Patents
Literature
80 results about "Direct-access storage device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A direct-access storage device (DASD) (pronounced /ˈdæzdiː/) is a secondary storage device in which "each physical record has a discrete location and a unique address". IBM coined the term DASD as a shorthand describing hard disk drives, magnetic drums, and data cells. Later, optical disc drives and flash memory units are also classified as DASD. The term DASD contrasts with sequential storage media such as magnetic tape, and unit record equipment such as card devices like card readers and punches.
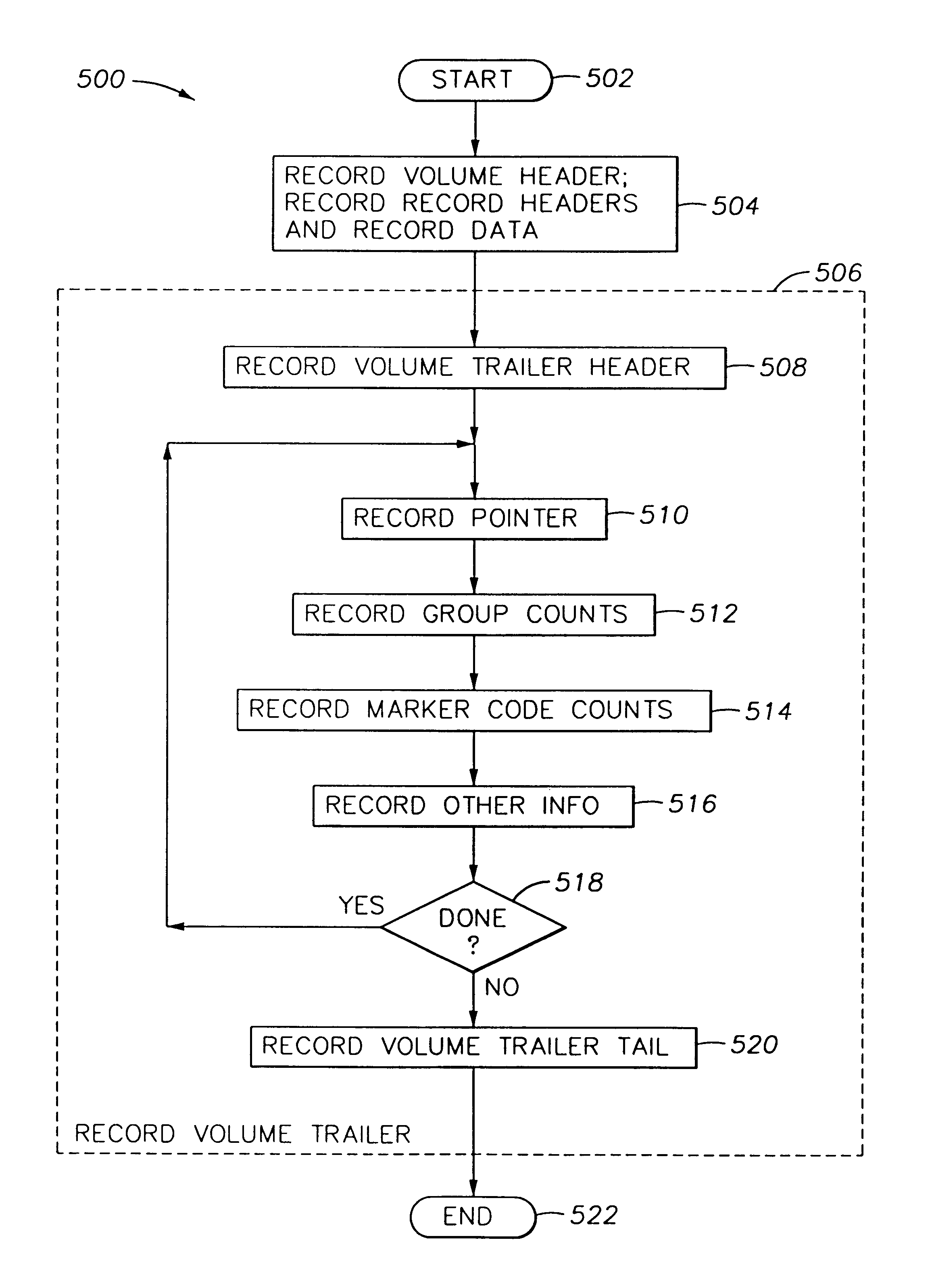
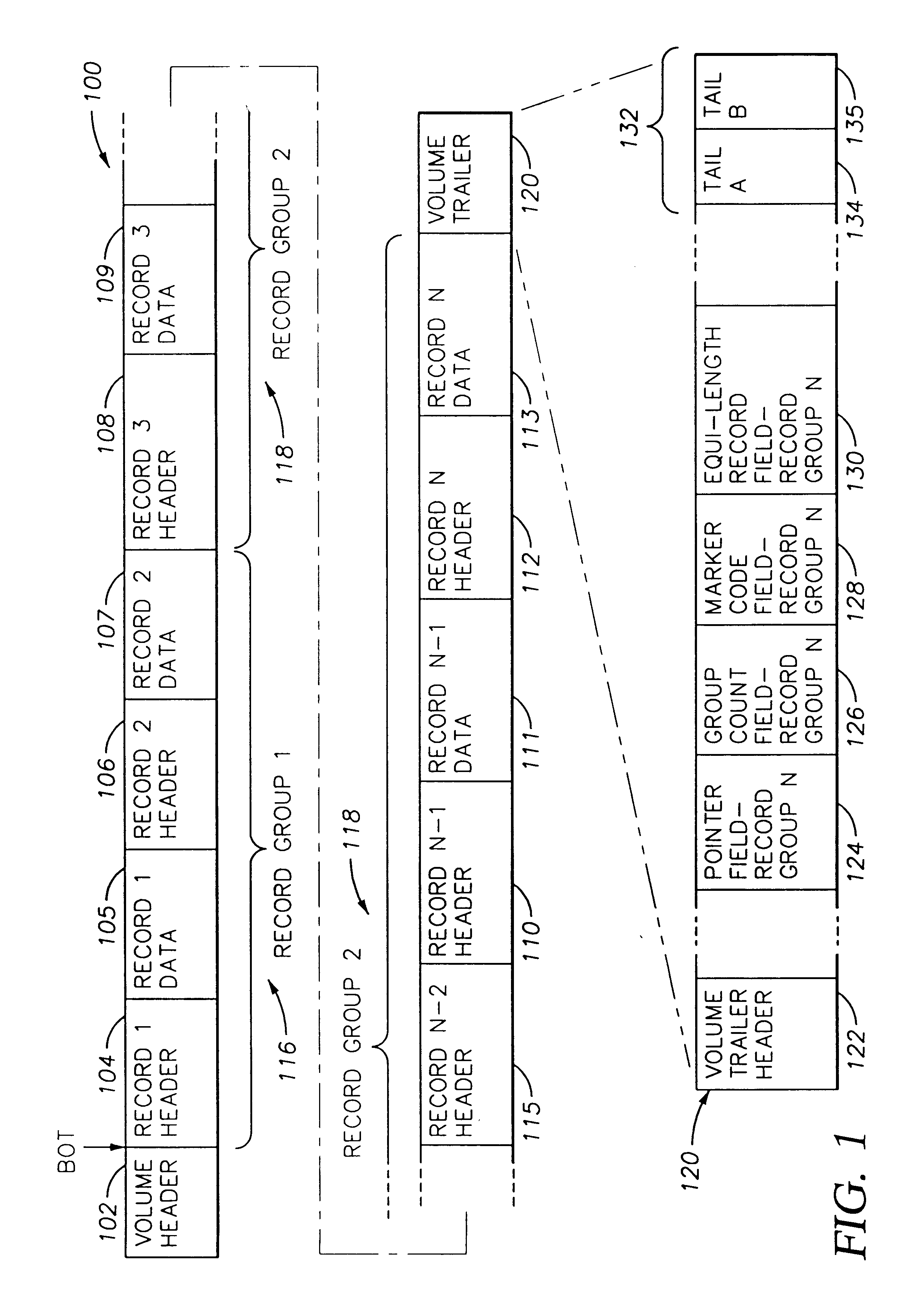
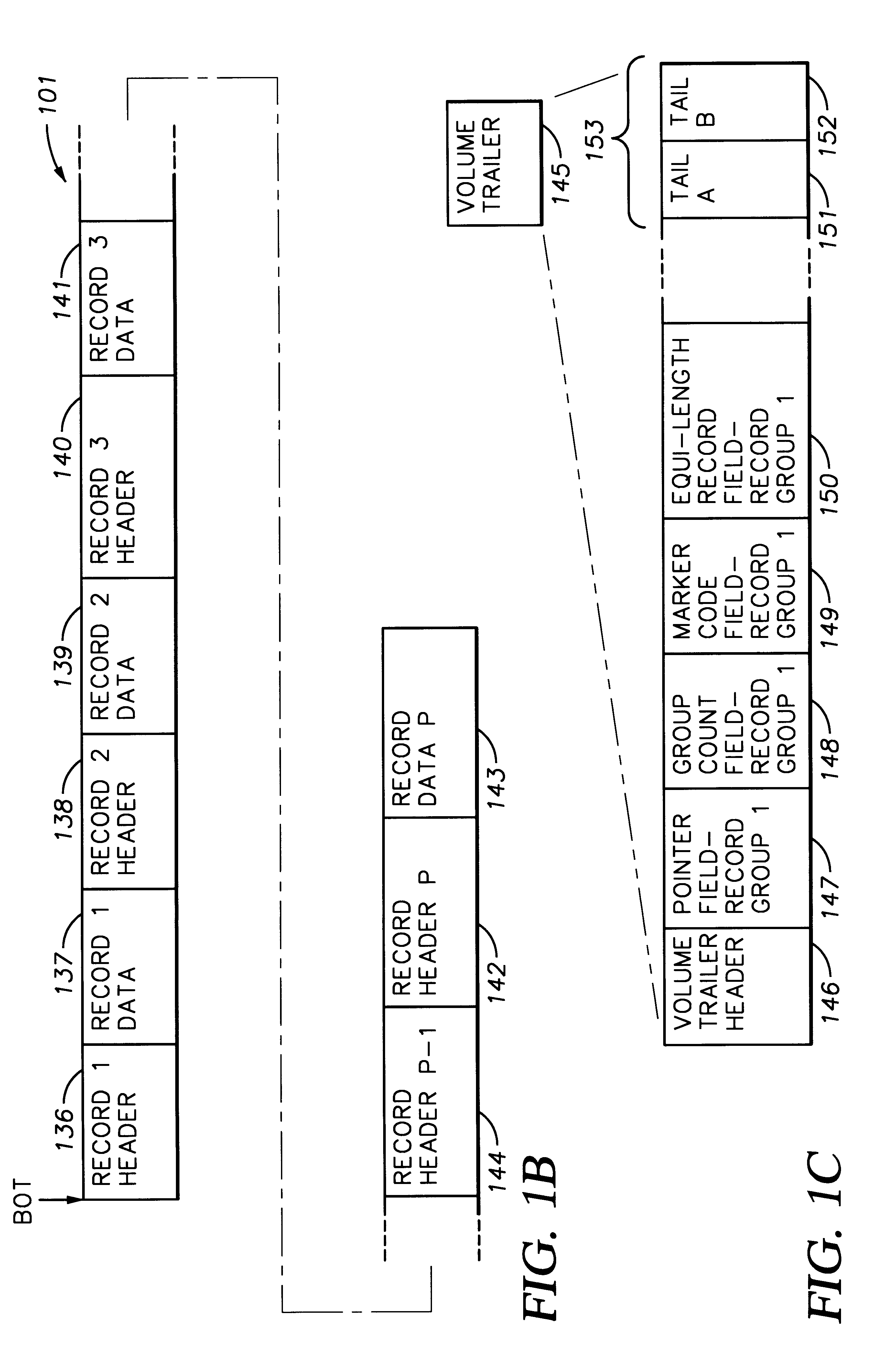
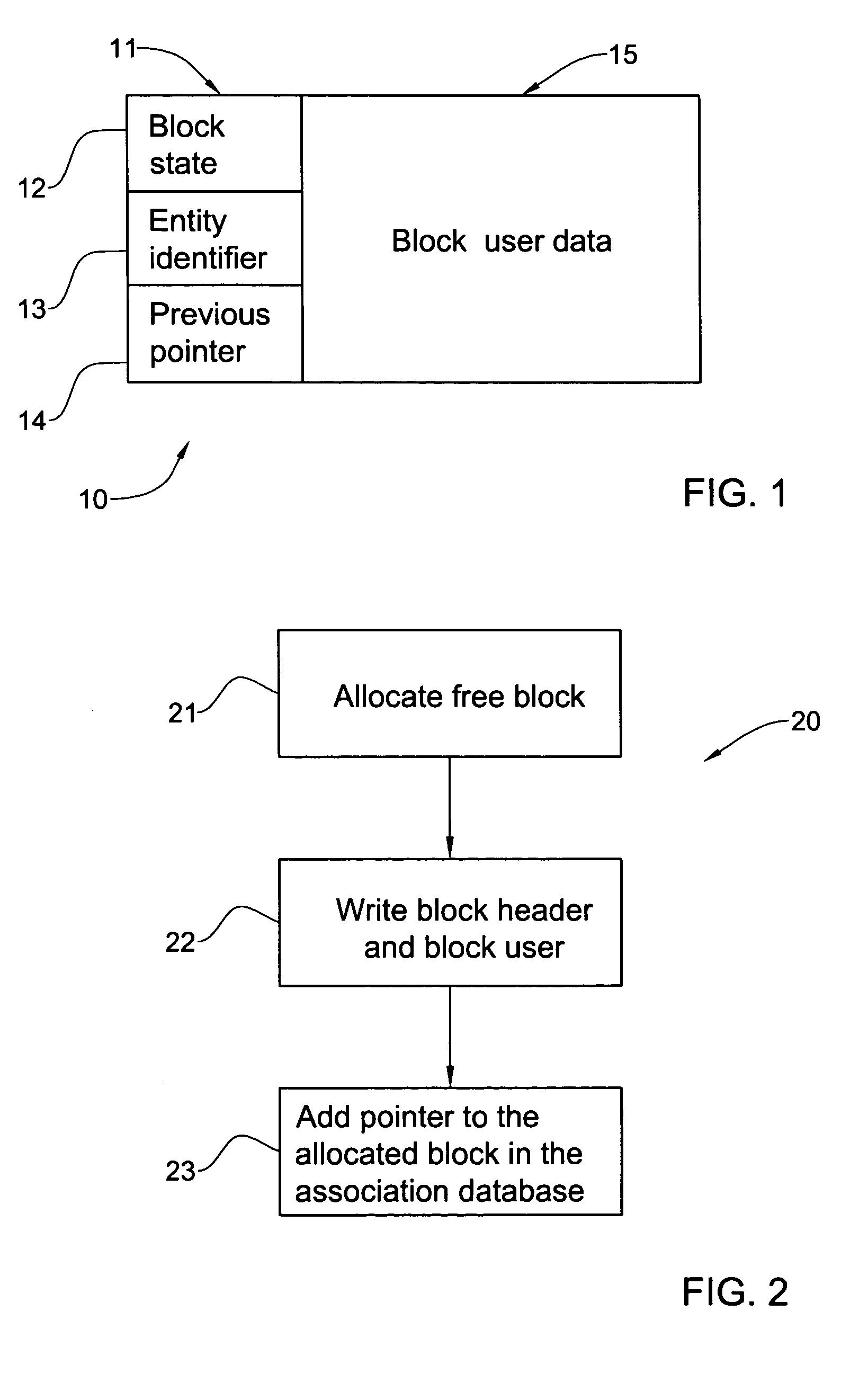
Storage and access of data using volume trailer
InactiveUS6343342B1Fast dataHigh speedInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital dataDirect-access storage device
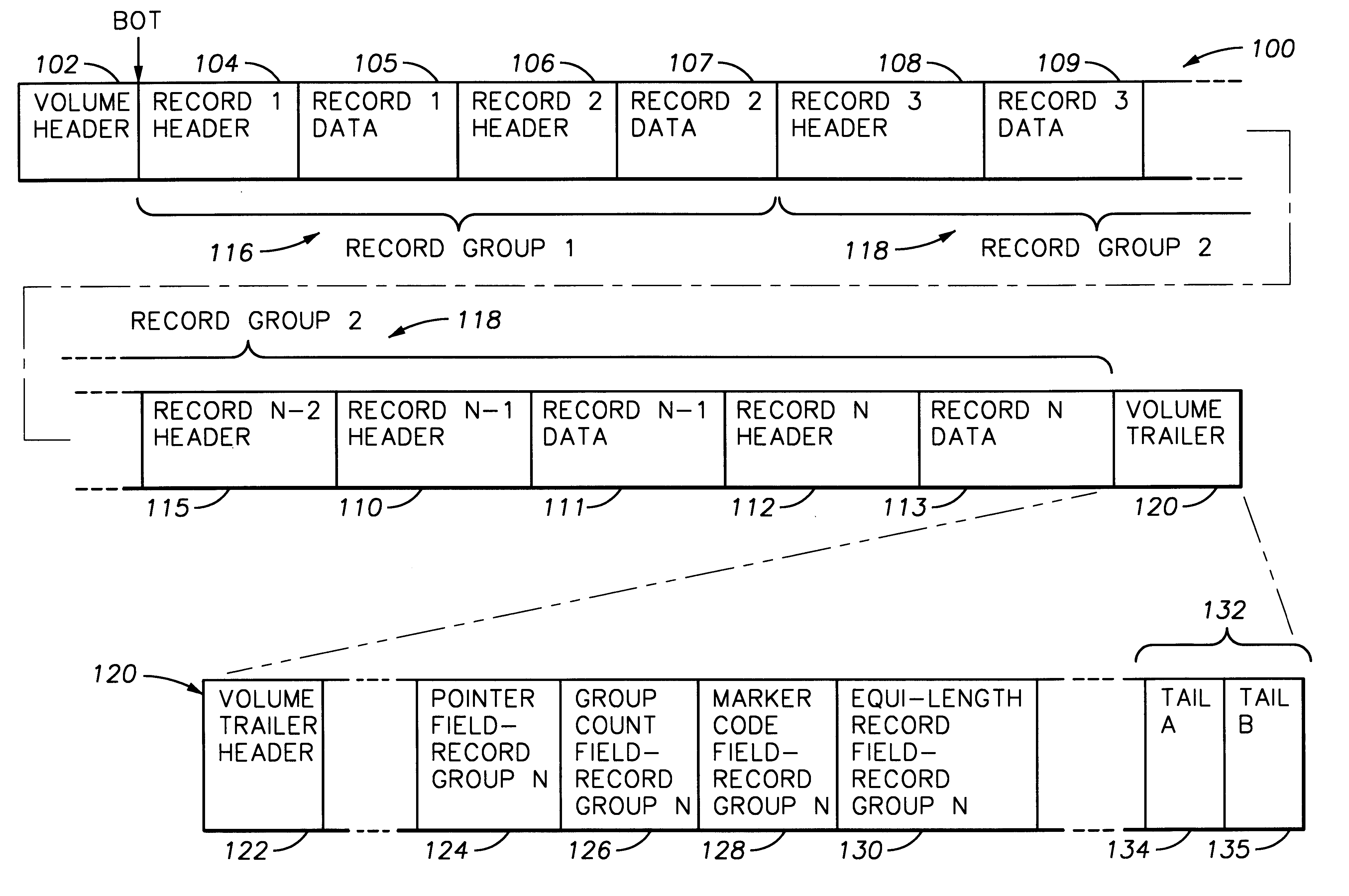
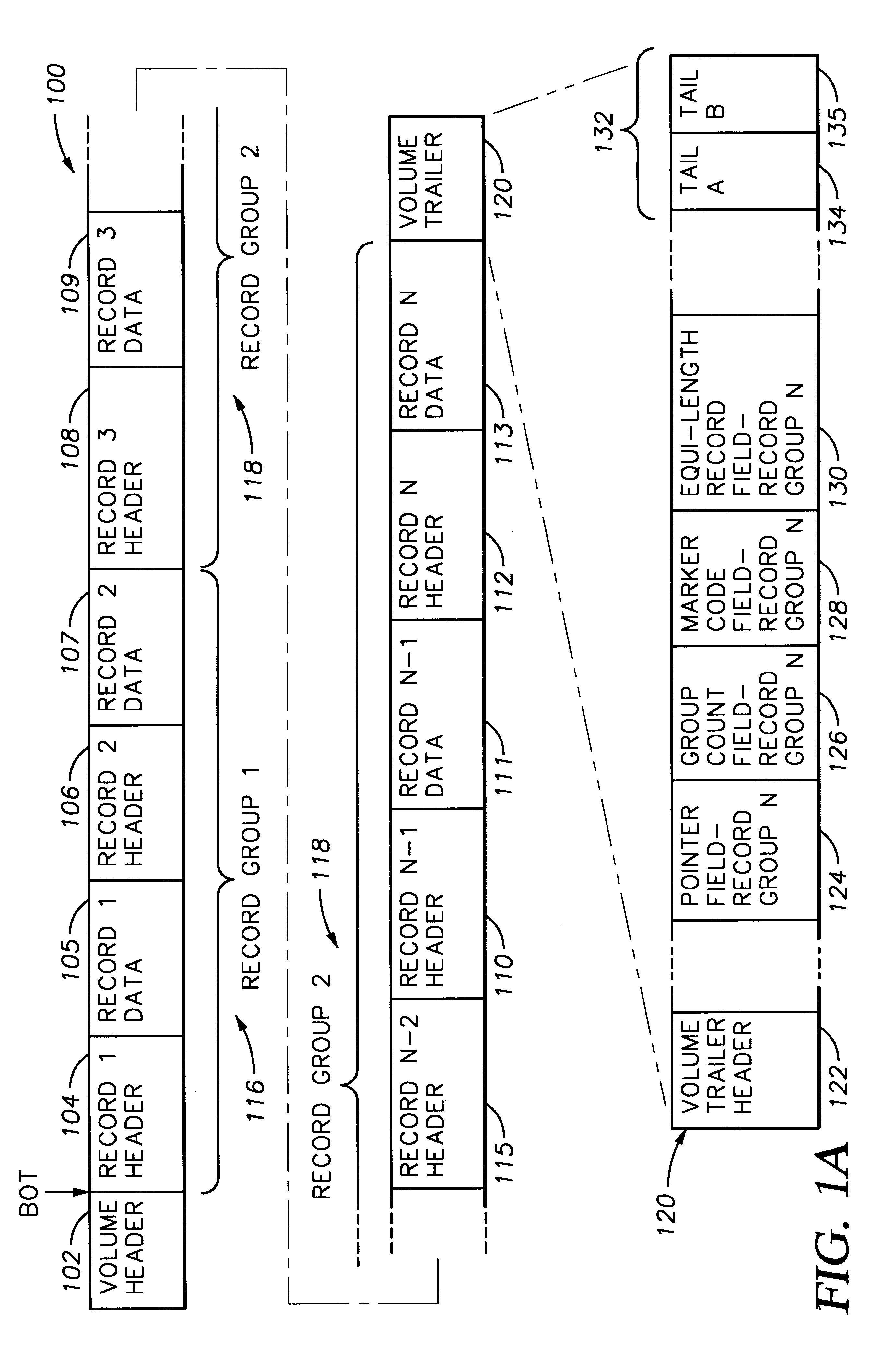
Digital data records are stored on a direct access storage device (DASD) in emulation of sequential-access media, the efficiency of storage and access of the data being improved by using a volume trailer containing various statistics about the records. Data is preferably stored in records, logically assembled into record groups. Interspersed with the records, there may be one or more marker codes, which function like tape marks among the various data records. The volume trailer contains pointers to each record group, record counts for each group, marker code counts for each group, and may also include fields showing whether records in a given record group are of equal length. The volume trailer may also include a volume trailer "tail", including a byte count for the entire volume trailer, and a unique sequence identifying the volume trailer. Statistics contained in the volume trailer enable substantially more efficient access of the data by a DASD. For example, record groupings, group counts, and / or marker code counts may be employed to perform operations such as locate, forward space file, and backward space file.
Owner:IBM CORP
Raid system with multiple controllers and proof against any single point of failure
A RAID system which functions despite any single point of failure is disclosed. The system has two or more controllers, a multiplicity of direct access storage devices arranged in racks, redundant connectors throughout, and an independent backplane, cables, power supply, and cooling system for each controller and for each rack of direct access storage devices. In a second embodiment, no backplane or midplane is included in the RAID system; rather each controller is connected directly with the direct access storage devices.
Owner:DIGI DATA CORP
Storage and access to scratch mounts in VTS system
InactiveUS6173359B1Fast and efficientInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital dataDirect-access storage device
A portion of digital data records are stored on a direct access storage device (DASD) in emulation of sequential-access media when the parent digital data records are transferred to a sequential-access media. The efficiency of storage and access to the data portion is improved by random-access recall of the data in the data portion, and by constructing a data portion trailer containing various statistics about the records for referencing the digital data and advancing to target data. The volume data portion trailer is constructed as read forward and forward space block operations are performed. Data is preferably stored in logically assembled records. Interspersed with the records, there may be one or more marker codes, which function like tape marks among the various data records. The volume trailer may contain pointers to each record, a record count and marker codes for the data portion. Statistics contained in the data portion trailer enable substantially more efficient access of the data by a DASD.
