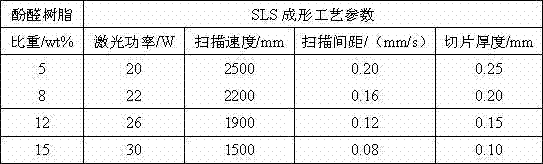
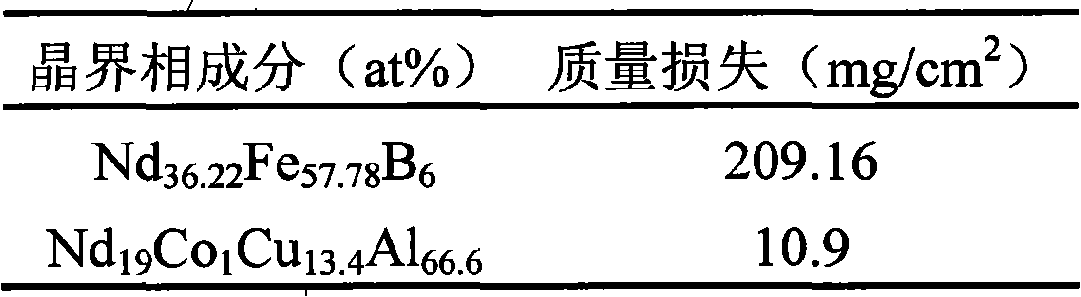
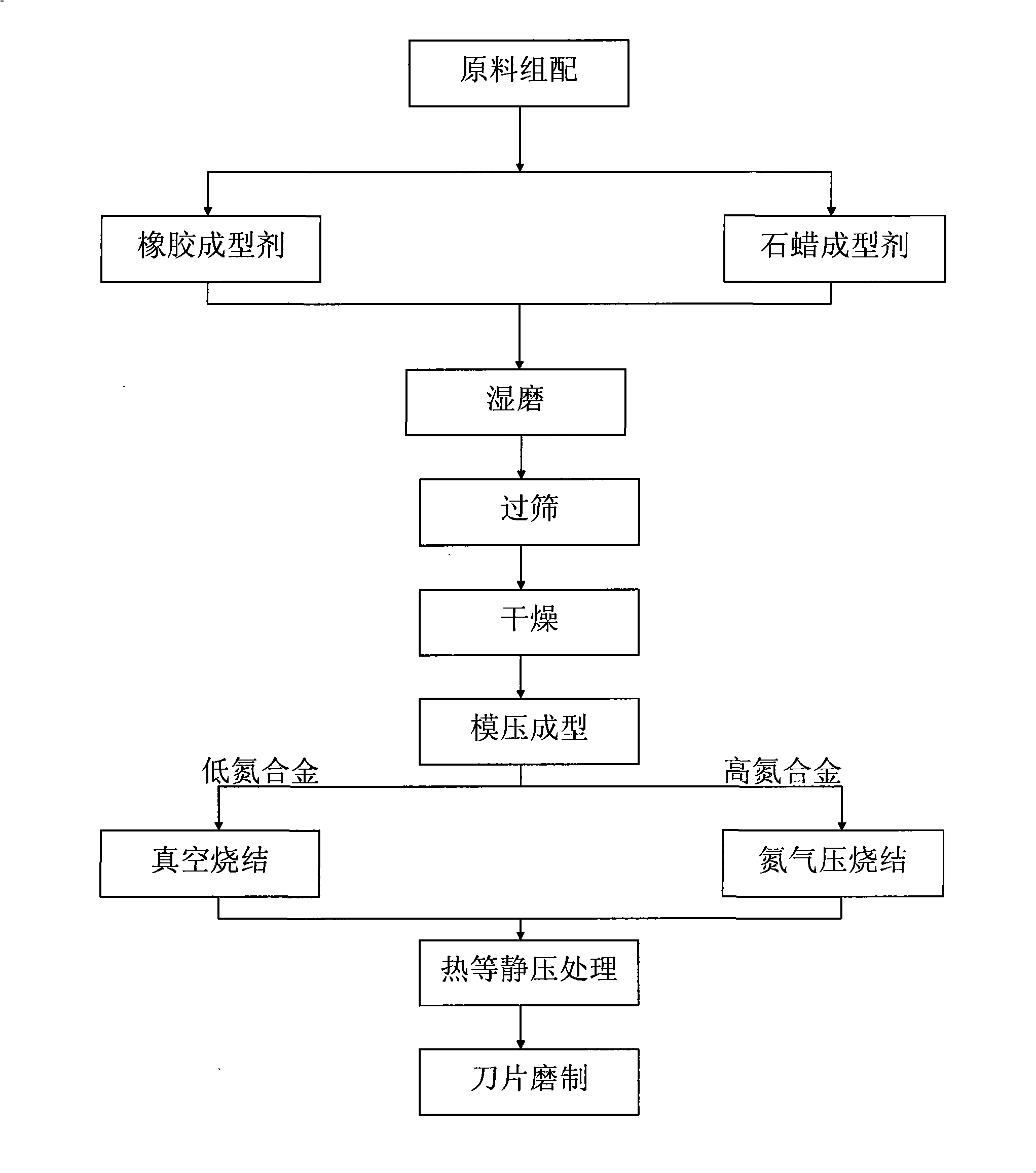
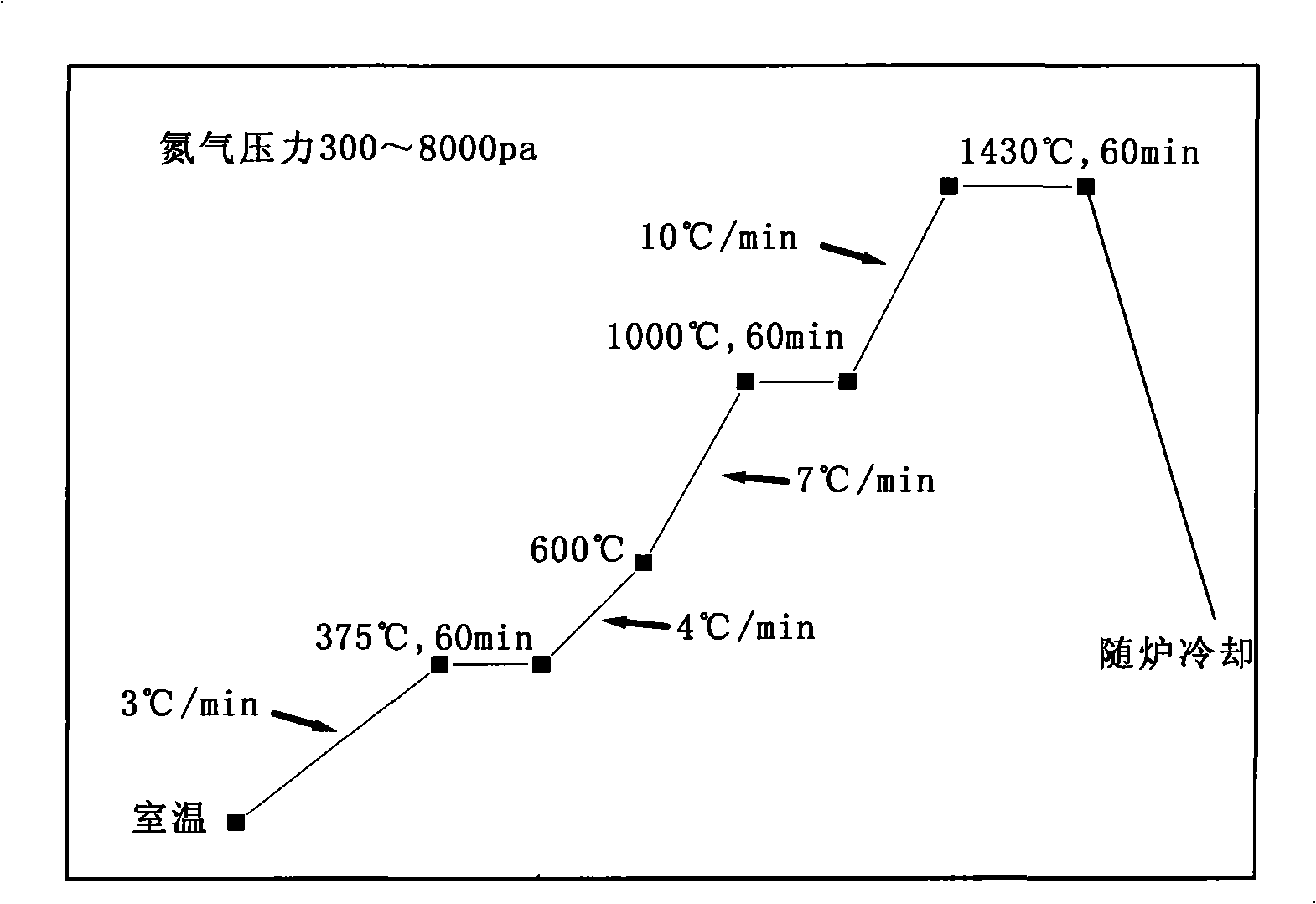
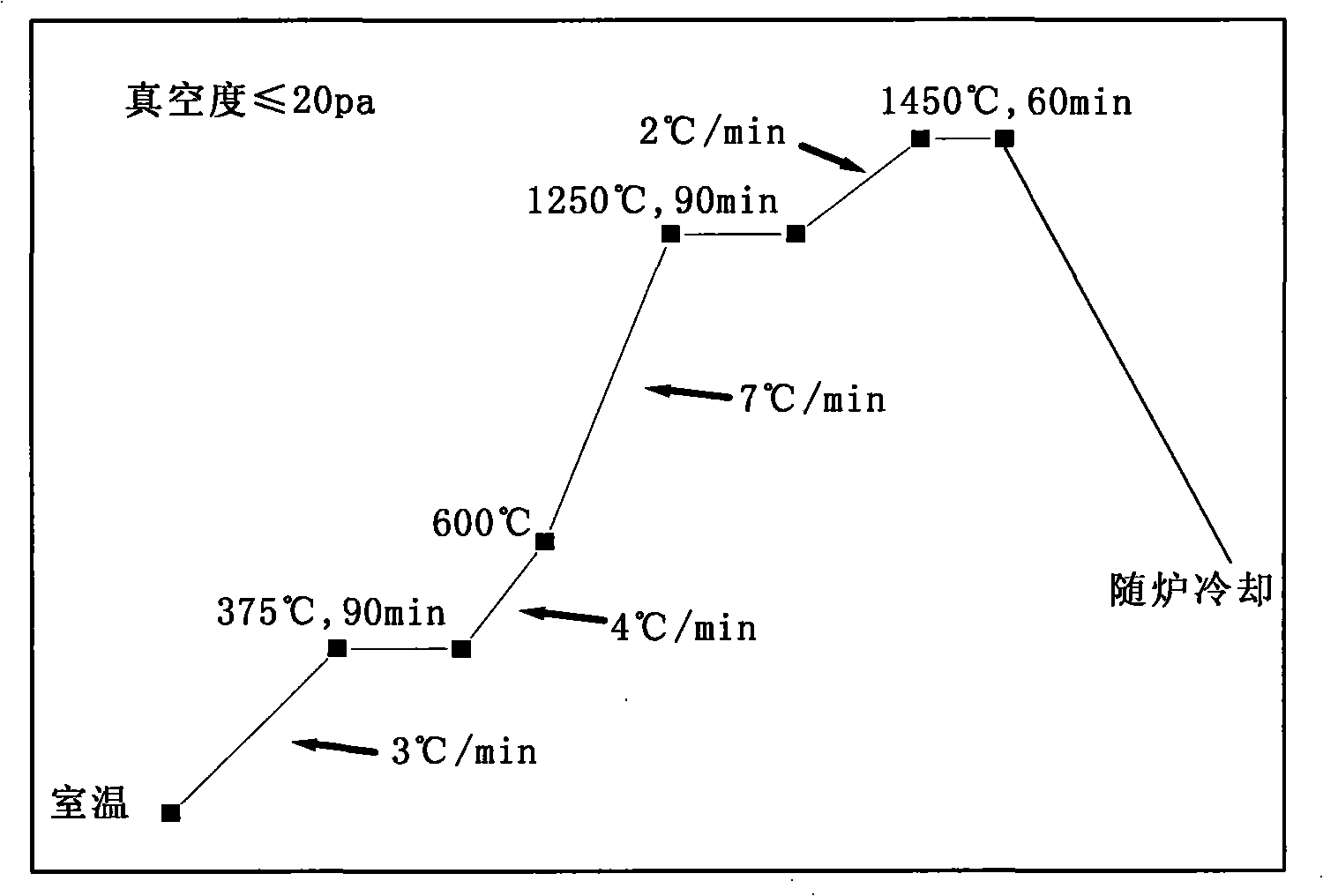
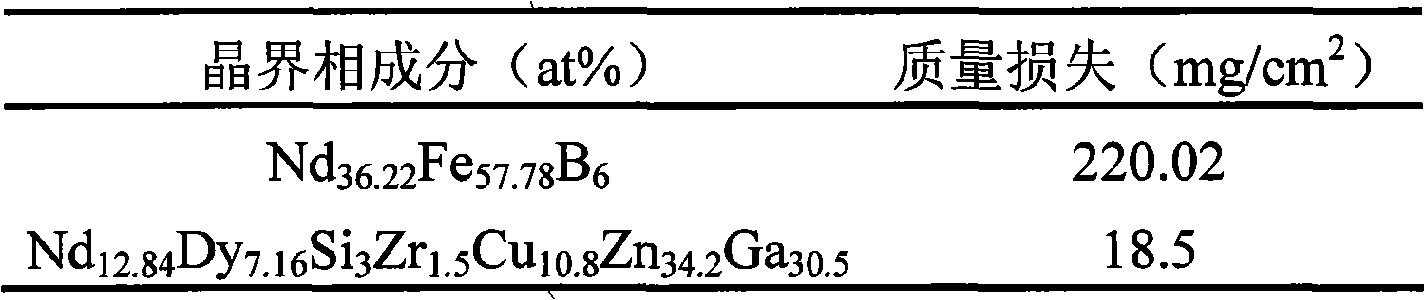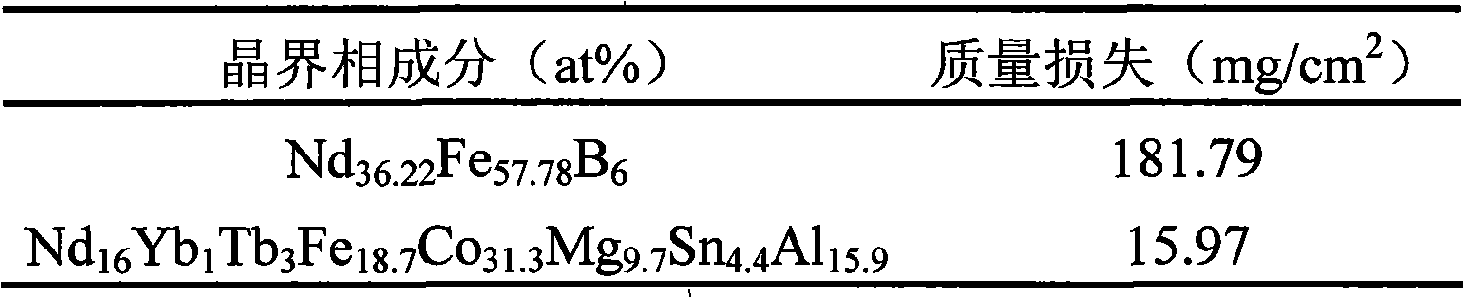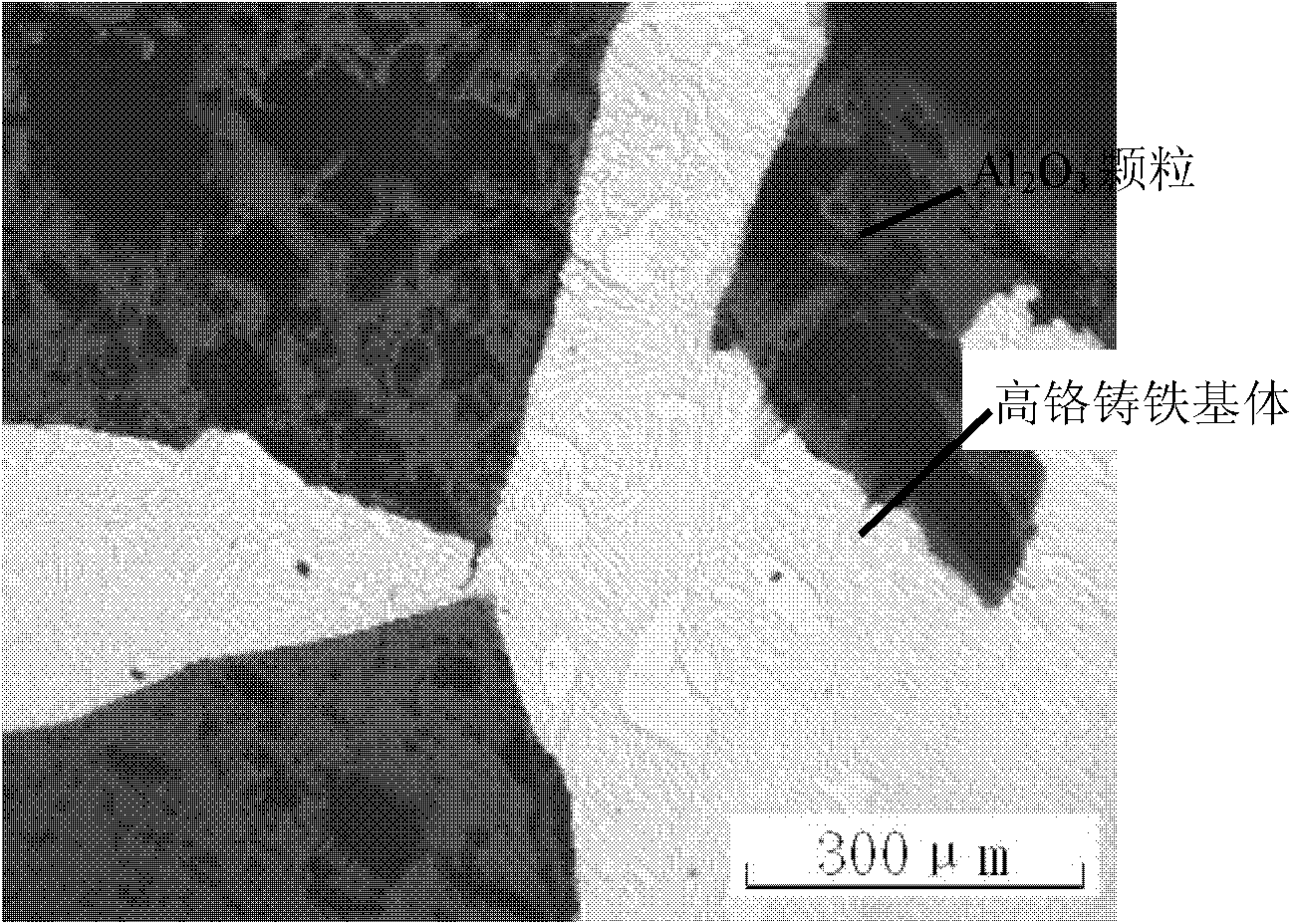Patents
Literature
2423 results about "Vacuum sintering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
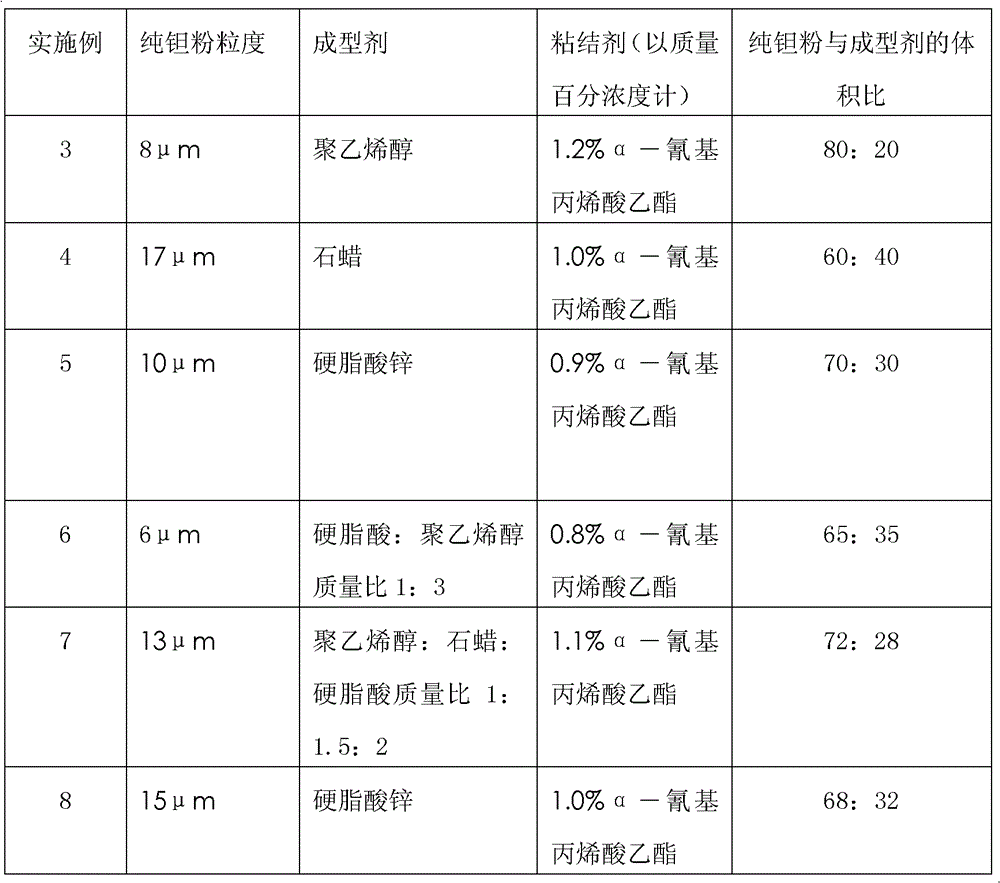
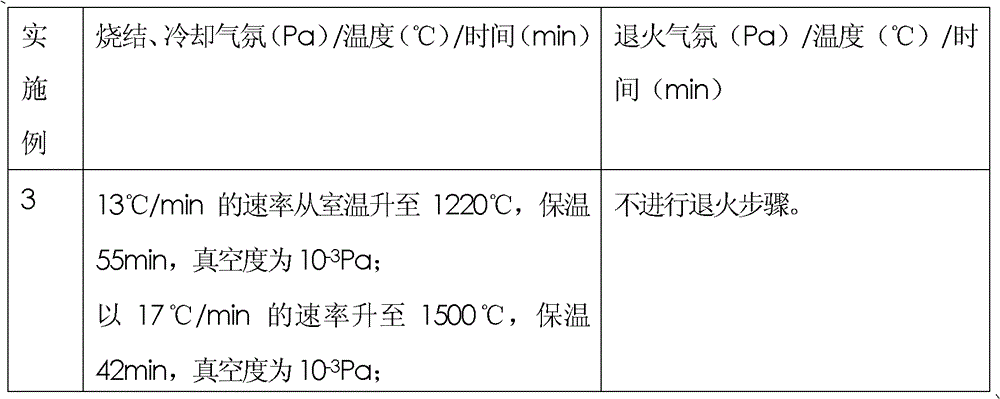
Method for preparing complexly shaped biomedical porous titanium molybdenum alloy implant body
InactiveCN102335742ADesign personalizationHigh dimensional accuracyIncreasing energy efficiencyProsthesisNatural boneMetallic materials
The invention provides a method for preparing a complexly shaped biomedical porous titanium molybdenum alloy implant body and belongs to the technical field of biomedical porous metallic material preparation. The method comprises the following steps of: taking a mixture of titanium and molybdenum metallic element powder and organic polymer powder as raw materials, and then preparing the biomedical porous titanium molybdenum alloy implant body by adopting the processes, such as three-dimensional modeling, selective laser-firing rapid forming, thermal de-greasing, vacuum sintering, and the like. The processing steps are simple, the period is short, the use ratio of materials is high, the cost is low, any complexly shaped porous titanium alloy implant body can be conveniently manufactured, and the method has efficiency and economic advantages in individual design and rapid manufacturing of the implant body. A titanium molybdenum alloy material prepared by using the method has the advantages that pore space is uniform, adjustment scopes of porosity, aperture ratio and aperture are wide, elasticity modulus and compression strength are in close proximity to natural bone, and the demand on biomechanical compatibility required by a biomedical material is met.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Grain boundary phase-reconstructed high-corrosion resistance Sintered NdFeB magnet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101320609ALow melting pointGuaranteed MagneticInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureElectrode potentialPowder mixture
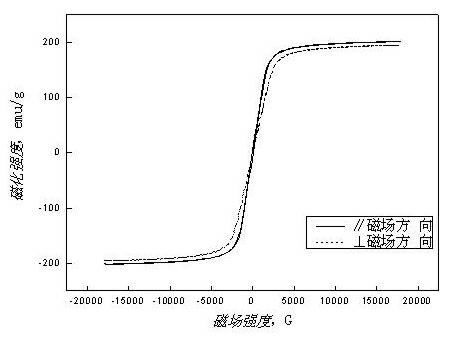
The invention discloses a sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet with high corrosion resistance and the grain boundary reconstruction and a preparation method thereof. The composition of the invention is that: NdeFe100-e-f-gBfMg, wherein, e is greater than or equal to 6 and equal to or less than 24, f is greater than or equal to 5. 6 and equal to or less than 7, g is greater than or equal to 0.03 and equal to or less than 8, M is one or some of elements Dy, Tb, Pr, Sm, Yb, La, Co, Ni, Cr, Nb, Ta, Zr, Si, Ti, Mo, W, V, Ca, Mg, Cu, Al, Zn, Ga, Bi, Sn and In; The method is that: main phrase alloy and reconstructed grain boundary phase alloy are respectively pulverized and mixed uniformly; the powder mixture is pressed to a mould in the magnetic field, and fabricated into a sintering magnet in a high vacuum sintering furnace. By the reconstruction of the grain boundary phase composition, the invention can obtain the grain boundary phase alloy with low melting point and high electrode potential, decrease the potential difference between the main phase and the grain boundary phase on the basis of ensuring the magnetic properties, promote the intrinsic corrosion resistance of magnet, and has the advantages of simple process, low cost and being suitable for the batch production. Therefore, by combining the grain boundary reconstruction and double alloy method, the sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet with high intrinsic corrosion resistance can be prepared.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High-wear resistant Ti (C, N)-base ceramet tool bit and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101302595AReliable guarantee of high nitrogen-carbon ratioReliable Guarantee of HardnessLow nitrogenWear resistant
