Patents
Literature
4417 results about "Voltage variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Voltage variation, relates to variation(change) of voltage magnitude when load changes from no load to full load(balanced loading), means it relates to voltage regulation((E-V)/V%). Voltage imbalance, relates to, change in voltage, with imbalance of load, in magnitude or phase(of three phase respect to standard rated, supply and phase(120 degree)),...
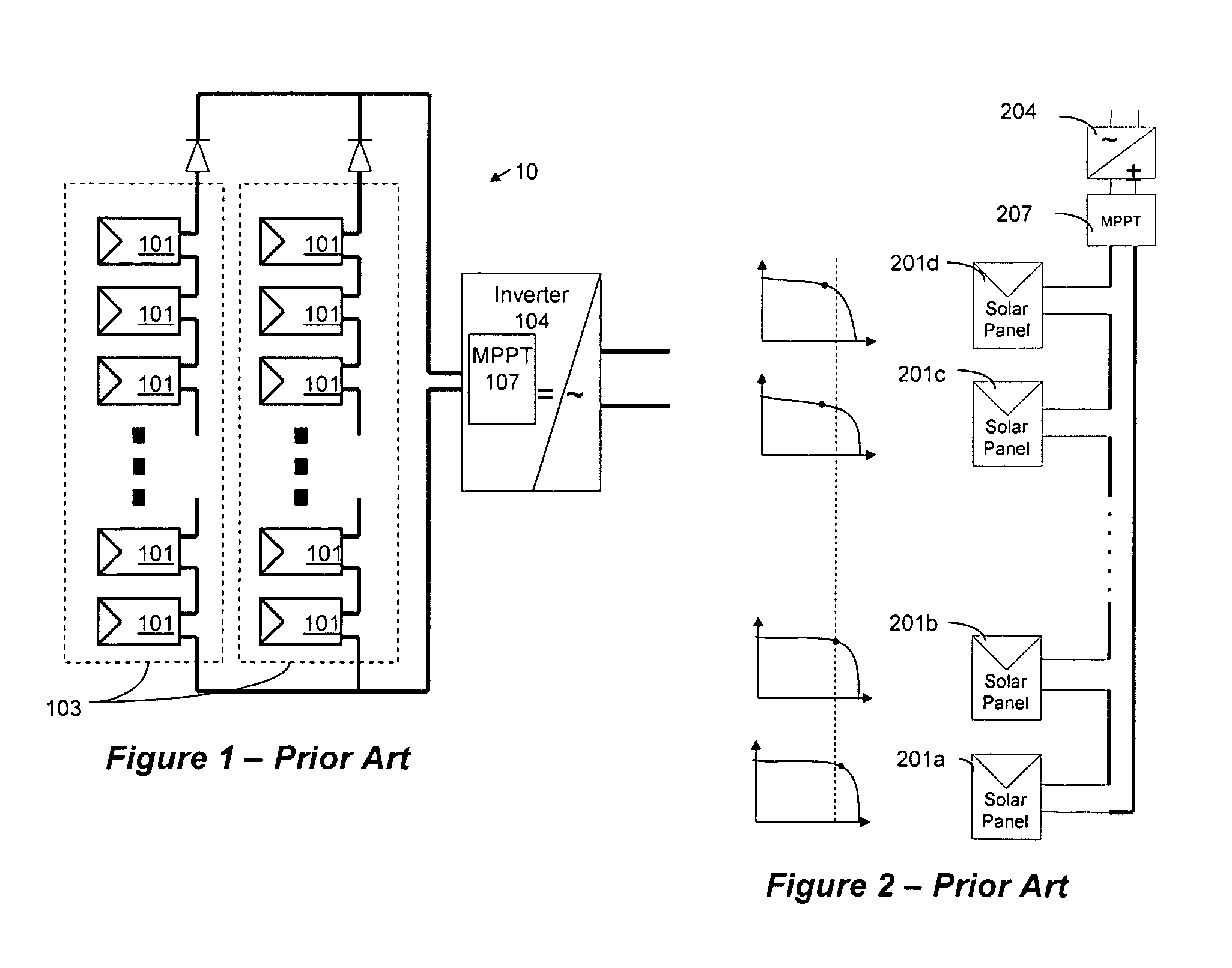
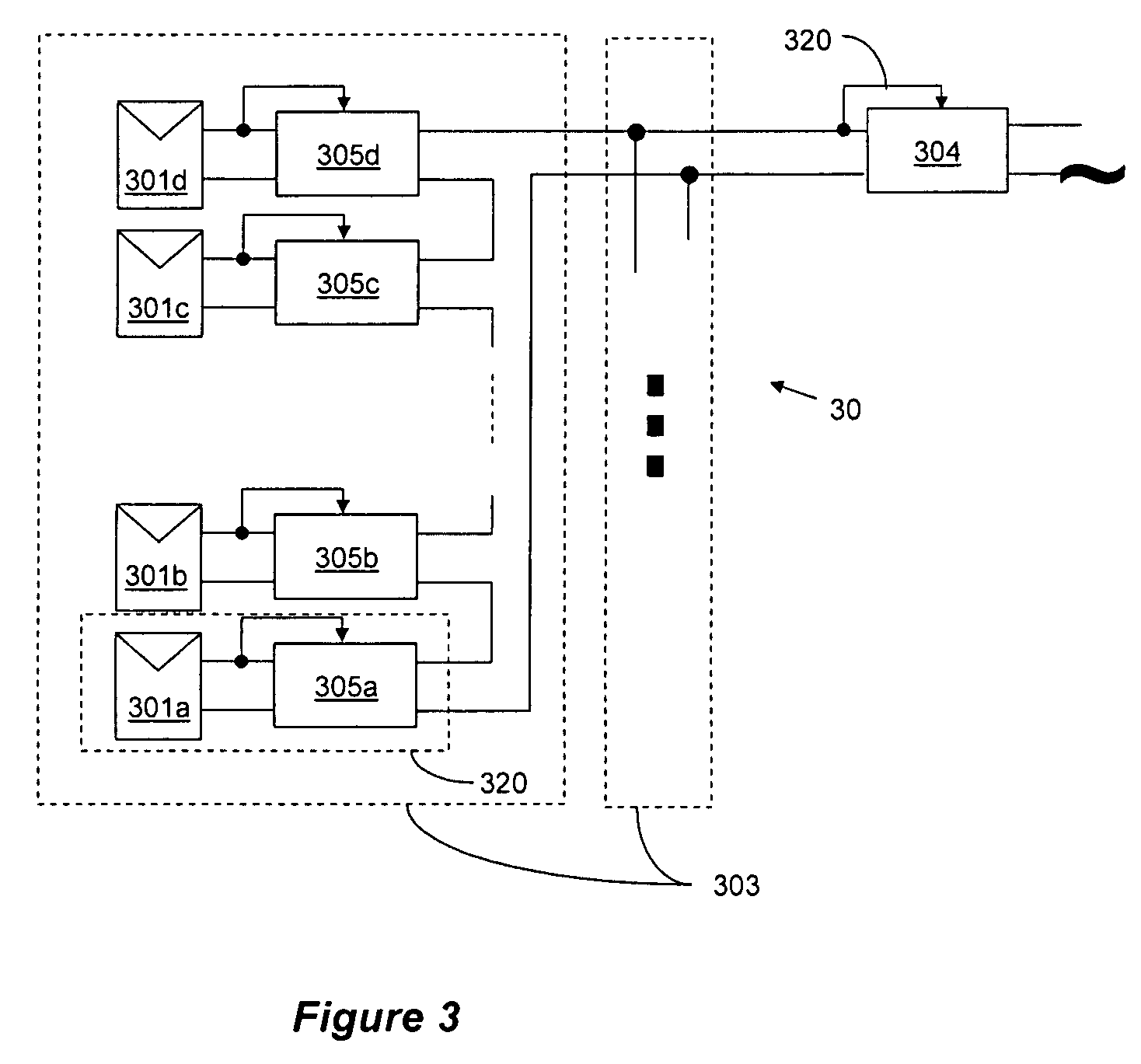
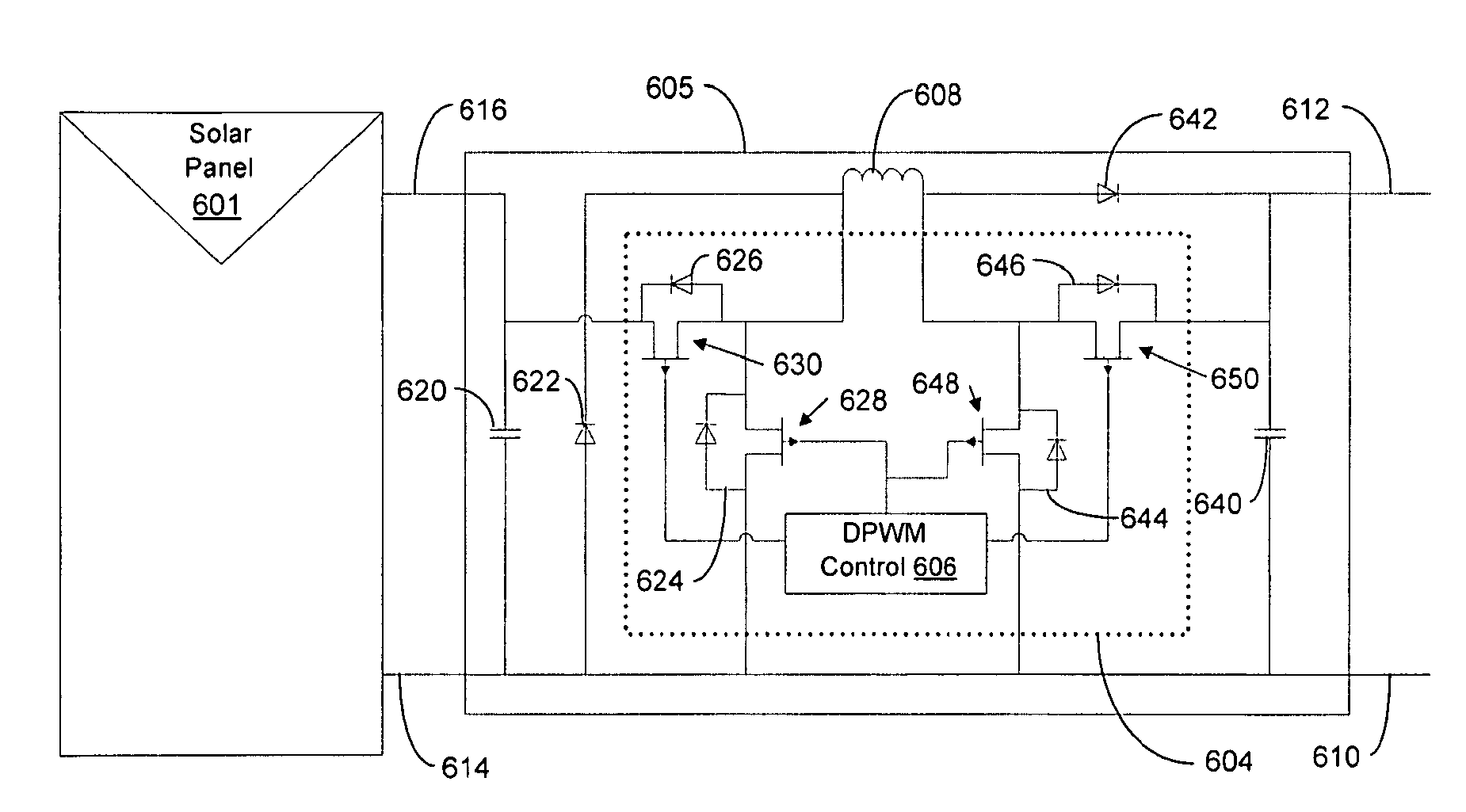
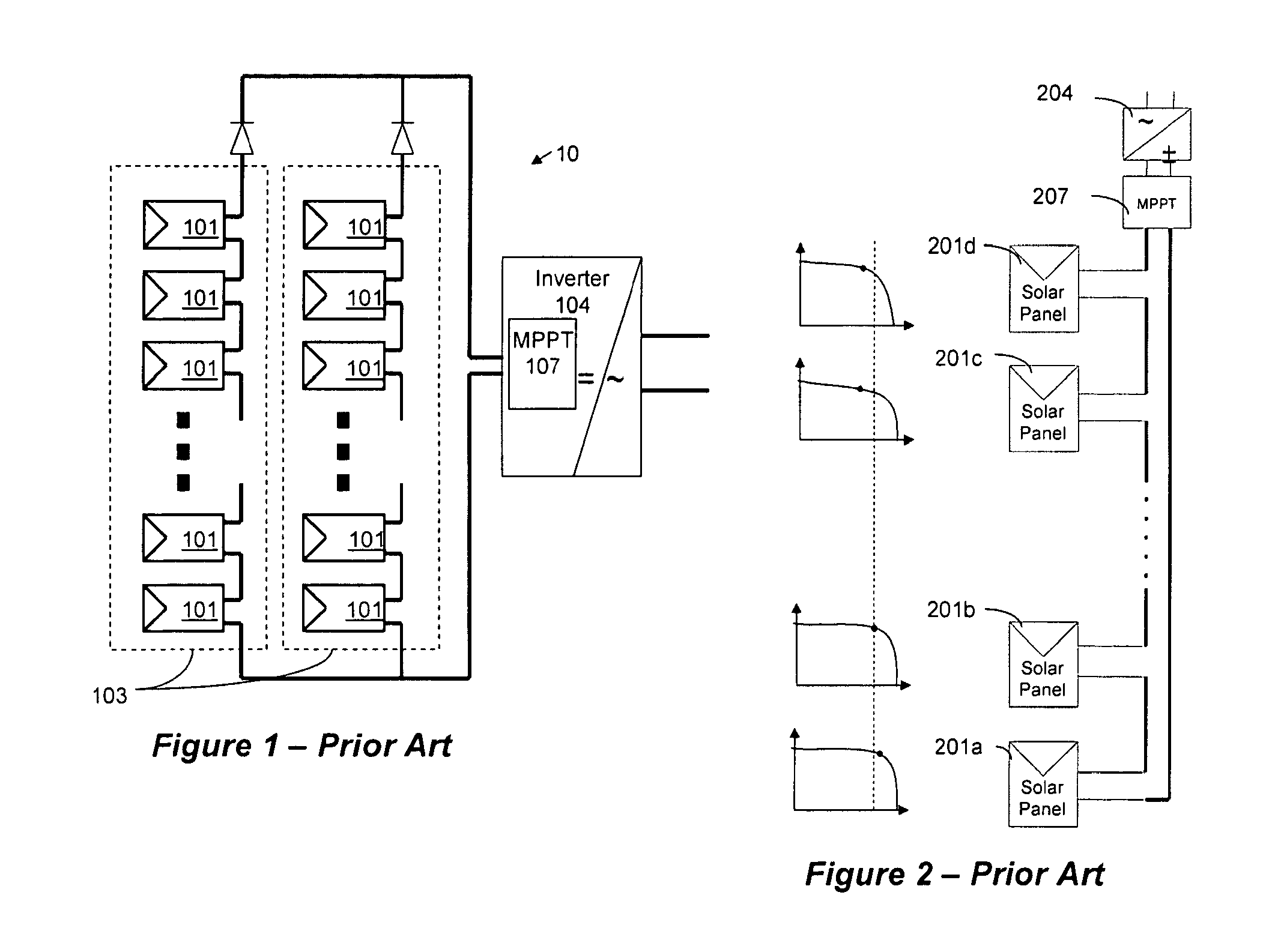
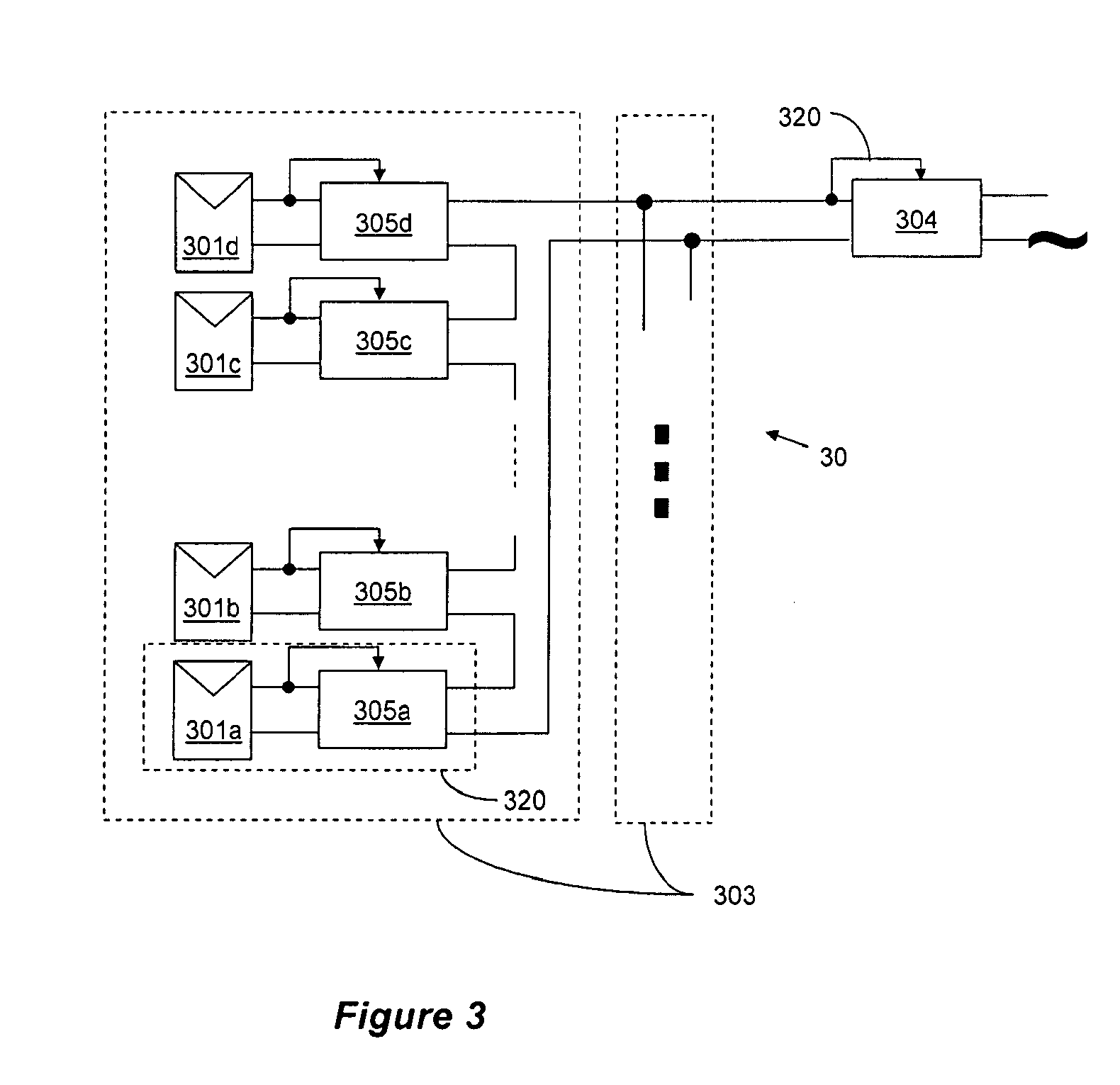
Distributed power harvesting systems using DC power sources
ActiveUS20080143188A1Improve reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsTransverterVoltage variation
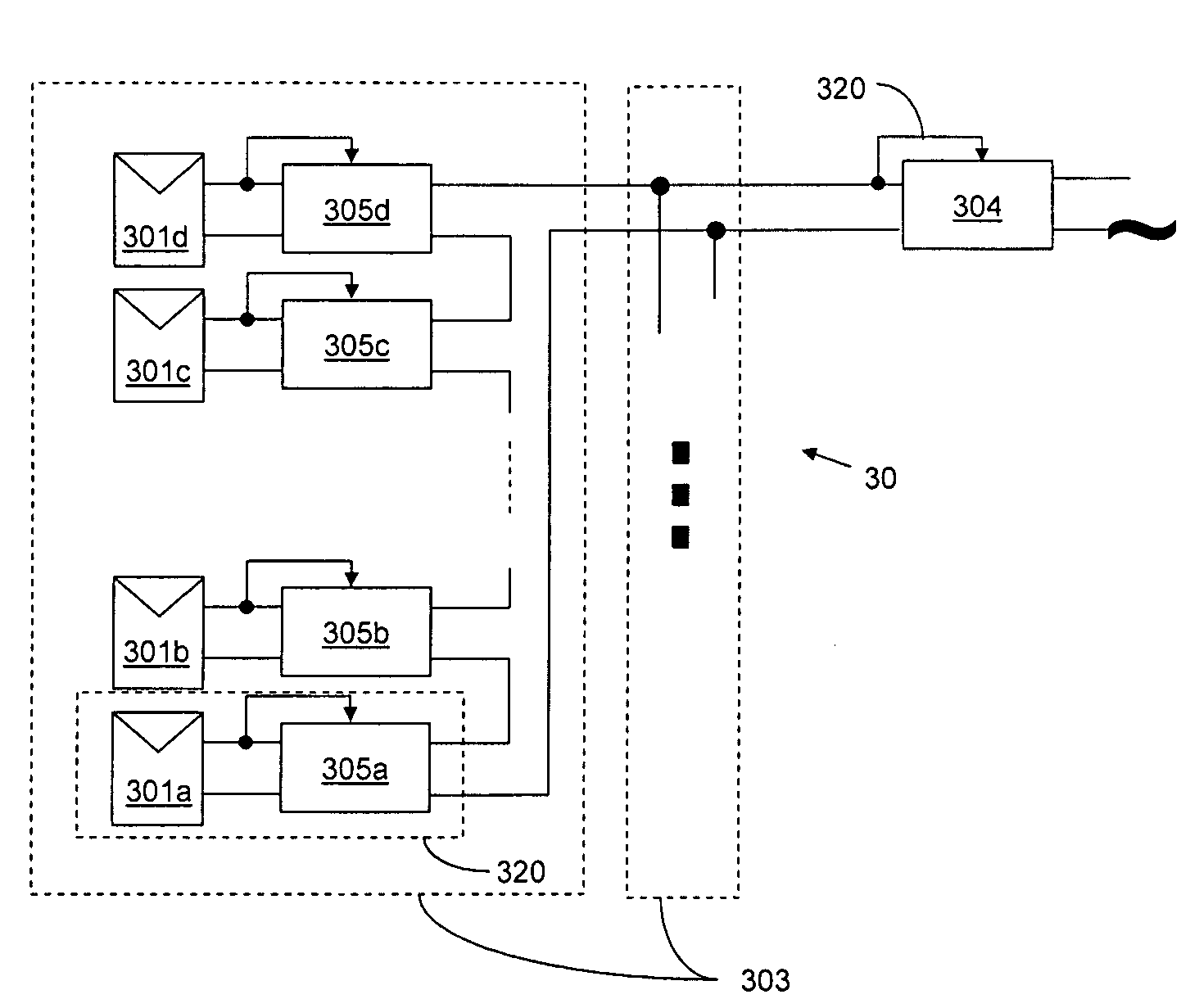
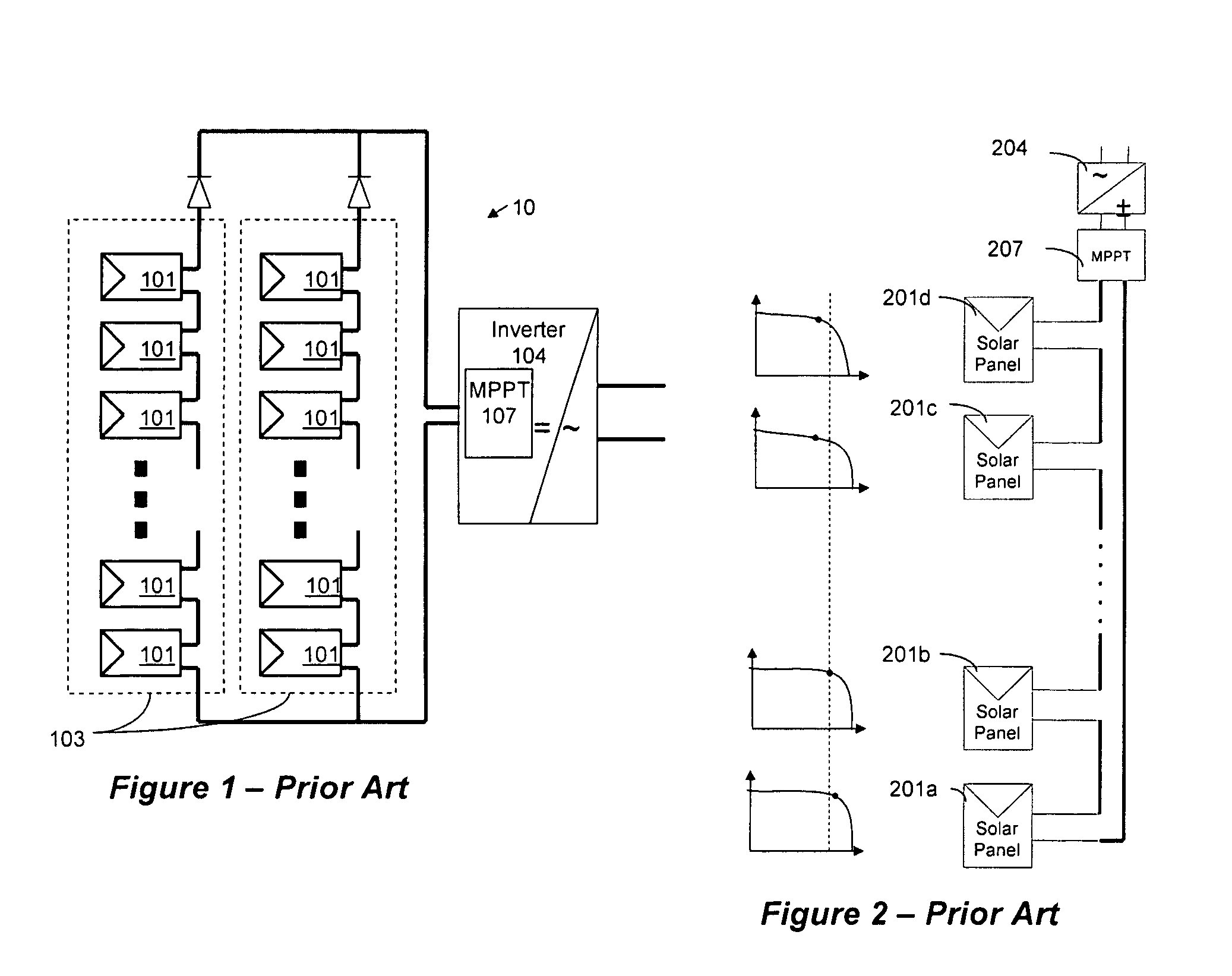
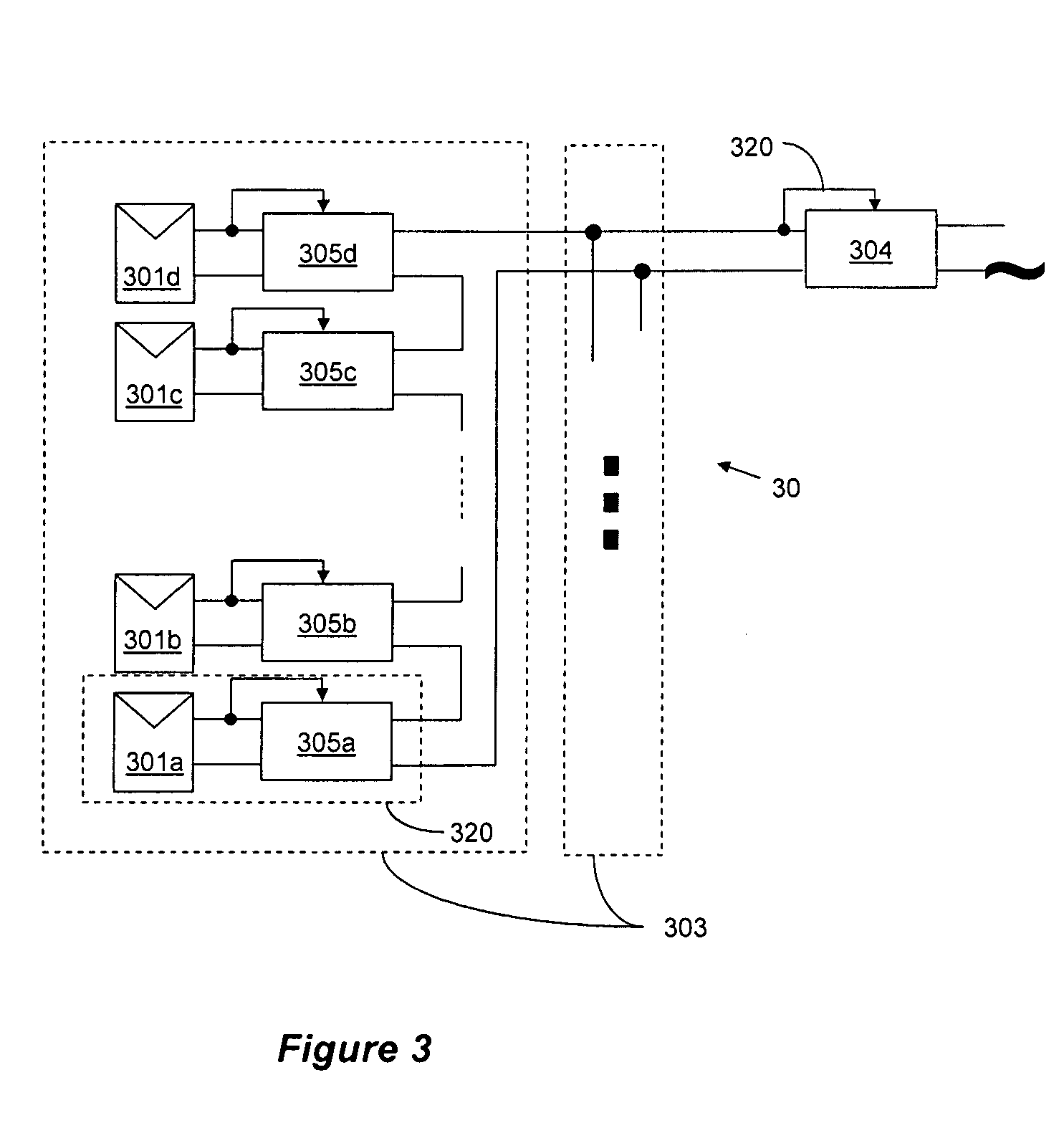
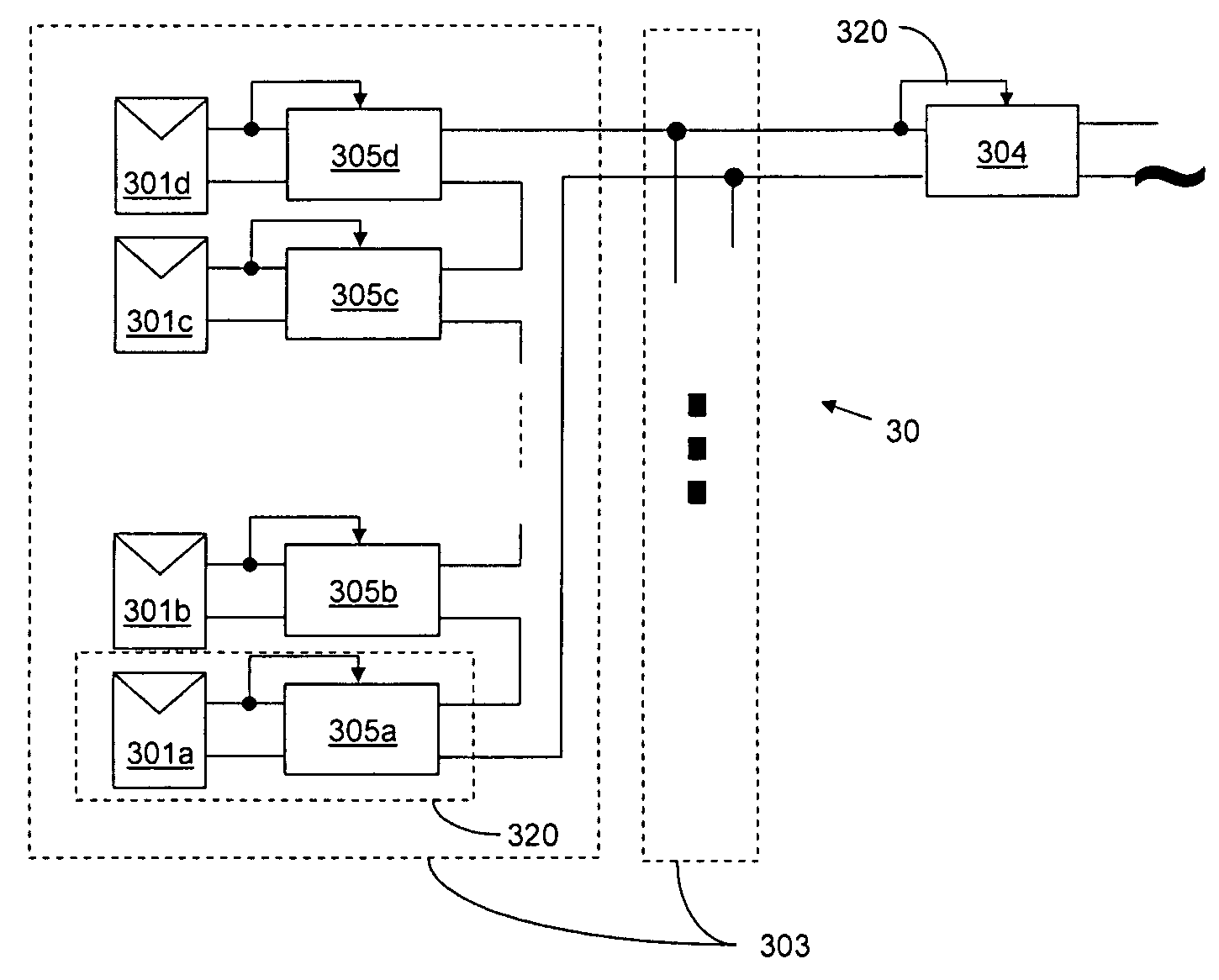
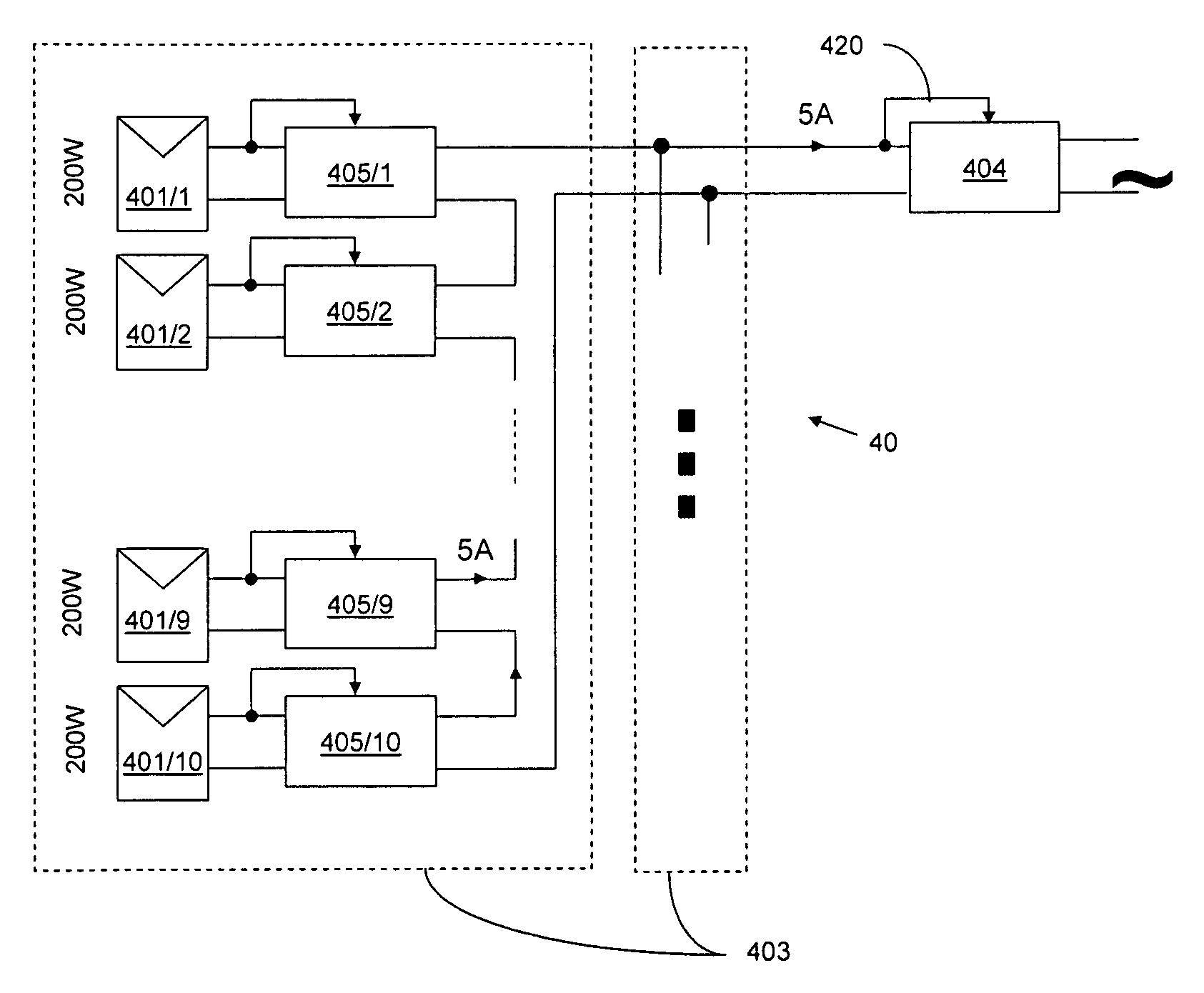
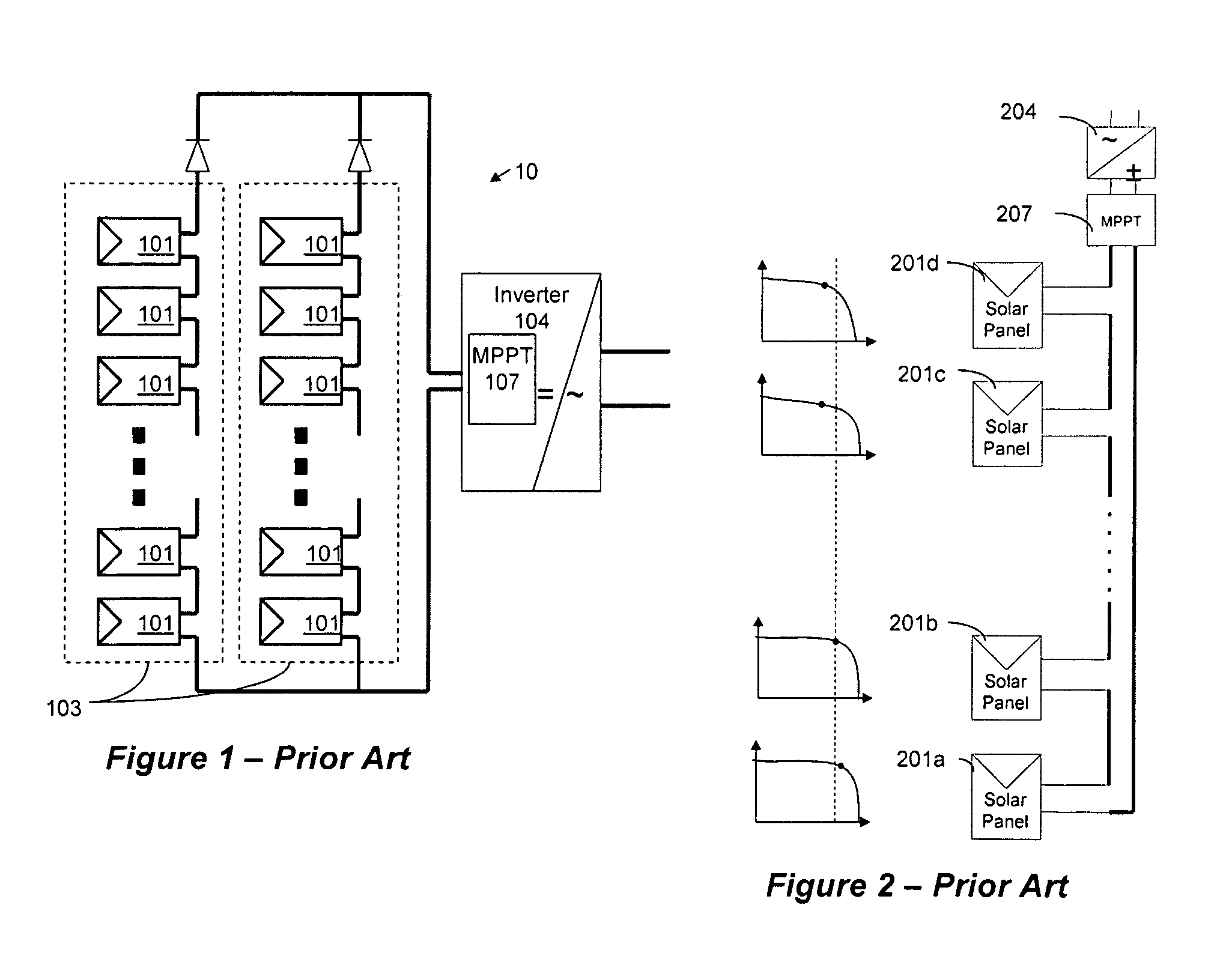
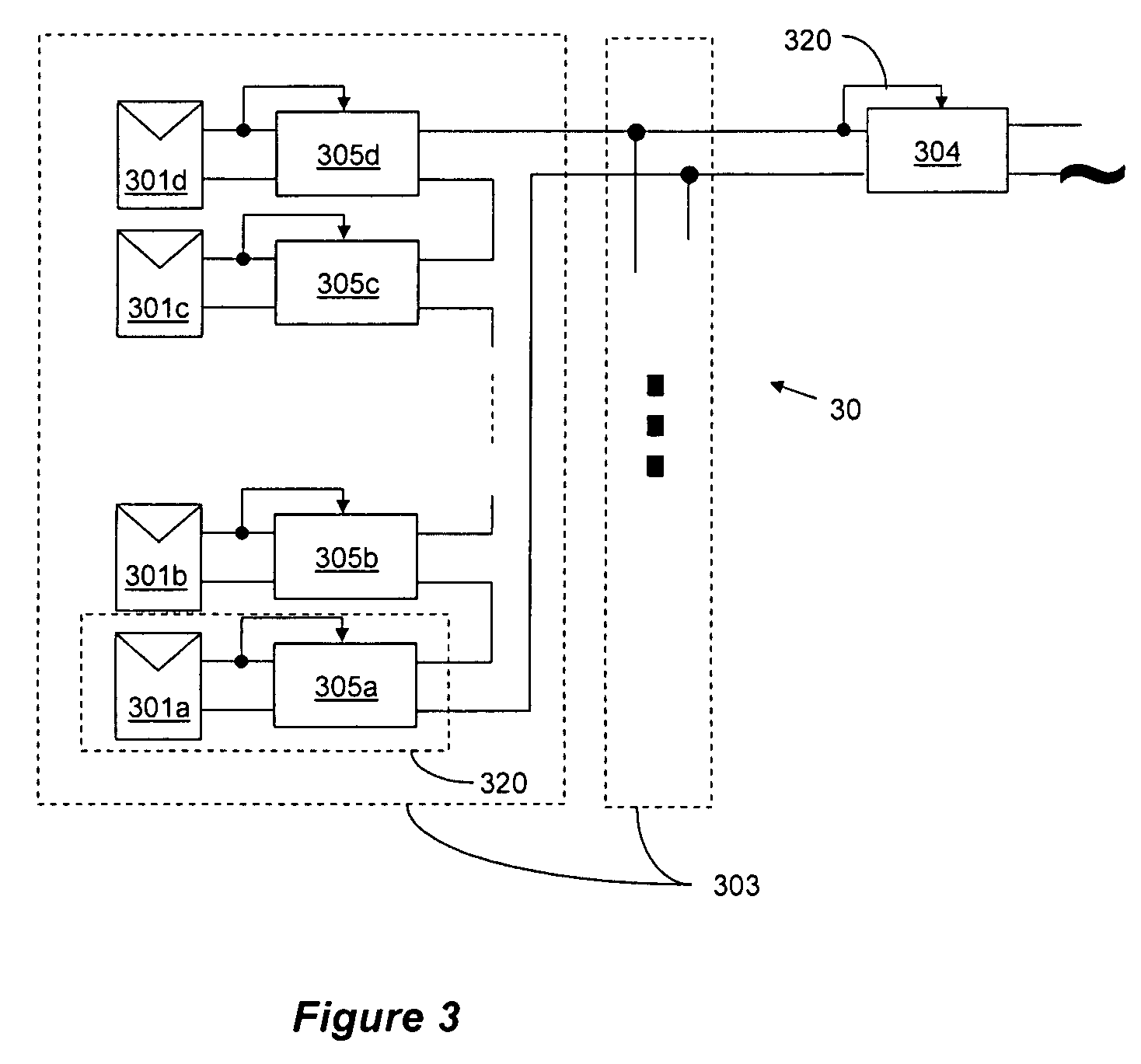
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
Method for distributed power harvesting using DC power sources
ActiveUS20080150366A1Improve reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsPower network operation systems integrationTransverterVoltage variation
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
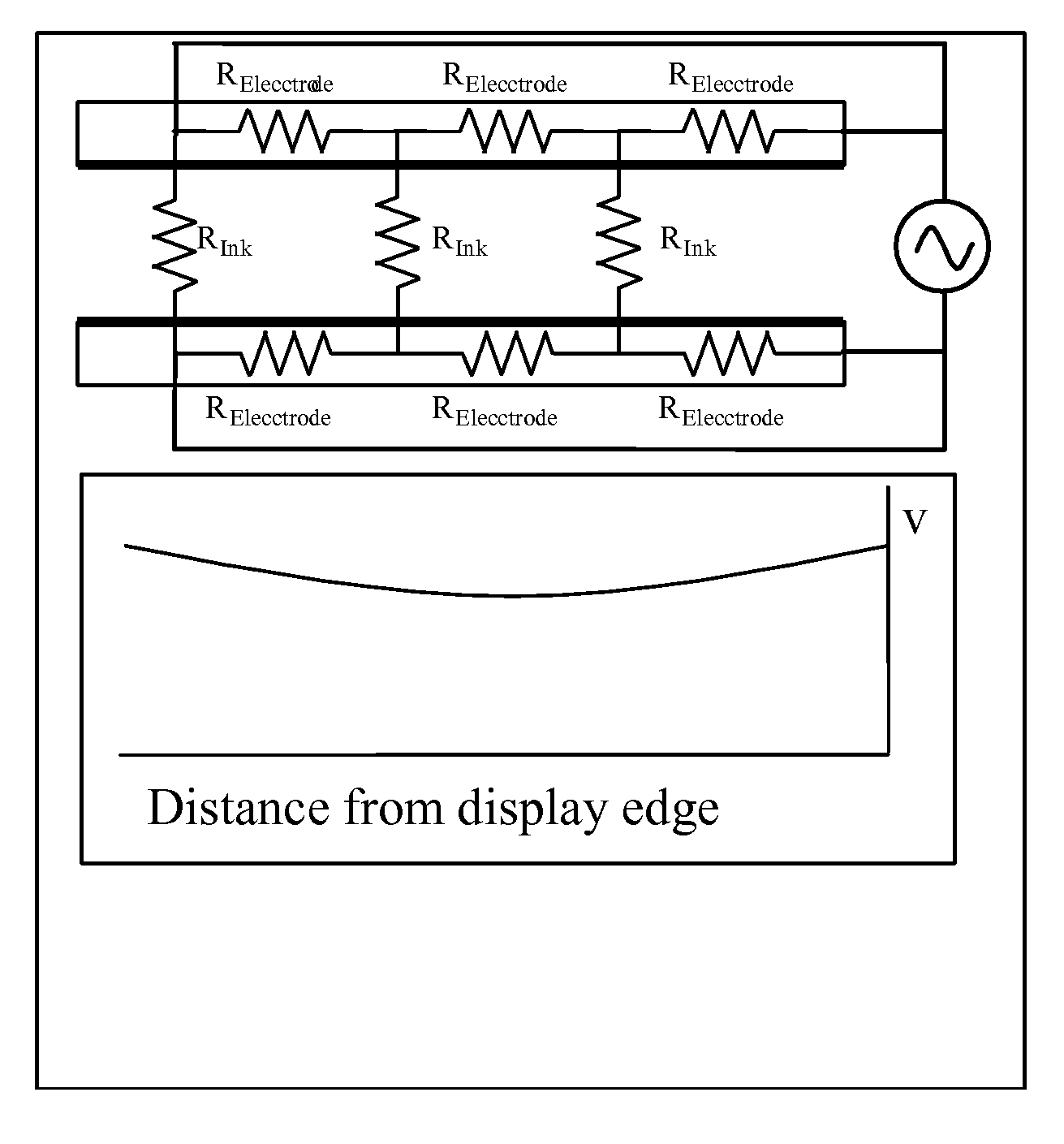
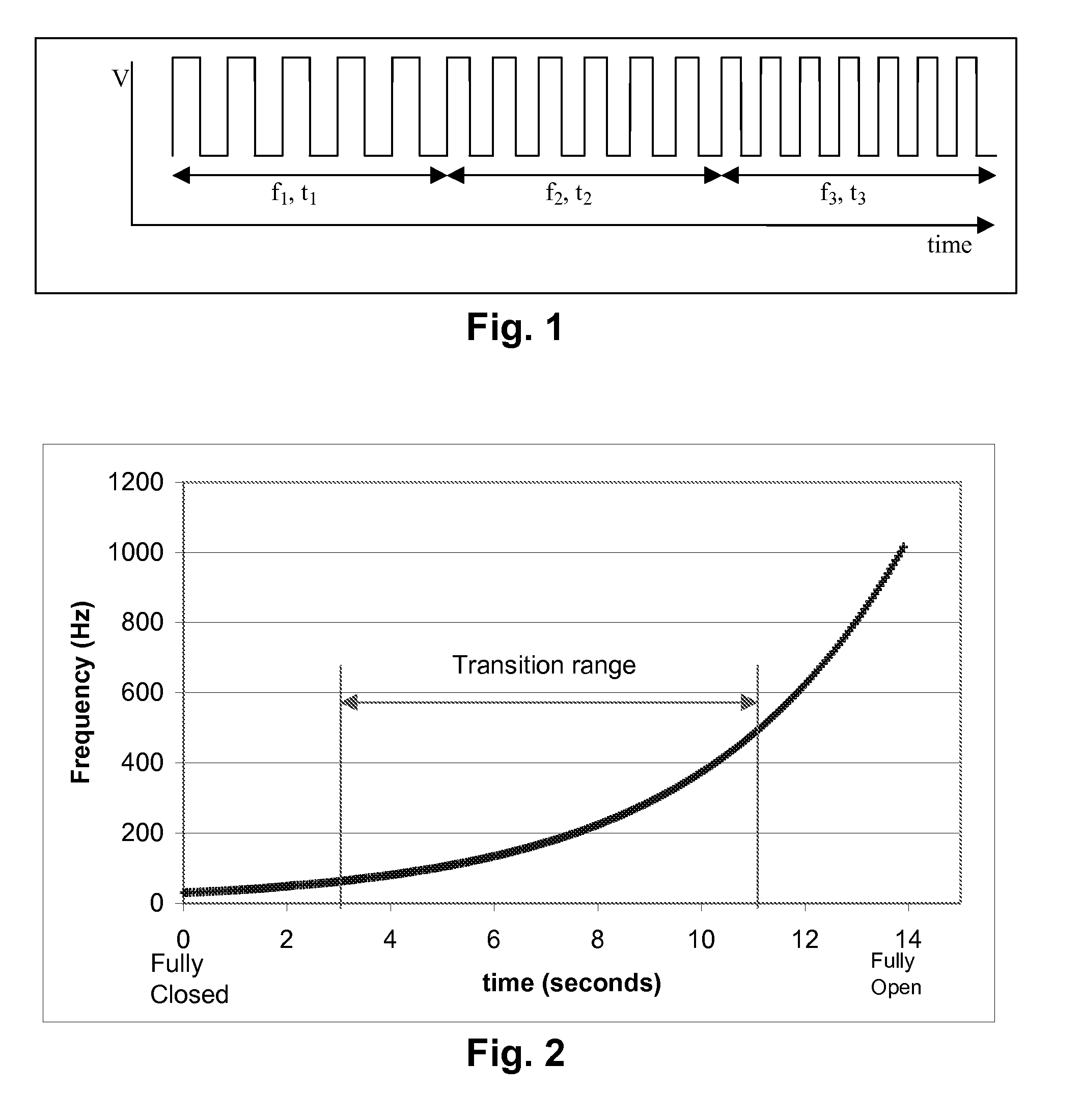
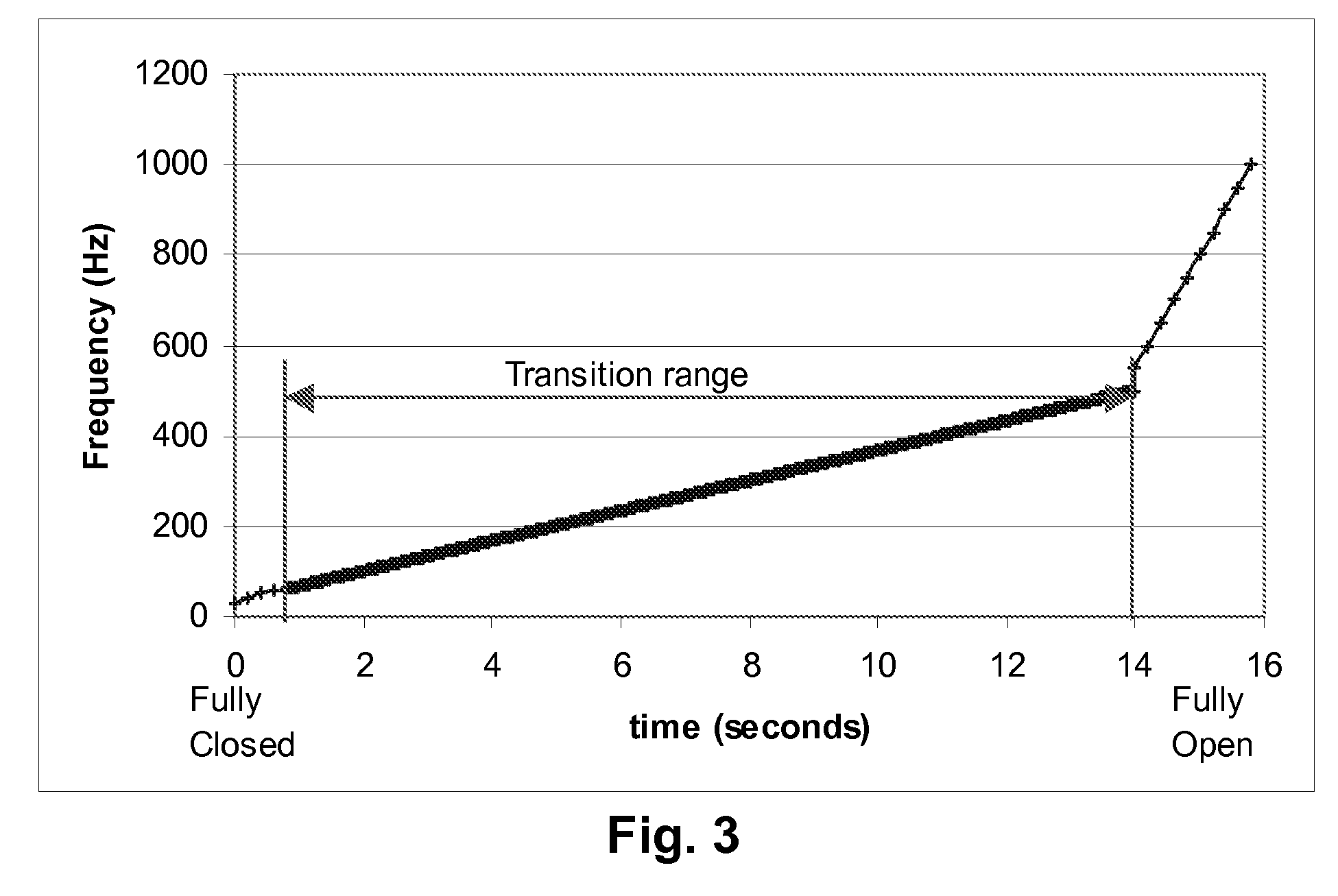
Methods for driving electrophoretic displays using dielectrophoretic forces
InactiveUS20080136774A1Significant energy savingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectrical conductorIntermediate frequency
A dielectrophoretic display is shifted from a low frequency closed state to a high frequency open state via at least one, and preferably several, intermediate frequency states; the use of such multiple frequency steps reduces flicker during the transition. A second type of dielectrophoretic display has a light-transmissive electrode through which the dielectrophoretic medium can be viewed and a conductor connected to the light-transmissive electrode at several points to reduce voltage variations within the light-transmissive electrode.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
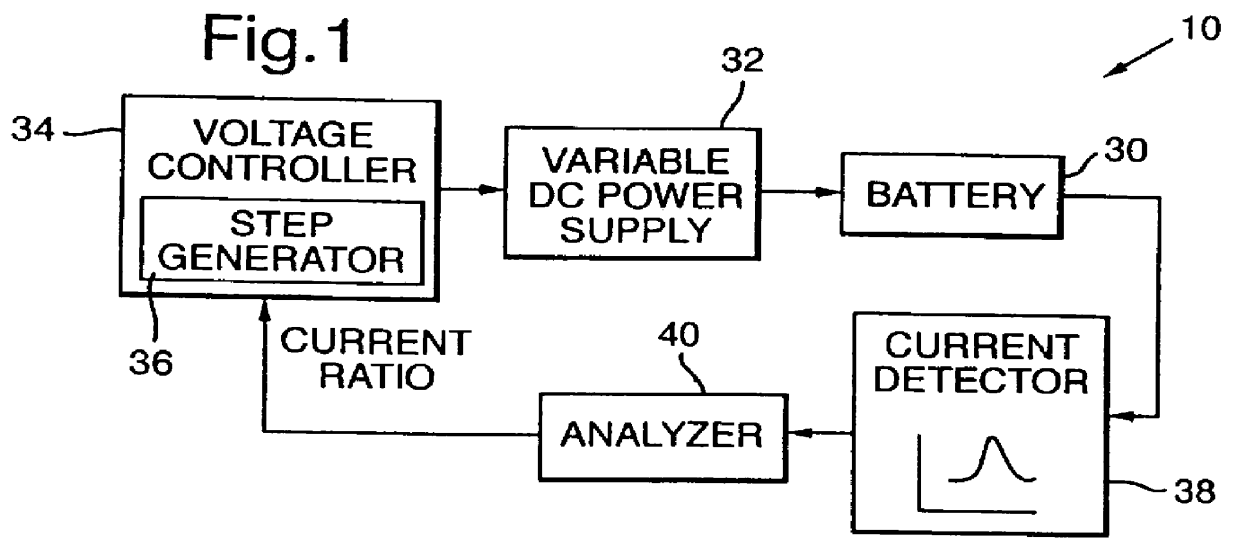
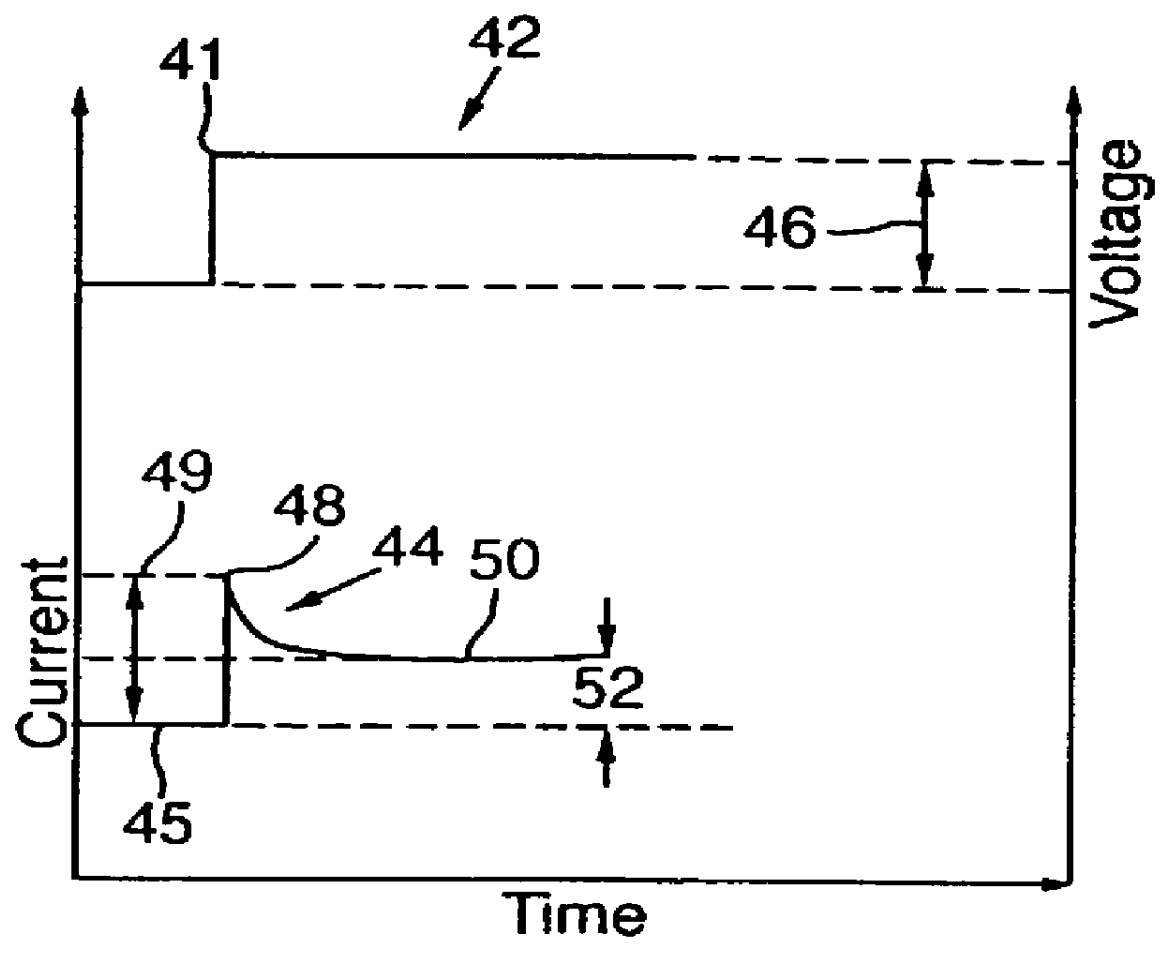
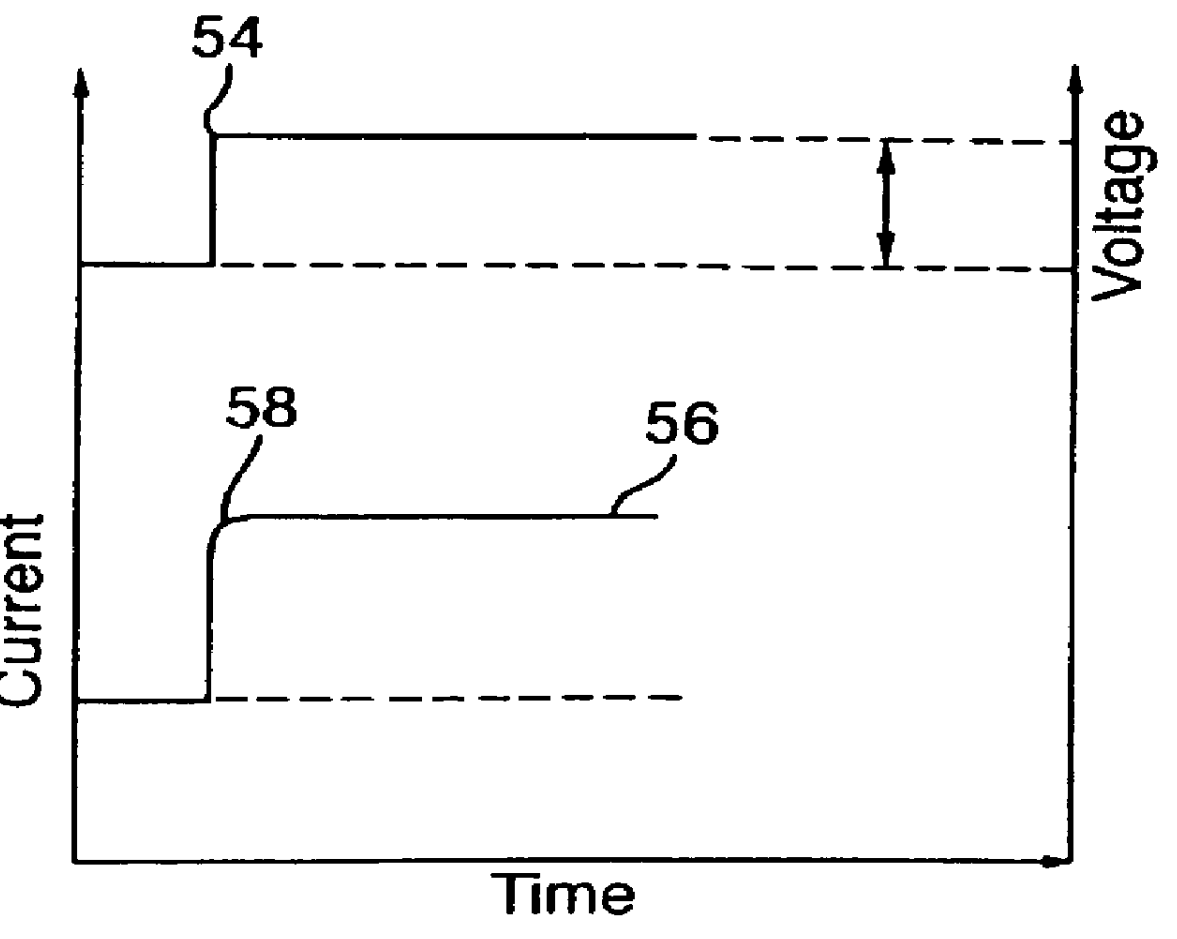
Method and apparatus for charging batteries
InactiveUS6037751AEfficient chargingLow charge acceptanceBatteries circuit arrangementsLead-acid accumulatorsCharge currentCurrent voltage
A method and apparatus for efficiently charging lead-acid batteries applies small voltage steps to probe the charging efficiency of a battery being charged. The application of a voltage step causes the current to change from a base current to a surge current immediately after the voltage step, and to decay asymptotically to a plateau current after the surge current. A current ratio, defined as the difference between the plateau current and the base current divided by the difference between the surge current and the base current, is used as an indicator of the charging efficiency. The output voltage of the power supply charging the battery is then adjusted according to the measured current ratio. A