Patents
Literature
53 results about "Spin-up" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spin-up refers to the process of a hard disk drive or optical disc drive accelerating its platters or inserted optical disc from a stopped state to an operational speed. The period of time taken by the drive to perform this process is referred to as its spin-up time, the average of which is reported by hard disks as a S.M.A.R.T. attribute. The required operational speed depends on the design of the disk drive. Typical speeds of hard disks have been 2400, 3600, 4200, 5400, 7200, 10000 and 15000 revolutions per minute (RPM). Achieving such speeds can require a significant portion of the available power budget of a computer system, and so application of power to the disks must be carefully controlled. Operational speed of optical disc drives may vary depending on type of disc and mode of operation (see Constant linear velocity).
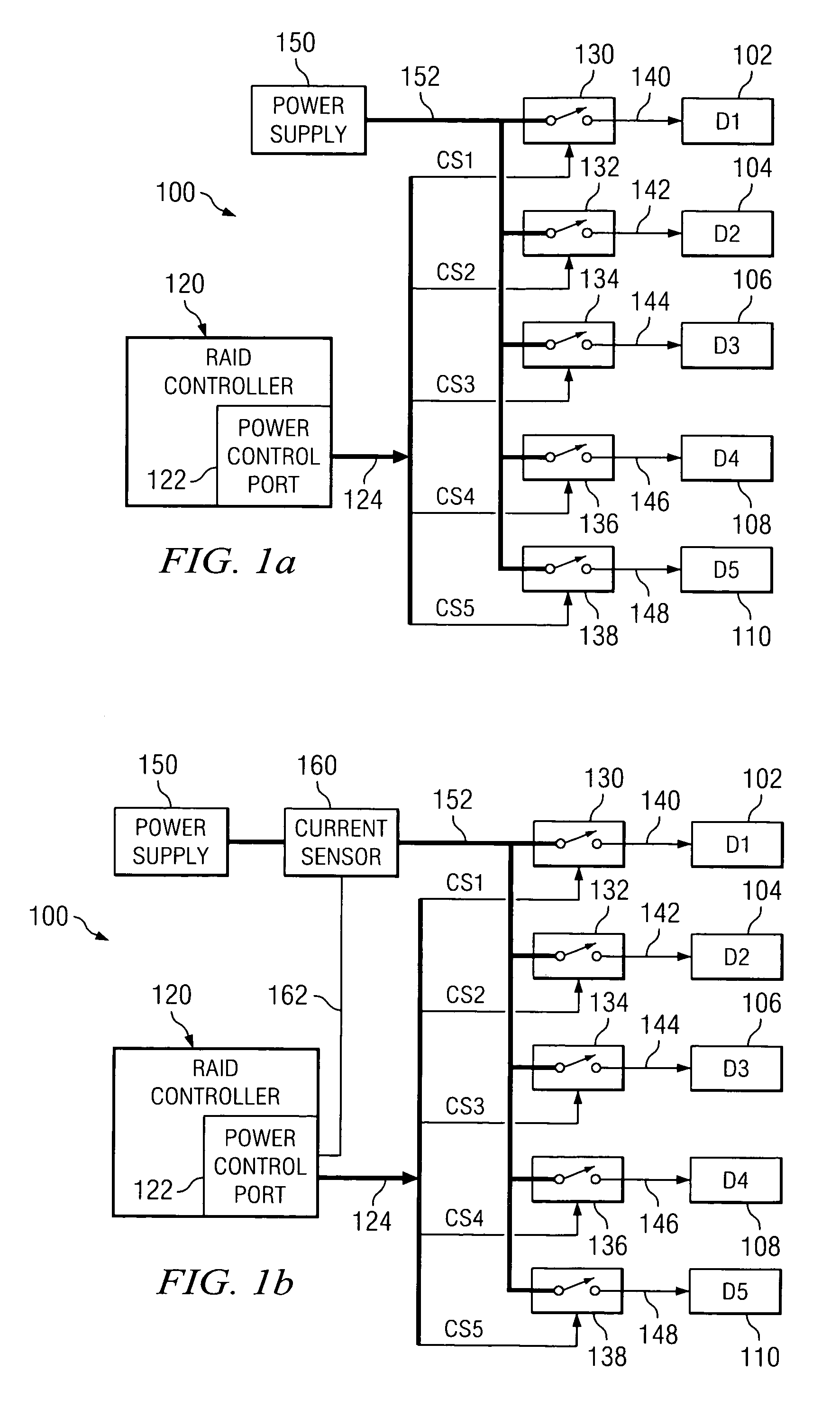
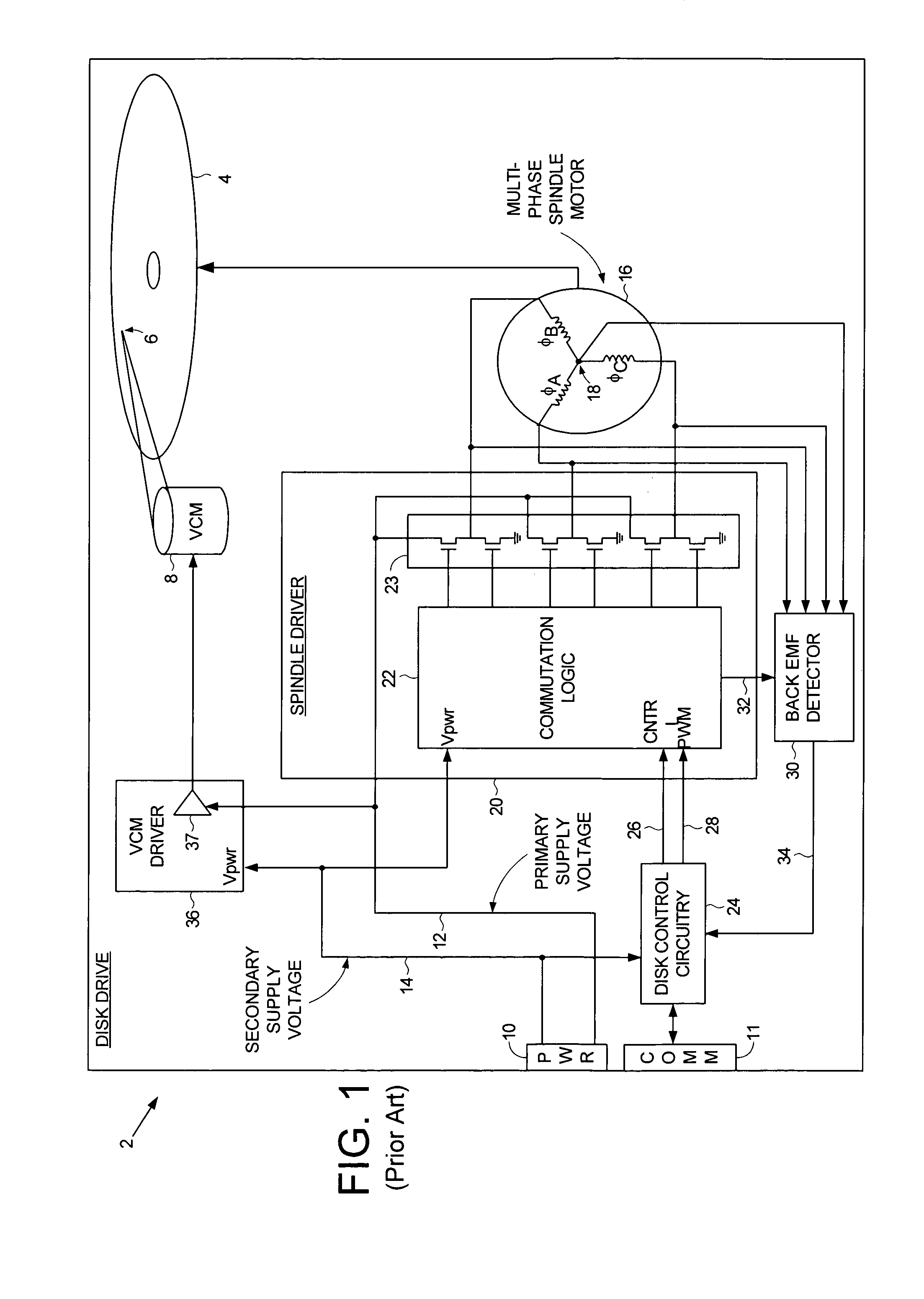
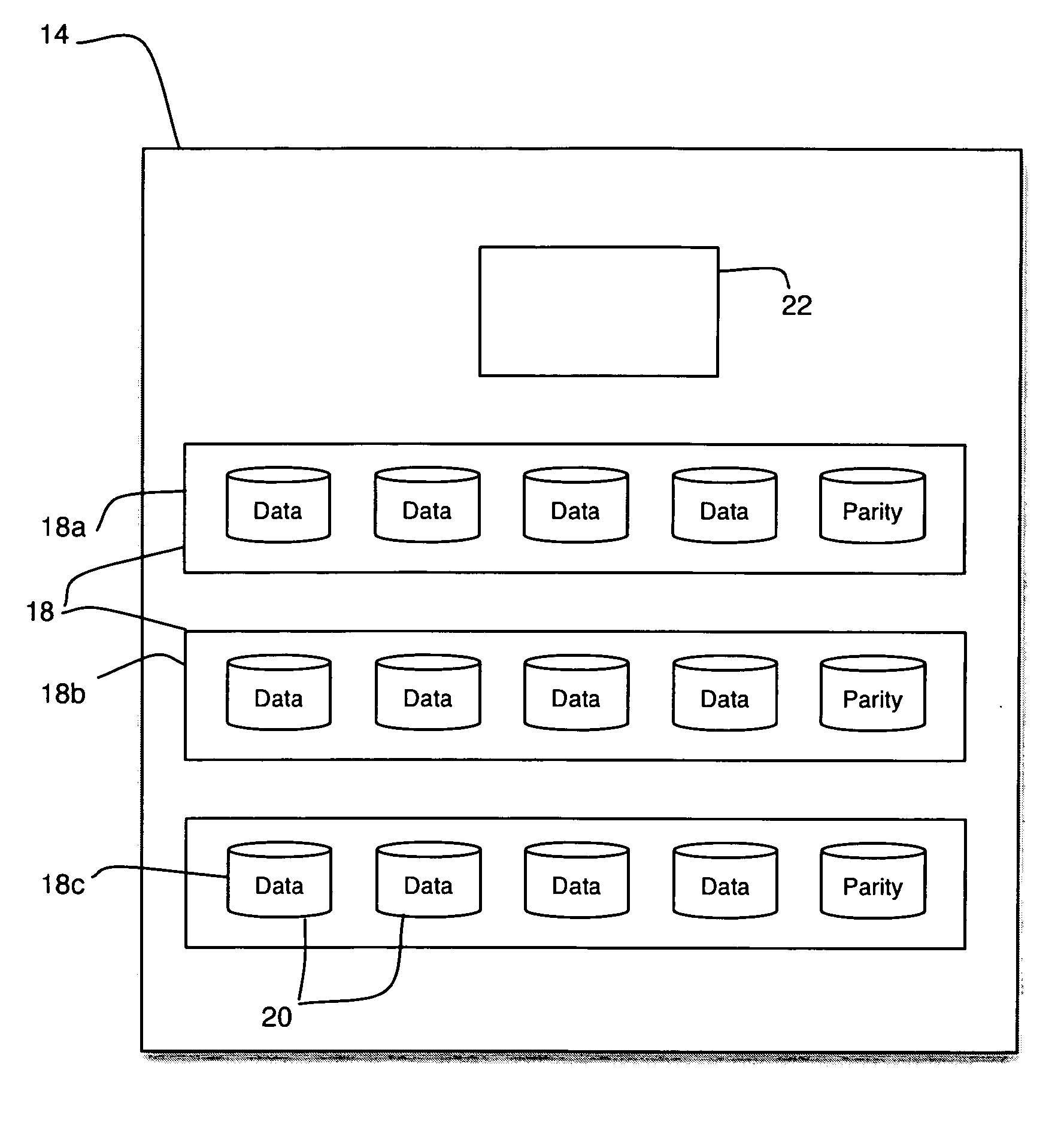
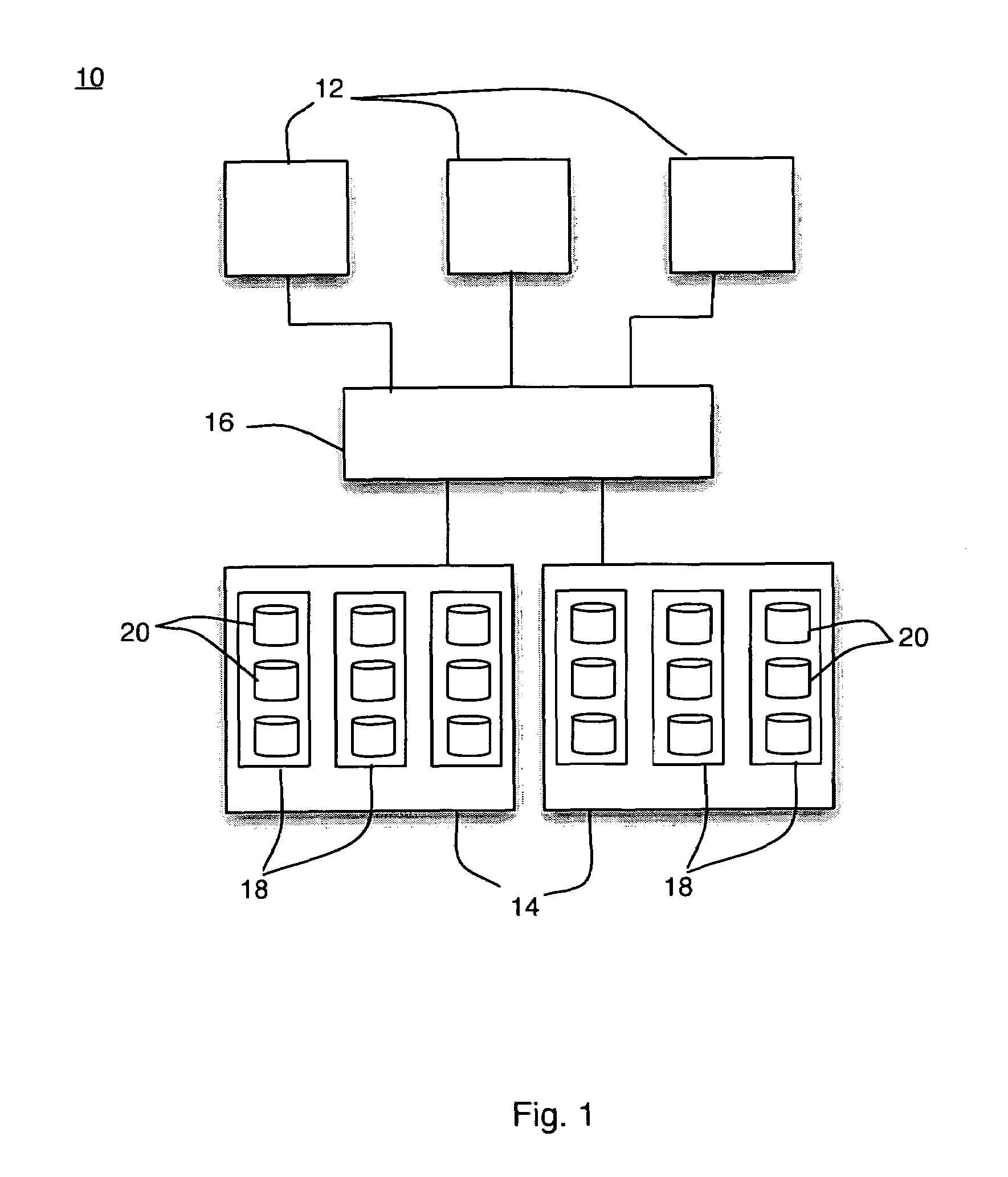
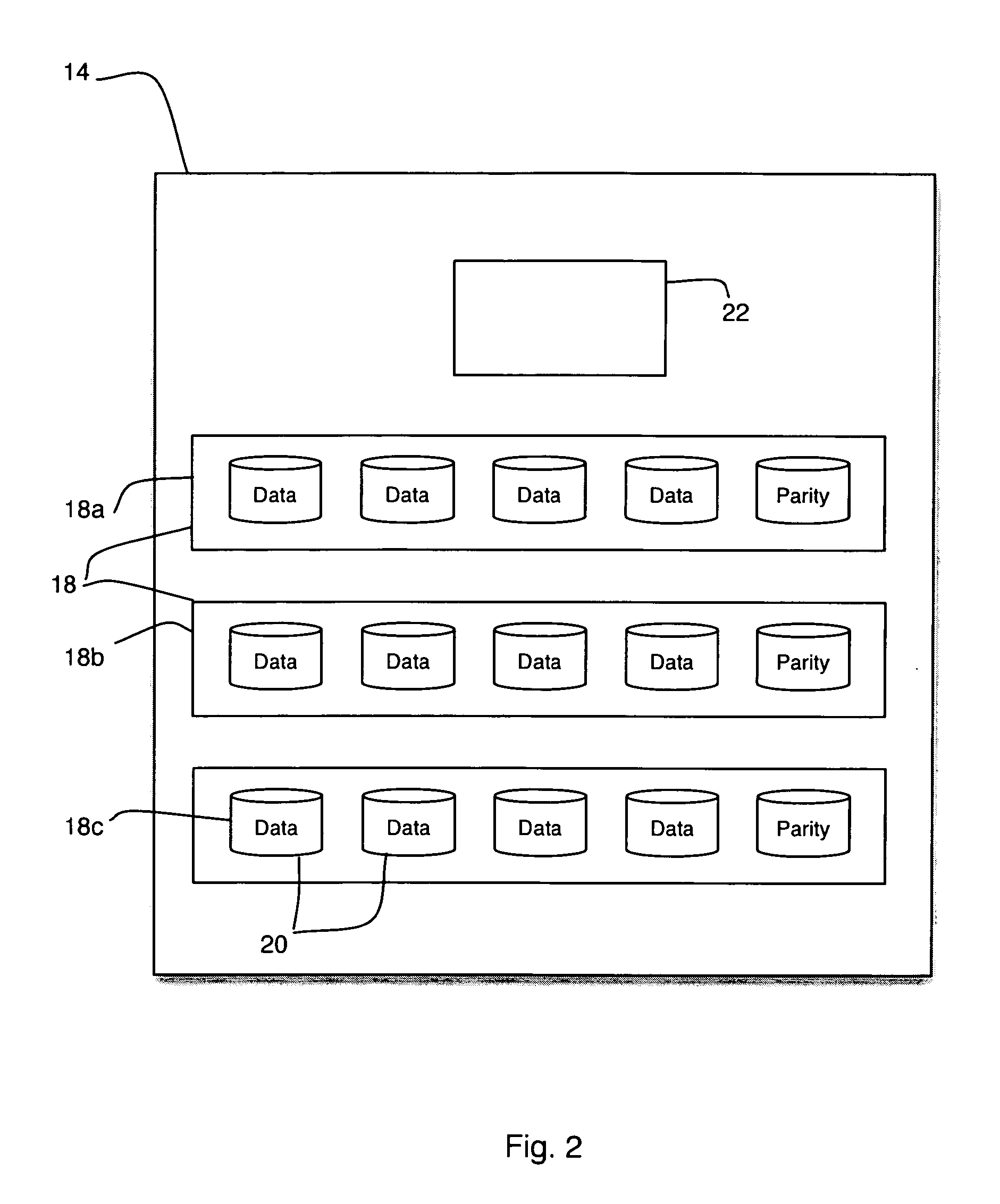
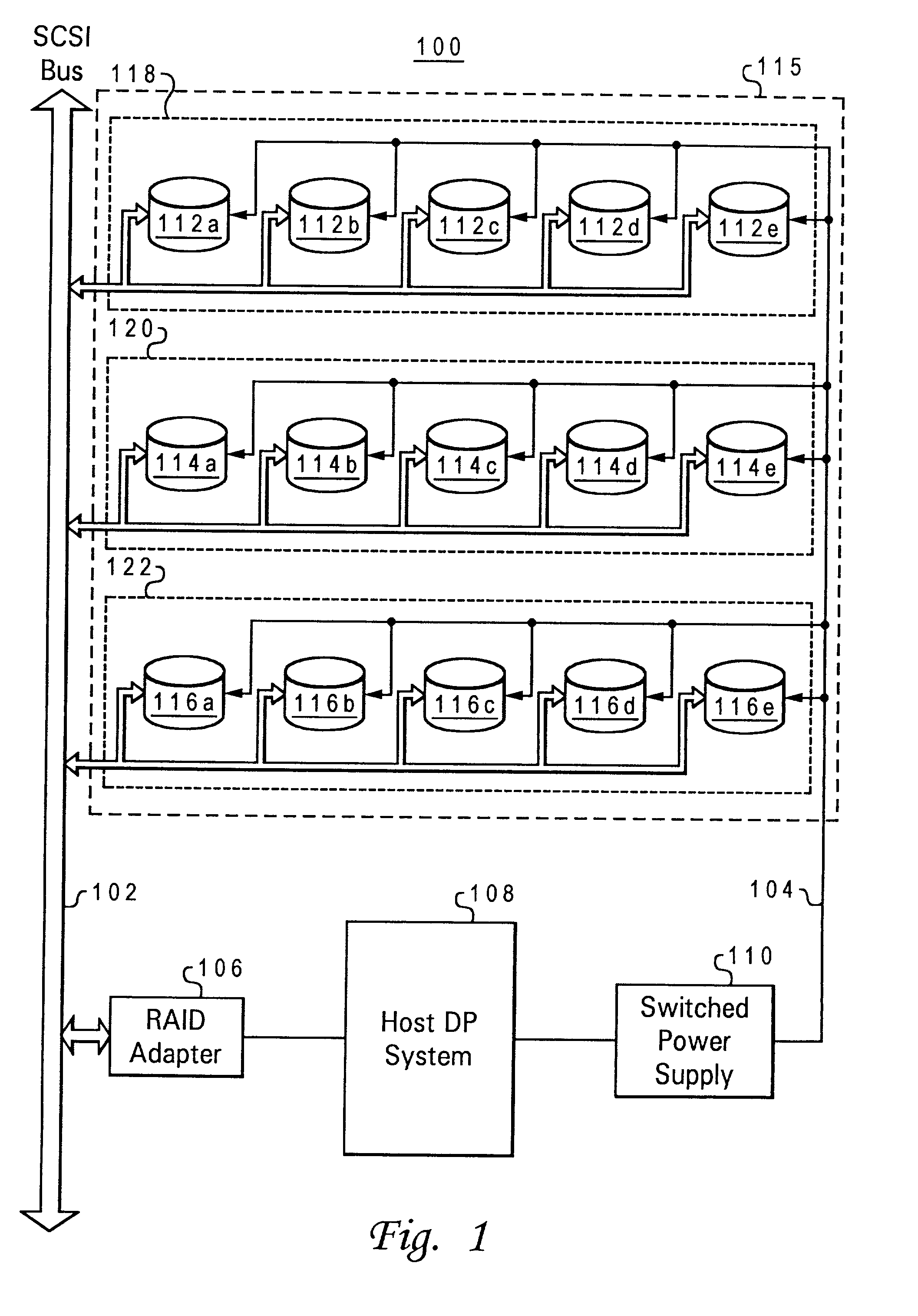
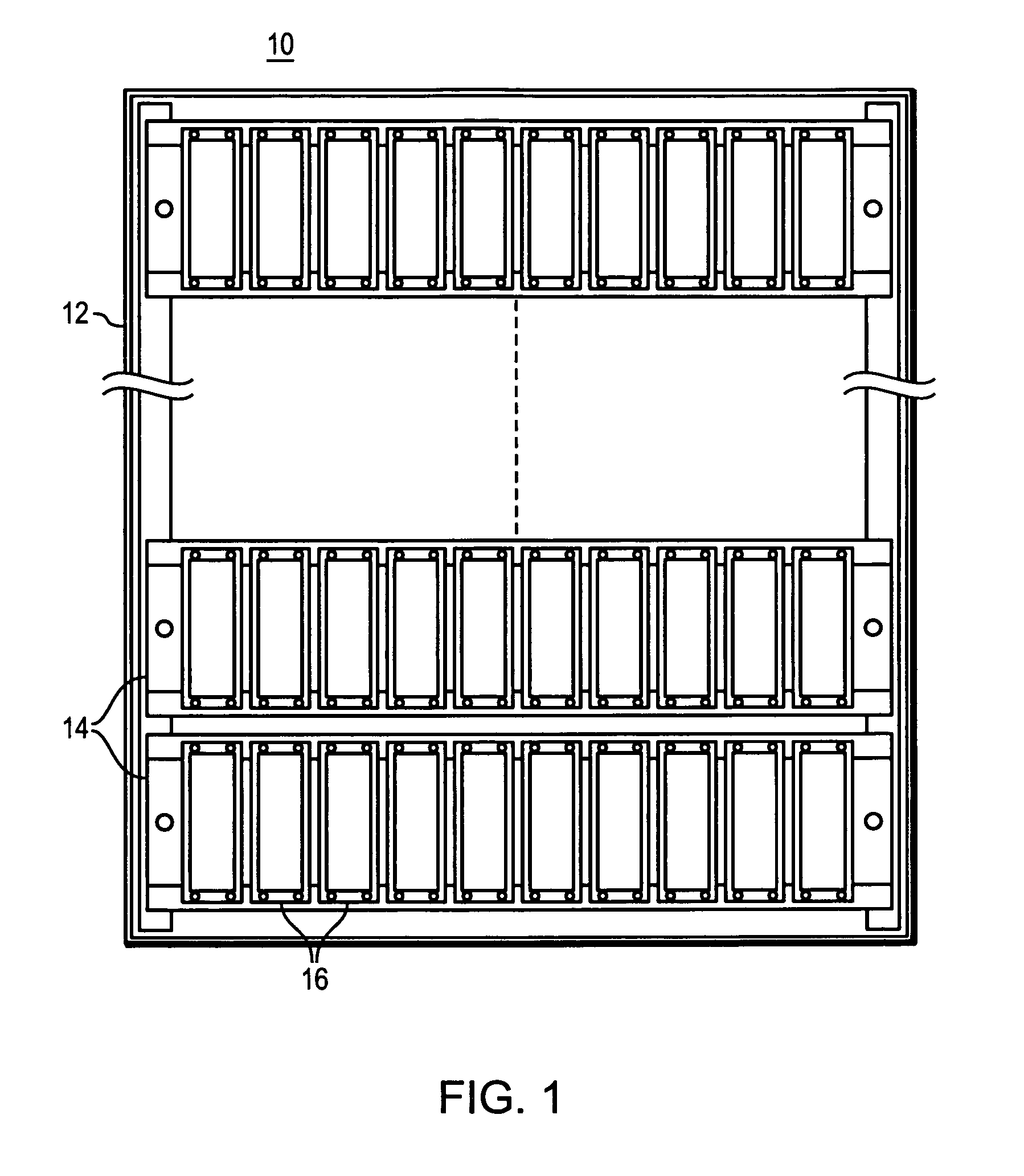
Method and apparatus for controlling power sequencing of a plurality of electrical/electronic devices
ActiveUS7370220B1Total current dropReduced Power RequirementsEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingControl powerClosed loop
A method and apparatus for managing power sequencing in a data storage system. The turn-on or spin-up sequence for the media drives in an array of media drives is selectively controlled such that the overall rush current is reduced. The individual drive components are characterized to determine a power profile for each such component. A closed-loop process is then used to manage and reduce peak power requirements when starting up or spinning up an array of media drives using the drive profiles. The media drives can also be organized as a plurality of sets of drives, and a power profile for each set of drives is used to manage and reduce peak power requirements.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
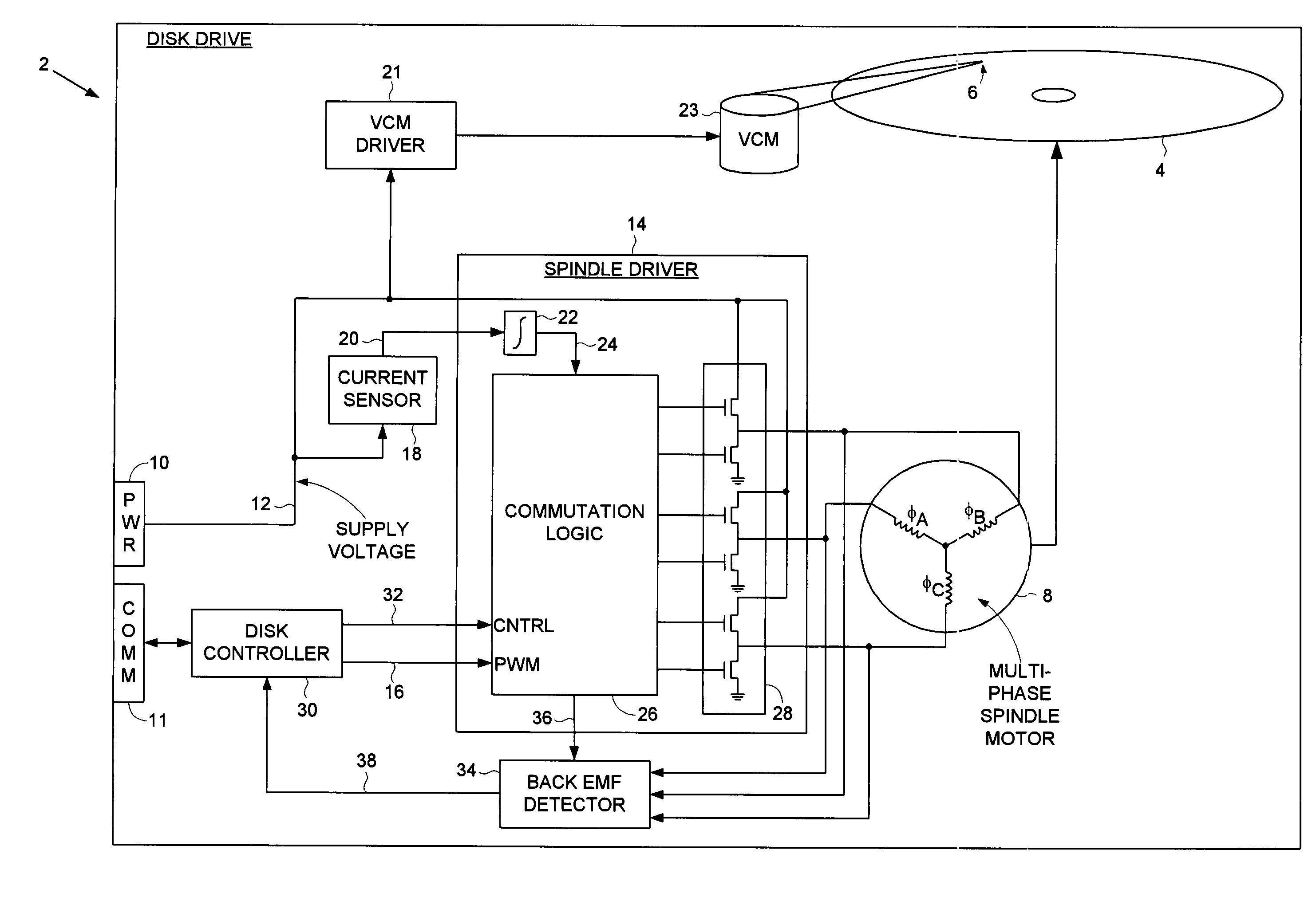
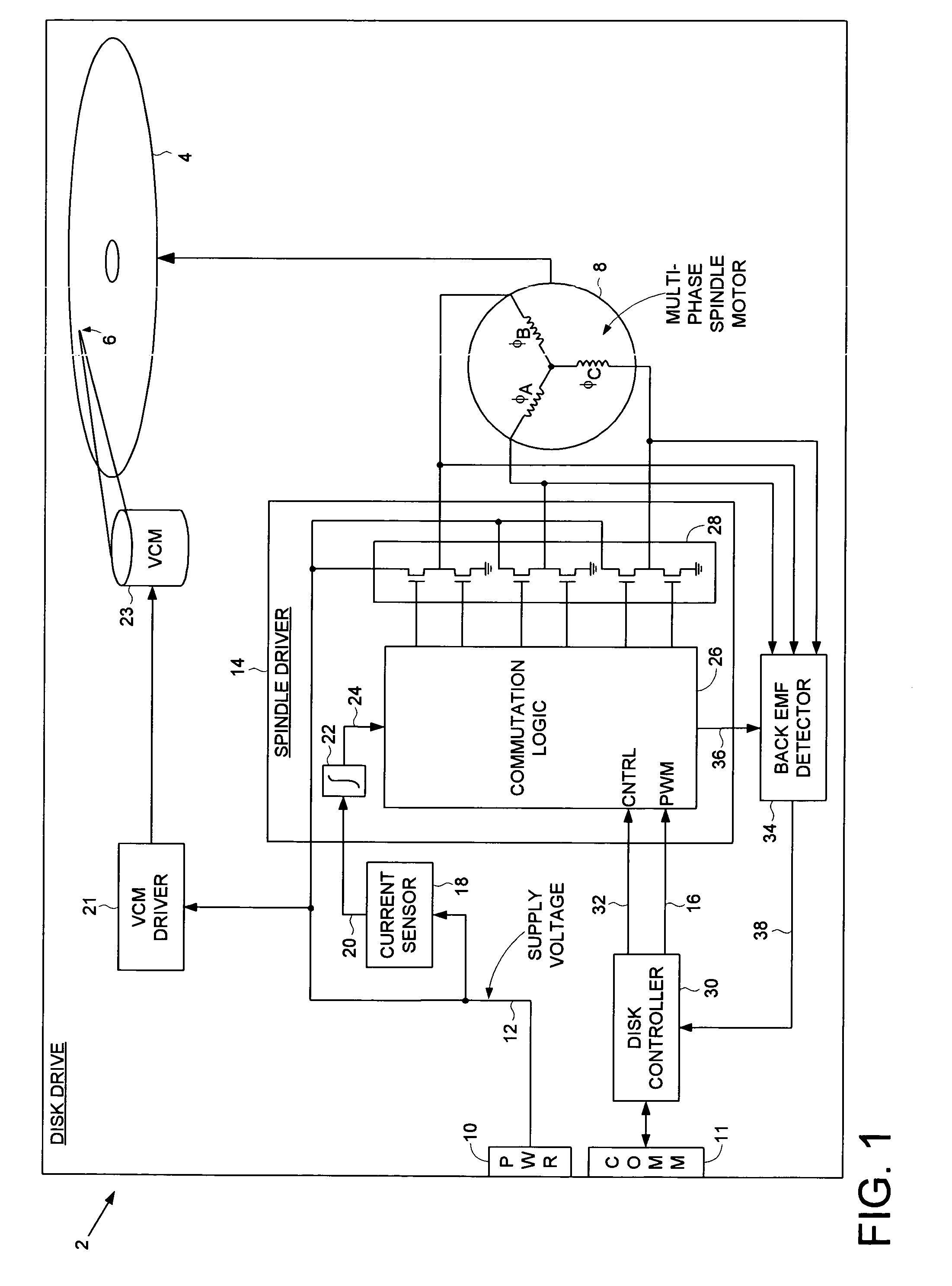
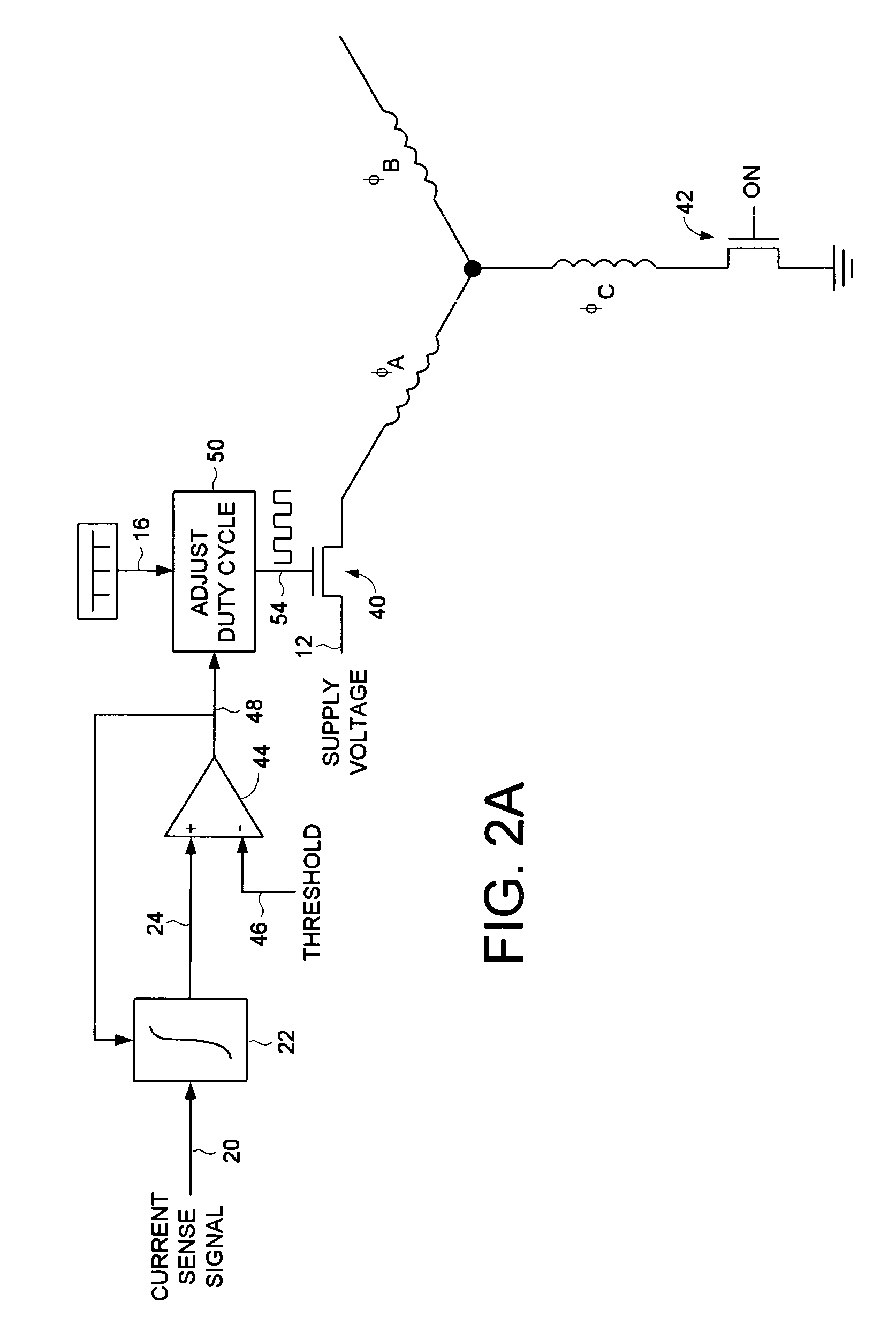
Decreasing spin up time in a disk drive by adjusting a duty cycle of a spindle motor PWM signal to maintain constant average input current
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a spindle motor for rotating a disk, wherein the current applied to the spindle motor is controlled by adjusting a duty cycle of a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal. A current sensor generates a current sense signal representing a current flowing from a supply voltage. The current sense signal is integrated to generate an integration signal. The integration signal is compared to a threshold, and the result of the comparison is used to adjust the duty cycle of the PWM signal. In this manner the disk drive draws essentially constant average input current from the supply voltage which decreases the spin up time of the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
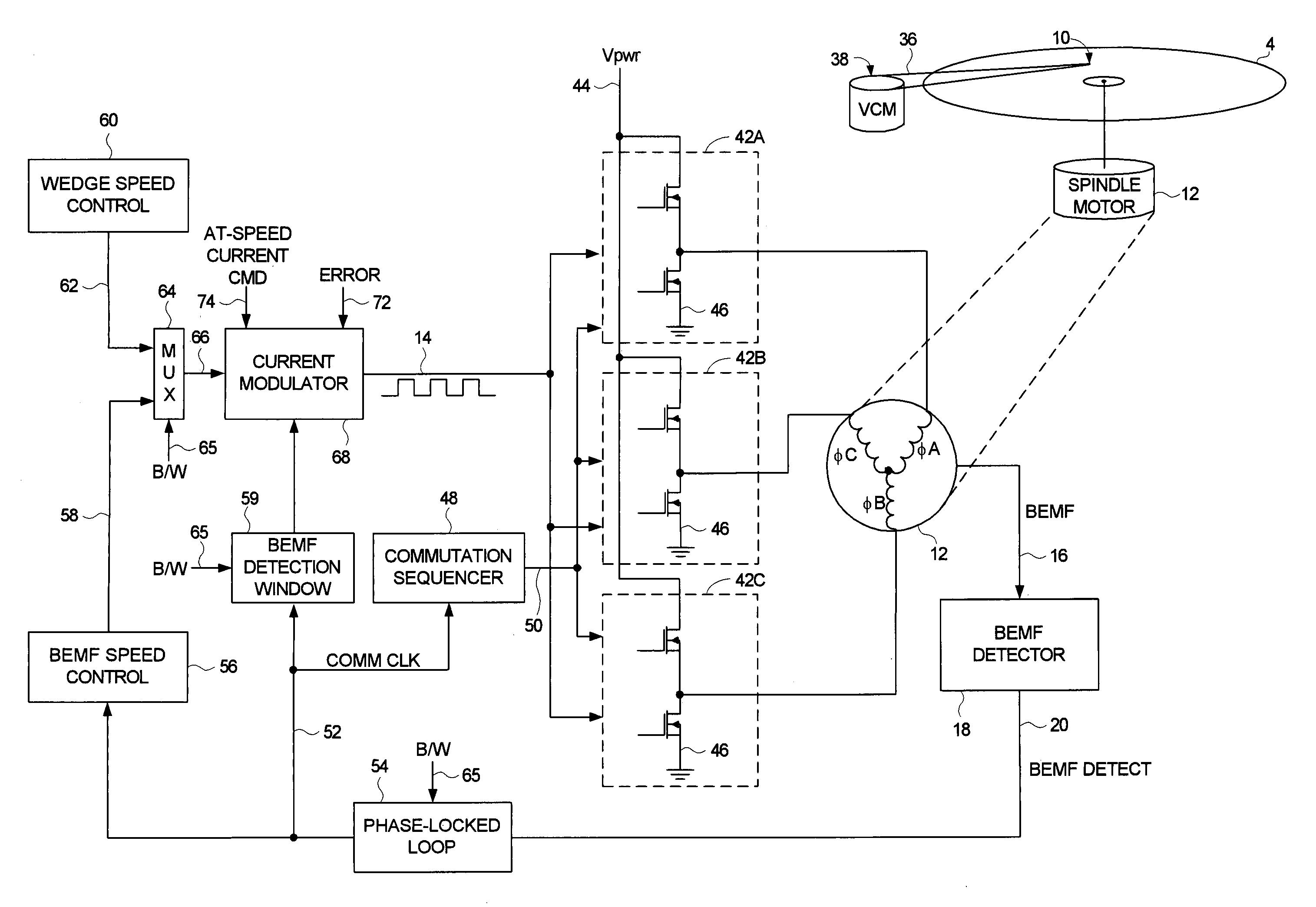
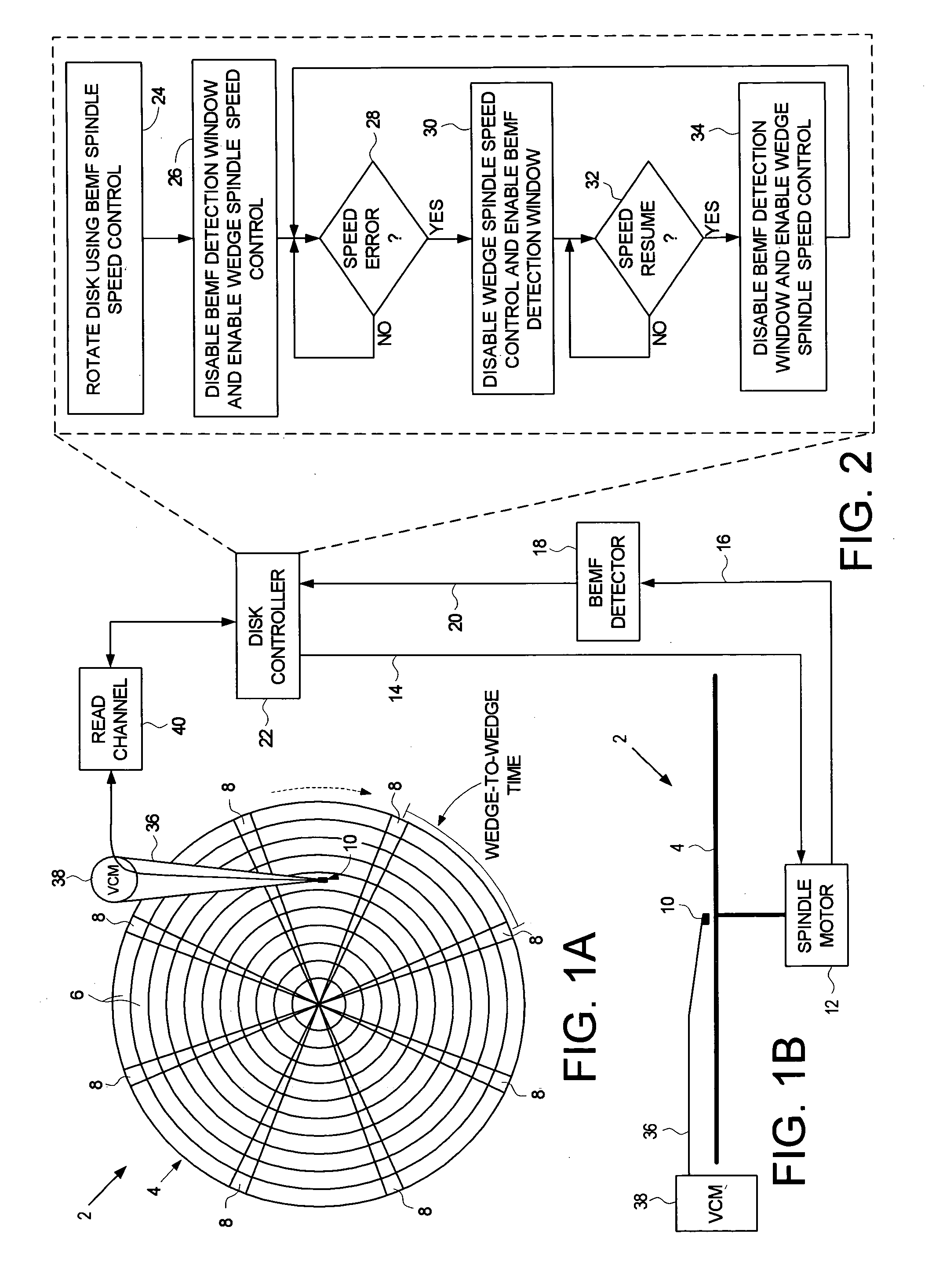
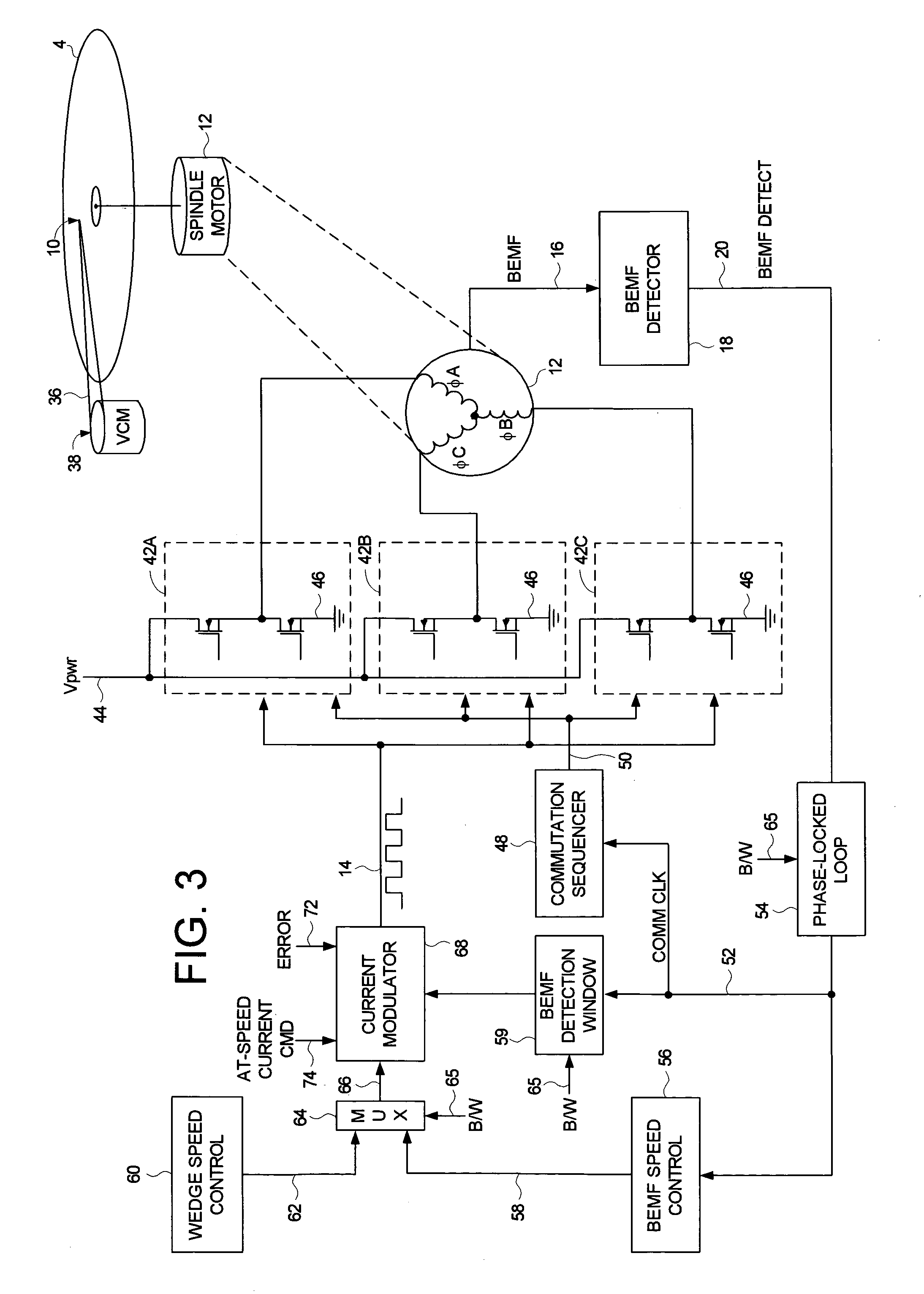
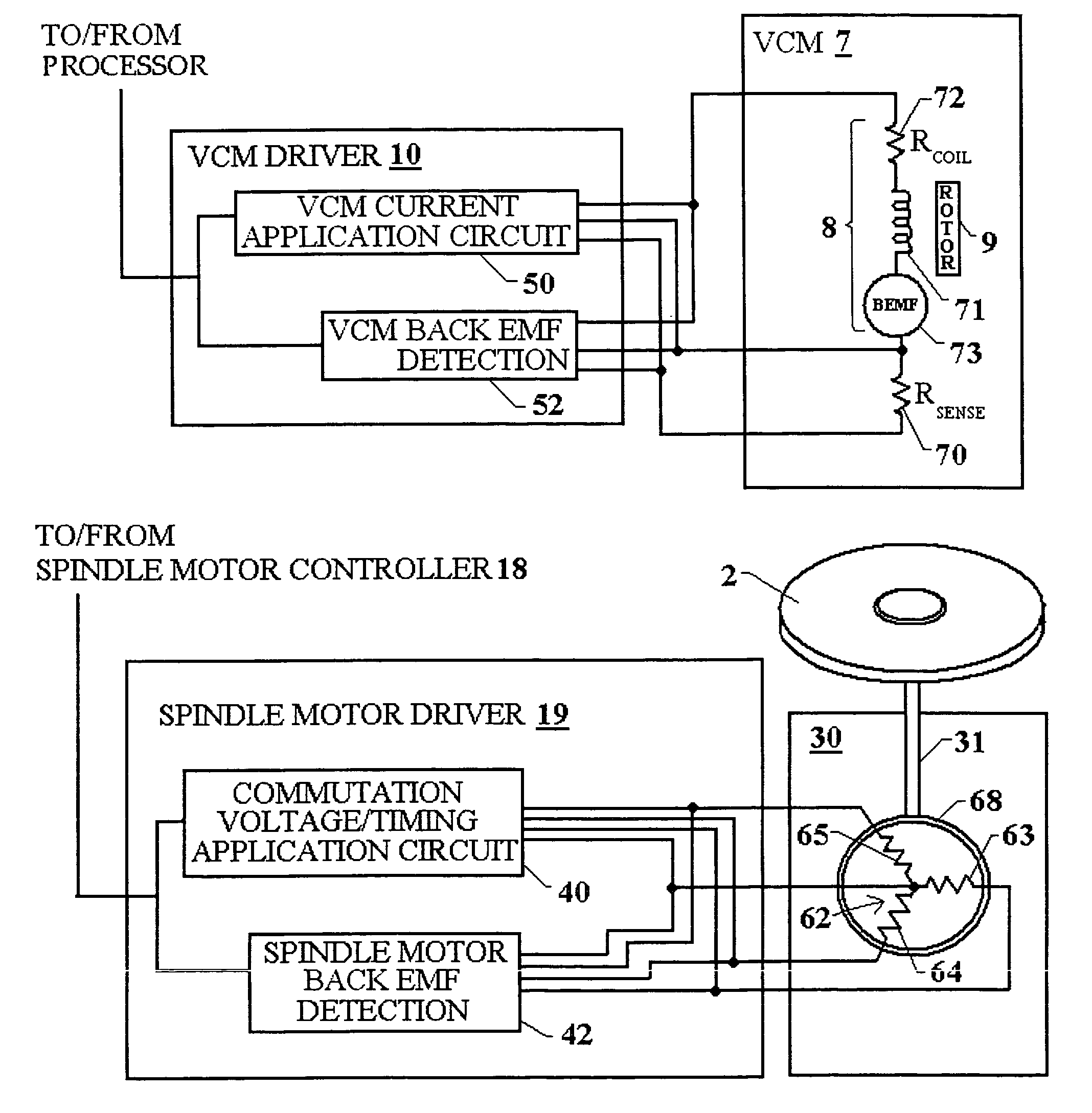
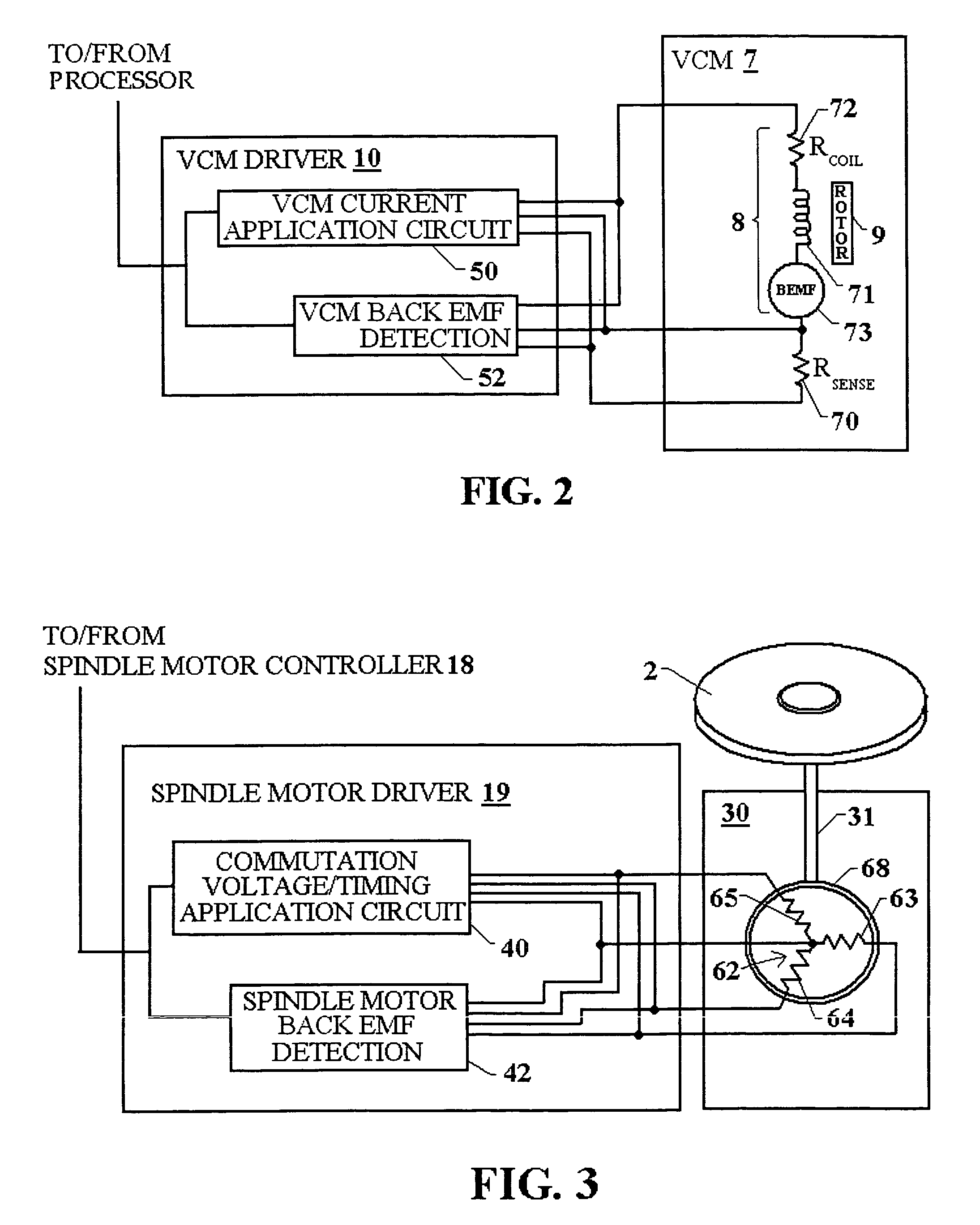
Disk drive disabling BEMF detection window to reduce acoustic noise while using wedge spindle speed control
InactiveUS6954324B1Reduce noiseRecord information storageCarrier speed control/regulation/indicationAcoustic noise reductionElectric machine