The invention provides a high-abrasion Ti(C, N) based metal ceramic tool and a preparation thereof. The Ti(C, N) based metal ceramic tool uses Ni and Co as a binder phase, is added with at least one carbonitride of Ti(Cx, N1-x) or (TiC)x plus (TiN)1-x as a basic batch, and consists of at least one composition of WC, Mo2C, Co, Ni, ZrC, Cr3C2, VC, TaC and NbC, and the balance being Ti(Cx, N1-x) or (TiC)x plus (TiN)1-x, wherein, an X value for adding the carbonitride of the Ti(C, N) based metal ceramic tool is as follows: X is less than or equal to 0.5 and more than or equal to 0.4, or the X is more than 0.5 and less than or equal to 0.7. The Ti(C, N) based metal ceramic tool is prepared according to the content of nitrogen by nitrogen pressure sintering or vacuum sintering combined with hot isostatic pressing treatment, thereby preventing nitrogen from escaping during the process of sintering high-nitrogen alloy, so that the high-nitrogen-carbon ratio in matrix and material hardness can be reliably guaranteed, and anti-oxidative abrasion property and anti-diffusive abrasion property of the material can be obviously increased through adding slight ZrC, Cr3C2, VC and other carbides into the basic batch; meanwhile, compactability and buckling strength of a low-nitrogen alloy structure can be obviously improved through optimally distributing each composition and content. The Ti(C, N) based metal ceramic tool is widely suitable for high-speed cutting tools of medium-low carbon steel and low alloy steel.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ceramic particle reinforced composite wear-resistant part and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101898238ASolve the problem of difficult penetrationImprove wear resistanceCeramic particleWear resistant
The invention relates to a ceramic particle reinforced composite wear-resistant part and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: ceramic particles and metal powder are mixed evenly to fill in a special mould; then the mixture along with the mould is placed in a vacuum sintering furnace to sinter, wherein metal powder and ceramic particles are bound together to form a perform; after cooled, the mould is opened to take the perform out and place the perform on the side of the end face of a casting mold cavity; parent metal material is smelted by a medium-frequency induction furnace to form molten metal; during the casting, the molten metal is poured, metal powder in the perform is molten to form a cast-penetration path under the heat of molten metal, thus the molten metal can easily penetrate ceramic particles to form particle reinforced composite material in situ; and the surface layer of the obtained wear-resistant part consists of parent metal and composite material. The wear resistance of the composite material prepared by the method of the invention is ensured and the composite material has high impact resistance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Method for increasing sintering Nd-Fe-B coercive force by adding nano-oxide in crystal boundary phase
