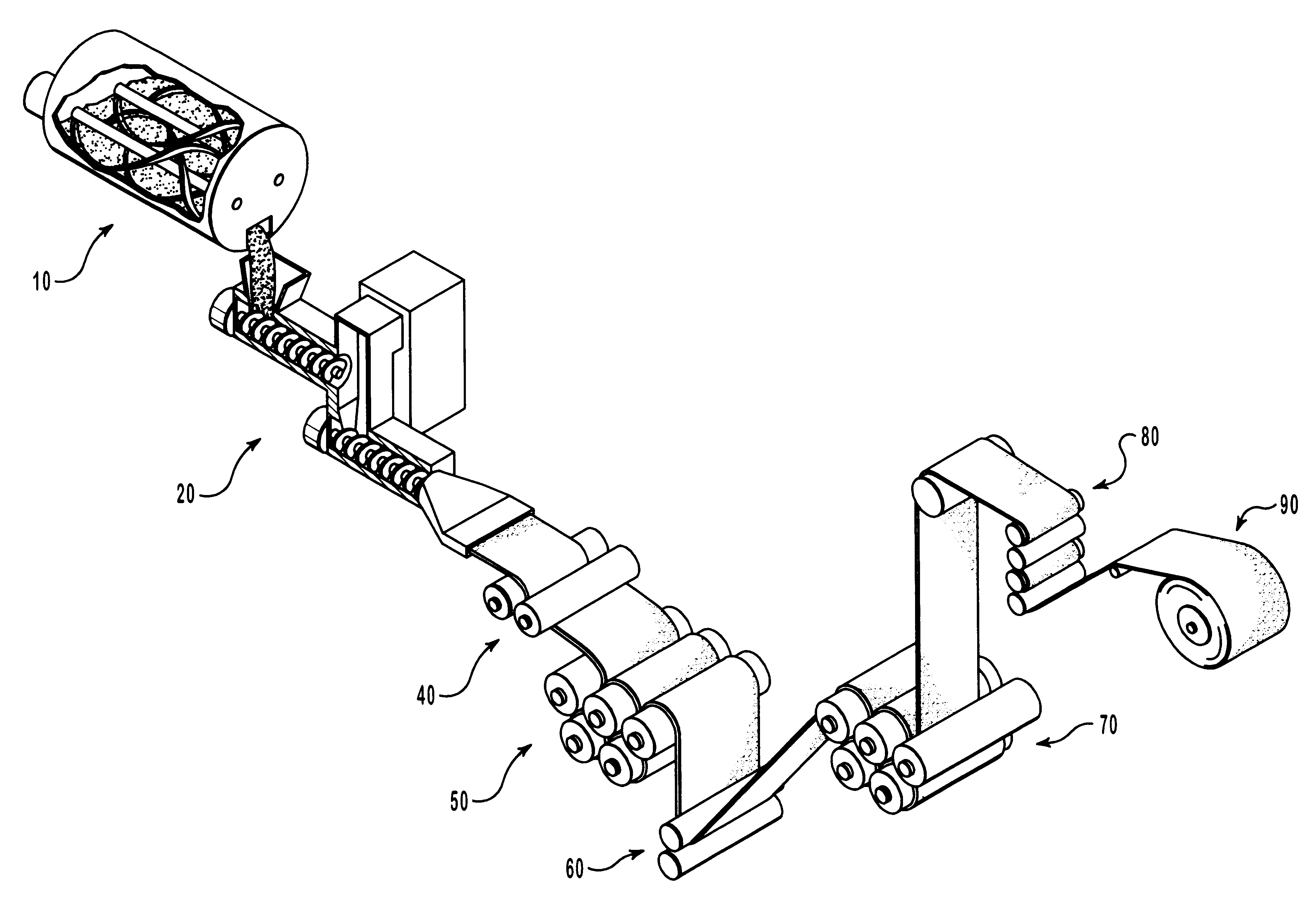
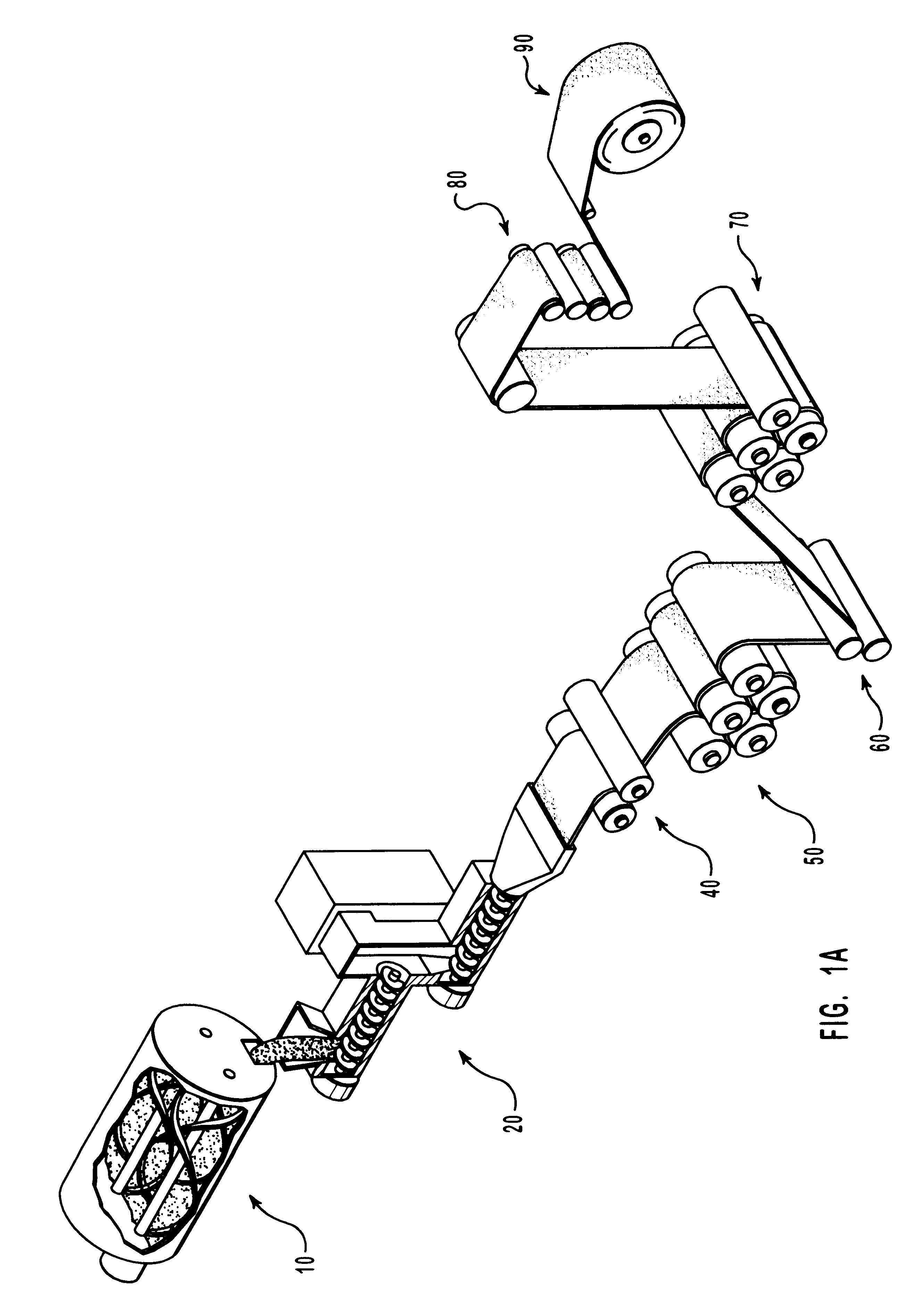
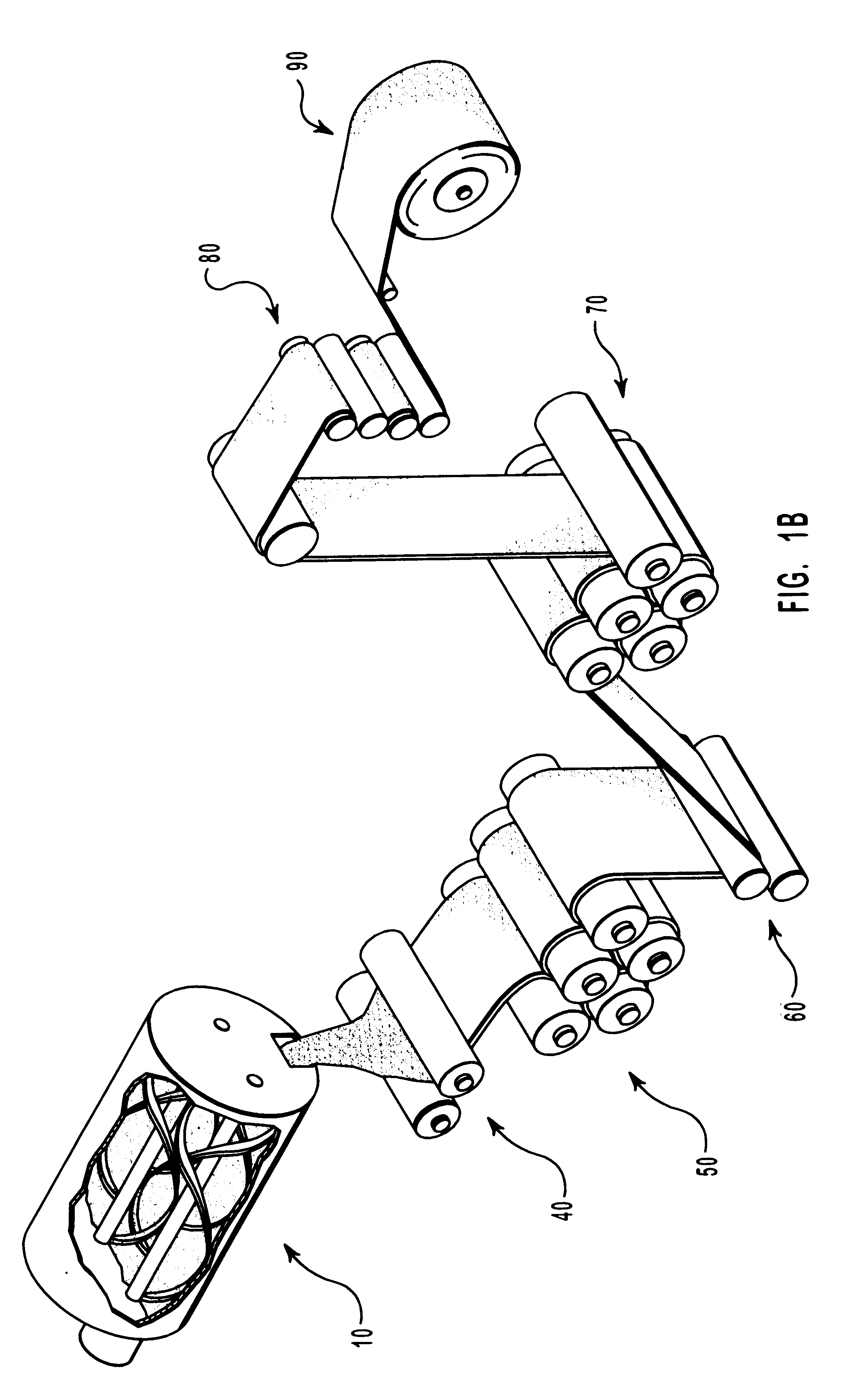
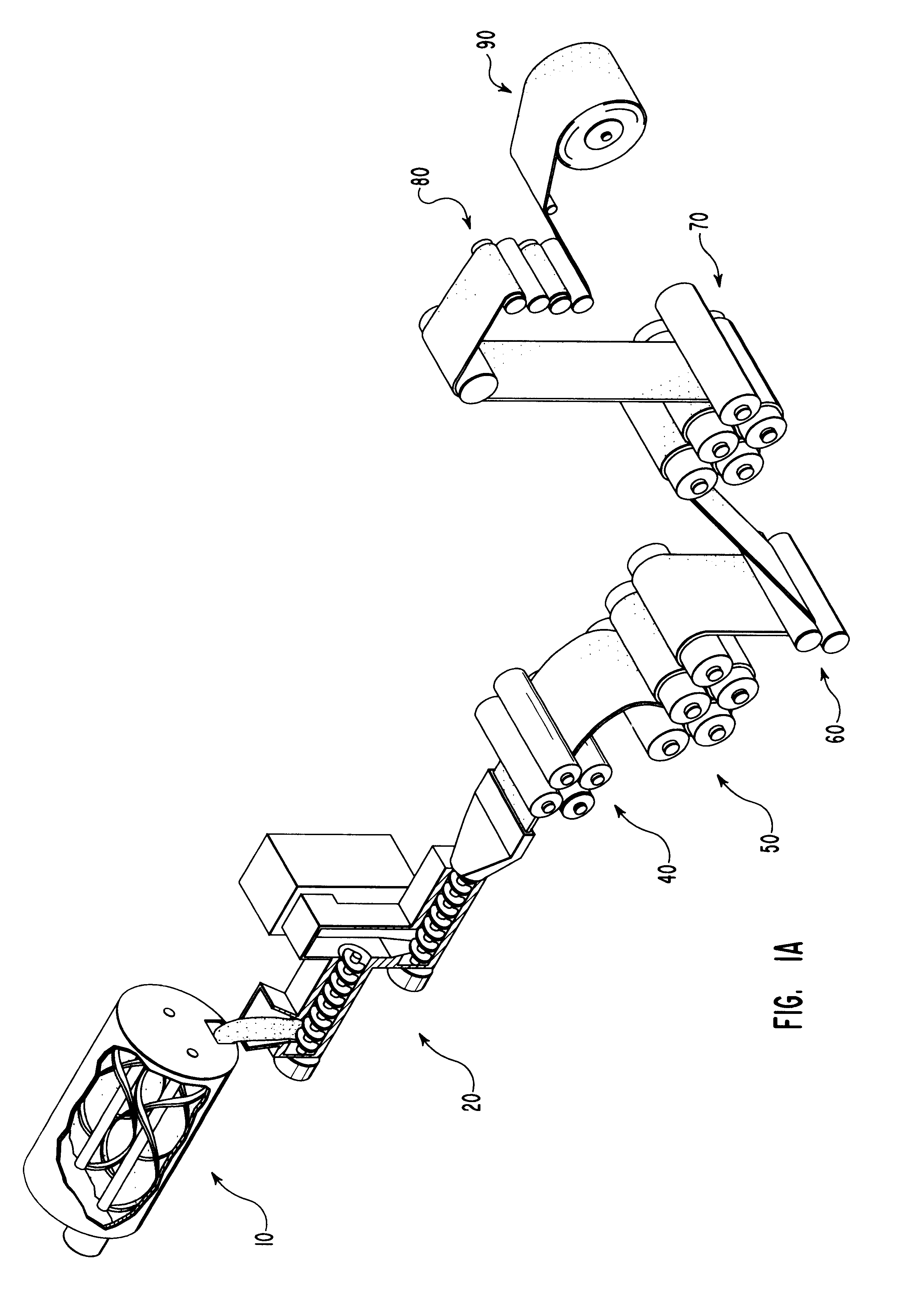
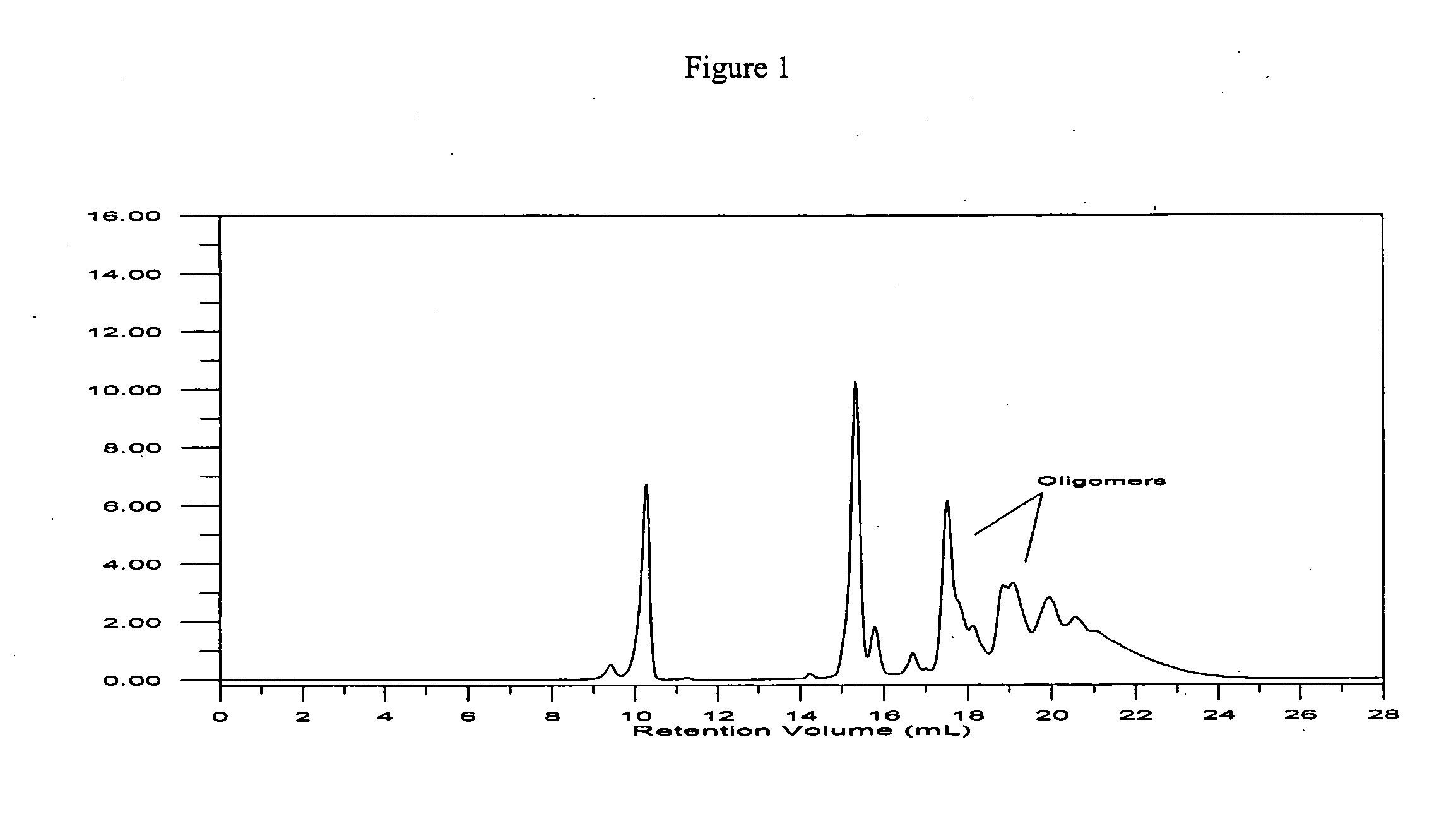
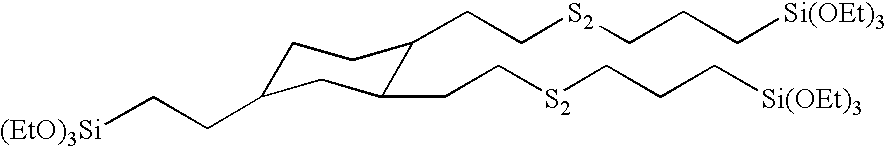
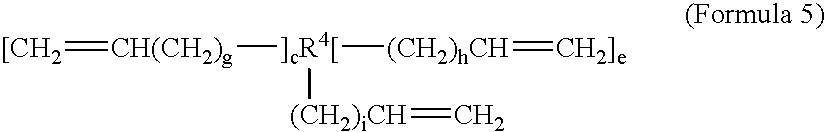Patents
Literature
6872 results about "Organic polymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
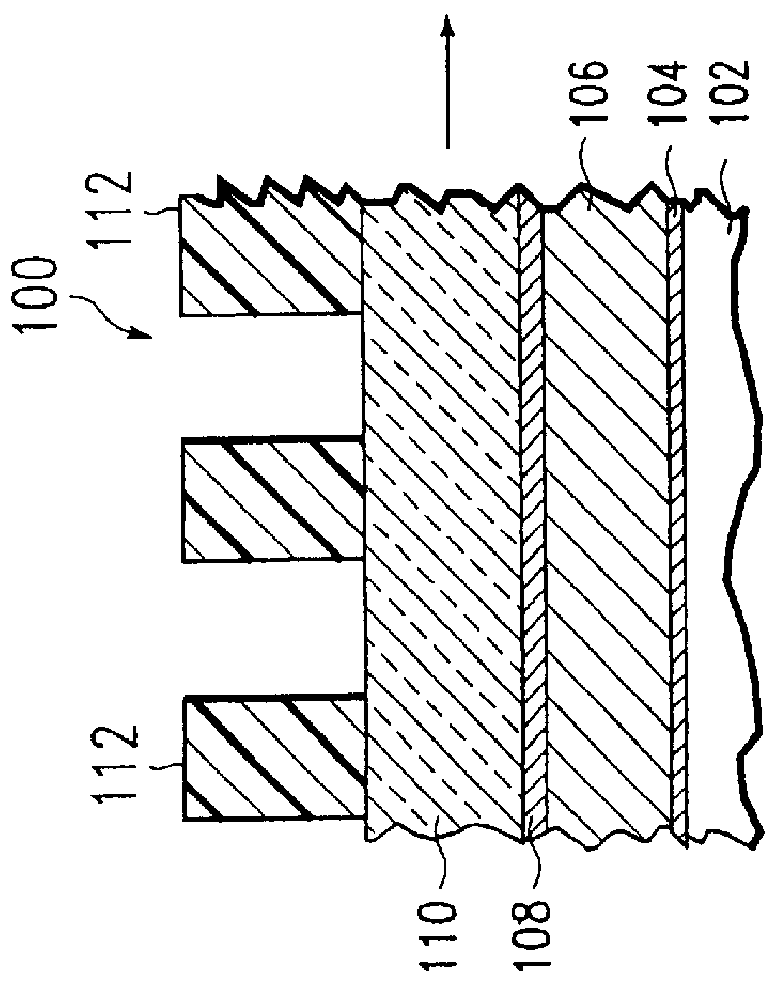
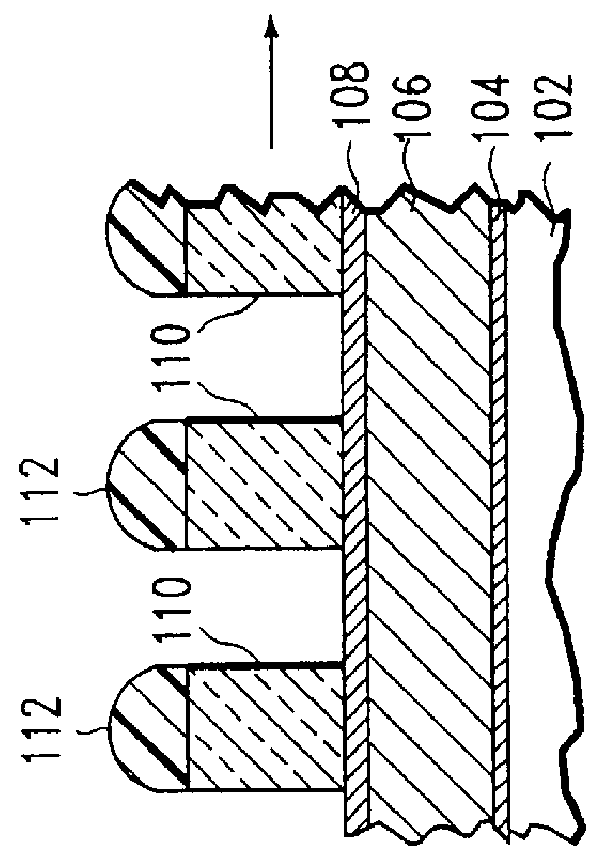
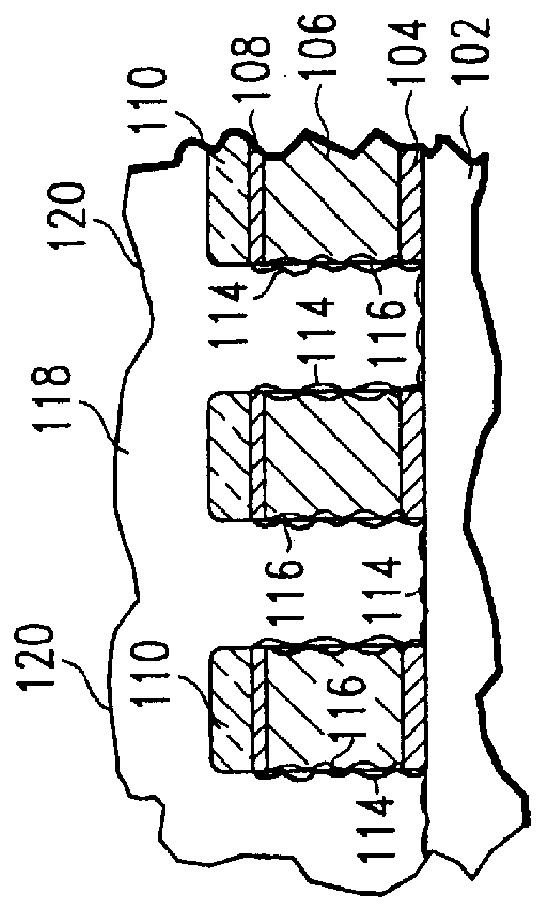
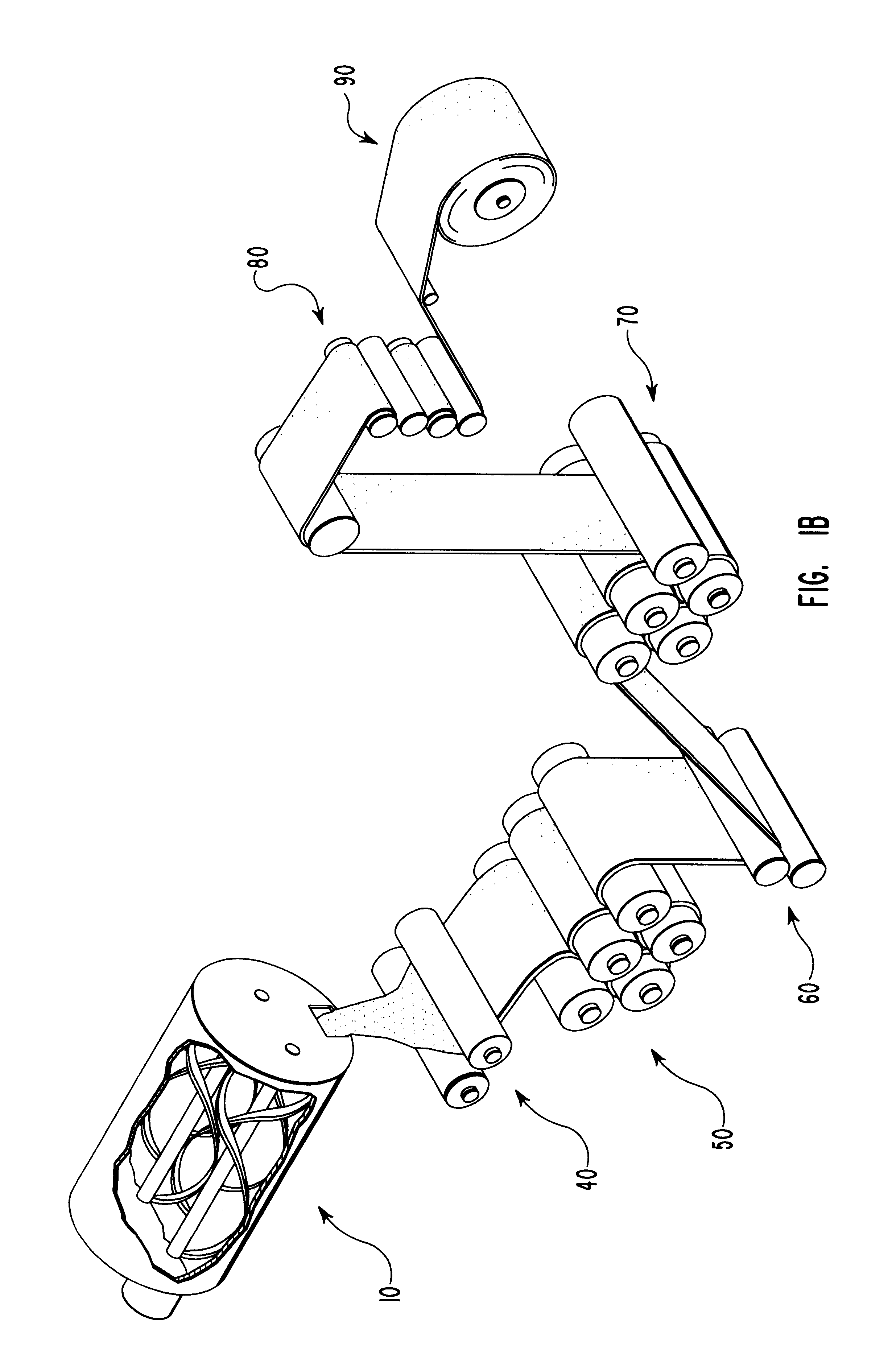
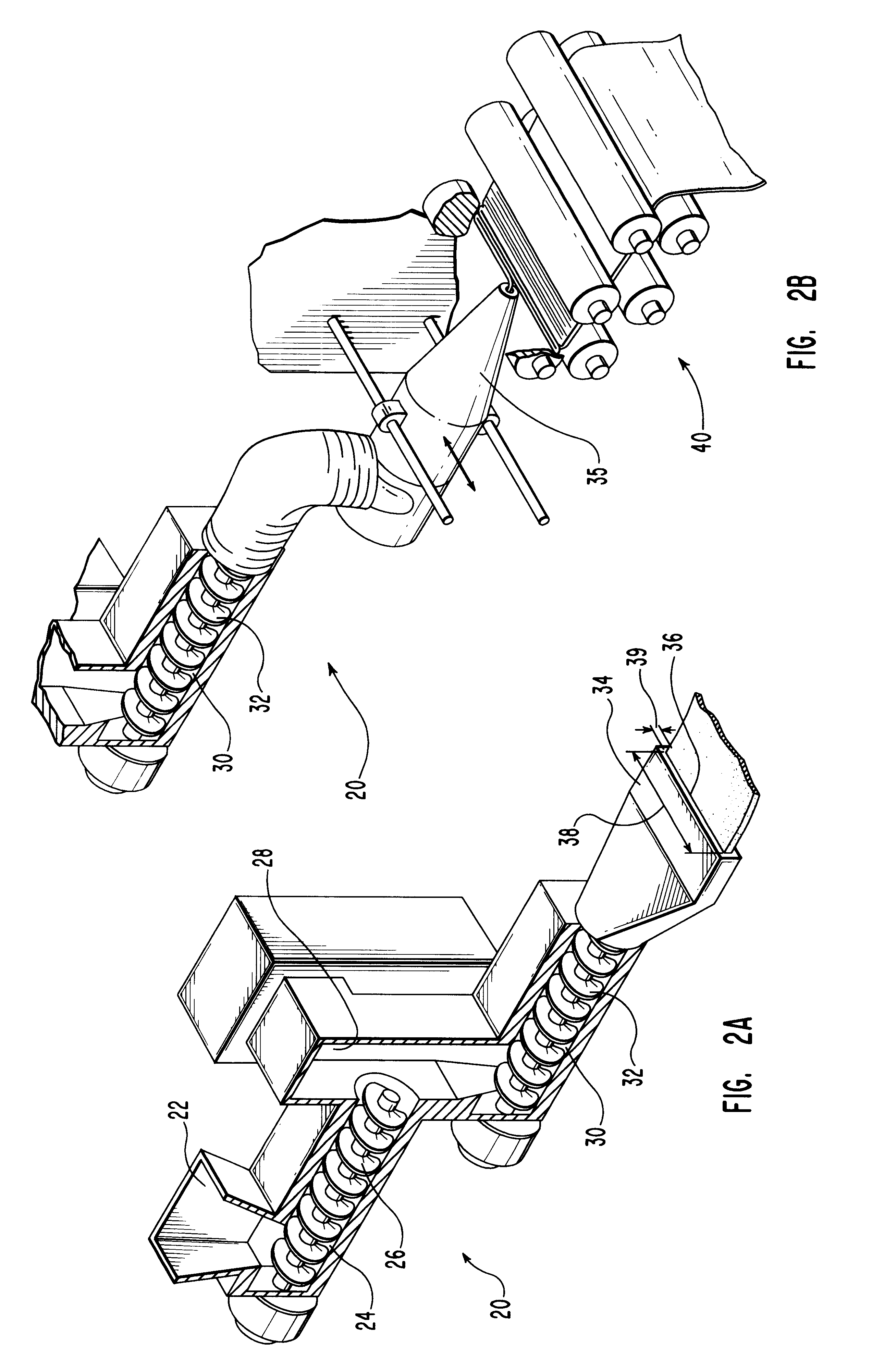
Method of etching patterned layers useful as masking during subsequent etching or for damascene structures
InactiveUS6080529APhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive polymerOrganic base
A first embodiment of the present invention pertains to a method of patterning a semiconductor device conductive feature while permitting easy removal of any residual masking layer which remains after completion of the etching process. A multi-layered masking structure is used which includes