Patents
Literature
468 results about "Adaptive optics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
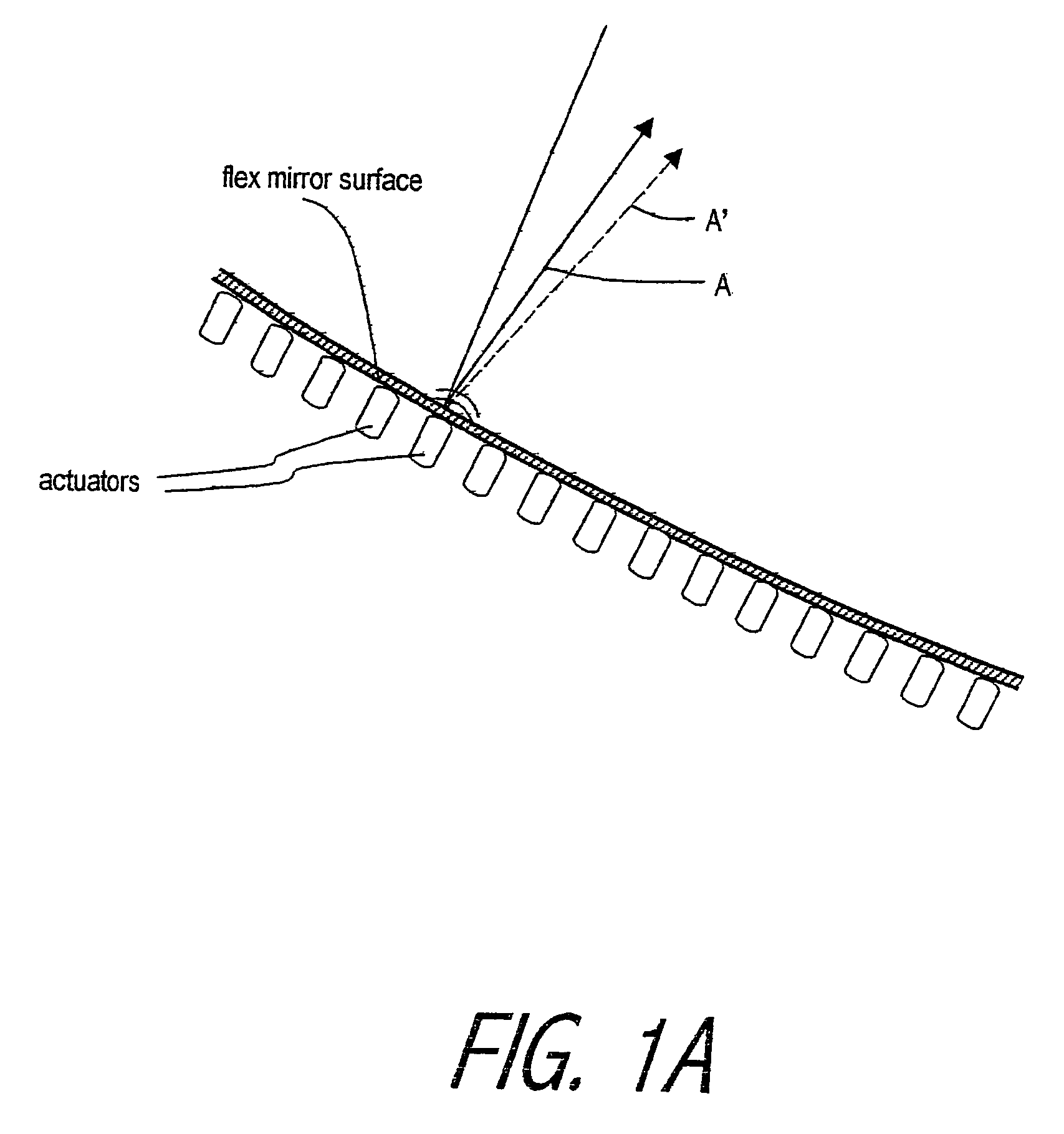
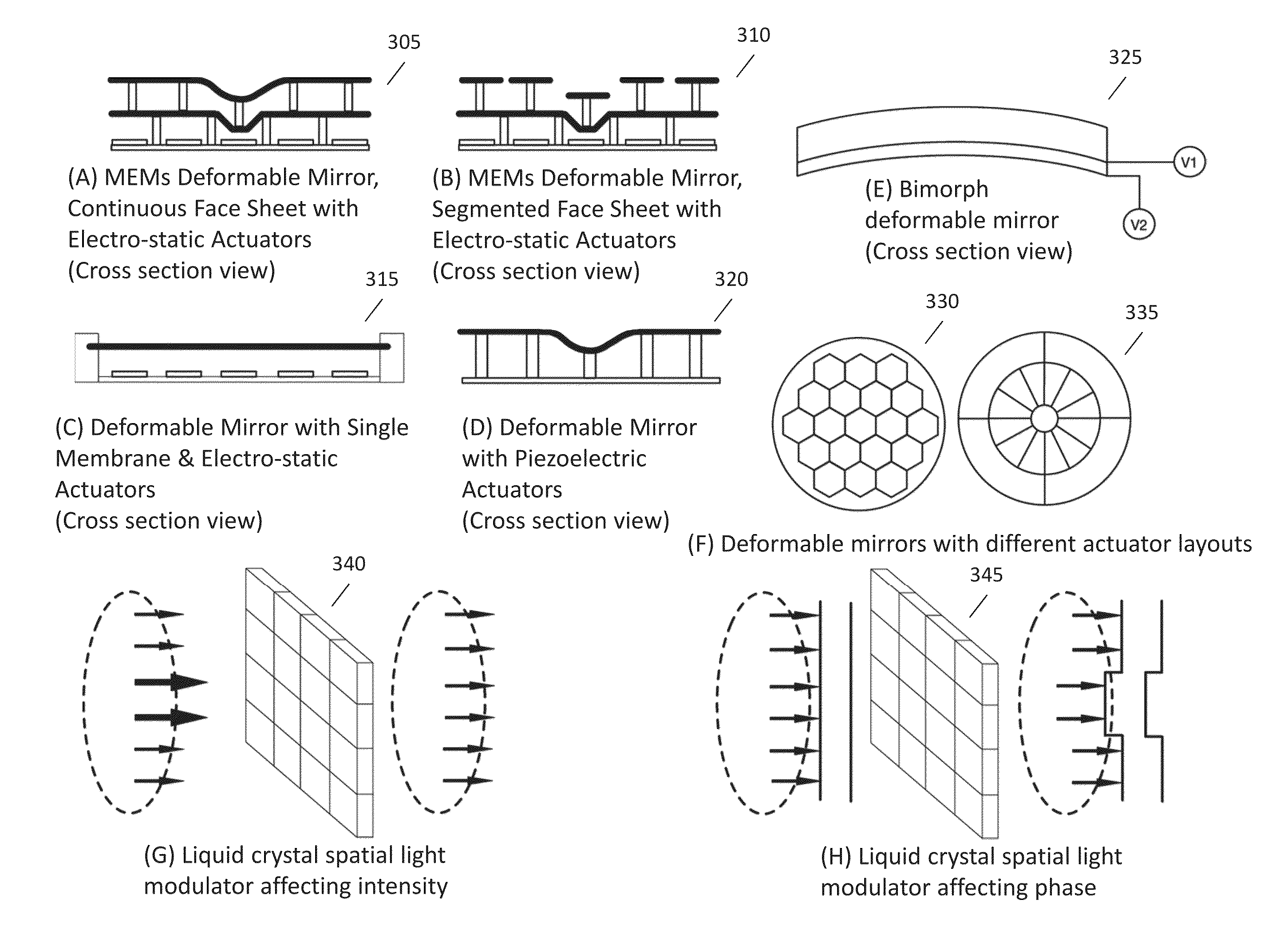
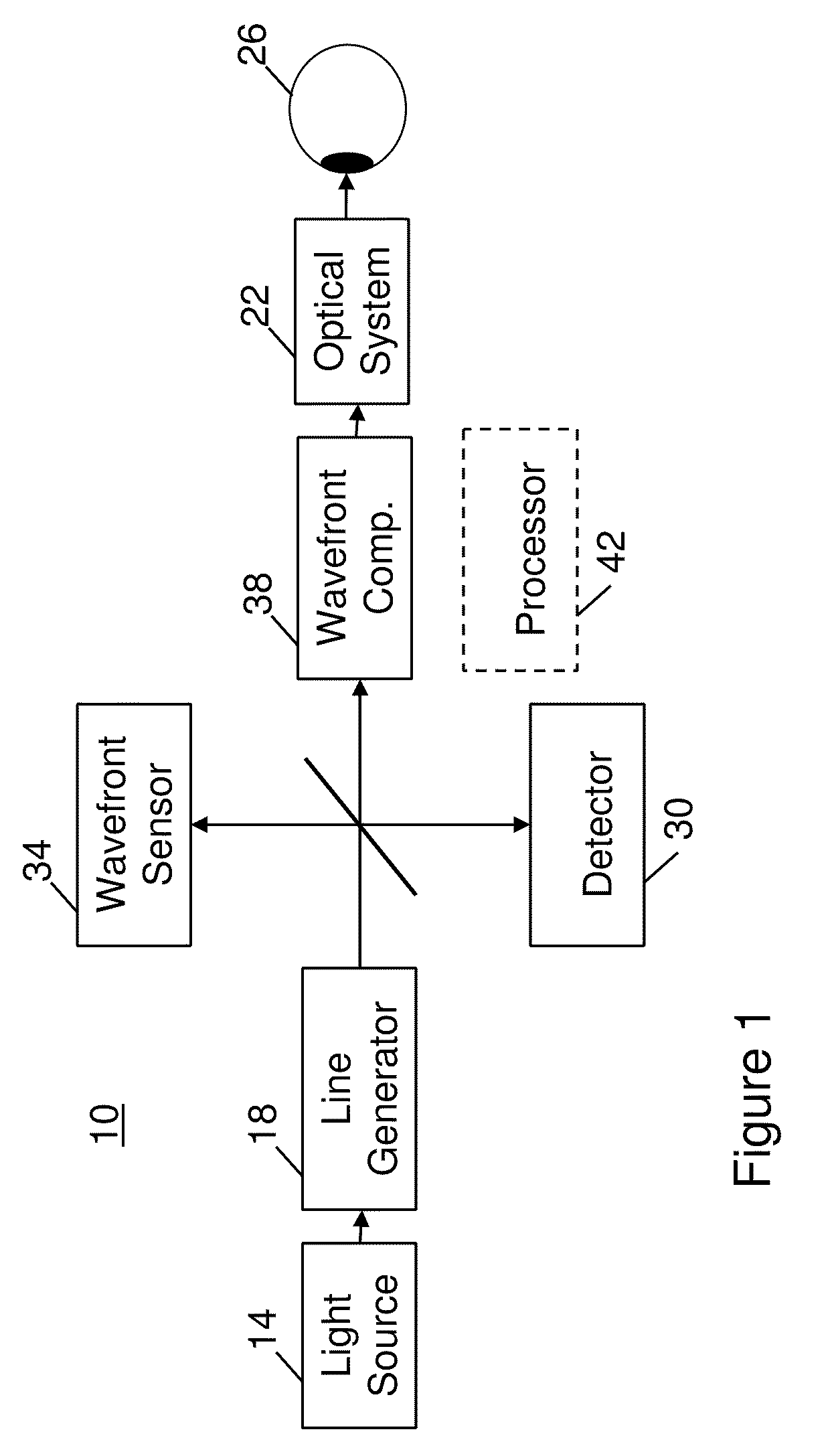
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of incoming wavefront distortions by deforming a mirror in order to compensate for the distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array.
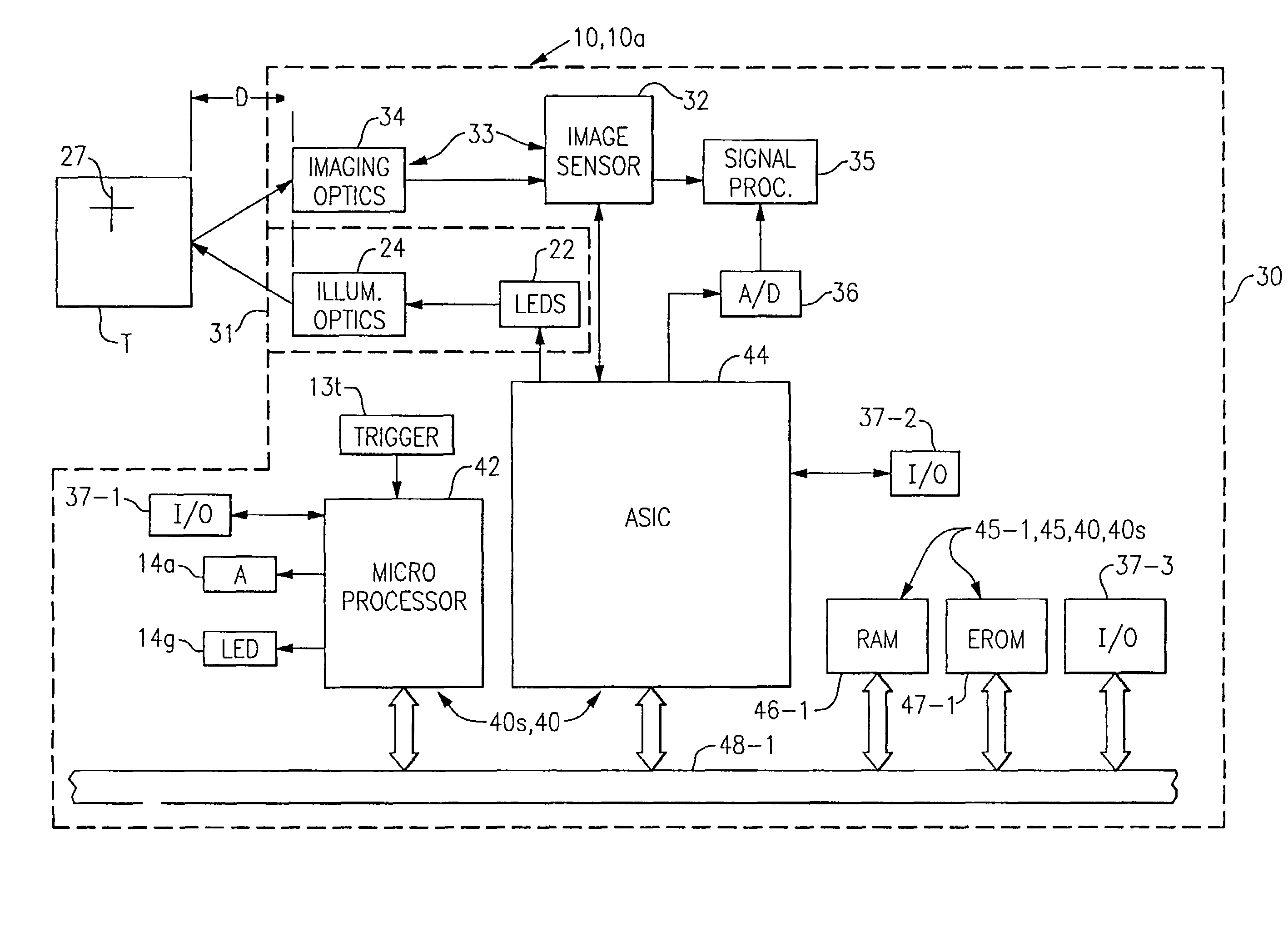
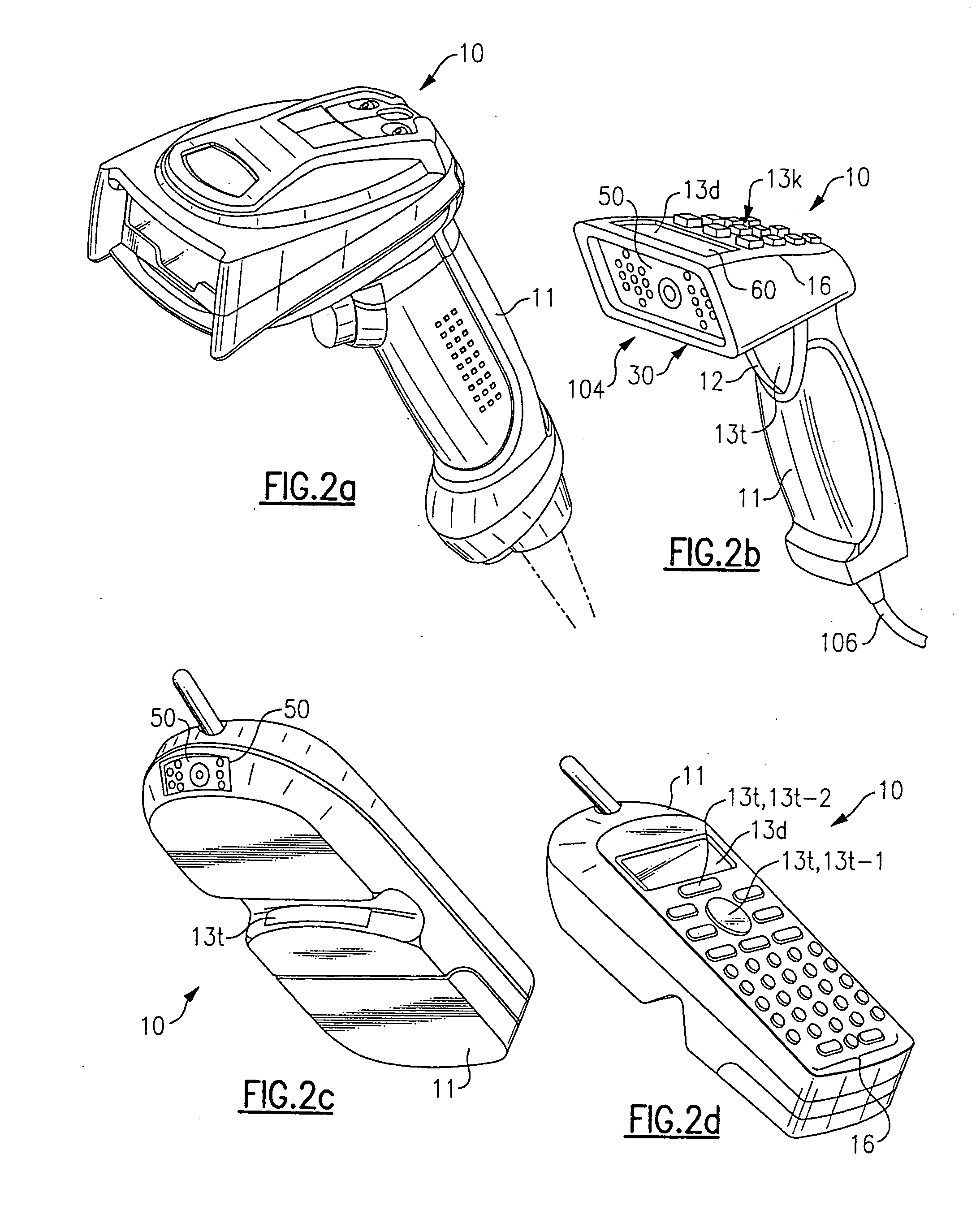
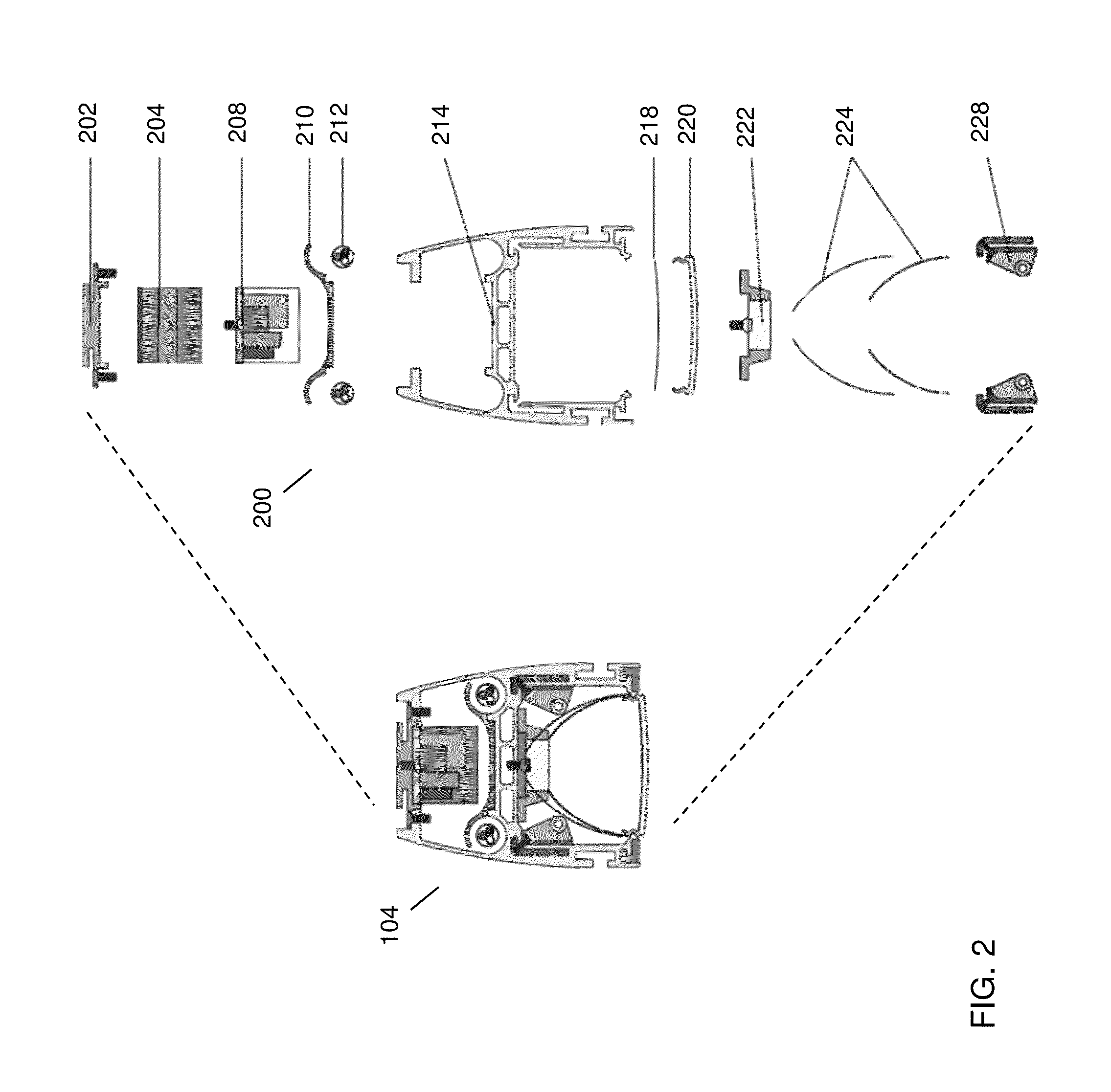
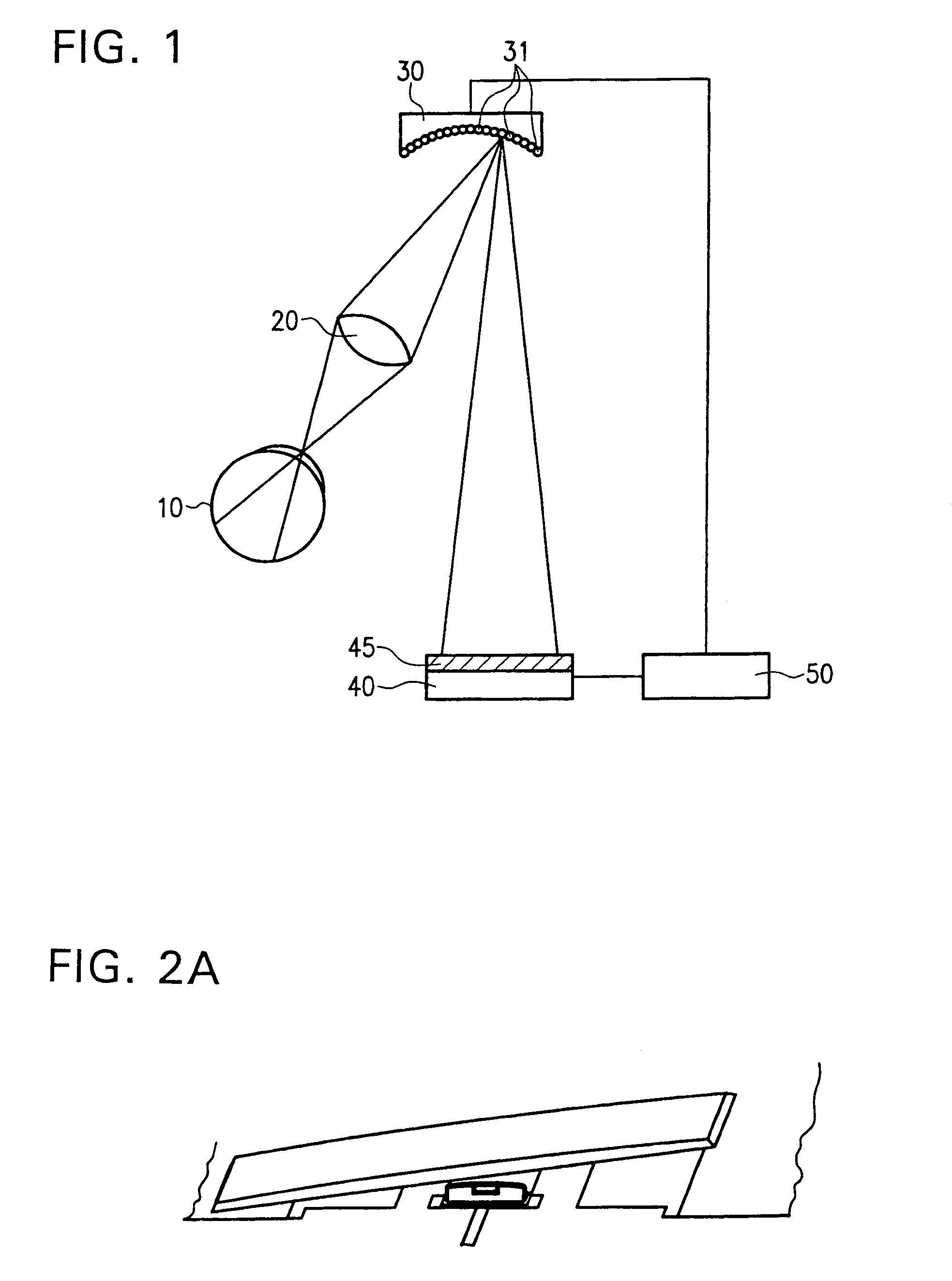
Adaptive optical image reader
InactiveUS7331523B2Character and pattern recognitionExposure controlDigital converterComputer science
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
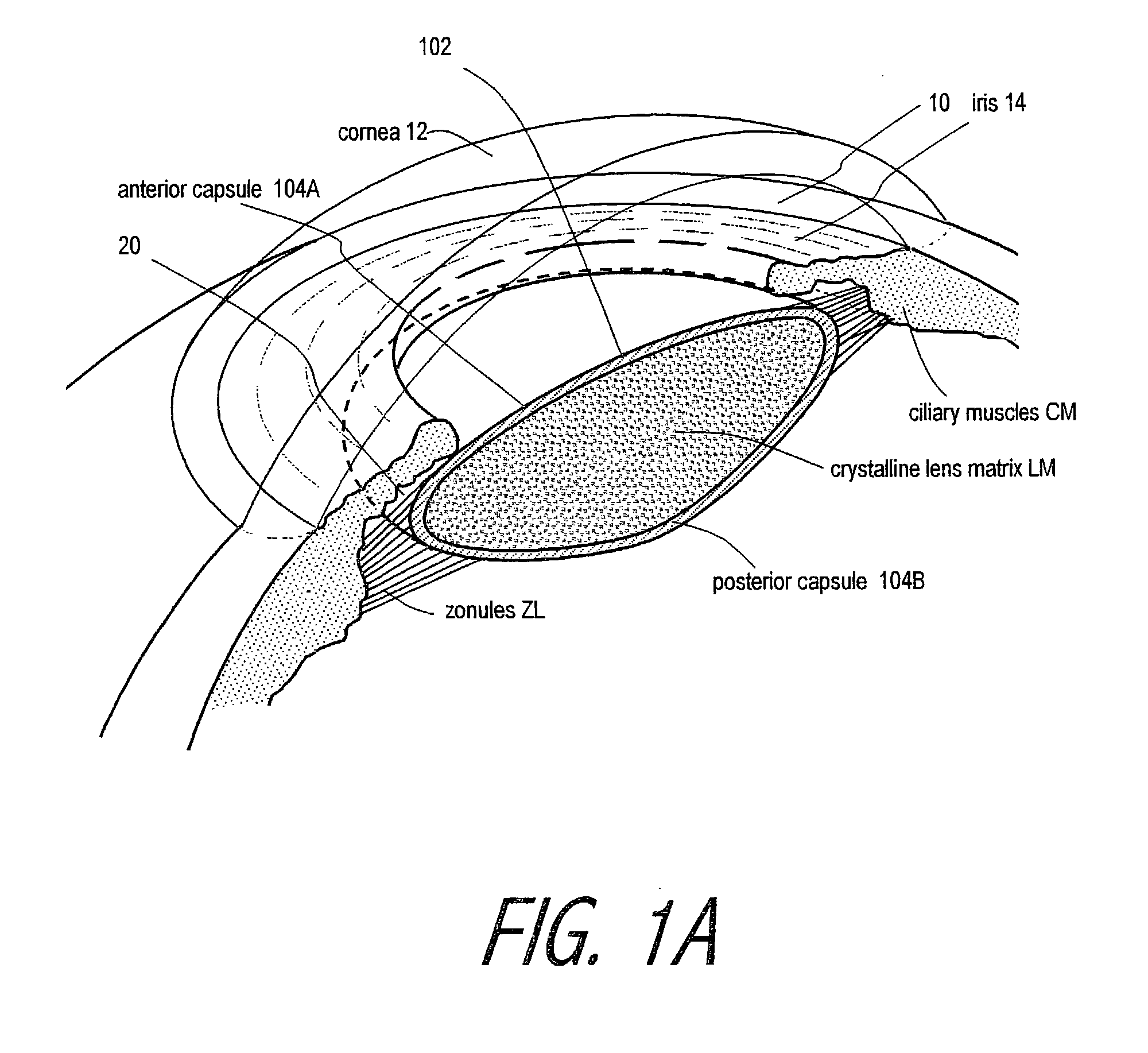
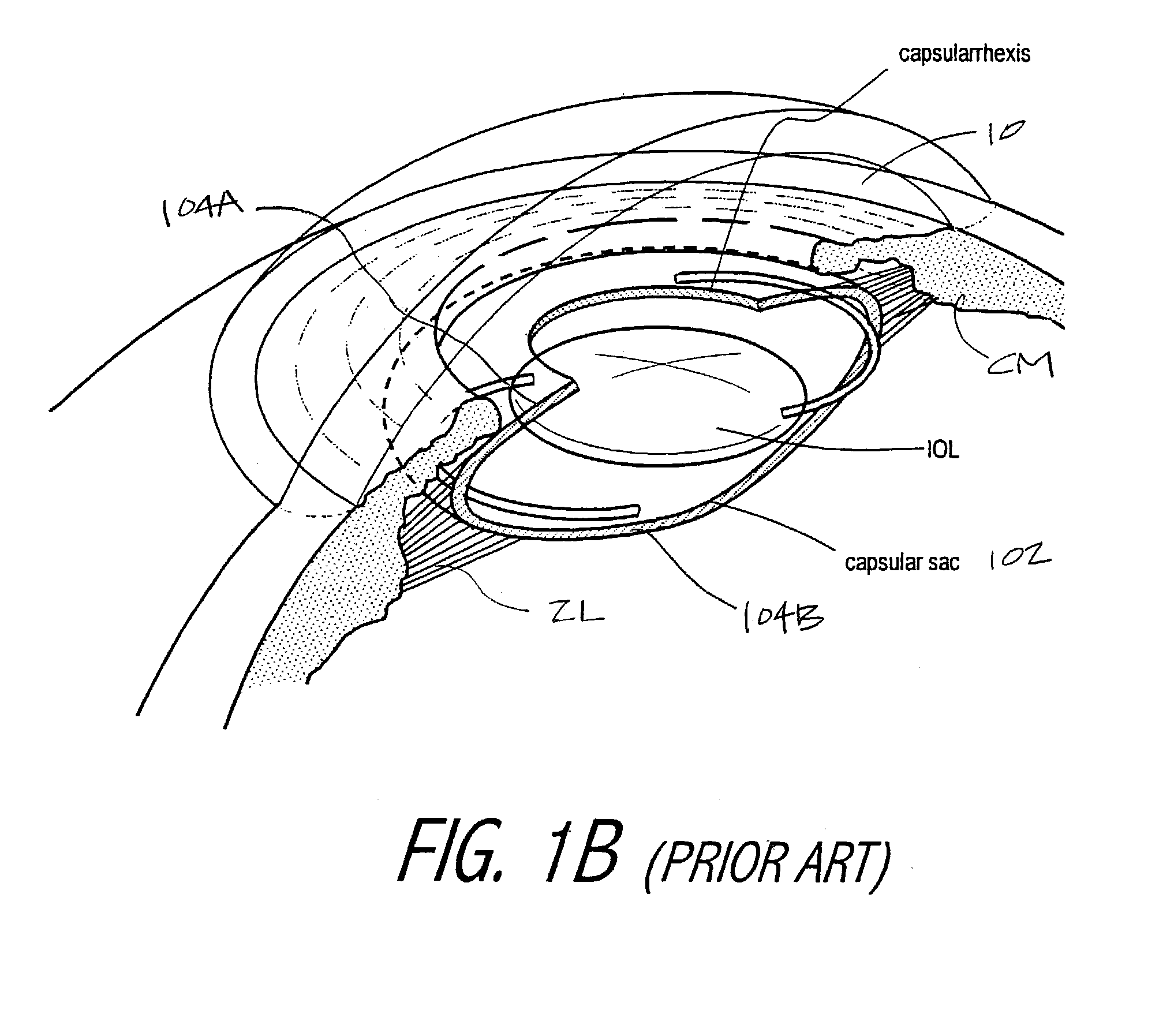
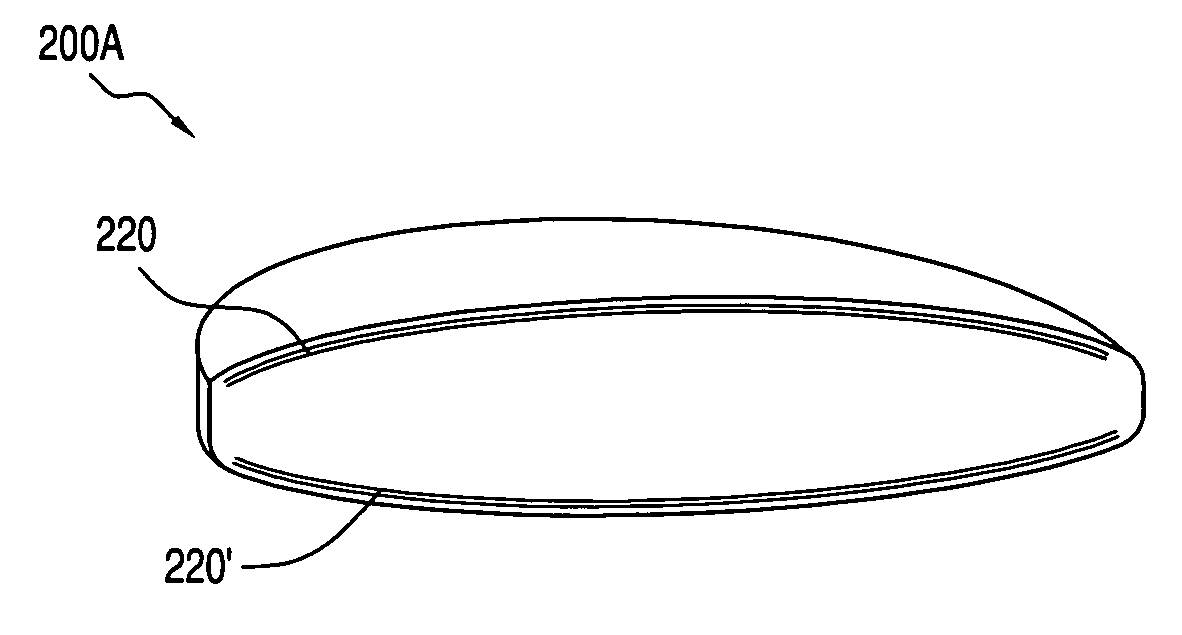
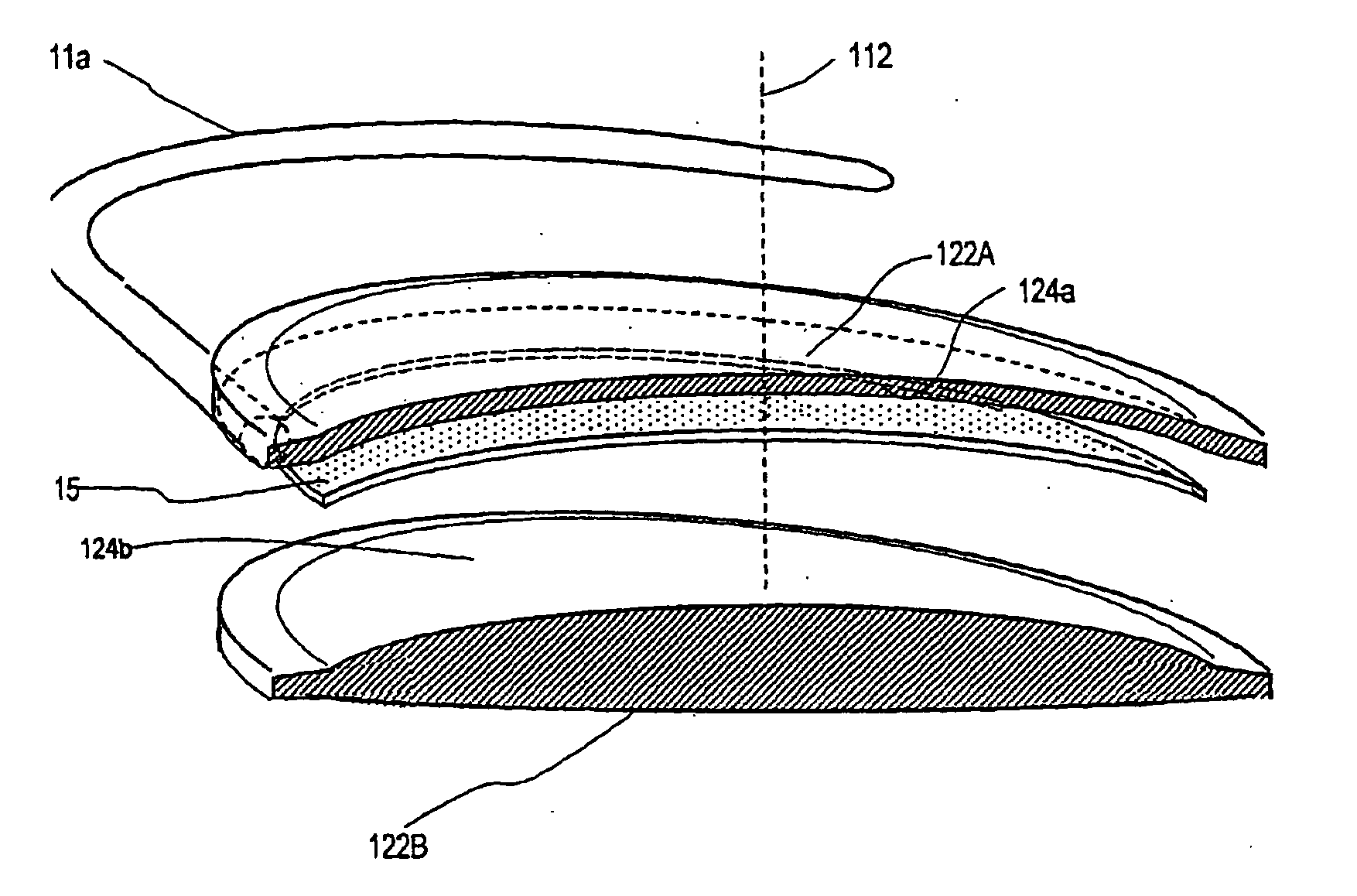
Ophthalmic devices, methods of use and methods of fabrication
InactiveUS20050021139A1Increase the adjustment rangeImproved force transmissionIntraocular lensElastomerYoung's modulus
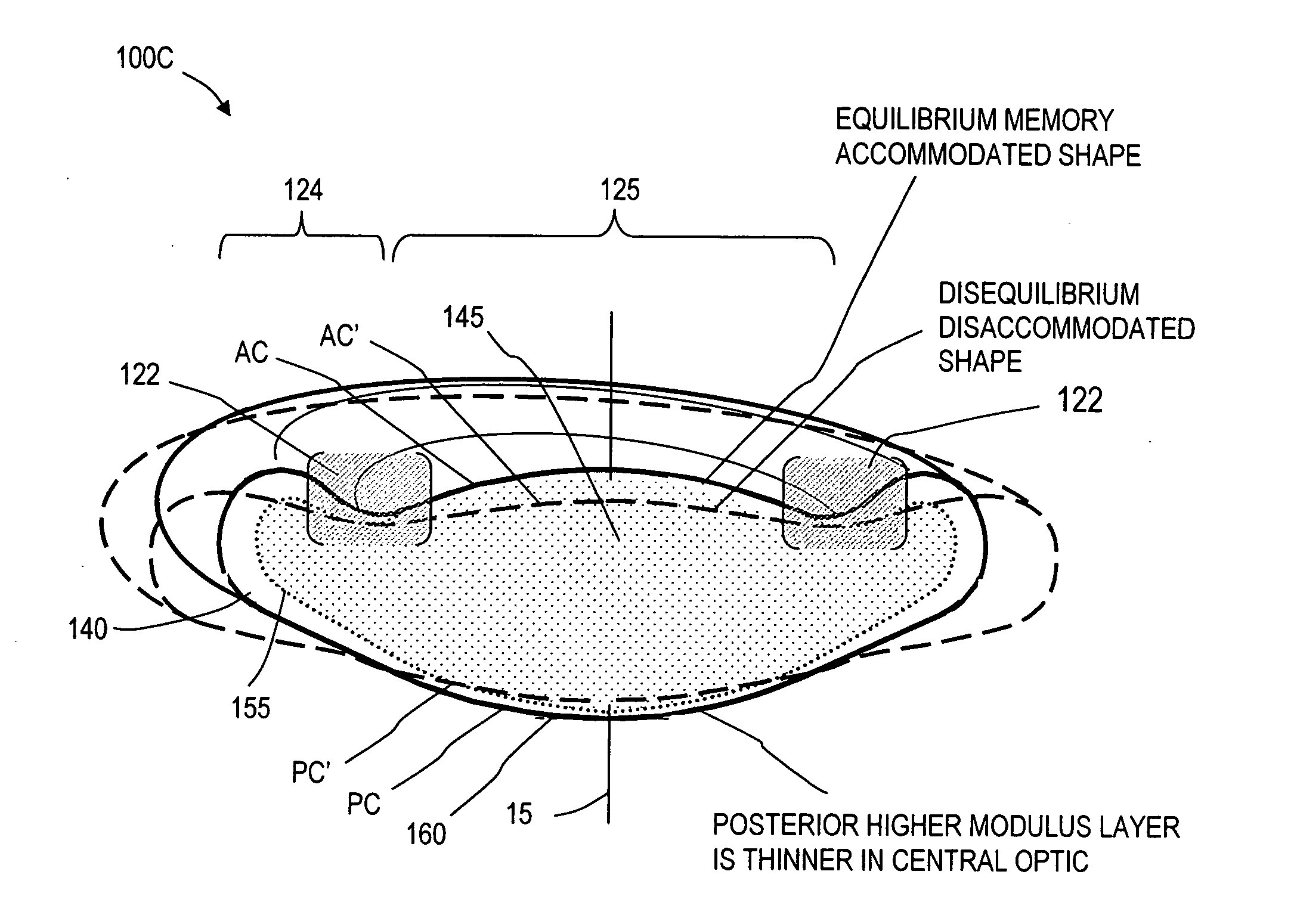
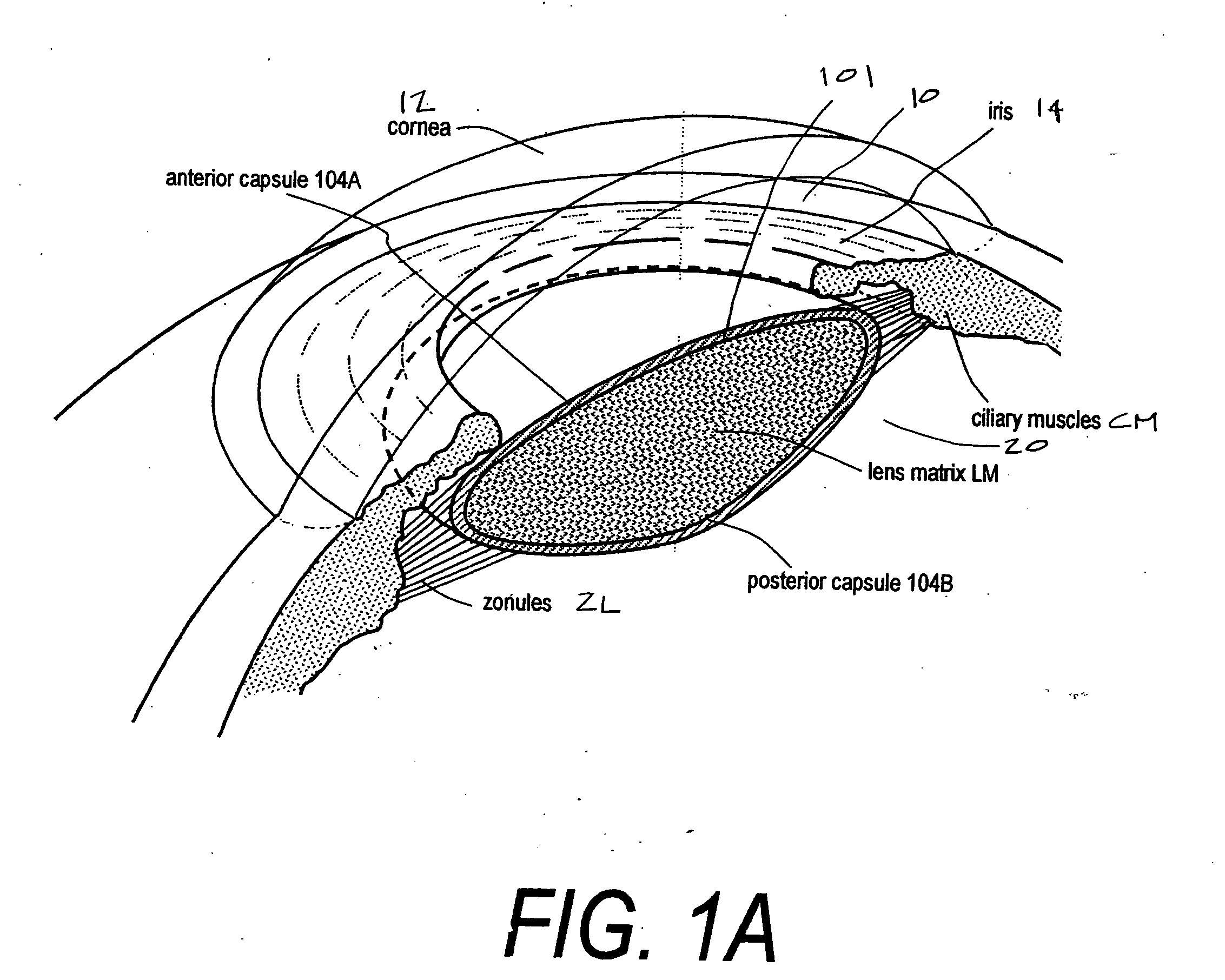
