Patents
Literature
1077 results about "Titanium metal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Formation of boron-doped titanium metal films with high work function
ActiveUS10083836B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHalogenTitanium metal
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Formation of boron-doped titanium metal films with high work function
ActiveUS20170025280A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium metalWork function
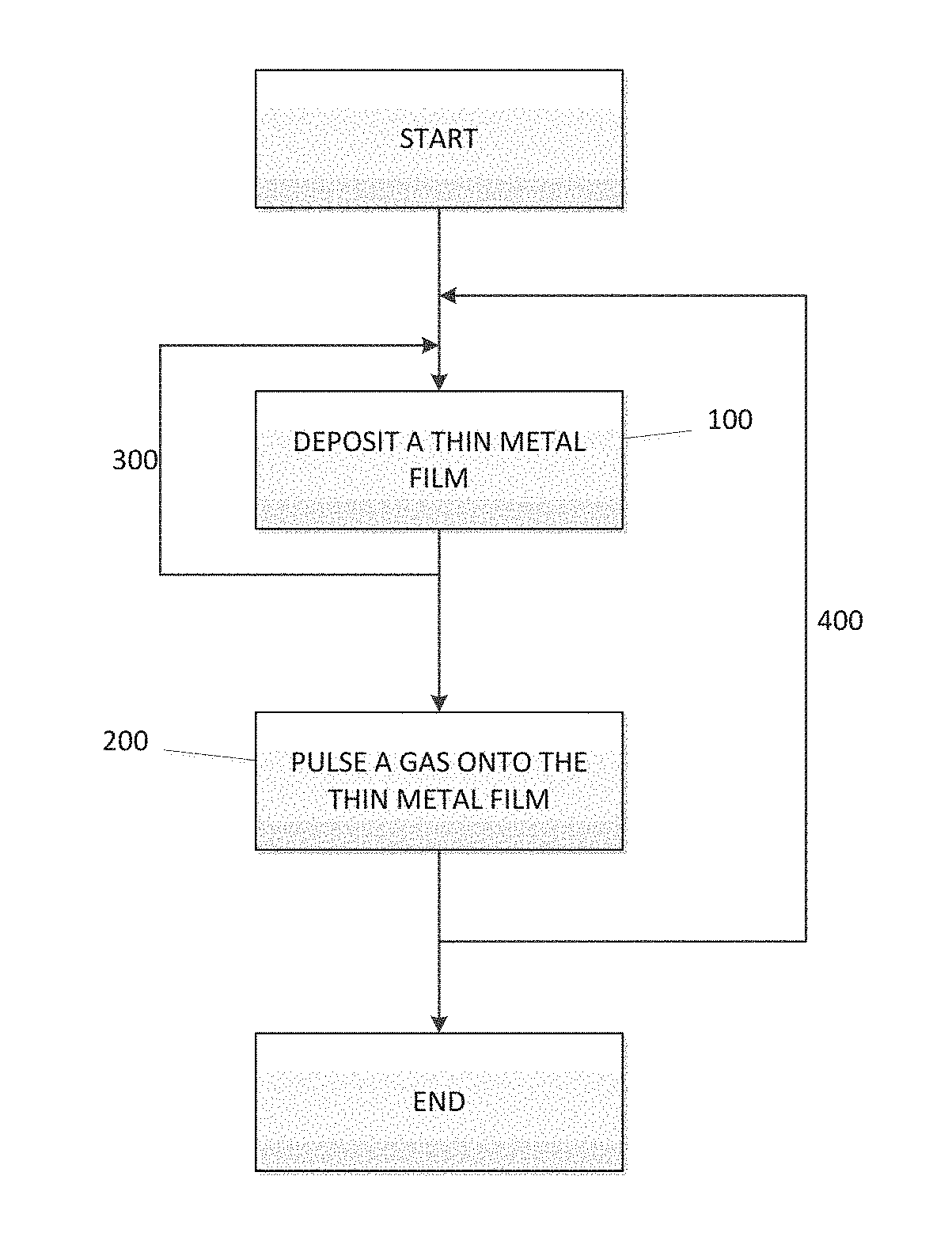
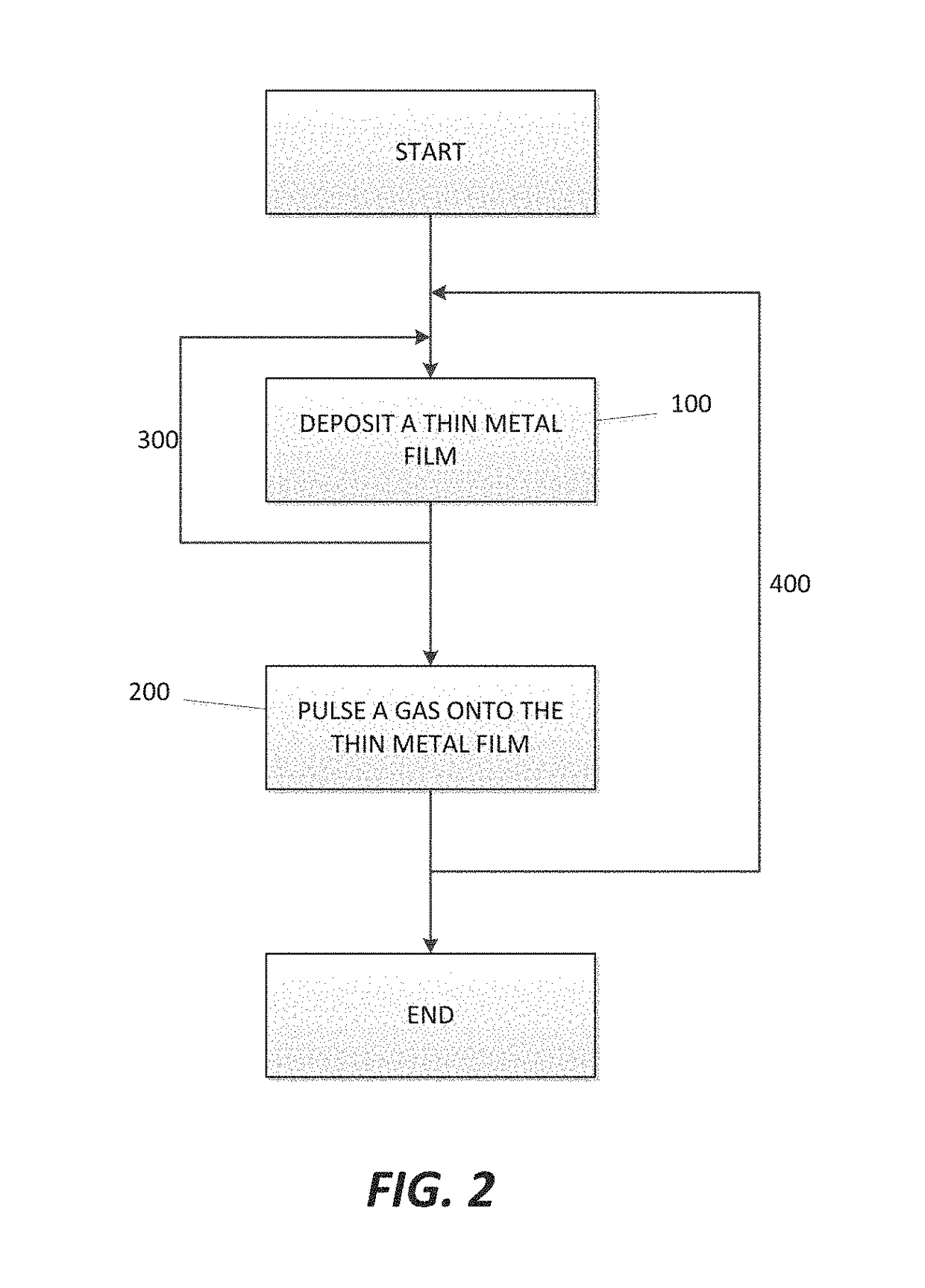
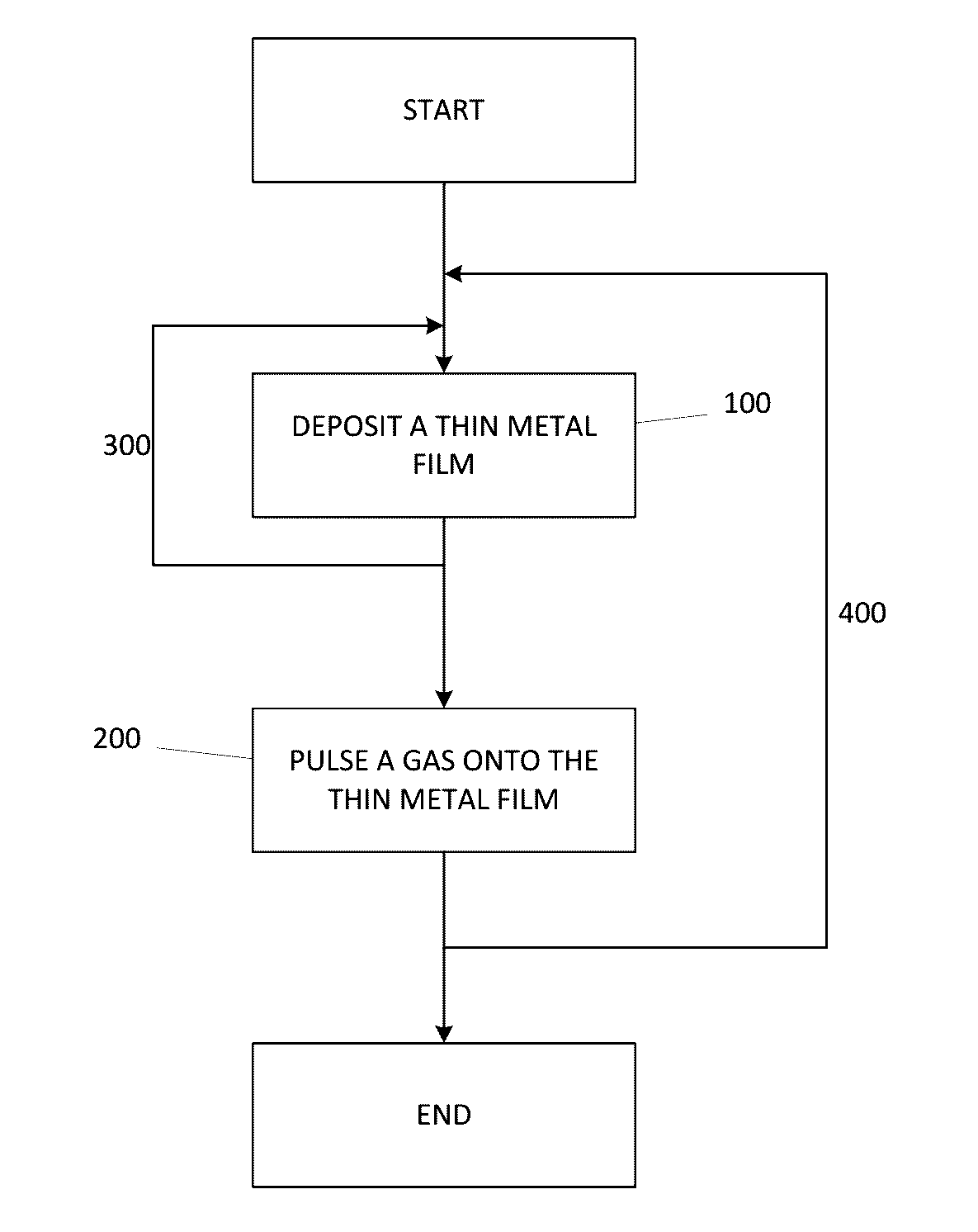
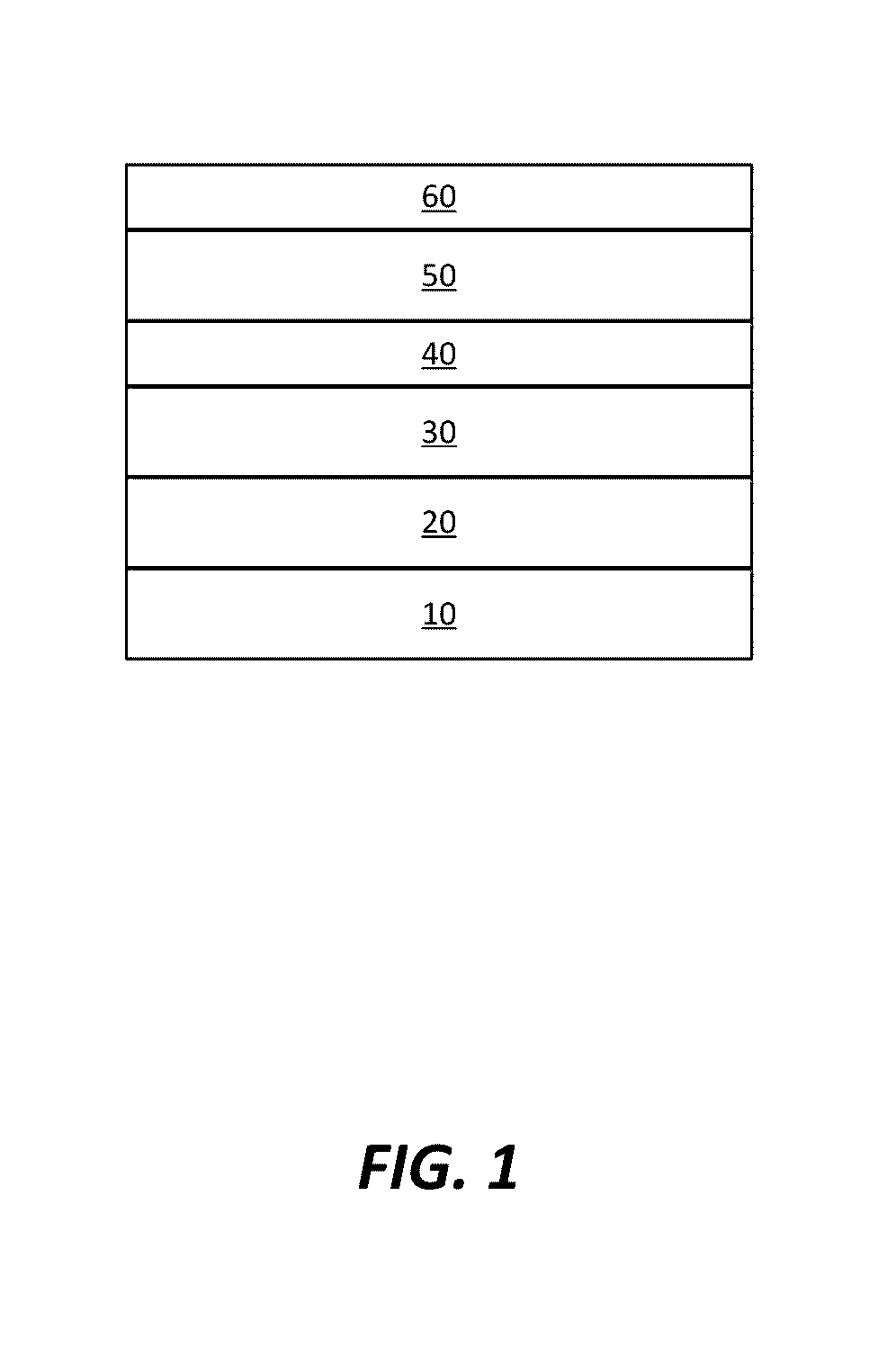
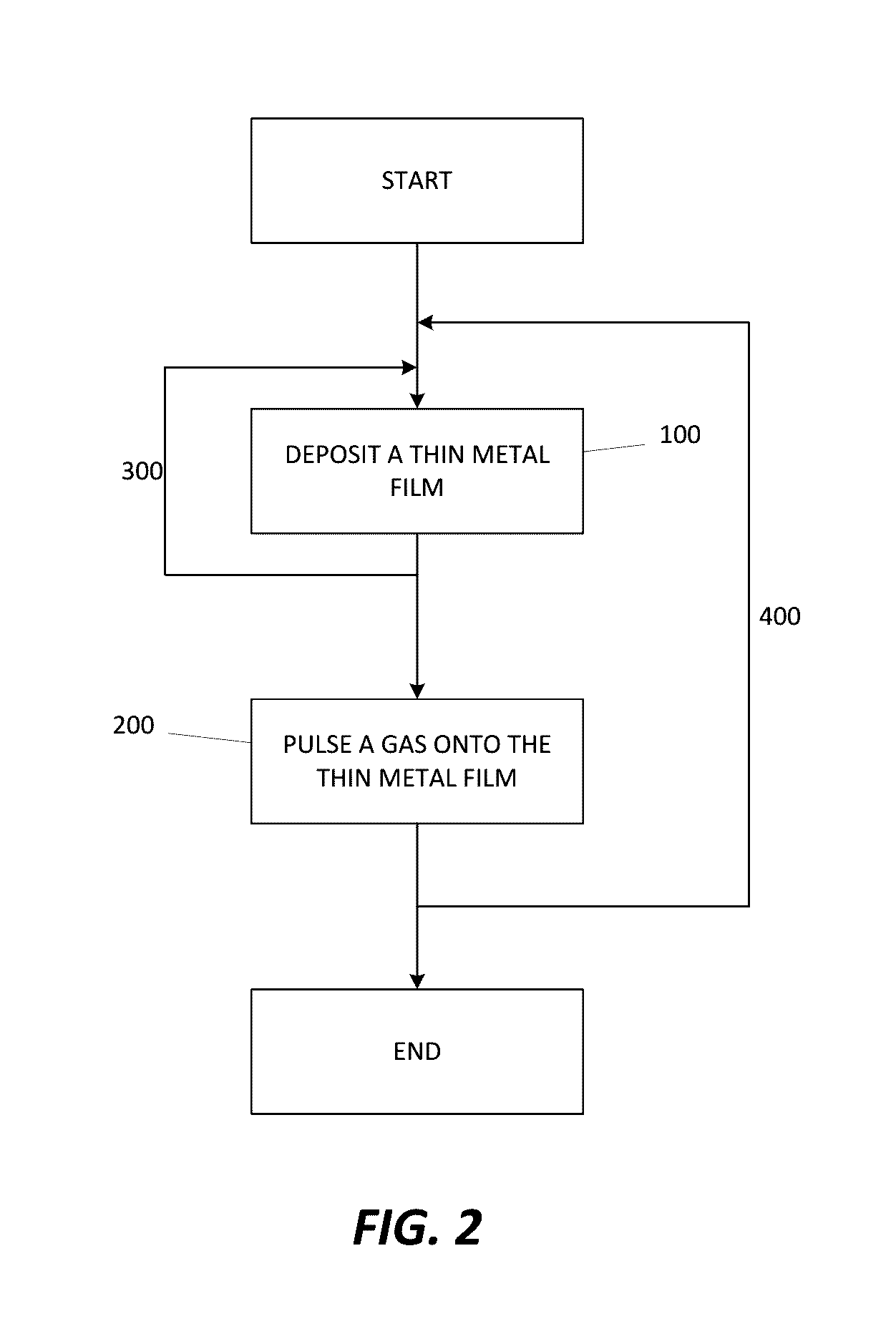
A method for forming a Boron doped metallic film, such as Titanium Boron Nitride, is disclosed. The method allows for creation of the metallic film with a high work function and low resistivity, while limiting the increase in effective oxide thickness. The method comprises a thin metallic layer deposition step as well as a Boron-based gas pulse step. The Boron-based gas pulse deposits Boron and allows for the removal of excess halogens within the metallic film. The steps may be repeated in order to achieve a desired thickness of the metallic film.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Preparation of poly(trimethylene terephthalate) with low level of di(1,3-propylene glycol)
A process of preparing poly(trimethylene terephthalate) containing less than 2.0 mole % of DPG comprising:(a) providing a molar amount of 1,3-propanediol:C1 to C4 dialkyl ester of terephthalic acid of 1.2:1 to 1.9:1,(b) reacting the 1,3-propanediol with the C1 to C4 dialkyl ester of terephthalic, acid to form bis(3-hydroxypropyl)terephthalate monomer in the presence of 10-100 ppm (as titanium metal) of an organic titanate catalyst, by weight of the poly(trimethylene terephthalate), and(c) polymerizing the bis(3-hydroxypropyl)terephthalate monomer to obtain the poly(trimethylene terephthalate); andpoly(trimethylene terephthalate) produced by the process.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
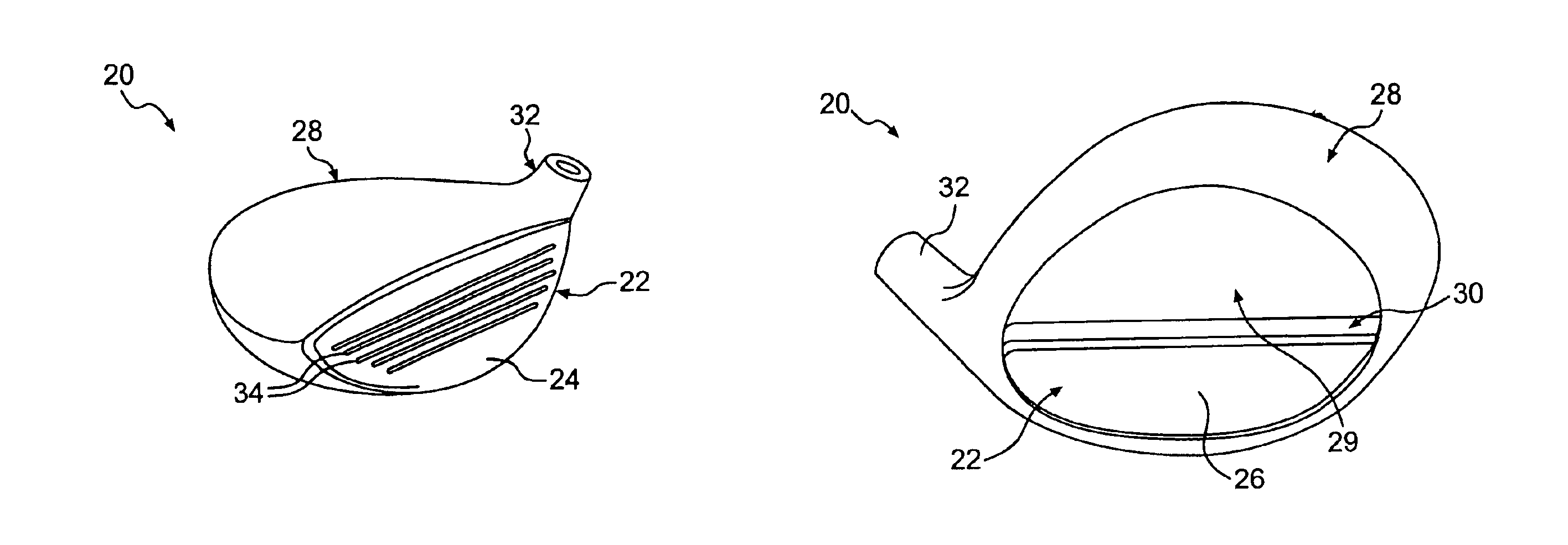
