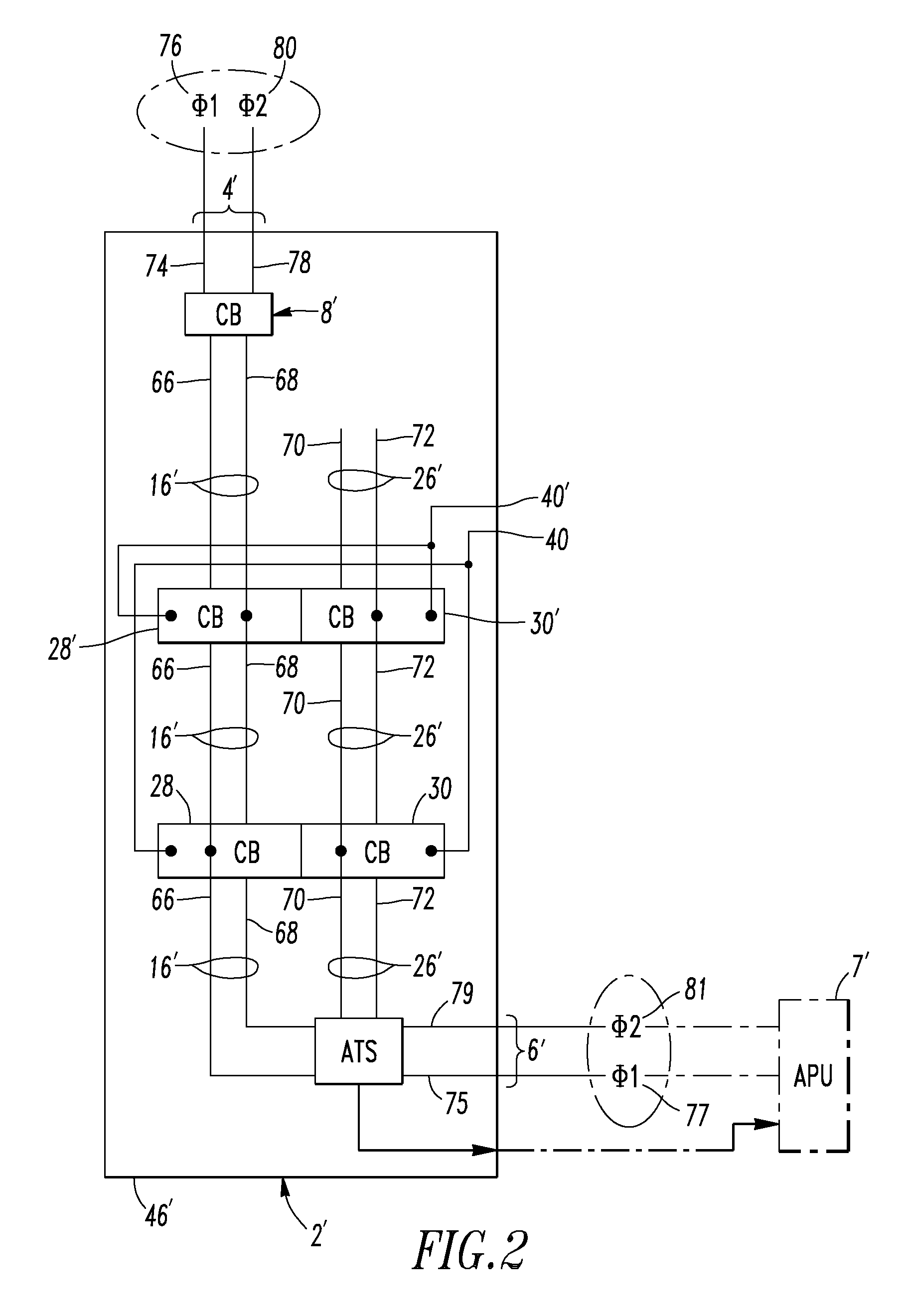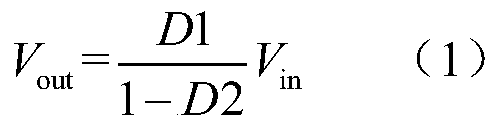Patents
Literature
126 results about "Load bus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
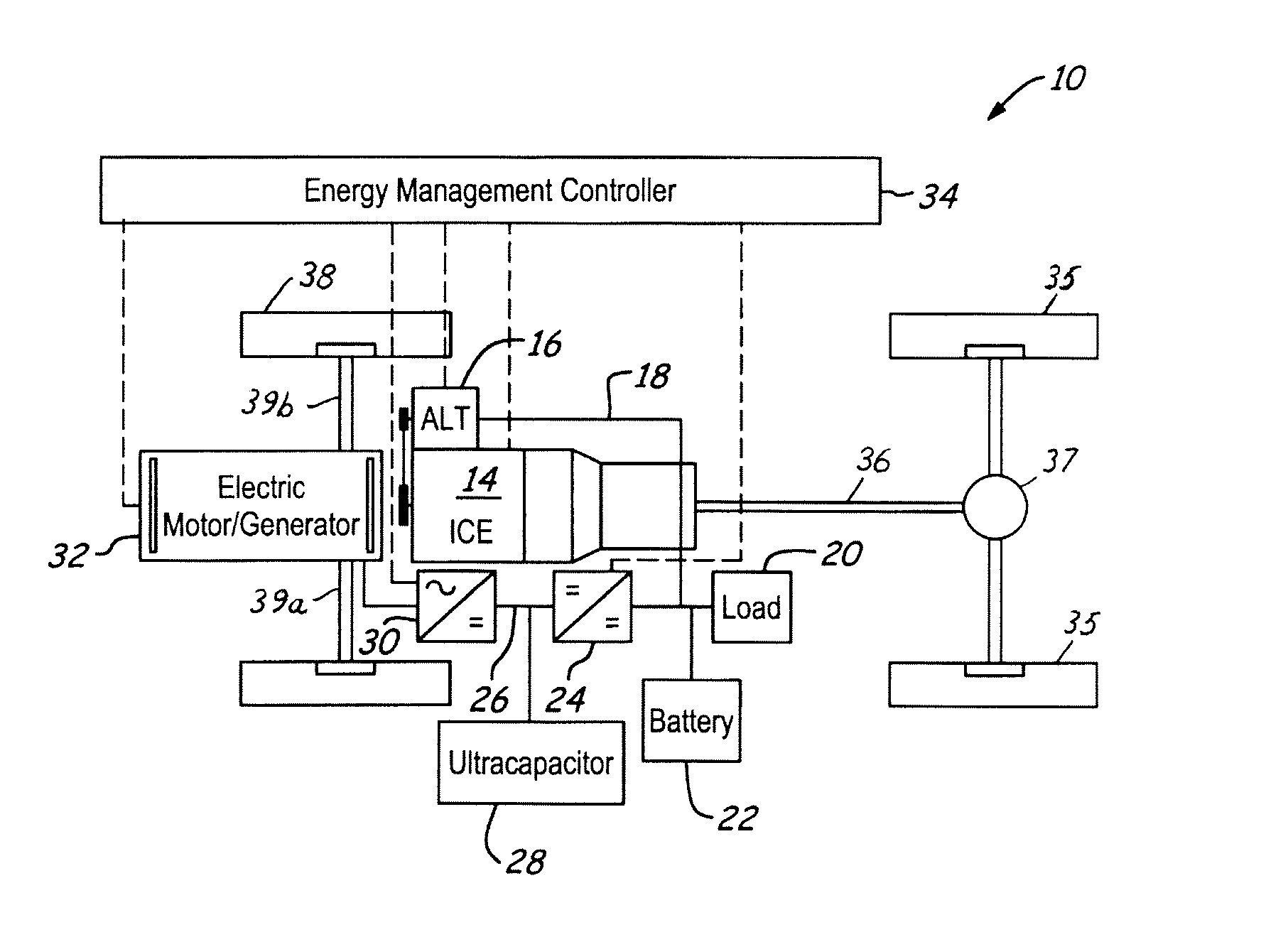
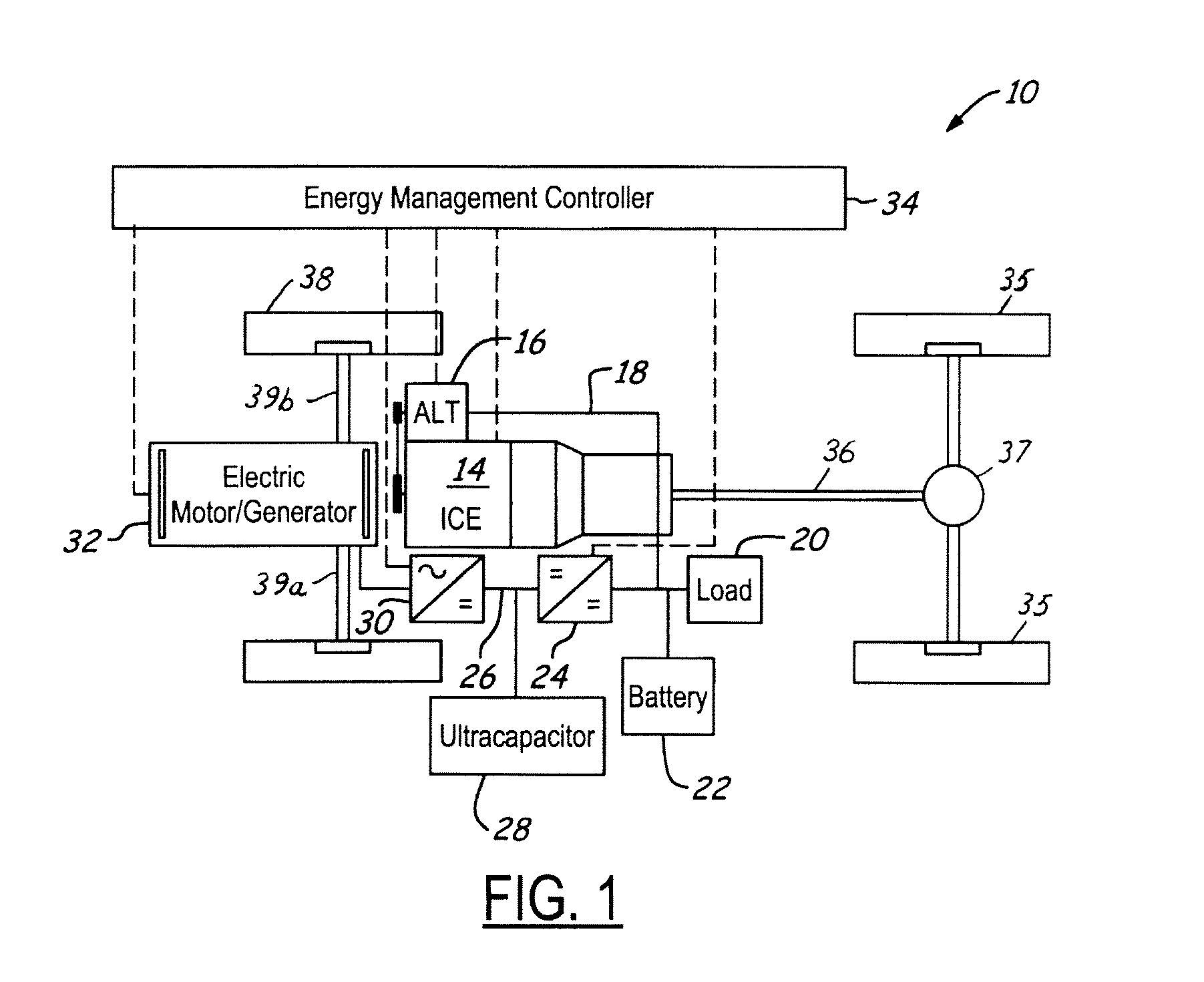
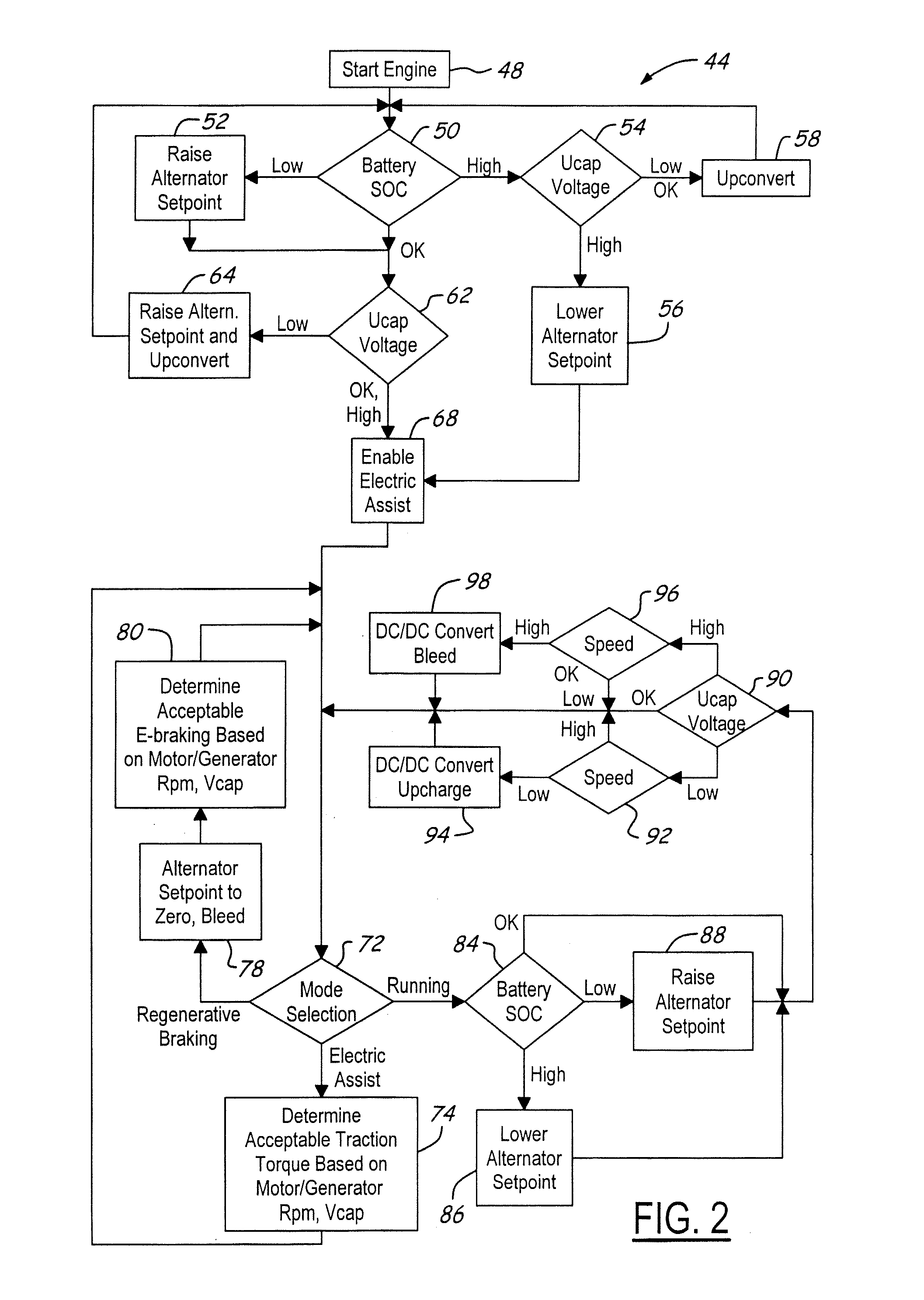
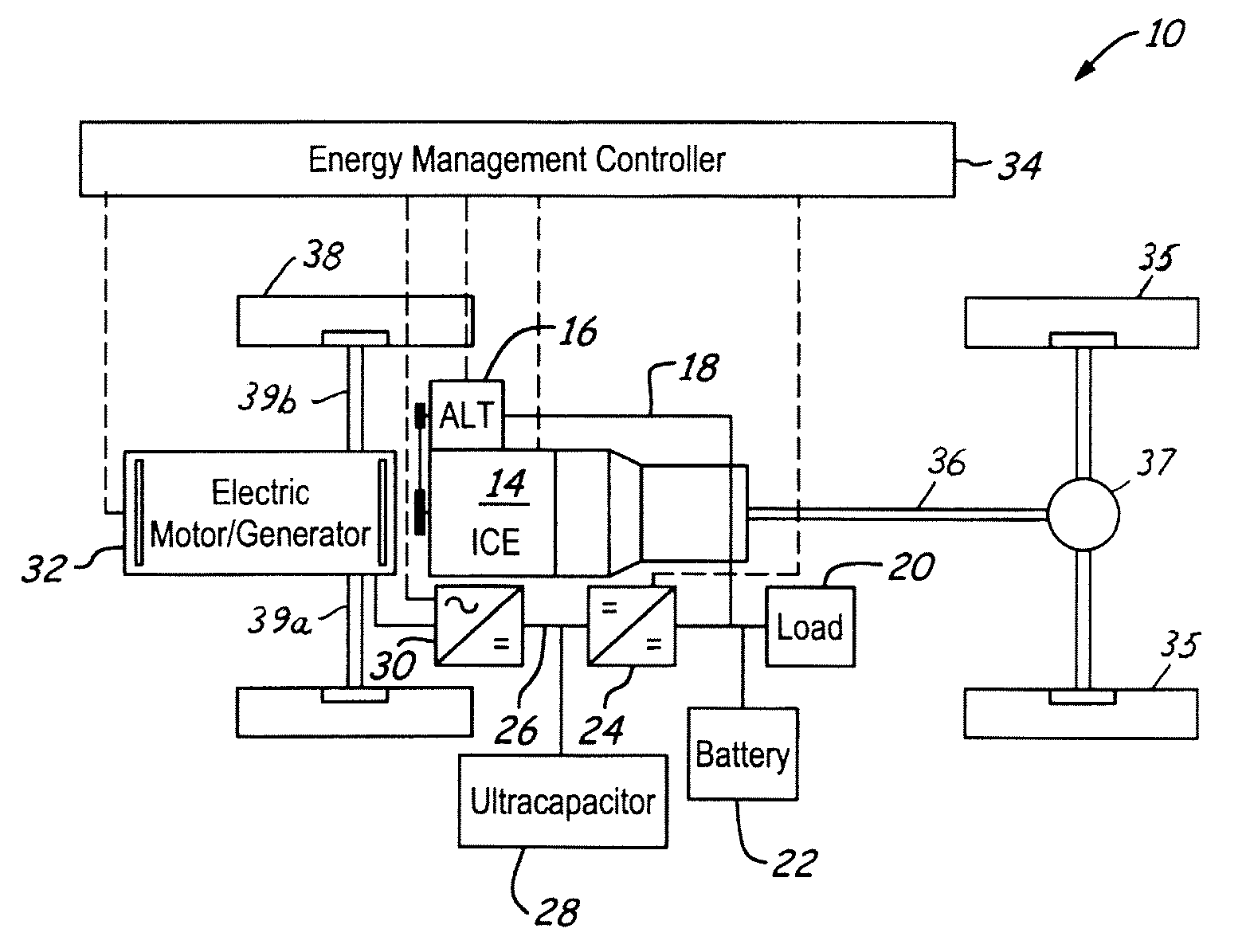
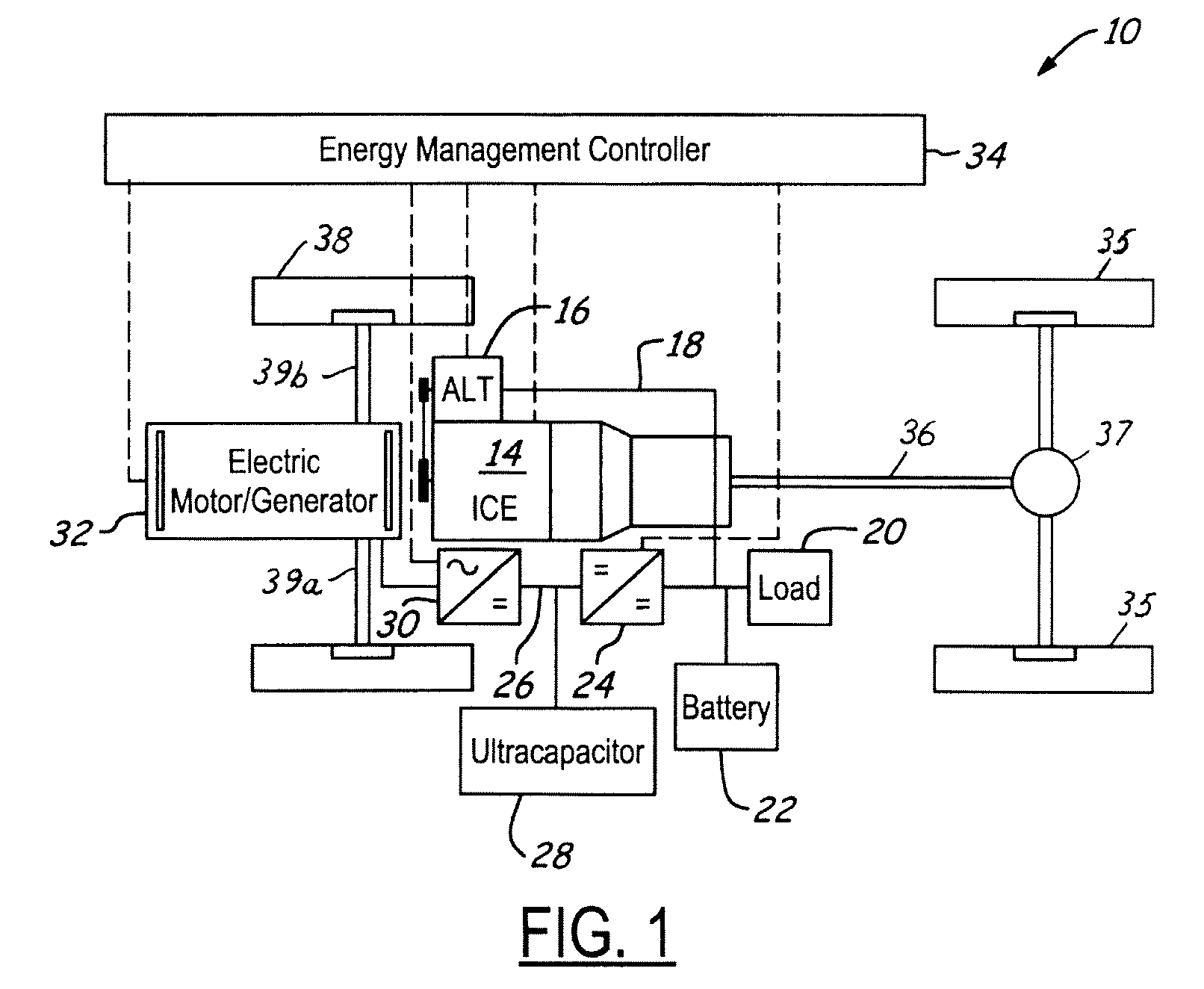
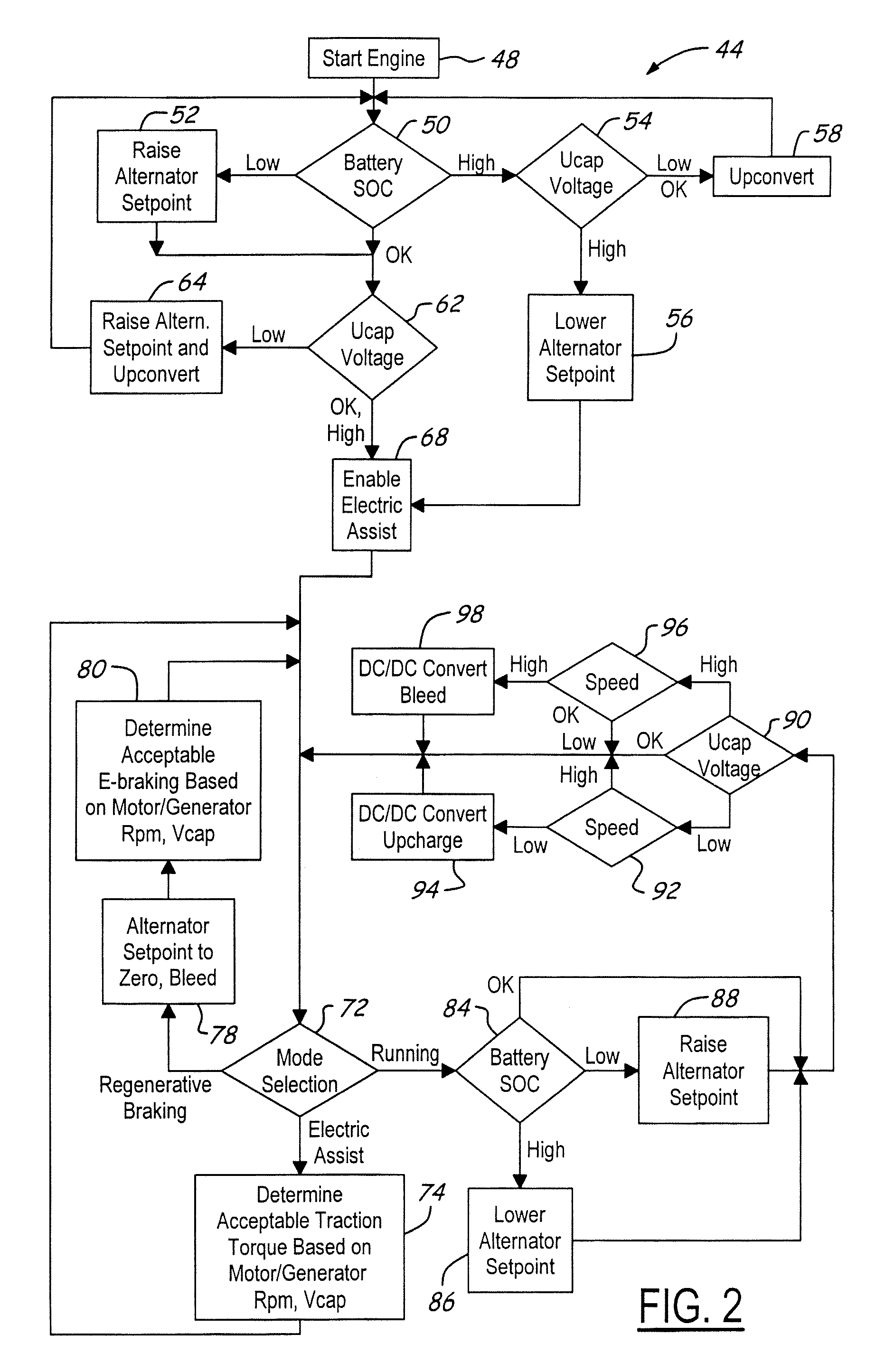
Stabilized electric distribution system for use with a vehicle having electric assist
A stabilized electric distribution system for use in a vehicle having electric assist. The system electrically couples an electric assist bus to an accessory load bus while protecting the first electrical bus from electric assist and regenerative braking induced voltage variations. An energy management controller selectively controls each of a electric motor / generator, a DC / DC converter, and an alternator to affect electric energy distribution within the system. Preferably, the electric energy distribution is controlled to maintain the first electrical bus voltage within a predefined voltage range.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Stabilized electric distribution system for use with a vehicle having electric assist
A stabilized electric distribution system for use in a vehicle having electric assist. The system electrically couples an electric assist bus to an accessory load bus while protecting the first electrical bus from electric assist and regenerative braking induced voltage variations. An energy management controller selectively controls each of a electric motor / generator, a DC / DC converter, and an alternator to affect electric energy distribution within the system. Preferably, the electric energy distribution is controlled to maintain the first electrical bus voltage within a predefined voltage range.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
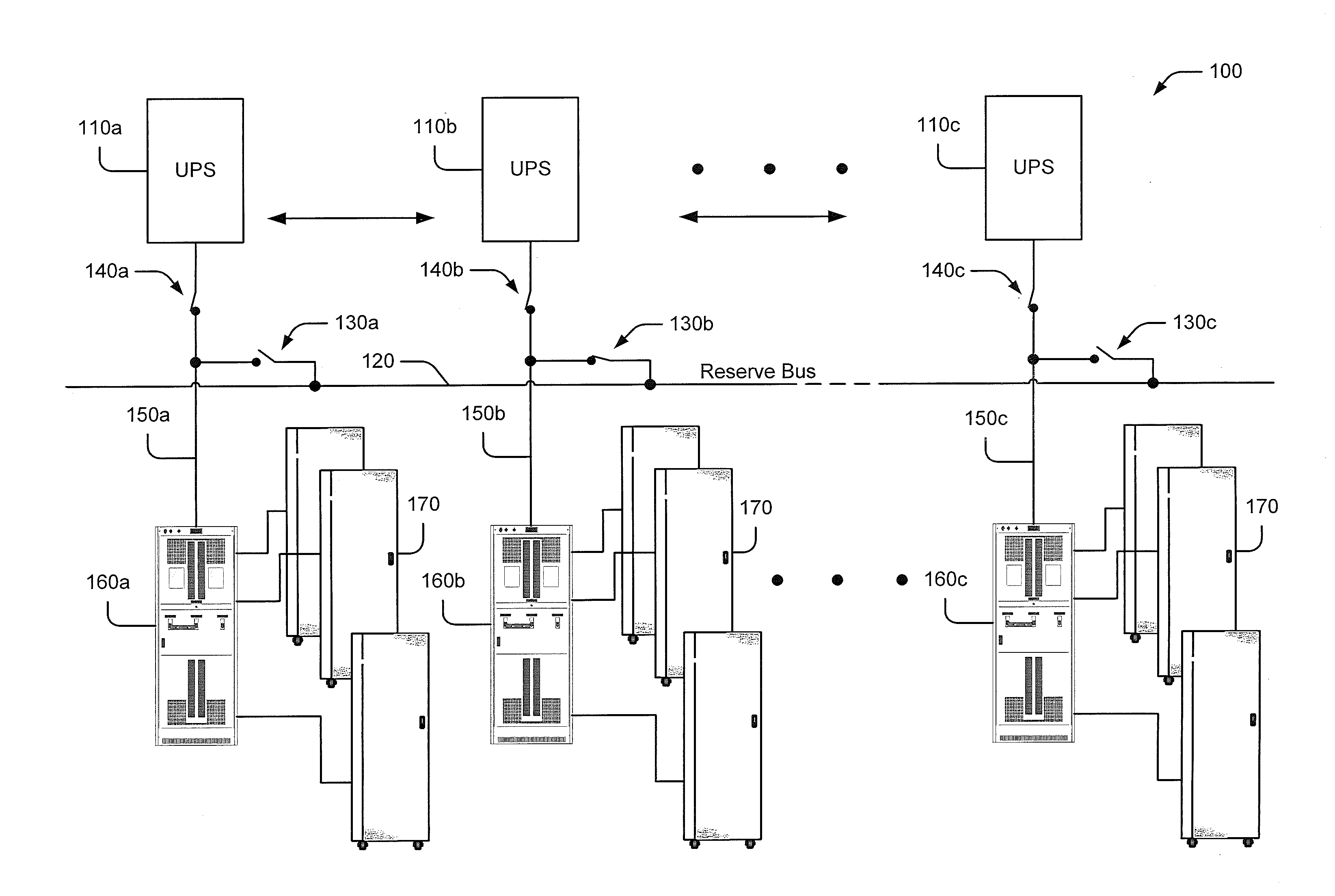
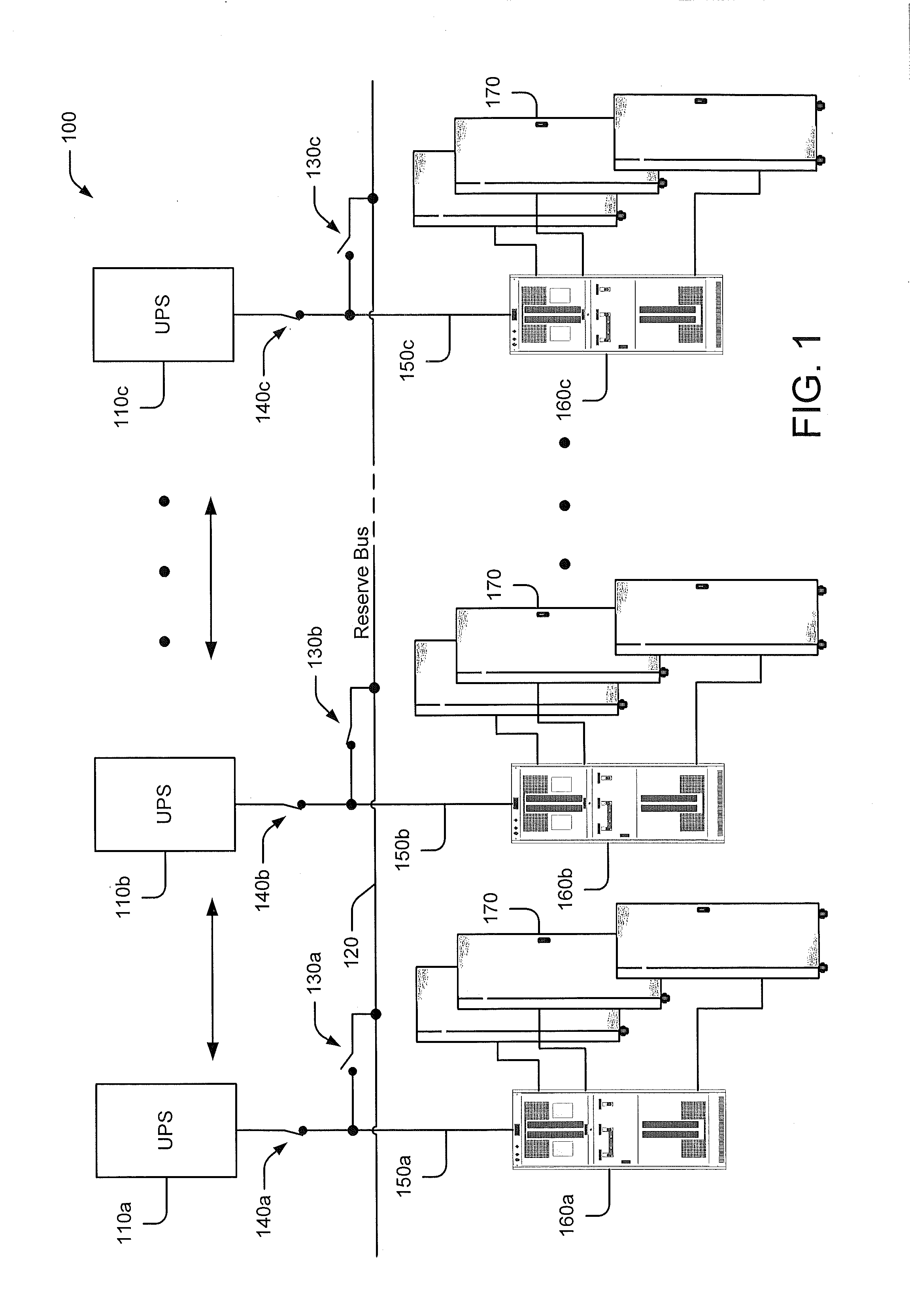
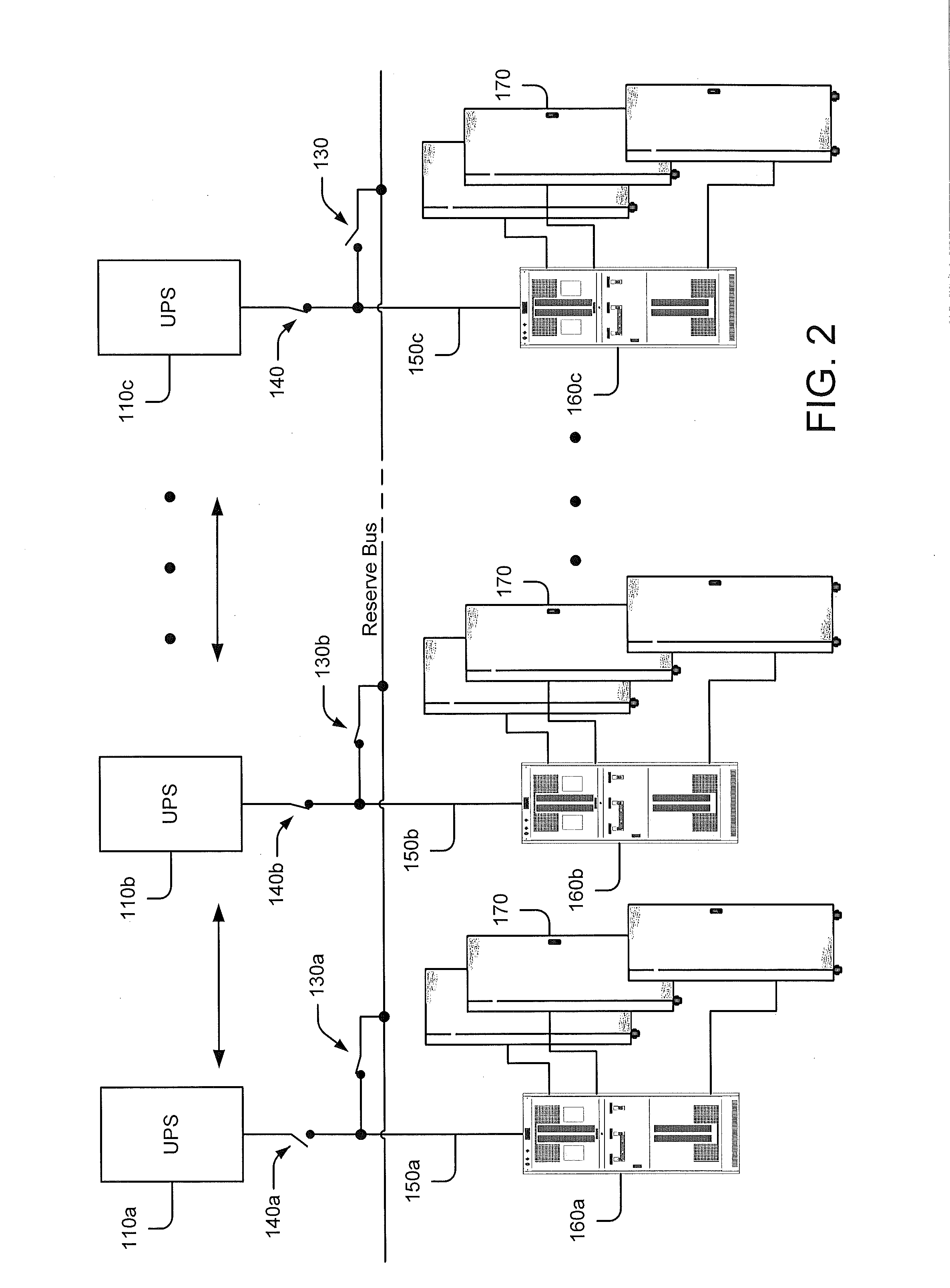
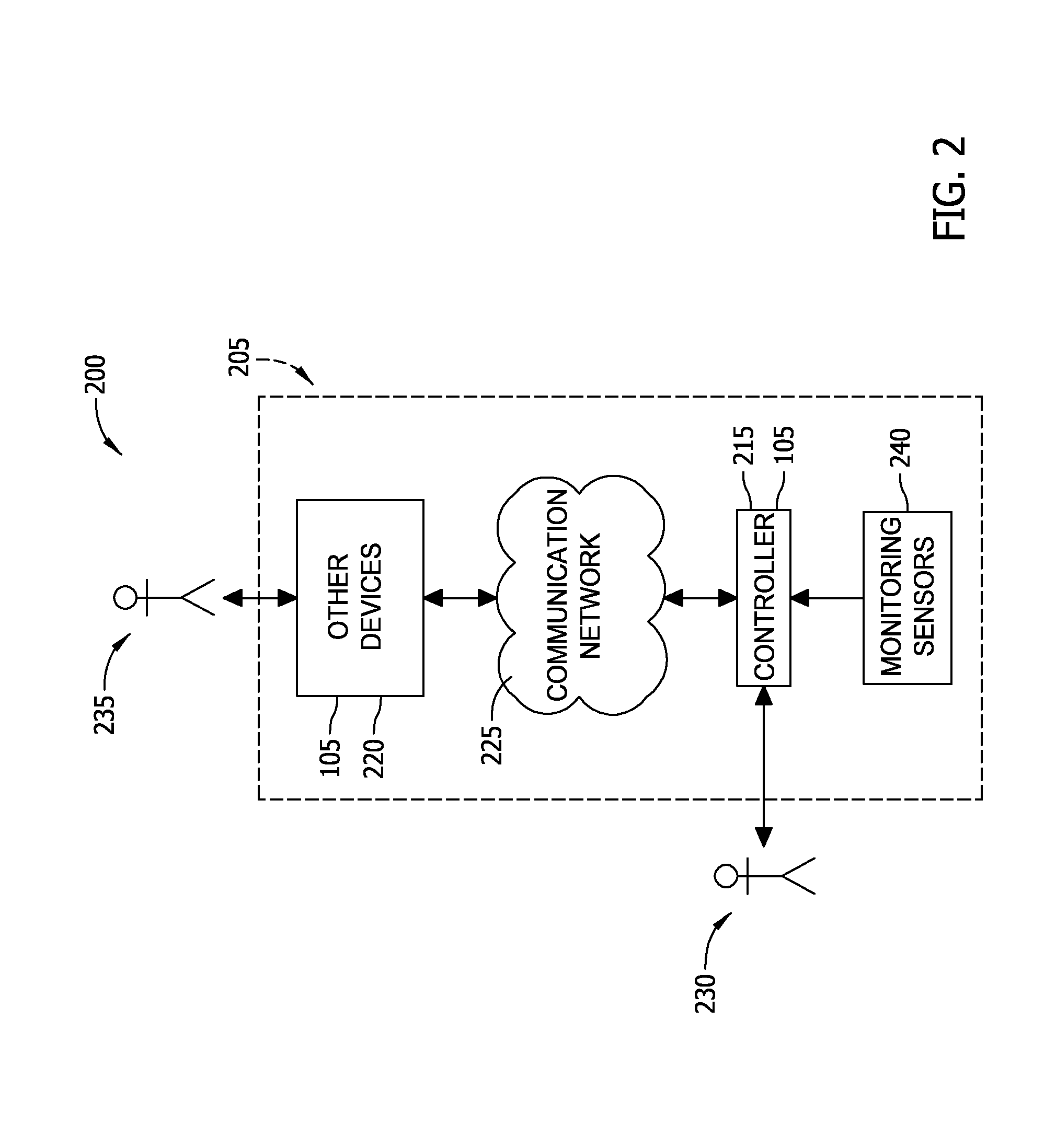
Data processing system power distribution using reserve bus
ActiveUS20130080793A1Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingData processing systemLoad bus
Some embodiments of the inventive subject matter provide a power distribution system for a data processing system. The power distribution system includes a plurality of uninterruptible power supply (UPS) units, respective ones of which are configured to be coupled to respective loads via respective load busses, at least one reserve bus, a switching circuit configured to selectively couple and decouple the UPS units and the load busses to and from the at least one reserve bus and a control circuit configured to control the switching circuit responsive to a state of the data processing system. The control circuit may be configured to cause the switching circuit to couple the first UPS unit to the at least one reserve bus concurrent with the first UPS unit being coupled to a first load via a first load bus.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