A disk drive is disclosed employing either back electromotive force (BEMF) spindle speed control mode or wedge spindle speed control mode. A BEMF detector monitors the BEMF voltage generated by the windings of the spindle motor to generate a BEMF speed error. The BEMF spindle speed control mode is used to spin up the disk to an operating speed, and the wedge spindle speed control to maintain the disk at the operating speed. While in the wedge spindle speed control mode, a BEMF detection window is disabled to reduce acoustic noise.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
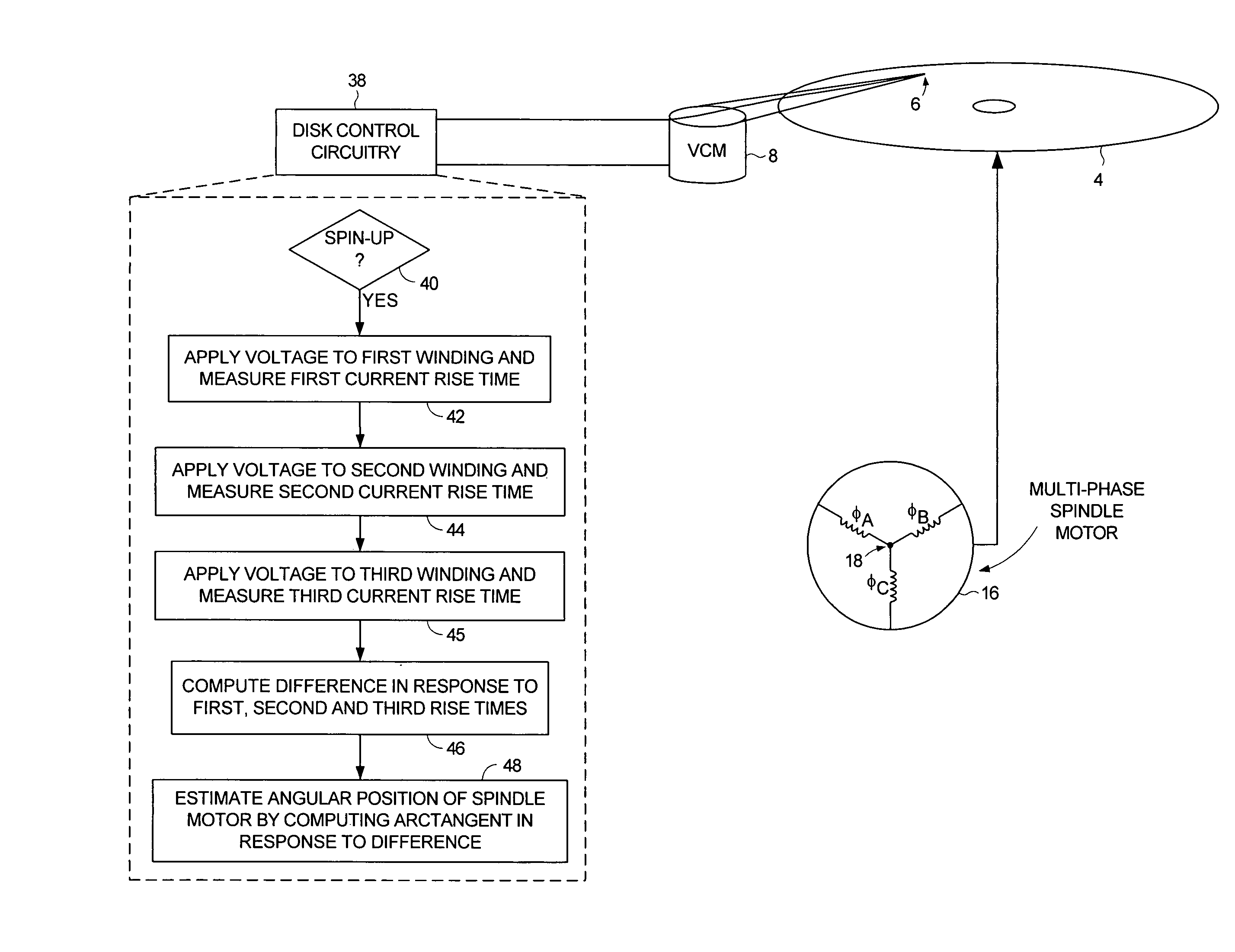
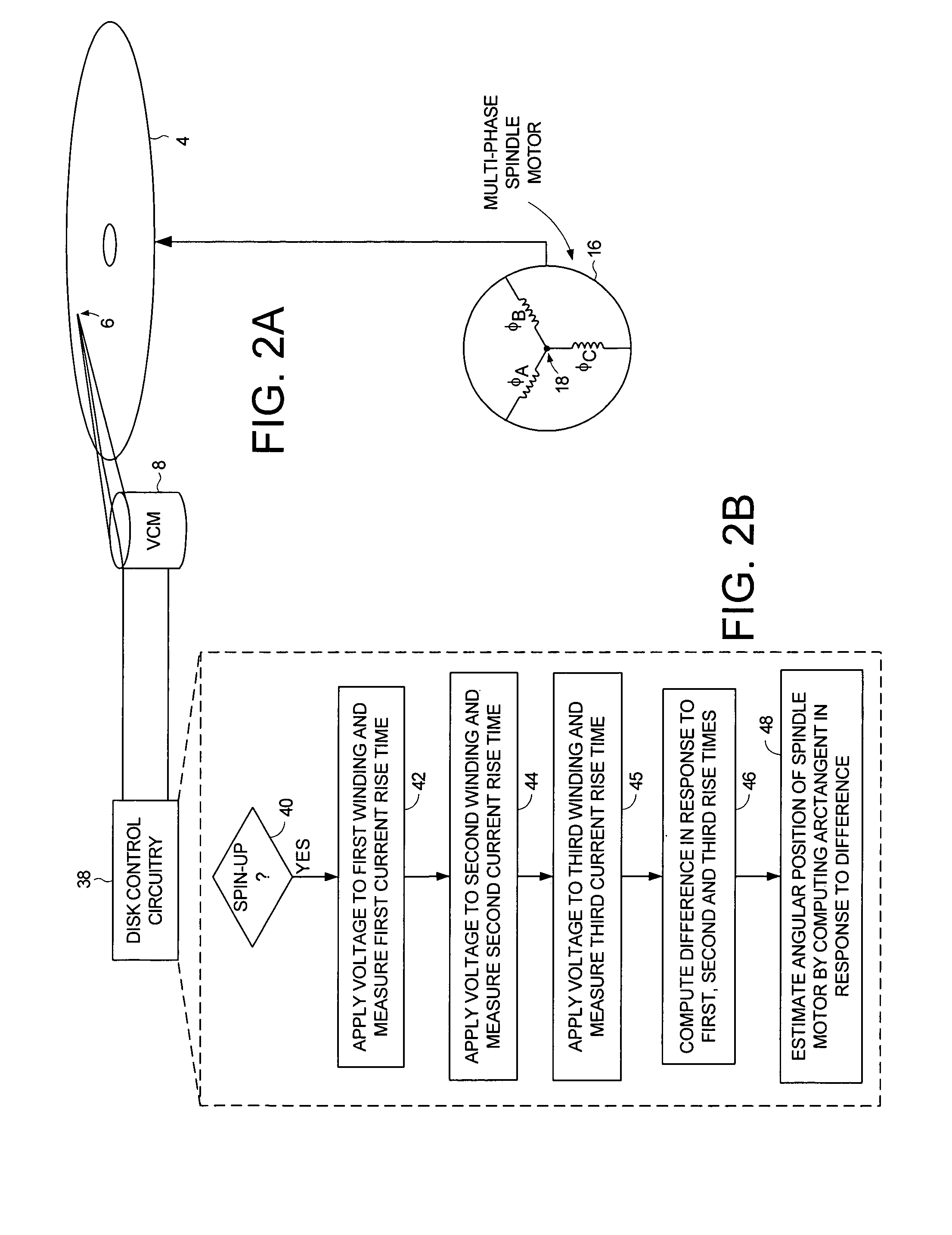
Disk drive estimating angular position of spindle motor during spin-up by computing differences in winding current rise times
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a spindle motor having a plurality of windings including at least a first winding, a second winding, and a third winding. During a spin-up operation, a voltage is applied to the first winding and a first rise time is measured for current flowing through the first winding to reach a predetermined threshold. A voltage is applied to the second winding and a second rise time is measured for current flowing through the second winding to reach a predetermined threshold. A voltage is applied to the third winding and a third rise time is measured for current flowing through the third winding to reach a predetermined threshold. A difference is computed in response to the first rise time, the second rise time, and the third rise time, and an angular position of the spindle motor is estimated by computing an arctangent in response to the difference.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Selective power management of disk drives during semi-idle time in order to save power and increase drive life span
ActiveUS7516348B1Extended disk drive lifeSignificant power savingEnergy efficient ICTDigital storageIdle timeData transmission
Redundancy in storage arrays is used to extend the life of disk drives and conserve power. In an exemplary storage array, a group of storage devices includes y storage devices. Data and redundant information is distributed across the y devices to provide m levels of redundancy. “Spun down devices” are provided by spinning down a set of one or more of up to m of the y storage devices. Meanwhile, data transfers to and from the group of storage devices continue to be serviced. After a predetermined time, the currently spun down disks can be spun up, and new spun down devices are provided by spinning down another set of one or more of m of the y storage devices. An array may include several groups of storage devices, each having its own value for y and m.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
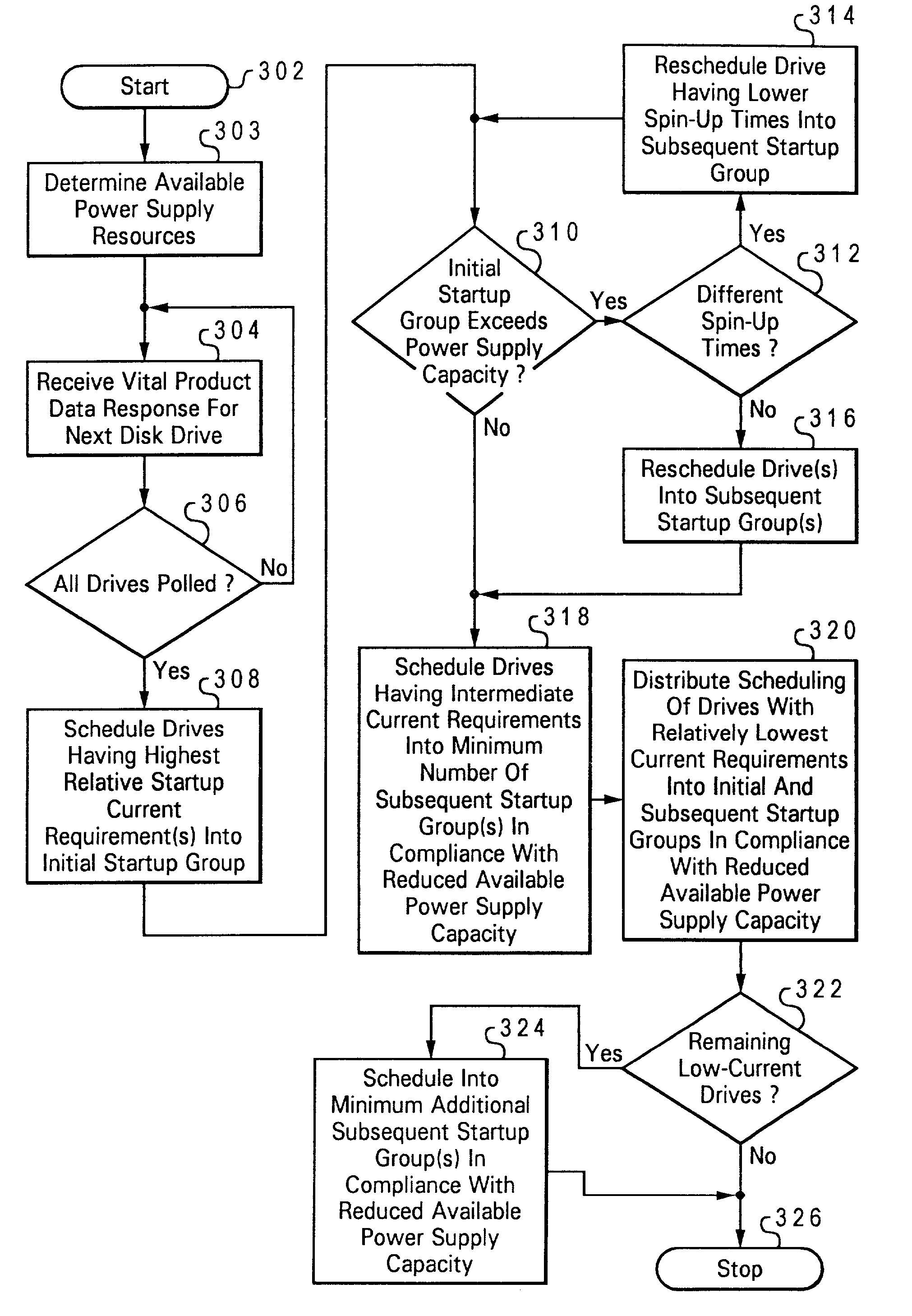
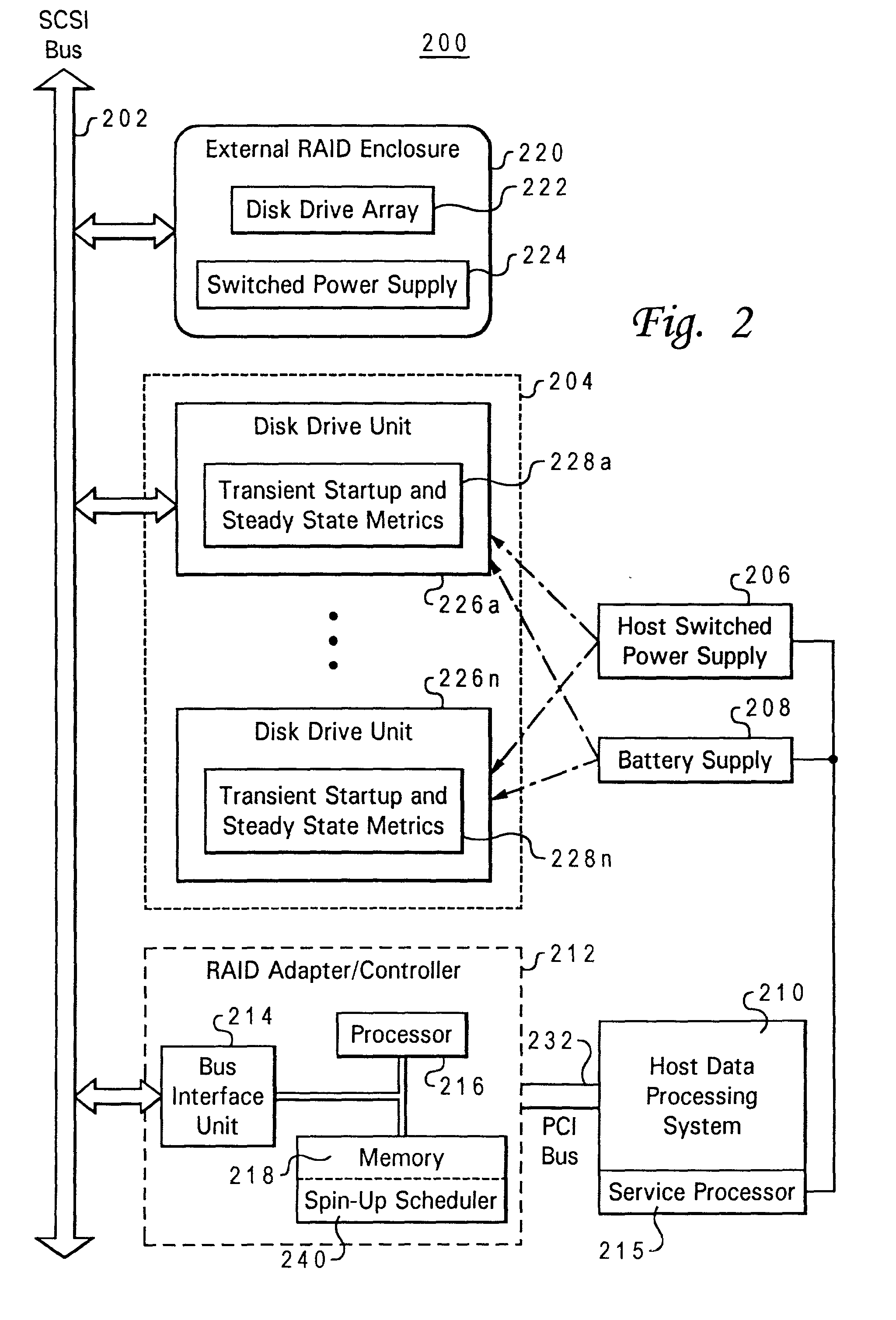
Adaptive startup policy for accelerating multi-disk array spin-up
A method and system for adaptively implementing a disk drive startup sequence for a disk drive array. Prior to a next disk drive spin-up sequence a currently available power supply resource capacity and a startup metric of each of the array disk drives are determined. Each of the disk drives are scheduled into designated startup groups as a function of both the determined currently available power supply resource capacity and the determined startup metric. The scheduling of disk drives into designated startup groups includes determining an activation sequence timing schedule for each of the disk drives. The activation sequence timing schedule determines the relative times at which spindle motors for each of said plurality of disk drives will be activated as a function of the determined startup metric for each of the disk drives and the available power supply resource capacity as reduced by the steady state power requirements of each of the startup groups.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Disk drive input sequencing for staggered drive spin-up
ActiveUS7305572B1Reduction in system peak power requirementSave budgetDisposition/mounting of recording headsDriving/moving recording headsControl theorySpin-up