a layer of high-temperature organic-based masking material overlaid by either a patterned layer of inorganic masking material or by a layer of patterned high-temperature imageable organic masking material. The inorganic masking material is used to transfer a pattern to the high-temperature organic-based masking material and is then removed. The high-temperature organic-based masking material is used to transfer the pattern and then may be removed if desired. This method is also useful in the pattern etching of aluminum, even though aluminum can be etched at lower temperatures. A second embodiment of the present invention pertains to a specialized etch chemistry useful in the patterning of organic polymeric layers such as low k dielectrics, or other organic polymeric interfacial layers. This etch chemistry is useful for mask opening during the etch of a conductive layer or is useful in etching damascene structures where a metal fill layer is applied over the surface of a patterned organic-based dielectric layer. The etch chemistry provides for the use of etchant plasma species which minimize oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, and bromine content.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrically conductive polymer composition
InactiveUS6184280B1Sufficient electrical conductivityImprove polymer propertiesOther chemical processesConductive materialPolymer scienceCarbon fibers
An electrically conductive polymer composition comprises a moldable organic polymer having hollow carbon microfibers and an electrically conductive white powder uniformly dispersed therein, the carbon fibers being present in an amount of 0.01 wt. % to less than 2 wt. % and the electrically conductive white powder being present in an amount of 2.5-40 wt. %, each percent range based on the total weight of the composition, the amounts of carbon microfibers and white powder being sufficient to simultaneously impart the desired electrical conductivity to the composition and white pigmentation to the composition.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP +1
Compound flocculant taking natural minerals as main components
InactiveCN104229957AEfficient removalApplicable to a wide range of PHWater resource protectionWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationDry weightNatural mineral
The invention discloses a compound flocculant taking natural minerals as main components. The compound flocculant is mainly prepared from the following components by weight percent: 60%-85% of natural minerals, 8%-38% traditional inorganic flocculant and 3%-10% of organic polymer flocculant. According to the invention, key points are as follows: in the compound flocculant taking natural minerals as main components, the weight of the natural minerals, the inorganic flocculant and the organic polymer flocculant is dry weight; and the compound flocculant is implemented to purification of civil engineering wastewater, natural water, industrial wastewater, oily wastewater, fluoride wastewater, food processing wastewater, auto parts processing wastewater, colored wastewater, clean wastewater, semiconductor processing wastewater, restaurant waste water, mine water, slaughter wastewater, grinding wastewater, sewage effluent and the like.