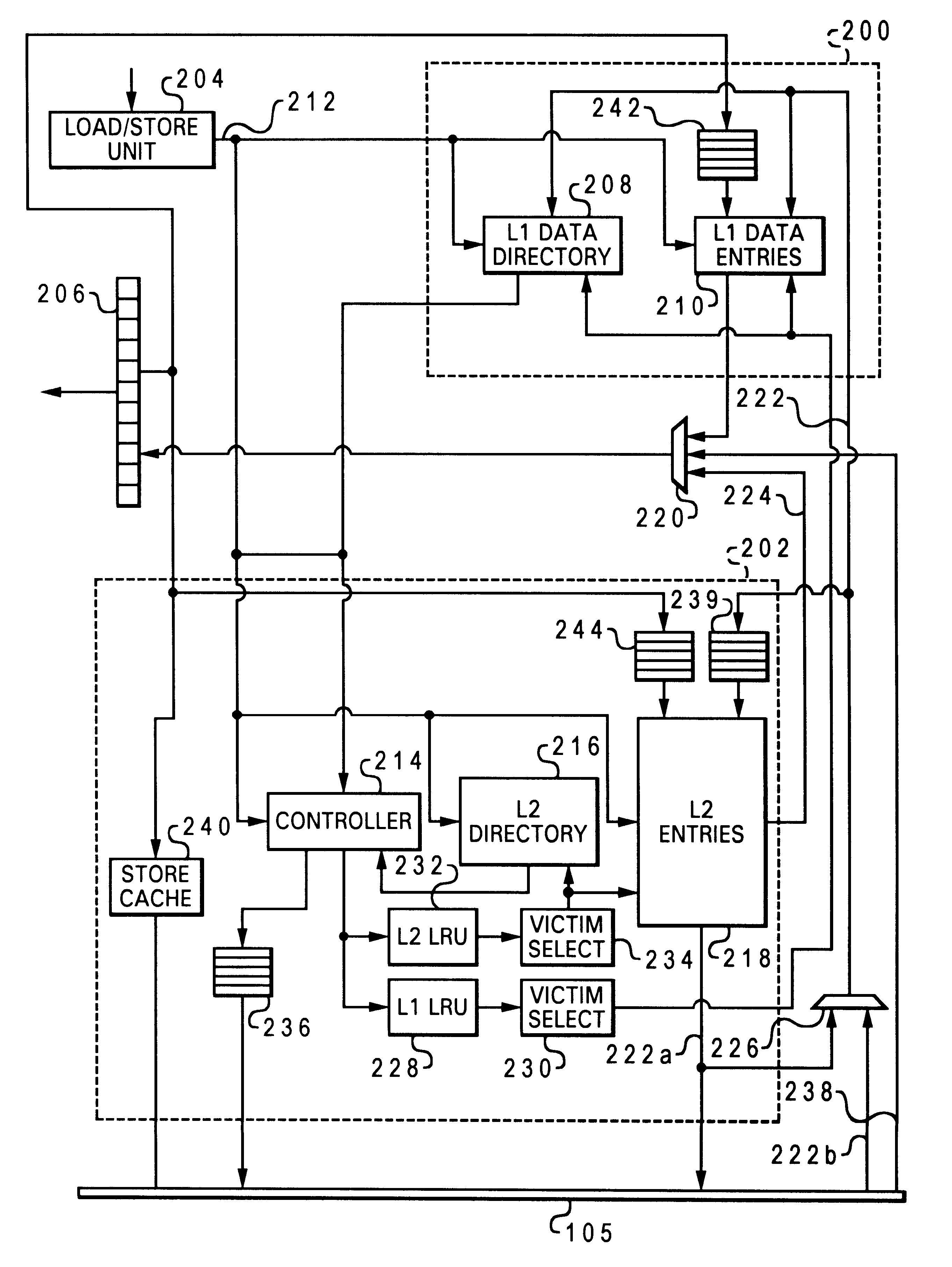
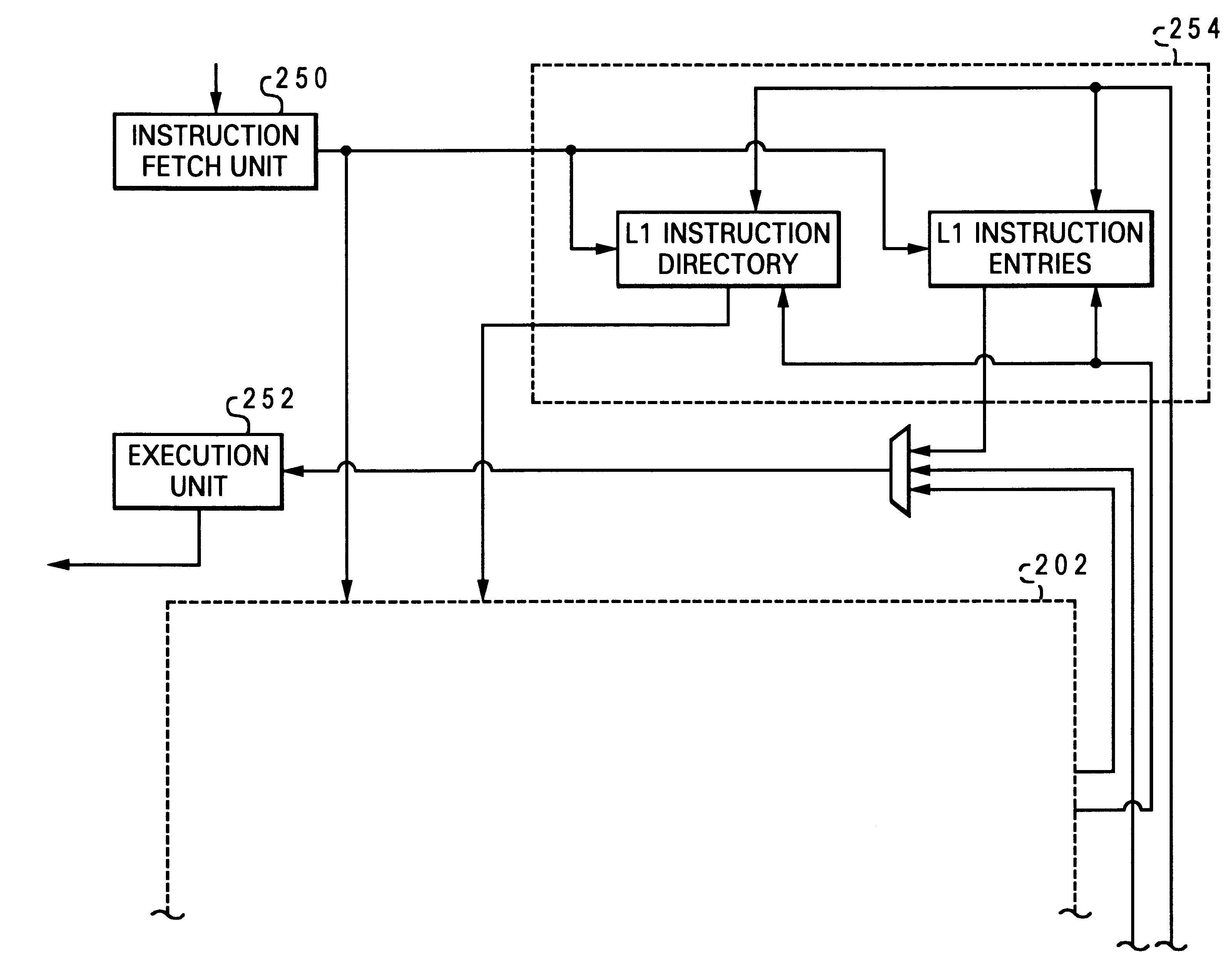
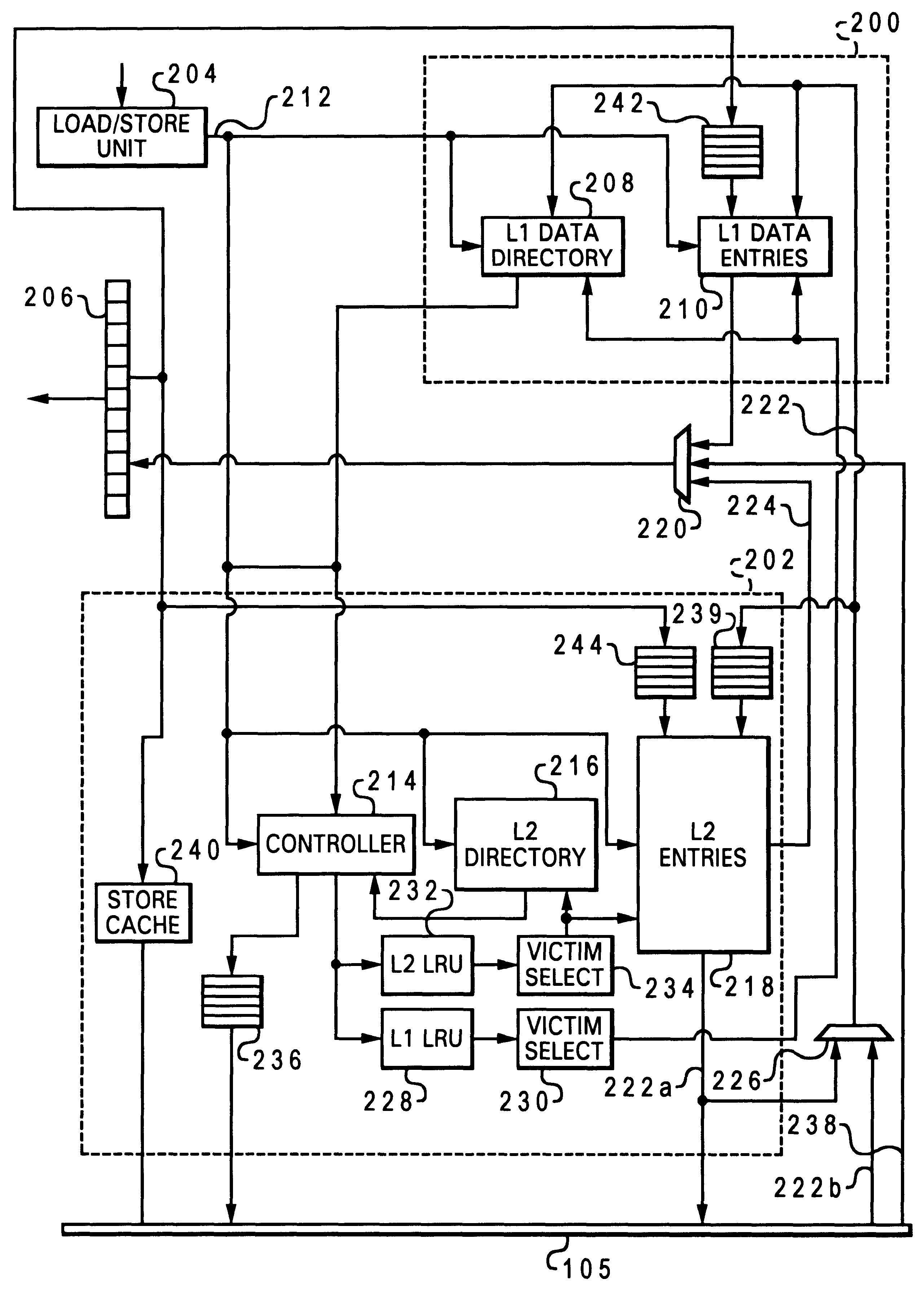
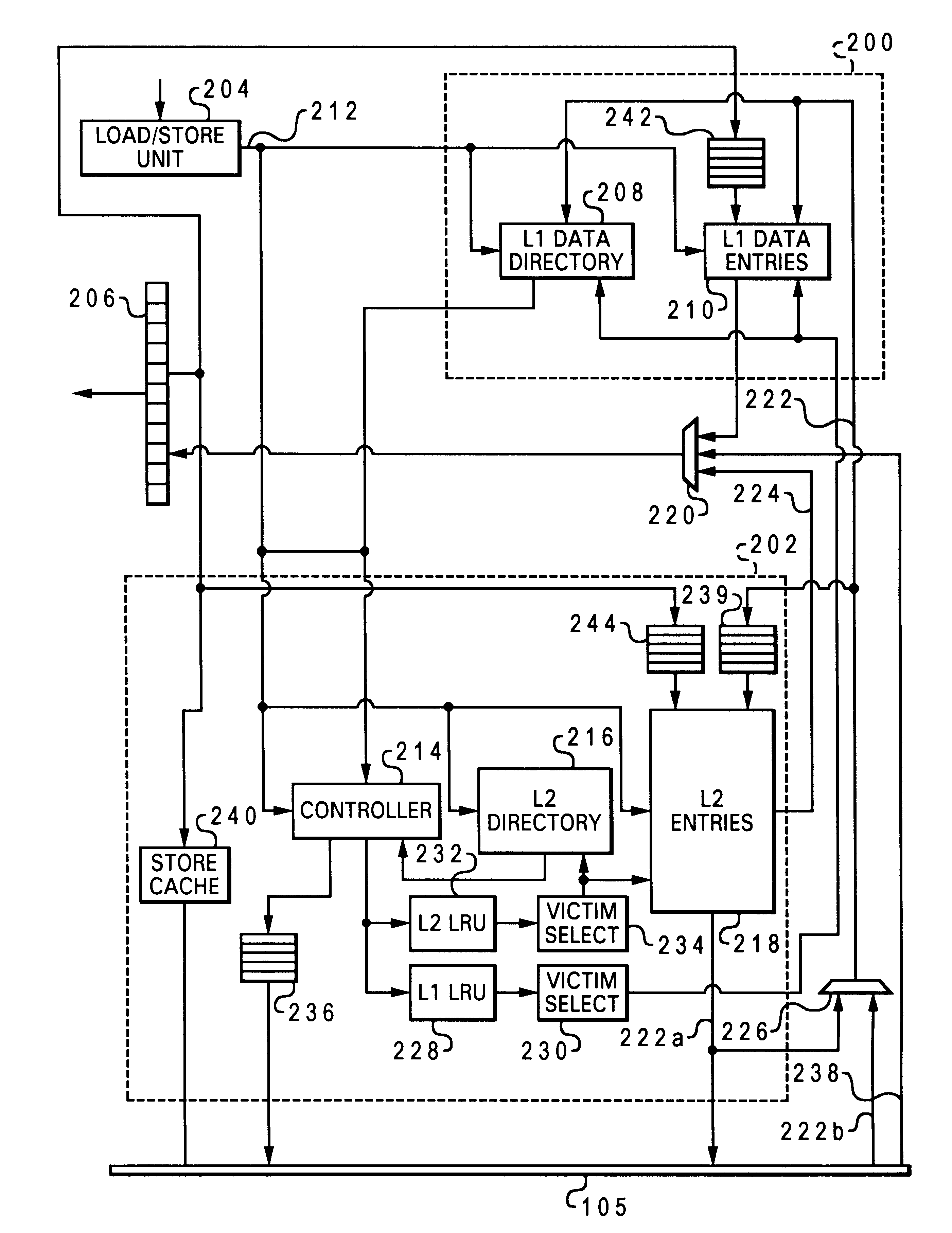
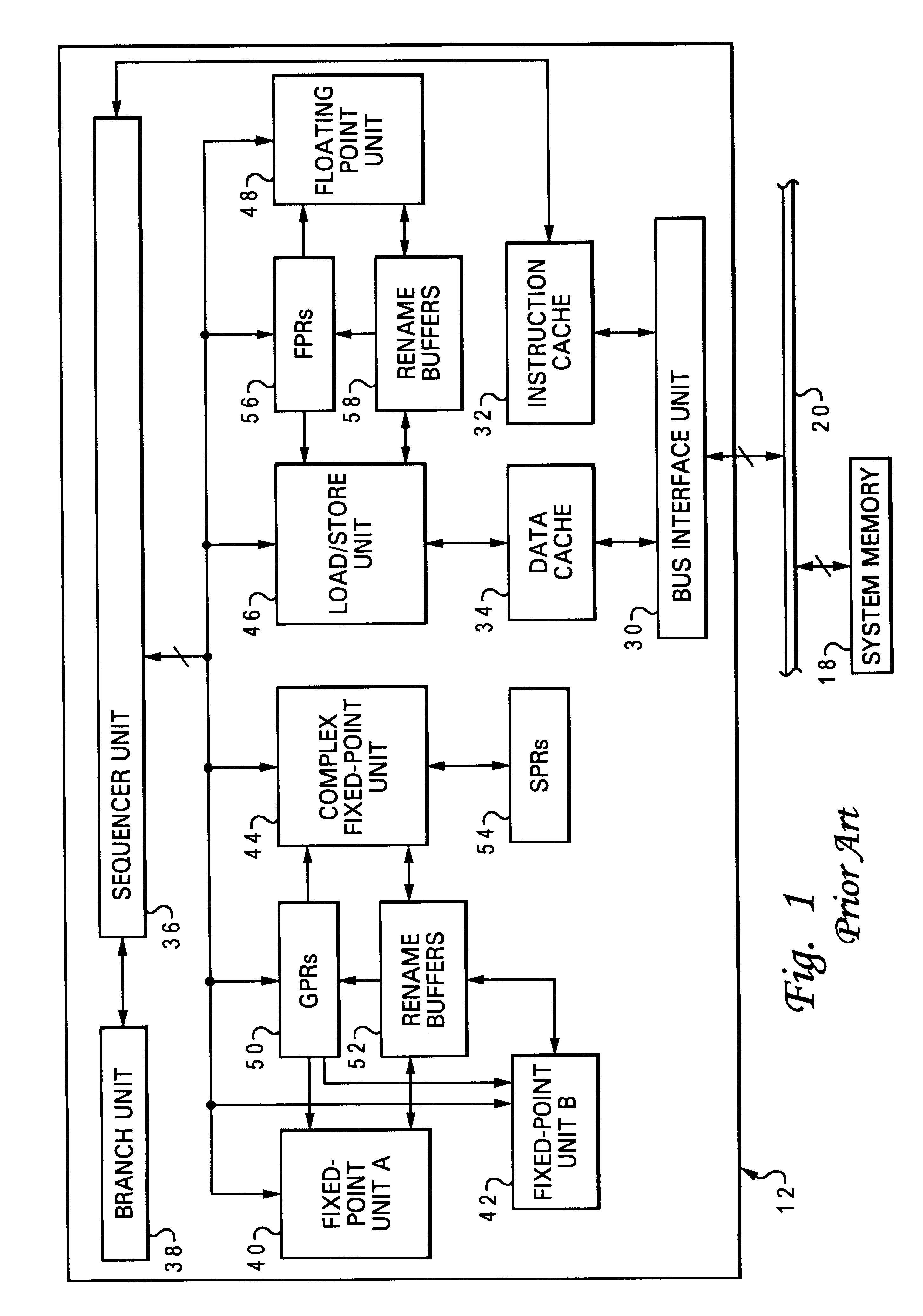
Layered local cache with lower level cache updating upper and lower level cache directories
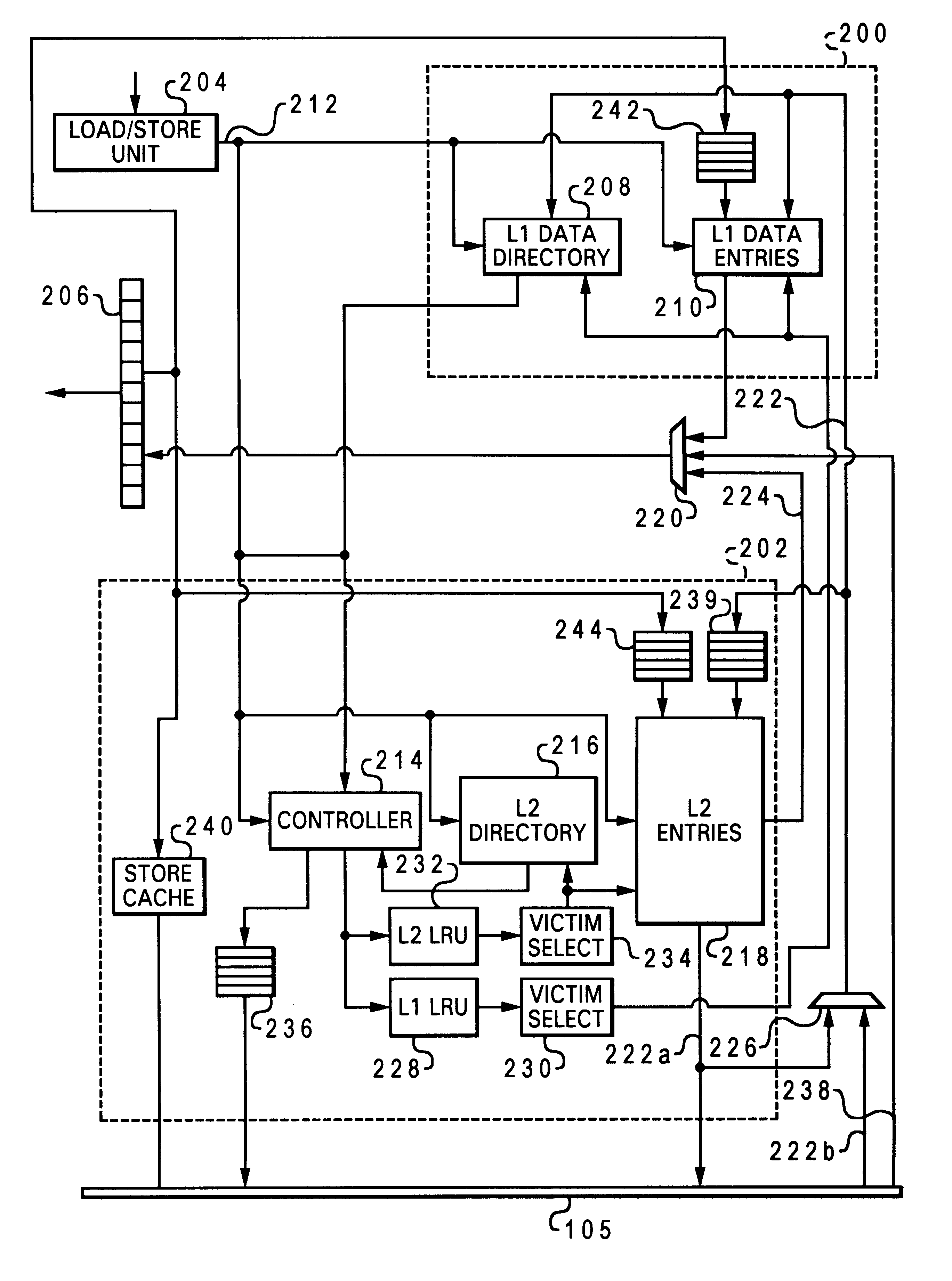
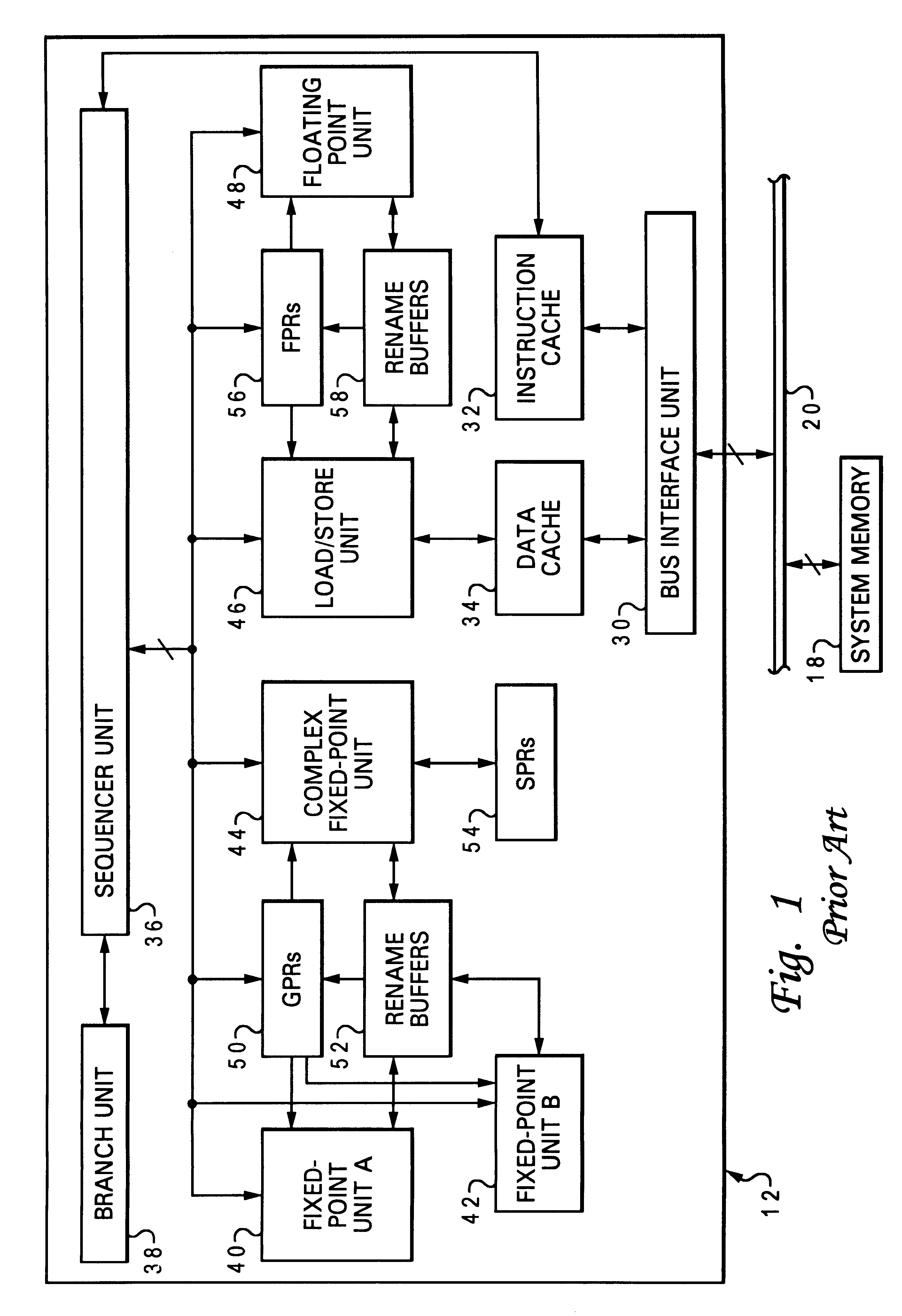
A method of improving memory access for a computer system, by sending load requests to a lower level storage subsystem along with associated information pertaining to intended use of the requested information by the requesting processor, without using a high level load queue. Returning the requested information to the processor along with the associated use information allows the information to be placed immediately without using reload buffers. A register load bus separate from the cache load bus (and having a smaller granularity) is used to return the information. An upper level (L1) cache may then be imprecisely reloaded (the upper level cache can also be imprecisely reloaded with store instructions). The lower level (L2) cache can monitor L1 and L2 cache activity, which can be used to select a victim cache block in the L1 cache (based on the additional L2 information), or to select a victim cache block in the L2 cache (based on the additional L1 information). L2 control of the L1 directory also allows certain snoop requests to be resolved without waiting for L1 acknowledgement. The invention can be applied to, e.g., instruction, operand data and translation caches.
Owner:IBM CORP
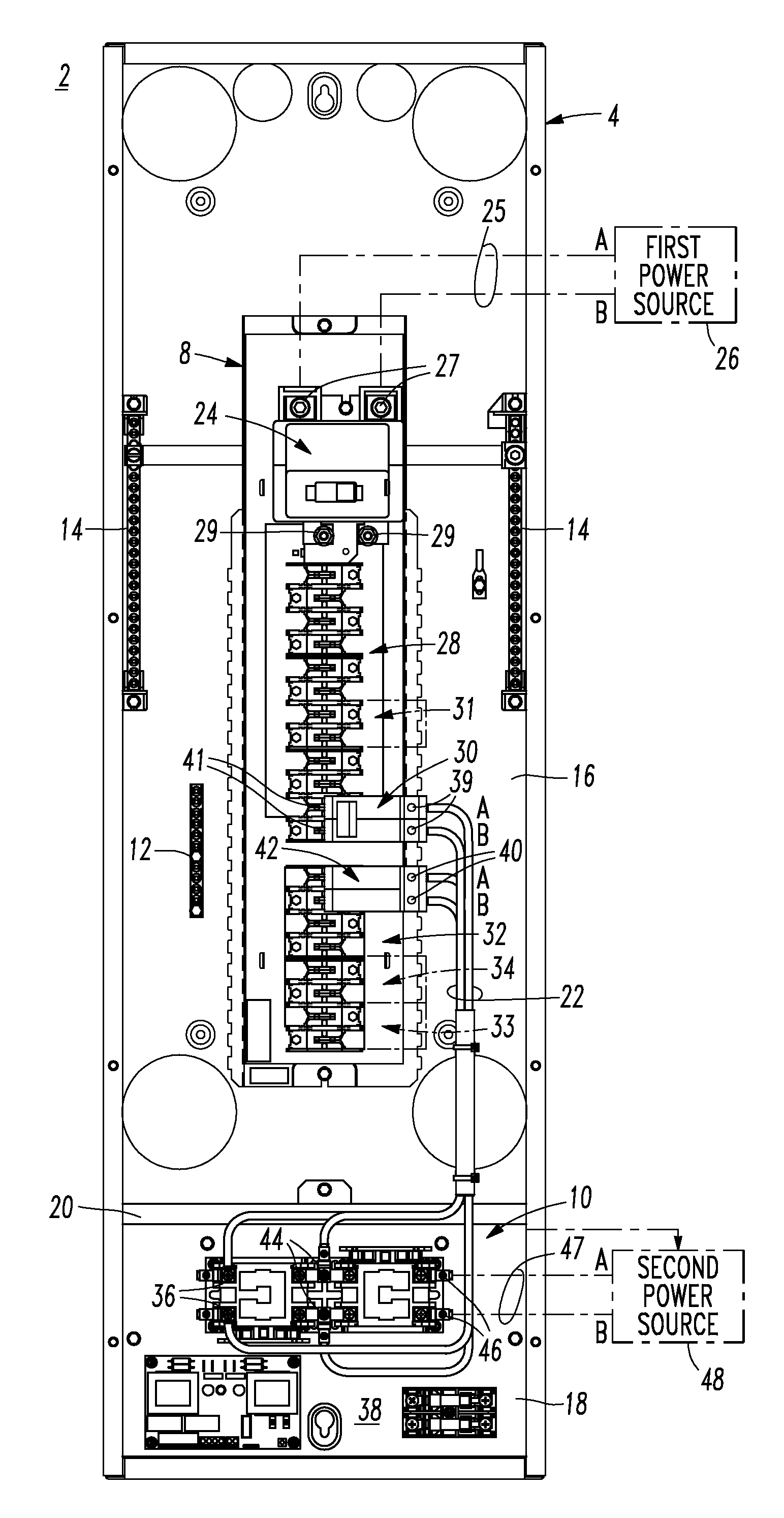
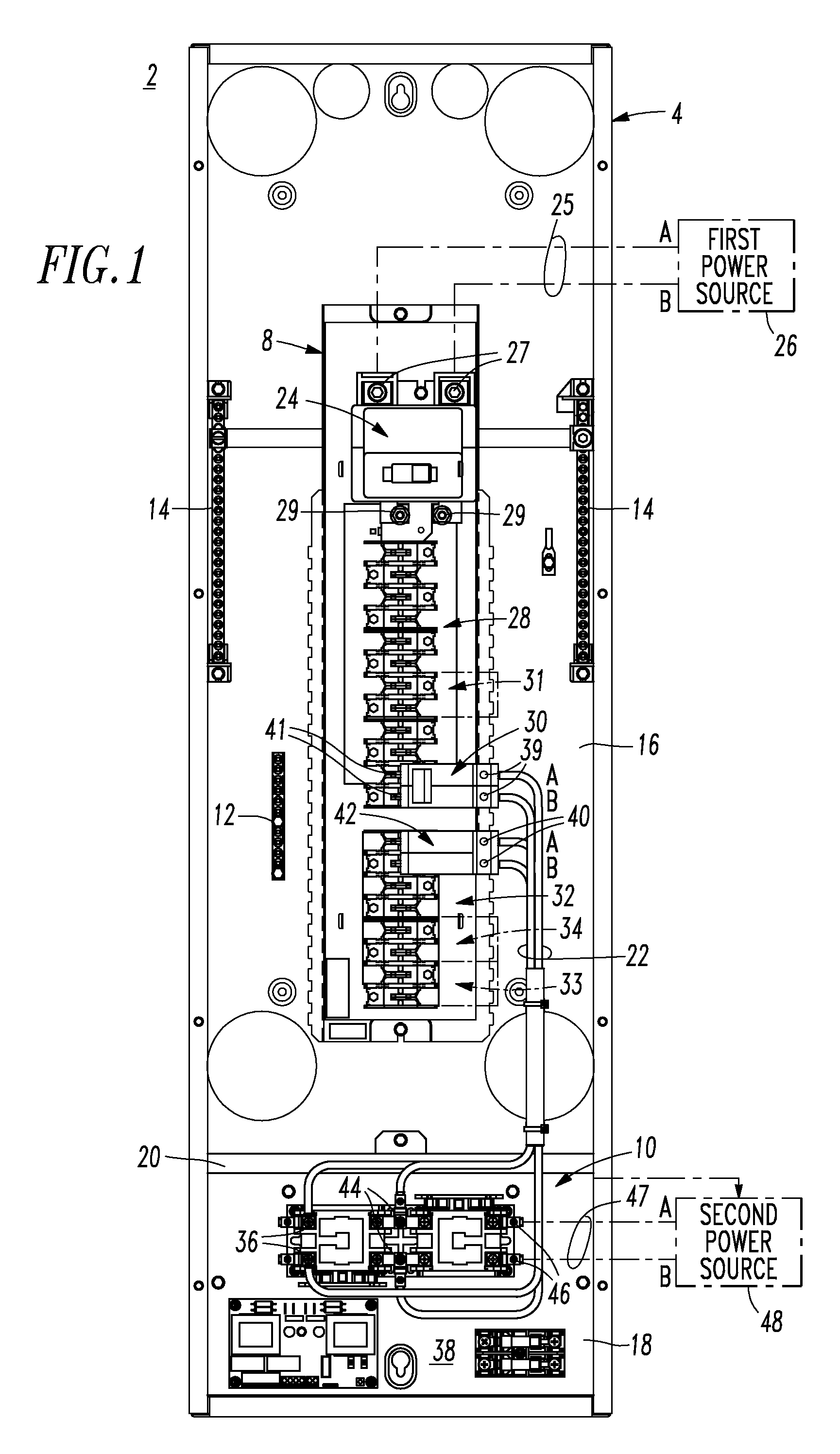
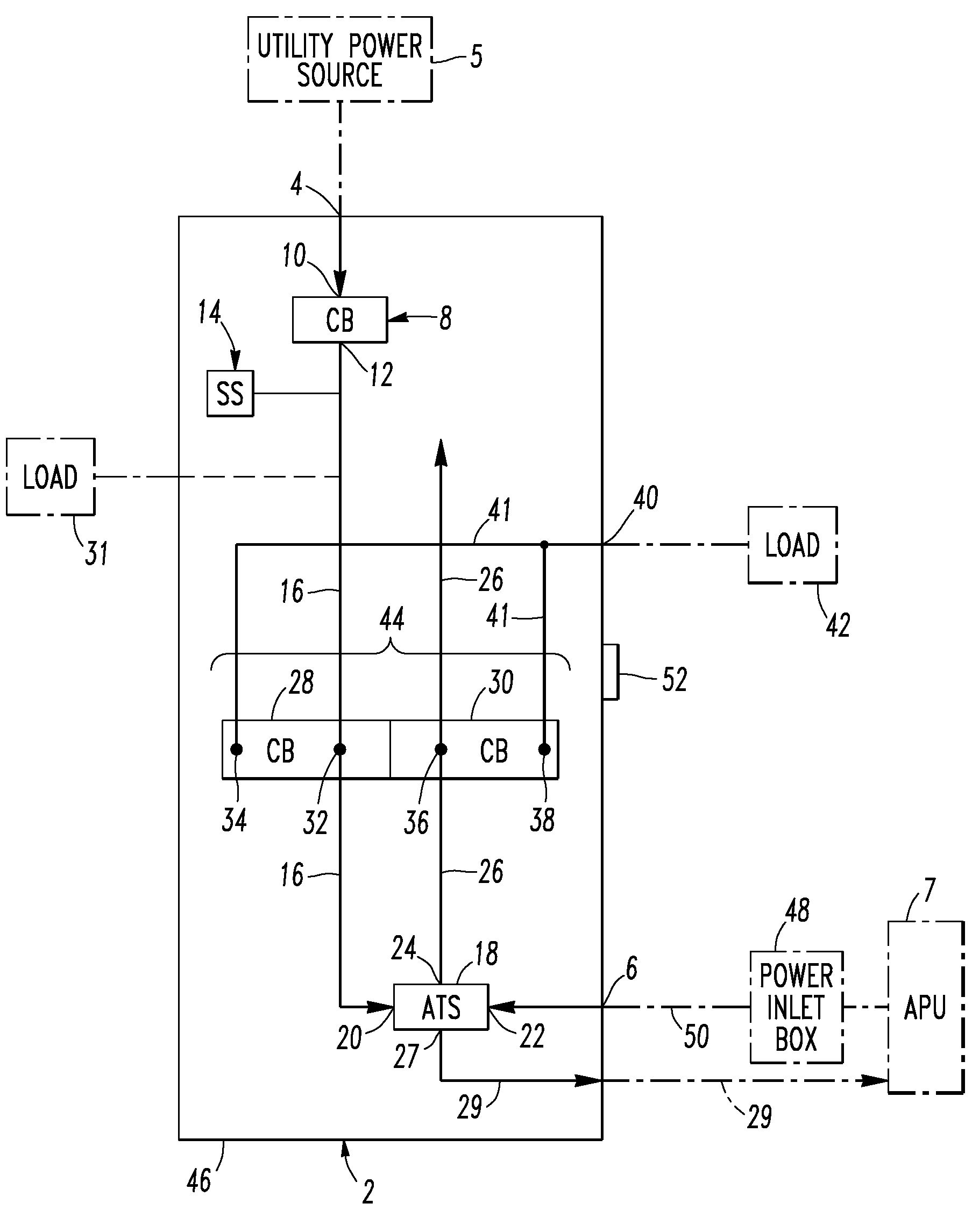
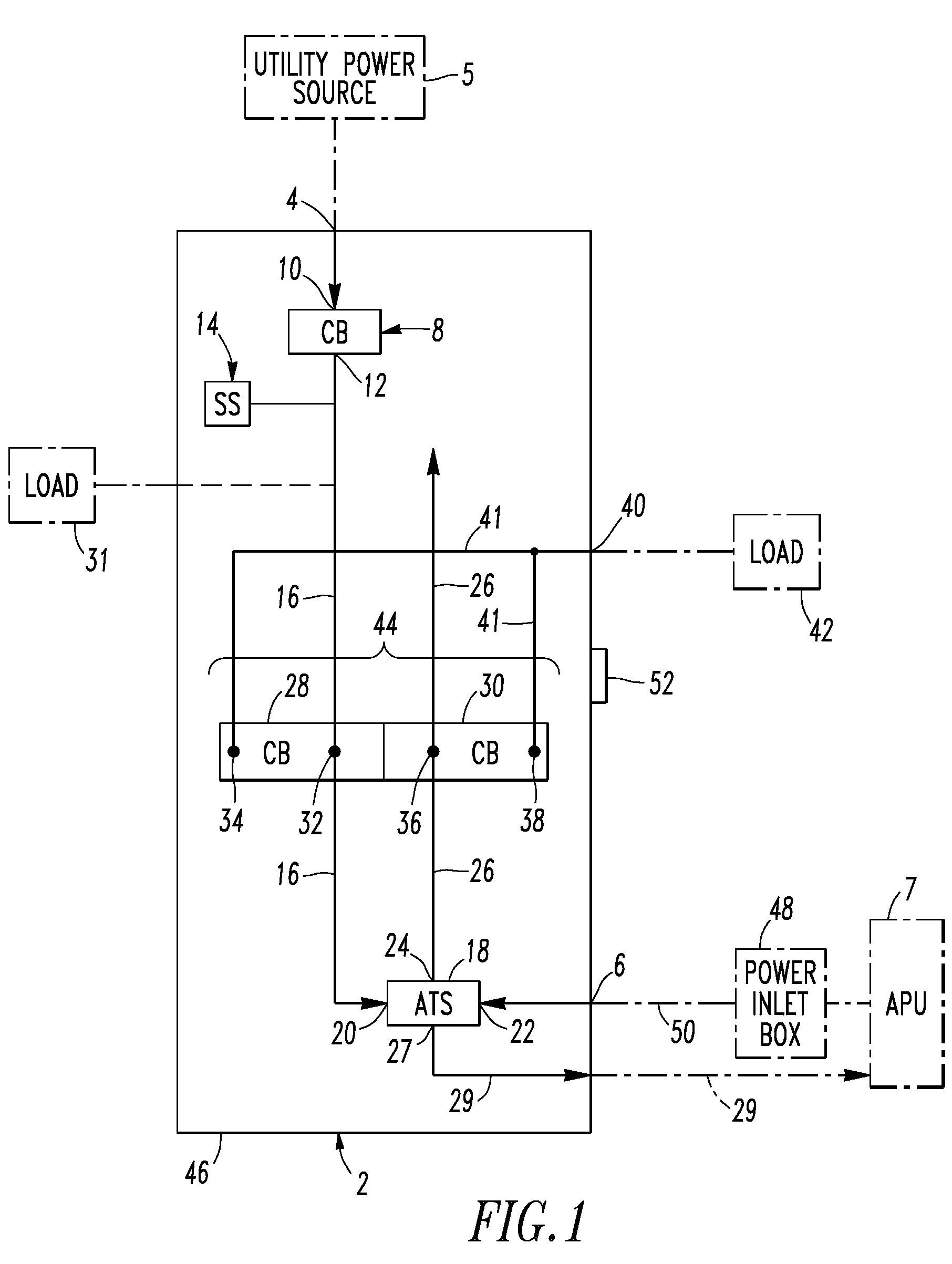
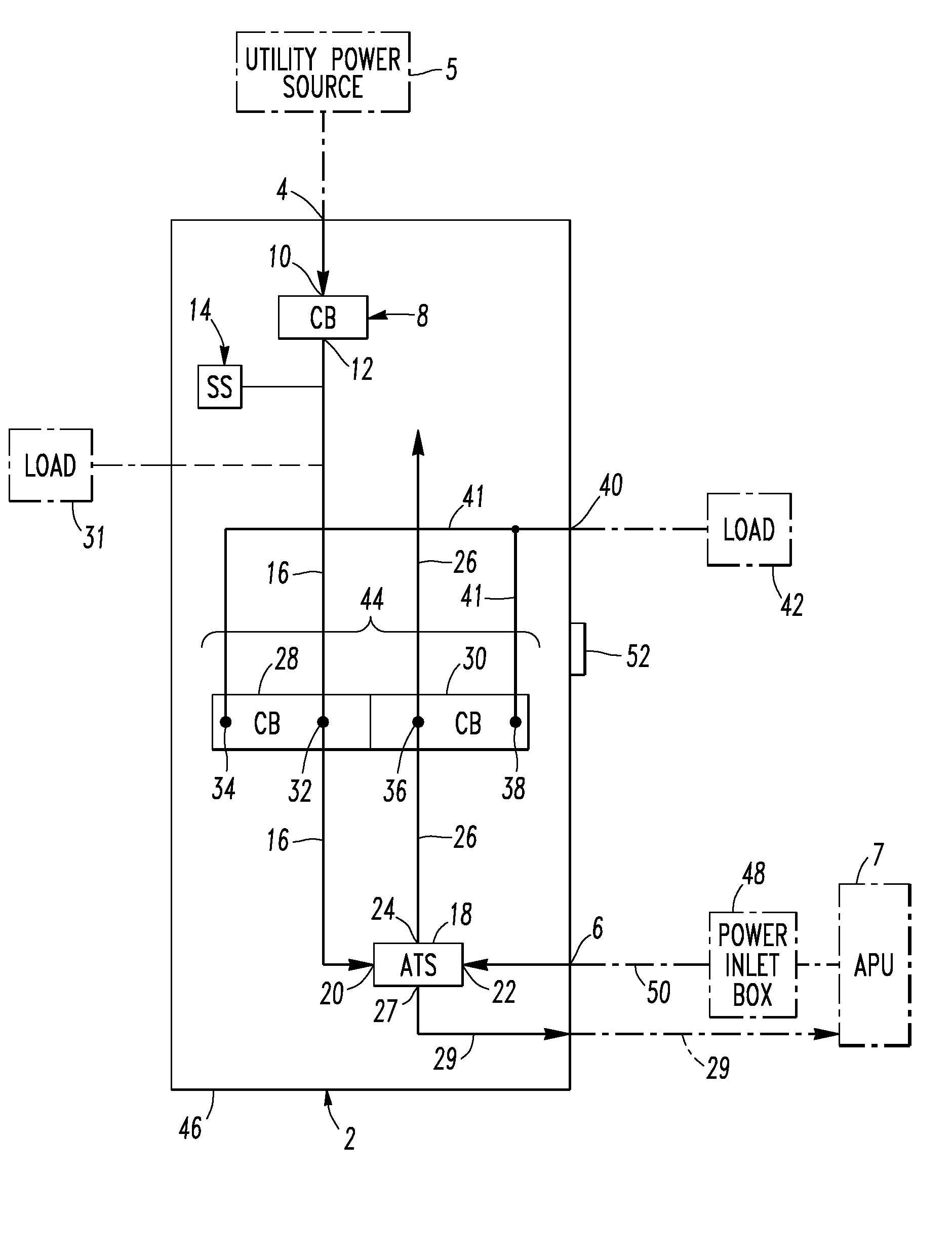
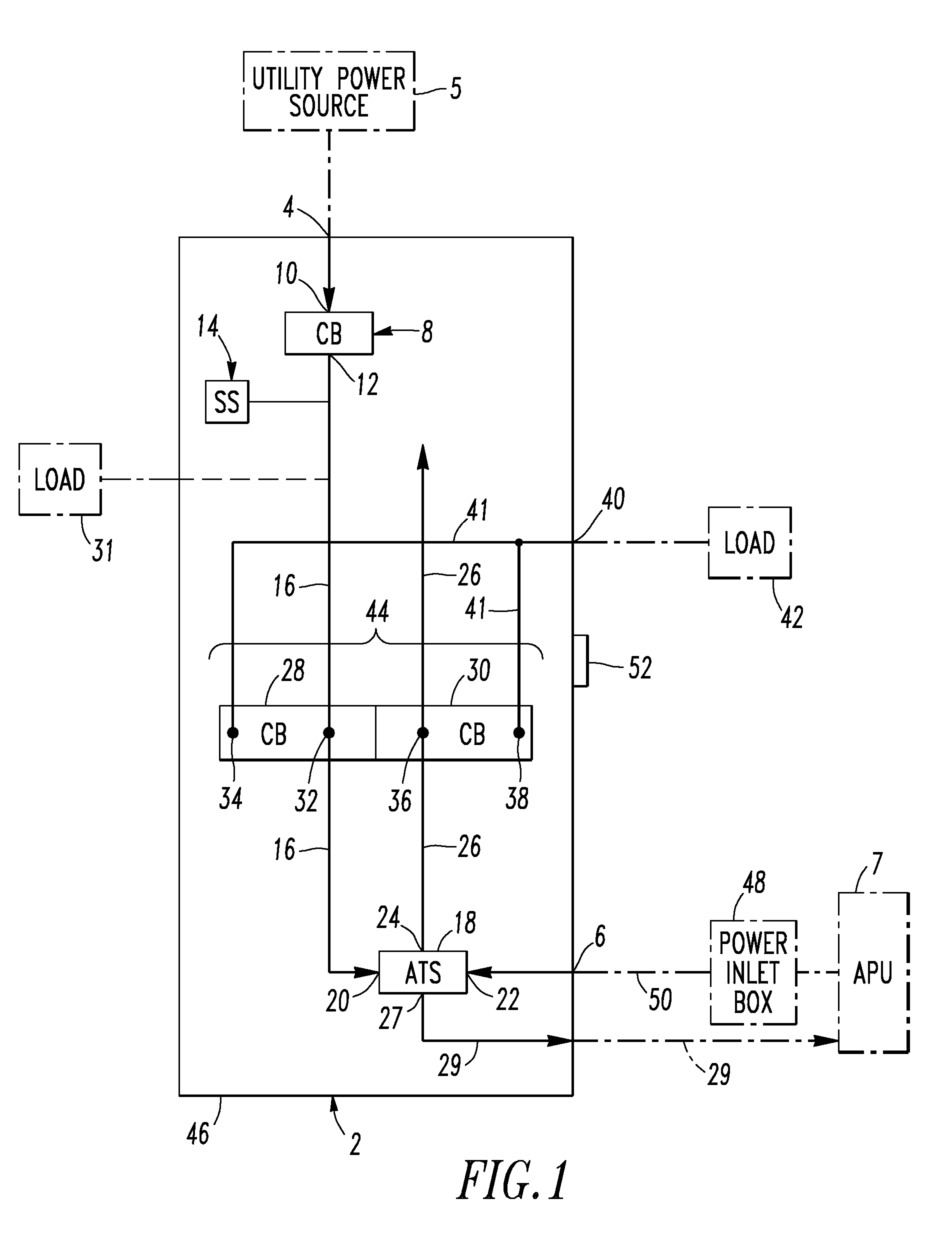
Electrical distribution panel including first non-critical load bus and second critical load bus
ActiveUS7599171B1Batteries circuit arrangementsSubstation/switching arrangement casingsEngineeringLoad bus
A load center includes an enclosure, a first power input, a second power input, a first circuit breaker having a line terminal electrically connected to the first power input and a load terminal, a first bus electrically connected to the load terminal, a number of independent second circuit breakers powered from the first bus, a second bus, a number of independent third circuit breakers powered from the second bus, and a transfer switch having a first input electrically connected to the first bus, a second input electrically connected to the second power input, and an output electrically connected to the second bus. The transfer switch selectively electrically connects one of its first and second inputs to its output. The first bus and the second circuit breakers power only a number of non-critical loads. The second bus and the third circuit breakers power only a number of critical loads.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Electrical distribution panel for a number of critical and non-critical loads