current-voltage slope, defined as the difference between the plateau current and the base current divided by the magnitude of the voltage step, may also be used as an indicator of the charging efficiency for controlling the charging process. Alternatively, in a current-controlled charging process, small current steps are used to probe the charging efficiency. For a current step, the induced voltage changes are measured, and a transient-plateau voltage ratio is calculated. The charging current is then adjusted according to the calculated voltage ratio.
Owner:MIDTRONICS
Method for distributed power harvesting using DC power sources
ActiveUS8013472B2Improve component reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsPower network operation systems integrationTransverterVoltage variation
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
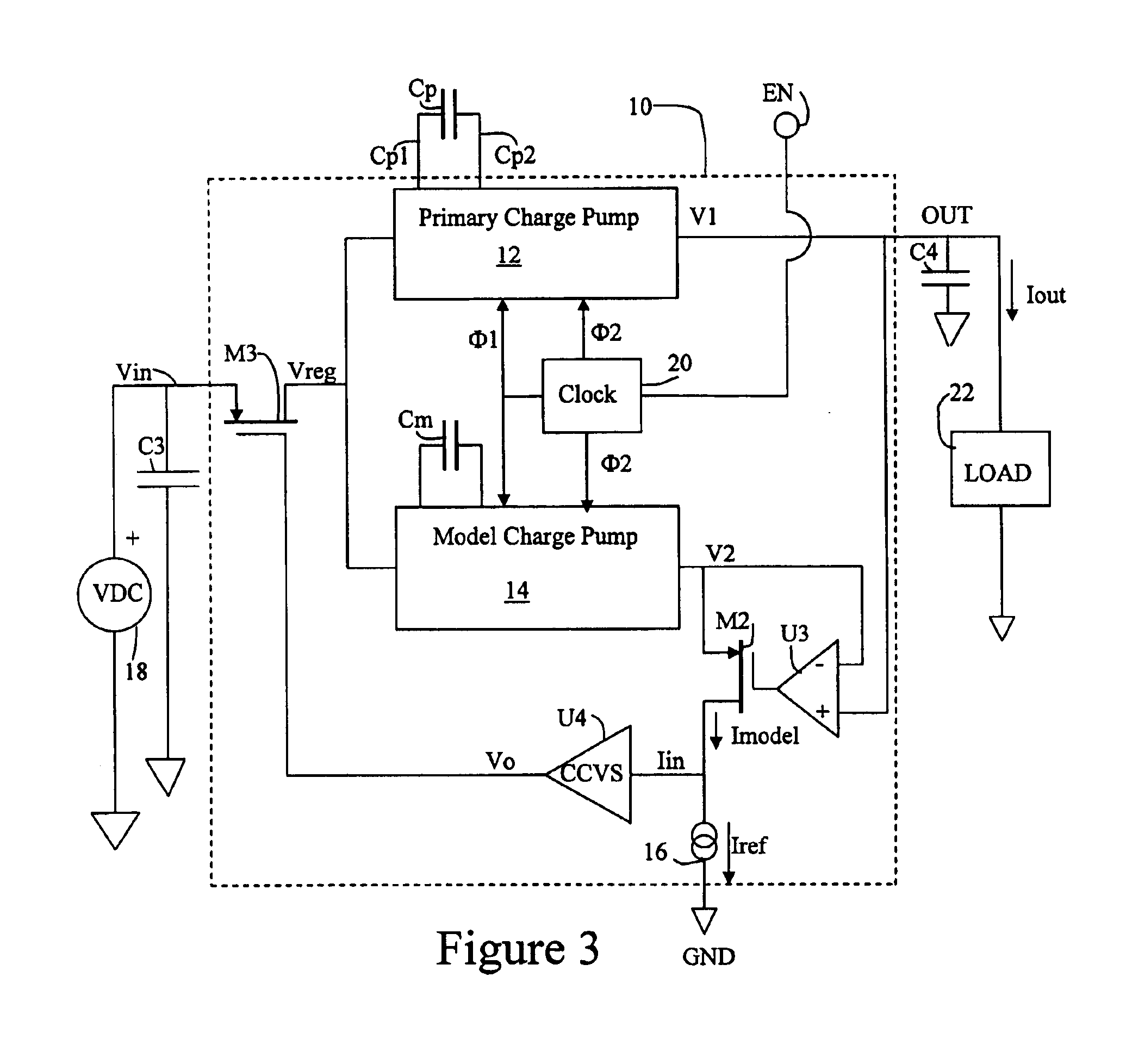
Integrated device providing current-regulated charge pump driver with capacitor-proportional current
InactiveUS6873203B1Low costApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceProportional control
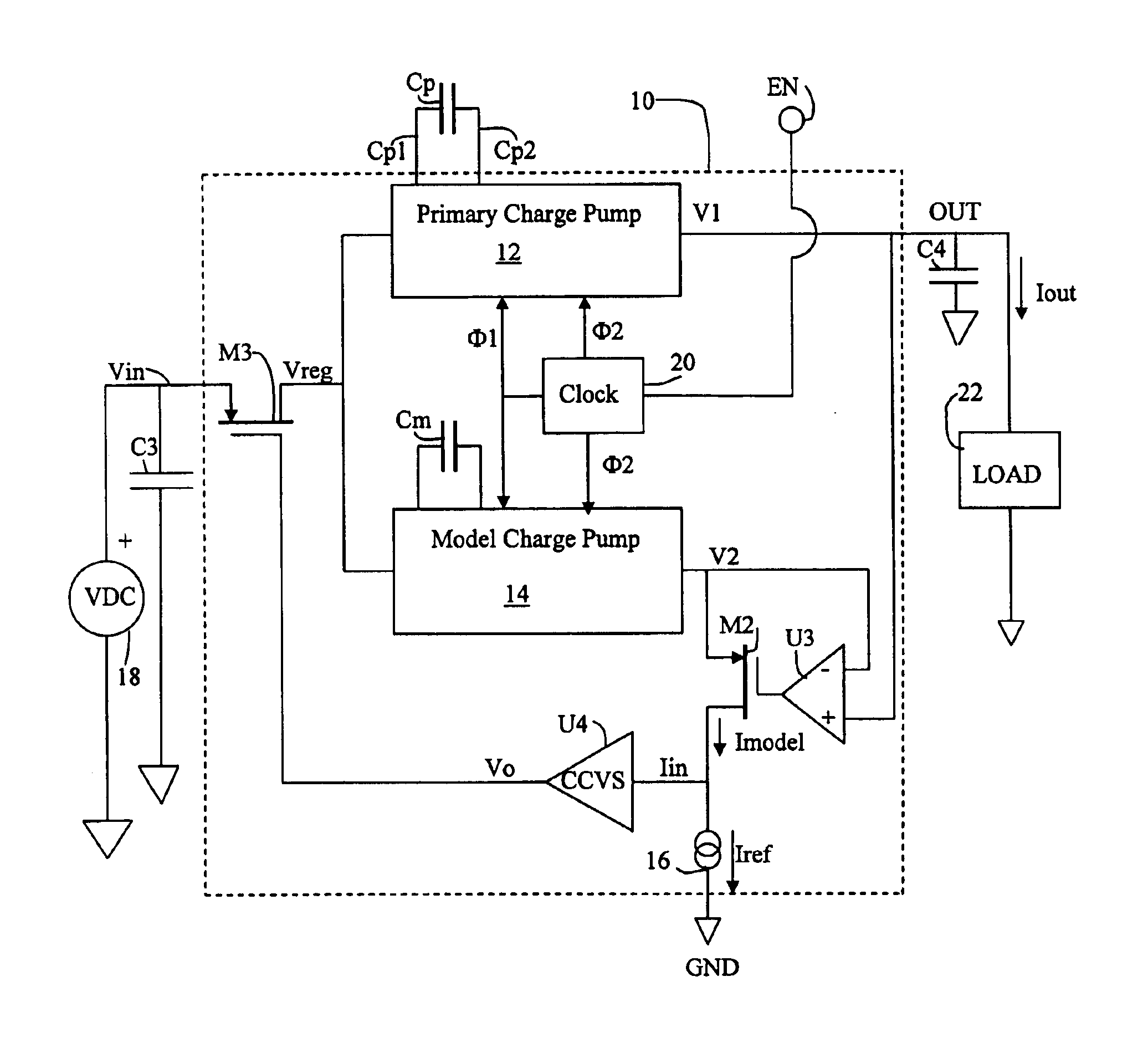
An integrated circuit regulates current flowing from a battery to a load without requiring an external current sense resistor. The IC includes a primary charge pump; a model charge pump; a current sense circuit, a first control circuit to force a voltage level at the output of the model charge pump to be equal to a voltage level at the output of the primary charge pump; and, a second control circuit to force a model current put out by the model charge pump to be equal to a reference current. Current passing through the primary charge pump is regulated at a level established by the capacitance value of an external flying capacitor irrespective of input voltage variation of the battery power source.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
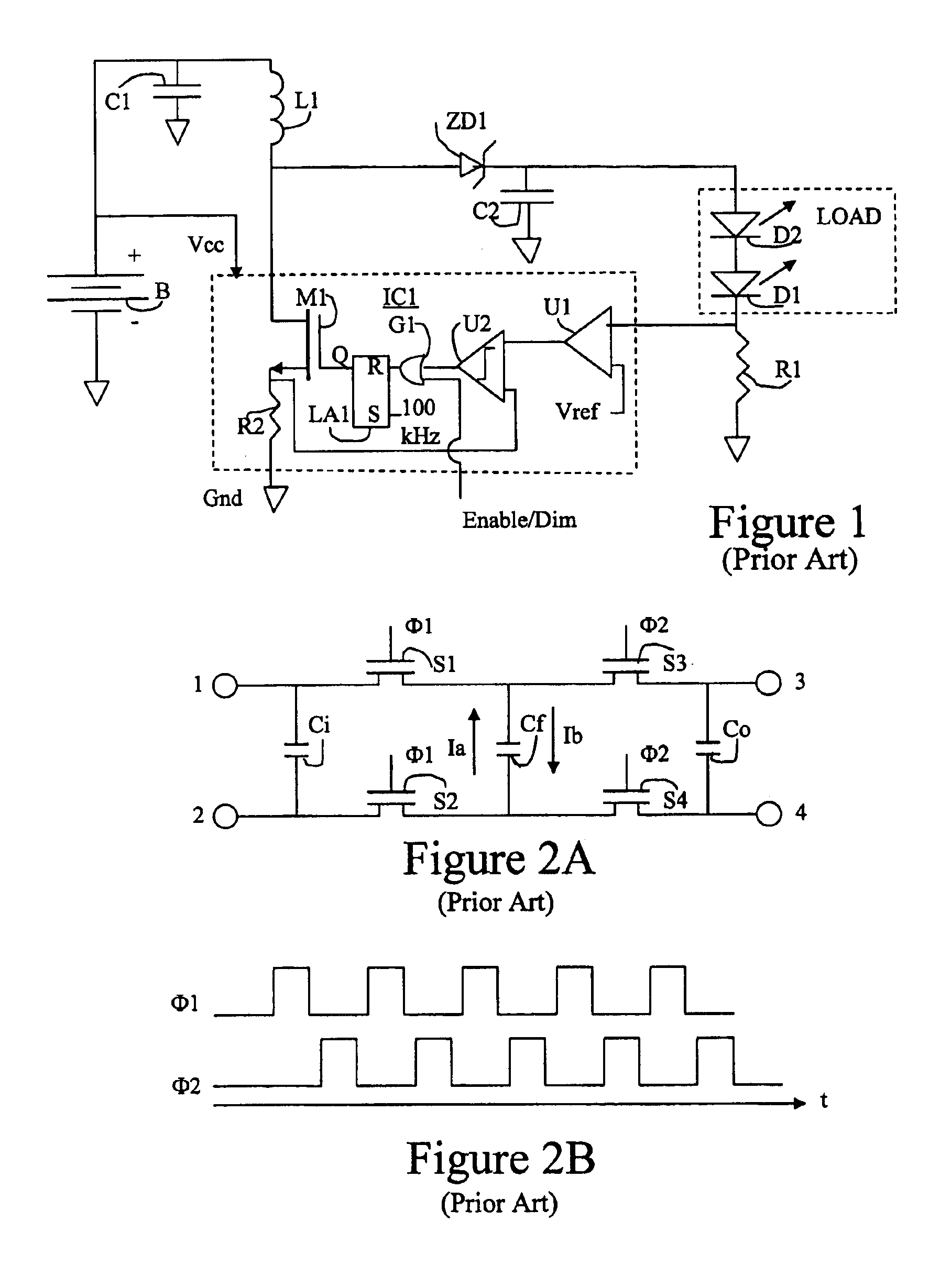
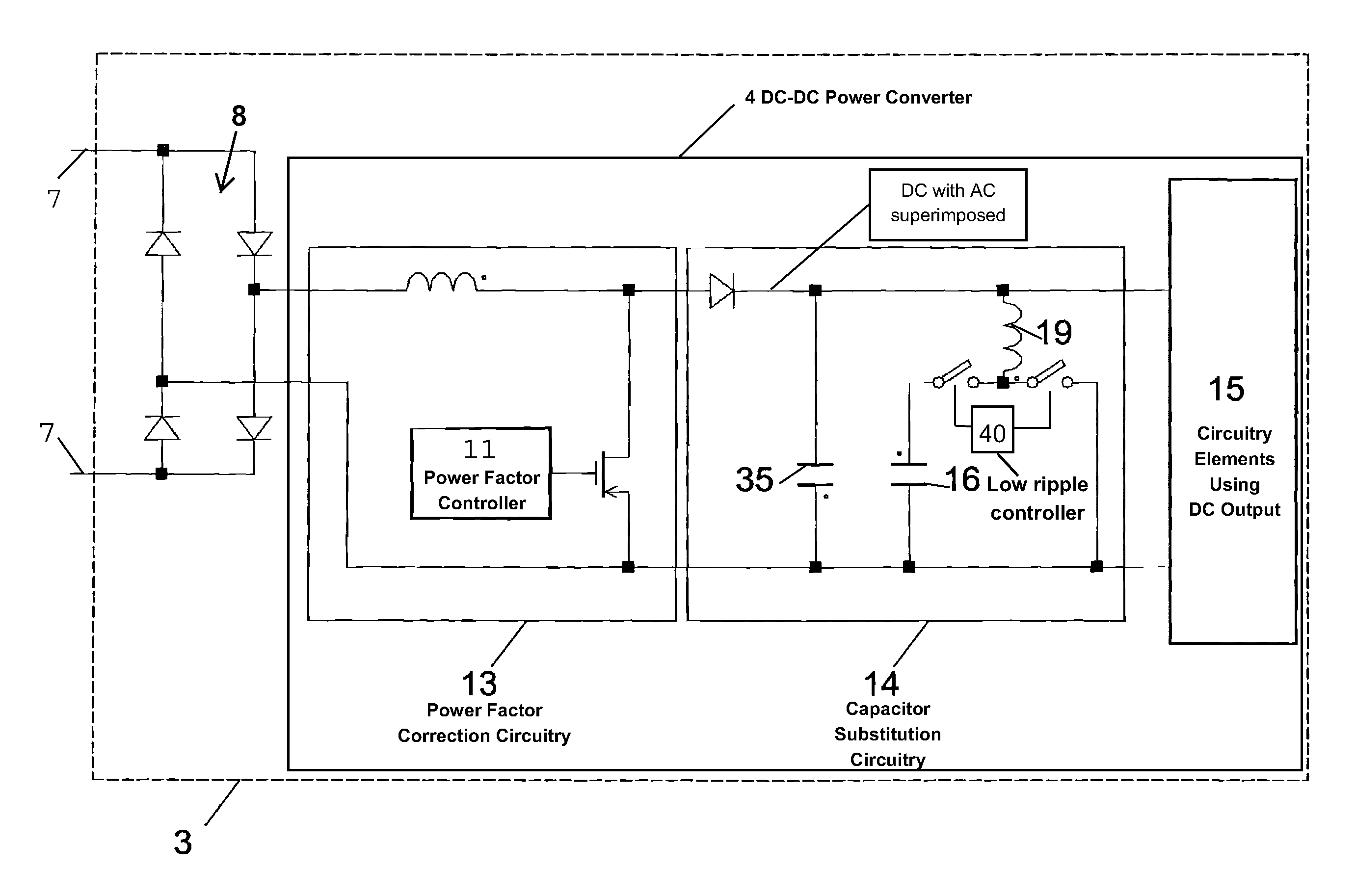
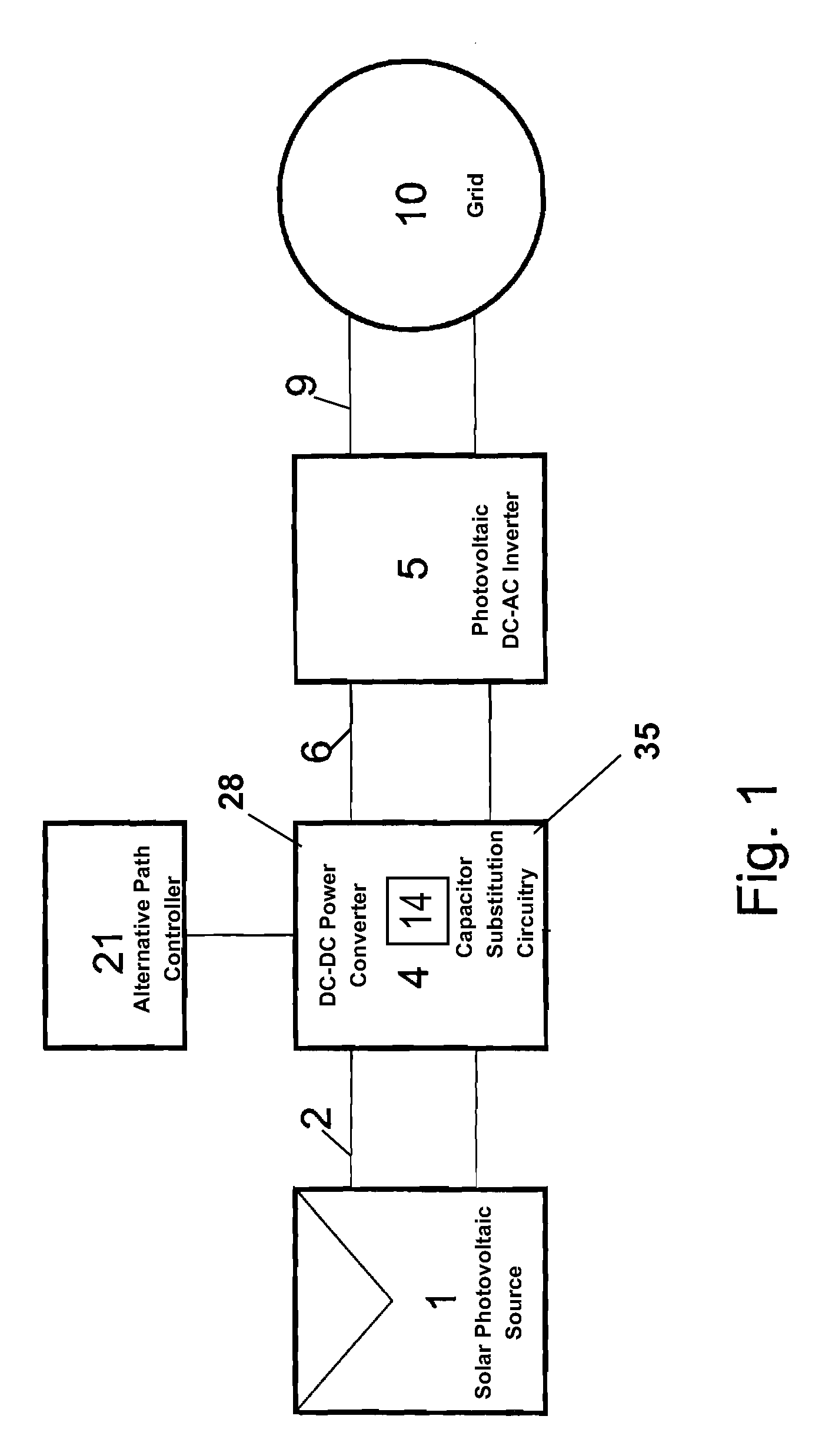
Solar power capacitor alternative switch circuitry system for enhanced capacitor life
InactiveUS7919953B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcBoost controllerEngineering
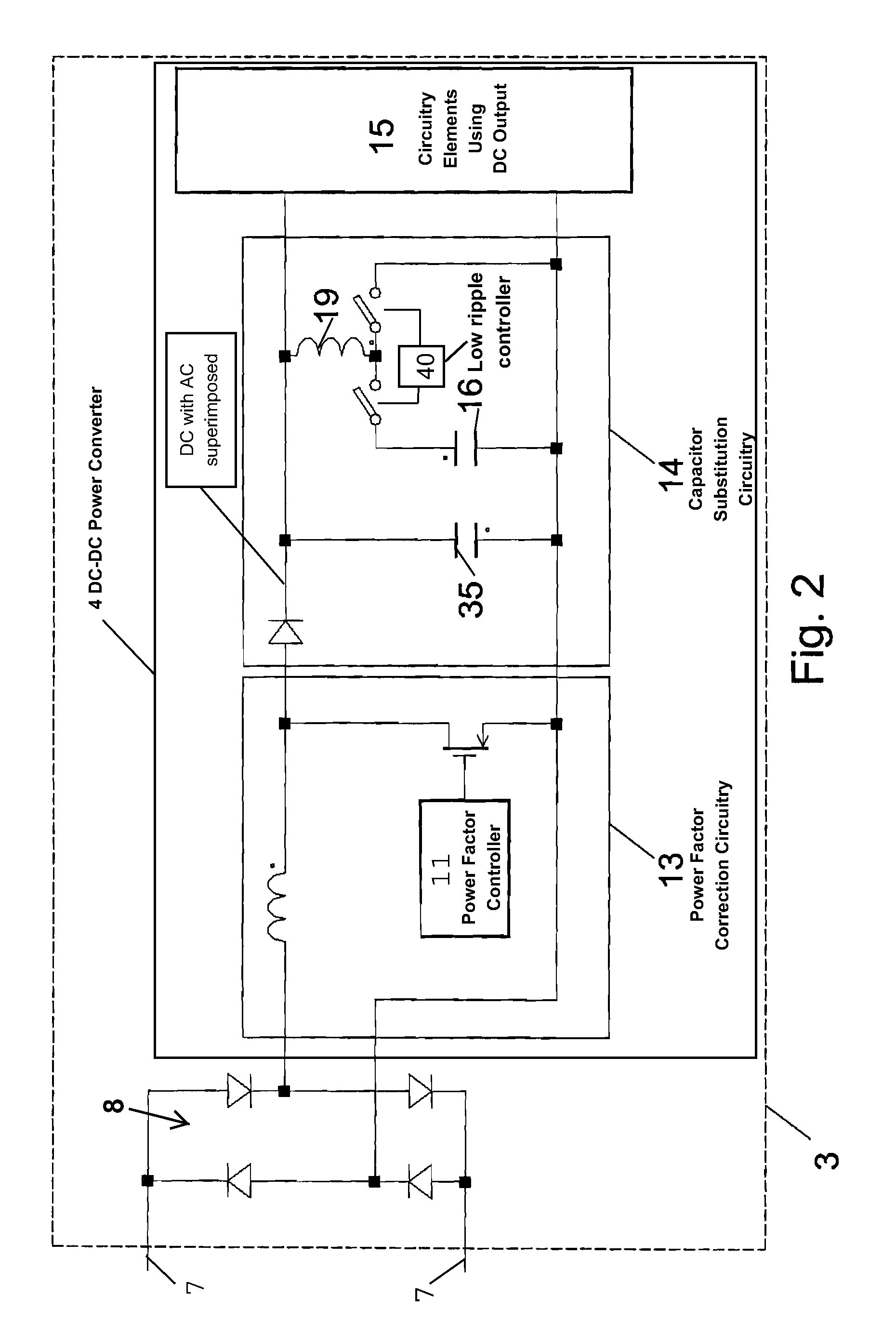
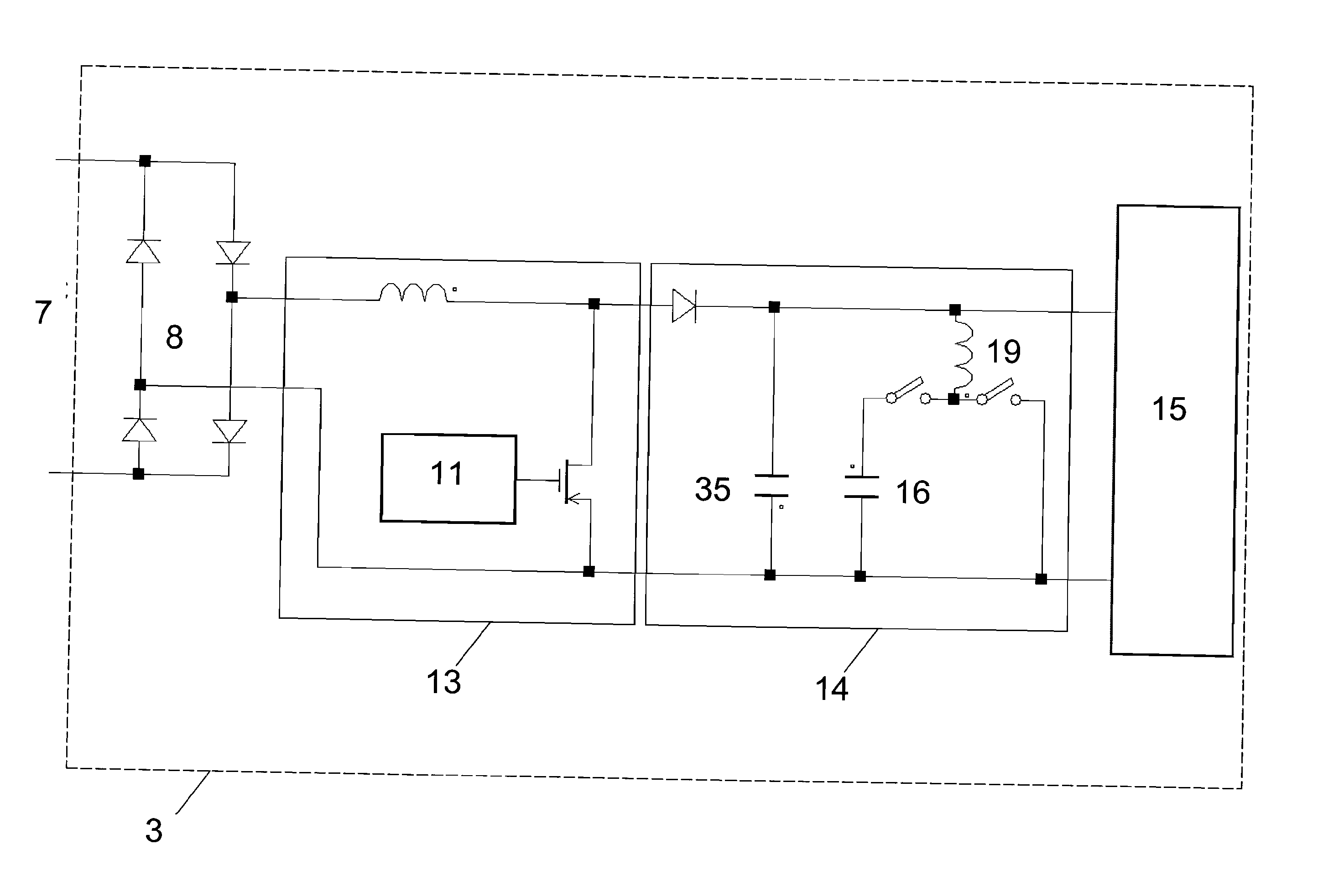
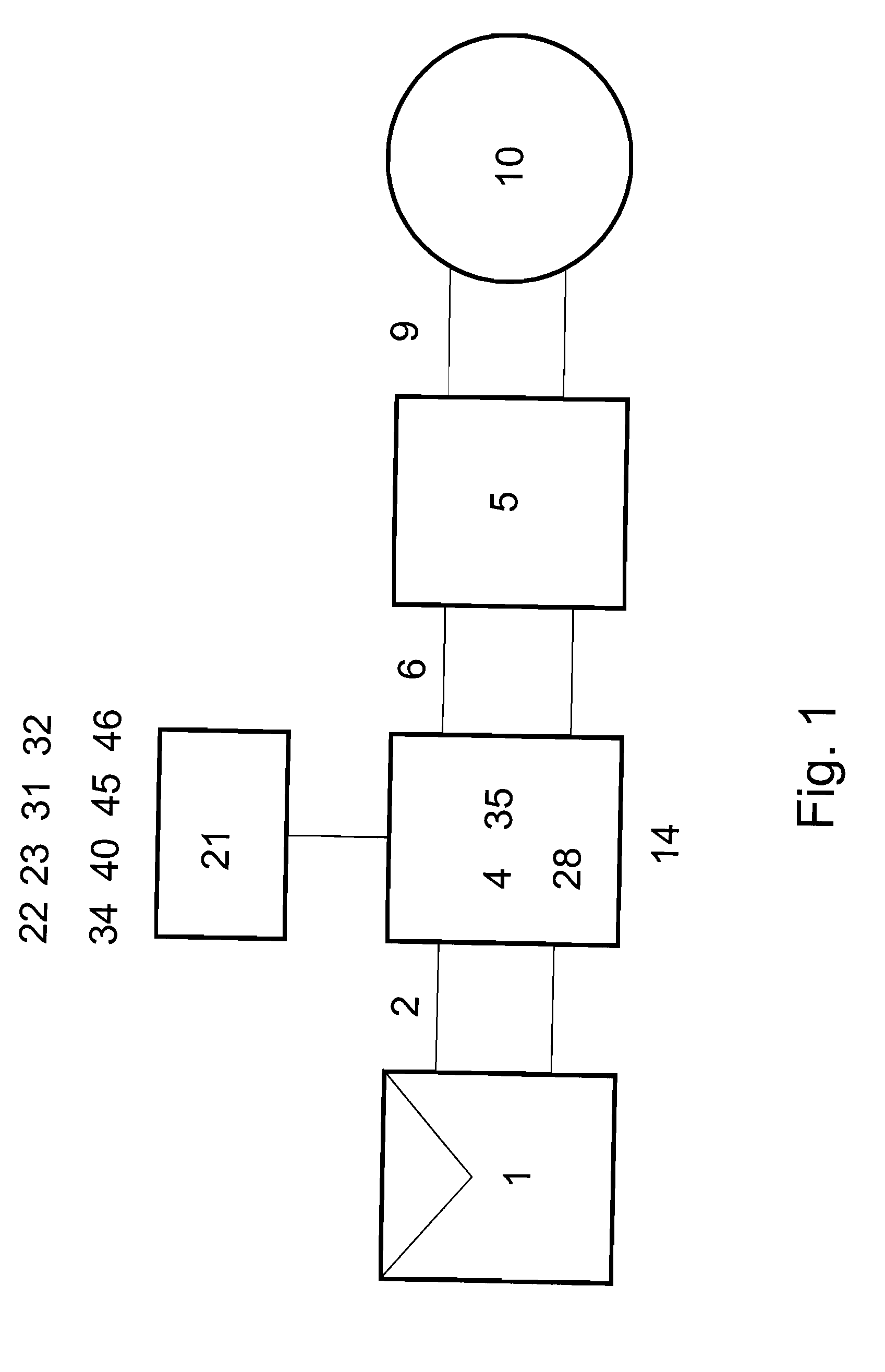
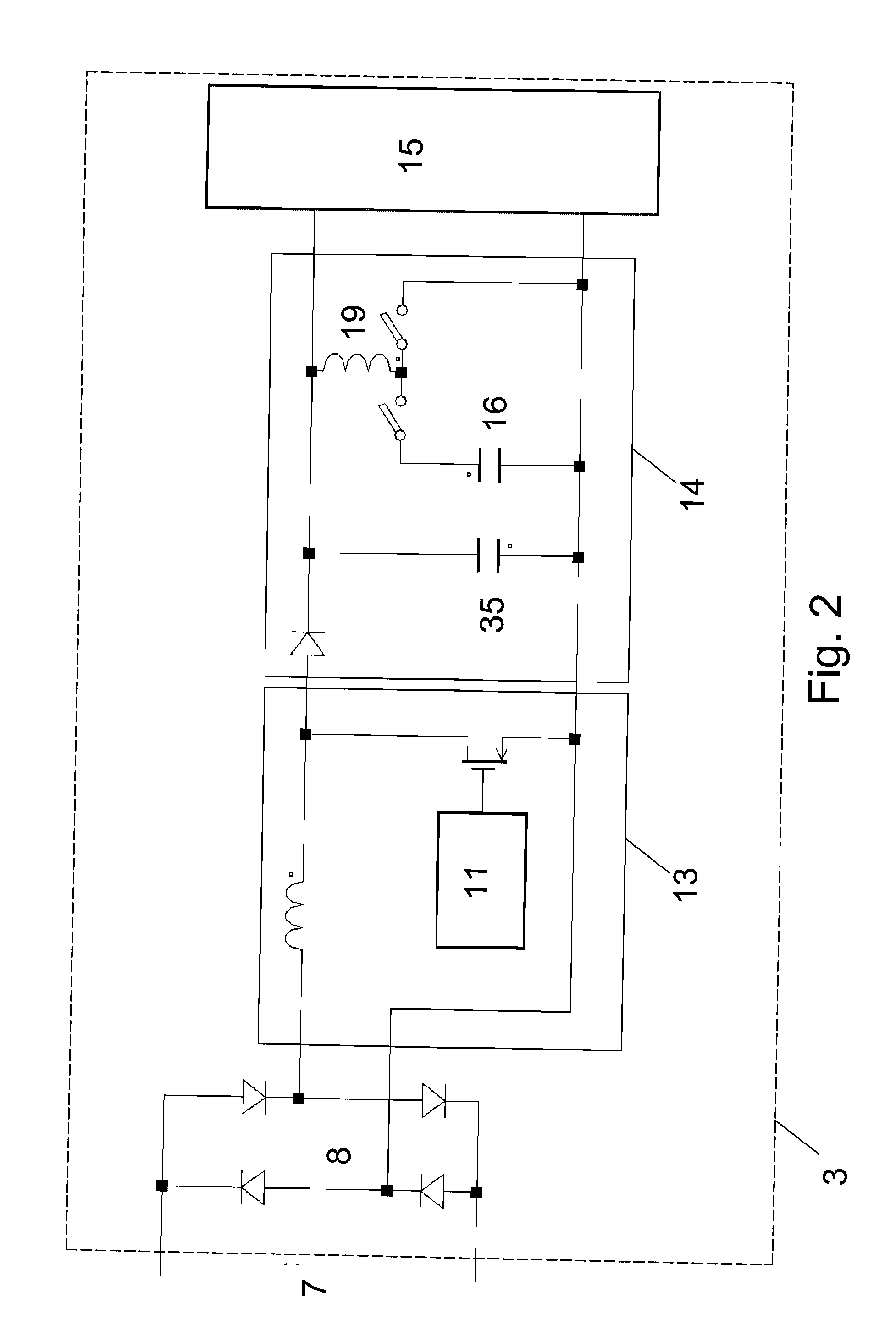
Reliability enhanced systems are shown where an short-lived electrolytic capacitor can be replaced by a much smaller, perhaps film type, longer-lived capacitor to be implemented in circuits for power factor correction, solar power conversion, or otherwise to achieve DC voltage smoothing with circuitry that has solar photovoltaic source (1) a DC photovoltaic input (2) internal to a device (3) and uses an enhanced DC-DC power converter (4) to provide a smoothed DC output (6) with capacitor substitution circuitry (14) that may include interim signal circuitry (28) that creates a large voltage variation for a replaced capacitor (16). Switchmode designs may include first and second switch elements (17) and (18) and an alternative path controller (21) that operates a boost controller (22) and a buck controller (23) perhaps with a switch duty cycle controller (32).
Owner:AMPT
Contactless electrical energy transmission system having a primary side current feedback control and soft-switched secondary side rectifier