Owner:IBM CORP
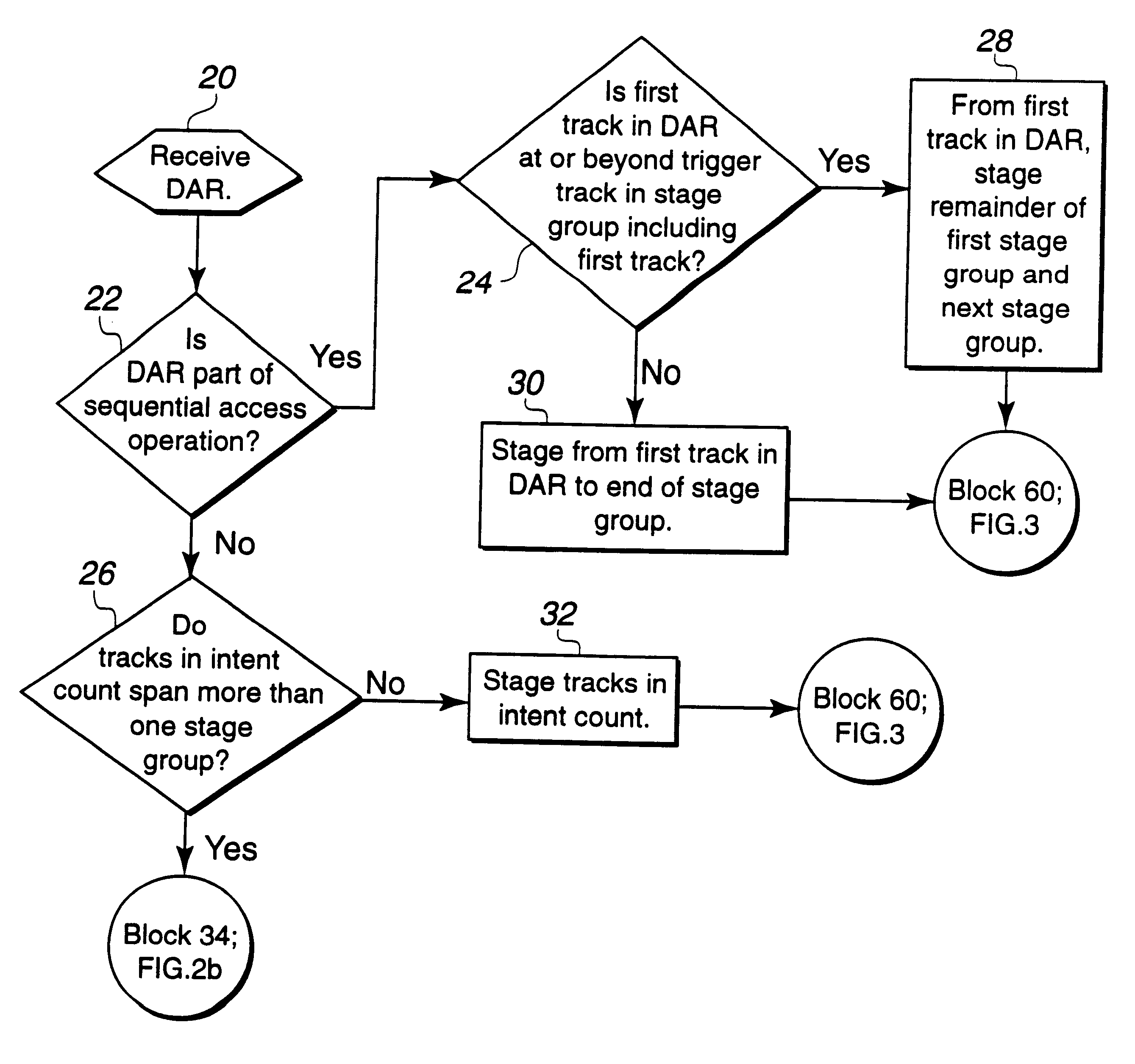
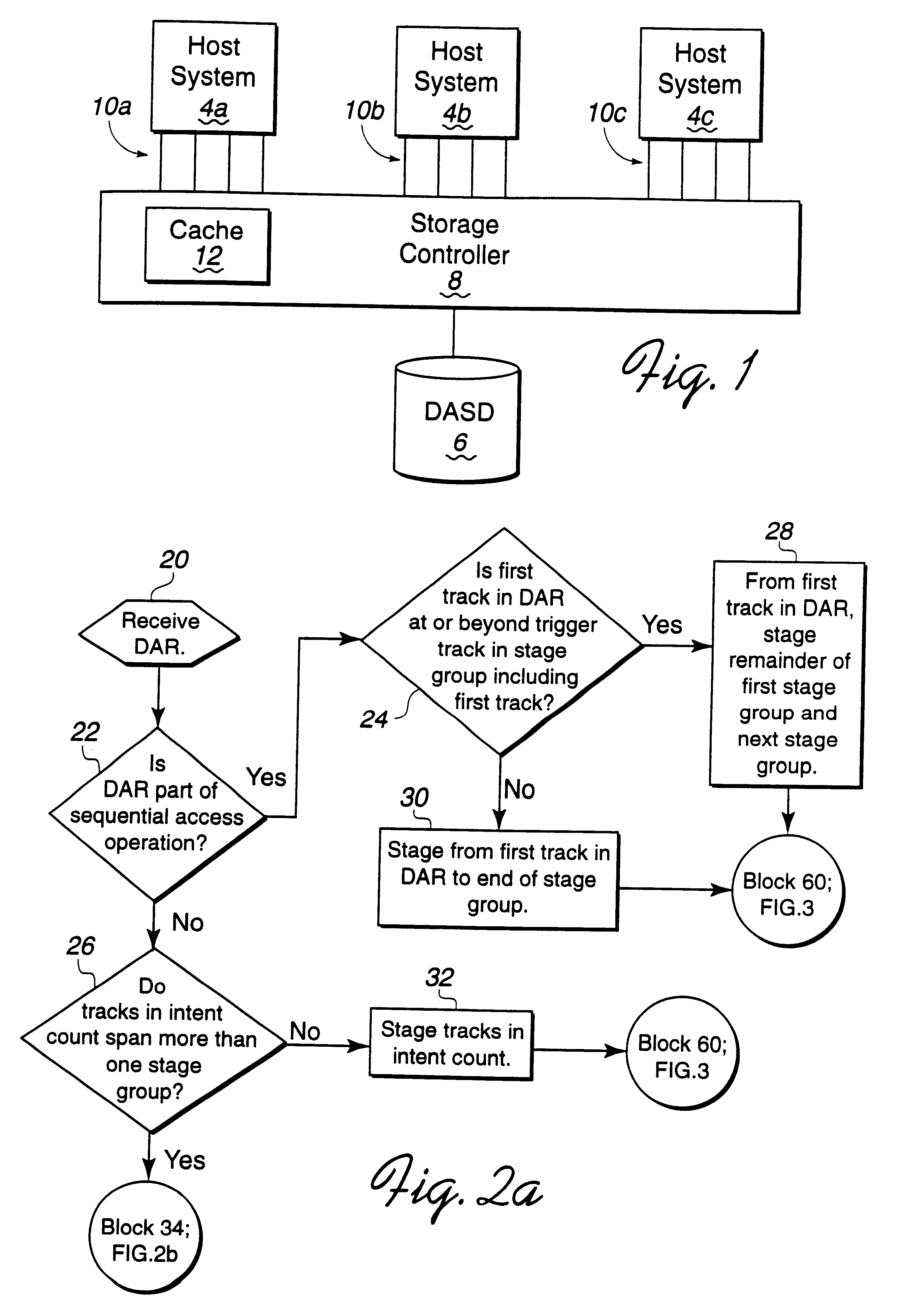
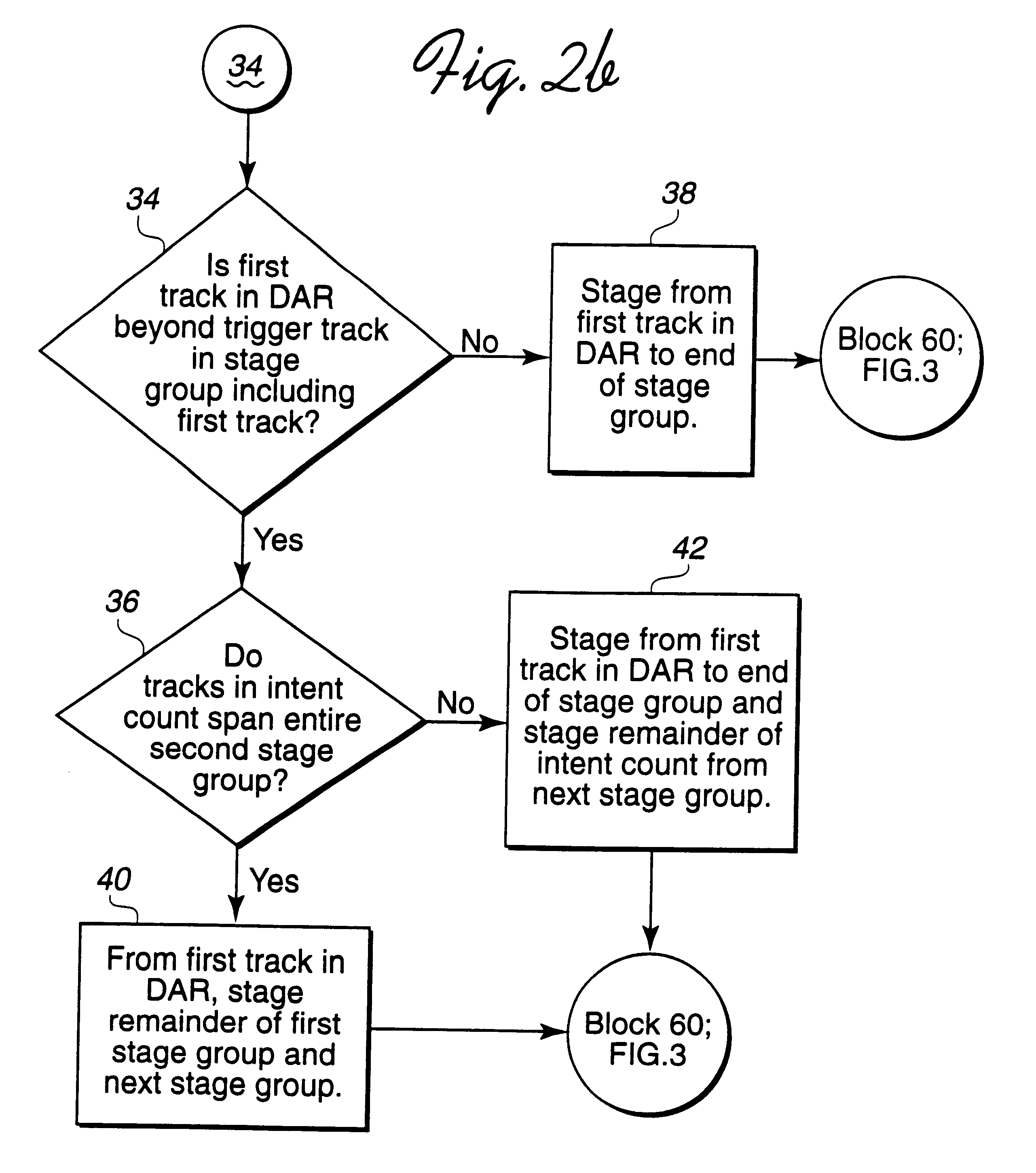
Method and system for staging data into cache
InactiveUS6381677B1Avoid a cache missSave memory spaceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData setDirect-access storage device
Disclosed is a system for caching data. After determining a sequential access of a first memory area, such as a direct access storage device (DASD), a processing unit stages a group of data sets from the first memory area to a second memory, such as cache. The processing unit processes a data access request (DAR) for data sets in the first memory area that are included in the sequential access and reads the requested data sets from the second memory area. The processing unit determines trigger data set from a plurality of trigger data sets based on a trigger data set criteria. The processing unit then stages a next group of data sets from the first memory area to the second memory area in response to reading the determined trigger data set.
Owner:IBM CORP
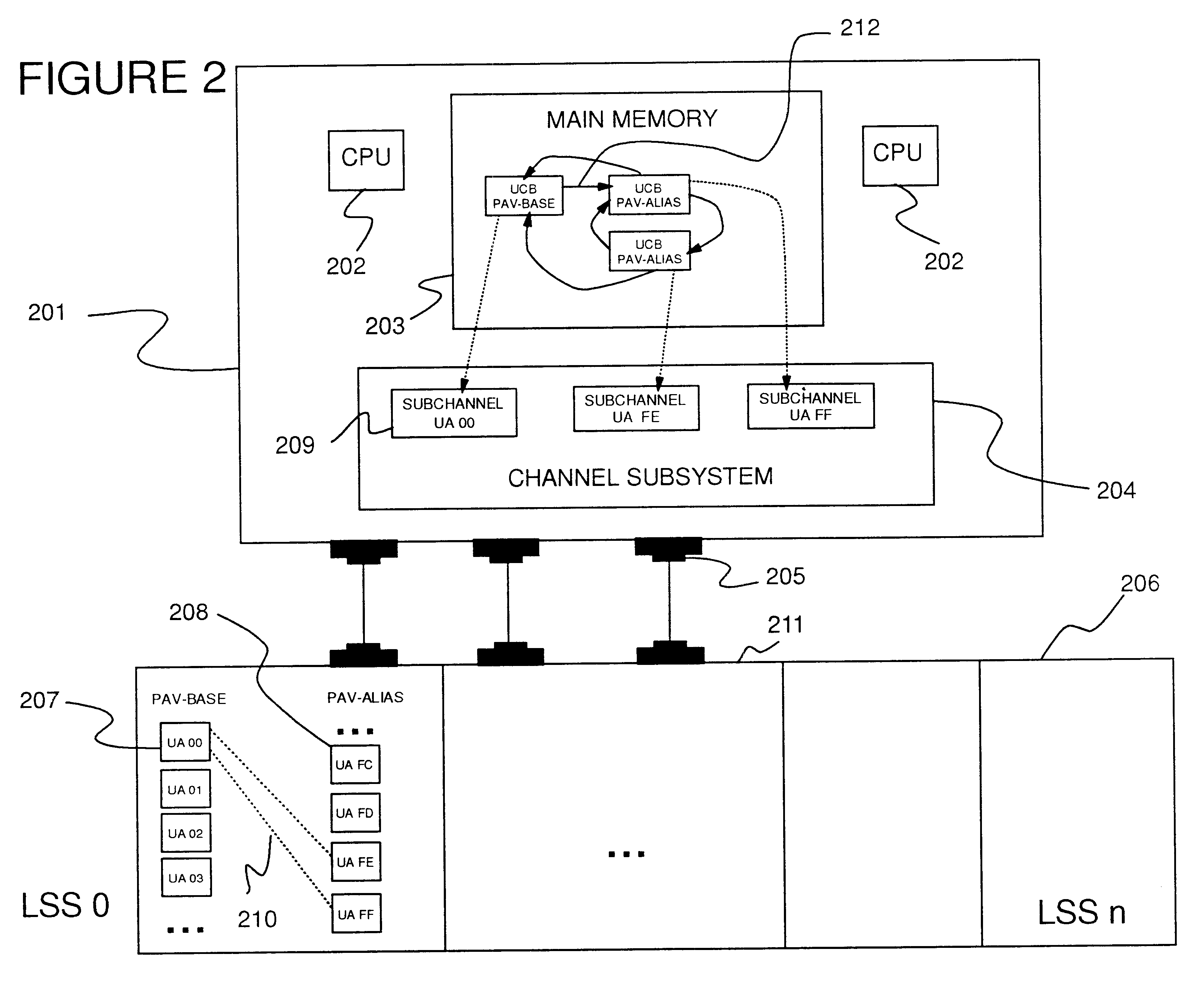
System for accessing an input/output device using multiple addresses
InactiveUS6170023B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingDirect-access storage deviceOutput device
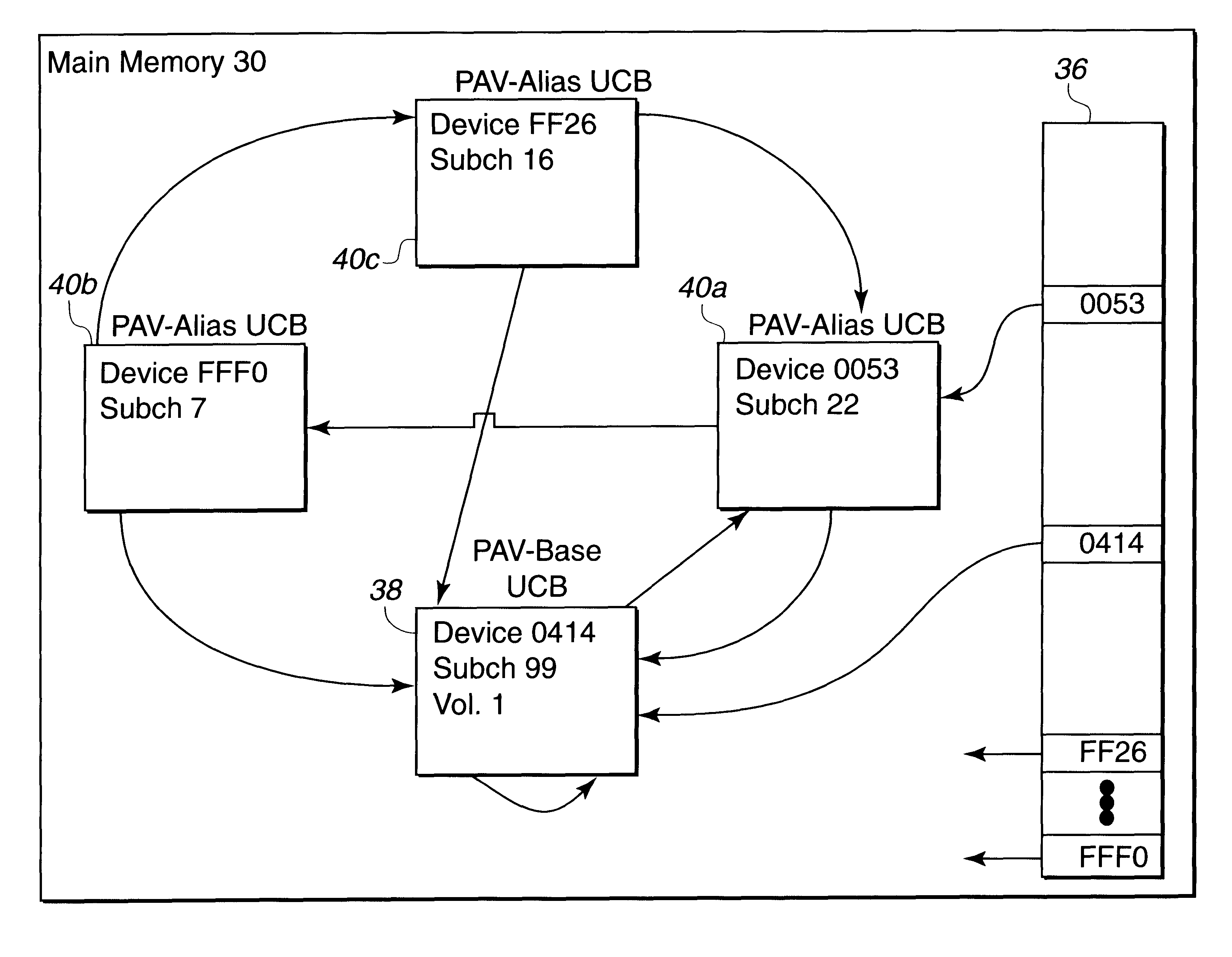
Disclosed is a system for performing input / output (I / O) operations with a processing unit. A processing unit, such as a host system, determines a base and associated alias addresses to address an I / O device, such as a direct access storage device (DASD). The processing unit associates the determined base and alias addresses to the I / O device. The association of base and alias addresses is maintained constant for subsequent I / O operations until the processing unit detects a reassignment of the association of base and alias addresses. The processing unit then determines an available base or alias address to use with an I / O operation and may concurrently execute multiple I / O operations against the I / O device using the base and alias addresses.
Owner:IBM CORP
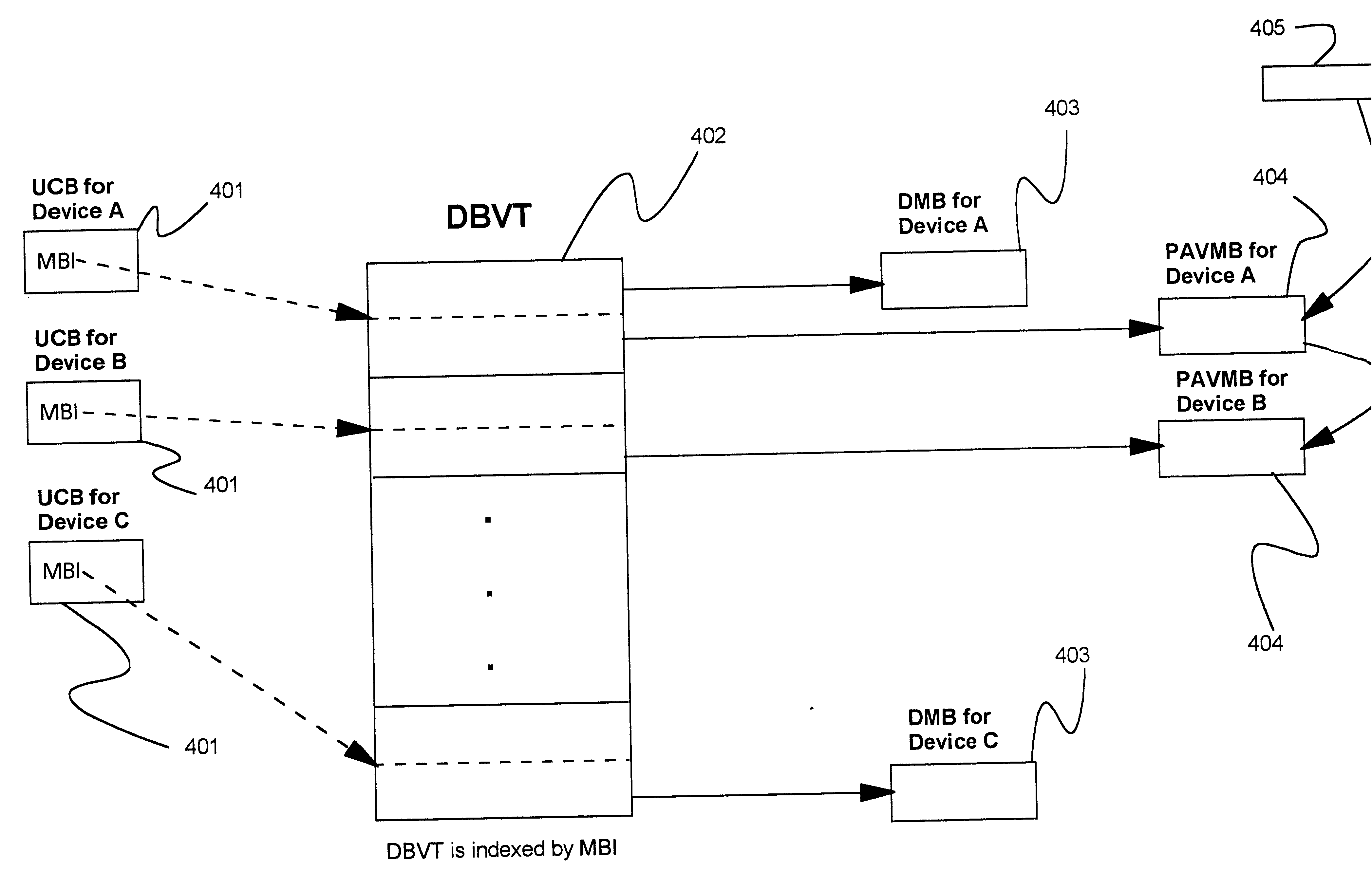
Method and system for dynamically assigning addresses to an input/output device
InactiveUS6185638B1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingDirect-access storage deviceComputerized system
Disclosed is a system for dynamically assigning alias addresses to base addresses referencing an I / O device, such as a direct access storage device (DASD). In the system, at least one base control block indicates a base address and a plurality of alias control blocks indicate a plurality of alias addresses. Each control block is associated with an address for addressing an I / O device. A processing unit, such as a host computer system, processes at least one alias control block associated with the I / O device and determines a base control block associated with the I / O device with which the alias control blocks are associated. The processing unit then binds at least one alias control block to the determined base control block. The bound base and alias control blocks provide different addresses to address the same I / O device. Further, the bound base and alias addresses address the same I / O device for subsequent I / O operations until the processing unit detects a reassignment of the association of base and alias addresses.
Owner:IBM CORP
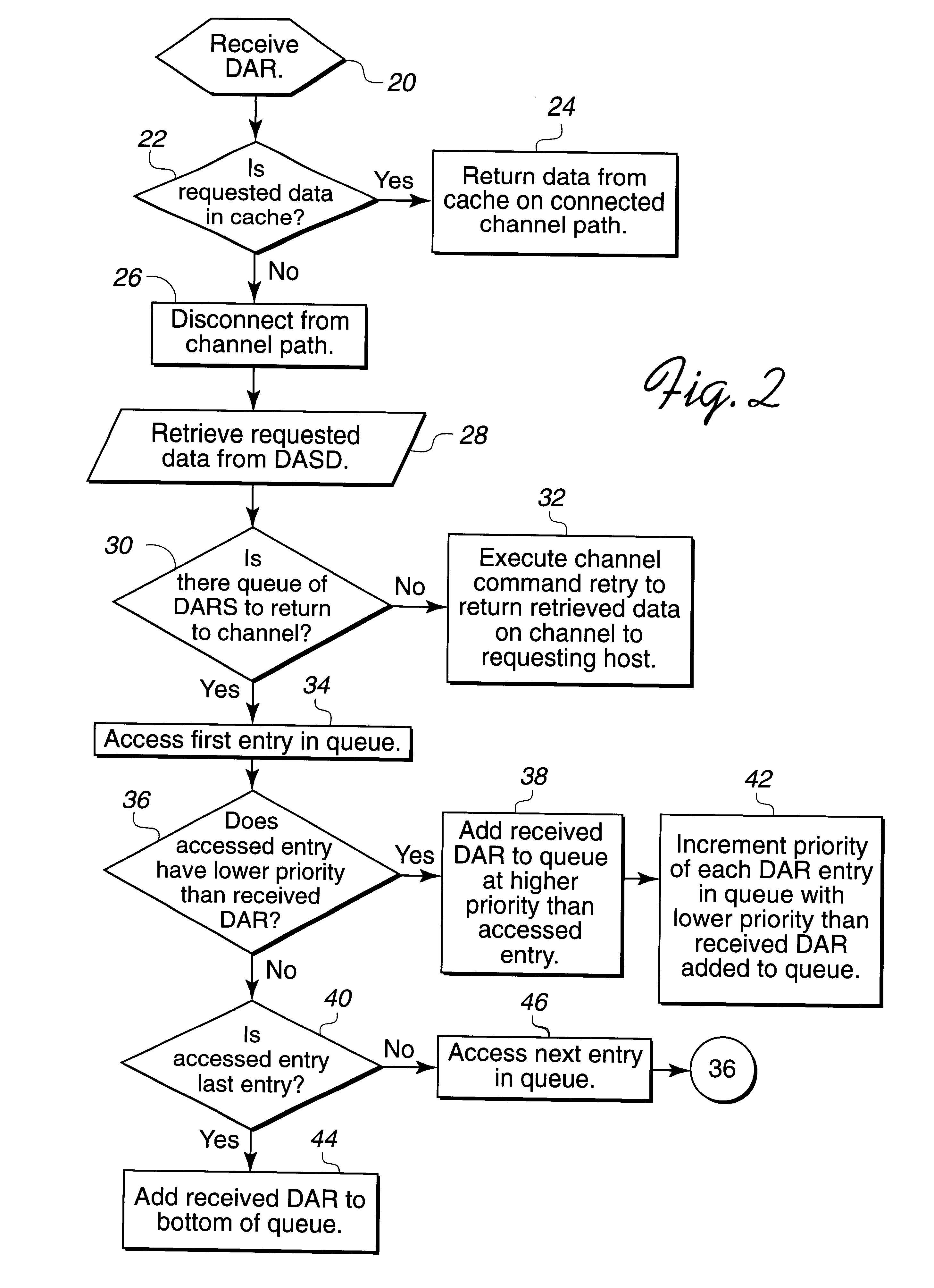
Input/output data access request with assigned priority handling
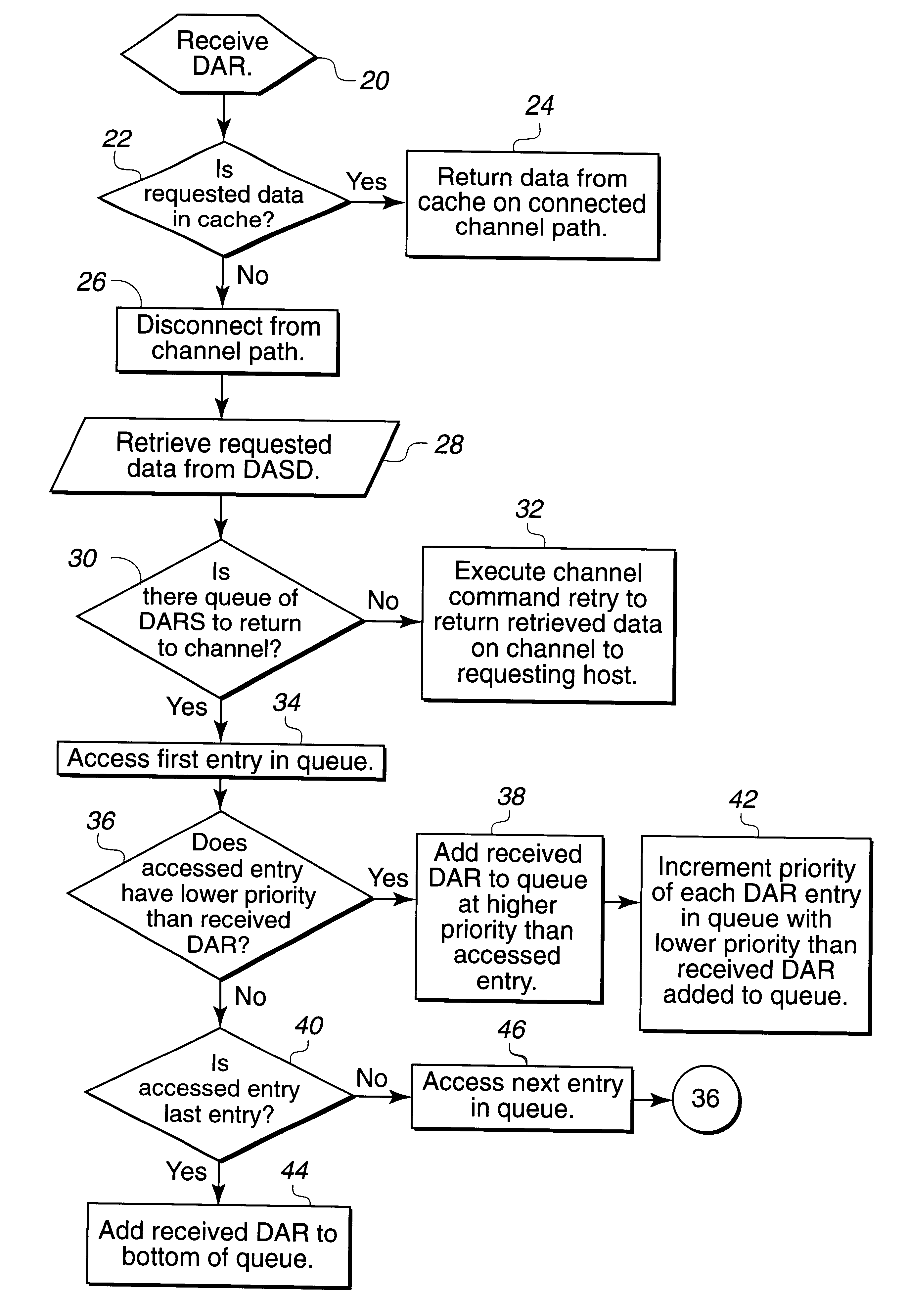
InactiveUS6253260B1Input/output to record carriersData conversionDirect-access storage deviceControl store
Disclosed is a system and method for processing a data access request (DAR). A processing unit, such as a storage controller, receives a DAR, indicating data to return on a channel, such as a channel connecting to a host system, and priority information for the received DAR. The processing unit retrieves the requested data for the received DAR from a memory area, such as a cache or direct access storage device (DASD), and determines whether there is a queue of data entries indicating retrieved data for DARs to transfer on the channel. The queued DARs include priority information. The processing unit processes at least one data entry in the queue, the priority information for the data entry, and the priority information for the received DAR to determine a position in the queue for the received DAR. The processing unit then indicates that the received DAR is at the determined position in the queue and processes the queue to select retrieved data to transfer on the channel to the host system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic management of addresses to an input/output (I/O) device
InactiveUS6622177B1Increase profitMultiple digital computer combinationsInput/output processes for data processingDirect-access storage deviceHosting environment
Disclosed is a method and computer program device for dynamically managing the assignment of alias addresses to base addresses referencing an input / output (I / O) device, such as a direct access storage device (DASD). Two distinct methods are disclosed. In one method, alias addresses are assigned based on the performance of the I / O devices. In this method, alias addresses are assigned to highly utilized devices, as indicated by device performance data, in order to maximize the efficient utilization of I / O device resources. In a second method, workload management principles are utilized to assign alias addresses. In this method, a correlation is made between each I / O device and the service classes utilizing each device. As in the first method, performance data is generated for each I / O device. Alias addresses are assigned to I / O devices experiencing queue delays as indicated by their performance data, if the device is associated with a service class that has failed to meet one or more processing goals. These methods may operate on a single host, or in a multi-host environment. The methods may be operated individually, or concurrently. Methods are disclosed to manage contention between concurrently operating assignment methods, and between multiple hosts concurrently operating one or more assignment methods.
