Patents
Literature
958 results about "Reluctance motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
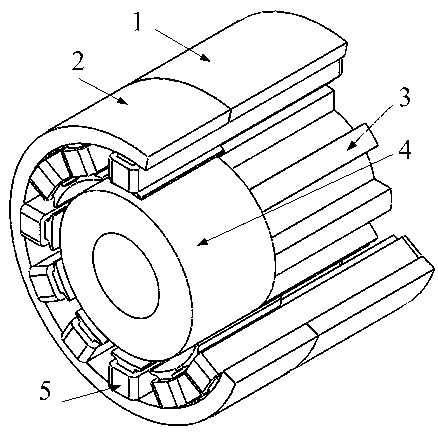
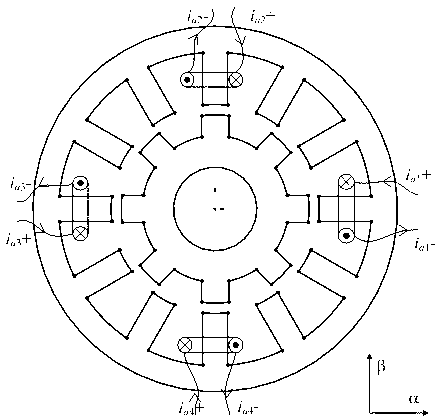
A reluctance motor is a type of electric motor that induces non-permanent magnetic poles on the ferromagnetic rotor. The rotor does not have any windings. It generates torque through magnetic reluctance.
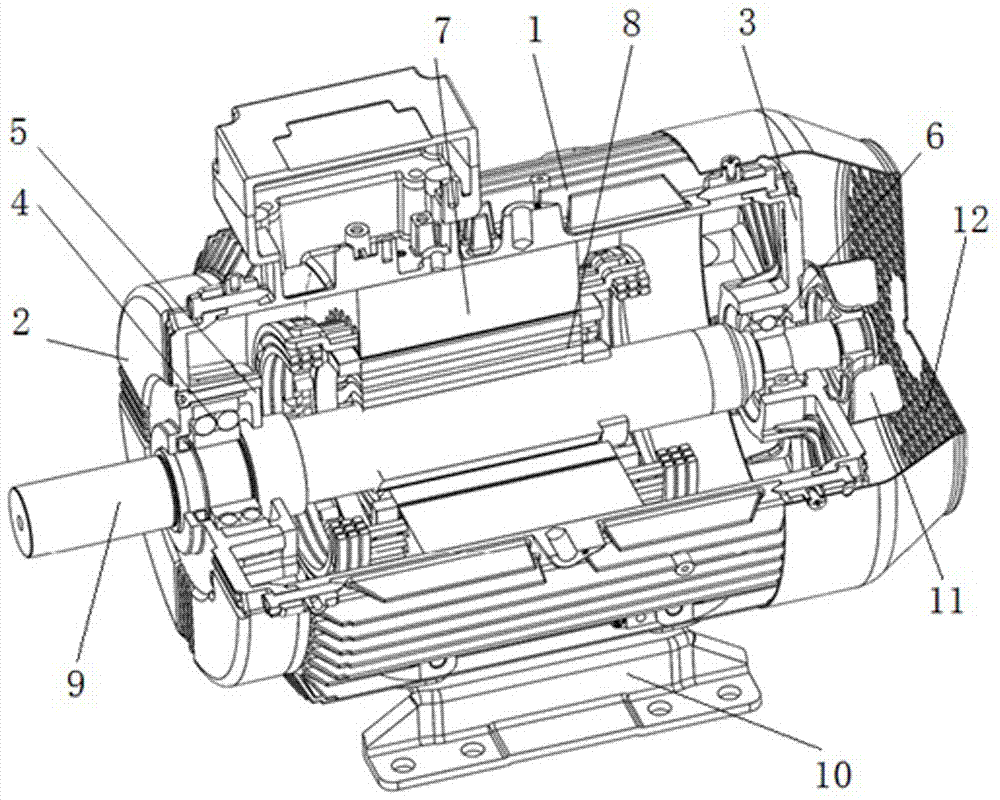
Reluctance motor with improved stator structure
InactiveUS20100123426A1Reduce efficiency of motorHigh cost of controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlReluctance motorEngineering
Owner:DENSO CORP
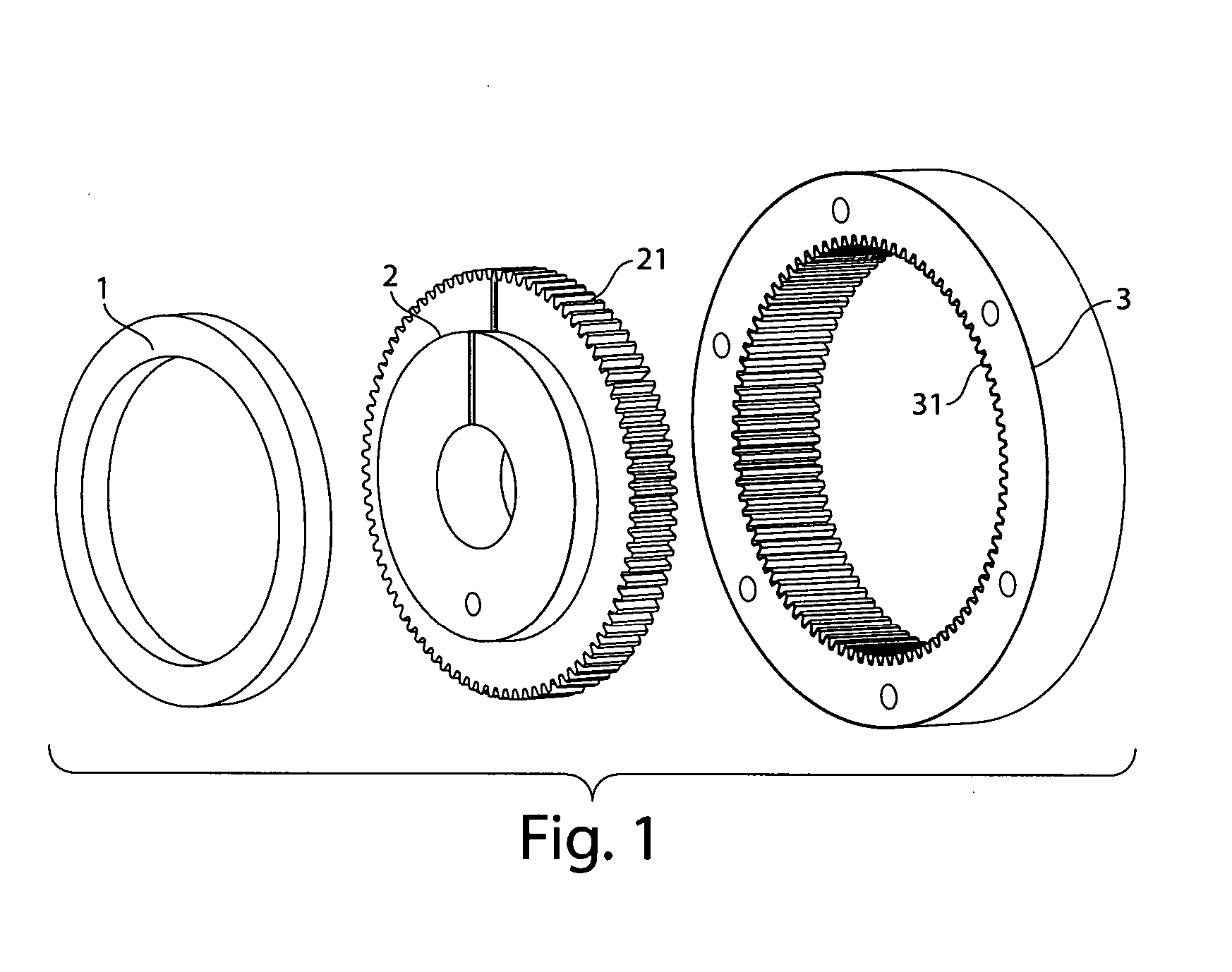
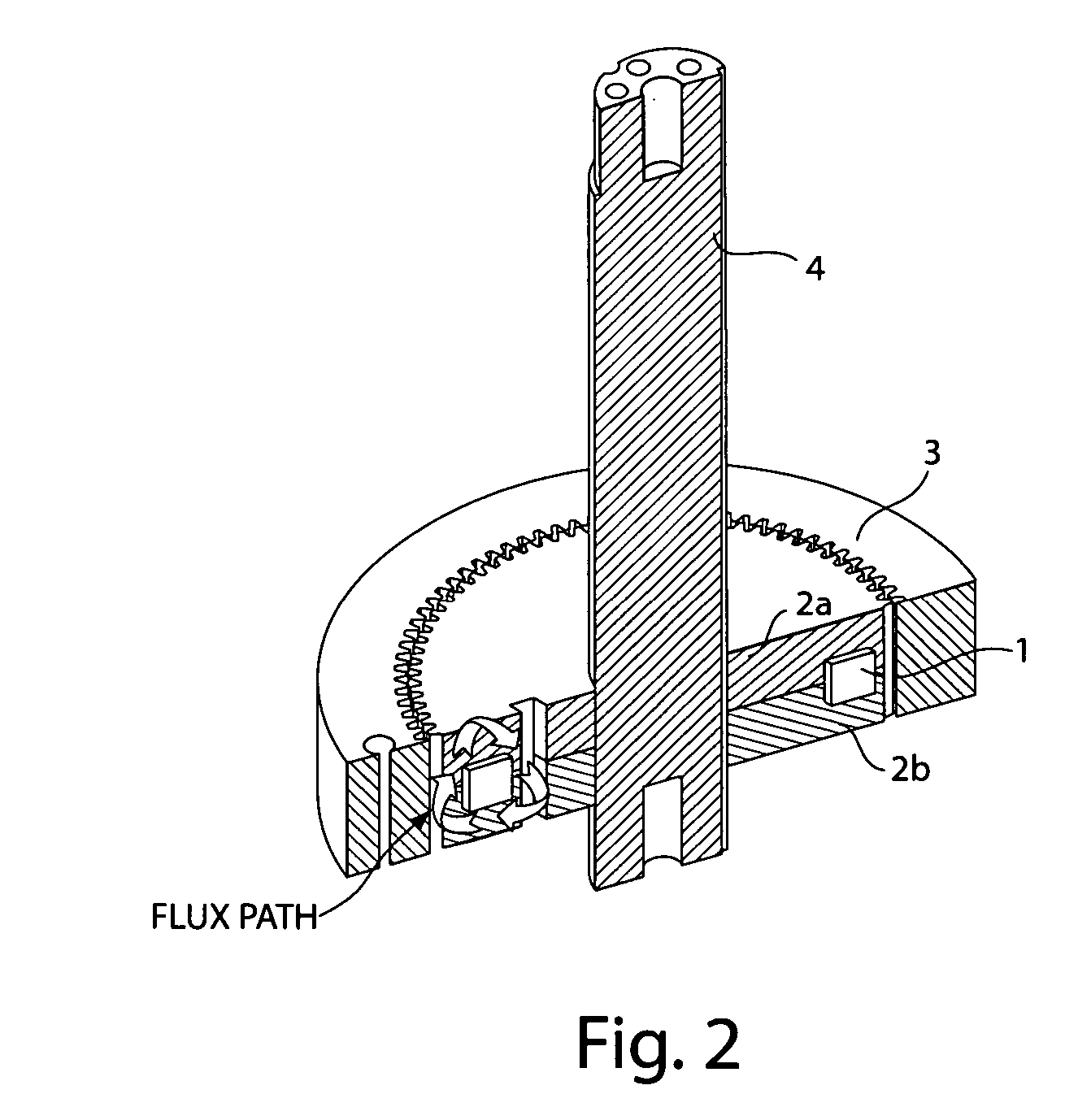
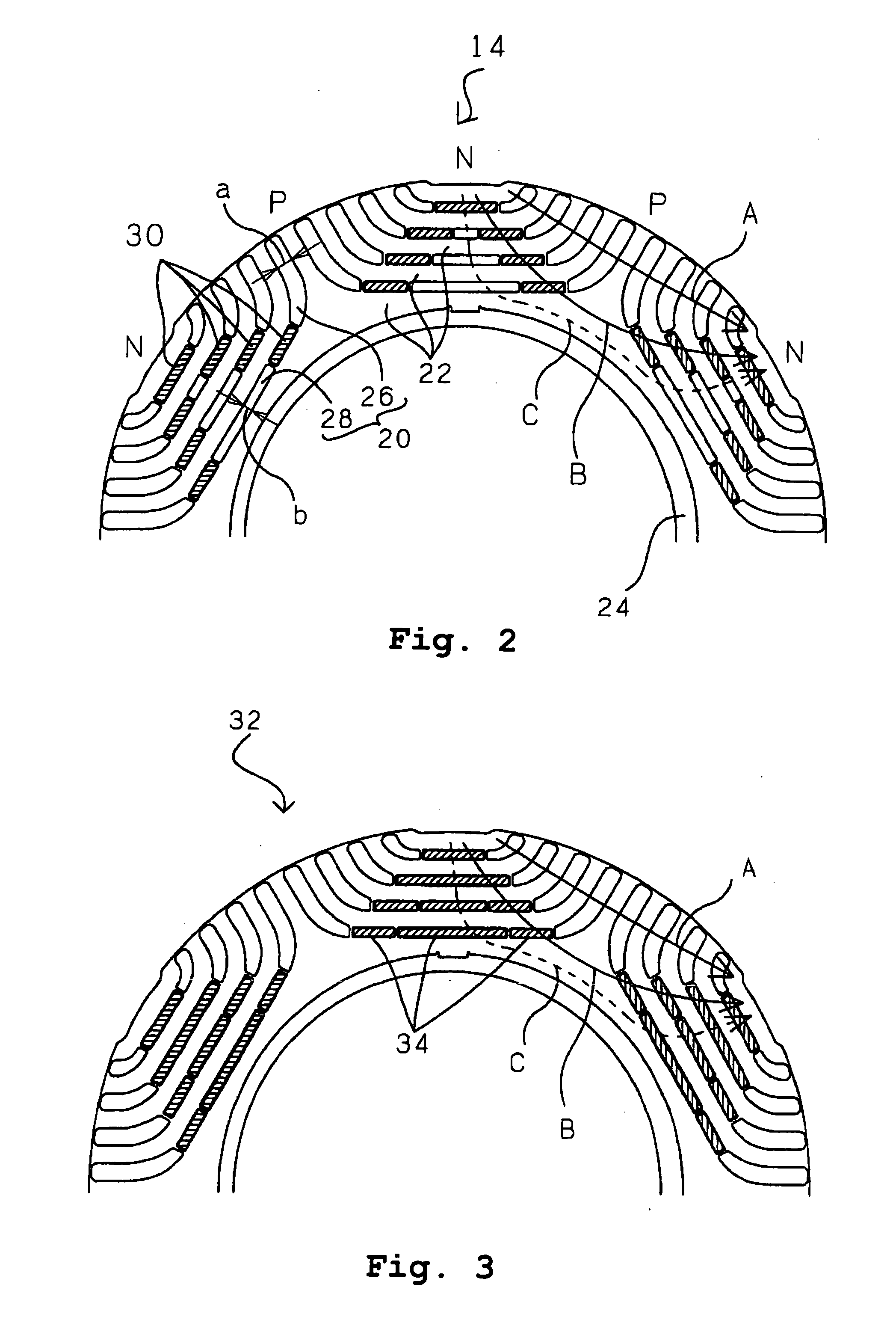
Reluctance motor
InactiveUS6121706ASynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic polesReluctance motor
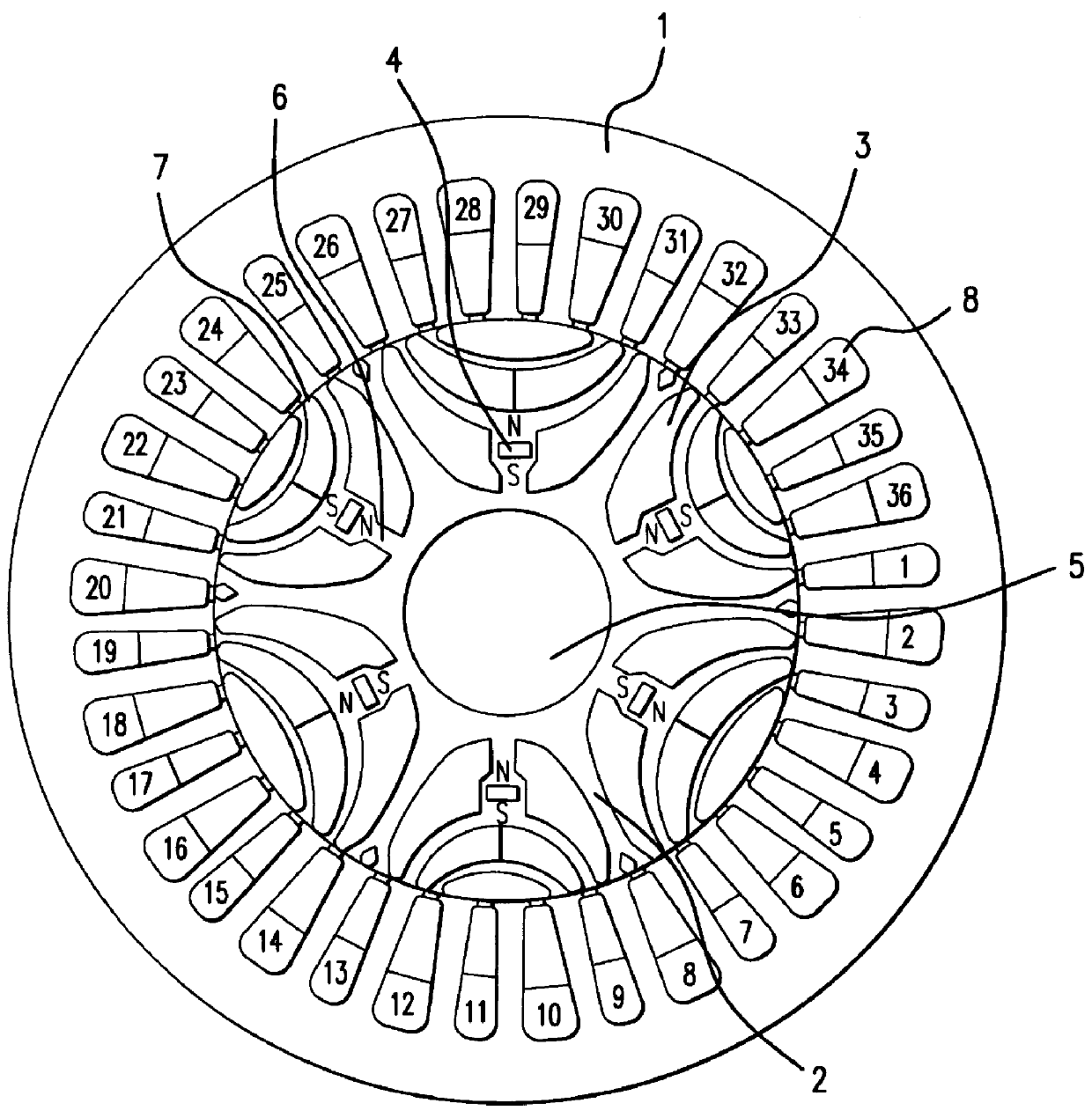
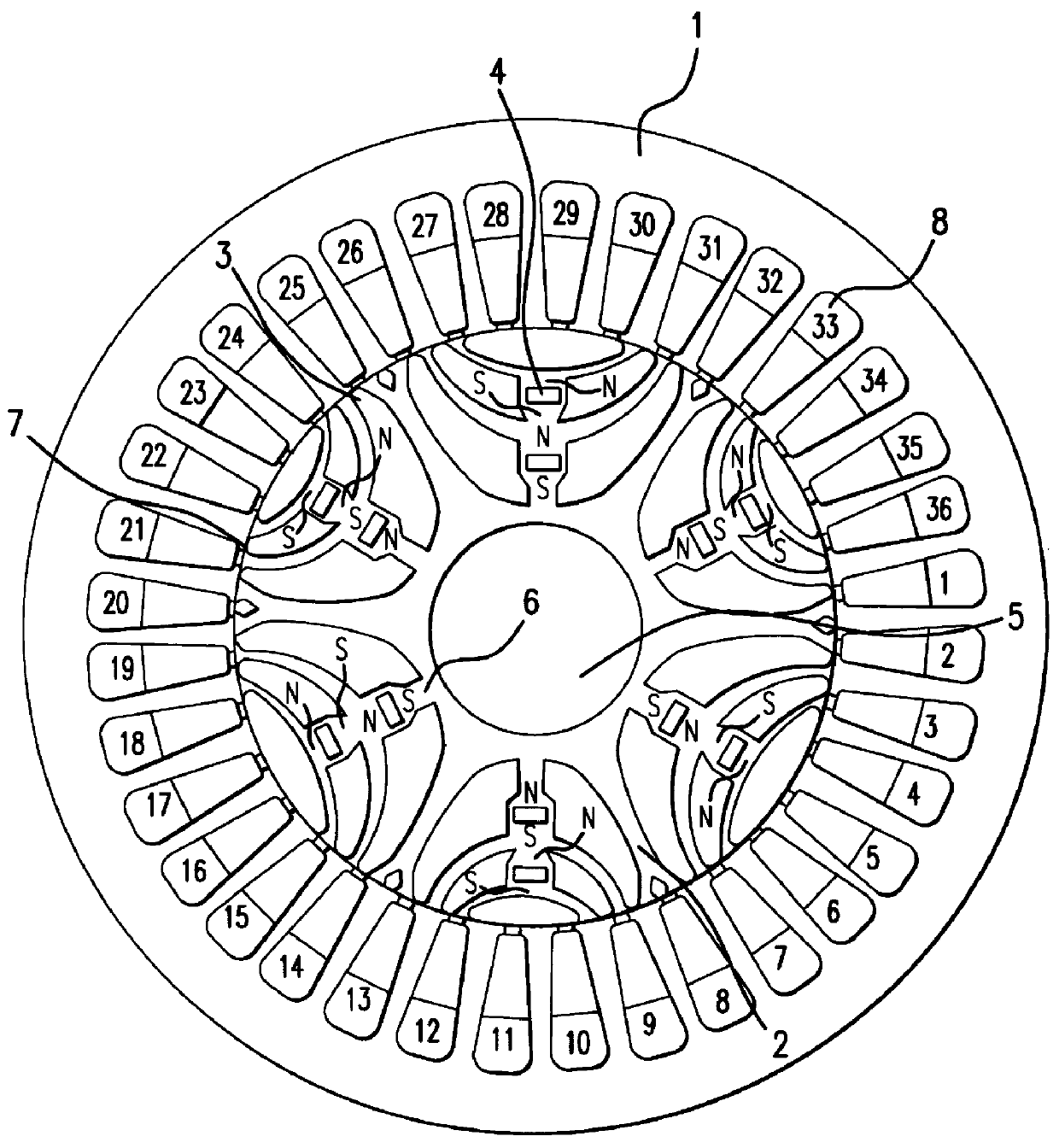
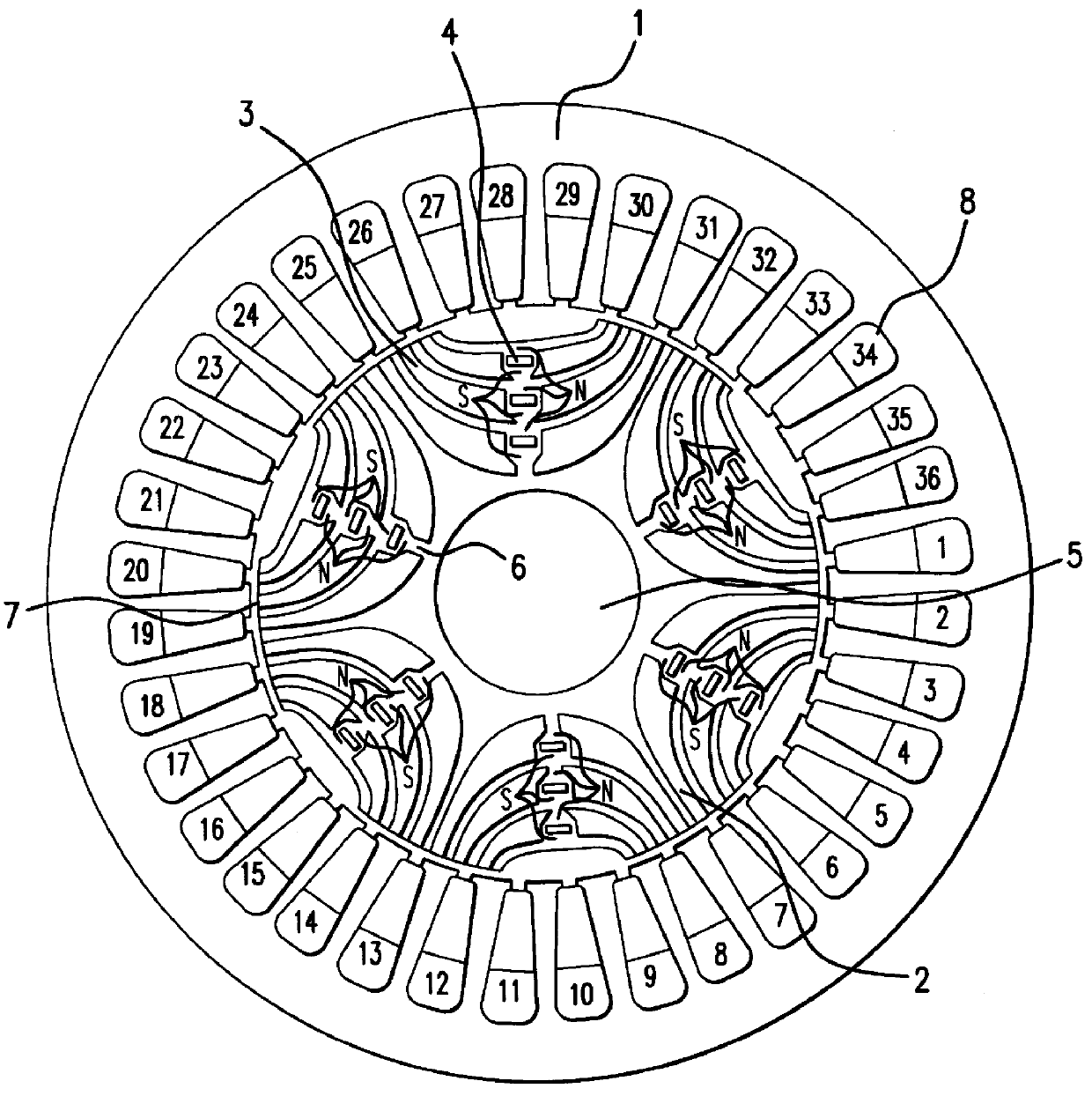
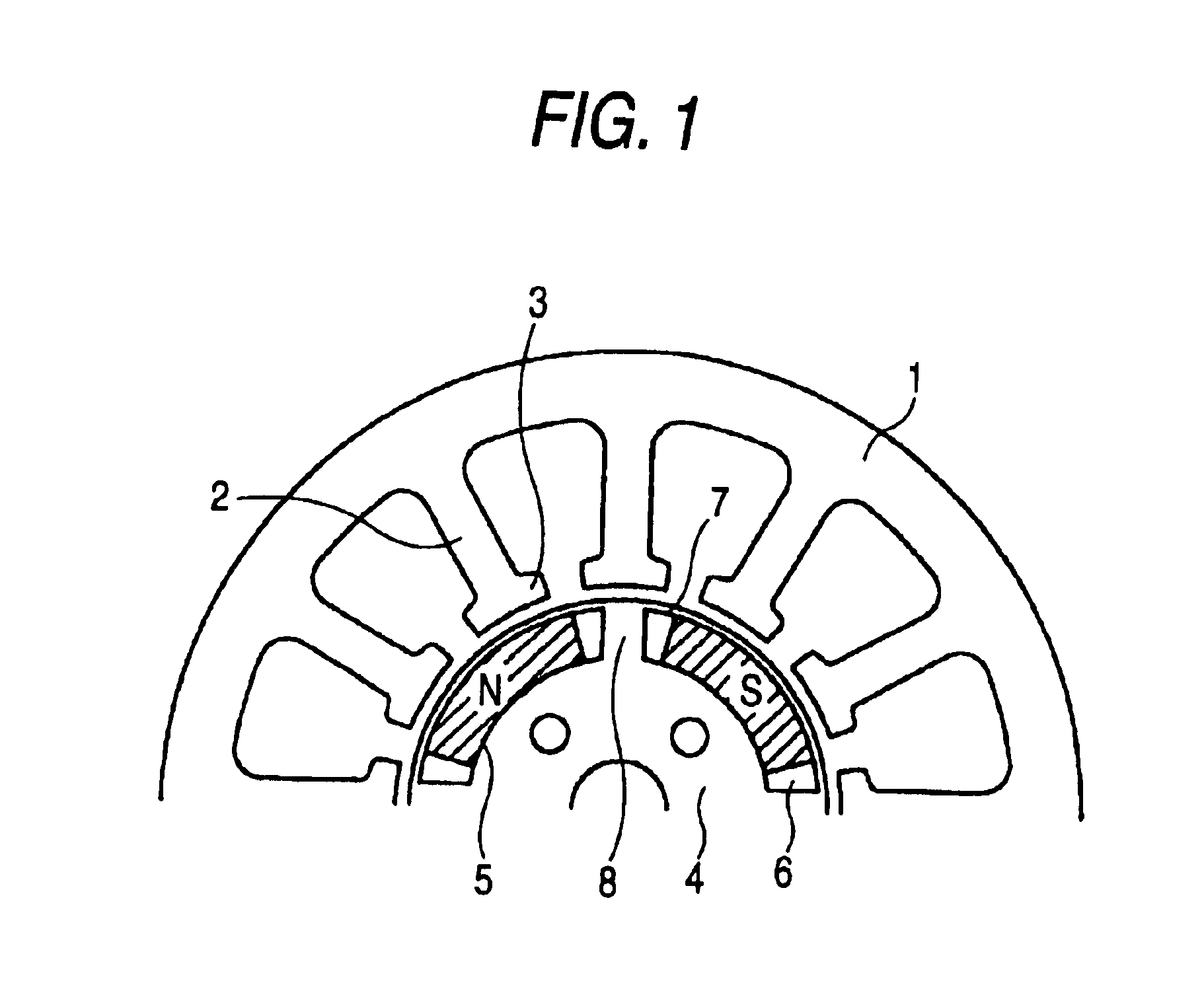
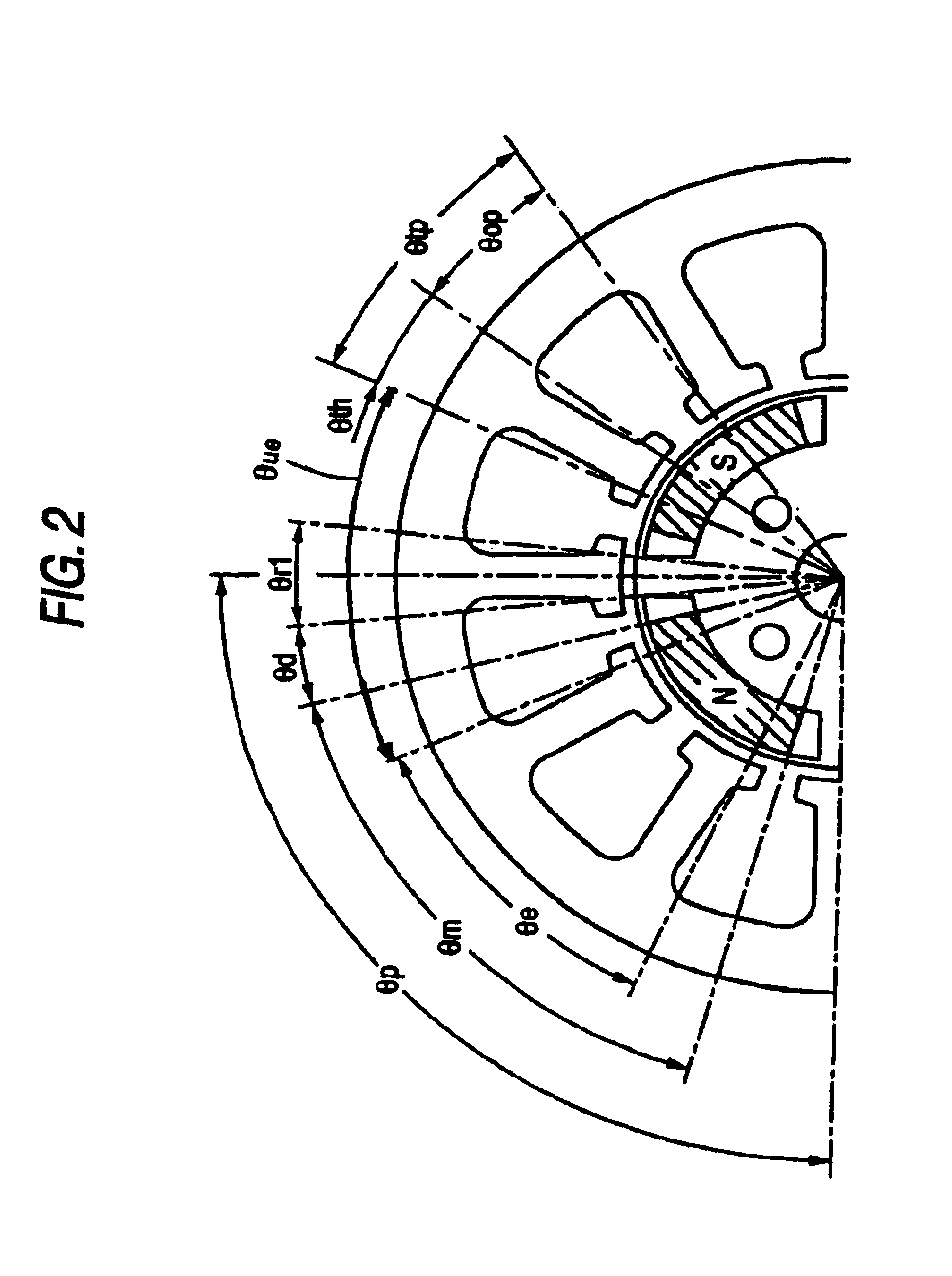
A reluctance motor is provided that reduces leaking magnetic flux. To generate magnetic flux between adjacent magnetic poles in a rotor 2, permanent magnets 4 are disposed in approximate centers of split magnetic paths near a borderline area between two magnetic poles in an internal portion of the rotor. Further, each of slots 8 in a stator 1 is wound with a coil of a corresponding phase such that the vector phase and amplitude expressed by the products of the number of coil turns and the amount of passing current, namely, ampere-turns, become almost identical for each of the slots. By reducing leaking magnetic flux according to this arrangement, generated torque can be increased. As the rotor mechanical strength is enhanced, the rotor can be safely driven at a higher speed. A practical motor is obtained that simultaneously achieves improved motor characteristics and reduced torque ripples.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Permanent magnet rotor type electric motor with different permanent magnet materials
InactiveUS6025667AMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesBrushless motorsPermanent magnet rotor
In an electric motor, such as a DC brushless motor or the like, having a permanent magnet in a rotor, each magnetic pole is formed of three permanent magnets, and the permanent magnets are made of at least two kinds of magnetic materials represented by ferrite magnet and rare-earth magnet. Thus, in a permanent magnet rotor type electric motor, a reluctance torque and a magnetic flux density can be selectively established, and cost is reasonable, corresponding to the quality.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Axial gap permanent magnet reluctance motor and method
InactiveUS20060131986A1Reduce axial loadReduction in iron reduces rotor inertiaMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsHarmonicElectric machine
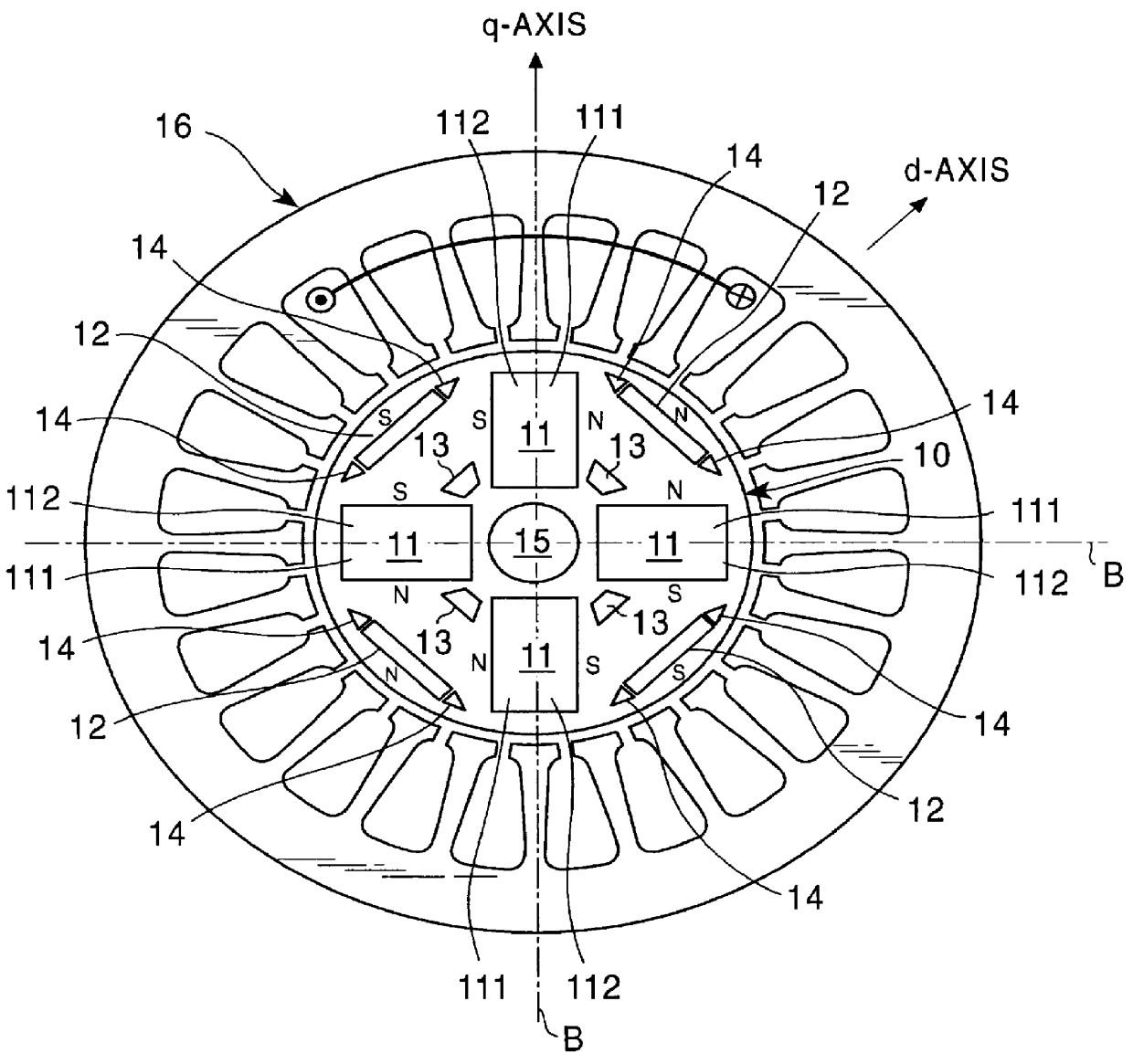
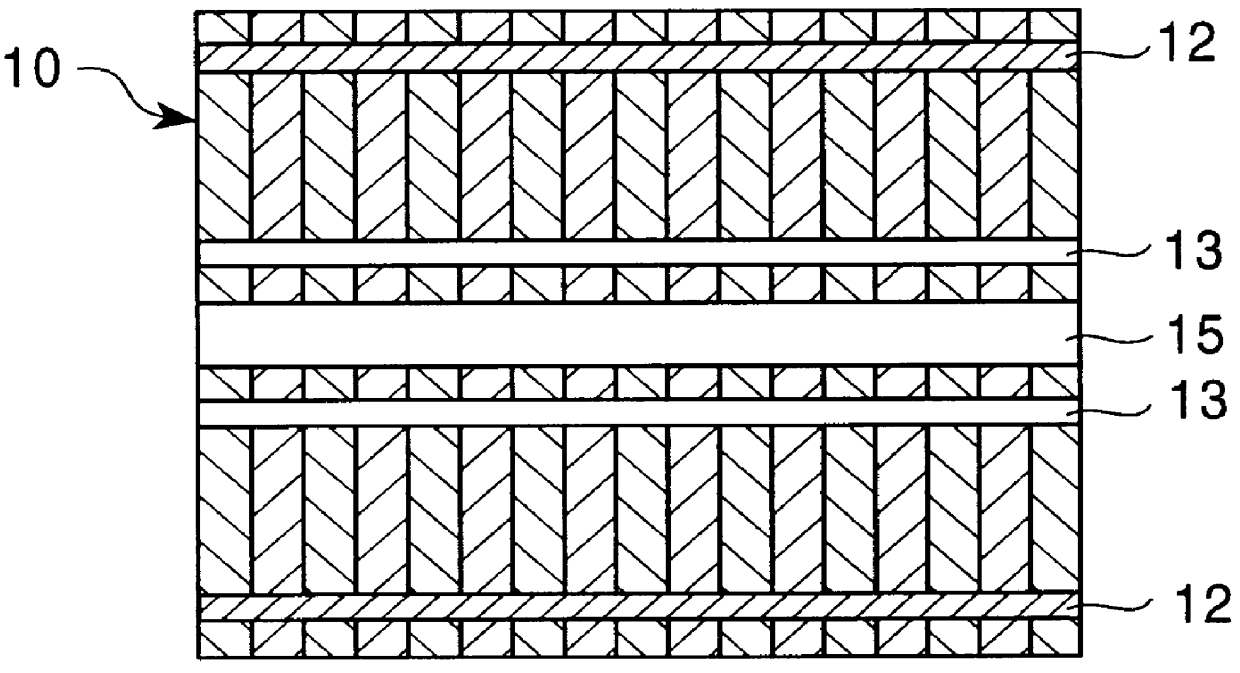
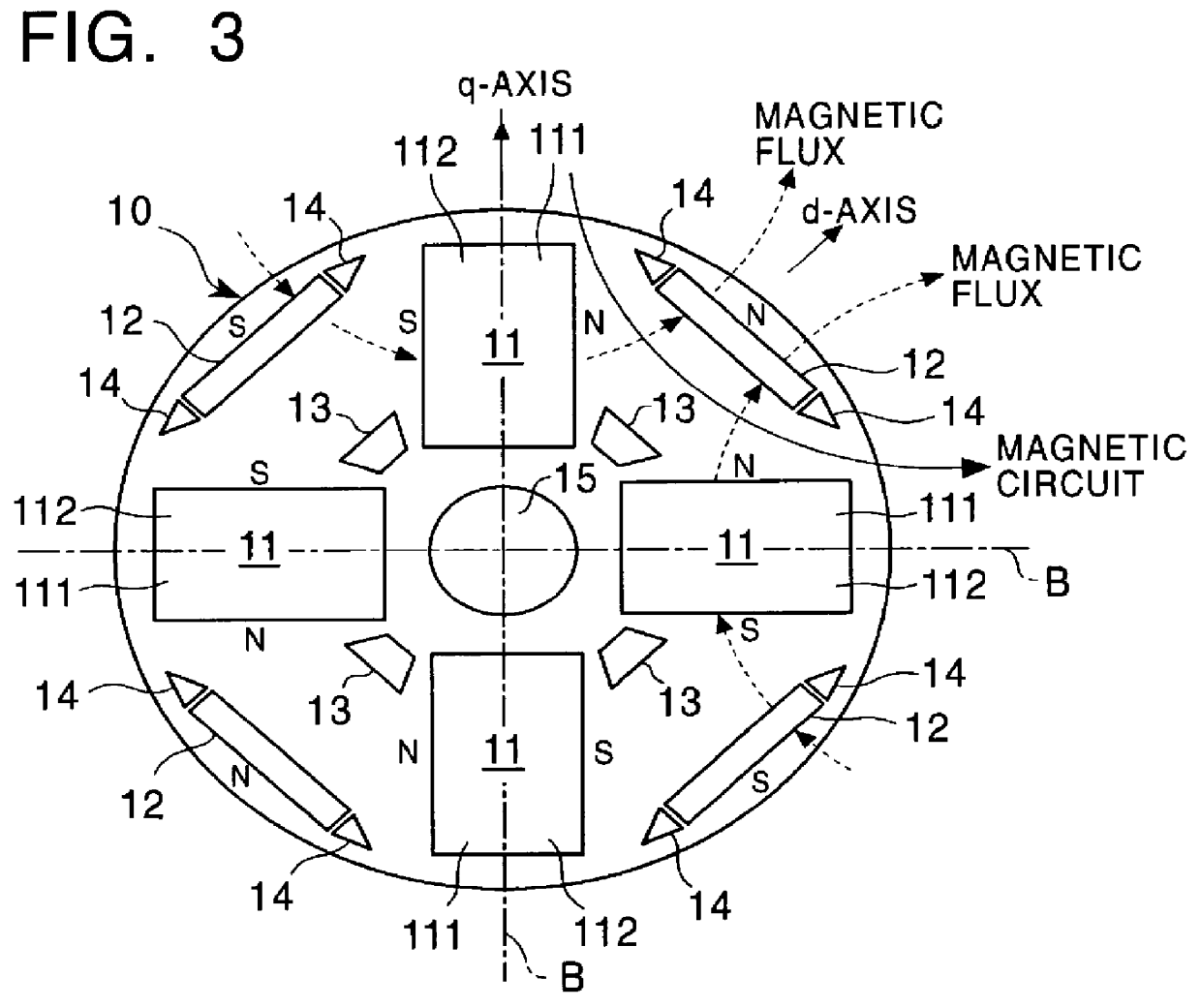
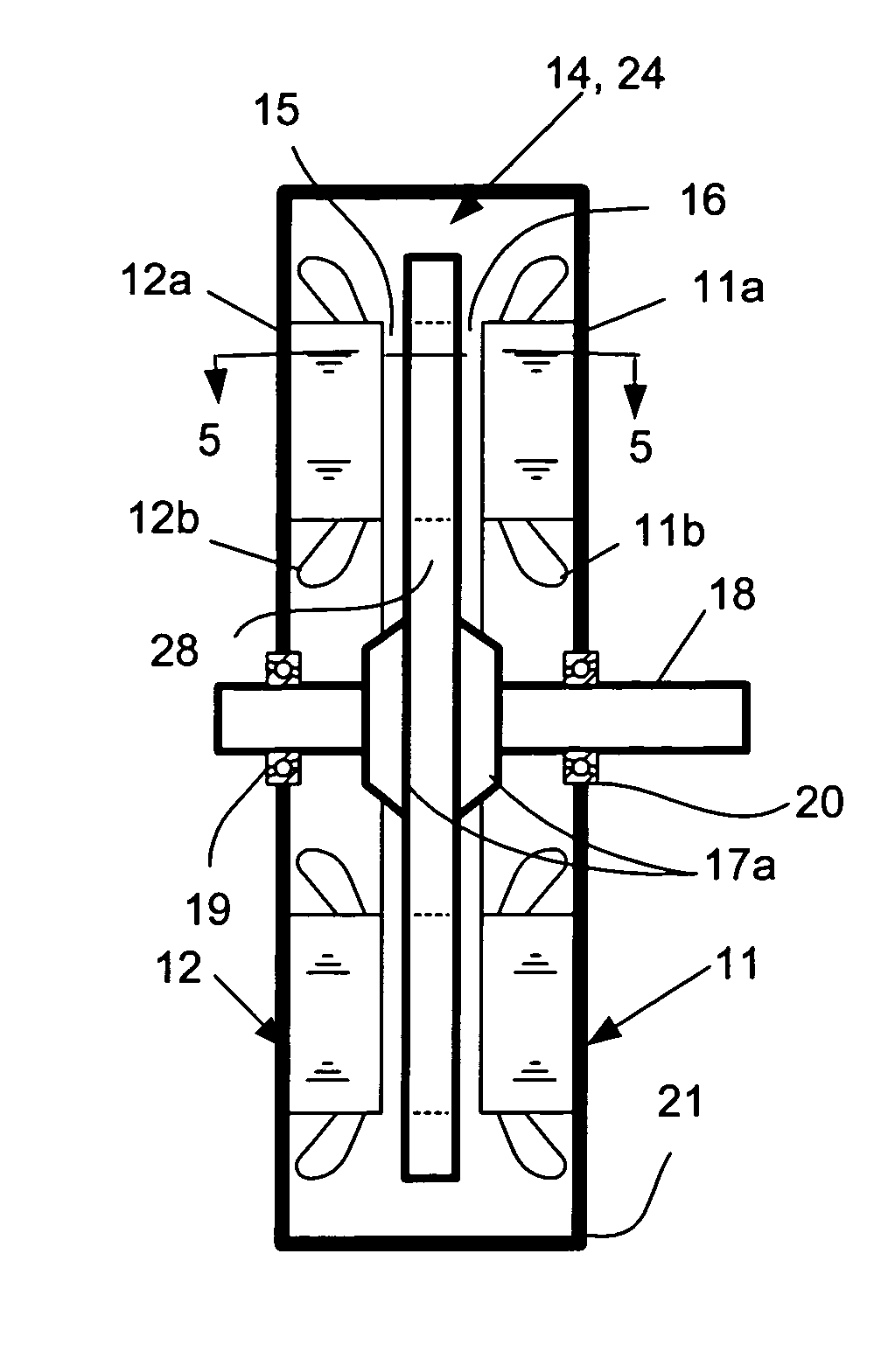
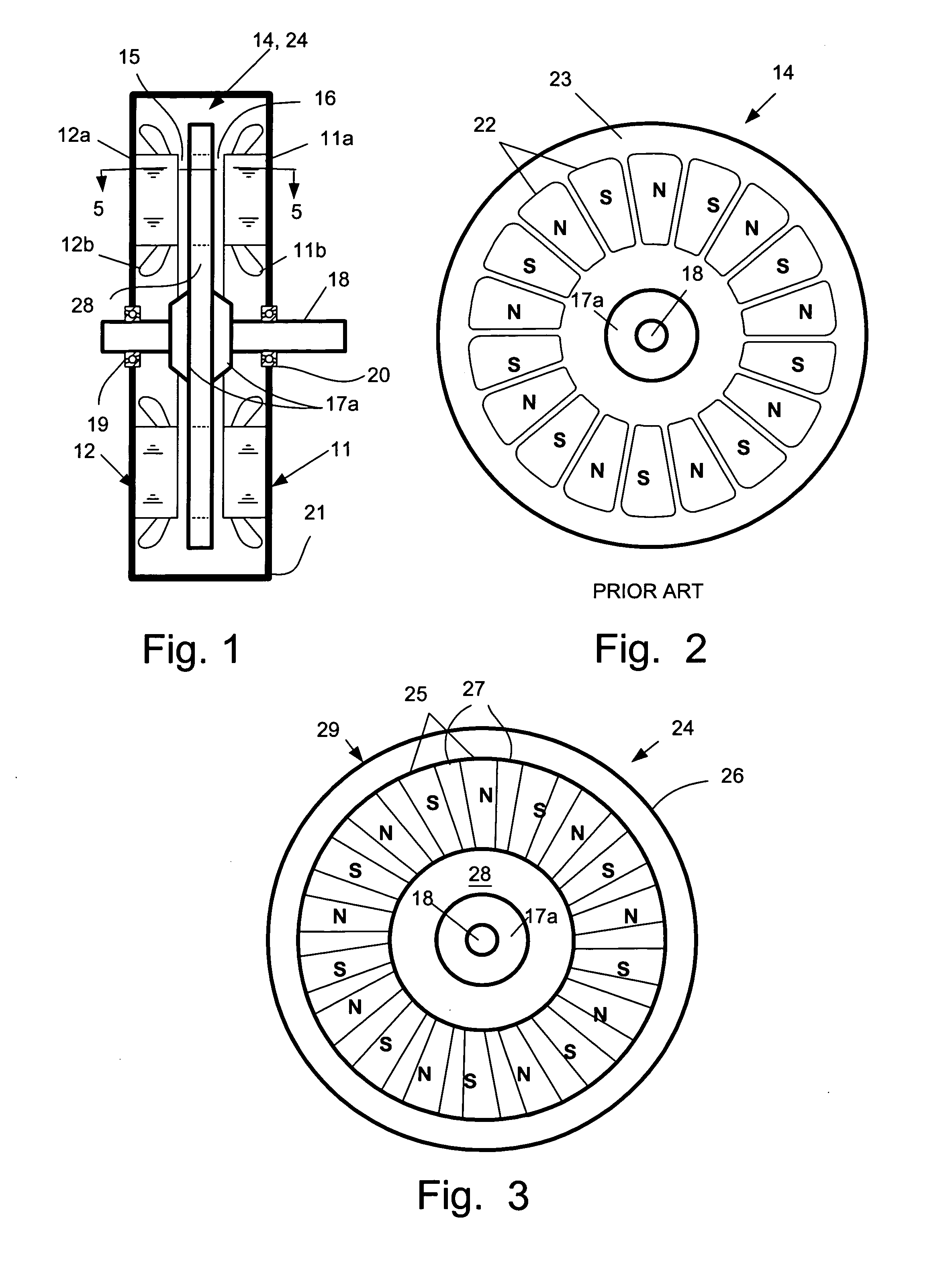
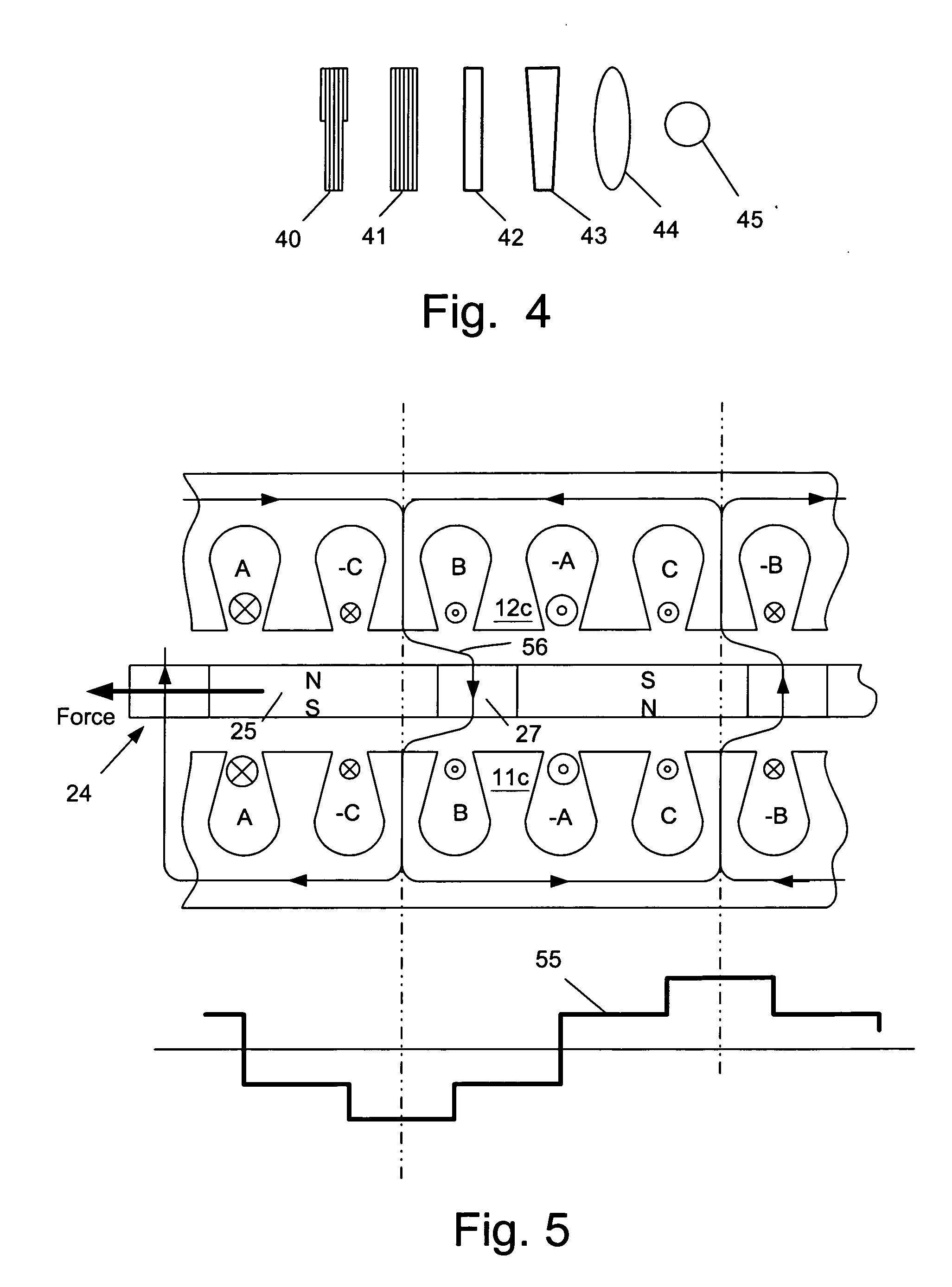
An electric machine (10) has a disk-shaped rotor (24) disposed in an operating space between two opposing stator assemblies (11, 12) to provide two axial air gaps (15, 16). The rotor (24) has a hub (28) and an outer ring (26) of non-magnetic material and is further provided with a plurality of permanent magnetic elements (25) for coupling flux that is induced by the magnetic field of the stator assemblies (11, 12). The permanent magnetic elements (25) are spaced apart and reluctance poles (27) are positioned in spaces between the magnetic elements (25) to couple additional flux induced by the magnetic field of the stator assemblies (11, 12). Various constructions and shapes (40-45) for the PM magnetic elements (25) are disclosed, and including PM covers (60) of ferromagnetic material for enhancing q-axis flux in the air gaps (15, 16) and for reducing harmonics where toothed stators are used. Methods of providing increased torque using the the various rotor constructions are also disclosed.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
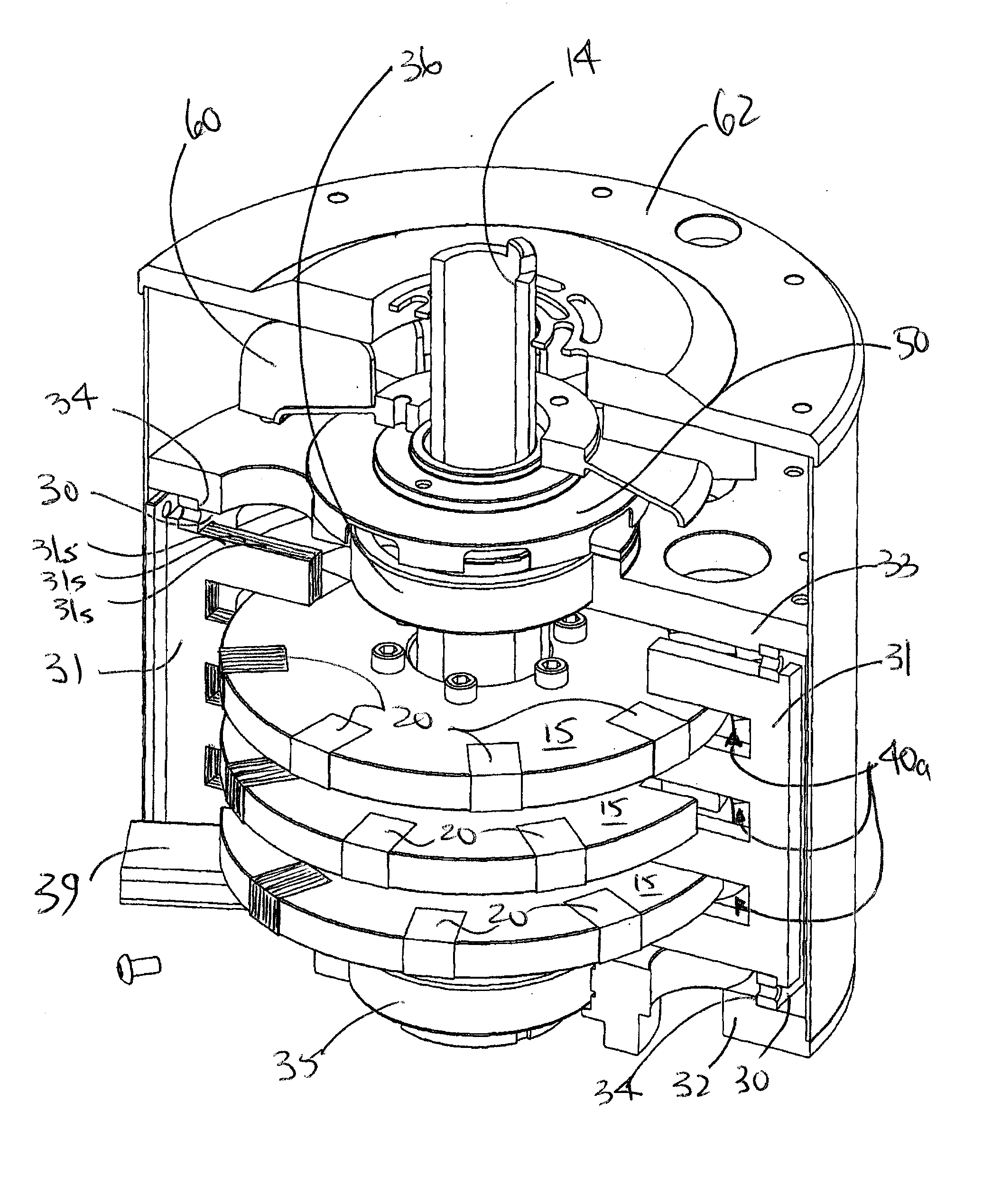
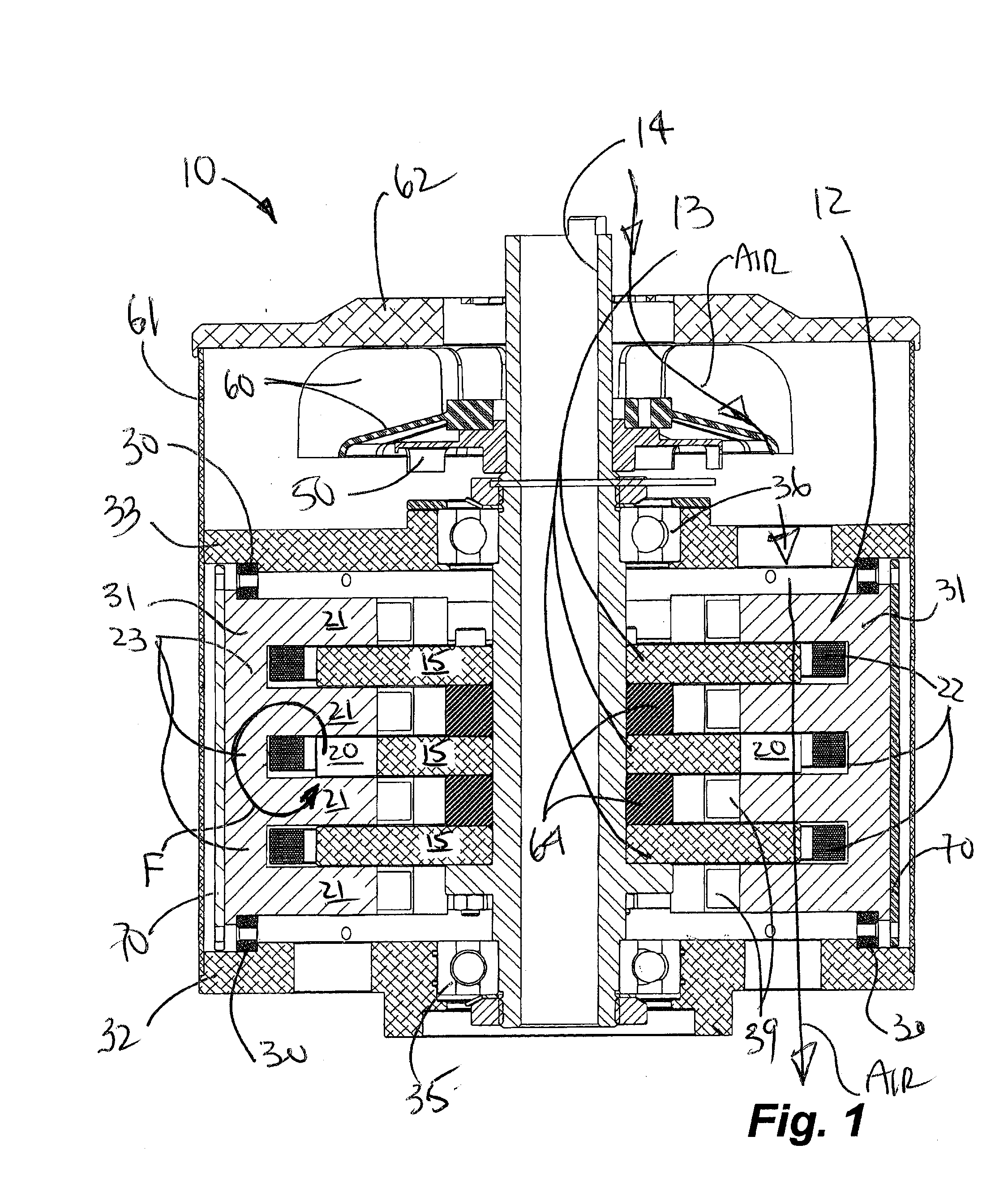
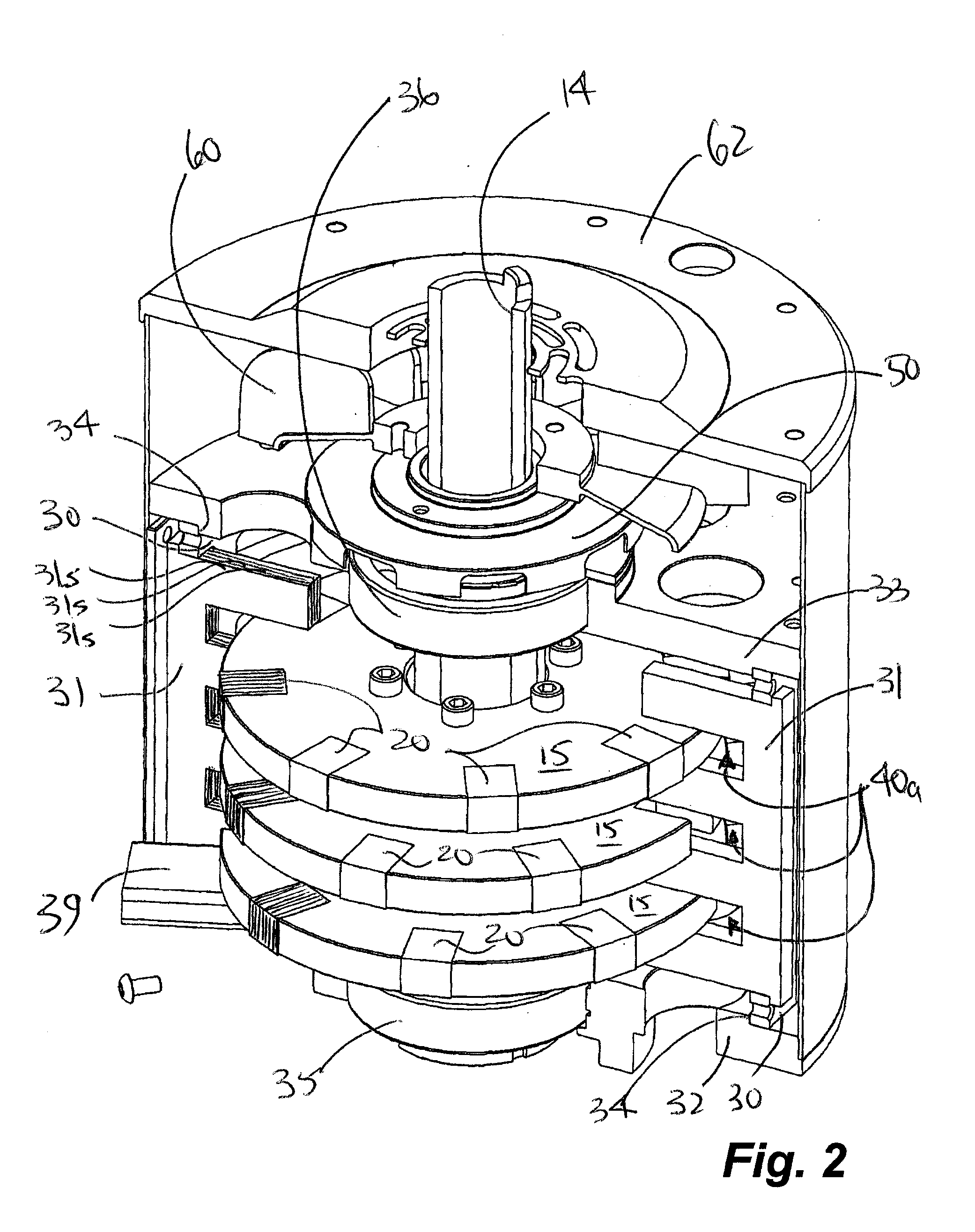
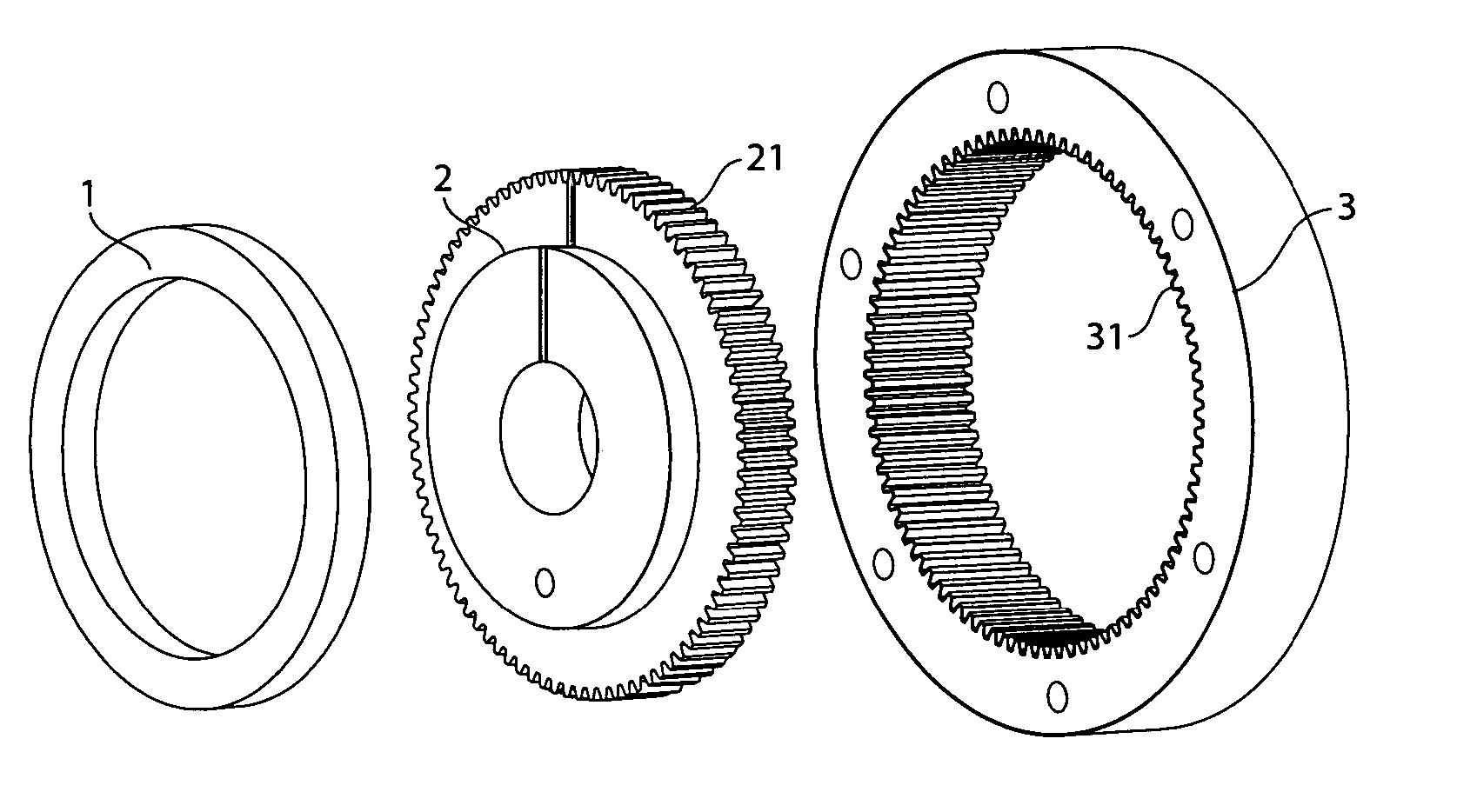
Axial flux switched reluctance motor and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20100295389A1Use minimizedIron and copper lossMagnetic circuitSynchronous motorsStator coilReluctance motor
