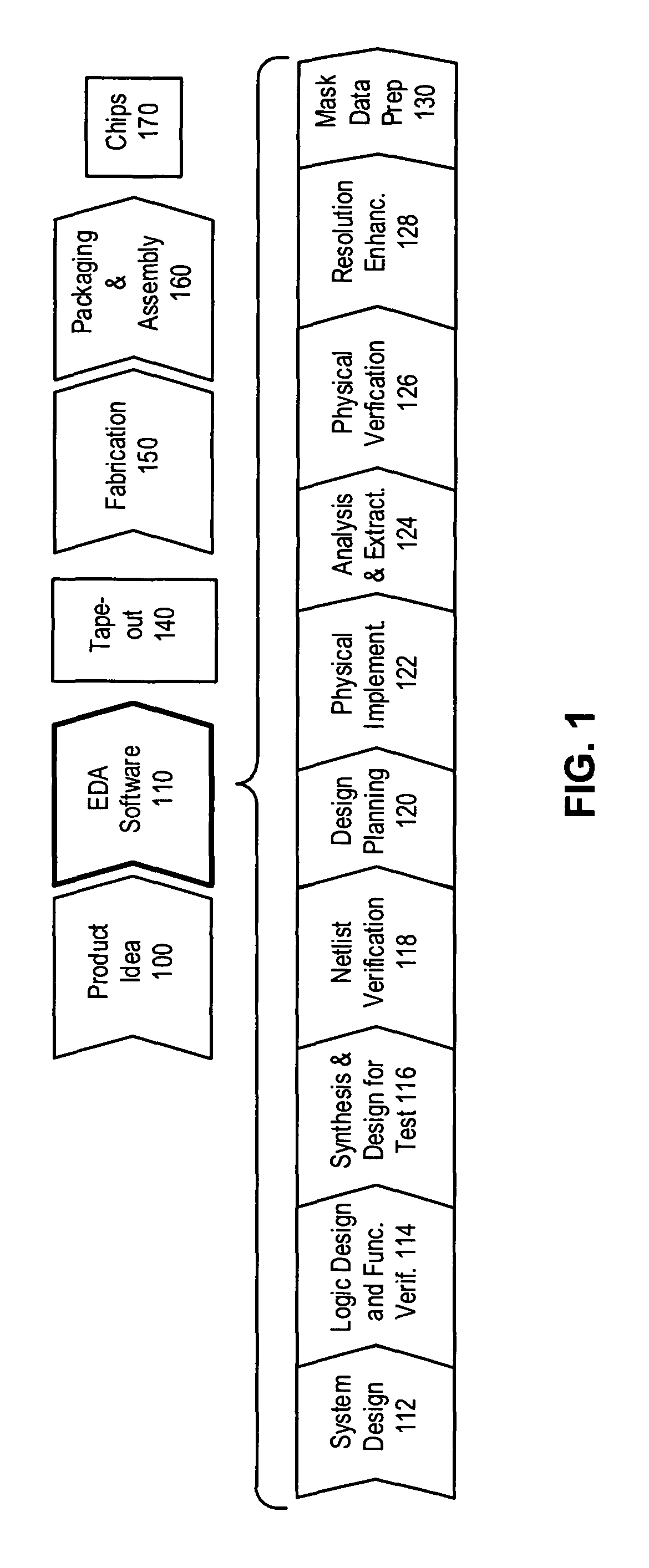
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Systematic variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Systematic Variation. In research and experimental situations, the term systematic variation generally denotes an anomaly or inaccuracy in observations which are the result of factors which are not under statistical control. An example of this could in testing water samples for harmful bacteria -- having no control over...
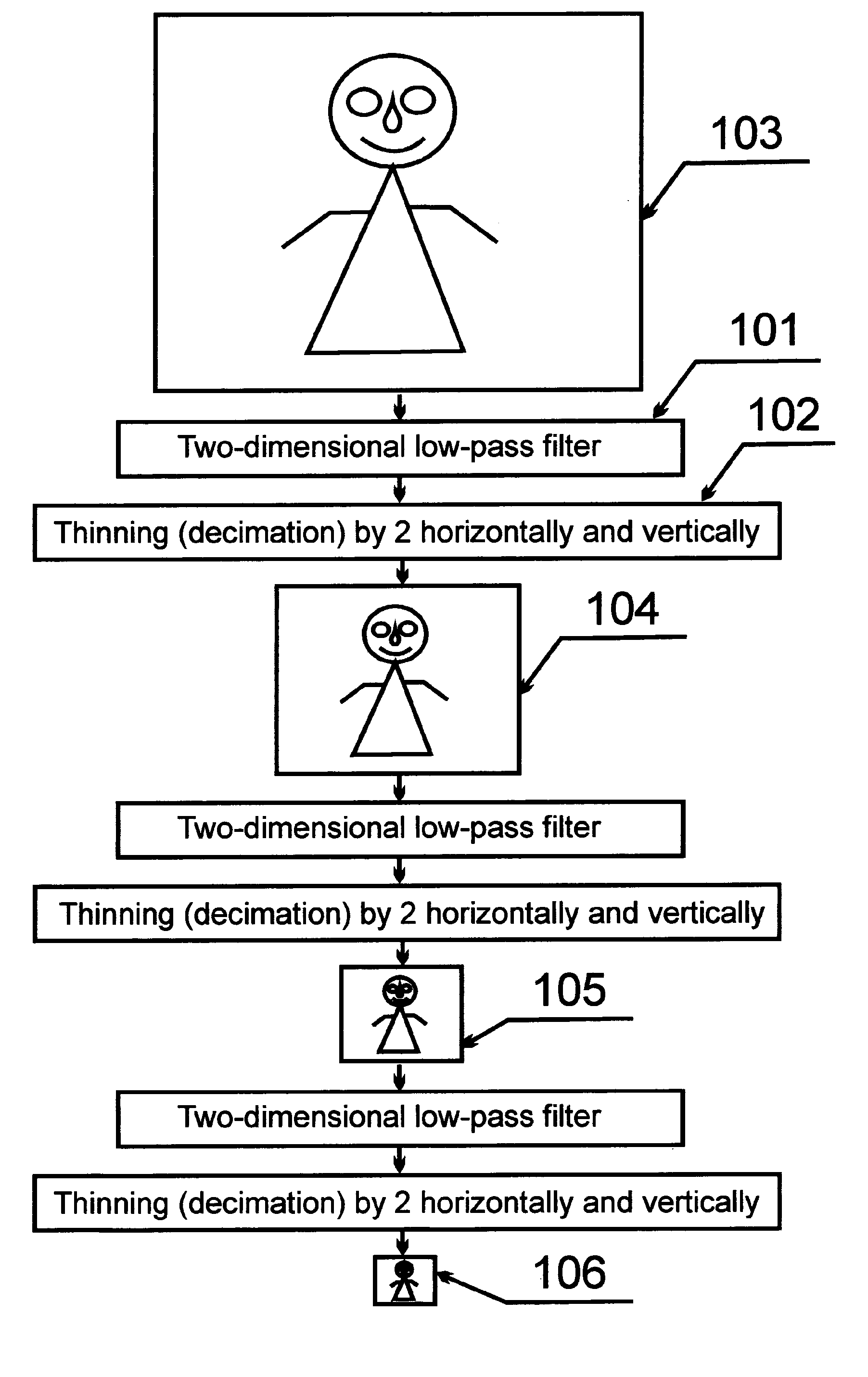
Method of encoding digital signals (variants), method of decoding digital signals (variants), device for implementation thereof (variants), and system for image transmission via limited throughput communication channels (variants)
InactiveUS20100226569A1Quality improvementImprove compression efficiencyCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionSystematic variationSelf adaptive
The invention relates to systems for a transmission of images via channels of communication with a limited capacity by means of application of compression of the images. The technical result consists in an increase of the compression degree upon encoding, and it allows to fulfill the transmission of such encoded images via the channel of communication with the limited capacity, therewith a high degree of the compression is provided without of increase of computational power of encoding device and without of distortions upon decoding. The result is obtained by the usage of more effective method of interpolation of restored subsamples, in this method there is used an adaptive and applicative set of samples, which restore a quantized signal, and this set of the samples allows to improve an accuracy of the interpolation with a number of the subsamples, which is necessary for the right interpolation that is simultaneously decreased one.
Owner:SIF CODEC
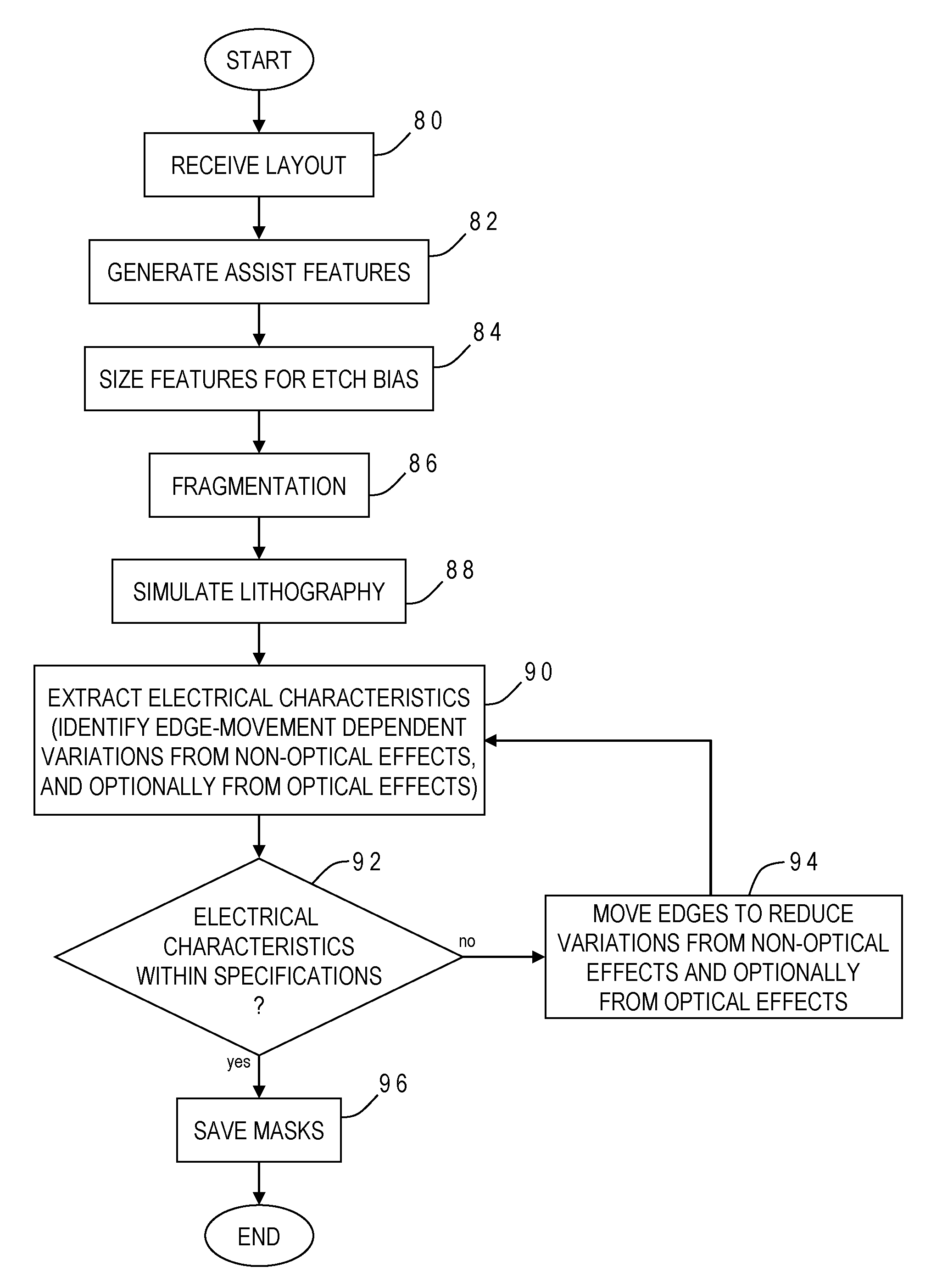
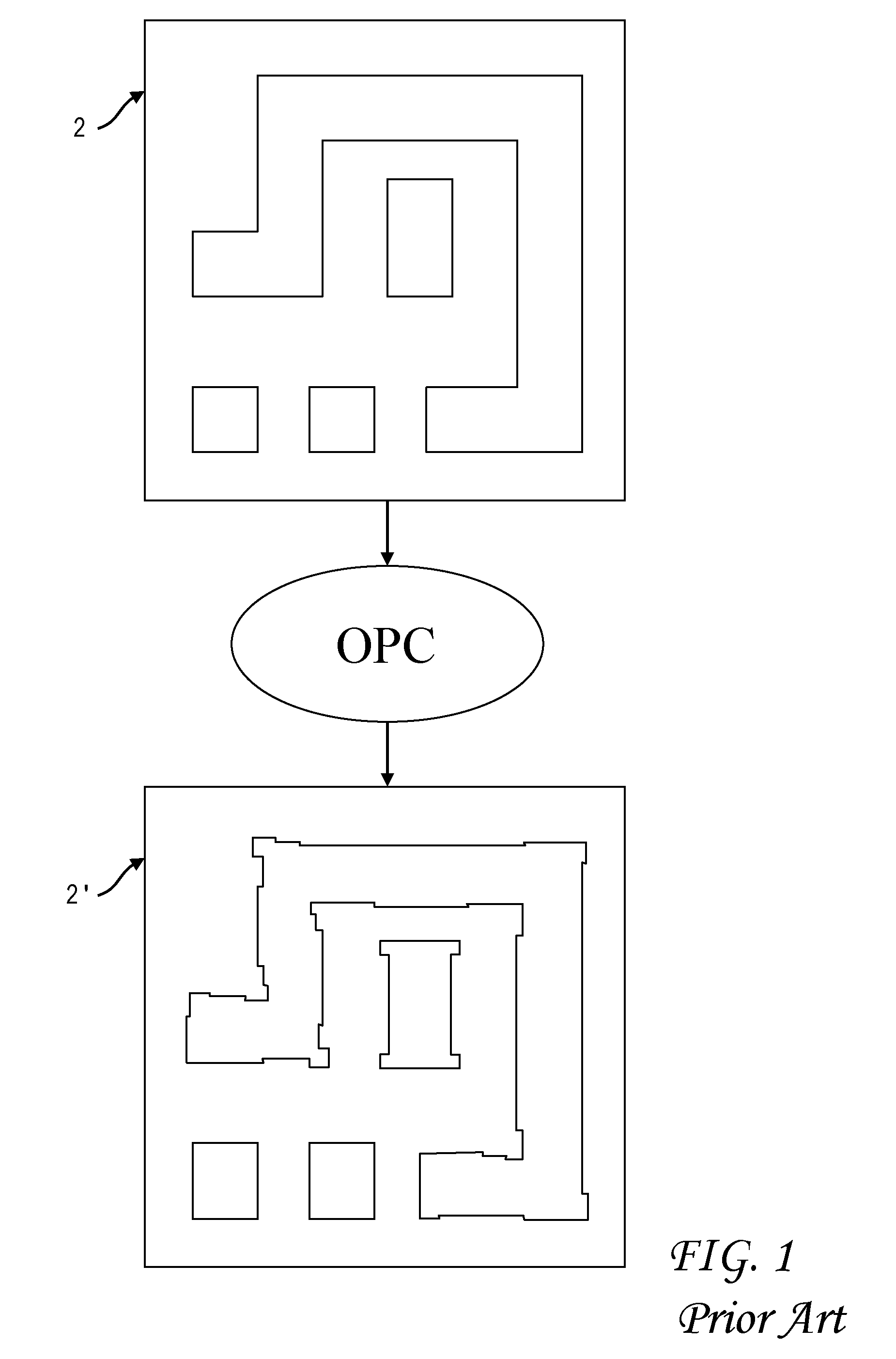
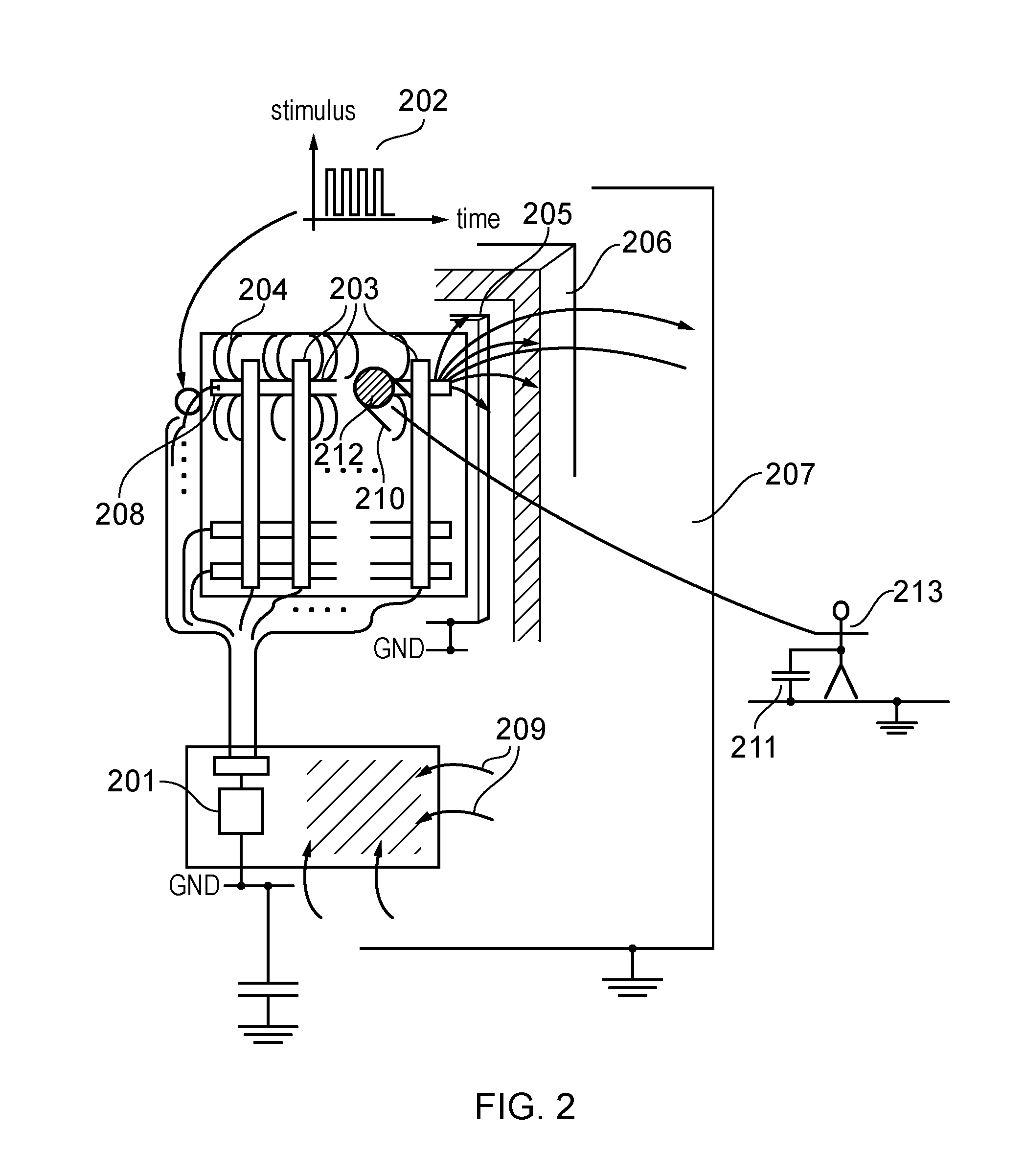
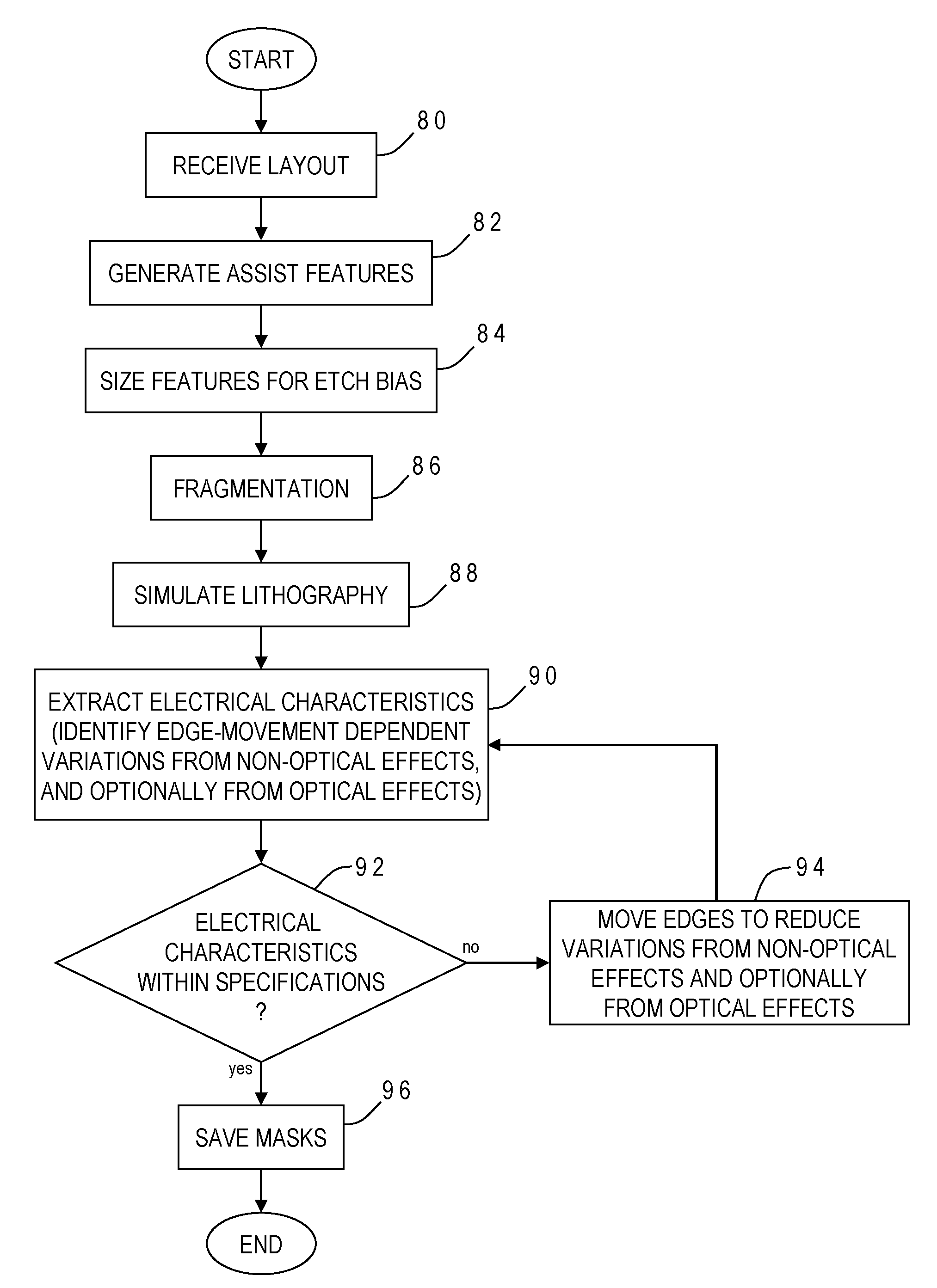
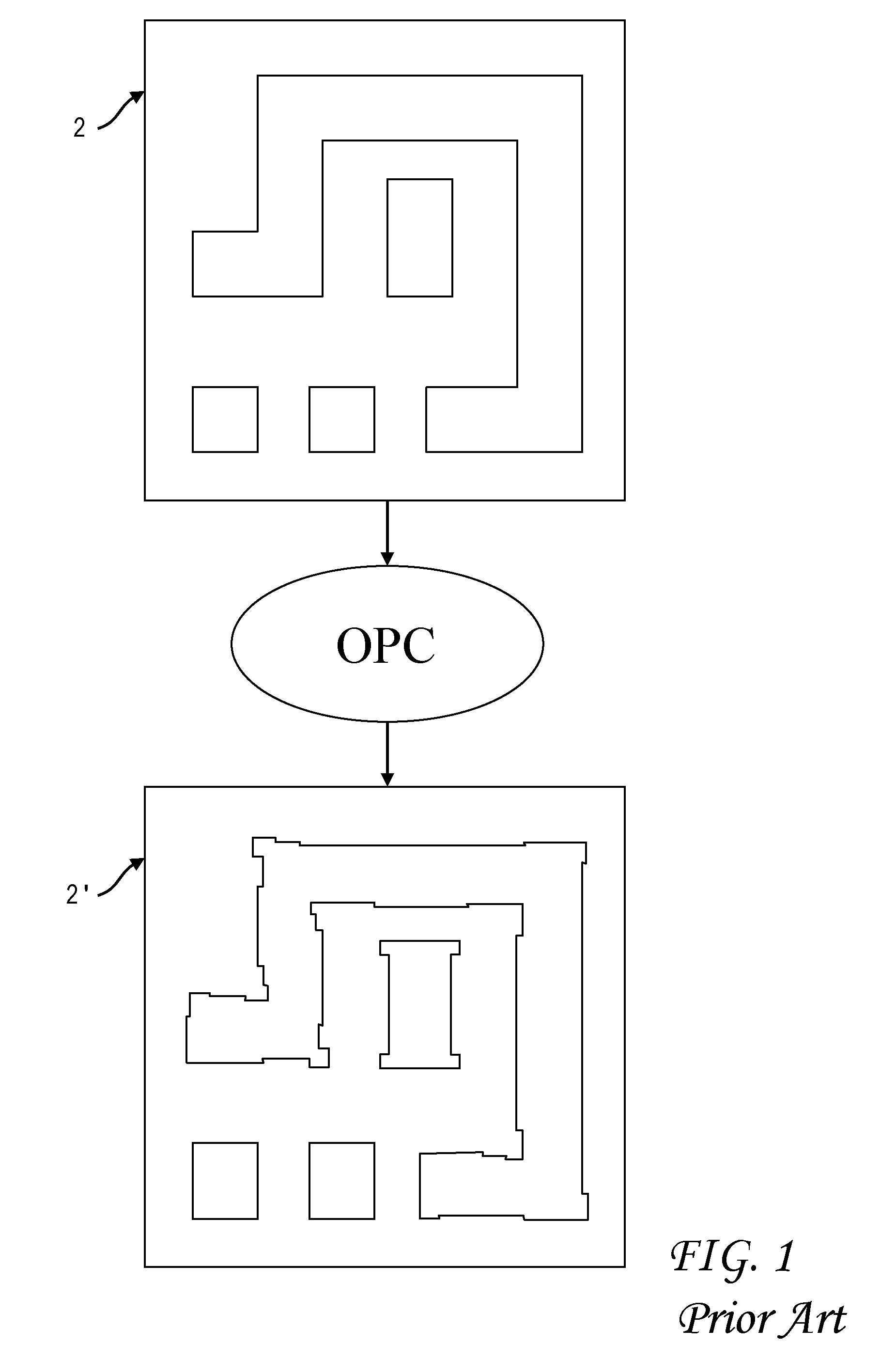
Electrically-driven optical proximity correction to compensate for non-optical effects
ActiveUS8103983B2Improve performancePhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentCapacitanceEngineering
A contour of a mask design for an integrated circuit is modified to compensate for systematic variations arising from non-optical effects such as stress, well proximity, rapid thermal anneal, or spacer thickness. Electrical characteristics of a simulated integrated circuit chip fabricated using the mask design are extracted and compared to design specifications, and one or more edges of the contour are adjusted to reduce the systematic variation until the electrical characteristic is within specification. The particular electrical characteristic preferably depends on which layer is to be fabricated from the mask: on-current for a polysilicon; resistance for contact; resistance and capacitance for metal; current for active; and resistance for vias. For systematic threshold voltage variation, the contour is adjusted to match a gate length which corresponds to an on-current value according to pre-calculated curves for contour current and gate length at a nominal threshold voltage of the chip.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
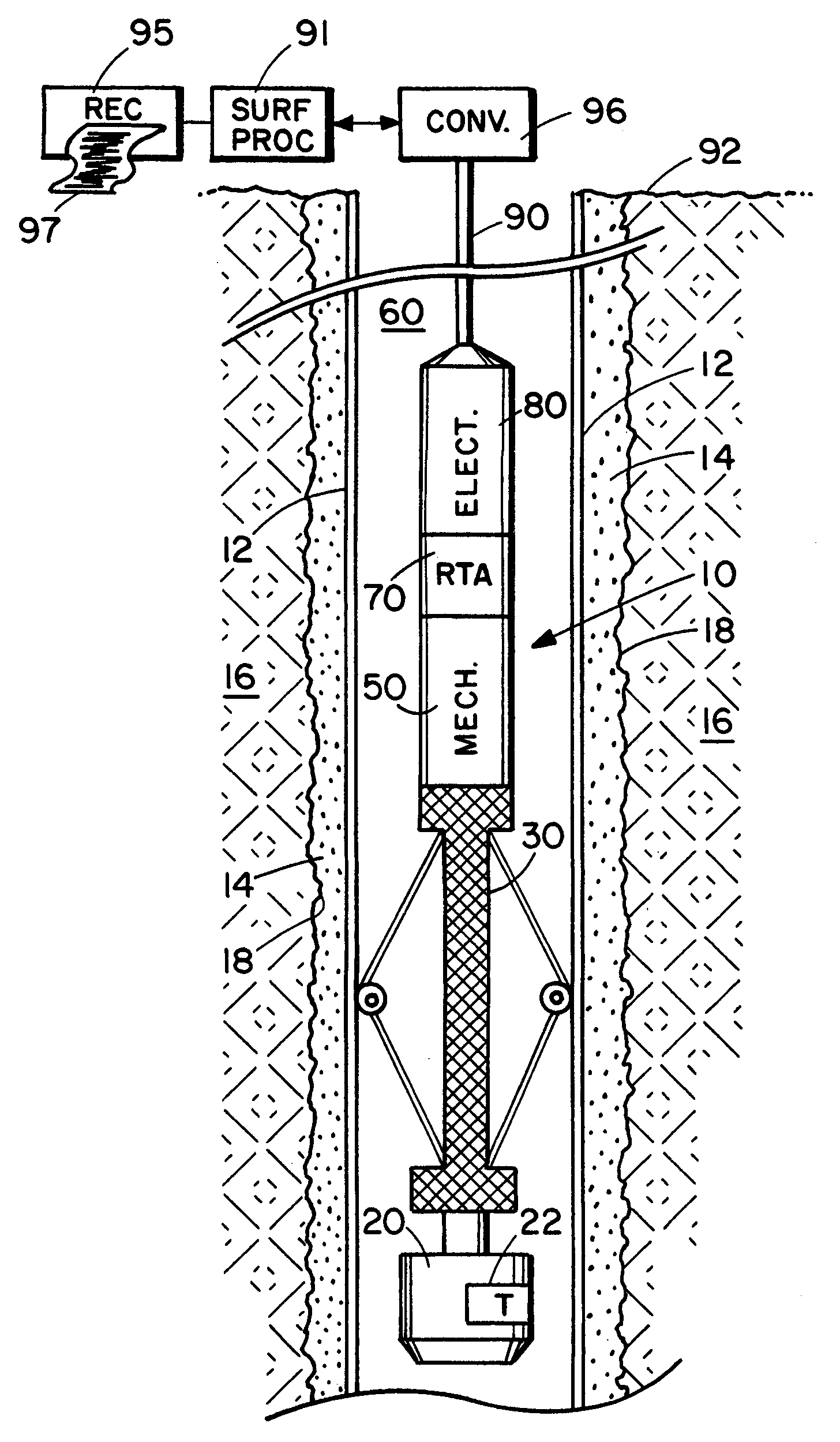
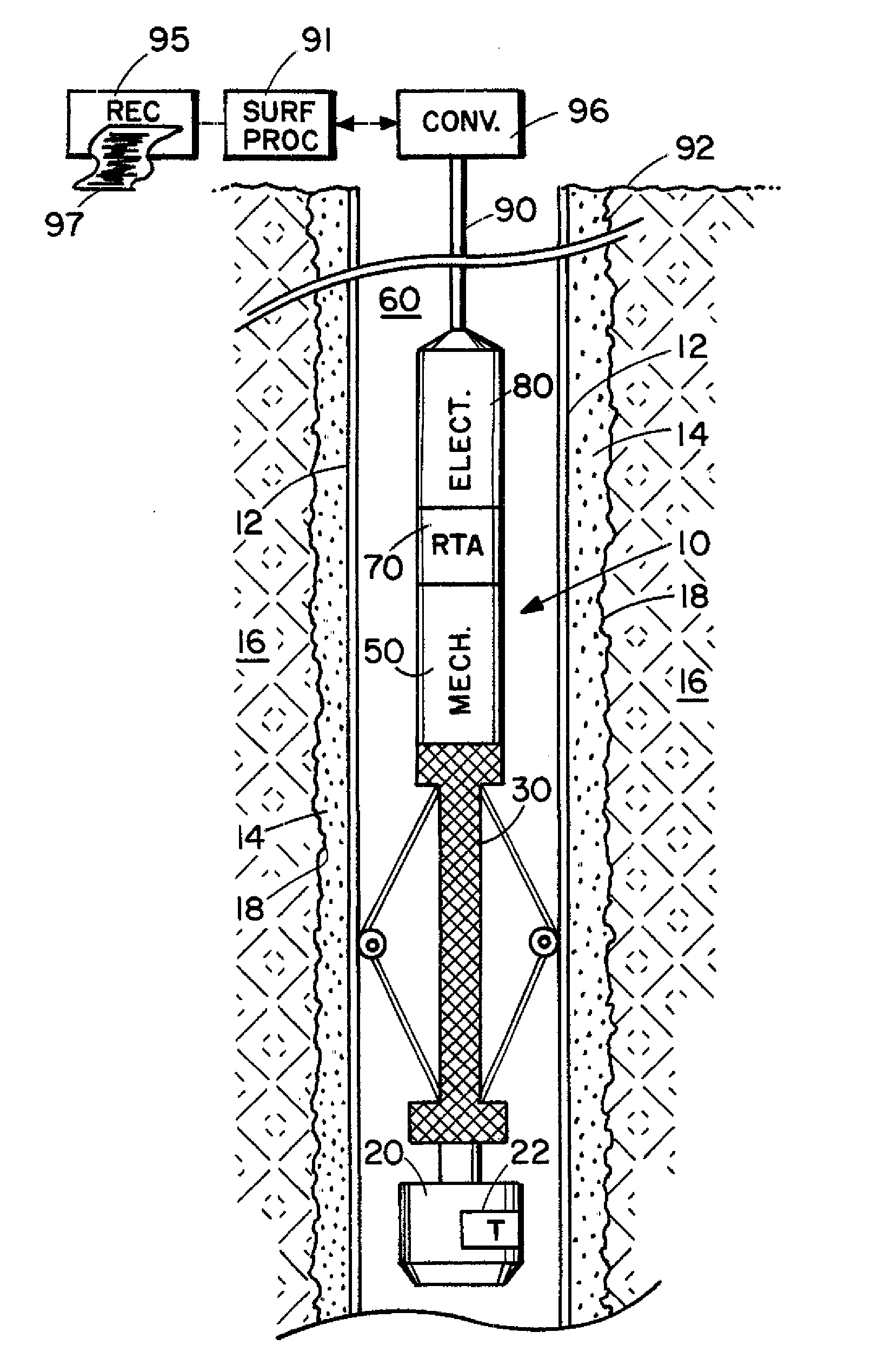
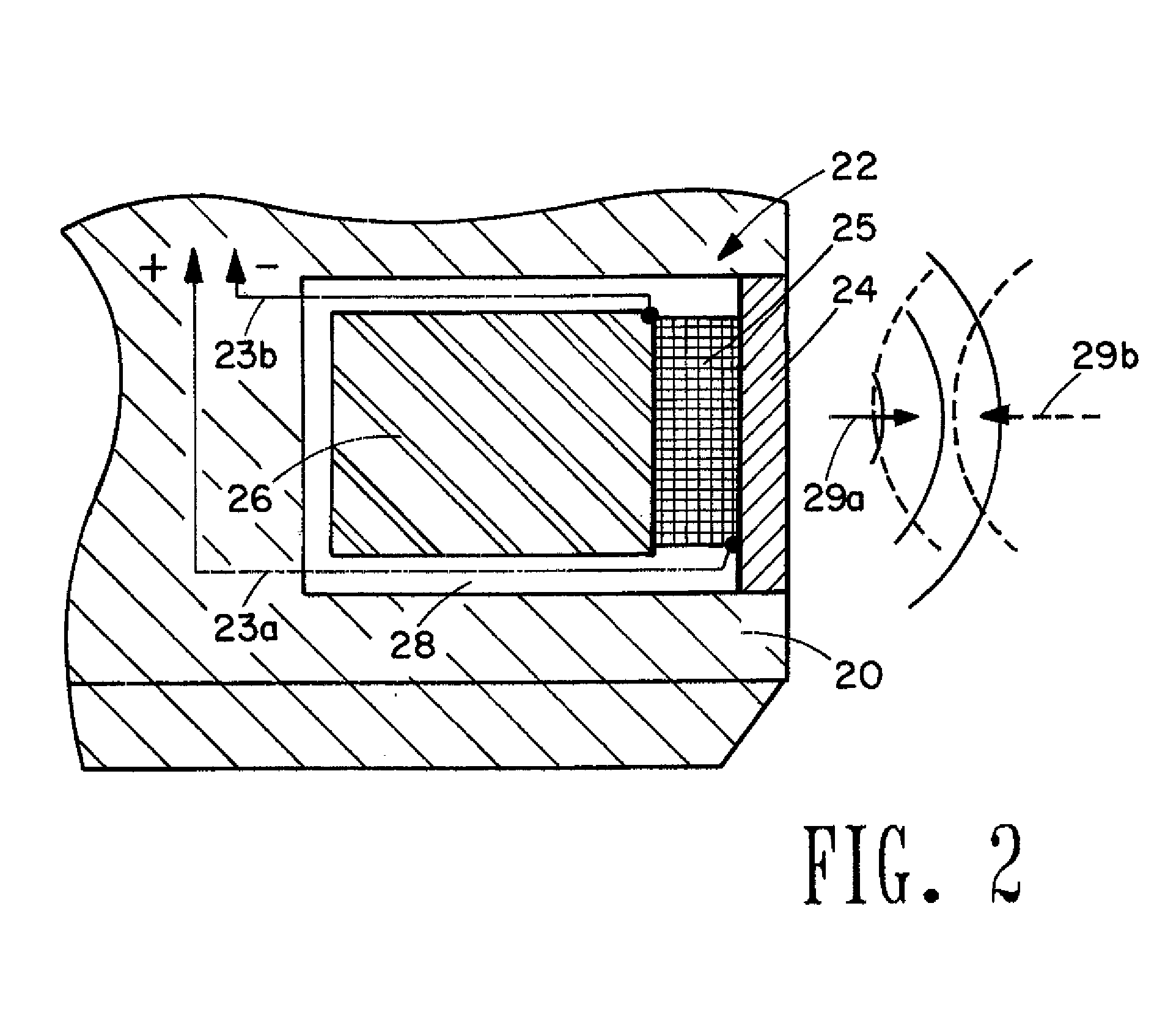
Ultrasonic cement scanner
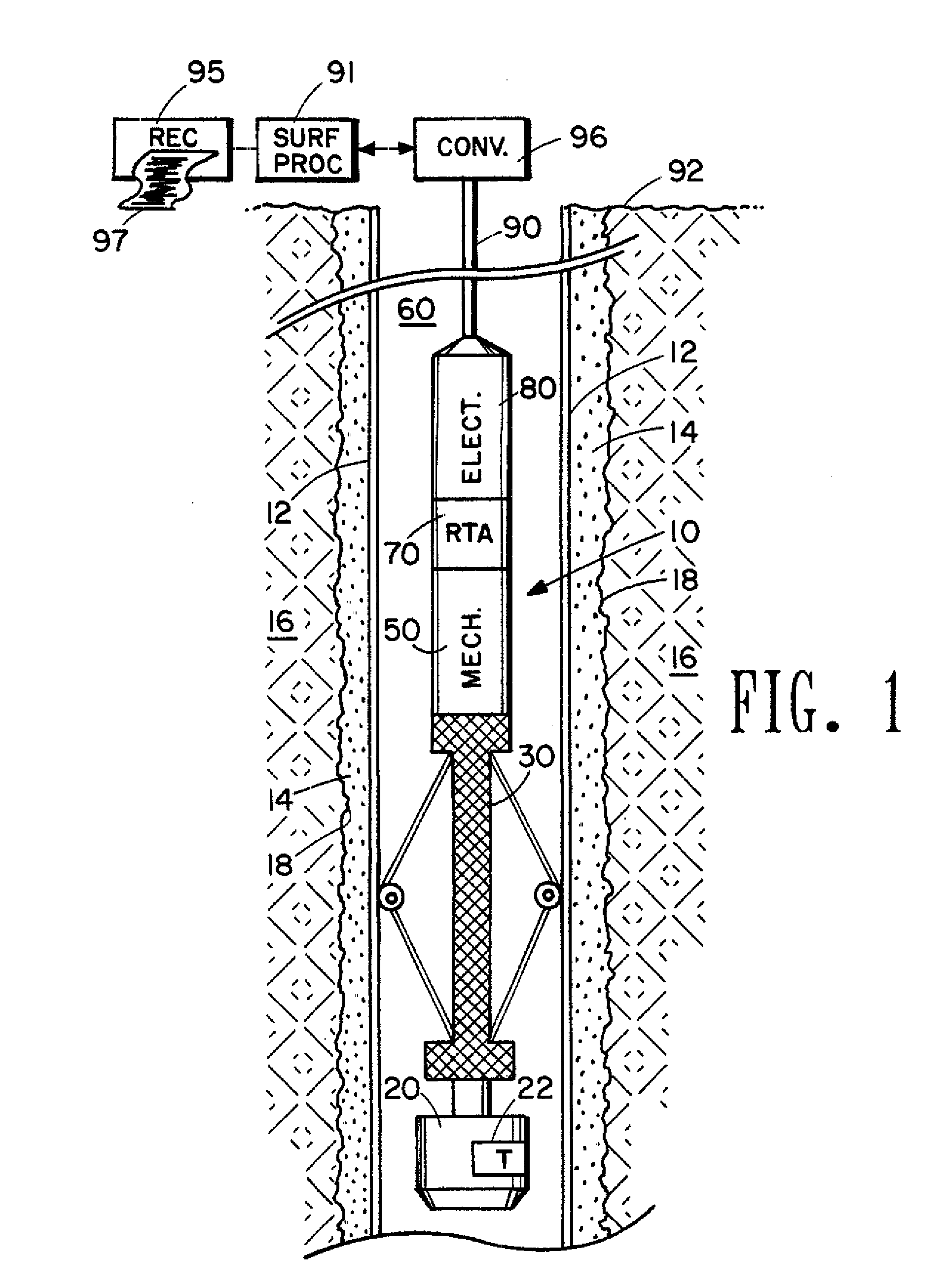
InactiveUS20060067162A1Minimizing telemetry band width requirementMinimization requirementsConstructionsSeismology for water-loggingSystematic variationFull wave
