Patents
Literature
35096results about How to "Reduce thickness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
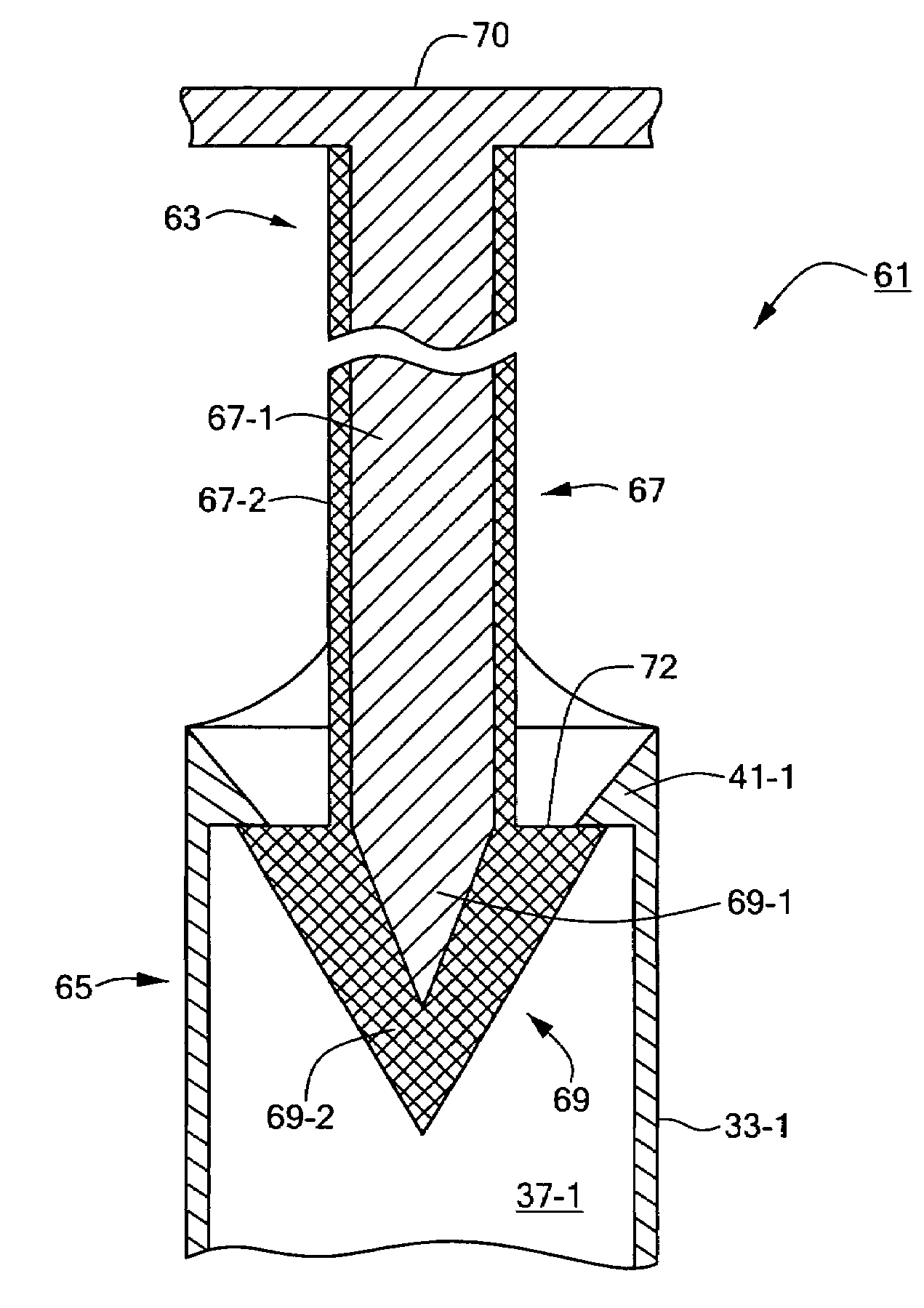
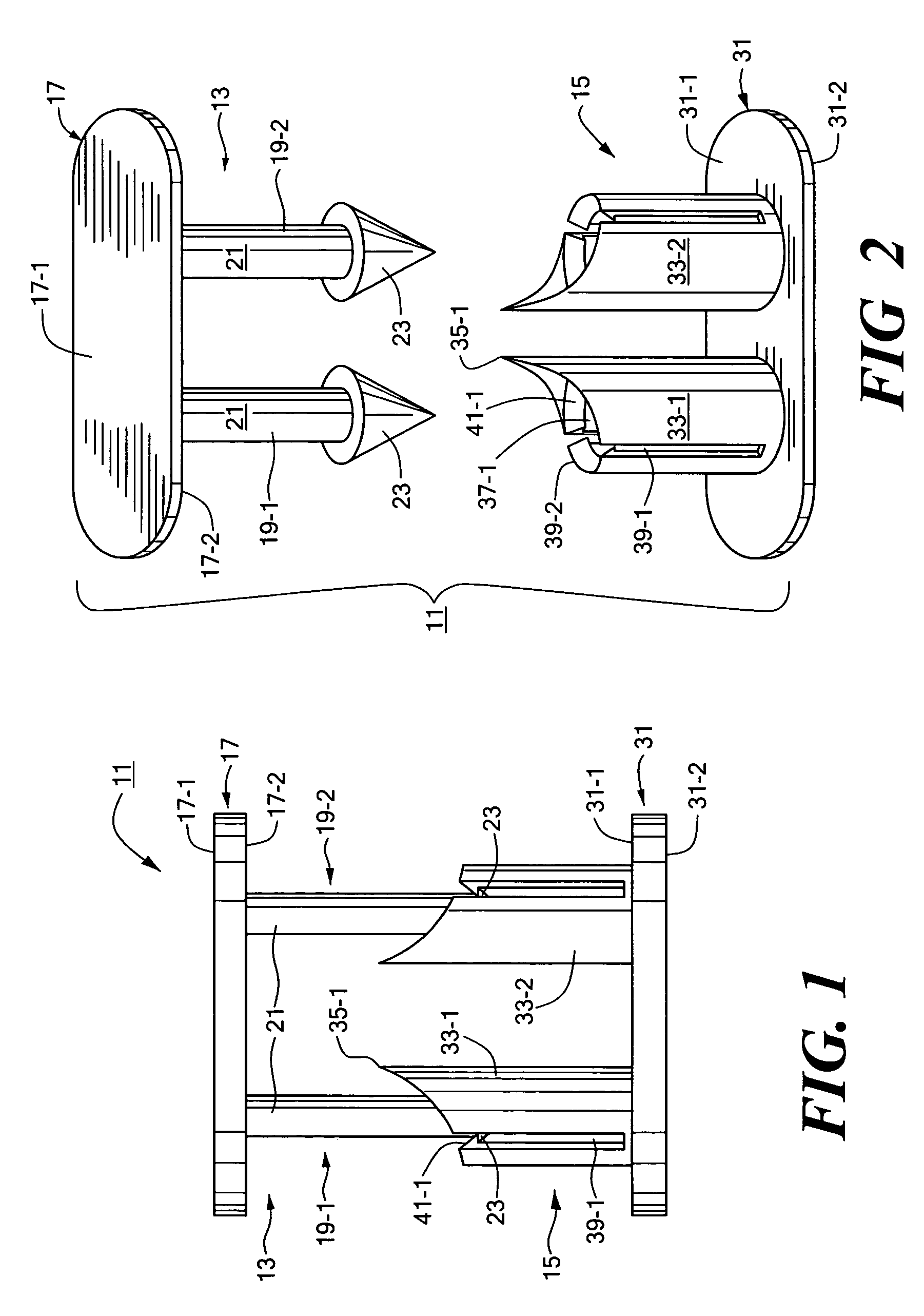
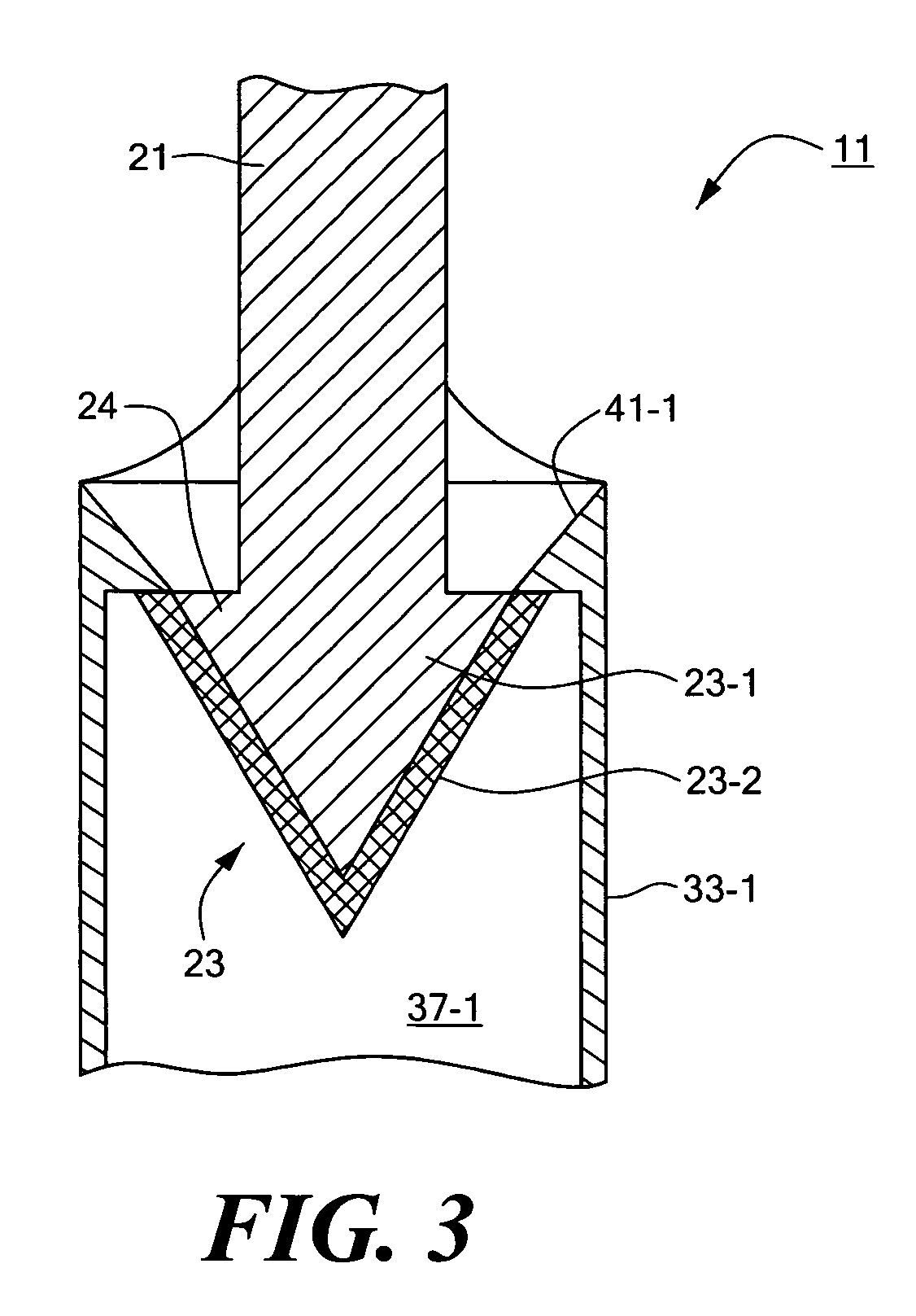
Impermanent biocompatible fastener
InactiveUS7442201B2Reduce thicknessDegrades more quicklySuture equipmentsSurgical adhesivesFastenerEngineering
A biocompatible fastener particularly well-suited for use in fundoplication procedures. In a preferred embodiment, the fastener is designed to break within the span of approximately three to six months after implantation and comprises a male portion and a female portion. The male portion includes a first base member, the first base member being generally flat and oval. A pair of male members are mounted on the bottom surface of the first base member, each male member comprising a cylindrical post extending downwardly from the bottom surface of the first base member and a conical head disposed at the bottom end of the post. The female portion includes a second base member, the second base member being generally flat and oval. A pair of sleeves are mounted on the top surface of the second base member and extend upwardly therefrom. Each sleeve defines a bore adapted to receive a head from a corresponding male member and has an inner flange formed thereon. The flange extends radially into the bore and is engageable with the head once the head has been inserted therepast so as to inhibit withdrawal of the head from the bore. Except for an outer coating on each of the two heads, the fastener is made entirely of a non-bioabsorbable material or a bioabsorbable material having a relatively slow degradation rate. By contrast, the outer coating is made of a bioabsorbable material having a relatively fast degradation rate. The thickness of the outer coating is appropriately selected so that degradation of the outer coating permits each head to be withdrawn past its flange after a desired period of time.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
