Patents
Literature
49results about How to "High depth resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
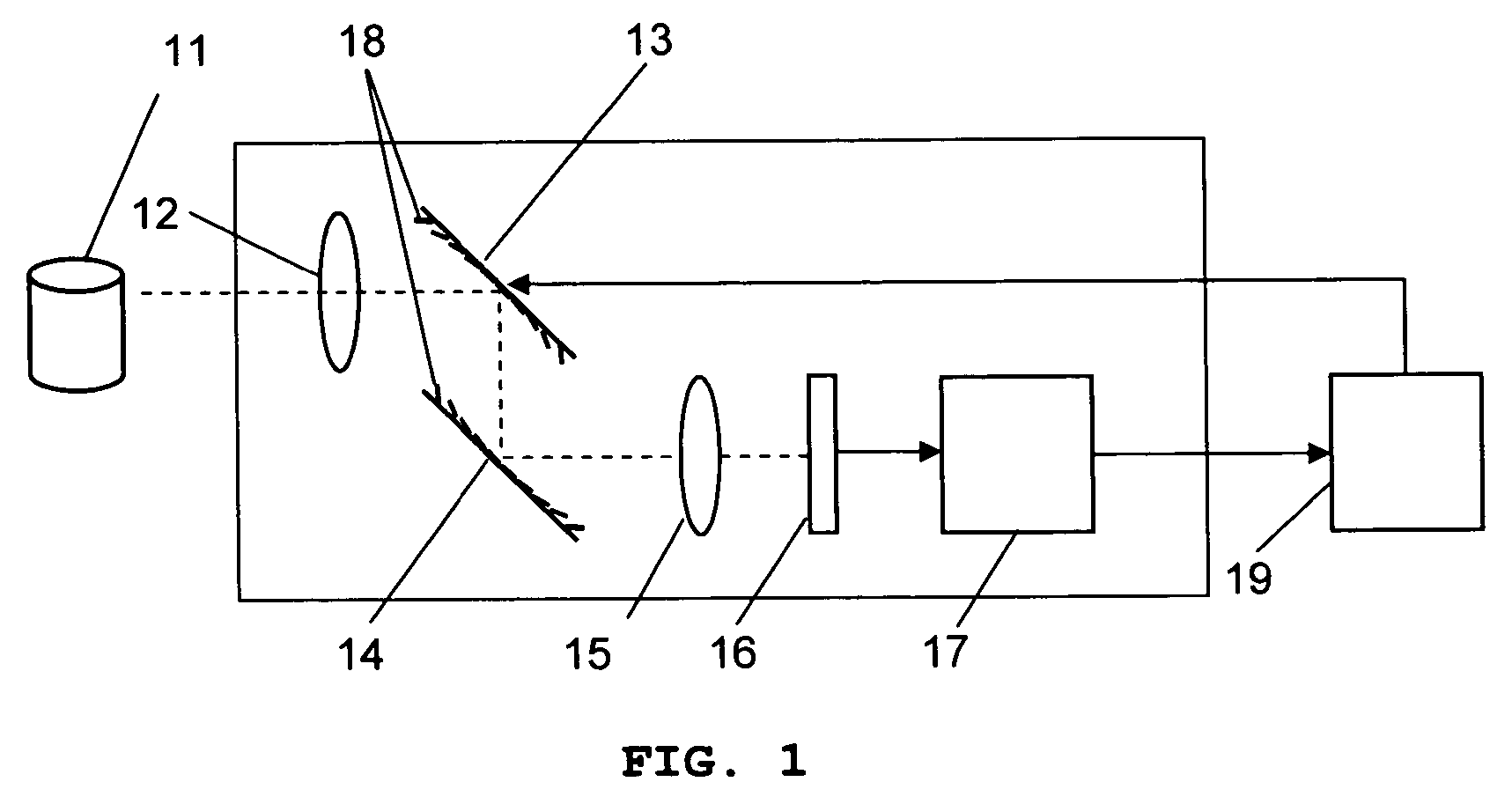
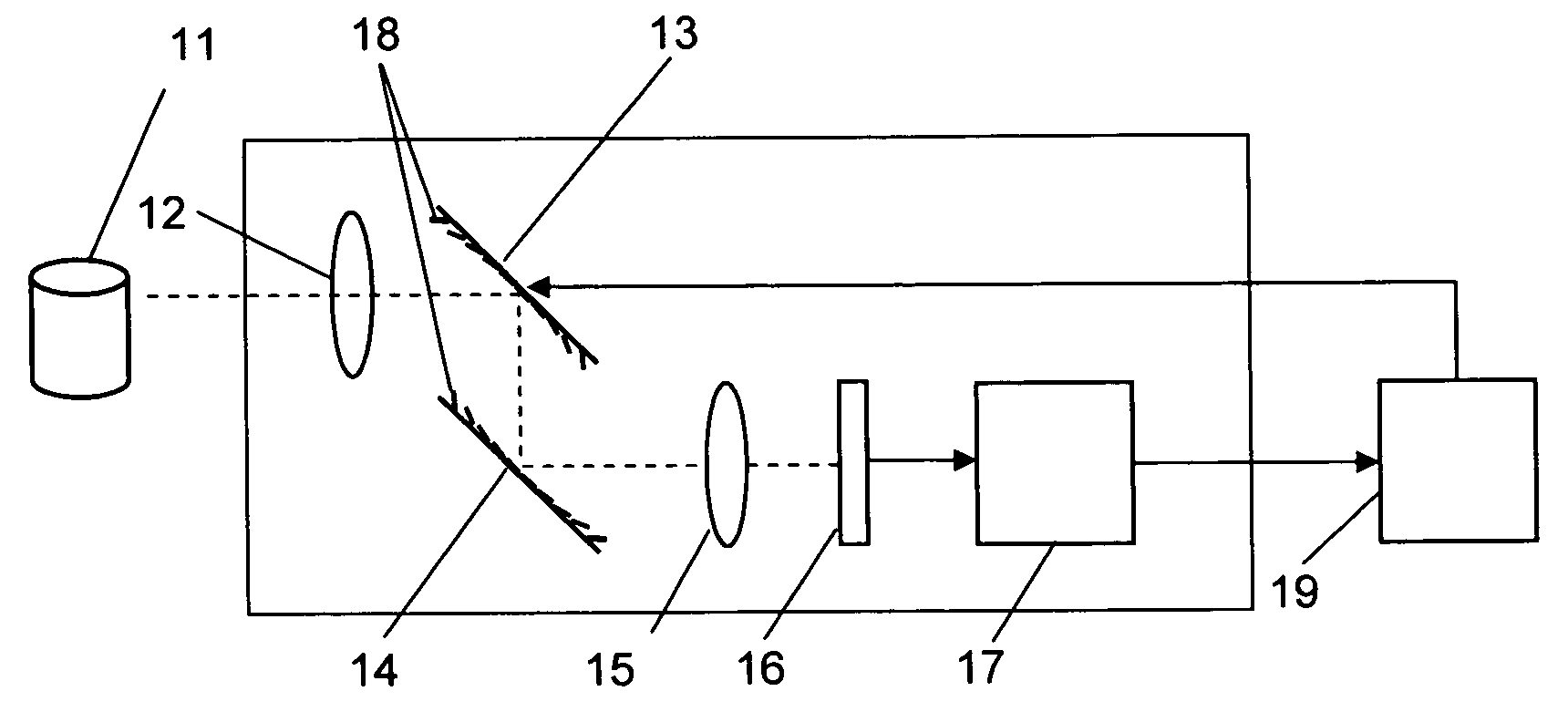
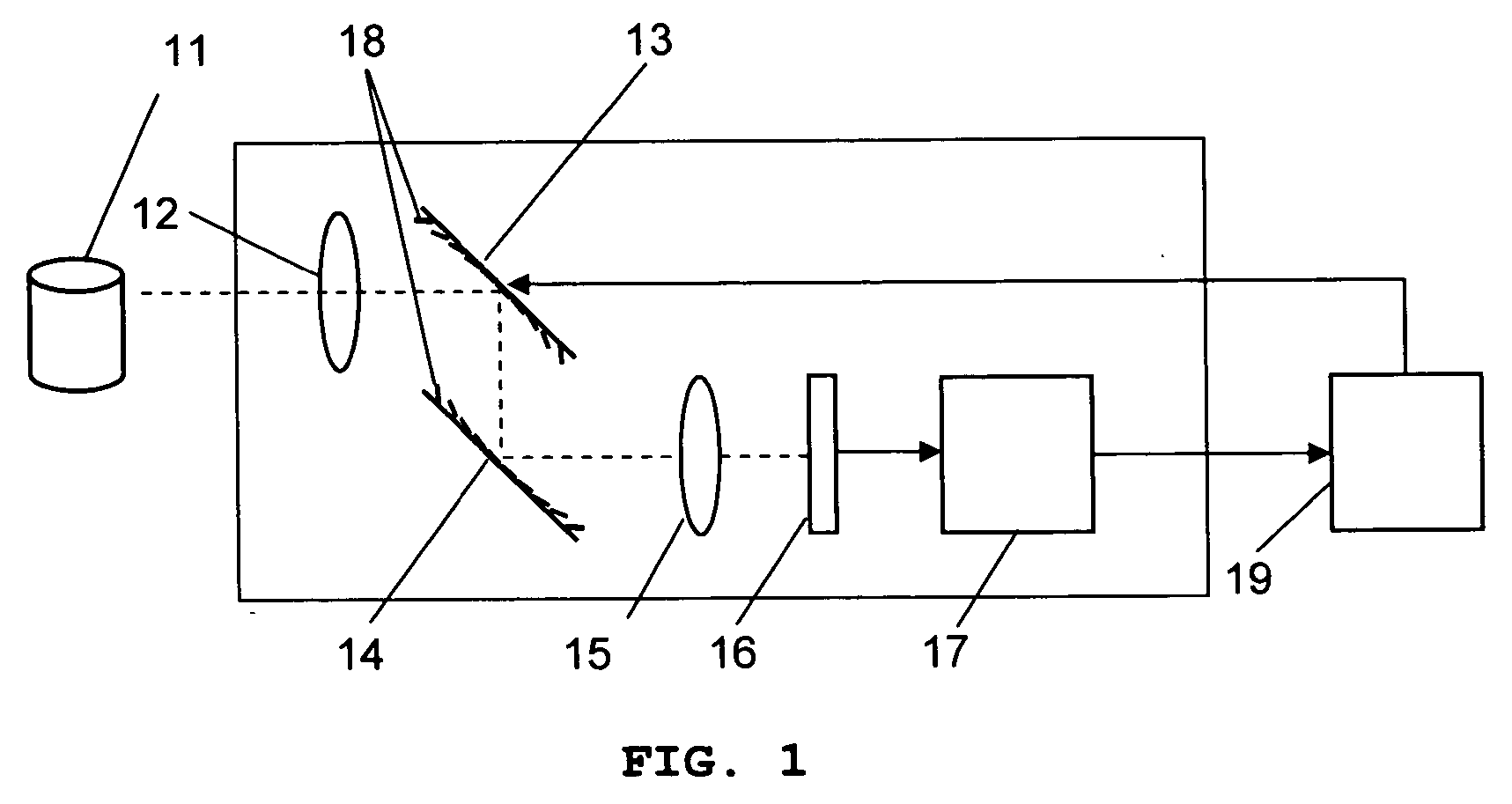
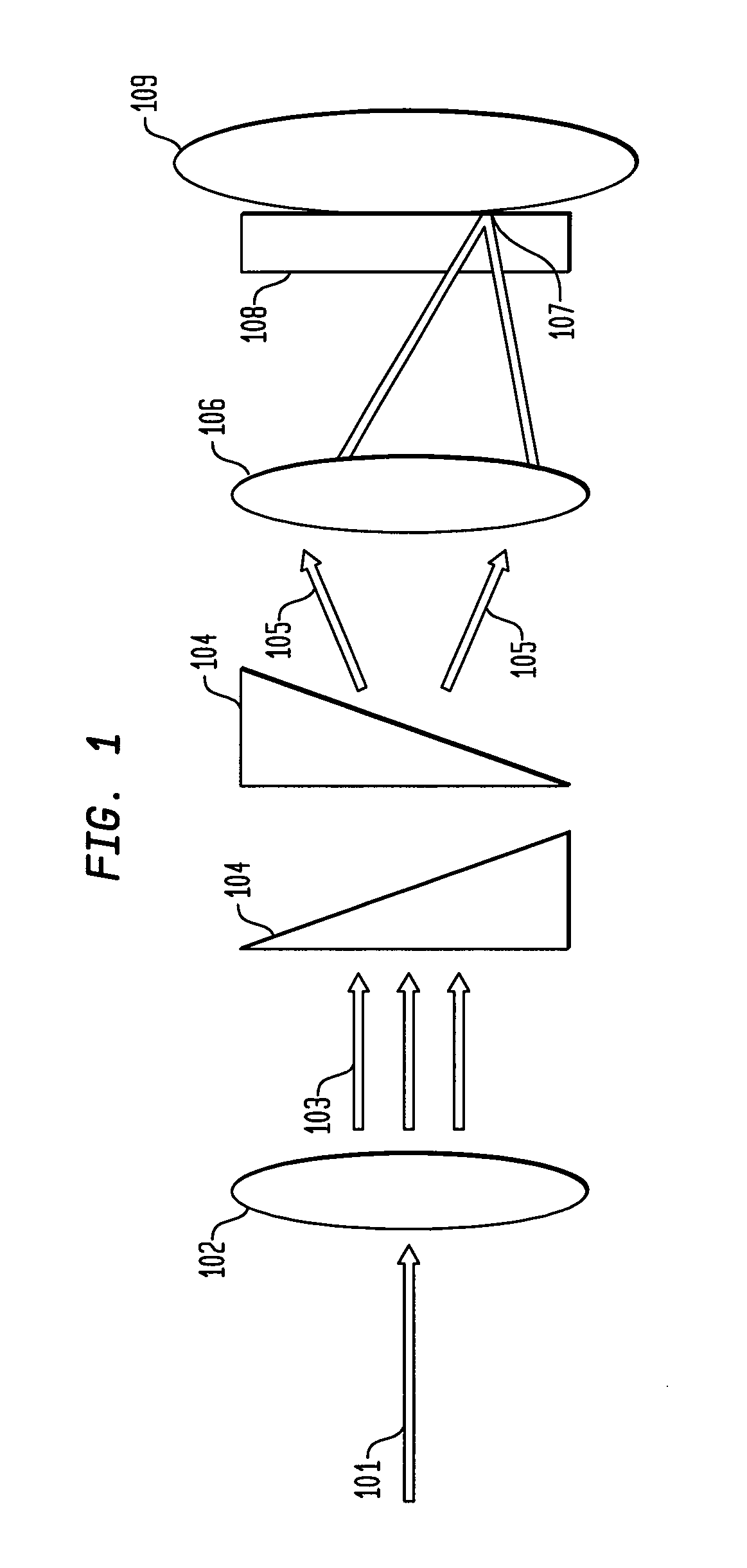
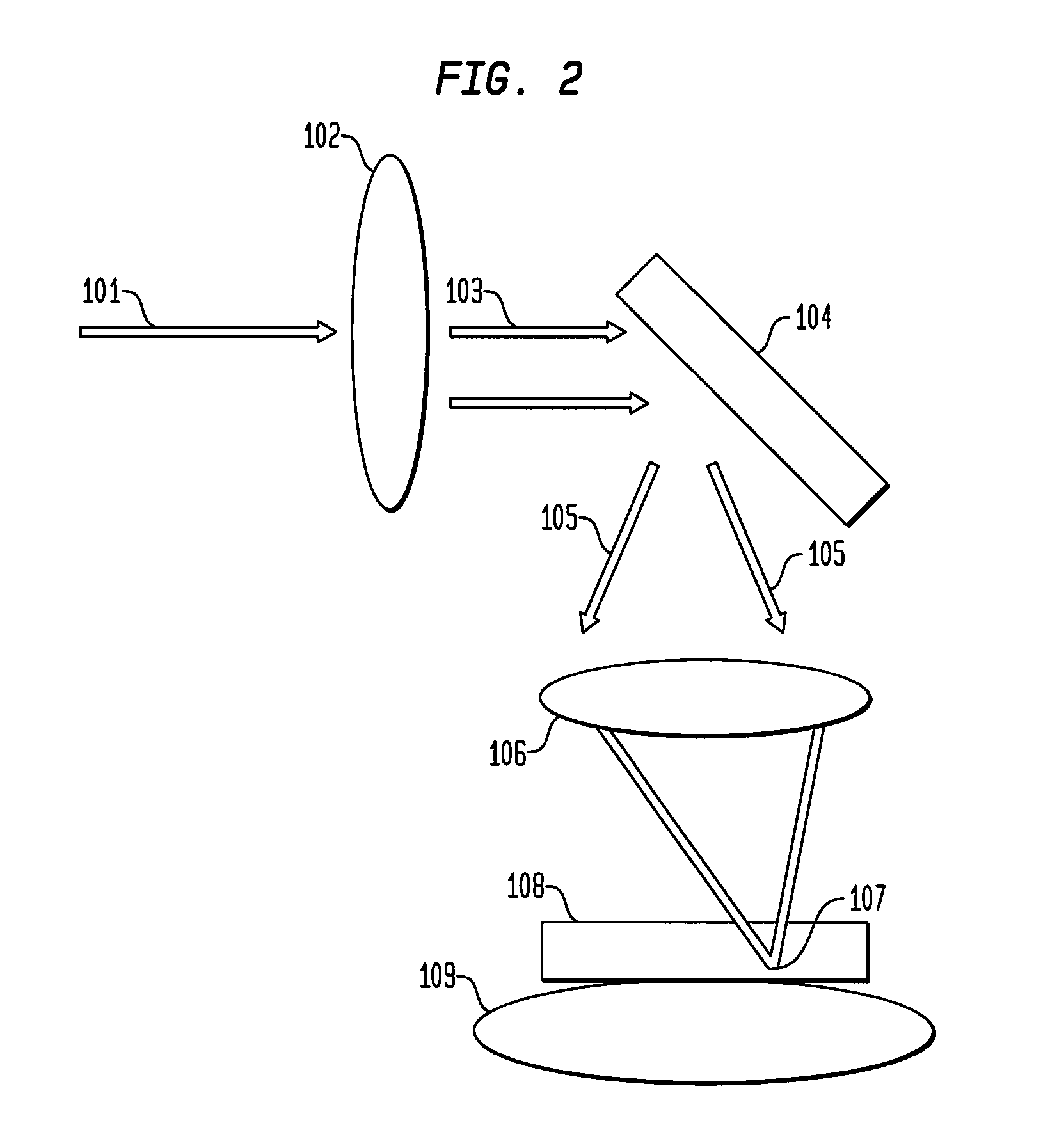
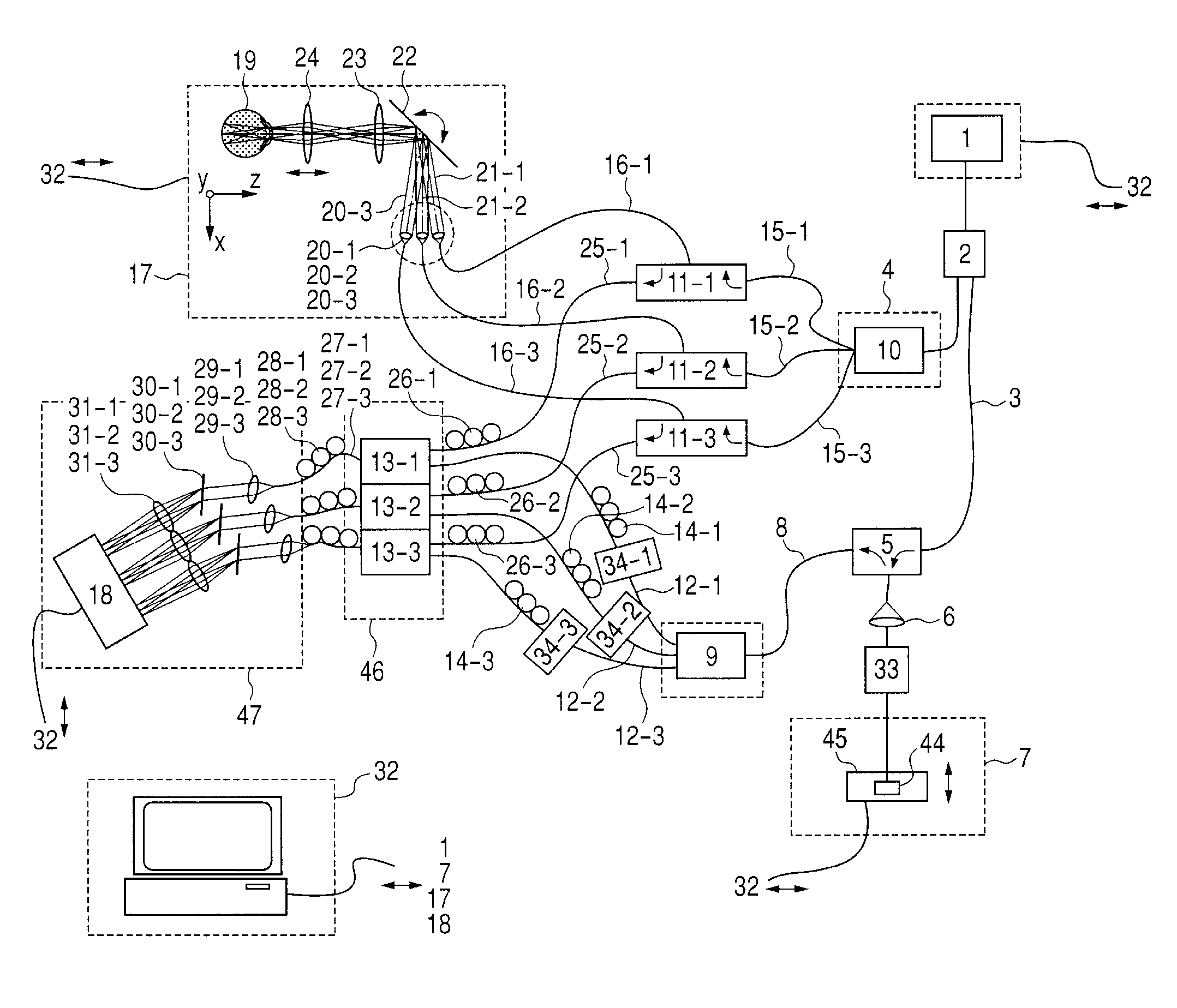
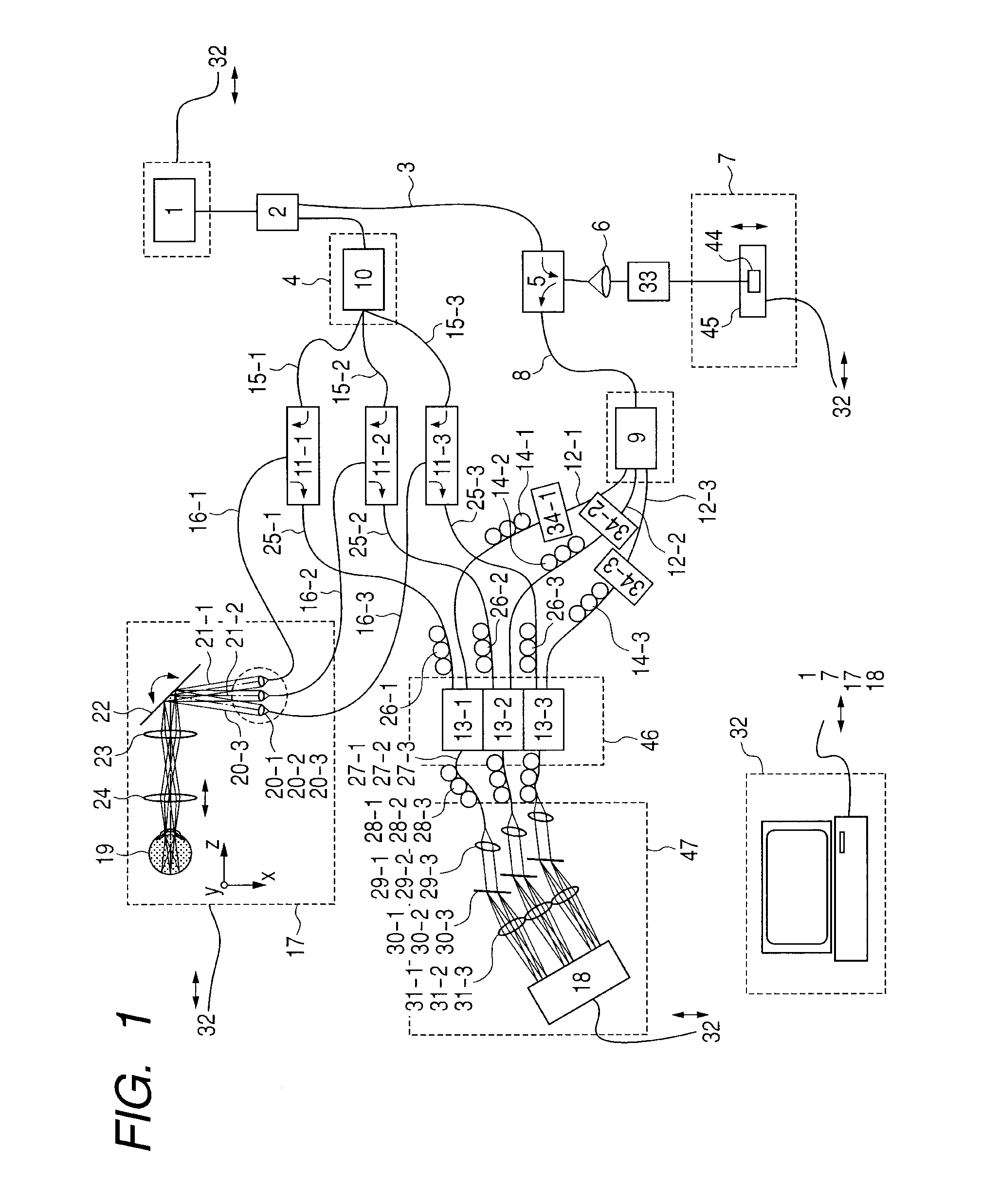
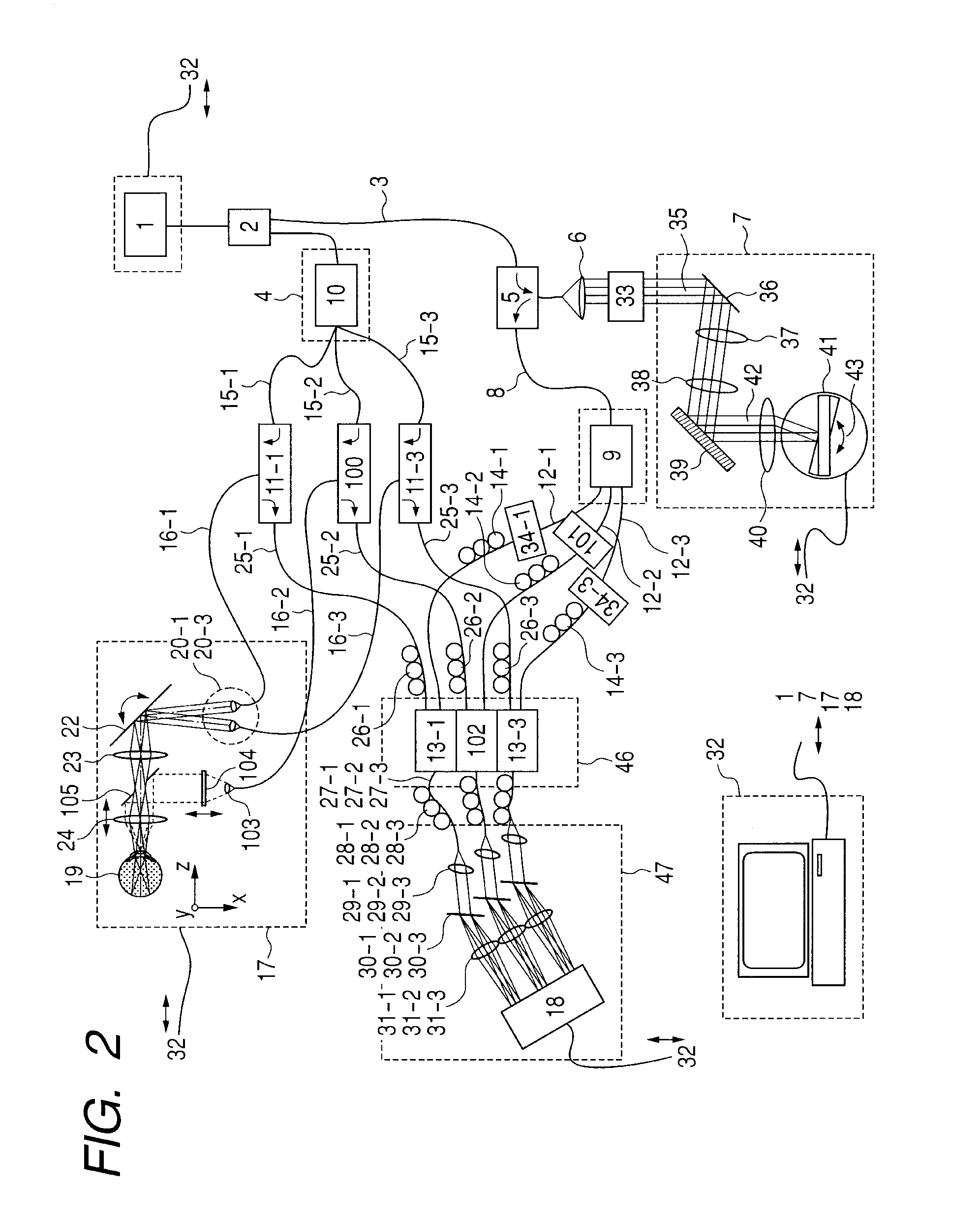
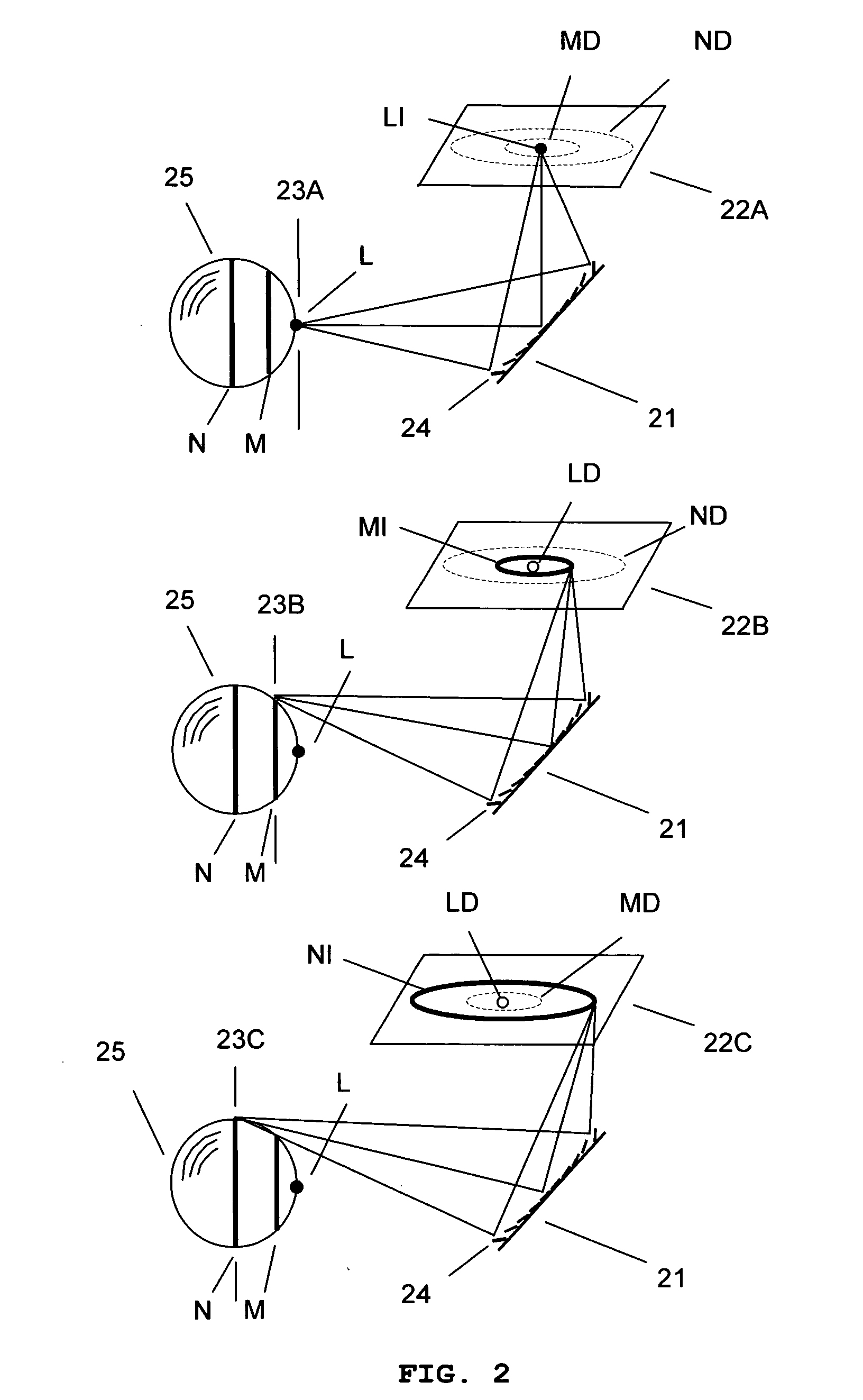
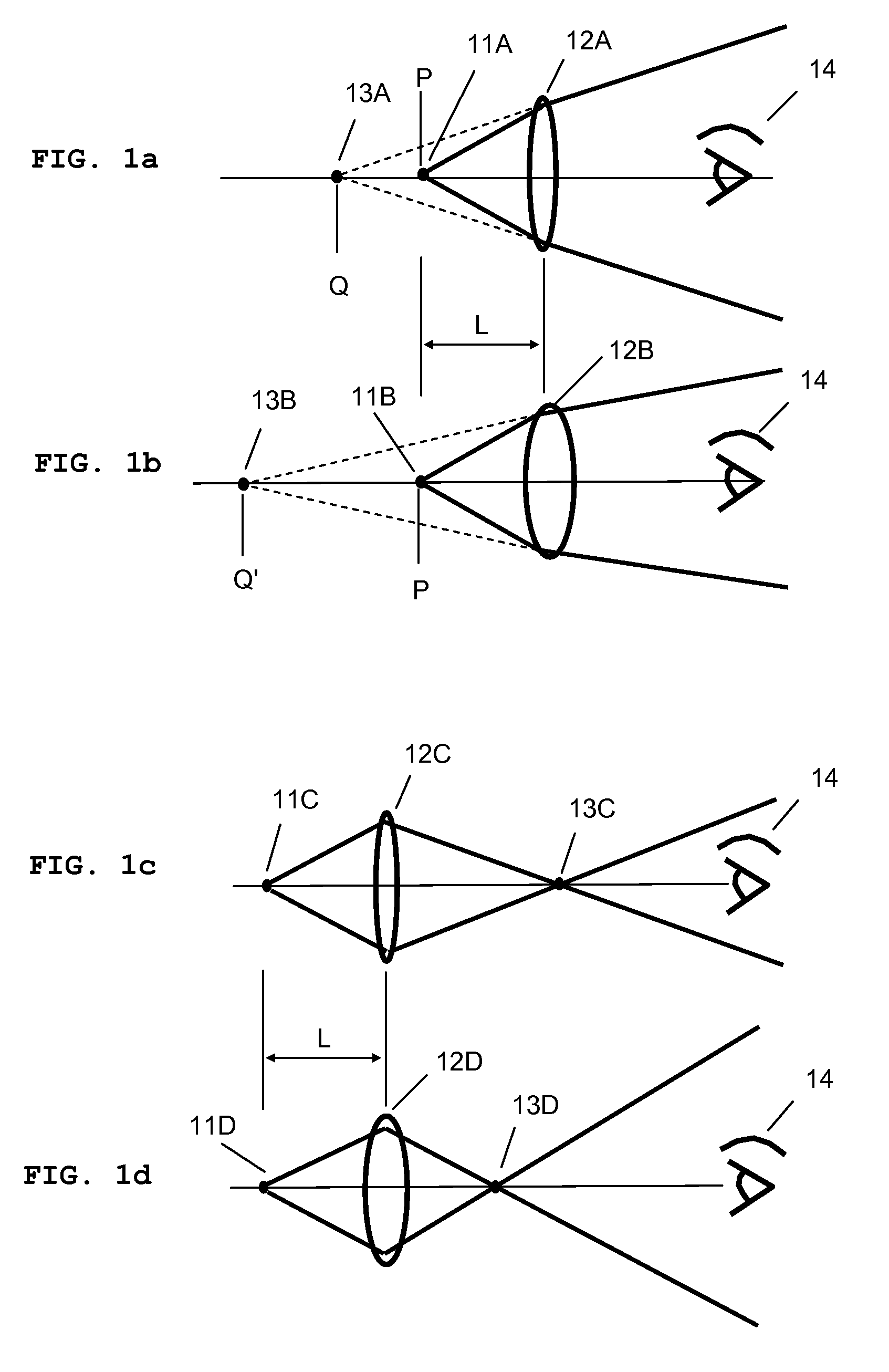
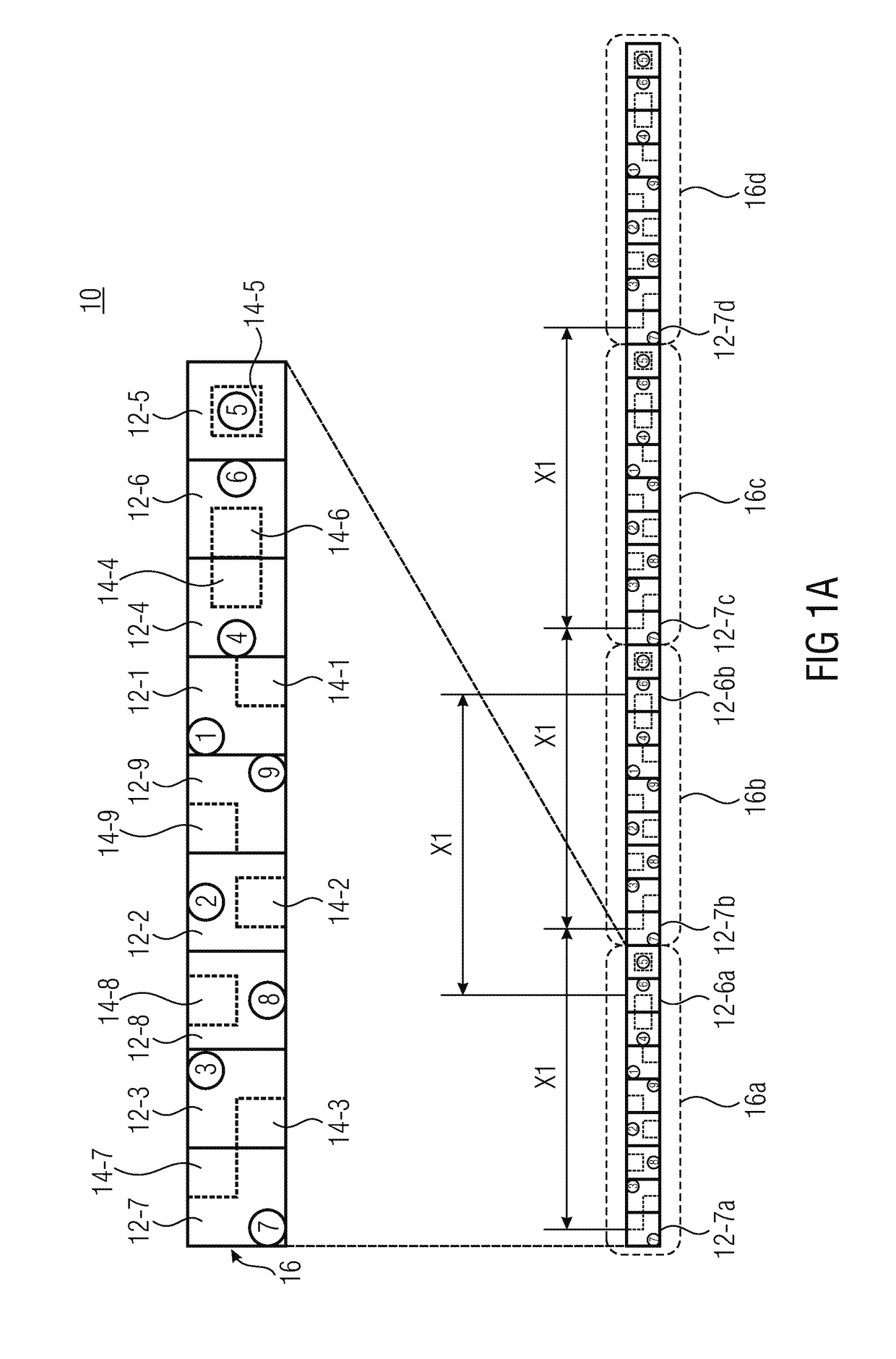
System and method for creating a stable optical interface
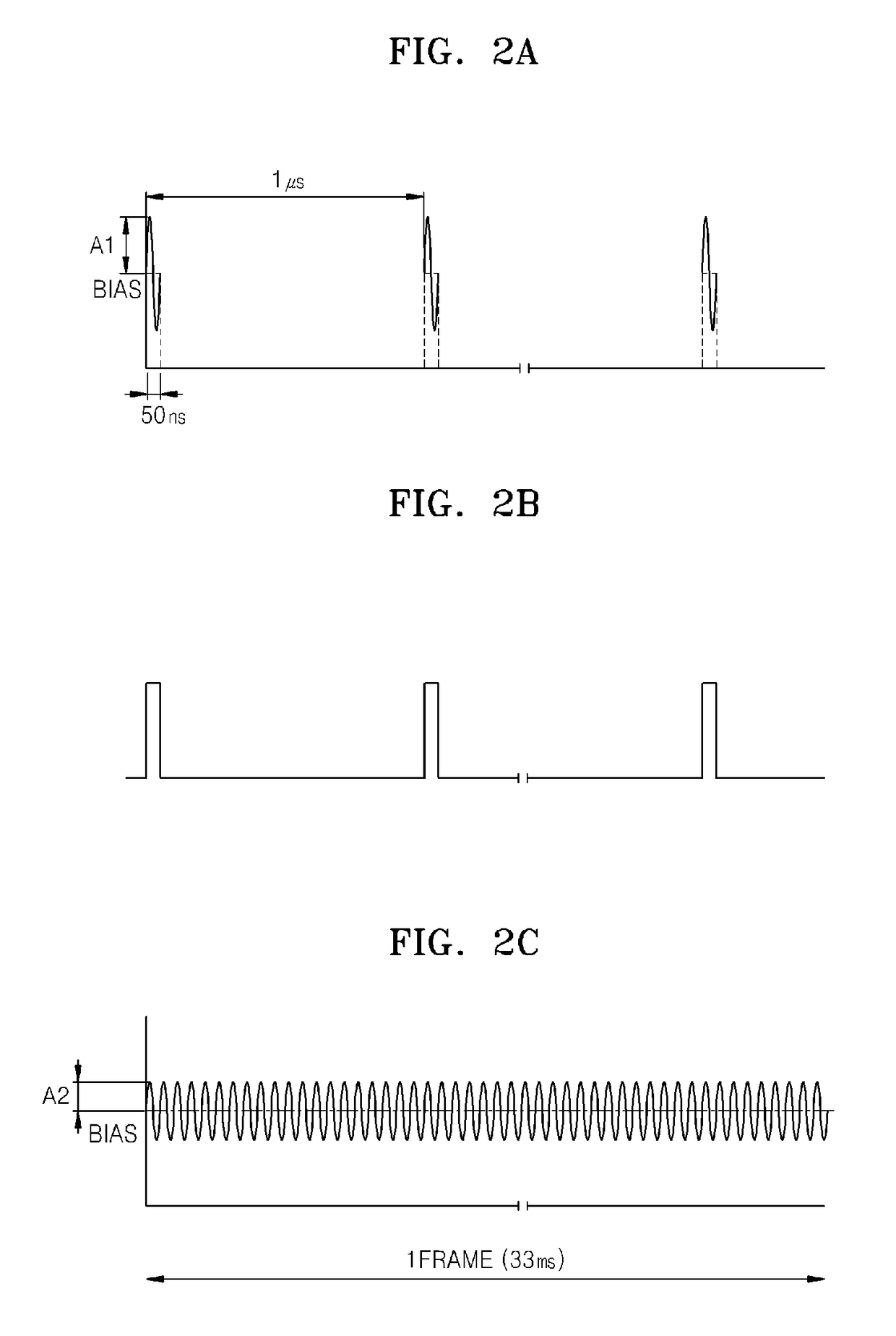
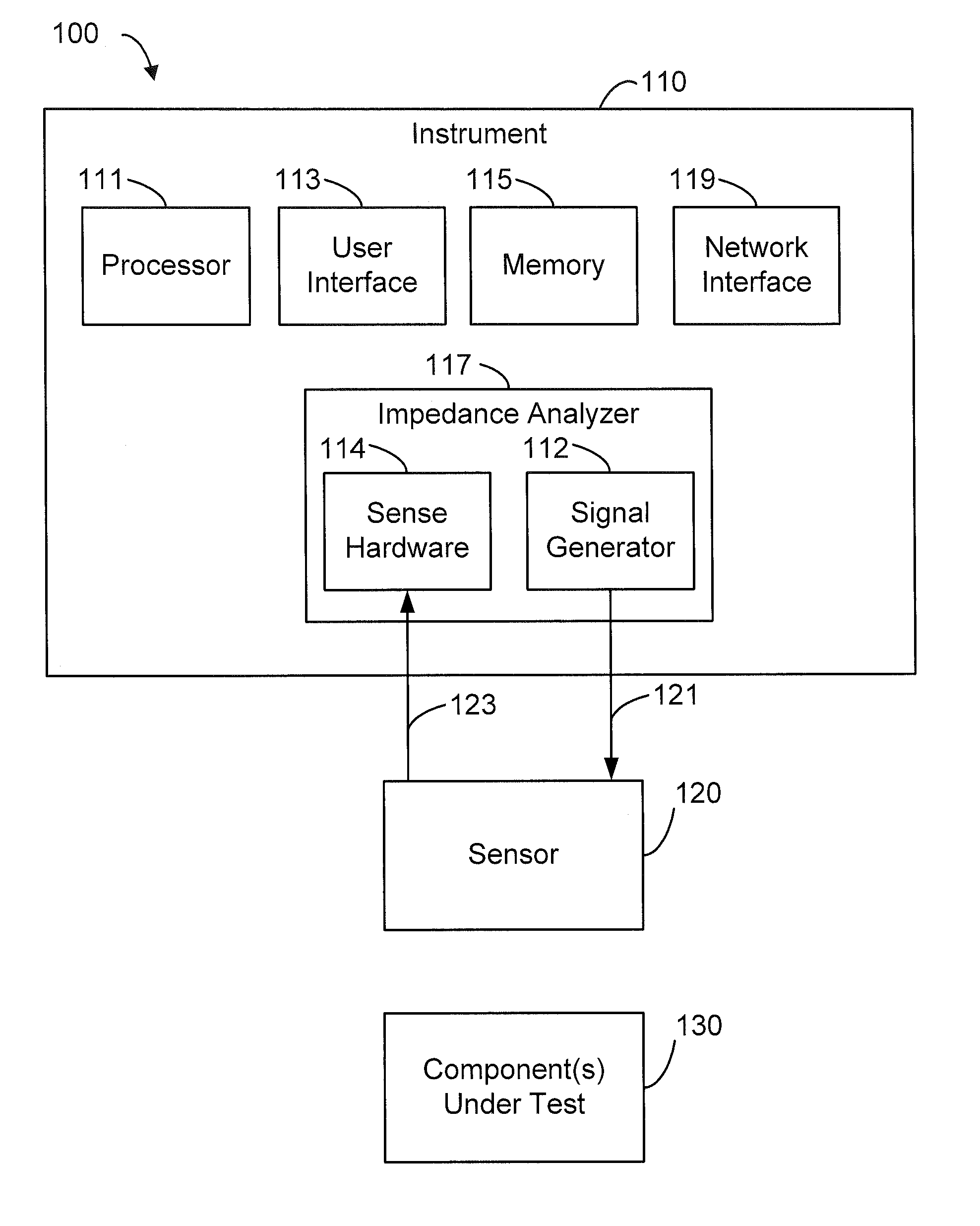
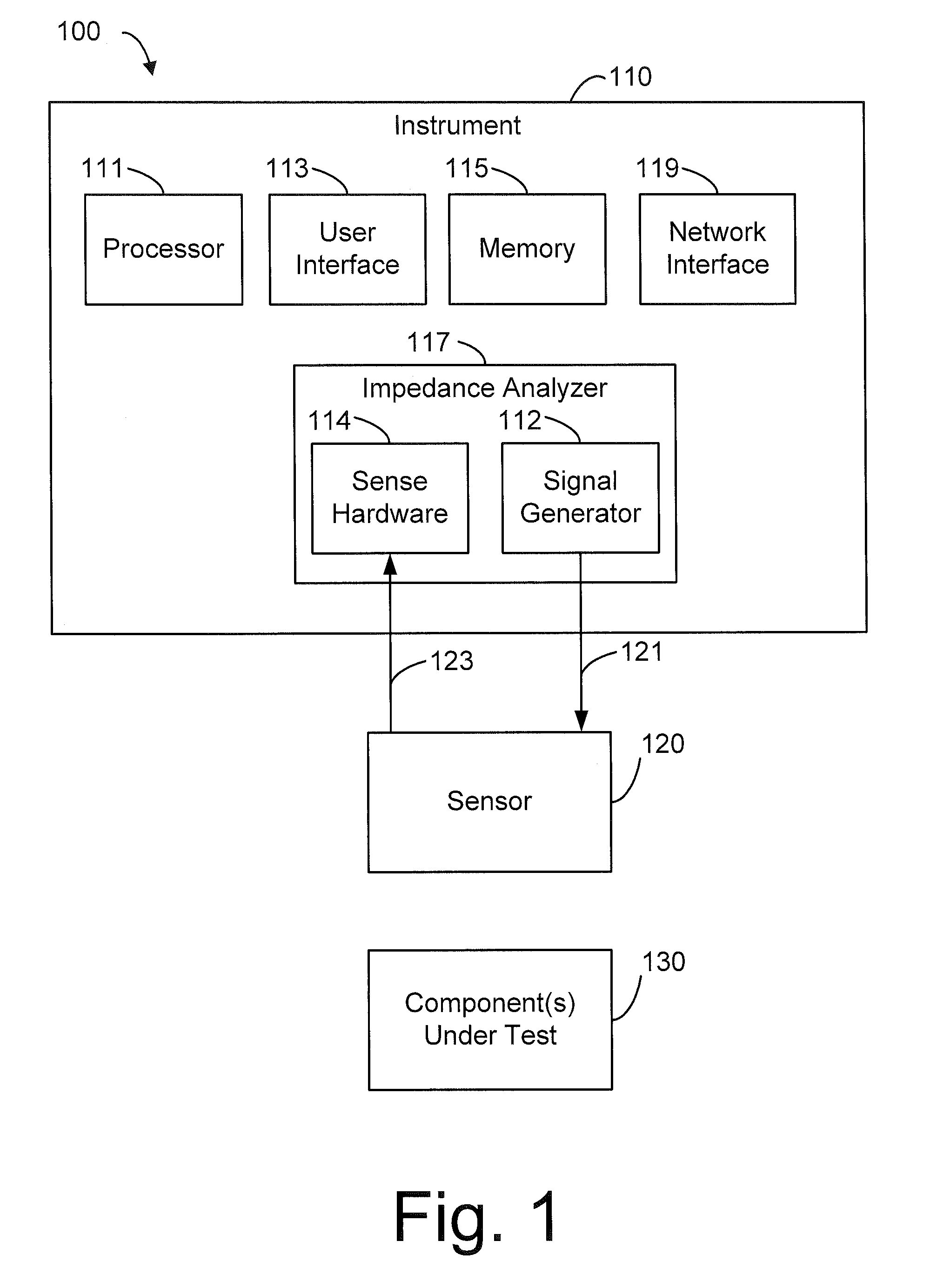
ActiveUS8219172B2High bandwidthReduce coherenceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRefractive indexLight beam
Owner:MASIMO CORP
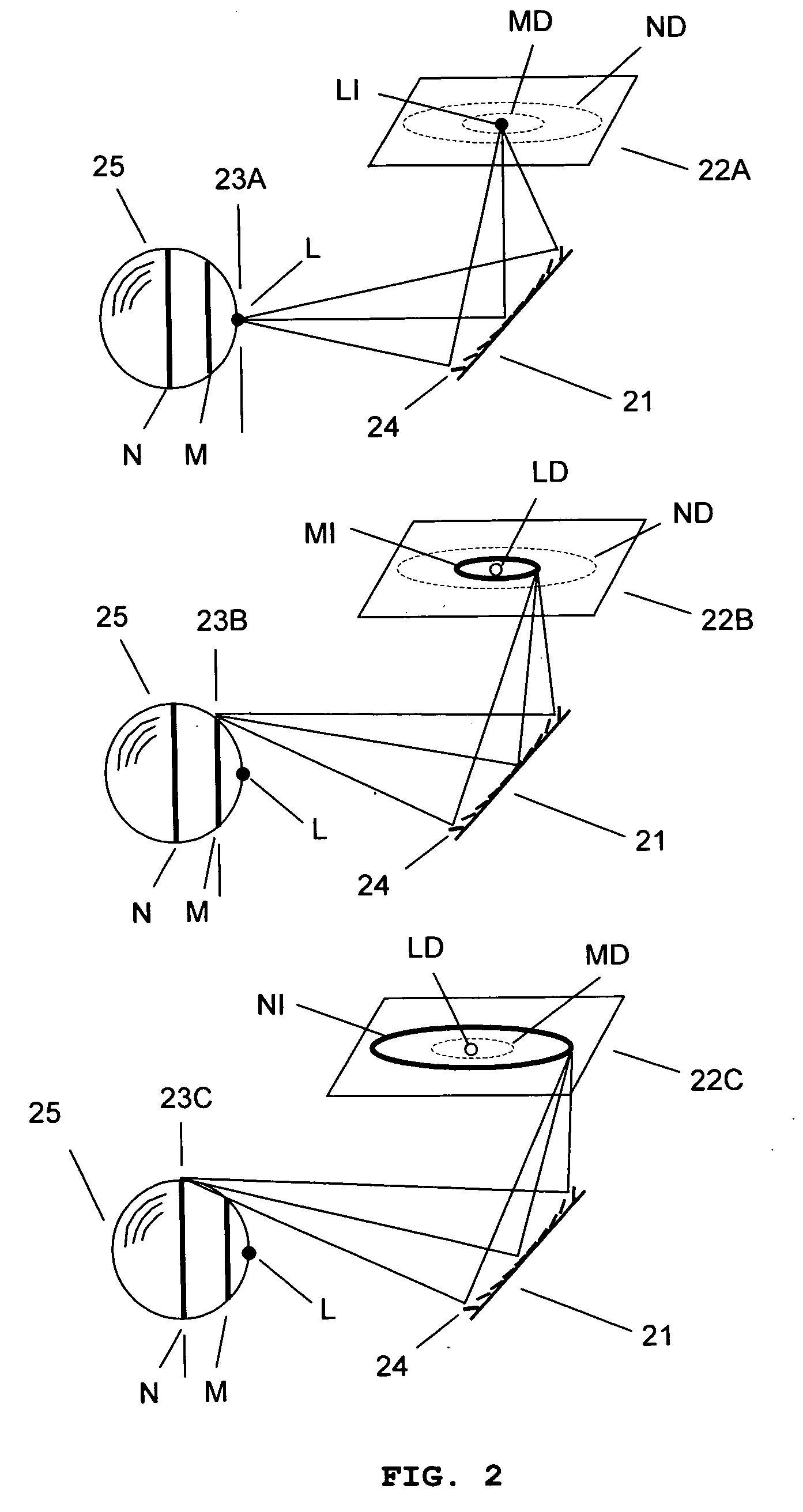
Full-field three-dimensional measurement method
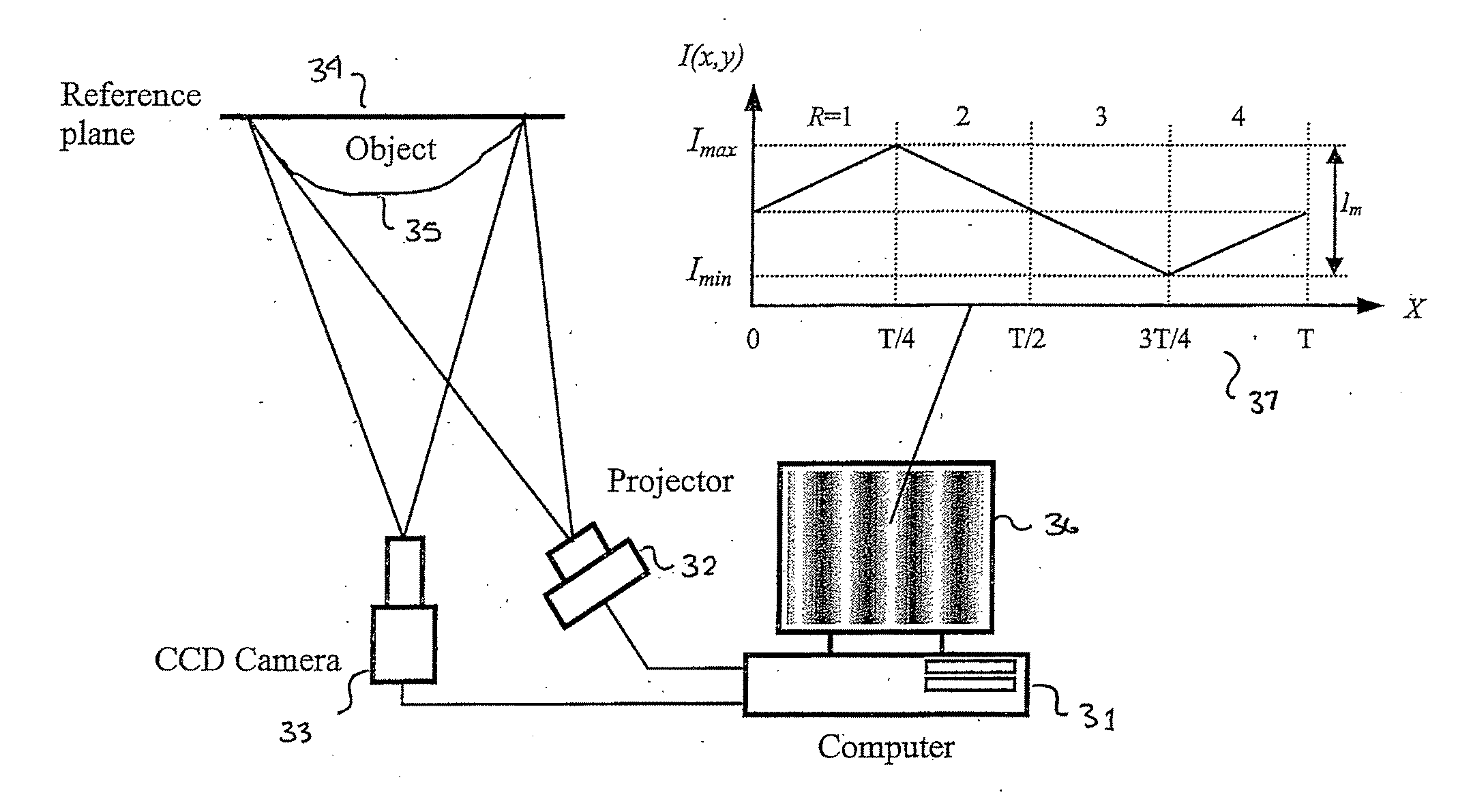
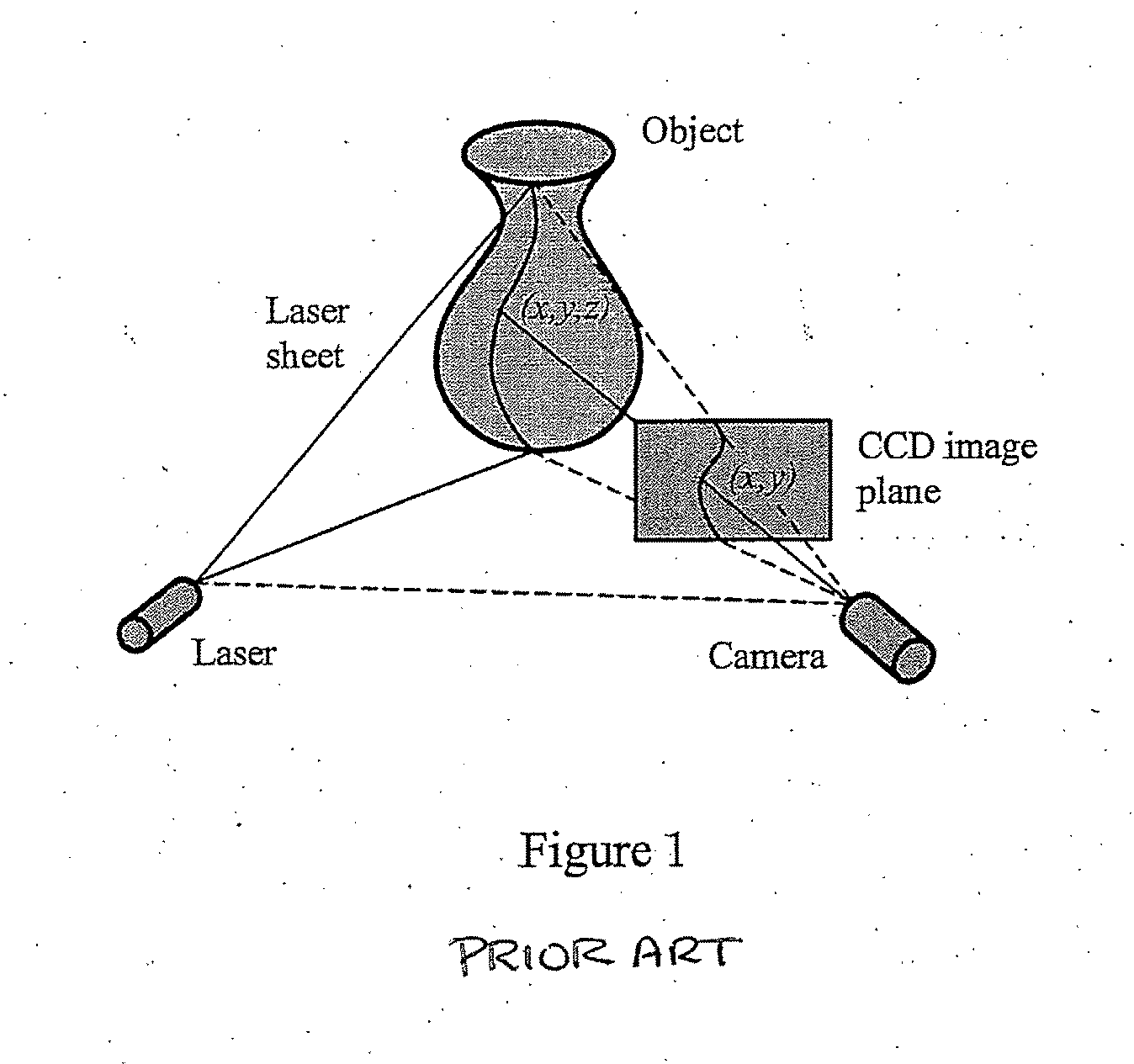
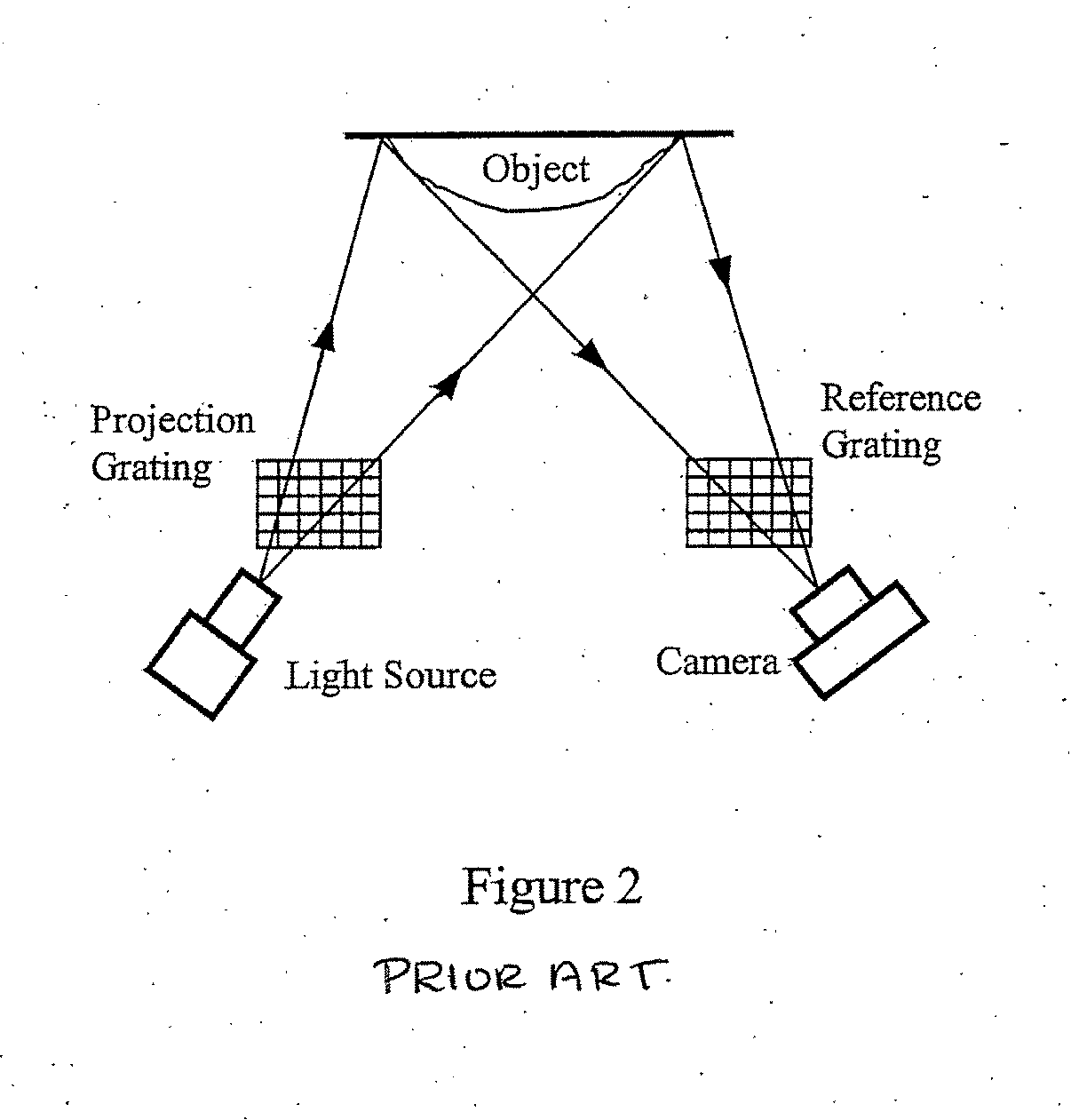
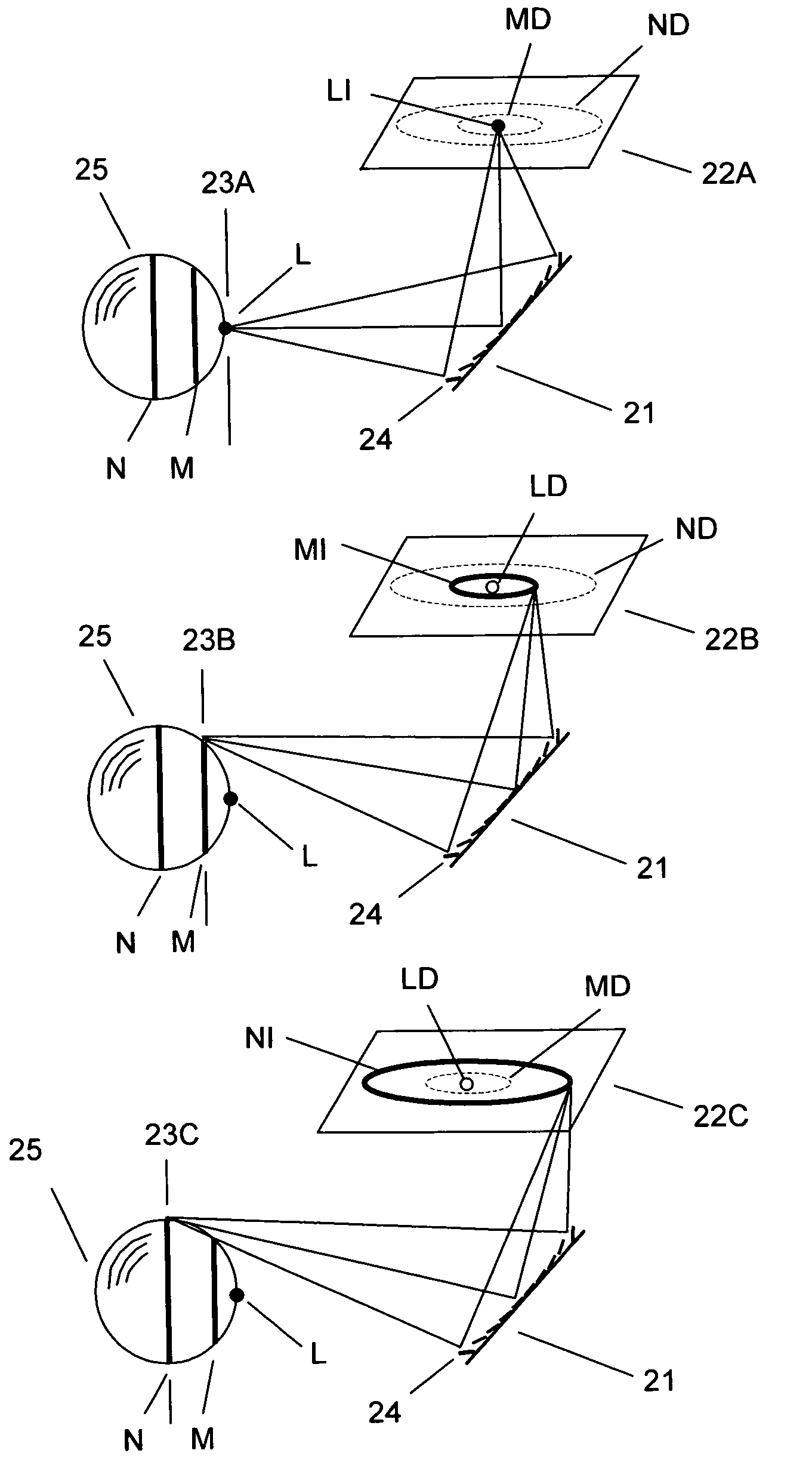
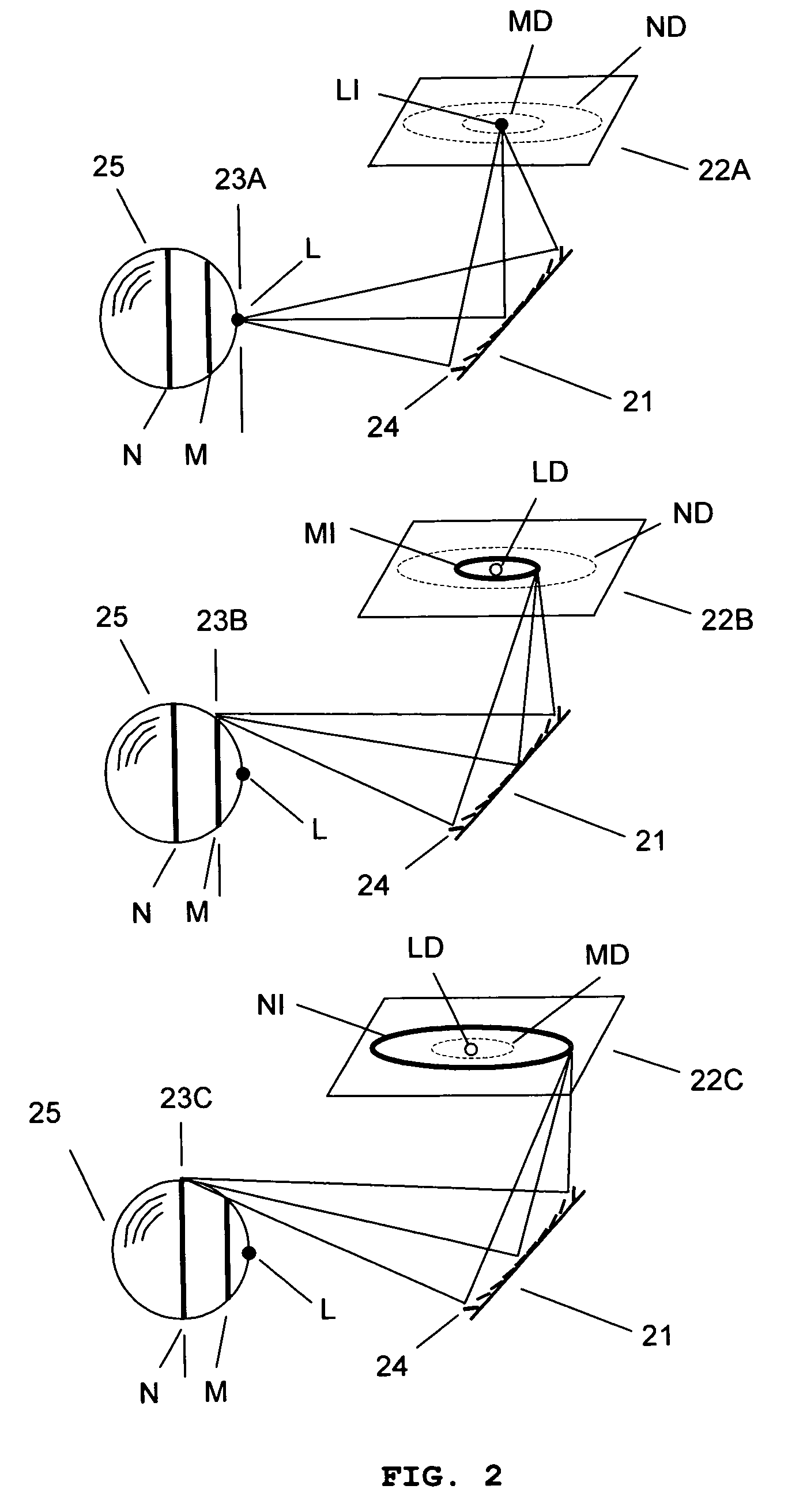
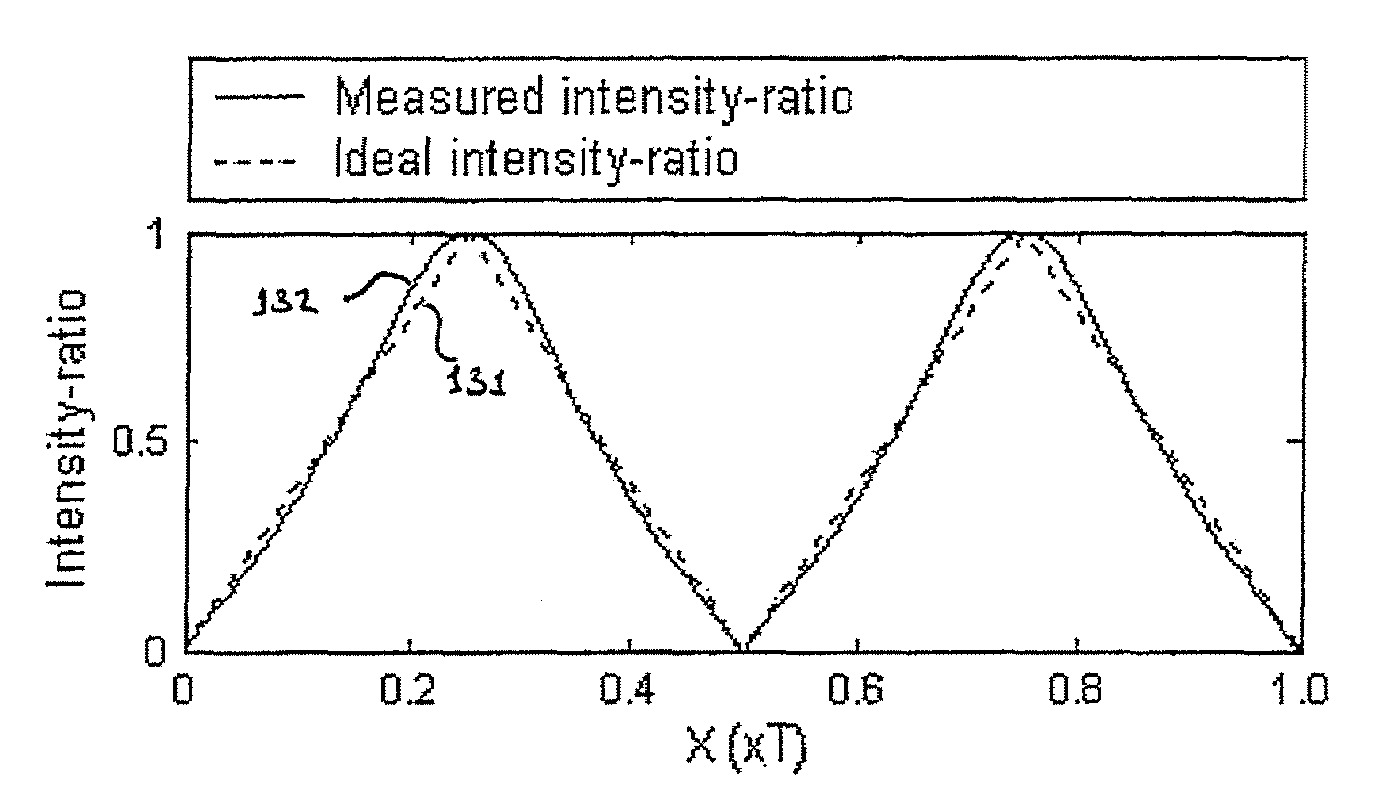
InactiveUS20070206204A1Improve processing speedSimple calculationUsing optical meansTriangulationFull field
A method and system for full-field fringe-projection for 3-D surface-geometry measurement, referred to as “triangular-pattern phase-shifting” is disclosed. A triangular grey-scale-level-coded fringe pattern is computer generated, projected along a first direction onto an object or scene surface and distorted according to the surface geometry. The 3-D coordinates of points on the surface are calculated by triangulation from distorted triangular fringe-pattern images acquired by a CCD camera along a second direction and a triangular-shape intensity-ratio distribution is obtained from calculation of the captured distorted triangular fringe-pattern images. Removal of the triangular shape of the intensity ratio over each pattern pitch generates a wrapped intensity-ratio distribution