An acoustic borehole logging system for parameters of a well borehole environs. Full wave acoustic response of a scanning transducer is used to measure parameters indicative of condition of a tubular lining the well borehole, the bonding of the tubular to material filling an annulus formed by the outside surface of the tubular and the wall of the borehole, the distribution of the material filling the annulus, and thickness of the tubular. A reference transducer is used to correct measured parameters for variations in acoustic impedance of fluid filling the borehole, and for systematic variations in the response of the scanning transducer. Corrections are made in real time. The downhole tool portion of the logging system is operated essentially centralized in the borehole using a centralizer that can be adjusted for operation in a wide range of borehole sizes.
Owner:PRECISION DRILLING TECH SERVICES GROUP +1
Nucleic acids encoding kinase and phosphatase enzymes, expression vectors and cells containing same
InactiveUS7517970B2Good quality crystalImprove crystallizationSugar derivativesHydrolasesActive enzymeSystematic variation
Methods for expressing active enzymes are described that involve co-expressing a first enzyme with a second enzyme that has an enzymatic activity that reverses a modification on the first enzyme and / or for identification of soluble and / or active catalytic domains by systematic variation of fragment lengths around catalytic domain boundaries.
Owner:PLEXXIKON INC
Touch sensor for non-uniform panels
ActiveUS20150028894A1Reduce and substantially eliminate variation in overlap areaStop capacitance variationResistance/reactance/impedenceElectric/magnetic position measurementsSystematic variationEngineering
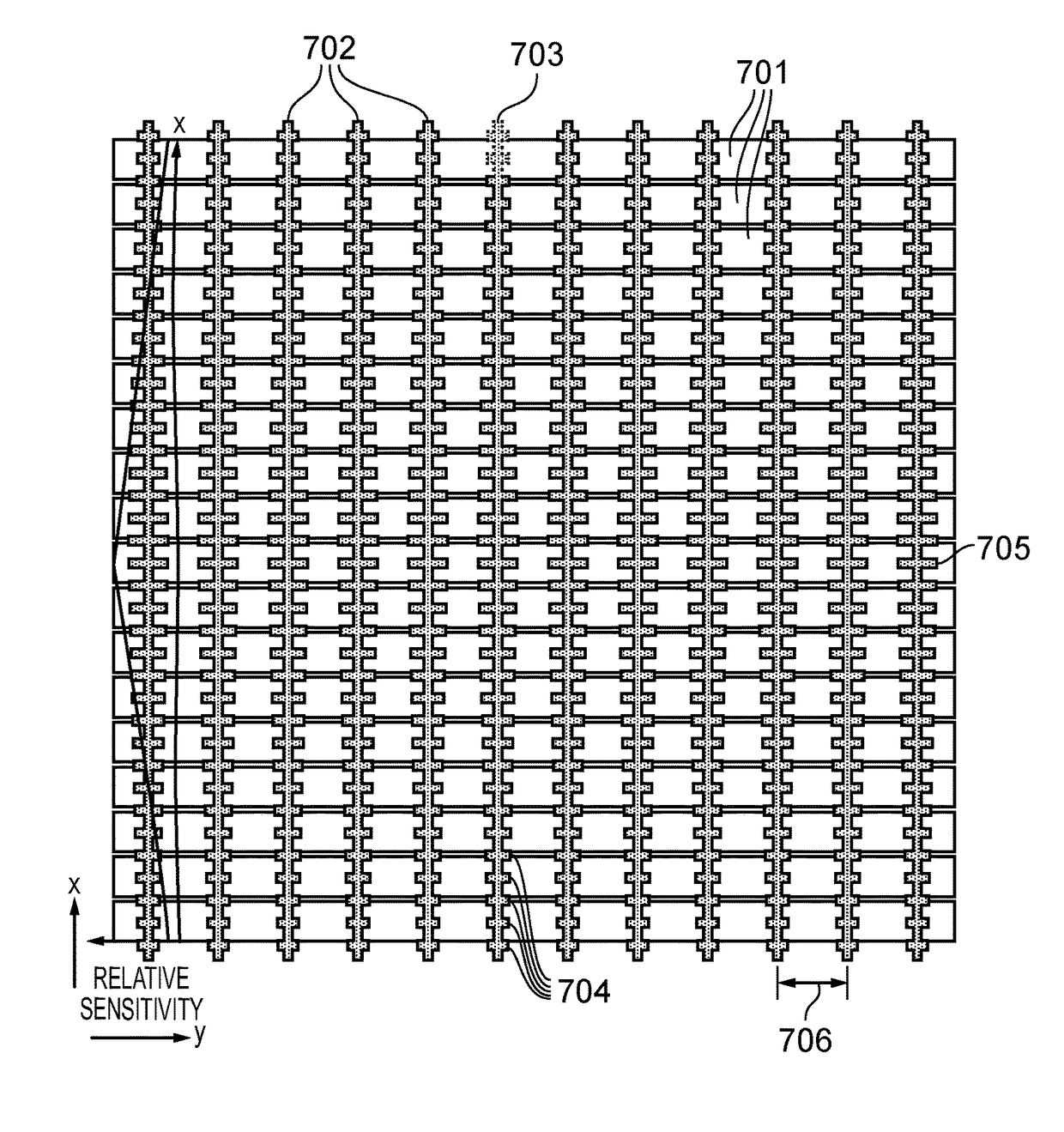
A two-dimensional capacitive touch sensor having a cover layer of varying thickness arranged on top of its electrode structure. An array of sensing nodes is formed between edge portions of the receiver electrodes and adjacent portions of the transmitter electrodes. To compensate for the varying thickness of the cover layer, the length of the edge portions per sensing node is varied to equalize node sensitivity across the sensor and thus suppress the systematic variation in node sensitivity which would otherwise arise as a result of the varying thickness of the cover layer.
Owner:TOUCHNETIX
Electrically-driven optical proximity correction to compensate for non-optical effects
ActiveUS20100122231A1Simple methodImprove performancePhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentCapacitanceEngineering
A contour of a mask design for an integrated circuit is modified to compensate for systematic variations arising from non-optical effects such as stress, well proximity, rapid thermal anneal, or spacer thickness. Electrical characteristics of a simulated integrated circuit chip fabricated using the mask design are extracted and compared to design specifications, and one or more edges of the contour are adjusted to reduce the systematic variation until the electrical characteristic is within specification. The particular electrical characteristic preferably depends on which layer is to be fabricated from the mask: on-current for a polysilicon; resistance for contact; resistance and capacitance for metal; current for active; and resistance for vias. For systematic threshold voltage variation, the contour is adjusted to match a gate length which corresponds to an on-current value according to pre-calculated curves for contour current and gate length at a nominal threshold voltage of the chip.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
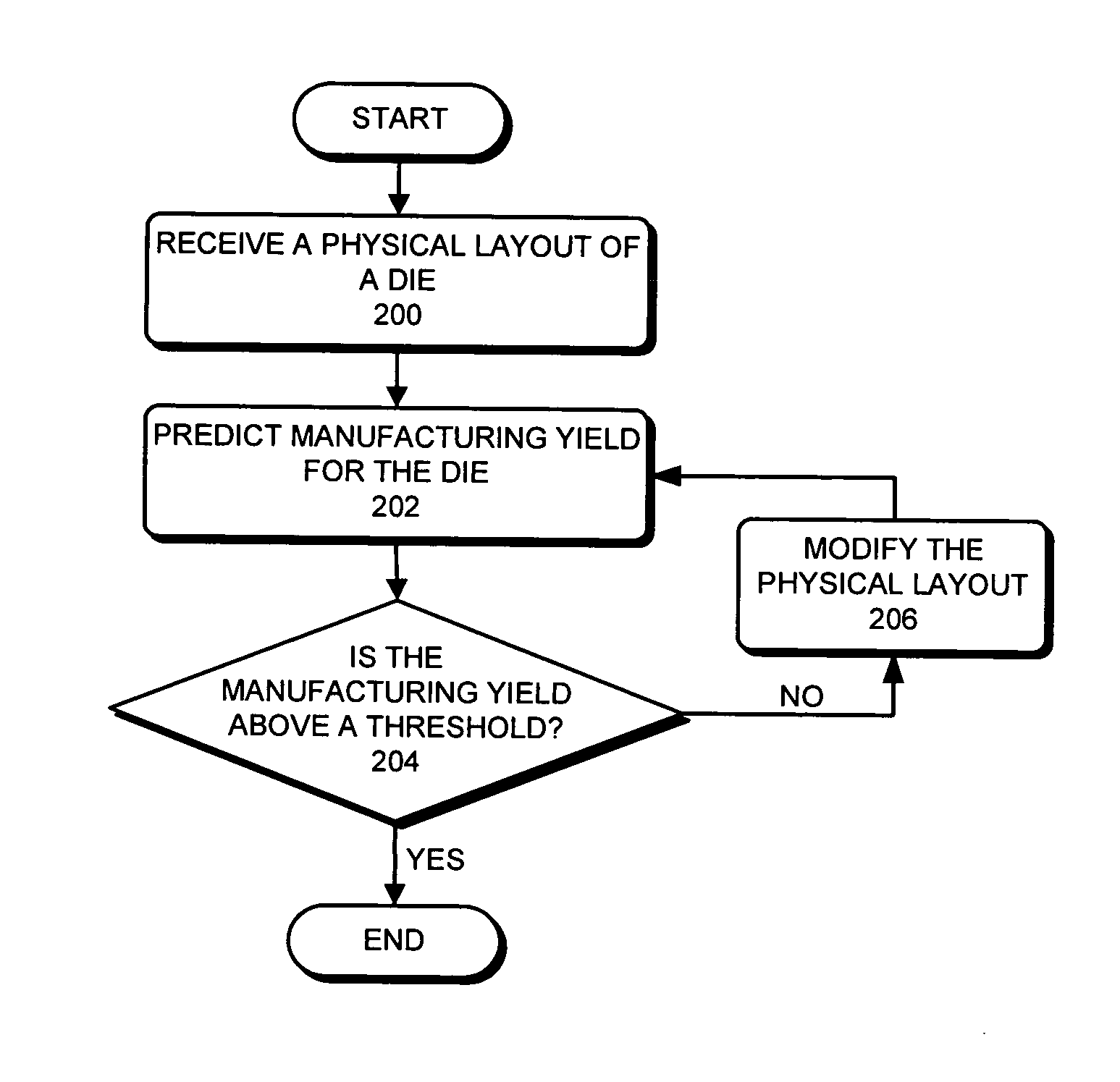
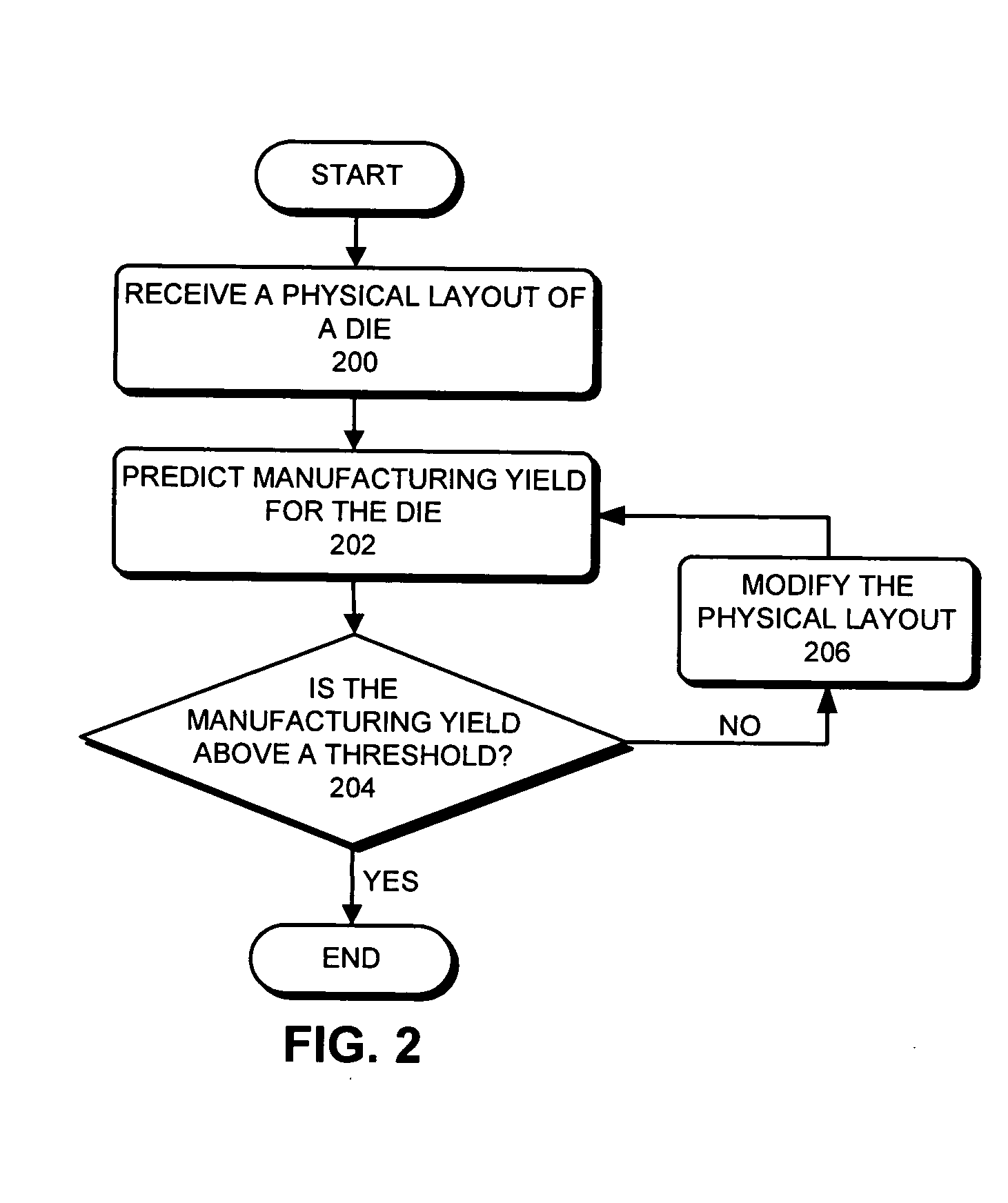
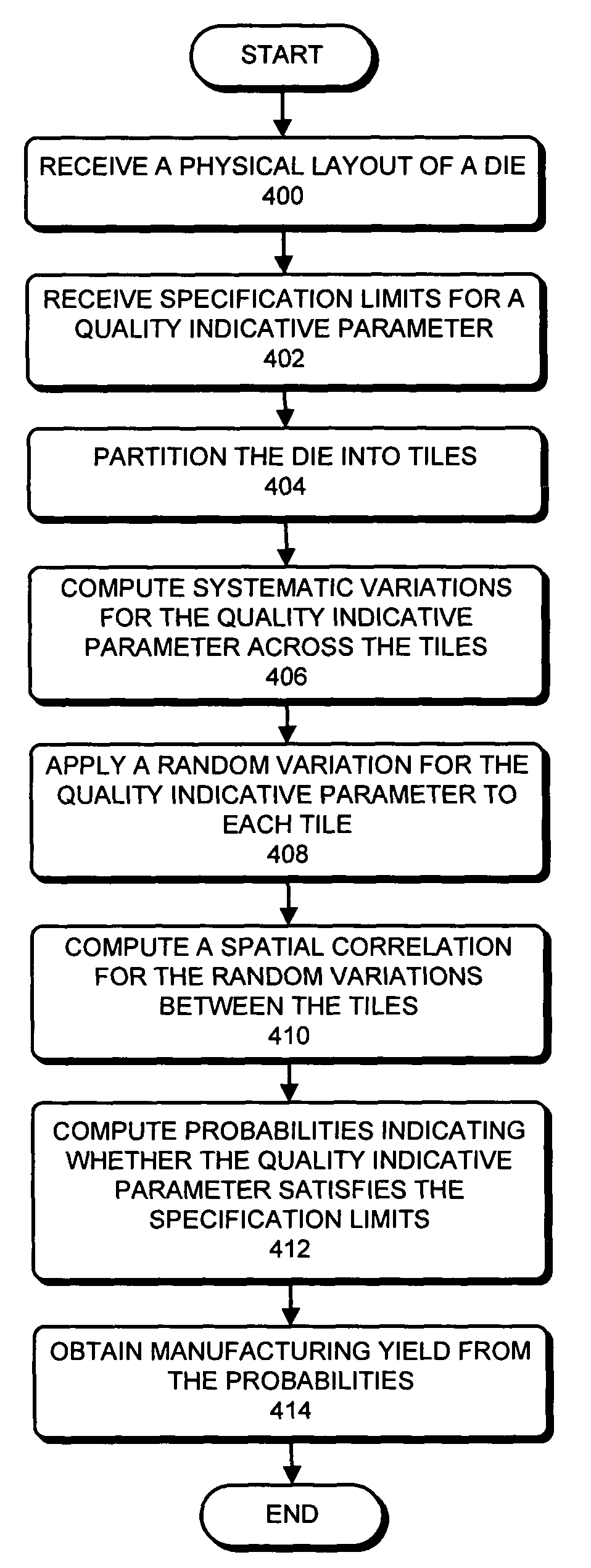
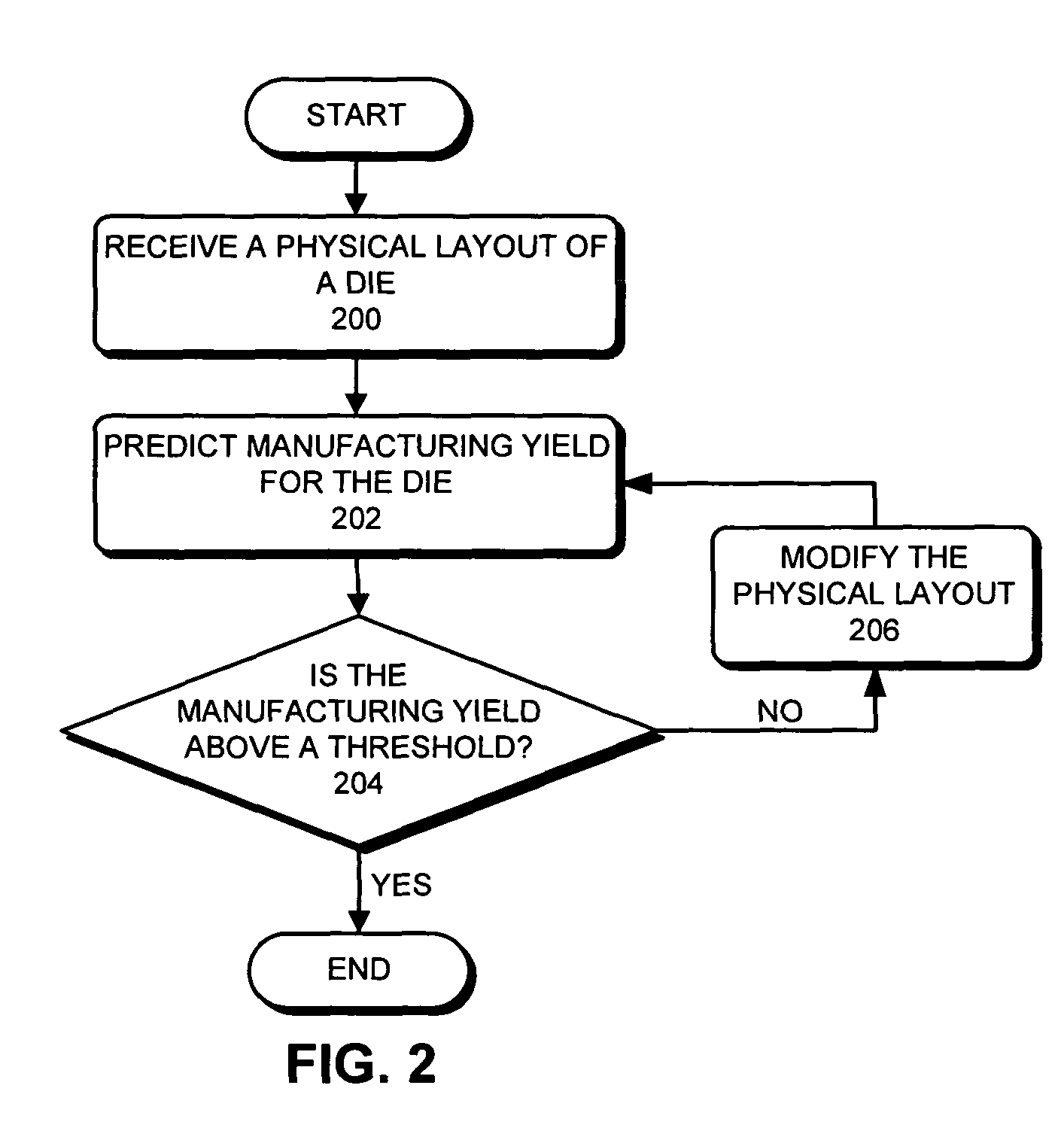
Predicting IC manufacturing yield by considering both systematic and random intra-die process variations
ActiveUS20070174797A1Reduce complexityProgramme controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSystematic variationDying processes