Disk drive spin-up is staggered to reduce peak power requirements. Spin-up of the drives is controlled by selectively delaying voltage inputs to the disk drives. Alternately, spin-up of the drives is controlled by staggering the timing of communications to the disk drives.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
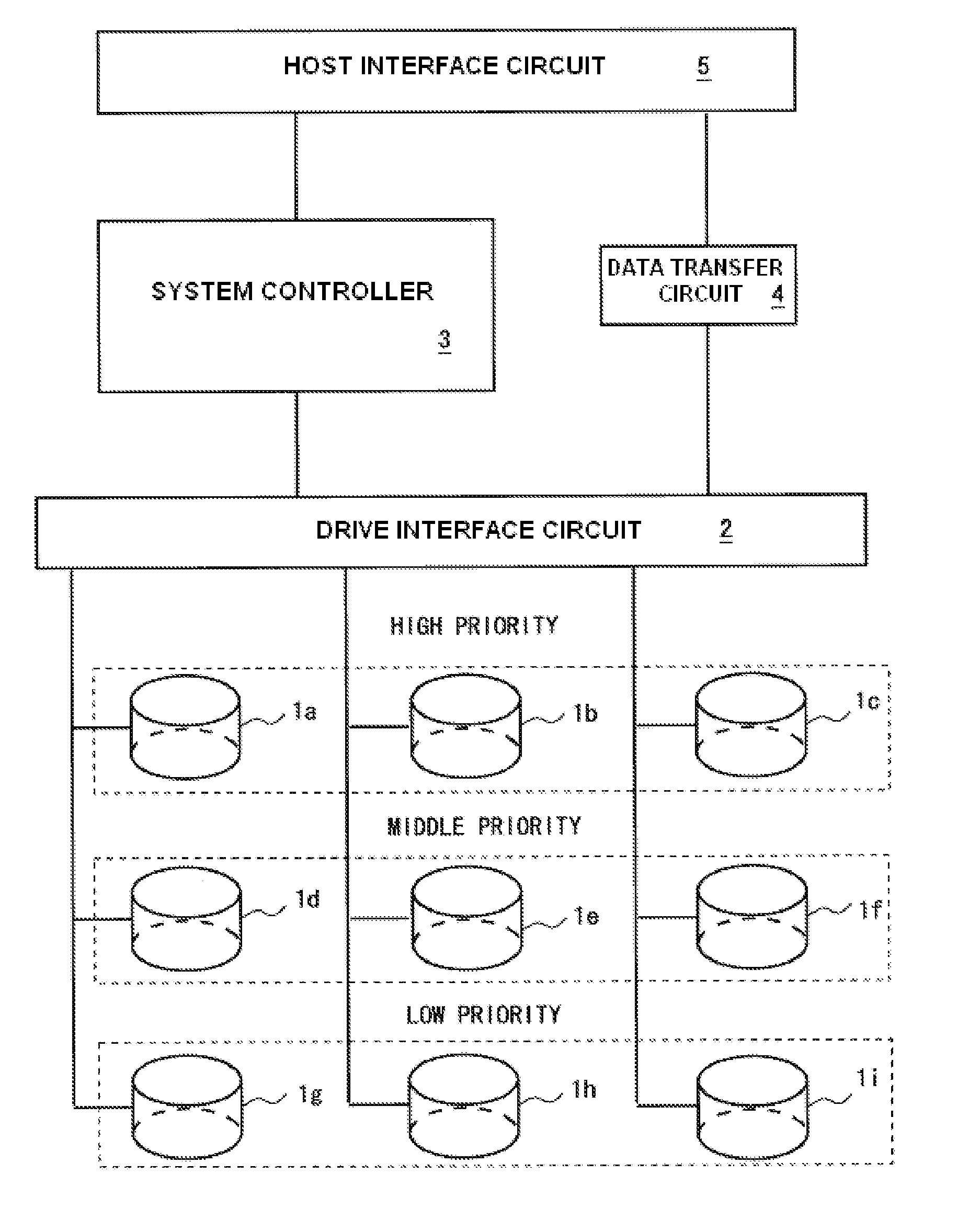
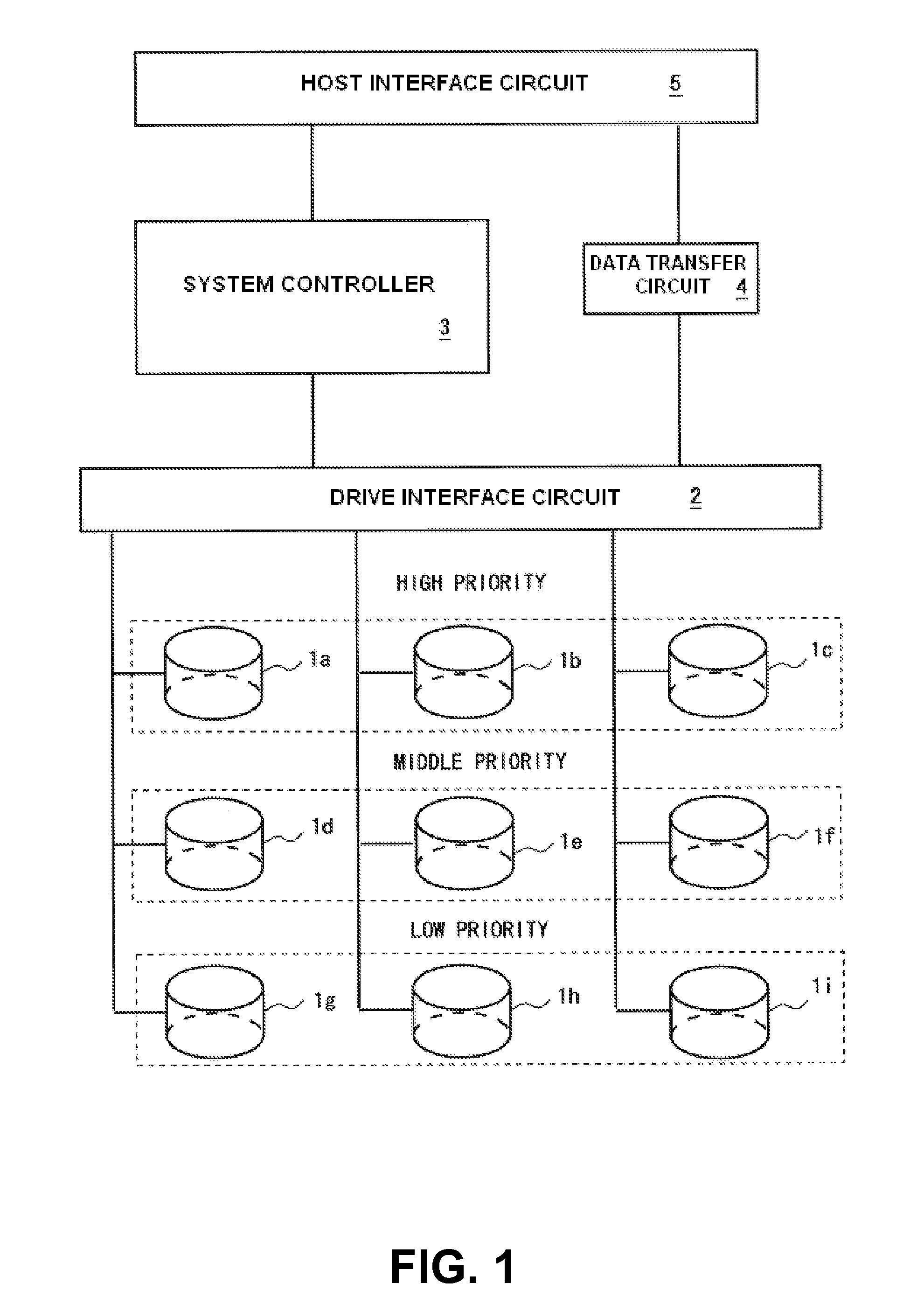
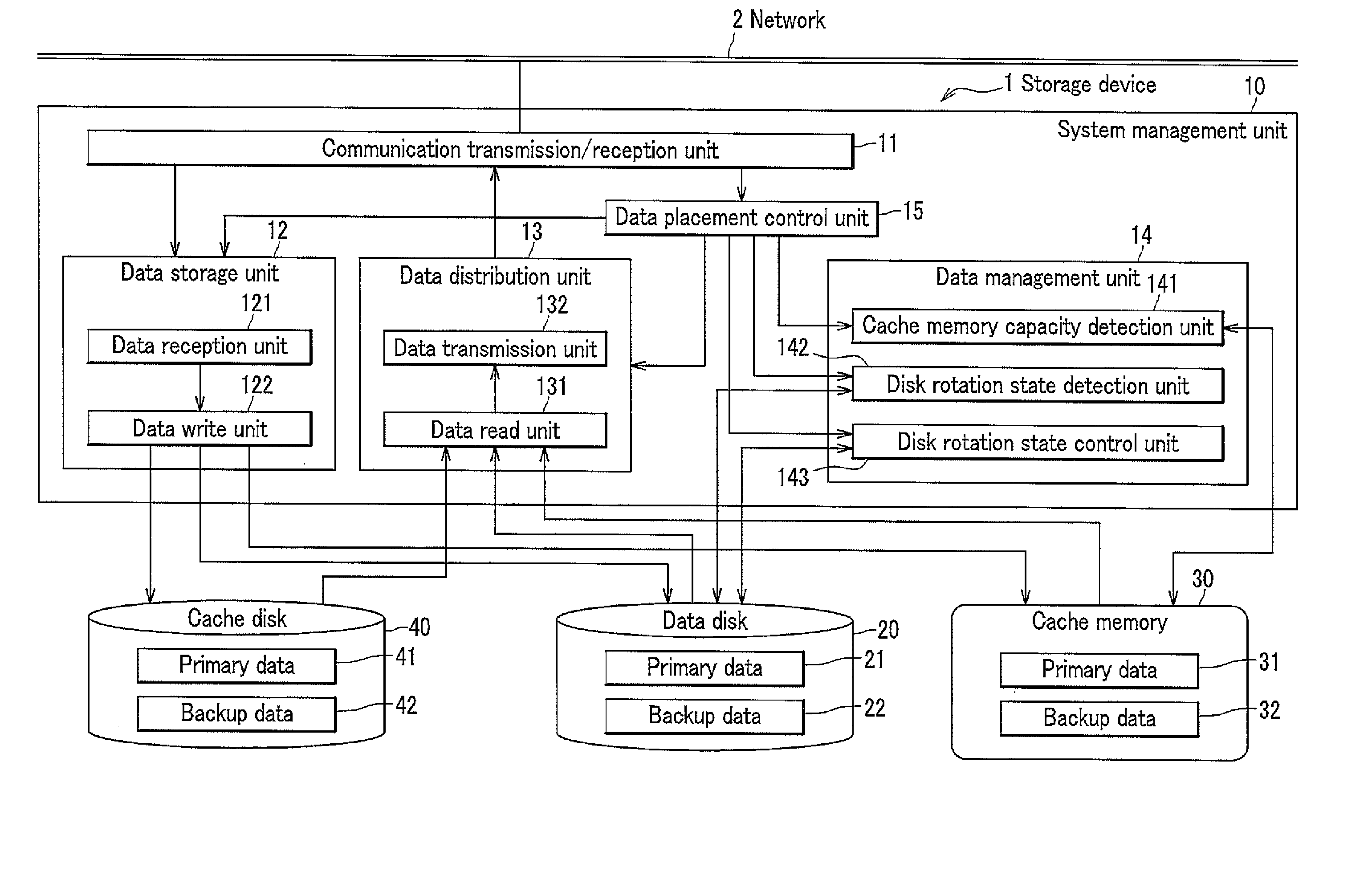
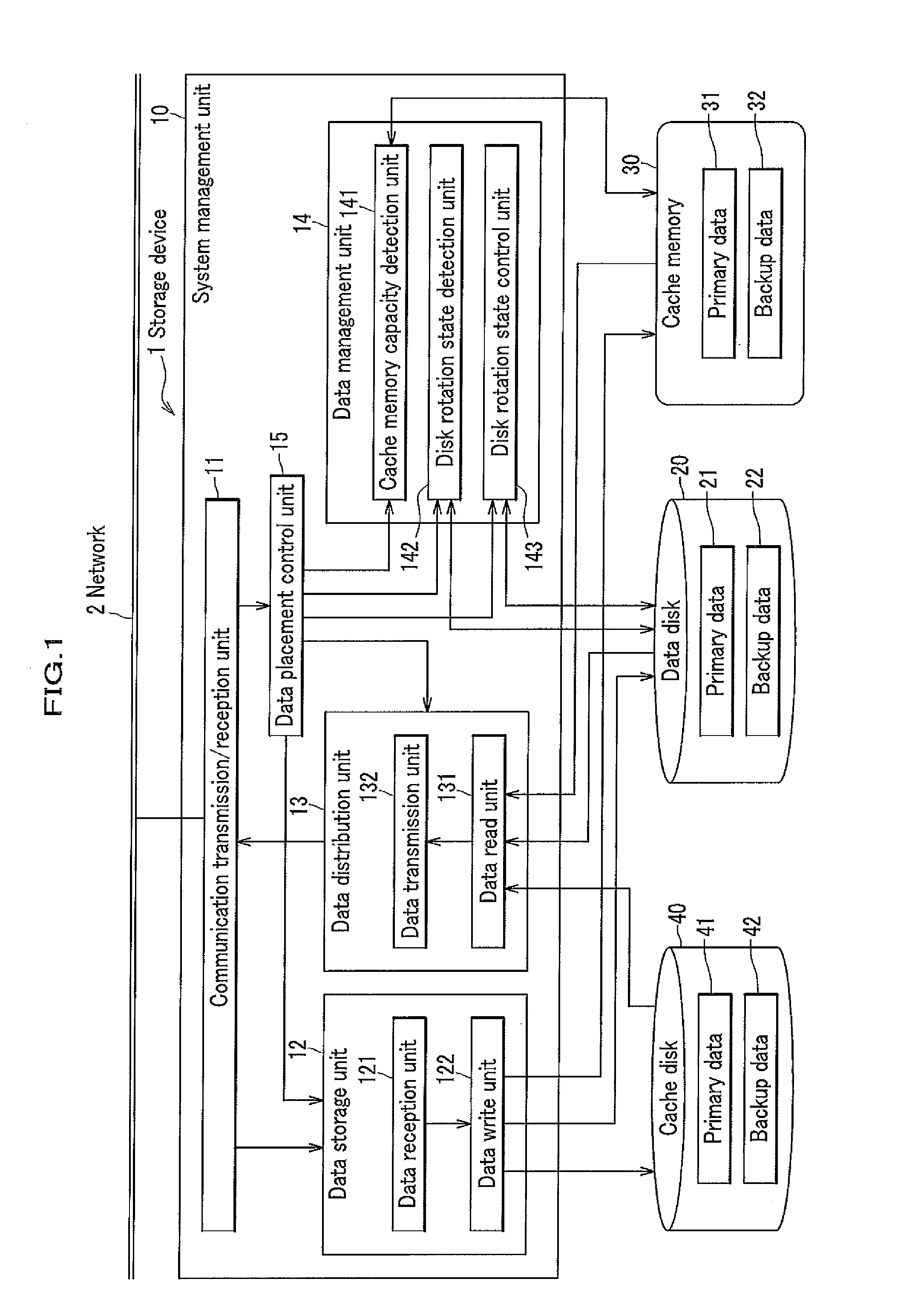
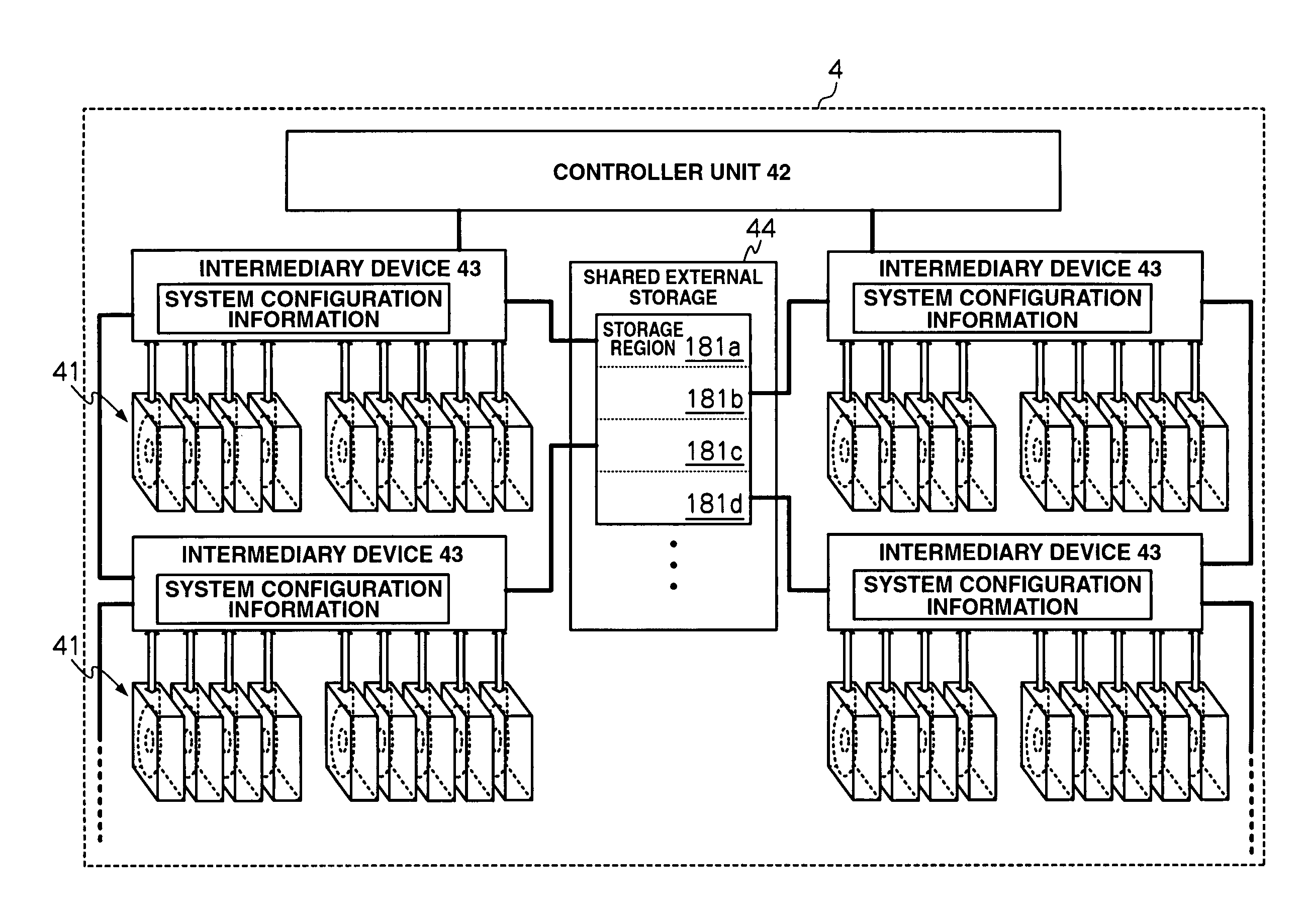
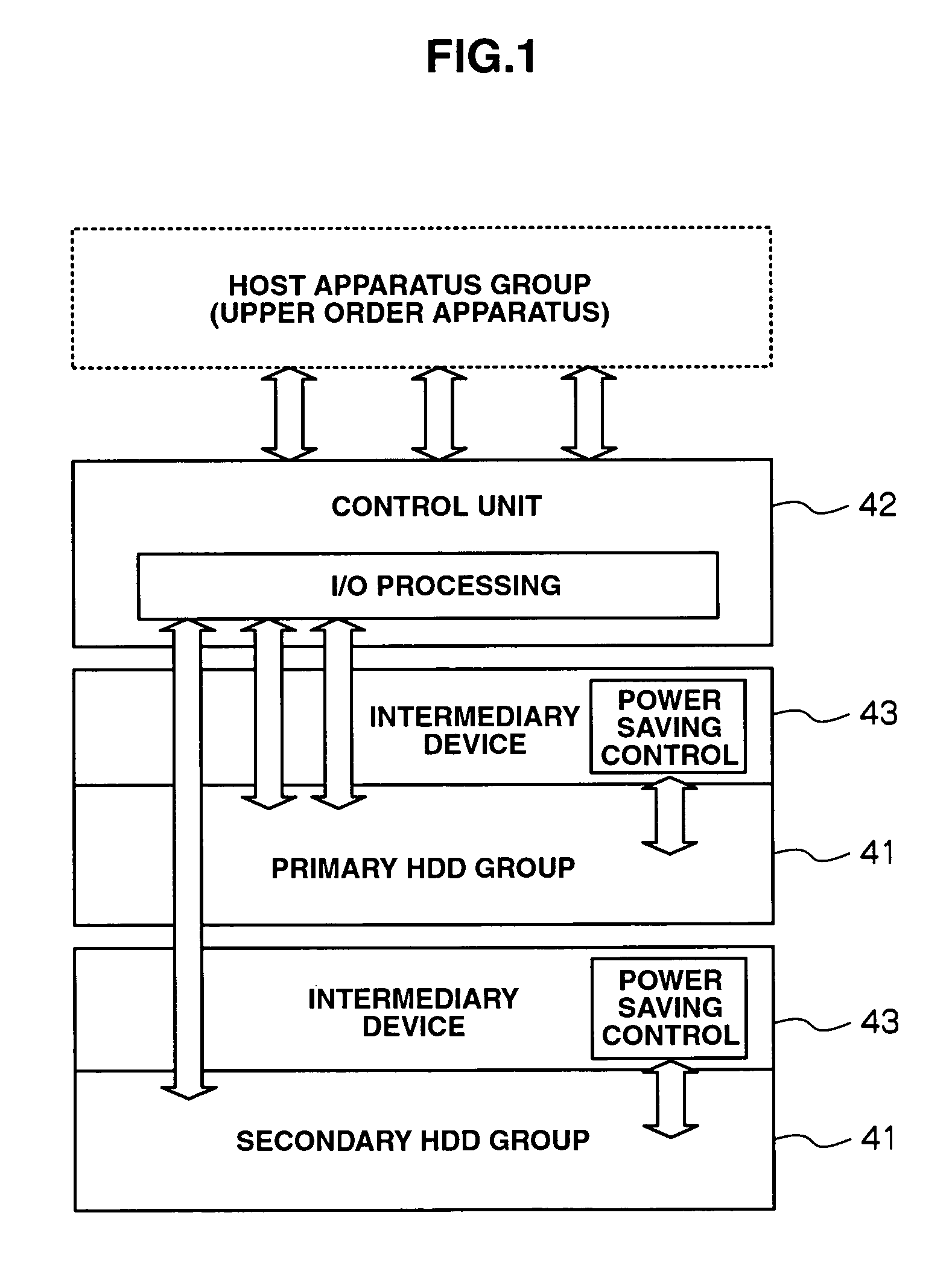
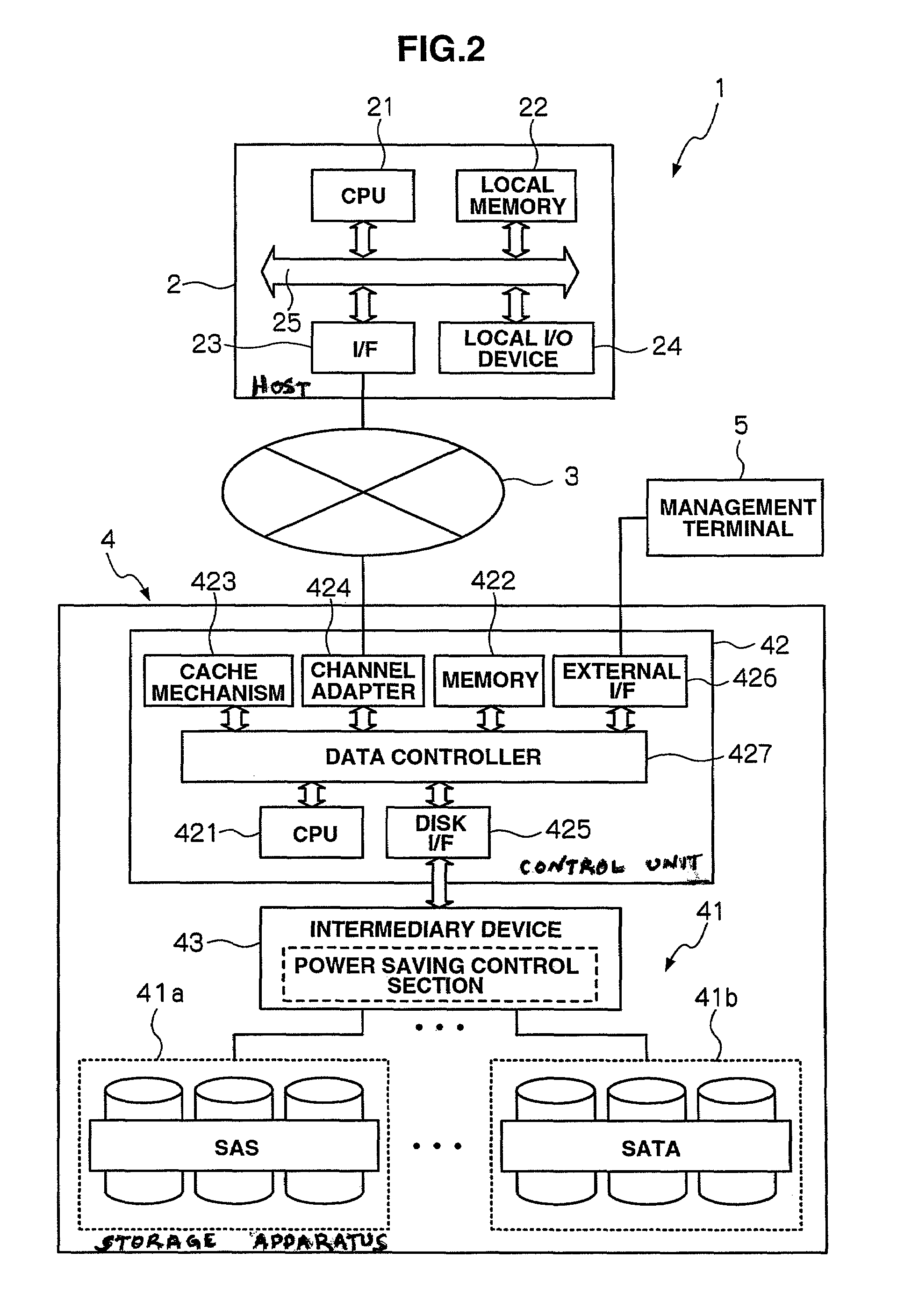
Storage apparatus and a data management method employing the storage apparatus
InactiveUS20080126616A1Increase consumptionIncrease in sizeEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareMaintenance management
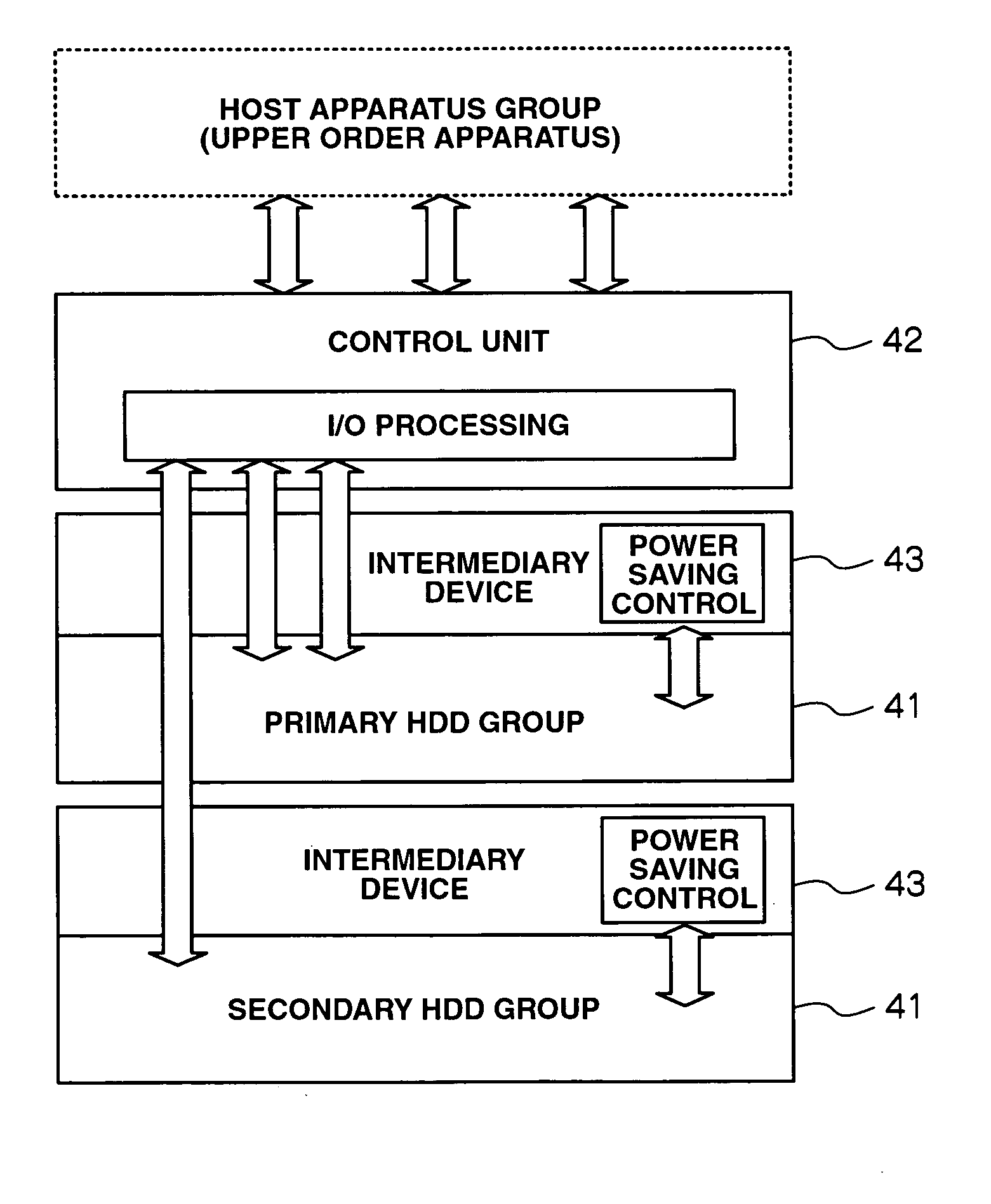
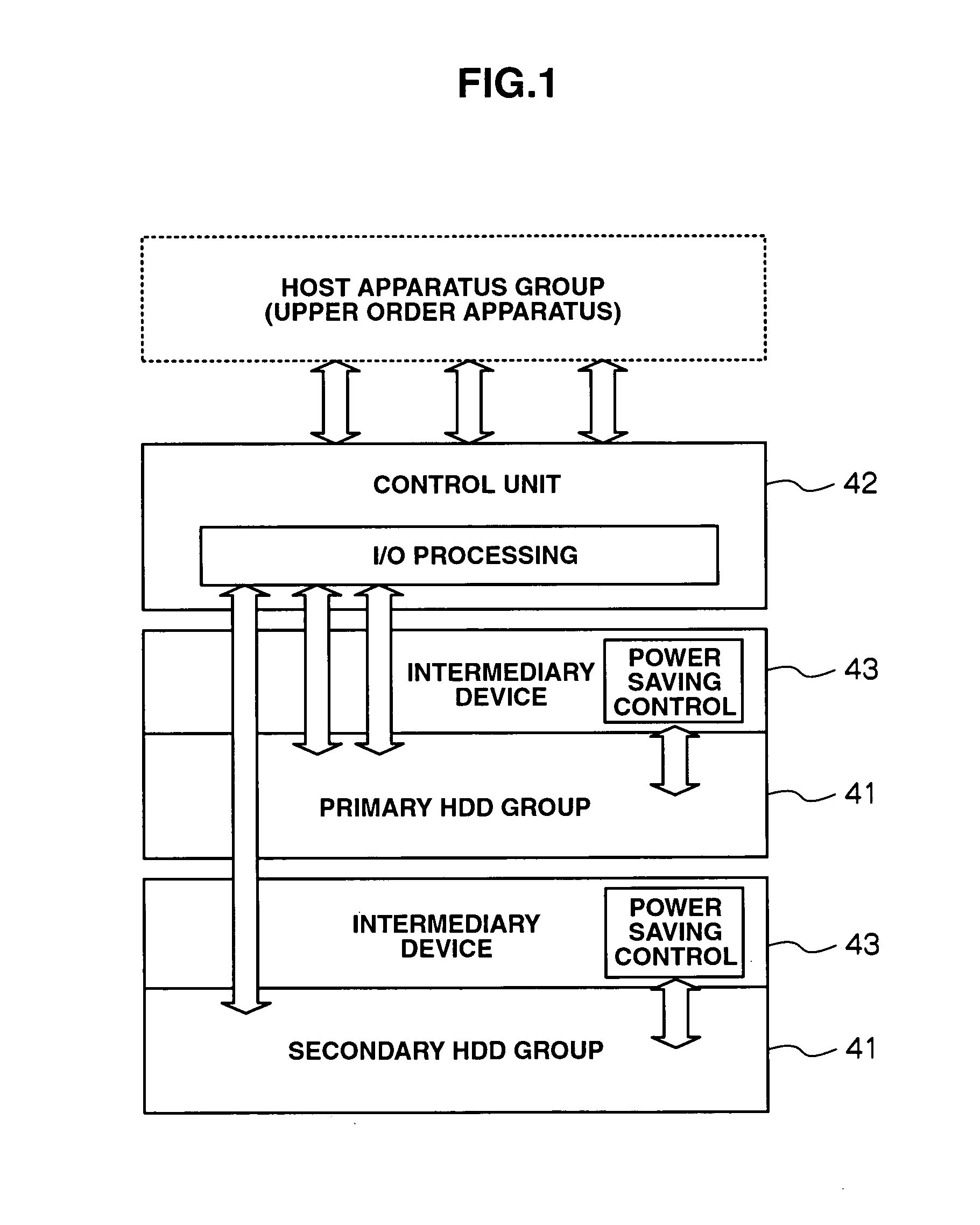
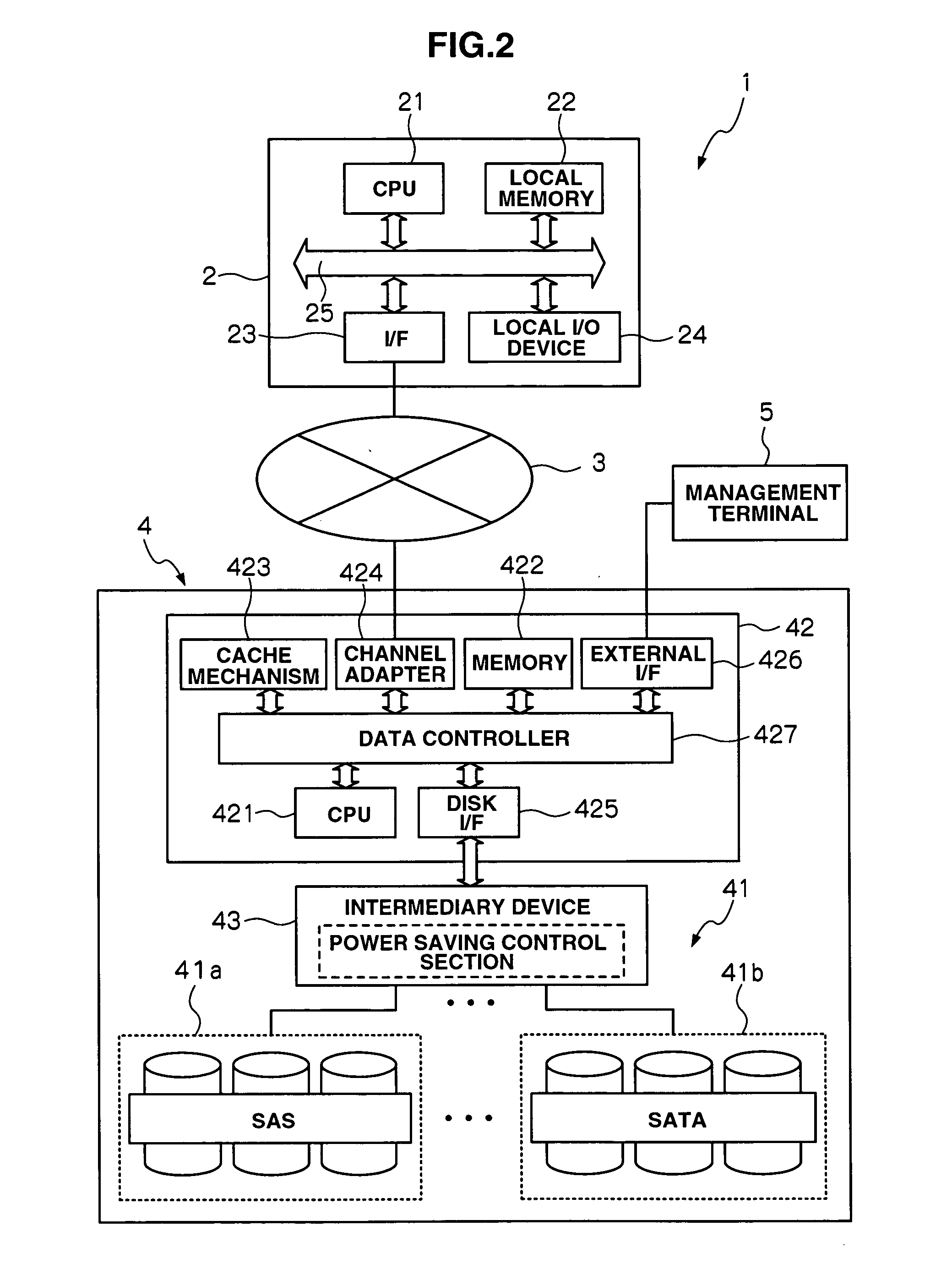
A storage apparatus is provided that is capable of reducing data maintenance management costs with a performance that is both highly reliable and fast. The present invention is storage apparatus where an intermediary device is arranged between a controller and a plurality of disk devices of different performances arranged in a hierarchical manner. The controller unit carries out I / O accesses to and from the disk devices via the intermediary devices based on access requests sent from host apparatus. The intermediary device includes a power saving control function for the disk device and carries out operation control such as spin off and spin up of disk devices in accordance with conditions set in advance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
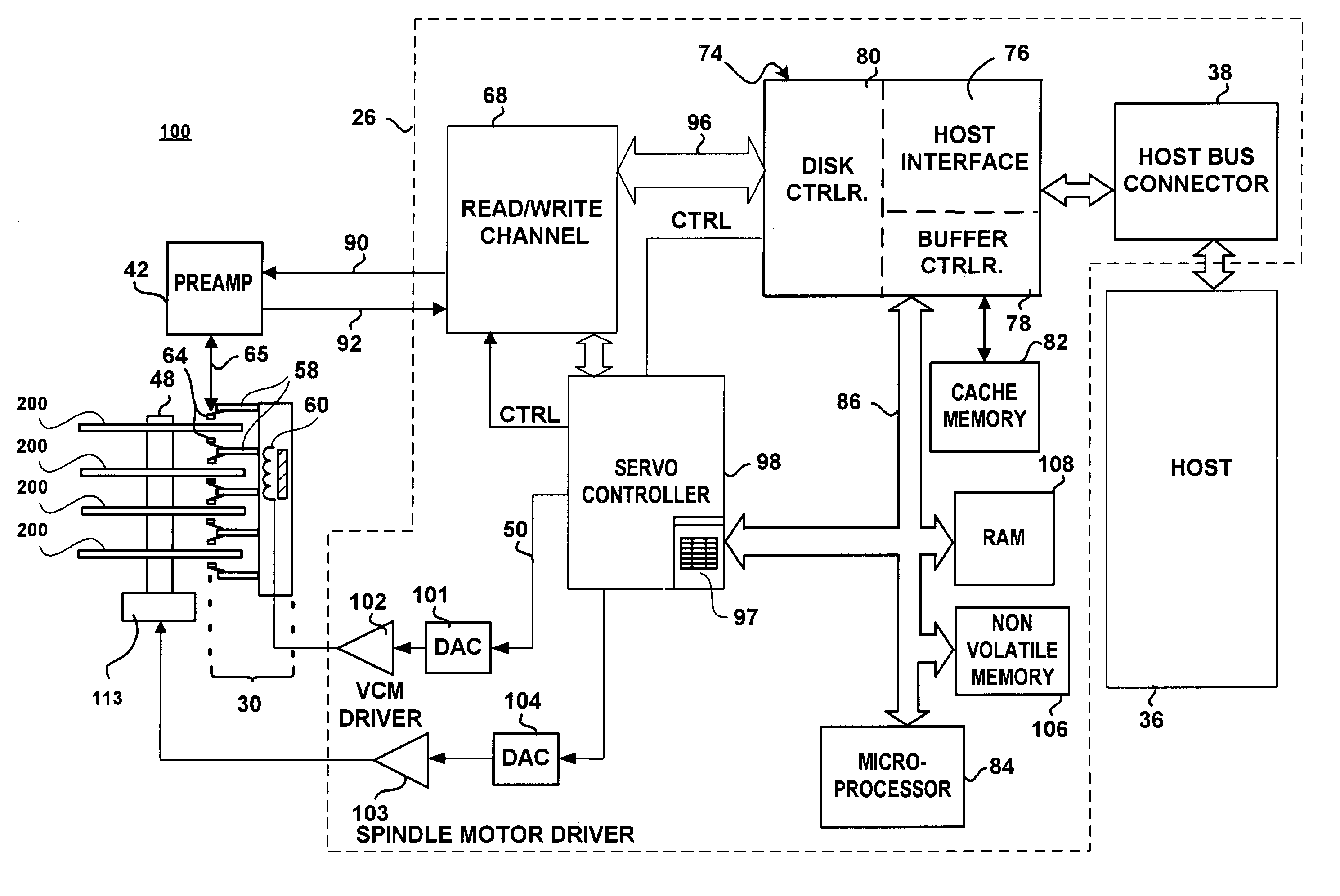
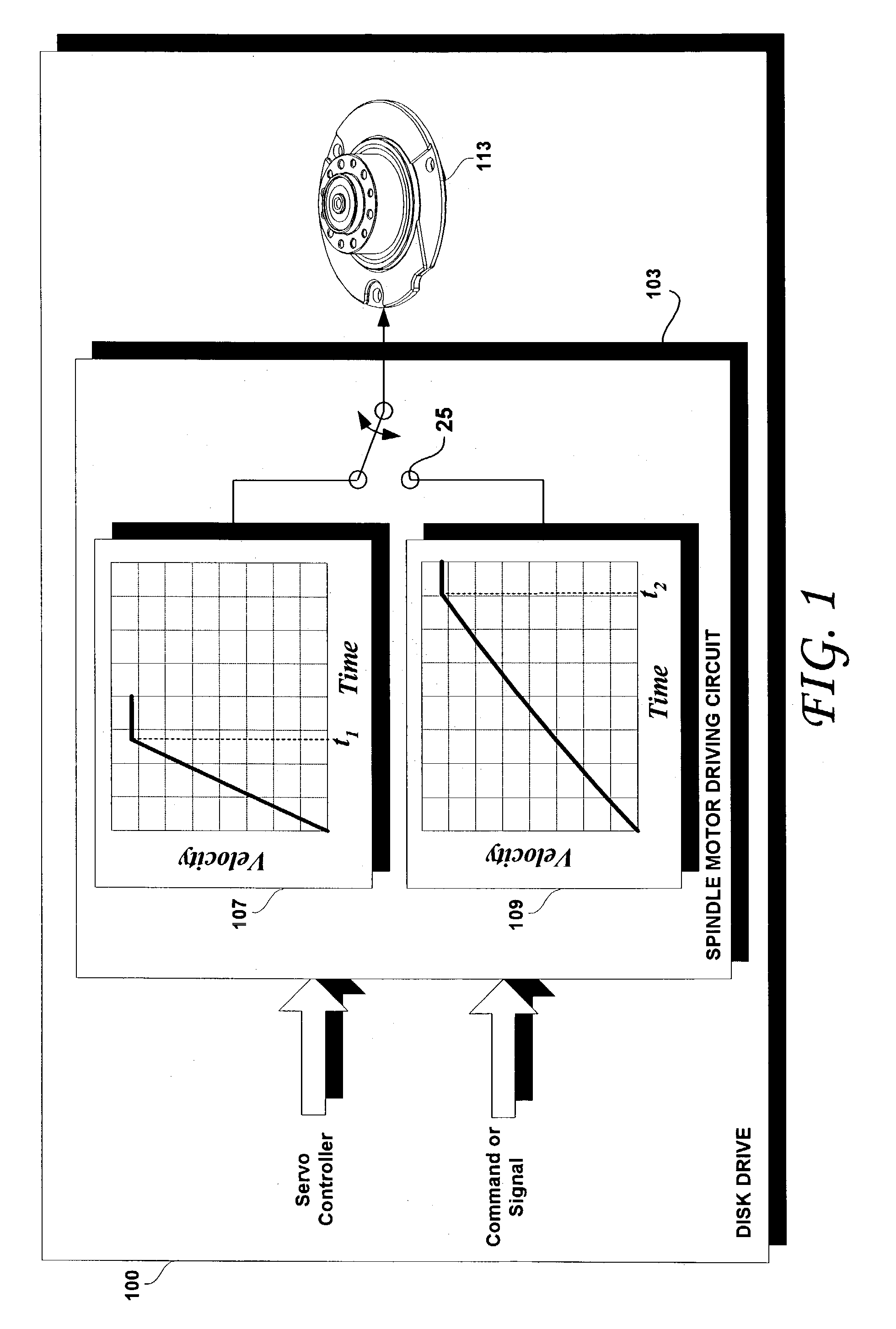
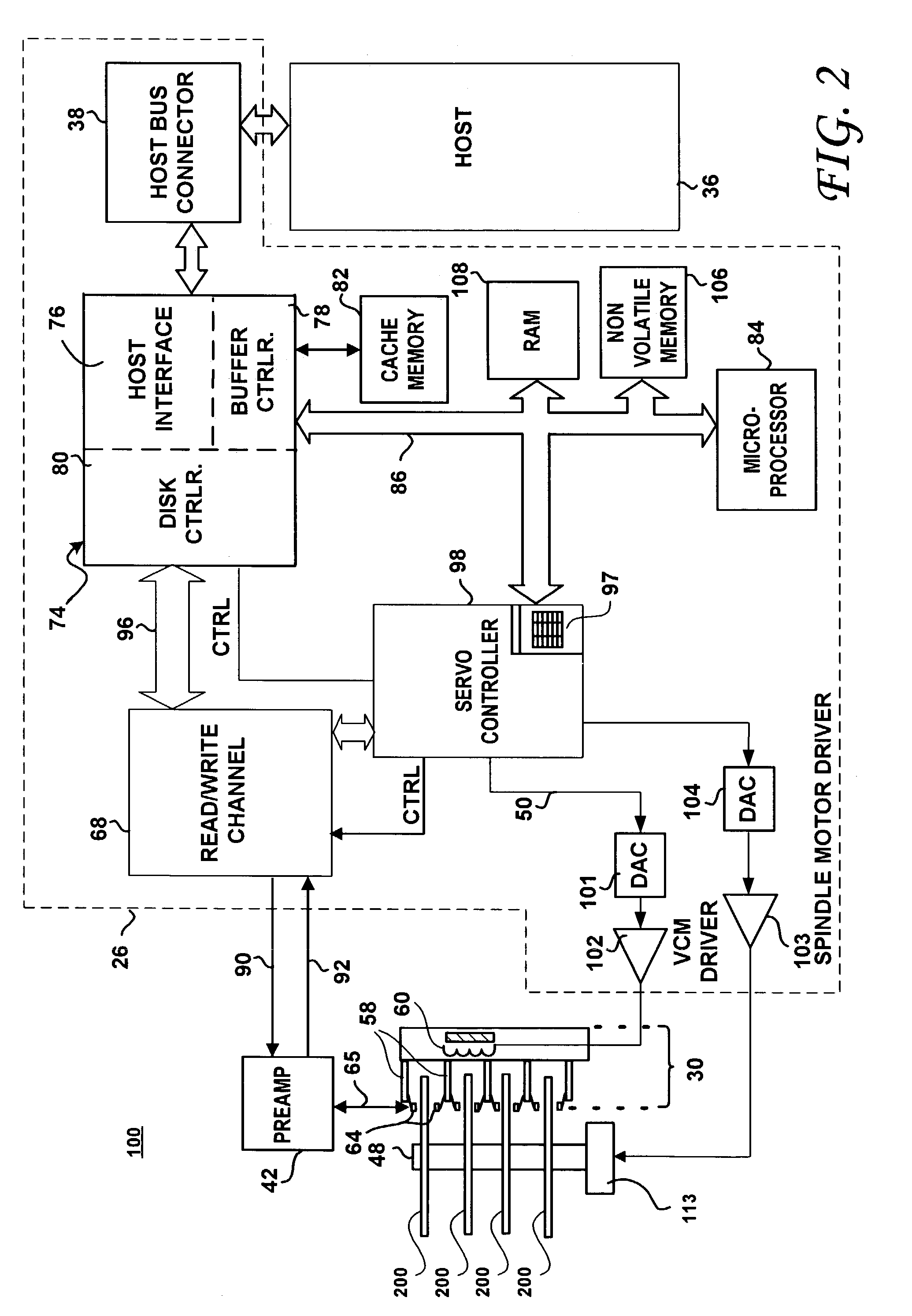
Disk drive and disk drive-containing device having selectively controllable spindle motor spin up profiles
InactiveUS6989953B1Keep for a long timeRecord information storageCarrier speed control/regulation/indicationElectric machineEngineering
A spindle motor in a disk drive is driven by a driving circuit that, upon receipt of a signal or command, selectively spins up the spindle motor according to a first spin up profile or according to a second spin up profile that is defined to provide a longer spin up time in comparison with the spin up time defined by the first spin up profile. The second spin up profile spins up the spindle motor in a longer period of time and / or generates less acoustic noise as compared to the first spin up profile.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
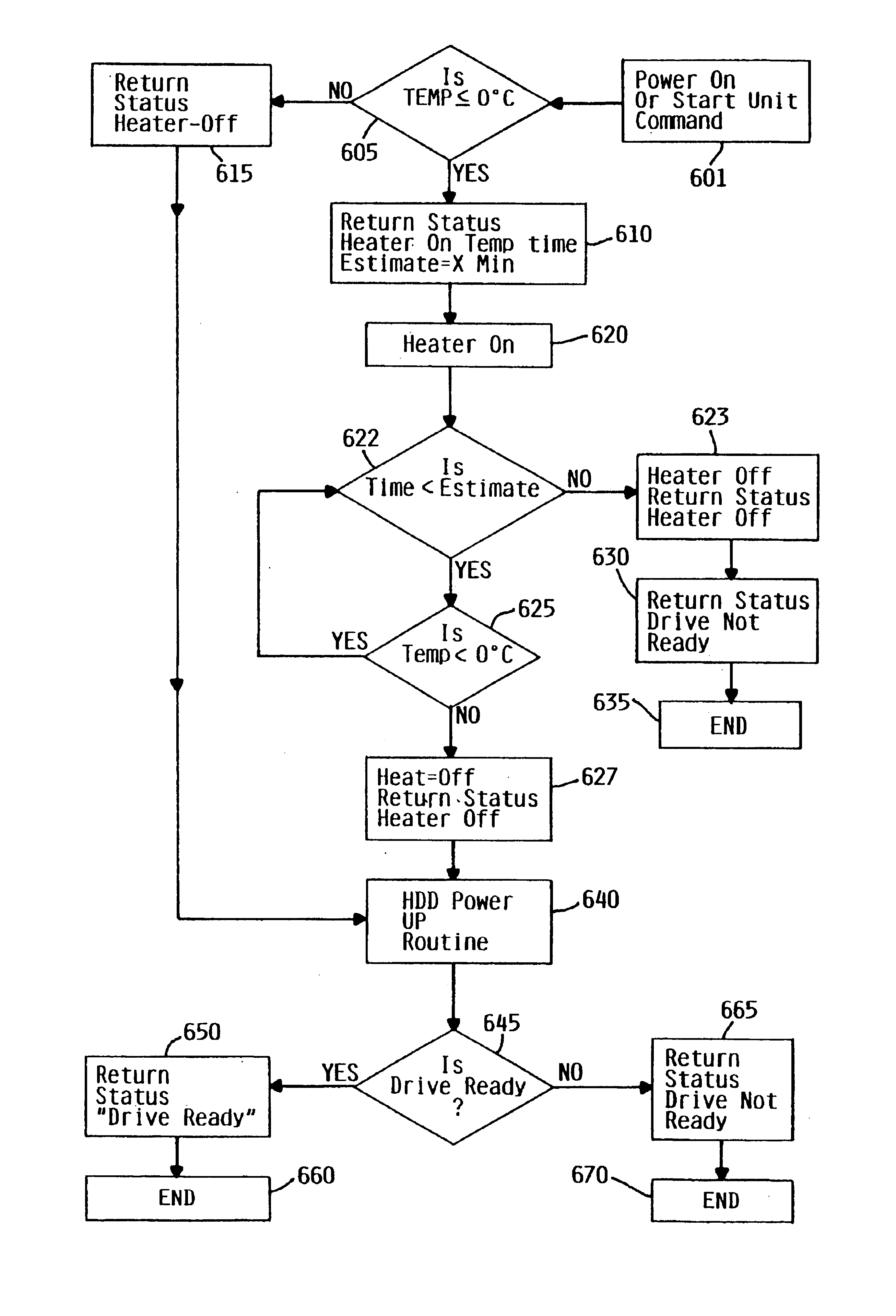
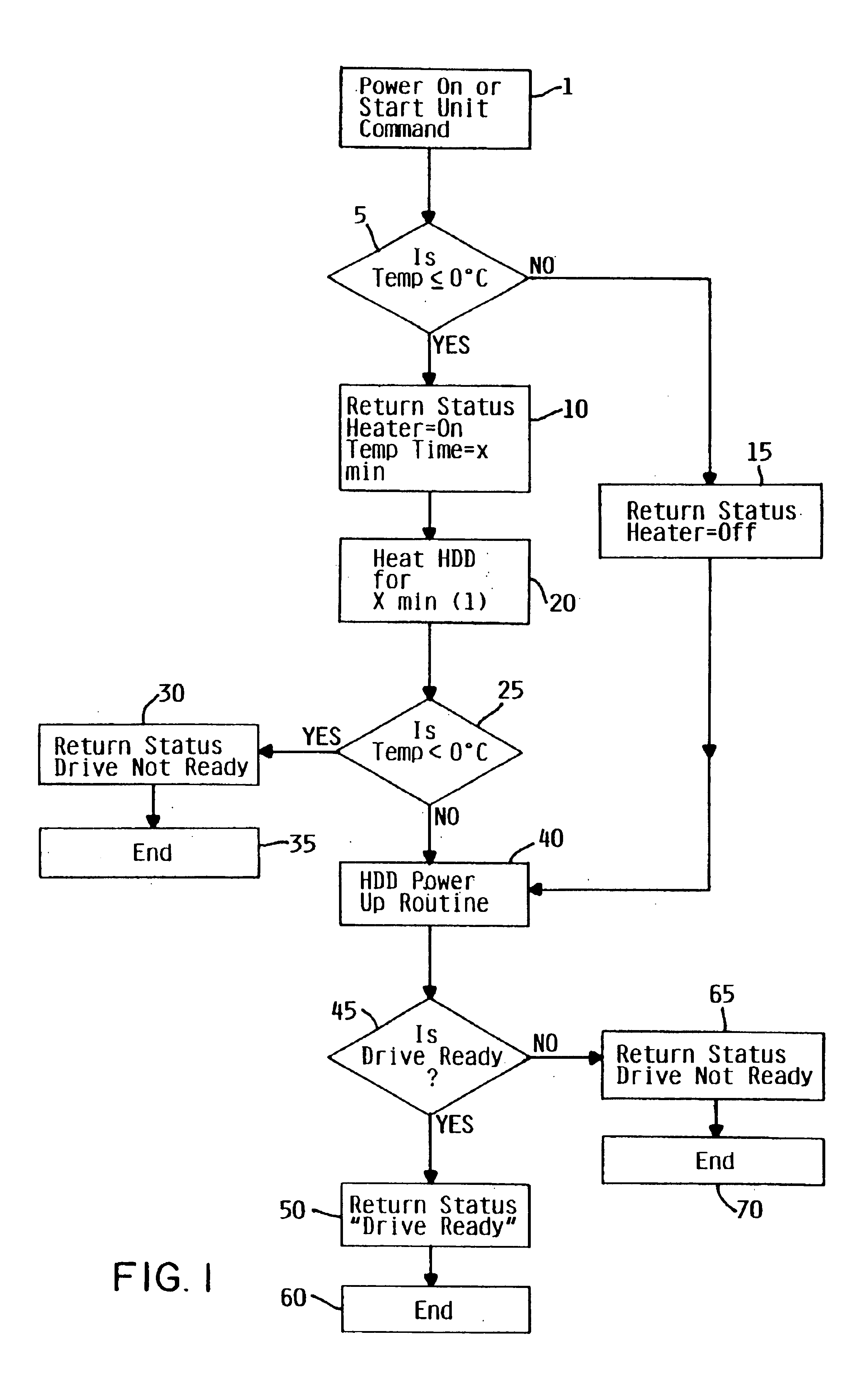
Method and apparatus for enabling cold temperature performance of a disk
InactiveUS6735035B1High torqueHigh viscosityCommutation monitoringApparatus for flat record carriersDirect-access storage deviceEngineering
In cold weather, the higher torque required for normal spinning operation of a spindle motor assembly in a direct access storage device due to the increased viscosity of the grease, is overcome by localizing the heating to the spindle motor assembly to reduce the viscosity of the grease, and then let a disk driven self heat during and after spin-up of the spindle motor assembly.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
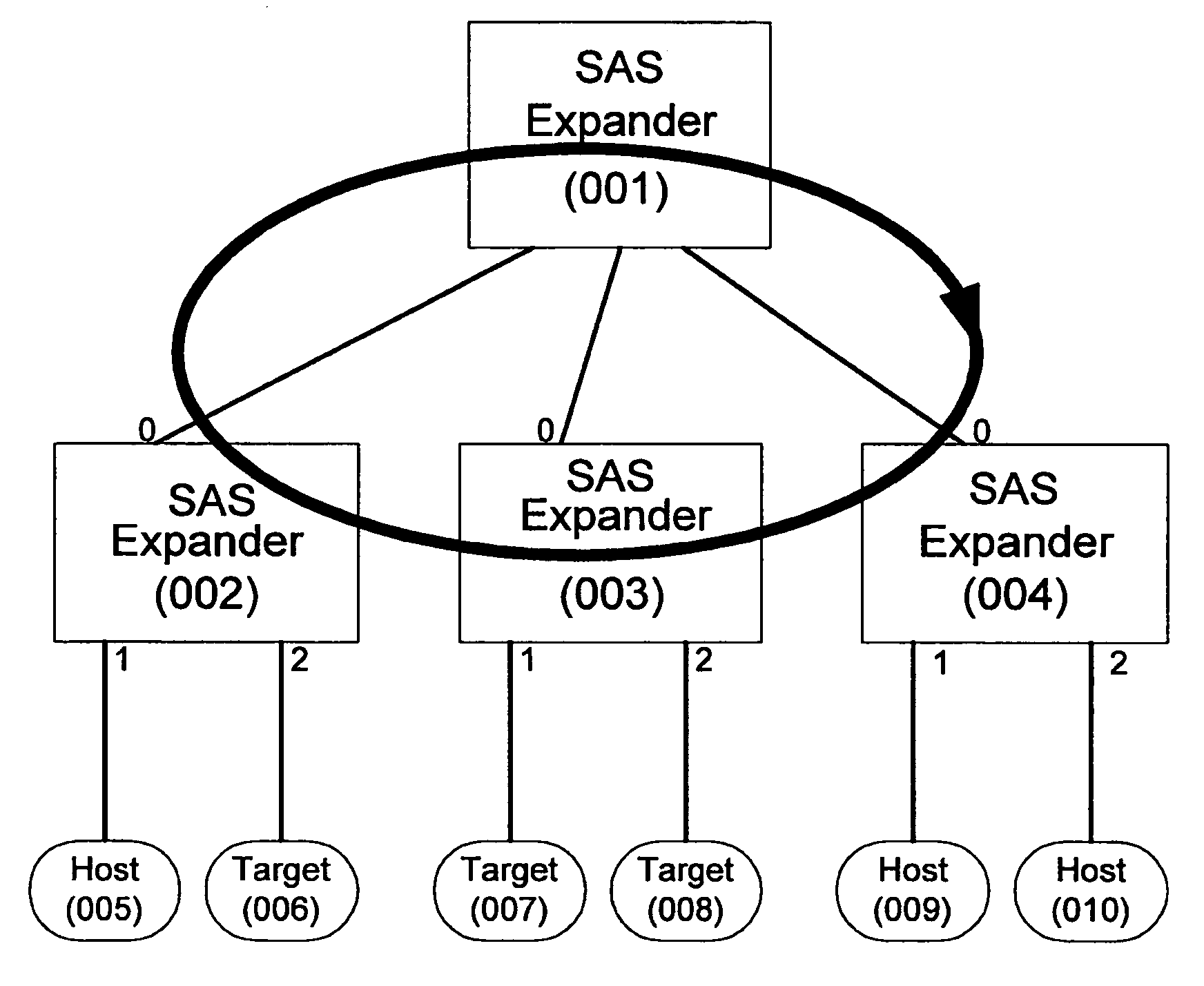
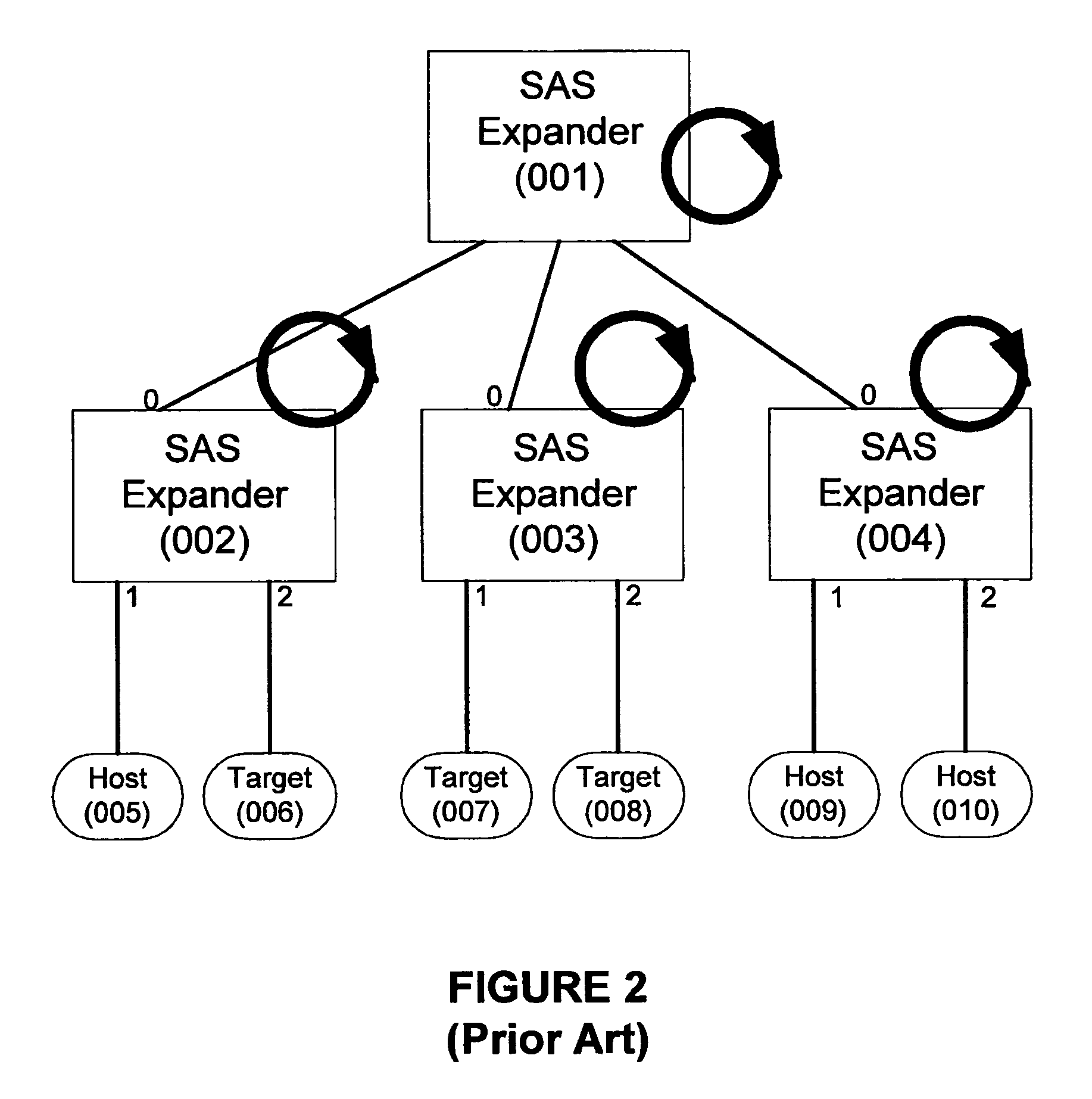
Hierarchical device spin-up control for serial attached devices
ActiveUS7474926B1Digital data processing detailsRecord information storageHard disc driveConnected device
