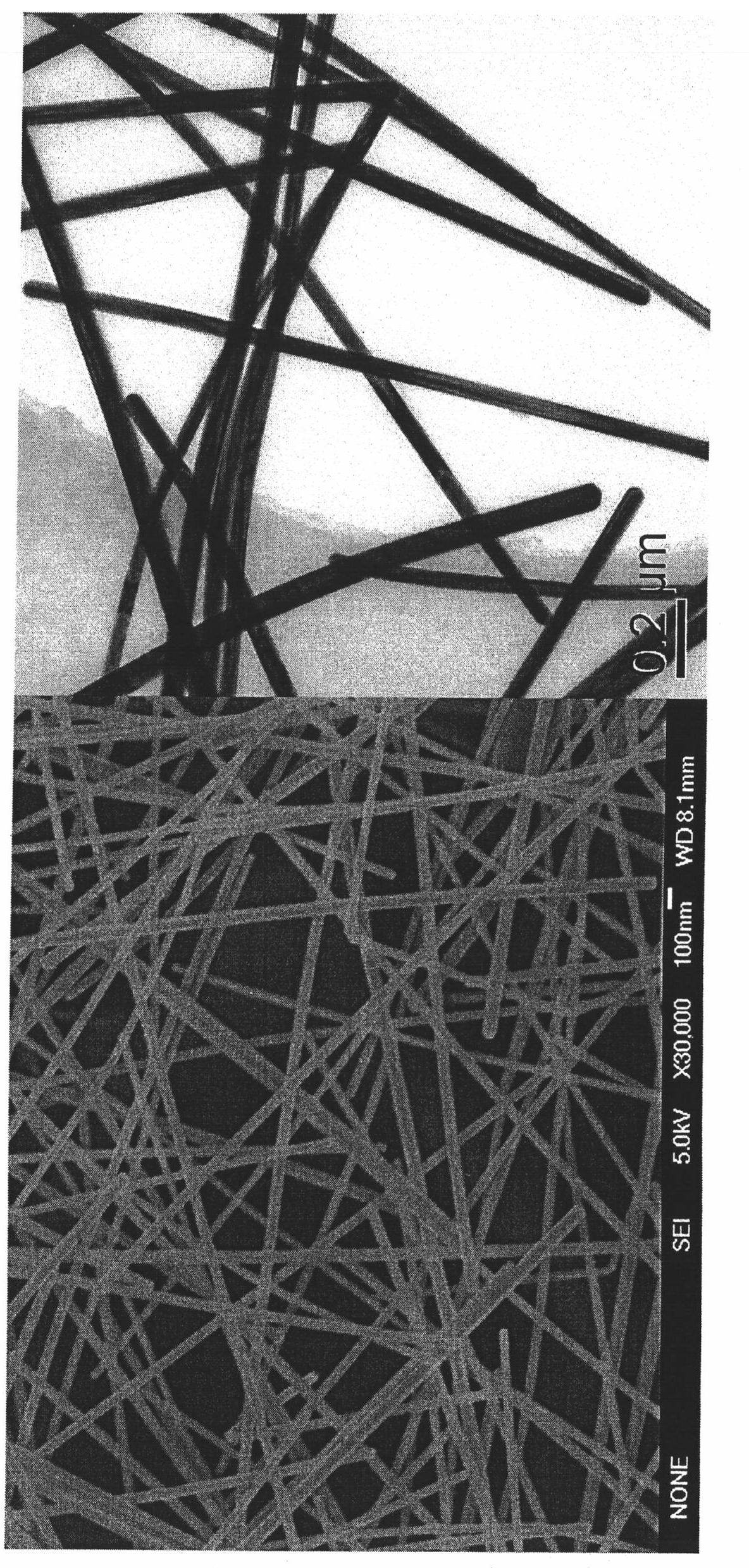
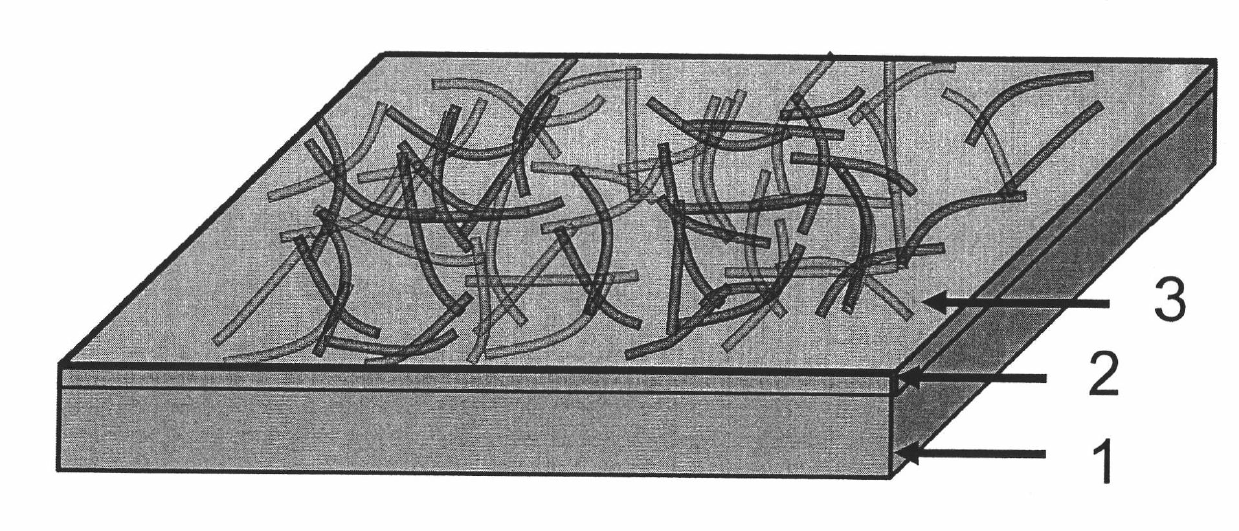
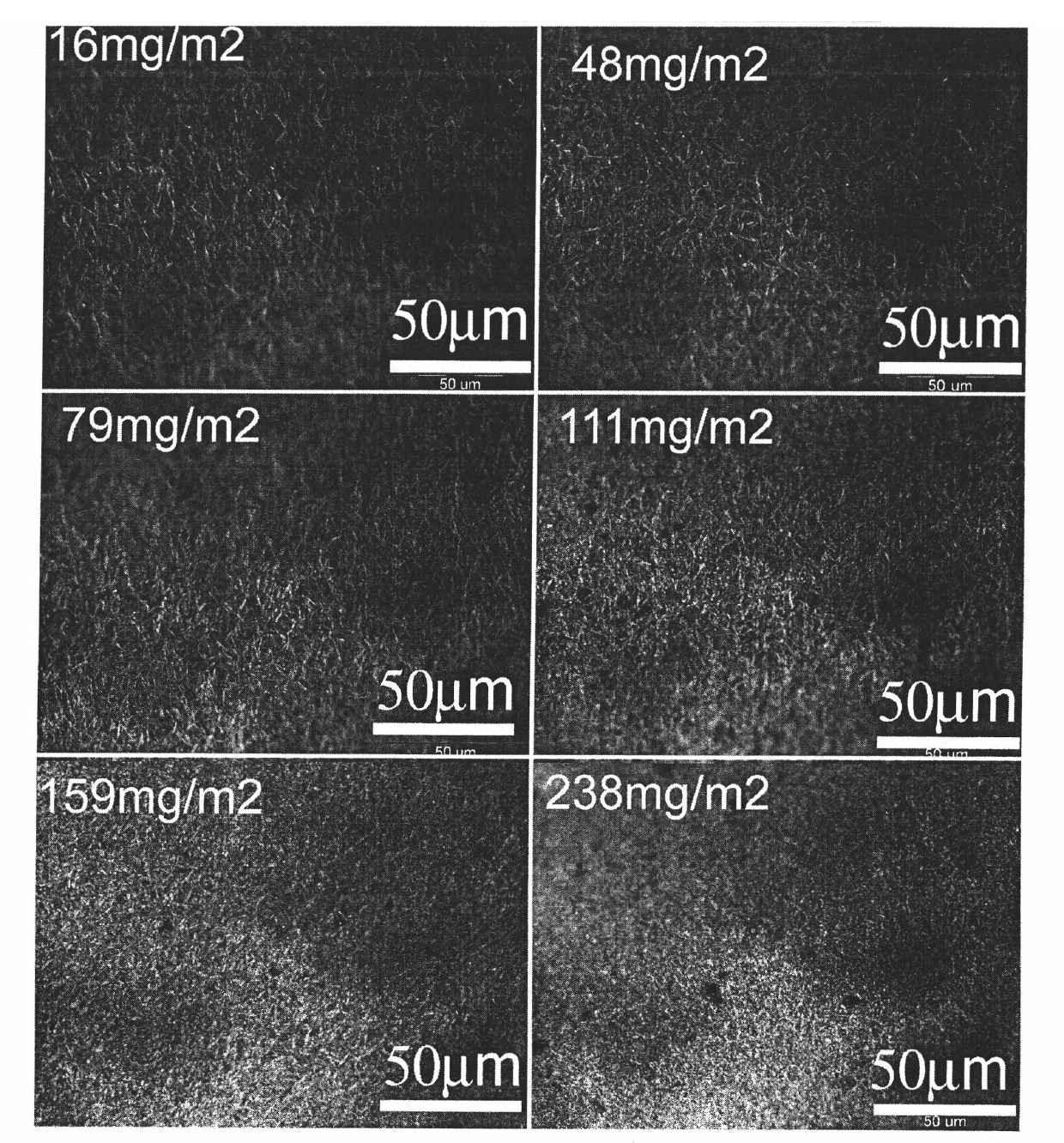
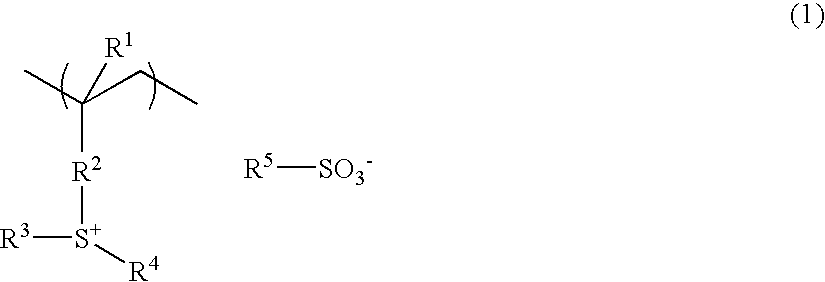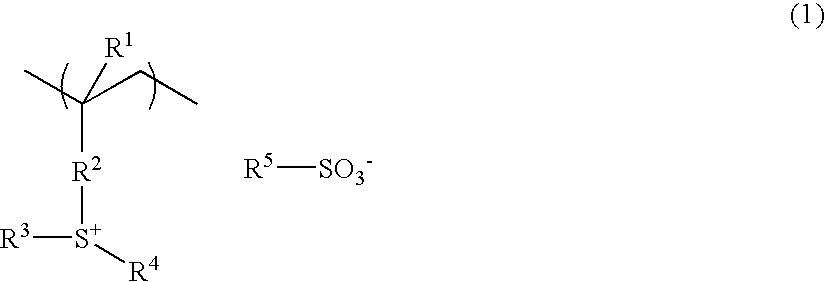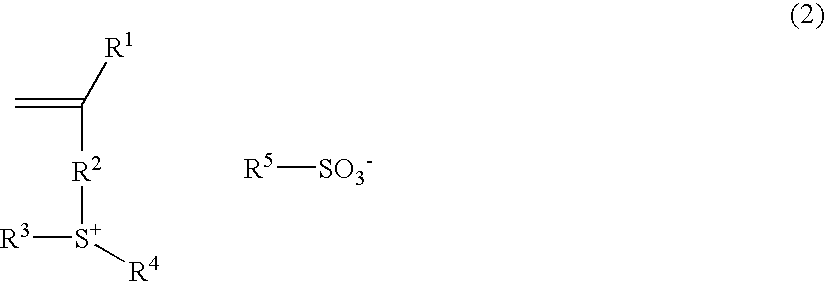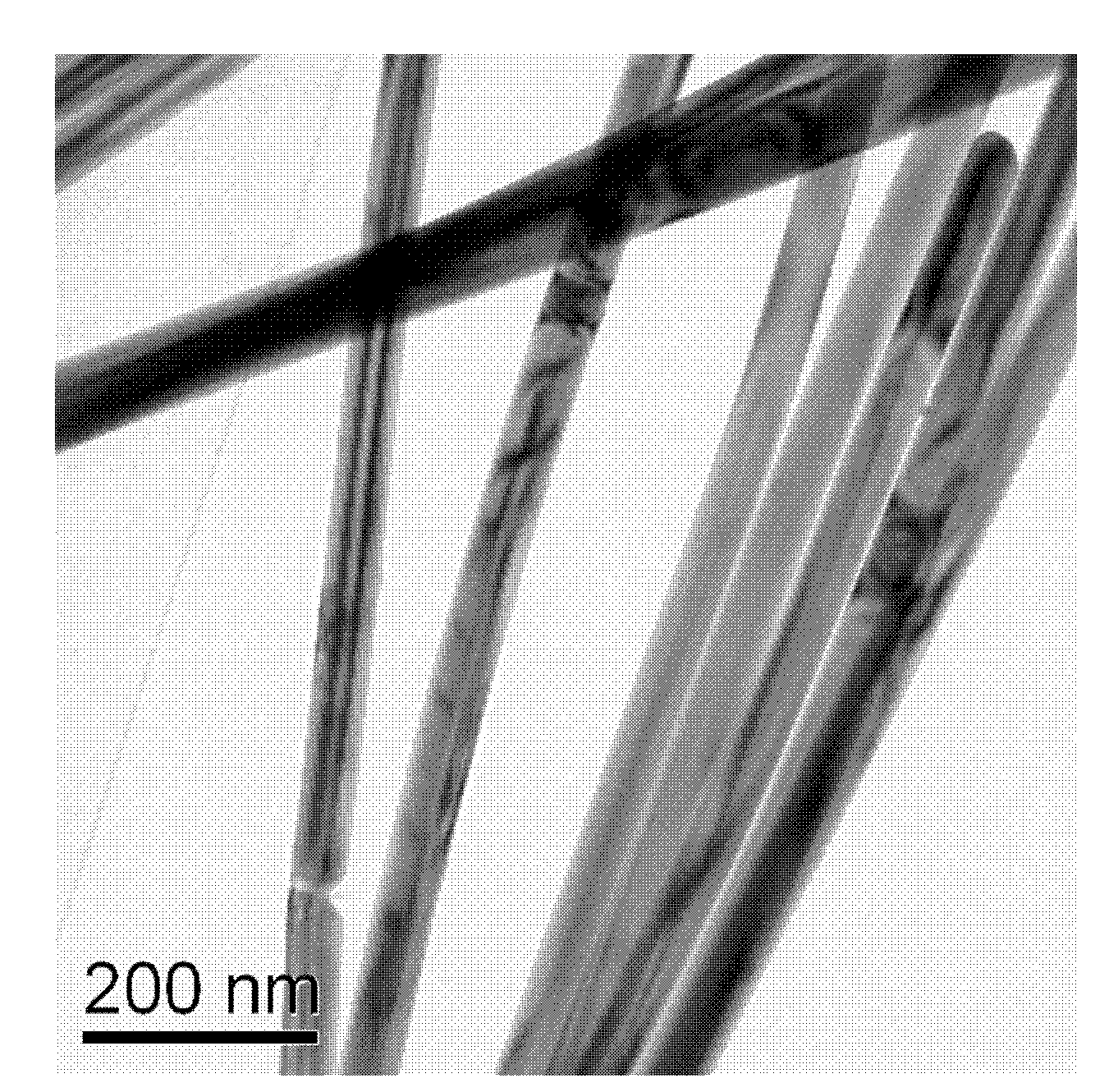Patents
Literature
3258results about How to "Reduce roughness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
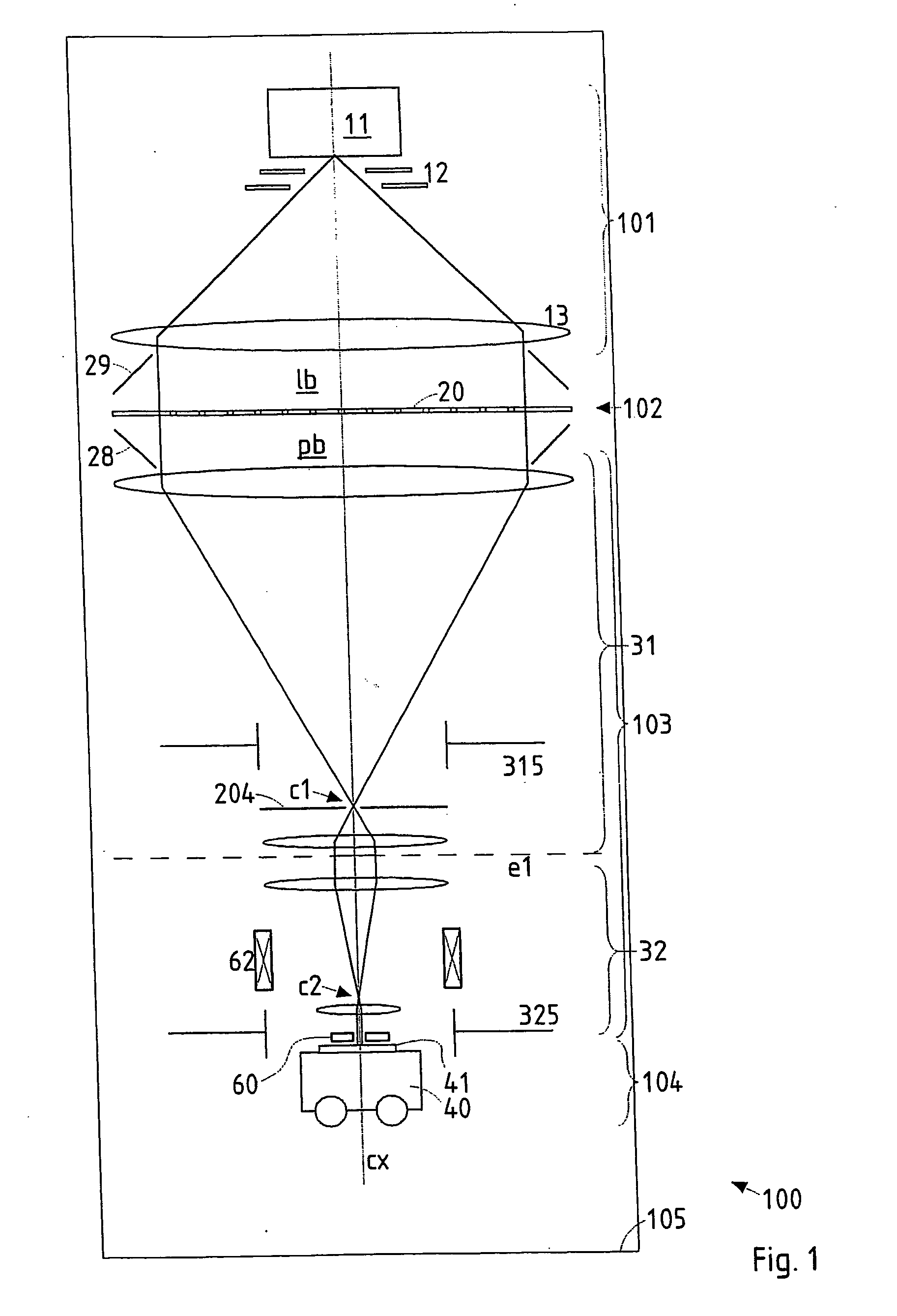
System and method for creating a stable optical interface
ActiveUS8219172B2High bandwidthReduce coherenceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRefractive indexLight beam
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Plasma processing method
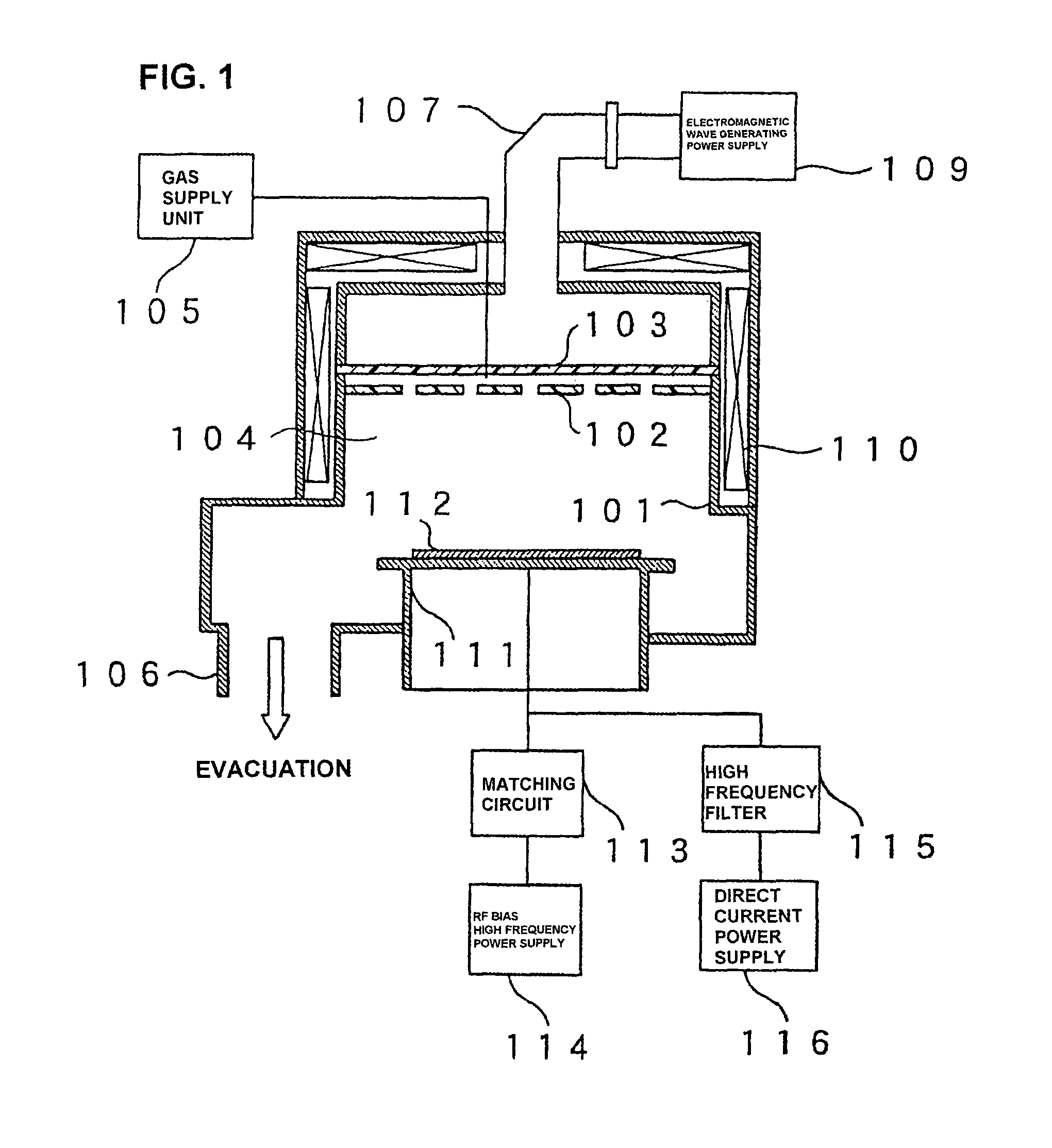
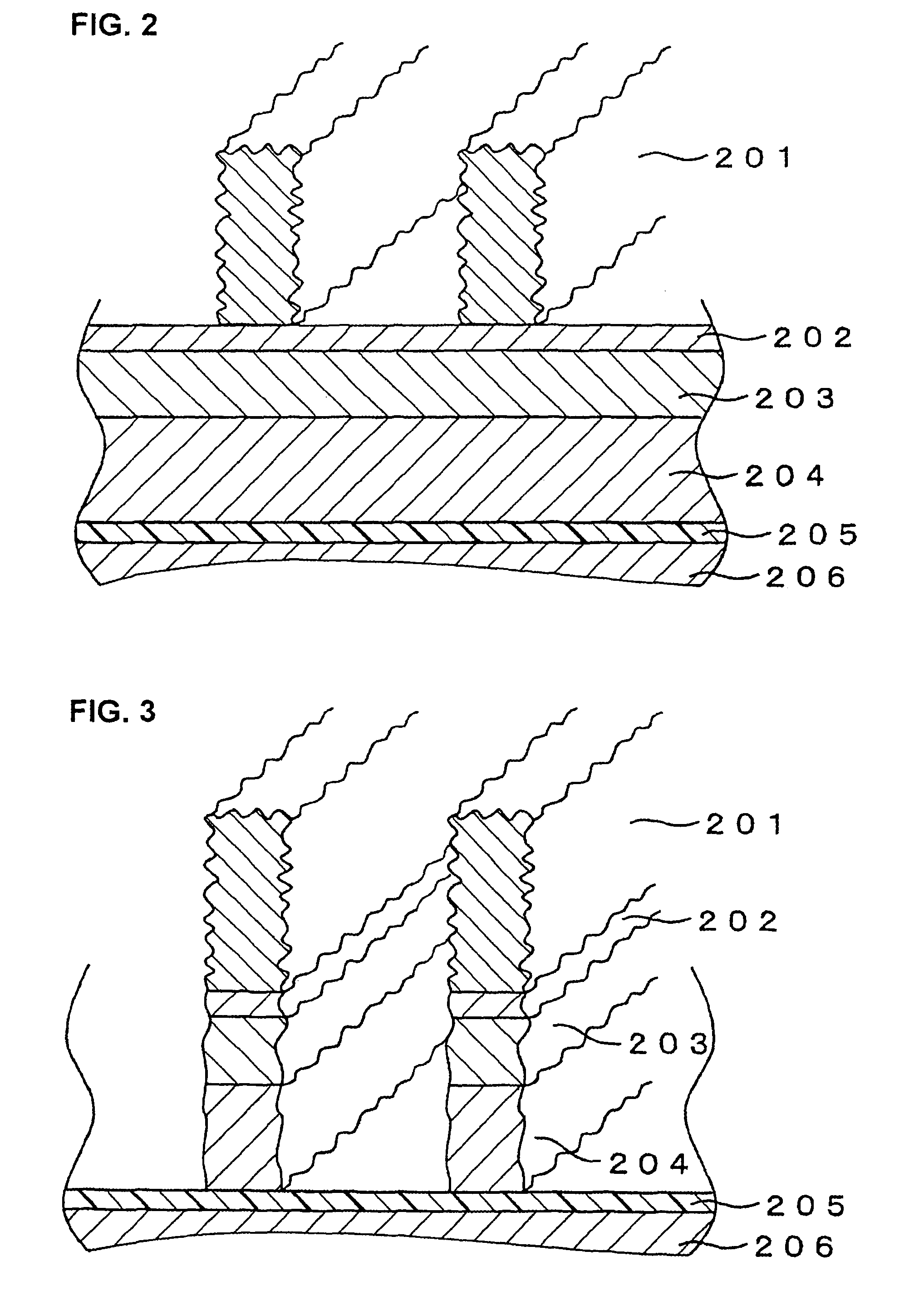
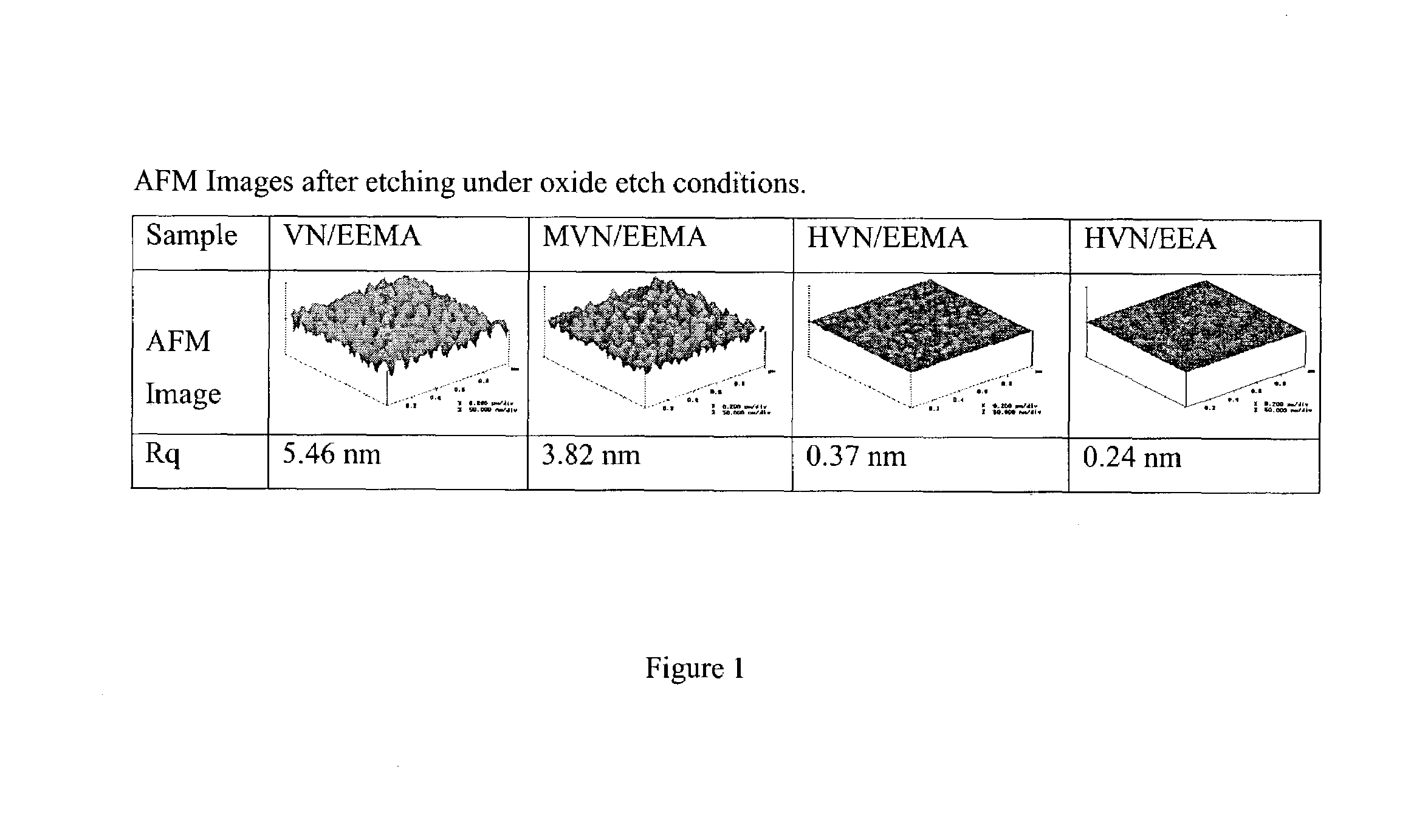
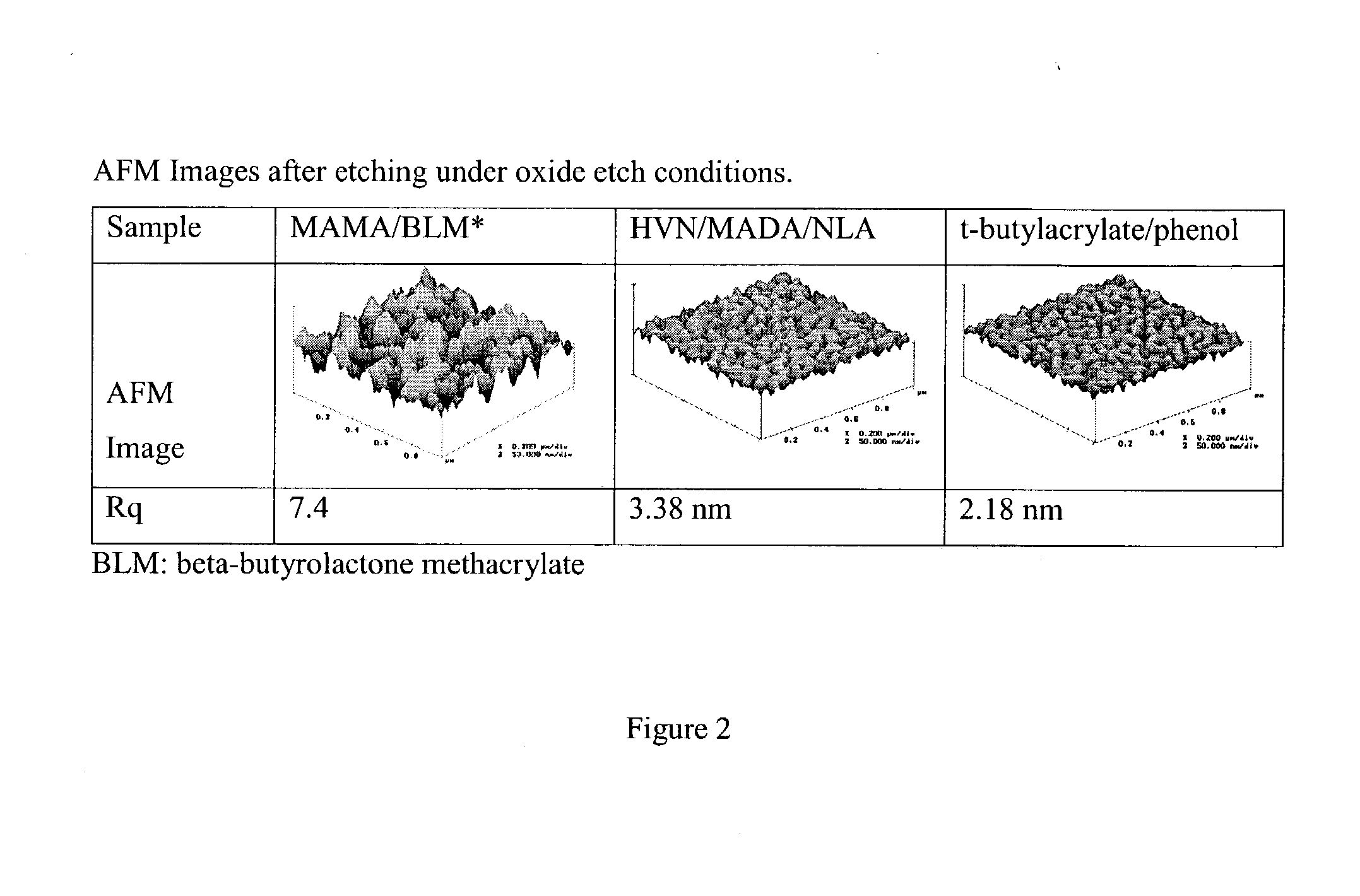
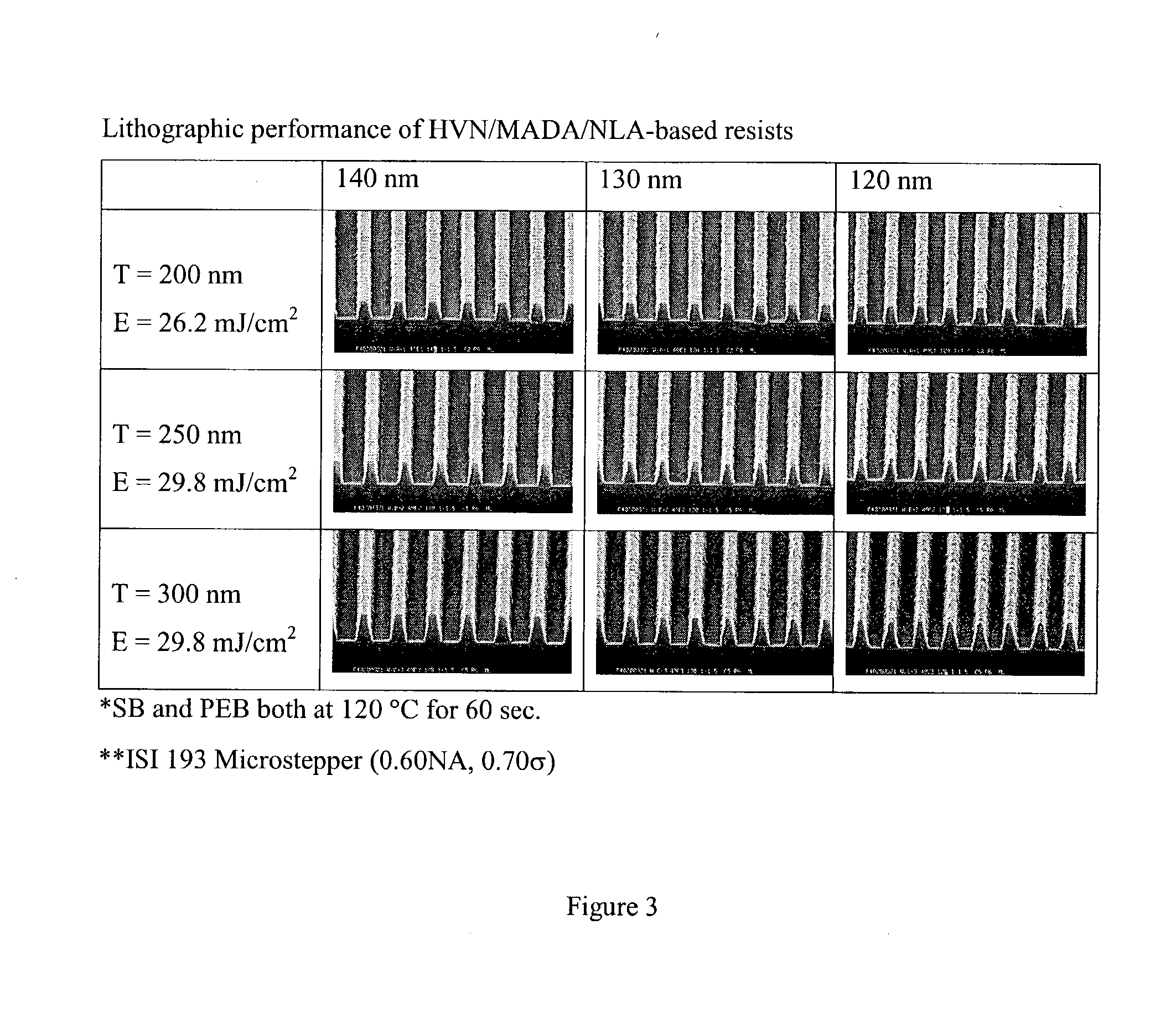
ActiveUS8497213B2Preventing deterioration of semiconductor device performanceReduce roughnessDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistNitrogen gas
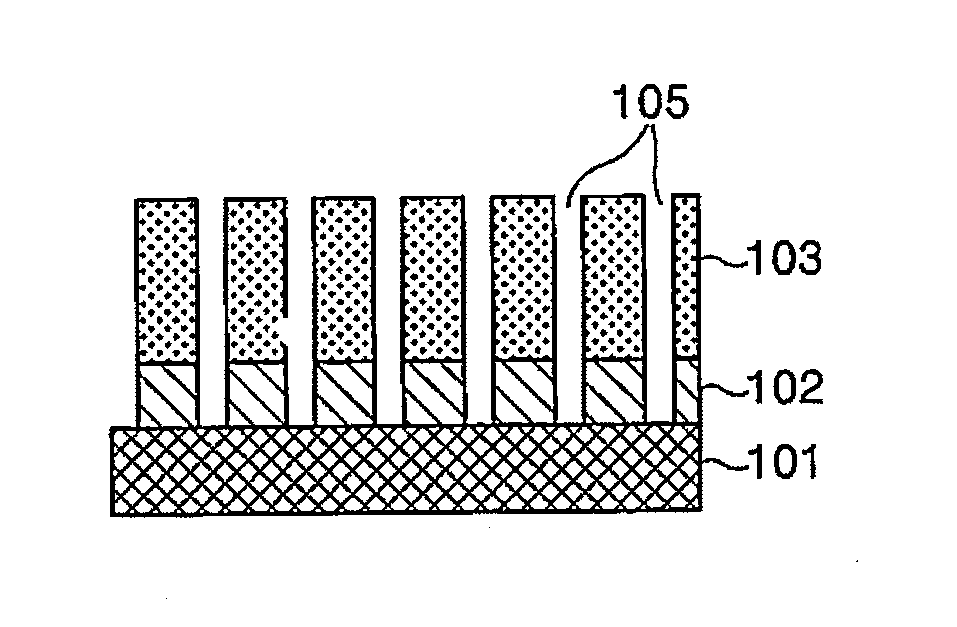
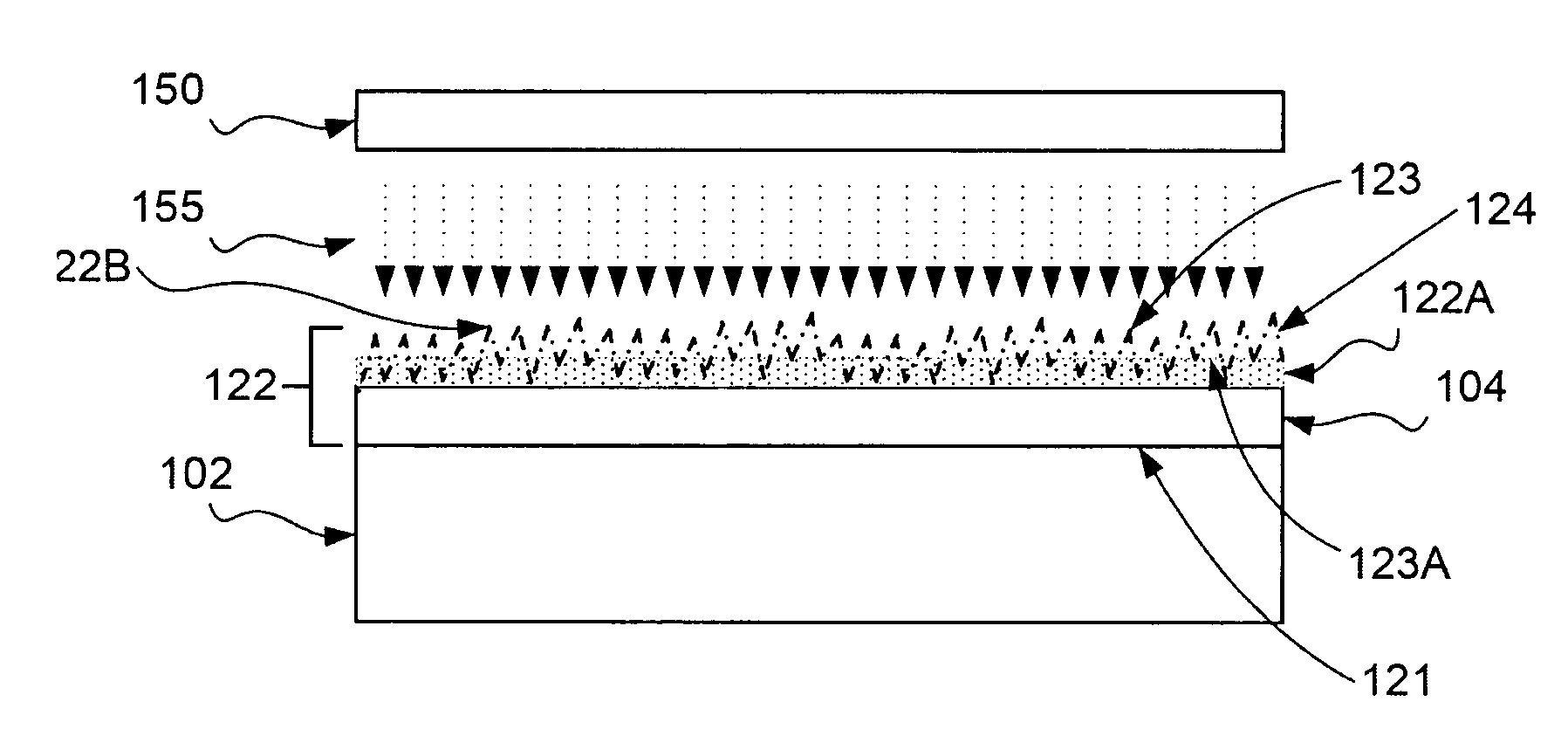
The invention provides a method for subjecting laminated thin films disposed below a photoresist mask pattern to plasma processing, wherein the roughness on the side walls of the formed pattern is reduced, and the LER and LWR are reduced. When etching a material to be processed to form a gate electrode including thin films such as a gate insulating film 205, a conducting layer 204, a mask layer 203 and an antireflection film 202 laminated on a semiconductor substrate 206 and a photoresist mask pattern 201 disposed on the antireflection film, prior to etching the mask pattern 201, plasma is generated from nitrogen gas or a mixed gas including nitrogen gas and deposition gas to subject the mask pattern 201 to a plasma curing process so as to reduce the roughness on the surface and side walls of the mask pattern 201, and then the laminated thin films 202, 203 and 204 disposed below the mask pattern 201 are subjected to a plasma etching process.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Laminated semiconductor substrate process for producing the same
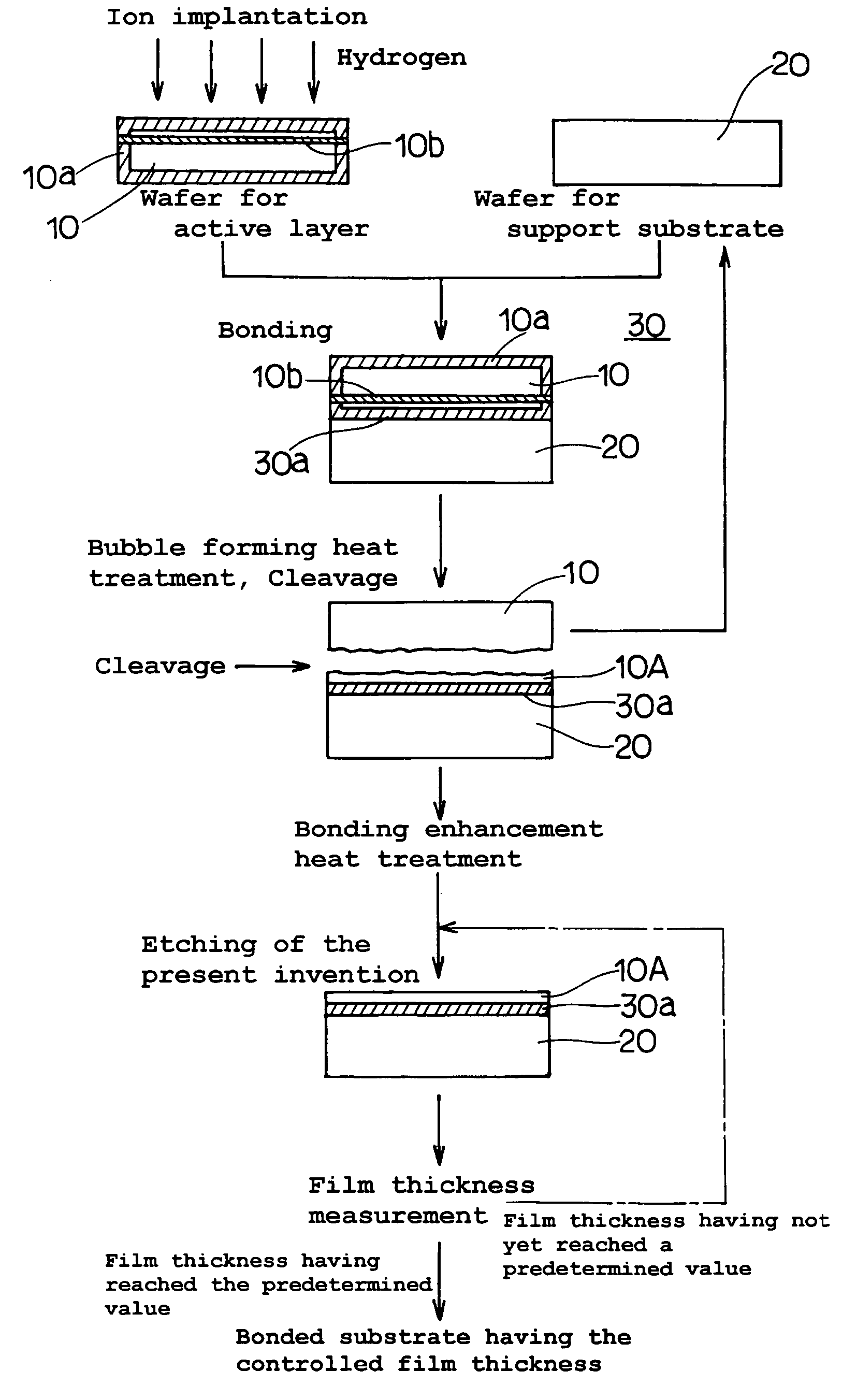
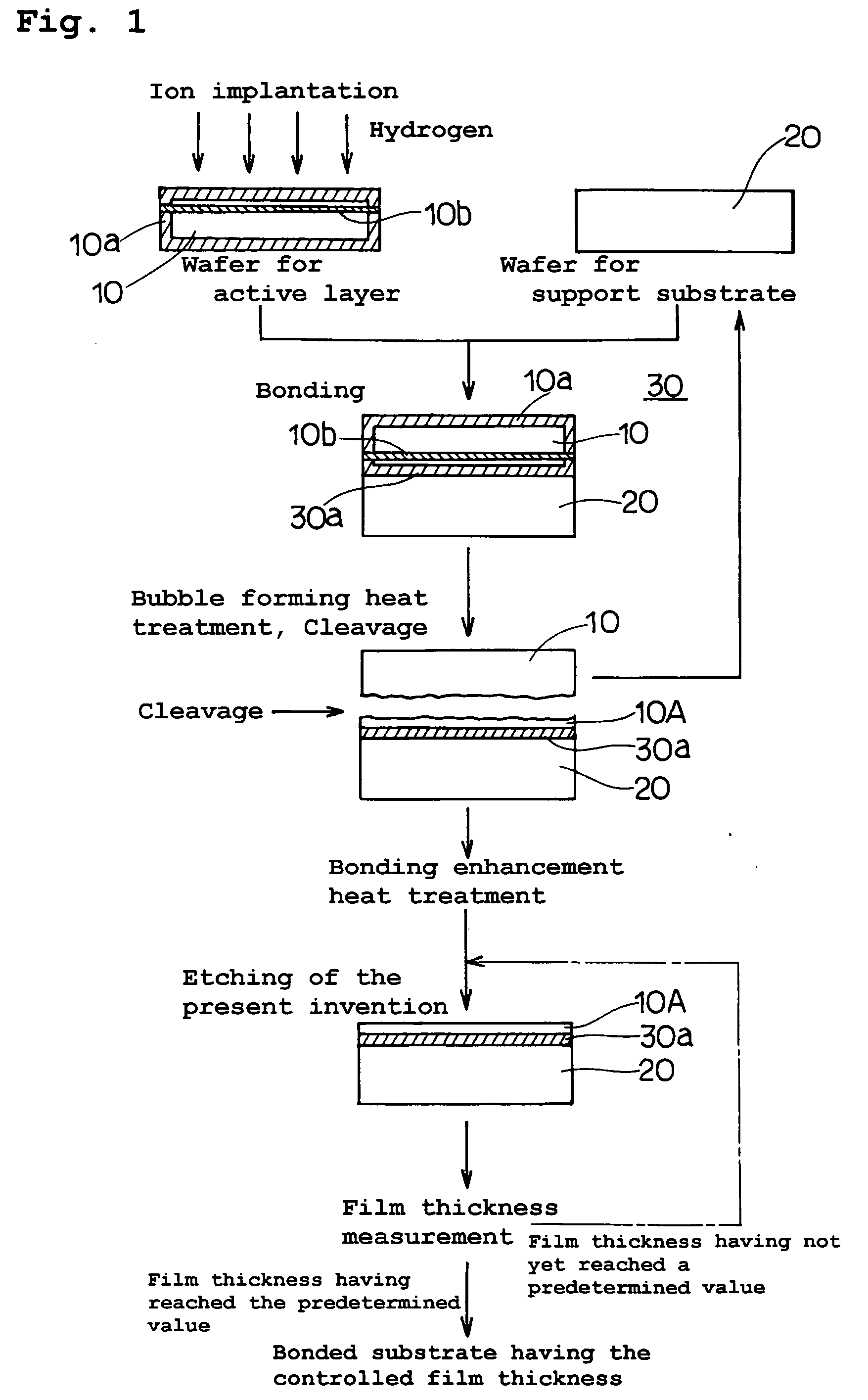
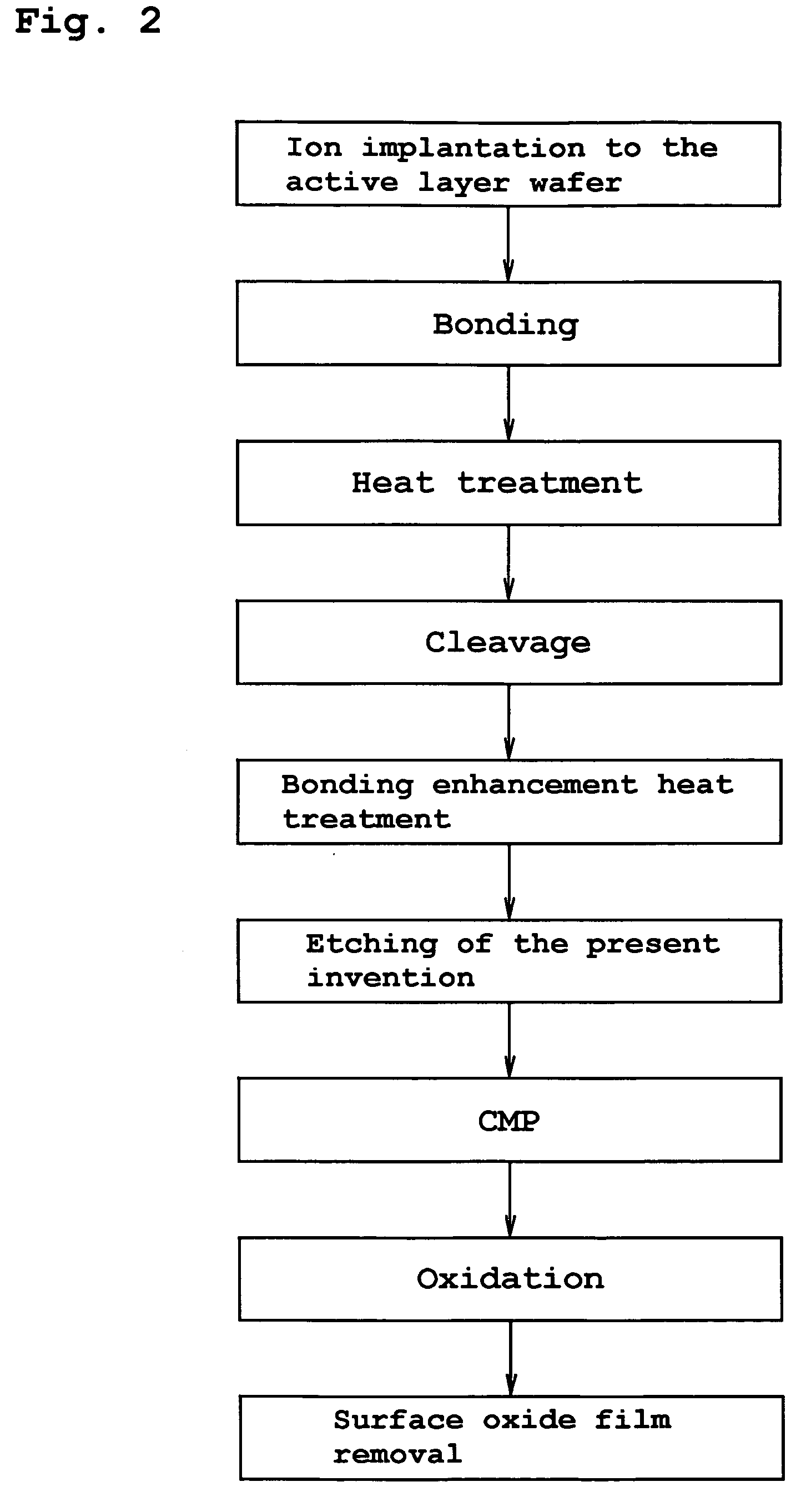
InactiveUS20060118935A1Simple processReduce surface roughnessDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEtchingSurface roughness
The present invention provides a bonded substrate fabricated to have its final active layer thickness of 200 nm or lower by performing the etching by only 1 nm to 1 μm with a solution having an etching effect on a surface of an active layer of a bonded substrate which has been prepared by bonding two substrates after one of them having been ion-implanted and then cleaving off a portion thereof by heat treatment. SC-1 solution is used for performing the etching. A polishing, a hydrogen annealing and a sacrificial oxidation may be respectively applied to the active layer before and / or after the etching. The film thickness of this active layer can be made uniform over the entire surface area and the surface roughness of the active layer can be reduced as well.