Owner:IBM CORP
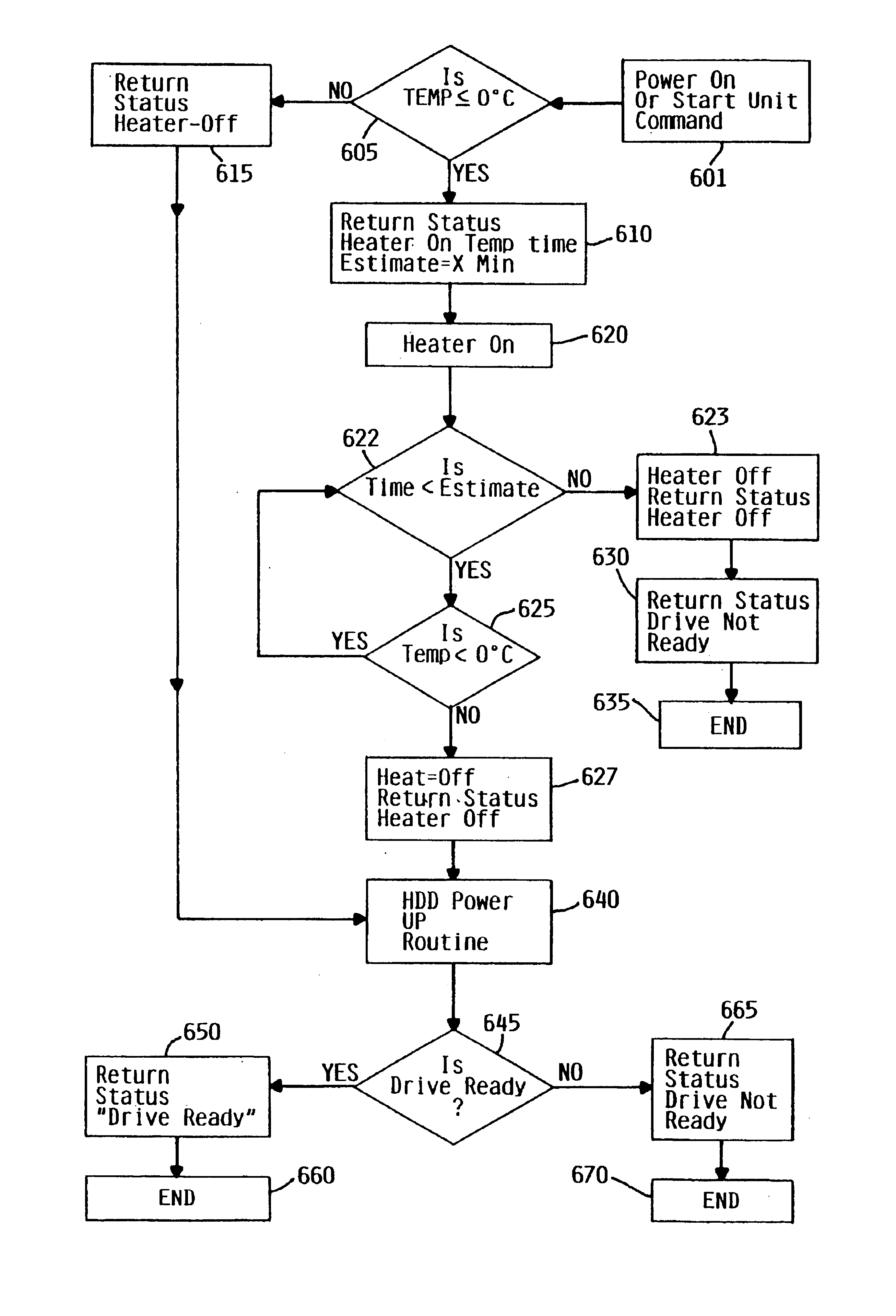
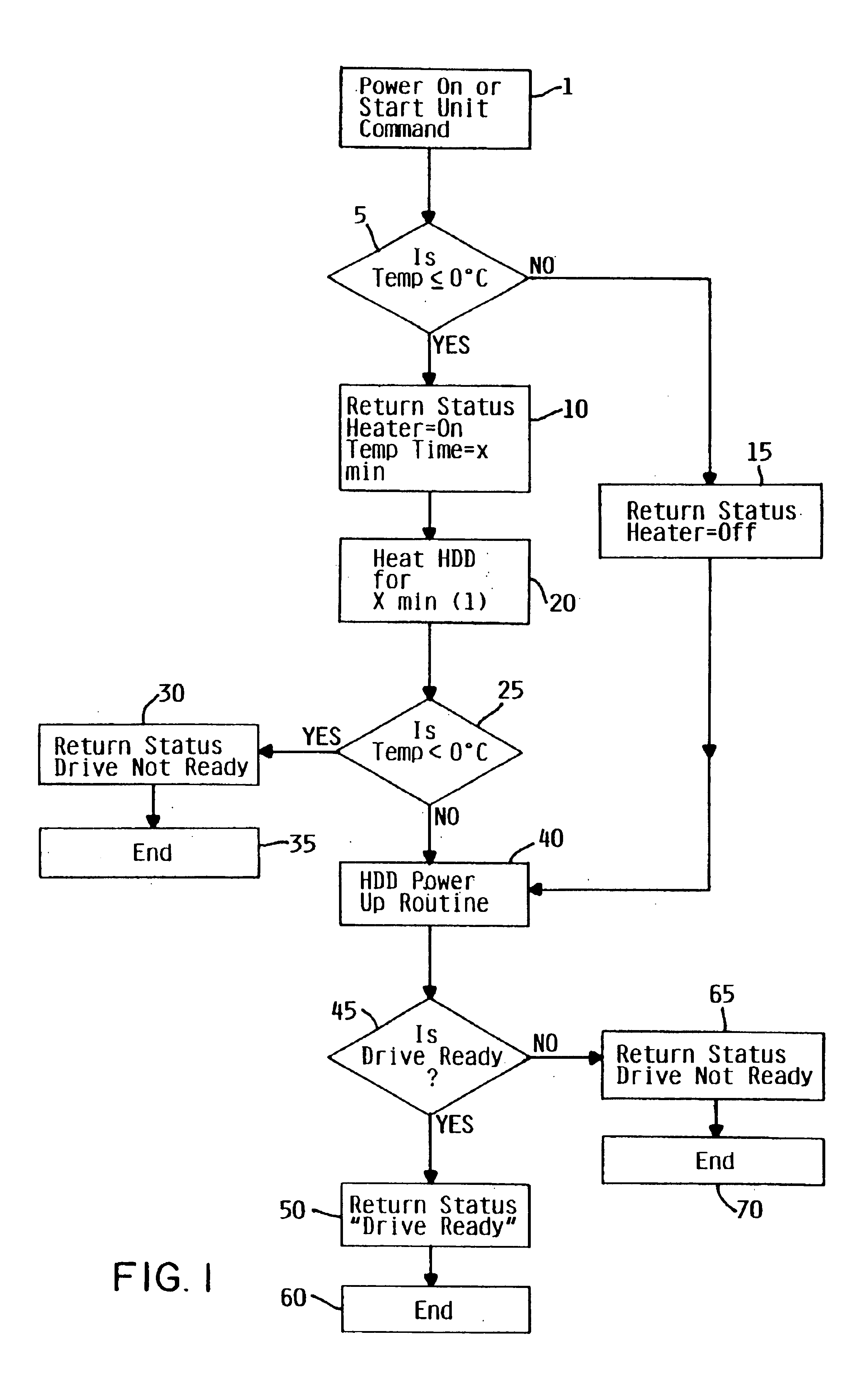
Method and apparatus for enabling cold temperature performance of a disk
InactiveUS6735035B1High torqueHigh viscosityCommutation monitoringApparatus for flat record carriersDirect-access storage deviceEngineering
In cold weather, the higher torque required for normal spinning operation of a spindle motor assembly in a direct access storage device due to the increased viscosity of the grease, is overcome by localizing the heating to the spindle motor assembly to reduce the viscosity of the grease, and then let a disk driven self heat during and after spin-up of the spindle motor assembly.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
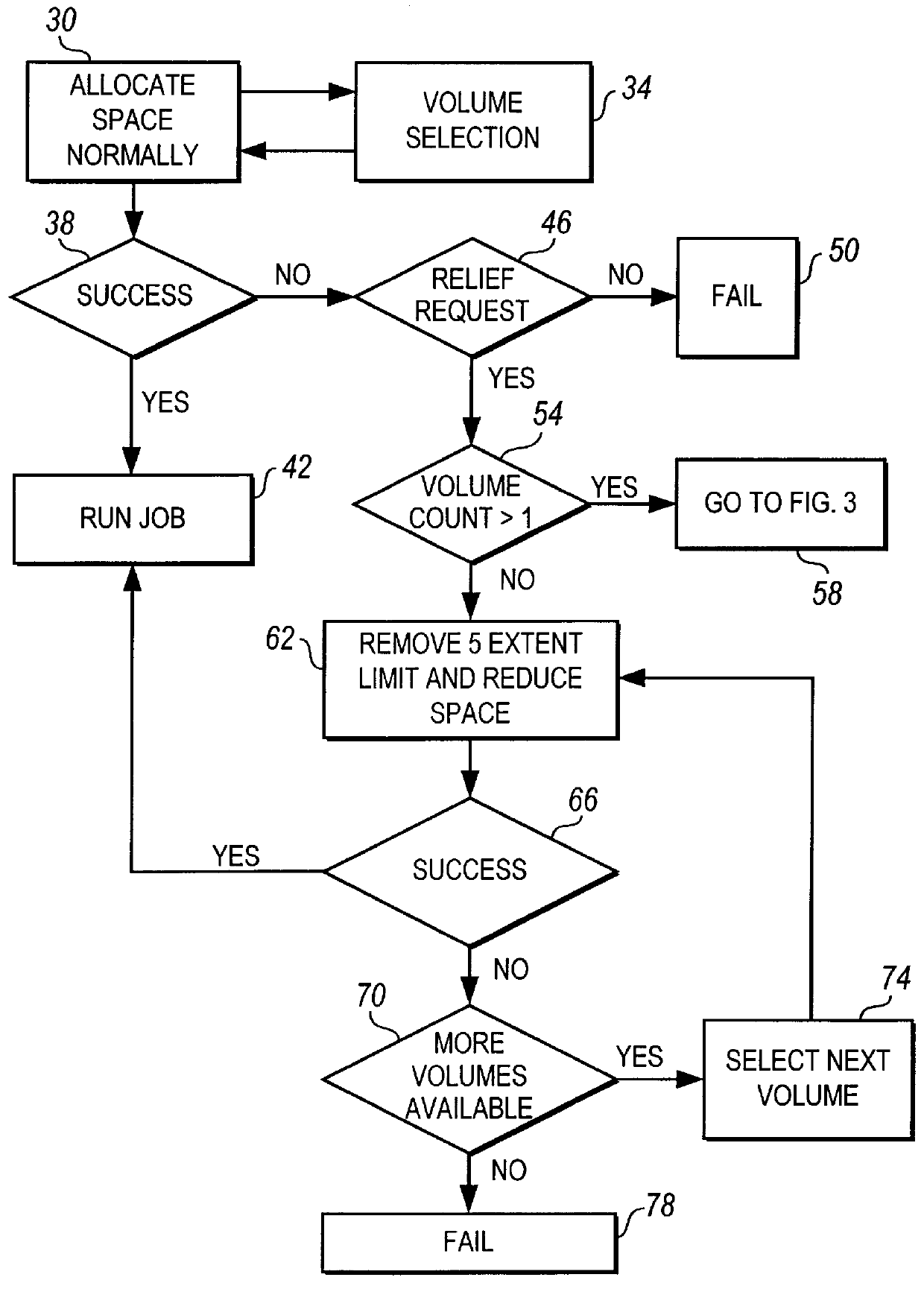
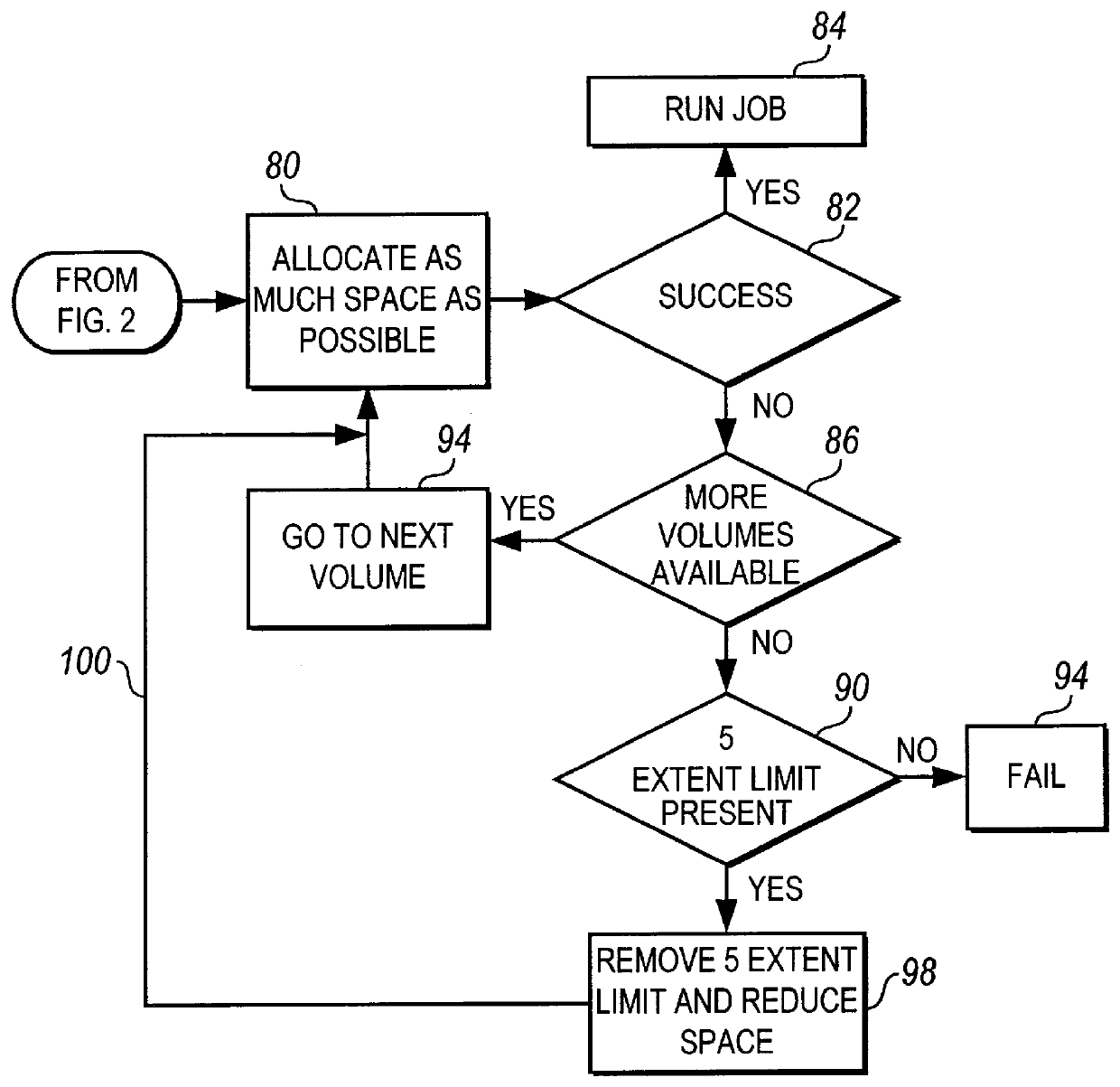
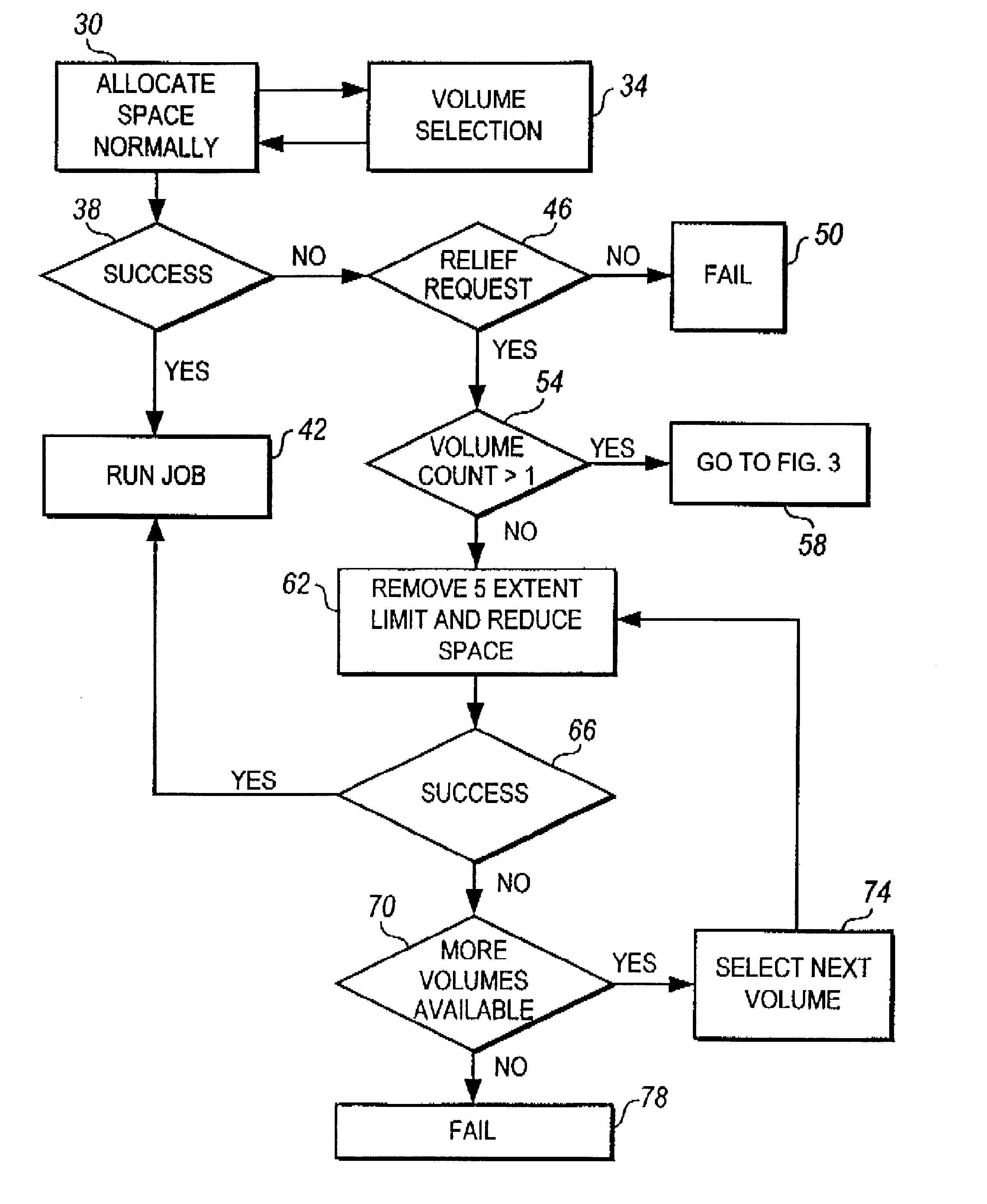
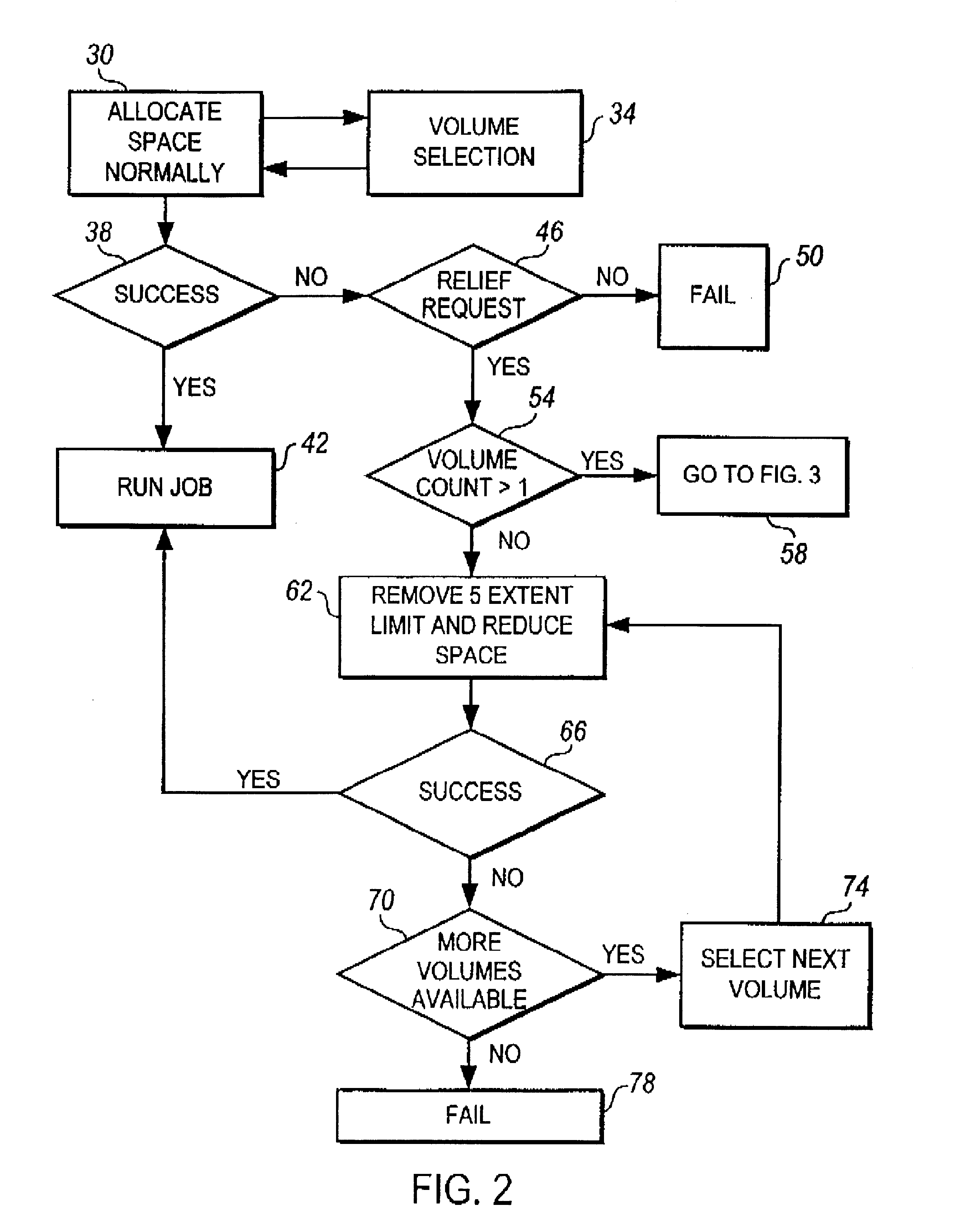
Method and apparatus for reducing space allocation failures in storage management systems
InactiveUS6088764AReducing space allocation errorReduce spacingInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirect-access storage deviceStorage management
A method and apparatus for reducing space allocation failures in a computer system that utilizes direct access storage devices to store data. The method comprises the steps of determining if authorization has been given to attempt to allocate an initial space request over more than one volume, and, if so, attempting to allocate space on a plurality of volumes. If the initial space request cannot be allocated on a plurality of volumes, the initial space request is reduced by a preset percentage, the five-extent limit is removed and an attempt is made to allocate the reduced space request on the plurality of volumes with the five extent limit removed. Alternatively, if authorization has not been given to attempt to allocate the initial space request over more than one volume, the initial space request is reduced by a preset percentage, the five-extent limit is removed and an attempt is made to allocate the reduced space request on a single volume.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
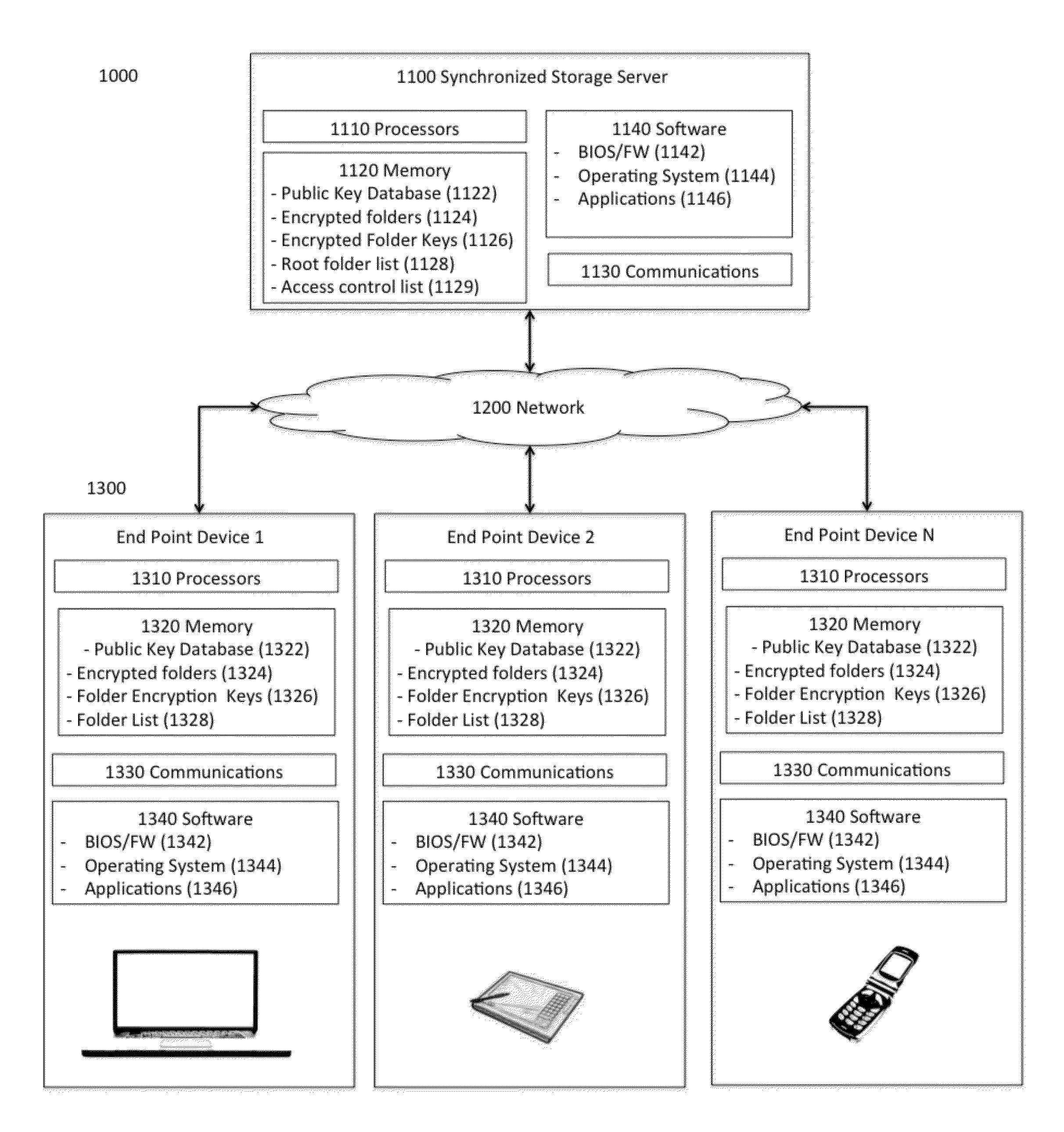
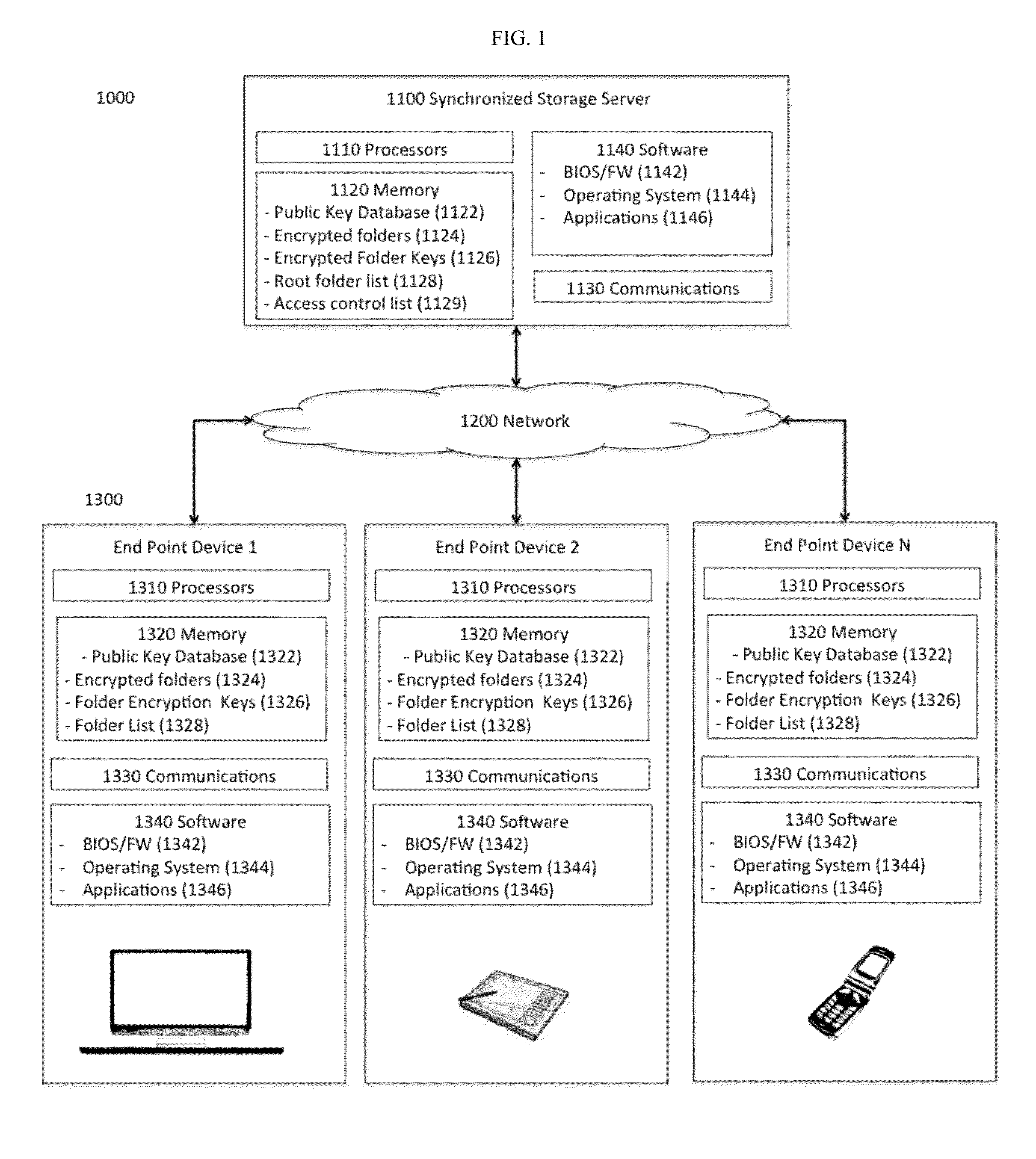
Secure Network Storage
ActiveUS20140281526A1User identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsDirect-access storage devicePointing device
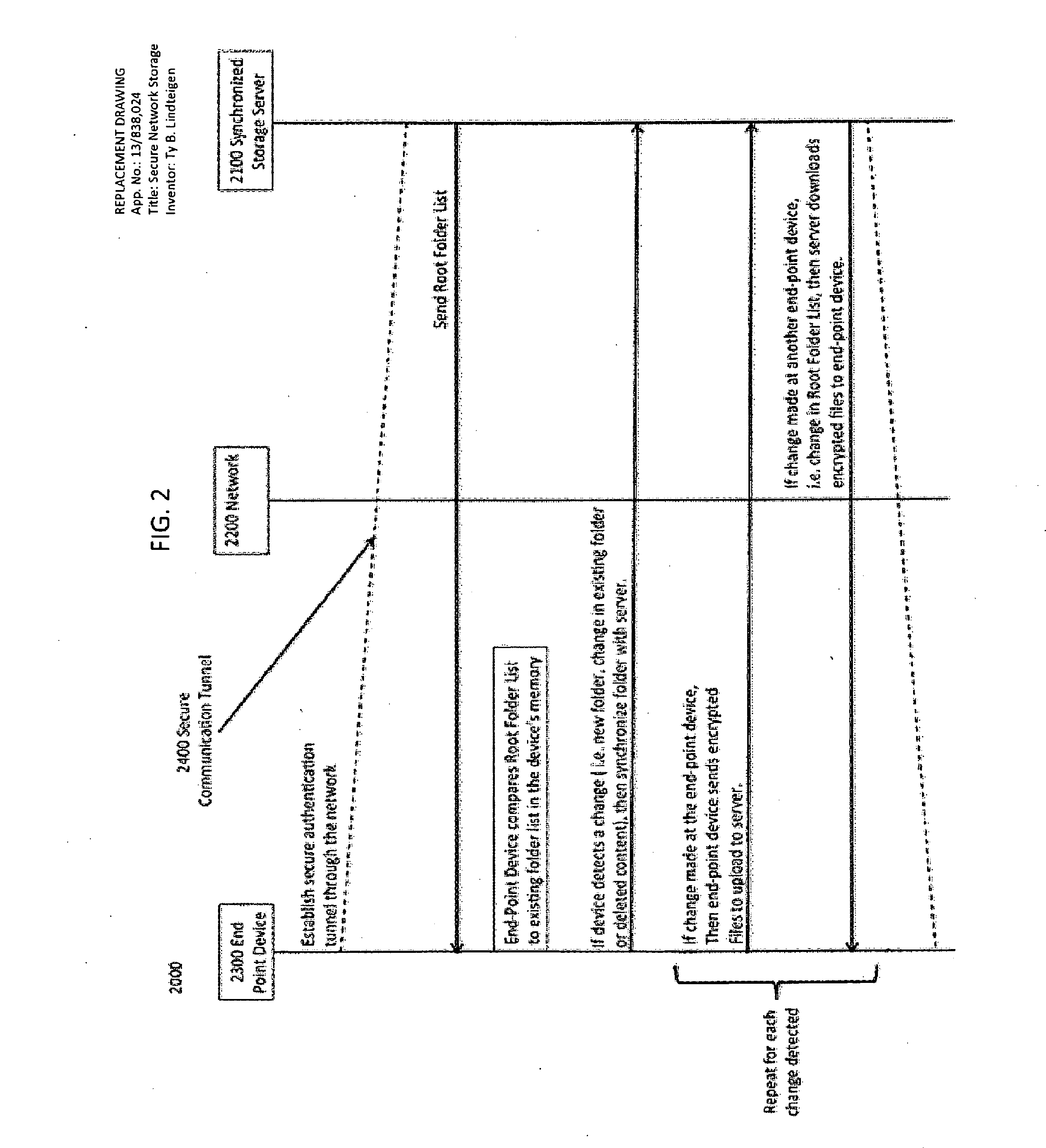
This invention includes apparatus, systems, and methods to secure data in a remote storage device where an end-point device does not have direct access to the storage device to secure the data, or the end-point device does not trust the storage device to adequately secure the data, comprising securing an authenticated communication between the end-point device and a synchronized storage server via a communication network. The synchronized storage server sends the end-point device a notification including the root folder list. The end-point device compares the sent root folder list to a previously stored root folder list in the end-point devices' memory. If the end-point device detects either a new root folder on the synchronized storage server, a change in an existing folder, or deleted content in a folder the end-point device will determine that a change is required to the stored data. Next the end-point device will synchronize with the synchronized storage server and create a new storage list. Finally, the synchronized storage server will send the end-point device a new encrypted folder encryption key which includes the encrypted file contents along with identifying information such as the server name and revision information.