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that predicts manufacturing yield for a die within a semiconductor wafer. During operation, the system first receives a physical layout of the die. Next, the system partitions the die into an array of tiles. The system then computes systematic variations for a quality indicative value to describe a process parameter across the array of tiles based on the physical layout of the die. Next, the system applies a random variation for the quality indicative parameter to each tile in the array of tiles. Finally, the system obtains the manufacturing yield for the die based on both the systematic variations and the random variations.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
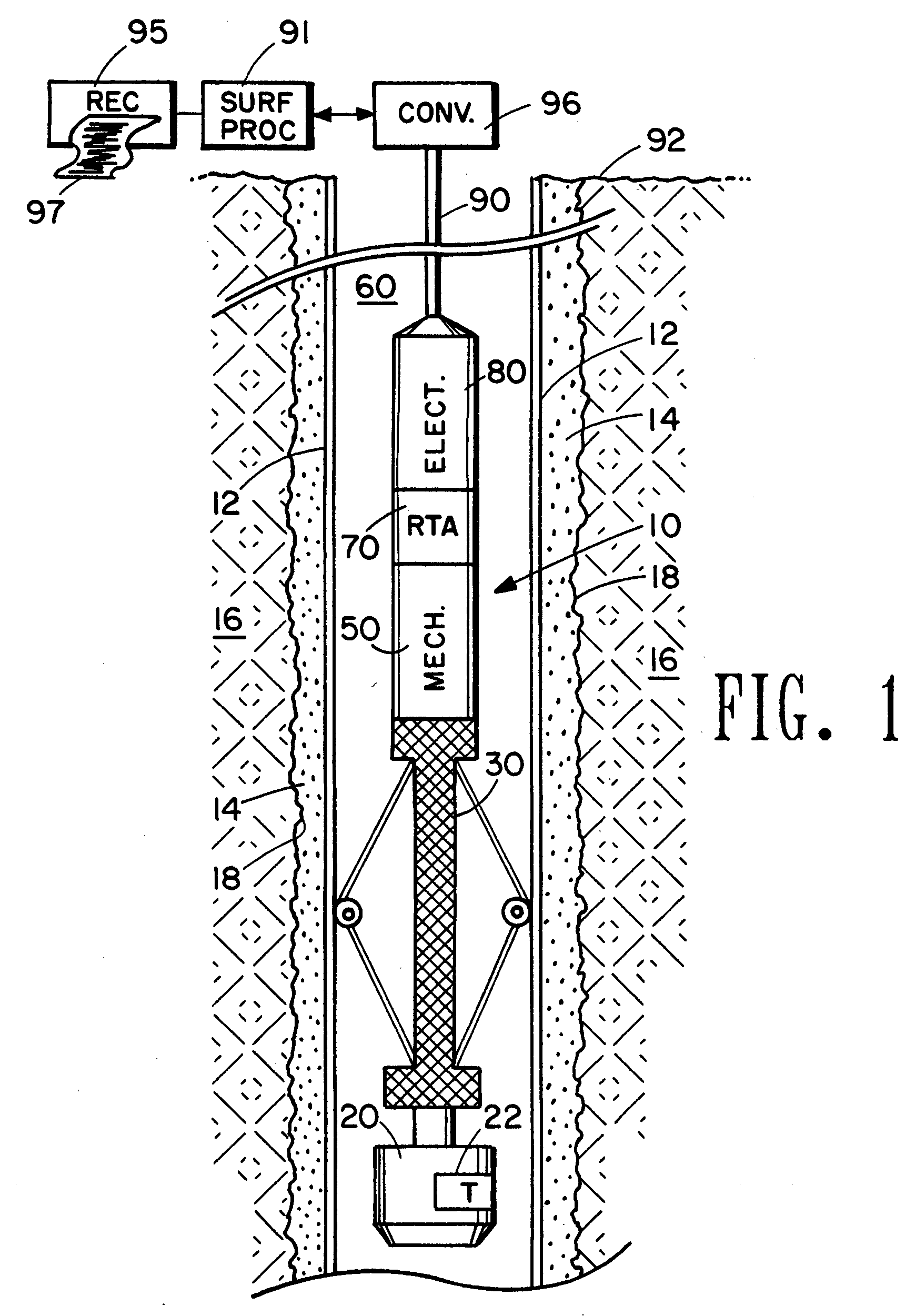
Ultrasonic cement scanner
InactiveUS20060262643A1Minimization requirementsConstructionsSeismology for water-loggingSystematic variationFull wave
An acoustic borehole logging system for parameters of a well borehole environs. Full wave acoustic response of a scanning transducer is used to measure parameters indicative of condition of a tubular lining the well borehole, the bonding of the tubular to material filling an annulus formed by the outside surface of the tubular and the wall of the borehole, the distribution of the material filling the annulus, and thickness of the tubular. A reference transducer is used to correct measured parameters for variations in acoustic impedance of fluid filling the borehole, and for systematic variations in the response of the scanning transducer. Corrections are made in real time. The downhole tool portion of the logging system is operated essentially centralized in the borehole using a centralizer that can be adjusted for operation in a wide range of borehole sizes.
Owner:PRECISION ENERGY SERVICES
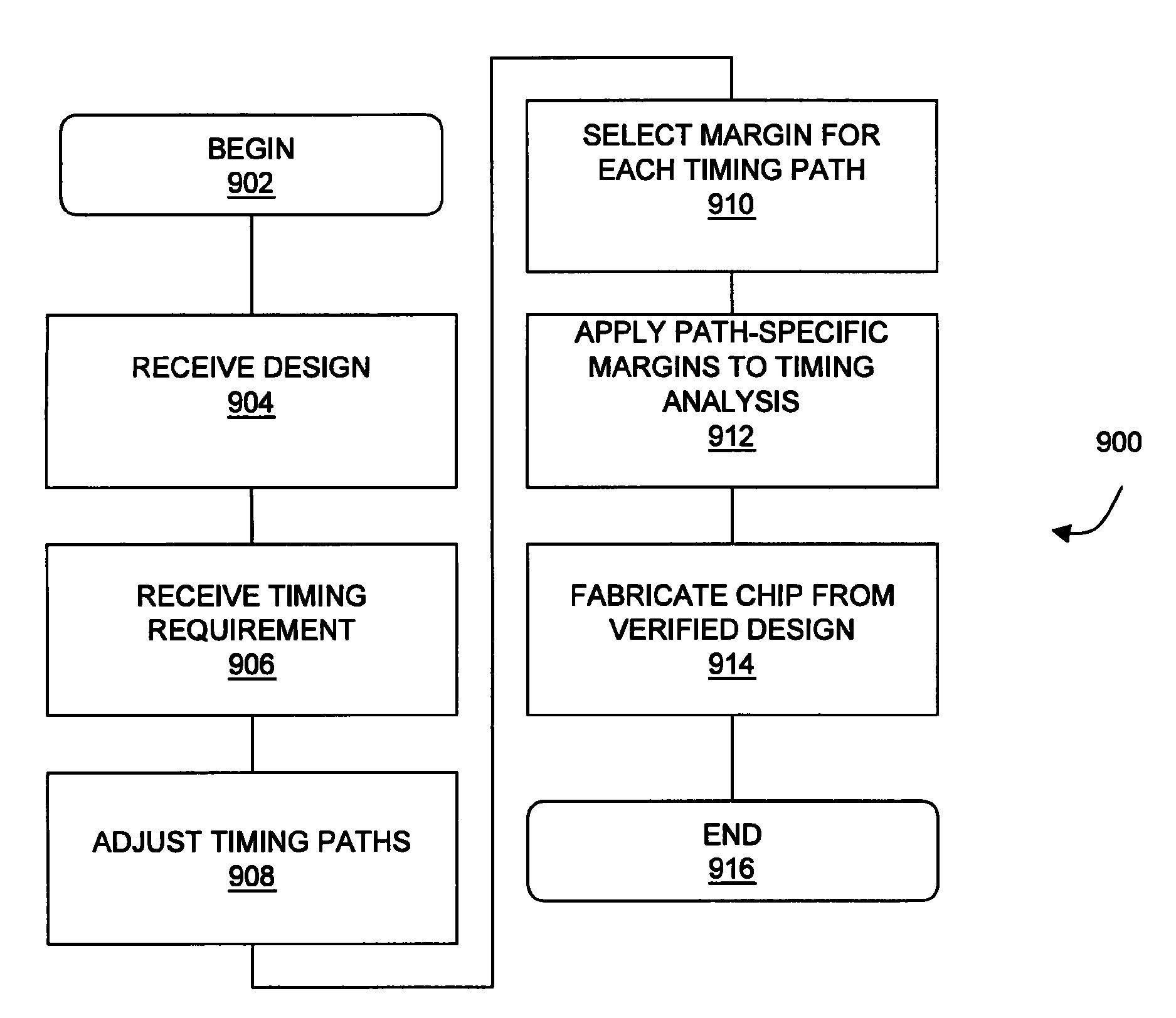
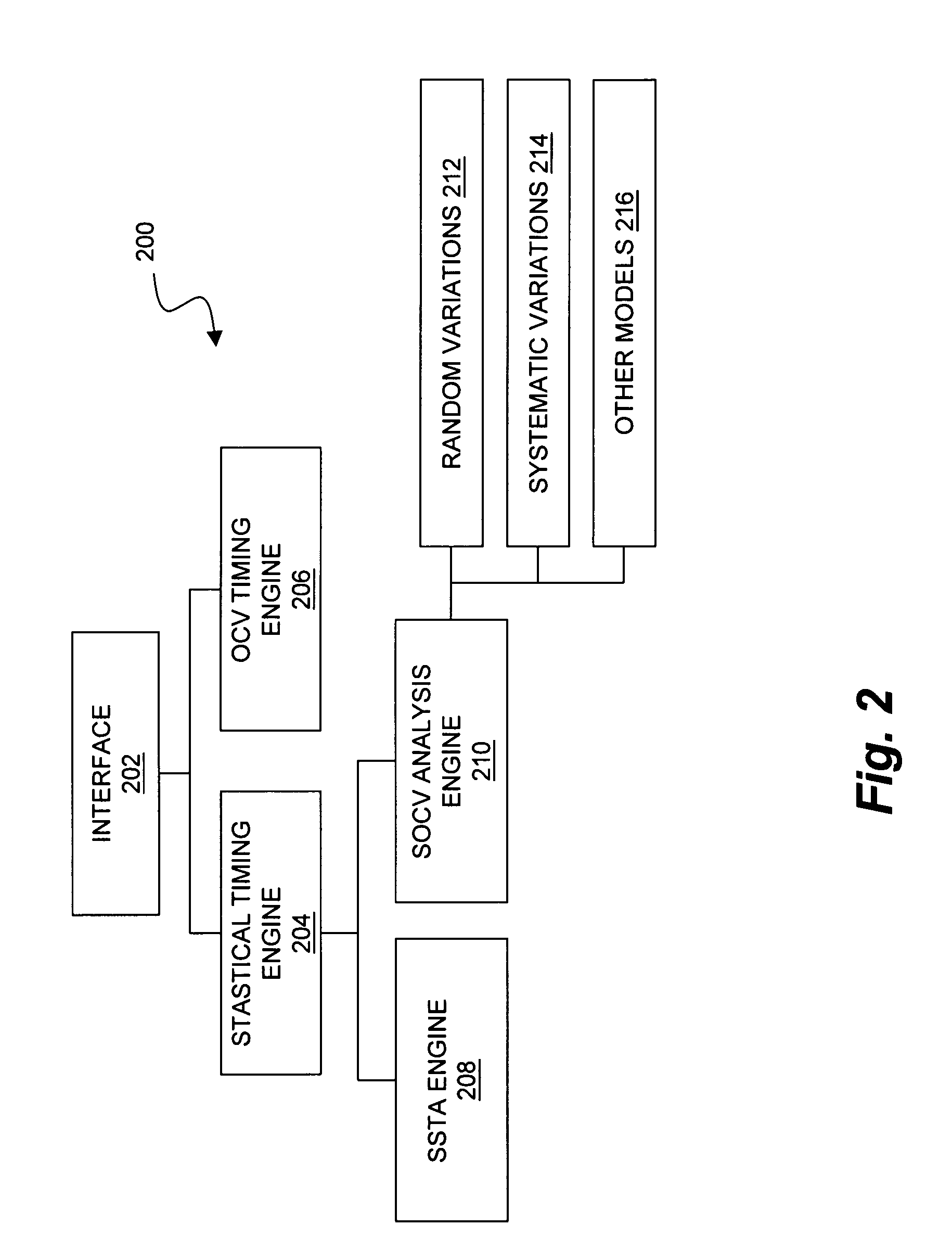
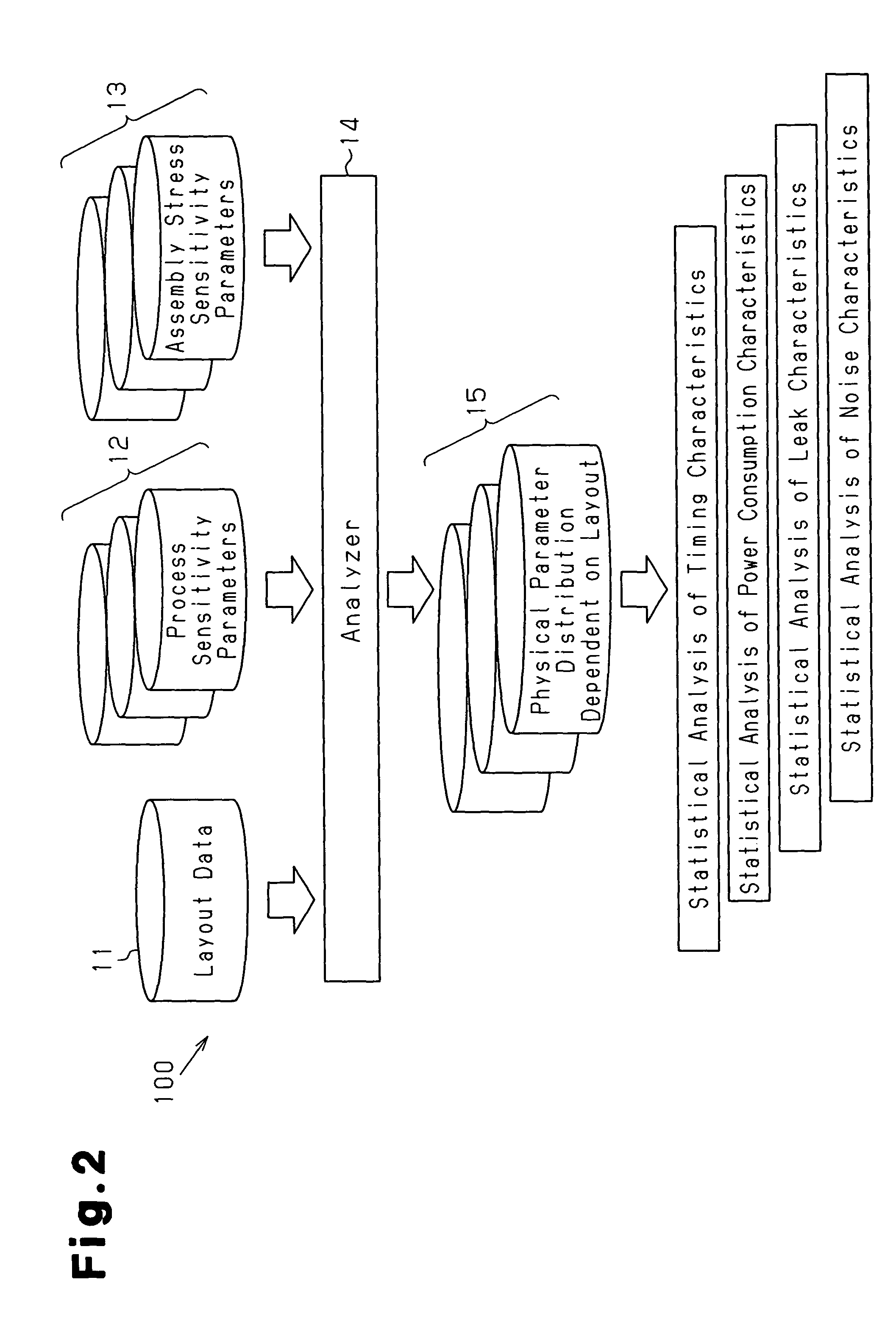
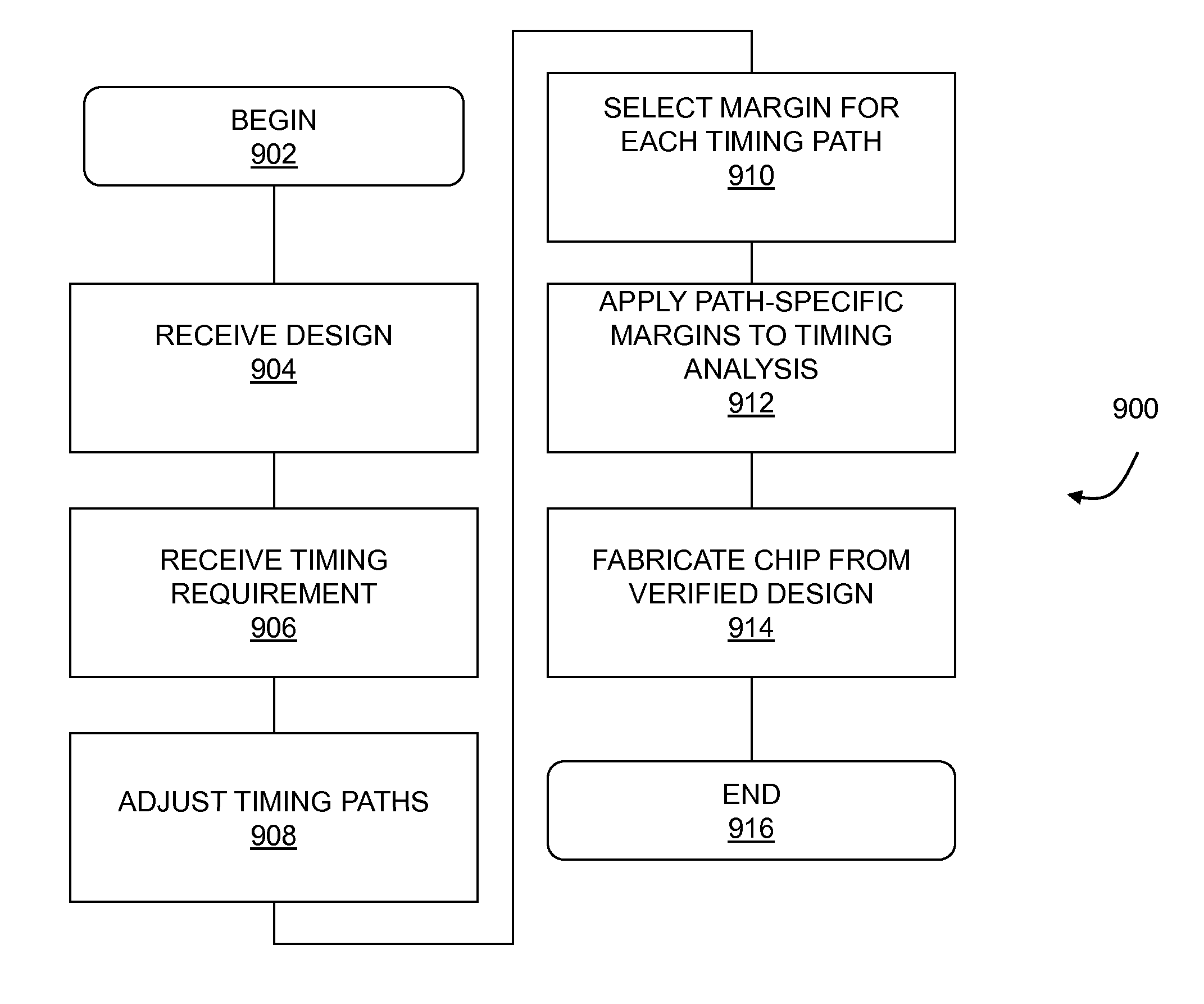
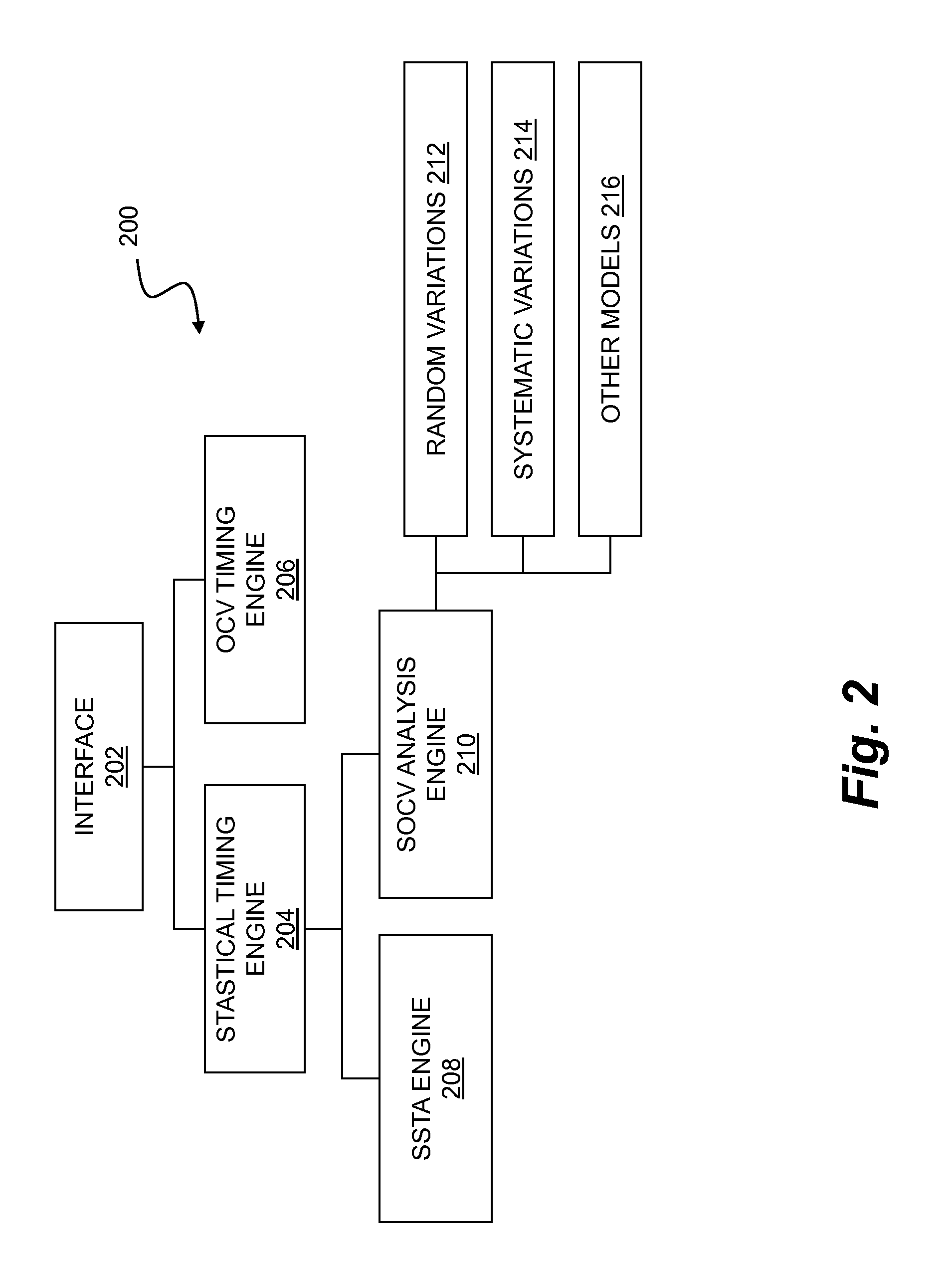
Timing analysis using statistical on-chip variation
ActiveUS7992114B1The result is accurateProbabilistic CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSystematic variationEngineering
A statistical on-chip variation approach to timing analysis permits the automated or semi-automated selection of design-specific margins without requiring complex statistical libraries. By separately addressing the impact of random and systematic variations on timing, a design-specific margin can be obtained and used in downstream OCV analysis. In addition, where statistical libraries are available for some portions of a design, these can be incrementally included in the timing analysis to obtain more accurate results.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
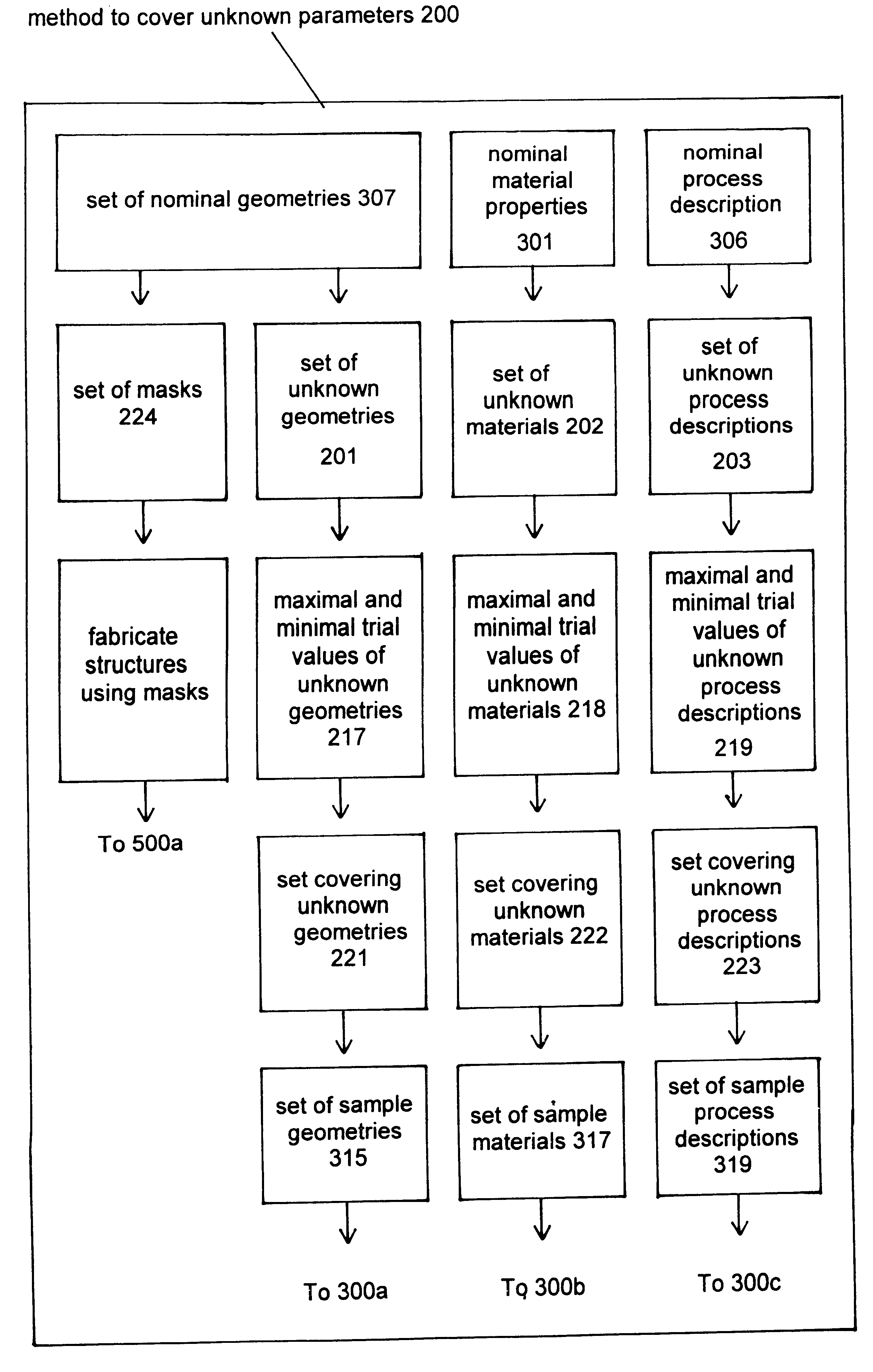
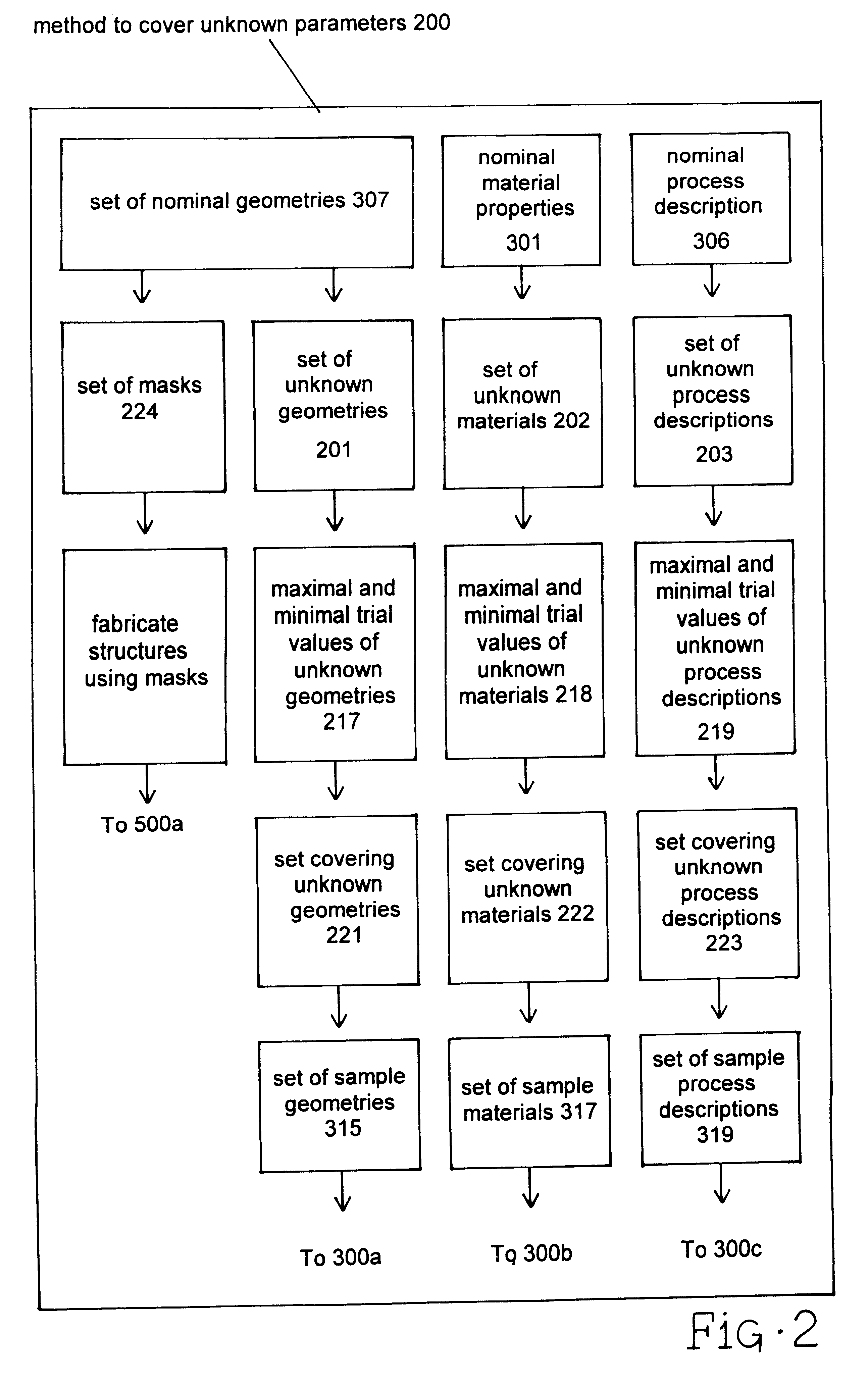
Characterization of microelectromechanical structures
Accurate characterization of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) geometry is critical for device design and simulation, for material property extraction, and for post-fabrication trimming. According to the present embodiment, a method for characterizing parameters describing MEMS structures resulting from the fabrication process or process variations is presented. According to the prefered embodiment, experimentally obtained natural frequencies are compared with numerical simulations to identify unknown values of structural parameters or parameter variations. Further, the prefered embodiment teaches how electrostatically-driven laterally resonant comb-drive MEMS test structures with prescribed changes in spring width are used to characterize systematic variations in process offsets and sidewall angles. The disclosed technique is both in-situ and non-destructive.