Owner:SUMCO CORP +1
Smooth SiConi etch for silicon-containing films
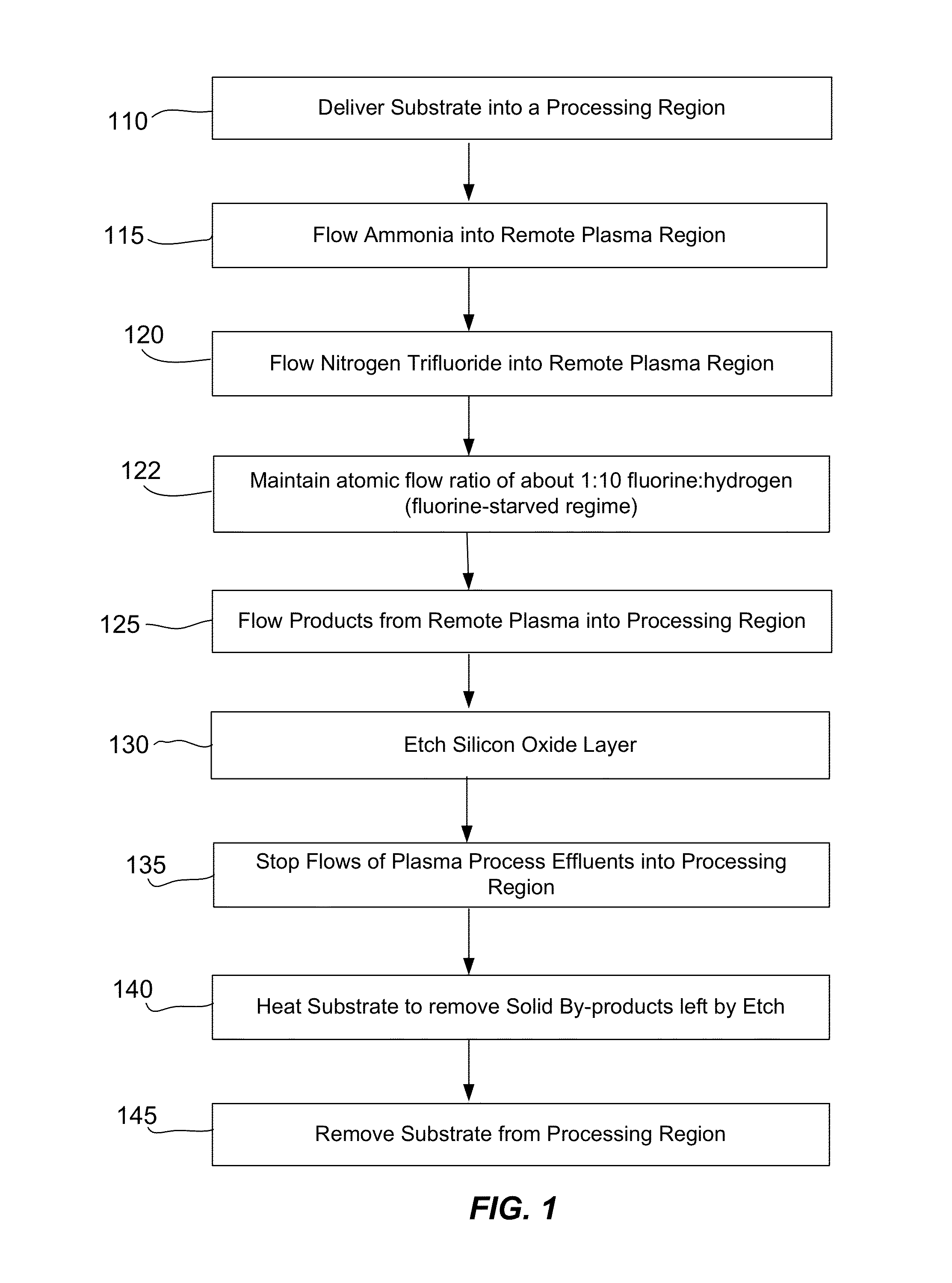
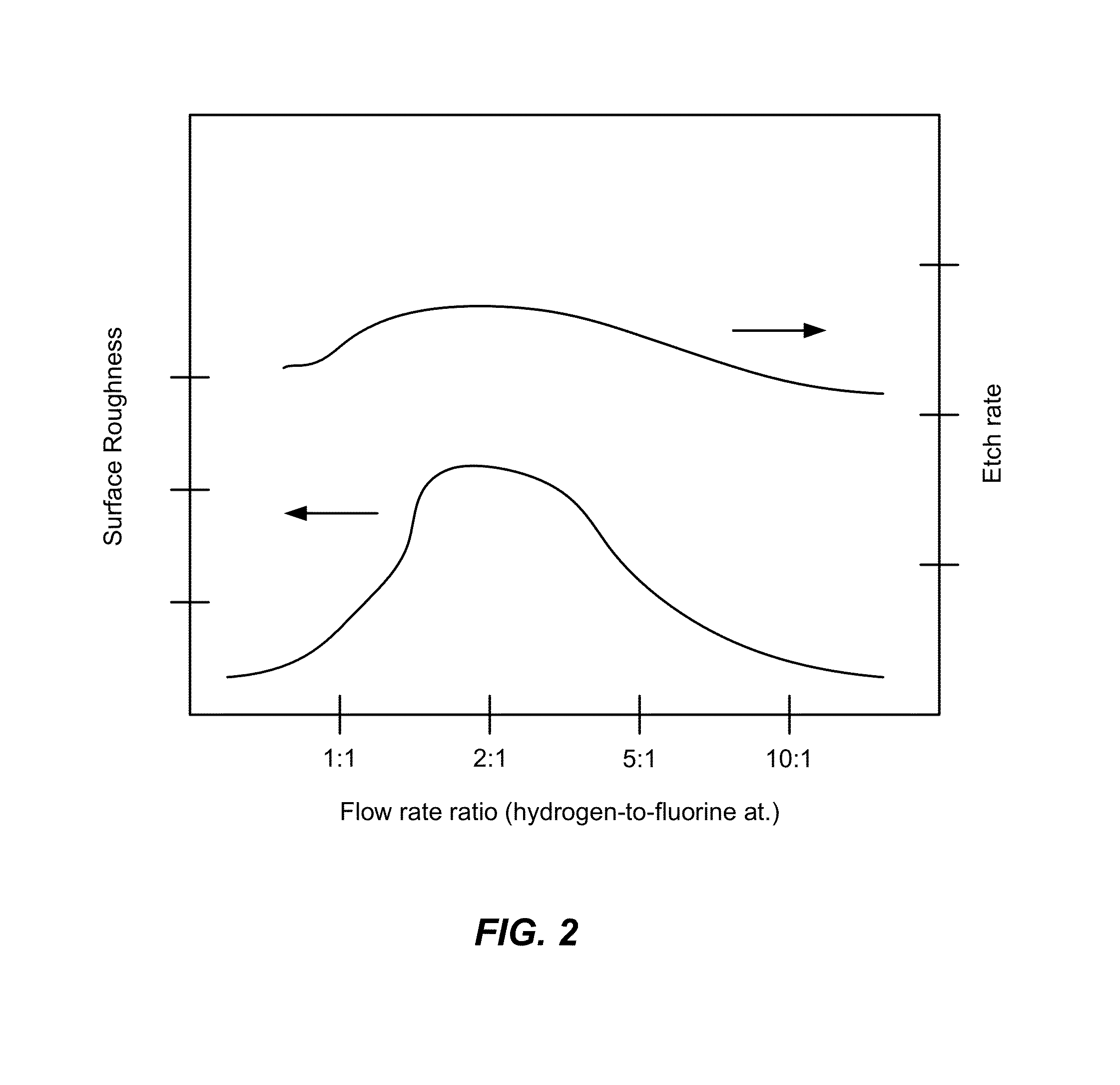
ActiveUS8501629B2Great and less flow ratioReduce roughnessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsHydrogenSurface roughness
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Plasma etching method and plasma etching apparatus
ActiveUS20140134847A1Reduce roughnessImproving cross-sectional shape of lineElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenSilicon oxide
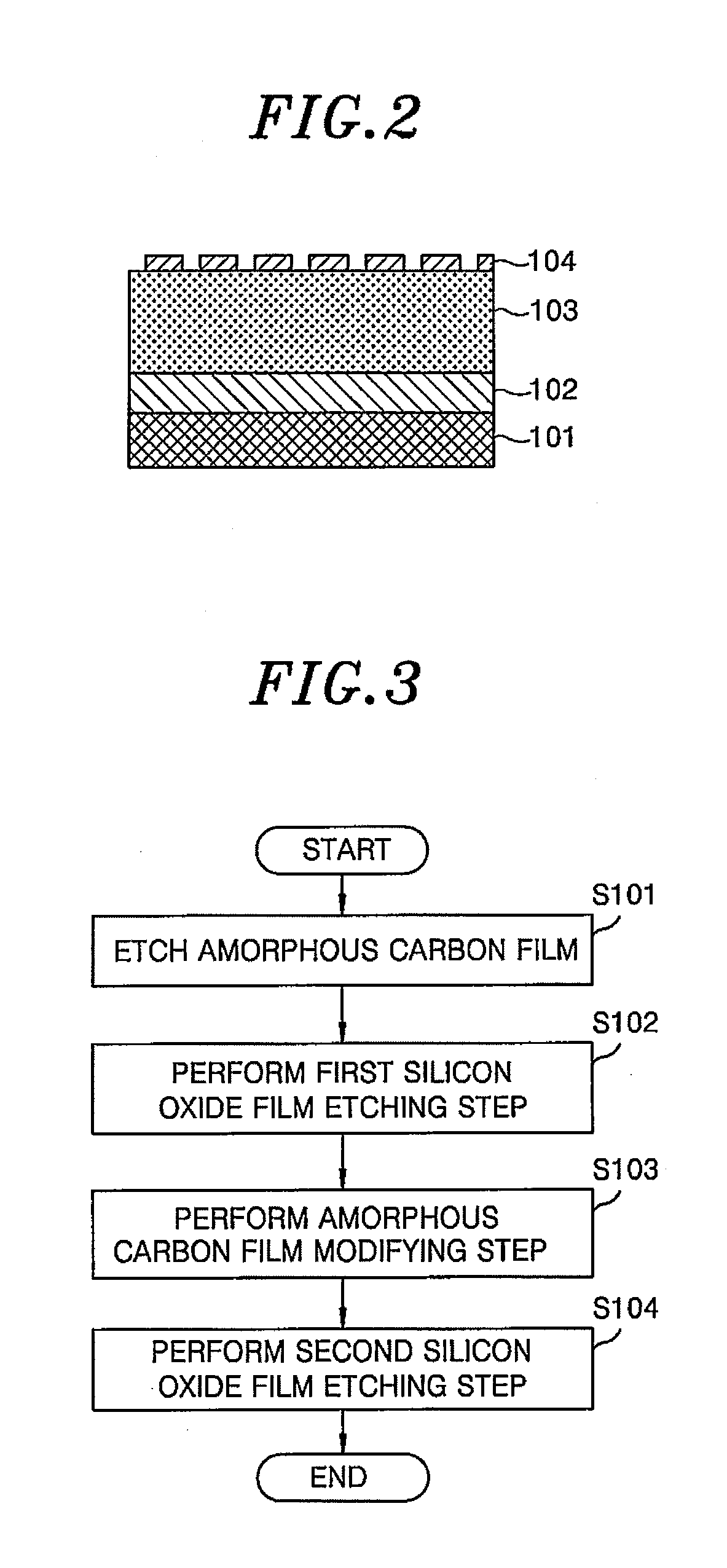
A plasma etching method includes etching an amorphous carbon film by a plasma of an oxygen-containing gas using, as a mask, an SiON film having a predetermined pattern formed on a target object, etching a silicon oxide film by a plasma of a processing gas using the amorphous carbon film as a mask while removing the SiON film remaining on the etched amorphous carbon film by the plasma of the processing gas. The plasma etching method further includes modifying the amorphous carbon film by a plasma of a sulfur-containing gas or a hydrogen-containing gas while applying a negative DC voltage to an upper electrode containing silicon after the SiON film is removed from the amorphous carbon film, and etching the silicon oxide film again by the plasma of the processing gas using the modified amorphous carbon film as a mask.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
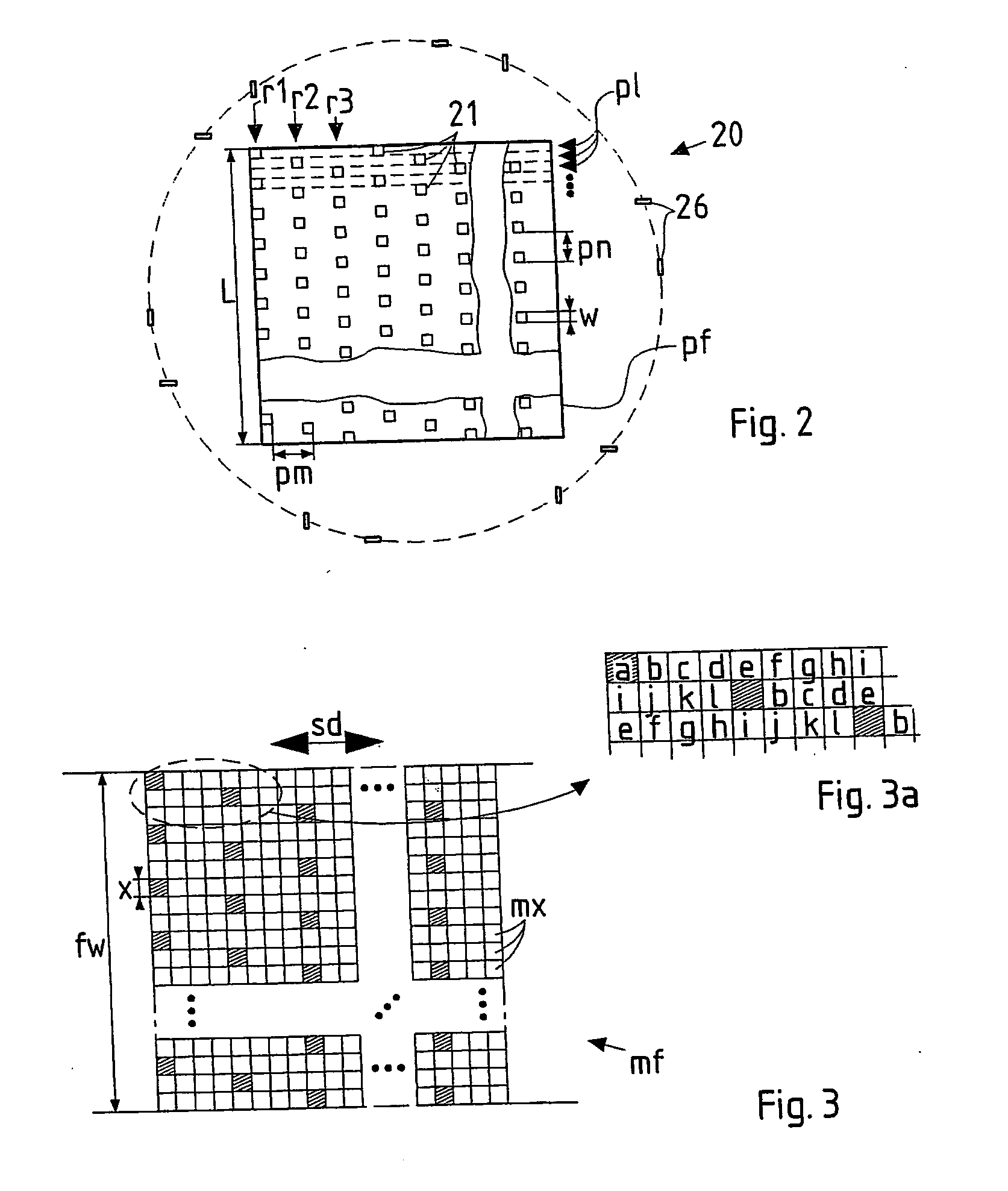
Advanced pattern definition for particle-beam processing
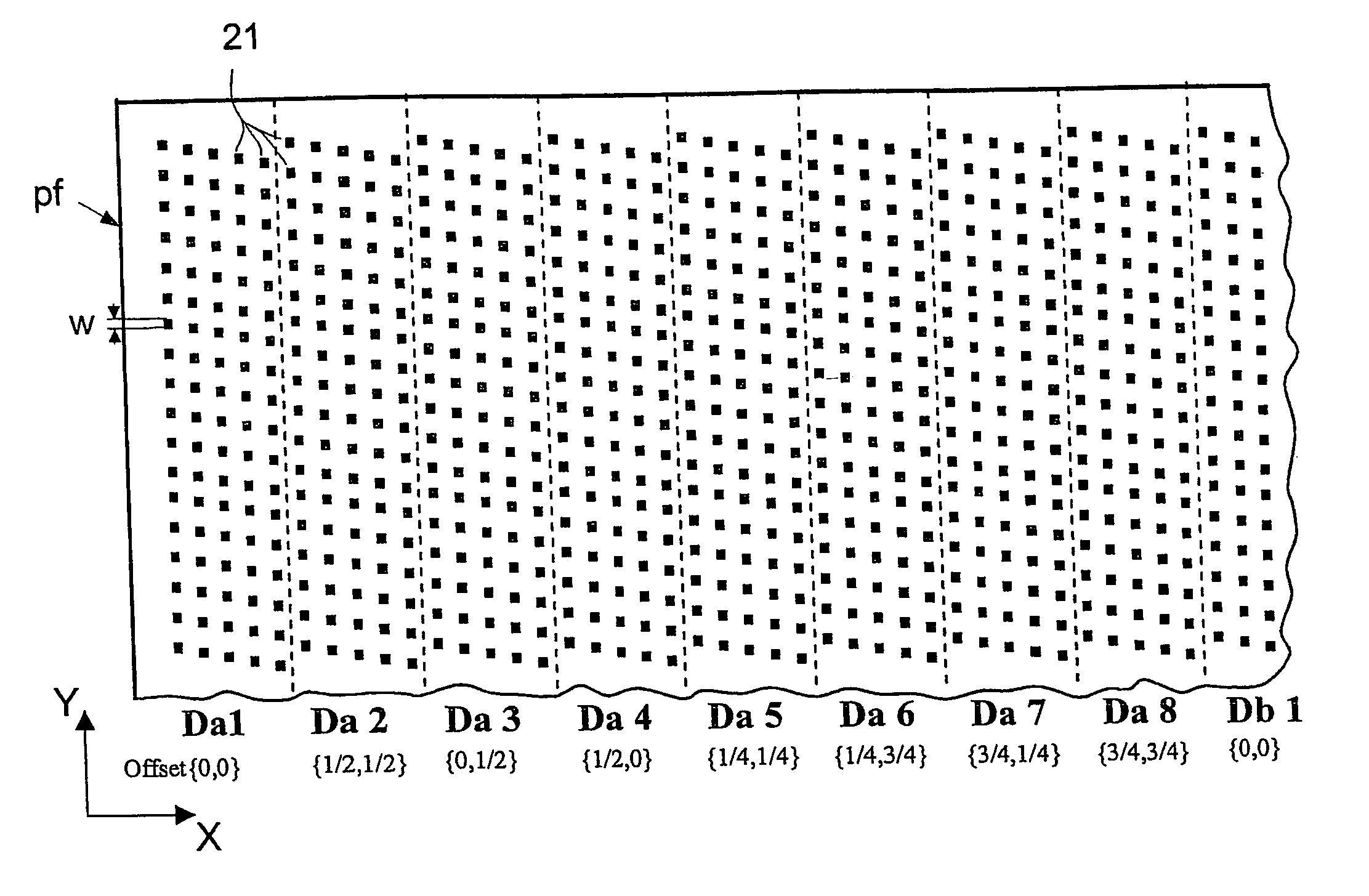
ActiveUS7276714B2High resolutionReduce roughnessElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsParticle beamMechanical engineering
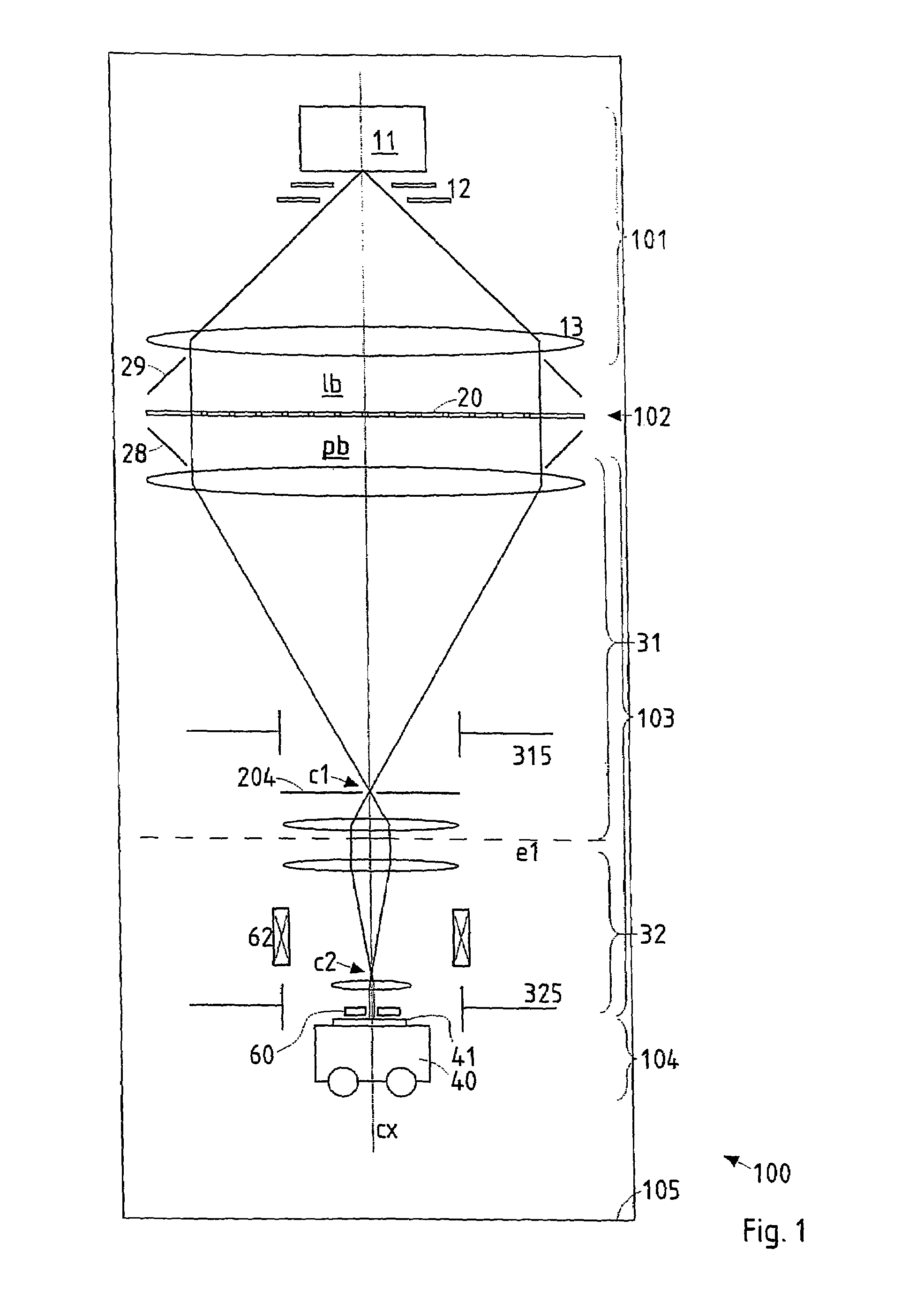
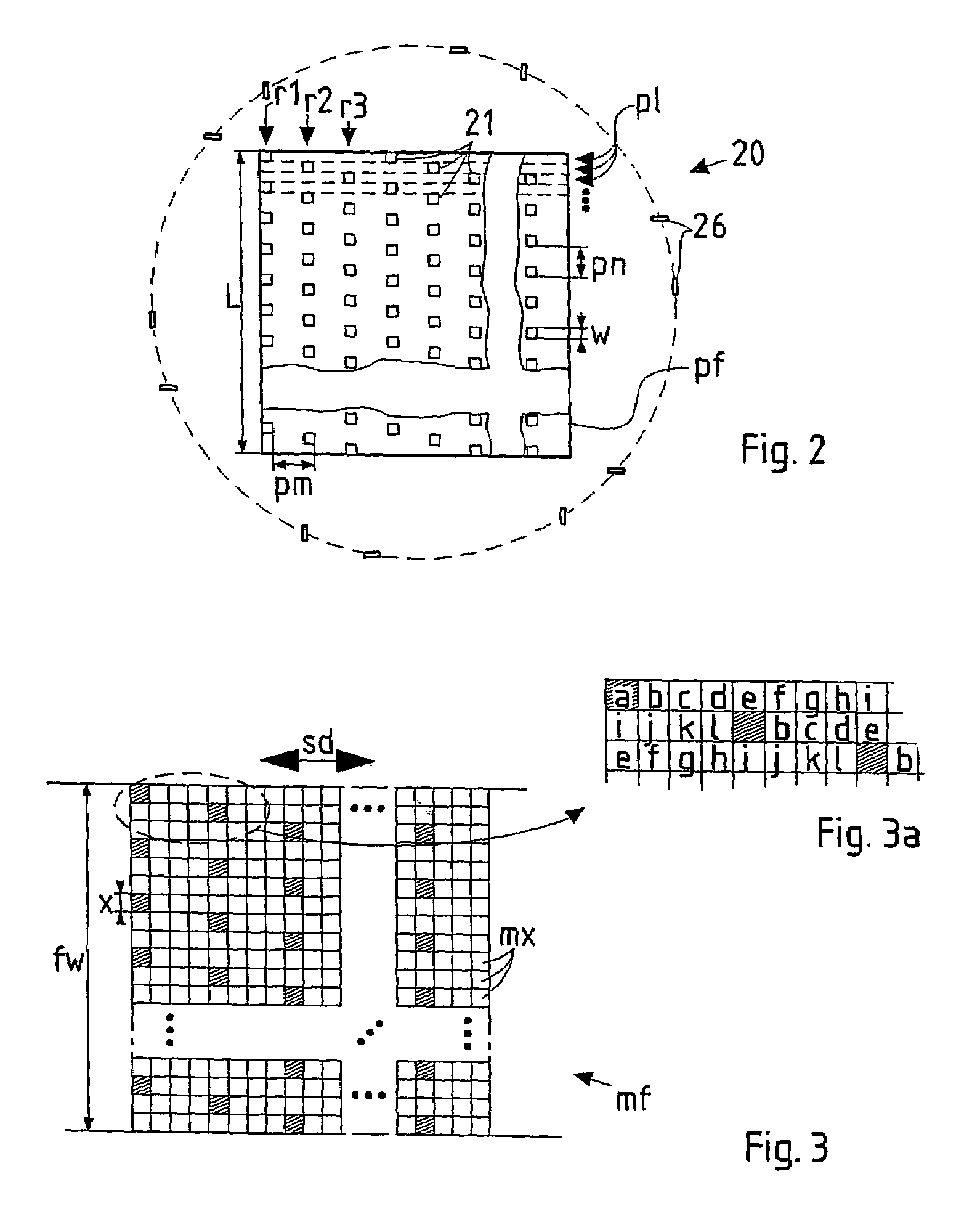
In a pattern definition device for use in a particle-beam processing apparatus a plurality of apertures (21) are arranged within a pattern definition field (pf) wherein the positions of the apertures (21) in the pattern definition field (pf) taken with respect to a direction (X, Y) perpendicular, or parallel, to the scanning direction are offset to each other by not only multiple integers of the effective width (w) of an aperture taken along said direction, but also multiple integers of an integer fraction of said effective width. The pattern definition field (pf) may be segmented into several domains (D) composed of a many staggered lines (pl) of apertures; along the direction perpendicular to the scanning direction, the apertures of a domain are offset to each other by multiple integers of the effective width (w), whereas the offsets of apertures of different domains are integer fractions of that width.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Thin film writer with multiplayer write gap
