Patents
Literature
6385results about "Single motor speed/torque control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
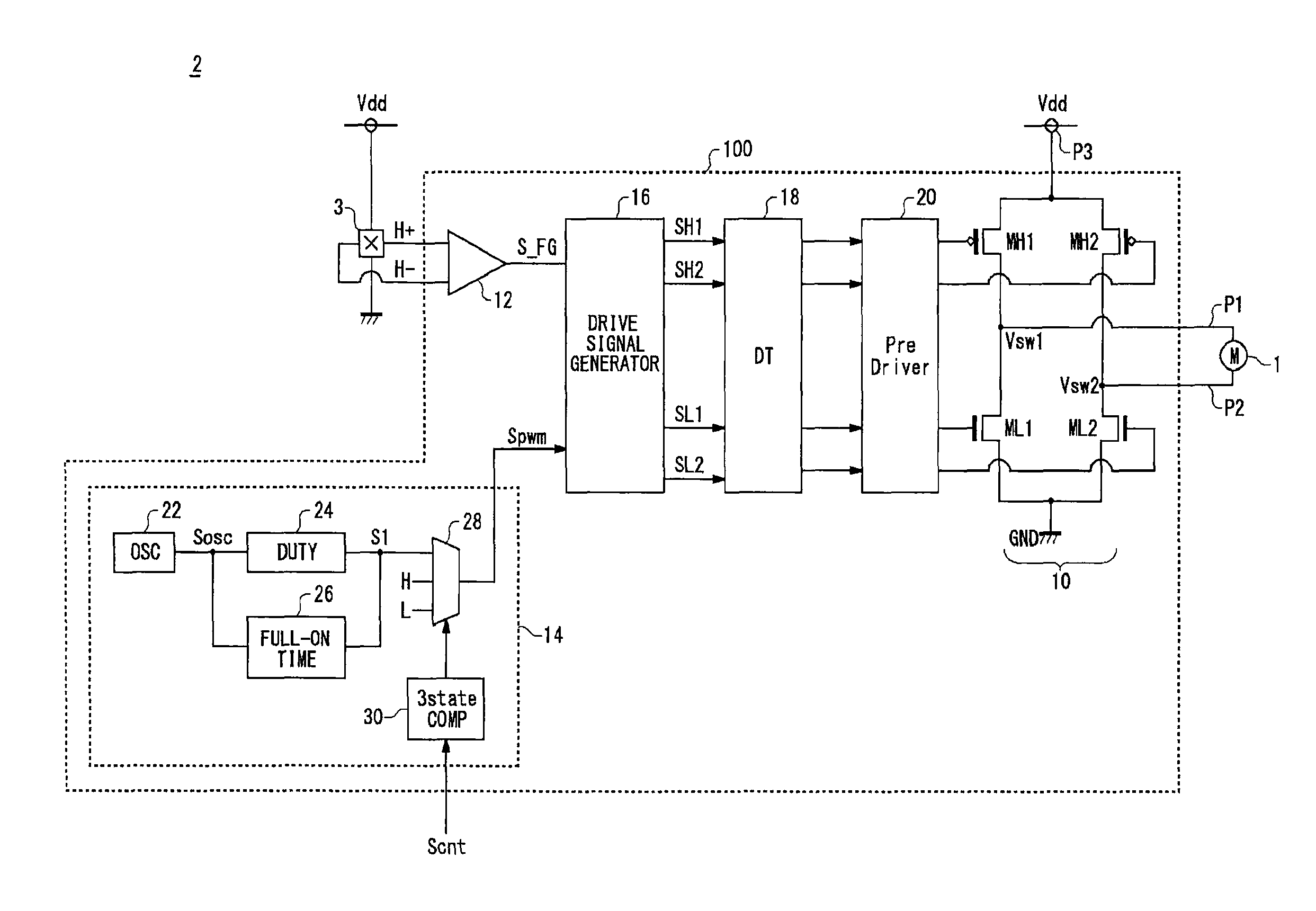
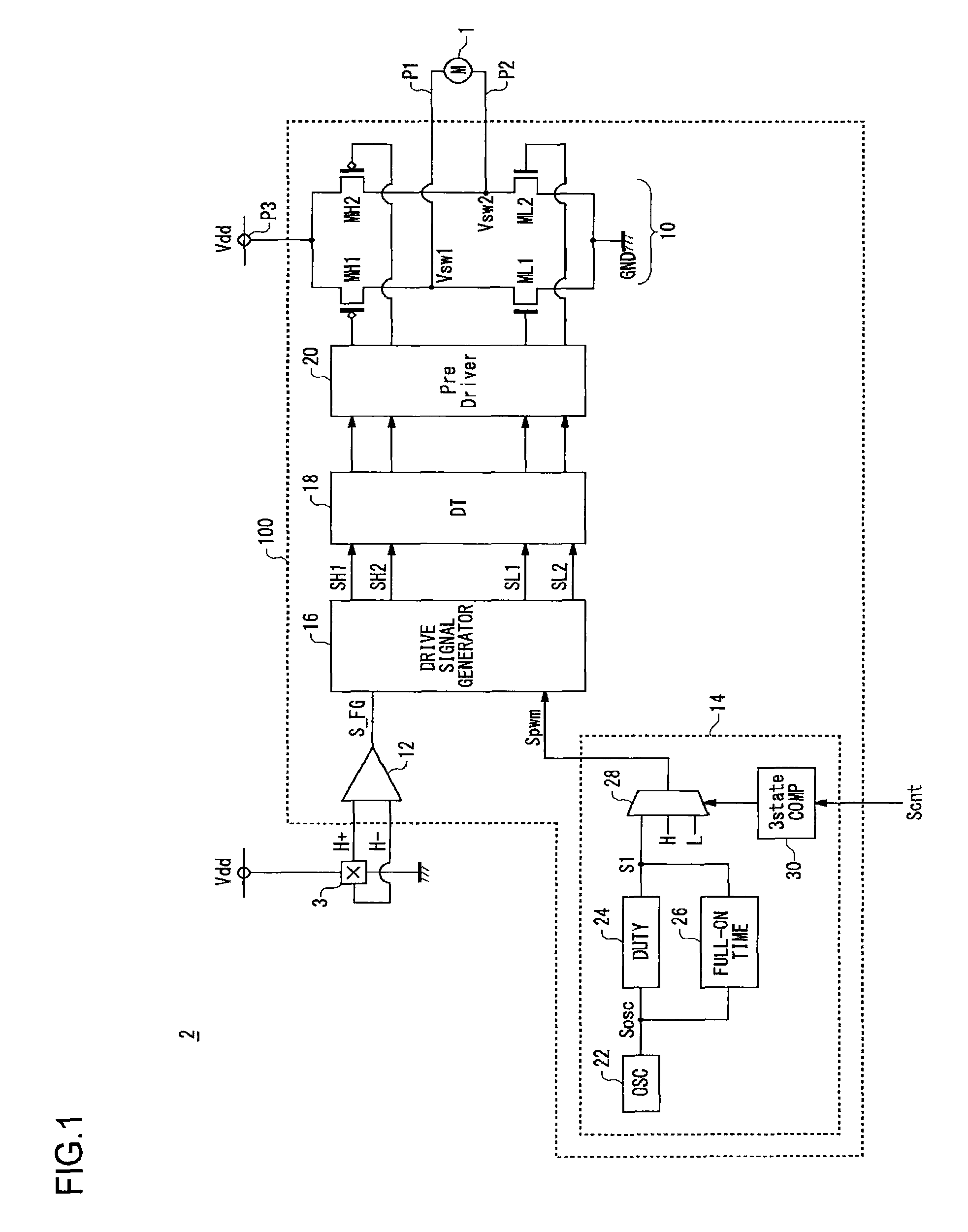
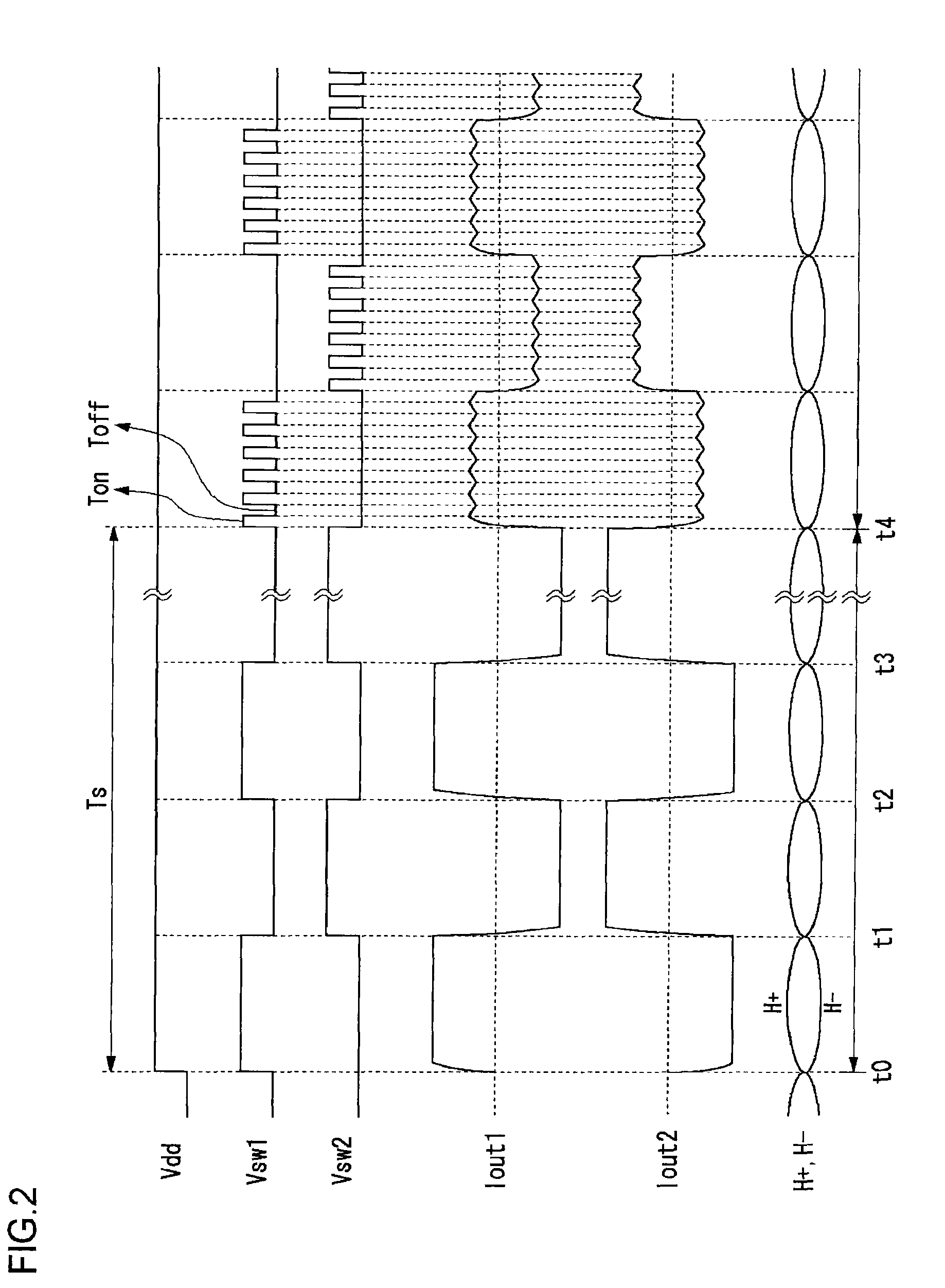
Motor drive circuit with short startup time
An H-bridge circuit is connected to a coil of the vibration motor that is to be driven. A comparator receives Hall signals indicating position information of a rotor of the vibration motor, and converts to an FG signal. A pulse width modulator generates a pulse-modulated pulse signal specifying energization time of the coil of the vibration motor. The pulse width modulator, in a first mode, after commencing start-up of the vibration motor, sets a duty ratio of the pulse signal to 100%, and after that, switches the duty ratio to a predetermined value in accordance with rotational frequency of the motor. In a second mode, the duty ratio of the pulse signal continues to be set to 100%. In a third mode, frequency and the duty ratio of the pulse signal are set based on a control signal of a pulse form inputted from outside. The control signal is used also in switching mode.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
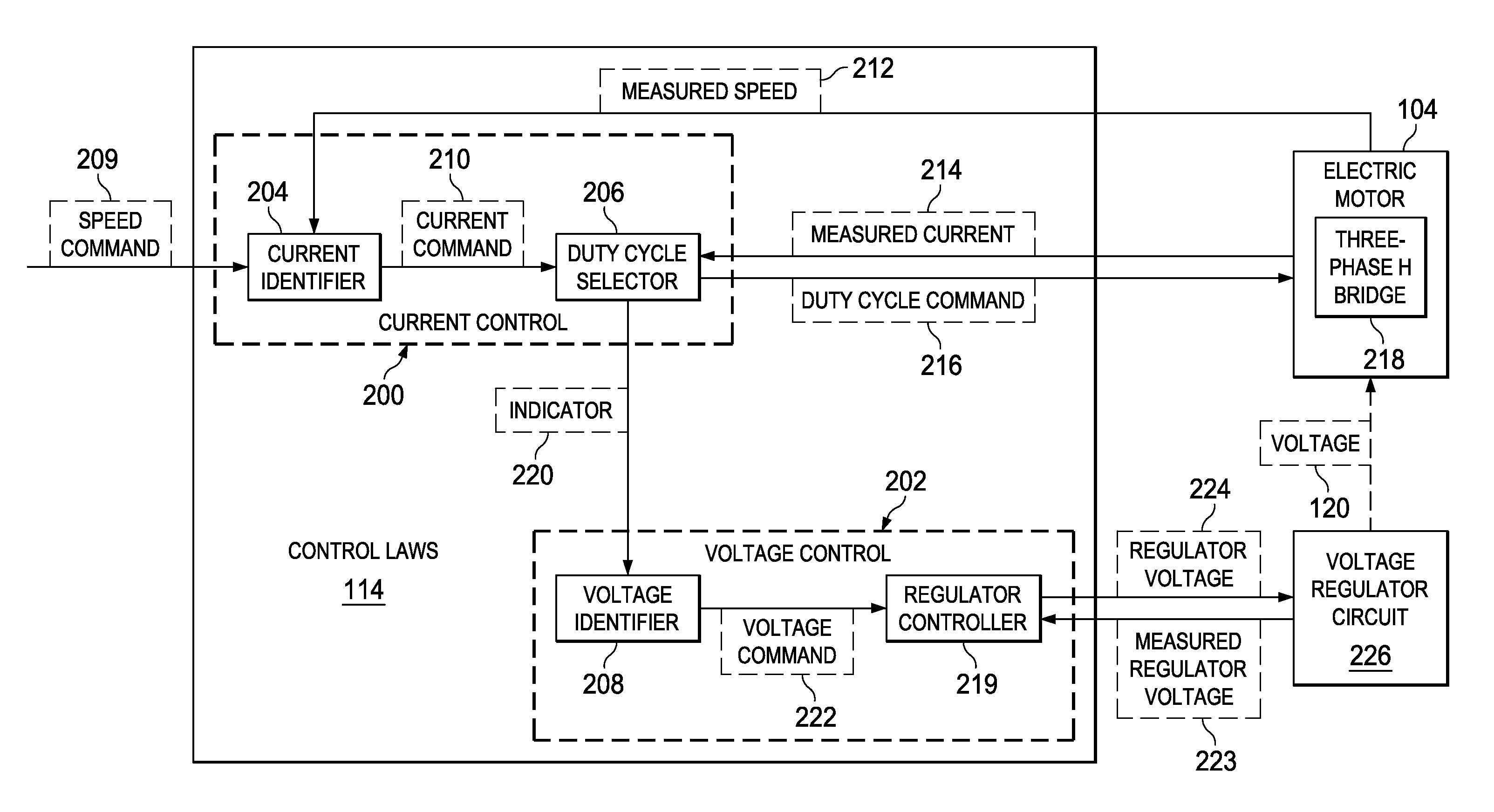
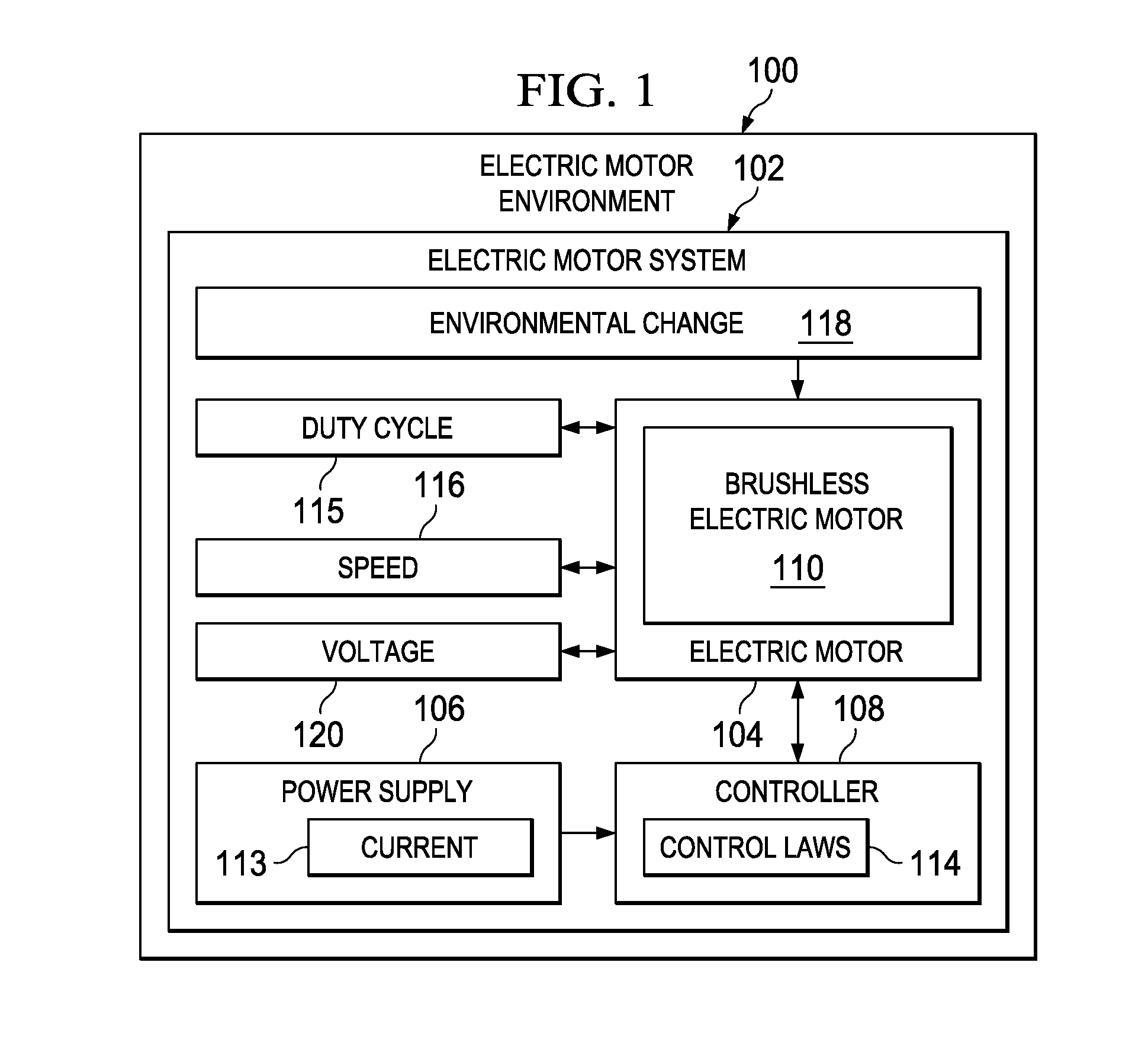
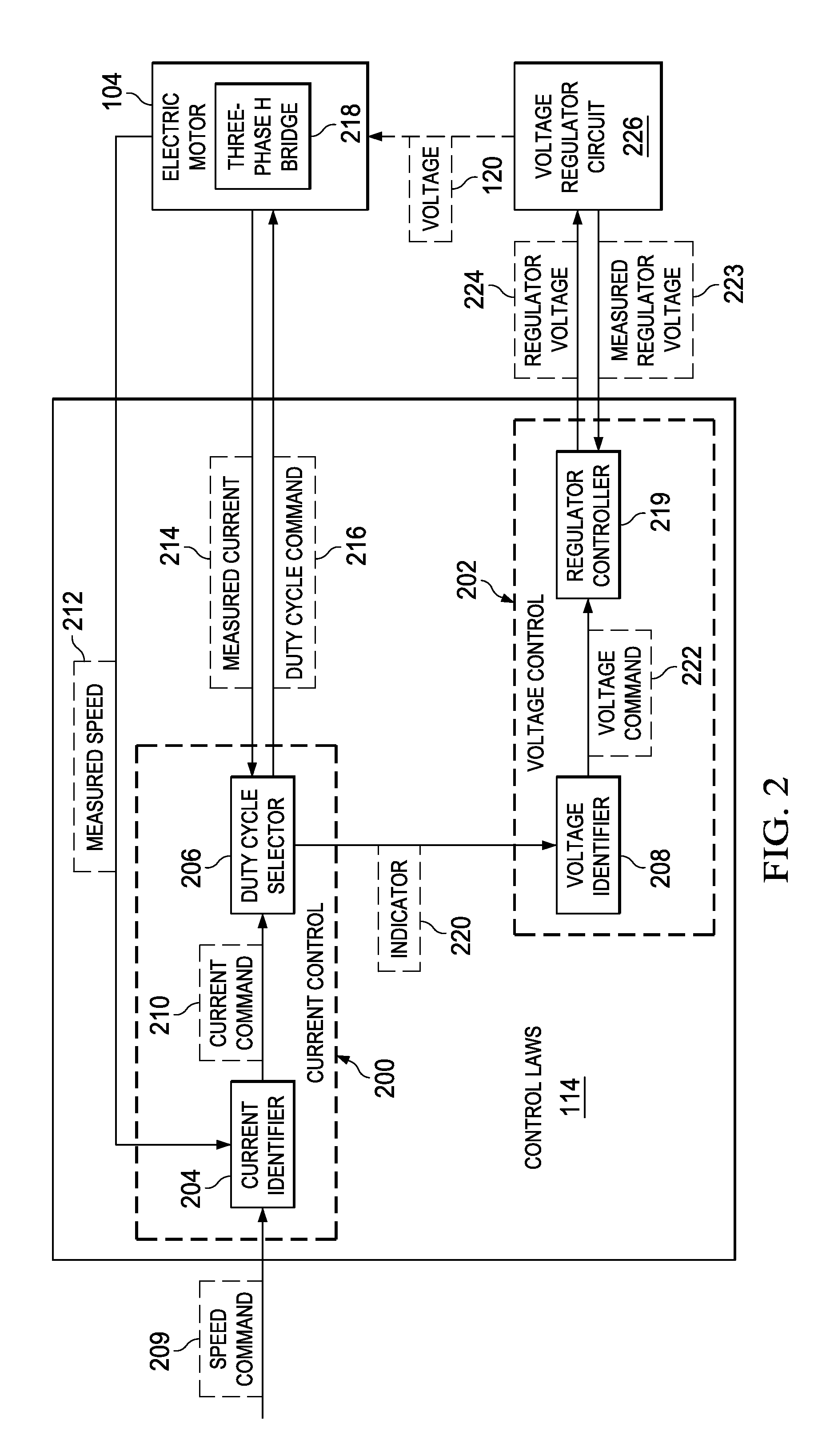
Active voltage controller for an electric motor
A method for controlling an electric motor. A desired speed is identified for the electric motor during operation of the electric motor. A voltage is identified to cause the electric motor to turn at the desired speed. The voltage is applied to the electric motor and actively controlled during operation of the electric motor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Motor controller
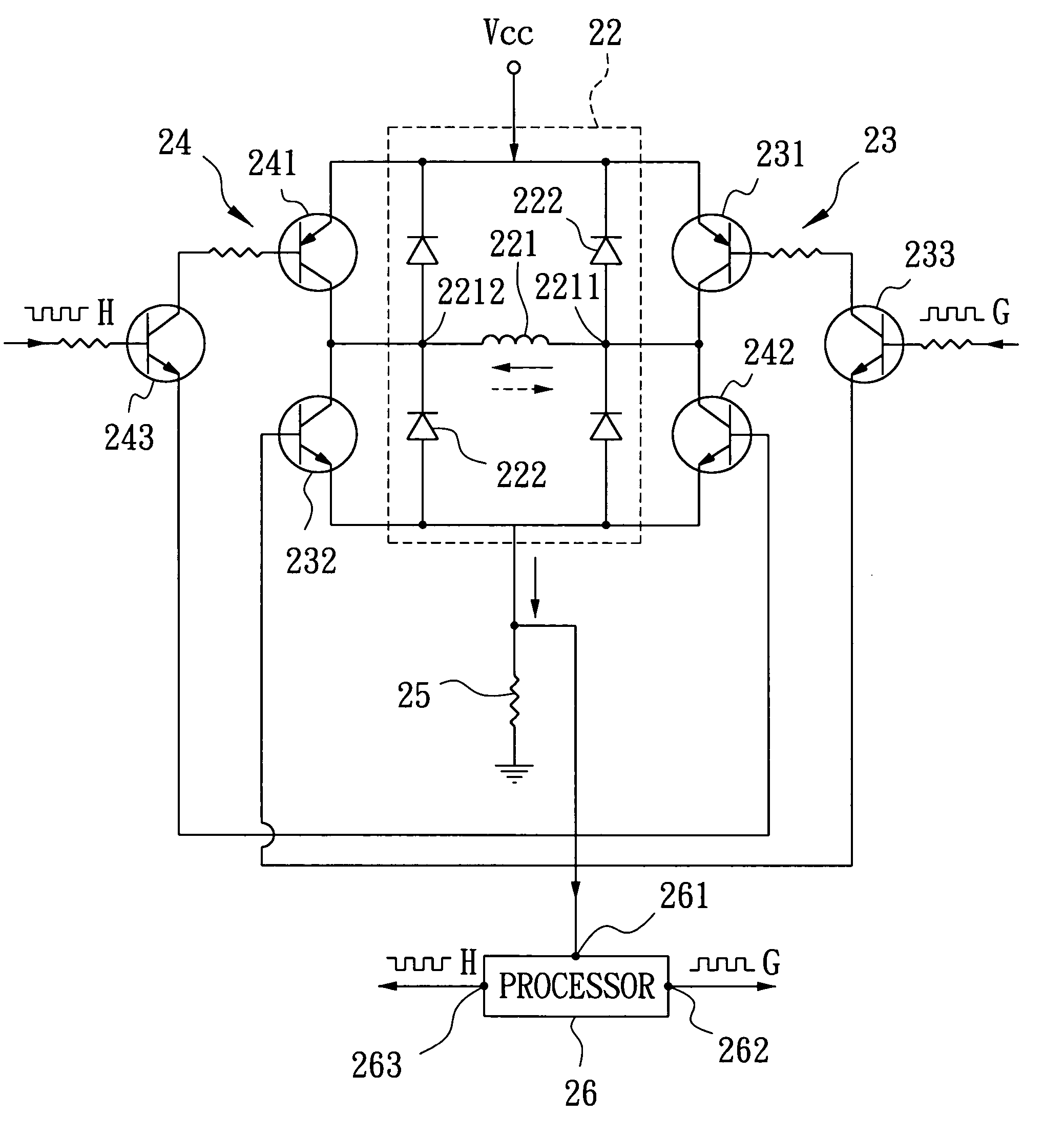
InactiveUS20070152612A1Accurate speed regulationAccurately control conduction and non-conduction of transistorsSingle motor speed/torque controlDynamo-electric converter controlElectricityVoltage drop
A motor controller includes a power source unit providing a direct current output, a drive unit including a drive coil, first and second transistor units, a voltage drop component, and a processor. The transistor units are coupled to the power source unit and the drive unit, and enable electricity to flow through the drive coil in a first direction when the first and the second transistor units are in conducting and non-conducting states respectively, and in an opposite second direction when the first and the second transistor units are in non-conducting and conducting states respectively. The voltage drop component has a first end coupled to the drive unit and a grounded second end. The processor is coupled to a junction of the drive unit and the voltage drop component, and provides first and second pulse-width-modulated signals to the first and second transistor units, respectively.