ActiveUS6934167B2Energy can transferEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSwitching frequencyEngineering
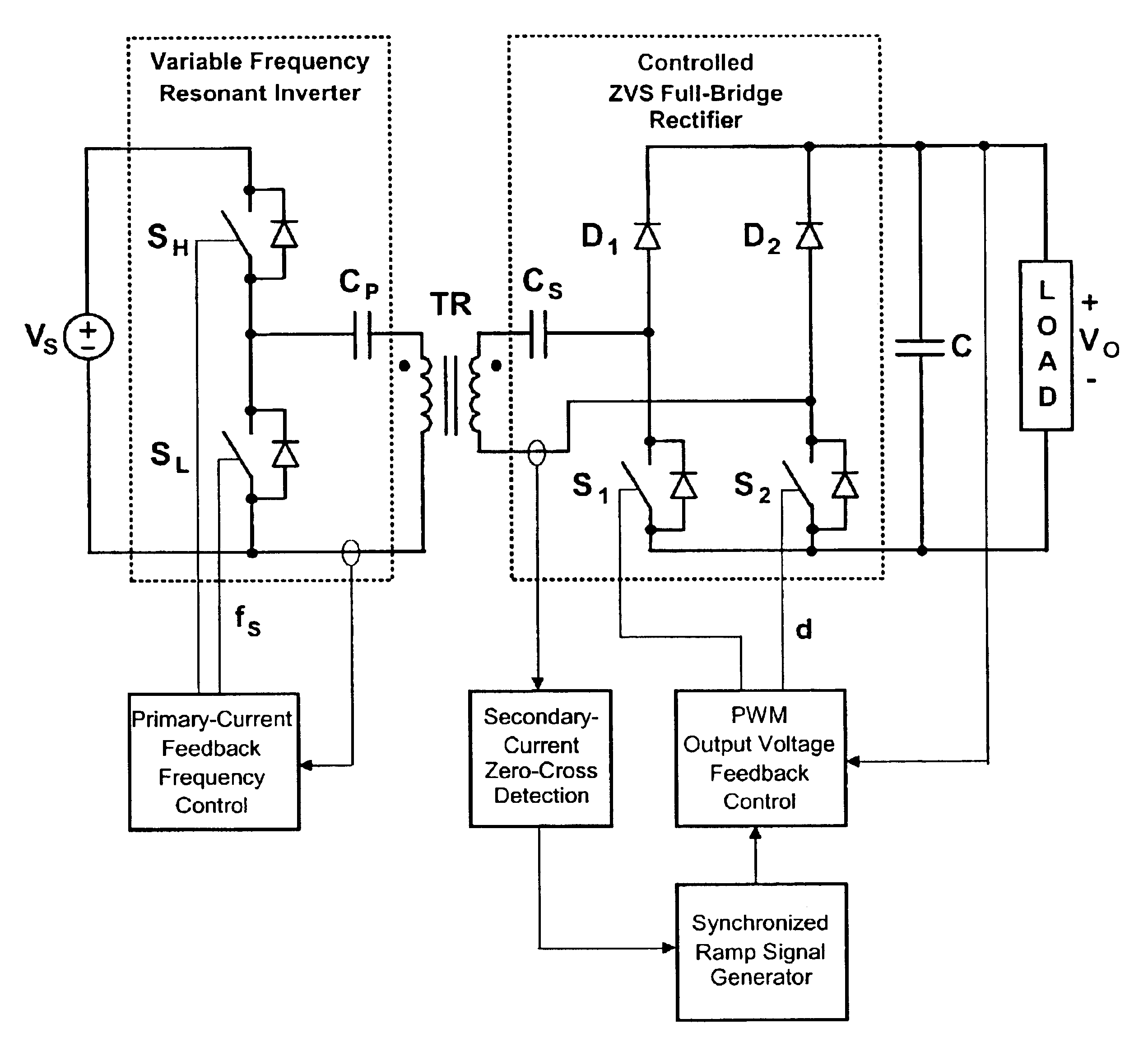
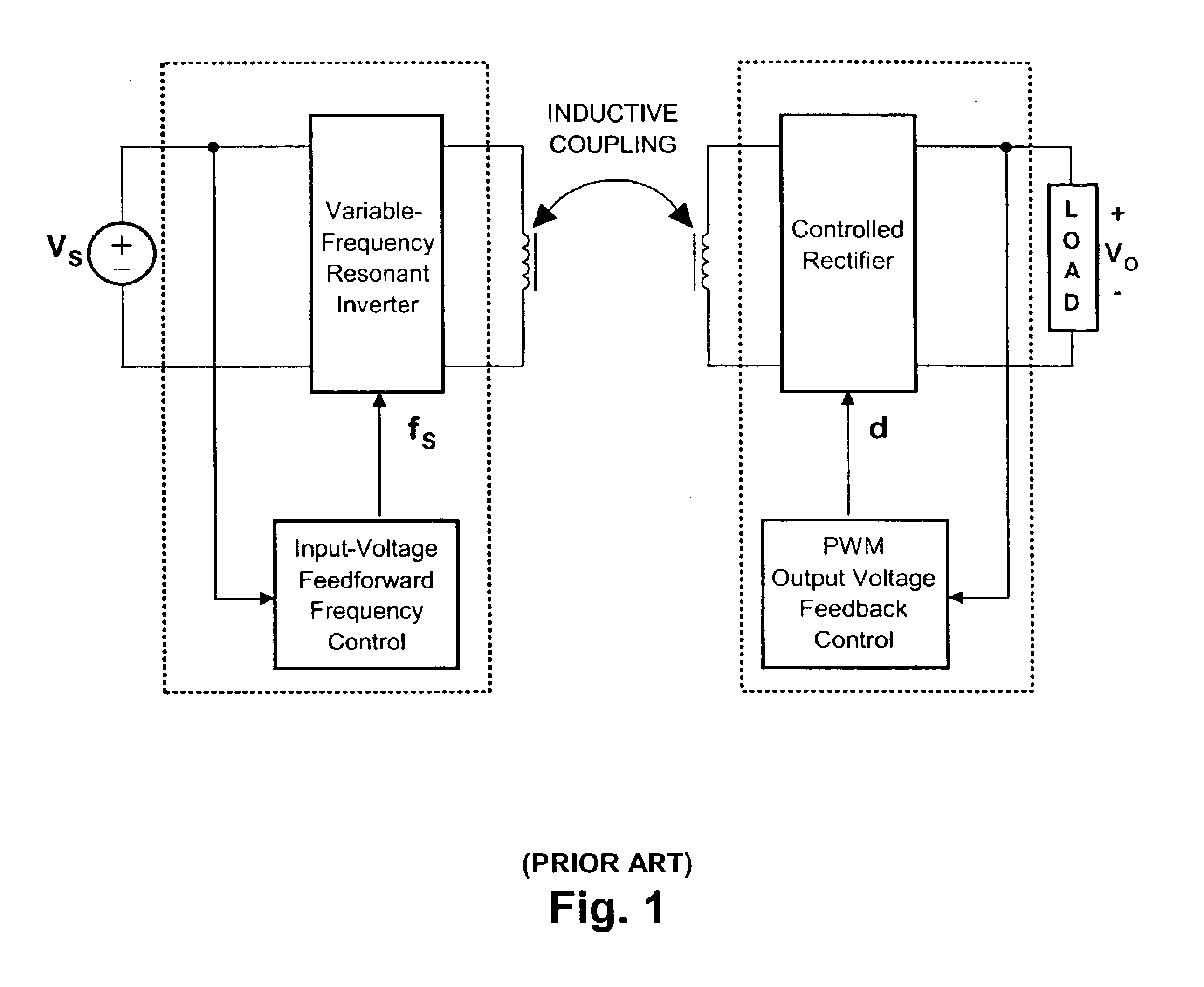
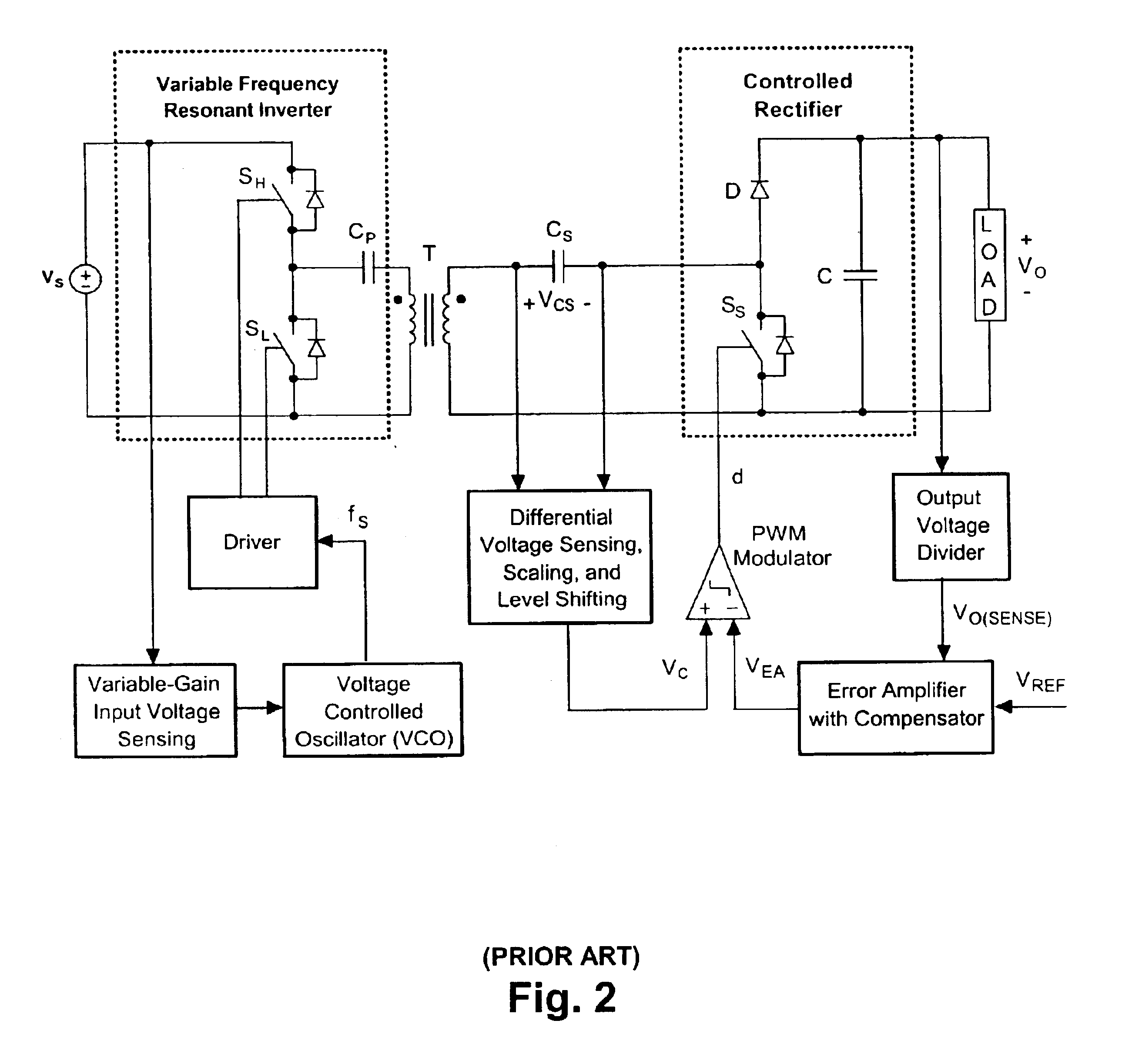
A contactless electrical energy transmission system includes a transformer having a primary winding that is coupled to a power source through a primary resonant circuit and a secondary winding that is coupled to a load through a secondary resonant circuit. The primary and secondary resonant circuits are inductively coupled to each other. A primary control circuit detects current changes through the primary resonant circuit to control the switching frequency of a controllable switching device for maintaining a substantially constant energy transfer between the primary winding and secondary winding in response to at least one of a power source voltage change and a load change. As a result, excessive circulating energy of the CEET system is minimized providing a tight regulation of the output voltage over the entire load and input voltage ranges without any feedback connection between the primary side and the secondary side.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Buck converter with inductor pre-energizing
ActiveUS7804282B2Simple control circuitDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterĆuk converter
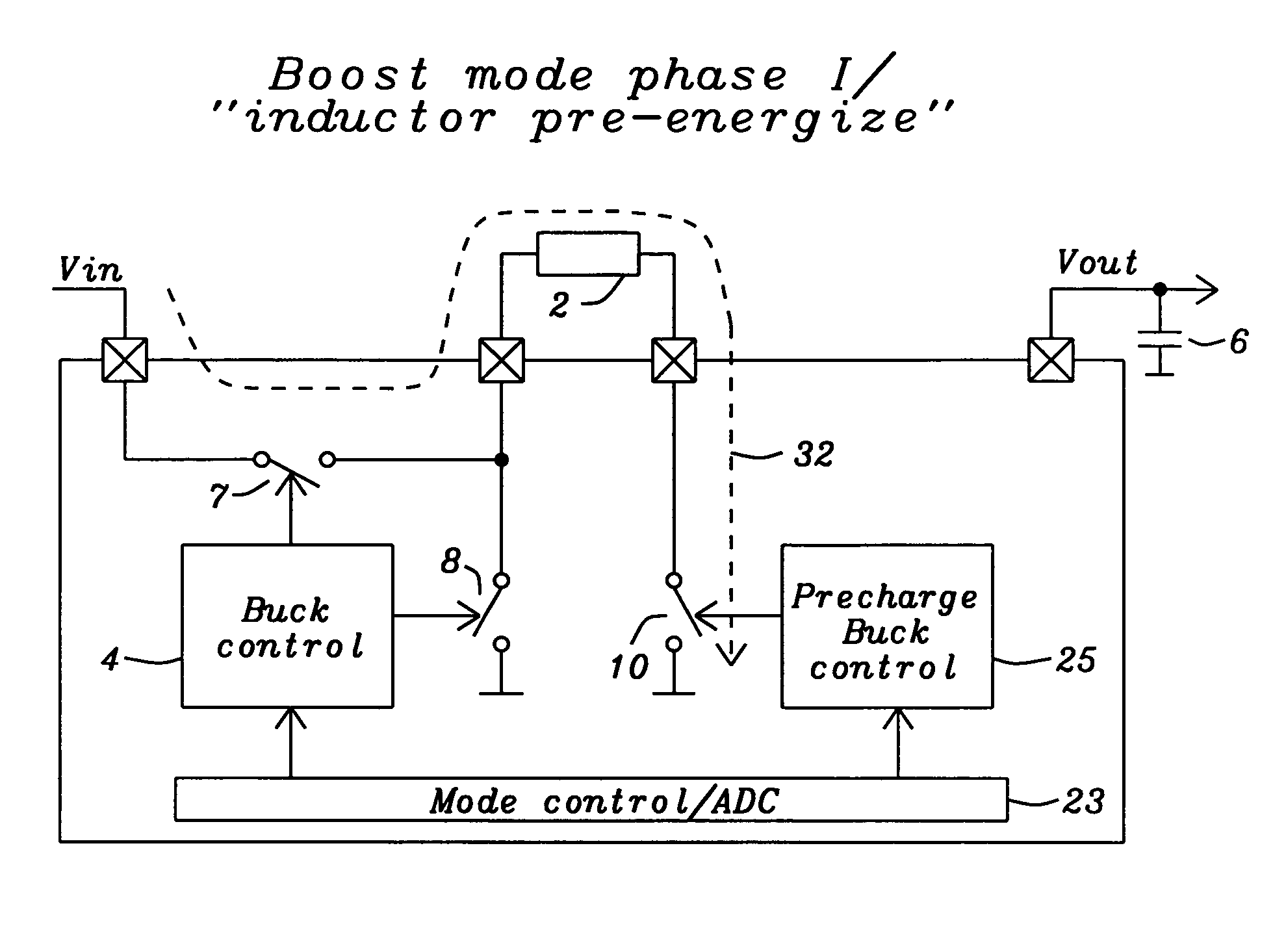
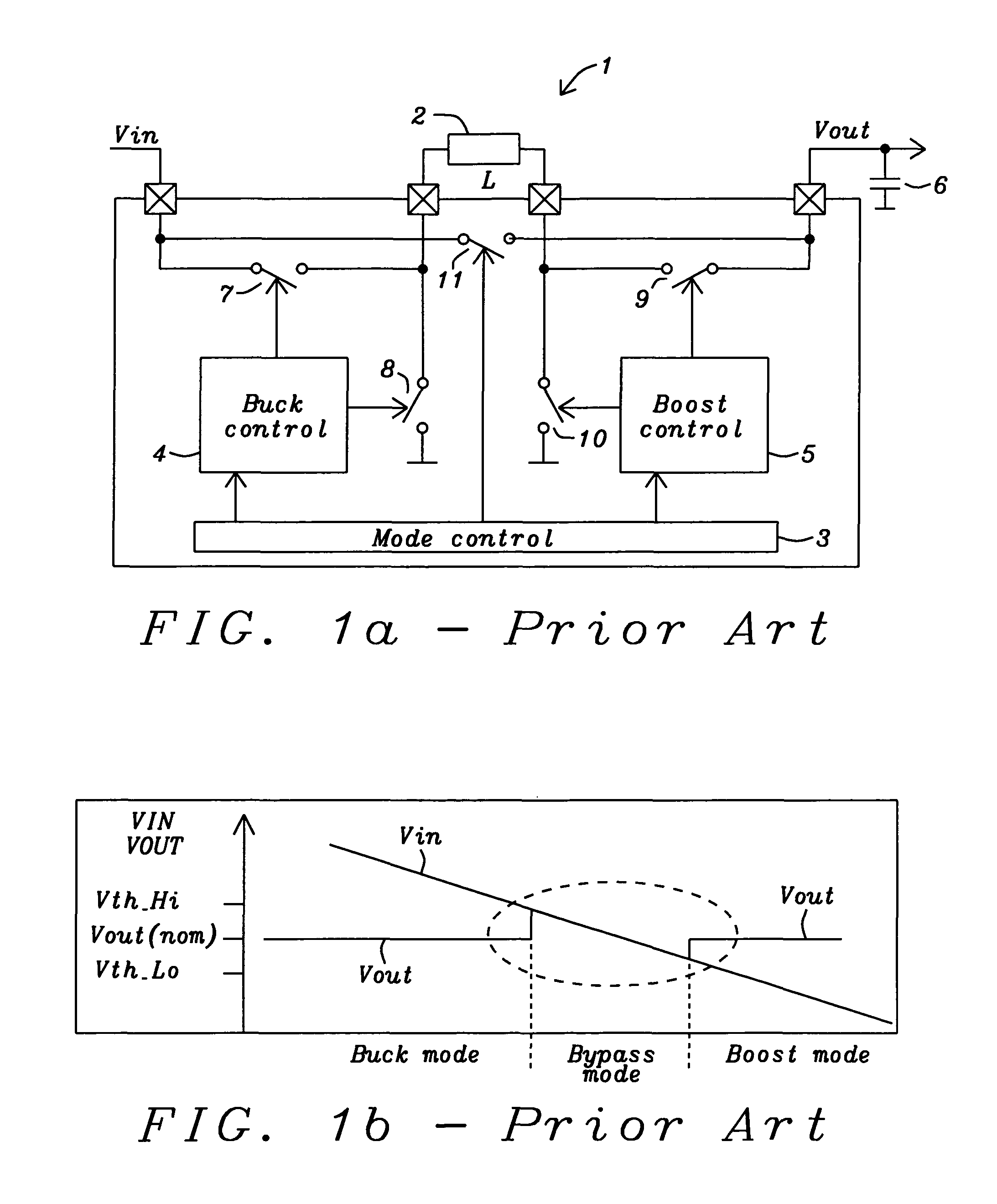
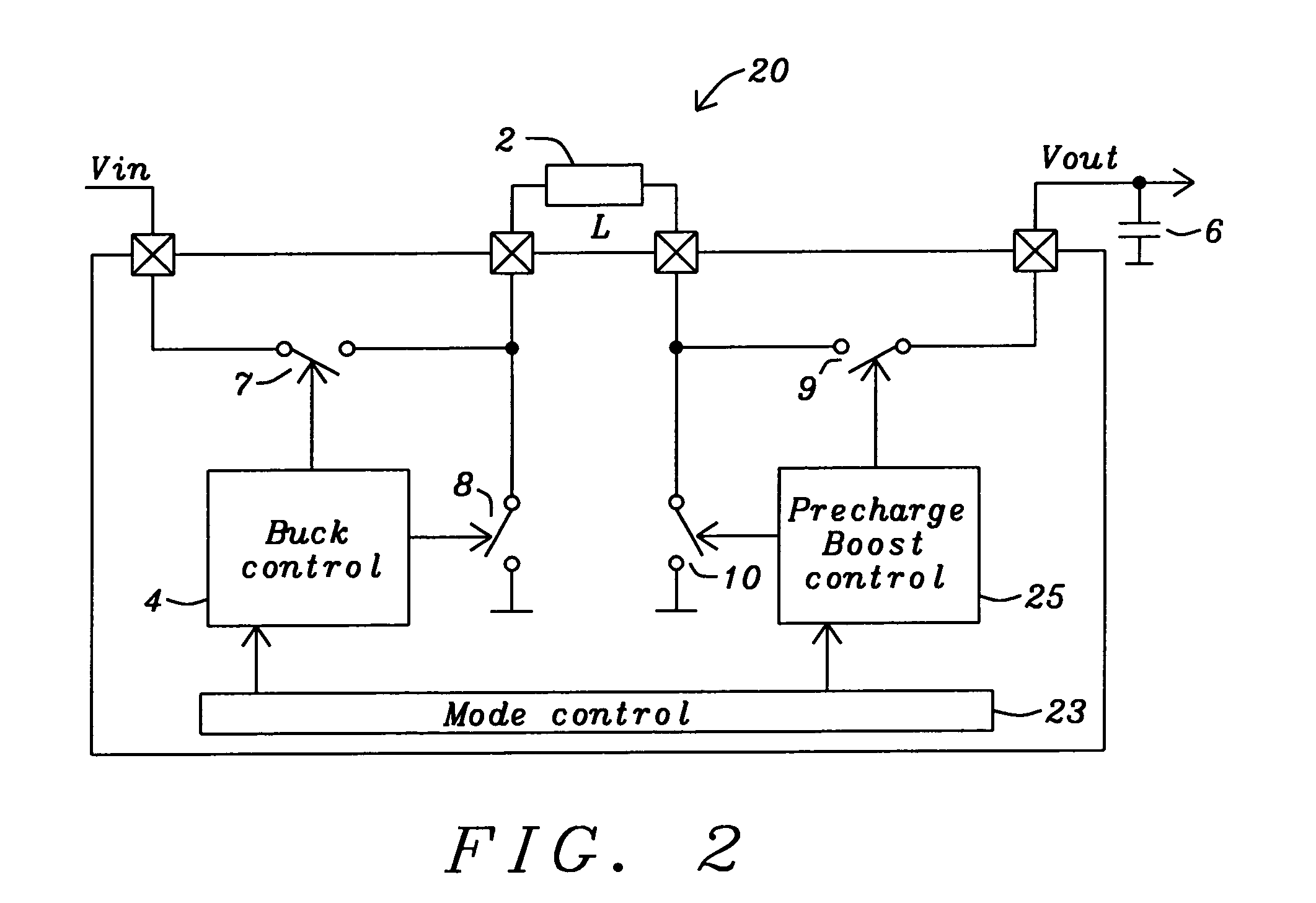
Circuits and methods to achieve a buck-boost converter, capable to achieve a constant output voltage by pre-charging of an inductor if the input voltage is close to the output voltage has been achieved. The prior art problem of output voltage variations occurring while the input voltage is close to the output voltage is avoided. In case the input voltage is lower than a defined threshold voltage or the duty cycle exceeds a defined maximum allowable level, the inductor of the converter is pre-charged followed by boosting of the energy of the inductor to the output of the converter. In both modes the control loops of the buck converter can be used for buck duty cycle control. The duration of the pre-charge depends upon the level of the input voltage, the lower the input level is the longer is the pre-charge performed.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Alternative Switch Power Circuitry Systems
InactiveUS20110181251A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcBoost controllerEngineering
Reliability enhanced systems are shown where an short-lived electrolytic capacitor can be replaced by a much smaller, perhaps film type, longer-lived capacitor to be implemented in circuits for power factor correction, solar power conversion, or otherwise to achieve DC voltage smoothing with circuitry that has solar photovoltaic source (1) a DC photovoltaic input (2) internal to a device (3) and uses an enhanced DC-DC power converter (4) to provide a smoothed DC output (6) with capacitor substitution circuitry (14) that may include interim signal circuitry (28) that creates a large voltage variation for a replaced capacitor (16). Switchmode designs may include first and second switch elements (17) and (18) and an alternative path controller (21) that operates a boost controller (22) and a buck controller (23) perhaps with a switch duty cycle controller (32).
