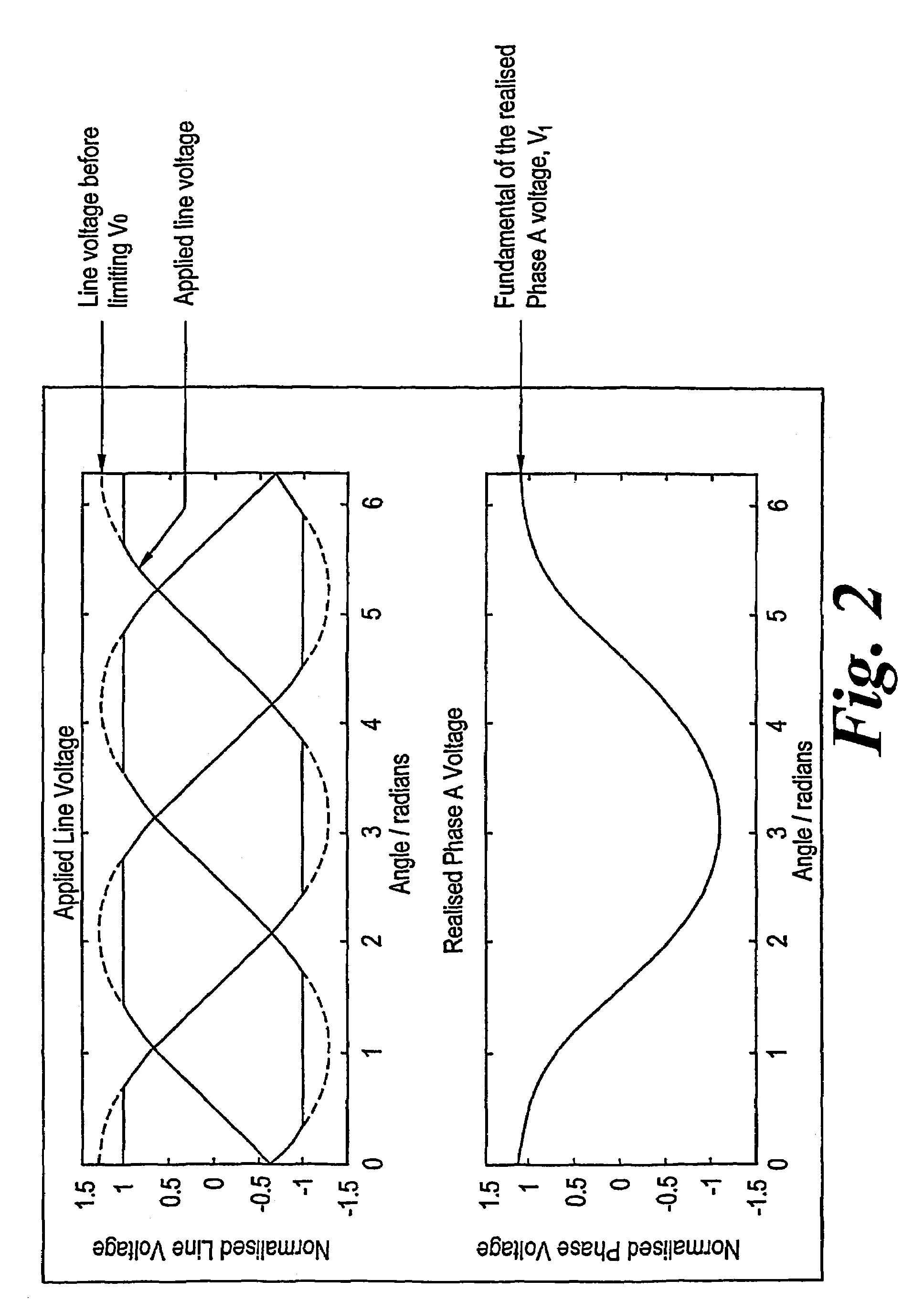
Patents
Literature
678results about "General control strategies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
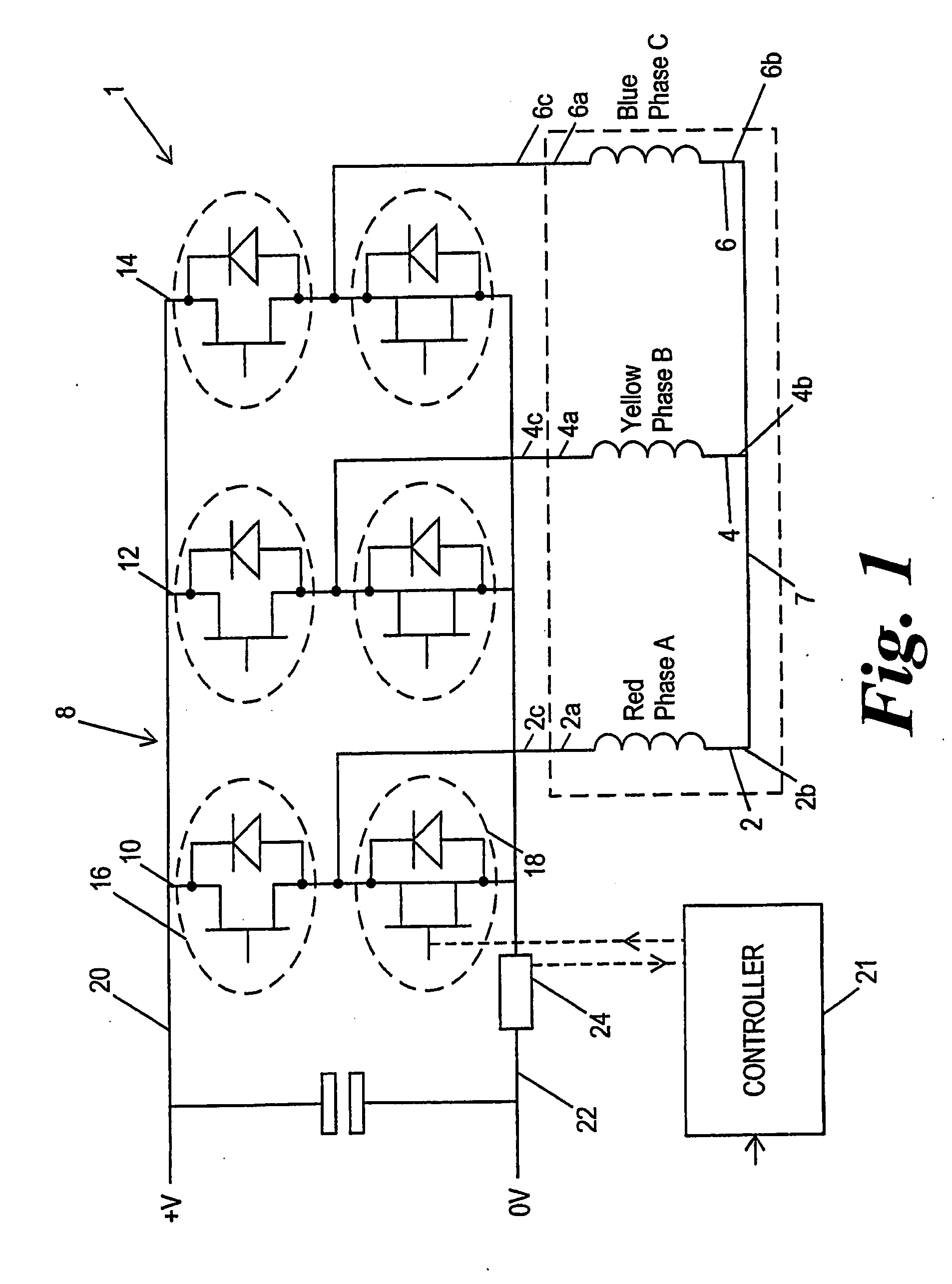
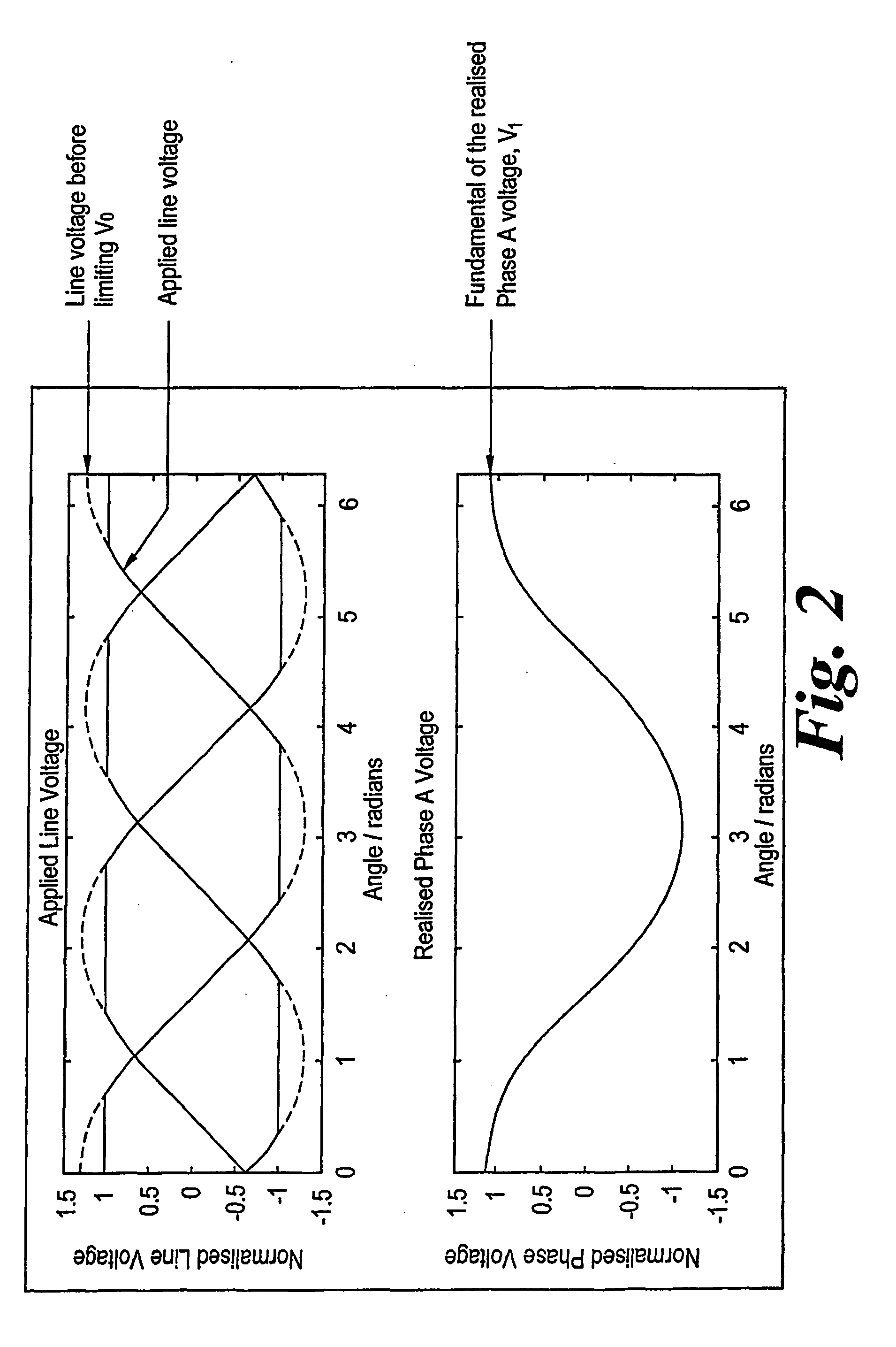
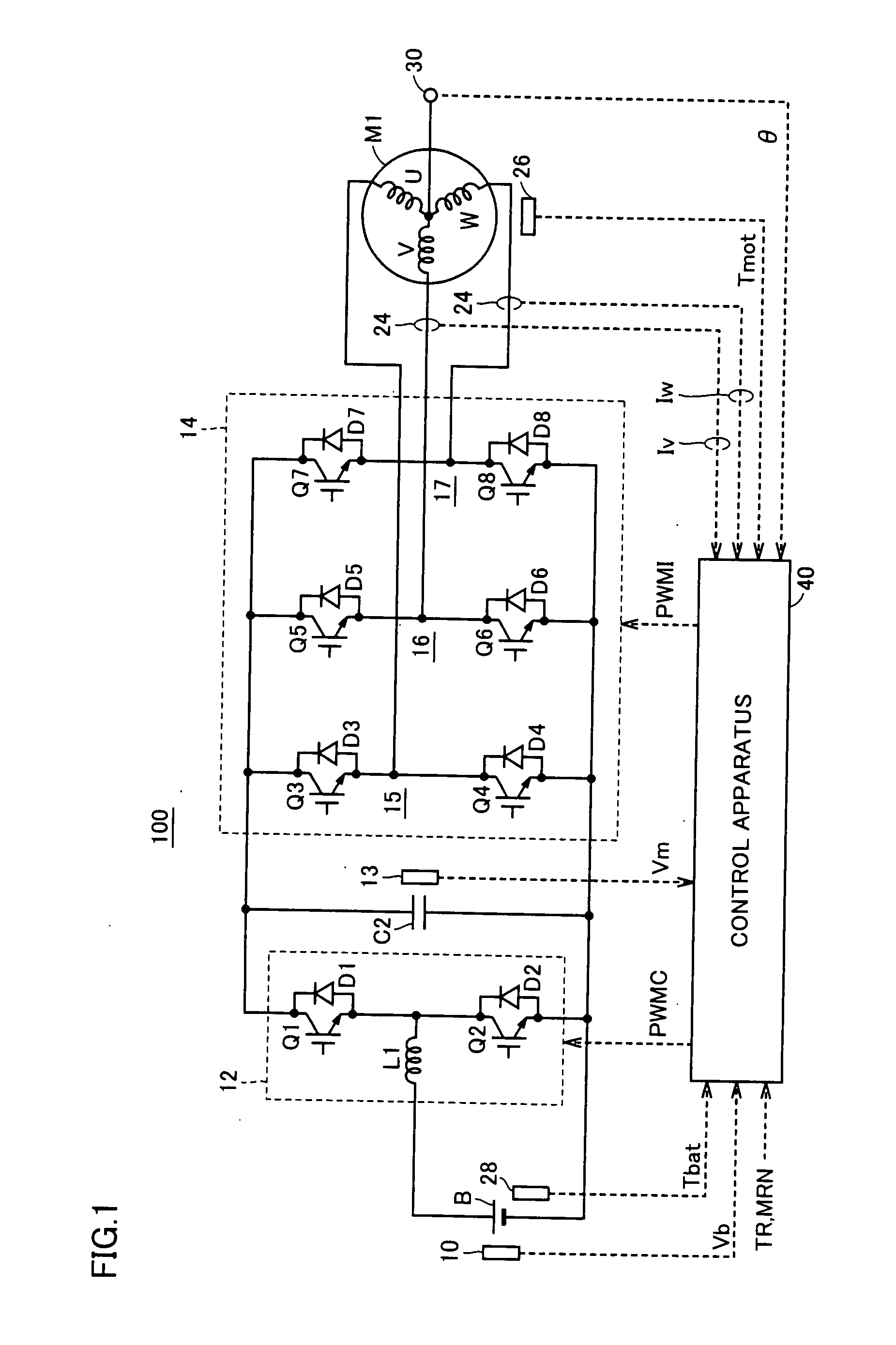
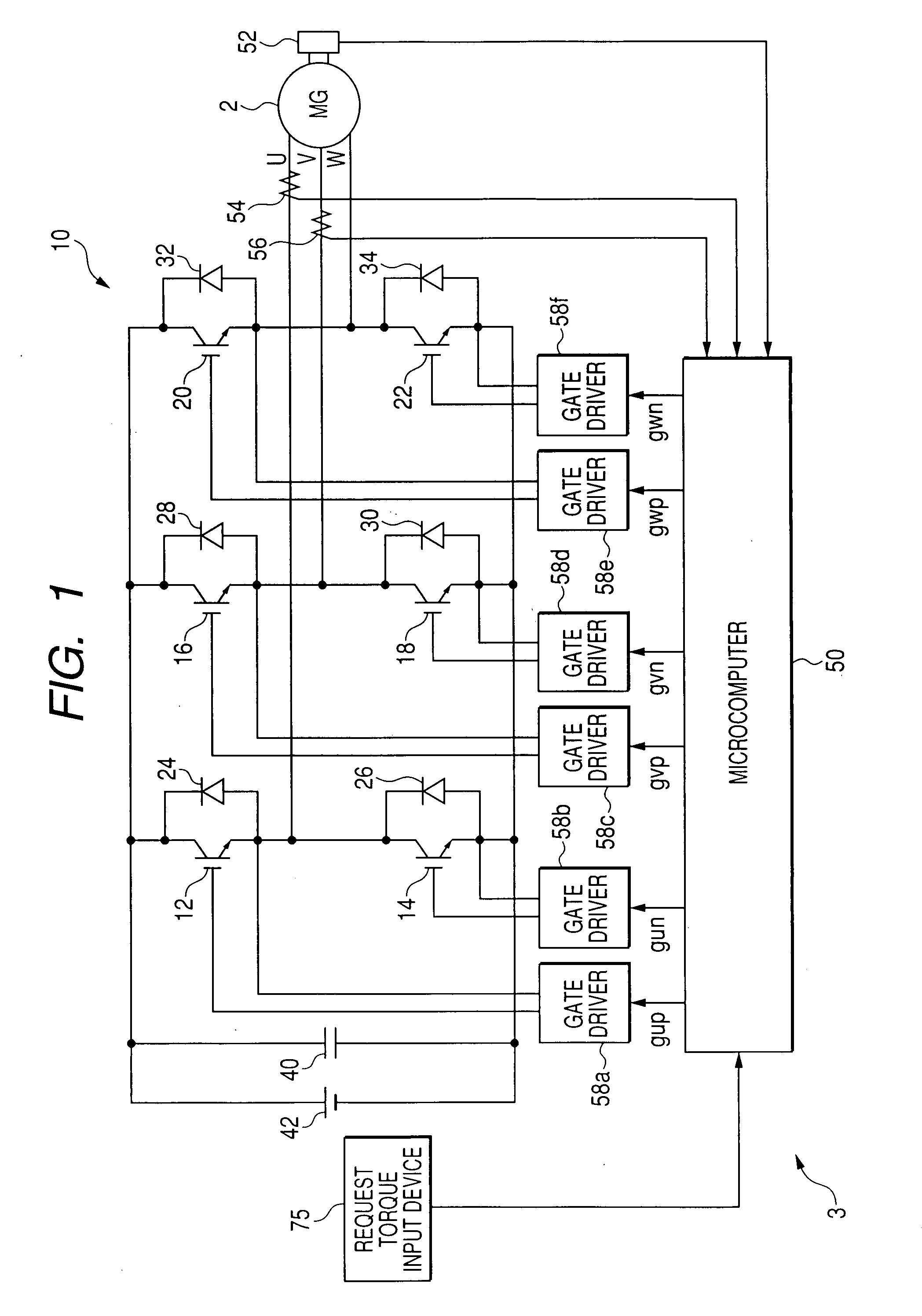
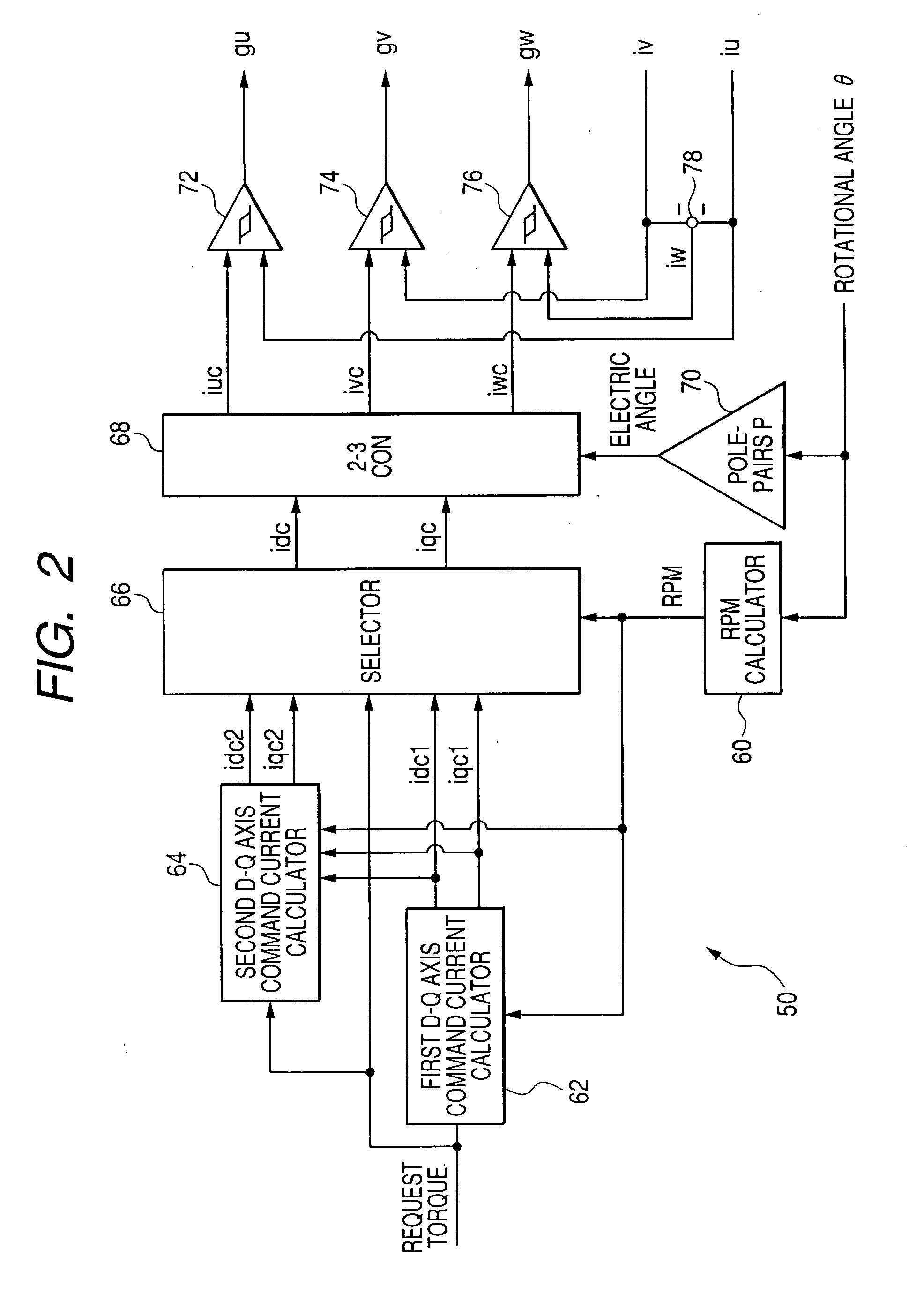
Synchronous and bi-directional variable frequency power conversion systems
InactiveUS6850426B2Facilitate easeLow costAc-dc conversion without reversalDc-dc conversionDigital controlAC power
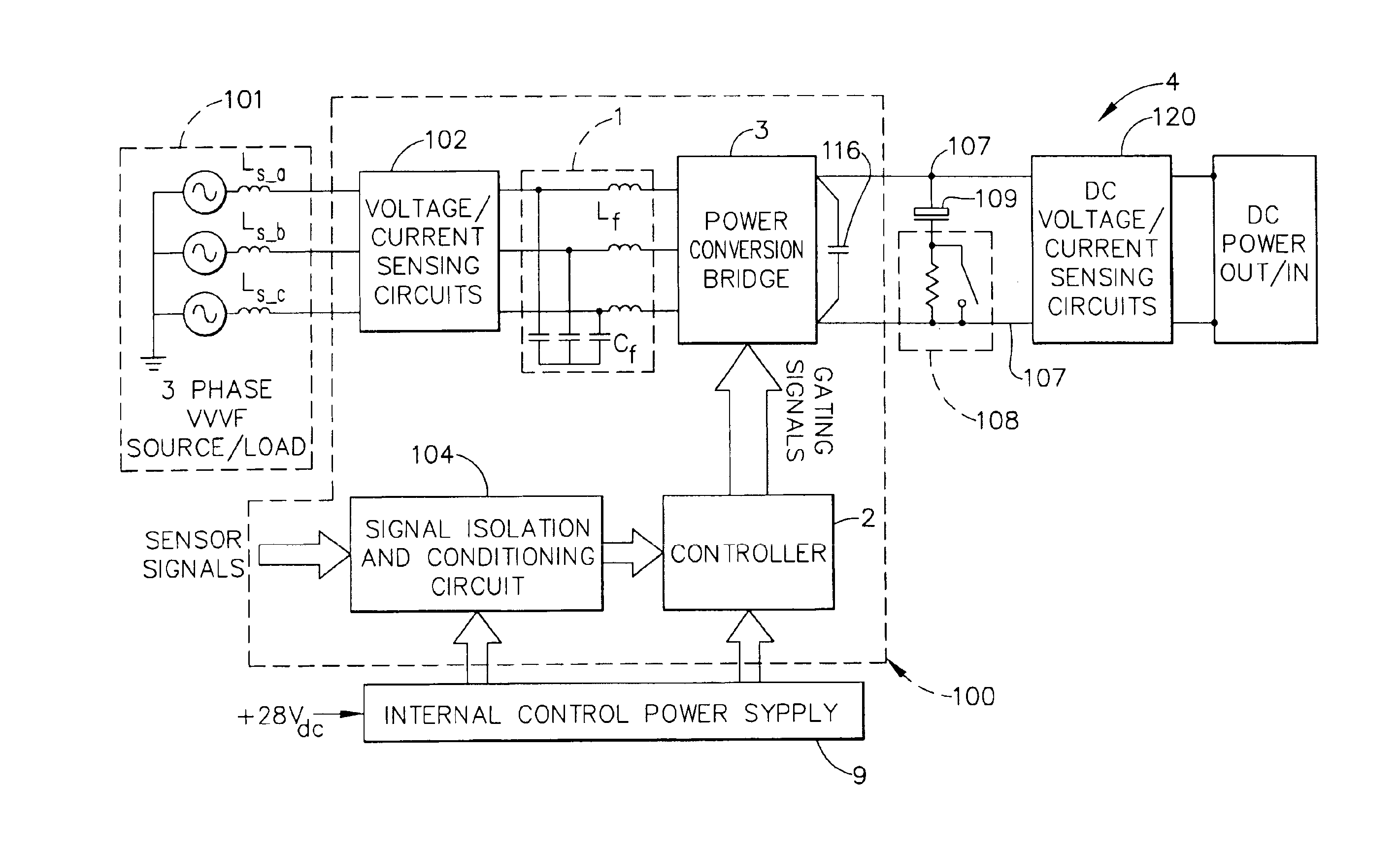
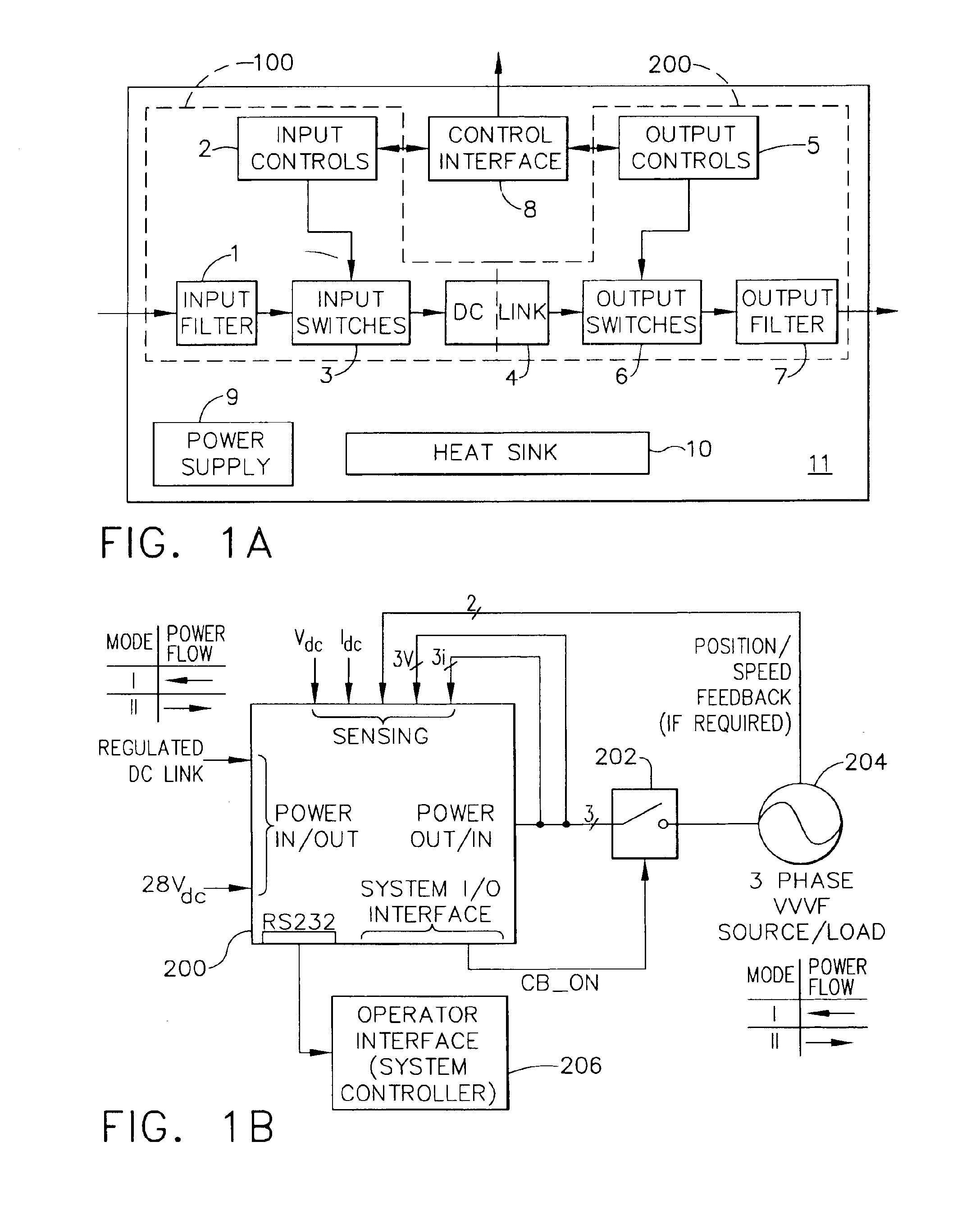
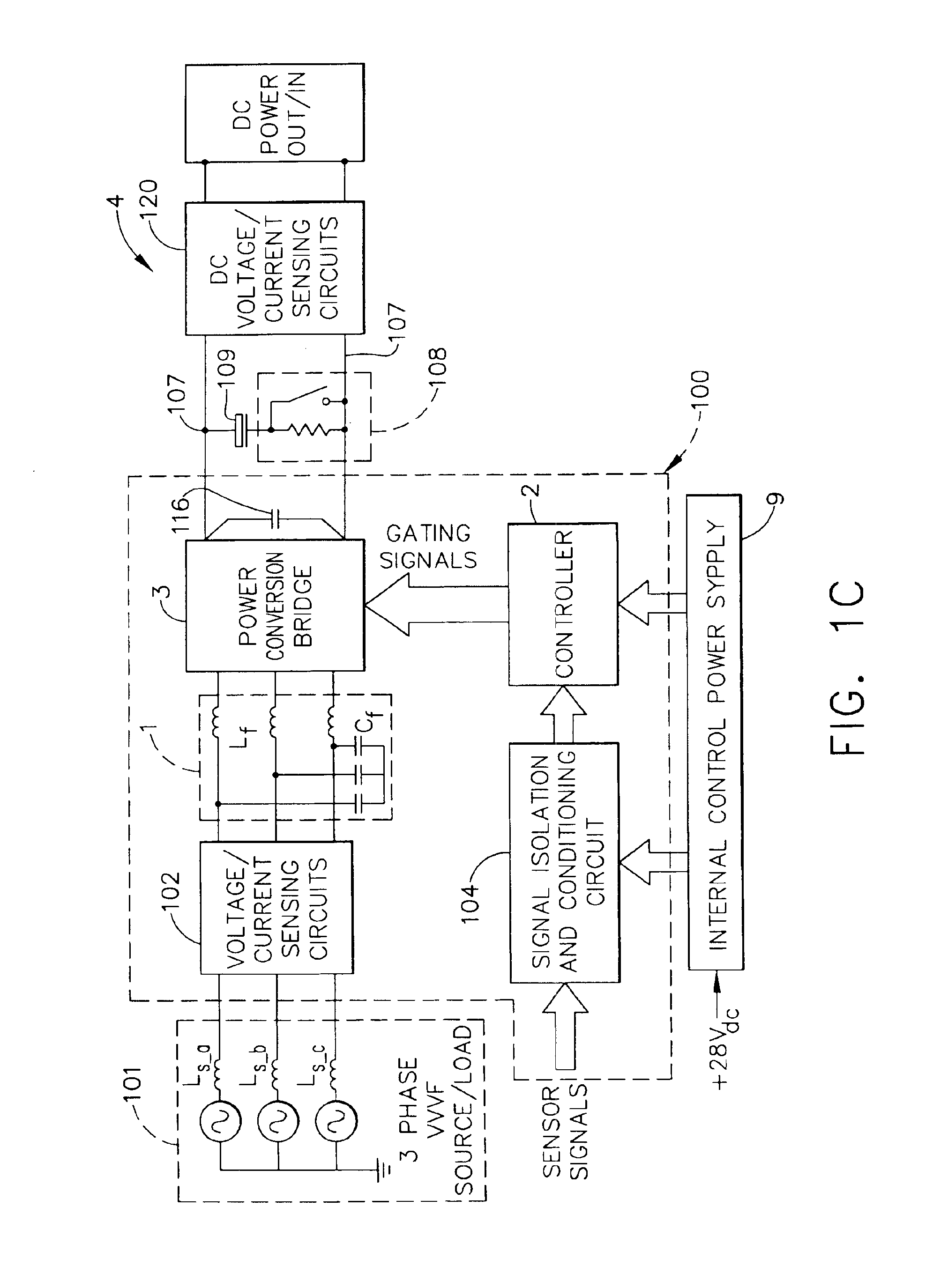
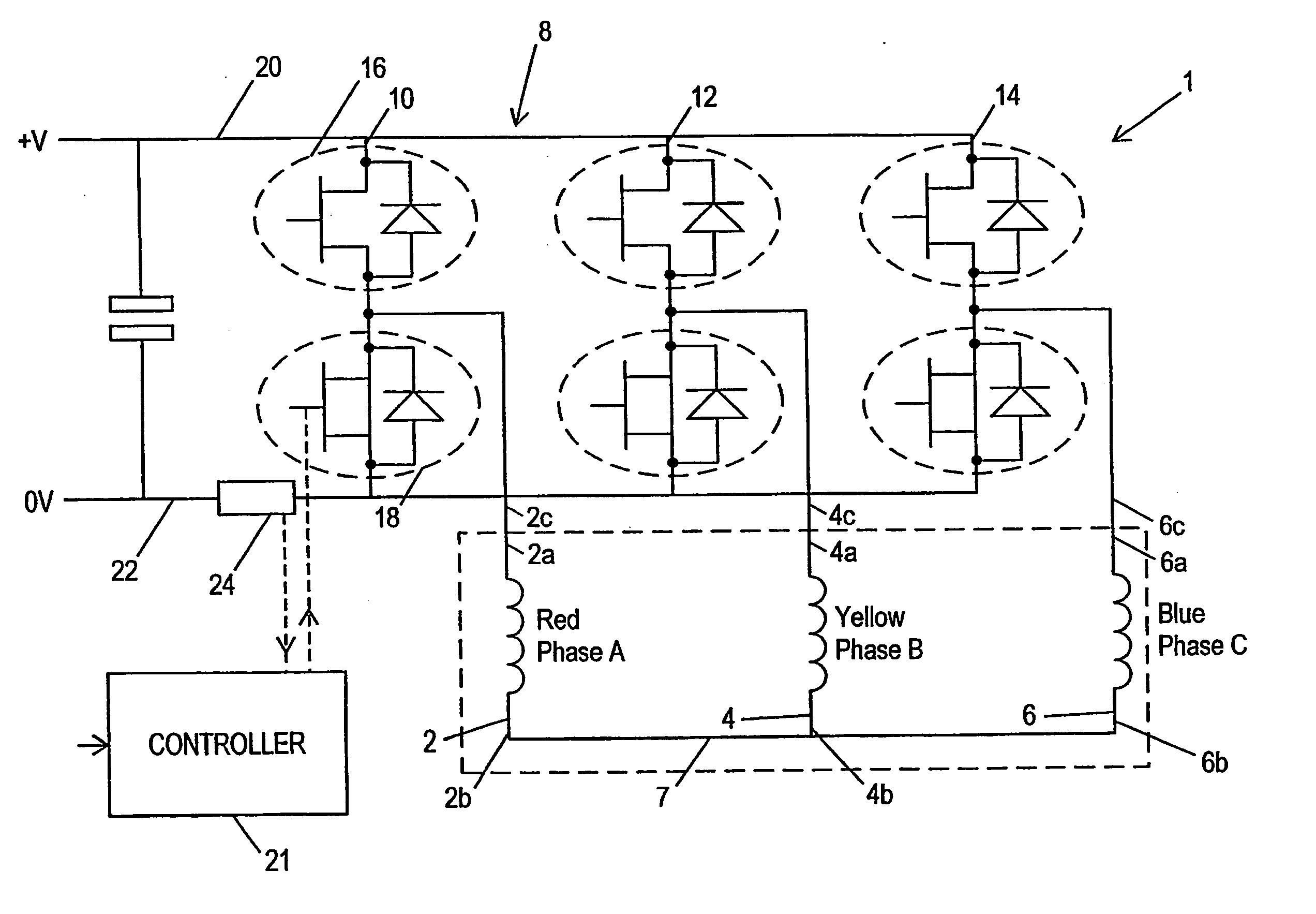
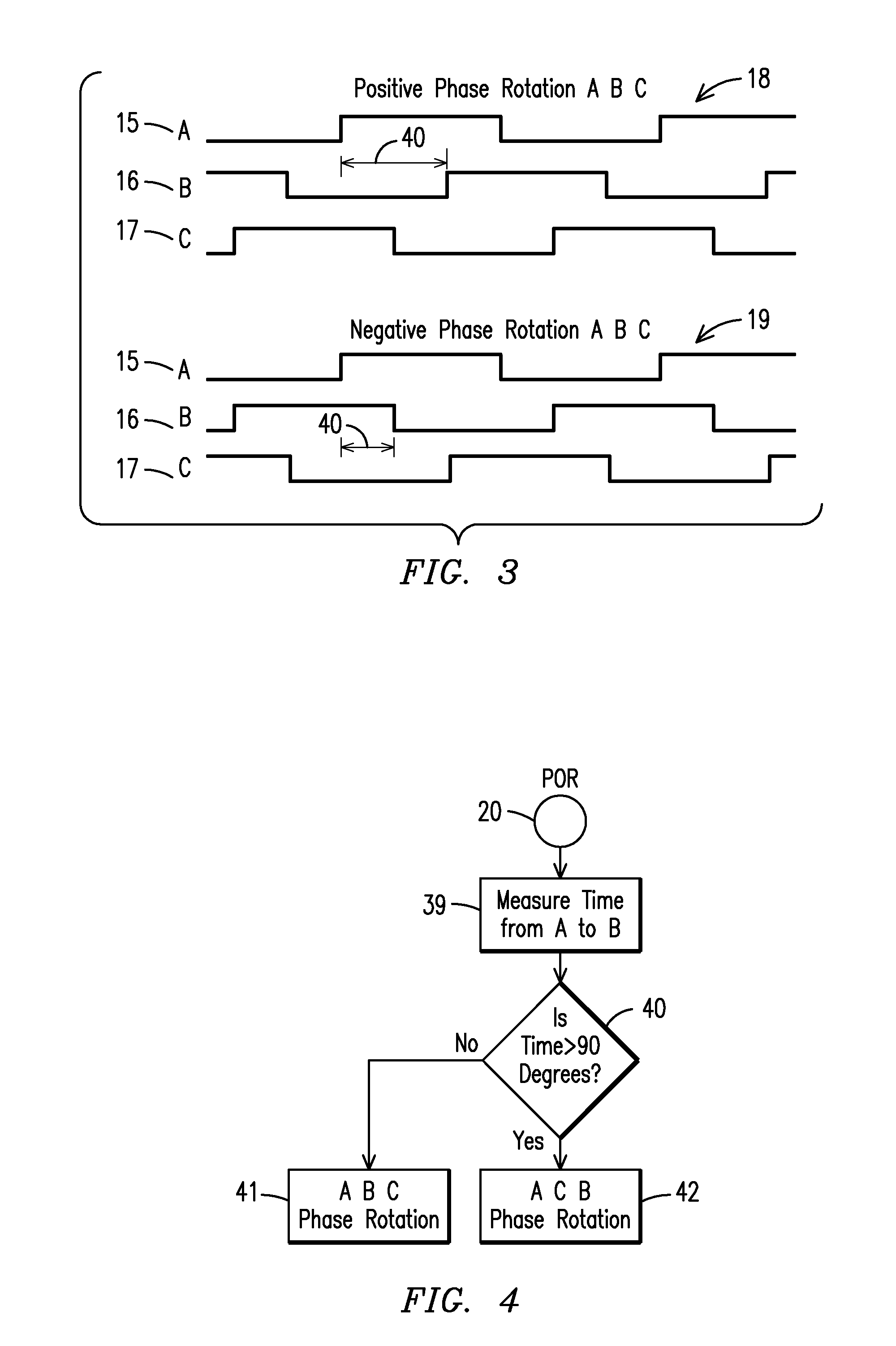
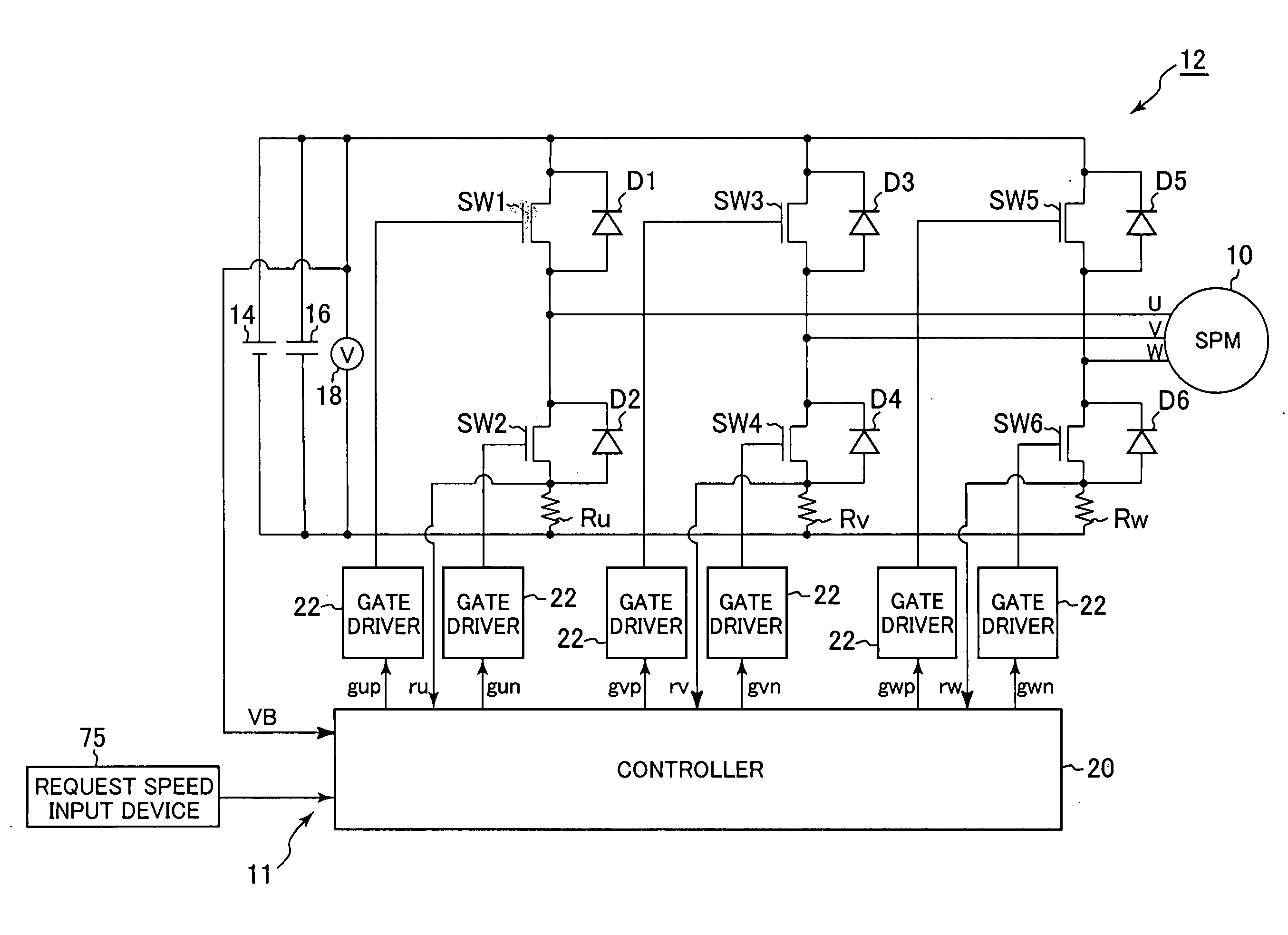
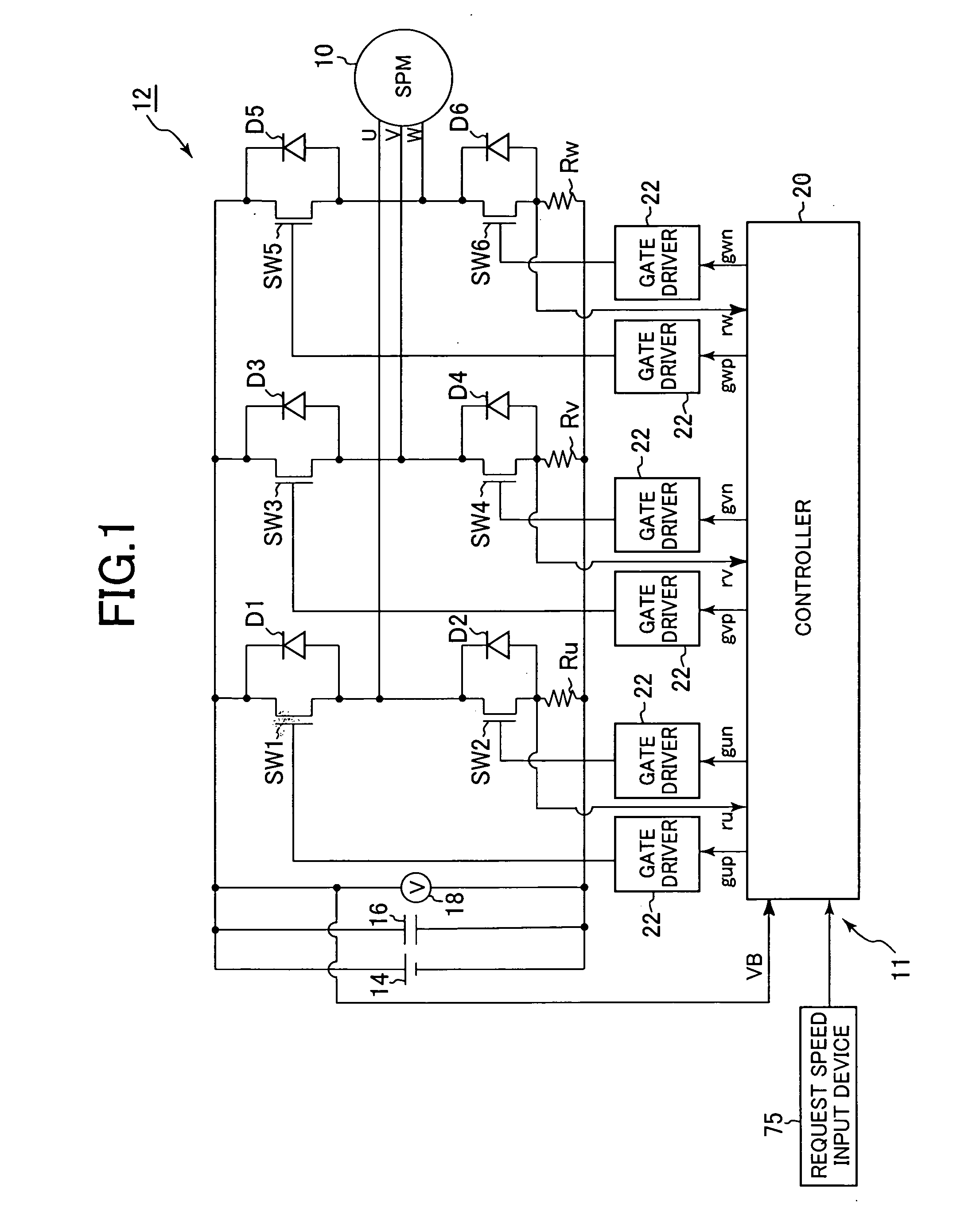
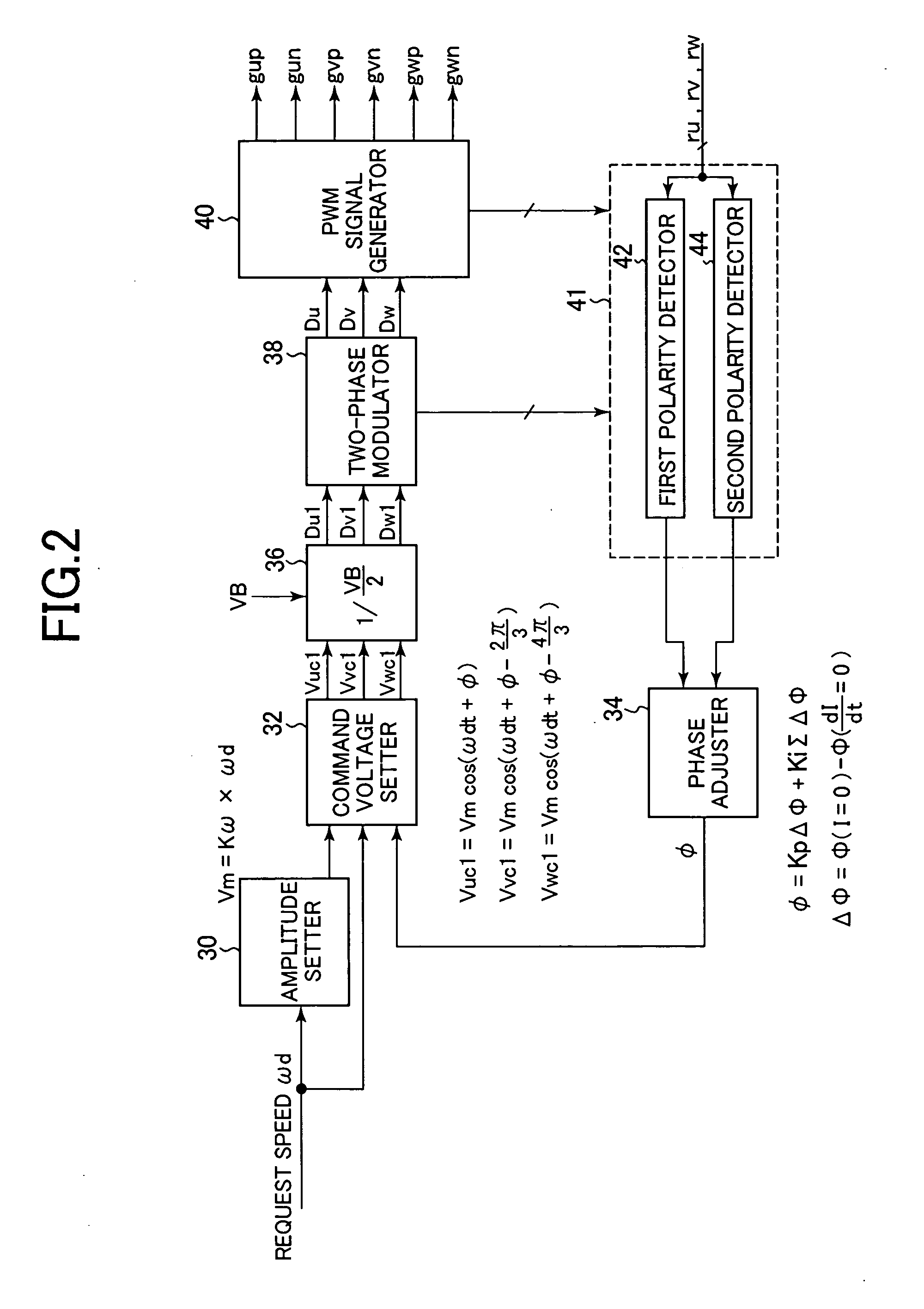
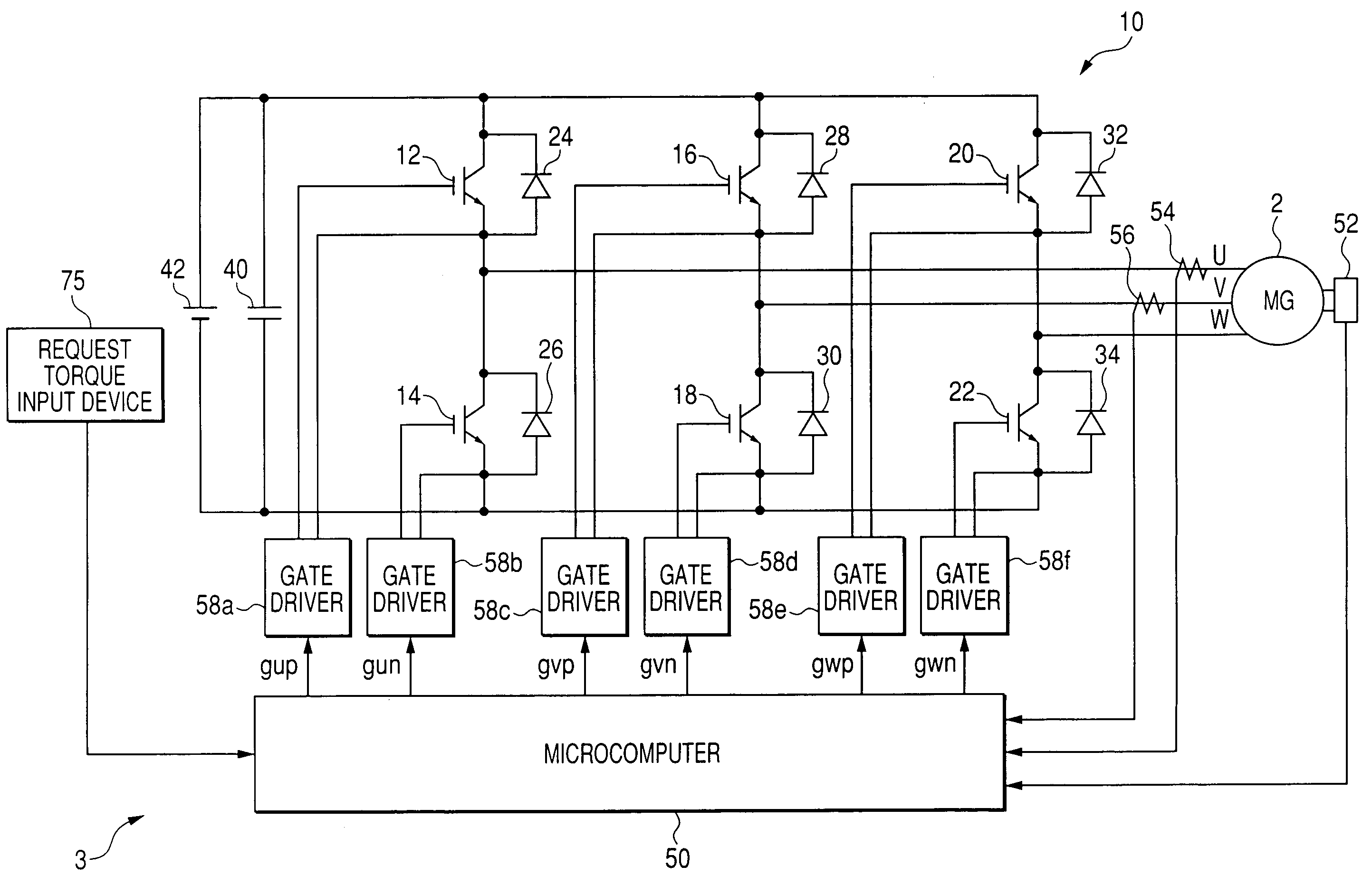
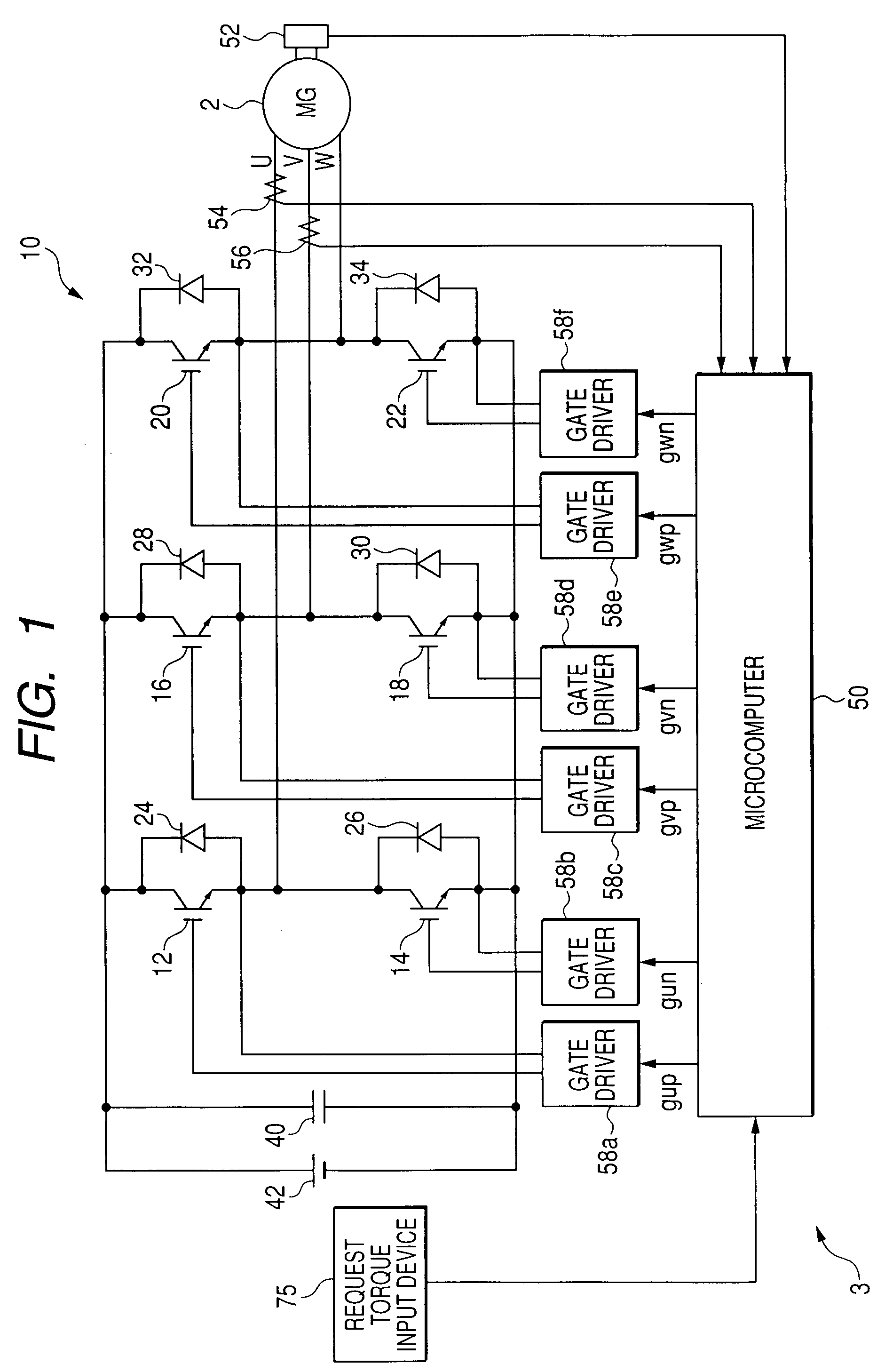
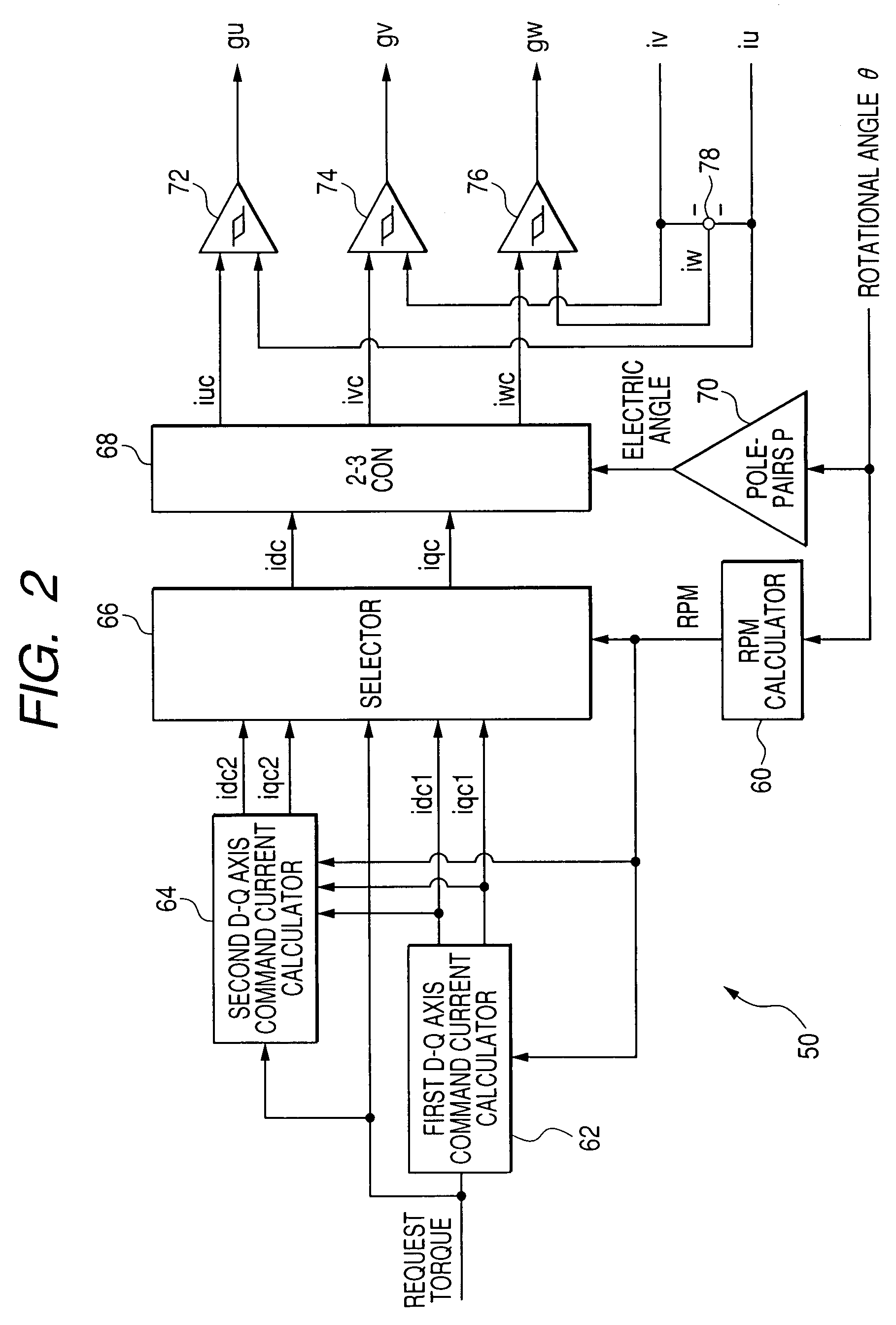
A synchronous bi-directional active power conditioning system (11) suitable for wide variable frequency systems or active loads such as adjustable speed drives which require variable voltage variable frequency power management systems is disclosed. Common power electronics building blocks (100, 200) (both hardware and software modular blocks) are presented which can be used for AC-DC, DC-AC individually or cascaded together for AC-DC-AC power conversion suitable for variable voltage and / or wide variable frequency power management systems. A common control software building block (2, 5) includes a digital control strategy / algorithm and digital phase lock loop method and apparatus which are developed and implemented in a digital environment to provide gating patterns for the switching elements (3, 6) of the common power-pass modular power electronics building blocks (100, 200).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Motor drive control with a single current sensor using space vector technique
InactiveUS20080079377A1Maximize magnitudeAvoid overlapSingle-phase induction motor startersSynchronous motors startersMotor driveElectric machine
A drive system for a three phase brushless AC motor is arranged to optimize the transistor switching pattern to improve power output whilst allowing current measurement in all of the phases using a single sensor. This is achieved by defining voltage demand vectors x where more than two states are required to meet a minimum state time requirement determined by the single sensor method, and calculating three or more state vectors which produce the demanded vector x whilst still allowing single current sensing. Various methods of optimising the PWM pattern so as to give maximum output whilst using single current sensing are also disclosed.