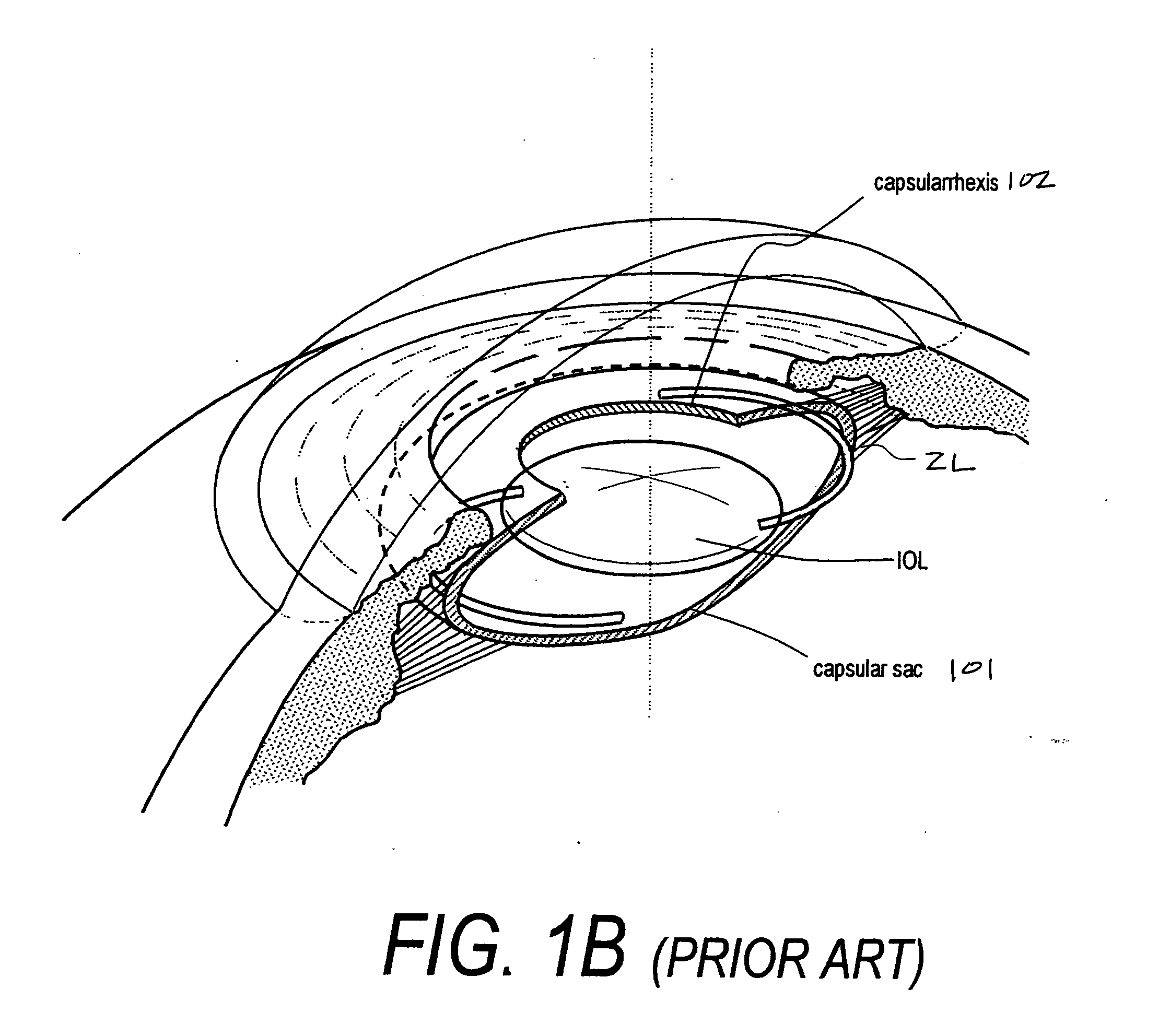
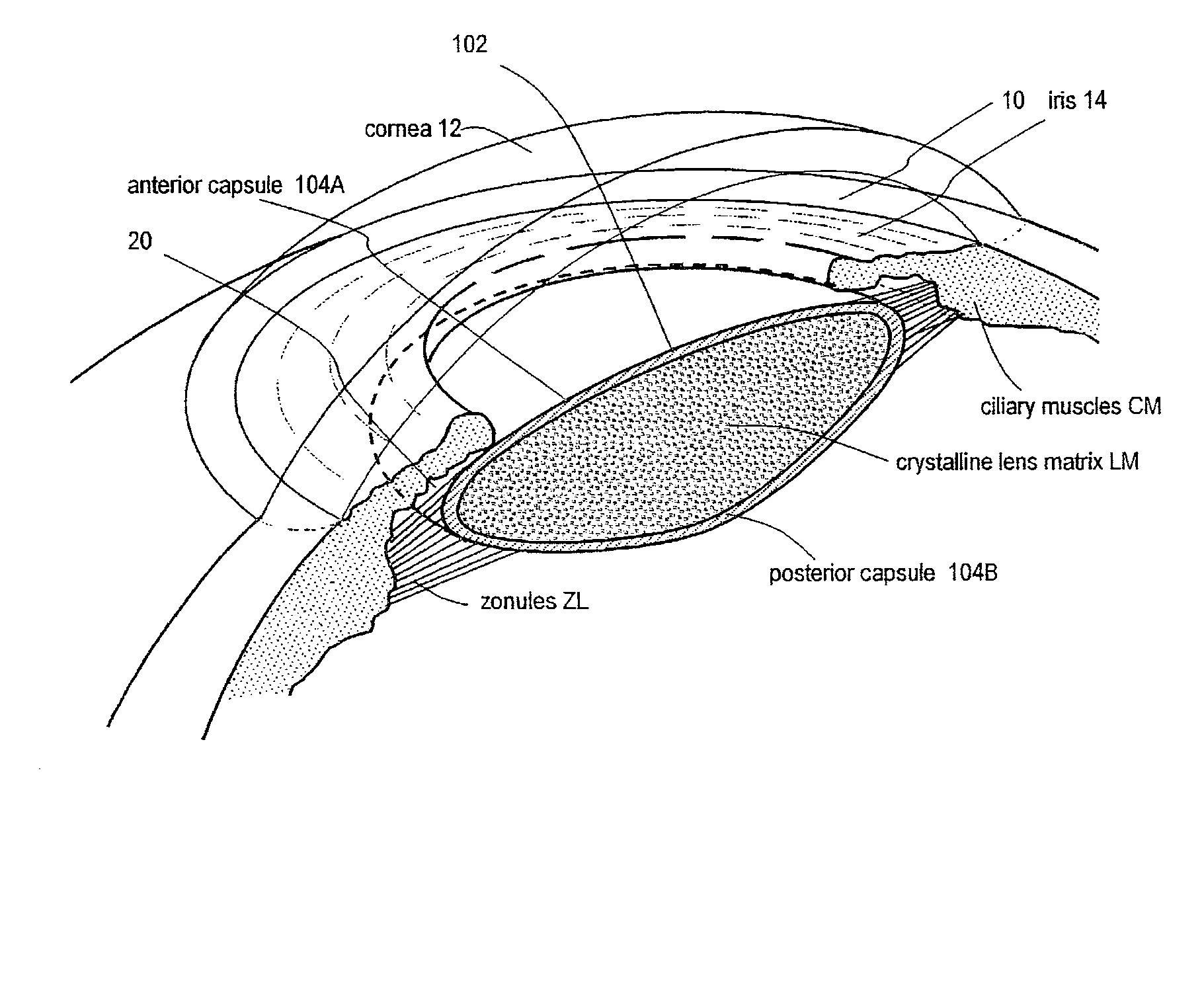
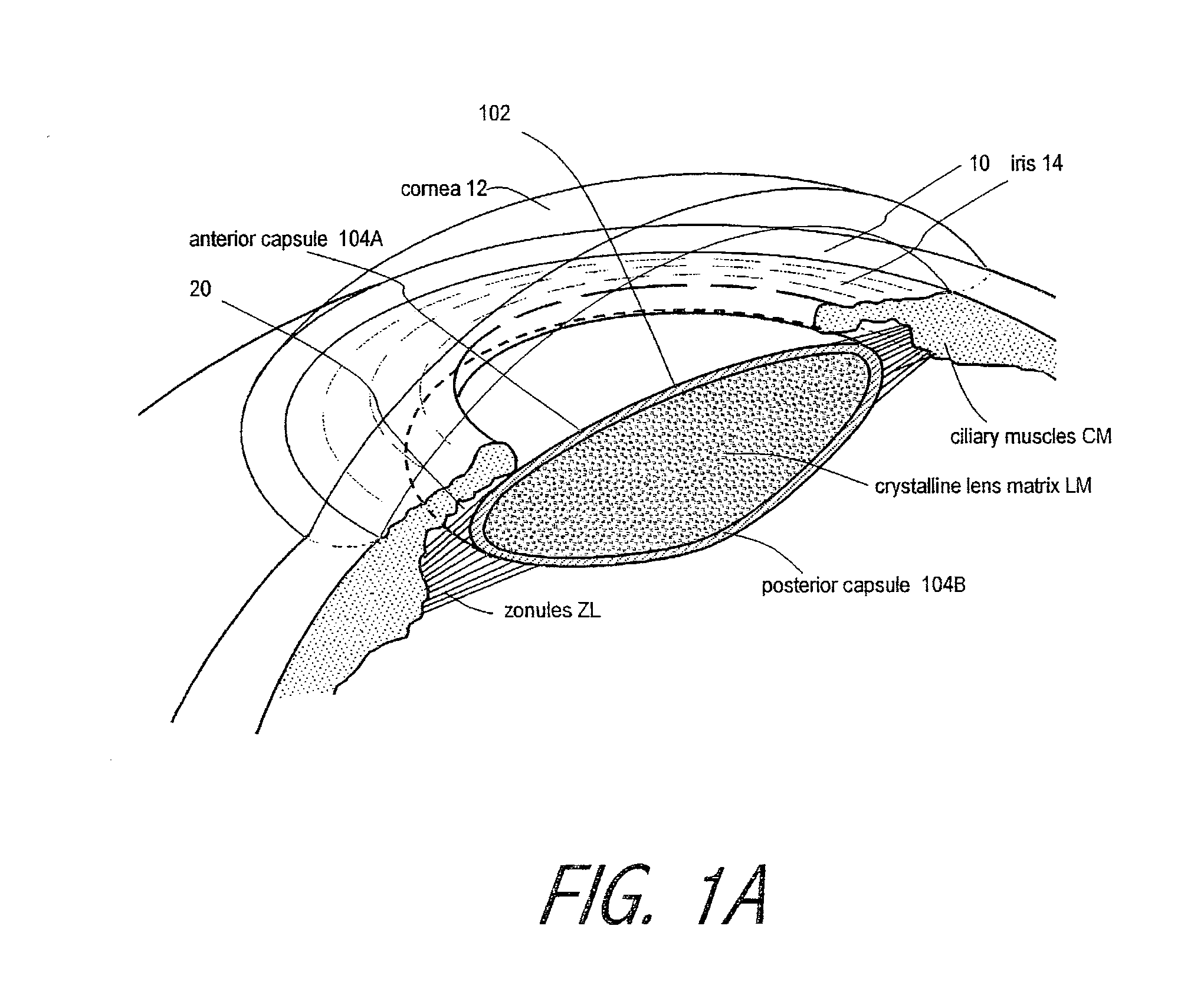
An adaptive optic for refractive lens exchange or cataract patients. The intracapsular implant comprises an elastomeric monolith with an equilibrium memory shape that imparts to the capsular sac's periphery the natural shape of the capsule in an accommodated state. In one embodiment, the monolith carries a recessed deformable central lens portion having an ultralow modulus that allows for high accommodative amplitude in response to equatorial tensioning. In a preferred embodiment, the adaptive optic defines an anisotropic modulus with a plurality of on-axis, rotationally symmetric elastomer block portions each having a different Young's modulus. The invention further provides composite materials for enhancing deformation of lens curvature, including the use of auxetic polymeric materials and negative stiffness materials. In preferred embodiments, at least a portion of the lens is fabricated of a shape memory polymer that provides a memory shape and a temporary shape with a reduced cross-sectional shape for introduction into the patient's eye.