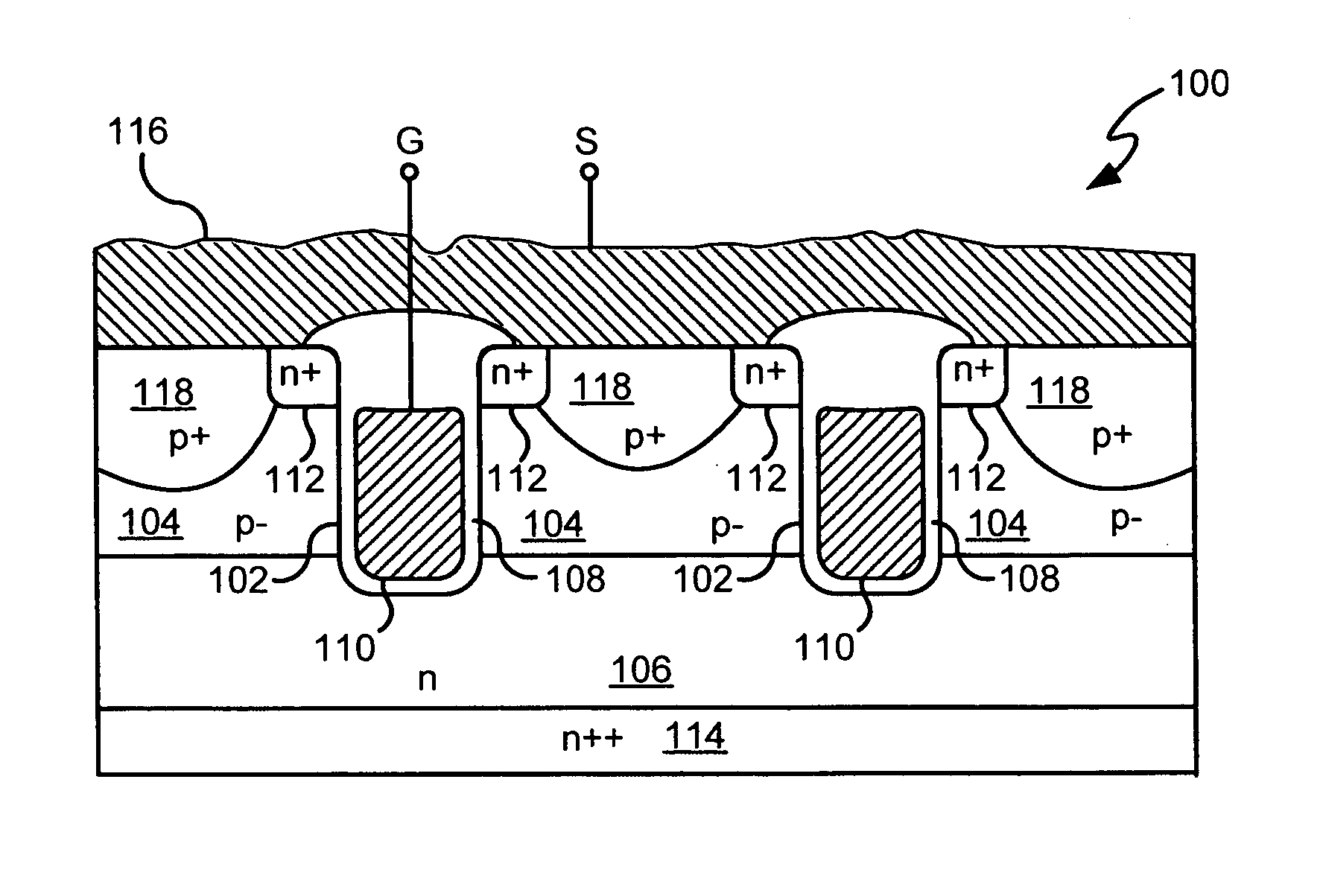
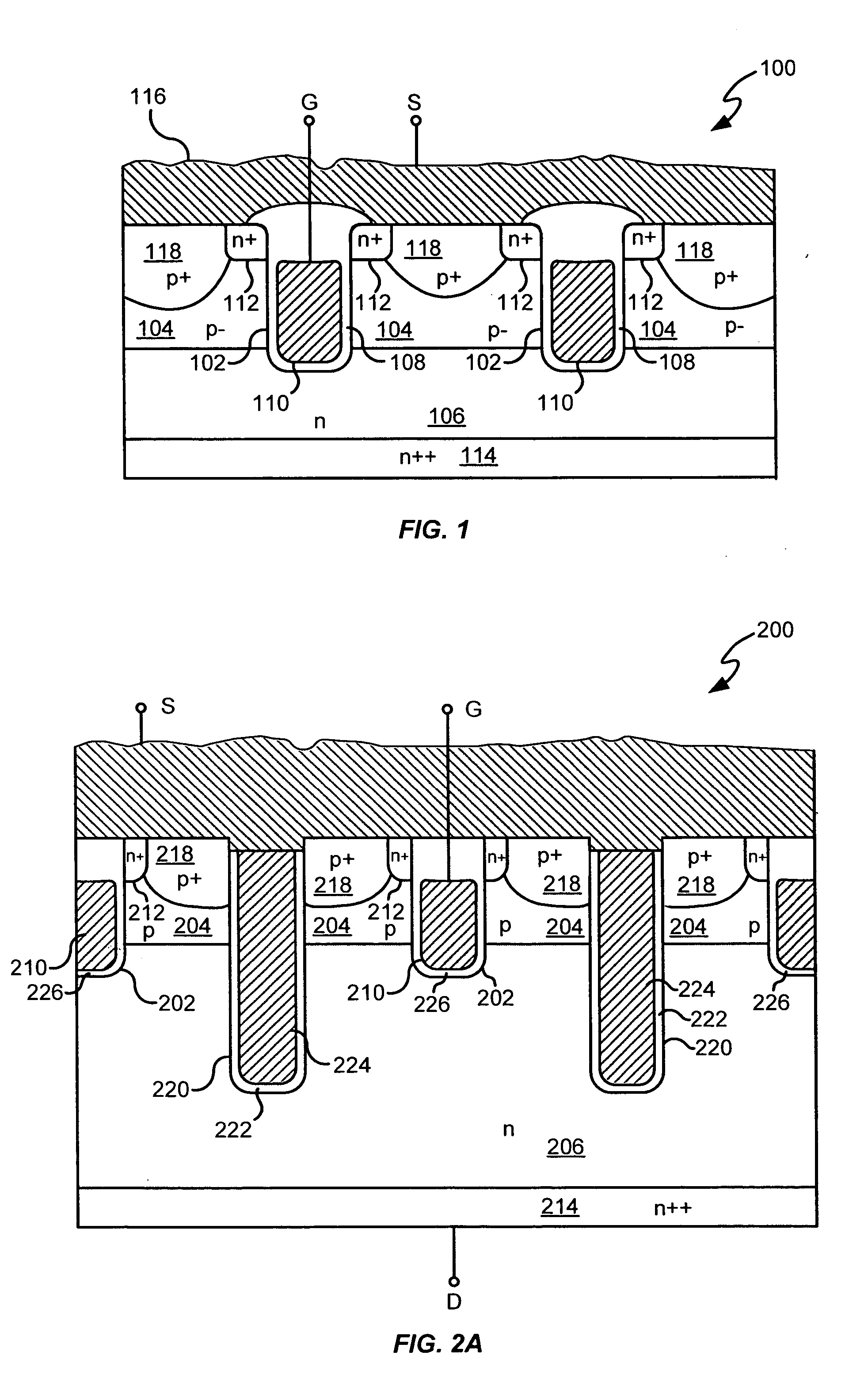
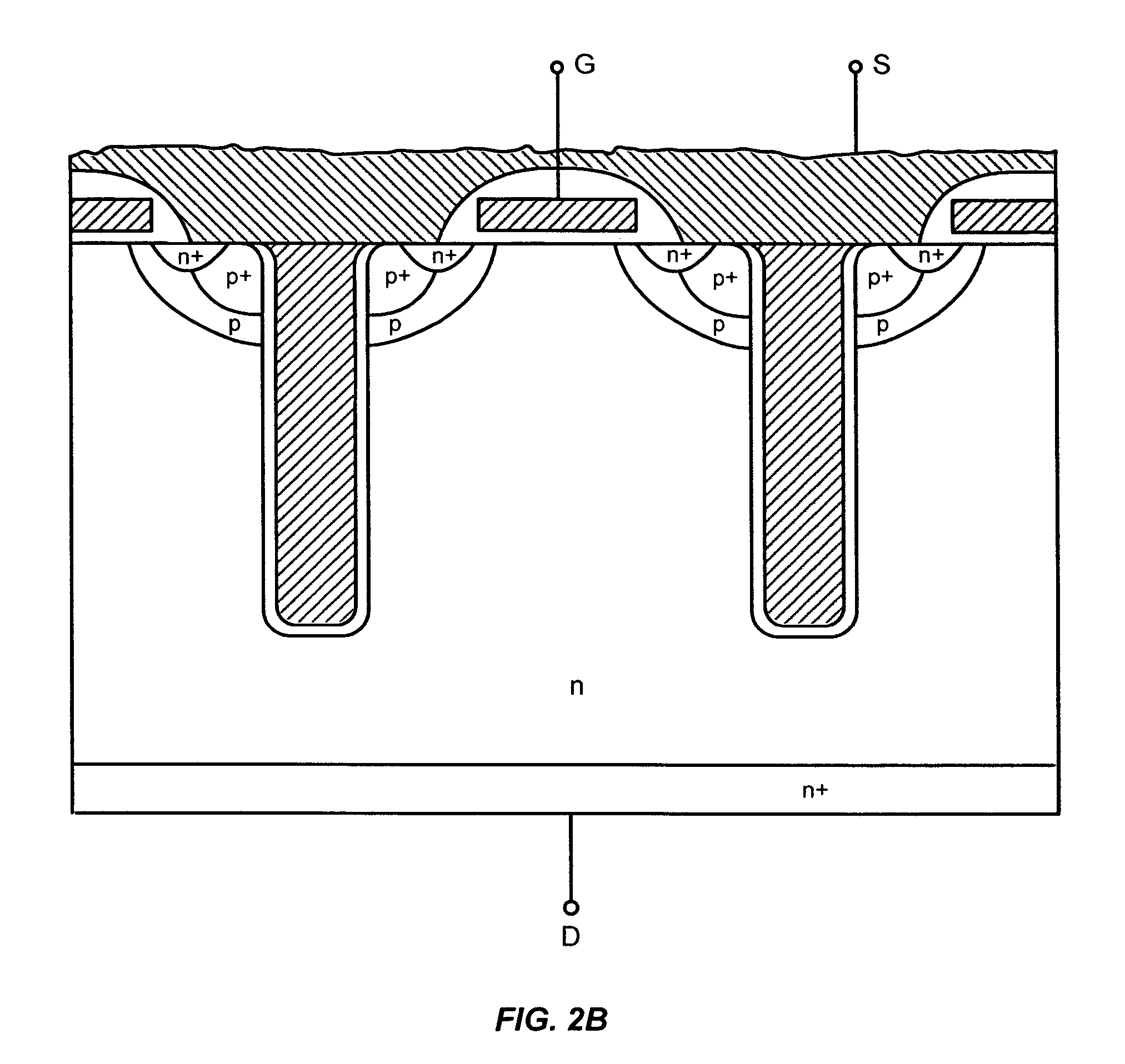
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20050167742A1Improved voltage performanceFast switching speedEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHigh voltage
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Use of high-k dielectric materials in modified ONO structure for semiconductor devices
InactiveUS6674138B1Reduced dimensionSacrificing charge trapping abilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor device
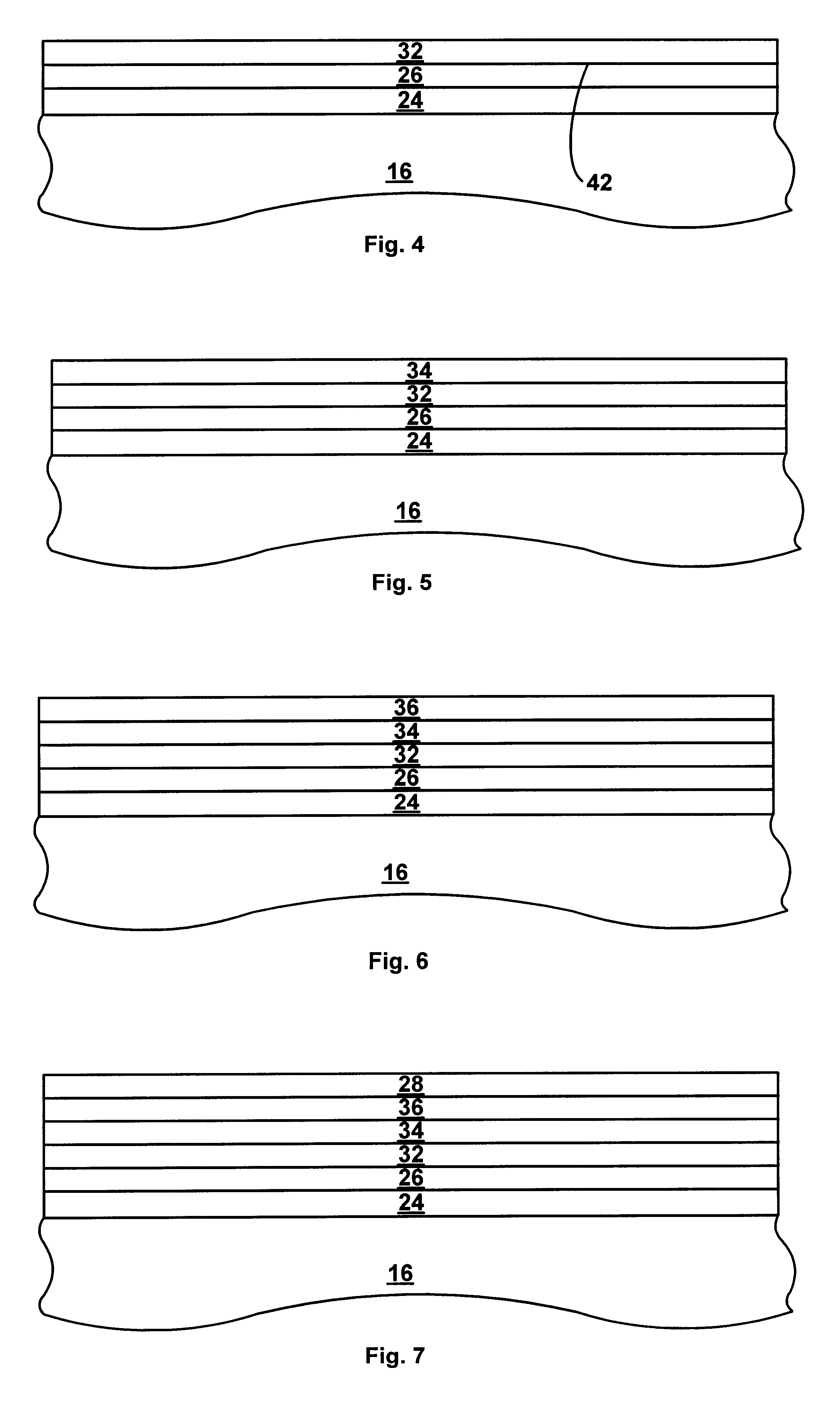
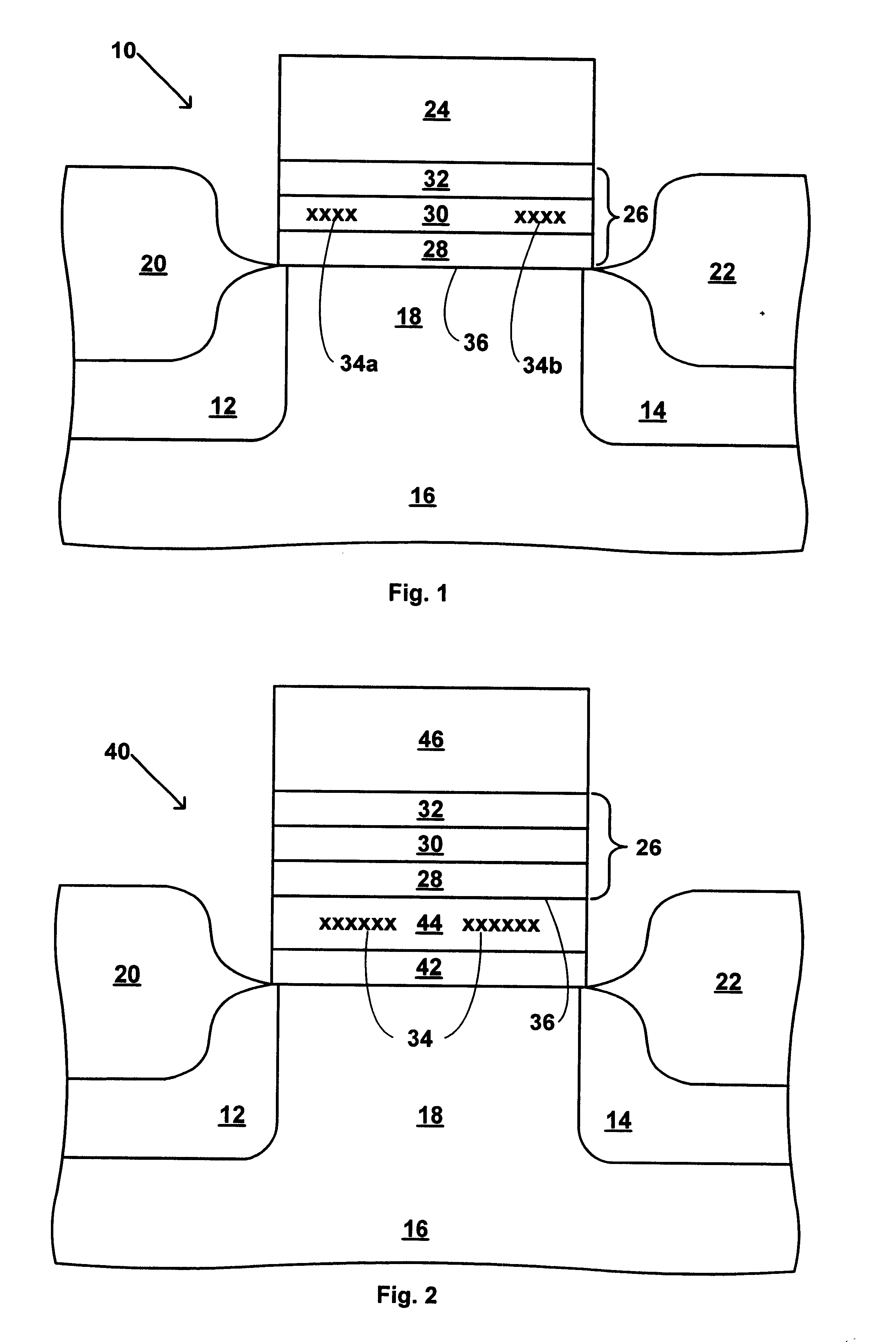
A process for fabrication of a semiconductor device including a modified ONO structure, including forming the modified ONO structure by providing a semiconductor substrate; forming a first oxide layer on the semiconductor substrate; depositing a layer comprising a high-K dielectric material on the first oxide layer; and forming a top oxide layer on the layer comprising a high-K dielectric material. The semiconductor device may be, e.g., a MIRRORBIT(TM) two-bit EEPROM device or a floating gate flash device including a modified ONO structure.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
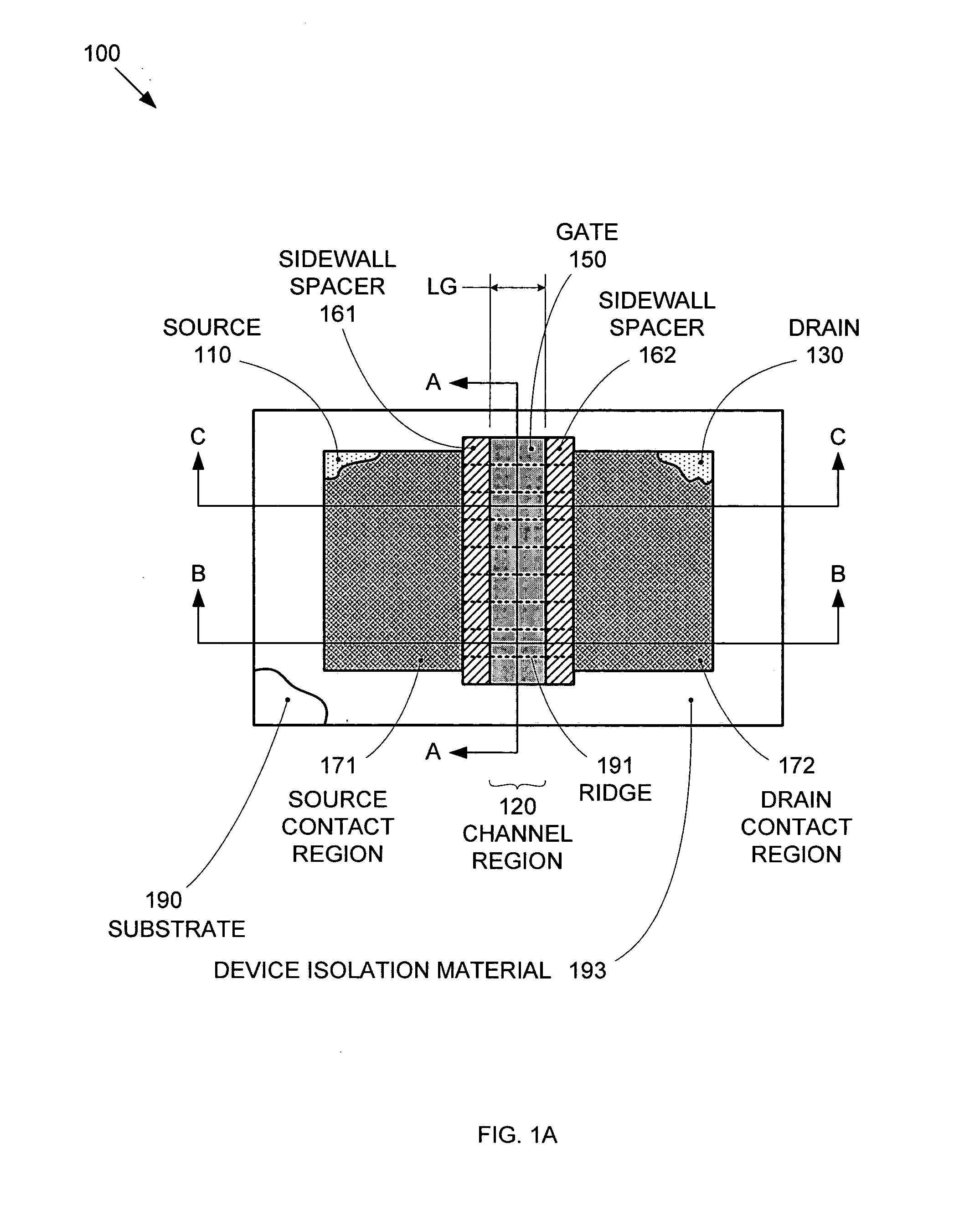
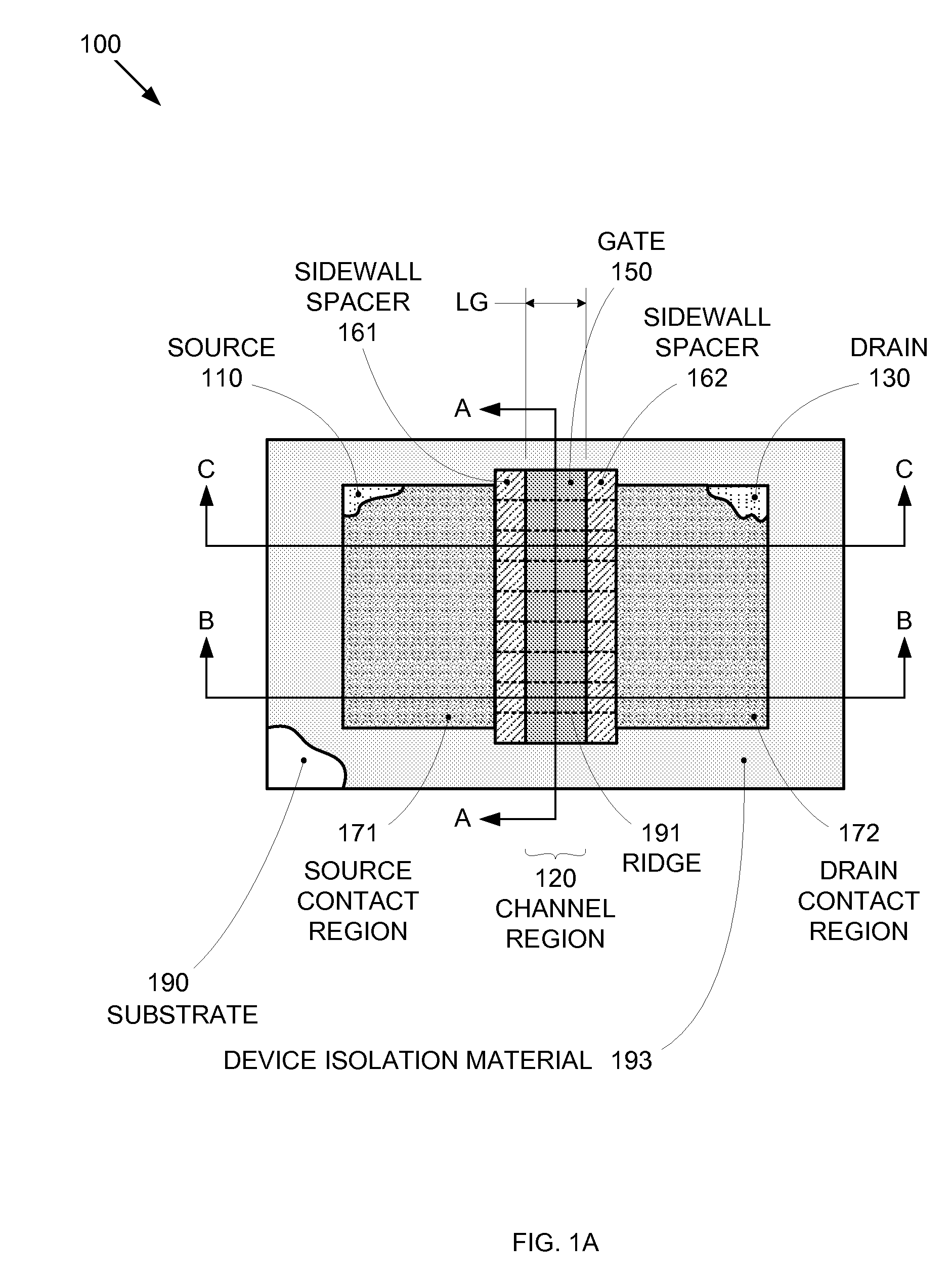
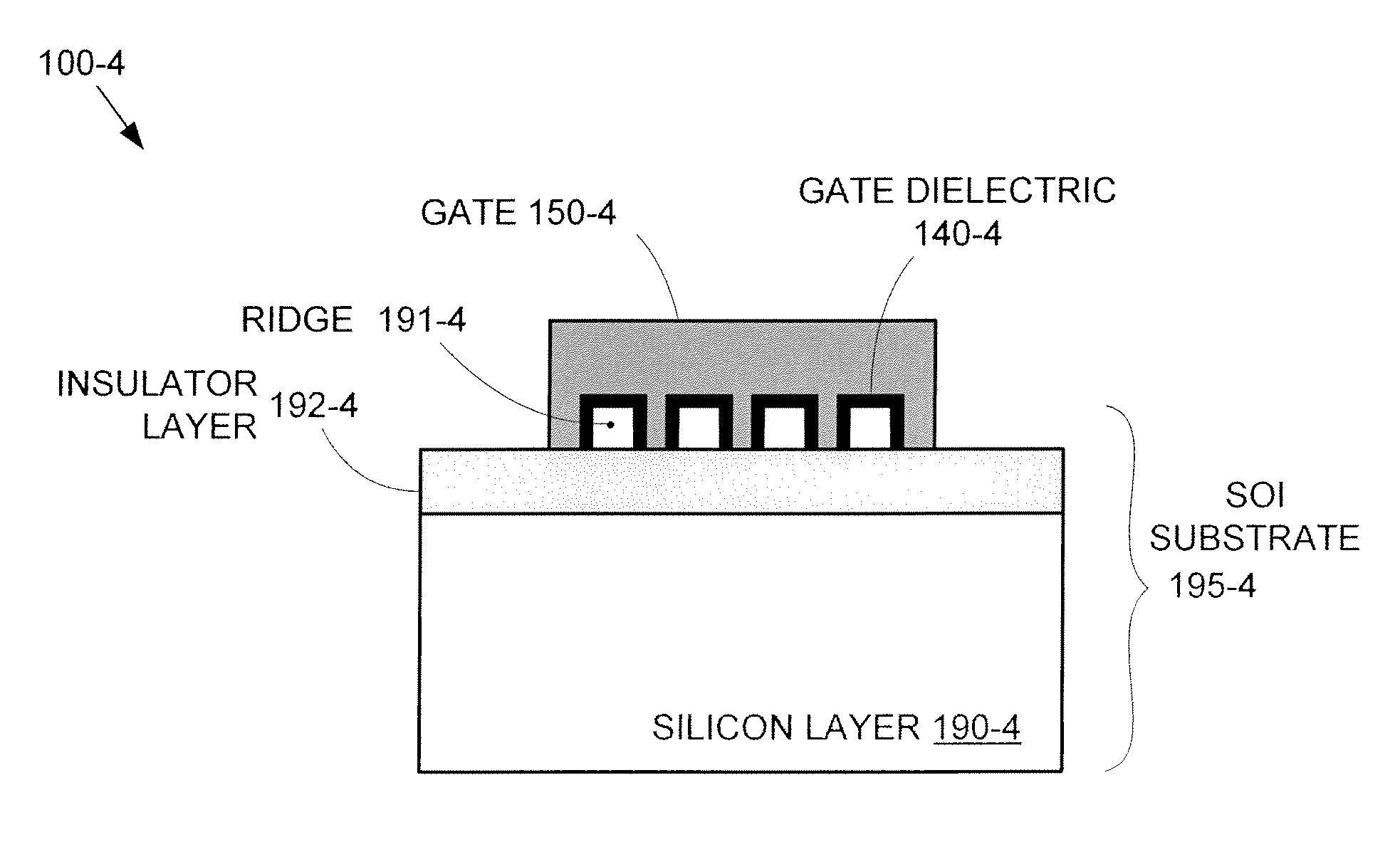
Segmented channel MOS transistor
ActiveUS7247887B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETLithographic artist
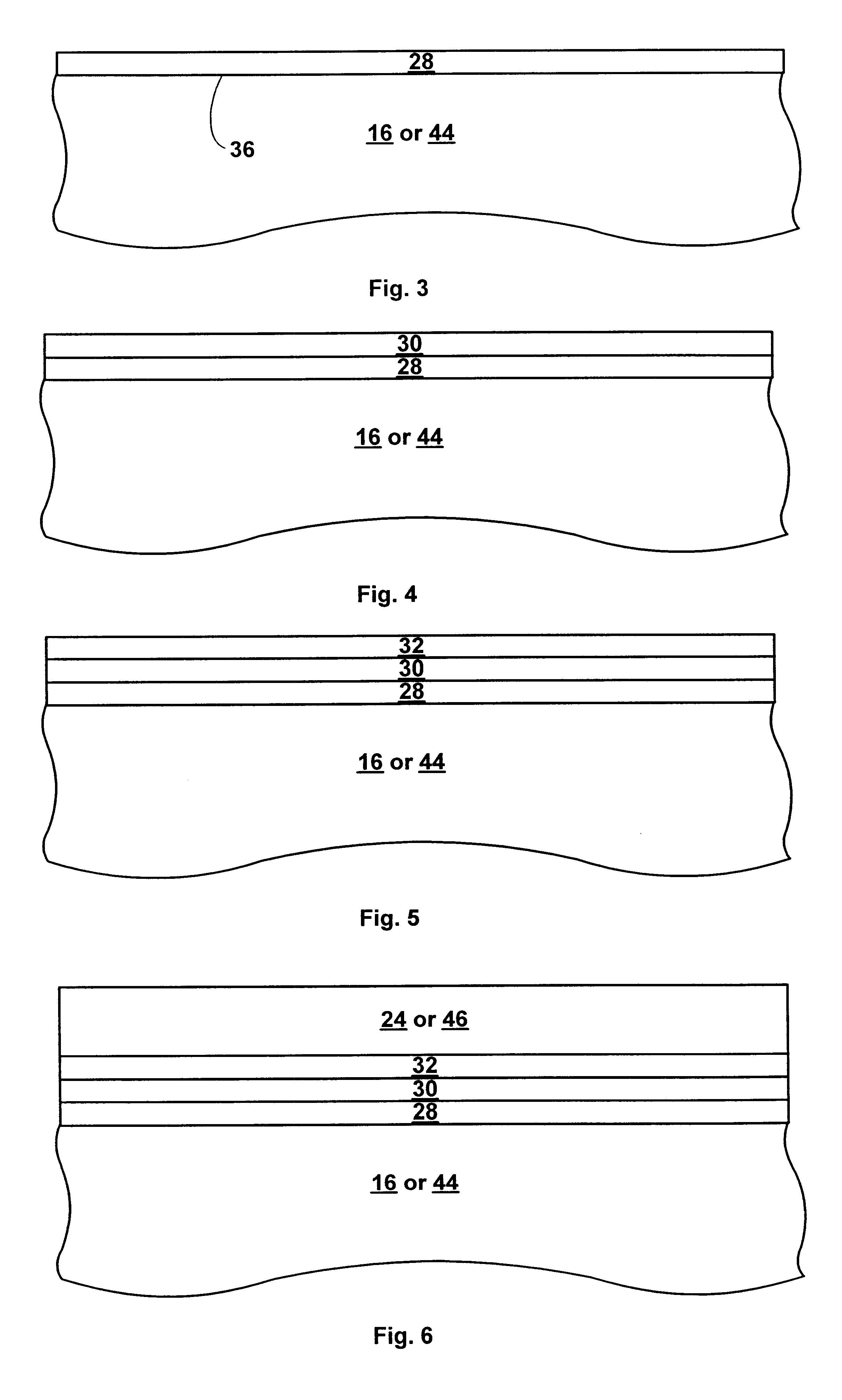
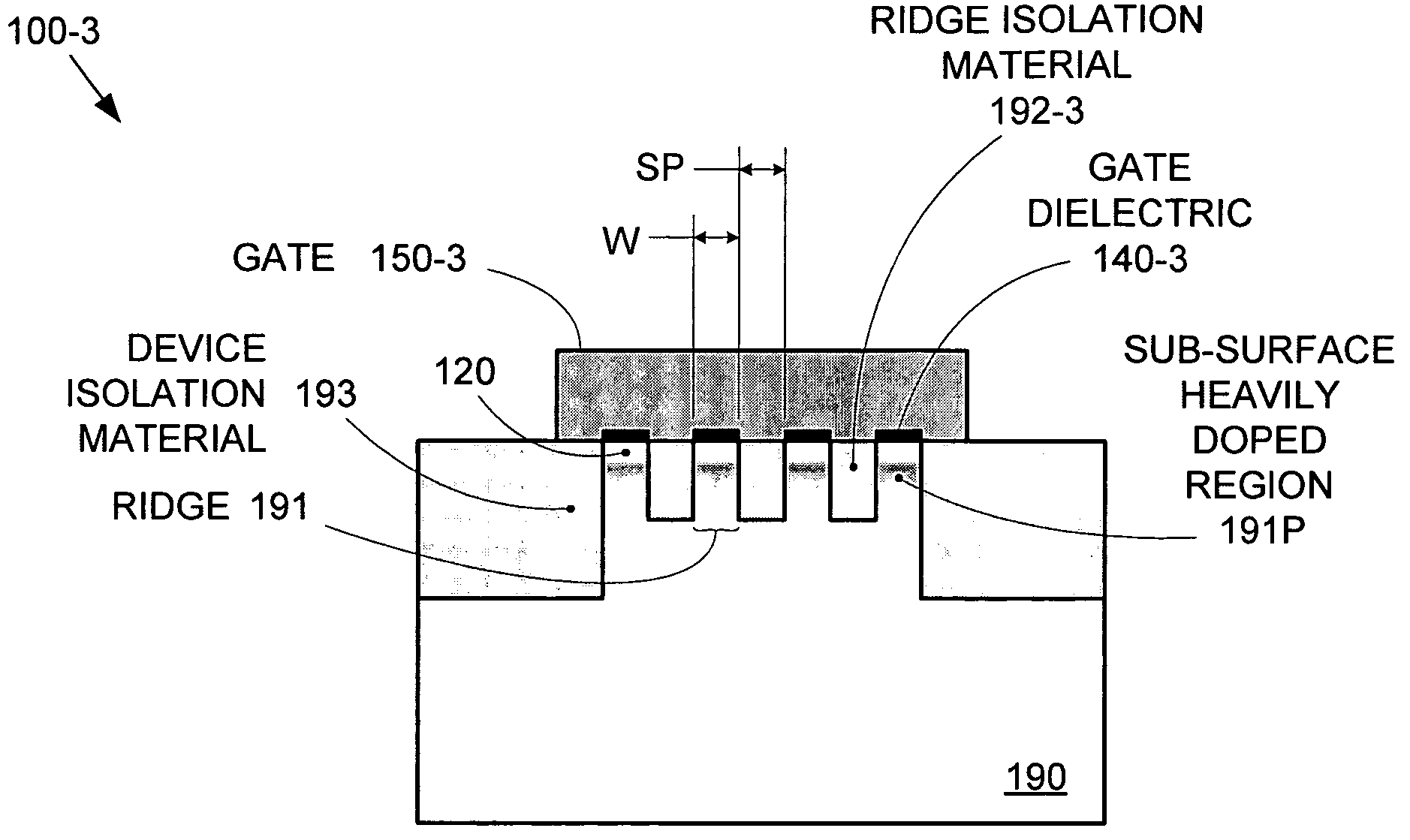