InactiveCN1688000ANot easily oxidizedIncrease the coercive force of the magnetInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureIngotGrain boundary
This invention discloses a method for increasing sintered Nd FeB coercive force by adding nm oxide in grain-boundary phase including the following steps: 1,applying casting technology to produce NdFeB ingot alloy or applying rapid hardening film technology to produce NdFeB rapid hardening film of with host phase alloy, applying casting technology to produce ingot alloy or rapid hardening film technology to get rapid hardening film or rapid quench technology to manufacture a rapid quench strip with the grain boundary phase alloy, 2, processing powder with the two alloys, 3, adding a nm oxide to the grain boundary phase alloy powder, 4, pressing the mixed powder into formation, 5, producing sintered magnetic body in a vacuum sintering oven.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for improving performance of sintered Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic material
ActiveCN101615459AEvenly distributed and orderlySolve bad problems such as α-Fe segregationInorganic material magnetismHigh energyPositive pressure
The invention relates to a method for improving performance of sintered Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic property by a rapid-hardening flake grain boundary diffusion heavy rare earth compound in rare earth material technical field, which comprises the following steps: 1) rapid-hardening technology is adopted to prepare an Nd-Fe-B alloy rapid-hardening flake; 2) a high-energy ball mill is used to prepare the heavy rare earth compound into powder particles with diameter being smaller than 1mu m; 3) the rapid-hardening flake is put into heavy rare earth compound turbid liquid to carry out ultrasonic coating; 4) the coated rapid-hardening flake is put into a sintered furnace filled with Ar2 to carry out positive pressure thermal diffusion; 5) ball milling, powder processing, orientation shaping, isostatic pressing and vacuum sintering are adopted to prepare the strip-casting flake after the heat treatment into a magnet. The chemical formula of the Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic material is NdxFe(100-x-y-z-xl)ByCozCuxl, and the mass percent is as follows: x is 30-31.5, y is 0.95-1, z is 1-1.2, and xl is 0-0.06. The magnet prepared by the invention improves the intrinsic coercivity on the basis of keeping the current magnetic energy product.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
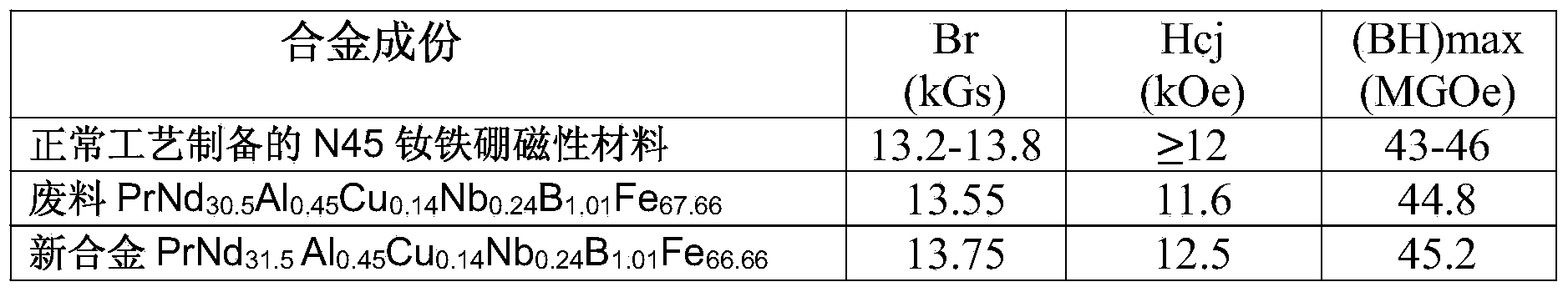
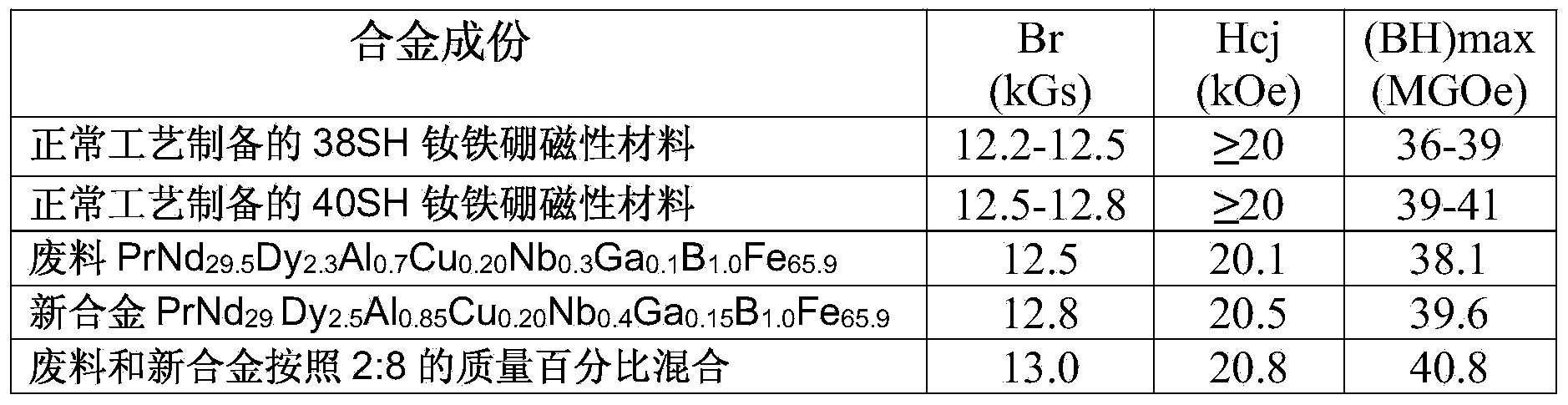
Method for preparing neodymium iron boron through regenerating waste material containing neodymium, iron and boron
ActiveCN103866127AFully absorb hydrogenImprove recycling ratesMagnetic materialsProcess efficiency improvementMetallurgyEconomic benefits
The invention provides a method for preparing neodymium iron boron through regenerating a waste material containing neodymium, iron and boron. The method comprises steps of (1) preprocessing the waste material; (2) correcting the components of the waste material; (3) crushing by hydrogen; (4) preparing into powder; (5) molding under a magnetic field; and (6) vacuum sintering. The method fully uses the waste material recycled in a production process, has high recovery rate of the waste material, can produce high performance product, has a simple and controllable flow, has high operability, uses no strong acid and strong base polluting the environment, is environment-friendly and energy-saving, and has high social and economic benefits.