Owner:YEN SUN TECH CORP
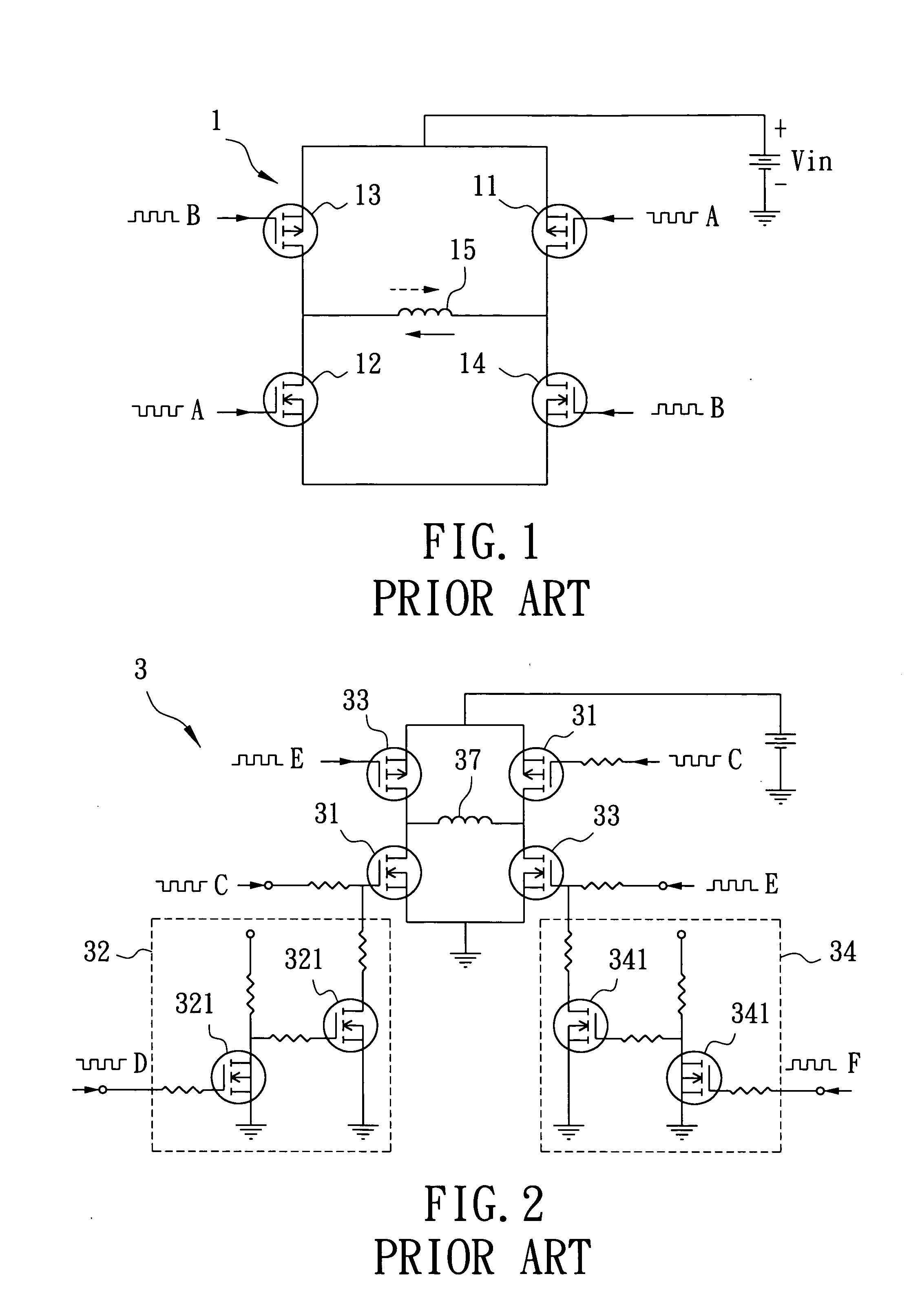
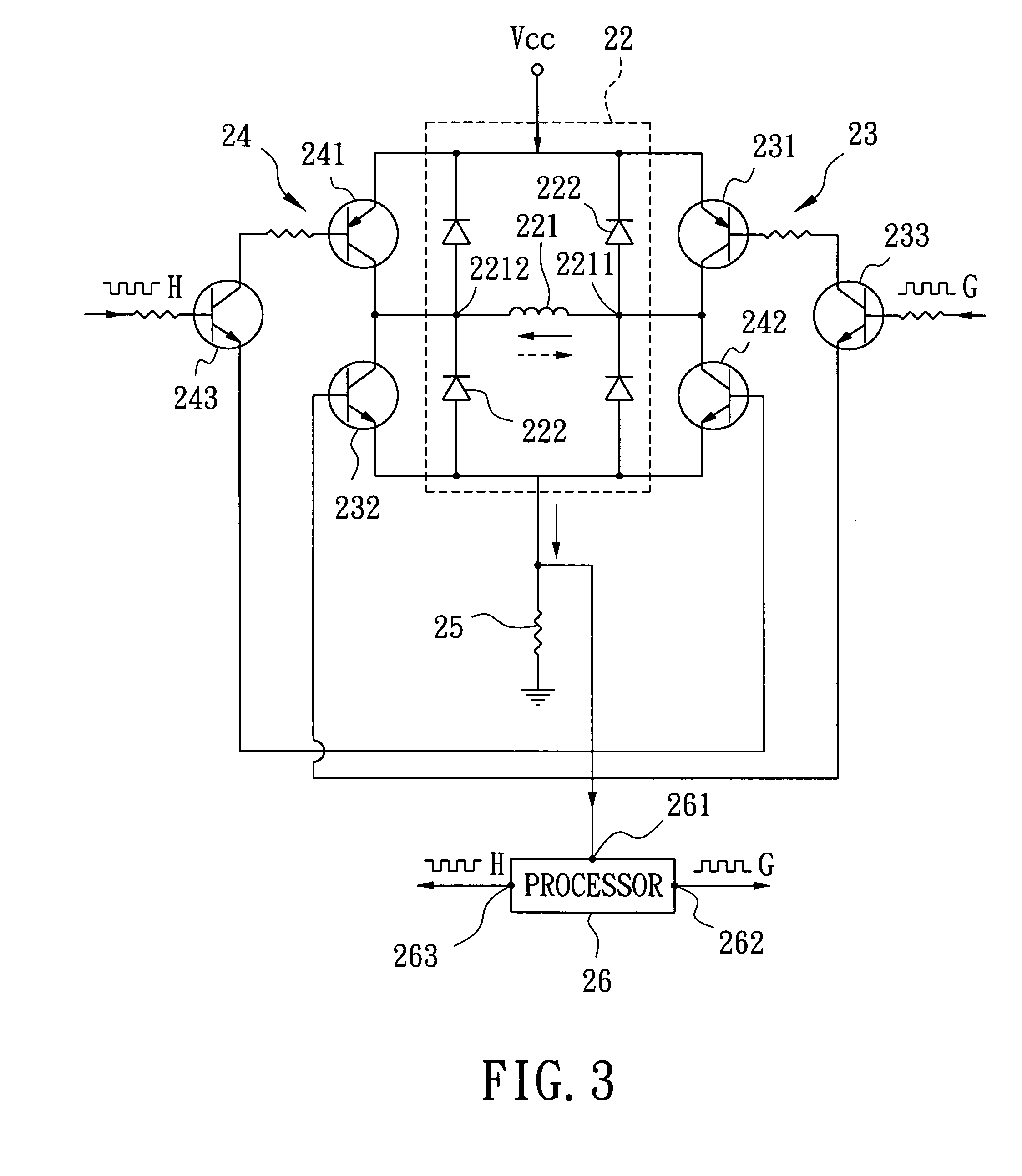
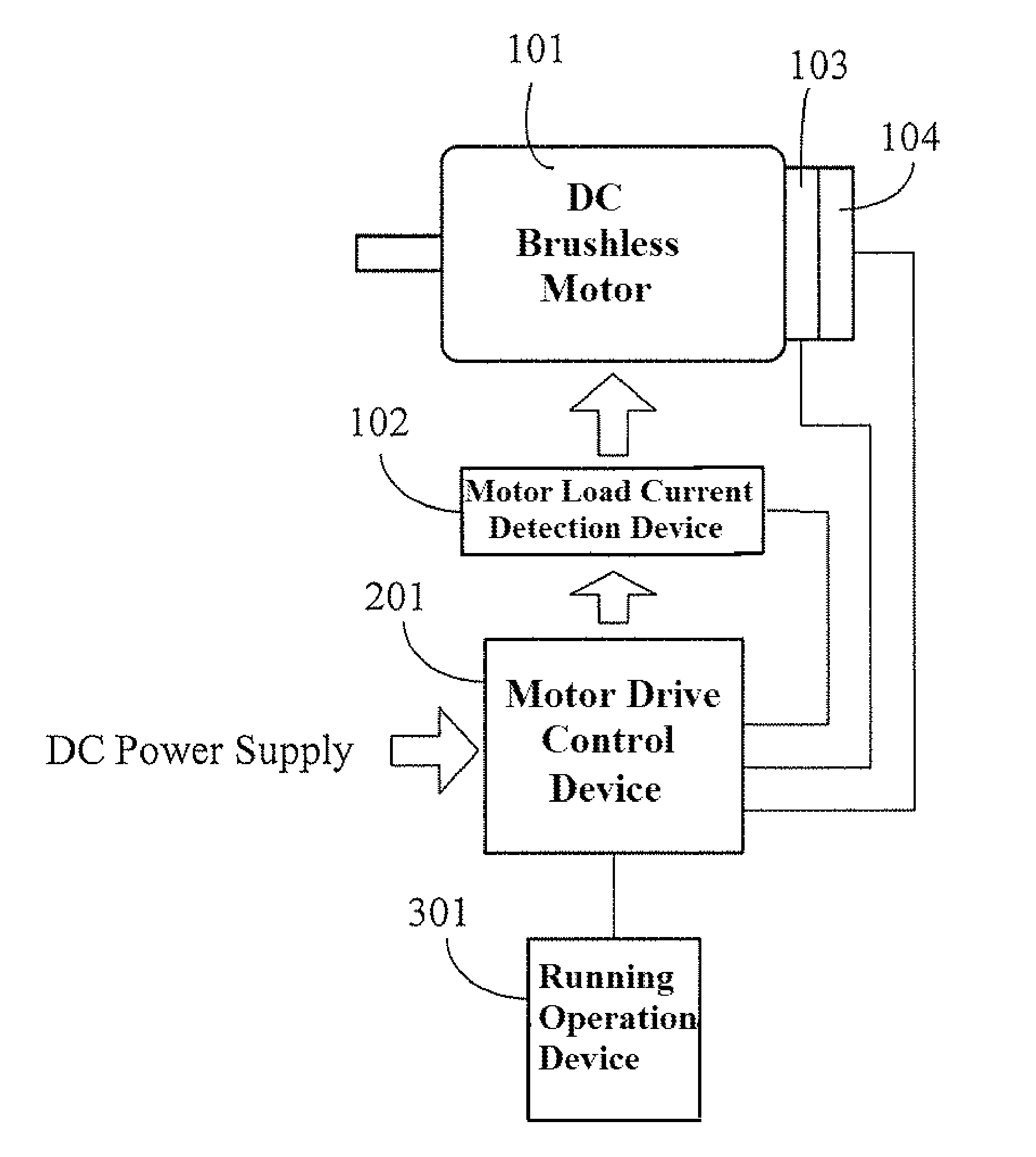
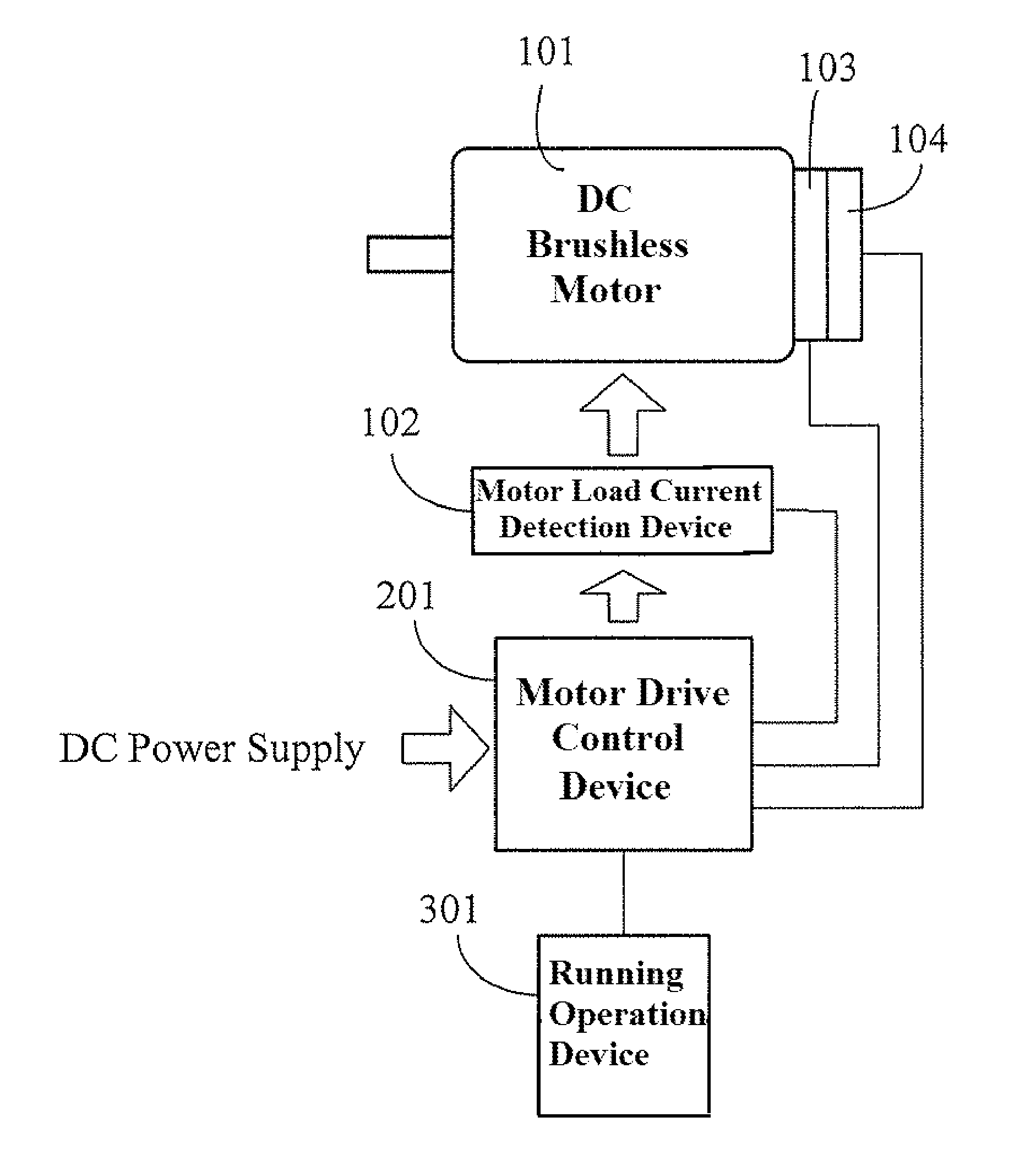
DC brushless motor drive circuit with speed variable-voltage
ActiveUS8288984B2Increase inputOvercome increased inductive impedanceTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersBrushless motorsMotor drive
For the present invention, under various running speeds statuses, the voltage supplied to the DC brushless motor is relatively increased or decreased on the basis of the internal setting of the motor drive control device according to the increased or decreased rotational output speed, so as to prevent the shortcoming of too much variation of the input impedance caused by the inductive reactance of the winding accordingly changed when the speed of the DC brushless motor is changed, specifically, to prevent the shortcoming of unable producing required torque resulting from the increased inductive reactance caused by increasing the rotational speed which makes the current value become too low when input by the original working voltage.
Owner:YANG TAI HER
Control circuit for a DC motor
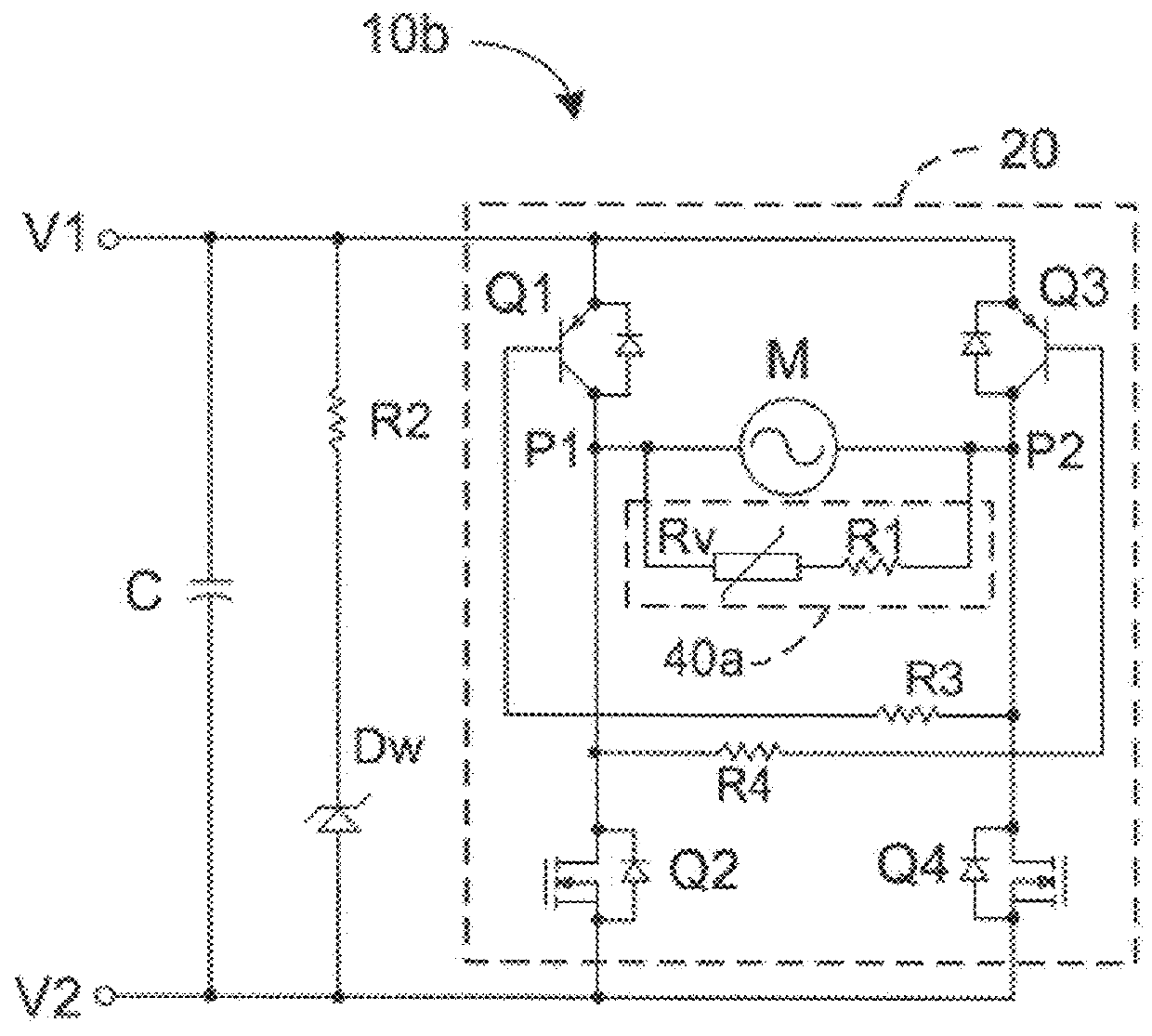
ActiveUS9385640B2Inhibit currentSingle motor speed/torque controlField or armature current controlControl circuitDC motor
A control circuit for a DC motor, has: a first and second input ports for connection to a DC source; a H-bridge driving circuit, having first and second switches connected in series between the input ports, and third and fourth switches connected in series between the input ports, a first output port between the first and second switches and a second output port between the third and fourth switches, and a shunt circuit and / or a blocking circuit. The motor is connected between the first and second output ports. The shunt circuit is connected between the first second output ports and has a resistance that will decrease in response to BEMF generated by the motor. The blocking circuit is connected in series with the motor between the output ports and has a resistance that increases in response to BEMF generated by the motor.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
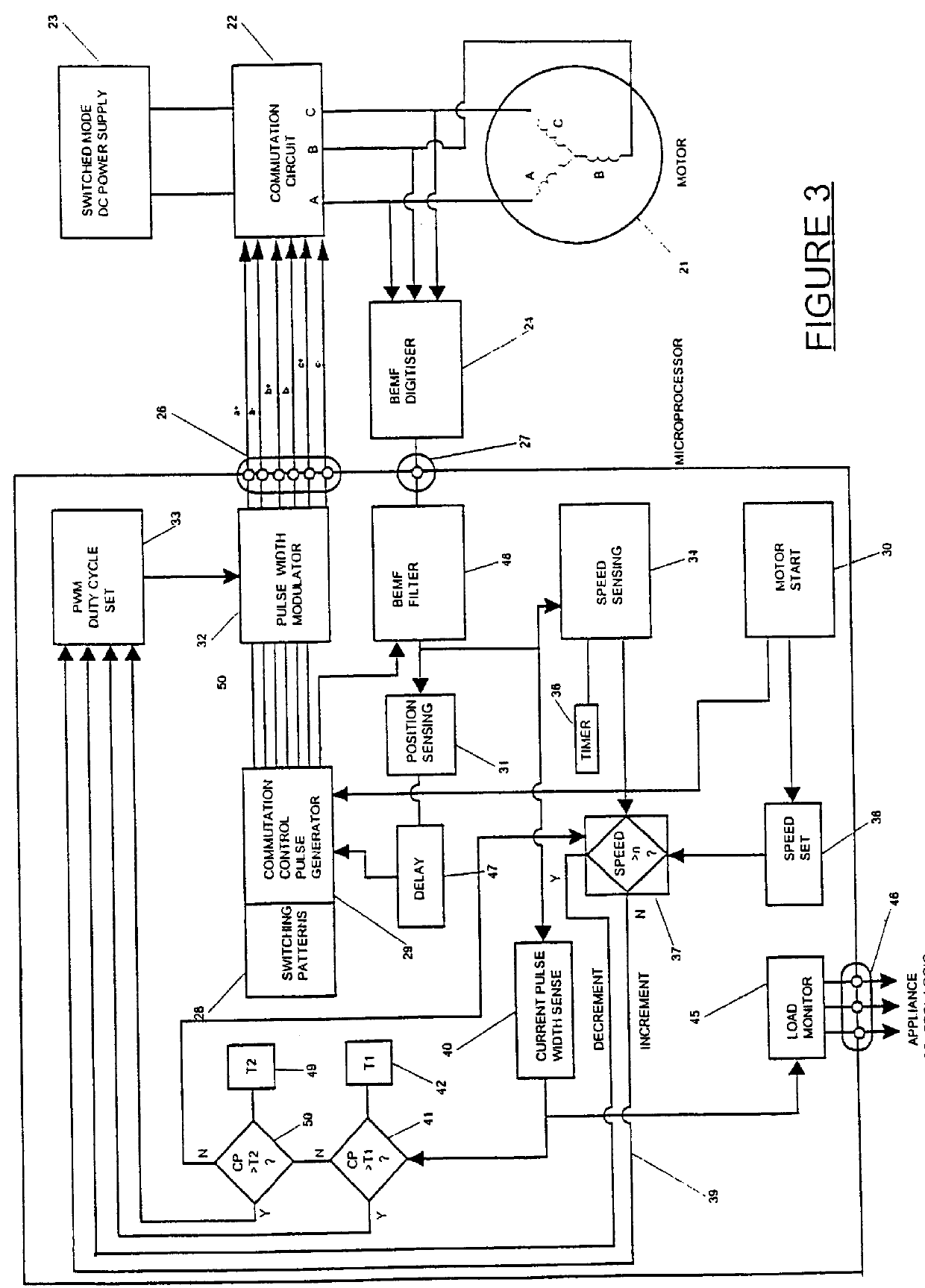
Brushless DC motor control
An electronically commutated brushless DC motor primarily for fractional horsepower applications of the type where at any instant one motor winding is unpowered and used to detect back EMF zero-crossings which information is used to initiate winding commutations. The duration of the pulse produced in this winding due to dissipation of stored energy by free-wheel diodes in parallel with the commutation devices after supply of current has been removed from this winding is used to provide a measure of motor current. This allows for simplified commutation device current limiting circuits and is available for control purposes which are a function of motor torque. There is also disclosed a method for maximizing useful power output by reducing the phase angle between the motor current and the back EMF. This is accomplished by introducing a delay in commutating the motor windings beyond the occurrence of each back EMF zero-crossing, with the delay being a function of the time between commutations.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
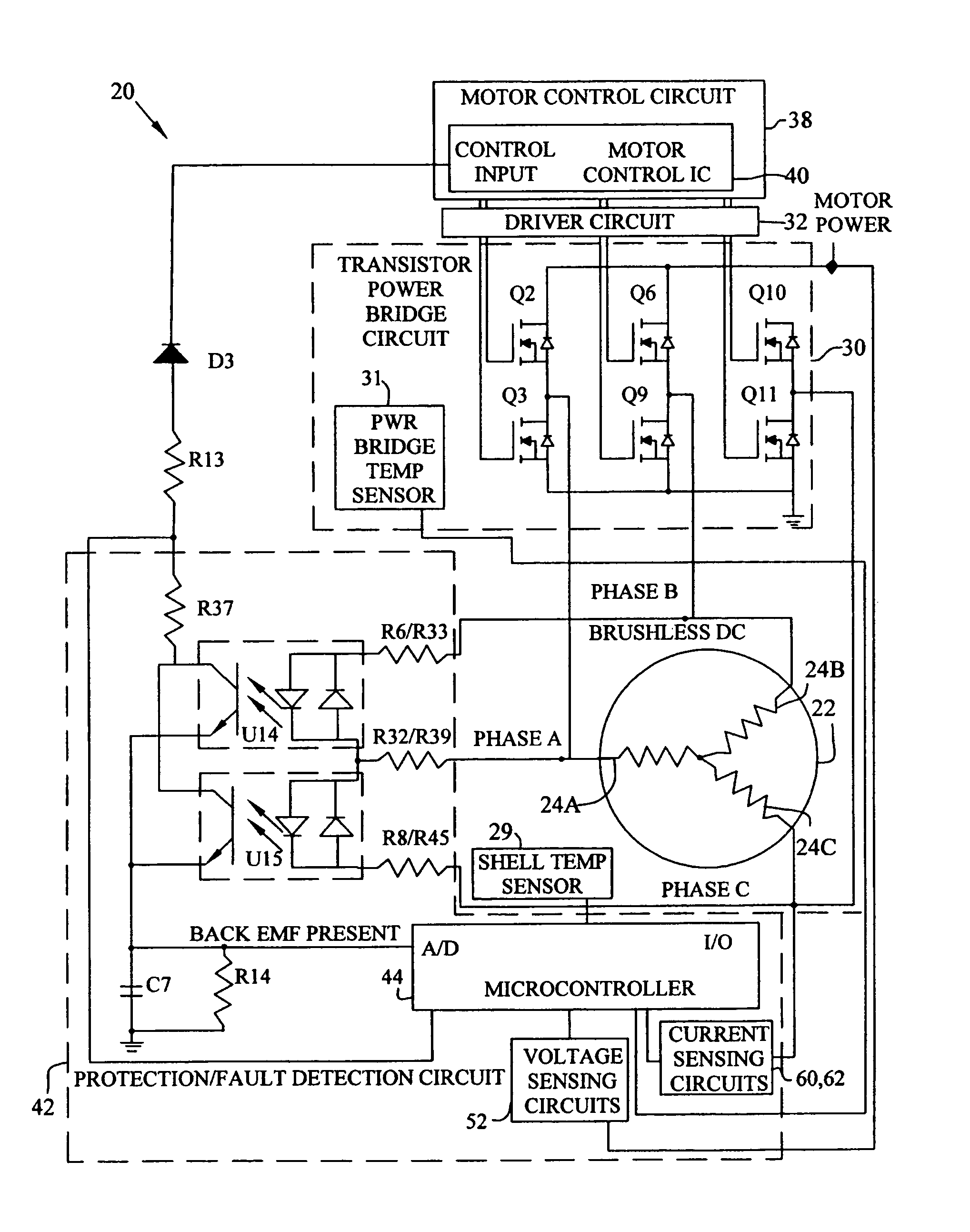
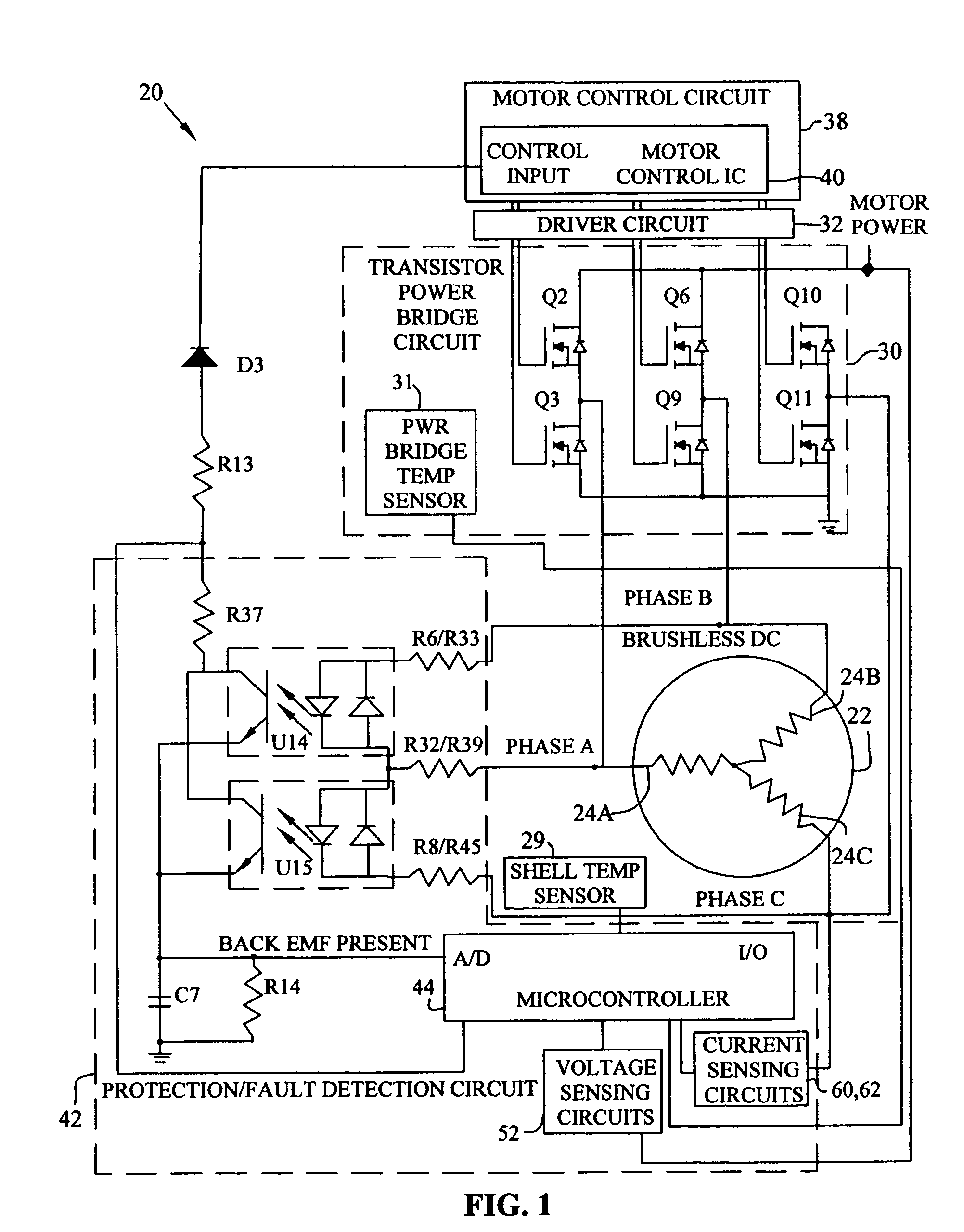
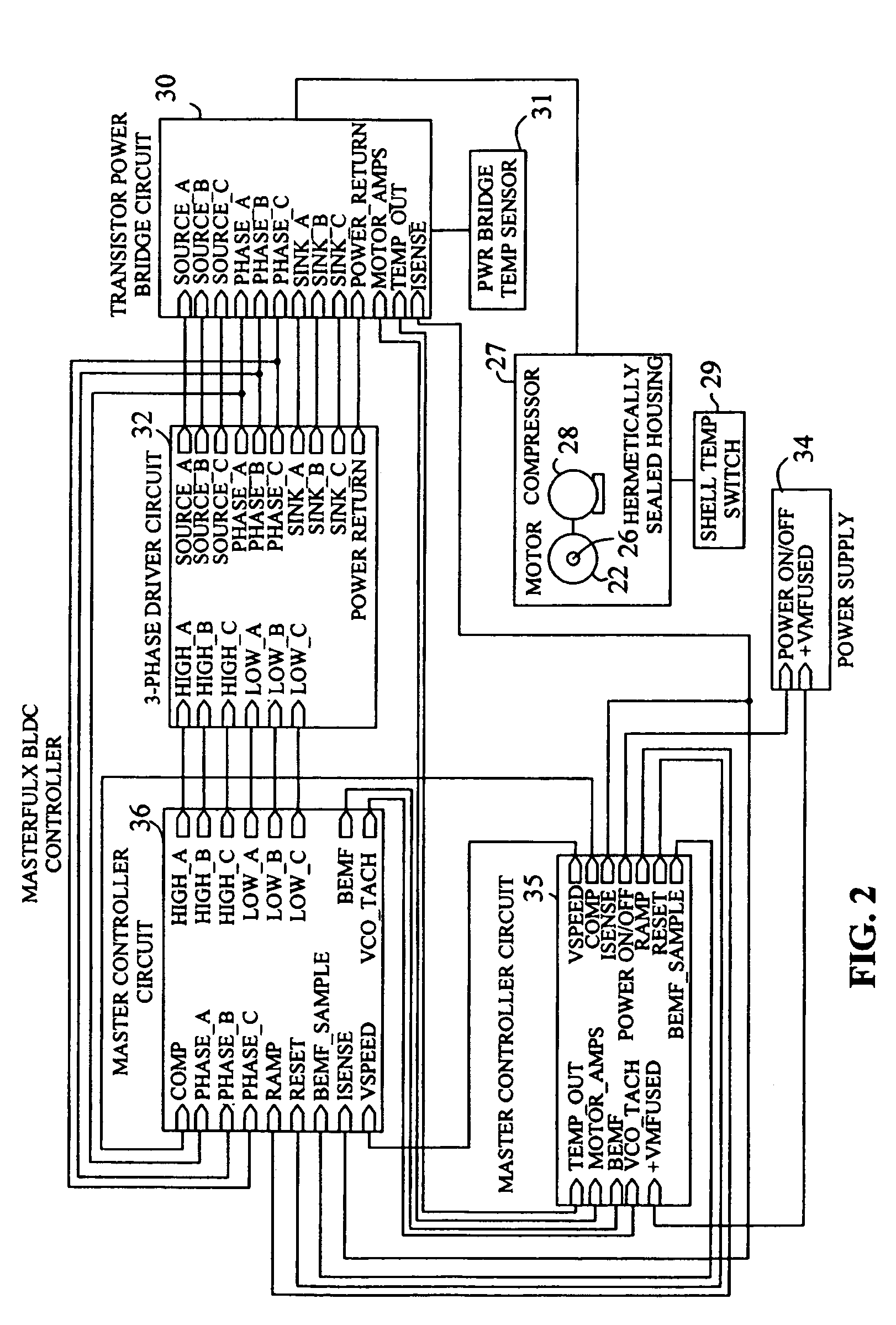
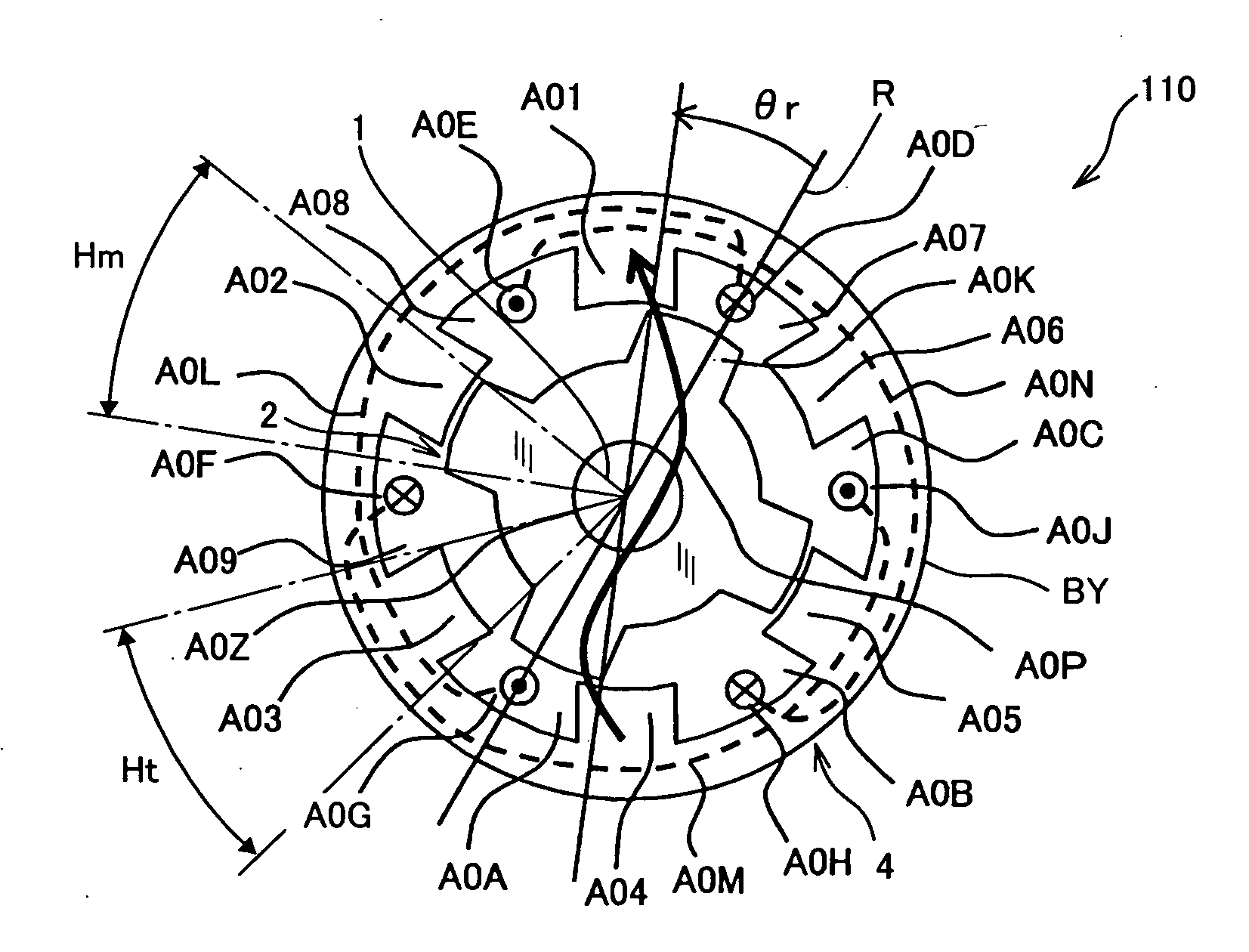
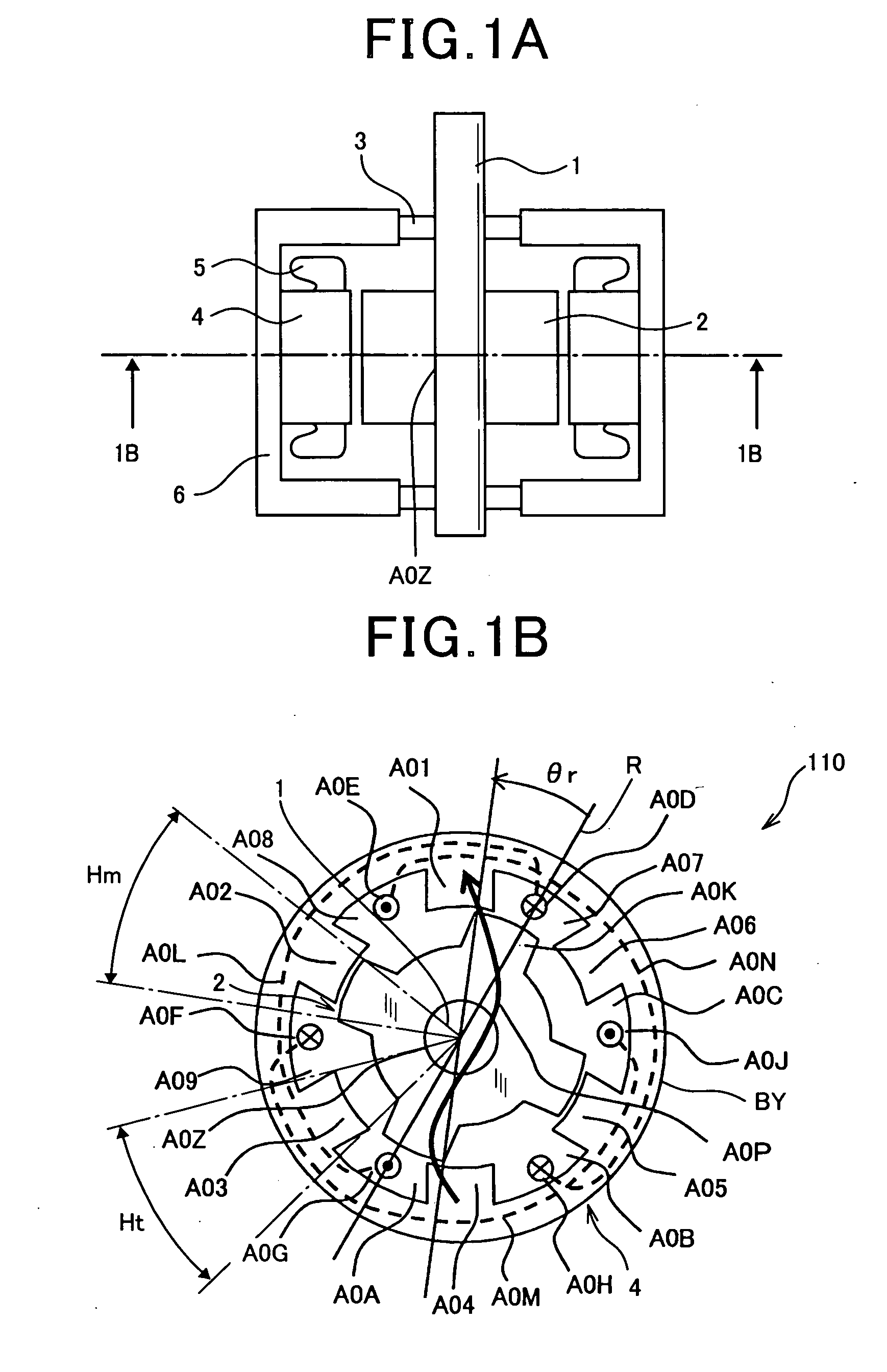
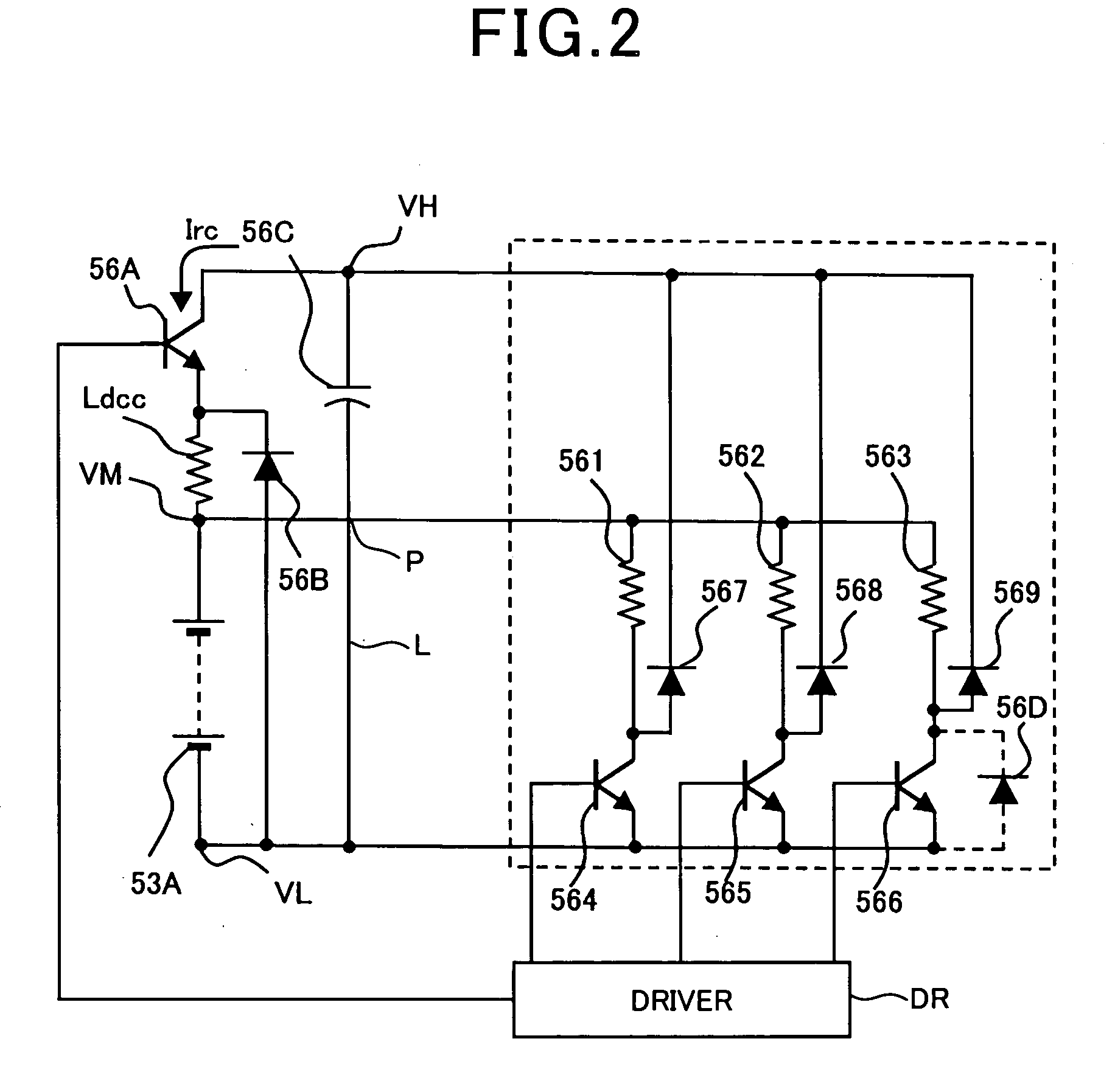
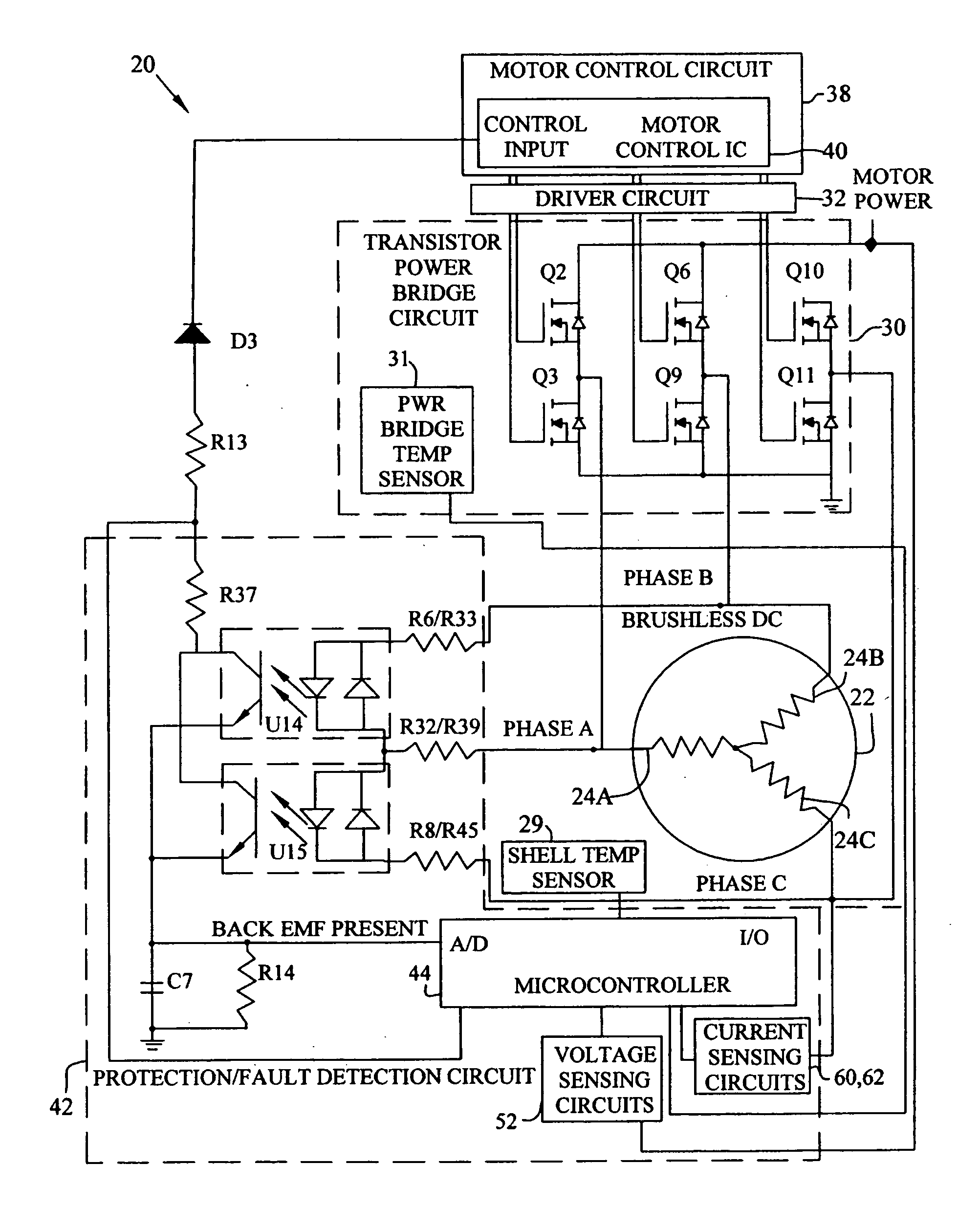
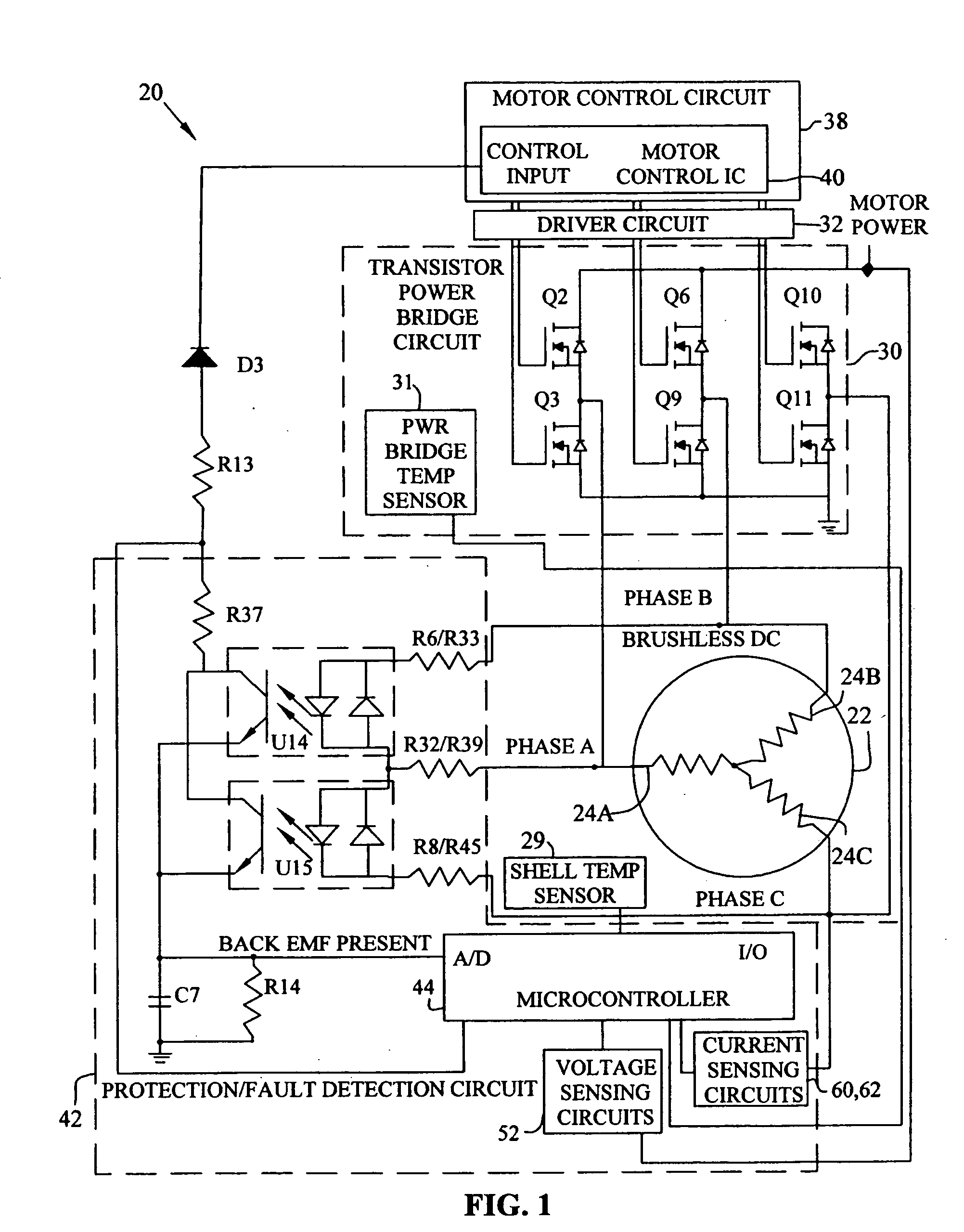
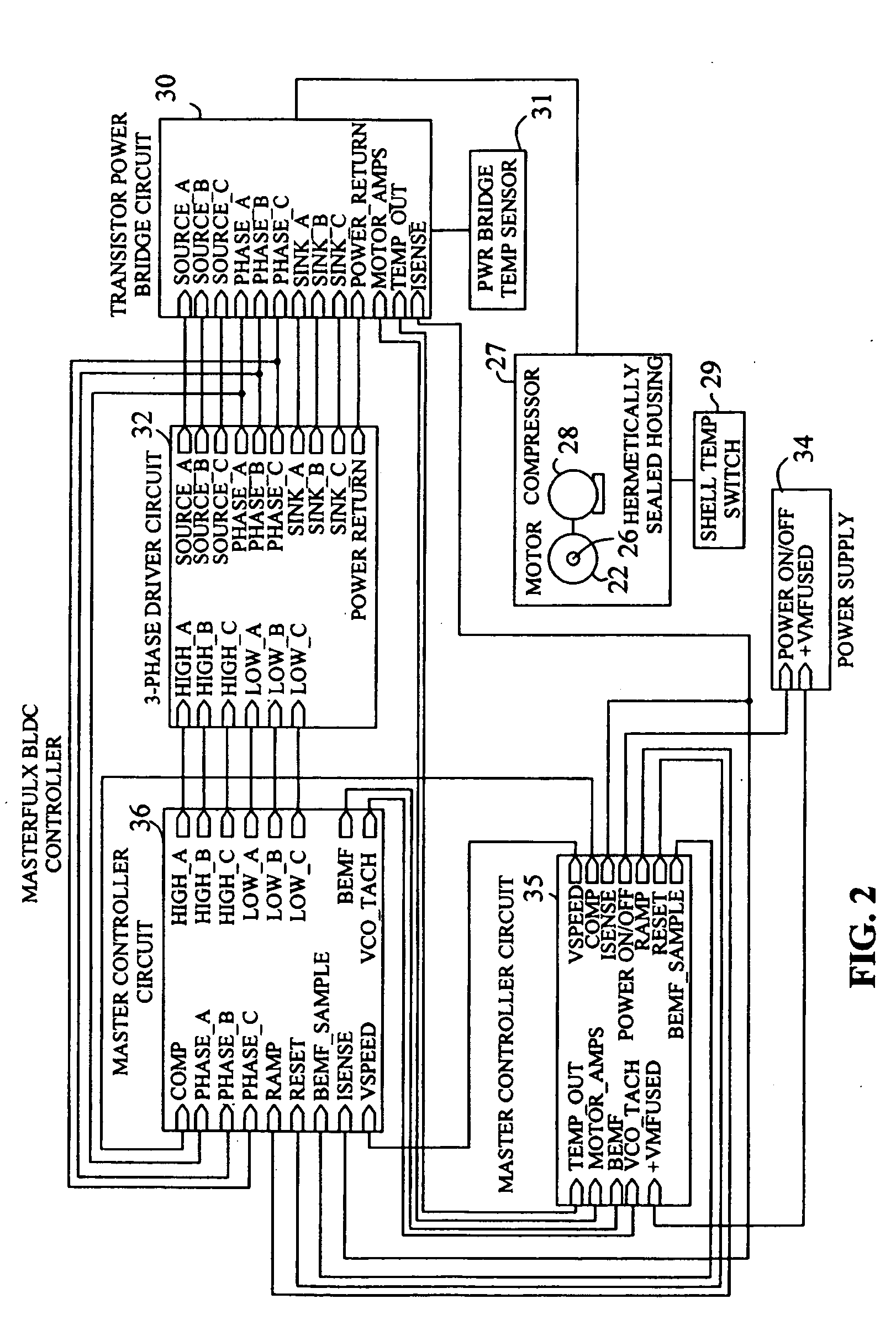
Brushless and sensorless DC motor control system with locked and stopped rotor detection
ActiveUS7042180B2Simple control methodEasily interfaceCommutation monitoringAC motor controlMotor speedDc motor control
