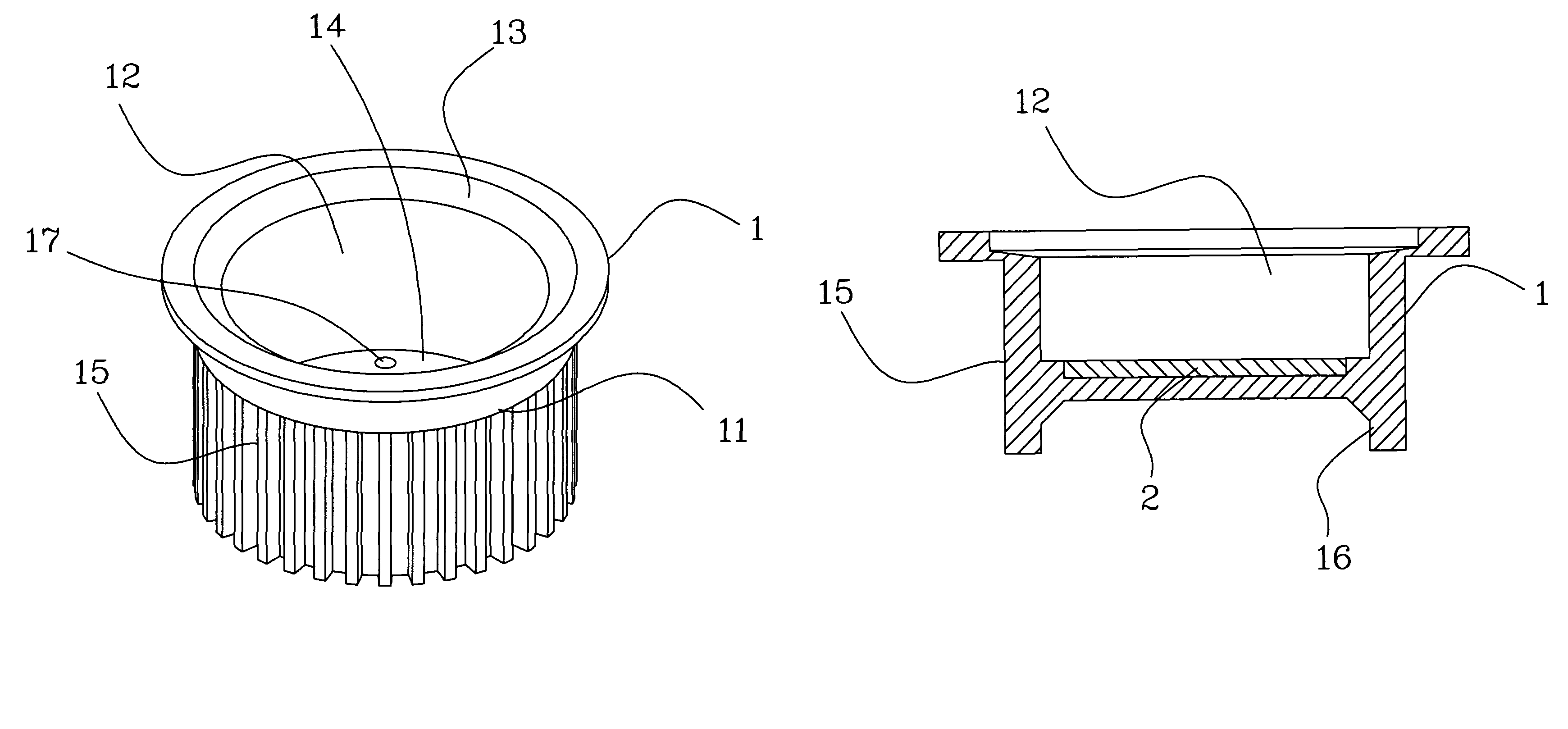
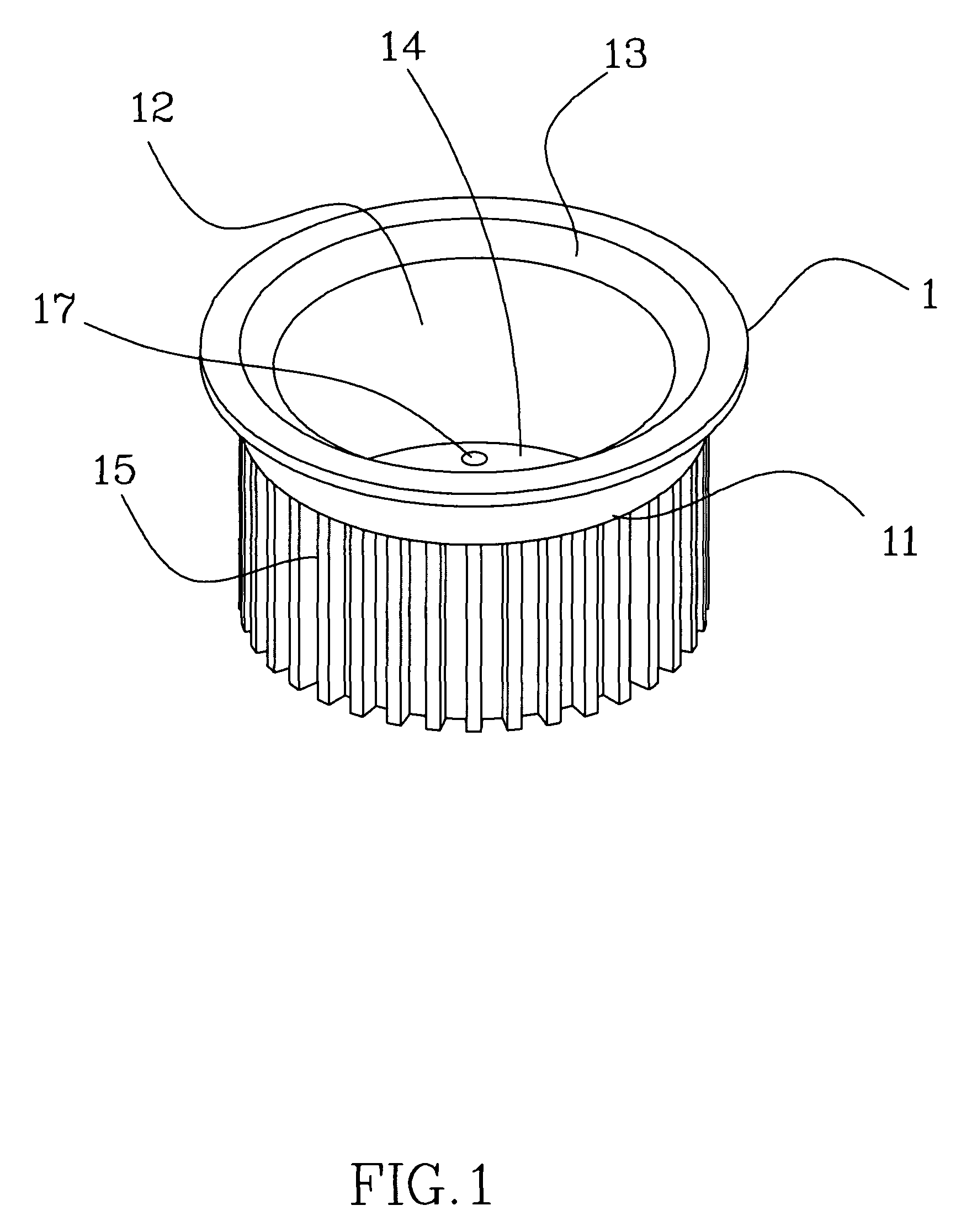
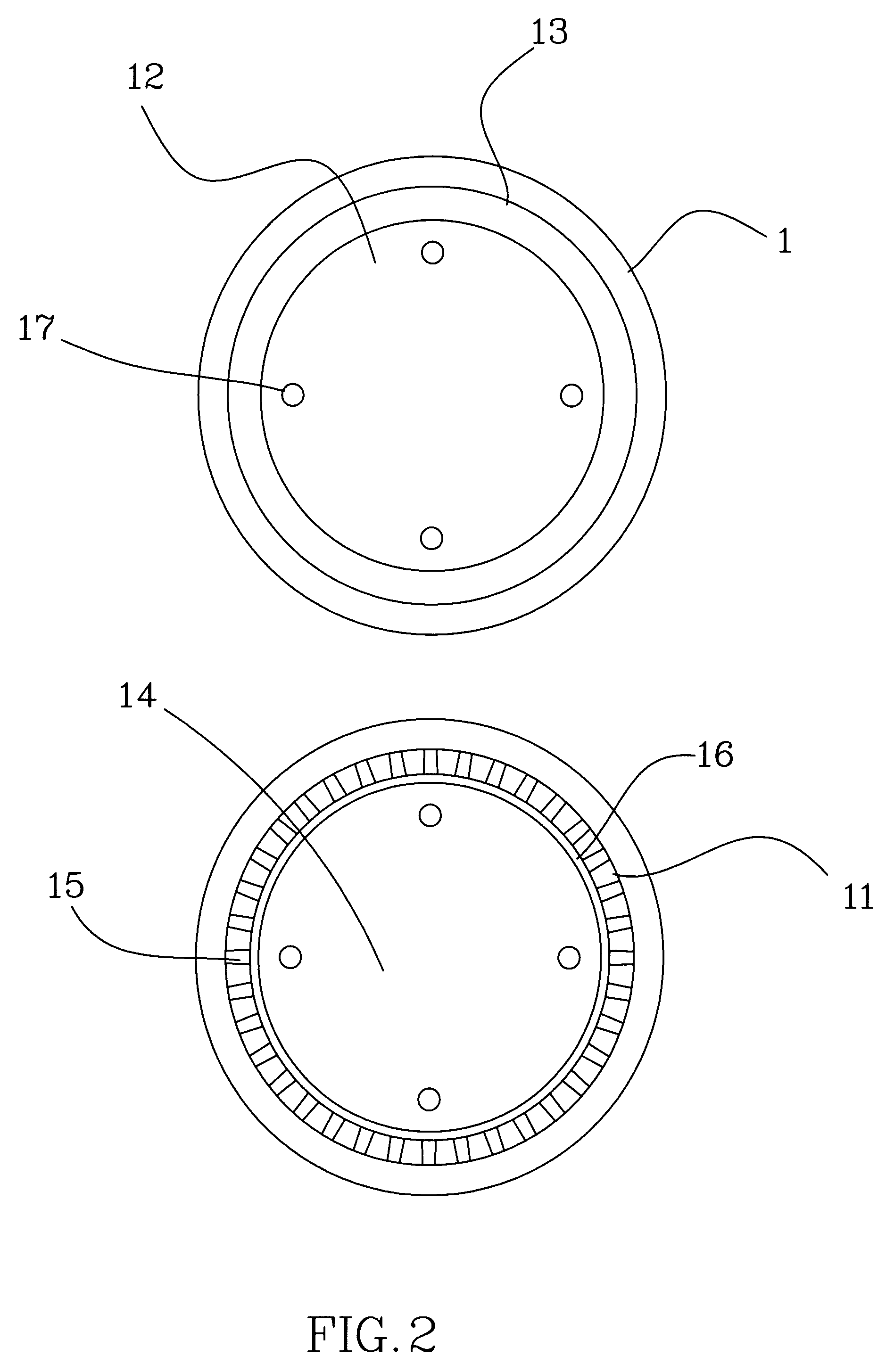
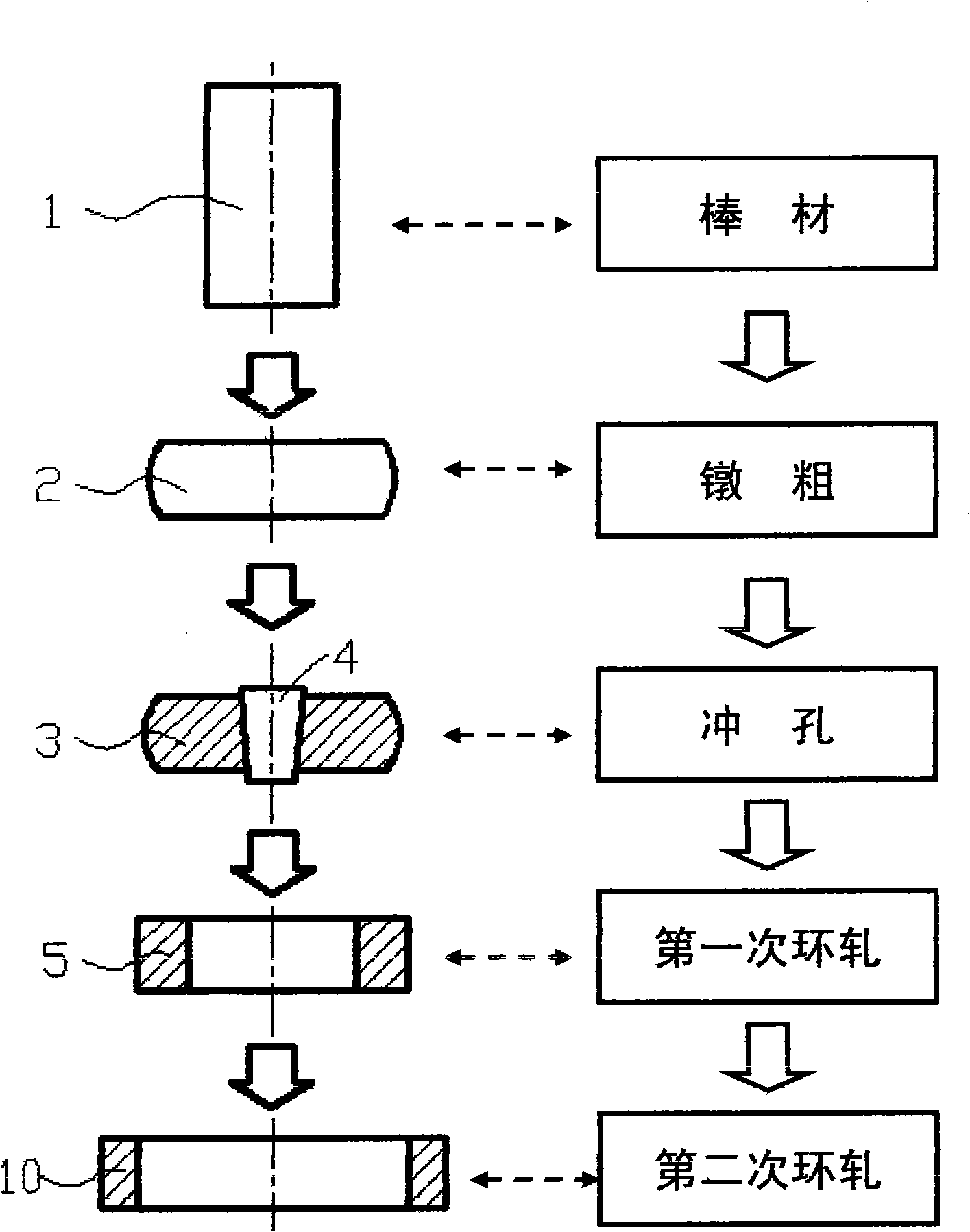
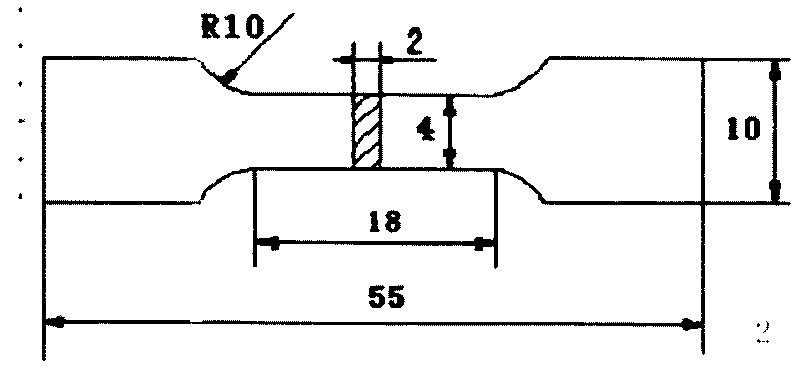
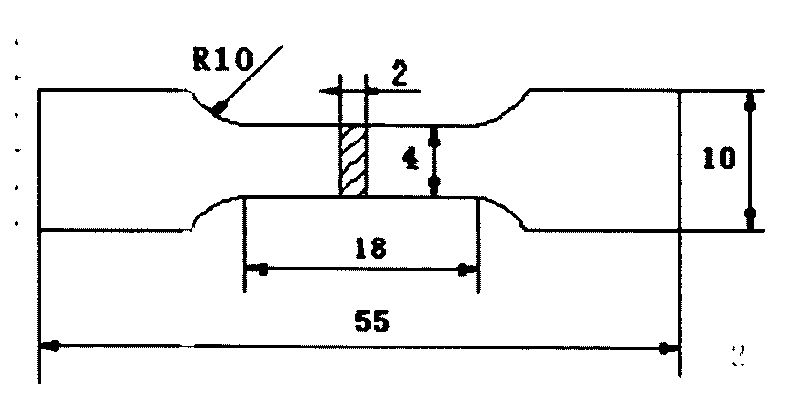
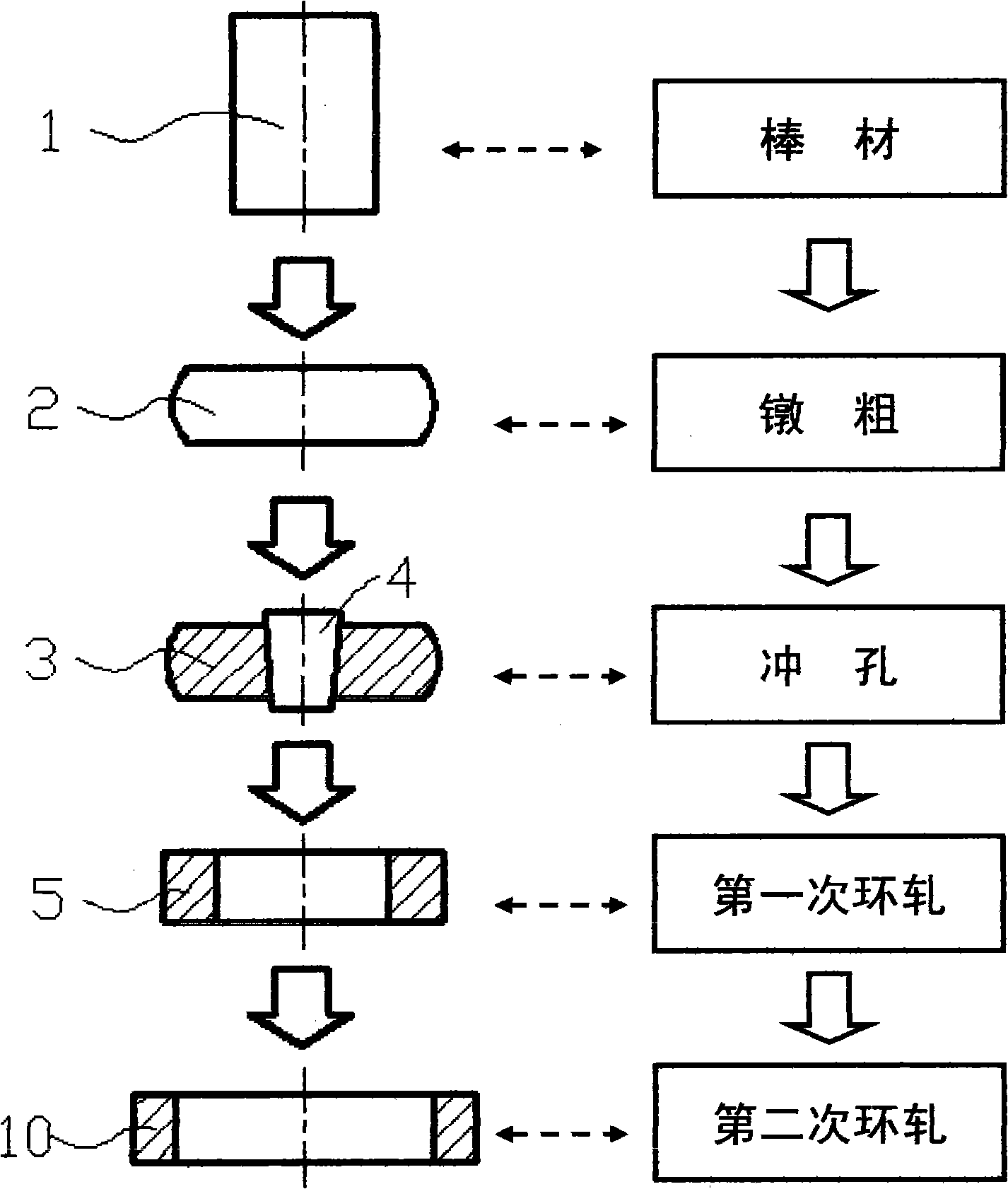
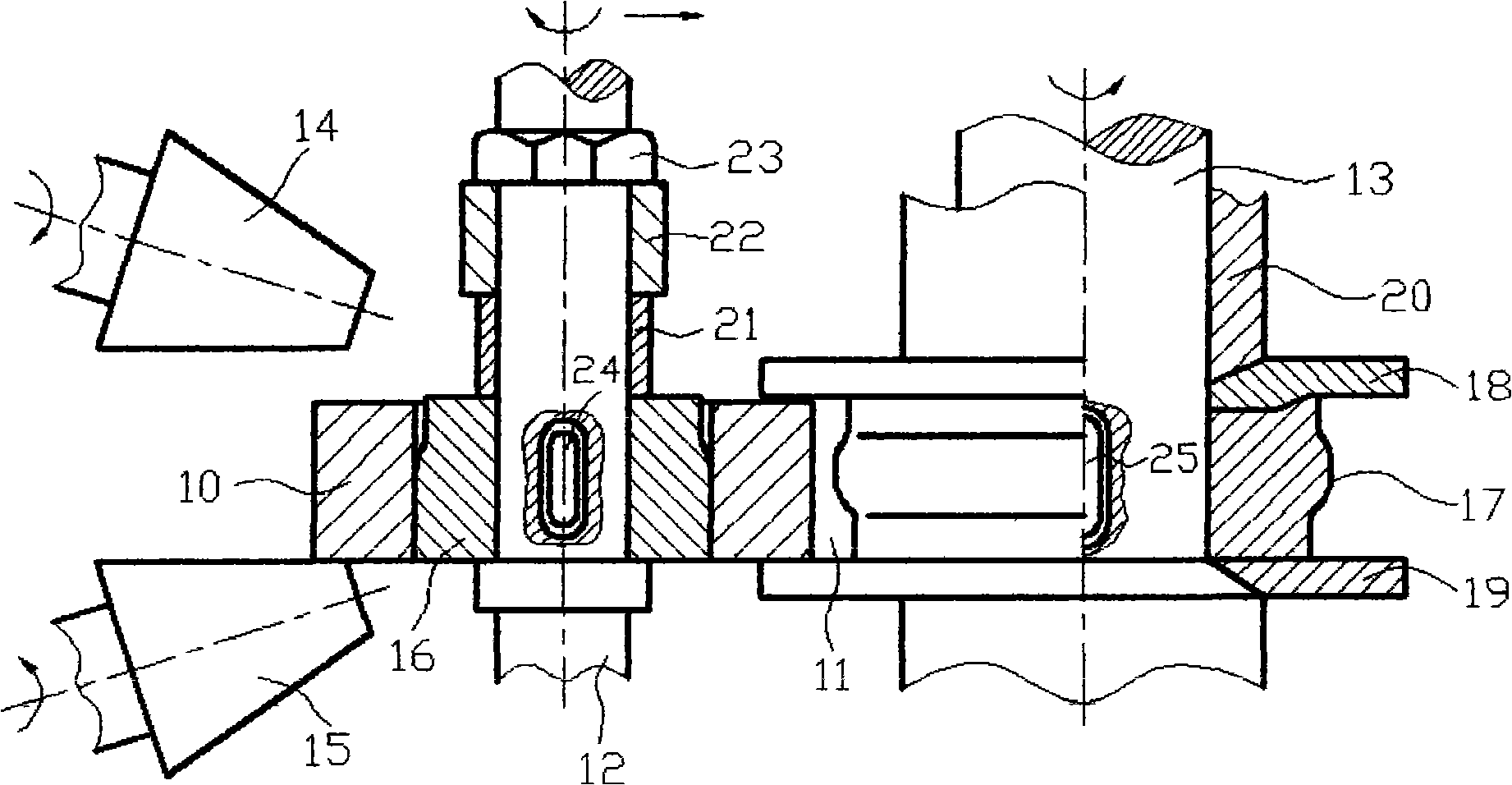
Patents
Literature
9186 results about "Forging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die. Forging is often classified according to the temperature at which it is performed: cold forging (a type of cold working), warm forging, or hot forging (a type of hot working). For the latter two, the metal is heated, usually in a forge. Forged parts can range in weight from less than a kilogram to hundreds of metric tons. Forging has been done by smiths for millennia; the traditional products were kitchenware, hardware, hand tools, edged weapons, cymbals, and jewellery. Since the Industrial Revolution, forged parts are widely used in mechanisms and machines wherever a component requires high strength; such forgings usually require further processing (such as machining) to achieve a finished part. Today, forging is a major worldwide industry.