Owner:CHINALCO JINYUAN RARE EARTH
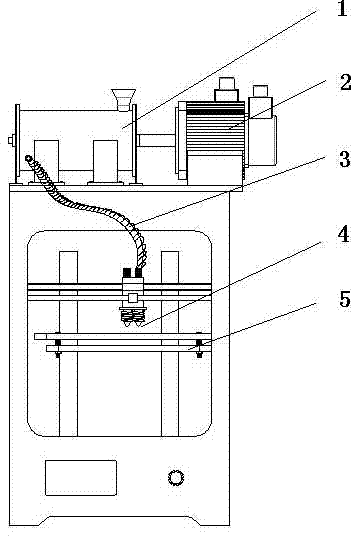
Metal 3D printing product production method by means of low-power laser sintering
InactiveCN103769586ACeramic shaping apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser sinteringAdhesive
The invention discloses a metal 3D printing product production method by means of low-power laser sintering. According to the metal 3D printing product production method, metal powder materials and thermoplastic molding adhesives are adopted to prepare a low-melting-point 3D metal printing raw material mixture; due to the fact that the thin-layer thermoplastic adhesives are formed on the surfaces of metal powder particles, low-power (smaller than 50 W) selective laser sintering or electron beam sintering 3D printer is used, the metal powder materials are stacked to be molded through surface layer thermoplastic adhesive low-temperature melting-cooling adhesive solidification, then metal part product green bodies can be printed through the prepared metal powder raw materials, the molded adhesives in the part green bodies are removed through thermal debinding or chemocatalysis debinding or other technologies, high-temperature sintering is conducted on the green bodies without the molded adhesives through a vacuum sintering method or an atmosphere protection sintering method, and alloying compact high-performance complex metal part products are produced. The metal 3D printing product production method by means of low-power laser sintering has the advantage that the 3D printing device and technology for producing the metal parts are low in cost.
Owner:王利民
Method and device for preparing high-silicon silicon steel sheet in static magnetic field with powder sintering method
ActiveCN102658367AAccurate control of silicon contentHigh densityInorganic material magnetismInlet valveExhaust pipe
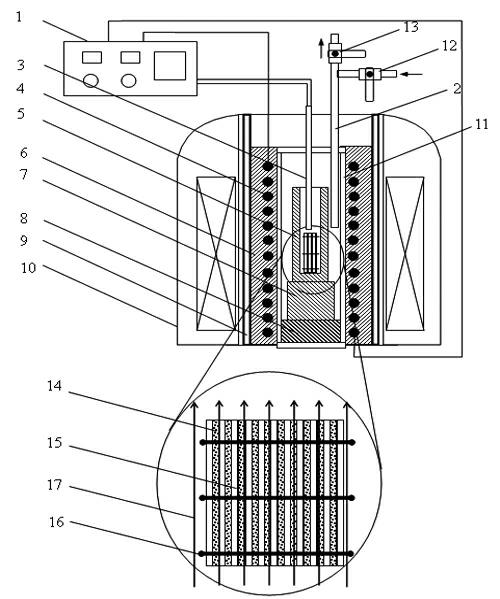
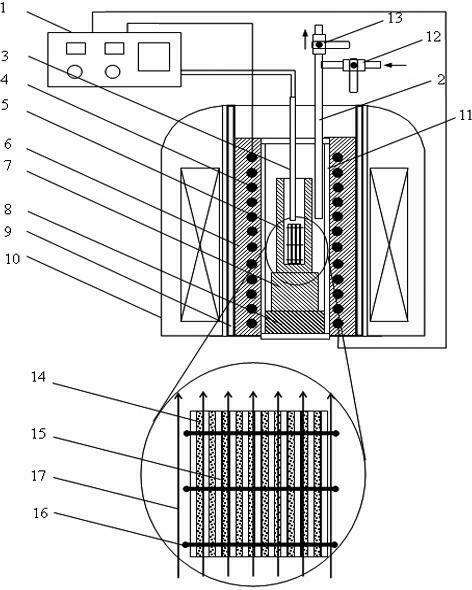
The invention relates to a method and device for preparing a silicon steel sheet in a static magnetic field with a powder sintering method. The specific process of the method consists of the following steps of: mixing Fe-Si powder; rolling into a plate blank; and sintering a Fe-6.5 weight percent Si green compact in a static magnetic field. In the method, 6.5 percent by weight of Si high-silicon steel with high density is obtained by using the influence of the magnetic field on the sintering densification and orientation process of a Fe-6.5 weight percent Si powder green compact, and an easily-magnetized axis is oriented along the magnetic field. An atmosphere / vacuum sintering device in a static magnetic field consists of a temperature control device, an exhaust pipe, a thermocouple, a heating element, a corundum crucible, a refractory fiber, a support block, a heat insulating block, a water-cooled bush, a static magnetic field generating device, a sealed corundum pipe, an inert gas inlet valve, a vacuum pumping valve, a Fe-6.5weight percent Si green compact, a thin corundum plate interlayer and a fixing molybdenum wire. The 6.5 percent Si silicon steel sheet prepared with the method has the advantages of near net molding, superior magnetic property, high orientation degree and the like, and has a remarkable industrial application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Toughened hard alloy and preparation method thereof
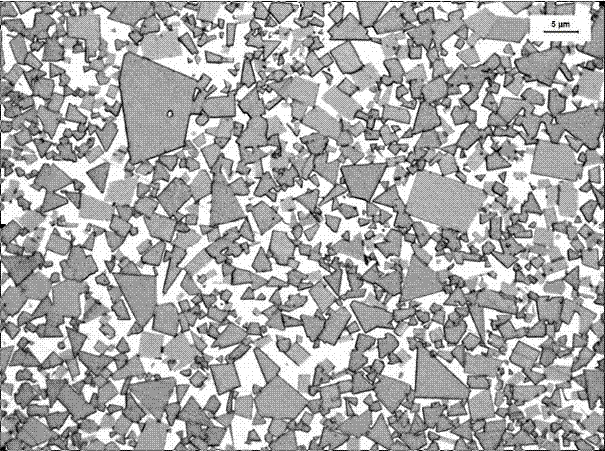
The invention discloses a high-toughness toughened hard alloy which comprises 10%-30% of Co or Co and Ni serving as a binding phase, 0-1.5% of Cr3C2 serving as an inhibitor, and the balance of hard phase WC, wherein the hard phase consists of WC crystalline grains with coarse, medium and fine grain sizes, the grain size of coarse grains is 9-15 mu m, the grain size of medium grains is 4-7 mu m, the grain size of the fine grains is less than 2 mu m, and the mean grain size of the hard phase WC is 1.6-3.2 mu m. The preparation method of the toughened hard alloy comprises the following steps of: preparing materials including 10%-30% of cobalt powder or cobalt powder and nickel powder, 0-1.5% of chromium carbide powder, and the balance of tungsten carbide powder, wherein Fsss grain size of the coarse grains WC is 9.0-11.0 mu m, the coarse grains WC account for 20%-42% of the prepared powder, the Fsss grain size of the medium grains WC is 4.0-6.0 mu m, the medium grains account for 10%-25% of the prepared powder, the Fsss grain size of the fine grains WC is 1.0-2.0 mu m, and the fine grains account for 20%-40% of the prepared powder; grinding, wherein a liquid paraffin forming agent which accounts for 2% of the prepared materials is added, mixed with absolute ethyl alcohol in a liquid-solid ratio of 300 ml / kg-350ml / kg, wet-ground for 20-28 hours according to the condition that the ratio of grinding media to material is 4:1, and sprayed and dried to obtain mixed materials; pressing; vacuum-sintering and isostatic-pressing and sintering. According to the invention, the toughness is improved on the premise of ensuring the hardness of the alloy, so that the operation field is expanded, special requirements of a cold-heating and cold-punching mould and a holt-rolling hard alloy roller ring are satisfied, and the service life of the high-toughness toughened hard alloy is prolonged.
Owner:ZHUZHOU HARD ALLOY GRP CO LTD
Method for preparing porous tantalum medical implant material through three-dimensional printing forming
ActiveCN102796909AFast molding speedHigh precisionAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyPorous tantalumBone tissue
The invention discloses a method for preparing a porous tantalum medical implant material. The method comprises the following steps of: feeding mixed tantalum power formed by mixing pure tantalum powder and a forming agent into a printing platform of a three-dimensional printer, and rolling and paving; spraying an adhesion agent by a printing head of the three-dimensional printer to adhere the mixed tantalum powder so as to form a two-dimensional plane; descending a working table 80 to 100 mu m, and processing the next layer; accumulating and forming layer by layer; removing the tantalum powder particles which are not adhered to obtain an initially formed sample; and performing aftertreatment such as degreasing, vacuum sintering, cooling and the like to obtain the porous tantalum medical implant material, wherein the volume ratio of the pure tantalum powder to the forming agent is (60-80):(20-40), and the adhesion agent is 1 mass percent alpha-cyanoacrylate adhesive. The pores of the porous tantalum medical implant material prepared by the method are completely communicated in a three-dimensional mode; the porous tantalum medical implant material prepared by the method is high in biocompatibility; and meanwhile, the mechanical property of the porous tantalum medical implant material prepared by the method is consistent with that of loading bone tissues of a human body.