Owner:张家领
Electrode structure for lithium secondary battery and secondary battery having such electrode structure
InactiveUS20060127773A1Small capacity reductionLarge capacityElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureElectrochemical responseConductive polymer
In an electrode structure for a lithium secondary battery including: a main active material layer formed from a metal powder selected from silicon, tin and an alloy thereof that can store and discharge and capable of lithium by electrochemical reaction, and a binder of an organic polymer; and a current collector, wherein the main active material layer is formed at least by a powder of a support material for supporting the electron conduction of the main active material layer in addition to the metal powder and the powder of the support material are particles having a spherical, pseudo-spherical or pillar shape with an average particle size of 0.3 to 1.35 times the thickness of the main active material layer. The support material is one or more materials selected from a group consisting of graphite, oxides of transition metals and metals that do not electrochemically form alloy with lithium. Organic polymer compounded with a conductive polymer is used for the binder. There are provided an electrode structure for a lithium secondary battery having a high capacity and a long lifetime, and a lithium secondary battery using the electrode structure and having a high capacity, a high energy density and a long lifetime.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods for the manufacture of sheets having a highly inorganically filled organic polymer matrix
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a highly inorganically filled matrix. Suitable inorganically filled mixtures are prepared by mixing together an organic polymer binder, water, one or more inorganic aggregate materials, fibers, and optional admixtures in the correct proportions in order to form a sheet which has the desired performance criteria. The inorganically filled mixtures are formed into sheets by first extruding the mixtures and the passing the extruded materials between a set of rollers. The rolled sheets are dried in an accelerated manner to form a substantially hardened sheet, such as by heated rollers and / or a drying chamber. The inorganically filled sheets may have properties substantially similar to sheets presently made from traditional materials like paper, cardboard, polystyrene, plastic, or metal. Such sheets can be rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued. They have especial utility in the mass production of containers, particularly food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Compositions and methods for manufacturing starch-based compositions
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, an auxiliary water-dispersible organic polymer, fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the auxiliary polymer to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and auxiliary polymer form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Methods for preparing coated drug particles and pharmaceutical formulations thereof
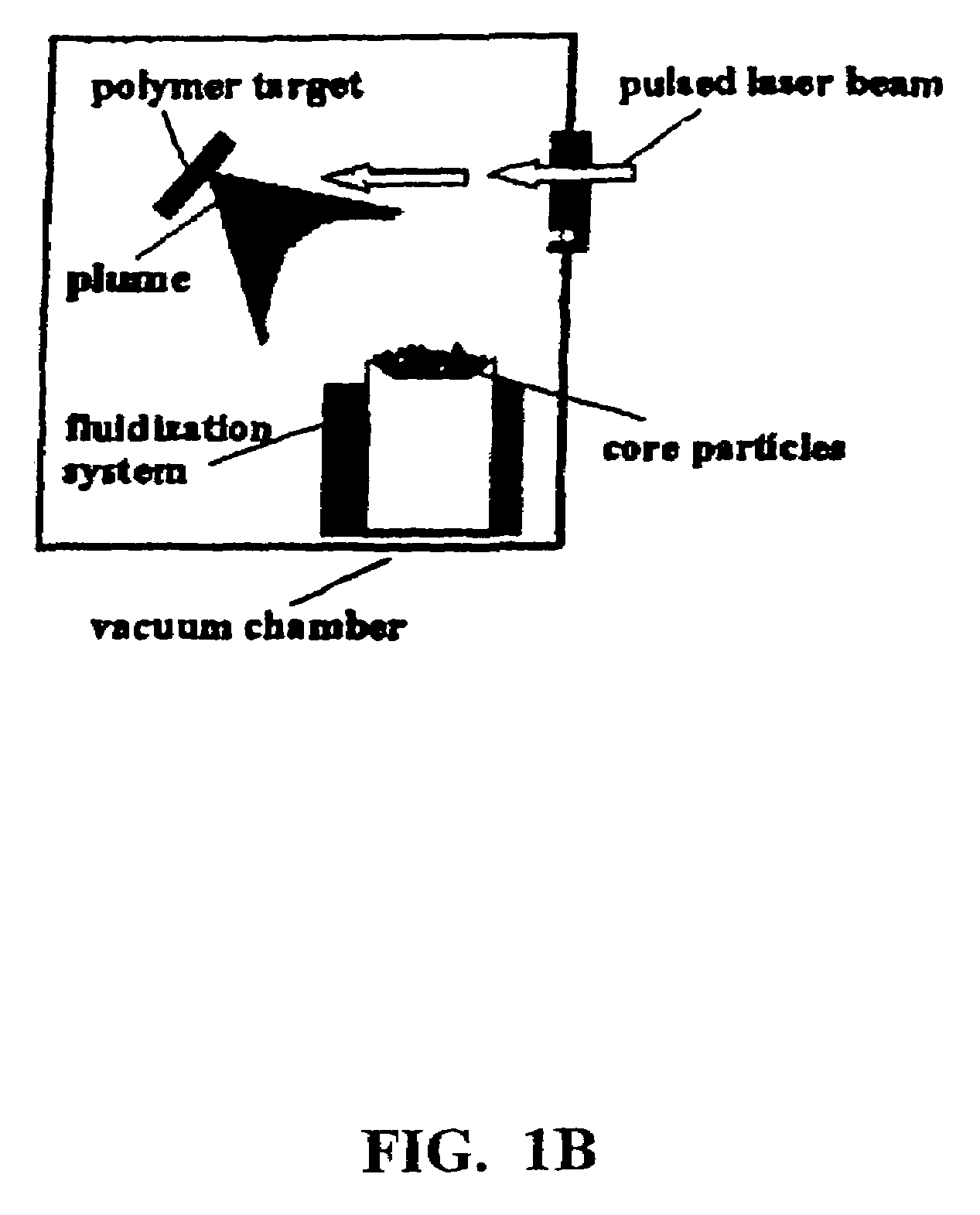
Disclosed are methods using pulsed laser ablation to prepare coated drug particles of uniform size and thickness. The coated drug particles ranged in size from several nanometers to several millimeters in diameter size, and were coated with organic polymer particle having average diameter sizes from about 1 to 50 nm. In illustrative embodiments, coated drug particles or drug delivery particles are disclosed comprising a biodegradable or biocompatible polymer coating having controlled thickness and controlled coating uniformity, that offer superior pharmaceutical properties for controlled delivery and increased bioavailability.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV PF +2
Method of pattern etching a low K dielectric layer
InactiveUS6331380B1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic baseOxygen
A first embodiment of the present invention pertains to a method of patterning a semiconductor device conductive feature while permitting easy removal of any residual masking layer which remains after completion of the etching process. A multi-layered masking structure is used which includes a layer of high-temperature organic-based masking material overlaid by either a patterned layer of inorganic masking material or by a layer of patterned high-temperature imageable organic masking material. The inorganic masking material is used to transfer a pattern to the high-temperature organic-based masking material and is then removed. The high-temperature organic-based masking material is used to transfer the pattern and then may be removed if desired. This method is also useful in the pattern etching of aluminum, even though aluminum can be etched at lower temperatures. A second embodiment of the present invention pertains to a specialized etch chemistry useful in the patterning of organic polymeric layers such as low k dielectrics, or other organic polymeric interfacial layers. This etch chemistry is useful for mask opening during the etch of a conductive layer or is useful in etching damascene structures where a metal fill layer is applied over the surface of a patterned organic-based dielectric layer. The etch chemistry provides for the use of etchant plasma species which minimize oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, and bromine content.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Fluorescent silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20130039848A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAntibacterial agentsDiseaseCellular component
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as polyethylene glycol) (PEG) The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo The nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker A therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle Radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle to permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by various imaging techniques.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
Medical electrode
An electrode providing electrical contact with a patient's skin includes a conductive member adapted for connection to an external electrical apparatus and a non-liquid film for electrically interfacing to said patient's skin, the liquid film being electrically and mechanically connected to said conductive member. The non-liquid film includes an electrically conductive organic polymer plasticized with a polyhydric alcohol with said organic polymer being derived from a monomeric mixture comprising from about 15 to 30 pph acrylic acid, 0.5 to 30 pph N-vinylpyrrolidone and 0.01 to 2 pph of a crosslinking agent. The monomeric mixture may further comprise from about 0.5 to 8 pph of a thickening agent selected from the group consisting of N-vinylpyrrolidone / acrylic acid copolymers, N-vinylpyrrolidone / vinylacetate copolymers, and N-vinylpyrrolidone / vinylimidazole copolymers.
Owner:AXELGAARD MANUFACTURING COMPANY INC
Medical electrode
An electrode providing electrical contact with a patient's skin includes a conductive member adapted for connection to an external electrical apparatus and a non-liquid water containing film for electrically interfacing to said patient's skin, the non-liquid film being electrically and mechanically connected to said conductive member. The non-liquid water containing film includes an electrically conductive organic polymer plasticized with a polyhydric alcohol with said organic polymer being derived from a monomeric mixture comprising from about 2 to 30 pph acrylic acid, 2 to 30 pph of a glycolvinylether and 0.01 to 1.5 pph of a crosslinking agent. Preferably the polyhydric alcohol is glycerol.
Owner:AXELGAARD MANUFACTURING COMPANY INC
Method for preparing complexly shaped biomedical porous titanium molybdenum alloy implant body
InactiveCN102335742ADesign personalizationHigh dimensional accuracyIncreasing energy efficiencyProsthesisNatural boneMetallic materials
The invention provides a method for preparing a complexly shaped biomedical porous titanium molybdenum alloy implant body and belongs to the technical field of biomedical porous metallic material preparation. The method comprises the following steps of: taking a mixture of titanium and molybdenum metallic element powder and organic polymer powder as raw materials, and then preparing the biomedical porous titanium molybdenum alloy implant body by adopting the processes, such as three-dimensional modeling, selective laser-firing rapid forming, thermal de-greasing, vacuum sintering, and the like. The processing steps are simple, the period is short, the use ratio of materials is high, the cost is low, any complexly shaped porous titanium alloy implant body can be conveniently manufactured, and the method has efficiency and economic advantages in individual design and rapid manufacturing of the implant body. A titanium molybdenum alloy material prepared by using the method has the advantages that pore space is uniform, adjustment scopes of porosity, aperture ratio and aperture are wide, elasticity modulus and compression strength are in close proximity to natural bone, and the demand on biomechanical compatibility required by a biomedical material is met.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Compositions used in manufacturing articles having an inorganically filled organic polymer matrix
InactiveUS6090195AReadily and inexpensively mass producedHigh strengthClosure lidsWrappersFiberPolymer science
Compositions, methods, and systems for manufacturing articles, particularly containers and packaging materials, having a highly inorganically filled matrix. Suitable inorganically filled mixtures are prepared by mixing together an organic polymer binder, water, one or more aggregate materials, fibers, and optional admixtures in the correct proportions in order to form an article which has the desired performance criteria. The inorganically filled mixtures are molded to fashion a portion of the mixture into a form stable shape for the desired article. Once the article has obtained form stability, such as by heating to remove water by evaporation, the article is removed from the mold and allowed to harden to gain strength. The articles may have properties substantially similar to articles presently made from traditional materials like paper, paperboard, polystyrene, plastic, or metal. They have especial utility in the mass production of containers, particularly food and beverage containers.