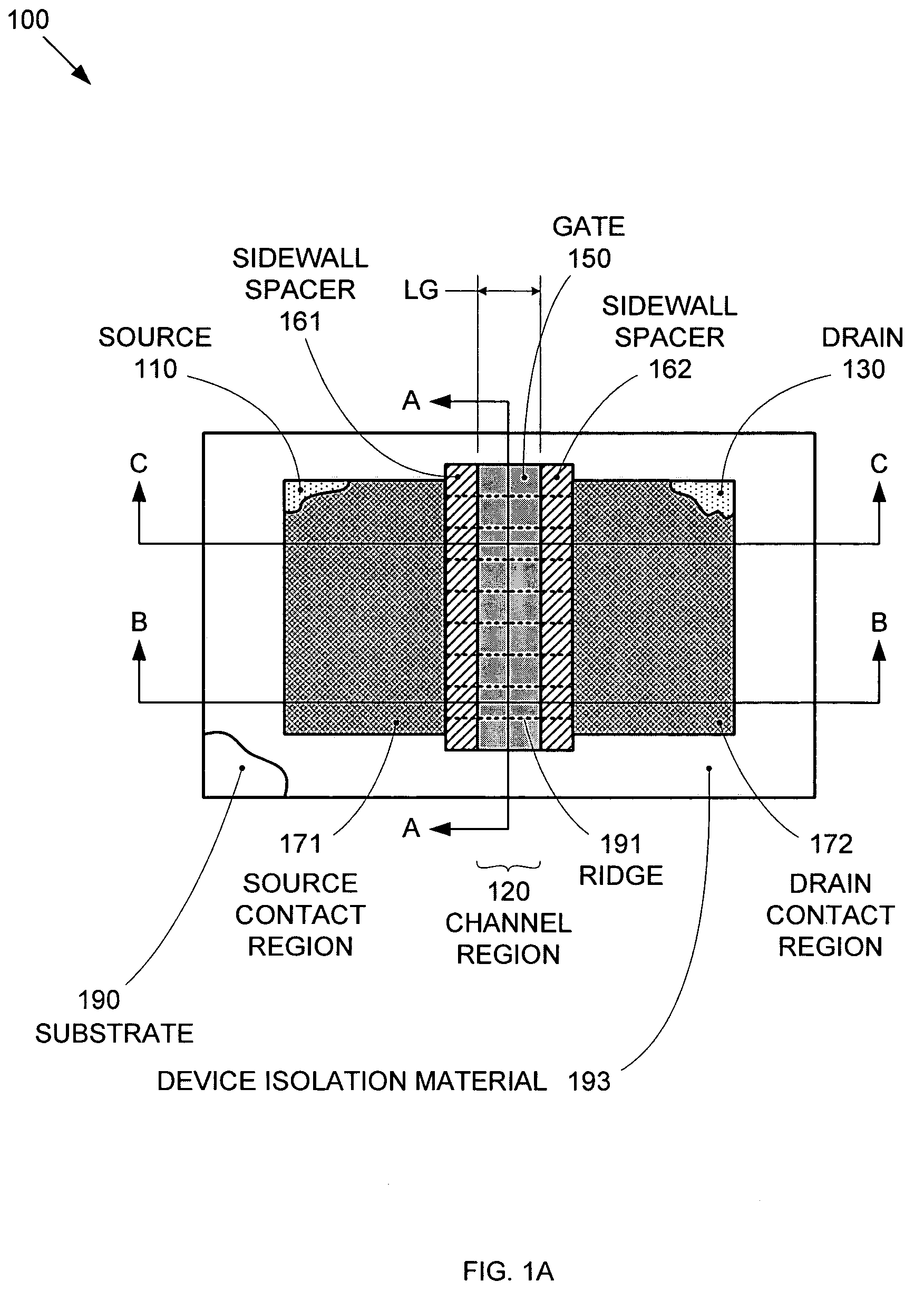
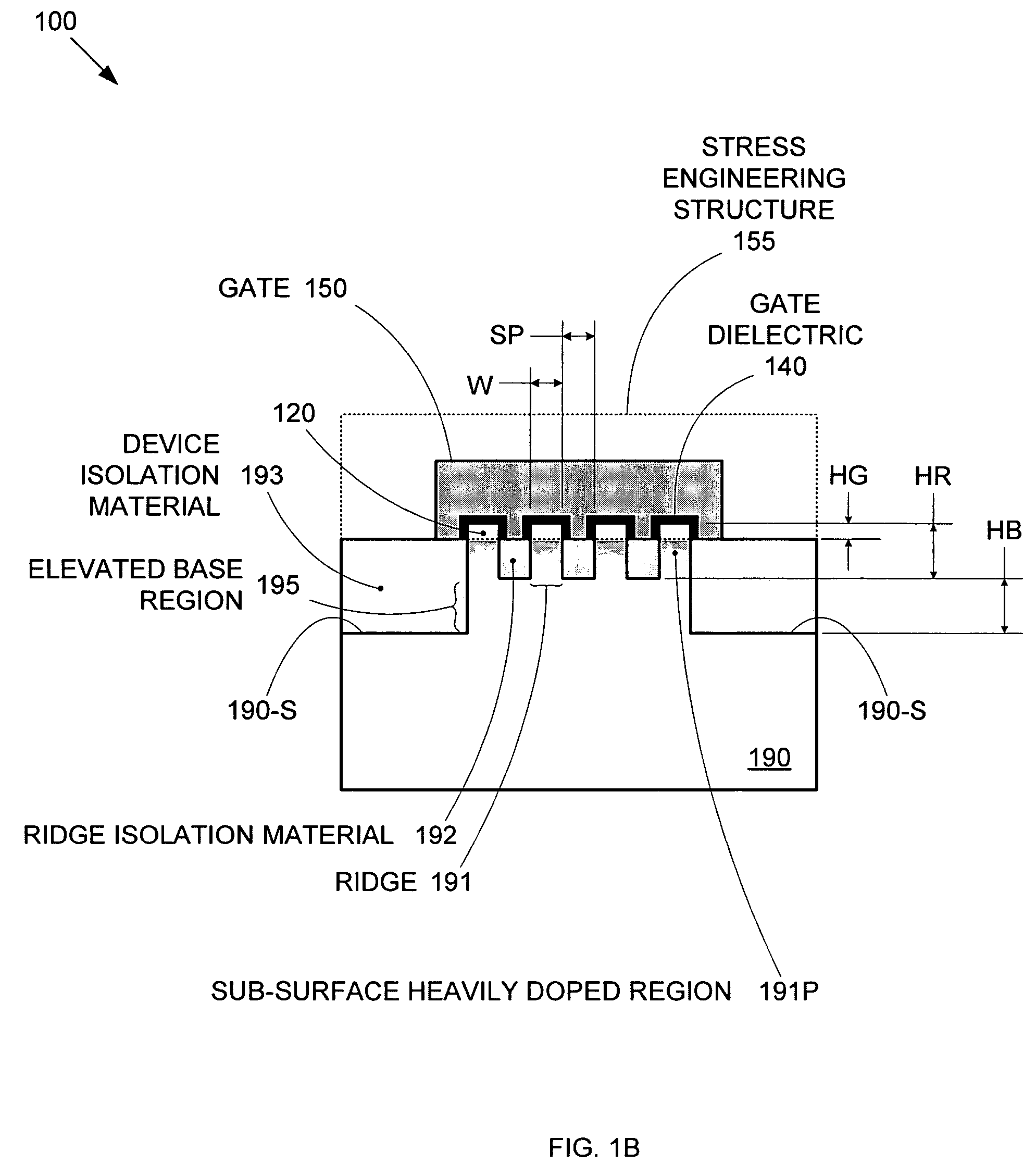
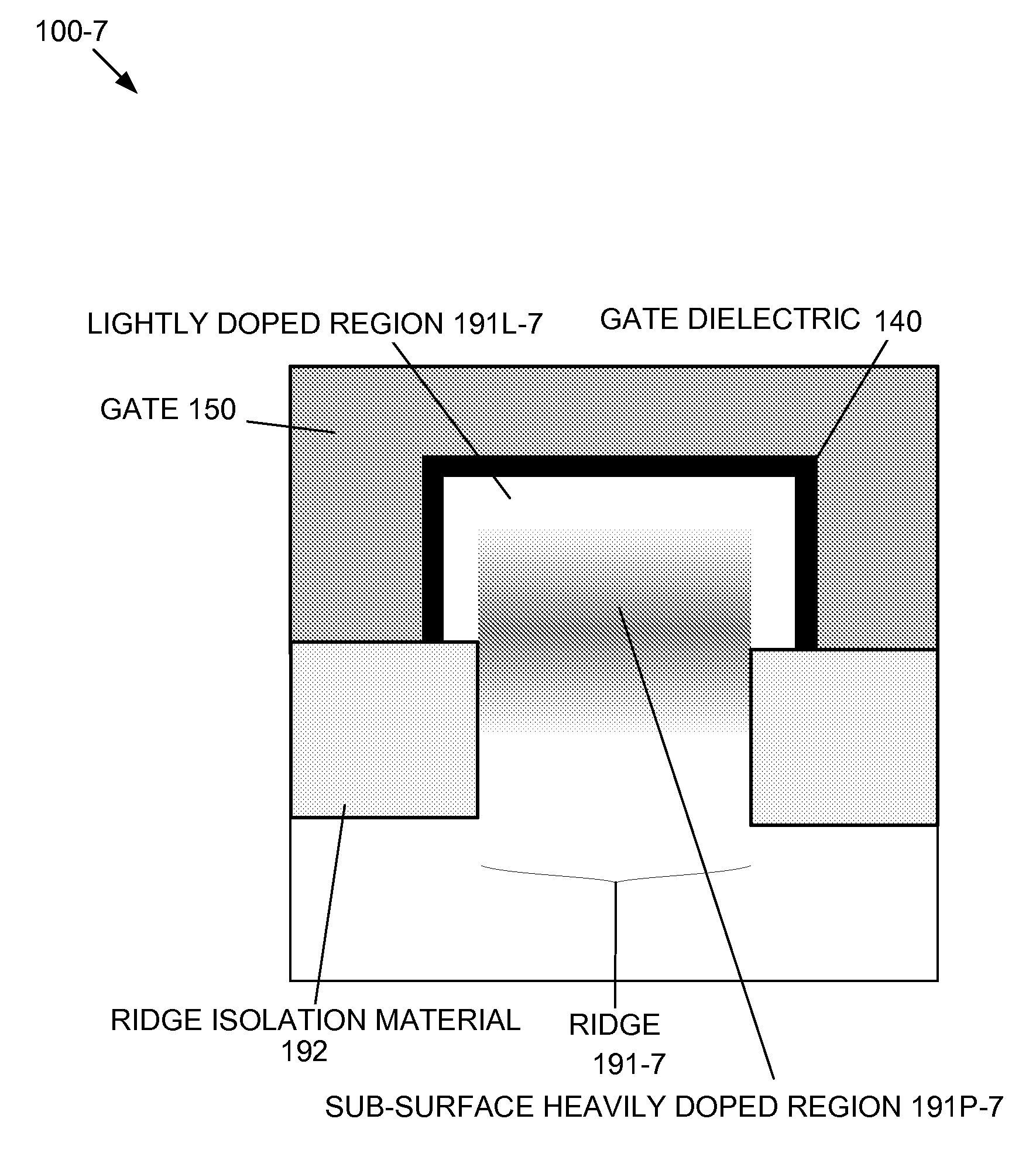
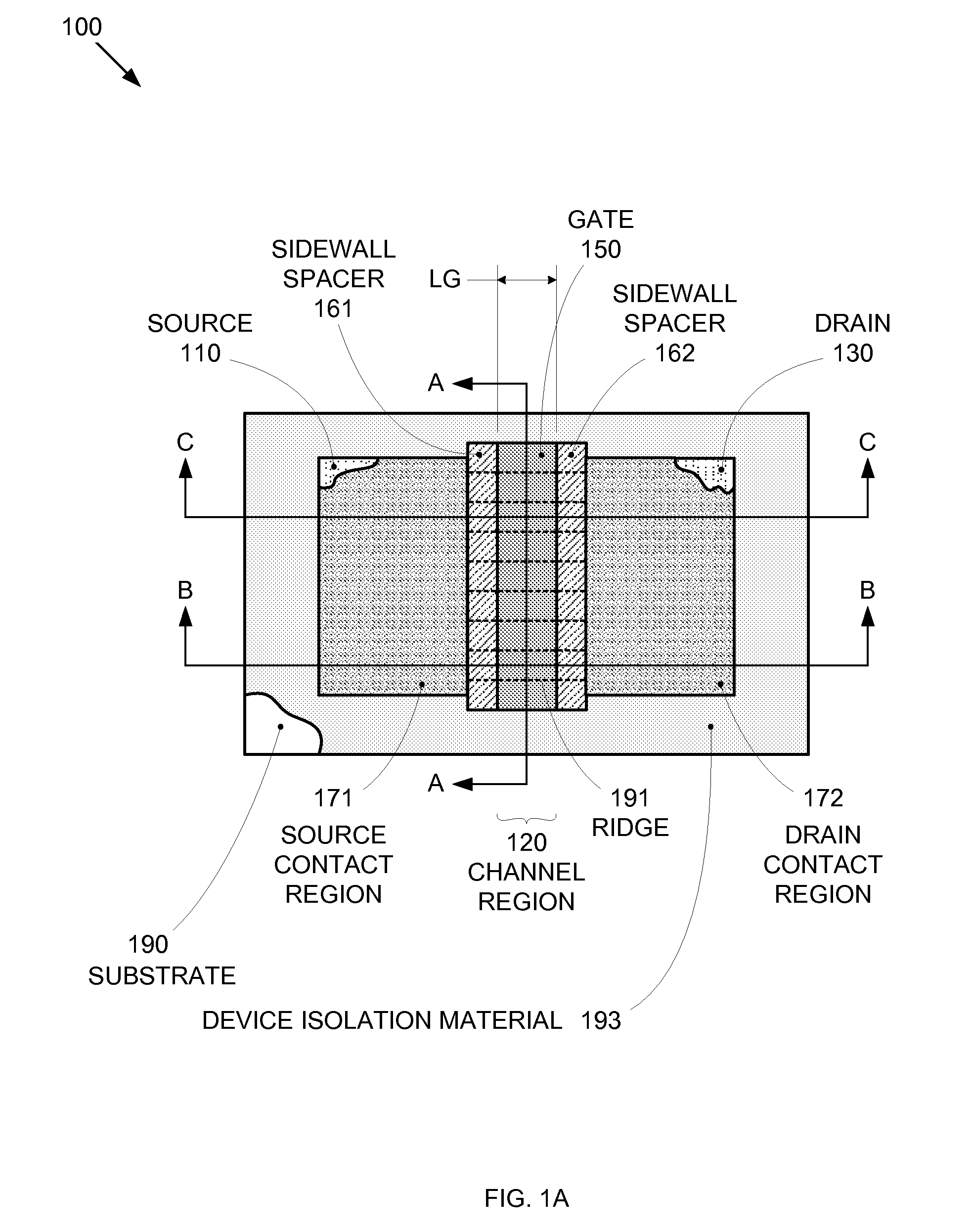
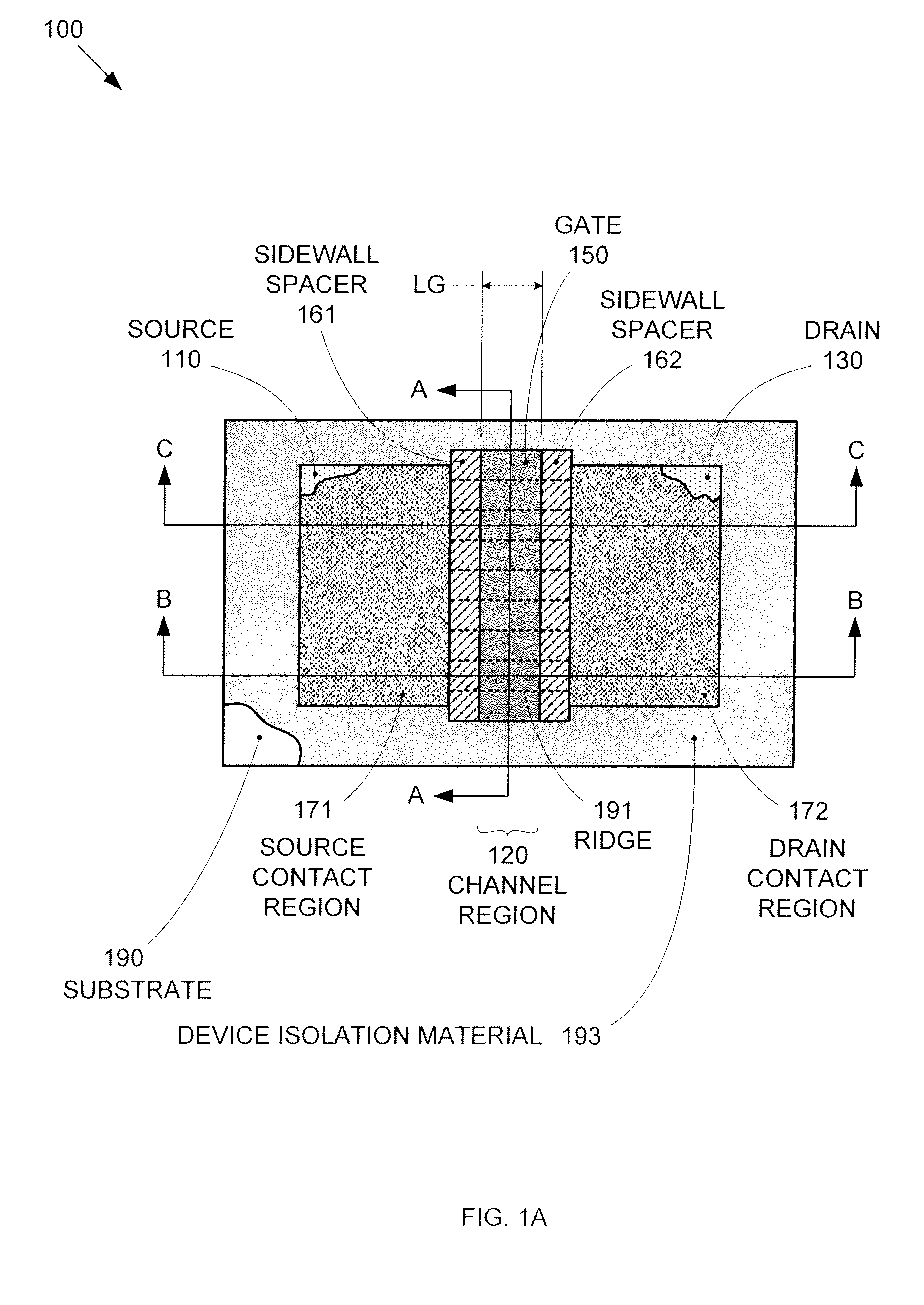
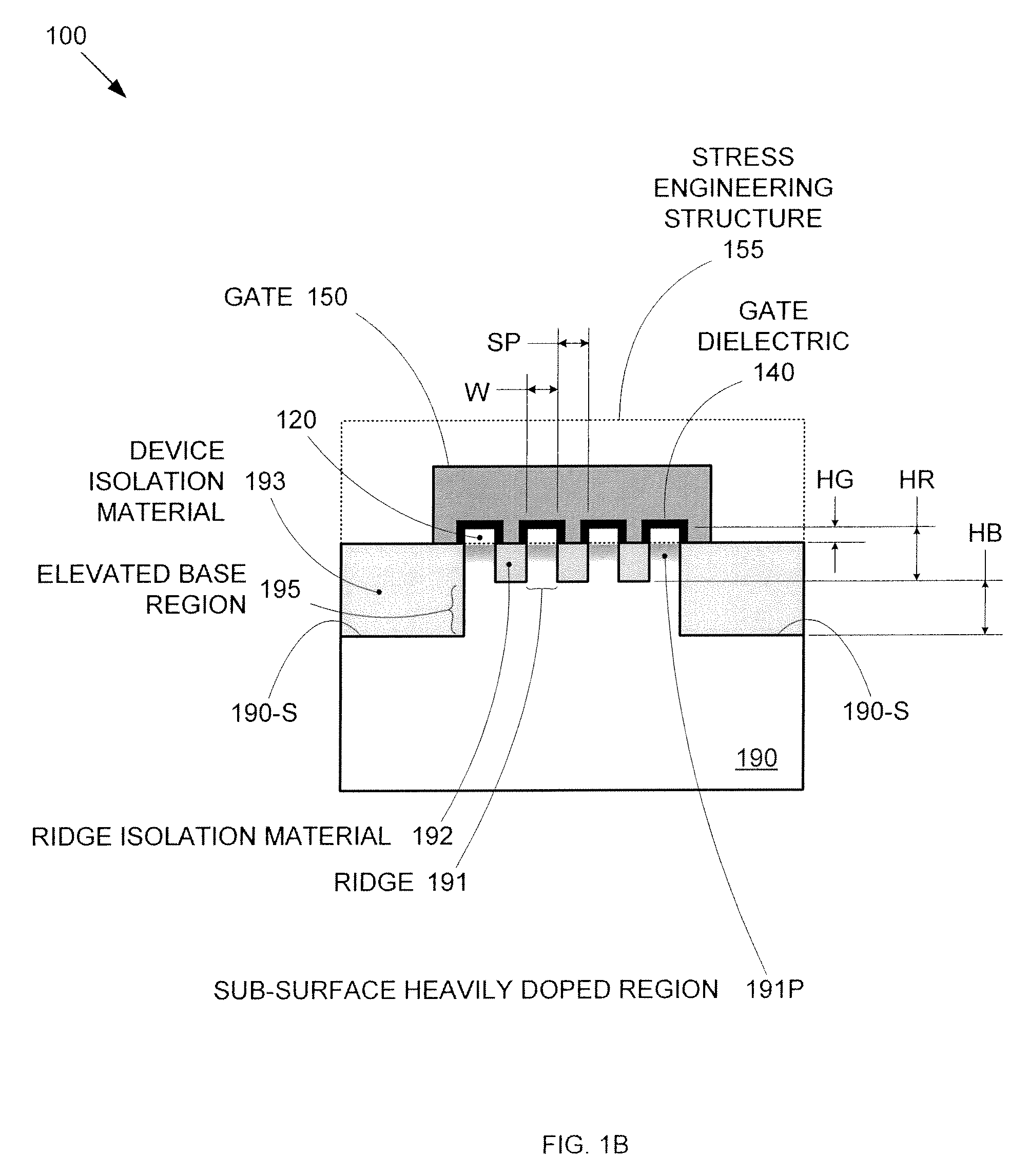
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Light emitting diode package with diffuser and method of manufacturing the same
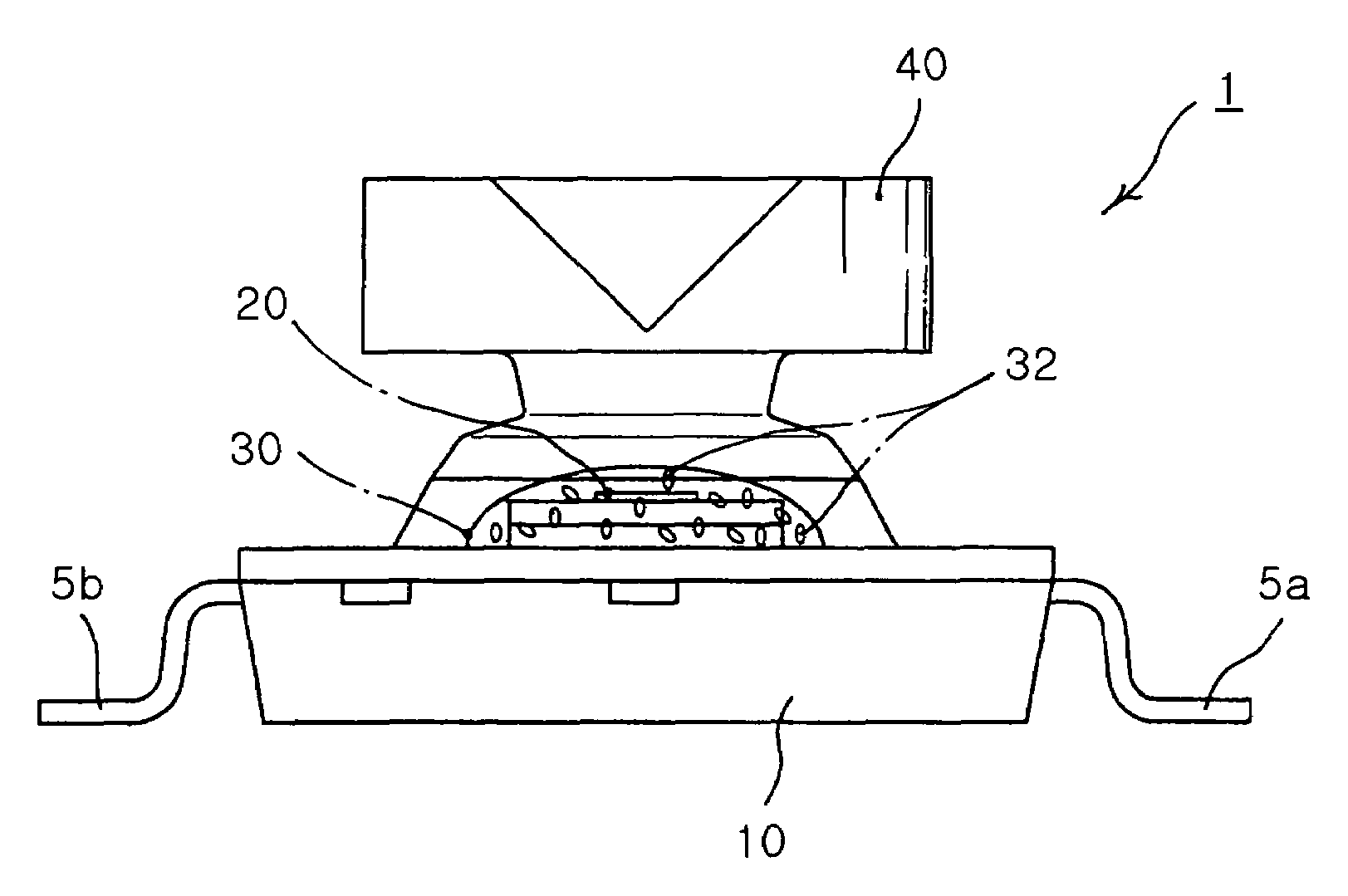
ActiveUS7501656B2Reduce thicknessIncrease freedomSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSealant
The invention relates to an LED package for facilitating color mixing using a diffuser and a manufacturing method of the same. The LED package includes a substrate with an electrode formed thereon, and an LED chip mounted on the substrate. The LED package also includes an encapsulant applied around the light emitting diode chip, containing a diffuser. The LED package further includes a lens part disposed on the light emitting diode chip and the encapsulant to radiate light in a wide angle. The LED package allows light from the light emitting diode chip to be emitted out of the package without distortion. The invention allows light to exit through the encapsulant containing the diffuser and the lens part, achieving uniform diffusion and emission of light from the LED chip, thereby increasing a radiating angle and obtaining a uniform light source.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Integrated circuit on corrugated substrate
ActiveUS7190050B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
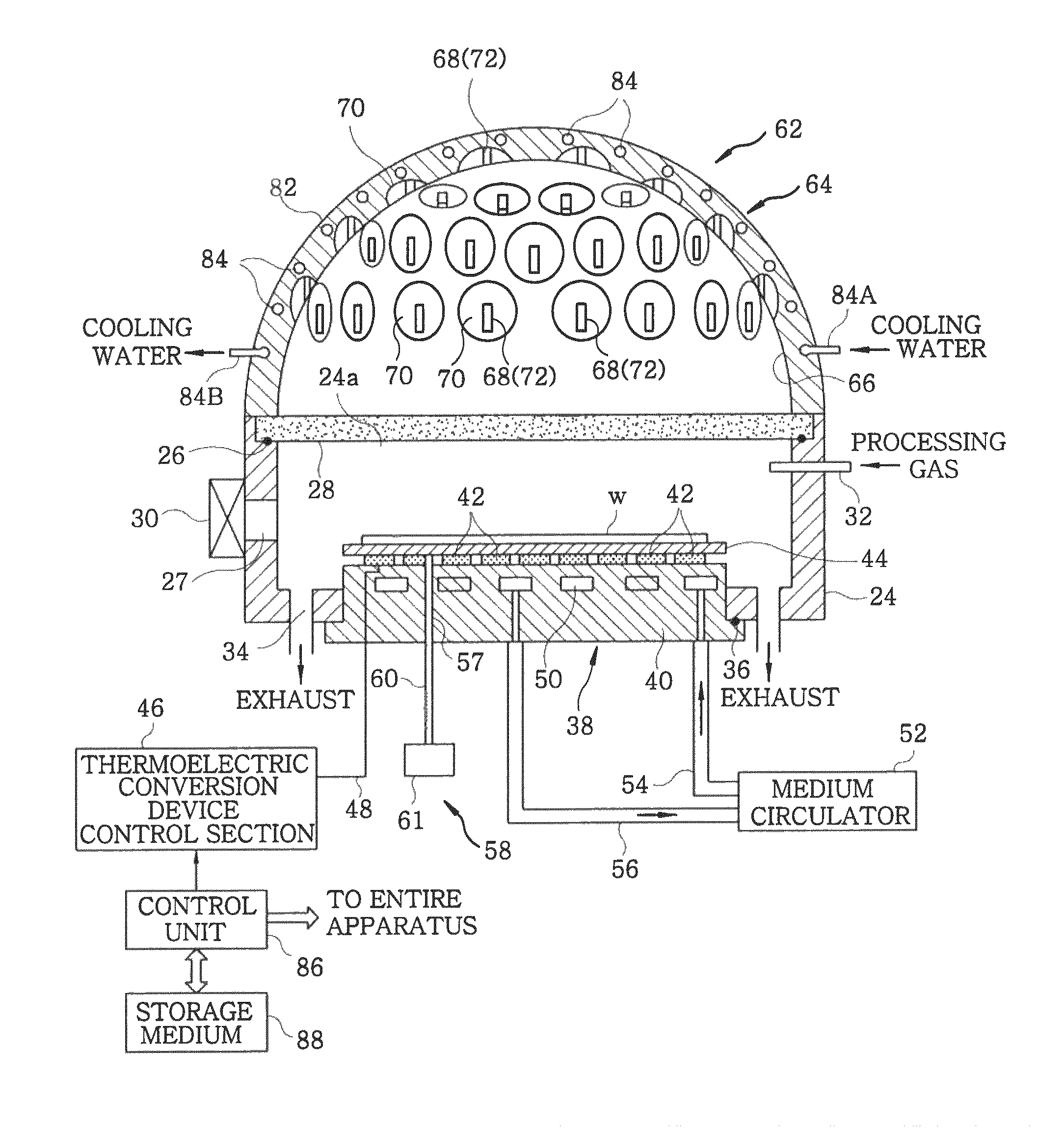
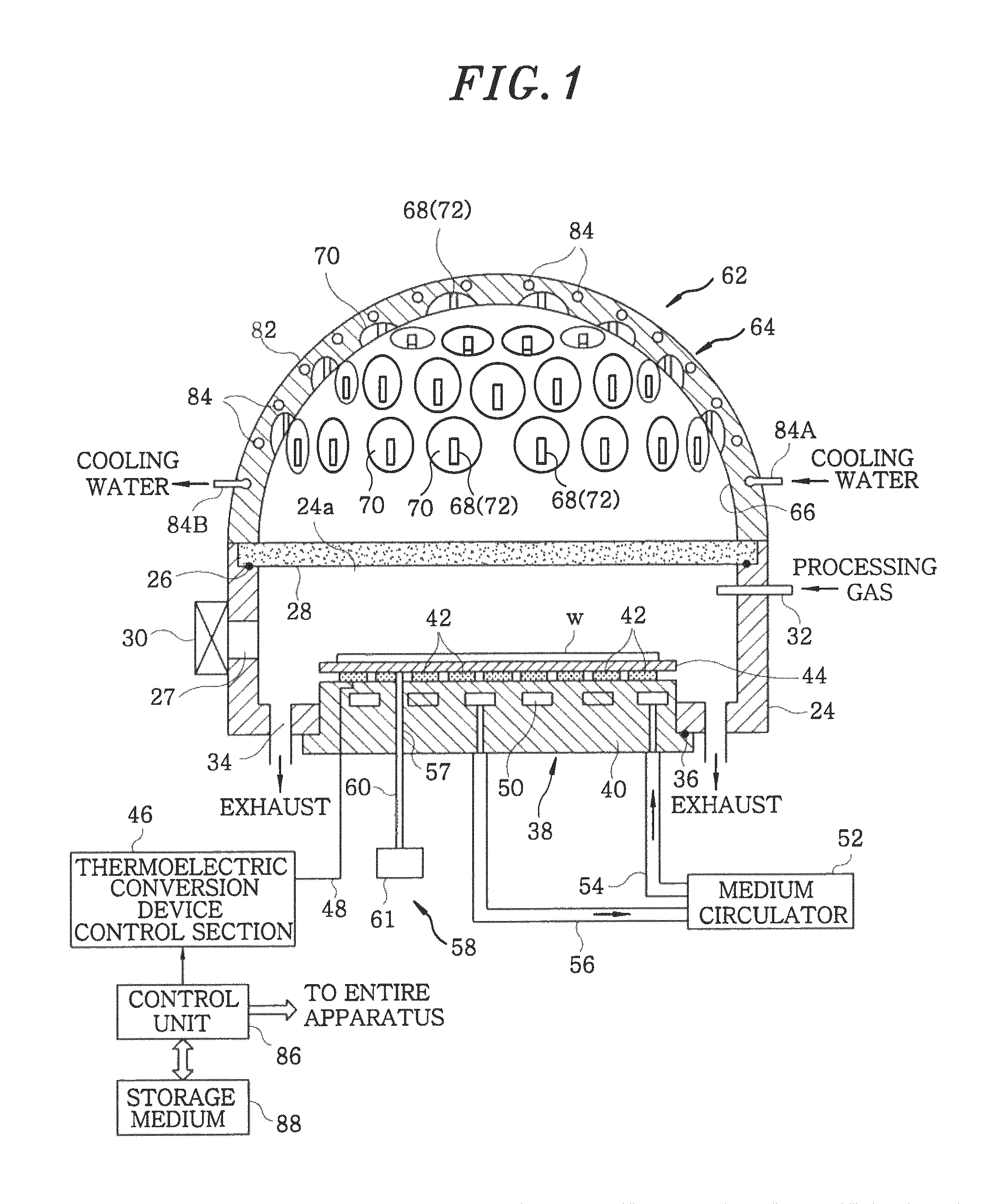
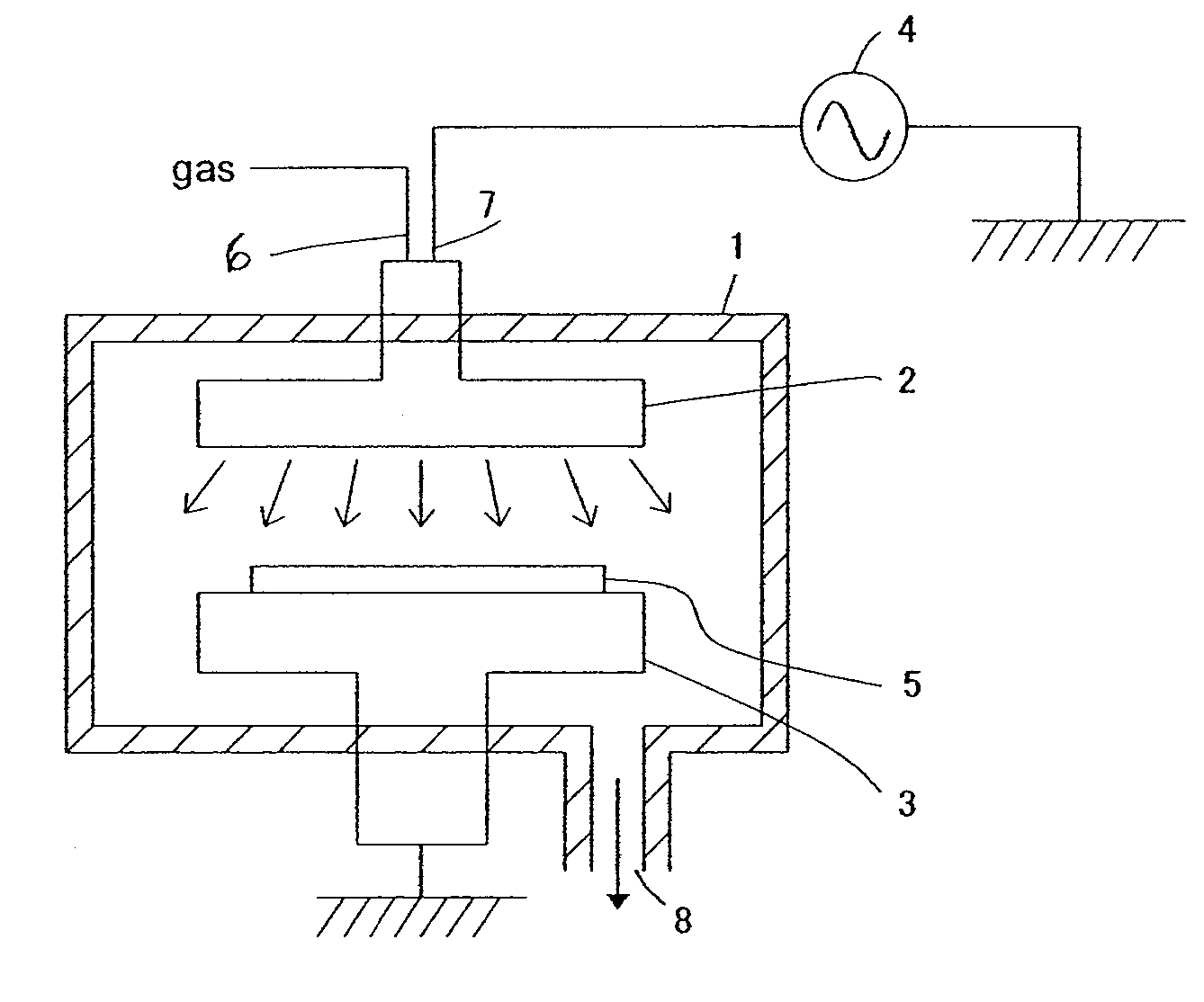
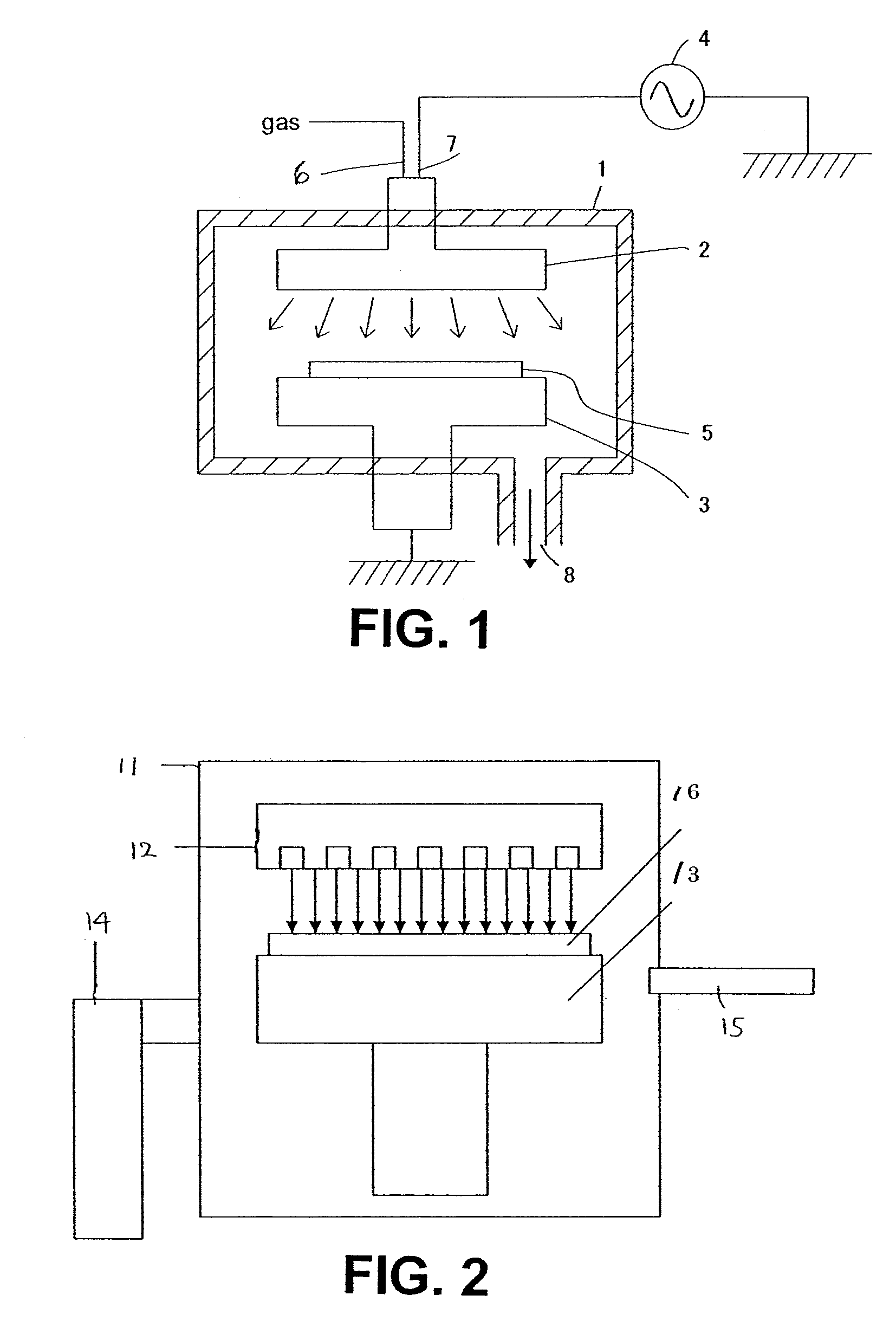
Heating apparatus, heat treatment apparatus, computer program and storage medium