Owner:SAIFE
Method and apparatus for enhanced data channel performance using read sample buffering
InactiveUS6937415B2Improve performanceModification of read/write signalsData buffering arrangementsChannel dataDirect-access storage device
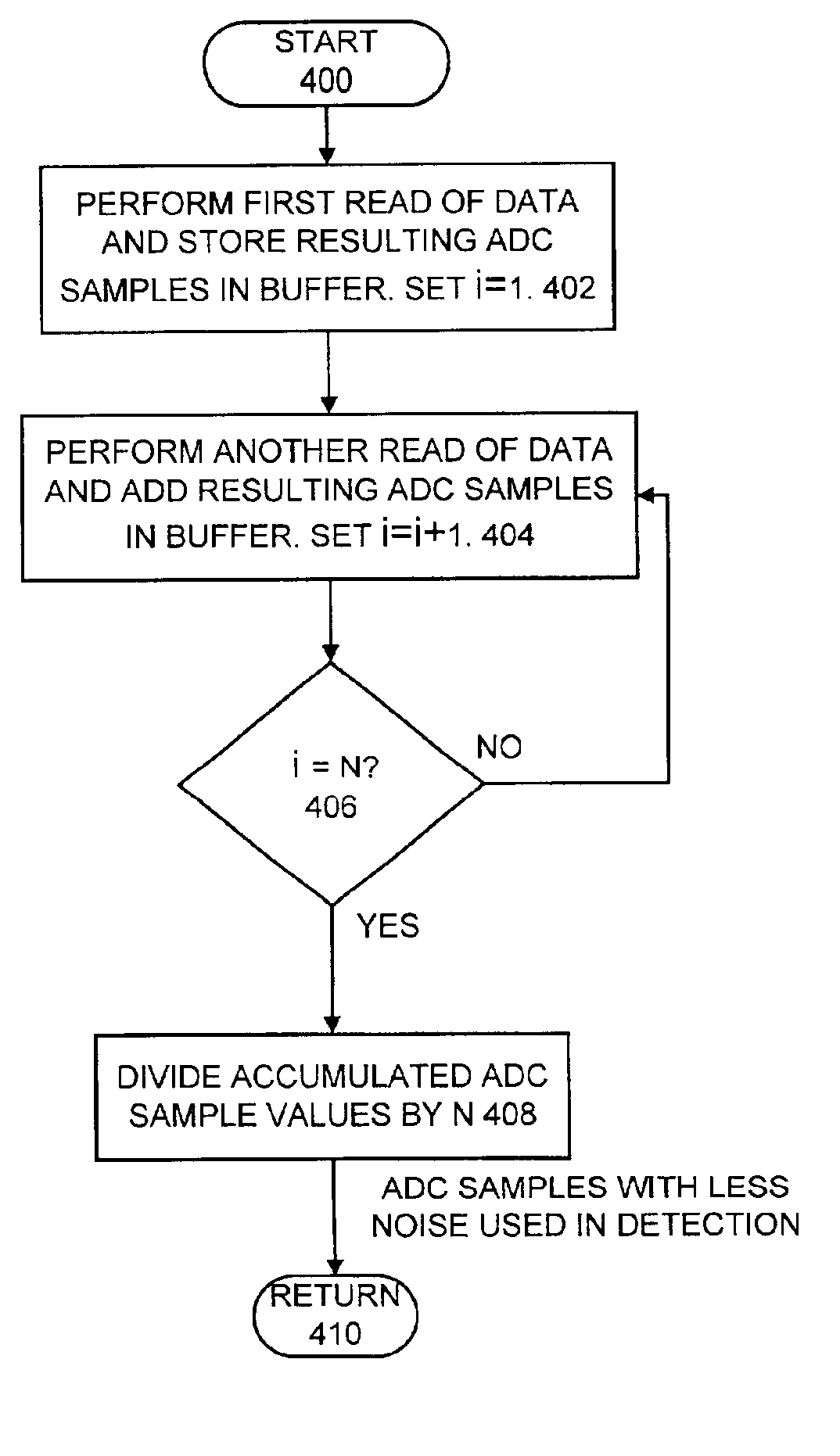
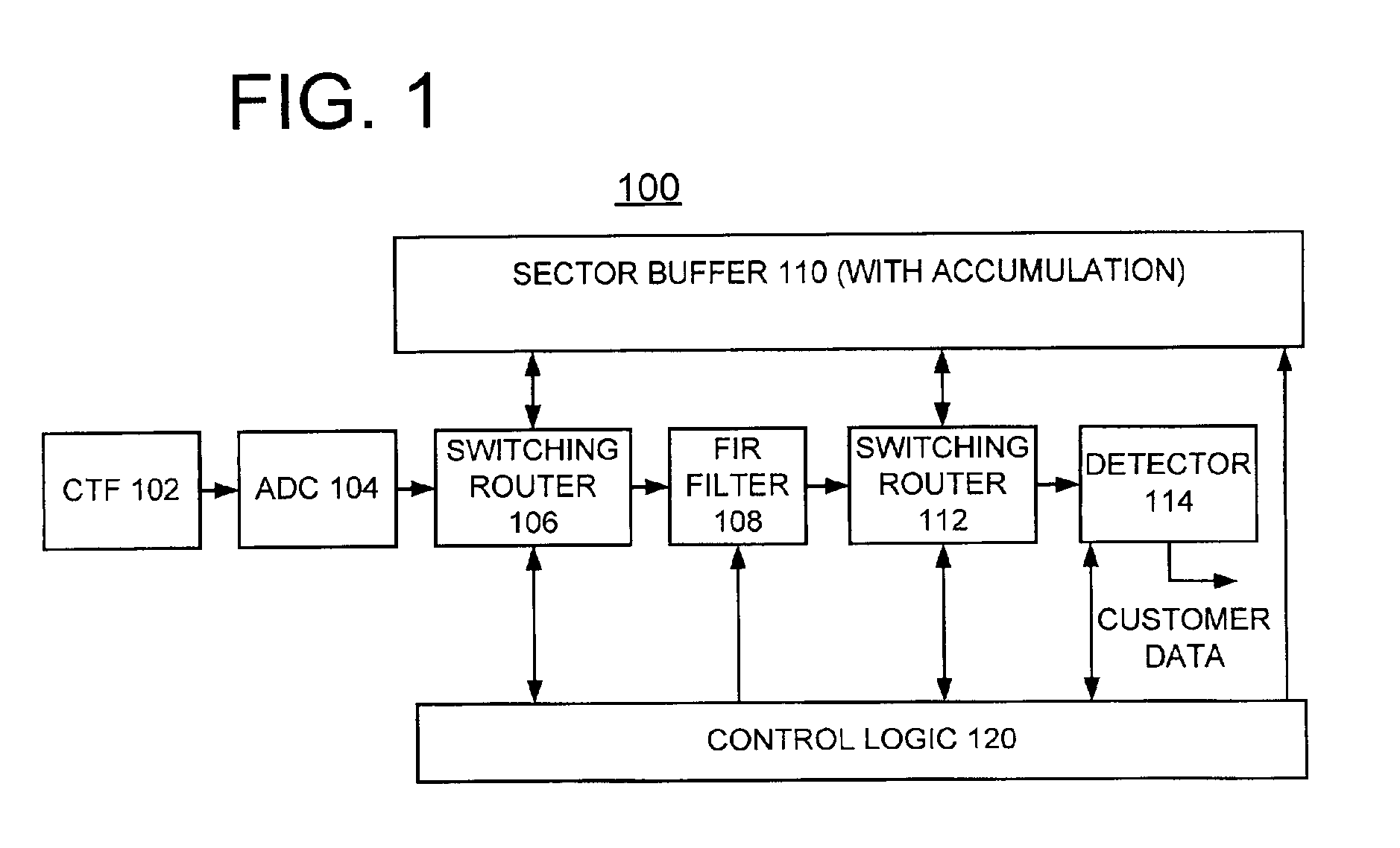
A method and apparatus are provided for implementing enhanced data channel performance using a read sample buffer in a direct access storage device (DASD). Disk data is read and stored in the read sample buffer. When a data recovery procedure (DRP) starts, the stored disk read data in the read sample buffer is detected. Error correction code (ECC) checking of the detected sample buffer disk data is performed to identify correctly recovered data. Using the disk read data stored in the read sample buffer enables data recovery without identification of a sync word. Also using the disk read data stored in the read sample buffer enables data recovery with changed channel data detection settings to recover the data. The read sample buffer can be used for accumulating read disk data from more than one read operation so that at least some channel noise is averaged out.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
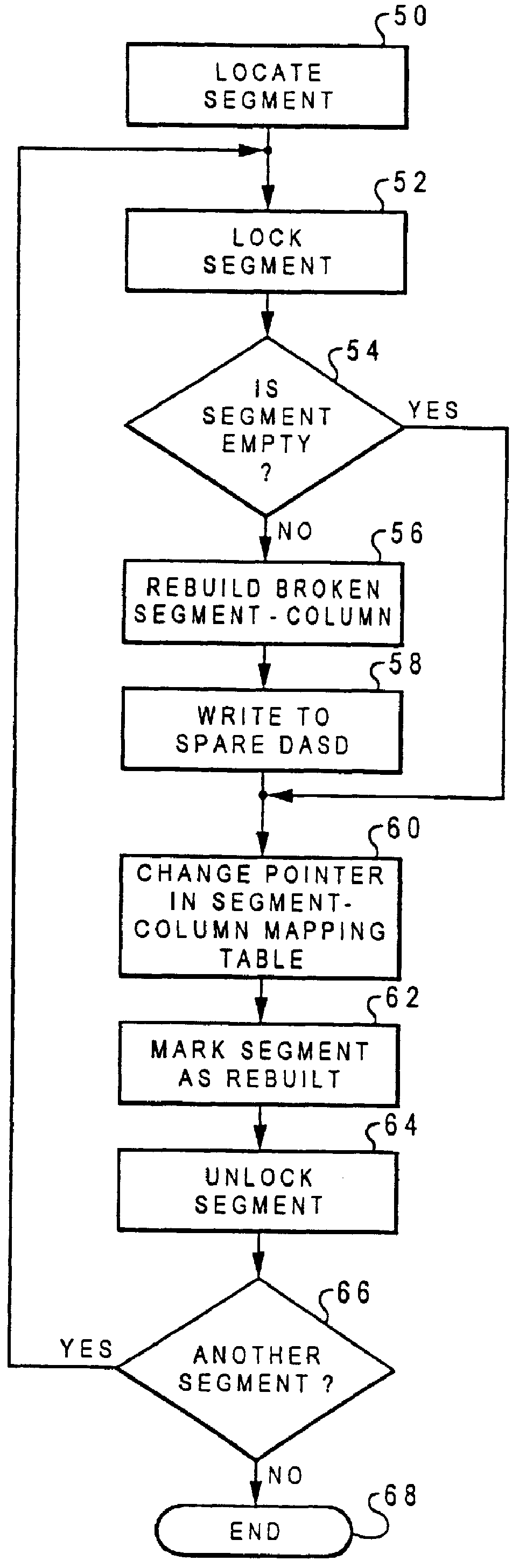
Method and system for rebuilding log-structured arrays
InactiveUS6021509ASimple methodRedundant data error correctionDirect-access storage deviceReal-time computing
A method for rebuilding contents of a malfunctioned direct access storage device within a log-structured array is disclosed. In accordance with the method and system of the present invention, each direct access storage device within a log-structured array is divided into multiple segment-columns, and each corresponding segment-column from each direct access storage device within the log-structured array forms a segment. A segment is first located within the direct access storage devices. A determination is made as to whether or not the segment is empty. In response to a determination that the segment is empty, a pointer is moved within a segment-column mapping table from pointing to a segment-column in the malfunctioned direct access storage device to point to a segment-column in a spare direct access storage device of the segment. In response to a determination that the segment is not empty, rebuilding contents of the segment-column in the malfunctioned direct access storage device to the segment-column in the spare direct access storage device, and moving the pointer within the segment-column mapping table from pointing to the segment-column in the malfunctioned direct access storage device to point to the segment-column in the spare direct access storage device of the segment. The process then returns to the determination step until all segment-columns within the malfunctioned direct access storage device are rebuilt.
Owner:IBM CORP
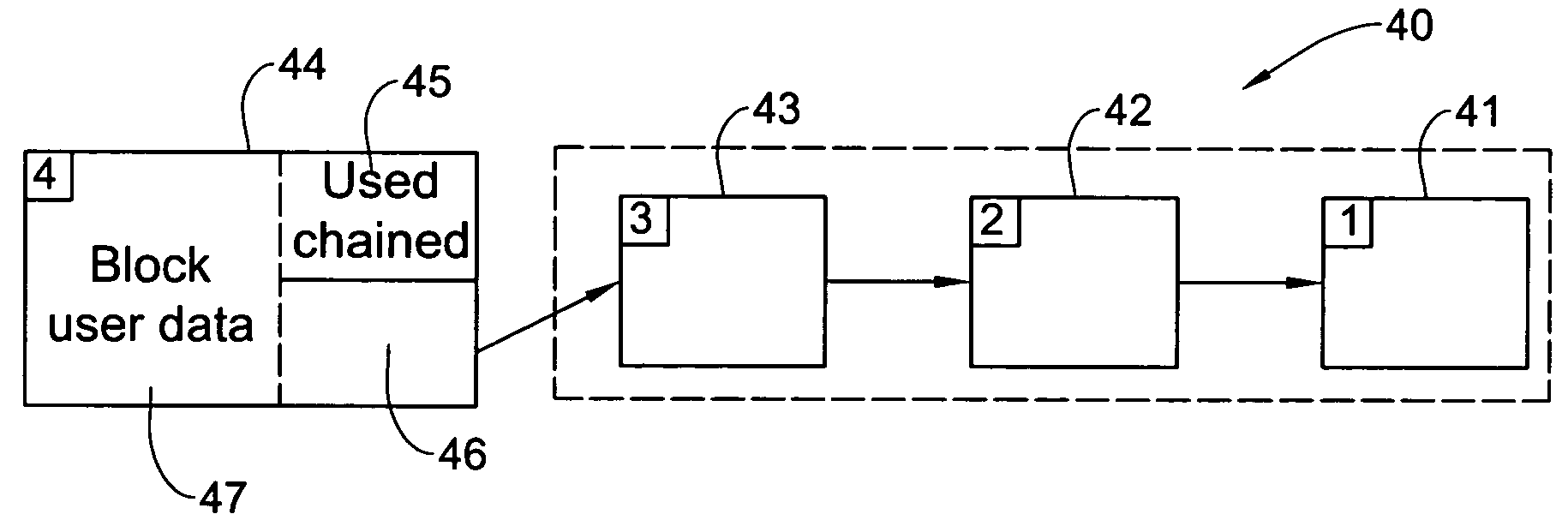
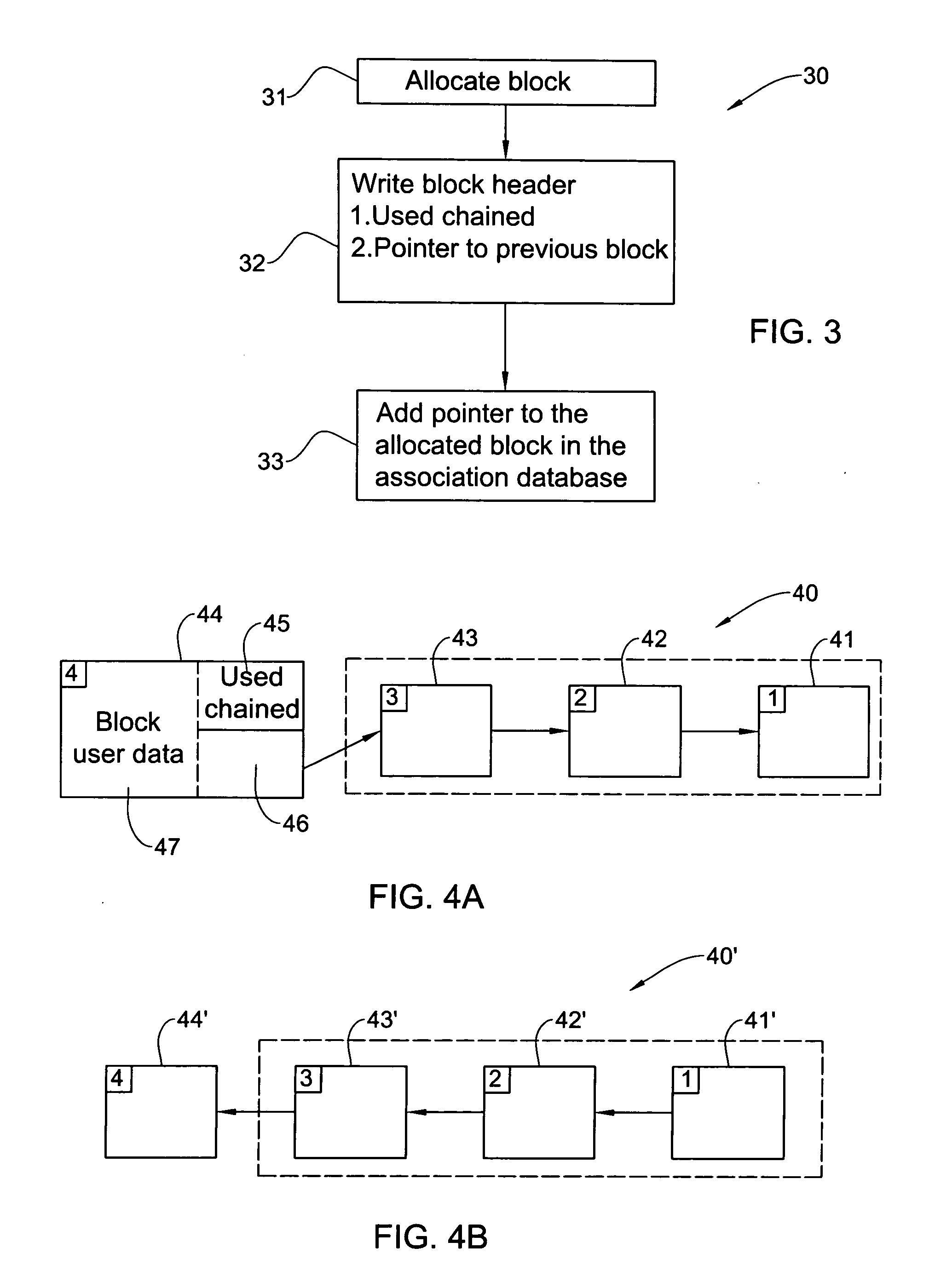
Chaining of blocks for optimal performance with DASD (Direct Access Storage Devices) free nonvolatile updates
InactiveUS20050097266A1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirect-access storage deviceRecovery procedure