Owner:AMPT
Apparatus for reducing power supply noise in an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6339338B1Reduce power supply noiseSuppress mutationDigital circuit testingVolume/mass flow measurementCapacitanceState variation
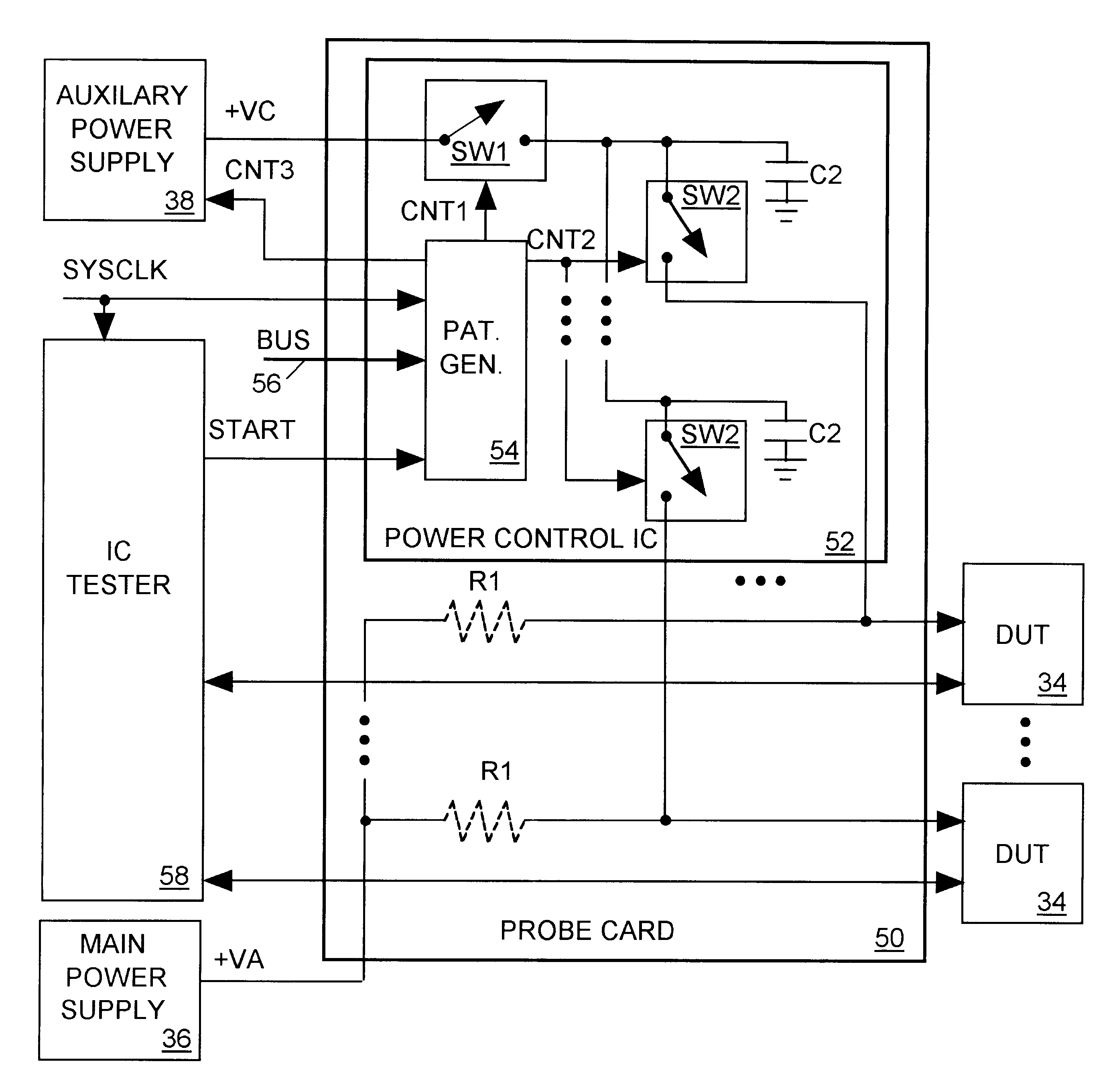
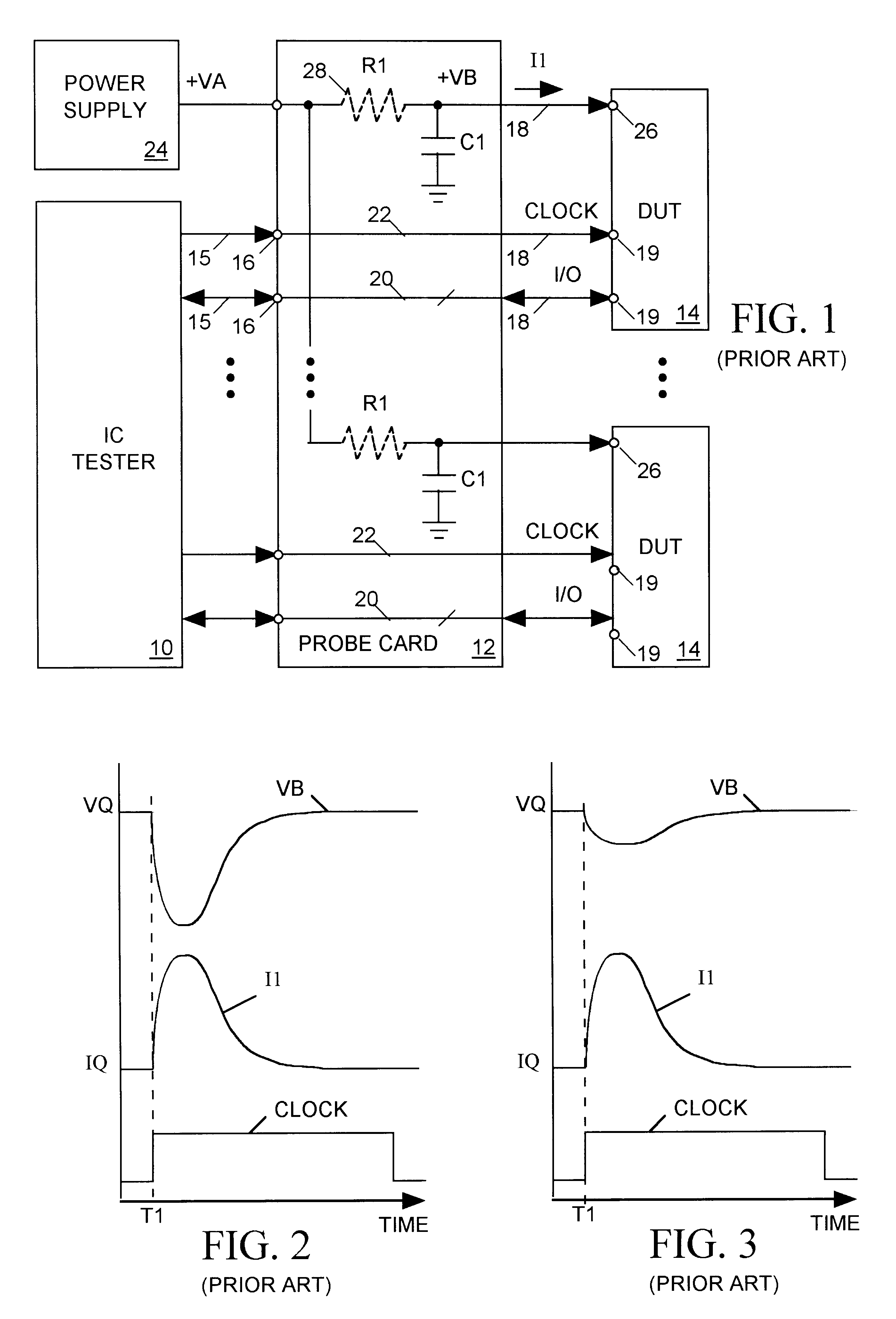
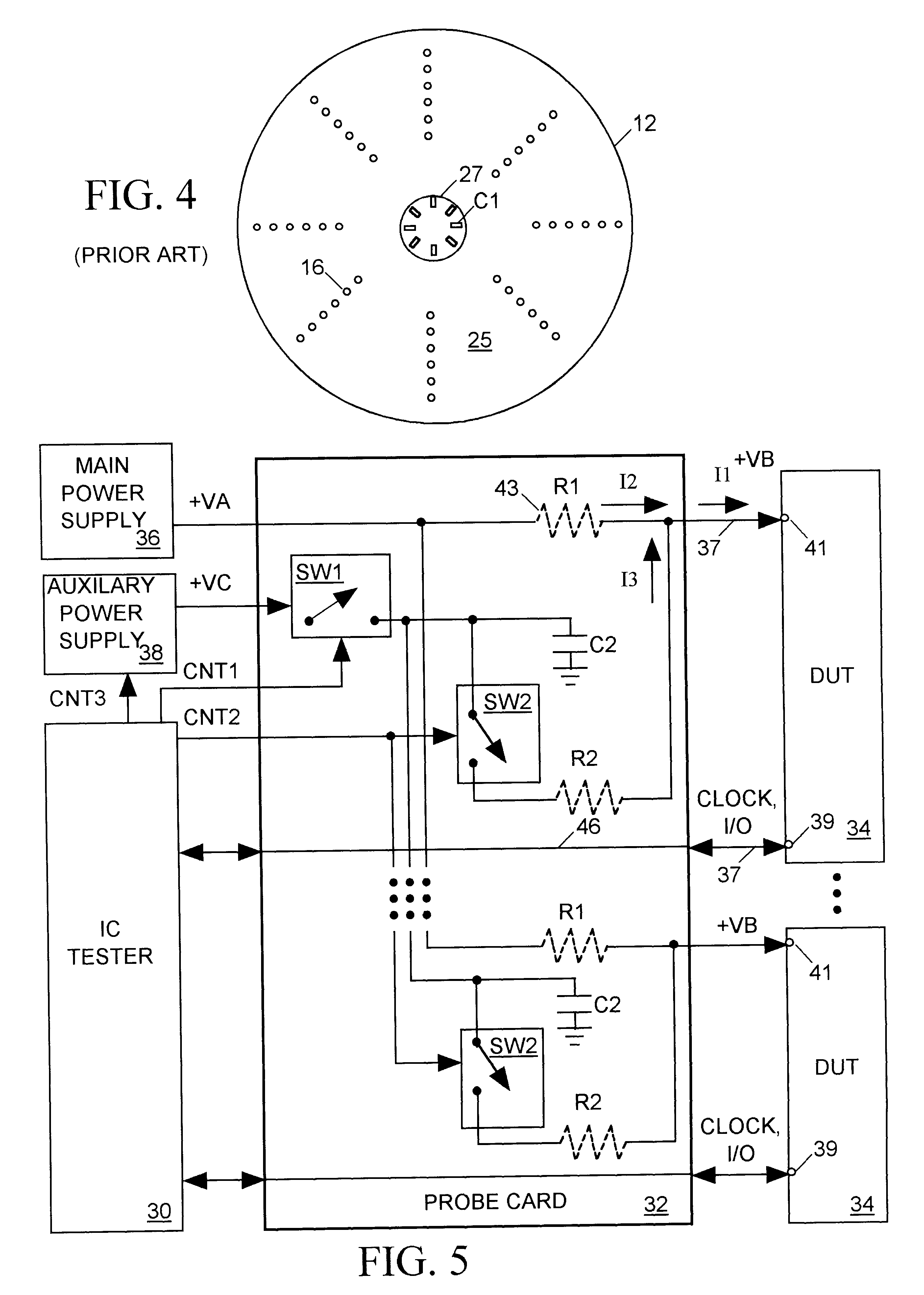
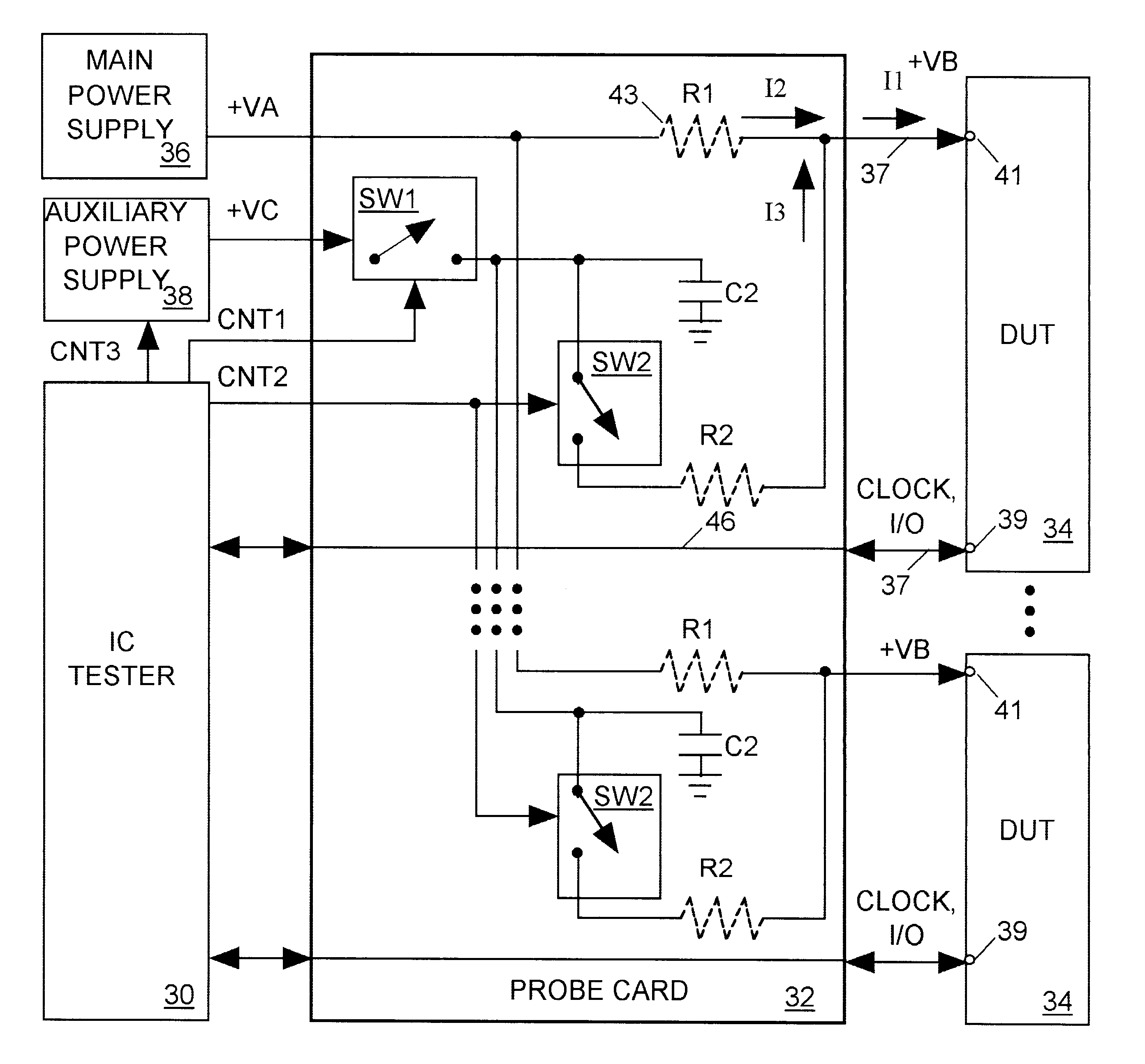
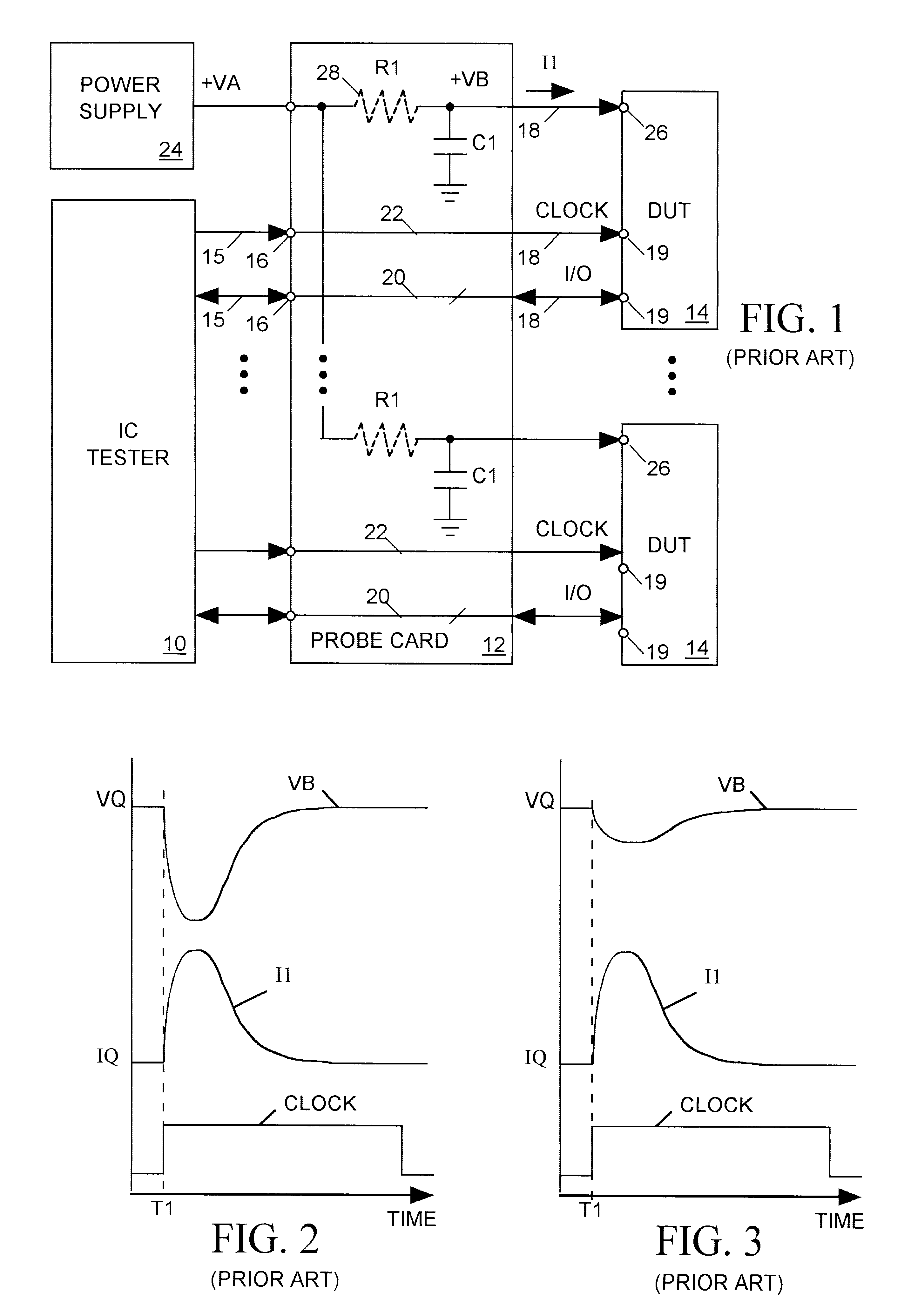
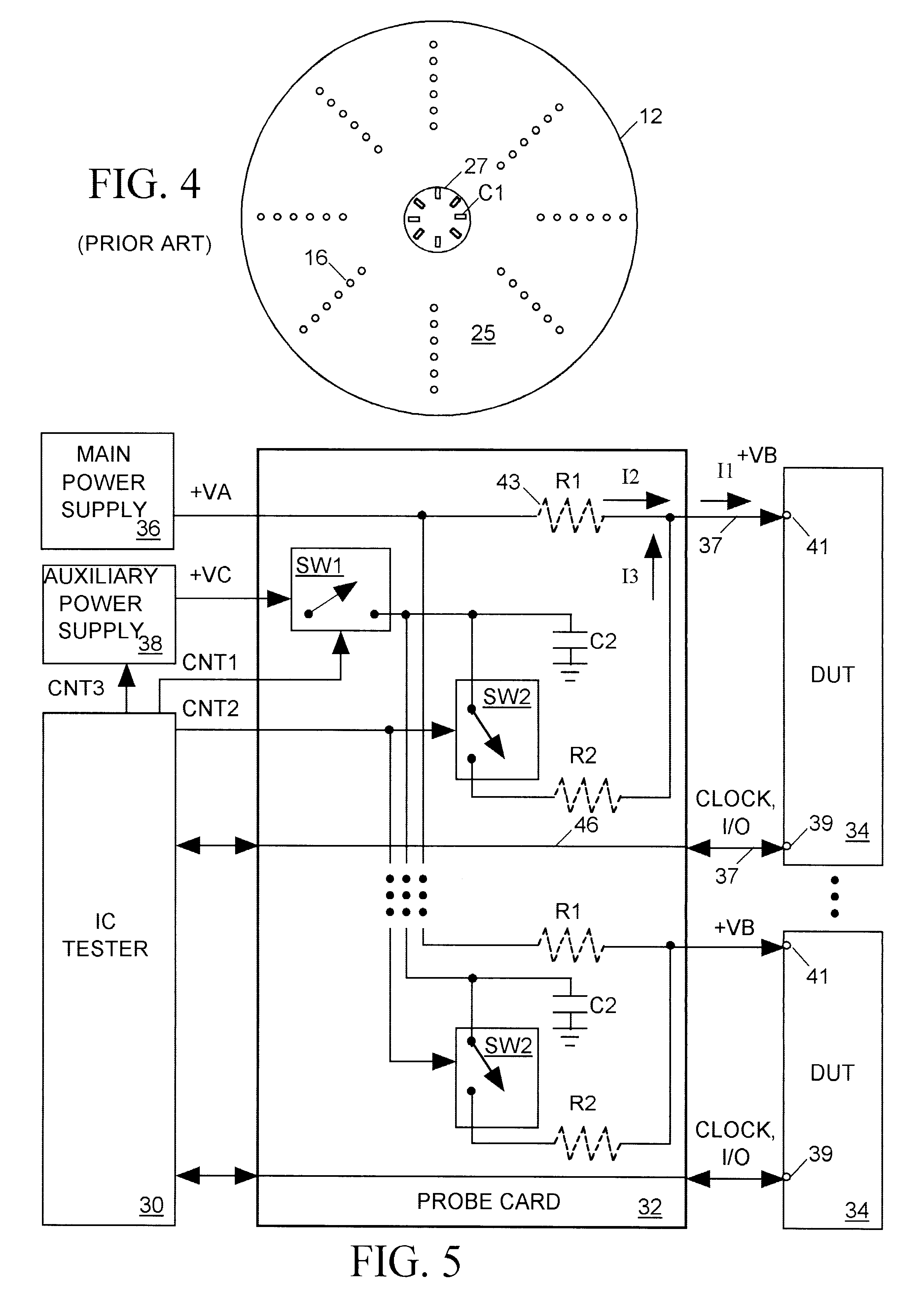
A main power supply continuously provides a current to a power input terminal of an integrated circuit device under test (DUT). The DUT's demand for current at the power input terminal temporarily increases during state changes in synchronous logic circuits implemented within the DUT. To limit variation (noise) in voltage at the power input terminal arising from these temporary increases in current demand, a charged capacitor is connected to the power input terminal during each DUT state change. The capacitor discharges into the power input terminal to supply additional current to meet the DUT's increased demand. Following each DUT state change the capacitor is disconnected from the power input terminal and charged to a level sufficient to meet a predicted increase in current demand during a next DUT state change.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Display apparatus and drive control method for the same
ActiveUS20100039422A1Avoid Threshold Voltage DriftInexpensive and simple circuit structureCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriving currentAcquired characteristic
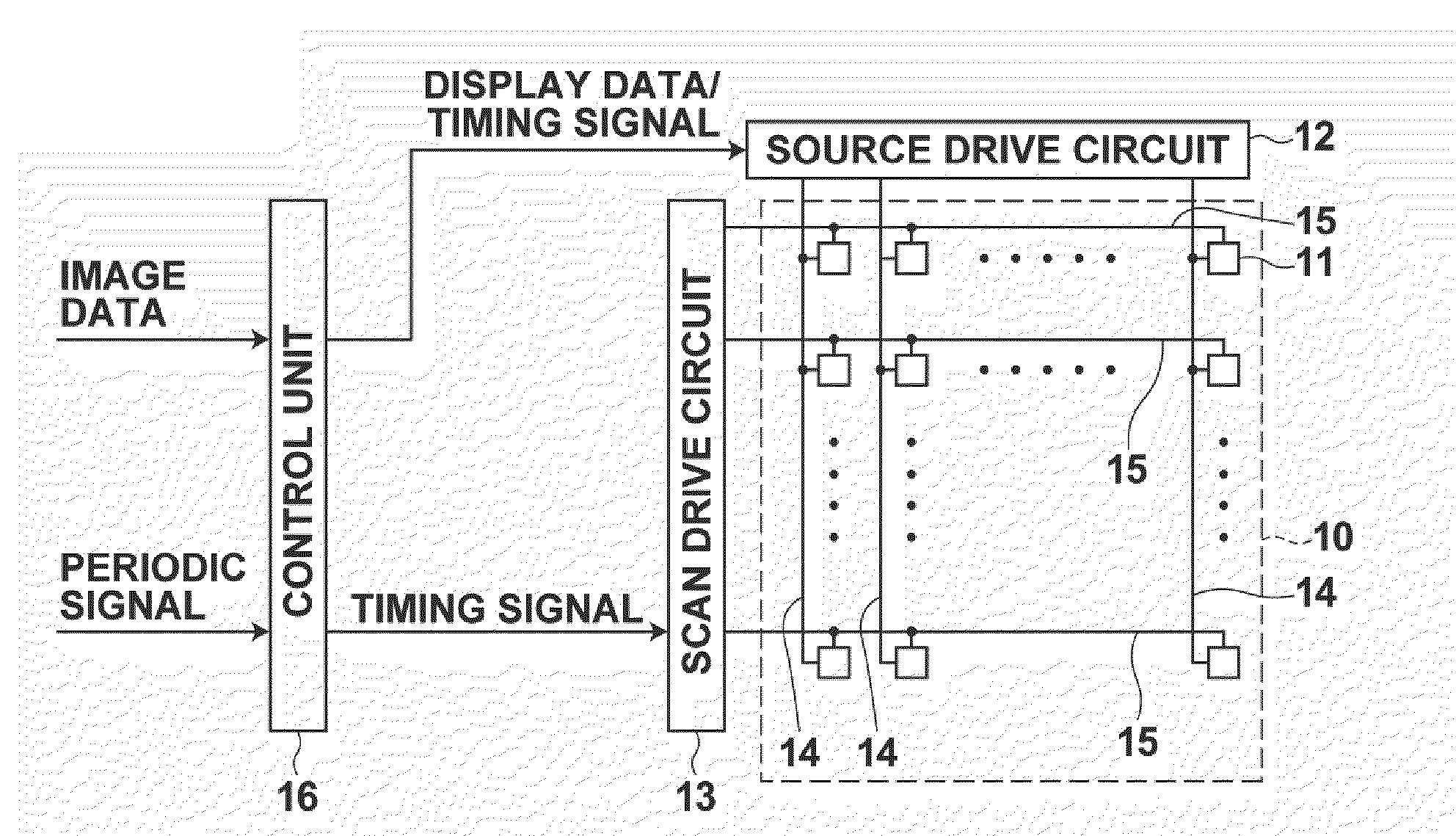
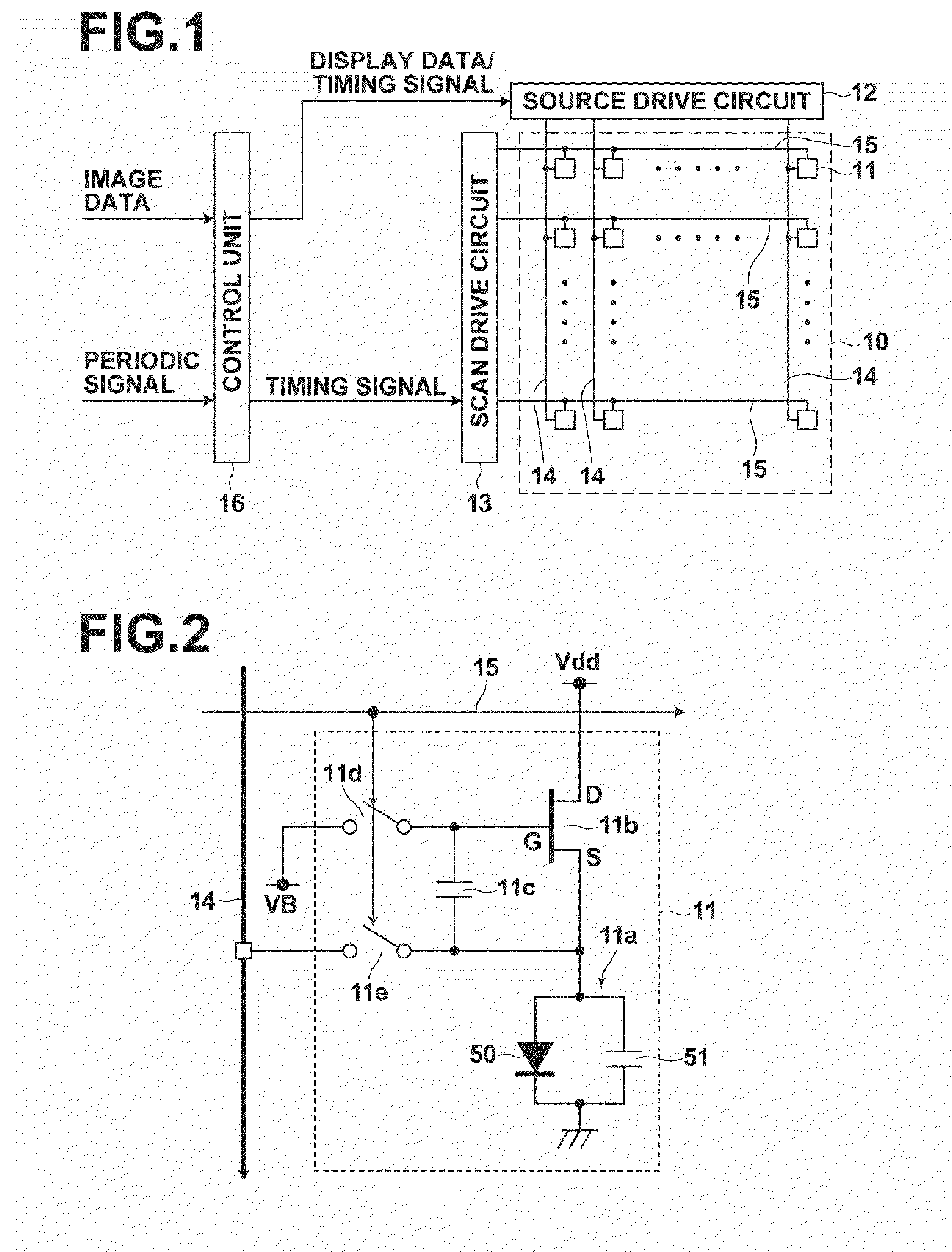
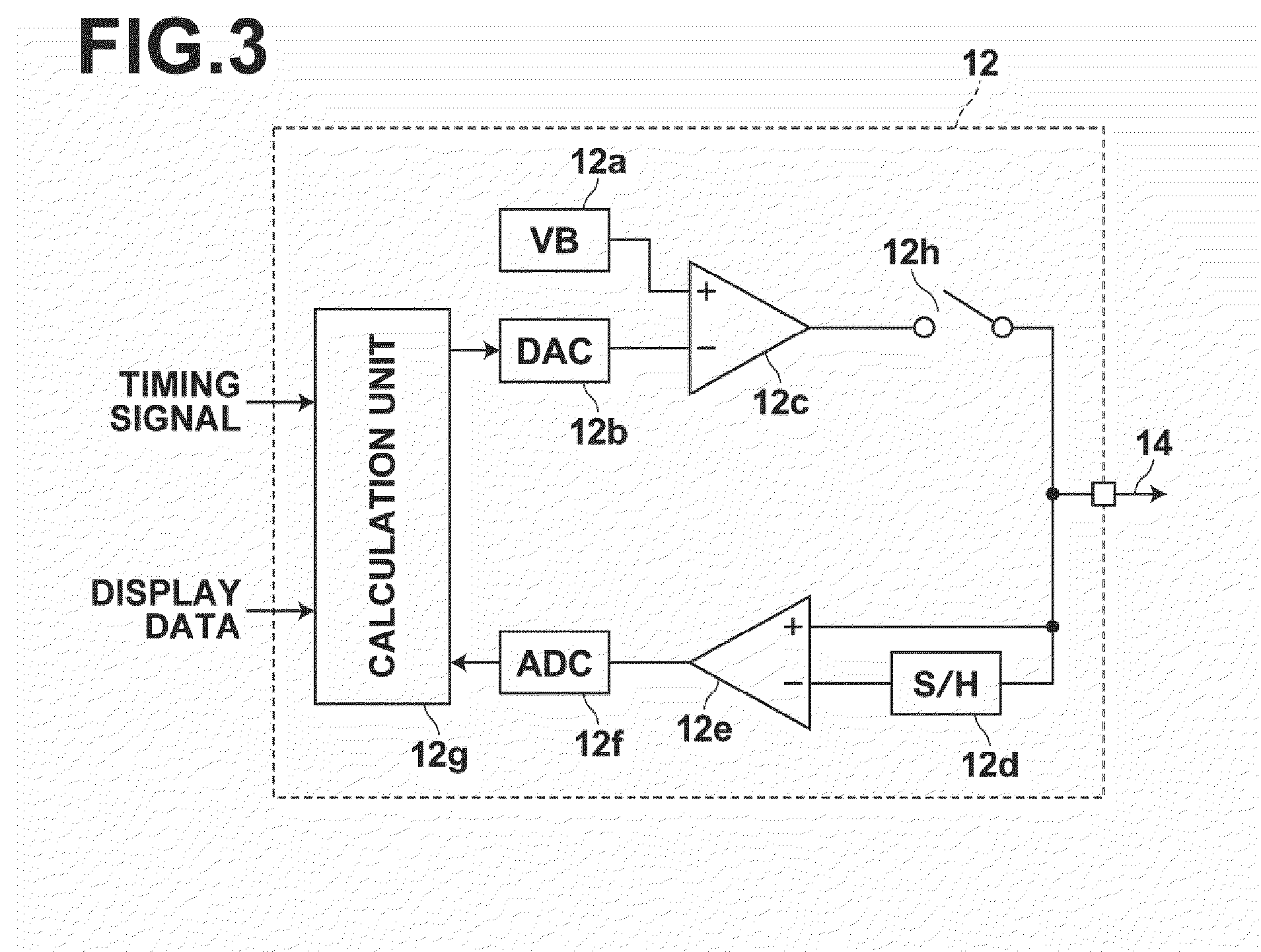
Supplying first and second measuring voltages to a source terminal of a drive transistor to obtain first and second voltage variations at the source terminal of the drive transistor when a parasitic capacitance of a light emitting element is charged by currents flowed through the drive transistor by the supply of the voltages, obtaining first and second current values of the drive current of the drive transistor based on the first and second voltage variations, obtaining characteristic values of the drive transistor based on the first and second measuring voltages and the first and second current values, and outputting a data signal based on the obtained characteristic values and a drive voltage of the drive transistor corresponding to the amount of emission of the light emitting element to the source terminal of the drive transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method of measuring threshold voltage for a NAND flash memory device
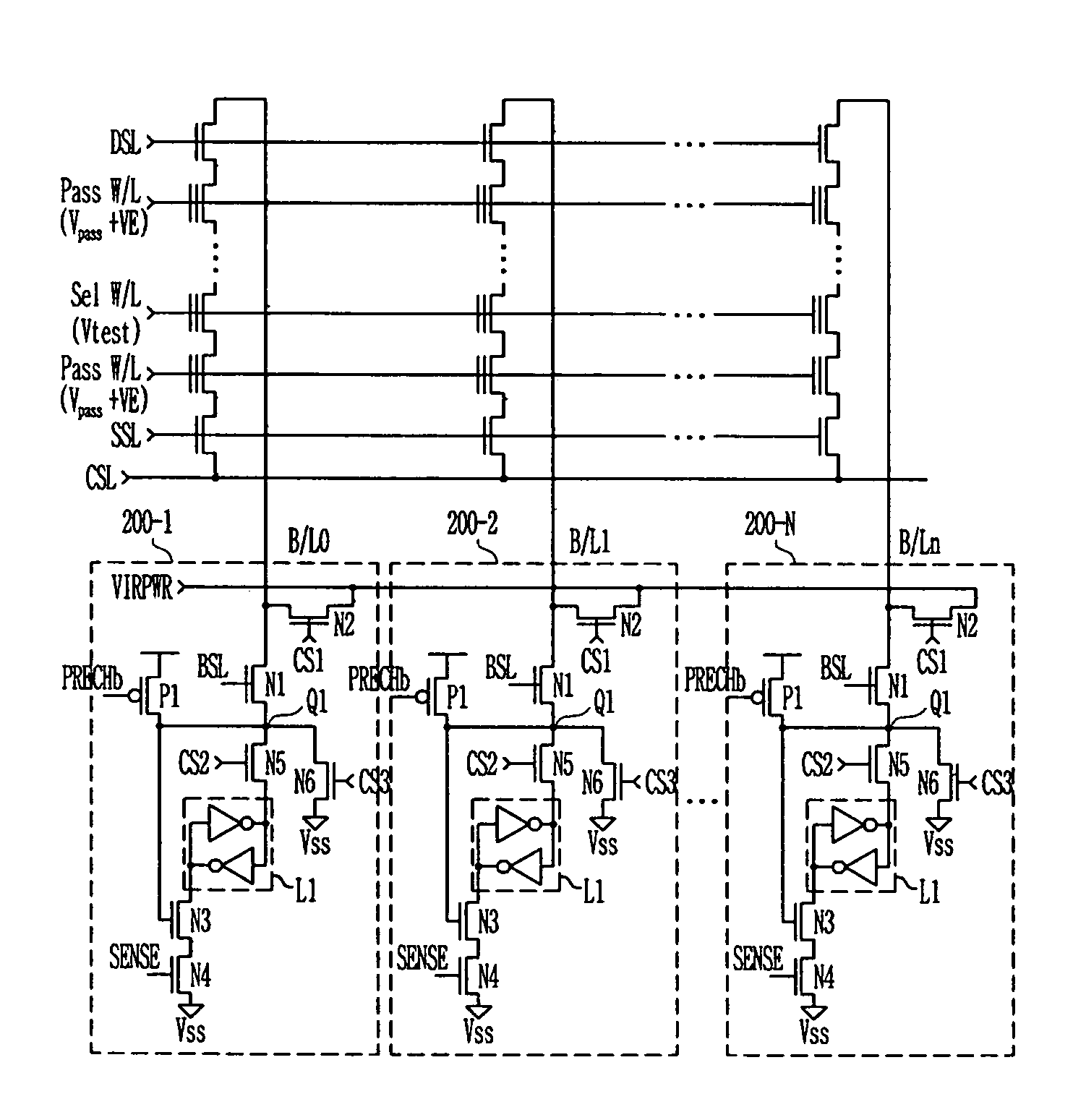
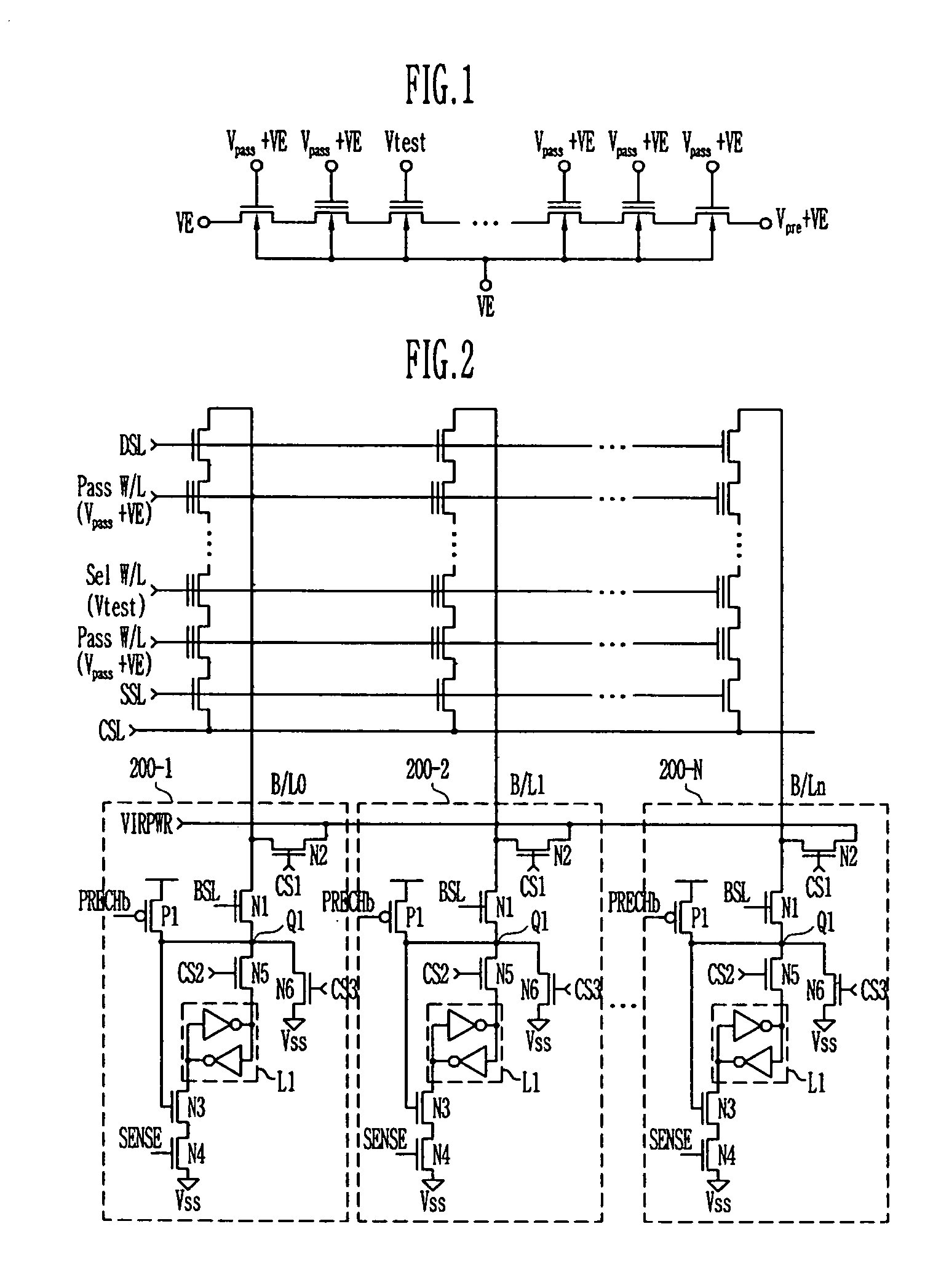
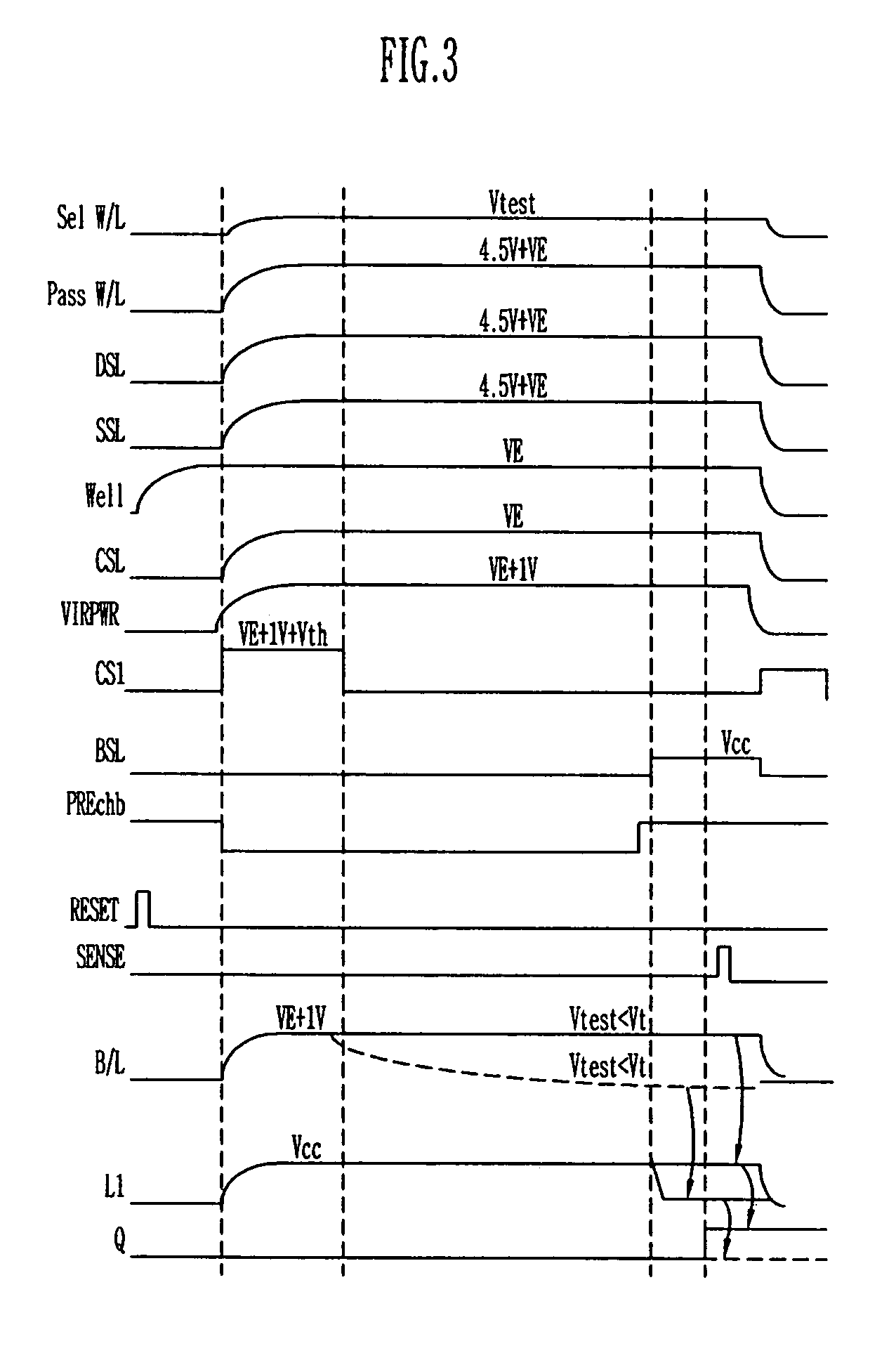
Provided is a method of measuring threshold voltages in a NAND flash memory device. In the method, a test voltage is applied to a wordline of selected memory cells to measure a distribution profile of threshold voltages of memory cells. A voltage summing up a pass voltage and an operation voltage is applied to wordlines of deselected cells. The operation voltage is applied to a well and a common source line. A voltage summing up a precharge voltage and the operation voltage is applied to a bitline. After then, a voltage variation on the bitline can be detected to measure a threshold voltage of a memory cell. A negative threshold voltage can be measured by applying a positive voltage with reference to a voltage, as the threshold voltage of the memory cell, set by subtracting the operation voltage from the test voltage in accordance with the bitline voltage variation.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
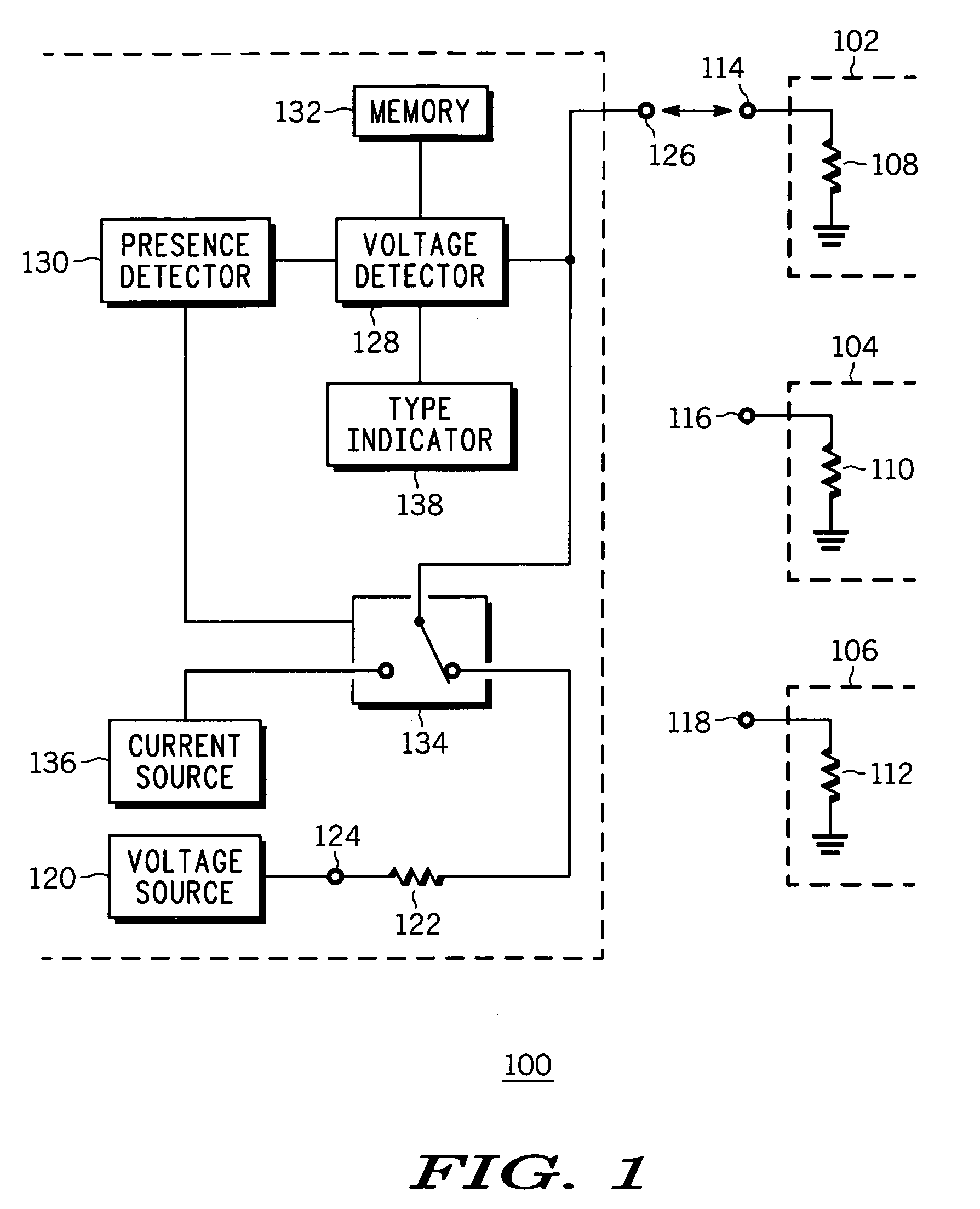
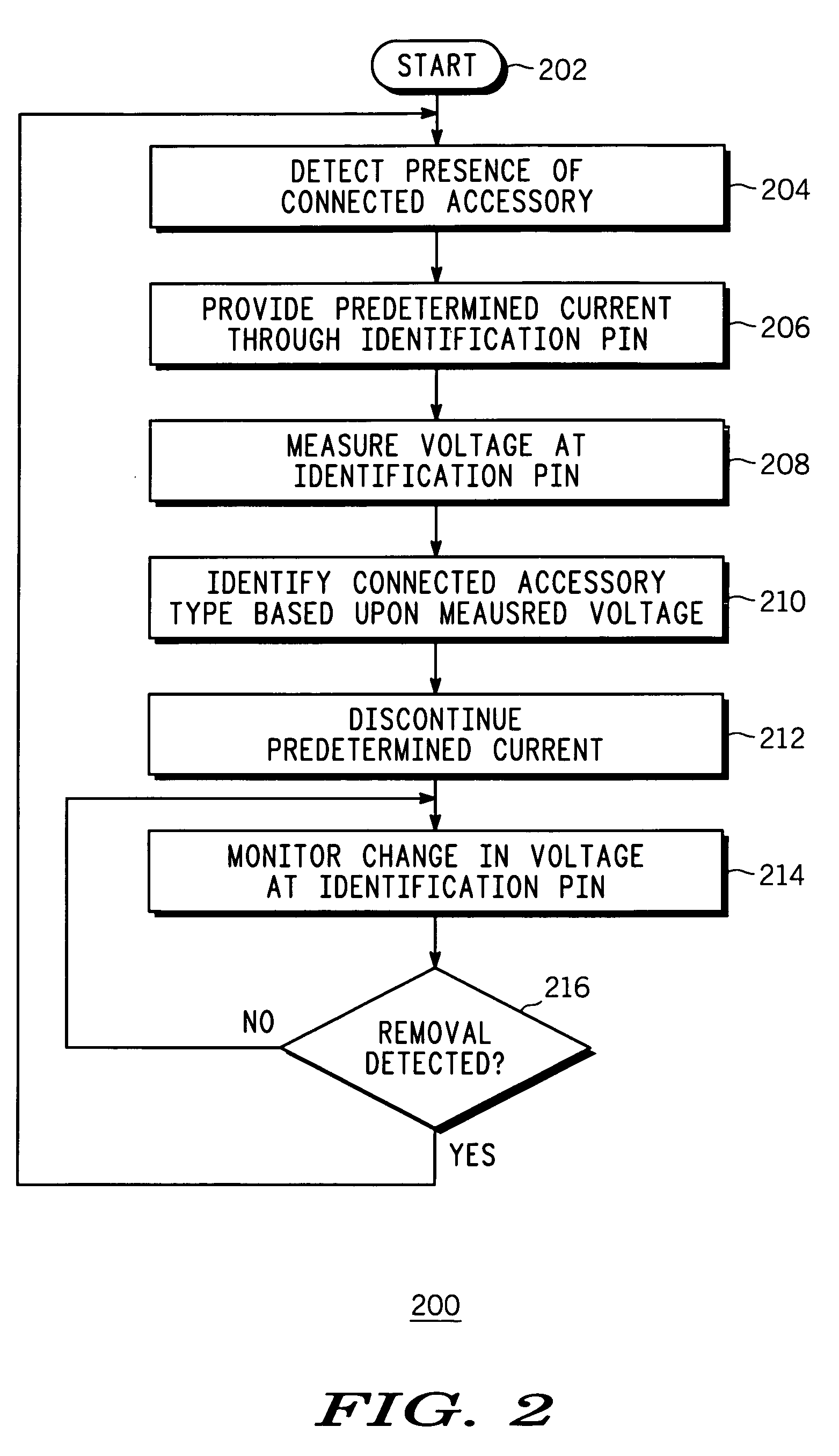
Accessory identifier in an electronic device
InactiveUS20050268000A1Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingUnique identifierVoltage source
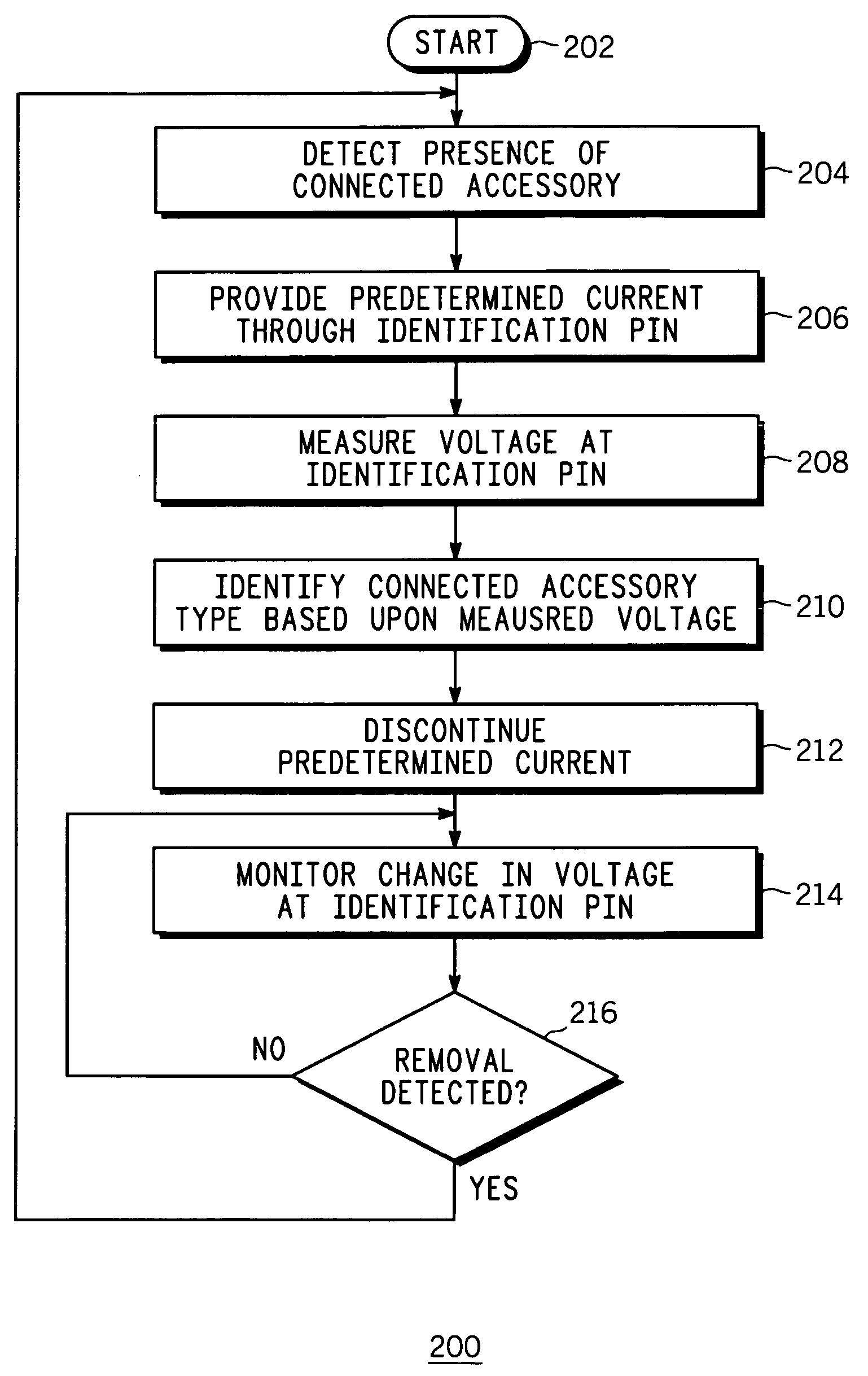