An axial flux switched reluctance motor utilizes one or more rotor discs spaced along a rotor shaft, each rotor disc having a plurality of rotor poles spaced along the periphery thereof. Stator elements are distributed circumferentially about the rotor discs and form pairs of radially extending stator poles for axially straddling the rotor discs. Stator coils as switched on to energize pairs of stator poles for forming an axial and radially inward flux path for rotating the rotor poles for minimizing the flux path before switching off the stator coil. Two or more rotor discs can be rotationally indexed for providing two or more motor phases. In manufacture, rotor discs and circumferentially extending stator coils about the periphery of each rotor disc are fit to a stator housing. Each stator element is then fit radially through the stator housing and secured thereto for straddling the rotor discs.
Owner:MSI MACHINEERING SOLUTIONS
Transverse flux switched reluctance motor and control methods
InactiveUS20060091755A1Eliminate end turn lossHigh densitySynchronous generatorsElectronic commutation motor controlTransverse fluxElectric machine
A variable reluctance motor and methods for control. The motor may include N motor phases, where N equals three or more. Each motor phase may include a coil to generate a magnetic flux, a stator and a rotor. A flux-carrying element for the rotor and / or stator may be made entirely of SMC. The stators and rotors of the N motor phases may be arranged relative to each other so that when the stator and rotor teeth of a selected phase are aligned, the stator and rotor teeth in each of the other motor phases are offset from each other, e.g., by an integer multiple of 1 / N of a pitch of the stator or rotor teeth. A fill factor of the coil relative to the space in which it is housed may be at least 60%, and up to 90% or more. The stator and rotor flux-carrying elements together may include at most three separable parts.
Owner:PRECISE AUTOMATION
Permanent magnet biased bearingless switched reluctance motor
InactiveCN102306995ARealize decoupling controlImprove efficiencyTorque ripple controlDynamo-electric machinesReluctance motorEngineering
The invention discloses a permanent magnet biased bearingless switched reluctance motor, which comprises stator back yokes, permanent magnets, stator suspension cores, stator torque cores, magnetic shields, suspension winding coils, torque winding coils, rotor cores and a shaft, wherein the stator suspension cores are wound with the suspension winding coils; the stator back yokes are arranged outside the stator suspension cores and connected with the stator suspension cores; the permanent magnets are arranged between the two stator back yokes; the magnetic shields and the stator torque cores are arranged in stator suspension core slots; the magnetic shields are positioned between the suspension stator windings and the stator torque cores; the rotor cores are arranged in the stator suspension cores and the stator torque cores; gas are reserved between the rotor cores and each of the stator suspension cores and the stator torque cores to form air gaps; and the shaft is arranged in the rotor cores. By the permanent magnet biased bearingless switched reluctance motor, decoupling control over torque and suspending power is realized to bring convenience to high-speed running; and a suspension biased magnetic flux is provided by the permanent magnets to reduce suspension power consumption and improve the efficiency of the motor.
Owner:南京埃克锐特机电科技有限公司
Electric start for a prime mover
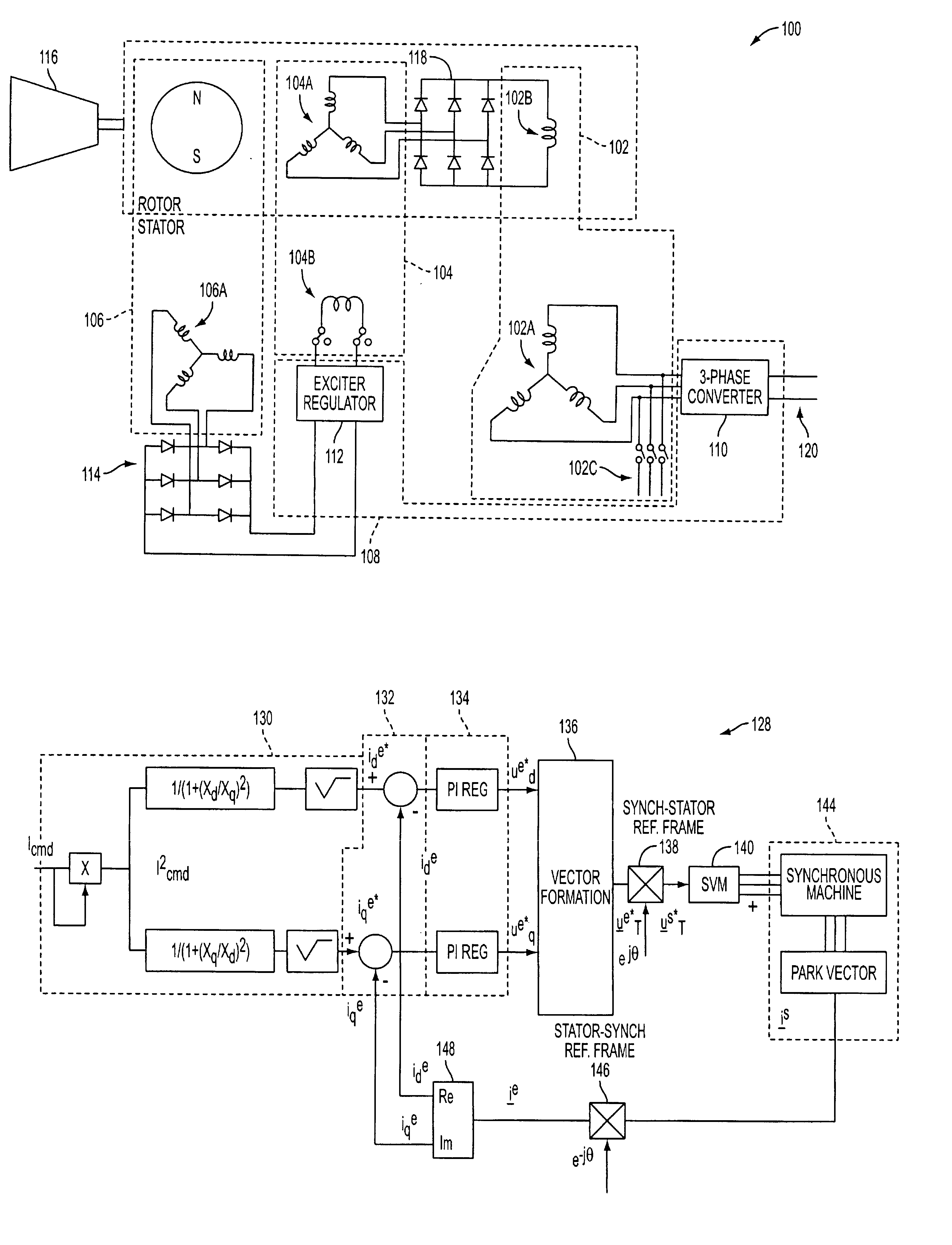
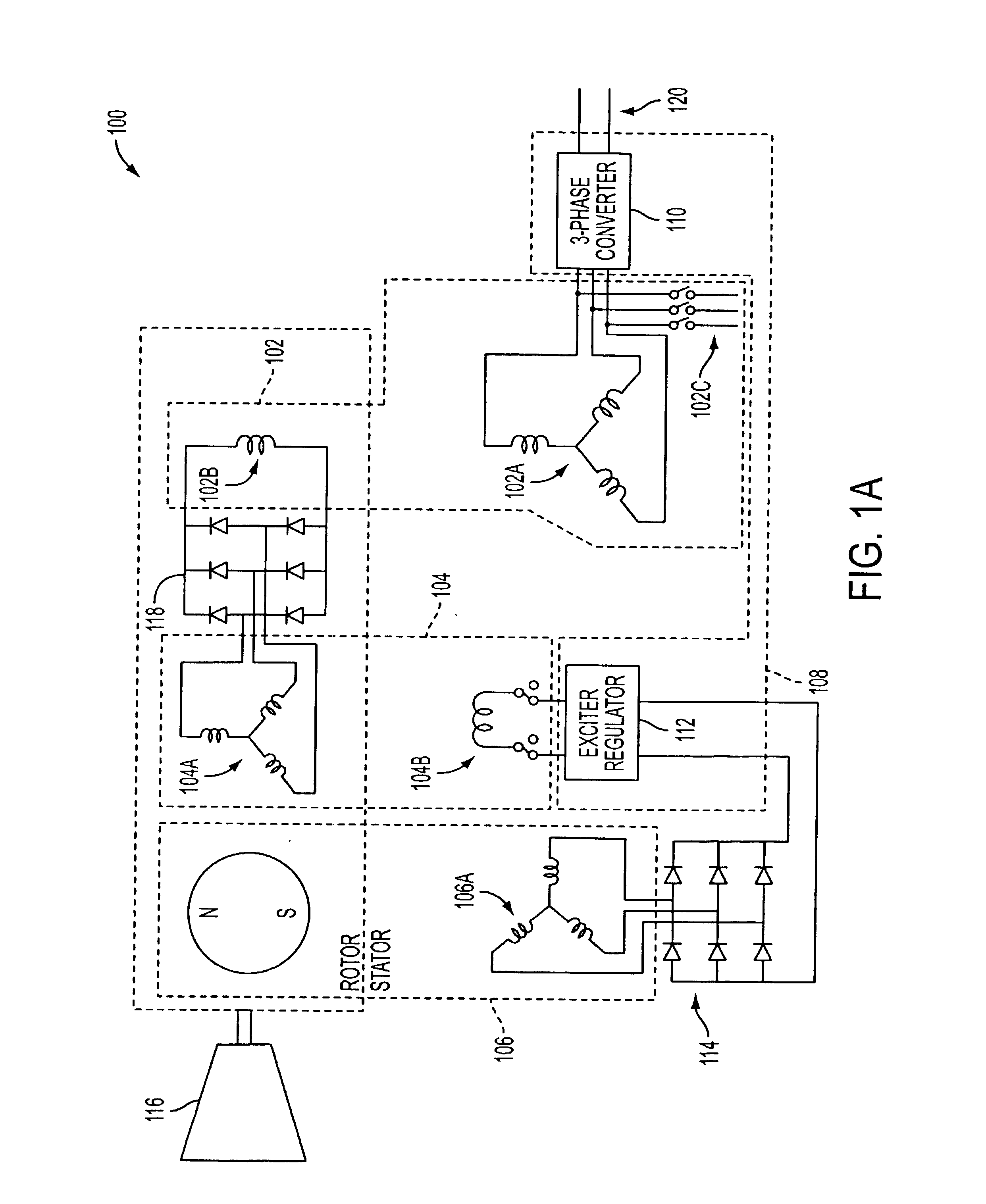
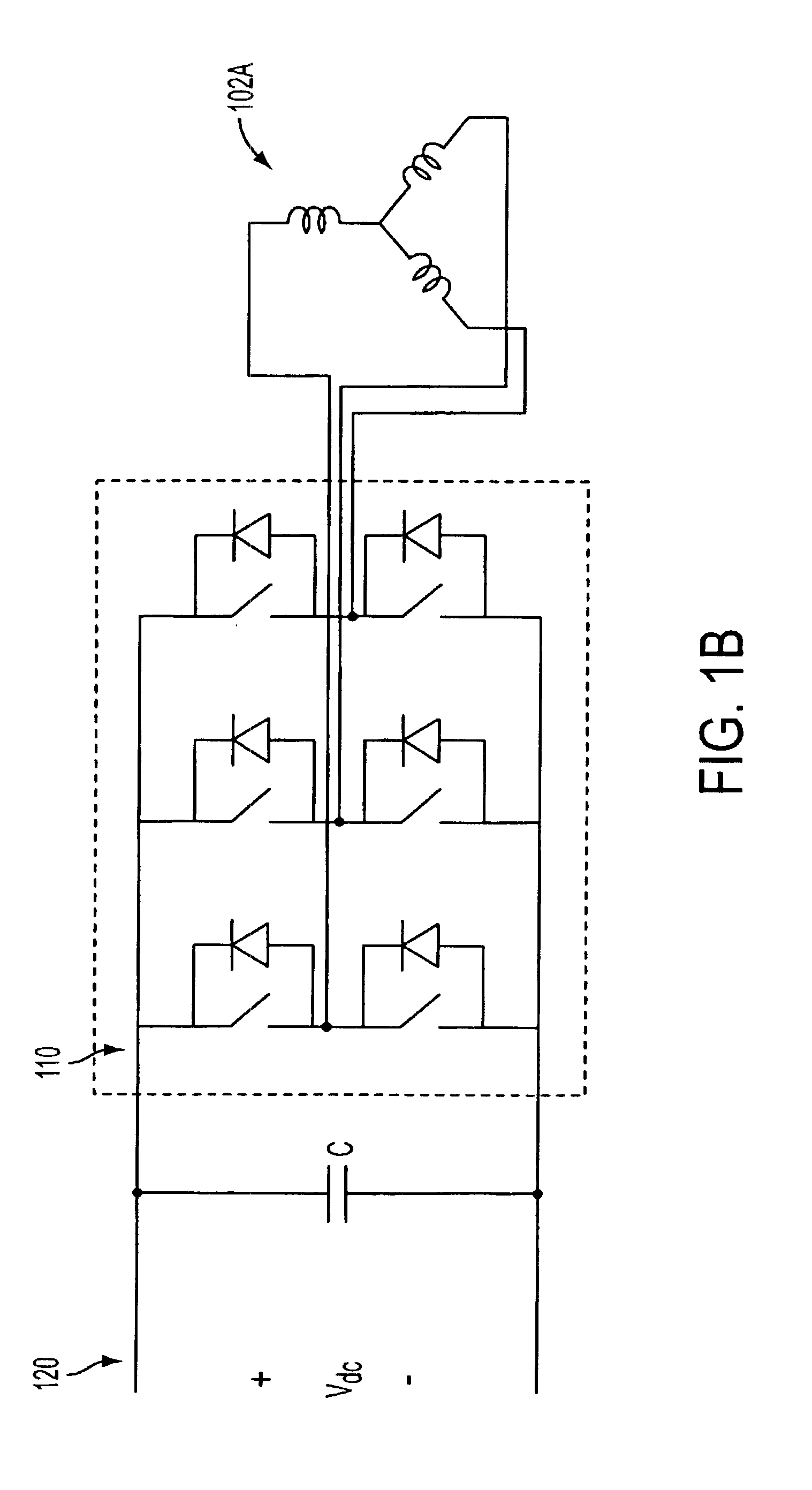
InactiveUS6847194B2Increasing main field fluxIncreasing the main field fluxMotor/generator/converter stoppersTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionStart timeMagnetic reluctance
A system and method for using reluctance torque or a combination of both reluctance and reaction torque components of an attached synchronous machine (102) to accelerate a prime mover (116), such as a gas turbine engine, within a desired start time. The system selects a mode of starting operation, and thereafter applies reluctance torque through a synchronous machine (102) armature winding (102A) excitation as a single, sufficient starting force in a first mode, or staged reluctance and reaction torque through the additional excitation of the synchronous machine (102) field winding (102B) excitation in a second mode, using existing power electronics and controls.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Composite excitation partitioned stator and rotor switched reluctance motor