Peen conditioning of titanium metal wood golf club heads
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Titanium comprising nanoparticles and related nanotechnology
ActiveUS7232556B2Increase volumeLow cost productionNitrogen compoundsGermanium dioxideNanoparticleTitanium metal
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Titanium comprising nanoparticles and related nanotechnology
ActiveUS20050191492A1Increase volumeLow cost productionNitrogen compoundsGermanium dioxideNanoparticleTitanium metal
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Polymetallic catalysts and method of preparing same
InactiveUS6054406AHigh elongationImprove propertiesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationSolubilityElectron donor
Disclosed is a polymetallic supported catalyst component comprising an activated anhydrous MgCl2 solid support which has been treated with at least one treatment of at least two halogen-containing transition metal compounds, wherein one is a halogen-containing titanium metal compound and one is a halogen-containing non-titanium transition metal compound, optionally, in the presence of an electron donor and the processes for producing the component. A catalyst for the polymerization of at least one alpha-olefin of the formula CH2=CHR, where R is H or a C1-12 branched or straight chain alkyl or substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl, by reacting this supported catalyst component with an organometallic cocatalyst, optionally in the presence of an electron donor, and the polymerization of at least one alpha-olefin with the catalyst are also disclosed. The resulting polymers, particularly propylene polymers, have a controllable atactic content, which is expressed herein in terms of its xylene solubility at room temperature (XSRT), wherein the ratio of the I.V. of the XSRT fraction to the I.V. of the bulk polymer is greater than or equal to 0.50.
Owner:MONTELL NORTH AMERICA
Method for electrowinning of titanium metal or alloy from titanium oxide containing compound in the liquid state
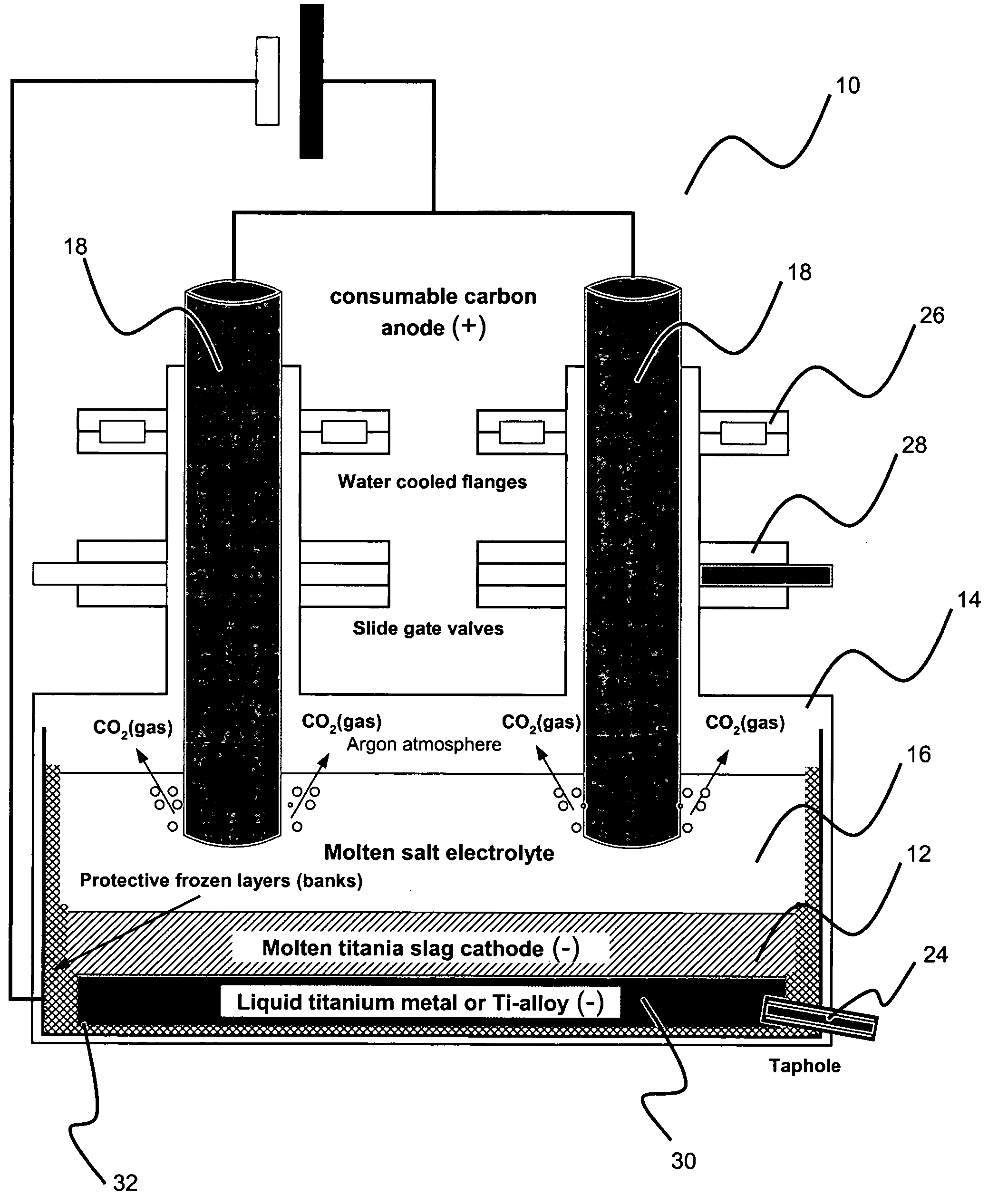
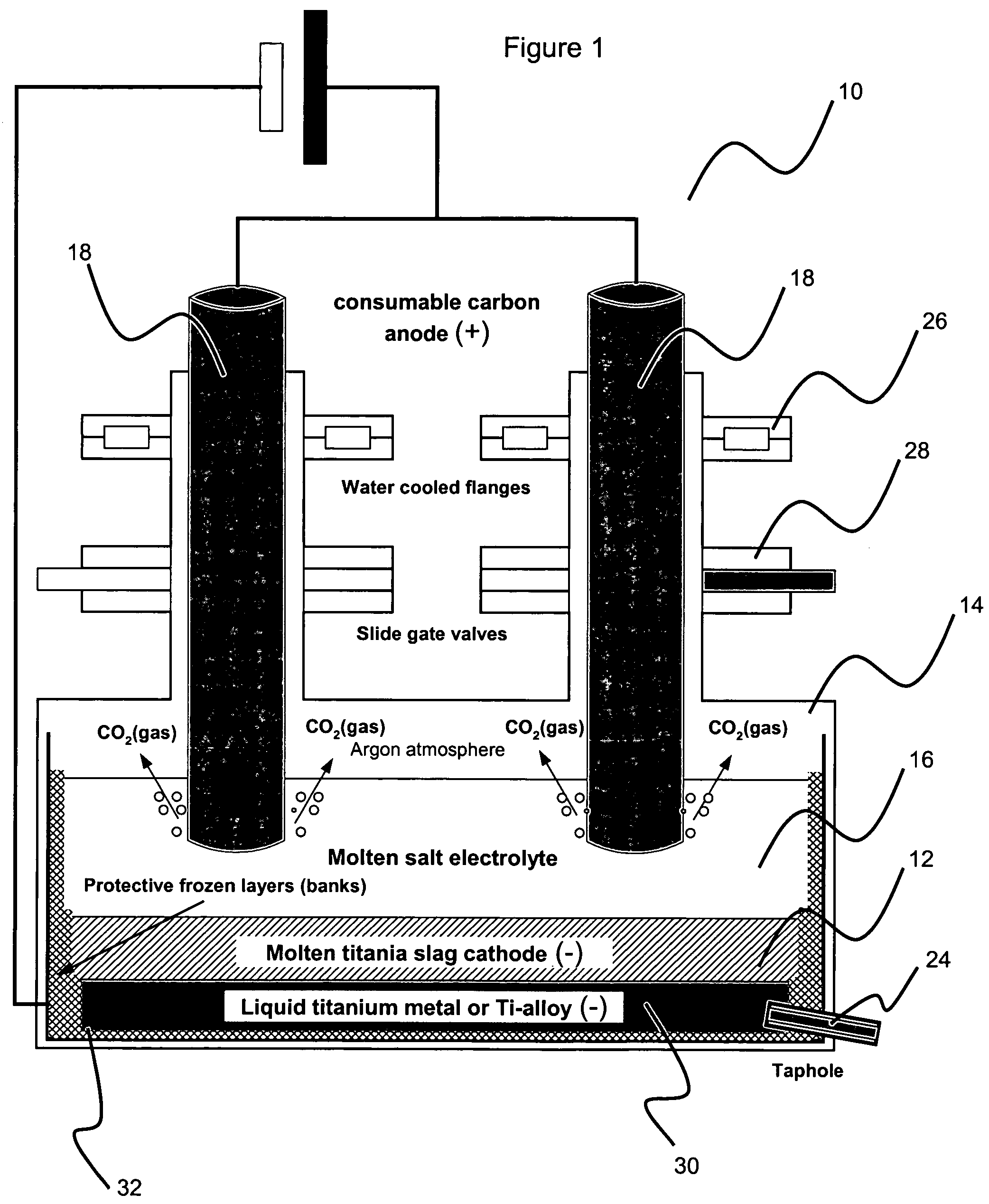