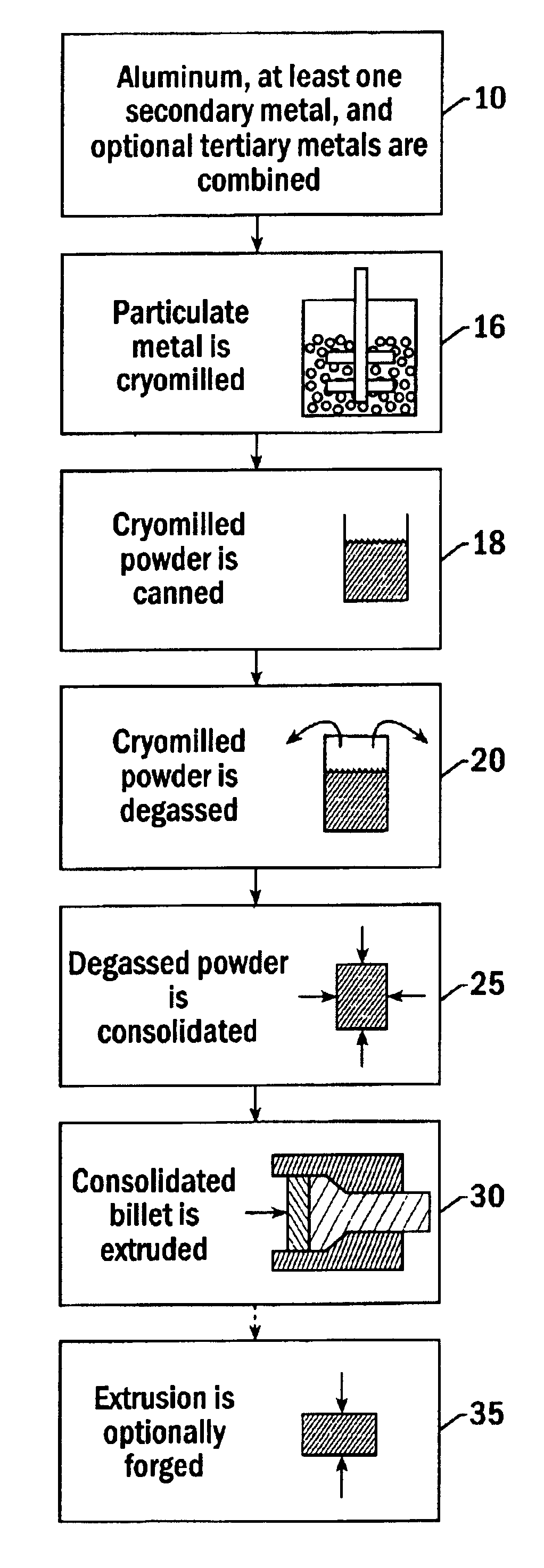
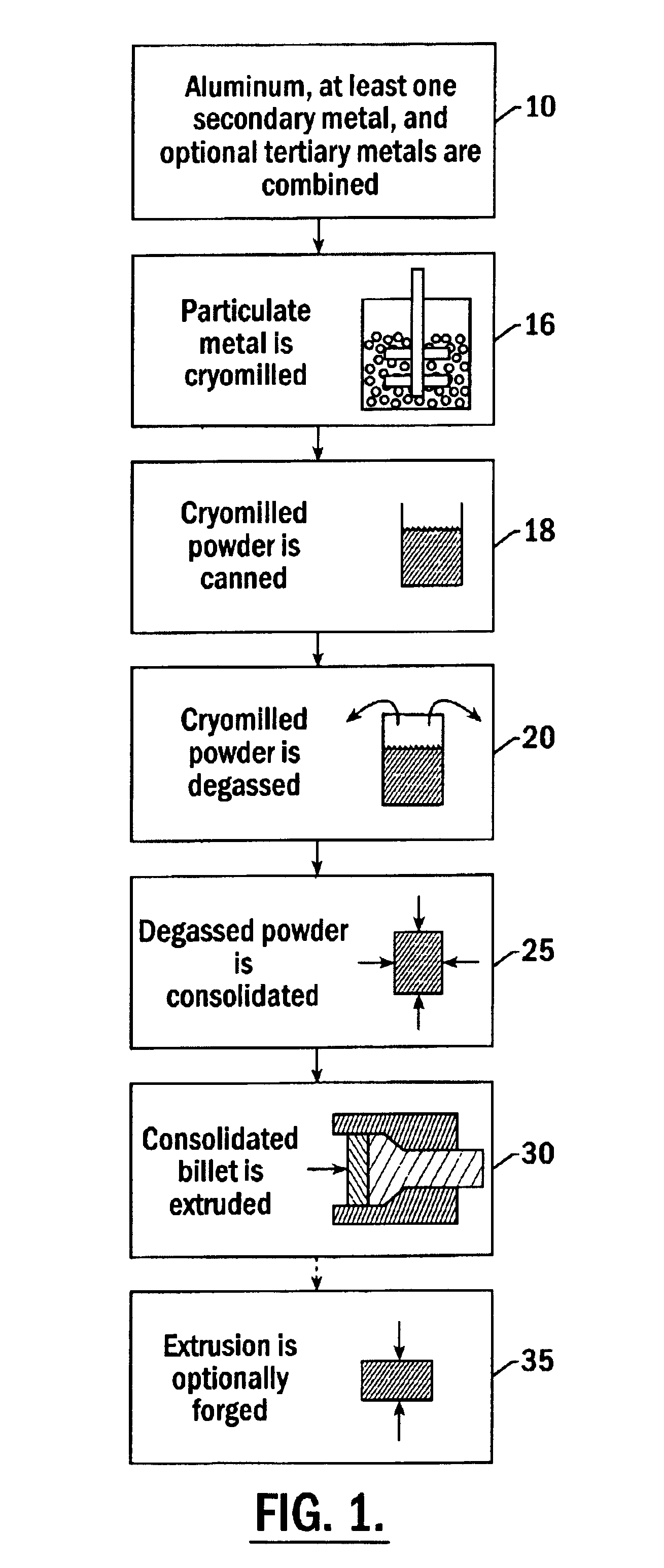
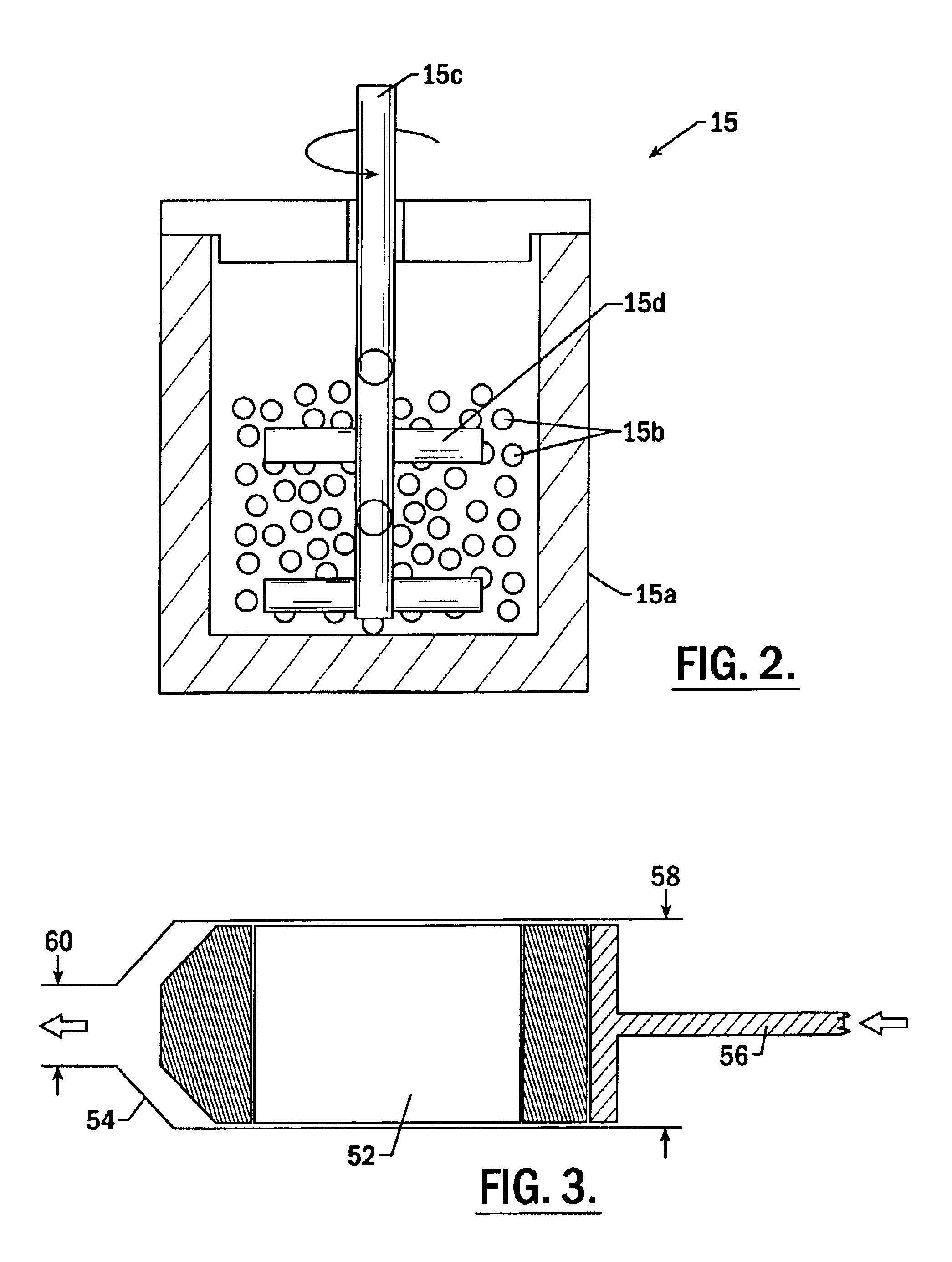
Method for preparing cryomilled aluminum alloys and components extruded and forged therefrom
InactiveUS6902699B2Stable structureHigh strengthTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusNanostructureAluminium alloy
High strength aluminum alloy powders, extrusions, and forgings are provided in which the aluminum alloys exhibit high strength at atmospheric temperatures and maintain high strength and ductility at extremely low temperatures. The alloy is produced by blending about 89 atomic % to 99 atomic % aluminum, 1 atomic % to 11 atomic % of a secondary metal selected from the group consisting of magnesium, lithium, silicon, titanium, zirconium, and combinations thereof, and up to about 10 atomic % of a tertiary metal selected from the group consisting of Be, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra, Sc, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Y, Nb, Mo, Tc, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd, W, and combinations thereof. The alloy is produced by nanostructure material synthesis, such as cryomilling, in the absence of refractory dispersoids. The synthesized alloy is then canned, degassed, consolidated, extruded, and optionally forged into a solid metallic component. Grain size within the alloy is less than 0.5 μm, and alloys with grain size less than 0.1 μm may be produced.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
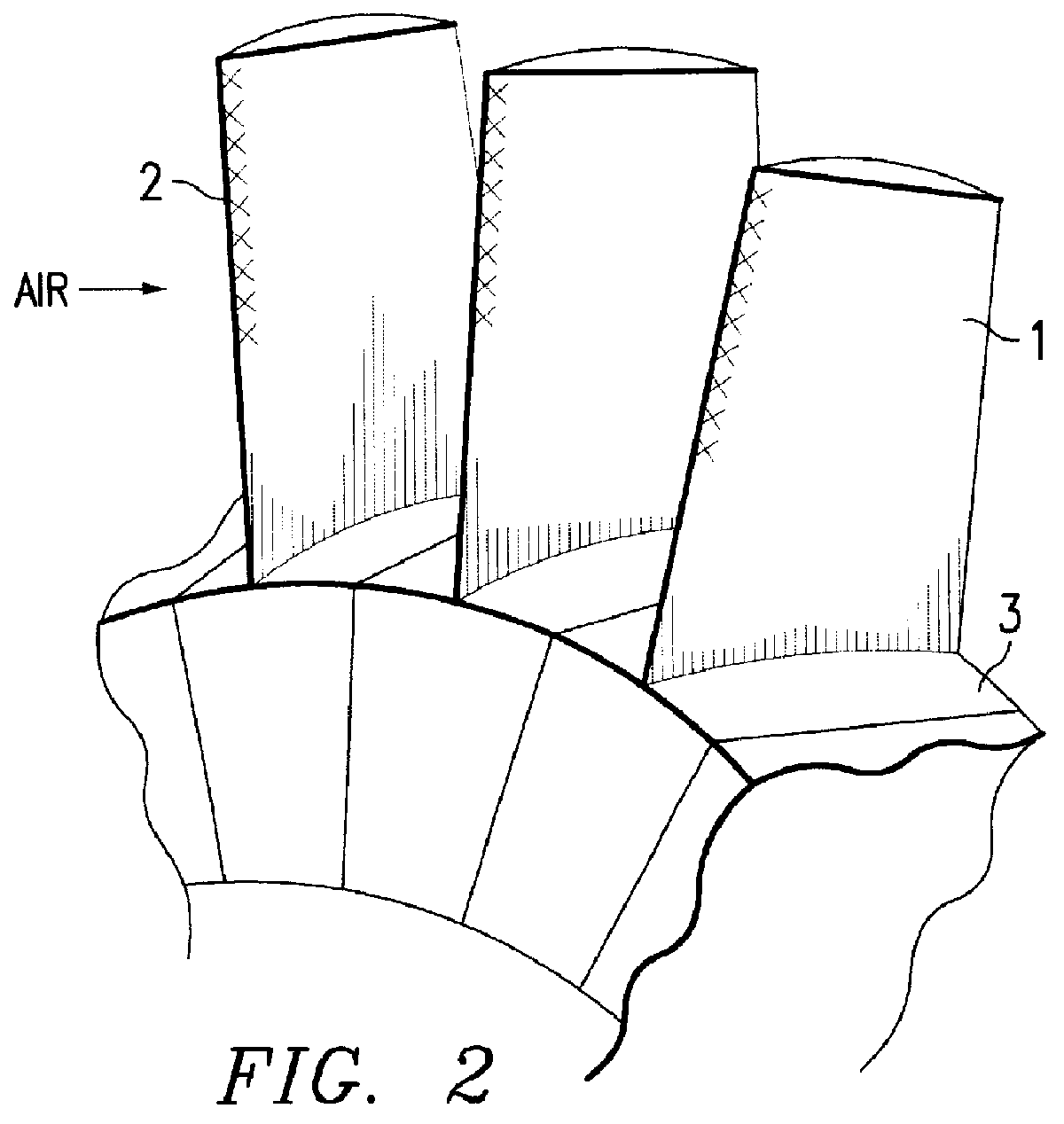
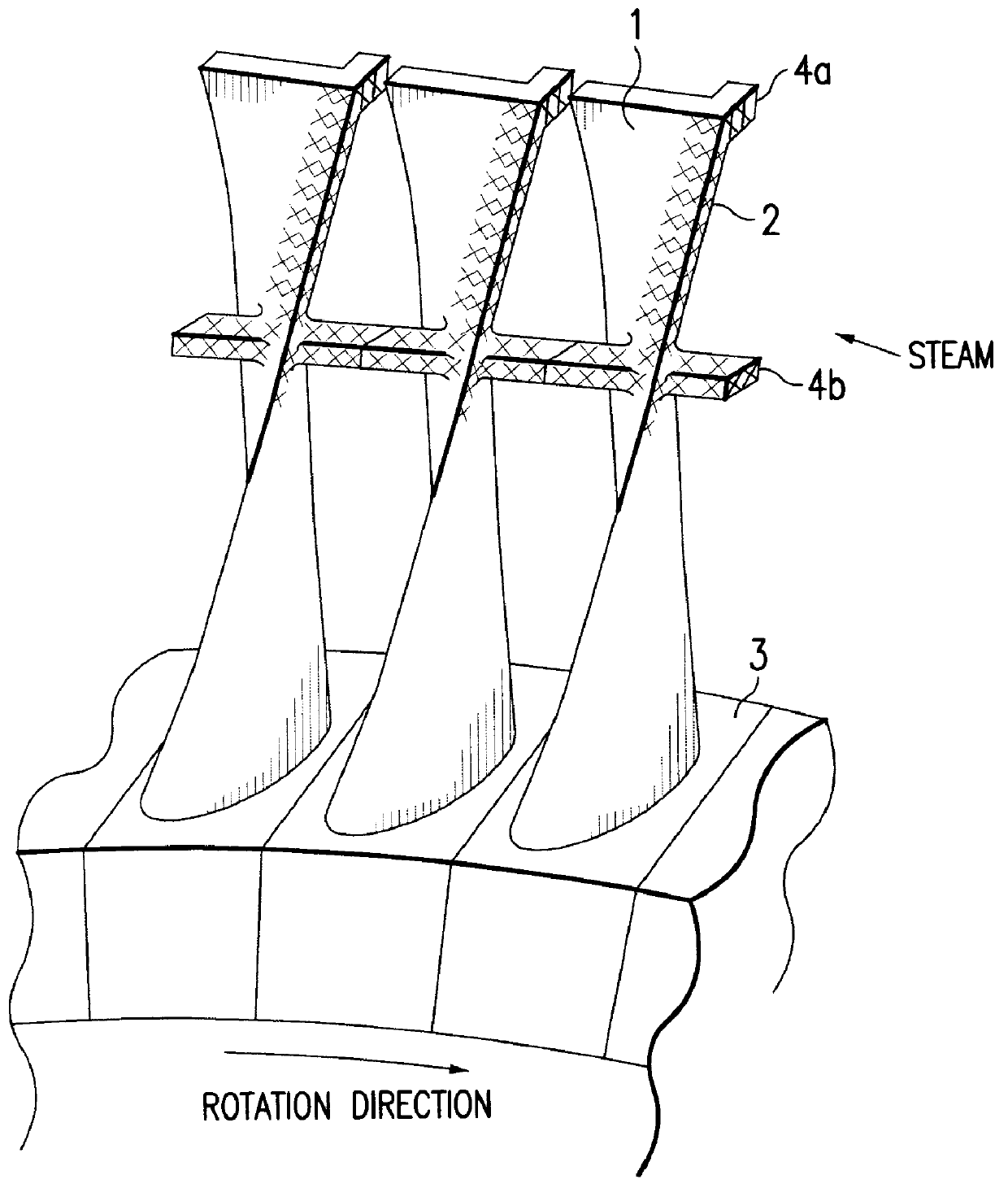
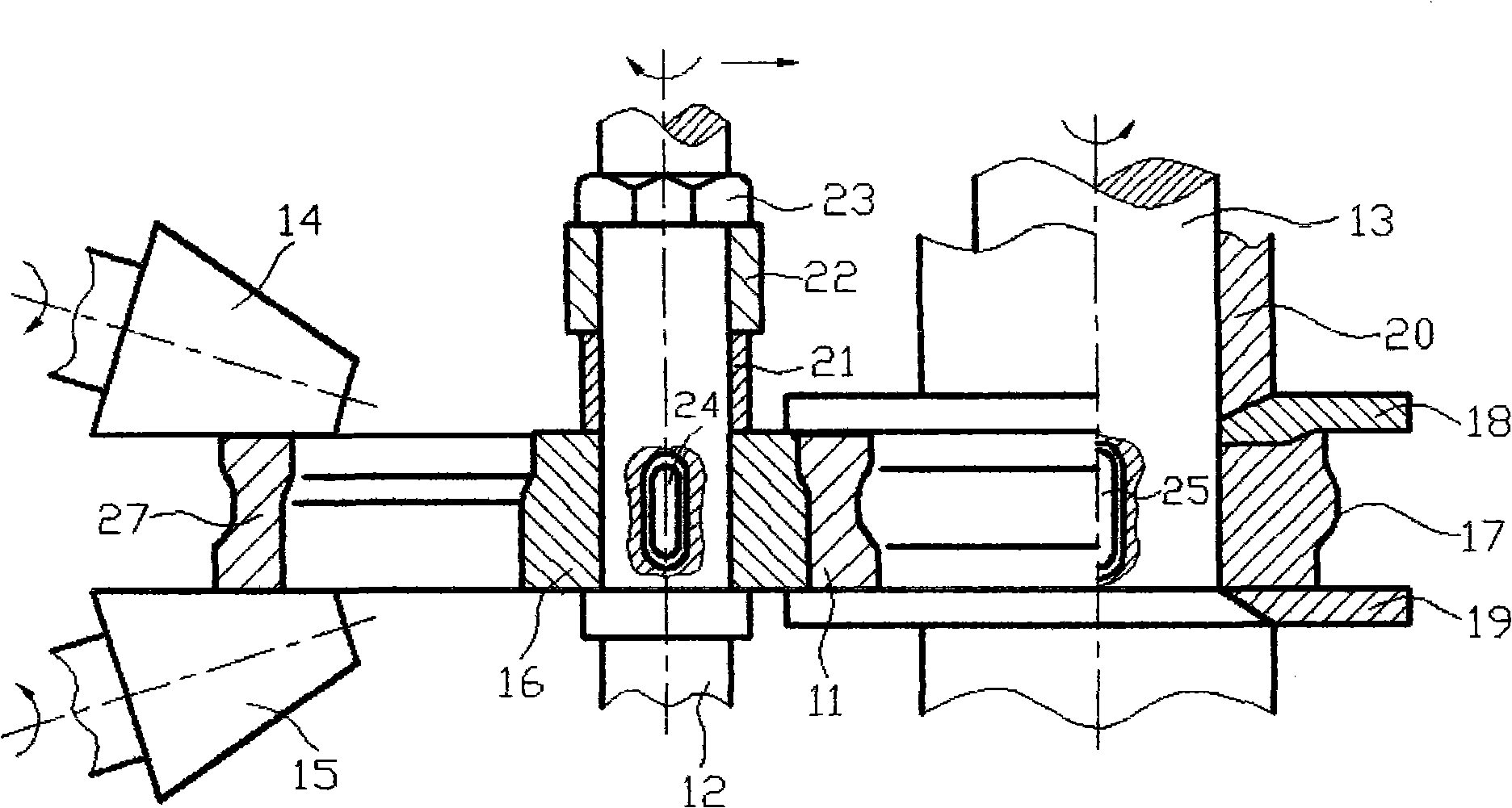
Method for producing titanium alloy turbine blades and titanium alloy turbine blades
InactiveUS6127044ALess abrasionSuperior in water droplet erosion resistancePropellersEngine manufactureLeading edgeTurbine blade
PCT No. PCT / JP95 / 01817 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 2, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 2, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 13, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 10066 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 20, 1997A method for producing titanium alloy turbine blades comprising the steps of (a) forming turbine blades of titanium alloy through hot forging or machining, (b) cooling leading edges on tip portions of the turbine blades including covers thereof formed through hot forging or machining faster than blade main body after final hot forging or solid solution treatment, and (c) heat treating the cooled turbine blades. With this method, it is possible to manufacture titanium turbine blades in an economical fashion and obtain titanium alloy turbine blades superior in reliability by preventing erosion.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