InactiveUS7616432B2Batteries circuit arrangementsSubstation/switching arrangement casingsElectricityLoad bus
An electrical distribution panel includes first and second power inputs, a first circuit breaker electrically between the first power input and a first load bus, a second load bus, an automatic transfer switch having a first input electrically connected to the first load bus, a second input electrically connected to the second power input, and an output electrically connected to the second load bus. The transfer switch selectively electrically connects one of the first and second inputs to the output thereof. Pairs of circuit breakers each includes a second breaker having a first terminal electrically connected to the first load bus, and a second terminal, a third breaker including a first terminal electrically connected to the second load bus, and a second terminal, a power output electrically connected to the second terminals, and an interlock cooperating with the circuit breaker pair to prevent both of them from being closed simultaneously.
Owner:EATON CORP
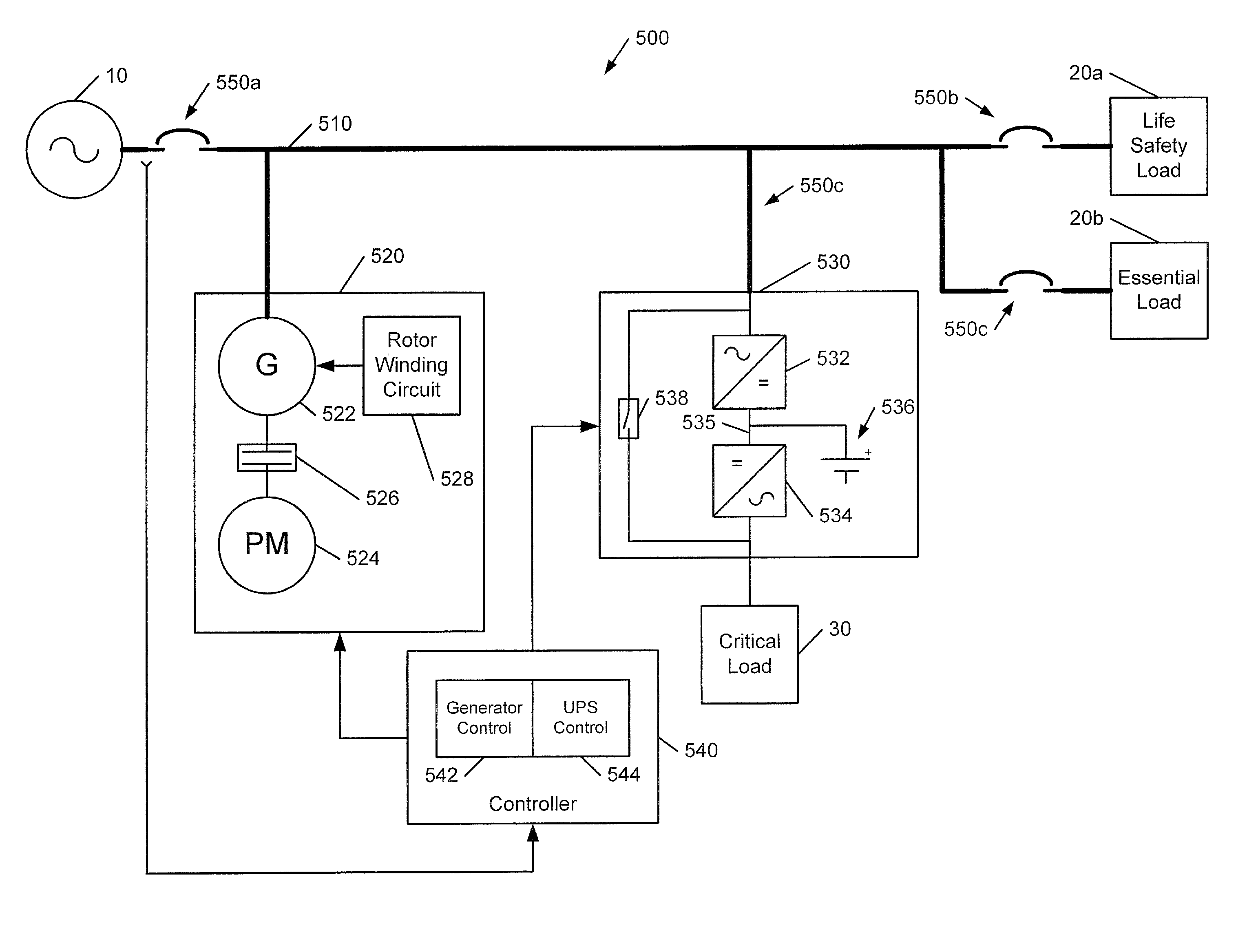
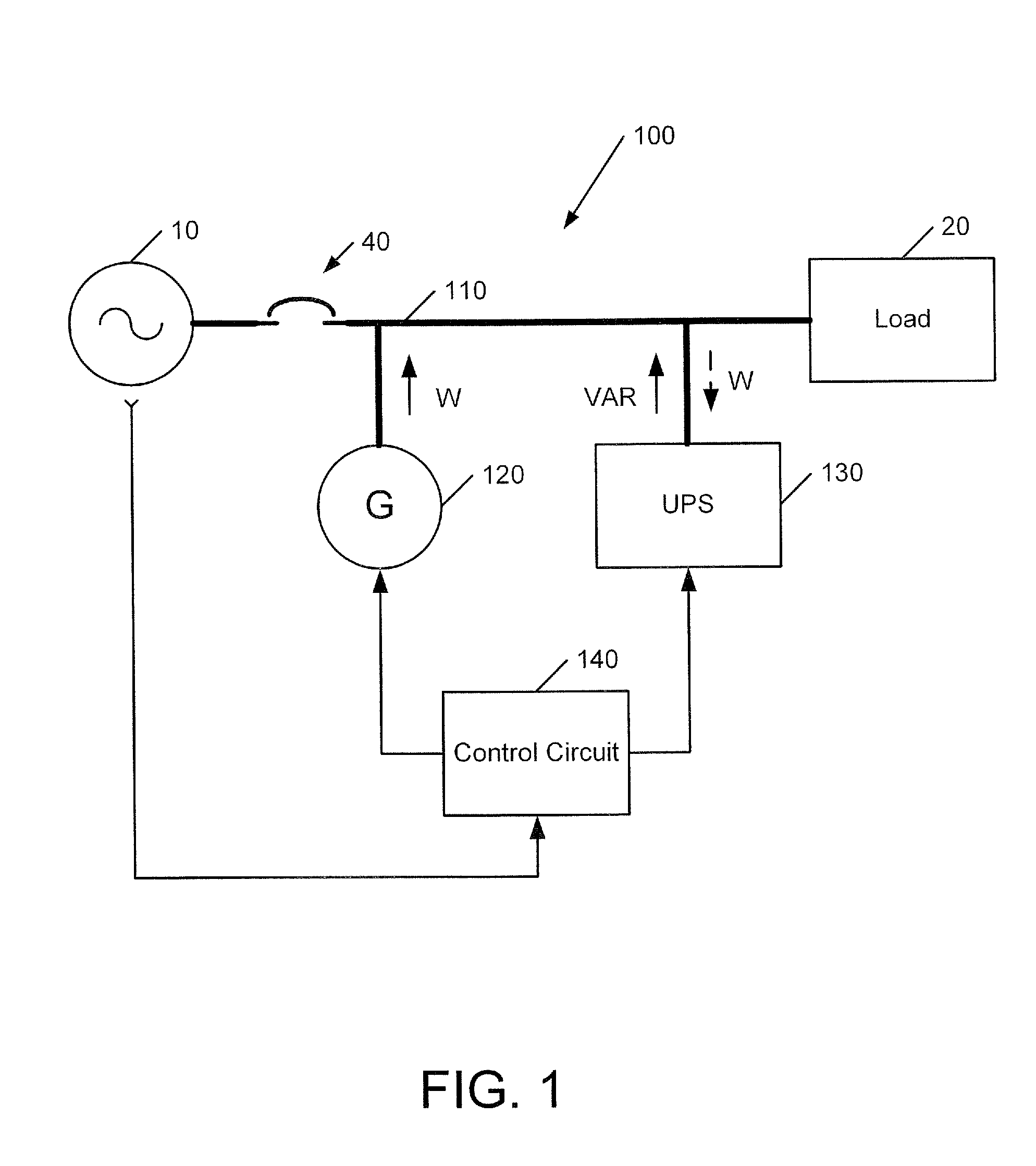
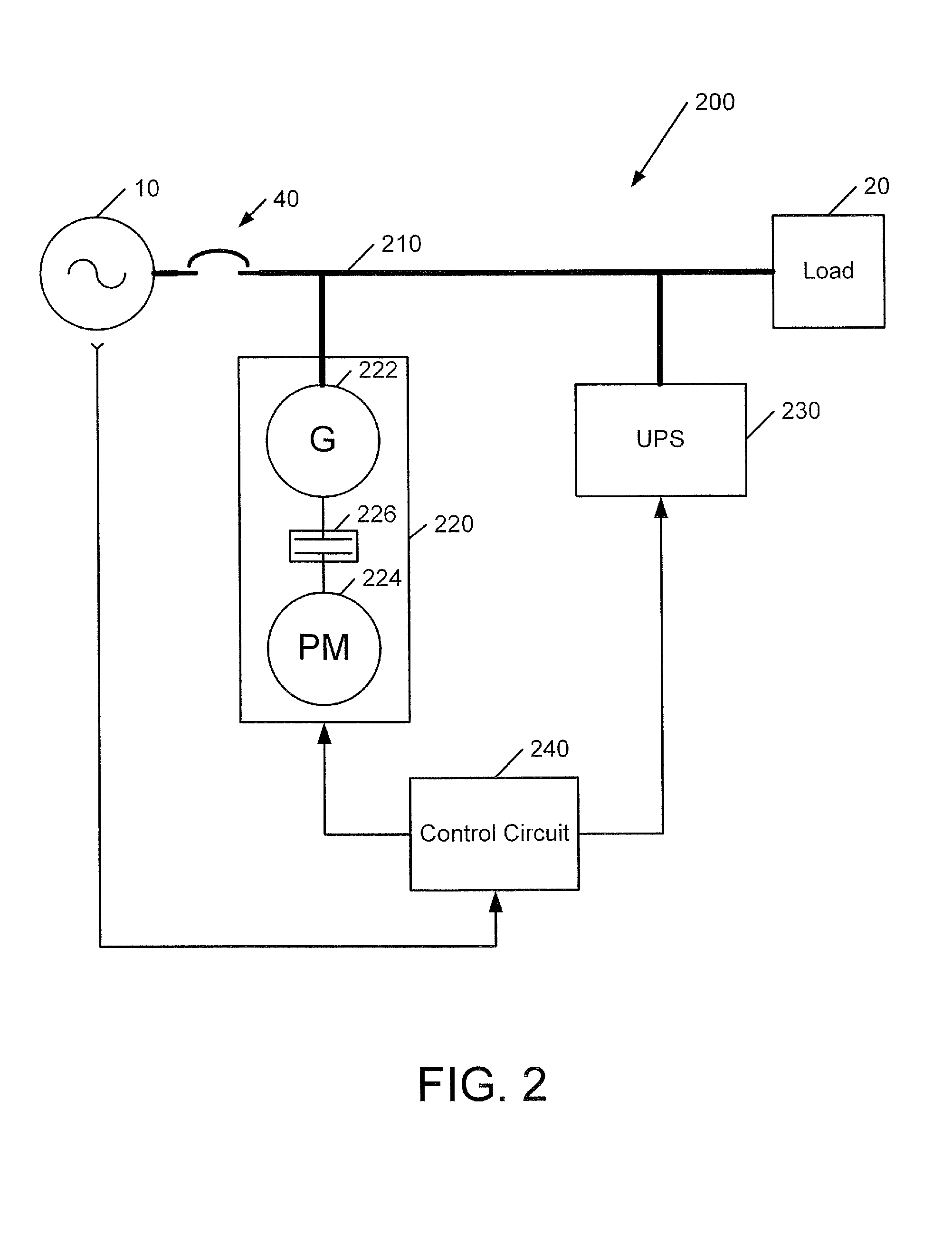
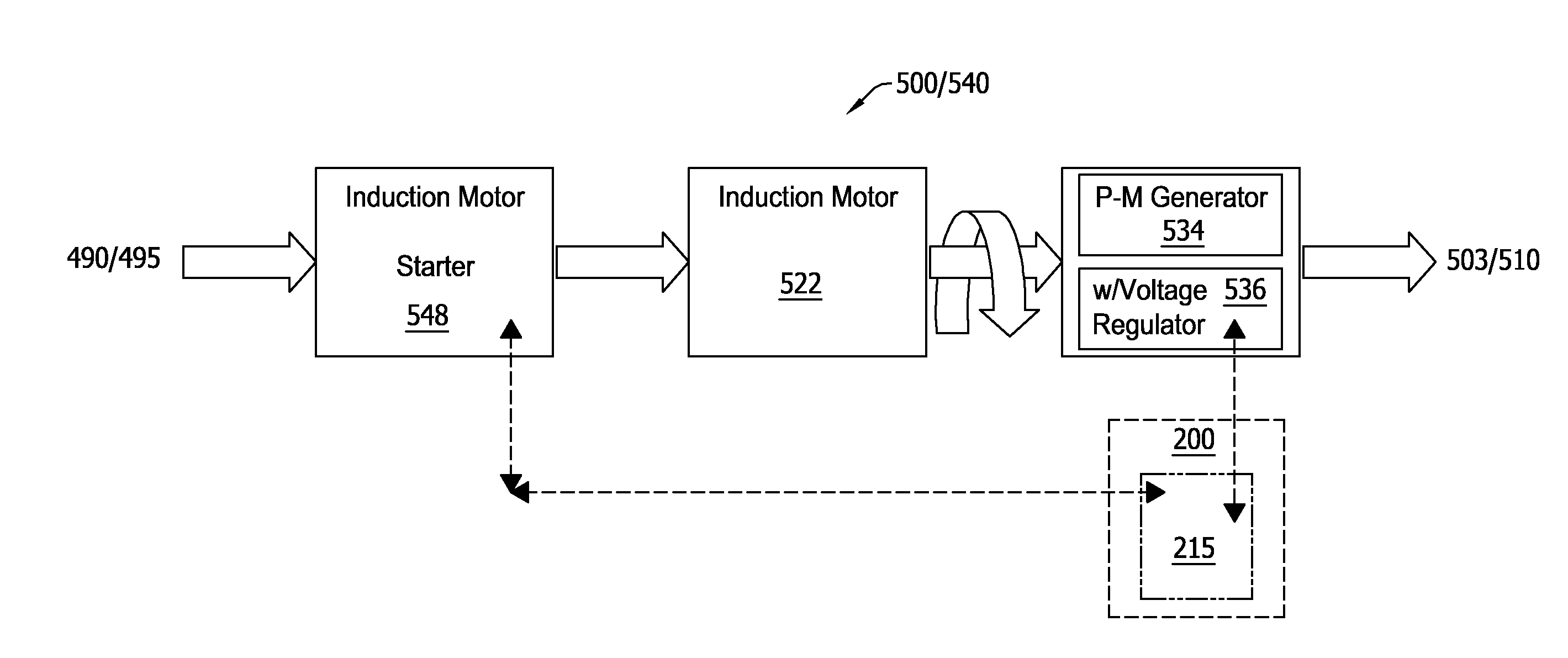
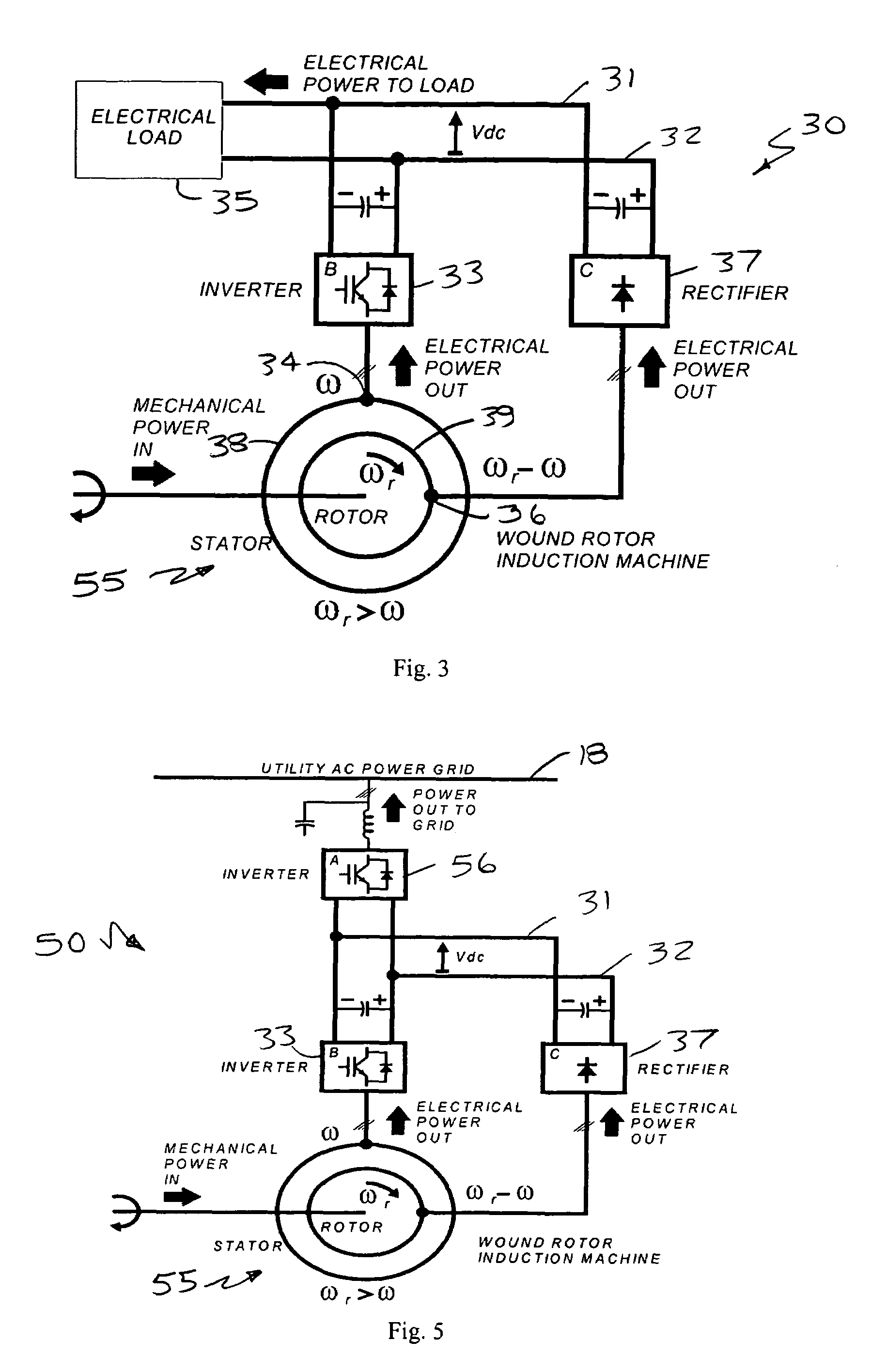
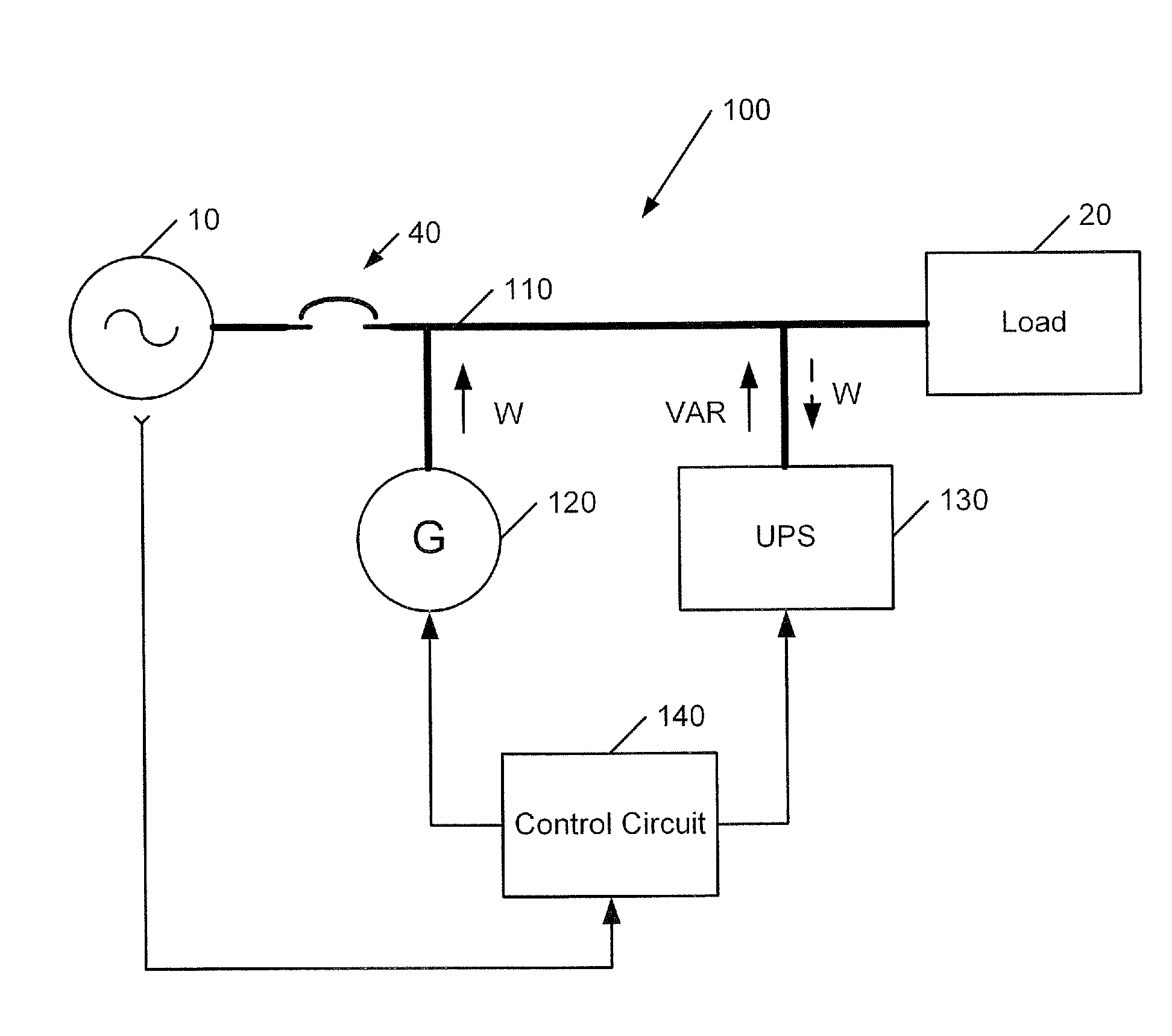
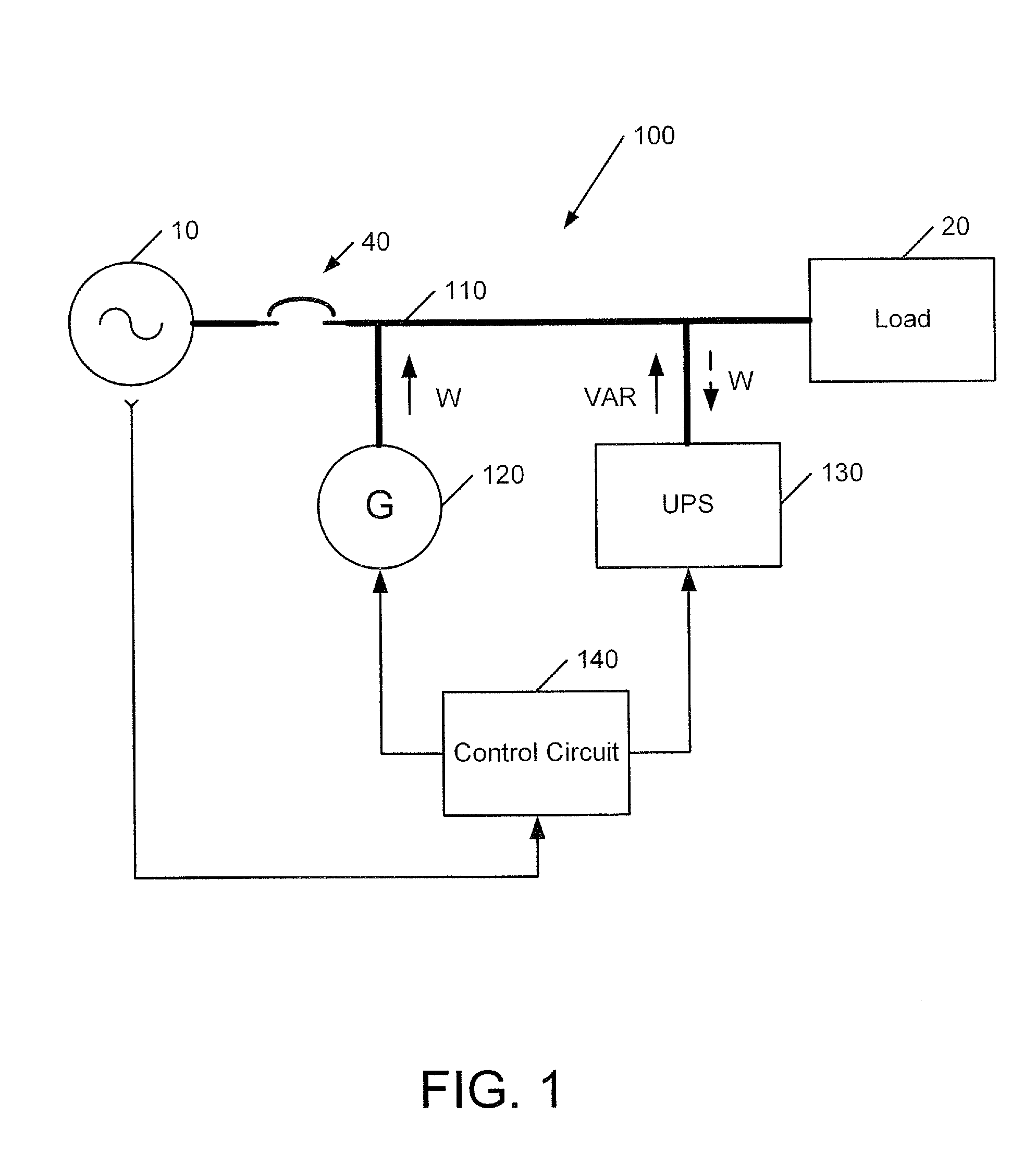
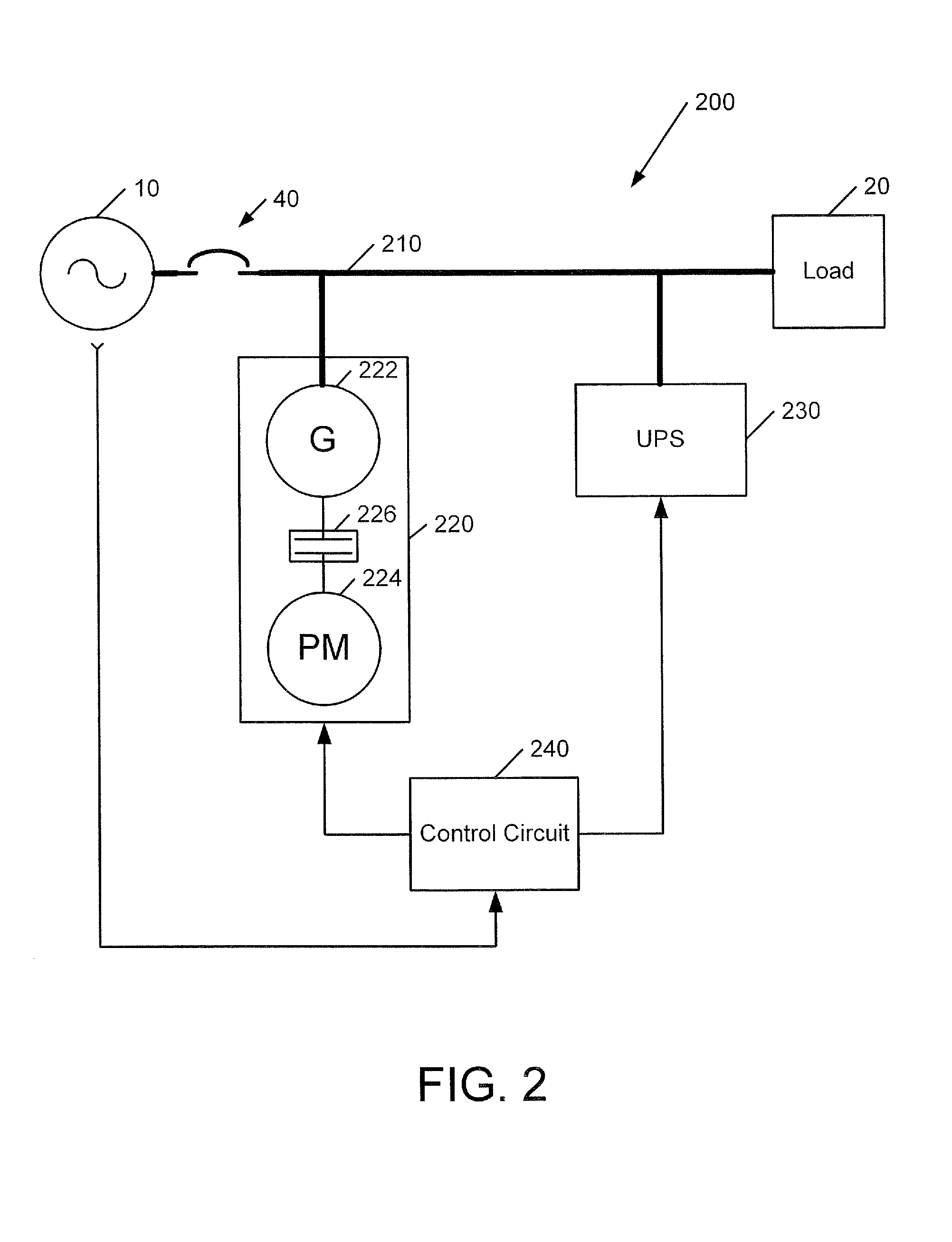
Power systems and methods using an induction generator in cooperation with an uninterruptible power supply
A power system includes a load bus configured to be connected to a power source, a generator and an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). The generator is operated as an induction generator to provide power to the load bus while providing reactive power to the load bus from the UPS. In some embodiments, prior to operating the generator as an induction generator, the generator is operated as an induction motor while the load bus is receiving power from the power source. Responsive to loss of the power source, the UPS may be used to maintain operation of the generator as an induction motor while the prime mover accelerates up to a speed sufficient to drive the generator as an induction generator.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD +1
Layered local cache mechanism with split register load bus and cache load bus
InactiveUS6405285B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationConcurrent instruction executionLoad busRelevant information