Owner:POWERVISION
Adaptive liquid crystal lenses
An adaptive optical lens device, system and method of using the same is composed of at least two planar substrates and at least one homogeneous nematic liquid crystal (LC) layer. One planar substrate has a spherical or annular ring-shaped Fresnel grooved transparent electrode within it, the other has a transparent electrode coated on its inner surface. The thickness of the LC layer is uniform. When a voltage is applied across the LC layer, a centro-symmetrical gradient distribution of refractive index within LC layer will occur. Therefore, the LC layer causes light to focus. By controlling the applied voltage, the focal length of the lens is continuously tunable.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
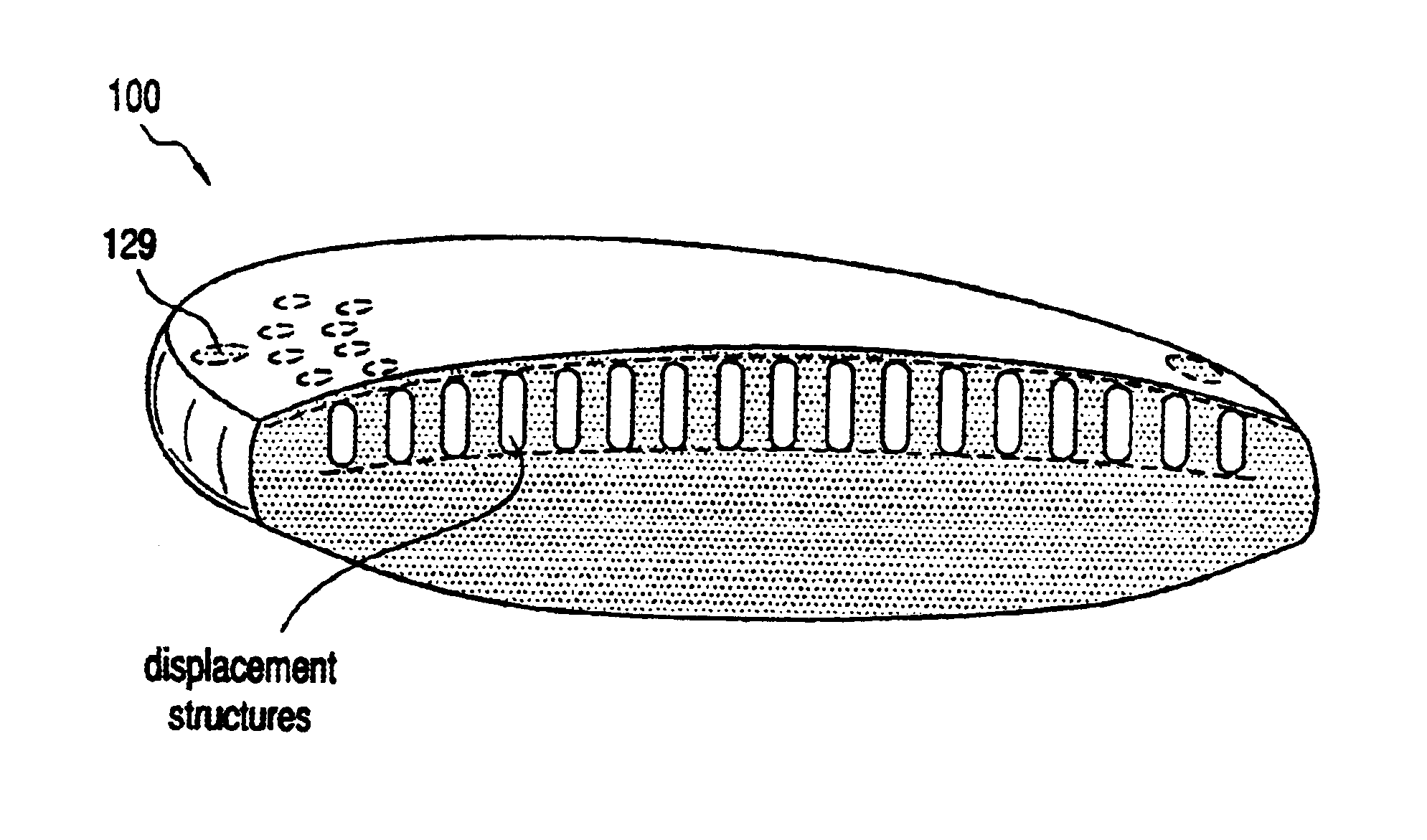
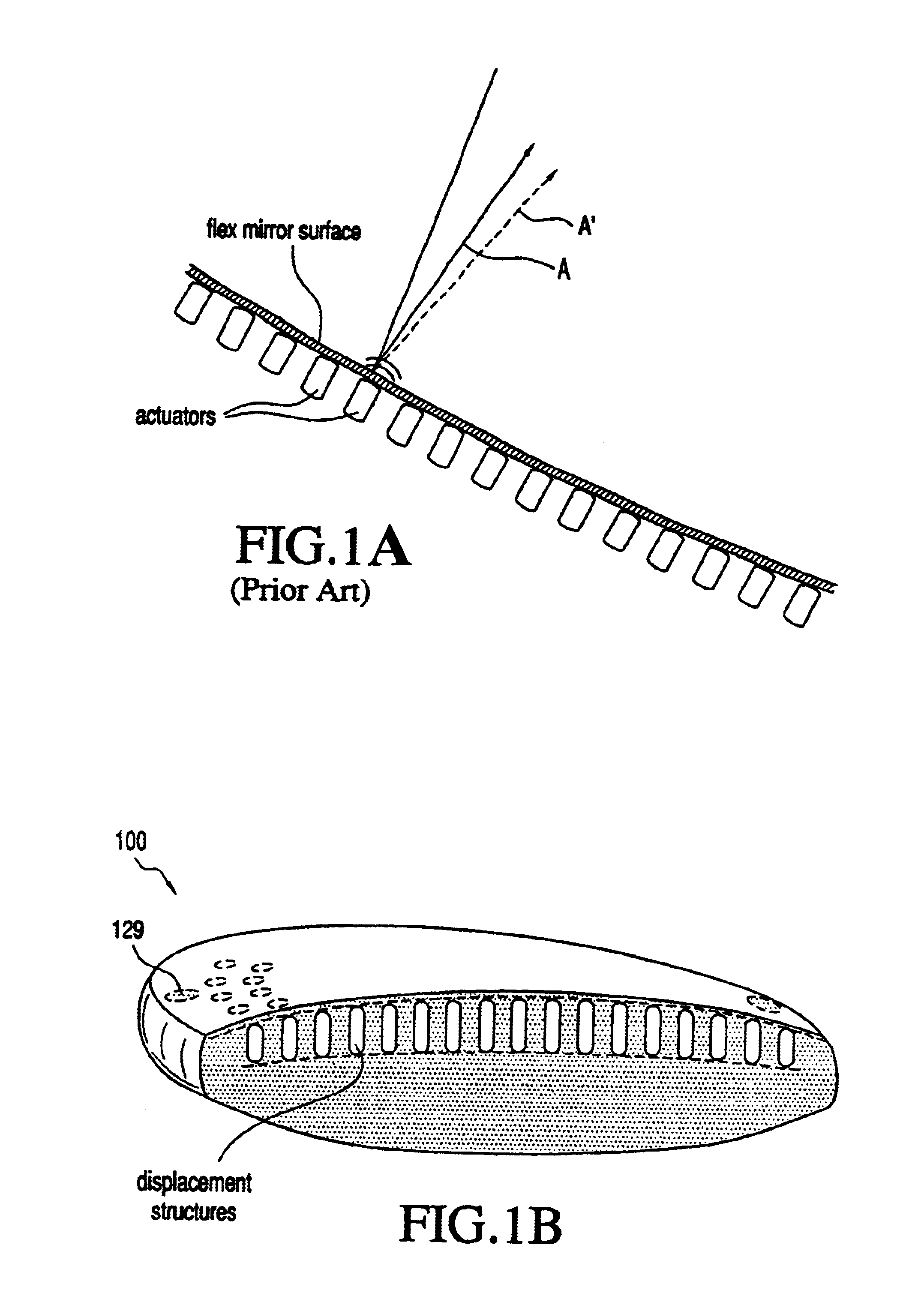
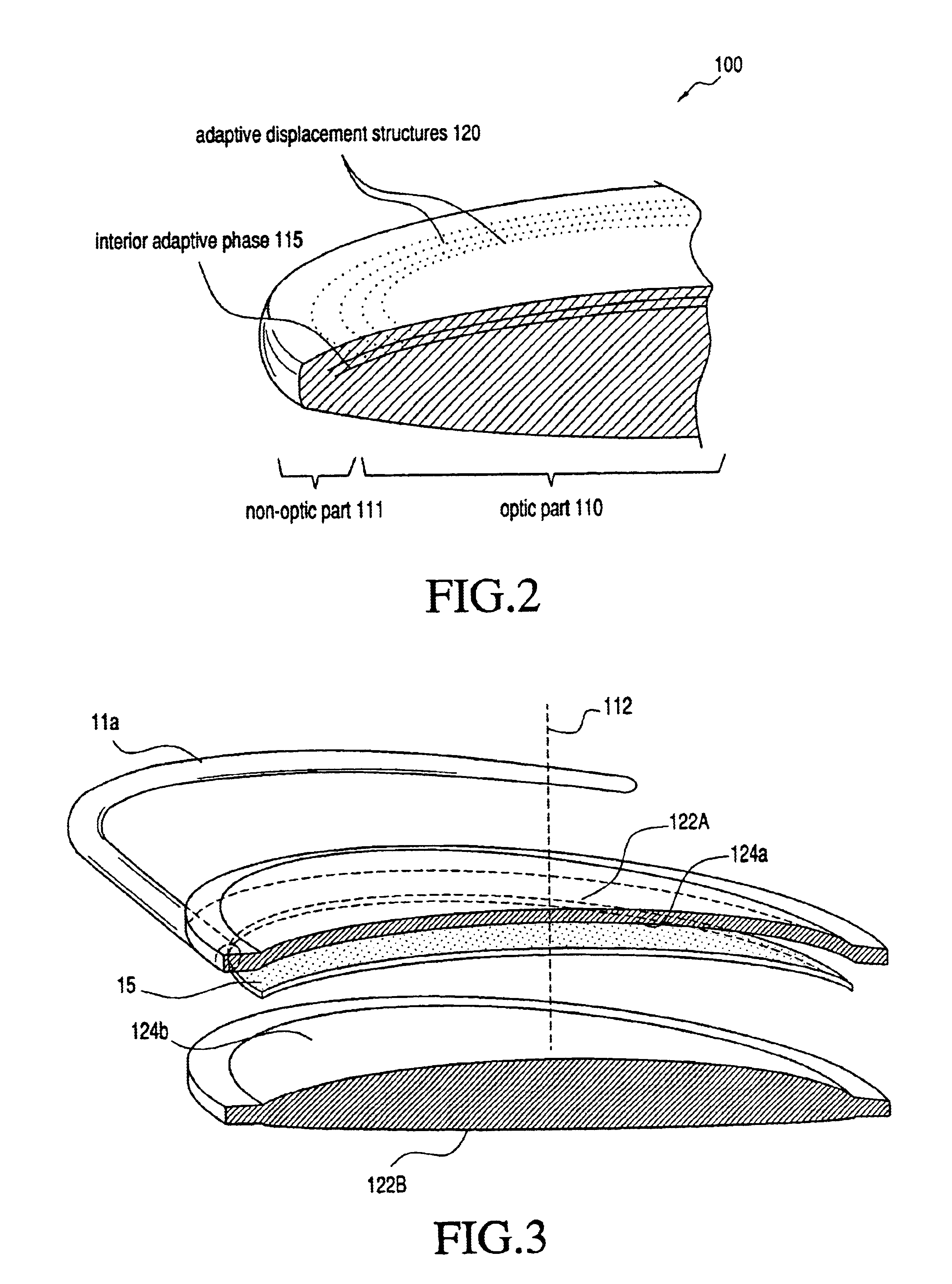
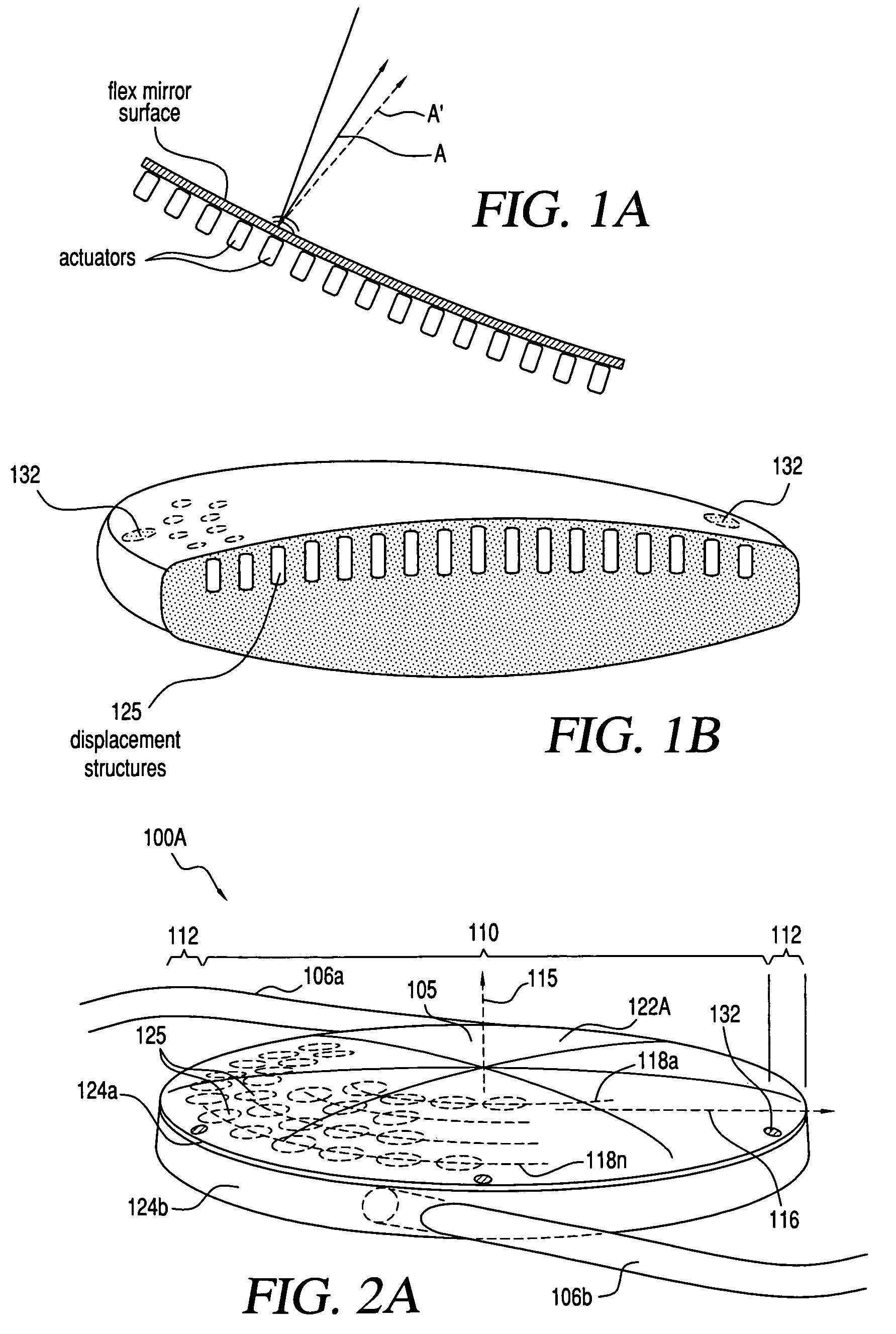
Adaptive optic lens and method of making
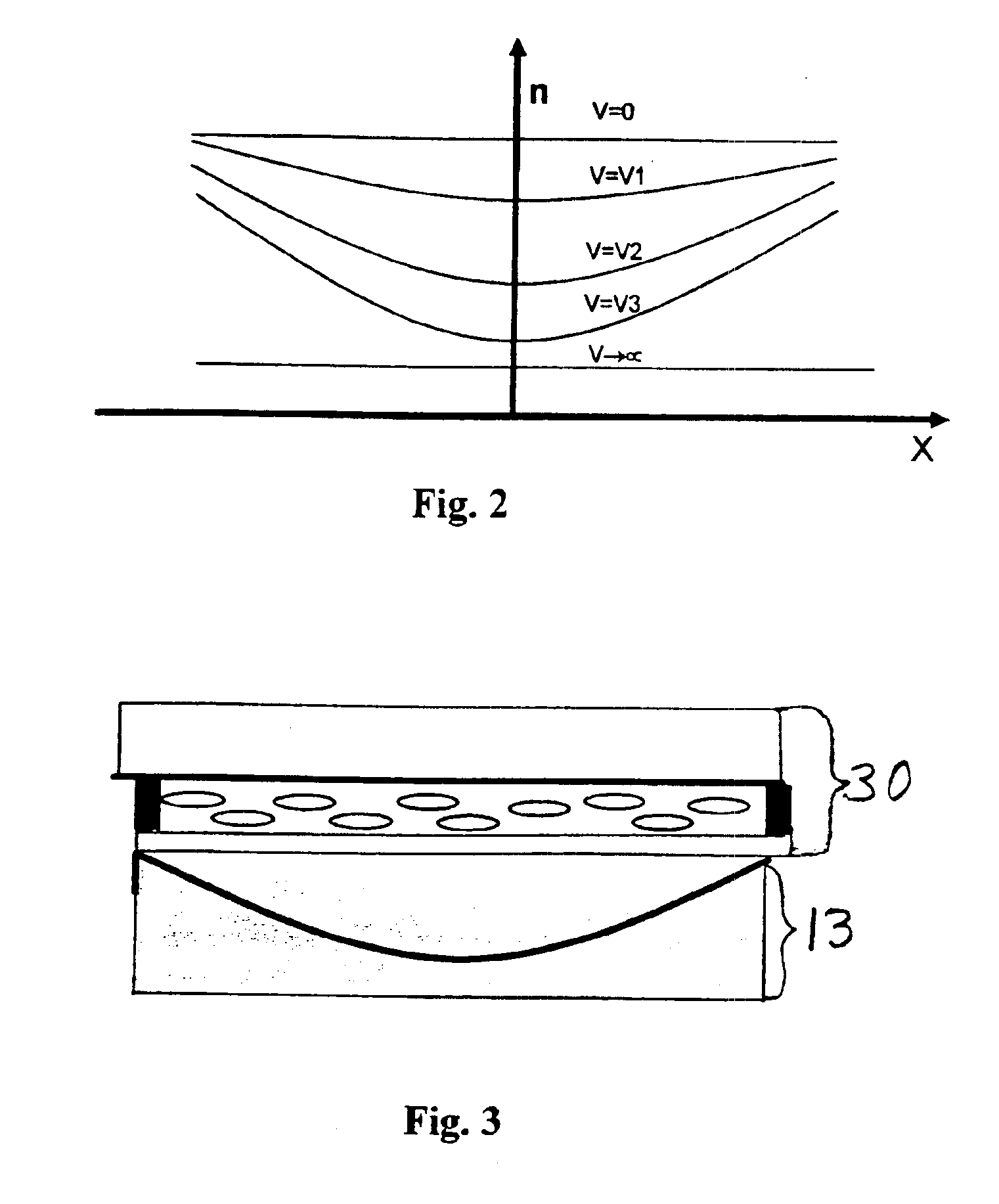
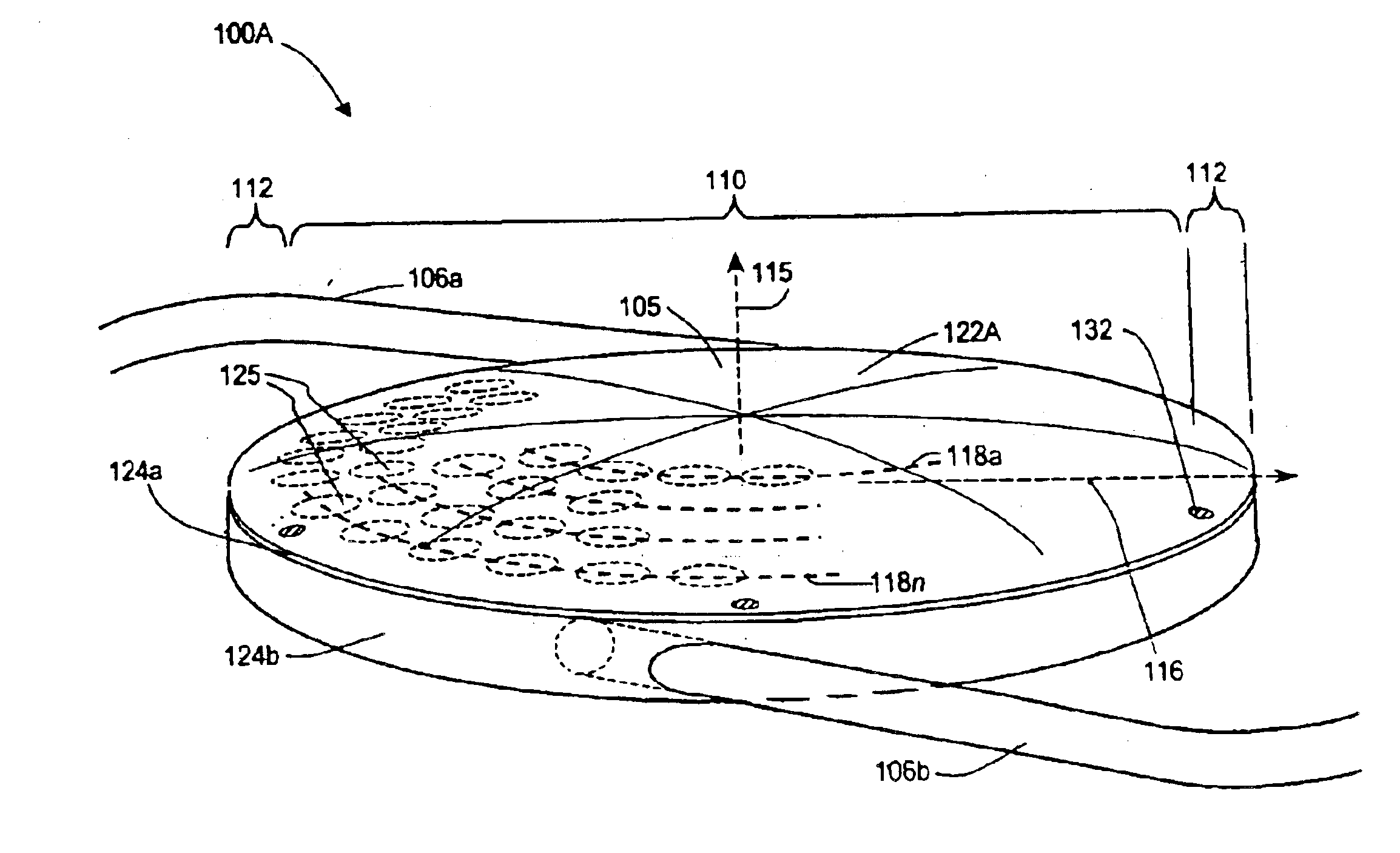
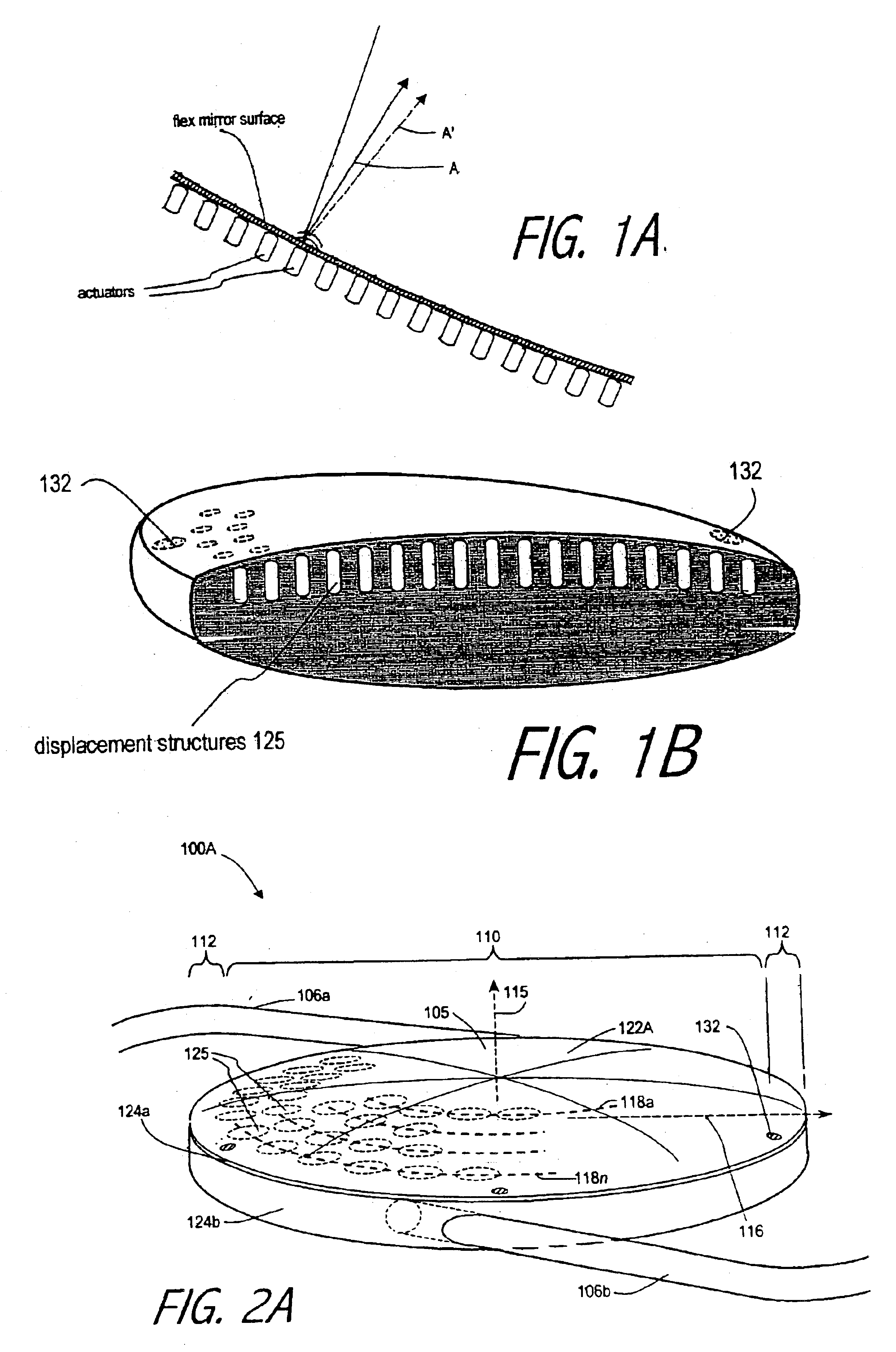
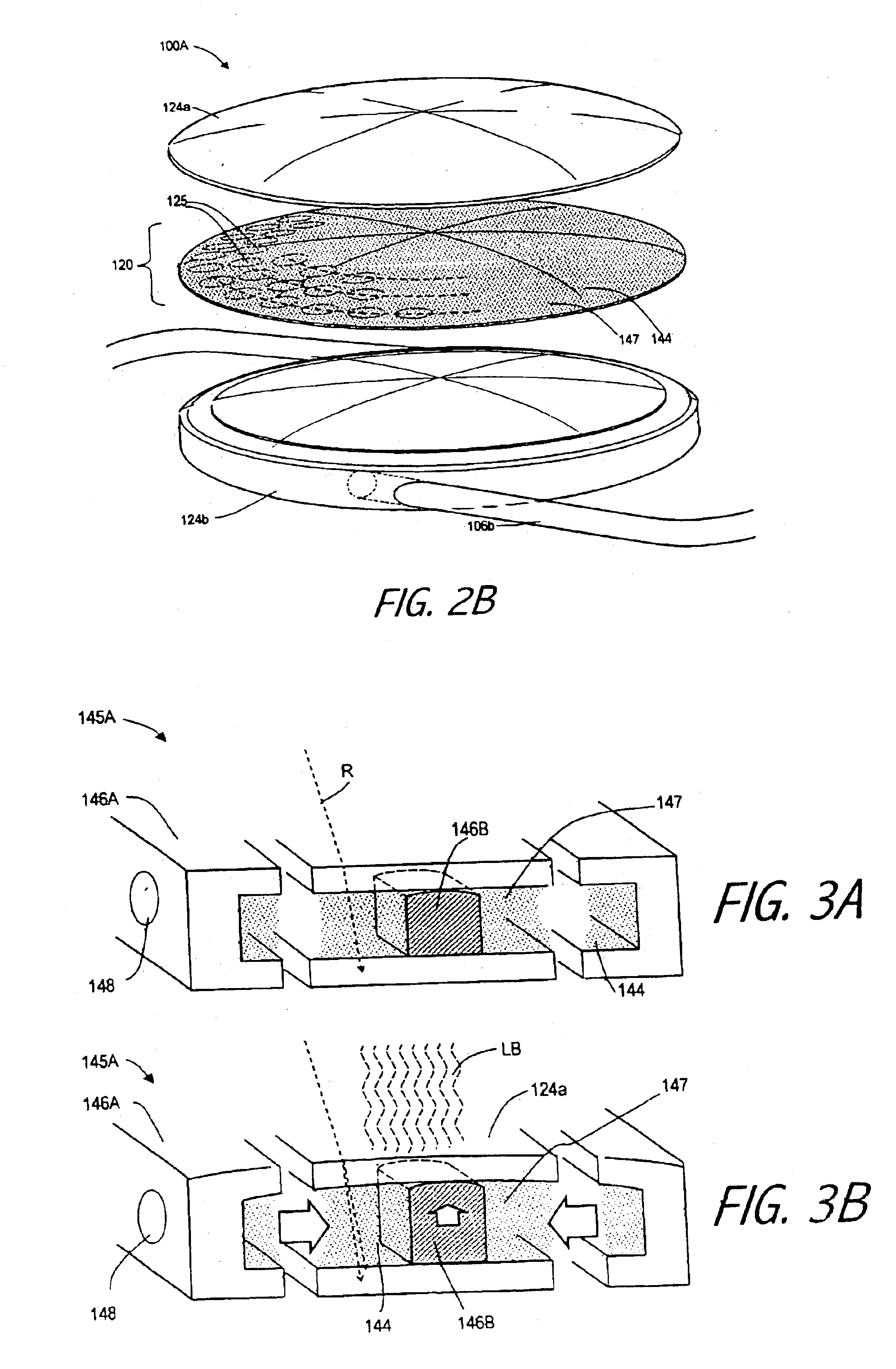
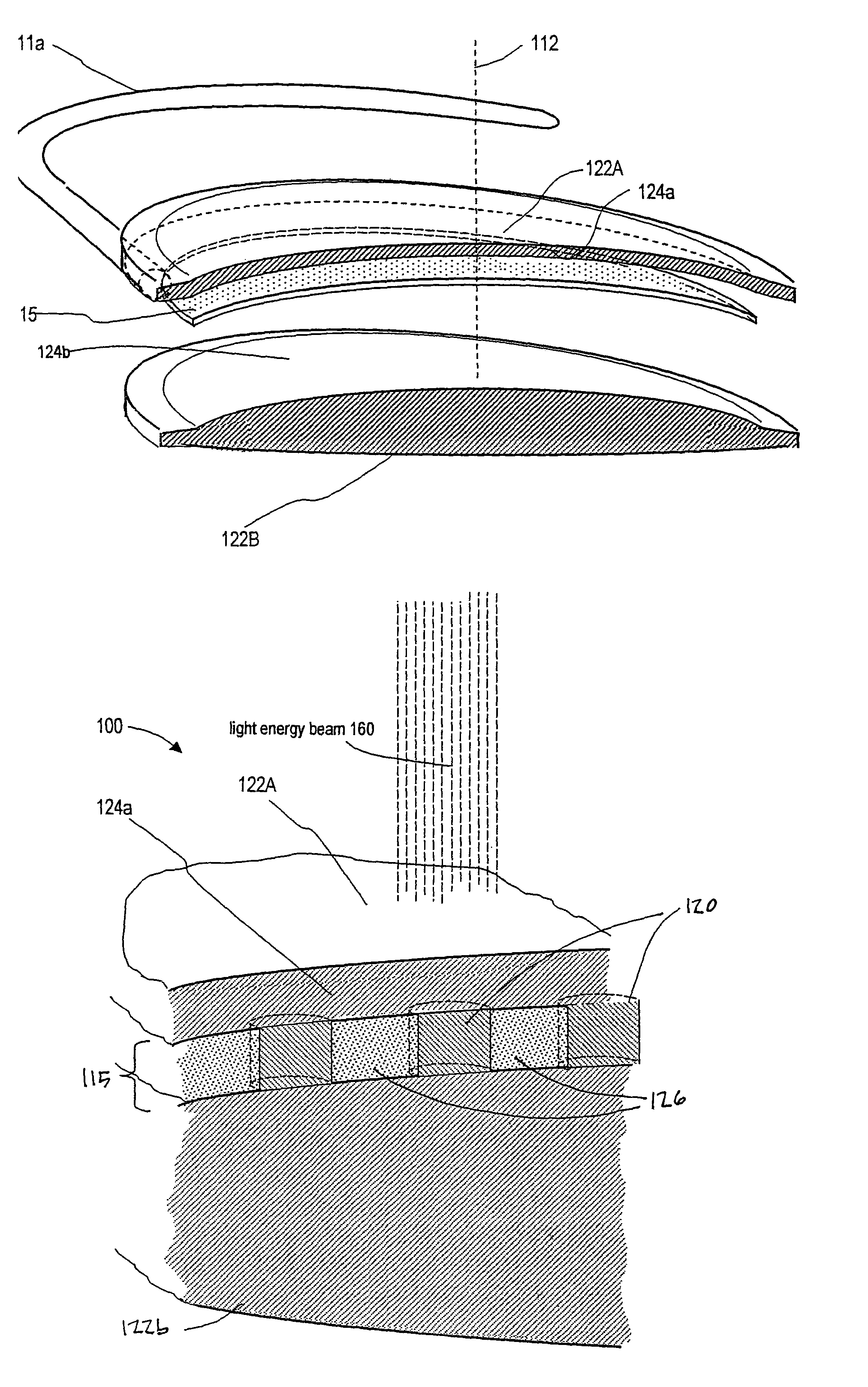
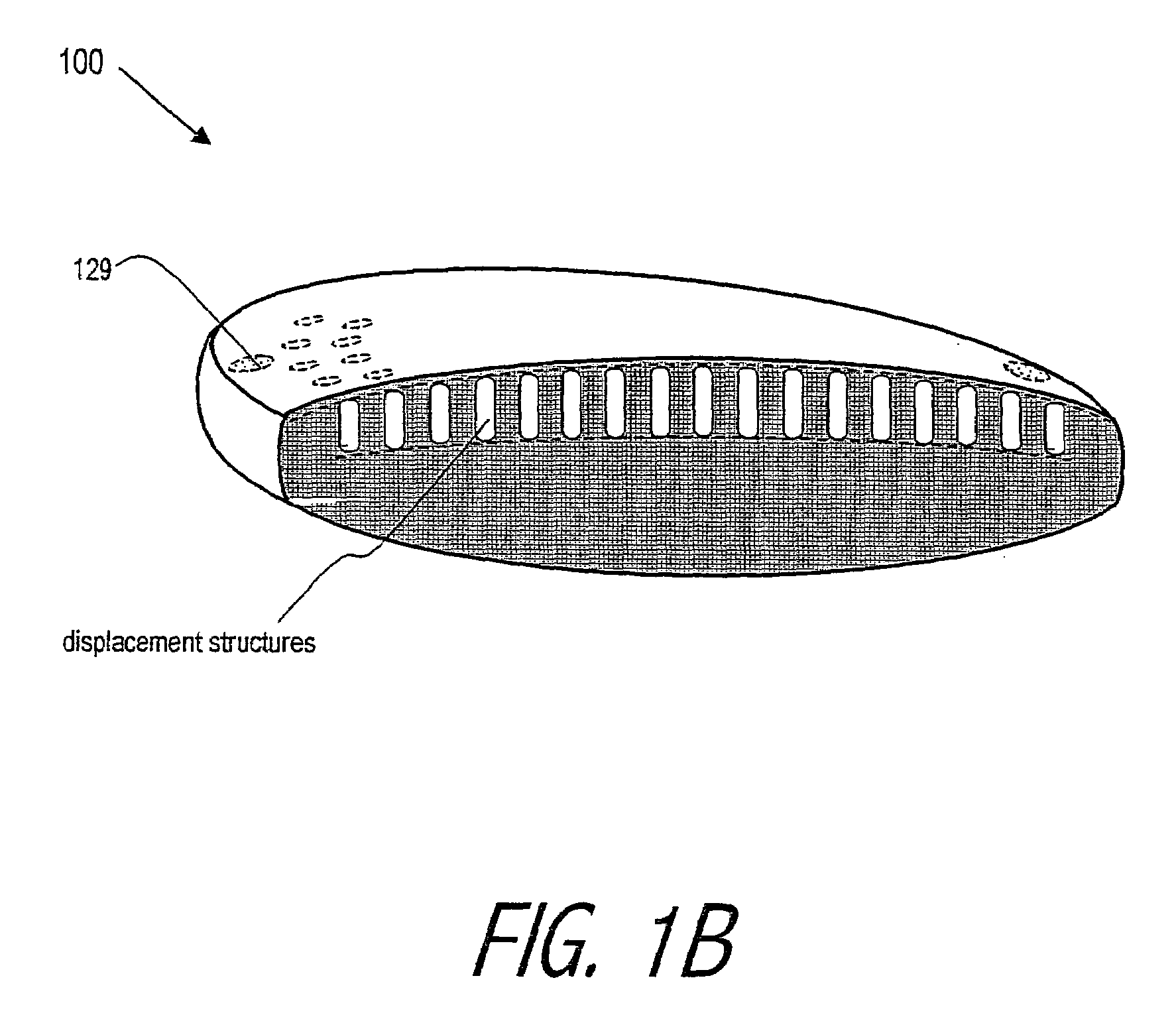
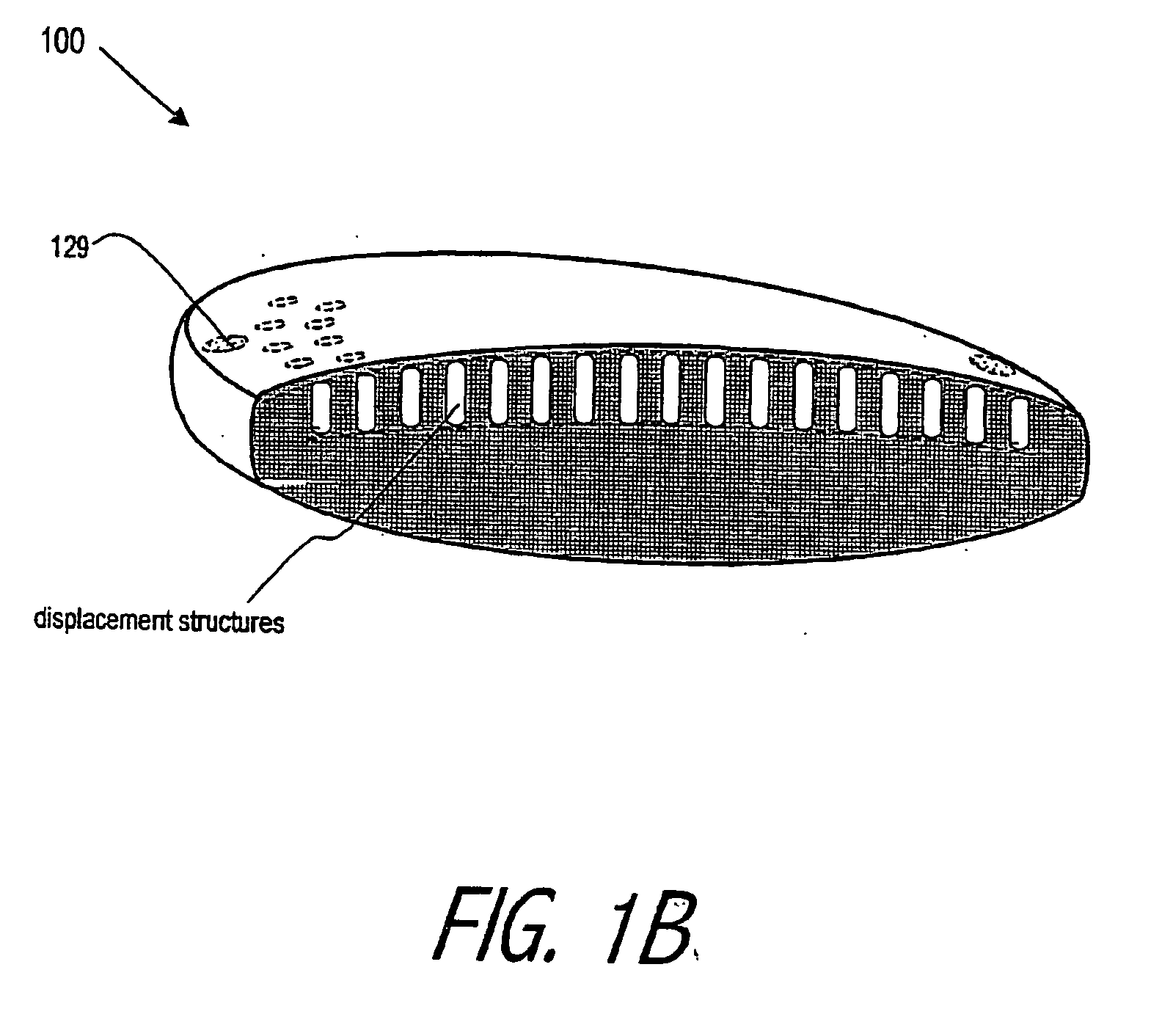
An lens for correcting human vision, for example an IOL, contact lens or corneal inlay or onlay, that carries and interior phase or layer comprising a pattern of individual transparent adaptive displacement structures. In the exemplary embodiments, the displacement structures are actuated by shape change polymer that adjusts a shape or other parameter in response to applied energy that in turn displaces a fluid media within the lens that actuates a flexible lens surface. The adaptive optic means of the invention can be used to create highly localized surface corrections in the lens to correct higher order aberrations-which types of surfaces cannot be fabricated into and IOL and then implanted. The system of displacement structures also can provide spherical corrections in the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Stabilized retinal imaging with adaptive optics
InactiveUS20070252951A1Improve understandingControl damageLaser surgeryUsing optical meansRetinal imagingLight beam
A system provides an optical image of an object. A first module tracks a reference feature of the object. A second module includes a source for an imaging beam, a scanning device to move the imaging beam along a portion of the object and a detection device receives a signal associated with an image of the portion of the object. The first module controls the position of the imaging beam relative to the reference feature to correct for the motion of the object. A third module detects a distortion of the object and compensates for the distortion.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
Adaptive optic lens system and method of use
InactiveUS6860601B2Reduce aberrationHigh order aberrationSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsCamera lensCorneal inlay
An lens for correcting human vision, for example an IOL, contact lens or corneal inlay or onlay, that carries and interior phase or layer comprising a pattern of individual transparent adaptive displacement structures. In one embodiment, the displacement structures are actuated by a shape memory polymer (SMP) material or other polymer that is adjustable in shape in response to applied energy. The SMP can be designed to be selectively adjustable in volumetric dimension, modulus of elasticity and / or permeability. The adaptive optic means of the invention can be used to create highly localized surface corrections in the lens to correct higher order aberrations-which types of surfaces cannot be fabricated into and IOL and then implanted. The system of displacement structures also can provide spherical corrections in the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Adaptive optical image reader
InactiveUS20050056699A1Data augmentationExtension of timeCharacter and pattern recognitionExposure controlDigital imageDigital converter
A digital image reading system including an image sensor and a computer that is programmed to adjust the frame rate of the image sensor, and to obtain a maximum frame rate of the image sensor for obtaining an acceptable image. An algorithm for adjusting the frame rate evaluates image parameters and calculates new exposure times, gain values, and exposure settings to support a maximum frame rate of the image sensor. A process for obtaining an acceptable image with an image reader evaluates an image signal level and adjusts the frame rate if the signal level is outside of a predetermined range. The process adjusts the image sensor to run at a maximum operational frame rate. A digital image reading system including multiple separate digitizers for use in various read environments and under various read conditions.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
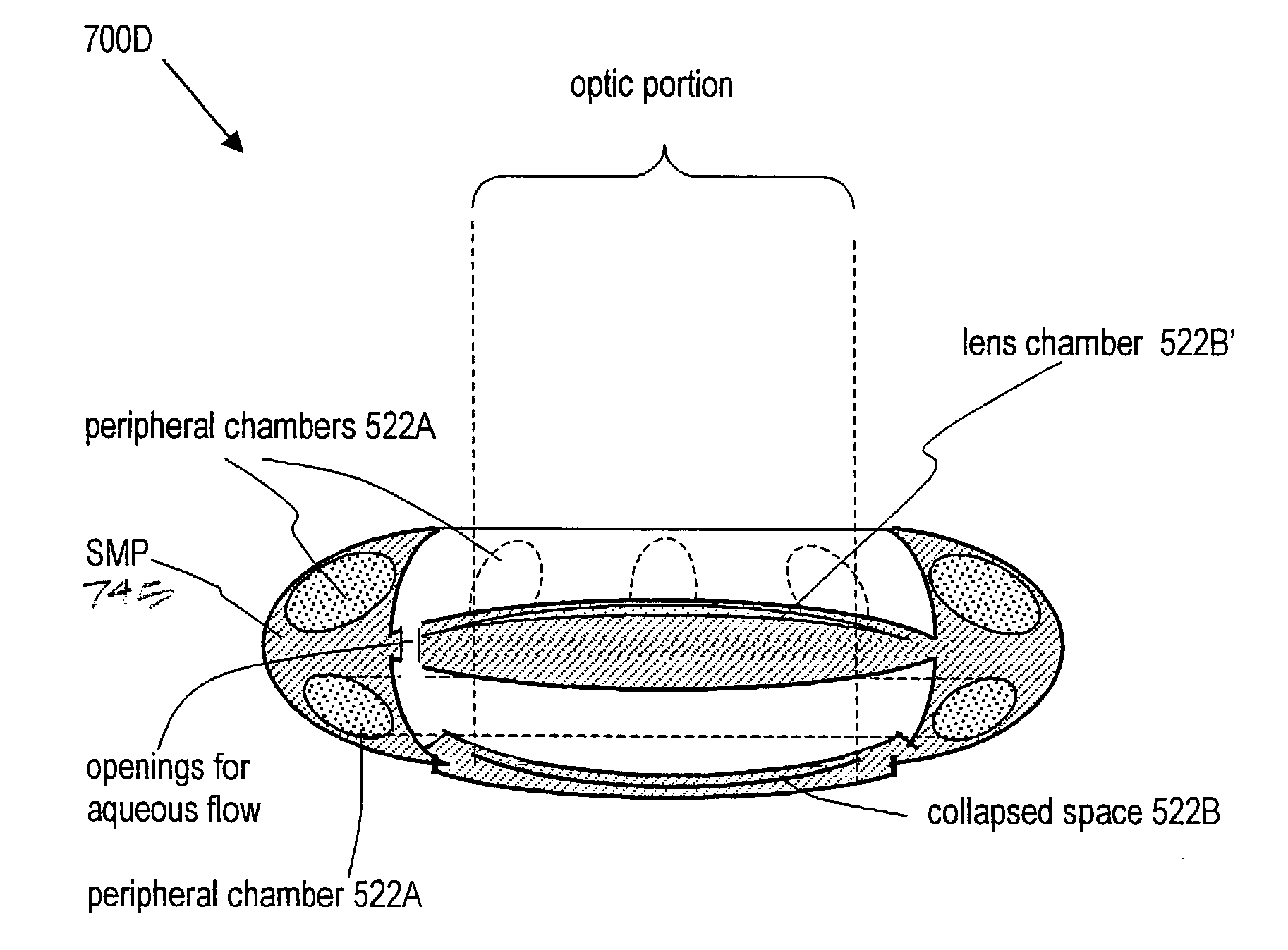
Intraocular implant devices
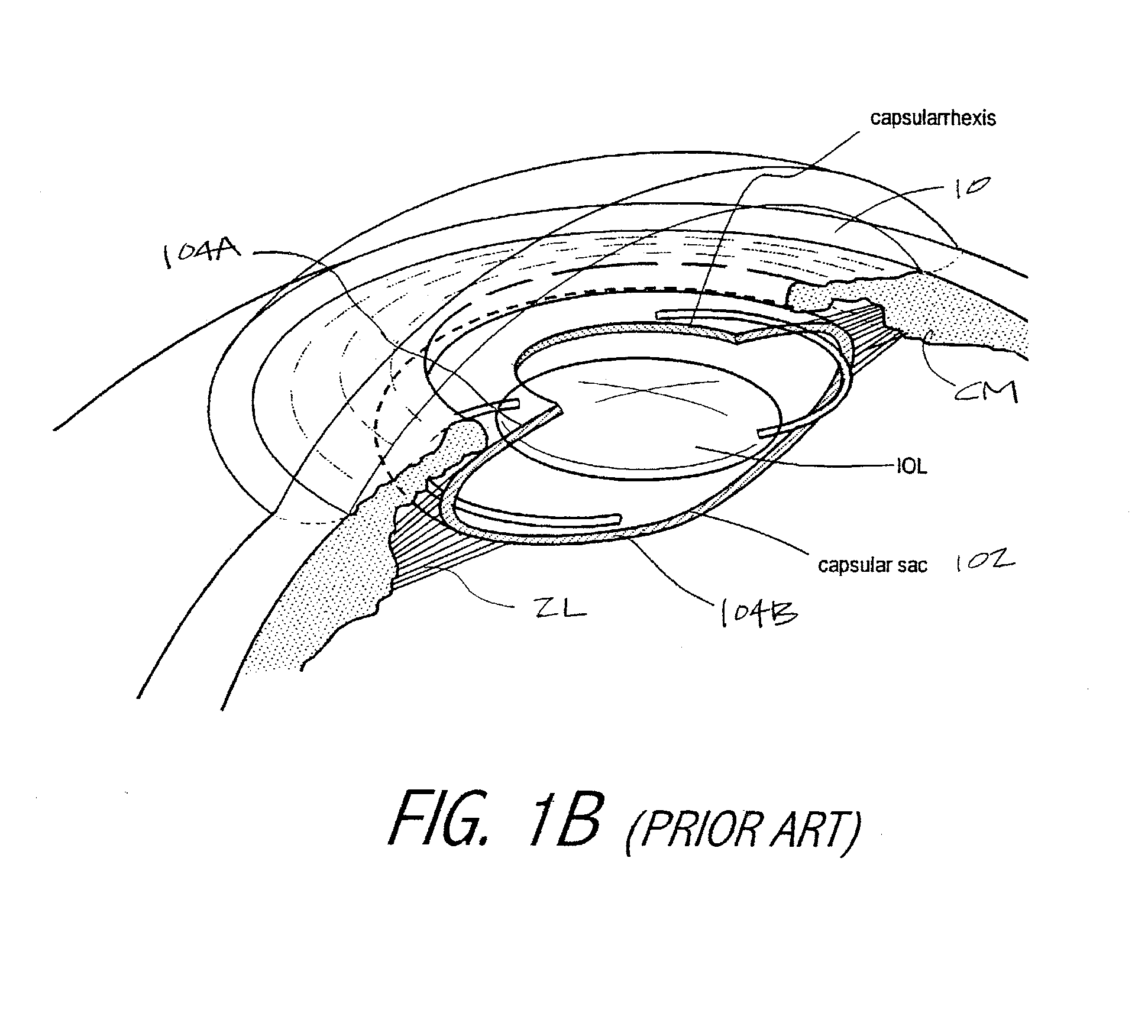