A system for managing variable sized pages of possibly non contiguous blocks in a Non-Volatile-Storage (NVS) for attaining a consistent NVS that survives malfunction events. Each page includes a self describing block or linked list of self describing blocks. the system includes: Volatile Storage storing auxiliary modules, means for performing an atomic “create a new page” procedure. Means for performing an atomic write “add block” procedure for adding a possibly non contiguous block to a page. The newly added block has a back pointer to a previous block in the page. Means for performing a “delete page” procedure for deleting all blocks in a page. Means for performing a recovery procedure for rolling backward the add block procedure and rolling forward the delete page procedure, in case of malfunction event, thereby attaining consistent NVS.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for reducing space allocation failures in storage management systems
InactiveUS6591334B1Reduce spacingInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirect-access storage deviceStorage management
A method and apparatus for reducing space allocation failures in a computer system that utilizes direct access storage devices to store data. The method comprises the steps of determining if authorization has been given to attempt to allocate an initial space request over more than one volume, and, if so, attempting to allocate space on a plurality of volumes. If the initial space request cannot be allocated on a plurality of volumes, the initial space request is reduced by a preset percentage, the five-extent limit is removed and an attempt is made to allocate the reduced space request on the plurality of volumes with the five extent limit removed. Alternatively, if authorization has not been given to attempt to allocate the initial space request over more than one volume, the initial space request is reduced by a preset percentage, the five-extent limit is removed and an attempt is made to allocate the reduced space request on a single volume.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
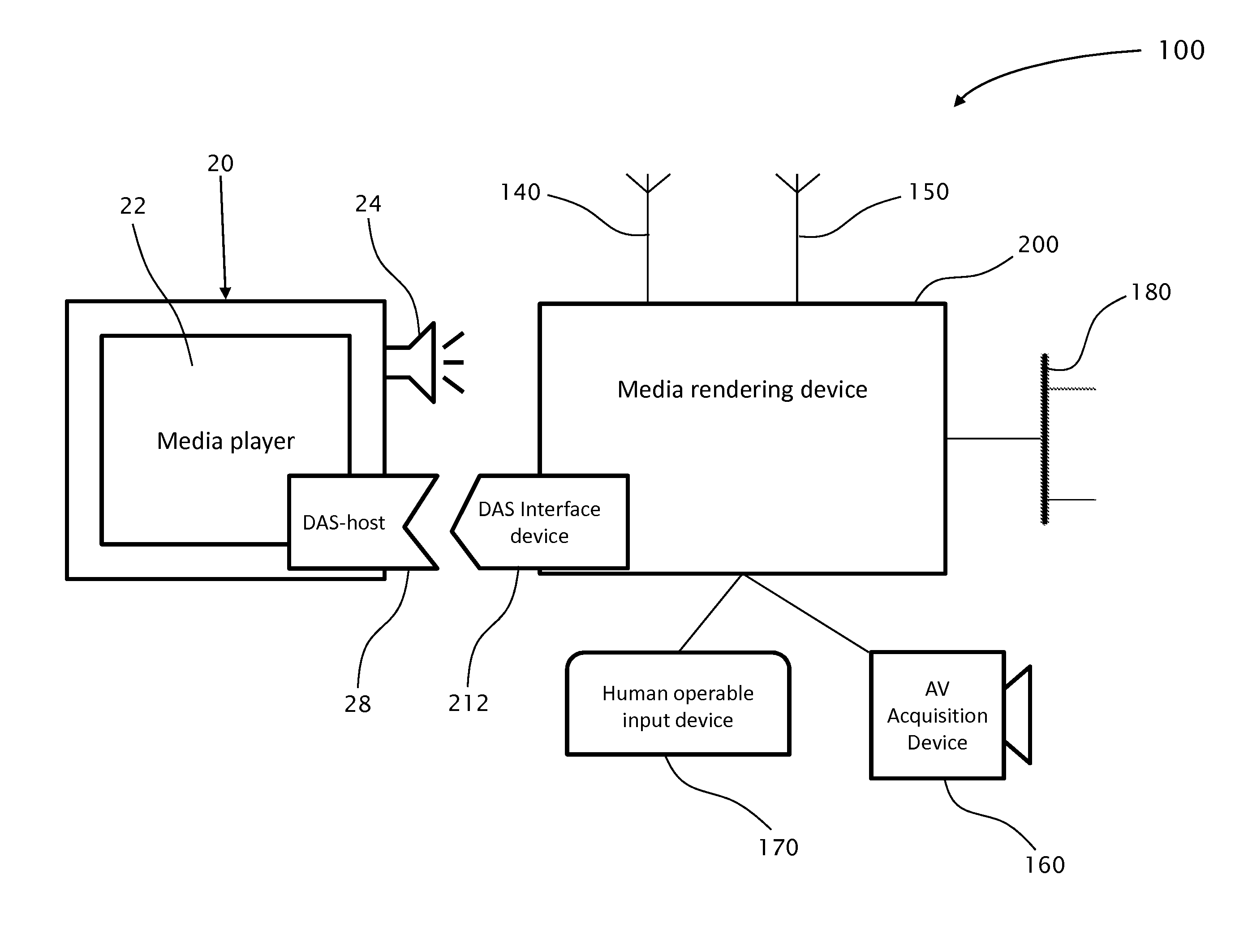
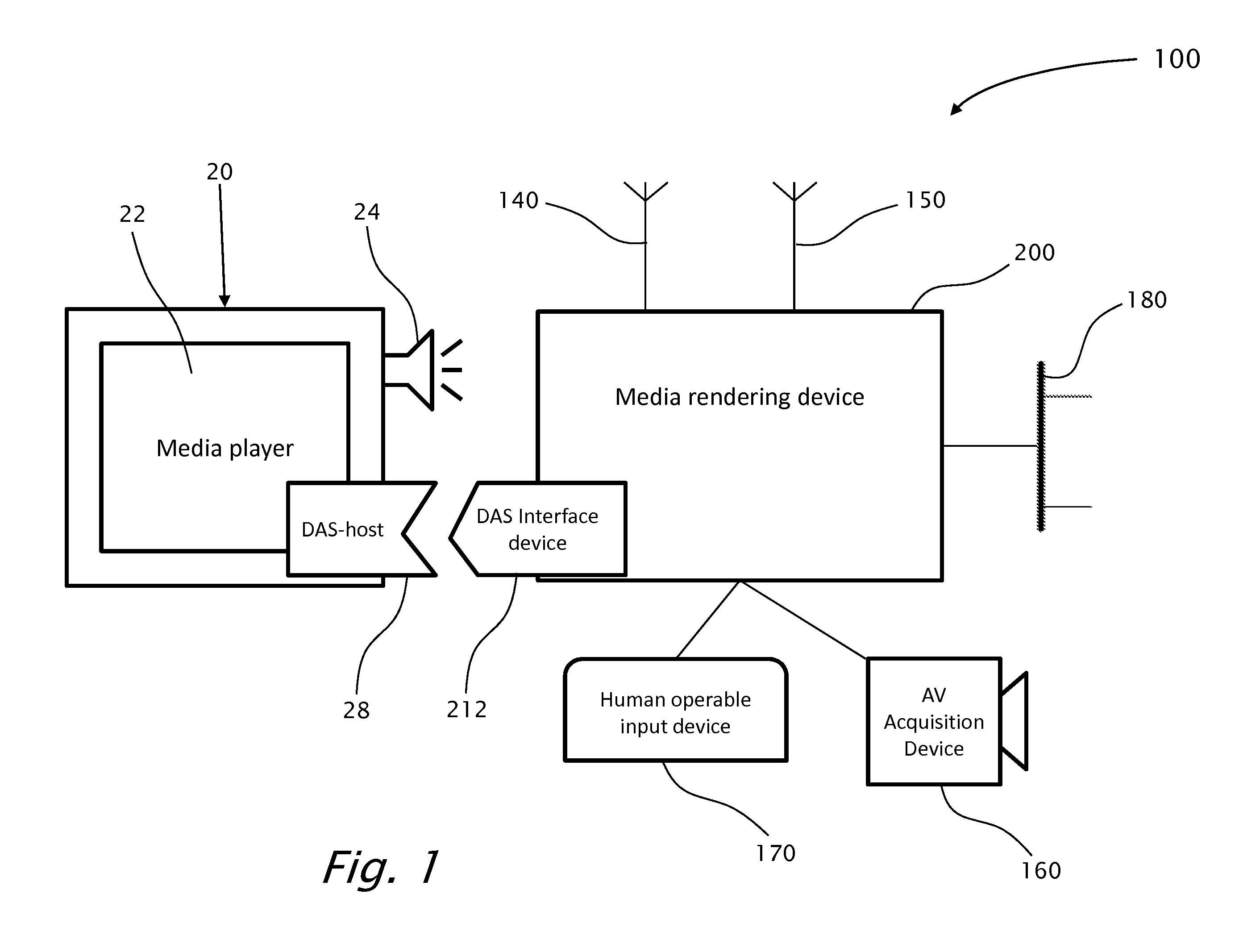
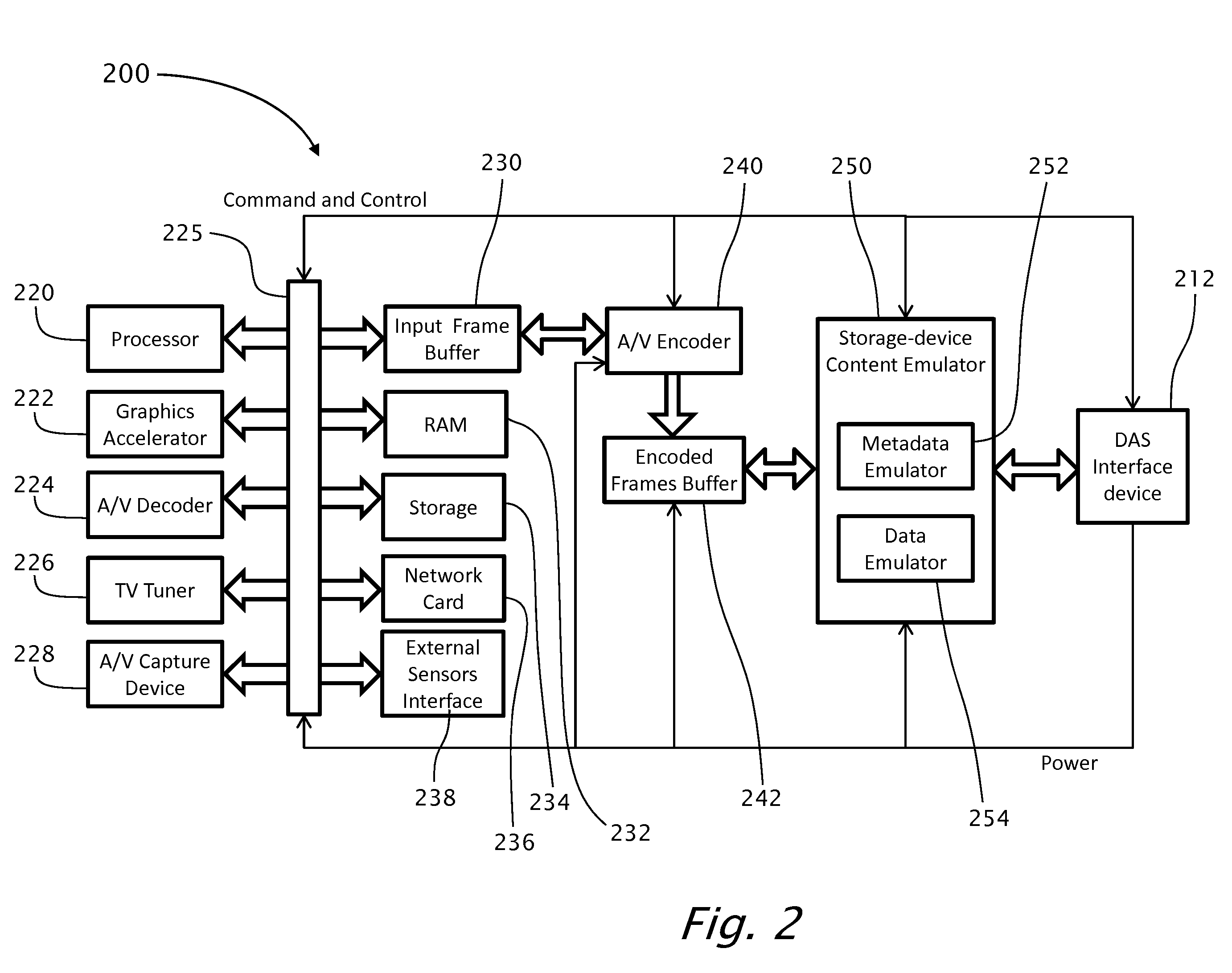
Method and apparatus for presenting interactive multimedia using storage device interface
InactiveUS20110255841A1Minimize wait delayImprove the display effectTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsDirect-access storage deviceData source
A media-rendering apparatus for real-time streaming of audio / video (AV) data to a media-player having one or more input direct-access-storage-device (DASD) interfaces, the apparatus including a real-time AV data source unit, an input frame buffer operatively coupled with the real-time AV data unit, an AV real-time encoder, an encoded-frames buffer, a power source, a storage-device content emulator and a DASD interface device for communicating with the media-player. Preferably, power is provided through the DASD interface device.
Owner:REMENNIK LEONID +1
Technique to support multiple forms of sas dasd
InactiveUS20080165490A1Digital data processing detailsRecord information storageMultiple formsDirect-access storage device
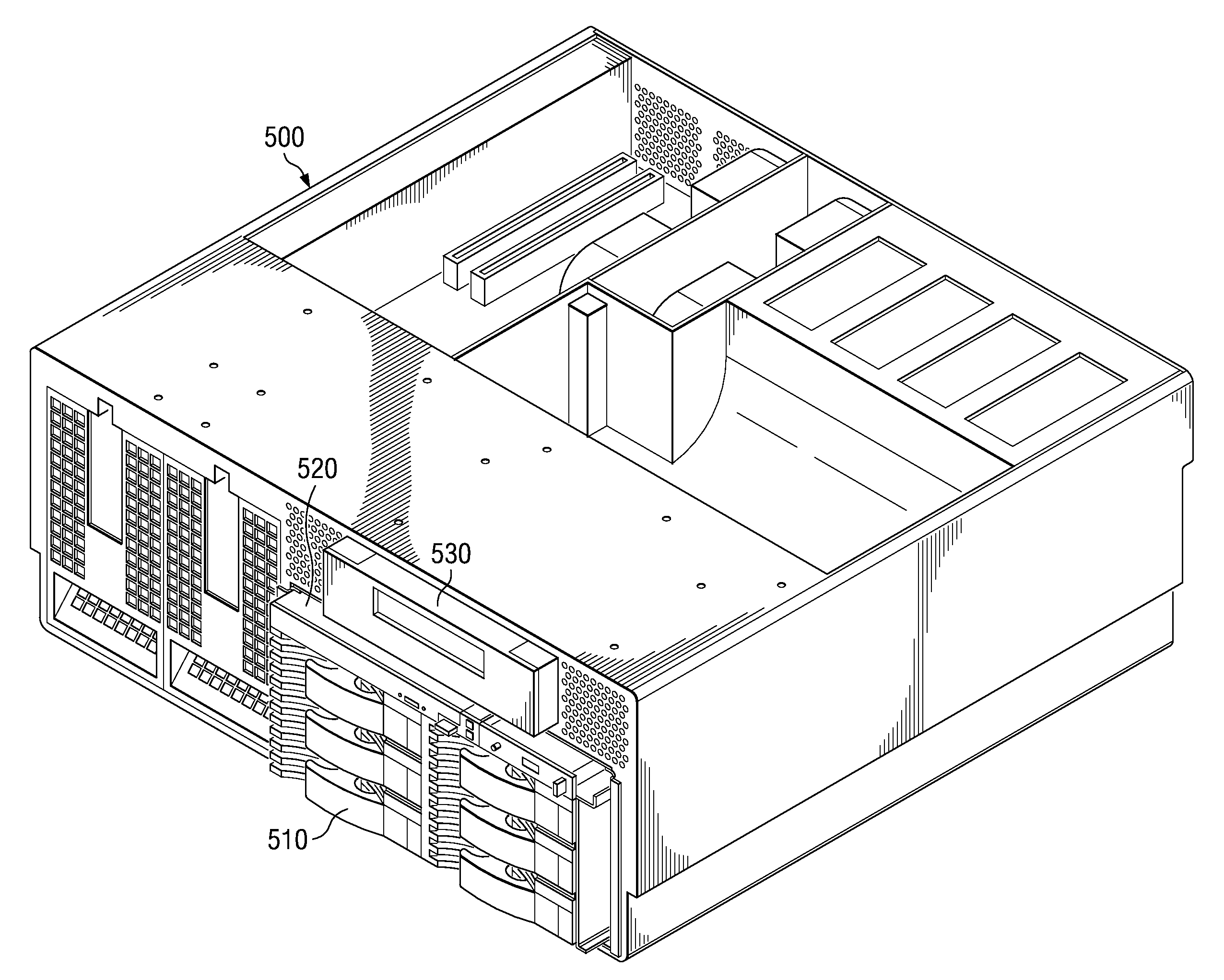
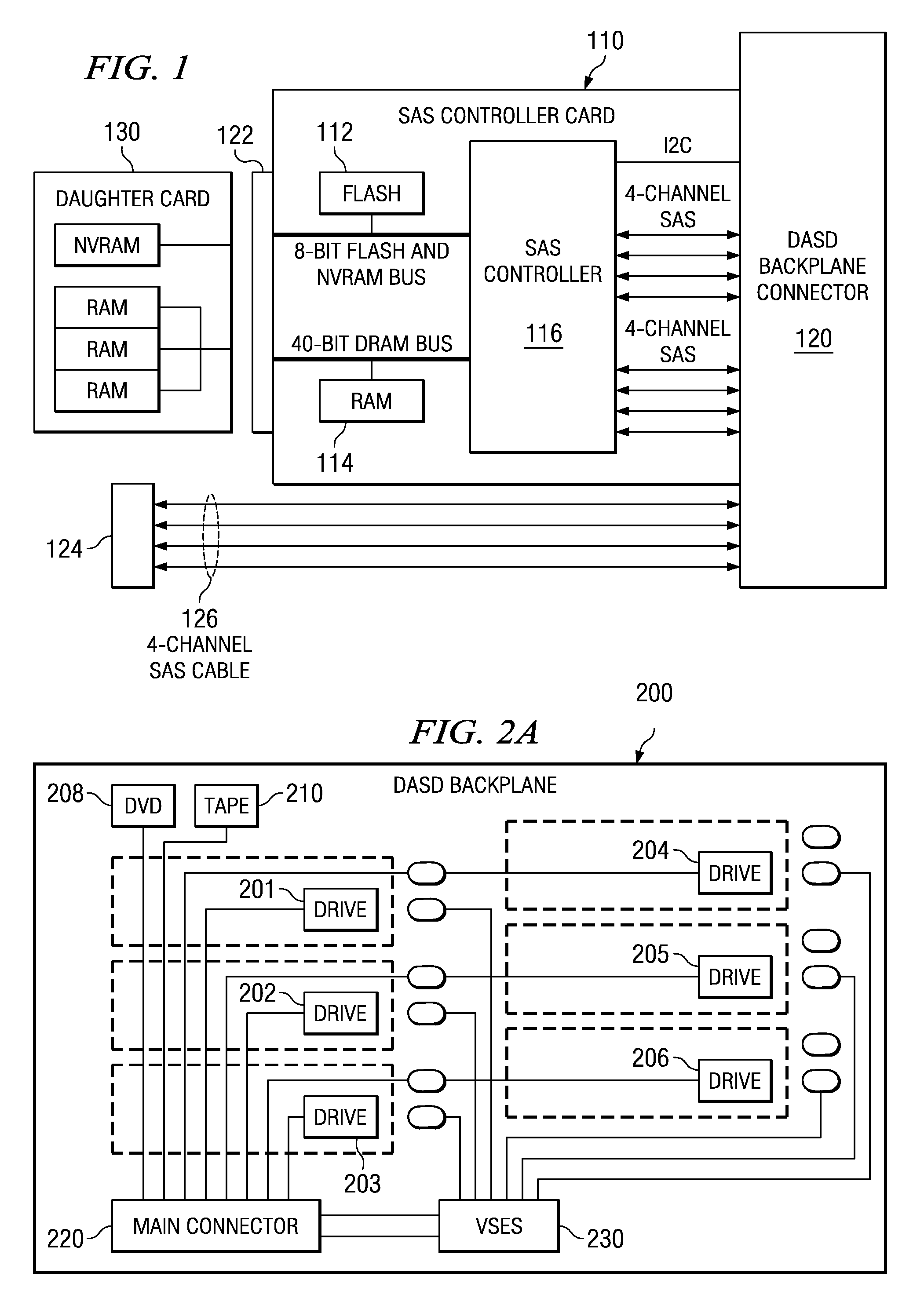
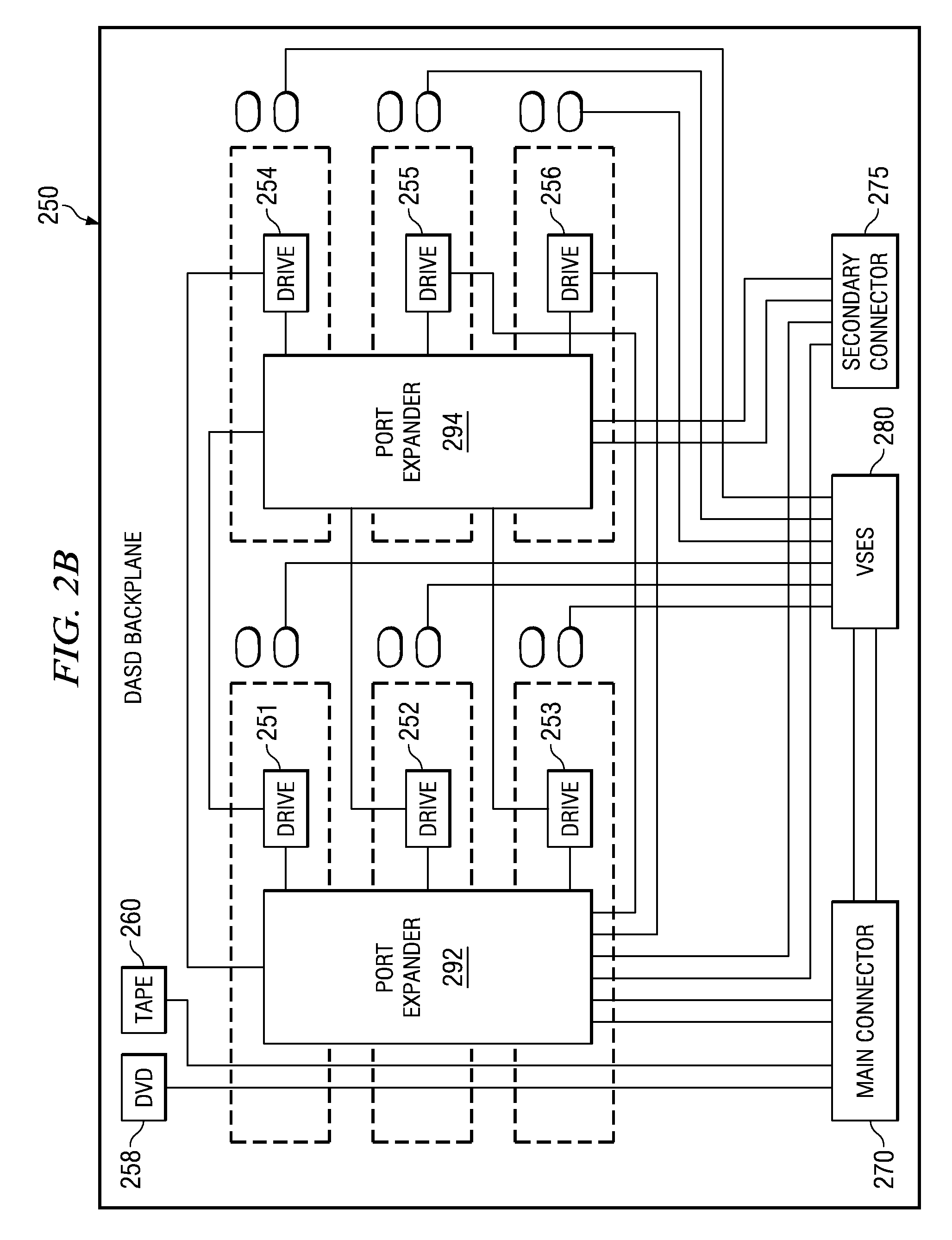
A computer chassis is provided that may accommodate direct access storage device cages for various form factors. A 3.5-inch direct access storage device (DASD) cage may support 3.5-inch serial attached SCSI (SAS) direct access storage devices. The 3.5-inch SAS DASD cage includes a DASD backplane with a main connector and eight SAS drive connectors. A SFF direct access storage device cage may support SFF SAS direct access storage devices. The SFF SAS DASD cage may include a DASD backplane with a main connector and two port expanders. The port expanders may support up to twelve SAS DASD with redundant SAS channel wiring and one external 4-channel SAS port.