Owner:CHONGQING RUNZE PHARM CO LTD
Preparation method of high-coercivity sintered Nd-Fe-B and product
InactiveCN104505206AIncrease profitImprove liquidityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare earthNitrogen
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-coercivity sintered Nd-Fe-B. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a main phase alloy powder and a grain boundary phase alloy powder; protecting the prepared main phase alloy powder and the grain boundary phase alloy powder by using nitrogen or argon in a protective medium, and uniformly mixing, wherein the mass percent of the added grain boundary phase alloy powder accounts for 0.1-10 percent; carrying out orientation profiling and cold isostatic pressing on the mixed alloy powder; in a vacuum sintering furnace, sintering a profiled magnet block for 2-4h at the temperature of 1000-1100 DEG C, then carrying out primary tempering for 2-4h at the temperature of 800-950 DEG C, and carrying out secondary tempering for 2-4h at the temperature of 450-650 DEG C to prepare the sintered Nd-Fe-B. The invention also discloses the high-coercivity sintered Nd-Fe-B. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, by virtue of low melting point auxiliary alloy, the wetting temperature between a grain boundary phase and a main phase is lowered, the wetting time is prolonged, the utilization ratio of heavy rare earth is increased, the used amount of rare earth is lowered, the process is simple, the cost is low, and the high-coercivity sintered Nd-Fe-B is suitable for mass production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device for producing metal 3D printing method product
The invention discloses a method and device for producing a metal 3D printing product. A low-melting-point thermoplastic 3D metal printing raw material mixture is prepared by adopting a method of combination between metal powder materials and forming adhesives, a 3D printer (please see the 3D printer in the figure) using a commercial FDM is slightly modified, a metal part product blank can be printed by using the prepared metal printing raw material mixture, the forming adhesives in a blank part are removed by using a thermal debinding method or a chemocatalysis debinding method or other technologies, high-temperature sintering is carried out on the blank without the forming adhesives by using a vacuum sintering method or an atmosphere protective sintering method, and a high-performance complex metal part product with alloying densification is produced. The method and device for producing the metal 3D printing product have the advantages that the device and the technology for protruding metal parts or parts made of other materials in a low-cost mode through a 3D printing method are developed.
Owner:王利民
High-strength tenacity agglomeration neodymium-iron-boron magnet reconstructed by crystal boundary phase and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101325109AImprove toughnessLow melting pointMagnetic materialsSintered magnetsGrain boundary
The invention discloses a high-obdurability Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet reconstructed by the grain boundary phase and the preparation method thereof. The Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet comprises the component of NdeFe100-e-f-gBfMg, wherein, e is more than or equal to 6 and less than or equal to 24, f is more than or equal to 5.3 and less than or equal to 6.4, and g is more than or equal to 0.01 and less than or equal to 6, and M is one or more elements of Dy, Tb, Pr, Sm, Ce, Yb, Co, Ni, Mn, Nb, Ta, Zr, Si, Ti, Mo, Ag, Au, Mg, Cu, Al, Zn, Ga, Bi, Sn and In; the preparation method comprises the following steps: main phase alloy and grain boundary phase alloy are respectively prepared into powder, and then the powder is intensively mixed; the mixed powder is pressed into the molded blank in the magnetic field; and the sintered magnet is obtained in a high-vacuum sintering oven. Through the restruction of the grain boundary phase component, the solution grain boundary phase alloy with low smelting point and high strength ductility is achieved, the obdurability of the grain boundary phase is enhanced on the basis that the magnetic property is guaranteed, thereby the high ductility of the magnet is enhanced, and the process is simple, the cost is low, and the magnet is suitable for the mass production, thereby the double-alloy method combined with the grain boundary restruction can be used for preparing the Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet with high obdurability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Preparation method of transparent fluorescent ceramic for LEDs (light-emitting diodes)
The invention discloses a preparation method of transparent fluorescent ceramic for LEDs (light-emitting diodes), which comprises the following steps: proportionally mixing high-purity ceramic raw material powder, a sintering assistant and fluorescent powder; adding into a ball milling tank, adding a ball milling medium and milling balls at the same time, and carrying out ball milling on the ball mill for some time; taking out the powder, drying, grinding and screening; sequentially carrying out dry press formation and cold isostatic compaction on the screened powder; sequentially carrying out vacuum sintering and hot isostatic compaction sintering on the formed billet; and carrying out annealing treatment to obtain the high-compactness transparent fluorescent ceramic for LEDs. In the formation and sintering steps, two different processes are respectively adopted, so that the prepared transparent fluorescent ceramic has higher compactness and better uniformity, and has better light emitting effect when being used for LED devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI SANSI ELECTRONICS ENG +2
Reactively sintered silicon carbide ceramic and production process
InactiveCN101508570AImprove performanceHigh mechanical strengthPolyvinyl alcoholTemperature resistance
The invention discloses a reaction sintering silicon carbide ceramics and a manufacturing technique thereof. The materials of the ceramics comprise: 5-8 parts by weight of SiC powder with a granularity of 10-90 mum, 2-3 parts by weight of SiC powder with a granularity of 0.1-10mum, 0.5-1 part by weight of carbon black powder, 0.3-0.8 part by weight of graphite powder and 0.1-0.3 part by weight of polyvinyl alcohol or carboxymethyl cellulose liquid; the silicon carbide ceramics is manufactured after the pulping of materials, slip casting, drying, vacuum sintering and sand removing and oxidization. The manufacturing technique of the invention is mature and reliable, the silicon carbide ceramics of the invention is fine in product performance and stable in quality, and hardness, temperature resistance, wear resistance and corrosion resistance thereof all reach the standard of international reaction sintering silicon carbide ceramics. In addition, the ceramics of the invention is widely applied to fields such as ceramics kiln furniture, desulphurization nozzles, metallurgy, chemical engineering and the like, and the size deformation rate of the product is less than 0.1%.
Owner:WEIFANG HUAMEI FINE TECHN CERAMICS
Method for preparing WC base hard alloy with high hardness and high toughness
The invention discloses a method for preparing a WC base hard alloy with high hardness and high toughness. Nano W powder, nano graphite powder and superfine Co powder or superfine Ni powder or superfine Co powder and superfine Ni powder with the specific surface area average granularity of smaller than 0.5 micron are used as raw materials; superfine Cr3C2 and rare earth are used as combined doping agents; the addition amount of the superfine Cr3C2 is controlled to account for 6-8 percent by mass of alloy binding agent; the addition amount of rare earth is controlled to account for 0.3-0.7 percent by mass of alloy binding agent in the terms of oxide; W-Co-C or W-Ni-C or a W-Co-Ni-C mixed material which is combined and doped by superfine Cr3C2 and rare earth is prepared by adopting a wet grinding process; an alloy press blank is prepared by adopting a die forming or hydrostaticisostatic forming process according to the product size and appearance characteristics; alloy is sintered by adopting a vacuum-sintering process or a pressure sintering process; and the alloy sintering temperature is controlled between 1,360 DEG C and 1,420 DEG C. According to the invention, WC base hard alloy with high crystalline perfection, pure plate-shaped crystal structure and isotropy can be prepared and the double-high performance characteristics of the alloy are realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG XIANGLU TUNGSTEN
Nano modified WC/Co cemented carbide material and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a nano-modified WC / Co hard alloy material and a method for manufacturing the same, which relate to a modified WC / Co hard alloy material and a method for manufacturing the same and avoids the problems of complicated preparation technology, high requirements for process parameters, updating of equipment, high cost and grain growing easily in the prior method for improving the comprehensive property. The nano-modified WC / cobalt hard alloy is made by nano-modified material and WC / cobalt alloy. The preparation method comprises the following: a step of mixing powder; a step of drying and screening; a step of mixing wax; a step of drying and screening; a step of press molding; and a step of vacuum sintering. Compared with the nano before modification, the hardness of the nano-modified WC / Co hard alloy material is increased to more than 1 HRA, the bending strength is increased by about 20 percent, the impact ductility is increased by about 40 to 50 percent, the elongation is increased by 20 to 40 percent, and the impact wear property is increased to more than 100 percent. The preparation method has a simple process and low requirements on process parameters, which compared with the powder metallurgy has the advantage of high ratio of property to price.
Owner:无锡海韵新材料科技有限公司
Method for preparing high performance sintered neodymium-iron-boron air stream millby hydrogenation
InactiveCN101051544AImprove powder output efficiencyIncrease the coercive force of the magnetInorganic material magnetismNitrogen gasCrusher
The method includes steps: (1) using casting technique to produce ingot of Nd-Fe-B alloy, or using quick hardening technique to produce quick hardening slices; (2) using hydrogen explosion technique or crusher to crash alloy of ingot or quick hardening slices into coarse powder; (3) through airflow grinding machine to produce fine powder from coarse powder; and mixed compressed gas from nitrogen and hydrogen is adopted by the airflow grinding machine; (4) mixing fine powder, gasoline, and antioxidant evenly by blender so as to obtain mixed powder; (5) molded blanks are pressed from mixed powder under 1.2-2.0T magnetic field; (6) molded blanks are sintered inside high vacuum sintering furnace at deg.C 1050-1120 for 2-4h; and through temper of heat treatment 2-4h at deg.C 500-650 so as to produce sintered magnet. Comparing with traditional technique, the invention produces magnet with high coercive force, and fine powder in high efficiency, is suitable to batch production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Manufacturing method of cam of engine camshaft
InactiveCN102000824AEliminate the problem of easy crackingSimple preparation processFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMass ratioVolumetric Mass Density
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of a cam of an engine camshaft, which is characterized by successively comprising the following steps of: (1) preparing raw materials, namely a mixed powder of iron, chromium, molybdenum, nickel, carbon and copper, and adding a lubricant with 0.1-1% mass ratio; (2) pressing the mixed powder on a pressing machine under the pressure greater than 600 MPa into a cam part with density greater than 7.3 g / cm<3>; (3) sintering the cam part at the temperature of 1100-1350 DEG C for more than 10-30 min in a vacuum sintering furnace or a continuous sintering furnace; and (4) thermally treating, determining the thermal treatment process according to the chemical composition requirements of the sintered part, quenching at the temperature of 800-1000 DEG C, maintaining the temperature for 30-45 min, or adopting high-frequency thermal treatment, tempering at the temperature of 150-400 DEG C, and maintaining the temperature for 110-130 min. The manufacturing method has the advantages of simple process, high product precision, great strength, good surface smoothness, lowered production cost and enhanced production efficiency.
