Patents
Literature
171results about How to "Small spot size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
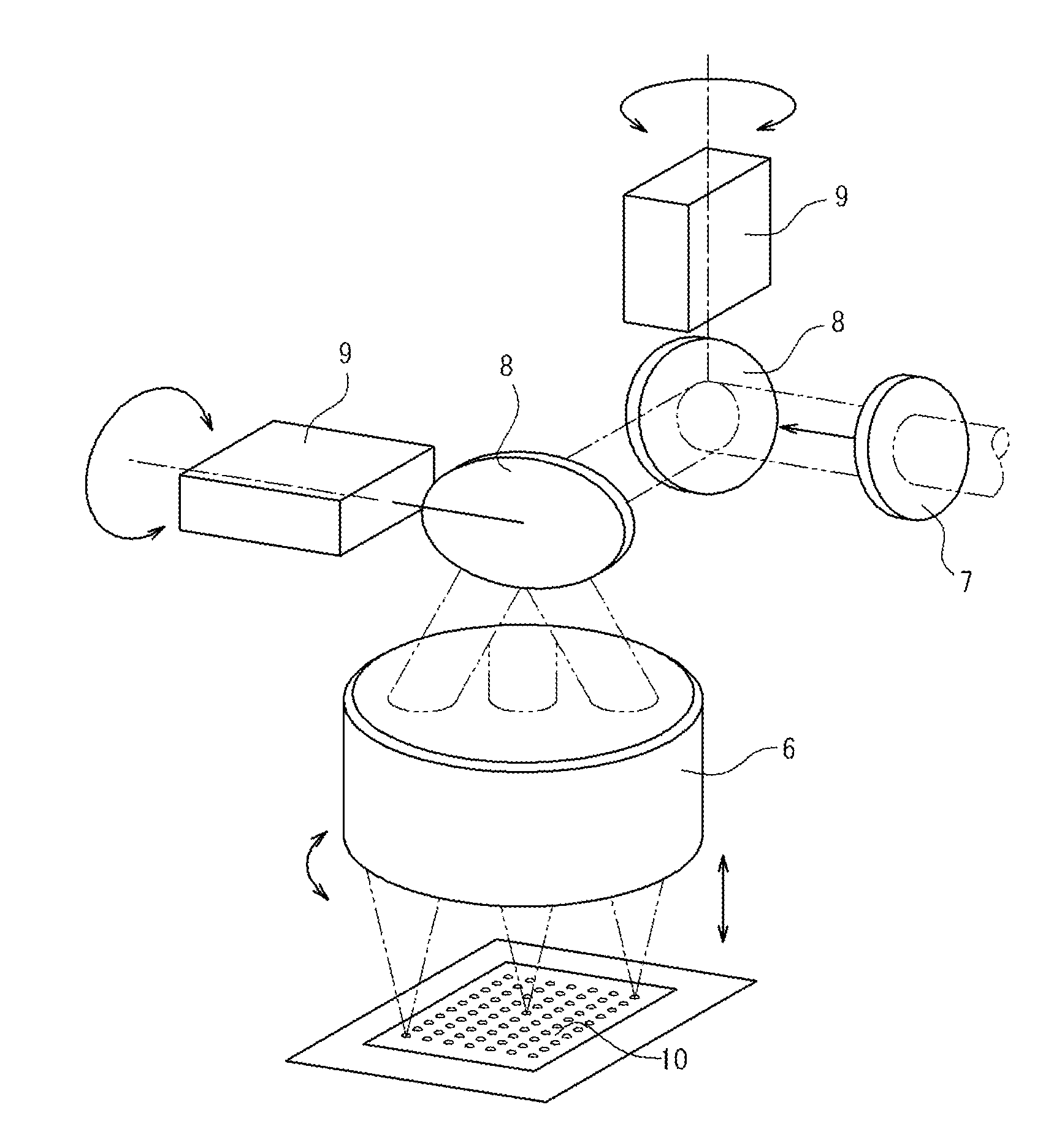
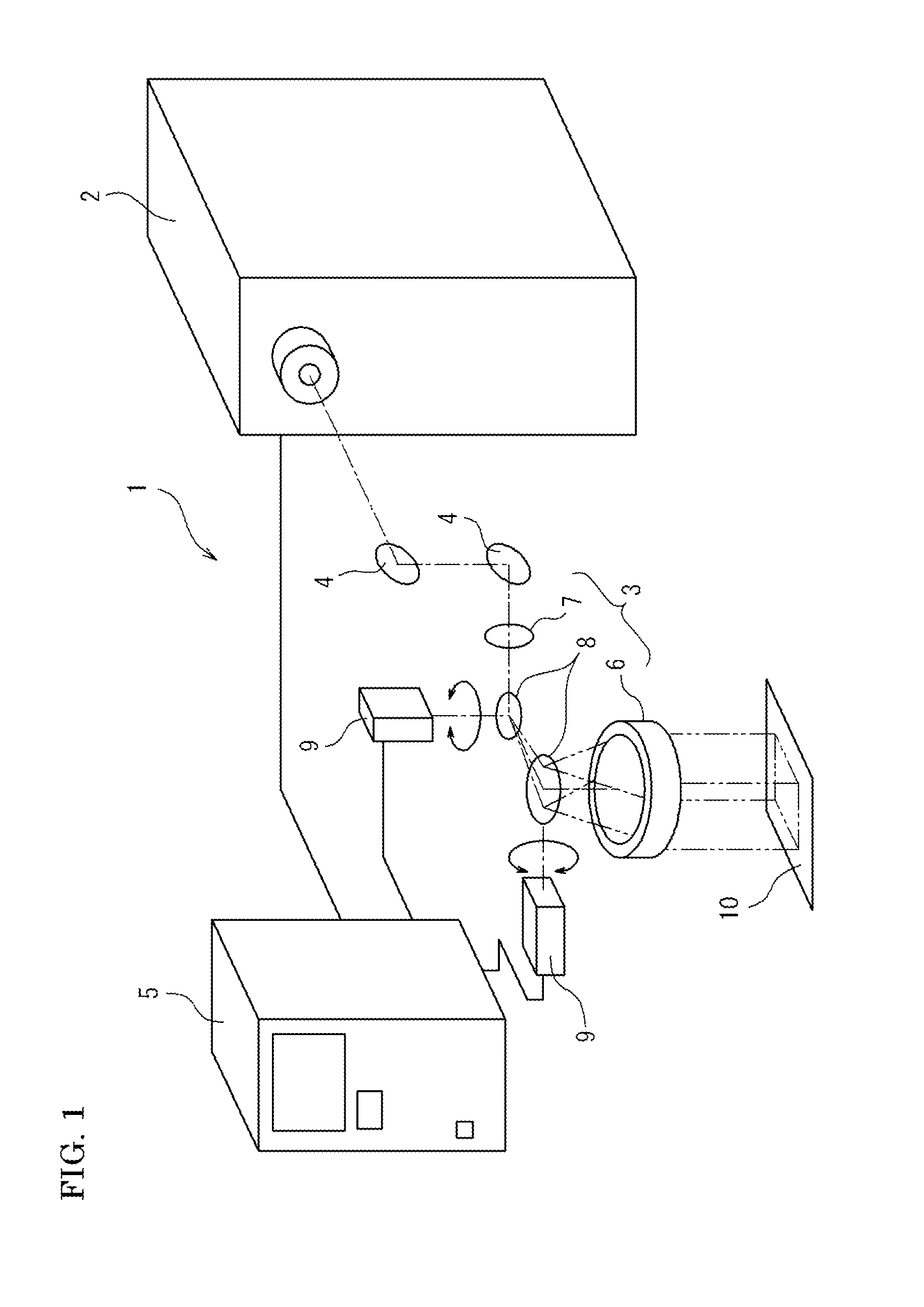
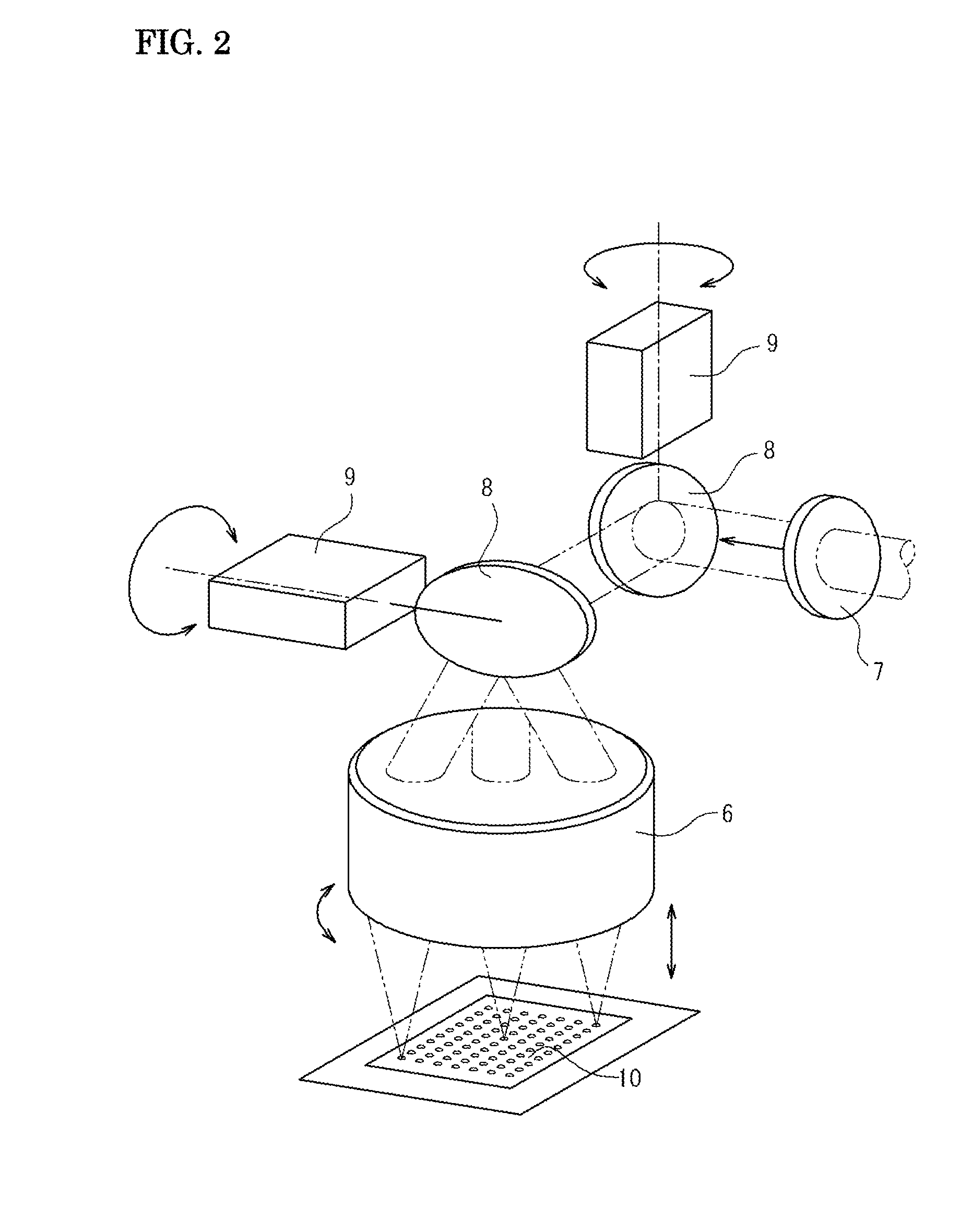
Apparatus and methods for additive-layer manufacturing of an article
ActiveUS20130270750A1Minimise impactSmall spot sizeAdditive manufacturing apparatusAuxillary shaping apparatusOptoelectronicsLaser beams
Apparatus is for additive layer manufacturing of an article from a material which can be rendered solid locally by application of a focused beam of laser radiation at a planar focal plane. The apparatus includes at least two laser beams, respective scanners for each laser beam for scanning the respective laser beams over a planar field, and a support movable stepwise to allow successive manufacturing layer cycles and for supporting material within the field. The entire planar field is common to each scanner and at least one scanner is tilted with respect to the planar field, and the at least one scanner is provided with a lens arranged to generate a focal plane tilted with respect to that scanner.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Wavefront sensing system employing active updating of reference positions and subaperture locations on wavefront sensor
ActiveUS20060024061A1Improve the situationSmall sizePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansWavefront sensorCommunications system
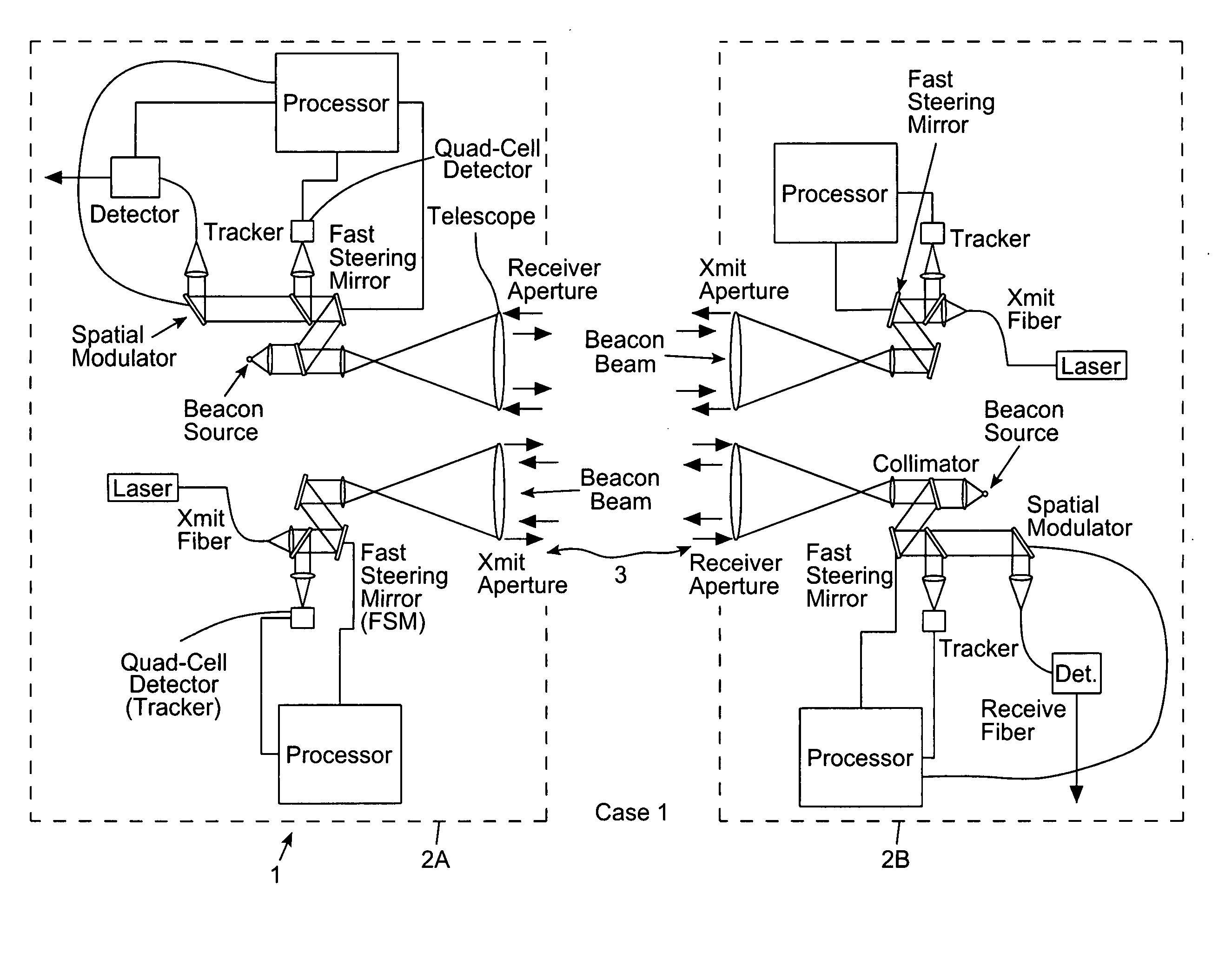
A free-space adaptive optical laser communication system having signal transmission and reception channels at all terminals in the communication system, wherein wavefront sensing (WFS) and wavefront correction mechanisms are employed along signal transmission and reception channels of all terminals in the communication system (i.e. adaptive optics) to improve the condition of the laser beam at the receiver (i.e. reduce the size of the spot a the detector plane). in the illustrative embodiment, the WFS mechanisms employ a novel WFS control process, in which active updating of reference positions and subaperture locations on the wavefront sensor. These WFS mechanism can be used in diverse application environments, including but not limited to FSO laser communication systems.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
Projection lens arrangement
ActiveUS20120091358A1Sufficient wafer throughputHigh resolutionThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersCamera lensLight beam
The invention relates to a charged particle multi-beamlet system for exposing a target using a plurality of beamlets. The system has a charged particle source, an aperture array, a beamlet manipulator, a beamlet blanker, and an array of projection lens systems. The charged particle source is configured to generate a charged particle beam. The aperture array is configured to define separate beamlets from the generated beam. The beamlet manipulator is configured to converge groups of the beamlets towards a common point of convergence for each group. The beamlet blanker is configured to controllably blank beamlets in the groups of beamlets. Finally, the array of projection lens systems is configured to project unblanked beamlets of the groups of beamlets on to the surface of the target. The beamlet manipulator is further adapted to converge each of the groups of beamlets towards a point corresponding to one of the projection lens systems.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Near-field light generator plate, thermally assisted magnetic head, head gimbal assembly, and hard disk drive
ActiveUS20080198496A1Easily projectedSmall spot sizeRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHard disc driveConductive materials
A near-field light generator plate 36 of the present invention is arranged to face a medium 10, and one portion 36b and other portion 36a in a medium-facing surface S thereof are made of their respective electroconductive materials different from each other. Since the one portion and the other portion in the medium-facing surface are made of the electroconductive materials different from each other, this medium-facing surface is formed by a surface removing step such as polishing or etching from the medium-facing surface side so that a difference between heights of the one portion and the other portion is readily made based on the difference of the materials.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Methods And Systems For Semiconductor Metrology Based On Polychromatic Soft X-Ray Diffraction
ActiveUS20190017946A1Increase measurement throughputSimultaneous measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyAngle of incidence