A method of improving memory access for a computer system, by sending load requests to a lower level storage subsystem along with associated information pertaining to intended use of the requested information by the requesting processor, without using a high level load queue. Returning the requested information to the processor along with the associated use information allows the information to be placed immediately without using reload buffers. A register load bus separate from the cache load bus (and having a smaller granularity) is used to return the information. An upper level (L1) cache may then be imprecisely reloaded (the upper level cache can also be imprecisely reloaded with store instructions). The lower level (L2) cache can monitor L1 and L2 cache activity, which can be used to select a victim cache block in the L1 cache (based on the additional L2 information), or to select a victim cache block in the L2 cache (based on the additional L1 information). L2 control of the L1 directory also allows certain snoop requests to be resolved without waiting for L1 acknowledgement. The invention can be applied to, e.g., instruction, operand data and translation caches.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus to maximize stored energy in UltraCapacitor Systems
InactiveUS7642755B2High energyReduce energy lossBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesLoad busVoltage reference
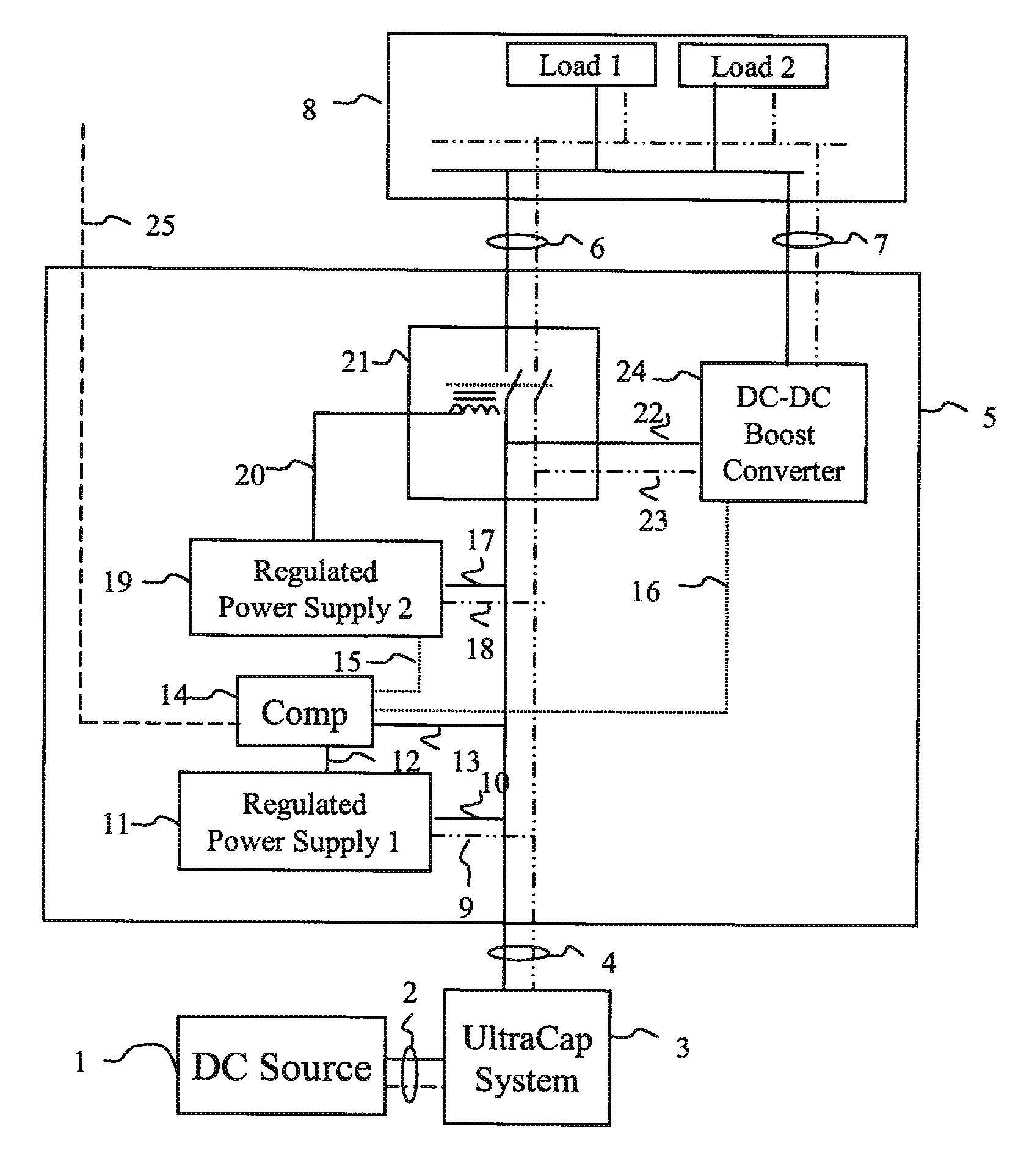
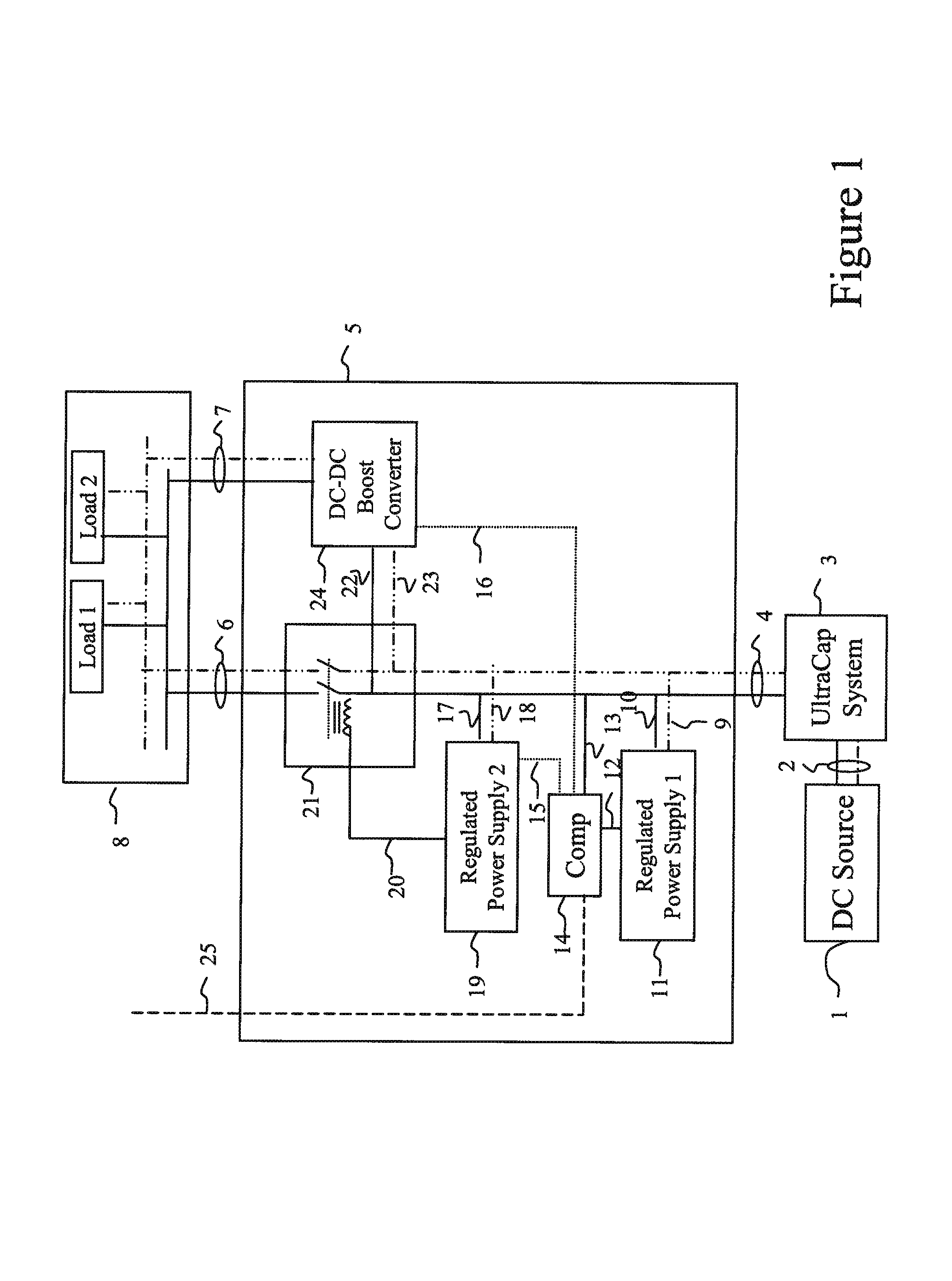
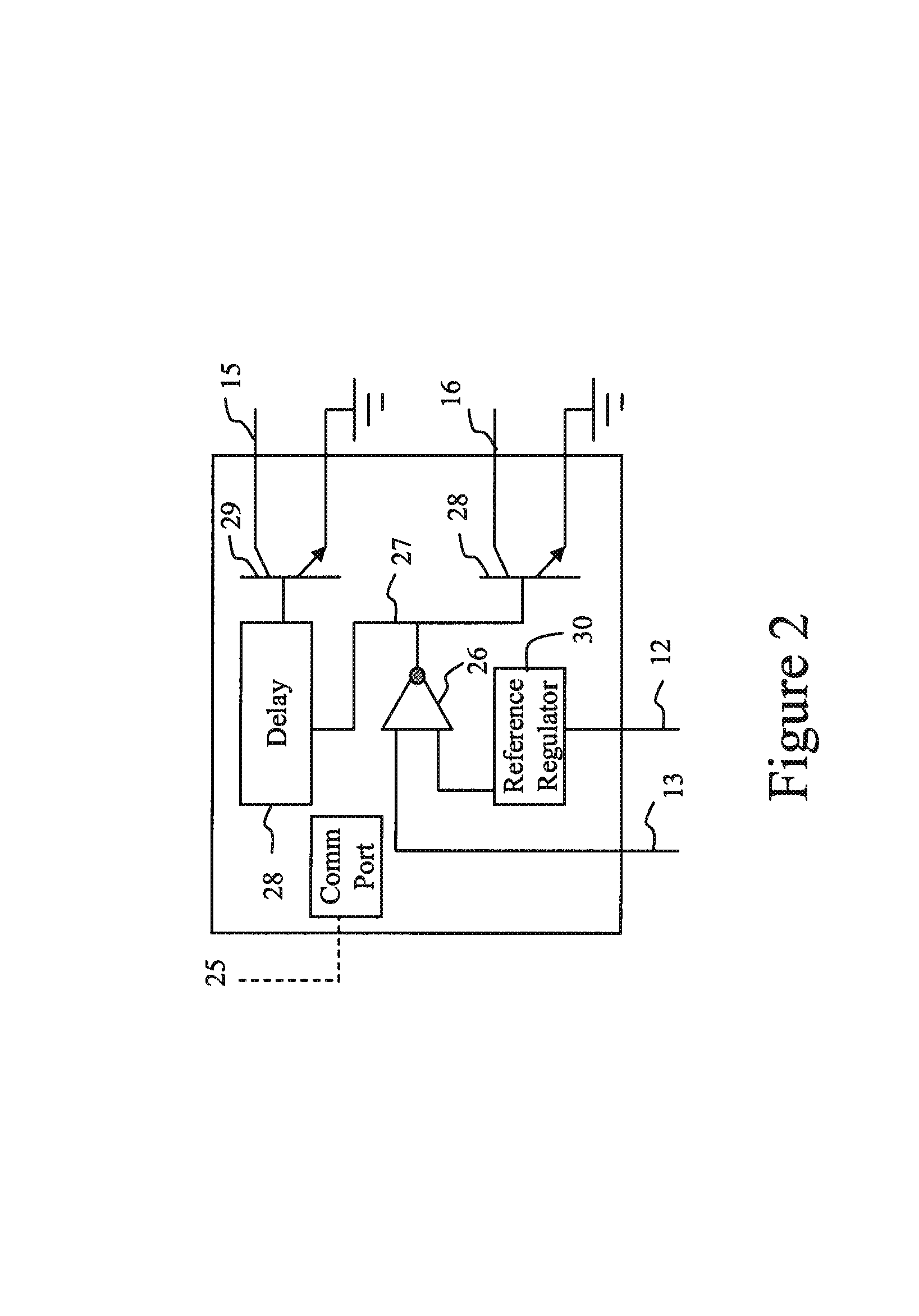
The control system for an UltraCapacitor (or “SuperCapacitor) based energy storage system consists of a relay switch, a voltage up-converting device (e.g. DC-DC converter), regulated power supplies and a comparator circuit. The comparator circuit compares the storage system output voltage with a reference voltage, causing the storage system output to be diverted through a voltage up-converting device when the said voltage has declined to a threshold value (typically set by the load requirements). Wide-input range power supplies enable consistent operation of the circuit as the UltraCapacitor system output bus voltage declines. The wide-range of input allowed by the up-converting device enables the continuance of power drain from the UltraCapacitors, i.e. more efficient use of available storage capacity, while maintaining the required output voltage to the load. Efficiency is increased by direct connection of the UltaCapacitor system to the load bus until its voltage falls below stated threshold. In the case of a given 48 VDC system electric motor application, 500% more energy is extracted from the UltraCapacitor system with the stated control system than would be permitted by the load voltage requirements without such system.
Owner:BARTILSON BRADLEY WAYNE
Queue-less and state-less layered local data cache mechanism