A method and apparatus are provided for controlling the powering-up or spin-up of devices such as hard drives using expanders in a SAS topology. The method and apparatus provides a mechanism to coordinate spin-up control among a topology of expanders. The present invention enables an expander to both process the reception of the NOTIFY command to spin up attached devices and to propagate such command to further expanders. Hierarchical spin-up control provides an advantageous, in-band mechanism that controls the expanders within the topology to limit the total number of devices powering-up at any given time.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Method and apparatus for pre-spinning rotor forgings
ActiveUS20100212422A1Relieve forging induced residual stressAvoid excessive rotationForce measurementStatic/dynamic balance measurementHigh densityRotation velocity
A method and system for relieving forging induced residual stresses in a rotor forging balances a pre-spin machine with the forging mounted thereon at a first rotational speed and then pre-spins the forging with it mounted on the machine at a substantially greater second rotational speed. A one per rev sensor is used for determining a weight placement angle and a vibration sensor is used for determining an amount of weight to add to a spinning assembly including the forging during the balancing. High-density non-metallic balance weights adhesively attached on an inside surface of the forging or spinning assembly may be used. The rotational inertia of the spinning assembly may be checked during a spin up period by determining a rate of rotational acceleration vs. torque applied to the spinning assembly and used to stop the pre-spinning if it is to great.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
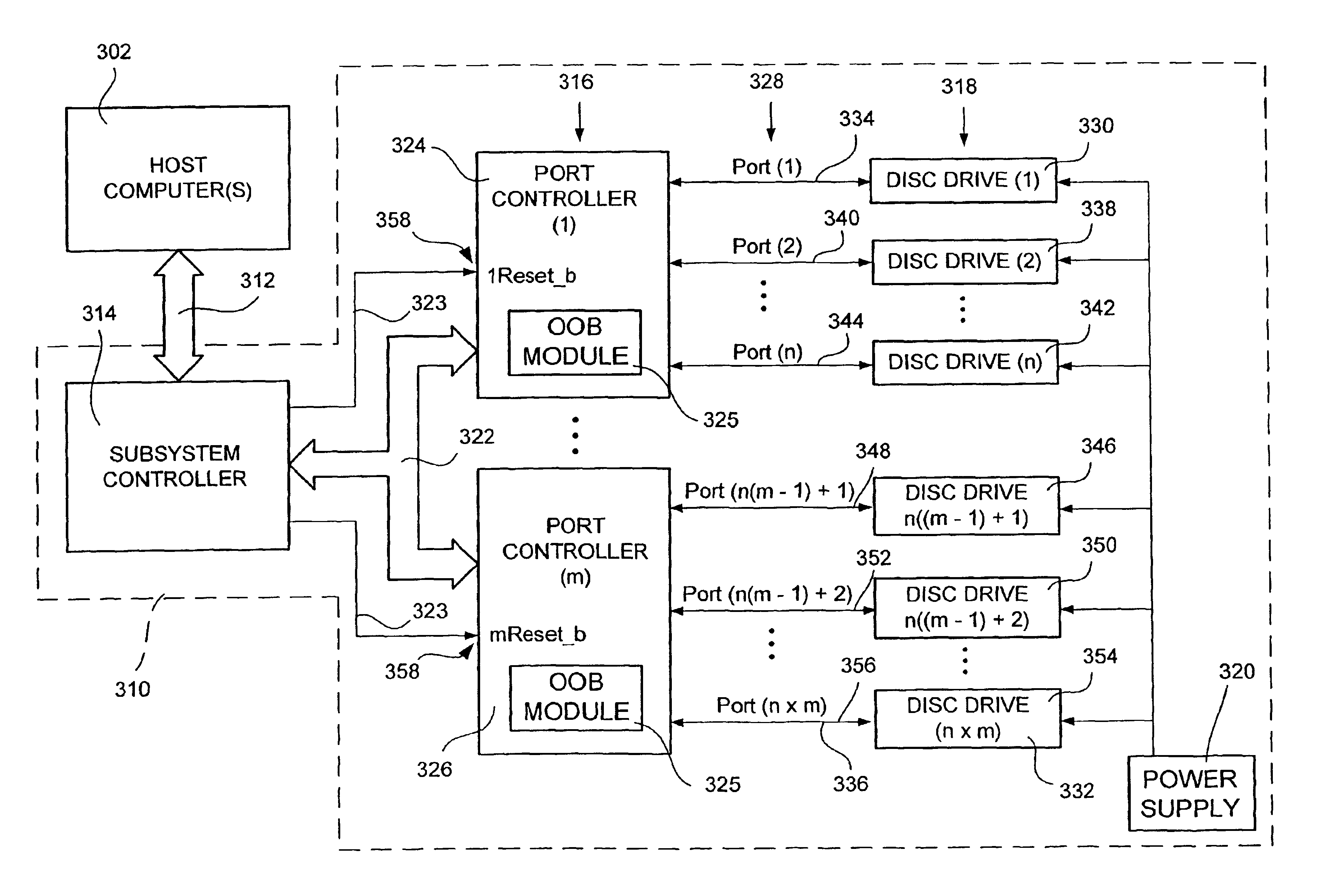
System for selectively controlling spin-up control for data storage devices in an array using predetermined out of band (OOB) signals
InactiveUS6915363B2Selective spin-up of the data storage devicesInput/output to record carriersRecord information storageComputer hardwareElectric machine
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
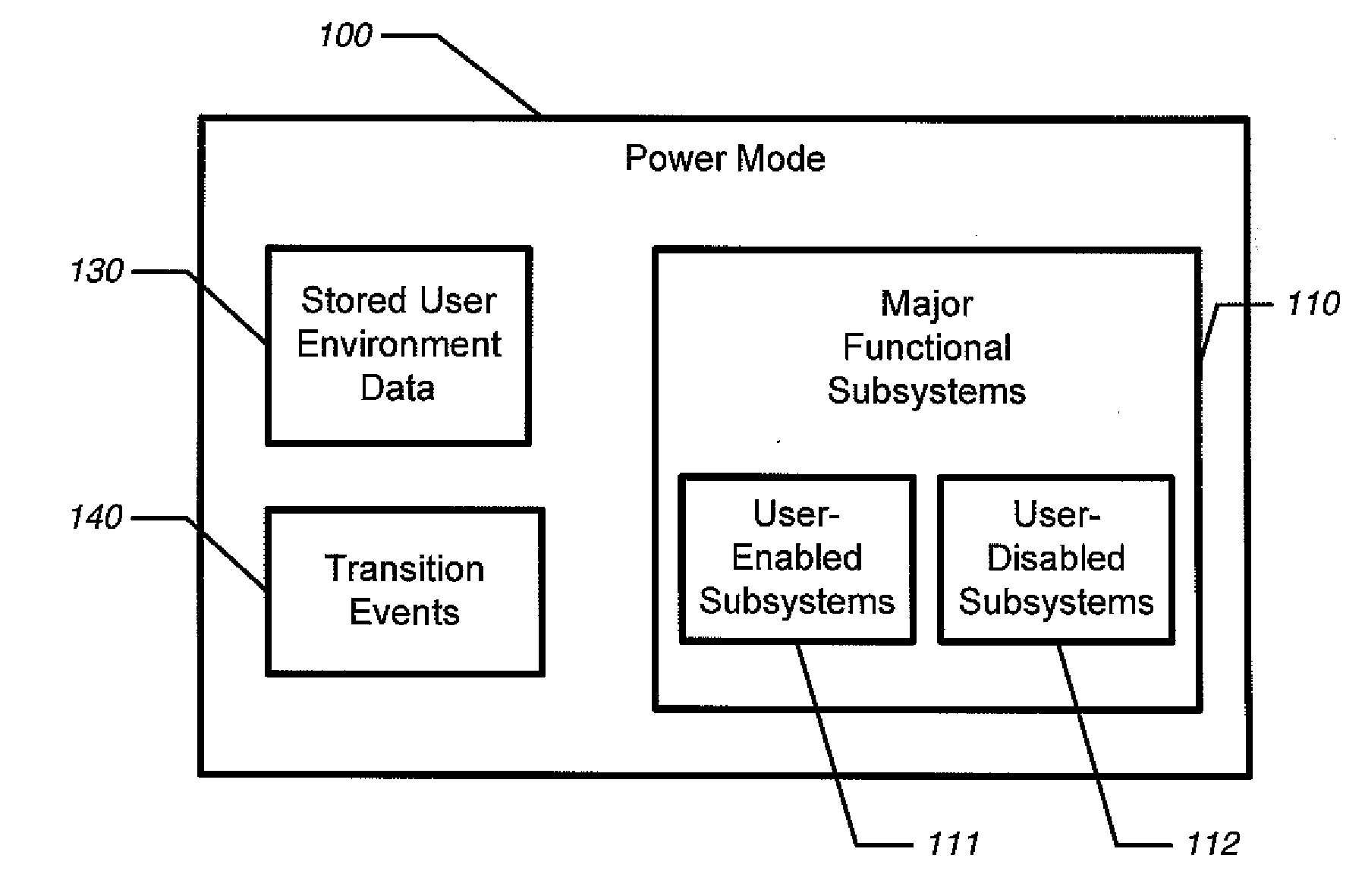
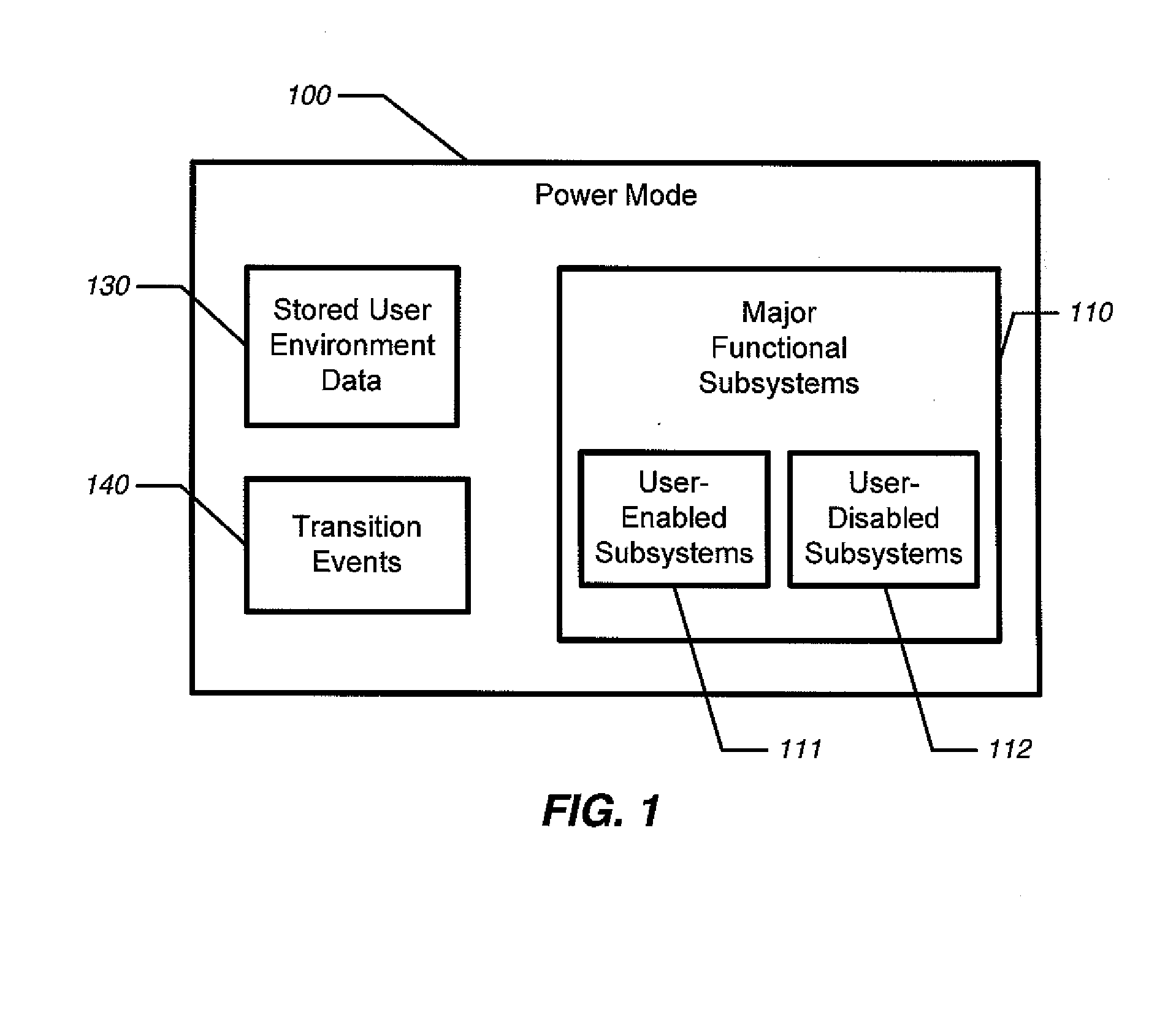
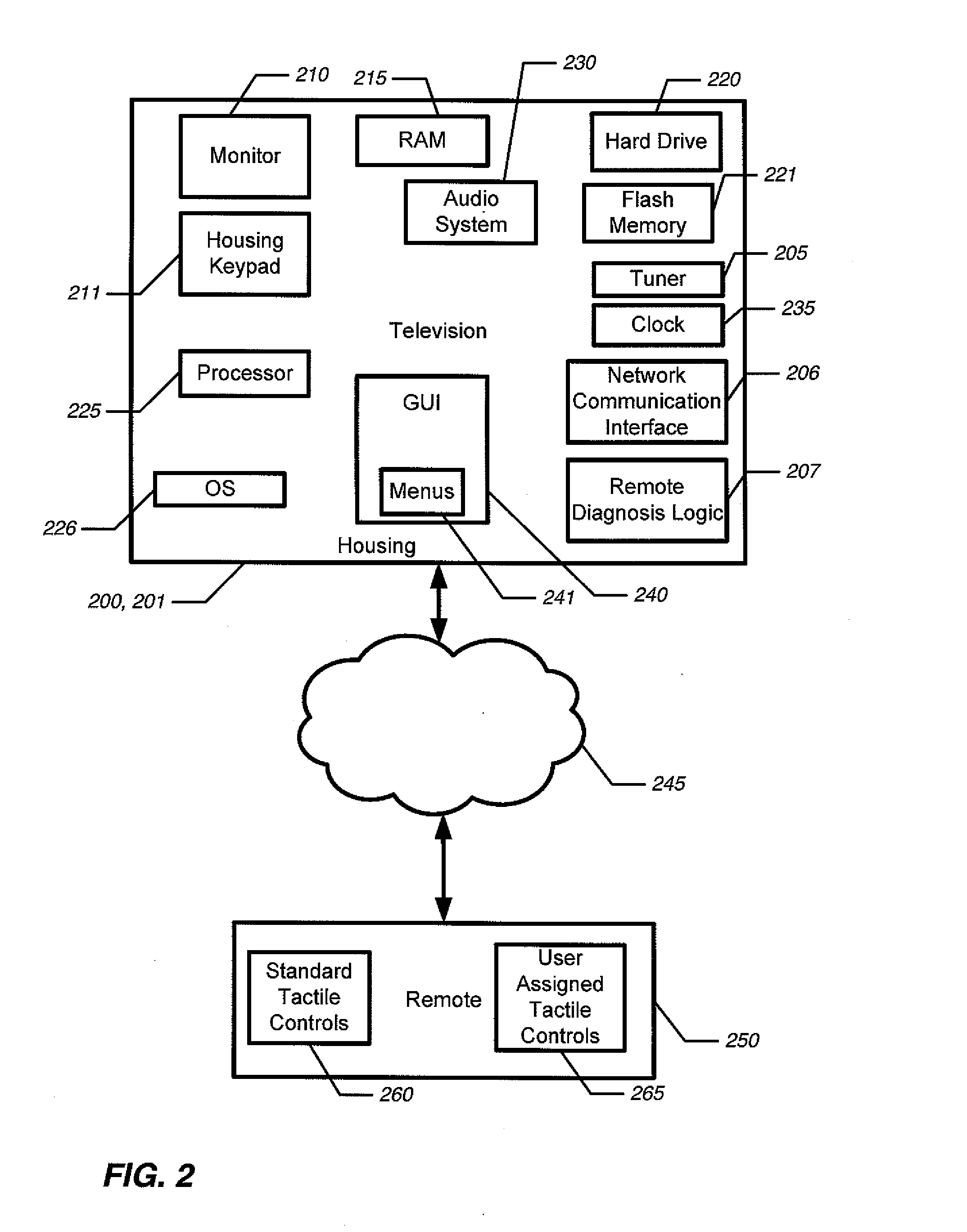
Television with energy saving and quick start modes
ActiveUS20120320280A1Consumes significant powerSave a lot of energyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPower modeEngineering
The present invention is a television that executes a process for transitioning between multiple power modes. Both the transition events and the power states may be factory-defined, or they may be user-configurable. The TV may have two sleep modes. In a quick-start mode, the screen is powered down but the operating system is spun-up, and possibly other major functional subsystems are user-enabled. In an energy-saving mode, fewer subsystems than quick-start mode, and possibly only components required to recognize a tactile control requesting a return to a power-on mode, may be enabled. Quick-start is less efficient than energy-saving mode, but results in much faster return to power-in mode. In some embodiments, power modes and transition events between them power modes may be automated, and either user defined or factory defined.
Owner:BBY SOLUTIONS
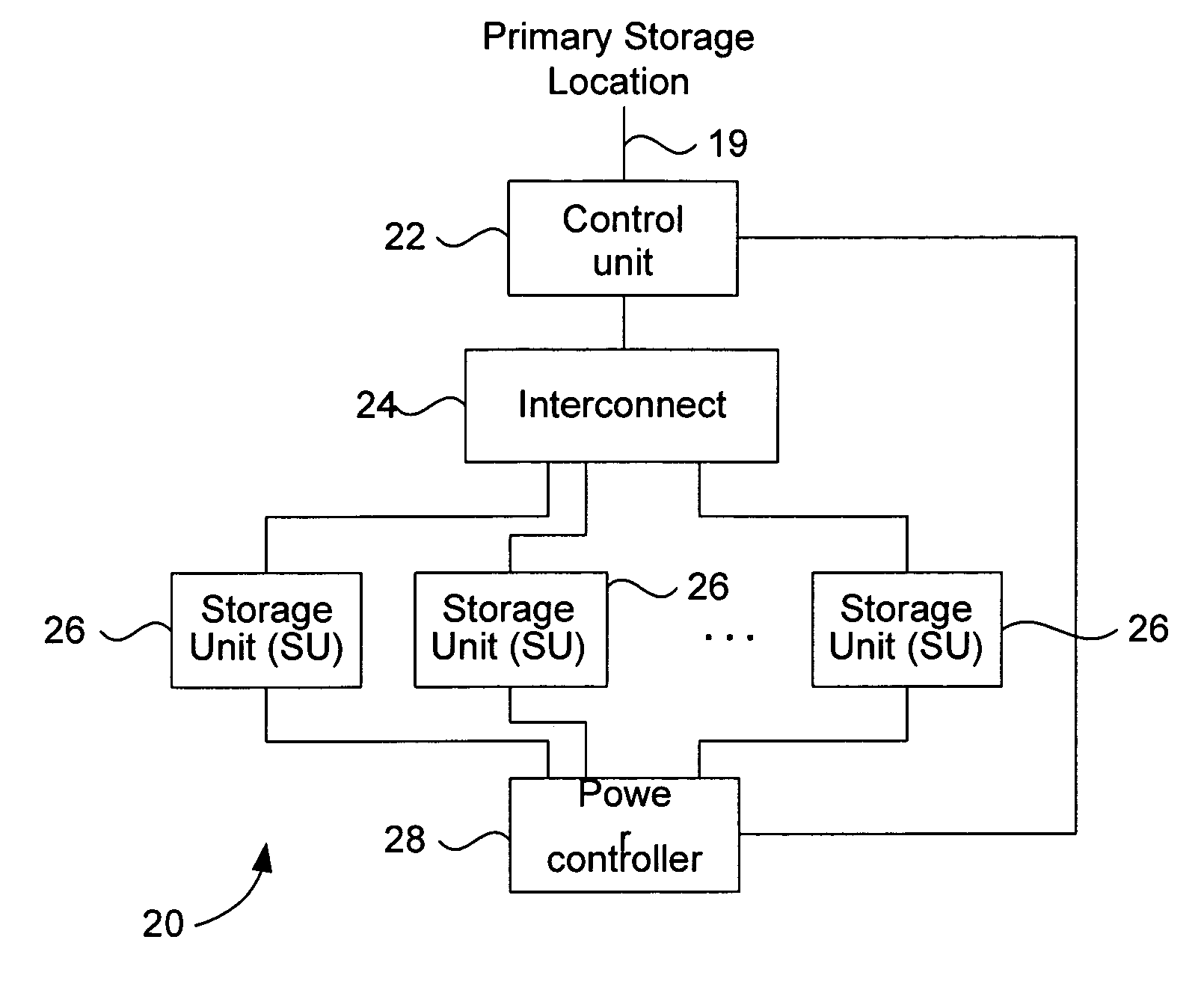
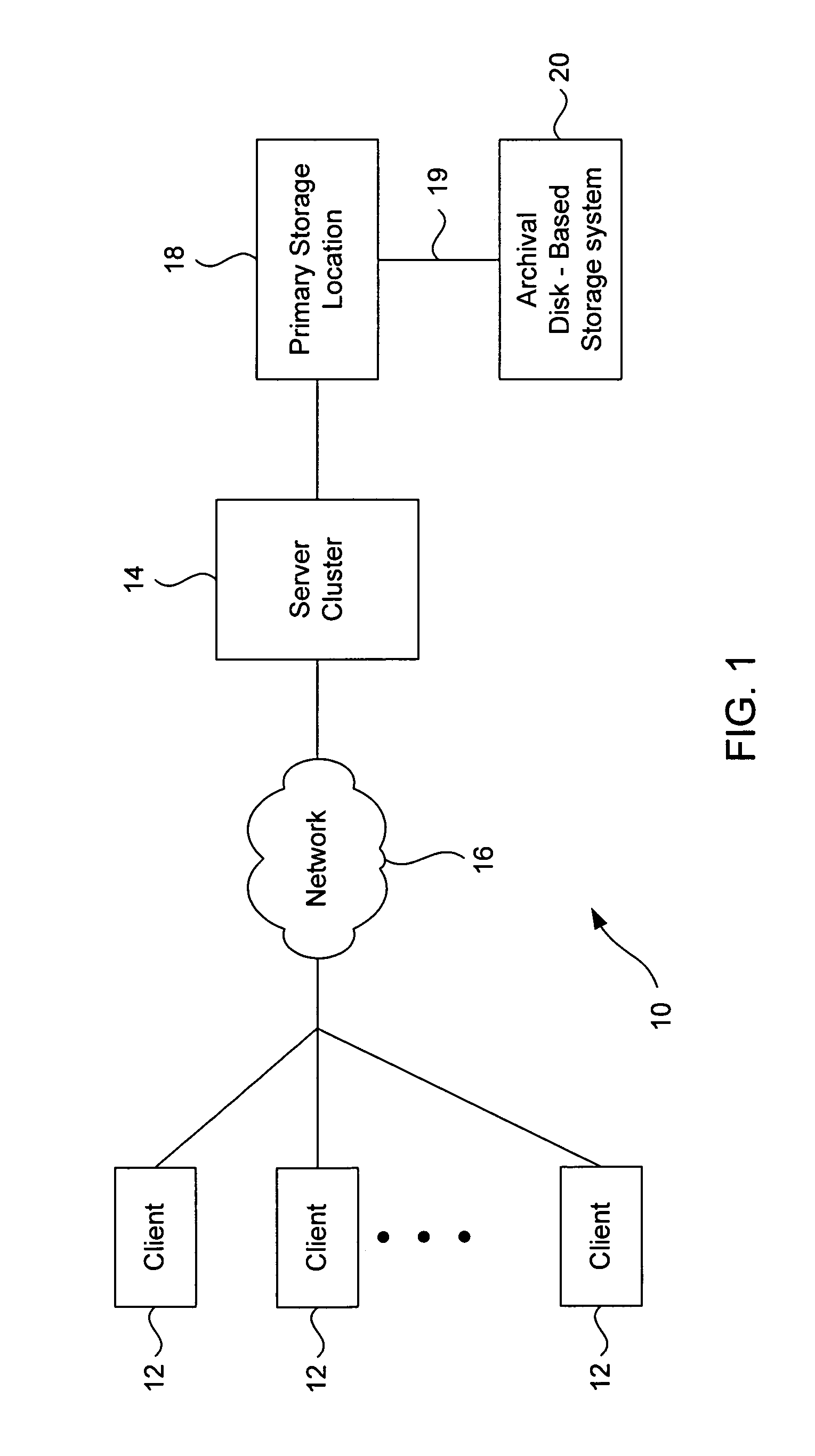
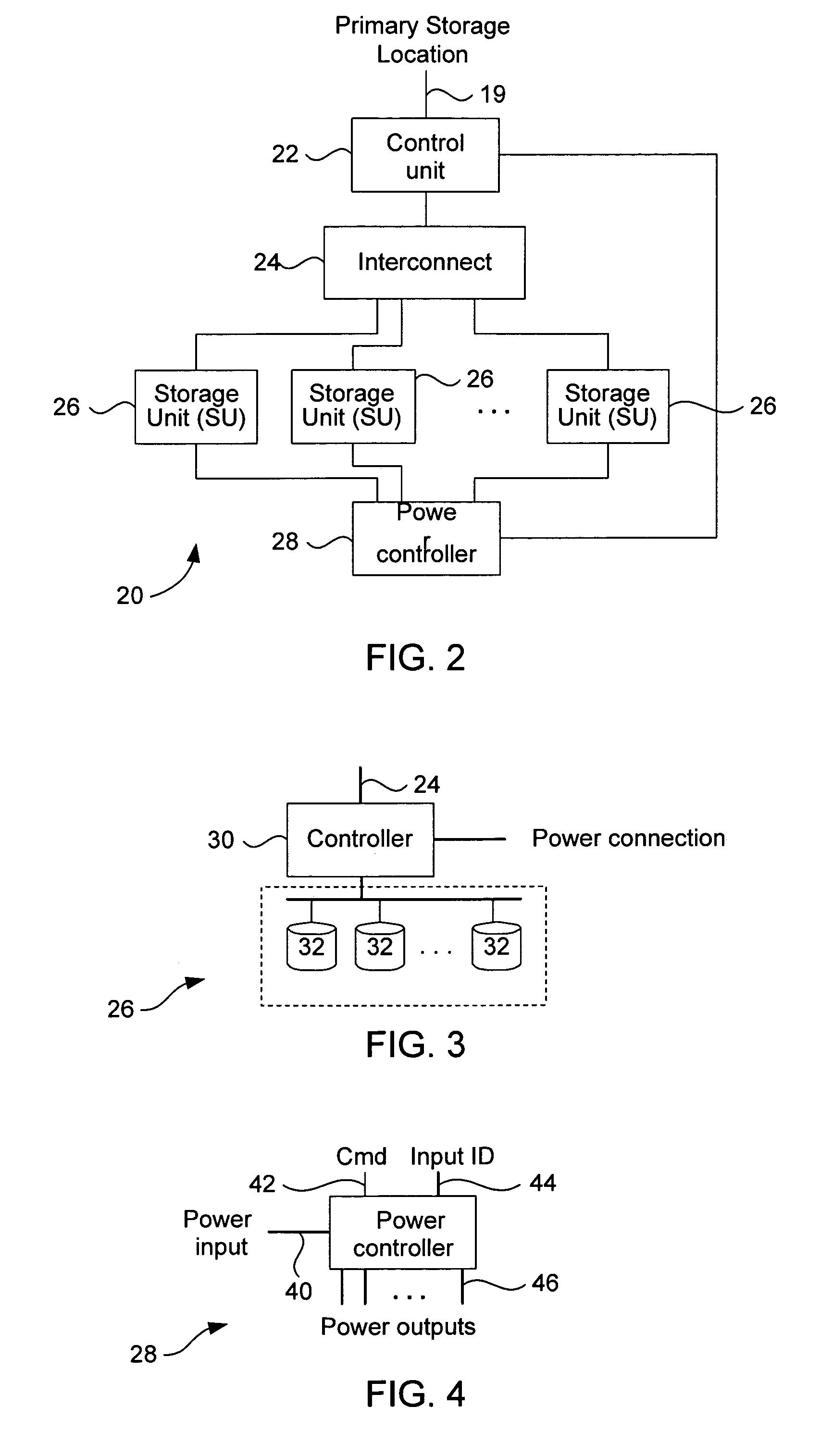
Archival data storage system and method
ActiveUS7007141B2Expand lifetimeIncreased longevityCombination recordingEnergy efficient ICTData integrityData storing
A disk-based archival storage system including a storage unit configured to store archival data, the storage unit including at least one spindle of disks configured to magnetically store archival data, an interconnect; and a control unit configured to process requests over the interconnect to either archive to or retrieve data from the storage unit. In one embodiment, the system includes a plurality of the storage units, each including at least one spindle of disks. The control unit controls the storage unit(s) in a master-slave relationship. Specifically the control unit is capable of issuing commands to selectively cause the storage unit(s) to shut down or power up, enter a running mode or a standby mode, cause the spindle of disk(s) to either spin up or spin down, and to perform a data integrity check of all the archival data stored in the storage system. In various other embodiments, the control unit runs algorithms that expand the lifetime and longevity of the disk spindles, optimizes power consumption, and performs data migration in the event a data integrity check identifies correctable errors.