Owner:EARTHSHELL SPE
Compositions and methods for manufacturing starch-based sheets
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, an auxiliary water-dispersible organic polymer, fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the auxiliary polymer to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and auxiliary polymer form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Memory device with active passive layers
InactiveUS6838720B2Improve read and write speedLong-term data retentionTransistorNanoinformaticsActive layerElectron mobility
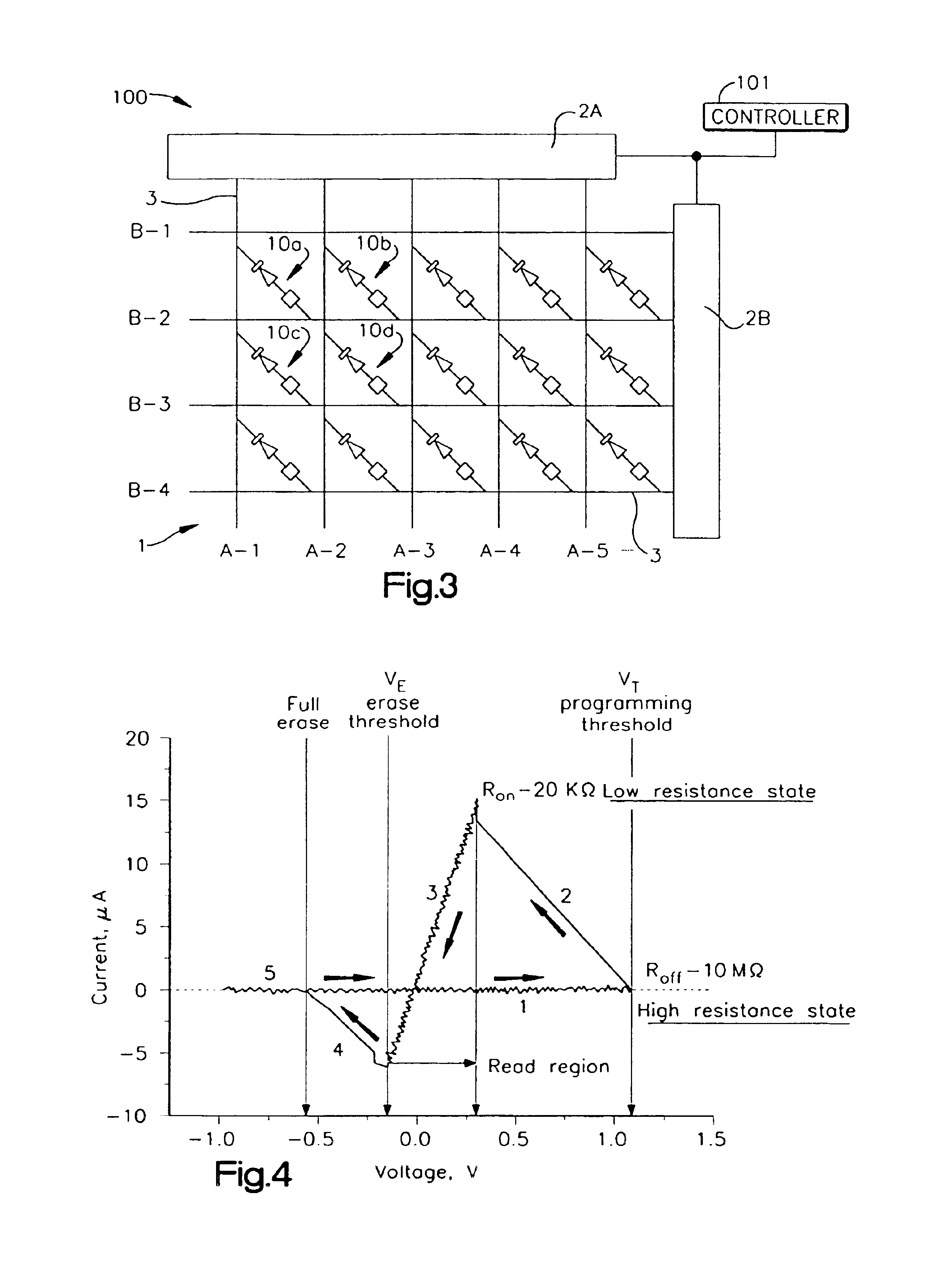
A memory including memory cells having active and passive layers may store multiple information bits. The active layer may include an organic polymer that has a variable resistance based on the movement of charged species (ions or ions and electrons) between the passive layer and the active layer. The passive layer may be a super-ionic material that has high ion and electron mobility. The active layer may be self-assembled from a monomer in a liquid or gas.
Owner:SPANSION LLC
Electrically conductive compositions and method of manufacture thereof
A method for manufacturing a conductive composition comprises blending a polymer precursor with a single wall carbon nanotube composition; and polymerizing the polymer precursor to form an organic polymer. The method may be advantageously used for manufacturing automotive components, computer components, and other components where electrical conductivity properties are desirable.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
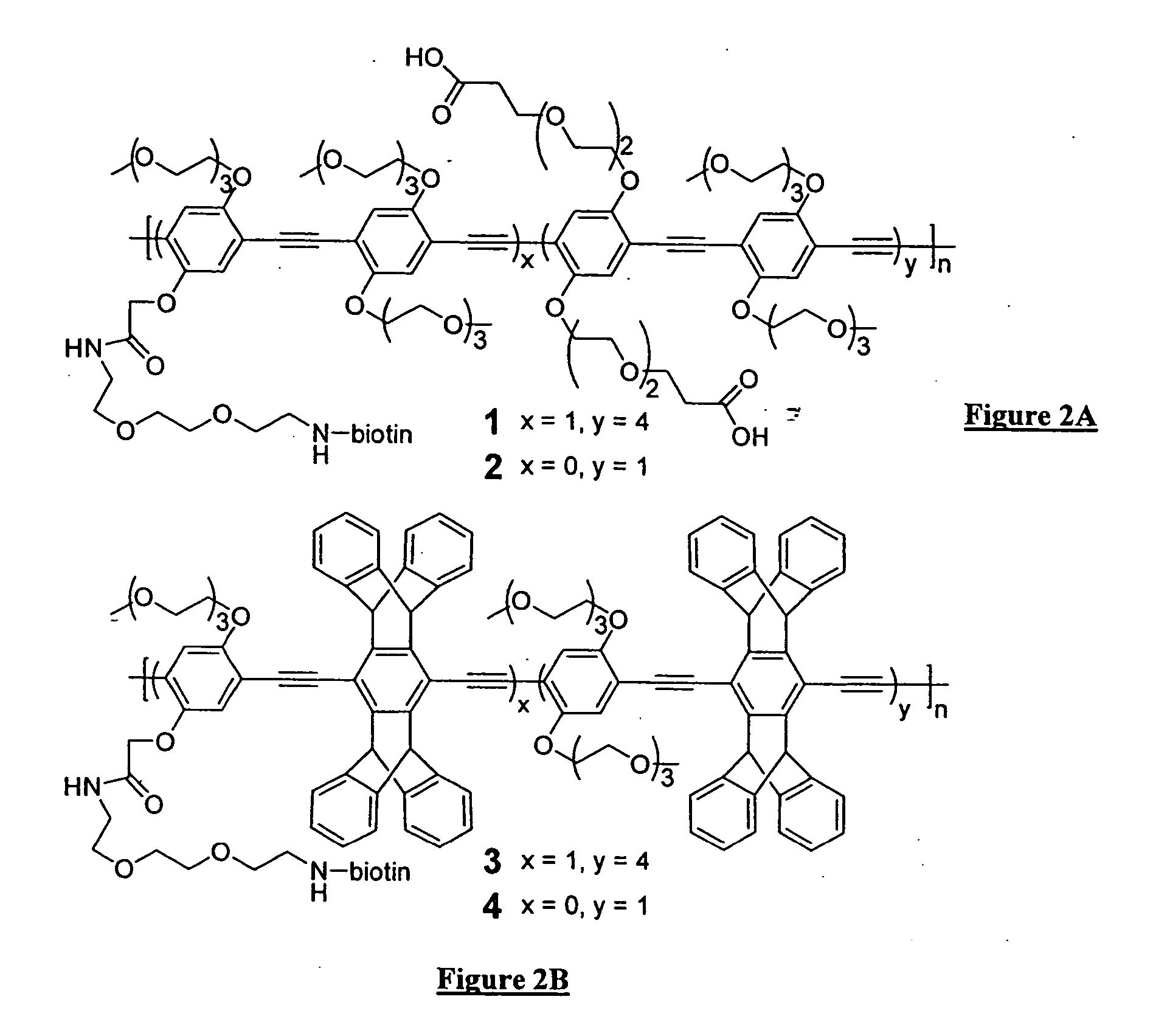
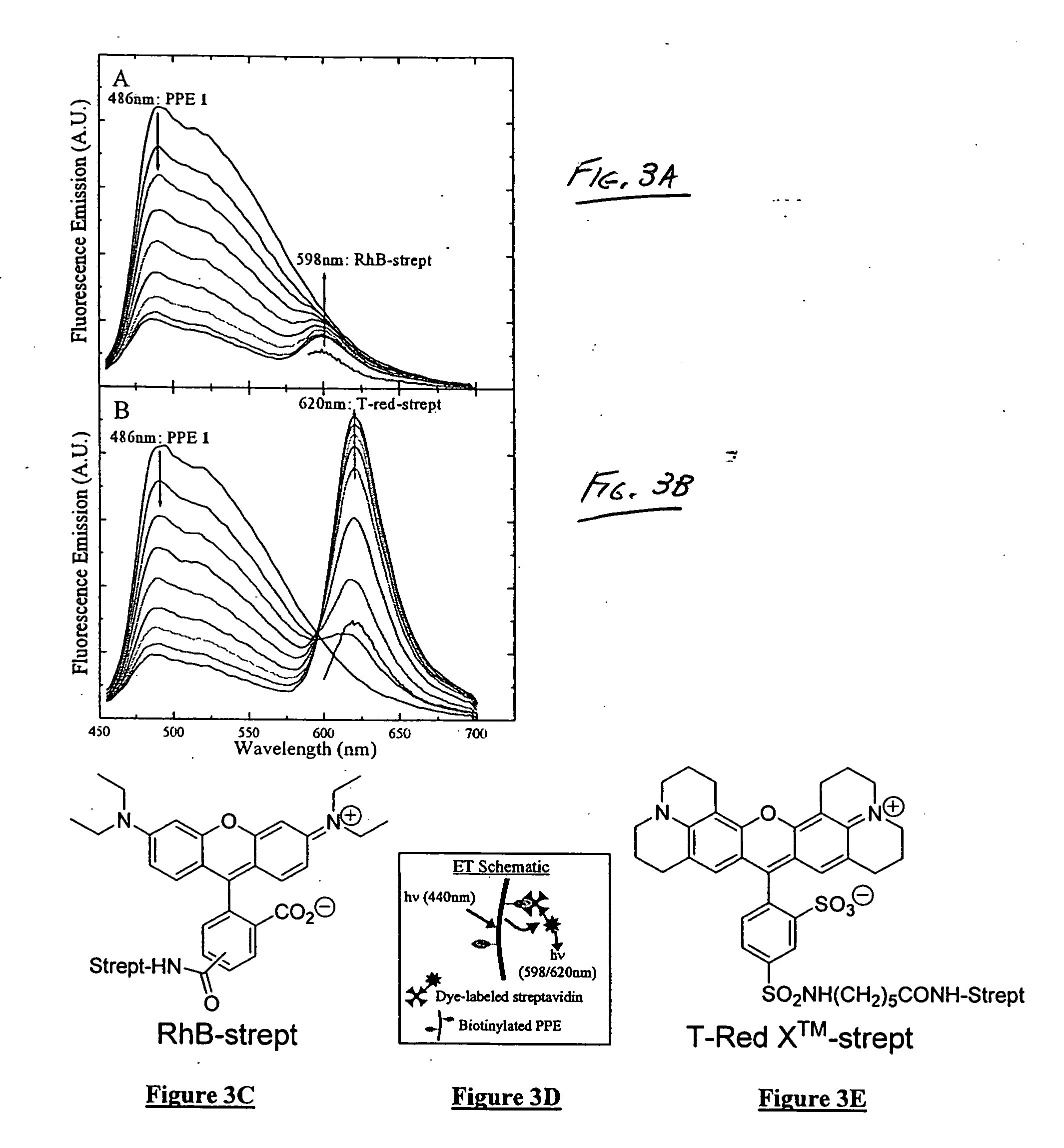
Polymers for analyte detection
InactiveUS20060127929A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceEscherichia coliFluorescence
The present invention generally relates to organic polymers able to participate in an analyte-recognition process, where an analyte facilitates an energy transfer between an energy donor and an energy acceptor. Certain embodiments of the invention make use of fluorescent conjugated polymers, such as poly(phenylene ethynylene)s and other polymers comprising pi-conjugated backbones. For example, one aspect of the invention provides a fluorescent conjugated polymer and an indicator that can interact with each other in the presence of an analyte to produce an emissive signal. In some cases, the interaction may include energy exchange mechanisms, such as Dexter energy transfer or the strong coupling effect. The interaction of the conjugated polymer and the indicator, in some instances, may be facilitated through specific interactions, such as a protein / carbohydrate interaction, a ligand / receptor interaction, etc. Another aspect of the invention provides for the detection of biological entities, for example, pathogenic bacteria such as E. coli, or viruses such as influenza virus. In some cases, biological recognition elements may be used to determine the biological entity, for instance, carbohydrates that can be used to specifically interact with at least part of the biological entity, such as a protein in the cell membrane of a bacterium. Still other aspects of the invention involve articles, devices, and kits using any of the above-described systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for the production of porous carbon-based molded bodies, and use thereof as cell culture carrier systems and culture systems
The present invention relates to methods for producing carbon-based molded bodies. In particular, the present invention relates to methods for producing porous carbon-based molded bodies by carbonizing organic polymer materials mixed with non-polymeric fillers and subsequently dissolving the fillers out from the carbonized molded bodies. The present invention further relates to methods for producing porous carbon-based molded bodies by carbonizing organic polymer materials mixed with non-polymeric fillers which are substantially completely decomposed during the carbonization. The present invention also relates to a method for producing porous carbon-based molded bodies by carbonizing organic polymer materials, the carbon-based molded bodies being partially oxidized following carbonization so as to produce pores. In addition, the present invention relates to porous molded bodies produced according to one of said methods and the use thereof, especially as cell culture carriers and / or culture systems.
Owner:CINVENTION AG
Pore forming material for porous body, manufacturing method of pore forming material for porous body, manufacturing method of porous body, porous body, and honeycomb structural body
InactiveUS7396586B2High porosityAvoid crackingSolid waste managementExhaust apparatusInorganic particleMicrosphere
The pore forming material for a porous body of the present invention comprises organic polymer particles and inorganic particles. As the embodiment thereof, there may be mentioned one having a structure in which the inorganic particles are contained in the organic polymer particles, and an aggregate body of the organic polymer particles and the inorganic particles. The inorganic particles may be inorganic micro-balloons, and the organic polymer particles may be organic micro-balloons.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Meniscus prosthesis