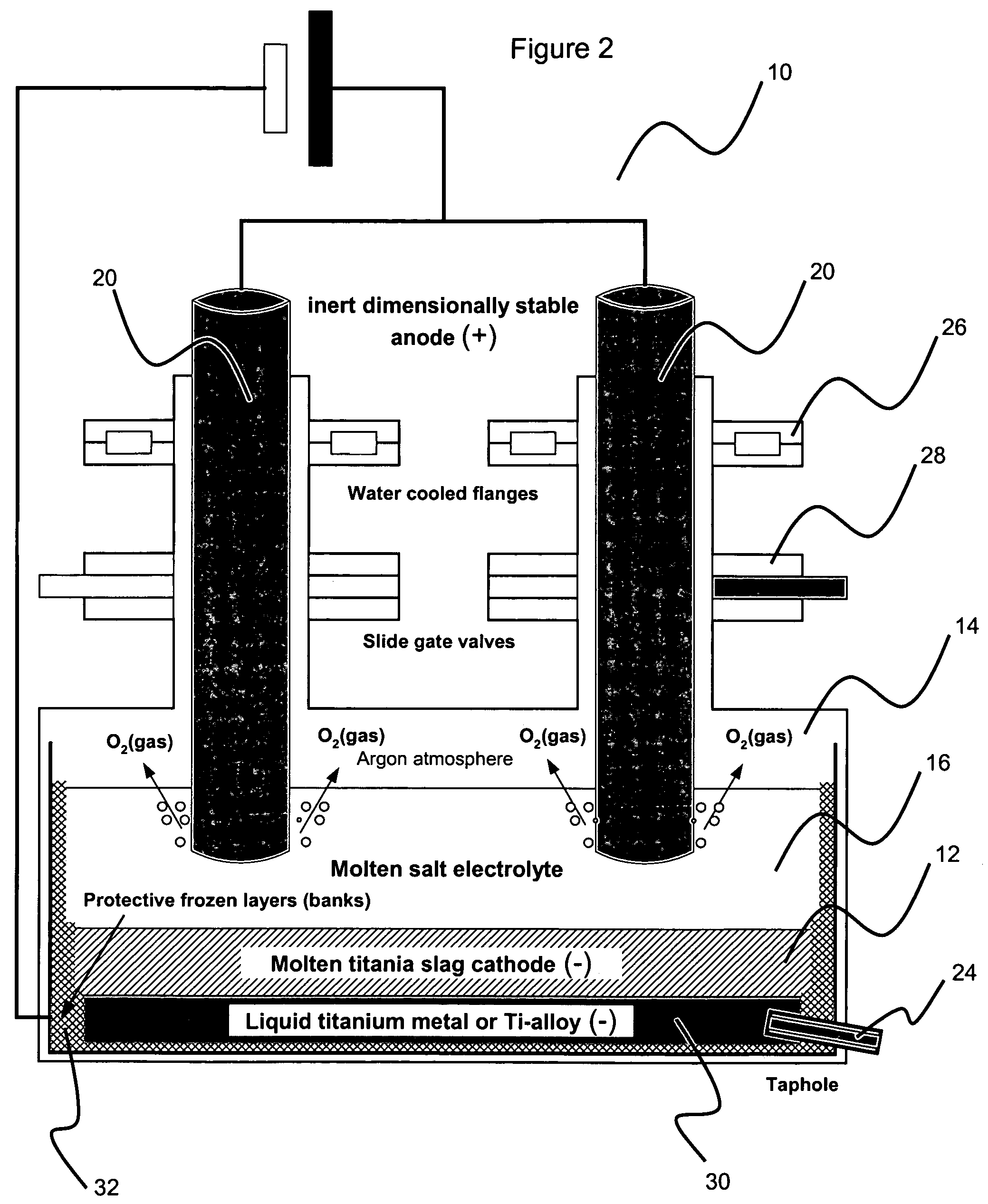
This invention relates to a method for electrowinning of titanium metal or titanium alloys from electrically conductive titanium mixed oxide compounds in the liquid state such as molten titania slag, molten ilmenite, molten leucoxene, molten perowskite, molten titanite, molten natural or synthetic rutile or molten titanium dioxide. The method involves providing the conductive titanium oxide compound at temperatures corresponding to the liquid state, pouring the molten material into an electrochemical reactor to form a pool of electrically conductive liquid acting as cathode material, covering the cathode material with a layer of electrolyte, such as molten salts or a solid state ionic conductor, deoxidizing electrochemically the molten cathode by direct current electrolysis. Preferably, the deoxidizing step is performed at high temperature using either a consumable carbon anode or an inert dimensionally stable anode or a gas diffusion anode. During the electrochemical reduction, droplets of liquid titanium metal or titanium alloy are produced at the slag / electrolyte interface and sink by gravity settling to the bottom of the electrochemical reactor forming, after coalescence, a pool of liquid titanium metal or titanium alloy. Meanwhile carbon dioxide or oxygen gas is evolved at the anode. The liquid metal is continuously siphoned or tapped under an inert atmosphere and cast into dense and coherent titanium metal or titanium alloy ingots.
Owner:QIT FER & TITANE INC
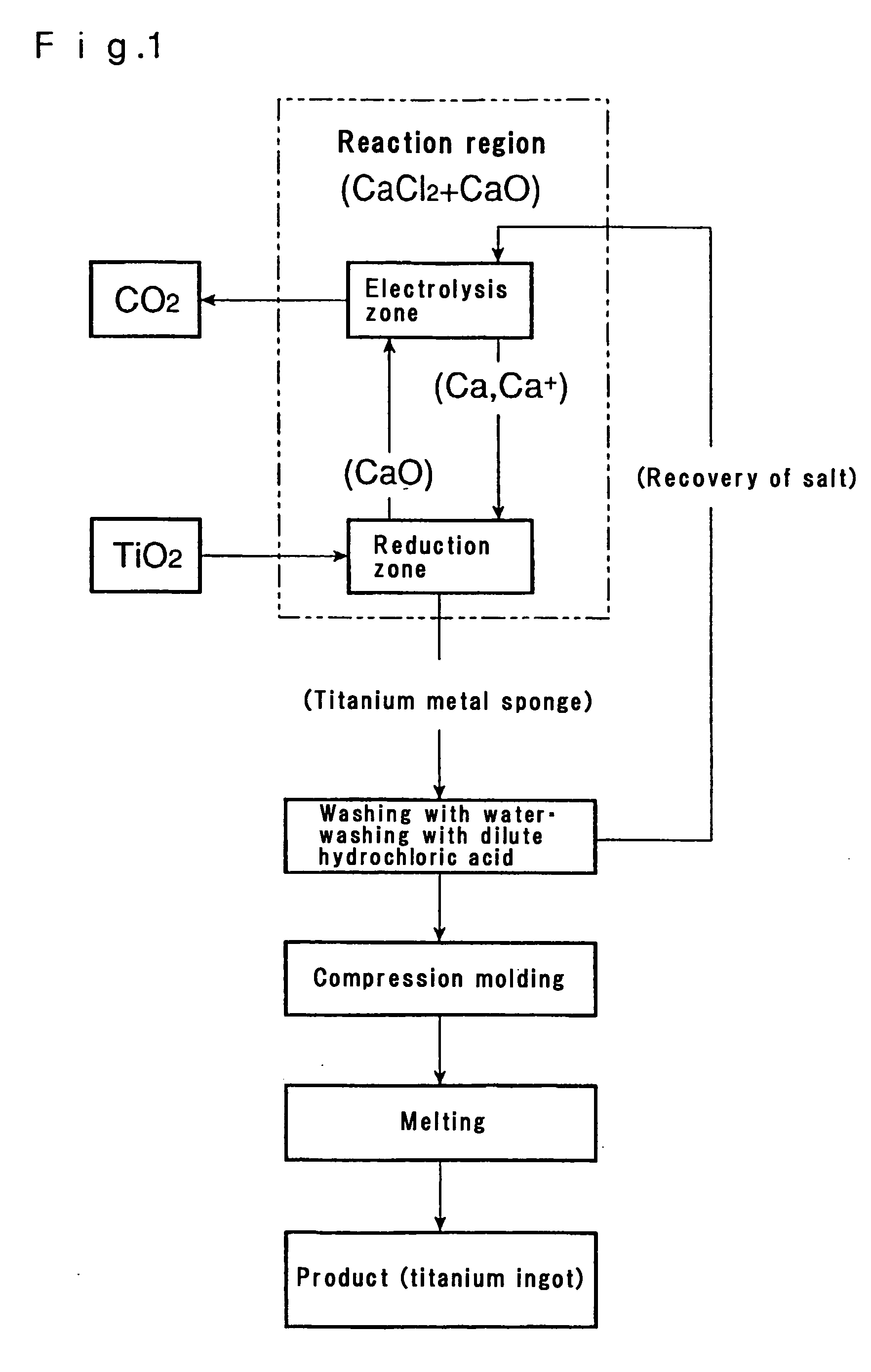
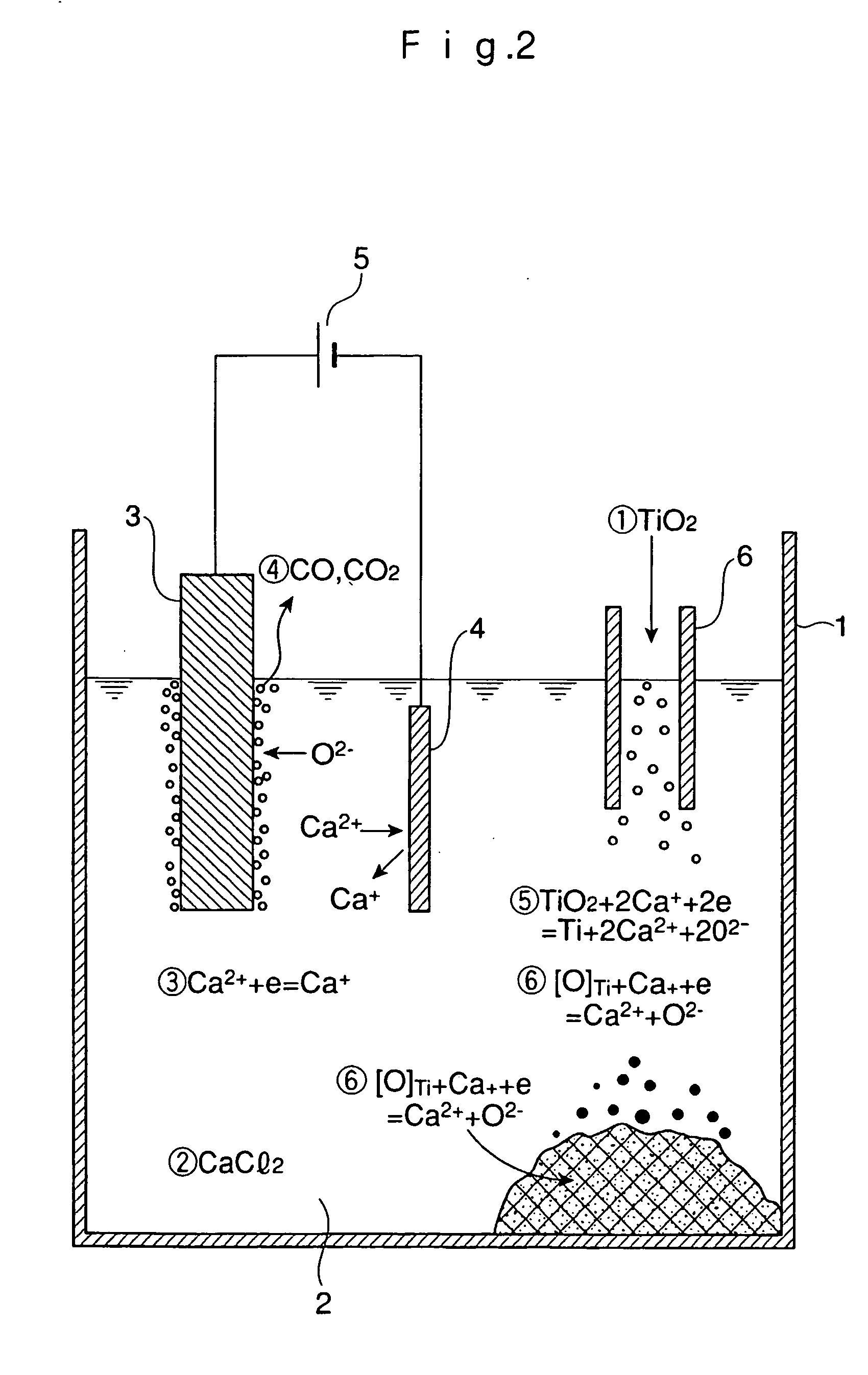
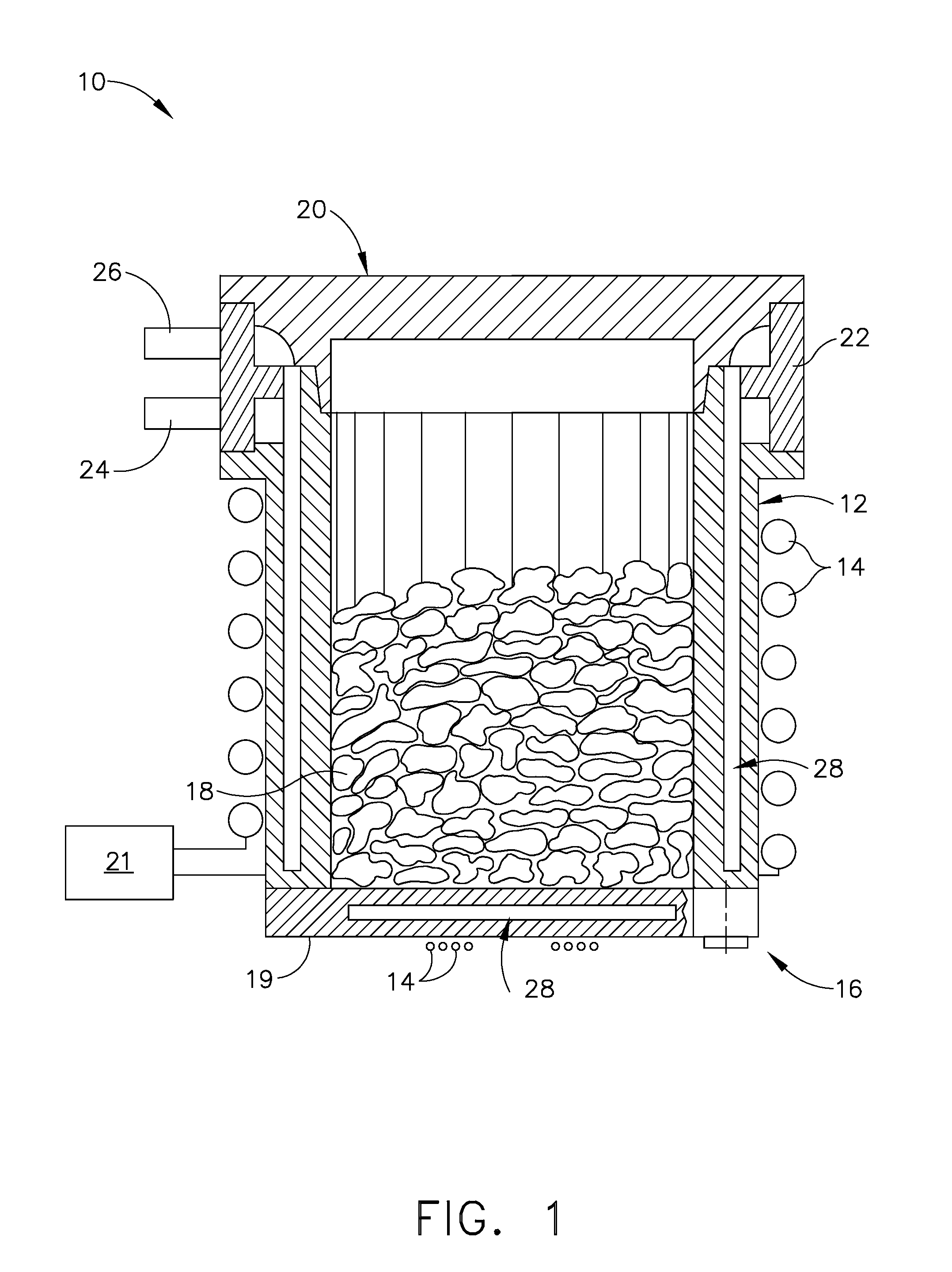
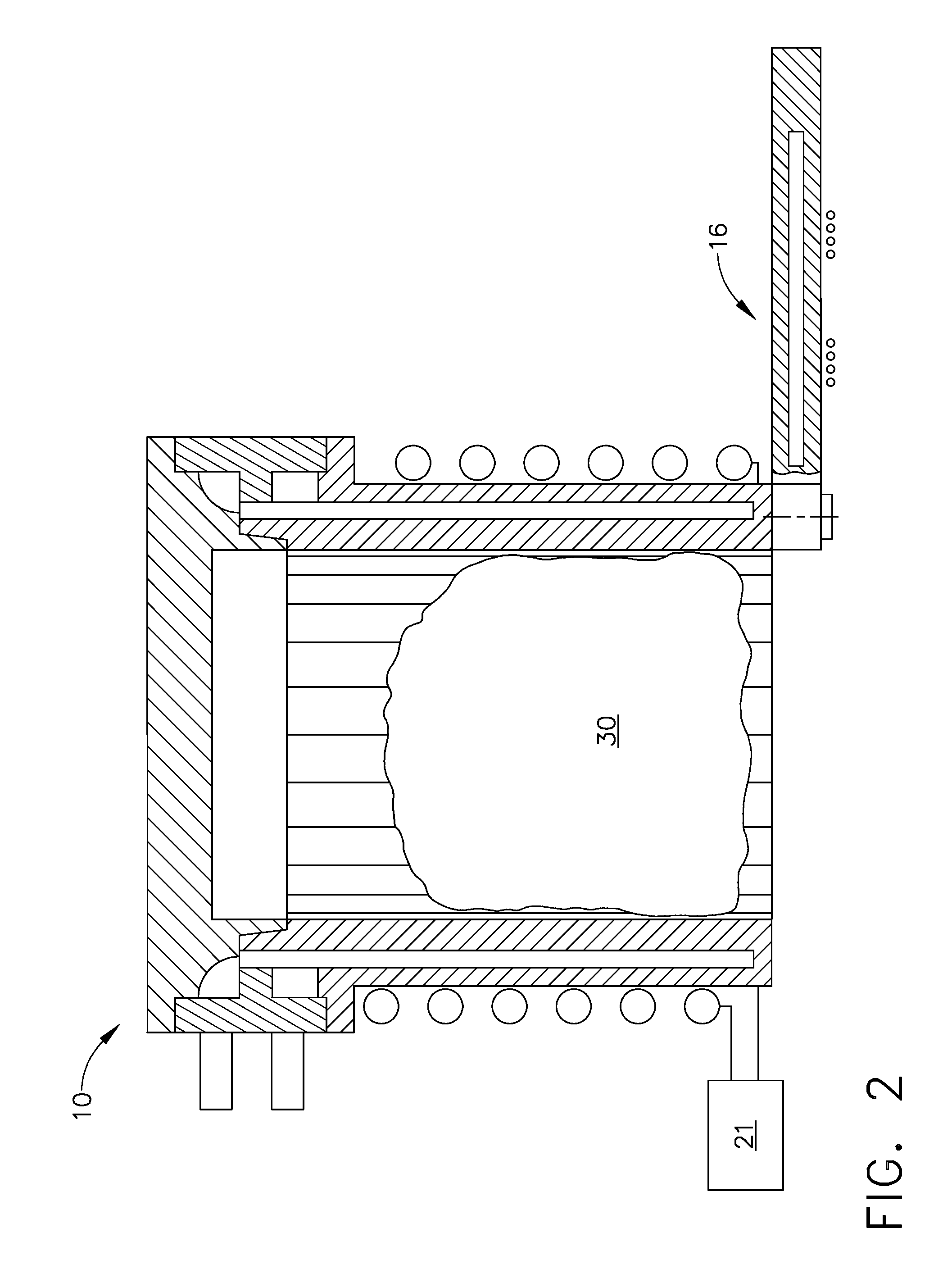
Method and apparatus for smelting titanium metal
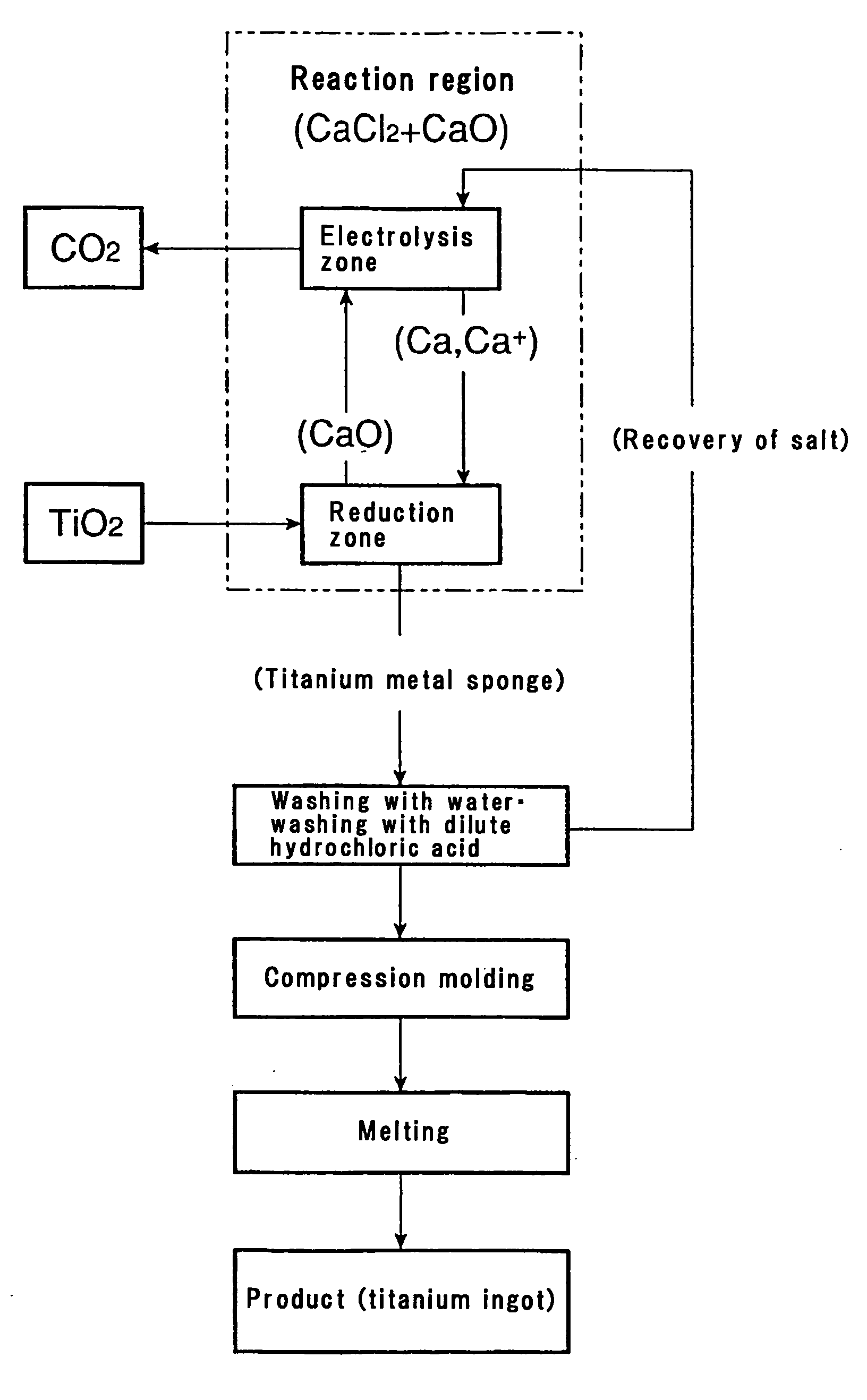
This invention relates to a method and an apparatus for smelting titanium metal by the thermal reduction of titanium oxide (TiO2) to titanium metal (Ti); a mixed salt of calcium chloride (CaCl2) and calcium oxide (CaO) contained in a reaction vessel is heated to form a molten salt which constitutes a reaction region, the molten salt in the reaction region