Methods and systems for performing measurements of semiconductor structures based on high-brightness, polychromatic, reflective small angle x-ray scatterometry (RSAXS) metrology are presented herein. RSAXS measurements are performed over a range of wavelengths, angles of incidence, and azimuth angles with small illumination beam spot size, simultaneously or sequentially. In some embodiments, RSAXS measurements are performed with x-ray radiation in the soft x-ray (SXR) region at grazing angles of incidence in the range of 5-20 degrees. In some embodiments, the x-ray illumination source size is 10 micrometers or less, and focusing optics project the source area onto a wafer with a demagnification factor of 0.2 or less, enabling an incident x-ray illumination spot size of less than two micrometers. In another aspect, active focusing optics project programmed ranges of illumination wavelengths, angles of incidence, and azimuth angles, or any combination thereof, onto a metrology area, either simultaneously or sequentially.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method and system for providing a high definition triangulation system
ActiveUS20080165357A1Precise positioningSmall spot sizeScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansOphthalmologyTriangulation
A triangulation system including a laser beam, optics focusing the laser beam on an object, a light detection unit detecting light reflected from the object due to impingement of the beam on the object, and an arrangement for determining, based on the detected light, object feature dimensions. The wavelength of the laser beam may be shorter than of infrared radiation, which allows for a reduced spot size without significant loss of depth of field. So as to reduce aberrations or a sensitivity to aberrations due to the shortened wavelength, the system may include (i) a polarization dependent coating matching the index of refraction of an element of the light detection unit to that of air for a range of angles, (ii) tilted projection optics, (iii) a prism wavefront corrector, and / or (iv) a positioning assembly, which provides for increased precision in positioning the laser diode with respect to a collimator lens.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Ultraviolet laser ablative patterning of microstructures in semiconductors
InactiveUS7157038B2High aspect ratioGreat depth of focusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesUltravioletSingle crystal
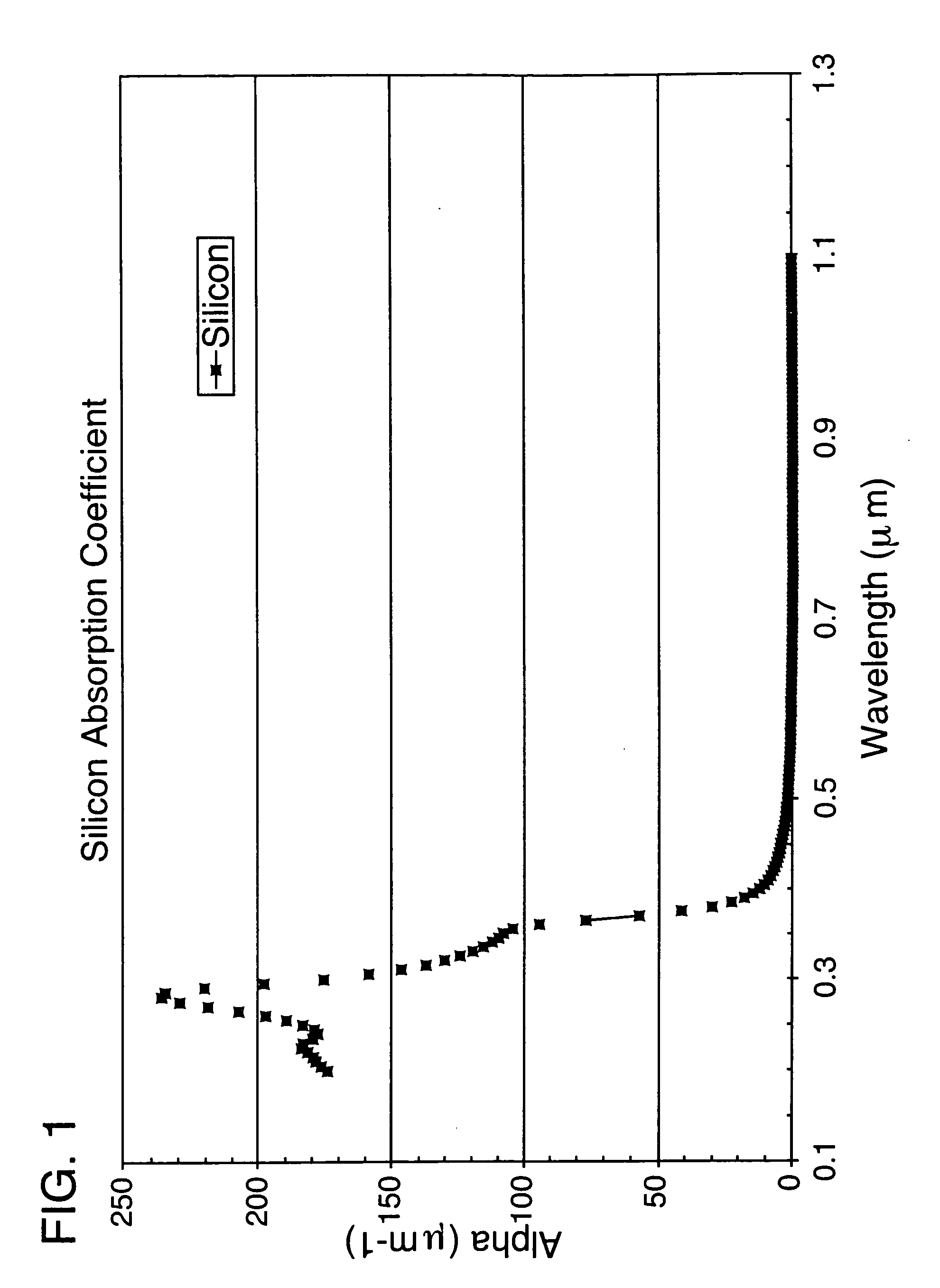
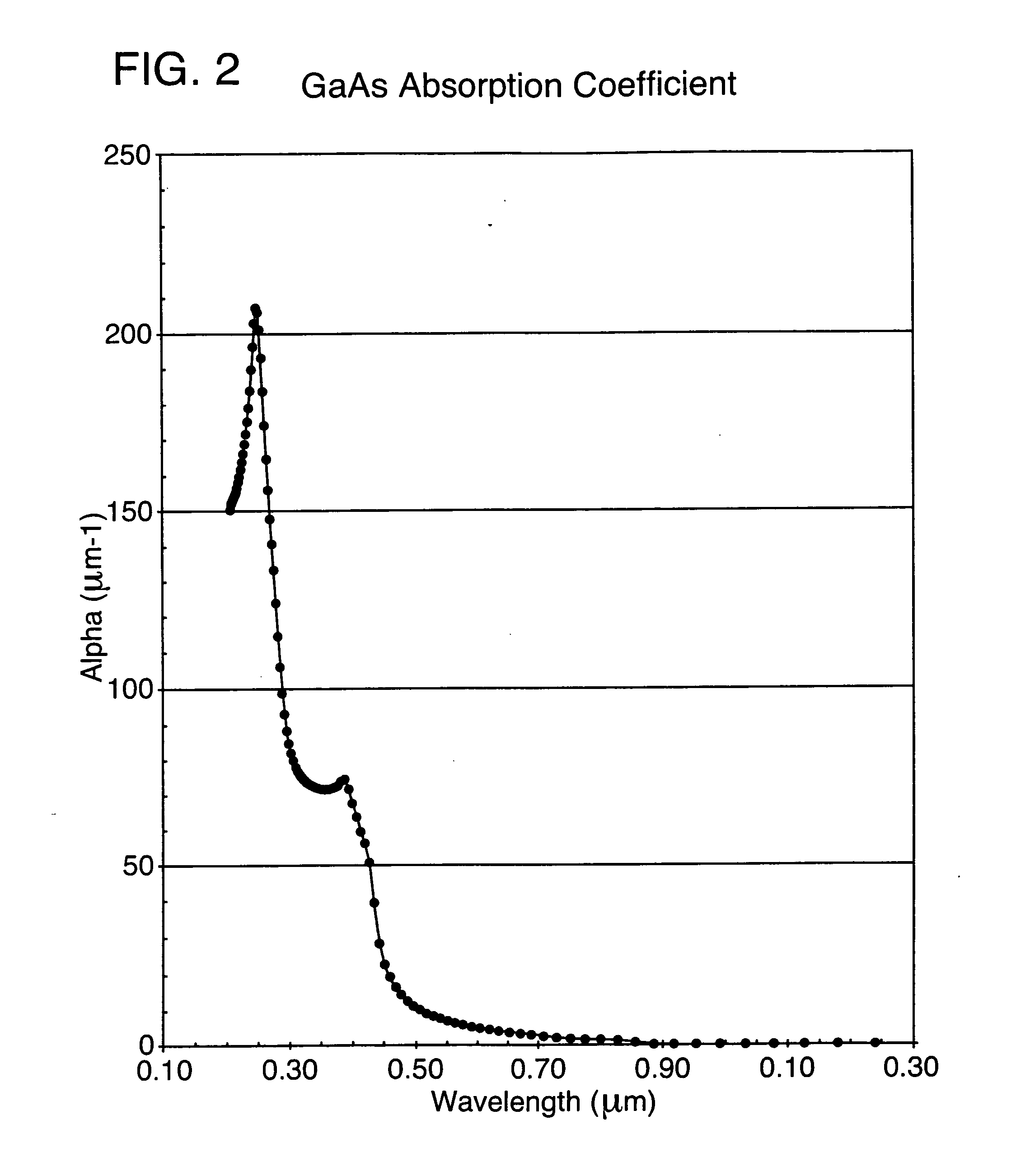
Patterns with feature sizes of less than 50 microns are rapidly formed directly in semiconductors, particularly silicon, GaAs, indium phosphide, or single crystalline sapphire, using ultraviolet laser ablation. These patterns include very high aspect ratio cylindrical through-hole openings for integrated circuit connections; singulation of processed die contained on semiconductor wafers; and microtab cutting to separate microcircuit workpieces from a parent semiconductor wafer. Laser output pulses (32) from a diode-pumped, Q-switched frequency-tripled Nd:YAG, Nd:YVO4, or Nd:YLF is directed to the workpiece (12) with high speed precision using a compound beam positioner. The optical system produces a Gaussian spot size, or top hat beam profile, of about 10 microns. The pulse energy used for high-speed ablative processing of semiconductors using this focused spot size is greater than 200 μJ per pulse at pulse repetition frequencies greater than 5 kHz and preferably above 15 kHz. The laser pulsewidth measured at the full width half-maximum points is preferably less than 80 ns.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Distance estimation using sound signals
ActiveUS20130064042A1Improve sound reproductionAccurate measurementMicrophonesLoudspeakersPath lengthSonification
An apparatus comprises a test signal generator (401) which generates an ultrasonic test signal by modulating an audio band test signal on an ultrasonic signal. The ultrasonic test signal is radiated from a parametric loudspeaker (403) and is demodulated by non-linearities in the air. A reflected audio signal may arise from reflections of an object, such as a wall. An audio band sensor (405) generates an audio band captured signal which comprises the demodulated reflected audio band signal. A distance circuit (407) then generates a distance estimate for the distance from the parametric loudspeaker (403) to the object in response to a comparison of the audio band captured signal and the audio band test signal. Specifically two signals may be correlated to determine a delay corresponding to the full path length. Based on the distance estimates an audio environment may be estimated and a sound system may be adapted accordingly.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Oct probe
InactiveUS20090190883A1Avoid ghostingAvoid it happening againMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterLight beamLight source