A motor control system for a brushless and sensorless DC motor for driving a compressor, pump or other application, includes a protection and fault detection circuit for detecting a locked rotor and a rotor which has stopped because of lost rotor phase lock. The motor control system also includes an off-the-shelf motor control integrated circuit having an input for disabling power outputs to the motor phase coils. The protection and fault detection circuit uses a back EMF sampling circuit coupled to the motor phase coils and momentarily disables power to the motor phase coils, via the motor control integrated circuit input, to determine if the motor rotor is rotating. The system also monitors supply voltage, supply current, temperature, and motor speed limits to detect faults and protect system components.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Reluctance motor with improved stator structure
InactiveUS20100123426A1Reduce efficiency of motorHigh cost of controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlReluctance motorEngineering
Owner:DENSO CORP
Brushless and sensorless DC motor control system with locked and stopped rotor detection
ActiveUS20050029976A1Easy to modifyEasily interfaceCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlMotor speedDc motor control
A motor control system for a brushless and sensorless DC motor for driving a compressor, pump or other application, includes a protection and fault detection circuit for detecting a locked rotor and a rotor which has stopped because of lost rotor phase lock. The motor control system also includes an off-the-shelf motor control integrated circuit having an input for disabling power outputs to the motor phase coils. The protection and fault detection circuit uses a back EMF sampling circuit coupled to the motor phase coils and momentarily disables power to the motor phase coils, via the motor control integrated circuit input, to determine if the motor rotor is rotating. The system also monitors supply voltage, supply current, temperature, and motor speed limits to detect faults and protect system components.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
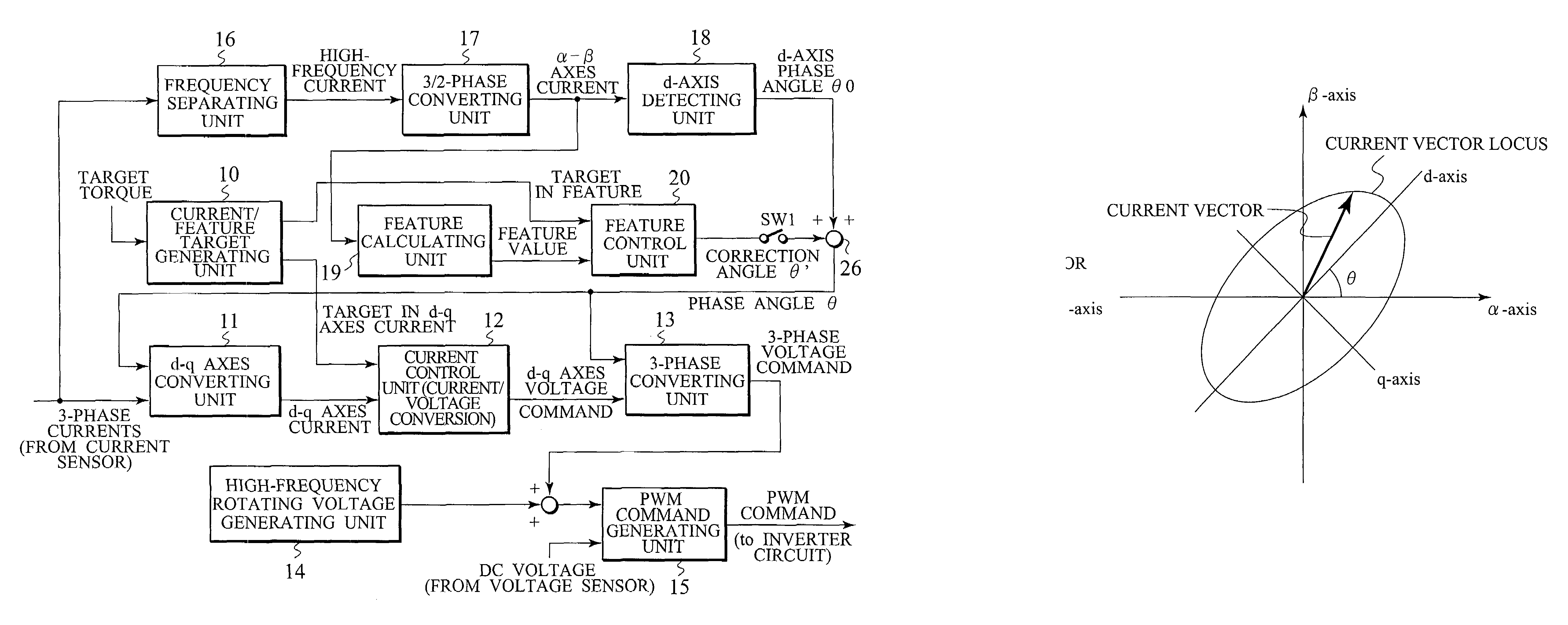
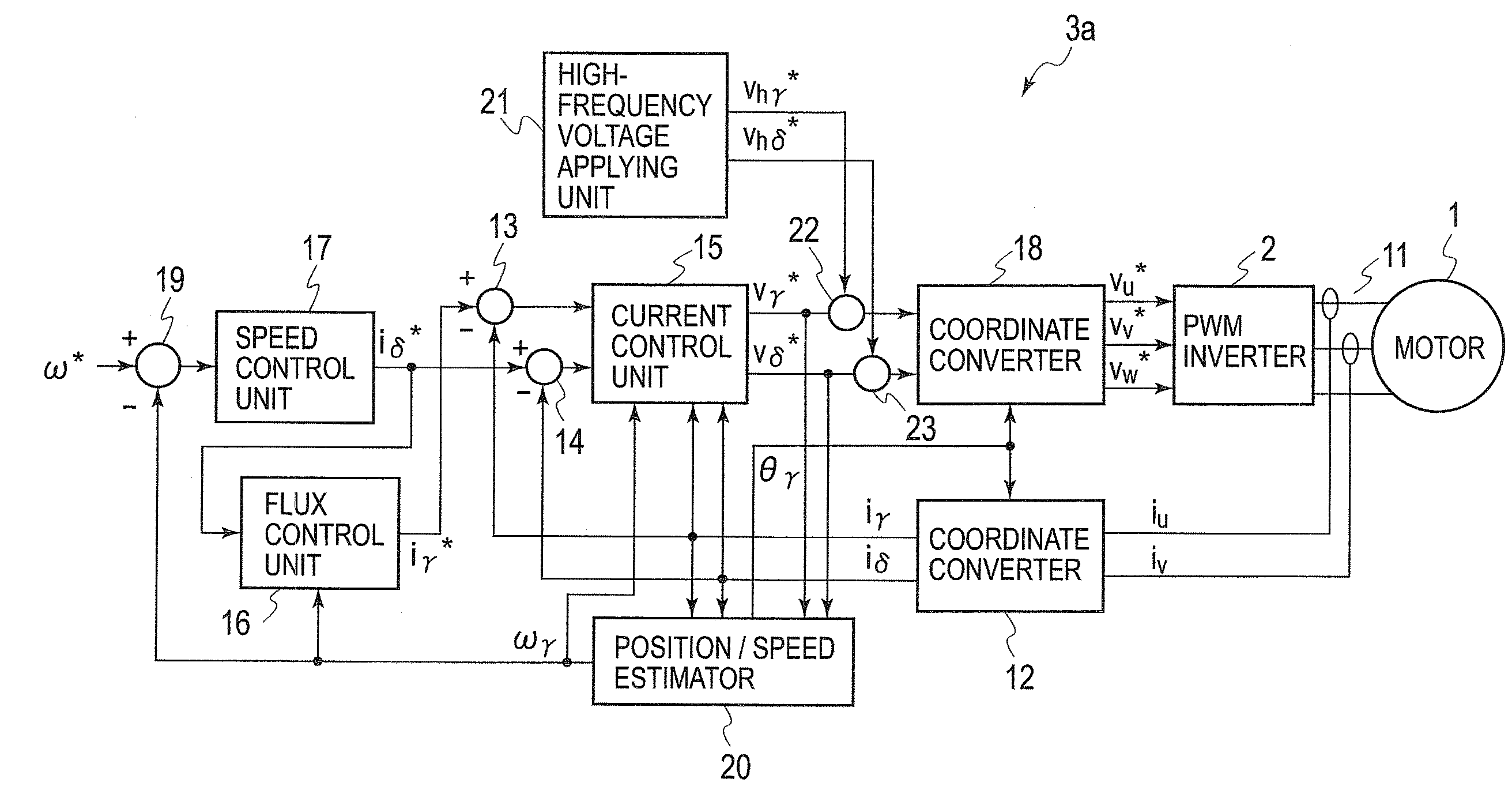
Control device for electric motor
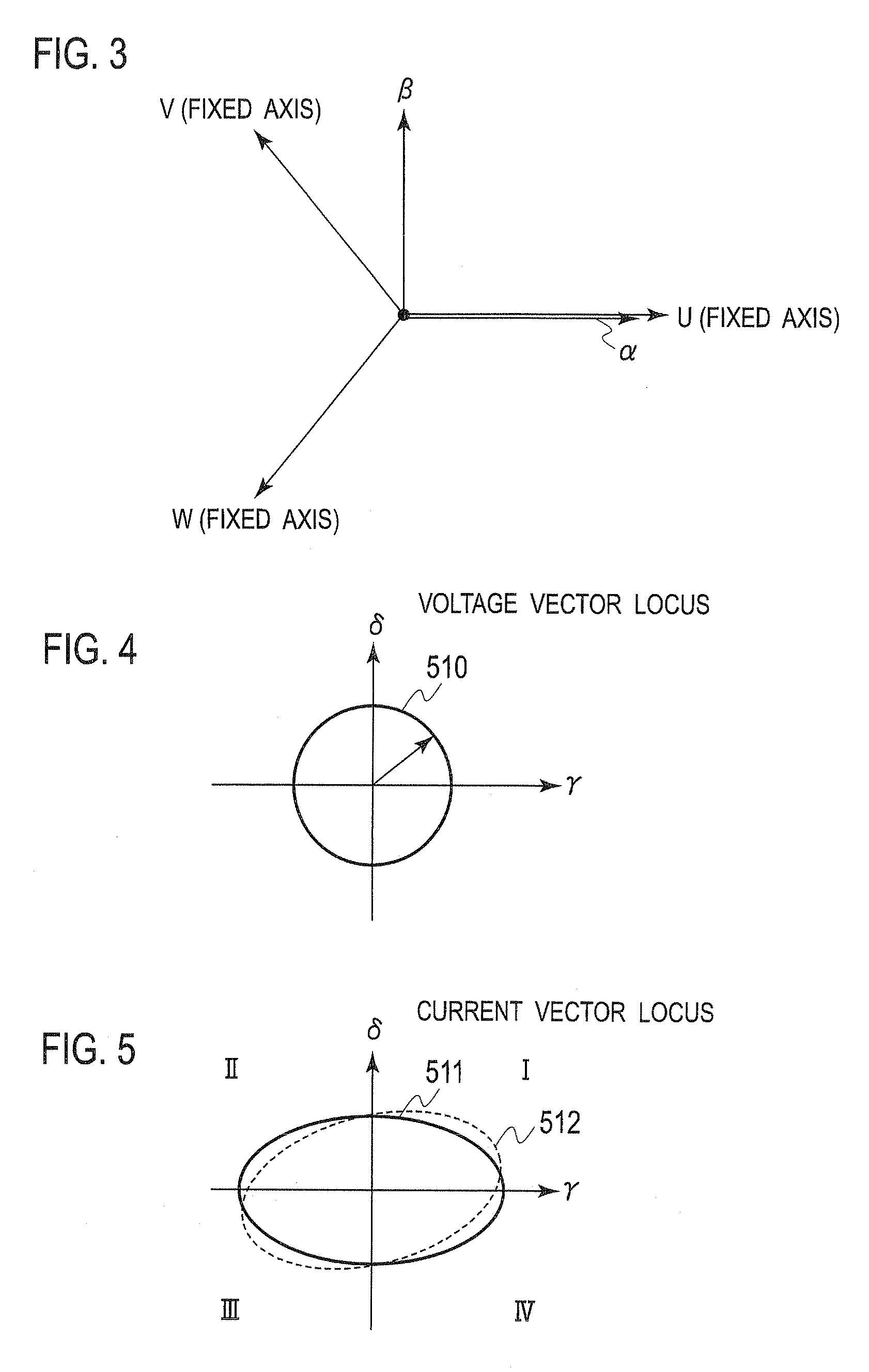
ActiveUS7005828B2Improve artSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlDriving currentAcquired characteristic
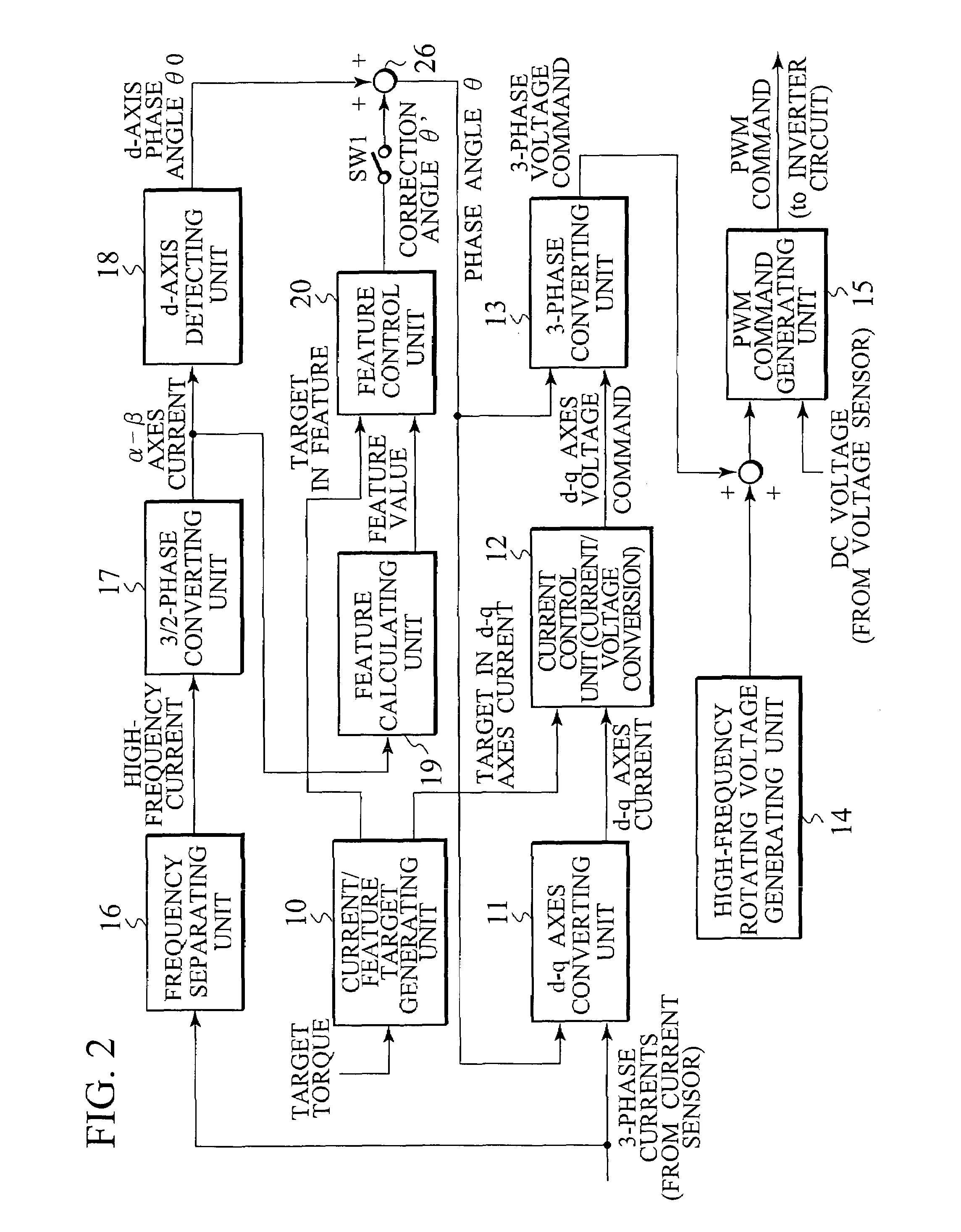
Corresponding to a target torque, the control device calculates a target value of a feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus and the length of the short axis and further superimposes a superimposed current on a drive current for the motor, the superimposed current having a frequency different from the frequency of the drive current. Further, the control device detects an actual value of the feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus of the superimposed current and the length of the short axis of the same and finally detects a phase angle of the motor based on the target value and the actual value for the feature. The manipulation of a detecting phase is performed by feedback of a feature obtained by the magnitude of the superimposed current. That is, when the actual feature is more than the target value, the detecting phase is advanced. Conversely, when the actual feature is less than the target value, the detecting phase is delayed.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Unconnected Motor, Drive Control Device Thereof, And Electric Power Steering Device Using Drive Control Device Of Unconnected Motor
InactiveUS20080067960A1Constant gainIncreased current consumptionMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectric power steeringControl signal
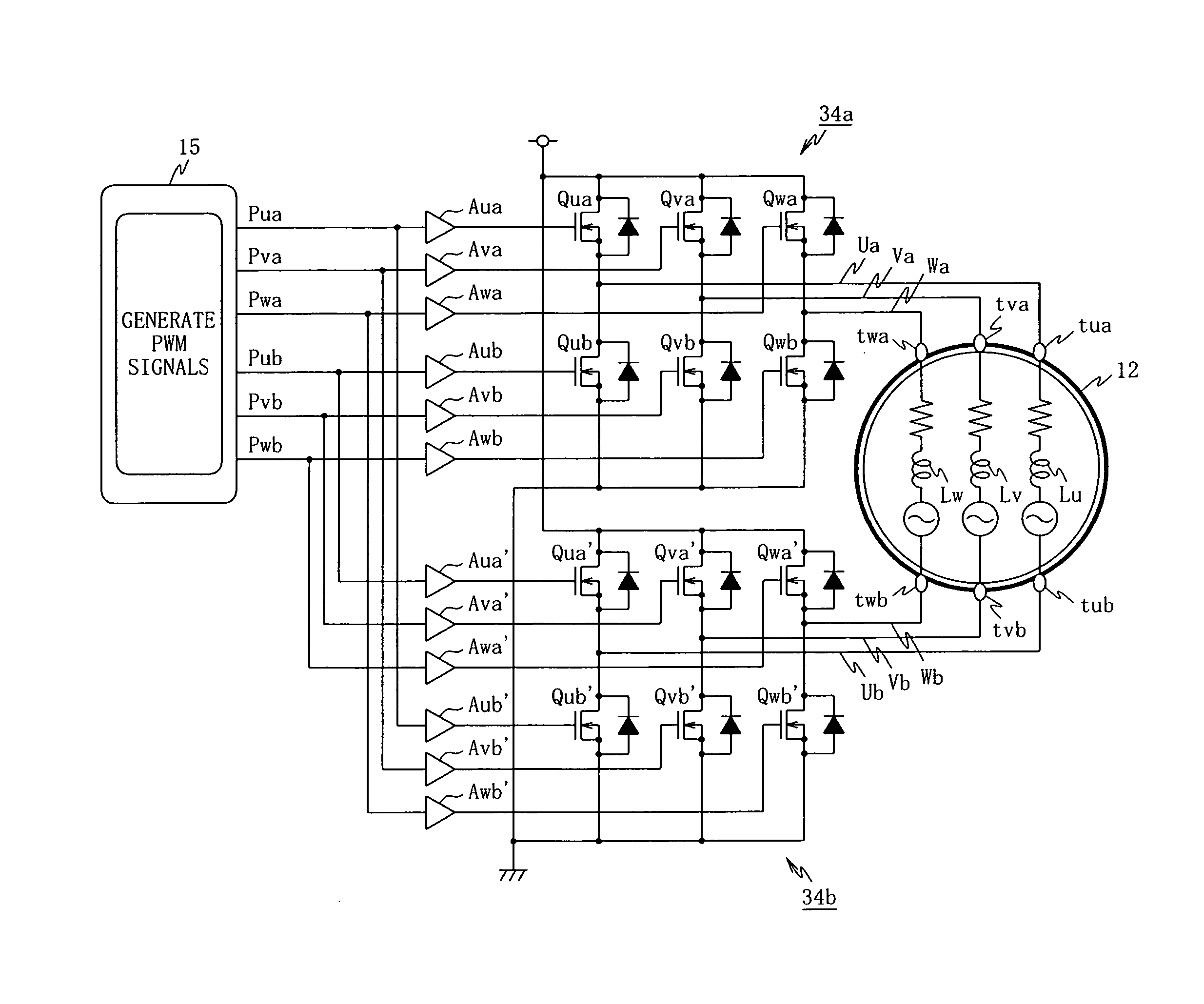
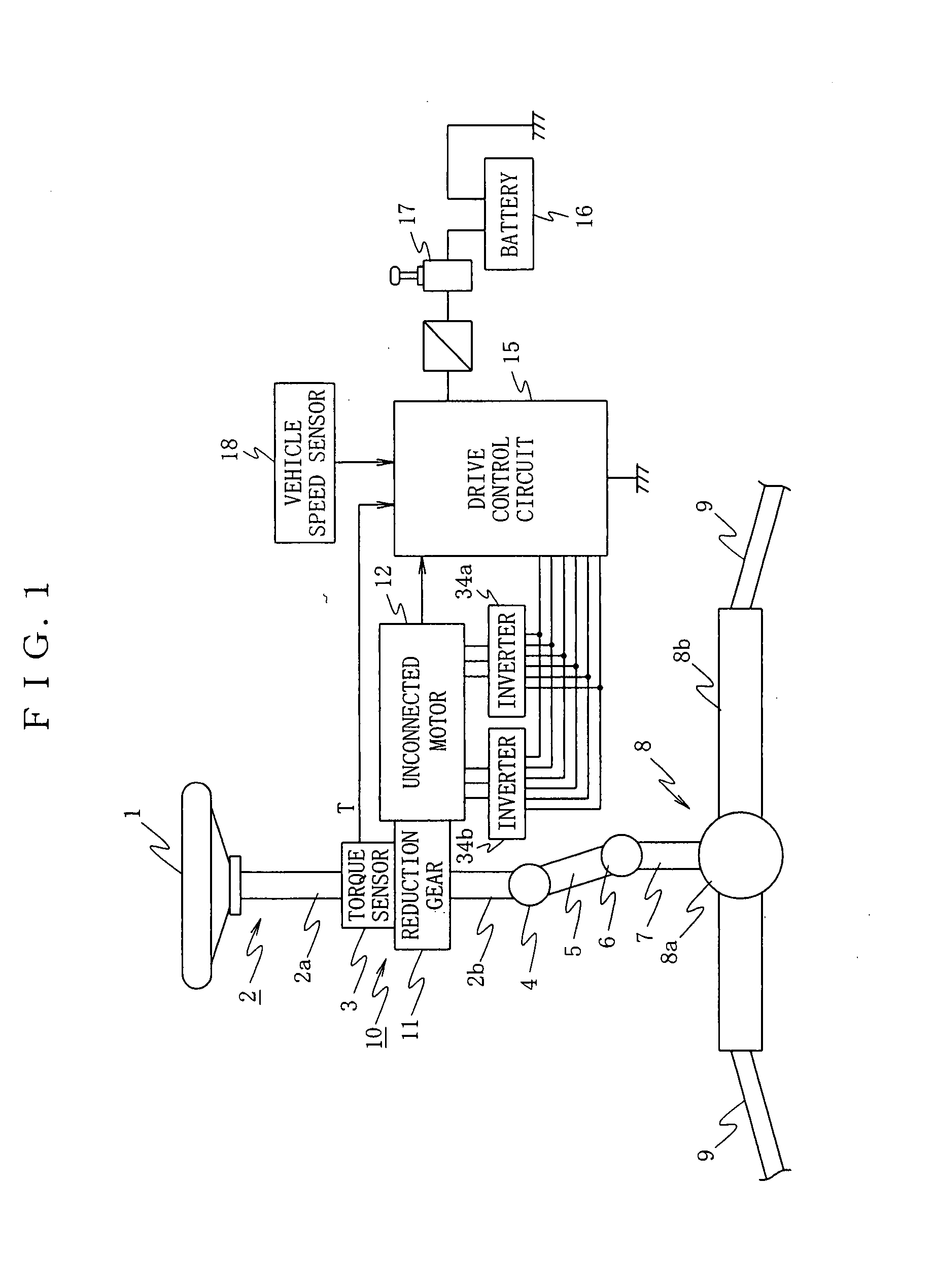
A drive control device of an unconnected motor capable of resolving power shortage and increasing motor output without using a boost circuit, and an electric power steering device using the unconnected motor. The drive control device comprises an unconnected motor (12) having a rotor in which permanent magnets are allocated and a stator opposing the rotor, in which armature winding Lu to Lw of a plurality (N number) of phases are independently arranged, a pair of inverter circuits (34a, 34b) individually connected to both ends of each armature winding, and a drive control circuit (15) which drives the pair of inverter circuits (34a, 34b) with a predetermined number (e.g. 2N) of PWM drive control signals.