InactiveUS6724569B1Easy to controlControl performanceConstruction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceElectrical conductorLower pole
Embodiments in accordance with the thin film write head of the present invention have a lower pole structure, an upper pole structure, and a multilayer write gap extending from an air bearing surface between the upper and lower pole structures. In preferred embodiments, the write gap comprises at least two of: (a) a first layer covering a lower pole tip portion of the lower pole structure, (b) a second layer covering turns of a semiconductor winding, or (c) a third layer covering a winding insulation stack. In more preferred embodiments, the write gap is formed of the first, the second, and the third write gap layers. An advantage of a write head with a multilayer write gap is that it allows better control of write gap thickness. As such, loss of write gap thickness can be compensated for by deposition of the second write gap layers, or by deposition of the third write gap layer. Some embodiments have one or more additional advantages in providing increased corrosion prevention, improving the integrity of conductor insulation, and / or improving the top pole magnetic material characteristics.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Through-silicon via and method for forming the same
InactiveUS20080079121A1Low costSecure characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerSemiconductor chip
A method for forming a through-silicon via includes the steps of defining a groove in each chip of a wafer which has a plurality of semiconductor chips; applying liquid polymer on the wafer to fill the groove; forming an insulation layer on a sidewall of the groove through patterning the polymer; forming a metal layer to fill the groove which is formed with the insulation layer on the sidewall thereof; and back-grinding a backside of the wafer to expose the metal layer filled in the groove.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method of manufacturing three-dimensional semiconductor device
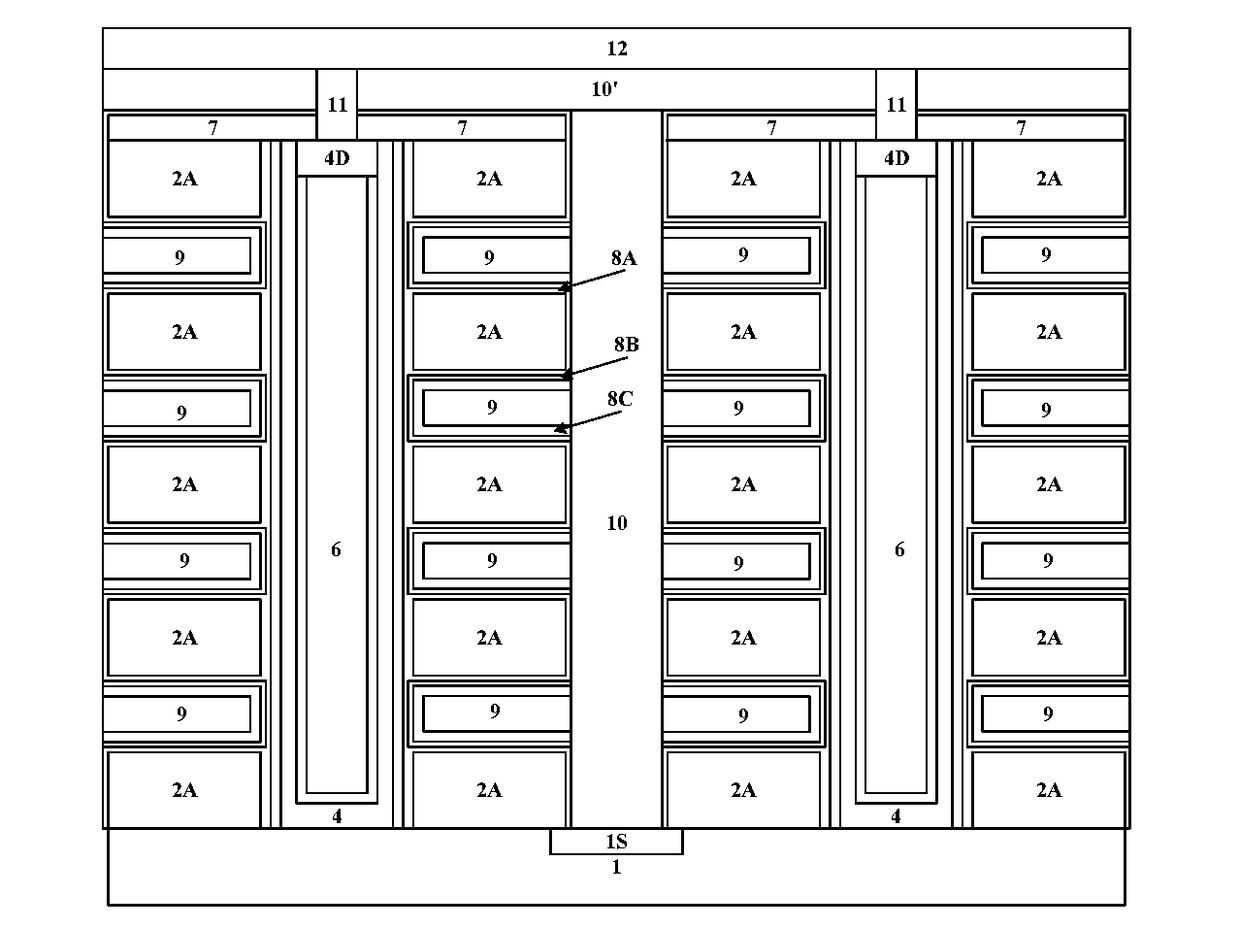
ActiveUS20170250193A1Reduce channel surface roughnessEnhance channel carrier mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrier mobilitySurface roughness