obtained by removing the discontinuity of the wrapped image with a modified unwrapping method. Intensity ratio-to-height conversion is used to reconstruct the 3-D surface coordinates of the object. Intensity-ratio error compensation involves estimating intensity-ratio error in a simulation of the measurement process with both real and ideal captured triangular-pattern images obtained from real and ideal gamma non-linearity functions. A look-up table relating the measure intensity-ratio to the corresponding intensity-ratio error is constructed and used for intensity-ratio error compensation. The inventive system is based on two-step phase-shifting but can be extended for multiple-step phase-shifting.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
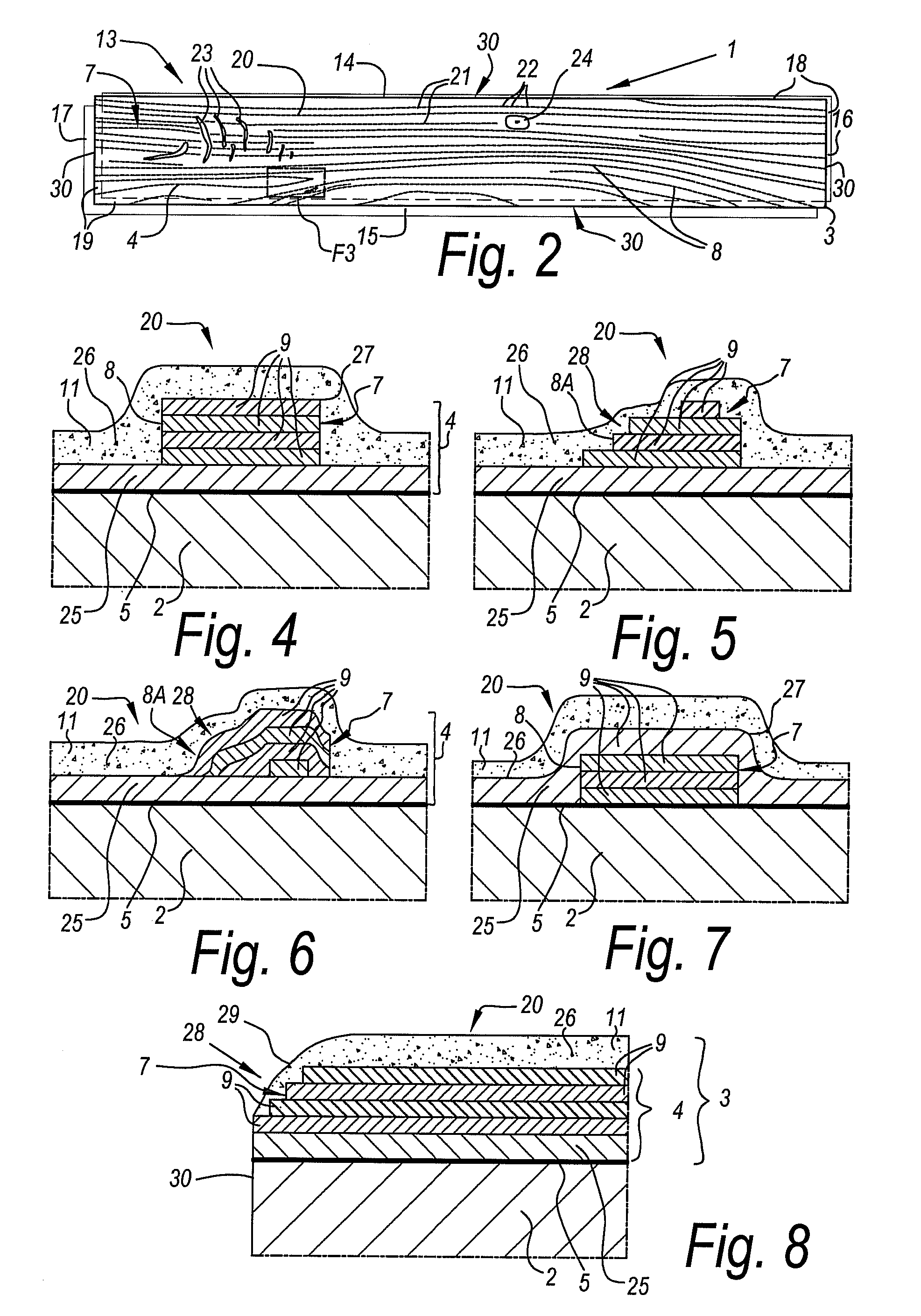
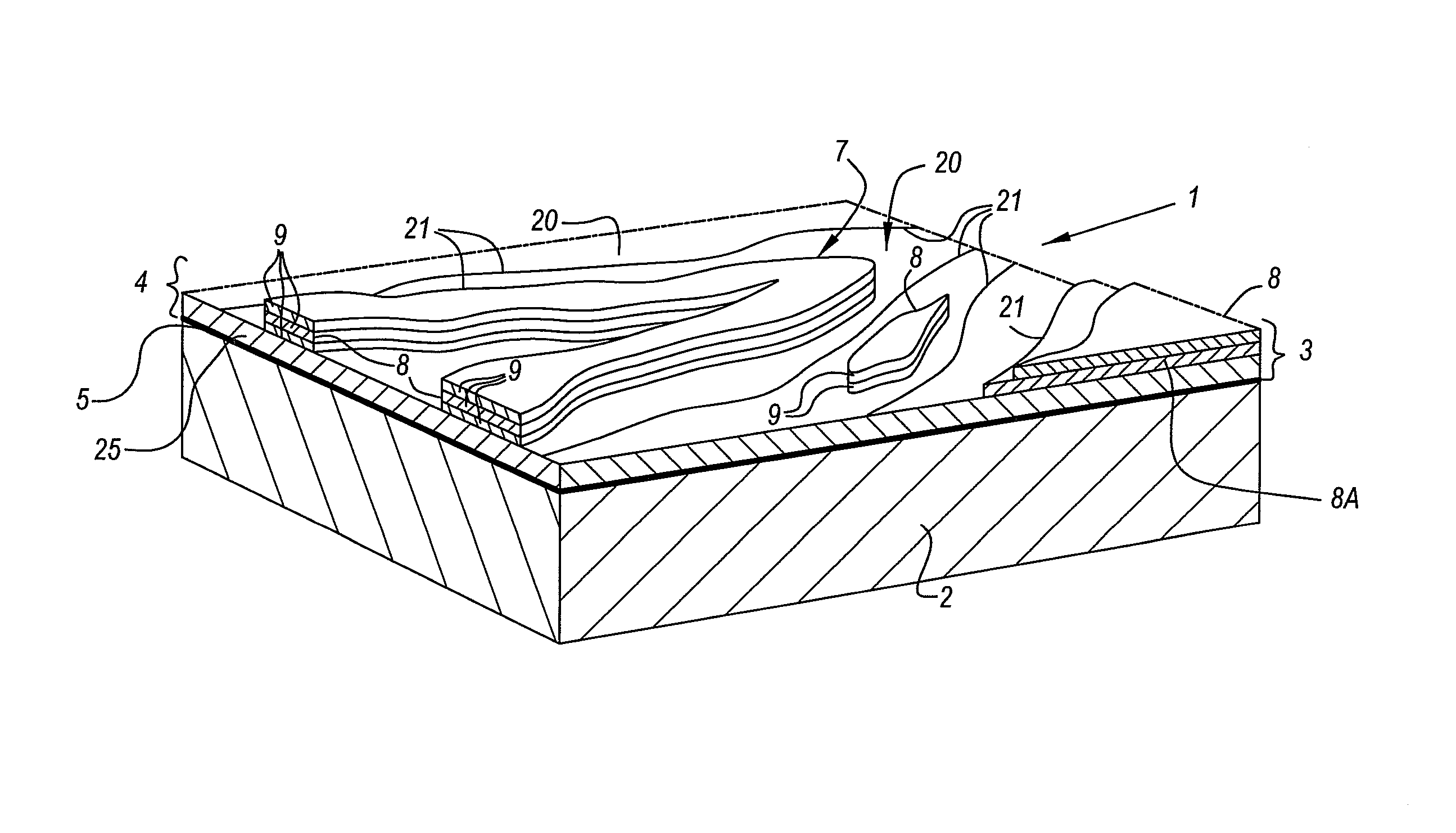
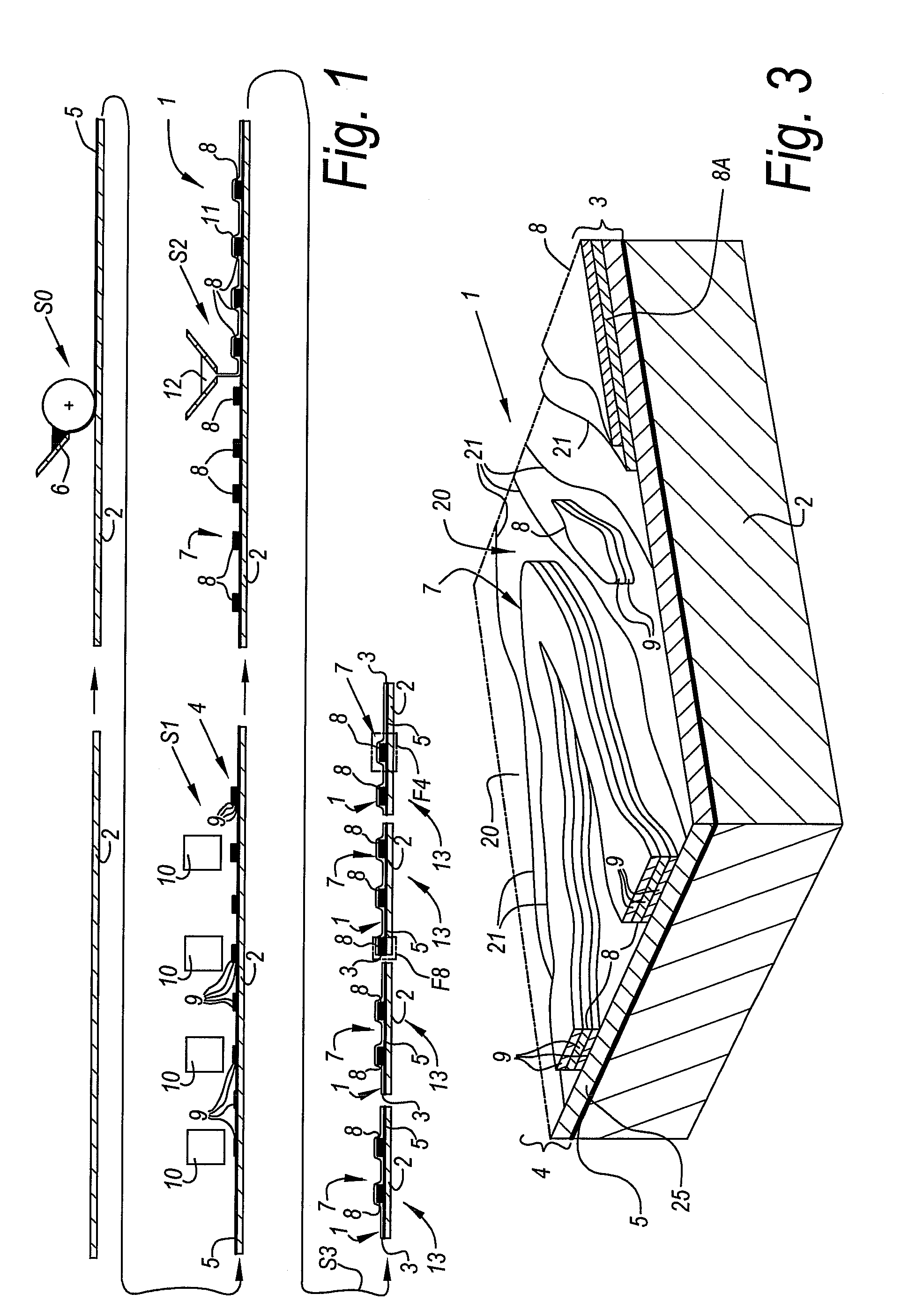
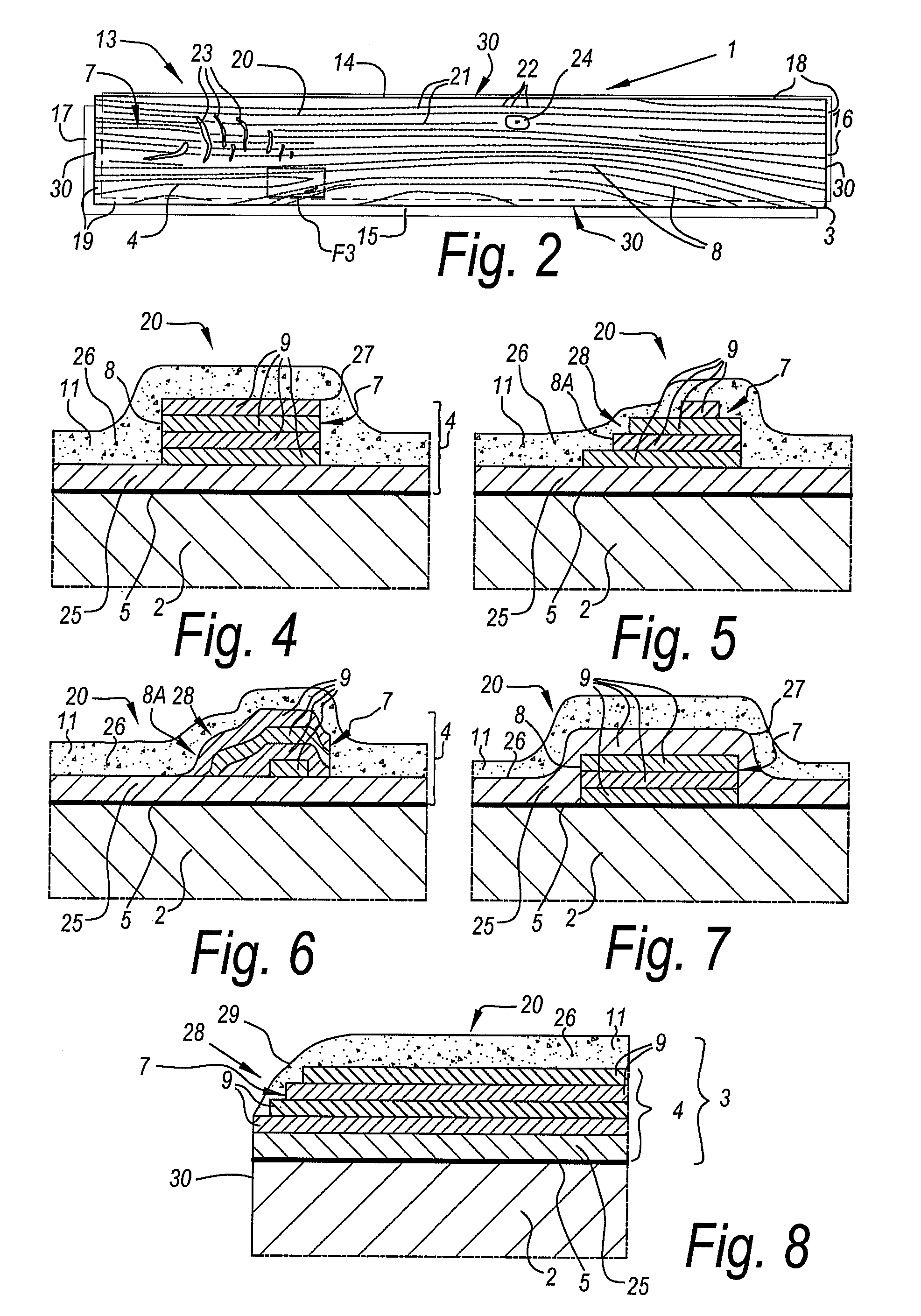
Method for manufacturing coated panels and coated panel
ActiveUS20090252925A1Significant changeComplex and more structureNatural patternsLayered productsEngineeringSurface plate
Owner:FLOORING IND LTD
Method for manufacturing coated panels
ActiveUS8465804B2Significant changeComplex and more structureNatural patternsOrnamental structuresEngineeringSurface plate
Owner:FLOORING IND LTD
Three-dimensional imaging system for pattern recognition
ActiveUS7212330B2High depth resolutionFast acquisition timeCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansDepth of fieldMicromirror array
The present invention provides a real-time three-dimensional pattern recognition imaging system having a variable focal length, a wide depth of field, a high depth resolution, a fast acquisition time, a variable magnification, a variable optical axis for tracking, and capability of compensating various optical distortions and aberrations, which enables pattern recognition systems to be more accurate as well as more robust to environmental variation. The imaging system for pattern recognition comprises one or more camera system, each of which has at least one micromirror array lens(MMAL), a two-dimensional image senor, and an image processing unit. A MMAL has unique features including a variable focal length, a variable optical axis, and a variable magnification.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Full-field three-dimensional measurement method