InactiveCN101764492ASmall resistance lossReduce lossMagnetic circuit stationary partsFault toleranceReluctance motor
The invention discloses a composite excitation partitioned stator and rotor switched reluctance motor belonging to the field of switched reluctance motors. The motor can be in a three-phase 6 / 4, four-phase 8 / 6 or three-phase 12 / 8 structure and the like and comprises U-shaped stator blocks, excitation coils, magnet vanes, permanent magnets, segmental rotor tooth blocks and a non-magnetic conduction rotor metallic sheath, wherein the segmental rotor tooth blocks are embedded into the non-magnetic conduction rotor metallic sheath; one magnet vane is arranged between two adjacent U-shaped stator blocks; the permanent magnets are embedded between two stator tooth notches of each U-shaped stator block; the excitation coils are wound on the yokes of the U-shaped stator blocks; and the excitation field generated by each excitation coil wound on the yoke of each U-shaped stator block is in parallel connection with the permanent magnetic field generated by the permanent magnet embedded between two stator tooth notches of the U-shaped stator block. The motor of the invention has high torque, small wind resistance loss when the rotor operates at high speed, small end winding, strong fault tolerance and low production cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Fault diagnosis method for power converter of switch reluctance motor
InactiveCN101551441AImprove operational reliabilityRapid identificationDynamo-electric machine testingPhase currentsDiagnosis methods
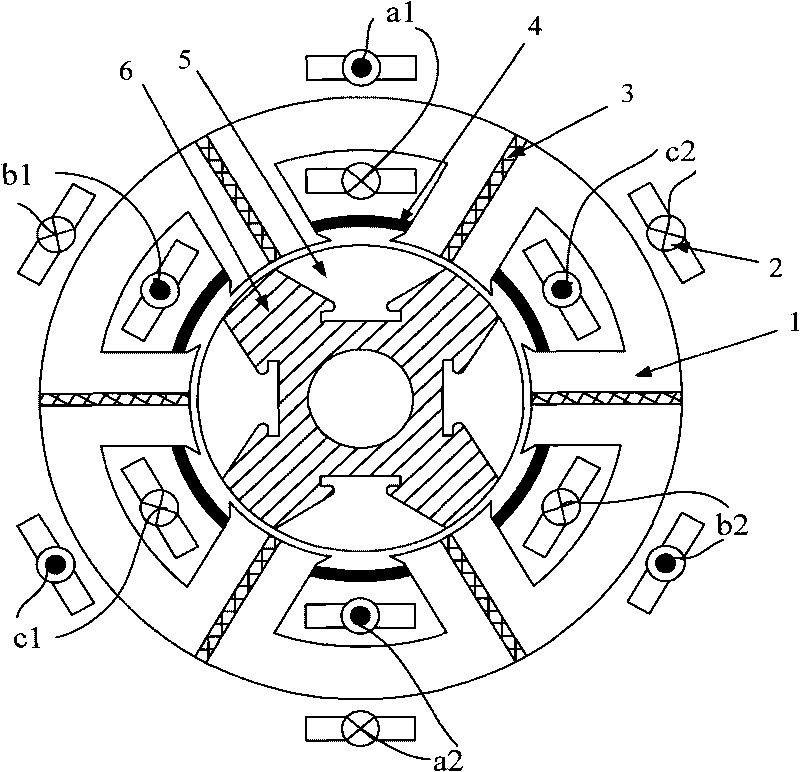
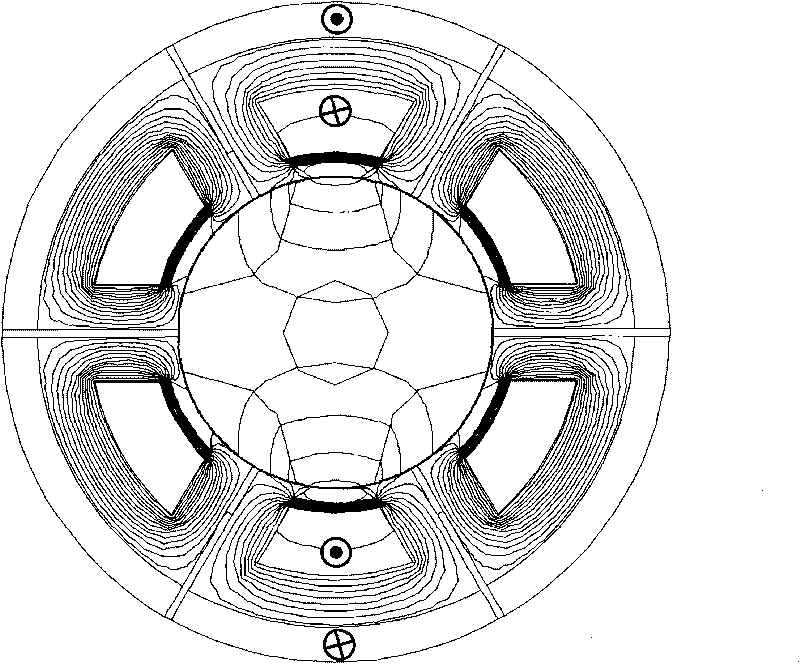
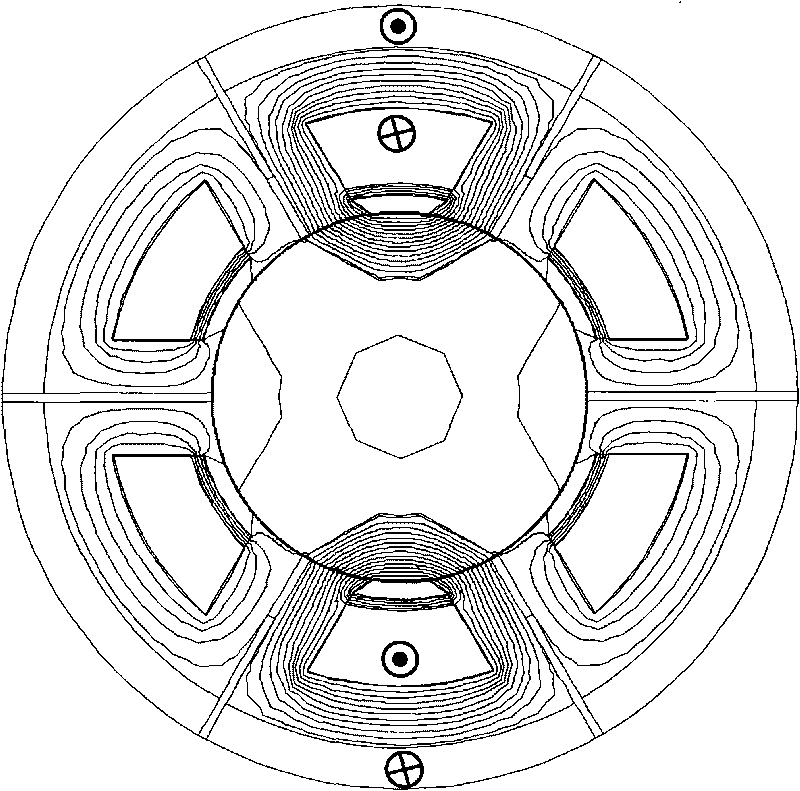
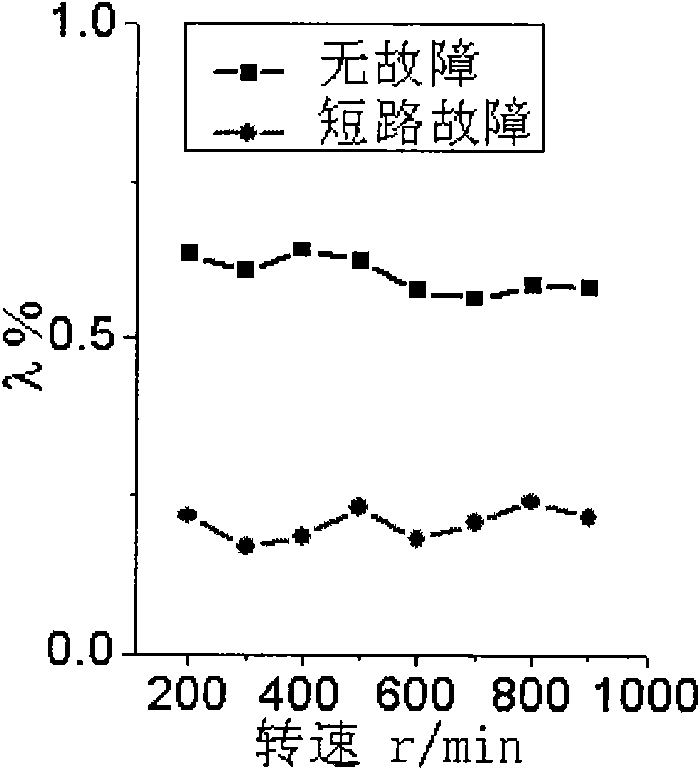
The invention relates to a fault diagnosis method for a power converter of a switch reluctance motor; current spectrum of the power converter phase of the switch reluctance motor is tested and used asfault characteristic quantity; and the proportion coefficient Lambada of relative spectrums ratio of the phase current is defined as the ratio of the amplitude of fundamental component of the phase current and the amplitude of direct current component of the phase current. If the coefficient of the relative spectrum ratio of all phase current is basically constant, the power converter does not occur fault; if the amplitudes of the direct current component and the fundamental component of a certain phase current are near to zero respectively, the phase occurs open fault; and compared with thecoefficient of the relative spectrum ratio of the phase current without fault, if the coefficient of the relative spectrum ratio of a certain phase current occurs obvious change, the phase occurs short fault. The method not only can be used for fault detection, discrimination for types of faults and positioning of fault phases when one phase of the power converter of the switch reluctance motor occurs fault, but also can be used for fault detection, discrimination for types of faults and positioning of fault phases when two or more than two phases of the power converter of the switch reluctance motor occur fault.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
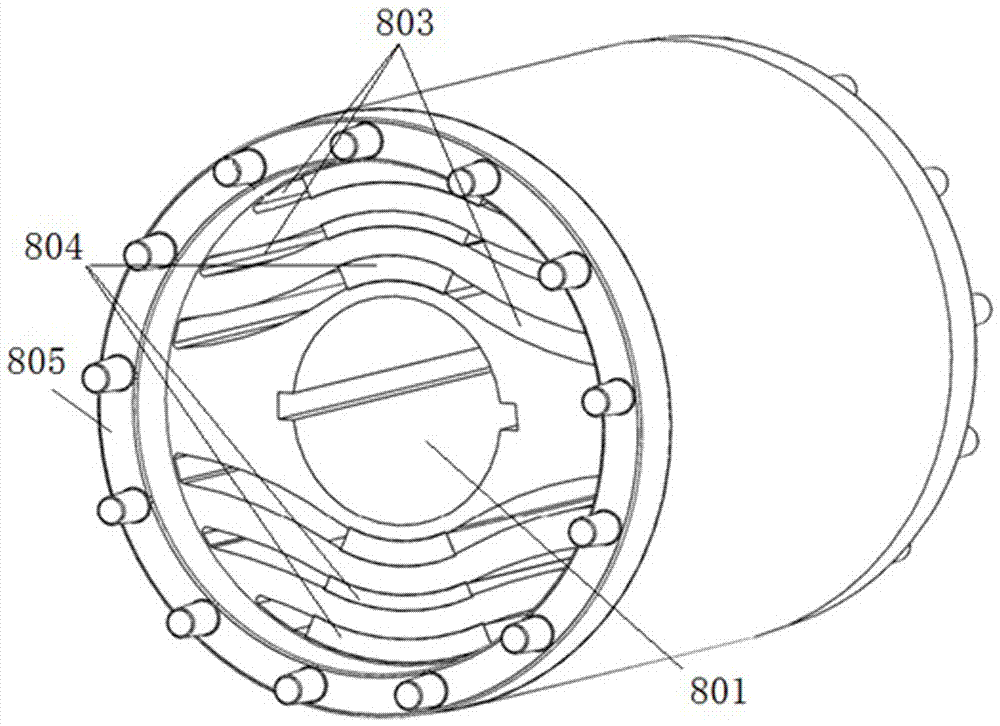
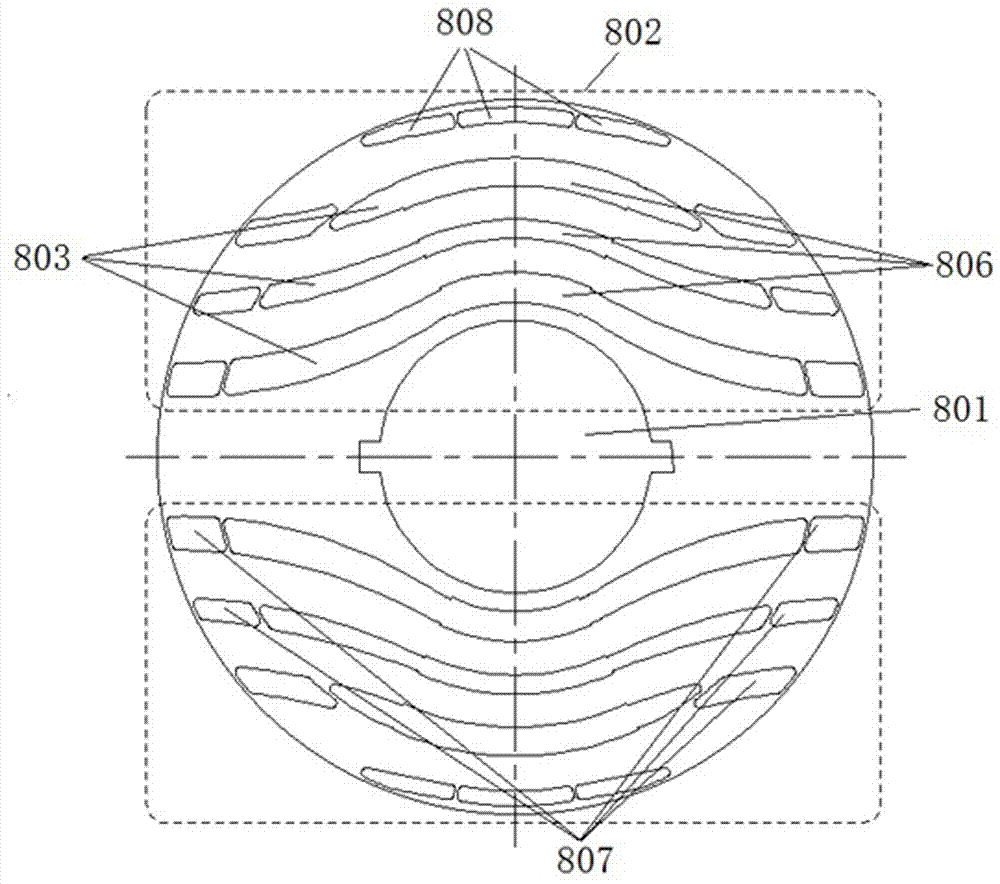
Reluctance motor
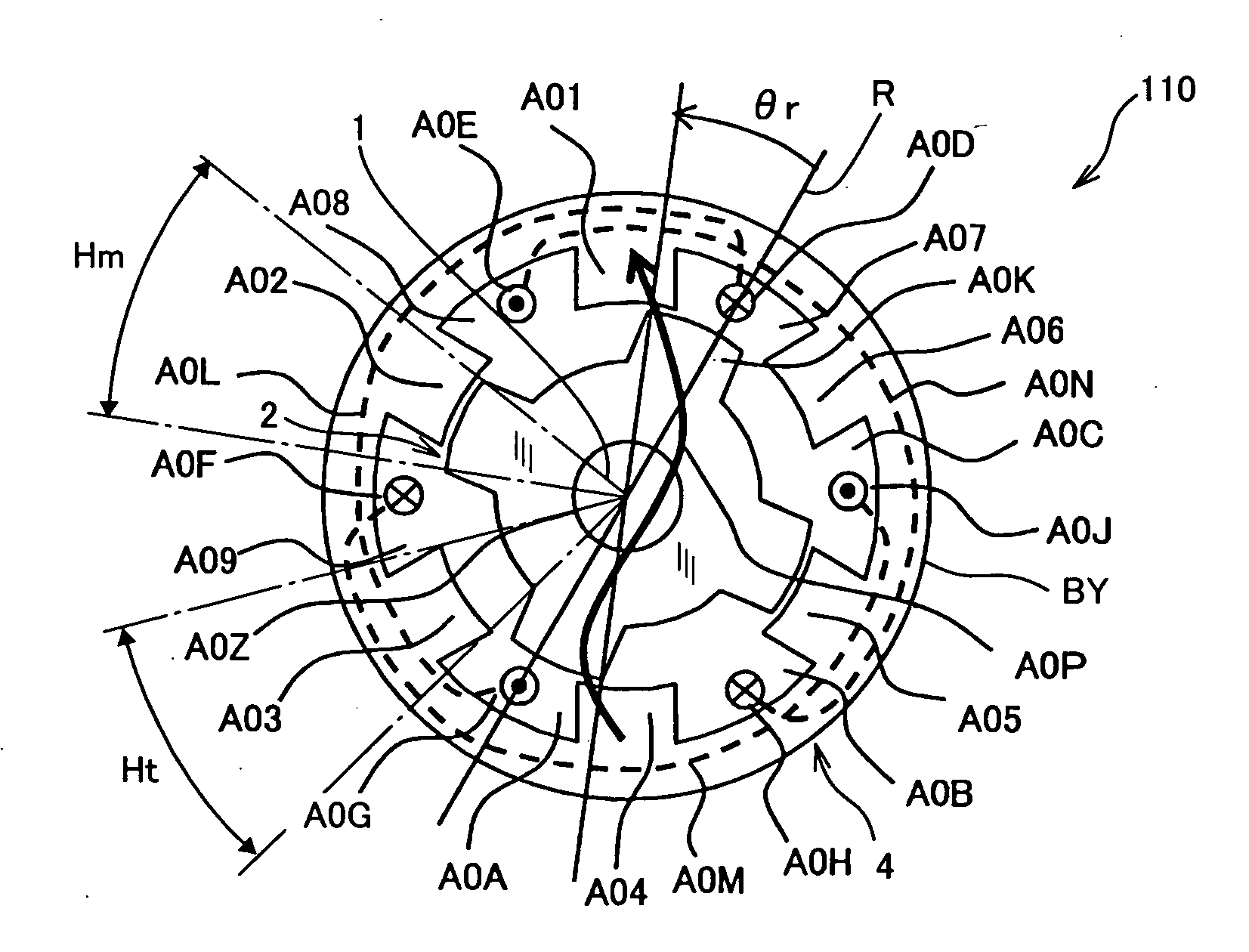
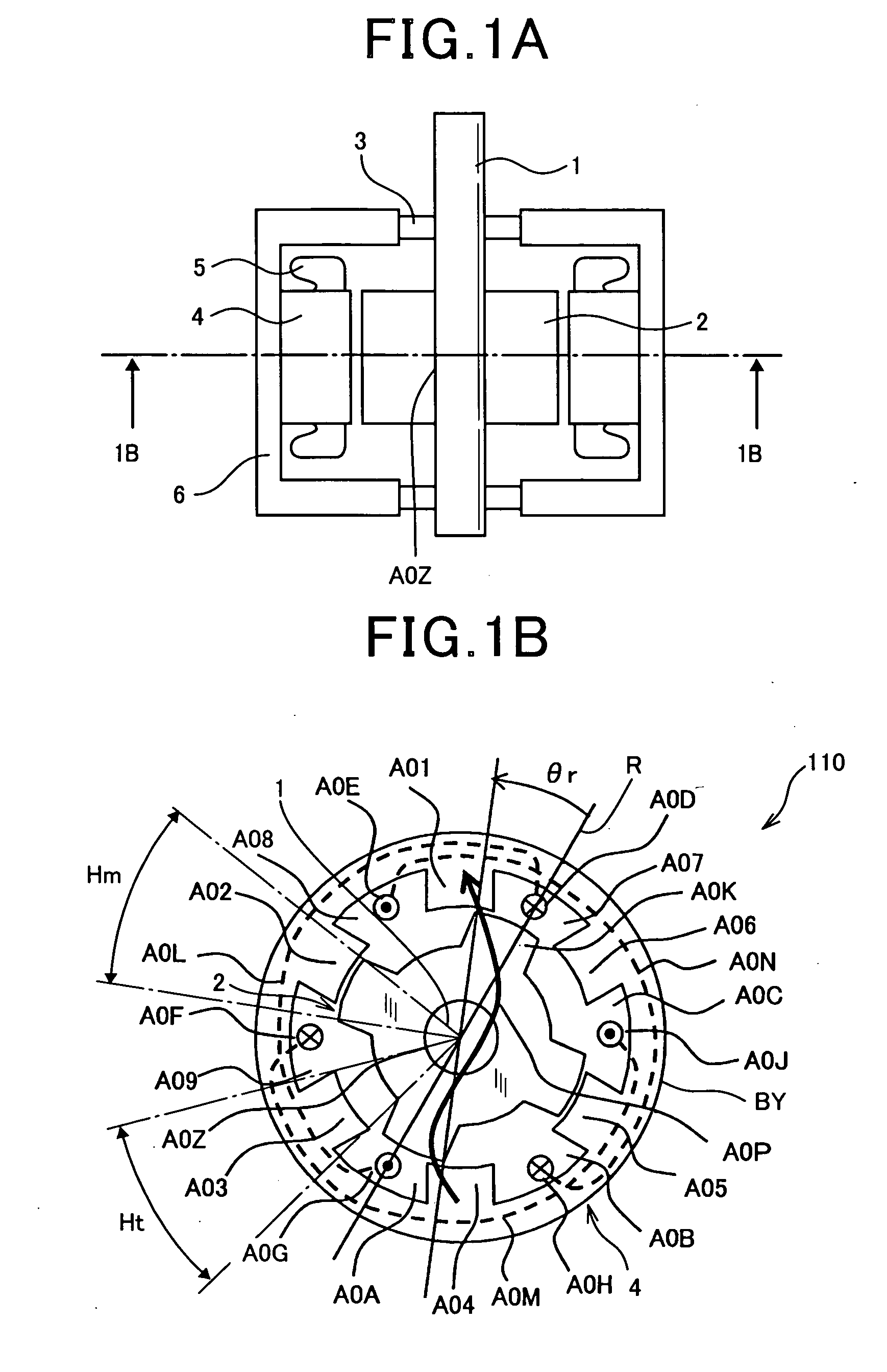
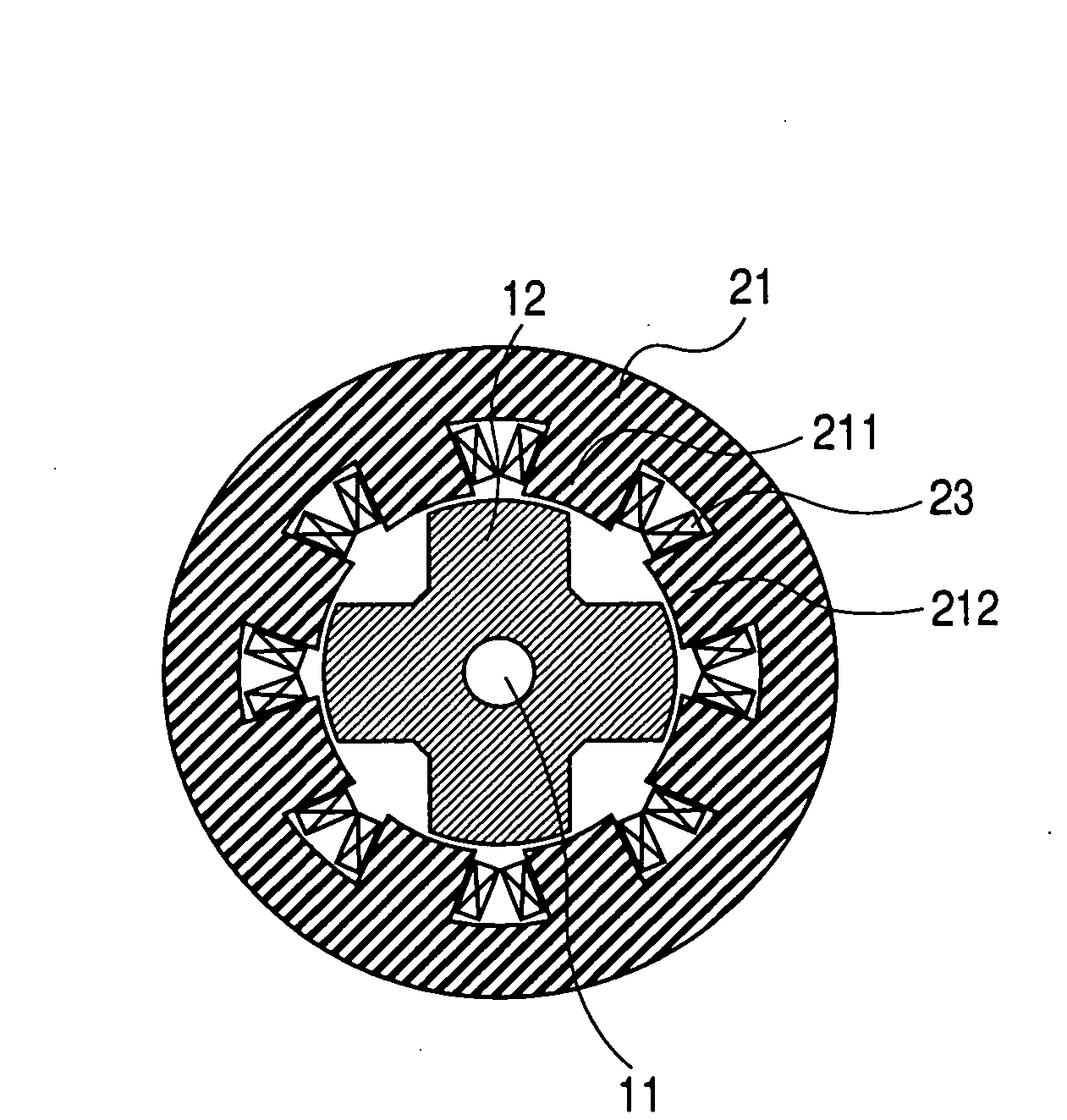
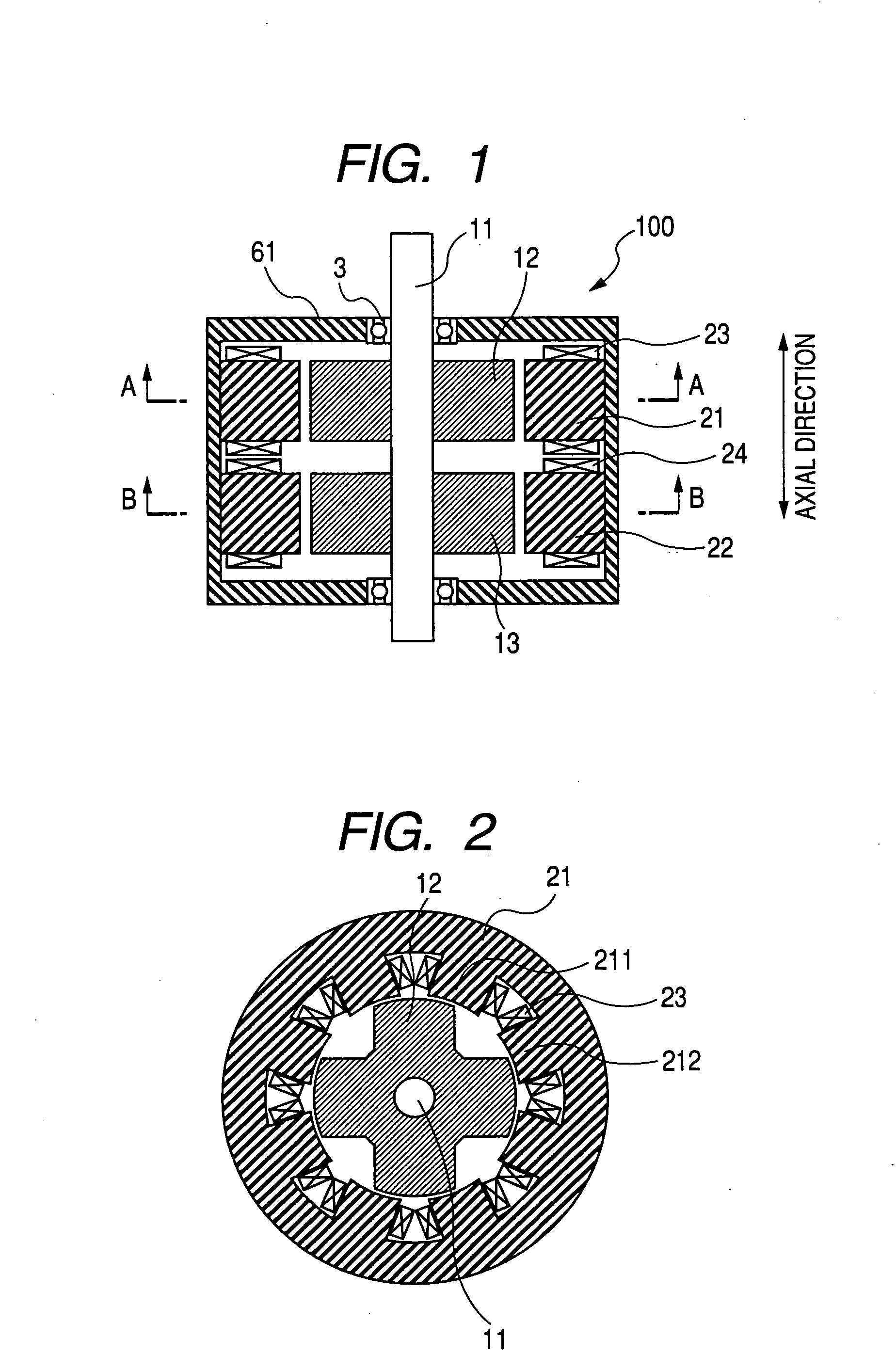
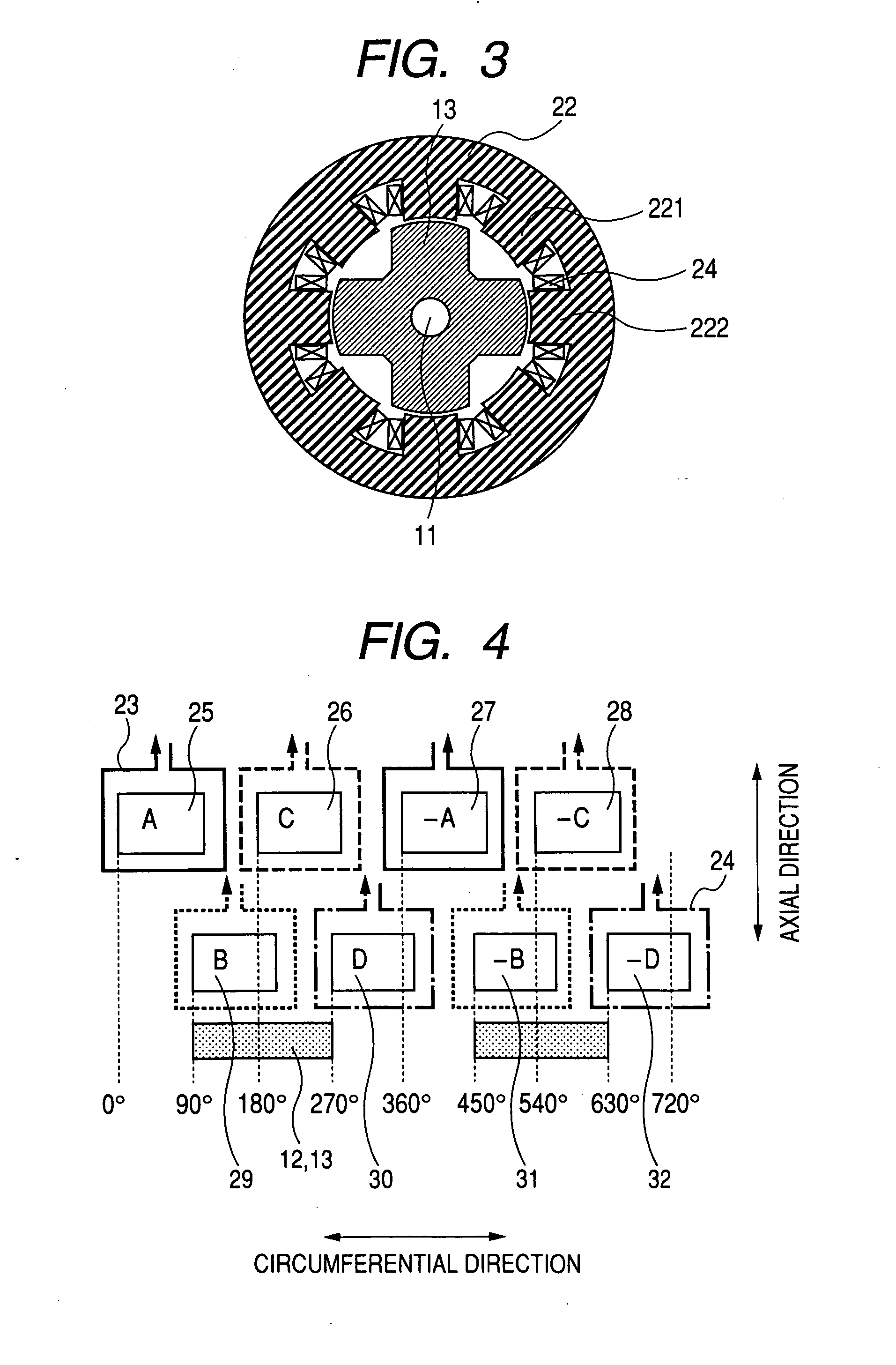
InactiveUS20070152527A1Increase the diameterSmall widthMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic reluctanceMagnetic poles
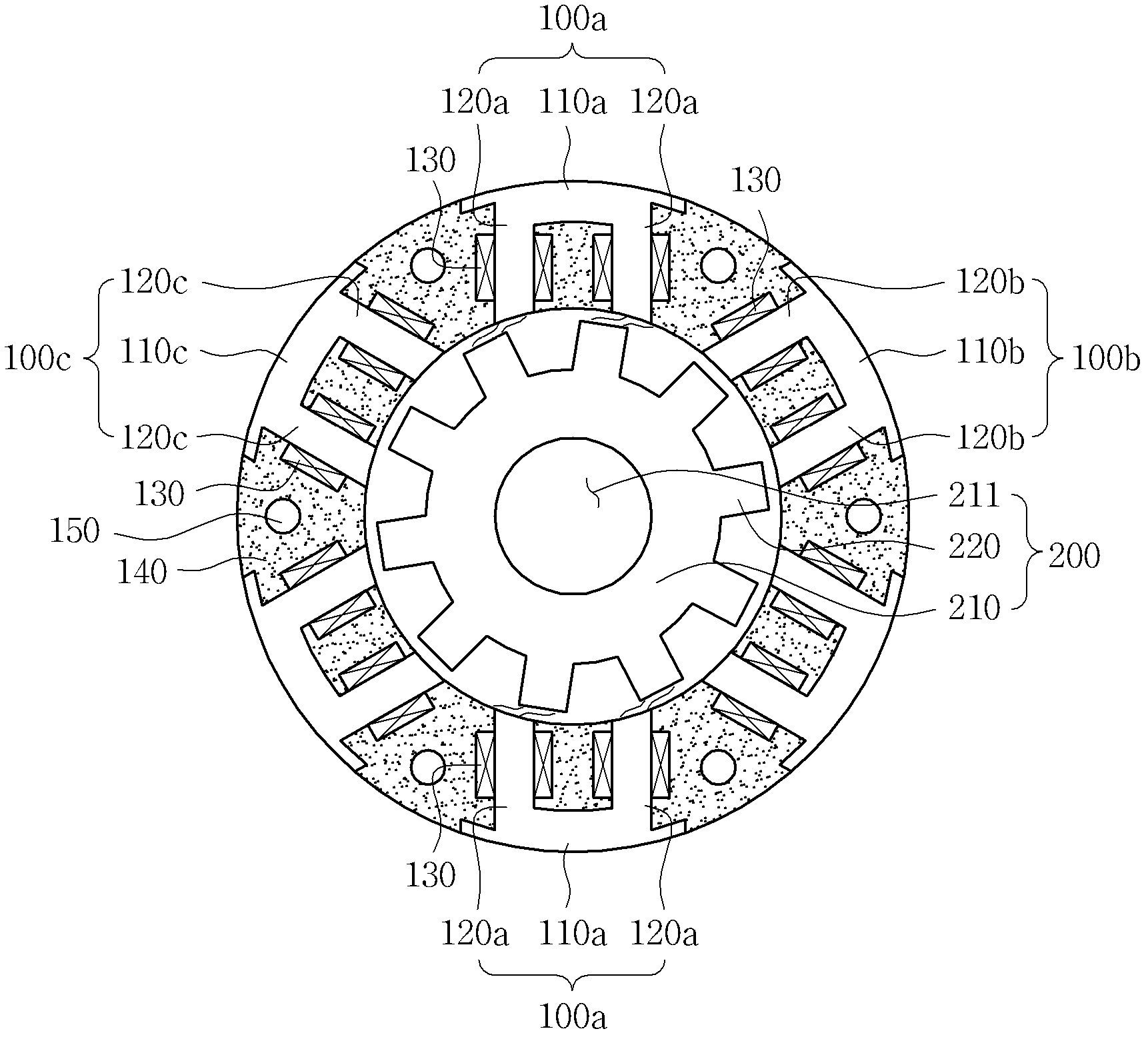
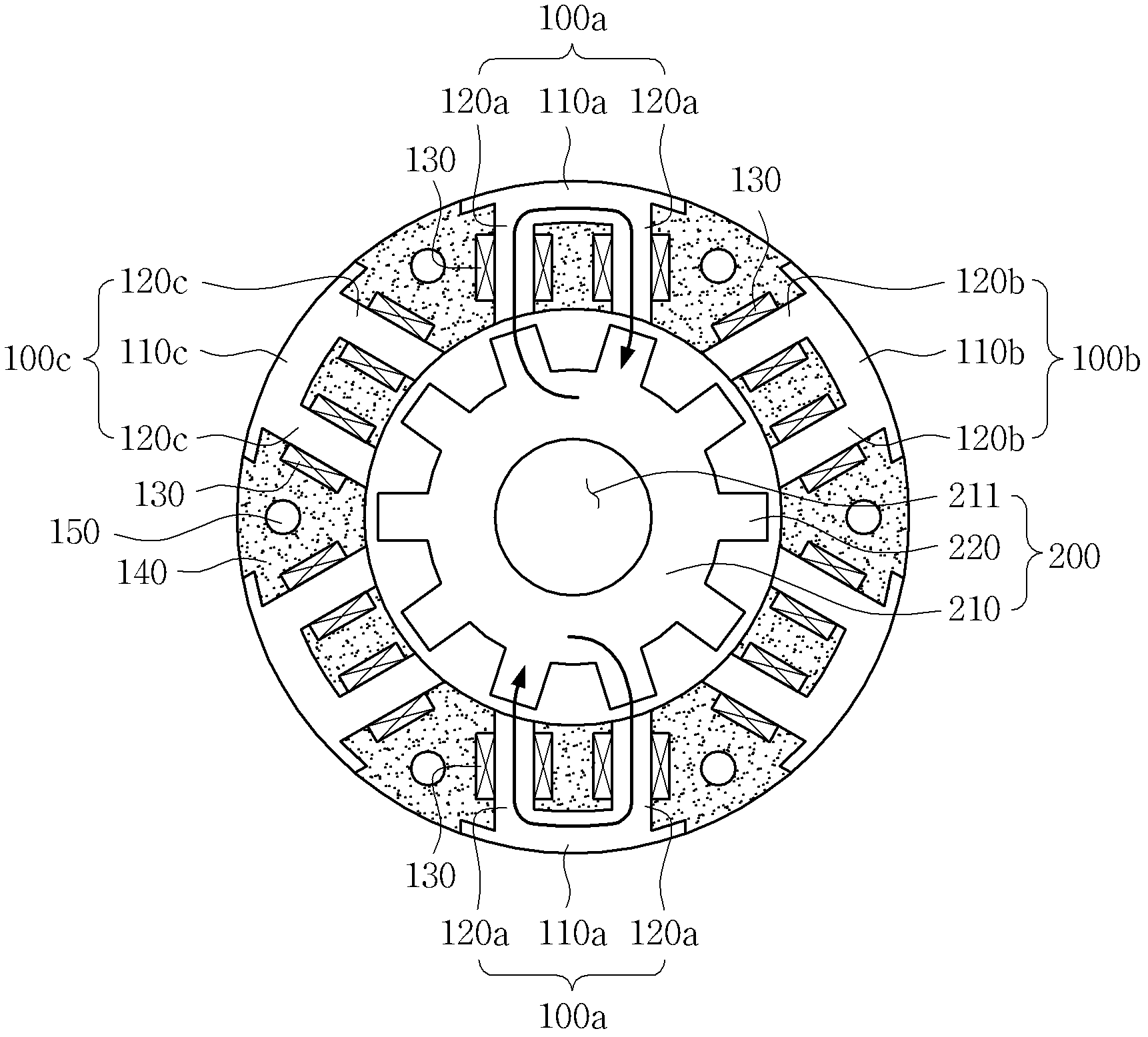
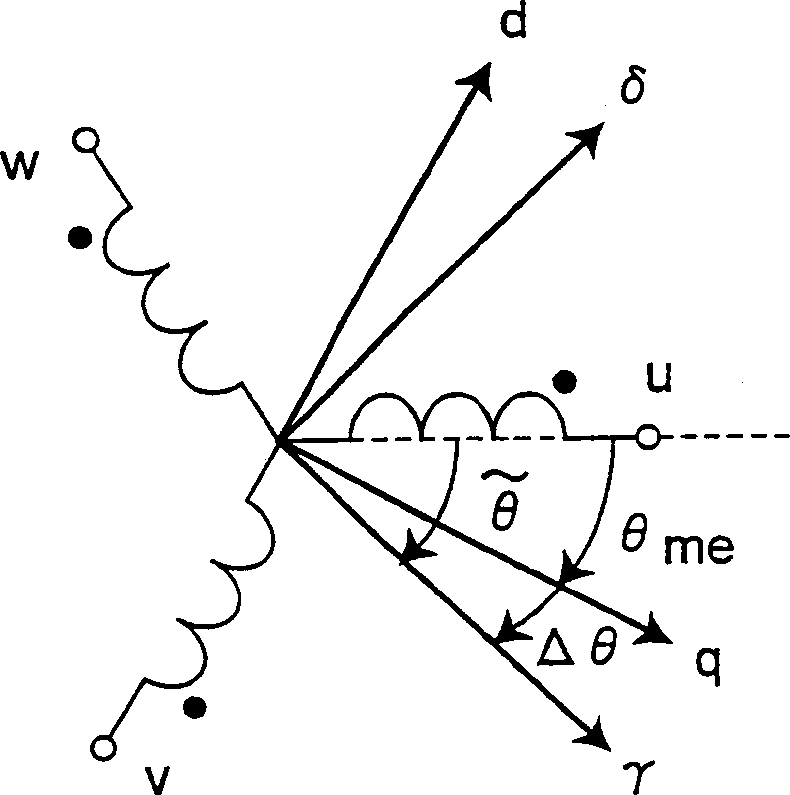
To form magnetic poles P on a rotor, a plurality of slits extending along a radial direction in a region close to the magnetic poles P and extending along a circumferential or chord direction in mid areas between the magnetic poles P are formed. The width b of circumferential slit segments extending along the circumferential or chord direction is narrower than the width a of radius slit segments extending along the radial direction. Permanent magnets are disposed in the narrowed segments of the slits to suppress leakage of magnetic flux. Thus, in a motor in which magnetic paths separated by the slits are formed on the rotor to provide regions having different magnetic reluctances in a circumferential direction of the rotor, a structure in which a through hole penetrated by an output shaft of the motor can have a large diameter is provided.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