Owner:COVENTOR
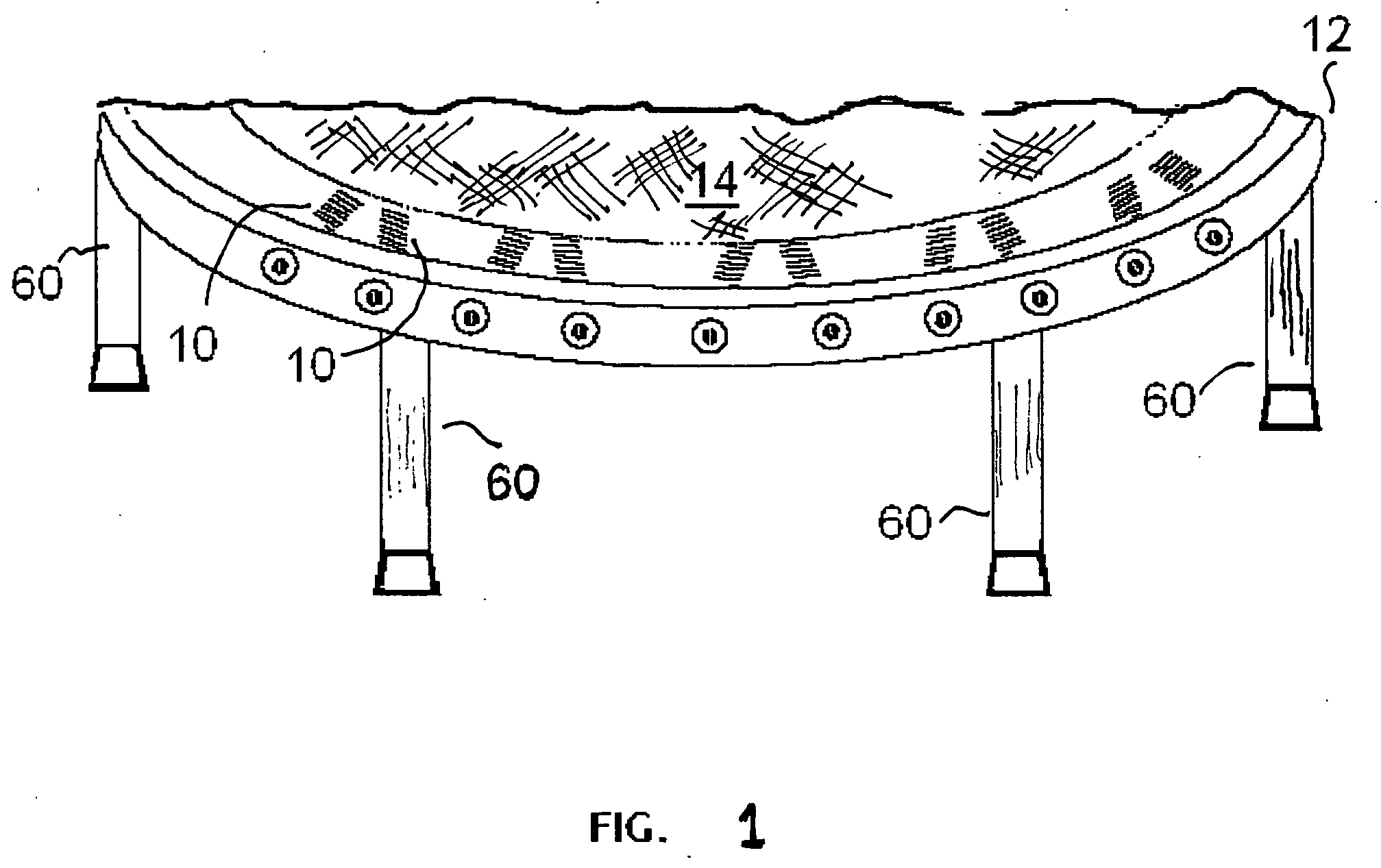
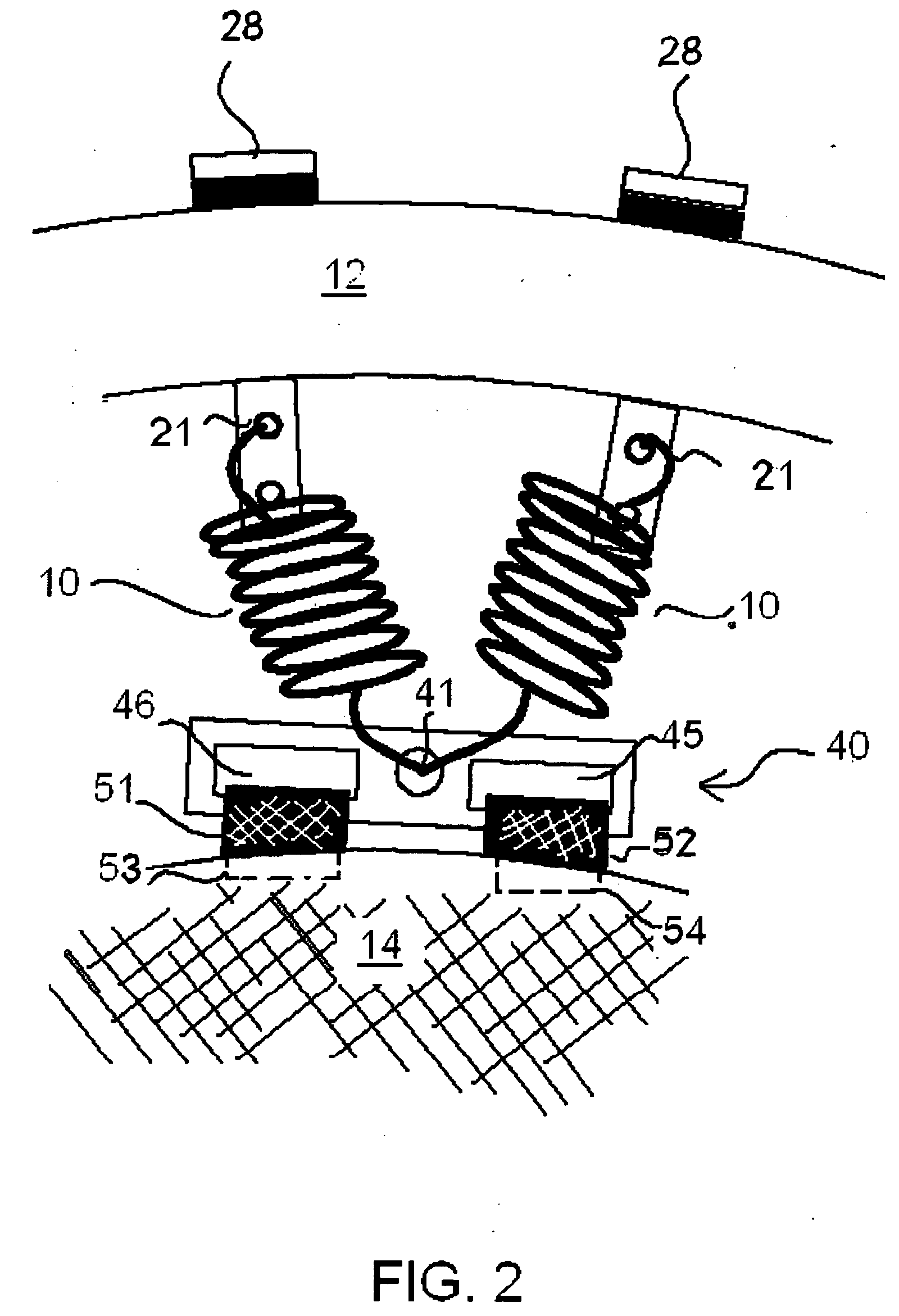
Trampoline with adjustable spring tension
Springs or other elastic connectors used to support a bed within the frame of a trampoline or the like are attached using methods that permit the adjustment and / or a systematic variation of the tension (or the travel distance required to reach limit of elasticity) between adjacent (or sets of adjacent) springs. These spring attachment methods adjust the energy absorption capacity of the tramnpoline bed, as well as increase the time it takes a given trampoline to absorb a given amount of energy, increasing the shock absorption time and thereby reducing the likelihood of an injury.
Owner:PUBLICOVER MARK W
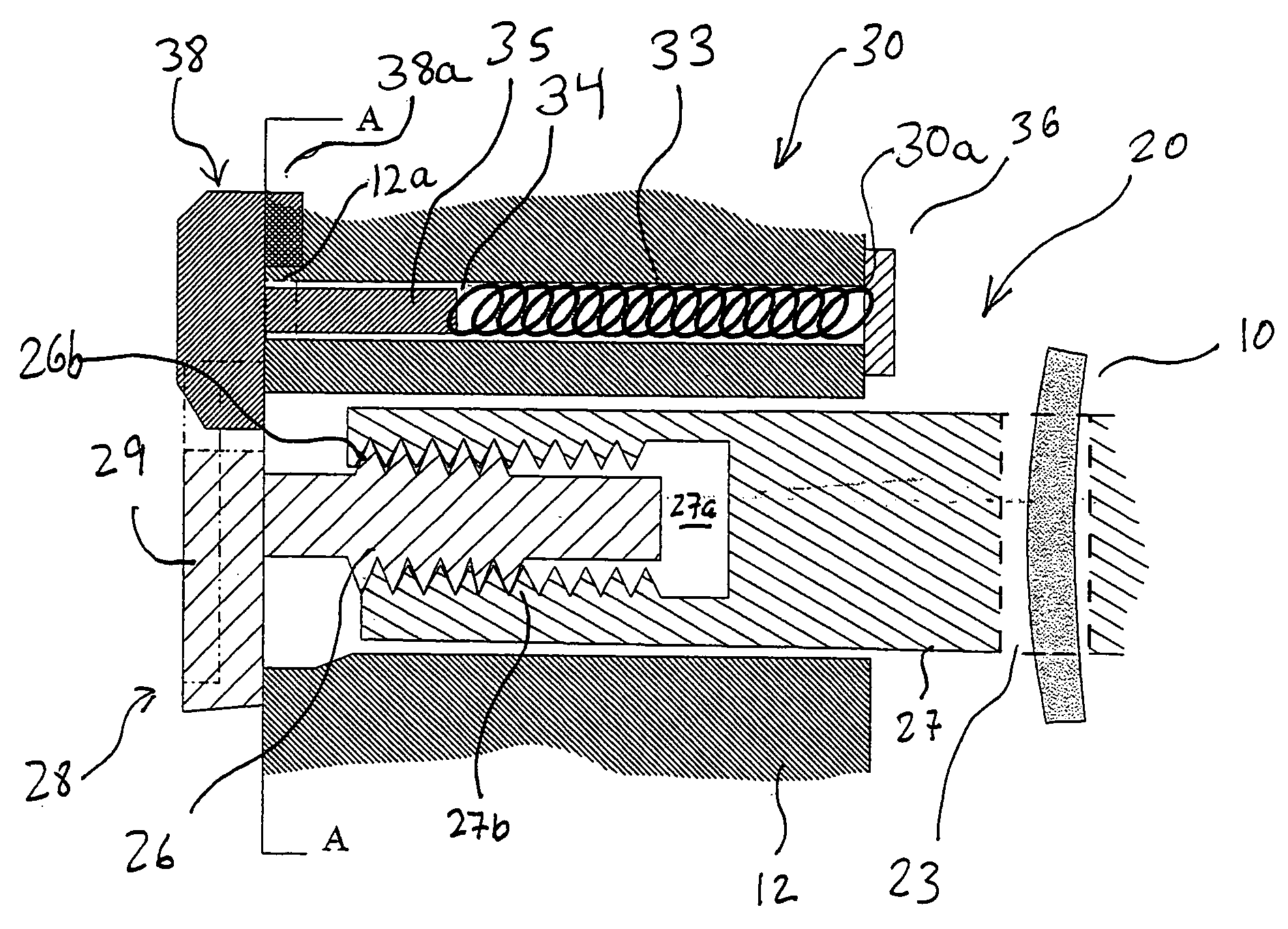
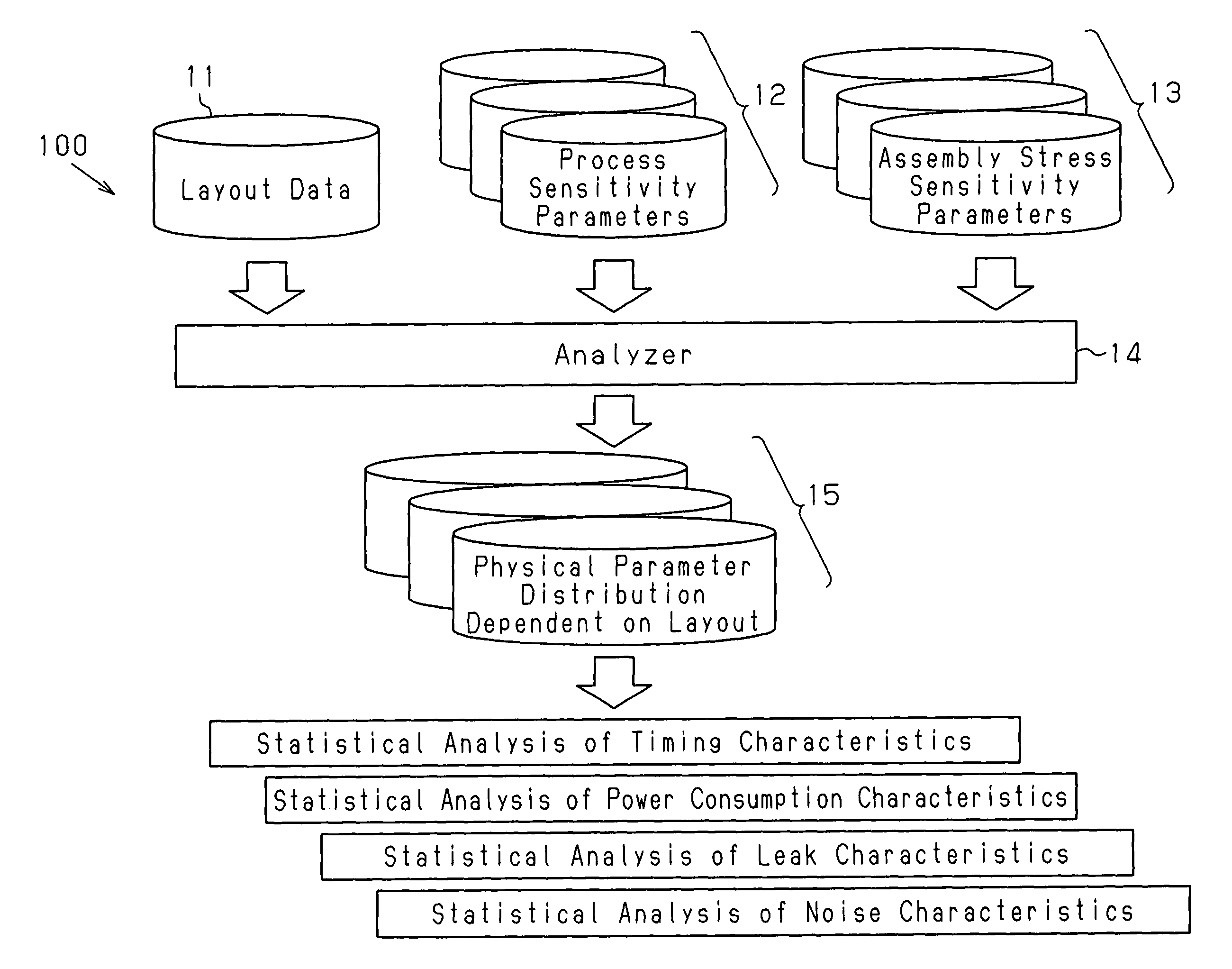
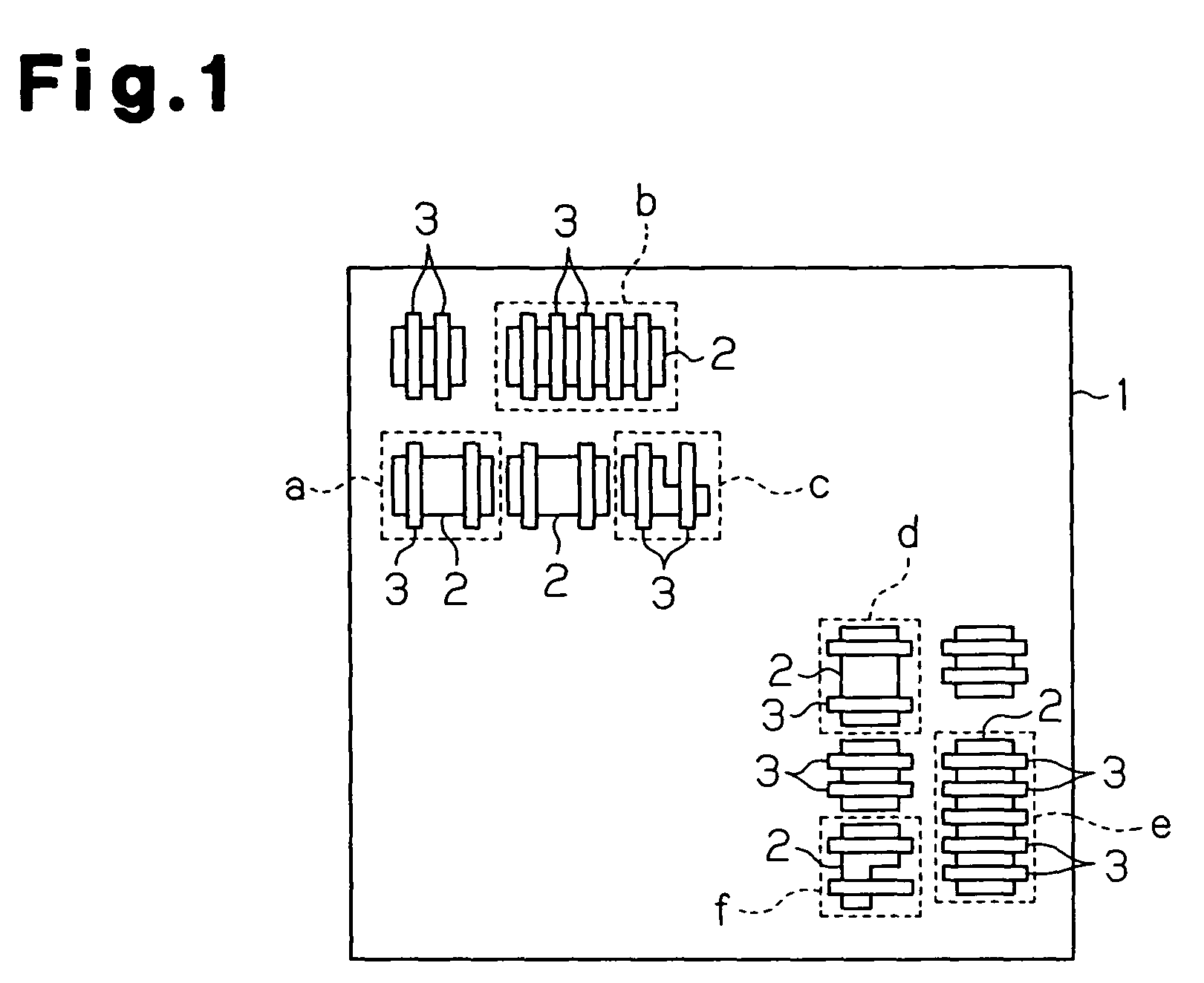
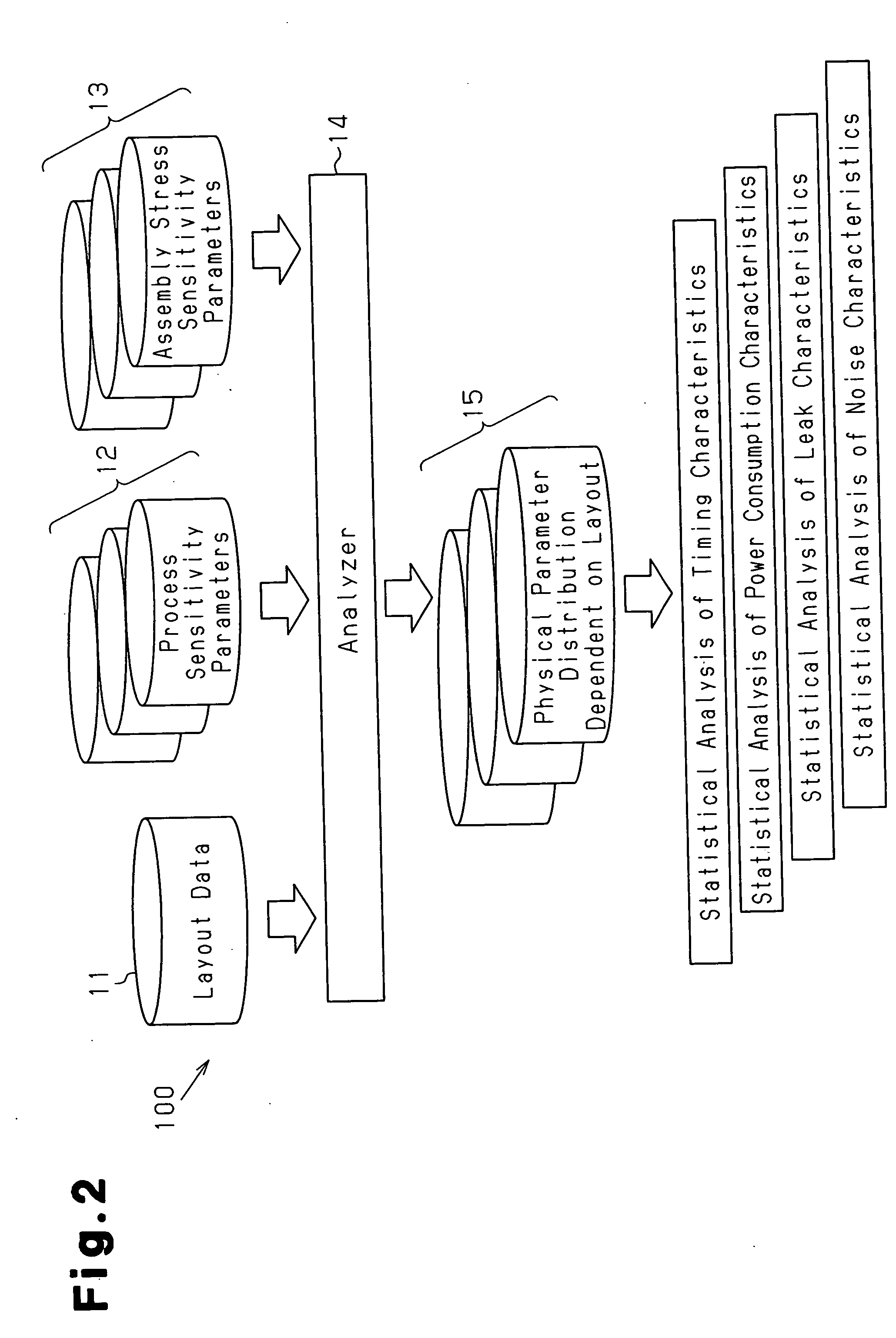
Layout analysis method and apparatus for semiconductor integrated circuit
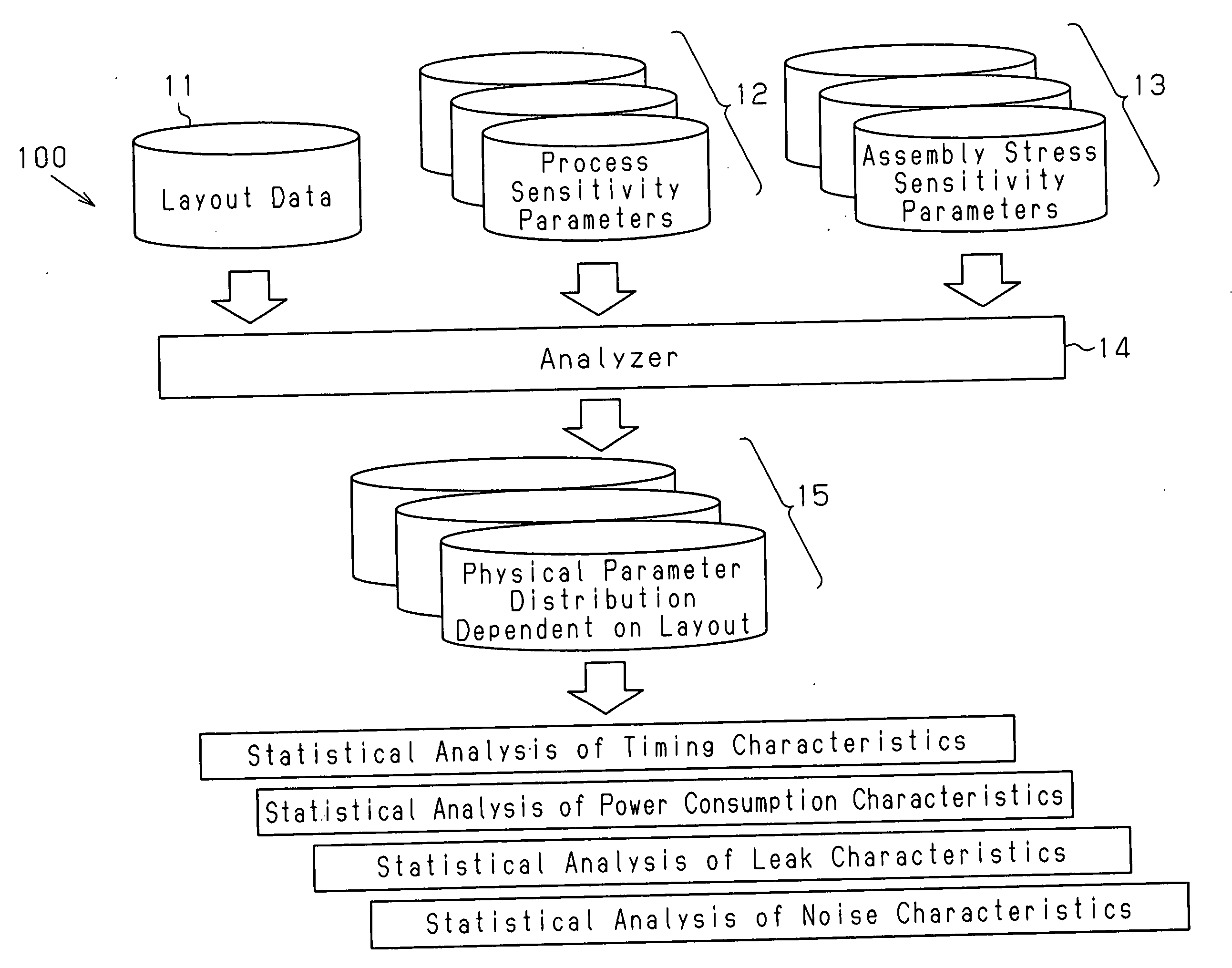
InactiveUS7802218B2Accurate identificationImprove analysis accuracyDetecting faulty computer hardwareOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSystematic variationEngineering
A method for analyzing a layout for a semiconductor integrated circuit, which includes a plurality of physical devices, to generate physical parameter distribution enabling accurate recognition of changes in transistor characteristics caused by systematic variations. The method includes holding systematic variation tables for physical parameters dependent on the layout of the semiconductor integrated circuit among physical parameters related to characteristics of the semiconductor integrated circuit, analyzing a design layout pattern of the semiconductor integrated circuit and selecting tables corresponding to the plurality of physical devices, and generating a physical parameter distribution based on the selected tables.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Statistical On-Chip Variation Timing Analysis
ActiveUS20110289465A1The result is accurateProbabilistic CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSystematic variationEngineering
A statistical on-chip variation approach to timing analysis permits the automated or semi-automated selection of design-specific margins without requiring complex statistical libraries. By separately addressing the impact of random and systematic variations on timing, a design-specific margin can be obtained and used in downstream OCV analysis. In addition, where statistical libraries are available for some portions of a design, these can be incrementally included in the timing analysis to obtain more accurate results.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
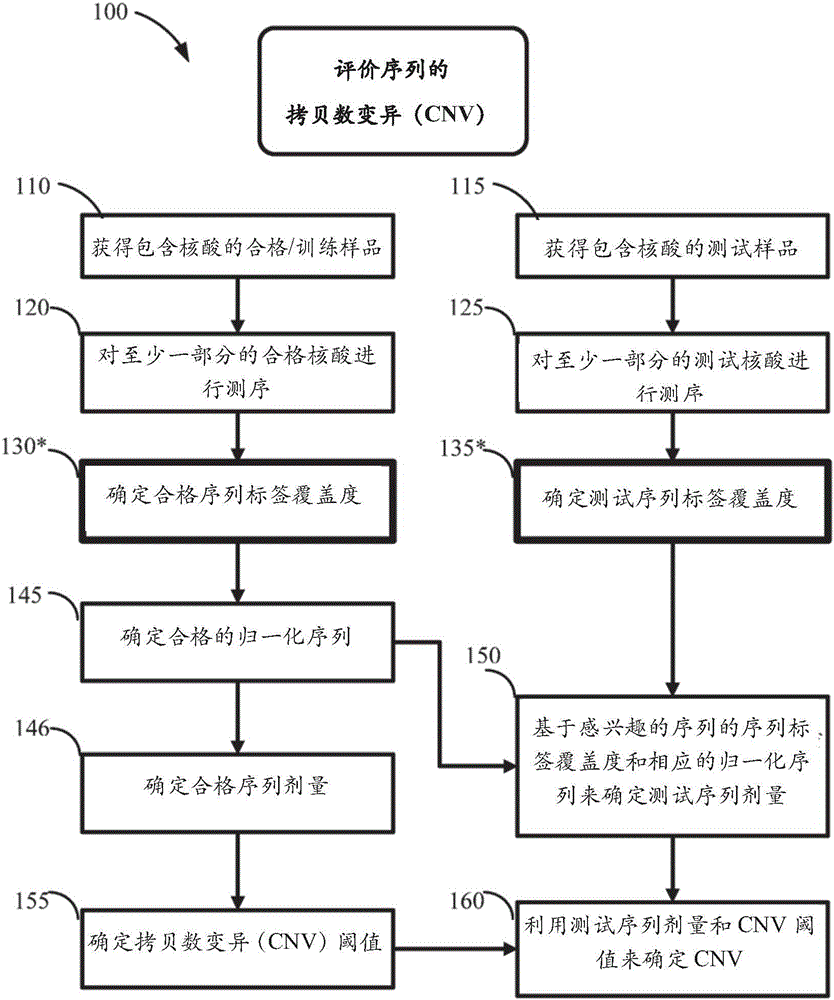
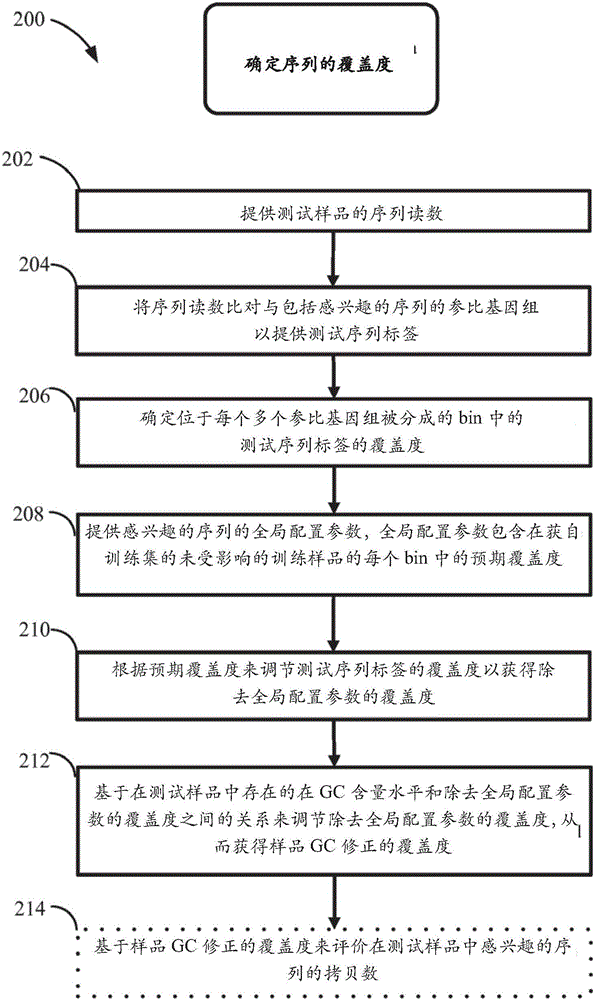
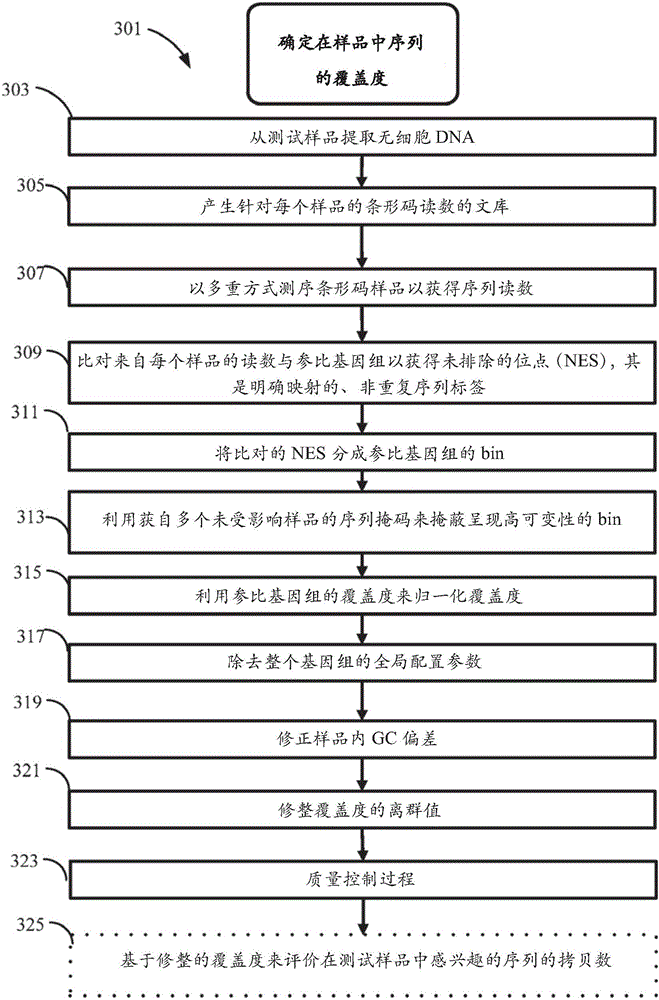
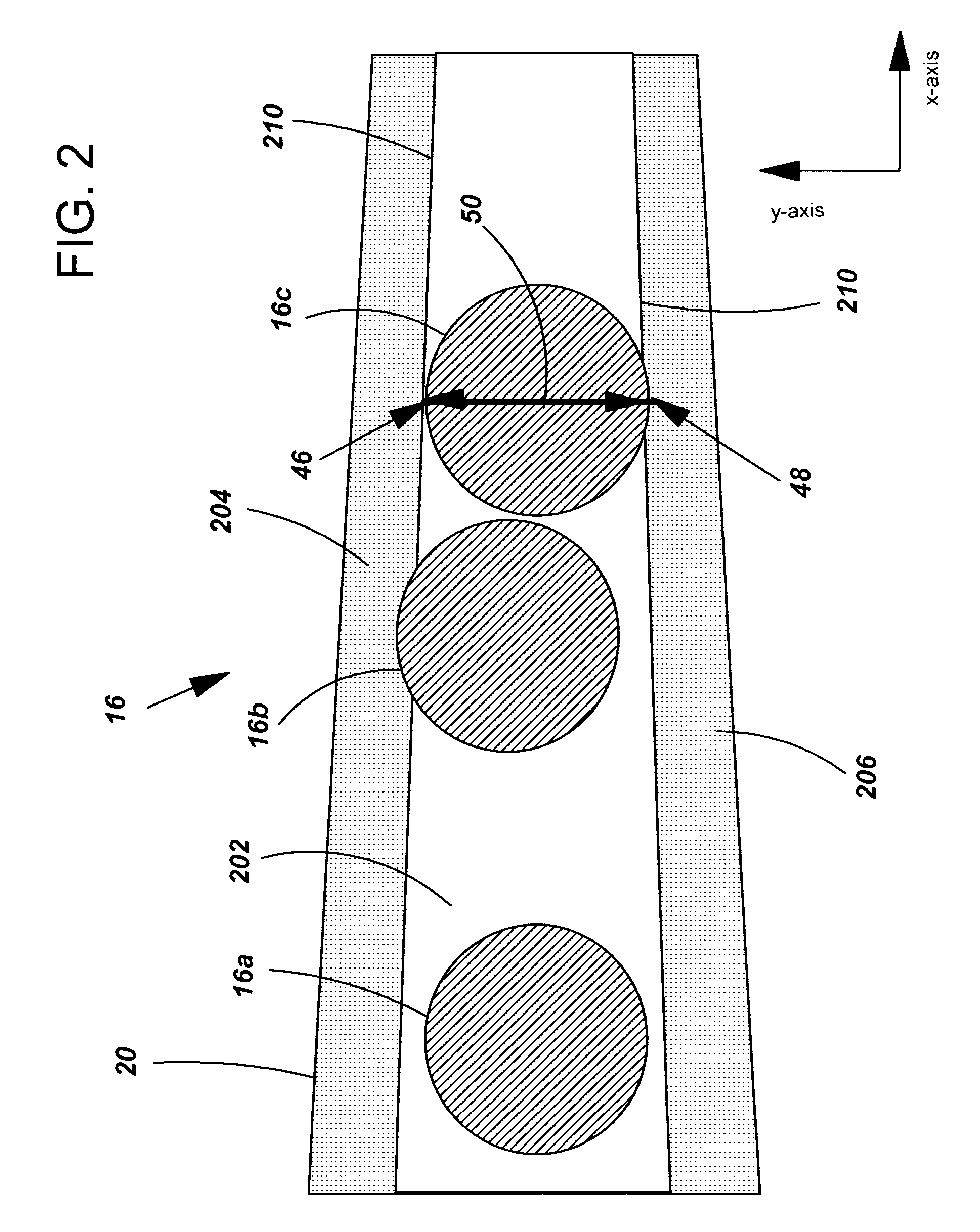
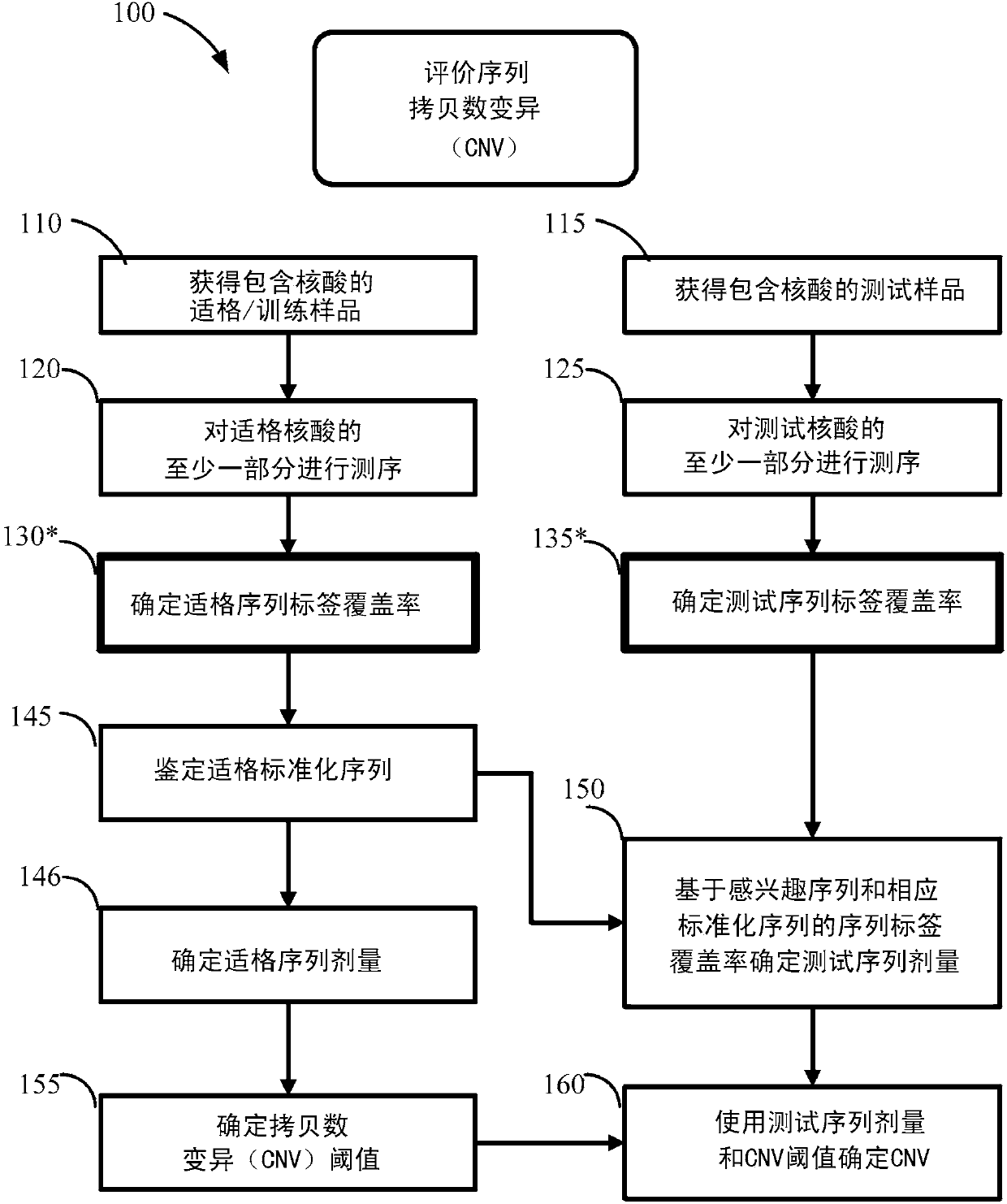
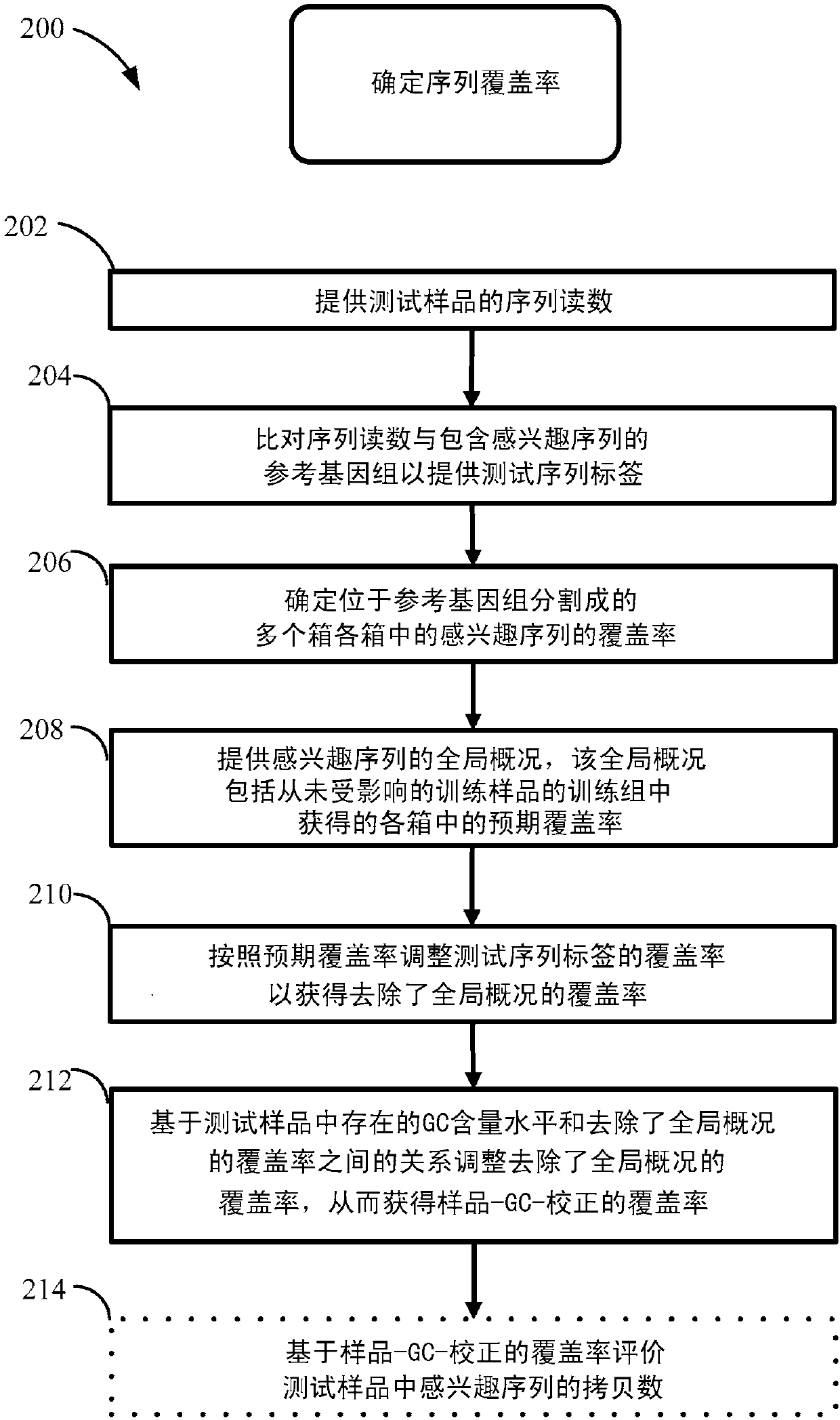
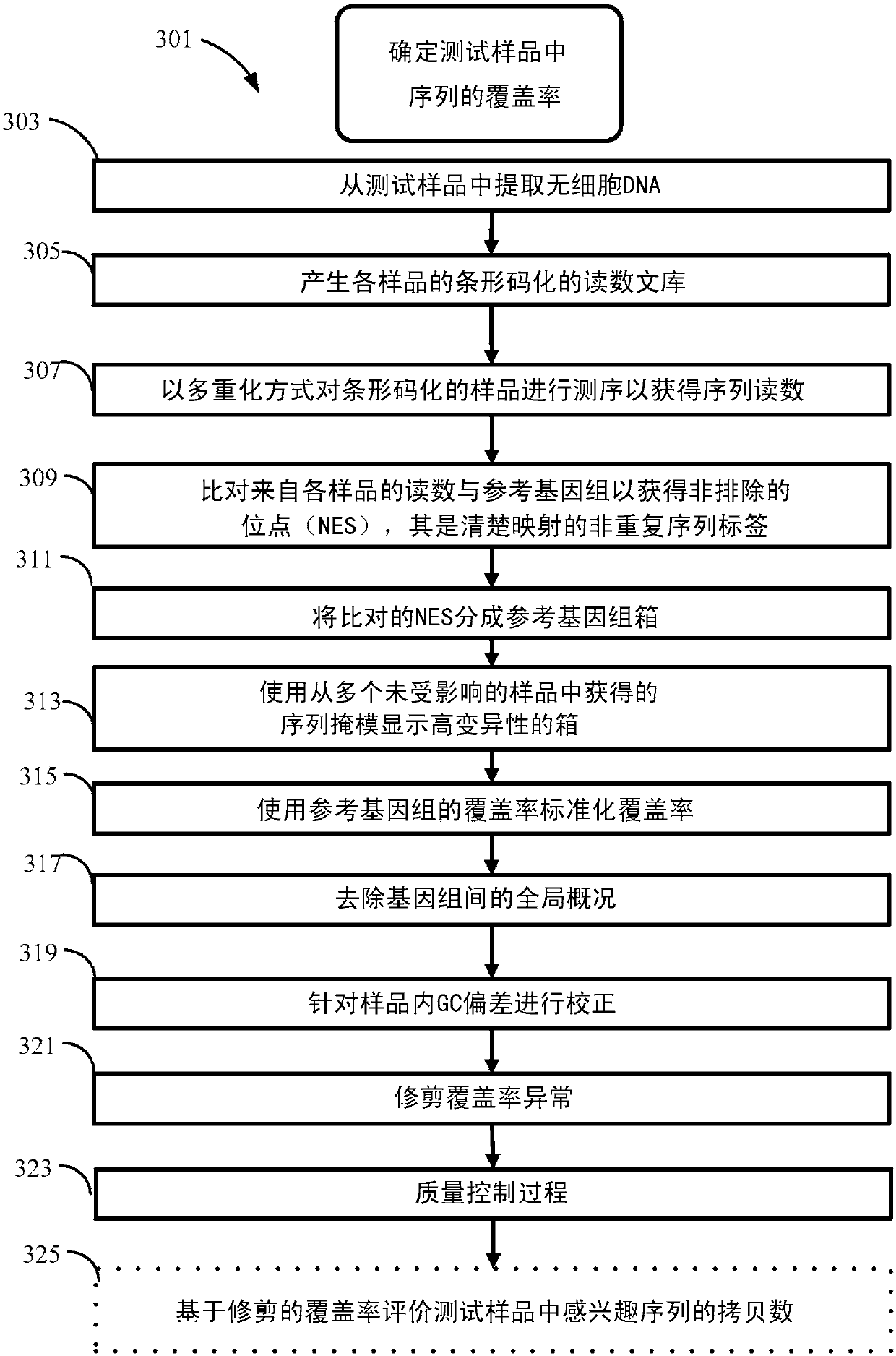
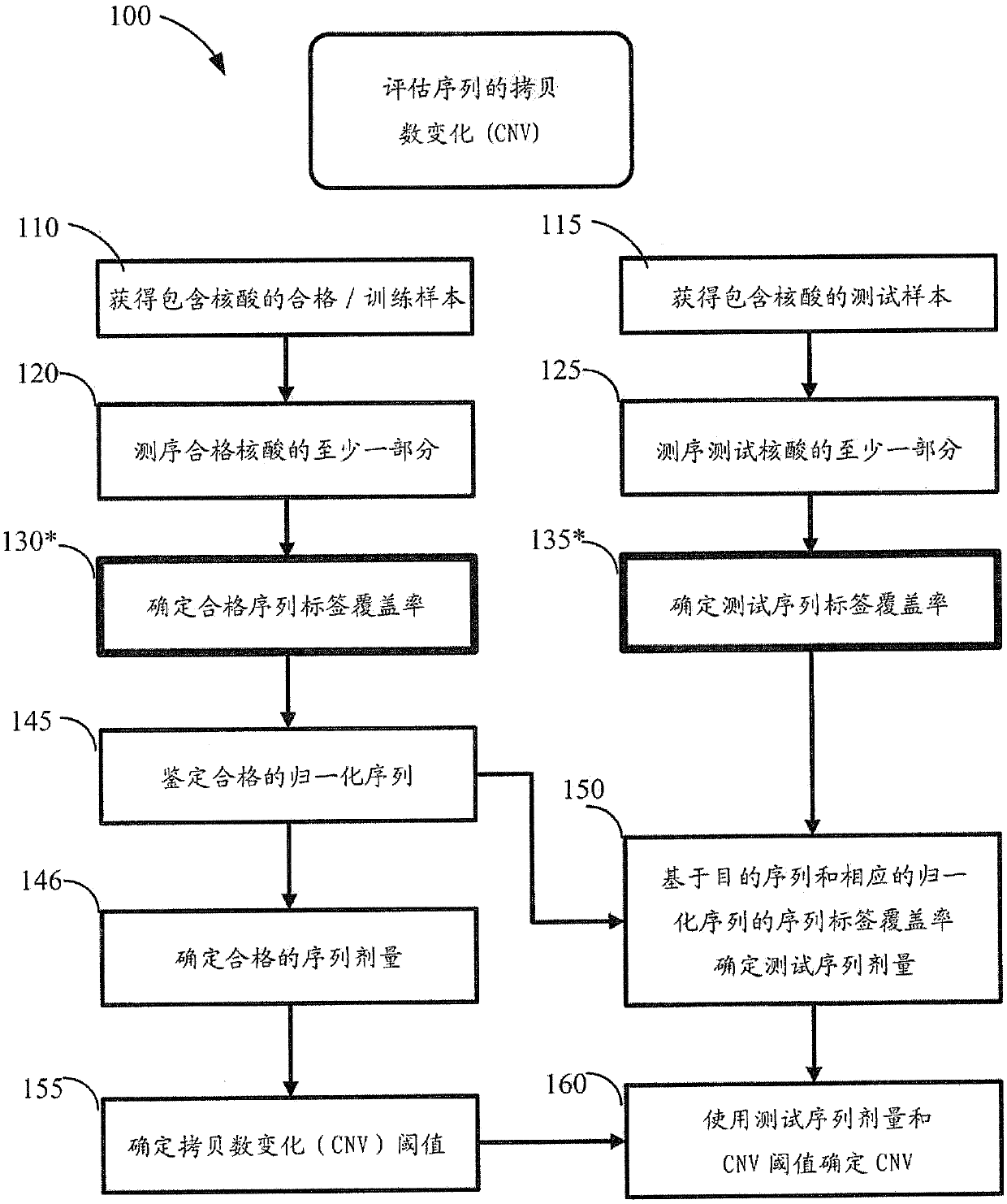
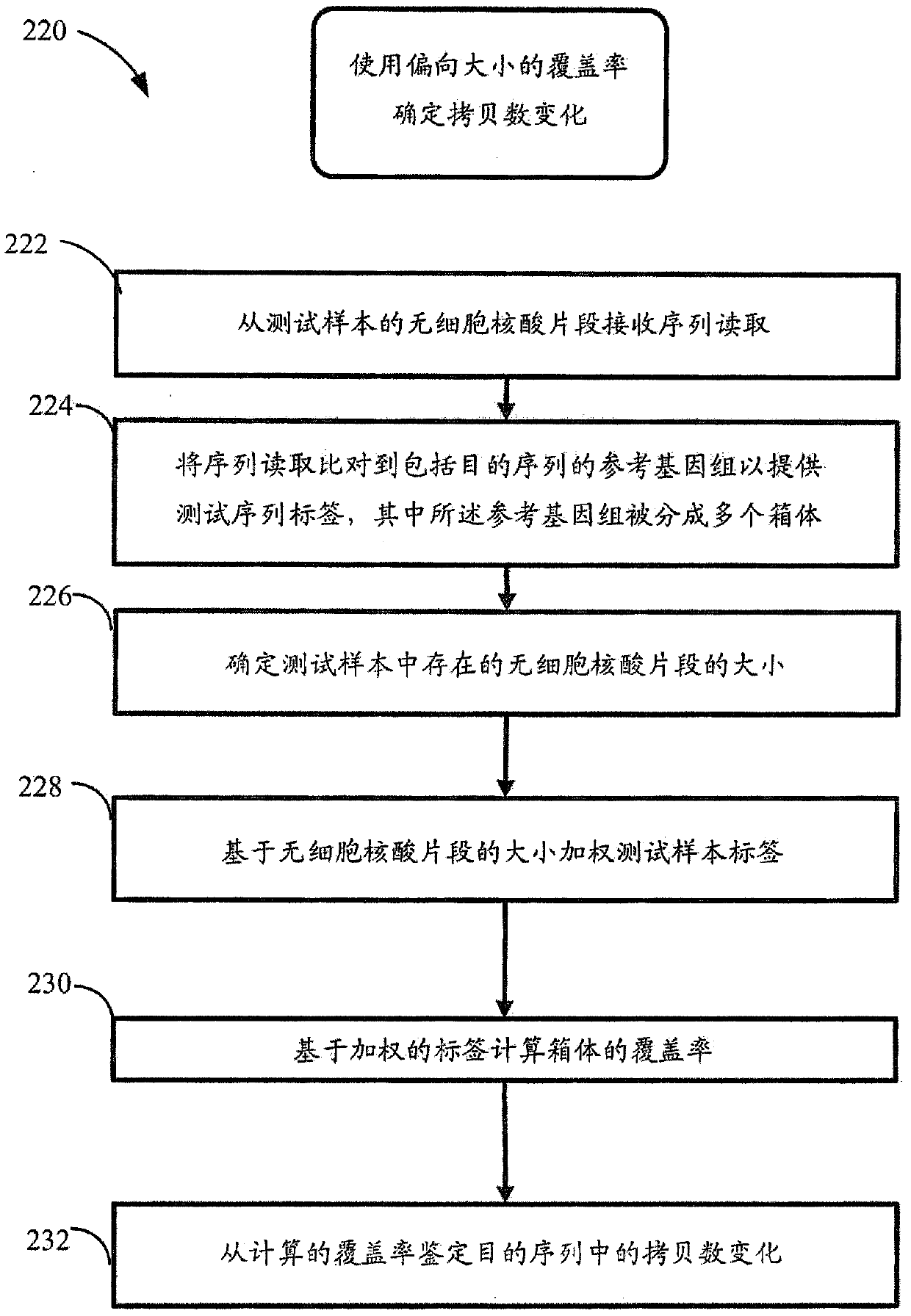
Method for improving the sensitivity of detection in determining copy number variations
