AC permanent magnet synergistic reluctance motor
A reluctance motor, permanent magnet technology, applied to synchronous motors with static armatures and rotating magnets, magnetic circuit rotating parts, synchronous machines, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient permanent magnet energy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Embodiment 1: This embodiment provides a unipolar permanent magnet synergistic reluctance motor whose rotor adopts a single-sided cantilever bracket and whose stator adopts compound excitation salient pole pairs. Its structure and shape are shown in the attached Figure 6-8 shown.
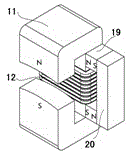
[0075] The stator of this embodiment is composed of a stator base 17 and four "composite excitation salient pole pairs", which are respectively arranged up, down, left, and right, with a gap of 90 degrees between them. "Composite excitation salient pole pair" consists of a "C-shaped" laminated iron core 11, an excitation coil 12 and a permanent magnet assembly 19, 20, as attached figure 2 As shown, the two port faces of the "C-shaped laminated iron core" face up and down, and the two port faces are arc-shaped. When the input excitation current of the excitation coil is zero, there is no magnetic polarity at the upper and lower port faces of the "C-shaped" laminated iron core, and the two m...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Embodiment 2: This embodiment provides a permanent magnet synergistic reluctance motor in which the rotor is a double-sided cantilever bracket and the stator compound excitation salient pole pair is unipolar. Its shape and structure are as follows: Figure 12-14 shown.
[0080] This embodiment is a special case of the first embodiment, that is, the combined structure of the motor shafts given in the two first embodiment.
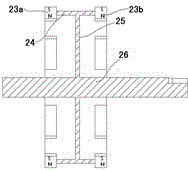
[0081] This embodiment adopts double-sided cantilever rotor support, and its structure is as attached Figure 9-11 As shown, the magnetic polarities of adjacent permanent magnets located on the same side of the support and on the same rotating surface are different, while the magnetic polarities of the two permanent magnets located on both sides of the support and at the same central angle are the same.
[0082] The eight compound excitation salient pole pairs of the motor stator in this embodiment are divided into two groups, with the disk in the ro...
Embodiment 3
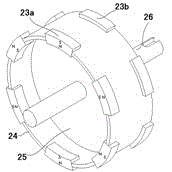
[0085] Embodiment 3: This embodiment provides another permanent magnet synergistic reluctance motor in which the rotor is a double-sided cantilever support and the stator composite excitation salient pole pair is unipolar. The structure and setting of the composite excitation salient pole pair on the stator The position is the same as that of embodiment two (see attached Figure 13-14 shown).
[0086] The difference between the present embodiment and the second embodiment is that the setting rules of the permanent magnets on the double-sided cantilever brackets are different, as shown in the attached Figure 15 And attached Figure 16 As shown, there is still a difference of 60 degrees between the radial centerlines of the six permanent magnets on one side of the cantilever bracket, and the magnetic polarity of two adjacent permanent magnets is different, but the six permanent magnets on one end of the cantilever bracket The permanent magnets and the six permanent magnets at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com