A deformable intracapsular implant device for shaping an enucleated lens capsule sac for use in cataract procedures and refractive lensectomy procedures. In one embodiment, the intraocular implant devices rely on thin film shape memory alloys and combine with the post-phaco capsular sac to provide a biomimetic complex that can mimic the energy-absorbing and energy-releasing characteristics of a young accommodative lens capsule. In another embodiment, the capsular shaping body is combined with an adaptive optic. The peripheral capsular shaping body carries at least one fluid-filled interior chamber that communicates with a space in a adaptive optic portion that has a deformable lens surface. The flexing of the peripheral shaping body in response to zonular tensioning and de-tensioning provides an inventive adaptive optics mechanism wherein fluid media flows between the respective chambers “adapts” the optic to increase and decrease the power thereof. In one embodiment, the capsular shaping body carries a posterior negative power adaptive optic that can be altered in power during accommodation to cooperate with an independent drop-in exchangeable intraocular lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Adaptive optic lens system and method of use
InactiveUS6966649B2Reduce aberrationHigh order aberrationSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsCamera lensCorneal inlay
An lens for correcting human vision, for example an IOL, contact lens or corneal inlay or onlay, that carries and interior phase or layer comprising a pattern of individual transparent adaptive displacement structures. In one embodiment, the displacement structures are actuated by a shape memory polymer (SMP) material or other polymer that is adjustable in shape in response to applied energy. The SMP can be designed to be selectively adjustable in volumetric dimension, modulus of elasticity and / or permeability. The adaptive optic means of the invention can be used to create highly localized surface corrections in the lens to correct higher order aberrations—which types of surfaces cannot be fabricated into and IOL and then implanted. The system of displacement structures also can provide spherical corrections in the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Accommodating Intraocular Lens
InactiveUS20100228344A1Minimal incisionSimplified lens exchangeIntraocular lensIntraocular lensCataract surgery
A deformable intracapsular implant device for shaping an enucleated lens capsule sac for use in cataract procedures and refractive lensectomy procedures. In one embodiment, the intraocular implant devices rely on thin film shape memory alloys and combine with the post-phaco capsular sac to provide a biomimetic complex that can mimic the energy-absorbing and energy-releasing characteristics of a young accommodative lens capsule. In another embodiment, the capsular shaping body is combined with an adaptive optic. The peripheral capsular shaping body carries at least one fluid-filled interior chamber that communicates with a space in a adaptive optic portion that has a deformable lens surface. The flexing of the peripheral shaping body in response to zonular tensioning and de-tensioning provides an inventive adaptive optics mechanism wherein fluid media flows between the respective chambers “adapts” the optic to increase and decrease the power thereof. In one embodiment, the capsular shaping body carries a posterior negative power adaptive optic that can be altered in power during accommodation to cooperate with an independent drop-in exchangeable intraocular lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
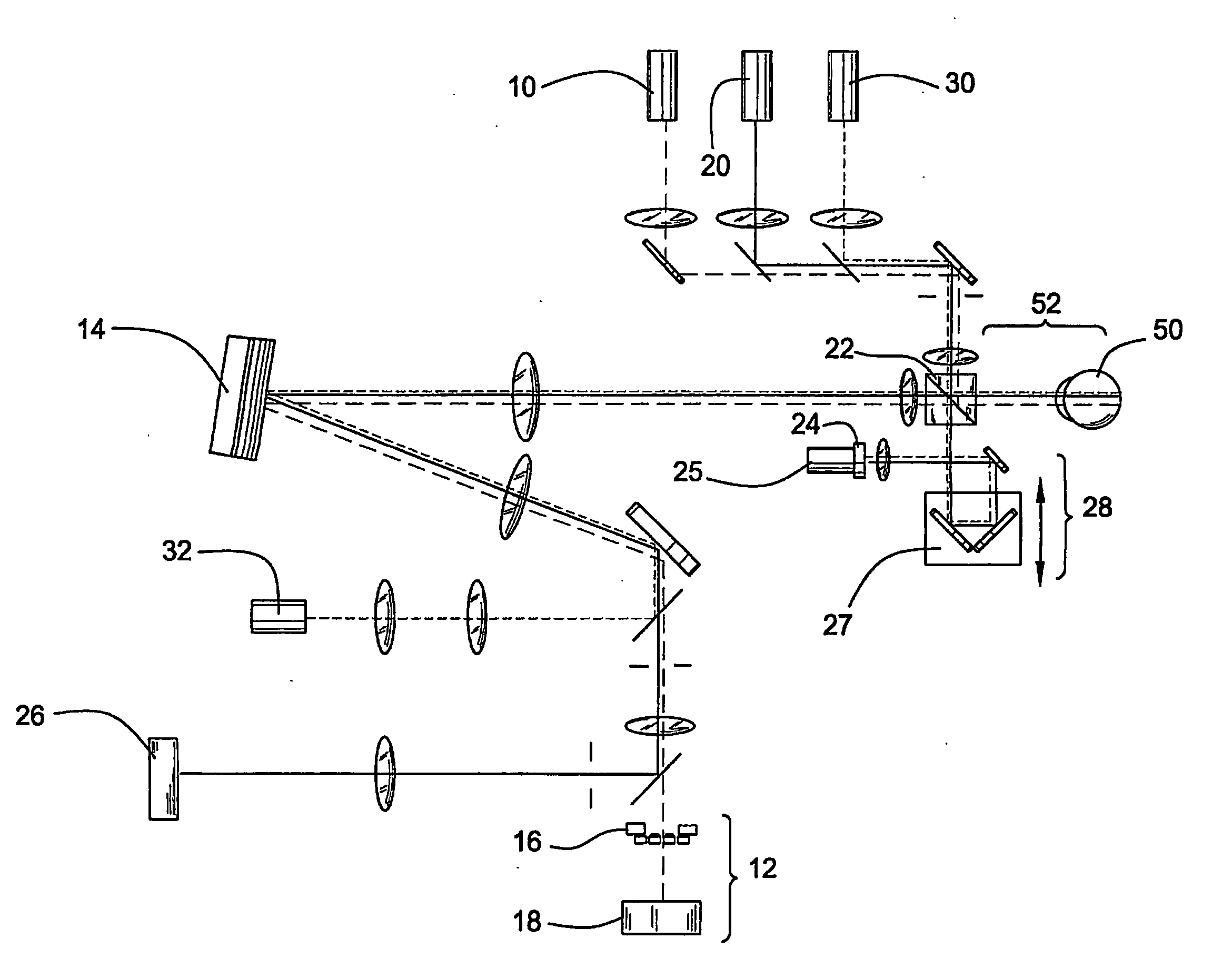
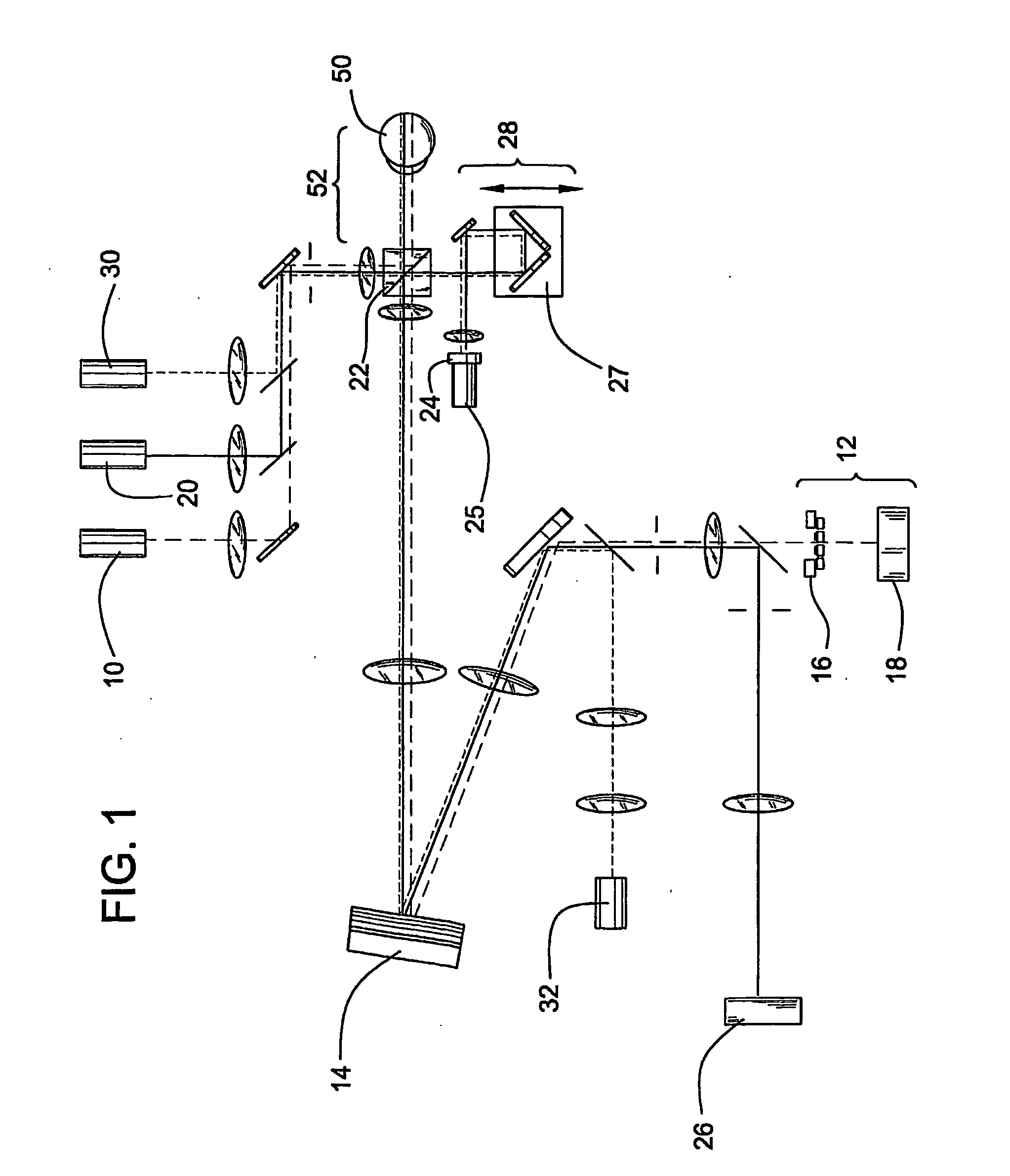
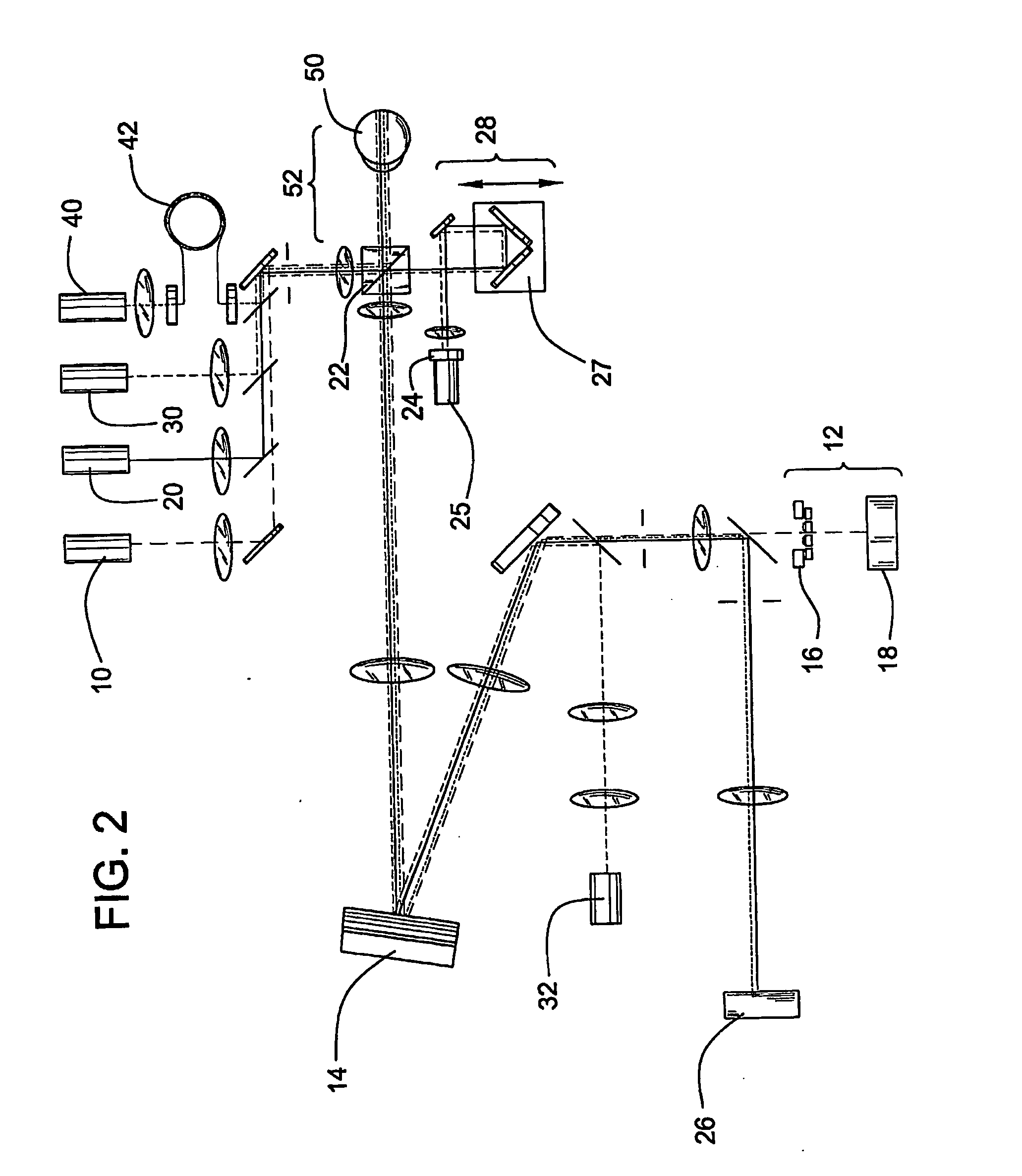
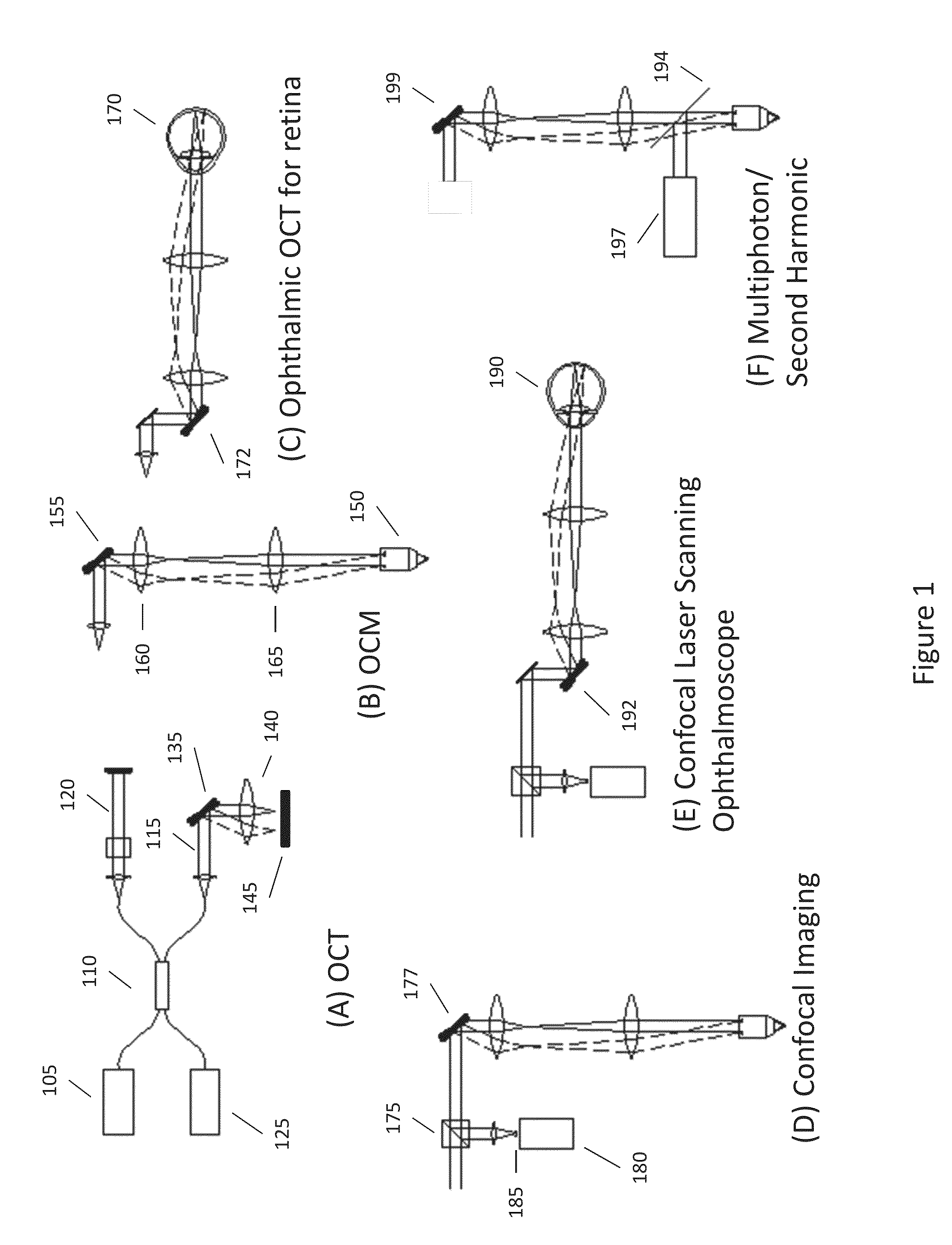
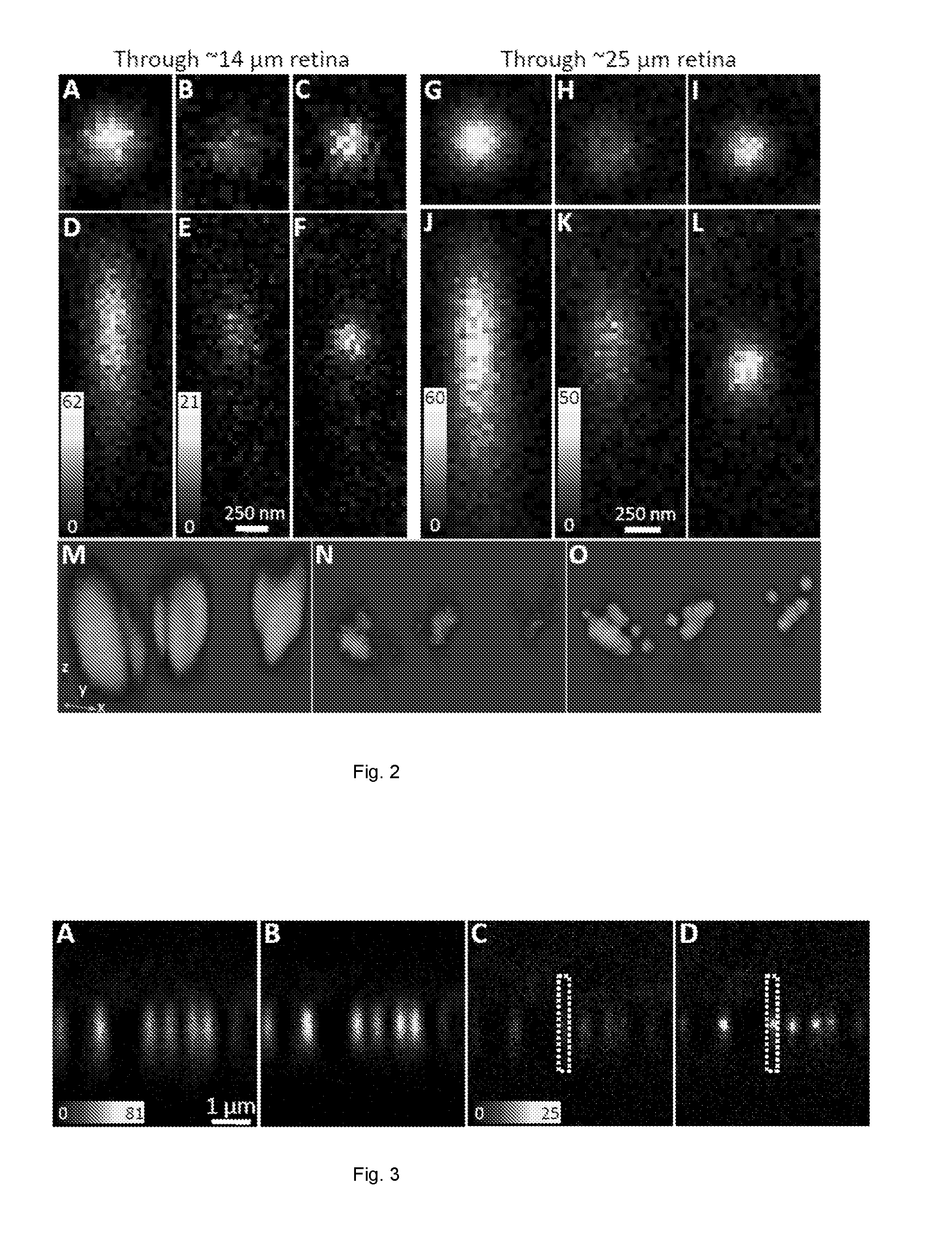
Method and apparatus for improving both lateral and axial resolution in ophthalmoscopy
The invention provides a method of optical imaging comprising providing a sample to be imaged, measuring and correcting aberrations associated with the sample using adaptive optics, and imaging the sample by optical coherence tomography. The method can be used to image the fundus of a human eye to provide diagnostic information about retinal pathologies such as macular degeneration, retinitis pigmentosa, glaucoma, or diabetic retinopathy. The invention further provides an apparatus comprising an adaptive optics subsystem and a two-dimensional optical coherence tomography subsystem.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Optical mapping apparatus
InactiveUS20070046948A1Easy to useHigh depth resolutionUsing optical meansOthalmoscopesOptical mappingTomography
Optical mapping apparatus for imaging an object, comprising an optical coherence tomography (OCT) system including an OCT source, an OCT reference path leading from the OCT source to an OCT receiver, an OCT object path leading from the object to the OCT coupler, an OCT depth scanner adapted to alter at least one of the OCT reference path and the OCT receiver path. A confocal system is provided including a confocal optical receiver a confocal path leading from the object to the confocal optical receiver via a confocal input aperture. An adaptive optics (AO) system is provided to correct optical aberrations in the OCT object path and the confocal path.