A method of manufacturing three-dimensional semiconductor device, comprising the steps of: forming a stack structure of a plurality of a first material layers and a second material layers on a substrate in the memory cell region; etching said stack structure to form a plurality of trenches; forming channel layers in said plurality of trenches; performing annealing treatment to at least one surface of the channel layers to reduce the surface roughness and the interface state. In accordance with the three-dimensional semiconductor device manufacturing method of the present invention, the formation of interface states is depressed by introducing a dummy channel sacrificial layer for the interface treatment on the channel surface and back surface, and / or the channel surface roughness is reduced by introducing a buffer layer on the channel surface and back surface during the treatment, which can improve the channel carrier mobility, improve the channel current as well as the reliability of the memory cell.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Advanced pattern definition for particle-beam processing
ActiveUS20050242302A1High resolutionReduced line edge roughnessElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsParticle beamA domain
In a pattern definition device for use in a particle-beam processing apparatus a plurality of apertures (21) are arranged within a pattern definition field (pf) wherein the positions of the apertures (21) in the pattern definition field (pf) taken with respect to a direction (X, Y) perpendicular, or parallel, to the scanning direction are offset to each other by not only multiple integers of the effective width (w) of an aperture taken along said direction, but also multiple integers of an integer fraction of said effective width. The pattern definition field (pf) may be segmented into several domains (D) composed of a many staggered lines (pl) of apertures; along the direction perpendicular to the scanning direction, the apertures of a domain are offset to each other by multiple integers of the effective width (w), whereas the offsets of apertures of different domains are integer fractions of that width.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Semiconductor on insulator structure made using radiation annealing
InactiveUS20070281172A1Healing damageReduce roughnessElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesWaferingIon implantation
Systems and methods for and products of a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) structure including subjecting at least one unfinished surface to a laser annealing process. Production of the SOI structure further may include subjecting an implantation surface of a donor semiconductor wafer to an ion implantation process to create an exfoliation layer in the donor semiconductor wafer; bonding the implantation surface of the exfoliation layer to an insulator substrate; separating the exfoliation layer from the donor semiconductor wafer, thereby exposing at least one cleaved surface; and subjecting the at least one cleaved surface to the laser annealing process.