A method and system for full-field fringe-projection for 3-D surface-geometry measurement, referred to as “triangular-pattern phase-shifting” is disclosed. A triangular grey-scale-level-coded fringe pattern is computer generated, projected along a first direction onto an object or scene surface and distorted according to the surface geometry. The 3-D coordinates of points on the surface are calculated by triangulation from distorted triangular fringe-pattern images acquired by a CCD camera along a second direction and a triangular-shape intensity-ratio distribution is obtained from calculation of the captured distorted triangular fringe-pattern images. Removal of the triangular shape of the intensity ratio over each pattern pitch generates a wrapped intensity-ratio distribution obtained by removing the discontinuity of the wrapped image with a modified unwrapping method. Intensity ratio-to-height conversion is used to reconstruct the 3-D surface coordinates of the object. Intensity-ratio error compensation involves estimating intensity-ratio error in a simulation of the measurement process with both real and ideal captured triangular-pattern images obtained from real and ideal gamma non-linearity functions. A look-up table relating the measure intensity-ratio to the corresponding intensity-ratio error is constructed and used for intensity-ratio error compensation. The inventive system is based on two-step phase-shifting but can be extended for multiple-step phase-shifting.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
Microscopy system with revolvable stage
InactiveUS20100177190A1High resolutionEnhance the imagePhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansRotational axisImage resolution