Owner:IBM CORP
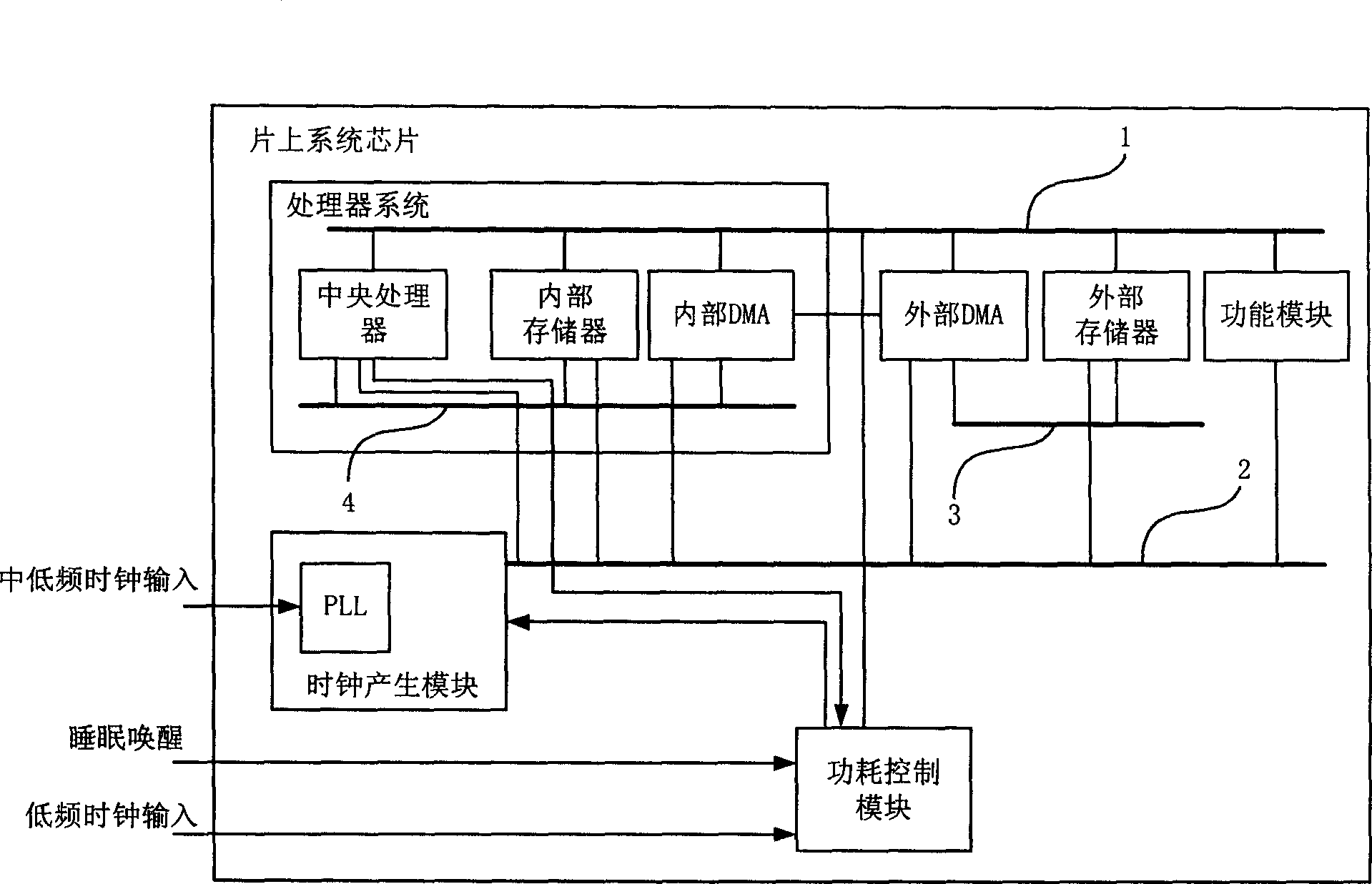
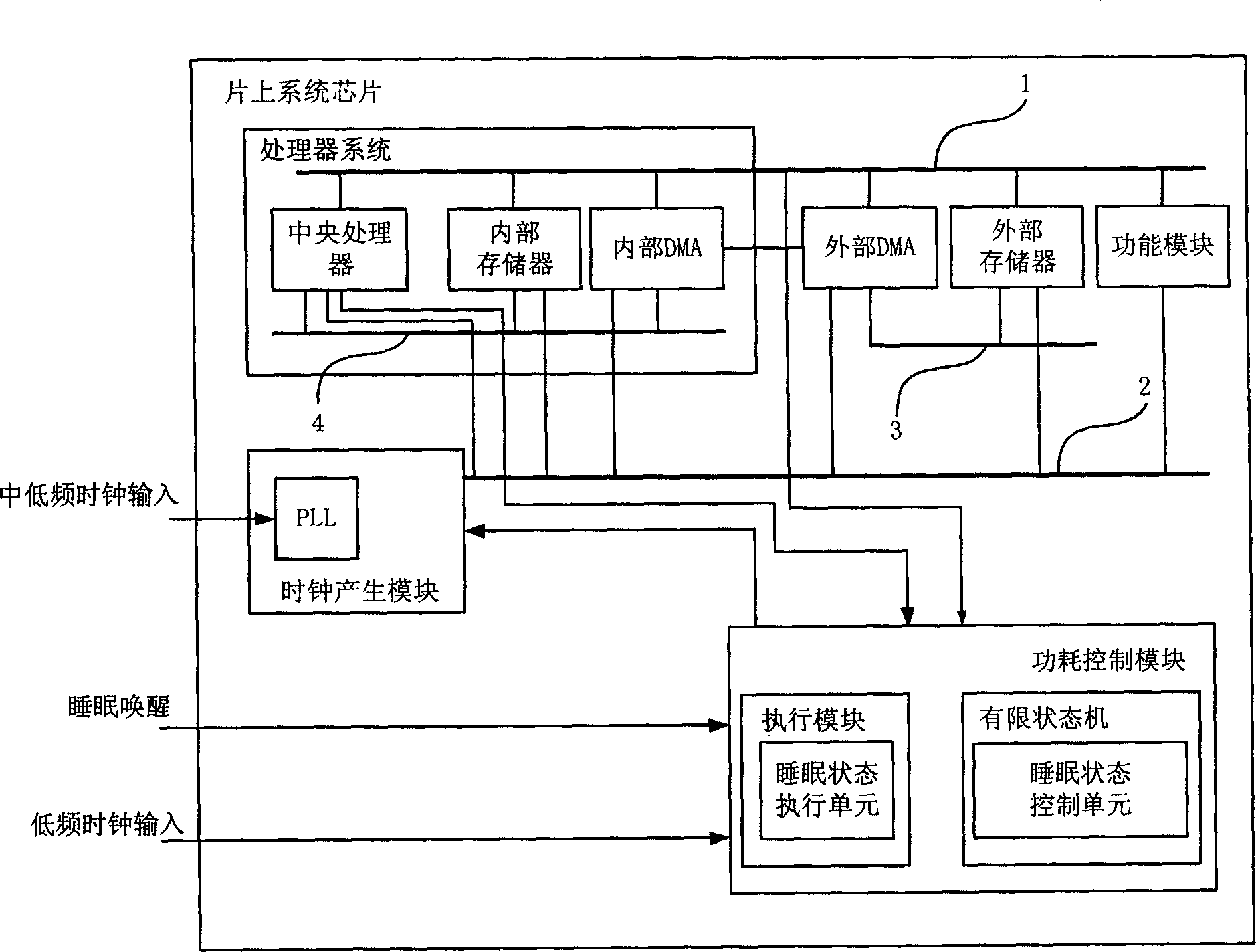
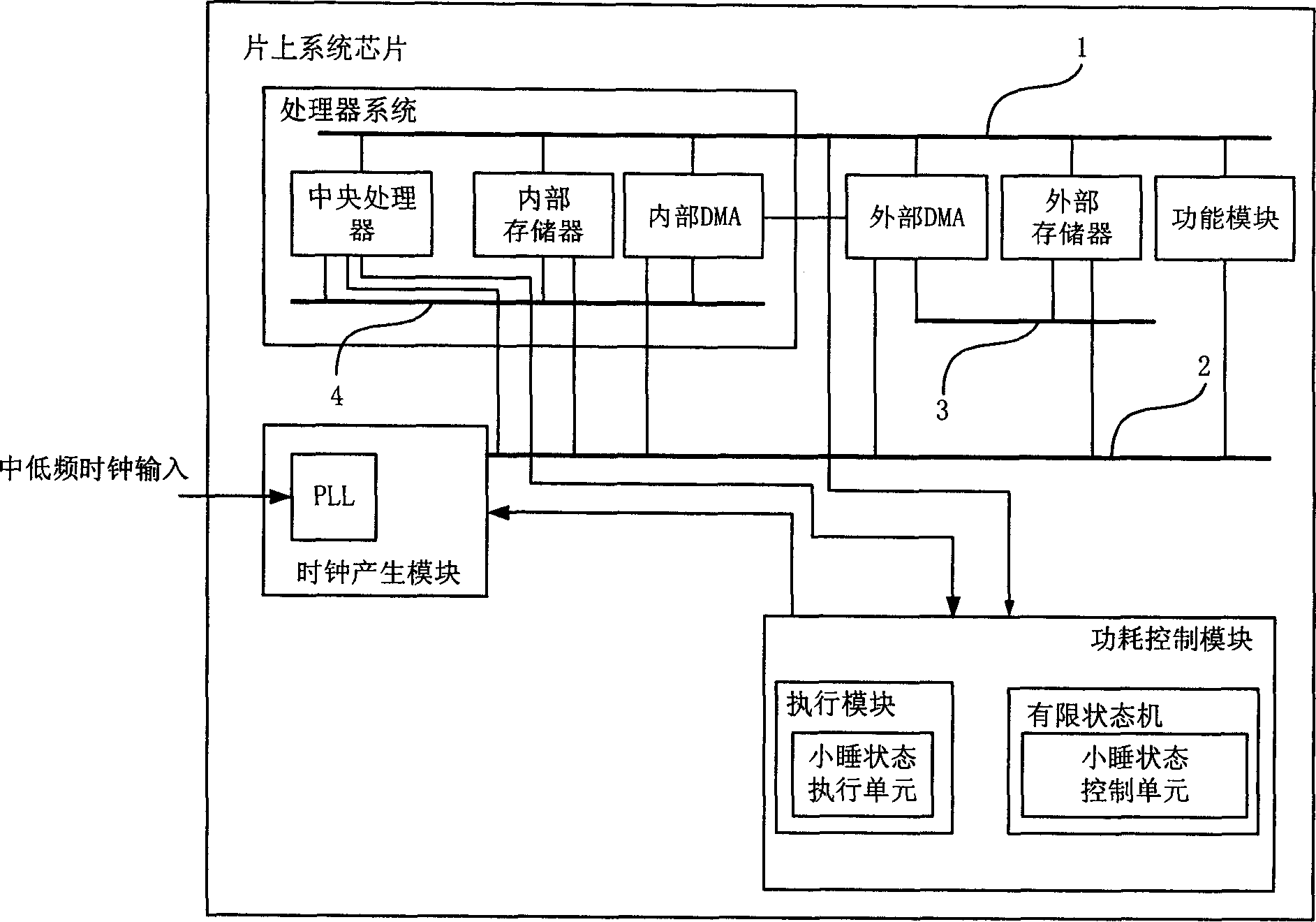
System-on-chip chip and its power consumption control method
InactiveCN1877494AControl power consumptionAchieve power savingPower supply for data processingControl powerDirect-access storage device
The invention discloses an on-chip system chip and a method for controlling its power consumption. The power consumption control module of the on-chip system chip has a sleep status control unit and a sleep status execution unit added; wherein the sleep status control unit controls the clock generating module via the sleep status execution unit according to the control information of the processor system to make clock generation module send high frequency clock signal to corresponding module. The inventive method comprises defining the work status of the central processor, each direct access storage device and corresponding storage devices; sending control information according to the above defined work status; outputting high frequency clock signal according to the control information by the clock generation module. The invention is characterized in that each module in the on-chip system chip sends corresponding control information to control power consumption.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SEMICON BEIJING
Implementing enhanced cover-mounted, auto-docking for multiple dasd configurations
InactiveUS20120113581A1Big advantageHigh densityDigital data processing detailsElectrical apparatus casings/cabinets/drawersElectricityHigh density
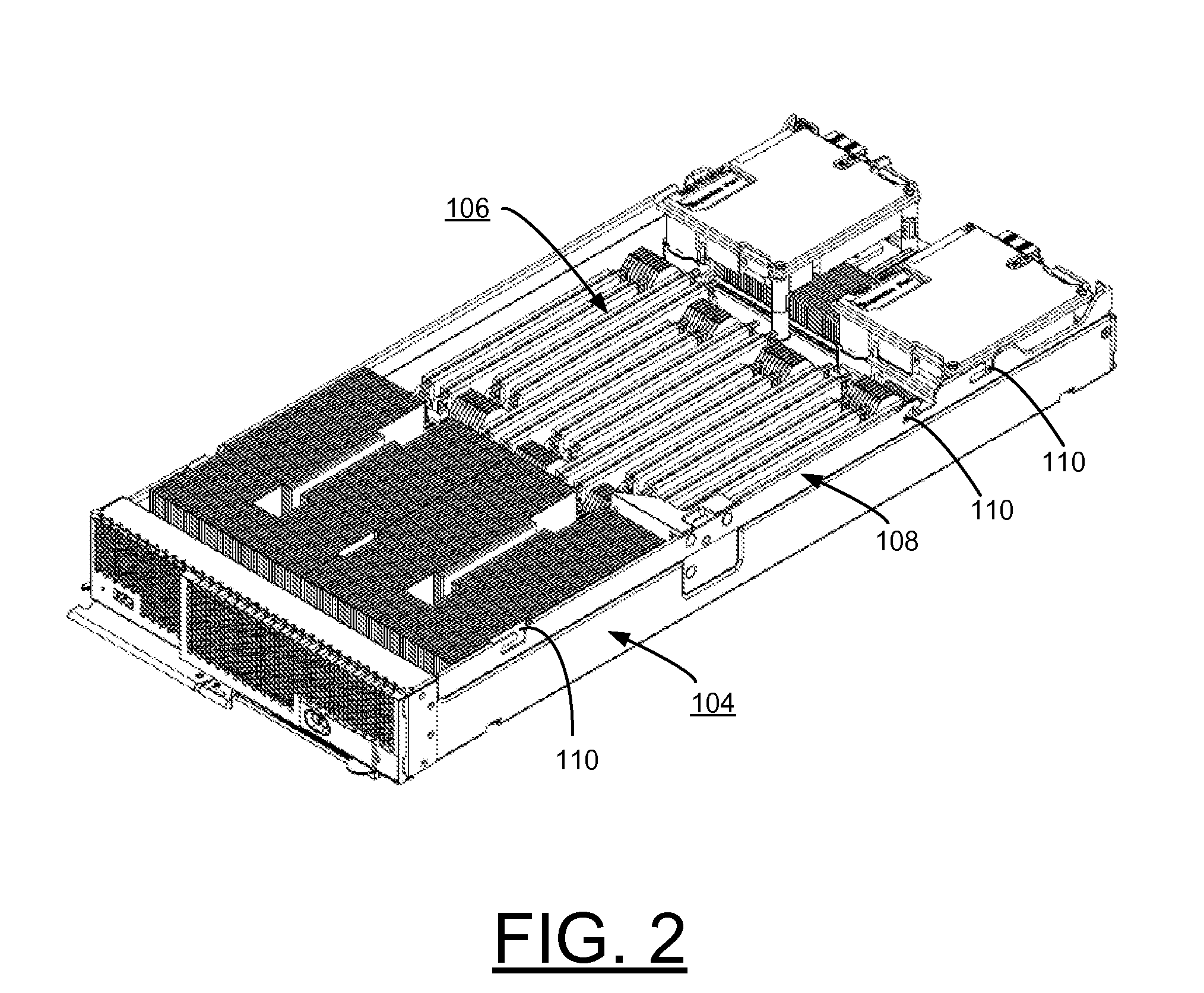
An enclosure assembly and system are provided for implementing cover-mounted, auto-docking for multiple DASD configurations in information technology equipment. A user selected direct access storage device (DASD) configuration is mechanically attached to an enclosure cover. A cover interposer card is mechanically attached to the enclosure cover and electrically connected to each DASD in the user selected DASD configuration. An electrical connector mates with the cover interposer card as the cover is installed through a sliding motion with a chassis and base planar of the enclosure assembly. A flexible cable interconnect attached to the mating electrical connector is connected to the base planar. The enclosure assembly enables high density, high performance modular server architectures without compromising processor performance or planar electrical architecture.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
In situ method and apparatus for detecting surface defects to identify handling damage in a disk drive
InactiveUS6154858ARecord information storageDigital signal error detection/correctionDirect-access storage deviceTransducer
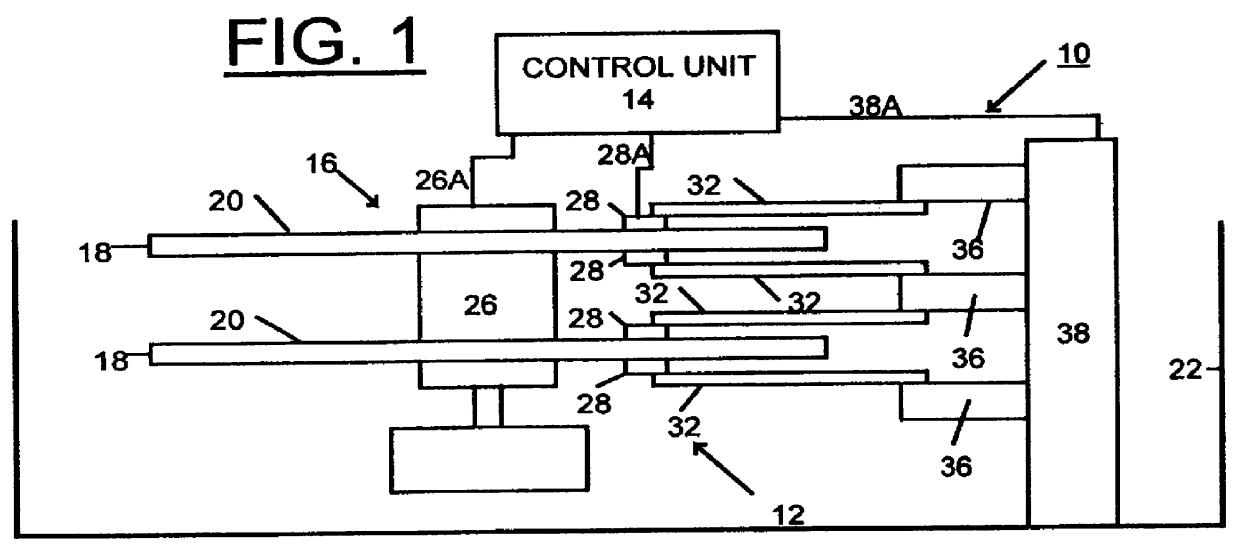
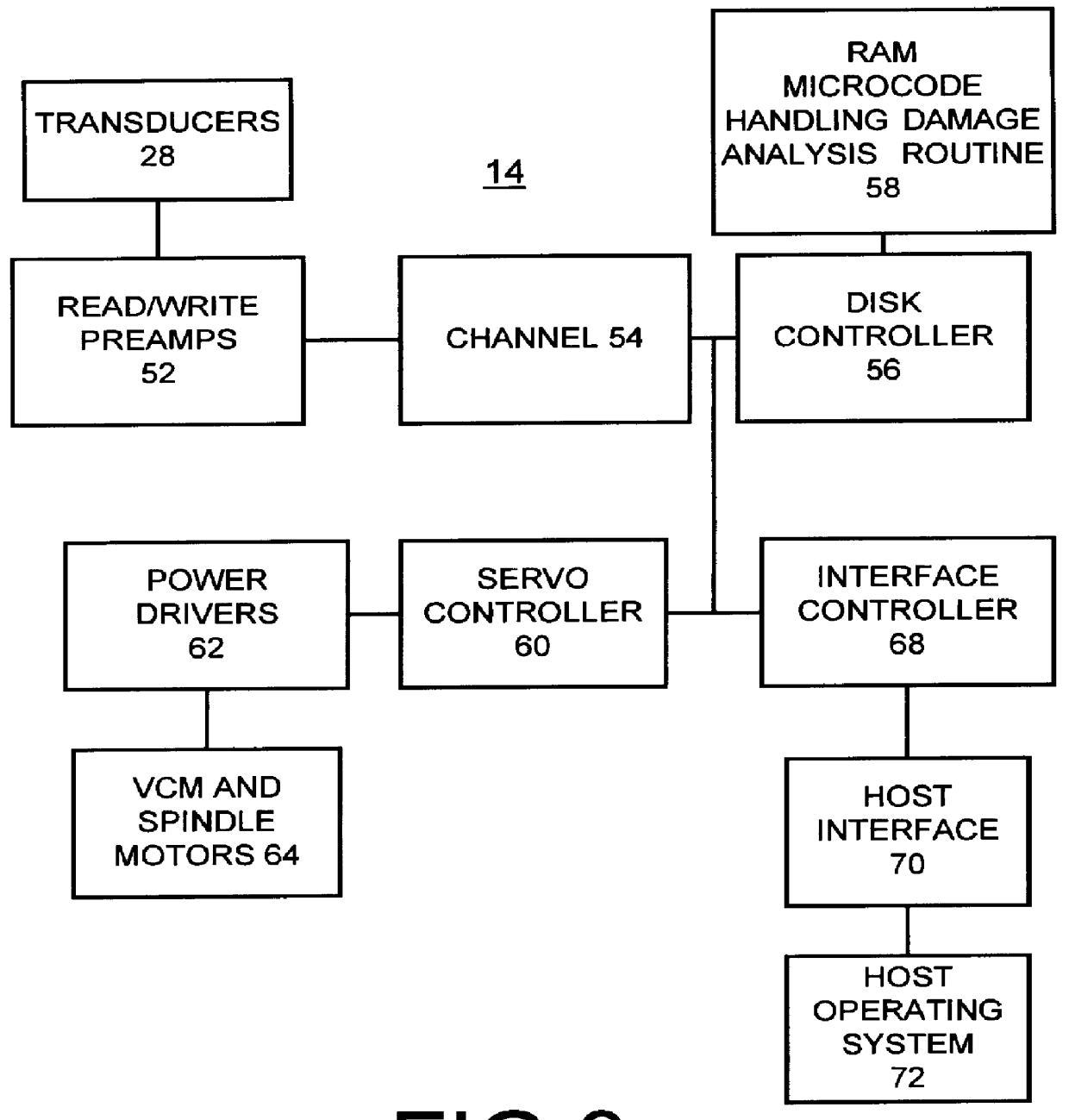
A method and apparatus are provided for detecting handling damage in a direct access storage device (DASD). The DASD has at least two magnetic disk surfaces provided by at least one disk mounted for rotation, and a corresponding transducer mounted for movement across each disk surfaces. A predefined test is performed to identify magnetic surface defects on each of the disk surfaces. The identified magnetic surface defects are utilized to identify cosited defects on at least two magnetic disk surfaces. Responsive to identifying a predefined number of cosited defects on at least two magnetic disk surfaces, handling damage is reported to the user. The method for detecting handling damage is performed responsive to a user request and following predetermined events during use of the direct access storage device.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Measuring fragmentation on direct access storage devices and defragmentation thereof
InactiveUS20090055450A1Digital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirect-access storage deviceFile system fragmentation
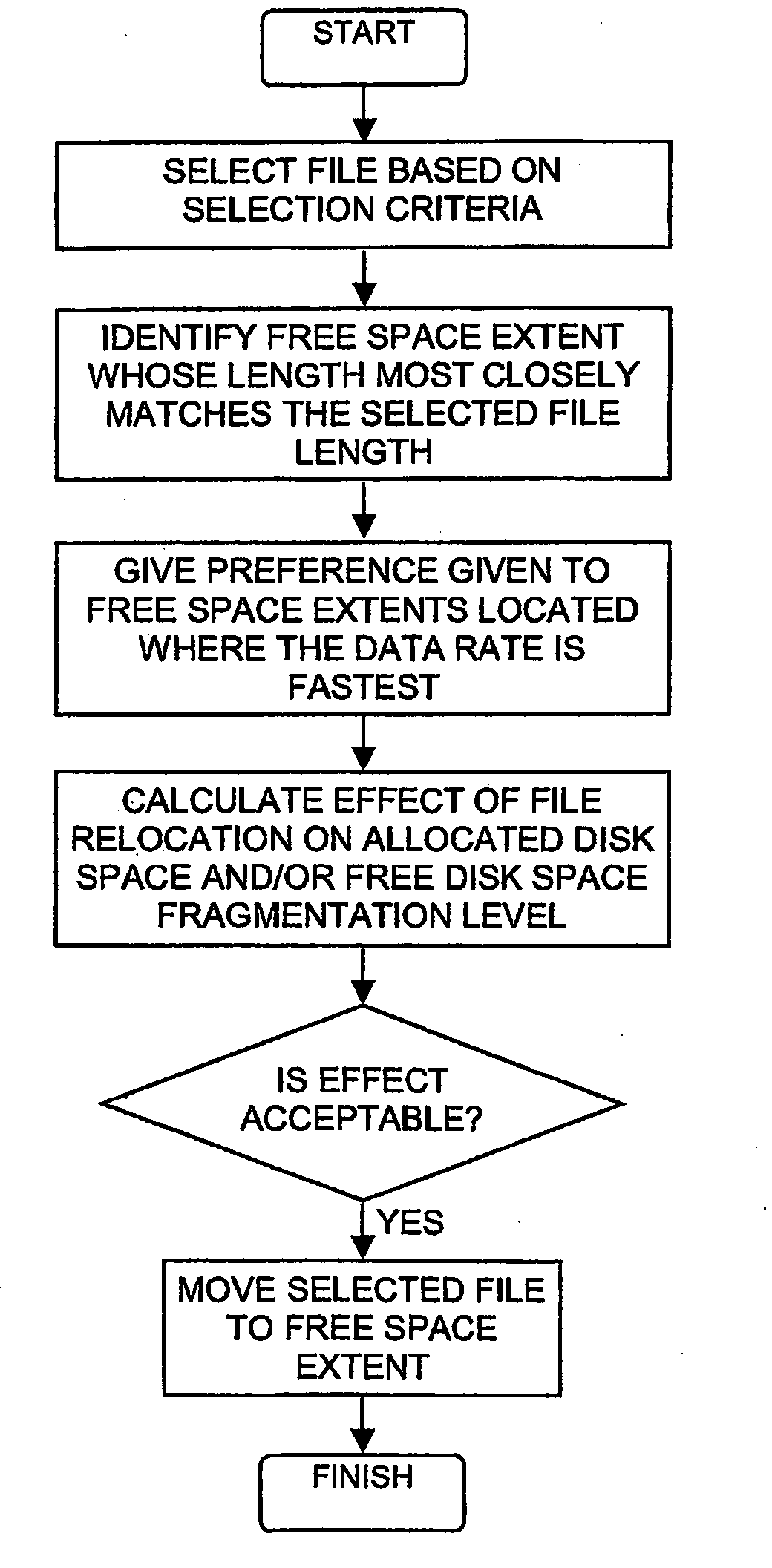
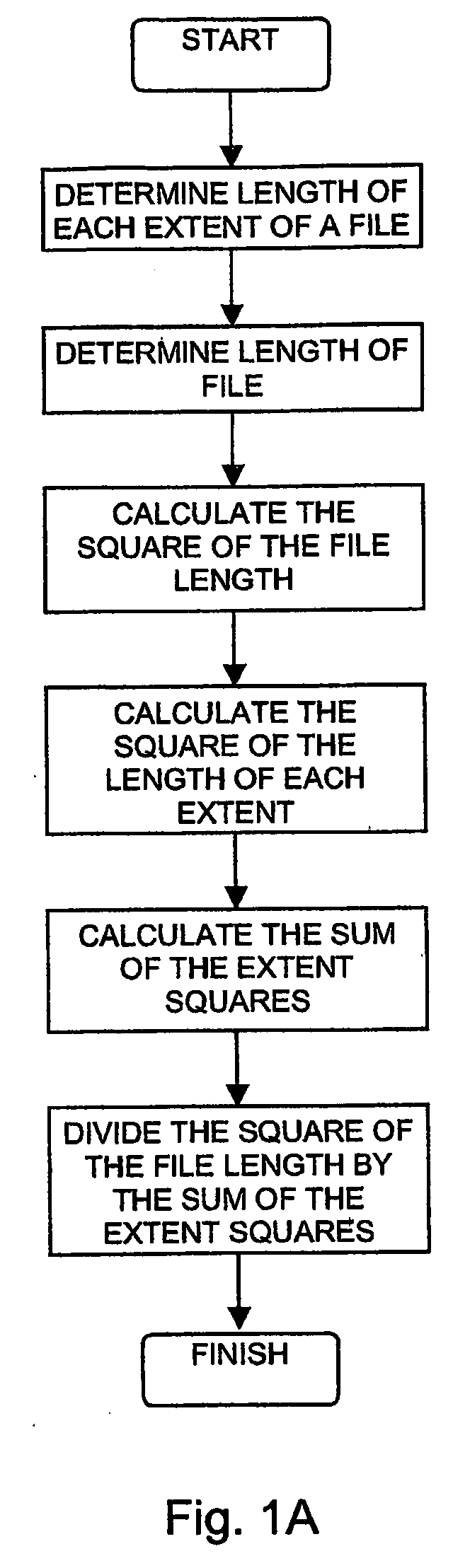
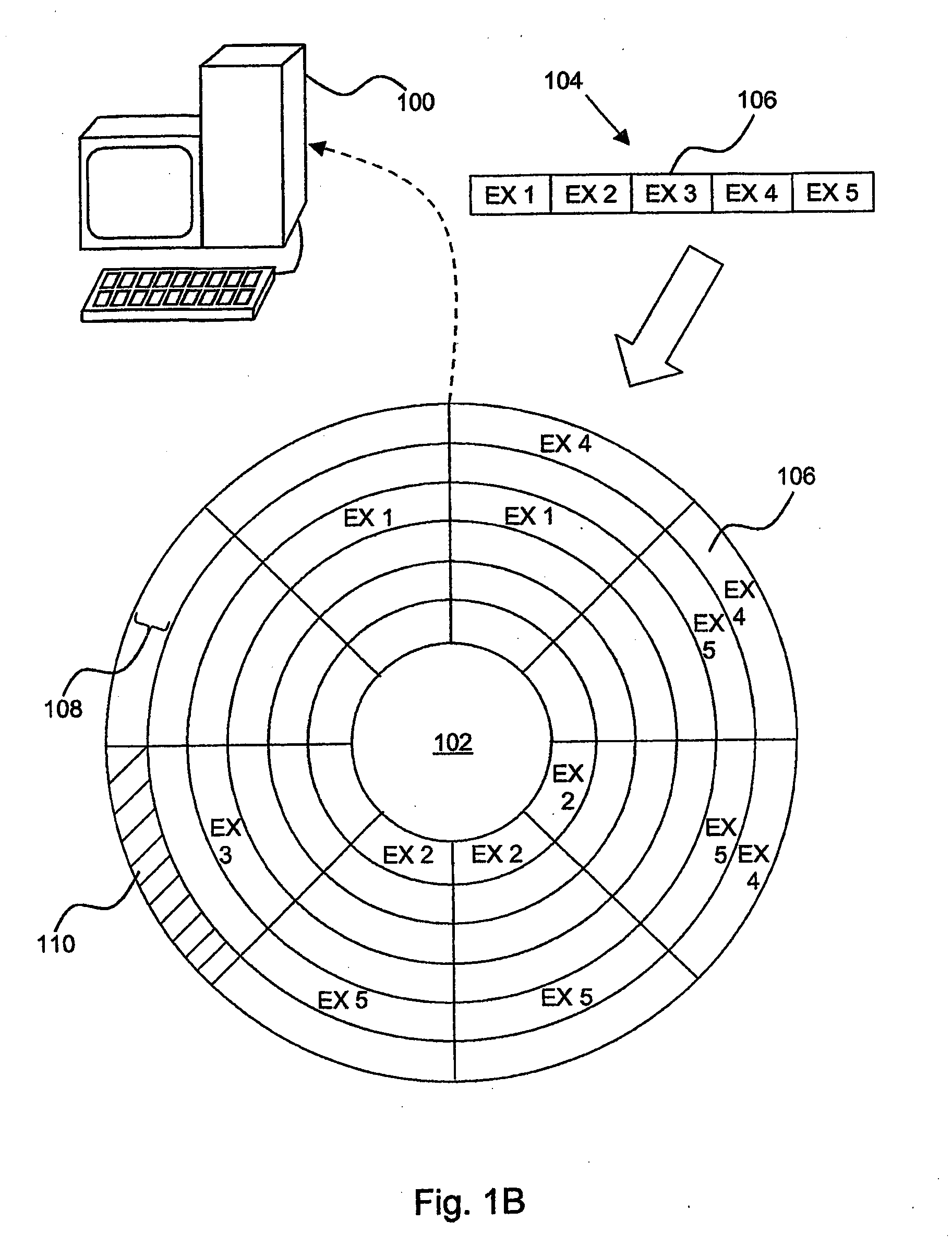
A method for determining file fragmentation and performing subsequent defragmentation, including measuring a file fragmentation factor, measuring a file extent distance factor, measuring a file fragmentation level, selecting a file stored as multiple extents on at least one disk, selecting a free space extent on the disk whose length most closely matches the length of the file, calculating a fragmentation level of the disk from a fragmentation factor and a file extent distance factor of free space extents or allocated space extents of the disk, calculating the effect that moving the file to the free space extent would have on the fragmentation level, and moving the file to the free space extent provided that doing so causes the fragmentation level to satisfy a criterion.