Owner:TRW LIMITED +1
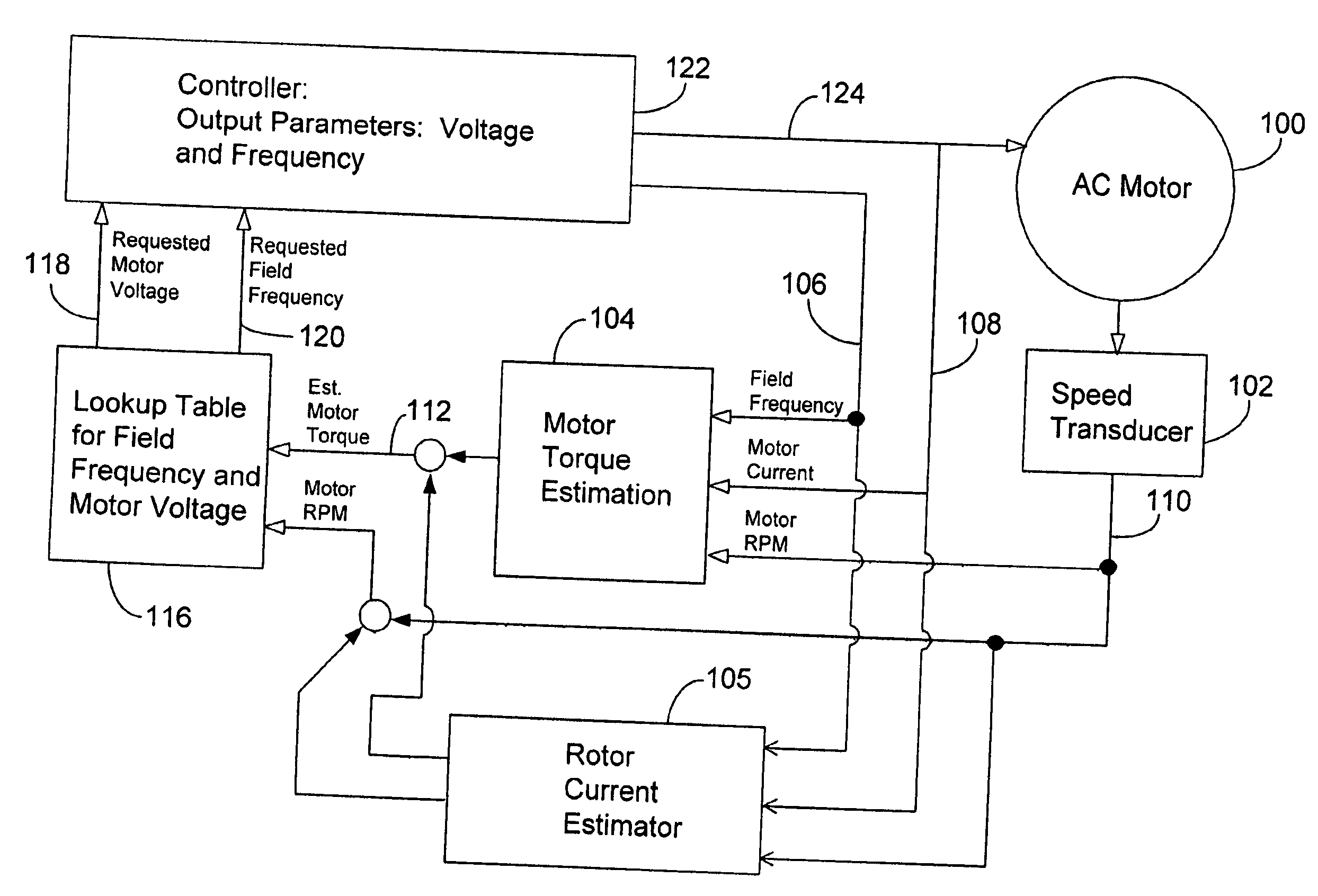
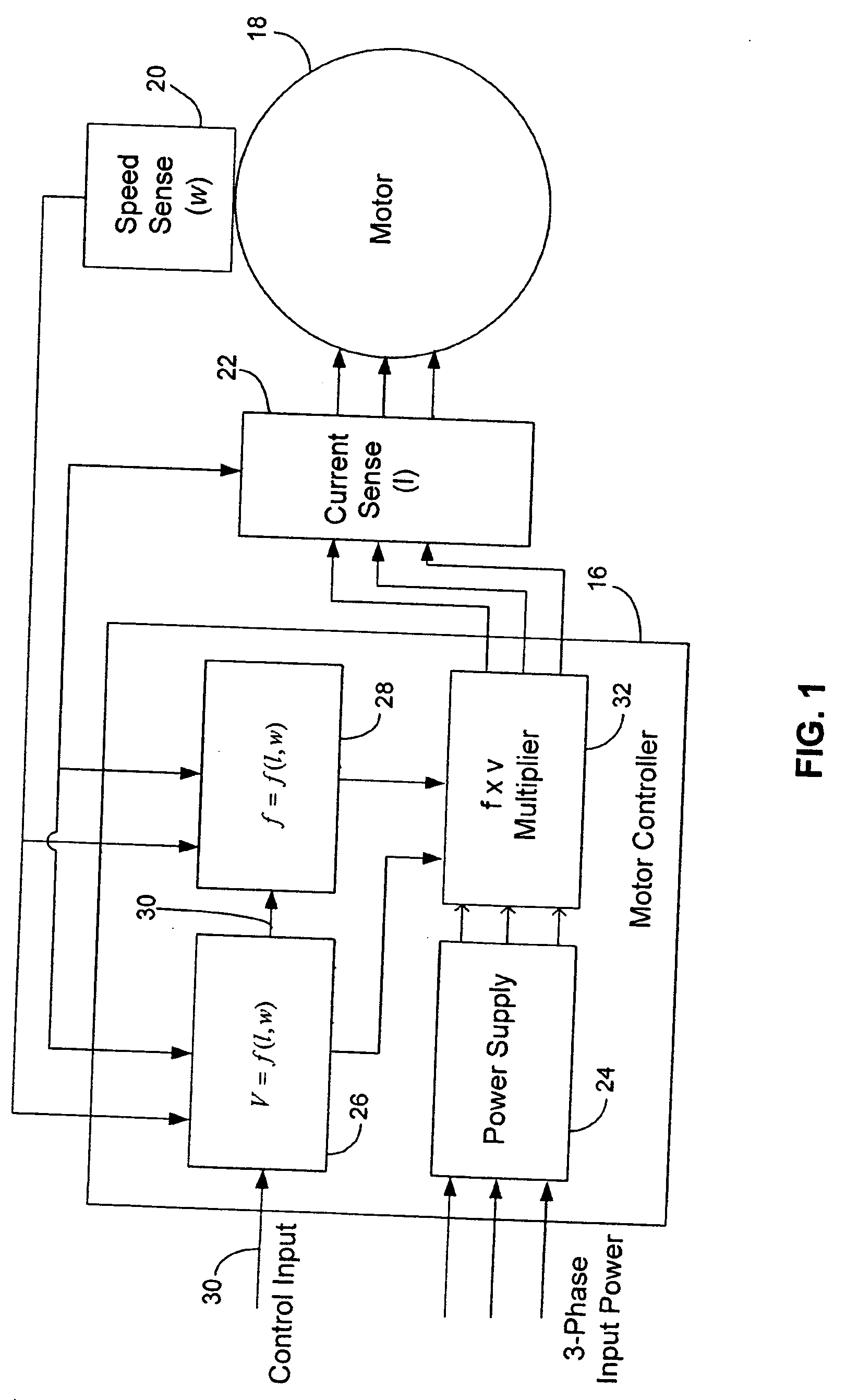
System and method for optimizing motor performance by varying flux
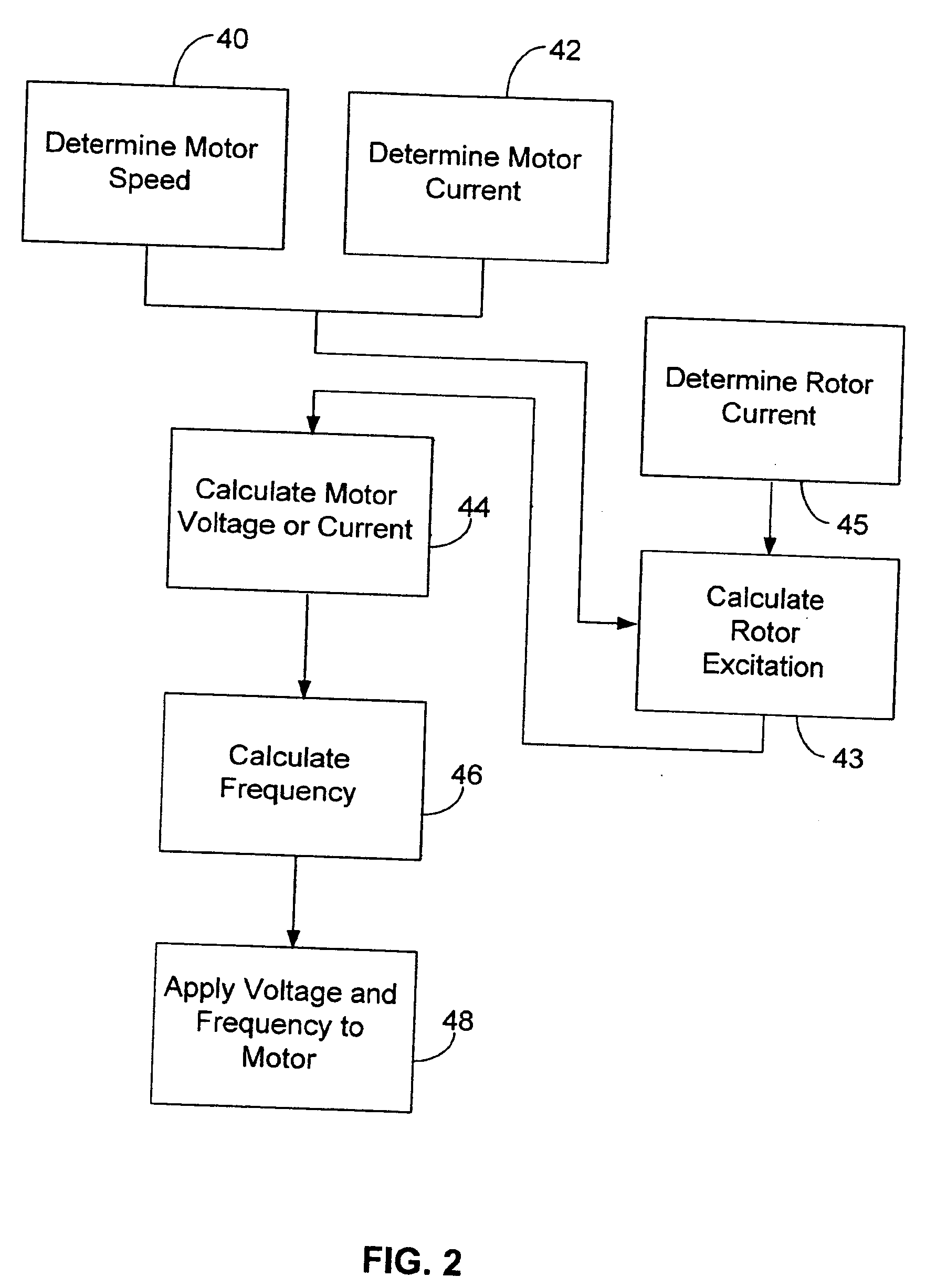
InactiveUS20060038530A1Easy to operateDC motor speed/torque controlGeneral control strategiesControl signalRotor flux
A system for operating an electric motor is described. The system has a torque estimator to determine a load on the motor and a controller configured to generate a motor control signal. The controller continuously adjusts the motor control signal in response to the load on the motor. The motor control signal optimizes the motor's performance by controlling the rotor flux of the motor. The motor control signal can control the voltage or current and frequency applied to the motor.
Owner:PATENT
Method to save energy for devices with rotating or reciprocating masses
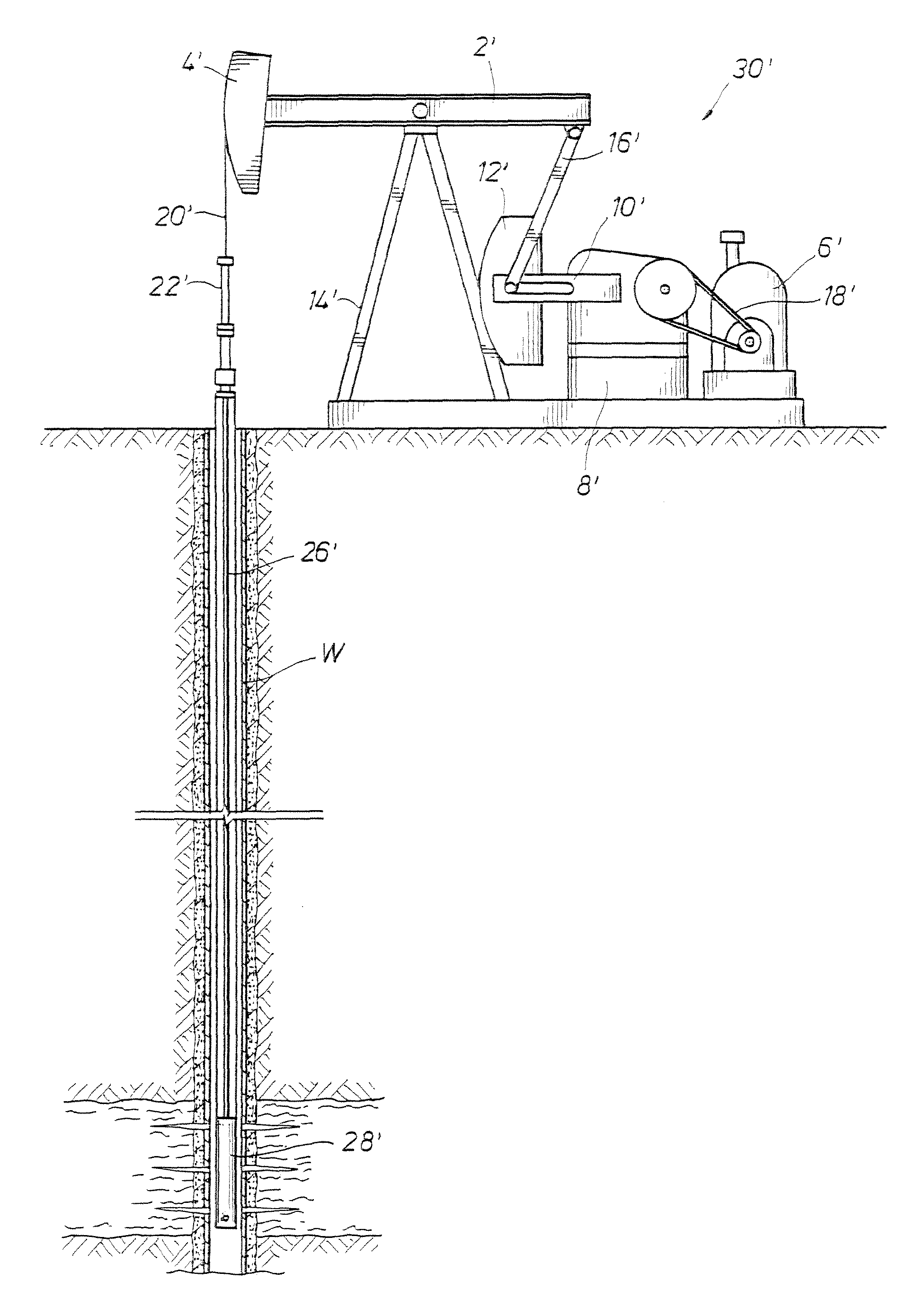
ActiveUS20110080130A1Highly variation of loadImprove energy savingMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlLoop controlReciprocating motion
A system and method are disclosed for turning off the voltage to a pump jack electric motor during predetermined periods of time to save energy. In the method, the motor's response to closed-loop control may be evaluated over several pump strokes. The periods of the pump stroke when it is feasible to turn off the motor may be identified. The consistency of the measurements over several strokes may be evaluated. The motor may be turned off during predetermined periods on subsequent pump strokes when each pump stroke shows sufficiently similar behavior to that predicted during the closed-loop control process. The system may return to the closed-loop control process after a predetermined period of time to adjust to any changes in the system.
Owner:THE POWERWISE GRP
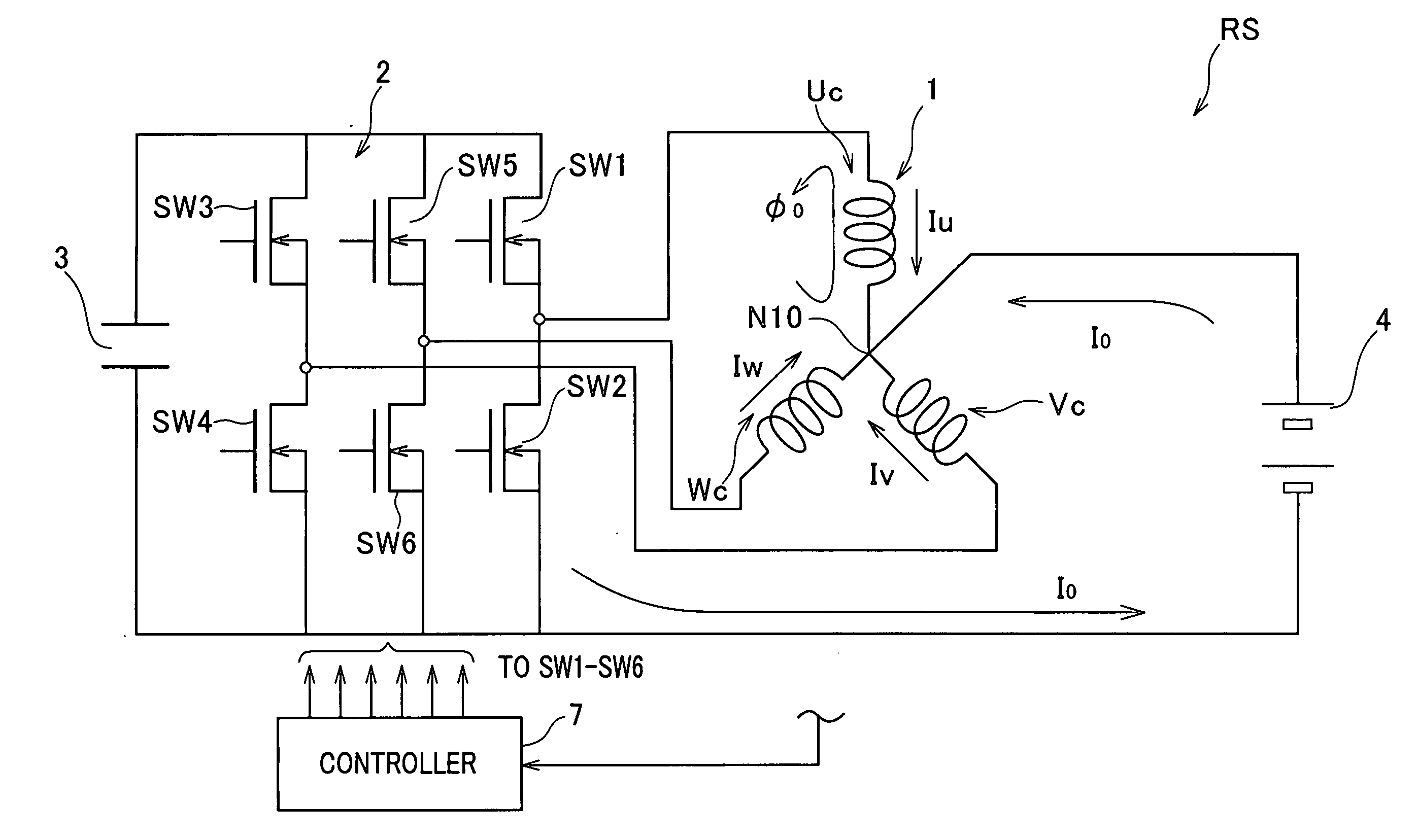
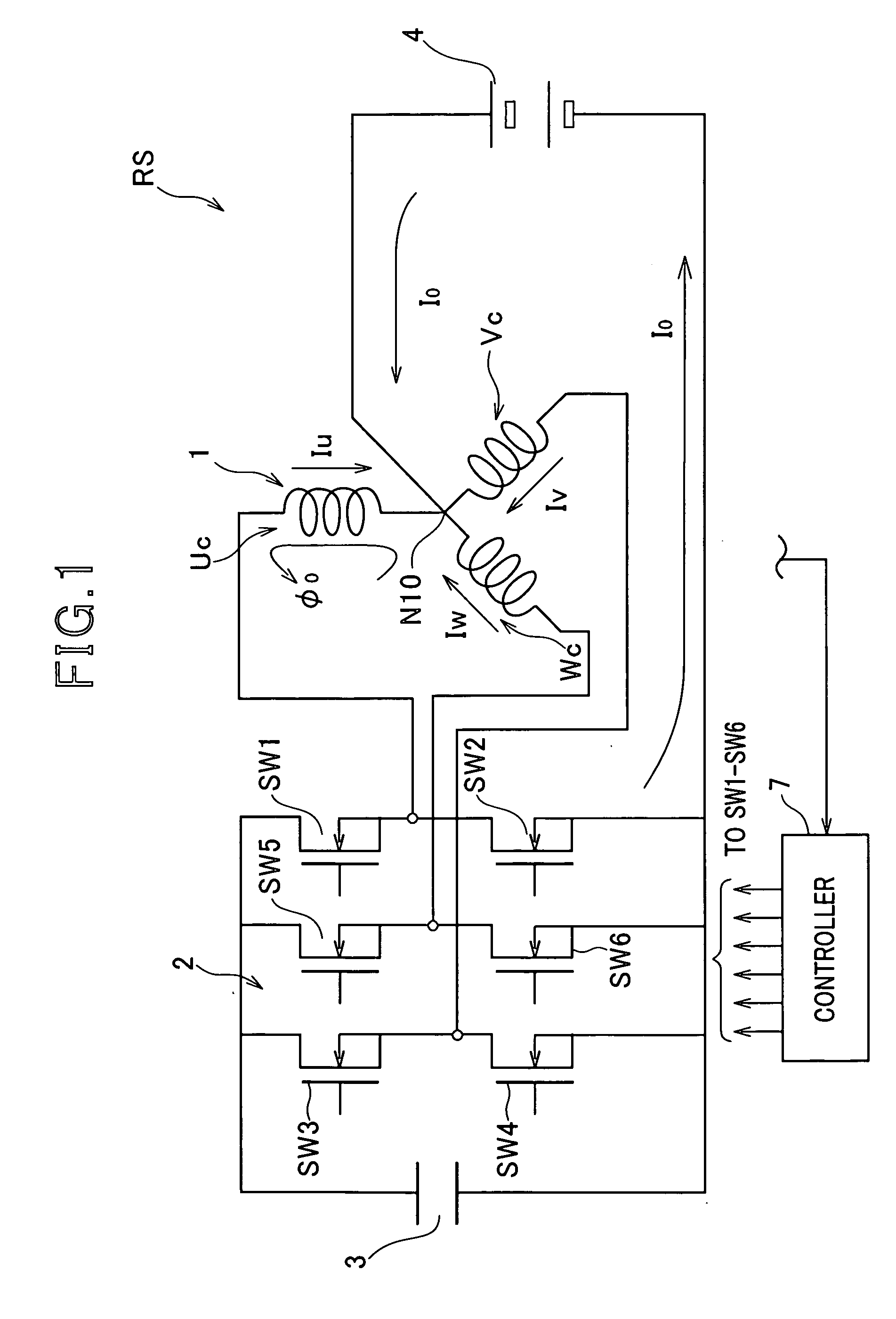
Rotary electric system designed to utilize zero-phase circuit
InactiveUS20080278102A1Good effectCreate torqueBatteries circuit arrangementsSynchronous motors startersSystems designElectric machine
In a rotary electric system, a rotary electric machine is provided with an armature core and star-connected multiphase windings with a neutral point wound in the armature core. Each of the star-connected multiphase windings has a predetermined winding configuration that prevents, when a zero-phase current is supplied from a direct current power source to the star-connected multiphase windings via the neutral point, a zero-phase magnetic flux created in the armature core based on the zero-phase current flowing in each phase winding of the star-connected multiphase windings from being cancelled out by a zero-phase magnetic flux created in the armature core based on the zero-phase current flowing in another one phase winding of the star-connected multiphase windings.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Permanent Magnet Motor with Field Weakening
InactiveUS20120126740A1Reduce field strengthField strength is alteredTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlConstant powerPermanent magnet motor
A permanent-magnet electrical machine is disclosed in which the rotor has a fixed back iron and movable back iron segments. When the movable back iron segments are in a first position, such as in contact with the fixed back iron, the field strength is high. When the movable back iron segments are in a second position in which the movable back iron segments are displaced away from the fixed back iron, the field strength is low. The ability to weaken the field strength causes the constant-power, speed ratio to be increased and thereby increases the utility of the motor for applications in which a wide speed range is desired. The disclosure applies to both permanent-magnet motors and generators. In an alternative embodiment, the stator ring is provided with a fixed portion and at least one movable stator segment.