is electrolyzed thereby converting the molten salt into a strongly reducing molten salt containing monovalent calcium ions (Ca<+>) and / or calcium (Ca), titanium oxide is supplied to the strongly reducing molten salt and the titanium oxide is reduced and the resulting titanium metal is deoxidized by the monovalent calcium ions and / or calcium. The method and the apparatus make it feasible to produce commercially titanium metal suitable for a variety of applications from titanium oxide.
Owner:NIPPON LIGHT METAL CO LTD
Surface heating type atomizer and electronic cigarette provided with same
The invention discloses a surface heating type atomizer and an electronic cigarette provided with same. The atomizer comprises a base and heating element, which are mutually connected; the heating element comprises a ceramic seat, an accommodating groove used for accommodating solid tobacco tar or paste is formed in the ceramic seat, a nano titanium metal heating material film is covered on the outer side of the ceramic seat; the electronic cigarette comprises an atomizer component and a cigarette rod component, which are mutually connected; the atomizer component comprises a cigarette holder, an atomizer tube, a first electrode connecting component and the atomizer, which are connected in sequence; the cigarette rod comprises a battery tube, as well as a second electrode connecting component, a battery and a control panel, which are arranged in the battery tube, the second electrode connecting component are connected with the battery through the control panel, a key switch connected with the control panel is arranged on the battery tube, and the first electrode connecting component and the second electrode connecting component are connected and conducted. The atomizer and the electronic cigarette provided with same have the advantages that the heating area is big, the atomization performance is good, the amount of the atomized oil smoke at a time is big, carbon deposition is avoided during the using process, the service life is long, and the atomizer and the electronic cigarette are energy-saving and environment-friendly.