An OCT probe has a sheath to be inserted into a subject; and an optical system within the sheath, for changing the direction of light which propagates from a light source through an optical fiber to irradiate the light onto the subject through a transparent portion of the sheath, and for reflecting the light beam, which is reflected by the subject, to guide the light into the optical fiber. A light output surface, for causing the light to be output from the reflecting surface in a direction obliquely inclined with respect to the inner surface of the sheath, and a reflected light sheath entrance preventing portion, for preventing light reflected by the inner surface of the sheath from entering the optical fiber, are provided in the optical system. The reflected light sheath entrance preventing portion may be formed by providing a cut planar surface portion on the lens.
Owner:NAMIKI PRECISION JEWEL CO LTD
Ultraviolet laser ablative patterning of microstructures in semiconductors
InactiveUS20060091126A1Improve aspect ratioGreat depth of focusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesIndium phosphideIntegrated circuit
Patterns with feature sizes of less than 50 microns are rapidly formed directly in semiconductors, particularly silicon, GaAs, indium phosphide, or single crystalline sapphire, using ultraviolet laser ablation. These patterns include very high aspect ratio cylindrical through-hole openings for integrated circuit connections; singulation of processed die contained on semiconductor wafers; and microtab cutting to separate microcircuit workpieces from a parent semiconductor wafer. Laser output pulses (32) from a diode-pumped, Q-switched frequency-tripled Nd:YAG, Nd:YVO4, or Nd:YLF is directed to the workpiece (12) with high speed precision using a compound beam positioner. The optical system produces a Gaussian spot size, or top hat beam profile, of about 10 microns. The pulse energy used for high-speed ablative processing of semiconductors using this focused spot size is greater than 200 μJ per pulse at pulse repetition frequencies greater than 5 kHz and preferably above 15 kHz. The laser pulsewidth measured at the full width half-maximum points is preferably less than 80 ns.
Owner:BAIRD BRIAN W +5
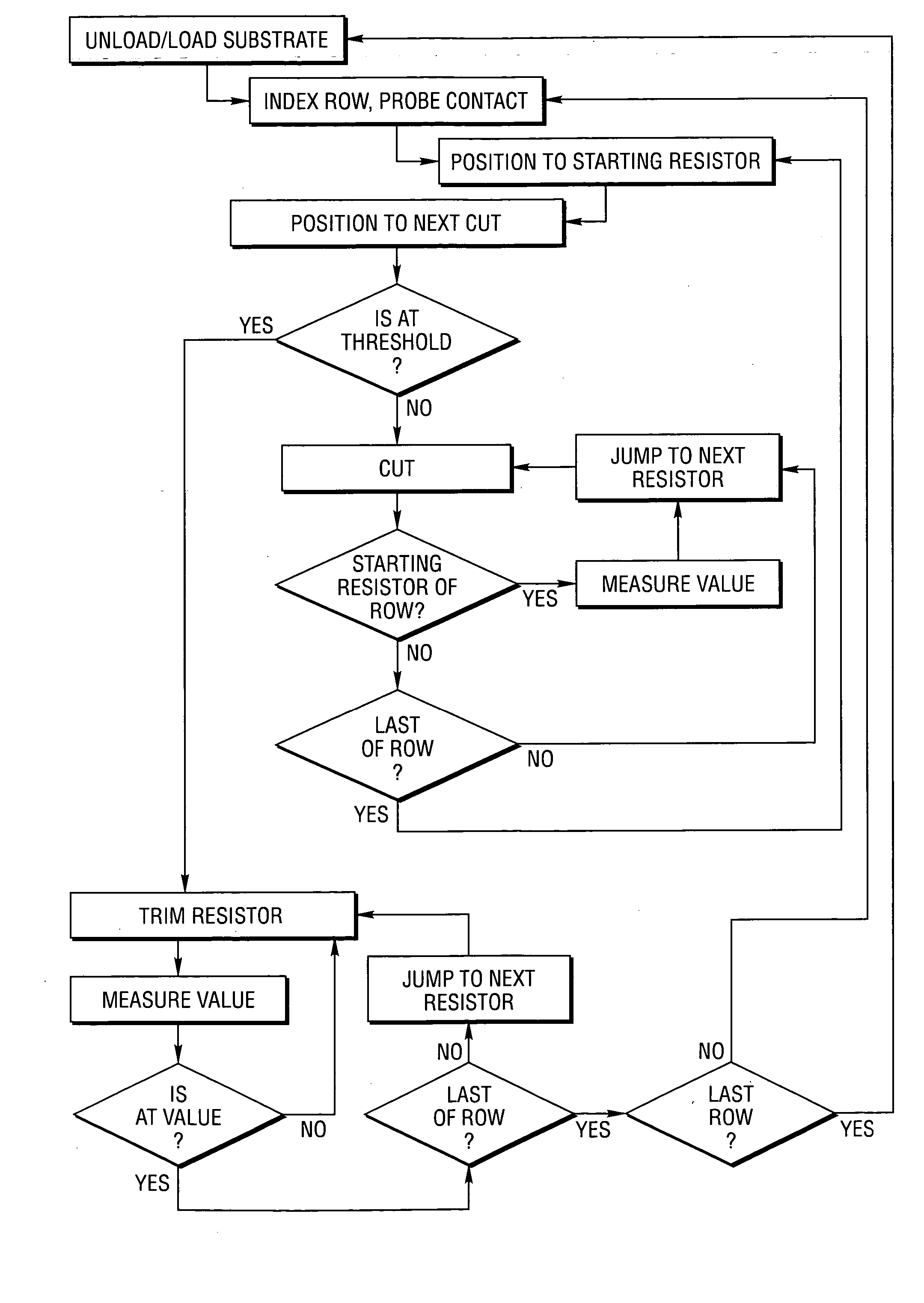
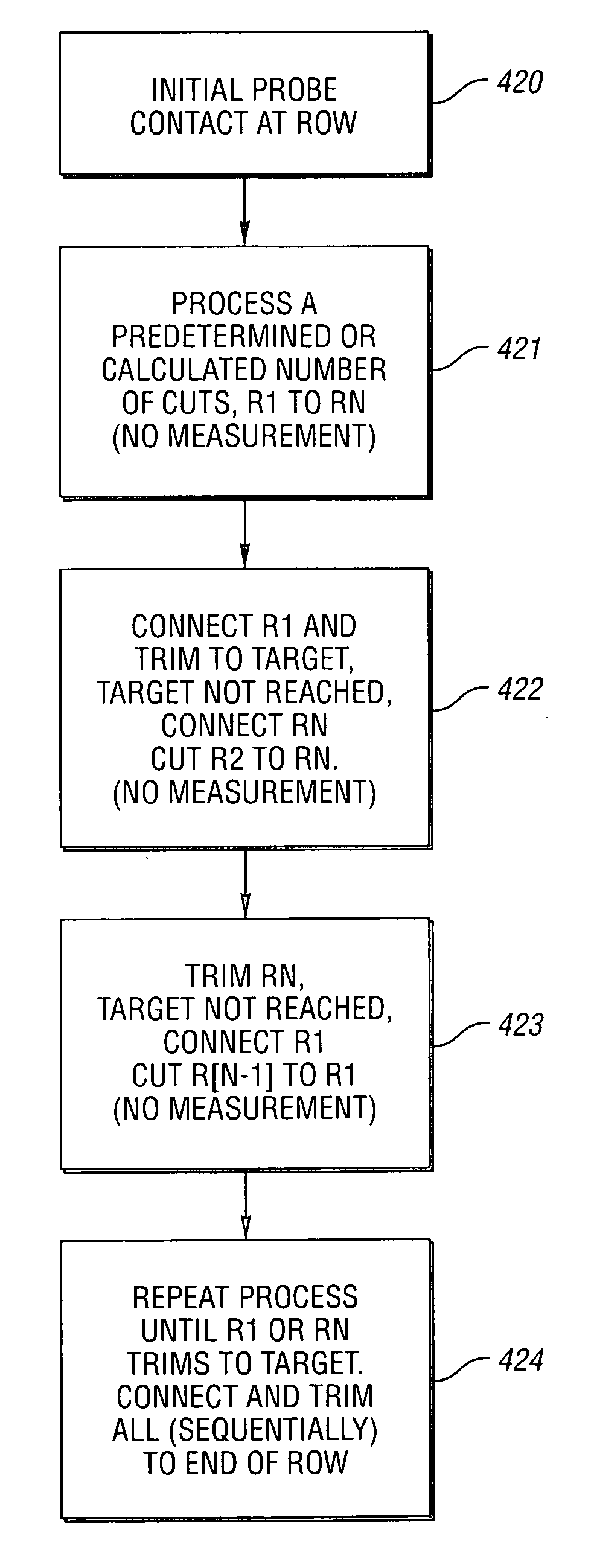
Method and system for high-speed precise laser trimming, scan lens system for use therein and electrical device produced thereby
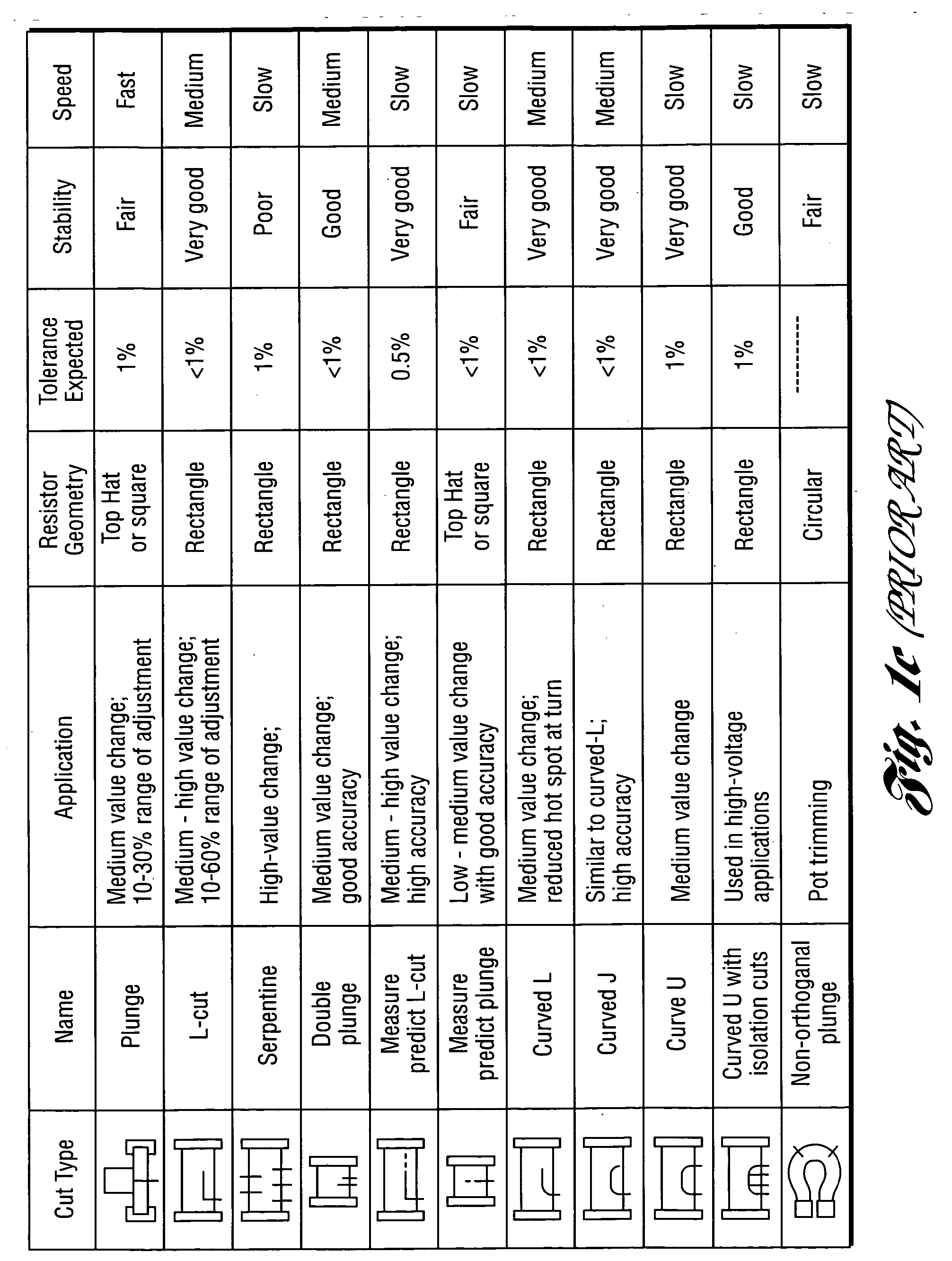
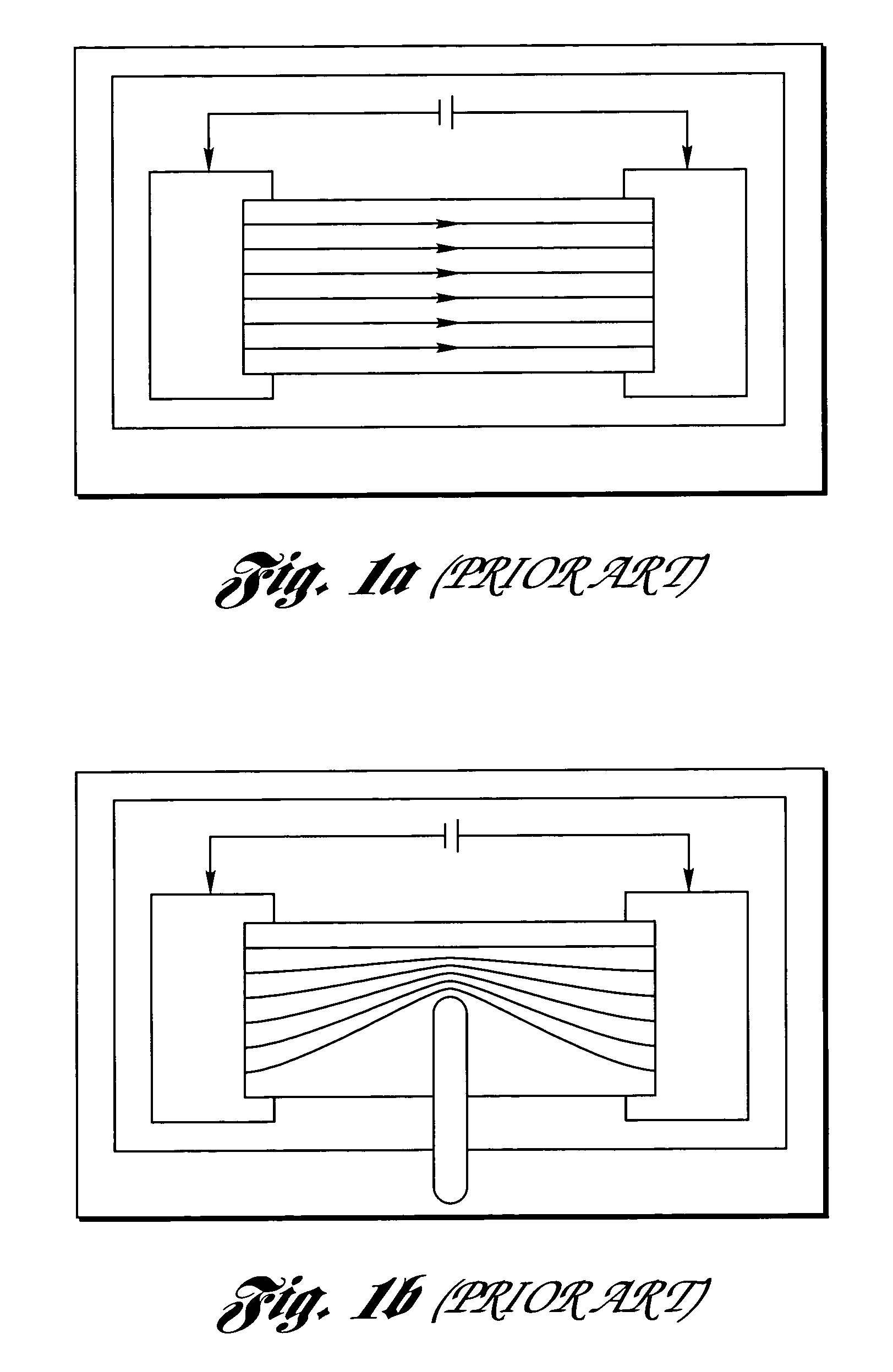
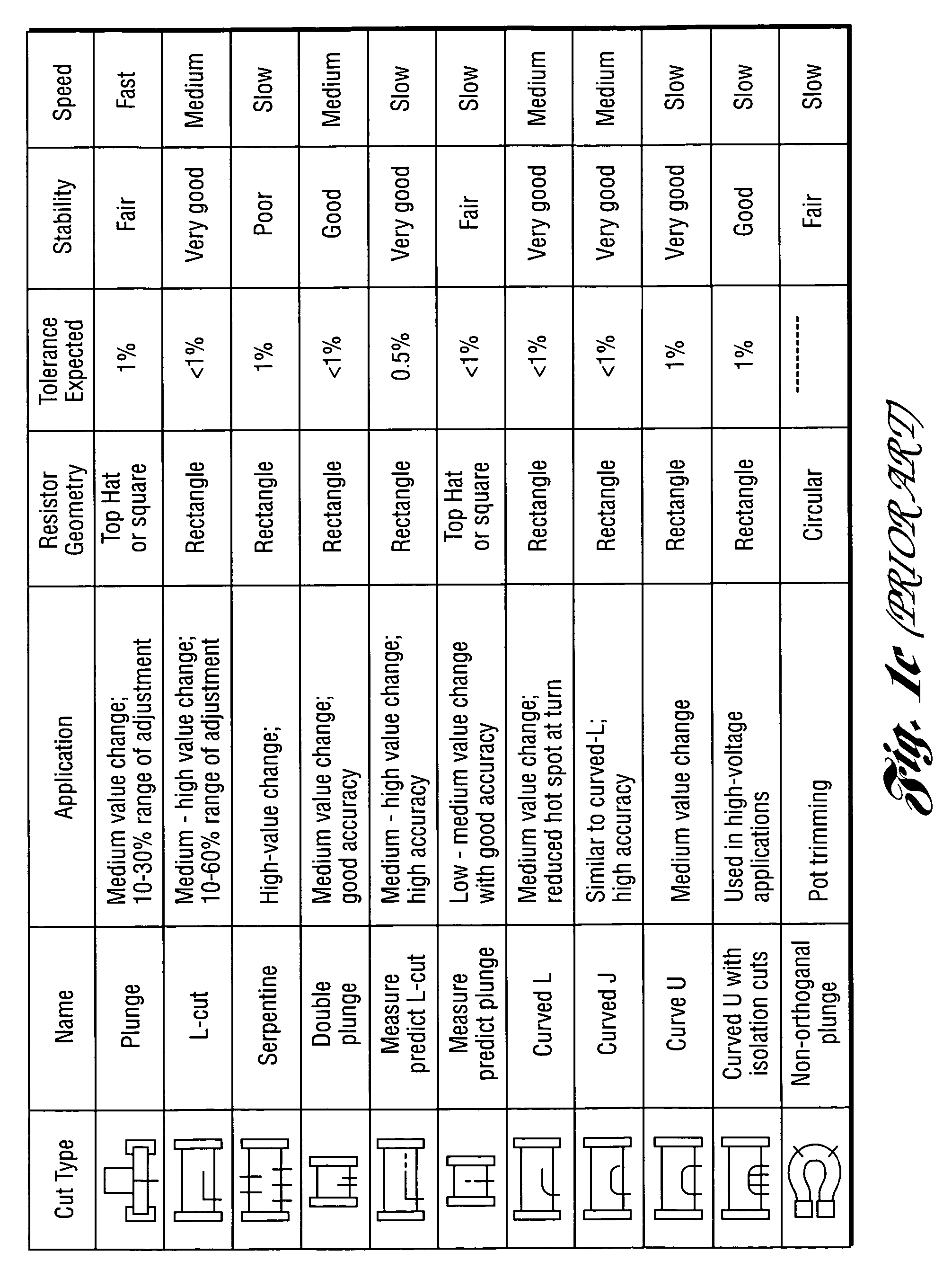
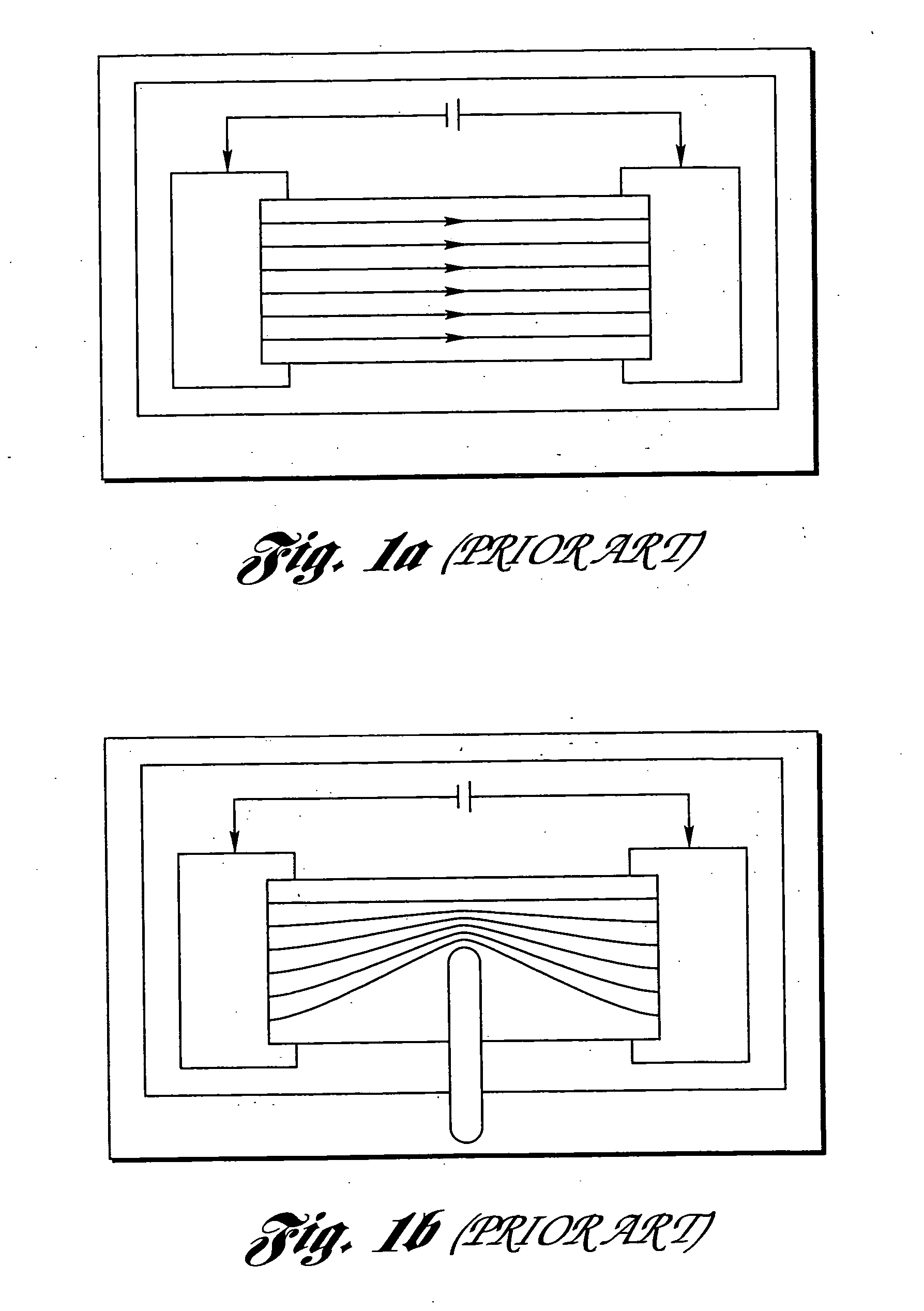
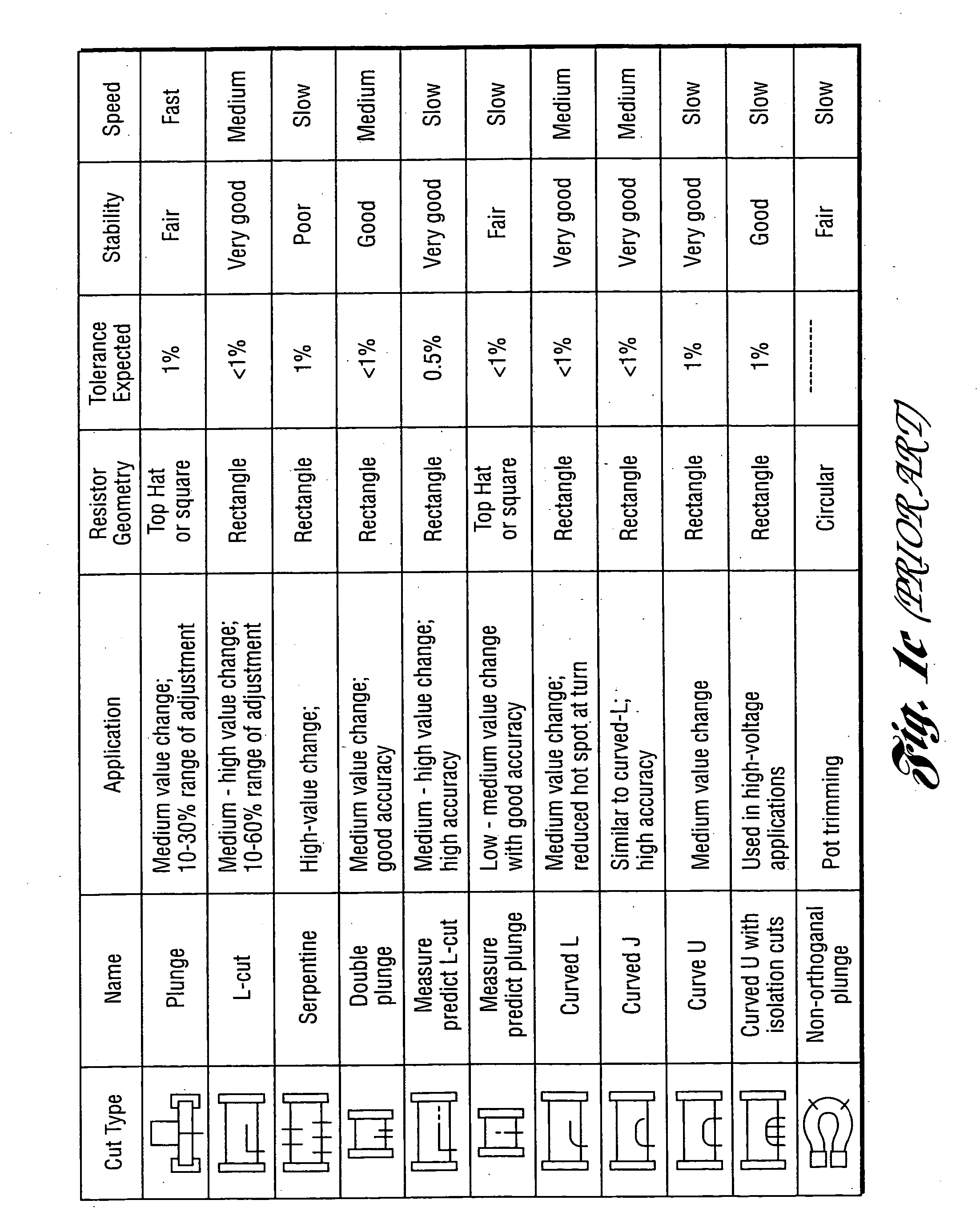
InactiveUS20060160332A1Small spot sizeTight toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistor manufactureElectricityHigh absorption
A method, system and scan lens system are provided for high-speed, laser-based, precise laser trimming at least one electrical element. The method includes generating a pulsed laser output having one or more laser pulses at a repetition rate. Each laser pulse has a pulse energy, a laser wavelength within a range of laser wavelengths, and a pulse duration. The method further includes selectively irradiating the at least one electrical element with the one or more laser pulses focused into at least one spot having a non-uniform intensity profile along a direction and a spot diameter as small as about 6 microns to about 15 microns so as to cause the one or more laser pulses to selectively remove material from the at least one element and laser trim the at least one element while avoiding substantial microcracking within the at least one element. The wavelength is short enough to produce desired short-wavelength benefits of small spot size, tight tolerance and high absorption, but not so short so as to cause microcracking.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Charged Particle Beam Device with Aperture
ActiveUS20070257207A1Reduce beam spot sizeImprove spatial resolutionRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsOptical axisMolecular physics
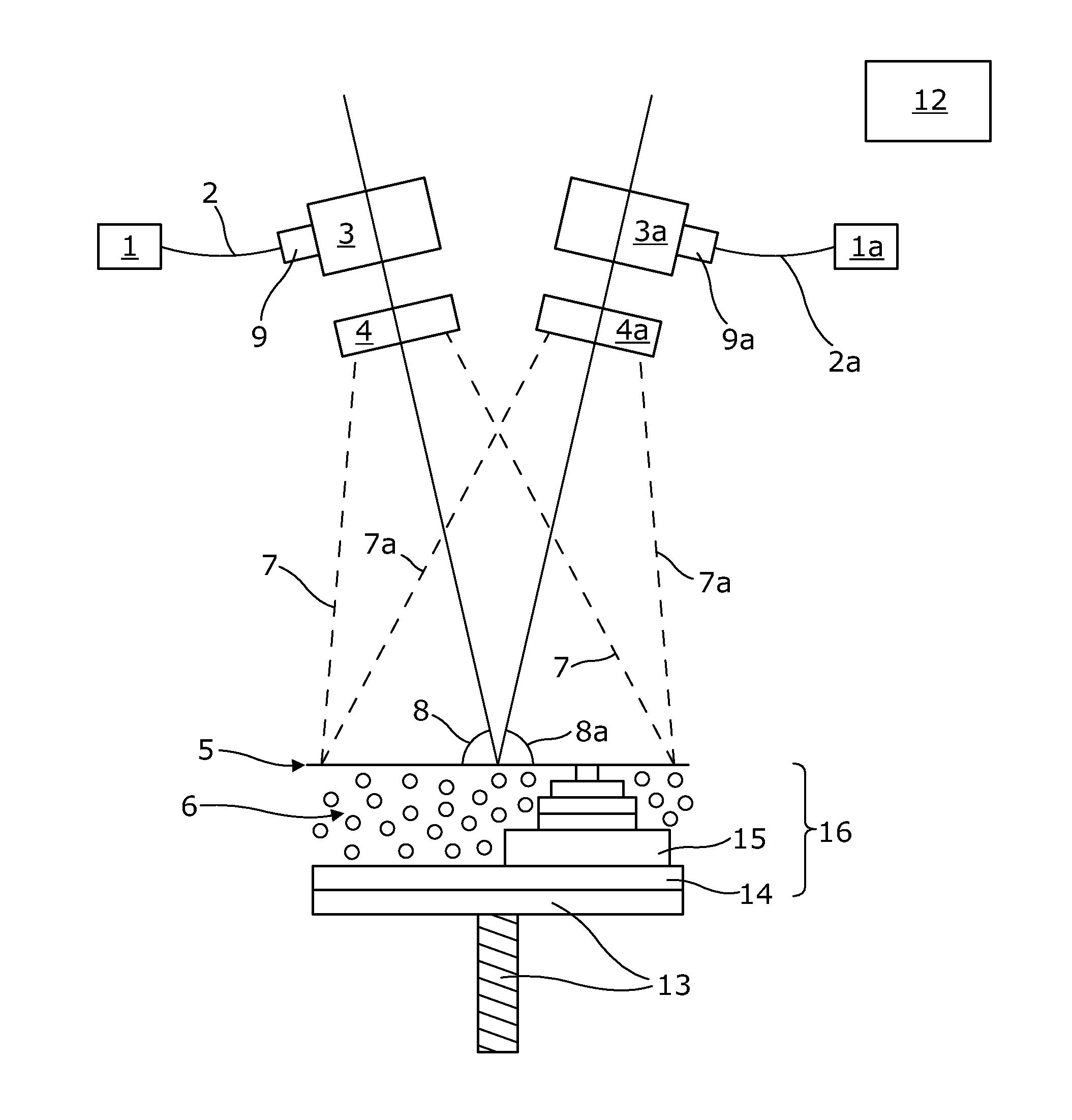
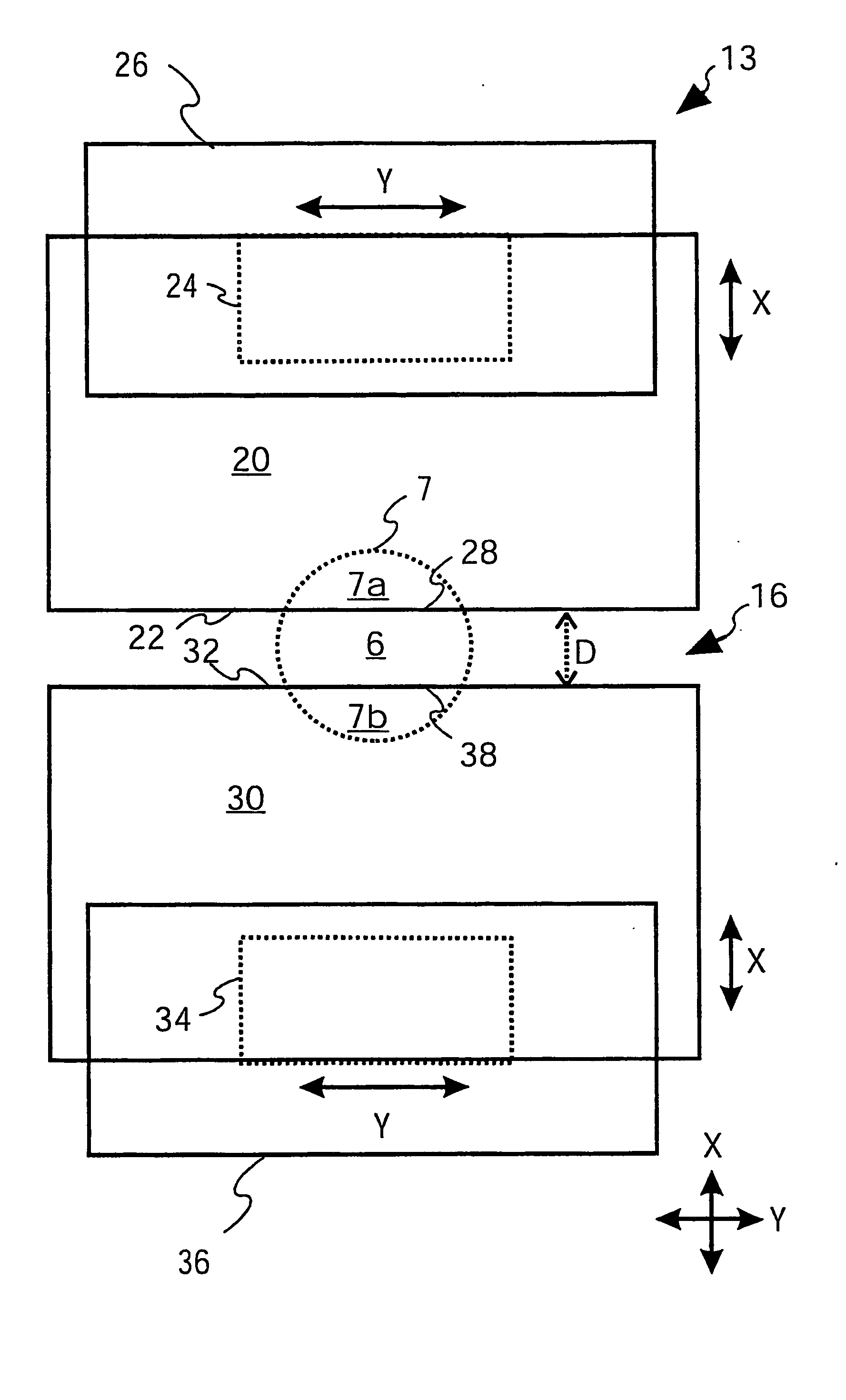
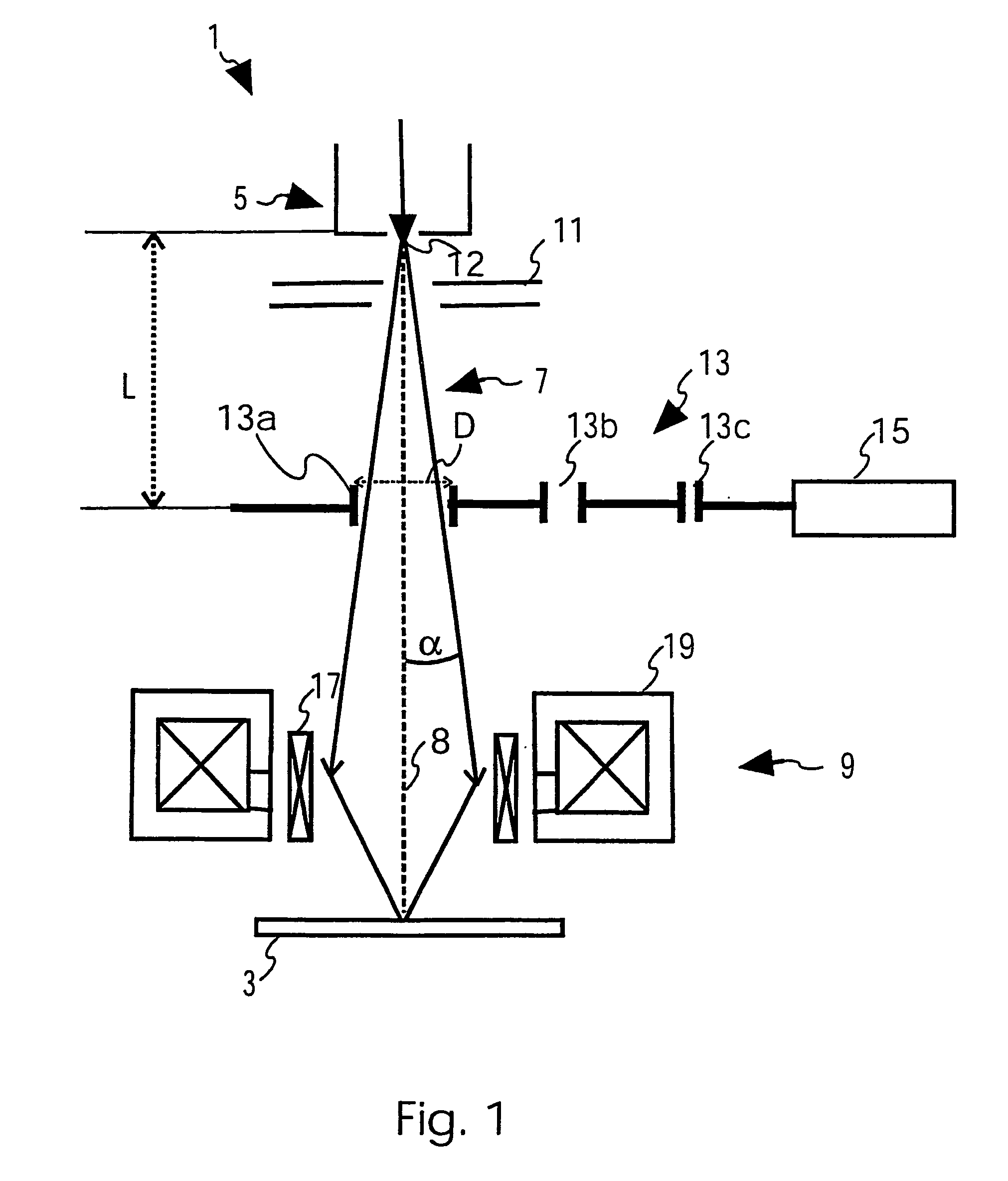
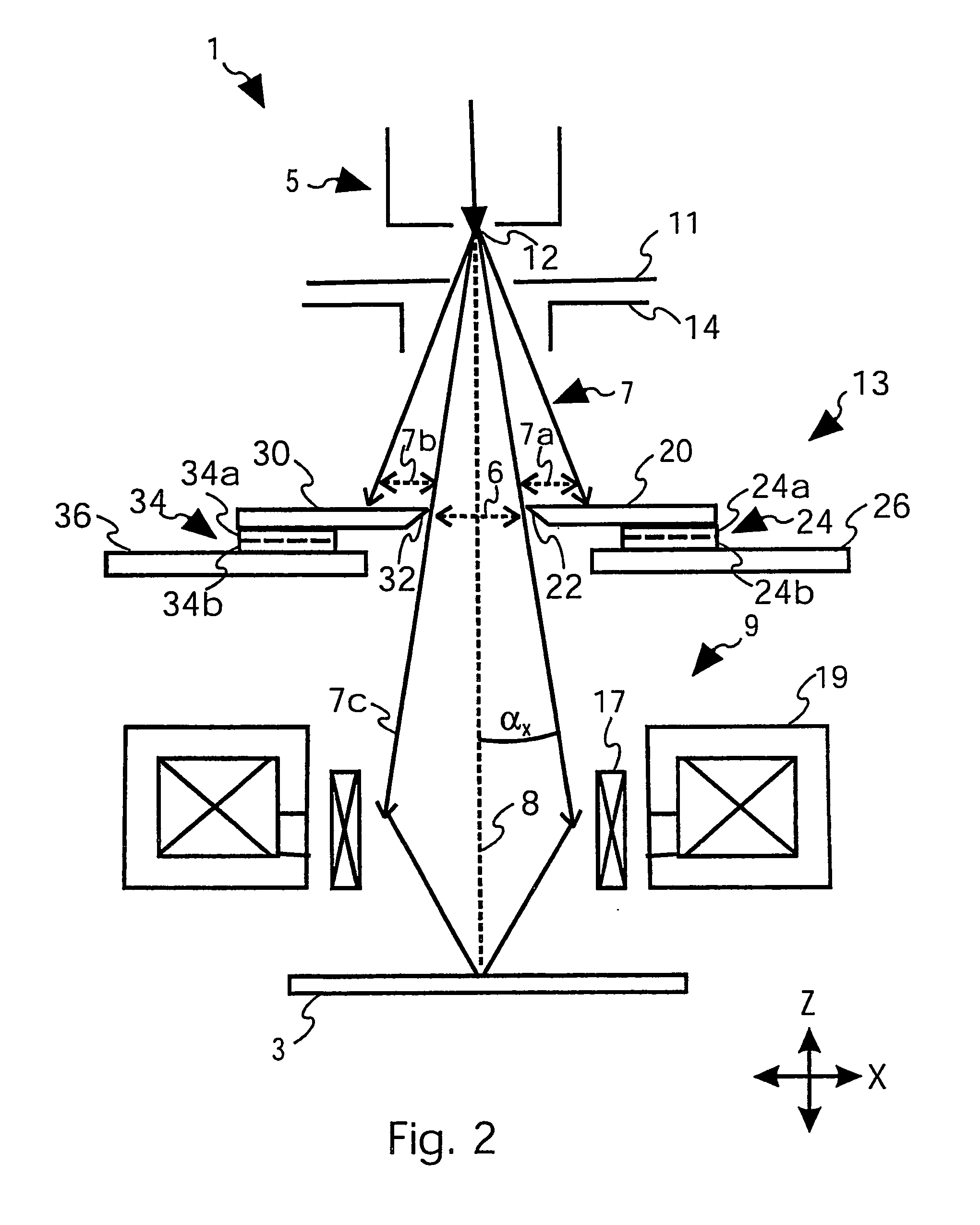
The present invention relates to a charged particle beam device (1) for inspecting or structuring a specimen (3) comprising a charged particle beam source (5) to generate a charged particle beam (7), a focussing lens (9) to focus the charged particle beam (7) onto the specimen (3), and an aperture system (13) for defining an aperture (6) for the charged particle beam (7). The aperture system (13) includes a first member (20) to block a first portion (7a) of the charged particle beam (7) between the charged particle beam source (5) and the focussing lens (9), a second member (30) to block a second portion (7b) of the charged particle beam (7) between the charged particle beam source (5) and the focussing lens (9), first means (24) for moving the first member (20) to adjust the size of the blocked first portion (7a) of the charged particle beam (7), and second means (34) for moving the second member (30) independently from the first portion (7b). With such aperture system (13), it is possible to freely adjust the size of the aperture (6) and align it to the optical axis (8) during operation.