AC permanent magnet synergistic reluctance motor
ActiveCN103560633AIncrease magnetic intensityImprove reaction speedMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsExcitation currentReluctance motor
The invention relates to an AC permanent magnet synergistic reluctance motor. The motor is characterized in that permanent magnets or permanent magnet components are combined with laminated cores in stator excitation salient pole pairs; when excitation coils do not have excitation current, the permanent magnets or the permanent magnet components and the laminated cores in the excitation salient pole pairs form locally closed magnetic circuits; when the excitation coils have the excitation current, the original closed permanent magnet magnetic circuits are opened and converged on the excitation magnetic circuits of the excitation salient pole pairs, and then compound excitation magnetic potential is produced on the two port surfaces of each salient pole of each excitation salient pole pair; when the magnetic port surfaces of the permanent magnets fixed to a rotor support are just opposite or coincide with the port surfaces of the stator excitation salient pole pairs, the shortest closed magnetic circuit with air gaps is formed. According to the AC permanent magnet synergistic reluctance motor, the magnetic induction intensity in the air gaps of the motor is greatly increased, the torque at the time of low rotation speed is increased, common magnetic circuit interference and flux leakage are reduced, electric energy is saved, and the power density of the motor and the use rate of equipment are further enhanced.
Owner:戴珊珊
Switched reluctance motor
InactiveUS20080278010A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh magnetic flux densitySynchronous generatorsSynchronous motorsMagnetic polesReluctance motor
A switched reluctance motor has a rotor and a stator. The stator has first and second stator magnetic pole groups sequentially placed in an axial direction of the rotor. First and second stator magnetic poles in each group are alternately arranged on a same circumference. The first stator magnetic poles are placed every electrical angle 2π and reversely magnetized to each other. The second stator magnetic poles are placed every electrical angle 2π and reversely magnetized to each other. The first magnetic pole is apart from the second magnetic pole by electrical angle π. Each stator magnetic pole in the first stator magnetic pole group is apart from that in the second magnetic pole group by electrical angle π / 2 in the circumferential direction.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and apparatus for estimating rotor position and for sensorless control of a switched reluctance motor
InactiveUS20060125427A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsSynchronous reluctance motor
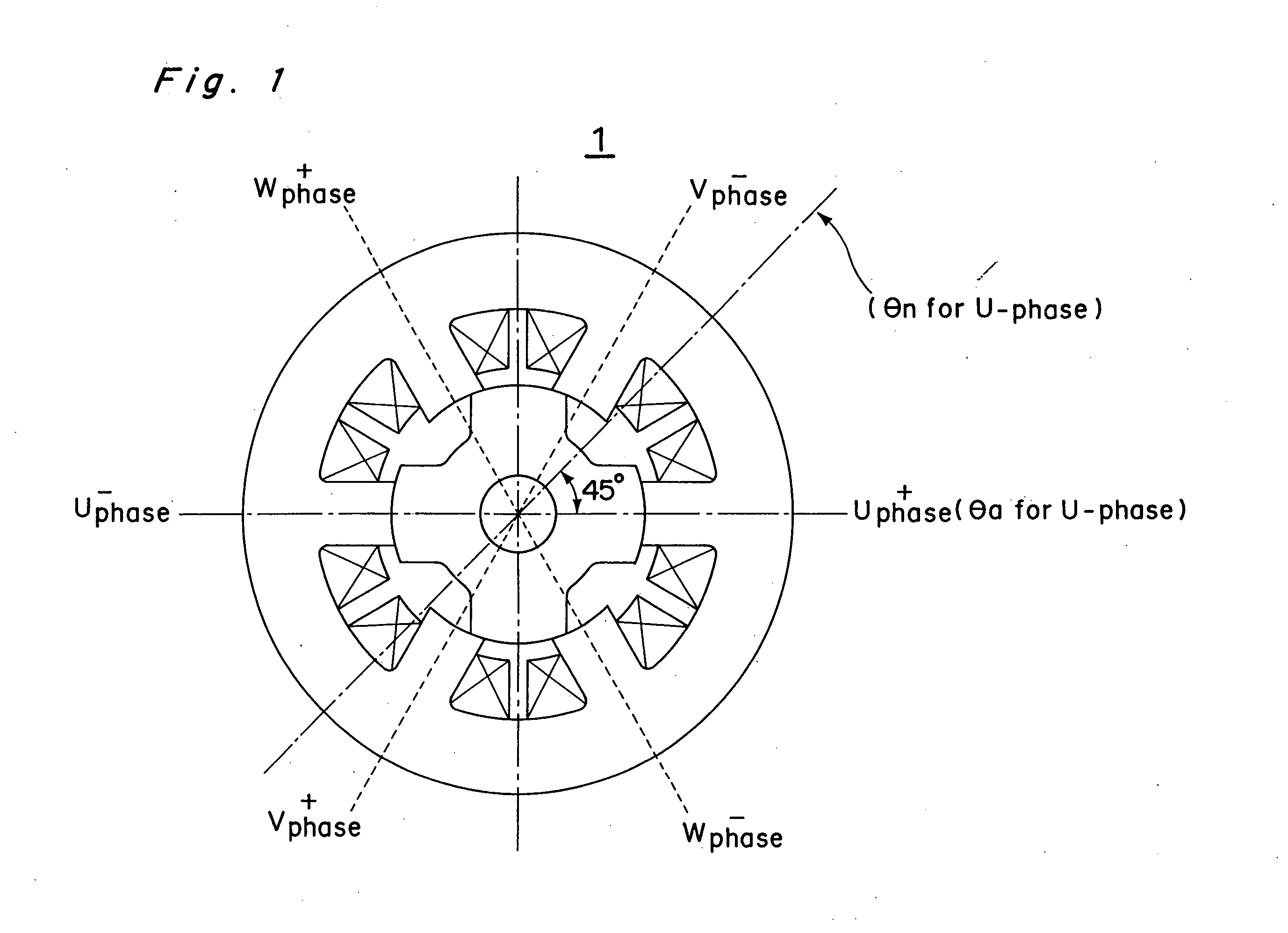
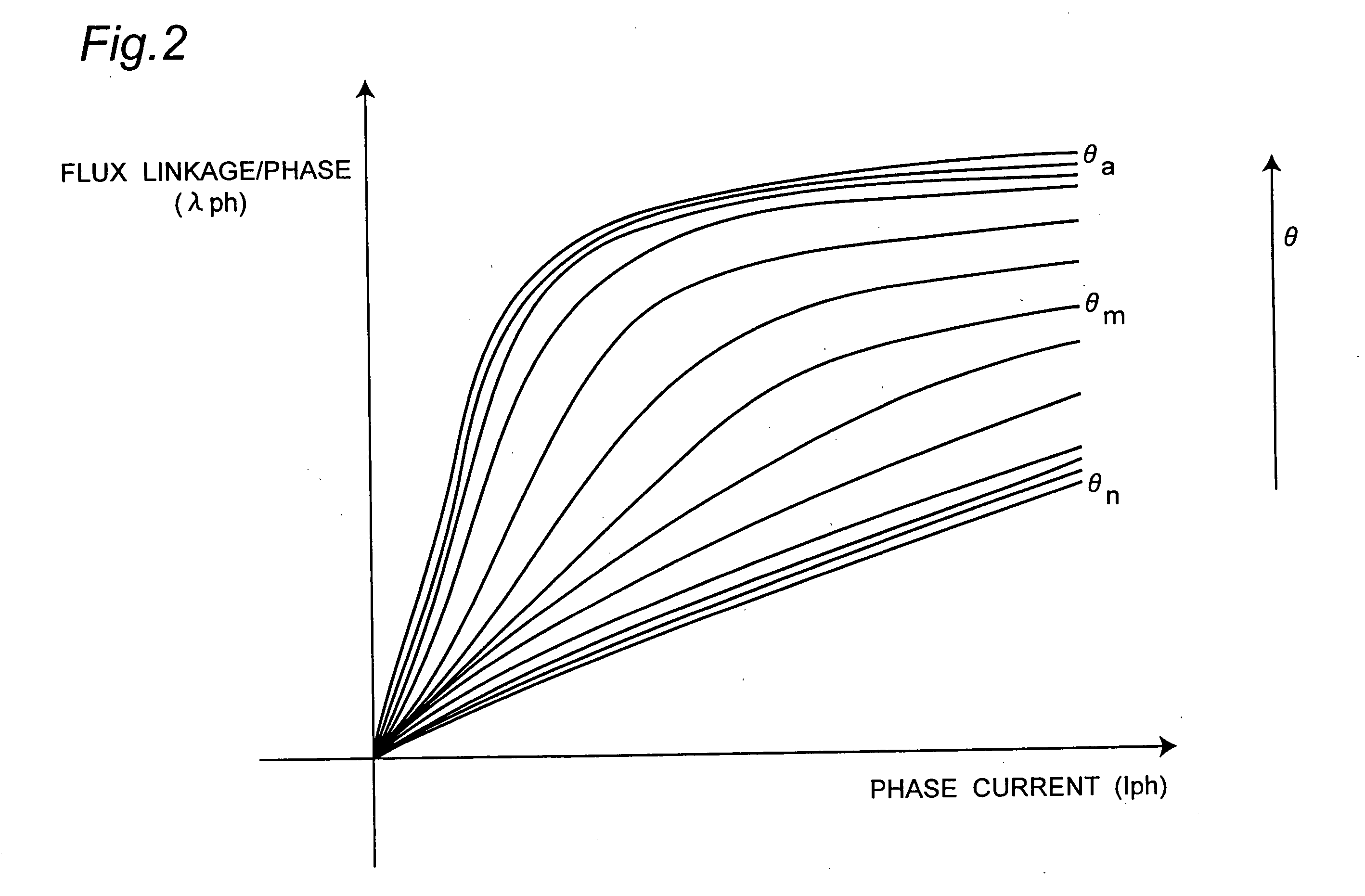
A discrete rotor position estimation method for a synchronized reluctance motor is provided. A d.c.-link voltage Vdc and a phase current Iph are sensed. A flux-linkage λph of an active phase is calculated from the sensed d.c.-link voltage Vdc and the sensed phase current Iph. The calculated flux-linkage λph is compared with a reference flux-linkage λr. The reference flux-linkage λr corresponds to a reference angle θr which lies between angles corresponding to aligned rotor position and non-aligned rotor position in the synchronized reluctance motor. An estimated rotor position θcal is obtained only once when the calculated flux-linkage λph is greater than the reference flux-linkage λr.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Rotor for line-start reluctance motor
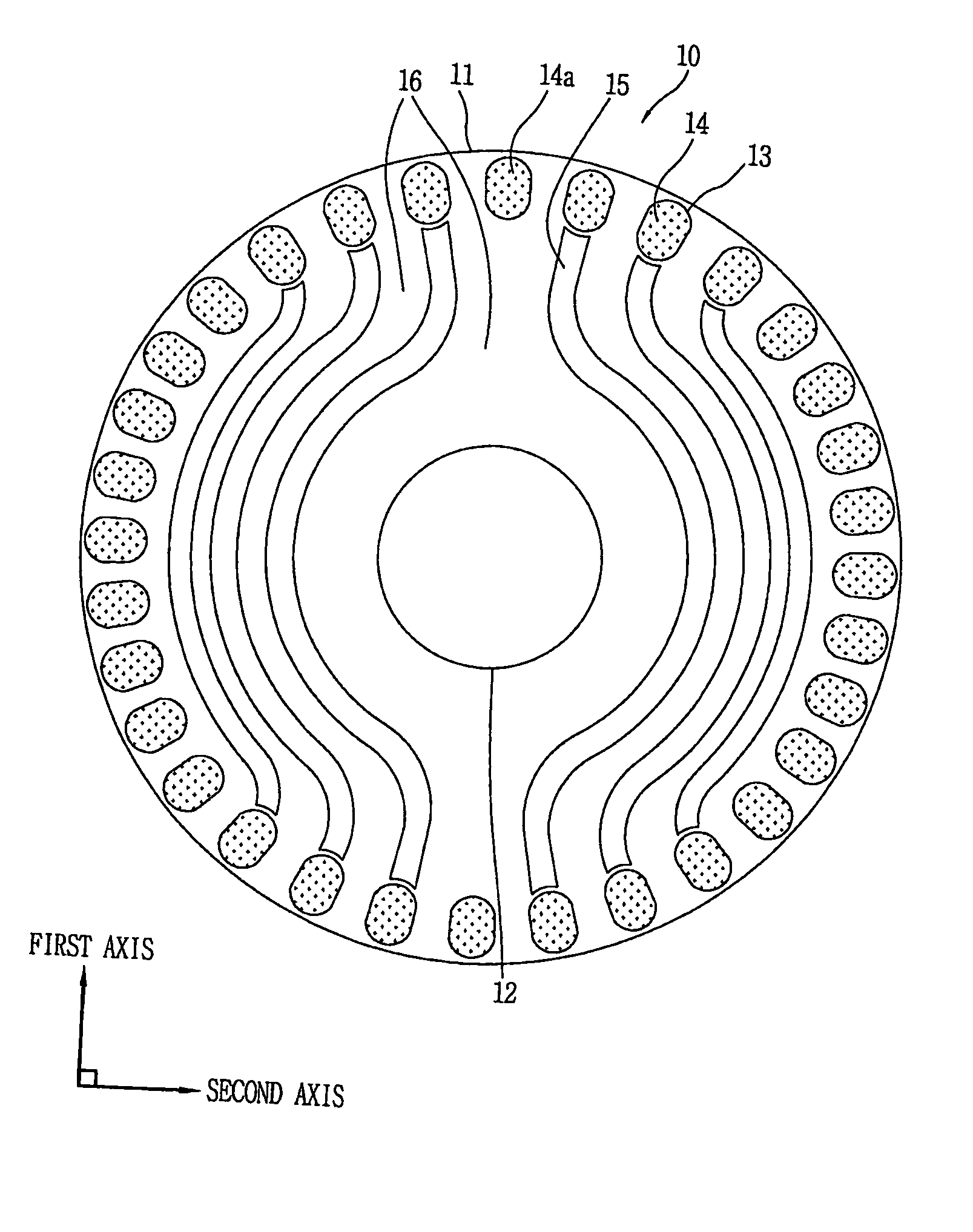
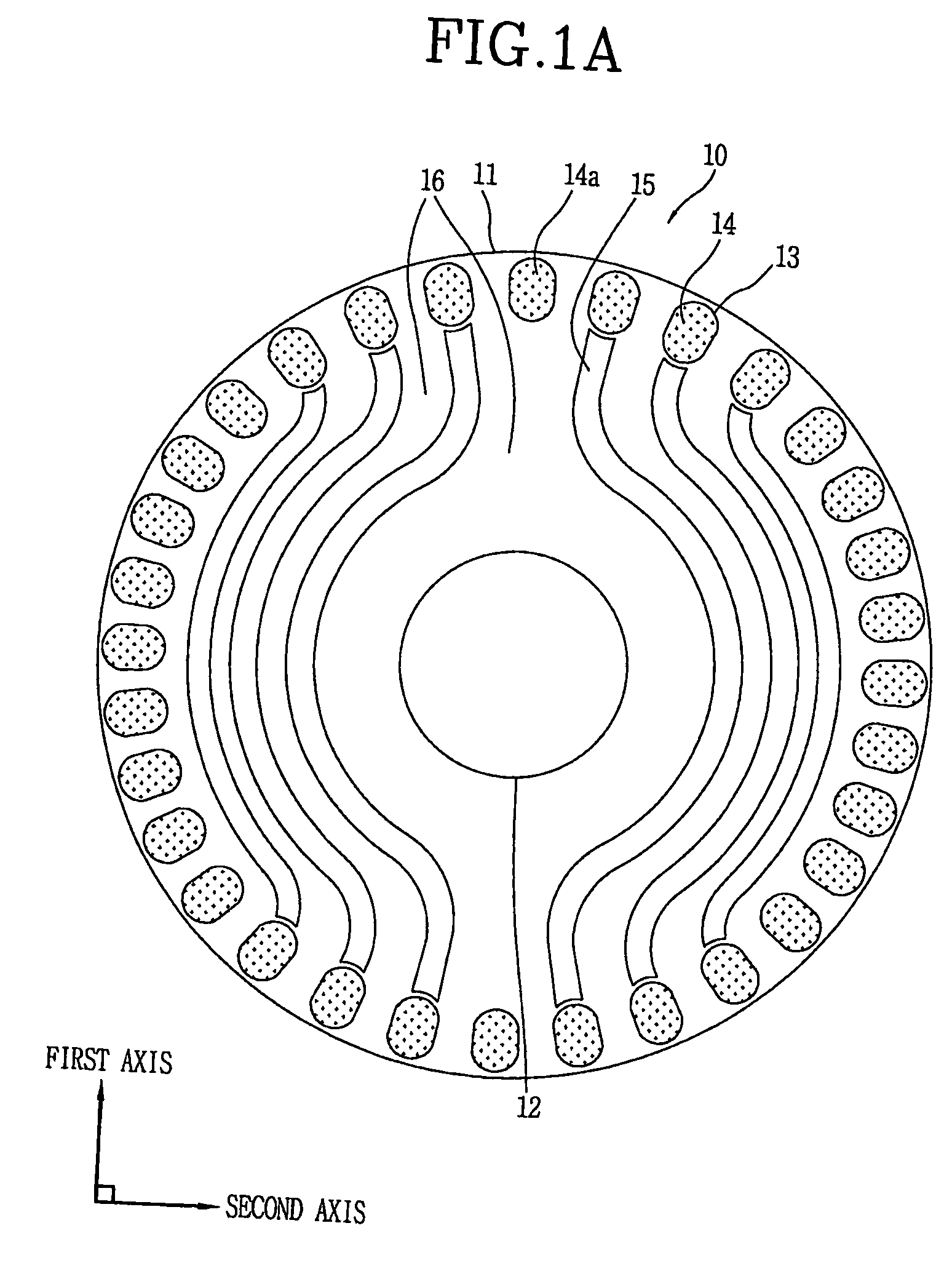
InactiveUS20060108888A1Shorten the timeReduce expensesMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorsPhysicsReluctance motor
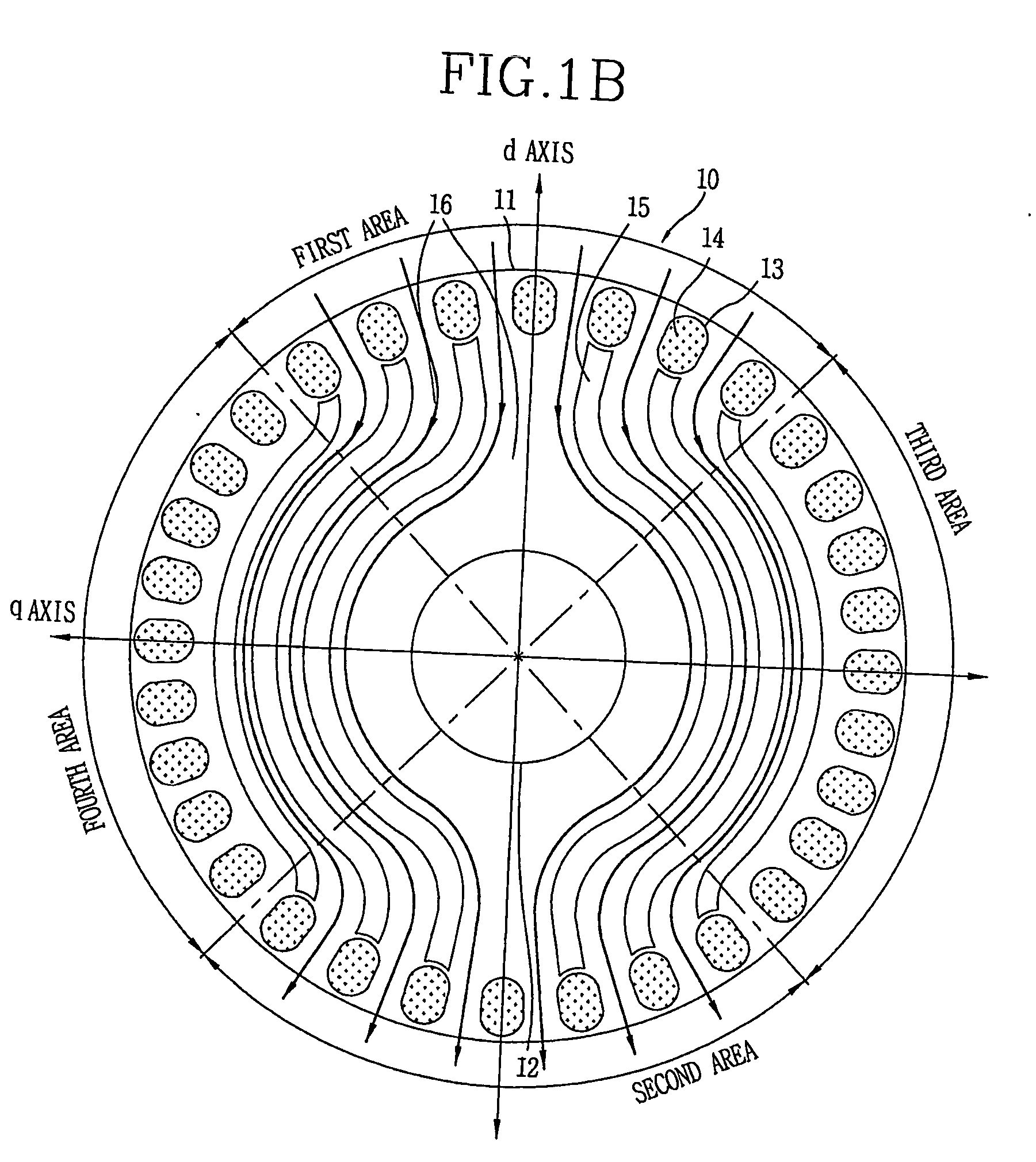
The present invention discloses a rotor for a line-start reluctance motor which improves core area efficiency to make flux flow in one direction. The rotor for the line-start reluctance motor includes a core having an axis coupling hole in a coupling direction of a shaft, a plurality of bars formed in the periphery of the core, and a plurality of flux barriers, one and the other ends of the flux barriers approaching the bars formed in first and second areas facing each other at a predetermined angle on a central line of a first axis on a core plane vertical to the coupling direction, at least parts of the centers of the flux barriers passing through a third or fourth area between the first and second areas, surrounding the axis coupling hole at predetermined intervals.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Multi-unit Modular Stackable Switched Reluctance Motor System with Parallely Excited Low Reluctance Circumferential Magnetic Flux loops for High Torque Density Generation