Owner:NSK LTD
Multiple power source system and apparatus, motor driving apparatus, and hybrid vehicle with multiple power source system mounted thereon
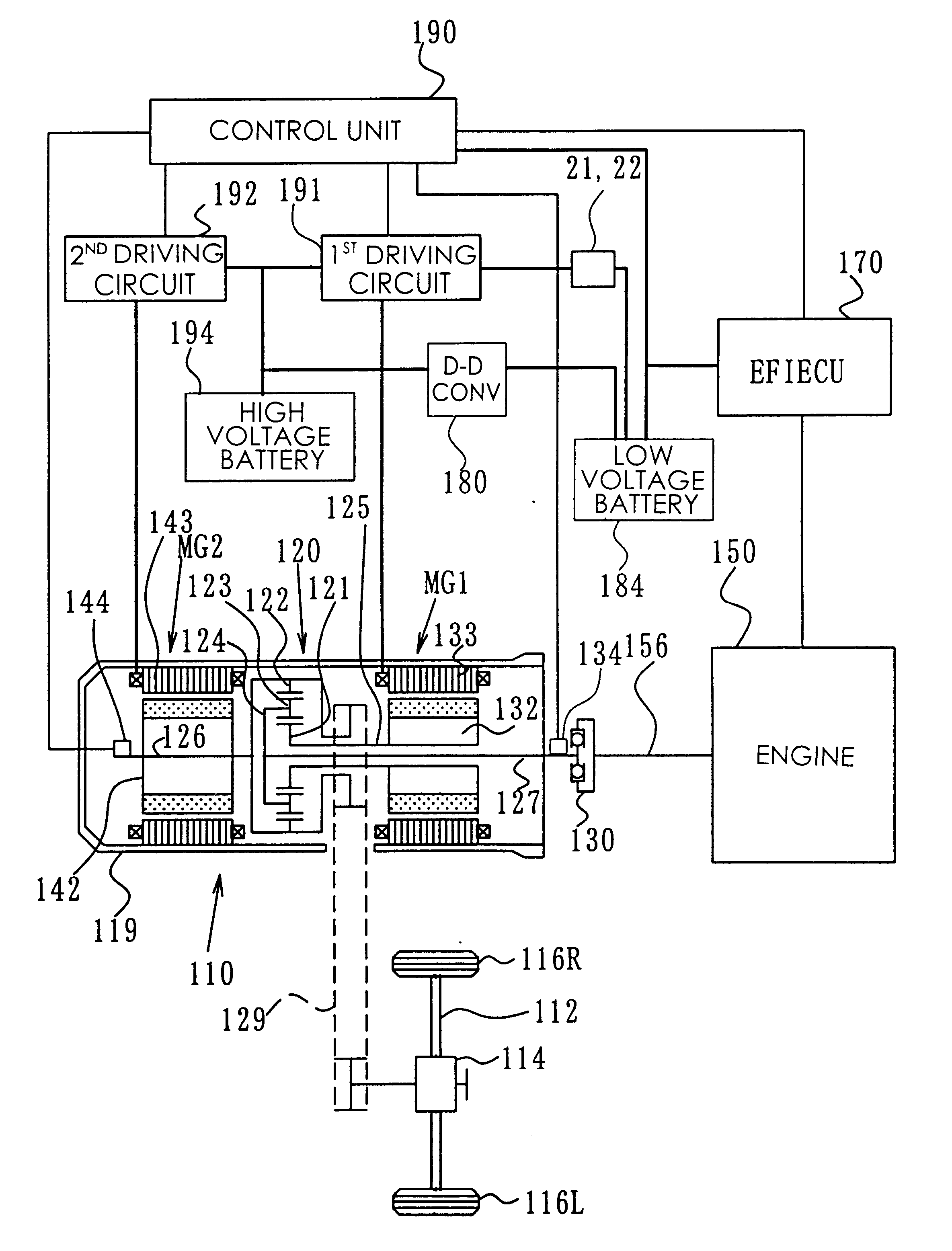
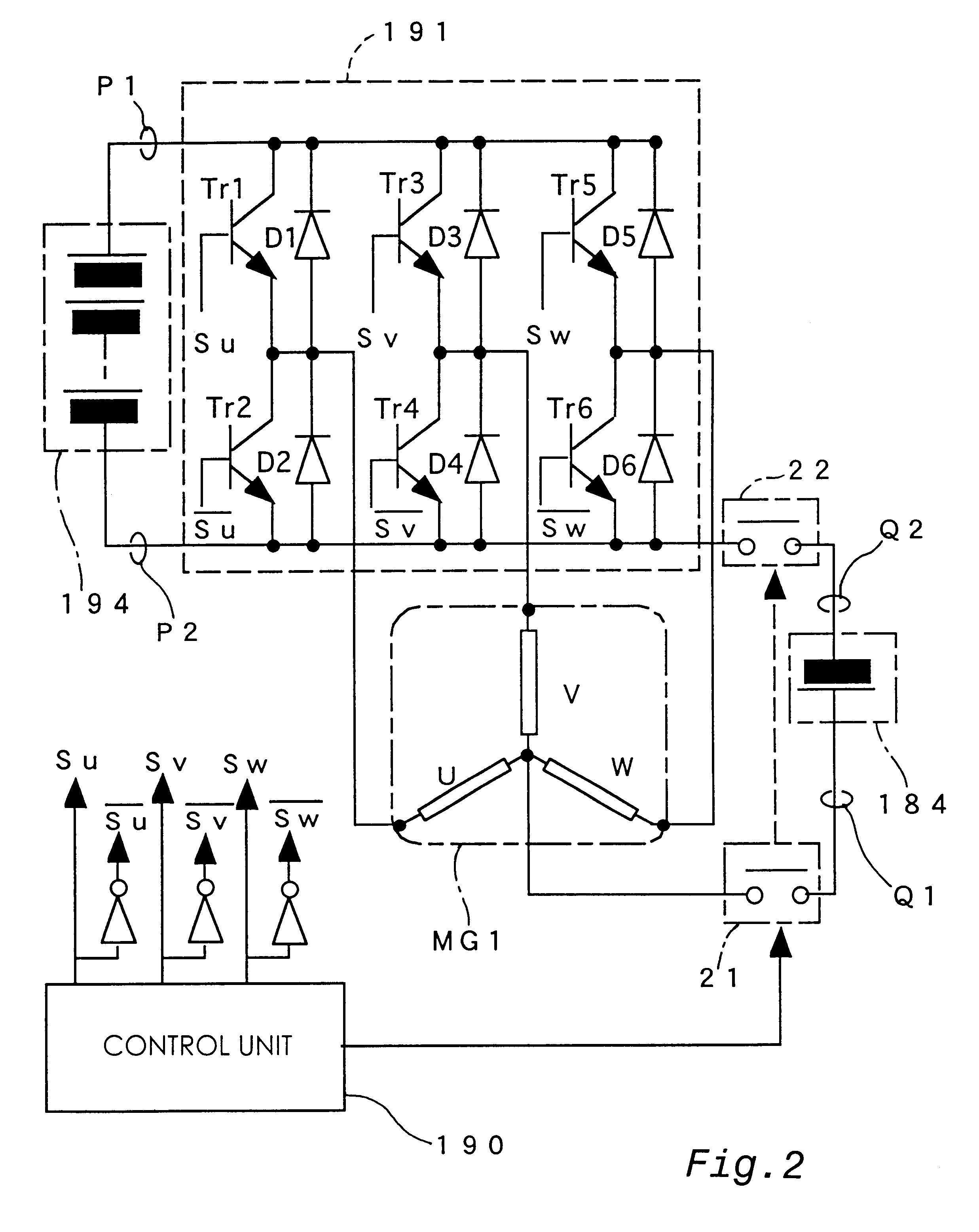
InactiveUS6476571B1Simple structureSimplify structure of apparatusSingle motor speed/torque controlAc-dc conversionElectrical batteryLow voltage
In a multiple power source system of the present invention that has an inverter connected to a reactance, such as three-phase coils in a motor, a high voltage battery is connected with a low voltage battery via one transistor (Tr2) and one diode (D2) included in the inverter and one phase coil (U-phase coil) of the three-phase motor. The transistor Tr2 is turned on to make the electric current flow from the low voltage battery to the U-phase coil. The transistor Tr2 is subsequently turned off at a preset timing, so that the electric energy accumulated in the reactance, that is, the U-phase coil, flows through the diode D1 into the high voltage battery and thereby charges the high voltage battery. This arrangement enables the charging process from the low voltage battery to the high voltage battery without any complicated circuit structure for the voltage step-up. The three-phase motor may be unipolar driven with transistors connected to one side of the inverter. The arrangement of the present invention does not require any complicated structure, which undesirably increases the size of the multiple power source system, in order to ensure mutual supplement of the electric energy between electric systems having a large difference in voltage, for example, an electric system for driving a hybrid vehicle and an electric system for its control circuit.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
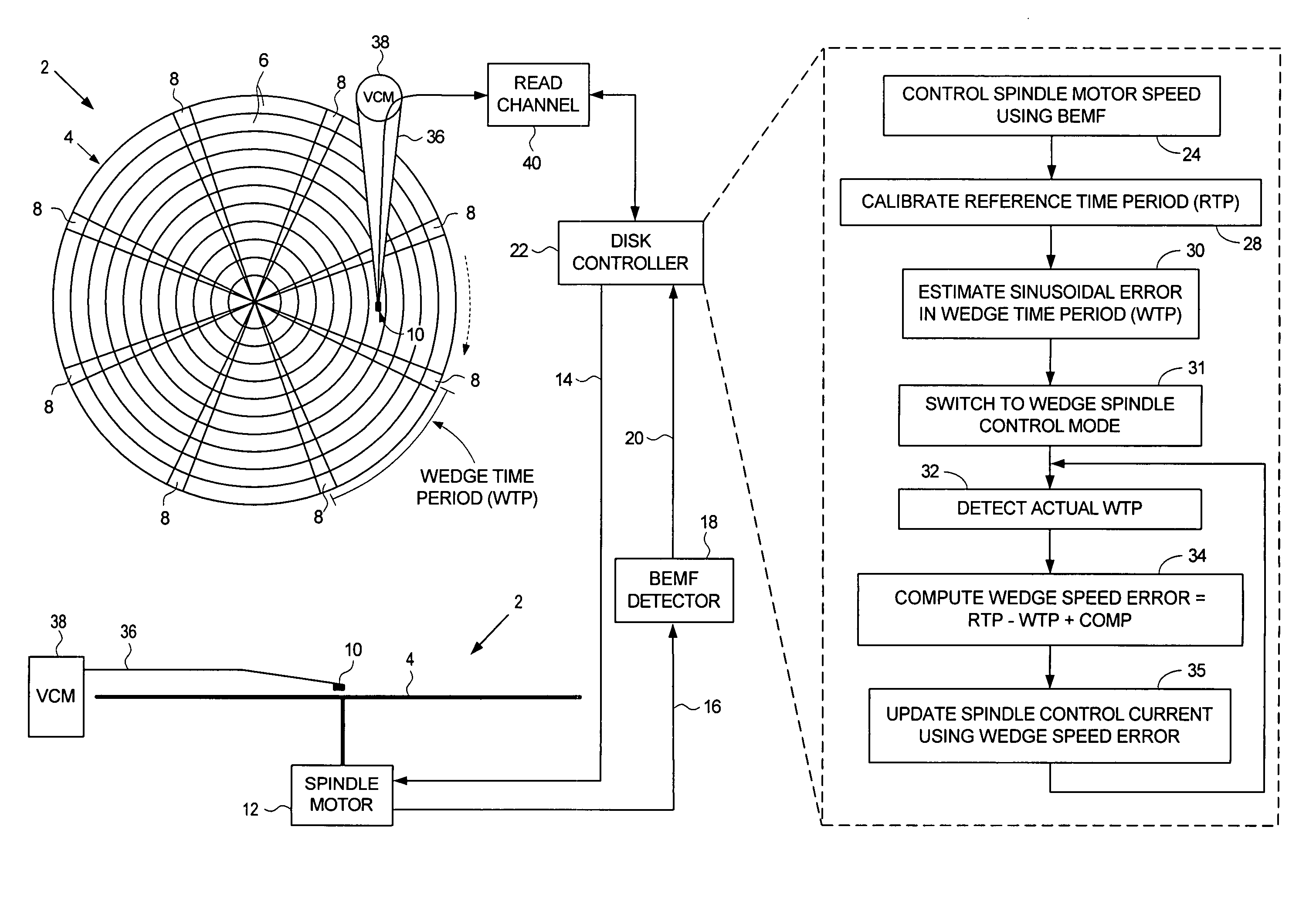
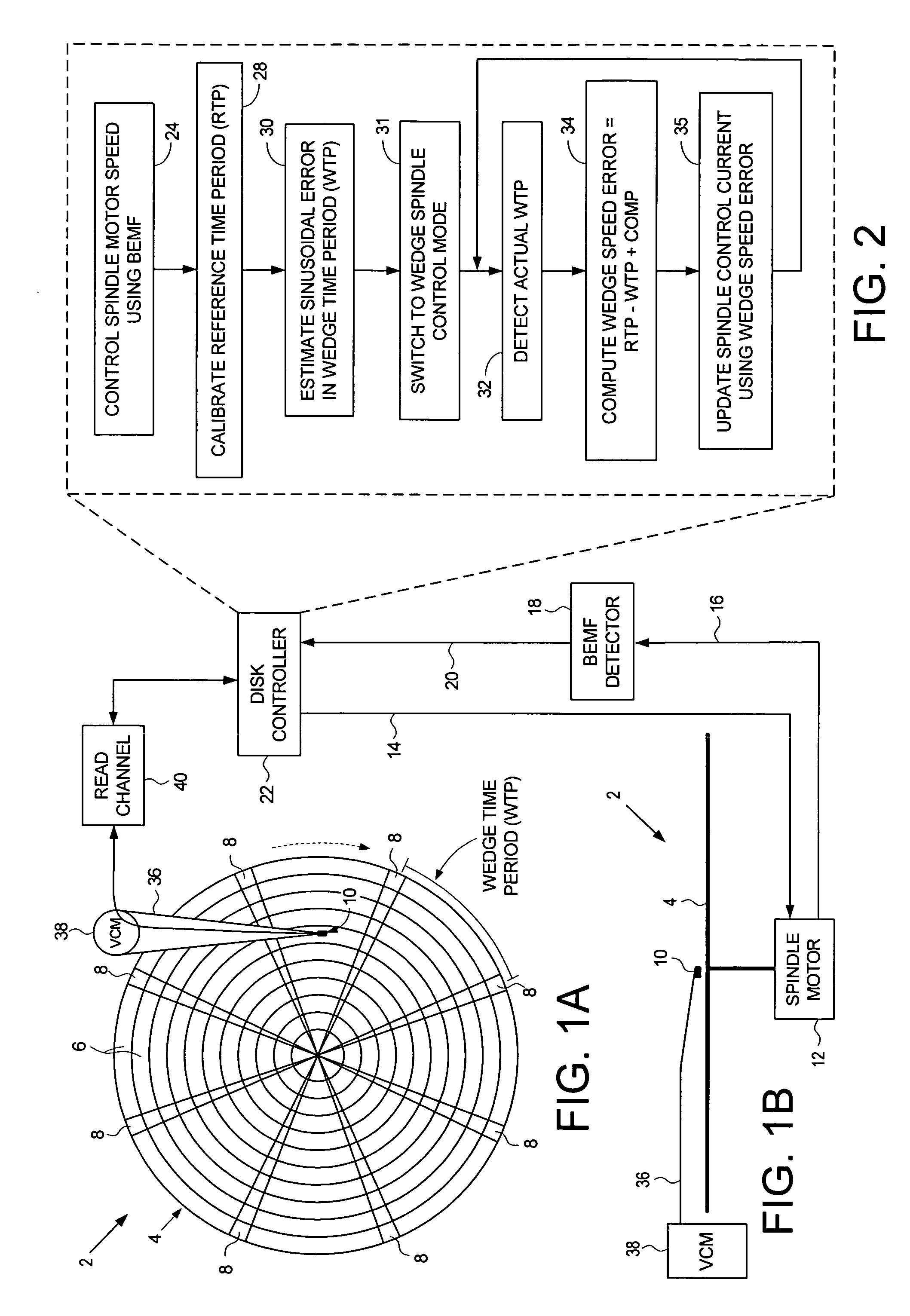
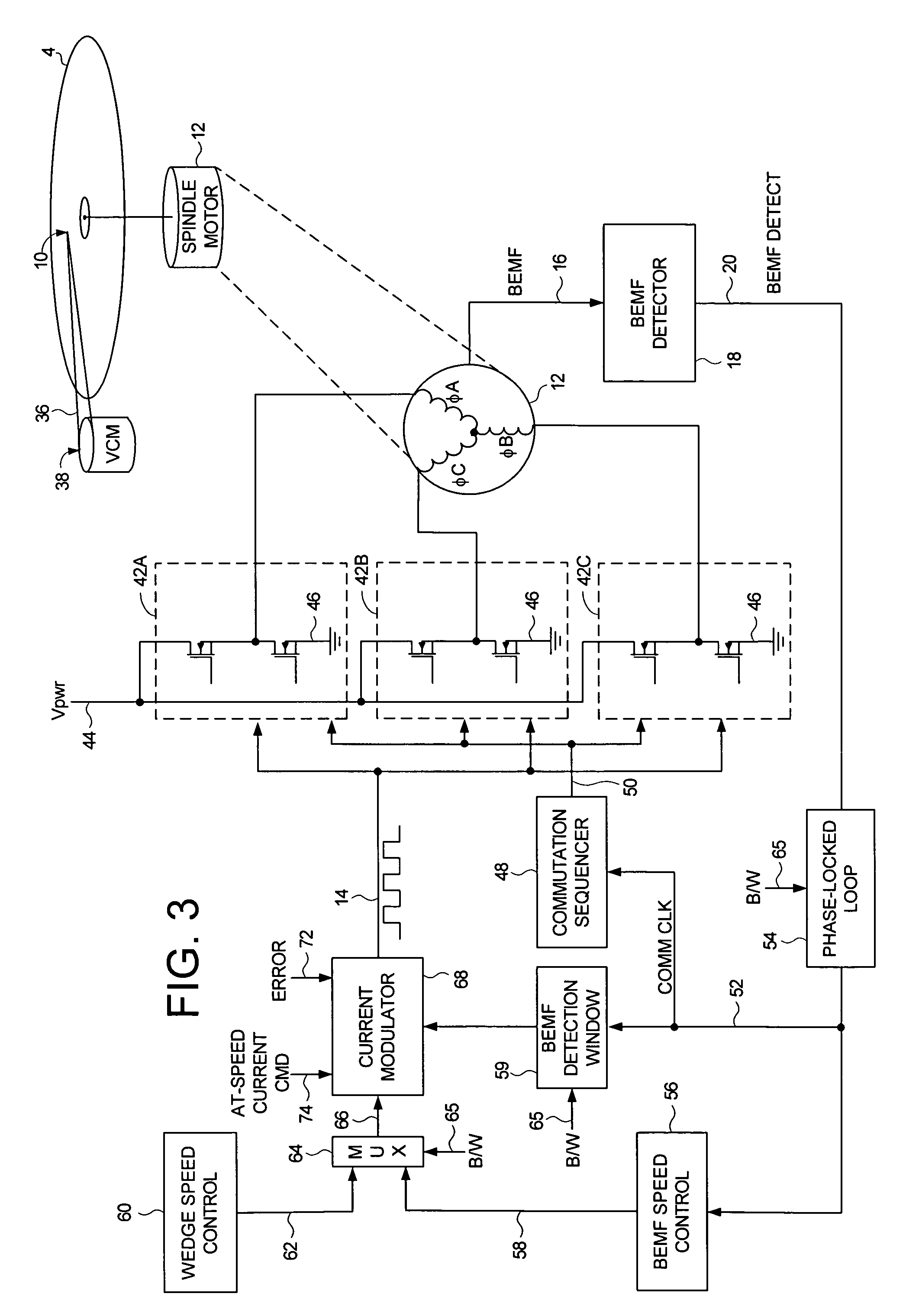
Disk drive employing wedge spindle speed control with eccentricity compensation
A disk drive is disclosed wherein a BEMF speed error is measured during a BEMF spindle speed control mode, and a spindle control current is updated in response to the BEMF speed error to drive the disk at an operating speed. A reference time period (RTP) is calibrated, and a sinusoidal error in a wedge time period (WTP) due to eccentricity in the disk rotating is estimated to generate an eccentricity compensation value. After switching to a wedge spindle speed control mode, an actual WTP is detected and a wedge speed error is generated in response to the RTP, the detected actual WTP, and the eccentricity compensation value. The disk is then maintained at the operating speed by updating the spindle control current in response to the wedge speed error.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System and method for controlling motor using parameter associated with magnetic flux
InactiveUS20080129243A1Reliably graspTorque ripple controlSynchronous motors startersDriving currentOperating point
A control method for a motor that rotates based on flux linkages to a winding member of the motor when the winding member is energized by a drive current is provided. The method includes storing magnetic-state information indicative of a relationship between each of a plurality of predetermined operating points of the drive current and a magnetic-state parameter associated with the flux linkages. The method includes obtaining at least one of command information associated with an operating state of the motor and detection information associated with the operating state of the motor. The method includes referencing the magnetic-state information with the use of the obtained at least one of the command information and detection information to obtain a value of the magnetic-state parameter based on a result of the reference. The method includes controlling an output of the motor based on the obtained value of the magnetic-state parameter.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Permanent magnetically excited electrical rotary drive
InactiveUS6278251B1Improve fault toleranceGuaranteed uptimeSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlPhase currentsElectricity
A permanent magnetically excited electrical rotary drive for a blood pump is proposed, comprising a permanent magnetic rotor and a stator, said stator comprising a drive winding having at least two loops for the production of a magnetic drive field which produces a torque on the rotor, with each loop belonging to a different electrical phase, furthermore comprising a setting device which supplies each loop in each case with a phase current or in each case with a phase voltage as a setting parameter, with the setting device comprising a separate power amplifier for each loop so that the setting parameter for each loop can be regulated independently of the setting parameter for the other loops.