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Disk drive spin control
InactiveUS20100157463A1Energy efficient ICTDC motor speed/torque controlElectric machineControl theory
A disk drive configured to control spindle spin is provided. The disk drive includes a spindle motor for spinning a disk configured for storing data, a nonvolatile memory comprising instructions associated with a first process for spin-up of the spindle motor from a power-on mode and the nonvolatile memory comprising instructions associated with a second process for spin-up of the spindle motor from a power save mode, a controller for determining which of the first or the second process for spin-up of the spindle motor to implement in accordance with the instructions stored in the nonvolatile memory and a motor driver for spinning up the spindle motor according to the first process or according to the second process for spin-up of the spindle motor.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System and method for rapid boot of secondary operating system
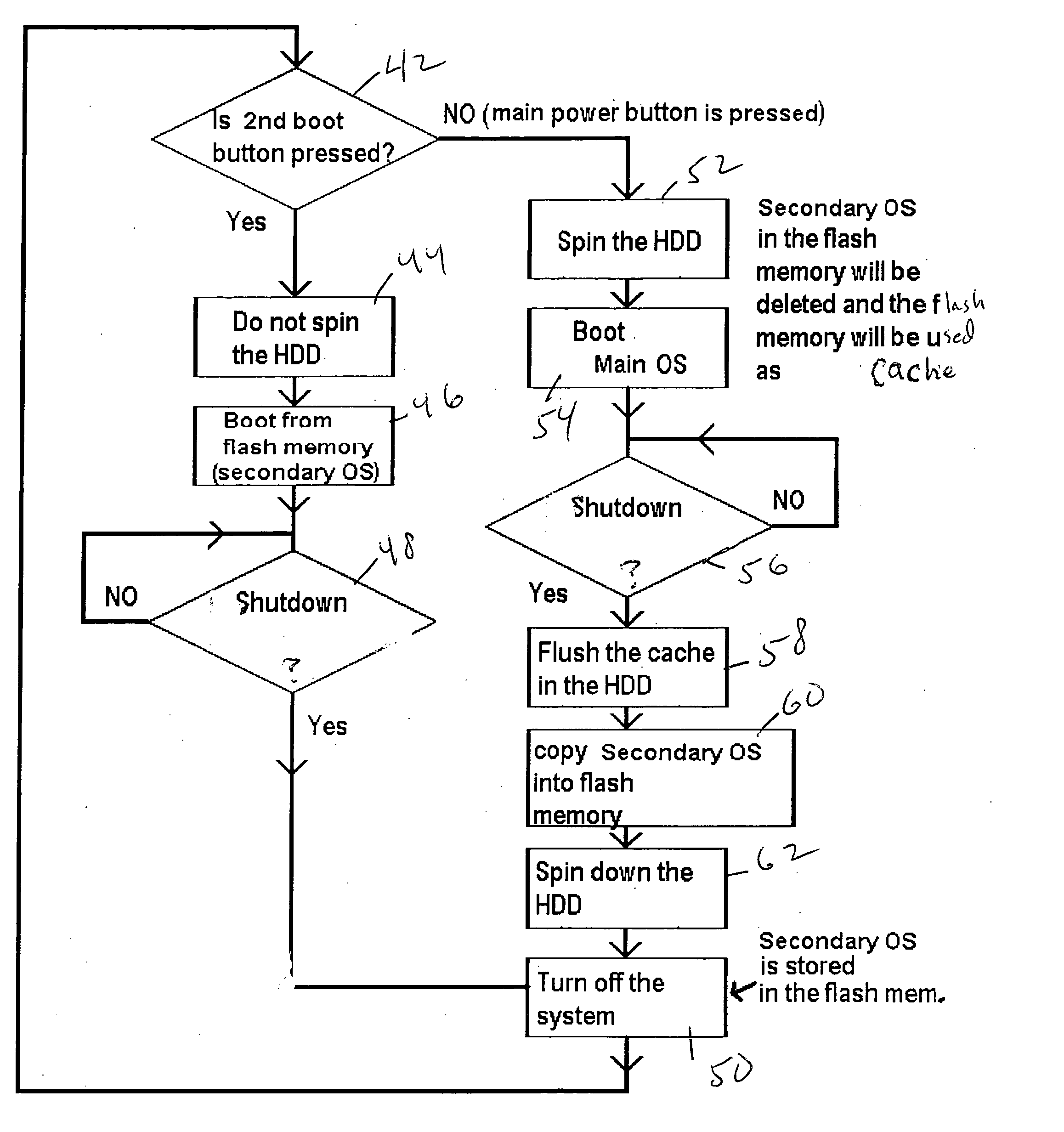
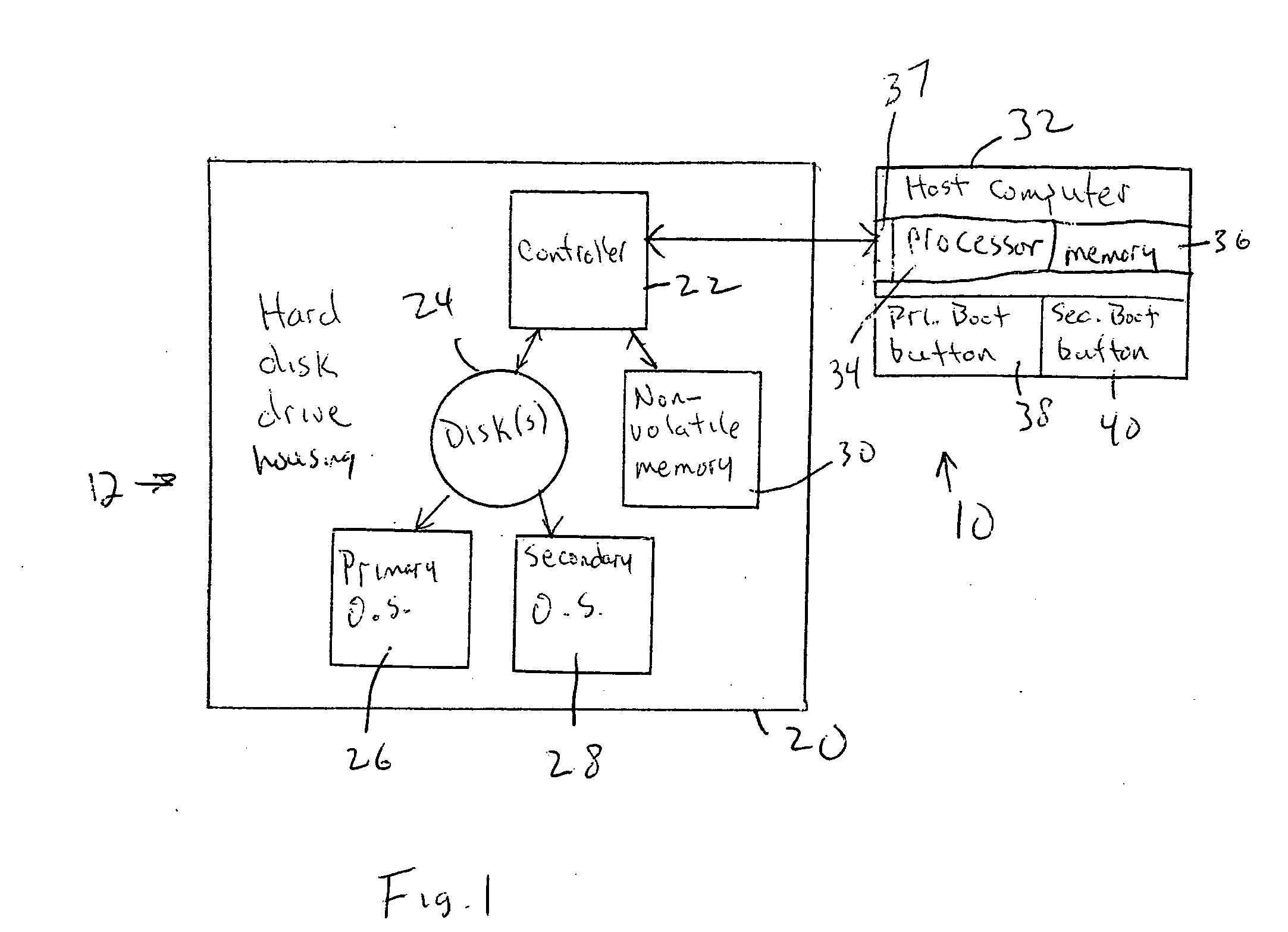
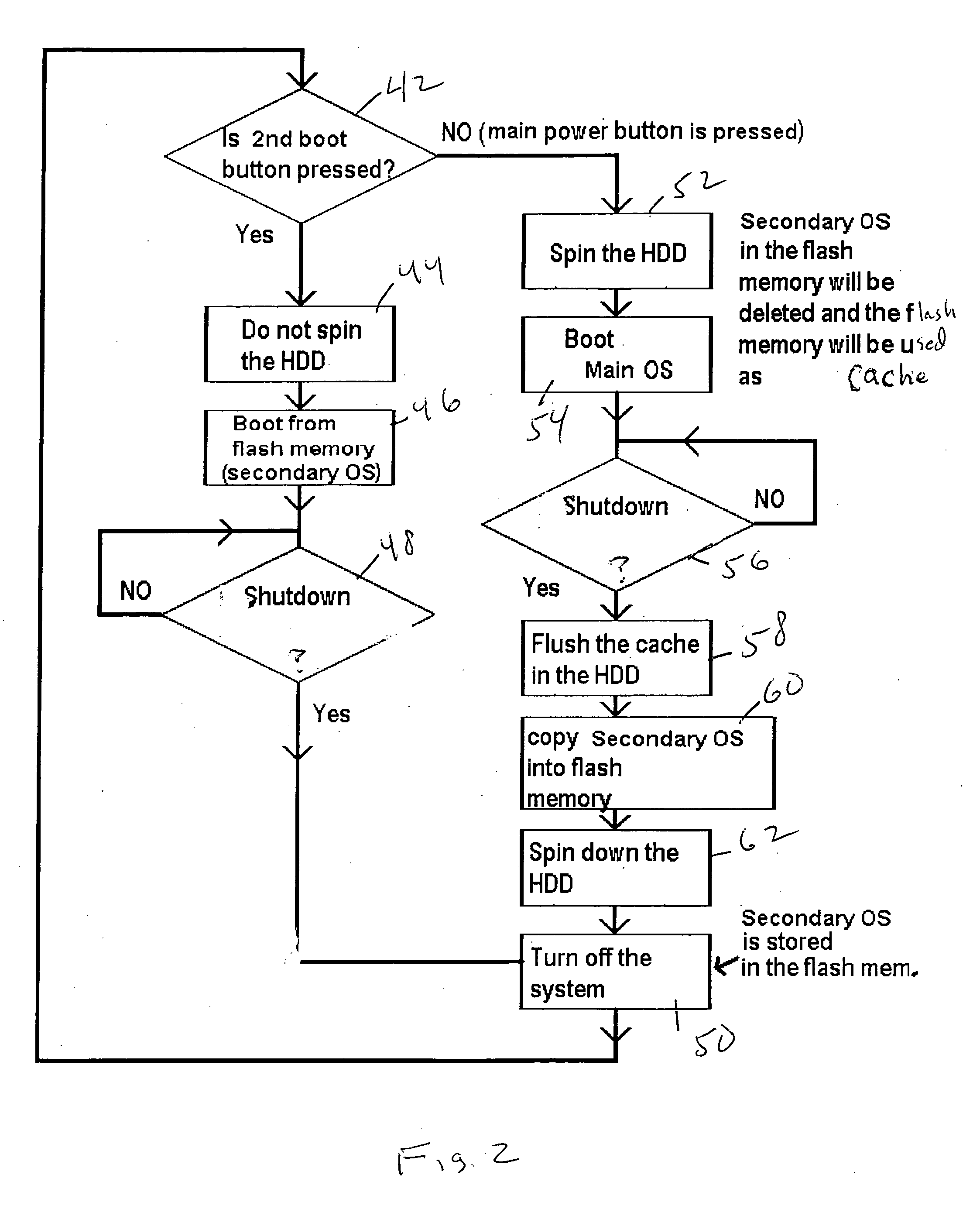
InactiveUS20060294357A1Reduce boot timeDigital computer detailsBootstrappingHard disc driveEngineering
The primary operating system of a computer such as a notebook computer is stored on disk in a hard disk drive and a smaller, secondary operating system such as an email operating system, wireless phone operating system, DVD player operating system, etc. is stored on disk and is transferred to flash memory within the HDD upon power-down of the primary operating system. In this way, should the user subsequently elect to power up the computer only for a limited secondary purpose, the user can elect to boot the associated secondary operating system from flash memory of the HDD without having to spin up the disks, saving energy and reducing boot time.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
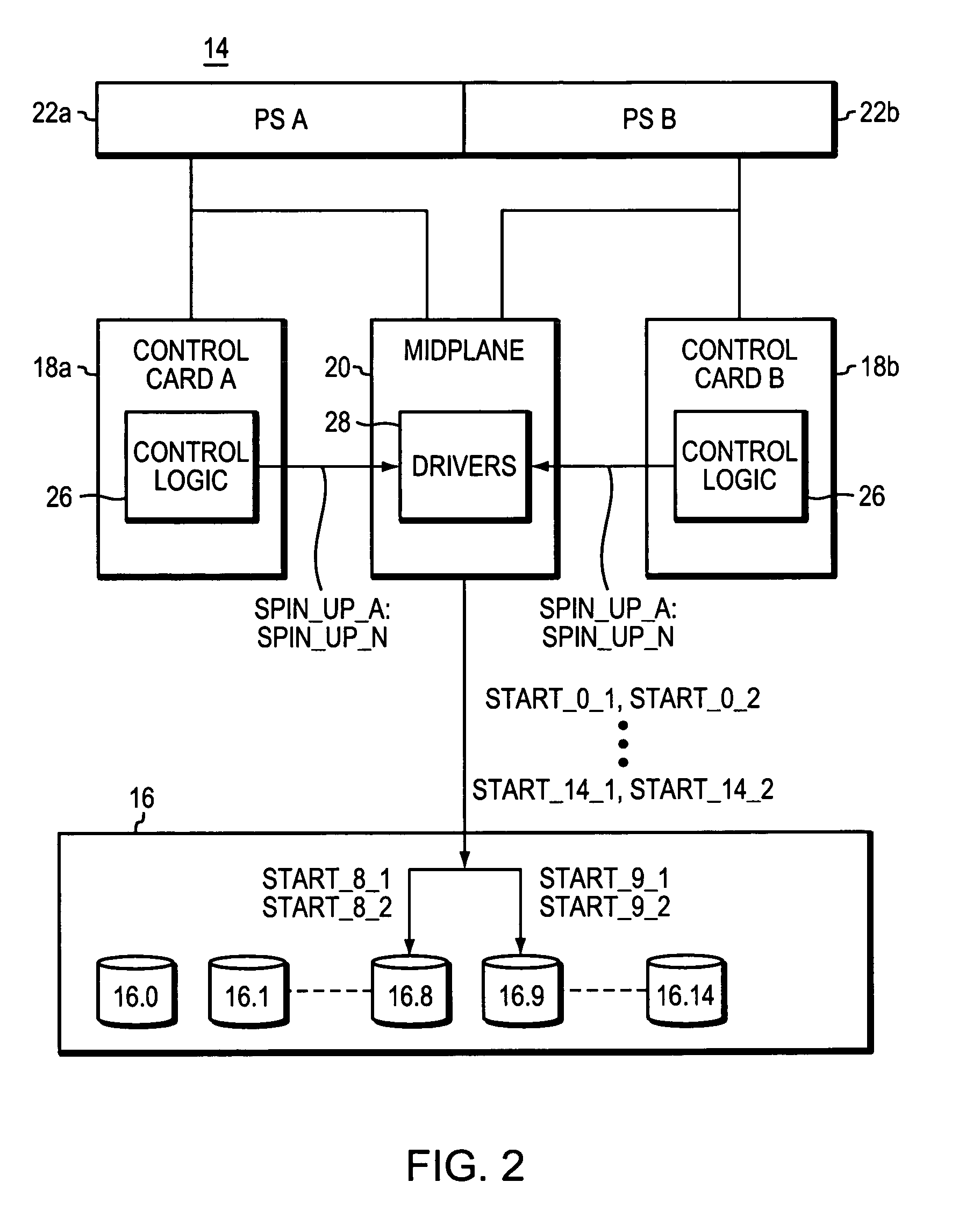
Managing disk drive spin up
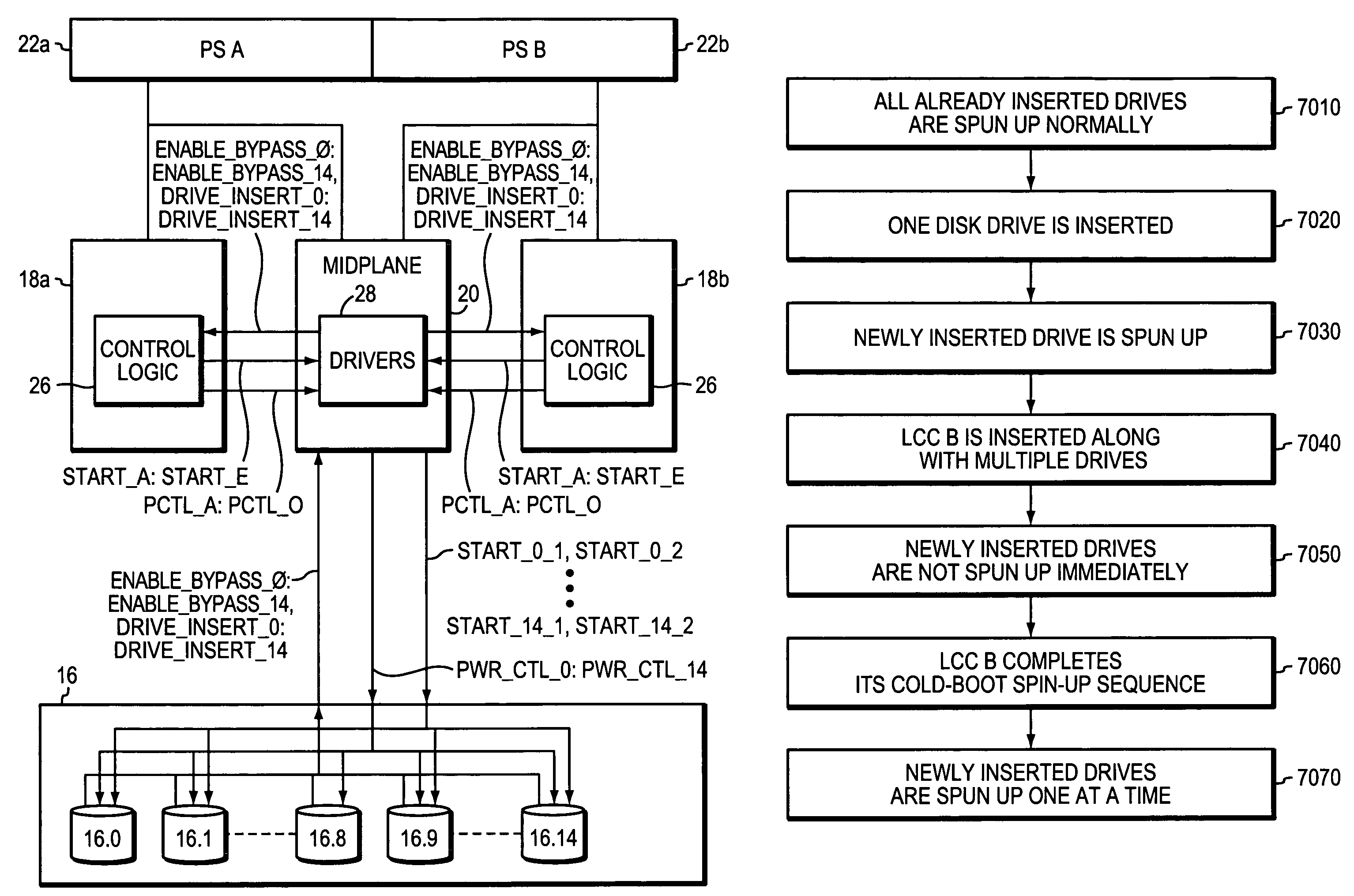
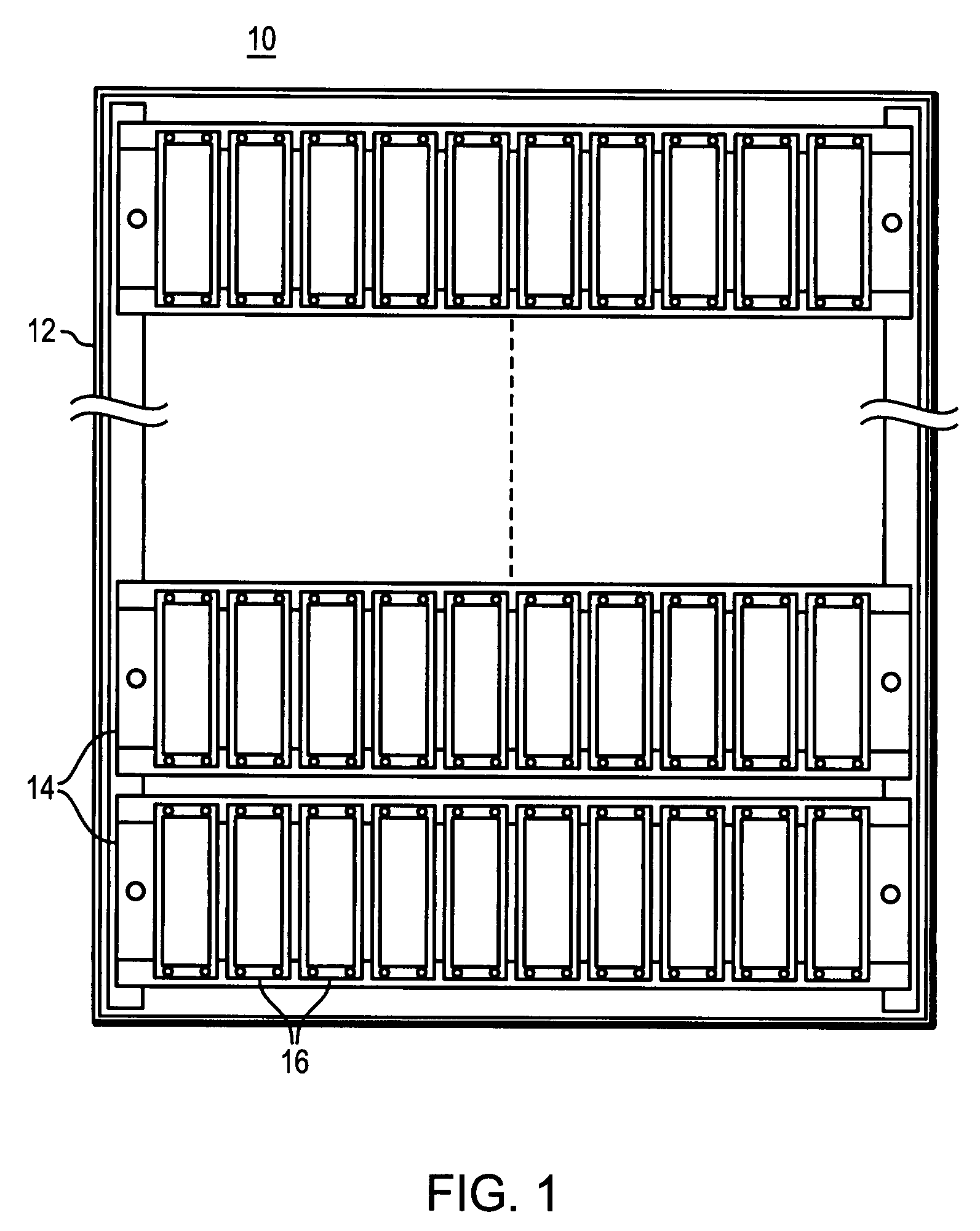
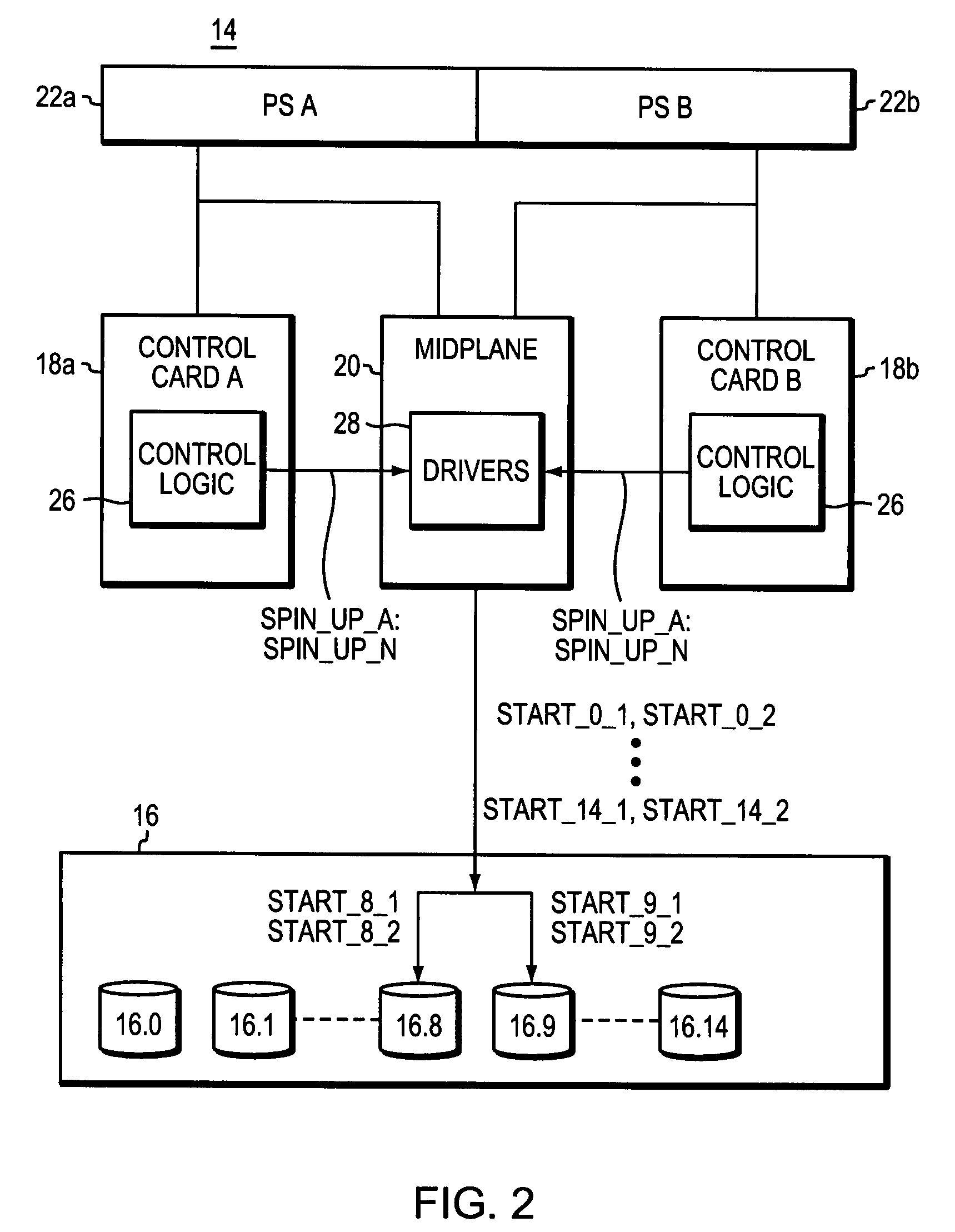
ActiveUS7440215B1Communication quickly and efficientlyQuickly and efficiently supplyFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageStable stateEngineering
Apparatus for use in managing disk drive spinup includes a plurality of disk drives newly inserted into a data storage system enclosure that is in an already powered up steady state. The apparatus also includes first and second control cards in the enclosure, and first control logic operable to cause the first and second control cards to coordinate to cause the disk drives to spin up in stages.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Operating a rotatable media storage device at multiple spin-speeds
InactiveUS20050141375A1Avoid excessive distanceCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsSpinsWorkload
A rotatable media storage device operates using multiple disk spin-speeds, e.g., a reduced spin-speed and a nominal spin-speed. A disk is spun up to a reduced spin-speed and an initial data transfer is began while the disk spins at the reduced spin-speed, if an amount of work that has been requested is below a threshold. The disk is spun up to a further spin-speed (e.g., a nominal spin-speed), which is greater than the reduced spin-speed, and the initial data transfer is began while the disk spins at the further spin-speed, if the amount of work that has been requested is above the threshold. Alternative embodiments using multiple disk spin-speeds are also provided.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Powering disk drive spinup