Owner:ICT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TESTING GESELLSCHAFT FUER HALBLEITERPRUEFTECHNIK GMBH
Plasmon shield to shape and reduce optical spot
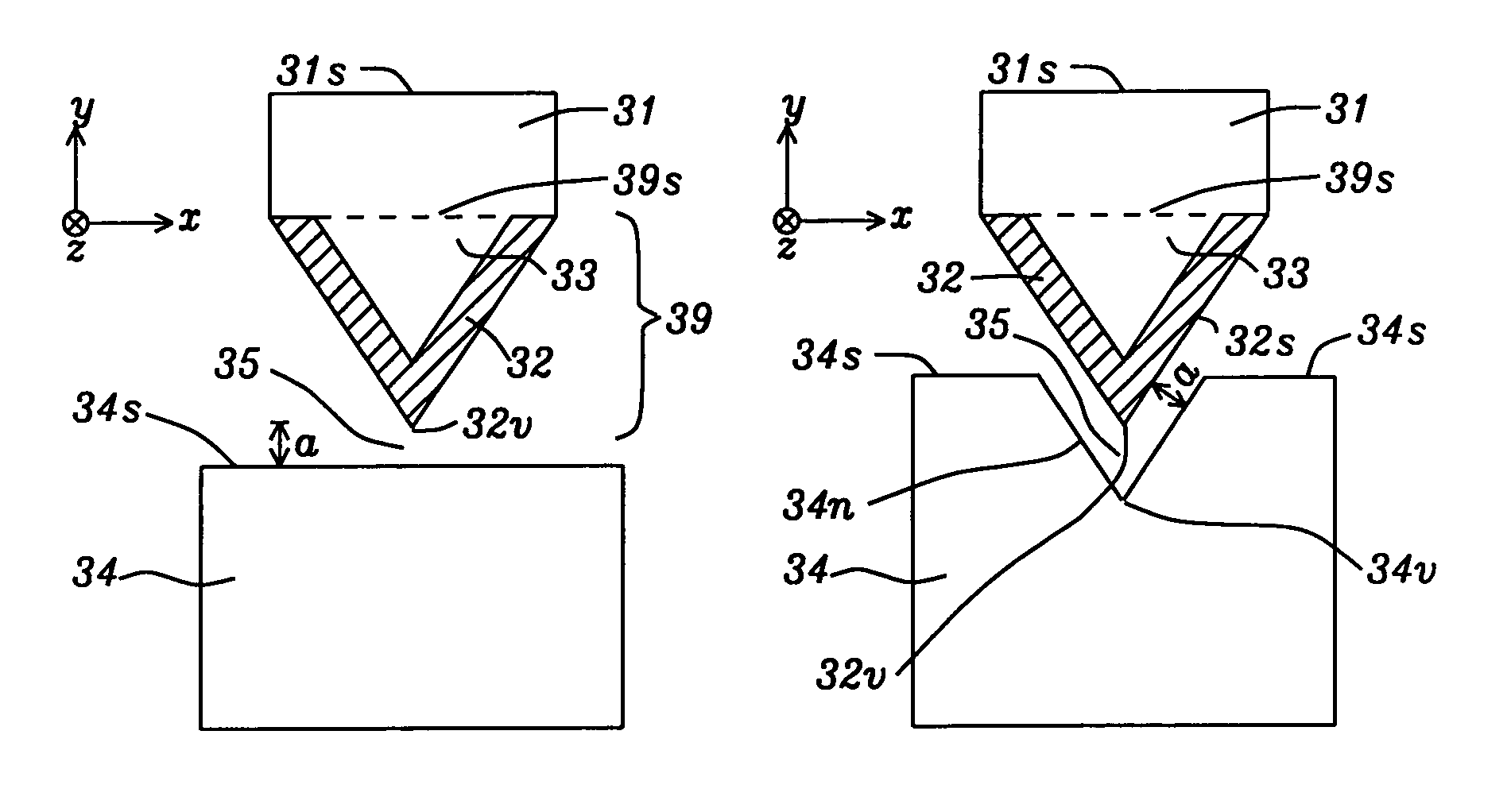
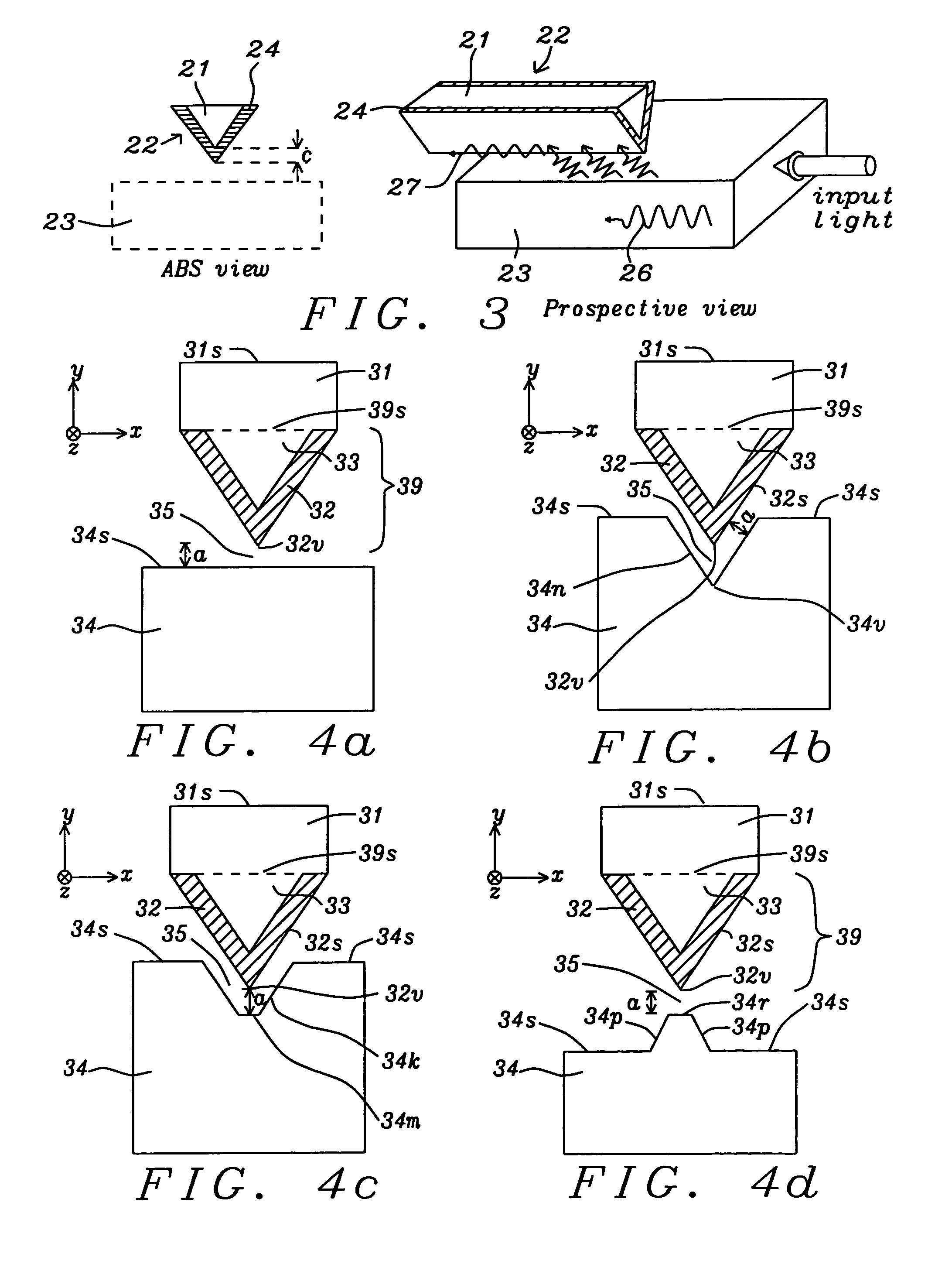
ActiveUS8036069B1Minimizing spot sizeReducing overall optical efficiencyCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsMagnetic mediaEngineering
A TAMR head is disclosed with a triangular shaped plasmon antenna covered on two sides with a plasmon layer that generates an edge plasmon mode along a vertex of the two plasmon sides formed opposite a main pole layer. A plasmon shield (PS) is formed along the ABS and opposite the vertex to confine an electric field from the edge plasmon mode within a small radius of the edge plasmon tip thereby reducing the optical spot size on the magnetic medium and enhancing writability. An end of a waveguide used to direct input electromagnetic radiation to the plasmon antenna adjoins a PS side opposite the ABS. In one embodiment, a magnetic shield may be formed along the ABS and adjoins the PS so that a first PS section terminates at the ABS and faces the vertex while a second PS section is formed between the magnetic shield and waveguide end.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Scanning system for inspecting anamolies on surfaces
InactiveUS20050110986A1Maintain consistencyReduce areaOptically investigating flaws/contaminationParticulatesOptical scanning
An optical scanning system and method for detecting anomalies, including pattern defects and particulate contaminants, on both patterned and unpatterned surfaces, using a light beam, scanning at a grazing angle with respect to the surfaces, a plurality of detectors and an interchannel communication scheme to compare data from each detector, which facilitates characterizing anomalies. The light beam illuminates a spot on the surface which is scanned over a short scan-line. The surface is moved in a manner so that the spot is scanned over its entire area in a serpentine fashion along adjacent striped regions. The plurality of detectors include groups of collector channels disposed circumferentially around the surface, a bright field reflectivity / autoposition channel, an alignment / registration channel and an imaging channel. The collector channels in each group are symmetrically disposed, in the azimuth, on opposite sides of the center of the scan line. The position of the collector channels, as well as the polarization of the beam, facilitates distinguishing pattern defects from particulate contaminants. The bright field reflectivity / autoposition channel is positioned to receive specularly reflected light that carries information concerning local variation in reflectivity, which is used to classify detected anomalies, as well as determine variations in the height of the surface. The alignment / registration channel is positioned to detect a maximum of the light scattered from the pattern on the surface to ensure that the streets of die present on the surface are oriented so as not to be oblique with respect to the scan line. The imaging channel combines the advantages of a scanning system and an imaging system while improving signal / background ratio of the present system.
Owner:NIKOONAHAD MEHRDAD +3
Imaging system
ActiveUS20110079730A1Sufficient wafer throughputHigh resolutionStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTarget surfaceLight beam
A charged particle multi-beamlet system for exposing a target (11) using a plurality of beamlets. The system comprises a charged particle source (1) for generating a charged particle beam (20), a beamlet aperture array (4D) for defining groups of beamlets (23) from the generated beam, a beamlet blanker array (6) comprising an array of blankers for controllably blanking the beamlets (23), a beam stop array (8) for blanking beamlets (23) deflected by the blankers, the beam stop array (8) comprising an array of apertures, each beam stop aperture corresponding to one or more of the blankers, and an array of projection lens systems (10) for projecting beamlets on to the surface of the target. The system images the source (1) onto a plane at the beam stop array (8), at the effective lens plane of the projection lens systems (10), or between the beam stop array (8) and the effective lens plane of the projection lens systems (10), and the system images the beamlet aperture array (4D) onto the target (11).