A prosthesis for placement into a joint space between two or more bones is disclosed. The prosthesis includes a body formed from a pre-formed solid one piece elastomer, wherein the elastomer is formed from a synthetic organic polymer that is biocompatible and has a modulus of elasticity and a mechanical strength between 0.5 MPa and 75 MPa. The body having a shape contoured to fit within a joint space between the femoral condyle, tubercle, and tibial plateau without any means of attachment.
Owner:CARTIVA INC
Methods, Systems, and Compositions for the Controlled Crosslinking of Well Servicing Fluids
Treating fluid compositions for use in hydrocarbon recovery operations from subterranean formations are described, as well as methods for their preparation and use. In particular, treating fluid compositions are described which comprise a liquid, a crosslinkable organic polymer material that is at least partially soluble in the liquid, a crosslinking agent that is capable of increasing the viscosity of the treating fluid by crosslinking the organic polymer material in the liquid, and a crosslinking modifier additive which can delay or accelerate the crosslinking of the treating fluid composition. Such compositions may be used in a variety of hydrocarbon recovery operations including fracturing operations, drilling operations, gravel packing operations, water control operations, and the like.
Owner:TUCC TECH LLC
Silated core polysulfides, their preparation and use in filled elastomer compositions
ActiveUS20080161477A1Good dispersion of fillerImprove productivityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSpecial tyresElastomerSilanes
This invention relates to novel sulfur-containing silane coupling agents, and organic polymers containing carbon-carbon double bonds. These novel silanes can be carried on organic and inorganic fillers. The invention also relates to articles of manufacture, particularly tires, made from the elastomer compositions described herein.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
Lithium ion conductive composite electrolyte and lithium ion secondary battery using same
ActiveUS20130230778A1Improve cycle performancePrevent electrolyte leakageNon-aqueous electrolyte cellsSecondary cellsComposite electrolyteConductive polymer
Provided is a lithium ion conductive composite electrolyte that can prevent leakage of electrolyte solution, and that have excellent cycle performance and lithium ion conductivity, and a lithium ion secondary battery. A lithium ion conductive composite electrolyte 1 is formed so that a lithium ion conductive polymer gel electrolyte is held in a porous body 2 formed from lithium ion conductive inorganic solid electrolyte particles and an organic polymer. The lithium ion conductive inorganic solid electrolyte particles are formed from a composite metal oxide that has a garnet structure, and is represented by the chemical formula Li7−yLa3−xAxZr2−yMyO12 (wherein 0≦x 3, 0≦y≦2, A is one of Y, Nd, Sm, and Gd, and M is Nb or Ta). A lithium ion secondary battery 11 includes the lithium ion conductive composite electrolyte 1 between a positive electrode 12 and a negative electrode 13.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Profile control oil-displacement agent for core-shell type inorganic/organic polymer composite microballoon
InactiveCN102485830AGood expansion performanceGood temperature and salt resistanceDrilling compositionCross-linkMicrosphere
The invention discloses a profile control oil-displacement agent for a core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon. A preparation method of the core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon comprises the following steps of carrying out surface modification of inorganic cores of inorganic nano-particles such as silica particles and magnetic particles, and carrying out graft polymerisation by a dispersion polymerization method or an inverse emulsion polymerization method to form polymer shells (such as polyacrylamide cross-linked copolymers) on the surfaces of the inorganic cores. The inorganic components and the organic components bind by chemical bonds so that the core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon has very stale structure. The core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon retains the advantages of polymer microballoons and inorganic particles, and has strong heat-resistant and mineralization-resistant capabilities, high plugging strength and good dilatancy. The core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon can move in rock pores and can plug the rock pores. When a plugging pressure difference is improved to a certain degree, elastic deformation of the core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon can be produced and the deformed core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon sequentially moves to a deep rock stratum part so that a liquid flow direction is changed gradually and a crude oil yield is improved. The profile control oil-displacement agent provided by the invention has a large potential.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Process for chromatographic separation of peptides and nucleic acid, and new high affinity ion exchange matrix