ActiveUS8041197B2Efficient solutionRapidly heating up and coolingDomestic stoves or rangesDrying solid materials with heatLength waveSemiconductor
A heating apparatus for heating a target object W is provided with a plurality of heating light sources, including LED elements for applying heating light having a wavelength within a range from 360 to 520 nm to the object. Thus, a temperature of only the shallow surface of the object, such as a semiconductor wafer, is increased / reduced at a high speed in uniform temperature distribution, irrespective of the film type.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS7345342B2Simple structureEasy to packEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHigh pressure
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Method for forming dielectric film in trenches by PEALD using H-containing gas
ActiveUS9455138B1Increase deposition rateHigh film thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical physicsNoble gas
A method for forming a dielectric film in a trench on a substrate by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) performs one or more process cycles, each process cycle including: (i) feeding a silicon-containing precursor in a pulse; (ii) supplying a hydrogen-containing reactant gas at a flow rate of more than about 30 sccm but less than about 800 sccm in the absence of nitrogen-containing gas; (iii) supplying a noble gas to the reaction space; and (iv) applying RF power in the presence of the reactant gas and the noble gas and in the absence of any precursor in the reaction space, to form a monolayer constituting a dielectric film on a substrate at a growth rate of less than one atomic layer thickness per cycle.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
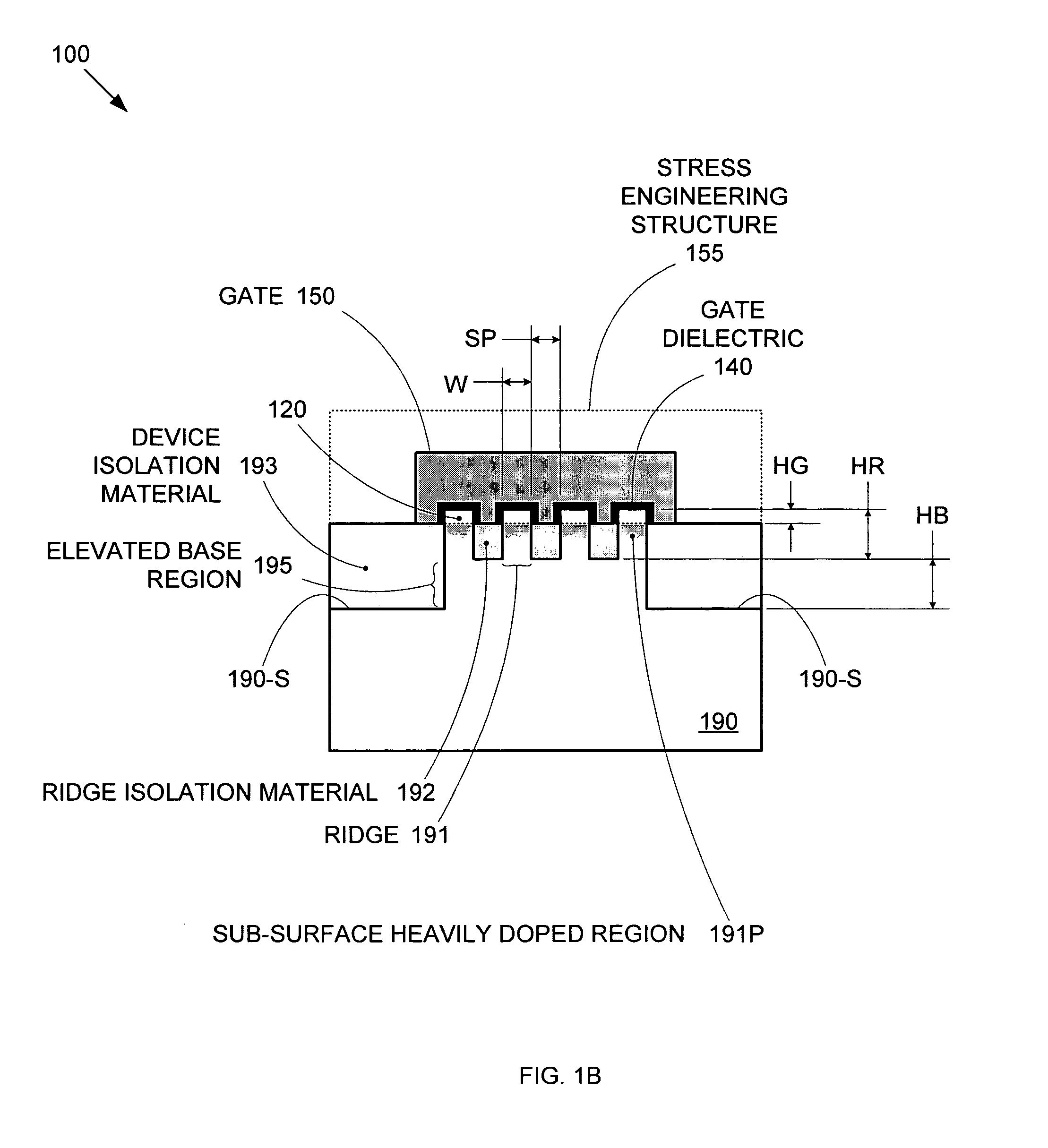