Owner:BILLER KOBY
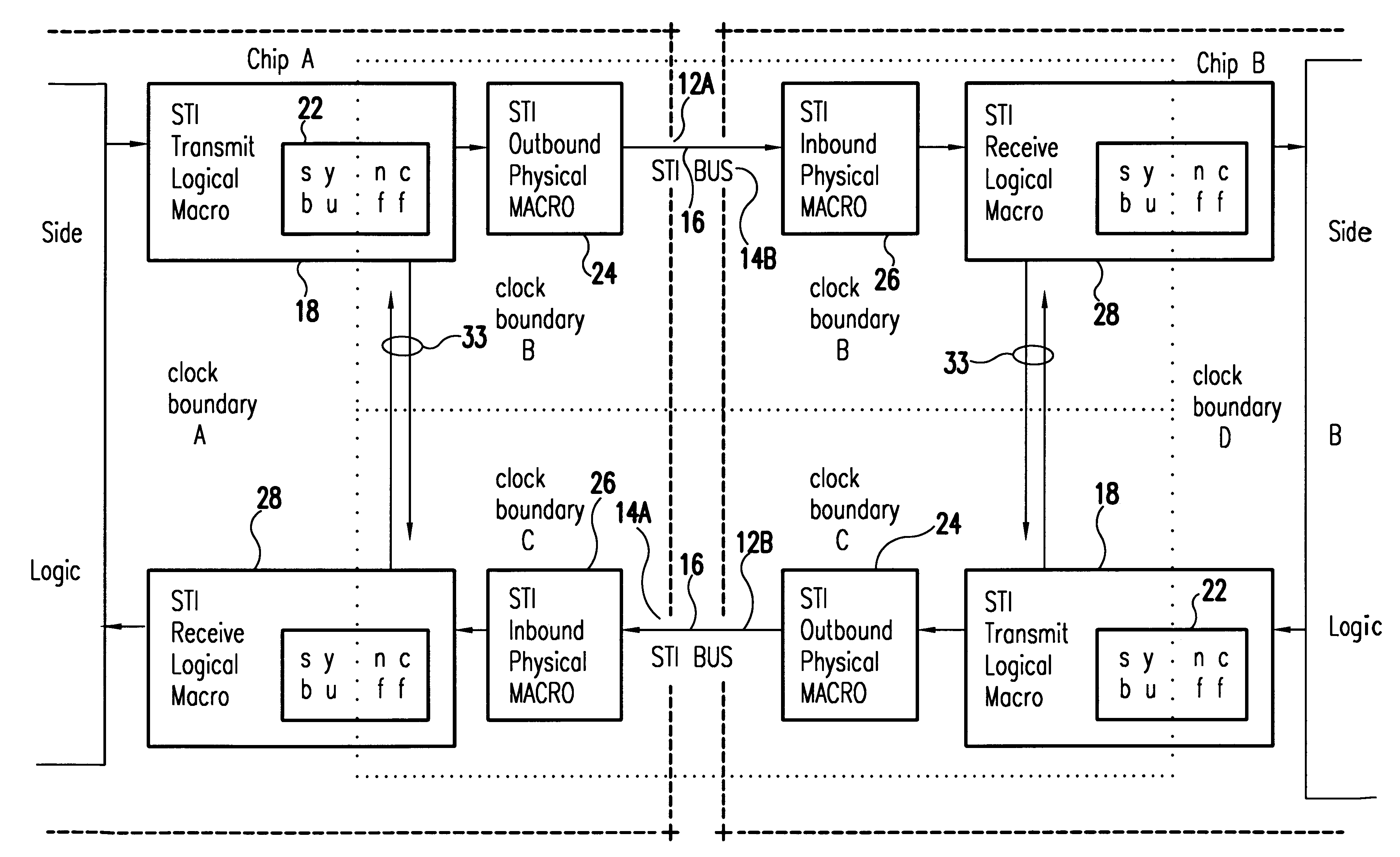
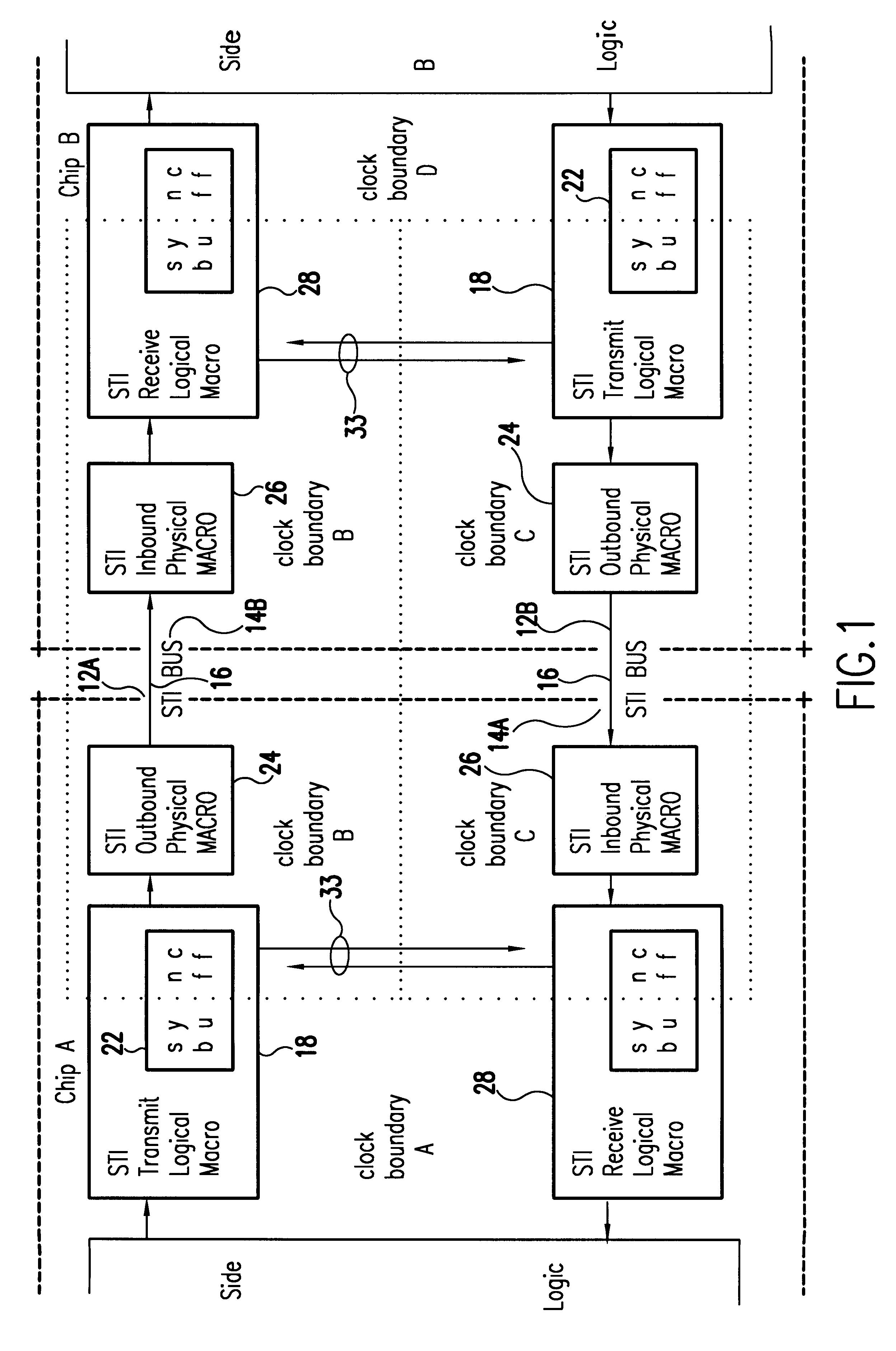
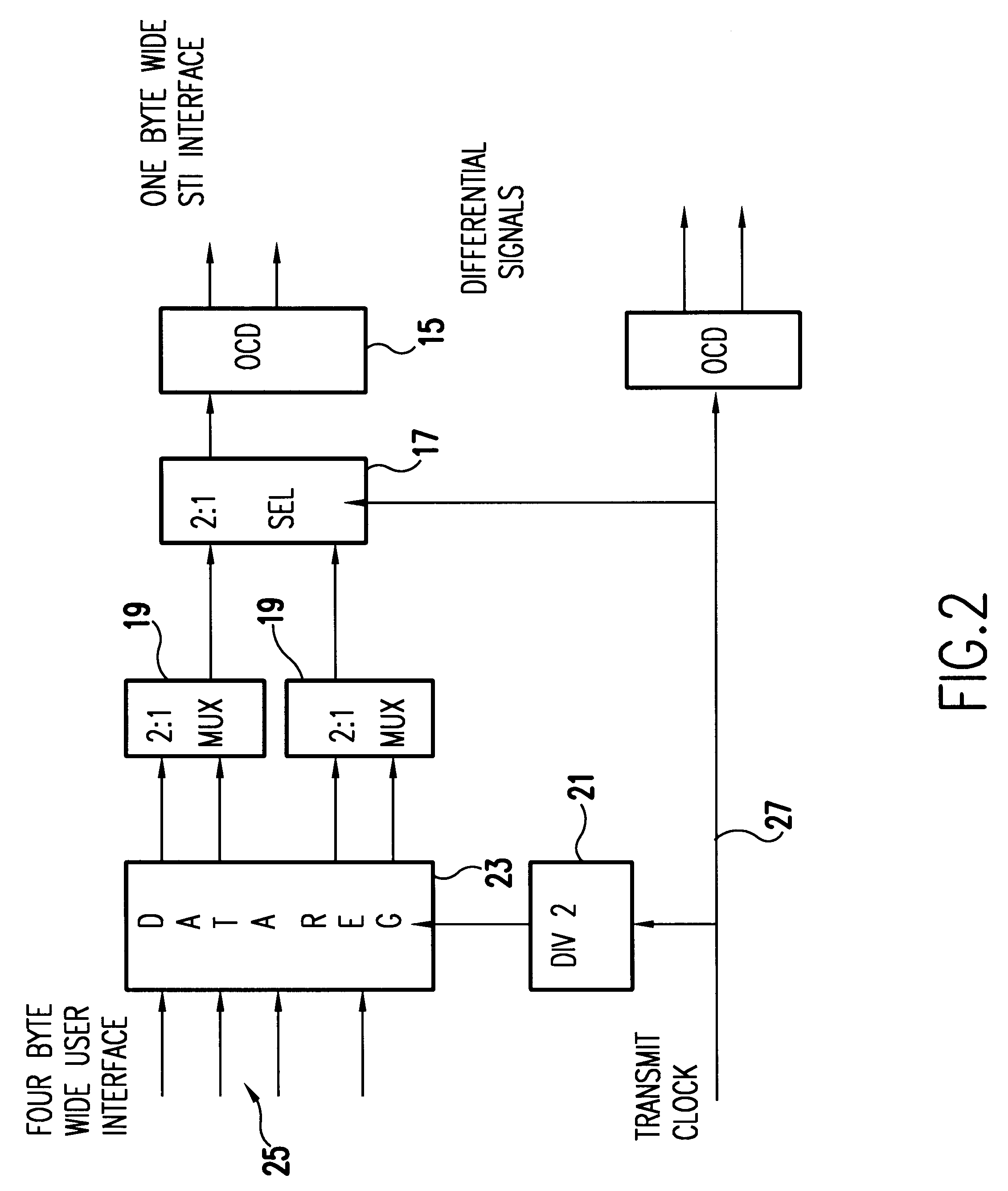
Self-timed parallel data bus interface to direct storage devices
InactiveUS6192482B1Low costImprove performanceError detection/correctionData resettingDirect-access storage deviceBus interface
An attached storage media link has a self-timed interface (STI) in which a clock signal clocks bit serial data onto a parallel, electrically conductive bus and the clock signal is transmitted on a separate line of the bus. The received data on each line of the bus is individually phase aligned with the clock signal, providing a high speed, cost effective interface to a direct access storage device.
Owner:IBM CORP
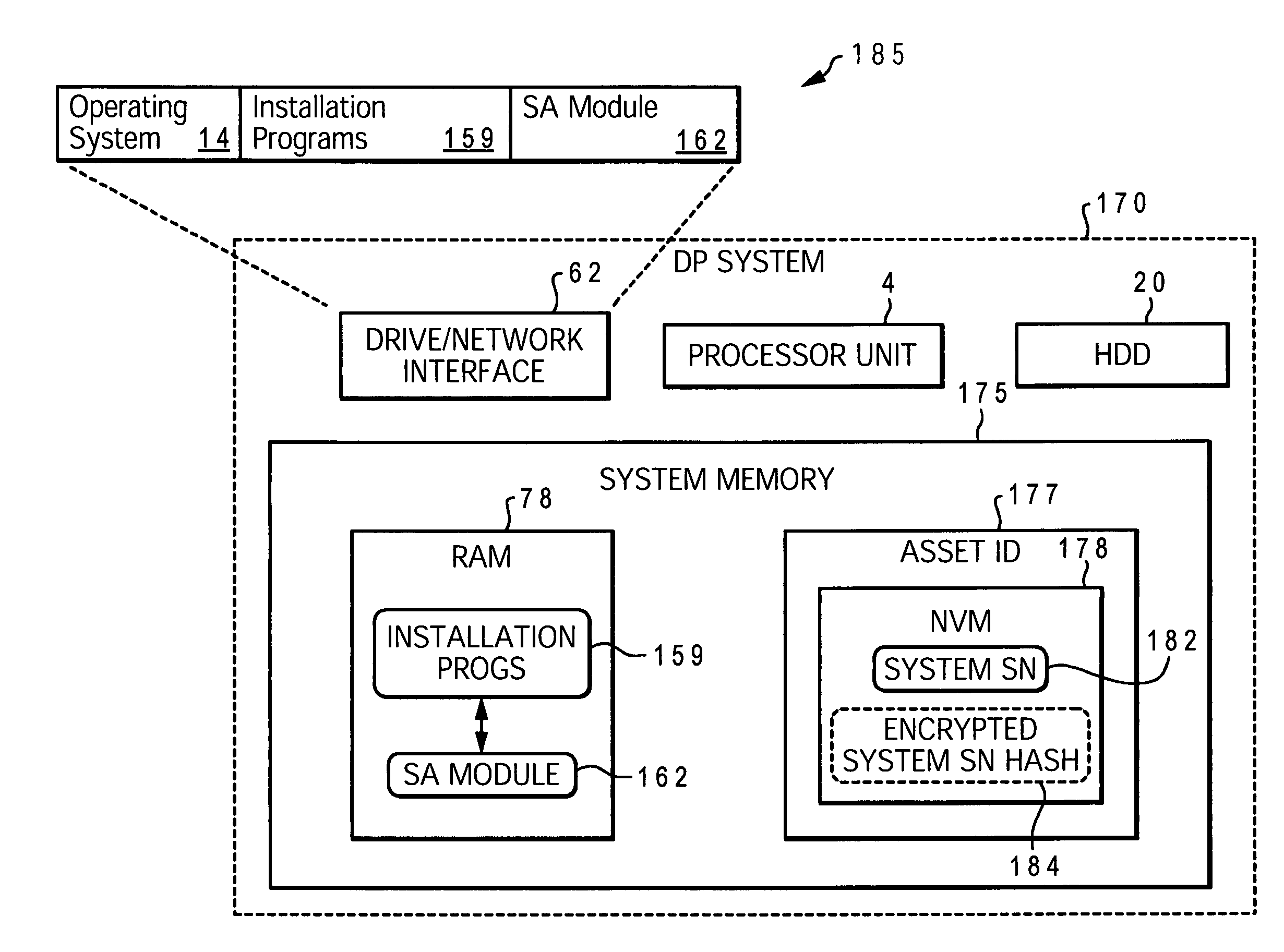
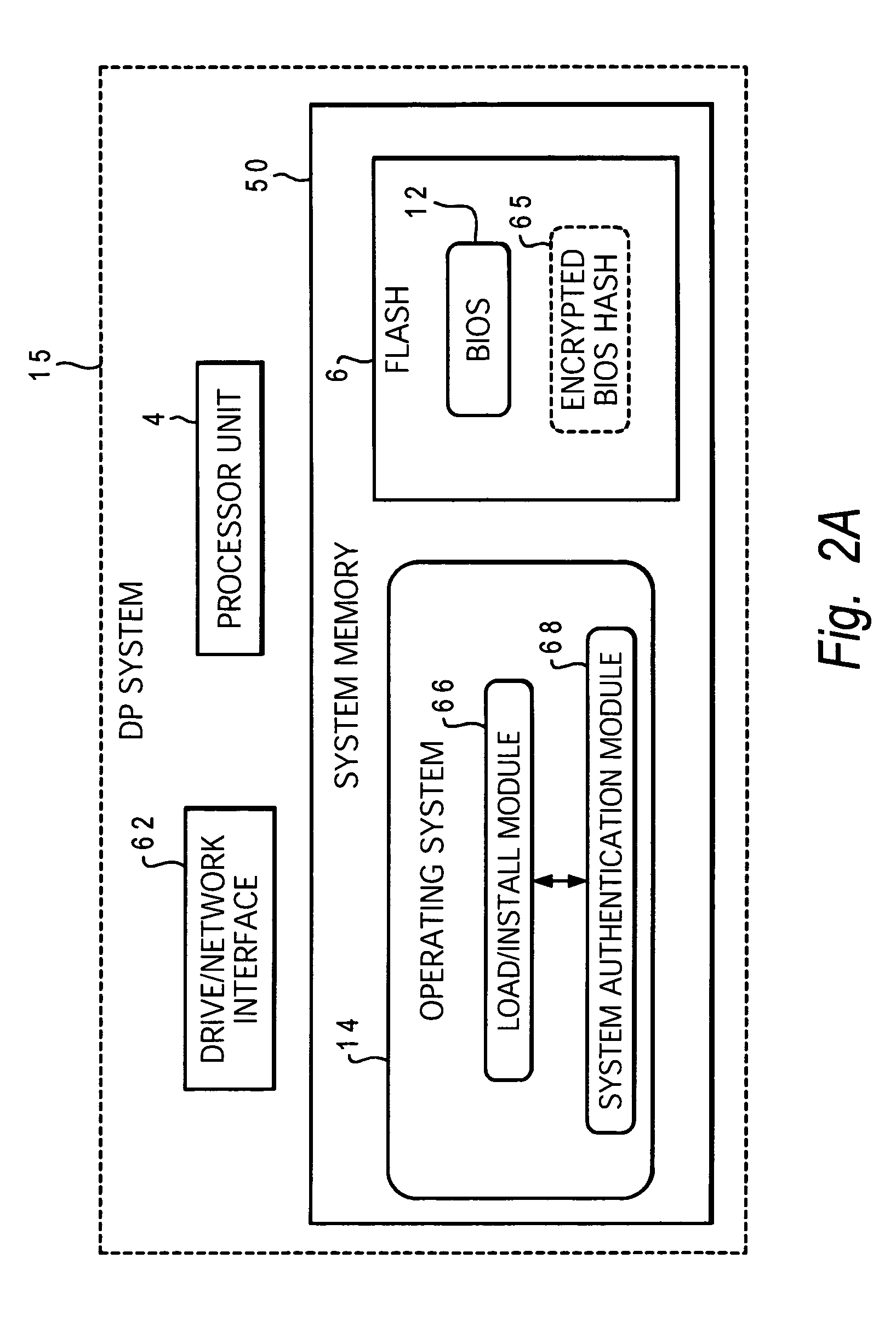
System and method for data processing system planar authentication
InactiveUS7490245B2User identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionData processing systemDirect-access storage device
Initially, a hardware inventory device is provided within the data processing system. UIC that uniquely identifies the data processing system is stored in a non-erasable memory of the hardware inventory device. An encrypted hash generated by combining the UIC and a BIOS hash is stored in the non-erasable memory of the hardware inventory device. In response to a loading of a software program previously installed within a direct access storage device of the data processing system, the following steps are performed: i. the encrypted hash is obtained from the non-erasable memory of the hardware inventory device; ii. the encrypted hash is decrypted; iii. a new hash is generated by using the UIC and a BIOS from the data processing system, and the decrypted hash is compared with the new hash; and iv. the software program loading is allowed to continue when the decrypted hash matches the new hash.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
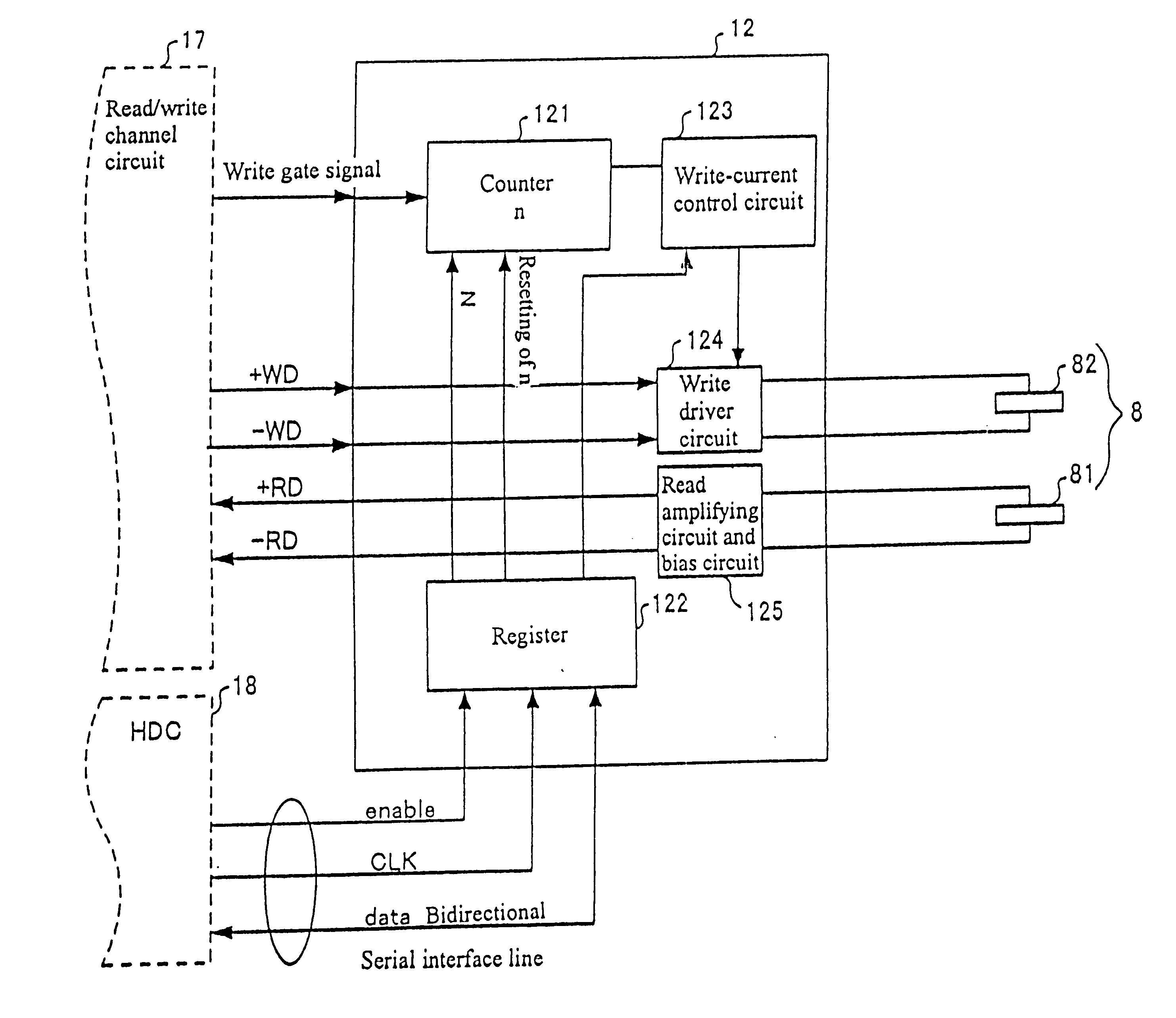
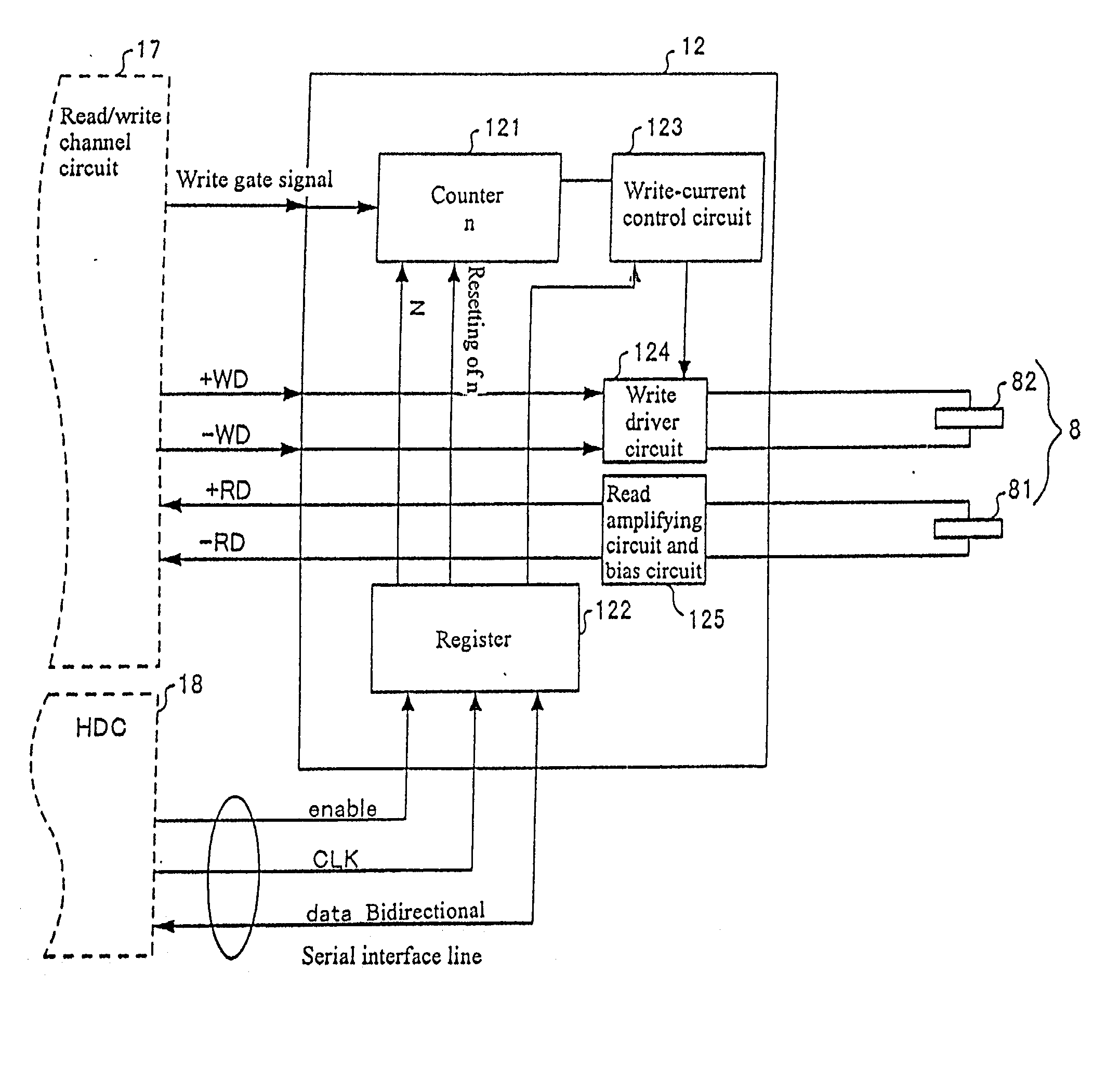
Method for controlling write current to a write head during data write on a hard disk
InactiveUS6798598B2Record information storageAnalogue recordingHard disc driveDirect-access storage device
A method for controlling write current to a write head during data write on a hard disk drive is disclosed. A direct access storage device includes a rotating storage medium in which data are magnetically written, a write head for writing data in the rotating storage medium, and a write current control circuit for changing write current-value settings to be supplied to the write head according to a predetermined elapsed time from the beginning of a write operation.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
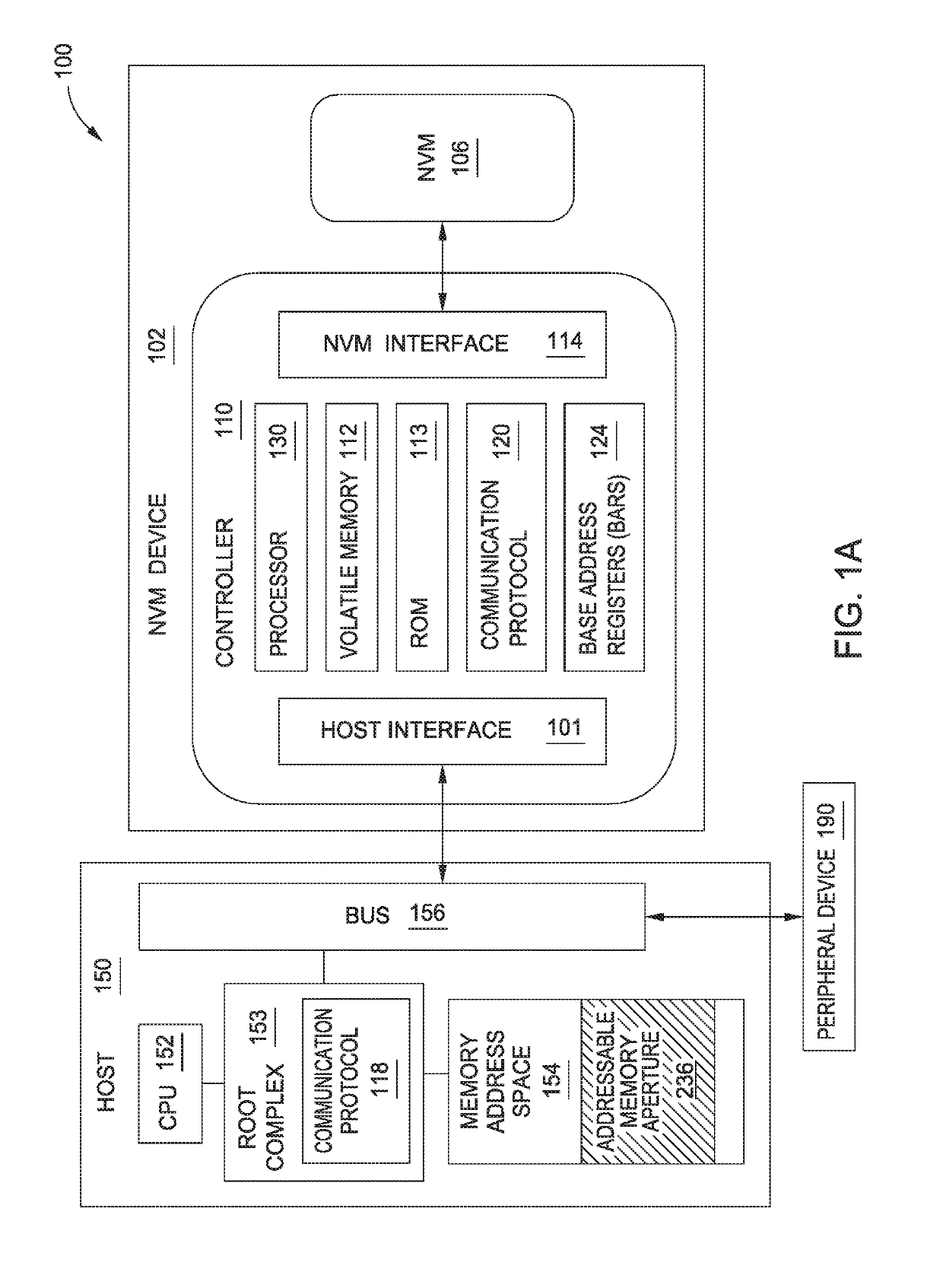
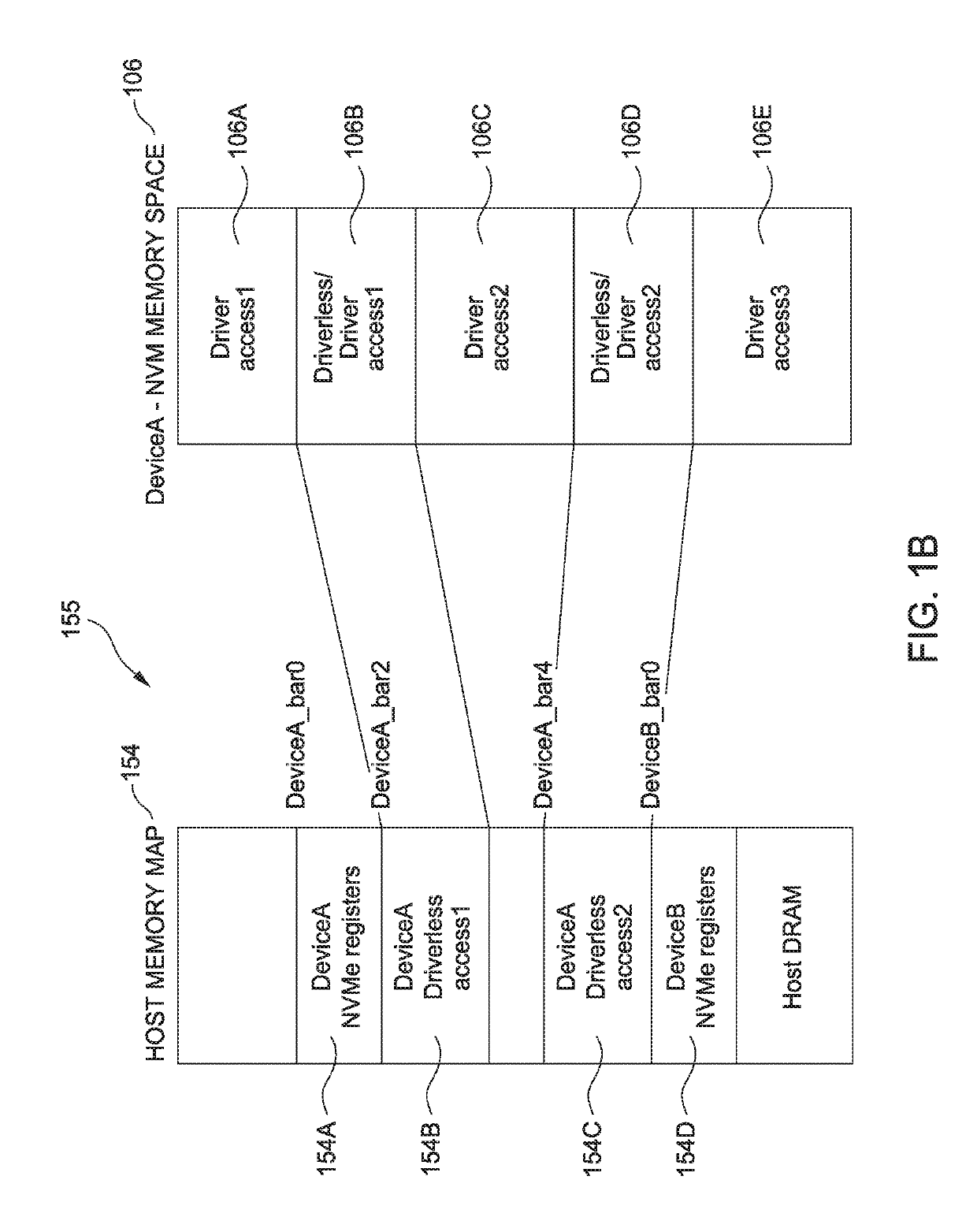
Direct host access to storage device memory space
ActiveUS20190188153A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersSpace mappingHost memory
Apparatuses and methods of directly accessing a memory space of a storage device by a host are provided. In one embodiment, a method of driverless access of a non-volatile memory of a non-volatile memory device by a host includes initializing a PCIe memory space mapping a portion of the non-volatile memory of the non-volatile memory device to a host memory space. The non-volatile memory is mapped through a PCIe link between the host and the non-volatile memory device. Load / store commands are sent to the PCIe memory space for driverless access. The method further includes negotiating an alignment size of the minimum transaction packet size to complete the load / store commands.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
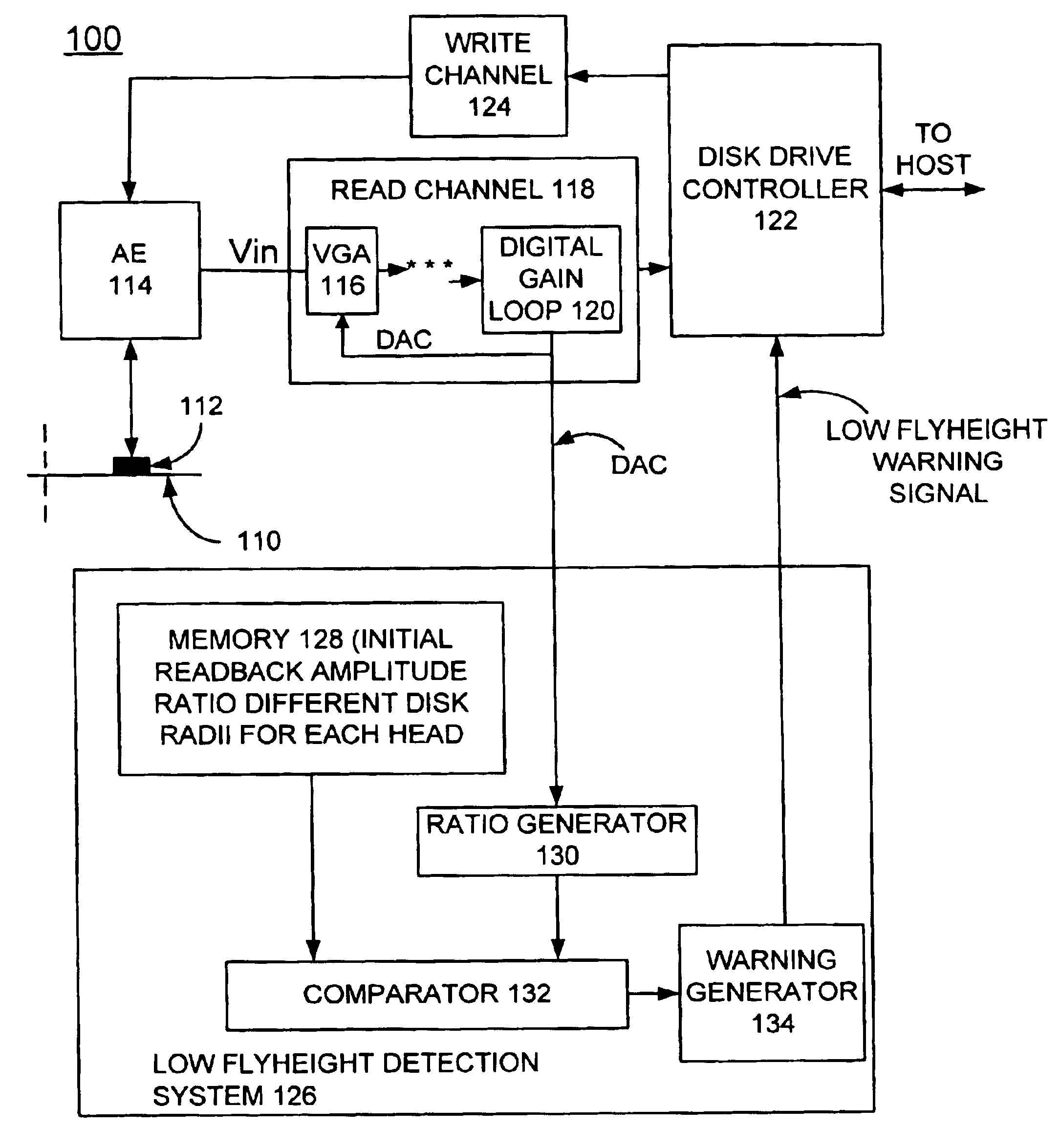
Method and system for implementing in situ low flyheight warning
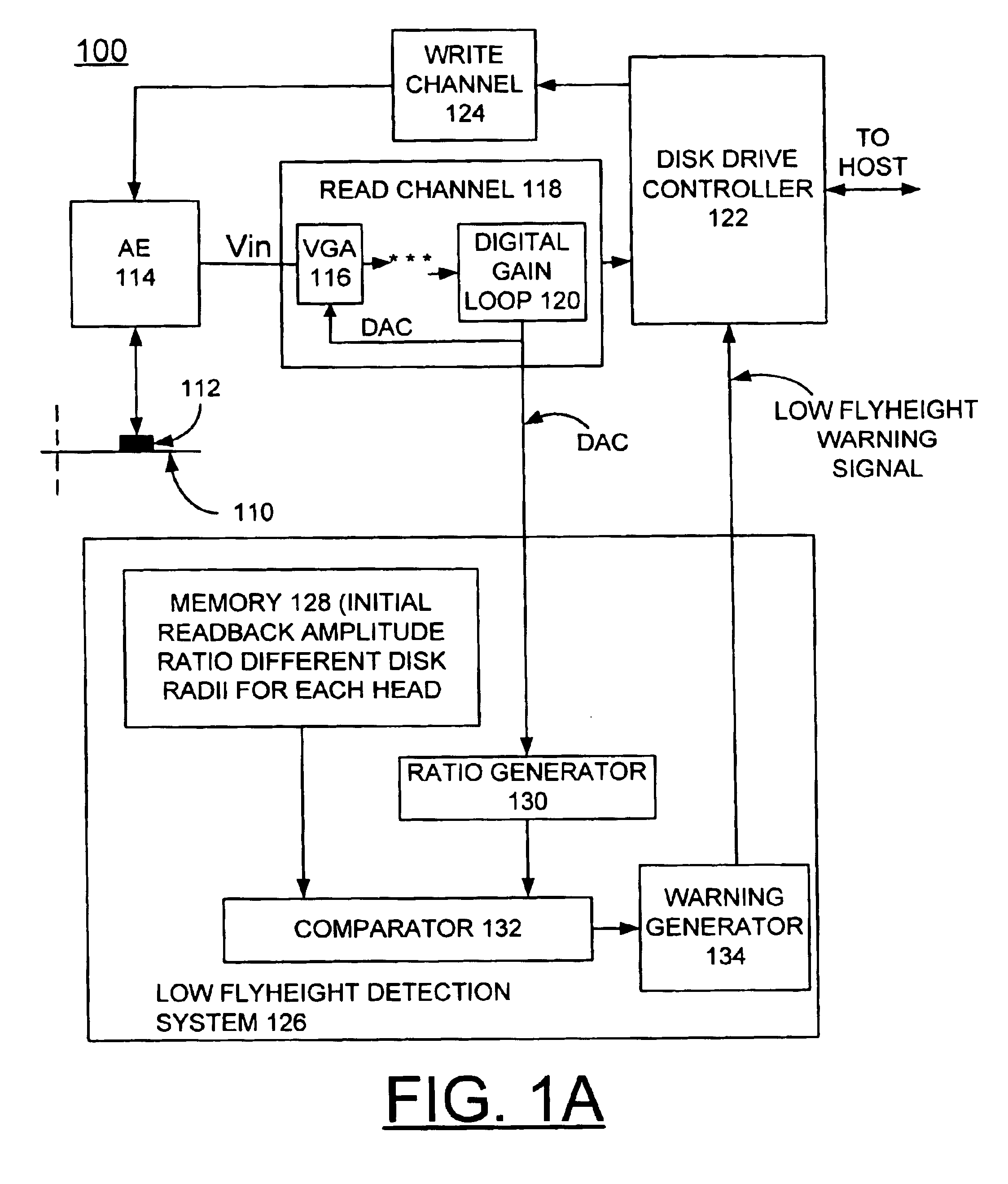
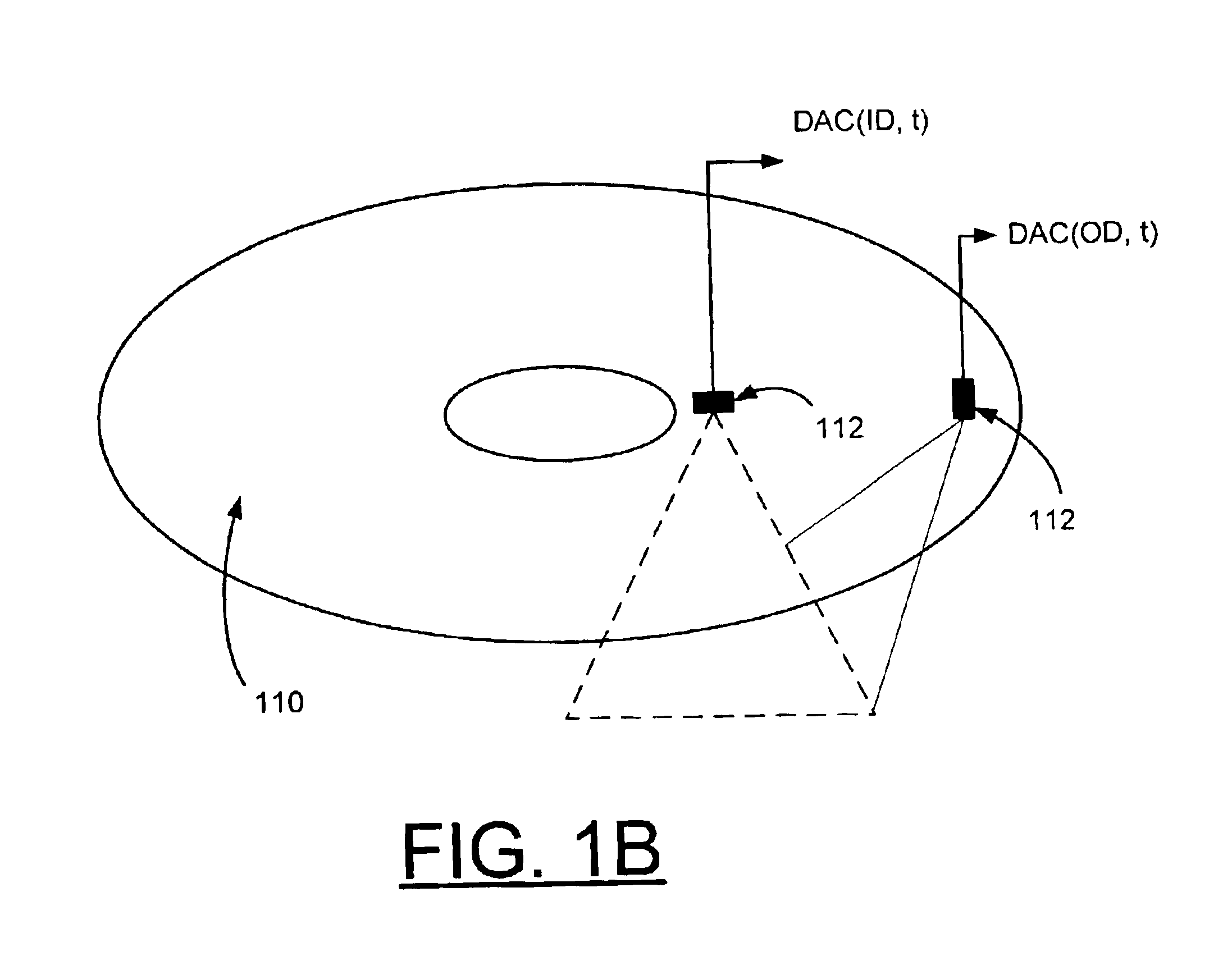
InactiveUS6906878B2Overcome disadvantagesDisc-shaped record carriersDriving/moving recording headsDirect-access storage deviceControl theory
A method and apparatus are provided for implementing in situ low flyheight warning in a direct access storage device (DASD). For each head in the DASD, a readback amplitude ratio is identified from two different disk radii. The initial ratio value is stored for each head in the DASD. During operation of the DASD, readback amplitude is monitored and an operating readback amplitude ratio is identified from two different disk radii. A change between the initial ratio value and the operating readback ratio is calculated and compared with a threshold value to identify a low-flying slider. A warning is generated responsive to the change value being greater than the threshold value.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Direct access storage device (DASD) with a variable spindle rotation speed