ActiveUS7873851B1Significant of expenseSignificant amount of powerEnergy efficient ICTSynchronous motors startersEngineeringSpin-up
A method is used in powering disk drive spinup. A disk drive is powered with a primary power source and is temporarily powered with a secondary power source in addition to the primary power source. The secondary power source powers the disk drive when the disk drive is spinning up.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Storage device, control method for same and system management program
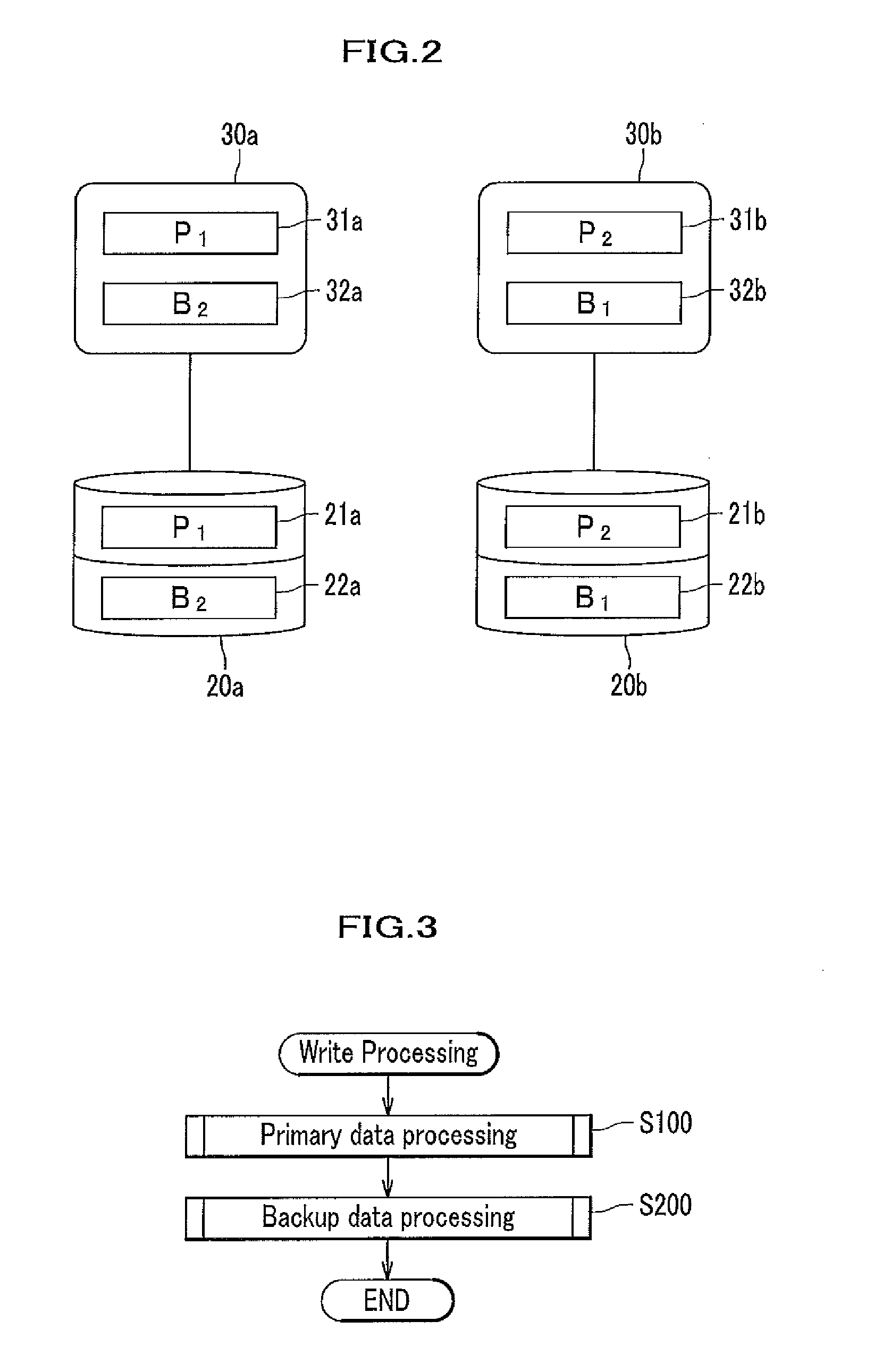
InactiveUS20120317354A1Saving of power consumptionSave power consumptionError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareSystems management
A storage device has plural data disks including a primary data area and a backup data area. Performance and reliability are secured while conserving power. A system management means includes a disk rotational state detection means, a disk rotational state control means for rotating or stopping a data disk, and a data placement control means for accessing the data disk to move the data. The data placement control means, if the data disk of the primary or backup side has been stopped at writing time, spins up and accesses thereof, and if the data disk of the primary or backup side has been stopped at reading time, prioritizes the side that is being rotated and accesses thereto, and if the data disk of the primary and backup side have both been stopped at reading time, spins up and accesses the side that has been stopped for the longer time.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
Storage apparatus for controlling power saving modes of multiple disk devices of different specifications
InactiveUS7730235B2Increase consumptionIncrease in sizeEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareControl power
A storage apparatus is provided that is capable of reducing data maintenance management costs with a performance that is both highly reliable and fast. The present invention is storage apparatus where an intermediary device is arranged between a controller and a plurality of disk devices of different performances arranged in a hierarchical manner. The controller unit carries out I / O accesses to and from the disk devices via the intermediary devices based on access requests sent from host apparatus. The intermediary device includes a power saving control function for the disk device and carries out operation control such as spin off and spin up of disk devices in accordance with conditions set in advance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
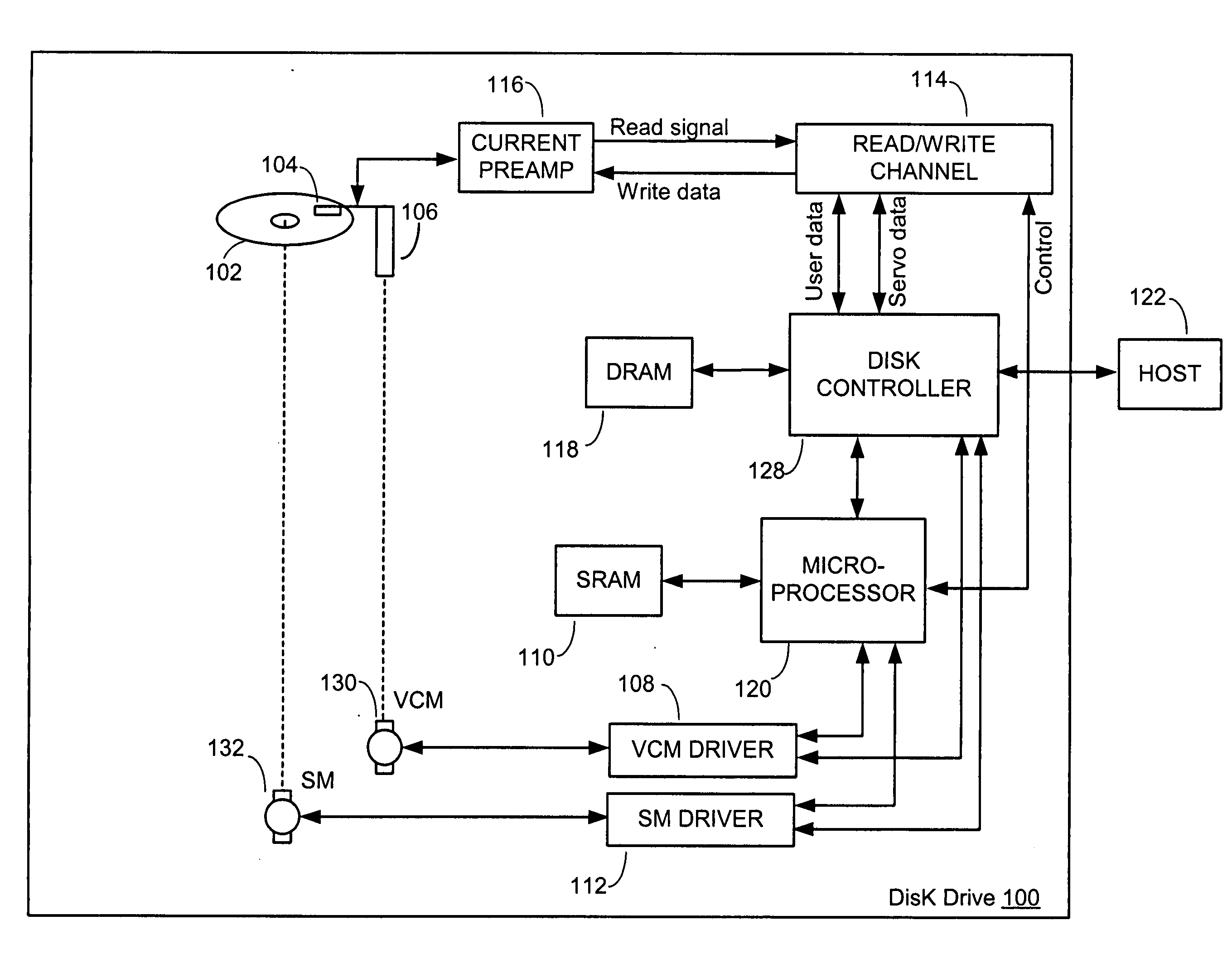
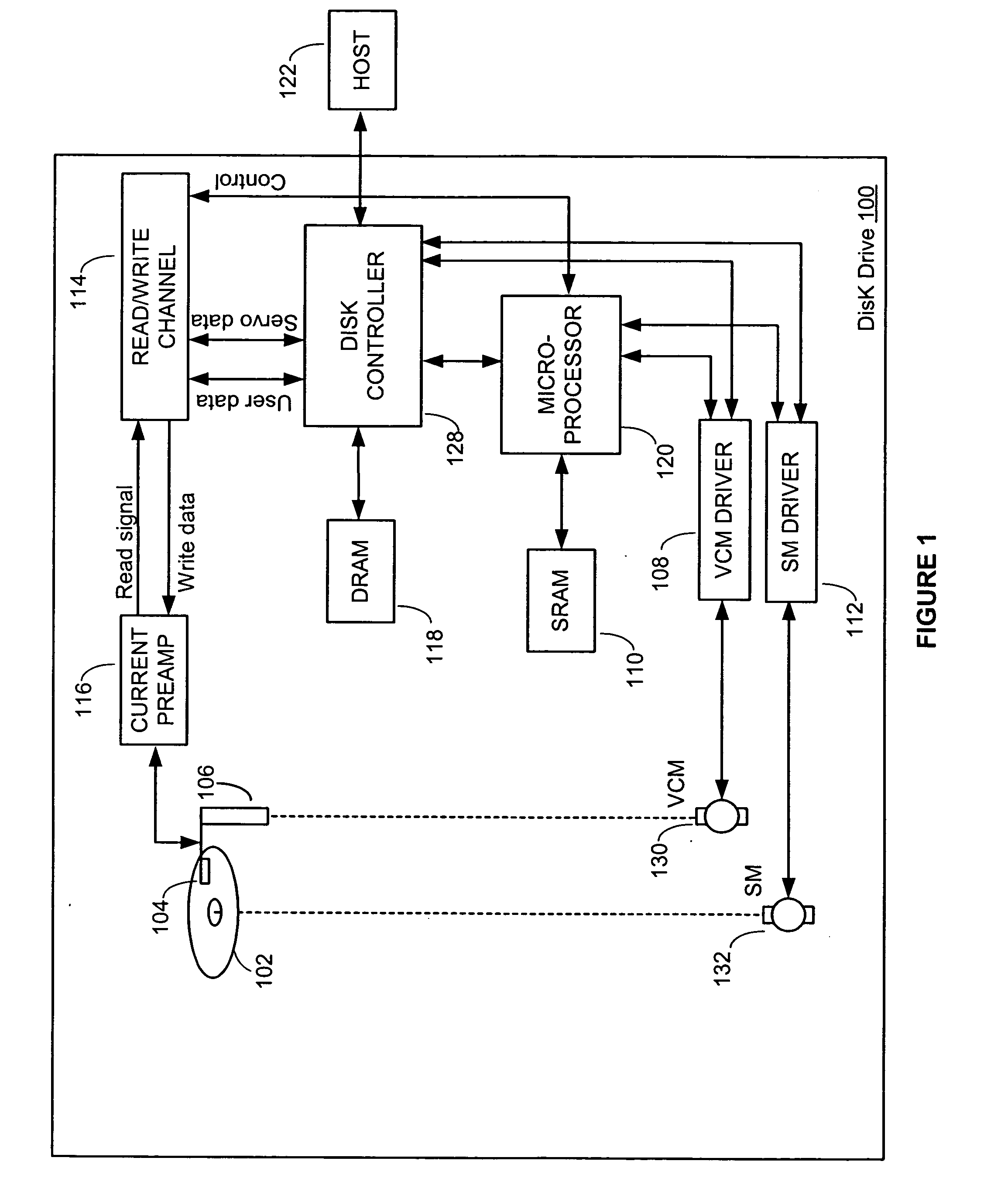
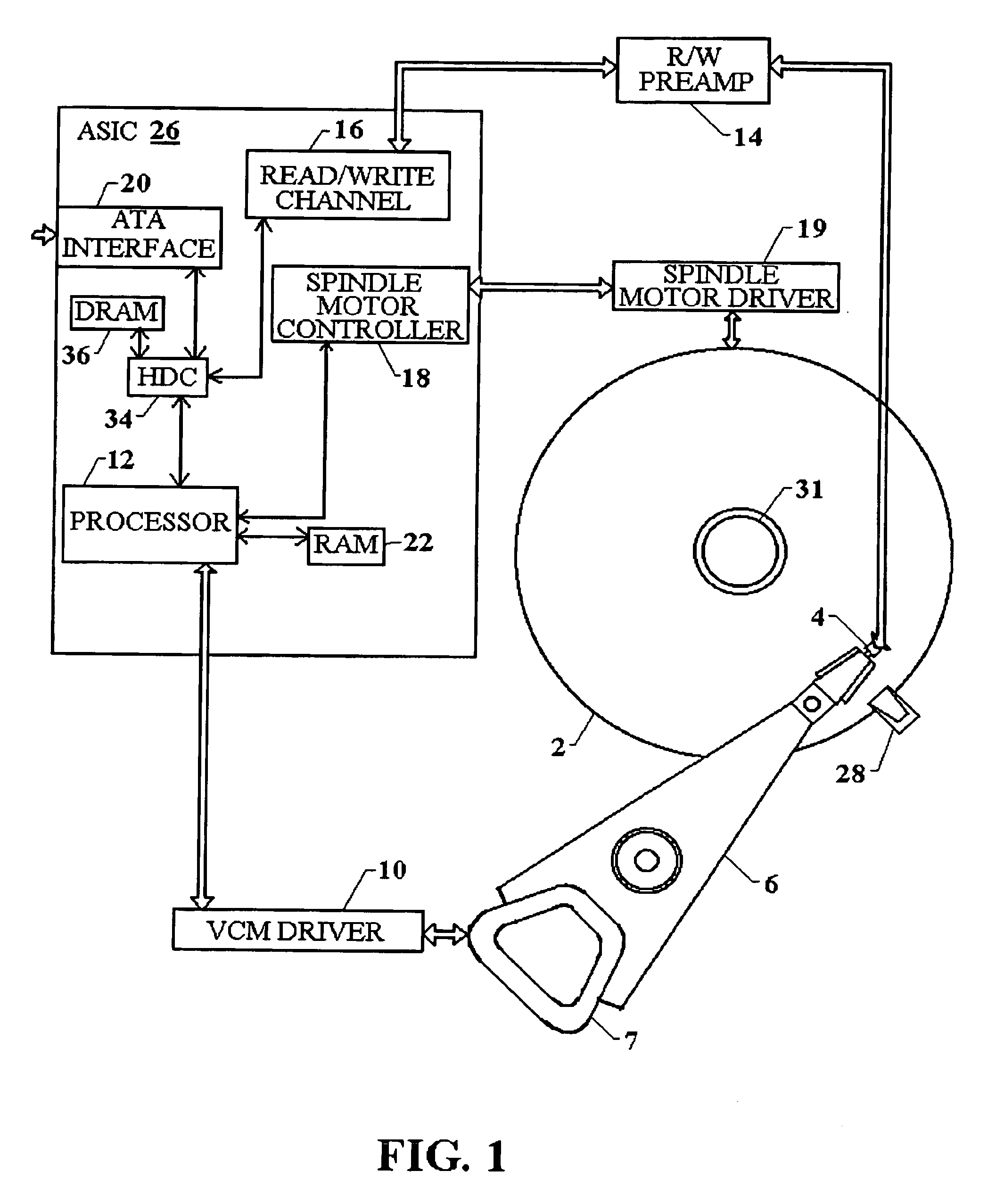
Apparatus for spindle bearing friction estimation for reliable disk drive startup
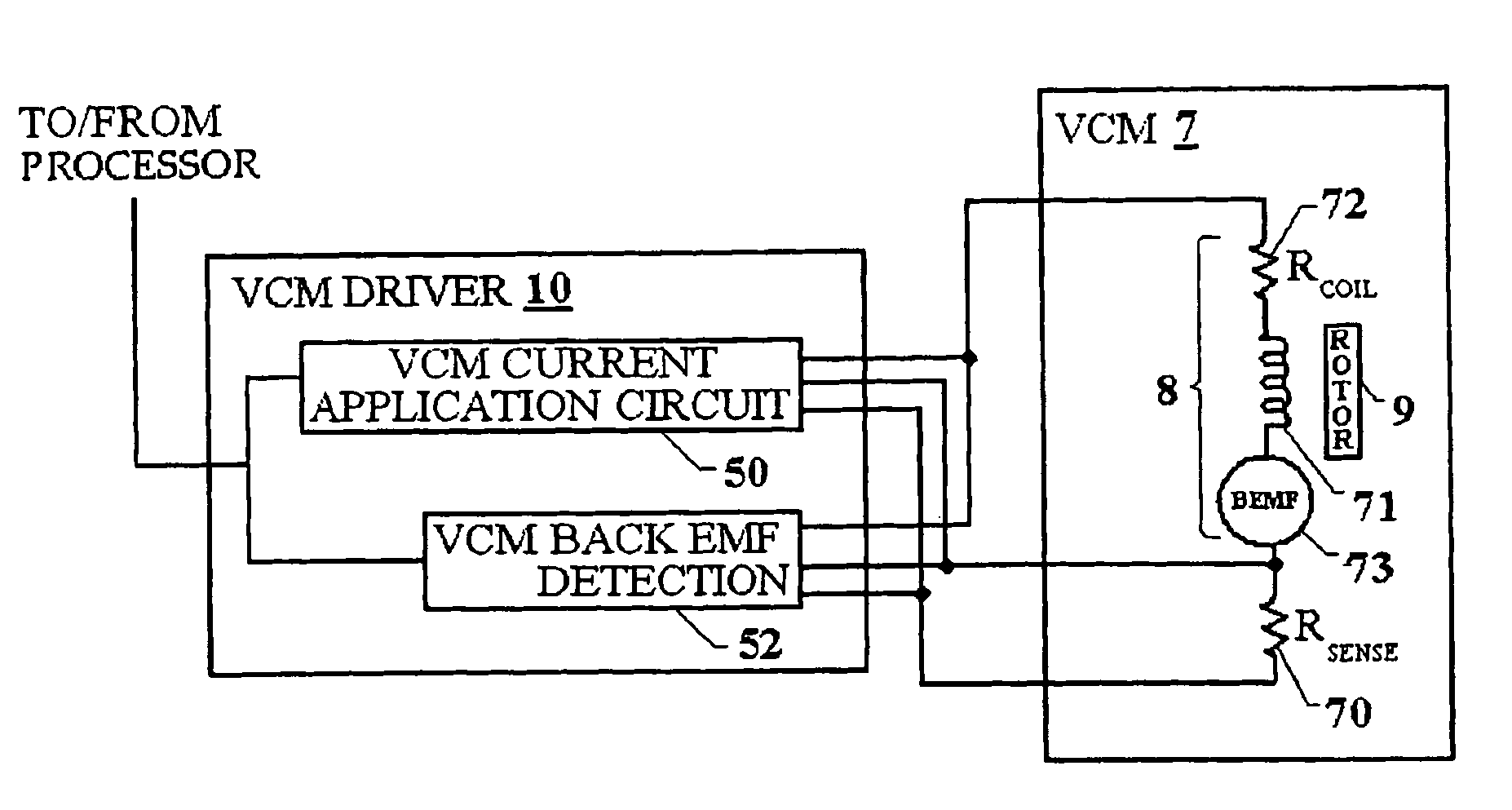
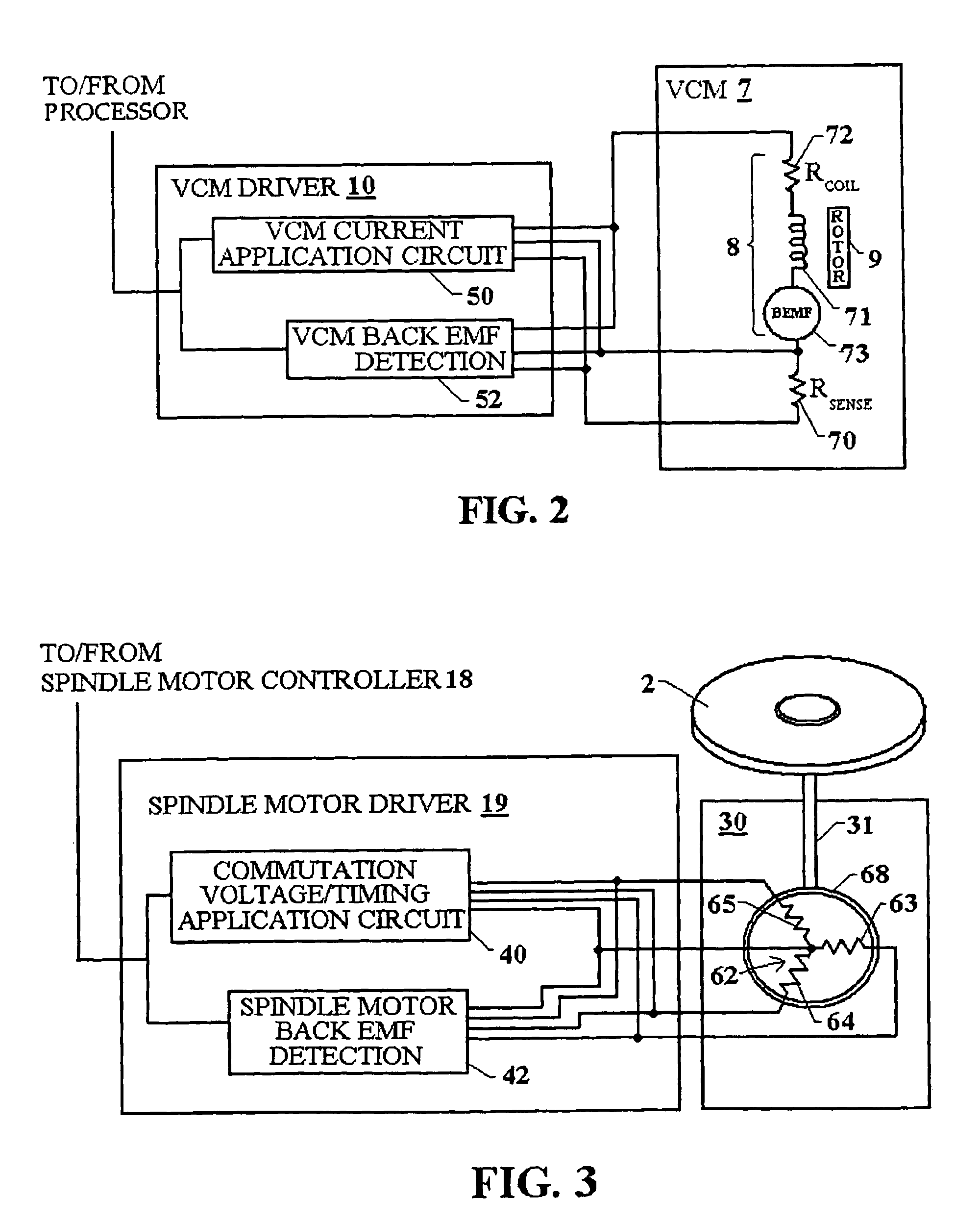
InactiveUS7005820B2Increased friction loadingImprove performance reliabilityDisc-shaped record carriersDC motor speed/torque controlElectrical resistance and conductanceElectromotive force