The invention discloses a method for improving the sensitivity of detection in determining copy number variations. Disclosed are methods for determining copy number variation (CNV) known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining copy number variation (CNV) of fetuses using maternal samples comprising maternal and fetal cell free DNA. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. Some embodiments disclosed herein provide methods to improve the sensitivity and / or specificity of sequence data analysis by removing within-sample GC-content bias. In some embodiments, removal of within-sample GC-content bias is based on sequence data corrected for systematic variation common across unaffected training samples. Also disclosed are systems and computer program products for evaluation of CNV of sequences of interest.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Multiple design database layer inspection
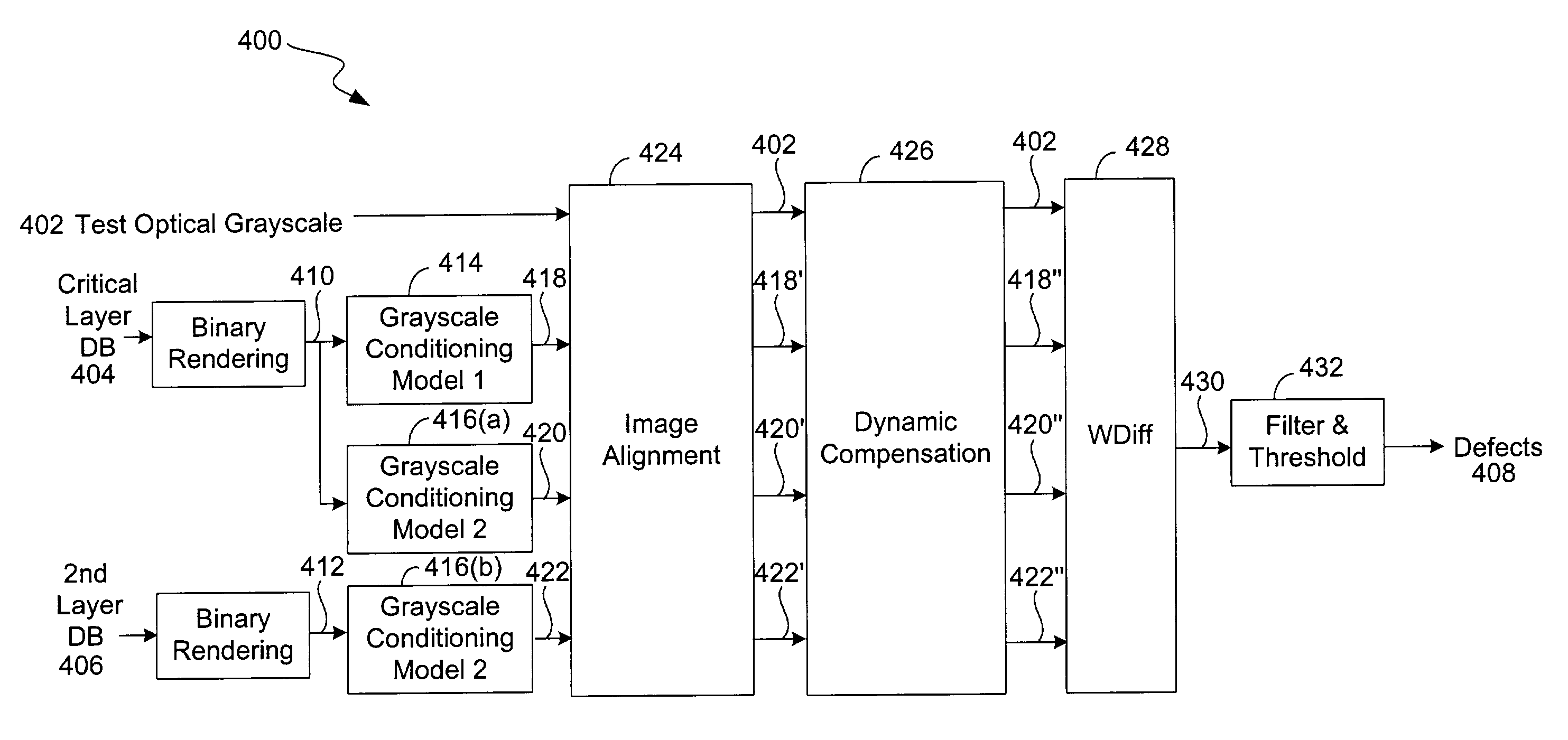
Techniques that use the design databases used in each of the expose / etch steps during construction of phase shift masks are described. A model or reference image is rendered, accounting for systematic variations, from the design databases to represent what a layer of the PSM should look like after processing. The reference image is compared to an optically acquired image of a specimen phase shift mask to find defects. The technique of the present invention can be used to inspect EAPSM, APSM and tritone masks. The technique inspects all layers in one pass and is therefore more efficient.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method and program for designing semiconductor integrated circuits, and semiconductor integrated circuit designing apparatus
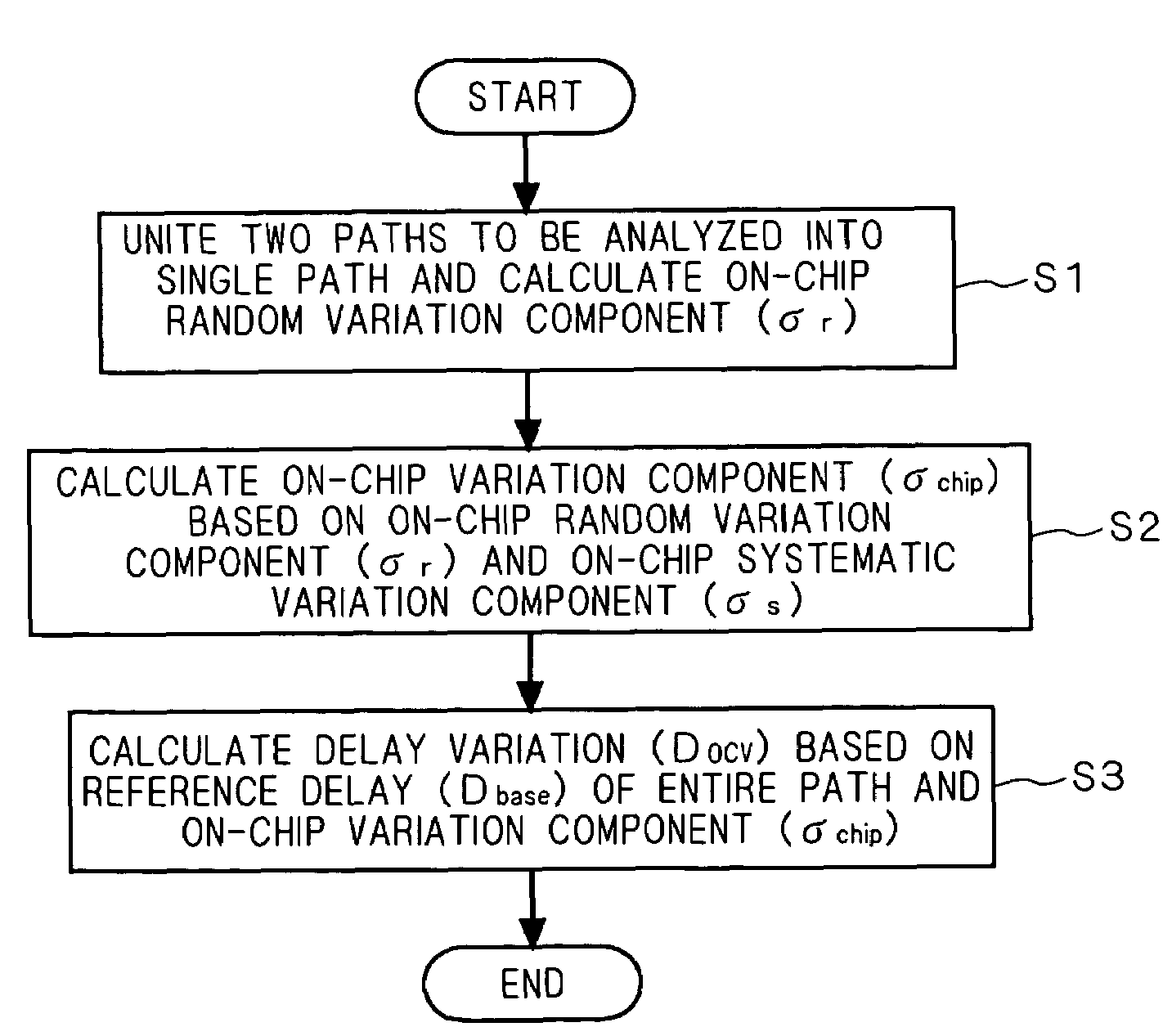
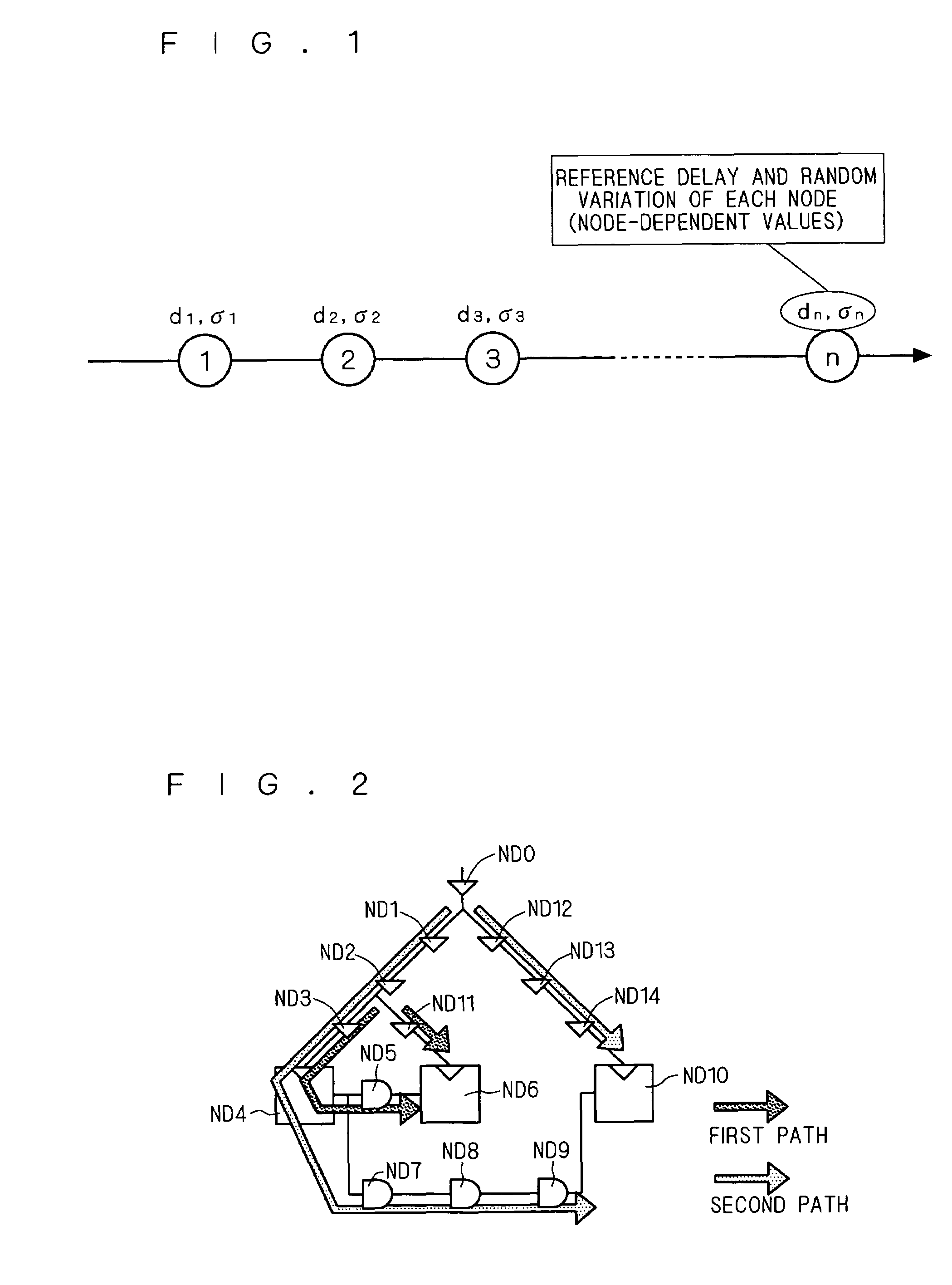
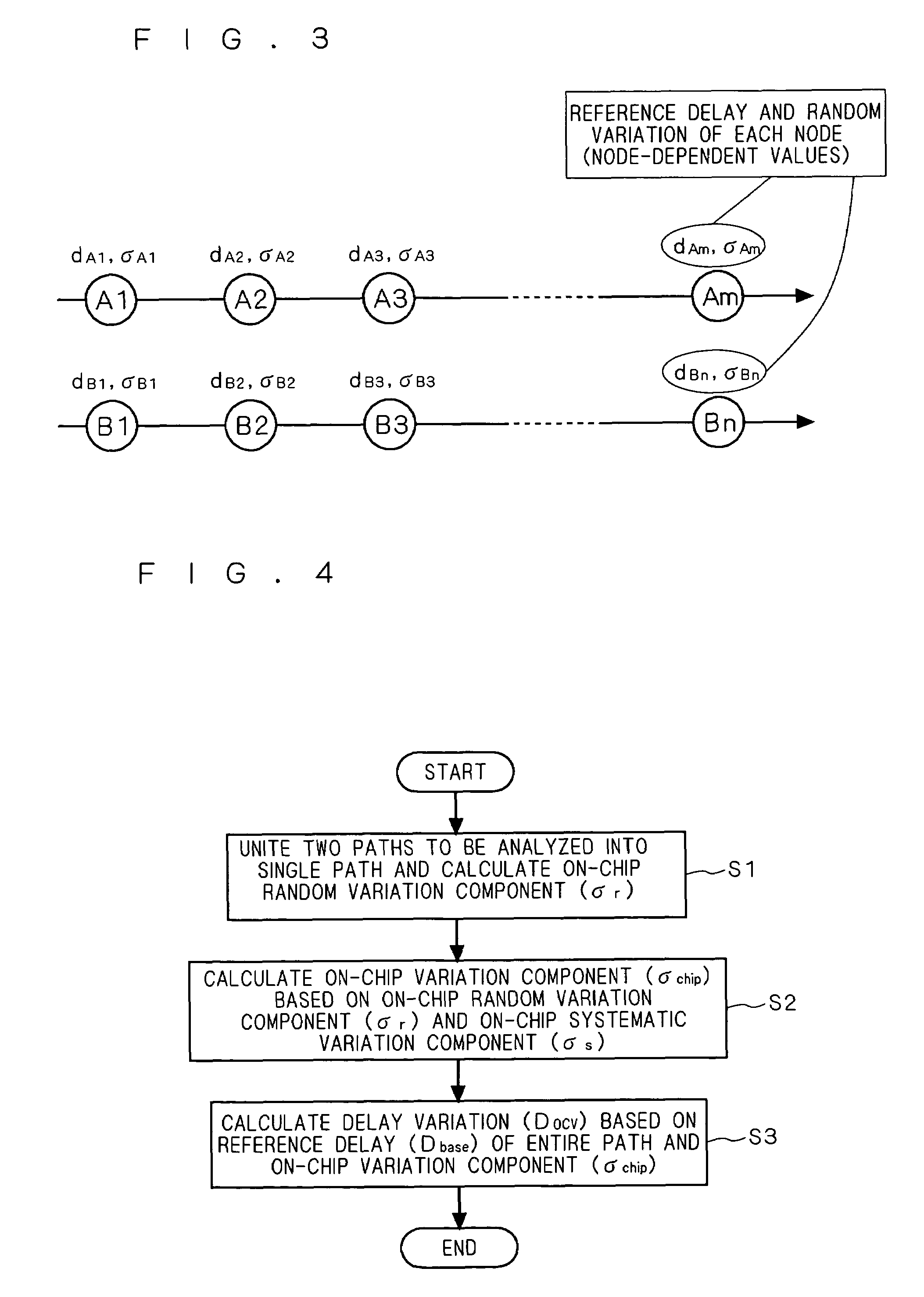
InactiveUS20070073500A1Improve performanceQuality improvementVoltage-current phase angleTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesSystematic variationComputer science
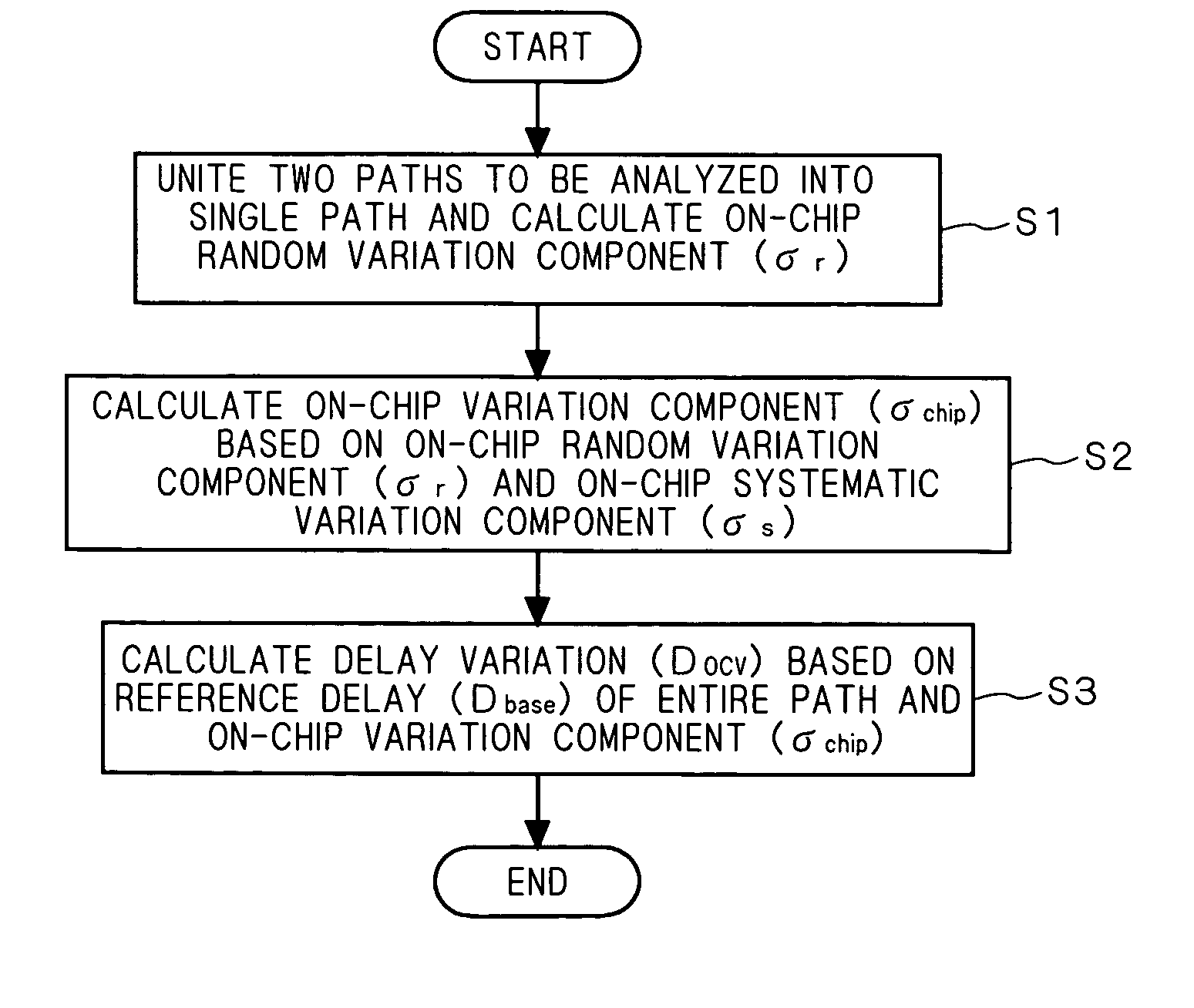
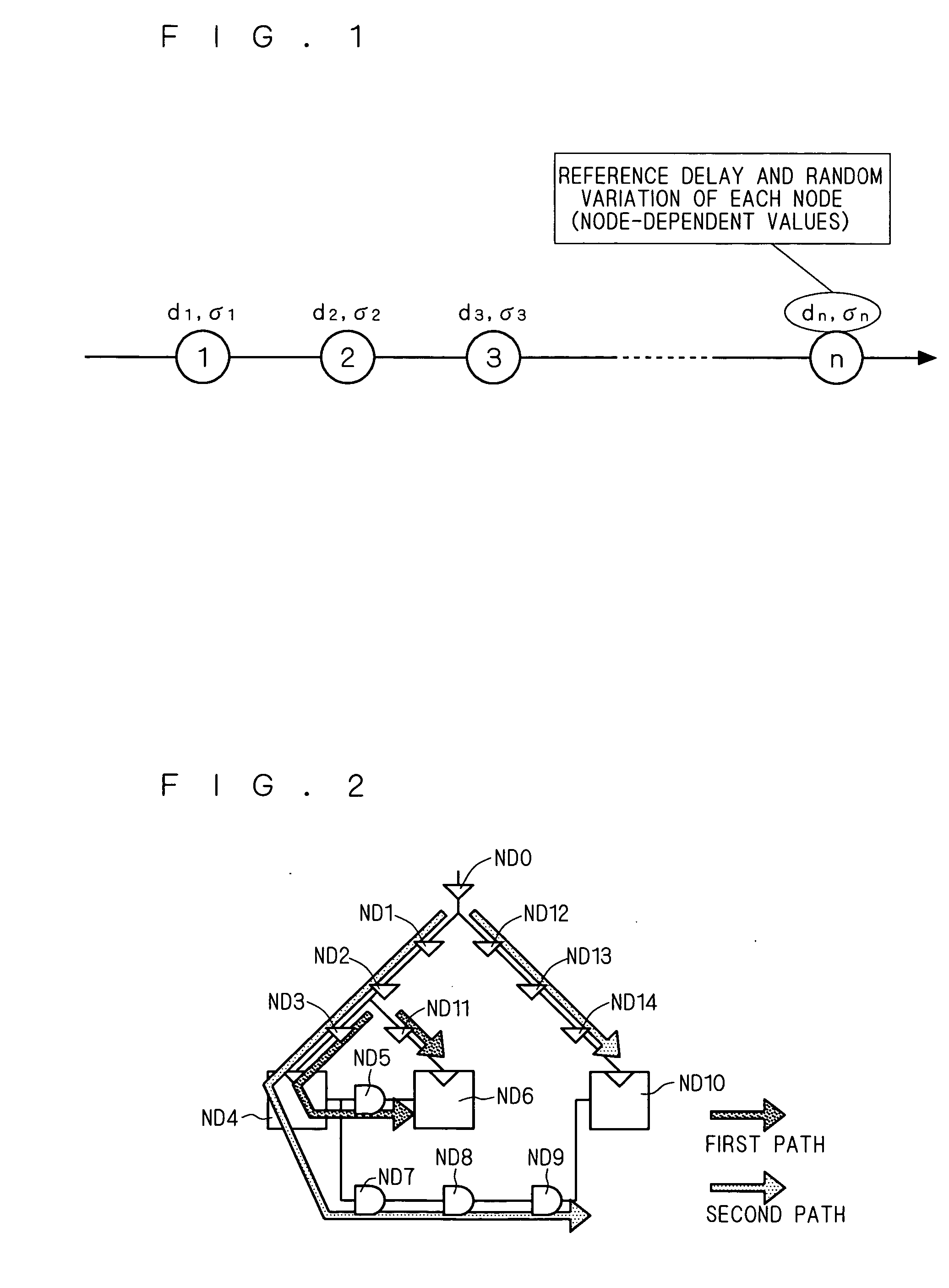
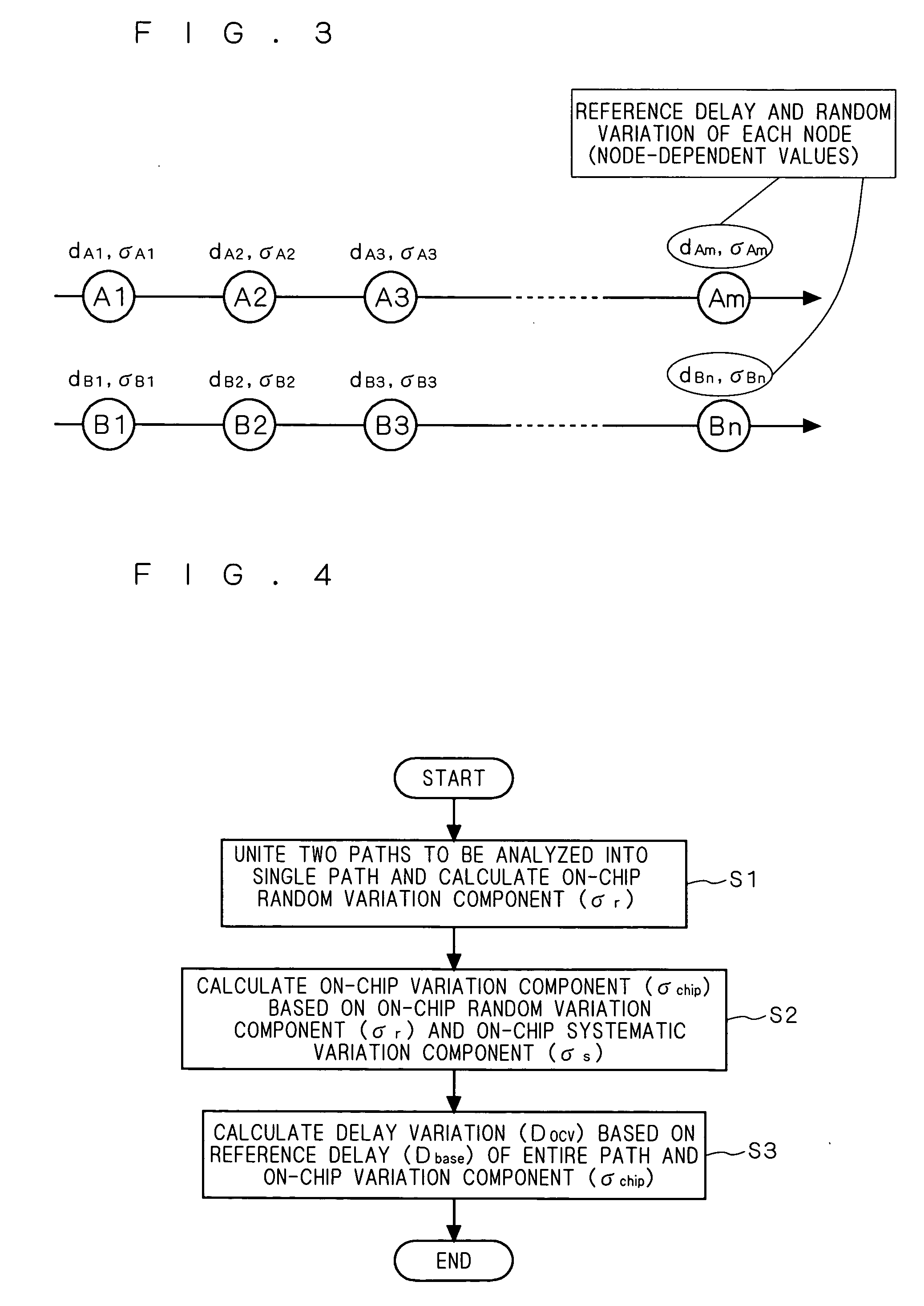
Two paths (arrival and required paths) as a target of analysis are united into a single path, and an on-chip random variation component σr about a plurality of nodes of the single path is calculated. Next, an on-chip variation component σchip is calculated on the basis of the on-chip random variation component σr and an on-chip systematic variation component σs. Subsequently, a delay variation Docv is calculated on the basis of a reference delay Dbase of the entire path and the on-chip variation component σchip.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Enzyme expression methods
InactiveUS20050176101A1Improve crystallizationLower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesHydrolasesSystematic variationActive enzyme
Owner:PLEXXIKON INC
Physically unclonable function pattern matching for device identification
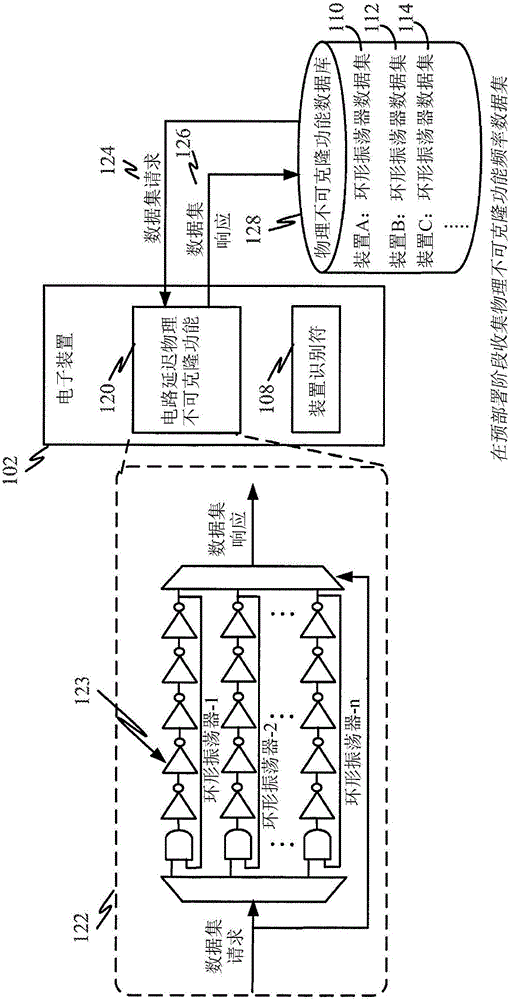
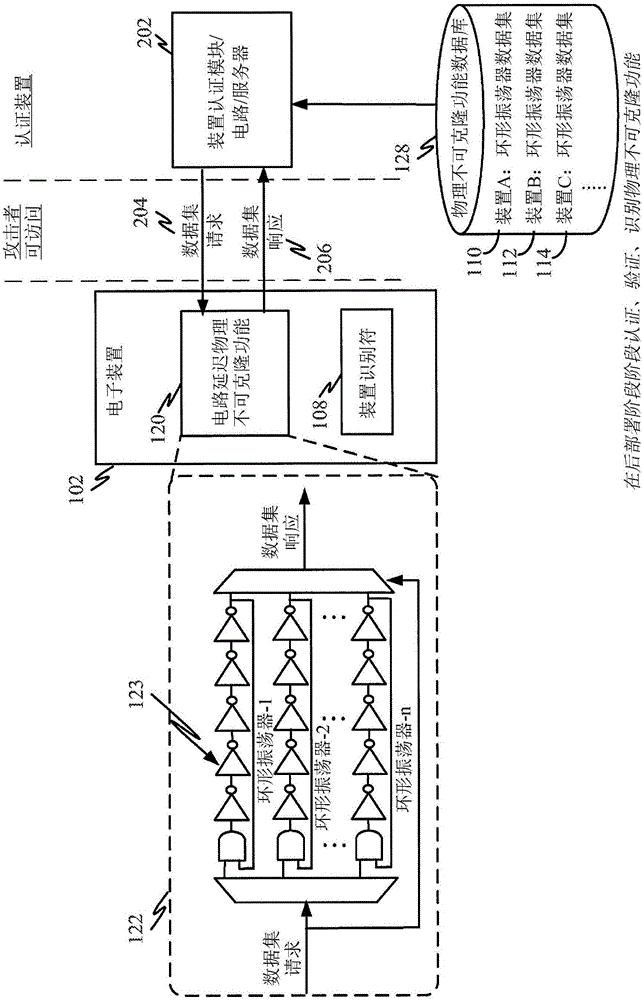
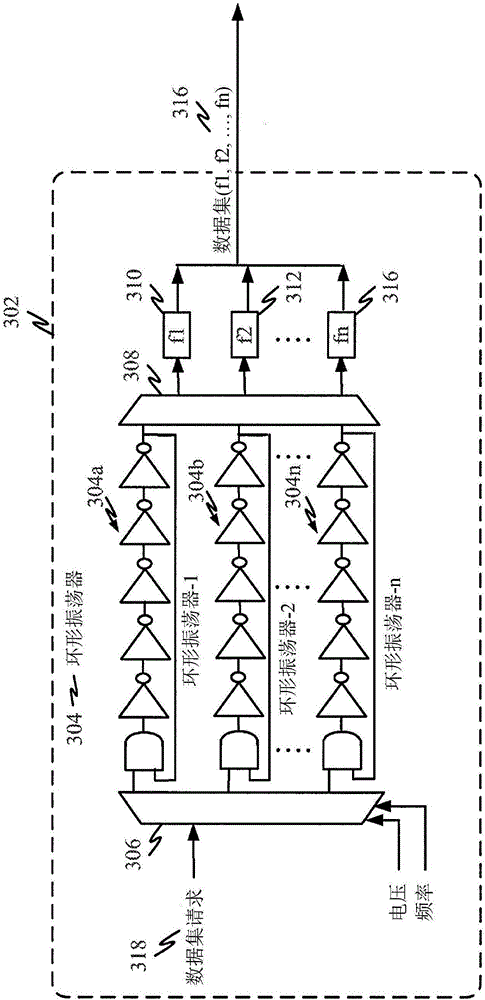
InactiveCN105850075AUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationComputer hardwareSystematic variation