InactiveUS6104566AWithout negative effectAC motor controlSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor driveDirect-access storage device
A method and apparatus are provided for variable spindle rotation speed in a direct access storage device (DASD). The direct access storage device (DASD) includes a multi-phase, brushless, direct current (DC) spindle motor. Speed and commutation control signals are applied to a plurality of spindle motor drivers for normally operating the plurality of spindle motor drivers in saturation mode while performing read and write operations. A spindle rotational speed is detected and compared with a predetermined spindle speed range. Responsive to the detected spindle rotational speed being within said predetermined spindle speed range, normal operations of the direct access storage device (DASD) are enabled. One or more write sync fields are provided on each surface of a magnetic disk media. The write sync field is used for timing write operations in the direct access storage device.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
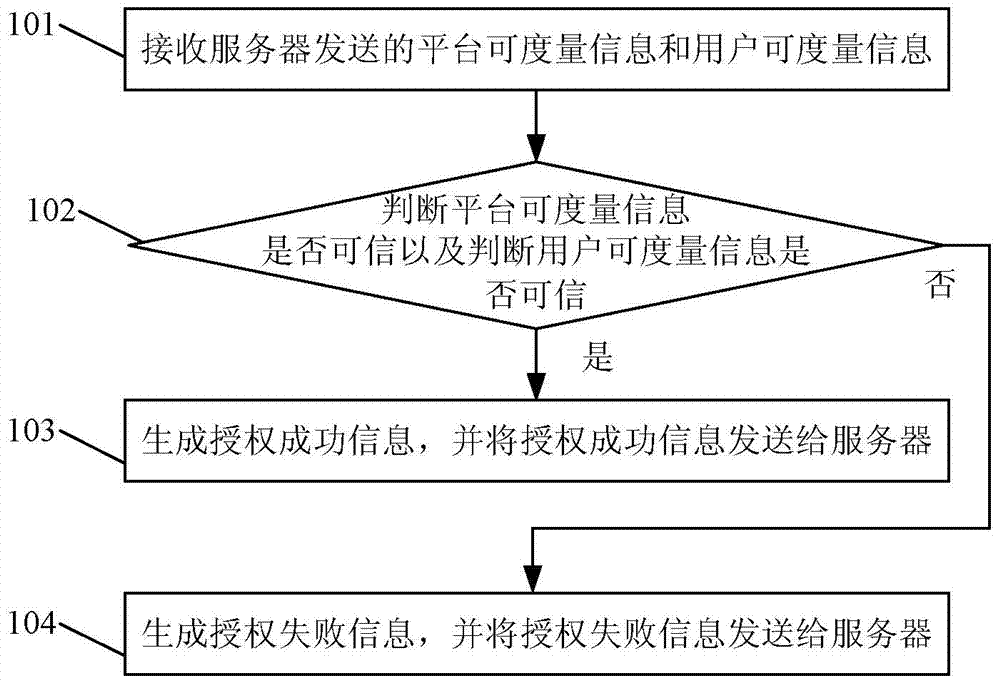
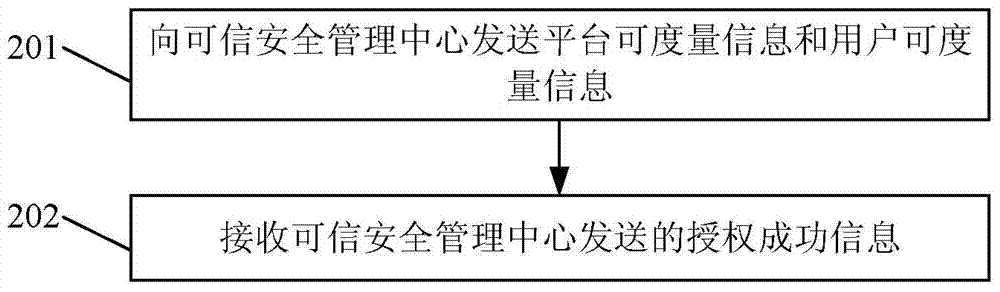
Credibility authorization method, system, credibility security management center and server
The invention discloses a credibility authorization method, a system, a credibility security management center and a server. The credibility authorization method comprises the followings steps: receiving platform metrizable information and user metrizable information transmitted by the server; judging whether the platform metrizable information is credible or not, and judging whether the user metrizable information is credible or not; if the platform metrizable information is credible and the user metrizable information is credible according to judgment, generating authorization success information; transmitting the authorization success information to the server. The server can only access storage equipment after receiving the authorization success information successfully, and an intruder can be prevented from accessing the storage equipment directly after the server is intruded, so that data in the storage equipment are effectively prevented from being accessed illegally.
Owner:CEC CYBERSPACE GREAT WALL
Method for controlling write current to a write head during data write on a hard disk
InactiveUS20020141094A1Record information storageAnalogue recordingHard disc driveDirect-access storage device
A method for controlling write current to a write head during data write on a hard disk drive is disclosed. A direct access storage device includes a rotating storage medium in which data are magnetically written, a write head for writing data in the rotating storage medium, and a write current control circuit for changing write current-value settings to be supplied to the write head according to a predetermined elapsed time from the beginning of a write operation.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Generation of higher-order harmonic sine and cosine sequences by indexing a first-order sine/cosine table
InactiveUS6556371B1Improve track registrationRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksDirect-access storage deviceHarmonic
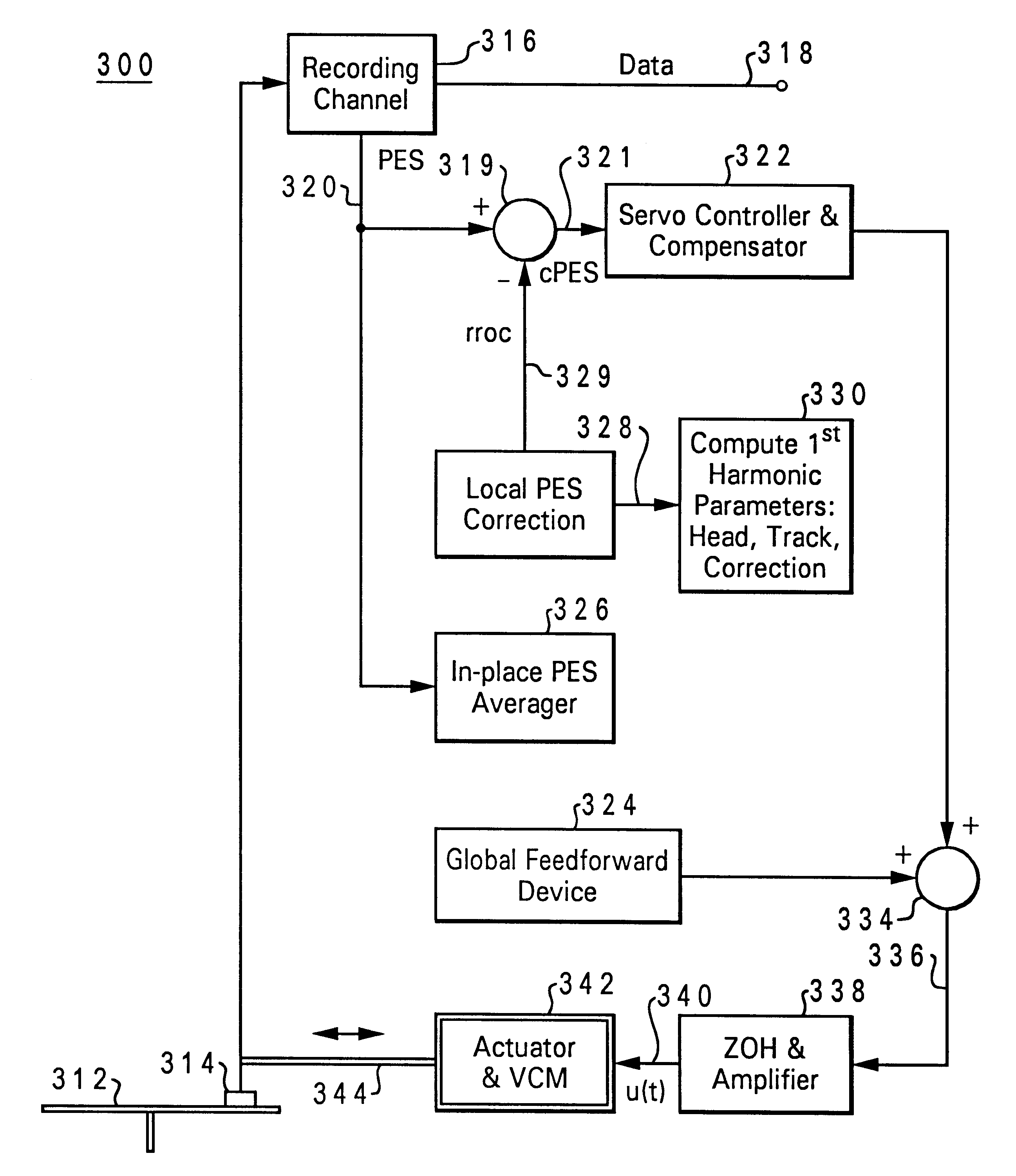
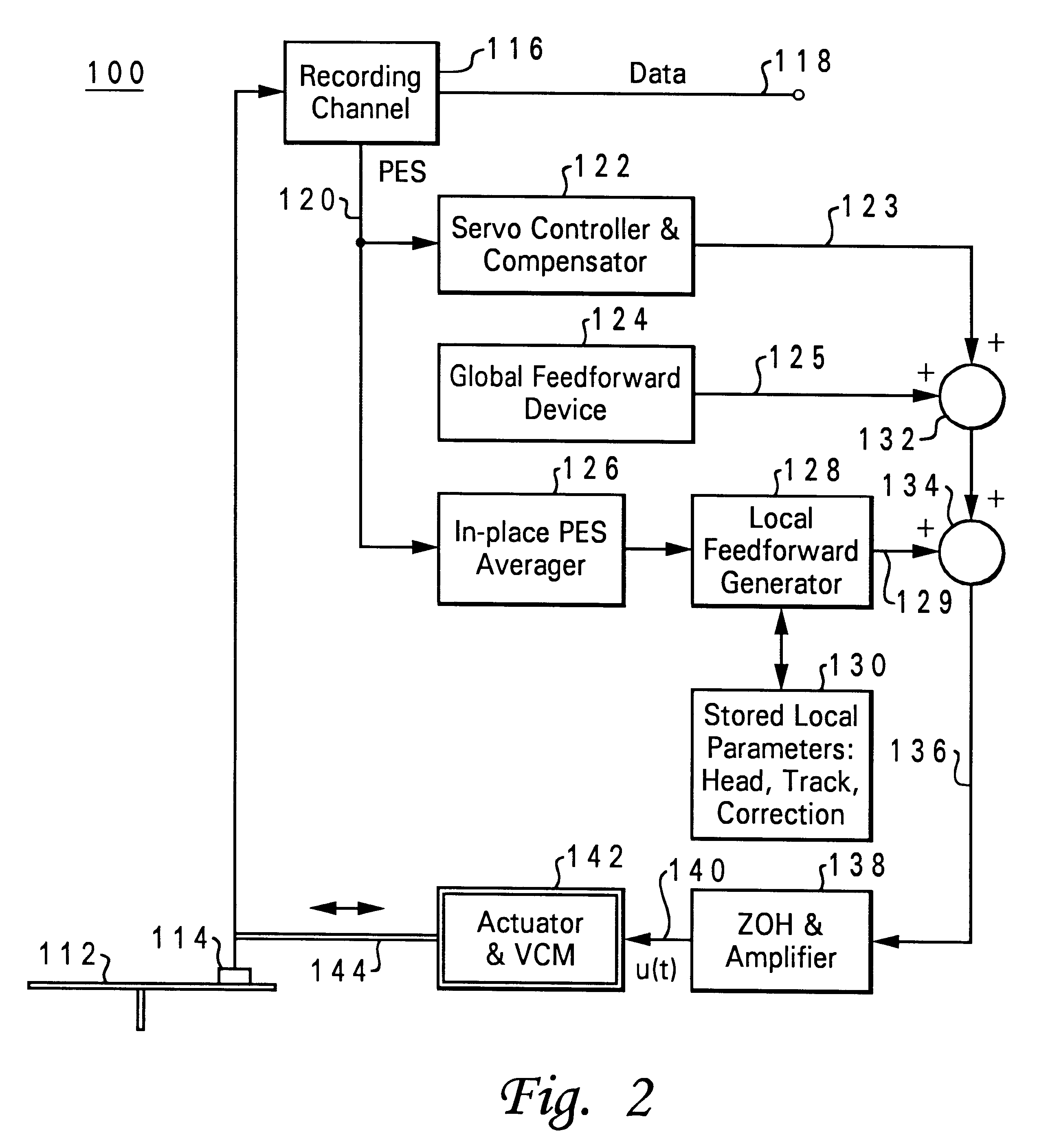
A method of generating a higher-order trigonometric sequence, by constructing a table having a first-order trigonometric sequence, indexing the table to yield a different sequence based on an order number of a desired higher-order harmonic, and catenating values in the table according to the different sequence to yield a higher-order trigonometric sequence whose order is the order number. The table may be a first-order sine sequence, with the method yielding a higher-order sine sequence, or the table may be a first-order cosine sequence, with the method yielding a higher-order cosine sequence. The table has a period N, and indexing is accomplished by computing pointer indices equal to (k*n)mod(N), where k is the order number, and 0<=n<N. In the special case where N is a multiple of 4, a single table may be used for both higher-order sine and higher-order cosine sequences. This method may be applied to the calculation of a local PES-correction value for at least one track of a direct access storage device. The local PES-correction value is then used to position a read / write head of the direct access storage device over the track. The PES-correction value for the track may be stored on a sector of the direct access storage device.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com