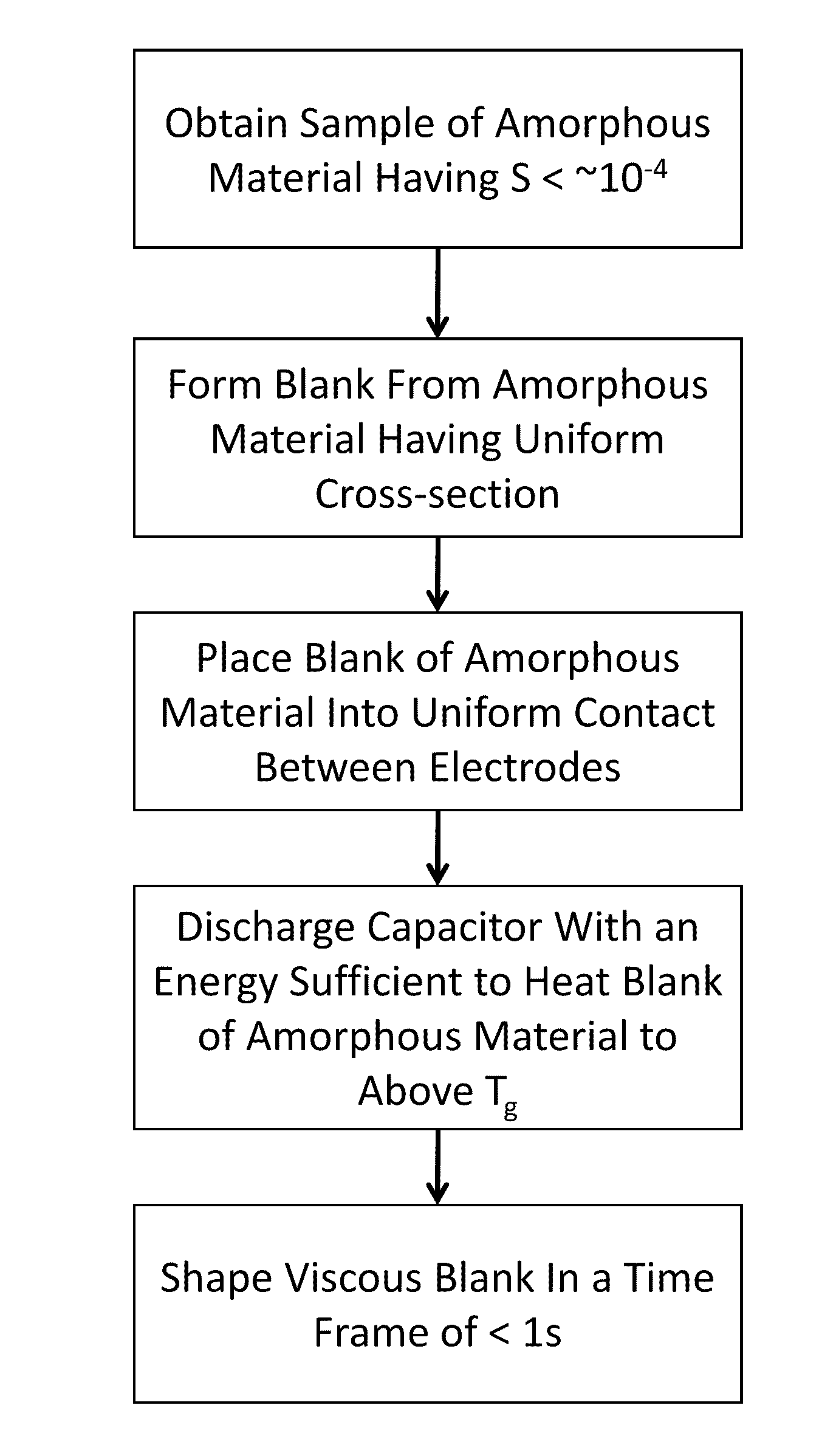
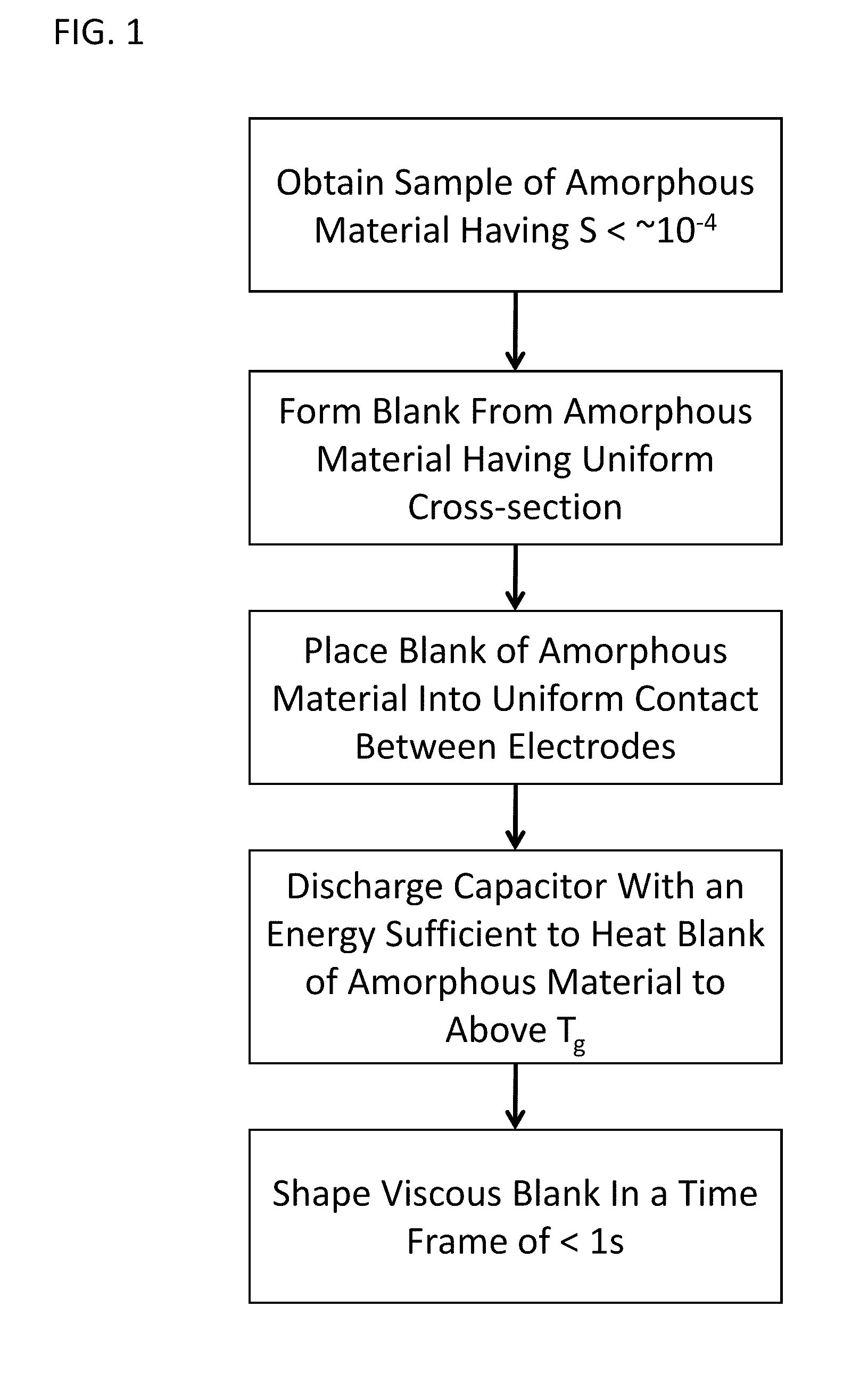
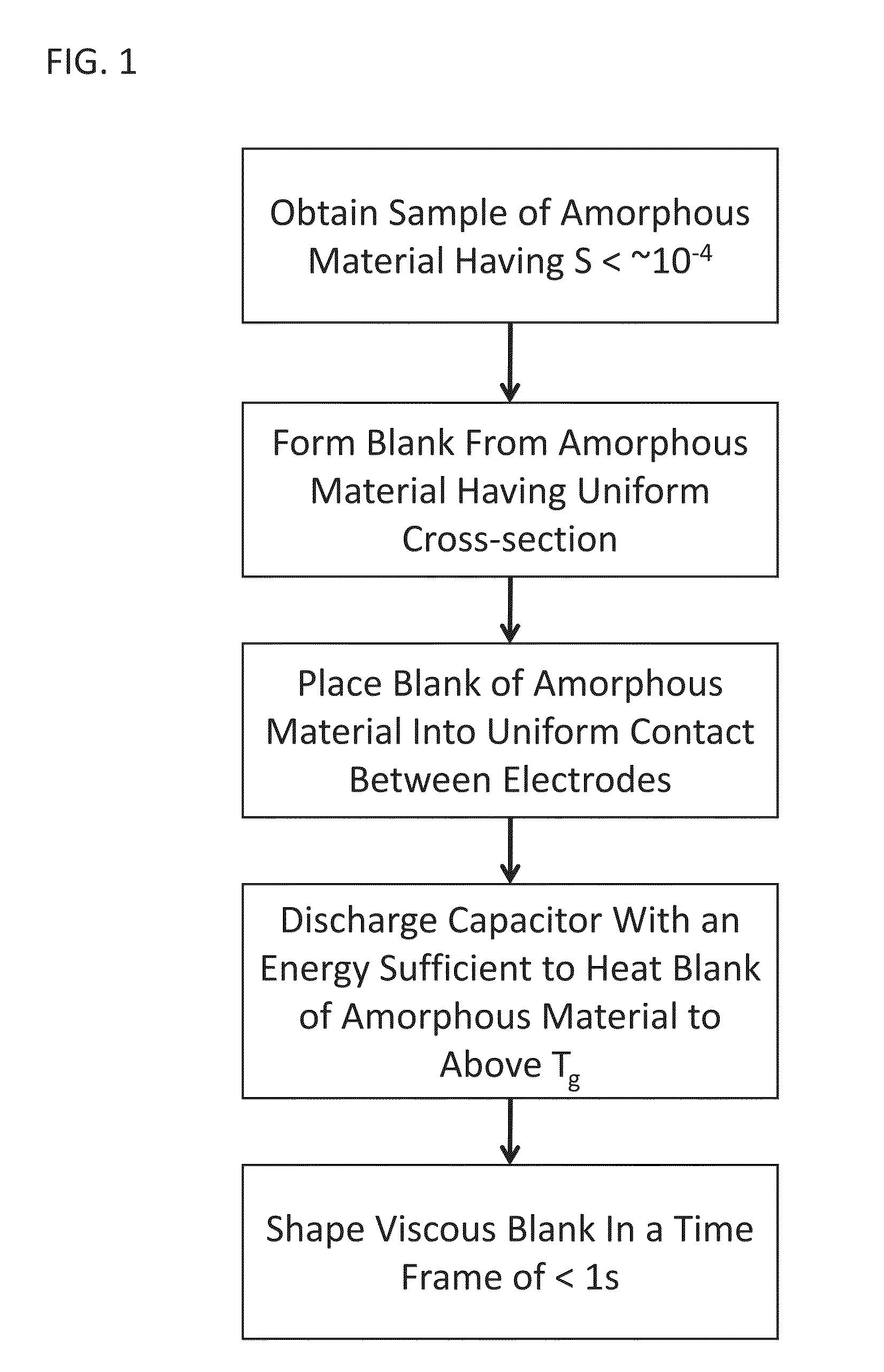
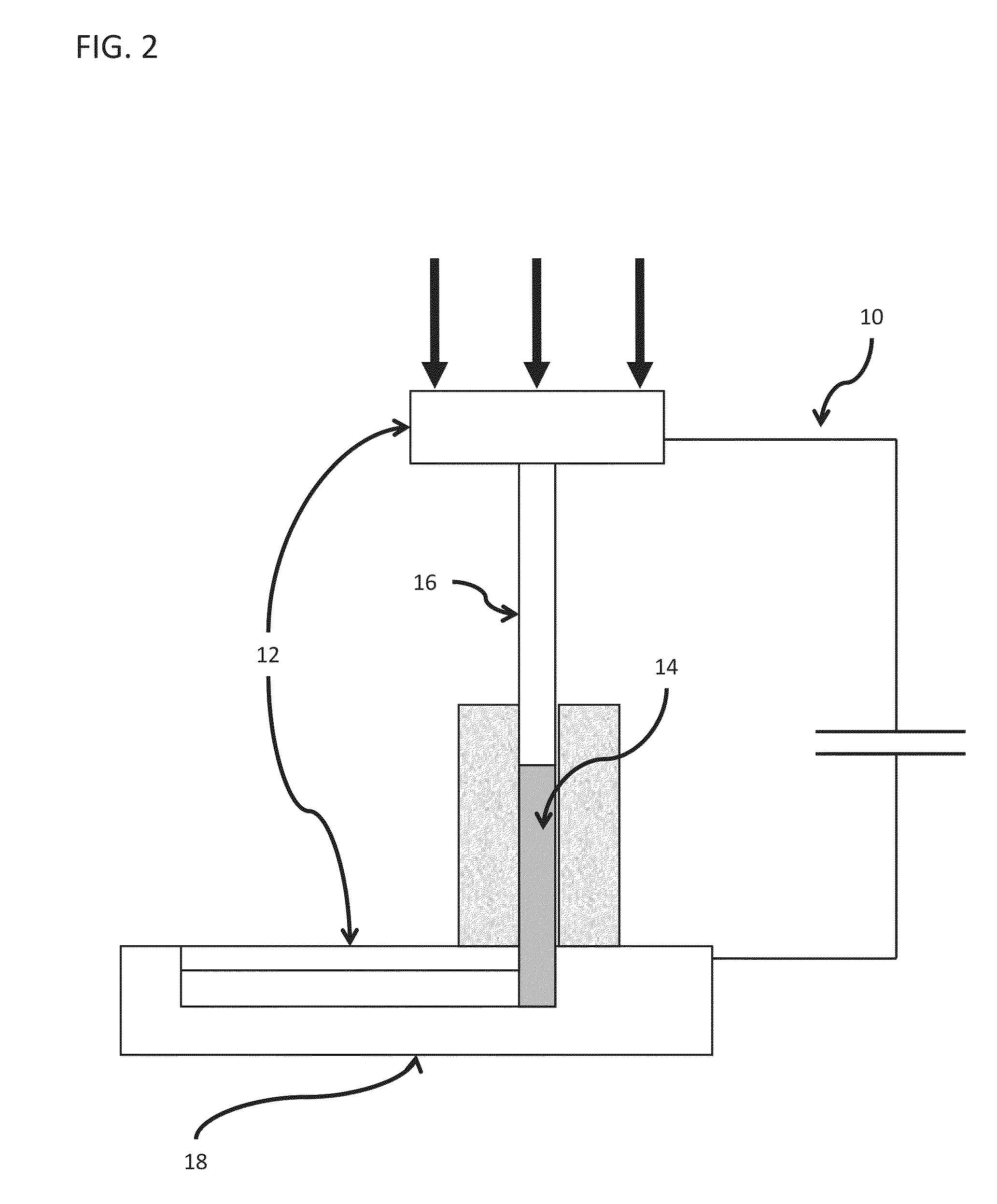
Forming of metallic glass by rapid capacitor discharge
ActiveUS20090236017A1Avoid failureAvoid thermal transport and development of thermalDielectric heatingShaping toolsAlloyGlass transition
An apparatus and method of uniformly heating, rheologically softening, and thermoplastically forming metallic glasses rapidly into a net shape using a rapid capacitor discharge forming (RCDF) tool are provided. The RCDF method utilizes the discharge of electrical energy stored in a capacitor to uniformly and rapidly heat a sample or charge of metallic glass alloy to a predetermined “process temperature” between the glass transition temperature of the amorphous material and the equilibrium melting point of the alloy in a time scale of several milliseconds or less. Once the sample is uniformly heated such that the entire sample block has a sufficiently low process viscosity it may be shaped into high quality amorphous bulk articles via any number of techniques including, for example, injection molding, dynamic forging, stamp forging, and blow molding in a time frame of less than 1 second.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
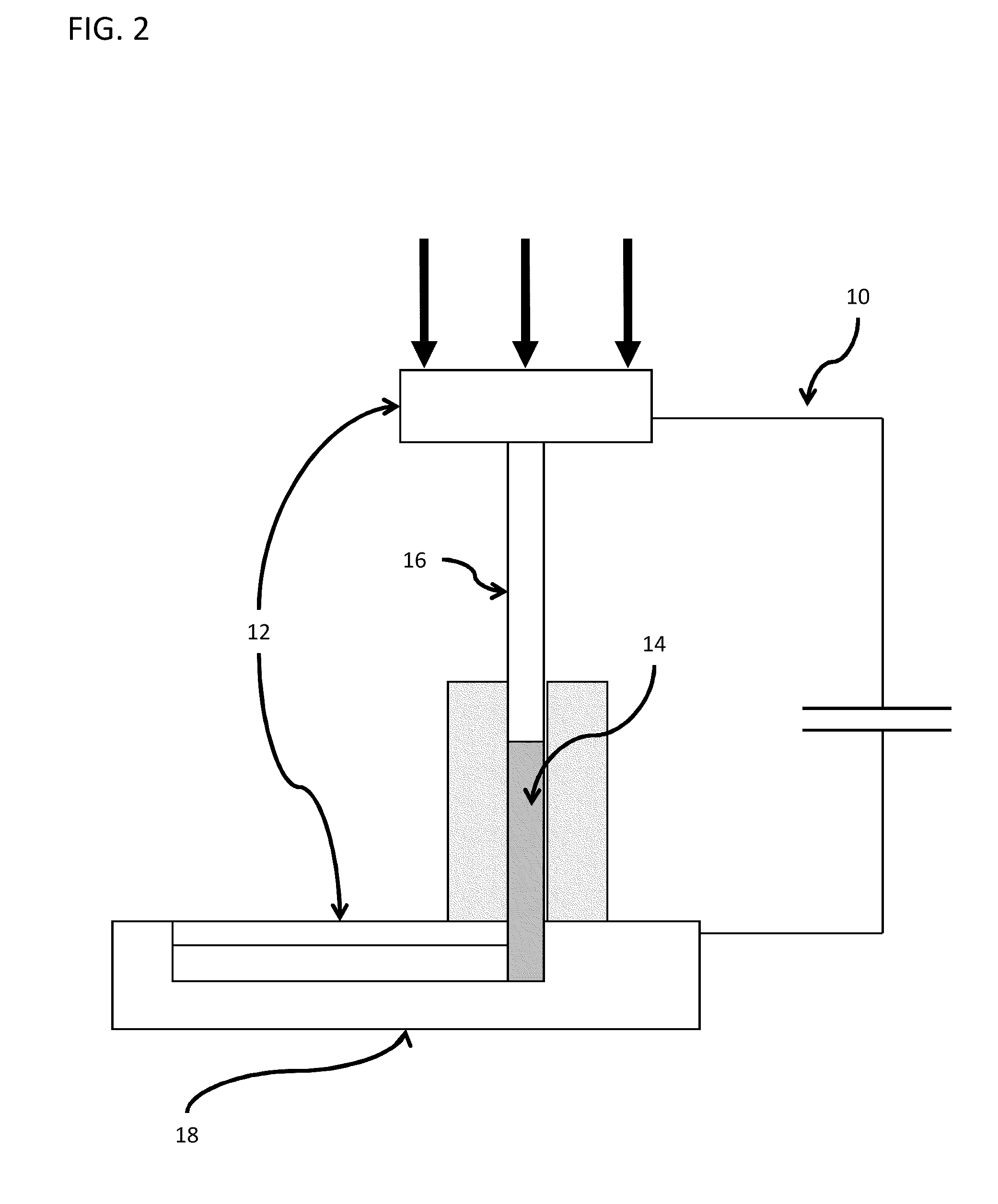
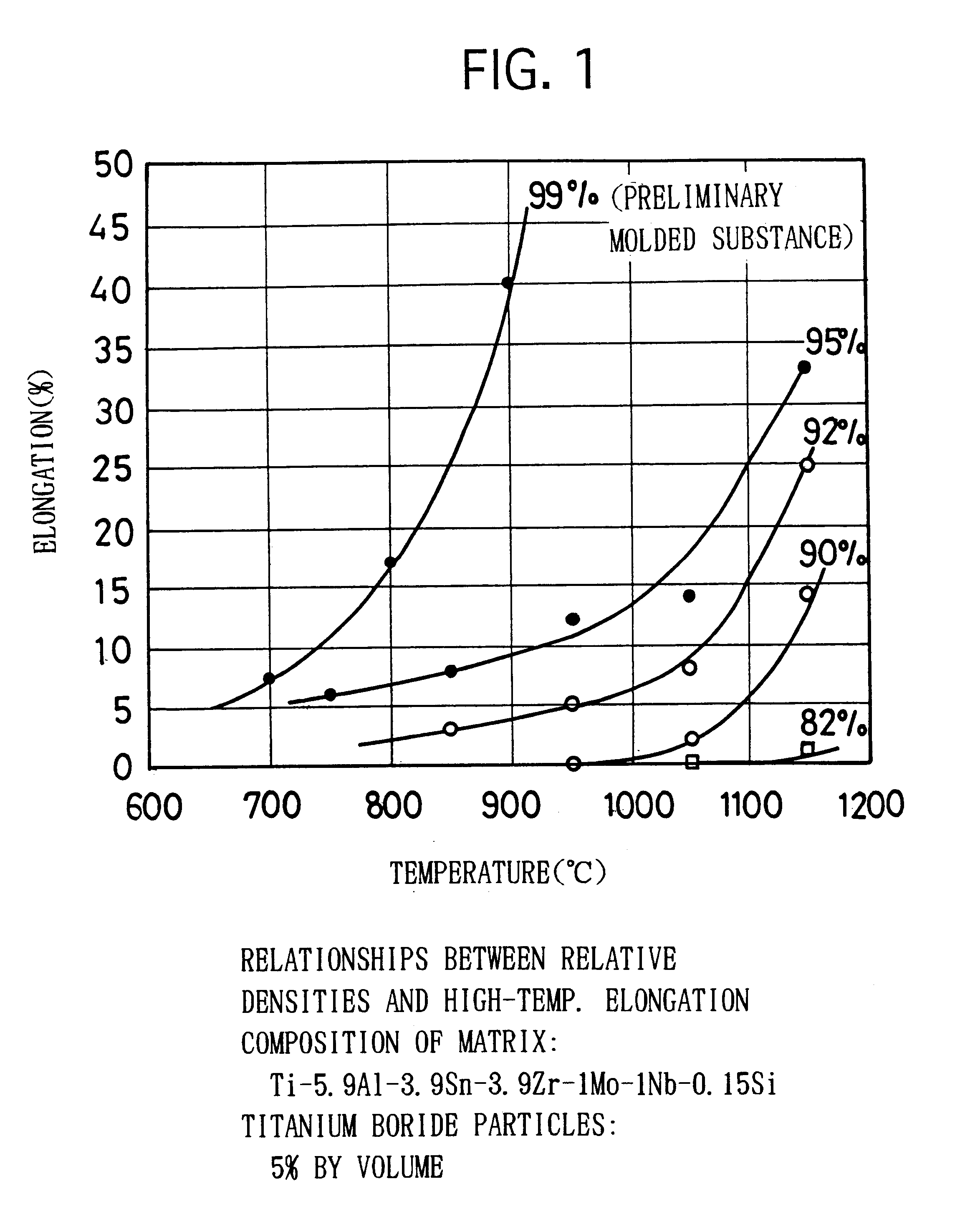
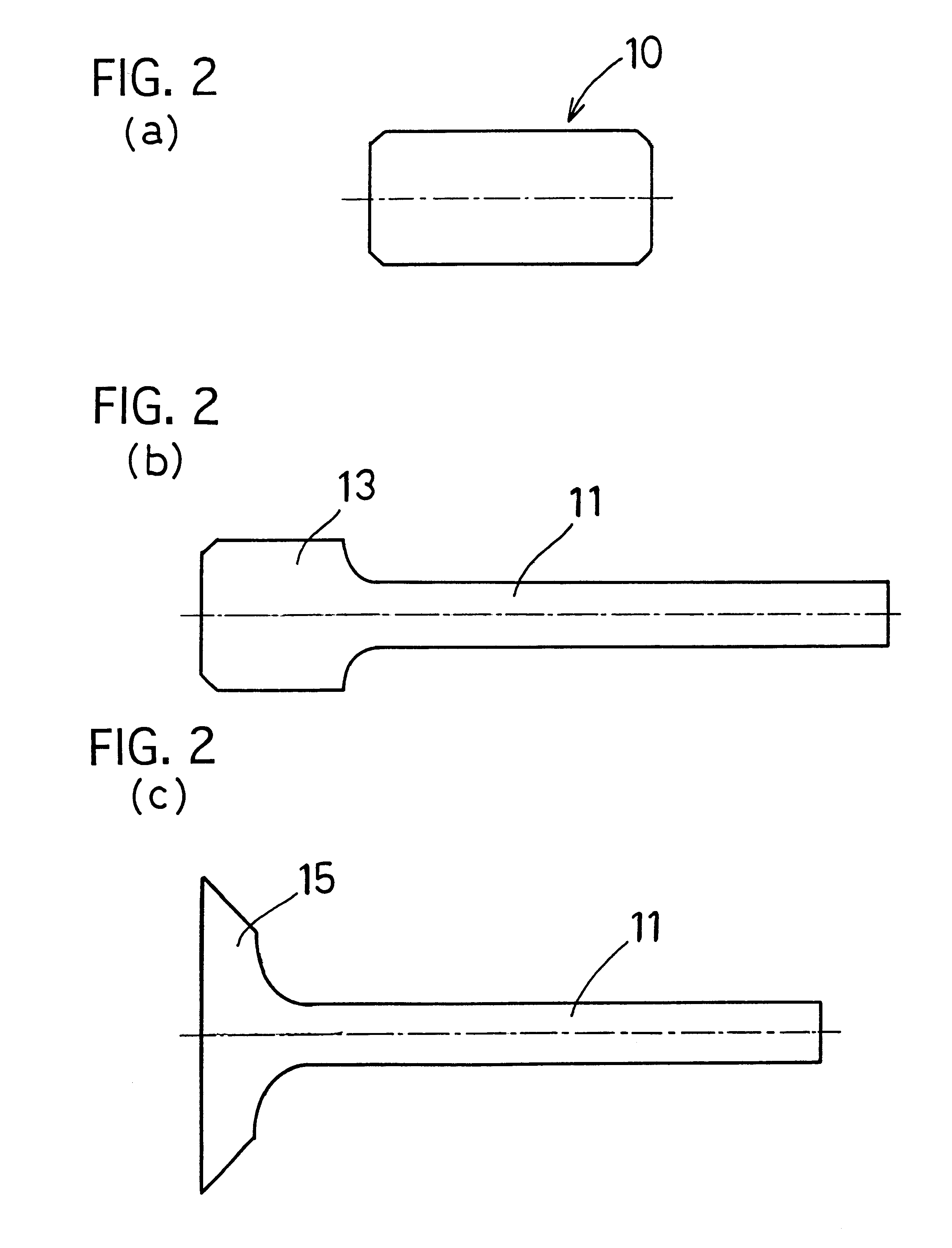
Process for forging titanium-based material, process for producing engine valve, and engine valve
InactiveUS6599467B1Degradation can be suppressedReduced strengthMetal-working apparatusMachines/enginesTitaniumEngine valve
The invention provides a process for forging a titanium-based material comprises the steps of: preparing a titanium-based sintered workpiece including at least one of ceramics particles and pores in a total amount of 1% or more by volume, the ceramics particles being thermodynamically stable in a titanium alloy; and heating the workpiece to a forging temperature and forging the same. In the production process, the pores or the ceramics particles inhibit the grain growth during forging. Accordingly, it is possible to carry out the forging at a relatively high temperature at which the titanium-based material exhibits a small resistance to deformation. Moreover, the titanium-based material can maintain an appropriate microstructure even after the forging. Consequently, the impact value and the fatigue strength are inhibited from decreasing.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