Owner:THORATEC CORPORTION
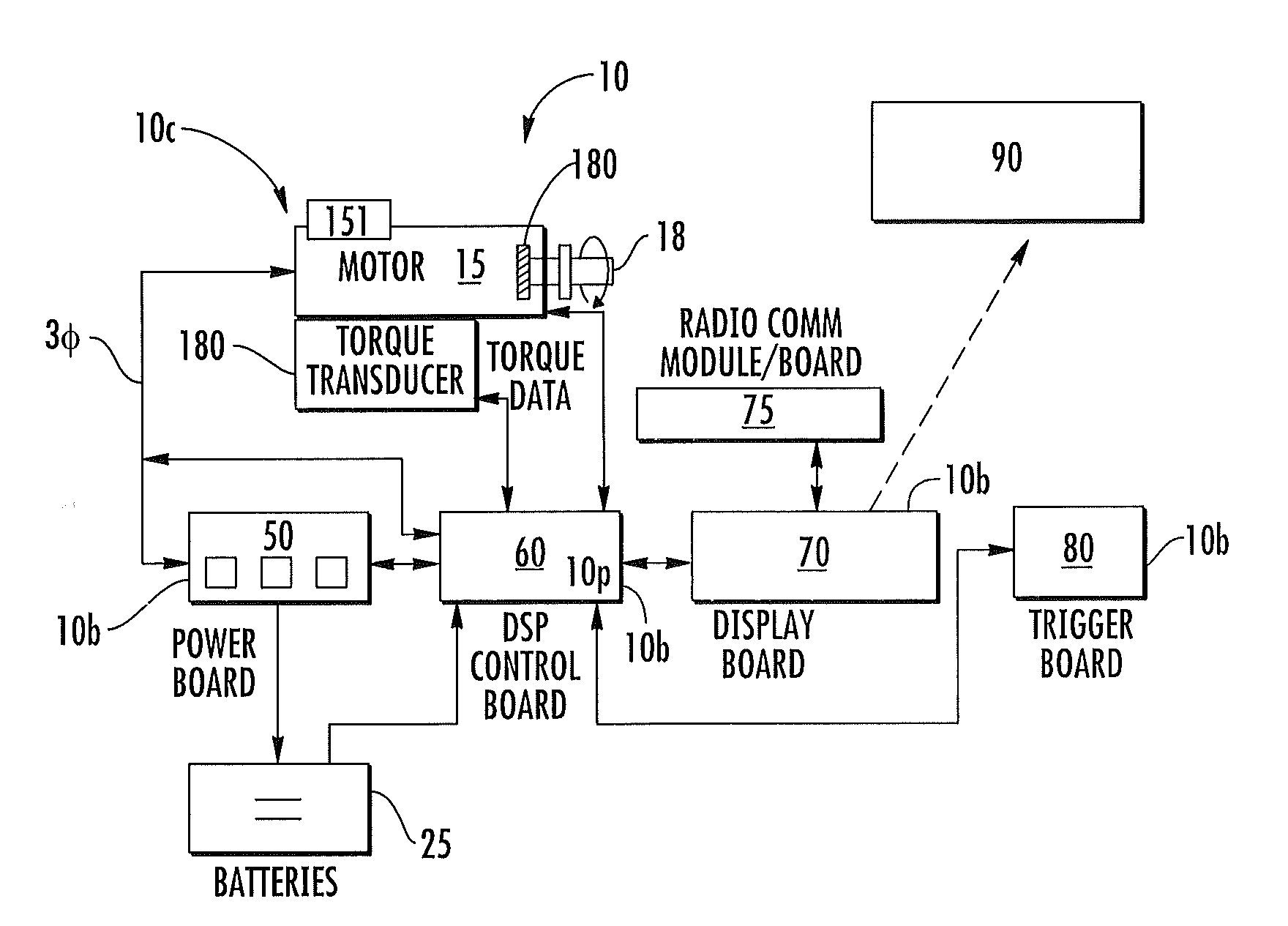
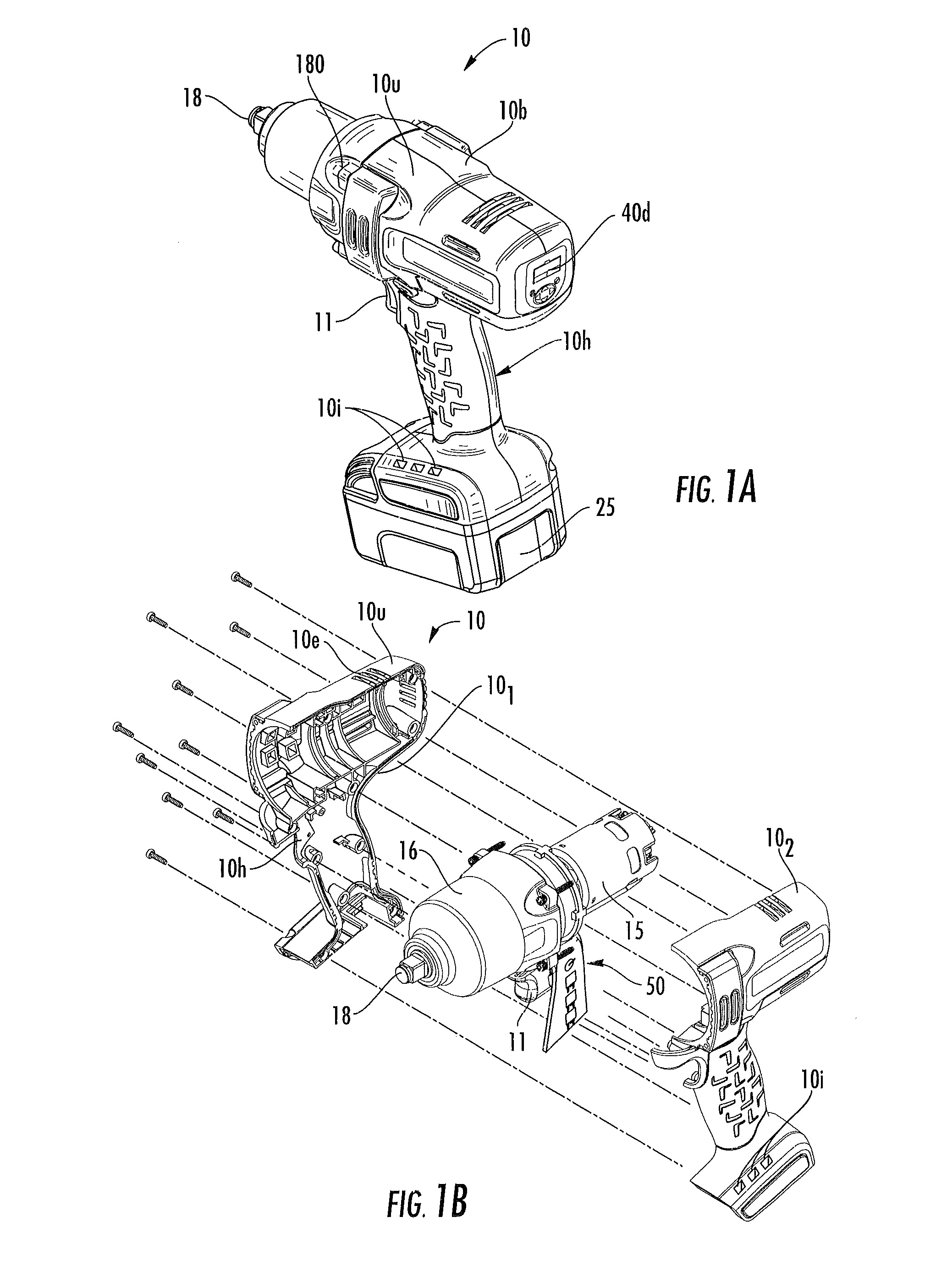
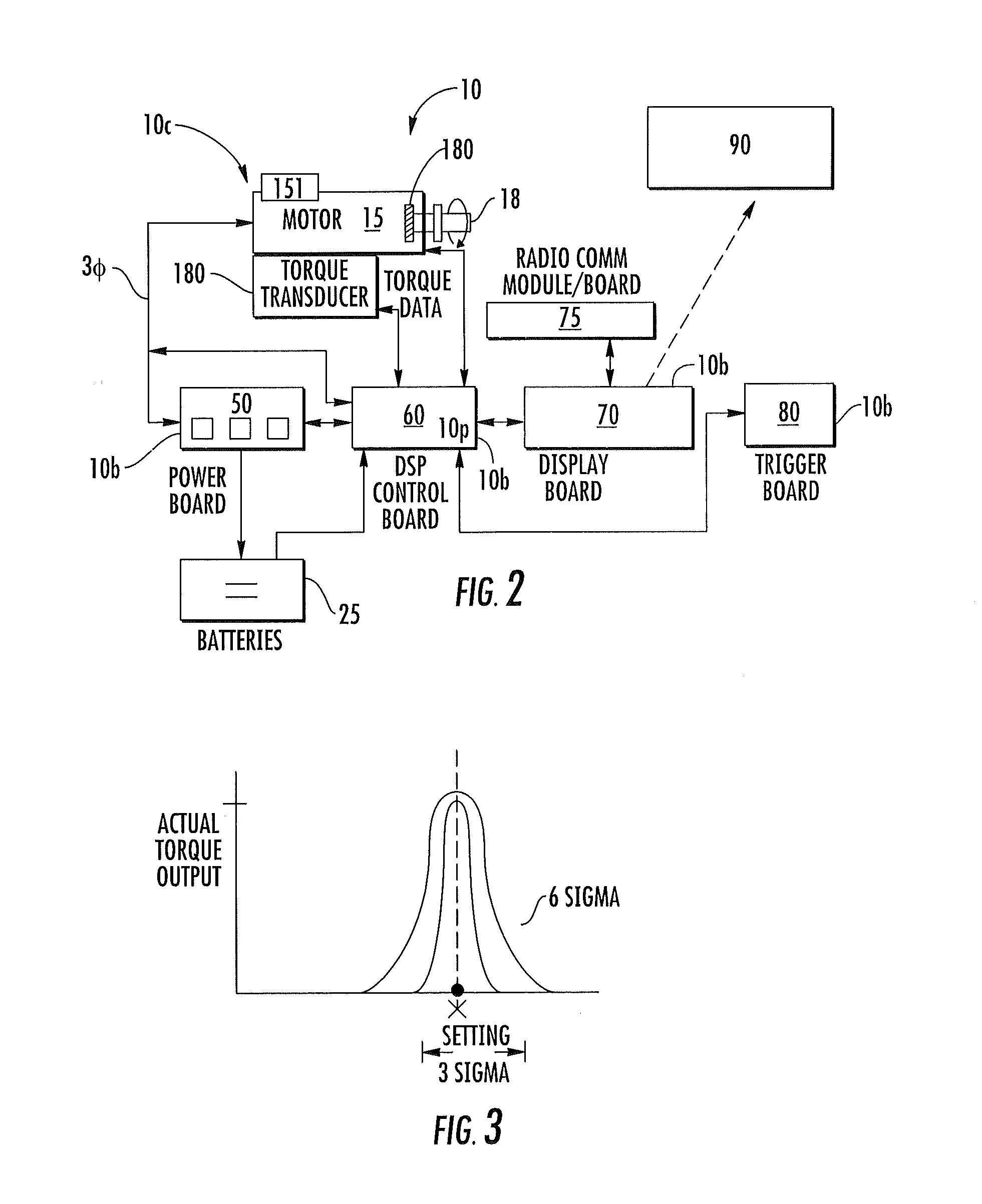
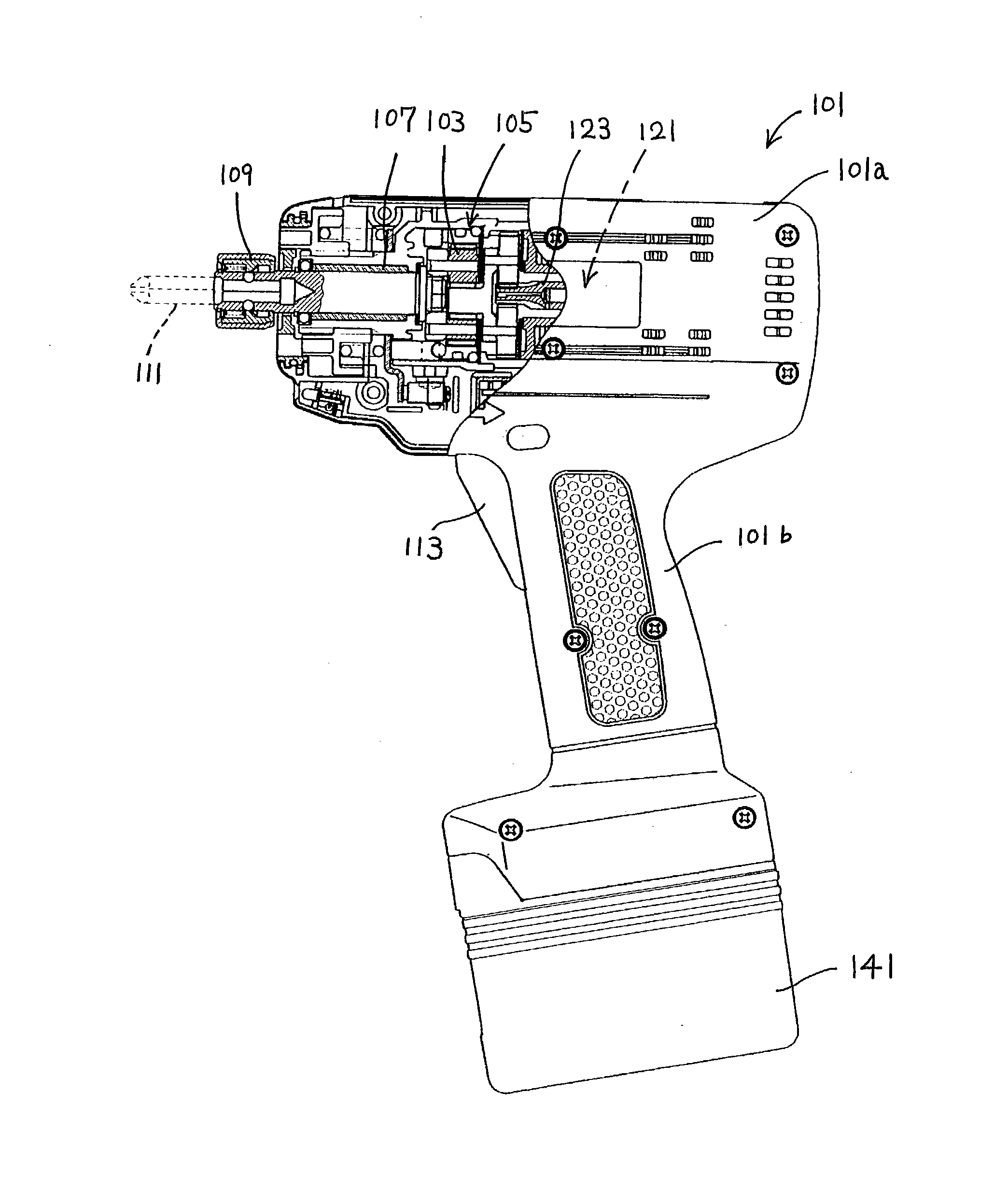
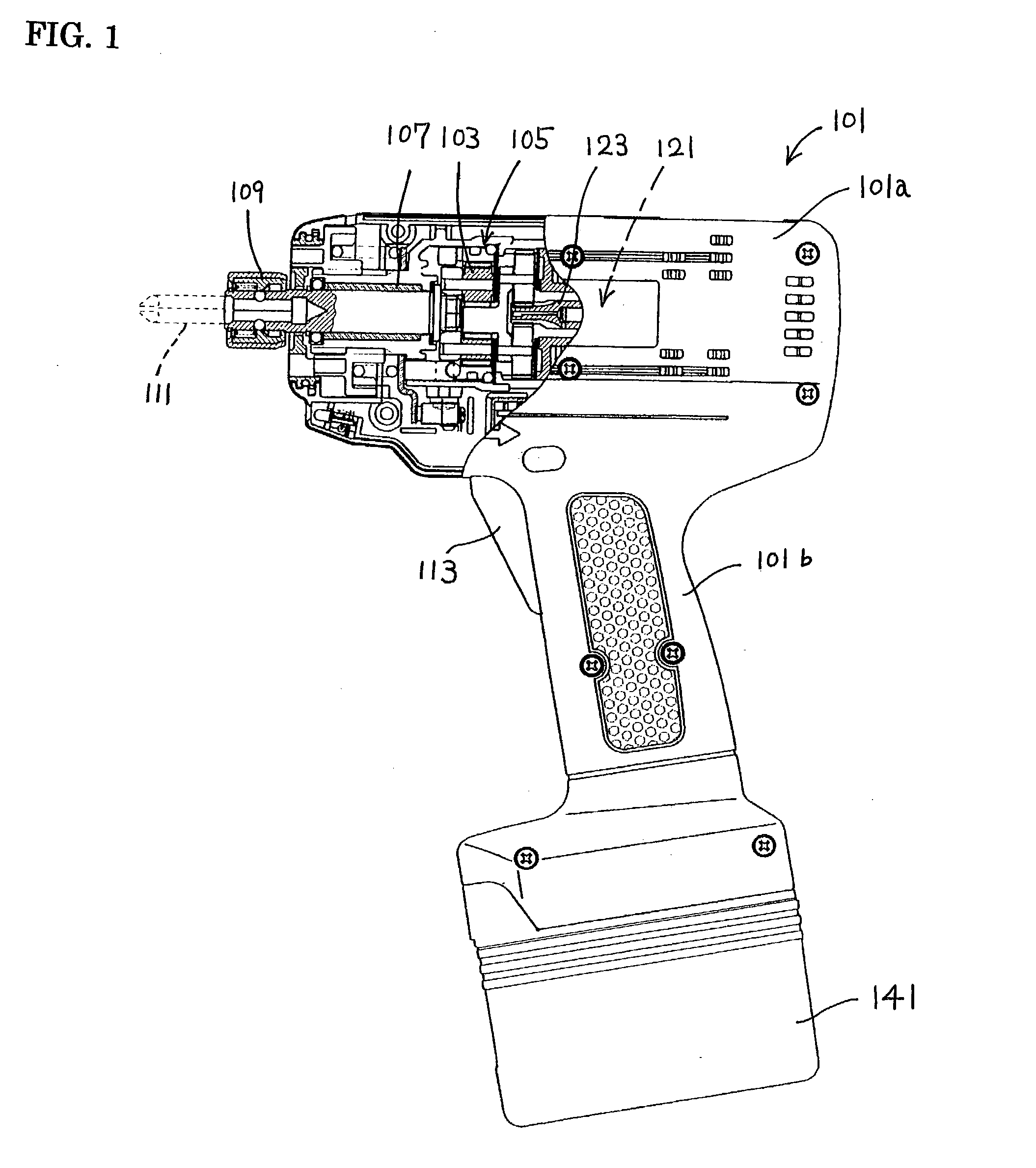
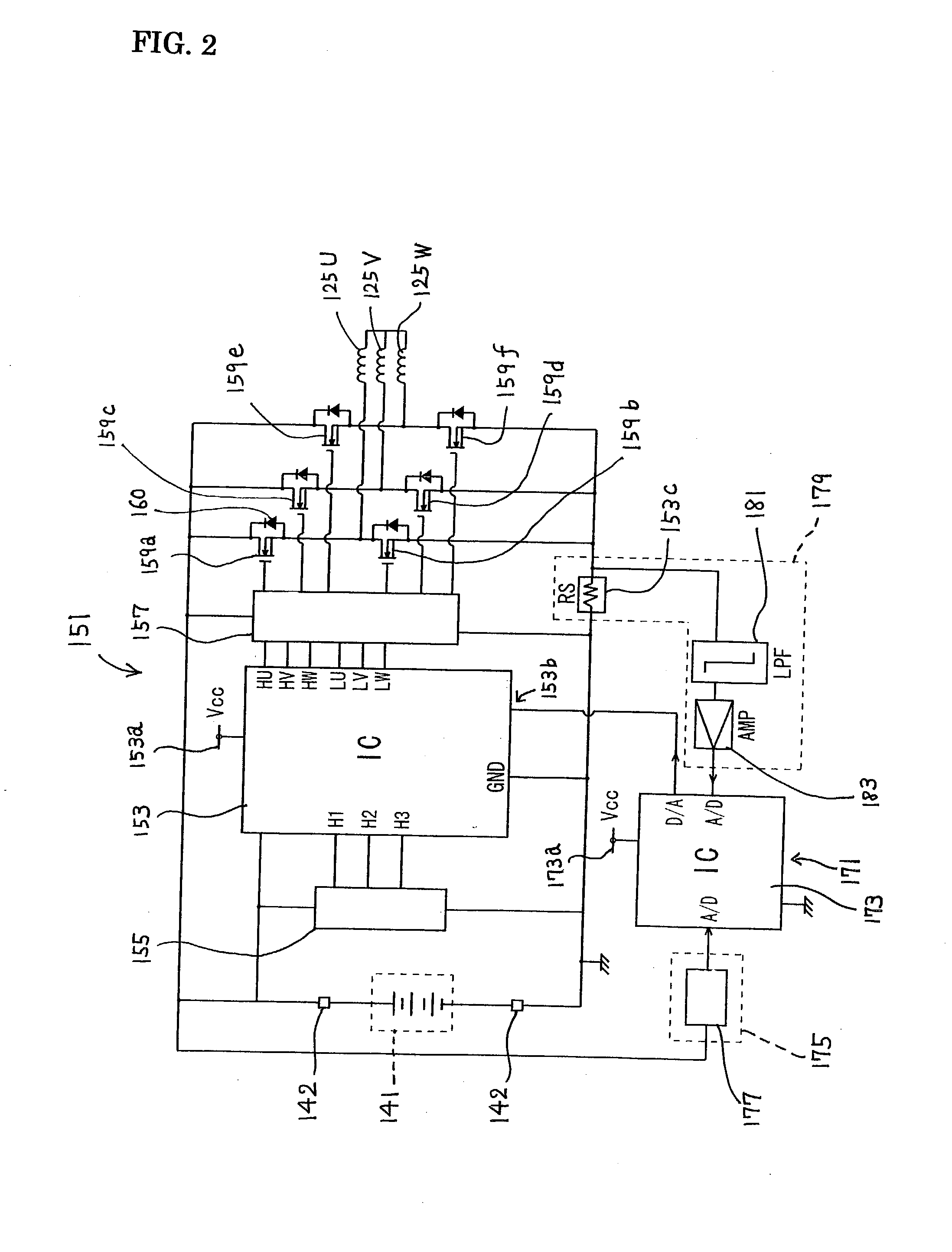
Precision-fastening handheld cordless power tools
ActiveUS20130193891A1Total current dropMotor/generator/converter stoppersSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor speedOn board
Cordless power tools include a pistol housing having an upper portion that merges into a downwardly extending handle, a DC motor residing in the upper portion of the housing, the DC motor having a rotor that drives an output shaft; a torque transducer on board the tool in communication with the output shaft; and a dynamic motor control circuit residing in the housing in communication with the motor and torque transducer. The dynamic motor control circuit includes a Kelvin resistor in communication with the motor for measuring motor current and digital hall switches in communication with the motor for measuring motor speed. The motor current can vary by at least 100 A during operation.
Owner:INGERSOLL RAND IND U S INC
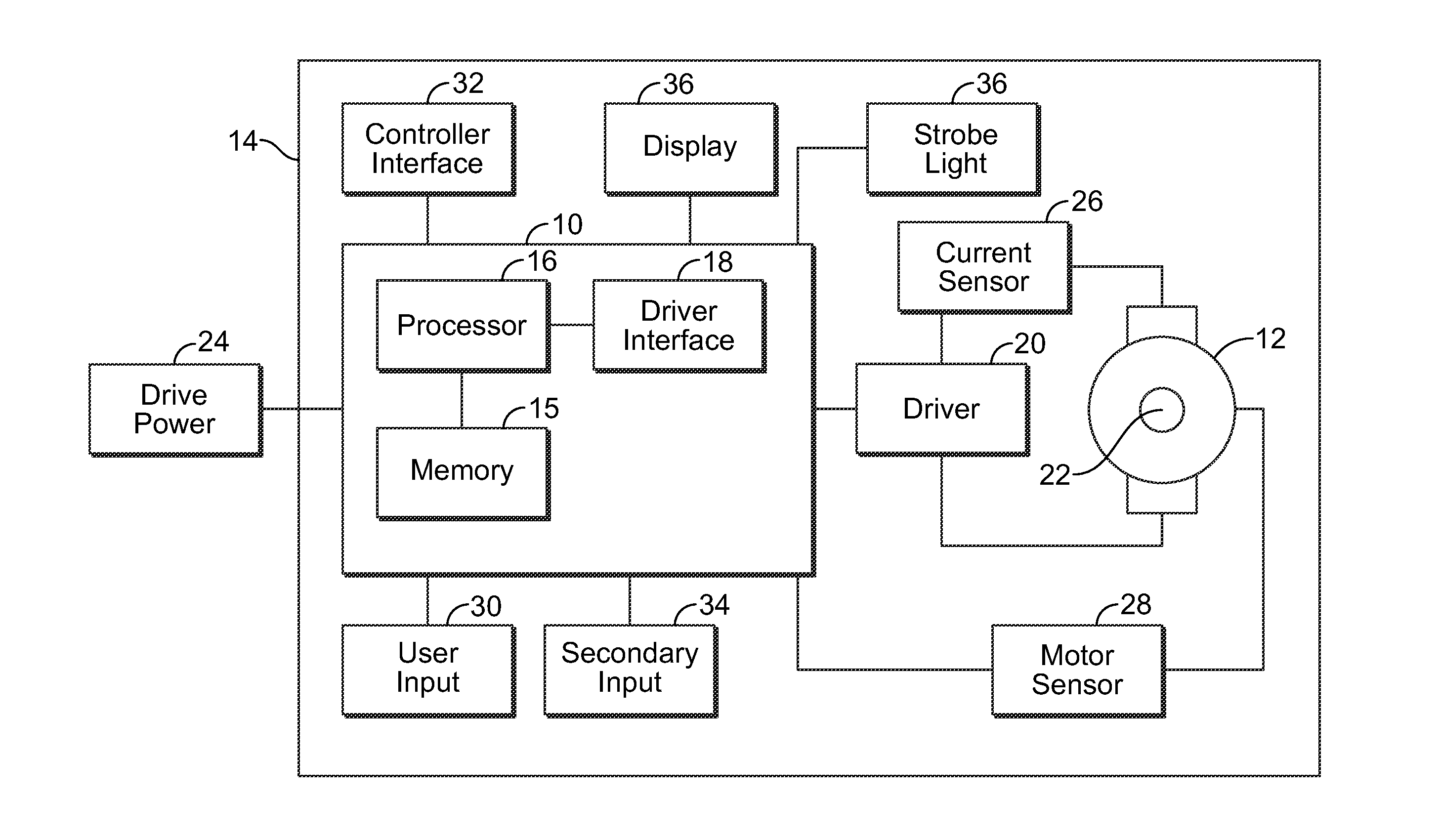
Programmable power tool with brushless DC motor
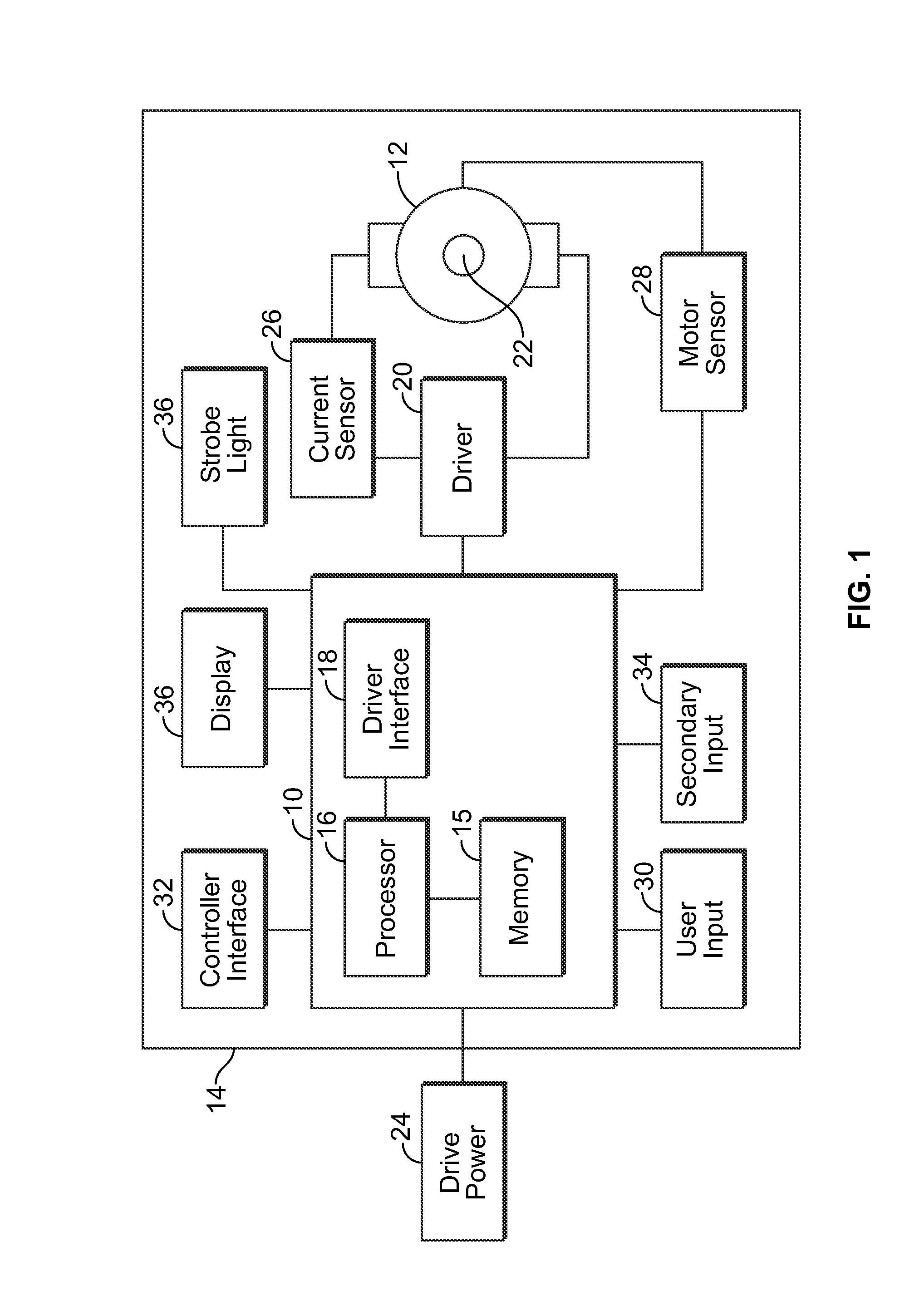
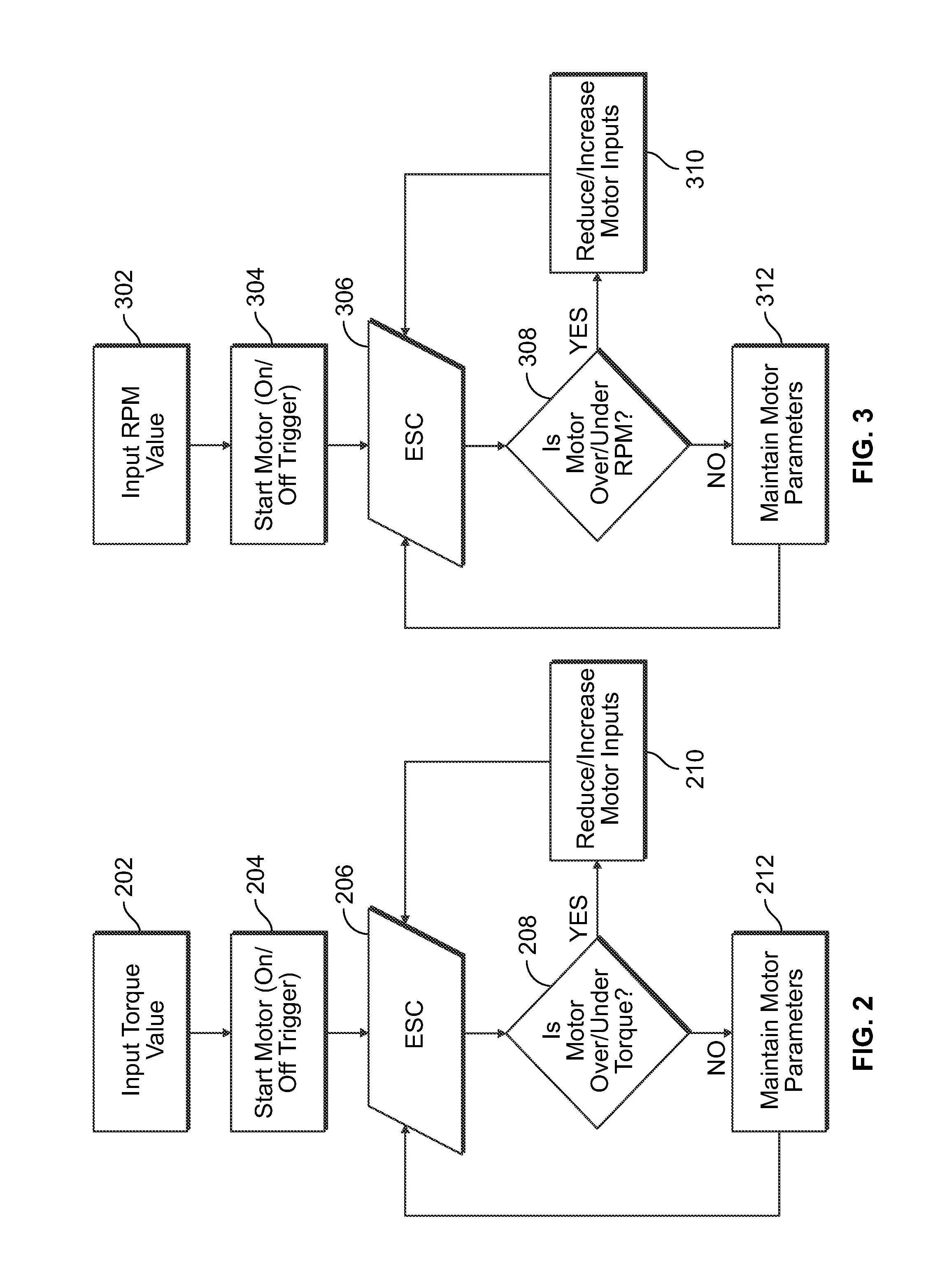
ActiveUS20130187587A1High performance featuresAccurate stopMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersEngineeringPower tool
A power tool that includes a brushless DC motor, one or more motor sensors, and a controller, such as, for example, an electronic speed control (ESC) circuit. The controller is adapted to provide instructions to control the operation of one or more parameters of the brushless DC motor. The controller is also adapted to receive feedback from one or more motor sensors that reflect whether the motor is attaining the one or more parameters. The controller may also be adapted to have a learning mode, in which feedback provided during use of the power tool is stored by the controller as a program so that the same operating parameters may be subsequently replicated by using the program to operate the tool. The controller may also use the feedback to adjust the operation of the motor so that the motor maintains one or more selected or programed operating parameters.