A microscopy system includes an image focusing module, a stage for supporting a sample, image collection unit for collecting sliced images of the sample acquired by the image focusing module, and an image fusion unit for fusing sliced images of the sample acquired from different observation angles. The stage supports the sample and is configured to be revolvable around a rotational axis which is substantially perpendicular to an extending direction from the sample to the image focusing module so that enabling the image focusing module to acquire sliced images of the sample from different observation angles. The image fusion unit is used for remapping the sliced images acquired from different observation angles into a reference coordinate system, converting anisotropic voxels resolution of the sliced images to isotropic resolution, and fusing the sliced images into a final image.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Three-dimensional imaging system for pattern recognition
ActiveUS20060098872A1Fast response timeLarge focal length variationCharacter and pattern recognitionDepth of fieldMicromirror array
The present invention provides a real-time three-dimensional pattern recognition imaging system having a variable focal length, a wide depth of field, a high depth resolution, a fast acquisition time, a variable magnification, a variable optical axis for tracking, and capability of compensating various optical distortions and aberrations, which enables pattern recognition systems to be more accurate as well as more robust to environmental variation. The imaging system for pattern recognition comprises one or more camera system, each of which has at least one micromirror array lens(MMAL), a two-dimensional image senor, and an image processing unit. A MMAL has unique features including a variable focal length, a variable optical axis, and a variable magnification.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
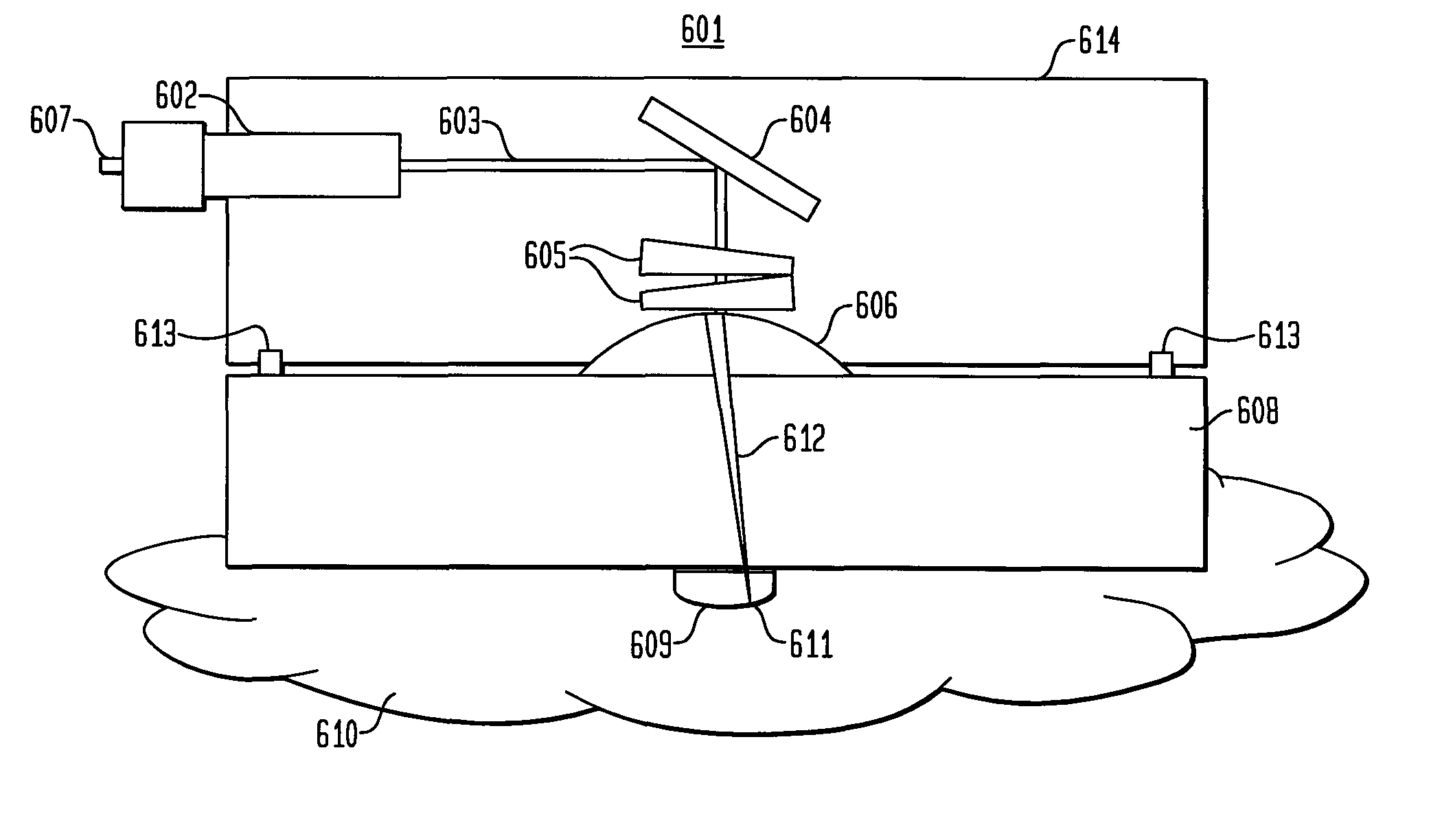
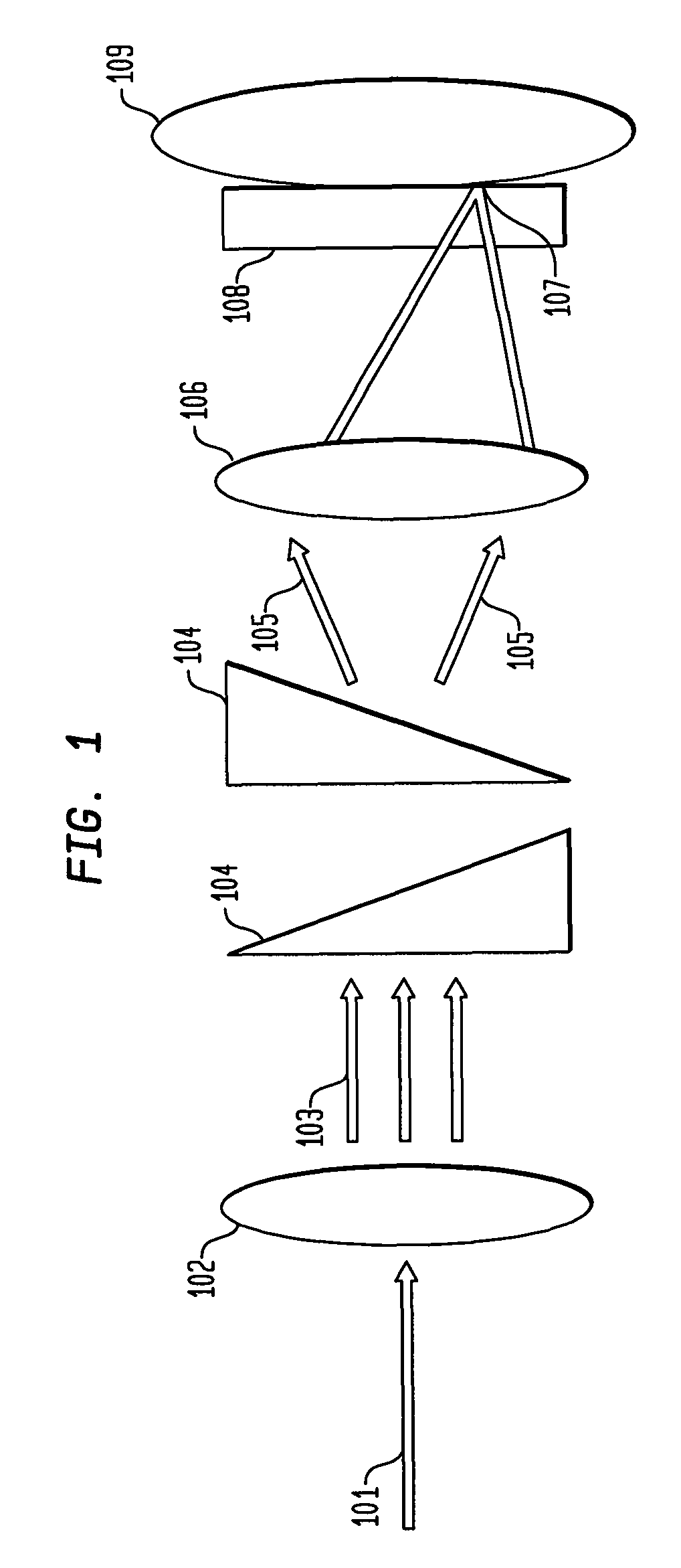
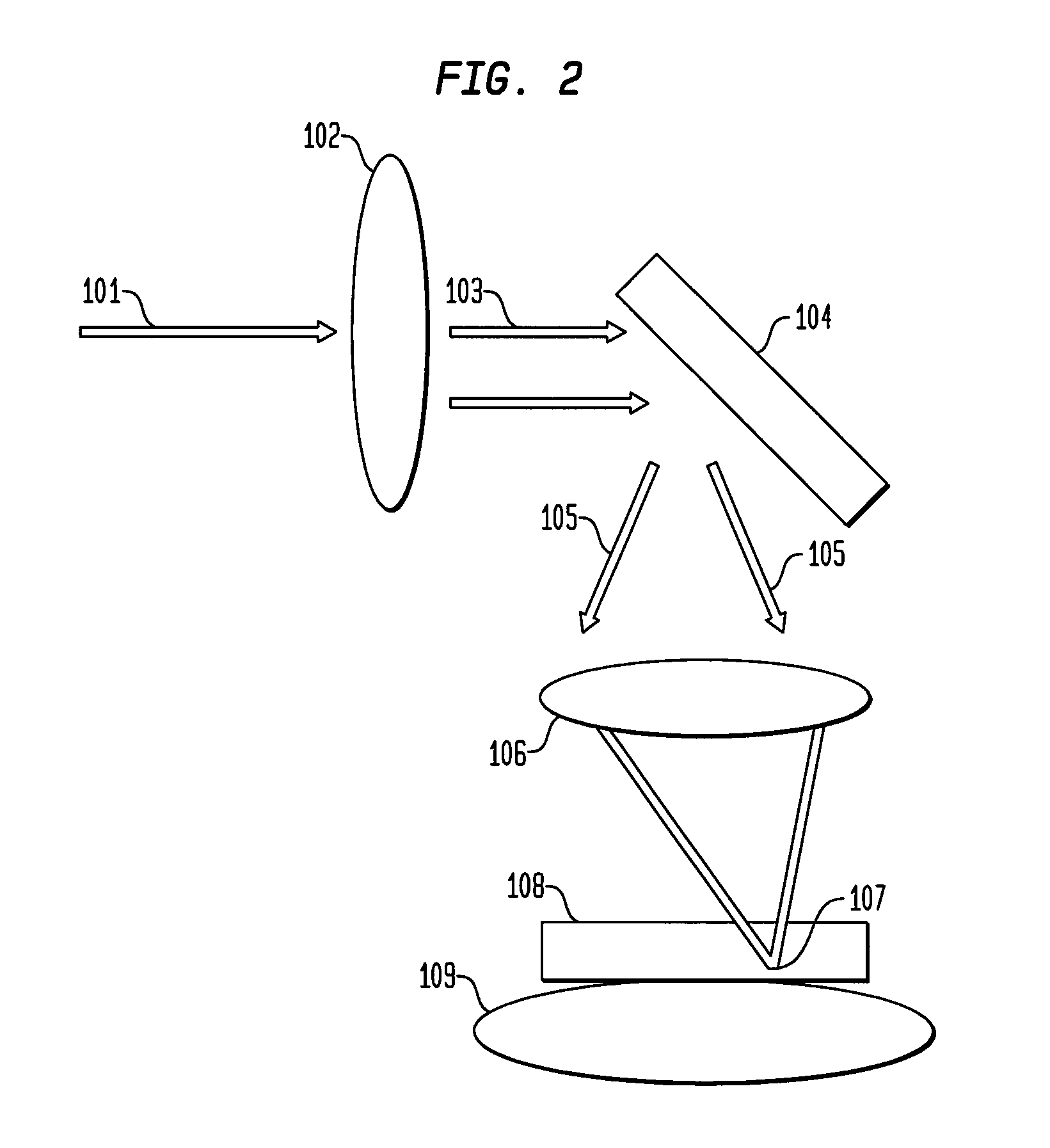
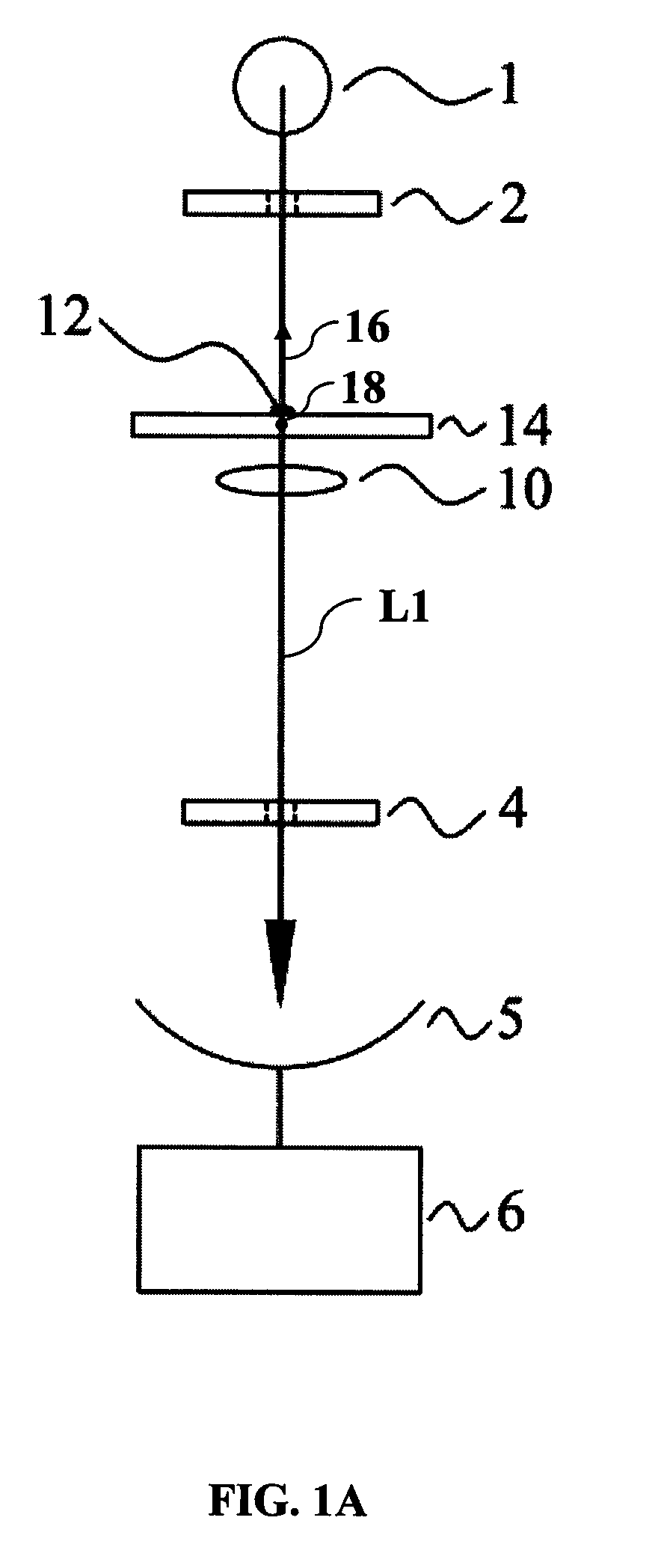
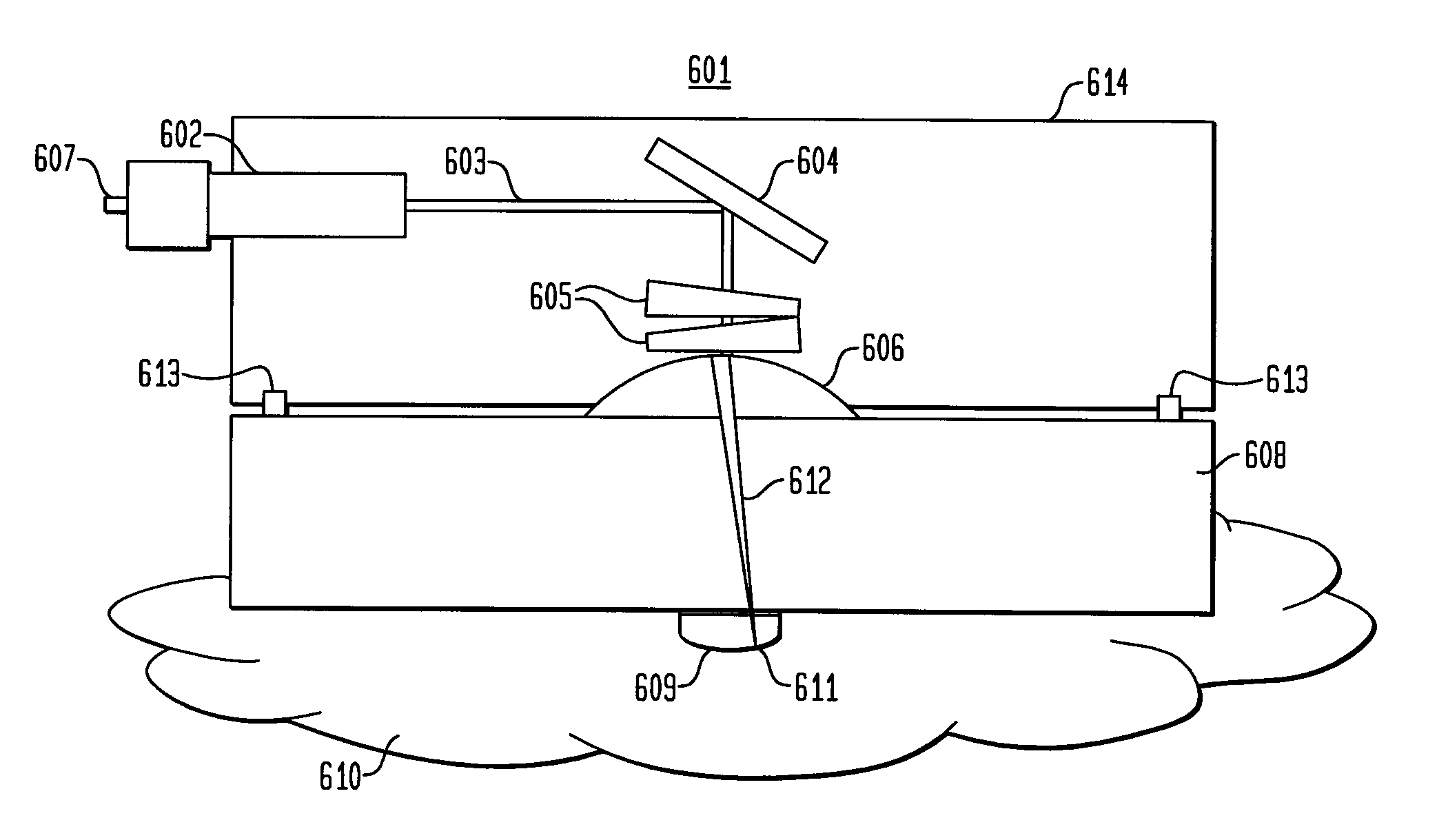
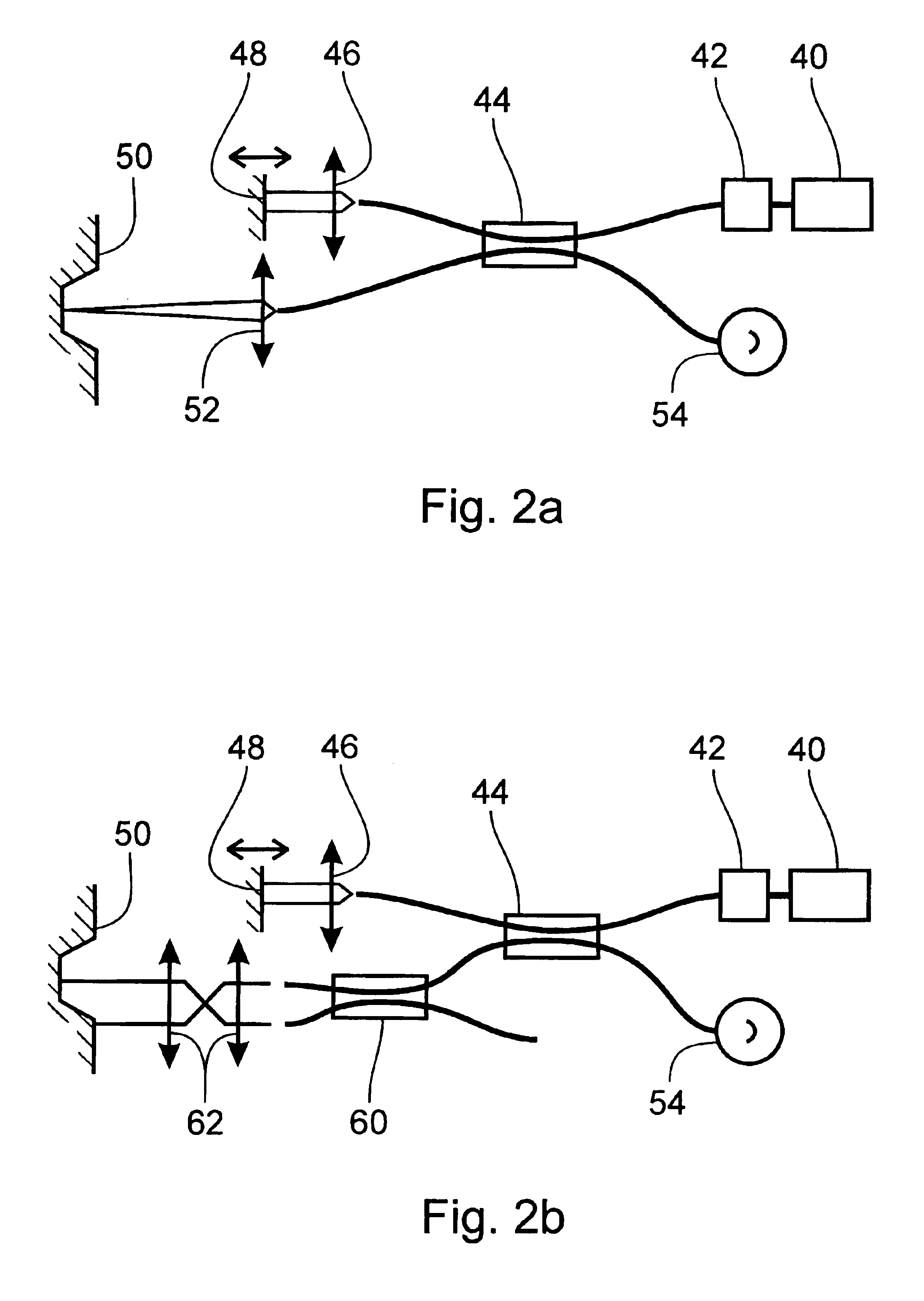