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Hydrophilic and phydrophobic mode sheet base special for biological chip
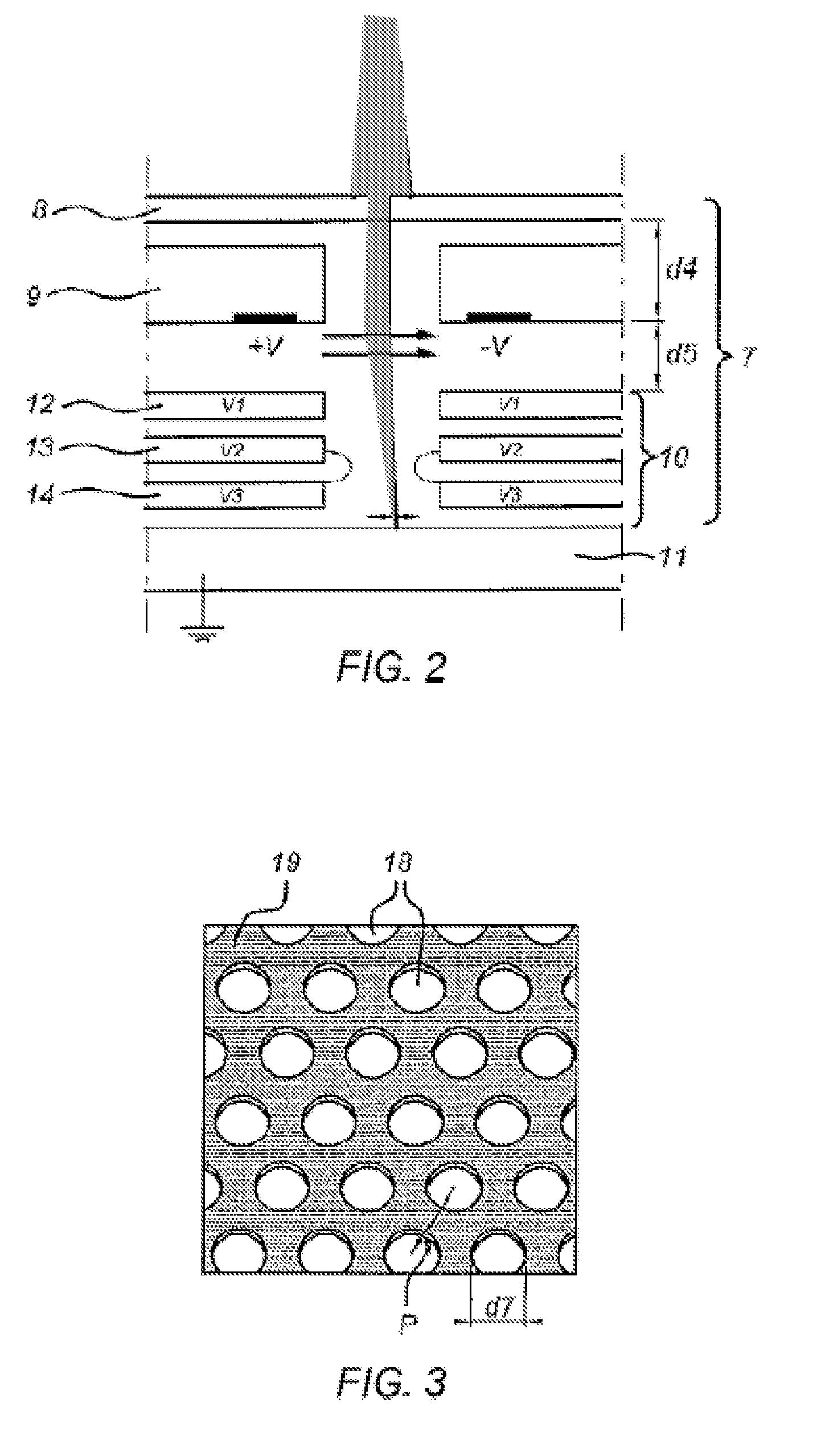
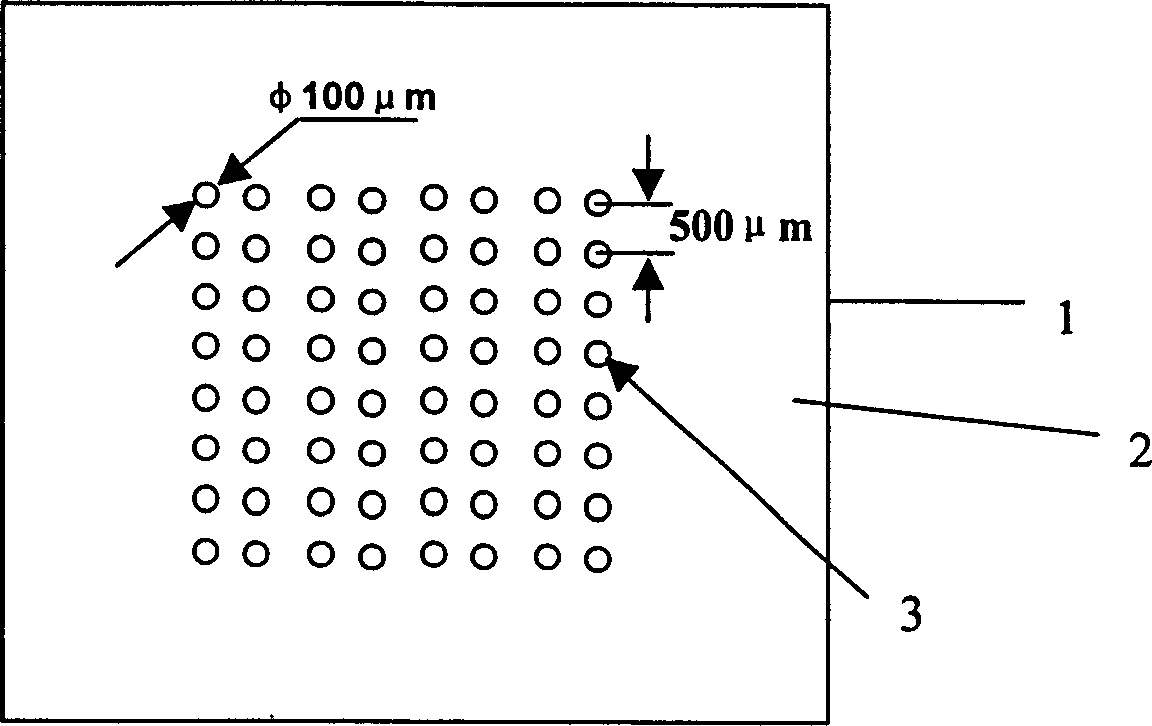
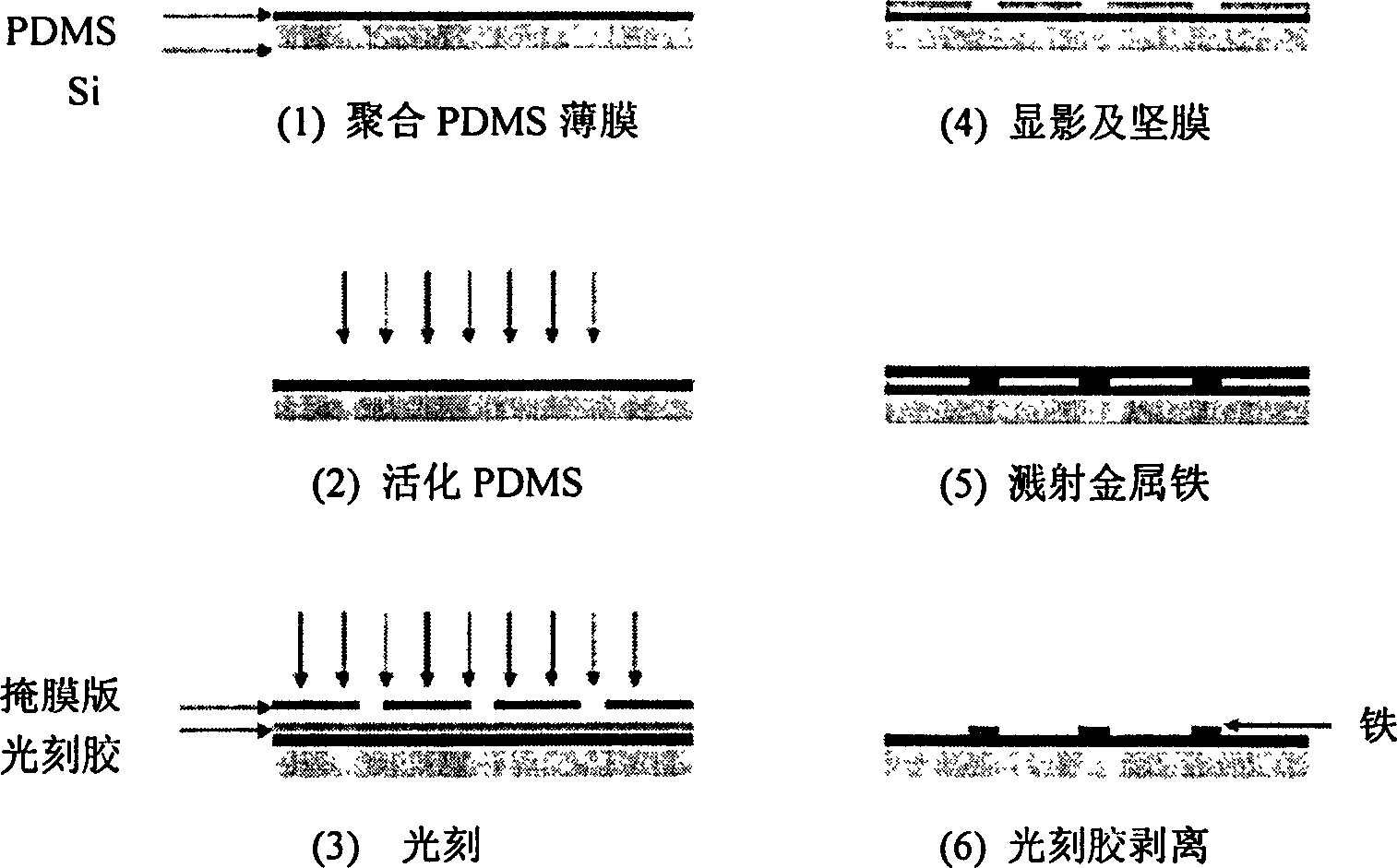
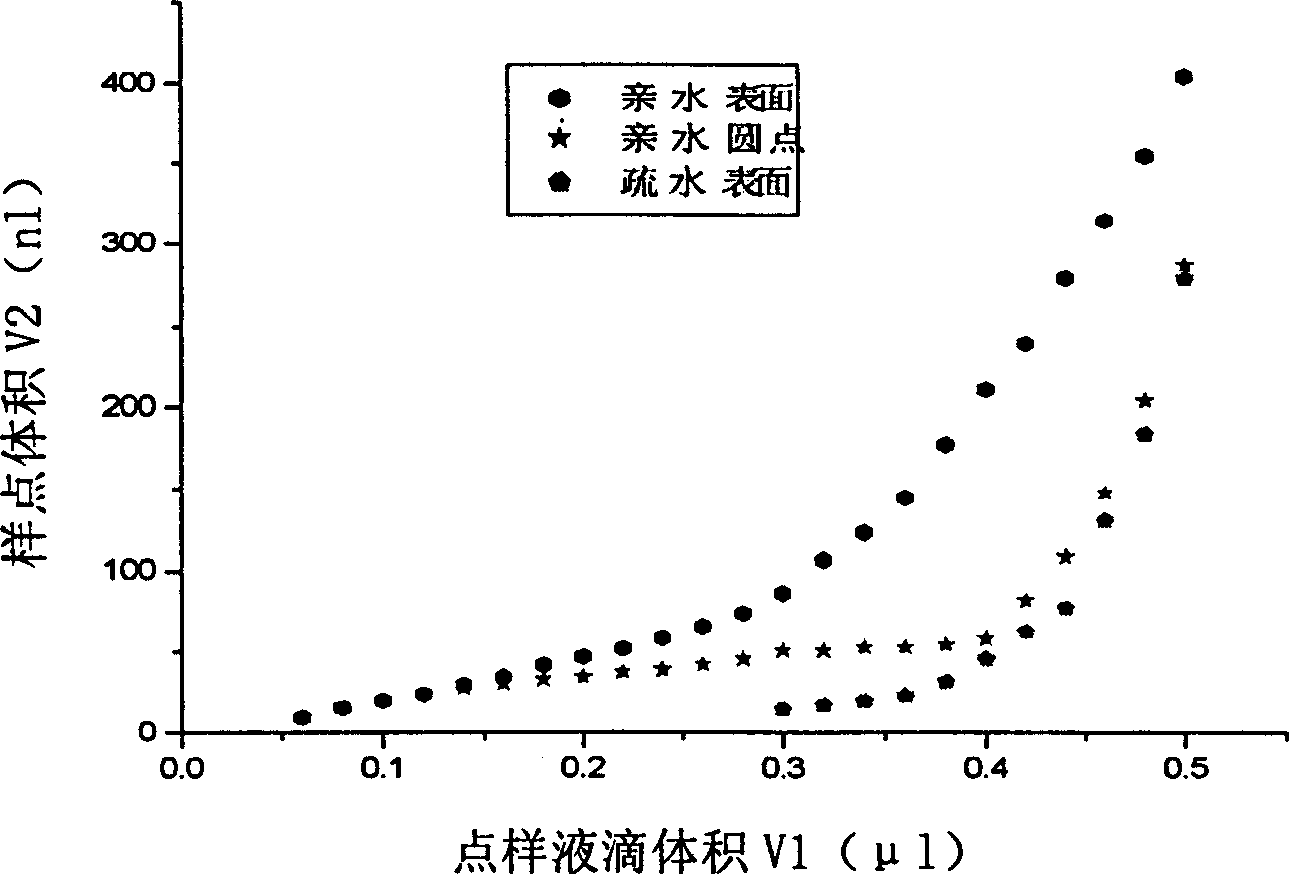
InactiveCN1858593ASmall spot sizeAvoid cross contaminationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFilm baseEngineering
This invention relates to a special hydrophilic and drain mode film base for biochips by providing a special hydrophilic and drain mode film base of a biochip having hydrophilic points in the same area and same size in a modified drain surface (thickness of the drain layer is 2-5mum) on a glass slide, silicon plate or other carriers, in which, shape, area, density and array arrangement can be decided according to the needs and the shape of the points are generally round, the film base has a substrate having a drain layer on the top surface and array hydrophilic points are distributed on the drain layer.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method and system for high-speed precise laser trimming and electrical device produced thereby
InactiveUS20060199354A1Precise TrimmingReduced stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistor manufactureHeat-affected zoneHigh absorption
A method and system are provided for high-speed, laser-based, precise laser trimming at least one electrical element along a trim path. The method includes generating a pulsed laser output with a laser, the output having one or more laser pulses at a repetition rate. A fast rise / fall time, pulse-shaped q-switched laser or an ultra-fast laser may be used. Beam shaping optics may be used to generate a flat-top beam profile. Each laser pulse has a pulse energy, a laser wavelength within a range of laser wavelengths, and a pulse duration. The wavelength is short enough to produce desired short-wavelength benefits of small spot size, tight tolerance, high absorption and reduced or eliminated heat-affected zone (HAZ) along the trim path, but not so short so as to cause microcracking. In this way, resistance drift after the trimming process is reduced.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Method and system for high-speed precise laser trimming, scan lens system for use therein and electrical device produced thereby
InactiveUS7358157B2Small spot sizeTight toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistor manufactureHigh absorptionPulse energy
A method, system and scan lens system are provided for high-speed, laser-based, precise laser trimming at least one electrical element. The method includes generating a pulsed laser output having one or more laser pulses at a repetition rate. Each laser pulse has a pulse energy, a laser wavelength within a range of laser wavelengths, and a pulse duration. The method further includes selectively irradiating the at least one electrical element with the one or more laser pulses focused into at least one spot having a non-uniform intensity profile along a direction and a spot diameter as small as about 6 microns to about 15 microns so as to cause the one or more laser pulses to selectively remove material from the at least one element and laser trim the at least one element while avoiding substantial microcracking within the at least one element. The wavelength is short enough to produce desired short-wavelength benefits of small spot size, tight tolerance and high absorption, but not so short so as to cause microcracking.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Method and system for high-speed precise laser trimming and scan lens for use therein