InactiveUS6090288ACation exchanger materialsComponent separationChromatographic separationTransferrin
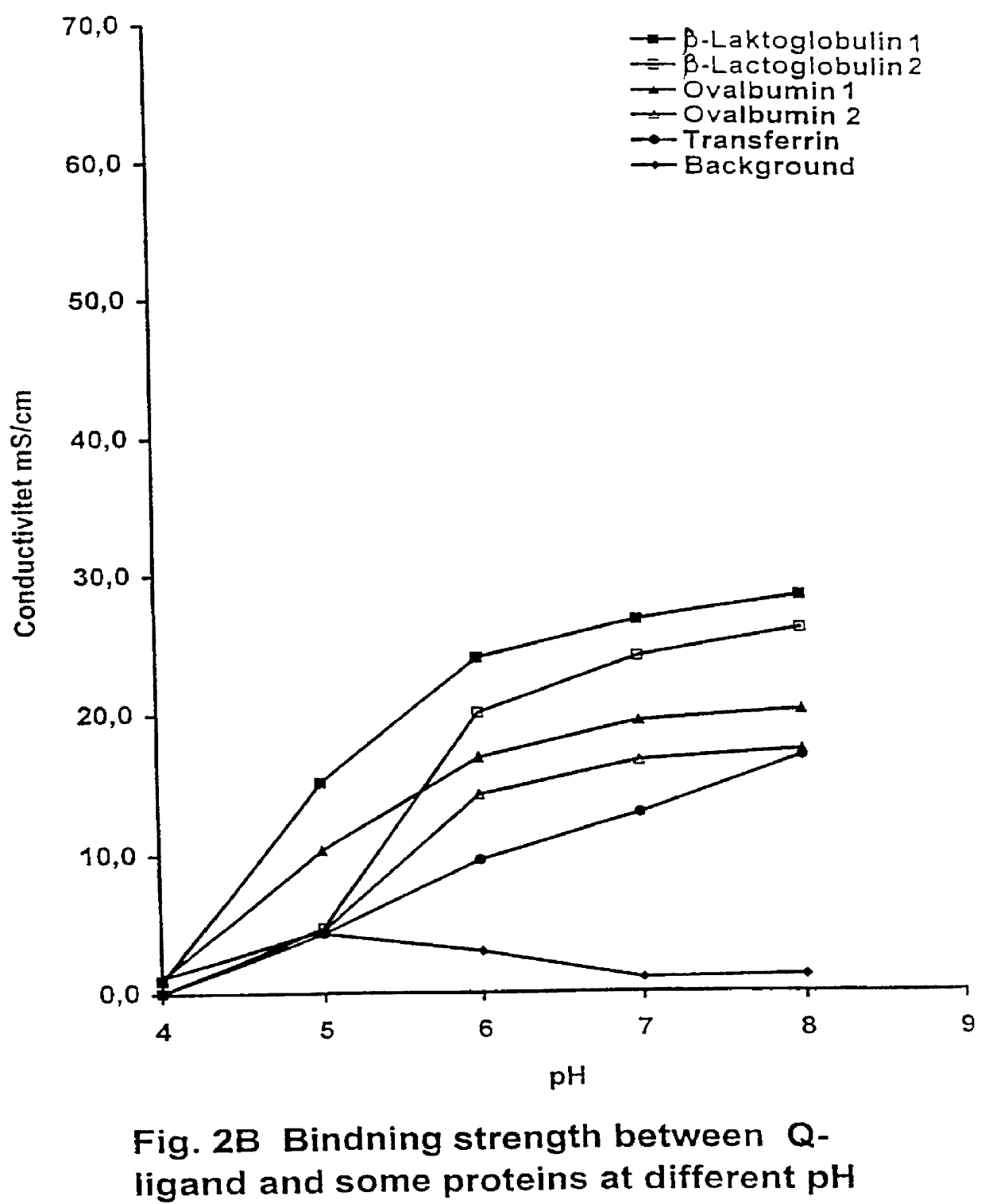
PCT No. PCT / SE97 / 00237 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 29, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 29, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 14, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 29825 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 21, 1997Process for separating off a peptide or a nucleic acid by an anion exchanger (I) characterized in that a) the anion exchanger (I) exhibits ligands, which (i) contain a primary, secondary or tertiary amino group and (ii) are covalently bound to an organic polymer (matrix), b) there on a carbon atom at a distance of 2 or 3 atoms away from an amino nitrogen in the ligands is a hydroxyl group or a primary, secondary or tertiary amino group, and c) the maximum elution ionic strength in the pH range 2-14 for at least one of the proteins transferrin, ovalbumin 1, ovalbumin 2, beta -lactoglobulin 1 and beta -lactoglobulin 2 on the anion exchanger is higher than the elution ionic strength required for a quaternary comparative ion exchanger.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIOPROCESS R&D
Organic solar cells including group IV nanocrystals and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050061363A1Promote absorptionEasy to manufactureMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureHeterojunctionOrganic solar cell
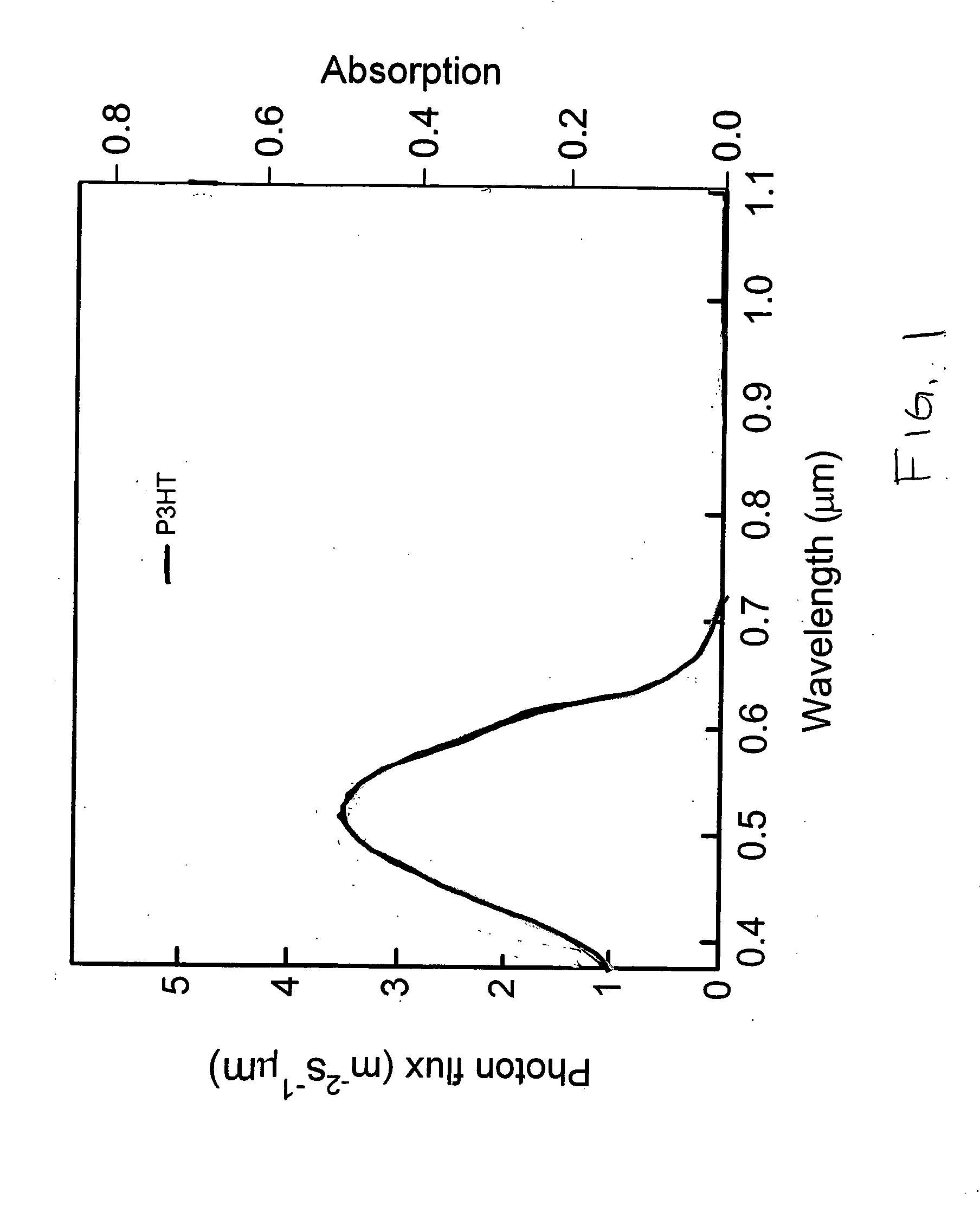
An improved organic solar cell converts light into electricity. The organic solar cell includes a cathode, an anode, and a bulk heterojunction material disposed therebetween. The bulk heterojunction material includes a plurality of group IV nanocrystals (e.g., silicon nanocrystals) disposed within an organic absorber (e.g., an organic polymer).
Owner:EVERGREEN SOLAR
Conductive thermoplastic compositions, methods of manufacture and articles derived from such compositions
Disclosed herein is an electrically conductive precursor composition comprising an organic polymer precursor; a single wall nanotube composition, wherein the single wall nanotube composition contains at least 0.1 wt % of production related impurities; and an optional nanosized conductive filler. A conductive composition comprises an organic polymer; a single wall nanotube composition, wherein the single wall nanotube composition contains at least 0.1 wt % of production related impurities; and a nanosized conductive filler.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Silver nanowire-based transparent conductive thin film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102087886AReduce roughnessReduce transmittanceConductive layers on insulating-supportsIndividual molecule manipulationPolyvinyl alcoholPolymethyl methacrylate
The invention provides a silver nanowire-based transparent conductive thin film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: forming a uniform adhesive layer on a substrate by organic polymer fluid; and forming a silver nanowire conductive layer on the adhesive layer, wherein silver nanowires can be firmly adhered to the adhesive layer. Through the adhesive layer, the firmness and the reliability of the silver nanowire transparent conductive thin film are greatly improved, the problem of easiness of falling of the silver nanowires is solved, and the selection range of the substrate is expanded. If the adhesive layer is formed by polyvinyl alcohol on a polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) substrate, the visible light transmittance reaches 84 percent when square resistance is 130.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Memory devices based on electric field programmable films
InactiveUS20050058009A1Easy to manufactureImprove device densityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesDielectric matrixElectricity
A composition for the formation of an electric field programmable film, the composition comprising a matrix precursor composition or a dielectric matrix material, wherein the dielectric matrix material comprises an organic polymer and / or a inorganic oxide; and an electron donor and an electron acceptor of a type and in an amount effective to provide electric field programming. The films are of utility in data storage devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Powder comprising silica-coated zinc oxide, organic polymer composition containing the powder and shaped article thereof
InactiveUS20060167138A1Help shapeSufficient UV shielding abilityPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyMicroparticleSilicon dioxide
A powder comprising silica-coated zinc oxide fine particles in which the surface of each particle is coated with silica, wherein large particles of 5 μm or more account for 0.1 mass % or less. A powder comprising surface-hydrophobicized silica-coated zinc oxide fine particles in which the silica-coated zinc oxide fine particles whose surfaces have been coated with silica are further treated with a hydrophobicity-imparting agent, wherein large particles of 5 μm or more account for 0.1 mass % or less.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com