Owner:CORNING INC
Silver nanowire-based transparent conductive thin film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102087886AReduce roughnessReduce transmittanceConductive layers on insulating-supportsIndividual molecule manipulationPolyvinyl alcoholPolymethyl methacrylate
The invention provides a silver nanowire-based transparent conductive thin film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: forming a uniform adhesive layer on a substrate by organic polymer fluid; and forming a silver nanowire conductive layer on the adhesive layer, wherein silver nanowires can be firmly adhered to the adhesive layer. Through the adhesive layer, the firmness and the reliability of the silver nanowire transparent conductive thin film are greatly improved, the problem of easiness of falling of the silver nanowires is solved, and the selection range of the substrate is expanded. If the adhesive layer is formed by polyvinyl alcohol on a polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) substrate, the visible light transmittance reaches 84 percent when square resistance is 130.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Resist composition and patterning process using the same
ActiveUS20060147836A1High resolutionReduced line edge roughnessRadiation applicationsPhotomechanical apparatusMeth-High resolution
There is disclosed a resist composition which comprises, at least, a polymer in which a sulfonium salt having a polymerizable unsaturated bond, a (meth)acrylate having a lactone or a hydroxyl group as an adhesion group, and a (meth)acrylate having an ester substituted with an acid labile group are copolymerized. There can be provided a resist composition with high resolution which has high sensitivity and high resolution to high energy beam, especially to ArF excimer laser, F2 excimer laser, EUV, X-ray, EB, etc., has reduced line edge roughness, and comprises a polymeric acid generator which has insolubility in water, and sufficient thermal stability and preservation stability.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
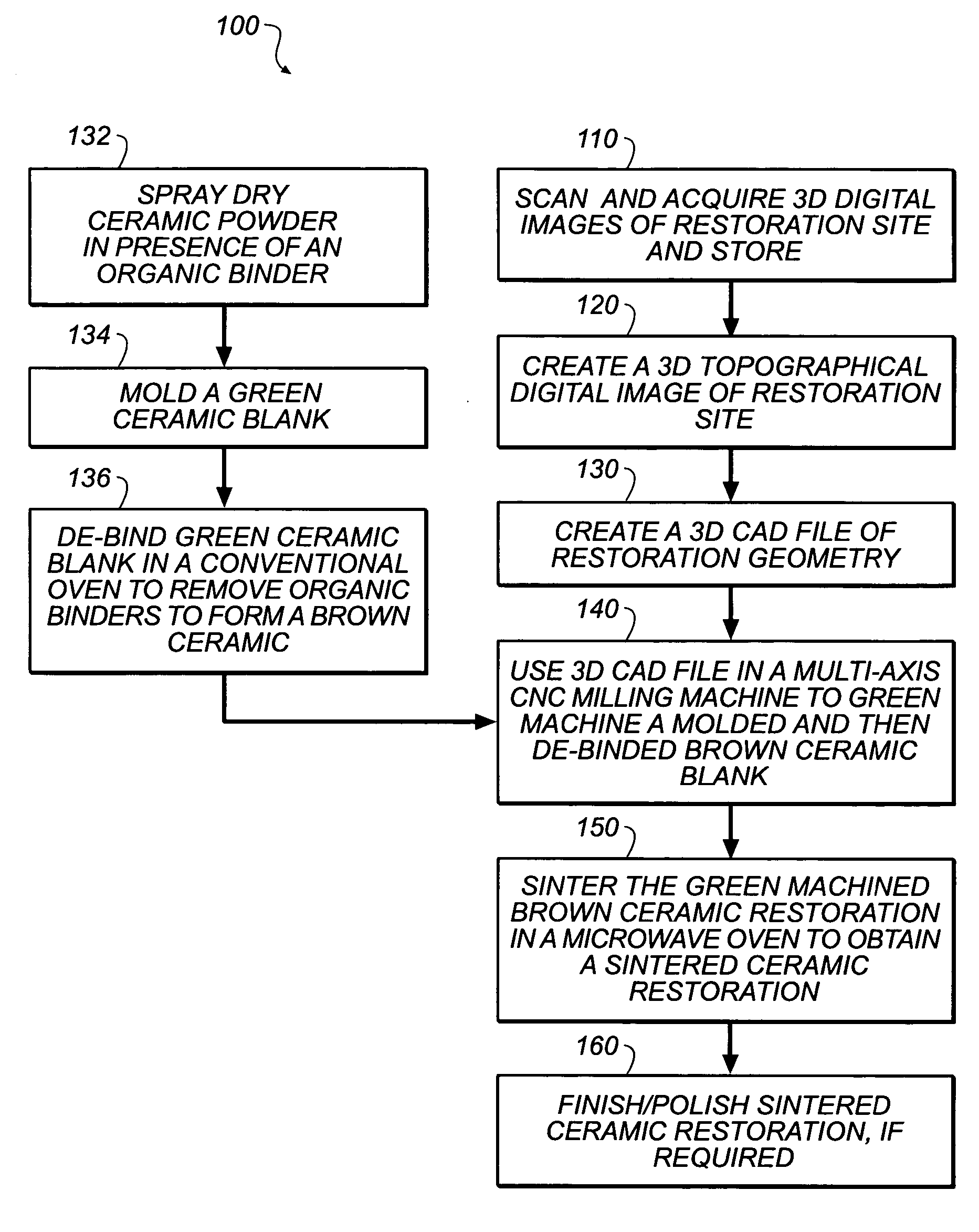
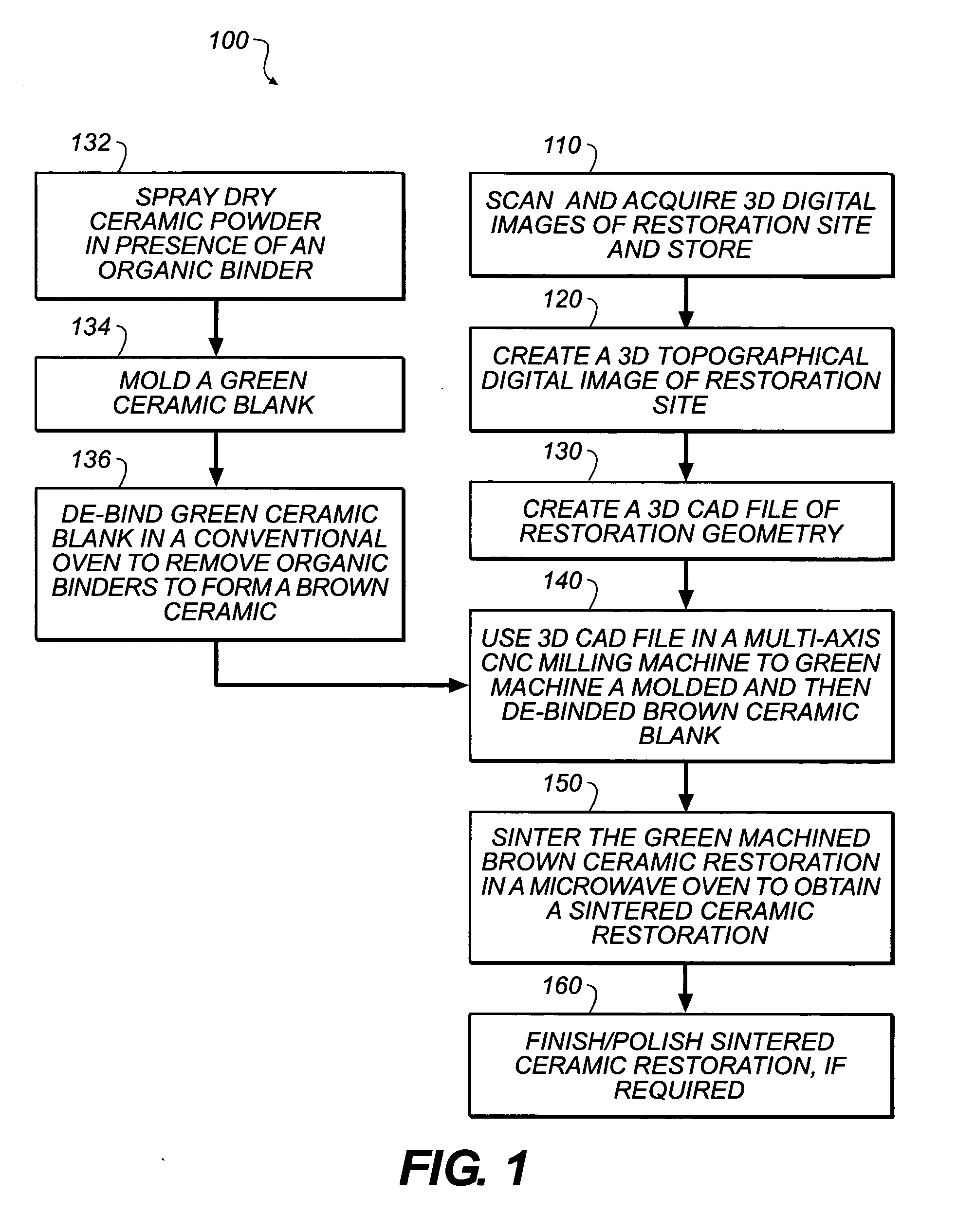
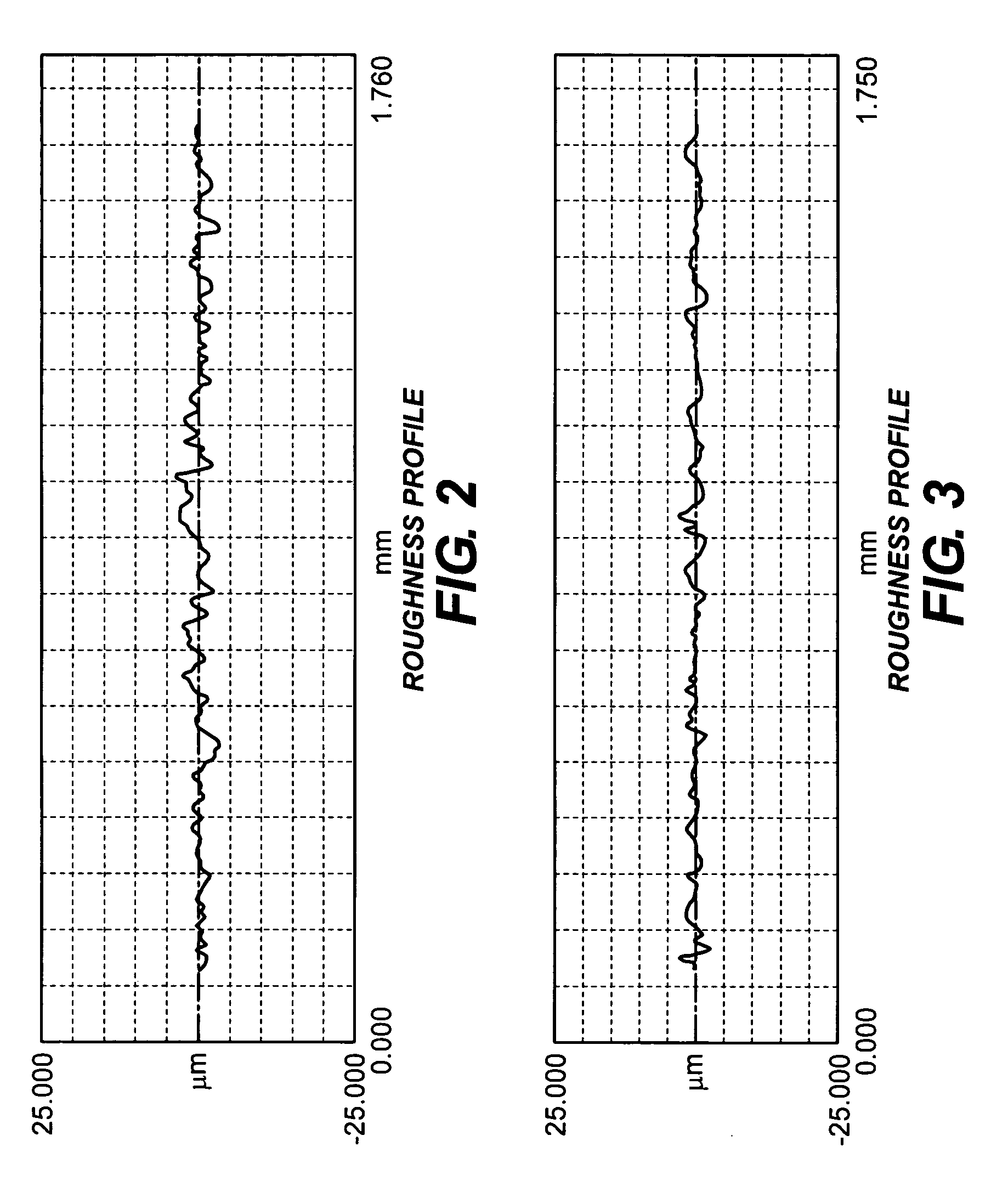
Method of making ceramic dental restorations
InactiveUS20050261795A1Without diminishing easeHigh speedTeeth fillingSpecial data processing applicationsHigh densityDental surgeon
Dental restorations can be made by acquiring a three-dimensional digitized image of a dental restoration site. A ceramic blank from which volatile organic binders have been removed, is then machined according to the three-dimensional digitized image to form a “brown” ceramic restoration. This material is then sintered using microwave energy to provide a high density ceramic dental restoration corresponding to the dental restoration site. This method can be carried out within a few hours thereby saving the patient several dental visits and enabling the dentist to better serve the patient directly in the office.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Photosensitive composition, compound for use in the photosensitive composition, and method of pattern formation with the photosensitive composition
ActiveUS20060040203A1Less apt to suffer pattern fallingReduce roughnessOrganic chemistryRadiation applicationsActinic RaysRadiation exposure
A compound which generates a sulfonic acid having one or more —SO3H groups and one or more —SO2— bonds upon irradiation with an actinic ray or a radiation; a photosensitive composition containing the compound; and a method of pattern formation with the photosensitive composition.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
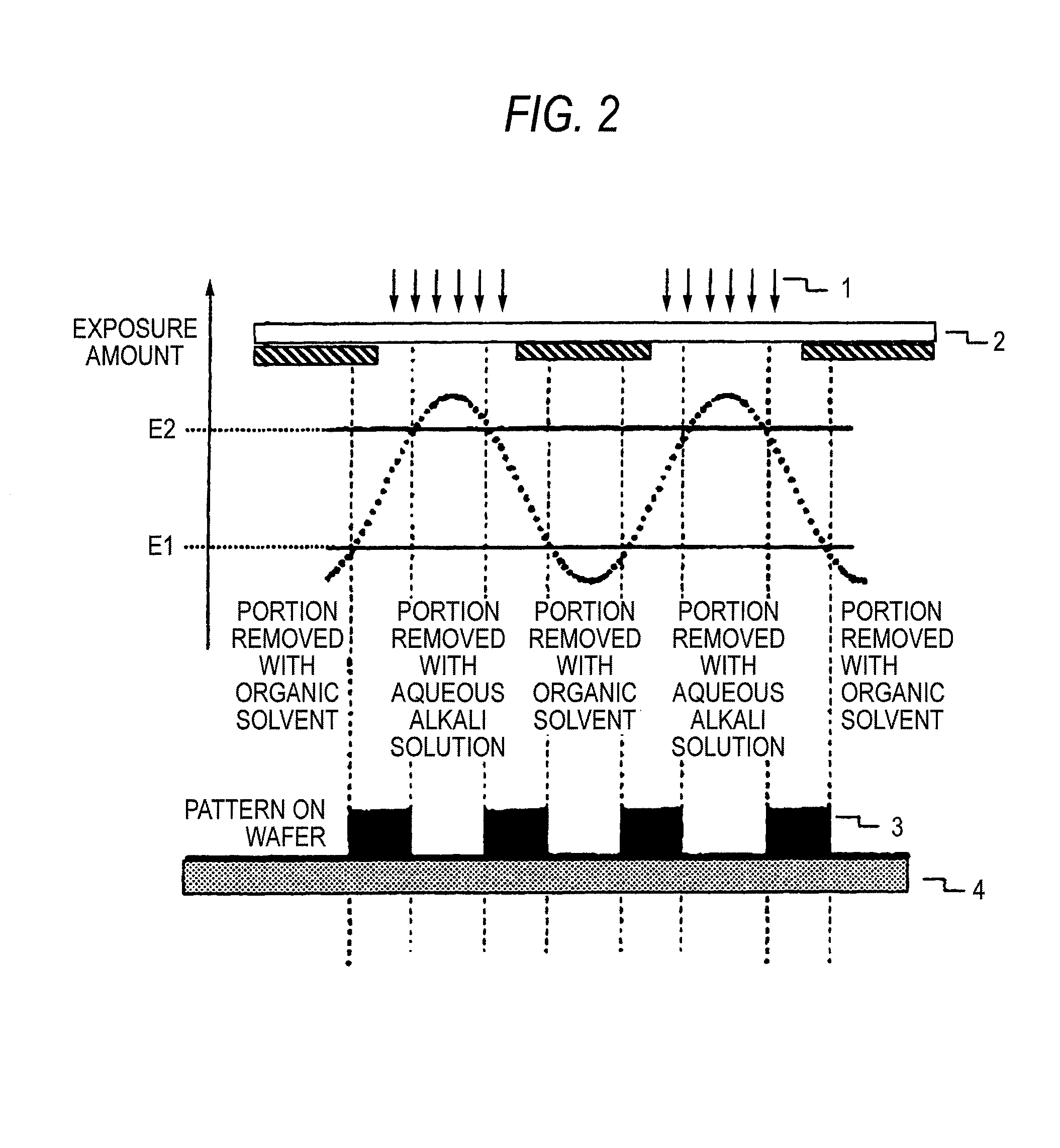
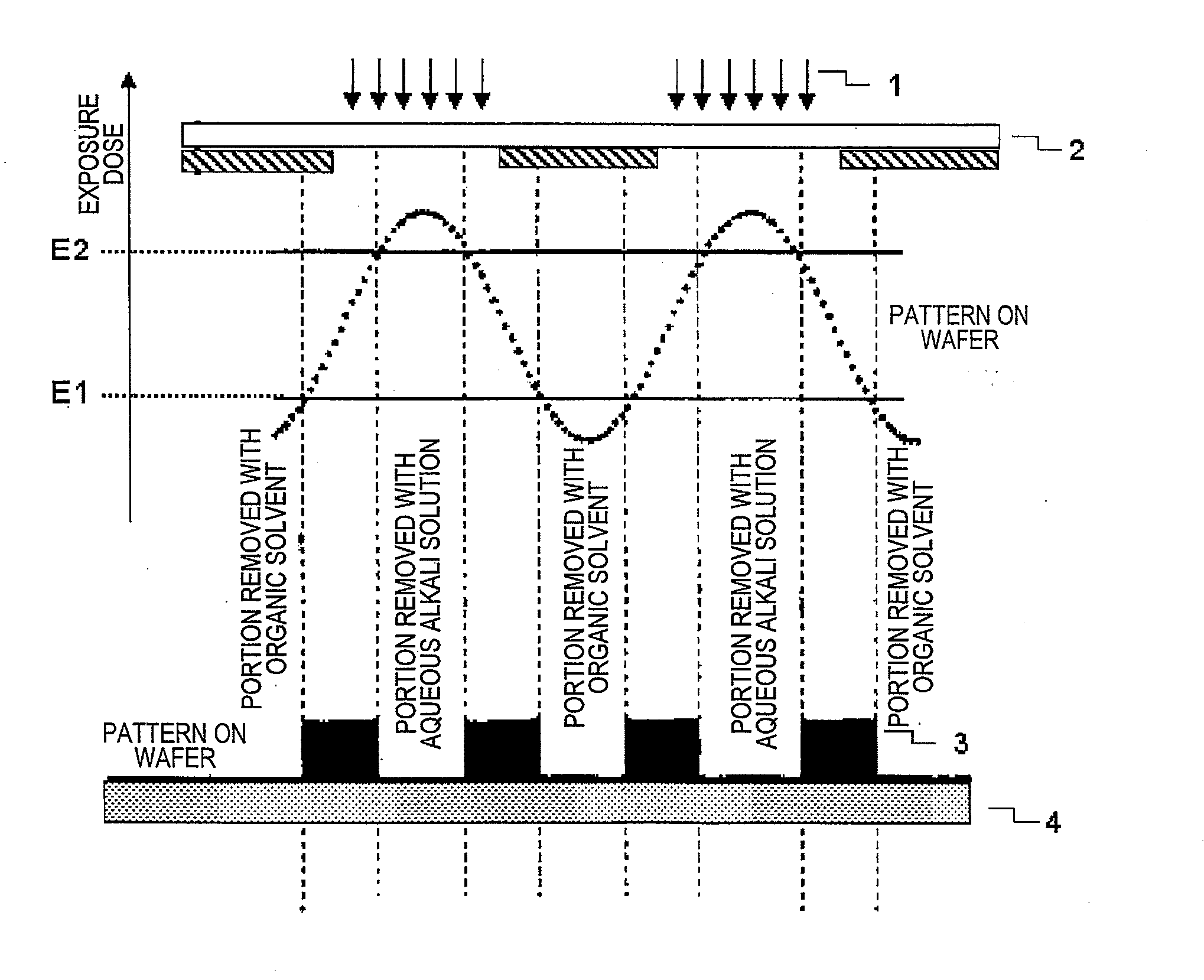
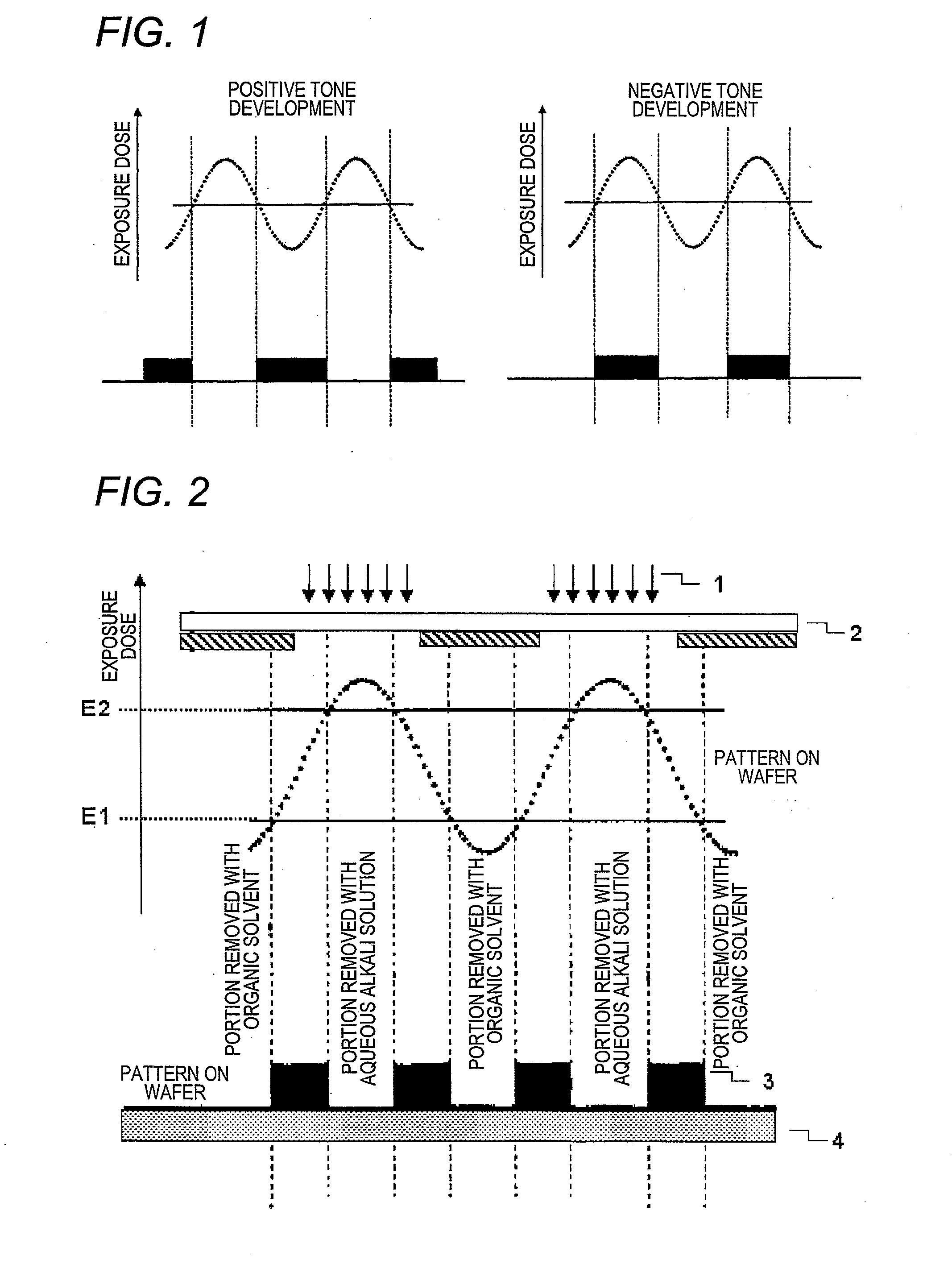
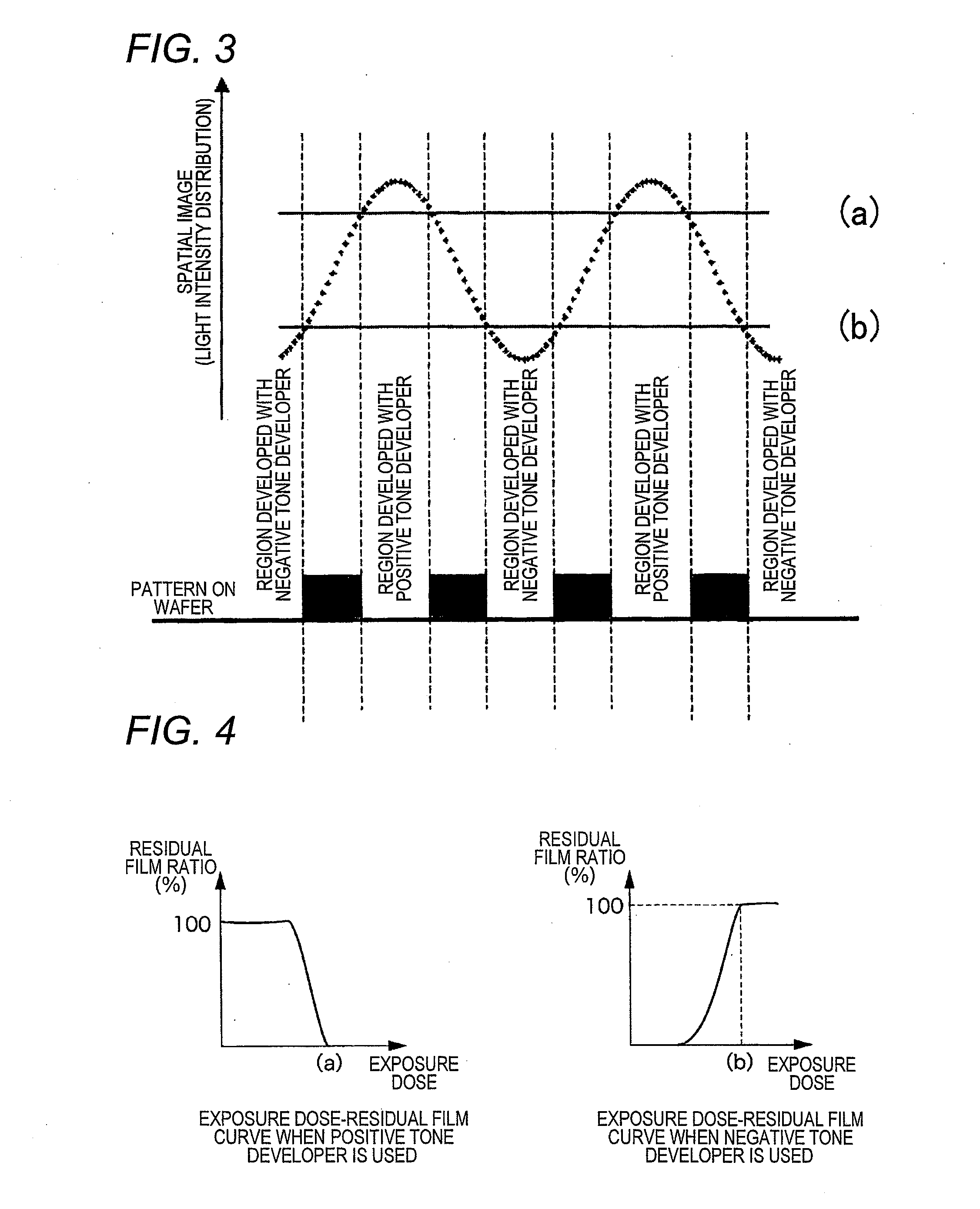