An apparatus (100) and a method (200) for an accessory identifier for identifying a connected accessory type from three or more accessory types (102, 104, 106) are provided. Each of the three or more accessory types (102, 104, 106) has a unique identifier resistor (108, 110, 112), which is accessible through an identification pin (114, 116, 118) and is linearly related to each other in resistance value. Using a voltage source (120), presence of the connected accessory (102) is detected (204) by monitoring a voltage change at the source pin (126). Once the presence is detected, a predetermined current is sent through the source pin (126) and the resulting voltage at the source pin (126) is measured (208), and based upon the measured voltage, the connected accessory type (102) is identified (210).
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
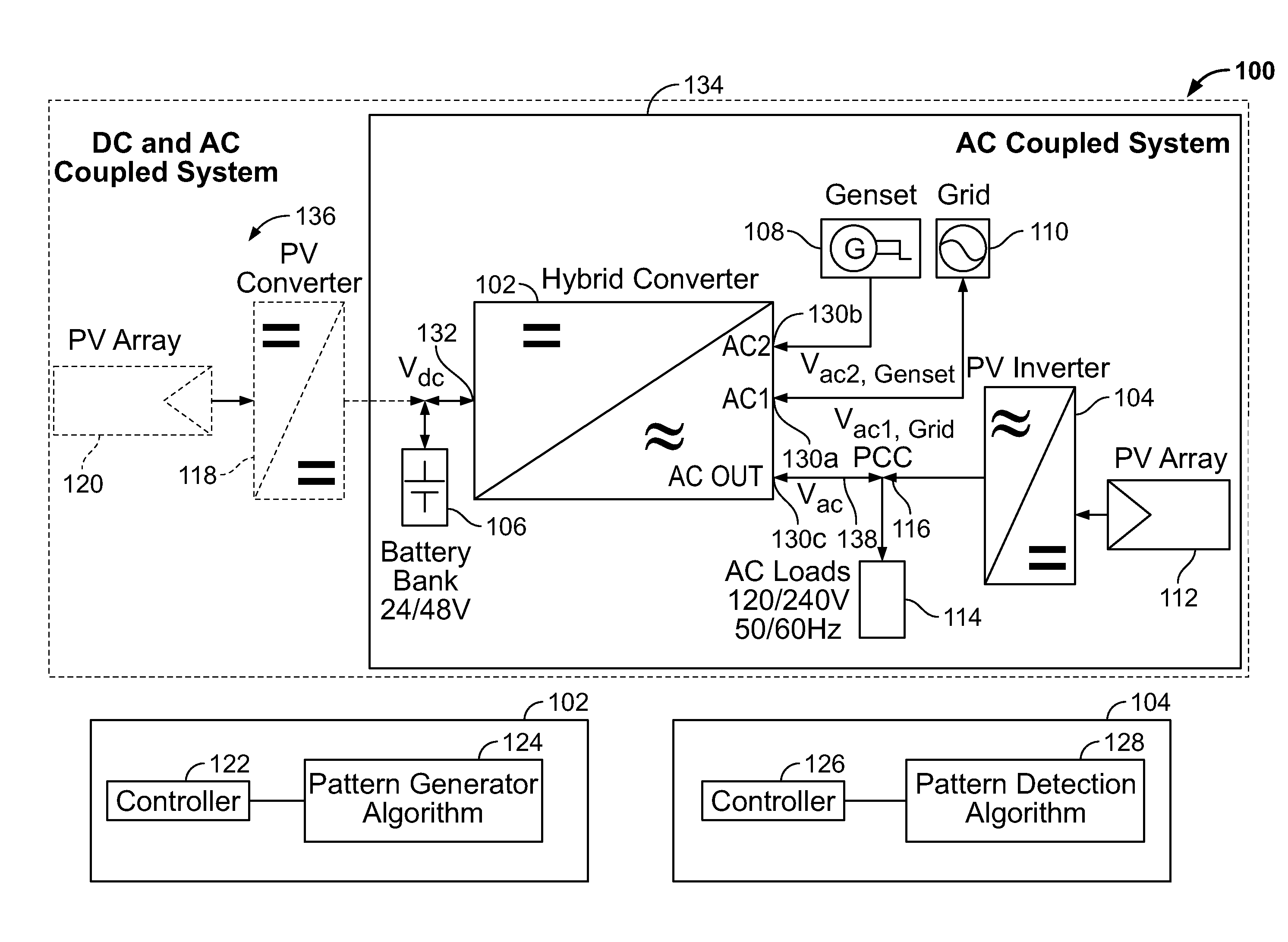
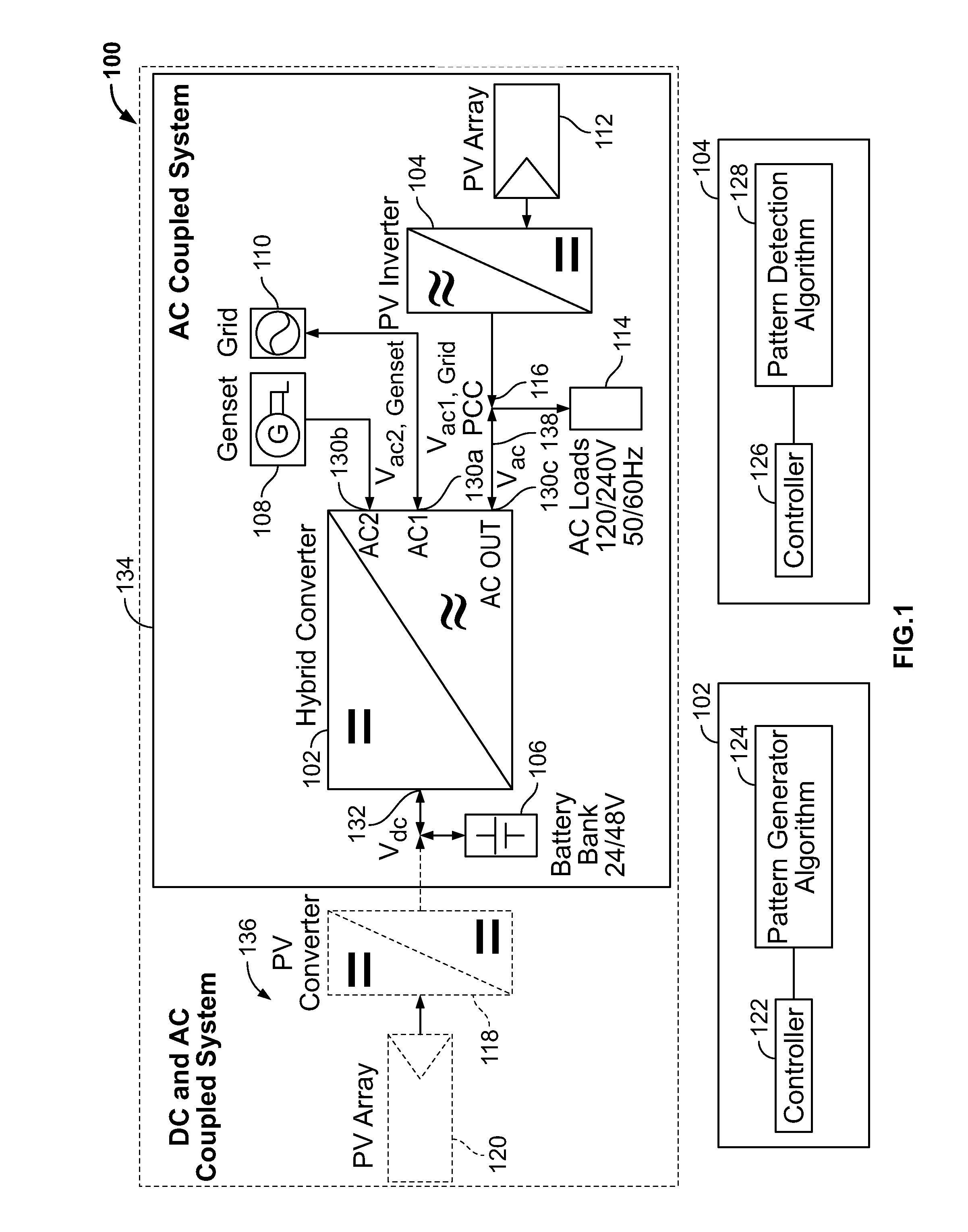
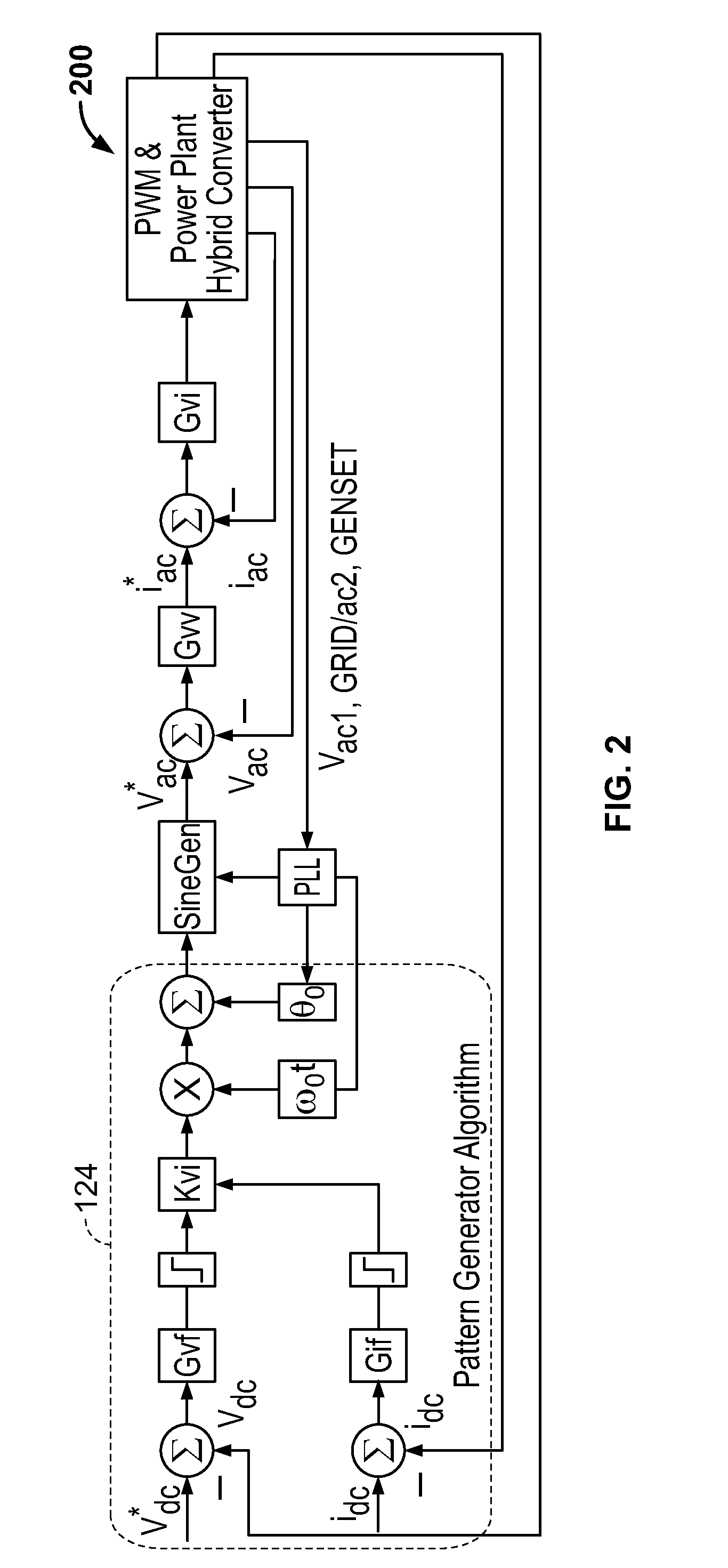
Ac connected modules with line frequency or voltage variation pattern for energy control
ActiveUS20110043160A1Maximize efficiencyEasy to controlBatteries circuit arrangementsPower supply linesIslandingEnergy control
A control strategy for distributed power generation modules in a power system that varies the line frequency or voltage according to a predetermined pattern to cause a PV inverter to modify its power output and thereby avoid overcharging a battery. When the power system operates in islanded mode, the AC load demand can be lower than the available energy from the PV array, causing the battery to become overcharged. To avoid this scenario, a hybrid inverter executes a pattern generator algorithm that varies the line frequency or voltage linearly, exponentially or any mathematical function or look-up tables. The PV inverter executes a pattern detection algorithm that detects the linear, exponential, or any mathematical function or look-up table change in the line frequency. In response, the PV inverter modifies its power output until an overcharging condition of the battery is removed. The line frequency / voltage can be varied within the anti-islanding limits to avoid premature disruption of the power system, and no additional settings are required at the device level in order to operate in any mode of operation: islanded, grid-connected or genset-connected.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOLAR INVERTERS USA
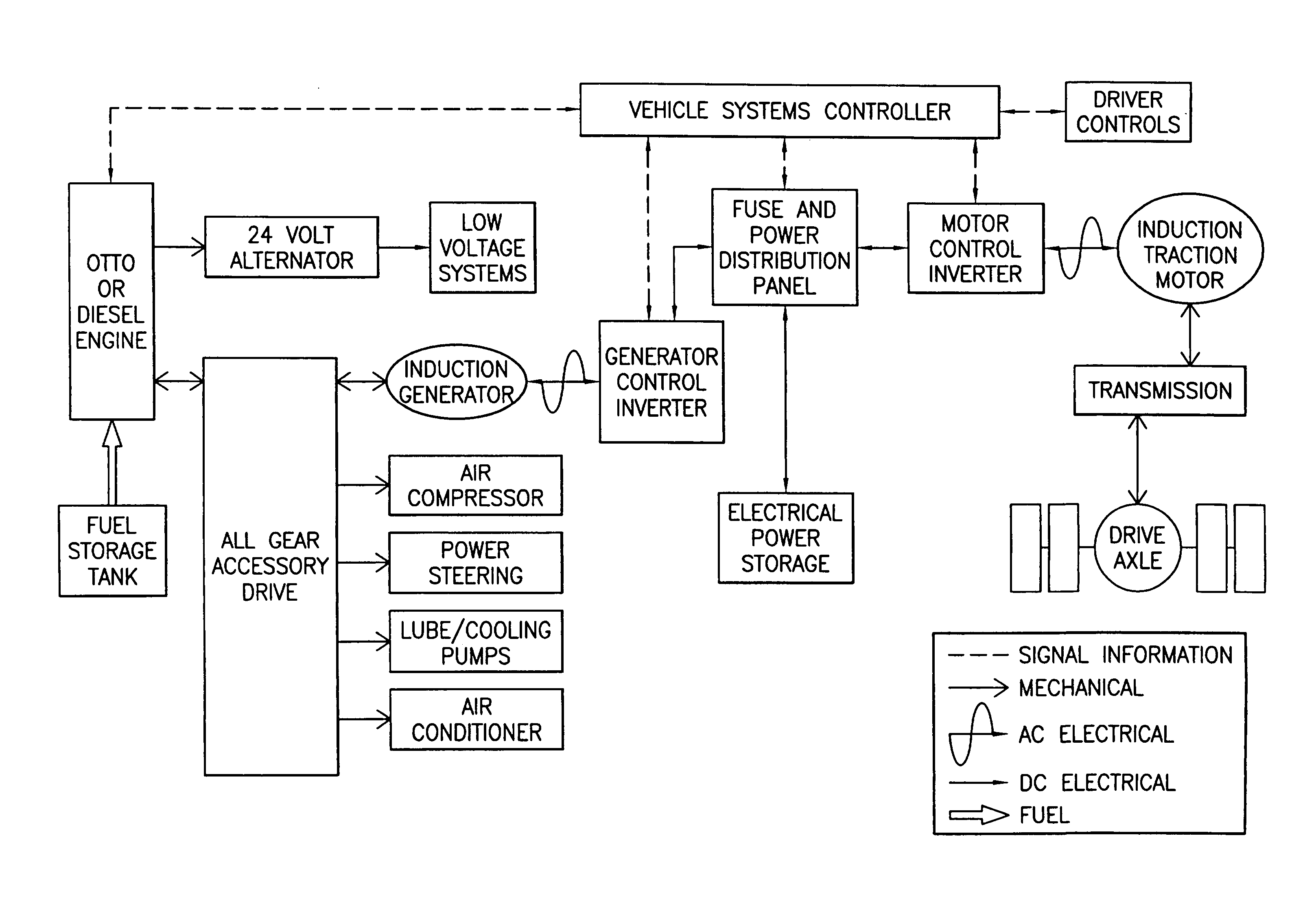
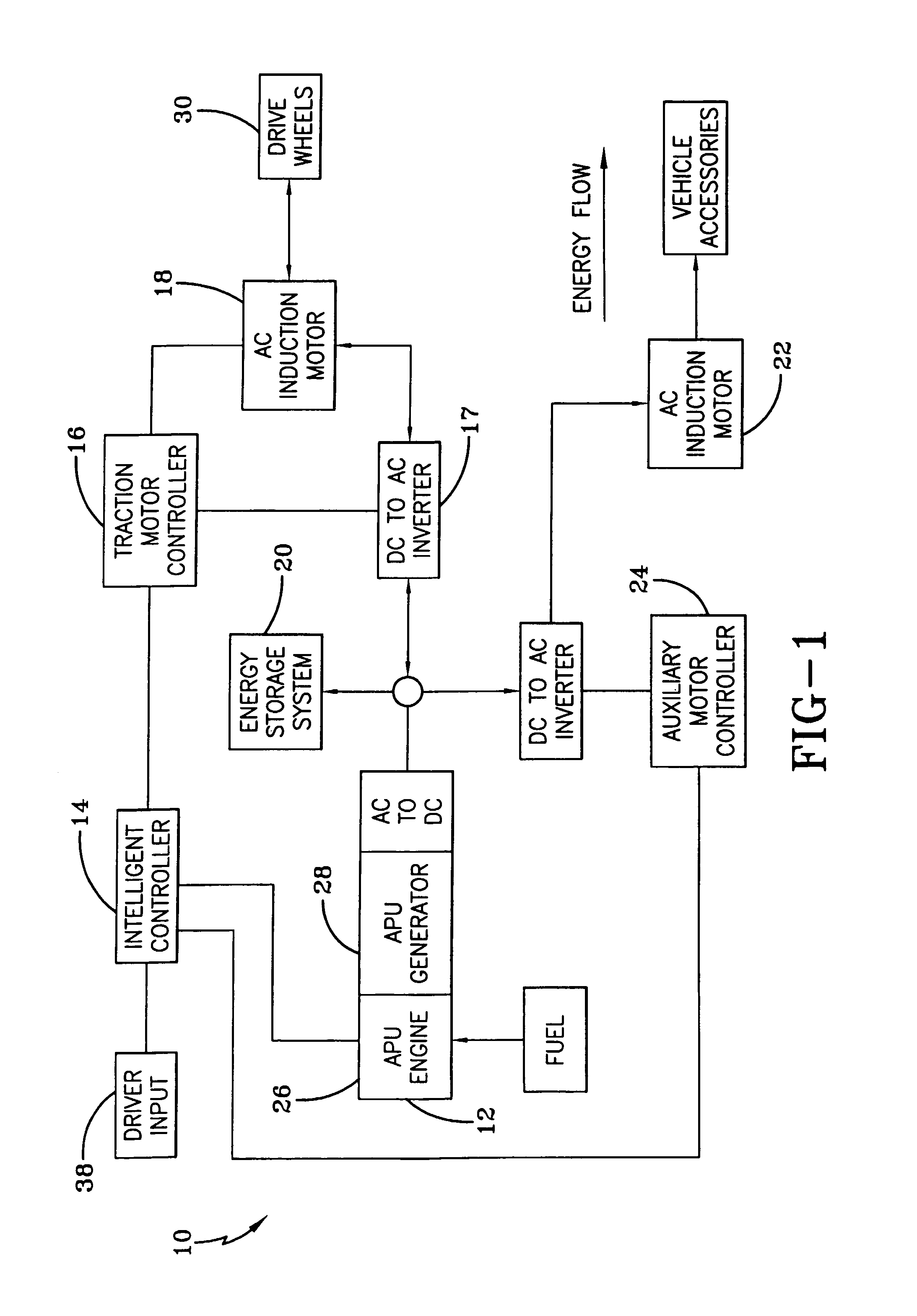
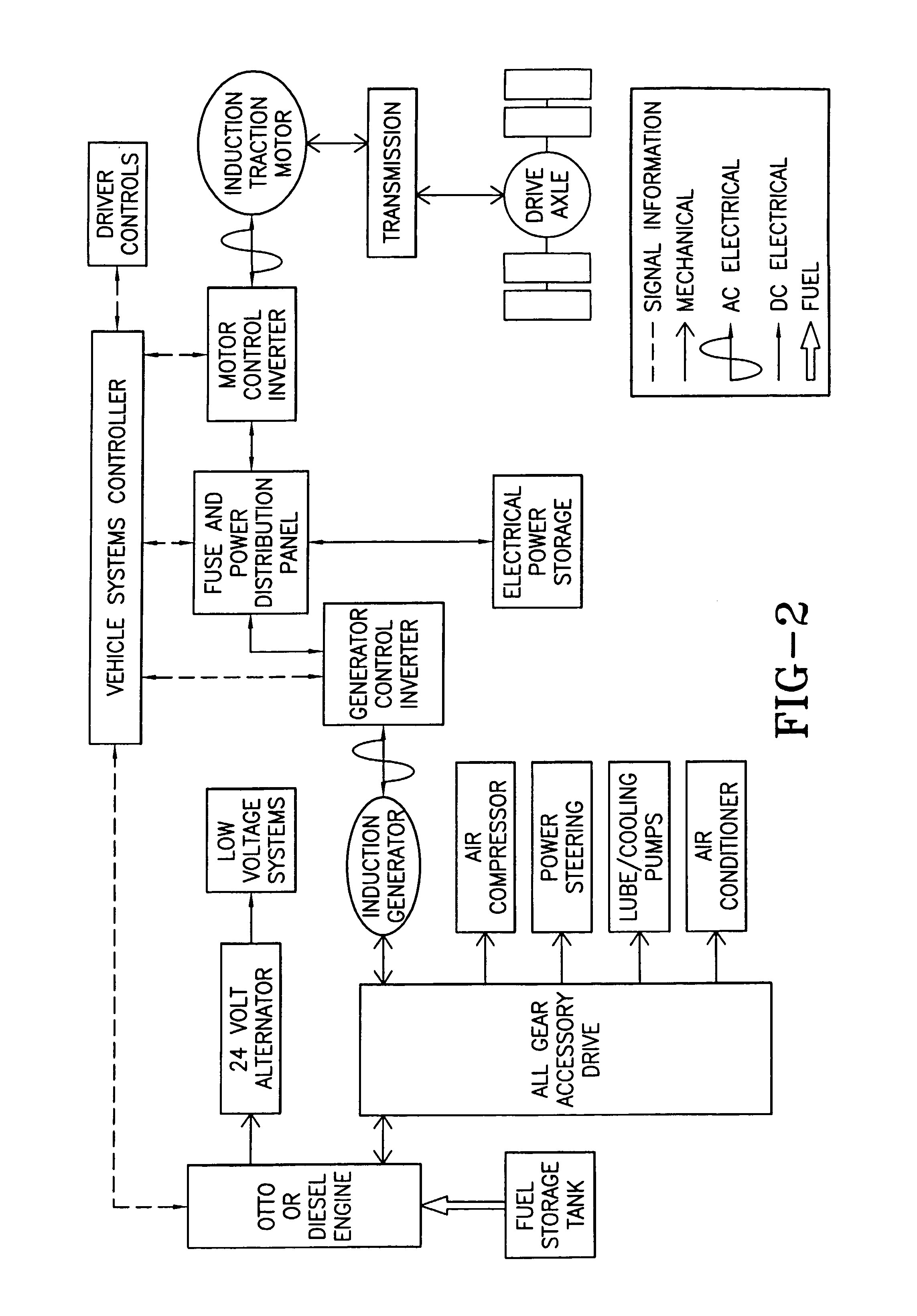
Hybrid electric vehicle
InactiveUS7252165B1Poor vehicle performanceImprove variationDigital data processing detailsVehicle sub-unit featuresLow voltageAuxiliary power unit
Owner:BOWLING GREEN STATE UNIV
Distributed Power Harvesting Systems Using DC Power Sources
InactiveUS20120175963A1Improve component reliabilitySafe operating voltageDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsTransverterEngineering
A system and method for combining power from DC power sources. Each power source is coupled to a converter. Each converter converts input power to output power by monitoring and maintaining the input power at a maximum power point. Substantially all input power is converted to the output power, and the controlling is performed by allowing output voltage of the converter to vary. The converters are coupled in series. An inverter is connected in parallel with the series connection of the converters and inverts a DC input to the inverter from the converters into an AC output. The inverter maintains the voltage at the inverter input at a desirable voltage by varying the amount of the series current drawn from the converters. The series current and the output power of the converters, determine the output voltage at each converter.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
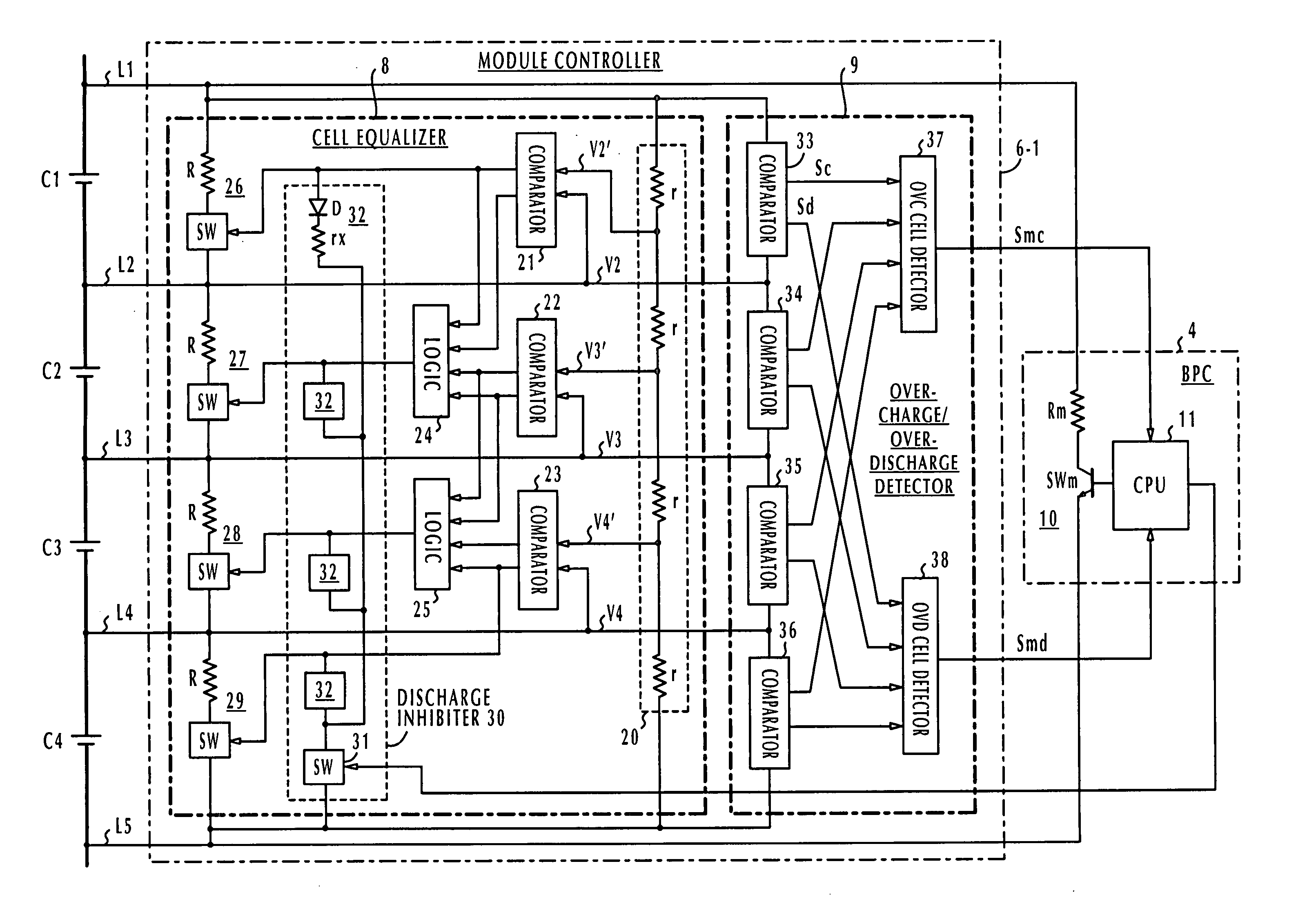
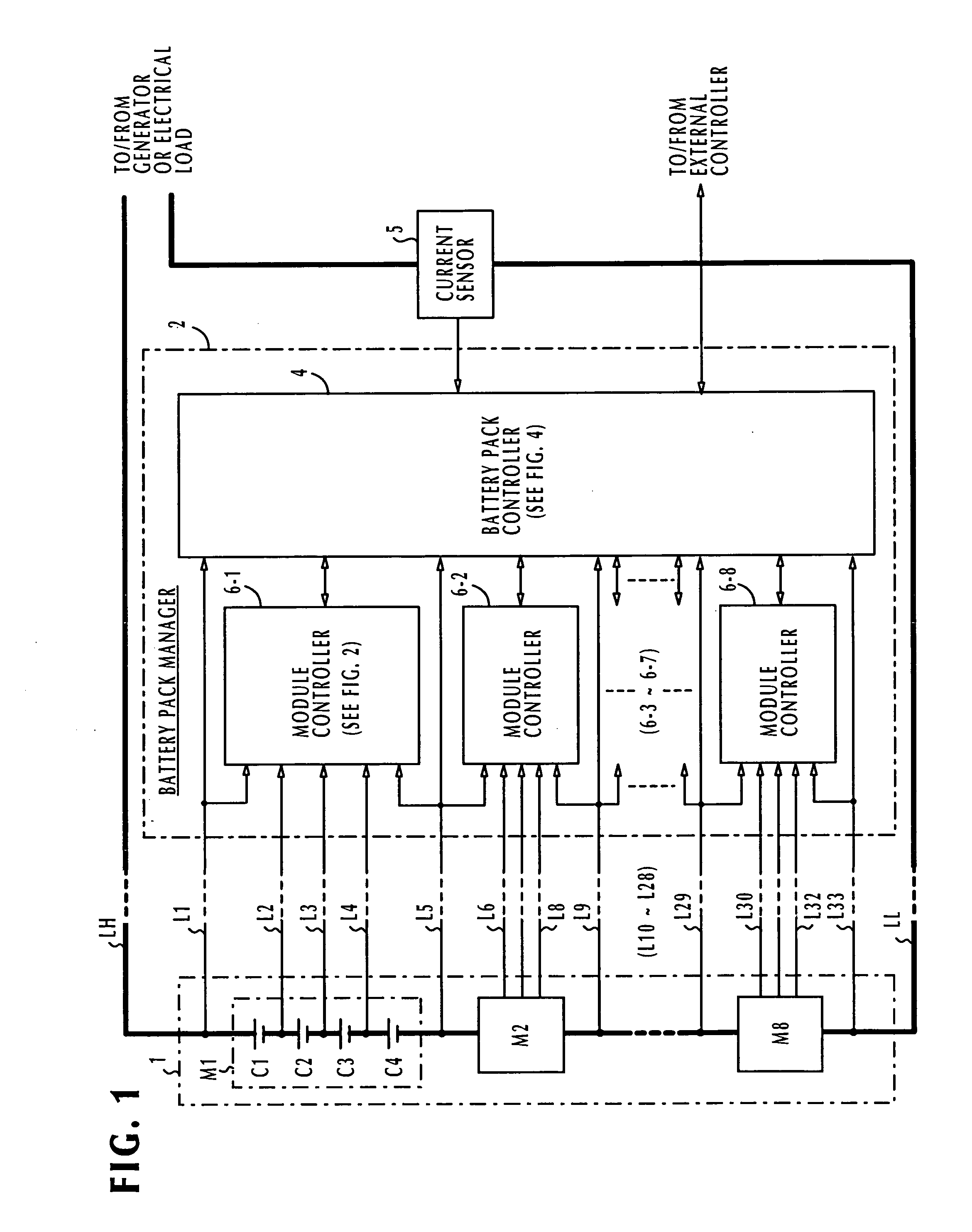
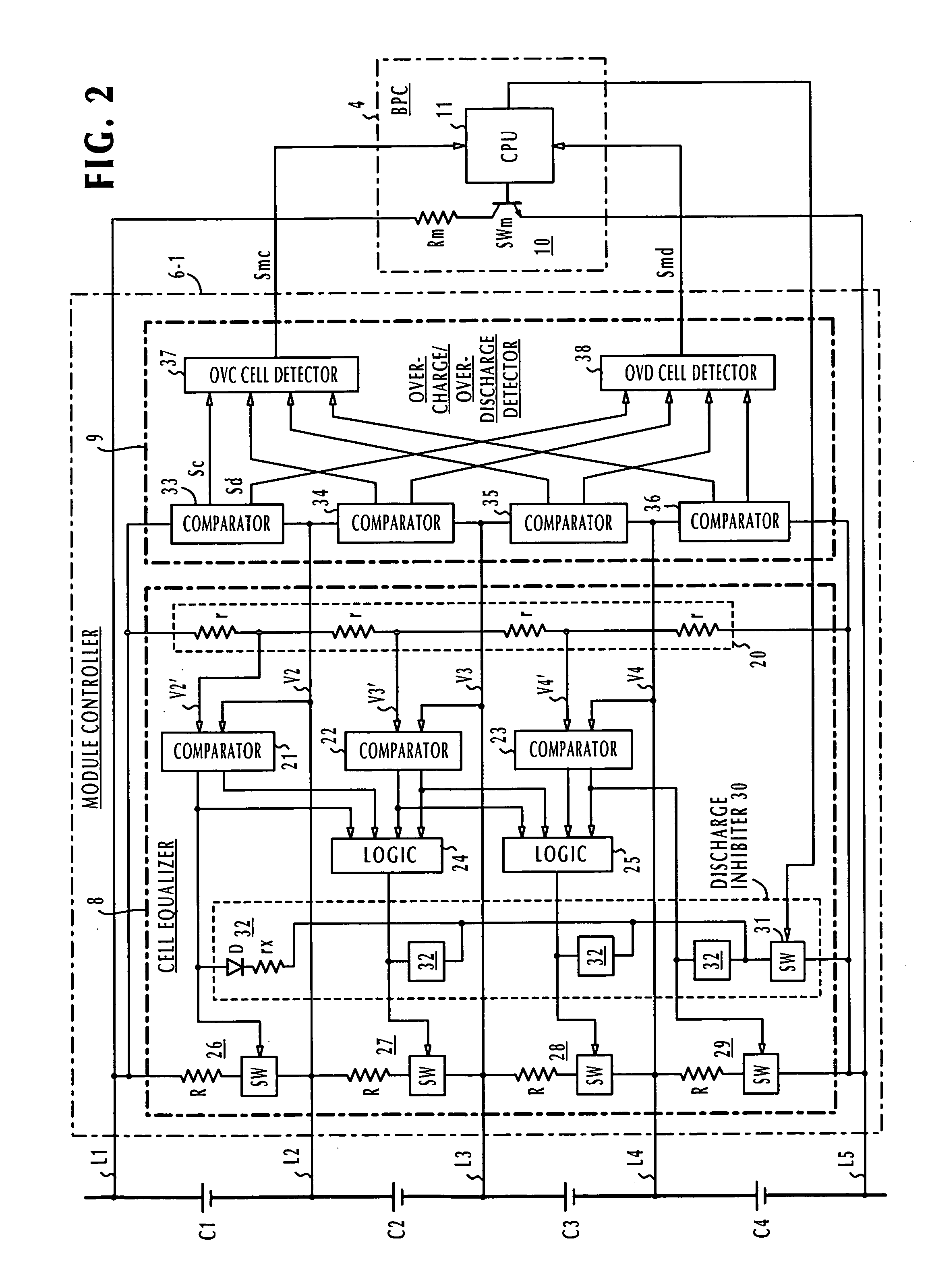
Battery pack manager
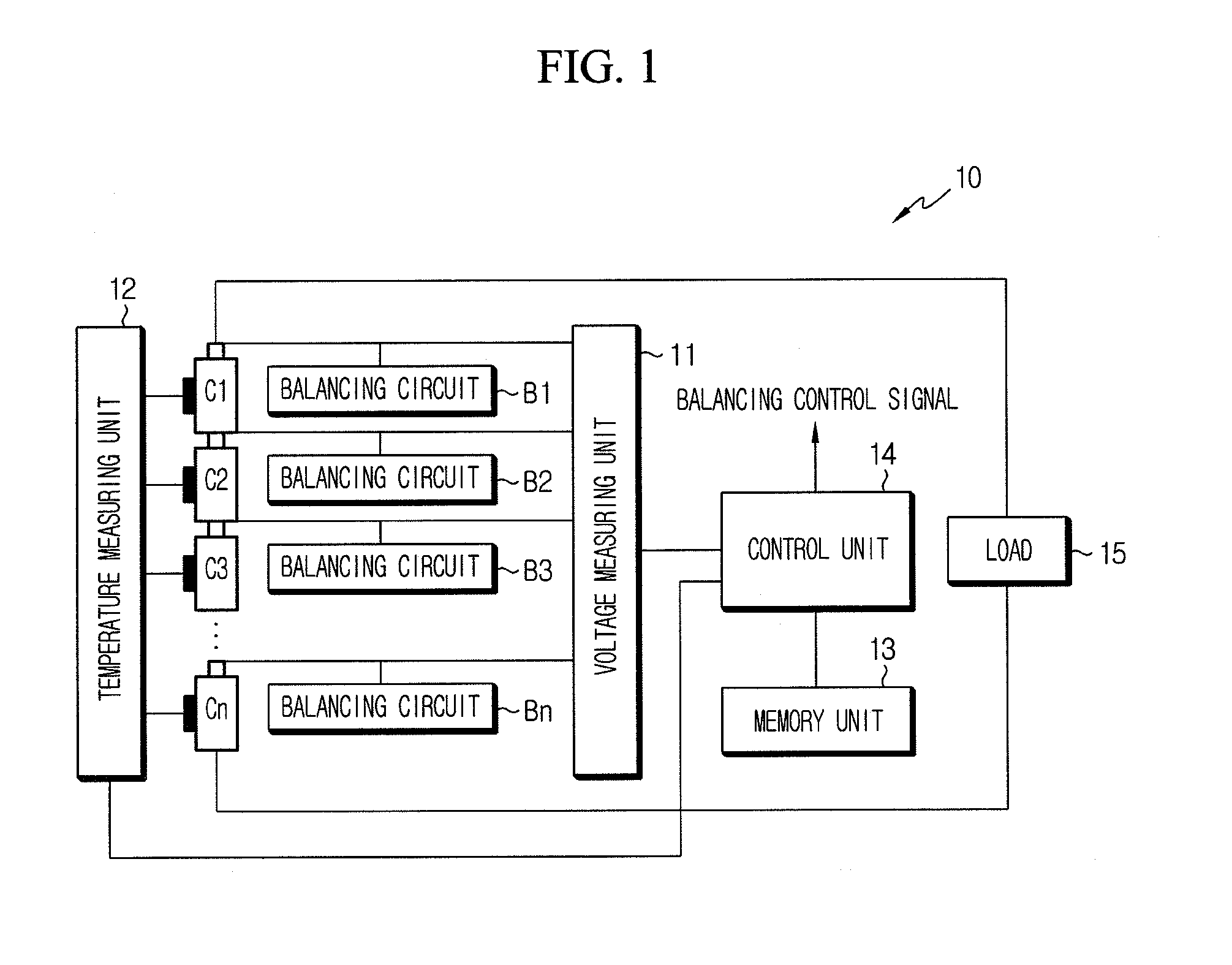