Owner:KENT UNIVERITY OF +1
Method and apparatus for improving both lateral and axial resolution in ophthalmoscopy
The invention provides a method of optical imaging comprising providing a sample to be imaged, measuring and correcting aberrations associated with the sample using adaptive optics, and imaging the sample by optical coherence tomography. The method can be used to image the fundus of a human eye to provide diagnostic information about retinal pathologies such as macular degeneration, retinitis pigmentosa, glaucoma, or diabetic retinopathy. The invention further provides an apparatus comprising an adaptive optics subsystem and a two-dimensional optical coherence tomography subsystem.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
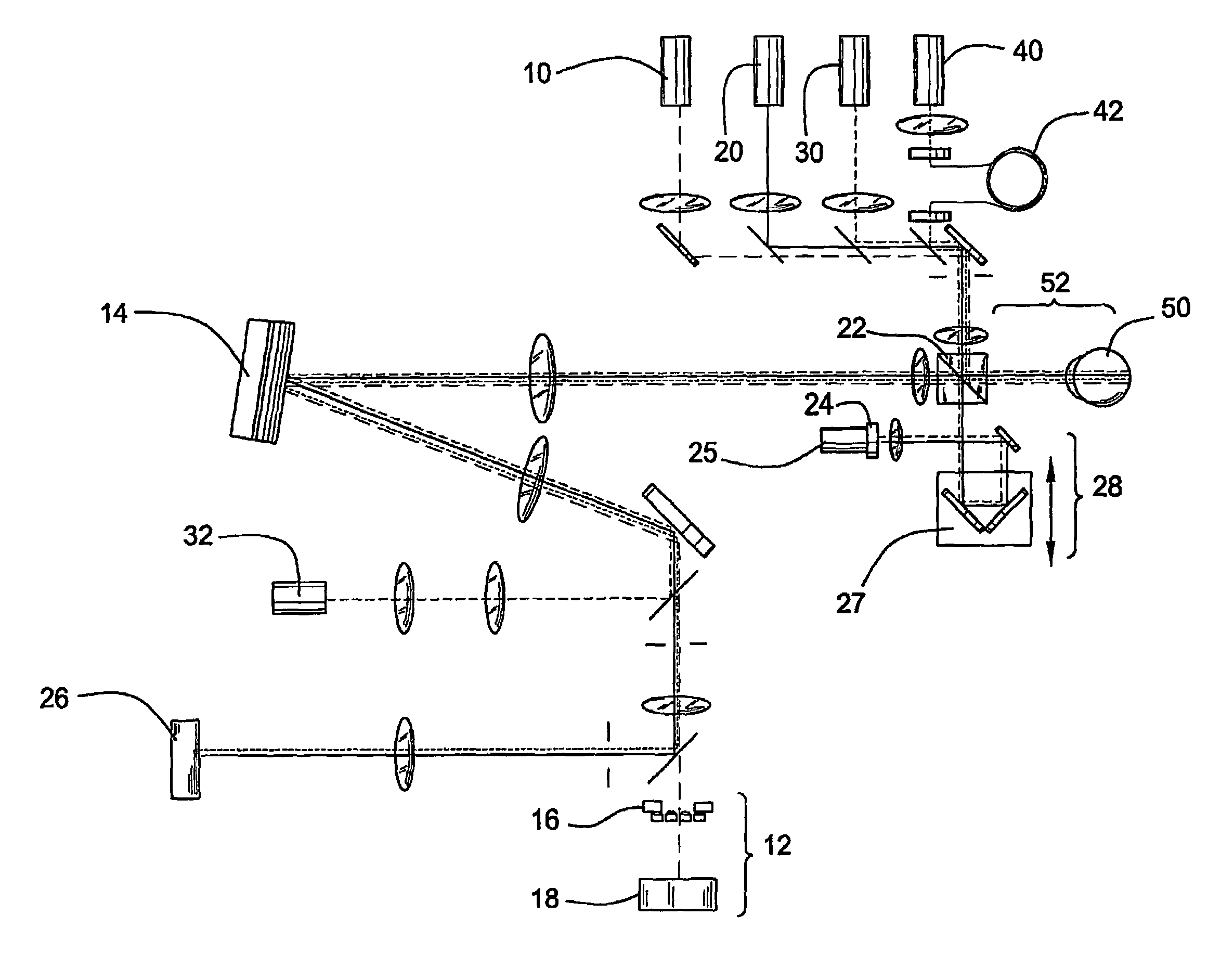
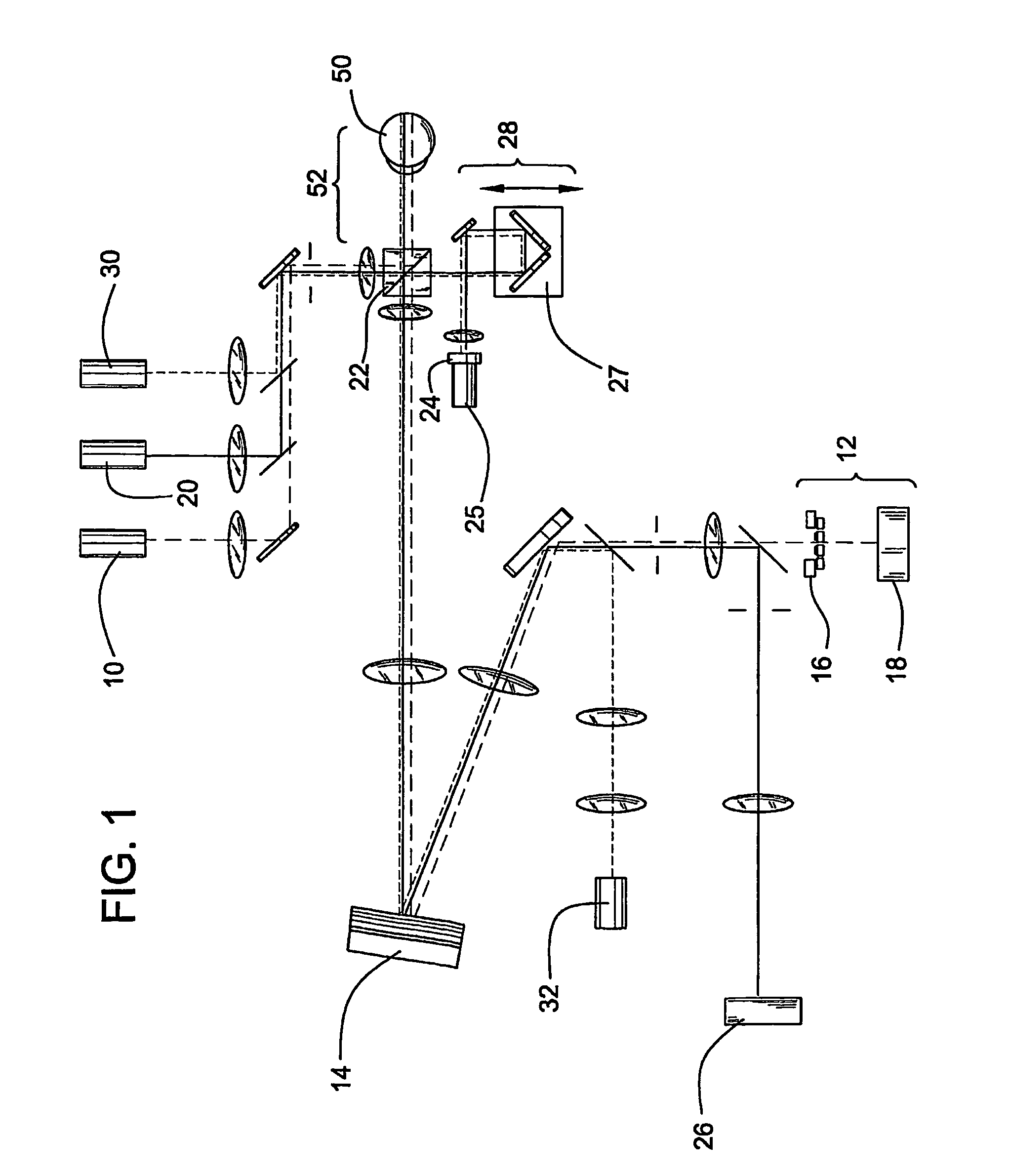
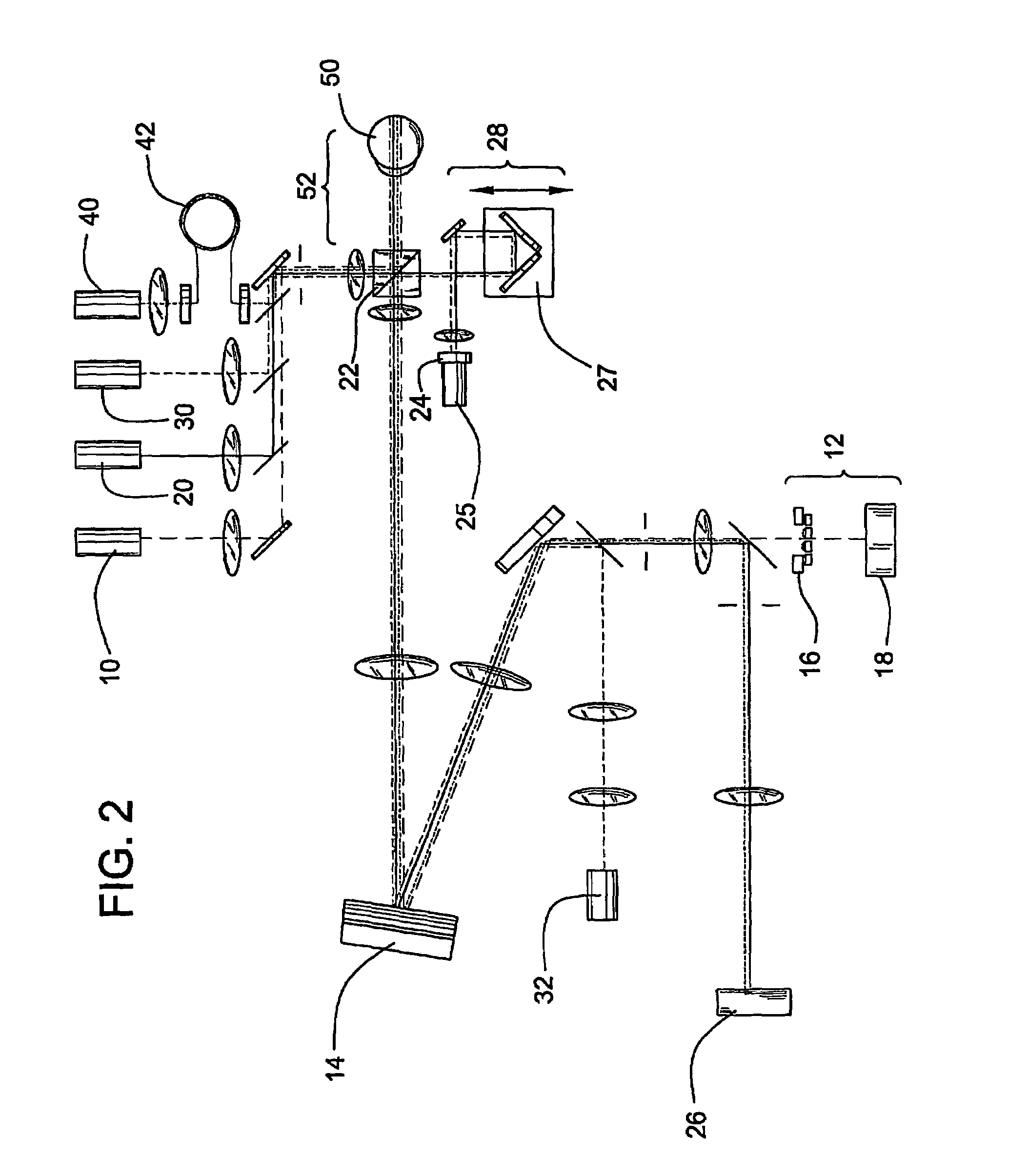
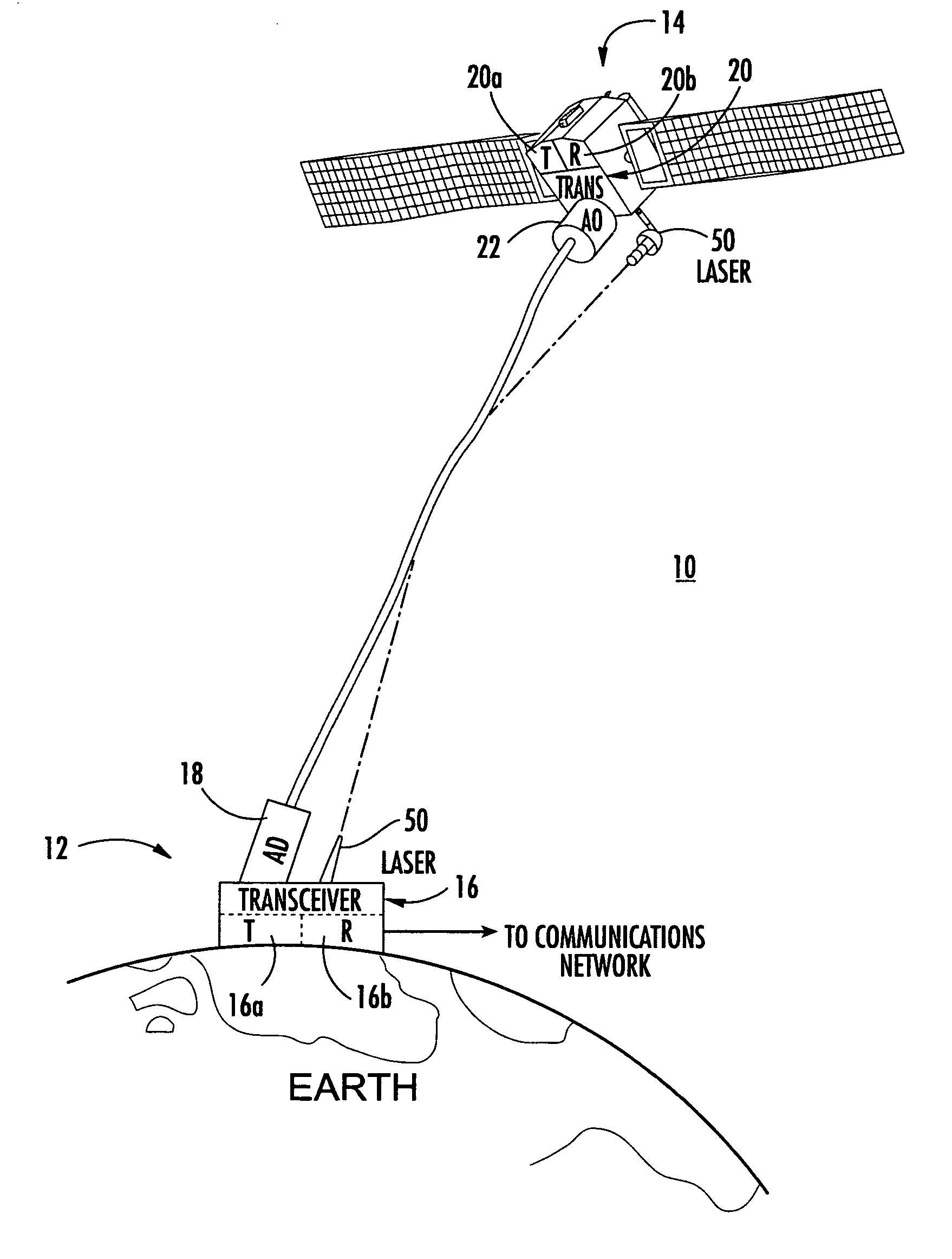
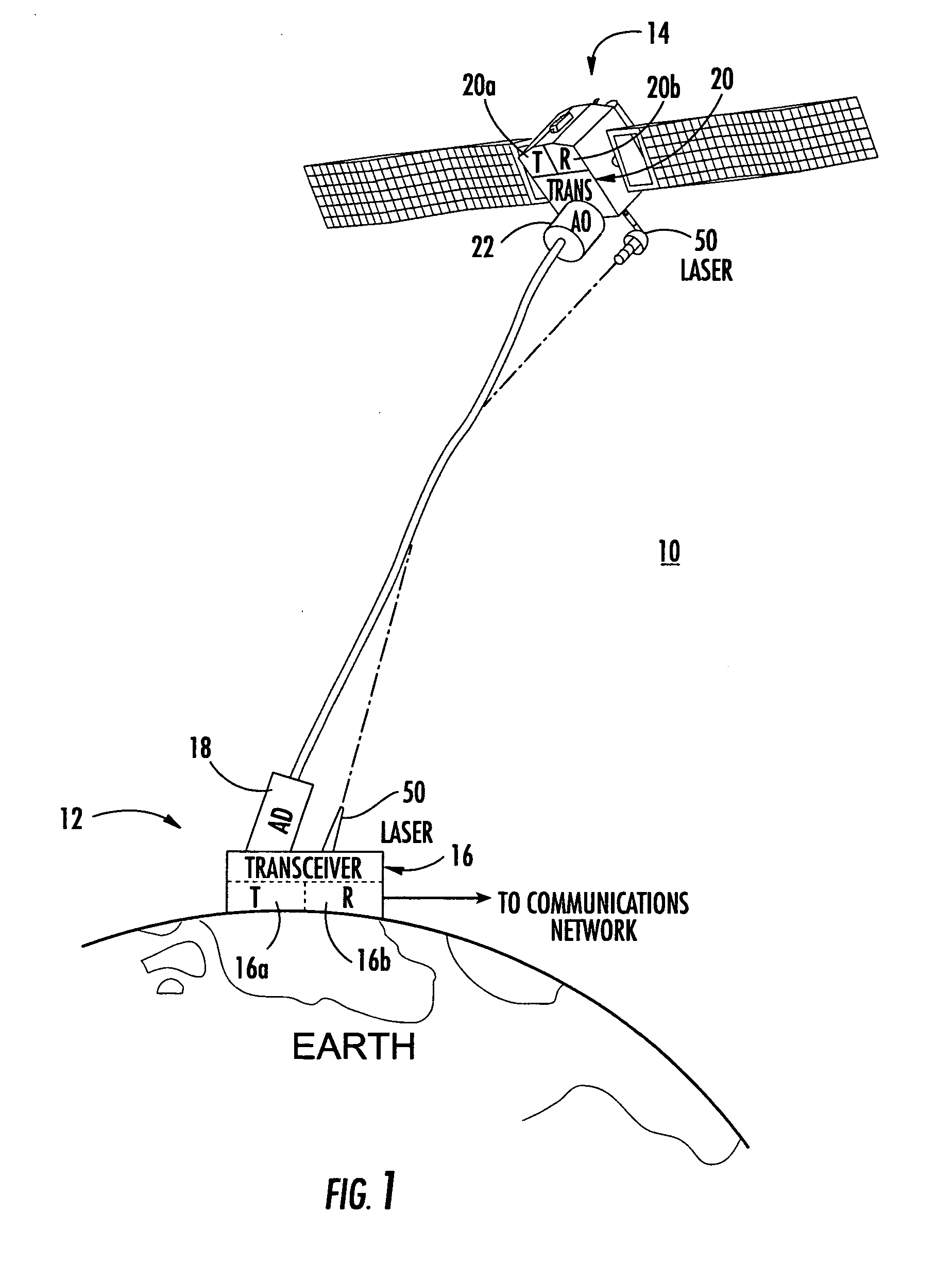
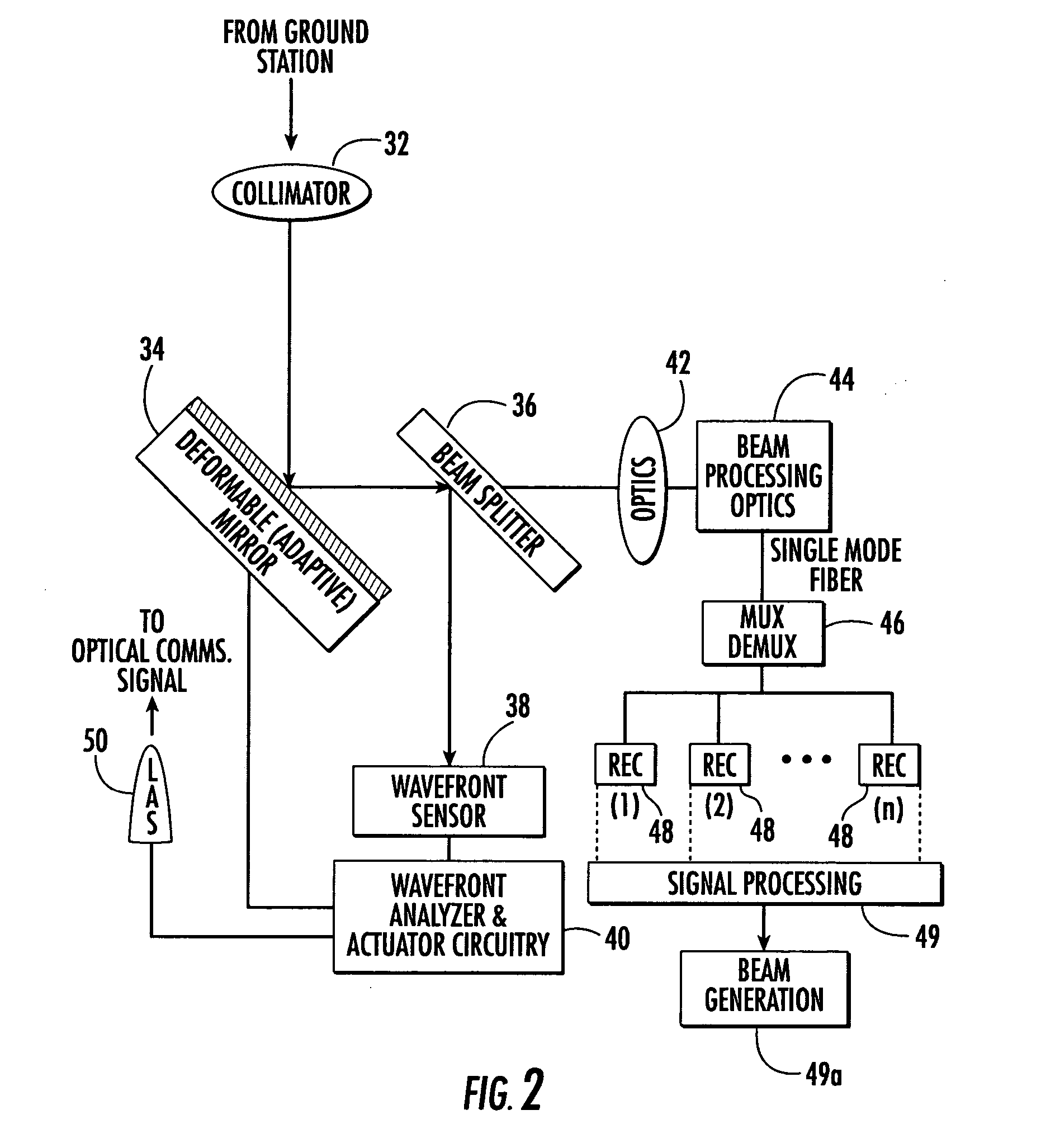
System and method of free-space optical satellite communications
InactiveUS20050100339A1Reduce and eliminate distortionIncrease volumeSatellite communication transmissionWavefrontTransceiver
A system and method of free-space optical satellite communications includes a ground station and transceiver for transmitting and receiving an optical communications signal. Adaptive optics at the ground station are operative with the transceiver for determining the shape of any distortions in the wavefront of the optical communications signal and compensating at the ground station for the distortions. A satellite includes a transceiver for transmitting and receiving the optical communications signal and includes adaptive optics for determining the shape of any distortions in the waveform of the optical communications signal and compensating at the satellite for the distortions.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
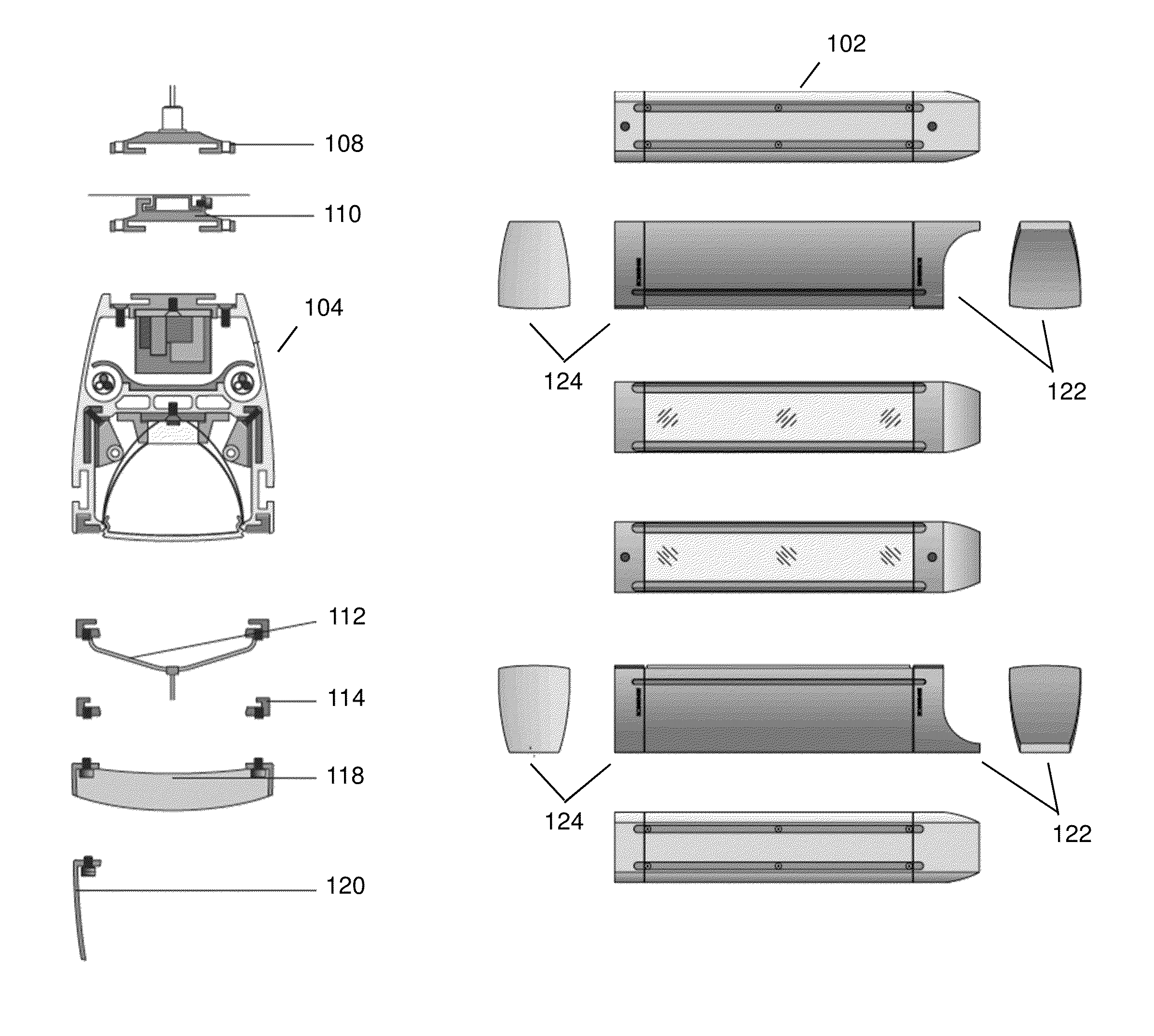
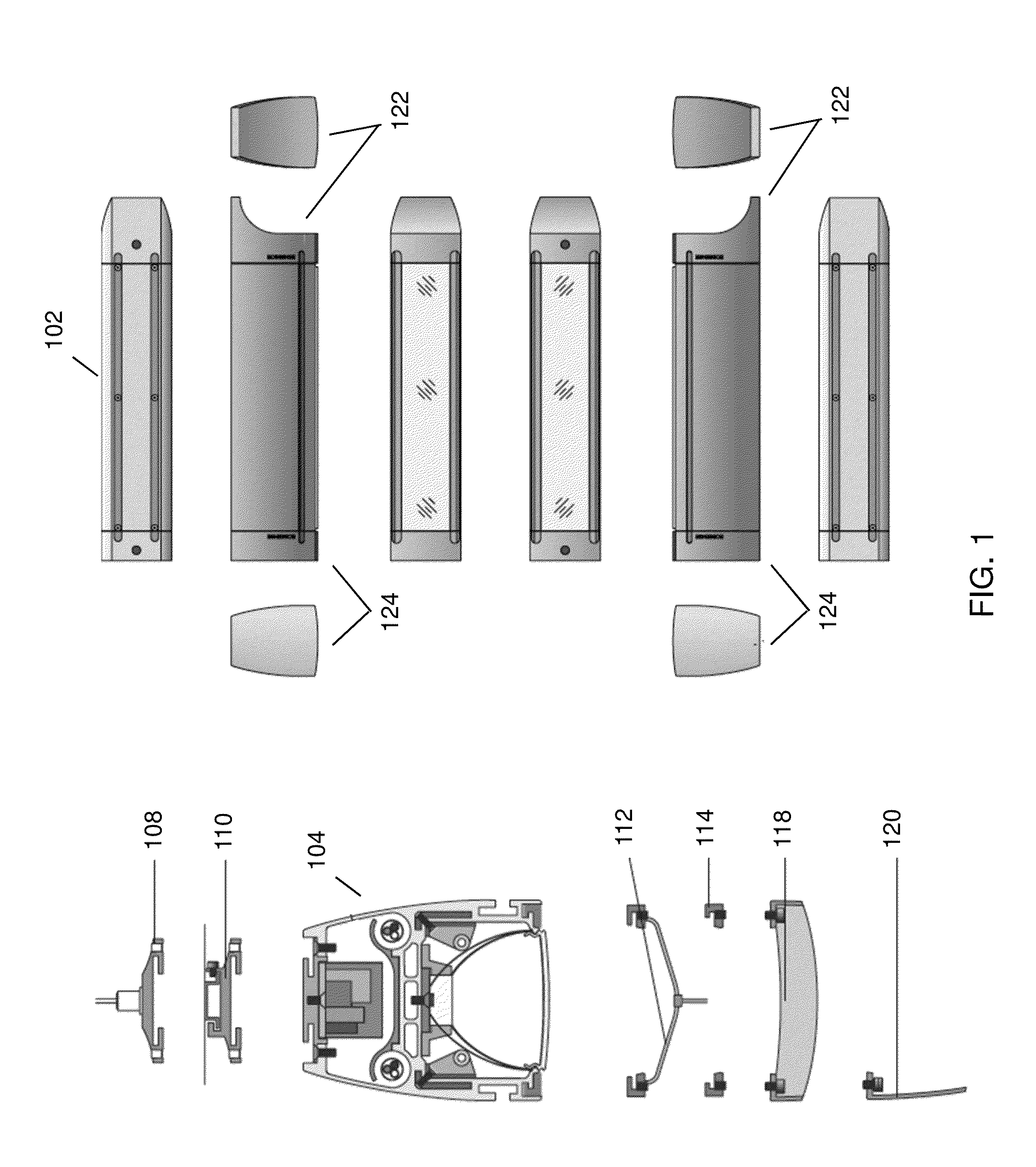
Linear LED light housing
ActiveUS20130094225A1Connection securityPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesElectricityEngineering
In embodiments of the present disclosure improved capabilities are described for a modular linear LED lighting system providing a flexible architectural slot lighting system with multiple configurations based on the same base body design with a performance of traditional lighting sources. The linear LED lighting system comprises at least one of a multiple attachment facility, multiple functional compartments, a linear series internal attachment facility, an end cap electrical interconnection facility, an adaptable optic facility, and a dimming facility.
Owner:KORRUS INC
Compact, low dispersion, and low aberration adaptive optics scanning system
ActiveUS20140104618A1Small sizeImprove instrument performanceEye diagnosticsUsing optical meansLight-adaptedLight beam
An adaptive optics scanning system using a beam projection module with four or more axes of motion that can project and control the position and angle of a beam of light to or from an adaptive optics element. The adaptive optics scanning system is compact in size, overcoming the challenges of a traditional lens and mirror based pupil relay design. The adaptive optics scanning system has little to no dispersion, chromatic aberration, and off-axis aberration for improved optical performance. The system and methods for calibrating and optimizing the system are described. A modular adaptive optics unit that scans and interfaces an adaptive optics element is described.
Owner:THORLABS INC
Adaptive optical devices with controllable focal power and aspheric shape
ActiveUS20130176628A1Limit ability to control optical propertyReduce optical aberrationLensRefractive indexEngineering
A fluidic lens may include an optical surface configured for deflection dominated by bending stress. An adjustable concentric load may be applied to the optical surface to cause a clear aperture region of the optical surface to deflect with generally spherical curvature. Adjusting the concentric load controls the radius of curvature. An adjustable uniformly-distributed load may be applied to the optical surface by fluid pressure that causes the clear aperture region to deflect with an aspheric shape. Adjusting the pressure controls the asphericity of curvature. First and second fluids having similar densities and different refractive indexes may be disposed on either side of a deflectable optical surface to help balance gravitational loading on either side of the optical surface, thereby reducing gravity-associated aberrations.