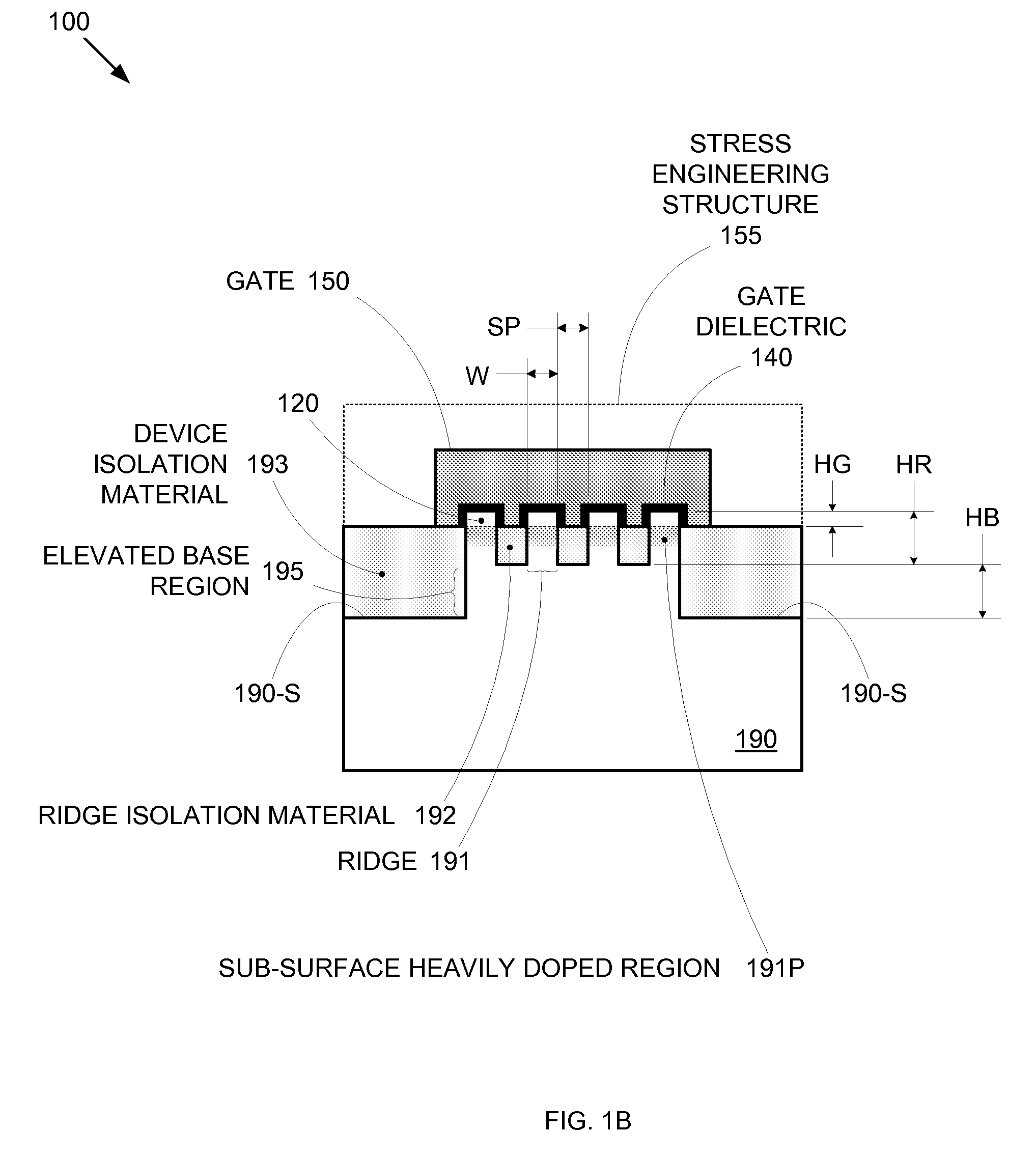
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with Multi Layer Regions
ActiveUS20070120156A1Increase costImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
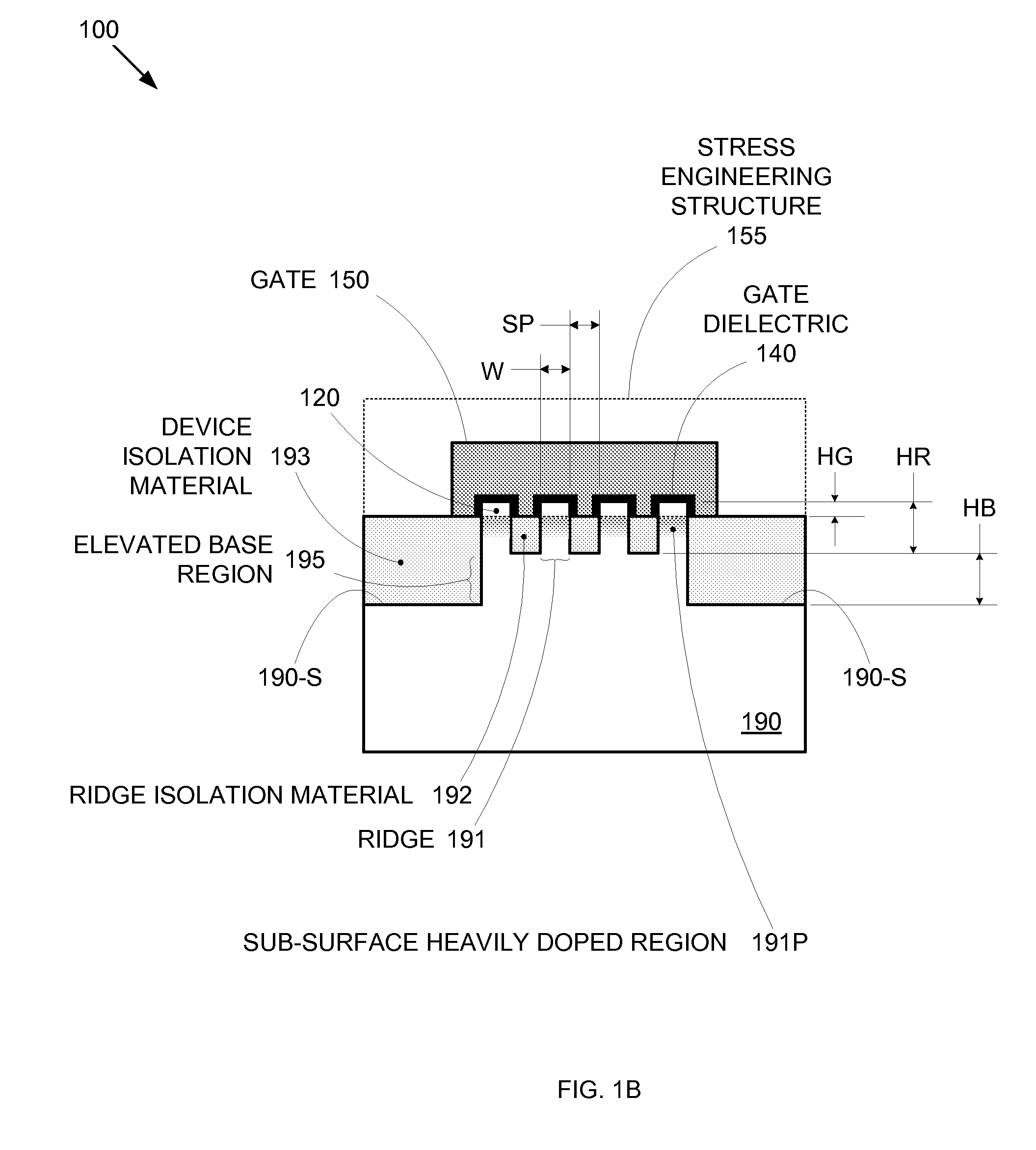
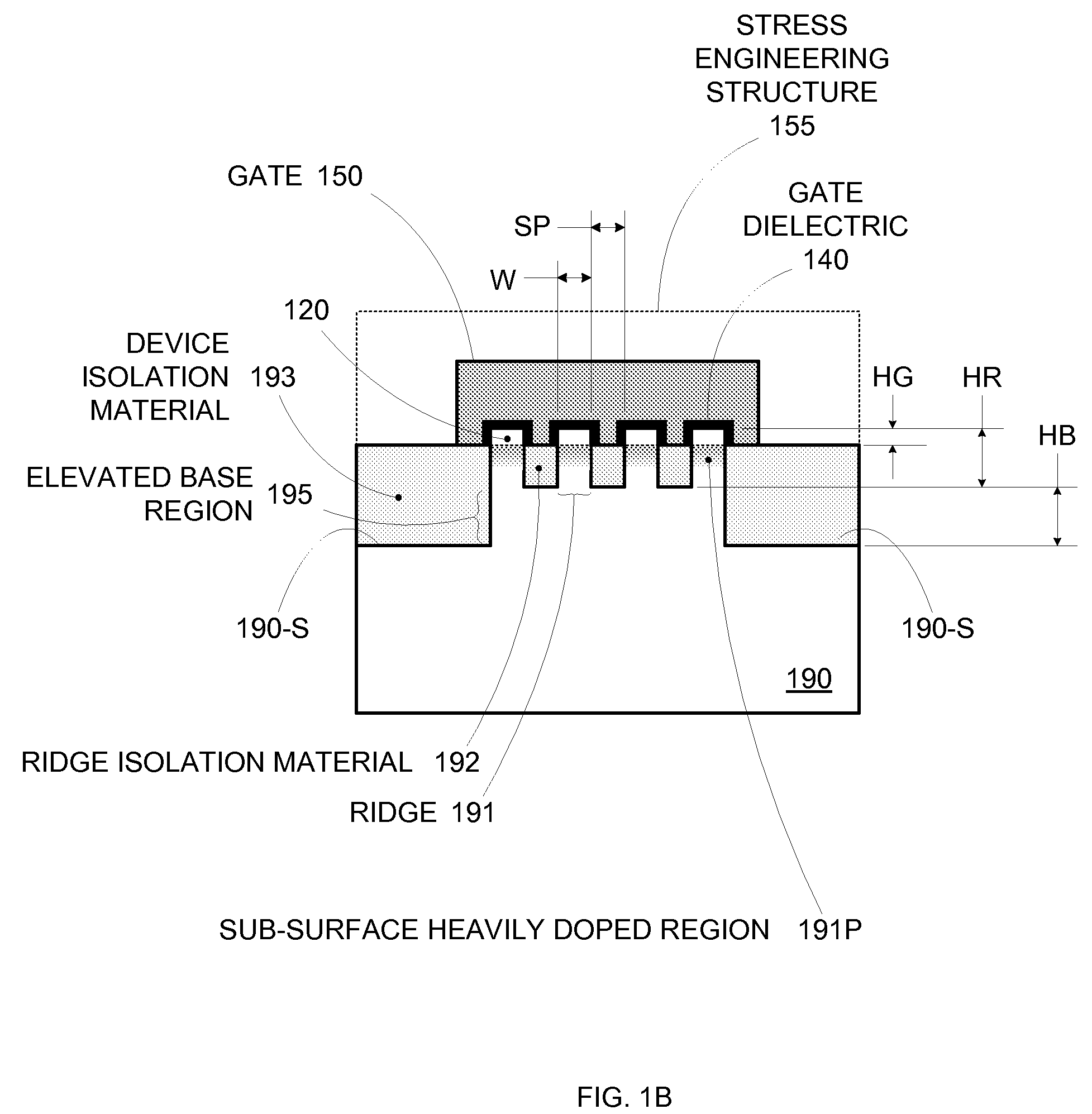
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Compositions with Improved Adhesion to Low Surface Energy Substrates
InactiveUS20080113094A1Excellent low surface energyImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsOrganic dyesOligomerEnd-group
Acrylic-based pressure sensitive adhesives are modified with a telechelic hydrocarbon oligomer. The oligomer comprises a hydrocarbon polymer chain or backbone and a functional end group, e.g., an oligomer prepared from a mono hydroxyl polybutadiene polymer and toluene diisocyanate. The oligomer attaches to the acrylic backbone of the polymer as a pendant group and in a preferred embodiment, the oligomer is mixed with the PSA shortly before the PSA is coated.
Owner:BRADY WORLDWIDE INC
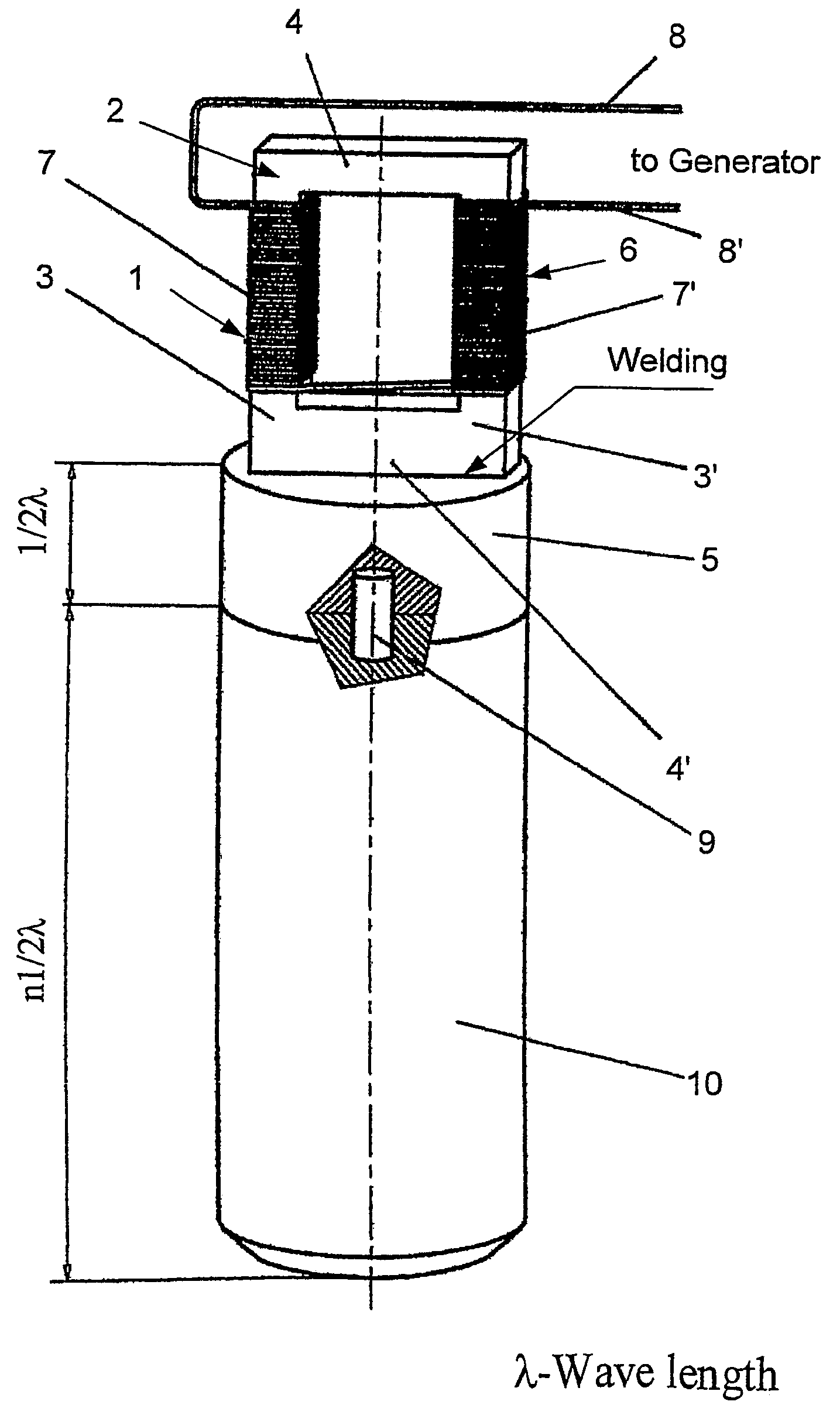
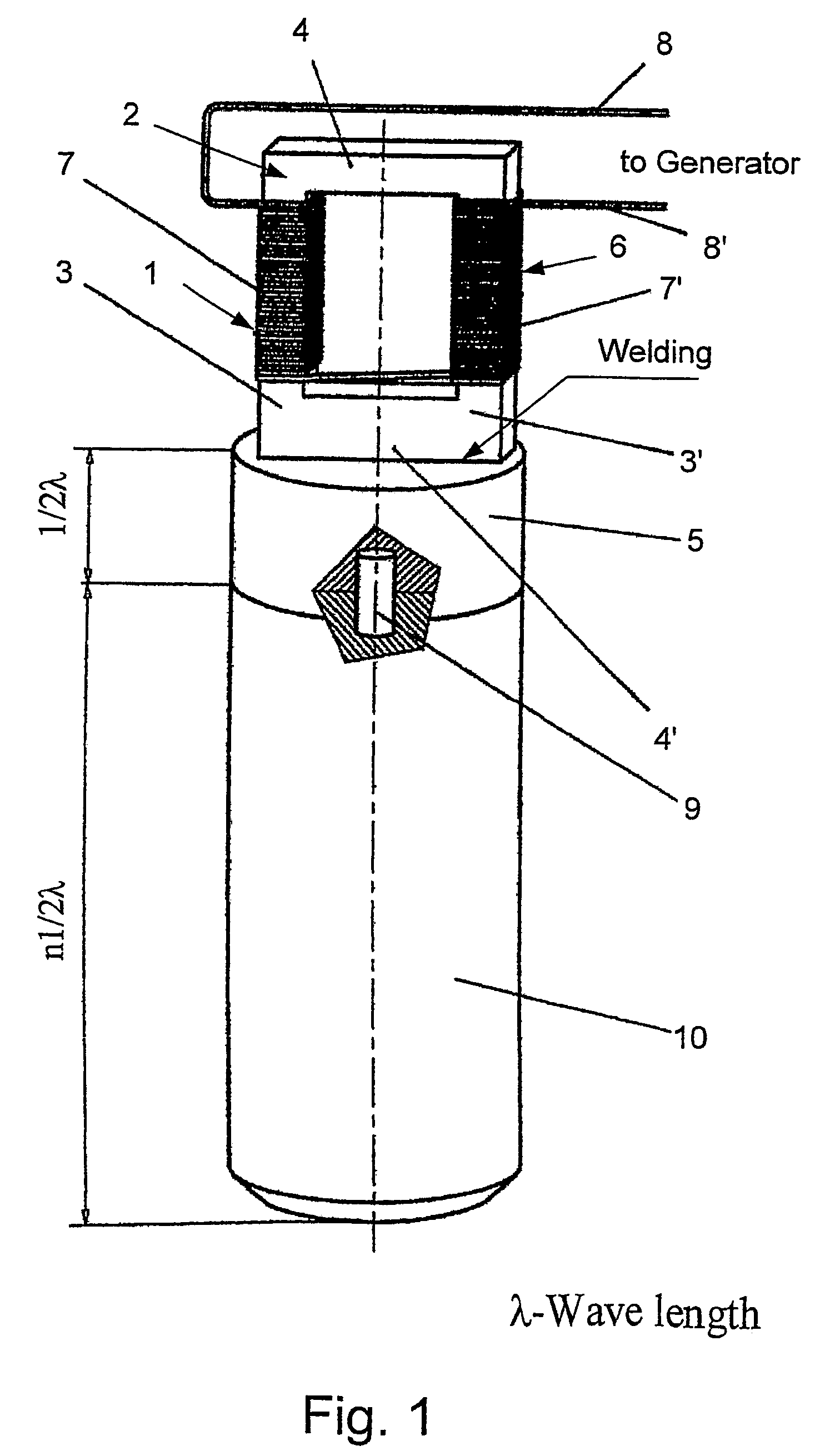
High power ultrasonic reactor for sonochemical applications
InactiveUS7157058B2Homogeneous distributionReduce thicknessMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentEngineeringMagnetostrictive transducers
Ultrasound device having a reaction chamber, which includes a magnetostrictive transducer and a horn transmitting ultrasound radiation substantially uniformly throughout the reaction chamber. The horn is hollow and is constituted by a cylinder having an empty inner chamber at its core defining a resonance chamber, which may be cylindrical and may comprise a plurality of sections of cylindrical shape or a central section of larger diameter and two terminal sections of smaller diameter.