InactiveUS20120001502A1Increased torque densityLow costMagnetic circuitSynchronous machinesFlux loopTransformer
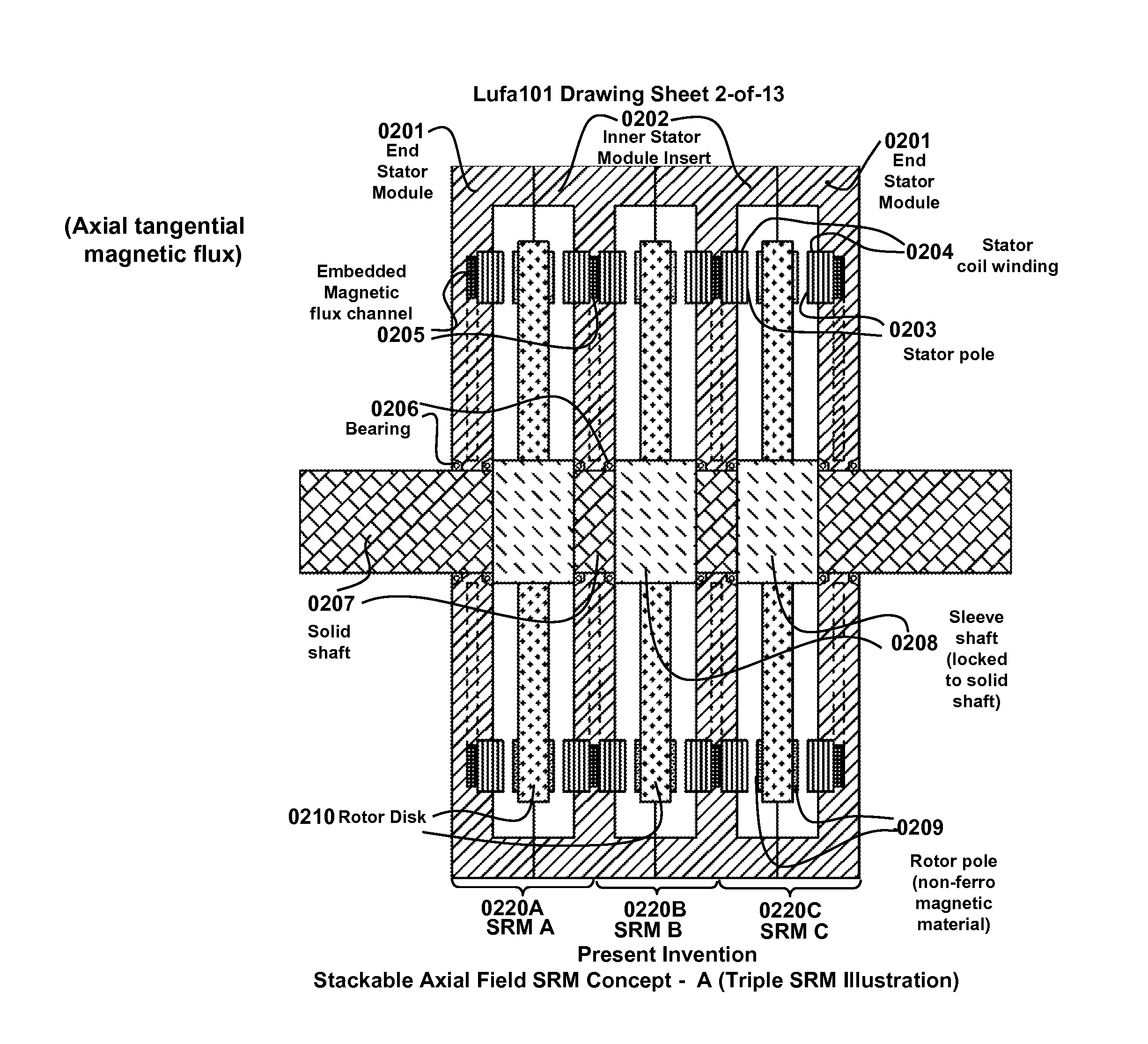
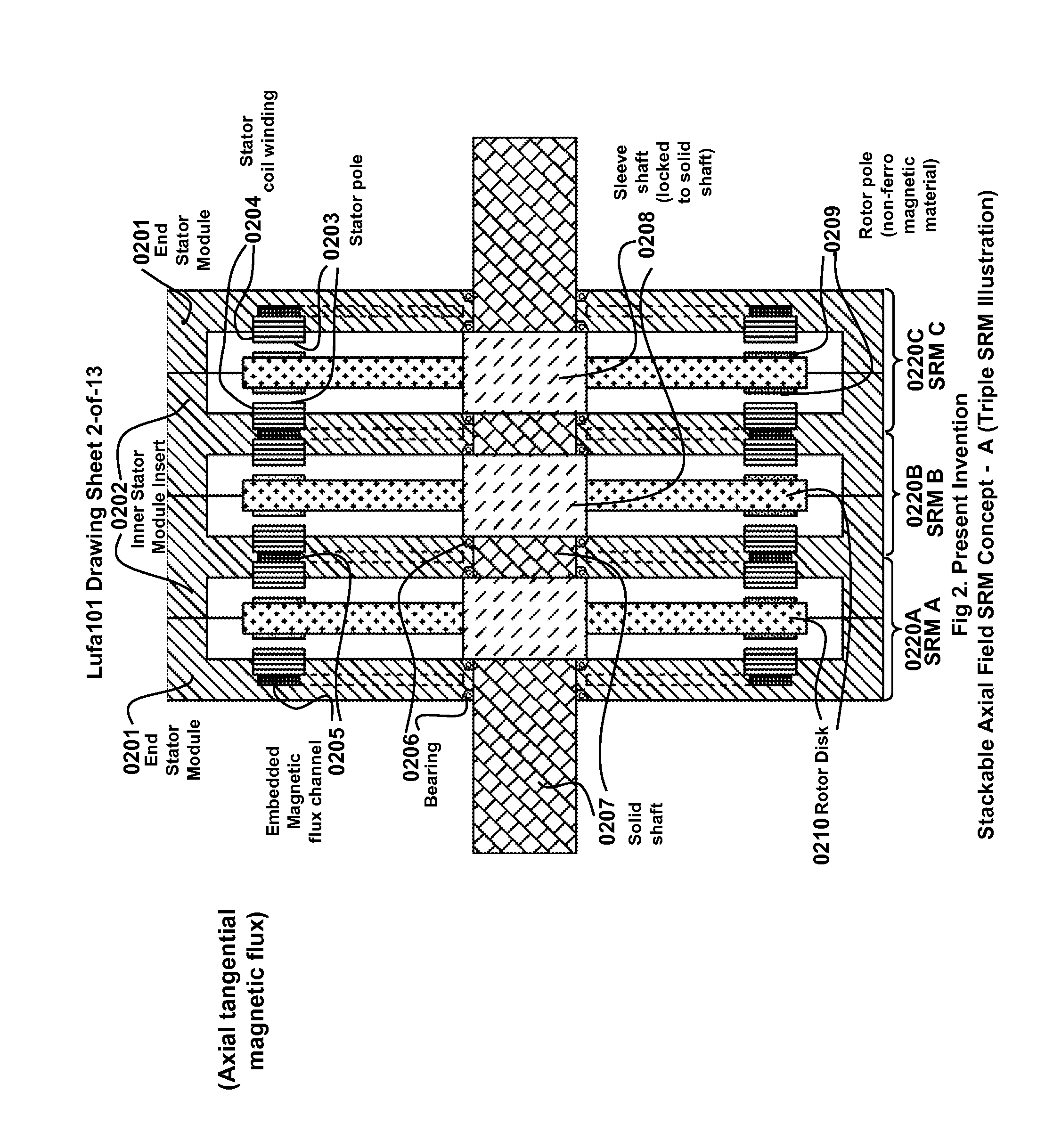
The present invention is a apparatus of multi-unit modular stackable switched reluctance motor system with parallely excited low reluctance circumferential magnetic flux loops for high torque density generation. For maximized benefits and advanced motor features, the present invention takes full combined advantages of both SRM architecture and “Axial Flux” architecture by applying “Axial Flux” architecture into SRM design without using any permanent magnet, by modularizing and stacking the “Axial Flux” SRM design for easy configuration and customization to satisfy various drive torque requirements and broad applications, and by incorporating an en energy recovery transformer for minimizing switching circuitry thus further lowering the cost and further increasing the reliability and robustness. Unlike prior arts, the present invention does not use any permanent magnet and this “Axial Flux” SRM system is modularized and stackable with many benefits.
Owner:LUSTONE TECH
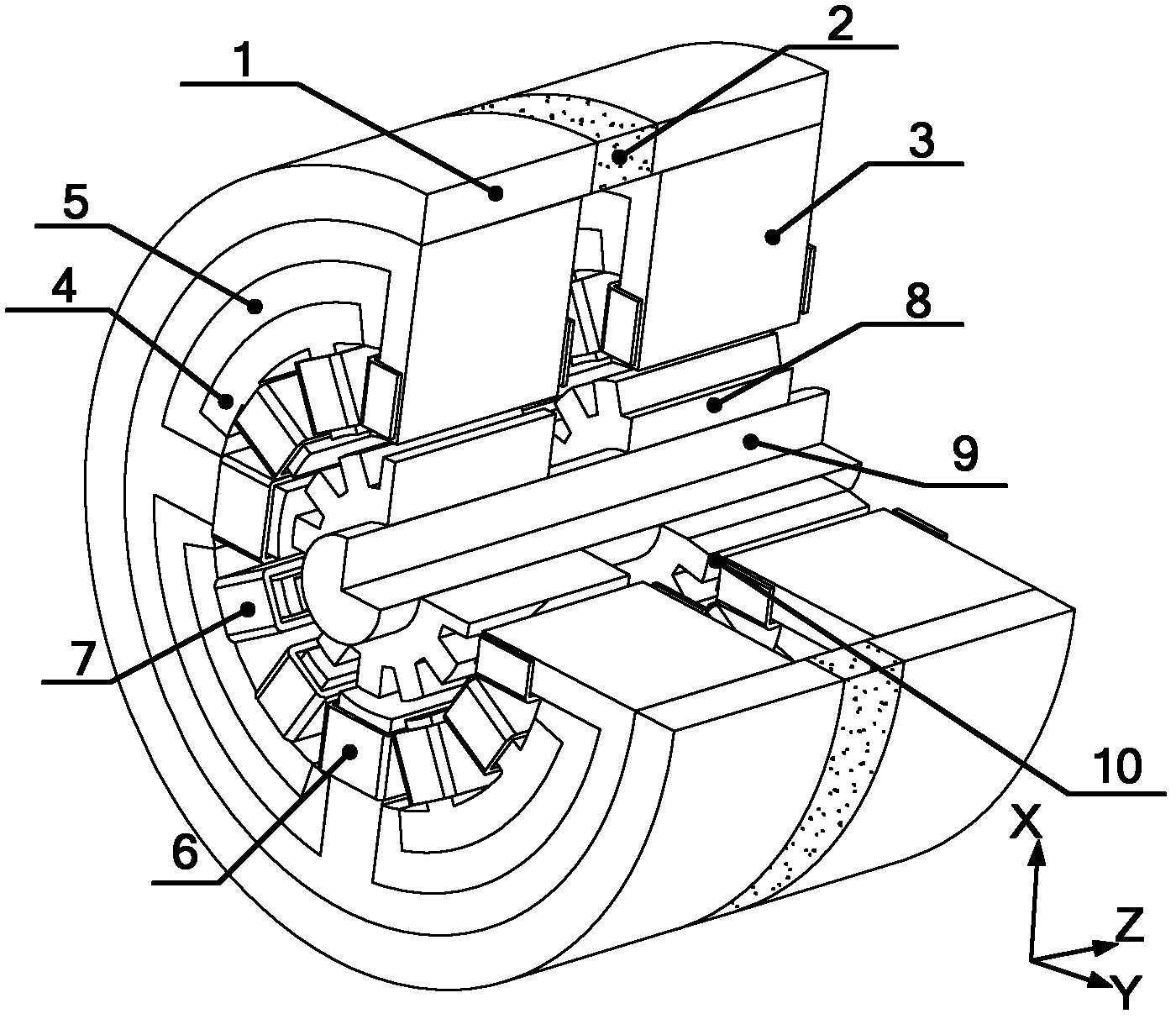
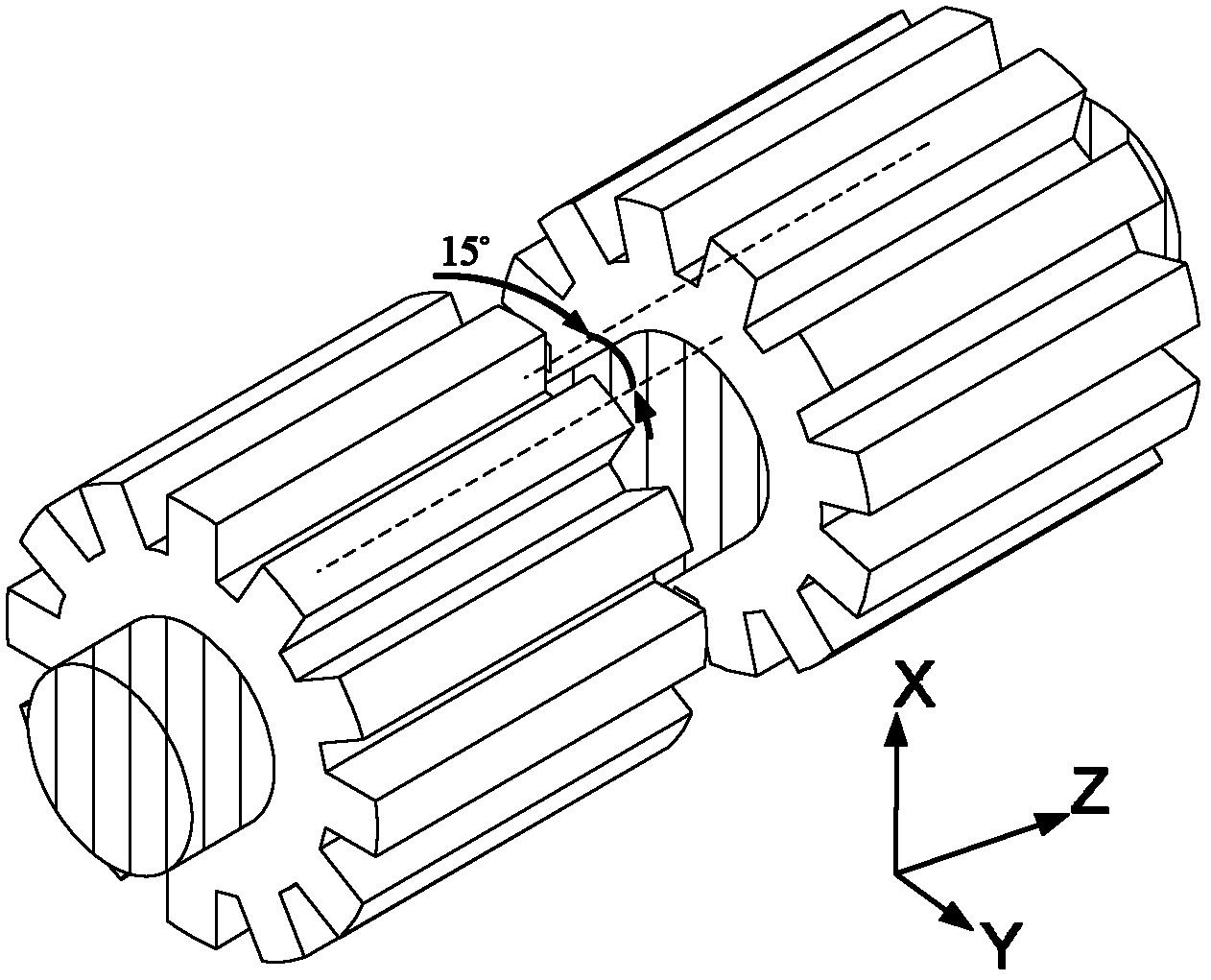
Bearingless switched reluctance motor and control method thereof
InactiveCN103296847AGive full play to high-speed adaptabilityReduce copper consumptionElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLoop controlPower flow
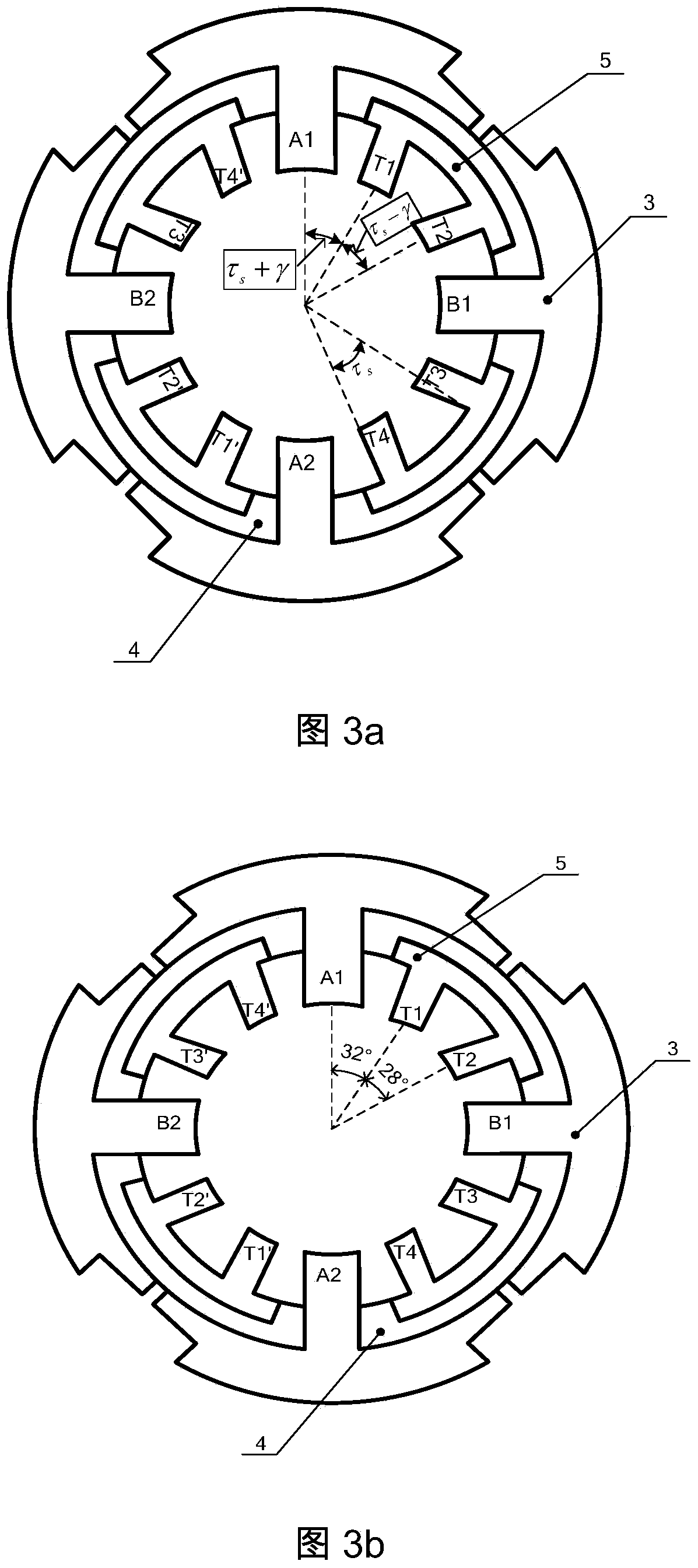
The invention provides a bearingless switched reluctance motor and a control method thereof. The difference between a rotor pole arc angle and a stator pole arc angle of the motor is 15 degrees, current of torque windings and suspension windings are controlled to generate suspension force, the current of the torque windings is controlled so as to generate torque, and current of the torque winding of each phase and turn-on and turn-off angle of the torque winding are regulated to achieve a speed closed loop; radial displacement of a rotor is detection, and radial force needed for rotor suspension is outputted via PID (proportion integration differentiation) regulators, so that closed-loop control of radial displacement of the rotor is achieved. The suspension windings are only excited and conducted in a maximum-inductance flat-top area and do not generate torque, so that the torque and the suspension force can be decoupled in control, and current magnitude of the torque windings and the suspension windings is optimized to make copper loss of the windings to be minimum; in addition, counter potential of the suspension windings and the torque windings is zero in the maximum-inductance flat-top area, and high-speed suspended running of the bearingless switched reluctance motor is benefitted so as to give full play to high-speed adaptability of the switched reluctance motor.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Switched reluctance motor
InactiveCN102810964AReduce stator weightReduce manufacturing costMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machinesReluctance motorMagnetic flux
Disclosed herein is a switched reluctance motor, including: a rotor provided with a plurality of salient poles protruded along an outer peripheral surface thereof; and a stator including a plurality of stator cores in a pi ([pi]) shape that have the rotor rotatably accommodated therein, are opposite to the plurality of salient poles, and have coils wound therearound, wherein a magnetic flux path is formed along the stator cores in the pi shape and the salient pole opposite thereto.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Composite-structure bearingless switched reluctance motor and control method thereof
InactiveCN103296935AGood suspensionReduce the impactMagnetic holding devicesLevitationElectric machine