Temperature of the disk drive is measured using components of the disk drive without the need of including a separate temperature sensor to optimize performance of the spindle motor during startup. To measure temperature, the resistance of the VCM winding is measured and used to estimate the spindle bearing temperature. Back emf is measured from VCM windings and used during startup to accurately determine actuator position. Because the VCM coil resistance varies significantly with temperature, coil resistance variations with temperature are determined to enable compensation for inaccuracies in determination of actuator velocity. This inferred temperature is then used to optimize the start up procedure for the spindle motor to accommodate the increased frictional loading of the spindle bearing. In this way an improved performance in the reliability and spin up operation time can be realized without the addition of a separate temperature measurement hardware element.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
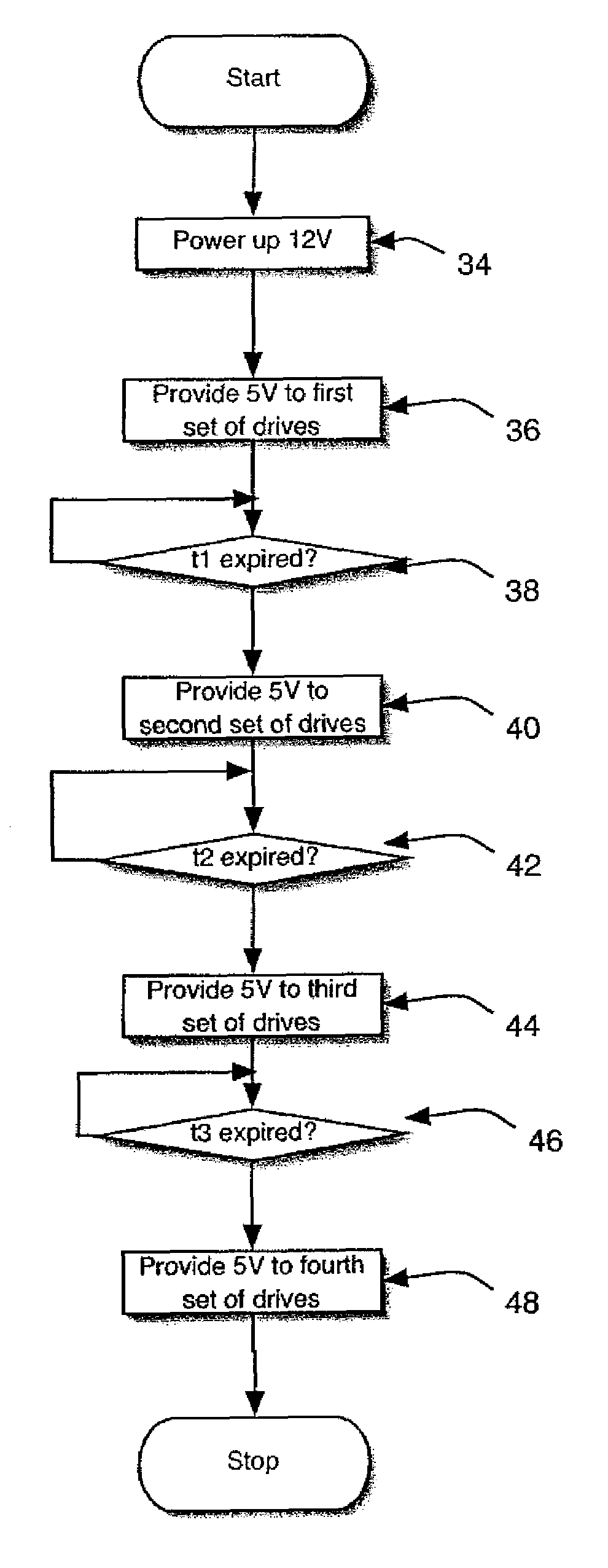
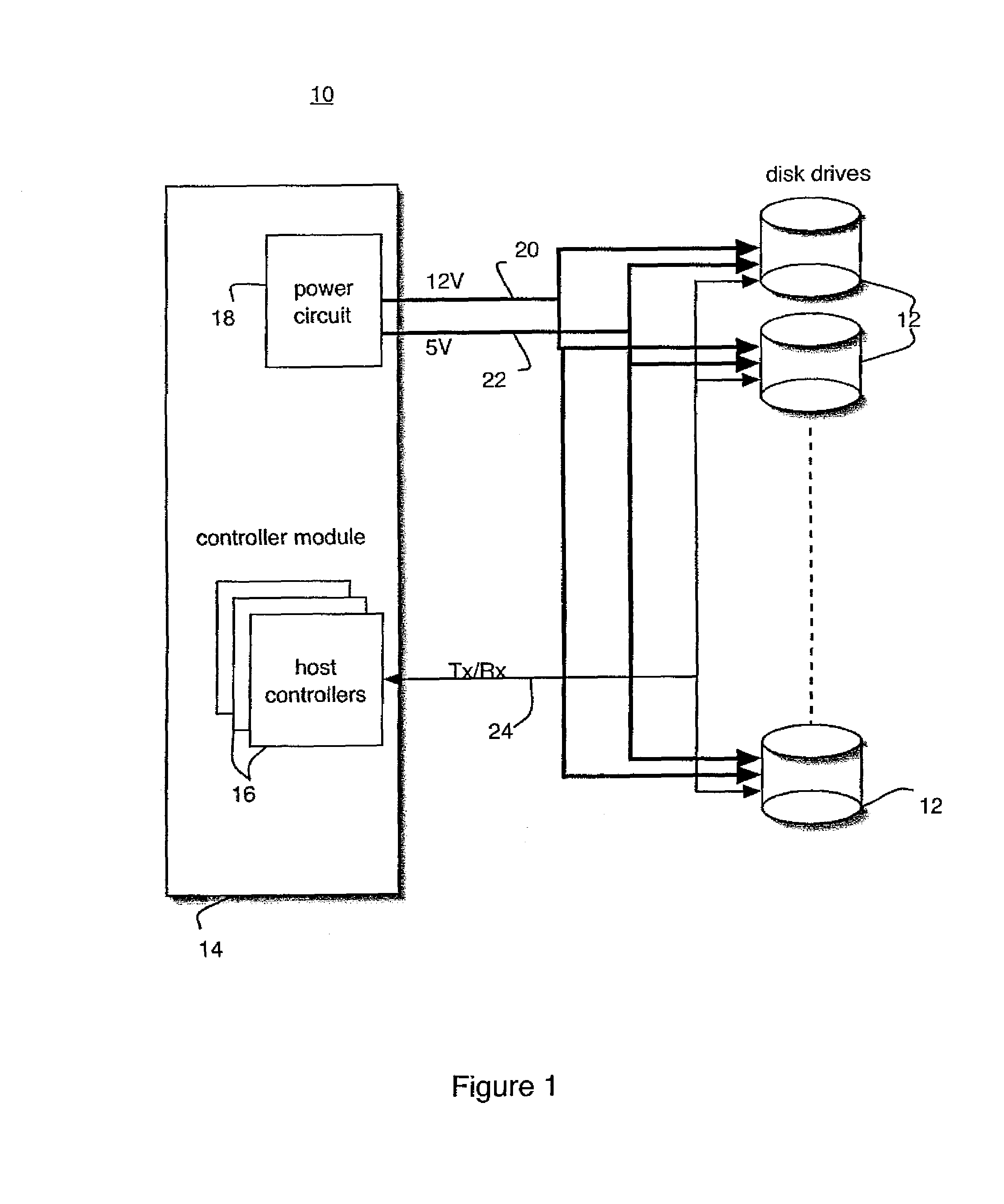
Method and control apparatus for controlling startup of multiple IDE-HDDs
InactiveUS7152173B2Reduce computing costTotal current dropEnergy efficient ICTInput/output to record carriersPeak currentControl equipment
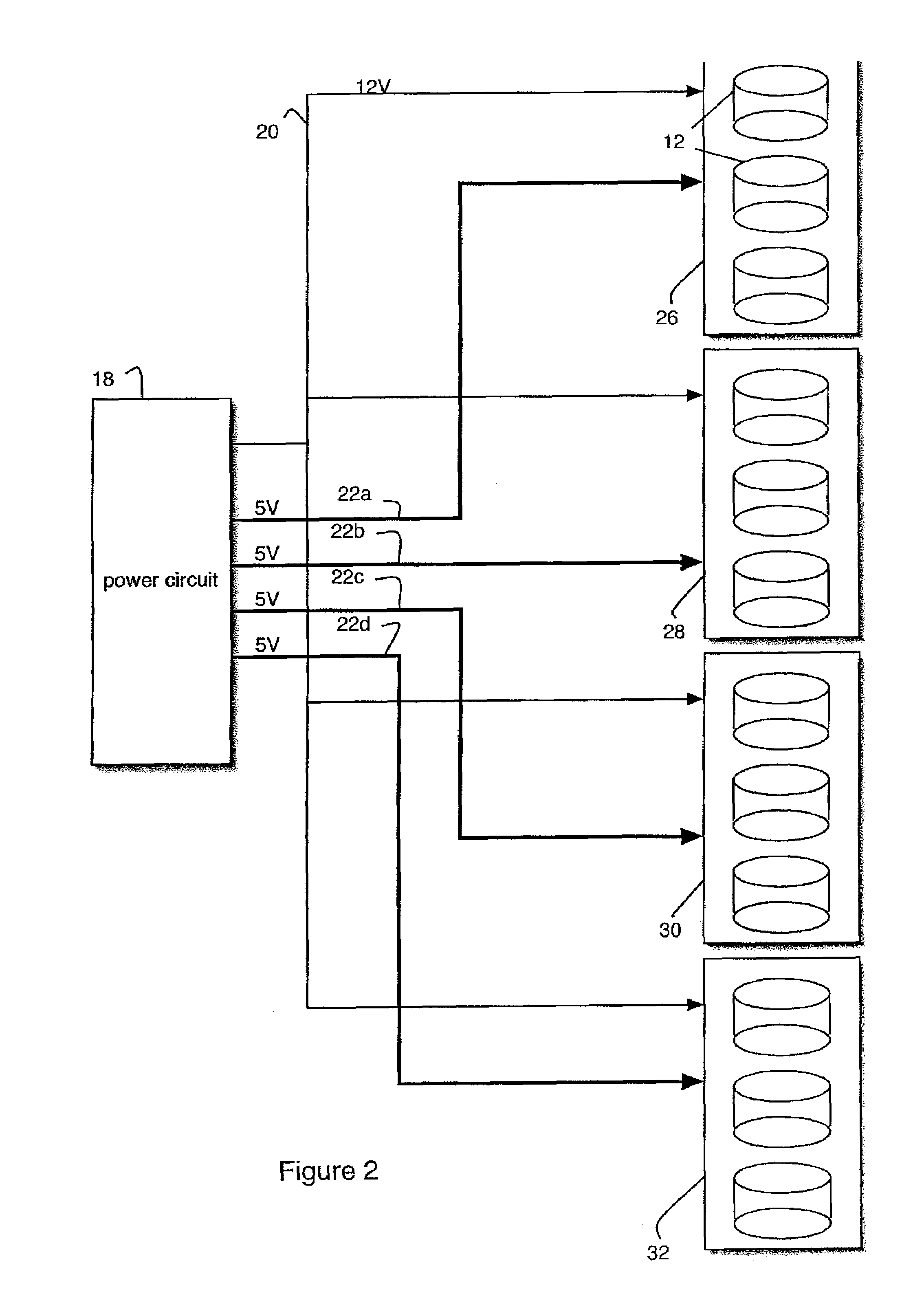
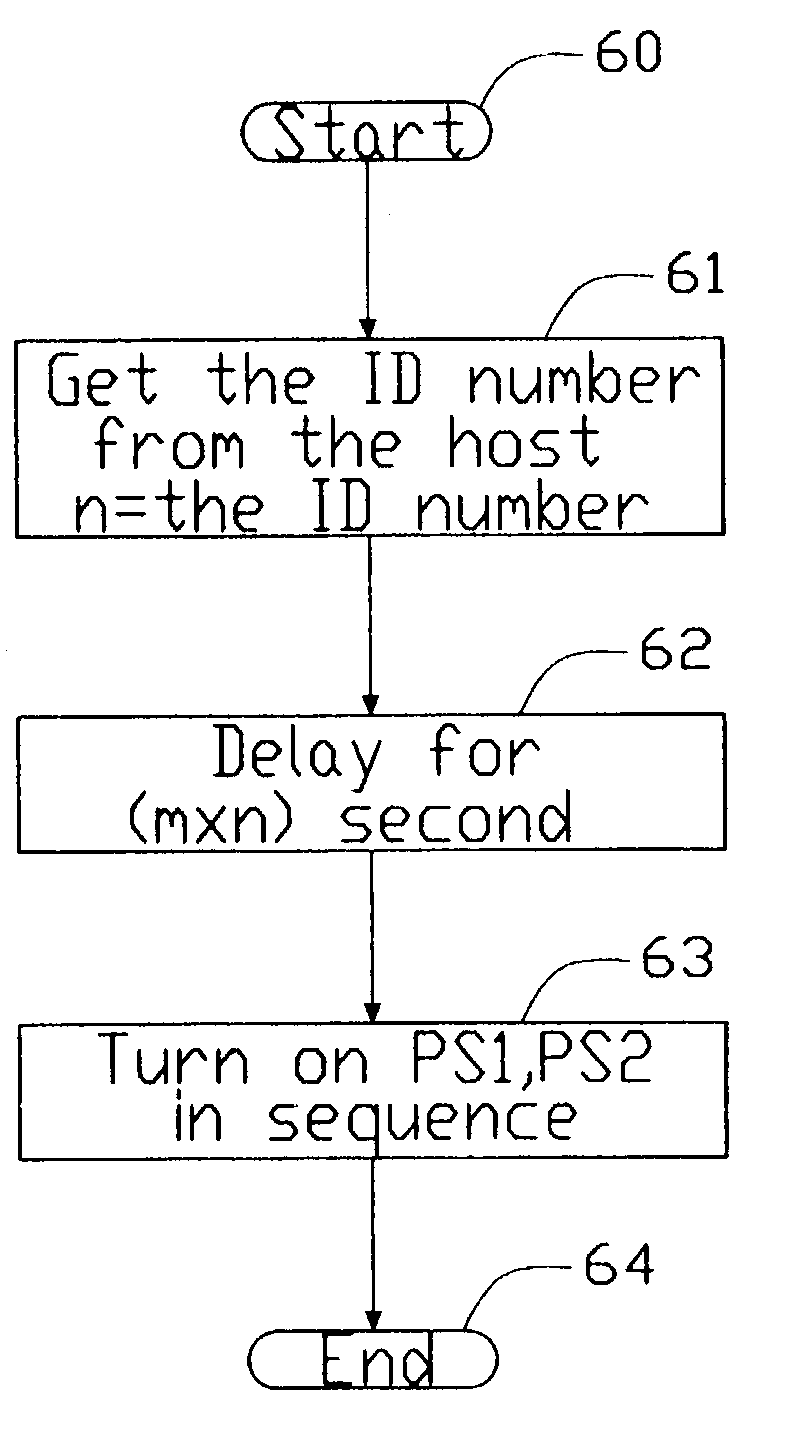
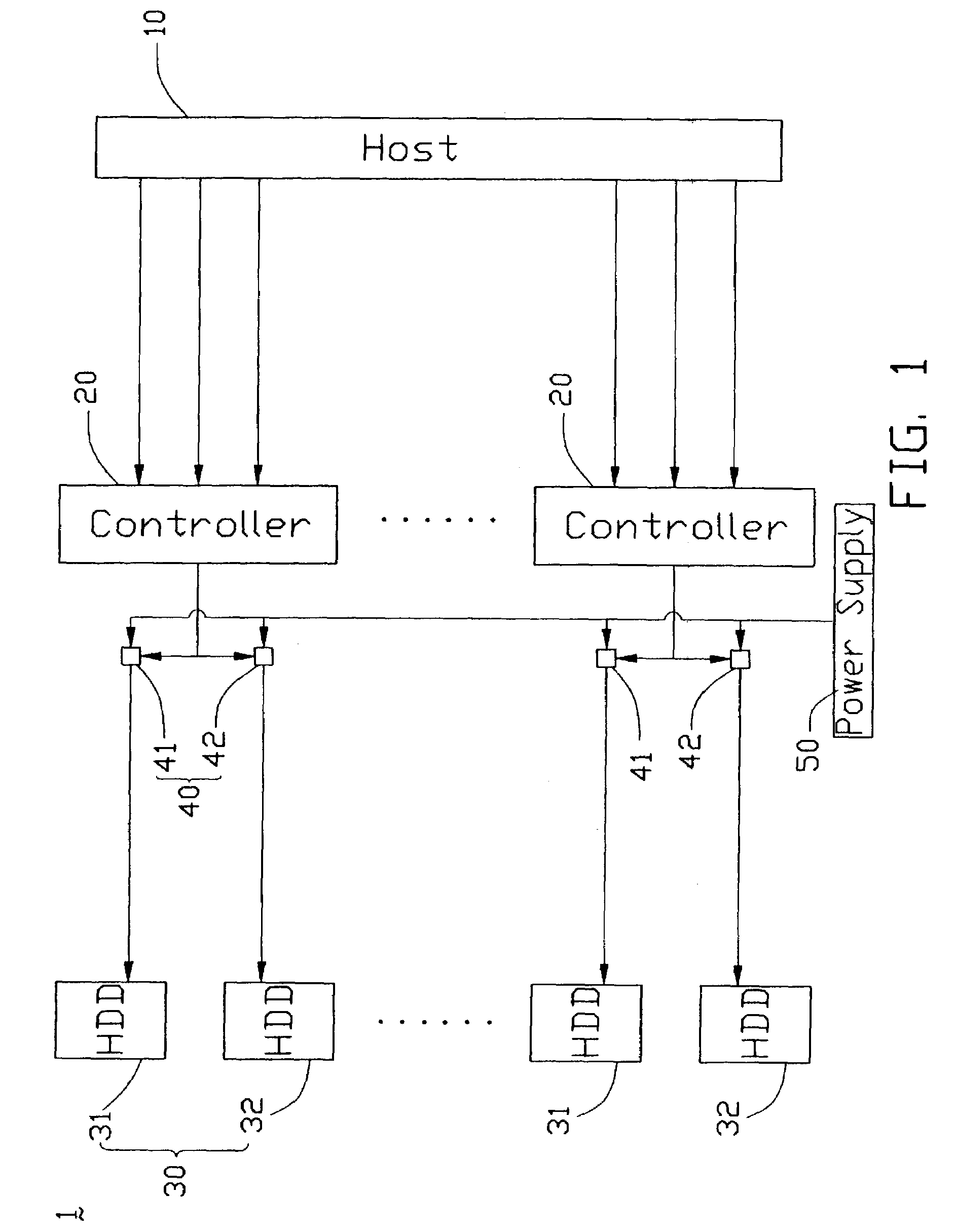
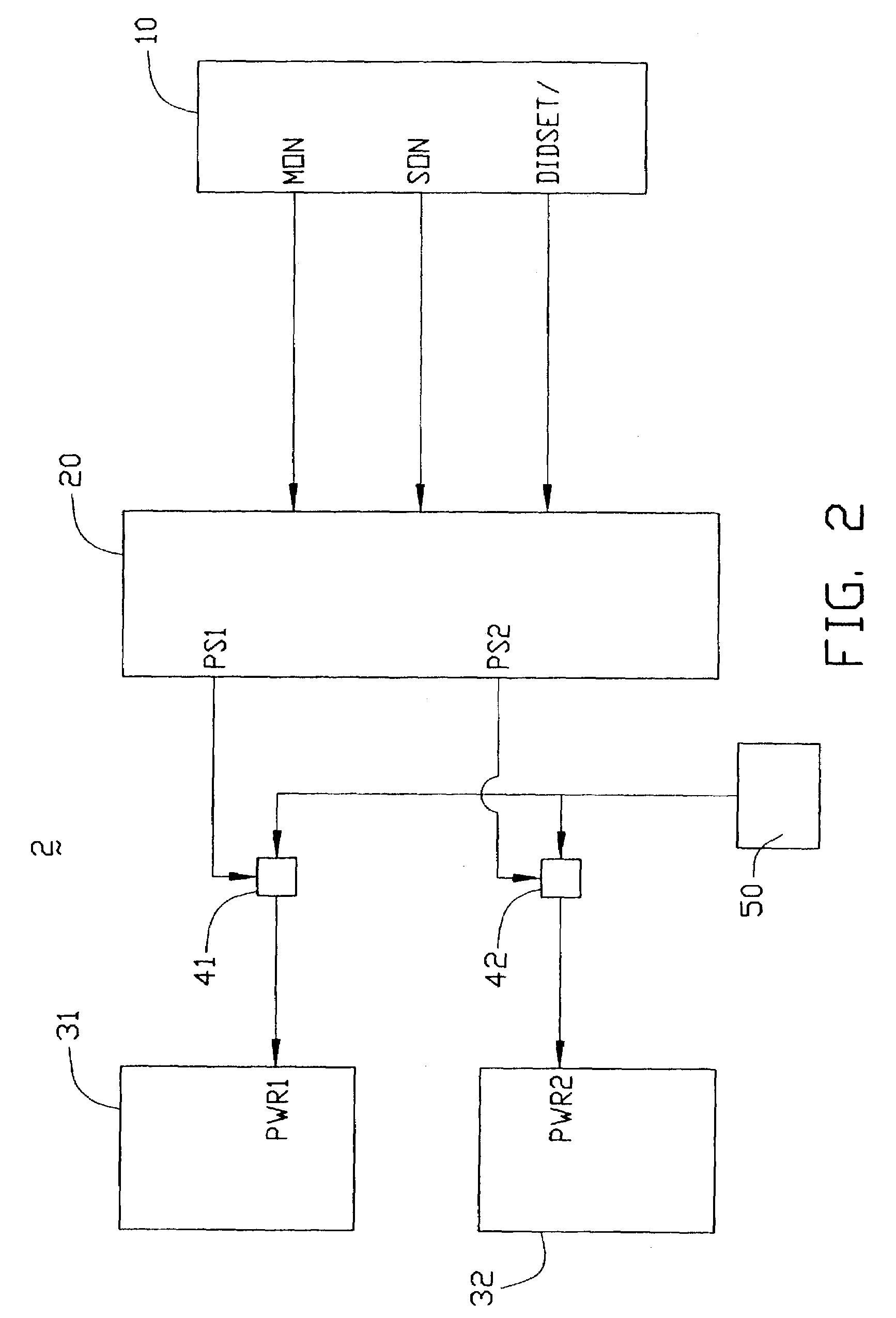
The present invention provides a method and a control apparatus (1) for sequentially controlling the spinning up of a number of IDE_HDDs (30) included in one computer or network server. The method and apparatus works by assigning different ID numbers to different pairs of IDE_HDDs and causing a delay between the start of spin up of each pair. The control apparatus includes a host (10), a plurality of controllers (20), a plurality of power switches (40) and a plurality of IDE_HDDs. When the control apparatus is booted up, each controller receives an ID number from the host and delays activating the power switches connecting a power supply (50) to the IDE_HDDs by a time proportional to the ID number. The present invention thereby avoids too high an instantaneous peak current during booting up and prevents the power supply from being burnt out.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
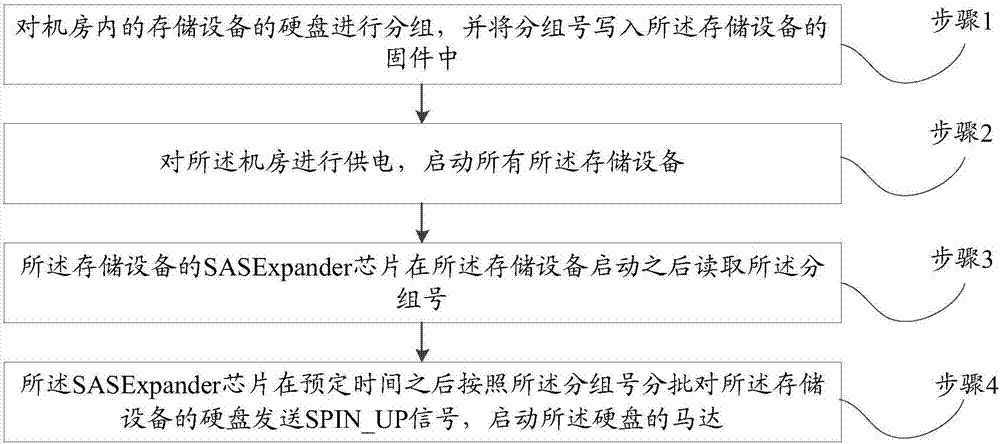
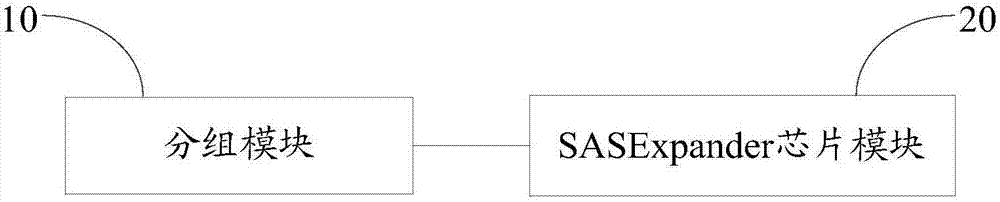
Hard disk staggered spin-up method and system
InactiveCN107402623AStaggered start implementationSimple methodVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingSpin-upComputer engineering
The invention discloses a hard disk staggered spin-up method and system. The method comprises the steps of 1, grouping hard disks of storage devices in a machine room, and writing group numbers into firmware of the storage devices; 2, supplying power to the machine room, thereby starting all the storage devices; 3, reading the group numbers after the storage devices are started by SASExpander chips of the storage devices; and 4, sending SPIN_UP signals to the hard disks of the storage devices in batches according to the group numbers after a predetermined time by the SASExpander chips, thereby starting motors of the hard disks. On the premise of not changing power supply logic of a power supply, the hard disks are grouped, the group numbers are written in the hard disks, and the SASExpander chips reads the group numbers and sends the SPIN_UP signals to the hard disks of the storage devices in batches to start the motors of the hard disks, so that hard disk staggered spin-up of all the devices in the machine room is realized; the realization method is relatively simple; batch staggered spin-up of the hard disks can be effectively realized; and serious consequences of power supply burnout, machine room fire and the like are avoided.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for spinning a multiphase motor for a disk drive system from an inactive state
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
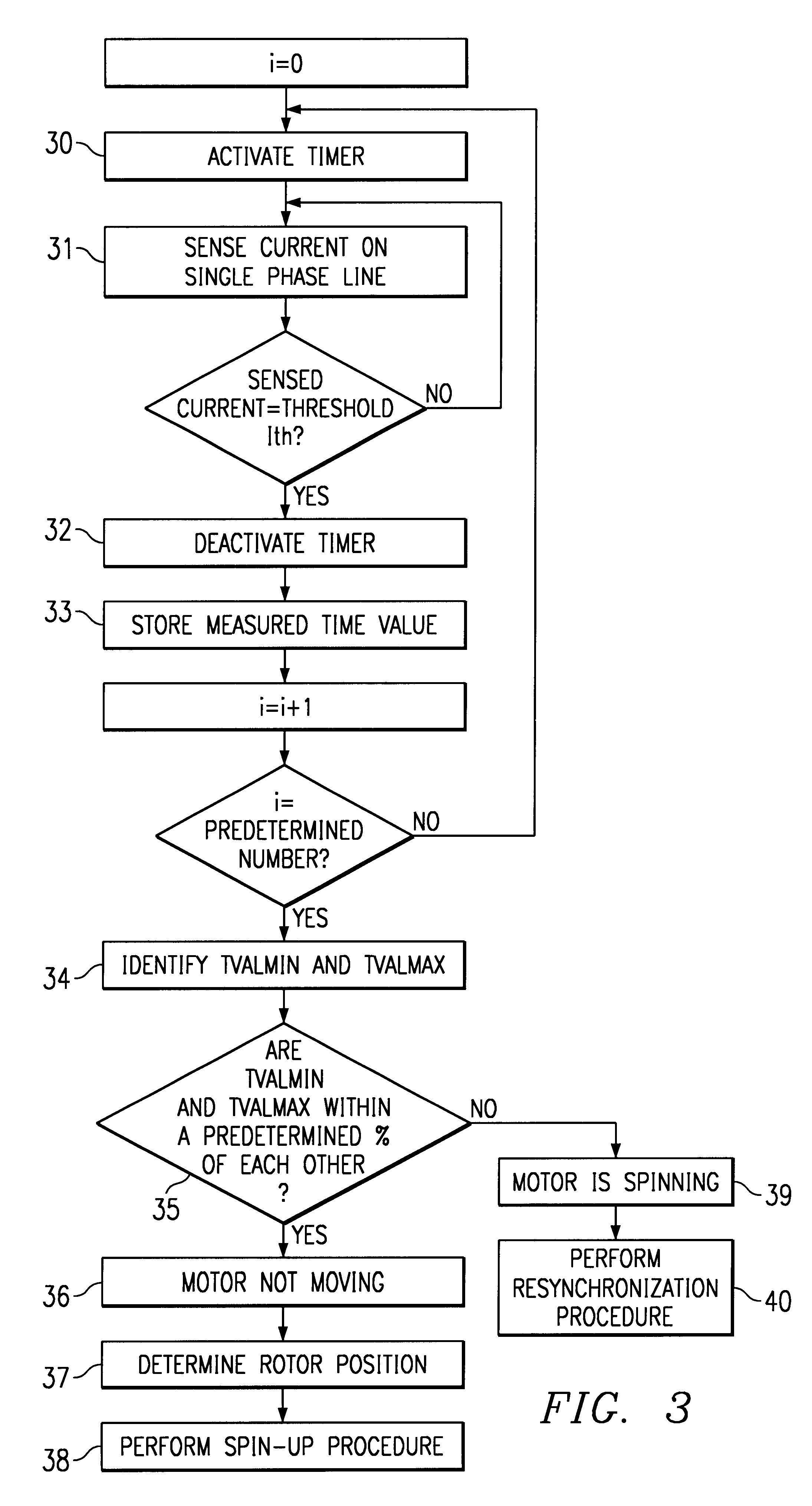
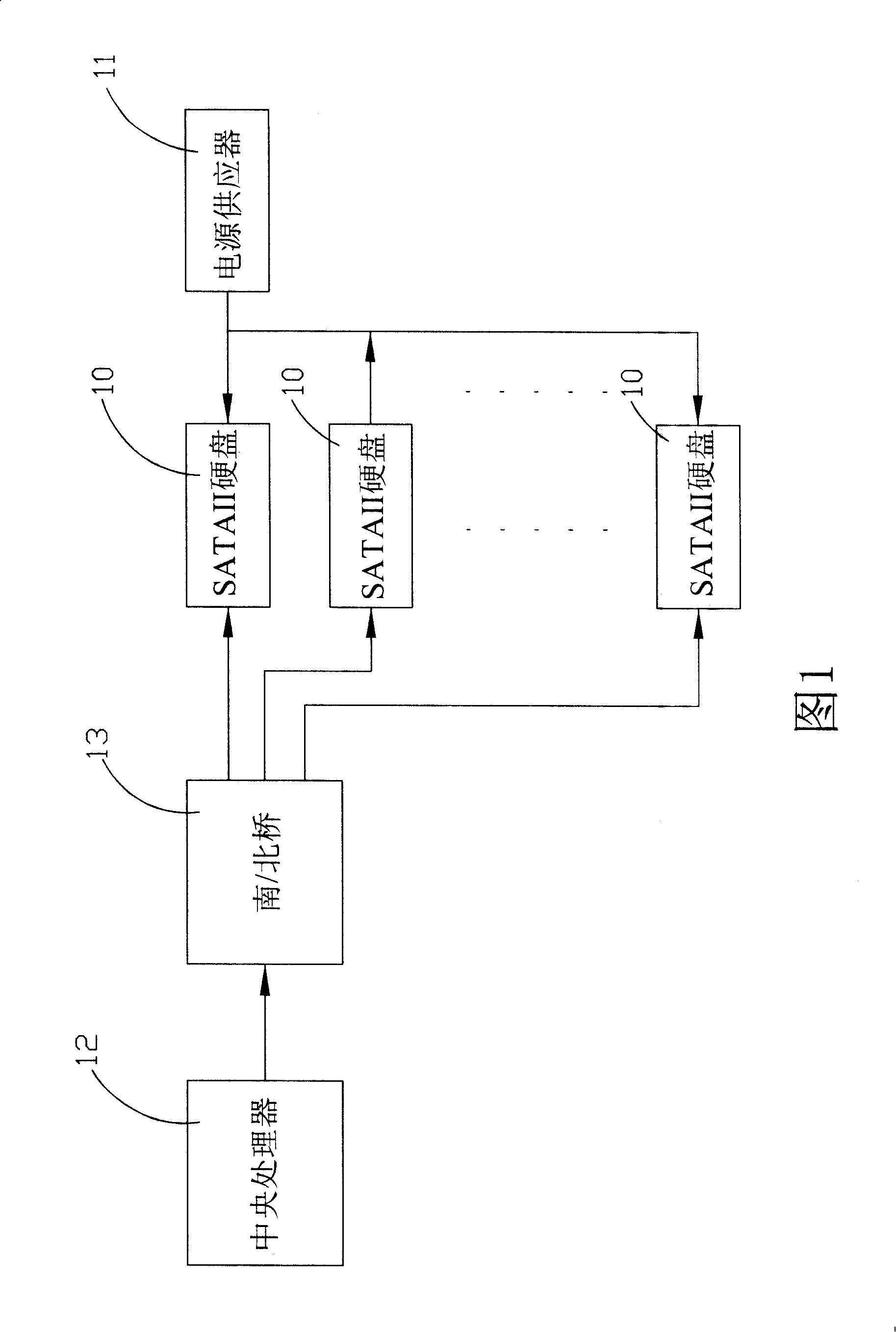
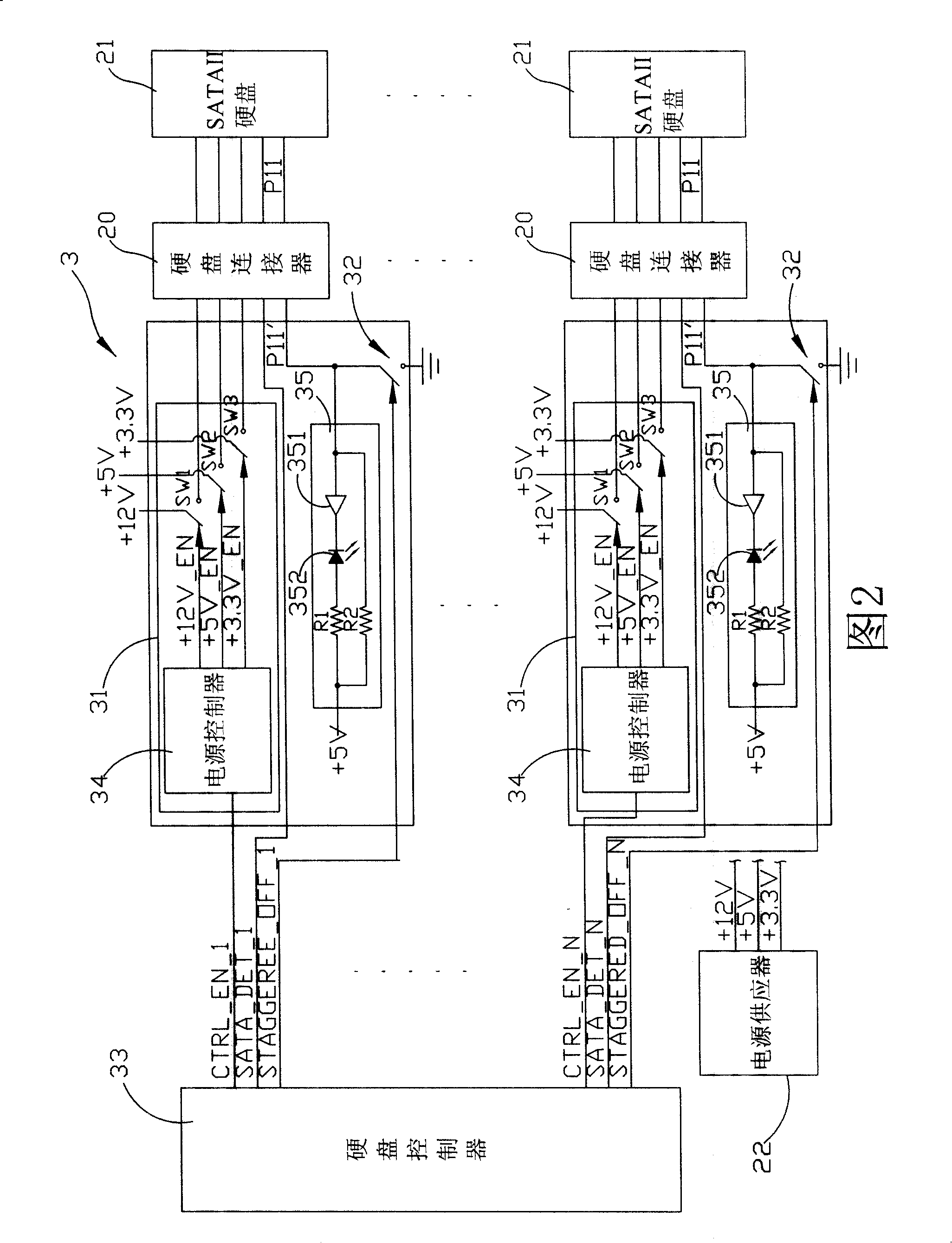
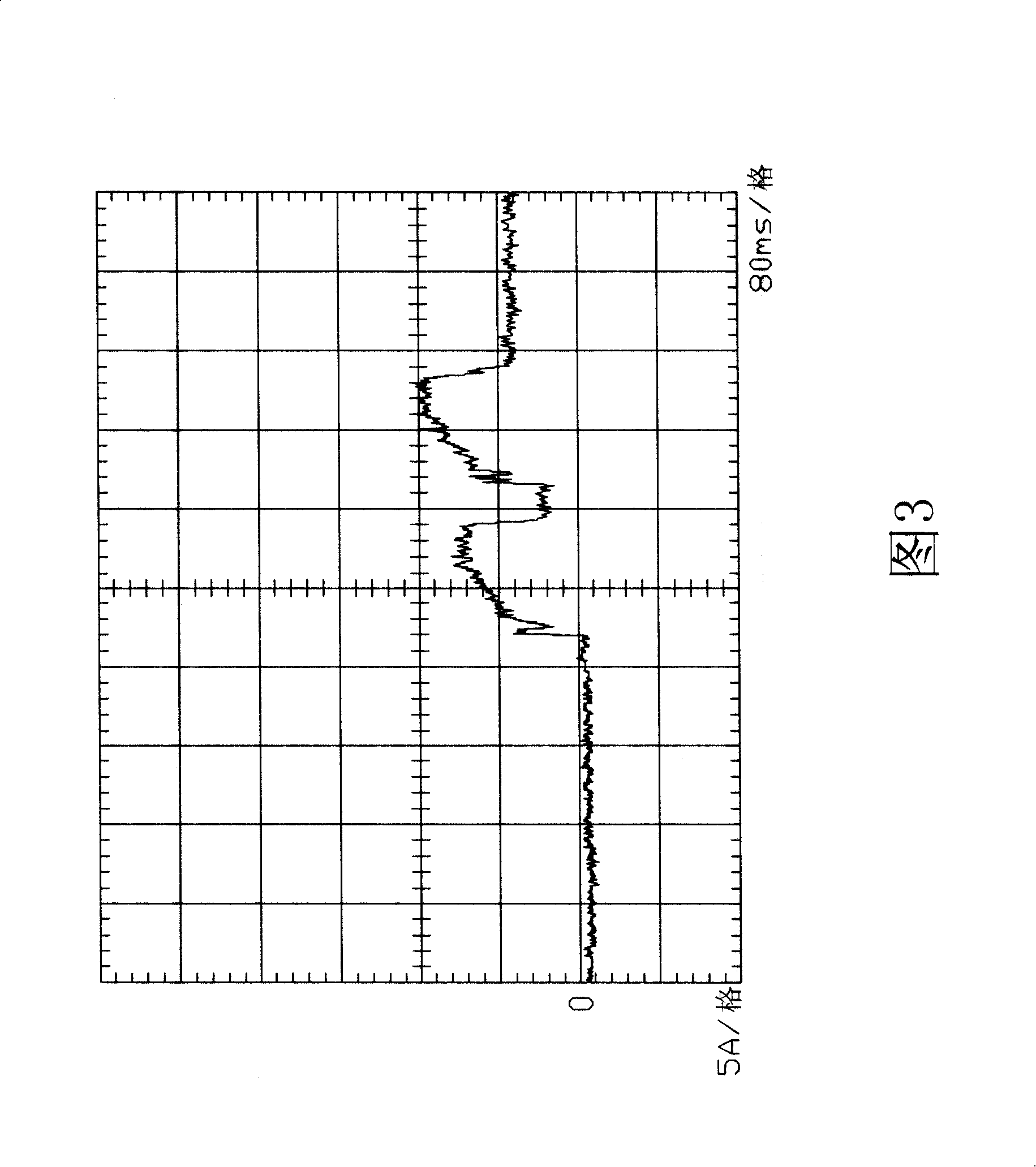
Hard disk startup sequence control circuit
InactiveCN101241417AAvoid overloadLow costInput/output to record carriersSequence controlElectricity