A method of improving memory access for a computer system, by sending load requests to a lower level storage subsystem along with associated information pertaining to intended use of the requested information by the requesting processor, without using a high level load queue. Returning the requested information to the processor along with the associated use information allows the information to be placed immediately without using reload buffers. A register load bus separate from the cache load bus (and having a smaller granularity) is used to return the information. An upper level (L1) cache may then be imprecisely reloaded (the upper level cache can also be imprecisely reloaded with store instructions). The lower level (L2) cache can monitor L1 and L2 cache activity, which can be used to select a victim cache block in the L1 cache (based on the additional L2 information), or to select a victim cache block in the L2 cache (based on the additional L1 information). L2 control of the L1 directory also allows certain snoop requests to be resolved without waiting for L1 acknowledgement. The invention can be applied to, e.g., instruction, operand data and translation caches.
Owner:IBM CORP
Auxiliary electric power system and method of regulating voltages of the same
ActiveUS20150073610A1Mechanical power/torque controlLevel controlElectric power transmissionLoad bus
An electric power system for a wind turbine includes at least one auxiliary load bus configured to transmit electric power to auxiliary equipment. The auxiliary load bus is further configured to receive electric power having a voltage within a first predetermined tolerance range. The system also includes at least one motor-generator set coupled to the auxiliary load bus. The motor-generator set is configured to receive electric power having a voltage within a second predetermined tolerance range and transmit electric power to the auxiliary load bus in the first predetermined tolerance range.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for upper level cache victim selection management by a lower level cache
InactiveUS6446166B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionLoad busRelevant information
A method of improving memory access for a computer system, by sending load requests to a lower level storage subsystem along with associated information pertaining to intended use of the requested information by the requesting processor, without using a high level load queue. Returning the requested information to the processor along with the associated use information allows the information to be placed immediately without using reload buffers. A register load bus separate from the cache load bus (and having a smaller granularity) is used to return the information. An upper level (L1) cache may then be imprecisely reloaded (the upper level cache can also be imprecisely reloaded with store instructions). The lower level (L2) cache can monitor L1 and L2 cache activity, which can be used to select a victim cache block in the L1 cache (based on the additional L2 information), or to select a victim cache block in the L2 cache (based on the additional L1 information). L2 control of the L1 directory also allows certain snoop requests to be resolved without waiting for L1 acknowledgement. The invention can be applied to, e.g., instruction, operand data and translation caches.