ActiveUS20060103351A1Without introducing complexityIncrease power consumptionCharge equalisation circuitMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringVoltage reference
In a battery pack manager that manages series-connected rechargeable unit cells, a cell equalizer equalizes the cell voltages by individually discharging the unit cells according to deviations from reference voltages. An overcharge / overdischarge detector detects an overcharge and an overdischarge state of each unit cell. An inhibit circuit prevents the cell equalizer from discharging the unit cells when the overcharge / overdischarge detector is activated to reduce the cell voltage variability, which would otherwise occur as a result of interference from the overcharge / overdischarge detector, so that the overcharge / overdischarge states of all unit cells can be determined with precision. Connecting lines of the unit cells are monitored to detect a line-cut. The inhibit circuit further inhibits the cell equalizer when the connecting lines are being monitored to reduce the cell voltage variability, which would otherwise occur as a result of interference from the line-cut detection, so that false line-cut detection is avoided.
Owner:DENSO CORP
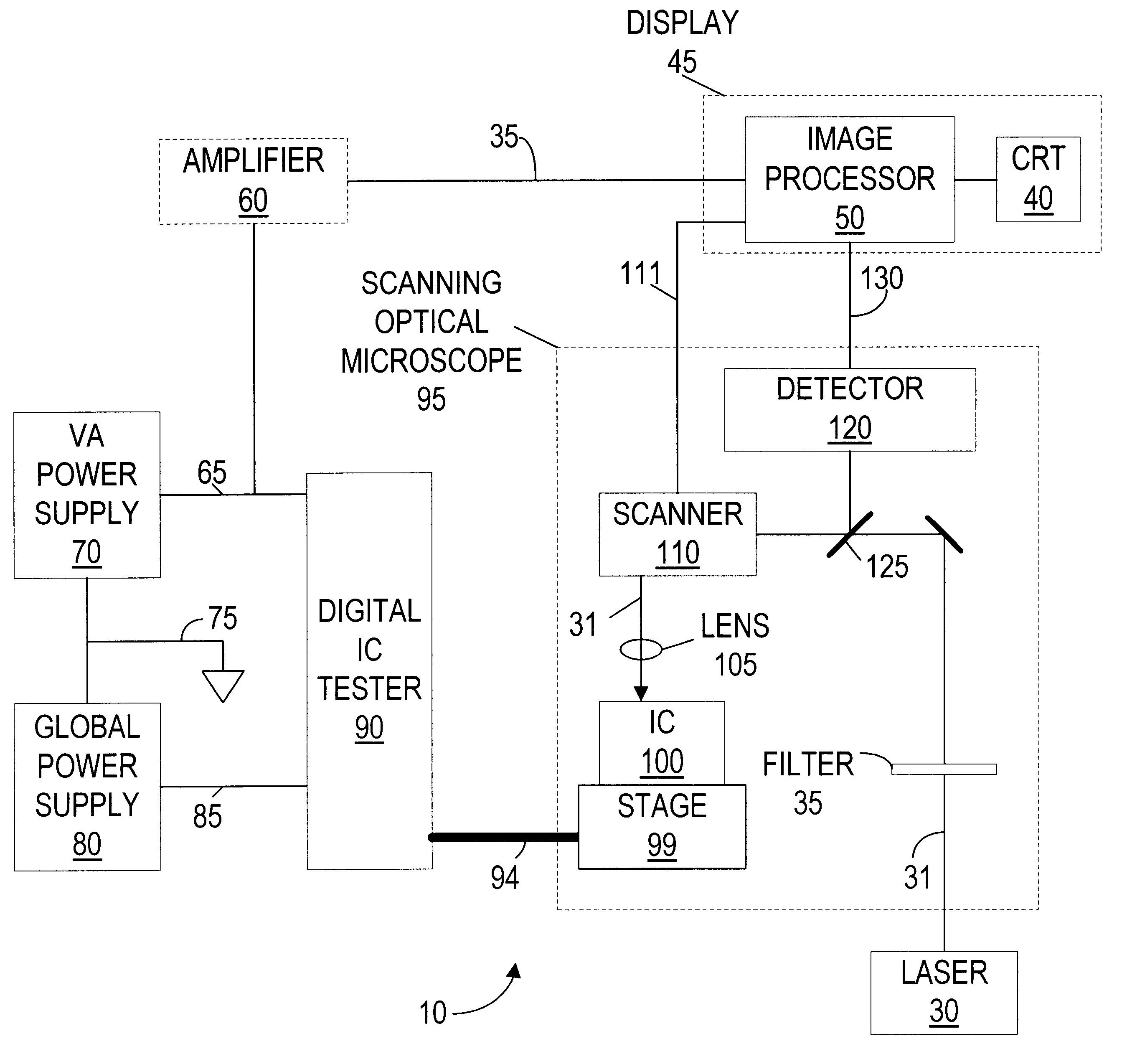
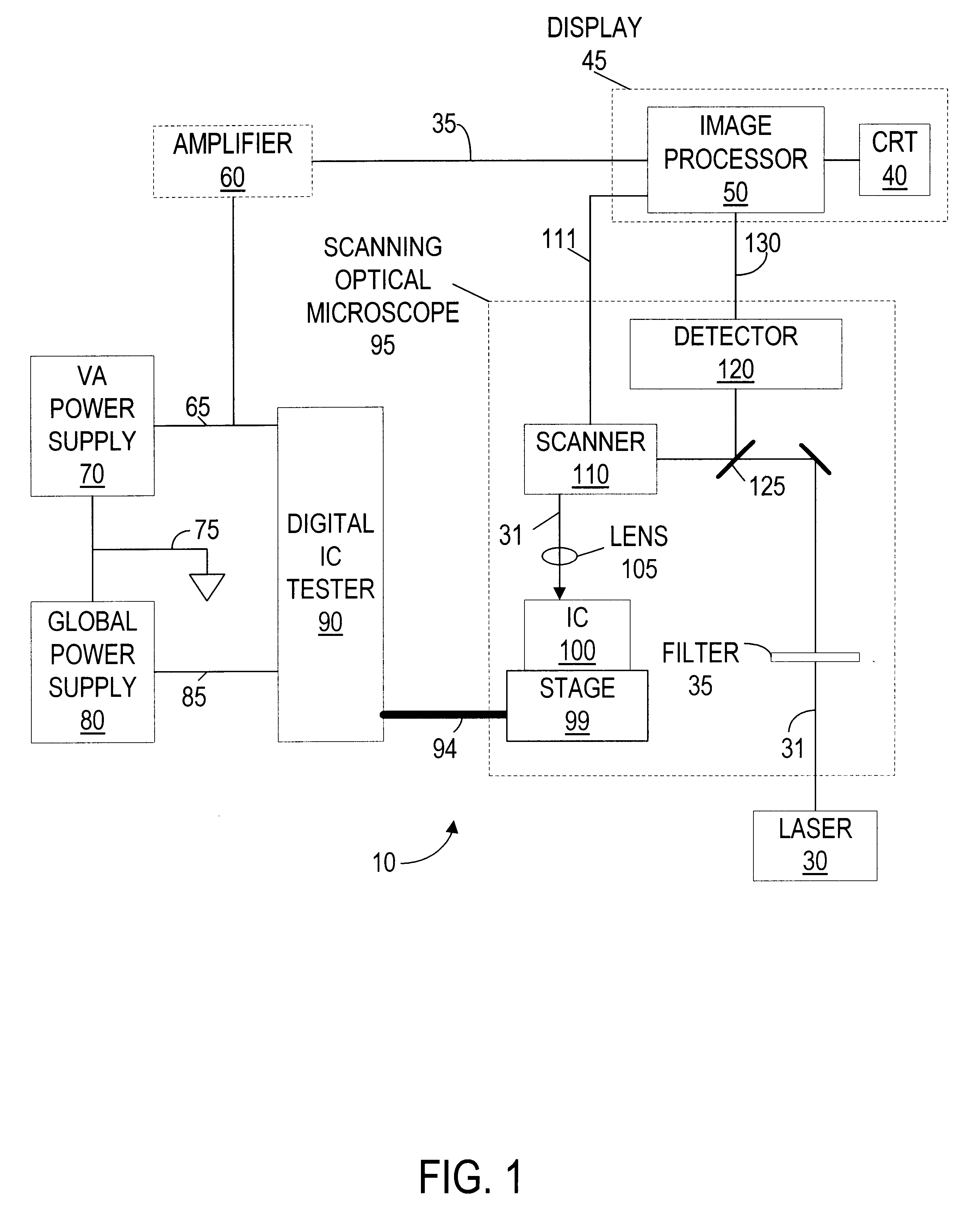
Laser intrusive technique for locating specific integrated circuit current paths
InactiveUS6617862B1Reduce the noise floorHigh sensitivityDigital circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingVoltage variationLaser beams
A method and apparatus for locating integrated circuit defects associated with different aspects of the integrated circuit industry. The integrated circuit is configured in a known failing mode, with a first power supply providing a constant voltage and variable current. Next, one or more additional dedicated power supplies are connected to various points of interest throughout the integrated circuit, wherein these dedicated power supplies have a preset current and the voltage is allowed to vary. The integrated circuit is then scanned with a laser beam, which induces current changes on in the integrated circuit especially in defective areas. These current changes then cause voltage changes on the dedicated power supplies. When such a voltage change occurs on the dedicated power supplies, its position is noted.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
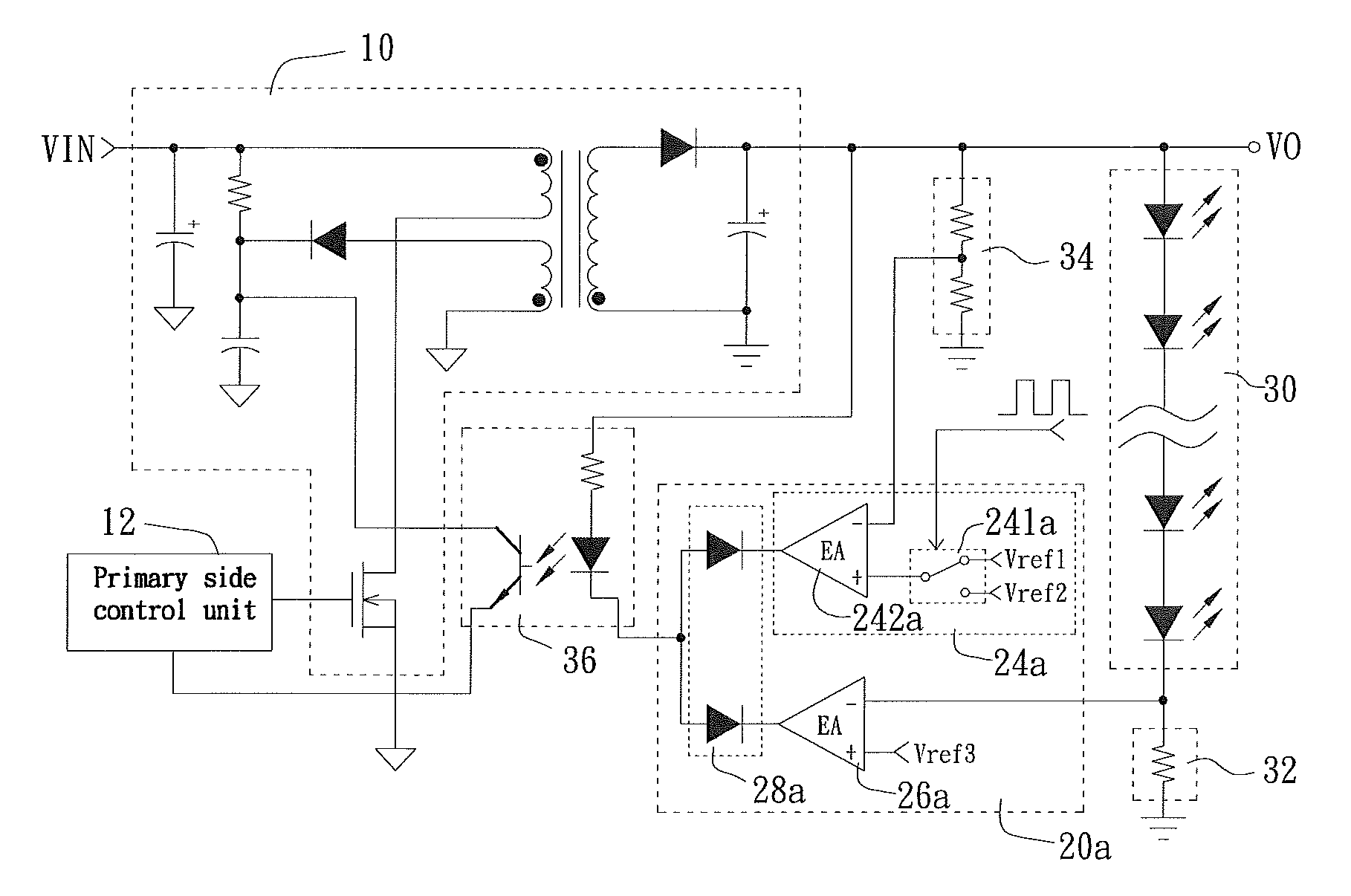
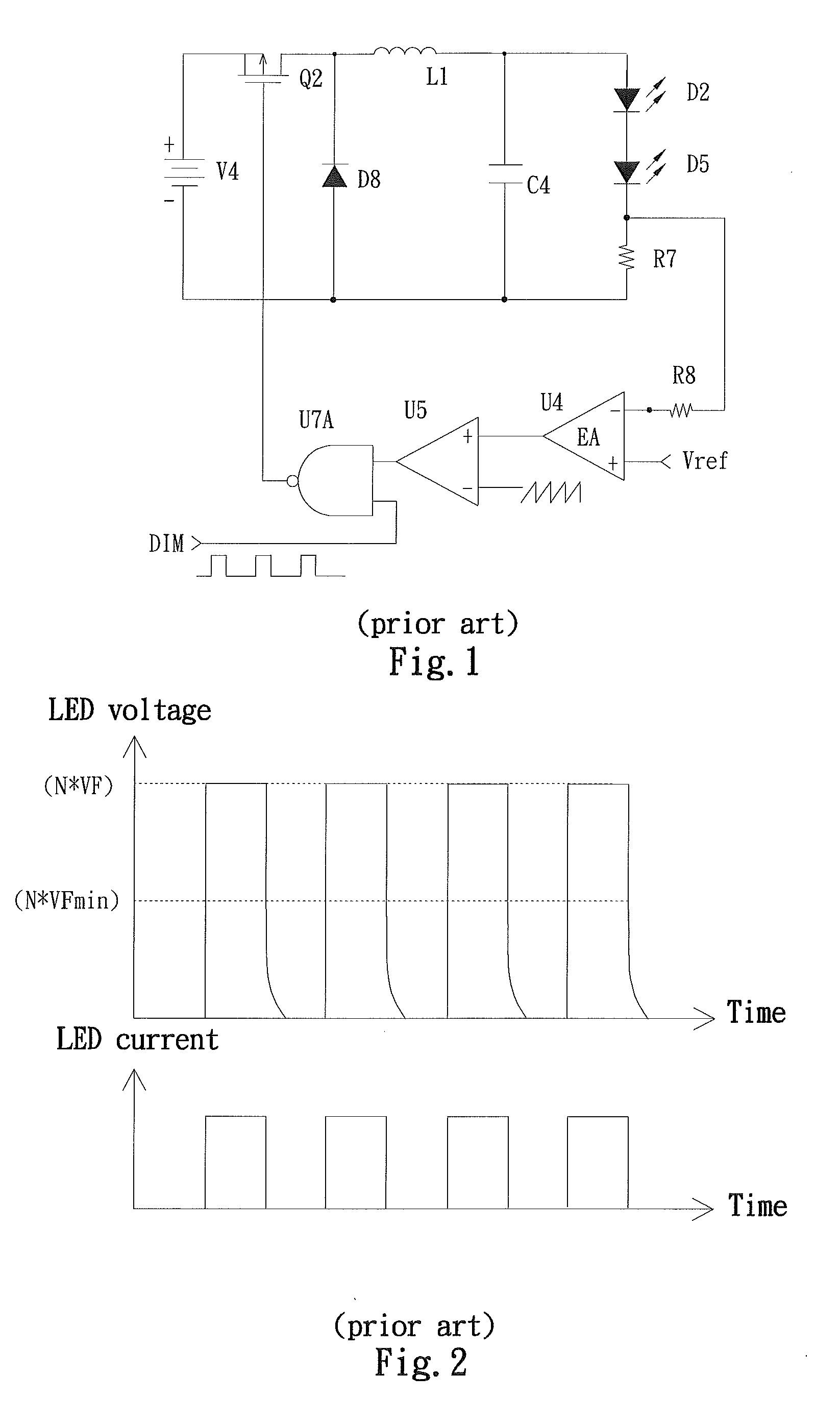
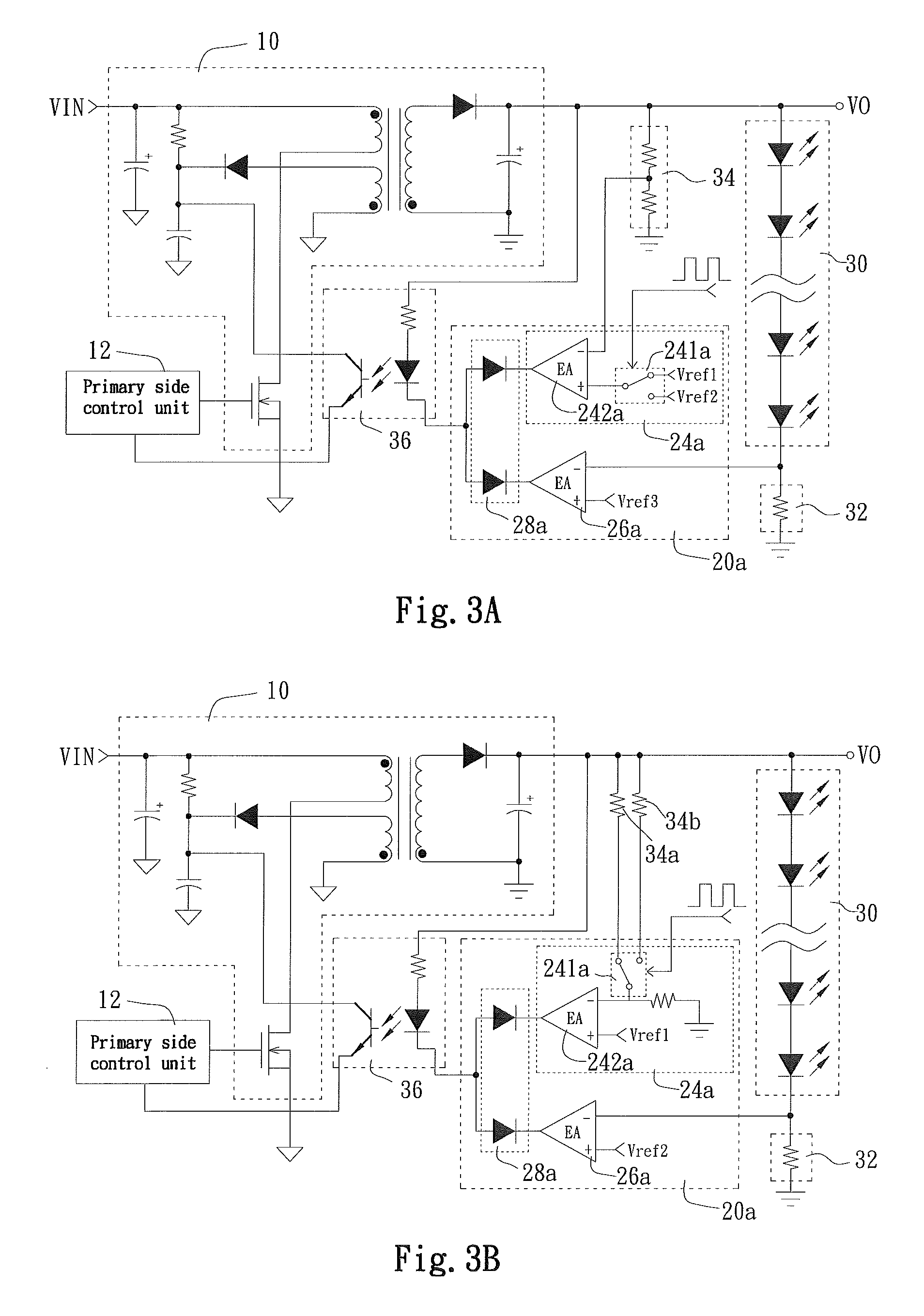
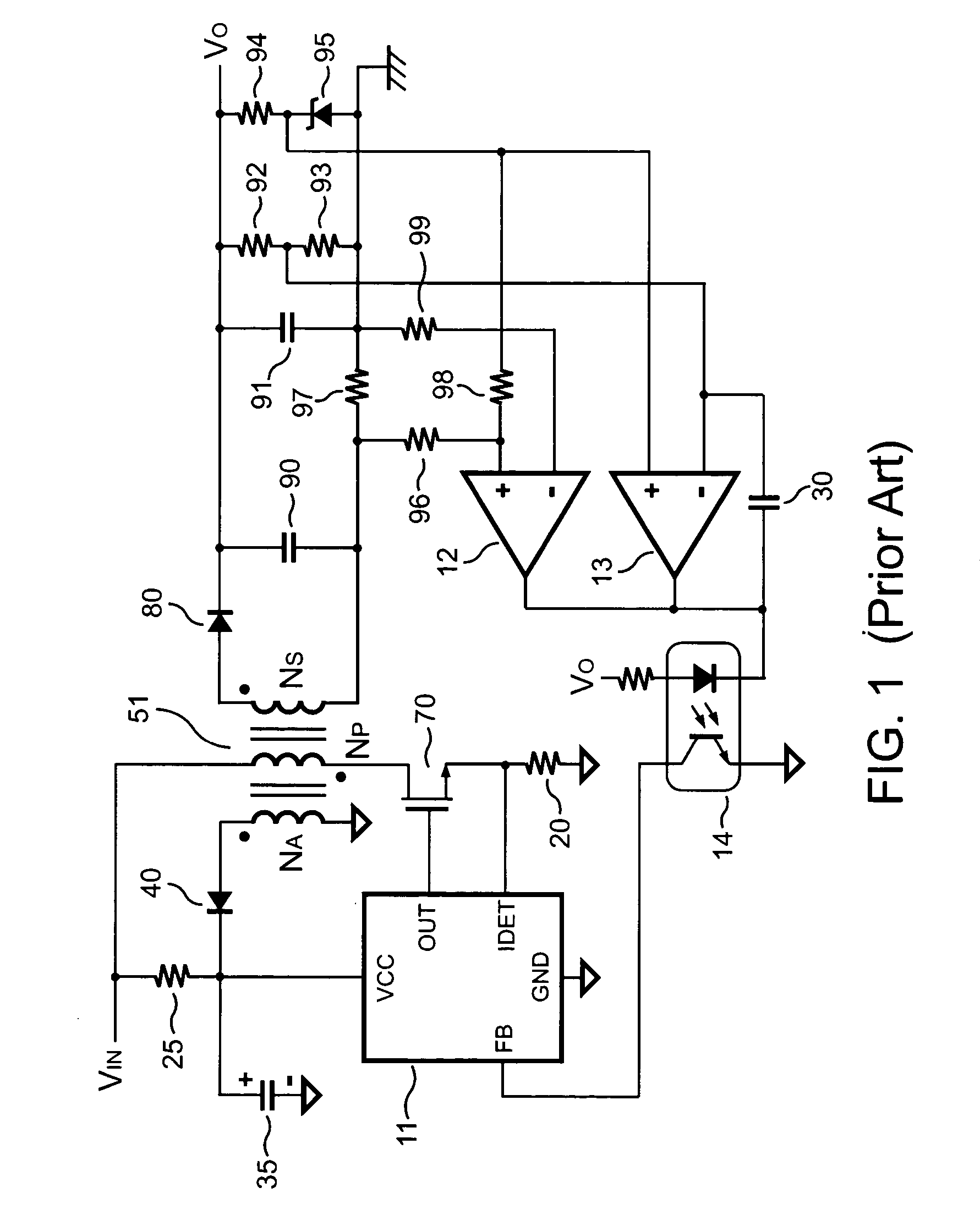
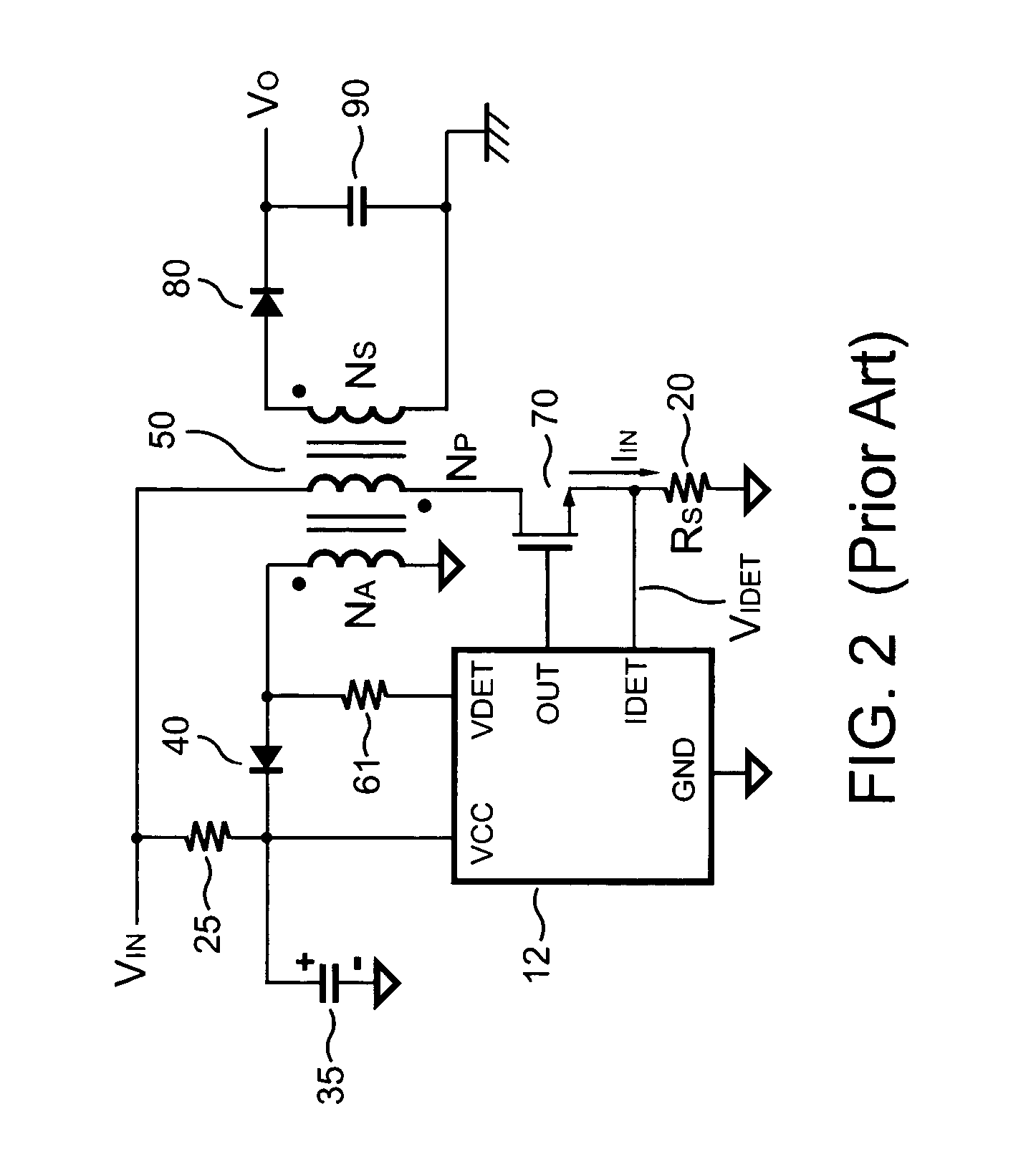
Light-emitting diode driving circuit and secondary side controller for controlling the same
InactiveUS7855520B2Low costLayout on a printed circuit board (PCB) may be simplifiedElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitEffect light
Owner:NIKO SEMICON
Predictive, adaptive power supply for an integrated circuit under test
InactiveUS6657455B2Suppress mutationReduce noiseDigital circuit testingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPower flowFeedback circuits
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
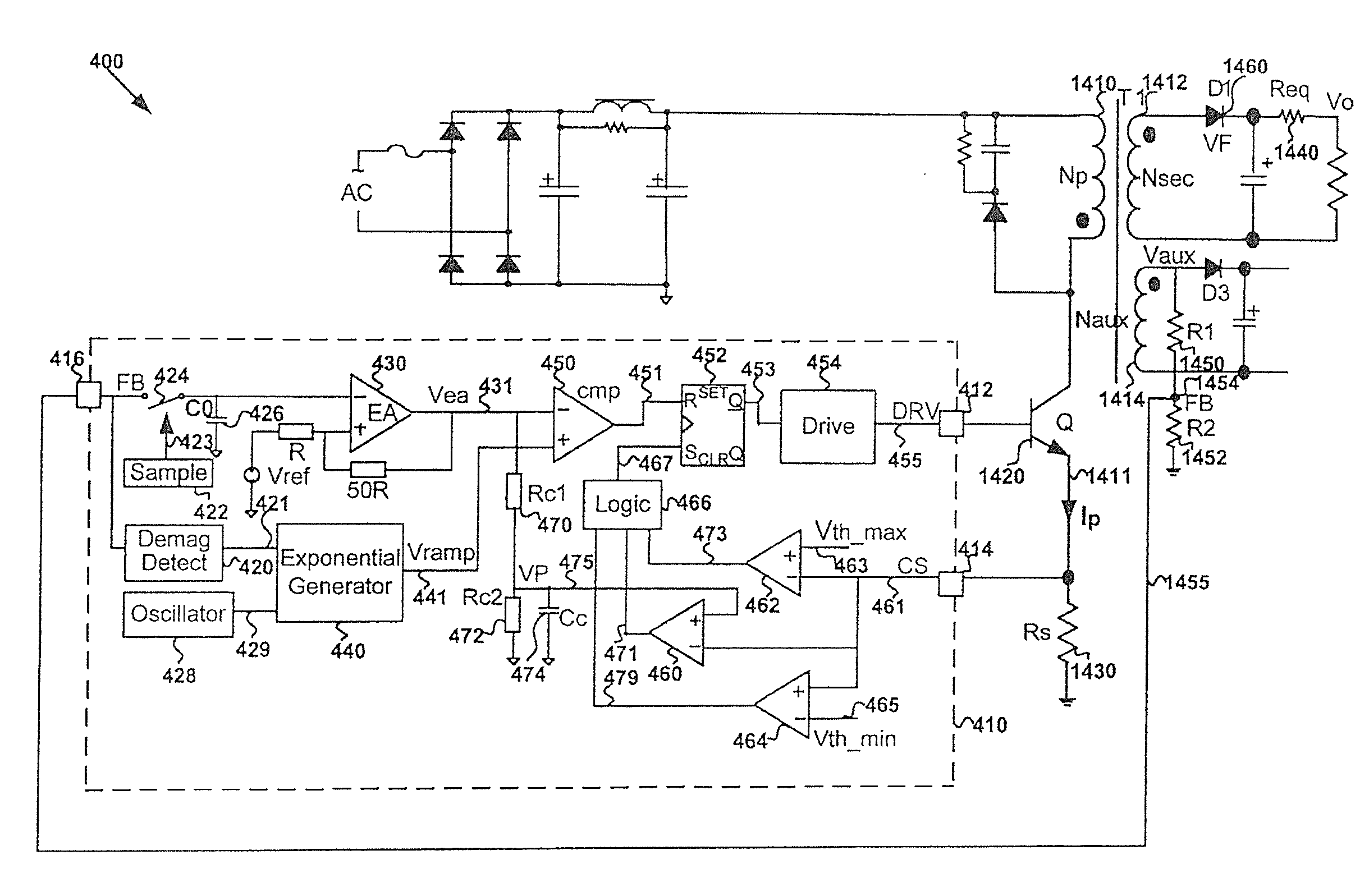
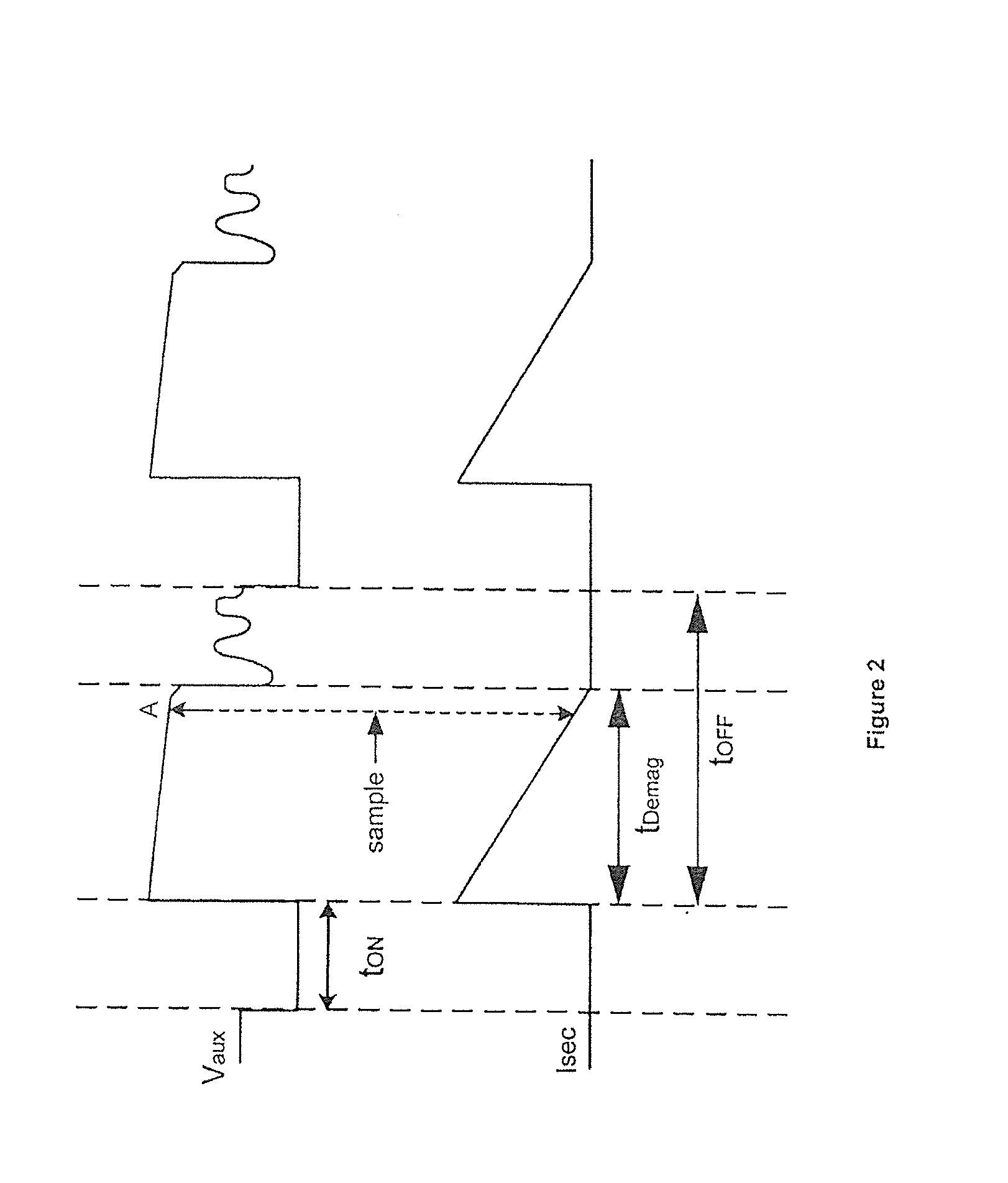
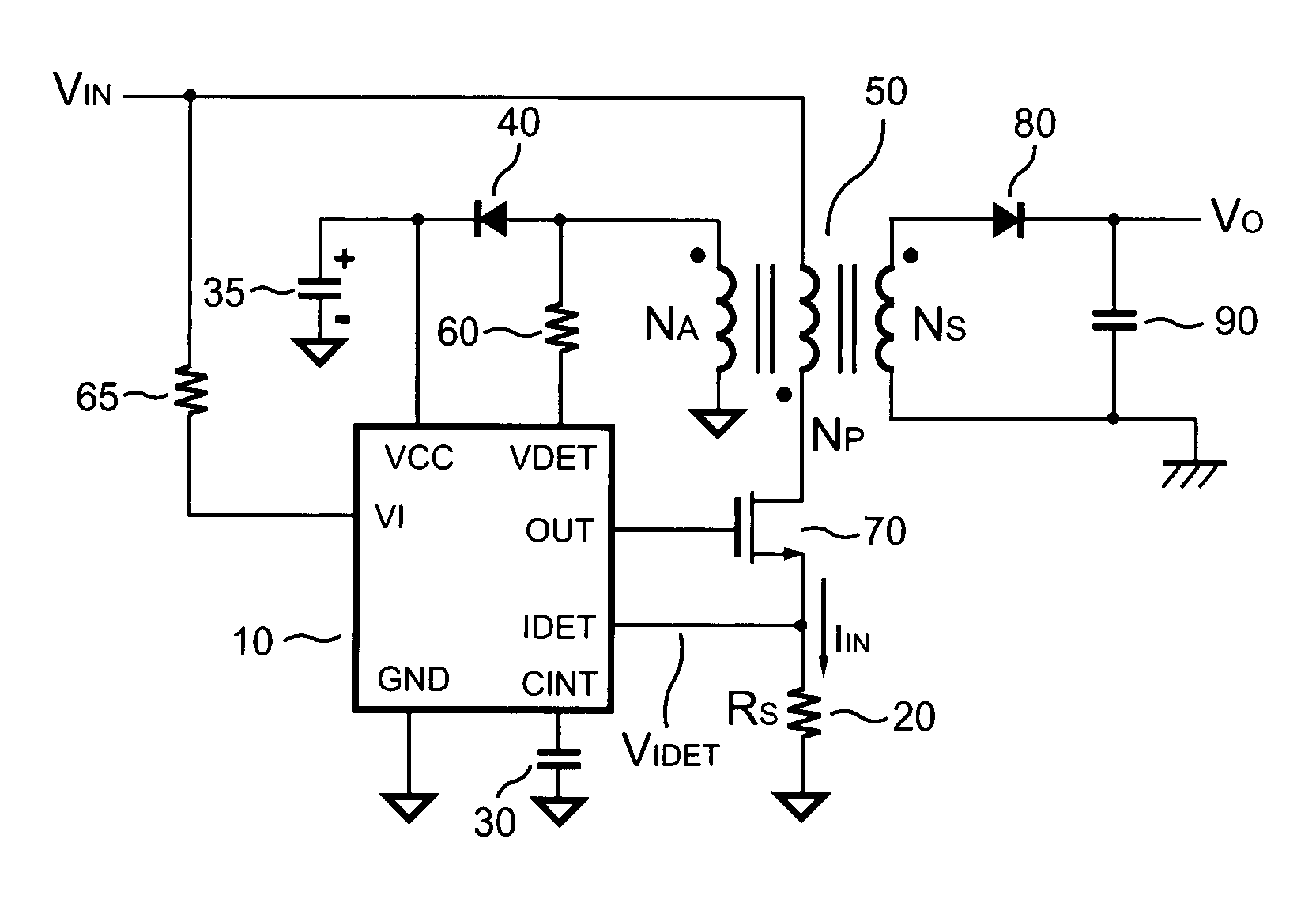
Systems and methods for flyback power converters with switching frequency and peak current adjustments based on changes in feedback signals
ActiveUS20130033905A1Increase frequencyIncreasing magnitudeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionPeak currentEngineering
System and method for regulating a power converter. The system includes a first comparator configured to receive a first input signal and a second input signal and generate a first comparison signal based on at least information associated with the first input signal and the second input signal, a pulse-width-modulation generator configured to receive at least the first comparison signal and generate a modulation signal based on at least information associated with the first comparison signal, a driver component configured to receive the modulation signal and output a drive signal to a switch to adjust a primary current flowing through a primary winding of the power converter, and a voltage-change-rate detection component configured to sample the feedback signal to generate a first sampled signal for a first modulation period and to sample the feedback signal to generate a second sampled signal for a second modulation period.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