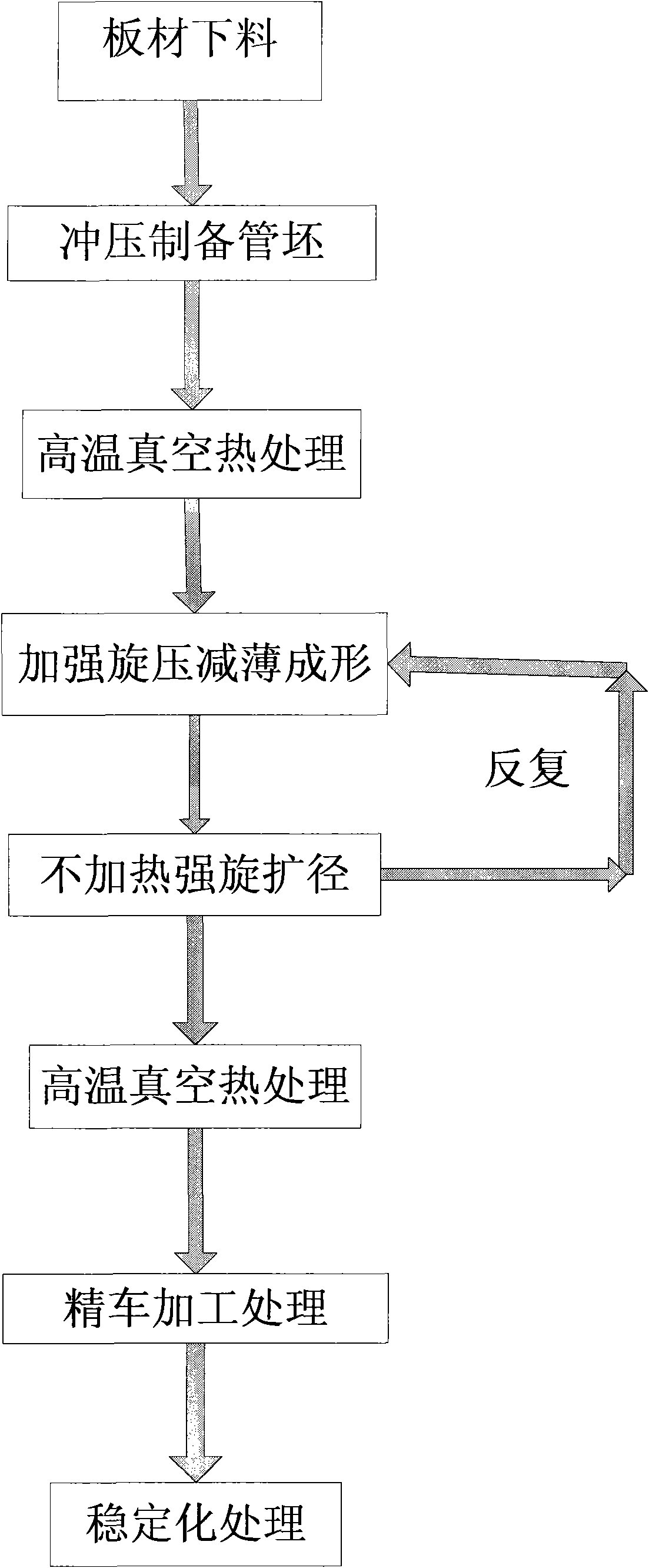
Integral forming method of large size thin-walled titanium alloy cylindrical part without welding line
ActiveCN101579804ASolve UtilizationSolving with longitudinal weldsFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesThinningLarge size
The invention provides an integral forming method of a large size thin-walled titanium alloy cylindrical part without a welding line. The integral forming method comprises the following steps of: (1) tube blank preparation by stamping; (2) high-temperature vacuum heat treatment; (3) heating power spinning thinning; (4) unheating power spinning diameter expanding; (5) repetitive and alternate conduction of steps (3) and (4) for 2-3 times; (6) high-temperature vacuum heat treatment; (7) finish turning treatment; and (8) stabilizing treatment. The integral forming method prepares the large size thin-walled titanium alloy cylindrical part without the welding line (wall thickness is 1-7mm) which has high precision and high performance by utilizing titanium alloy plates and adopting a composite technique combining a stamping method, a spinning method and a stabilizing treatment method, and solves the problems of low material utilization ratio, having longitudinal welding lines, low precision of tube performance and the like in the forging and roll bending welding forming of the large size titanium alloy thin-walled tubes.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH
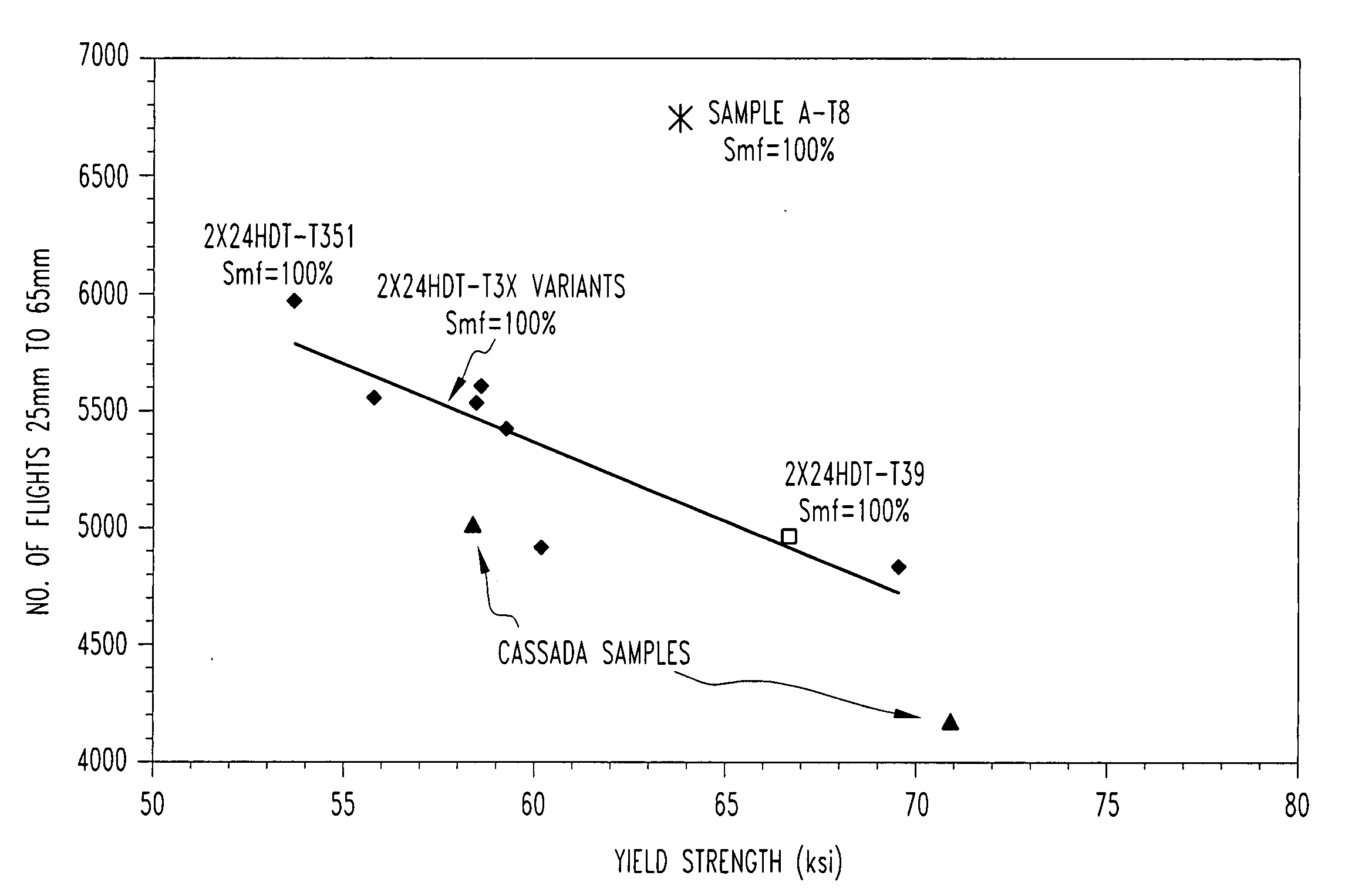
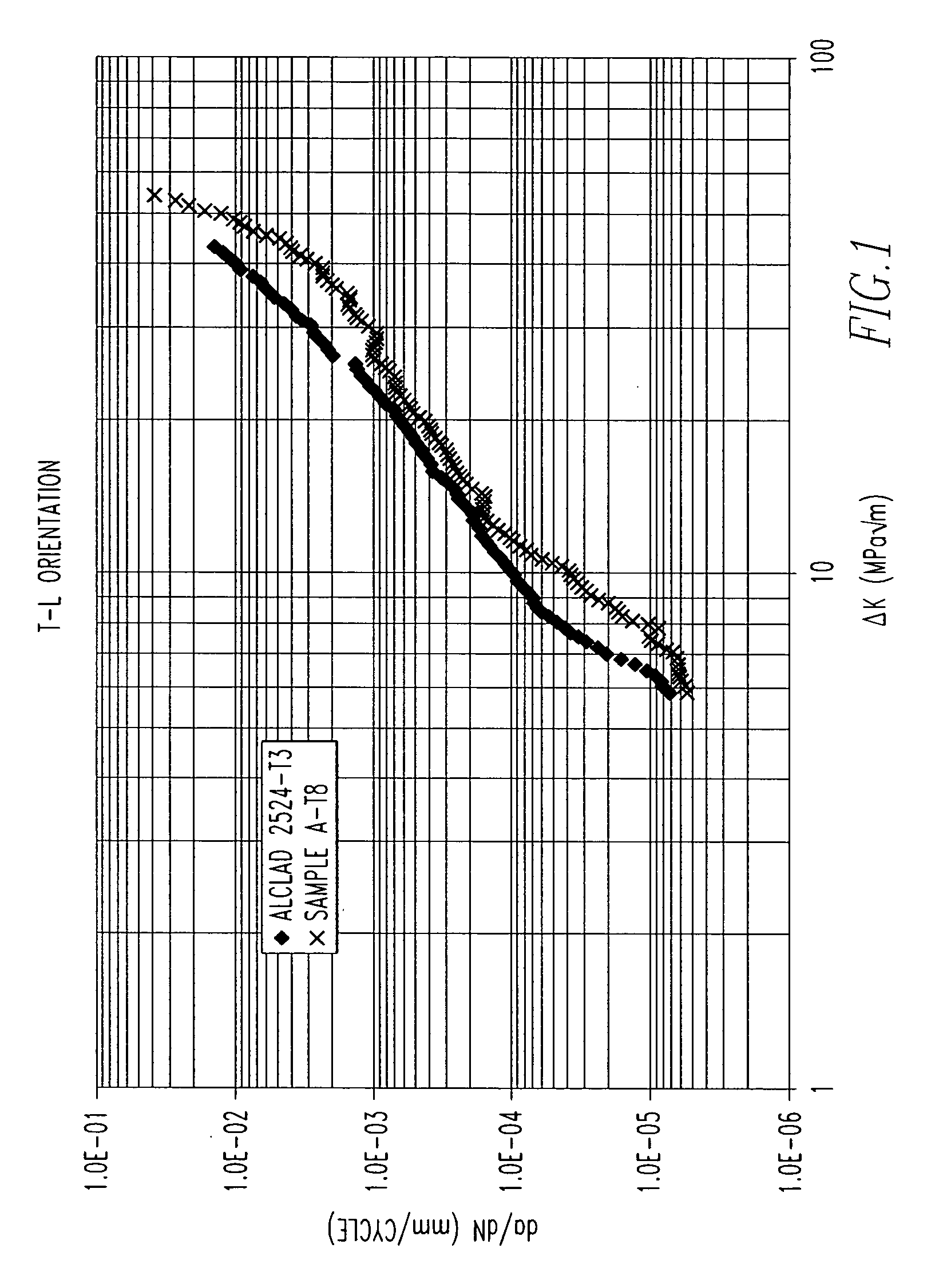
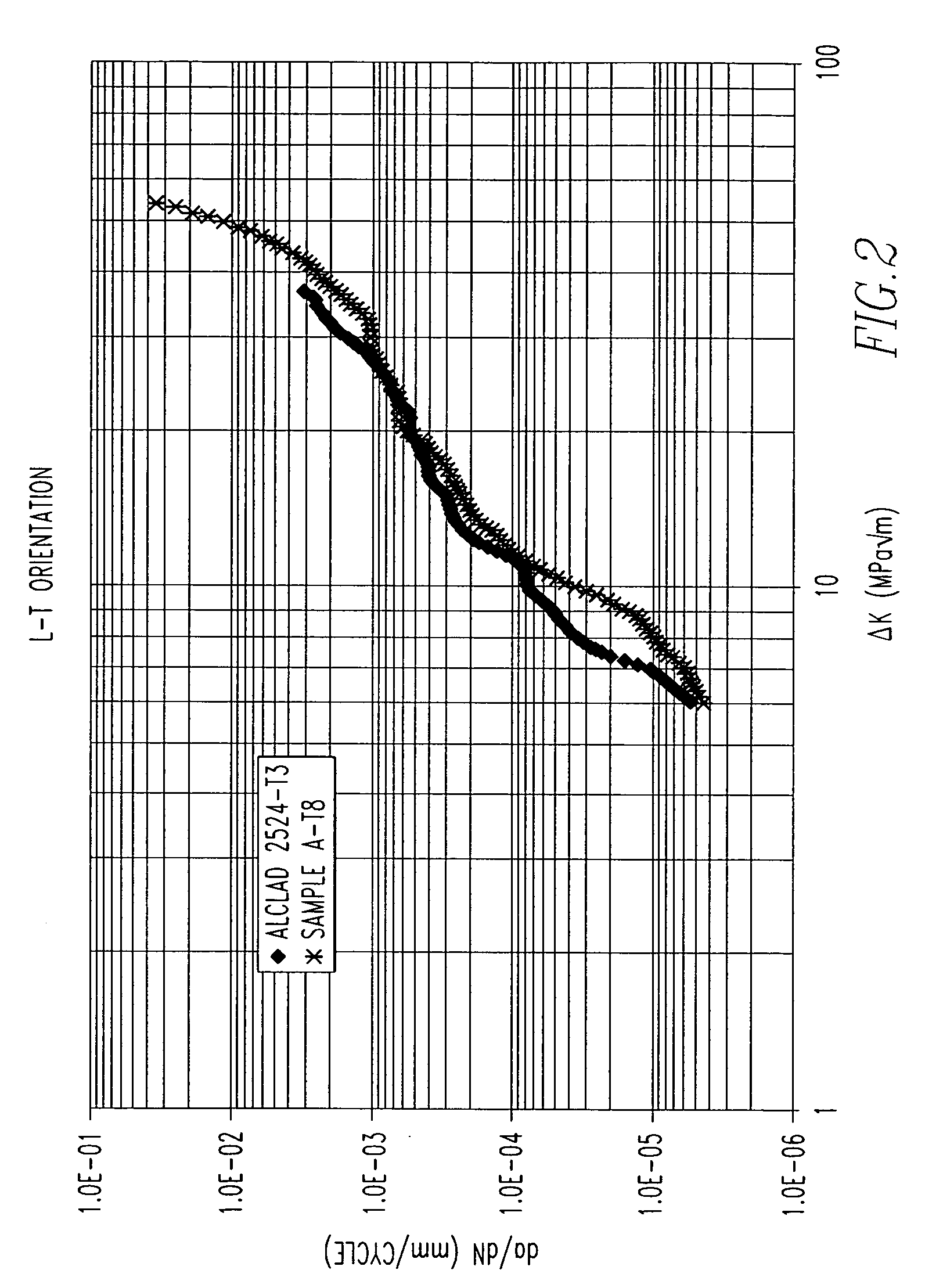
2000 Series alloys with enhanced damage tolerance performance for aerospace applications
The invention provides a 2000 series aluminum alloy having enhanced damage tolerance, the alloy consisting essentially of about 3.0-4.0 wt % copper; about 0.4-1.1 wt % magnesium; up to about 0.8 wt % silver; up to about 1.0 wt % Zn; up to about 0.25 wt % Zr; up to about 0.9 wt % Mn; up to about 0.5 wt % Fe; and up to about 0.5 wt % Si, the balance substantially aluminum, incidental impurities and elements, said copper and magnesium present in a ratio of about 3.6-5 parts copper to about 1 part magnesium. The alloy is suitable for use in wrought or cast products including those used in aerospace applications, particularly sheet or plate structural members, extrusions and forgings, and provides an improved combination of strength and damage tolerance.