Owner:HOLOCHIP
Method for determining vision defects and for collecting data for correcting vision defects of the eye by interaction of a patient with an examiner and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS6997555B2Easy to catchGood utilization basisRefractometersSkiascopesElectronic control systemComputer science
There is now provided a method for determining vision defects and for collecting data for correcting vision defects of the eye. The method comprises projecting an image into the eye of the patient with an adaptive optical system having adaptive optical elements. The optical characteristics of the optical elements can be individually changed by an electrical signal. The presence of distortions of the image as perceived by the patient is determined by interaction of the patient with the examiner. By way of an electronic control system the optical characteristics of the adaptive optical elements are changed through outputting of an electrical signal to obtain a modified image with minimized distortions in the eye of the patient. The optical characteristics of the adaptive optical elements, as modified, are determined and vision correcting data for the eye being examined are computed from the optical characteristics of the adaptive optical elements, as modified. The method not only takes into consideration the aberrations of the optical imaging system but also the properties of reception and signal processing in the human brain. The method is further characterized in that the correction data for the aberrations of the human eye that impair the vision can be obtained by a measuring method that is actively physiologically evaluated beforehand. There is also provided an apparatus for determining vision defects and for collecting data for correcting vision defects.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Adaptive optic lens and method of making
An lens for correcting human vision, for example an IOL, contact lens or corneal inlay or onlay, that carries and interior phase or layer comprising a pattern of individual transparent adaptive displacement structures. In the exemplary embodiments, the displacement structures are actuated by shape change polymer that adjusts a shape or other parameter in response to applied energy that in turn displaces a fluid media within the lens that actuates a flexible lens surface. The adaptive optic means of the invention can be used to create highly localized surface corrections in the lens to correct higher order aberrations-which types of surfaces cannot be fabricated into and IOL and then implanted. The system of displacement structures also can provide spherical corrections in the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
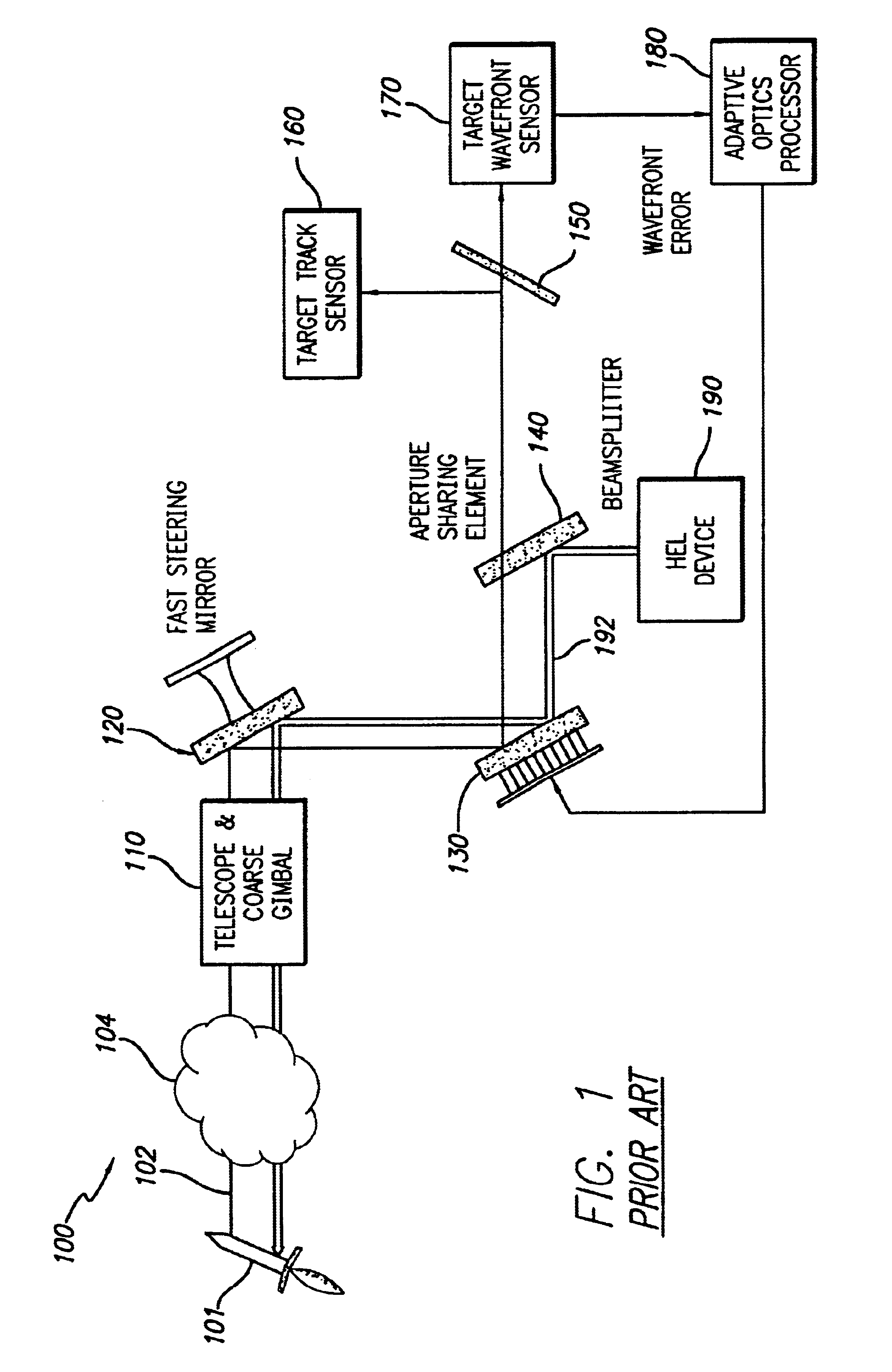
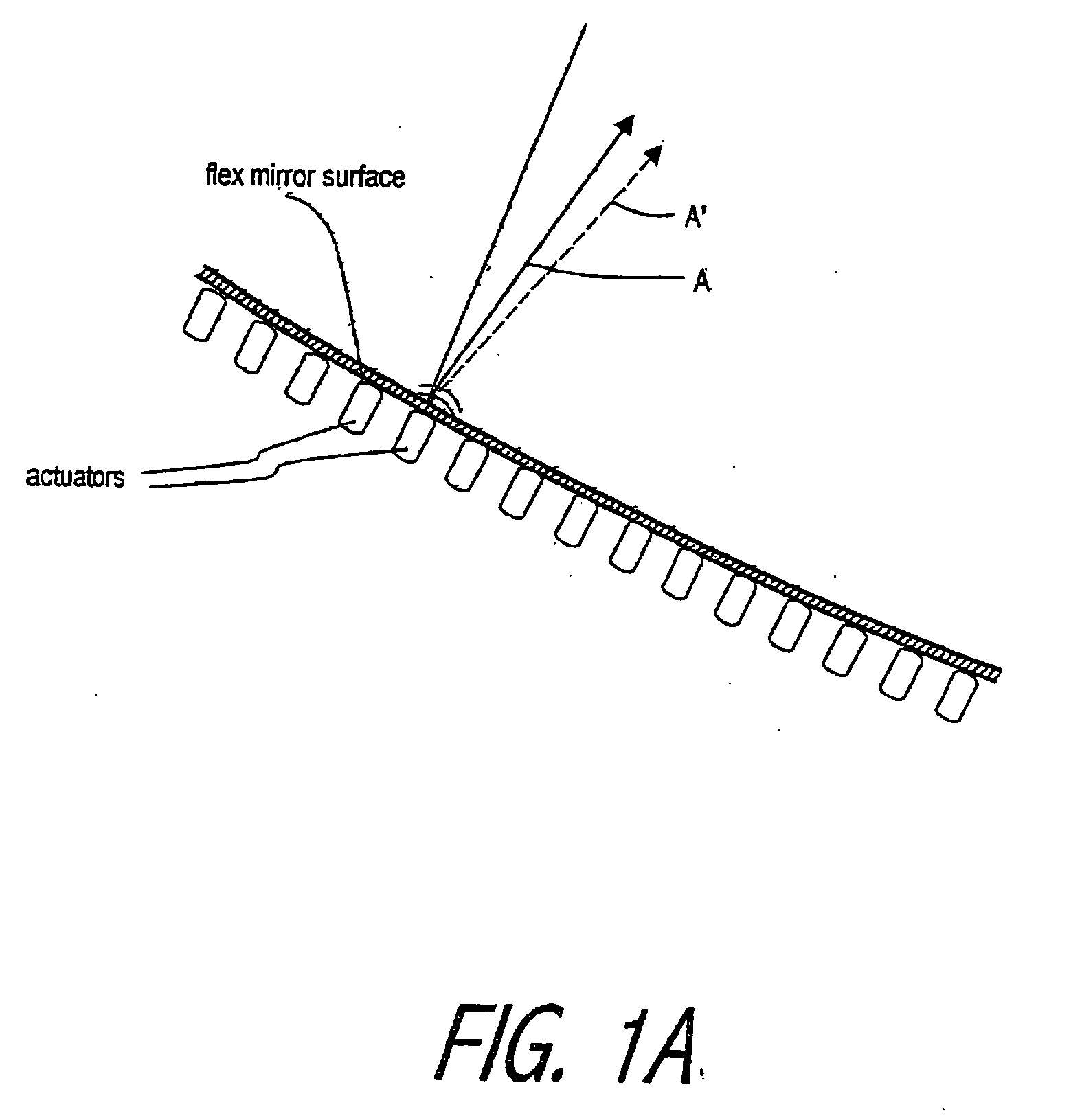
System and method for effecting high-power beam control with adaptive optics in low power beam path
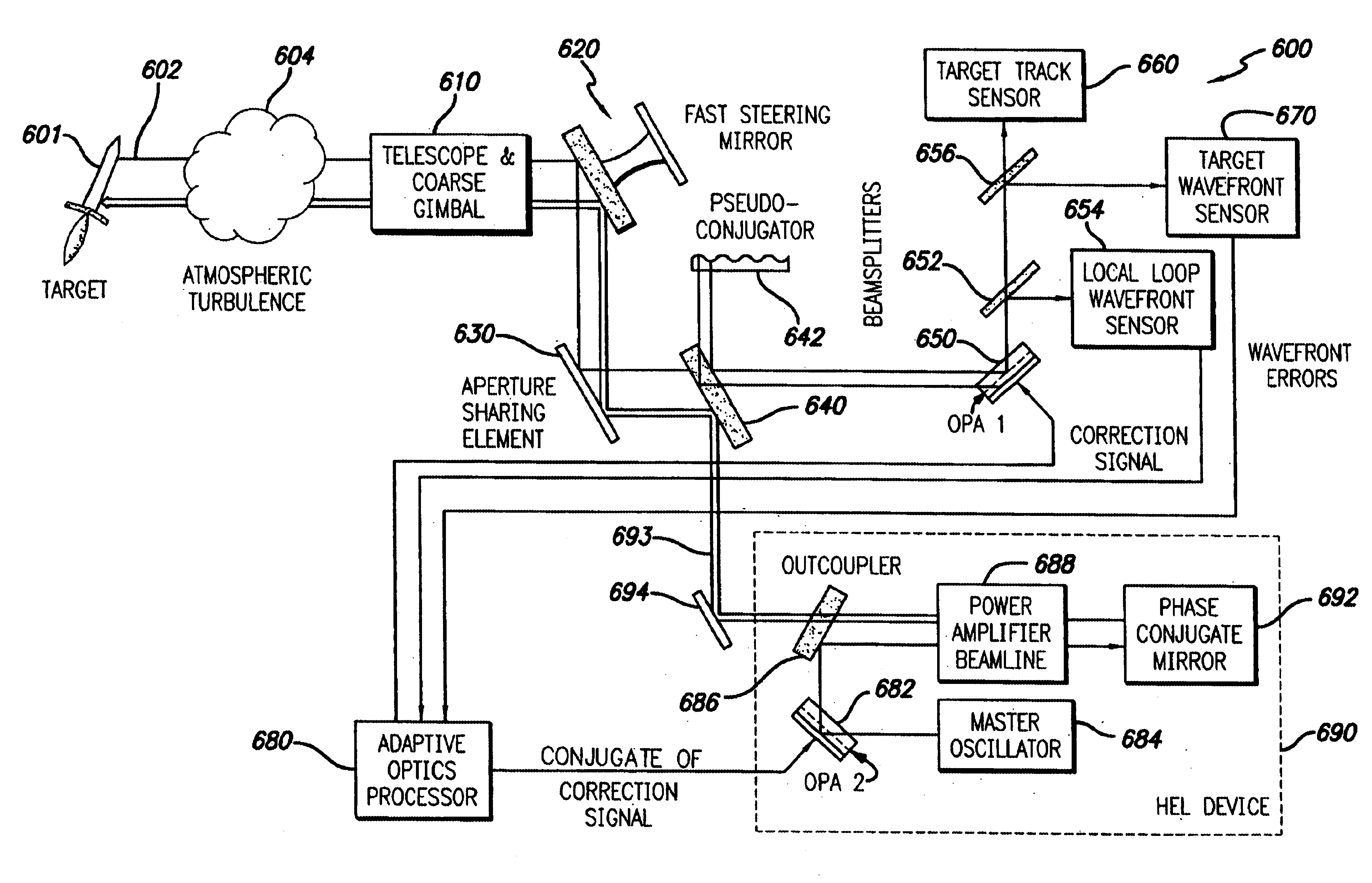
InactiveUS20030062468A1Photometry using reference valueBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsEngineeringTelescope
A beam control system and method which utilizes the wavefront reversal property of nonlinear optical phase conjugation to permit incorporation of a liquid crystal OPA within the low power legs of the beam control system, thereby affording the advantages of the OPA without the power limitations thereof. The invention is adapted for use with a beacon for illuminating a target with a first beam of electromagnetic energy. The system includes a telescope (1010) for receiving a target return comprising a reflection of the first beam from the target. An optical phased array (1050) is included for correcting for aberrations in the wavefront of the target return. A mechanism is included for ascertaining the correction applied by the optical phased array to the target return. The mechanism applies the correction to a third beam which ultimately is the output beam. In the illustrative embodiment, the first beam of electromagnetic energy is optical energy and the mechanism includes a first phase conjugate mirror (1091) adapted to conjugate electromagnetic energy output by the third mechanism and a second phase conjugate mirror (1092) adapted to conjugate the output of the first phase conjugate mirror. The fourth mechanism further includes an amplifier (1088) for boosting the signal output by the second phase conjugate mirror (1092) to provide the output beam.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
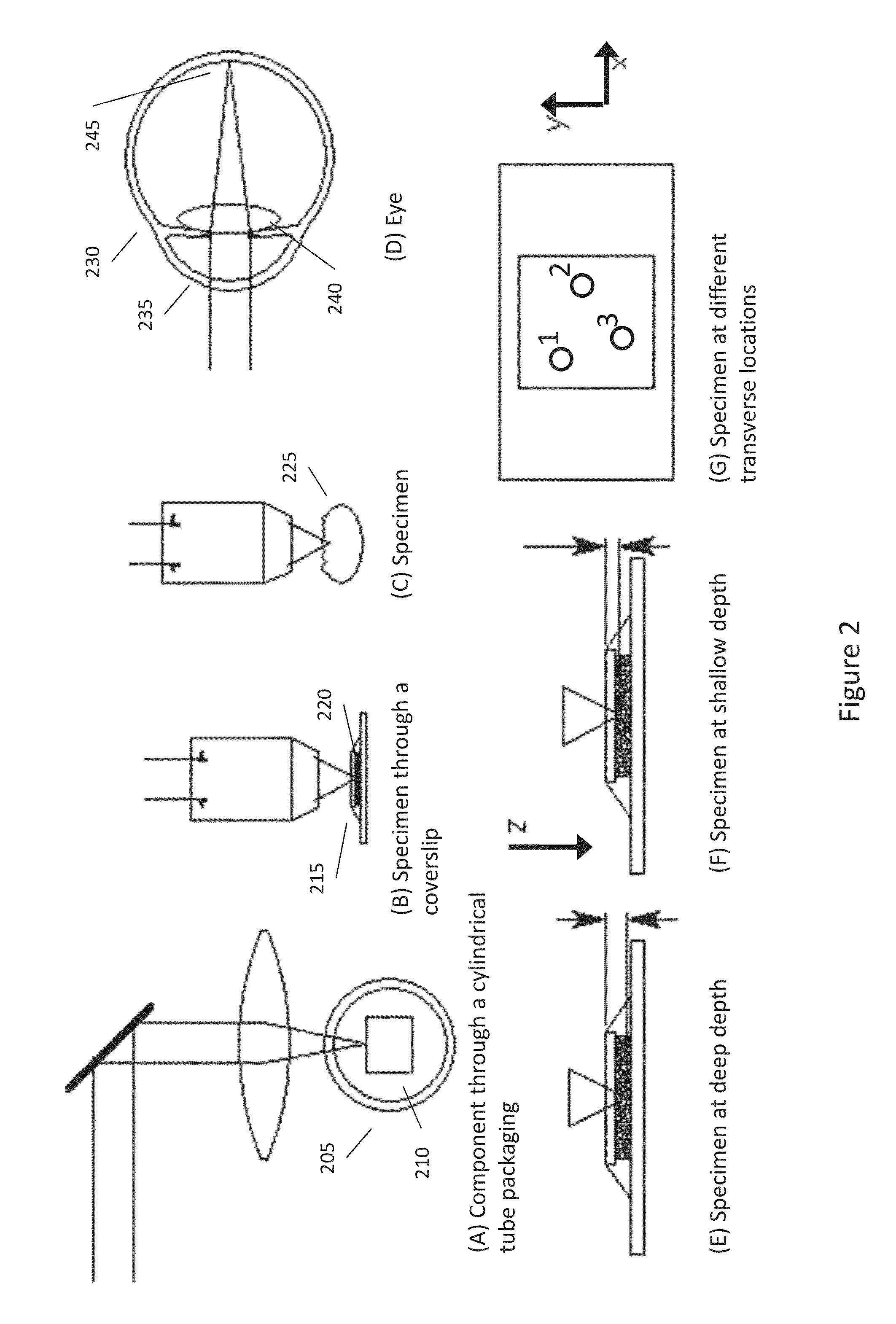
Adaptive-scanning optical microscope
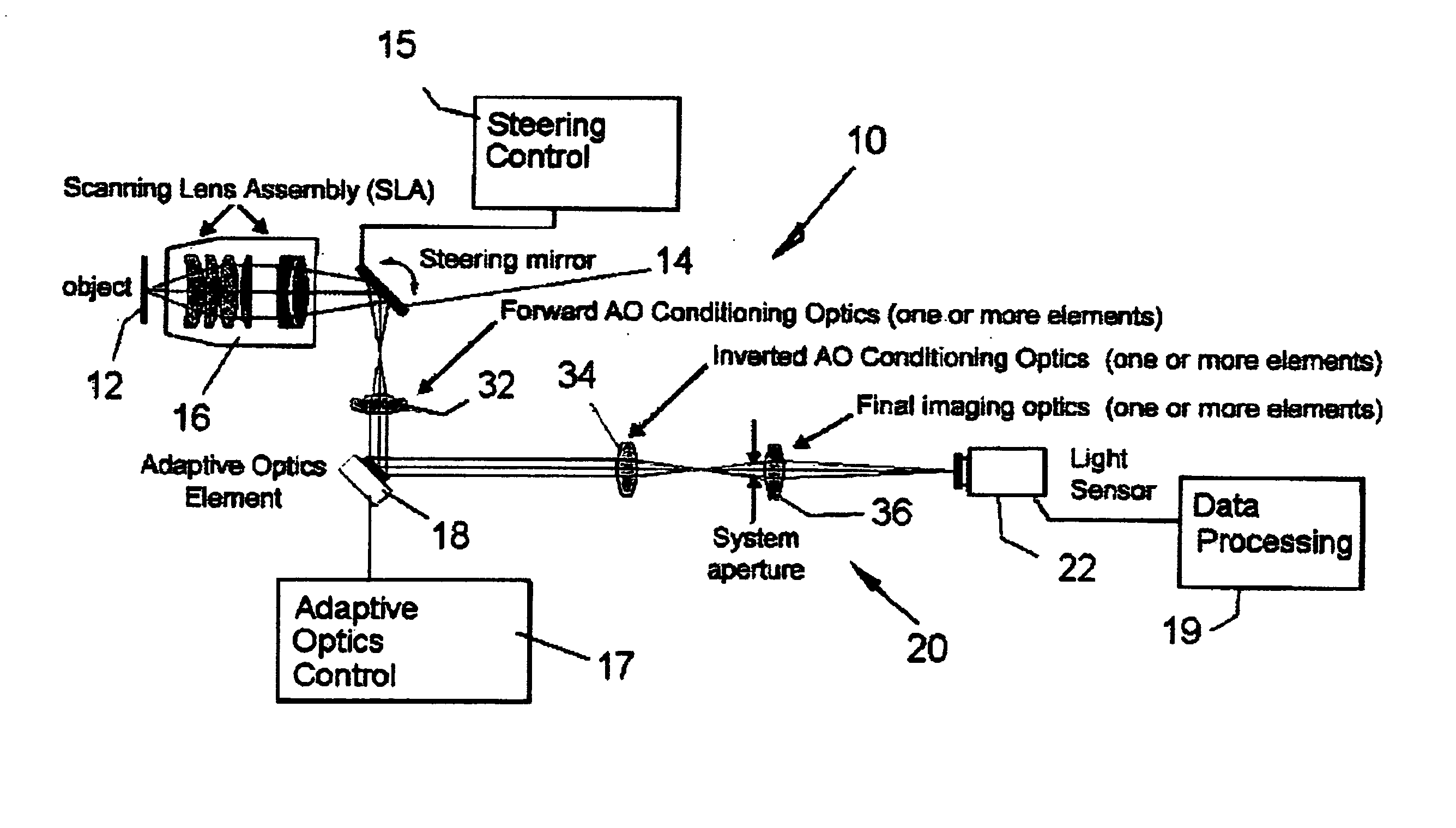
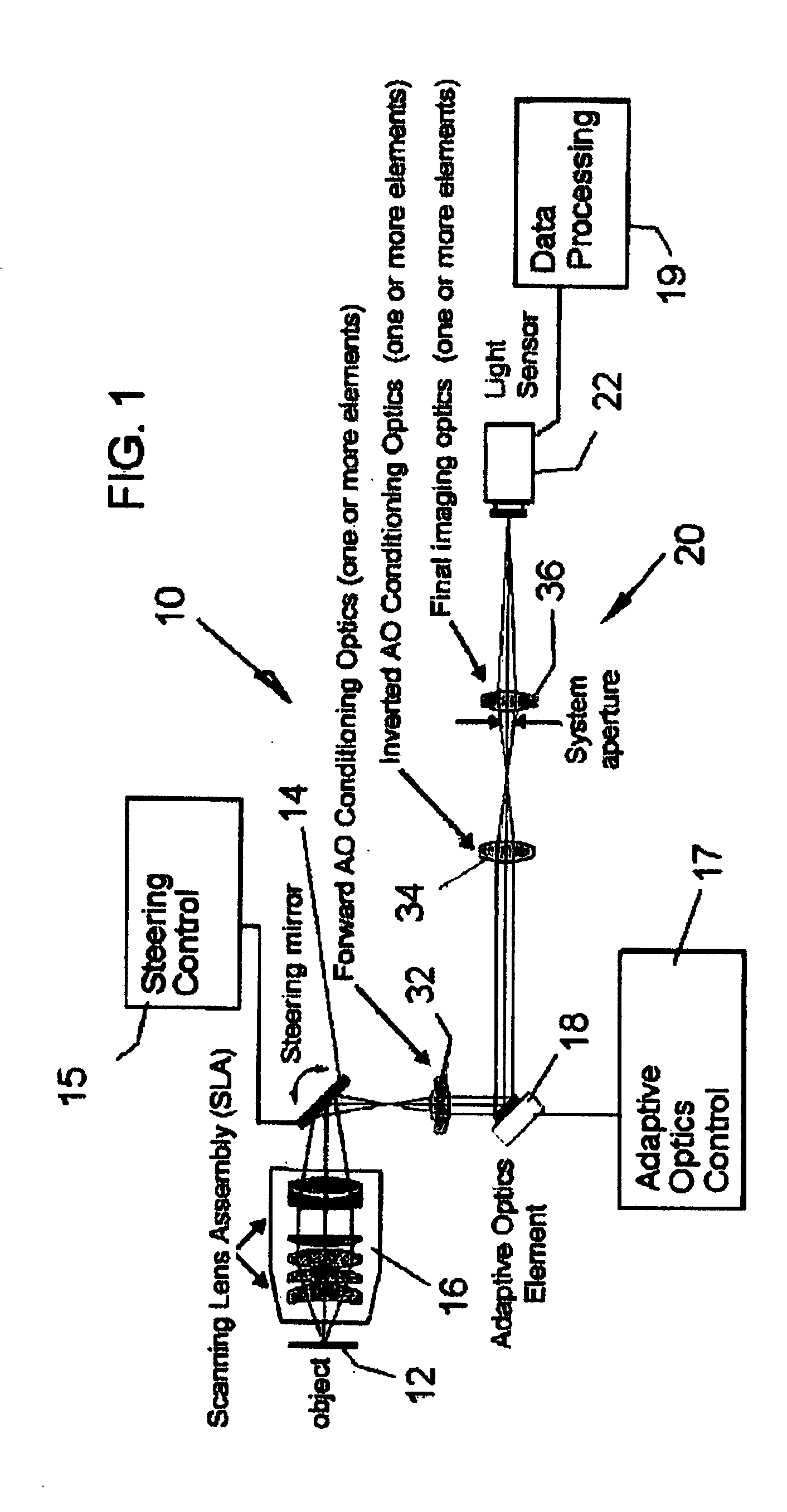
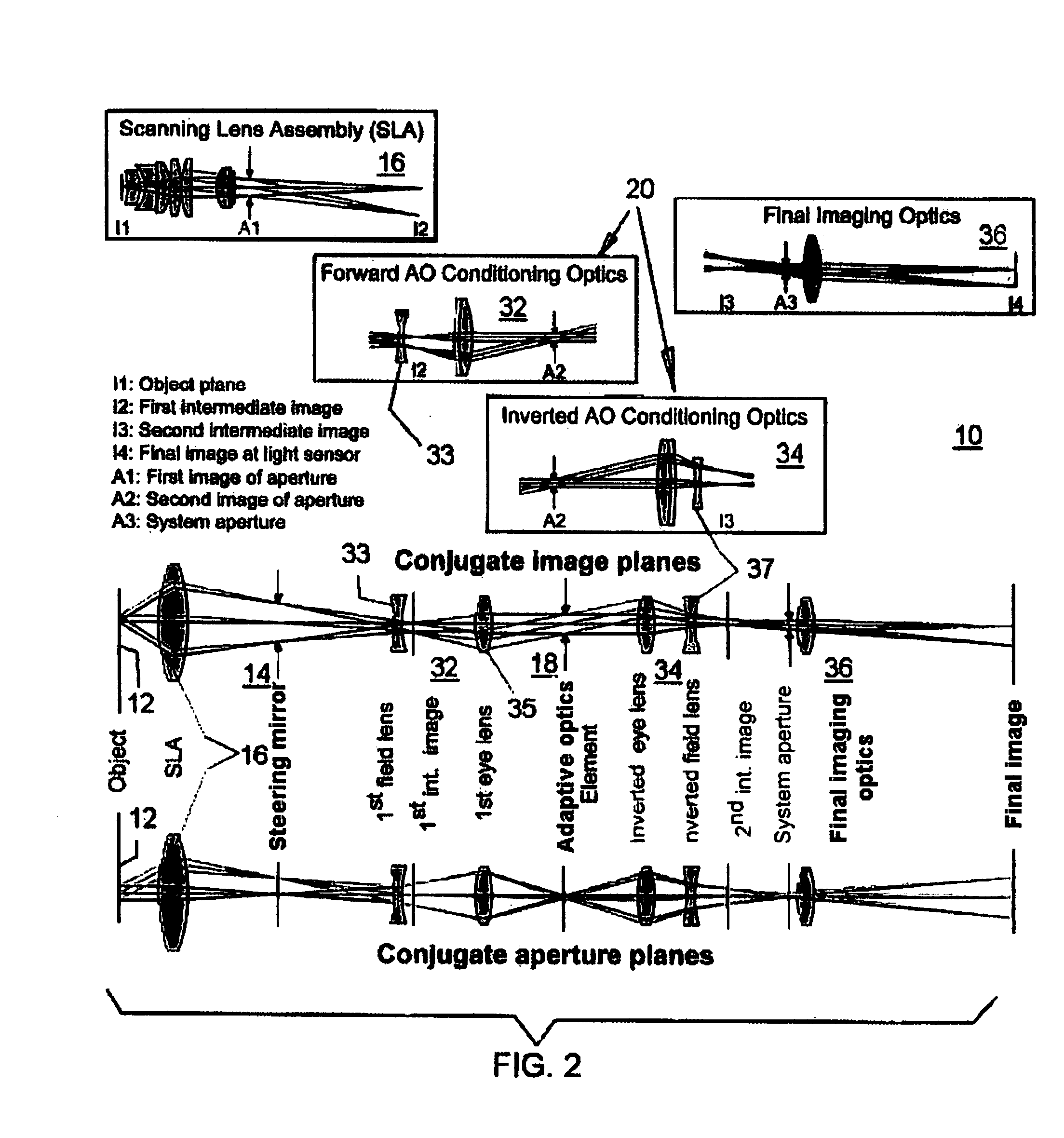
ActiveUS20070253057A1Improve performanceScanner lens is simplifiedMicroscopesPosition dependentOptical aberration