Owner:CURRENT MOTOR
Motor drive system using potential at neutral point
ActiveUS20100320945A1Reduce rippleTorque ripple controlSynchronous motors startersMotor driveElectric machine
According to input parameters, a controller carries out: generation of a voltage command value for each of d- and q-axes; conversion of the voltage command value for each of the d- and q-axes into a voltage command value for each of the multiphase windings; and control of a multiphase inverter based on the voltage command value for each of the multiphase windings. The controller adds, to the voltage command value for the q-axis, a first compensation voltage value for compensating torque ripples to thereby output a compensated voltage command value for the q-axis. The first compensation voltage value contains m-th harmonic components in the AC motor and varies depending on the rotational angle of the rotor, the m corresponding to the number of phase of the multiphase windings. The controller uses, as the voltage command value for the q-axis, the compensated voltage command value for the q-axis.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Motor drive apparatus and motor drive method
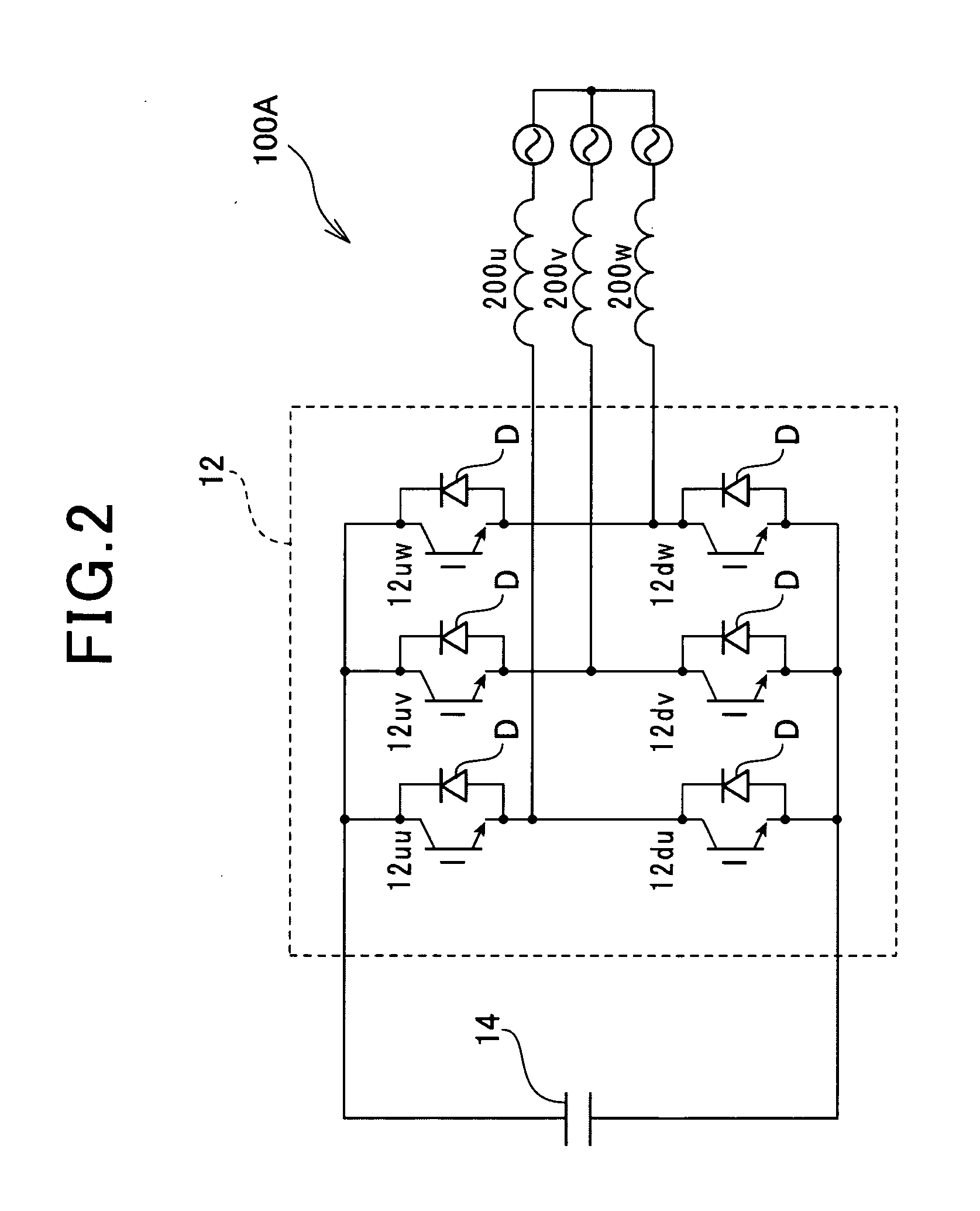
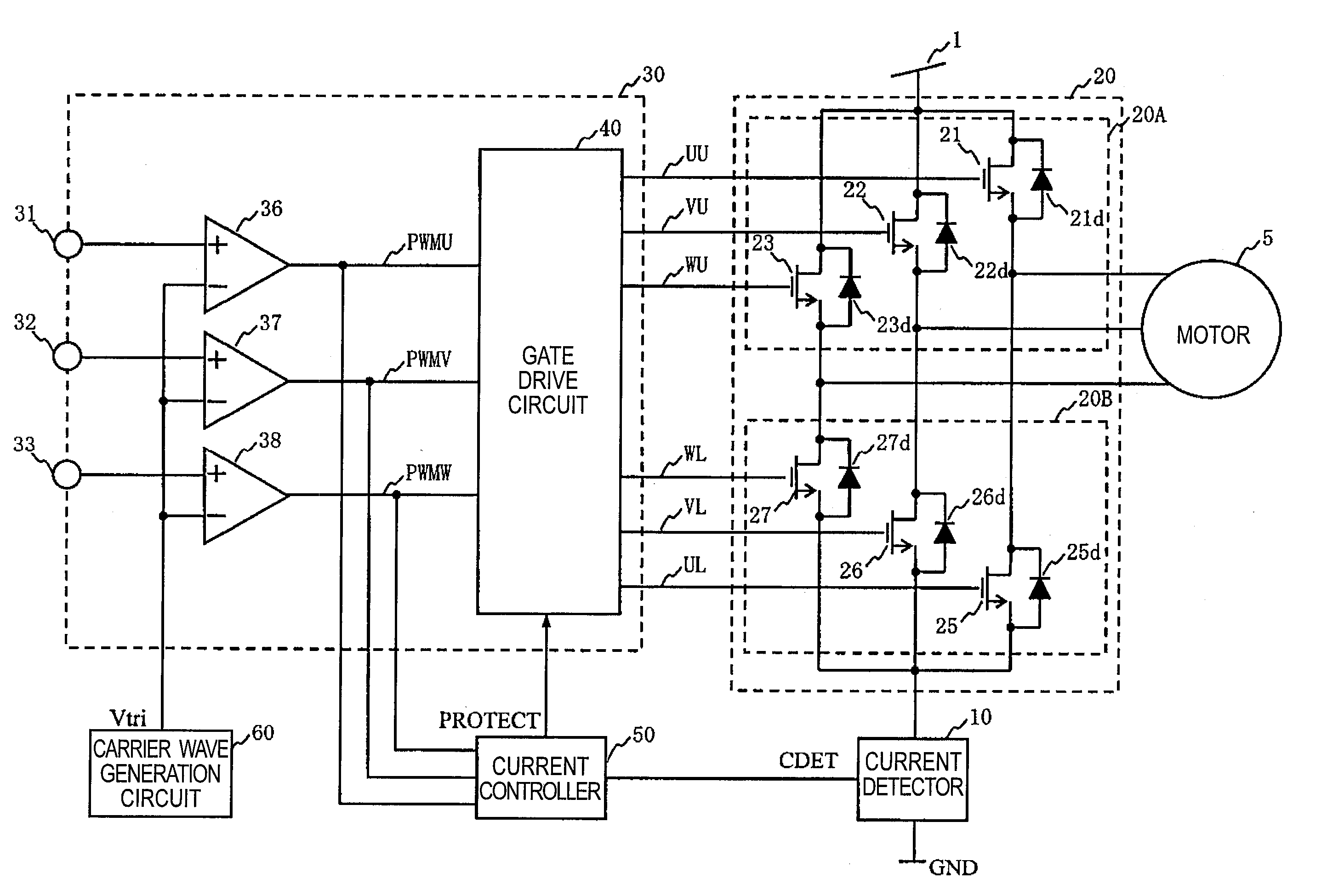
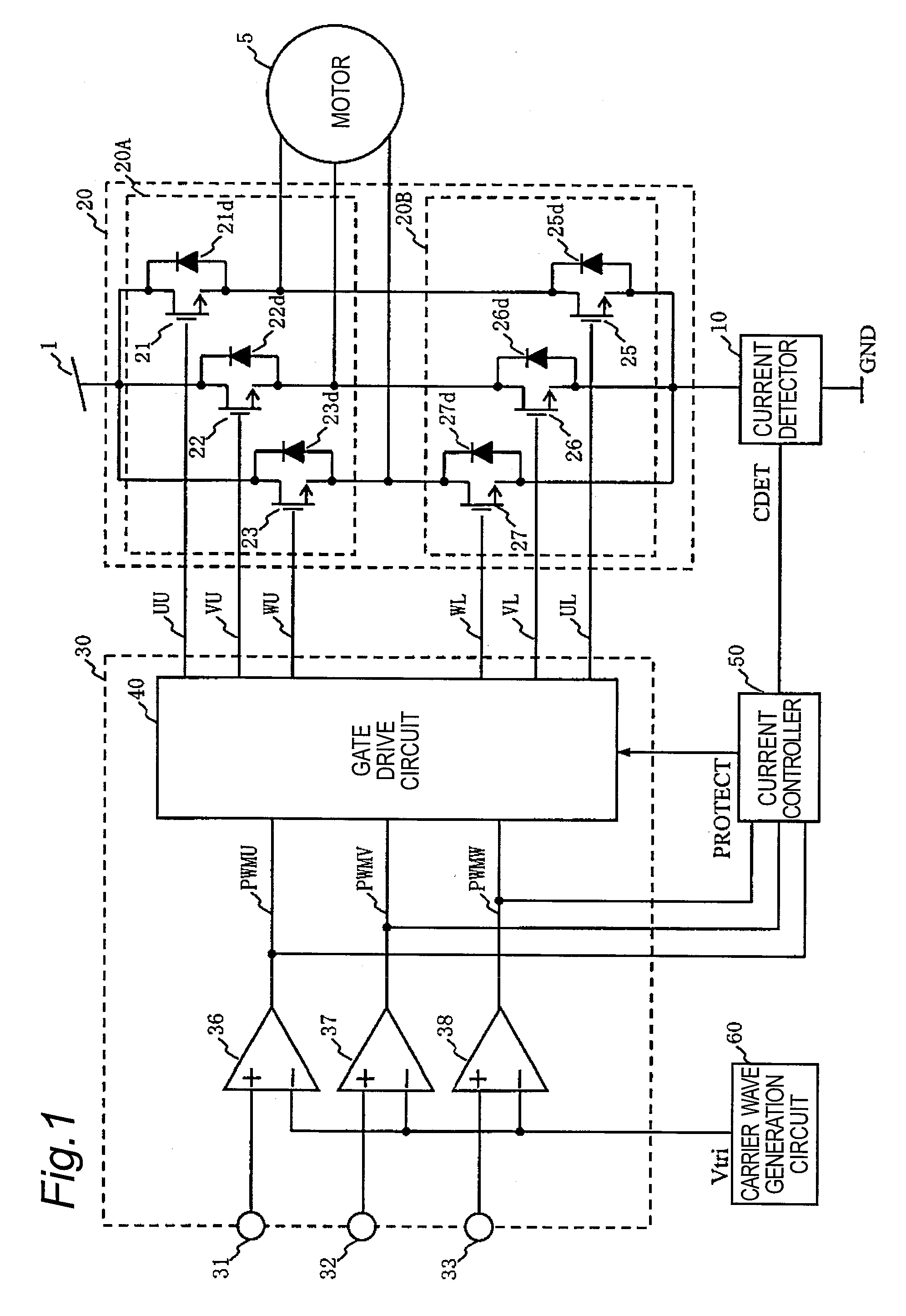
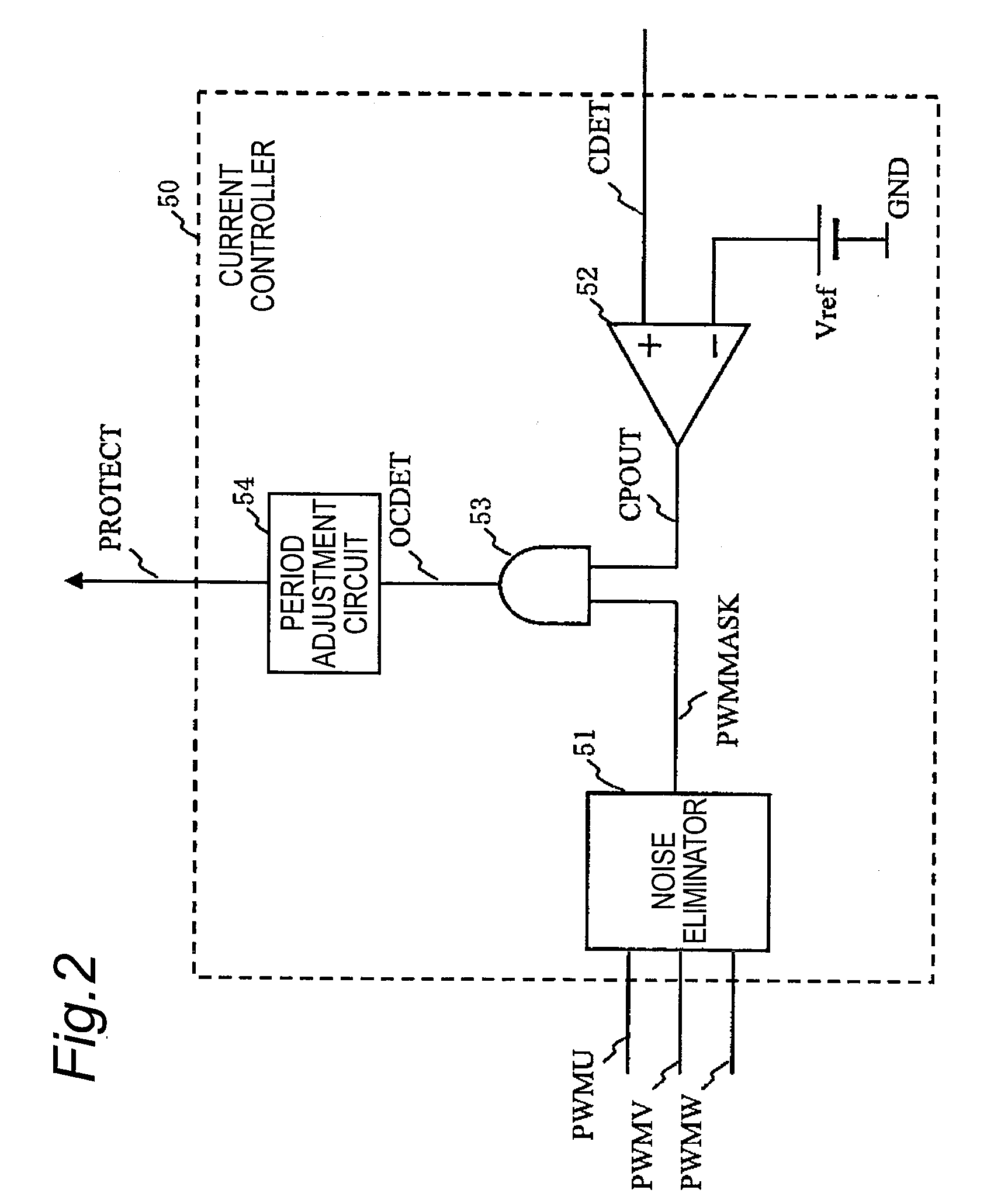
InactiveUS20080231219A1High voltageAccurate detectionSynchronous motors startersEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDriving currentCurrent limiting
To reduce noise by limiting a current peak value to a predetermined value or less and by smoothing the waveforms of drive currents during the current limitation, switching control means (30) according to the present invention turns ON all of one-side drive transistors selected from the high-side drive transistors (21, 22 and 23) and the low-side drive transistors (25, 26 and 27) of power supply means (20) for a predetermined period, and turns OFF all of the other-side drive transistors for a predetermined period in response to a current control signal for the current peak value to a predetermined value or less.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Drive method for brushless motor and drive control apparatus therefor
ActiveUS7157870B2Improve efficiencyReduce current consumptionMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersBrushless motorsPhase control
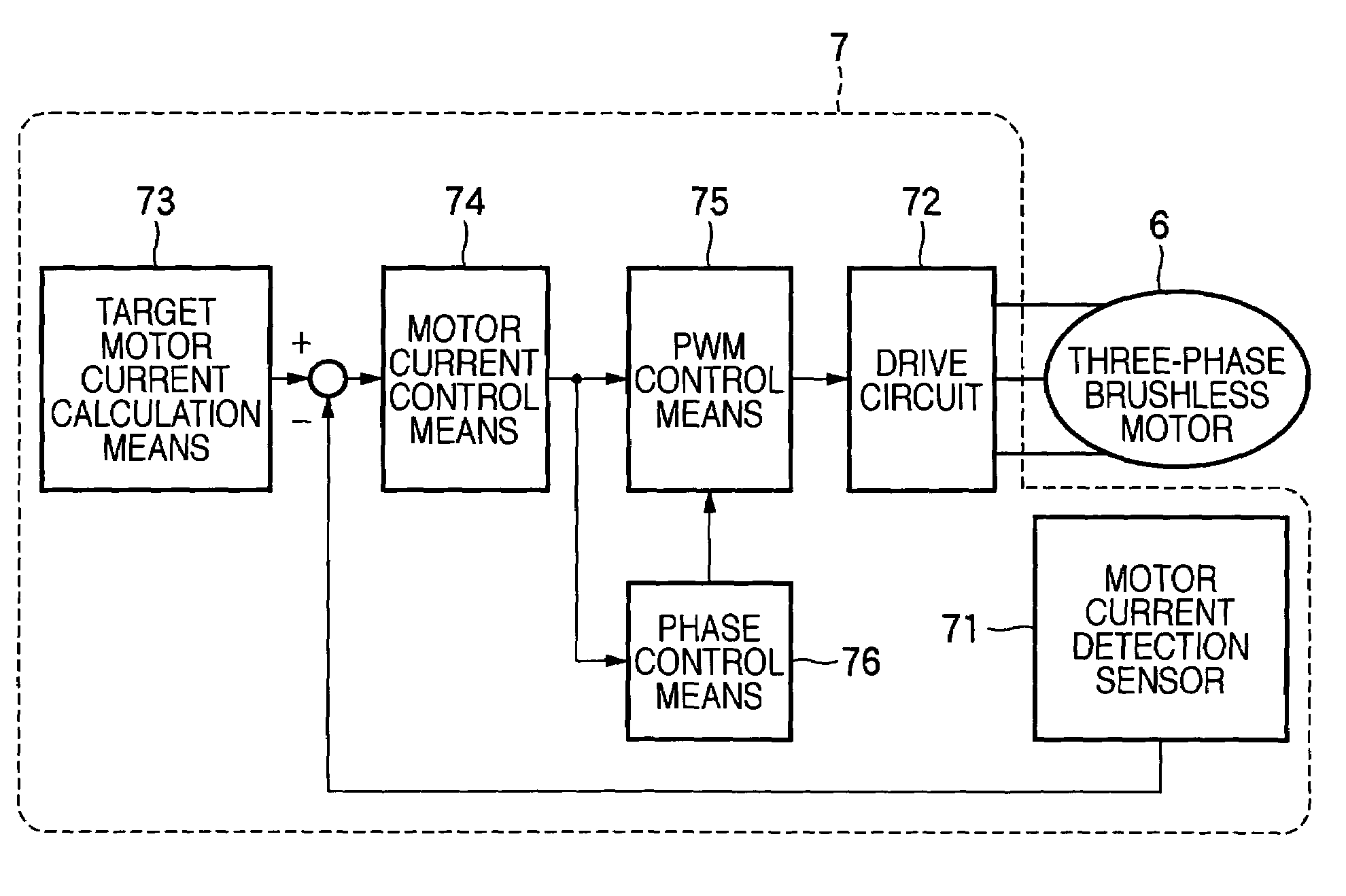
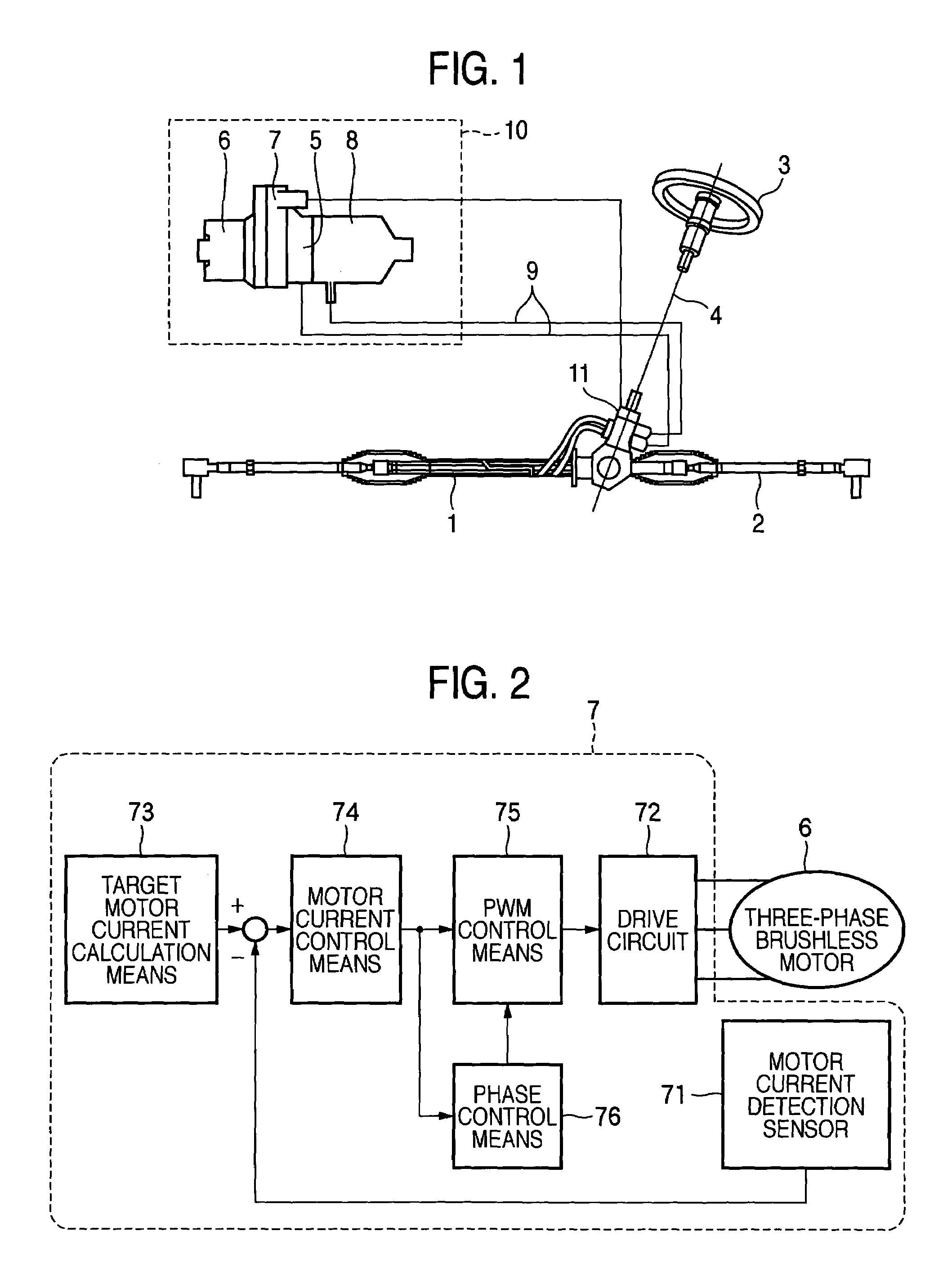
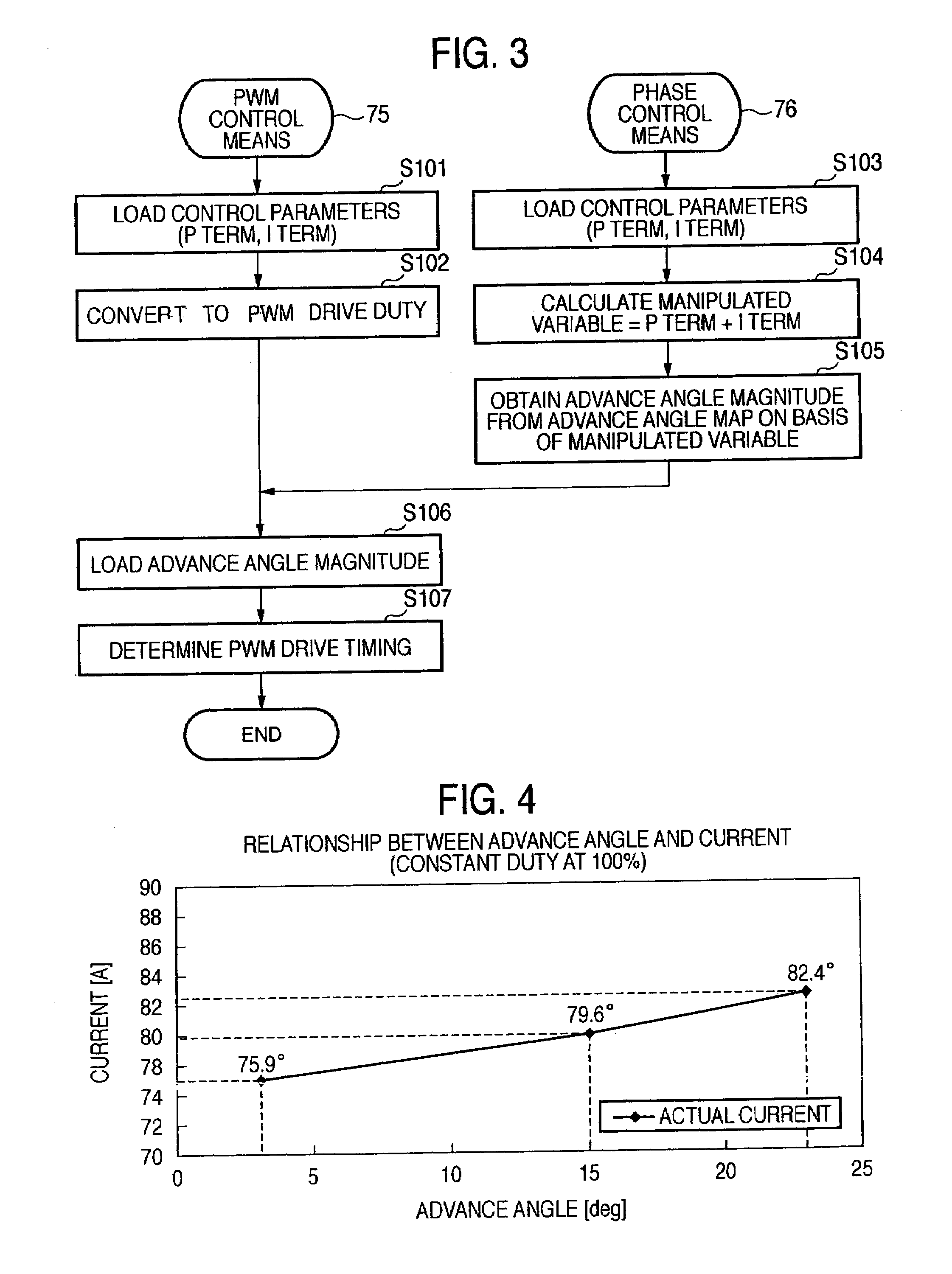
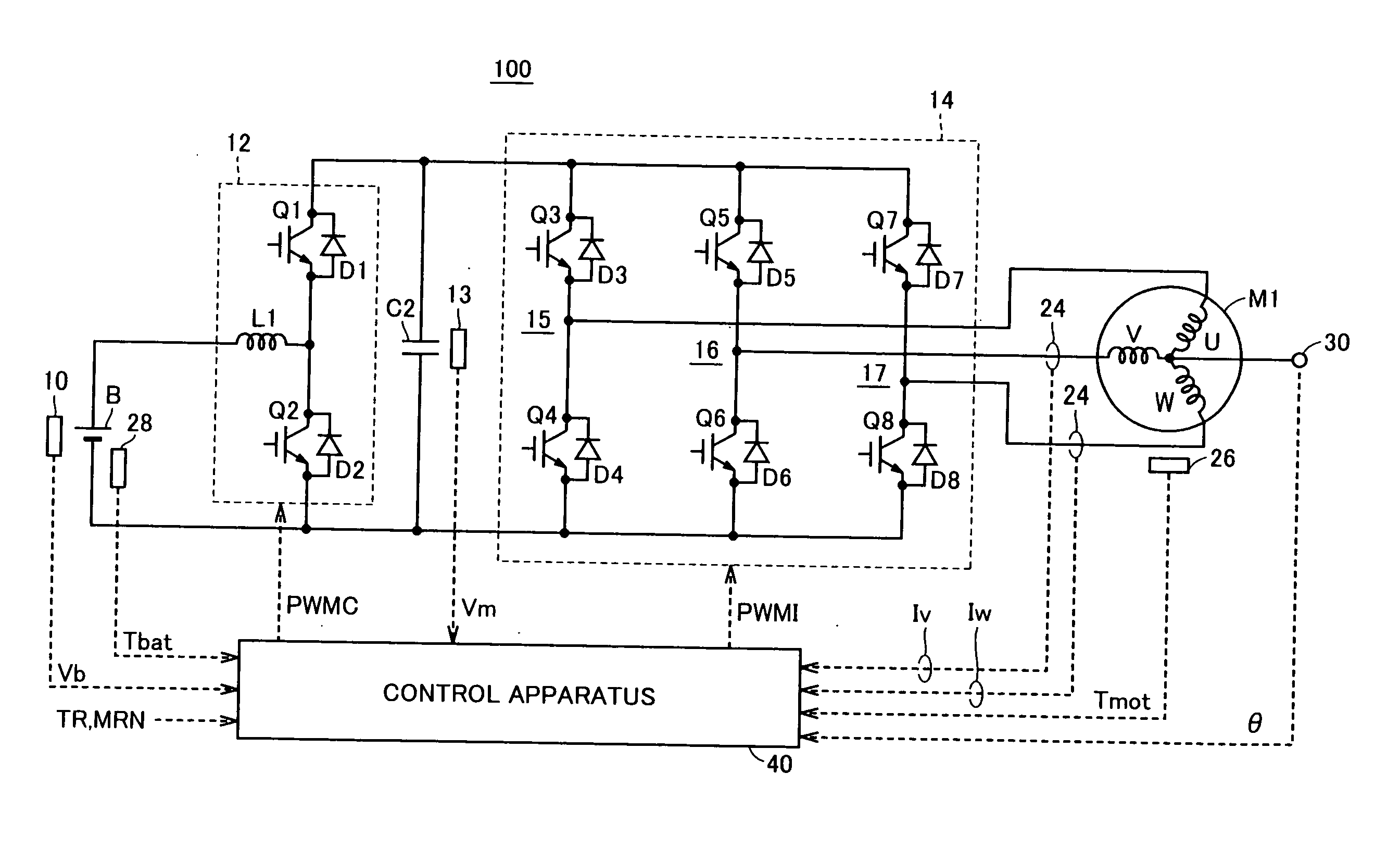
A drive method for a brushless motor and a drive control apparatus therefor, in which control parameters are calculated by motor current control means (74 in FIG. 2) in accordance with the deviation between a target motor current value and an actual motor current value, a manipulated variable is computed by phase control means (76) on the basis of the calculated control parameters, an advance angle magnitude is computed from the relationship between a manipulated variable and an advance angle magnitude as designed and created beforehand, on the basis of the computed manipulated variable, and the value of the conduction phase angle of a drive circuit (72) as set on the basis of a motor current signal is corrected with the information of the computed advance angle magnitude.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Secondary Battery Control Apparatus and Secondary Battery Control Method
InactiveUS20080143281A1Energy loss is increased and reducedTemperature can be quickly and easilySingle motor speed/torque controlTemperatue controlElectrical resistance and conductanceInternal resistance
When it is determined that a battery temperature is lower than a threshold value, an inverter control circuit alternately switches an operation point of an AC motor between an optimum operation point and a motor loss increase point. At the motor loss increase point, an increase in the amplitude of the motor current increases copper loss occurring in the three-phase coil of the AC motor. On the other hand, at the optimum operation point, a reduction in the amplitude of the motor current reduces copper loss. Corresponding to the cyclical increase / reduction in the copper loss, the battery is cyclically charged / discharged by the electric power corresponding to the copper loss. The change in the battery current occurred by the charge / discharge causes the internal resistance to generate heat, whereby the temperature of the battery is increased. The foregoing temperature increase operation is prohibited when the motor temperature exceeds an allowable temperature with which the operation efficiency of the AC motor is ensured.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