Owner:ARCONIC TECH LLC
Aluminum alloy having superior strength-toughness combinations in thick gauges
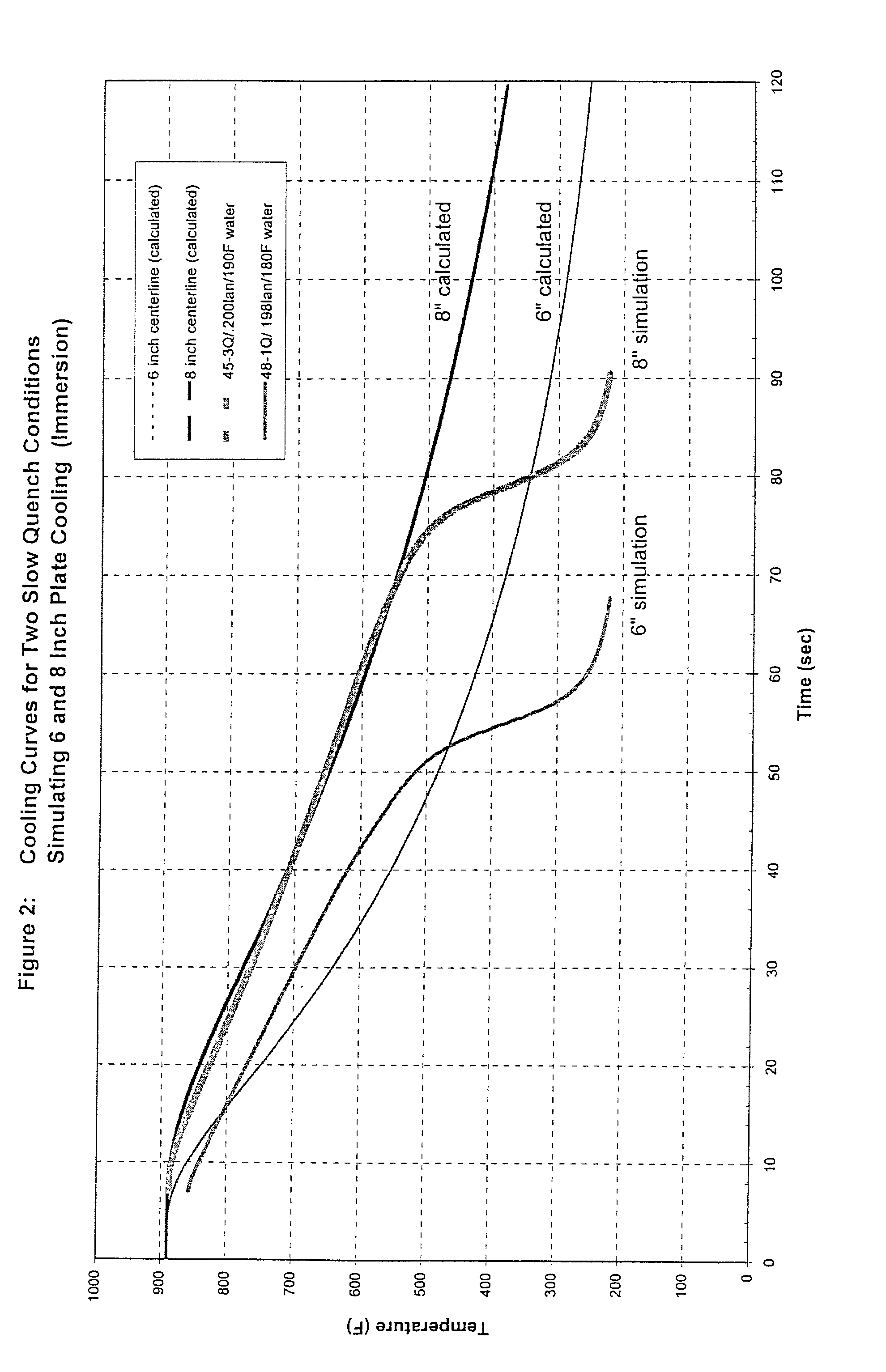
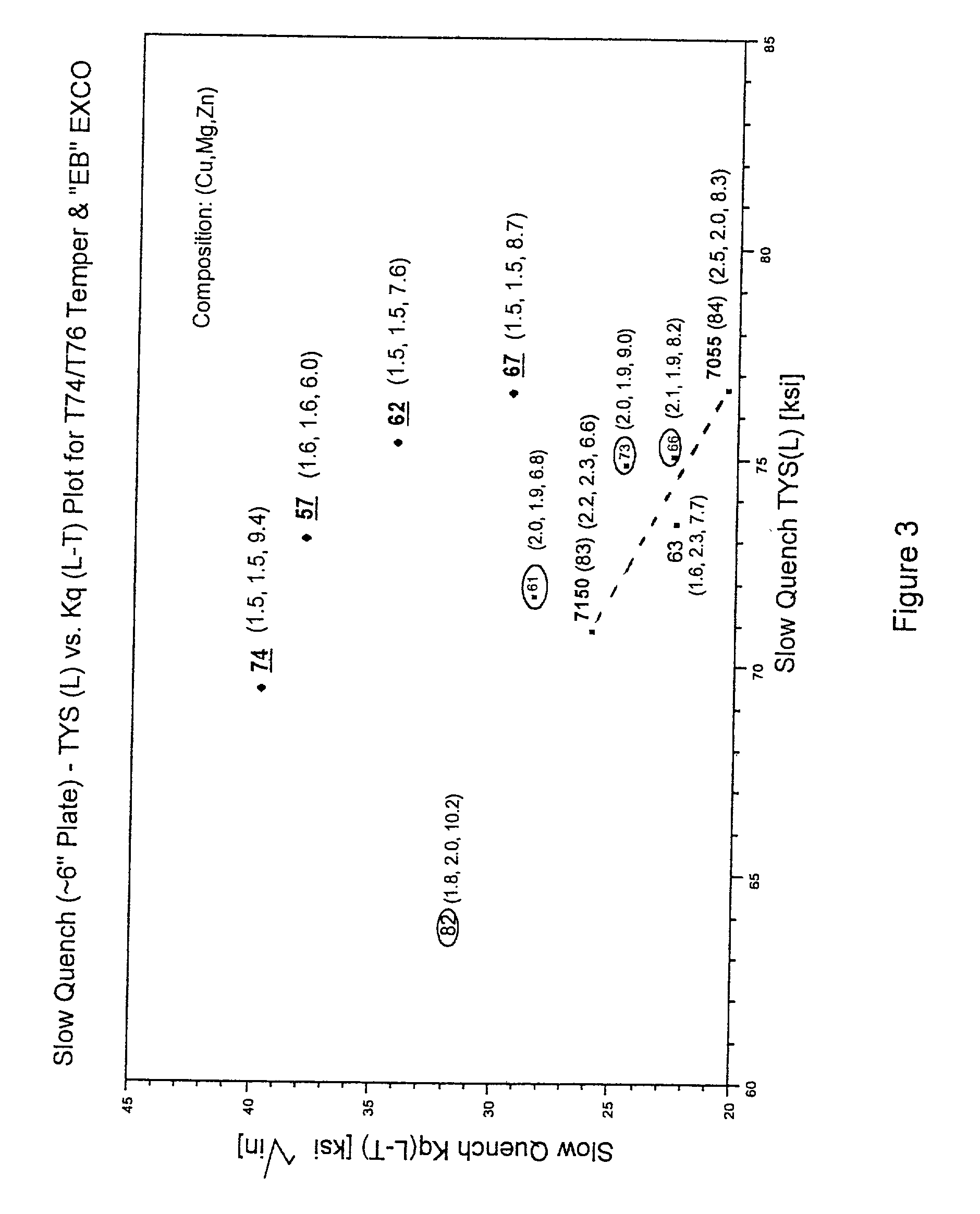
A 7XXX series aluminum alloy having reduced quench sensitivity suitable for use in aerospace structural components, such as integral wing spars, ribs, extrusions and forgings comprises, in weight %: 6 to 10 Zn, 1.3 to 1.9 Mg, 1.4 to 2.2 Cu, wherein Mg<=Cu+0.3, one or more of 0 to 0.4 Zr, up to 0.4 Sc, up to 0.2 Hf, up to 0.4 Cr, up to 1.0 Mn and the balance Al plus incidental additions including Si, Fe, Ti and the like plus impurities. By controlling the Mg content to 1.3 to 1.7 wt. %, limiting Mg<=Cu+0.3 and 6.5<=Zn<=8.5, the alloy provides significantly improved combined strength and fracture toughness in heavy gauges. For example, in a six-inch thick plate there is provided a combination of about 75 ksi quarter-plane tensile yield strength (L) with a fracture toughness (L-T) of about 33 ksi{square root}in which progresses by artificial aging / tempering to a combined strength and fracture toughness of about 67 ksi tensile yield strength (L) and a fracture toughness (L-T) of about 40 ksi{square root}in. The alloy product possesses equally attractive combinations of strength and fracture toughness when intentionally quenched slowly following solution heat treatment so as to lessen dimensional distortion, particularly in shapes of varying cross section.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
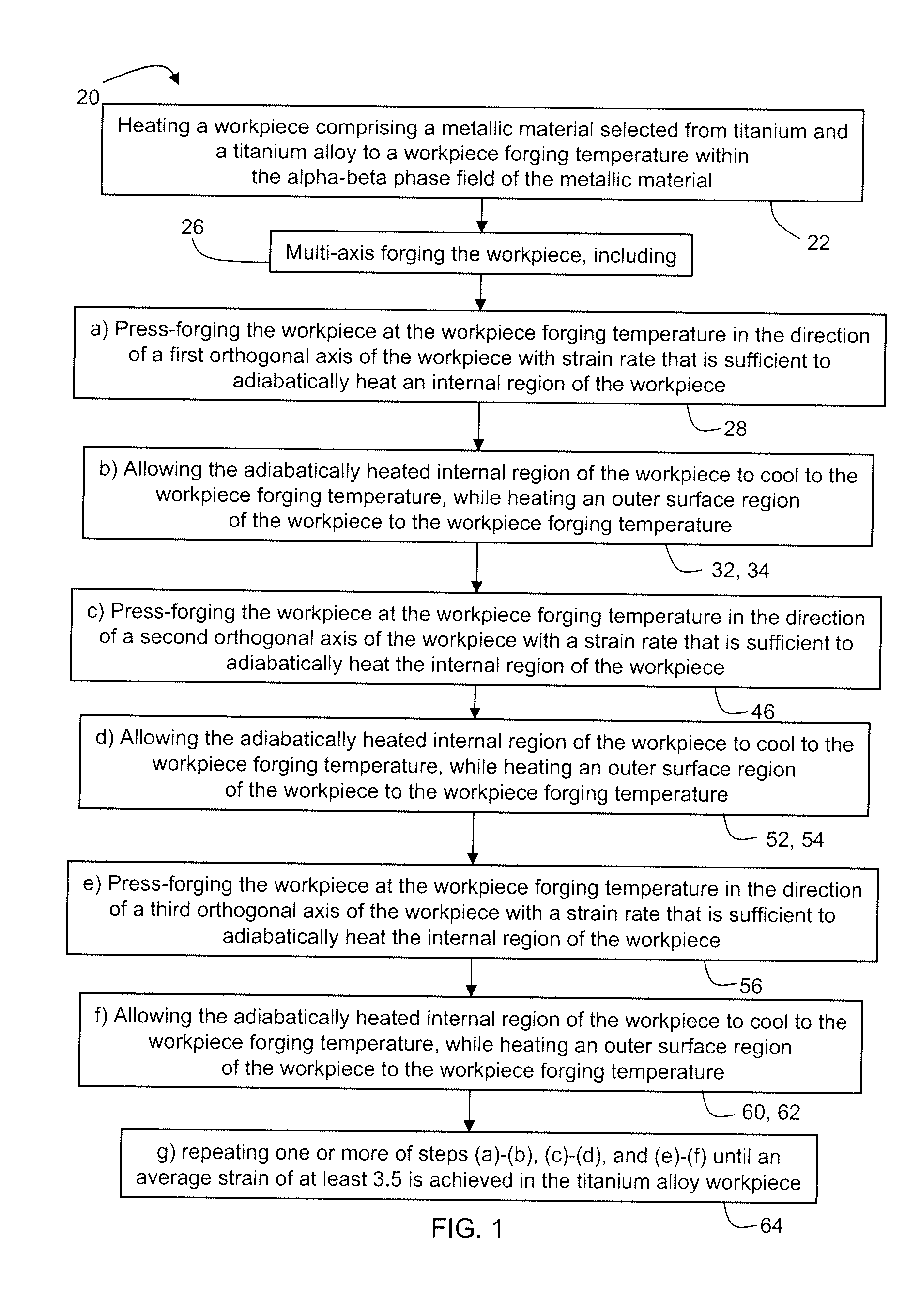
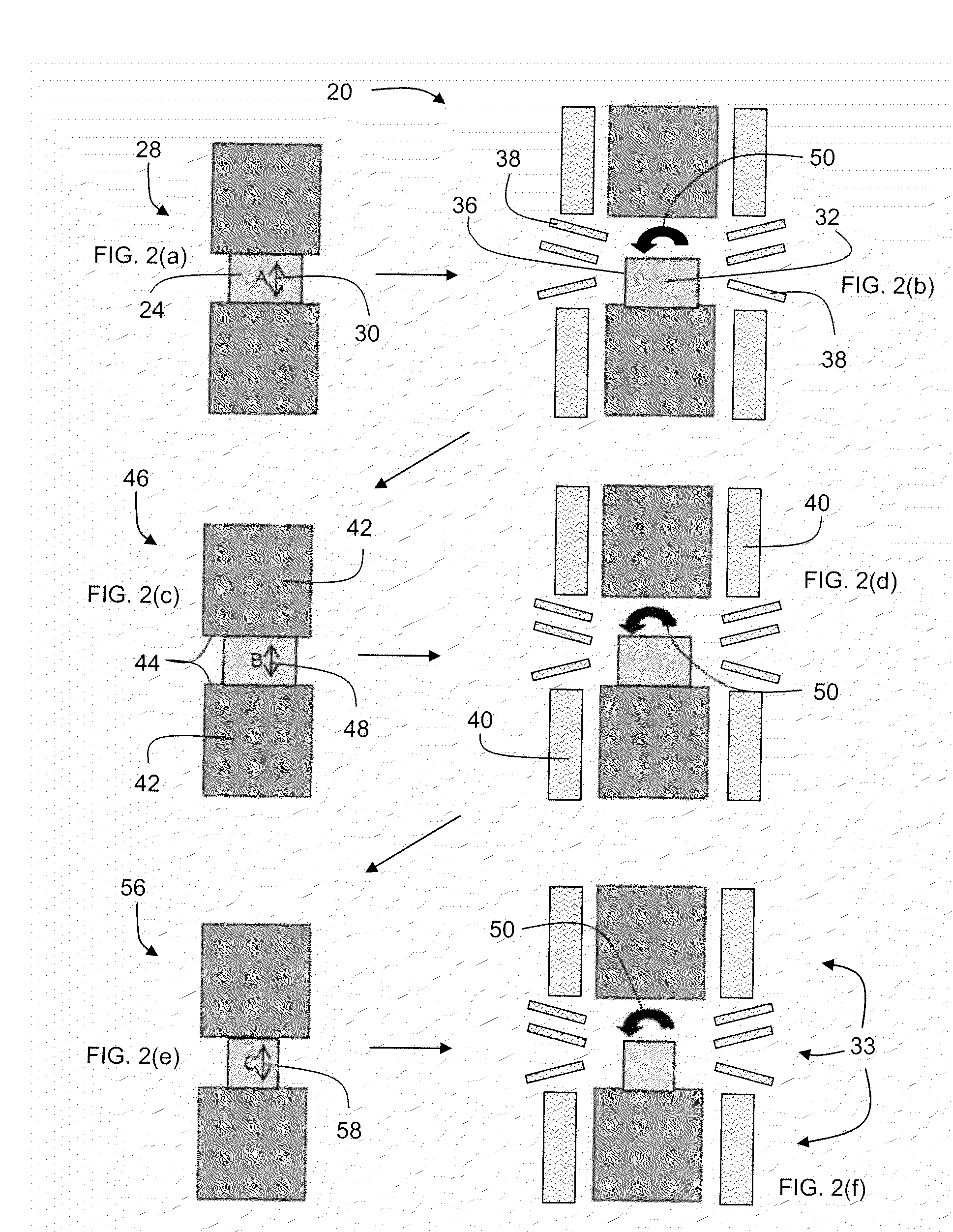
Processing Routes for Titanium and Titanium Alloys
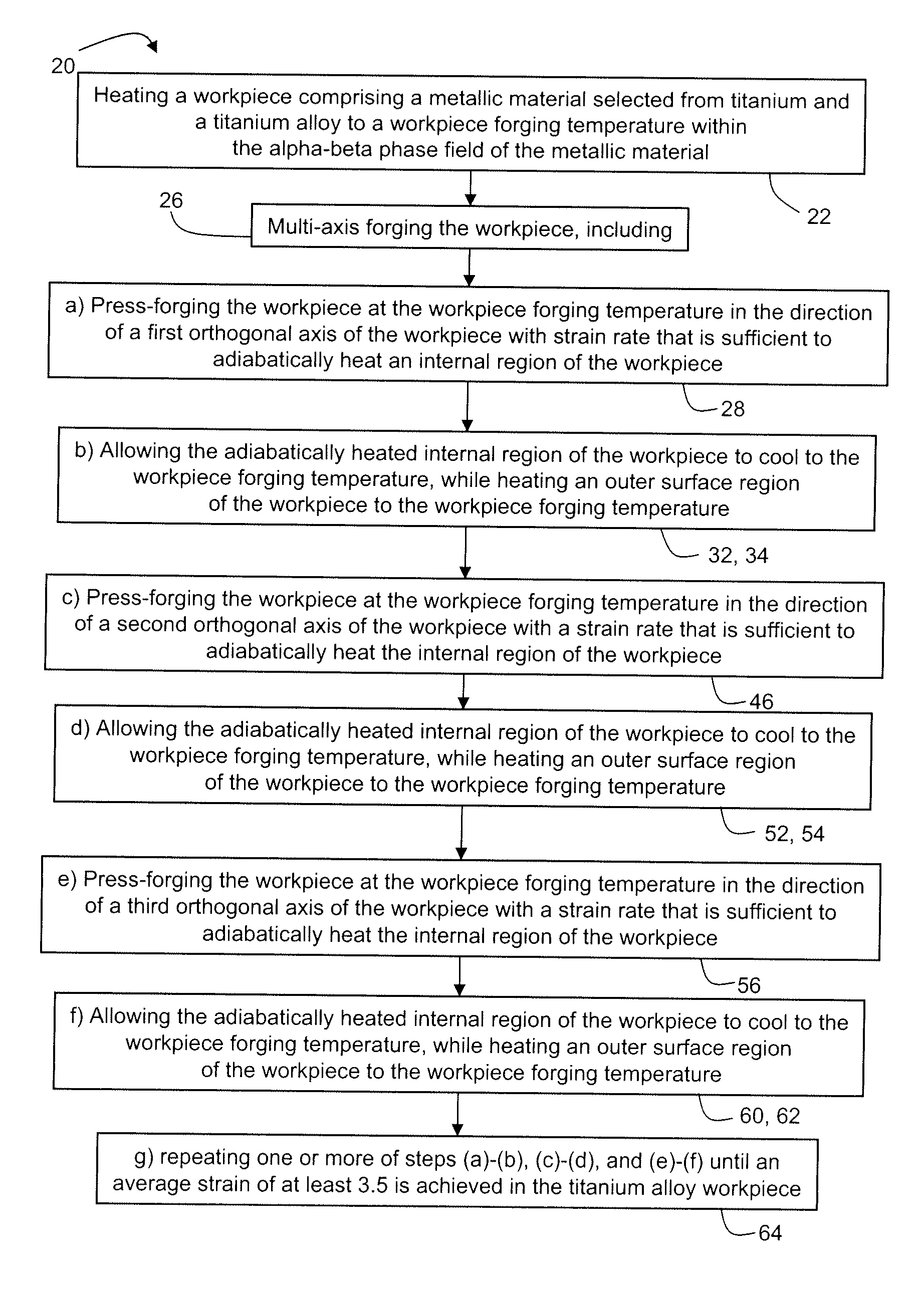
Methods of refining the grain size of titanium and titanium alloys include thermally managed high strain rate multi-axis forging. A high strain rate adiabatically heats an internal region of the workpiece during forging, and a thermal management system is used to heat an external surface region to the workpiece forging temperature, while the internal region is allowed to cool to the workpiece forging temperature. A further method includes multiple upset and draw forging titanium or a titanium alloy using a strain rate less than is used in conventional open die forging of titanium and titanium alloys. Incremental workpiece rotation and draw forging causes severe plastic deformation and grain refinement in the titanium or titanium alloy forging.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES LLC
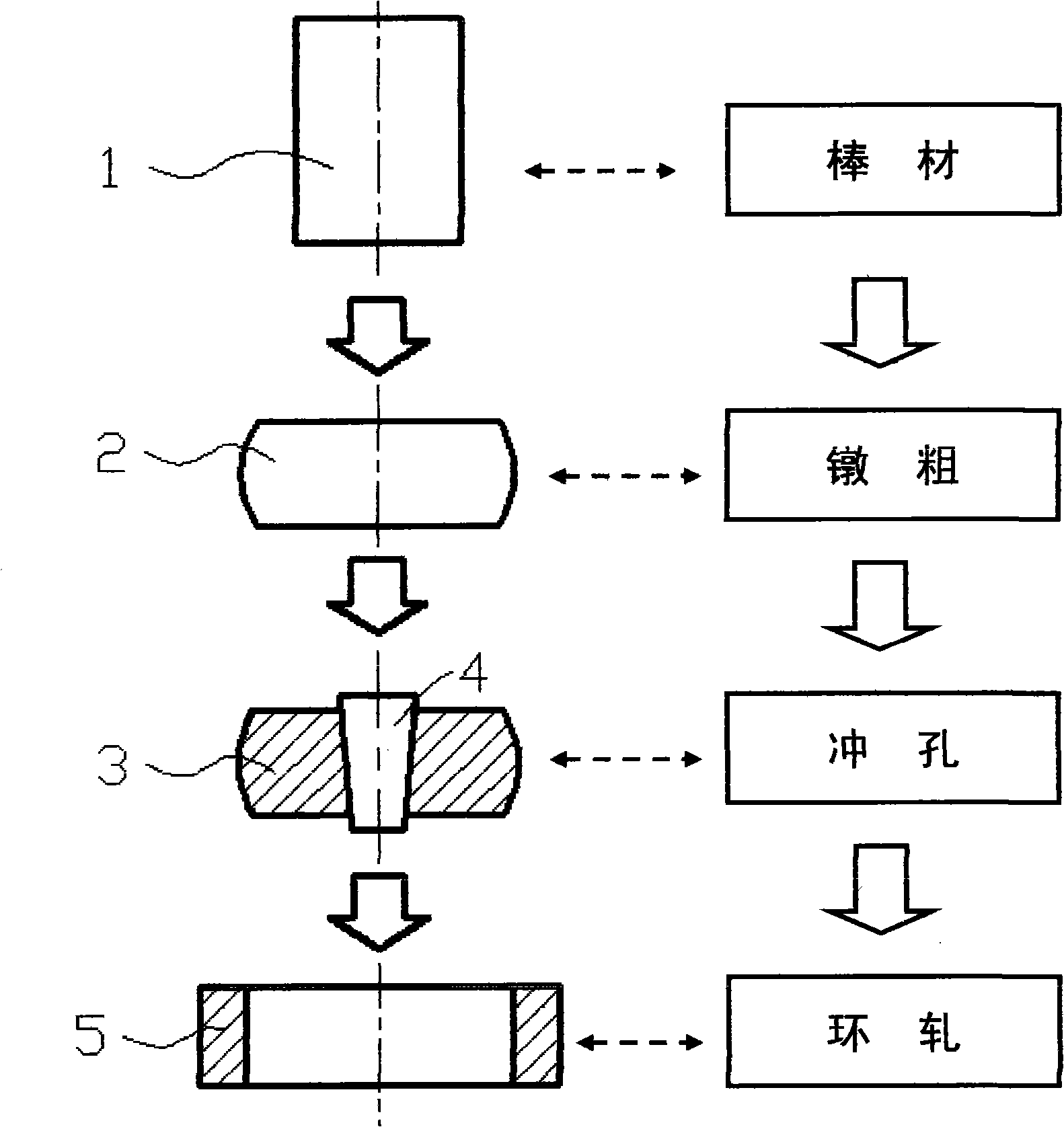
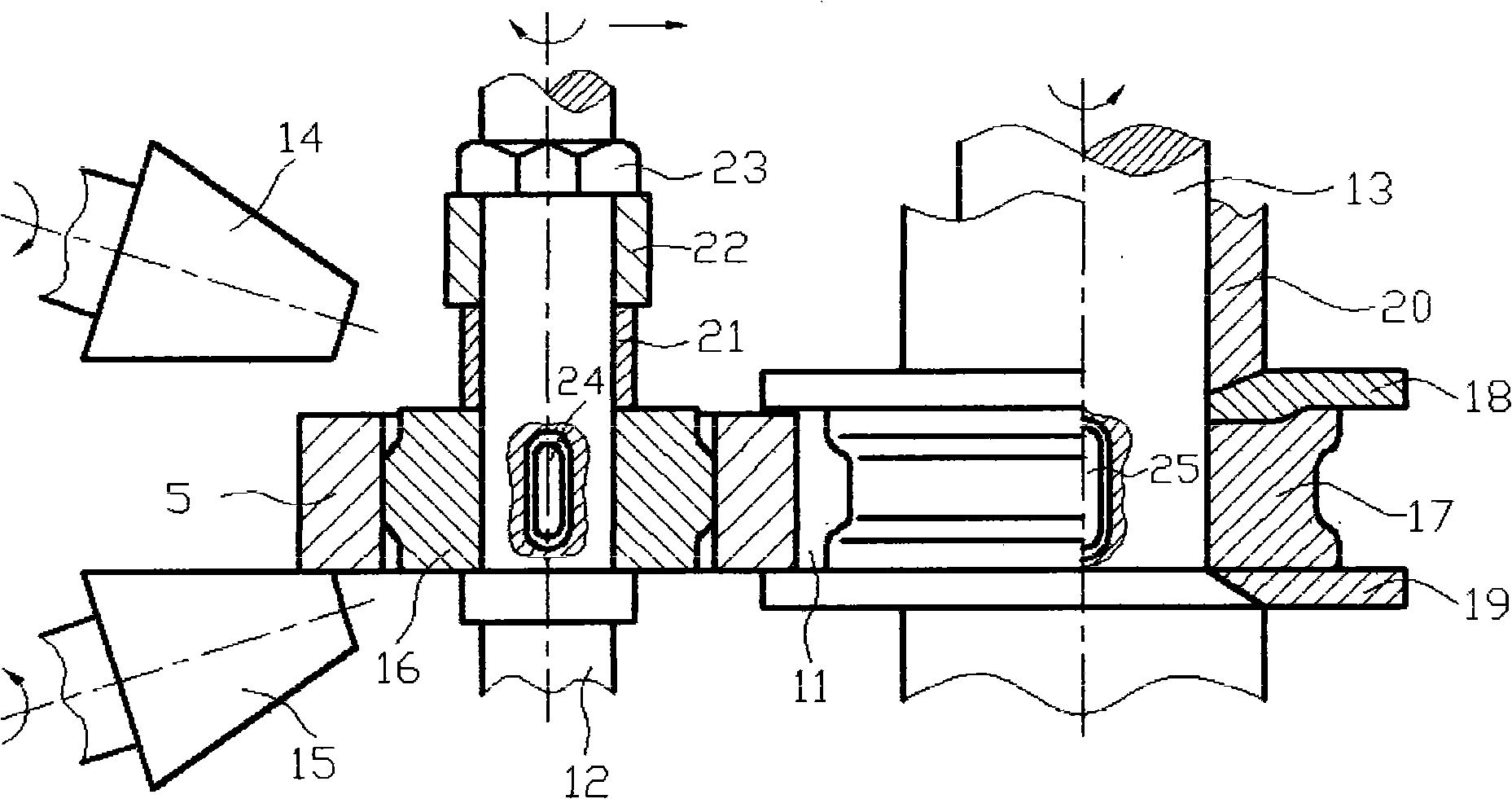
Method for rolling and shaping stainless steel special-shaped ring forging
The invention discloses a rolling and shaping method for a stainless steel heterotypic ring forging in order to obtain the alloy heterotypic ring forgings with excellent tissues and properties as well as realize accurate rolling. The method includes the following steps: alloy bar material is heated, carried out continuous upsetting and deformed by 50 to 55 percent, so as to be made into a solid cake and then is punched again to lead the alloy bar material to be made into a hollow round cake after the aperture dimension of the alloy bar material is 30 to 35 percent of the dimension of the outer diameter thereof; a rectangle pre-rolling blank is obtained after the hollow round cake is heated, rolled circularly and deformed by 40 to 45 percent; the pre-rolling blank is heated and arranged in a rolling die of a ring rolling machine and forms a heterotypic ring forging after being rolled and deformed by 50 to 55 percent in a section groove. When in expansion, the broadening speed of the pre-rolling blank along the radial direction is 2mm / s to 15mm / s with radial rolling force of 20000kg to 120000kg. The method is mainly used for the shaping of the heterotypic ring forging of an aeroengine. The method can be adopted to obtain the heterotypic ring forging that is arranged in a flow line along the outline of a part.