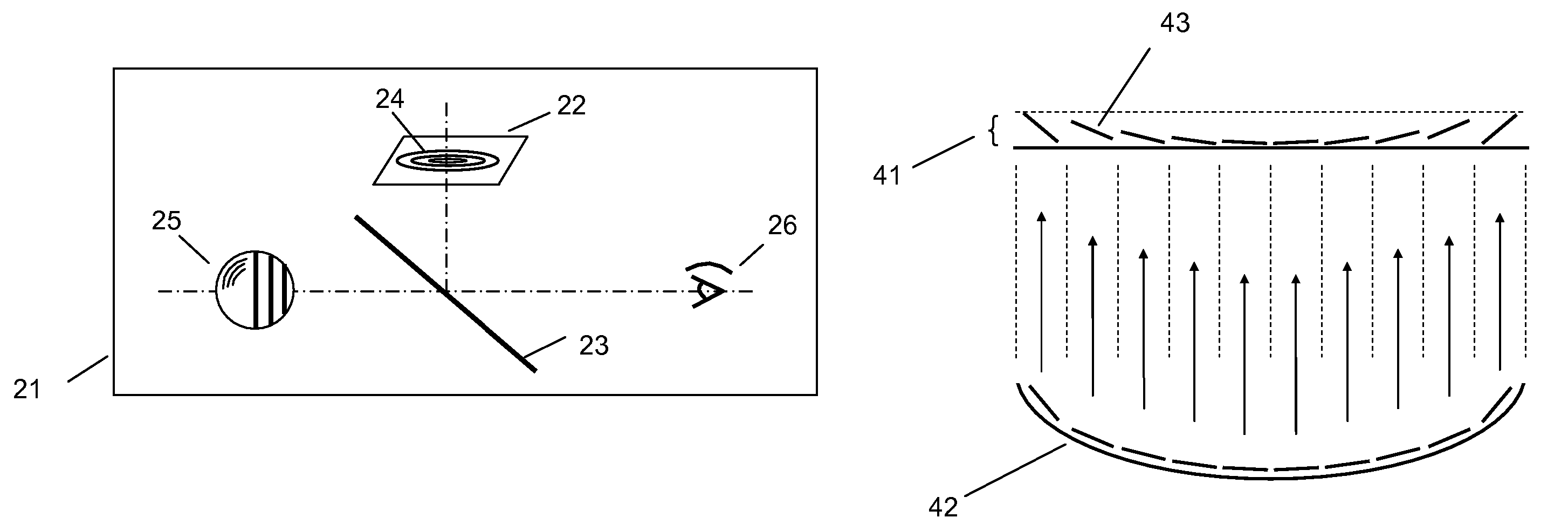
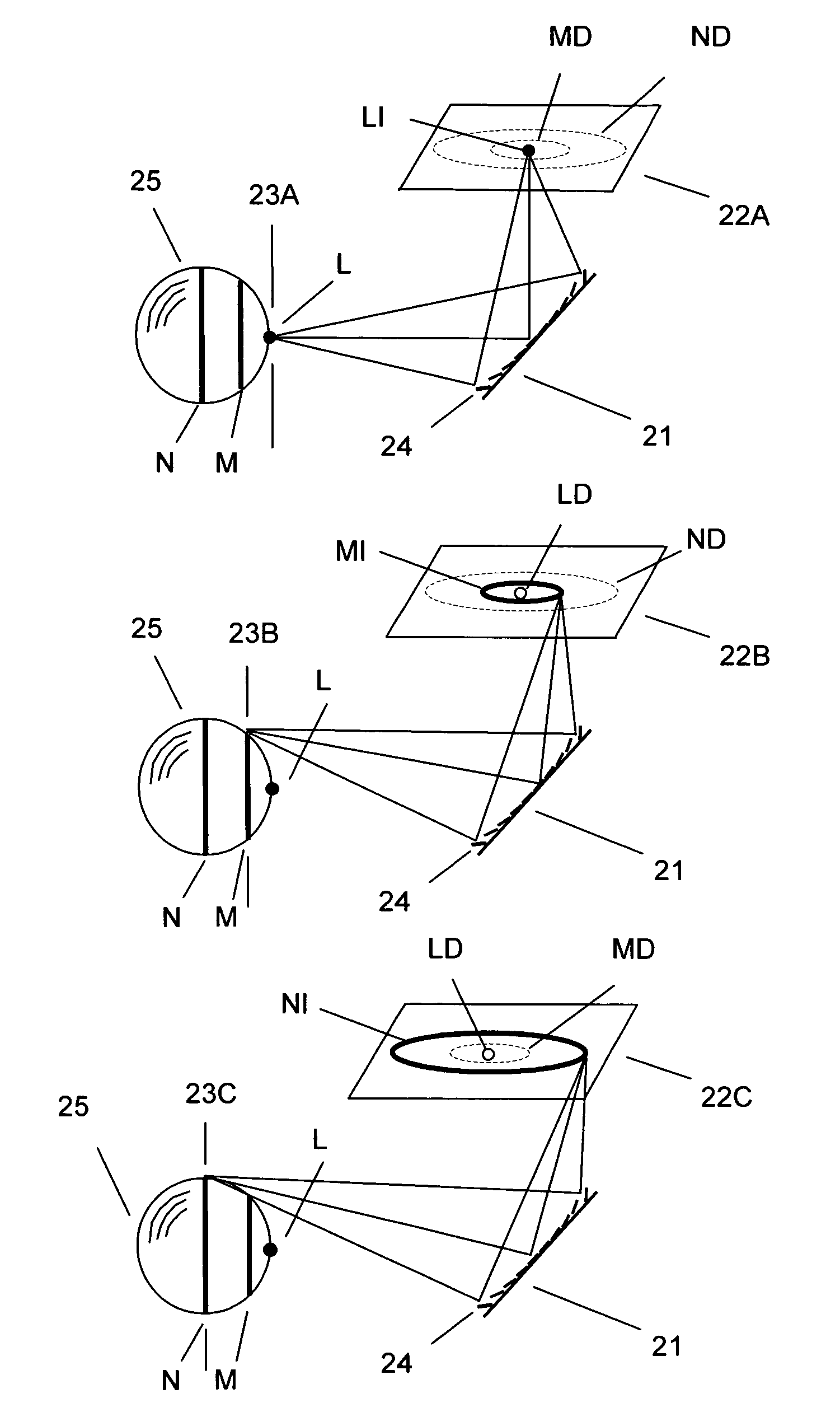
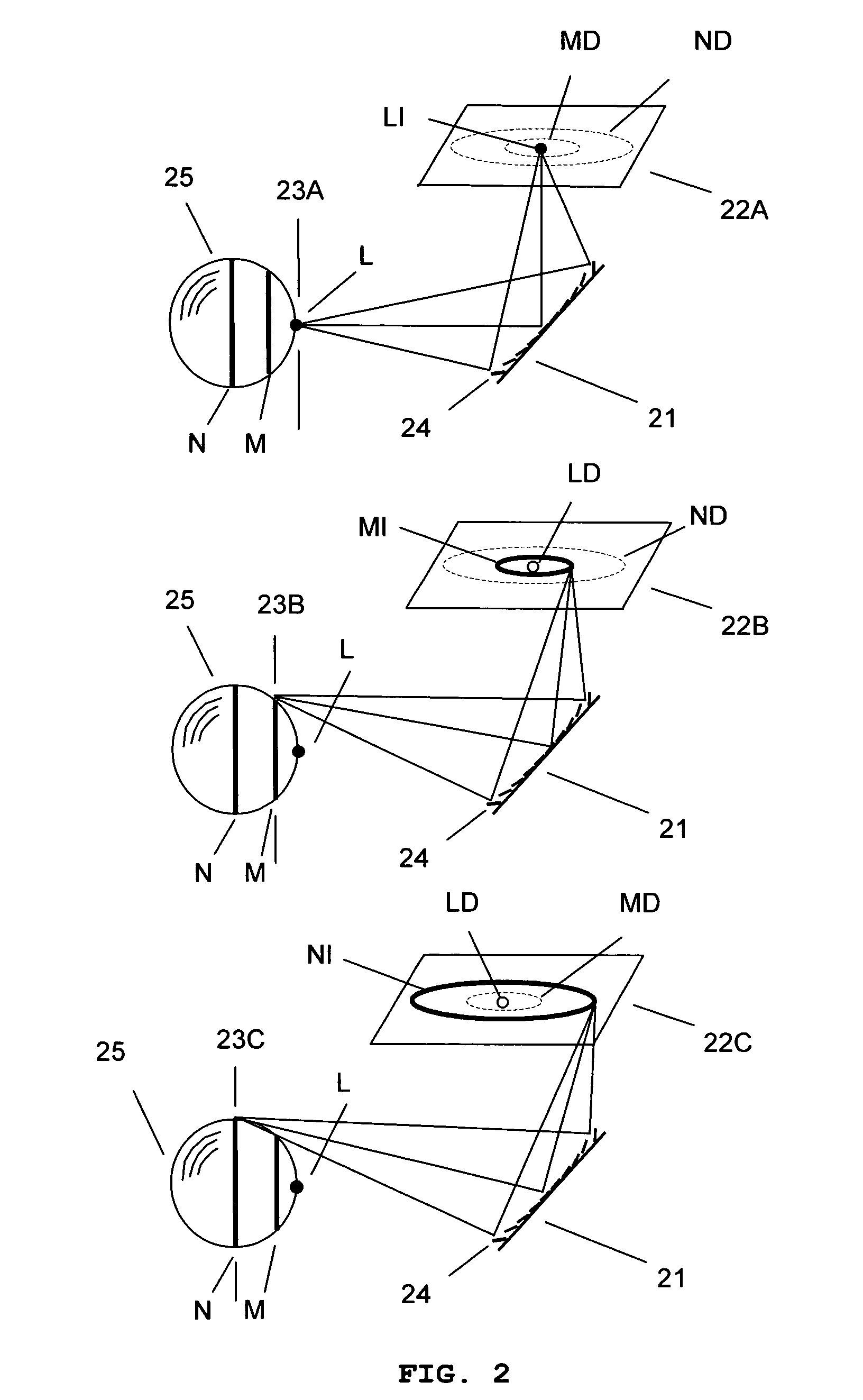
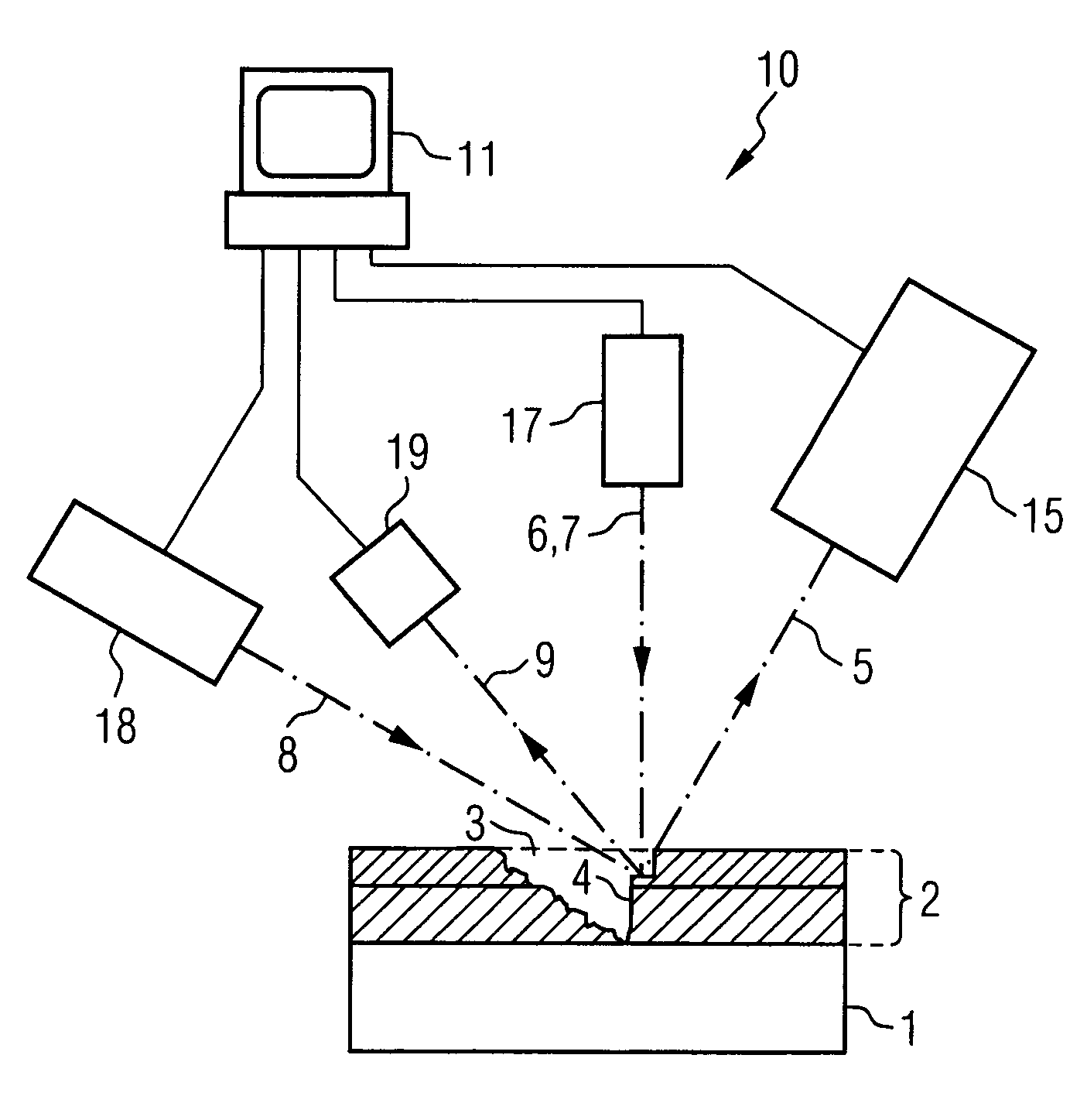
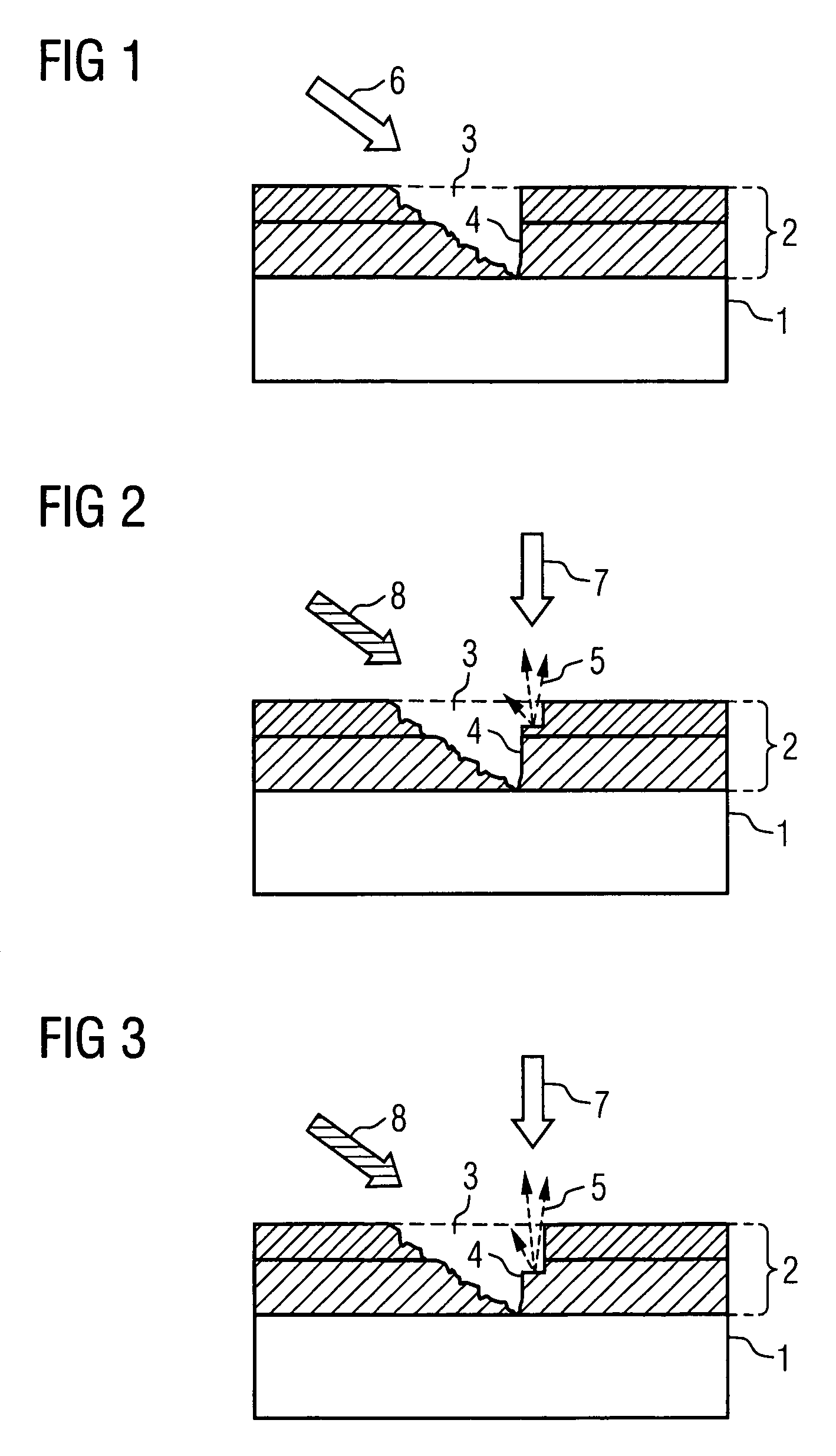
System and method for creating a stable optical interface
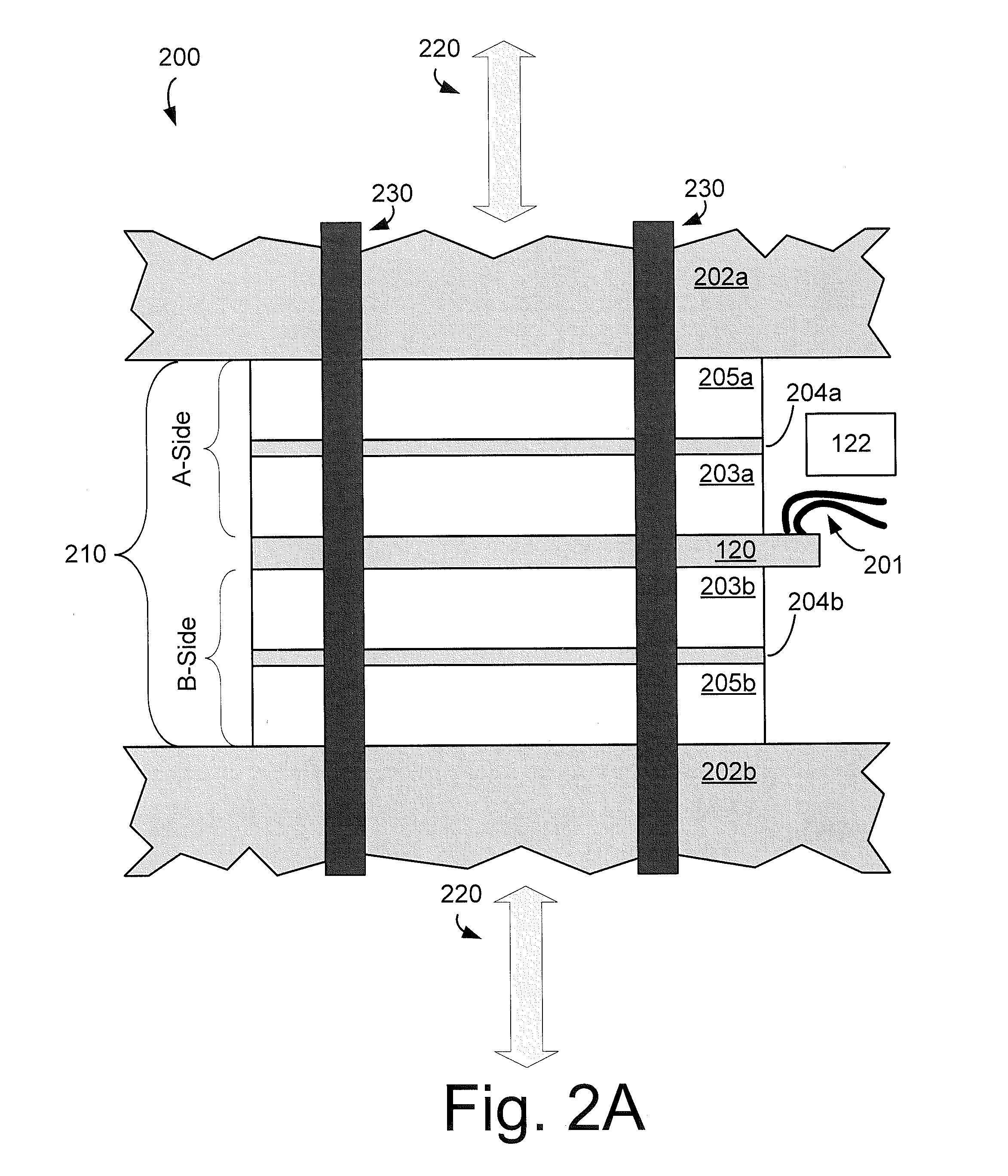
ActiveUS20070219437A1Simple interfaceOptical coupling efficiency is decreasedDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSkin surfaceRefractive index
A system and a method for creating a stable and reproducible interface of an optical sensor system for measuring blood glucose levels in biological tissue include a dual wedge prism sensor attached to a disposable optic that comprises a focusing lens and an optical window. The disposable optic adheres to the skin to allow a patient to take multiple readings or scans at the same location. The disposable optic includes a Petzval surface placed flush against the skin to maintain the focal point of the optical beam on the surface of the skin. Additionally, the integrity of the sensor signal is maximized by varying the rotation rates of the dual wedge prisms over time in relation to the depth scan rate of the sensor. Optimally, a medium may be injected between the disposable and the skin to match the respective refractive indices and optimize the signal collection of the sensor.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
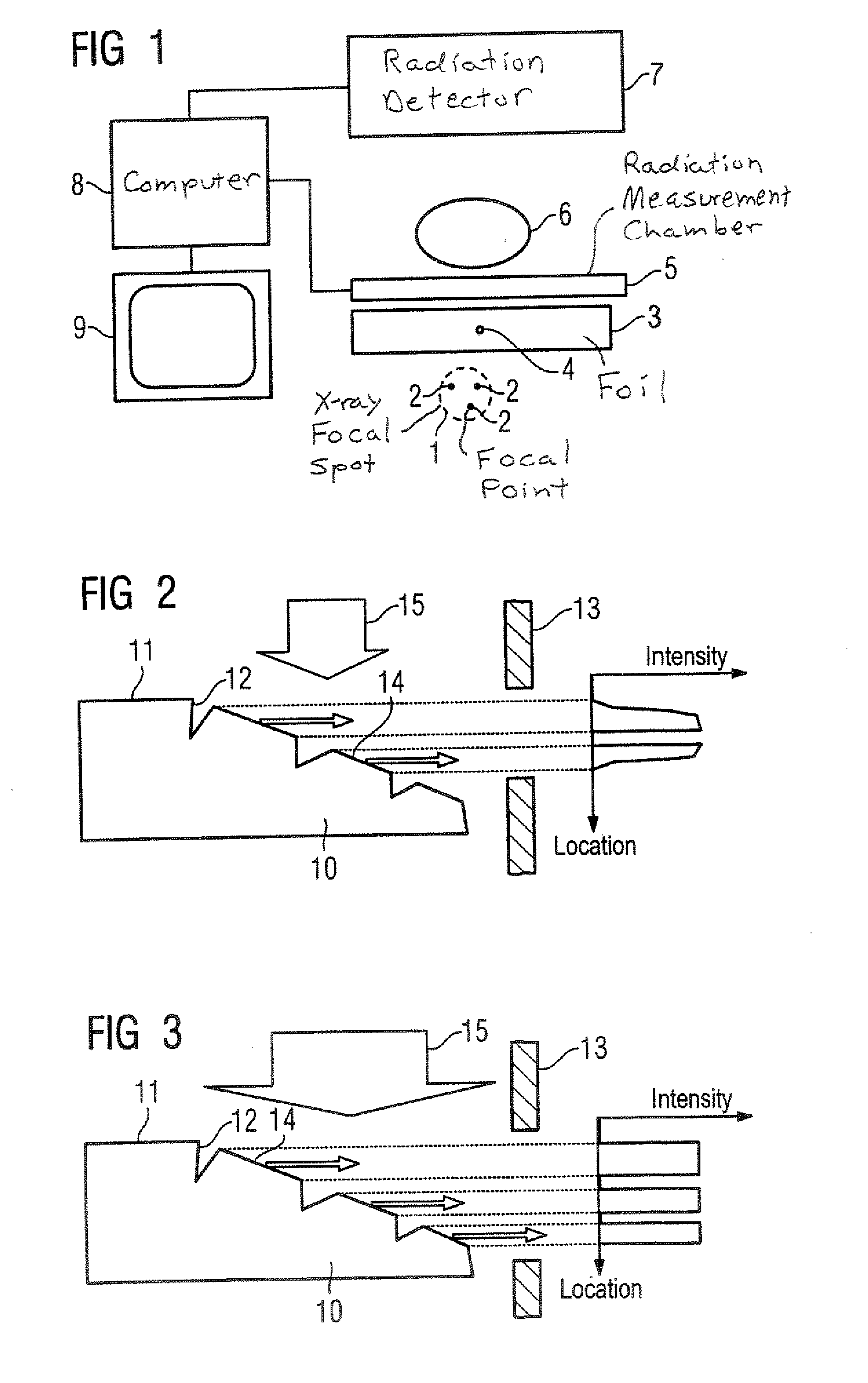
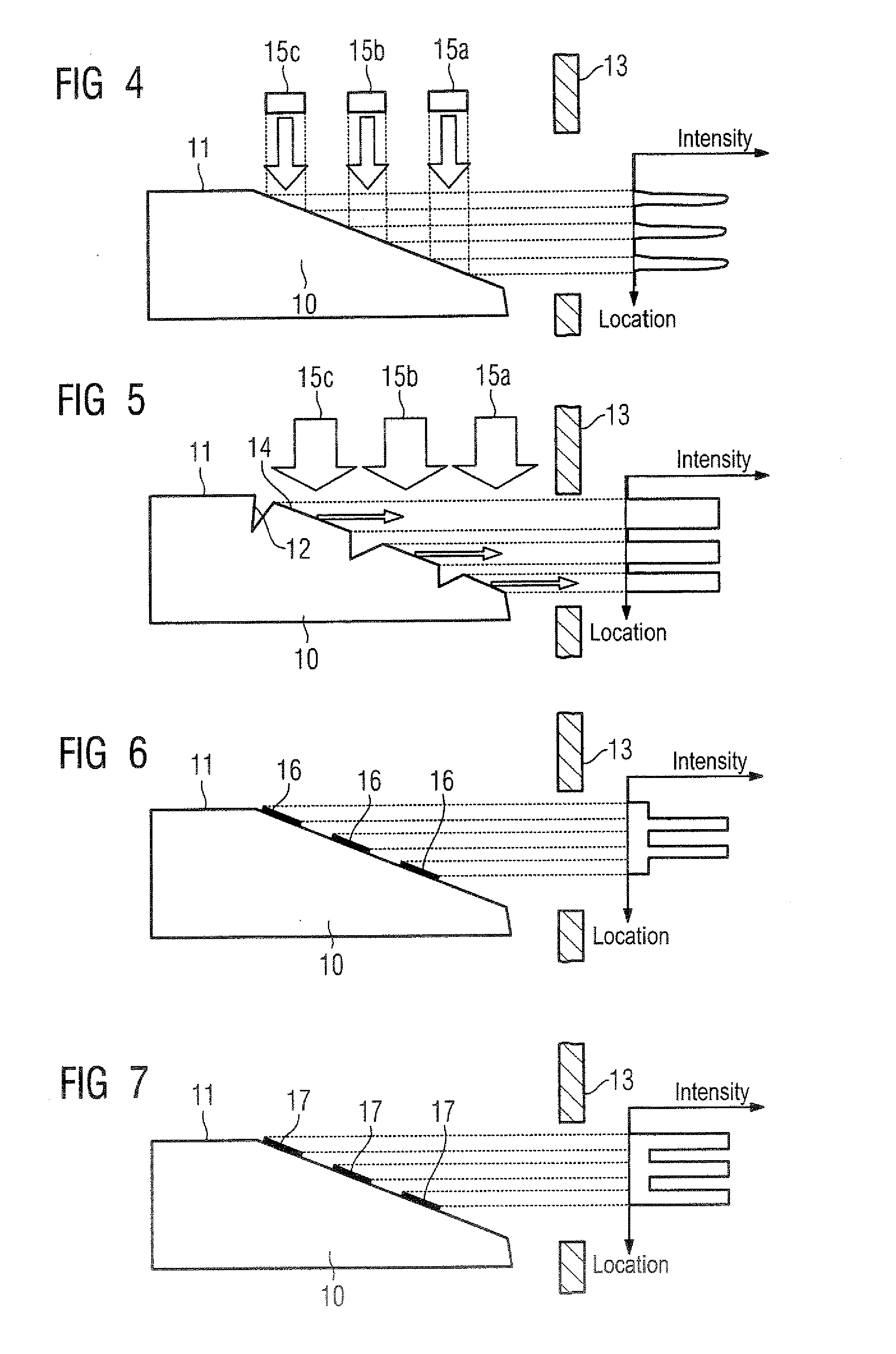
X-ray system having an x-ray generator that produces an x-ray focal spot with multiple intensity maxima
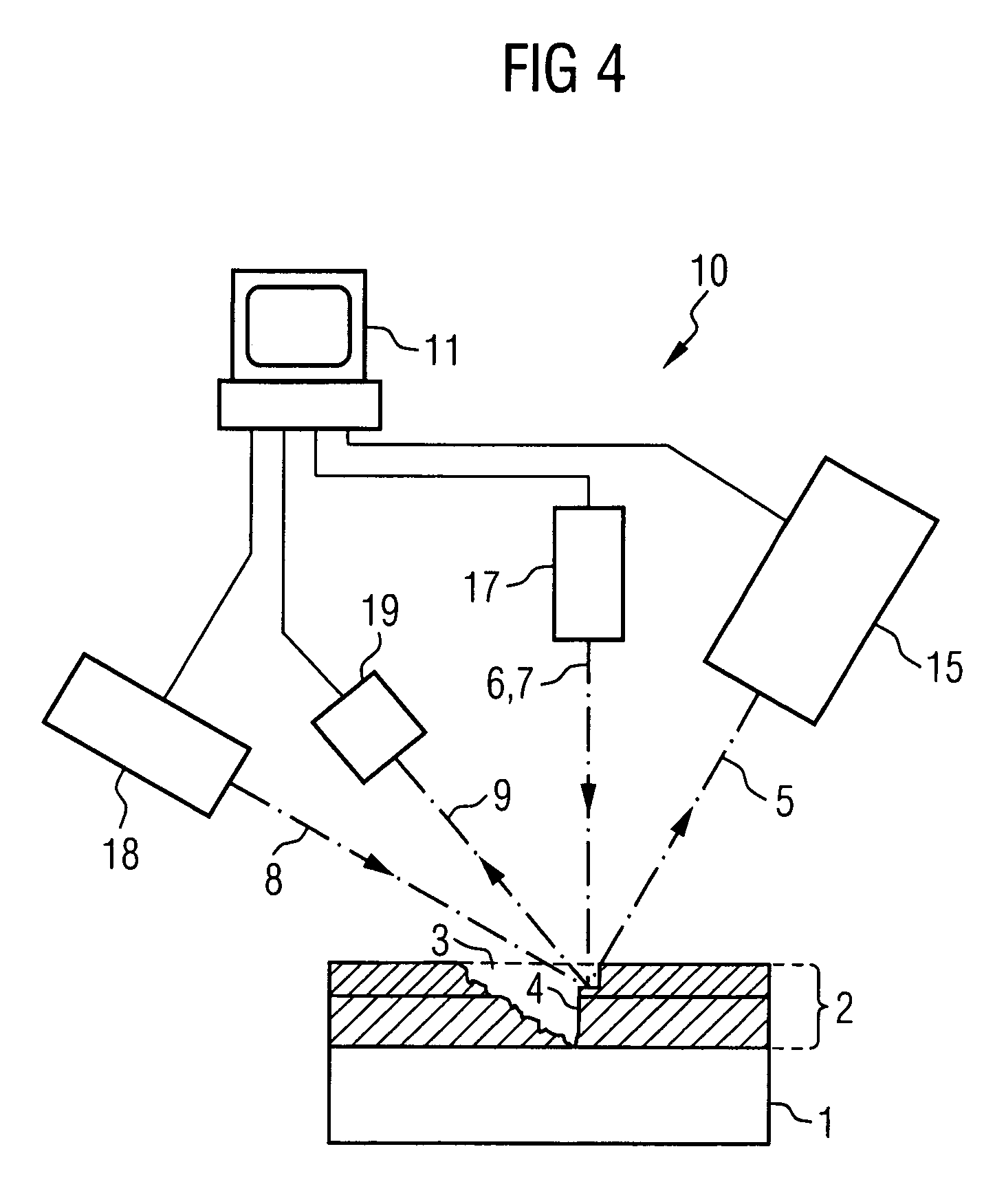
InactiveUS20070153979A1High resolutionBetter signal to noise ratioImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayX ray image
A system for generation of an x-ray image with high resolution has an x-ray generator that produces an x-ray focal spot with a number of intensity maxima. The partial x-ray images corresponding to each of the intensity maxima are subsequently reconstructed into an x-ray image of high resolution using an algorithm taking into account the spatial distribution.