Owner:NBTM NEW MATERIALS GRP
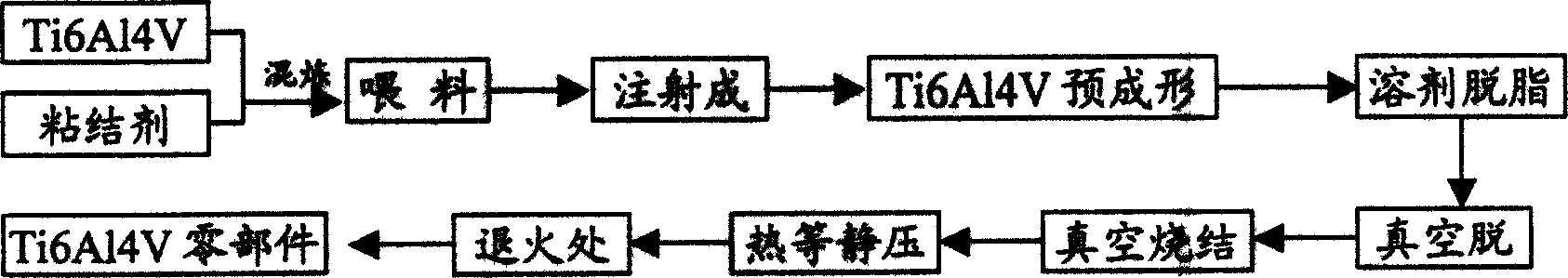
Ti6Al4V alloy injection forming method
An injection moulding technology for the Ti6A14V alloy workpiece includes such steps as steps as providing Ti6A14V powder, proportionally mixing it with adhesive for 1.5-2 hr, granulating, injection moulding, thermal vacuum degreasing in the mixture of absolut alcohol and vinyl trichloride, vacuum sintering, isostatic pressure treating and annealing. Its advantages are high mechanical performance and high size precision.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
High saturated magnetic flux density and low loss manganese-zinc ferrite material and its preparing method
ActiveCN1749209ASimple manufacturing methodLower sintering temperatureInorganic material magnetismVolumetric Mass DensityNanometre
The present invention discloses high saturated magnetic flux density and low loss manganese manganese-zinc ferrite material and its preparation process. The manganese-zinc ferrite material contains: Fe2O3 52-54 mol%, MnO 33-40 mol%, ZnO 8-13 mol%, supplementary components CaCO3 100-600 ppm, SiO2 50-300 ppm and other metal oxides. The preparation process includes the steps of: mixing material, pre-sintering, adding supplementary components, secondary ball milling, forming and sintering. The supplementary components are common oxide grains, and this result in easy adding and low cost. The preparation process of the manganese-zinc ferrite material has relatively low pre-sintering and sintering temperature and relaxed requirement on sintering apparatus, may be completed in common vacuum sintering furnace, and easily realized in industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method for preparing rare earth-doped yttrium aluminum garnet transparent ceramic
ActiveCN101985397AHigh linear transmittanceImprove mechanical propertiesRare-earth elementSpray Granulation
The invention relates to a method for preparing rare earth-doped yttrium aluminum garnet transparent ceramic. In the invention, high-transparency polycrystalline ceramic is prepared by using commercial powdered Y2O3, Al2O3 and Re2O3, of which the purities are over 99.9 percent, as main raw materials and by spray granulation dry pressing molding process and vacuum reaction and sintering, wherein the Re may be one or several of trivalent rare earth elements such as Nd<3+>, Yb<3+>, Cr<3+>, Er<3+>, Ce<3+>, Sm<3+> and Eu<3+>; MgO or CaO or tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) or SiO2 is used as a sintering assistant; a certain amount of bonding agent, plasticizer and dispersant is added; the oxides, sintering assistant and additive are mixed and added into a liquid medium, and the mixture is ball-milled and mixed for 0.5 to 100 hours; after the powder materials are mixed uniformly, the powder is made into spherical or approximately spherical grains; blanks formed by drying pressing isostatic forming are degreased; sintering the blanks in a vacuum sintering furnace; and annealing after sintering. The transmissivity at a laser wavelength of the rare earth-doped yttrium aluminum garnet transparent ceramic prepared by the method is more than or equal to 77 percent.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for manufacturing driving gear of motorcycle clutch
InactiveCN102000825ASolve the small densityEliminates crack-prone defectsFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesVolumetric Mass DensitySurface smoothness
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a driving gear of a motorcycle clutch, which is characterized by sequentially comprising the following steps of: (1) preparing a raw material, namely mixed powder of iron, chromium, molybdenum, nickel, carbon and copper, and adding a required amount of lubricant; (2) pressing the mixed powder into a driving gear part with the density of more than 7.3g / cm<3> on a pressing machine with the pressure of more than 600MPa; (3) sintering, namely sintering the driving gear part in a vacuum sintering furnace or a continuous sintering furnace at the temperature of between 1,100 and 1,350 DEG C for 10 to 120 minutes; and (4) performing heat treatment, namely determining a heat treatment process according to the chemical component requirement of the sintered part, quenching at the temperature of between 800 and 1,000 DEG C, preserving heat for 30 to 45 minutes, tempering at the temperature of between 150 and 400 DEG C, and preserving heat for 110 to 130 minutes. The method has the advantages that: the manufacturing process is simple; the driving gear has high accuracy, strength and surface smoothness; and the problem that a die is easy to crack because the forging process is performed at a high temperature is effectively solved, so that production cost is reduced, and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:NBTM NEW MATERIALS GRP