Owner:SHENZHEN BUDDY TECH DEV CO LTD
Method of preparing hydroxyl apatite bioceramic film by plasma micro-arc oxidization method
InactiveCN101054708AComposition is stableStable structureSurface reaction electrolytic coatingPlasma electrolytic oxidationMicro arc oxidation
The present invention relates to a process for preparing hydroxylapatite bio-ceramic membranes at titanium or titanium alloy surfaces by utilizing differential arc oxidation process. Firstly, preparing electrolytic solution A by using calcium ion salts and phosphate radical ion-containing salts, or preparing electrolytic solution B by adding metal silver ions to the electrolytic solution A; or preparing electrolytic solution C by adding metal silicon ions to the electrolytic solution A; and then, selecting titanium or titanium alloy as anodes and putting them respectively into the electrolytic solution A, B and C, selecting the non-corrodible steel container for containing the electrolytic solutions as cathodes, controlling conditions such as impulse electrical source positive phase voltage, frequency for differential arc oxidation of titanium or titanium alloy, then hydroxylapatite bio-ceramic membrane layers possessing different performances are prepared. Said titanium based bio-ceramic compound material prepared according to said process possesses not only intensity and toughness of metals but also biological activity of hydroxylapatites, and is capable of being applied in the fields such as jackstraw chirurgery implantation body and tooth planting body.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Improvement method for titanium alloy laser 3D printing
ActiveCN104928513AEasy to printImprove wettabilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusTitanium metalTitanium alloy
The invention discloses an improvement method for titanium alloy laser 3D printing and relates to an improvement method for laser 3D printing. The improvement method for titanium alloy laser 3D printing solves the problems that titanium alloy and components prepared through laser 3D printing at present are low in strength level and heat resistant temperature, the metallographic structure is thick and big and not even, the metallographic structure grows to be big in the subsequent heat treatment modification process, the technological parameter selectable range in subsequent heat treatment is narrow, the mechanical property improvement is limited, and the plasticity level of the alloy and the components is low. The improvement method includes the steps that firstly, titanium or titanium alloy powder is evenly mixed with improved raw material powder in a ball milling mode; secondly, laser 3D printing is conducted. The metallographic structure of a laser 3D titanium metal product prepared through the mode of execution is thin and small, a subsequent heat treatment window can be greatly expanded, a balanced structure formed by high-temperature annealing can be achieved, long-time solution strengthening processing or annealing processing can be conducted, the even metallographic structure is obtained, and the mechanical performance of the metallographic structure is greatly improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Titanium metal vacuum cup and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103405104AThermal insulationImprove corrosion resistanceDrinking vesselsVacuum pumpingTitanium metal
The invention provides a titanium metal vacuum cup and a manufacturing method thereof, belongs to the technical field of daily necessities, and solves the technical problems that a conventional vacuum cup is lower in corrosion resistance and attractiveness and the like. The vacuum cup comprises an outer cup body and an inner cup body, wherein the inner cup body is sleeved with the outer cup body; the orientation of cup rims of the inner cup body and the outer cup body is identical; the inner cup body and the outer cup body are sealed and fixed annularly at the cup rims; a vacuum interlayer is arranged between the inner cup body and the outer cup body; and both the outer cup body and the inner cup body are made of titanium metal pieces. The manufacturing method of the vacuum cup comprises the procedures as follows: a, blank preparation; b, expansion molding; c, cup bottom sheet installation; d, tailless vacuum pumping; and e, finished product blanking. The titanium metal vacuum cup has the advantages of good corrosion resistance, high attractiveness and the like.
Owner:亚钛军创(金华)控股有限公司
Method for preparing nano oxide dispersion reinforced superfine crystal tungsten-based composite material
The invention provides a method for preparing a nano oxide dispersion reinforced superfine crystal tungsten-based composite material. The method comprises the following steps of: taking 0.1 to 1 weight percent of micro tungsten powder, nano yttrium oxide powder or yttrium metal powder and 0 to 2 weight percent of titanium metal powder or molybdenum powder or tantalum powder, blending the materials, mechanically alloying the materials, sintering discharge plasma and the like to prepare the superfine crystal tungsten composite material. The method has the following advantage that: the nearly full-densification superfine crystal tungsten-based composite material can be obtained by the method for preparing the nano oxide dispersion reinforced superfine crystal tungsten-based composite material. Complex phase doping of yttrium oxide or yttrium metal and titanium metal, molybdenum or tantalum powder not only realizes sintering densification of tungsten at a lower temperature, but also inhibits grain growth of tungsten crystals during sintering. The tungsten crystal grain size of the yttrium oxide reinforced superfine crystal tungsten-based composite material prepared by adopting the method is less than or equal to 3 microns, and the composite material has good mechanical property and thermal shock resistance.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
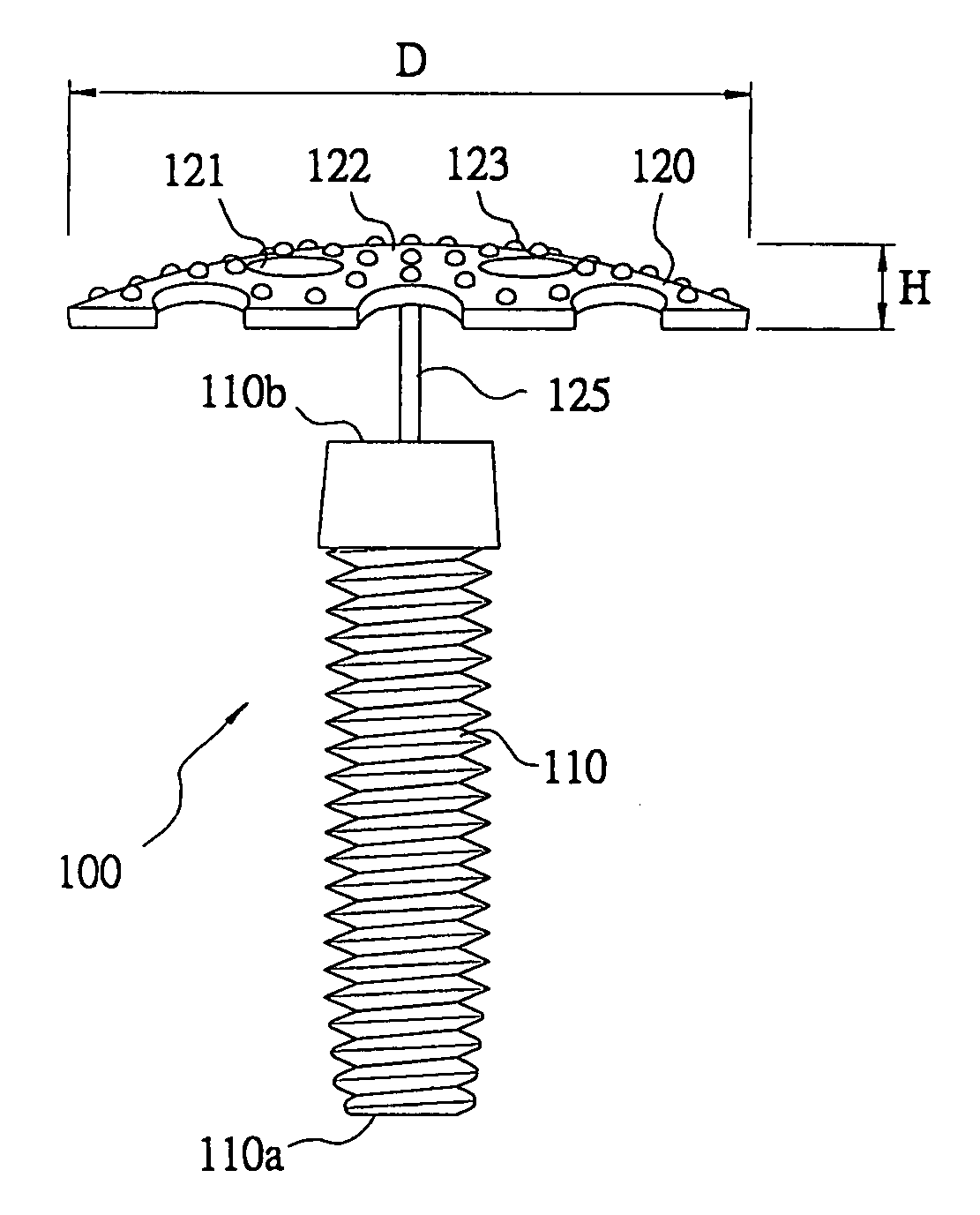
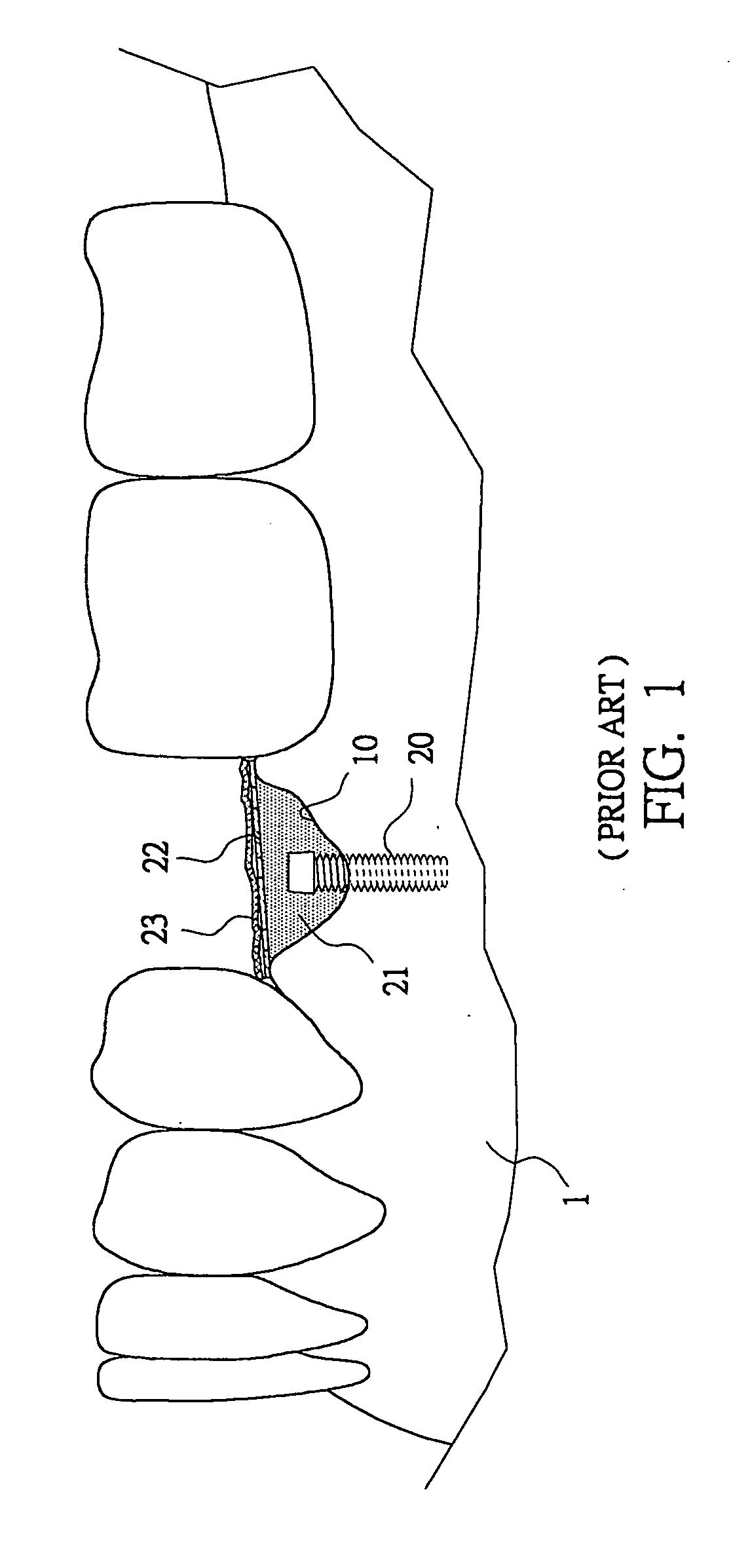
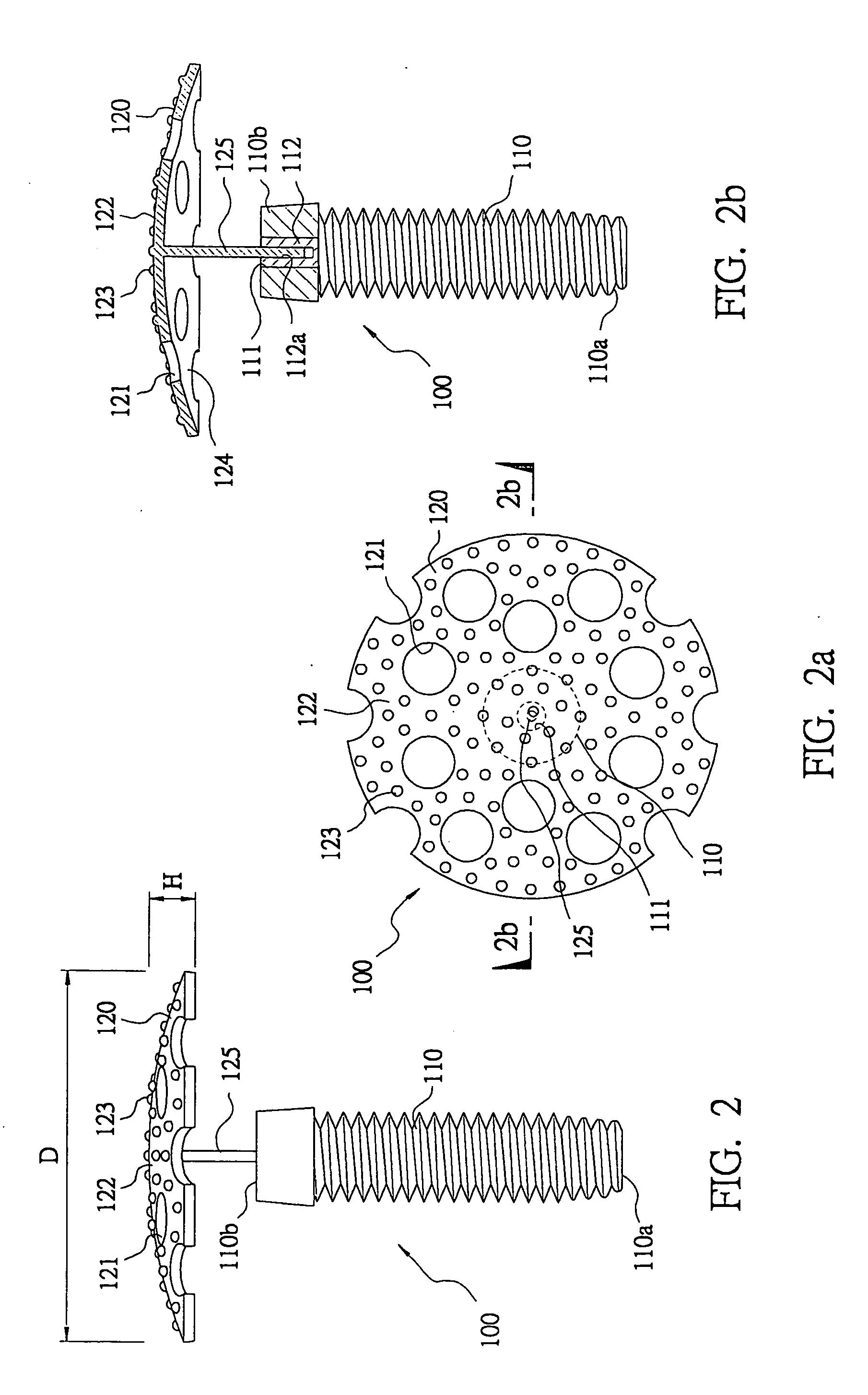
Titanium-mesh umbrella device for bone grafting
InactiveUS20060008773A1Quick placementInsufficient improvementDental implantsBone implantTitanium metalTissue membrane
A titanium-mesh umbrella for bone grafting used to combine with conventional implant and to hold bone graft in proper position during dental implant placement procedure, comprises: a titanium metal shank with one end as implant end and the other end having a pin hole at its center to form a mounting portion; a titanium-mesh with its surface having a plurality of screen meshes, wherein said titanium-mesh encircles an area with a diameter in horizontal direction and forms a projecting umbrella surface with a curvature in perpendicular direction, a rough surface being formed on said projecting umbrella surface, said umbrella type titanium-mesh being able to position quickly on the mounting portion of said metal shank to form an umbrella structure. Thus, the titanium metal umbrella can be positioned quickly during dental implant placement procedure, so that the guide tissue membrane can be securely attached, a space for bone graft growing can be maintained, and the operation duration can be shortened.