Owner:TRANSFORM SR BRANDS LLC
Permanent magnet synchronous motor and controller therefor
InactiveUS20050248306A1Low costReduce impactTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsLoop control
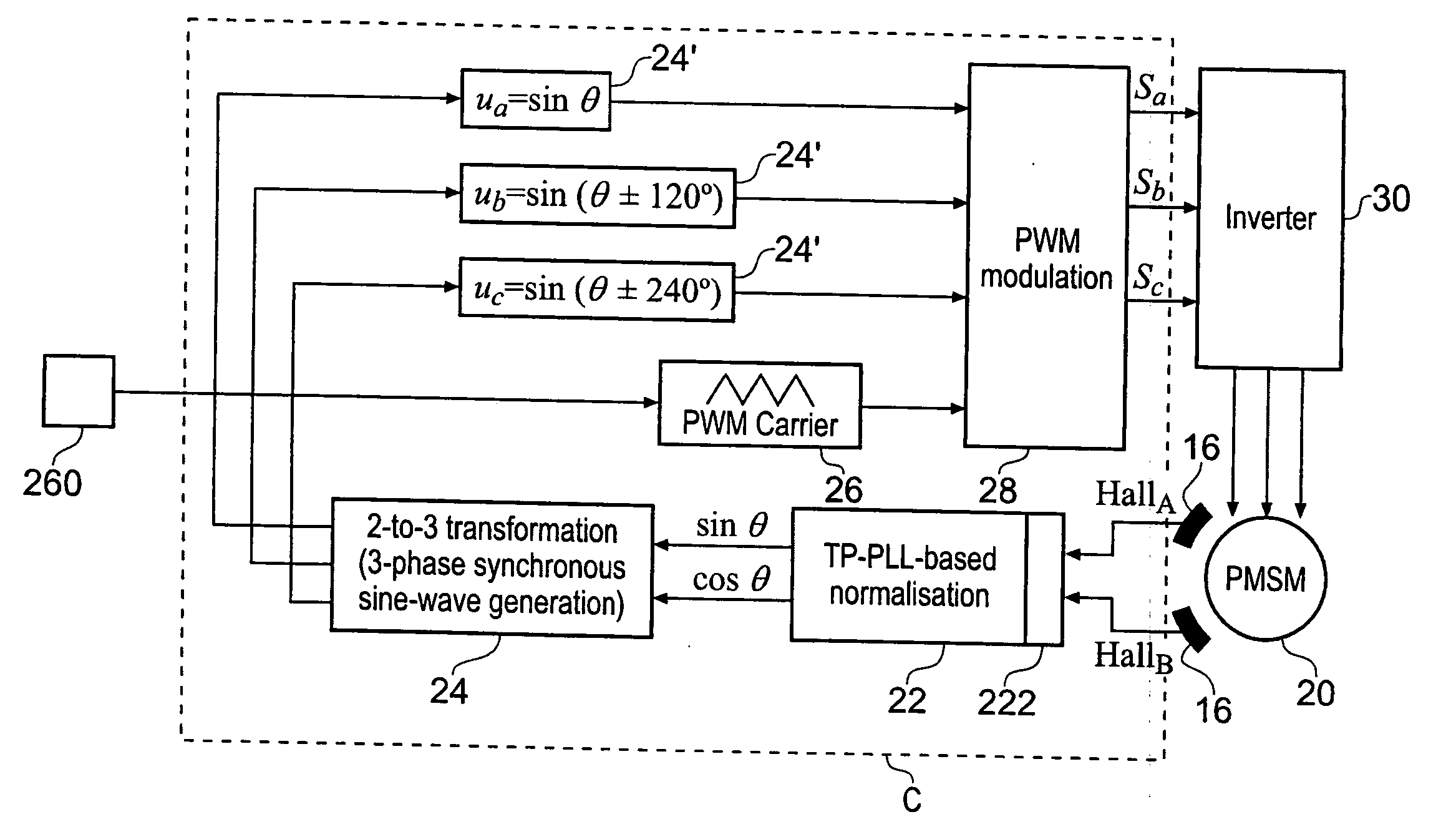
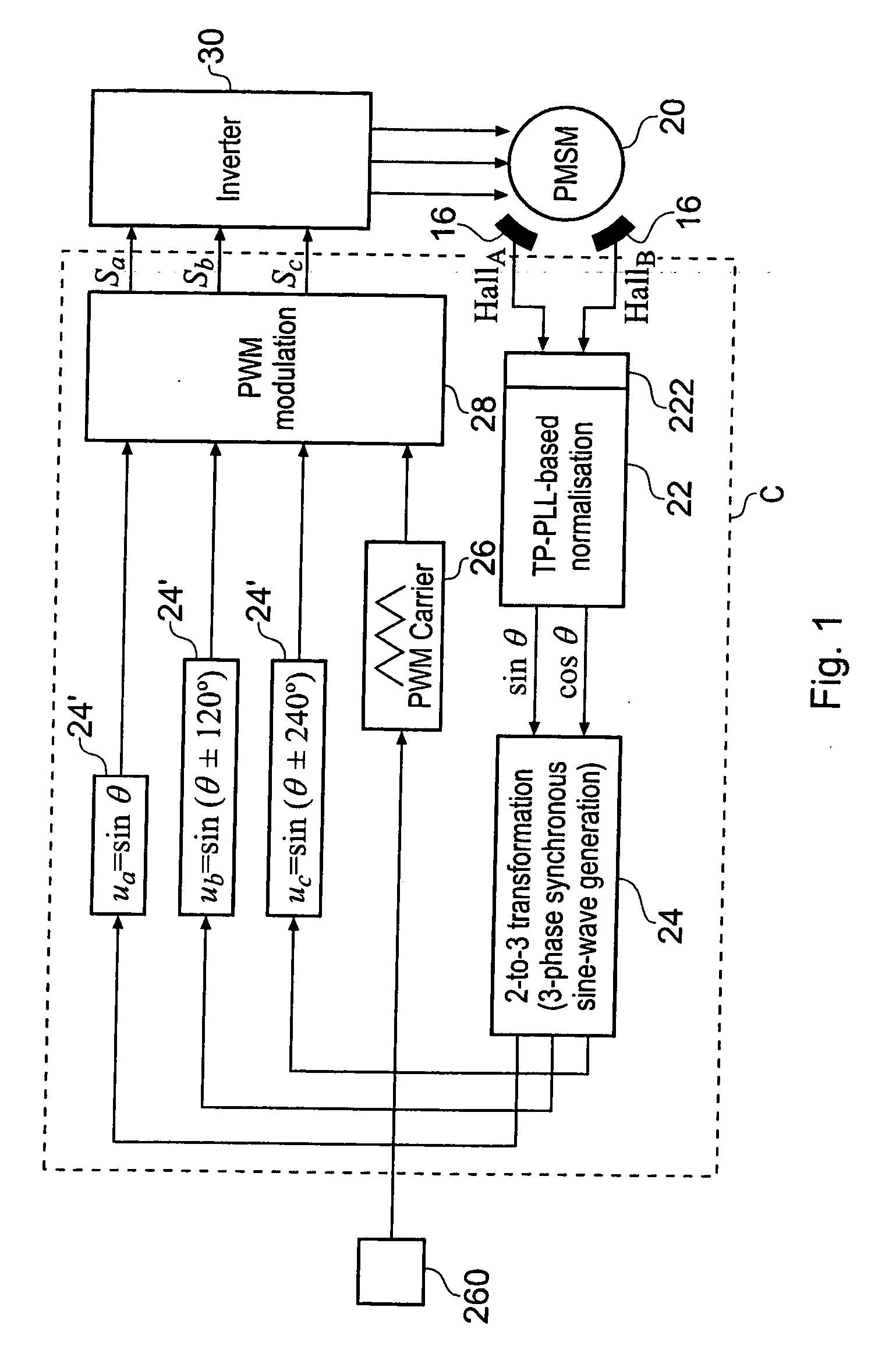
A low-cost sine-wave drive for a 3-phase permanent magnet synchronous AC machines (PMSM) in open-loop control is based on the measurements of two linear Hall sensors. The two Hall sensors are excited by a magnetic ring with the same pole number as the PMSM rotor magnet and sinusoidal flux distributions. The output signals of the Hall sensors are unified through a two-phase-type phase-lock-loop in order to reduce the impact of the sensor mounting non-uniformity during mass production. The peak torque and speed of motor is simply controlled by adjusting the amplitude of pulse-width-modulation carrier. Smooth torque control is achieved due to sinusoidal 3-phase currents. Such a simple sine-wave drive can be achieved with or without the assistance of a micro-controller unit (MCU). No current sensor is required for the motor phase current detection. This motor can be used in industrial applications where there is no strict requirement on torque response and constant speed control of PMSM machines.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
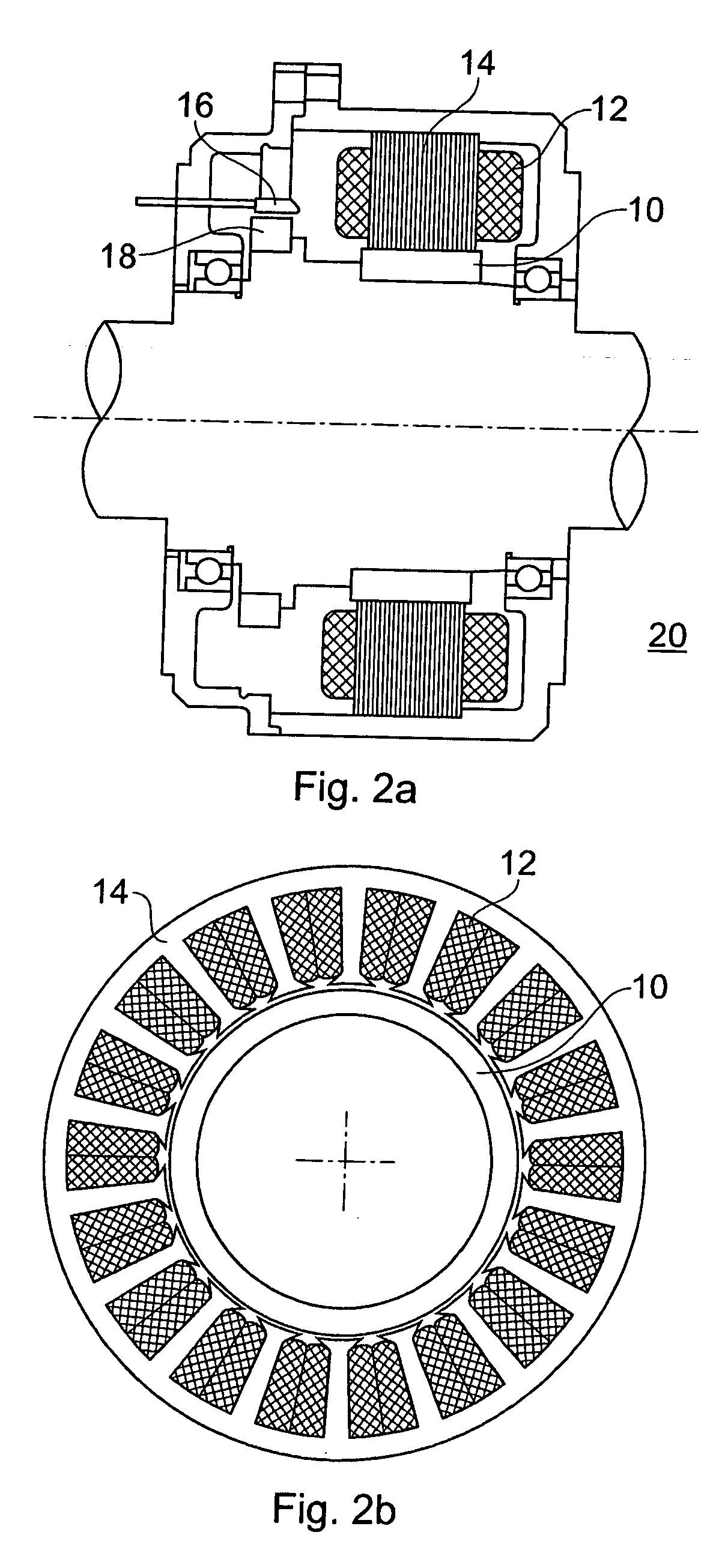
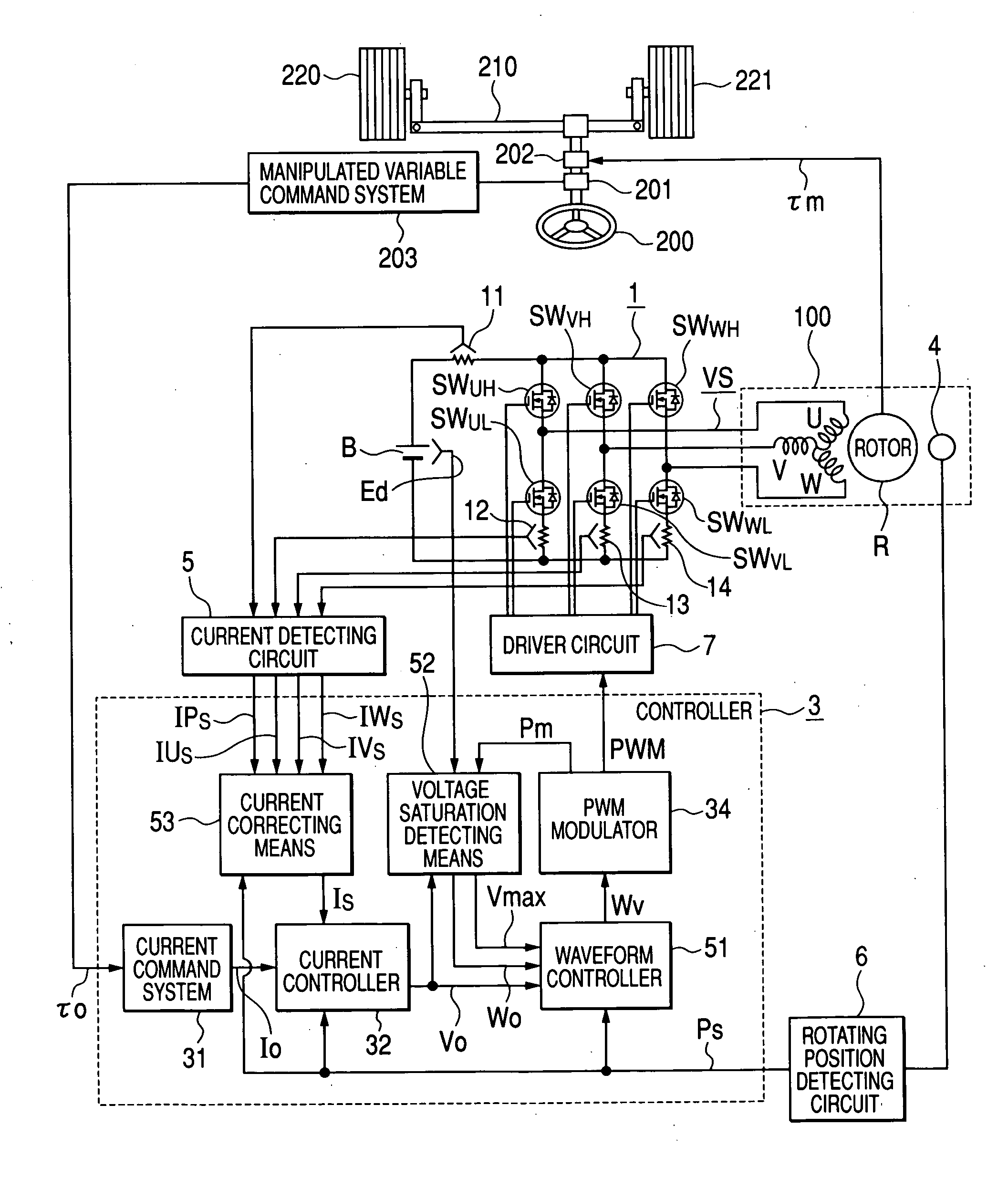
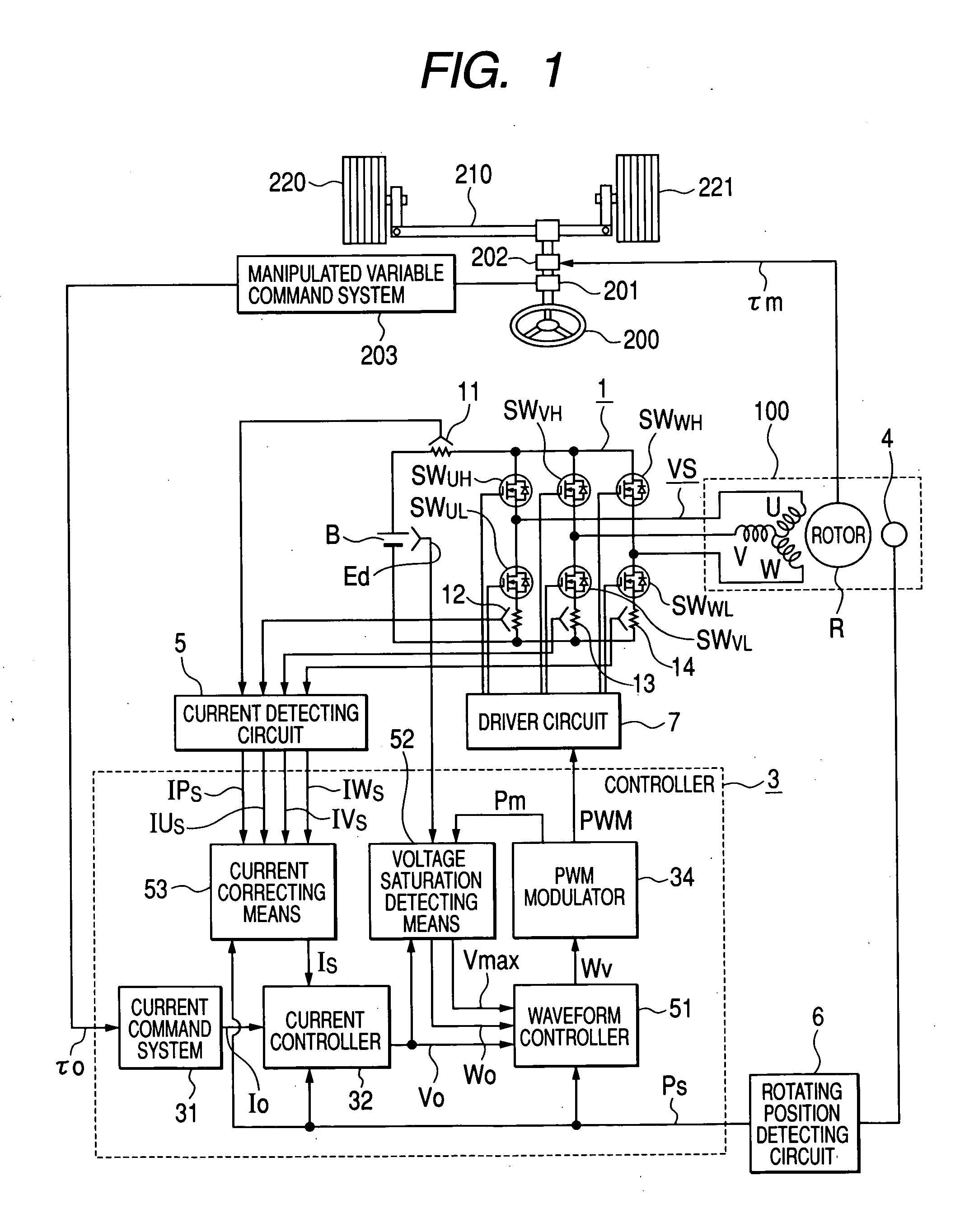
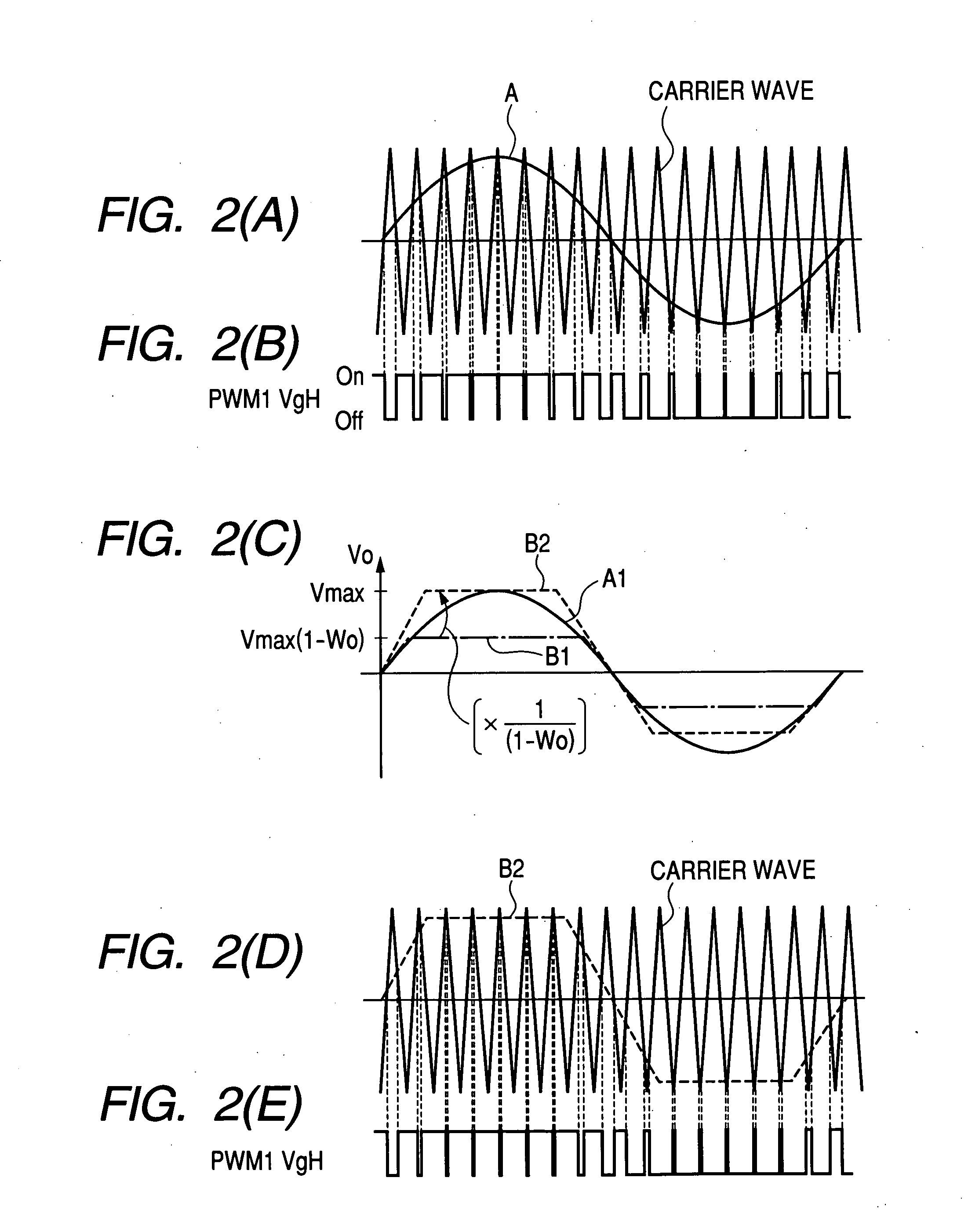
Motor drive apparatus, electric actuator and electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20060001392A1Increase driving speedHigh areaTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringHigher order harmonics
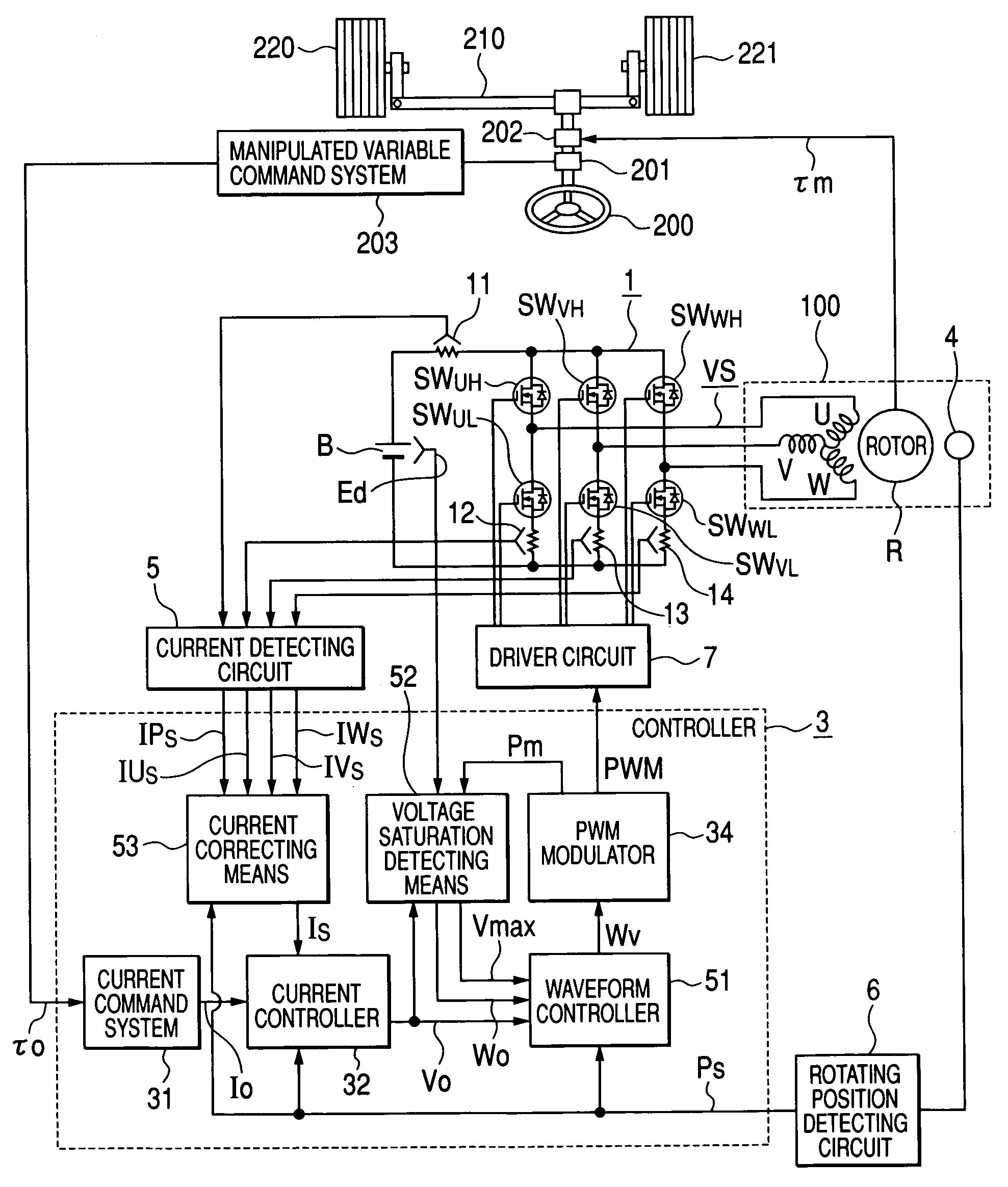
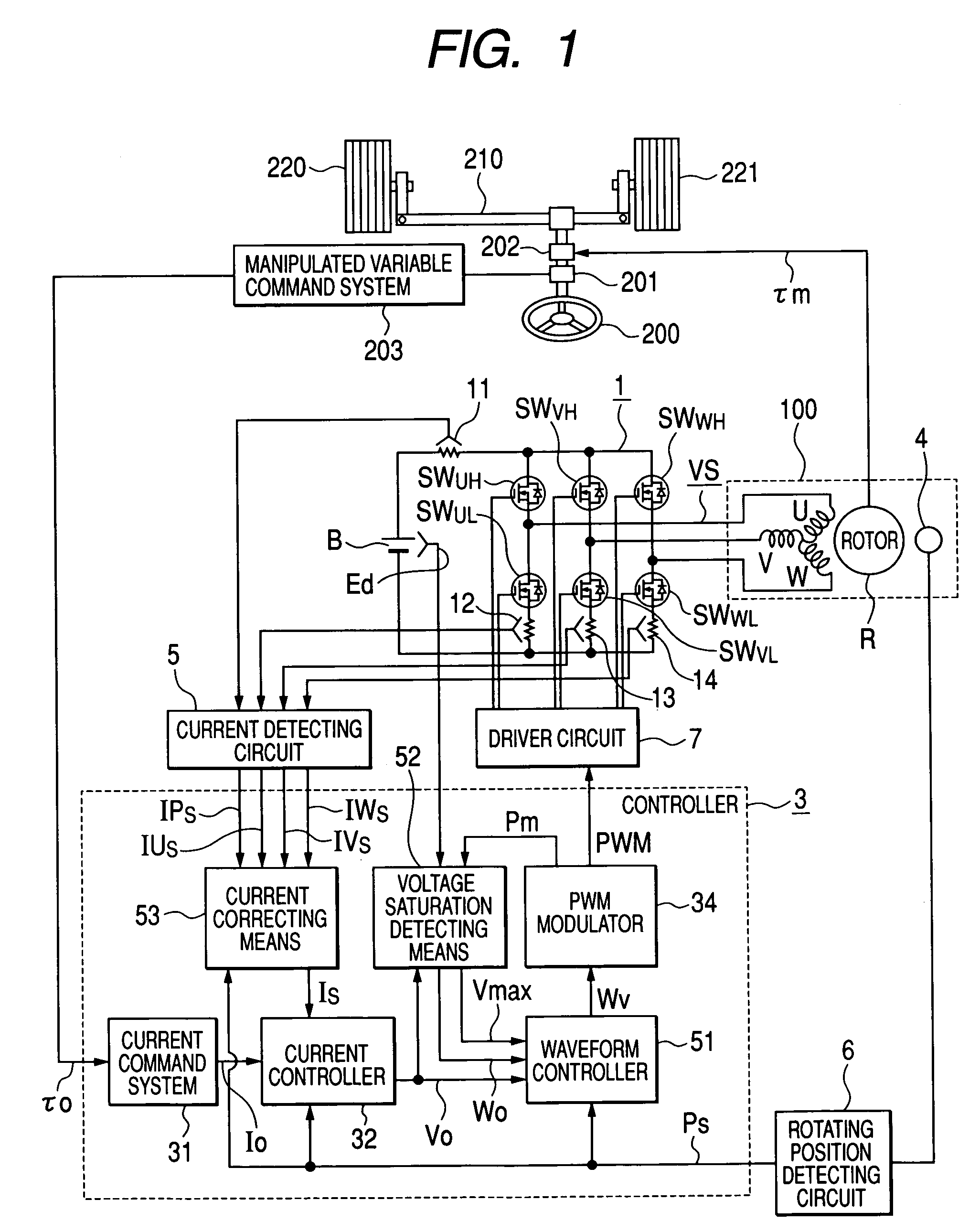
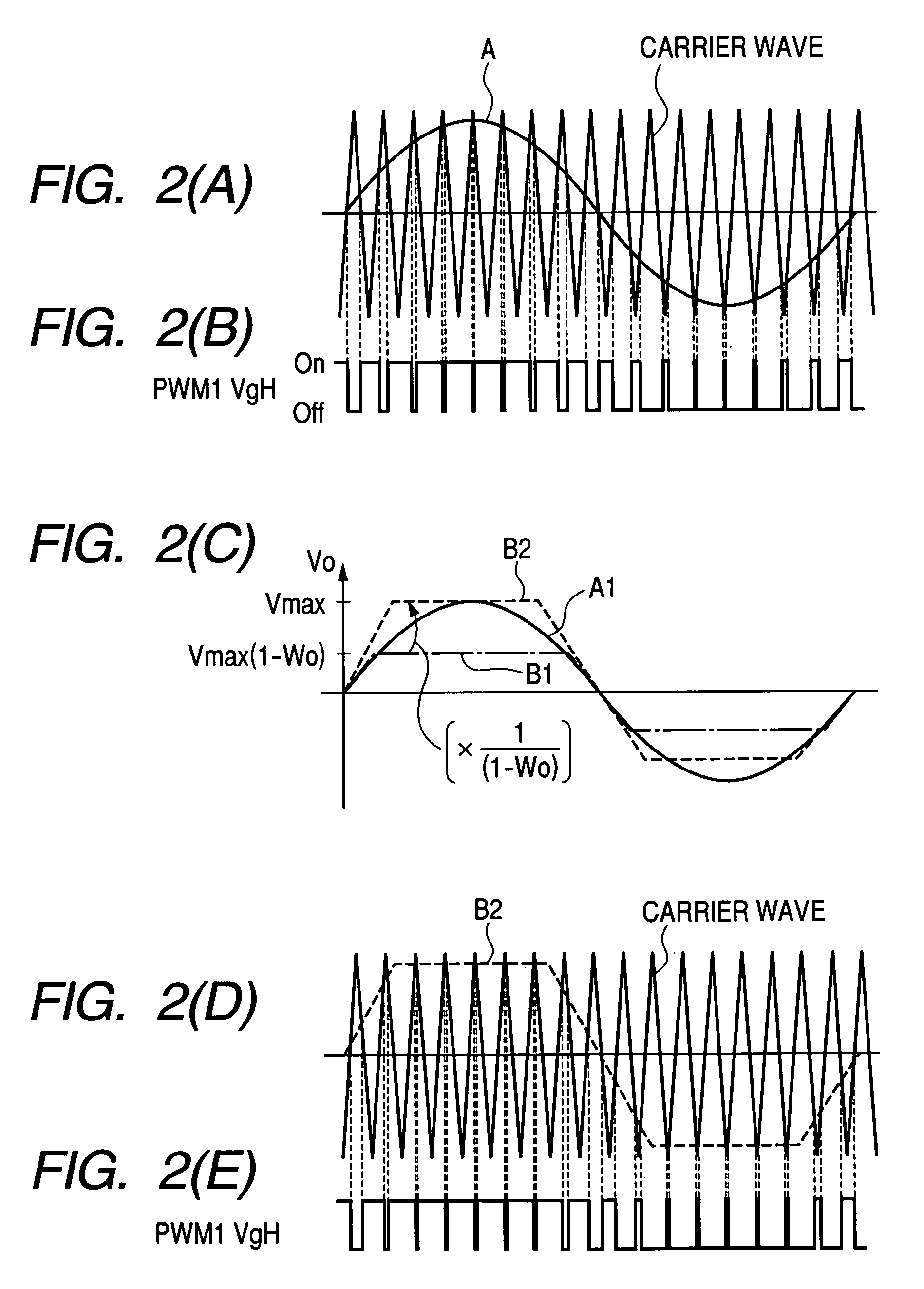
In an operation range of an actuator subjected to quick acceleration and deceleration, a motor drive apparatus, an electric actuator and an electric power steering apparatus capable of continuous torque control up to the high drive speed and high torque area. A controller comprises a voltage saturation detecting means for detecting the voltage saturation of the output voltage of an inverter circuit, based on the battery voltage, and a waveform controller that converts the drive waveform of the inverter circuit into the waveform created by superimposing harmonics of high odd-numbered order on a sinusoidal wave as a fundamental wave of the modulated wave modulated by a PWN carrier wave; and continuously changes the ratio of superimposing the high-order harmonics in response to the voltage saturation detected by a voltage saturation detecting means. This arrangement allows the controller to continuously change the drive waveform of the inverter circuit.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Motor drive apparatus, electric actuator and electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS7161323B2Increase torqueTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringMotor drive
The disclosure concerns a a motor drive apparatus, an electric actuator and an electric power steering apparatus capable of continuous torque control up to the high drive speed and high torque area, in order to enable quick acceleration and deceleration. A controller comprises a voltage saturation detecting apparatus for detecting the voltage saturation of the output voltage of an inverter circuit, based on the battery voltage, and a waveform controller that converts the drive waveform of the inverter circuit into the waveform created by superimposing harmonics of high odd-numbered order on a sinusoidal wave as a fundamental wave of the modulated wave modulated by a PWN carrier wave; and continuously changes the ratio of superimposing the high-order harmonics in response to the voltage saturation detected by a voltage saturation detecting means. This arrangement allows the controller to continuously change the drive waveform of the inverter circuit.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
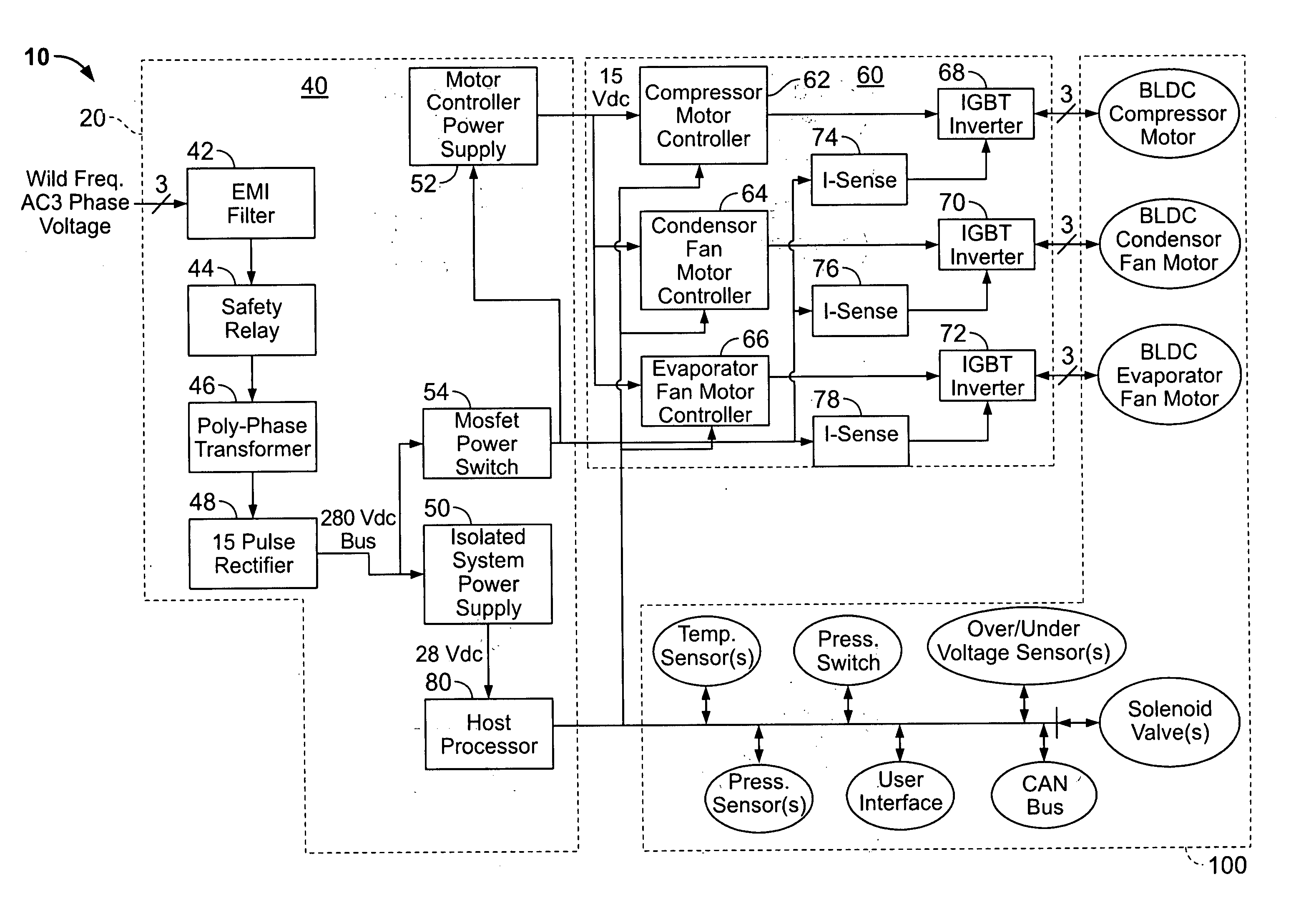
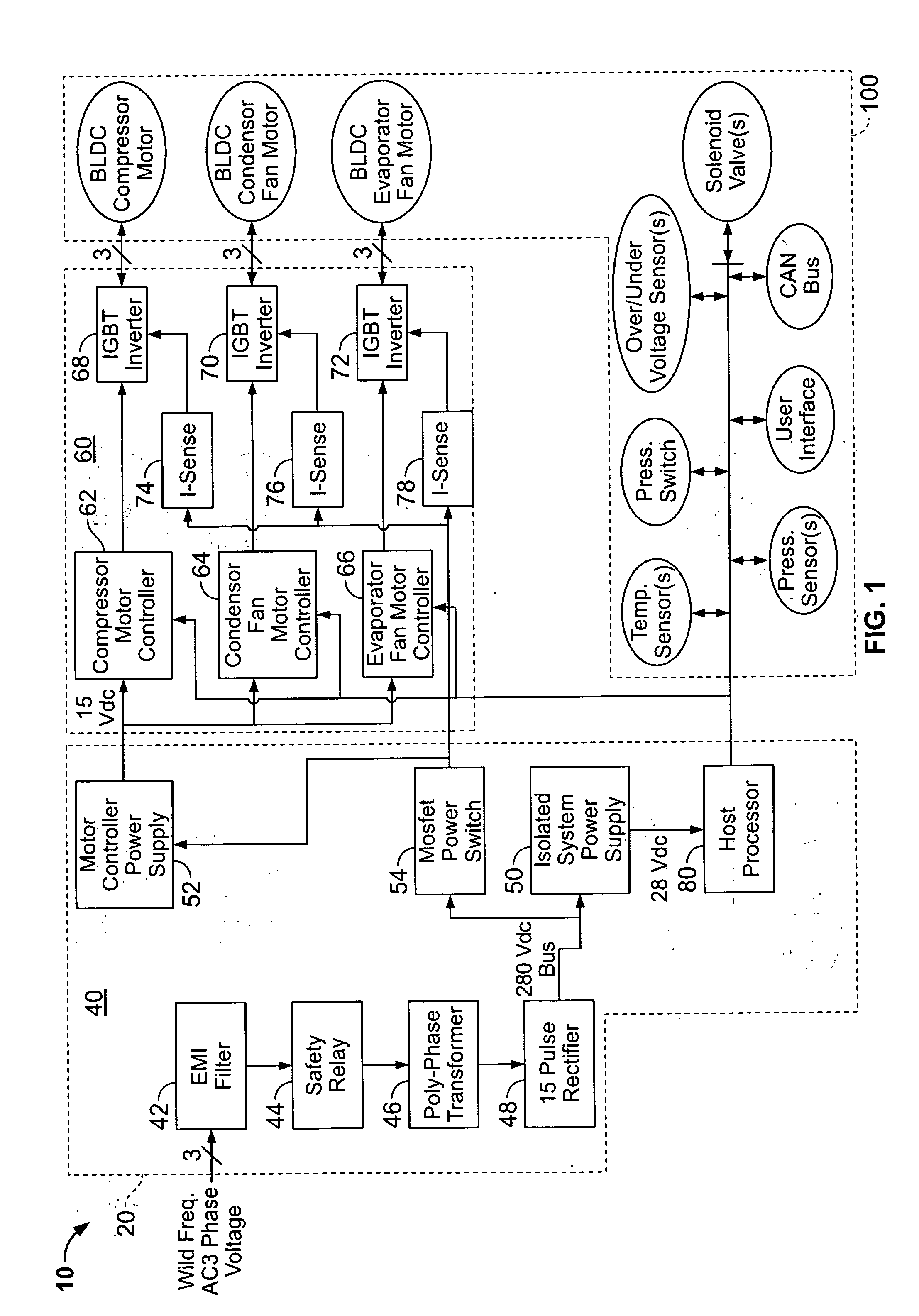
Wild frequency avionic refrigeration system and controller therefor
ActiveUS20080115512A1Air-treating devicesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleAviationControl signal
A wild frequency avionic refrigeration system and a controller therefore are provided. One embodiment of the refrigeration system includes: a refrigeration LRU including a vapor cycle system with a brushless DC compressor motor, a brushless DC condenser motor, a brushless DC evaporator motor and a plurality of sensors configured to output operating parameter data relative to the vapor cycle system; a power module configured to convert a wild frequency AC input voltage to at least one DC output voltage; a motor control module in communication with the brushless DC compressor, condenser and evaporator motors; and a processing module in communication with the plurality of sensors and the motor control module, wherein the processing module, according to the operating parameter data, outputs control signals to the motor control module for independently driving the brushless DC compressor, condenser and evaporator motors.