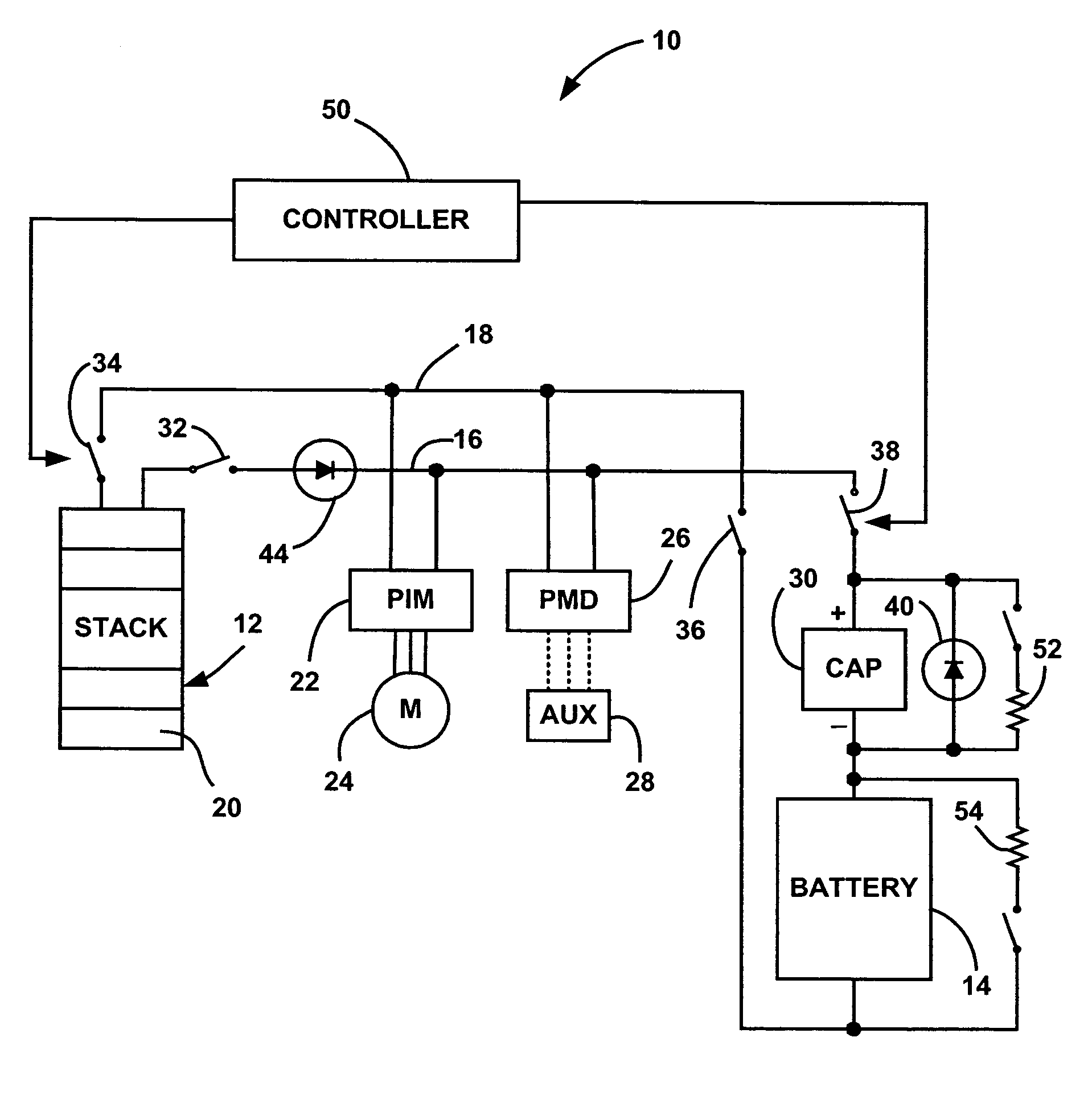
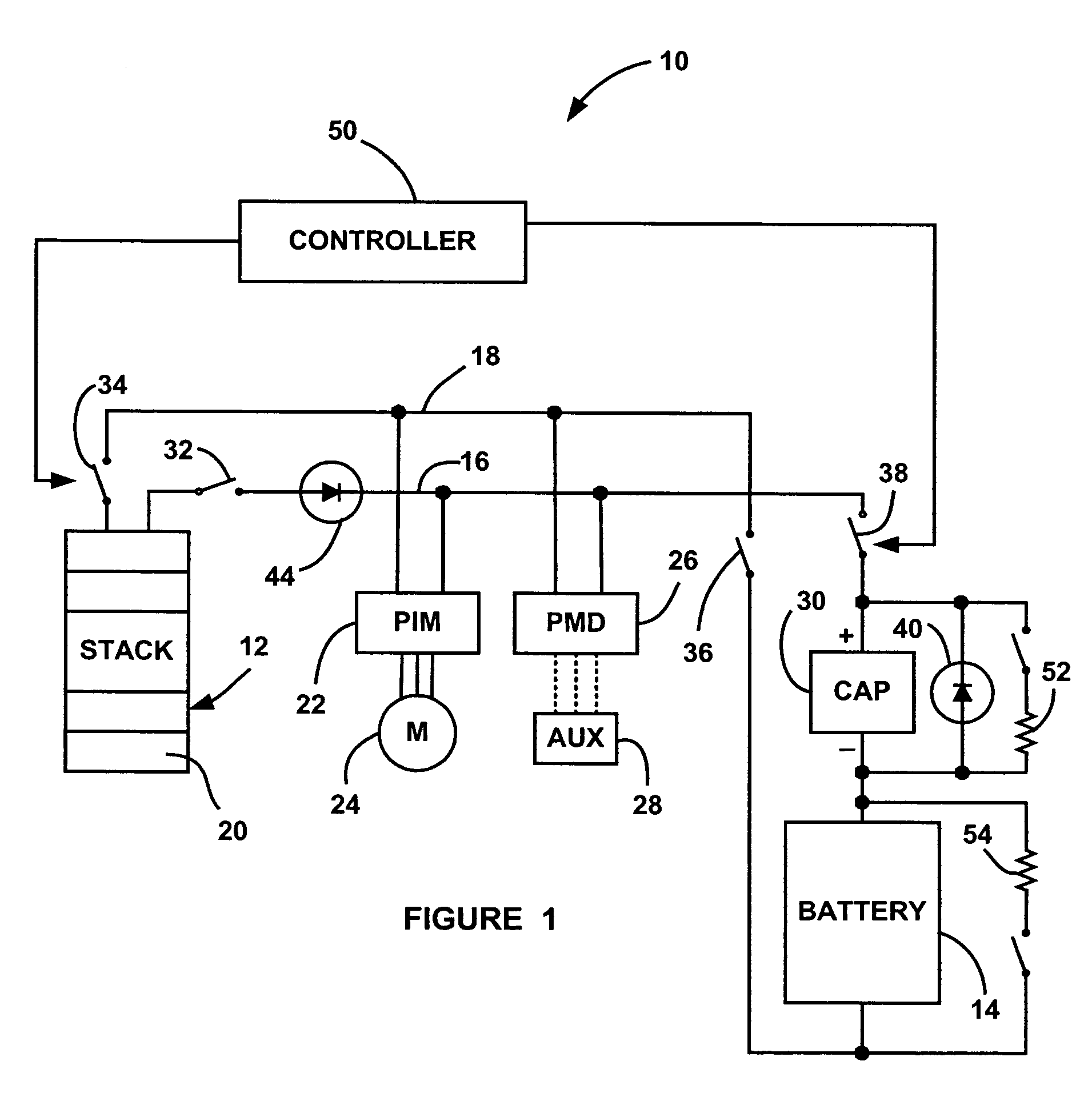
Hybrid fuel cell system with battery capacitor energy storage system
A fuel cell system that employs a super capacitor and battery electrically coupled in series with each other and in parallel with a fuel cell stack on a power bus line. As the voltage on the power bus line changes over the operating requirements of the system, the super capacitor is charged and discharged over a relatively large voltage swing, such as an 85% SOC swing. The super capacitor equalizes or voltage matches the voltage variation on the power bus line as set by the stack voltage to the voltage of the battery. Therefore, the battery, while providing the majority of the energy and power during charge and discharge, has a relatively small defined SOC swing, which acts to maintain the battery life. The system can also include a diode electrically coupled in parallel with the super capacitor that provides reverse voltage protection and electrical power by-pass.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
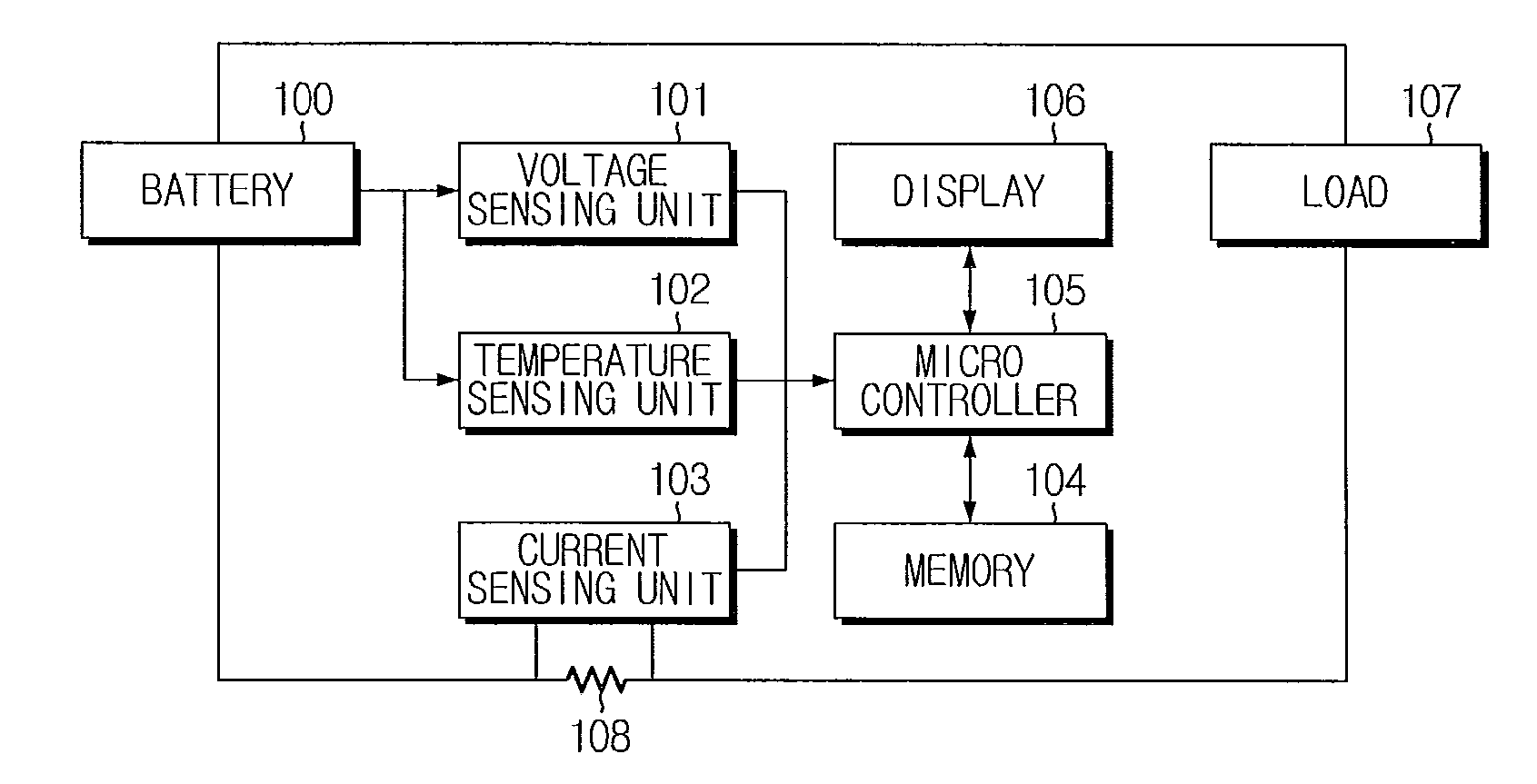
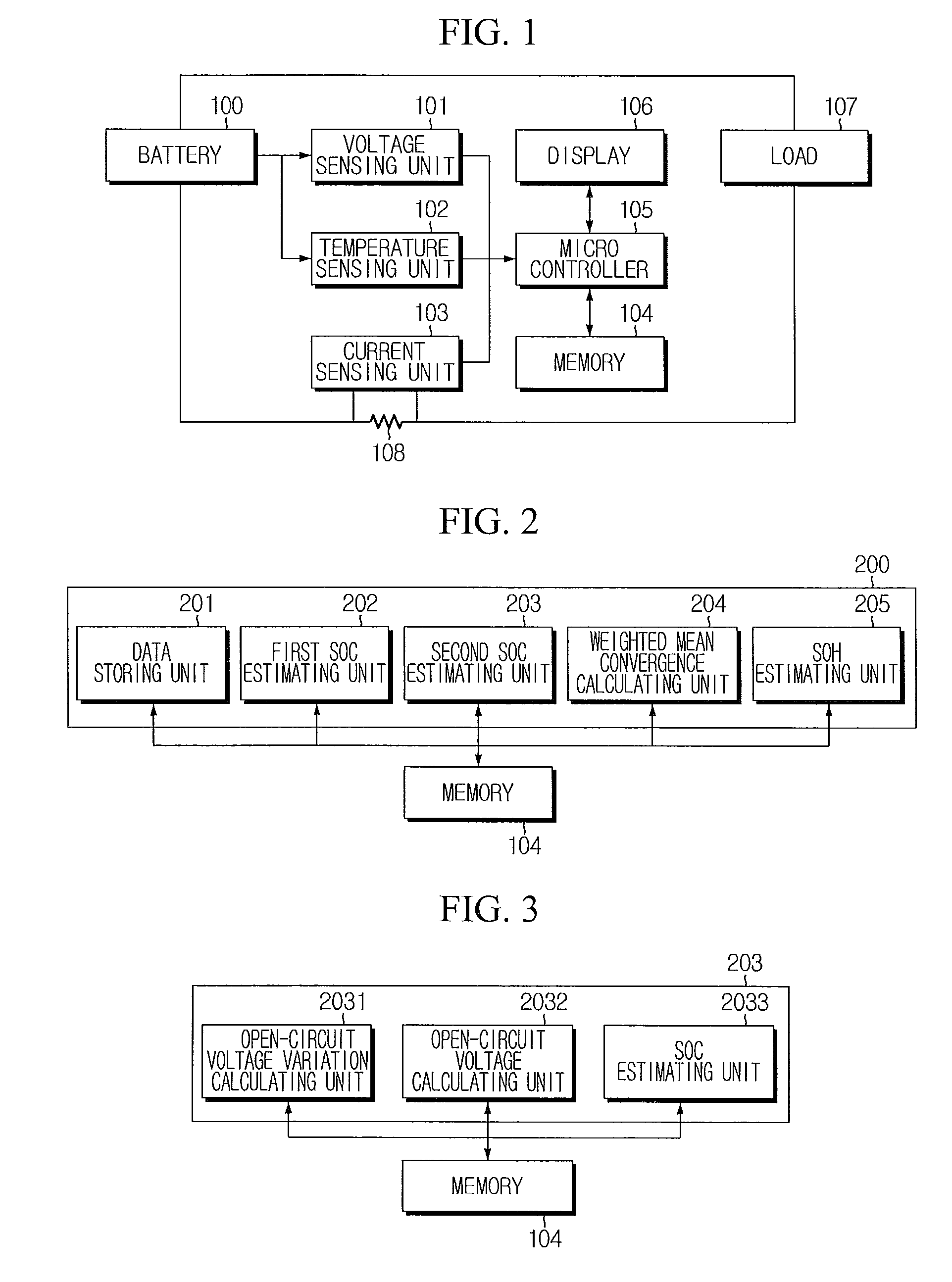
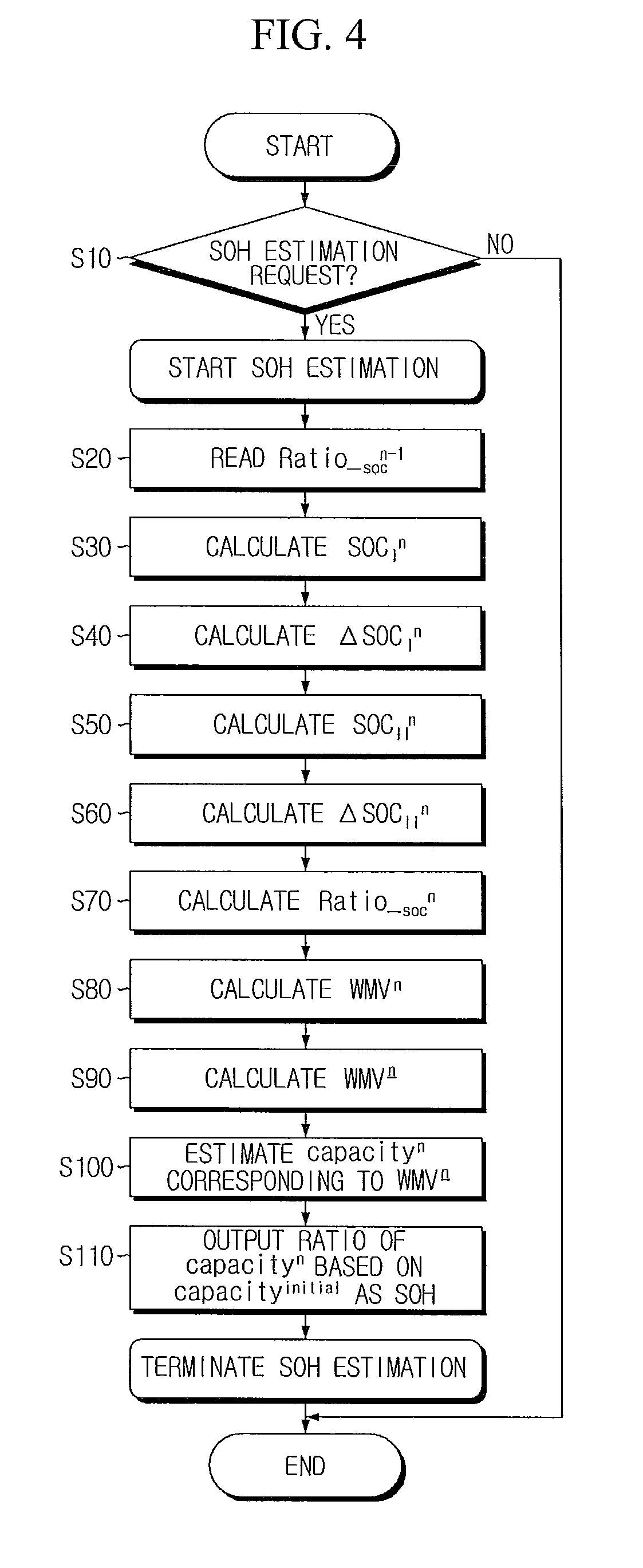
Apparatus and method for estimating state of health of battery based on battery voltage variation pattern
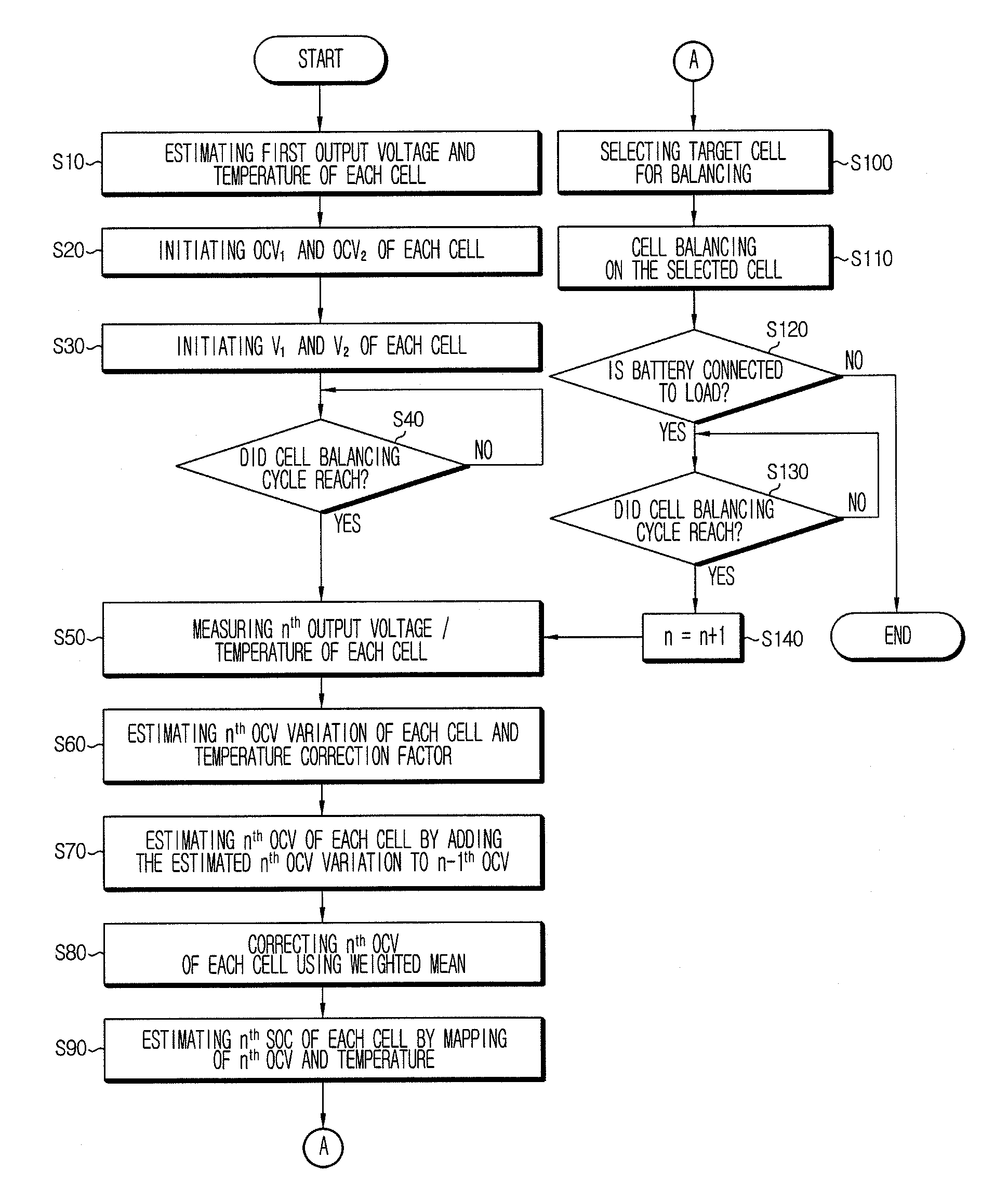
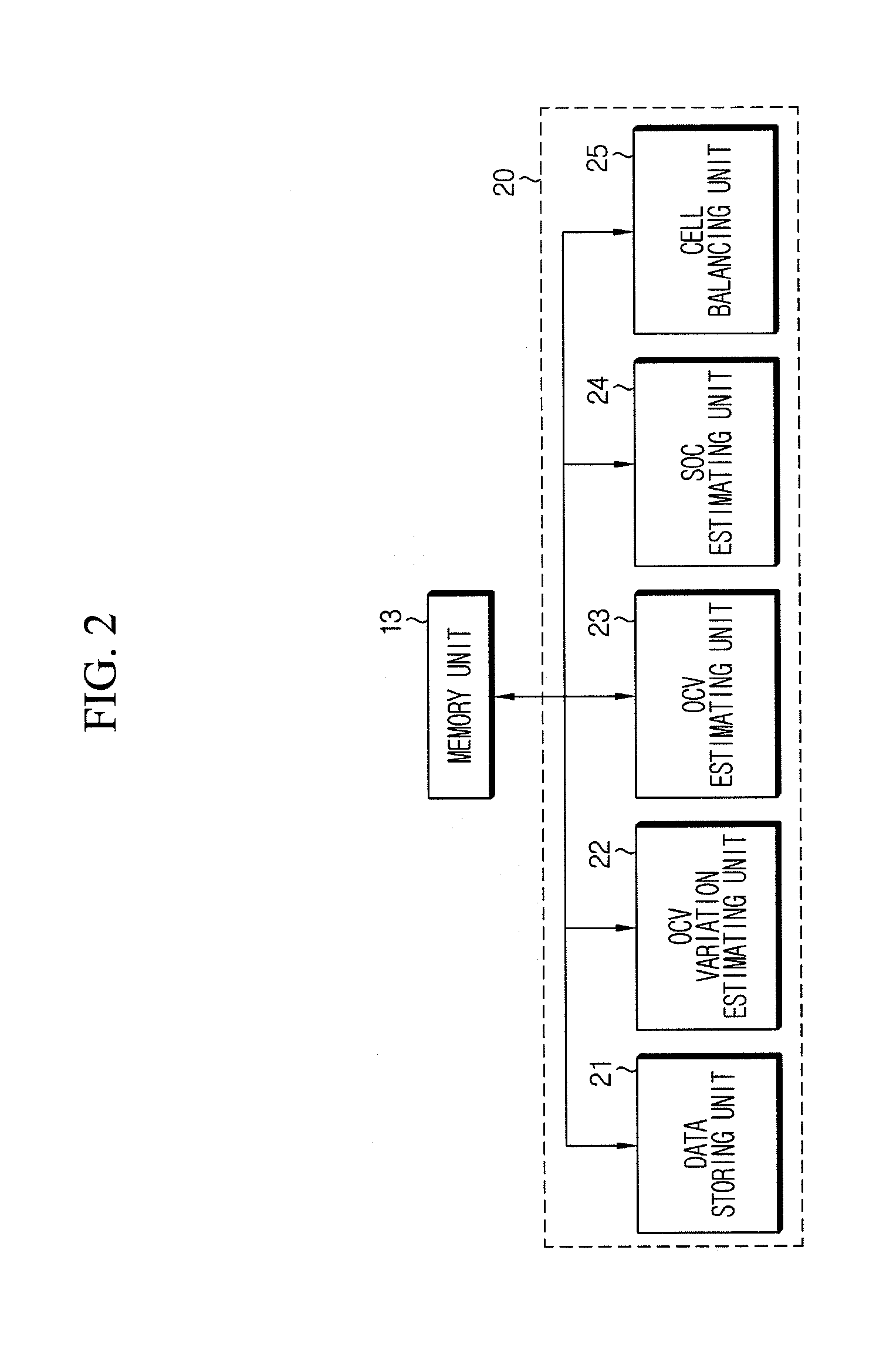
ActiveUS20100036626A1Improve accuracyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesState of healthEngineering
An apparatus estimates SOH of a battery based on a battery voltage variation pattern. A data storing unit obtains and stores battery voltage, current and temperature data from sensors, at each SOH estimation. A first SOC estimating unit estimates first SOC by current integration using the battery current data. A second SOC estimating unit estimates open-circuit voltage from the voltage variation pattern, and calculates and stores second SOC corresponding to the open-circuit voltage and temperature using correlations between the open-circuit voltage / temperature and SOC. A weighted mean convergence calculating unit calculates and stores convergence value for weighted mean value of ratio of the second SOC variation to the first SOC variation. A SOH estimating unit estimates capacity corresponding to the weighted mean convergence value using correlation between the weighted mean convergence value and the capacity, estimates relative ratio of the estimated capacity to an initial capacity, and stores it as SOH.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Light-emitting diode driving circuit and secondary side controller for controlling the same
InactiveUS20090237007A1Small voltage changeLow costElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitEffect light
A light-emitting diode (LED) driving circuit and a secondary side controller for controlling the same control an output voltage of the LED driving circuit at a first driving voltage or a second driving voltage. When the output voltage is controlled at the first driving voltage, an LED module driven by the LED driving circuit is in a stably lighting state; and when the output voltage is controlled at the second driving voltage, the output voltage is approximately a threshold voltage of the LED module but higher than zero volt, so that the LED module is close to not emitting light. Therefore, in a dimming operation, the variation of voltage applied across the LED module is smaller than that in the conventional LED driving circuits to thereby protect the LED module against an excessive voltage stress and avoid the problem of inaccurate dimming.