A method is provided for using obtaining a reproducible device identifier from a physically unclonable function. An authentication device may receive a first physically unclonable function (PUF) dataset from the electronic device, the first PUF dataset including characteristic information generated from a physically unclonable function in the electronic device. The authentication device may then identify a pre-stored PUF dataset corresponding to the electronic device. Authentication of the electronic device may be performed by correlating the pre-stored PUF dataset and the first PUF dataset for the electronic device, wherein such correlation is based on a pattern or distribution correlation the pre-stored PUF dataset and the first PUF dataset. Because such correlation is performed on datasets, and not individual points, systematic variations can be recognized by the correlation operation leading to higher correlation than point-by-point comparisons.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and program for designing semiconductor integrated circuits, and semiconductor integrated circuit designing apparatus
InactiveUS7512920B2Improve performanceQuality improvementVoltage-current phase angleTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesSystematic variationComputer science
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Optical spot geometric parameter determination using calibration targets
A method, system and computer program product for determining a geometric parameter of an optical spot of a light beam are disclosed. A method comprises: providing a calibration target, the calibration target including a systematic variation in a parameter; measuring the calibration target with respect to the systematic variation using the light beam to obtain a plurality of measurements; and analyzing the measurements and the systematic variation to determine the geometric parameter of the optical spot.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Detecting fetal sub-chromosomal aneuploidies and copy number variations
ActiveCN106795558AMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsSequence analysisSystematic variation
Disclosed are methods for determining copy number variation (CNV) known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions, including syndromes related to CNV of subchromosomal regions wherein the bins from the unaffected training samples used as controls have a coverage similar to the coverage of the region inspected for CNV. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining CNV of fetuses using maternal samples comprising maternal and fetal cell free DNA. Some embodiments disclosed herein provide methods to improve the sensitivity and / or specificity of sequence data analysis by removing within-sample GC-content bias. In some embodiments, removal of within-sample GC-content bias is based on sequence data corrected for systematic variation common across unaffected training samples. In some embodiments, syndrome related biases in sample data are also removed to increase signal to noise ratio. Also disclosed are systems for evaluation of CNV of sequences of interest.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Methodology and system for teaching reading
InactiveUS20170148341A1Reduce confusionWork lessReadingNatural language data processingSystematic variationConfusion
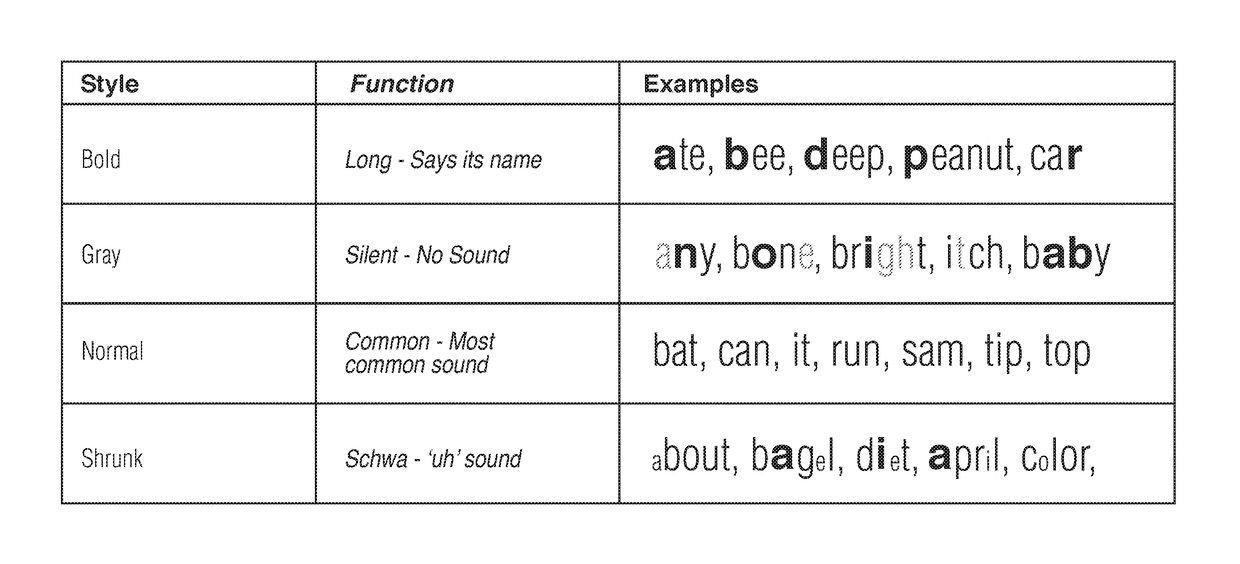
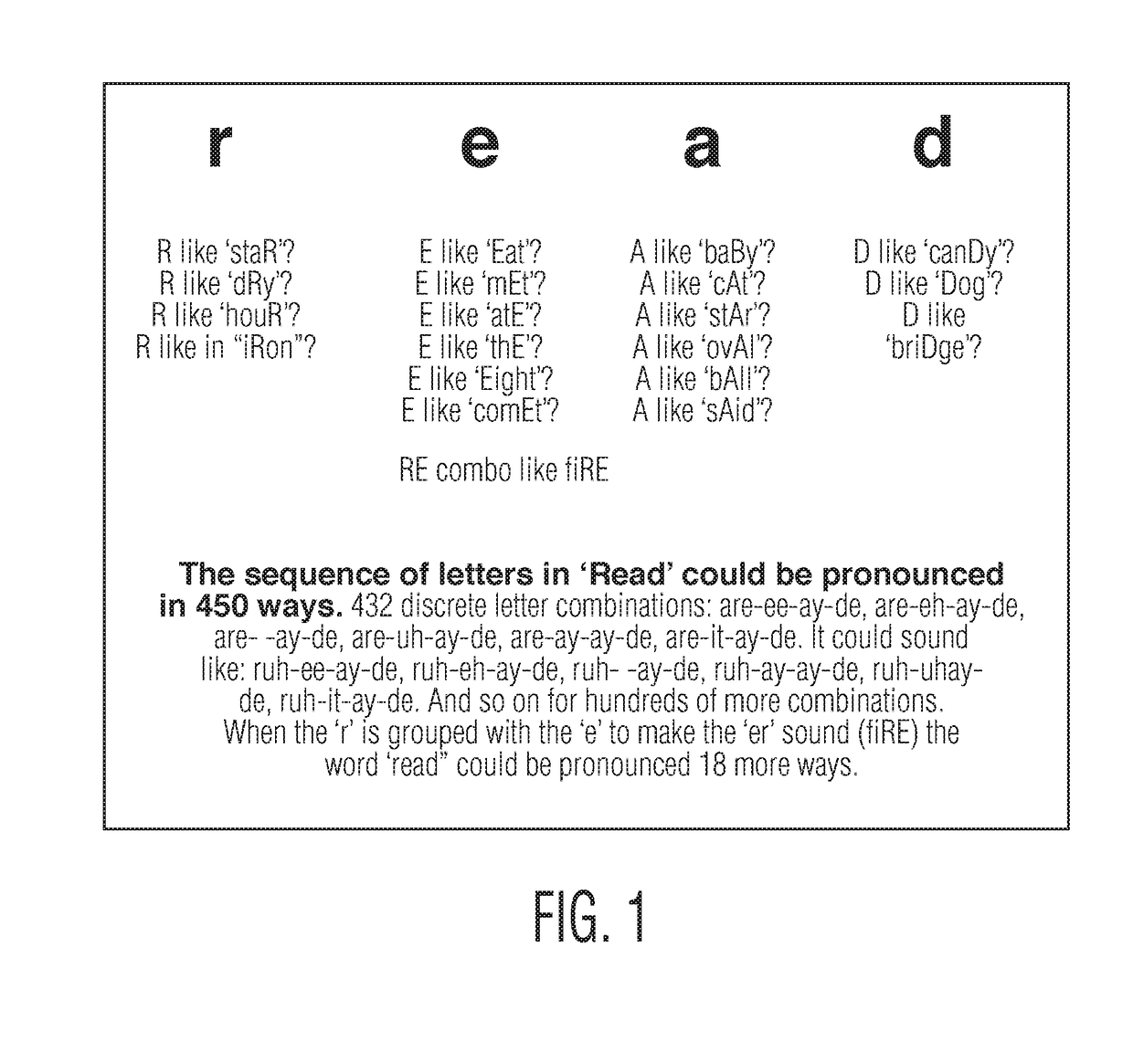
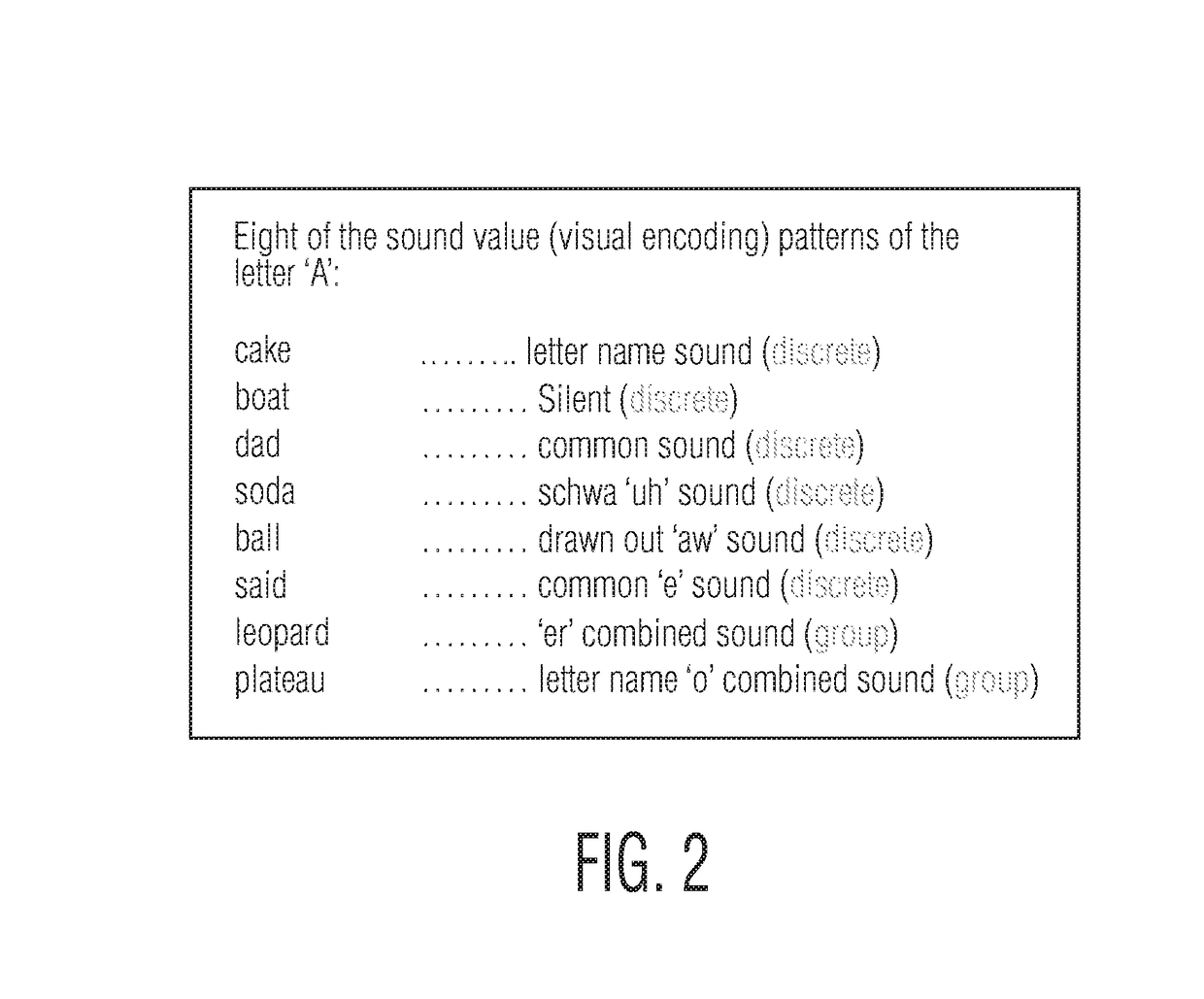