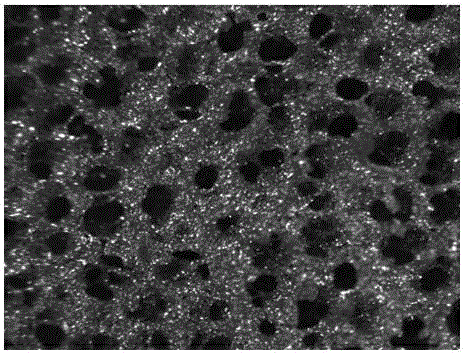
Porous tantalum serving as medical metal implanted material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102205144AReduce contentImprove mechanical propertiesMetal-working apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPorosityNeck structure
The invention relates to porous tantalum serving as a medical metal implanted material and a preparation method thereof. The porous tantalum has a pore three-dimensional communicating distribution foam structure, wherein a solution which is prepared from an organic adhesive and a dispersant and tantalum powder are adopted to prepare a tantalum powder slurry; the tantalum powder slurry is poured into an organic foam body and soaked until the tantalum powder slurry is filled in the pores of the organic foam body, drying is carried out so as to remove the dispersant in the organic foam body which is poured with the tantalum powder slurry, and ungreased treatment is carried out in the presence of inert gas so as to remove the organic adhesive and the organic foam body, and vacuum sintering is carried out so as to prepare the porous sintered body; on a foam framework which is formed by accumulated sintered pure tantalum powder, and a sintering neck structure exists among tantalum powder particles; and the tantalum powder is annealed in vacuum and subjected to conventional post-treatment. The porous tantalum has the advantages of high porosity, uniform and communicated porous distribution, uniform sintered microstructure particles, remarkable sintering neck, ensured excellent chemical performance and especially excellent ductibility.
Owner:CHONGQING RUNZE PHARM CO LTD
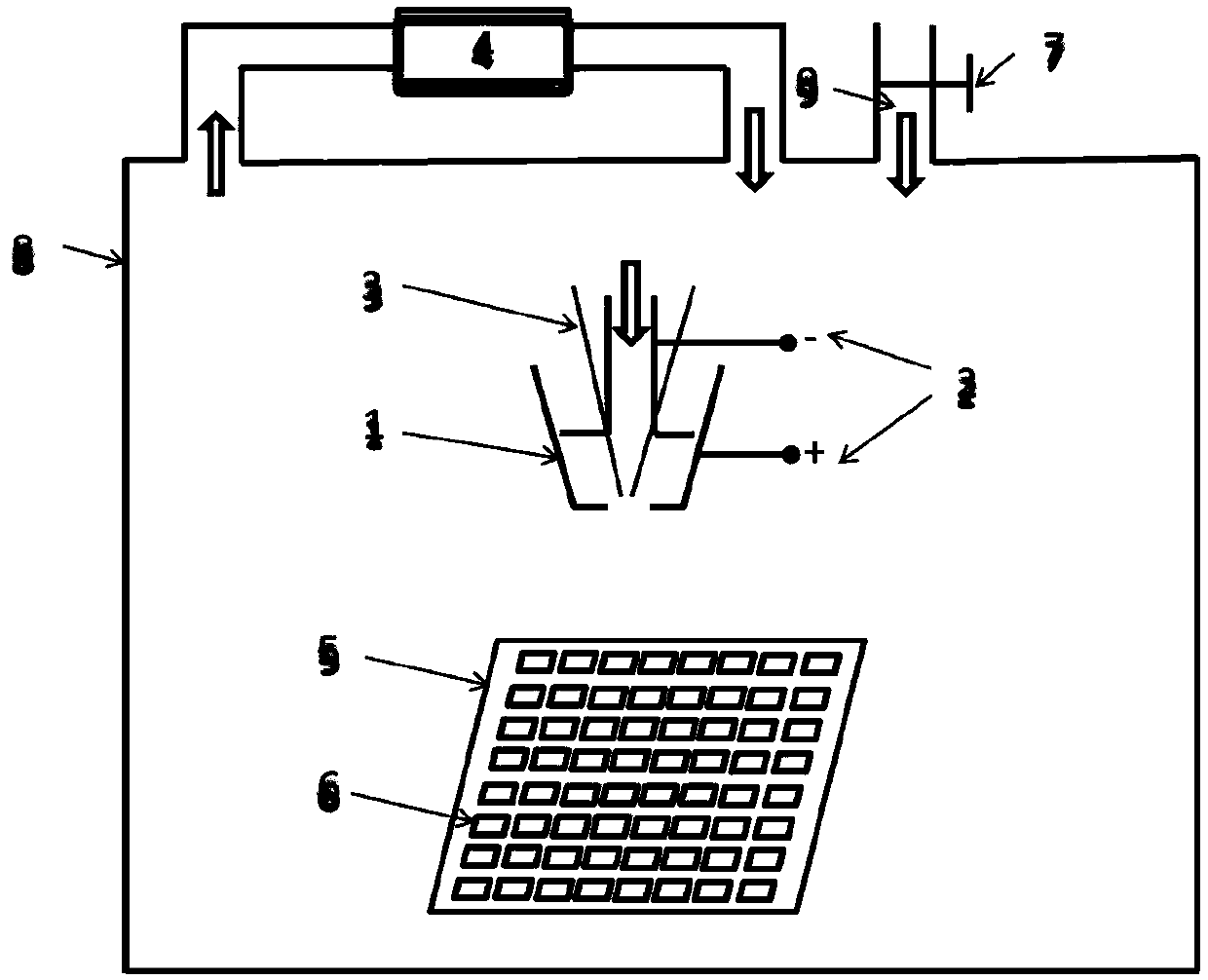
Composite technique of preparing lacunaris titanium coating by using cold spraying and vacuum sintering
InactiveCN101032633AGood pore uniformityHigh bonding strengthImpression capsSurgeryArtificial boneTitanium alloy
The present invention discloses composite cold spraying and vacuum sintering process for preparing porous titanium coating. Mixed titanium-magnesium powder is first sprayed onto the roughened titanium or titanium alloy substrate to form composite titanium-magnesium coating, which is then sintered at high vacuum and high temperature to obtain porous titanium coating. Thus produced porous titanium coating has no oxide, thickness greater than 0.5 mm, opened and communicated pore structure, pores of 30-200 microns, porosity of 30-65 %, and metallurgical combination with the substrate with combination strength higher than 60MPa and elastic modulus adjustable in 30-50 GPa. The present invention is suitable for making bearing hard tissue implant, such as artificial joint, artificial bone, artificial tooth root, etc. with improved long term stability.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Preparation of oriented hole silicon carbide porous ceramic
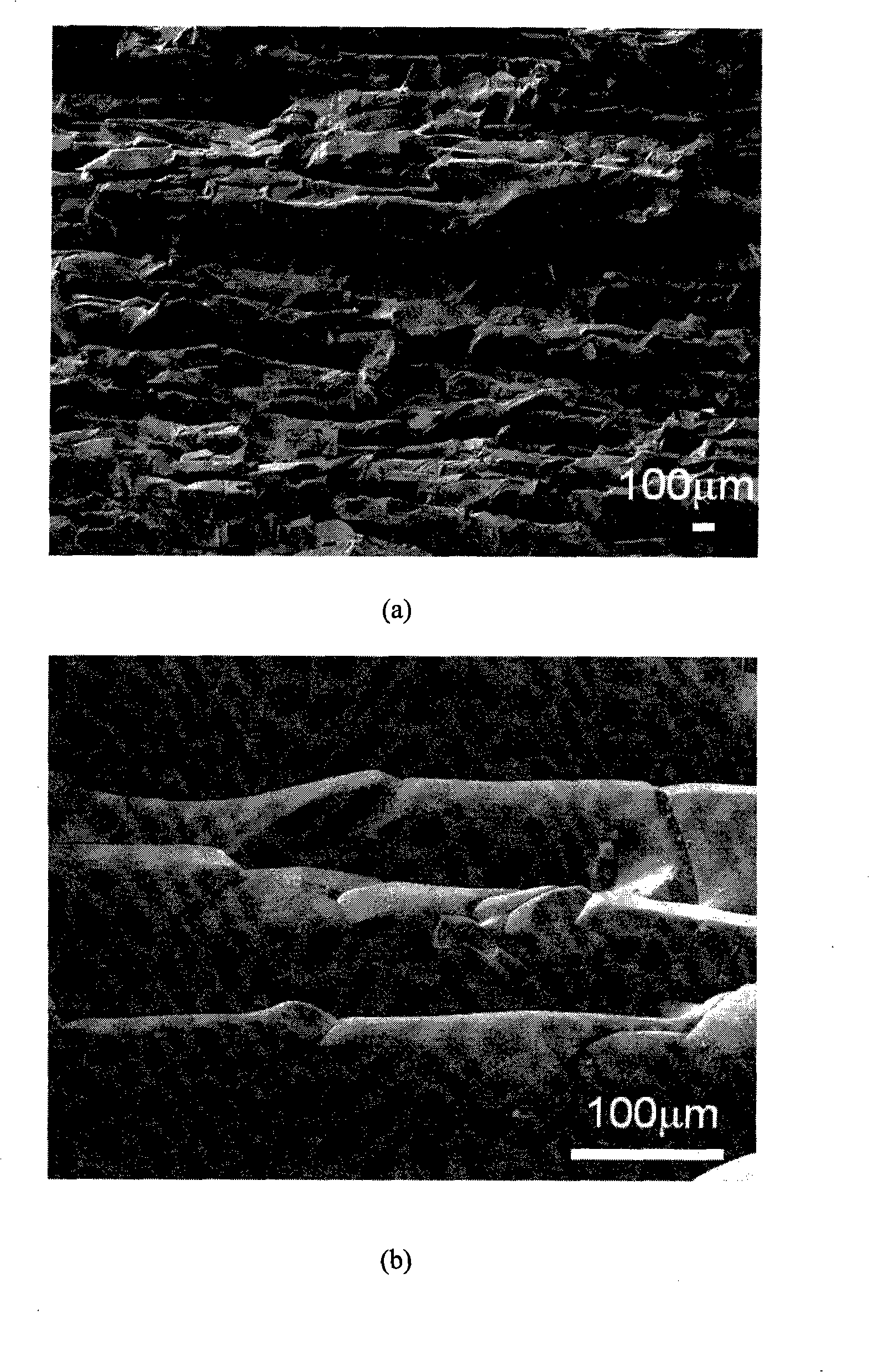
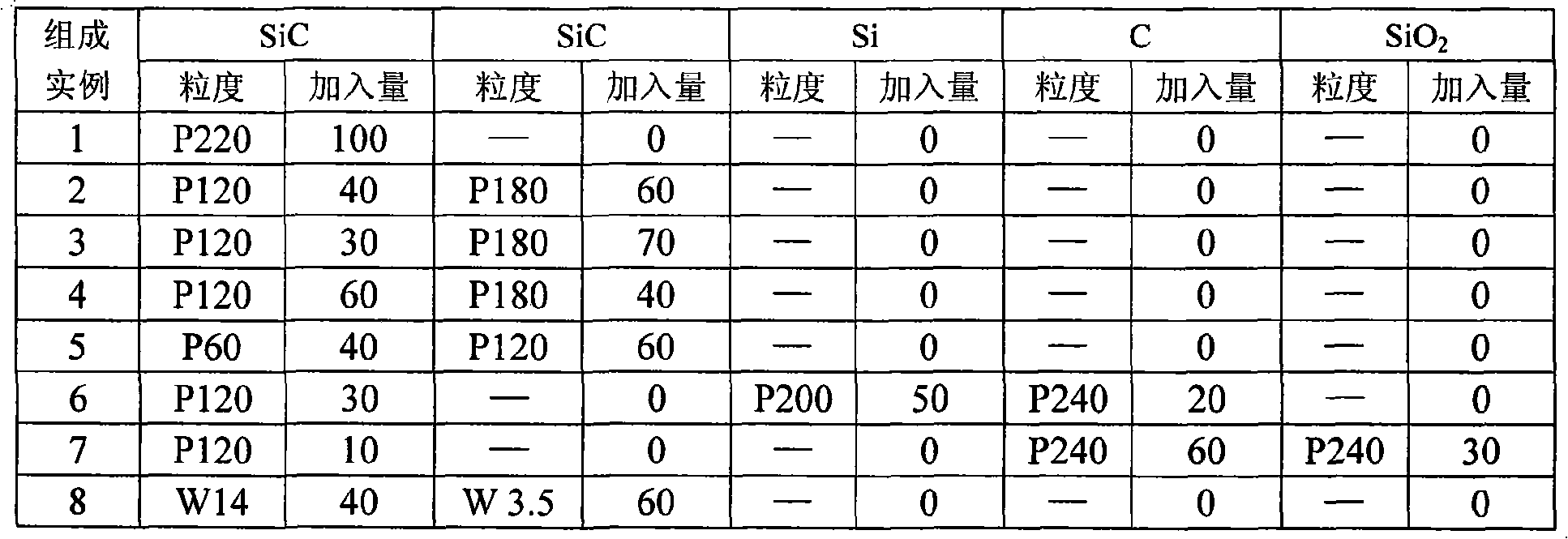
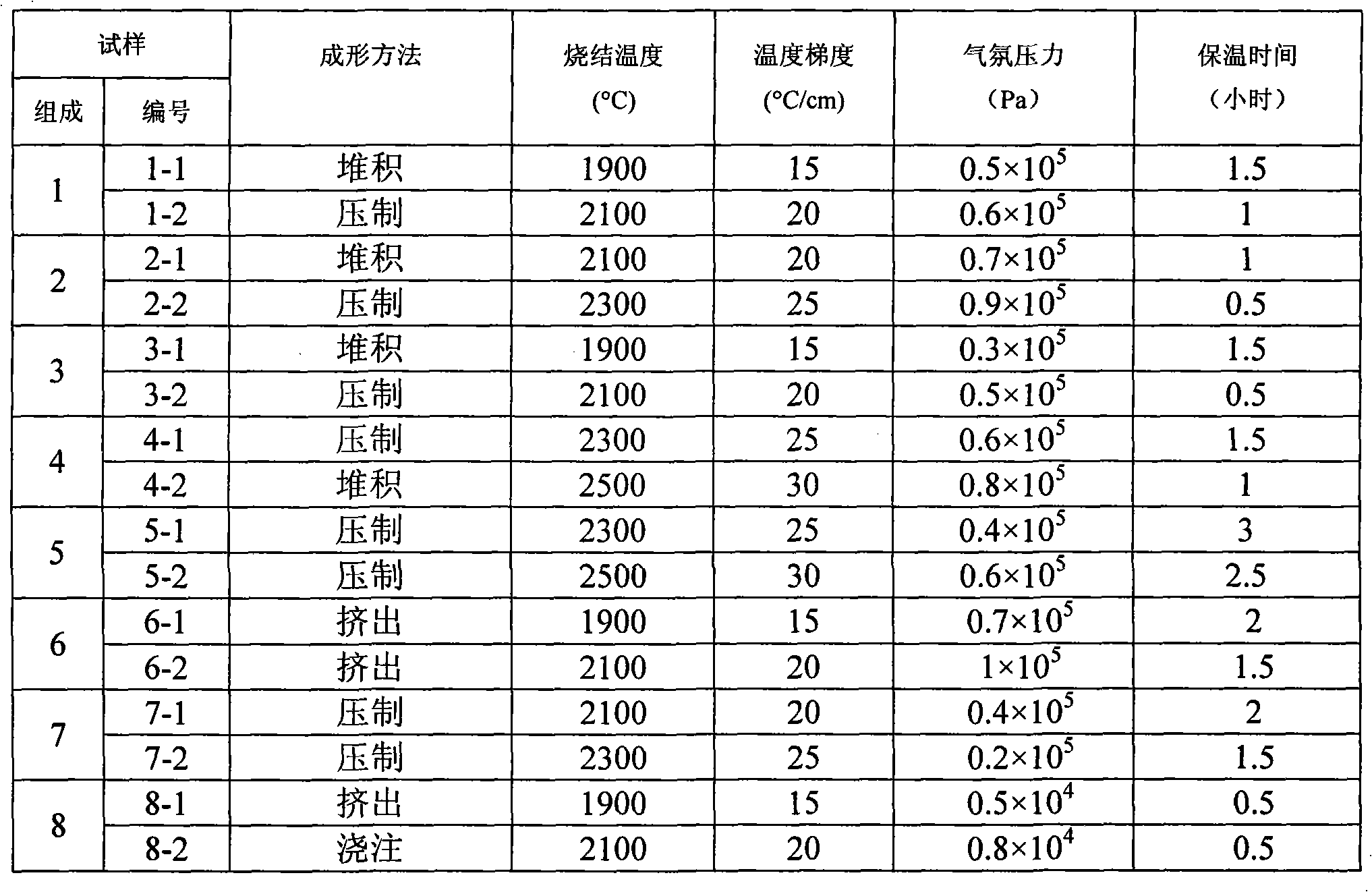
InactiveCN101323524AControl evaporation-condensation directionAdjust evaporation-condensation rateCeramicwareGranularitySaggar
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous silicon-carbide ceramic provided with oriented pores. Firstly, according to weight percentage, 0 to 30 percent of carbon powder, 0 to 50 percent of silicon powder and 0 to 60 percent of silica are added into the 10 to 100 percent of the basic material of silicon-carbide; wherein, the granularity of the silicon-carbide is W3.5 to P220, and one granularity or two granularities are adopted for graduation; then the equally mixed materials are processed through powder accumulation or normal ceramic forming process to obtain a green compact which is put into a graphite crucible or a saggar; the graphite crucible or saggar is placed into a vacuum sintering furnace provided with a temperature field with a temperature grade from 15 to 30 DEG C / cm, and then the temperature is raised to 1900 to 2500 DEG C in an argon environment and with pressure of 0.2 to 1 multipliedby 10 <5>Pa, and the insulation work for the graphite crucible or saggar is preserved for 0.5 to 3 hours; finally the temperature naturally falls down under air protection and the sintered body is taken out, namely, the recrystallization porous silicon-carbide ceramic provided with oriented pores is obtained.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Preparation method of bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone
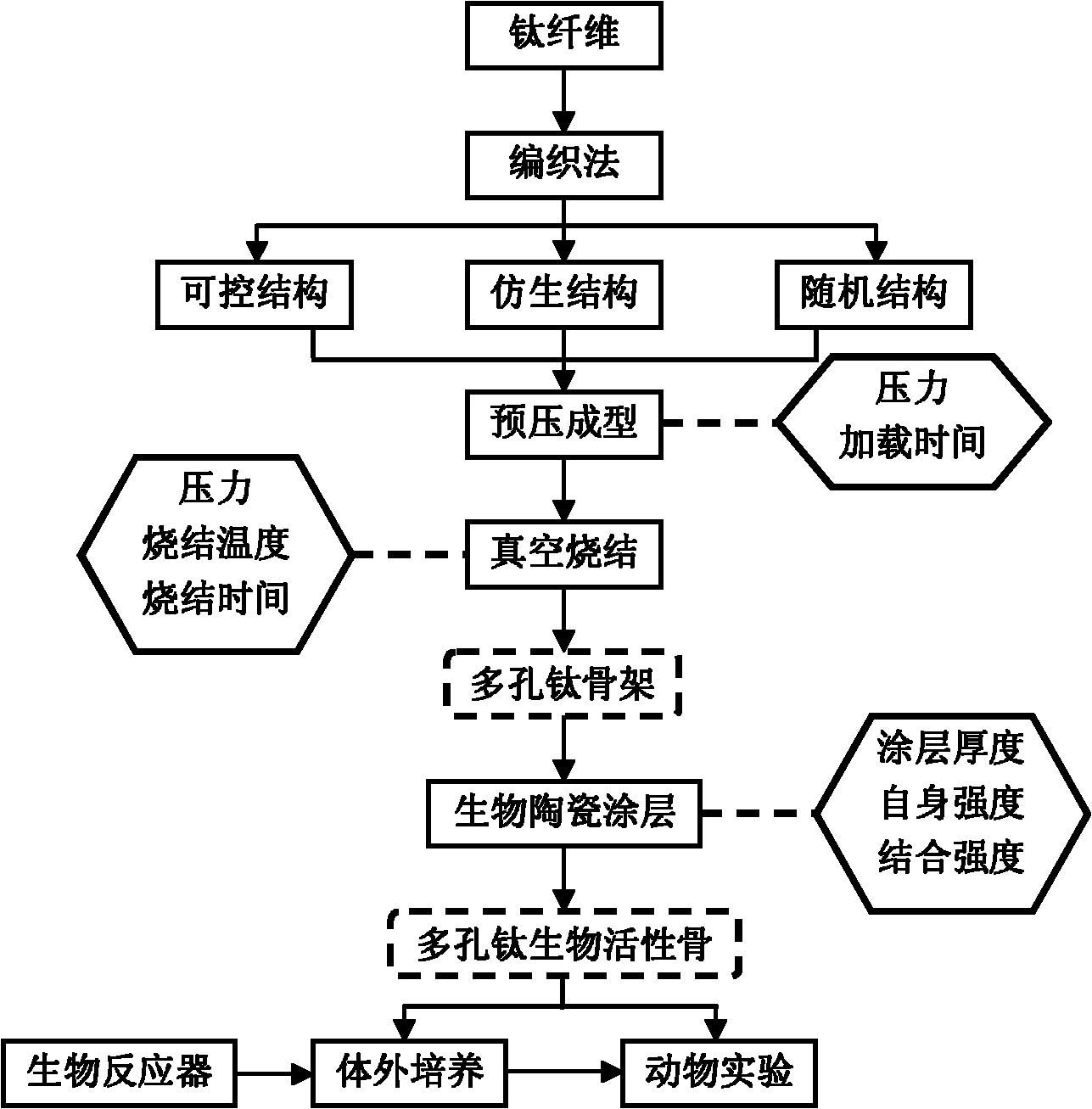
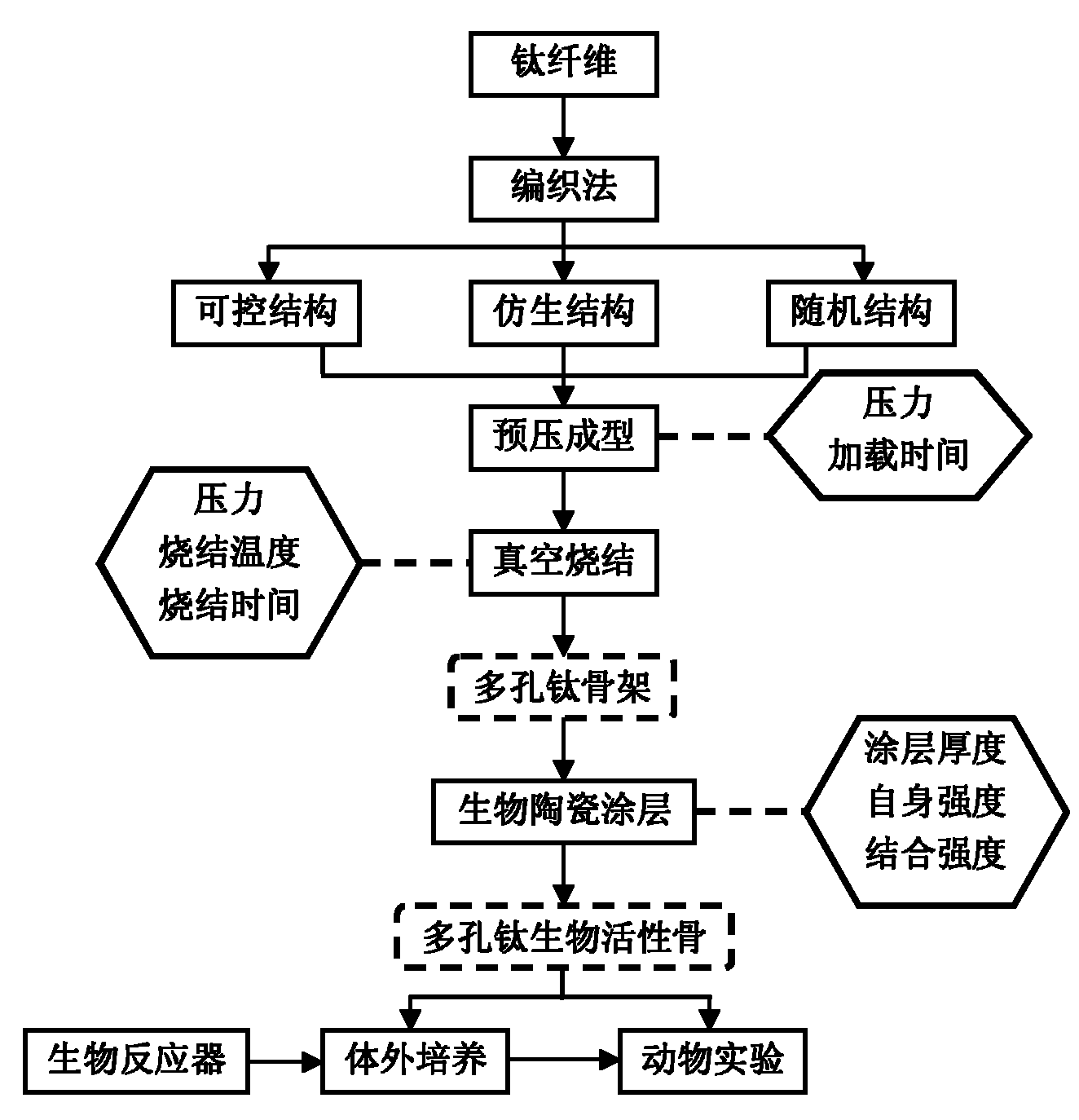