InactiveUS20070178714A1Precise TrimmingReduced stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistor manufactureHigh absorptionHeat-affected zone
A method, system and scan lens for use therein are provided for high-speed, laser-based, precise laser trimming at least one electrical element along a trim path. The method includes generating a pulsed laser output with a laser, the output having one or more laser pulses at a repetition rate. A fast rise / fall time, pulse-shaped q-switched laser or an ultra-fast laser may be used. Beam shaping optics may be used to generate a flat-top beam profile. Each laser pulse has a pulse energy, a laser wavelength within a range of laser wavelengths, and a pulse duration. The wavelength is short enough to produce desired short-wavelength benefits of small spot size, tight tolerance, high absorption and reduced or eliminated heat-affected zone (HAZ) along the trim path, but not so short so as to cause microcracking. In this way, resistance drift after the trimming process is reduced.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Metal layer having aperture, method of forming the same, light delivery module including metal layer having aperture, and heat assisted magnetic recording head including the same
InactiveUS20080055343A1Power throughput can be diminishedSmall spot sizeRecording by magnetic meansLayered productsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingLight delivery
A metal layer having an aperture for delivering light, a method of forming the same, a light delivery module including the metal layer having the aperture, and a heat assisted magnetic recording head including the same are provided. The aperture of the metal layer has an inlet and an outlet of different sizes, and also has curved side surfaces. Also, the light delivery module includes the metal layer at an output end thereof, and the heat assisted magnetic recording head includes the light delivery module as an optical heating unit.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH INT
Laser atom probe
ActiveUS7683318B2Less heatHeat dissipation fastLaser detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationArrival timeAtom probe
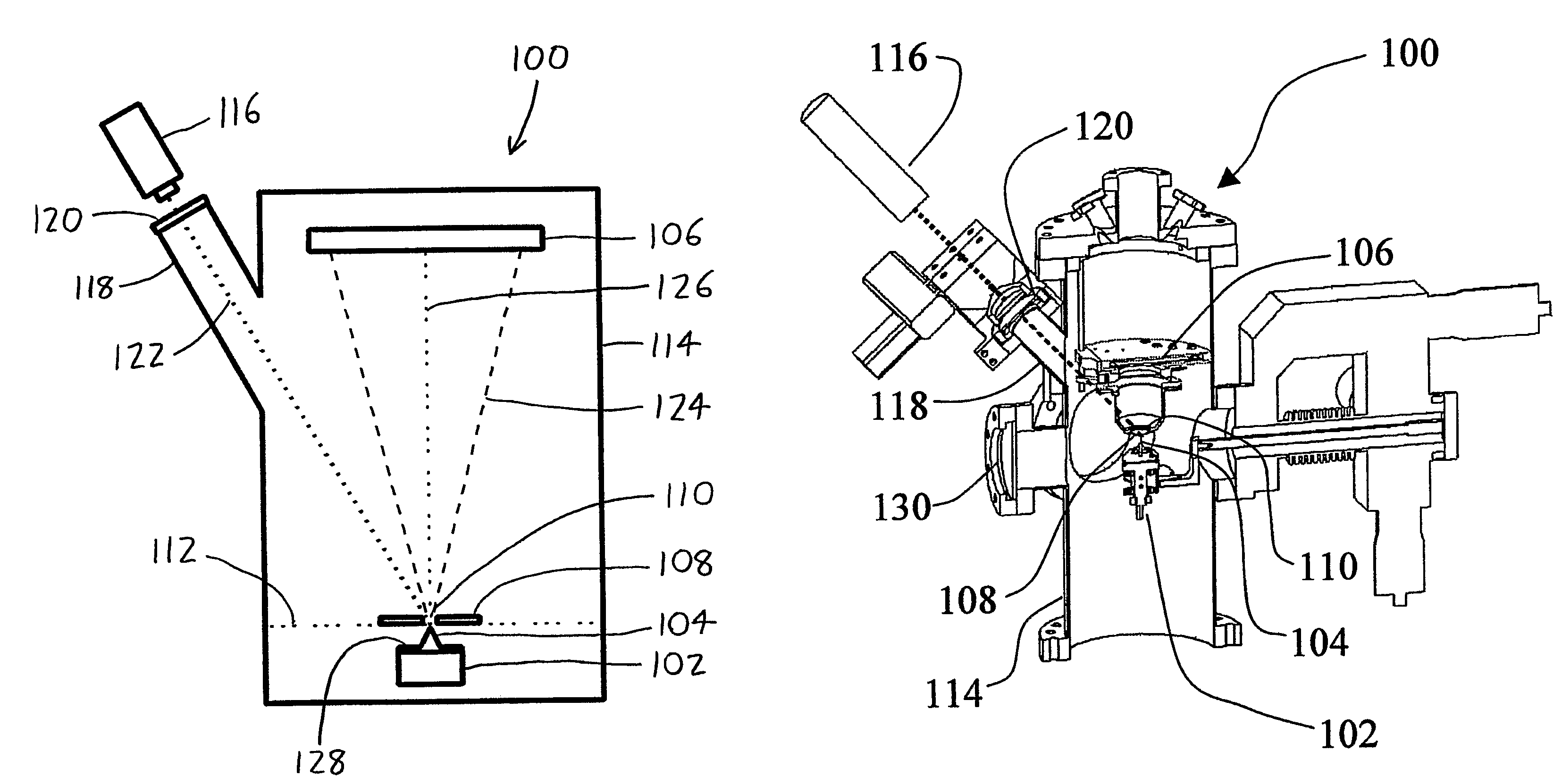
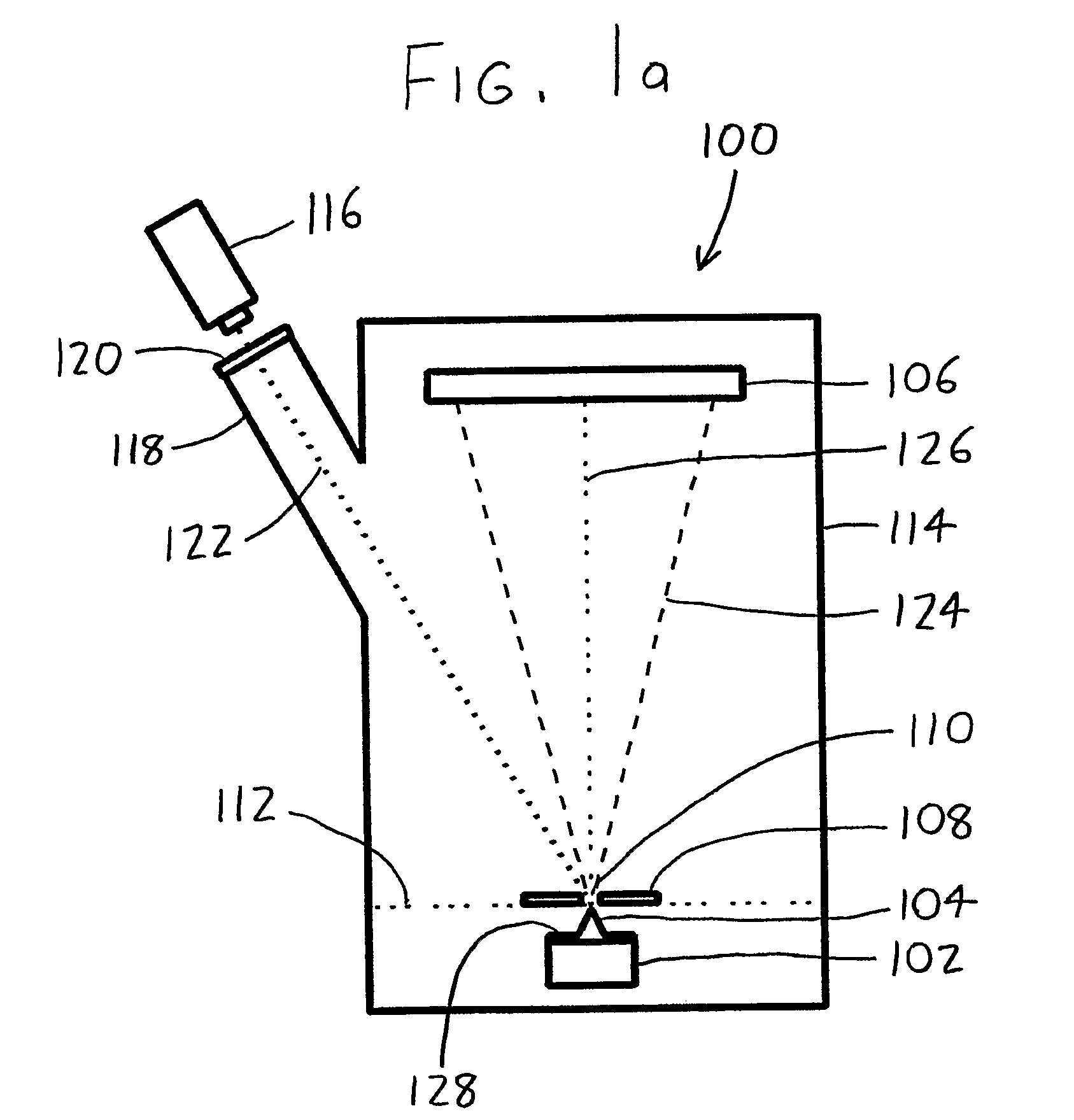
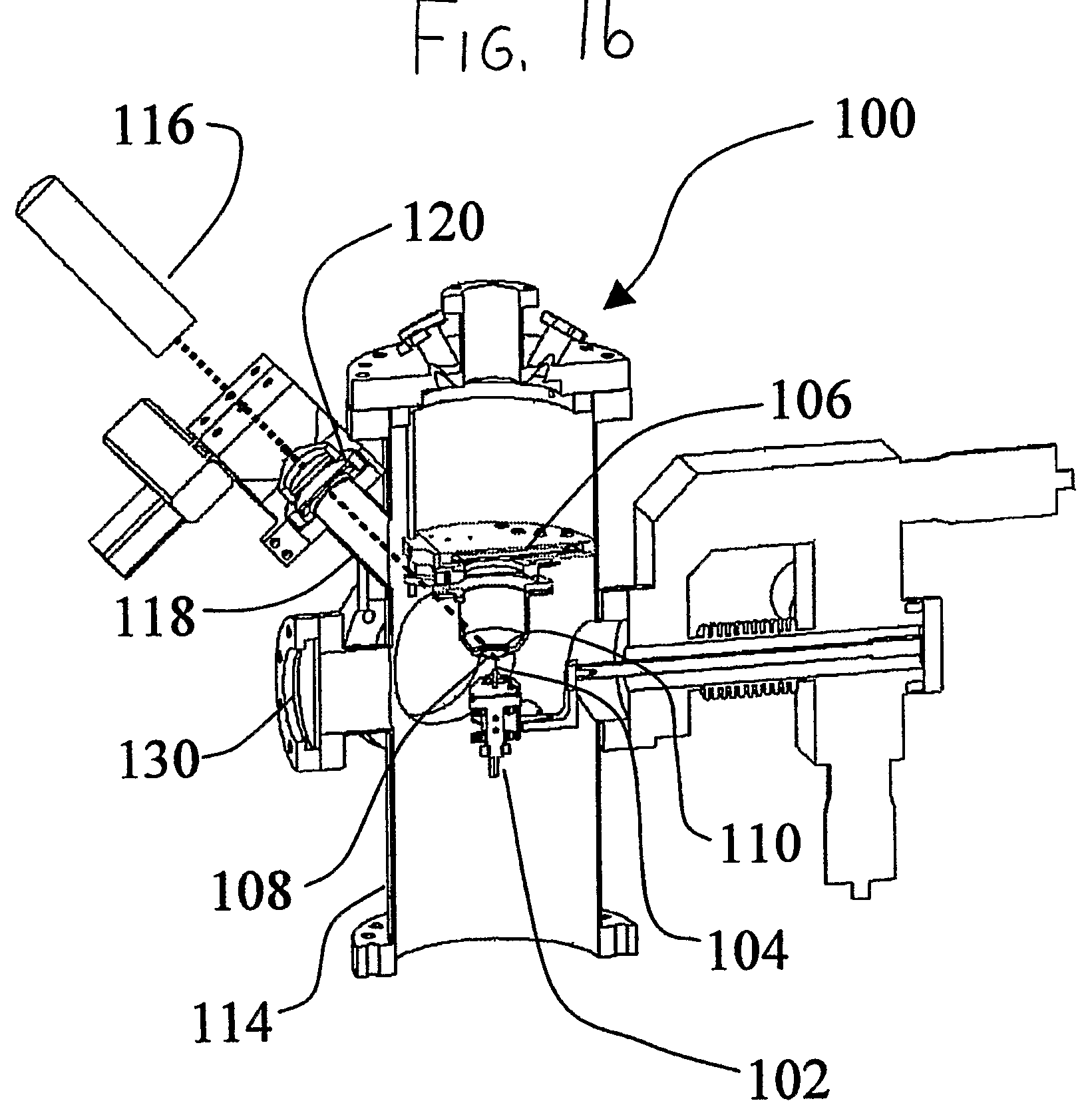
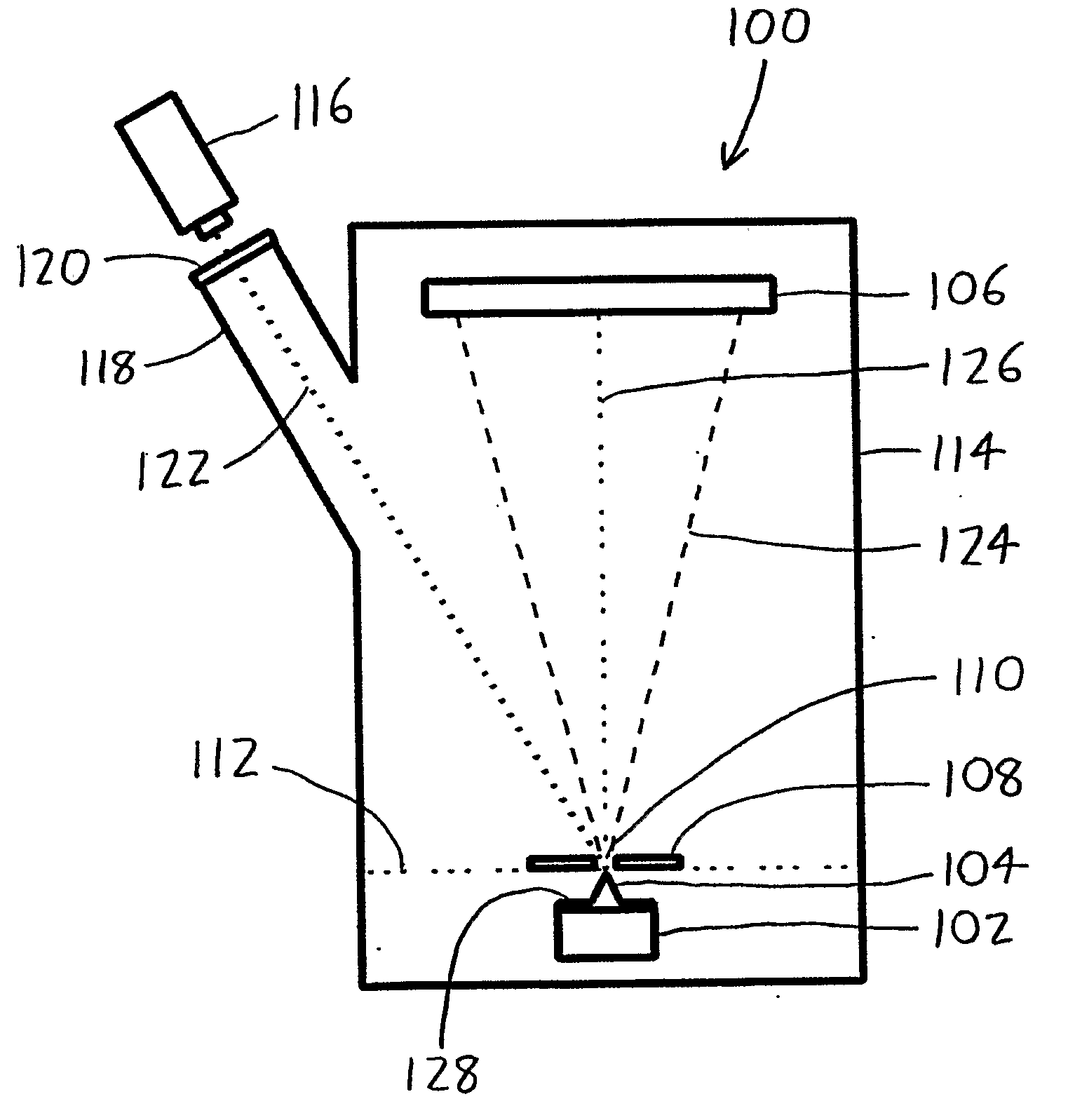
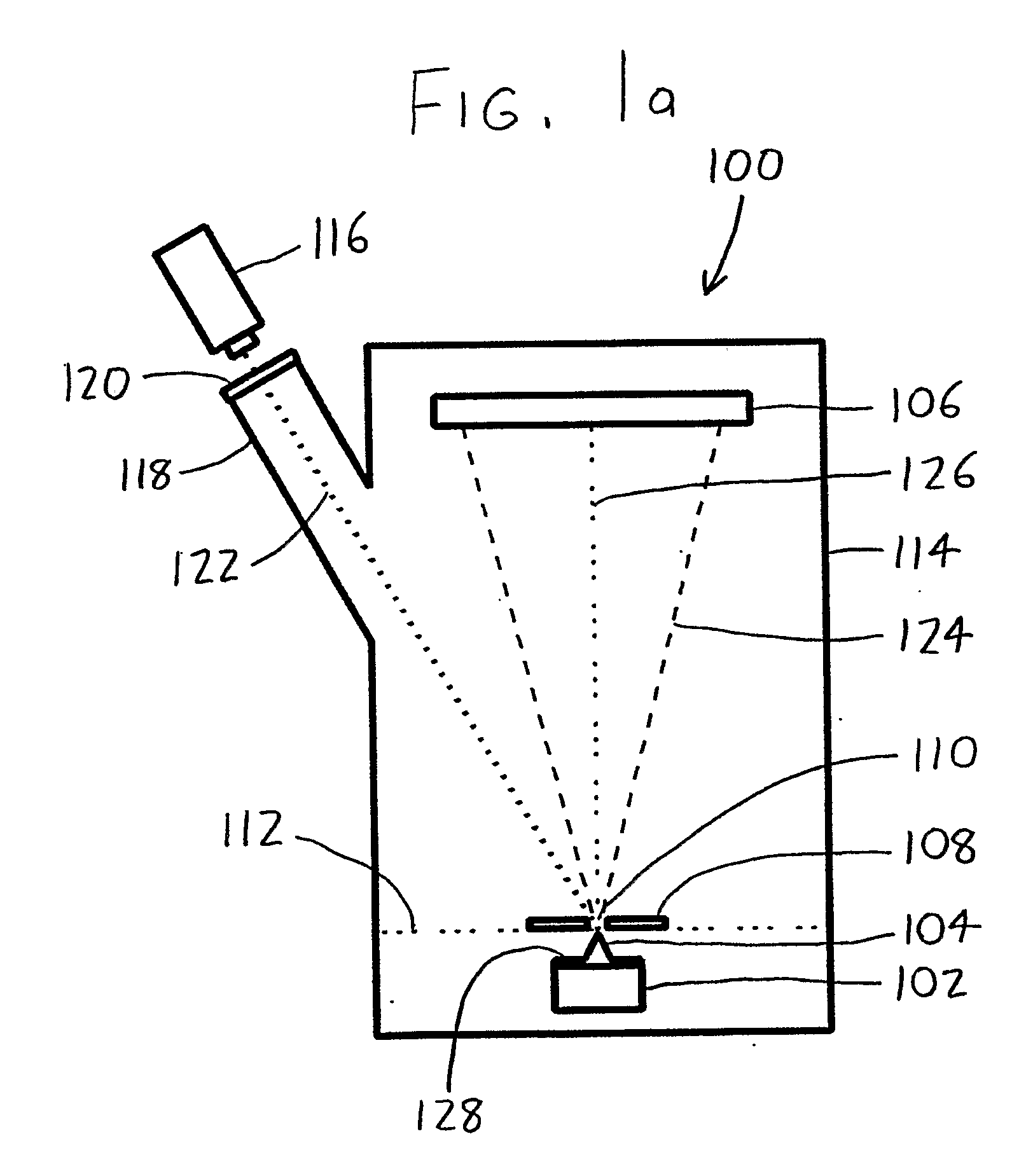
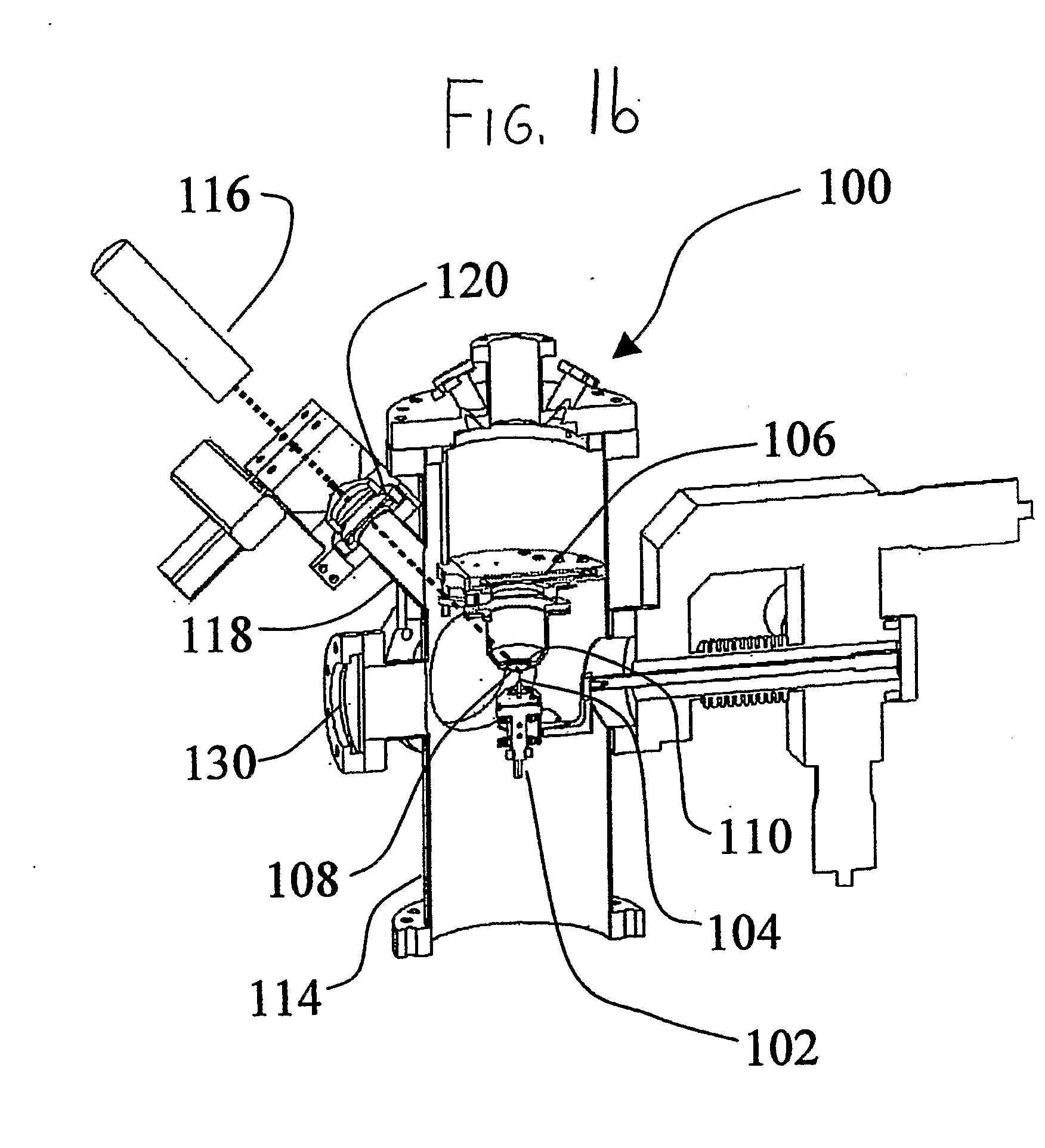
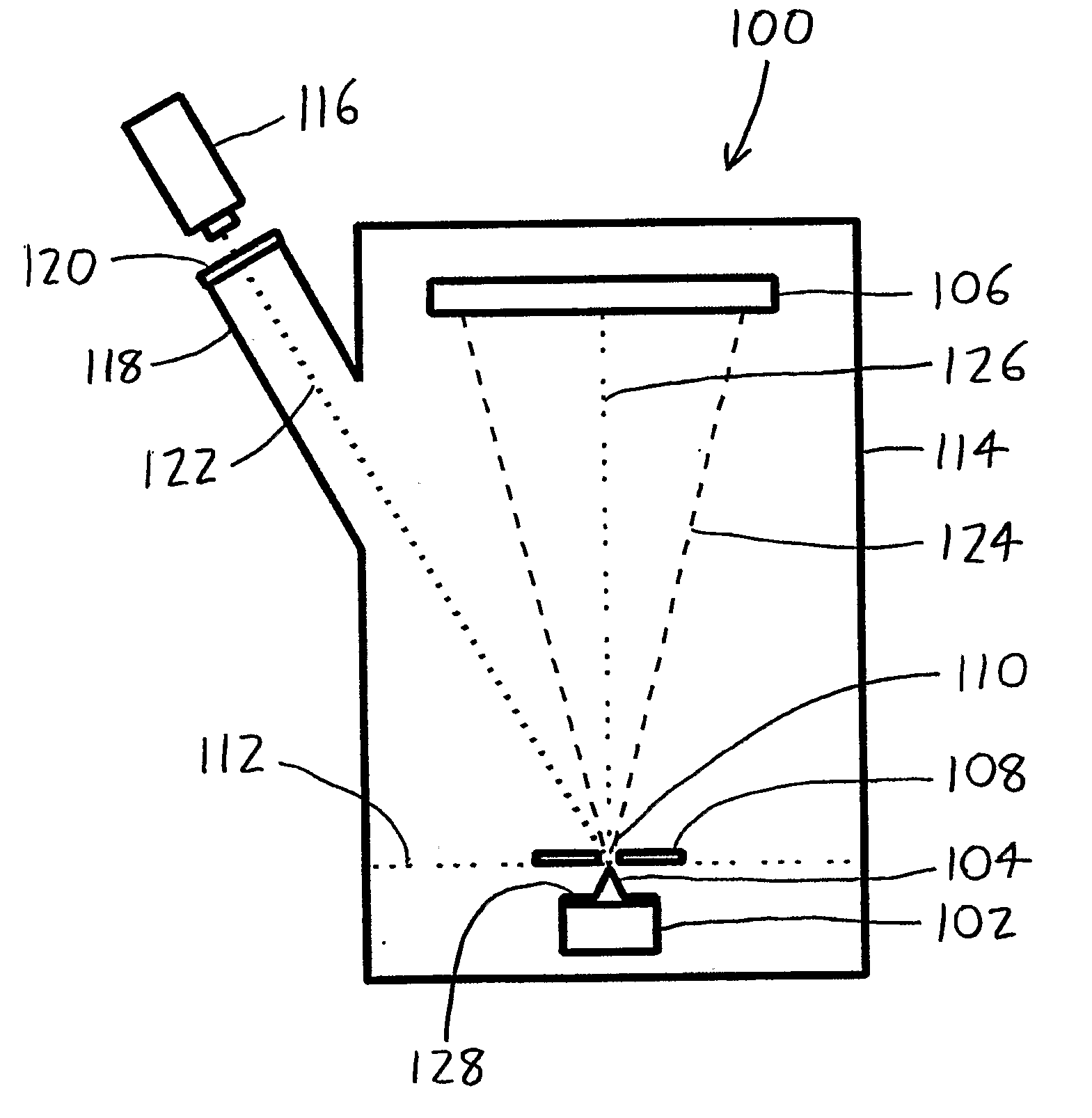
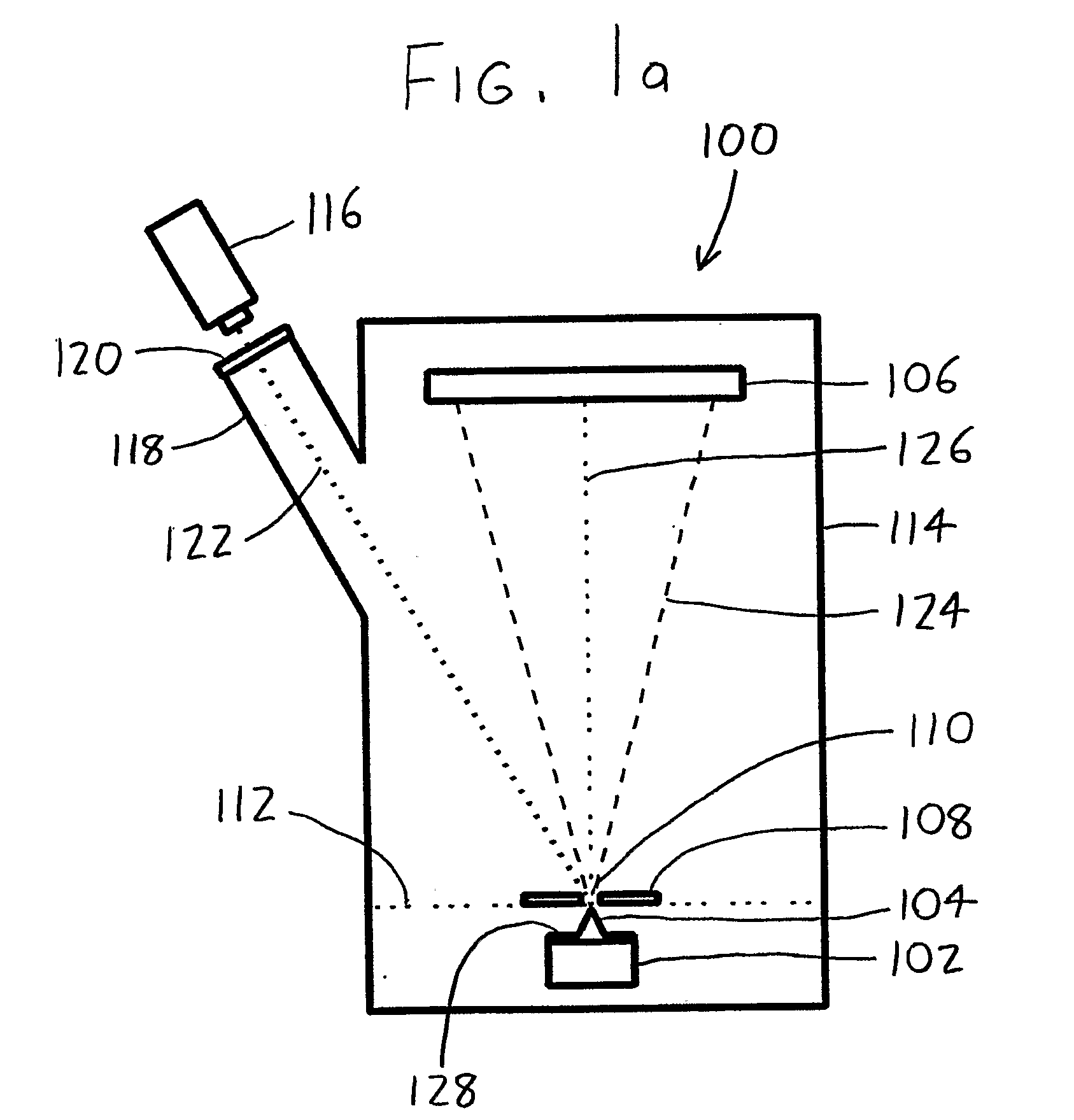
A laser atom probe (100) situates a counter electrode between a specimen mount and a detector (106), and provides a laser (116) having its beam (122) aligned to illuminate the specimen (104) through the aperture (110) of the counter electrode (108). The detector, specimen mount (102), and then be pulsed to bring the specimen to ionization. The timing of the laser pulses may be used to determine ion departure and arrival times allowing determination of the mass-to-charge ratios of the ions, thus their identities. Automated alignment methods are described wherein the laser is automatically directed to areas of interest.