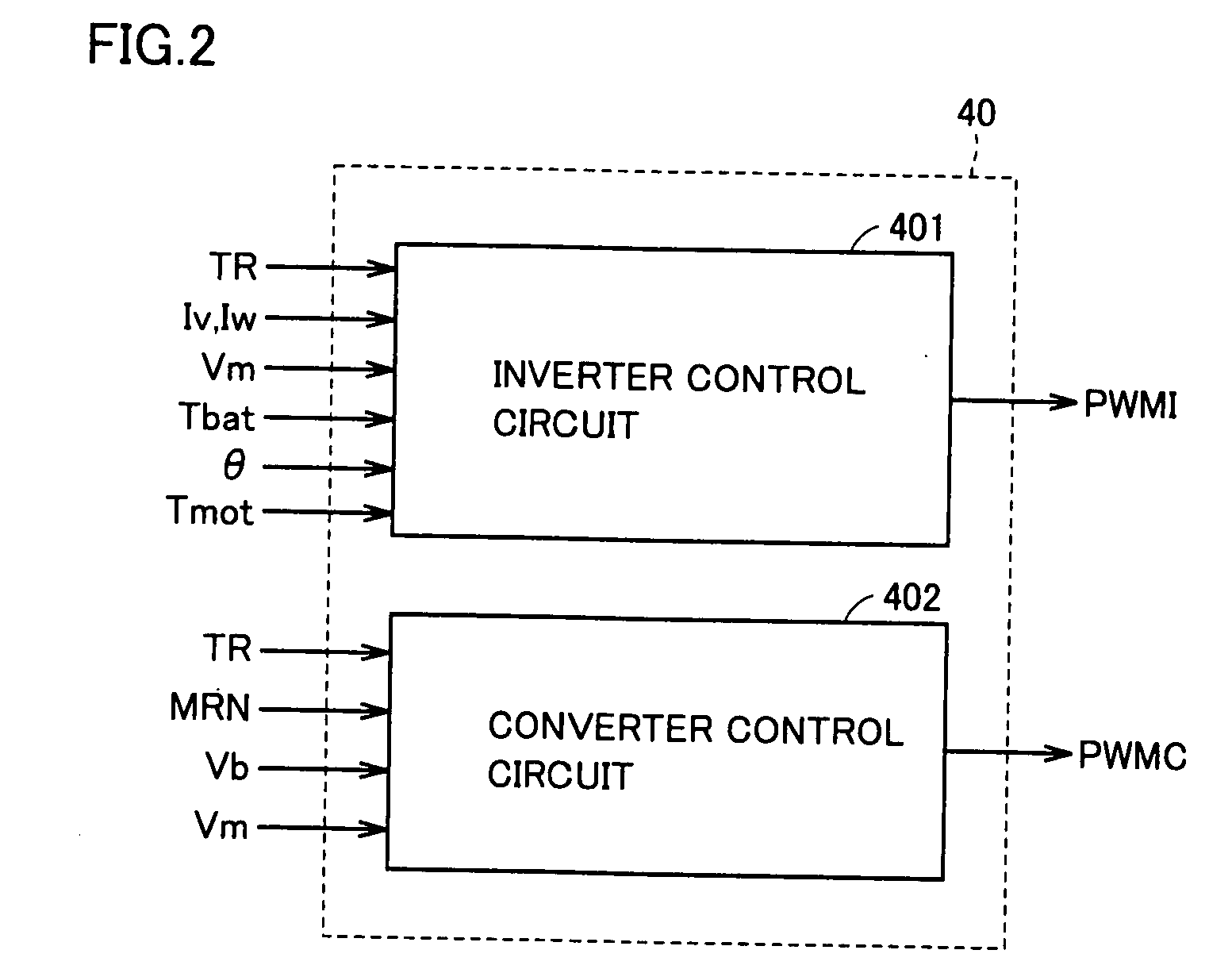
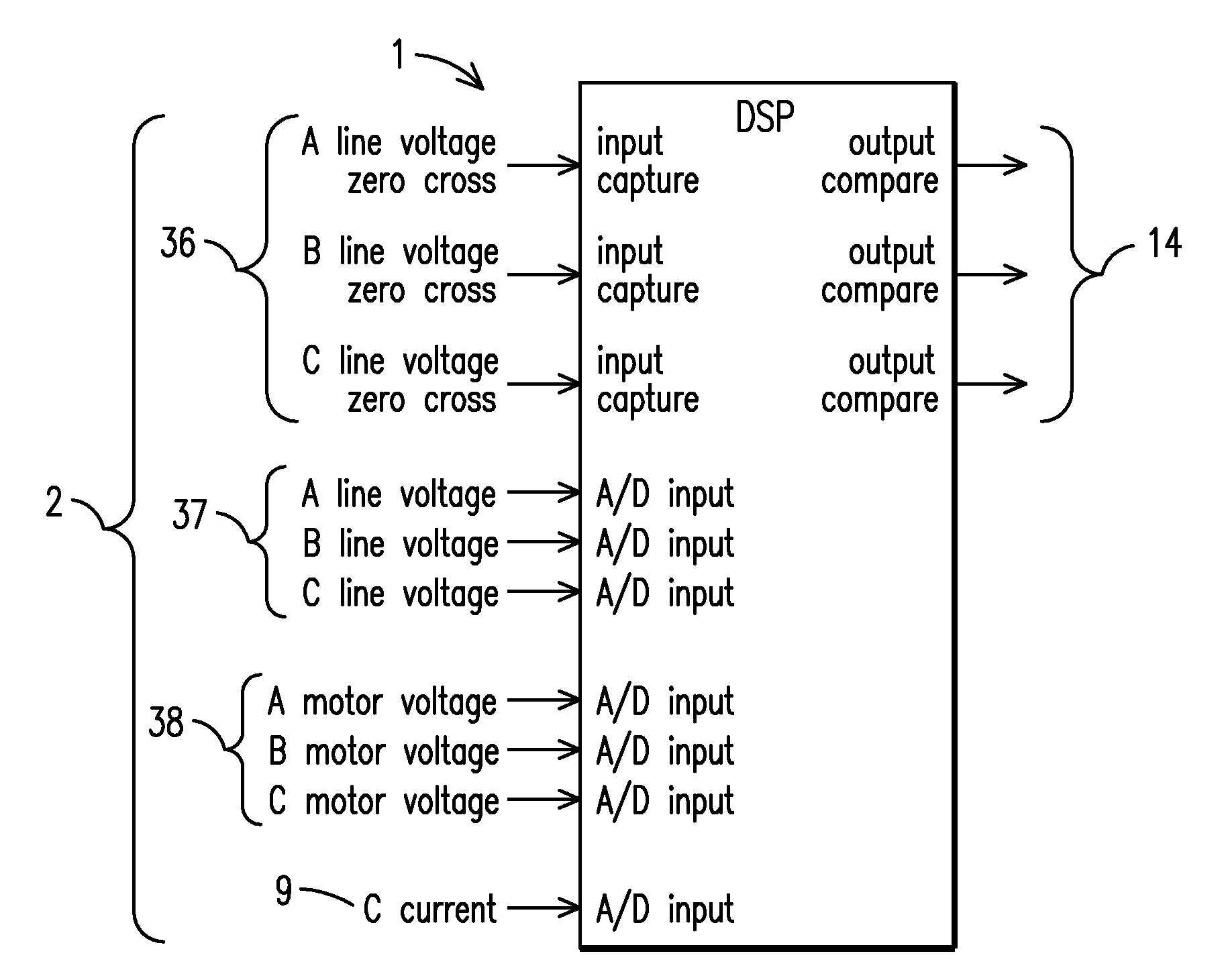
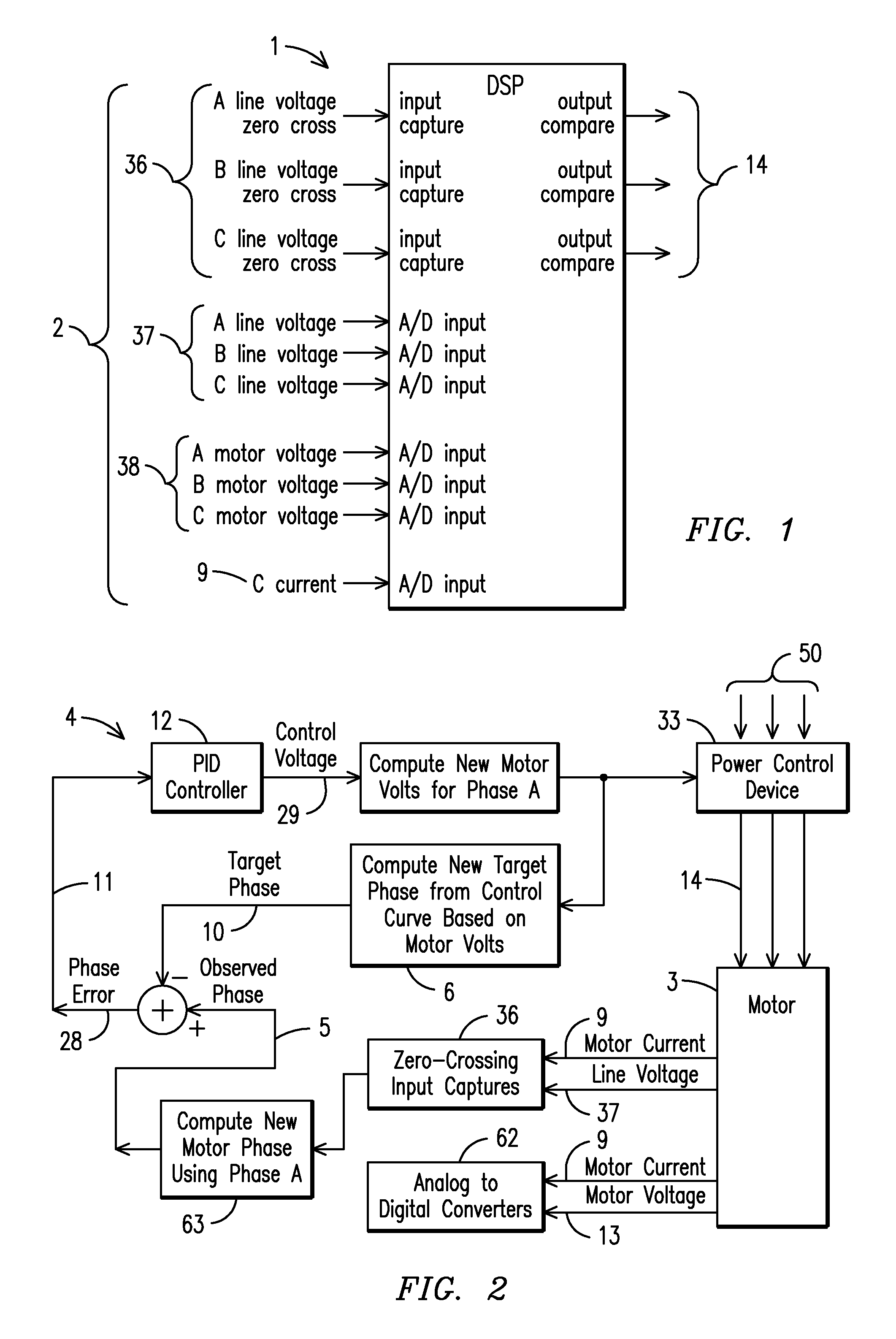
Motor controller system and method for maximizing energy savings
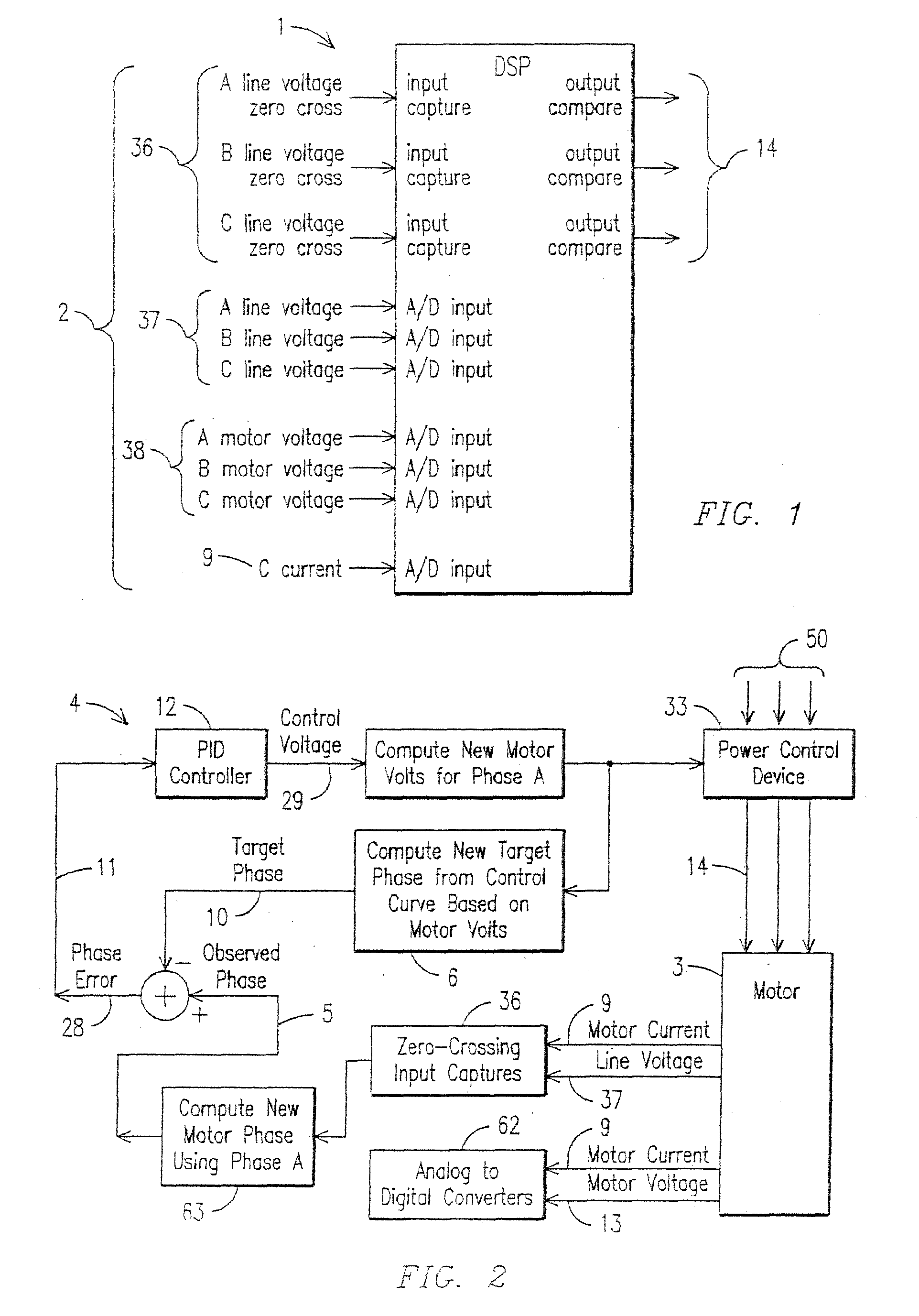
ActiveUS20100013427A1Maximize energy savingSave energyMotor control for low load efficiencyMotor/generator/converter stoppersTarget controlInduction motor
A motor controller (4) and method for maximizing the energy savings in an AC induction motor (3) at every load wherein the motor is calibrated at two or more load points to establish a control line (6), which is then programmed into a non-volatile memory (30) of the motor controller. A DSP-based closed-loop motor controller observes the motor parameters of the motor such as firing angle / duty cycles (23), voltage (37), current (9) and phase angles to arrive at a minimum voltage necessary to operate the motor at any load along the control line. The motor controller performs closed-loop control to keep the motor running at a computed target control point, such that maximum energy savings are realized by reducing voltage through pulse width modulation.
Owner:THE POWERWISE GRP
Control system for multiphase rotary machines
ActiveUS20080246426A1Enough timeSingle-phase induction motor startersEmergency protective circuit arrangementsControl systemEngineering
A control system aims at converting, via a switching circuit, a direct current voltage into an alternating current voltage to be applied to multiphase windings of a multiphase rotary machine to thereby control rotation of the multiphase rotary machine. In the control system, a command voltage determiner determines a command voltage value for an alternating current voltage to be applied to the multiphase windings based on a zero crossing of a line-to-line current and a zero crossing of the amount of change in the line-to-line current. A driving unit drives the switching circuit on and off based on the determined command voltage value to thereby modulate the direct current voltage to the alternating current voltage to be applied to the multiphase windings.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Motor driving device, motor driving method, and electronic device
InactiveUS20050275362A1Small sizeLow costElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsWind driven
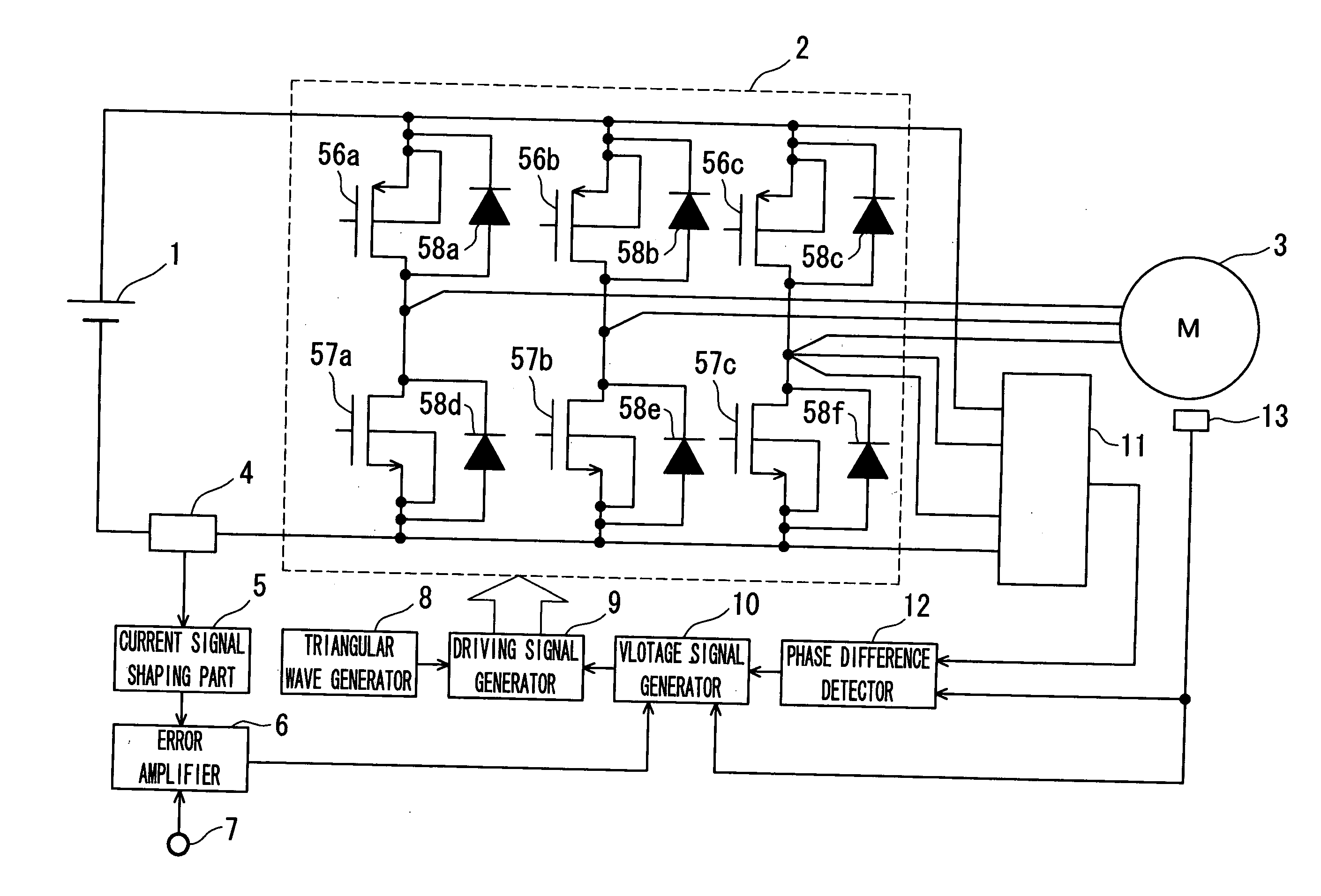
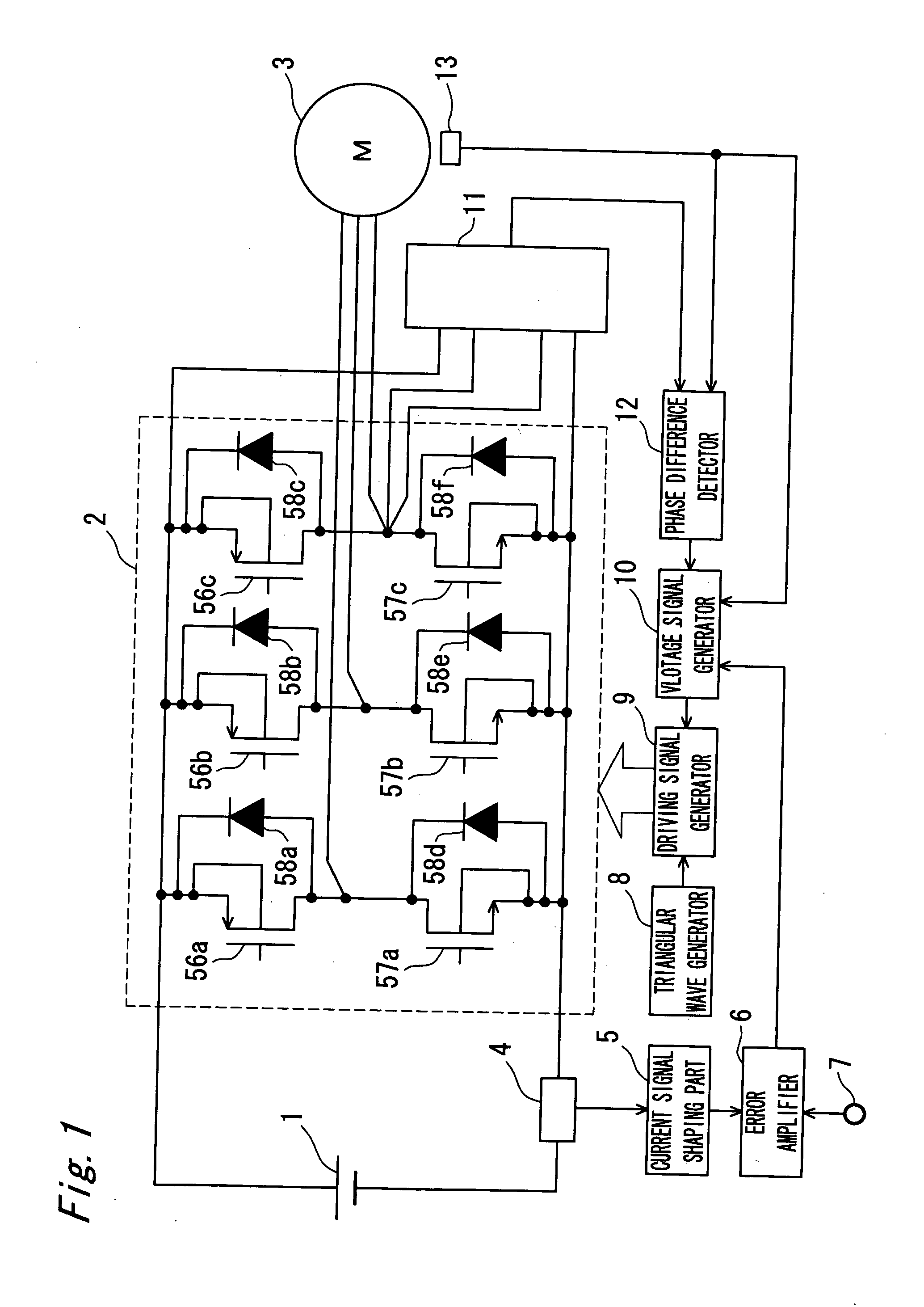
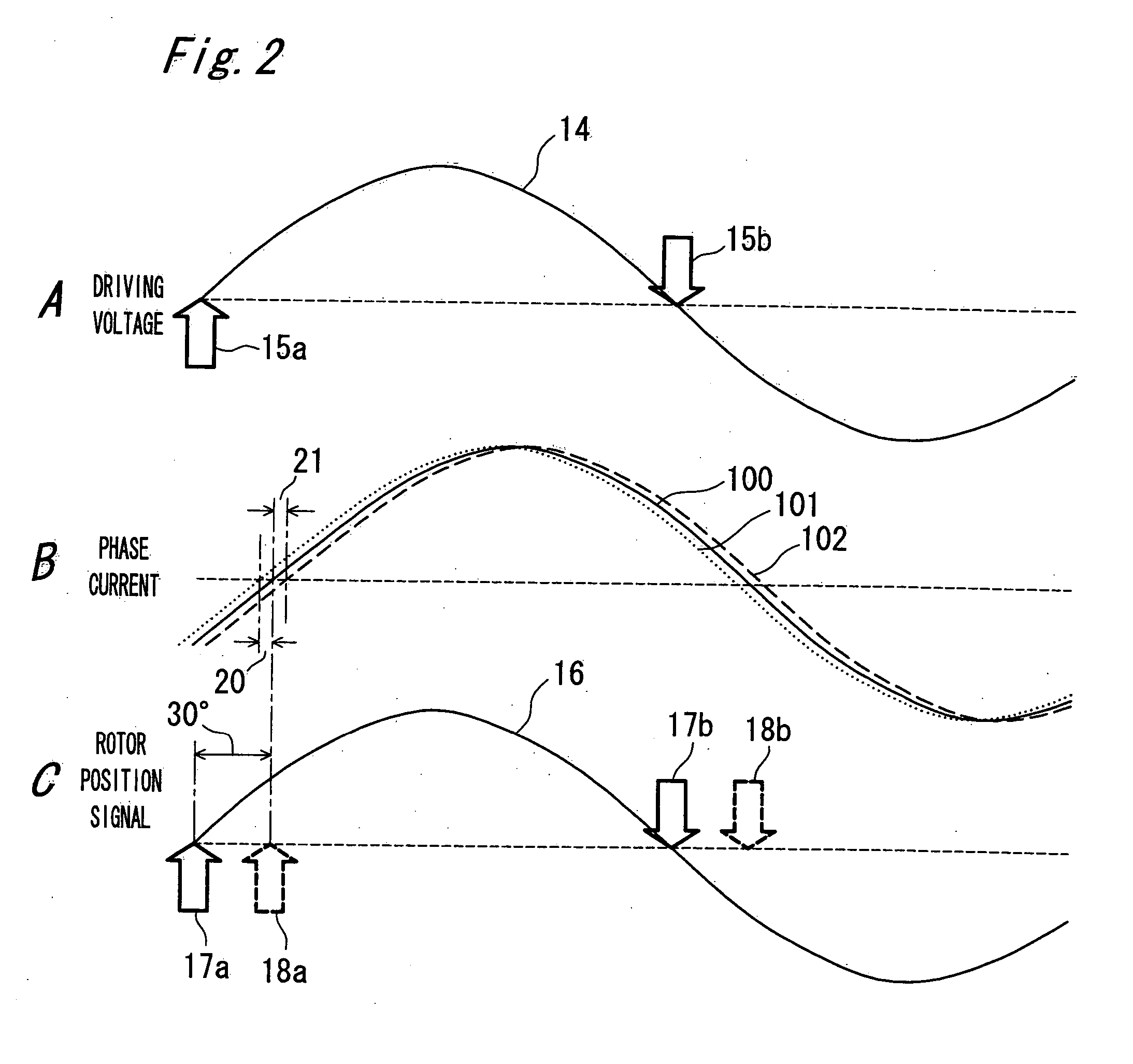
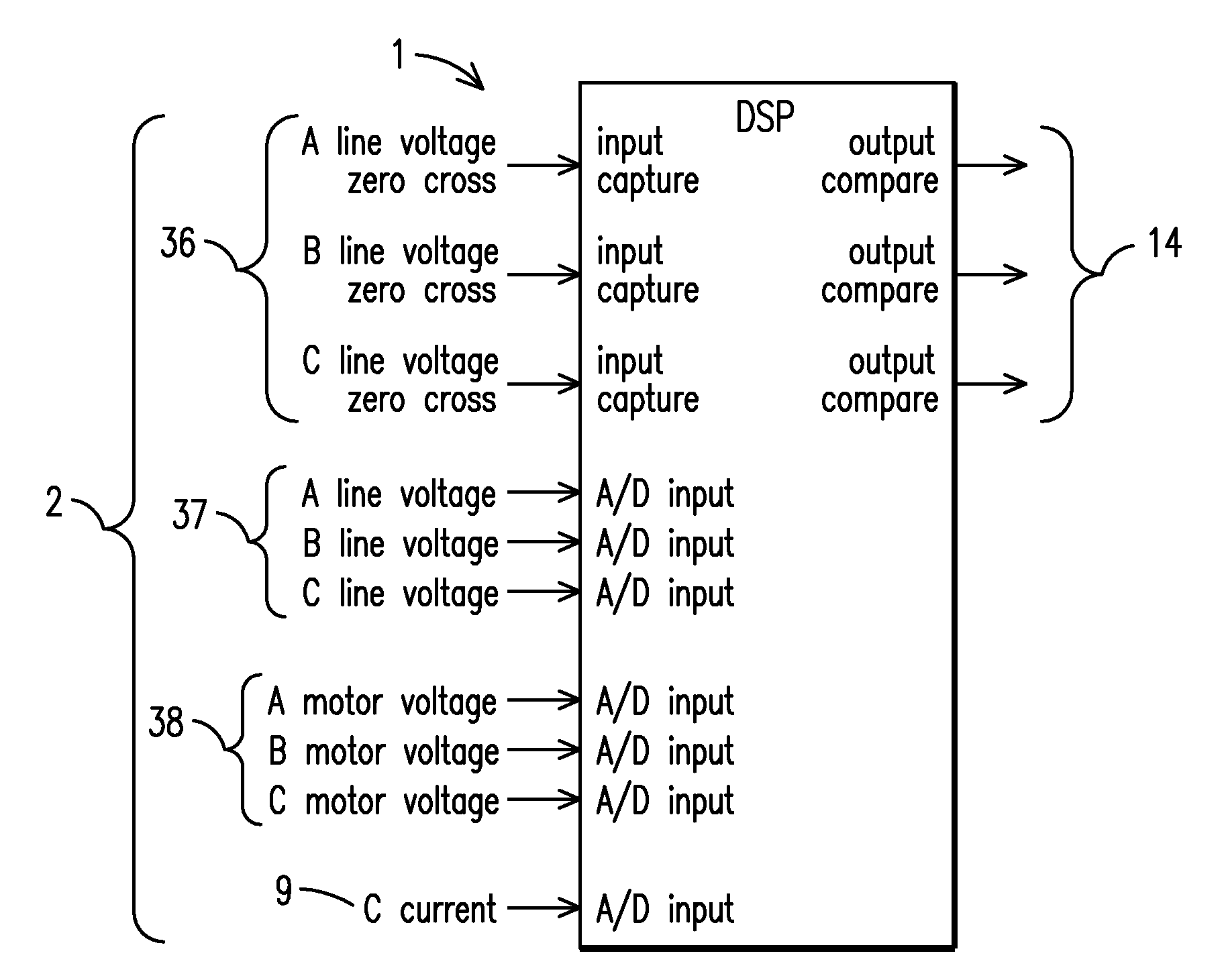
A motor driving device that is low in cost and capable to control the phase of a motor with high efficiency and with accuracy. A motor driving device includes a motor driving part, a rotor position detector, a current phase detector, a voltage signal generator, and a driving signal generator. The motor driving part has a plurality of half bridge circuits in which a high potential side drive transistor and a low potential side drive transistor are connected in series to each other, and a connection point therebetween serves as a stator winding driving terminal of each phase of a motor. The rotor position detector detects a rotor position of the motor and outputting a rotor position signal. The current phase detector detects the phase of a phase current flowing in the stator winding driving terminal. The voltage signal generator controls and generates a voltage profile signal such that a first phase difference that is a difference between the phase of the phase current and the phase of the rotor position signal is kept to a predetermined electrical angle. The driving signal generator generates a PWM signal that drives the drive transistor of each phase depending on the voltage profile signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Motor controller system and method for maximizing energy savings
ActiveUS20100117588A9Maximize energy savingSave energyMotor control for low load efficiencyMotor/generator/converter stoppersLoop controlInduction motor
A motor controller (4) and method for maximizing the energy savings in an AC induction motor (3) at every load wherein the motor is calibrated at two or more load points to establish a control line (6), which is then programmed into a non-volatile memory (30) of the motor controller. A DSP-based closed-loop motor controller observes the motor parameters of the motor such as firing angle / duty cycles (23), voltage (37), current (9) and phase angles to arrive at a minimum voltage necessary to operate the motor at any load along the control line. The motor controller performs closed-loop control to keep the motor running at a computed target control point, such that maximum energy savings are realized by reducing voltage through pulse width modulation.