An adaptive scanning optical microscope has a scanner lens assembly for acquiring images from different parts of an object plane and for forming a preferably curved image field having at least some aberration which varies as a function of the part of the object plane from which the image is acquired. A steering mirror selects the field of view and steers light from the object and along a light path from the object plane to a final image plane. An adaptive optics element receives the steered light from the object and compensates for the field position dependent optical aberrations and additional optics are along at least part of the light path for conditioning and focusing the light as it moves from the steering mirror, past the adaptive optics element and to the final image plane.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
System and method for effecting high-power beam control with adaptive optics in low power beam path
InactiveUS6809307B2Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringTelescope
A beam control system and method which utilizes the wavefront reversal property of nonlinear optical phase conjugation to permit incorporation of a liquid crystal OPA within the low power legs of the beam control system, thereby affording the advantages of the OPA without the power limitations thereof. The invention is adapted for use with a beacon for illuminating a target with a first beam of electromagnetic energy. The system includes a telescope (1010) for receiving a target return comprising a reflection of the first beam from the target. An optical phased array (1050) is included for correcting for aberrations in the wavefront of the target return. A mechanism is included for ascertaining the correction applied by the optical phased array to the target return. The mechanism applies the correction to a third beam which ultimately is the output beam. In the illustrative embodiment, the first beam of electromagnetic energy is optical energy and the mechanism includes a first phase conjugate mirror (1091) adapted to conjugate electromagnetic energy output by the third mechanism and a second phase conjugate mirror (1092) adapted to conjugate the output of the first phase conjugate mirror. The fourth mechanism further includes an amplifier (1088) for boosting the signal output by the second phase conjugate mirror (1092) to provide the output beam.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
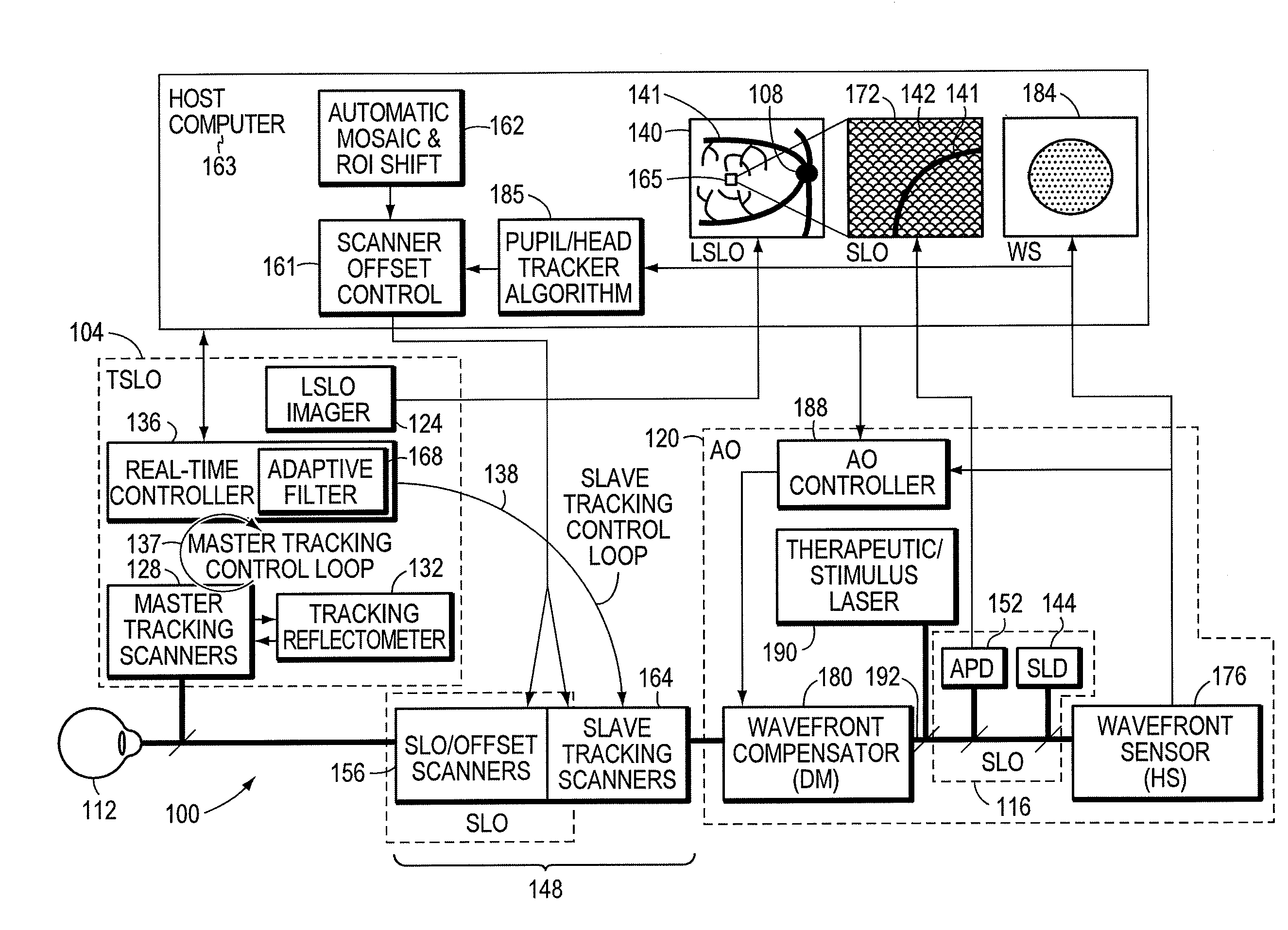
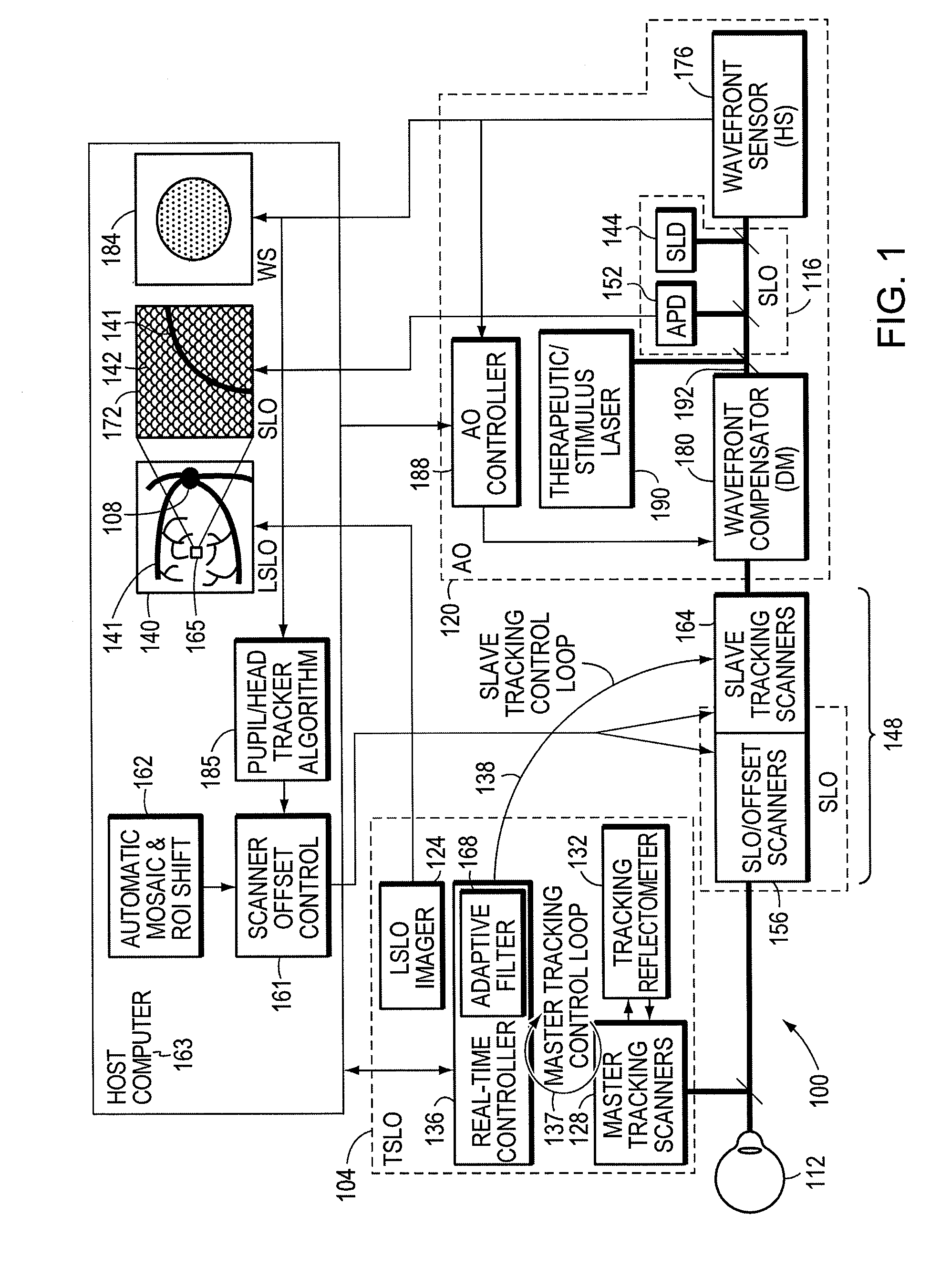
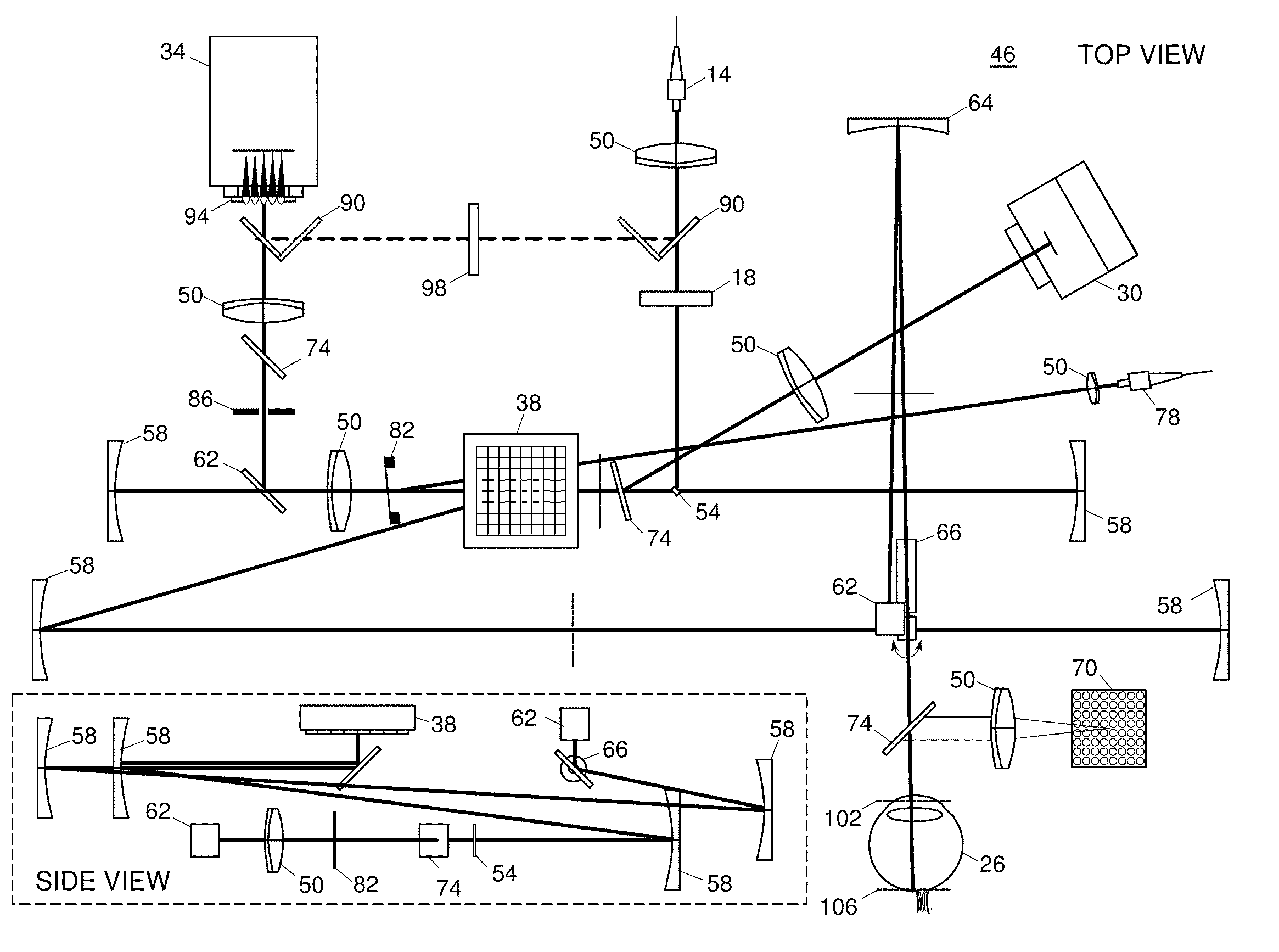
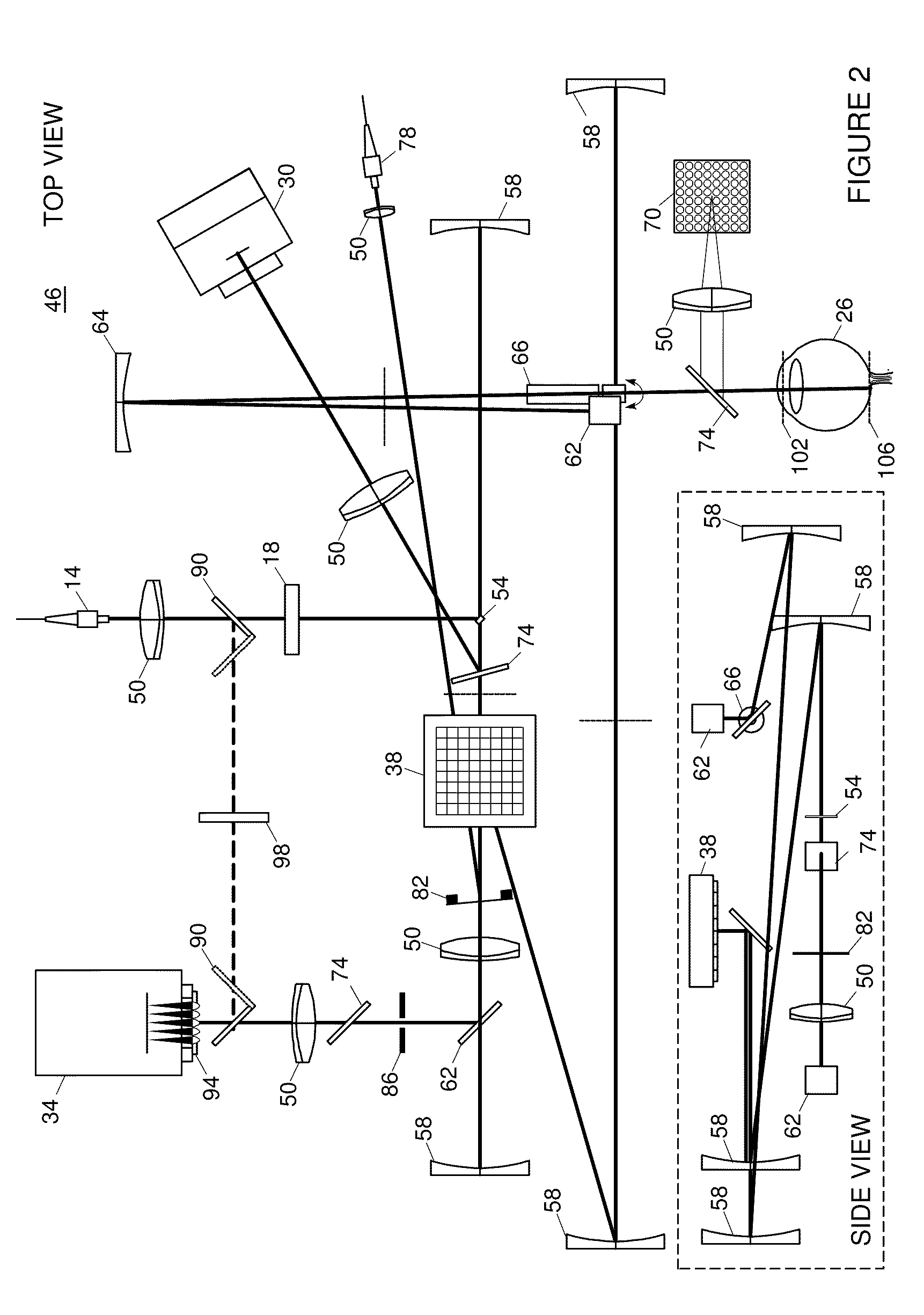
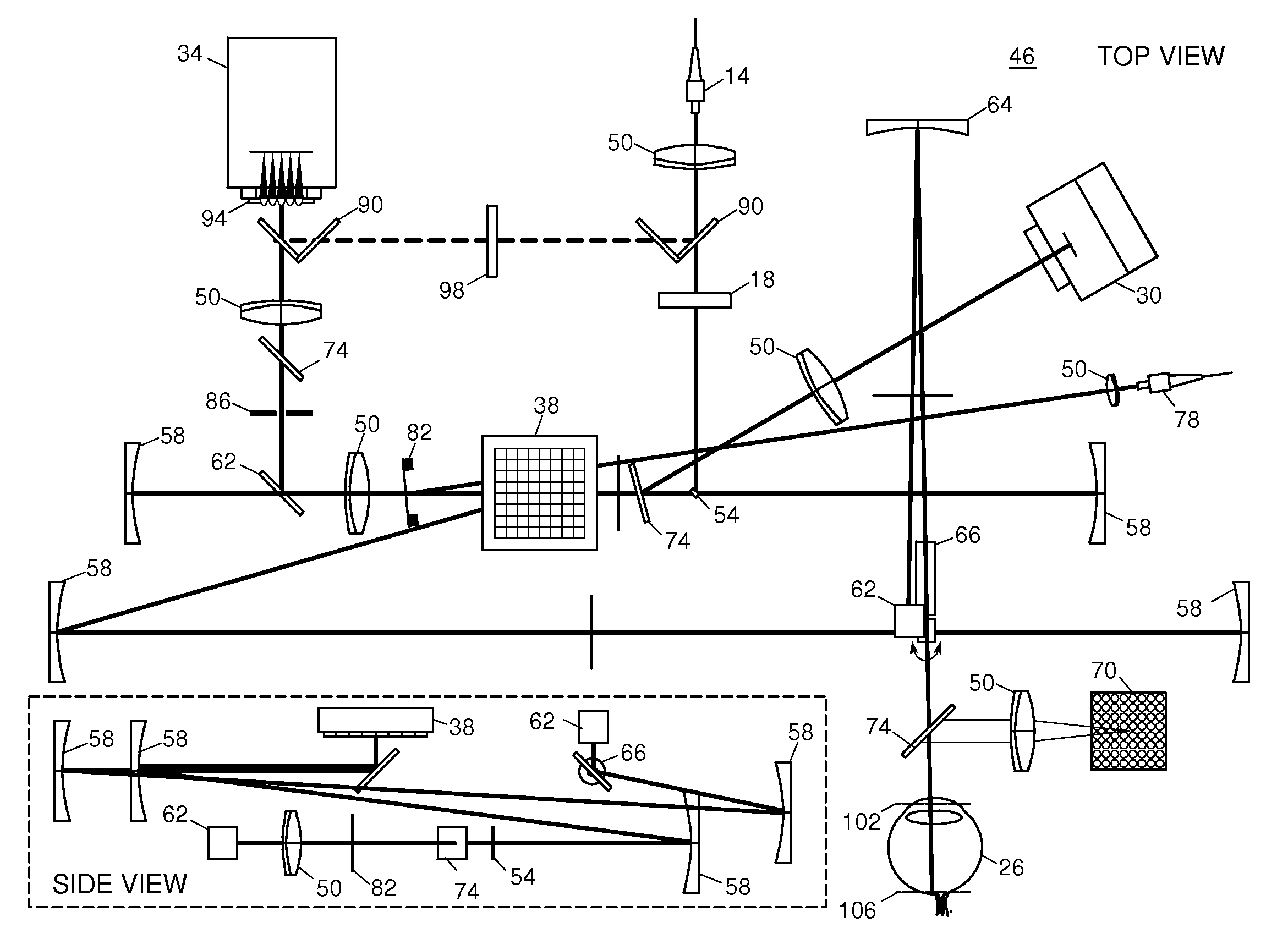
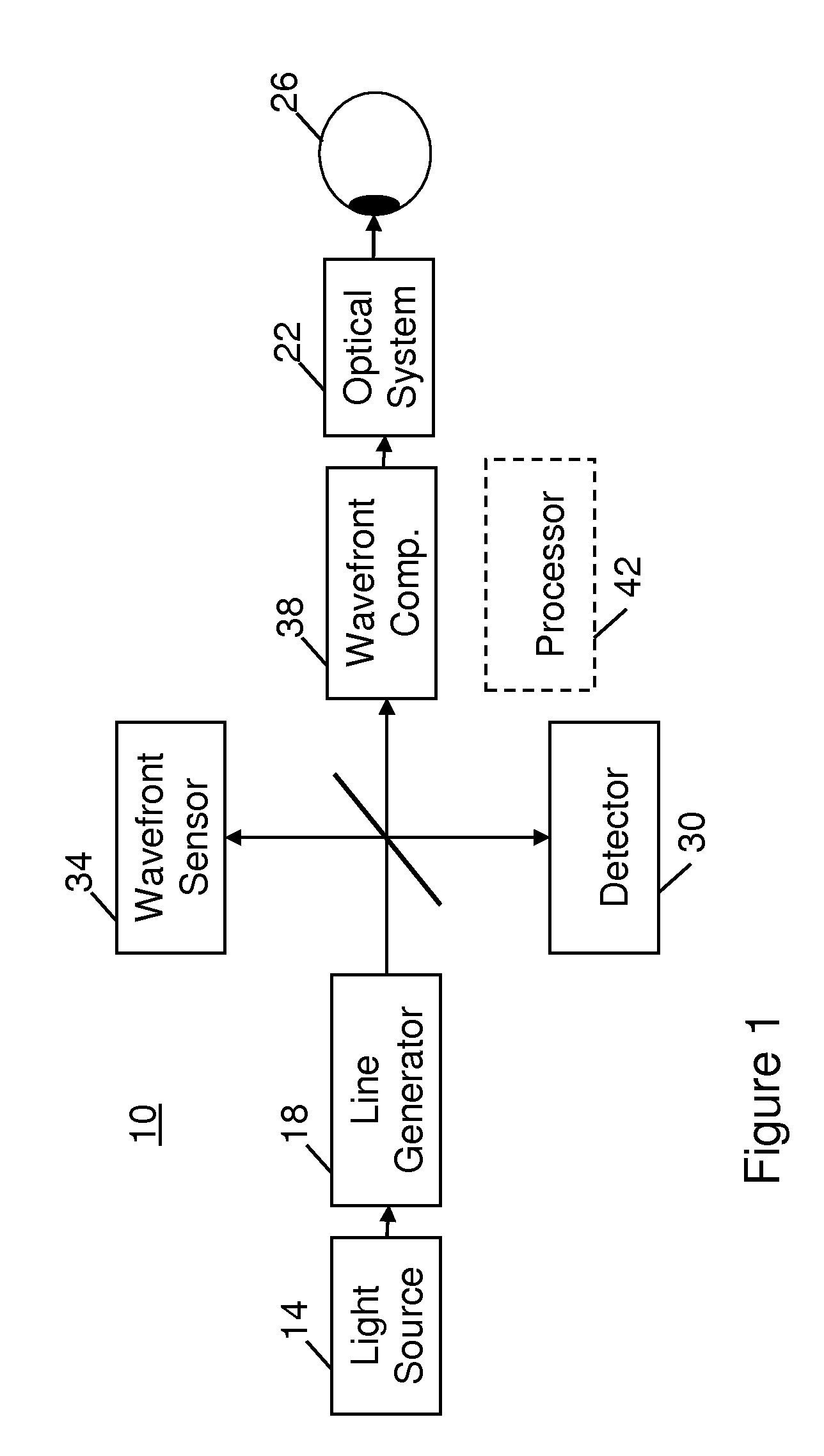
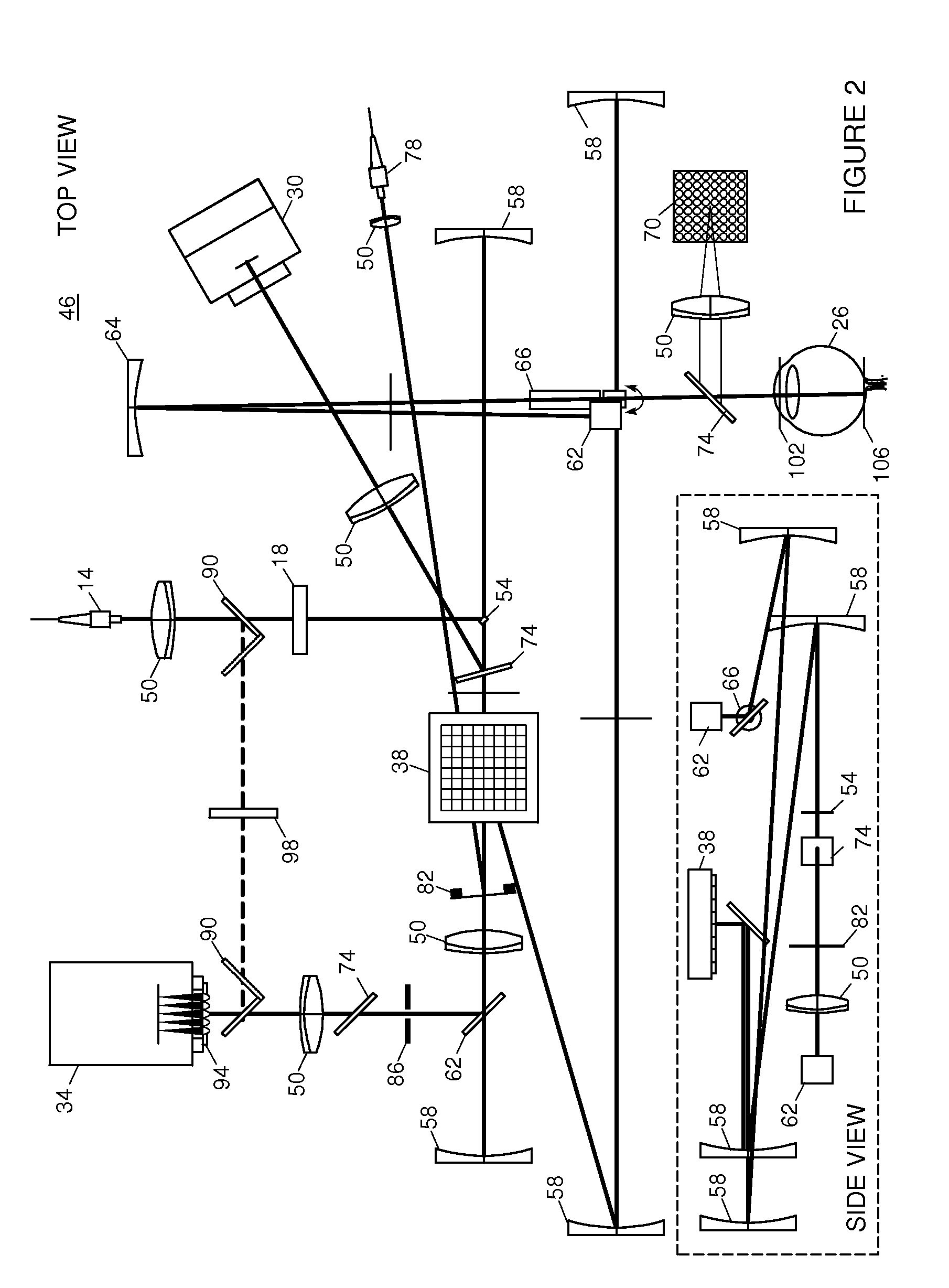
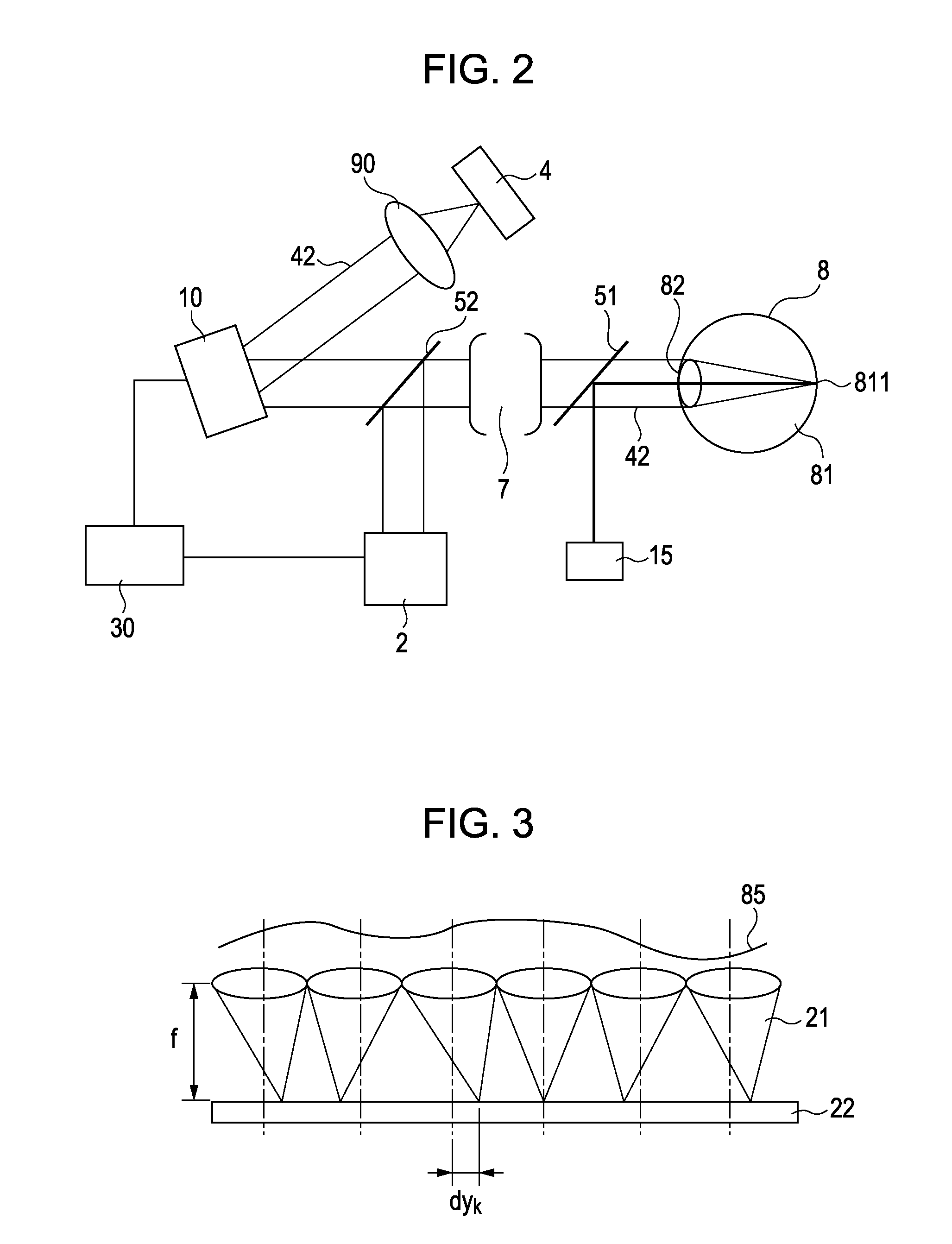
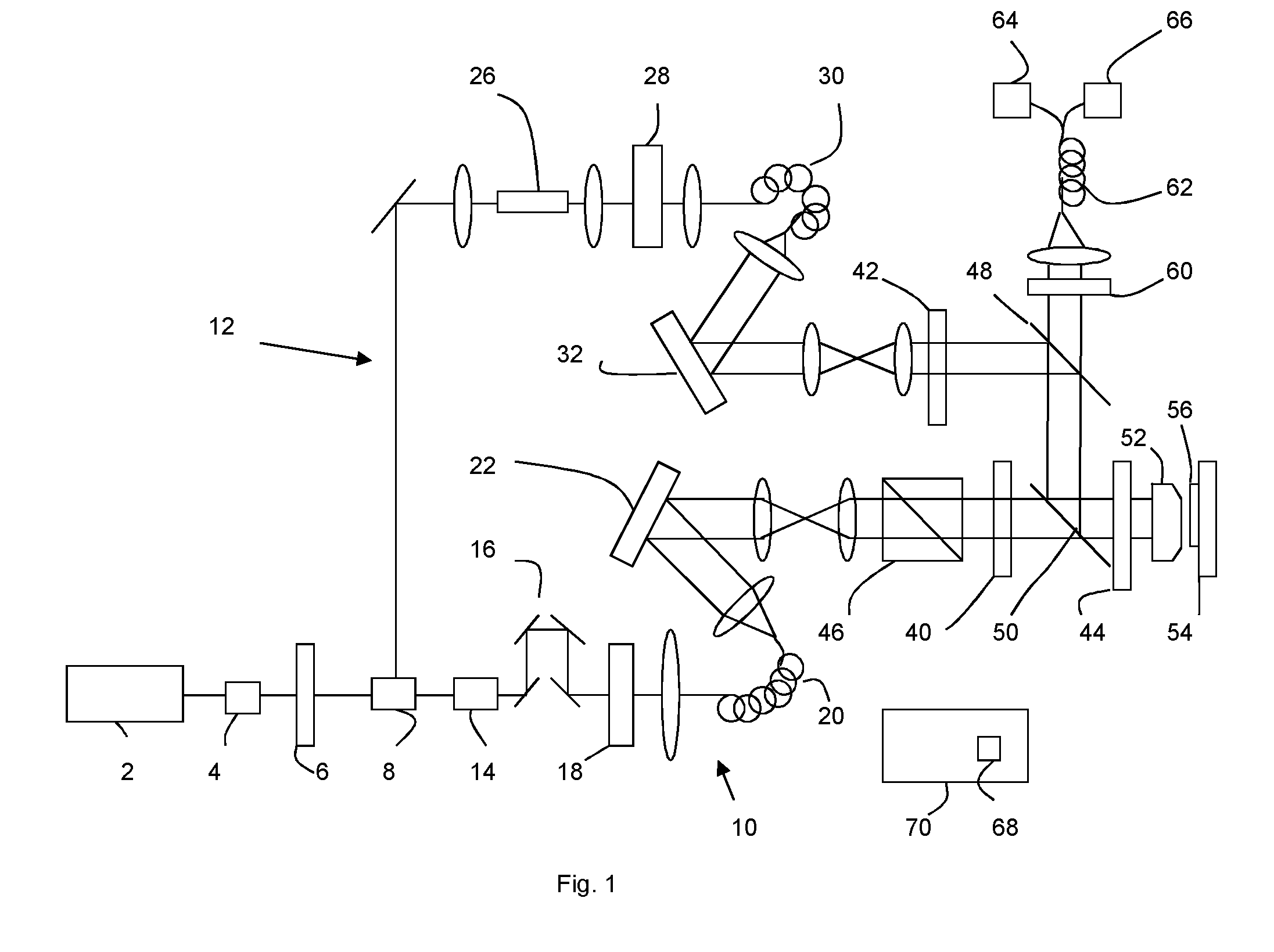
Adaptive optics line scanning ophthalmoscope
ActiveUS8201943B2Improve understandingSimplied optics, high-speed scanning componentsEye diagnosticsOptical ModuleOphthalmoscopes
A first optical module scans a portion of an eye with a line of light, descans reflected light from the scanned portion of the eye and confocally provides output light in a line focus configuration. A detection device detects the output light and images the portion of the eye. A second optical module detects an optical distortion and corrects the optical distortion in the line of light scanned on the portion of the eye.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
Adaptive Optics Line Scanning Ophthalmoscope
ActiveUS20100195048A1Advance understanding of visionCompact and simplifiedEye diagnosticsOptical ModuleOphthalmology
A first optical module scans a portion of an eye with a line of light, descans reflected light from the scanned portion of the eye and confocally provides output light in a line focus configuration. A detection device detects the output light and images the portion of the eye. A second optical module detects an optical distortion and corrects the optical distortion in the line of light scanned on the portion of the eye.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
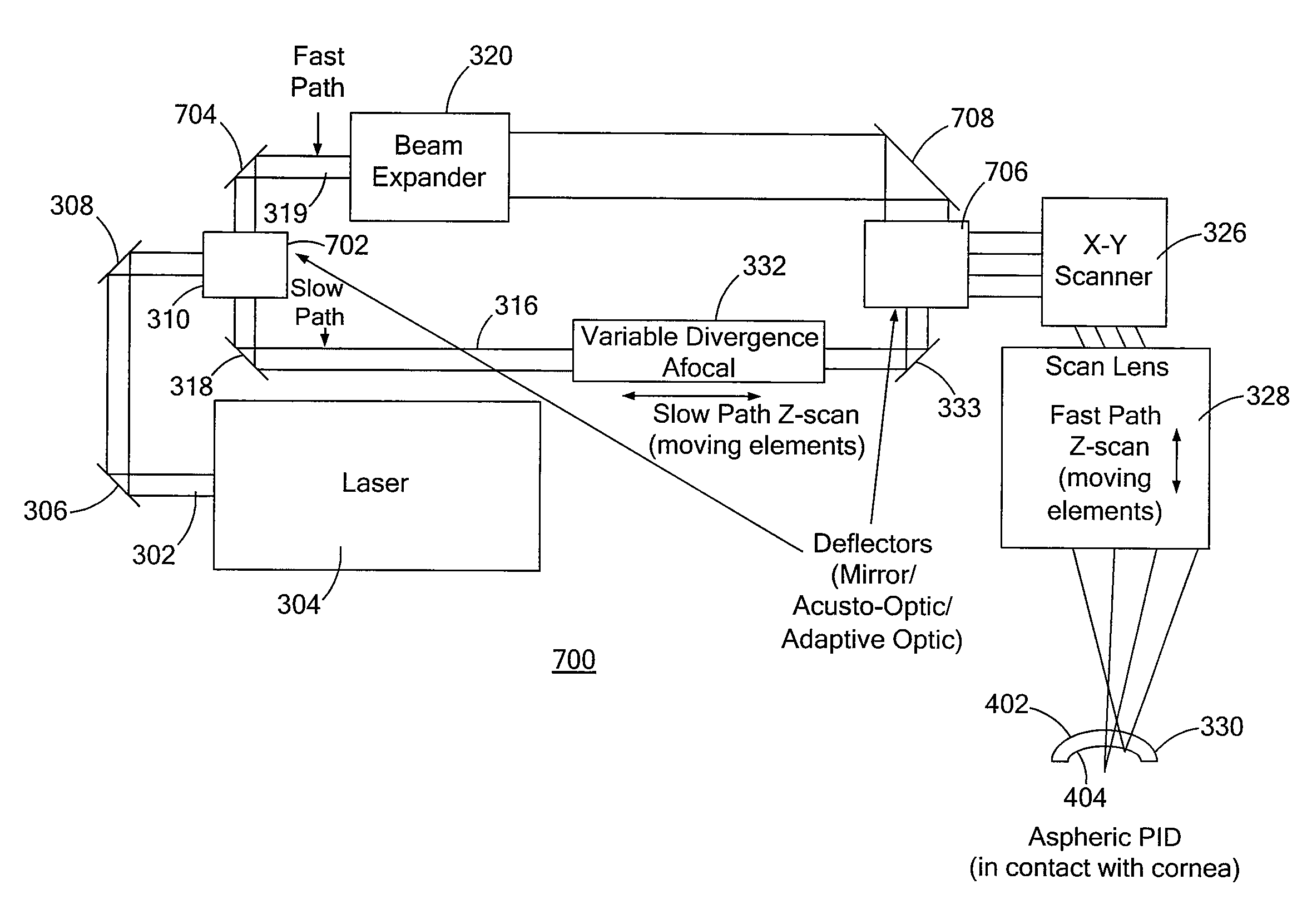
System and method for laser generated corneal and crystalline lens incisions using a variable f/# optical system with aspheric contact interface to the cornea or rotating and adaptive optics
ActiveUS20120271286A1Reduce complexityMaximum flexibilityLaser surgeryPolarising elementsFast pathSelf adaptive