Owner:LIAO JUNG YEN
Catalyzer for CO low-voltage gas-phase synthesizing of oxalic ester and method of preparing the same
InactiveCN101138722AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationTitanium metalGas phase
The present invention belongs to the oxalate preparation technical field and aims to provide a catalyst for synthesis of low pressure, high activity and high selectivity oxalate in a CO low-pressure gas phase, and a preparation method for the catalyst. The catalyst mainly uses the palladium metal as a main activated component, titanium and cerium as a promoter, and modified Alfa-Al2O3 as a carrier. The select content of palladium metal is 0.1 to 3.0 percent of the carrier weight, the content of the titanium metal is 0.02 to 1.5 percent of the carrier weight, and the content of the cerium metal is 0.01 to 0.75 percent of the carrier weight. The catalyst is manufactured with the method of immersion. The catalyst is manufactured with the method of immersion. Proven by experiments, the catalyst of the present invention is provided with the very high reaction activity and oxalate selectivity in the reaction to synthesize dimethyl oxalate or diethyl oxalate with carbon monoxide and nitrite. Moreover, the catalyst can resist affection by oxygen, hydrogen, water steam and other impurities. The catalyst is provided with the long usable life and the stable reaction performance, and can be easily controlled.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Titanium-containing lubricating oil composition
ActiveUS20070132274A1Improve fuel economyImprove wear characteristicsVehicle seatsWindowsTitanium metalPhysical chemistry
A lubricating oil composition comprising a) an oil of lubricating viscosity having a viscosity index of at least about 95; b) at least one calcium detergent; c) at least one oil soluble titanium compound; d) at least one friction modifier; and e) at least one metal dihydrocarbyldithiophosphate compound. The composition has a Noack volatility of about 15 wt. % or less, and contains from about 0.05 to about 0.6 wt. % calcium from the calcium detergent, titanium metal in an amount of at least about 10 ppm up to about 1500 ppm titanium from the titanium compound, and phosphorus from the metal dihydrocarbyldithiophosphate compound in an amount up to about 0.1 wt. %.
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL
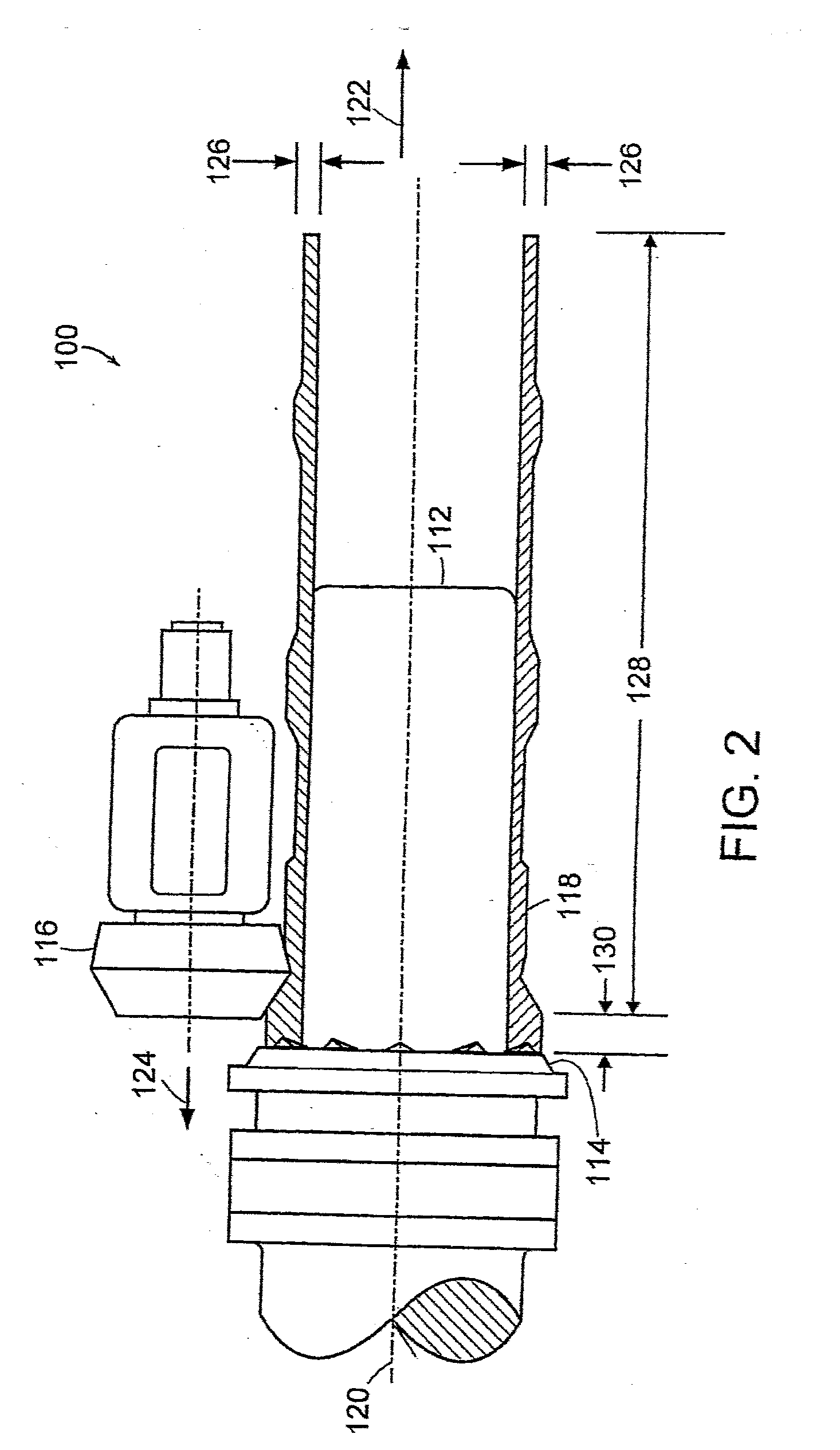
Flowforming Gun Barrels and Similar Tubular Devices
InactiveUS20100236122A1Efficient manufacturingStrong and light weightBarrelsHollow articlesTitanium metalTitanium
Gun barrels and similar tubular devices for repeatedly guiding fired projectiles are fabricated from superalloys, titanium metals, tantalum metals, and similar metal materials by a flowforming process. Combinations of these metals are also flowformed to produce gun barrels and projectile-guiding tubes. In addition, inner liners for such barrels and tubes are made with these metals and flowforming processes. These barrels and tubular devices can withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments. The flowforming process is efficient and produces strong, yet thin and / or light weight, gun barrels and similar tubular devices.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES LLC
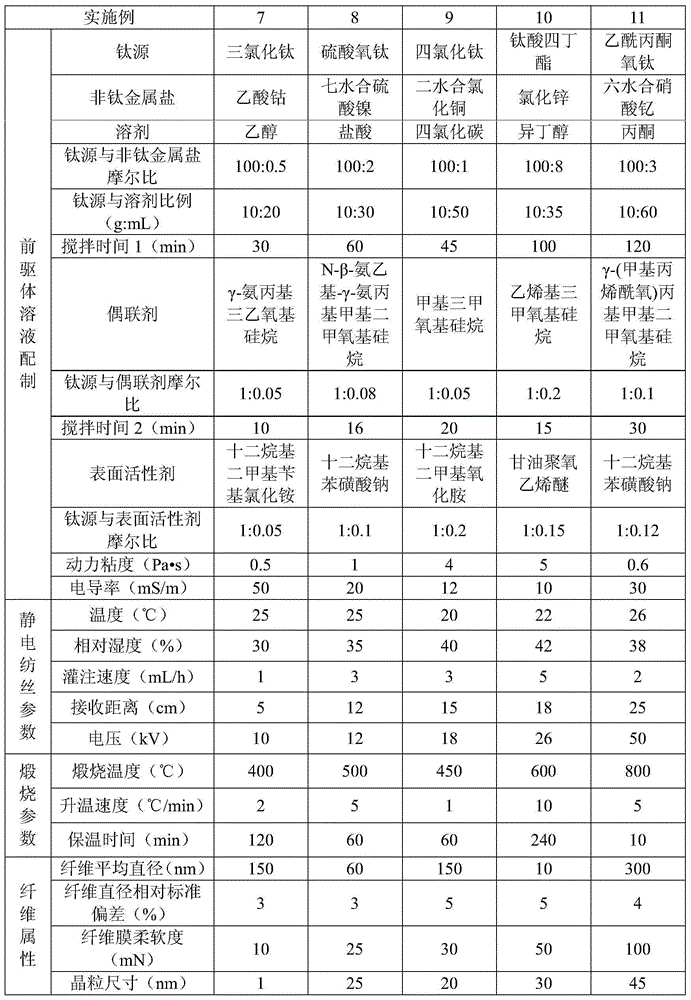
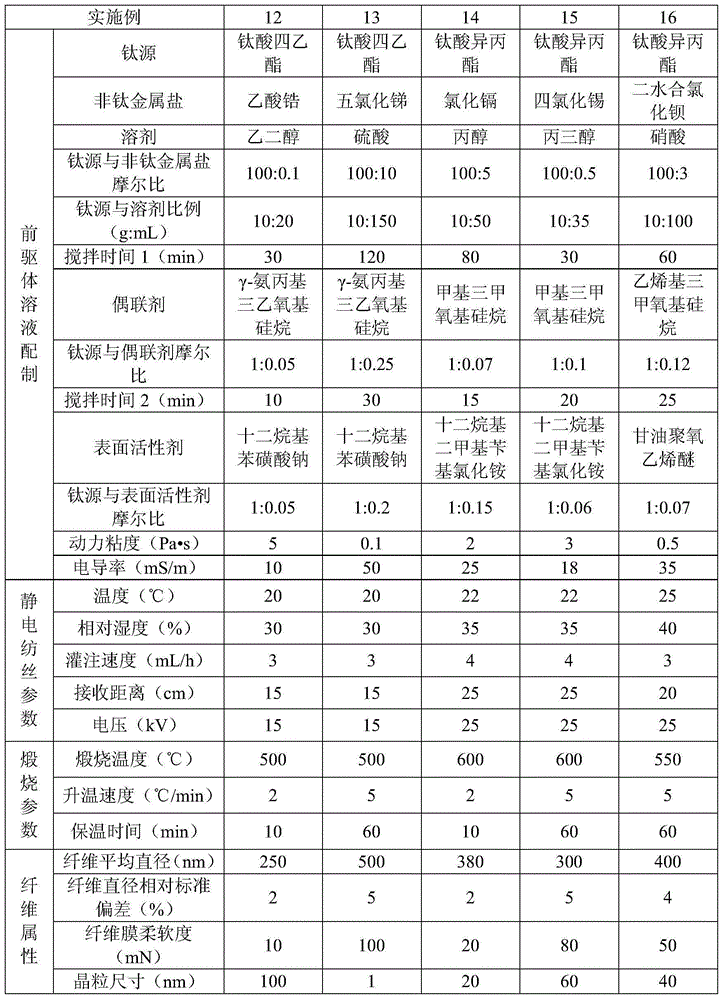
Flexible titanium oxide nanofiber membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104153123AImprove flexibilityHigh yieldHeating/cooling textile fabricsNon-woven fabricsFiberTitanium metal
The invention relates to a flexible titanium oxide nanofiber membrane and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes firstly dissolving a titanium source and a non-titanium metal salt in solvent, and sequentially adding coupling agent and surfactant to be uniformly mixed and obtain stable precursor solution with interpenetrating three-dimensional network structure molecular chains; then making the precursor solution into a precursor fiber membrane through an electrospinning technique; burning the precursor fiber membrane in the air to obtain the flexible titanium oxide nanofiber membrane. The preparation method is simple and low in cost, the obtained titanium oxide nanofiber membrane is good in flexible and has promising application prospect in the fields such as air purification, water treatment, hydrogen production by photodecomposition, dye-sensitized solar cells, lithium ion batteries and self-cleaning environment protection and energy sources.
Owner:嘉兴富瑞邦新材料科技有限公司
Brake disks and methods for coating
A lightweight brake disk is made of a Titanium alloy and coated with a coating material that is hard and wear resistant. The aesthetically pleasing, wear resistant coating overlays wear surfaces and portions of the brake disk that will be visible when the brake disk is installed on the vehicle. The coating includes a first layer of a metal, such as amorphous Titanium metal, and a second layer that preferably includes a Nitride, Boride, Carbide or Oxide of the metal used in the first layer. The coating is preferably applied using a physical vapor deposition source such as a cathodic arc source with a controlled gas atmosphere.