Owner:NIKO SEMICON
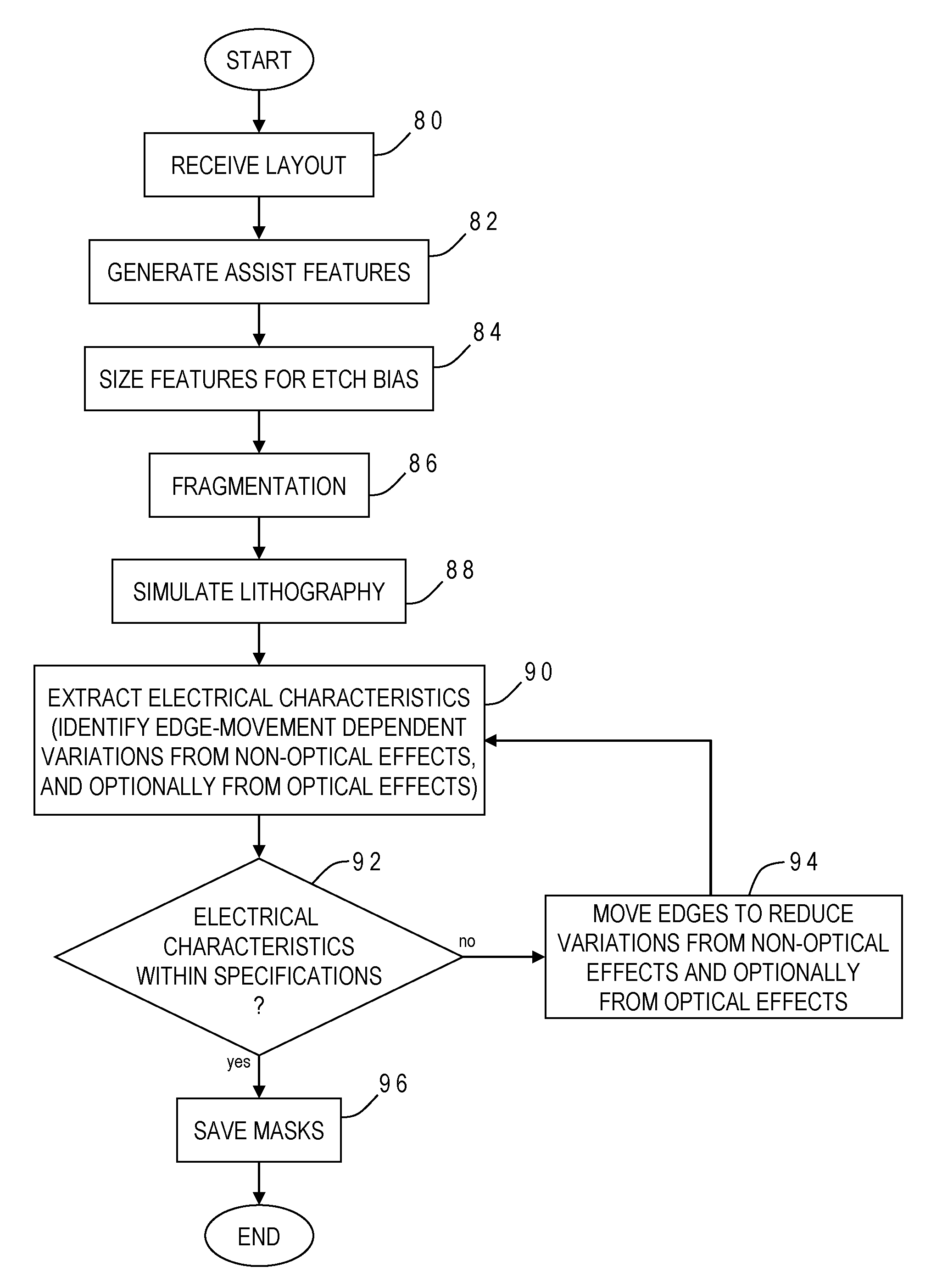
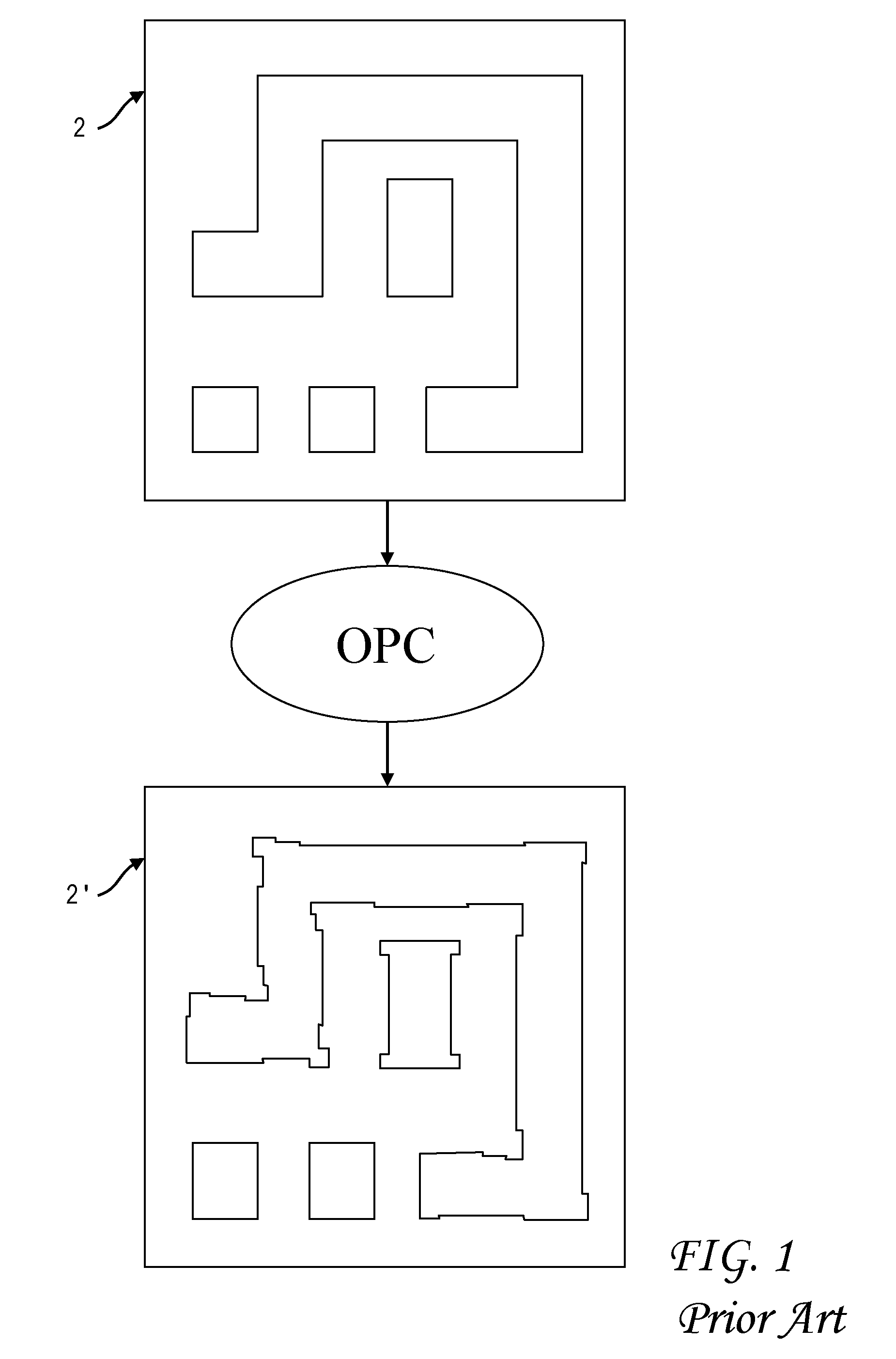
Electrically-driven optical proximity correction to compensate for non-optical effects
ActiveUS8103983B2Improve performancePhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentCapacitanceEngineering
A contour of a mask design for an integrated circuit is modified to compensate for systematic variations arising from non-optical effects such as stress, well proximity, rapid thermal anneal, or spacer thickness. Electrical characteristics of a simulated integrated circuit chip fabricated using the mask design are extracted and compared to design specifications, and one or more edges of the contour are adjusted to reduce the systematic variation until the electrical characteristic is within specification. The particular electrical characteristic preferably depends on which layer is to be fabricated from the mask: on-current for a polysilicon; resistance for contact; resistance and capacitance for metal; current for active; and resistance for vias. For systematic threshold voltage variation, the contour is adjusted to match a gate length which corresponds to an on-current value according to pre-calculated curves for contour current and gate length at a nominal threshold voltage of the chip.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
AC LED lamp involving an LED string having separately shortable sections
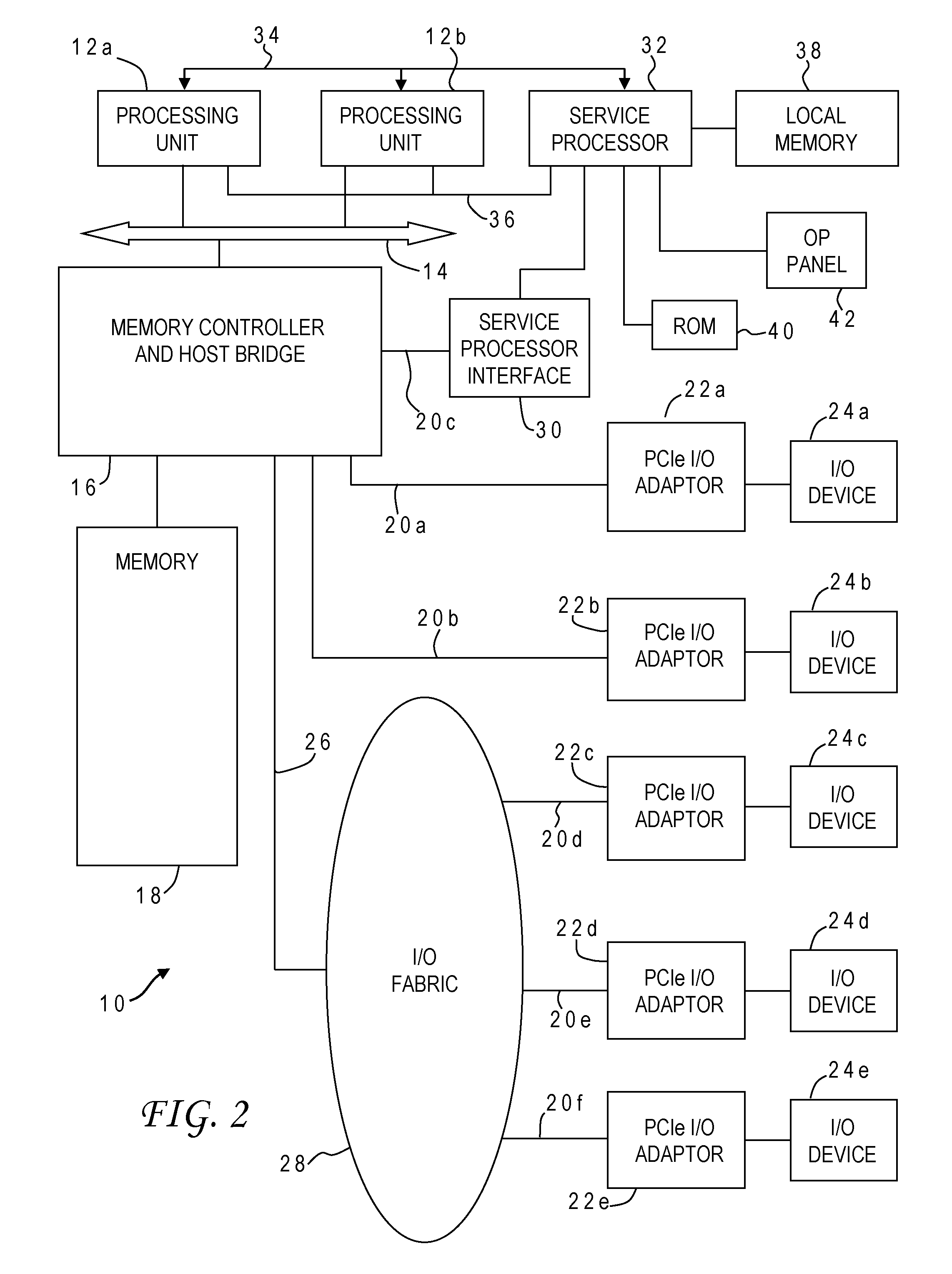
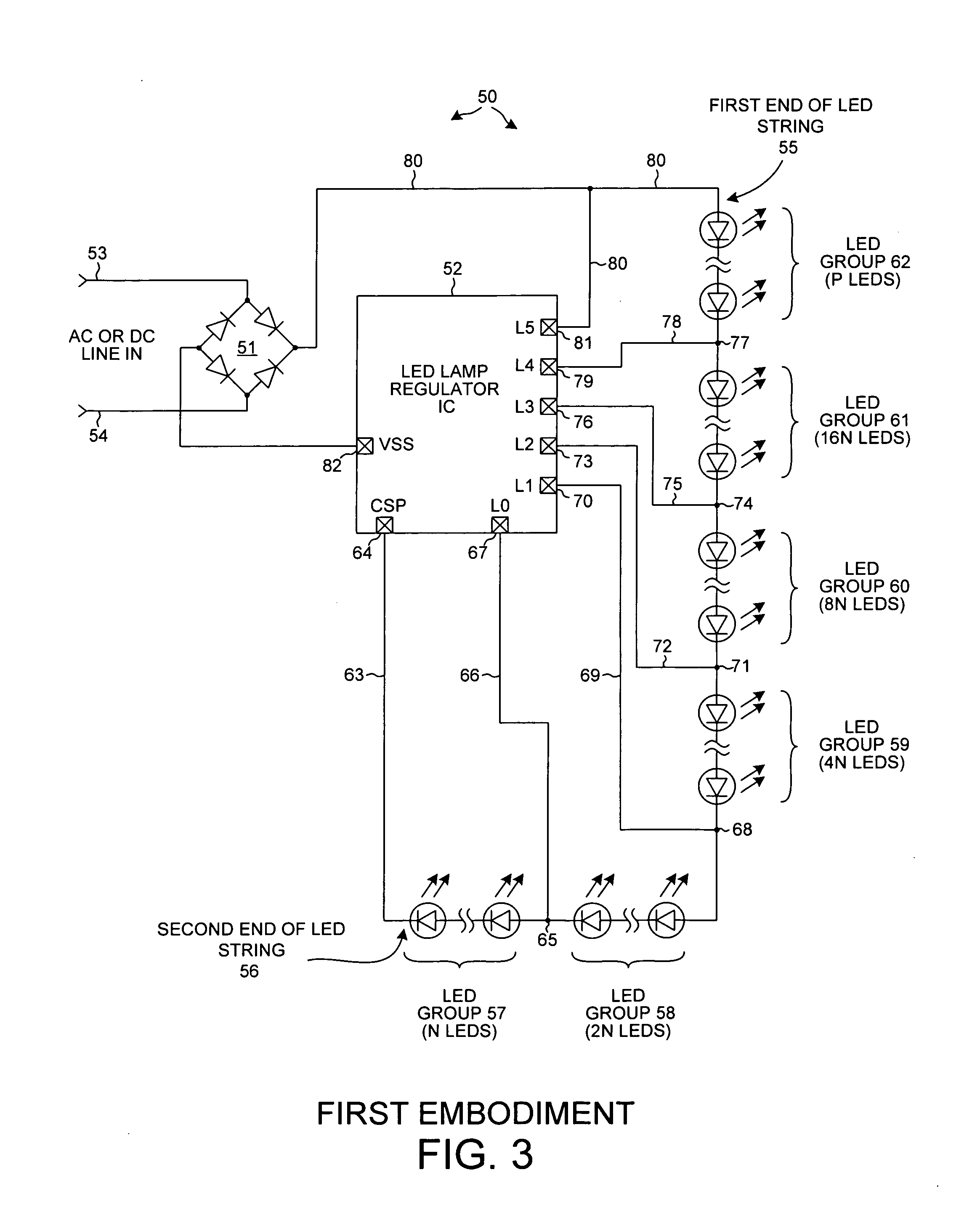
ActiveUS20110227490A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPower switchingEngineering
An LED lamp includes a rectifier, an integrated circuit and a string of series-connected LEDs. The lamp receives an incoming AC signal such that a rectified version of the signal is present across the LED string. The integrated circuit includes a plurality of power switches. Each power switch is coupled so that it can separately and selectably short out a corresponding one of several groups of LEDs in the string. As the voltage across the string increases the integrated circuit controls the power switches such that the number of LEDs through which current flows increases, whereas as the voltage across the string decreases the integrated circuit controls the power switches such that the number of LEDs through which current flows decreases. LED string current flow is controlled and regulated to provide superior efficiency, reliability, anti-flicker, regulation against line voltage variations, power factor correction, and lamp over-voltage, over-current, and over-temperature protection.
Owner:ACTIVE SEMI
Cell balancing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20100085009A1Eliminate needAccurately estimates OCVCharge equalisation circuitMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansActive cellAccurate estimation
Disclosed is a cell balancing apparatus and method using a voltage variation pattern of a battery cell, which measures voltage of each cell, estimates OCV or SOC of each cell using a voltage variation pattern of each cell including a present voltage and a past voltage, and eliminates a deviation in OCV or SOC between the cells through comparison of the estimated OCV or SOC of each cell. In estimating the OCV of each cell, an output voltage error due to IR drop is corrected. Thus, SOC of each cell may be accurately estimated. And, an accurate estimation of SOC may render substantial elimination for a SOC deviation of each cell. Furthermore, SOC estimating using an output voltage leads to an active cell balancing even during charge and discharge of battery, thereby minimizing an SOC deviation of each cell.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
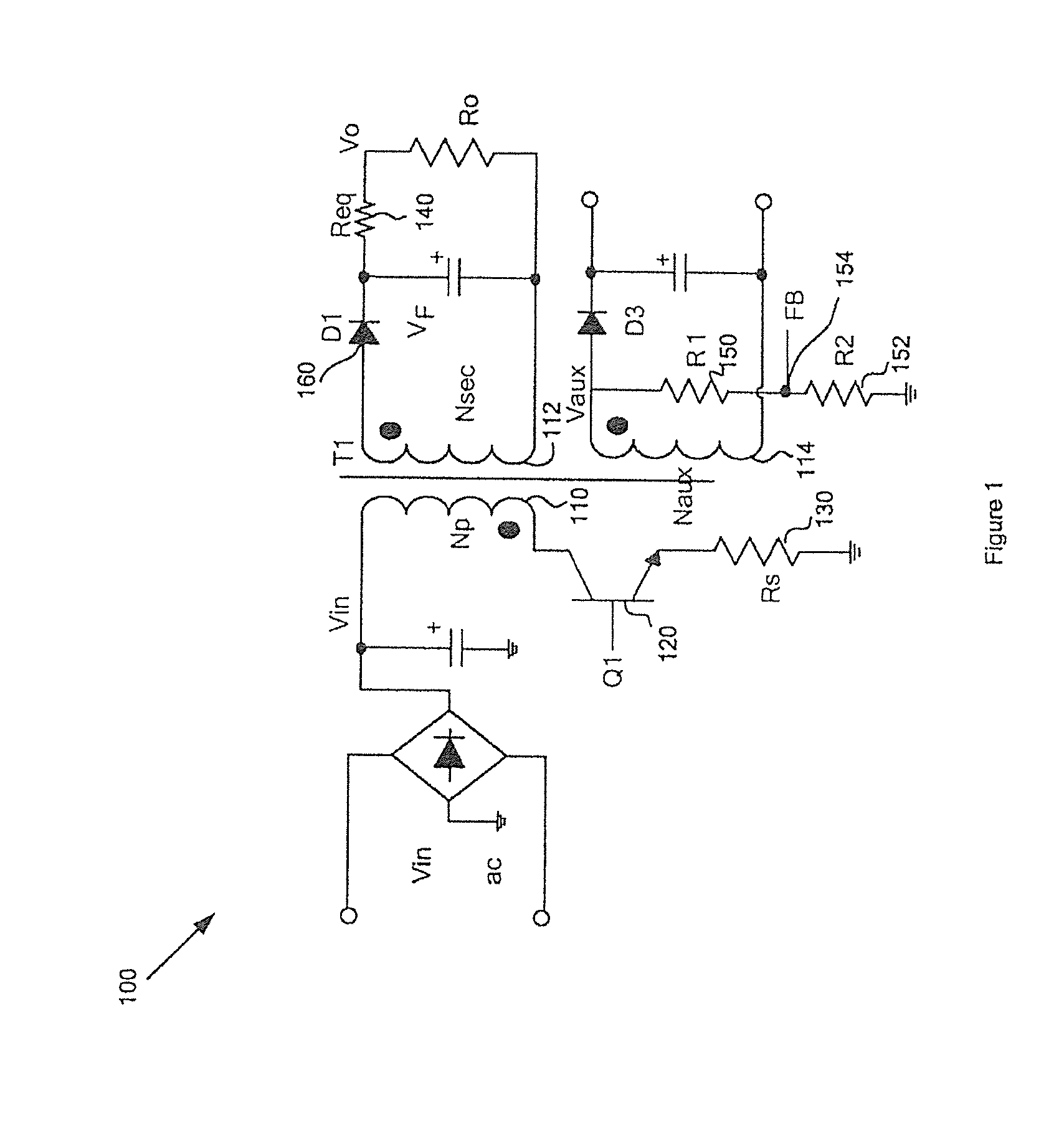
Power-mode controlled power converter
A power-mode controlled power converter is capable of supplying a constant output voltage and output current. A PWM controller generates a PWM signal in response to a voltage sampled from a transformer auxiliary winding. A programmable current-sink and a detection resistor compensate for a voltage drop of an output rectifier. A low-pass filter integrates a switching-current voltage to an average-current signal. An attenuator produces an input-voltage signal from a line-voltage input signal. The PWM controller multiplies the average-current signal with the input-voltage signal to generate a power-control signal. An error-amplifier compares the power-control signal with a power-reference voltage to generate a limit voltage. The limit voltage controls the power delivered from a primary-side circuit to a secondary-side circuit of the power-mode controlled power converter. Since the power-reference voltage varies in proportional to output voltage variations, a constant output current is therefore achieved.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
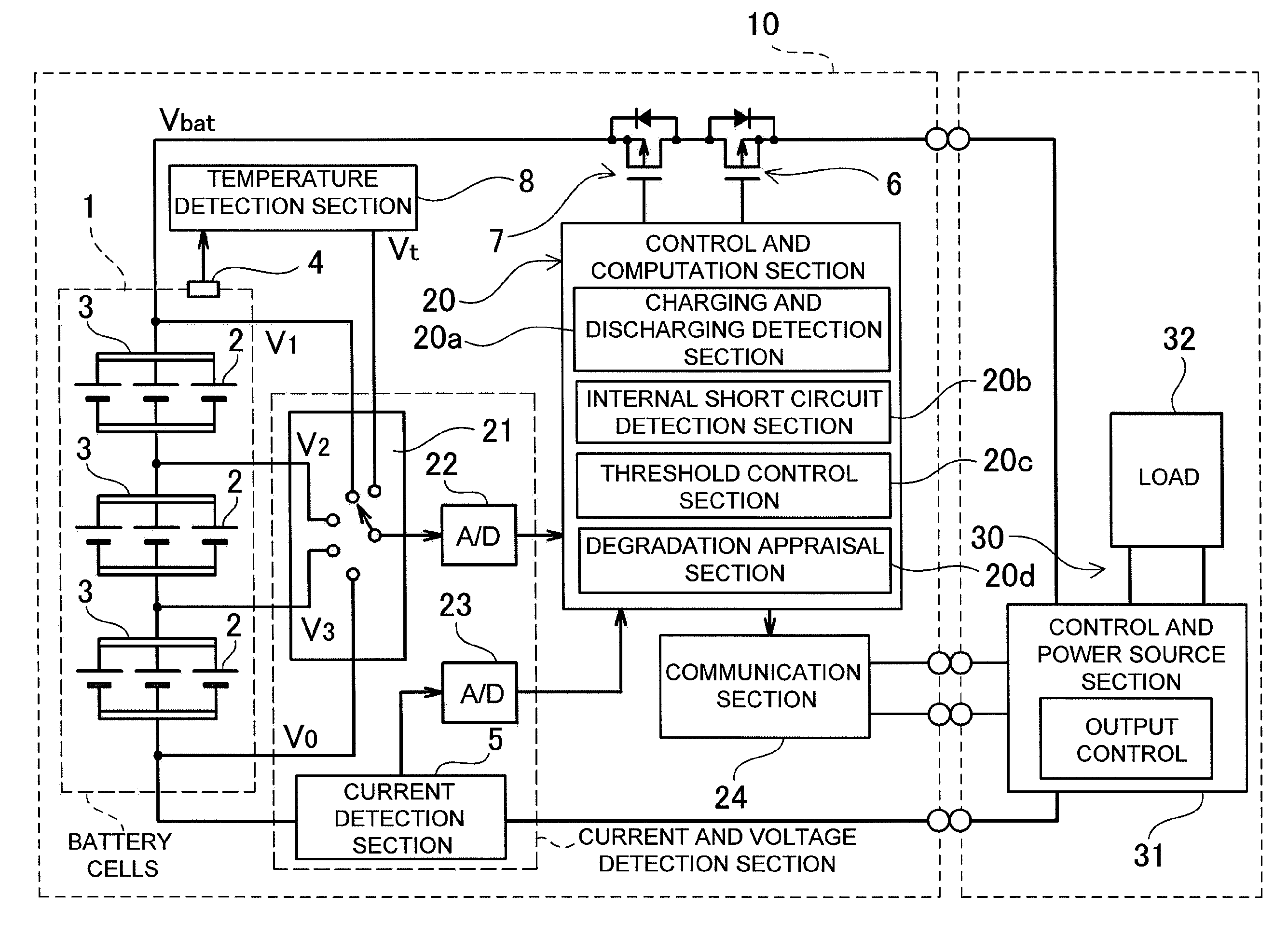
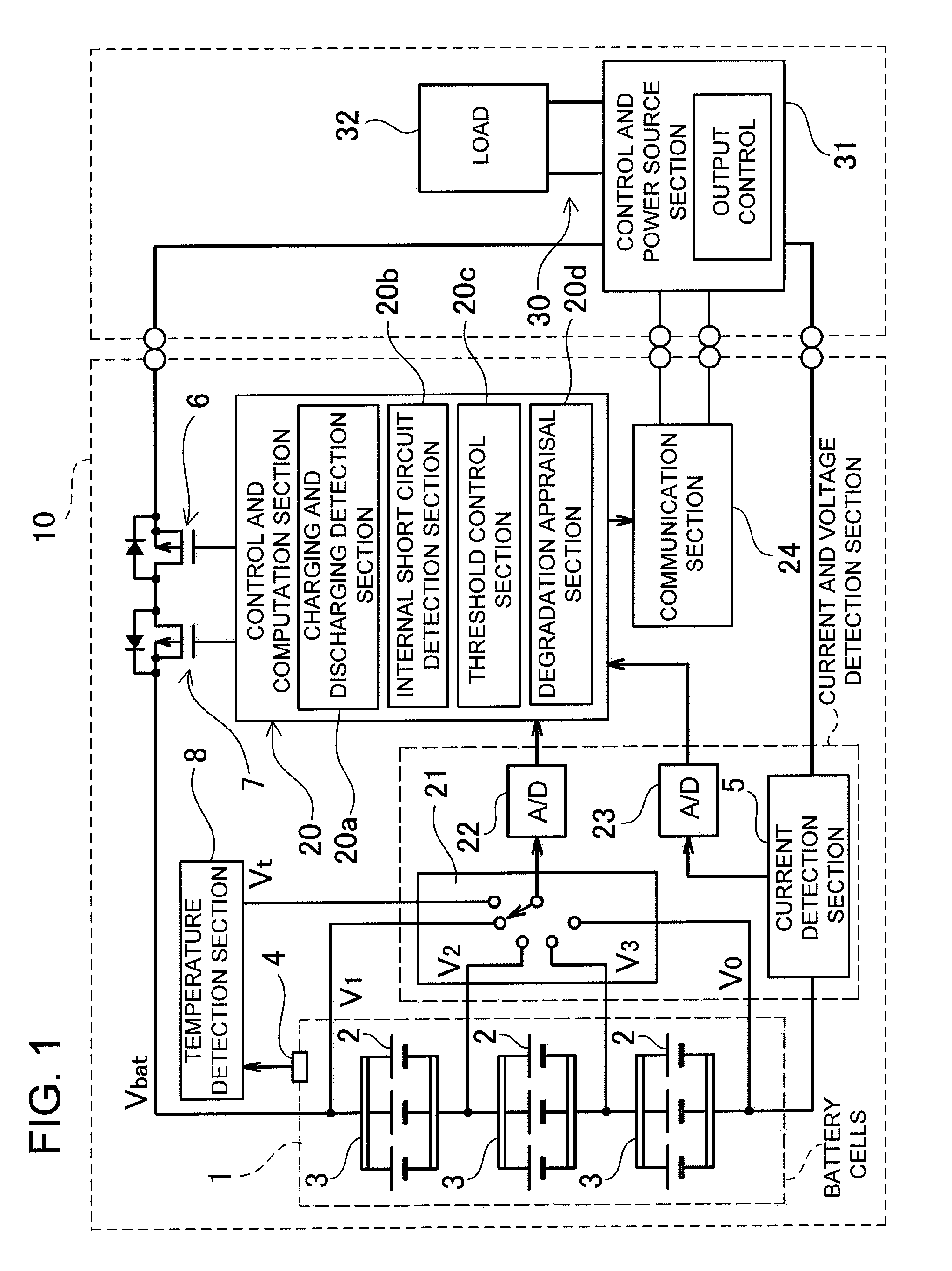
Rechargeable battery abnormality detection apparatus and rechargeable battery apparatus
ActiveUS20100194398A1Reliable detectionEffective preventionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCell component detailsBattery degradationAnomaly detection
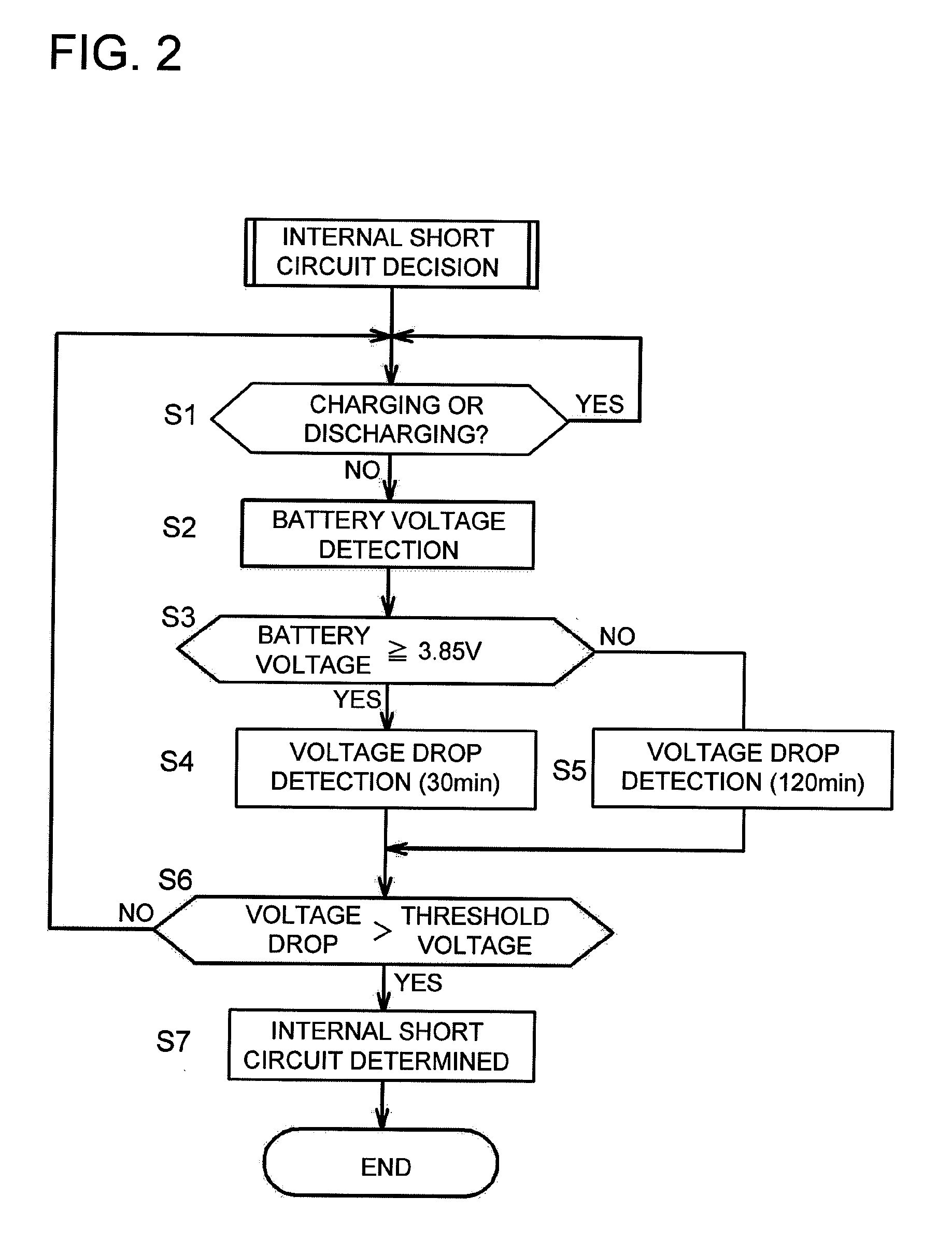
The rechargeable battery abnormality detection apparatus is provided with an internal short circuit detection section (20b) that monitors rechargeable battery (1) voltage change when no charging or discharging takes place, and detects internal short circuit abnormality when battery voltage drop during a predetermined time period exceeds a preset threshold voltage; a degradation appraisal section (20d) that judges the degree of rechargeable battery degradation; and a threshold control section (20c) that incrementally increases the threshold voltage according to the degree of degradation determined by the degradation appraisal section (20d).
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com