The invention relates to a composite-structure bearingless switched reluctance motor and a control method thereof and belongs to the field of bearingless switched reluctance motors and control methods thereof. A torque stator and a levitation stator are axially stacked to form a stator; a winding is wound on teeth of the stator and passes the torque stator and the levitation stator, and the winding is wound in a central winding manner; a rotor comprises a torque rotor and a levitation rotor, the torque rotor and the levitation rotor are axially stacked in the stator, the torque rotor is located below the torque stator, the torque stator and the torque rotor are equal in axial length, and the levitation stator corresponds to the levitation rotor while the levitation stator and the levitation rotor are equal in axial length; the levitation stator is in a pole shoe structure, and the polar arc angle of the levitation stator is larger than that of the torque stator. Levitation and torque decoupled control is achieved; the control method is simple; radial bearing force is large; the motor is fine in levitating performance. Levitation control is achieved by minimum inductance zone; the levitating current has low effect on torque current, and interphase coupling effect is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Bearing-free switch reluctance motor having axial-direction parallel hybrid structure and control method of motor
ActiveCN105024507AGood high-speed suspension performanceLow costElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMagnetic bearingElectric machine
The invention discloses bearing-free switch reluctance motor having an axial-direction parallel hybrid structure and a control method of said motor. A motor stator is composed of a reluctance motor stator and a magnetic bearing stator. A rotor is composed of a salient pole rotor and a cylinder rotor. The windings are composed of torque windings and suspension windings. The torque windings are composed of reluctance motor windings and wide-tooth windings and the number of the torque windings is identical to phase number m. The suspension windings are two and are arranged in the radial direction. The magnetic bearing stator is composed of four E-shaped structures and the width of each middle tooth is twice of the rest. According to the invention, suspension current is calculated according to a suspension force direction. Current of the torque windings and switching-on and switching-off angles of a power circuit are controlled separately and rotation speed and torque are controlled in real time. Current of the two suspension windings is controlled separately, suspension forces are regulated in real time and mutual decoupling is realized in rotation and suspension. According to the invention, the quantity of control variables is small; suspension control is simple; and a power converter of a suspension system is low in cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
2-magnetic-pole controller-free self-starting permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor
InactiveCN107994698APrevent the risk of high temperature demagnetizationImprove securityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsSynchronous reluctance motorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a 2-magnetic-pole controller-free self-starting permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor, and relates to the field of the synchronous reluctance motor. At current, the reluctance motor can be only in operation by being equipped with a special controller, and needs a large number of rare earth permanent magnet material, so that the cost is high. The 2-magnetic-pole controller-free self-starting permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor comprises a machine base, a front end cover, a back end cover, a front bearing, a front bearing inner cover,a back bearing, a back bearing inner cover, a line stator, a rotor iron core, a rotary shaft, a bottom foot, a fan blade and a fan cover; the rotor iron core is formed by multiple iron core stampingsheets with two magnetic poles in an overlaying manner; rotary shaft holes are formed in the centers of the iron core stamping sheets; the two magnetic poles both comprise radially arranged reluctancegrooves of the same number; a fan-shaped permanent magnet is arranged in the middle of each reluctance groove; and an aluminum cast mouse cage is arranged on the periphery, on the outer sides of thereluctance grooves of the iron core stamping sheets, of the rotor iron core. By virtue of a combination of a permanent magnet synchronous motor and the synchronous reluctance motor in the technical scheme, and by combination of the aluminum cast mouse cage, use of a permanent magnet material is reduced, and high operation also can be realized without a controller, so that the motor cost is obviously lowered.