Owner:THE POWERWISE GRP INC
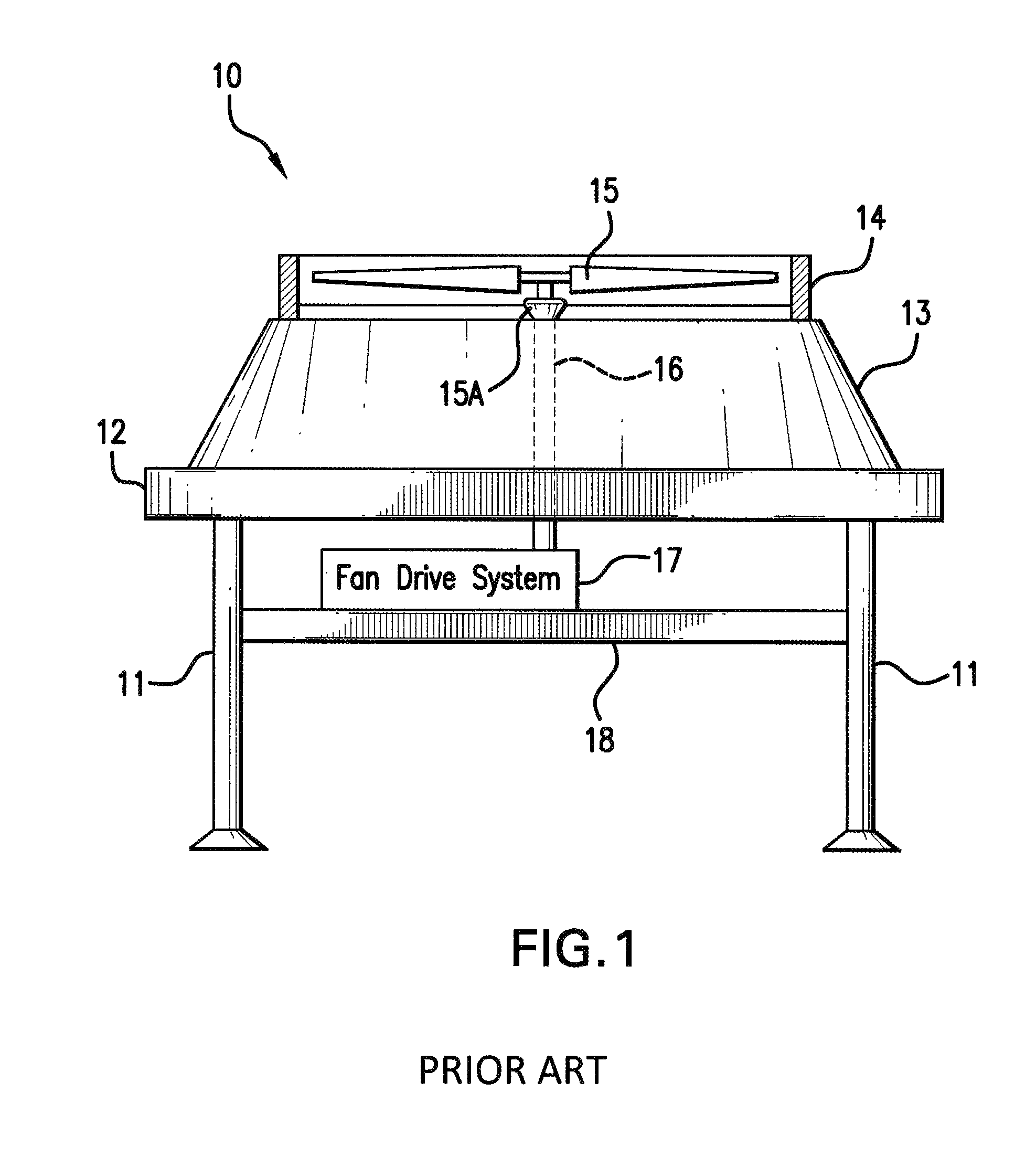
Integrated Fan Drive System For Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger (ACHE)
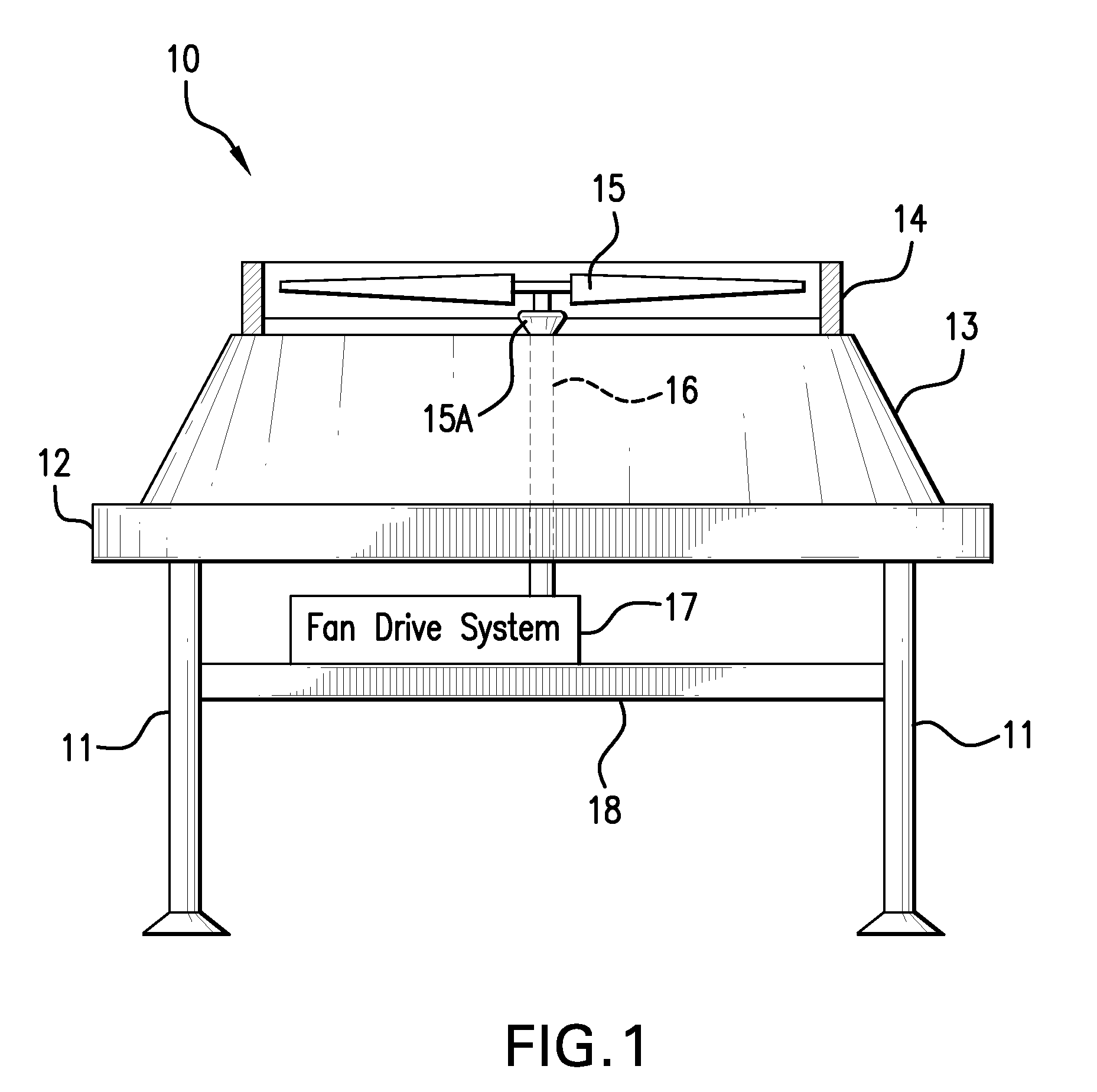
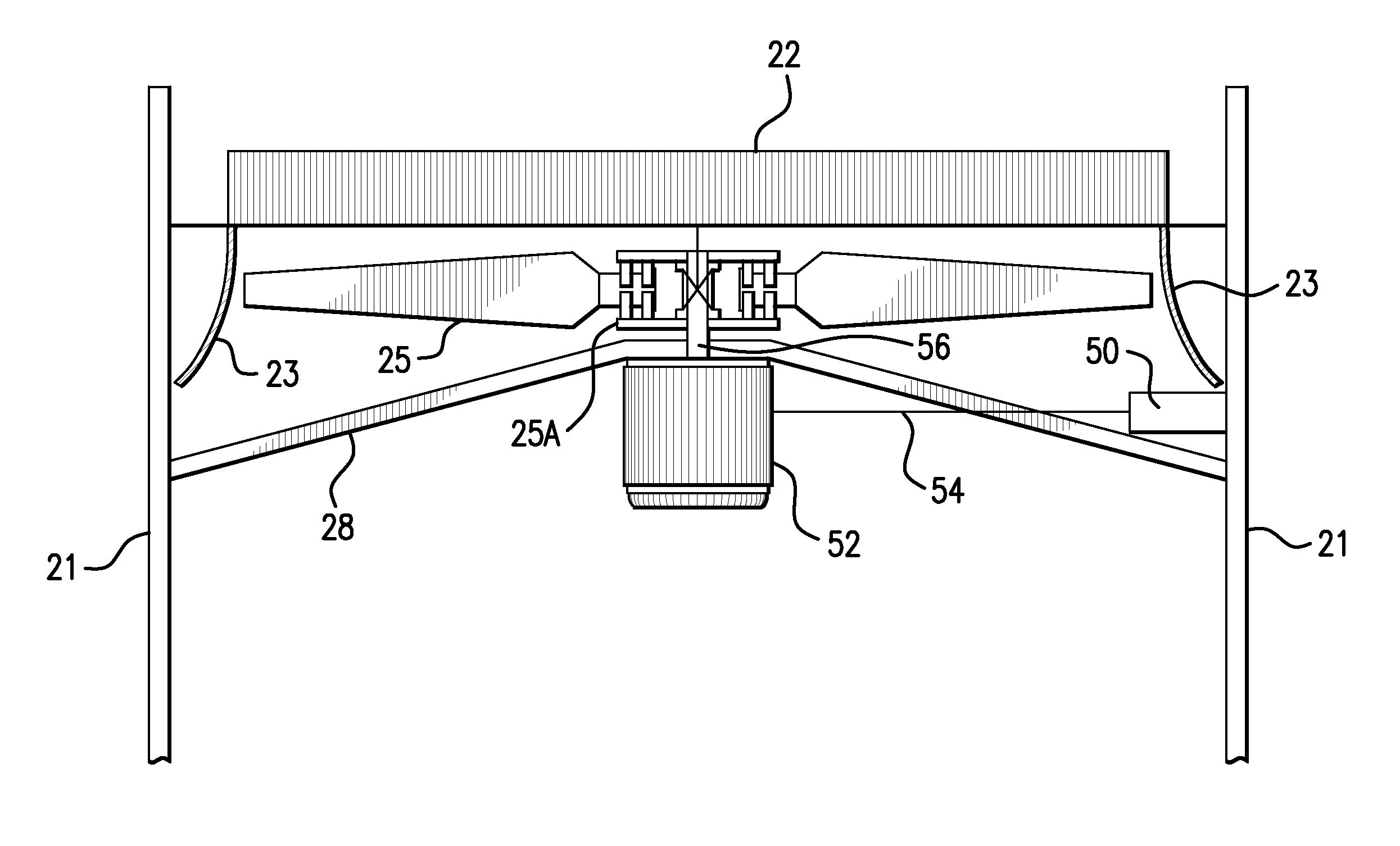
ActiveUS20100193163A1Eliminate disadvantagesEliminate the problemSpace heating and ventilationSolid-state devicesMotor speedLow speed
An integrated fan drive system for air-cooled heat exchangers. The integrated fan drive system has a high-torque, low speed permanent magnet motor having a rotatable shaft, a fan that is directly connected to the rotatable shaft, and a variable frequency drive device in electrical signal communication with the permanent magnet motor to control the rotational speed of the permanent magnet motor. The high-torque, permanent magnet motor comprises no more than two bearings in operative association with the shaft. The variable frequency drive device has a variable frequency controller that has an input for receiving AC power and an output for providing electrical signals that control the operational speed of high-torque, permanent magnet motor. The variable frequency drive device also includes a user interface in electronic data signal communication with the variable frequency controller to allow a user to input motor speed control data. Other embodiments of the invention are described herein.
Owner:PRIME DATUM
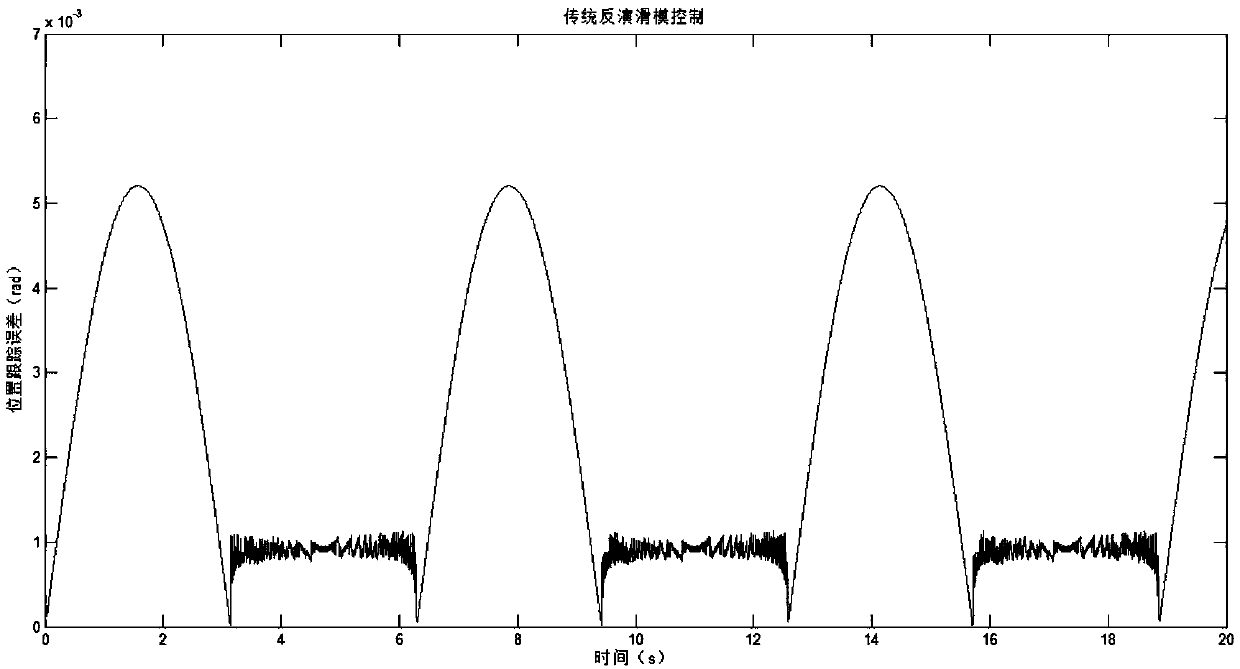
Method for controlling slip mode variable structure of brushless direct current motor based on power exponential reaching law
InactiveCN108233788AImproved speed response performanceImprove control qualitySingle motor speed/torque controlGeneral control strategiesProportional controlMode control
The invention provides a method for controlling a slip mode variable structure of a brushless direct current motor based on a power exponential reaching law. The method comprises the following steps of S1, analyzing a mathematics model of the brushless direct current motor; S2, designing a slip mode controller; combining a power reaching law and an exponential reaching law, so as to obtain the improved reaching law-power exponential reaching law, and calculate the slip mode control rate at the current time; S3, setting a current loop and a speed loop for controlling the brushless direct current motor, wherein the current loop adopts the integral and proportional control type, and the speed loop adopts the slip mode variable structure control type using the power reaching law; S4, repeatedly updating the value of slip mode control rate i, so as to control the brushless direct current motor. The method has the advantages that the control quantity on the brushless direct current motor adopts three adjustable parameters, so that the control and adjusting are more flexible; a control strategy with high control quality, simple type and convenient implementing on the brushless direct current motor is provided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Control system for multiphase rotary electric machines
A control system controls, based on a comparison between a waved real current to be supplied to a multiphase rotary electric machine and a hysteresis region established by a waved command signal, a switching timing of a switching element of an inverter to which a direct current voltage is applied to thereby match the waved real current with a waved request current. A determining unit determines whether a workload associated with rotation of the portion of the multiphase rotary electric machine is equal to or greater than a corresponding predetermined value. When it is determined that the workload is equal to or greater than the predetermined value, a changing unit changes the waved command signal from being set to the waved request current so as to determine the switching timing of the switching element based on a positional relation between the waved request current and the changed waved command signal.
Owner:DENSO CORP
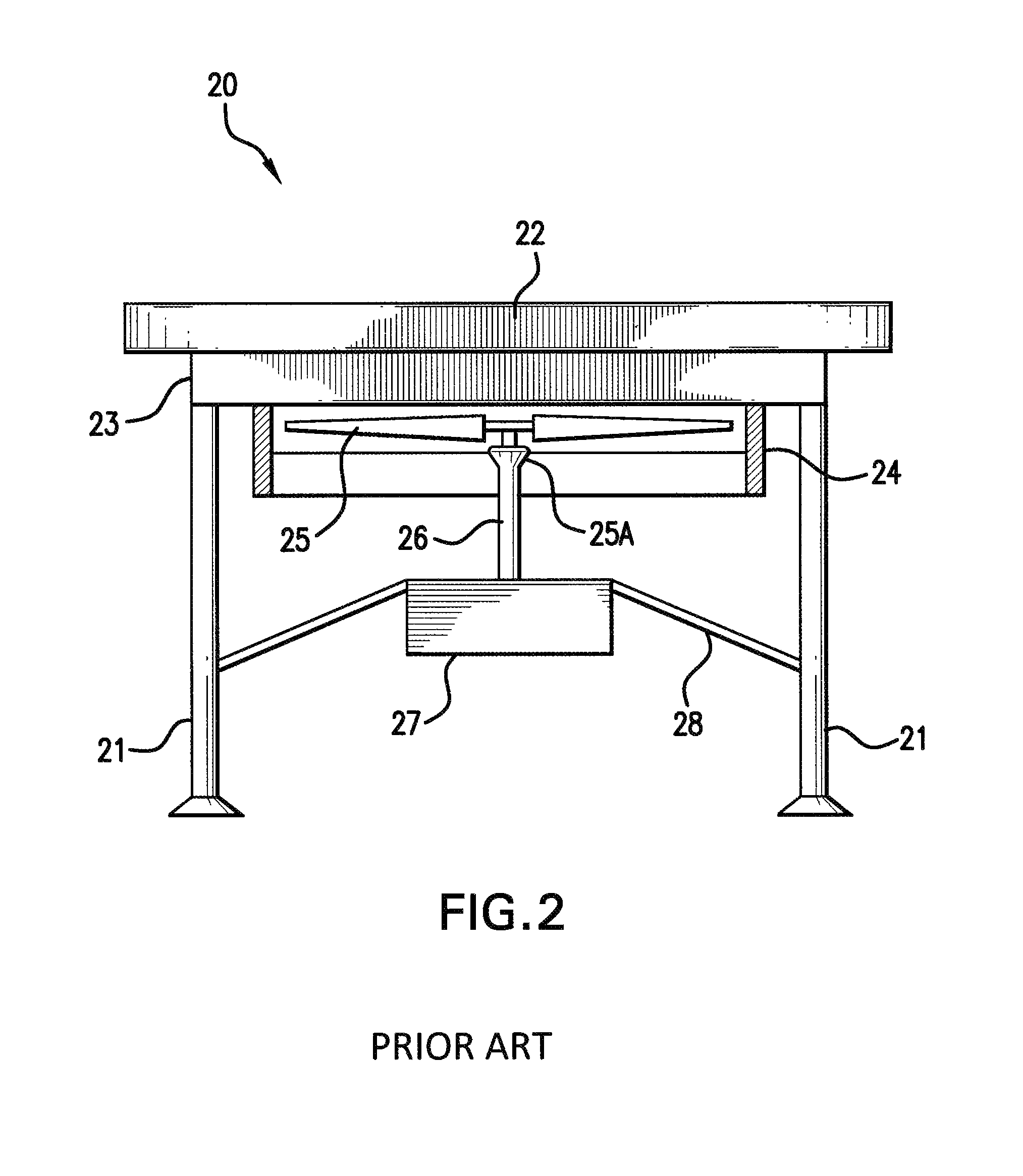
Integrated fan drive system for air-cooled heat exchanger (ACHE)
An integrated fan drive system for air-cooled heat exchangers. The integrated fan drive system has a high-torque, low speed permanent magnet motor having a rotatable shaft, a fan that is directly connected to the rotatable shaft, and a variable frequency drive device in electrical signal communication with the permanent magnet motor to control the rotational speed of the permanent magnet motor. The high-torque, permanent magnet motor comprises no more than two bearings in operative association with the shaft. The variable frequency drive device has a variable frequency controller that has an input for receiving AC power and an output for providing electrical signals that control the operational speed of high-torque, permanent magnet motor. The variable frequency drive device also includes a user interface in electronic data signal communication with the variable frequency controller to allow a user to input motor speed control data. Other embodiments of the invention are described herein.