Owner:GUIZHOU ANDA AVIATION FORGING
Variable density golf club
InactiveUS7815523B2Improving the club head moment of inertiaEnlarging the sweet spotGolf clubsRacket sportsHeel-and-toeMoment of inertia
A golf club head having portions of varying density is disclosed and claimed. The club head includes a body with a recess in the back between the heel and toe and extending toward the sole. An insert that is configured to matingly correspond to the recess is positioned within the recess. The insert has a lower specific gravity than the club head body, biasing the club head mass toward the club head perimeter. The insert can form a muscle of the club head. The club head is forged, and the recess is formed by machining. After the insert is positioned within the recess, the club head-insert combination is subjected to additional forging and finishing steps. The present invention increases the club head moment of inertia and / or enlarges the club head sweet spot while retaining the golfer's ability to work the golf ball and shape the golf shot. The present invention can be used with forged, blade, and muscle back clubs, which have not heretofore been enhanced in these manners.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Thermal module
InactiveUS7845393B2Uniform and tight crystal phase structureImprove cooling efficiencyLayered productsDigital data processing detailsMetalThermal conductivity
A thermal module includes a body press-forged from magnesium alloy that is heated to a softened status and having a peripheral wall and a recessed chamber surrounded by the peripheral wall, and a contact surface member prepared from a high thermal conductivity metal material and bonded to the recessed chamber of the body during press-forging of the body.
Owner:JIING TUNG TEC METAL
Method for rolling and shaping titanium alloy special-shaped ring forging
ActiveCN101279345AReduce manufacturing costHigh dimensional accuracyMetal rollingTitanium alloyAbnormal shaped
The invention discloses a rolling and shaping method for a titanium alloy heterotypic ring forging in order to obtain the alloy heterotypic ring forgings with excellent tissues and properties as well as realize accurate rolling. The method includes the following steps: alloy bar material is heated, carried out continuous upsetting and deformed by 65 to 70 percent, so as to be made into a solid cake and then is punched again to lead the alloy bar material to be made into a hollow round cake after the aperture dimension of the alloy bar material is 30 to 35 percent of the dimension of the outer diameter thereof; a rectangle ring blank is obtained after the hollow round cake is heated, rolled circularly and deformed by 25 to 30 percent; a rectangle pre-rolling blank is obtained after the rectangle ring blank is heated, rolled circularly and deformed by 25 to 30 percent again; the pre-rolling blank is heated and arranged in a rolling die of a ring rolling machine and becomes a heterotypic ring forging after being rolled and deformed by 40 to 45 percent in a section groove of the die. When in expansion, the broadening speed of the pre-rolling blank along the radial direction is 2mm / s to 15mm / s with a radial rolling force of 40000kg to 220000kg. The method is mainly used for the shaping of the heterotypic ring forging of an aeroengine or a gas turbine. The method can be adopted to obtain the heterotypic ring forging that is arranged in a flow line along the outline of a part.
Owner:GUIZHOU ANDA AVIATION FORGING
Device for preparing semi-solid alloy rheological slurry or blank
ActiveCN101618438AOvercome the disadvantages of large and complex structure and high investment costLow investment costCrucibleSemi solid
The invention discloses a device for preparing semi-solid metal and alloy slurry, which mainly comprises an electromagnetic stirrer, an insulating layer, an external cooling controller, a valve, a draft tube, a preparation crucible, an insulating crucible cover, a standing crucible, a melting crucible and a thermocouple. The middle part of the preparation crucible is provided with an internal cooling controller, and the outer wall of the internal cooling controller forms a clearance with the inner wall of the preparation crucible. The device can be connected with a press-casting machine, an extruder, a continuous casting machine and a forging machine, wherein the press-casting machine consists of a press-casting fixed die, a press-casting movable die, an injection chamber and a punch head; the extruder consists of a right extrusion die profile, a left extrusion die profile, an extrusion cylinder and an extrusion rod; the continuous casting machine consists of a tundish, a crystallizer, a cooling water nozzle and a traction mechanism; and the forging machine consists of a forging die cavity and a forging die. The device has the advantages that the device has simple and compact structure, low investment cost and strong practicability; the temperature field and tissue of the prepared slurry are distributed evenly; the semi-solid alloy slurry is pure, does not bubble and has good self cleanness; and the device can produce large-specification semi-solid slurry or blank, and is quite suitable for the preparation and formation of the semi-solid slurry or the blank.
Owner:有研金属复材技术有限公司
Aluminum alloy forgings and process for production thereof
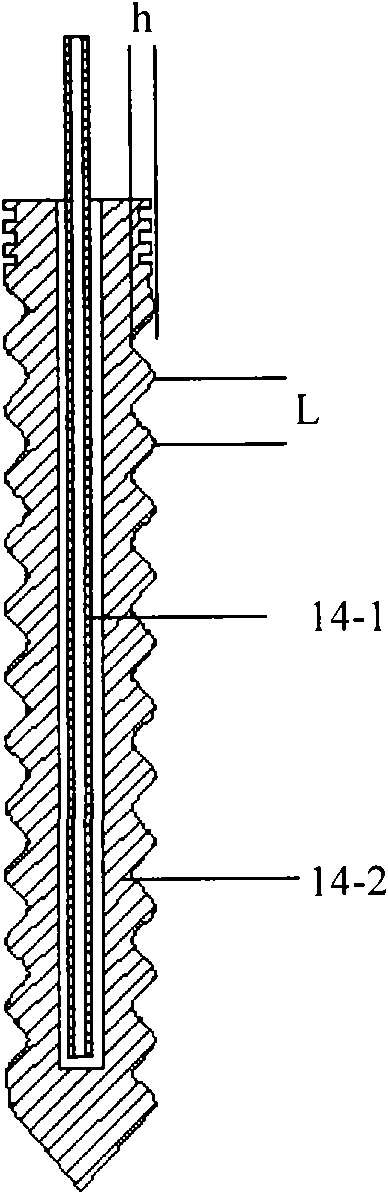
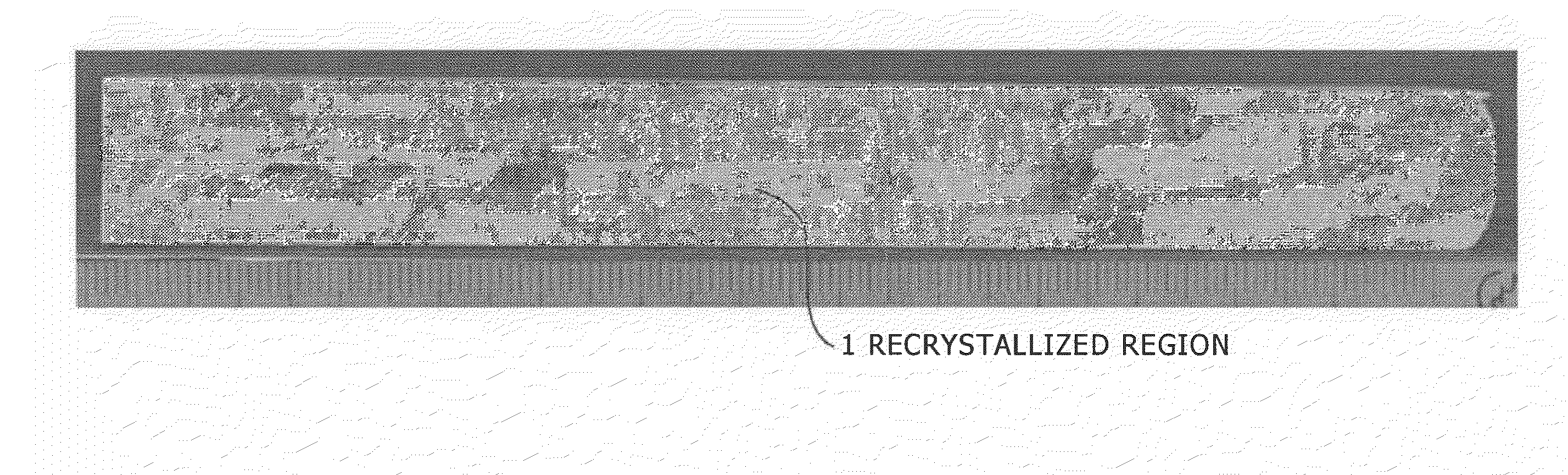
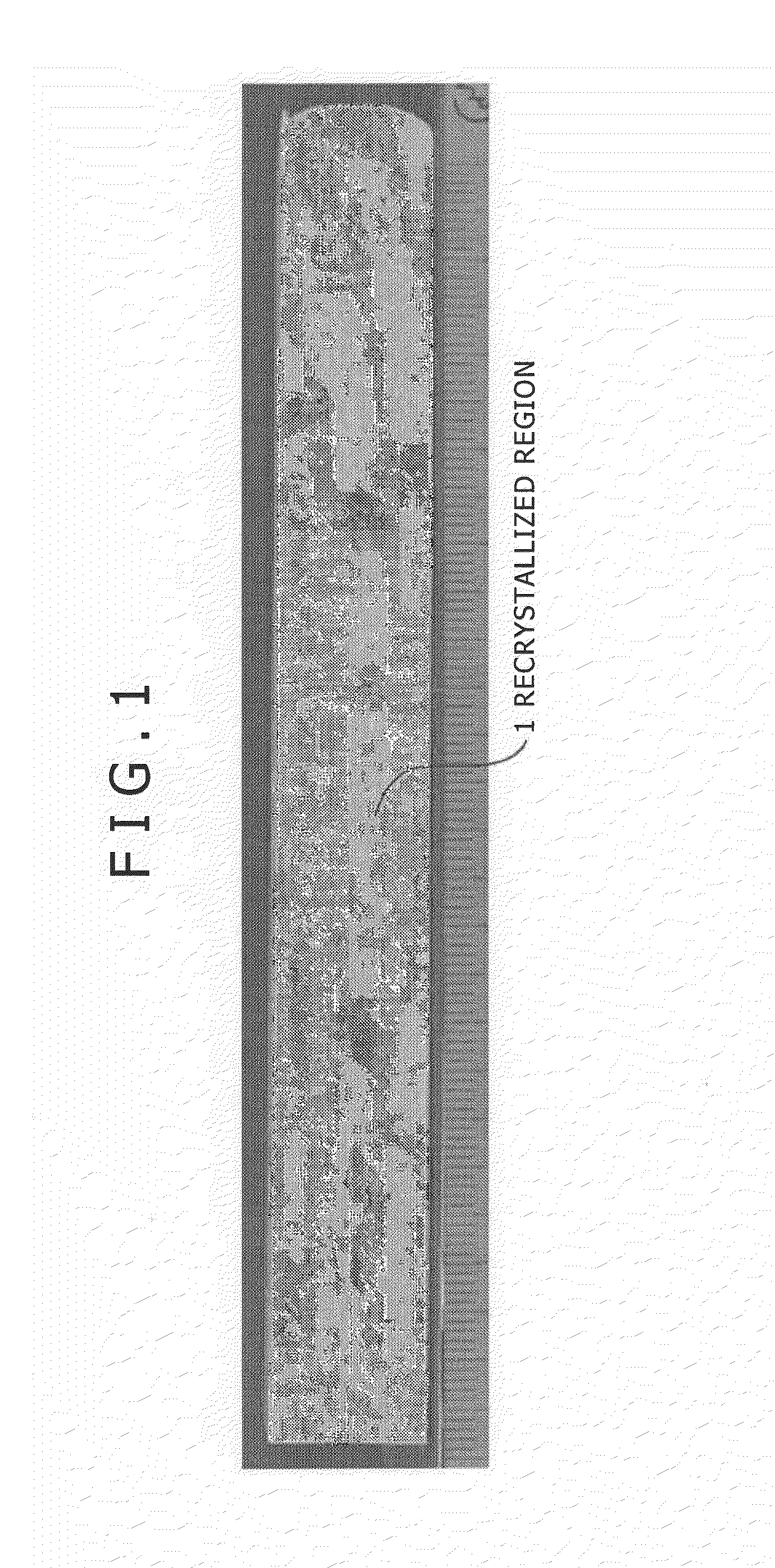
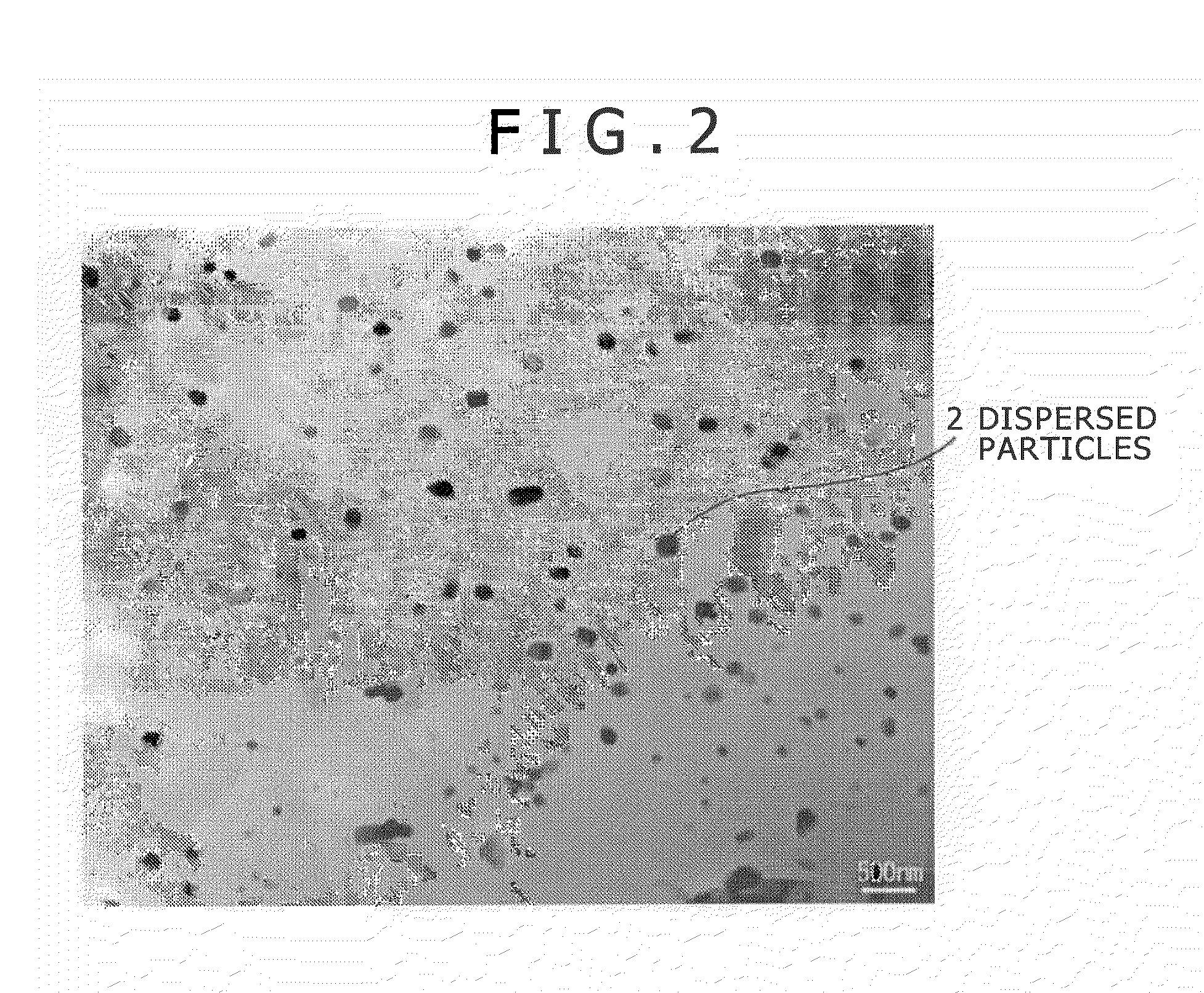
There are provided an aluminum alloy forging having high strength, toughness, and resistance to corrosion in response to the thinning of automotive underbody parts, and a process for production thereof.The aluminum alloy forging includes an aluminum alloy containing predetermined amounts of Mg, Si, Mn, Fe, Zn, Cu, Cr, Zr, and Ti with the balance being composed of Al and inevitable impurities, and having a hydrogen gas concentration of 0.25 ml / 100 g of Al. In the aluminum alloy forging mentioned above, the area ratio of Mg2Si having a maximum length of 0.1 μm or above is 0.15% or below, the recrystallization ratio of the aluminum alloy is 20% or below, and a size distribution index value defined by V / r of dispersed particles of the aluminum alloy (V: the area ratio [%] of the dispersed particles, and r: the average radius [nm] of the dispersed particles) is 0.20 or above.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Short-flow casting and rolling composite forming method for ferrule piece
The invention relates to a short-flow casting and rolling composite forming method for a ferrule piece, which belongs to a machining and forming method for a large-sized ferrule piece and mainly overcomes the technical difficulty that the conventional rolling method has high material waste and serious energy waste. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the short-flow casting and rolling composite forming method for the ferrule piece comprises the steps of alloy melting, molten steel refining, centrifugal casting of a ring blank, hot rolling and expanding, rough machining, heat treatment and finish machining, wherein the molten steel refining refers to external refining with an LF furnace and argon stirring to obtain high-purity molten steel; the centrifugal casting of the ring blank comprises that the refined molten steel is centrifugally cast at the temperature of 1,600 DEG C to form the ring blank, and meanwhile the cast blank grains are thinned by adopting electromagnetic stirring; and the hot rolling and expanding comprise that when the ring blank casting is solidified and the temperature drops to initial forging temperature of 1,200 DEG C, the rolling and expanding are directly performed on a rolling and expanding machine, the feeding amount is controlled during rolling and expanding, and the rolling-expanding ratio is 2 to 3.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Cold-forging technique of gear shaft
InactiveCN101332488ALow flow resistanceReduce the bearing unit extrusion forceForging/hammering/pressing machinesMetallic material coating processesGear wheelPre stress
The invention relates to a cold forging technology for a gear shaft; the cold forging technology is characterized in that a new technology of the cold forging forming of the inside and outside and split flow forging, a volume split flow space is arranged between the gear shaft diameter and a concave die, the metal flow resistance is reduced and the unit extruding force carried by the die is lowered by split flow; high-strength die steel and split structure are adopted to produce a gear hole forming die; the concave die is produced by adopting three-layer sleeve prestressed structure so as to improve the compression resistance of the die; a punch is made from an alloy steel material and used for the cold forging and precision forming of a complex gear form blind hole, which improves the forming quality and production efficiency of the gear hole, and lowers the consumption of the raw materials markedly. The cold forging technology of the invention has the advantages of achieving the smooth forming of the gear form blind hole, improving the production efficiency greatly, and improving the quality of the gear hole and the qualification rate of the product markedly.
Owner:SHANGHAI DONGFU COLD FORGING MFG
Method for rolling and shaping aluminum alloy special-shaped ring forging
InactiveCN101279344AReduce manufacturing costHigh dimensional accuracyMetal rollingAbnormal shapedAero engine
The invention discloses a rolling and shaping method for an aluminum alloy heterotypic ring forging in order to obtain the alloy heterotypic ring forgings with excellent tissues and properties as well as realize accurate rolling. The method includes the following steps: alloy bar material is heated, carried out continuous upsetting and deformed by 50 to 55 percent, so as to be made into a solid cake and then is punched again to lead the alloy bar material to be made into a hollow round cake after the aperture dimension of the alloy bar material is 30 to 35 percent of the dimension of the outer diameter thereof; a rectangle pre-rolling blank is obtained after the hollow round cake is heated, rolled circularly and deformed by 40 to 45 percent; the pre-rolling blank is heated and arranged in a rolling die of a ring rolling machine and forms a heterotypic ring forging after being rolled and deformed by 50 to 55 percent in a section groove. When in expansion, the broadening speed of the pre-rolling blank along the radial direction is 2mm / s to 15mm / s with a radial rolling force of 20000kg to 120000kg. The method is mainly used for the shaping of the heterotypic ring forging of an aeroengine. The method can be adopted to obtain the heterotypic ring forging that is arranged in a flow line along the outline of a part.