Owner:IBM CORP
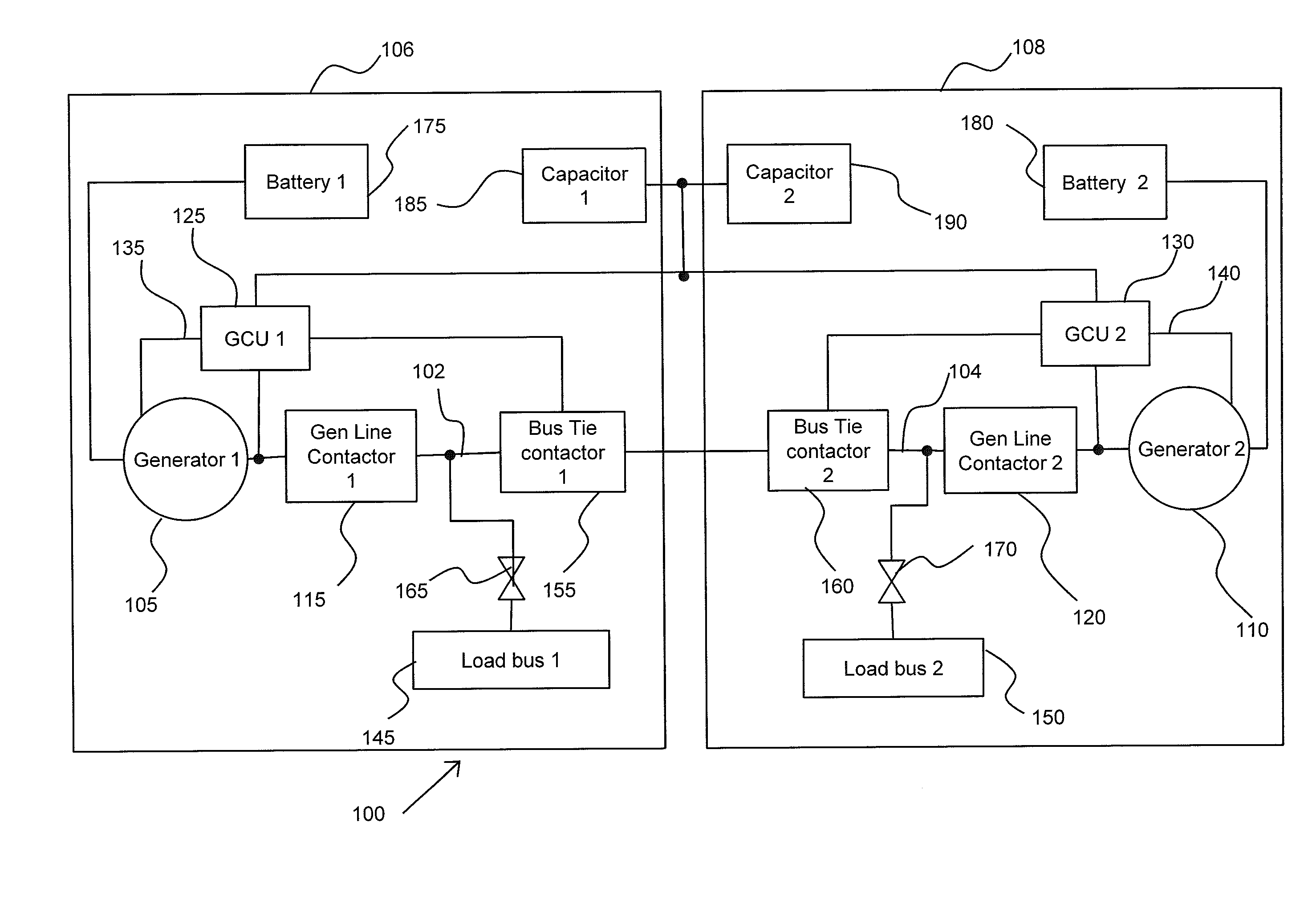
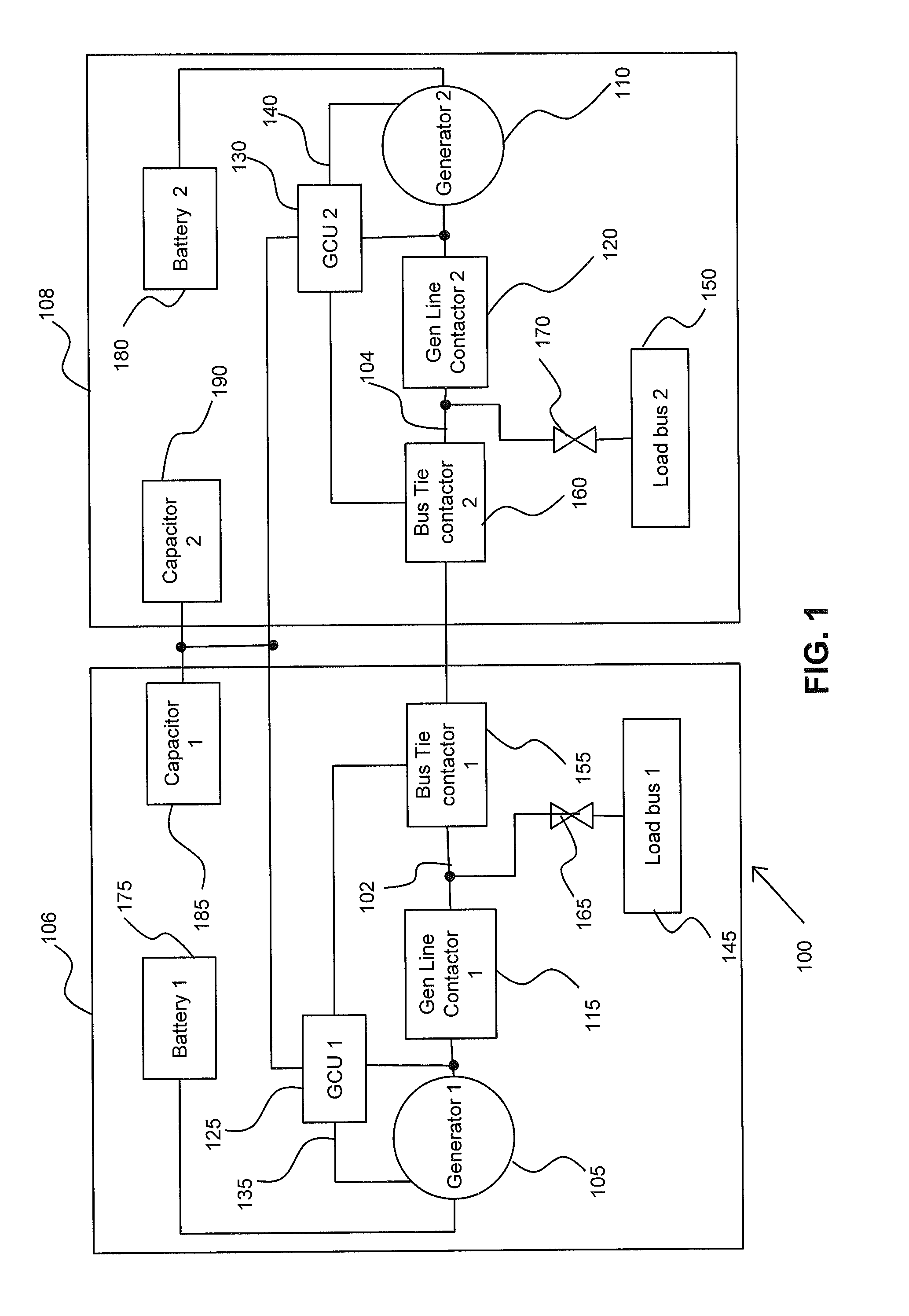
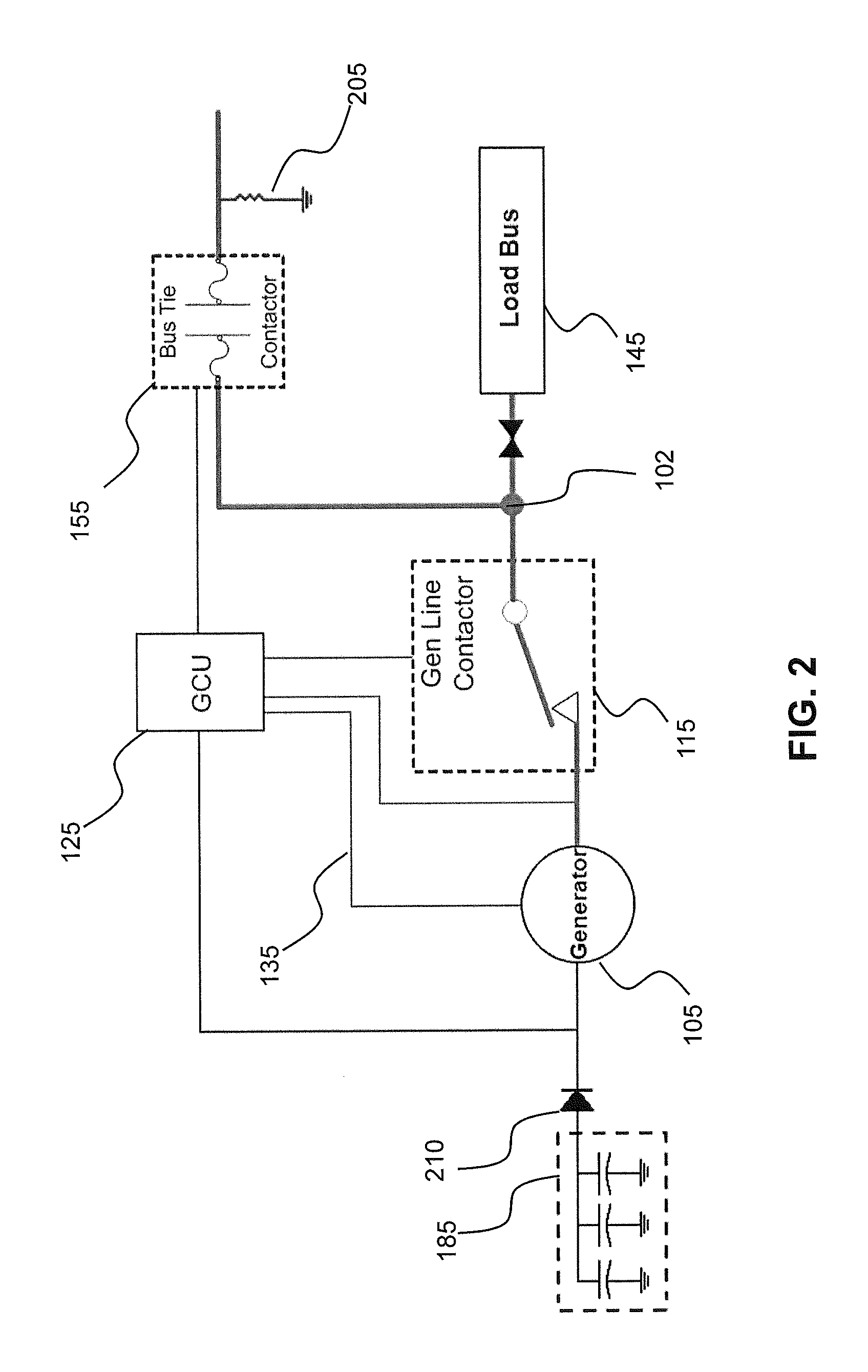
Fault clearing without a DC backup power source
ActiveUS20130215536A1Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentLoad busProtection system
An electrical power protection system, includes a generator configured for supplying Direct Current (DC) power to a load bus, the load bus in electrical communication with a bus circuit; a generator control unit being configured for regulating the output voltage supplied by the generator; a bus contactor in serial communication with the bus circuit, the bus contactor including logic circuits configured for detecting an overcurrent in the bus circuit, the overcurrent representative of a ground fault in the bus circuit; and a capacitor bank coupled to the generator for selectively supplying an excitation voltage through a diode switch to the generator during the ground fault in the bus circuit.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
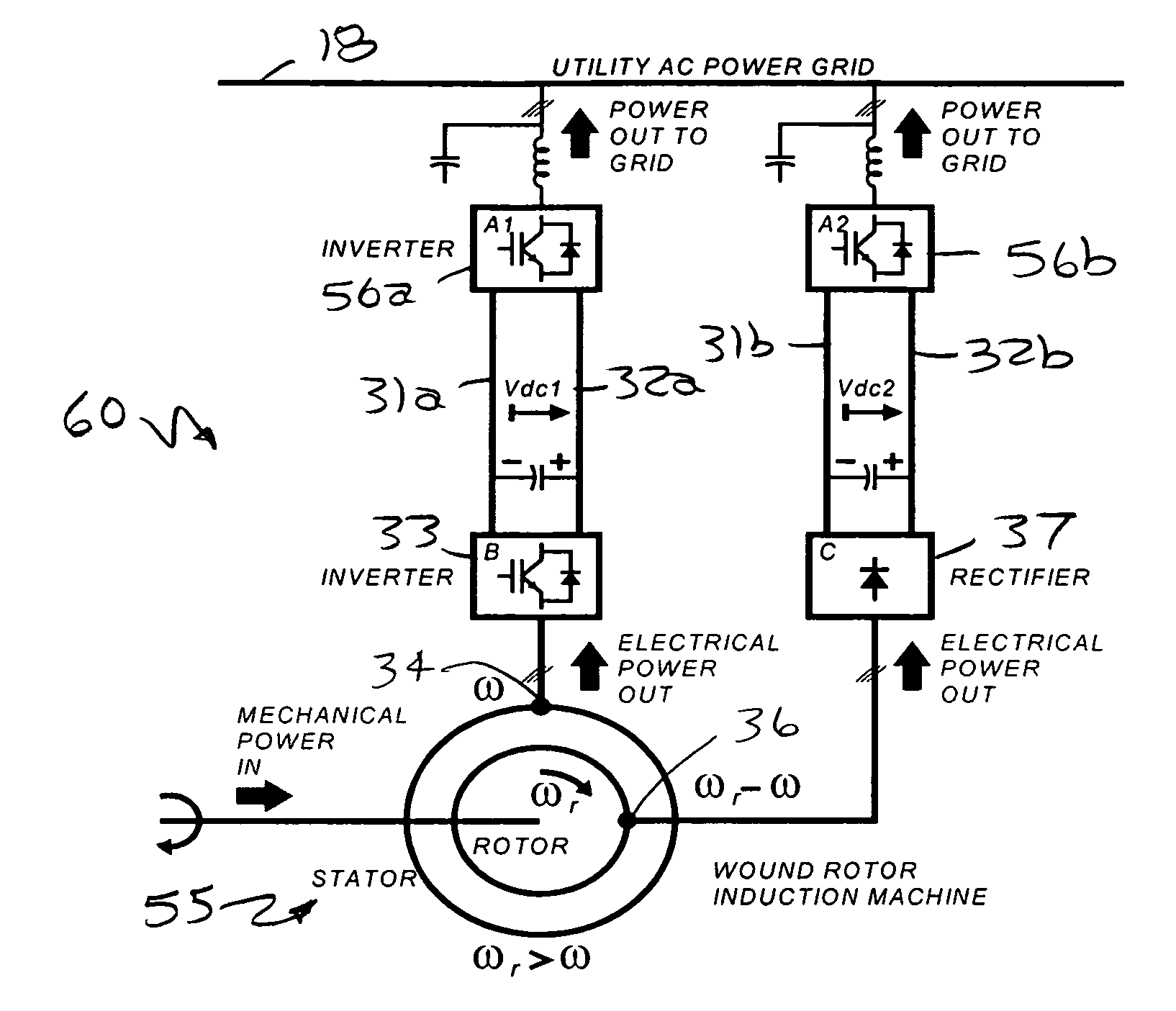
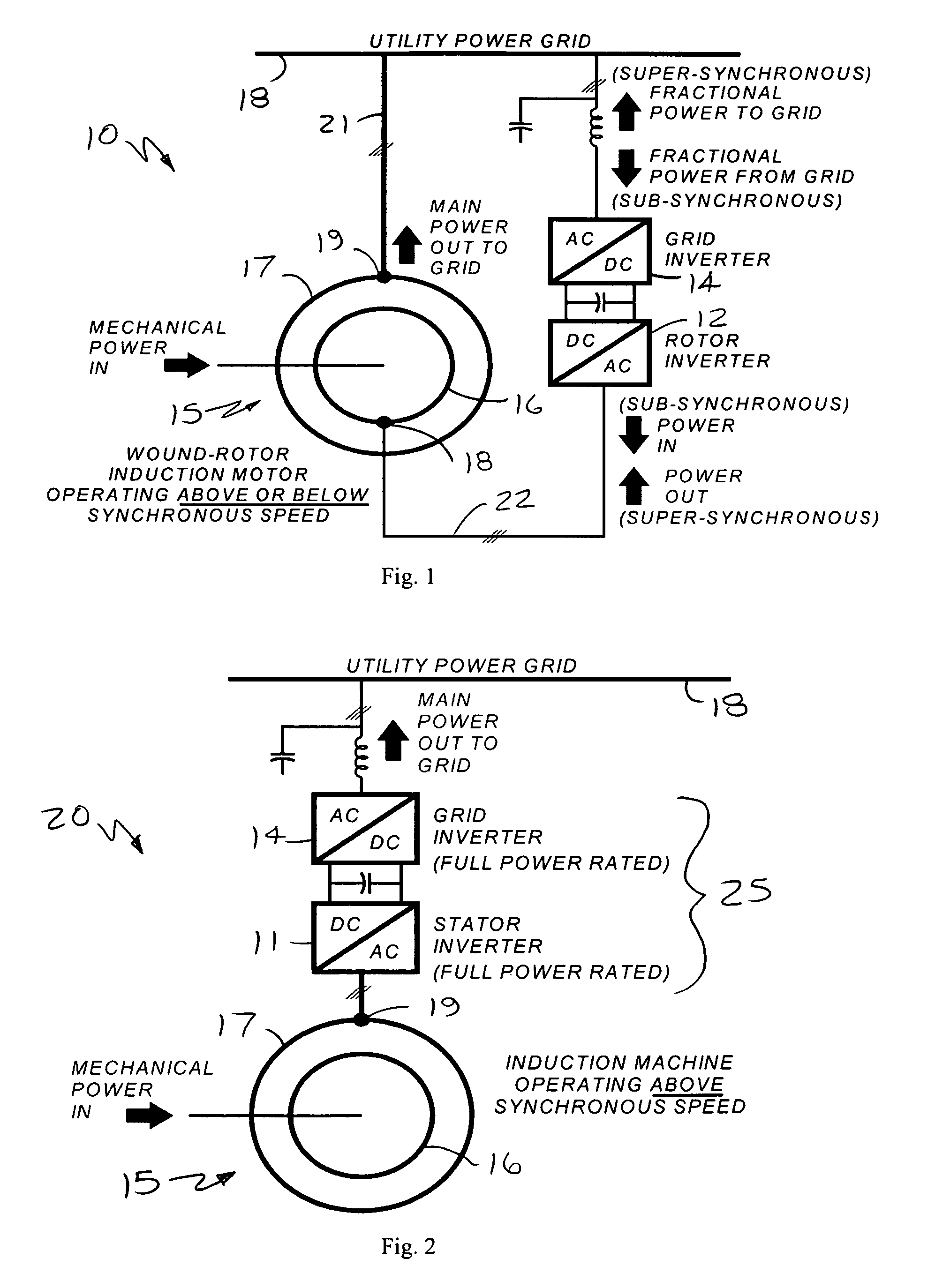
Slip-controlled, wound-rotor induction machine for wind turbine and other applications
InactiveUS7554302B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlConstant frequencyLoad bus
Owner:PERFECT GALAXY INT
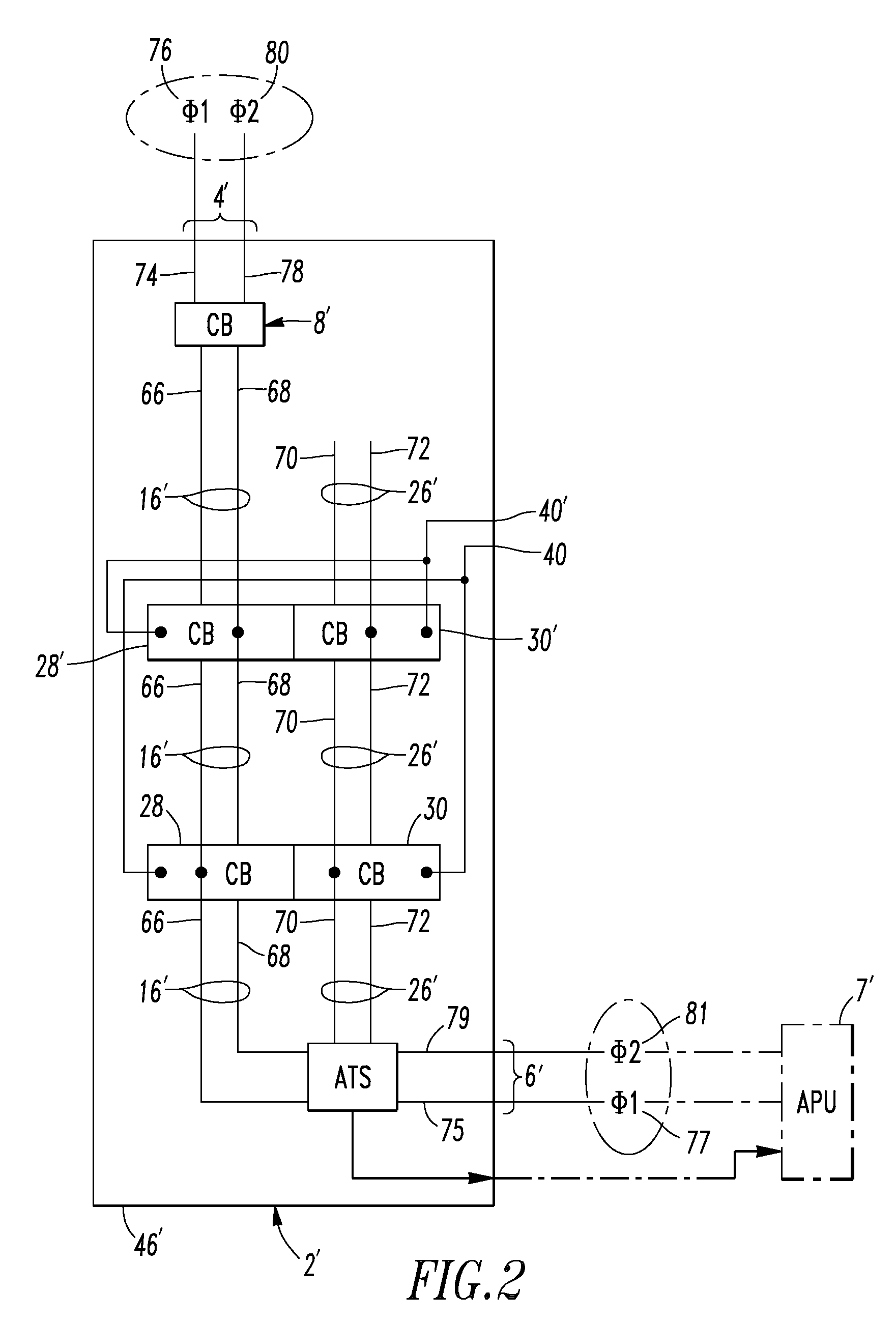
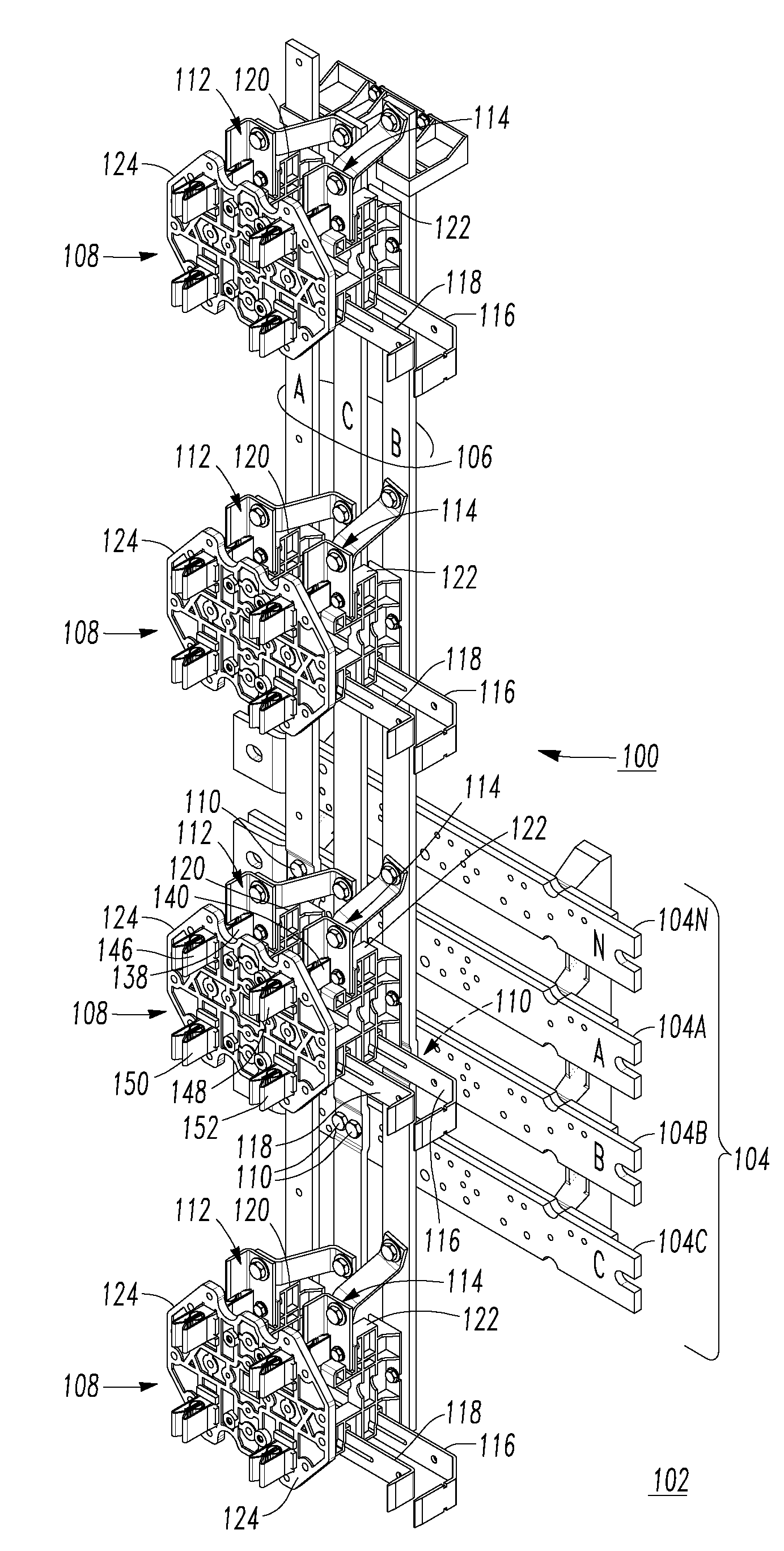
Power circuit breakers with offset vertical quick disconnect adapters to allow plugging onto a line and a load bus in different planes
InactiveUS20060002056A1Easy to installEasy to removeBus-bar/wiring layoutsSwitchgear detailsLoad busEngineering
An offset assembly for a circuit breaker includes at least one two plane member having a first plate and a second plate. The first and second plates are joined at an edge and extend generally perpendicular to each other. The second plate is structured to be coupled to the quick disconnect and the first plate is structured to be coupled to the circuit breaker terminal so that the second plate is not aligned with the centerline of the circuit breaker terminal.