A system for visual encoding of words to assist learning to read including systematic variations in the appearance of letters which may look like morphic analogs of the sound variations they suggest (for example, barely visible grey for silent letters). By improving how letters cue sounds (like the alphabet originally did), visual encoding reduces the cognitive processing work that most impedes and endangers the progress of beginning and struggling readers (disambiguating letter-sound relationship confusion).
Owner:BOULTON DAVID A +5
Layout analysis method and apparatus for semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20070106967A1Accurate identificationImprove analysis accuracyDetecting faulty computer hardwareOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSystematic variationAnalysis method
A method for analyzing a layout for a semiconductor integrated circuit, which includes a plurality of physical devices, to generate physical parameter distribution enabling accurate recognition of changes in transistor characteristics caused by systematic variations. The method includes holding systematic variation tables for physical parameters dependent on the layout of the semiconductor integrated circuit among physical parameters related to characteristics of the semiconductor integrated circuit, analyzing a design layout pattern of the semiconductor integrated circuit and selecting tables corresponding to the plurality of physical devices, and generating a physical parameter distribution based on the selected tables.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
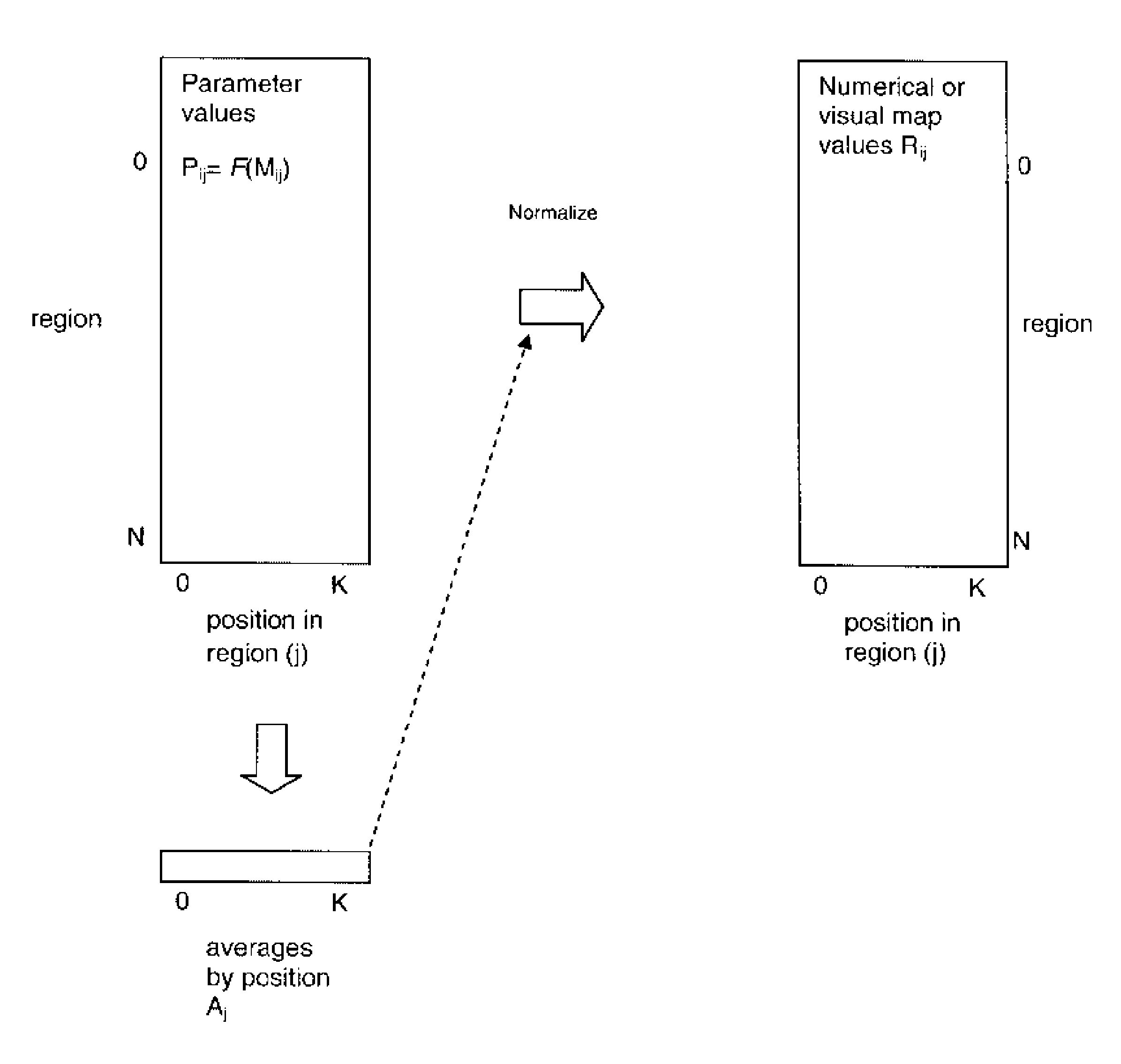
Techniques for filtering systematic differences from wafer evaluation parameters
InactiveUS7991574B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceResistance/reactance/impedenceColor mappingSystematic variation
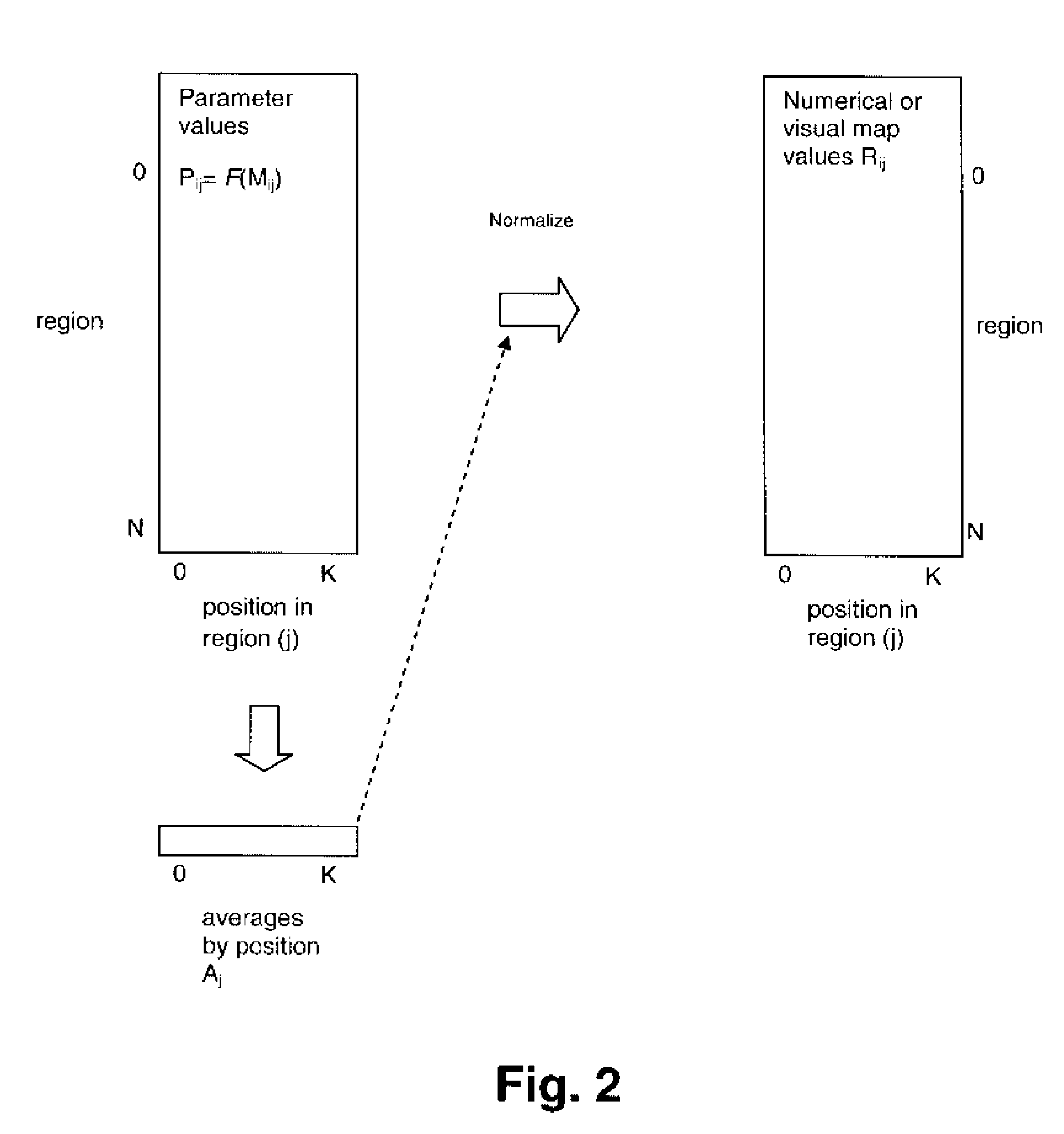
A method, system and computer program product for filtering systematic differences from wafer evaluation parameters provides an efficient visual display and numerical map technique for observing wafer-level process variation. Measurement data is gathered from electronic circuits at multiple positions within multiple regions on one or more wafers and parameters are computed from the measurement data, which may be the measurement data values themselves. The set of parameters is filtered for expected systematic variation by computing a set of normalization values from the set of parameters and normalizing the data according to the normalization values. The normalized parameter set is then either presented in a visual display, e.g., by color mapping, or arranged in a numerical map of parameter value by location.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Touch sensor for non-uniform panels
ActiveUS9612101B2Reduce and substantially eliminate variation in overlap areaStop capacitance variationElectric/magnetic position measurementsUsing electrical meansSystematic variationEngineering
A two-dimensional capacitive touch sensor having a cover layer of varying thickness arranged on top of its electrode structure. An array of sensing nodes is formed between edge portions of the receiver electrodes and adjacent portions of the transmitter electrodes. To compensate for the varying thickness of the cover layer, the length of the edge portions per sensing node is varied to equalize node sensitivity across the sensor and thus suppress the systematic variation in node sensitivity which would otherwise arise as a result of the varying thickness of the cover layer.