Owner:BAUMANN JOACHIM +5
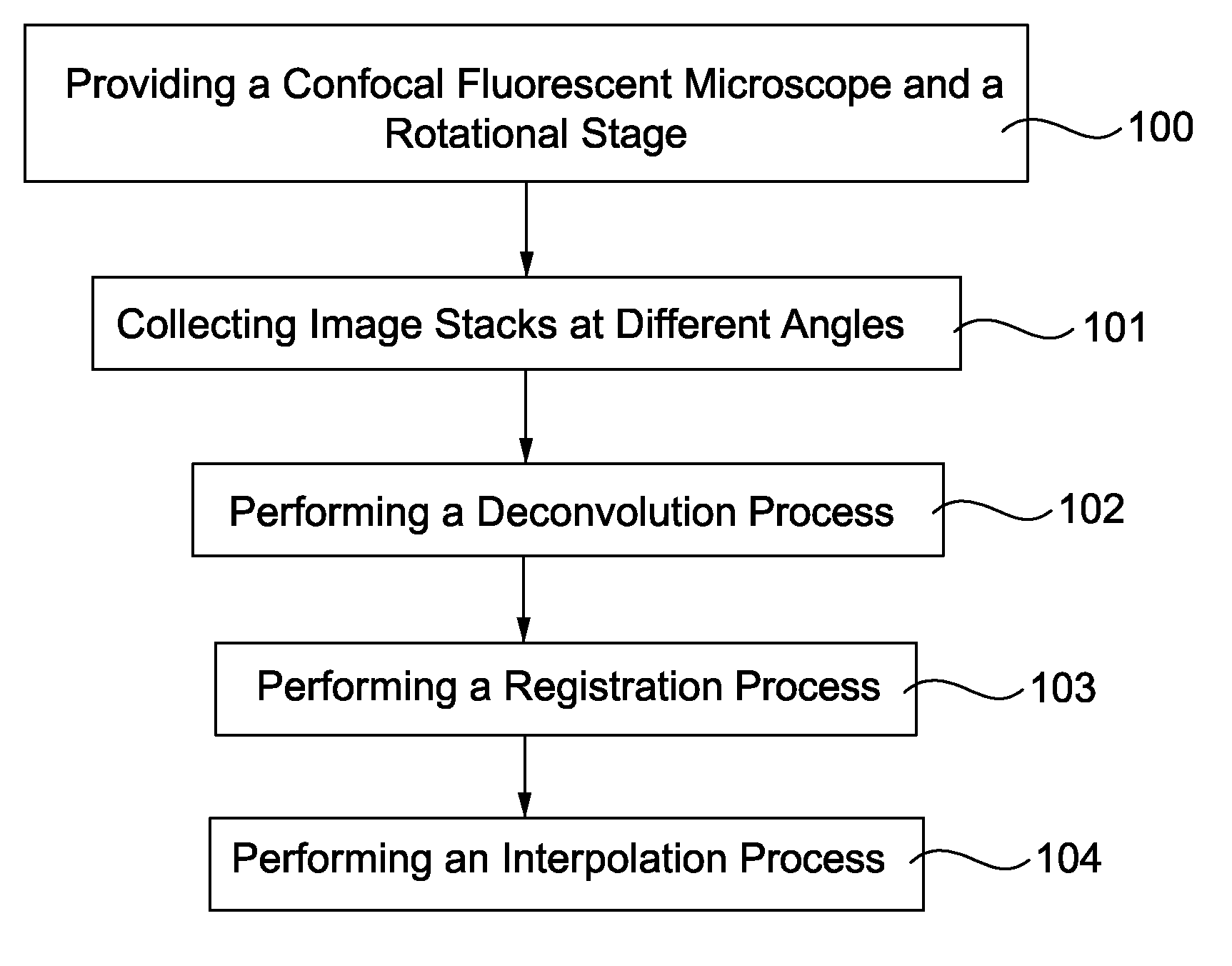
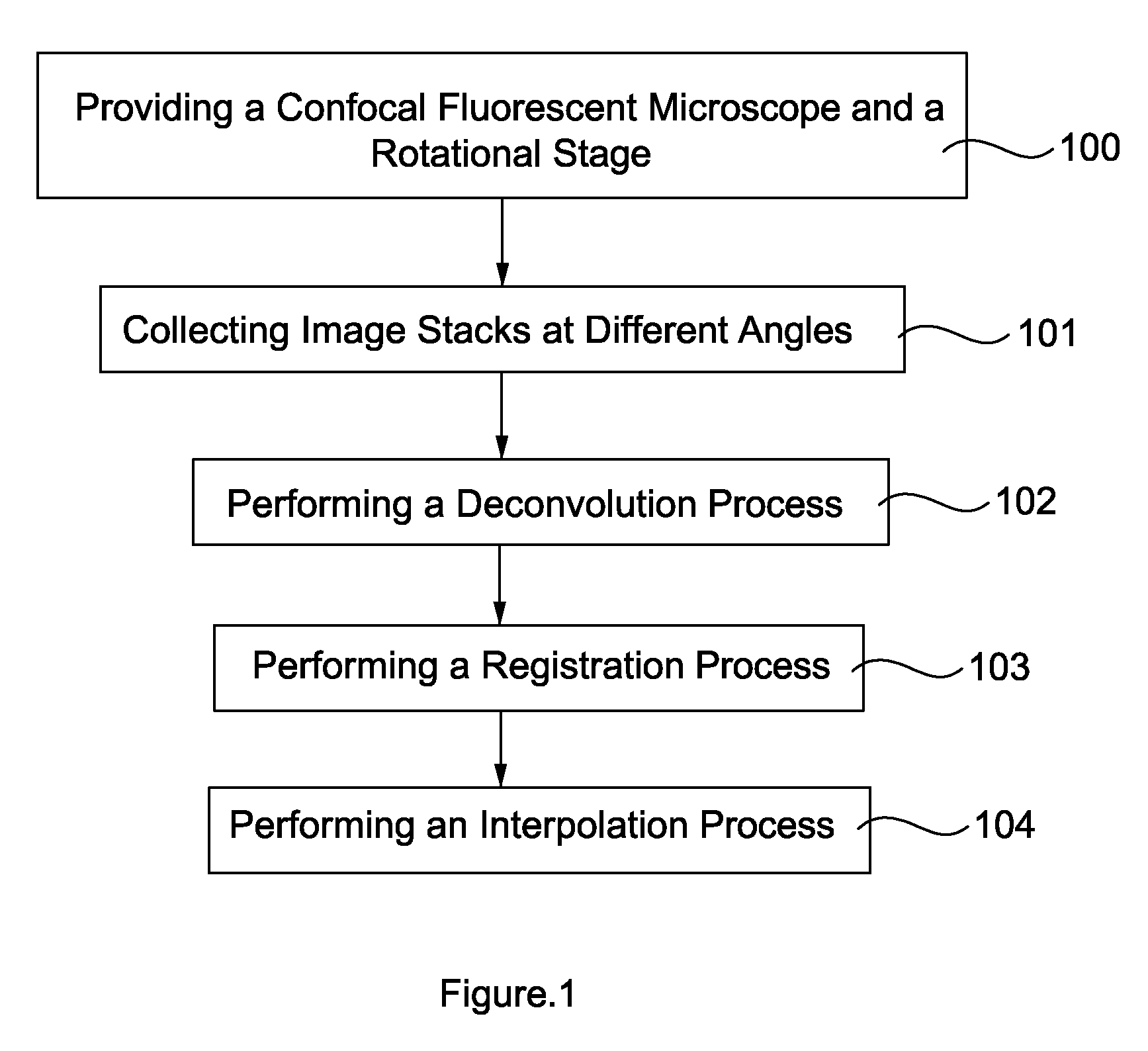
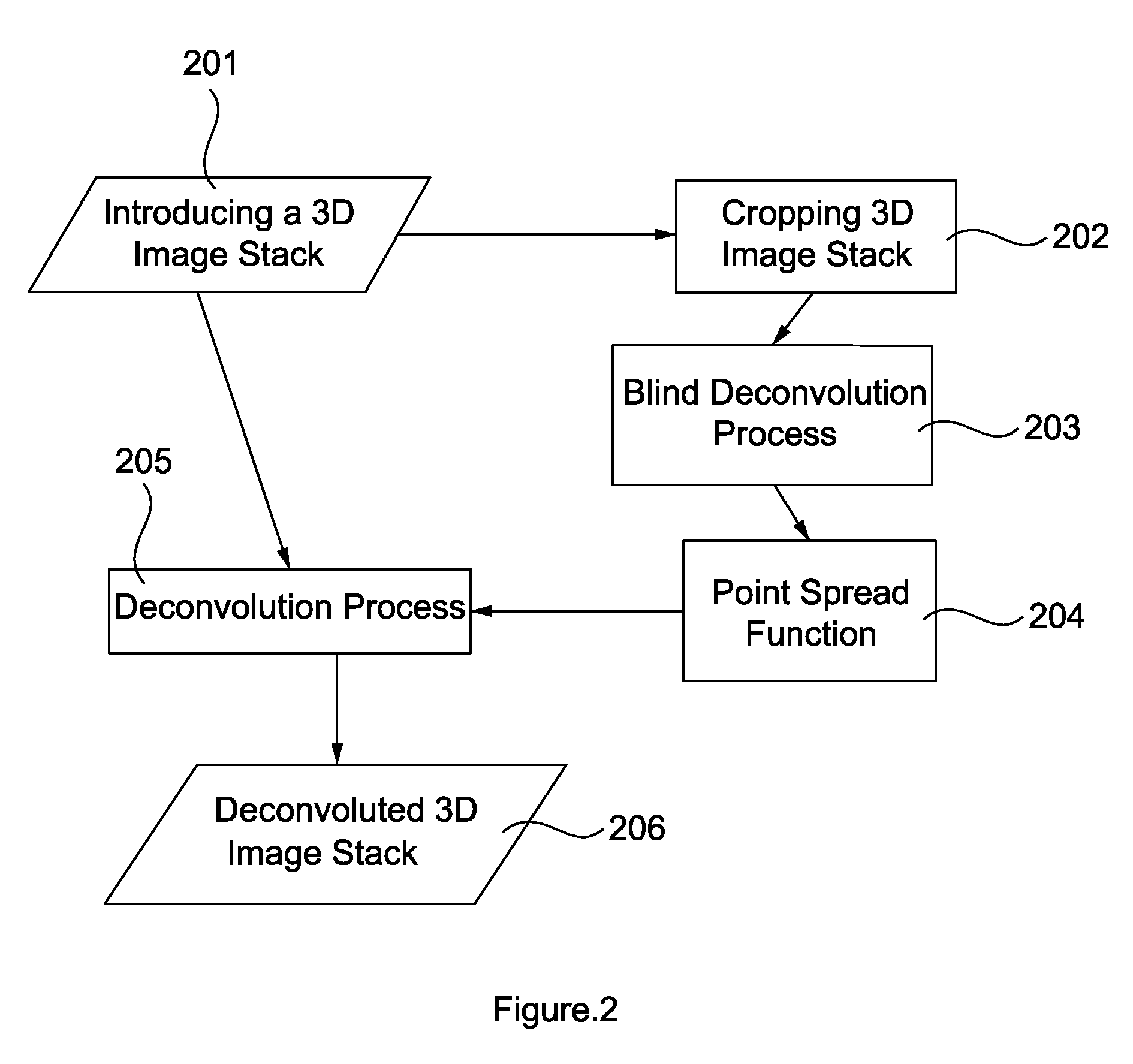
Method of Enhancing 3D Image Information Density
ActiveUS20120194646A1Enhancing D image information densityPoor resolutionGeometric image transformationMicroscopes3d imageFluorescence
A method of enhancing 3D image information density, comprising providing a confocal fluorescent microscope and a rotational stage. 3D image samples at different angles are collected. A deconvolution process of the 3D image samples by a processing unit is performed. A registration process of the deconvoluted 3D image samples by the processing unit is performed. An interpolation process of the registered 3D image samples by the processing unit is performed to output a 3D image in high resolution.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Three-dimensional display using variable focal length micromirror array lens
ActiveUS20060232498A1Improve image qualityAberration compensationMirrorsProjectorsThree dimensional displayComputer graphics (images)
A three-dimensional display device includes a two-dimensional display displaying a depthwise image, and a variable focal length micromirror array lens receiving light from the two-dimensional display and forming a corresponding image in the required location in space. Each depthwise image represents a portion of an object or scene having the same image depth, and the two-dimensional display displays one depthwise image at a time. The focal length of the variable focal length micromirror array lens changes according to the depth of the depthwise image being displayed. The variable focal length micromirror array lens has enough speed and focusing depth range for the realistic three-dimensional display.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Mammography apparatus
ActiveUS20150036796A1Improve image qualityDecreasing acquisitionRadiation diagnostic device controlTomosynthesisPath lengthX-ray
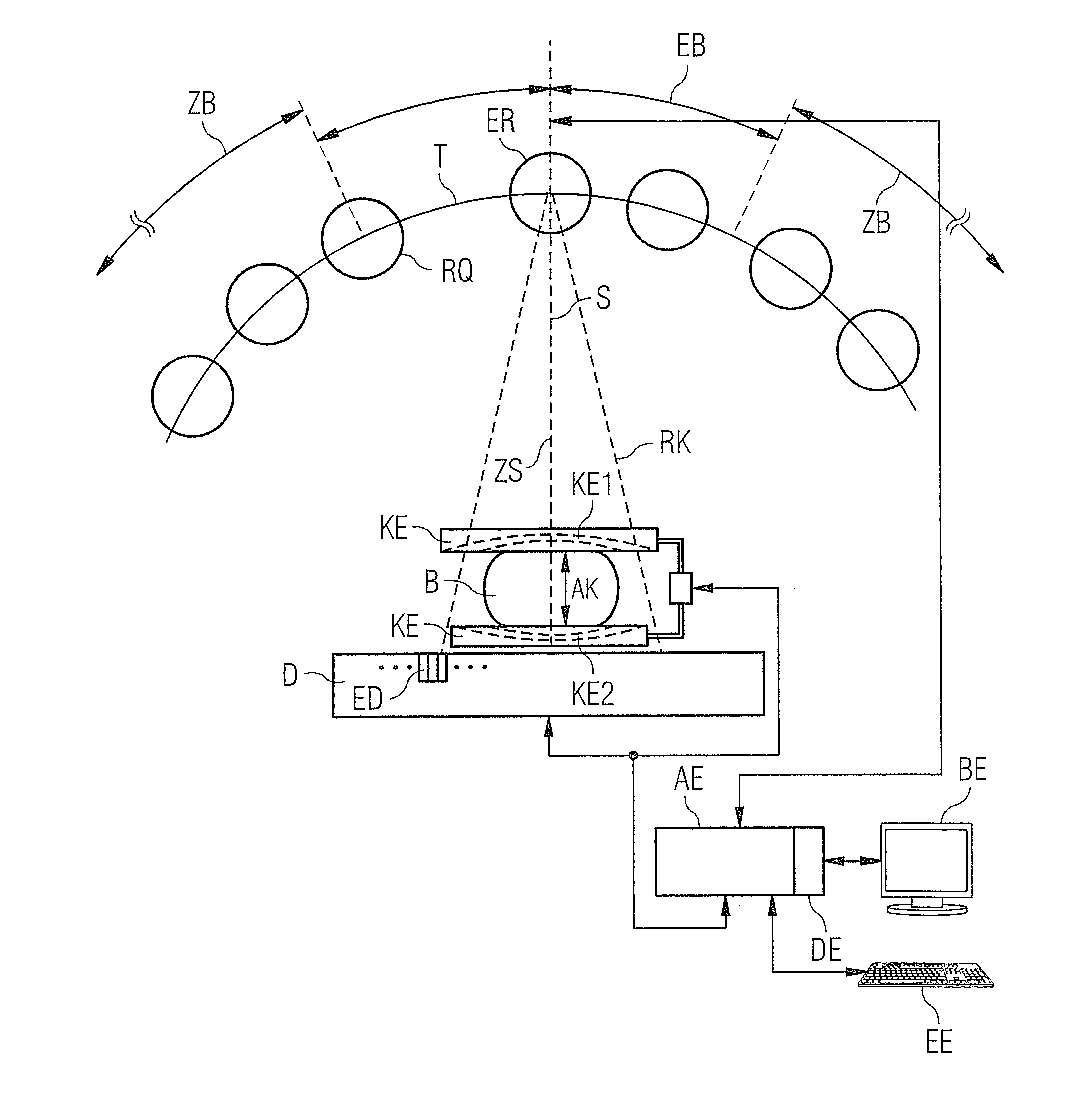
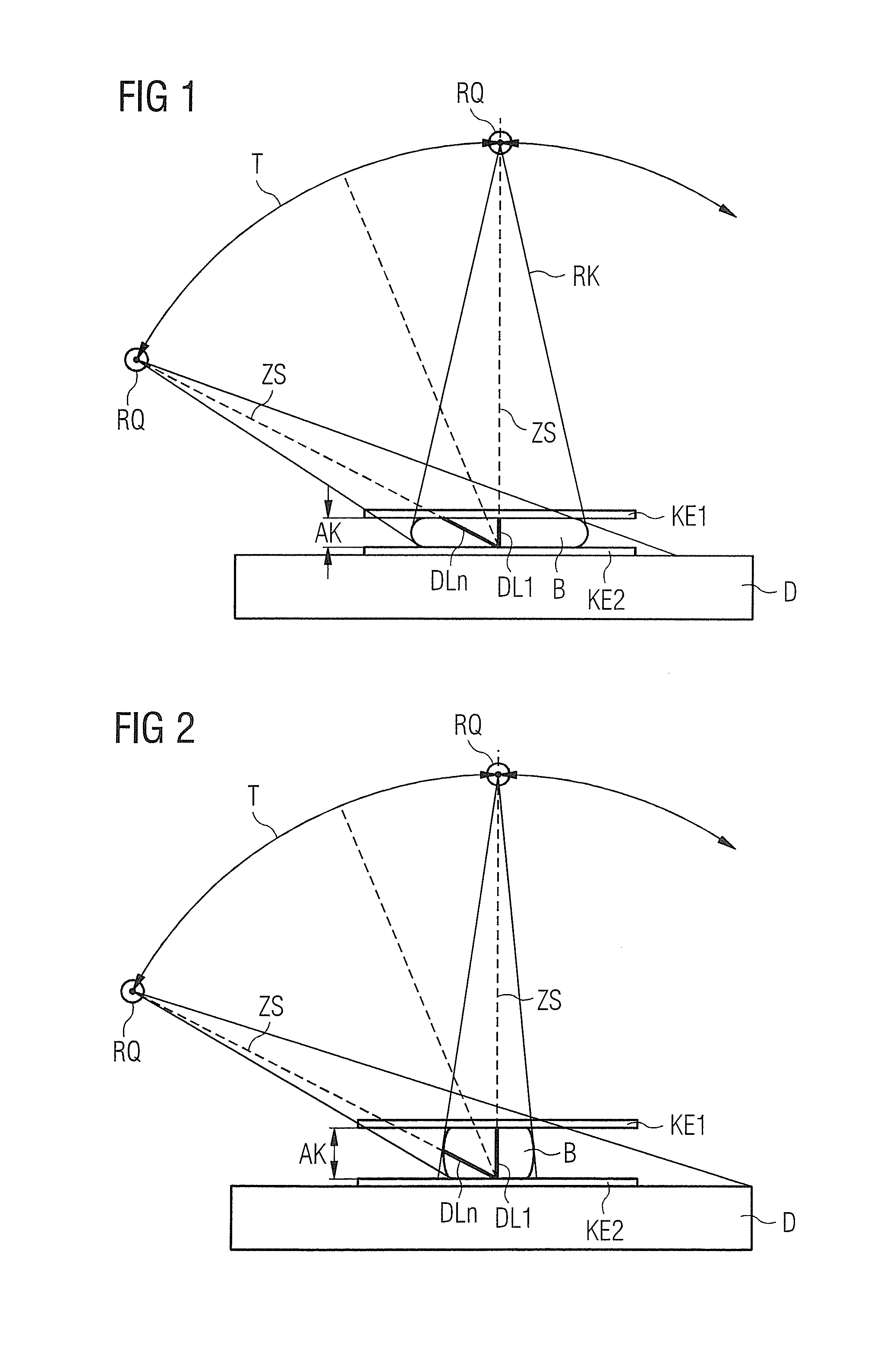
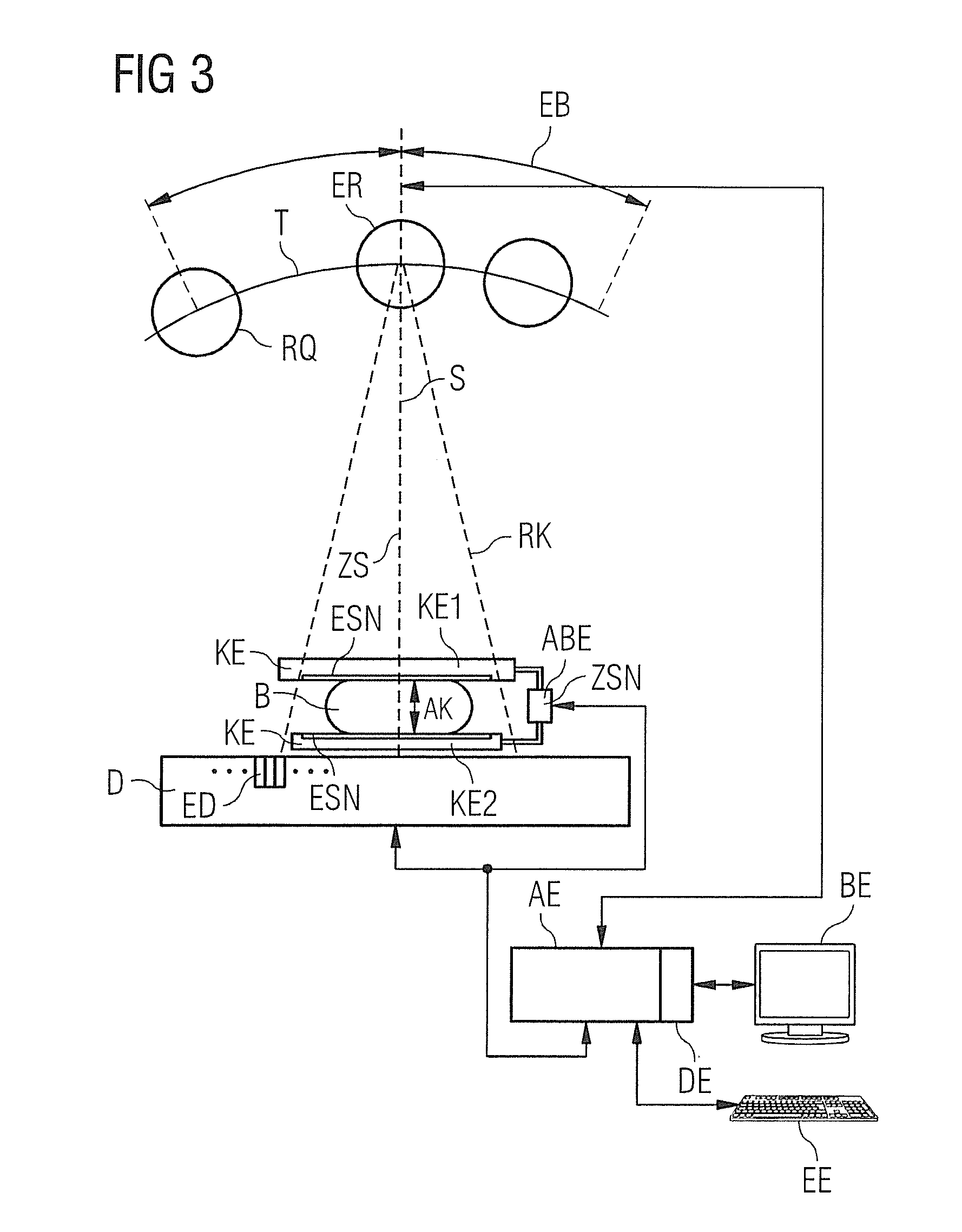
In a mammography apparatus, a deflection of an x-ray source aligned on a radiation detector is predetermined depending on the size of a breast compressed in the compression unit and / or the density of the breast tissue. Given an increasing deflection on an arc-shaped trajectory of the x-ray source, the compression of the breast is reduced at least once so that the path of the x-rays through the breast stays within a predetermined path length, starting from a first compression in a first x-ray acquisition.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and System for Motion Adaptive Fusion of Optical Images and Depth Maps Acquired by Cameras and Depth Sensors
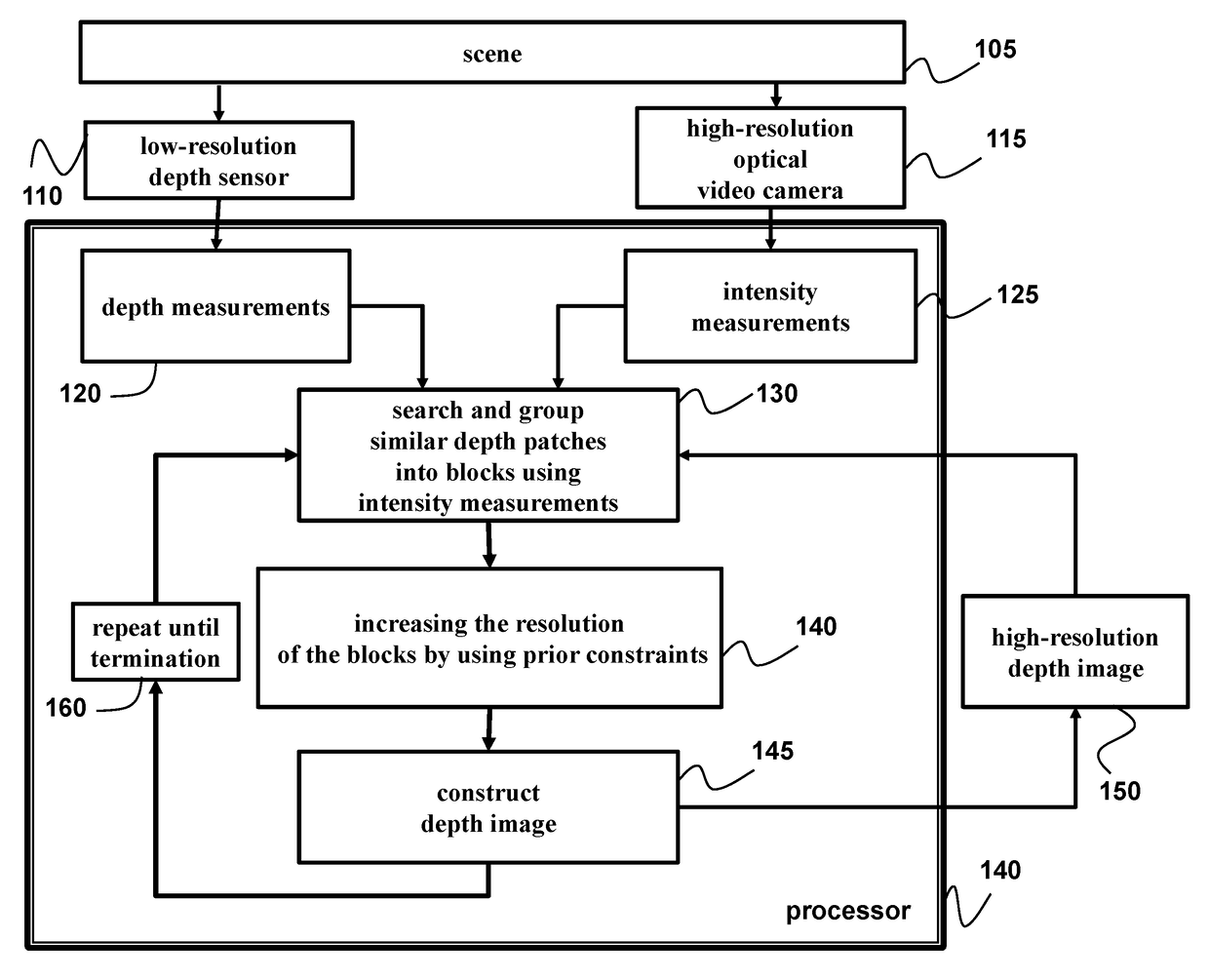
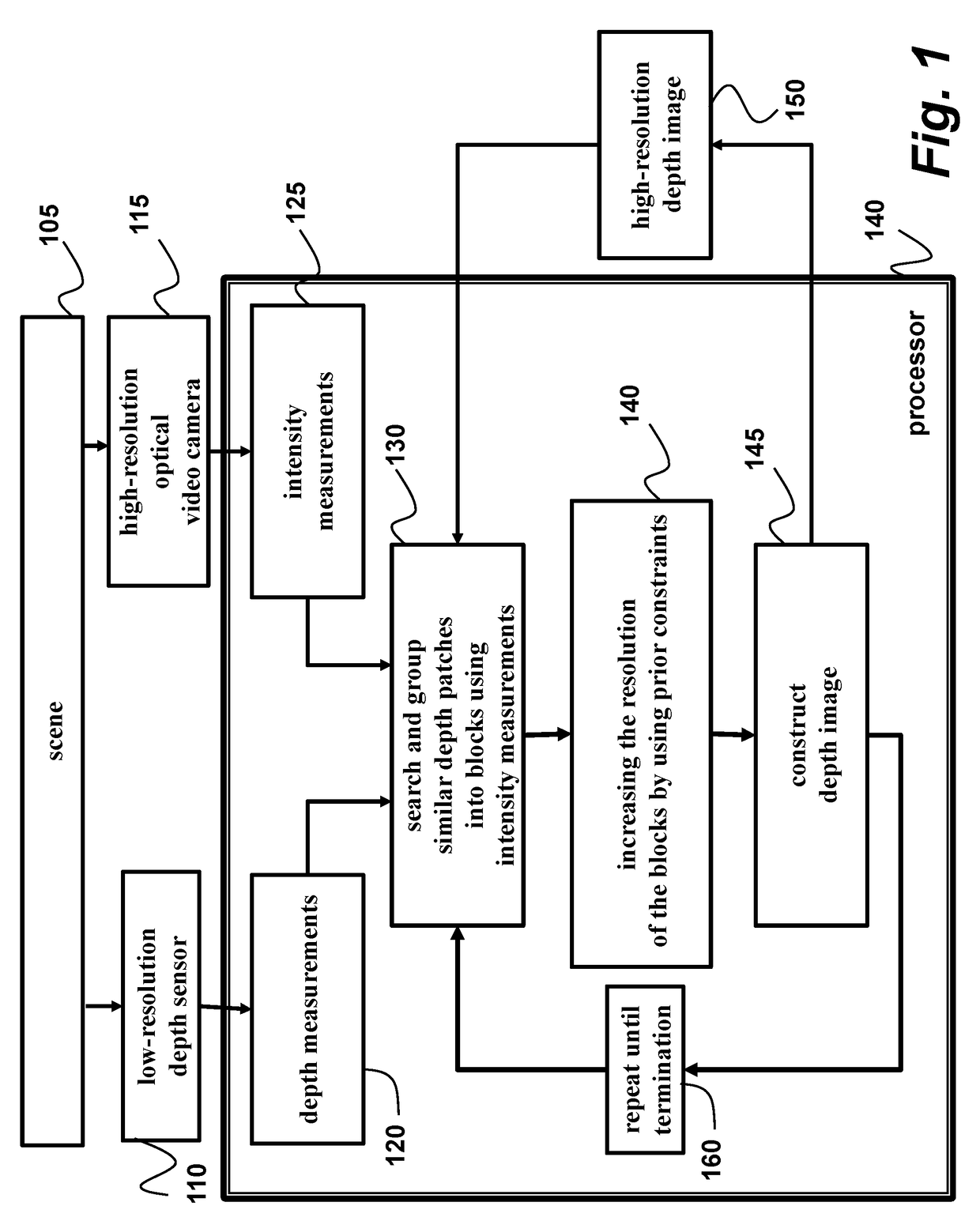
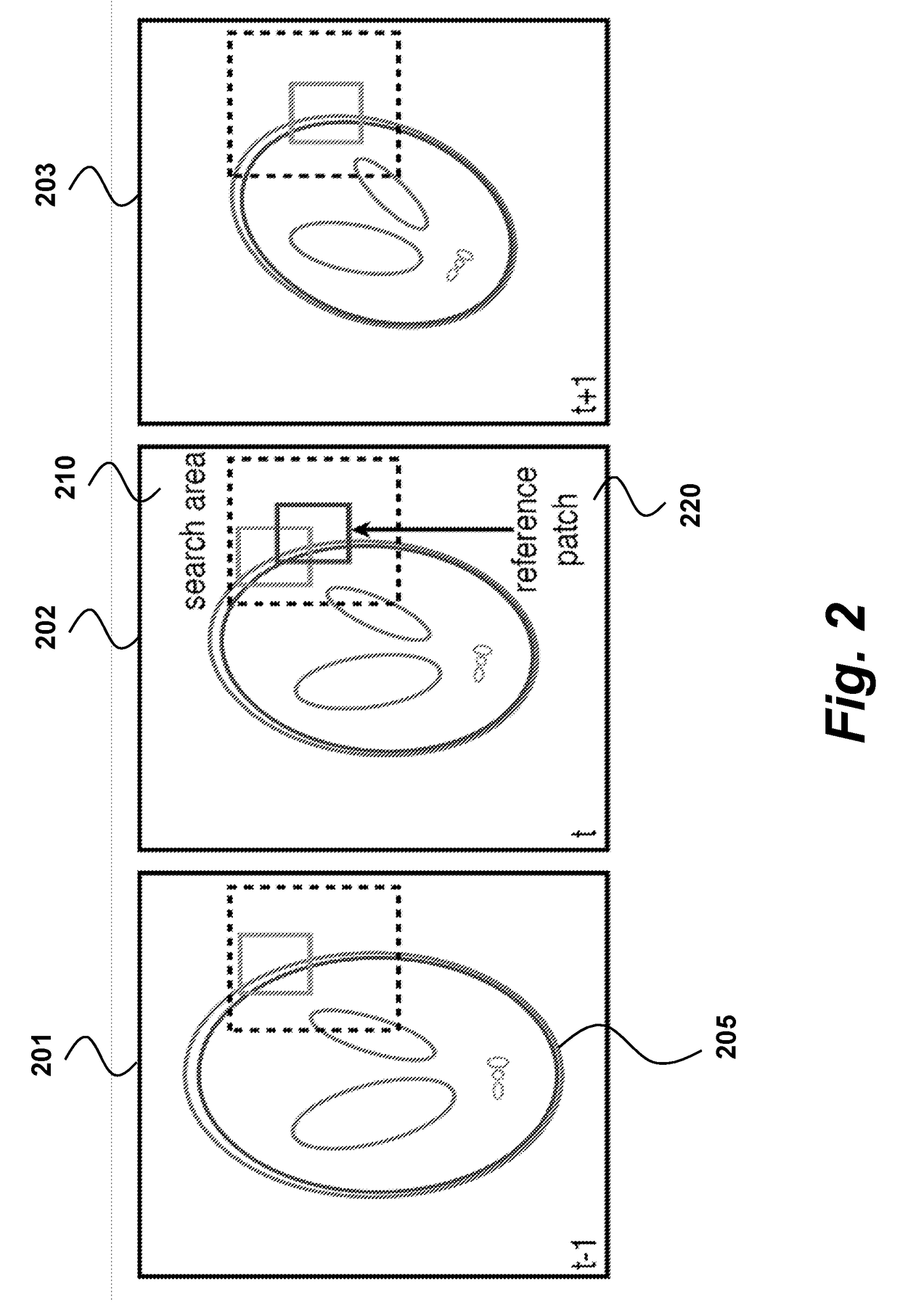
ActiveUS20170180639A1High resolutionSpatial resolution is lowImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage resolutionDepth map
A method and system for fusing sensed measurements includes a depth sensor to acquire depth measurements of a scene as a sequence of frames, and a camera configured to acquire intensity measurements of the scene as a sequence of images, wherein a resolution of the depth sensor is less than a resolution of the camera. A processor searches for similar patches in multiple temporally adjacent frames of the depth measurements, groups the similar patches into blocks using the intensity measurements, increases a resolution of the blocks using prior constraints to obtain increased resolution blocks, and then constructs a depth image with a resolution greater than the resolution of sensor from the increased resolution blocks.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional compositional mapping of heterogeneous materials
InactiveUS6873419B2Rapid and accurate three-dimensional compositionalRapid and accurate depth profileAnalysis by thermal excitationUsing optical meansCoherence lengthLaser ablation
Laser ablation combined with spectrometric analysis is a good tool for determining the composition of heterogeneous materials. By measuring the depth of an ablation crater at a target of a heterogeneous material, it is possible to generate a compositional profile as a function of the depth. It is also possible to generate a 3 dimensional profile by depth profiling of a plurality of craters. The depth measurement is conducted in situ and in real time so that the evolution of composition as a function of the depth can be measured. An interferometric technique with a short coherence length light is one of the preferred embodiments for measuring the depth in situ and in real time.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Multi-aperture device and method for detecting an object region
ActiveUS20160255330A1High depth resolutionMiniaturization of the image detecting devicesSteroscopic systemsSub regionOptics