The pesent invention provides a SATAII hard start sequence control circuit, for controlling the start sequence of SATAII hard inserting in multiple hards connector, and SATAII hard has a start interlaced start mode controlled by a driving software, the circuit is electrically connected one-to-one with these hard connectors by multiple power control units to control SATAII hards inserted in the hard connectors timing output by power, and multiple switch elements are electrically connected one-to-one with these hards connectors, and a hard controller detects whether these hards connectors is inserted with SATAII hards or not, when detecting the multiple hardware connectors inserting in the SATAII hardware, the relative power control units separately supply to these STATII hardwares after inhibiting staggered spin-up mode of these SATAII hardwares by the corresponding switch units. Thereafter, the overload of the power caused by multiple SATAII hardwares start at the same time is avoided.
Owner:MITAC COMP (SHUN DE) LTD +1
Method for spindle bearing friction estimation for reliable disk drive startup operation
InactiveUS7009354B2Increased friction loadingImprove performance reliabilityReducing temperature influence on carrierMotor/generator/converter stoppersActuatorCounter-electromotive force
Temperature of the disk drive is measured using components of the disk drive without the need of including a separate temperature sensor to optimize performance of the spindle motor during startup. To measure temperature, the resistance of the VCM winding is measured and used to estimate the spindle bearing temperature. Back emf is measured from VCM windings and used during startup to accurately determine actuator position. Because the VCM coil resistance varies significantly with temperature, coil resistance variations with temperature are determined to enable compensation for inaccuracies in determination of actuator velocity. This inferred temperature is then used to optimize the start up procedure for the spindle motor to accommodate the increased frictional loading of the spindle bearing. In this way an improved performance in the reliability and spin up operation time can be realized without the addition of a separate temperature measurement hardware element.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Managing disk drive power states
ActiveUS7856563B1Significant of expenseSignificant amount of powerEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementSpin-upElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
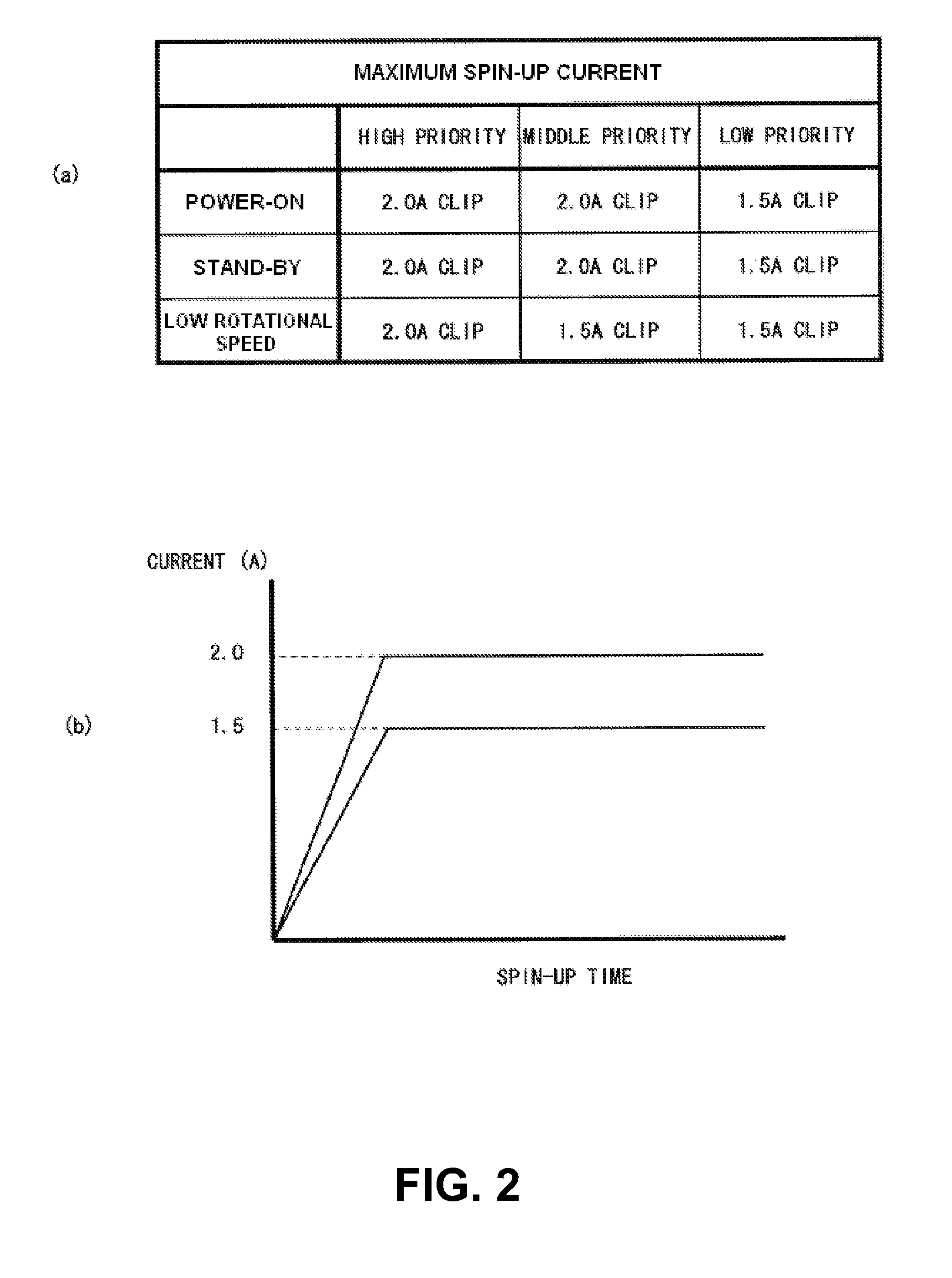
Ensuring Rate Of Spin-Up/Spin-Down Cycles For Spindle Motor In A Hard Disk Drive Does Not Exceed Rate Spindle Motor Is Designed To Handle
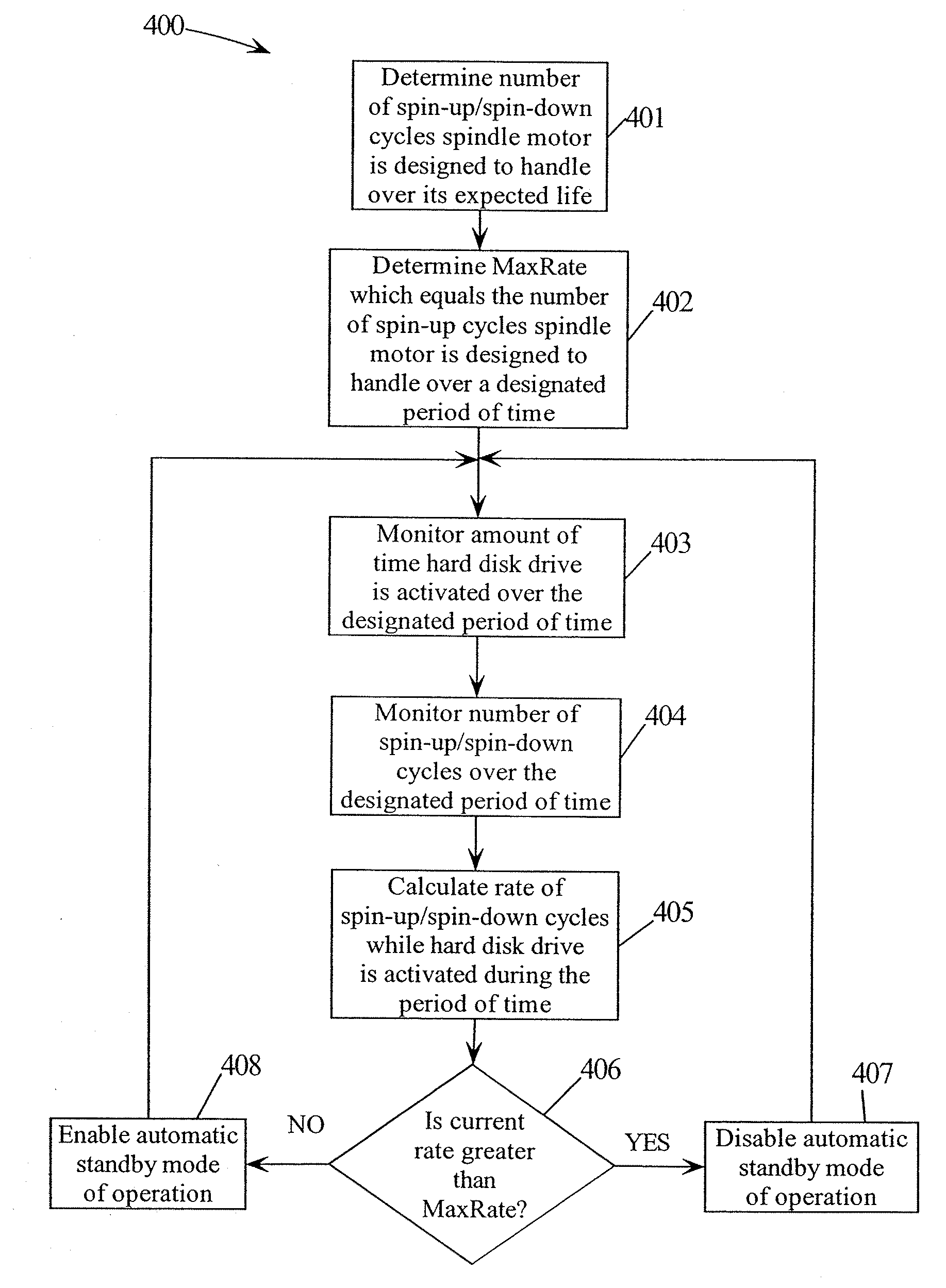
InactiveUS20060274445A1Reduce probabilityExcessive wearDriving/moving recording headsFilamentary/web record carriersHard disc driveTime segment
A method, computer program product and hard disk drive for restricting a rate of spin-up / spin-down cycles for a spindle motor in a hard disk drive. The firmware in the hard disk drive determines a maximum rate of spin-up / spin-down cycles the spindle motor is designed to handle over a designated period of time based on the number of spin-up / spin-down cycles the spindle motor is designed to handle over its expected lifetime. The firmware disables the automatic standby mode of operation if a calculated rate of spin-up / spin-down cycles during the designated period of time is greater than the maximum rate of spin-up / spin-down cycles the spindle motor is designed to handle over the designated period of time. By disabling the automatic standby mode of operation, the rate of spin-up / spin-down cycles will be reduced as the spindle motor will not incur a spin-up / spin-down cycle until the automatic standby mode of operation is enabled.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com