Owner:MOLECULAR METALLURY
Pure-titanium metal surface micro-arc oxidation treatment electrolyte and antimicrobial bioactive coating preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102146577AImprove antibacterial propertiesImprove biological activitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingProsthesisPlasma electrolytic oxidationMicro arc oxidation
The invention discloses pure-titanium metal surface micro-arc oxidation treatment electrolyte and an antimicrobial bioactive coating preparation method thereof, belongs to a medical titanium metal surface modification technology, and aims to provide a micro-arc oxidation treatment electrolyte which can remarkably improve pure-titanium metal surface bioactivity and coating bonding strength and a coating preparation method thereof. The electrolyte comprises a compound system including the components of calcium acetate, sodium phosphate and a zinc oxide precursor, wherein the phosphorous ion concentration is 0.5 to 1.0 M, the molar ratio of Ca to P is 0.2 to 1.0, and the designed Zn<2+> concentration accounts for 10 to 20 percent of the total concentration. A biological composite coating is directly generated on the surface of a titanium metal surface in-situ by adopting the electrolyte and a micro-arc oxidation technology. The coating has high bonding strength with a substrate, dense inner layer, coarse and porous outer layer, high bioactivity and high antibacterial property; moreover, the used raw materials are easy to obtain; the process is simple and easy to operate; and the electrolyte has stability, reusability, and low production cost and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIAMUSI UNIVERSITY
Methods for centrifugally casting highly reactive titanium metals
Methods for centrifugally casting a highly reactive titanium metal involving providing a cold wall induction crucible having a plurality of induction coils and a removable bottom plate, using a power source to heat a titanium metal charge in the induction crucible to obtain a molten metal, preheating a secondary crucible and placing the preheated secondary crucible into a centrifugal casting machine, positioning the centrifugal casting machine having the secondary crucible beneath the induction crucible, withdrawing the bottom plate of the induction crucible and turning off the power source to the induction crucible to allow the molten metal to fall from the induction crucible into the secondary crucible, and accelerating the secondary crucible to centrifugally force the molten metal into a casting mold to produce a cast component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
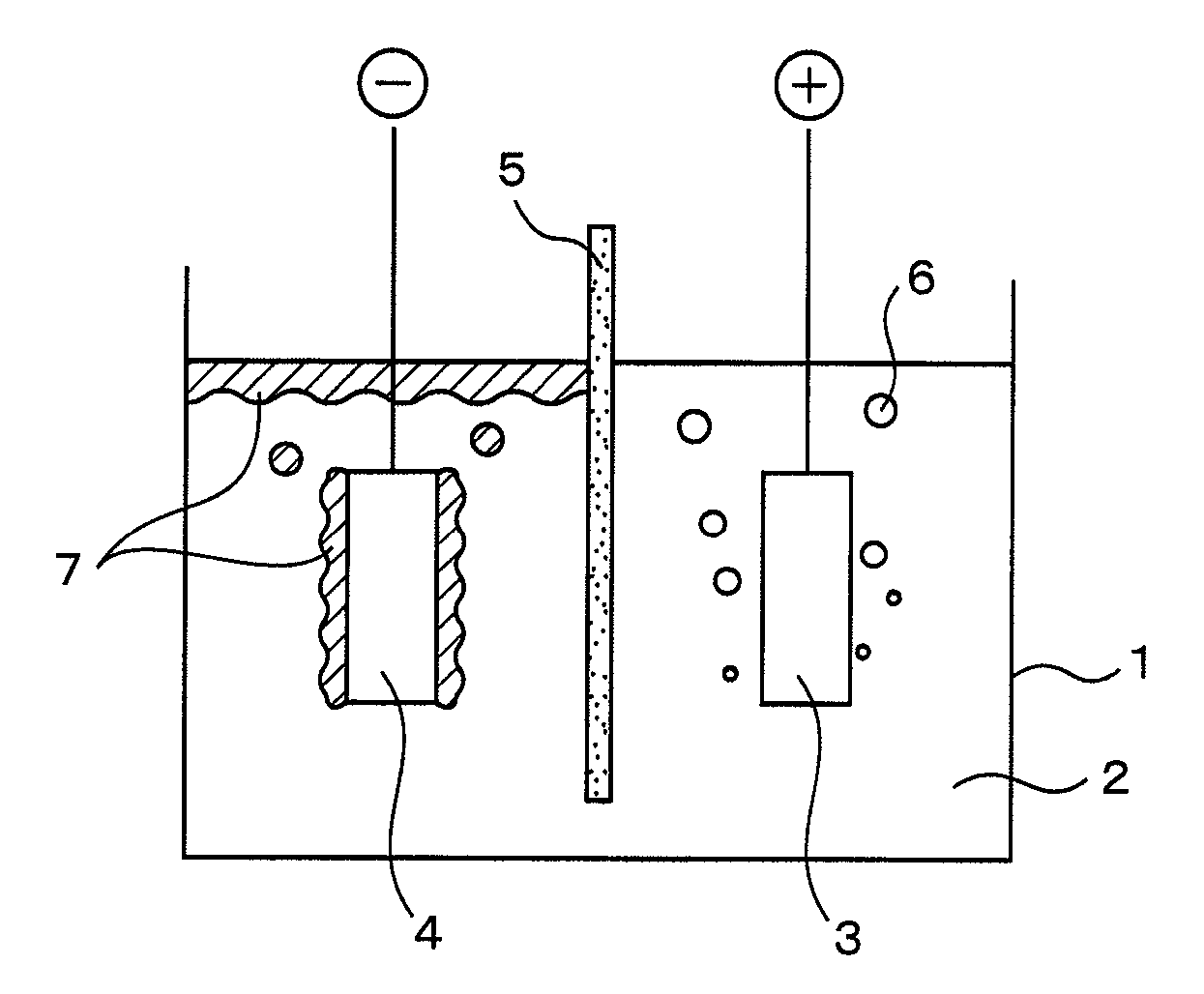
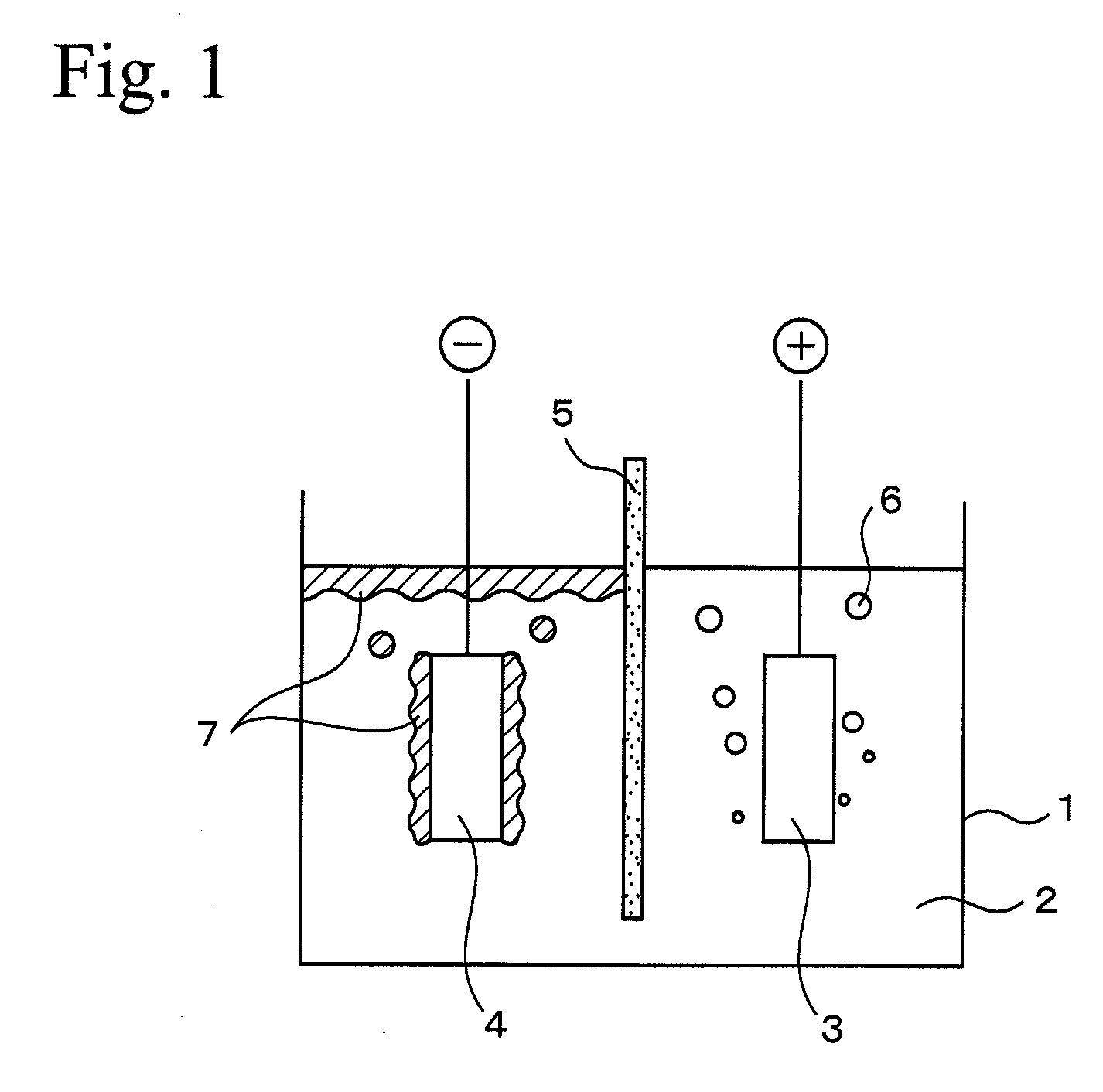
Method for Production of Metal by Molten-Salt Electrolysis and Method for Production of Titanium Metal
InactiveUS20080053838A1Effective recoveryReduce solubilityElectrolysis componentsMetal chlorideElectrolysis
A method for production of metal by molten-salt electrolysis is a method for production of metal by molten-salt electrolysis which is performed by filling molten salt of a metal chloride in an electrolysis vessel having an anode and a cathode, and a molten salt which reduces solubility of the metal in the molten salt is used.
Owner:TOHO TITANIUM CO LTD +1
Preparation method of bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone
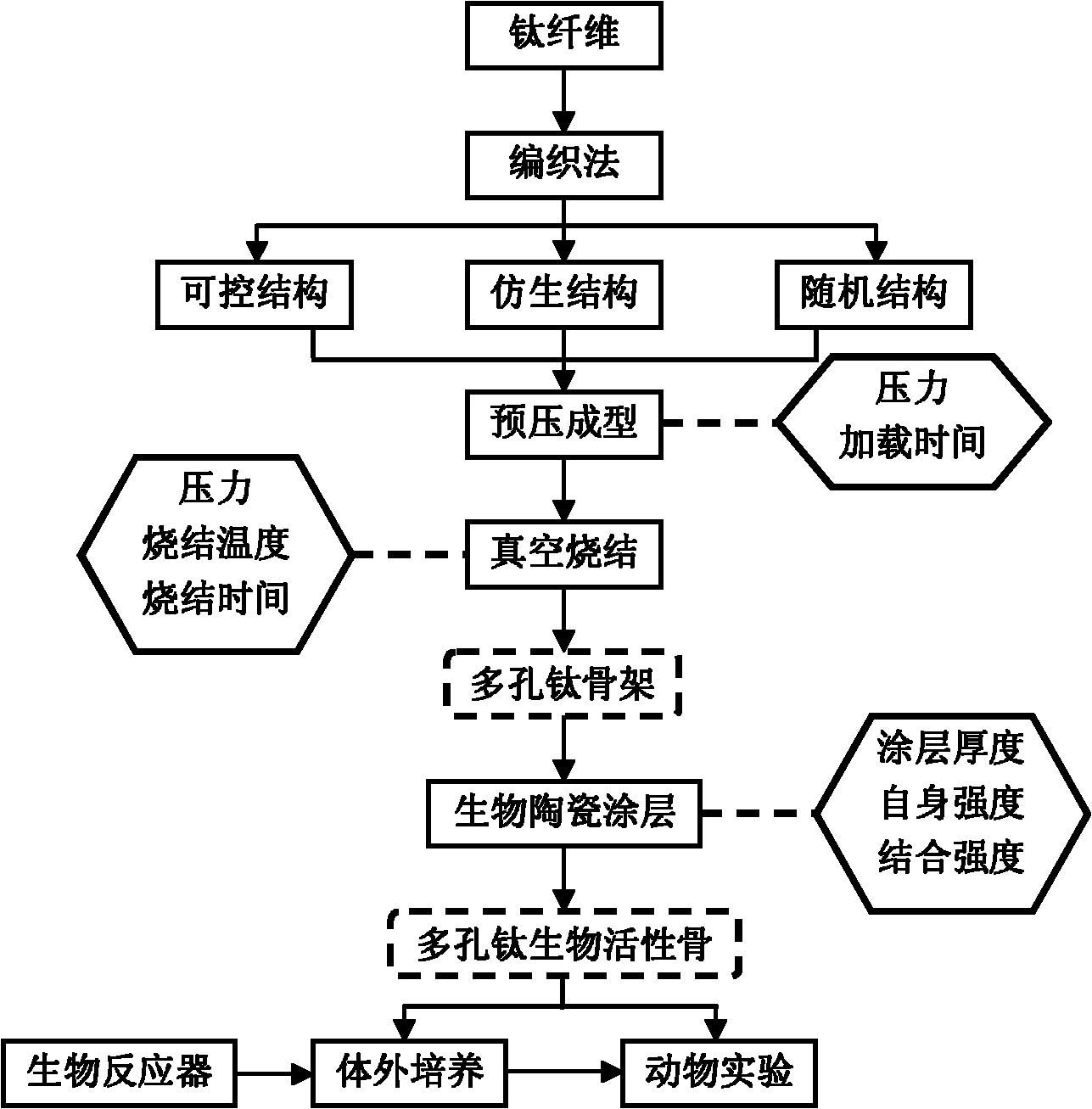
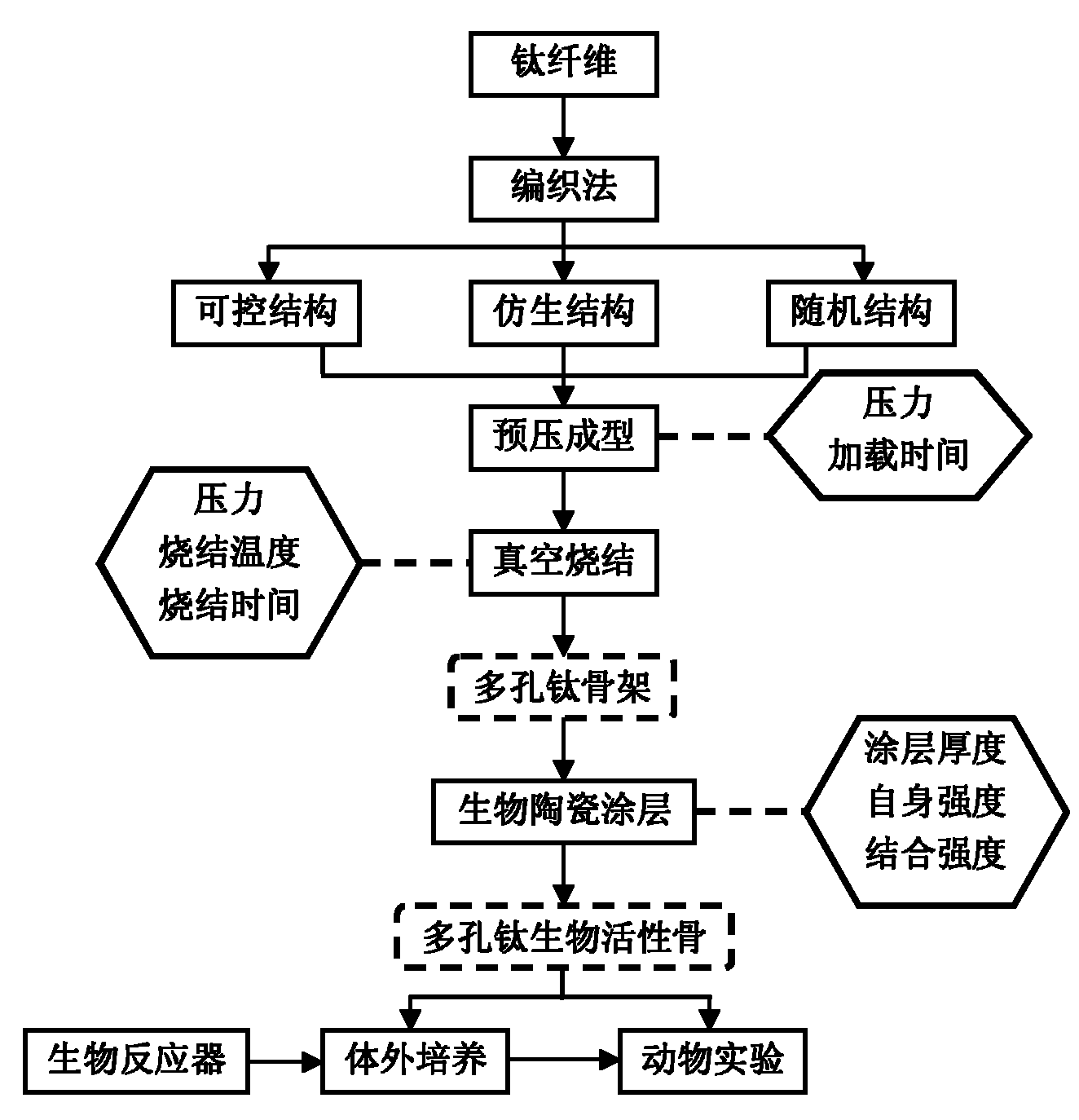
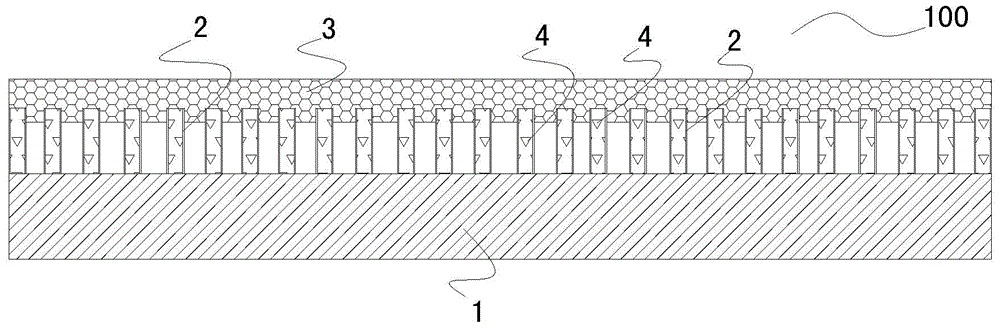
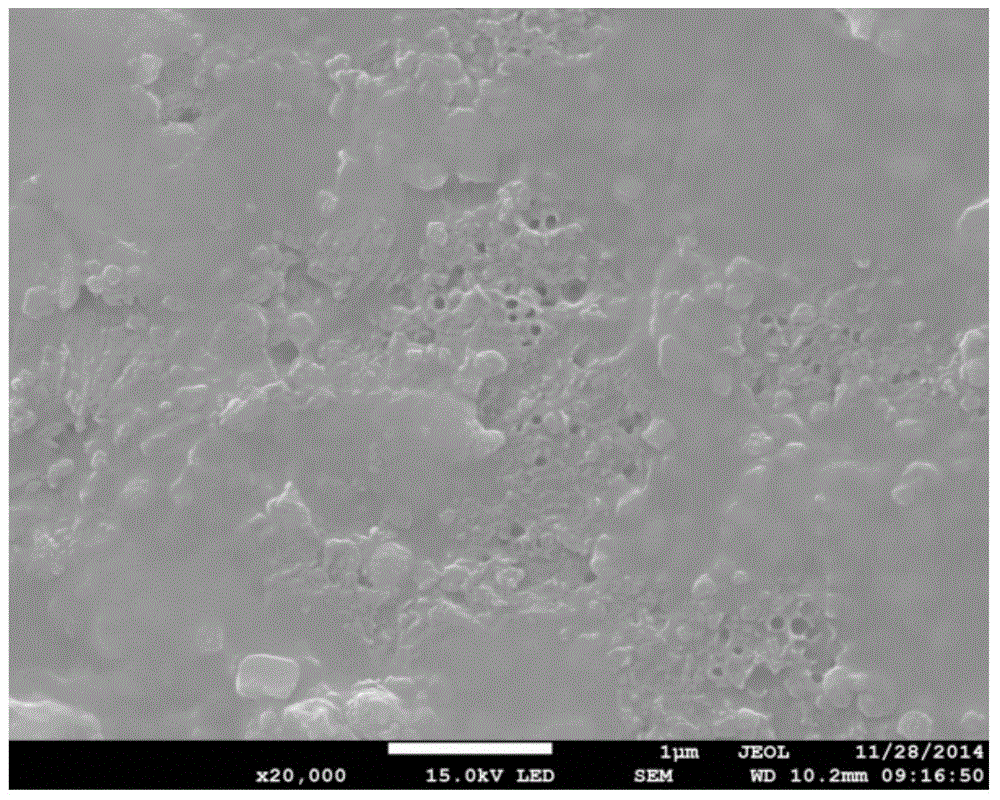
InactiveCN101889912AHave biological propertiesBiologically activeBone implantCoatingsFiberPrincipal stress
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone, belonging to the biomedical engineering field. In the invention, a three-dimensional weaving method is utilized, a titanium metal fiber wire is constructed into a controllable structure model, a random structure model and a bionic structure model which can stimulate the bone trabecula and principal stress line of a human bone, and then is prepared into the porous titanium artificial bone through prepressing molding and vacuum sintering, after that, a sol-gel method is utilized to manufacture a gradient coating or a complex coating on the surface of the porous titanium artificial bone, so that the gradient coating transiting from titanium dioxide to bio-ceramics or the bio-ceramics-titanium dioxide complex coating is formed on the surface of the porous titanium artificial bone to obtain the bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone. The preparation method not only can protect the titanium metal skeleton and prevent titanium ions from dissociating to enter a human body, but also can ensure that the titanium metal skeleton the surface of which is coated with the bio-ceramics has the biological characteristics, therefore, the bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone can be applied to repairing clinical segmental defect of long bones.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Bioactive film on titanium metal surface and its sand blasting-micro arc oxidizing compounding process
InactiveCN1974876ASolve for bond strengthAddressing Binding StabilitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingPlasma electrolytic oxidationMicro arc oxidation
The present invention relates to film on the surface of medical titanium-base metal material and its sand blasting-micro arc oxidizing compounding process. Through the first surface sand blasting treatment of titanium or titanium alloy material and the subsequent micro arc oxidizing in electrolyte solution containing phosphate radical ion and calcium ion and with the titanium or titanium alloy material as anode, stainless steel or titanium as cathode and DC power source or DC pulse power source, one bioactive film is in-situ formed on the surface of the titanium or titanium alloy material. The bioactive film of rough porous hydroxyapatite has surface roughness Ra of 2-4.5 micron, no interface with the substrate, elastic modulus reaching that of bone and excellent bioactivity, and may be used as the substitute for femur, hip joint, tooth root, etc. The bioactive film has optimized combination strength, stability and bioactivity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Medical titanium metal implant material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104826159AImprove biological activityImprove adhesionCoatingsProsthesisTitanium metalNanotube