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Optical coherence tomographic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20120026463A1High depth resolutionLow lightInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansSingle sampleTomographic image
Optical coherence tomographic imaging apparatus creating tomographic image of inspection object includes light splitting means for splitting light from light source into a single reference light and a single sample light, optical path length changing means for changing optical path length of the single reference light, reference light splitting means for splitting the single reference light whose optical path length is changed into a plurality of reference lights, sample light splitting means for splitting the single sample light into a plurality of sample lights, irradiation means for irradiating the inspection object by leading the plurality of sample lights thereto, interference signal forming means for combining returning lights of the plurality of the sample lights from the inspection object irradiated by the irradiation means with the plurality of reference lights passed through the reference-light path, and interference signal obtaining means for obtaining an interference signal from the interference signal forming means.
Owner:CANON KK
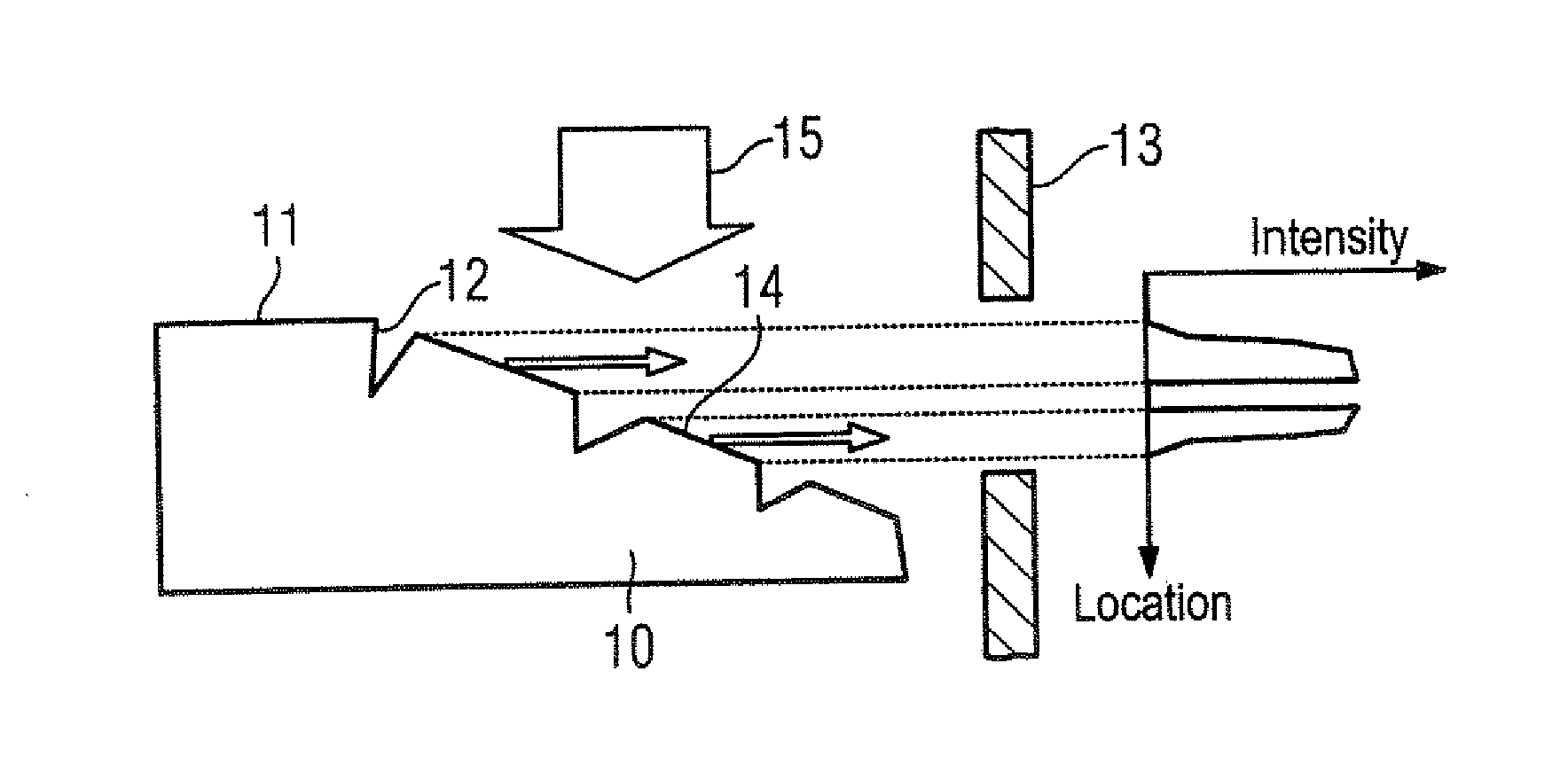
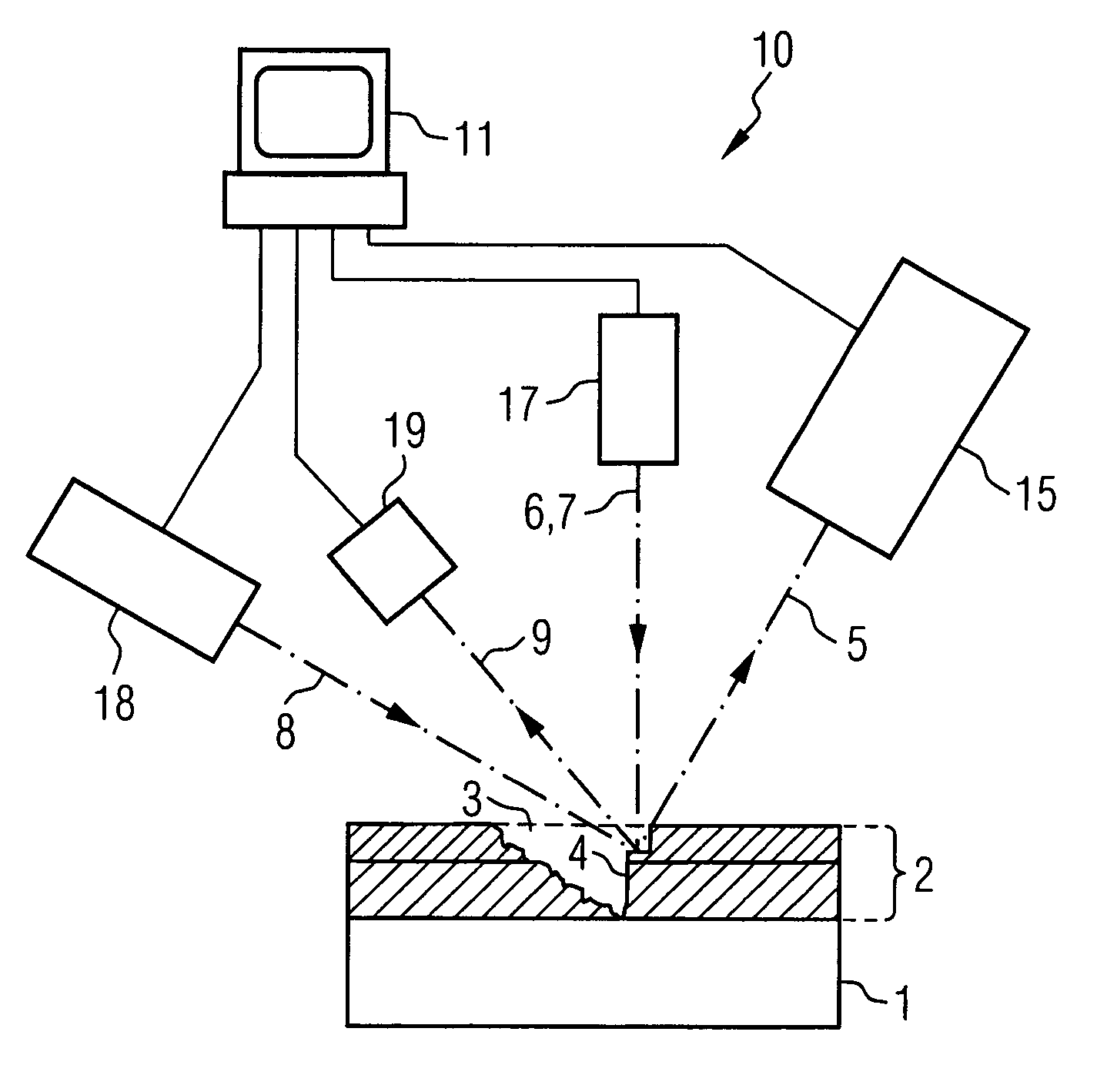
Method and apparatus for the depth-resolved characterization of layer of a carrier
InactiveUS20060076494A1Improve accuracyHigh lateral spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIon beamPhysics
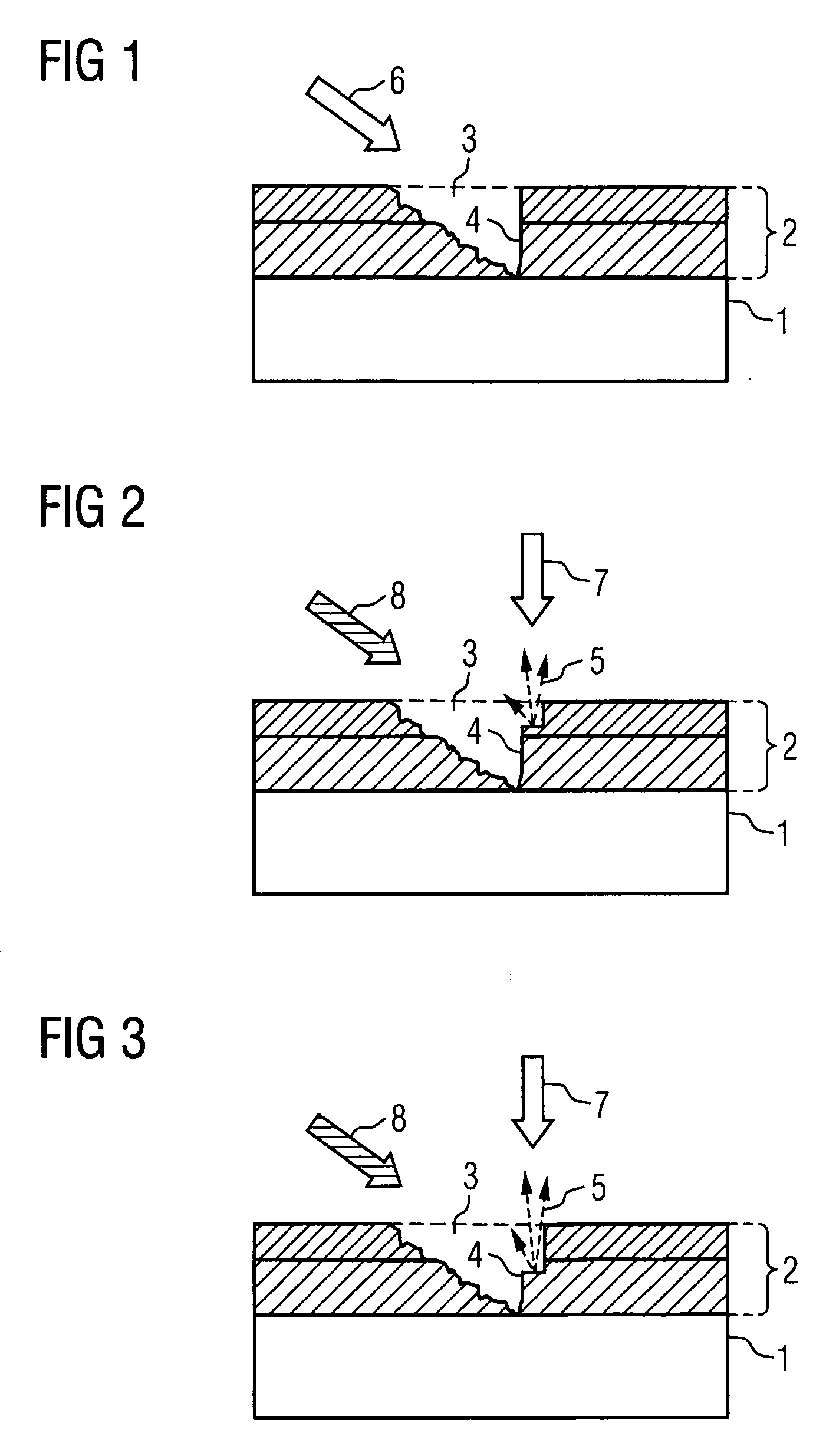
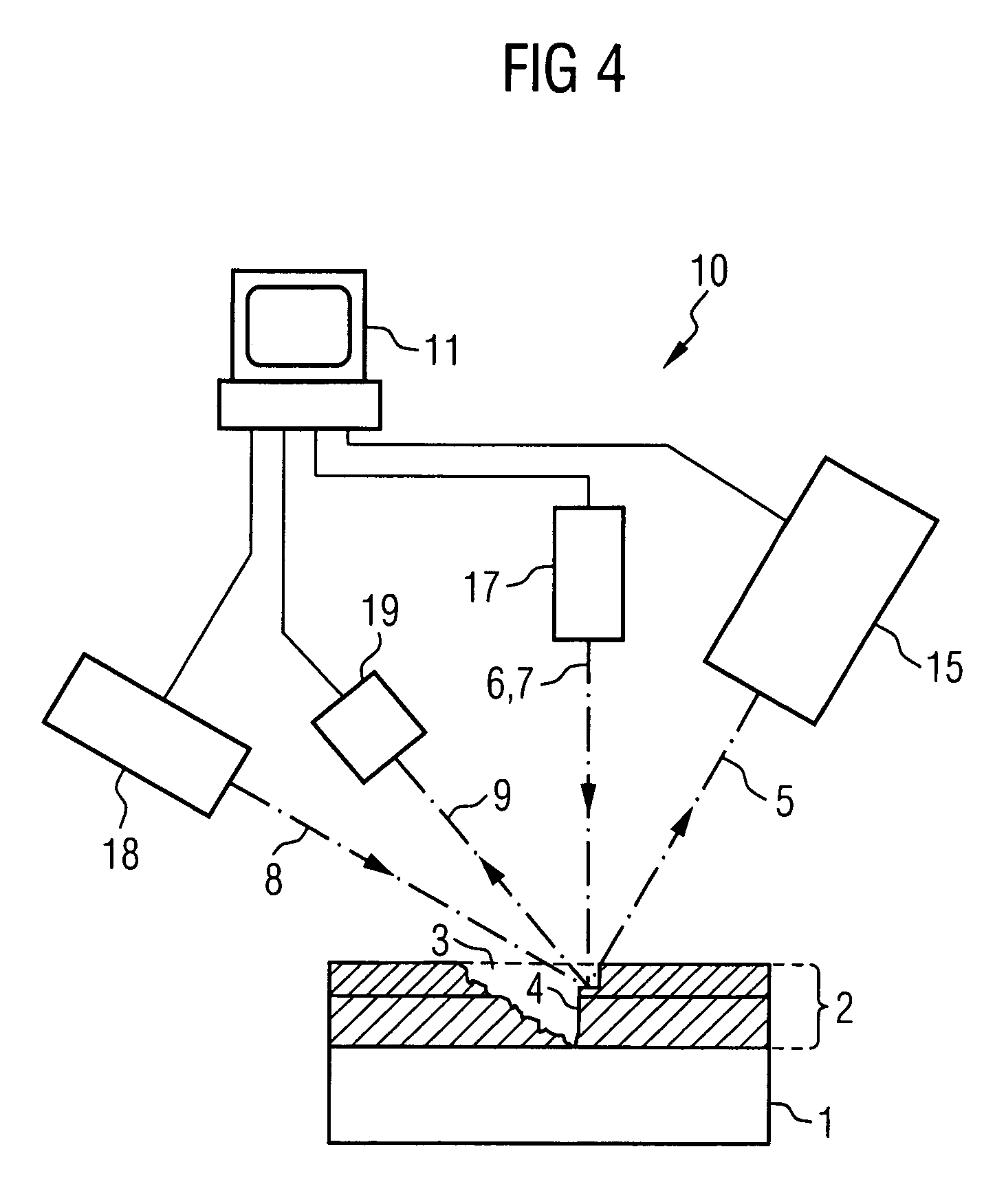
The present invention relates to a method for the depth-resolved characterization of a layer of a carrier. This involves firstly producing a cutout in the layer of the carrier with a sidewall and subsequently removing carrier material adjoining the sidewall with the aid of an ion beam. During the removal process, images of the sidewall are recorded and material compositions of the removed carrier material are determined as well. A depth-resolved characterization of the layer of the carrier is carried out on the basis of a correlation of the determined material compositions of the removed carrier material with the recorded images of the sidewall, layer depths being assigned to the material compositions of the removed carrier material with the aid of the images of the sidewall. The invention furthermore relates to an apparatus for carrying out this method.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Three-dimensional imaging system for robot vision
ActiveUS20070188883A1Clear imagingEasy CalibrationMirrorsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingField of view
The present invention provides a three-dimensional imaging system for robot vision, which is capable of three-dimensional positioning of objects, object identification, searching and tracking of an object of interest, and compensating the aberration of the system. The three-dimensional imaging system for robot vision comprises one or more camera systems, each of which has at least one variable focal length micromirror array lens, an imaging unit, and an image processing unit. The variable focal length micromirror array lens used in the three-dimensional imaging system for robot vision has unique features including a variable focal length, a variable focal axis, and a variable field of view with a fast response time.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
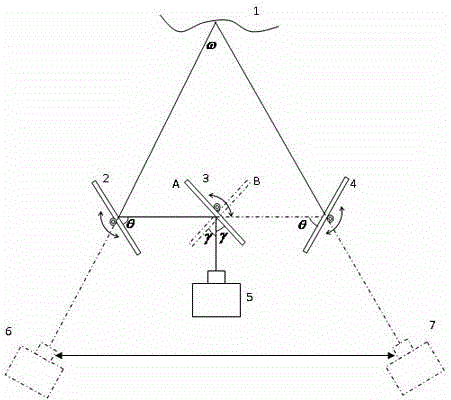
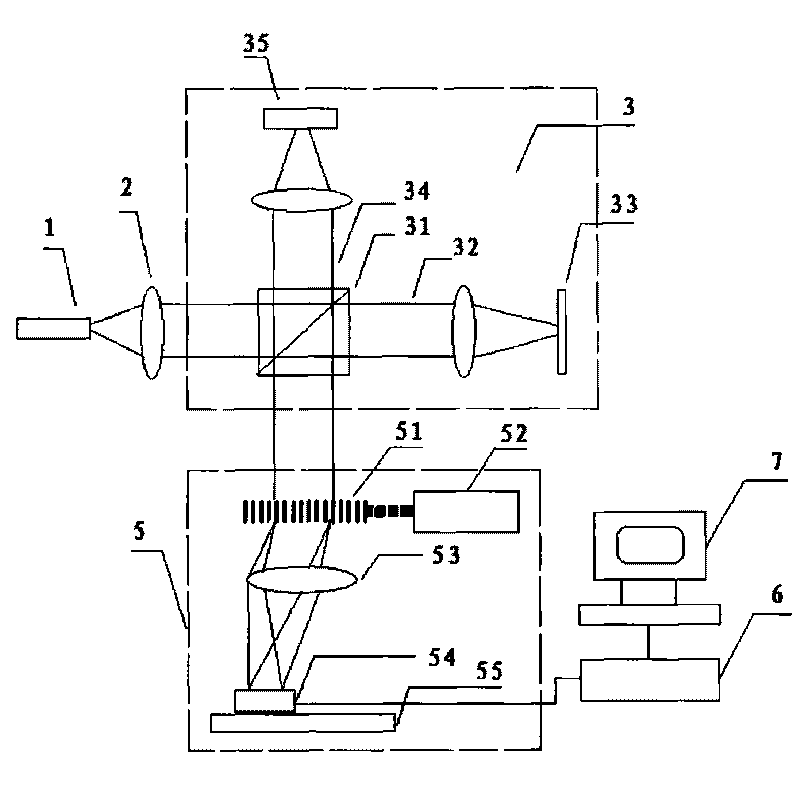
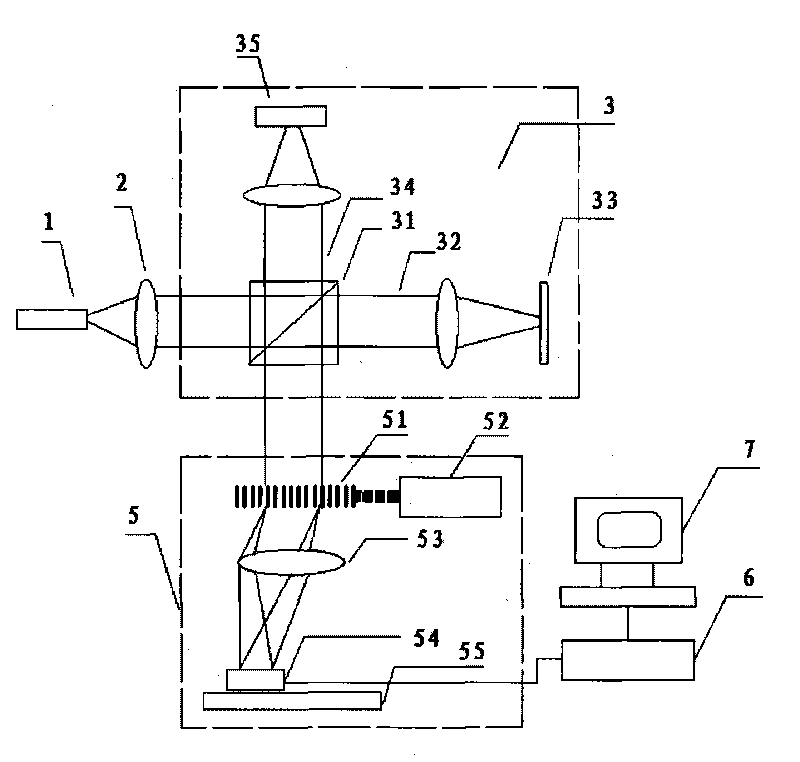
Device utilizing single camera for achieving binocular vision three-dimensional imaging
InactiveCN104460220AReduce internal referenceHigh depth resolutionUsing optical meansStereoscopic photographyInverse correlationImage resolution
The invention discloses a device utilizing a single camera for achieving binocular vision three-dimensional imaging. The device comprises the camera arranged behind an object to be measured, a left view image reflecting module for reflecting a left view image of the object to the camera, and a right view image reflecting module for reflecting a right view image of the object to the single camera. The single camera is utilized for replacing two cameras in a traditional method, a system is simplified, camera internal parameters to be calibrated are reduced, and the difficulty of system calibration is lowered; in addition, in binocular vision, the positive correlation between the depth resolution of three-dimensional imaging and the distance of the two cameras is formed, the inverse correlation is formed between the depth resolution of three-dimensional imaging and the distance from the object to the camera is formed, three galvanometers can rotate around the axis, and therefore the system can obtain the high depth resolution for objects of different depths.