Owner:NANO SIZE
Method of IC production using corrugated substrate
ActiveUS7265008B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceLaser detailsSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with narrowed base regions
ActiveUS7508031B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably produced. Ridges on the corrugated substrate can be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials, high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Ink-jet recording head with piezoelectric device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6142615AIncrease in piezoelectric constantIncrease the driving voltagePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionPiezoelectric actuatorsPiezoelectric coefficient
A piezoelectric device for an ink jet print head that has a greater displacement at a low drive voltage. The ink-jet recording head includes a vibration plate, on which is mounted one or more piezoelectric devices that change the volumes of pressure chambers upon application of a voltage. The device is mounted at least on one face of a pressure chamber substrate that is to be filled with ink. Such piezoelectric device includes a second piezoelectric layer having a piezoelectric constant g of a constant value or higher; and a first piezoelectric layer having a dielectric constant of a specific value or higher. Since the piezoelectric constant d of the piezoelectric device correlates with the product of the largest piezoelectric constant g and the largest dielectric device of the piezoelectric devices, a piezoelectric constant d larger than in the conventional case, i.e., having a greater displacement, can be obtained.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with high-permittivity dielectric isolation material
ActiveUS7605449B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method of manufracturing increasing reliability of copper-based metallization structures in a microstructure device by using aluminum nitride
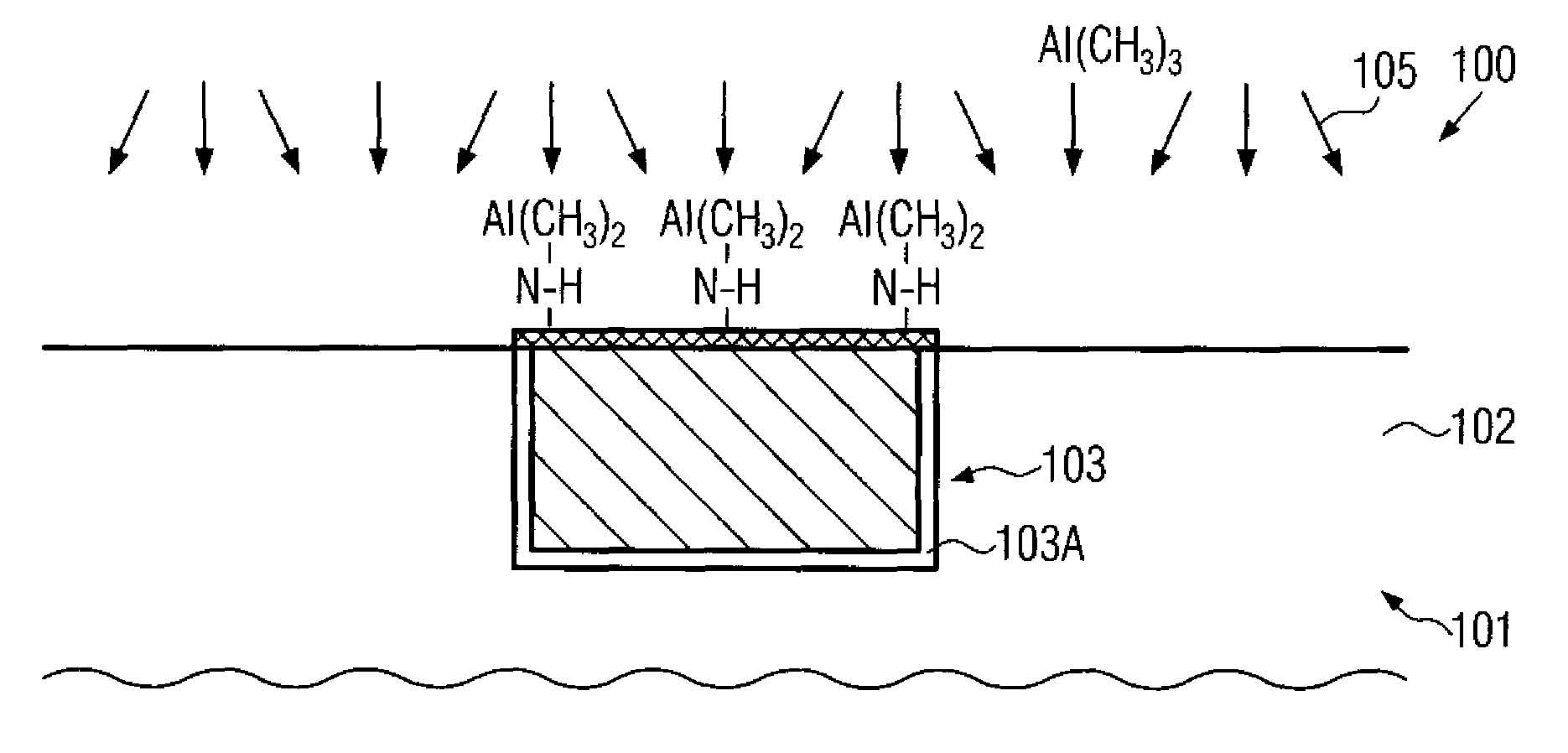
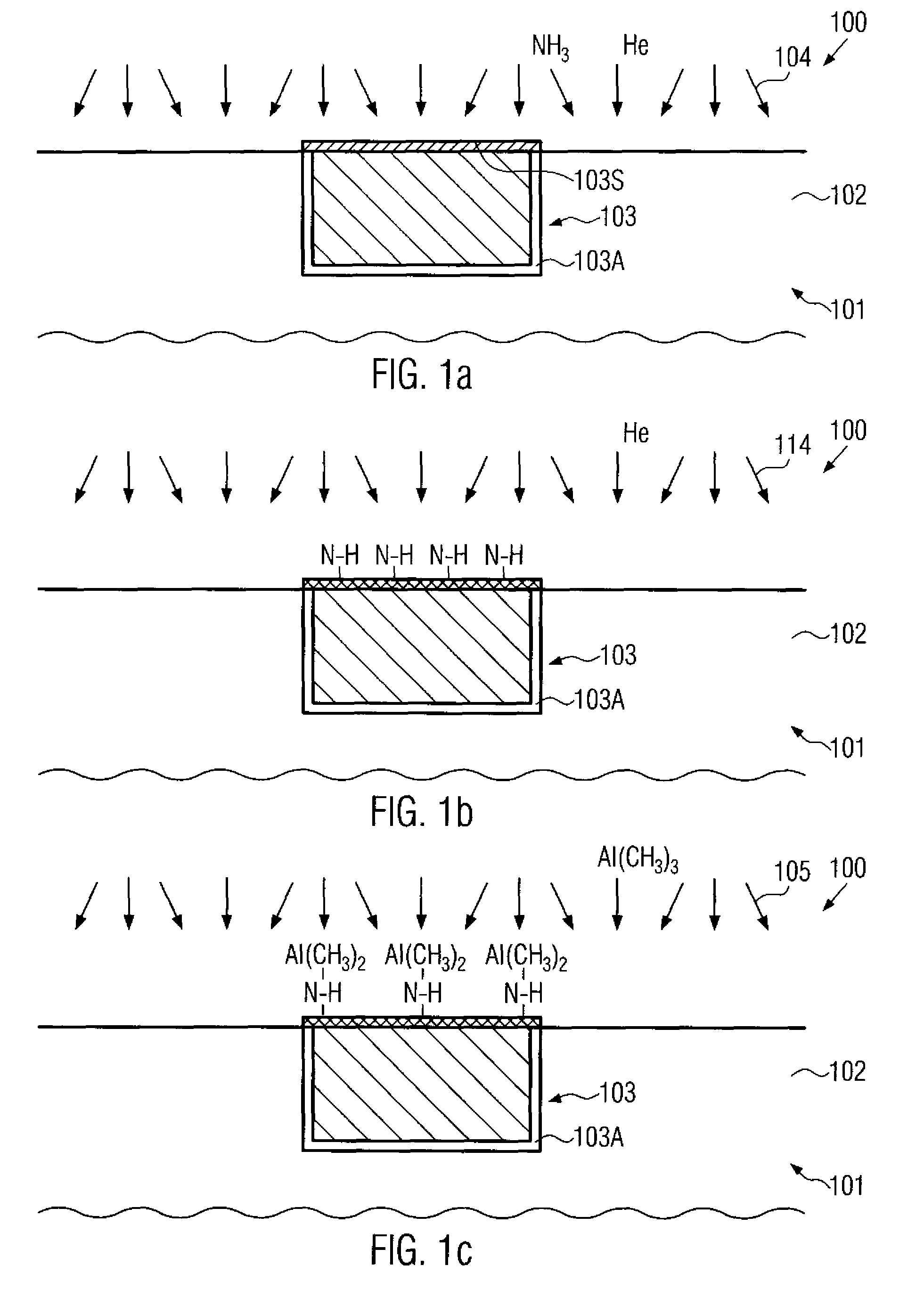
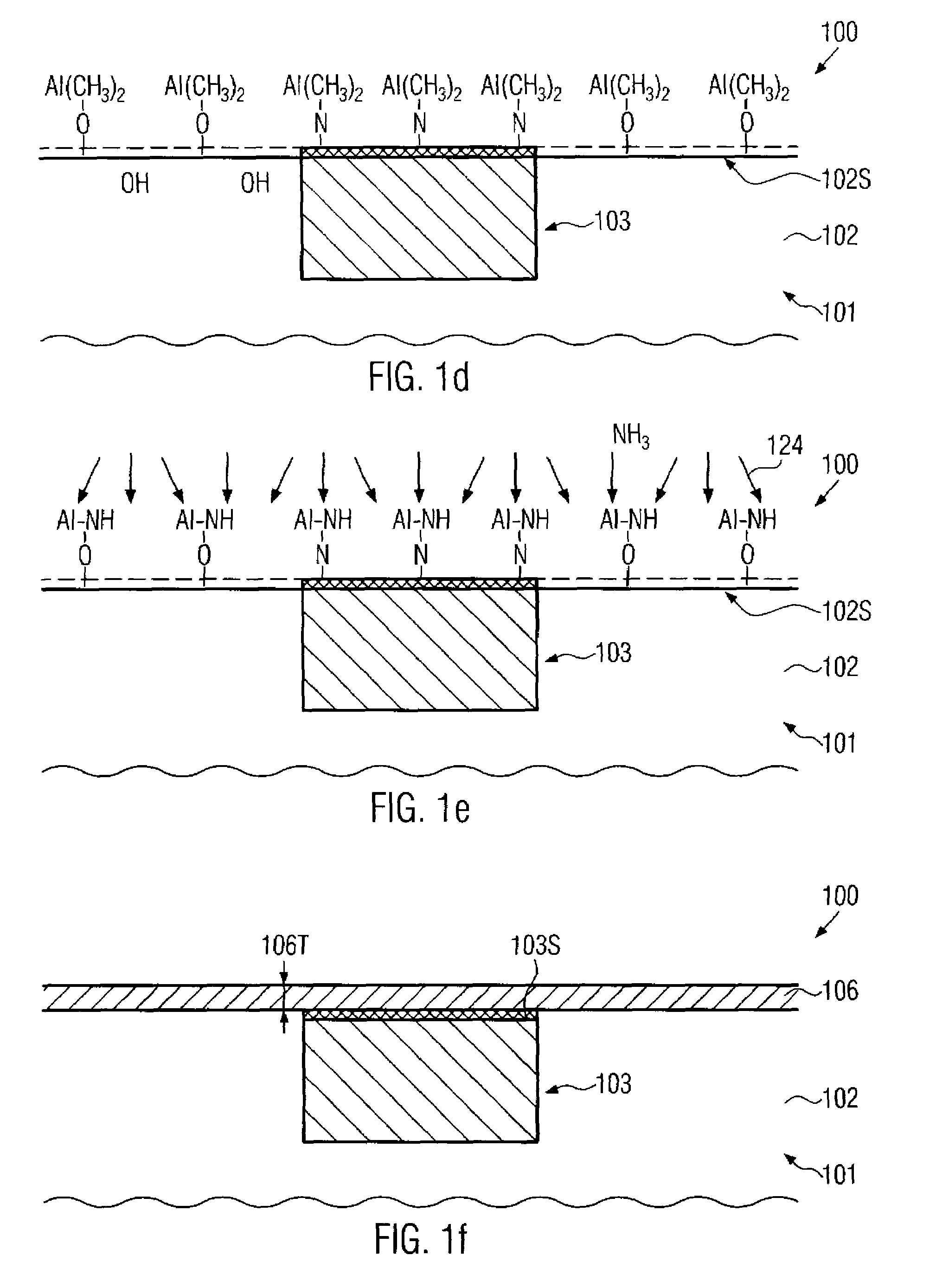
ActiveUS7829460B2Reduce parasitic capacitanceEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSelf limitingPermittivity
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
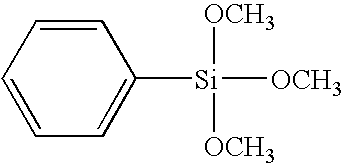
Method for forming insulation film
InactiveUS7354873B2Reduce distanceGood film densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma reactionResidence time
A method for forming an insulation film having filling property on a semiconductor substrate by plasma reaction includes: vaporizing a silicon-containing hydrocarbon having a Si—O bond compound to provide a source gas; introducing the source gas and a carrier gas without an oxidizing gas into a reaction space for plasma CVD processing; and forming an insulation film constituted by Si, O, H, and optionally C or N on a substrate by plasma reaction using a combination of low-frequency RF power and high-frequency RF power in the reaction space. The plasma reaction is activated while controlling the flow of the reaction gas to lengthen a residence time, Rt, of the reaction gas in the reaction space.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Integrated Circuit On Corrugated Substrate
ActiveUS20070132053A1Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETSemiconductor materials
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method for forming insulation film
InactiveUS7582575B2Reduce trafficReduce volumeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma reactionResidence time
A method for forming an insulation film on a semiconductor substrate by plasma reaction includes: vaporizing a silicon-containing hydrocarbon having a Si—O bond compound to provide a source gas; introducing the source gas and a carrier gas without an oxidizing gas into a reaction space for plasma CVD processing; and forming an insulation film constituted by Si, C, O, and H on a substrate by plasma reaction using a combination of low-frequency RF power and high-frequency RF power in the reaction space. The plasma reaction is activated while controlling the flow of the reaction gas to lengthen a residence time, Rt, of the reaction gas in the reaction space.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
OLED device with embedded chip driving
ActiveUS7999454B2Small sizeReduce thicknessDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesHemt circuitsElectric current flow