Owner:EATON CORP
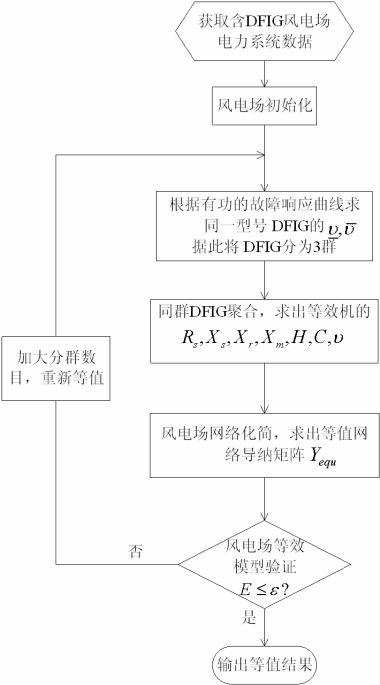
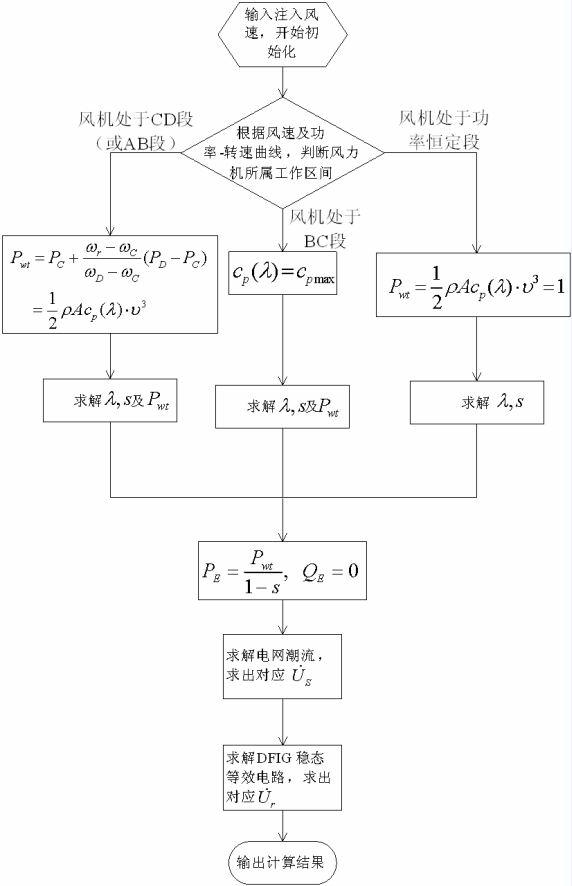
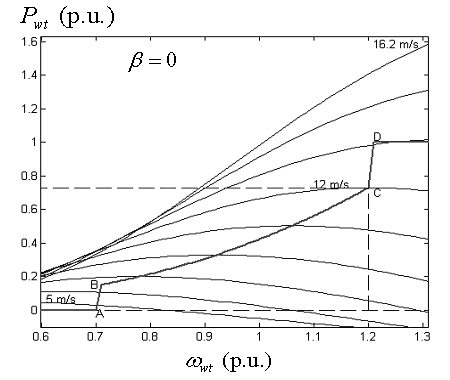
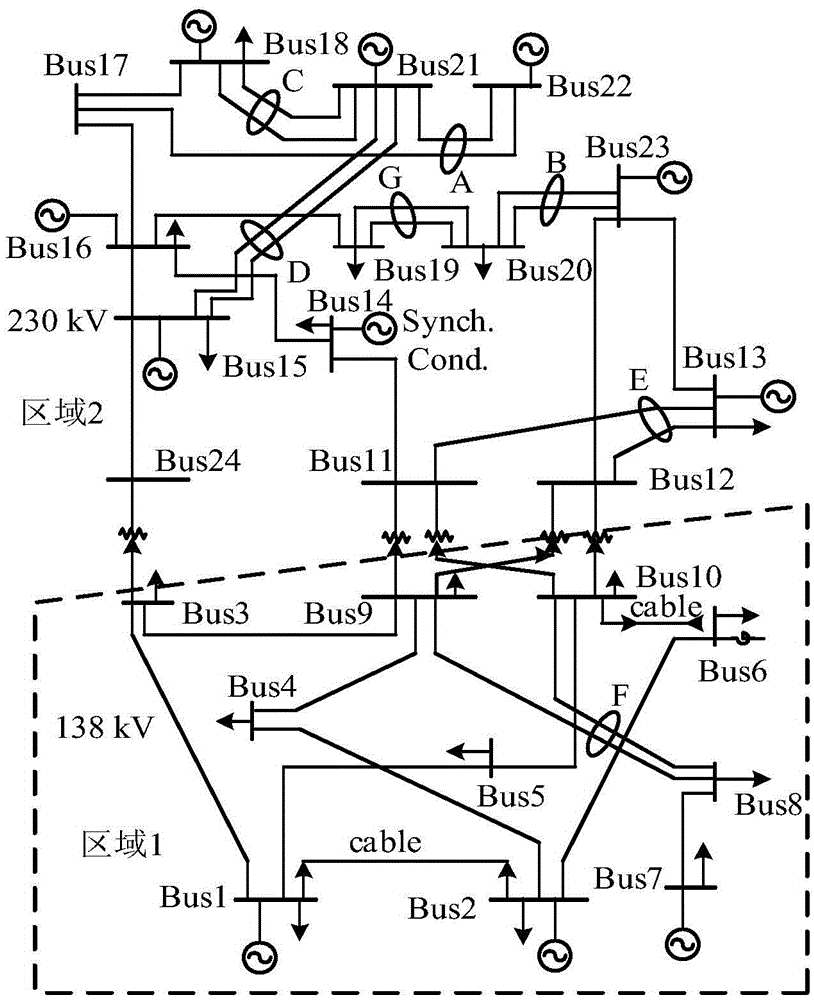
Variable-speed double-fed wind power station clustering equating method based on mechanical and electrical dynamic characteristics
InactiveCN102624309AImprove homeostasisHigh precisionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationTransient stateLoad bus
The invention discloses a variable-speed double-fed wind power station clustering equating method based on mechanical and electrical dynamic characteristics. Firstly, a system containing a wind power station is quickly initialized to determine an initial operating point. According to the types of selected double-fed wind generators and by means of offline calculation, the wind speed upper limit and the wind speed lower limit of the remarkable change of transient-state electrodynamic potential dynamic characteristics of the wind generators are determined, and the wind generators are divided into three clusters. Secondly, the double-fed wind generators in the same cluster are respectively connected to an equivalent double-fed wind generator node through a complex ratio transformer, and interbuses, load buses, transient-state internal potential buses increased during equivalent and phase shift transformers in the wind power station are eliminated to obtain an equivalent network. Thirdly, according to the connection relation of an equivalent circuit of the wind generator and the principle of unchanged output mechanical power, equivalent wind generator parameters and equivalent wind speed are deduced. The variable-speed double-fed wind power station clustering equating method comprehensively considers electromechanical dynamic similarity degree of the double-fed wind generators and is particularly suitable for accurate equivalent operation of the wind power station with complex connection and large wind speed difference.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
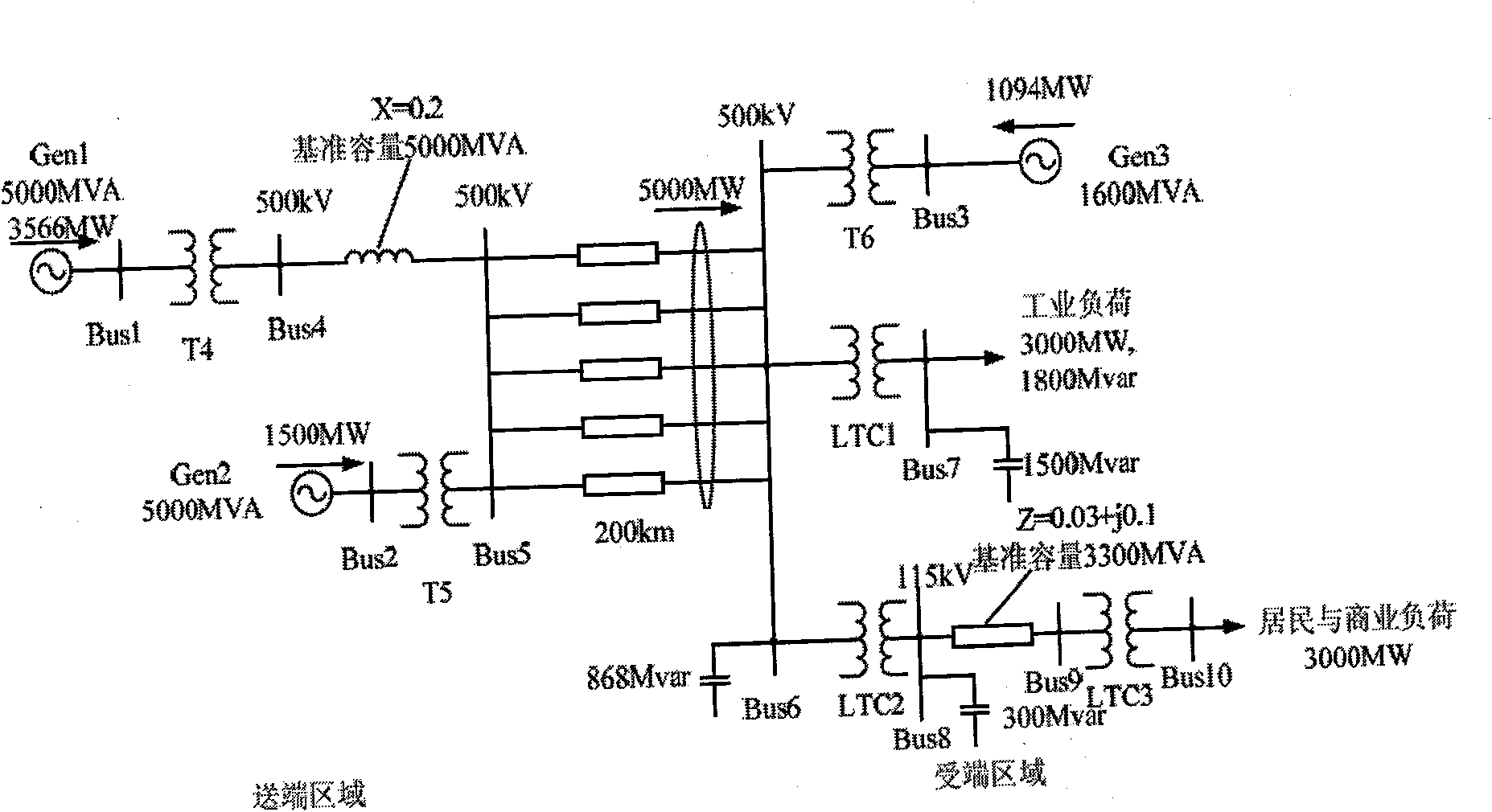
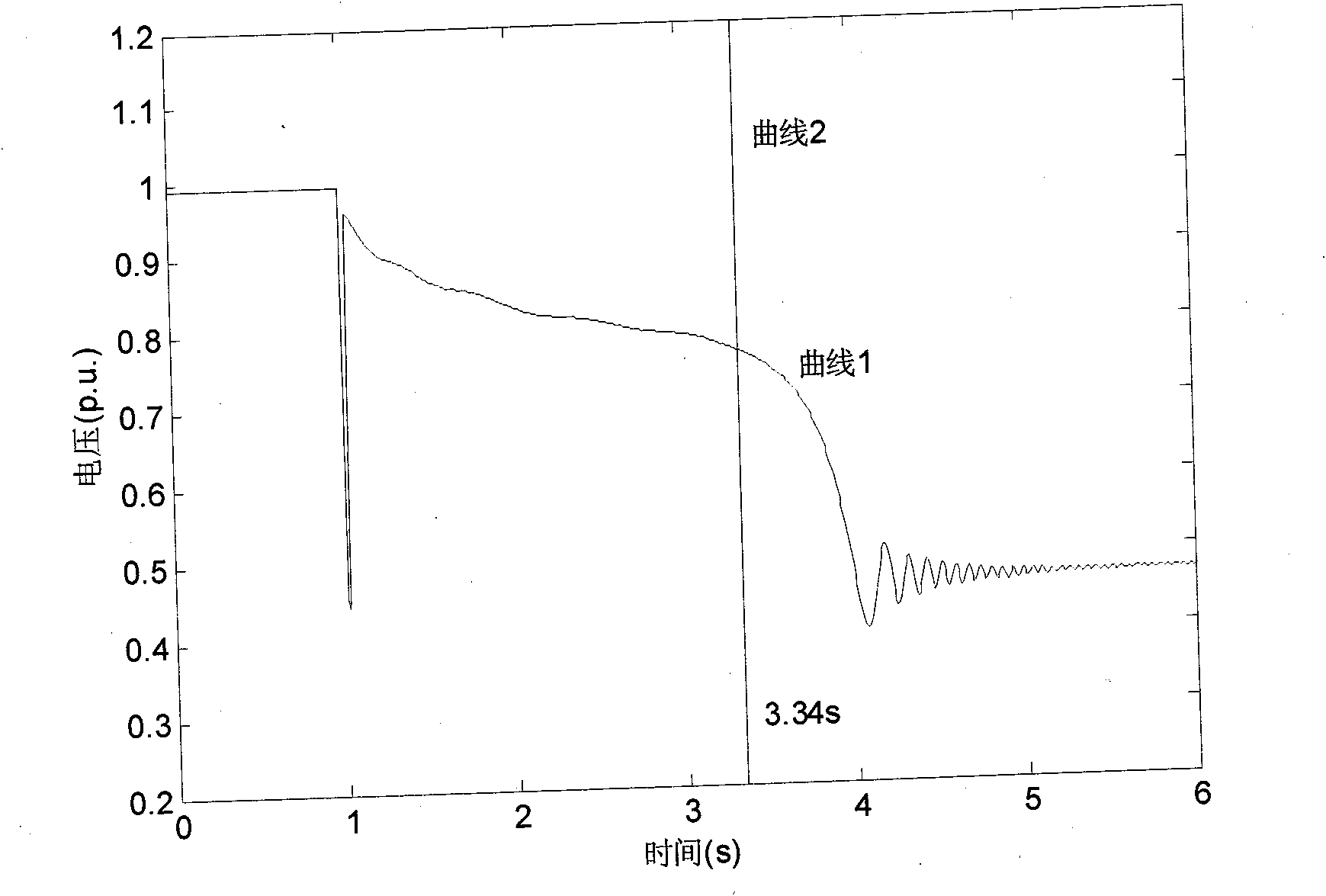
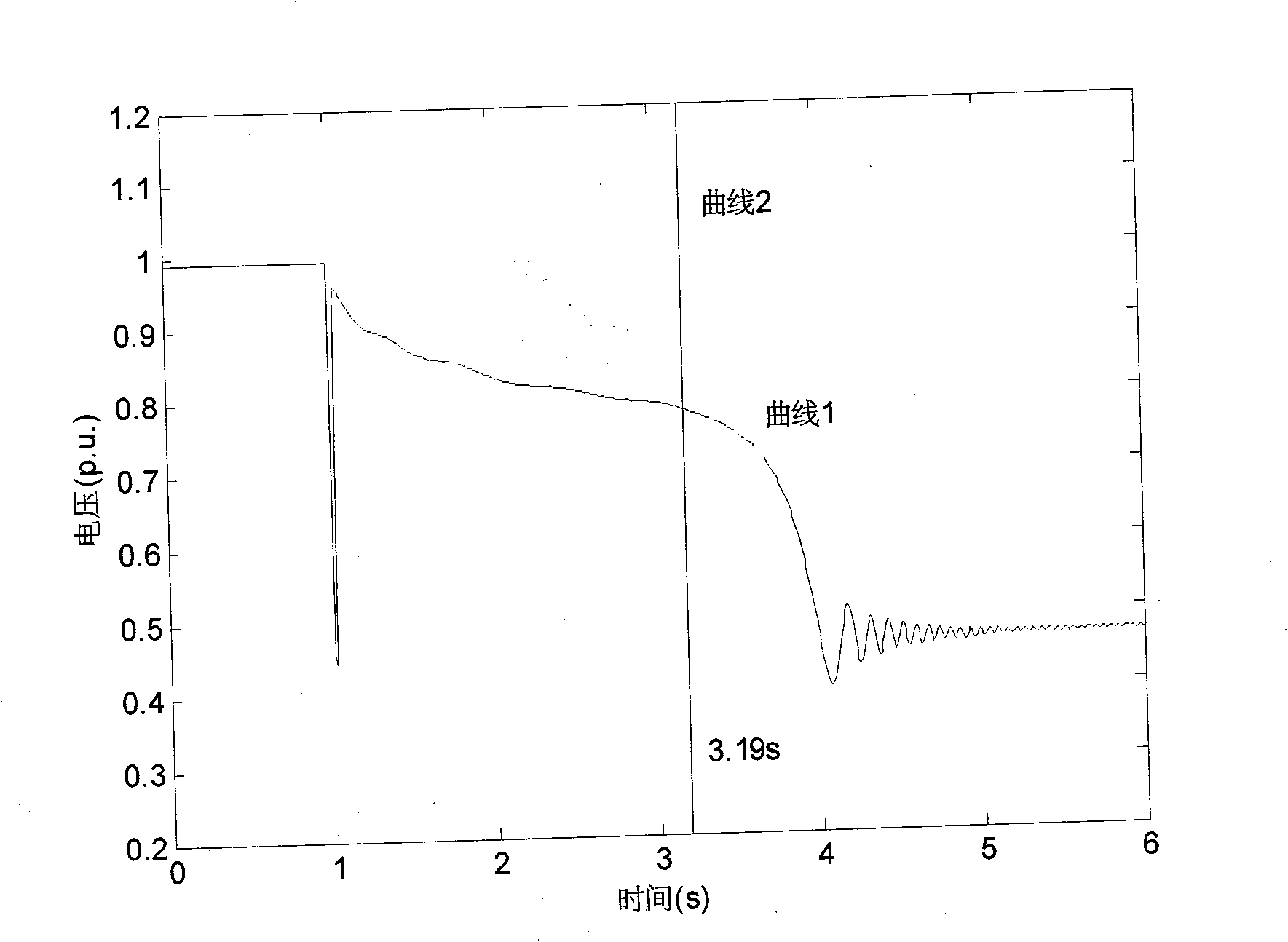
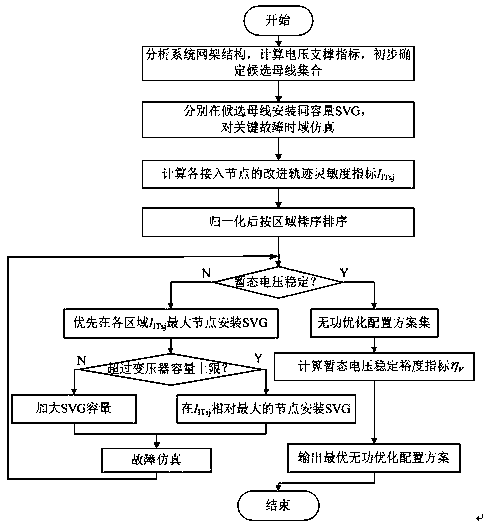
Method for judging power transmission network transient voltage stability based on area rule
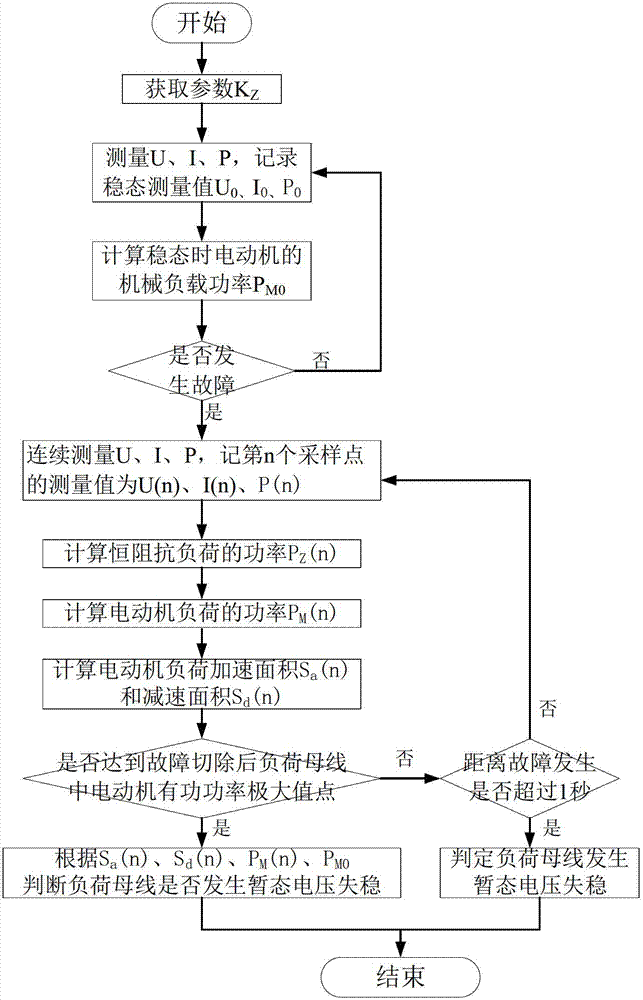
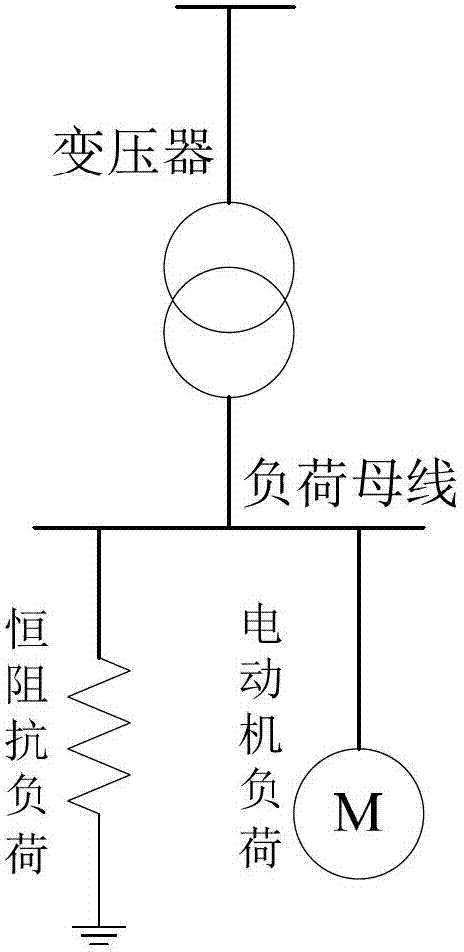
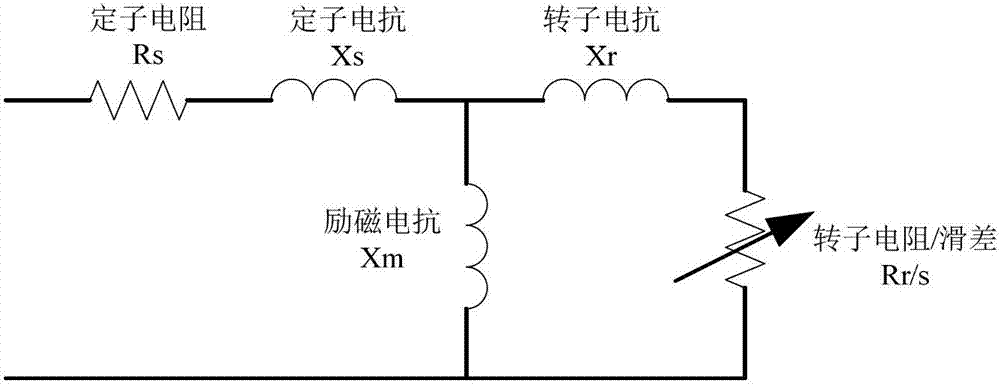
The invention relates to a method for judging power transmission network transient voltage stability based on an area rule, which belongs to the technical field of power transmission network stability control. The method for judging comprises the steps of: calculating the motor acceleration area and deceleration area according to the active power change of a motor in a disturbed load bus, and through comparing the acceleration area with the deceleration area as well as the active power after disturbing the motor with the active power before disturbing the motor, quickly judging whether the load bus has unstable transient voltage or not. The method for judging has the advantages of clear physical meaning, simplicity in realization, accurate judging and the like; and the method is applied to online real-time monitoring and control of power transmission network transient voltage stability and can accurately and quickly judge the transient voltage stability of the disturbed load bus, so that advantages can be provided for subsequent correction control.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Power circuit breakers with offset vertical quick disconnect adapters to allow plugging onto a line and a load bus in different planes
InactiveUS7173811B2Easy to installEasy to removeBus-bar/wiring layoutsSwitchgear detailsLoad busPower circuits
An offset assembly for a circuit breaker includes at least one two plane member having a first plate and a second plate. The first and second plates are joined at an edge and extend generally perpendicular to each other. The second plate is structured to be coupled to the quick disconnect and the first plate is structured to be coupled to the circuit breaker terminal so that the second plate is not aligned with the centerline of the circuit breaker terminal.
Owner:EATON CORP
High performance store instruction management via imprecise local cache update mechanism
A method of improving memory access for a computer system, by sending load requests to a lower level storage subsystem along with associated information pertaining to intended use of the requested information by the requesting processor, without using a high level load queue. Returning the requested information to the processor along with the associated use information allows the information to be placed immediately without using reload buffers. A register load bus separate from the cache load bus (and having a smaller granularity) is used to return the information. An upper level (L1) cache may then be imprecisely reloaded (the upper level cache can also be imprecisely reloaded with store instructions). The lower level (L2) cache can monitor L1 and L2 cache activity, which can be used to select a victim cache block in the L1 cache (based on the additional L2 information), or to select a victim cache block in the L2 cache (based on the additional L1 information). L2 control of the L1 directory also allows certain snoop requests to be resolved without waiting for L1 acknowledgement. The invention can be applied to, e.g., instruction, operand data and translation caches.