Owner:WOLONG ELECTRIC GRP CO LTD
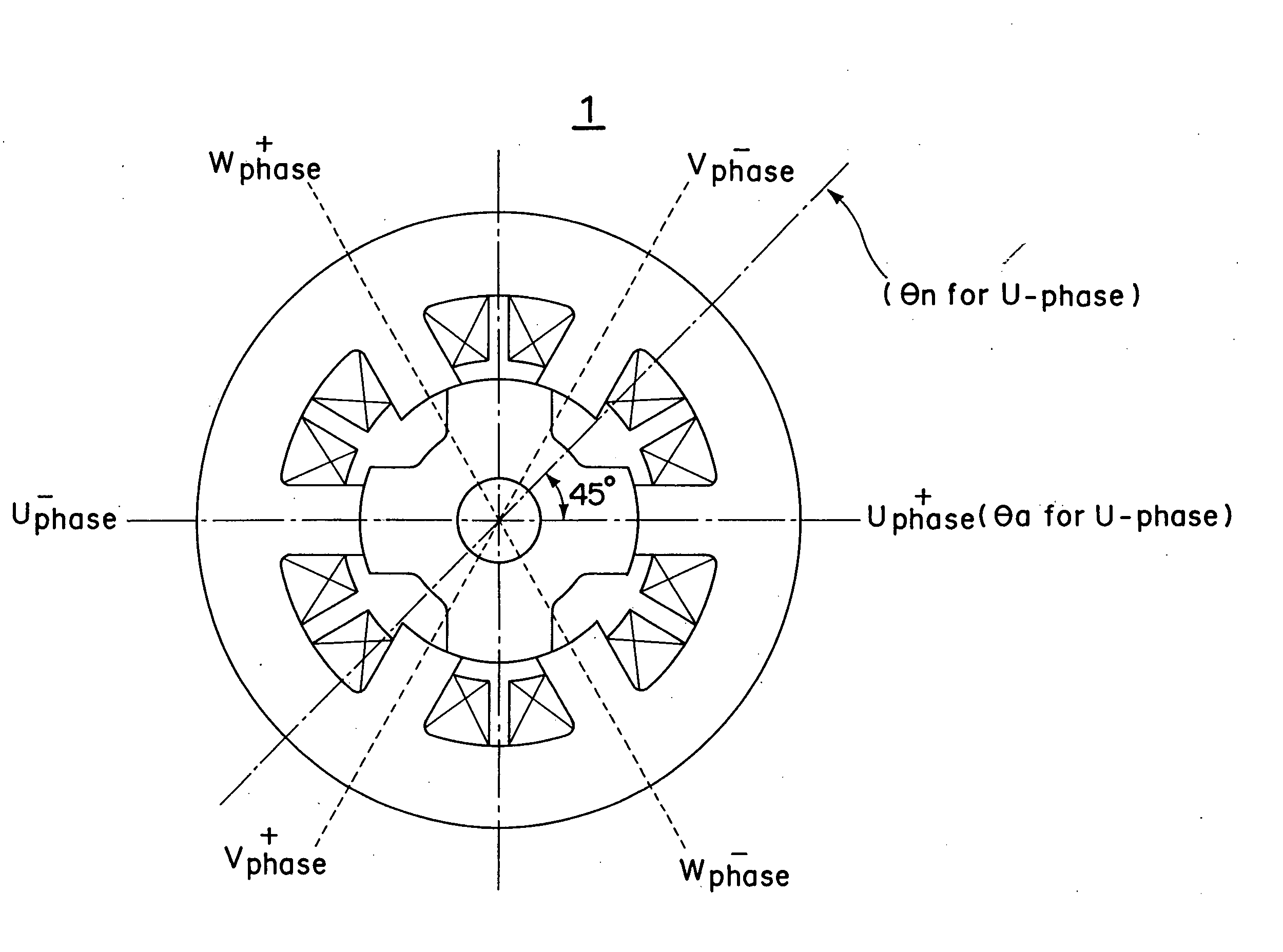
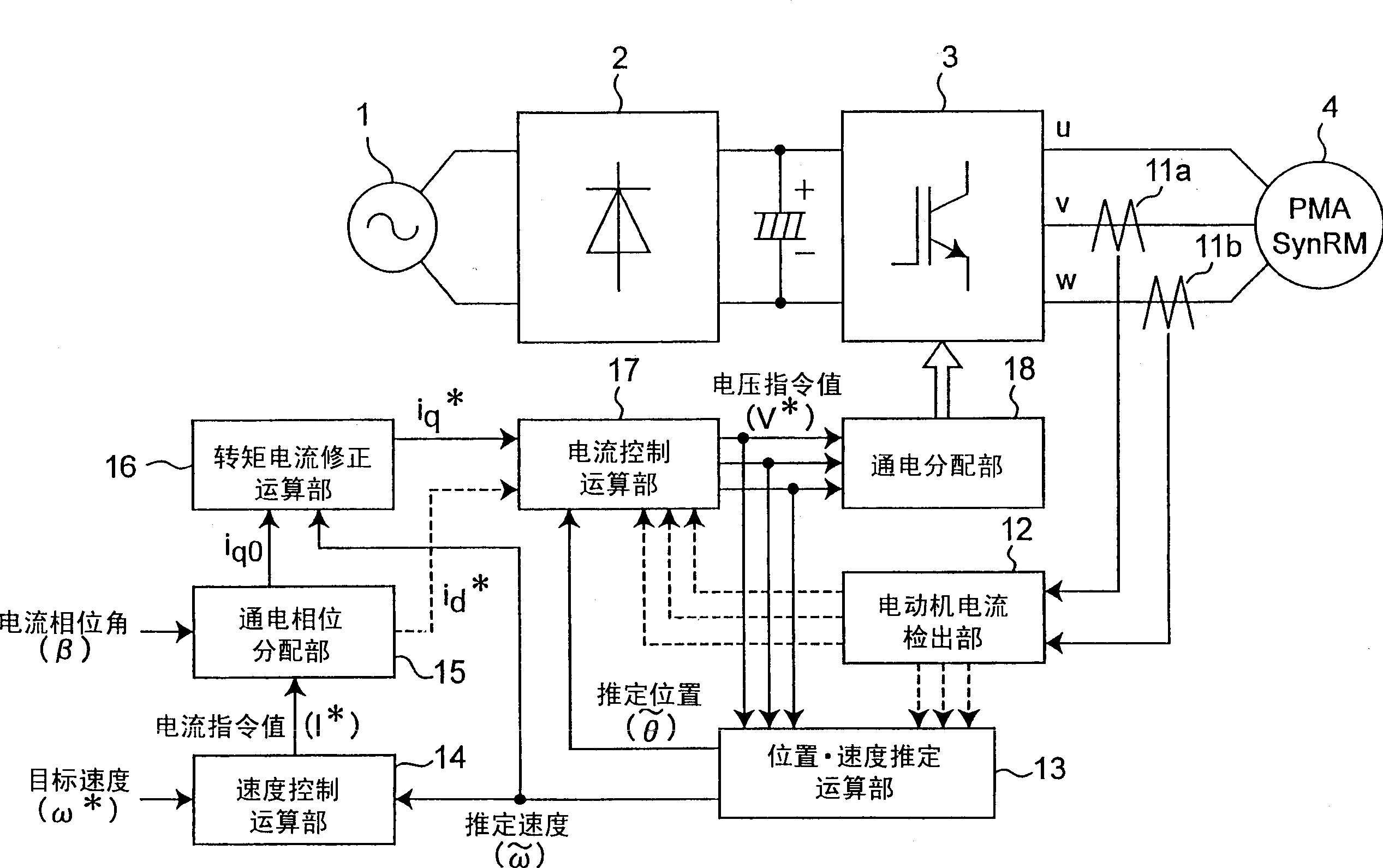
Synchronuos reluctance motor control device
InactiveCN1516918ASuppress changesReduce vibrationElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlSynchronous reluctance motorLoad torque
A control apparatus of a synchronous reluctance motor includes a torque current correction unit (16) that generates a torque current command tracing a load torque so as to make the output torque of the motor coincide with the load torque. the control apparatus may further include a position and speed estimation unit (13) that estimates the position and speed based on three phase voltage equation to improve control performance in a voltage saturation state.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Mixed excitation short-magnetic-circuit variable-reluctance motor
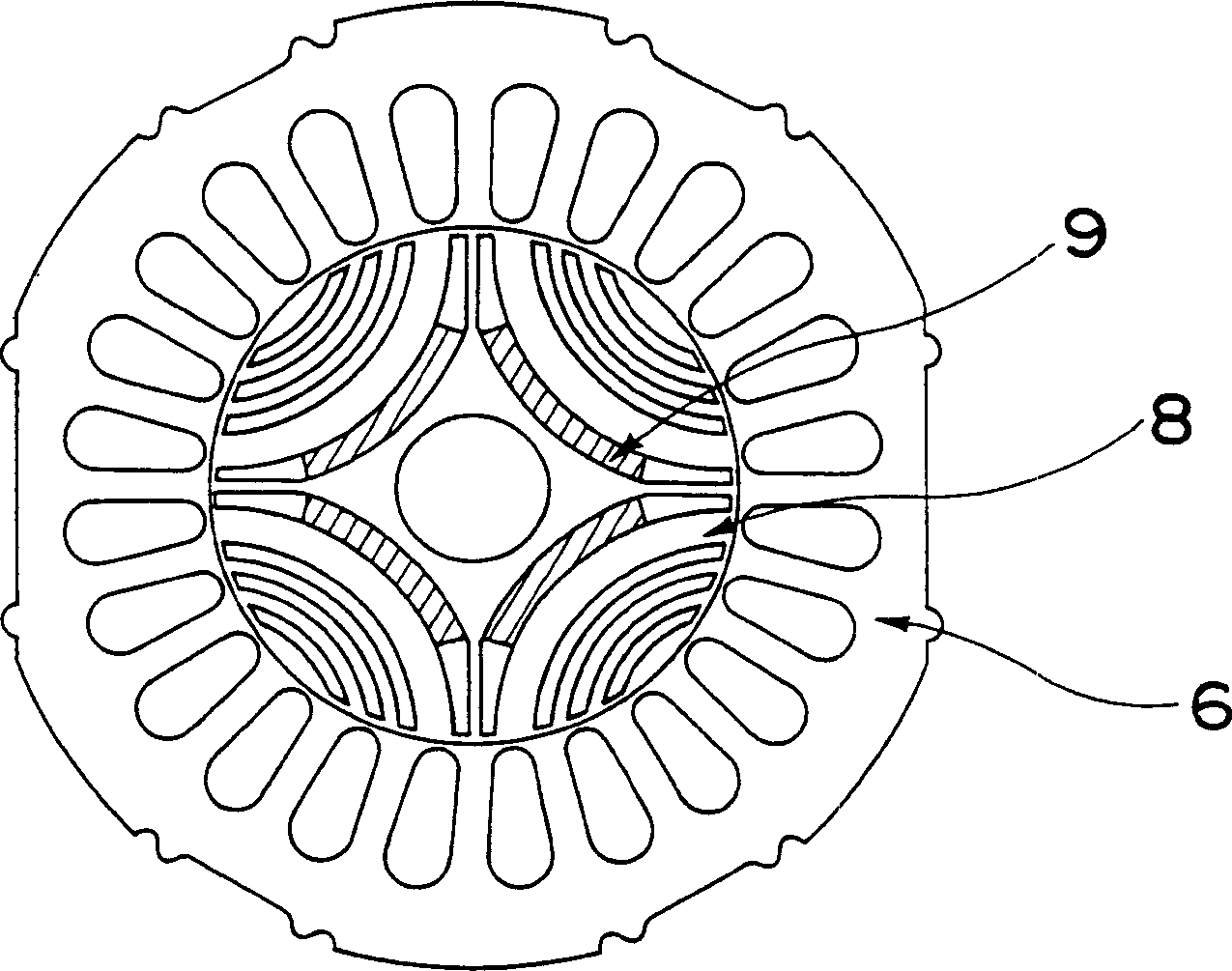
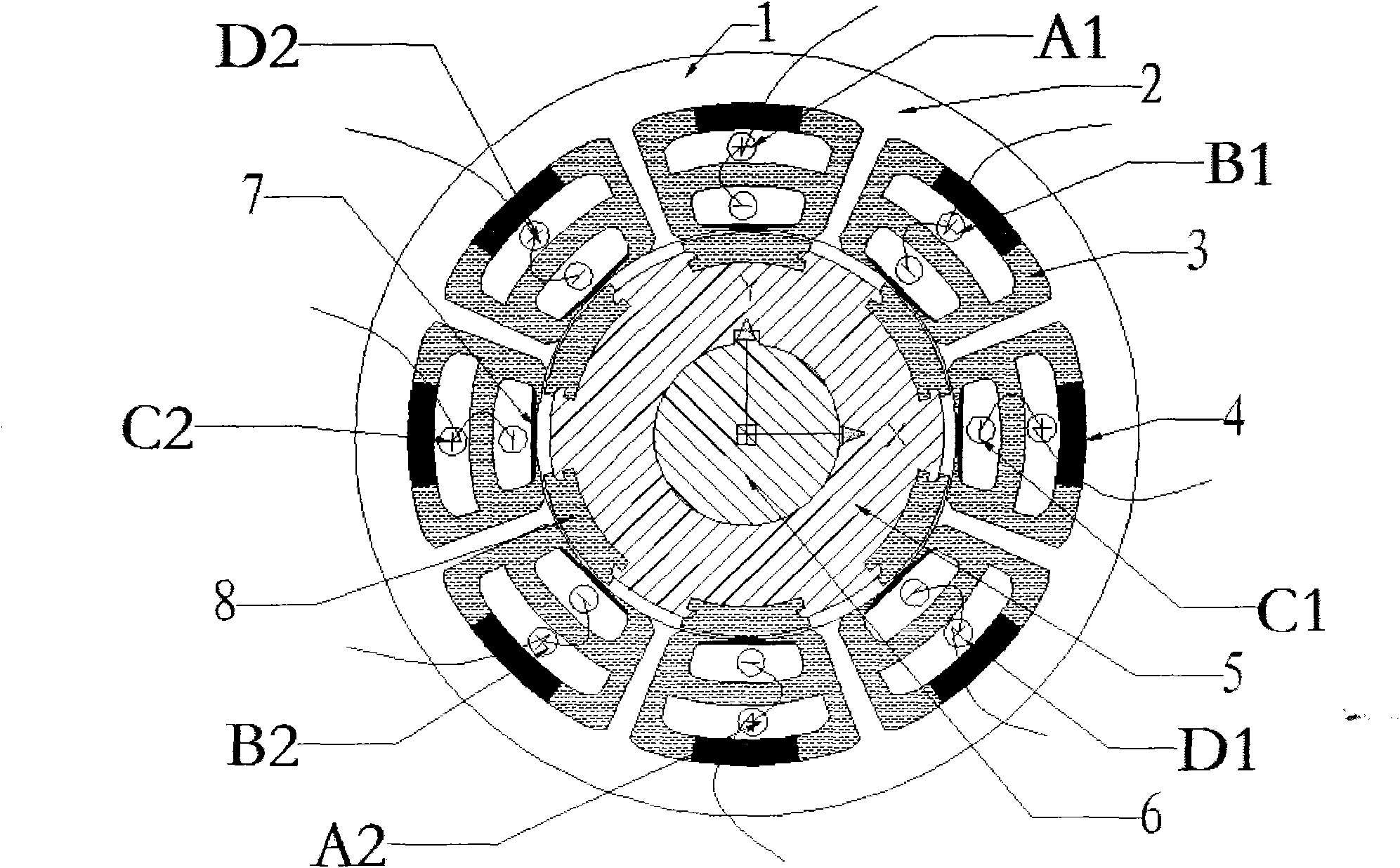
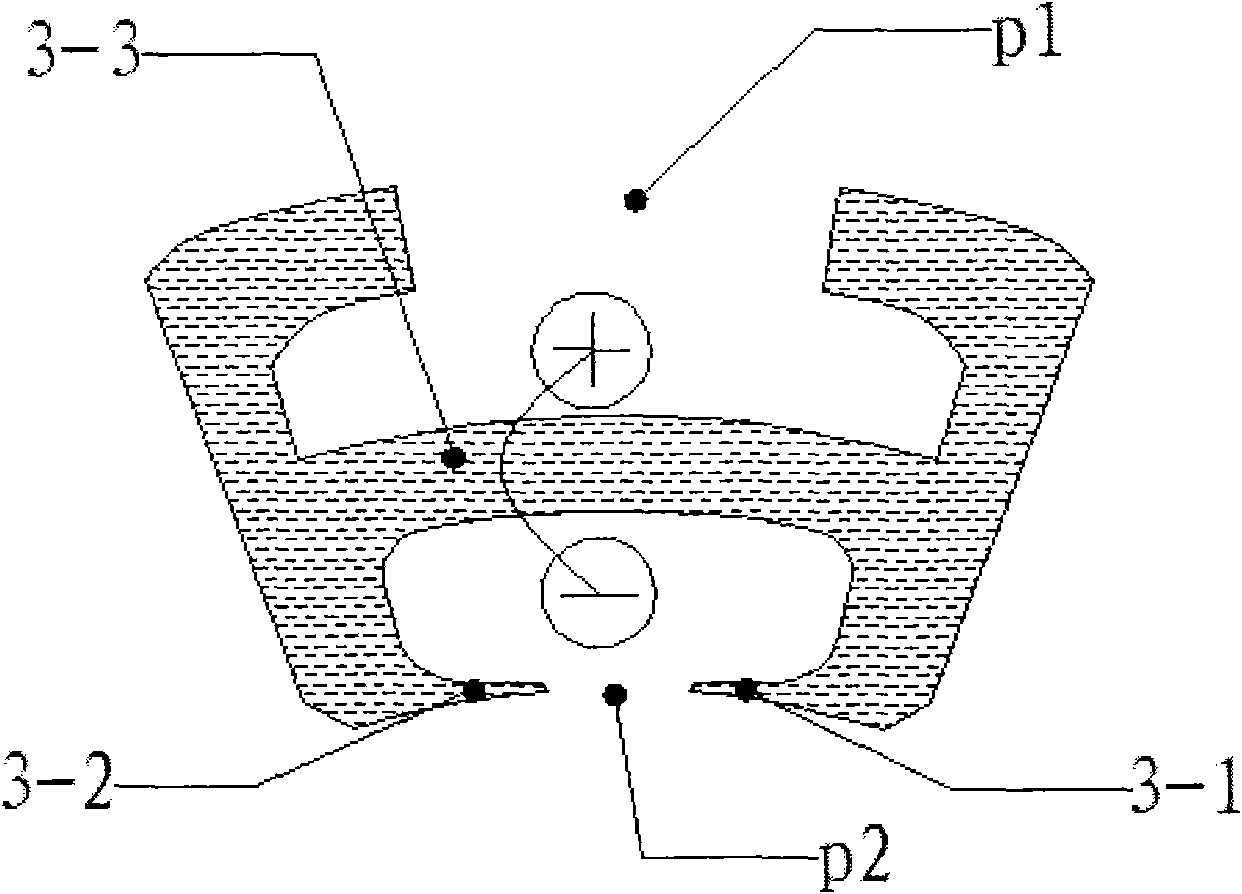
InactiveCN102315746AEasy to installFlexibleMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsNoise levelElectrical polarity
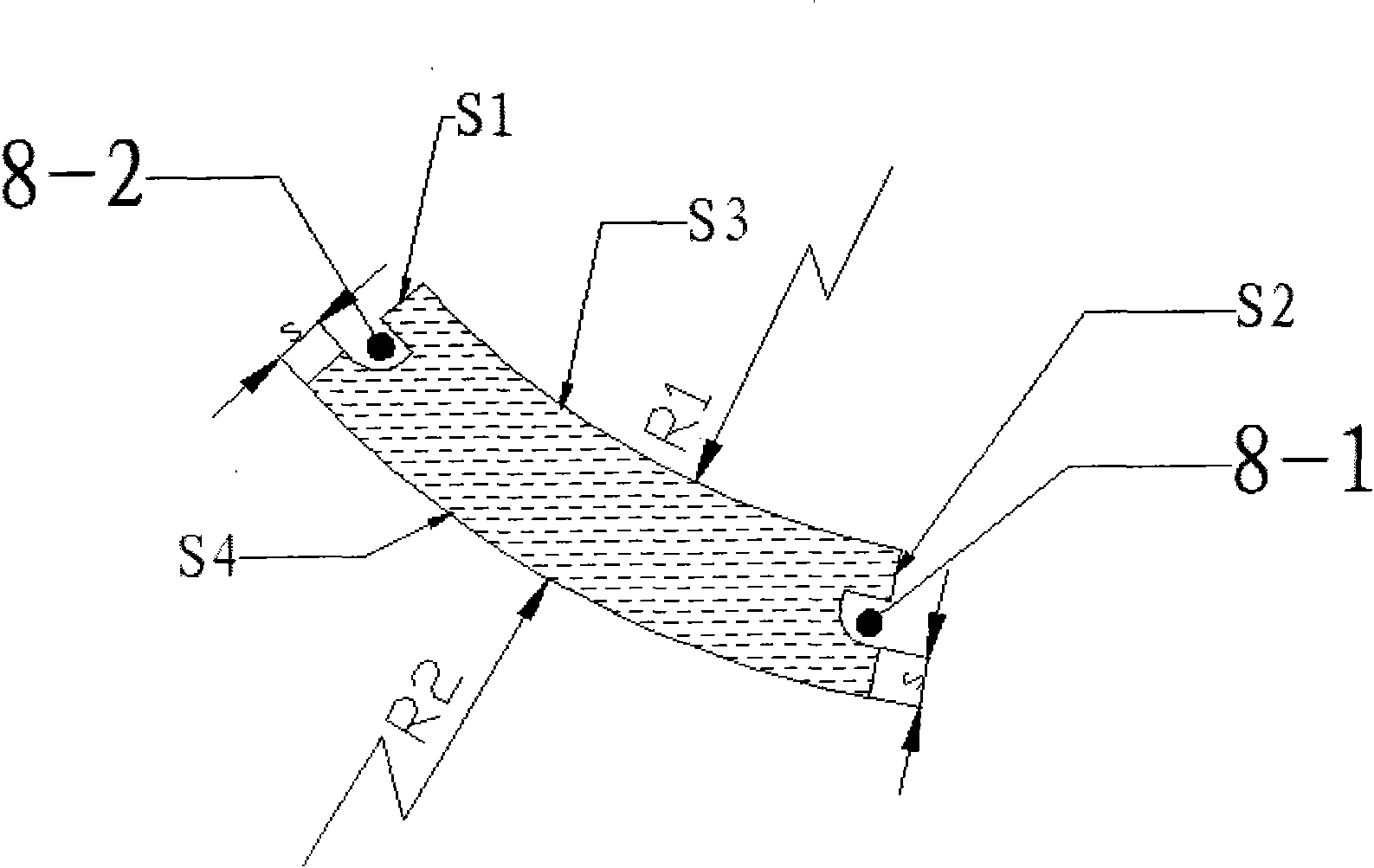
The invention discloses a mixed excitation short-magnetic-circuit variable-reluctance motor 1 as well as a stator structure and a rotor structure thereof. An inner circular face t of a base part 2 of the mixed excitation short-magnetic-circuit variable-reluctance motor is provided with modules 2-1 which protrude inwards in a preset interval angle; the stator part comprises a plurality of H-shaped stator sections 3 and first permanent magnets 4 (1) arranged at all the H-shaped stator sections p1, and the polarities of the permanent magnets of the stator sections are opposite; an exciting winding coil is embedded into two stator slots of each H-shaped stator section 3; and the rotor part comprises a rotor body 5 and a plurality of annular body rotor sections 8 arranged on the rotor body and / or second permanent magnets 4 (2), wherein the second permanent magnets are arranged on the s3 surfaces of the annular body rotor sections, and open grooves 8-1 and 8-2 are arranged on the lateral surfaces of the annular body rotor sections. According to the invention, the rotating force of the variable-reluctance motor can be increased, the energy density is improved, the torque ripple and the vibration and noise level are reduced, the performance is stable, and the size is smaller under the requirement of same output torque.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
12/14 bearingless permanent magnet biased switched reluctance motor
InactiveCN103715945AStable suspension forceDynamo-electric machinesMagnetic holding devicesReluctance motorElectromagnetic torque
A 12 / 14 bearingless permanent magnet biased switched reluctance motor is formed by a stator back yoke, permanent magnets, stator suspension force iron cores, magnetism isolation sleeves, stator torque iron cores, a rotor iron core, suspension force winding coils, torque winding coils and a shaft. The inner side of the stator back yoke is provided with the stator suspension force iron cores; the permanent magnets are embedded between the stator back yoke and the stator suspension force iron cores; the magnetism isolation sleeves are arranged between the stator suspension force iron cores and the stator torque iron cores; the stator suspension force iron cores and the stator torque iron cores are wound with the suspension force winding coils and the torque winding coils respectively; and the stator suspension force iron cores and the stator torque iron cores are internally provided with the rotor iron core, and the rotor iron core is internally provided with the shaft. The permanent magnets provide a bias magnetic field, so that motor loss is reduced and axial length is reduced; meanwhile, through the adjustment of the positions of stator torque iron core teeth, electromagnetic torque of the motor is increased, and torque pulsation is reduced; and the defects of an original 12 / 14 bearingless switched reluctance motor are totally overcome from two aspects, and the efficiency of the motor is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Motor with separated permanent magnet torque and reluctance torque and its optimal efficiency control
ActiveUS20180323665A1Reduce processing difficultyGreater reluctance torqueElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlSurface mountingReluctance motor
The invention proposes a new motor with separated permanent magnet torque and reluctance torque. Meanwhile, the optimal efficiency control method for this motor is proposed. This invention belongs to the field of motor and its drive system. The proposed motor includes 3 stators and 1 rotor (composed of 2 axial rotors and 1 radial rotor), the radial stator employs distributed winding, the axial stator adopts concentrated winding. The distributed winding and the radial reluctance rotor structure contribute to higher reluctance torque, while the concentrated winding and the surface mount permanent magnet structure offer higher permanent magnet torque. In the view of the magnetic circuit, the axial magnetic circuit generates the permanent magnet torque, and the radial magnetic circuit generates the reluctance torque. By using the decoupling of axial and radial magnetic circuits, the separation and the independent control of the permanent magnet torque and the reluctance torque are realized. Each stator and rotor of the invention can be processed independently, and the modular installation can be processed, thereby reducing the difficulty of the motor processing.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Brushless DC motor
InactiveUS6867526B2Reduce decreaseMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsBrushless motorsMagnetic reluctance
A bridge (8) in conformity with a tooth opening angle of the stator (1) is provided between a permanent magnet (5) and a permanent magnet (5) in a rotor (4), so that a magnetic flux for a reluctance torque is made to pass an inner side of the permanent magnet (5). An opening angle of each of ribs (7) on both sides of the permanent magnet (5) is set to be equal to or smaller than the teeth interval opening angle and equal to or larger than a half thereof. Thereby, reluctance of the rib (7) against a magnetic flux in a circumferential direction is increased and leakage of the magnetic flux of the permanent magnet (5) is prevented.