Owner:PRIME DATUM
Motor control device, robot hand, robot, and motor control method
ActiveCN103107767AControl speedProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectric motor controlRobot handData signal
A motor control device controls a motor using an angle data signal and a rotational speed signal output from a rotation detector detecting a rotation state of a rotating shaft of the motor. The motor control device includes a speed control unit that outputs a torque instruction signal corresponding to a difference between the rotational speed of the rotating shaft and a speed instruction using the speed instruction of the rotating shaft and the rotational speed signal, a limit value setting unit that sets a torque limit value indicating the maximum value of the torque applied to the rotating shaft, and a torque limit control unit that limits the torque of the rotating shaft driven by the torque instruction signal to the torque limit value or less.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
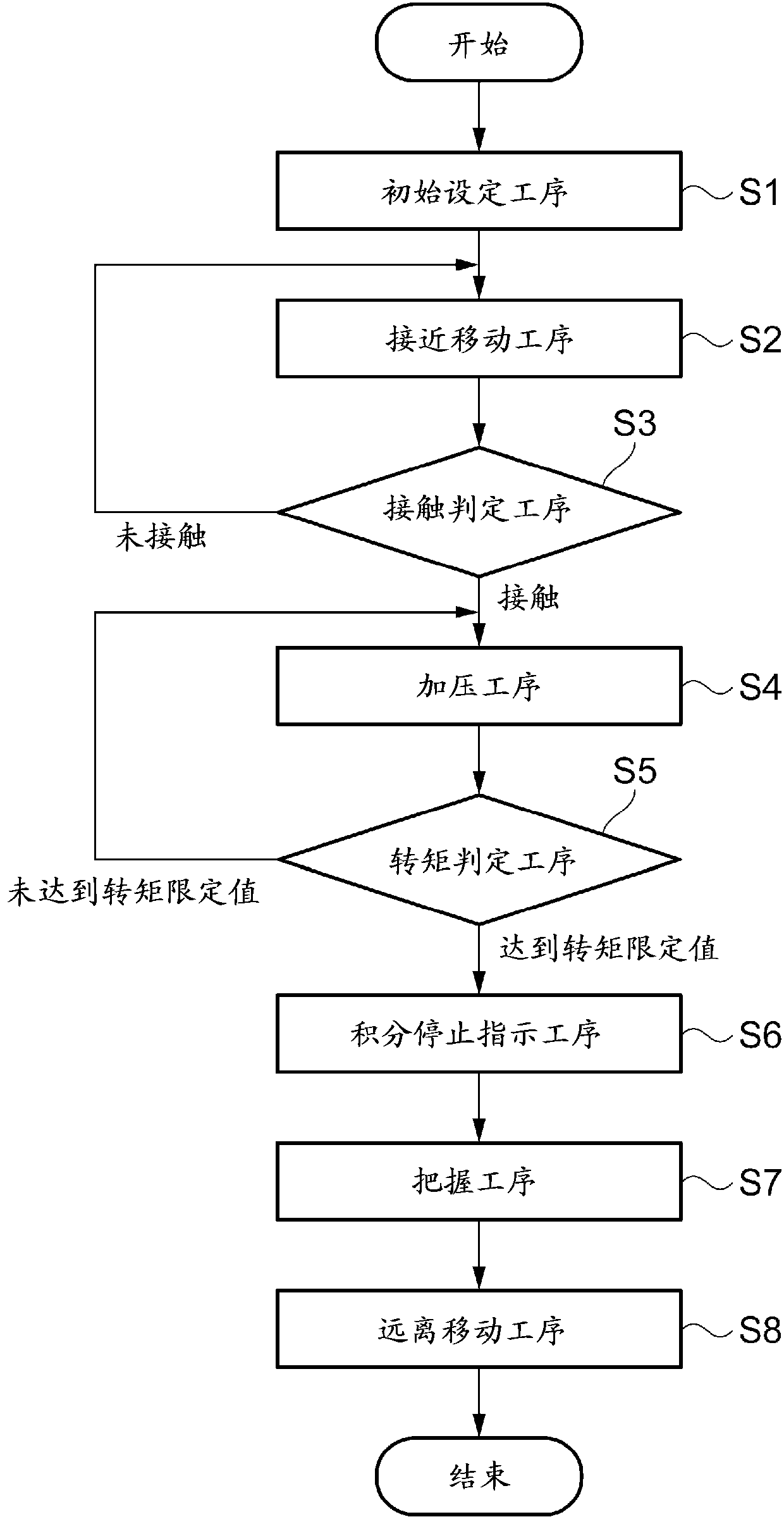
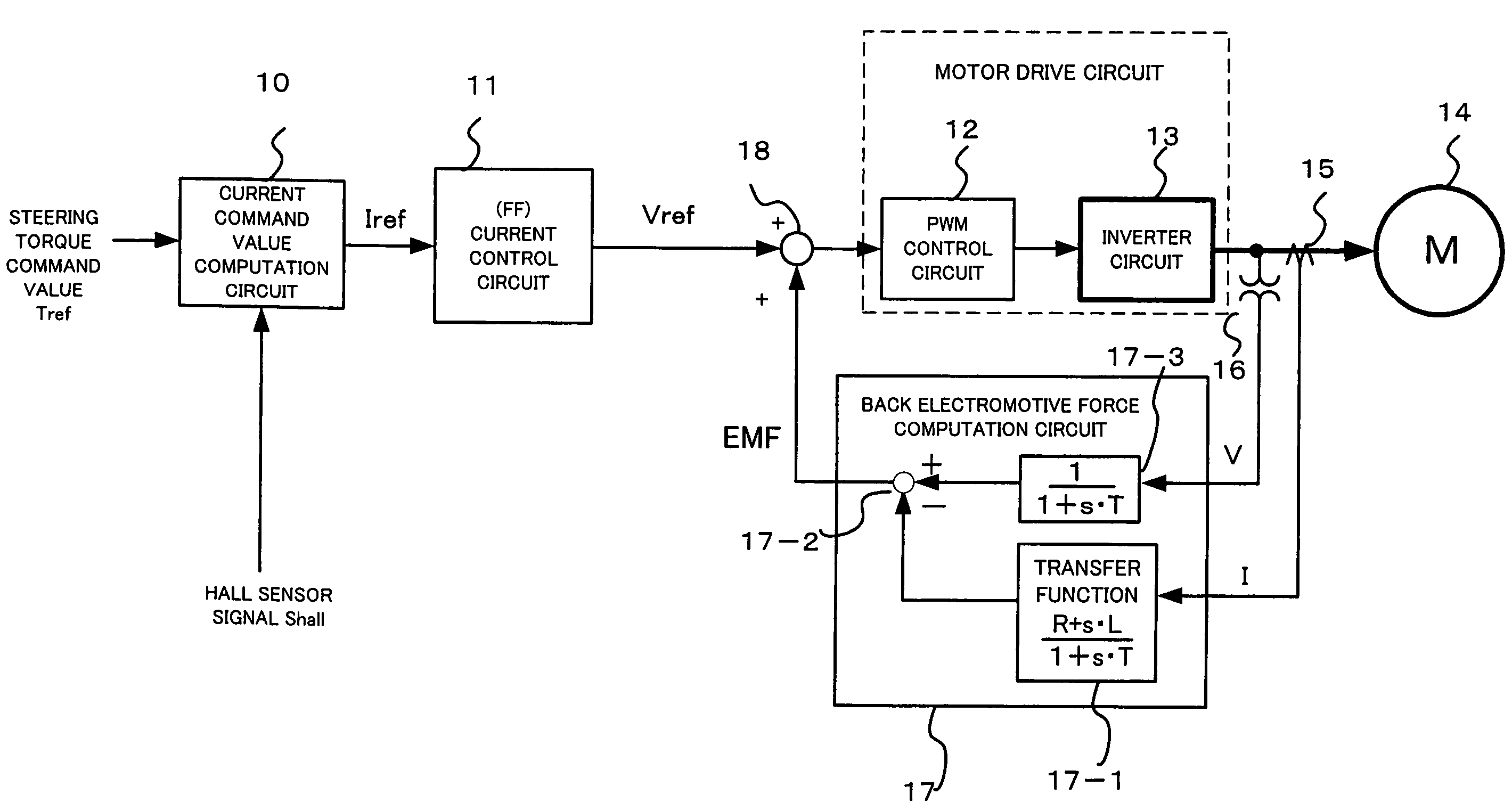
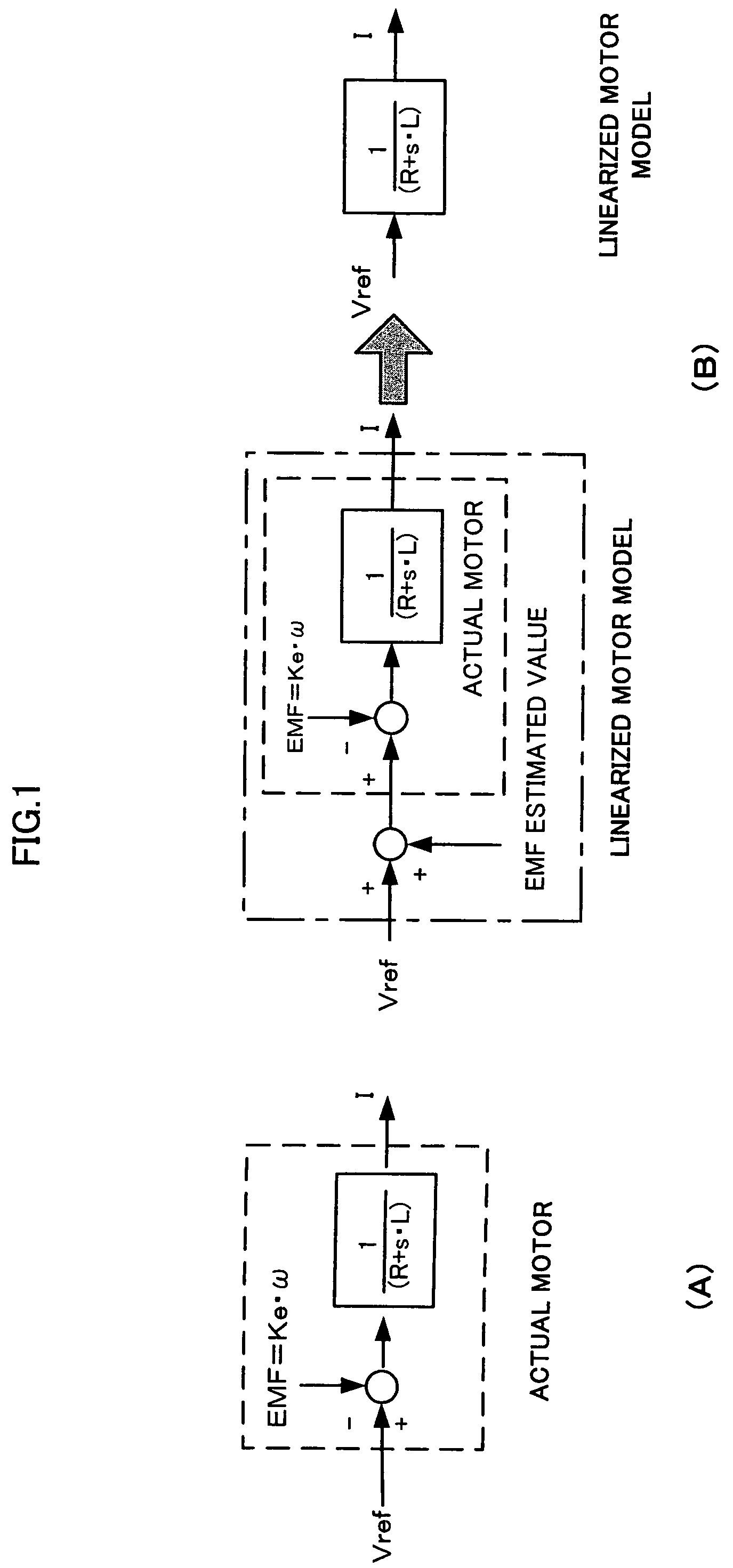
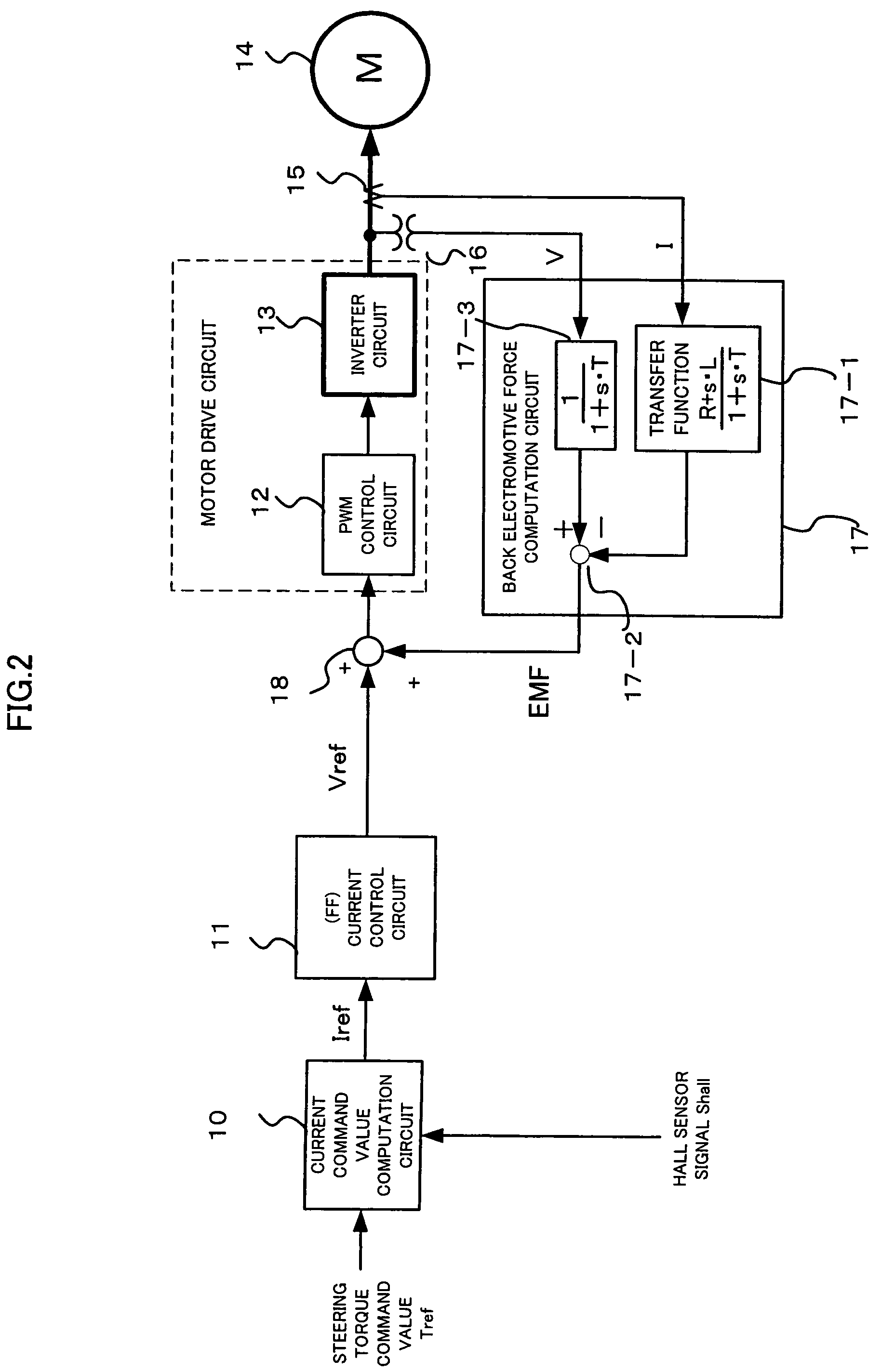
Controller for electric power steering device
InactiveUS7574294B2Digital data processing detailsSingle motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringEngineering
Owner:NSK LTD +1
Apparatus and method for detecting phase currents of inverter
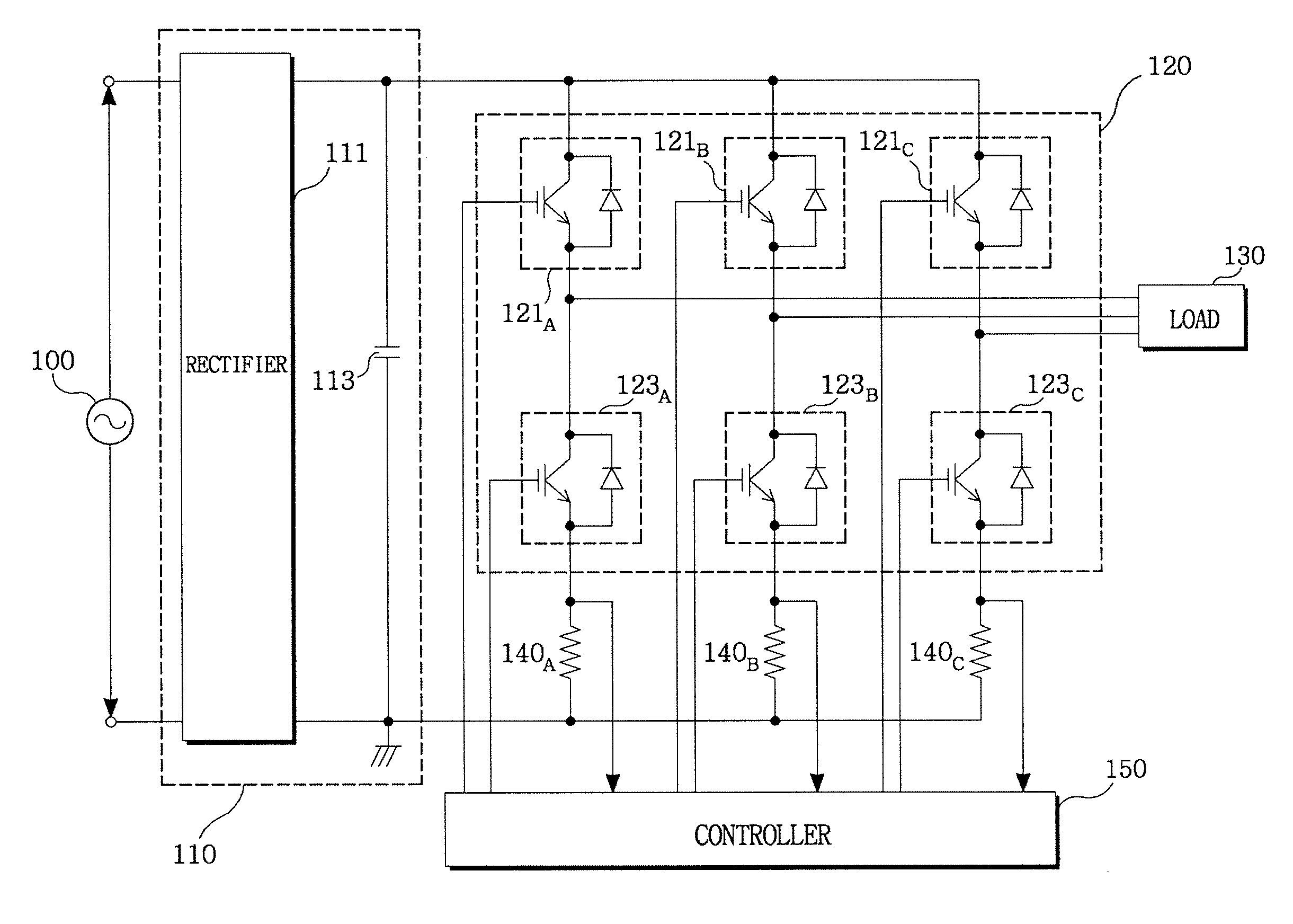
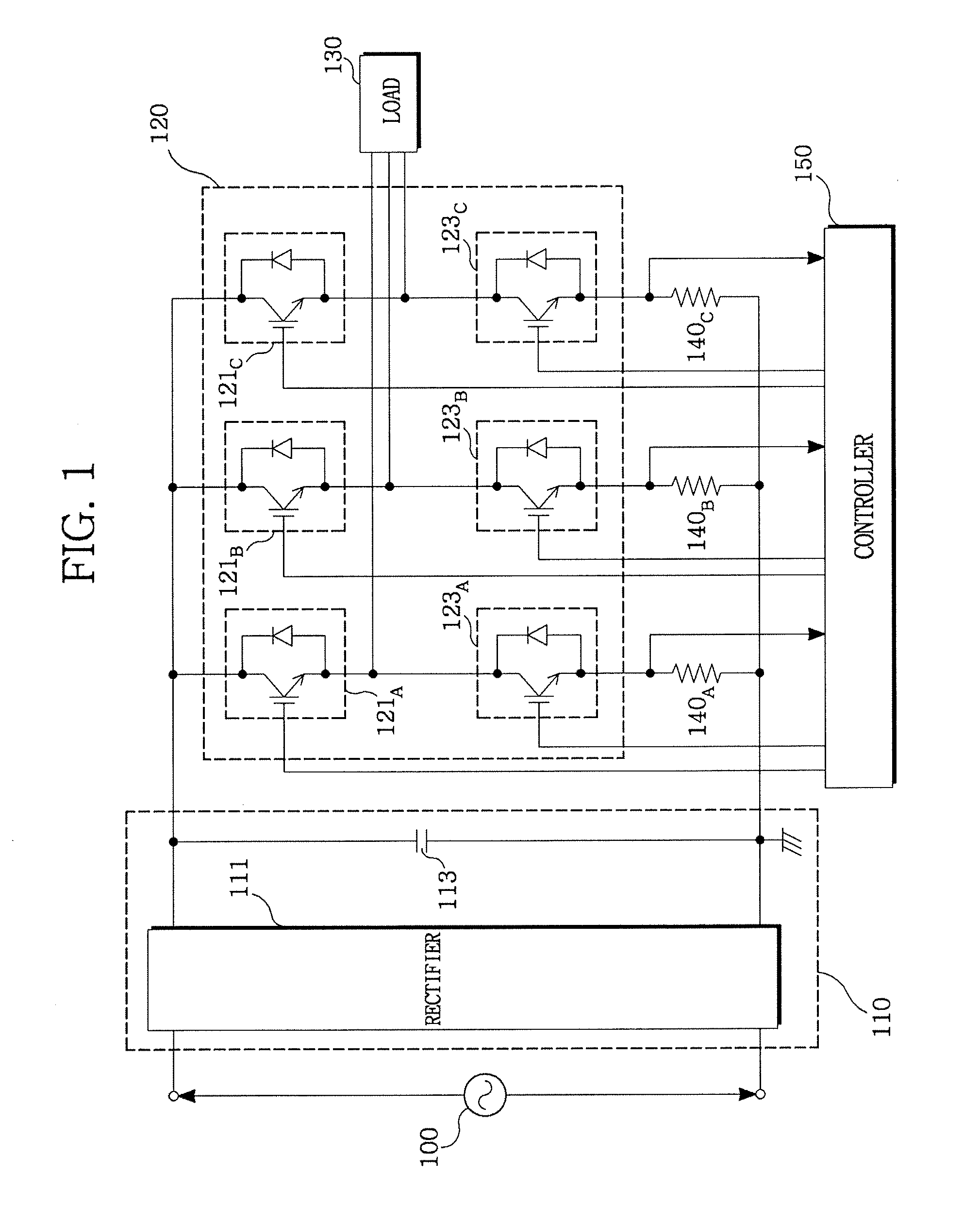
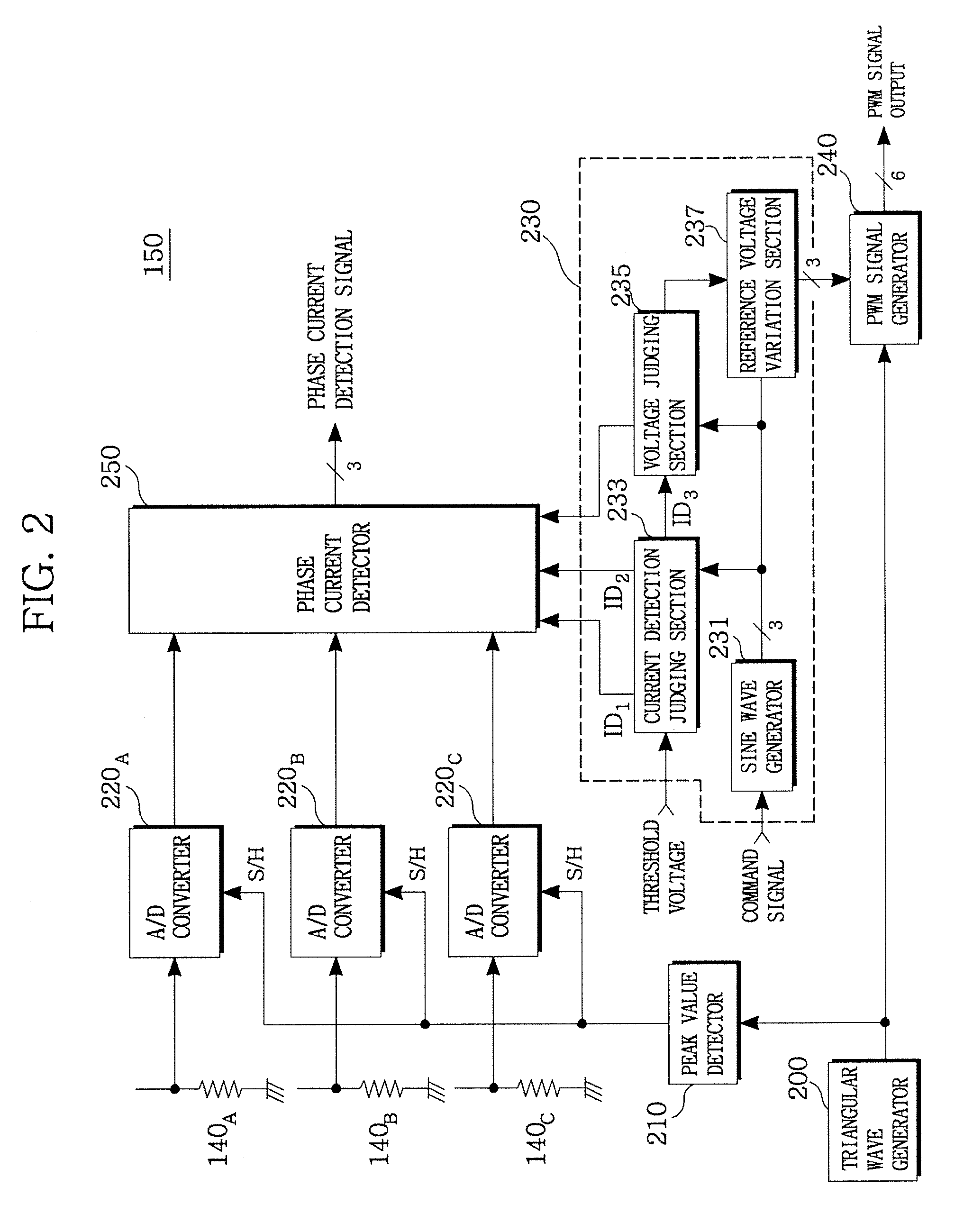
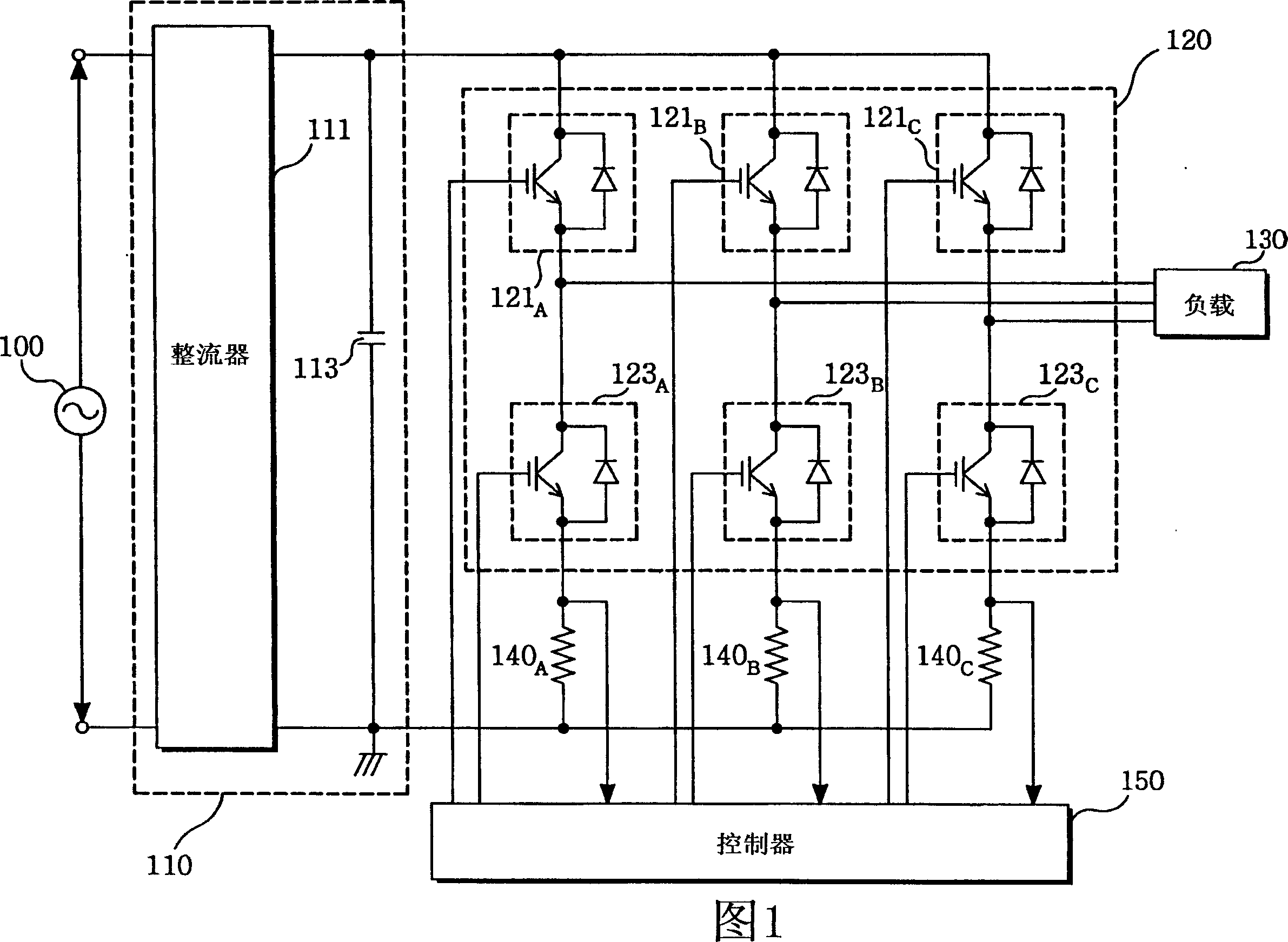
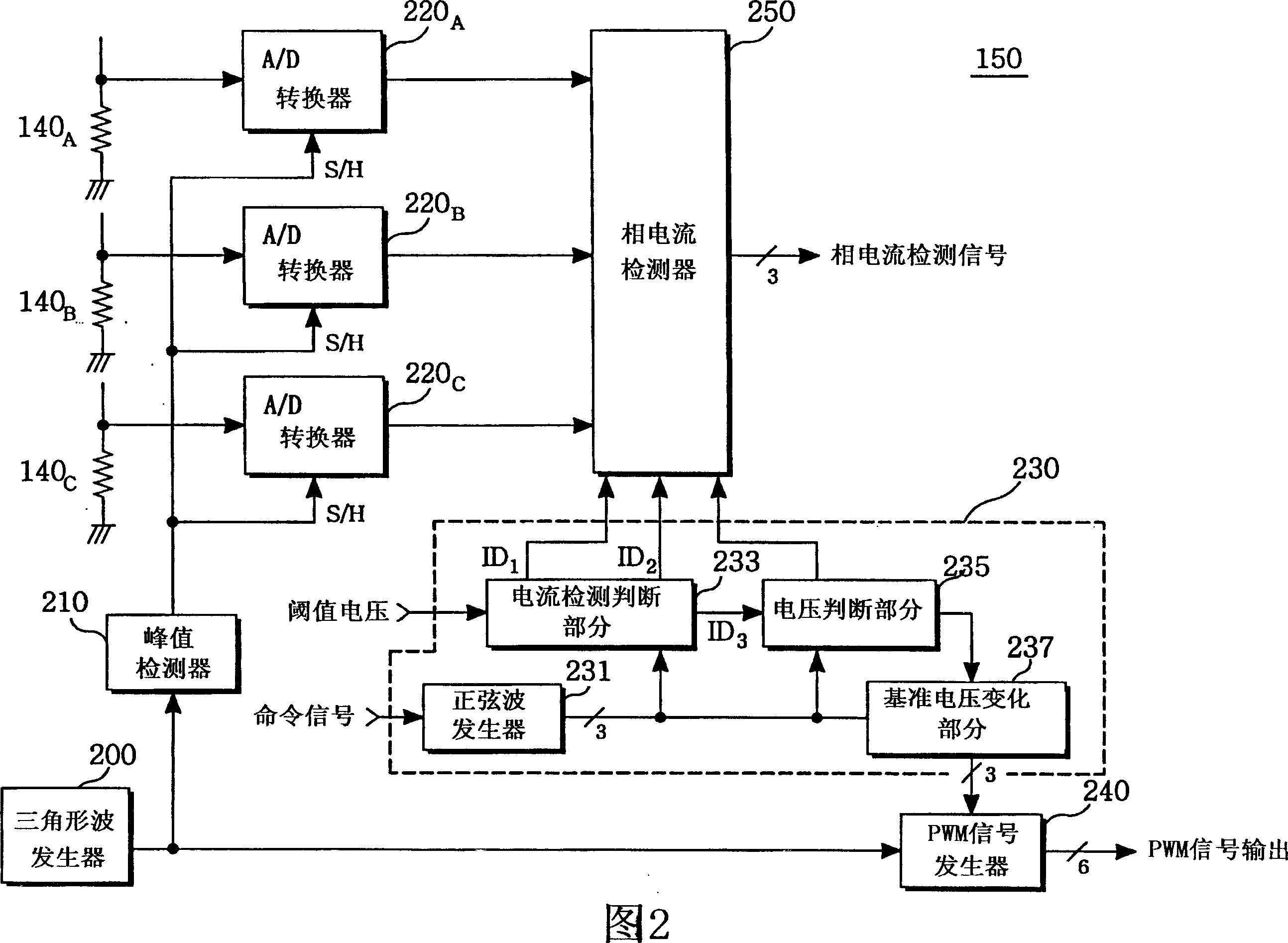
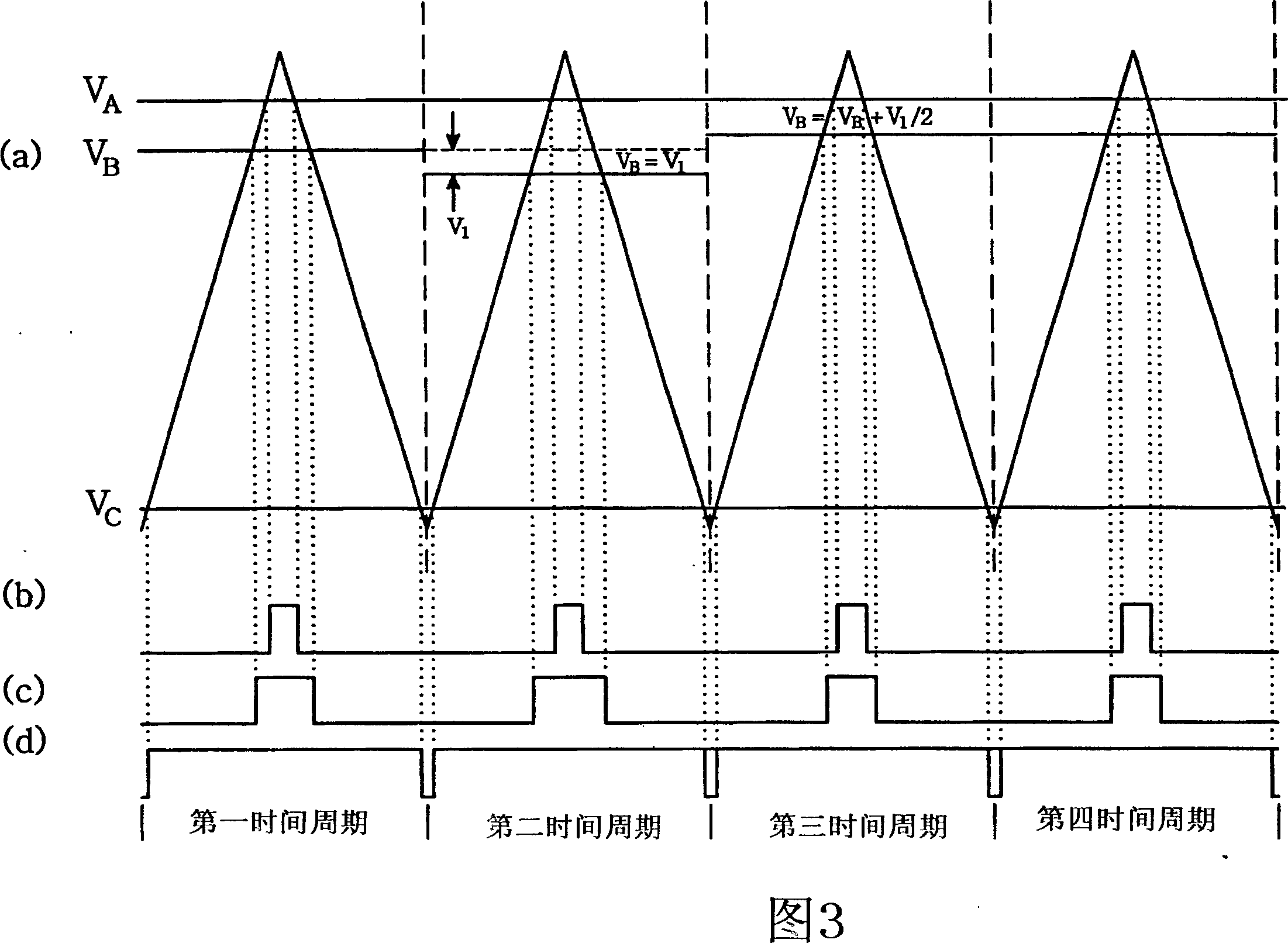
ActiveUS20070152676A1Minimum pulse widthElectric motor controlConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPhase currentsVoltage reference
The present invention previously sets a threshold voltage, compares the set threshold voltage with a reference voltage, and judges whether a minimal pulse width of a PWM signal is obtained. When a pulse width of one PWM signal is equal to or greater than the minimal pulse width, but each pulse width of two PWM signals is less than the minimal pulse width, a sine wave voltage corresponding to one of the two PWM signals less than the minimal pulse width is varied to a threshold voltage to detect two phase currents, and a remaining one phase current is calculated based on the two detected phase currents. After the phase current was detected by varying the threshold voltage, a level difference between an original sine wave voltage and the threshold voltage is set as a compensation voltage, and the sine wave voltage is compensated by the compensation voltage.