Owner:IBM CORP
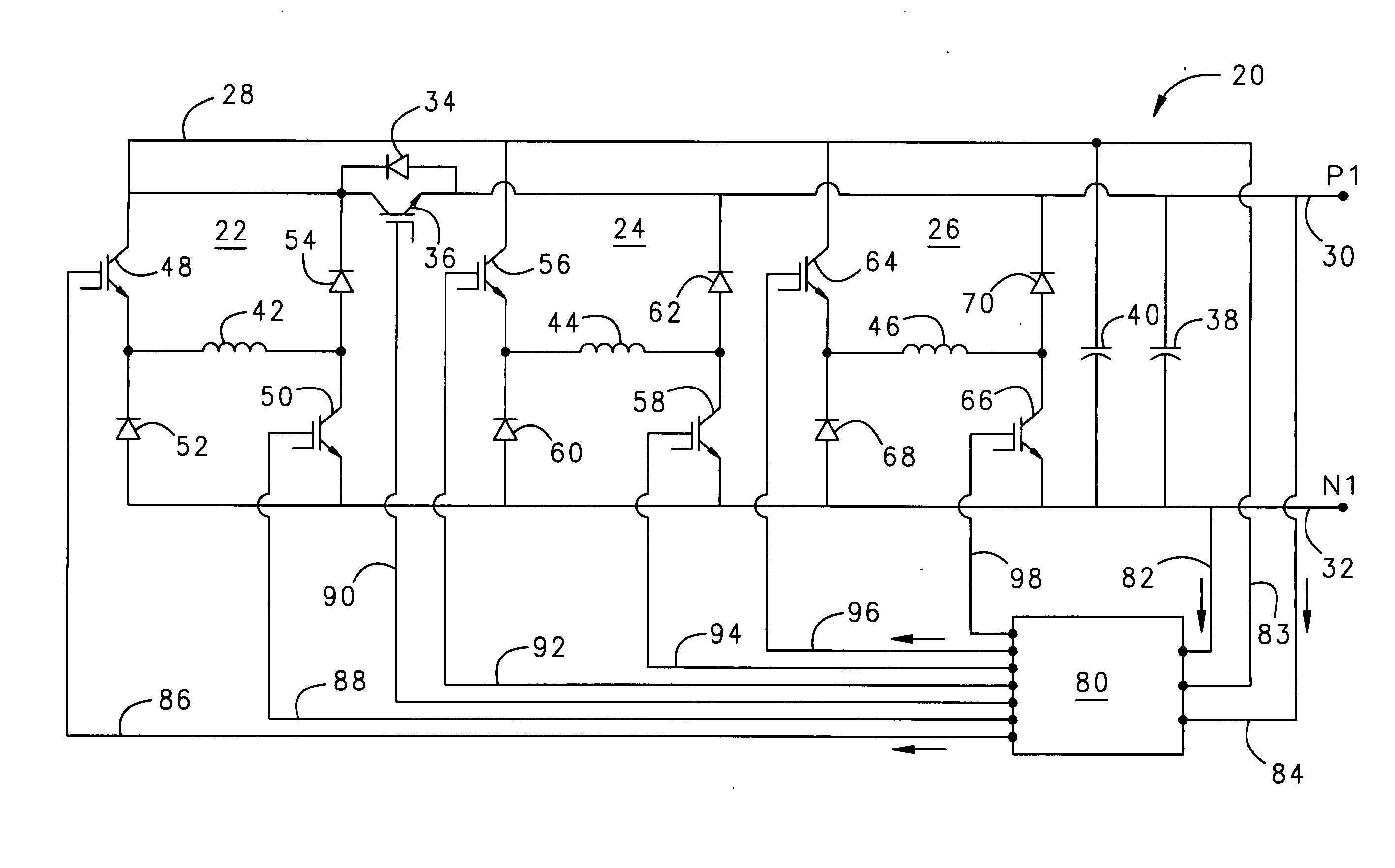
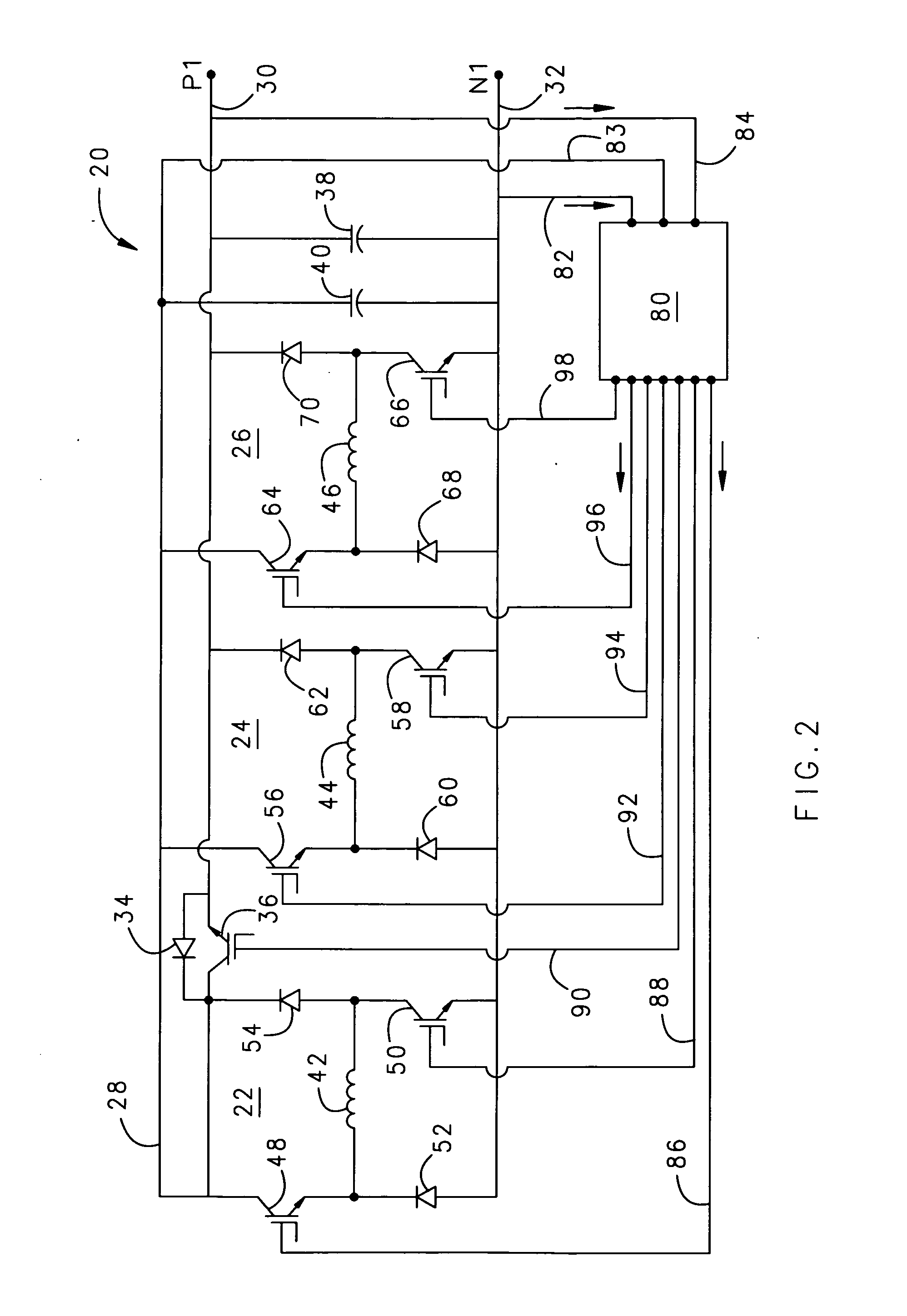
Self-excitation of switched reluctance generators during load bus faults
InactiveUS20080042611A1Reduce weightEliminate needElectronic commutation motor controlBatteries circuit arrangementsLoad busSelf excited
A self-excited, switched reluctance generator obtains excitation energy from a capacitor bank via an excitation bus during normal operation. During a short-circuit or load fault, one or more phases of the generator provide power to the excitation bus while the remaining phases send current to a faulted positive bus. The system does not require an external battery or power source for excitation energy. The system is capable of resuming normal operation after the load bus fault.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Electrical distribution panel for a number of critical and non-critical loads
InactiveUS20090225501A1Avoid positioningBatteries circuit arrangementsSubstation/switching arrangement casingsElectricityLoad bus
An electrical distribution panel includes first and second power inputs, a first circuit breaker electrically between the first power input and a first load bus, a second load bus, an automatic transfer switch having a first input electrically connected to the first load bus, a second input electrically connected to the second power input, and an output electrically connected to the second load bus. The transfer switch selectively electrically connects one of the first and second inputs to the output thereof. Pairs of circuit breakers each includes a second breaker having a first terminal electrically connected to the first load bus, and a second terminal, a third breaker including a first terminal electrically connected to the second load bus, and a second terminal, a power output electrically connected to the second terminals, and an interlock cooperating with the circuit breaker pair to prevent both of them from being closed simultaneously.
Owner:EATON CORP
Meter socket assembly employing phase balancing bus jumpers and meter center employing the same
ActiveUS7400495B1Substation/switching arrangement detailsTime integral measurementElectricityLoad bus
A meter center includes three feeder bus bars, three supply bus bars, each supply bus bar being electrically connected to a corresponding feeder bus bar, and a number of meter socket assemblies. Each meter socket assembly includes two bus jumpers, each bus jumper including a first end and a second end, the second end of a first bus jumper being selectively electrically connected to a first supply bus bar, the second end of a different second bus jumper being selectively electrically connected to a different second supply bus bar, two load bus bars, insulative support members coupled to a number of the supply bus bars, the insulative support members including a first end coupled to the bus jumpers and an opposite second end supporting the load bus bars, and a meter socket including terminals electrically connected to the first ends of the bus jumpers and to the load bus bars.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Transient state and medium and long-term voltage stability distinguishing method based on power current reversal
ActiveCN101630839AAdaptableEasy to useElectrical testingAc network circuit arrangementsTransient stateLoad bus
The invention provides a method for judging whether voltage has unstability in the transient state and medium and long-term process after an electrical power system has disturbance; if load current or current on a sending and receiving end connecting line is increased to lead a load or a receiving end system not to obtain higher power, and after the situation lasts for a period of time, the voltage of a load bus or a connecting line receiving end bus is lowered to be lower than a certain threshold value, so voltage of the load bus or the receiving end system has unstability. The method overcomes the defect that the existing method is lack of theory support and solves the problem that the accuracy of the judgment result can not be determined; the method has the characteristics of strong applicability, simple use and little calculated amount, and can be applied to the estimation and judgment for the transient state and medium and long-term voltage stability in the electrical power system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
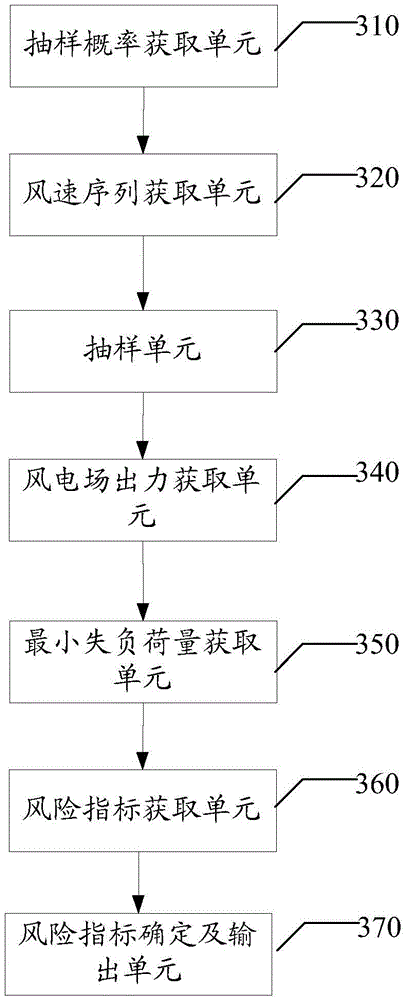
Method and system for evaluating operational risk of wind power farms in combination with weather and wind speed
The invention provides a method for evaluating operational risk of wind power farms in combination with weather and wind speed, comprising the following steps of: a, determining outage probability of equipment components under the current weather within an evaluation cycle; b, constructing a time sequence through an ARMA model and performing matrix transformation, thereby obtaining a wind speed sequence of each wind power farm; c, obtaining a system state according to the outage probability of the current weather, and performing sampling through a non-sequential Monte Carlo method; d, adding 1 to number of sampling, obtaining wind speed of each wind power farm at the current time, and calculating output of each wind power farm; e, according to output of each wind power farm, screening out a load bus meeting a preset condition, and corresponding load shedding value of the load bus, accumulating the load shedding value, and taking the accumulated value as minimum loss load quantity of the system; f, according to the minimum loss load quantity, calculating a risk indicator; g, when risk indicator variance is less than precision each time, returning back to the step d; and otherwise, outputting the risk indicator. By implementation of the method and the system provided by the invention, accuracy and reliability of evaluation of operational risk of the wind power farms can be improved, and evaluation result can be more scientific and rational, and has extensibility.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU
Power Systems and Methods Using an Induction Generator in Cooperation with an Uninterruptible Power Supply
ActiveUS20090021080A1Batteries circuit arrangementsLoad balancing in dc networkLoad busInduction motor
A power system includes a load bus configured to be connected to a power source, a generator and an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). The generator is operated as an induction generator to provide power to the load bus while providing reactive power to the load bus from the UPS. In some embodiments, prior to operating the generator as an induction generator, the generator is operated as an induction motor while the load bus is receiving power from the power source. Responsive to loss of the power source, the UPS may be used to maintain operation of the generator as an induction motor while the prime mover accelerates up to a speed sufficient to drive the generator as an induction generator.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED +1
Transient voltage control method
PendingCN110768263AMeet voltage stability requirementsSolve the problem of low discrimination of practical transient voltage evaluation indicatorsAc network voltage adjustmentReactive power compensationTransient statePower compensation
The invention discloses a transient voltage control method. The method can quantitatively evaluate transient voltage stability based on transient voltage stability margin index, and combines improvedvoltage reactive trajectory sensitivity to optimize a reactive configuration scheme of an AC / DC receiving-end power grid. The method comprises the following steps: to begin with, in combination with voltage stability requirements of a power system for a load bus and a pivot bus, limiting transient minimum voltage and steady-state recovery voltage levels, and for the idea of assigning different weights according to different drop degrees, constructing a transient voltage stability margin index based on a multi-binary table; then, proposing a voltage stability support (VSS) index for the condition of a multi-direct-current feed-in receiving-end power grid, and screening a candidate bus for reactive power compensation; then, improving the voltage reactive track sensitivity index by utilizingthe transient voltage stability margin index; and finally, providing an AC / DC receiving-end power grid dynamic reactive power optimization configuration scheme combining the improved voltage reactivepower track sensitivity and the transient voltage stability margin index.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
High performance load instruction management via system bus with explicit register load and/or cache reload protocols
A method of improving memory access for a computer system, by sending load requests to a lower level storage subsystem along with associated information pertaining to intended use of the requested information by the requesting processor, without using a high level load queue. Returning the requested information to the processor along with the associated use information allows the information to be placed immediately without using reload buffers. A register load bus separate from the cache load bus (and having a smaller granularity) is used to return the information. An upper level (L1) cache may then be imprecisely reloaded (the upper level cache can also be imprecisely reloaded with store instructions). The lower level (L2) cache can monitor L1 and L2 cache activity, which can be used to select a victim cache block in the L1 cache (based on the additional L2 information), or to select a victim cache block in the L2 cache (based on the additional L1 information). L2 control of the L1 directory also allows certain snoop requests to be resolved without waiting for L1 acknowledgement. The invention can be applied to, e.g., instruction, operand data and translation caches.
Owner:IBM CORP
Spacecraft reconfigurable power supply system architecture
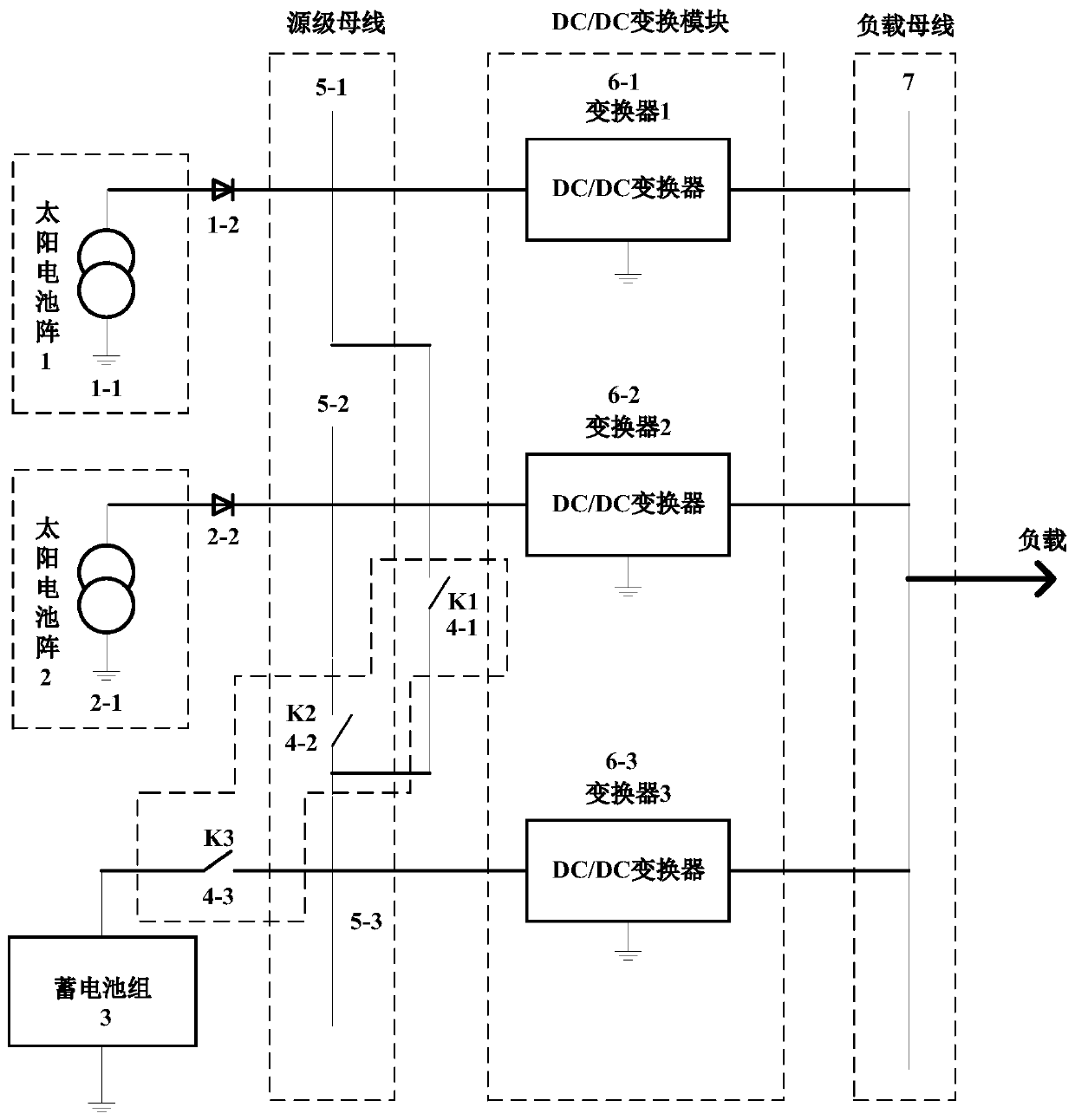
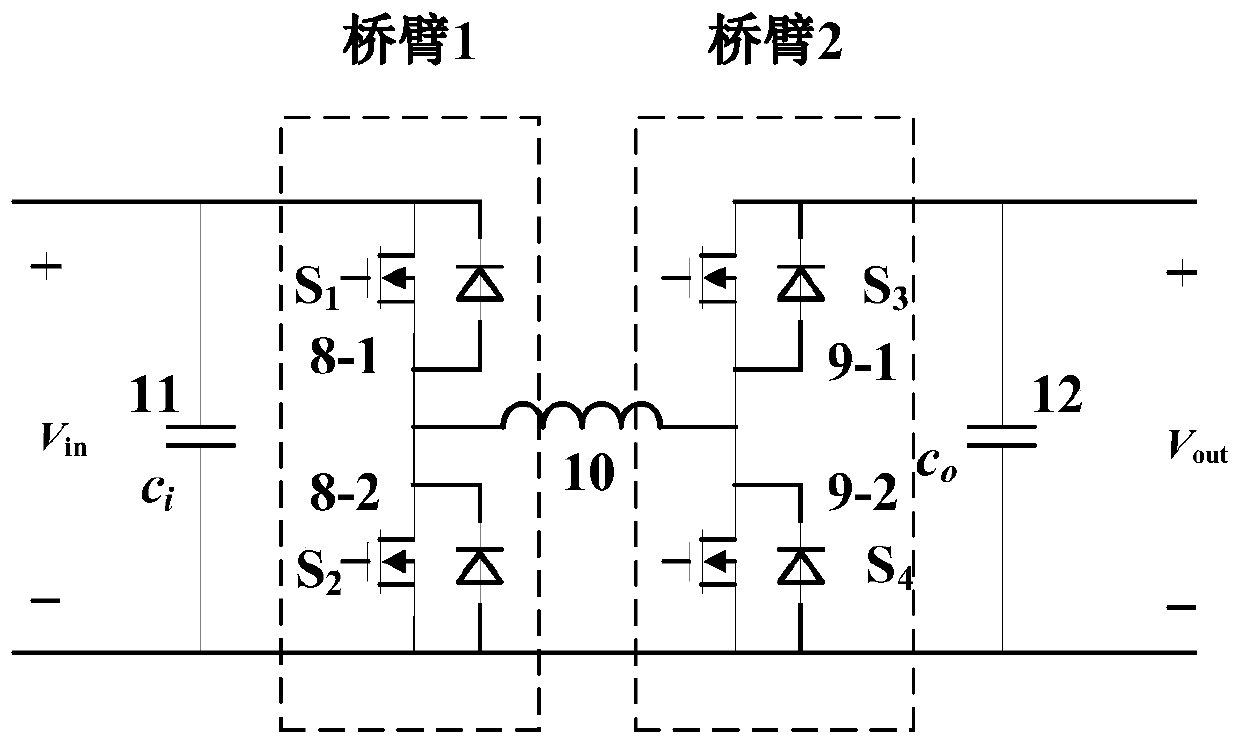
ActiveCN110148995AFlexible structureHigh specific powerBatteries circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionEngineeringSolar cell
The invention provides a spacecraft reconfigurable power supply system architecture comprising a solar cell array, a storage battery pack, a source bus, a function switch module, a DC / DC converter module and a load bus. The solar cell array and the storage battery pack are taken as a source electrode and are connected to a segmented source busbar through the function switch module, and the sourcebus is connected to the load bus through the DC / DC converter module to realize energy conversion. The DC / DC converter has the ability to reconstitute a MPPT module, a battery charging module, a battery discharging module and other functional modules, the switching of various working modes of a power supply system is carried out the function switch module and a reconstruction algorithm, the defectsof fixed module, non-variable function and large system of a traditional spacecraft power system module are solved, and the power system output capability upgrade, energy expansion upgrade, fault reconfiguration and modular design are achieved. The architecture is simple and flexible and has high reliability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPACE POWER SOURCES
Method for identifying candidate prevention and control measure of self-adaptive external-environmental electric power system
InactiveCN101976827ASatisfy securityFulfil requirementsTesting/monitoring control systemsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLoad busEnvironmental effect
The invention relates to a method for identifying the candidate prevention and control measure of a self-adaptive external-environmental electric power system, which is applicable to dynamically identifying plant stations and electric power equipment influenced by disasters, judging the prevention and control measure losing or recovering the regulating capability and having the changed regulatingrange or cost and online dynamically adjusting the usable control measure of prevention and control aid decision making and the regulating range and the control cost thereof. The candidate preventionand control measure integrates two tasks of online automatic identification comprising the identification of the plant stations and the equipment influenced by the disasters and adjustment of prevention and control measure spaces, i.e. the plant stations and the equipment (containing load buses) influenced by external environments are online dynamically and quantitatively evaluated according to the information, such as the probability of transmission line faults caused by the disasters and the like, and then the regulating range and the regulating cost of the measure are automatically corrected according to the influenced conditions of the equipment, so that the prevention and control results are adapted to the real-time external environments, and the feasibility and the economical property of the aid decision making are ensured.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGXI ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
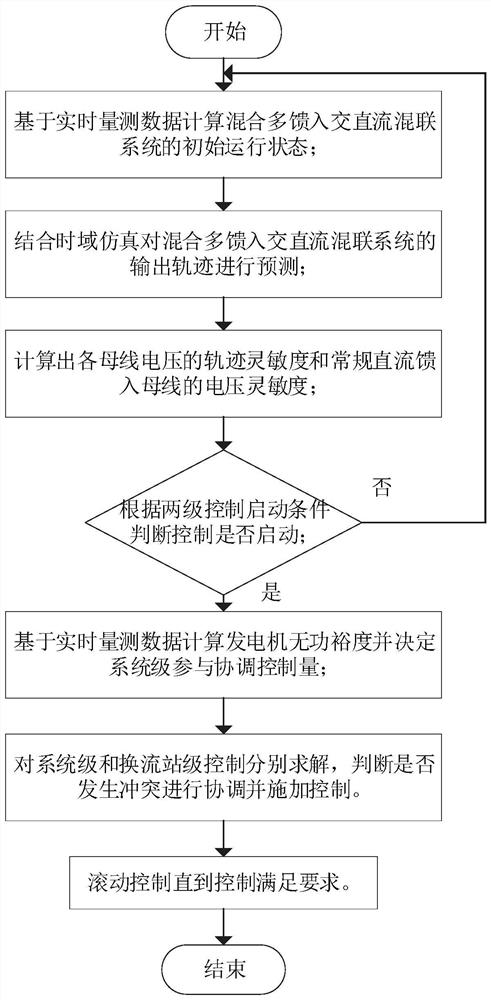
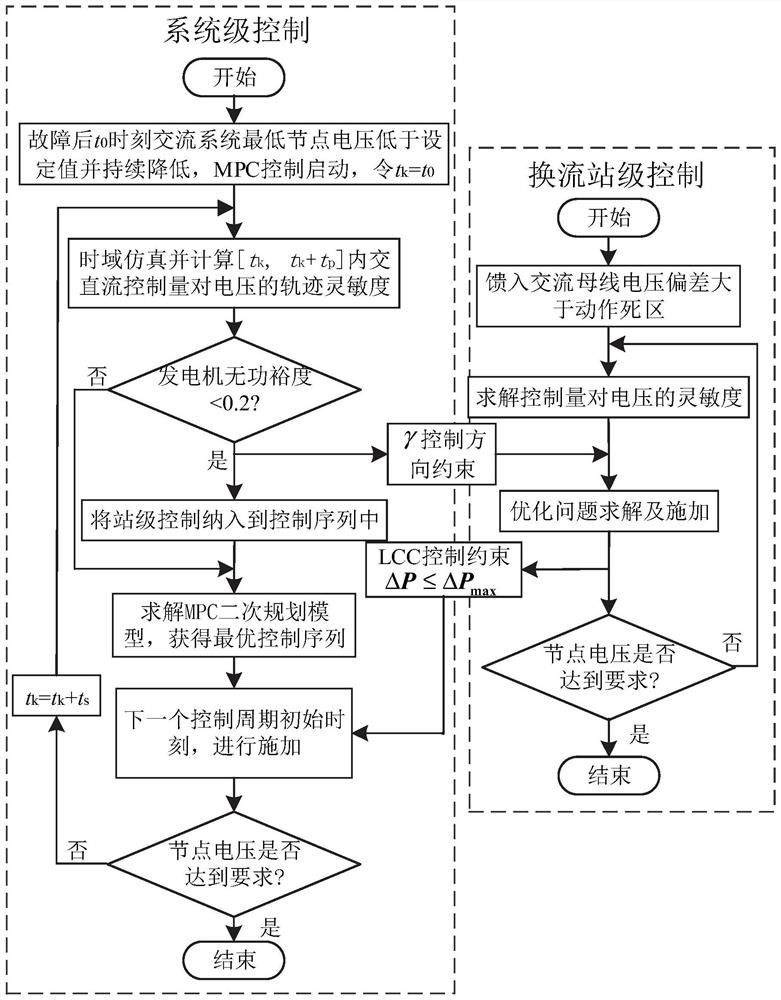
Hierarchical coordination voltage control method and system for hybrid multi-infeed AC/DC hybrid system
ActiveCN111682571AIncrease controllable marginImprove medium and long-term voltage stabilityElectric power transfer ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsLoad busHybrid system
The invention provides a hierarchical coordination voltage control method and system for a hybrid multi-infeed AC / DC hybrid system. The method comprises the following steps: 1, calculating the track sensitivity of each bus voltage and the voltage sensitivity of each control quantity to a direct-current feed-in bus; 2, judging whether system-level control and converter station-level control are started or not; 3, calculating the reactive power margin of the generator based on the wide-area measurement data, and determining whether the system-level participation coordination control quantity comprises a converter station-level control quantity or not; 4, optimizing and solving a corresponding optimal control sequence of voltage stability coordination control; 5, judging whether the control quantities in the two-stage optimal control sequences of the system and the converter station conflict or not, if yes, selecting the control quantities according to a coordination control rule for application, detecting whether the load bus voltage meets a preset requirement or not after application, and if yes, exiting coordination control; otherwise, repeating the steps 1-5 until the voltage of the load bus meets the preset requirement. And the medium-and-long-term voltage stability of the system can be improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com