Owner:KOYO SEIKO CO LTD
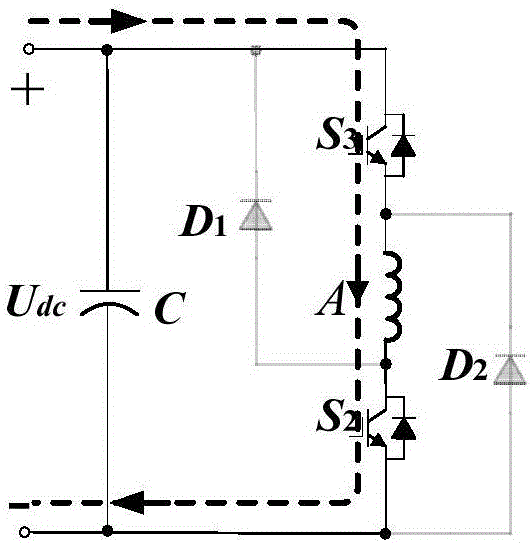
Low-cost detection system and method of winding current of switching reluctance motor
ActiveCN106707167AReduce volumeLow costCurrent/voltage measurementDynamo-electric machine testingWork patternElectric machine
The invention discloses a low-cost detection system and method of winding current of a switching reluctance motor. The low-cost detection system comprises a switching reluctance motor, an improved asymmetric semi-bridge converter, a rotor position detection device, a current sensor and a controller; different working modes, caused by the fact that conducting ranges are different, of the winding current of two adjacent phases of stators are analyzed; conditions that the winding current of the two adjacent phases of stators has an overlapping interval and does not have the overlapping interval are discussed, and an improved asymmetric semi-bridge converter topology is provided; and the quantity of electronic devices is reduced, and the winding current of each phase of the stator can be reconstructed through only one current sensor without any voltage loss. According to the low-cost detection system and method, the volume and cost of a motor system are reduced, the system is more compact, and the reliability of the motor performance is extremely improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
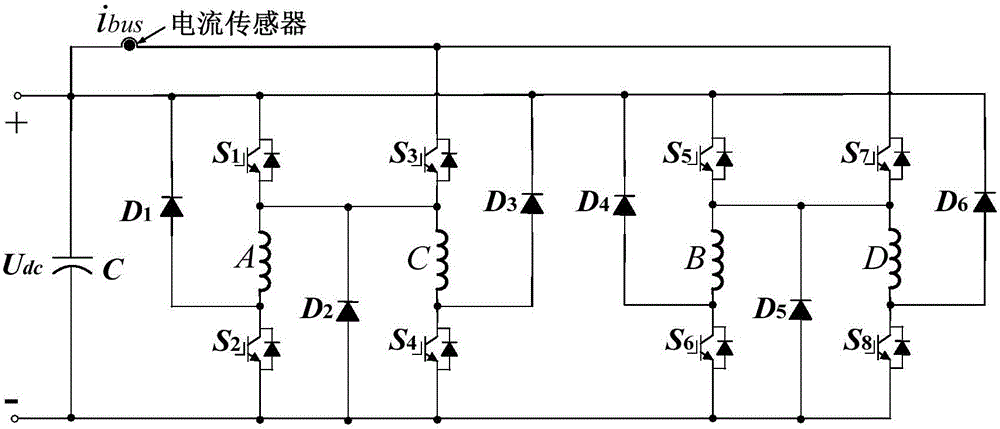
Switched reluctance motor system based on bus current sampling and winding current obtaining method thereof
ActiveCN104767430AEffective refactoringReduce usageAC motor controlElectric motor controlPhase currentsImpulse frequency
The invention discloses a switched reluctance motor system based on bus current sampling. The switched reluctance motor system comprises a switched reluctance motor, a power converter, a rotating speed detecting device, current sensors and a controller. The phase current of the SRM system is analyzed, the influence on the phase current waveform by different open sections is discussed, and the phase current overlapping and non-overlapping conditions in a current chopping section are analyzed. According to the phase current overlapping condition, high-frequency impulses are injected into all under-phase tubes in an overlapping section, A / D sampling is triggered at the pulse low level to discompose the direct-current bus current, the injection high-frequency impulse frequency and the A / D sampling frequency are highly synchronous, information of all the open sections is combined, phase currents in all the phase conducting sections can be effectively rebuilt, the use quantity of the sensors is reduced, the system cost and size are greatly reduced, the switched reluctance motor system is more compact, and the problem that as gains of the single current sensors of all the phases are unequal, voltage drop is unbalanced is solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and system for lowering torque pulsation of switched reluctance motor by current adaptive control
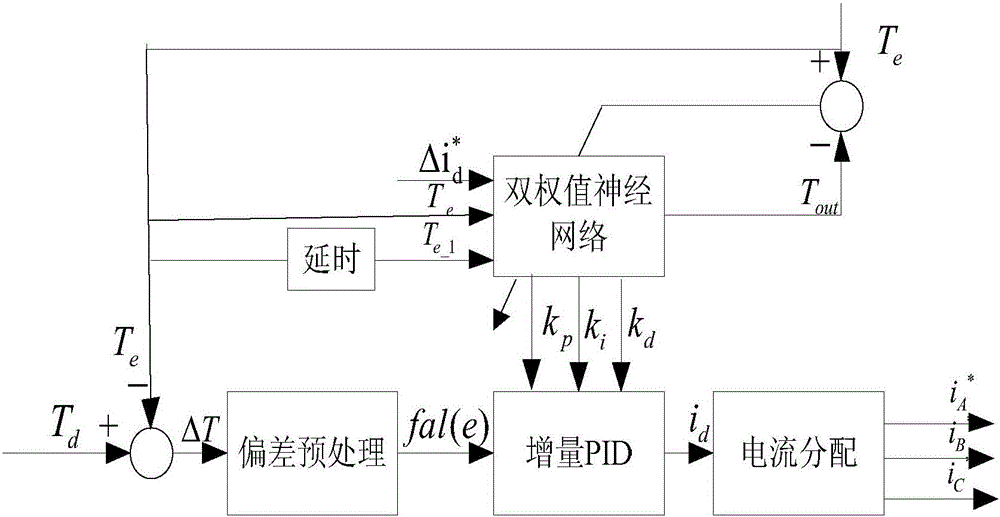
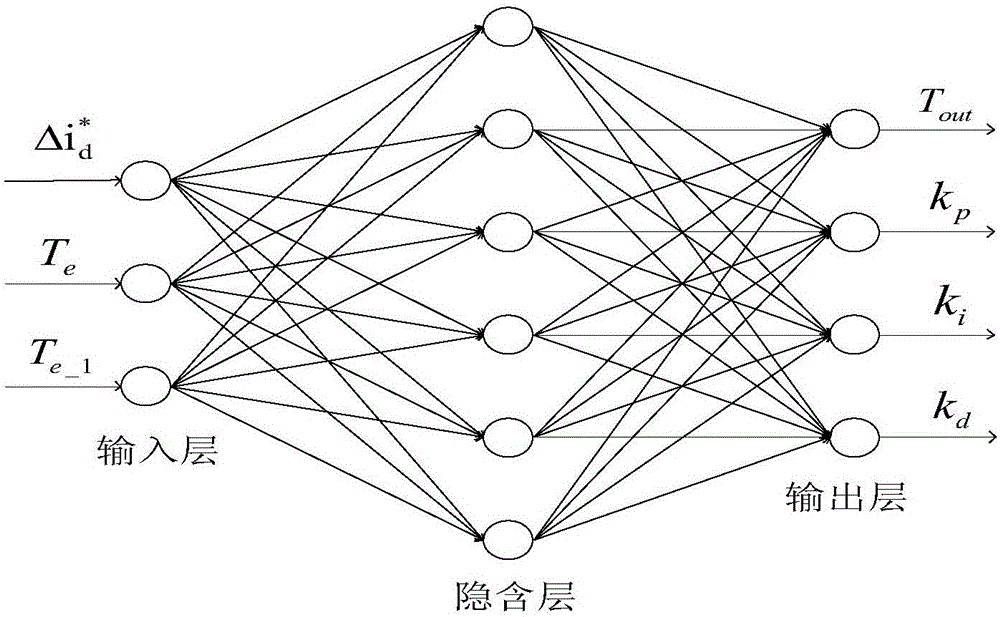
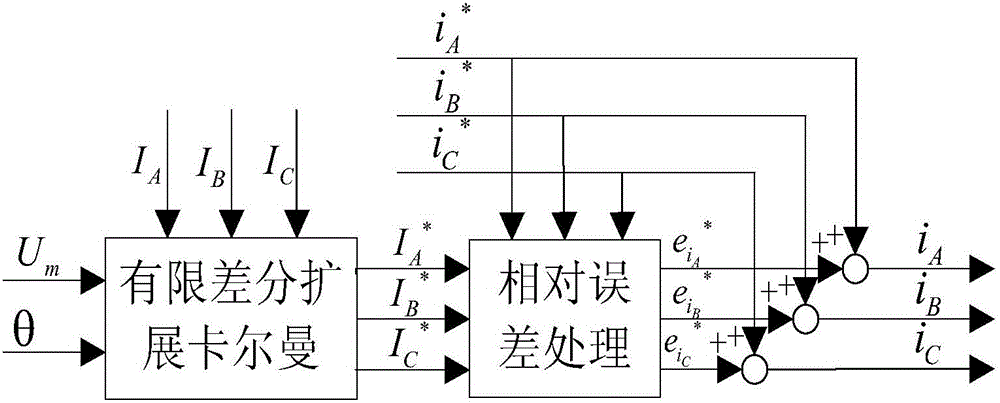
InactiveCN106357192ASuppression of torque rippleImprove predictive performanceGeneral control strategiesObserver controlHysteresisReference current
The invention relates to a method and system for lowering torque pulsation of a switched reluctance motor by current adaptive control; the method comprises: preprocessing a deviation: subjecting the torque deviation to nonlinear conversion; solving torque estimated output and adaptive PID (proportion integration differentiation) control coefficient by using double-weight neural network; acquiring current set total current by PID control calculation, and acquiring each phase control current via current allocation; predicting current feed-forward compensation control by finite difference extended Kalman filter, and effectively inhibiting and lowering torque pulsation of the switched reluctance motor by joint action of adaptive PID control and prediction-based current feed-forward compensation control. Current, torque and rotor position sensors are connected with a signal processor, the signal processor executes modules of the method, compensated three-phase reference current is output to control a power converter of the motor via a current hysteresis controller, and torque pulsation of the switched reluctance motor is significantly and effective inhibited.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Permanent magnet auxiliary synchronized reluctance motor rotor and motor thereof and installation method of motor
InactiveCN102790457AImprove operational reliabilityImprove resistance to demagnetizationMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous reluctance motorReluctance motor
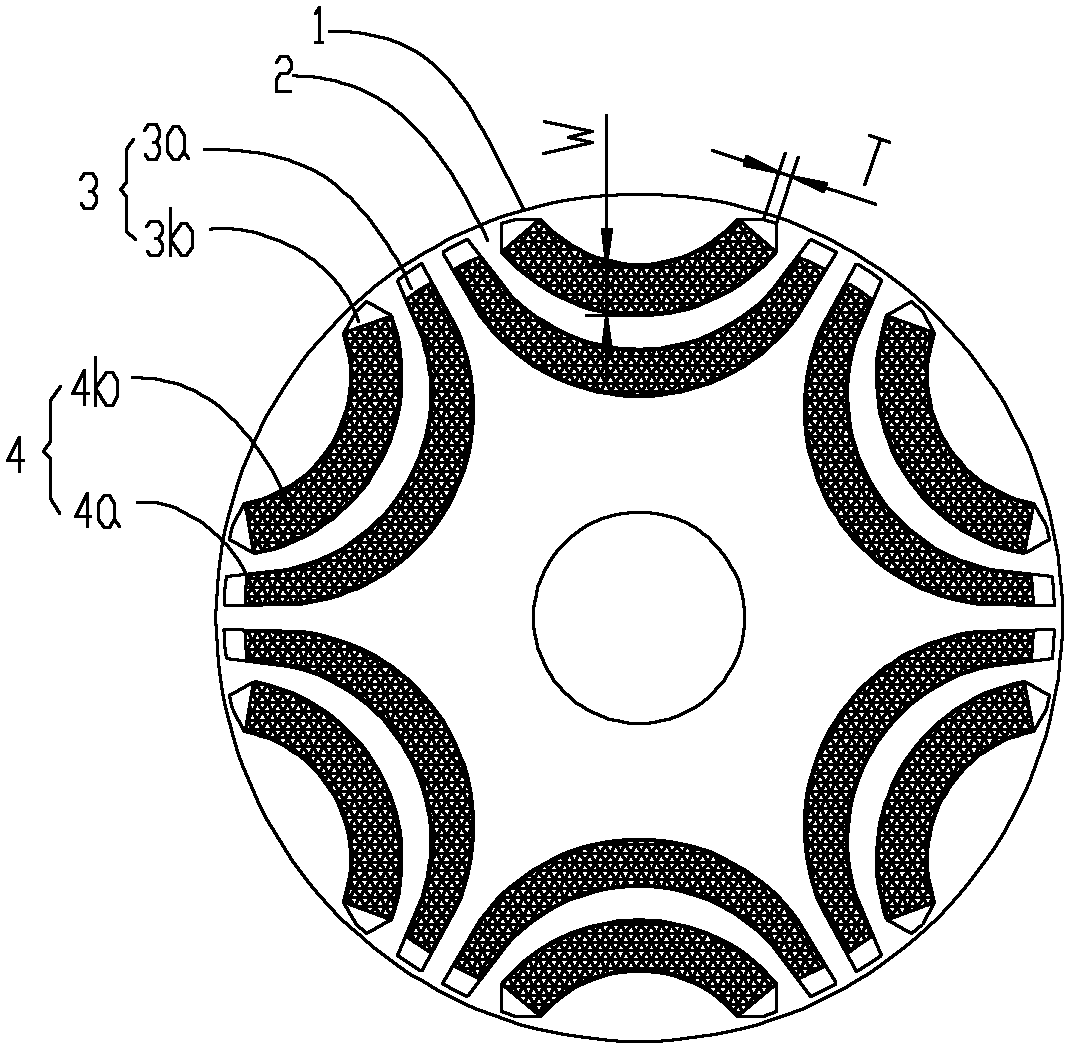
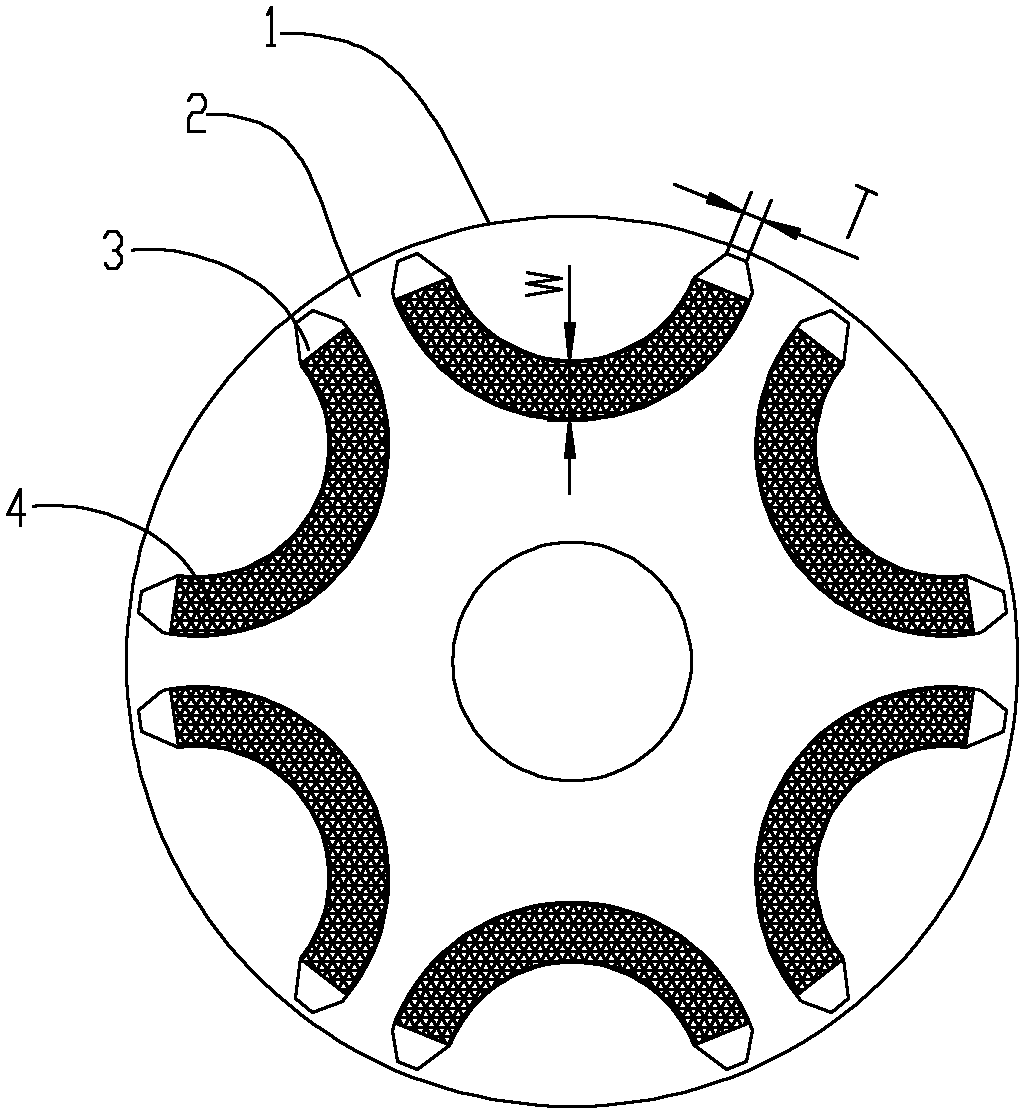
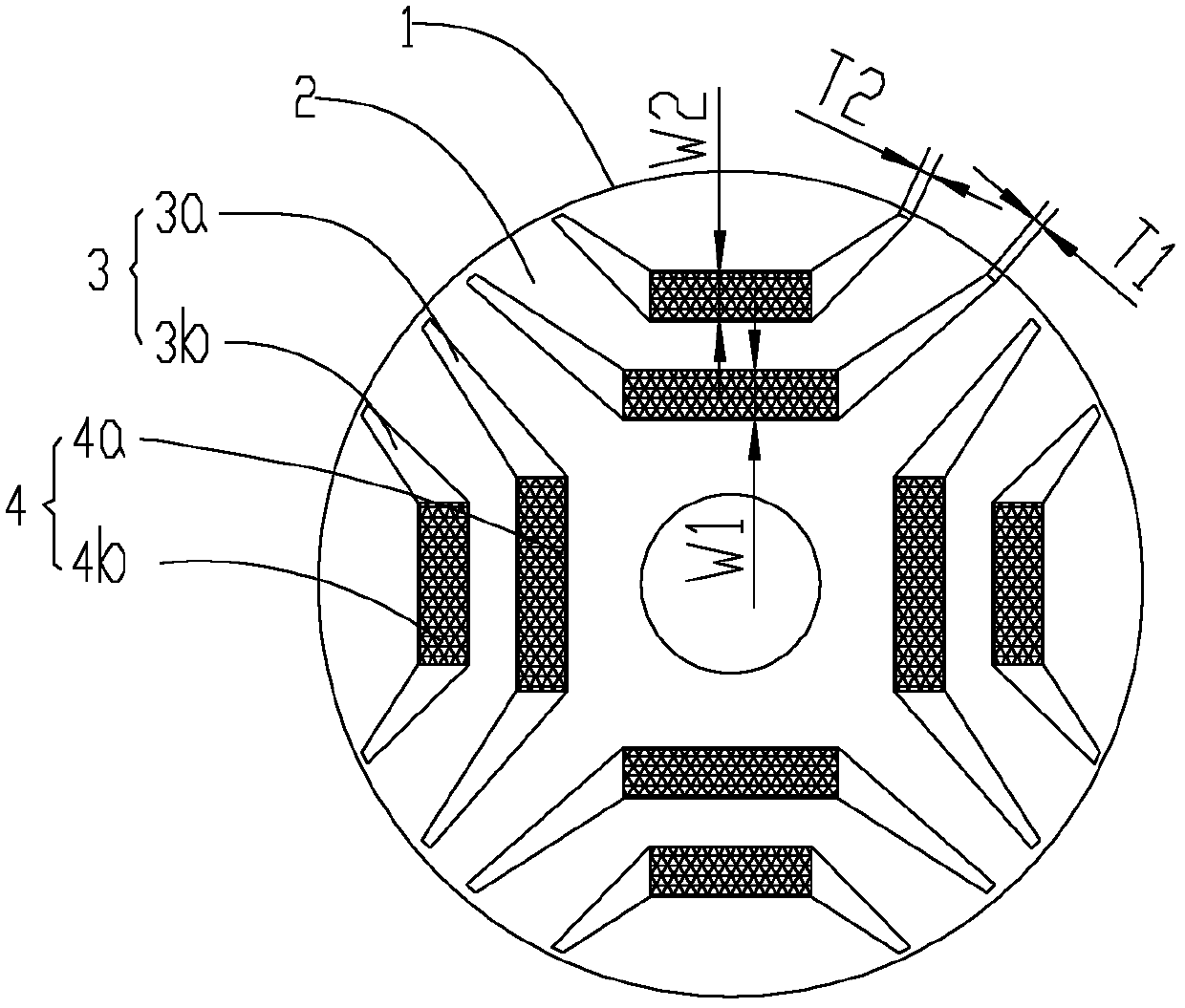
The invention provides a permanent magnet auxiliary synchronized reluctance motor rotor, a motor thereof and an installation method of the motor. The permanent magnet auxiliary synchronized reluctance motor rotor comprises a rotor iron core and a plurality of permanent magnet groups, a plurality of permanent magnet groove groups are uniformly distributed on the rotor iron core with rotor axis serving as a circle centre in a peripheral direction, each permanent magnet groove group comprises a single layer or multilayer of permanent magnet grooves, the number of the permanent magnet groups is identical to that of the permanent magnet groove groups, each permanent magnet group comprises a single layer or multilayer of permanent magnets which are respectively embedded into the permanent magnet grooves of the corresponding permanent magnet groove groups, the permanent magnets in each permanent magnet group have the same polarity, the polarities of the two adjacent permanent magnet groups are opposite, the end portion of at least one layer of permanent magnet groove in the plurality of permanent magnet groove groups is a sharpened end provided with a cutting face, and width T of the sharpened end cutting face of a permanent magnet groove with the sharpened end and middle width W meet the following relation. By means of the motor rotor, the motor thereof and the installation method of the motor, the whole demagnetization resistant capacity and operation reliability of the motor are improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE REFRIGERATION TECH CENT OF ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com