Owner:BE AEROSPACE INCORPORATED
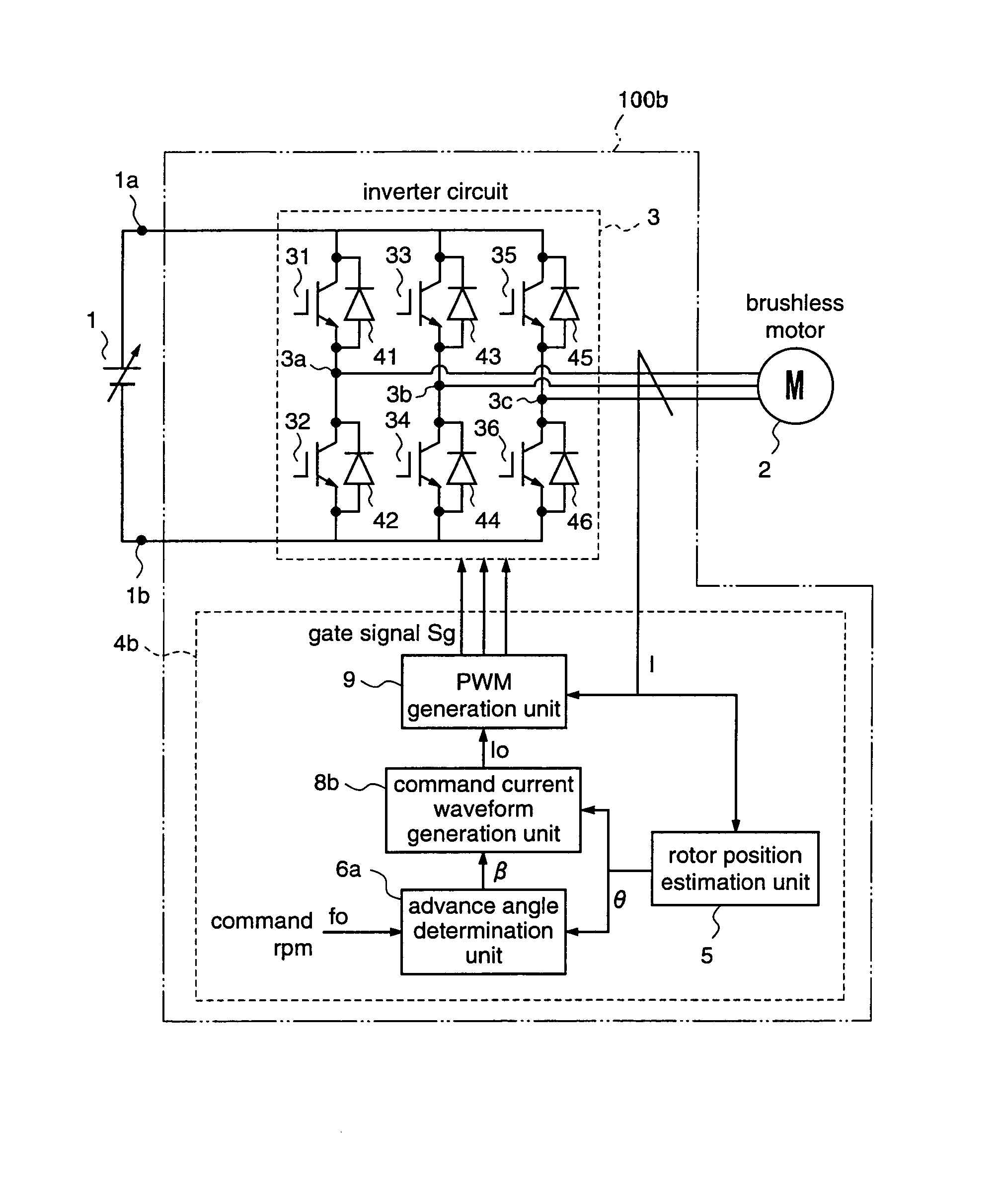
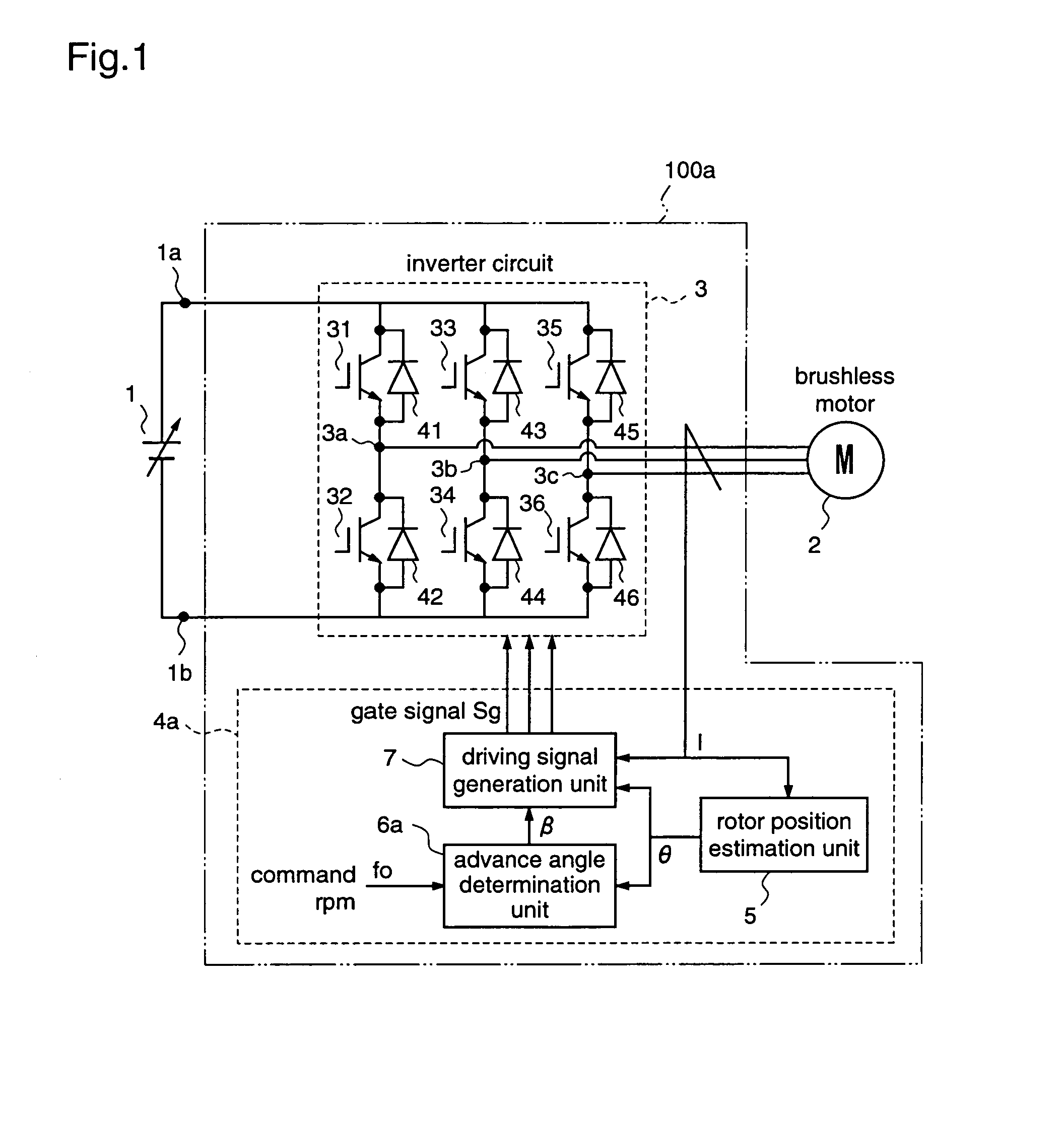
Motor driving apparatus
ActiveUS7176644B2Low costIncrease freedomSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsBrushless motorsMotor drive
A motor driving apparatus includes an inverter circuit for converting an output voltage of a power supply into a three-phase AC and outputting the same to the brushless motor, a rotor position estimation unit for estimating a rotor position of the brushless motor, and an inverter control unit for controlling the inverter circuit so that the brushless motor is driven by a current based on the estimated rotor position. The inverter control unit determines an advance angle of the current supplied to the brushless motor with respect to the estimated rotor position so as to minimize a deviation between a command rpm and an actual rpm. Therefore, it is possible to perform stable weak field control for the brushless motor, independently from the input voltage of the inverter circuit, without using predetermined control variables such as table values.
Owner:III HLDG 7
Power tool
It is an object of the present invention to provide a technique to increase efficiency of the output torque of the blushless motor to drive a power tool. A representative power tool may comprise a tool bit, a brushless motor to drive the tool bit, a battery to operate the brushless motor and a control device. The control device may operate the brushless motor by means of the battery. The control device may include an advance angle controlling section to control an advance angle of the brushless motor. According to the present teachings, the advance angle of the brushless motor may be determined based upon indexes that reflect working condition of the tool bit when the brushless motor is under the operation. By reflecting the working condition of the tool bit to the determination of the advance angle of the brushless motor, the brushless motor can be operated with higher efficiency under the various working condition such as a hard joint operation and a soft joint operation.
Owner:MAKITA CORP
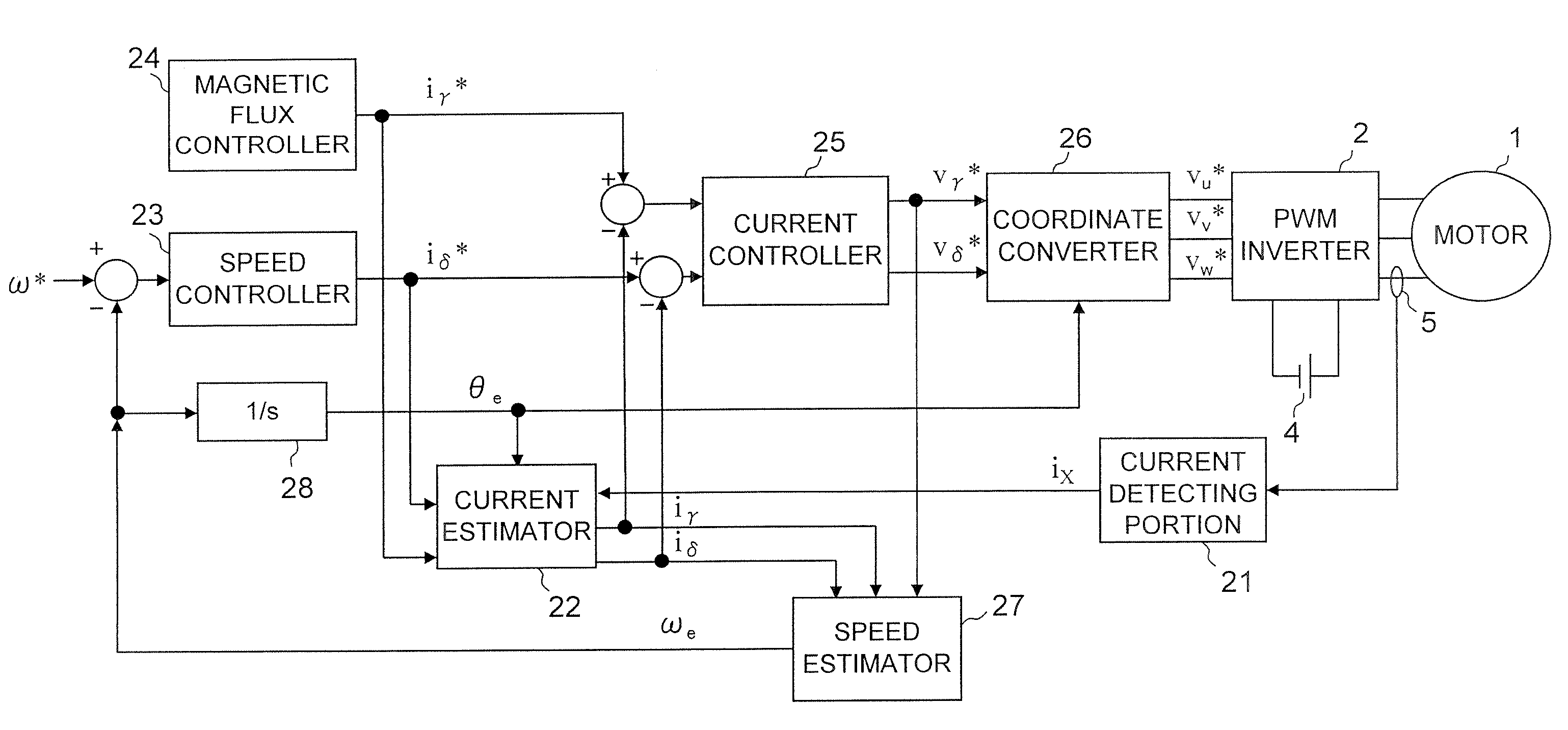
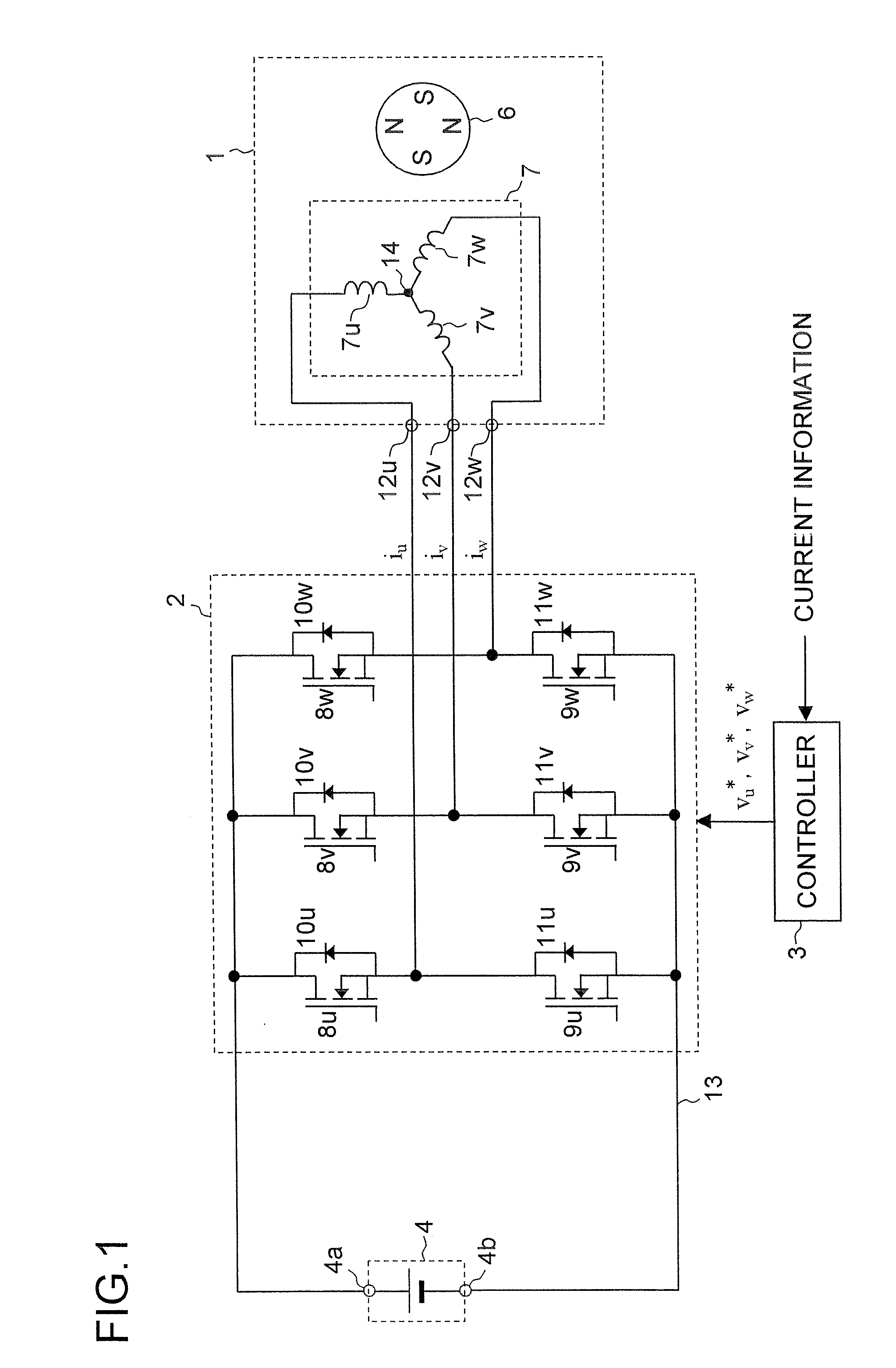
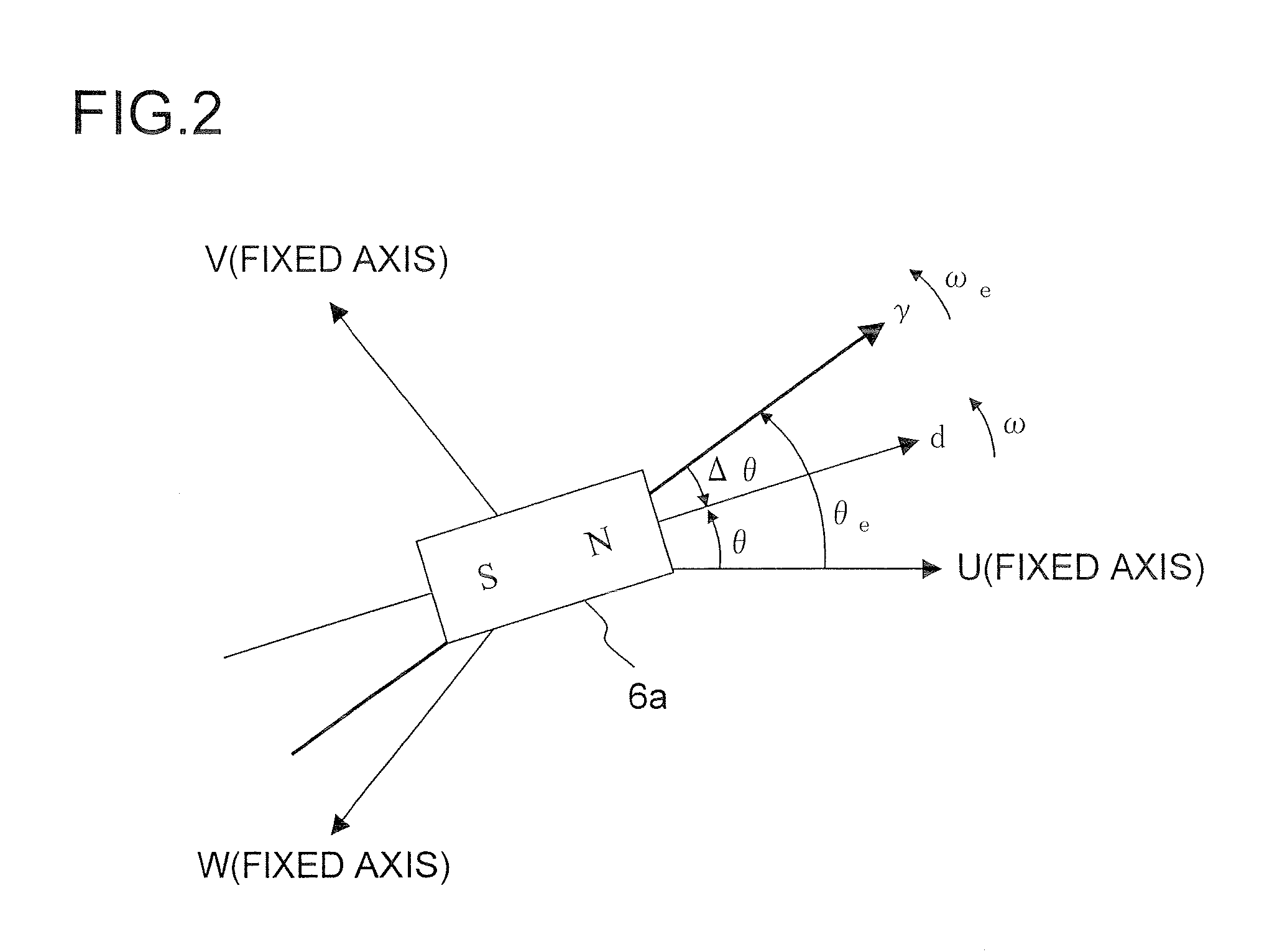
Motor control device
A motor control device includes a current detecting portion that detects phase current of one phase among three phase currents supplied from an inverter to a motor, and a current estimator that estimates phase current of phases other than the detected phase current by using a specified current value indicating current to be supplied to the motor, and derives control current corresponding to the specified current value from the estimated phase current and the phase current of one phase. The motor control device controls the motor via the inverter so that the control current follows the specified current value.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
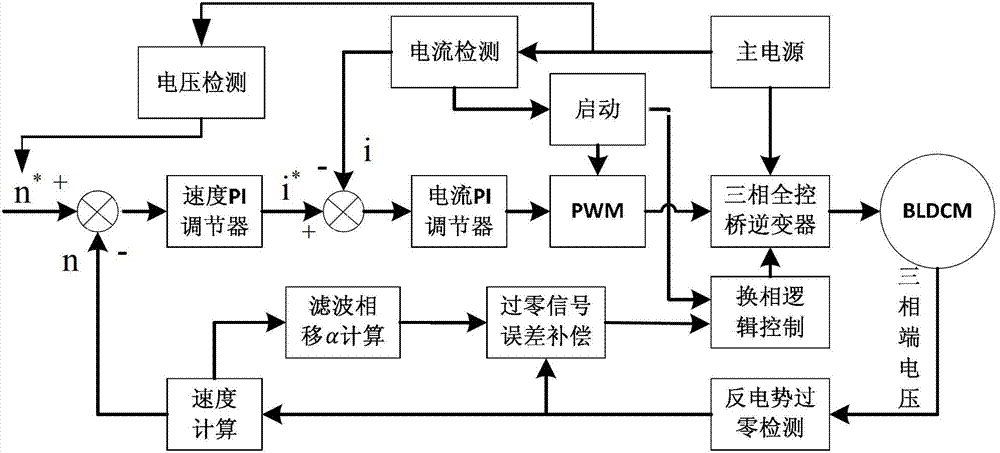
Position sensor-free double closed-loop speed regulation control method for brushless DC motor
InactiveCN103248294AAccurate control of different speedsSolve the problems of large volume and low speed accuracyTorque ripple controlSingle motor speed/torque controlClosed loopEngineering
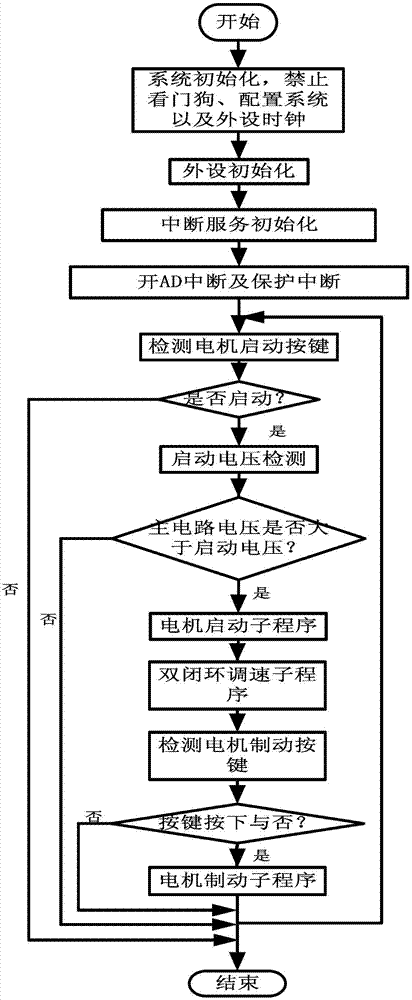
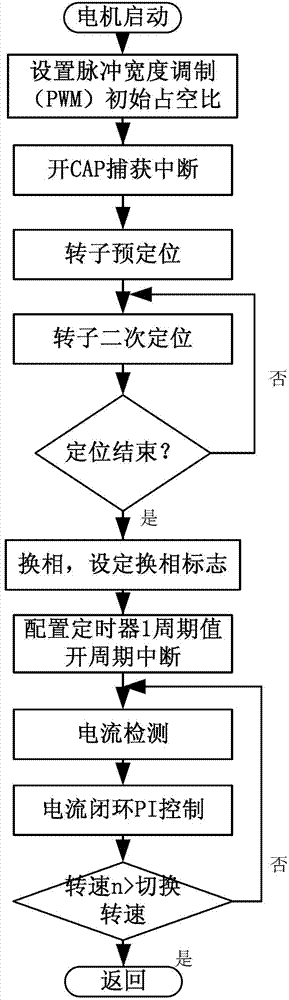
A position sensor-free double closed-loop speed regulation control method for a brushless DC motor comprises the following steps: (1) initializing functional modules and peripherals; (2) opening AD (Analog-Digital) interruption and protection interruption; (3) detecting the start key of the motor, judging whether to start the motor, if yes, executing the next step, and if not, continuing to execute the step; (4) starting voltage detection, judging whether the voltage of a main circuit is larger than starting voltage, if yes, executing the next step, and if not, returning to the step (3); (5) entering a motor starting subprogram and beginning operating the motor; (6) entering a double closed-loop speed regulation subprogram, and regulating the rotational speed and the current of the motor according to voltage value; and (7) detecting a motor brake key, judging whether to press the key, if yes, entering a motor brake subprogram, and if not, returning to the step (3). The method provided by the invention overcomes the defects of larger size, low rotational speed accuracy and the like of the conventional motor controller, can accurately control different rotational speeds of the motor, and can simultaneously realize counter electromotive force zero-cross comparison position sensor-free reversing and Hall position signal reversing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Variable-flux motor drive system