InactiveCN101889912AHave biological propertiesBiologically activeBone implantCoatingsFiberPrincipal stress
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone, belonging to the biomedical engineering field. In the invention, a three-dimensional weaving method is utilized, a titanium metal fiber wire is constructed into a controllable structure model, a random structure model and a bionic structure model which can stimulate the bone trabecula and principal stress line of a human bone, and then is prepared into the porous titanium artificial bone through prepressing molding and vacuum sintering, after that, a sol-gel method is utilized to manufacture a gradient coating or a complex coating on the surface of the porous titanium artificial bone, so that the gradient coating transiting from titanium dioxide to bio-ceramics or the bio-ceramics-titanium dioxide complex coating is formed on the surface of the porous titanium artificial bone to obtain the bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone. The preparation method not only can protect the titanium metal skeleton and prevent titanium ions from dissociating to enter a human body, but also can ensure that the titanium metal skeleton the surface of which is coated with the bio-ceramics has the biological characteristics, therefore, the bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone can be applied to repairing clinical segmental defect of long bones.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Grain boundary diffusion method for neodymium-iron-boron magnet
ActiveCN106409497AImprove coercive forceImprove uniformityElectrophoretic coatingsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementDiffusion methods
The invention discloses a grain boundary diffusion method for a neodymium-iron-boron magnet. The method comprises the following specific steps: preparing main-phase alloy powders through the neodymium-iron-boron powder metallurgy technique; preparing grain boundary powders of a low-melting-point rare earth alloy through the rare earth alloy powder metallurgy technique; evenly mixing the main-phase alloy powders and the grain boundary powders of the low-melting-point rare earth alloy according to a certain proportion; carrying out orienting compression in a magnetic field to prepare a neodymium-iron-boron magnet blank, and carrying out sintering of the neodymium-iron-boron magnet blank for 3 to 5 hours at a temperature of 1,000 to 1,100 DEG C, so as to prepare a sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet; coating the magnet surface with a low-melting-point rare earth alloy layer through electrophoresis; and placing the magnet in a vacuum sintering furnace for secondary tempering heat treatment. The method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the coercivity of the magnet is improved while the residual magnetism is hardly reduced; the diffusion depth of heavy rare earth elements in the magnet can be improved; the uniformity of the magnet after the diffusion is improved; and the method is applicable for batch production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DONGYANG DMEGC RARE EARTH MAGNET CO LTD
Preparation method for R-Fe-B-series sintering magnet
InactiveCN103745823AImprove coercive forceImprove diffusivityPermanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementThermal spraying
The invention relates to a preparation method for an R-Fe-B-series sintering magnet. The preparation method for the R-Fe-B-series sintering magnet comprises the following steps of firstly, preparing an R-Fe-B-series sintering magnet with the thickness of 1-10mm by using the conventional method; secondly, spraying DyTb alloy with the thickness of 10-200 micrometers and the Dy mass percent of 60%-90% on the surface of the sintering magnet in a sealing box at an Ar gas protective atmosphere by using a thermal spraying method; and finally, placing the sintering magnet with the DyTb alloy on the surface in a vacuum sintering furnace, and performing heat treatment on the sintering magnet in a vacuum or Ar gas protective atmosphere at the temperature of 750-1000 DEG C so that heavy rare earth elements such as Tb and Dy enter the sintering magnet along a crystal boundary by diffusion. The DyTb alloy is sprayed on the surface of the sintering magnet by using the thermal spraying method, the problem of waste on resources due to high volatility of the Dy is solved, a phenomenon that production only depends on the heavy rare earth Tb with quite low content is avoided, the treatment speed is high, the coating is uniform, the yield is high, and the coercivity of the magnet after heat treatment is performed on the magnet is greatly improved.
Owner:YANTAI ZHENGHAI MAGNETIC MATERIAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com