Pattern forming method, and resist composition, developer and rinsing solution used in the pattern forming method
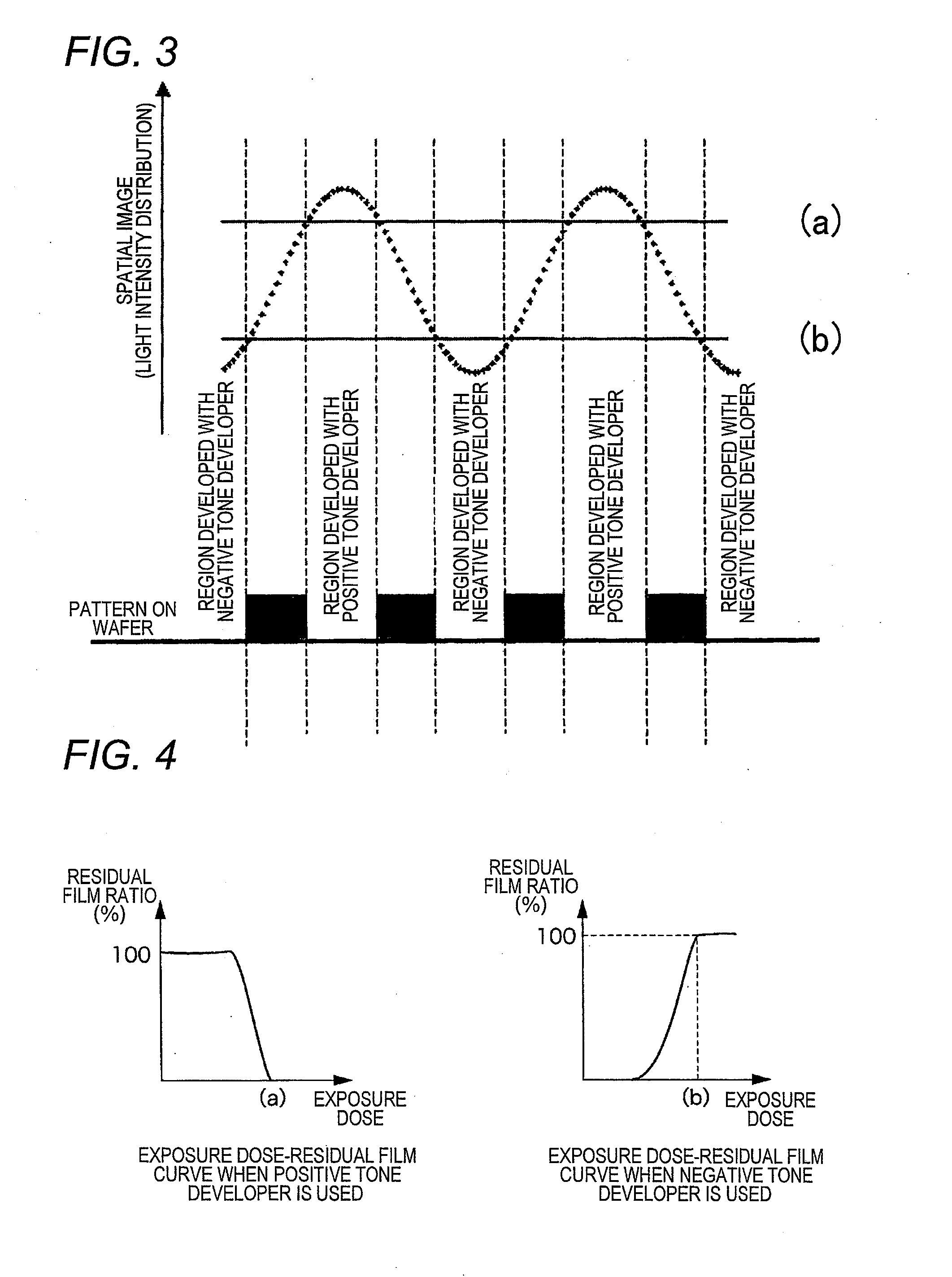
ActiveUS8017304B2Molding stabilityReduce roughnessPhotosensitive materialsPhotoprinting processesDispersityActinic Rays
A pattern forming method comprising a step of applying a resist composition whose solubility in a negative tone developer decreases upon irradiation with an actinic ray or radiation and which contains a resin having an alicyclic hydrocarbon structure and a dispersity of 1.7 or less and being capable of increasing the polarity by the action of an acid, an exposure step, and a development step using a negative tone developer; a resist composition for use in the method; and a developer and a rinsing solution for use in the method, are provided, whereby a pattern with reduced line edge roughness and high dimensional uniformity can be formed.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Resins and photoresist compositions comprising same
InactiveUS7244542B2Improve photolithographic effectConvenient and smoothPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsArylResist
Provided are new resins that comprise carbocyclic aryl units with hetero substitution units and photoresists that contain such resins. Particularly preferred photoresists of the invention comprise a deblocking resin that contains hydroxy naphthyl units and can be effectively imaged with sub-200 nm radiation such as 193 nm radiation.
Owner:SHIPLEY CO LLC
Surface treatment process of copper foil for high-Tg halogen-free plate
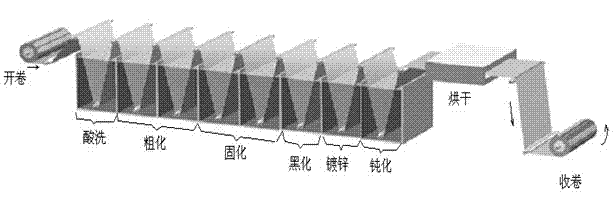
InactiveCN102418129AHigh peel strength and corrosion resistanceStrong antioxidantAnodisationCopper foilHexavalent chromium
The invention relates to a surface treatment process of a copper foil for a high-Tg halogen-free plate, belonging to the technical field of a production process of a high-precision electrolytic copper foil. In the surface treatment process provided by the invention, a structure shape of a coarsening layer is changed by using a special mixed additive in a coarsening step so as to improve anti-stripping strength; an ultra-fine nanoscale electroplated nickel-zinc alloy is used as a barrier layer to assure the corrosion resistance of the copper foil. Internal properties and pressure plate back color of the copper foil which is treated by the process provided by the invention are similar with those of the copper foil which is imported abroad; the anti-stripping strength on the high-Tg (Tg170) and the halogen-free plate is more than 1.5 N / mm; and the copper foil has characteristic of environmental friendliness and does not contain harmful matters, such as arsenic, antimony, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG JINBAO ELECTRONICS
Pattern forming method, and resist composition, developer and rinsing solution used in the pattern forming method
InactiveUS20100040971A1Reduced line edge roughnessGood size uniformityPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDispersityActinic Rays
A pattern forming method comprising a step of applying a resist composition whose solubility in a negative tone developer decreases upon irradiation with an actinic ray or radiation and which contains a resin having an alicyclic hydrocarbon structure and a dispersity of 1.7 or less and being capable of increasing the polarity by the action of an acid, an exposure step, and a development step using a negative tone developer; a resist composition for use in the method; and a developer and a rinsing solution for use in the method, are provided, whereby a pattern with reduced line edge roughness and high dimensional uniformity can be formed.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
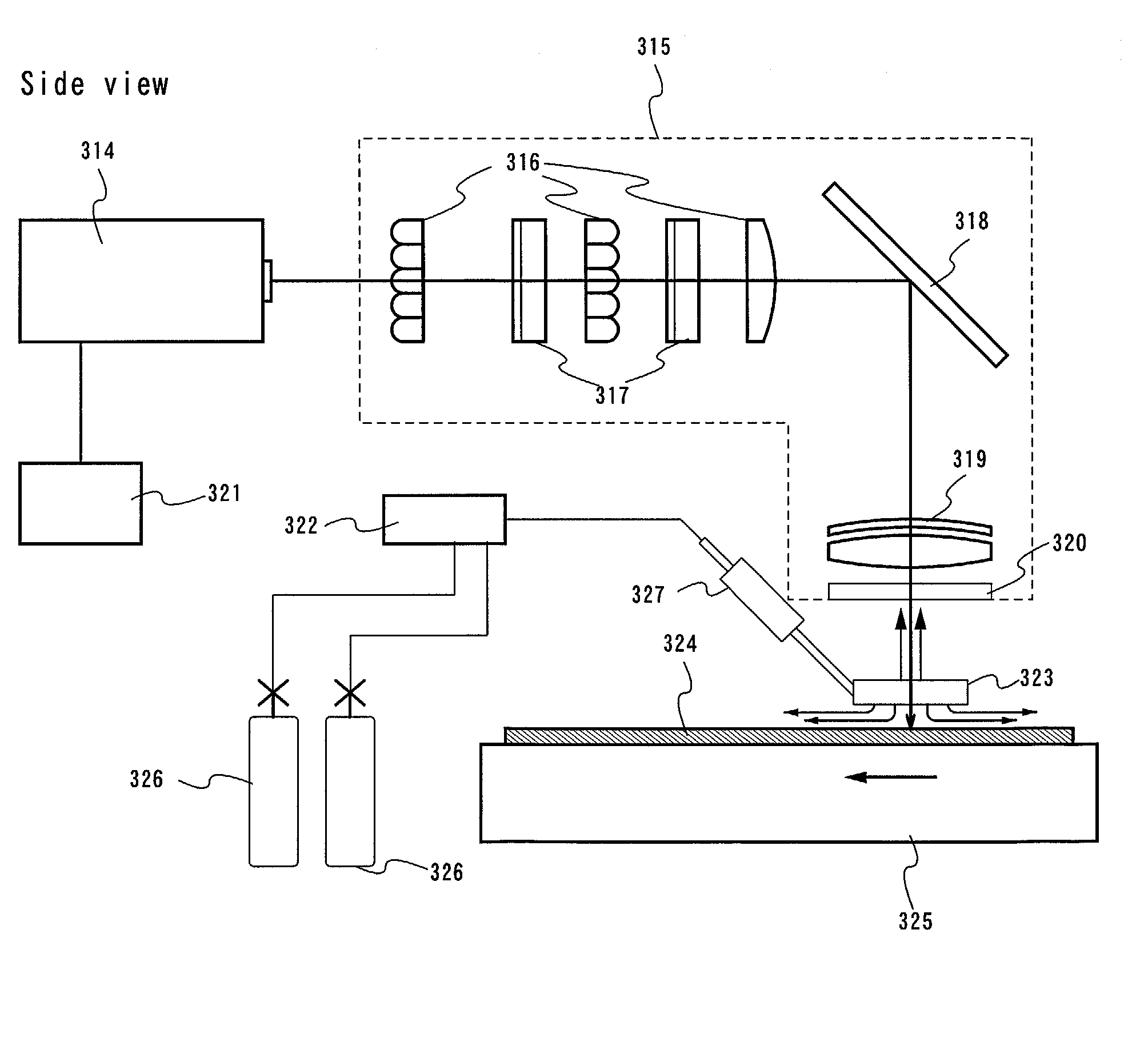
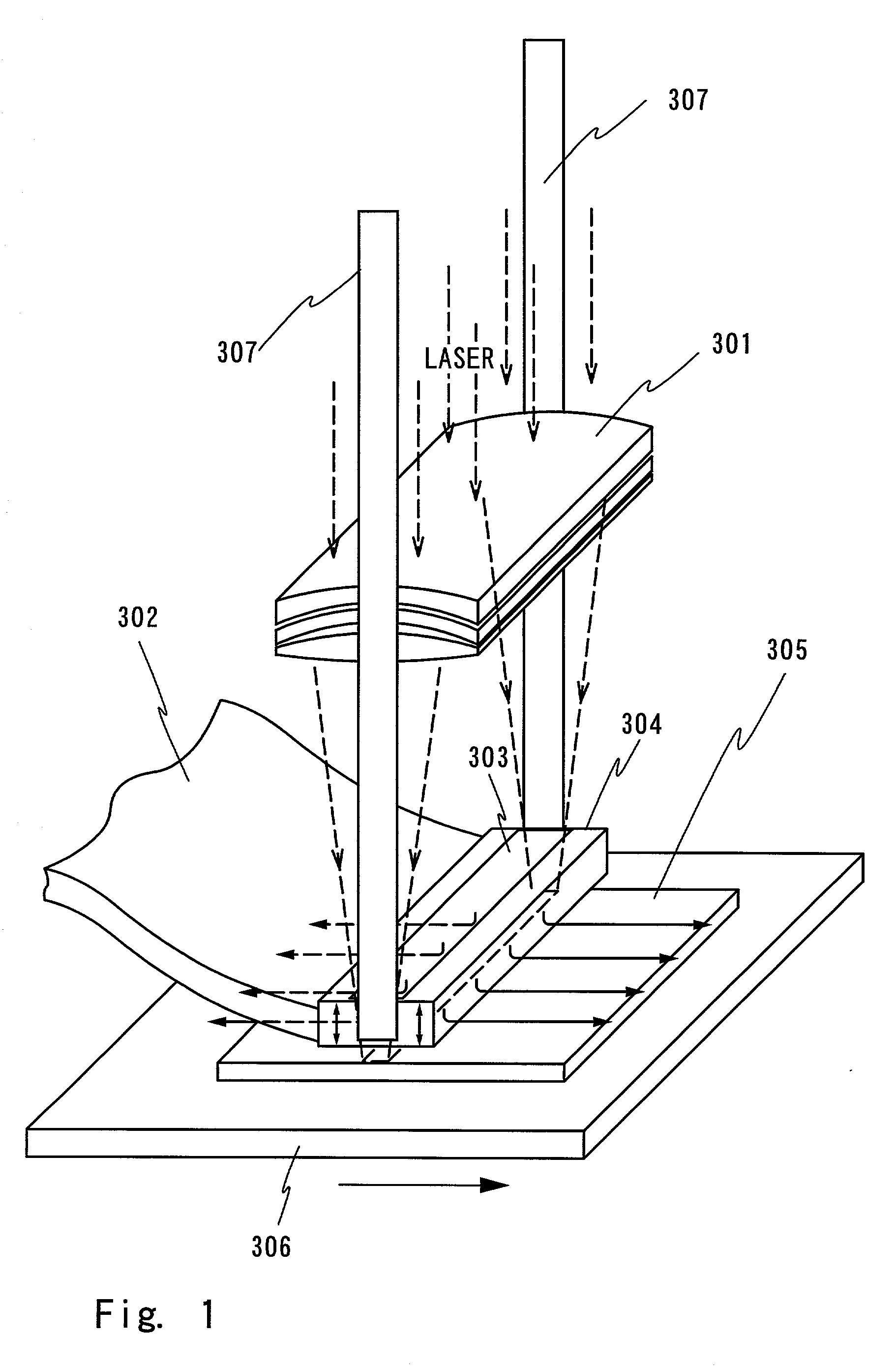
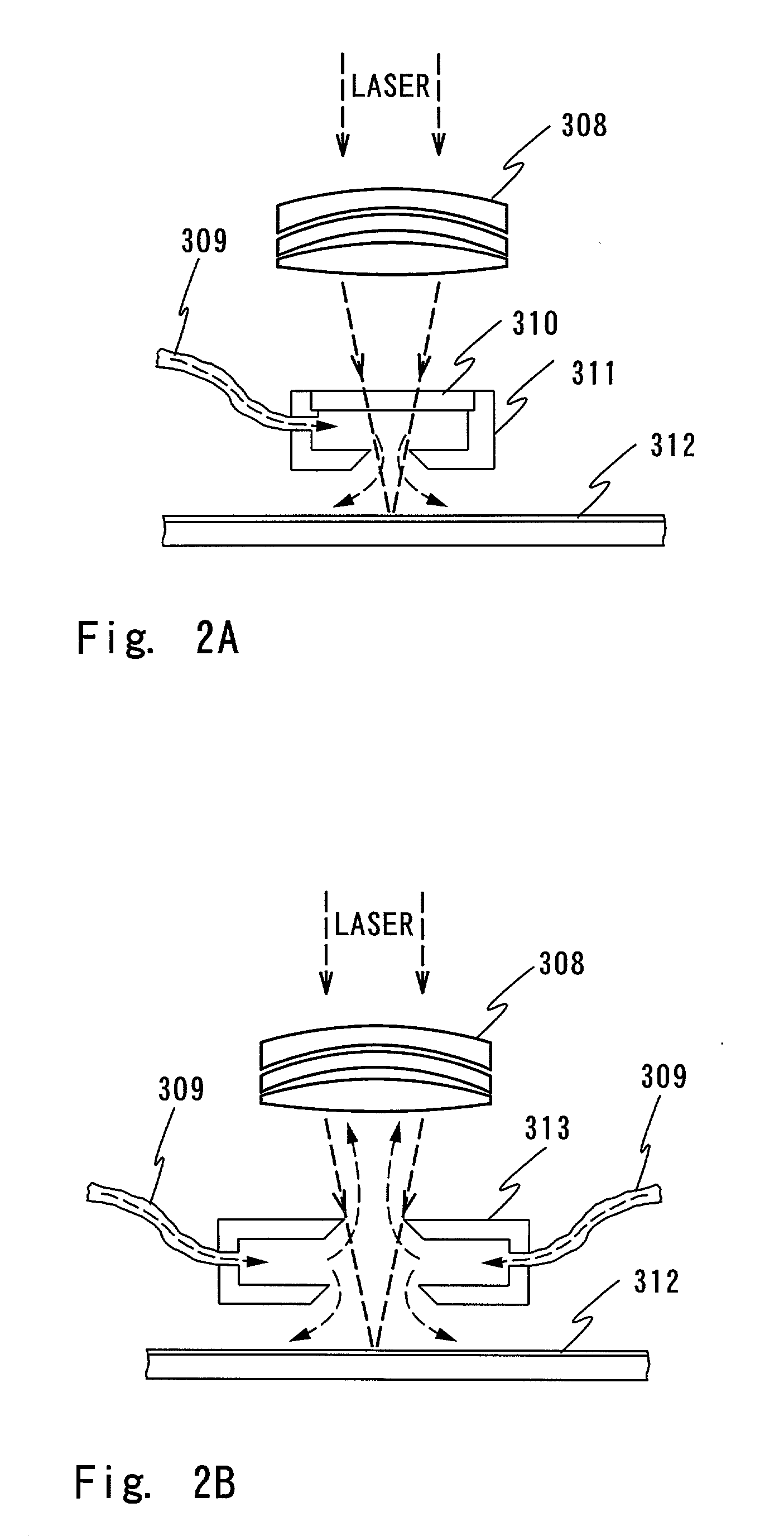
Laser irradiating apparatus and method of manufacturing semiconductor apparatus