ActiveUS20090261774A1Prevent braking forceImprove securityMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlMotor drivePermanent magnet motor
A variable-flux motor drive system including a permanent-magnet motor including a permanent magnet, an inverter to drive the permanent-magnet motor, and a magnetize device to pass a magnetizing current for controlling flux of the permanent magnet. The permanent magnet is a variable magnet whose flux density is variable depending on a magnetizing current from the inverter. The magnetize device passes a magnetizing current that is over a magnetization saturation zone of magnetic material of the variable magnet. This system improves a flux repeatability of the variable magnet and a torque accuracy.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
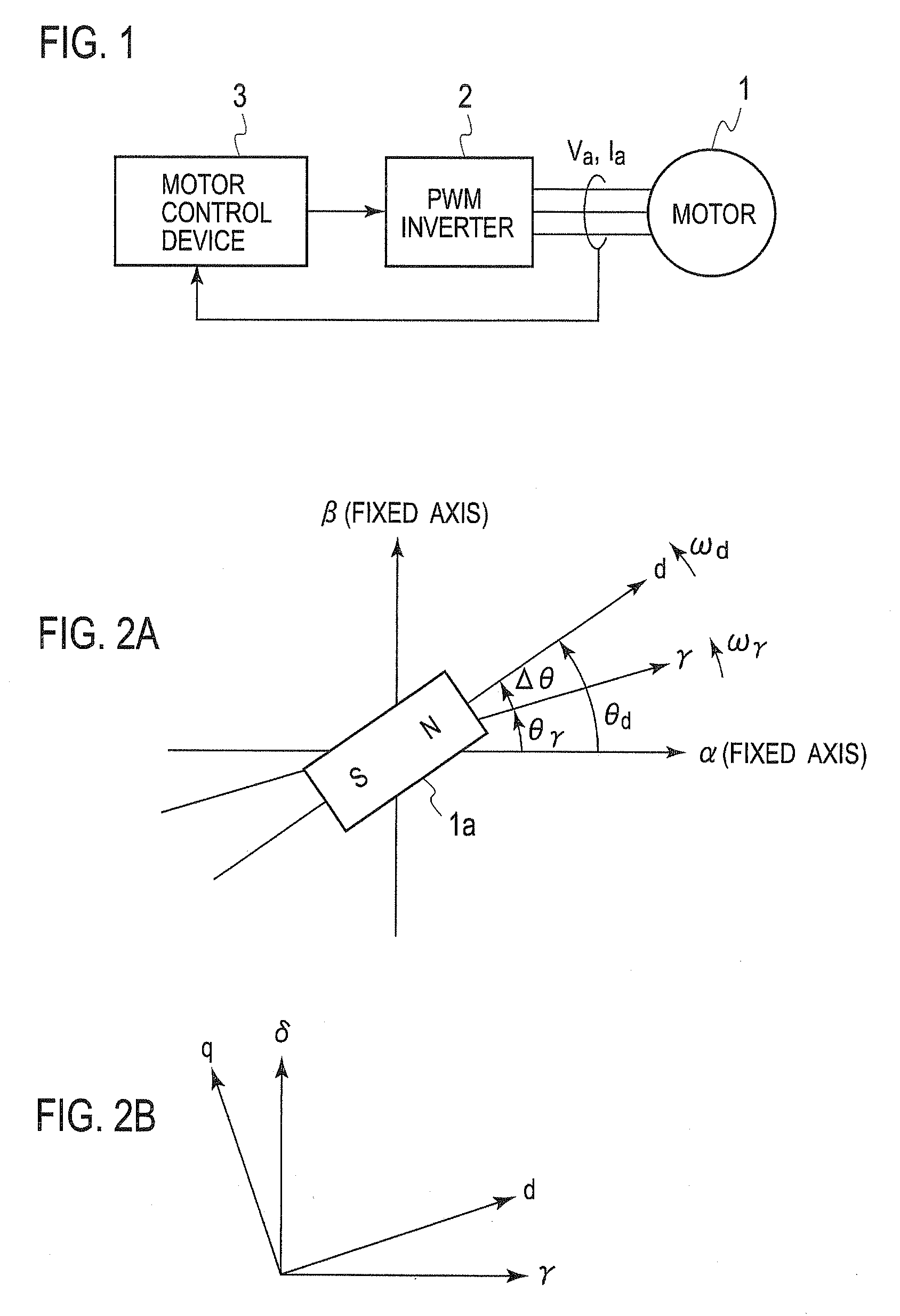
Sensorless controller of AC motor and control method
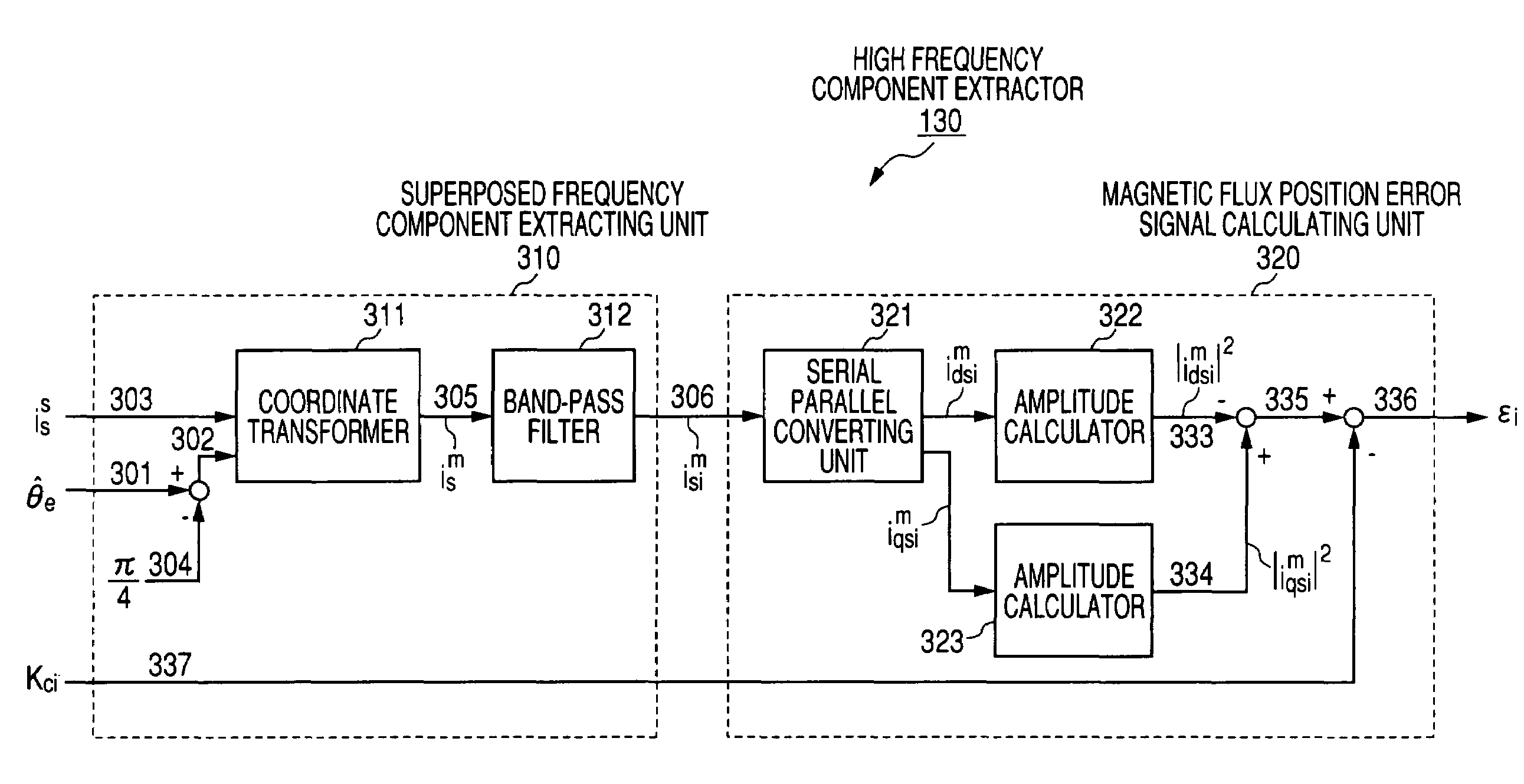
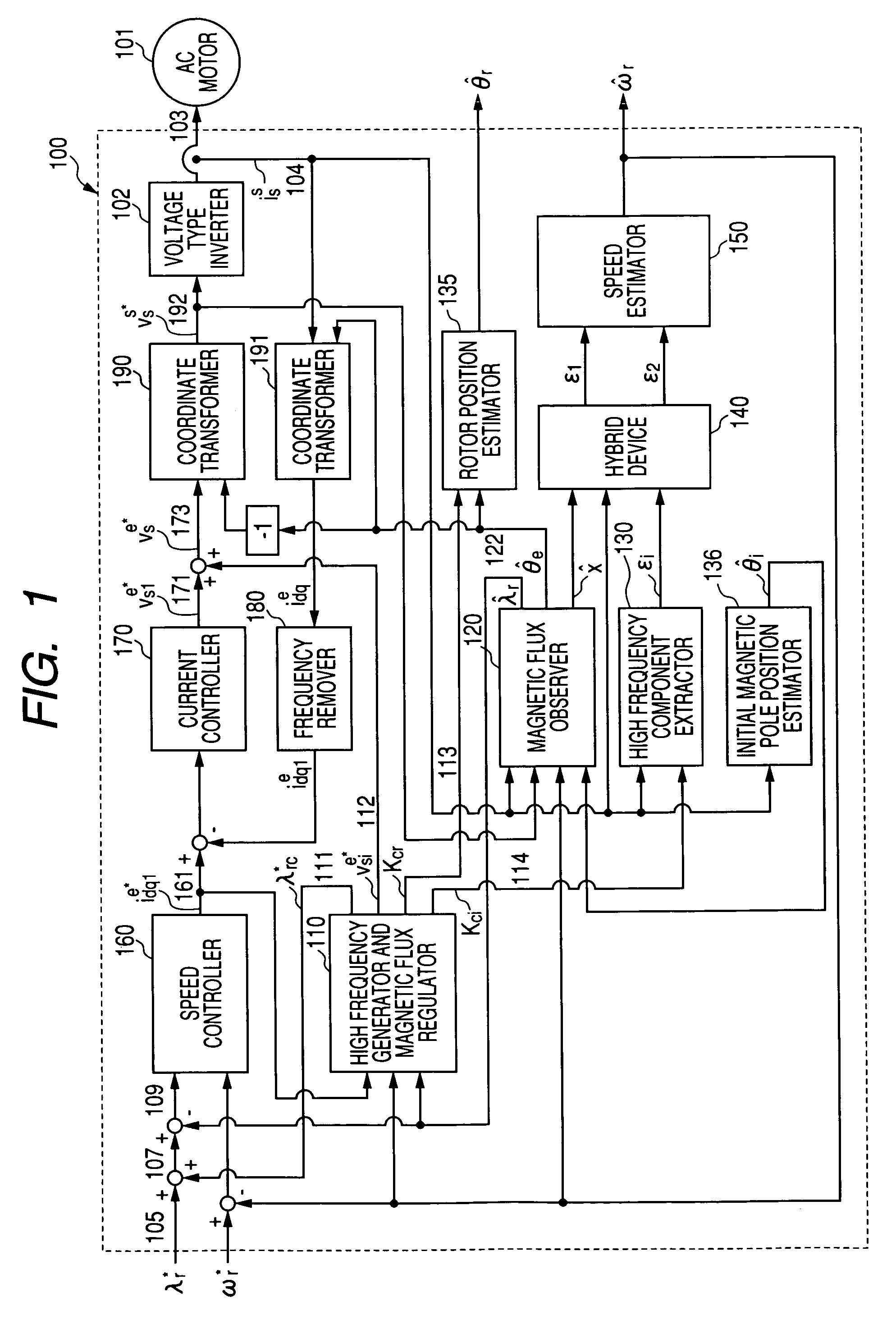
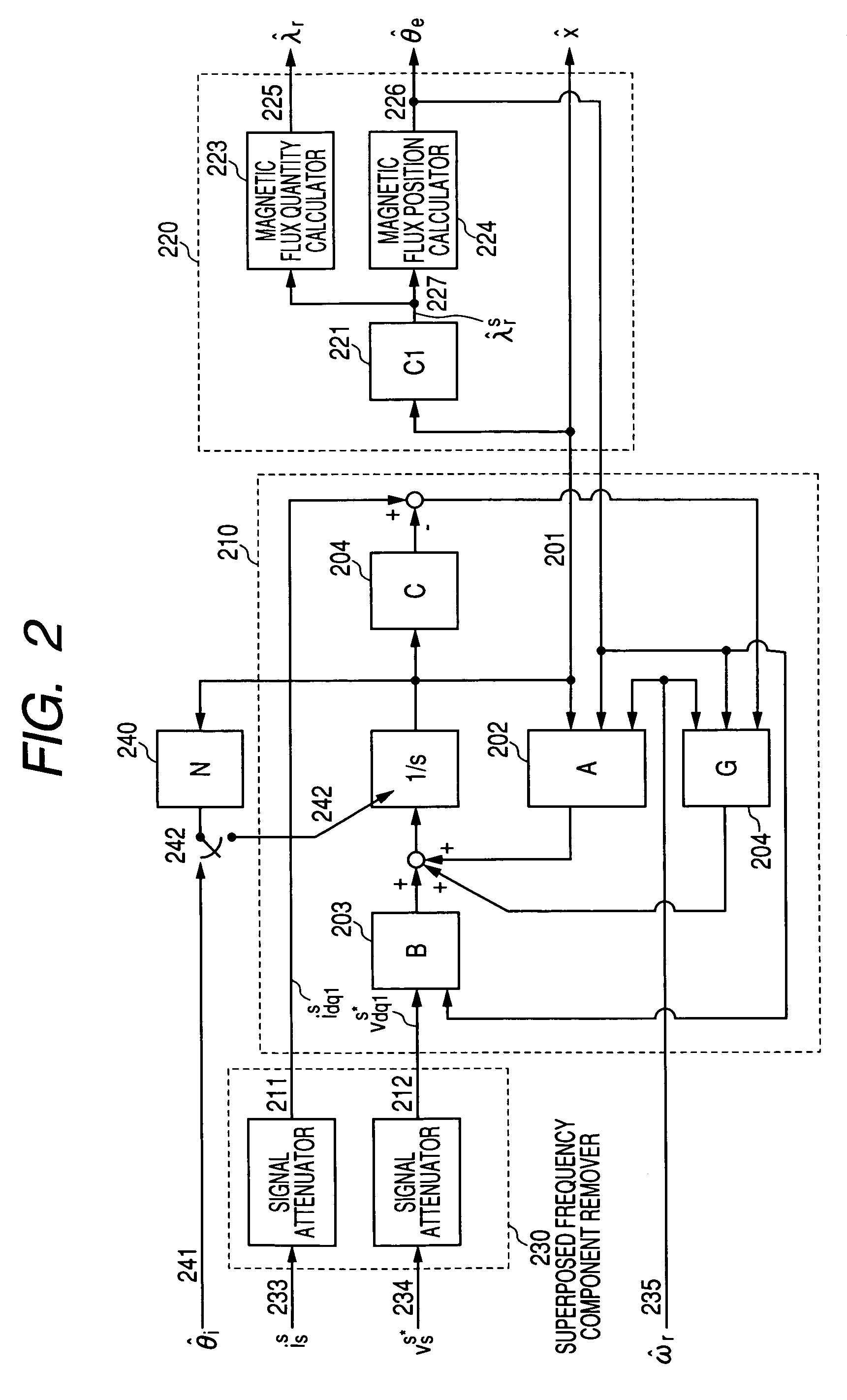
InactiveUS7045988B2Improve efficiencyMagnetic saliency at the high frequency is reducedVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlLow speedSignal on
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
Motor Control Device
ActiveUS20100045218A1Stable positionShort amount of timeSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsMagnetic polesEngineering
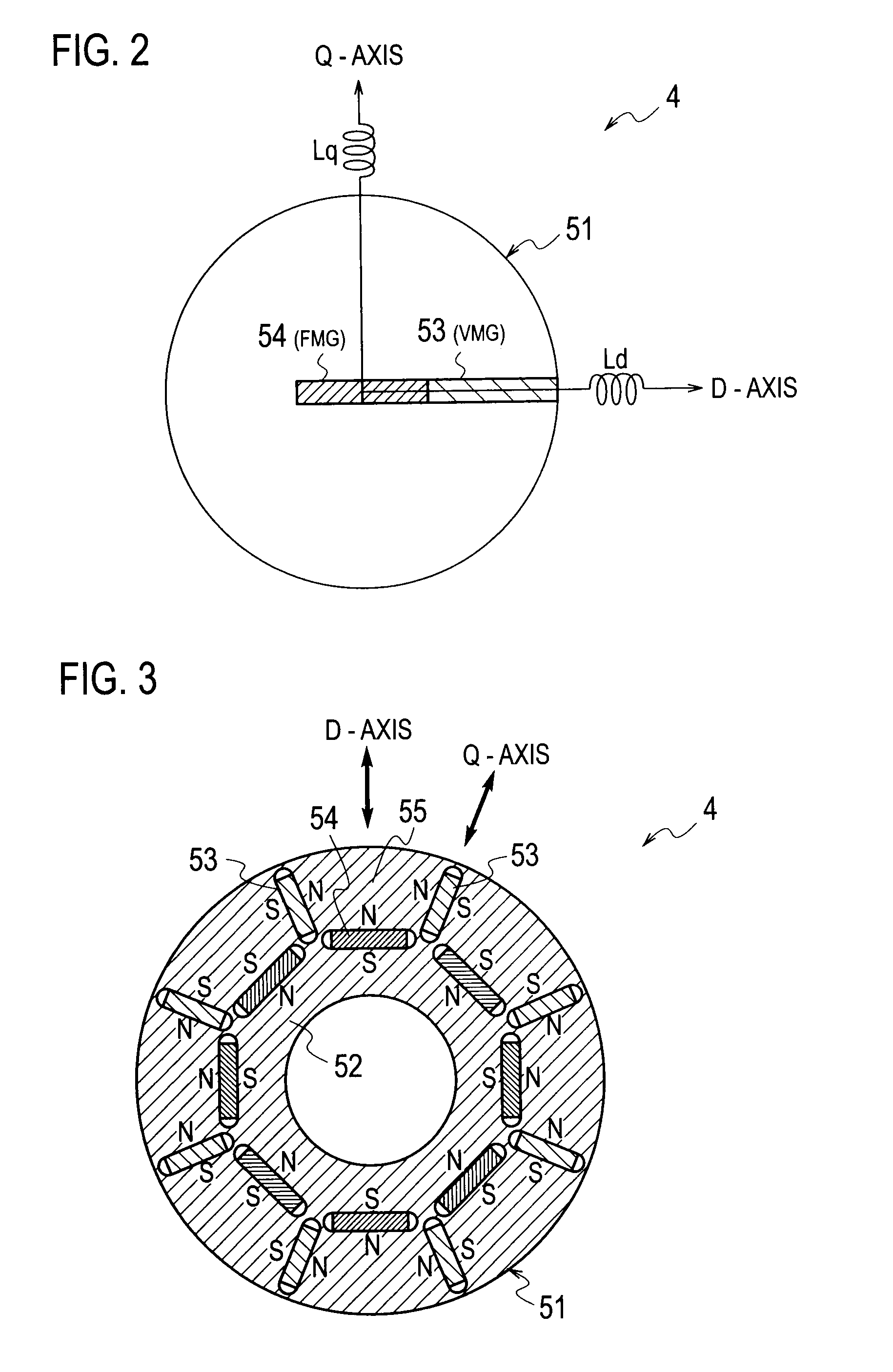
To estimate an initial magnetic pole position in a short time, estimated axes for control that correspond to the d-axis and the q-axis are set as the γ-axis and the d-axis, and a high frequency rotation voltage or alternating voltage on the γδ coordinate system is applied to the motor. A high frequency current ih that flows in the motor due to the application of the high frequency voltage is extracted from a detected motor current (armature current) and a direct current component (ihγ×ihd)DC of a product of the γ-axis and d-axis components of the high frequency current ih is derived. On the other hand, the γ′-axis component ichγ and the δ′-axis component ichd of the high frequency current ih that are shifted by p / 4 in electric angle from the γ-axis and the d-axis are obtained and a direct current component of their product (ichγ×ichd)DC is obtained. Thereafter, the magnetic pole position is estimated by computing the axial error Δθ between the γ-d axes utilizing the two direct current components.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
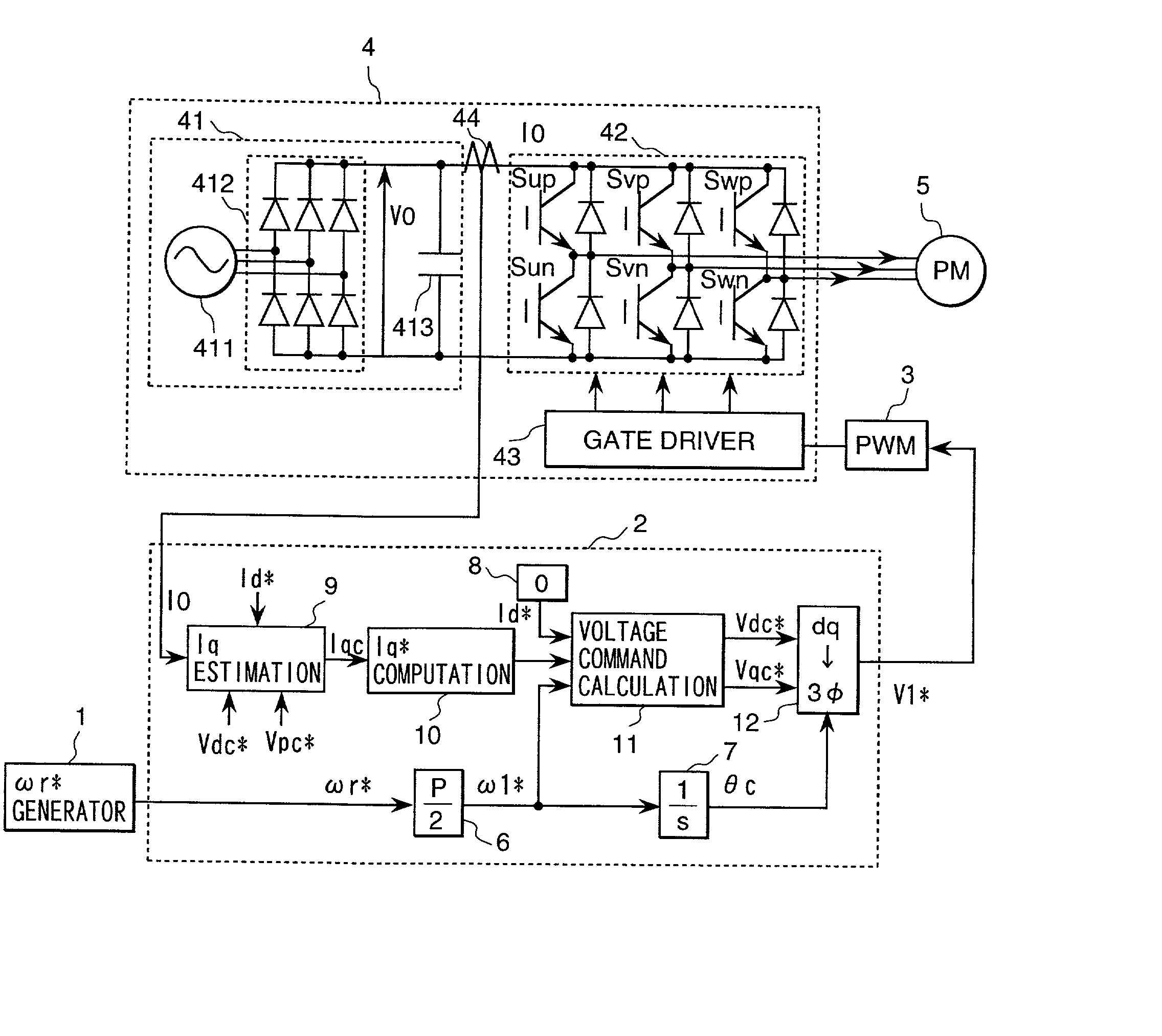
Sensorless control system for synchronous motor
InactiveUS20030030404A1DC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motors startersSynchronous motorDc current
A synchronous motor drive system in accordance with the present invention detects a DC current of an inverter which drives a synchronous motor, and based on the magnitude of the current, estimates torque current components that flow through the motor, and then based on the estimated value, determines the voltage which is applied to the motor, and finally estimates and computes the magnetic pole axis located inside the motor using the estimated value of the torque current.
Owner:HITACHI JOHNSON CONTROLS AIR CONDITIONING INC
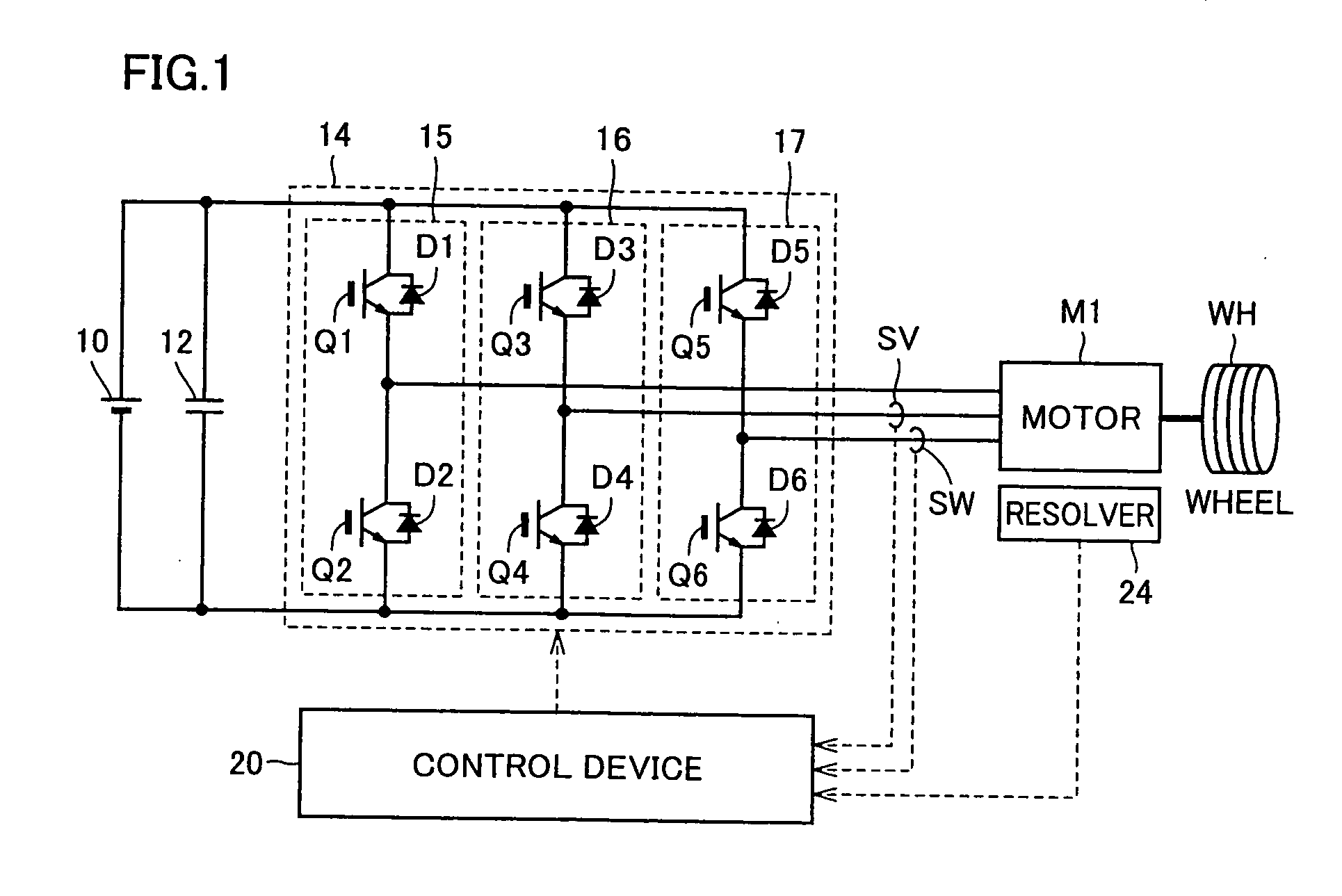
Vehicle equipped with motor and inverter
ActiveUS20100052583A1Reduce noiseIncrease fuel consumptionSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsFrequency changerDrive wheel
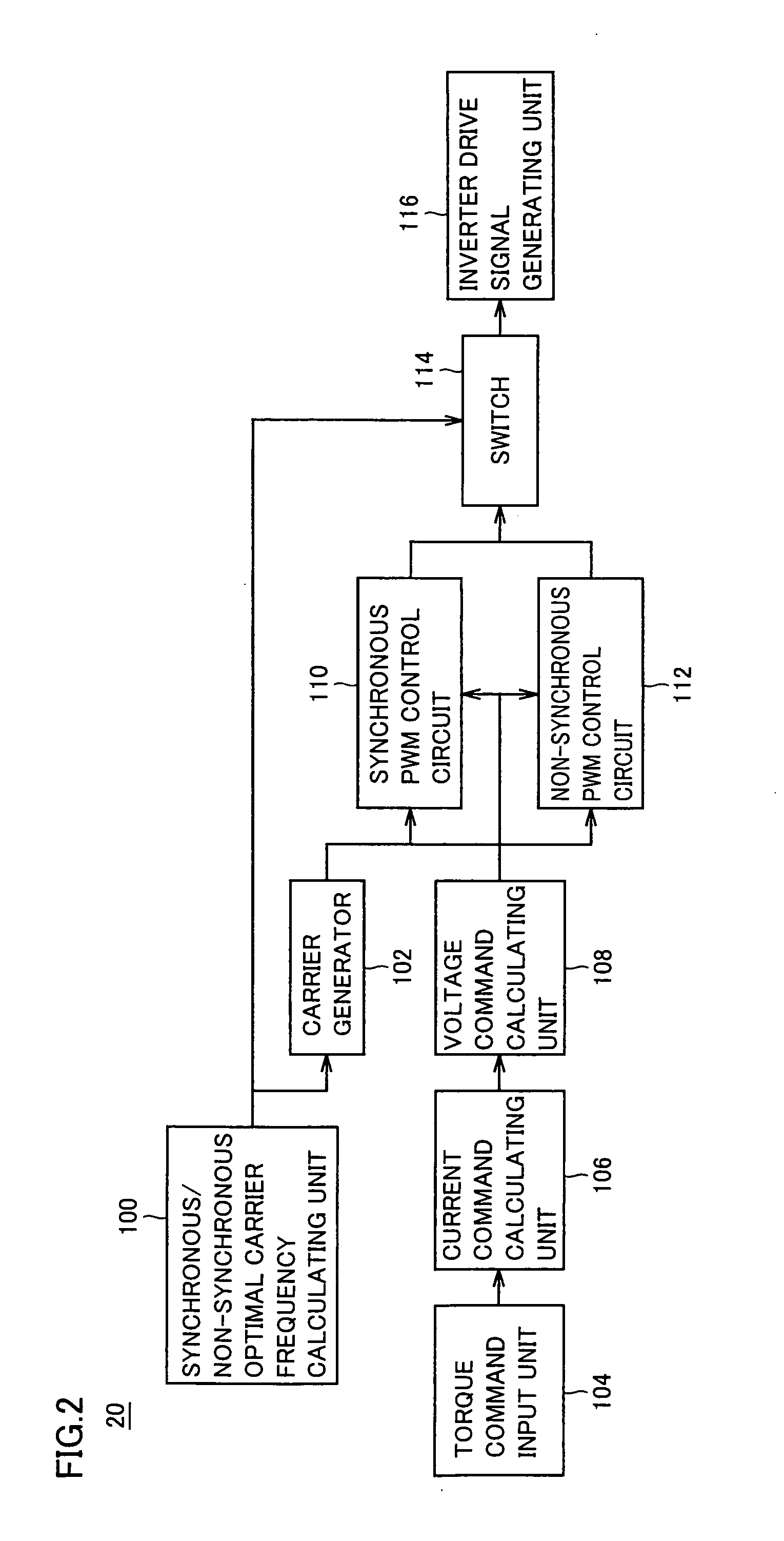
A vehicle includes a motor for driving wheels WH, an inverter to drive the motor, and a control device to perform PWM control of the inverter. The control device performs synchronous PWM control in a case where an electric current supplied to the motor by the inverter or torque generated in the motor is larger than a threshold value; and performs the synchronous PWM control or non-synchronous PWM control in a case where the electric current or the torque is smaller than the threshold value and sets carrier frequency or a pulse number of the PWM control to be higher than the case where the electric current or the torque is larger than the threshold value. Thereby, it is possible to provide a vehicle of achieving reduction of noise, reduction of cost and improvement of fuel consumption in a balanced manner.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com