An electroluminescent device having a plurality of current driven pixels arranged in rows and columns, such that when current is provided to a pixel it produces light, including each pixel having first and second electrodes and current responsive electroluminescent media disposed between the first and second electrodes; at least one chiplet having a thickness less than 20 micrometers; including transistor drive circuitry for controlling the operation of at least four pixels, the chiplet being mounted on a substrate and having connection pads; a planarization layer disposed over at least a portion of the chiplet; a first conductive layer over the planarization layer and connected to at least one of the connection pads; and a structure for providing electrical signals through the first conductive layer and at least one of the connection pads of the chiplet so that the transistor drive circuitry of the chiplet controls current to the four pixels.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD +1
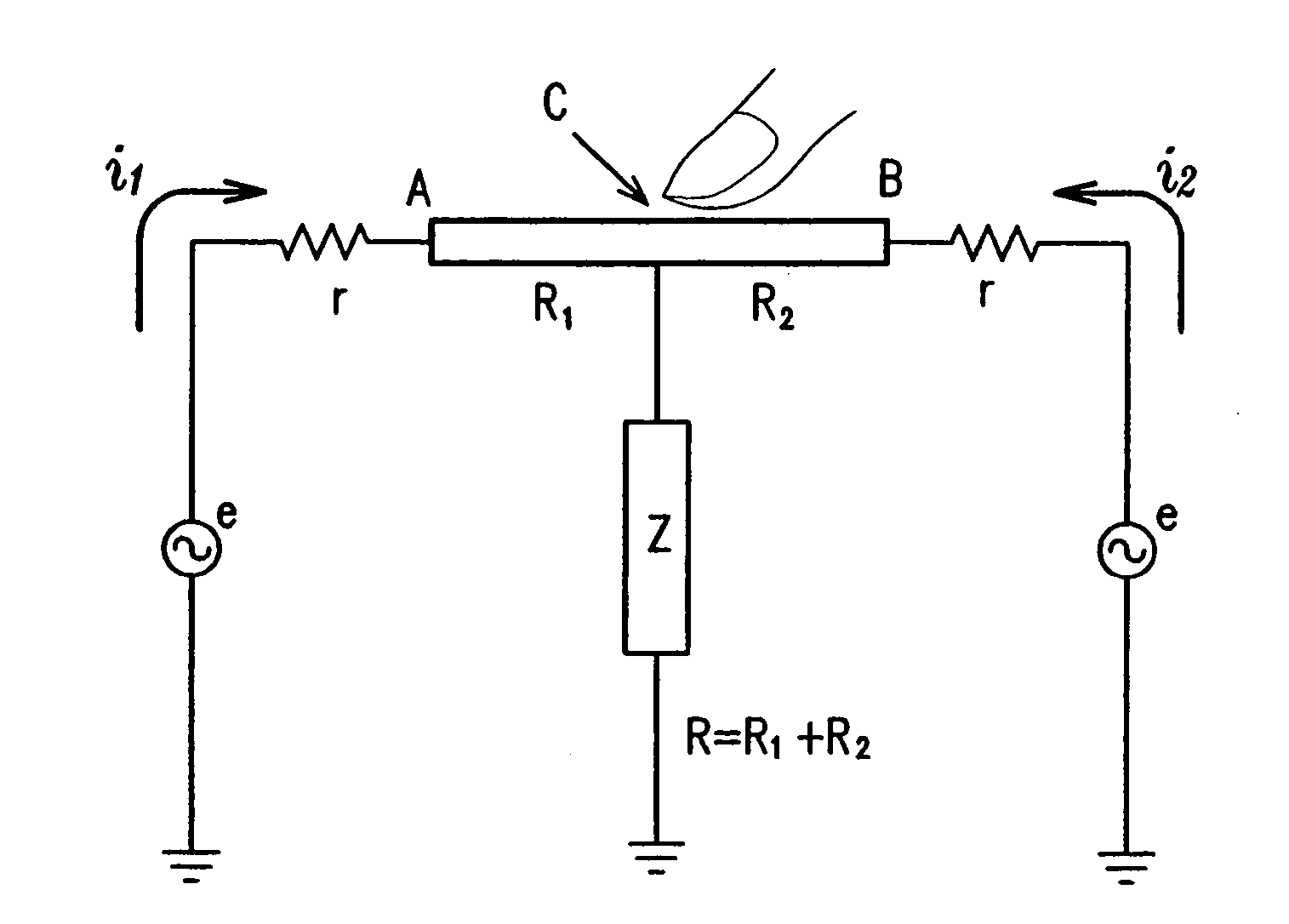
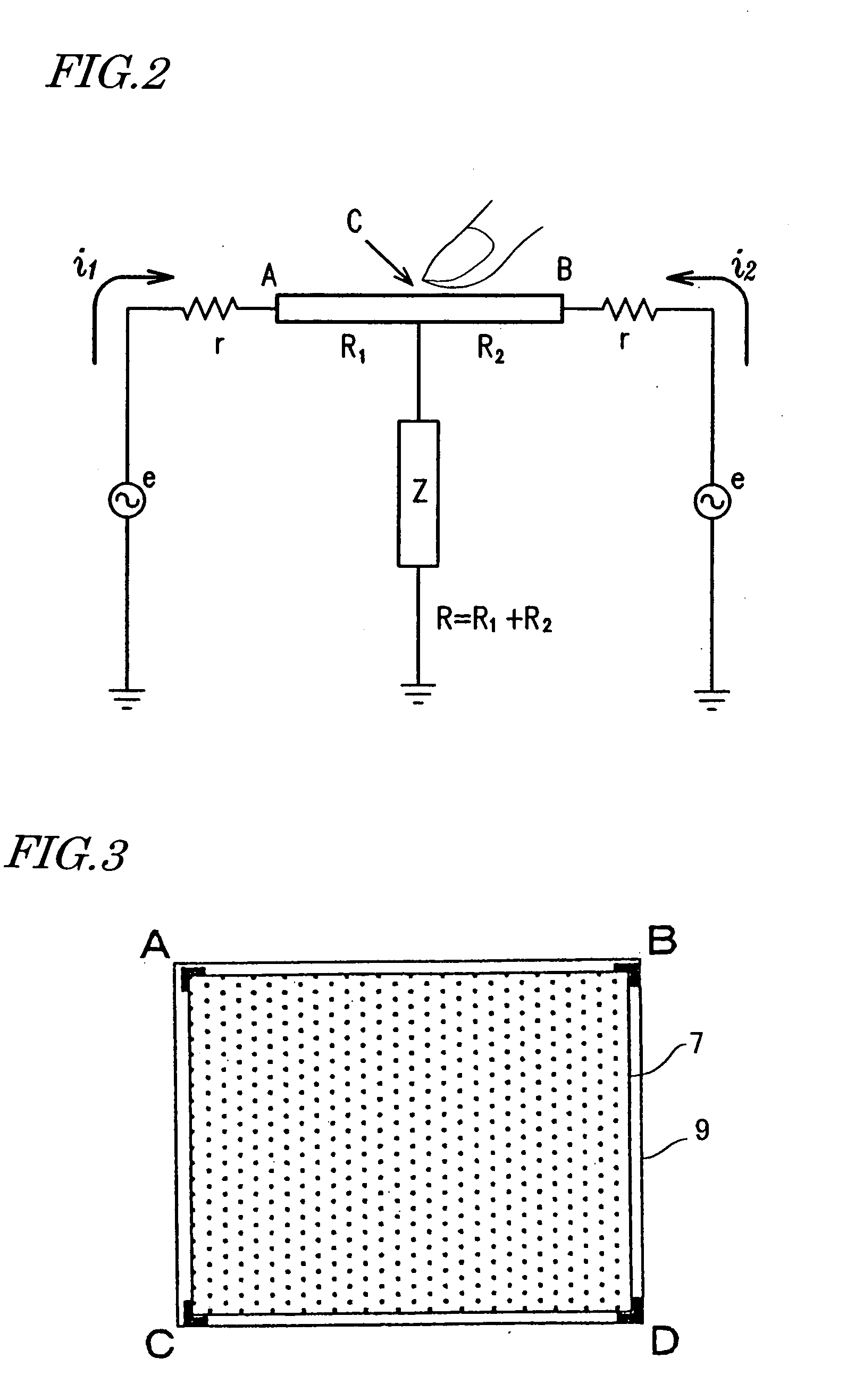
Touch sensor, display with touch sensor, and method for generating position data
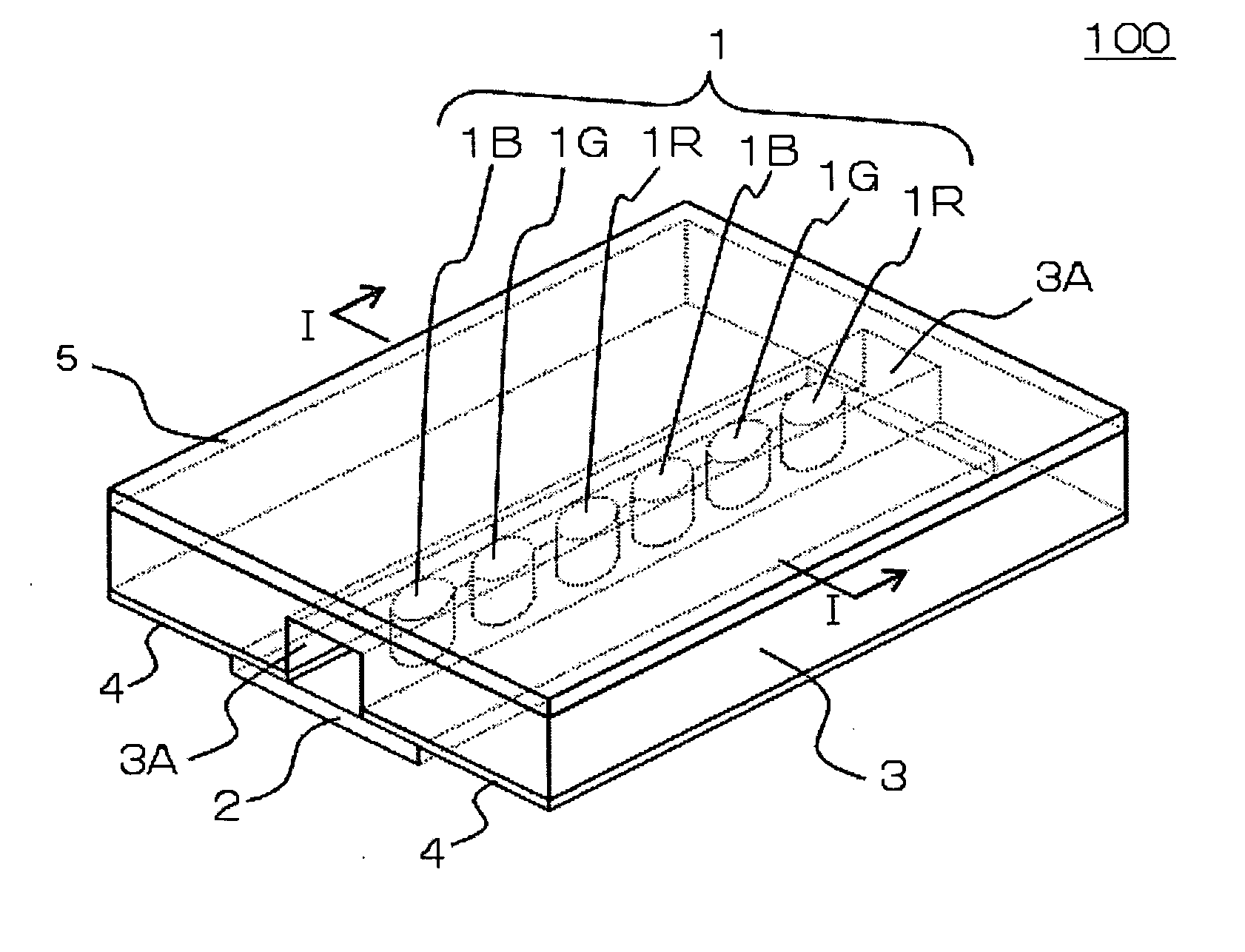
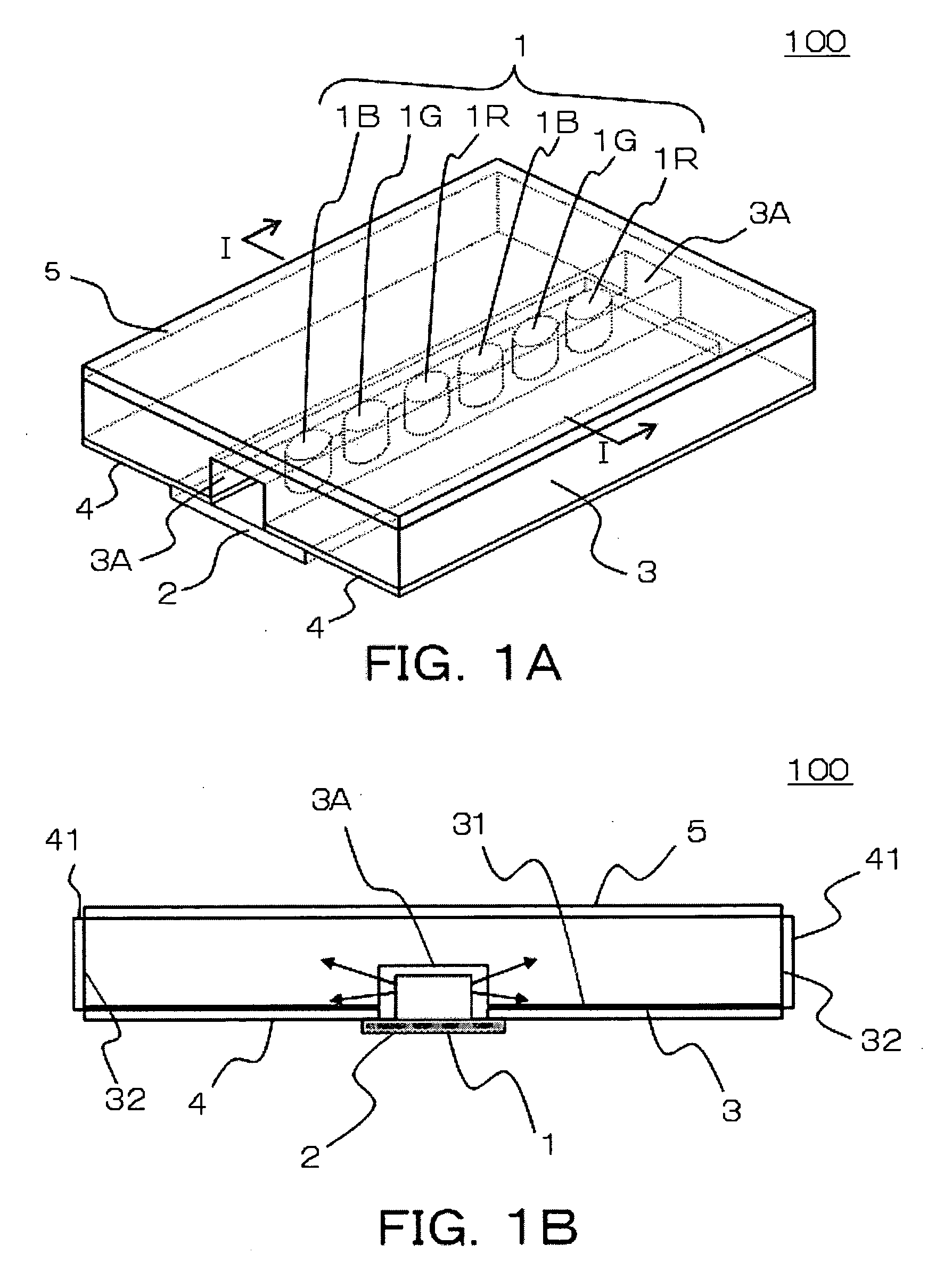
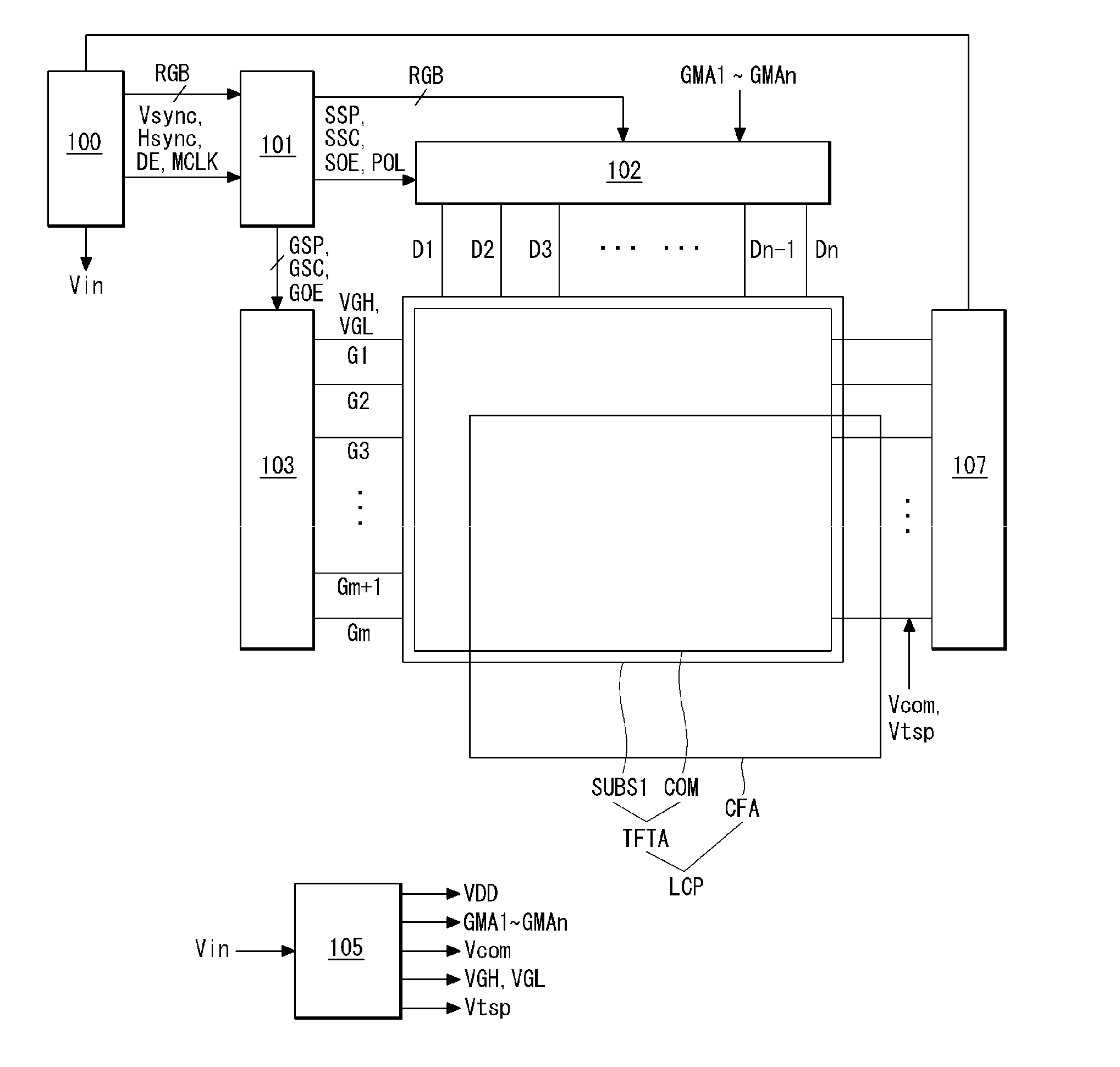
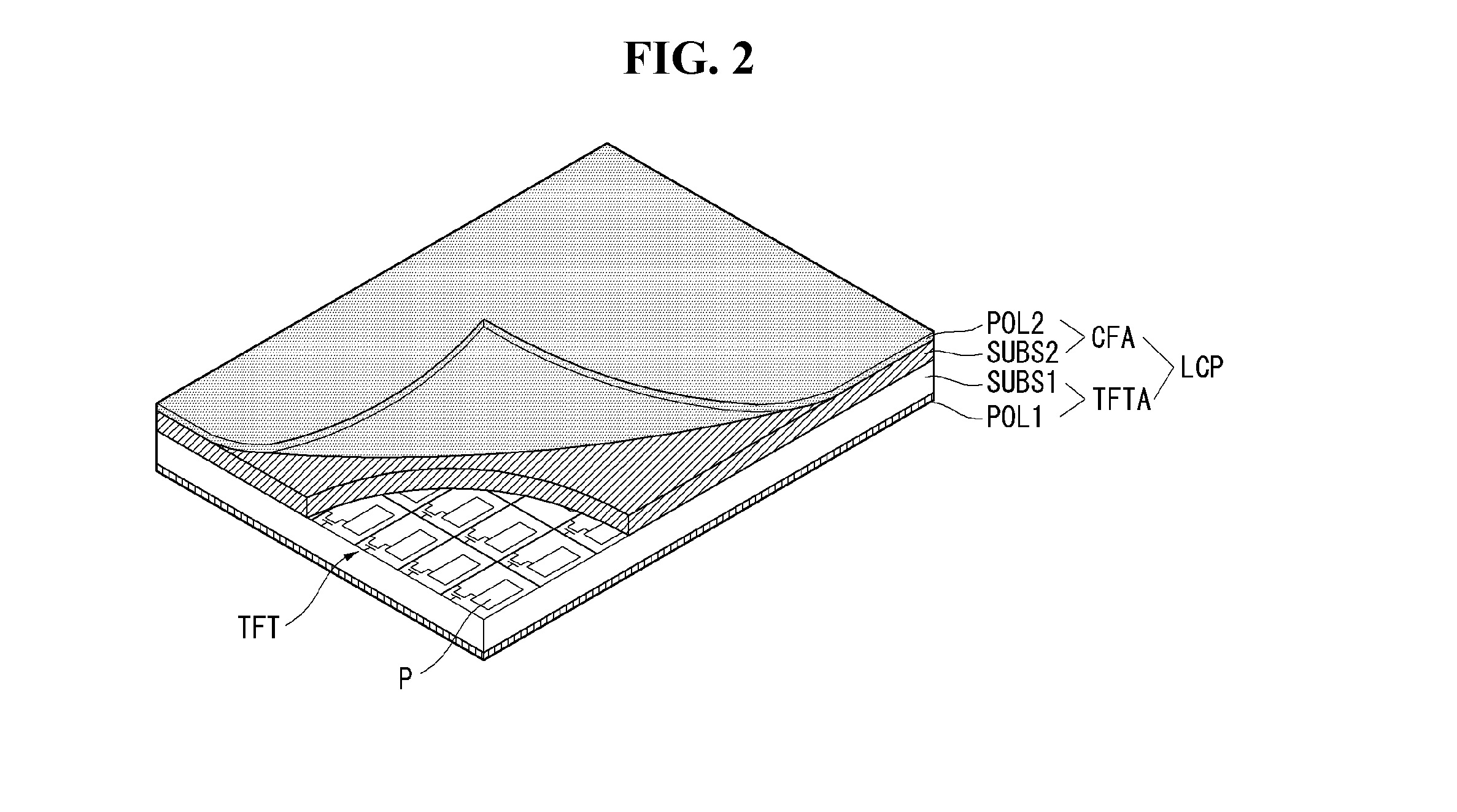
ActiveUS20040217945A1Not deteriorate display performanceEffectively downsizedCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsElectricityVoltage
A display device with a touch sensor according to the present invention includes an active matrix substrate 4A and a transparent counter electrode 7. On a first surface of the active matrix substrate, multiple pixel electrodes are arranged in matrix. The transparent counter electrode is opposed to the first surface of the active matrix substrate. The display device further includes a first circuit, a second circuit and a switching circuit. The first circuit supplies a voltage or a current to the transparent counter electrode for display purposes. The second circuit detects currents flowing from a number of points on the transparent counter electrode. And the switching circuit selectively connects electrically one of the first and second circuits to the transparent counter electrode.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Method for forming insulation film
InactiveUS20050161434A1Quality improvementIncreasing the thicknessElectrical controlDecorative surface effectsSubstrate surfaceElectron
In a process involving the formation of an insulating film on a substrate for an electronic device, the insulating film is formed on the substrate surface by carrying out two or more steps for regulating the characteristic of the insulating film involved in the process under the same operation principle. The formation of an insulating film having a high level of cleanness can be realized by carrying out treatment such as cleaning, oxidation, nitriding, and a film thickness reduction while avoiding exposure to the air. Further, carrying out various steps regarding the formation of an insulating film under the same operation principle can realize simplification of the form of an apparatus and can form an insulating film having excellent property with a high efficiency.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Use of high-K dielectric material for ONO and tunnel oxide to improve floating gate flash memory coupling
InactiveUS6617639B1Enhanced couplingReduce equivalent oxide thicknessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCouplingDielectric layer
A floating gate flash memory device including a substrate comprising a source region, a drain region, and a channel region positioned therebetween; a floating gate electrode positioned above the channel region and separated from the channel region by a tunnel dielectric material layer; and a control gate electrode positioned above the floating gate electrode and separated from the floating gate electrode by an interpoly dielectric layer, the interpoly dielectric layer comprising a modified ONO structure having a bottom dielectric material layer adjacent to the floating gate electrode, a top dielectric material layer adjacent to the control gate electrode, and a center layer comprising a nitride and positioned between the bottom dielectric material layer and the top dielectric material layer, in which the tunnel dielectric material layer, and at least one of the bottom dielectric material layer and the top dielectric material layer, comprise a high-K dielectric material.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Use of high-K dielectric material in modified ONO structure for semiconductor devices
InactiveUS6642573B1Reduced dimensionSacrificing charge trapping abilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricSemiconductor
A process for fabrication of a semiconductor device including a modified ONO structure, comprising forming the modified ONO structure by providing a semiconductor substrate; forming a first dielectric material layer on the semiconductor substrate; depositing a silicon nitride layer on the first dielectric material layer; and forming a top dielectric material layer, wherein at least one of the bottom dielectric material layer and the top dielectric material layer comprise a mid-K or a high-K dielectric material. The semiconductor device may be, e.g., a SONOS two-bit EEPROM device or a floating gate flash device including the modified ONO structure.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Backlight unit and liquid crystal display device using the same
InactiveUS20060002146A1Efficient mixingLittle color changeOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayLight guide
Light emitted in side surface directions from side-emitting red, green, and blue LEDs which are arranged on an LED array substrate is introduced into a light guide from side surfaces of a groove-shaped recessed portion, and propagates in the light guide. Thus, the three colors are mixed. The light further propagates in the light guide while being reflected at both side end surfaces of the light guide by the function of a reflective sheet and the like. Thus, color mixing progresses. Further, the light is reflected upward by diffuse reflective means provided on the lower surface of the light guide, and emitted as backlight light to the outside through a diffuse sheet.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
Golf club having an improved face plate
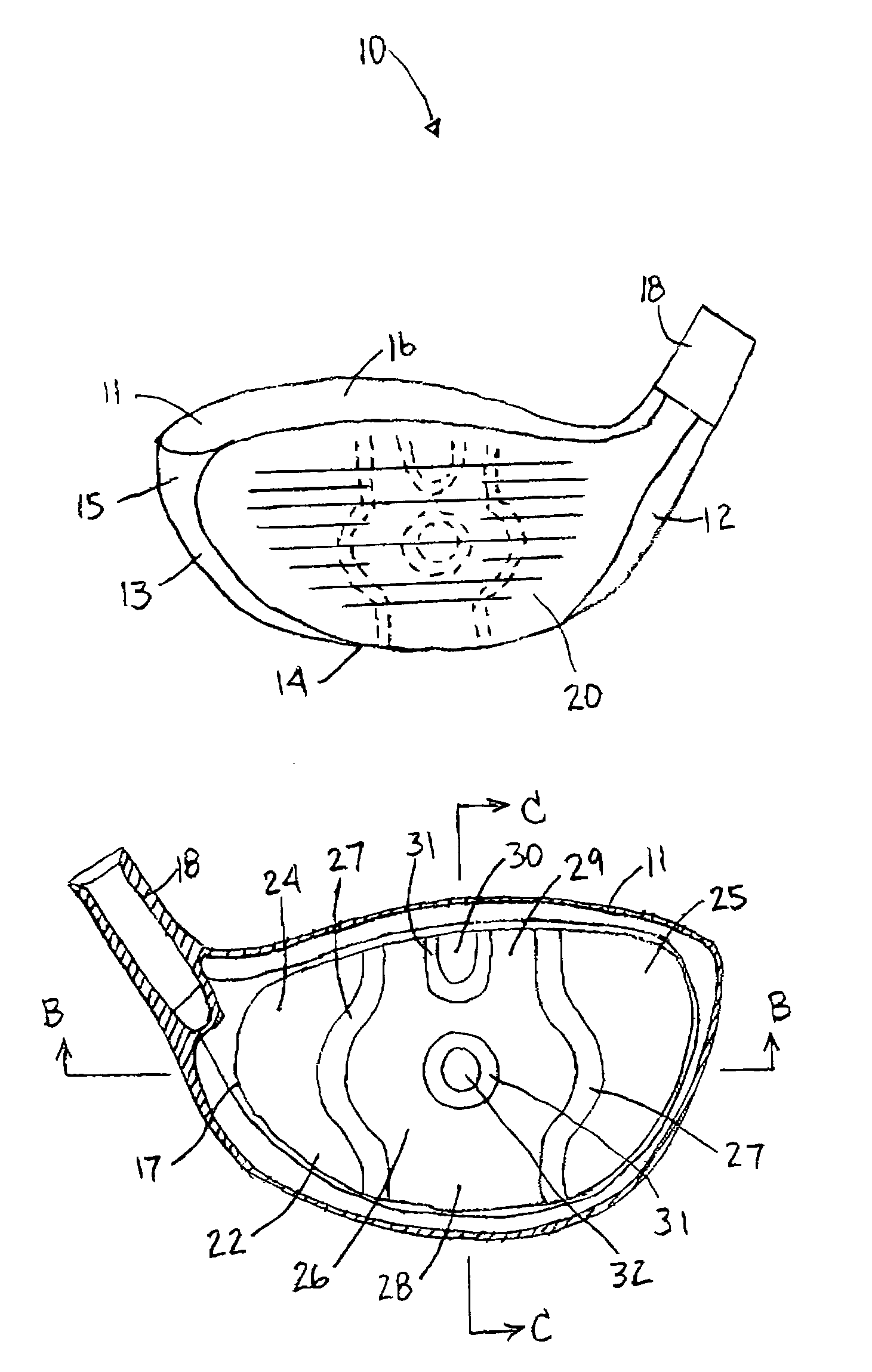
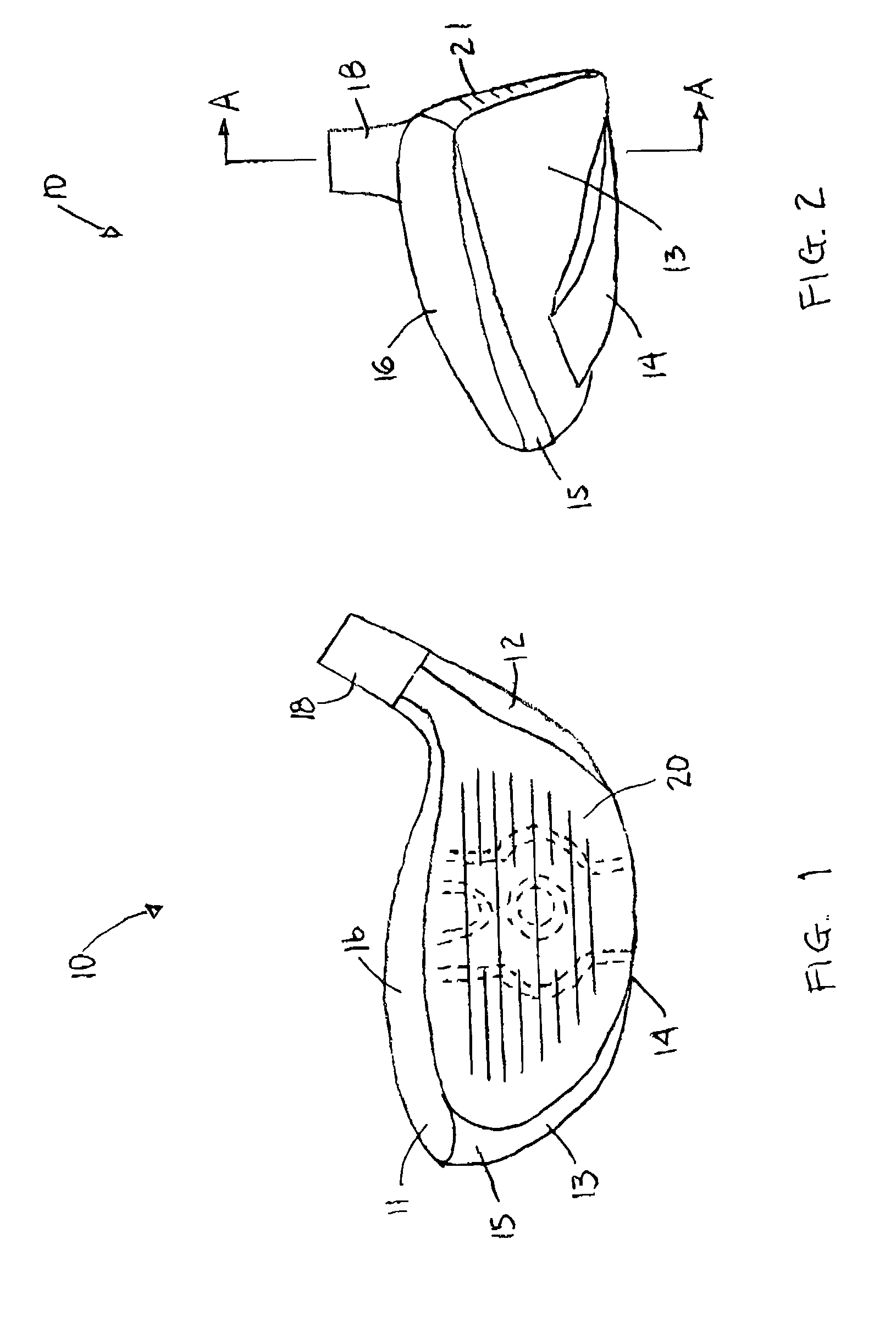
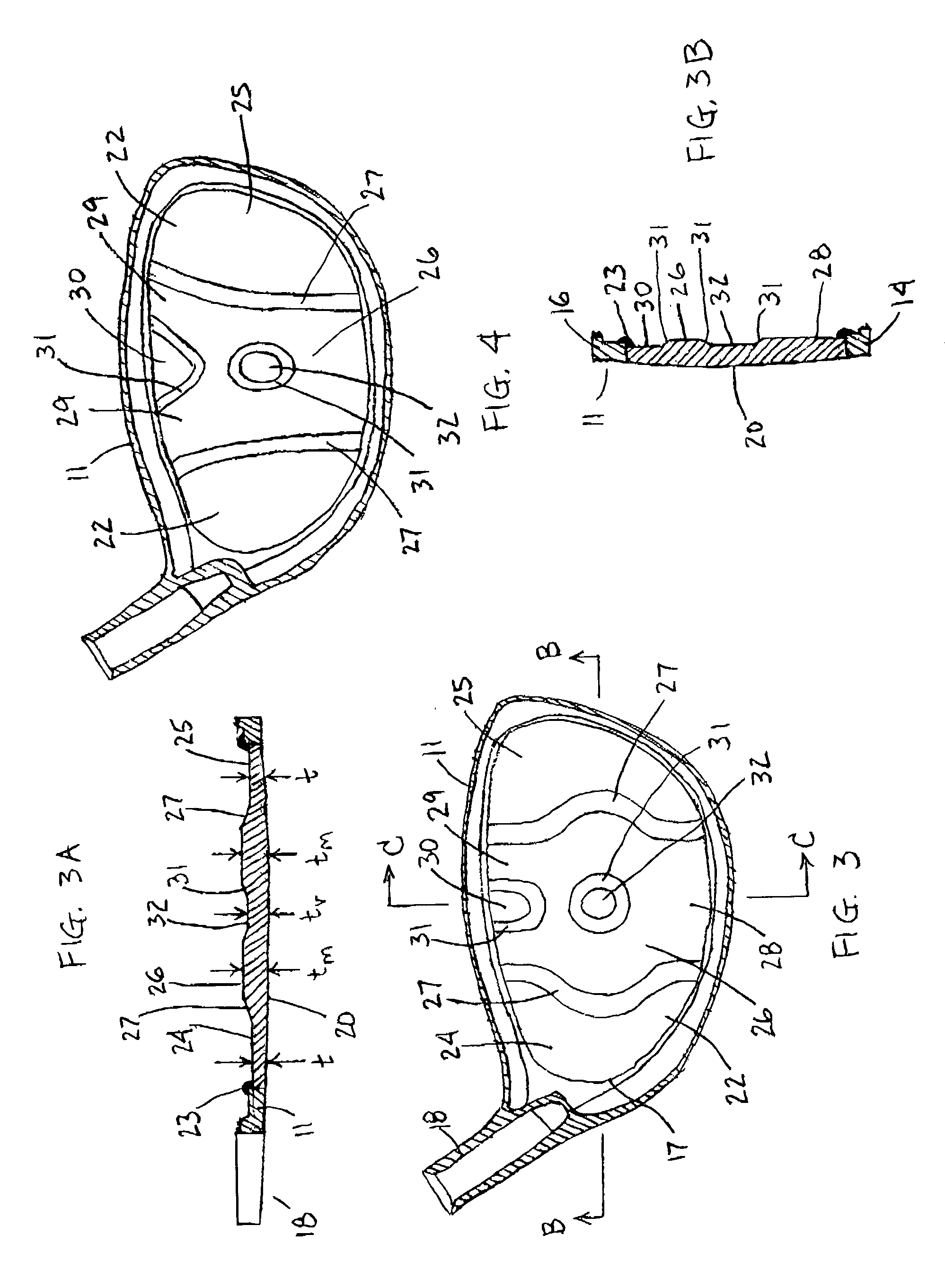
InactiveUS6997820B2Increasing the thicknessReduce thicknessGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringMetallic materials
A golf club head is provided having an increased sweet spot across its club face. A preferred construction includes a face plate having vertical zone of increased thickness and a central region having a reduced thickness. An upward extension of the vertical zone comprises divergent segments separated by an upper region of reduced thickness. The face plate material is preferably metallic, but in alternative embodiments may be formed of a composite or non-metal material. Methods for manufacturing a golf club head having a face plate with the thicknesses of the present invention include forging and machining techniques. The club head may be a wood-type or iron.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
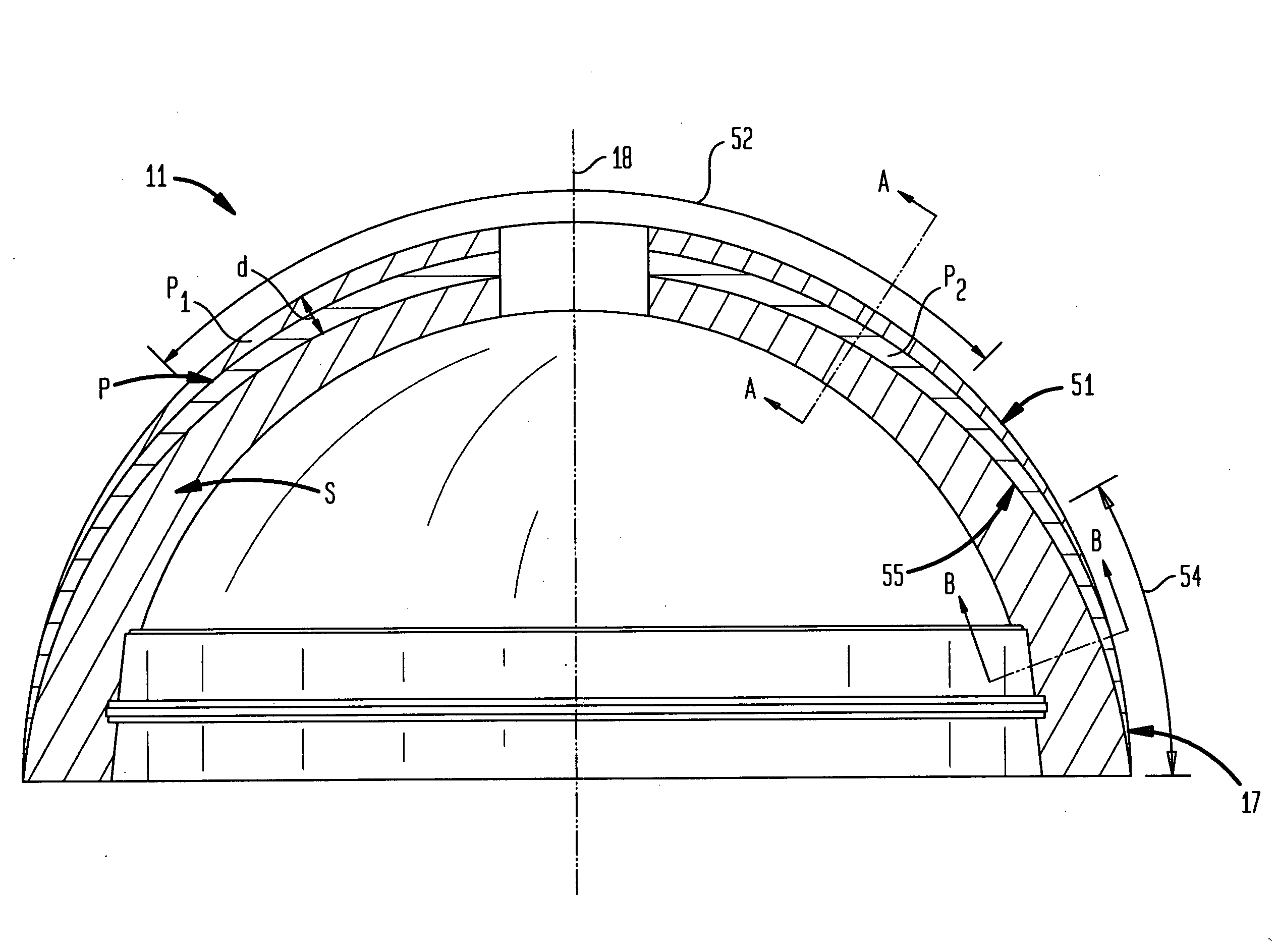
Gradient porous implant
ActiveUS20070150068A1Optimize performanceOptimizes various mechanical and biological requirements of the implants performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantPorous metalMedical treatment
An implantable medical device includes a porous metal foam or foam-like structure having pores defined by metal struts or webs wherein the porous structure has directionally controlled pore characteristics. The pore characteristics controlled include one or more of the metal structure porosity, pore size, pore shape, pore size distribution and strut thickness. The pore characteristics may vary in one or more directions throughout the structure. Preferably the pore characteristics are controlled to match the porous metal structure to various mechanical and biological requirements of different regions of the structure in order to optimize aspects of the implants performance and may vary not only over the surface of the porous structure but through the depth of the porous structure. The thickness of the porous metal structure may also be modified to establish a thickness profile that optimizes mechanical and biological requirements of the implants performance. Acetabular cup embodiments of the invention are described. Various methods of manufacturing implants having directionally controlled pore characteristics are described.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
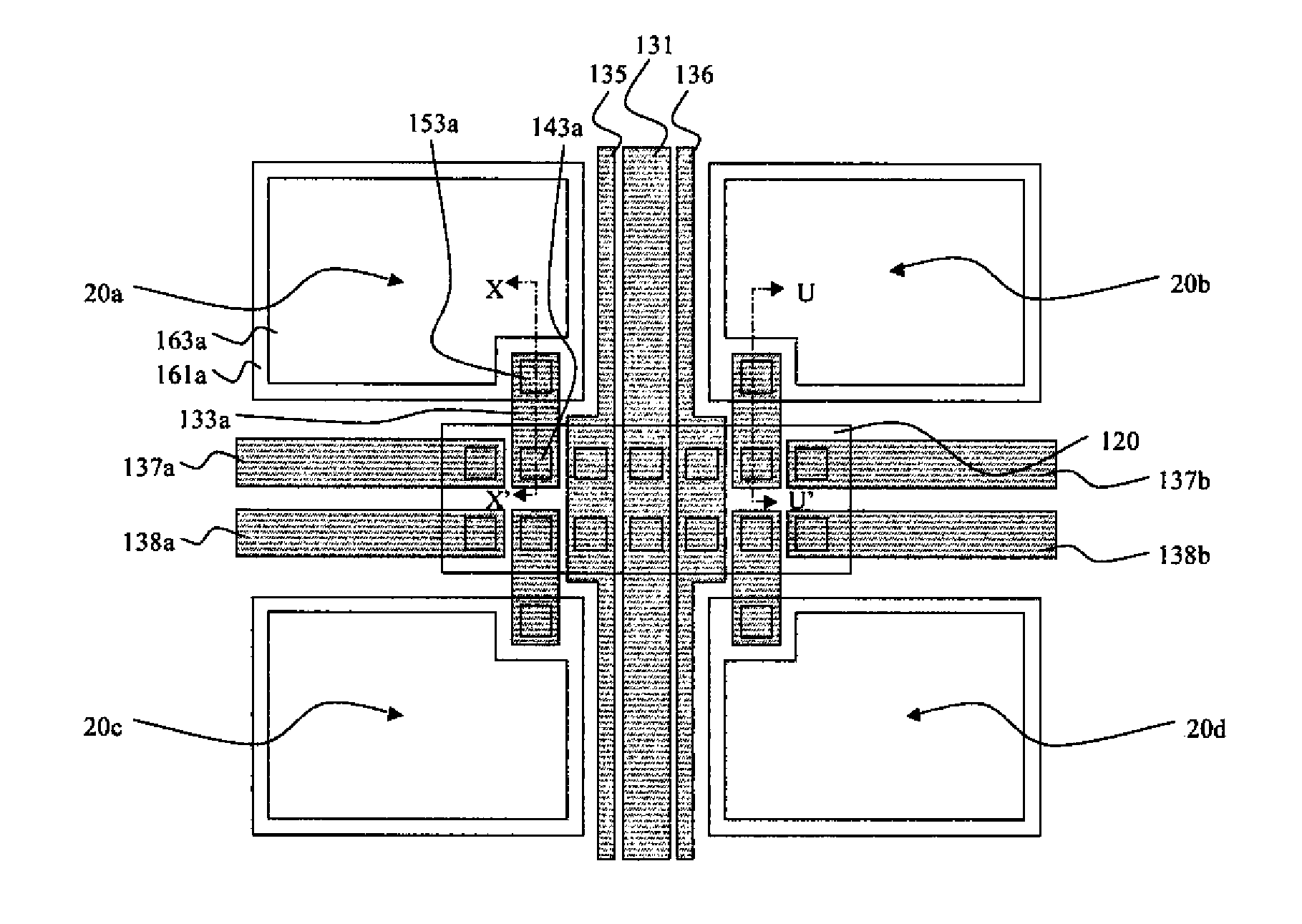
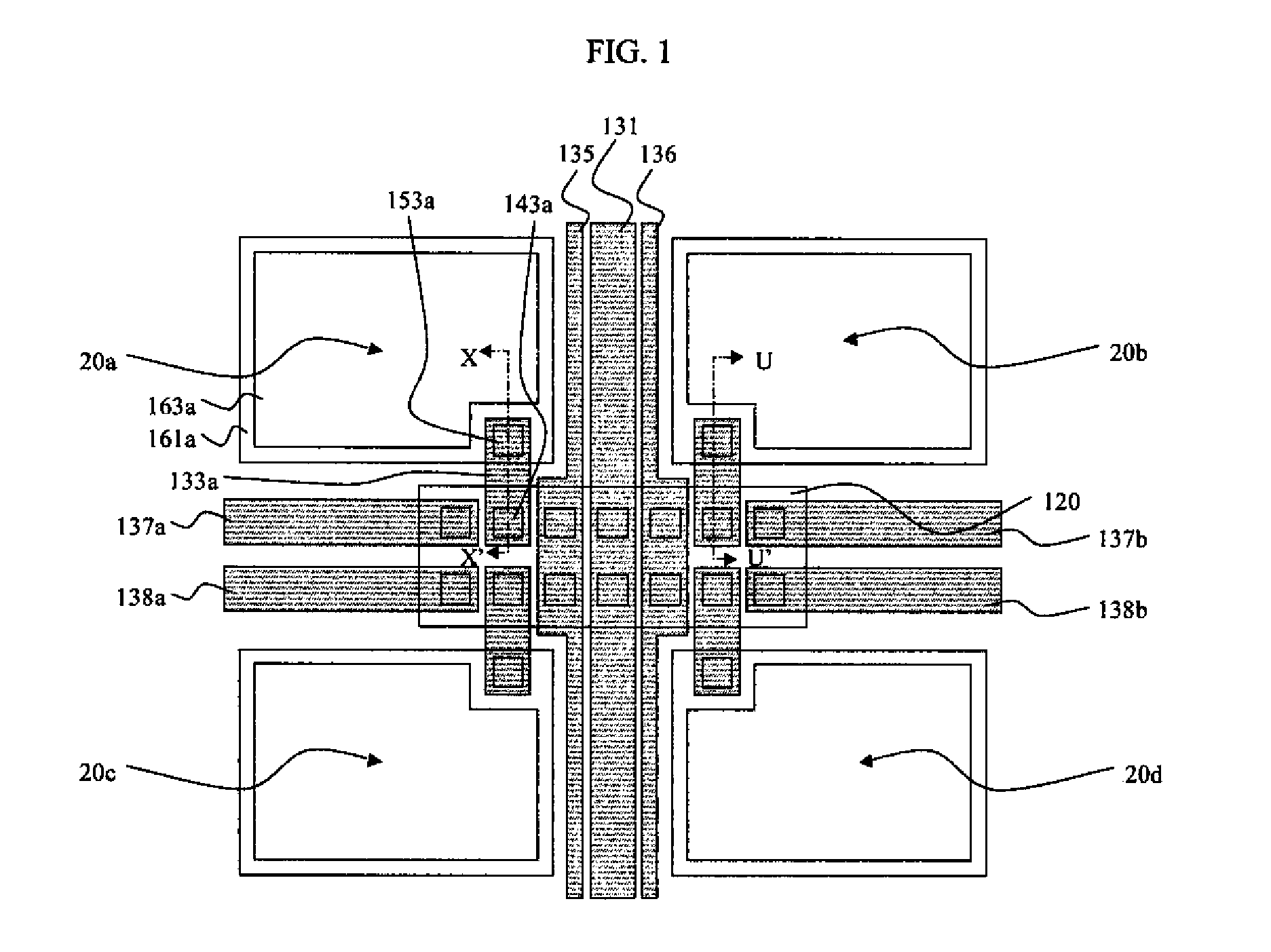
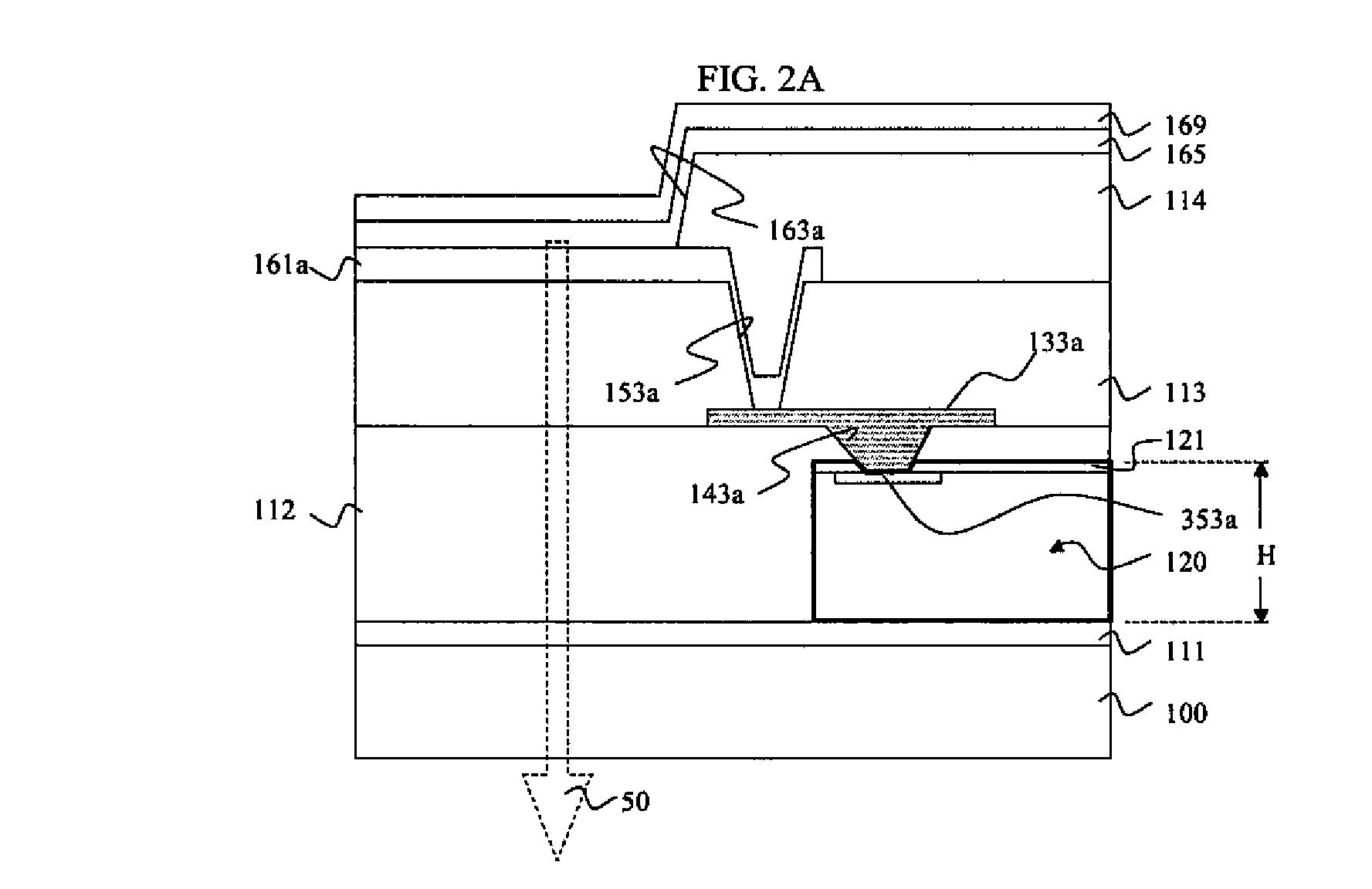
Touch sensor integrated display device
ActiveUS20120218199A1Reduce thicknessIncreased durabilityStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceEngineering
A touch sensor integrated display device is provided comprising gate lines and data lines formed on a substrate to be intersected with each other, a plurality of pixel electrodes formed at intersections between the gate lines and the data lines, and a common electrode formed to overlap the plurality of pixel electrodes through an insulating film disposed between the common electrode and the plurality of pixel electrodes, wherein the common electrode includes at least two touch electrodes, each of which is connected to at least one of signal lines arranged in one of a first direction and a second direction crossing the first direction.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Device and method for locking two building boards
Owner:FLOORING TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com