InactiveUS20020153360A1Improve featuresGrowth inhibitionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusVolumetric Mass DensityLaser light
First laser light is irradiated (energy density of 400 to 500 mj / cm2) to a semiconductor film 102 in an atmosphere containing oxygen in order to obtain a semiconductor film 102b having large depressions and projections on the surface. Then, an oxidized film 105a formed by the irradiation of the first laser light is removed. After that, an inert gas with an oxygen density of 10 ppm or below is blown thereto, and, at the same time, second laser light is irradiated thereto (the energy density is higher than that of the irradiation of the first laser light). Thus, the surface of the semiconductor film 102b is flattened, and a semiconductor film 102c having fewer depressions and projections on the surface can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
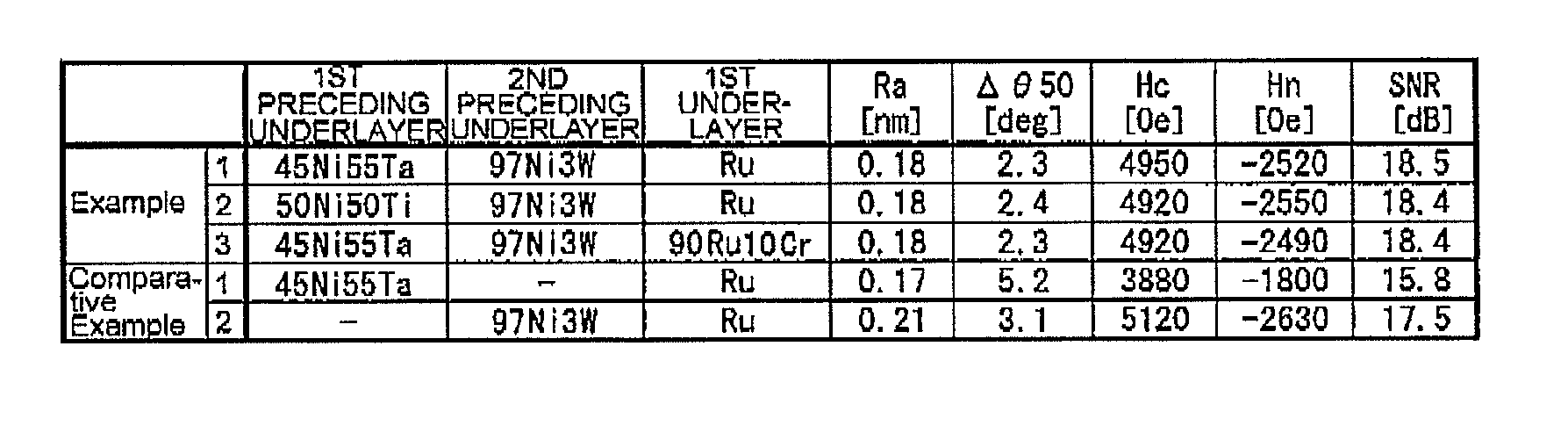
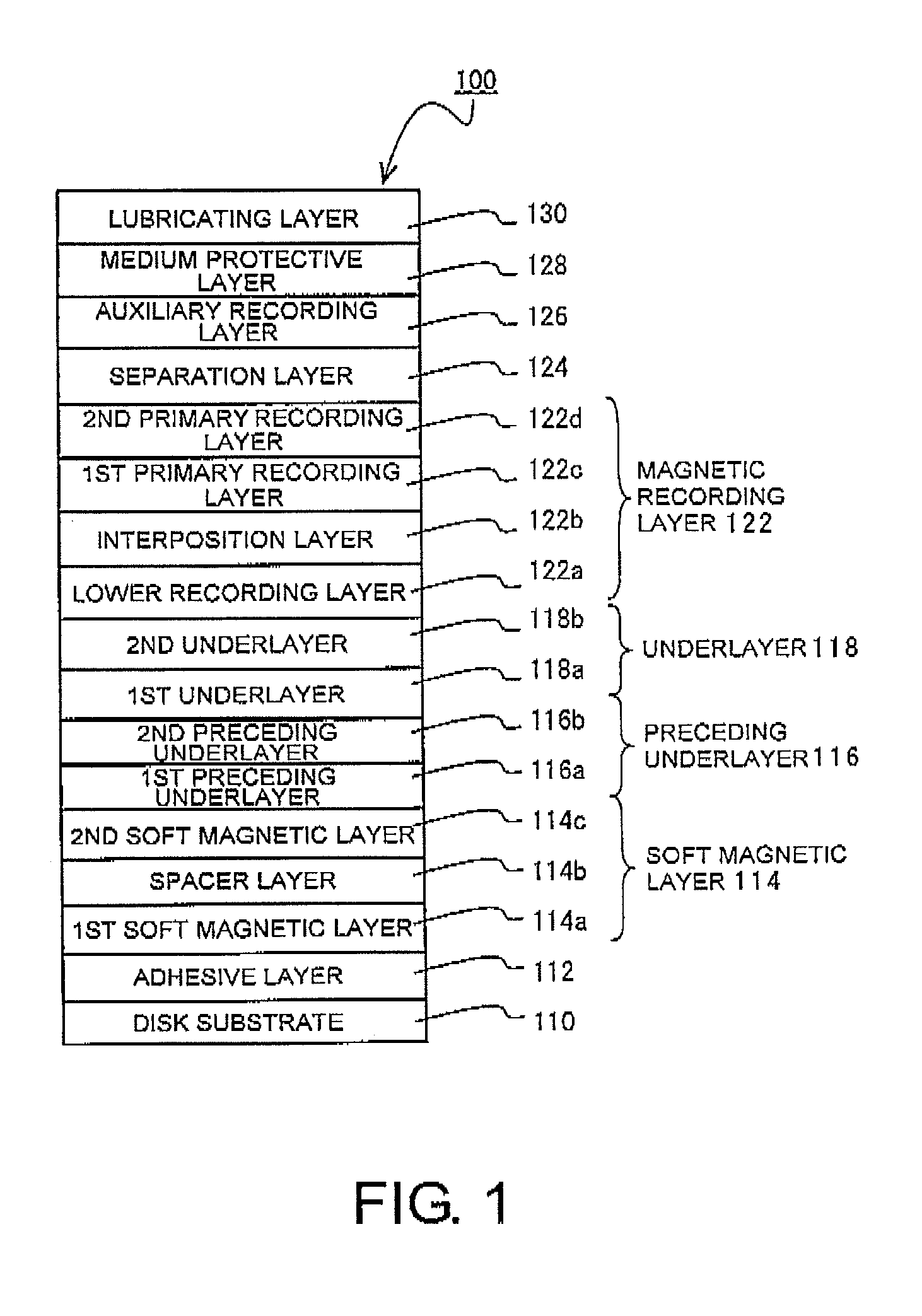
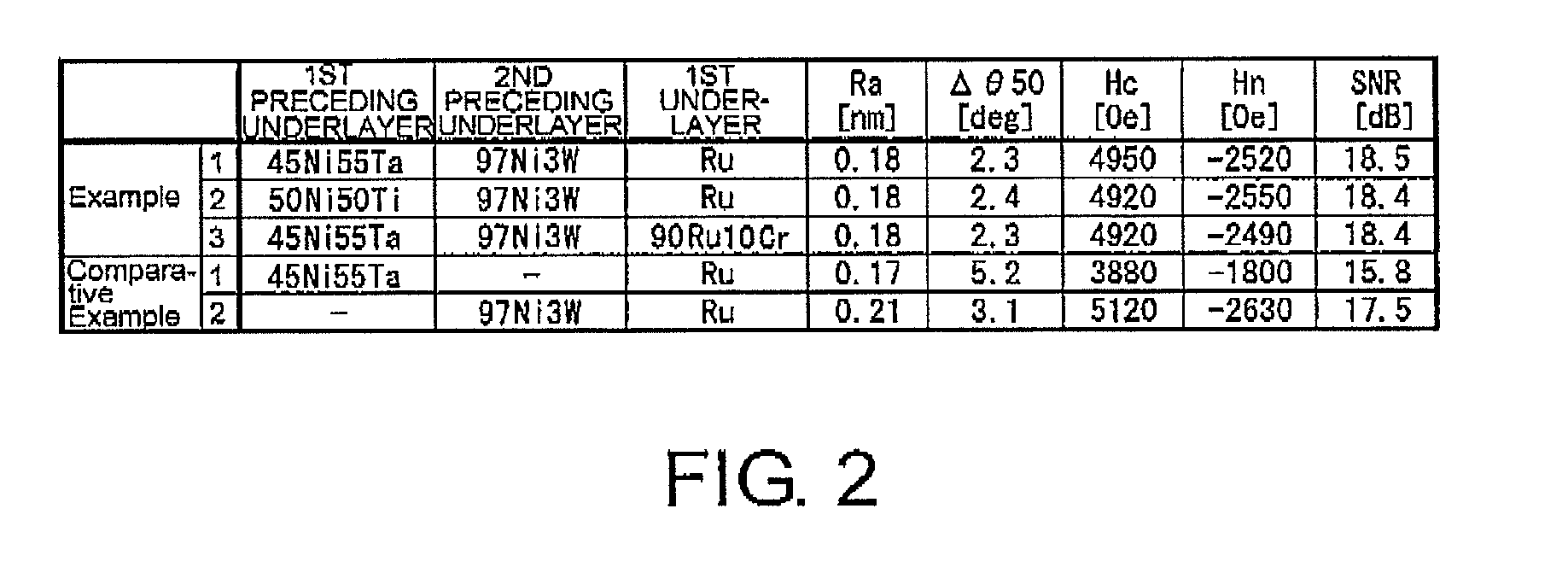
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8431258B2Reduce roughnessCrystallinity is disorderedRecord information storageDisk carriersCrystal orientationOptoelectronics
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium comprises a magnetic recording layer that records a signal, an underlayer formed of Ru or Ru compound below the magnetic recording layer, a non-magnetic layer formed of a non-magnetic material below the underlayer to control crystal orientation of the underlayer, a soft magnetic layer provided below the non-magnetic layer, and a substrate on which the magnetic recording layer, the underlayer, the non-magnetic layer, and the soft magnetic layer are formed. The non-magnetic layer comprises a first non-magnetic layer formed above the soft magnetic layer and a second non-magnetic layer formed above the first non-magnetic layer. The first non-magnetic layer is formed of amorphous Ni compound while the second non-magnetic layer is formed of crystalline Ni or crystalline Ni compound.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic carrier and two-component developer
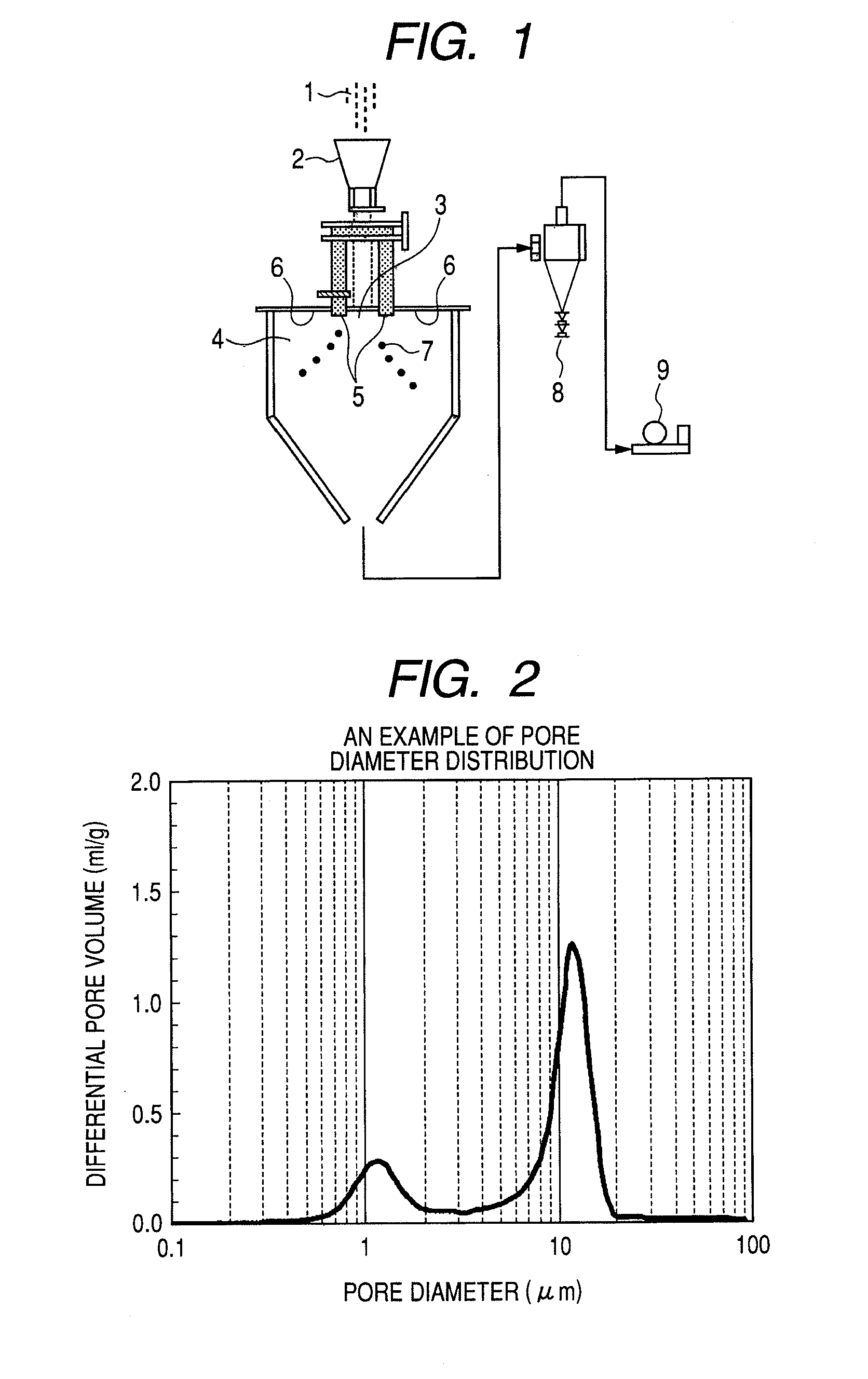
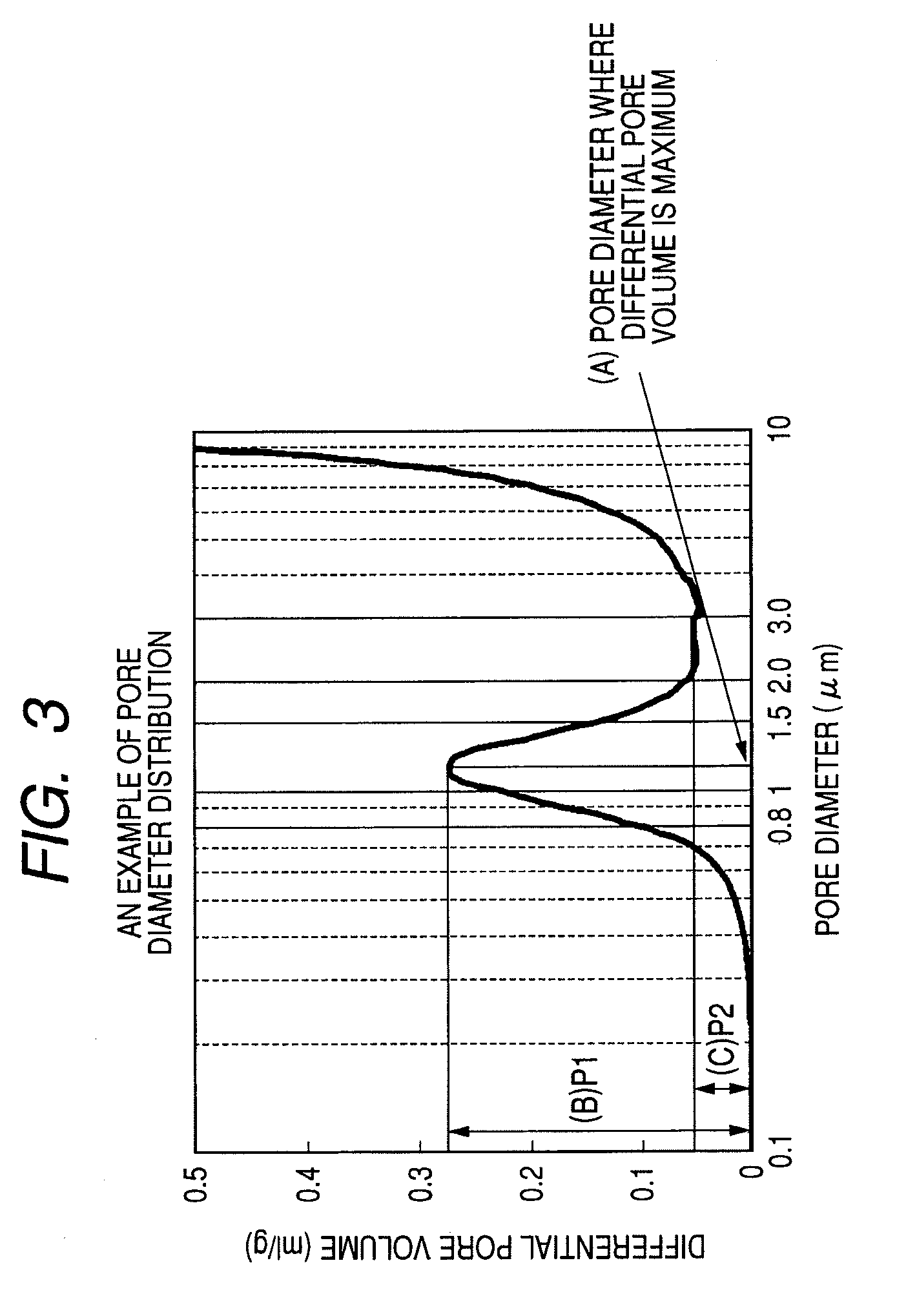
A magnetic carrier and two-component developer are provided alleviating coarse images, fogging when printing is done after a copier body is left standing for one week in a high temperature and high humidity environment and carrier adhesion after extensive operation in a low image ratio. The magnetic carrier includes magnetic carrier particles including porous magnetic core particles and a resin, wherein in a mercury intrusion method applied to the porous magnetic core particles, a pore diameter in which a differential pore volume in the specific pore diameter range becomes maximum is in a specific range, and when the maximum value of a differential pore volume in the specific pore diameter range is defined as P1 and the maximum value of a differential pore volume in the specific pore diameter range is defined as P2, P1 is in a specific range and the ratio P2 / P1 is in a specific range.
Owner:CANON KK
Technique and apparatus for manufacturing flexible and moisture resistive photovoltaic modules
InactiveUS20090159119A1Reduce roughnessFinal product manufacturePV power plantsElectricityElectrical battery
An apparatus and method of making moisture resistant solar cells, strings and modules is provided. The method includes reducing the roughness of the finger patterns by coating them fully or partially with a surface preparation film. The surface preparation film firmly attaches itself to underlying finger patterns and electrical leads while forming a smooth surface on which a moisture barrier film is subsequently deposited. Process flows to obtain moisture resistive solar cells, solar cell strings are described.