Owner:GUIZHOU ANDA AVIATION FORGING
Oxide dispersion strengthening low activity martensitic steel material and preparation thereof
The invention discloses an oxide dispersion strengthened low-activation martensitic steel. A substrate is a CLAM steel and contains 0.2 to 0.5 percent of Y2O3 and 0.10 to 0.50 percent of Ti. The method comprises the following steps that: CLAM steel powder, Y2O3 powder and Ti powder are evenly mixed and put in a sealed container for degassing, subjected to mechanical alloying, hot isostatic pressing or hot-pressing sintering and densification molding under the protection of high-purity argon gas, then subjected to hot squeezing or forging and rolling and other machining and molding processes, and the needed section material is prepared; and finally, the section material is subjected to the treatment of quenching and tempering to prepare the oxide dispersion strengthened low-activation martensitic steel ODS-CLAM. The oxide dispersion strengthened low-activation martensitic steel has the advantages that: the low-activation martensitic steel realizes a martensite-based alloy with oxide strengthening phases evenly dispersed and distributed and crystal grains of a reasonable size, can be used as a structural steel material, has the characteristics of strong neutron irradiation resistance, good high-temperature performance, low activation, etc. and is suitable for a fusion reactor and other environments with strong neutron irradiation and high-temperature.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for manufacturing high-strength 7055 aluminum alloy forge piece formed by spraying
The invention belongs to a manufacturing technology of aluminum alloy and relates to a method for manufacturing a high-strength 7055 aluminum alloy forge piece formed by spraying. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: (a) melting components of 7055 alloy in an intermediate frequency furnace; (b) degassing, deslagging, refining and filtering an aluminum alloy fusant; (c) forming the filtered fusant by spraying to obtain a columnar aluminum alloy ingot blank; (e) carrying out hot extrusion on the aluminum alloy ingot blank formed by spraying; (f) constantly cutting the extrusion ingot as required and then carrying out free forging; (g) carrying out blocker-type forging and / or stamp forging on the blank after the free forging to obtain a stamp forging piece; and (h) carrying out T6 heat treatment on the stamp forging piece. A large-specification and high-property 7055 product can be obtained by using the method which is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU HAORAN SPRAY FORMING ALLOY
Steel forging manufacturing process for deep-sea Christmas tree equipment connectors
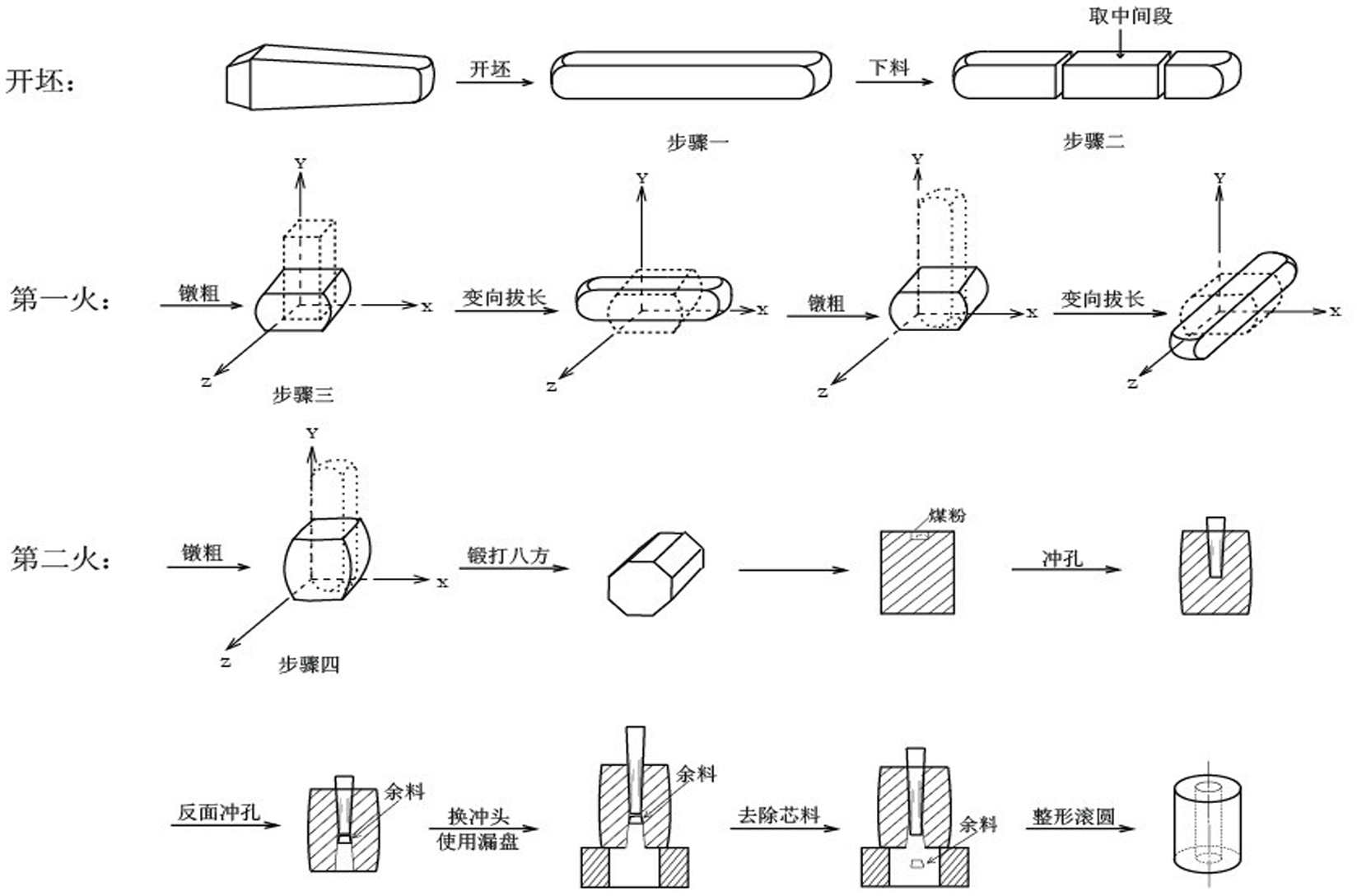
ActiveCN102071367AEliminate the problem of increased toughnessImprove forging qualityMetal-working apparatusPunchingEngineering
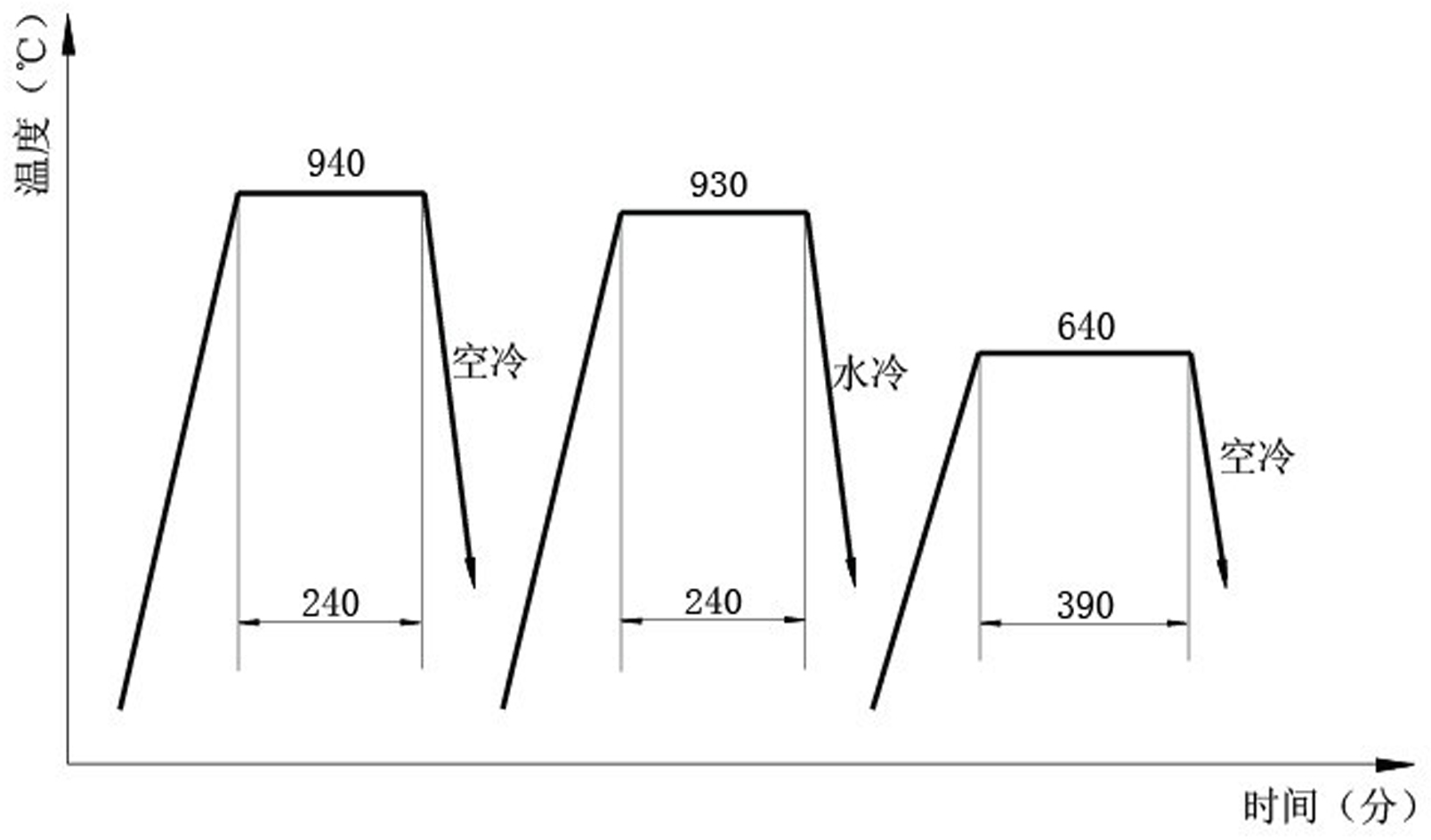
The invention relates to a steel forging manufacturing process for deep-sea Christmas tree equipment connectors, which comprises the following steps: (1) using chromium-nickel-molybdenum low-alloy steel as the blank material; (2) selecting square ingots, heating to 1220 DEG C, cogging, pulling out the material, sawing, and taking the middle section as the blank; (3) heating to the initial forging temperature, upsetting in the directions of three-dimensional coordinates, and drawing out to obtain the isotropic blank; (4) upsetting and forging the blank to obtain an octagonal prism, punching, circularly rolling and shaping to obtain a cylindrical forging stock with a hole; (5) carrying out rough machining on the cylindrical forging stock with a hole to obtain a cylindrical workpiece with a hole; (6) heating the cylindrical workpiece with a hole to 940 DEG C, and cooling in the air to room temperature; (7) heating the cylindrical workpiece with a hole subjected to the step (6), to 930 DEG C, and quenching with water; and (8) heating the cylindrical workpiece with a hole subjected to the step (7), to 640 DEG C, and cooling in the air to room temperature.
Owner:NANJING DEV ADVANCED MFG
Method and apparatus for pre-spinning rotor forgings
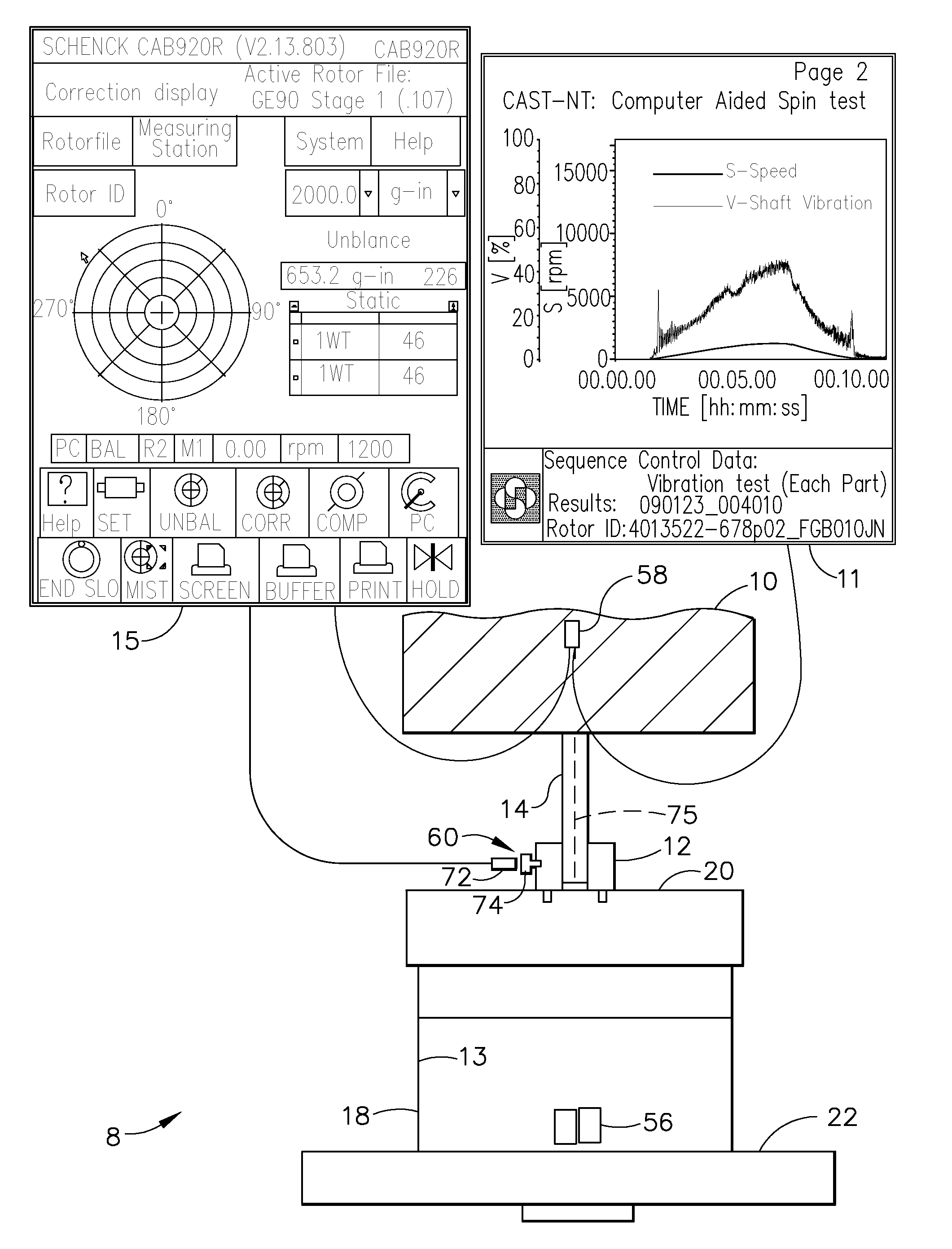
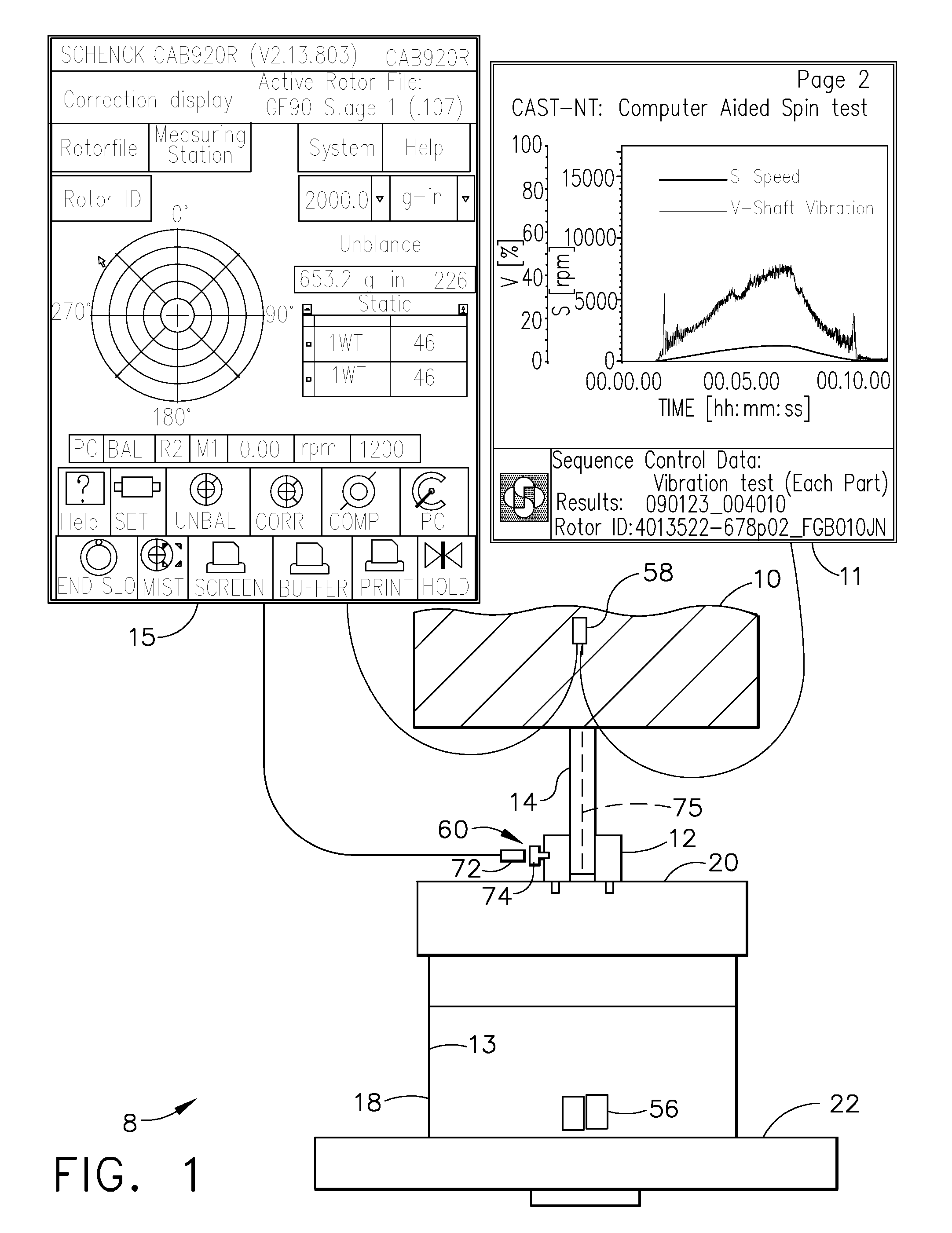
ActiveUS20100212422A1Relieve forging induced residual stressAvoid excessive rotationForce measurementStatic/dynamic balance measurementHigh densityRotation velocity
A method and system for relieving forging induced residual stresses in a rotor forging balances a pre-spin machine with the forging mounted thereon at a first rotational speed and then pre-spins the forging with it mounted on the machine at a substantially greater second rotational speed. A one per rev sensor is used for determining a weight placement angle and a vibration sensor is used for determining an amount of weight to add to a spinning assembly including the forging during the balancing. High-density non-metallic balance weights adhesively attached on an inside surface of the forging or spinning assembly may be used. The rotational inertia of the spinning assembly may be checked during a spin up period by determining a rate of rotational acceleration vs. torque applied to the spinning assembly and used to stop the pre-spinning if it is to great.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
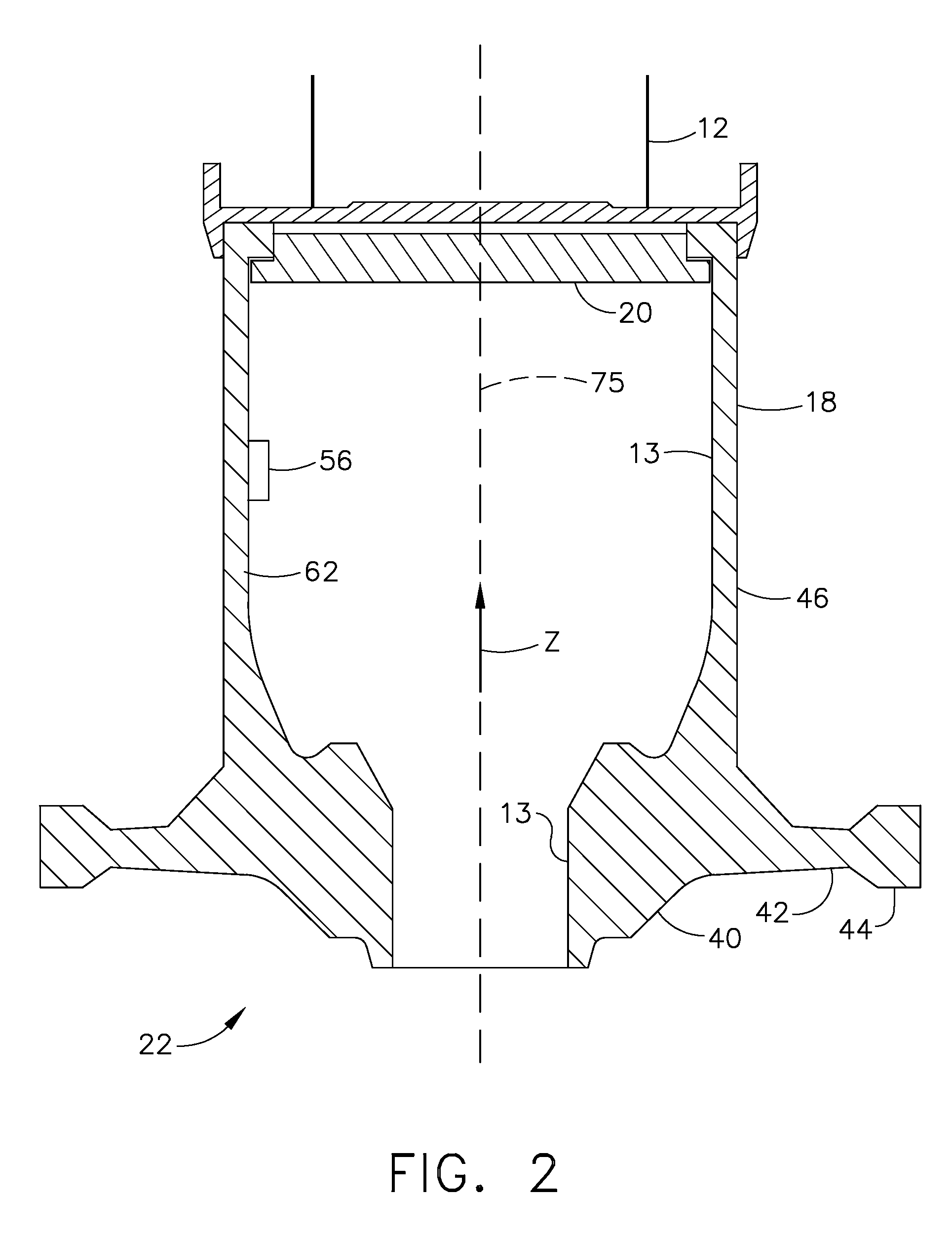
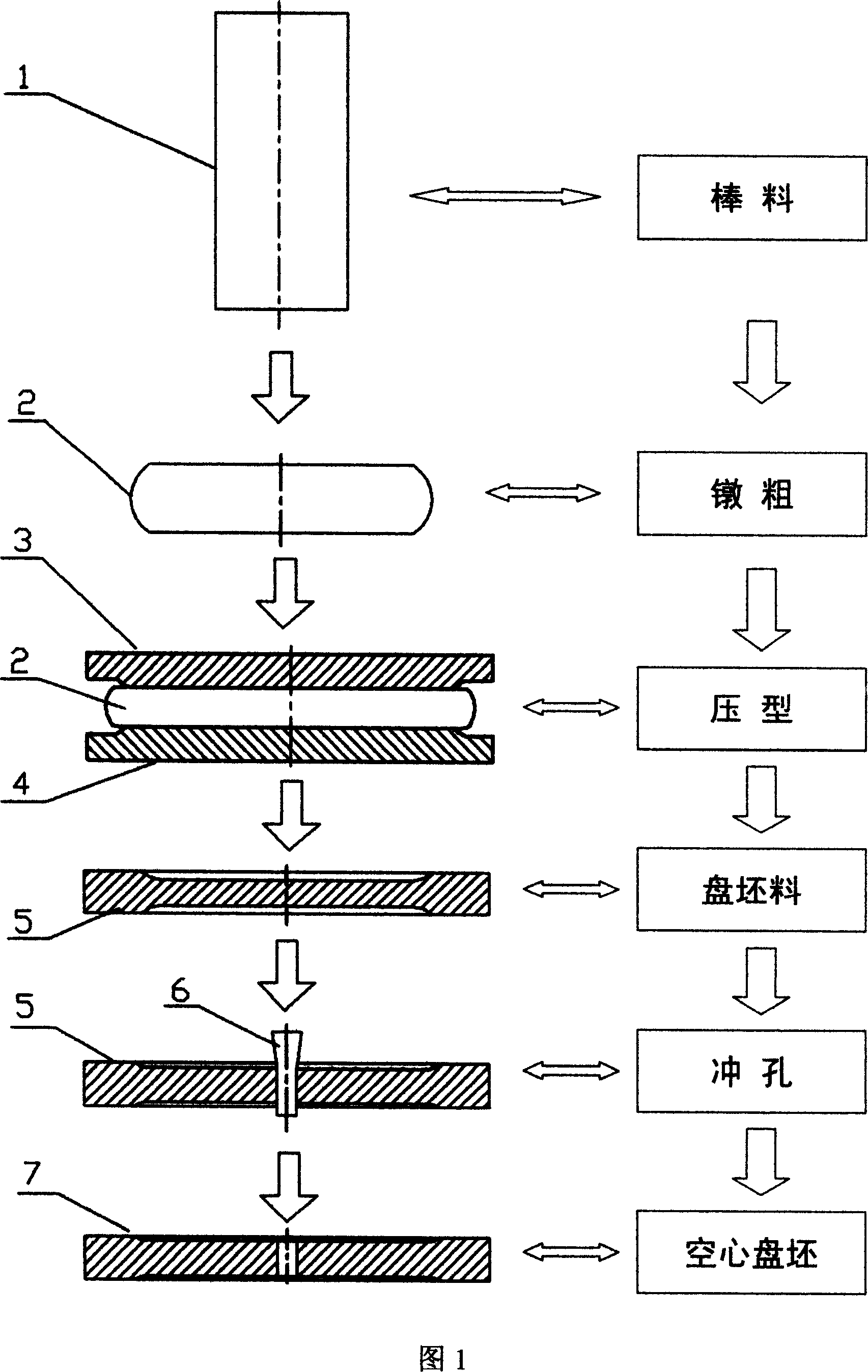
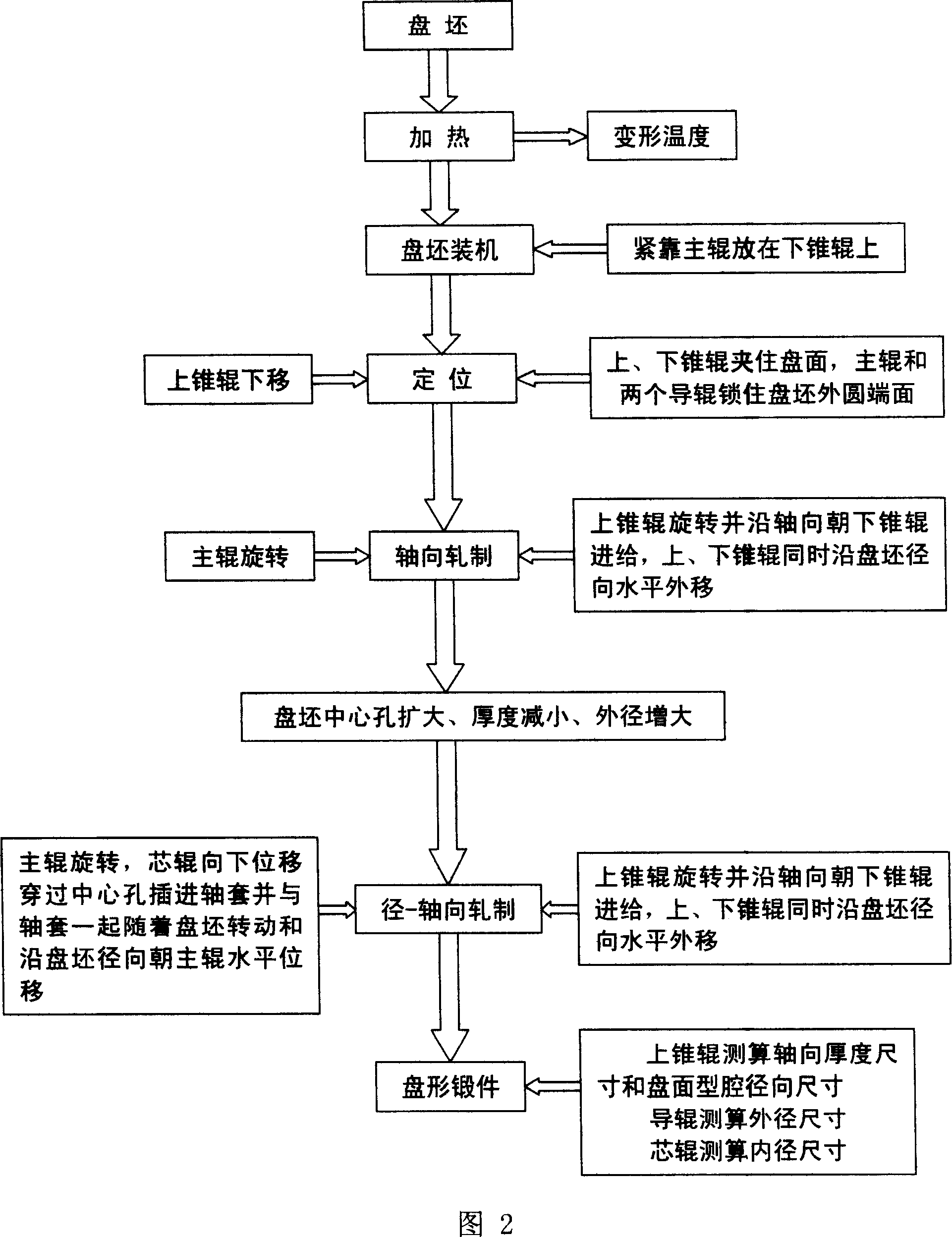
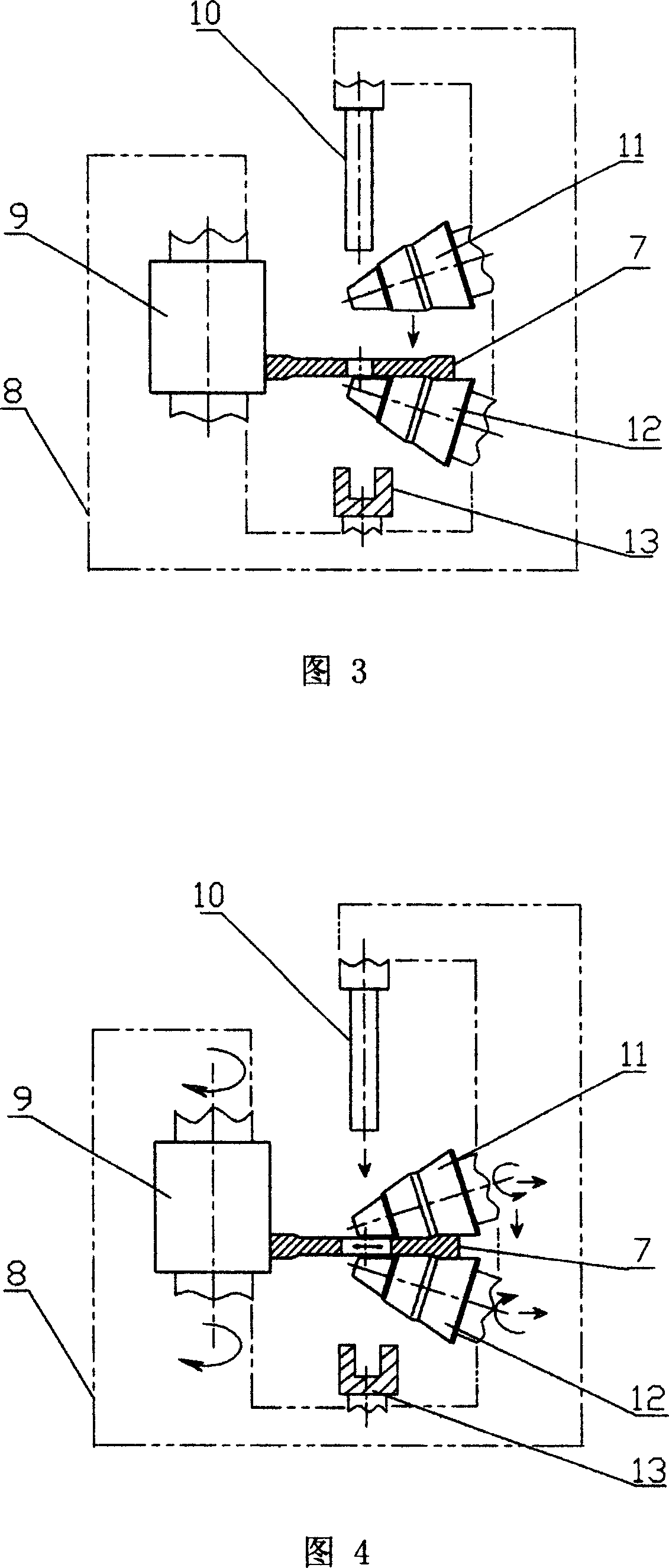
Rolling forming process for large hollow disc forging
ActiveCN101020282ARadial wall thickness reductionReduce axial thicknessRoll force/gap control deviceMeasuring devicesMaterials scienceMetal
The technological process of rolling and forming large hollow disc forging includes the steps of: deforming metal rod material, heating, upsetting to form cake blank, profiling to obtain disc blank, punching hole to obtain hollow disc blank, heating, locating, axial rolling, radial and axial rolling, and measuring size to obtain hollow disc forging. The rolling process has axial rolling force of (2-5)x10<5> kg, radial rolling force of (5-20)x10<4> kg, and broadening speed of 5-15 mm / s. The rolled disc forging has outer diameter of 800-3000 mm, inner diameter of 300-2000 mm and thickness of 30-250 mm. By means of altering the conic size and sizes of the conic roll, disc forgings of different sizes may be rolled. The present invention can form disc forging continuously and form large forging in small apparatus.
Owner:GUIZHOU ANDA AVIATION FORGING
Process for preparing biomedical beta-titanium alloy
InactiveCN101724764AImprove performanceHigh strengthImpression capsFurnace typesMaterials processingQuenching
The invention discloses a process for preparing a biomedical beta-titanium alloy. The process comprises the following steps: A) alloy preparation; B) surface coating; C) hot forging and cogging; D) hot rolling; E) cold rolling and molding; and F) heat treatment. In the process, the material is manufactured to a 2mm plate after the beta-titanium alloy is subjected to high vacuum electric arc melting, repeated stirring, casting, phase transformation point measuring, homogenization under the protection of vacuum and argon, coating, hot forging, hot rolling, cold rolling, solid solution, water quenching, artificial aging and water cooling so as to prepare the biomedical beta-titanium alloy with excellent comprehensive performance. The process is a biomedical beta-titanium preparation process capable of improving the material strength, abrasion resistance and corrosion resistance, reducing the elasticity modulus of the material, and maintaining excellent manufacturing and molding performance of the material.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Tantalum sputtering target and method for preparation thereof
InactiveUS20050155856A1Enhancing evenness (uniformity)Quality improvementCellsVacuum evaporation coatingCrystal structureIngot
Provided is a tantalum sputtering target having a crystal structure in which the (222) orientation is preferential from a position of 10% of the target thickness toward the center face of the target, and a manufacturing method of a tantalum sputtering target, including the steps of forging and recrystallization annealing, and thereafter rolling, a tantalum ingot or billet having been subject to melting and casting, and forming a crystal structure in which the (222) orientation is preferential from a position of 10% of the target thickness toward the center face of the target. As a result, evenness (uniformity) of the film is enhanced, and quality of the sputter deposition is improved.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Method for rolling and shaping nickel-based high-temperature alloy special-shaped ring forging