The invention provides a medical titanium metal implant material and a preparation method thereof. The medical titanium metal implant material includes a titanium metal, titania nanotubes grown on the titanium metal surface in a matrix arrangement, a biodegradable superpolymer coating the end face of a titania nanotube layer in the matrix arrangement and sealing the titania nanotubes, and an anti-inflammatory antibacterial drug loaded in the titania nanotubes. The medical titanium metal implant material has the characteristics of being high in drug loading capacity and capable of making drug properties of the drug slowly released.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Expansion connecting method for titanium and aluminium dissimillar non-ferrous metal
InactiveCN1943956ASimple and fast operationLow costHot-dipping/immersion processesNon-electric welding apparatusTitanium metalTitanium
The diffusion connecting method for dissimilar non-ferrous metals, such as titanium and aluminum, belongs to the field of material processing technology. The connection process includes the following steps: 1. plating assisting treatment of the surface of metal titanium; 2. aluminum immersing treatment of the surface of metal titanium; 3. cleaning treatment of the surface of metal titanium; 4. cleaning treatment of the surface of metal aluminum to be connected; 5. superposing titanium and aluminum and assembling connecting part; and 6. vacuum diffusion connecting. The connection process is simple, low in cost and high in connecting effect and the present invention provides one new way for the connection between dissimilar non-ferrous metals.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Bipolar zero-gap type electrolytic cell
ActiveUS20060042935A1Preventing gas vibrationStable electrolysisCellsElectrode shape/formsInternal pressureTitanium metal
A bipolar zero-gap electrolytic cell comprising an anode comprising an anode substrate constituted of a titanium expanded metal or titanium metal net of 25 to 70% opening ratio, which anode after coating the substrate with a catalyst has a surface of 5 to 50 μm unevenness difference maximum and has a thickness of 0.7 to 2.0 mm. In this electrolytic cell, the possibility of breakage of ion exchange membrane is low, and the anolyte and catholyte have a concentration distribution falling within given range. With this electrolytic cell, stable electrolysis can be performed for a prolonged period of time with less variation of cell internal pressure.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
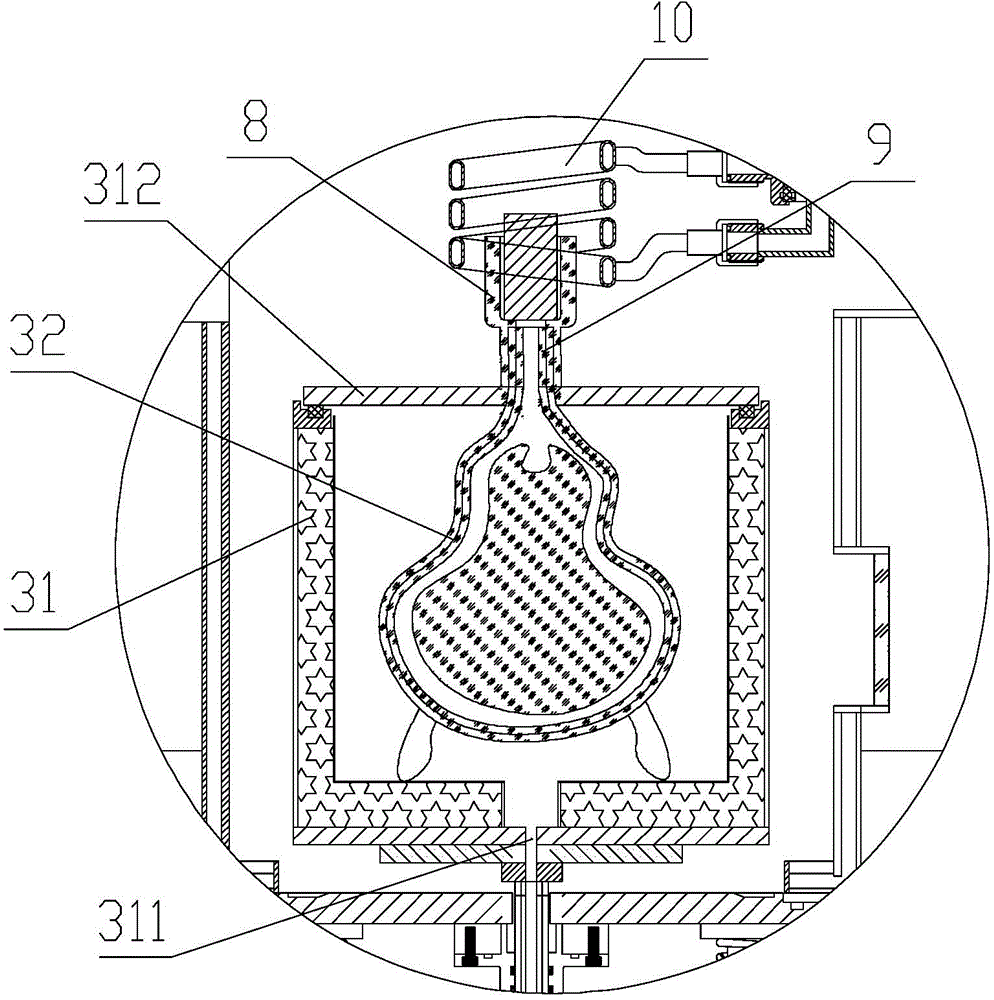
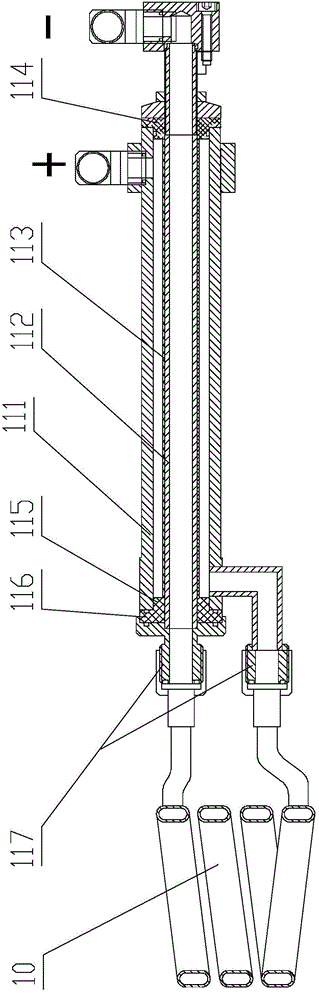
Titanium-based alloy induction melting bottom leakage type vacuum suction casting device and control method
The invention discloses a titanium-based alloy induction melting bottom leakage type vacuum suction casting device and a control method, relates to the technical field of titanium-based alloy melting suction casting and solves the problems of low efficiency, high cost, complicated technology and the like of an existing titanium-based alloy melting suction casting device. The titanium-based alloy induction melting bottom leakage type vacuum suction casting device provided by the invention can be used for carrying out vacuum induction melting on titanium-based alloy by adopting a ceramic crucible; since no any shielding effect works on an electromagnetic force by ceramic, all electromagnetic induction energy generated by an induction coil can totally act on titanium metal, energy saving and environment protection are realized, the utilization rate of metal raw materials is up to 60%-70%, and the metal cost is greatly reduced; an isolating layer is formed on the inner surface of a crucible body of the ceramic crucible, materials which are used for manufacturing the isolating layer comprise yttrium oxide, the yttrium oxide has good inertia on the titanium metal under high temperature and can be used for isolating ceramic materials which can react with the titanium metal during a melting process, and titanium-based alloy melting is enabled to be reliably proceeded.
Owner:北京博瑞杰特科技发展有限公司
Three-phase three-dimensional electrode photoelectric catalytic reactor and application thereof
InactiveCN102424452AGuaranteed equal aerationGood mass transfer effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsTitanium metalUltraviolet
The invention relates to a three-phase three-dimensional electrode photoelectric reactor and application thereof. The reactor comprises a reactor shell, a titanium metal net anode, a stainless steel or graphite cathode, a gas distribution board, a double-layer U-shaped quartz pipe as well as a light source UV (ultraviolet) lamp, a three-dimensional particle electrode and clapboards placed in the quartz pipe. According to the three-phase three-dimensional photoelectric reactor provided by the invention, a non-homogeneous three-dimensional electrode and a photocatalysis technique are ingeniously combined, not only are the oxidation of the anode and the reduction of the cathode utilized, but also the synergism of.OH, H2O2, -OH and other active substances generated by an electric field and photocatalysis are utilized, the surfaces of TiO2 particles are continuously renewed, and the reaction system is organically harmonized, thus the organic matter degradation reaction is more thorough, and the decolorizing rate in printing and dyeing wastewater treatment can reach 97.09%. A large reaction chamber is uniformly divided into 2-6 small reaction chambers by the clapboards, thus a group of 2-6 control experiments can be carried out under the reaction conditions of the same voltage, light source, reaction time and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com