Owner:TOUCHNETIX
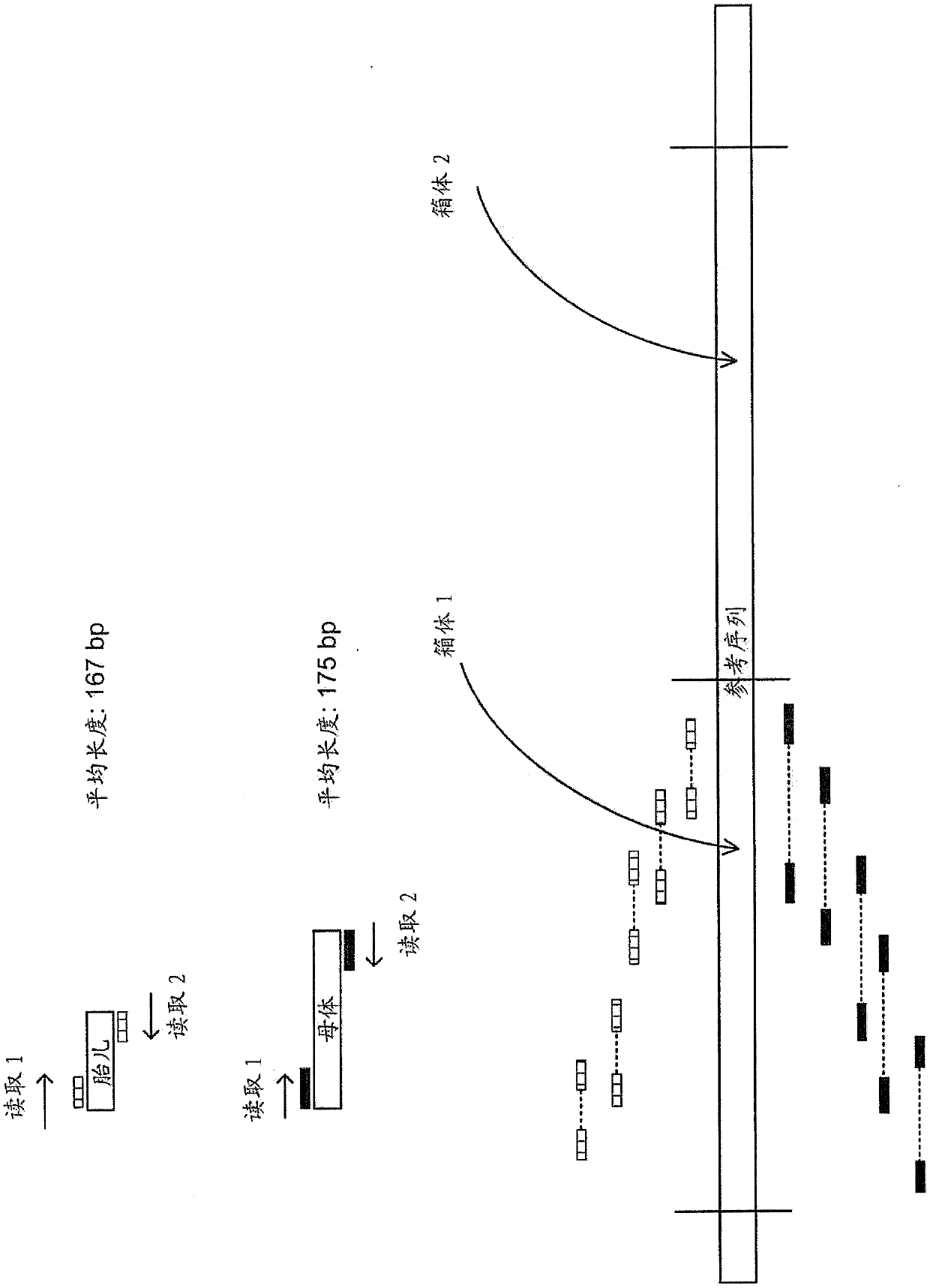
USing cell-free DNA fragment size to determine copy number variations
Disclosed are methods for determining copy number variation (CNV) known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining copy number variation (CNV) of fetuses using maternal samples comprising maternal and fetal cell free DNA. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. Some embodiments disclosed herein provide methods to improve the sensitivity and / or specificity of sequence data analysis by deriving a fragment size parameter, such as a size-weighted coverage or a fraction of fragments in a size range. In some embodiments, the fragment size parameter is adjusted to remove within-sample GC-content bias. In some embodiments, removal of within-sample GC-content bias is based on sequence data corrected for systematic variation common across unaffected training samples. Also disclosed are systems and computer program products for evaluation of CNV of sequences of interest.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Predicting IC manufacturing yield by considering both systematic and random intra-die process variations
ActiveUS8000826B2Reduce complexityProgramme controlError detection/correctionSystematic variationDying processes
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that predicts manufacturing yield for a die within a semiconductor wafer. During operation, the system first receives a physical layout of the die. Next, the system partitions the die into an array of tiles. The system then computes systematic variations for a quality indicative value to describe a process parameter across the array of tiles based on the physical layout of the die. Next, the system applies a random variation for the quality indicative parameter to each tile in the array of tiles. Finally, the system obtains the manufacturing yield for the die based on both the systematic variations and the random variations.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
System and apparatus for dual transducer ultrasonic testing of package seals
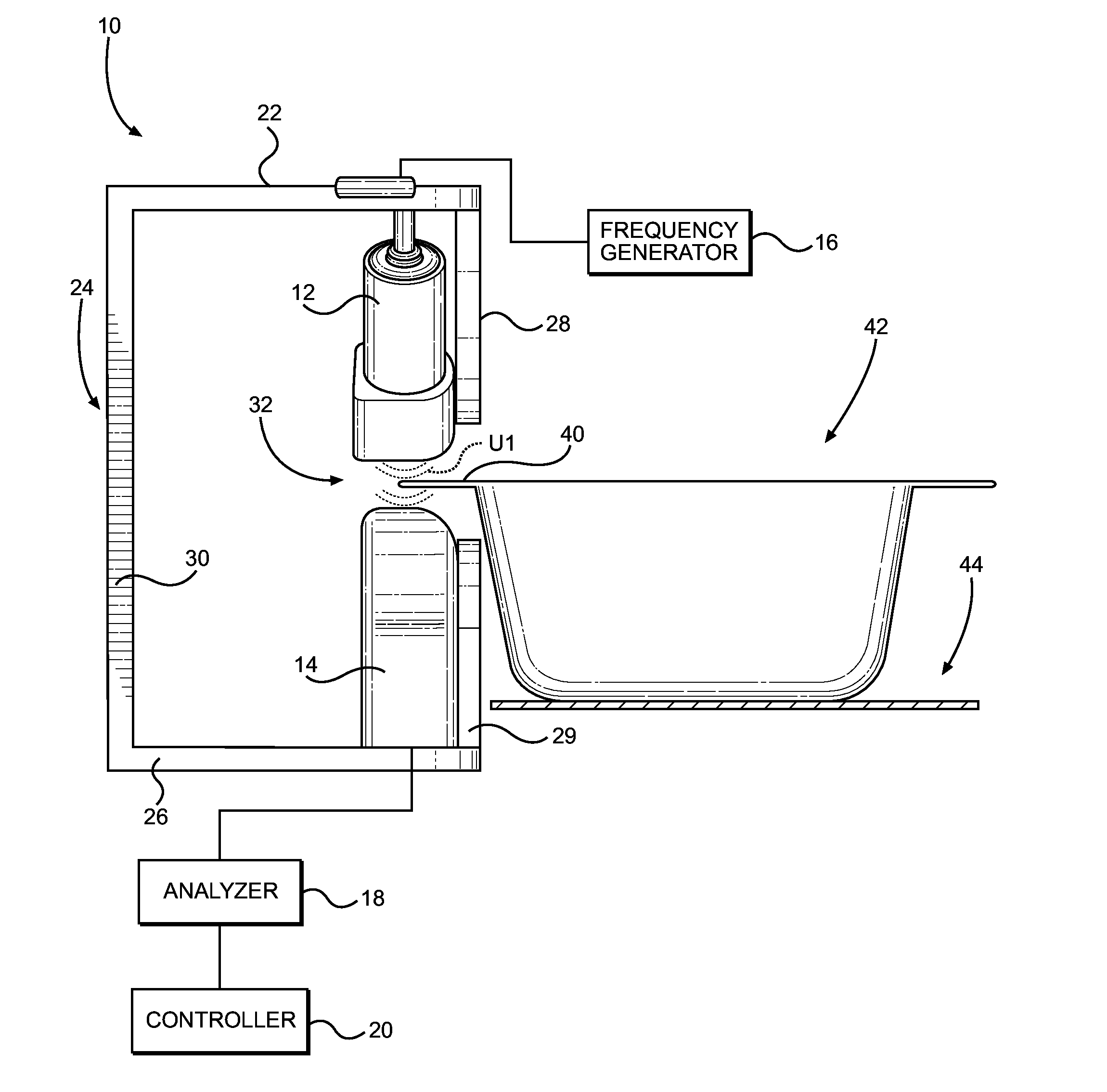
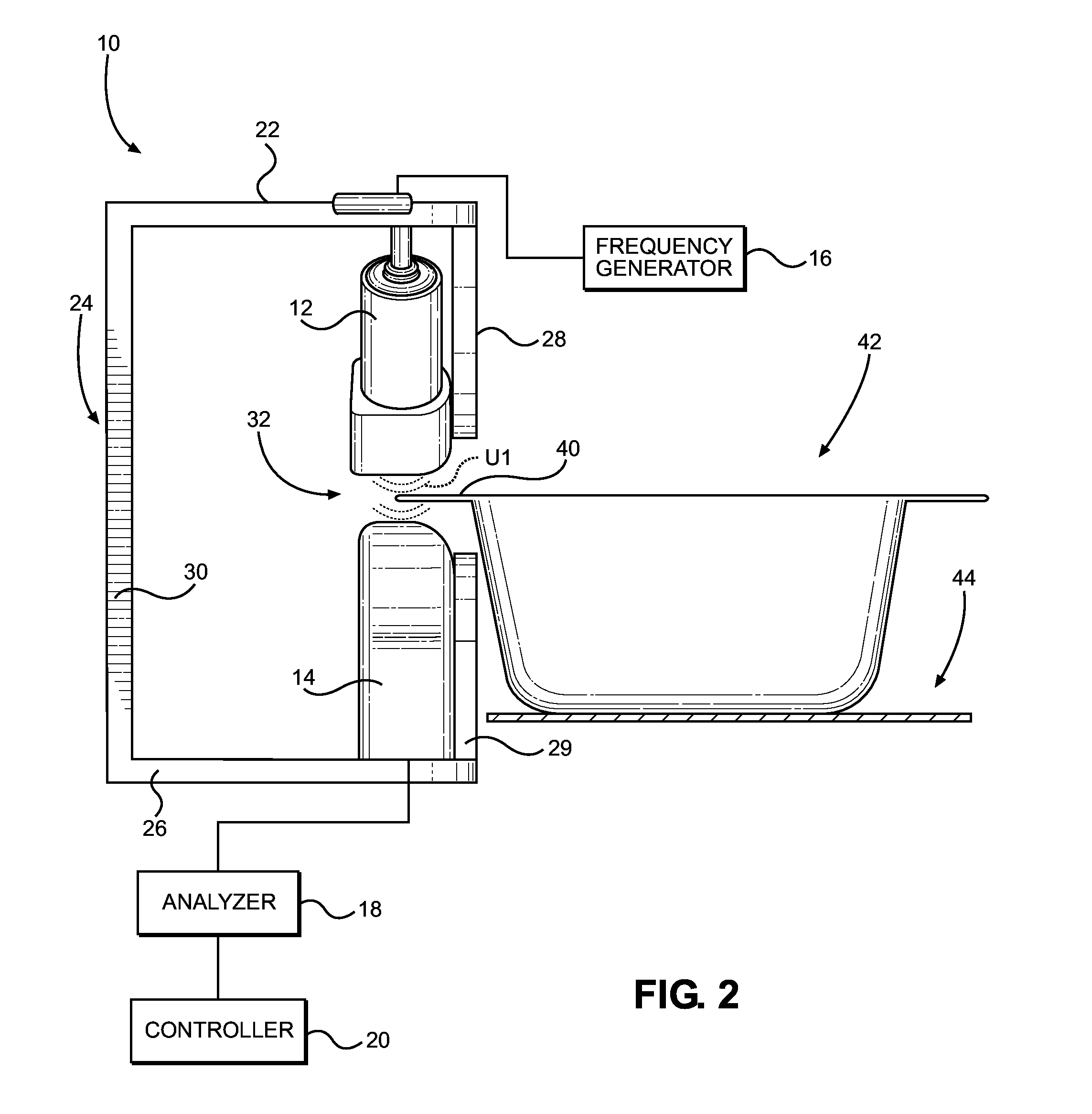
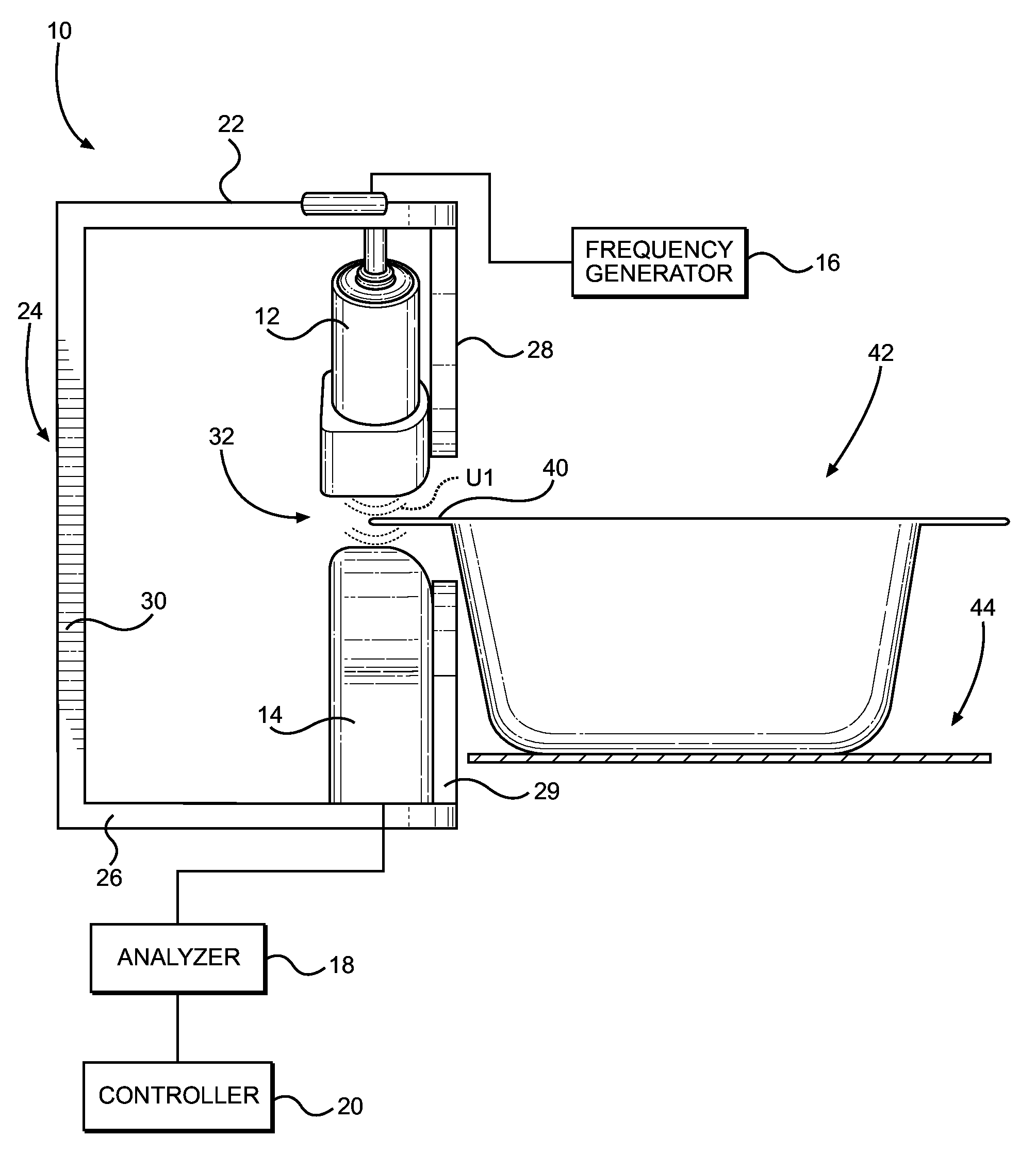
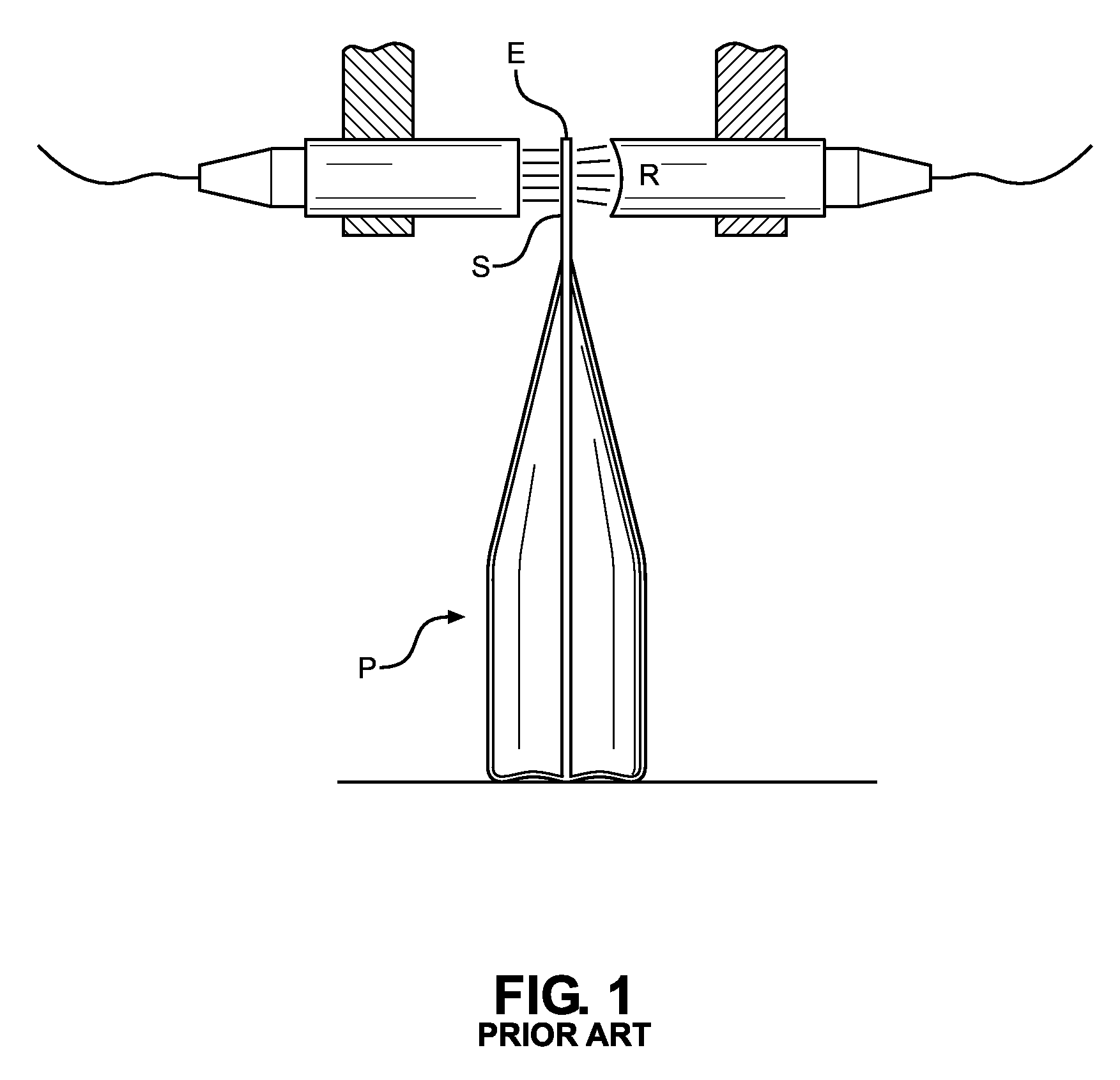
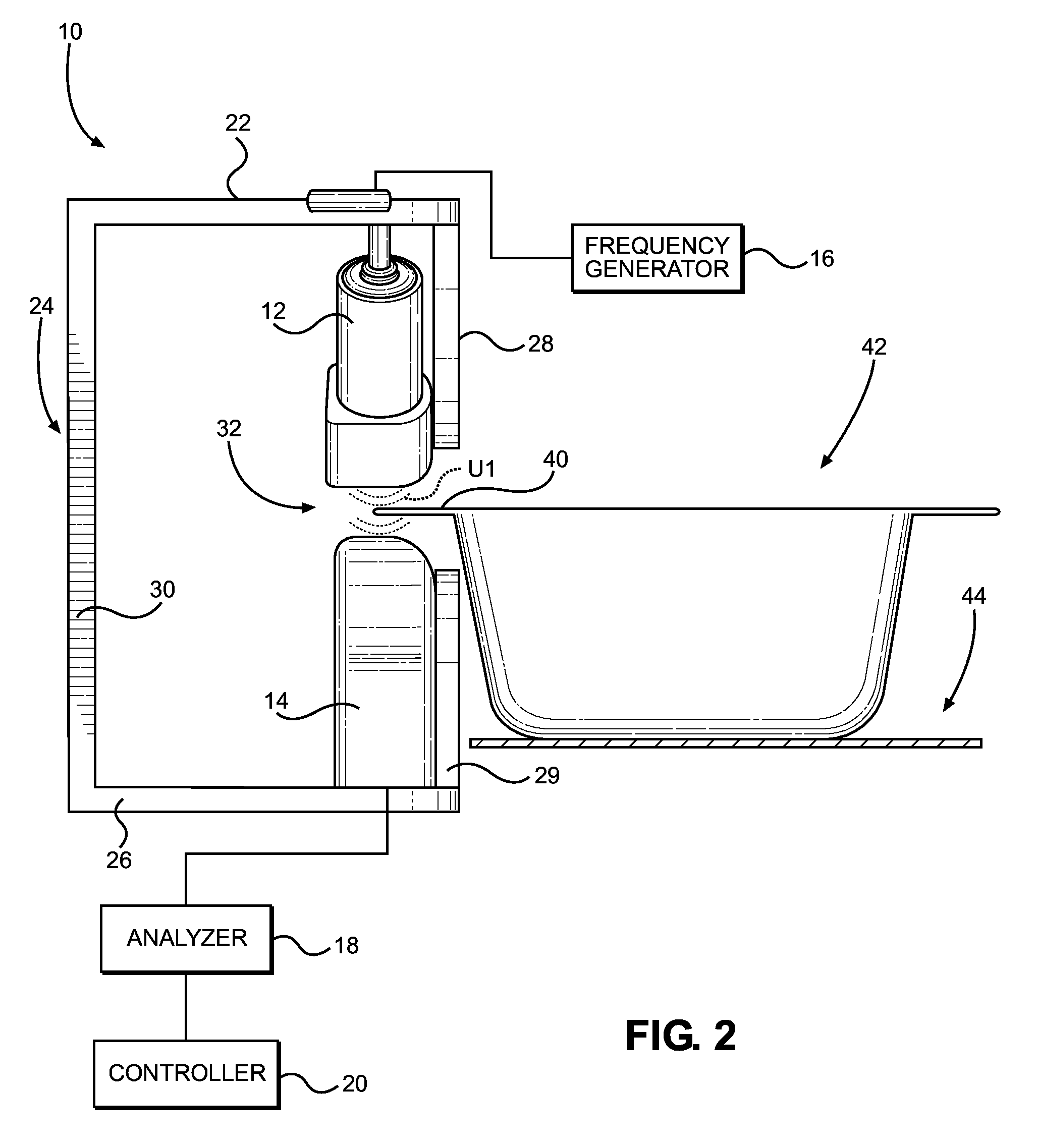
ActiveUS20150293061A1Eliminates systematic variationEliminate variationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetic property measurementsSignal responseSystematic variation
An airborne ultrasonic testing system includes two sets of ultrasound transmitters and receivers, an ultrasound frequency generator, a computer analyzer, and a controller. The ultrasound transmitters and opposing receivers are fixedly mounted at oblique angles from a support. A seal-receiving slot is defined between the transmitters and receivers, and is sized to receive a sealed edge portion of a container to be tested. The ultrasound transmitters preferably emit respective ultrasound streams that encounter a top surface of a sealed edge portion of the container at an angle between approximately 0-45 degrees, and most preferably, approximately 45 degrees. The angle of ultrasound emission of the first transmitter may be inverse of the angle of emission of the second transmitter. The signal response of each pair of receivers can be processed individually or combined to produce a summary test result of the two measurements that eliminates systematic variation associated with material variation.
Owner:PACKAGING TECH & INSPECTION
System and apparatus for dual transducer ultrasonic testing of package seals
ActiveUS9448208B2Eliminate variationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDomestic articlesSignal responseSystematic variation
An airborne ultrasonic testing system includes two sets of ultrasound transmitters and receivers, an ultrasound frequency generator, a computer analyzer, and a controller. The ultrasound transmitters and opposing receivers are fixedly mounted at oblique angles from a support. A seal-receiving slot is defined between the transmitters and receivers, and is sized to receive a sealed edge portion of a container to be tested. The ultrasound transmitters preferably emit respective ultrasound streams that encounter a top surface of a sealed edge portion of the container at an angle between approximately 0-45 degrees, and most preferably, approximately 45 degrees. The angle of ultrasound emission of the first transmitter may be inverse of the angle of emission of the second transmitter. The signal response of each pair of receivers can be processed individually or combined to produce a summary test result of the two measurements that eliminates systematic variation associated with material variation.
Owner:PACKAGING TECH & INSPECTION LLC
Varying feature size in resist across the chip without the artifact of "grid-snapping" from the mask writing tool
ActiveUS6870168B1Feature size in resistSmall spot sizeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesResistSystematic variation
A method for creating a pattern on a substrate, the method includes the steps of imprinting a first pattern on the substrate; and imprinting a second substantially similar pattern which is mis-registered with regard to the first pattern so that the combination of the first and second patterns cause a systematic variation in a final size of defined elements across the substrate.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com