Owner:SUZHOU JIANGAO OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Adjustable frequency domain optical coherence chromatography imaging method and system thereof
ActiveCN101750146AChange the non-adjustable situationLarge depth rangeInterferometric spectrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsSpectral widthGrating
The invention relates to a frequency domain optical coherence chromatography imaging method and a system thereof with adjustable detection depth range and depth resolution ratio; a variable cycle grating is used for frequency domain optical coherence chromatography imaging, and the light spectrum detection depth and the light spectrum detection resolution ratio of a frequency domain interference signal are changed by adjusting the grating period and the lateral position of the detector, so as to realize the frequency domain optical coherence chromatography imaging with adjustable frequency domain optical coherence chromatography imaging. The invention can be matched with the usage of a wide spectral width light source, the problem that the pixel array length of the detector is limited when the spectral width is wider, and different imaging requirements of uses for obtaining large detection depth range or / and deeper depth resolution ratio can be met.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three-dimensional display using variable focal length micromirror array lens
ActiveUS7350922B2Easy constructionRealistic image representationMirrorsProjectorsComputer graphics (images)Micromirror array
A three-dimensional display device includes a two-dimensional display displaying a depthwise image, and a variable focal length micromirror array lens receiving light from the two-dimensional display and forming a corresponding image in the required location in space. Each depthwise image represents a portion of an object or scene having the same image depth, and the two-dimensional display displays one depthwise image at a time. The focal length of the variable focal length micromirror array lens changes according to the depth of the depthwise image being displayed. The variable focal length micromirror array lens has enough speed and focusing depth range for the realistic three-dimensional display.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Three-dimensional imaging system for robot vision
ActiveUS7410266B2Clear imagingEasy CalibrationMirrorsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingField of view
The present invention provides a three-dimensional imaging system for robot vision, which is capable of three-dimensional positioning of objects, object identification, searching and tracking of an object of interest, and compensating the aberration of the system. The three-dimensional imaging system for robot vision comprises one or more camera systems, each of which has at least one variable focal length micromirror array lens, an imaging unit, and an image processing unit. The variable focal length micromirror array lens used in the three-dimensional imaging system for robot vision has unique features including a variable focal length, a variable focal axis, and a variable field of view with a fast response time.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
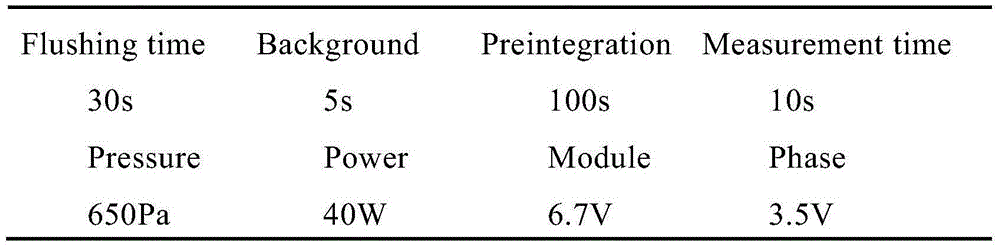
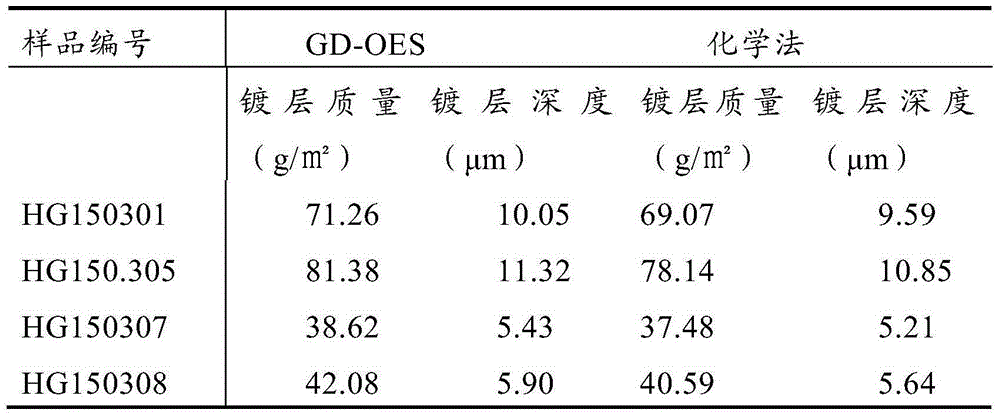
Method for measuring depth and quality of plating of galvanized plate through glow discharge spectrometer
InactiveCN105181676AFast test resultsReduce operating proceduresAnalysis by electrical excitationUsing optical meansUltimate tensile strengthSpectrometer
The invention discloses a method for measuring depth and quality of plating of a galvanized plate through a glow discharge spectrometer and aims to provide a method for rapidly, accurately and efficiently measuring the depth and the quality of the plating of the galvanized plate. The method comprises steps as follows: an instrument is debugged, center positioning and curve calibration are performed, accordingly, the instrument is in the optimum state, a sample is cut into sample blocks with appropriate sizes, the surfaces of the taken sample blocks are flat and don't have defects, the sample is arranged in a spectrometer sample chamber after surface dirt is wiped and removed, intensity of spectral lines is measured, a changing curve of the intensity of each element with time is obtained, the curve is subjected to analysis and calculation, and the depth and the quality of the plating of the galvanized plate are obtained.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
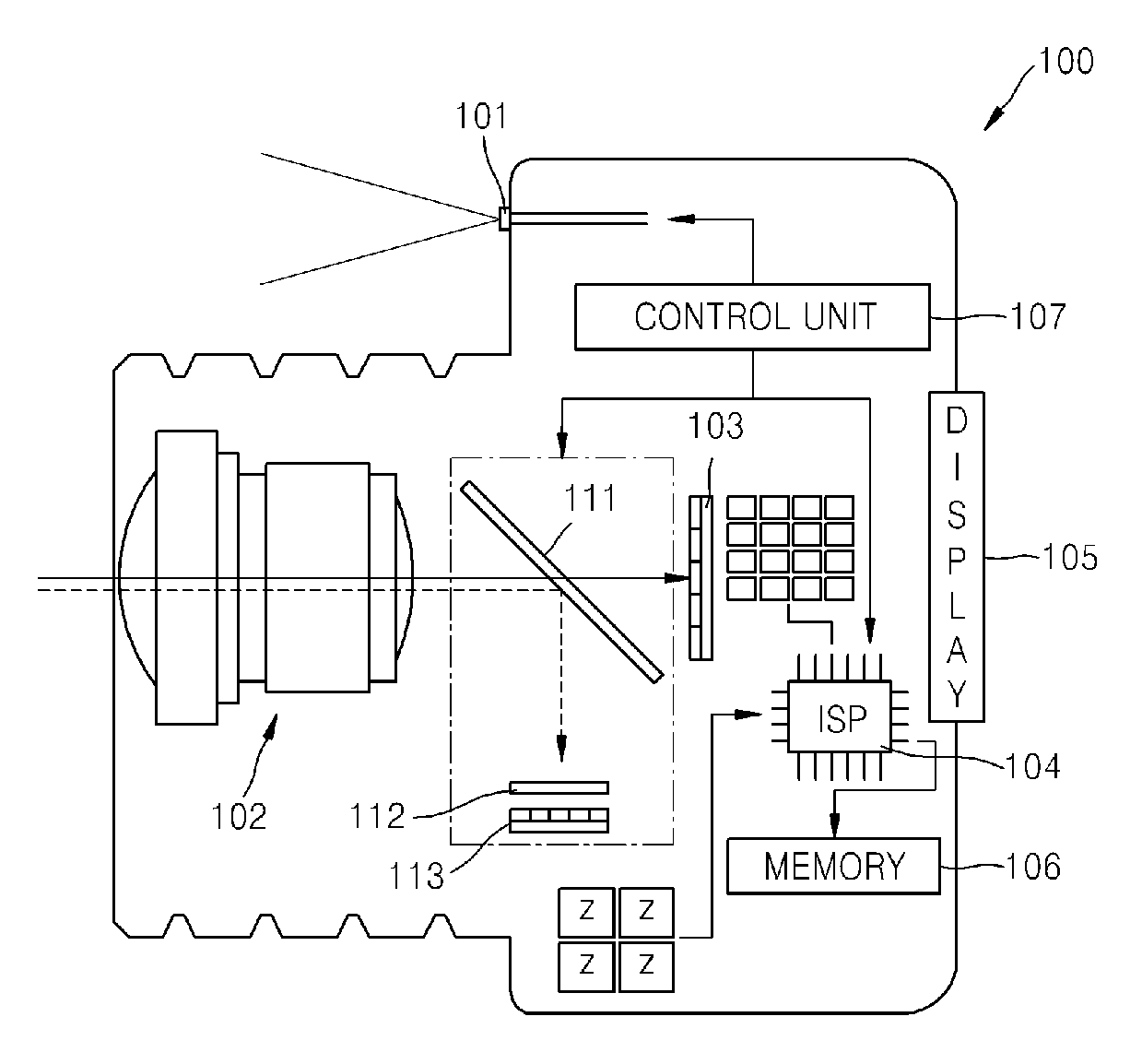
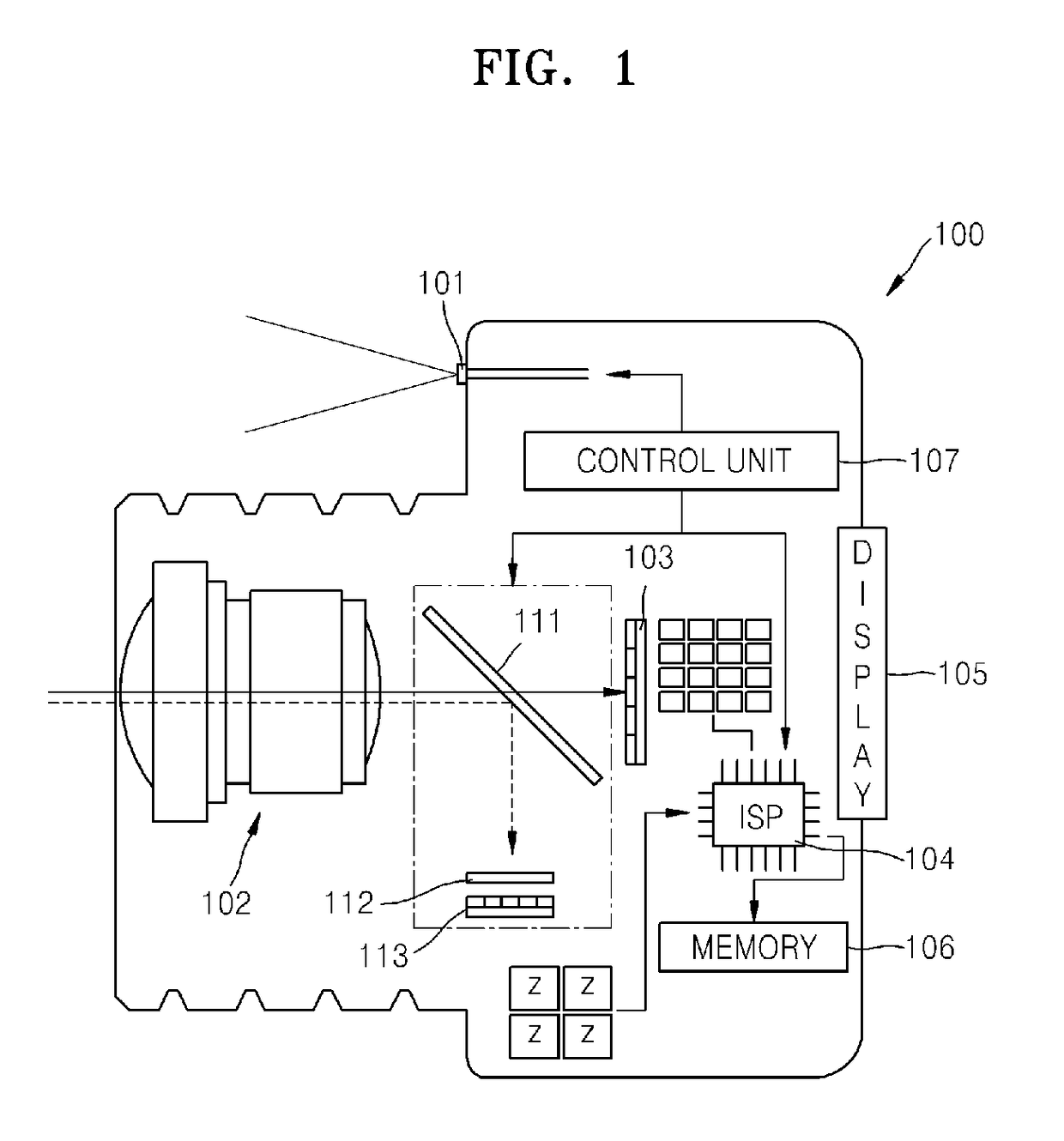
3D image acquisition apparatus and method of driving the same
ActiveUS9894347B2High depth resolutionReduce power consumptionElectromagnetic wave reradiationSteroscopic systemsAcquisition apparatus3d image
Provided is a 3-dimensional (3D) image acquisition apparatus and a method of driving the same. The 3D image acquisition apparatus includes a light source, an optical shutter, an image sensor, an image signal processor, and a controller. The light source is configured to project illumination light on an object. The optical shutter is configured to modulate the illumination light reflected from the object with a predetermined gain waveform. The image sensor is configured to generate a depth image by detecting the illumination light modulated by the optical shutter. The image signal processor is configured to calculate a distance from the 3D image acquisition apparatus to the object using the depth image generated by the image sensor. The controller is configured to control an operation of the light source and an operation of the optical shutter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for load and additional property measurement
ActiveUS9207131B2Avoid corrosionHigh depth resolutionForce measurement by measuring frquency variationsForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationEngineeringCorrosion
A system and method for measuring load and an additional property using a sensor gasket embedded between two components. The sensor gasket may include a sensor layer and a conductive layer. A gap between the sensor layer and conductive layer may be filled with a load sensitive material. The thickness of the load sensitive material varies with the load applied to the two components between which the sensor gasket sits. The sensor operates in a first mode to obtain a sensor measurement that depends on the distance between the sensor layer and conductive layer. The sensor measurement then used to estimate the applied load. The sensor operates in a second mode to estimate a property of one or both of the components. The property of interest may be cracking, material loss due to corrosion, temperature, or another property of the component.
Owner:JENTEK SENSORS
Mammography apparatus with X-ray sources arranged at different distances from the chest
InactiveUS8605854B2High depth resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayBreast tissue
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Multi-aperture device and method for detecting an object region
ActiveUS9769458B2High depth resolutionMiniaturization of the image detecting devicesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOpticsSub region
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and apparatus for the depth-resolved characterization of a layer of a carrier
InactiveUS7358491B2Improve accuracyHigh lateral spatial resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementIon beamCarrier material
The present invention relates to a method for the depth-resolved characterization of a layer of a carrier. This involves firstly producing a cutout in the layer of the carrier with a sidewall and subsequently removing carrier material adjoining the sidewall with the aid of an ion beam. During the removal process, images of the sidewall are recorded and material compositions of the removed carrier material are determined as well. A depth-resolved characterization of the layer of the carrier is carried out on the basis of a correlation of the determined material compositions of the removed carrier material with the recorded images of the sidewall, layer depths being assigned to the material compositions of the removed carrier material with the aid of the images of the sidewall. The invention furthermore relates to an apparatus for carrying out this method.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
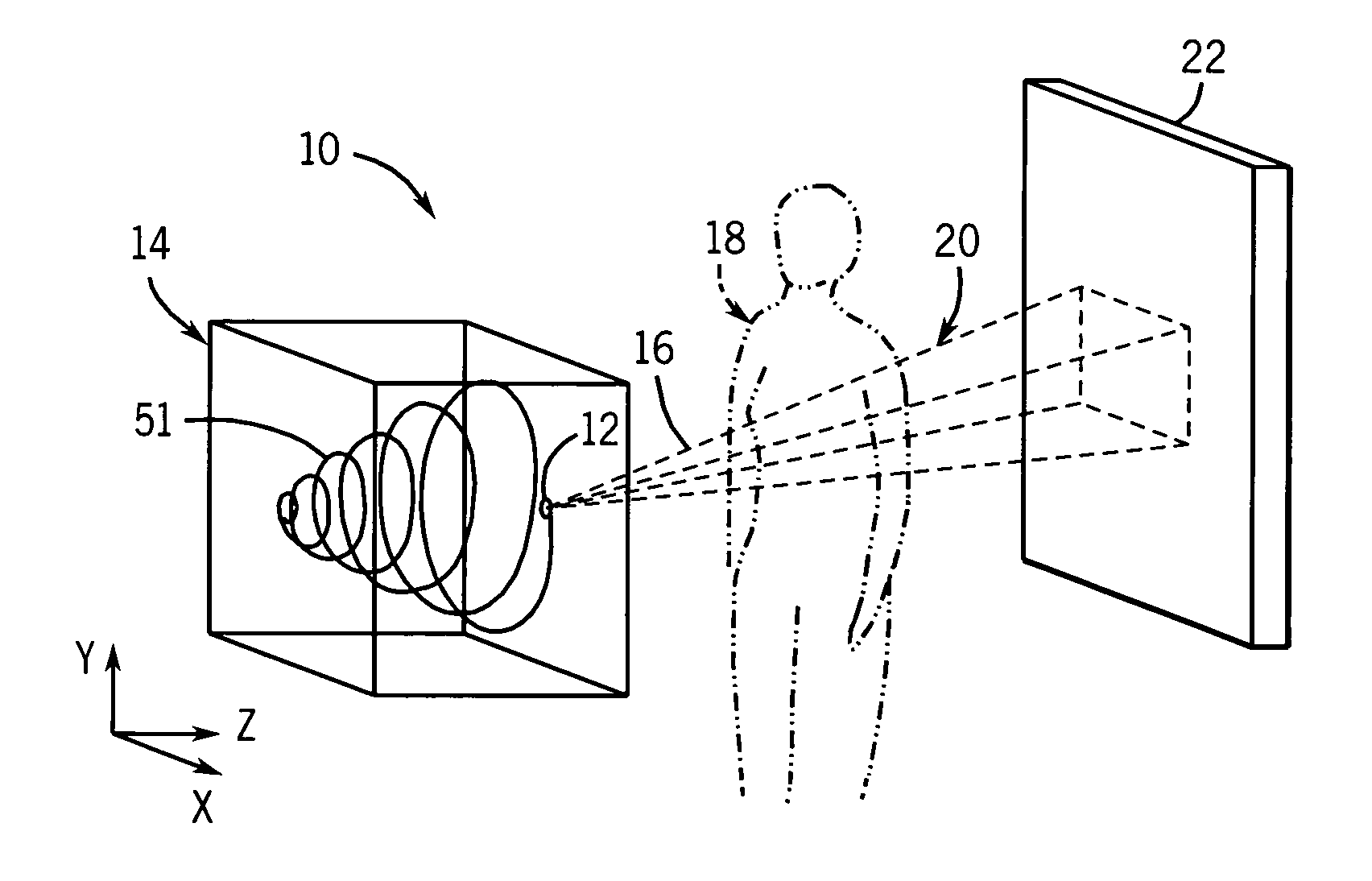
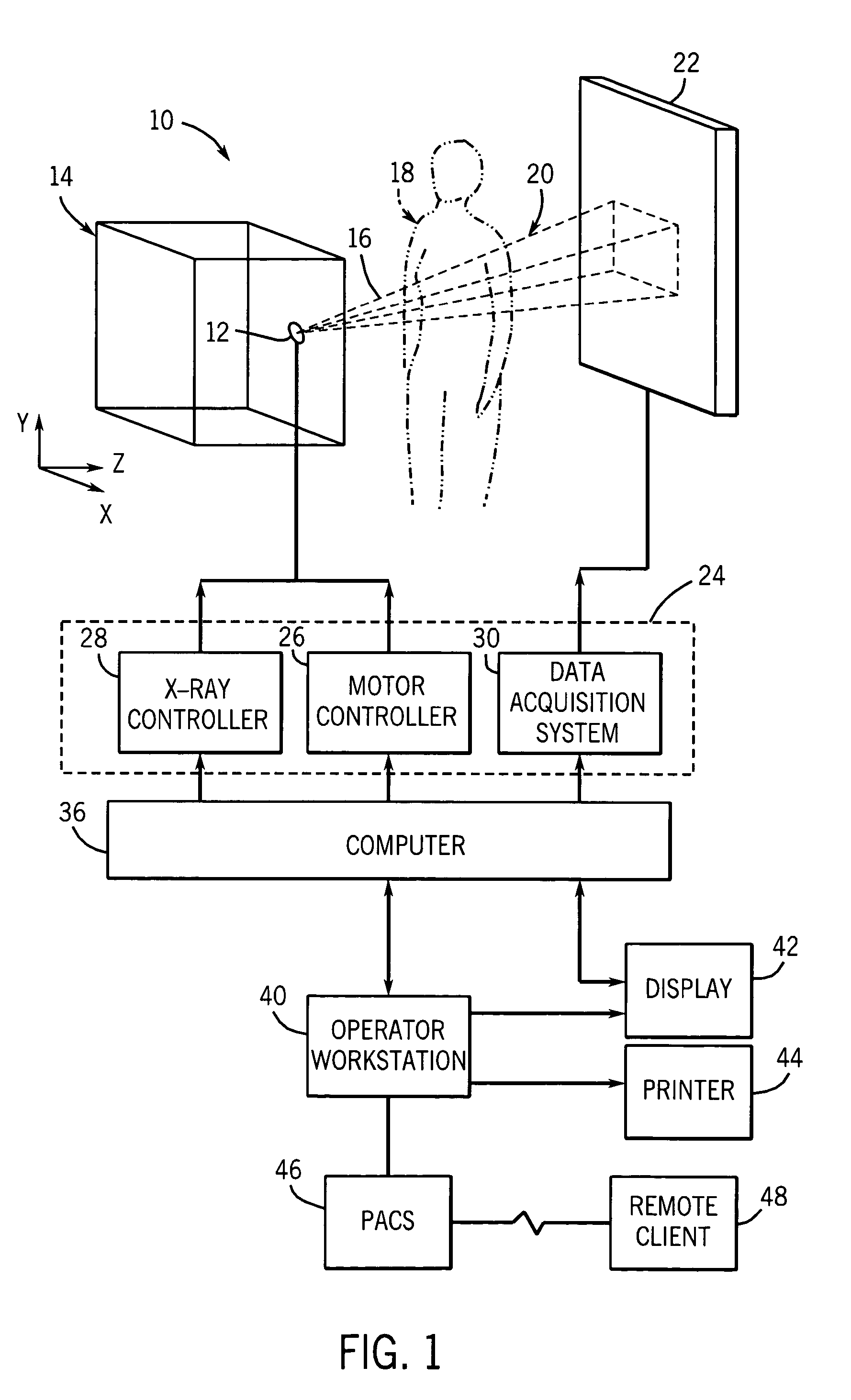
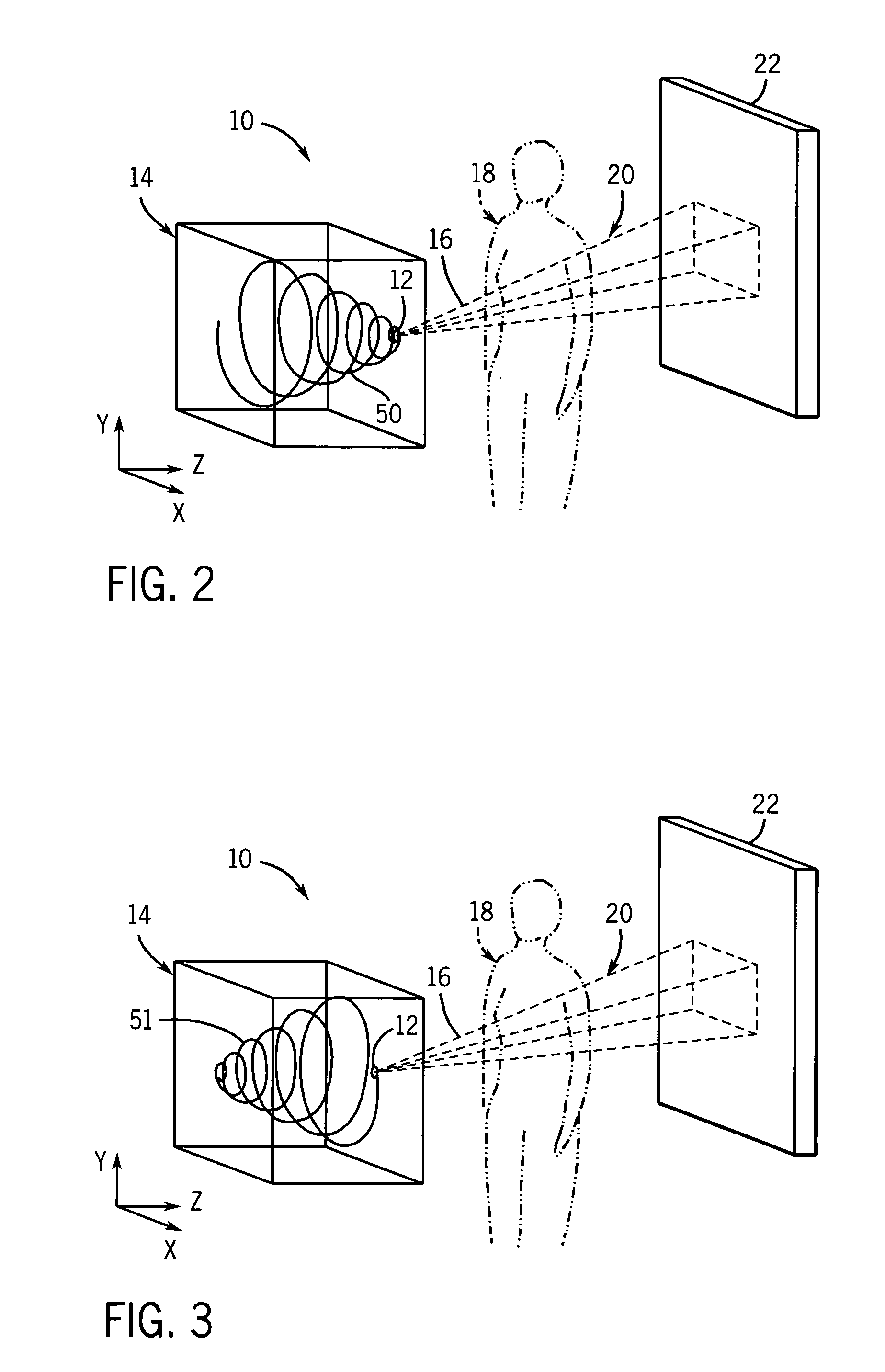
Method and system for imaging a volume using a three-dimensional spiral scan trajectory
InactiveUS7046759B2High depth resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisHelical scan
A technique is provided for improving the depth resolution of tomosynthesis images. The technique provides for the use of spiral scan trajectories. The X-ray source may moved along the spiral scan trajectory, acquiring projection data at various locations on the trajectory which are offset in the z-direction, i.e., in a direction perpendicular to the detector. Projection data acquired at different positions in the z-direction may be used to generate three-dimensional, tomosynthesis images having improved depth resolution.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com