The invention discloses a rolling and shaping method for a nickel-based high temperature alloy heterotypic ring forging in order to obtain the alloy heterotypic ring forgings with excellent tissues and properties as well as realize accurate rolling. The method includes the following steps: alloy bar material is heated, carried out continuous upsetting and deformed by 60 to 65 percent so as to be made into a solid cake and then is punched again to lead the alloy bar material to be made into a hollow round cake after the aperture dimension of the alloy bar material is 30 to 35 percent of the dimension of the outer diameter thereof; a rectangle ring blank is obtained after the hollow round cake is heated, rolled circularly and deformed by 20 to 25 percent; a rectangle pre-rolling blank is obtained after the rectangle ring blank is heated, rolled circularly and deformed by 20 to 25 percent again; the pre-rolling blank is heated and arranged in a rolling die of a ring rolling machine and becomes a heterotypic ring forging after being rolled and deformed by 40 to 45 percent in a section groove of the die. When in expansion, the broadening speed of the pre-rolling blank along the radial direction is 2mm / s to 15mm / s with a radial rolling force of 40000kg to 220000kg. The method is mainly used for the shaping of the heterotypic ring forging of an aeroengine or a gas turbine. The method can be adopted to obtain the heterotypic ring forging that is arranged in a flow line along the outline of a part.
Owner:GUIZHOU ANDA AVIATION FORGING
Injection molding of metallic glass by rapid capacitor discharge
ActiveUS20130025814A1Avoid failureAvoid thermal transport and development of thermalFoundry mouldsHeat treatment process controlAlloyInjection molding machine
An apparatus and method of uniformly heating, rheologically softening, and thermoplastically forming magnetic metallic glasses rapidly into a net shape using a rapid capacitor discharge forming (RCDF) tool are provided. The RCDF method utilizes the discharge of electrical energy stored in a capacitor to uniformly and rapidly heat a sample or charge of metallic glass alloy to a predetermined “process temperature” between the glass transition temperature of the amorphous material and the equilibrium melting point of the alloy in a time scale of several milliseconds or less. Once the sample is uniformly heated such that the entire sample block has a sufficiently low process viscosity it may be shaped into high quality amorphous bulk articles via any number of techniques including, for example, injection molding, dynamic forging, stamp forging, sheet forming, and blow molding in a time frame of less than 1 second.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Middle-duty and heavy-duty automobile knuckle stamp forging extruding compound technology
ActiveCN101607294AShort preparation cycleIncrease profitForging/hammering/pressing machinesProduction rateHeavy duty
A middle-duty and heavy-duty automobile knuckle stamp forging extruding compound technology overcomes the disadvantages of low material utilization and large device investment of the traditional production technology, utilizes flexibility of preforming by a stamping hammer and structure characteristic of a press extrusion die and adopts stamping hammer production technology and press extrusion compound technology. The main technical scheme includes a series of technical measures of vertically splitting of blank material by mould with V-shaped cutting edge and locally enclosed structure, preforging of cavity damping stripe, finish forging of locally enclosed structure, hot extrusion forming of steering space and the like, parameter requirements and corresponding moulds and devices. The invention has the characteristics that device investment of stamping hammer production technology is small, structure is simple, and equipment manufacturing period is short; production technological flow is reasonable and processing is easy; and the invention also has the characteristics that product quality is good and productivity is high; and material utilization is obviously higher than that of any original knuckle processing technology and production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUBEI TRI RING FORGING
Controlled-forging controlled-cooling processing technology of bearing ring prepared by GCr15
The invention relates to a controlled-forging controlled-cooling processing technology of a bearing ring prepared by GCr15, comprising the following steps of: quenching the bearing ring in cooling fluid at final forging temperature of 850-950 DEG C and at fluid outlet temperature of 350-550 DEG C; when heating the bearing ring to the temperature of 450-550 DEG C, after preserving the temperature for 1h-3h, discharging the bearing ring from a boiler and cooling the bearing ring to room temperature; when heating the bearing ring to the temperature of 650-690 DEG C again, preserving the temperature for 1h; when continuously heating the bearing ring to the temperature of 740-780 DEG C, after preserving the temperature for 2-3h, cooling the bearing ring to the temperature of 680-690 DEG C and preserving the temperature for 2-4 hours; finally, when cooling the bearing ring to the temperature of 550-600 DEG C at the speed of 10 DEG C / h, cooling o the bearing ring to the room temperature along with the boiler by air; quenching a machined semi-finished bearing ring; when heating to the temperature of 810-830 DEG C, after preserving the temperature for 45-60min, discharging the machined semi-finished bearing ring from the boiler and quenching the machined semi-finished bearing ring in oil; and when heating the machined semi-finished bearing ring to the temperature of 160-200 DEG C after being quenched, preserving the temperature of the machined semi-finished bearing ring for 4h, discharging the machined semi-finished bearing ring from the boiler and cooling the machined semi-finished bearing ring to the room temperature by air. According to the invention, carbides, martensite crystals and austenite crystals of the bearing ring are refined, network carbides are improved or eliminated and impact ductility and fatigue life are improved.
Owner:LUOYANG BEARING RES INST CO LTD
Metal part manufacturing system and method adopting micro-casting-forging and milling-grinding in-situ composite
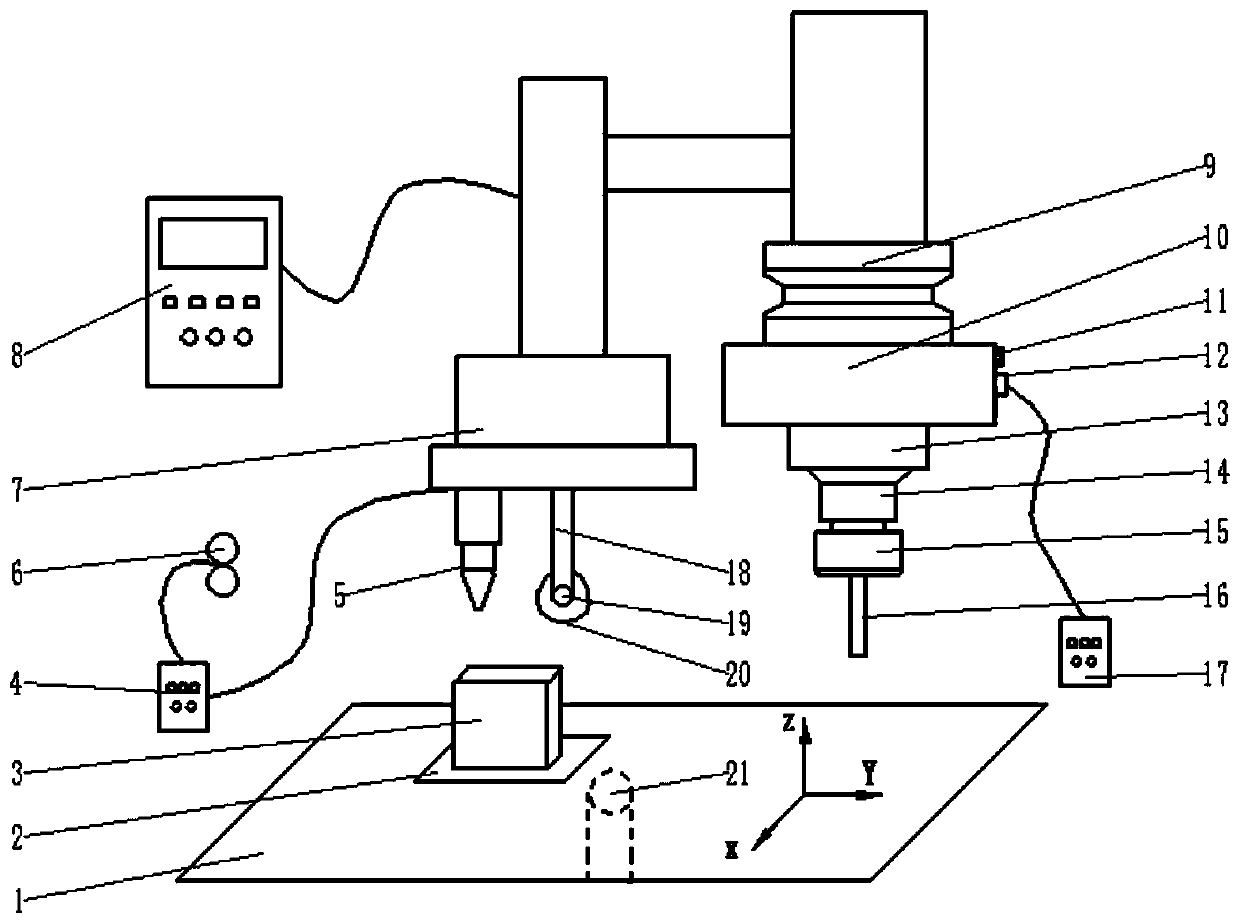
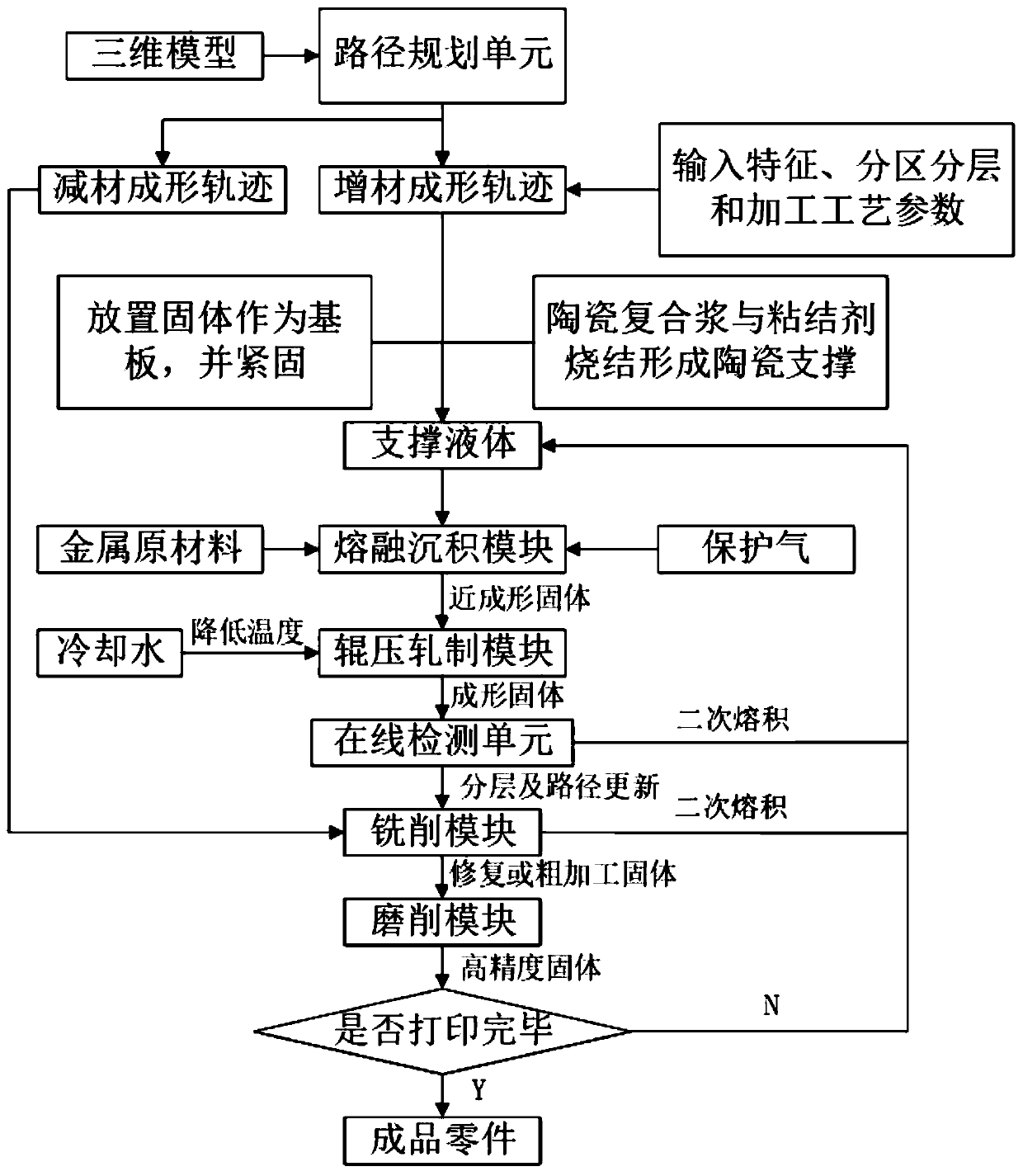
InactiveCN110076566AImprove tissue mechanical propertiesImprove processing efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusOther manufacturing equipments/toolsEngineeringManufacturing systems
The invention belongs to the field of metal part manufacturing, and particularly discloses a metal part manufacturing system and method adopting the micro-casting-forging and milling-grinding in-situcomposite. The system involves a micro-casting-forging module, a milling module, a five-axis linkage workbench and a control device, wherein the micro-casting-forging module is connected with the milling module and comprises a fusion deposition sub-module and a roller-pressing rolling sub-module, the five-axis linkage workbench is positioned below the micro-casting-forging module and the milling module, and is used for containing metal parts to be formed, and the control device is connected with the fusion deposition sub-module, the roller-pressing rolling sub-module, the milling module and the five-axis linkage workbench. According to the system and method, micro-casting-forging and a milling process are composited to process and manufacture the metal parts, so that the problems that whenthe metal parts are made through the additive manufacturing, the structure is not uniform, the deformation is serious, the residual stress is large, the structure performance is poor, and the surfacequality is poor are solved, and the system and method is especially suitable for processing a high-performance complicated special-shaped element.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Flying-shear main-transmission gearwheel steel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102162069AReduce the effect of heat treatment distortionOvercoming brittlenessGear grindingHobbing
The invention discloses a flying-shear main-transmission gearwheel steel and a preparation method thereof. The flying-shear main-transmission gearwheel steel comprises the following elements in percentage by mass: 0.10-0.20% of C, 2.00-3.00% of Cr, 2.50-3.50% of Ni, 0.4-1.00% of Mo, 0.10-0.40% of Si, 0.40-1.00% of Mn, at most 0.25% of Cu, at most 0.1% of Al, at most 0.020% of P, at most 0.015% ofS, at most 30ppm of O, at most 100ppm of N and at most 2ppm of H. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) smelting according to the percentage by mass to obtain a forging stock; (2)forging; (3) carrying out normalizing heat treatment; (4) carrying out gear hobbing; (5) carrying out surface carburization quenching heat treatment; and (6) carrying out gear grinding. The inventionenhances the bearing capacity and reliability of the gearwheel, and satisfies the production demands of high-carbon high-alloy steel and enhanced specifications, thereby having wide popularization and application prospects.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com