Owner:CAMECA INSTR
Laser atom probe methods
ActiveUS20070181826A1Increase profitEfficient analysisPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansArrival timeIonization
A laser atom probe (100) situates a counter electrode between a specimen mount and a detector (106), and provides a laser (116) having its beam (122) aligned to illuminate the specimen (104) through the aperture (110) of the counter electrode (108). The detector, specimen mount (102), and / or the counter electrode may be charged to some boost voltage and then be pulsed to bring the specimen to ionization. The timing of the laser pulses may be used to determine ion departure and arrival times allowing determination of the mass-to-charge ratios of the ions, thus their identities. Automated alignment methods are described wherein the laser is automatically directed to areas of interest.
Owner:CAMECA INSTR
Laser Atom Probe
ActiveUS20070205358A1Increase profitEfficient analysisLaser detailsTime-of-flight spectrometersLight beamArrival time
A laser atom probe (100) situates a counter electrode between a specimen mount and a detector (106), and provides a laser (116) having its beam (122) aligned to illuminate the specimen (104) through the aperture (110) of the counter electrode (108). The detector, specimen mount (102), and then be pulsed to bring the specimen to ionization. The timing of the laser pulses may be used to determine ion departure and arrival times allowing determination of the mass-to-charge ratios of the ions, thus their identities. Automated alignment methods are described wherein the laser is automatically directed to areas of interest.
Owner:CAMECA INSTR
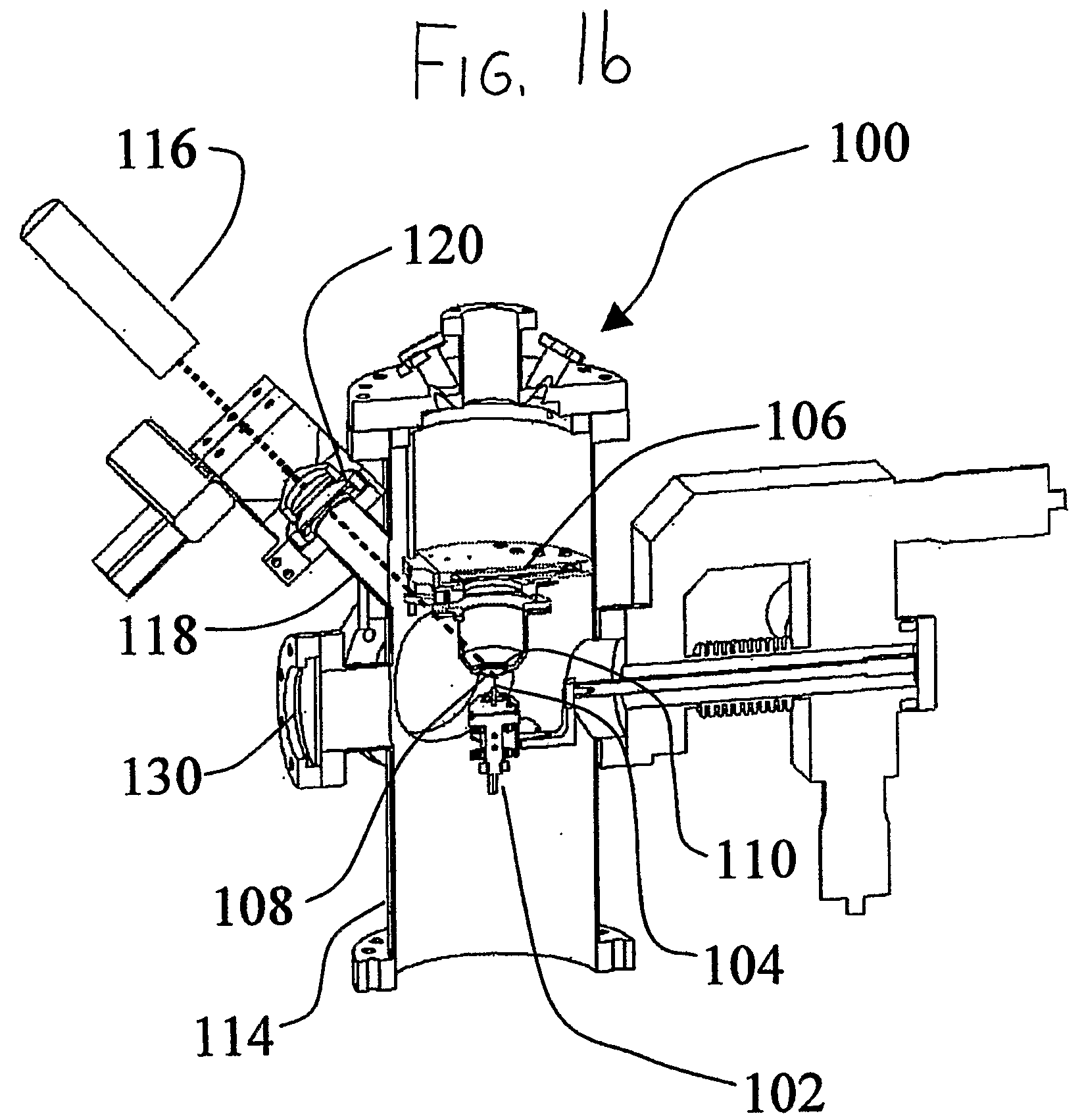
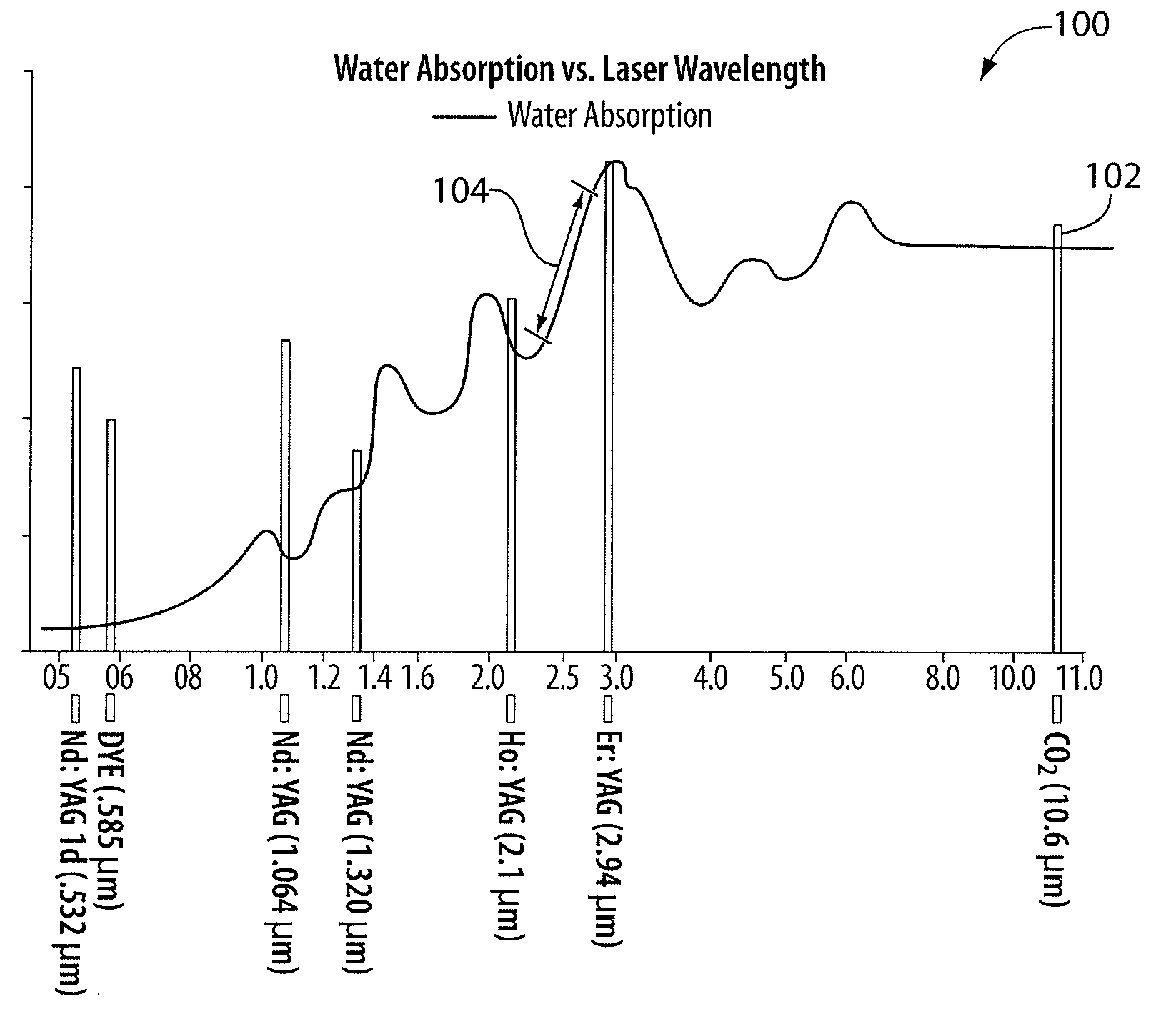
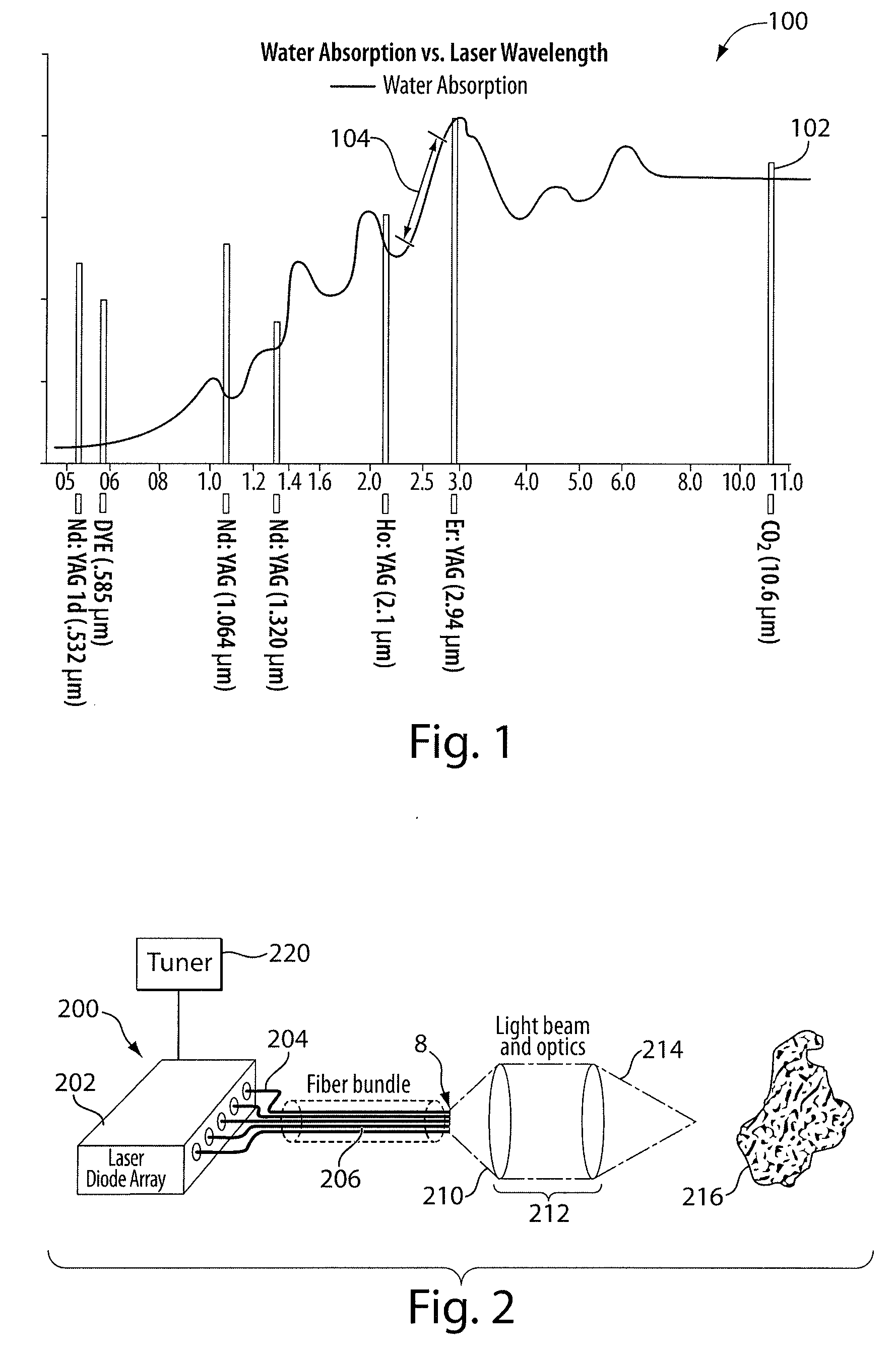
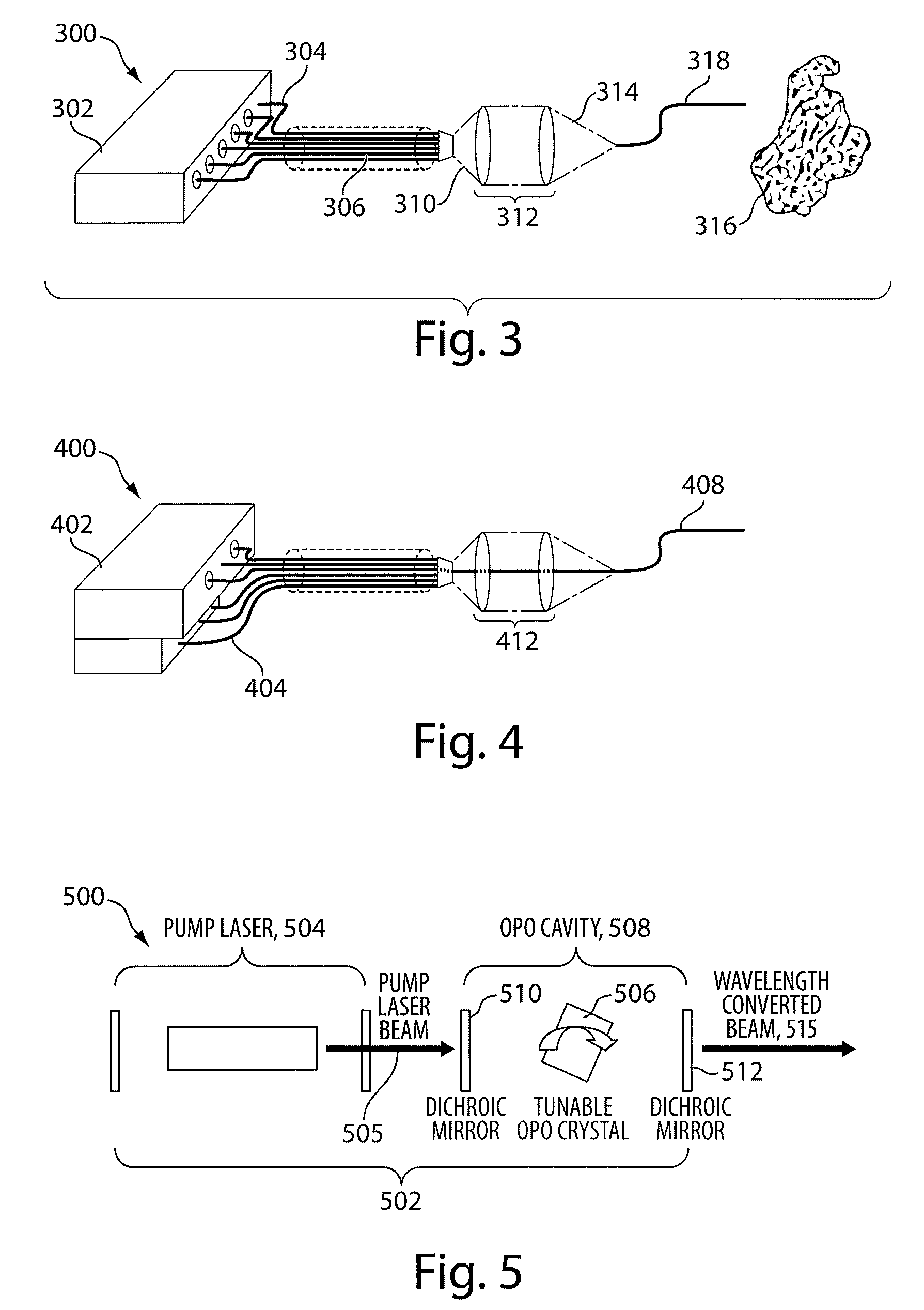
System and Method for Lasers in Surgical Applications
ActiveUS20090275927A1Convenient for surgical useSmall spot sizeExcitation process/apparatusSurgical instrument detailsLength wavePhysics
Disclosed is a surgical laser system. The system includes a laser generator to generate laser radiation to cause water absorption levels that approximate water absorption levels achieved with a CO2 laser, and one or more fibers coupled to the laser generator to deliver the generated laser radiation. In some embodiments, the laser generator is configured to generate radiation at multiple possible wavelengths in a range of between about 2.4 μm to about 2.75 μm.