Owner:SOLOPOWER
Hollow-core optical fiber and method of making same
InactiveUS20050185908A1Increase surface tensionReduce surface tensionGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreFiberSurface roughness
An optical fiber having a cladding region surrounding a core region having an elongate core hole, the inner or outer surface of the core hole having a surface roughness with a spatial period equal to or less than 5 μm by a spectral power below 0.0017 nm2μm−1. A method of making an optical fiber including a cladding region having an arrangement of elongate cladding holes in a matrix material, surrounding an elongate core region having an elongate core hole, the method including the step of increasing the surface tension of the matrix material prior to or during the step of heating and drawing the fiber.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Silver nanowire transparent conductive film based on thermoplastic transparent polymer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102270524ASolve the problem of easy falling offGood chemical stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyConductive layers on insulating-supportsPolymer scienceFilm base
The invention provides a structure and a preparation method of a silver nanowire transparent conductive film based on a thermoplastic transparent polymer, which is characterized in that the silver nanowire conductive network is uniformly spread on a hard substrate, and then the The method makes a continuous silver nanowire conductive network embedded on the surface of a thermoplastic transparent polymer, and part of the surface of the silver nanowire is exposed to the air to form a silver nanowire conductive film based on the thermoplastic transparent polymer.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
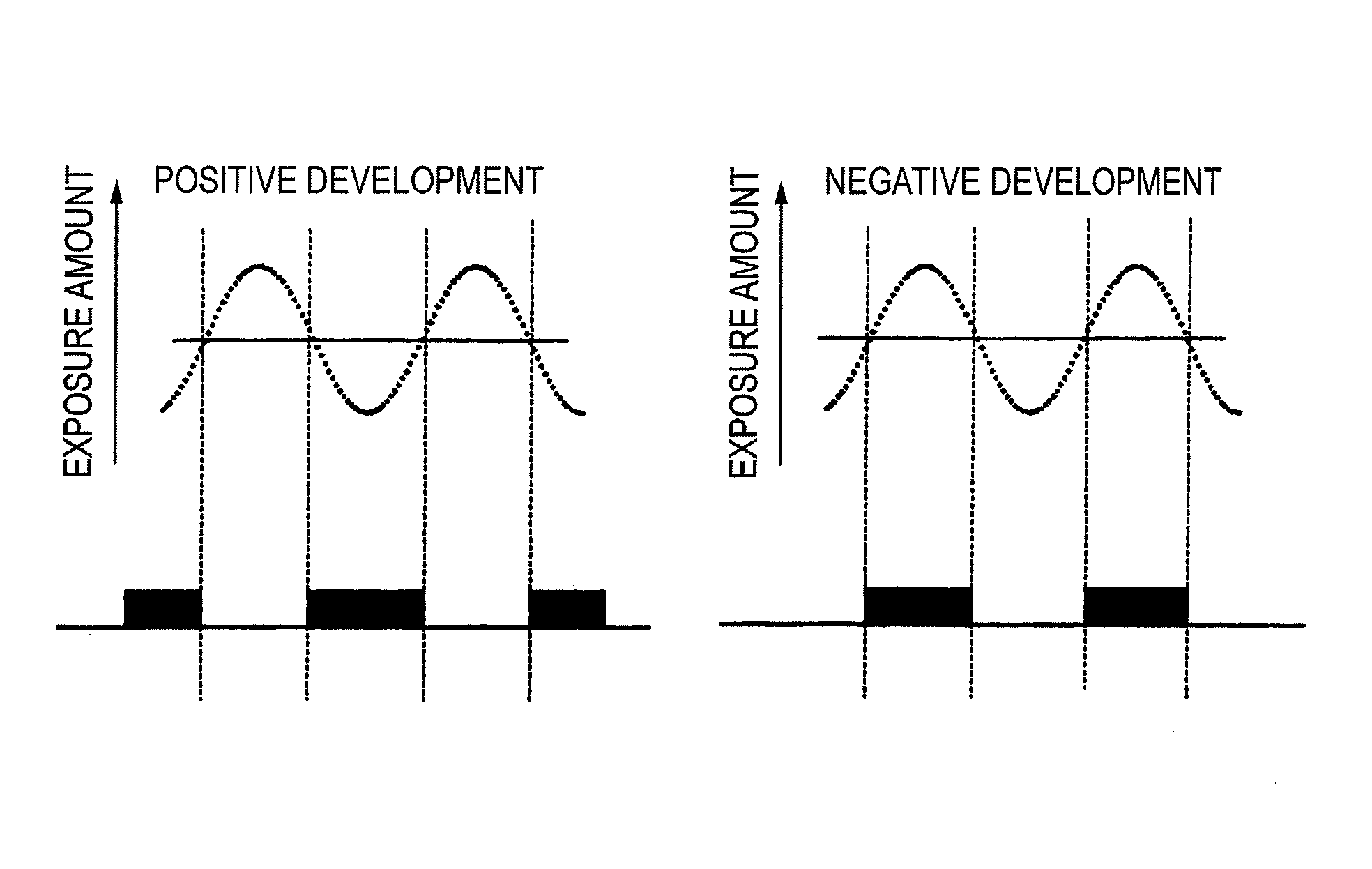
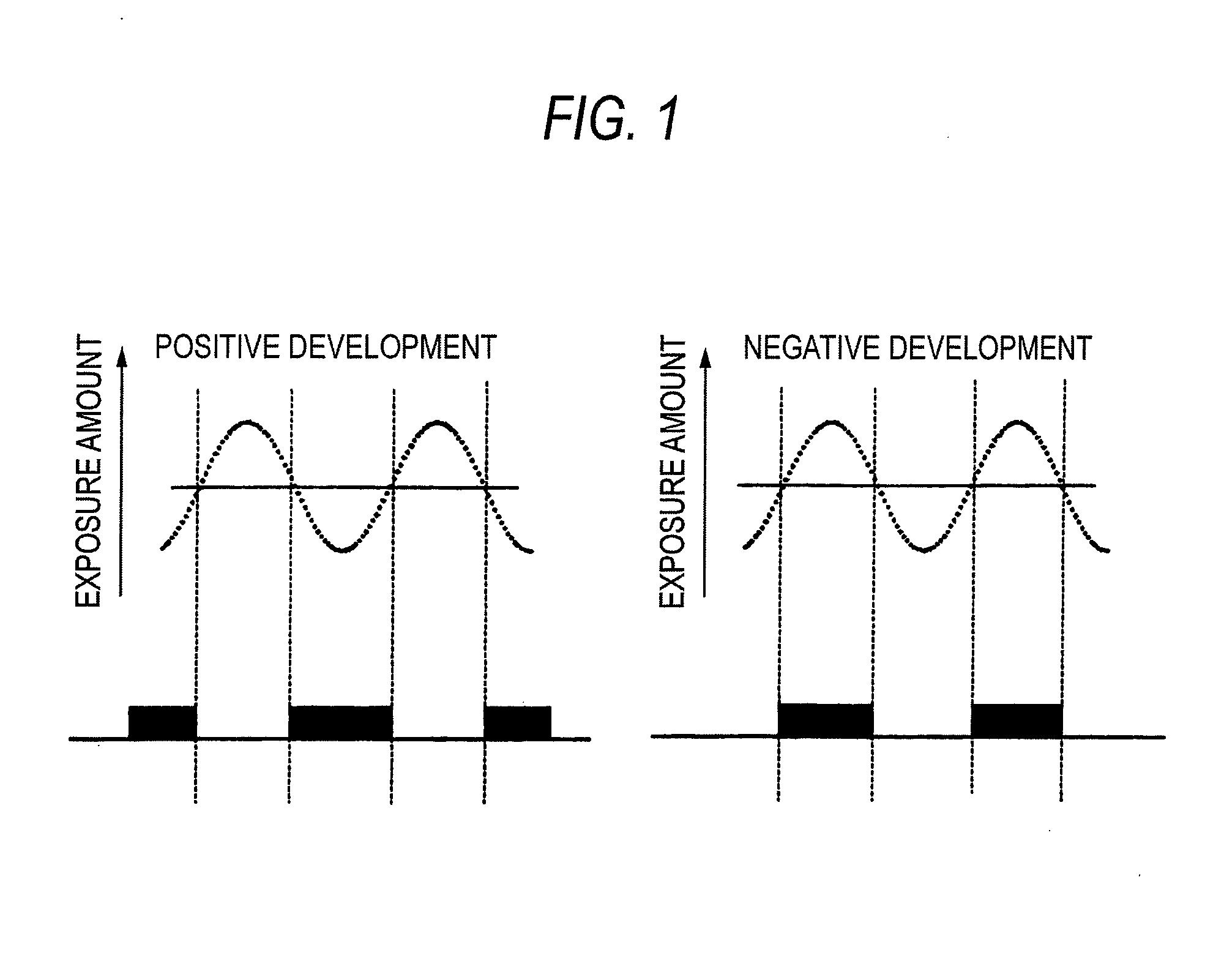
Method of forming patterns
ActiveUS20080318171A1Enhanced in-plane uniformity of line widthReduced line edge roughnessPhotosensitive materialsPhoto-taking processesActinic RaysRadiation exposure
A method of forming patterns includes (a) coating a substrate with a resist composition for negative development to form a resist film having a receding contact angle of 70 degrees or above with respect to water, wherein the resist composition for negative development contains a resin capable of increasing the polarity by the action of an acid and becomes more soluble in a positive developer and less soluble in a negative developer upon irradiation with an actinic ray or radiation, (b) exposing the resist film via an immersion medium, and (c) performing development with a negative developer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Pattern forming method, and resist composition, developer and rinsing solution used in the pattern forming method
ActiveUS20100040972A1Reduced line edge roughnessGood size uniformityPhotosensitive materialsPhotoprinting processesDispersityActinic Rays
A pattern forming method comprising a step of applying a resist composition whose solubility in a negative tone developer decreases upon irradiation with an actinic ray or radiation and which contains a resin having an alicyclic hydrocarbon structure and a dispersity of 1.7 or less and being capable of increasing the polarity by the action of an acid, an exposure step, and a development step using a negative tone developer; a resist composition for use in the method; and a developer and a rinsing solution for use in the method, are provided, whereby a pattern with reduced line edge roughness and high dimensional uniformity can be formed.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Semiconductor on insulator structure made using radiation annealing
InactiveUS7579654B2Healing damageReduce roughnessElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesIon implantationSemiconductor
Owner:CORNING INC
Electrolytic solution for integrated circuit copper wire laying electrodeposition
InactiveCN101481812AImprove surface topographyReduce roughnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCopper wirePhysical chemistry
The invention provides an electrolyte used in integrated circuit copper cabling electrodeposition, which comprises the following components and contents: 50-200g / liter of copper sulphate, 50-220g / liter of sulphuric acid, 10-150 milligram / liter of chloridion, 5-200 milligram / liter of inhibitor, 5-50 milligram / liter of accelerator, 0.5-20 milligram / liter of leveling agent and the rest of deionized water. As the electrolyte contains the chloridion, inhibitor and accelerator, the surface appearance is improved after electrodeposition and the roughness concentration is reduced. And the leveling agent can increase the adsorption of the accelerator on the surface of electrodes in the deposition process, and then increases the surface improvement effect of the accelerator; the surface roughness of the clad layer is further reduced; the orientation of the clad layer obtained by deposition Cu (111) is dominant; after deposition, the surface dendrite growth mode disappears; and the surface has no hole defects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050077591A1Improve electrical performanceReduce surface roughnessTransistorSolid-state devicesSchottky barrierSurface layer
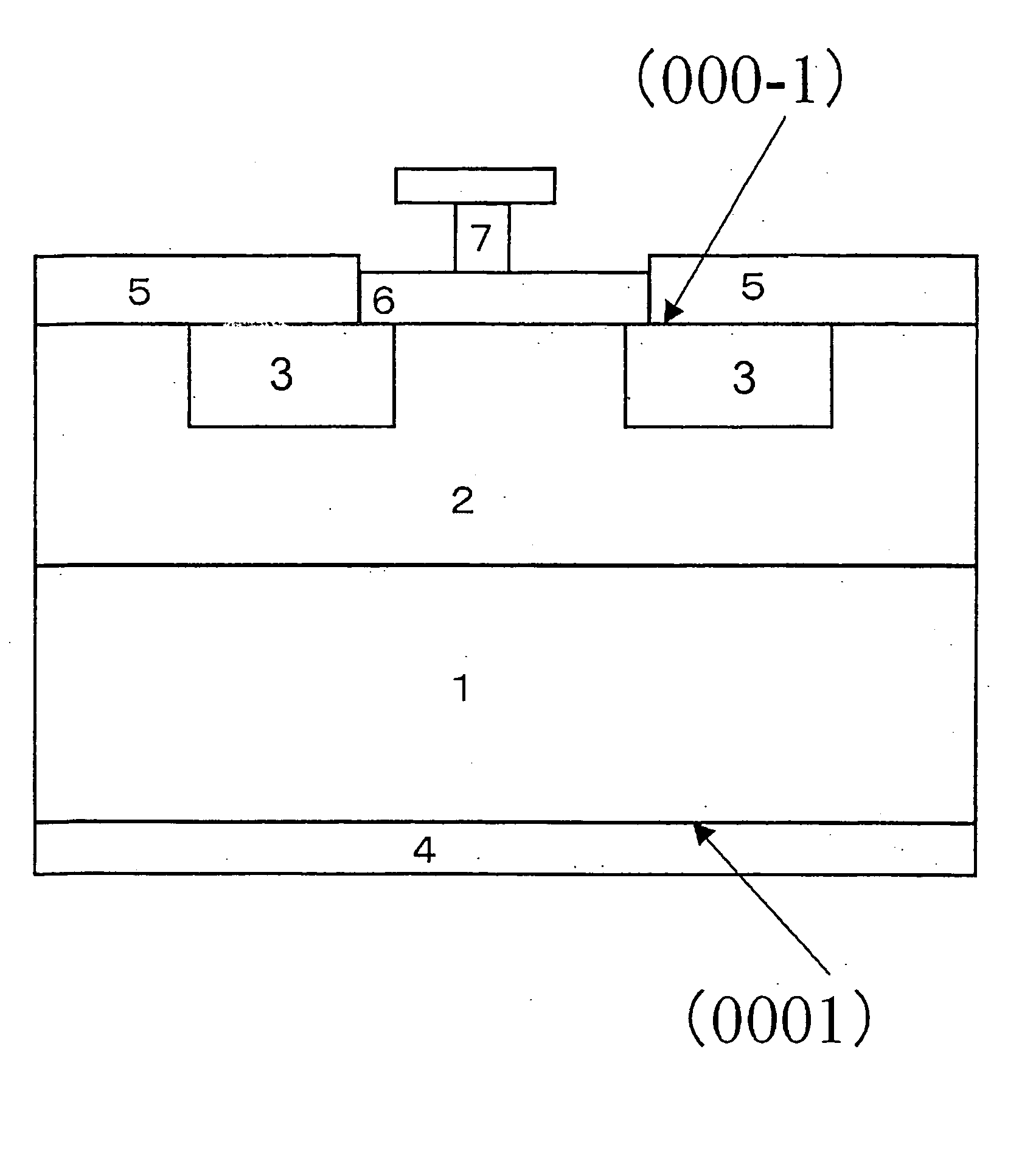
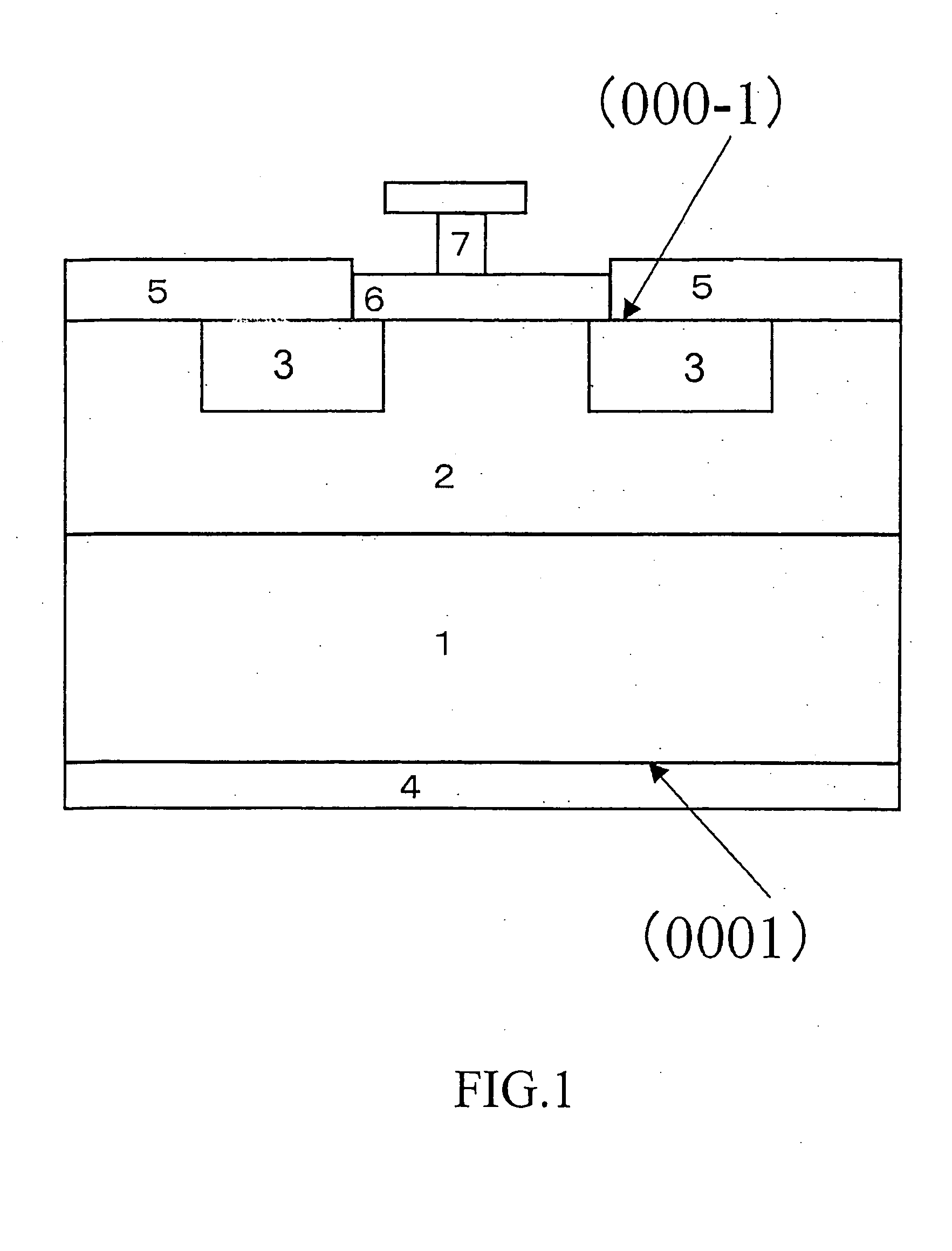
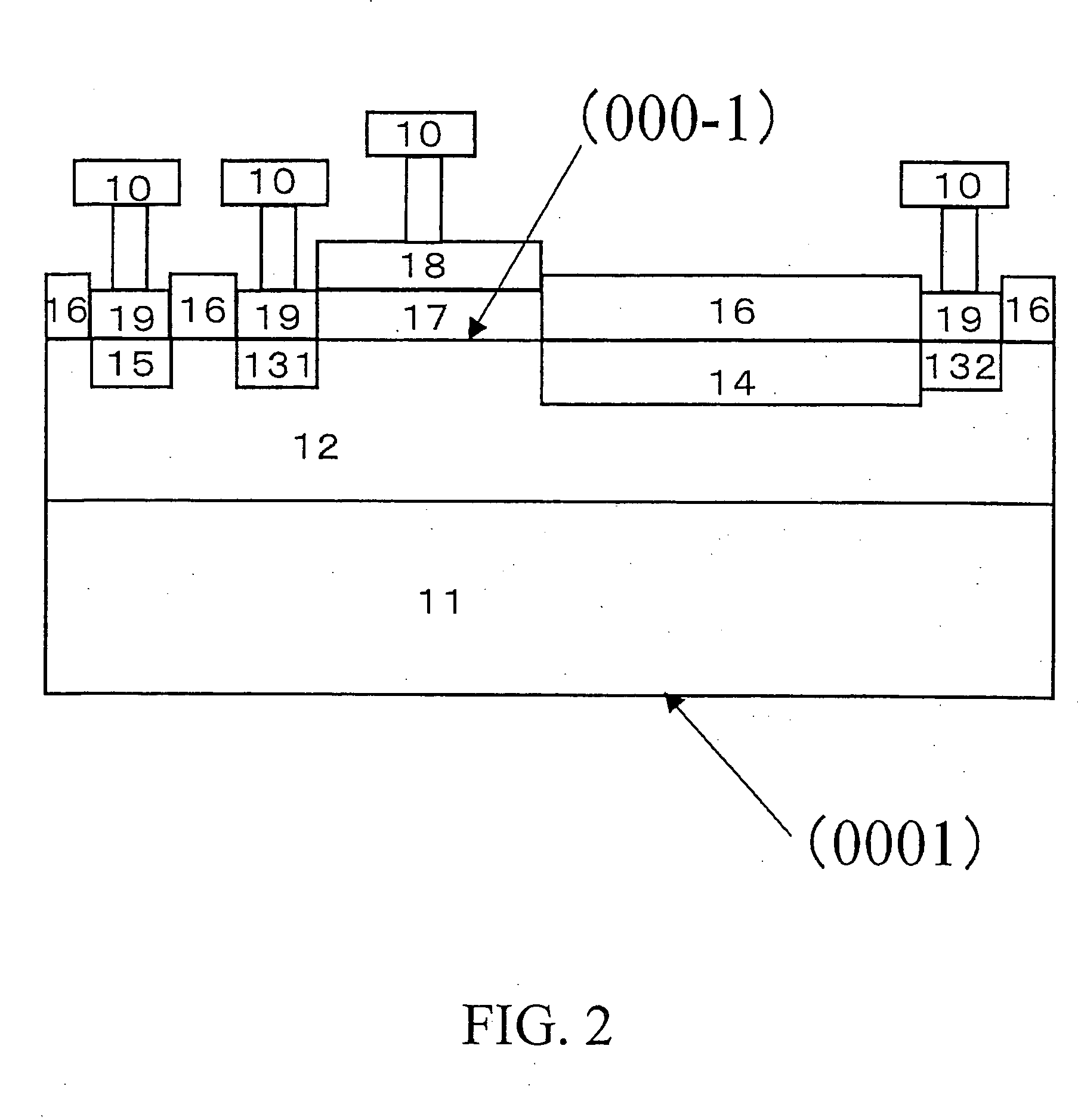
A semiconductor device formed on a silicon carbide semiconductor substrate comprises an epitaxial layer formed on a surface sloping (or inclining) by 0 to less than 1 degree from a (000-1) face of the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate, wherein at least one of a P type semiconductor area or an N type semiconductor area is selectively formed in the epitaxial layer by ion implantation, a metal electrode is formed so as to contact a surface layer of the P type semiconductor area or the N type semiconductor area, a rectification function is shown between the metal electrode and the P type semiconductor area or the N type semiconductor area, and the semiconductor device is formed on the silicon carbide semiconductor substrate of a Schottky barrier diode or a PN type diode.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com