A laser system including a laser source that generates a laser beam and an optical switch that receives the laser beam and sends the laser beam to either a fast path or a slow path, wherein the F / # of the fast path is lower than the F / # of the slow path. The laser system includes an afocal optical system in the slow path and receives the laser beam from the optical switch and an x-y scanner that receives either a laser beam from the slow path or a laser beam from the fast path. The laser system including a scan lens system that performs a z-scan for the scanning laser beam only in the case wherein the scanning laser beam is generated from the laser beam in the fast path. The laser system including an aspheric patient interface device that receives a laser beam from the scan lens system.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
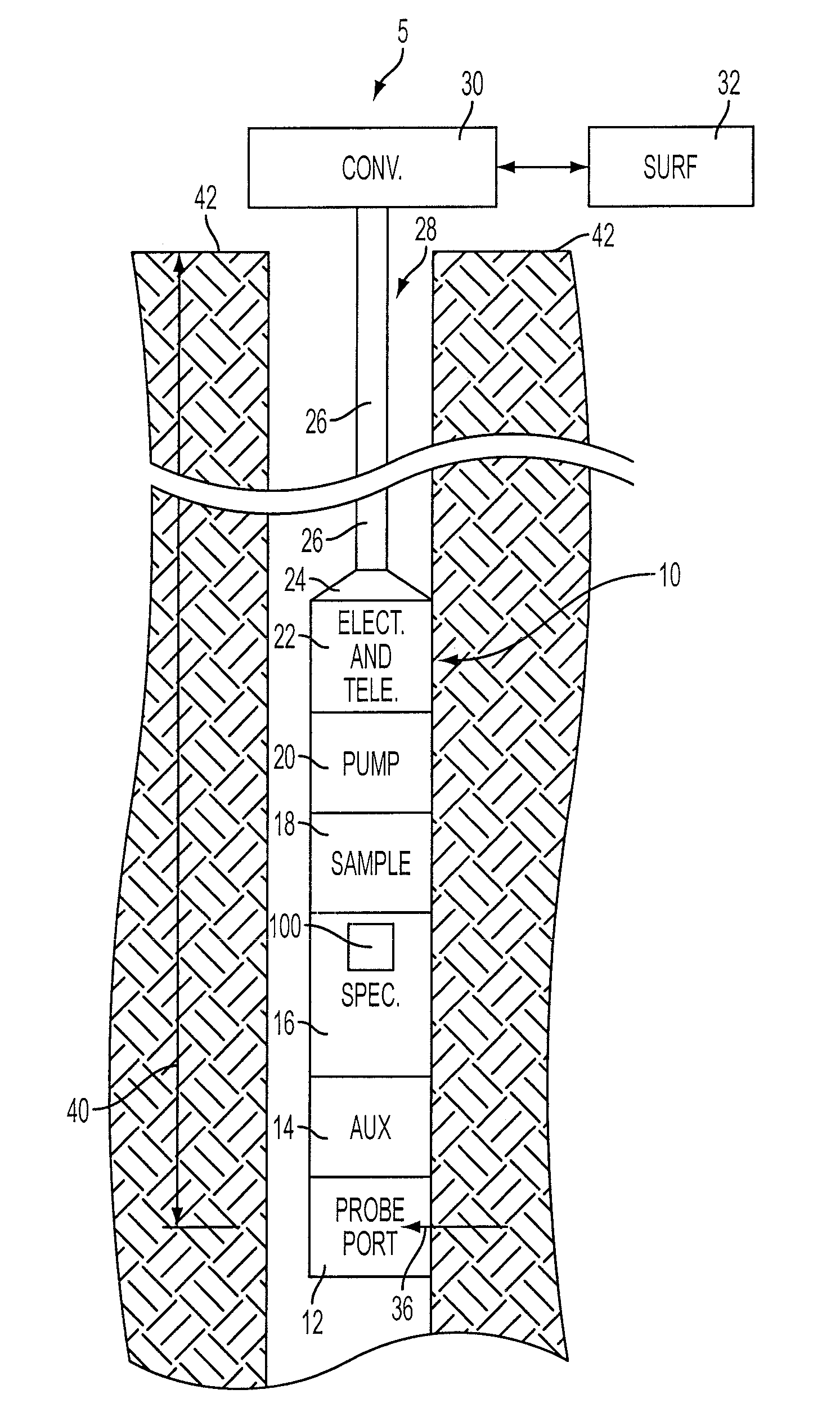
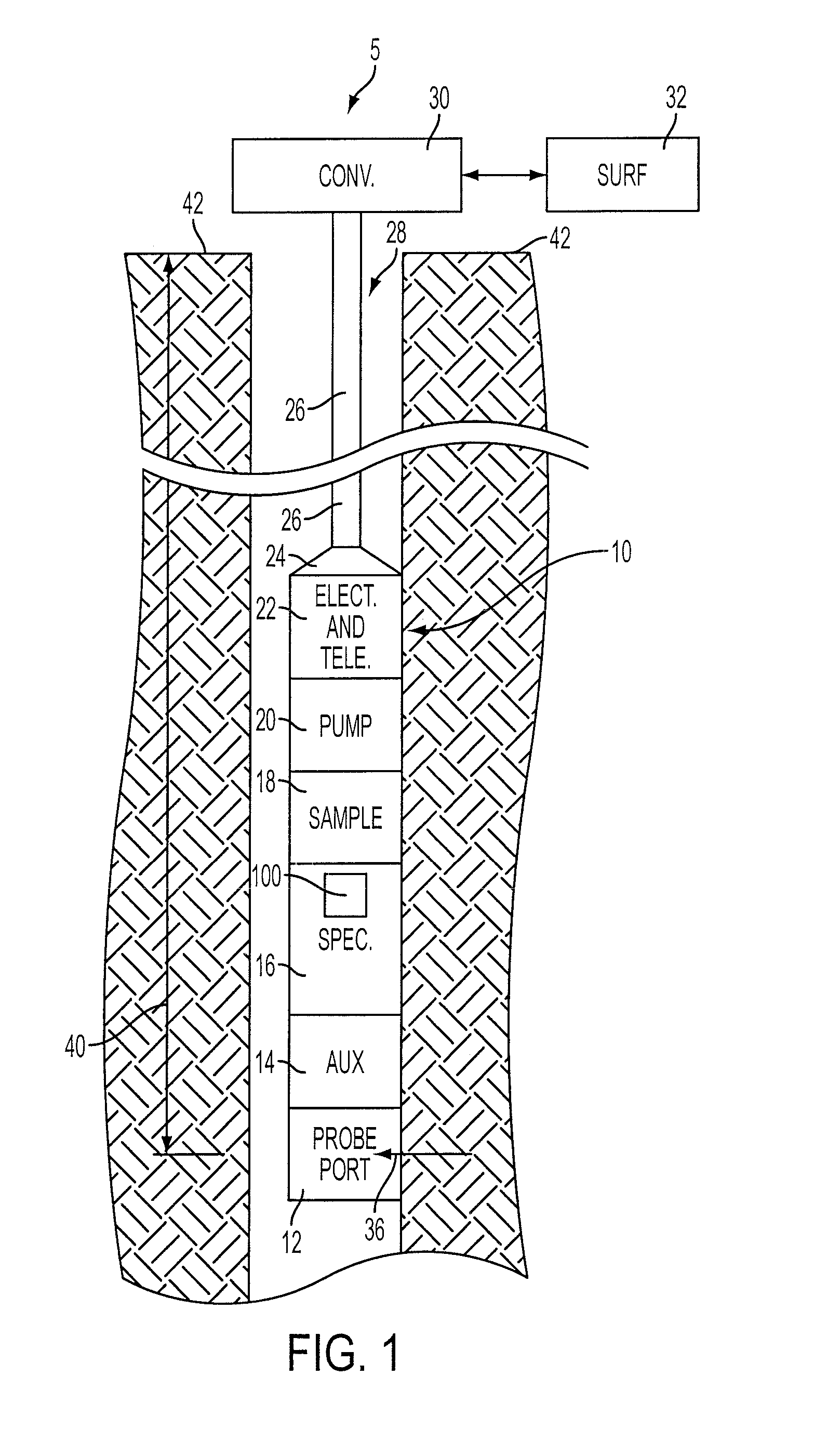
Method and Apparatus for Performing Spectroscopy Downhole within a Wellbore
An analysis system, tool, and method for performing downhole fluid analysis, such as within a wellbore. The analysis system, tool, and method provide for a tool including a spectroscope for use in downhole fluid analysis which utilizes an adaptive optical element such as a Micro Mirror Array (MMA) and two distinct light channels and detectors to provide real-time scaling or normalization.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
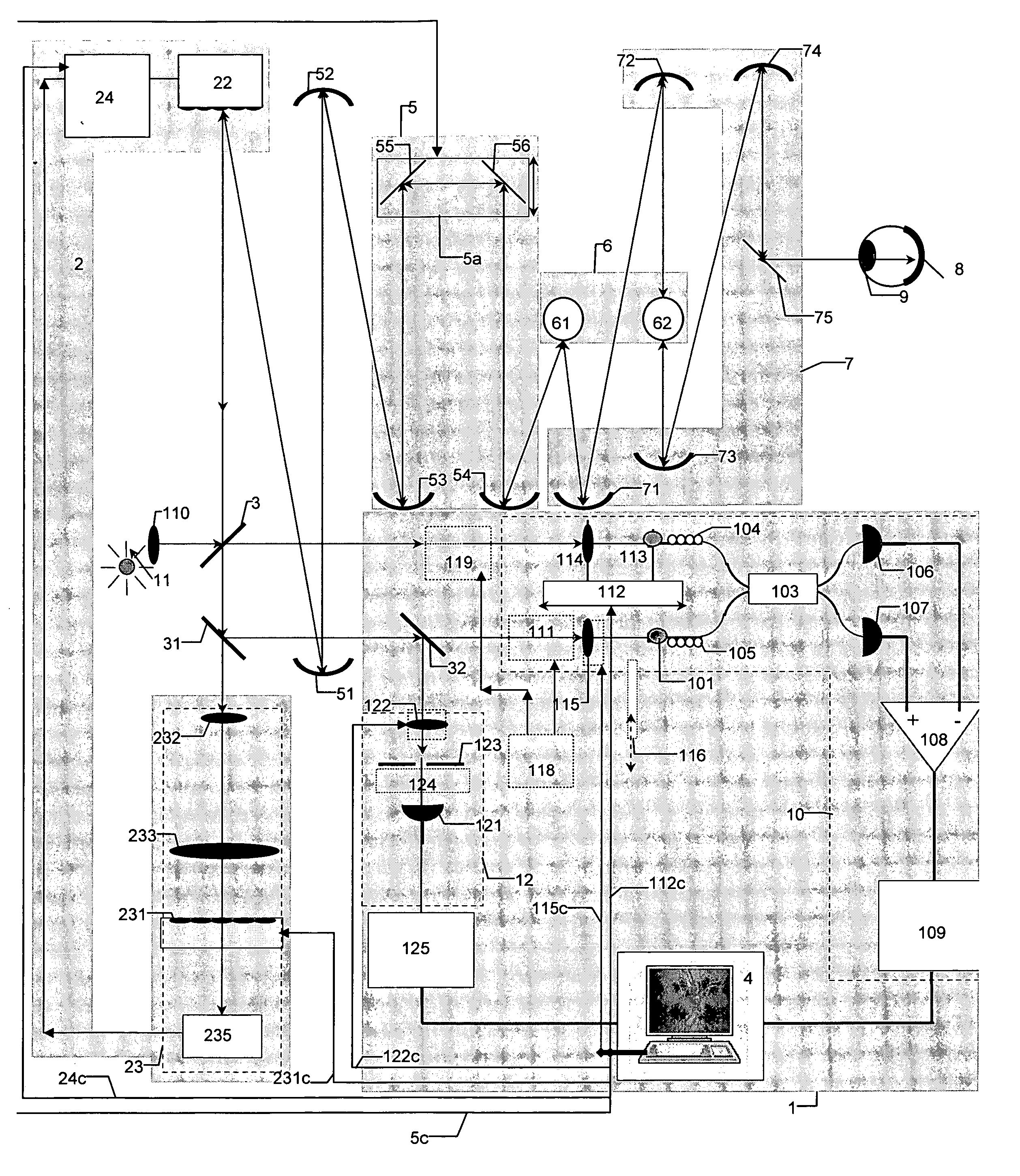
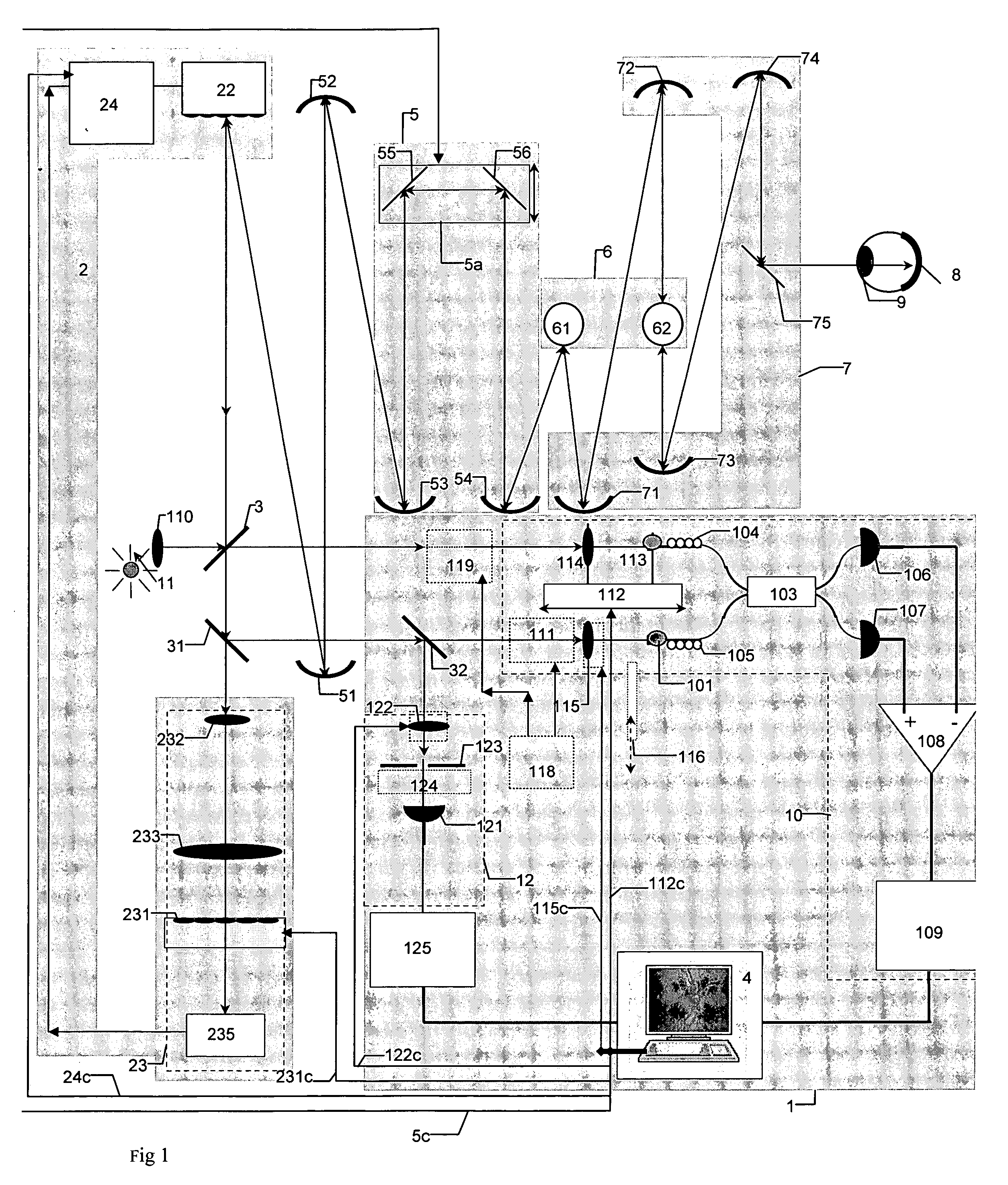
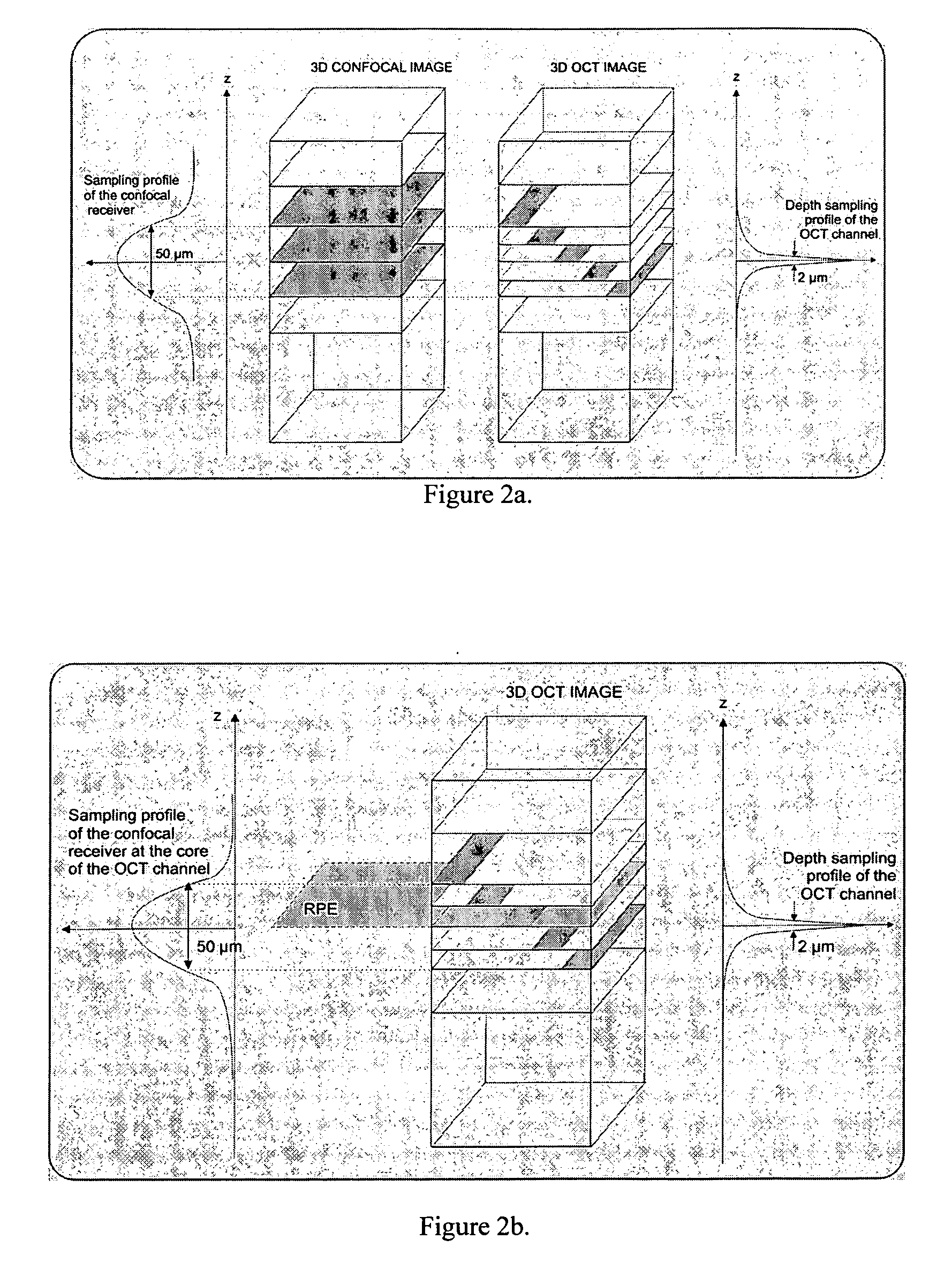
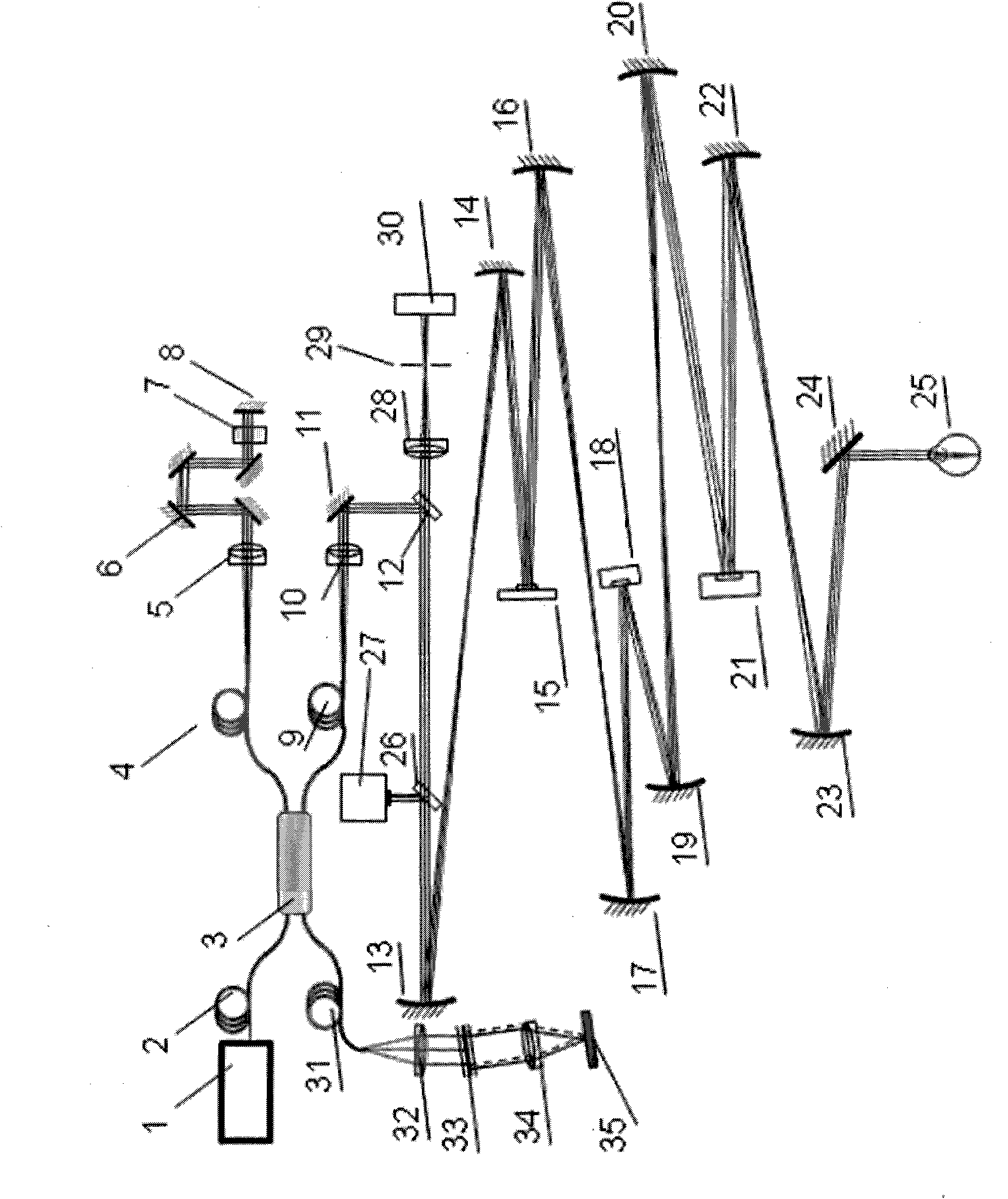
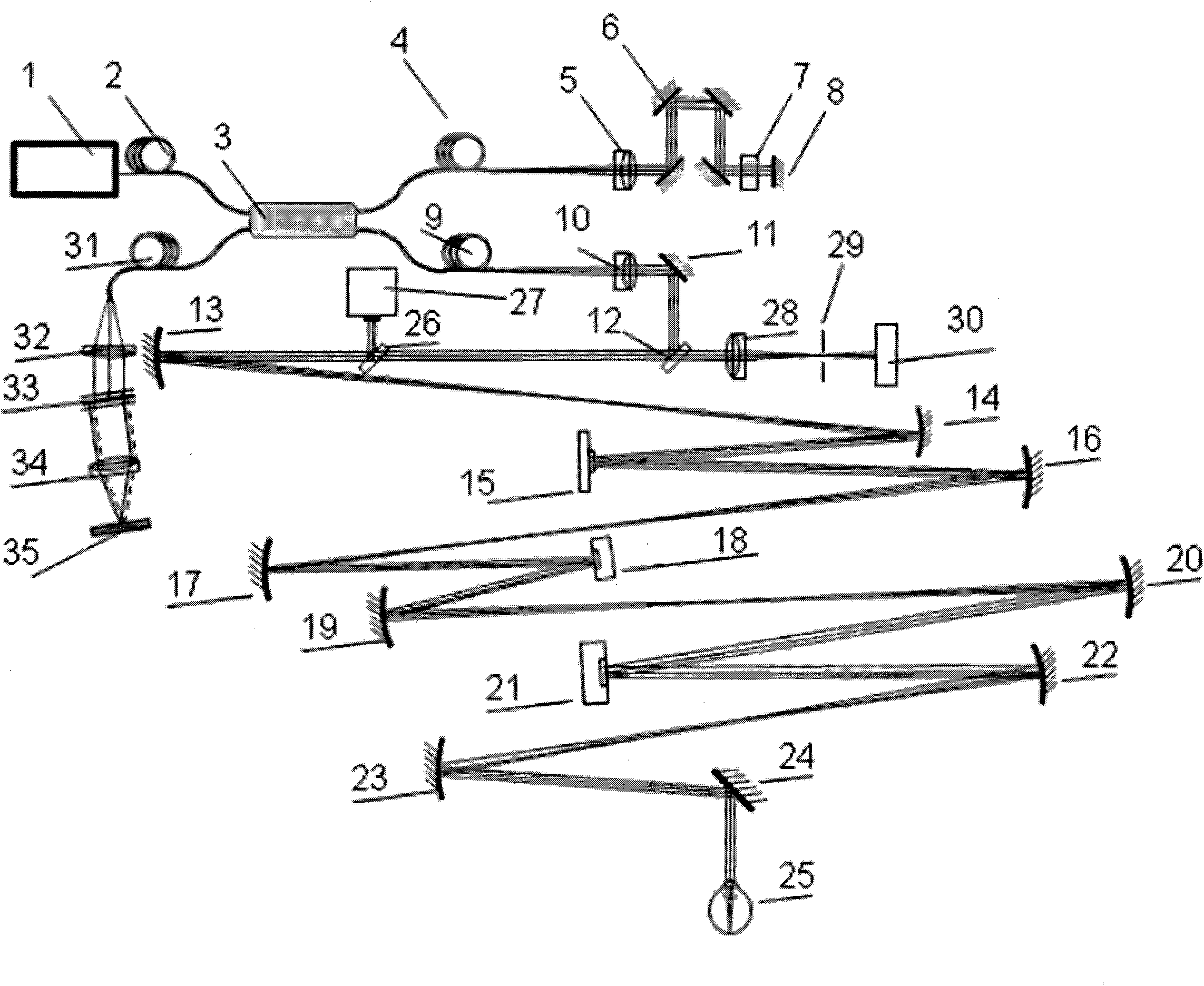
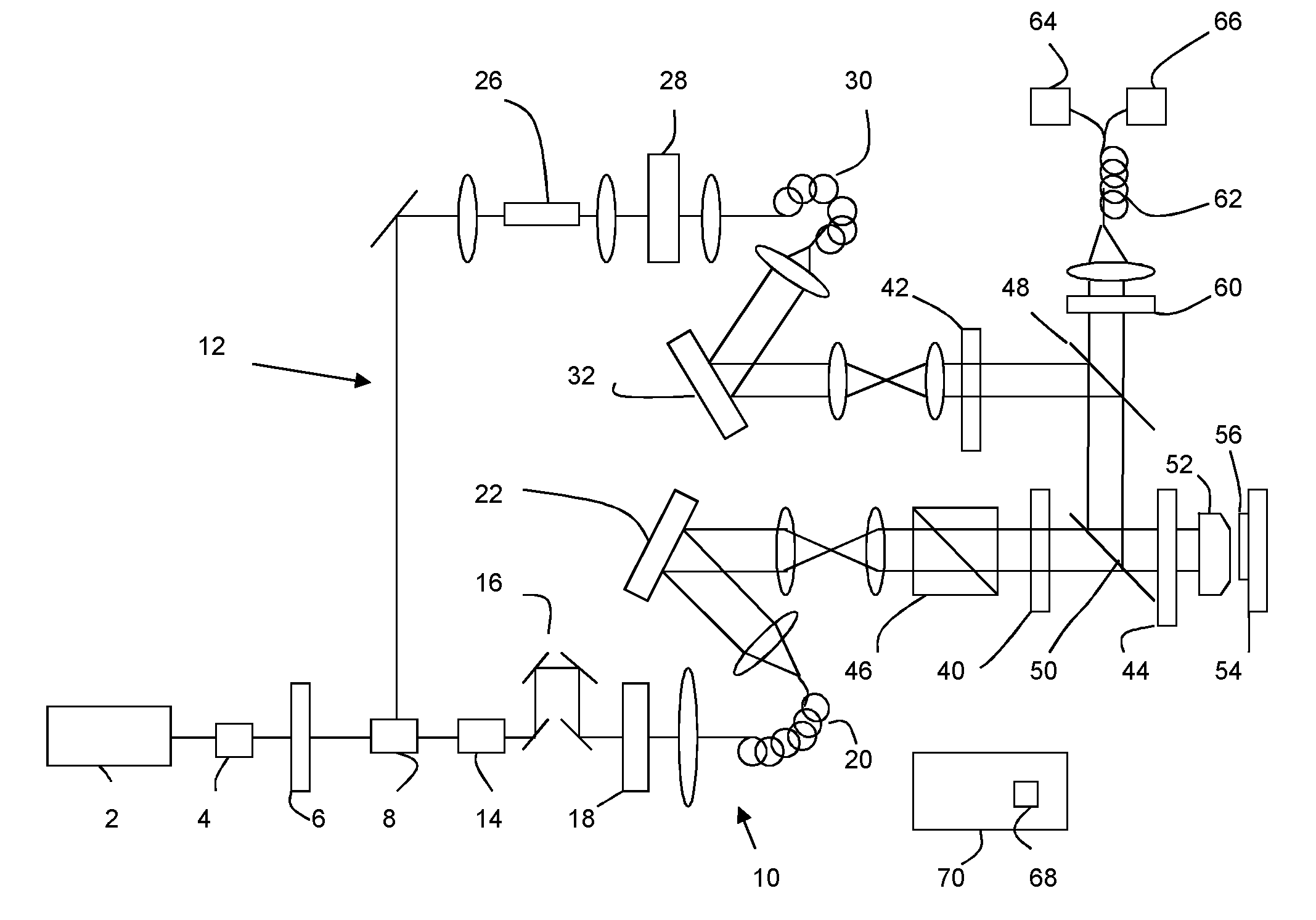
Confocal scanning and optical coherence tomograph based on self-adaptive optical technology
ActiveCN101869466AImproving Resolution in Longitudinal Sectional ImagingIncreased imaging resolution in transverse slicesPhase-affecting property measurementsEye diagnosticsReflecting telescopeImage detection
A confocal scanning and optical coherence tomograph based on self-adaptive optical technology comprises a light source component, a scanning and lighting light path component, an aberration detection and correction component, a confocal imaging detection component, a reference arm component and an optical coherence tomography detection component, wherein the components are linked by optical fiber and / or spherical reflecting telescopes; one part of low-coherent light emitted by the light source component enters into the reference arm component and then returns along the original path and the other part enters into the samples to be detected through the aberration detection and correction component and the scanning and lighting light path component in sequence and then returns from the samples to be detected along the original path; one part of the returning light is reflected to the aberration detection and correction component by a spectroscope and the other part is transmitted to another spectroscope and then is split into two parts, one part enters into the confocal imaging detection component and the other part enters into the optical coherence tomography detection component after being coupled with the light returning from the reference arm component. The tomograph can realize high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of the objects to be detected.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROCLEAR MEDICAL INSTR
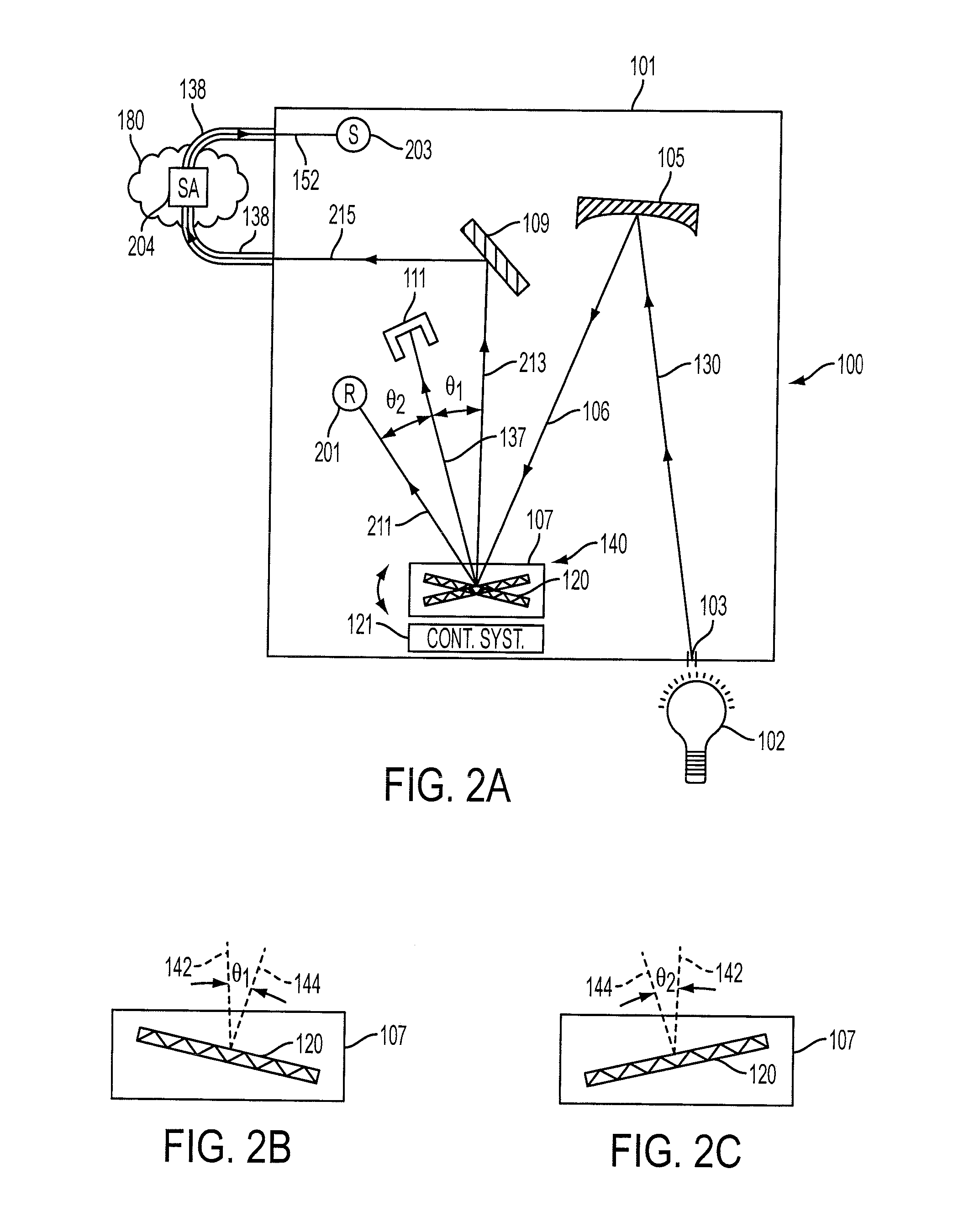
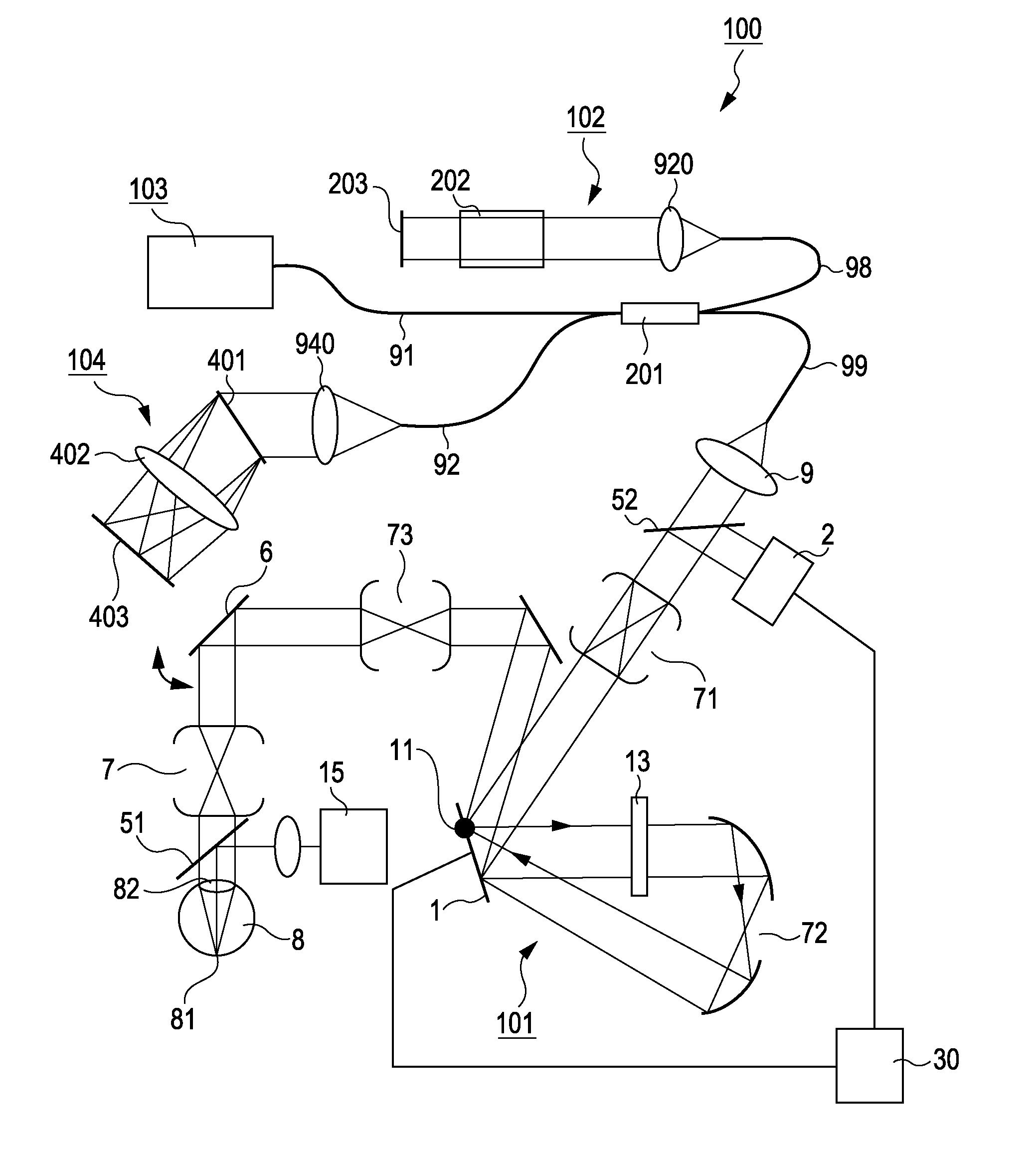
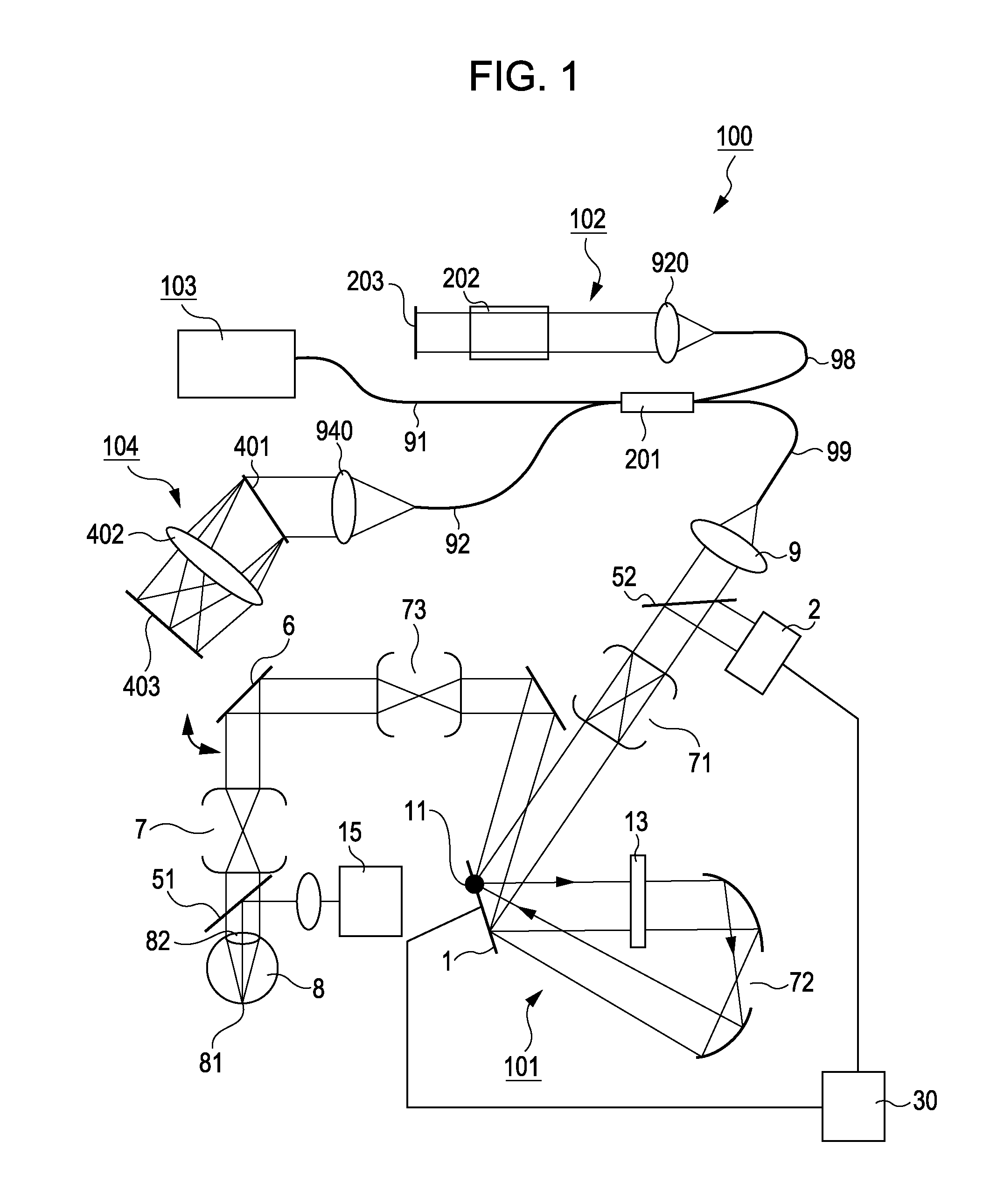
Adaptive optics apparatus that corrects aberration of examination object and image taking apparatus including adaptive optics apparatus
InactiveUS20110096292A1Reduce the impactImprove light utilization efficiencyLight polarisation measurementNon-linear opticsOptical polarizationAdaptive optics
An adaptive optics apparatus includes a first light modulating unit configured to perform modulation in a polarization direction of one of two polarized light components in light emitted from a light source, a changing unit configured to rotate the light modulated by the first light modulating unit by 90 degrees, a second light modulating unit configured to modulate the light changed by the changing unit in the polarization direction, and an irradiating unit configured to irradiate a measurement object with the light modulated by the second light modulating unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Stimulated emission depletion microscopy
ActiveUS20150226950A1Reduce optical aberrationMaximising metricPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersStimulated emissionBrightness perception
Aberrations in stimulated emission depletion microscopy are corrected using an adaptive optics approach using a metric which combines both image sharpness and brightness. Light modulators (22,32) are used to perform aberration correction in one or more of the depletion path (10), the excitation path (12), or the emission path from sample to detector.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Adaptive optic lens system and method of use
Owner:ALCON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com