Owner:LUMENIS LTD
Light condensing optical system, laser processing method and apparatus, and method of manufacturing fragile material
ActiveUS20100065537A1Reduce intensitySmall spot sizeRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansLaser processingLight spot
A condensing optical system having a condensed light spot with a small size and a large focal depth without causing a problem of a decrease in intensity of the condensed light spot or discontinuity of an intensity distribution in front and rear areas of a focal position is provided. The condensing optical system that condenses a laser beam generated by a laser source at a predetermined focal length is designed to satisfy Expressions (a) to (d), thereby producing 3rd and 5th spherical aberrations:|Z8|≧0.1λ or |Z15|≧0.05λ, (a)Z8 / Z15≧3 or Z8 / Z15<1, (b)|Z8|<1.4λ, and (c)|Z15|<0.5λ, (d)where λ is a wavelength, Z8 is an 8th coefficient of coefficients of the Zernike fringe polynomial of wavefront aberration corresponding to a 3rd order spherical aberration, and Z15 is a 15th coefficient of the coefficients of the Zernike fringe polynomial of wavefront aberration corresponding to a 5th spherical aberration.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
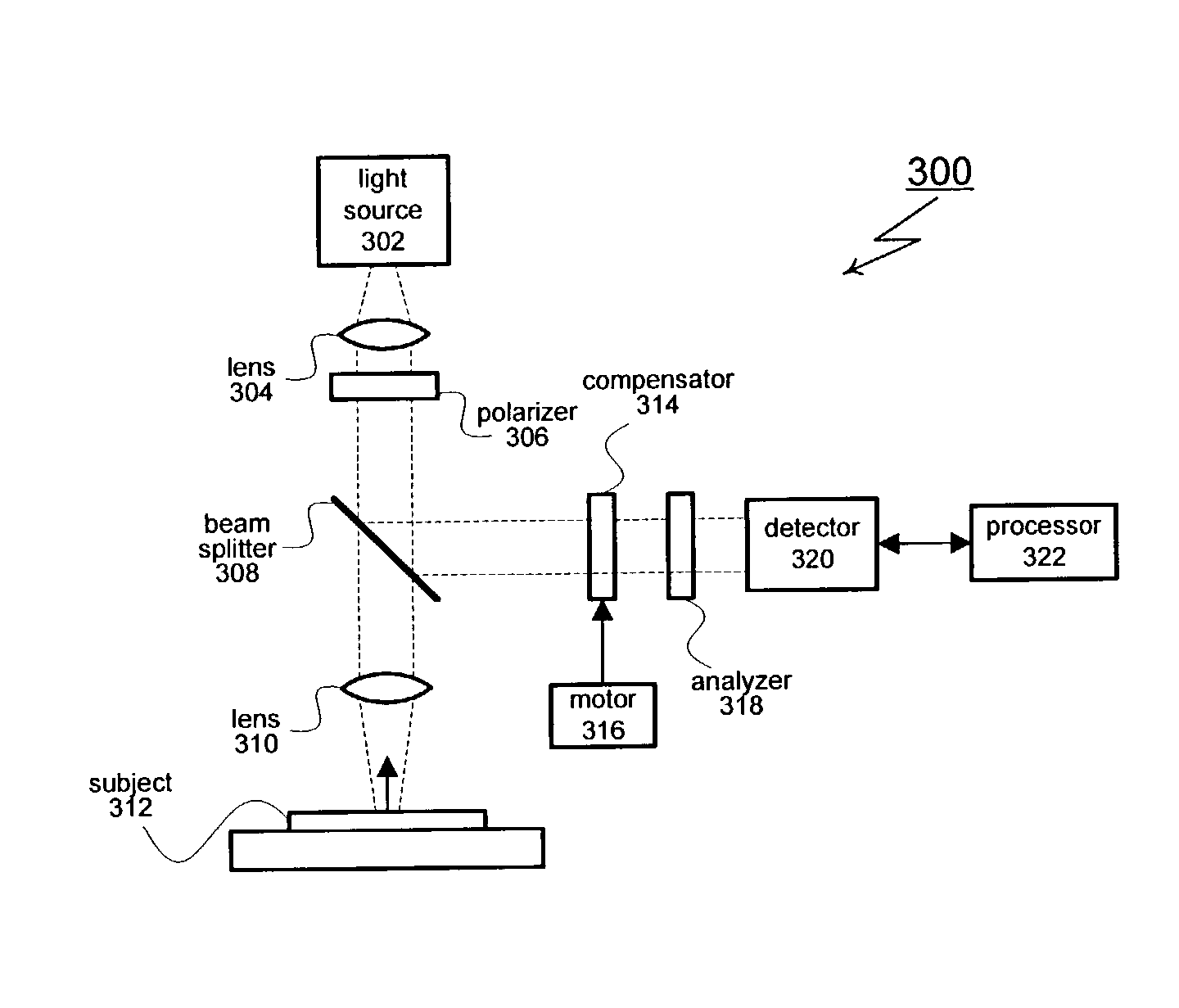
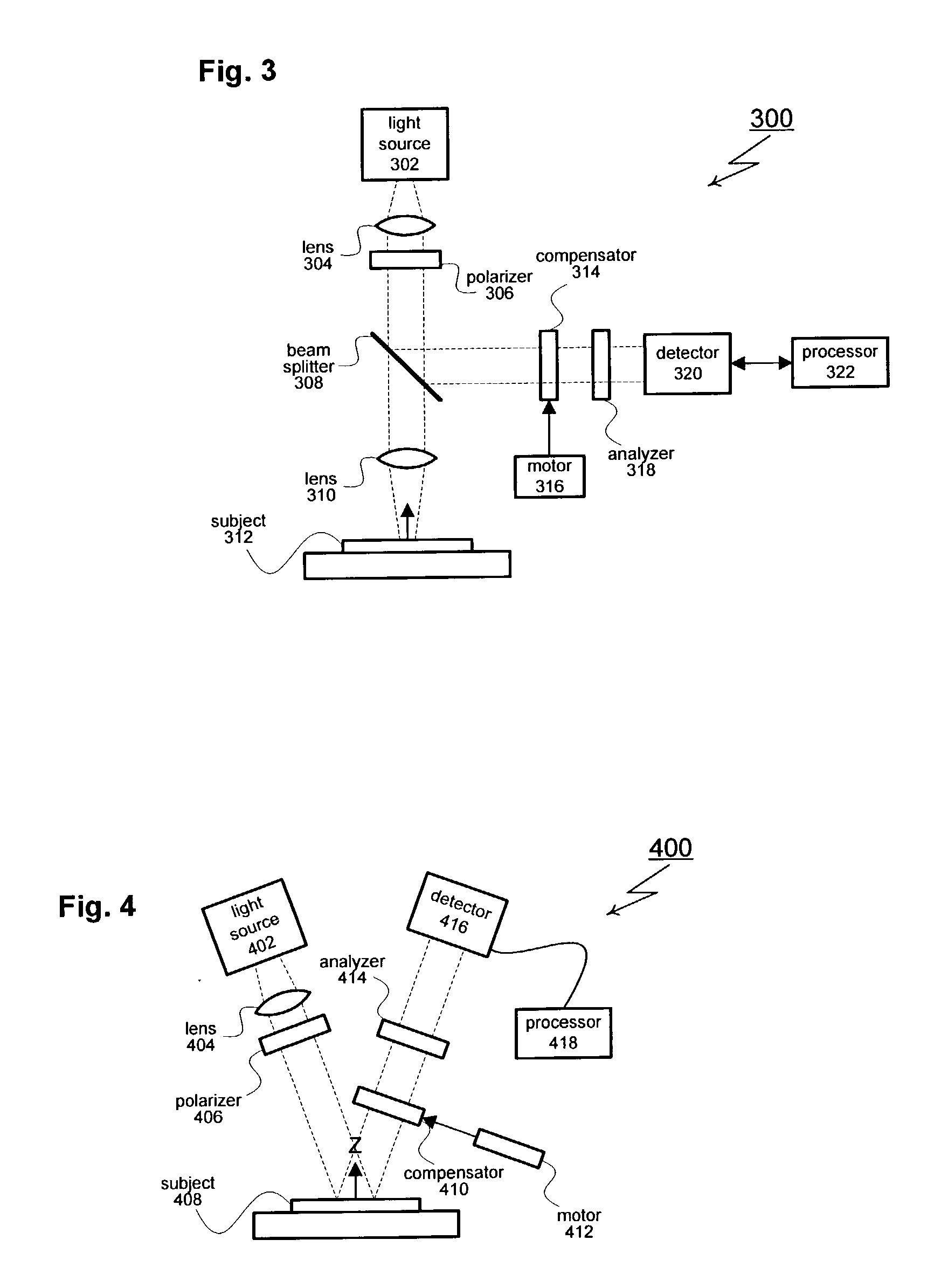
Spectroscopic ellipsometer and polarimeter systems
InactiveUS7336361B1Minimize stressMinimize stress induced birefringence.Material analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementPolarimeterPolarizer
A spectroscopic ellipsometer or polarimeter system having a source of a polychromatic beam of electromagnetic radiation, a polarizer, a stage for supporting a material system, an analyzer, a dispersive optics and a detector system which comprises a multiplicity of detector elements, there being apertures before the stage for supporting a material system, and thereafter, the system further having at least one multi-element lens and optionally being present in an environmental control chamber.
Owner:J A WOOLLAM CO
Optical coupling device and process for fabrication thereof
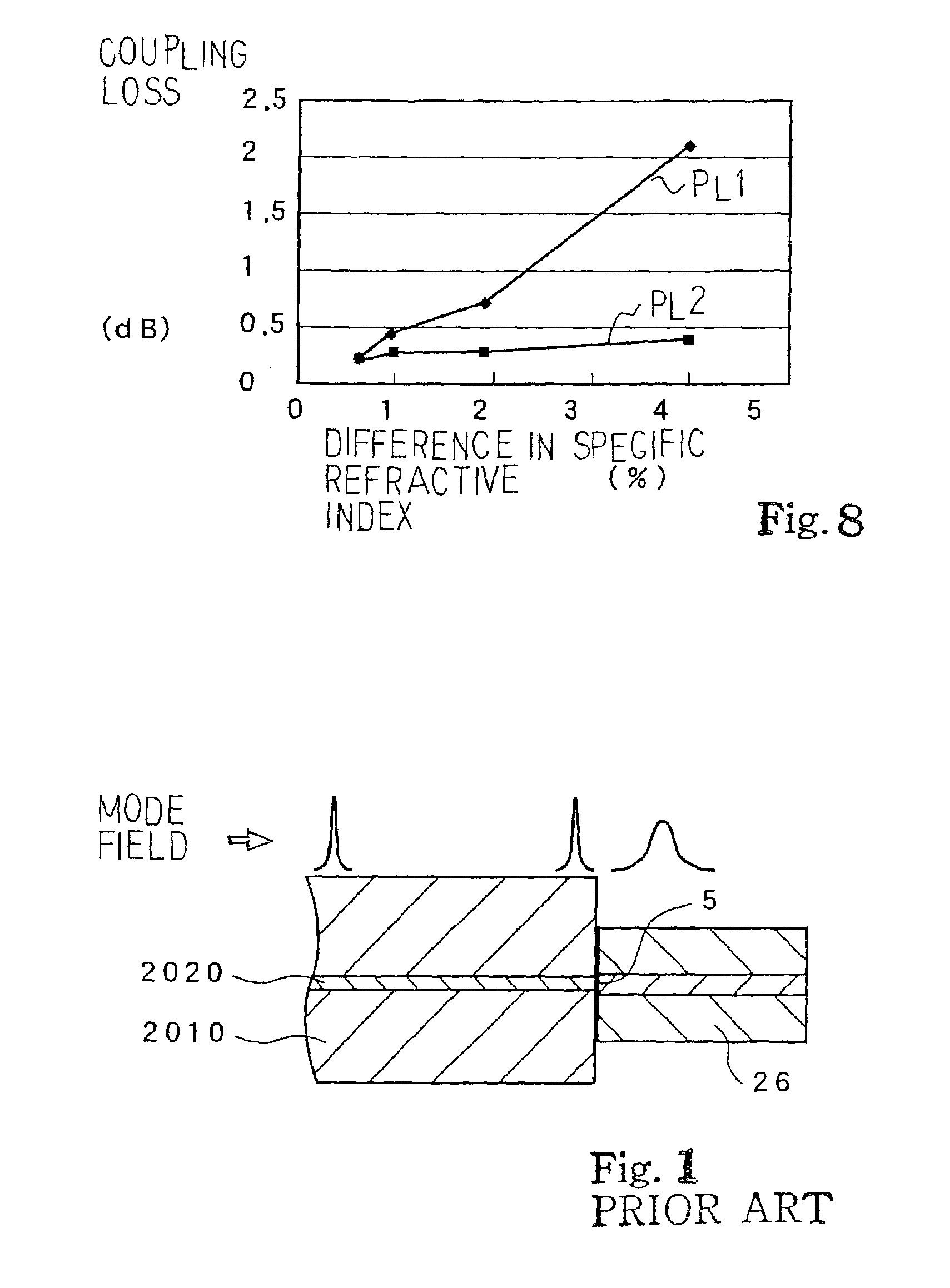
InactiveUS7099540B2Increase of coupling lossSmall spot sizeCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexComputational physics
An optical coupling device has an optical wave-guide varied in difference in specific refractive index between a clad layer and a core layer, and the optical wave-guide serves as a convergent / divergent spot size converter; since reduction in cross section of the core layer is not required for the convergent / divergent spot size converter so that the optical coupling device is produced at a high production yield.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical measurement device and method
ActiveUS20050275845A1Small spot sizeCertain level of sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesOptical pathOptical measurements
A system and method are presented for measurement on an article. The system comprises an illuminator for producing light of at least one predetermined wavelength range; an optical system; a displacement arrangement; and a control system. The optical system is configured to define at least a measurement channel, and comprises a light directing assembly for directing an input light beam, propagating along an input light path from the illuminator, onto the article and directing a light beam returned from the illuminated region of the article to at least one light detector. The displacement arrangement is associated with at least the light directing assembly of the optical system, and is configured and operable by the control system to rotate said at least light directing assembly of the optical system with respect to a stage supporting the article about a rotational axis substantially normal to the stage.
Owner:NOVA MEASURING INSTR LTD
Scatterometry to simultaneously measure critical dimensions and film properties
ActiveUS20050041250A1Spot be very smallAccurately analyzedPolarisation-affecting propertiesUsing optical meansPolarizerAngle of incidence
An ellipsometer includes a light source for generating a probe beam of polychromatic light for interacting with a sample. A polarizer is used to impart a known polarization state to the probe beam and the polarized probe beam is directed against the sample at a shallow angle of incidence. A rotating compensator is used to impart phase retardations to the polarization state of the reflected probe beam. After passing through the compensator, the probe beam passes through a second polarizer (analyzer). After leaving the analyzer, the probe beam is received by a detector. The detector translates the received probe beam into a signal that includes DC, 2ω and 4ω signal components (where ω is the angular velocity of the rotating compensator). A processor analyzes the signal using the DC, 2ω and 4ω components allowing simultaneous evaluation of both critical dimensions and film parameters.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
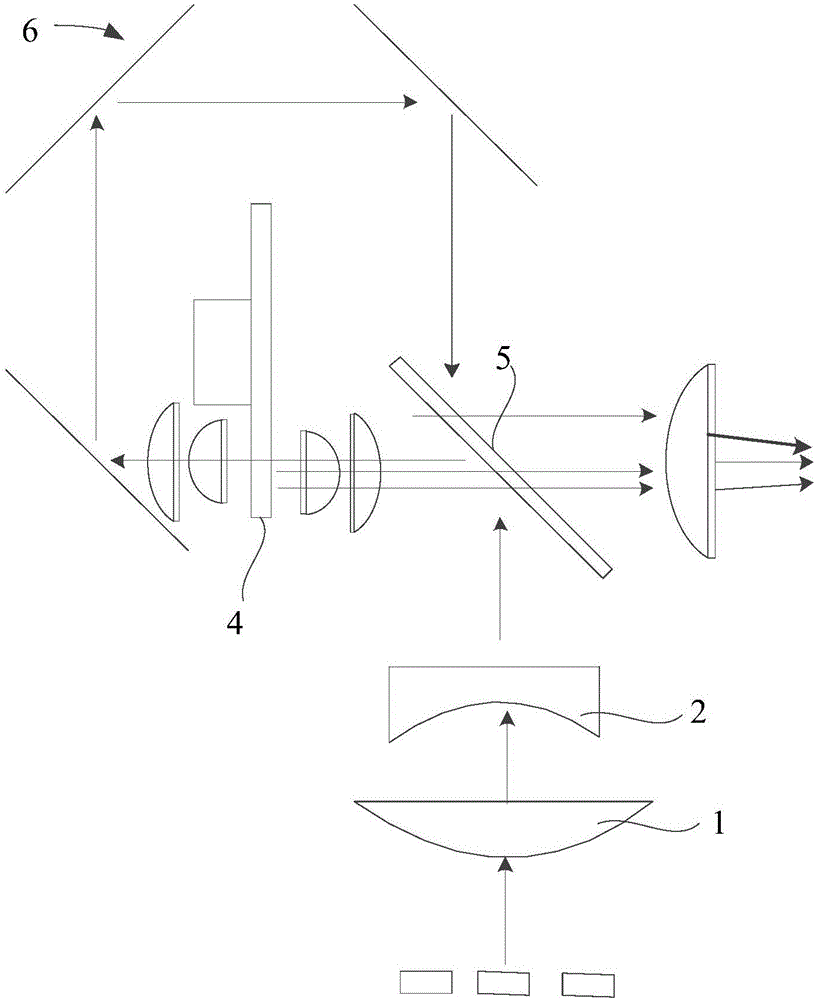
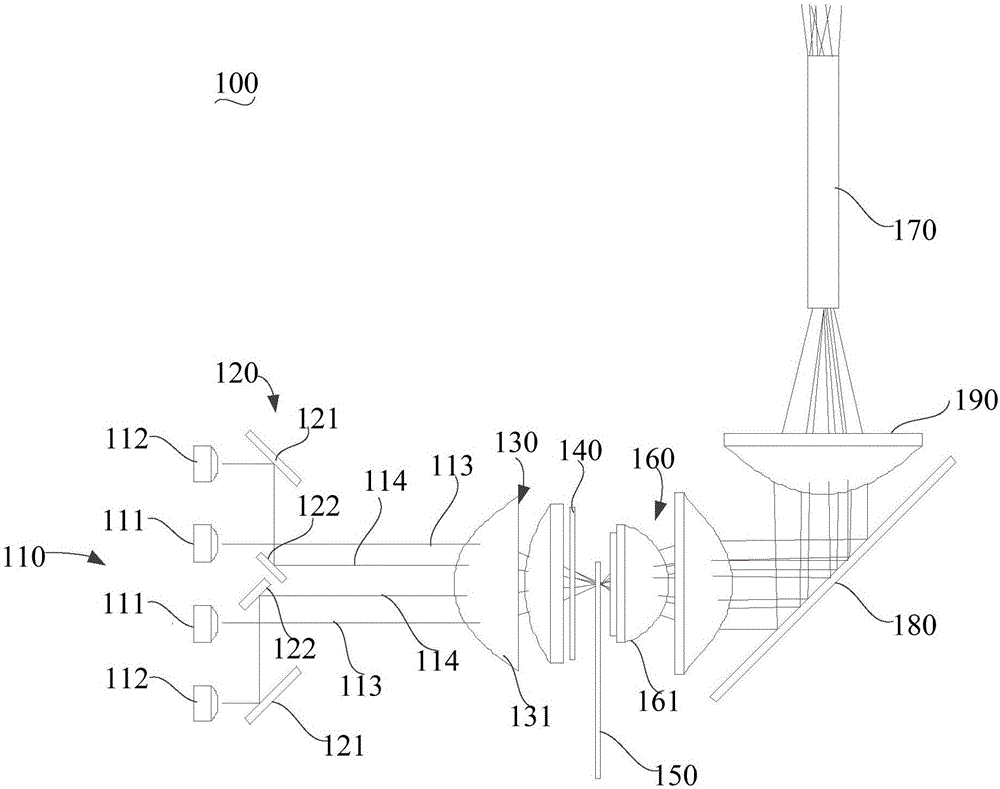
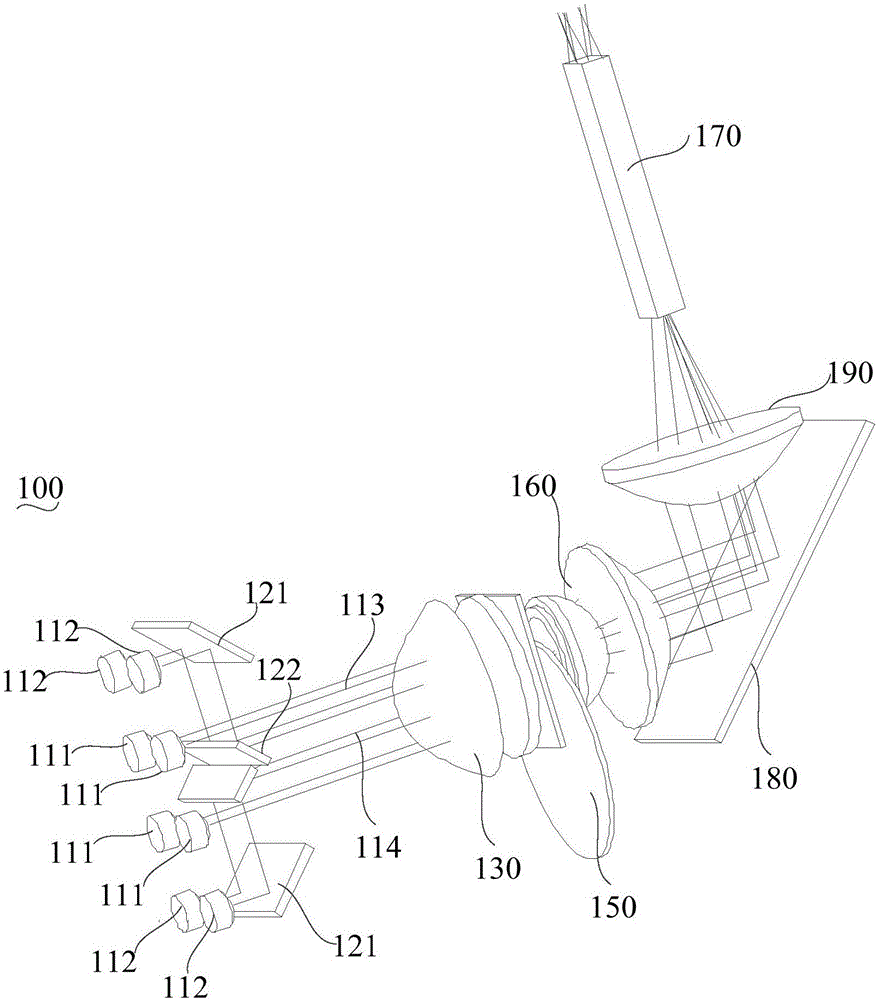
Laser light source and laser projection device
The invention provides a laser projection device and a laser light source thereof. The laser light source comprises a laser array and a plurality of beam-contraction reflectors. The laser array consists of a main laser and secondary lasers arranged at the two sides of the main laser; the main laser is arranged at the middle part of the laser array and emits a main light beam; and the secondary lasers emit secondary light beams. The beam-contraction reflectors include first reflection planes and second reflection planes. According to the laser light source, the secondary light beams emitted by the secondary lasers are reflected by the first reflection planes and the second reflection planes and thus the secondary light beams located at the two sides of the main light beam approach the main light beam, thereby achieving an objective of beam contraction. Therefore, a telescopic system with a small diameter dimension can meet the using requirement; the size of the overall laser light source is reduced; and microminiaturization development of the laser projection device can be realized well.
Owner:HISENSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com