Owner:LS IND SYETEMS CO LTD
Motor controlling method and apparatus thereof
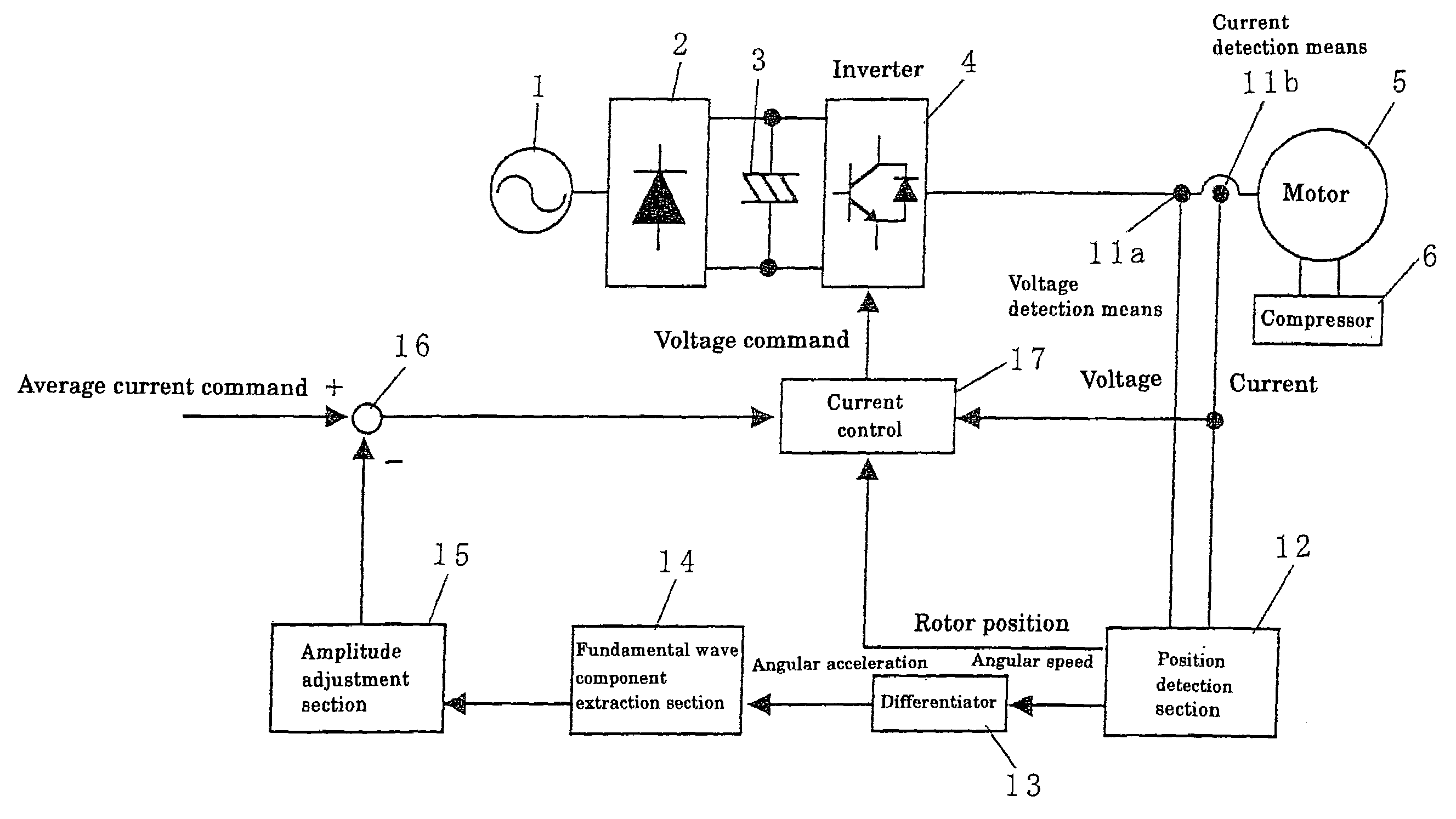
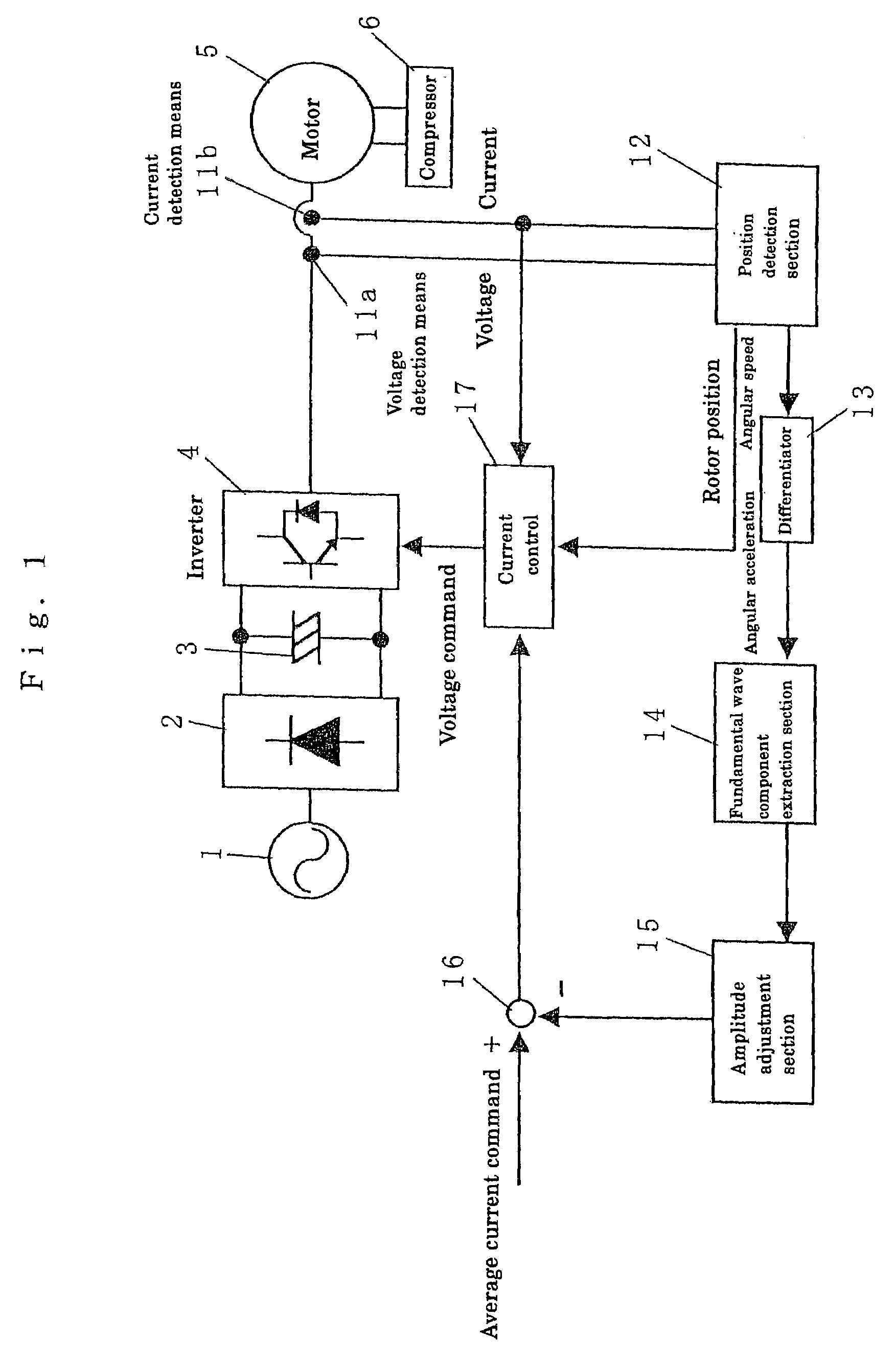
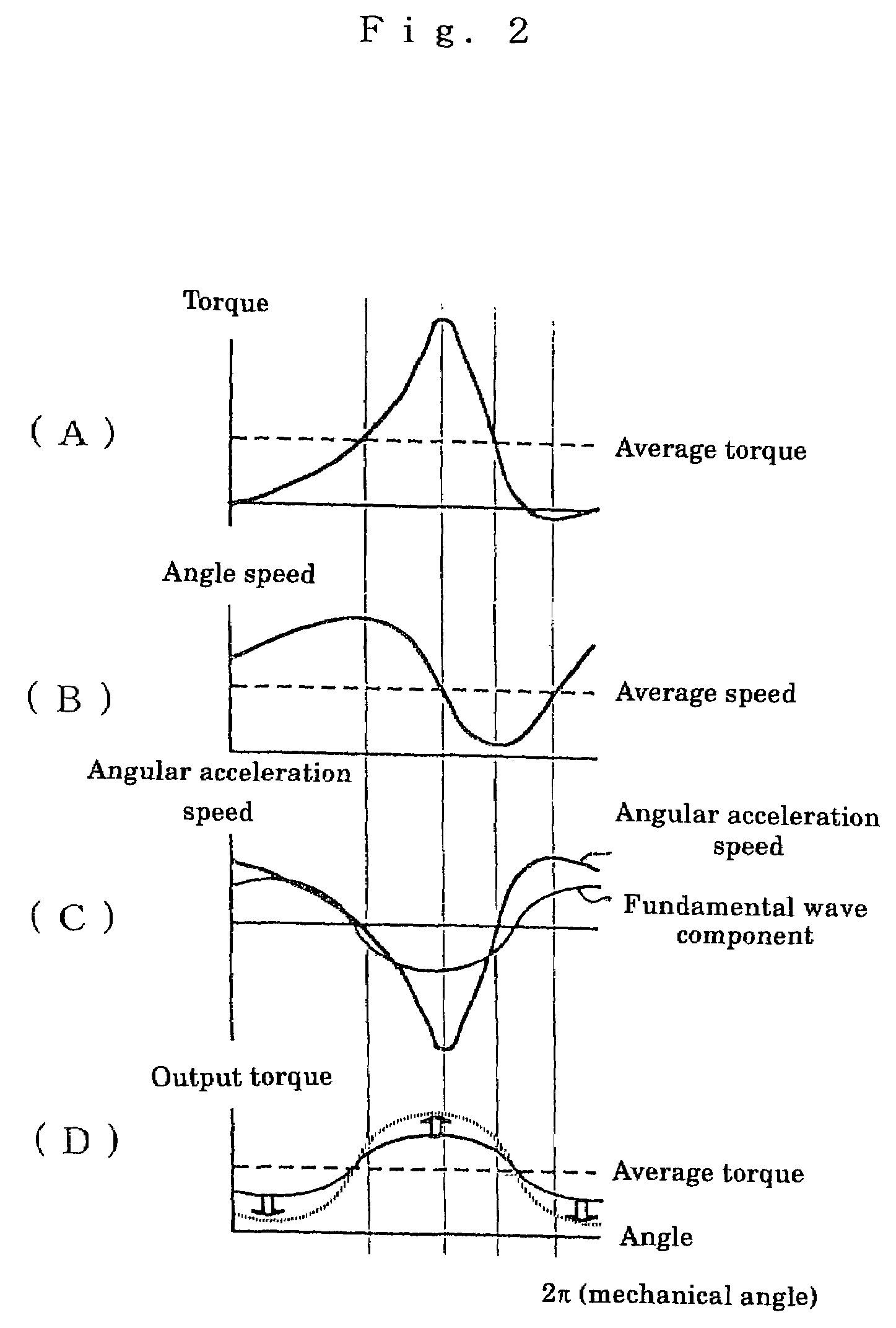
ActiveUS7075260B2Convenient and accurateSuppresses speed changesTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlLocation detectionDifferentiator
A voltage detection section and current detection section detect a voltage and current supplied to a motor, and the detected voltage and current are supplied to a position detection section. An angular speed output from the position detection section is supplied to a differentiator to output an angular acceleration. A fundamental wave component extraction section extracts a fundamental wave component of the angular acceleration, and the extracted fundamental wave component is supplied to an amplitude adjustment section. The output of the amplitude adjustment section is subtracted from the average current command by a subtraction section. This subtraction result, current detection value, and the rotor position from the position detection section are supplied to a current control section to carry out the current control operation so as to obtain a current command. The current command is supplied to an inverter to control the voltage and current so as to suppress the speed changing due to the load torque changing. Thus, stability is improved, and a decrease in cost is realized.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Motor drive control with a single current sensor using space vector technique
InactiveUS7308192B2Enough timeAvoid changeVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor driveElectric machine
A drive system for a three phase brushless AC motor that is operative to optimize a transistor switching pattern to improve power output while allowing current measurement in all of the phases using a single sensor. This is achieved by defining a voltage demand vector where more than two states are required to meet a minimum state time requirement determined by the single sensor and calculating three or more state vectors that produce the demand vector while still allowing single current sensing.
Owner:TRW LIMITED +1
Method and system for lowering torque pulsation of switched reluctance motor by current adaptive control
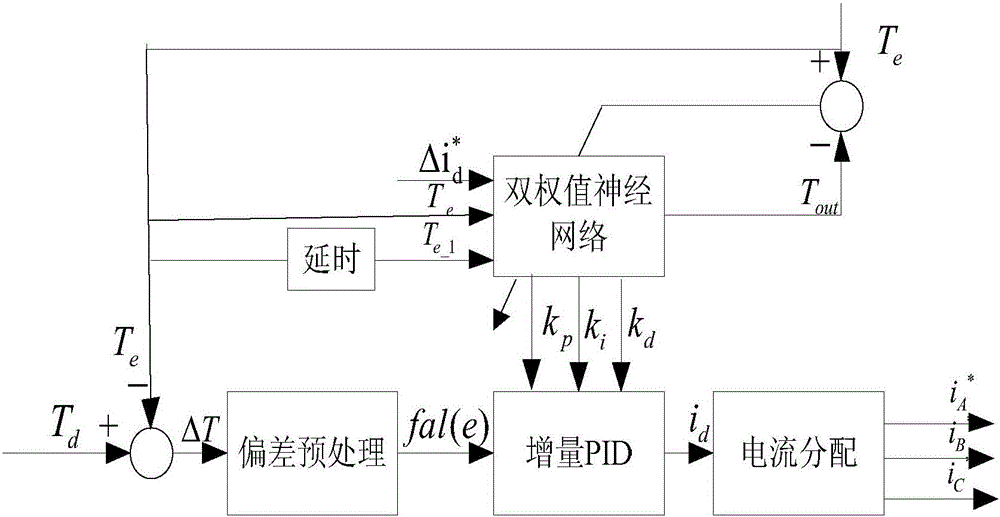
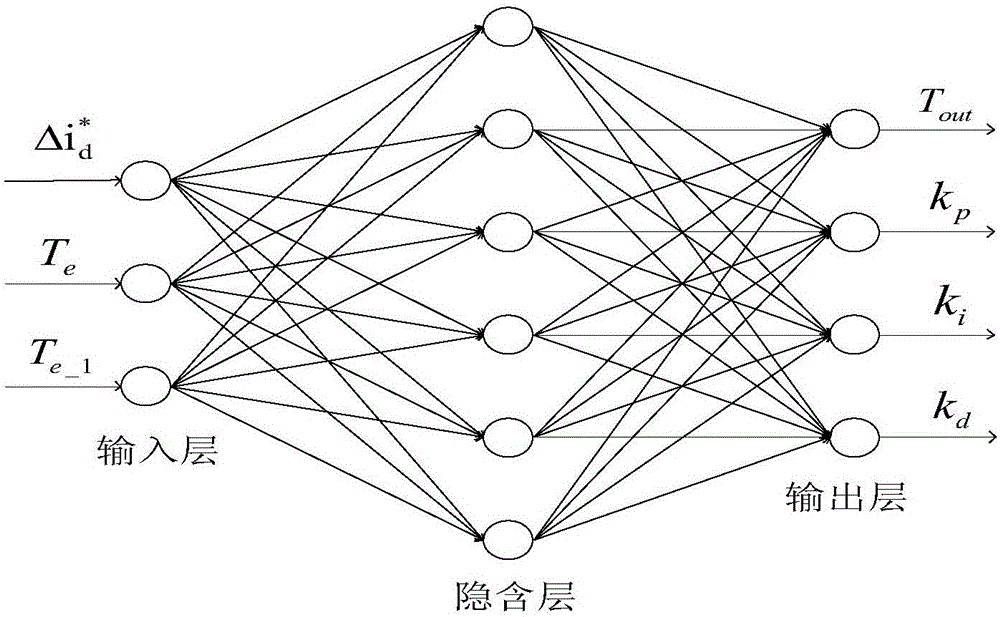
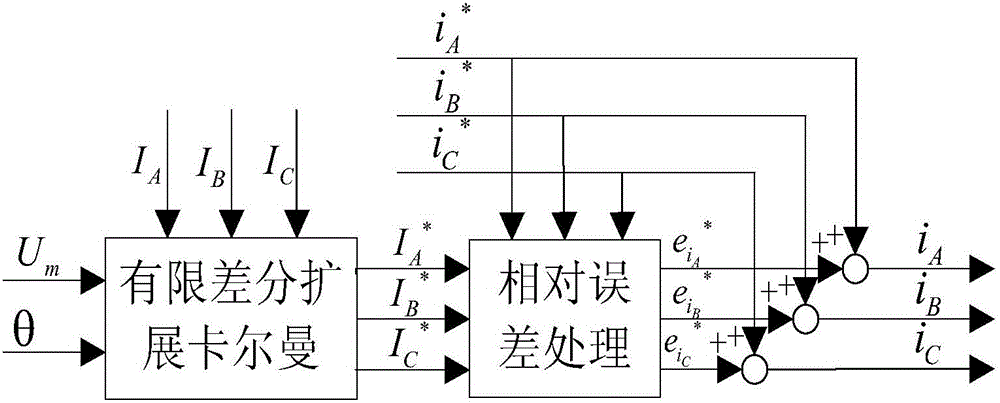
InactiveCN106357192ASuppression of torque rippleImprove predictive performanceGeneral control strategiesObserver controlHysteresisReference current
The invention relates to a method and system for lowering torque pulsation of a switched reluctance motor by current adaptive control; the method comprises: preprocessing a deviation: subjecting the torque deviation to nonlinear conversion; solving torque estimated output and adaptive PID (proportion integration differentiation) control coefficient by using double-weight neural network; acquiring current set total current by PID control calculation, and acquiring each phase control current via current allocation; predicting current feed-forward compensation control by finite difference extended Kalman filter, and effectively inhibiting and lowering torque pulsation of the switched reluctance motor by joint action of adaptive PID control and prediction-based current feed-forward compensation control. Current, torque and rotor position sensors are connected with a signal processor, the signal processor executes modules of the method, compensated three-phase reference current is output to control a power converter of the motor via a current hysteresis controller, and torque pulsation of the switched reluctance motor is significantly and effective inhibited.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Apparatus and method for detecting phase currents of inverter
The present invention previously sets a threshold voltage, compares the set threshold voltage with a reference voltage, and judges whether a minimal pulse width of a PWM signal is obtained. When a pulse width of one PWM signal is equal to or greater than the minimal pulse width, but each pulse width of two PWM signals is less than the minimal pulse width, a sine wave voltage corresponding to one of the two PWM signals less than the minimal pulse width is varied to a threshold voltage to detect two phase currents, and a remaining one phase current is calculated based on the two detected phase currents. After the phase current was detected by varying the threshold voltage, a level difference between an original sine wave voltage and the threshold voltage is set as a compensation voltage, and the sine wave voltage is compensated by the compensation voltage.
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
Control system for multiphase rotary electric machines
A control system controls, based on a comparison between a waved real current to be supplied to a multiphase rotary electric machine and a hysteresis region established by a waved command signal, a switching timing of a switching element of an inverter to which a direct current voltage is applied to thereby match the waved real current with a waved request current. A determining unit determines whether a workload associated with rotation of the portion of the multiphase rotary electric machine is equal to or greater than a corresponding predetermined value. When it is determined that the workload is equal to or greater than the predetermined value, a changing unit changes the waved command signal from being set to the waved request current so as to determine the switching timing of the switching element based on a positional relation between the waved request current and the changed waved command signal.
Owner:DENSO CORP
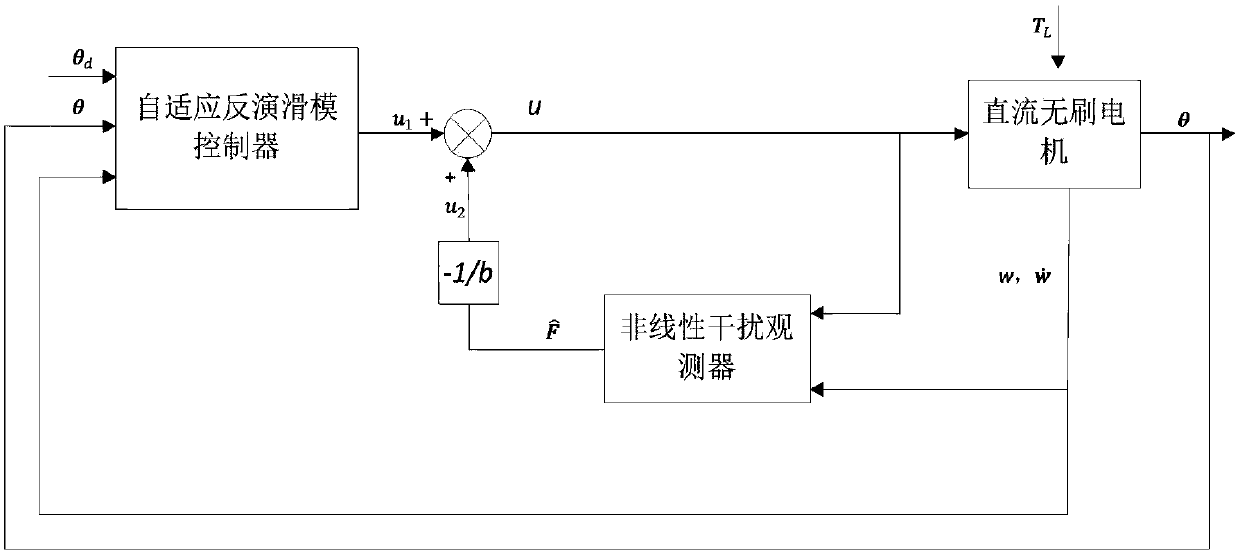
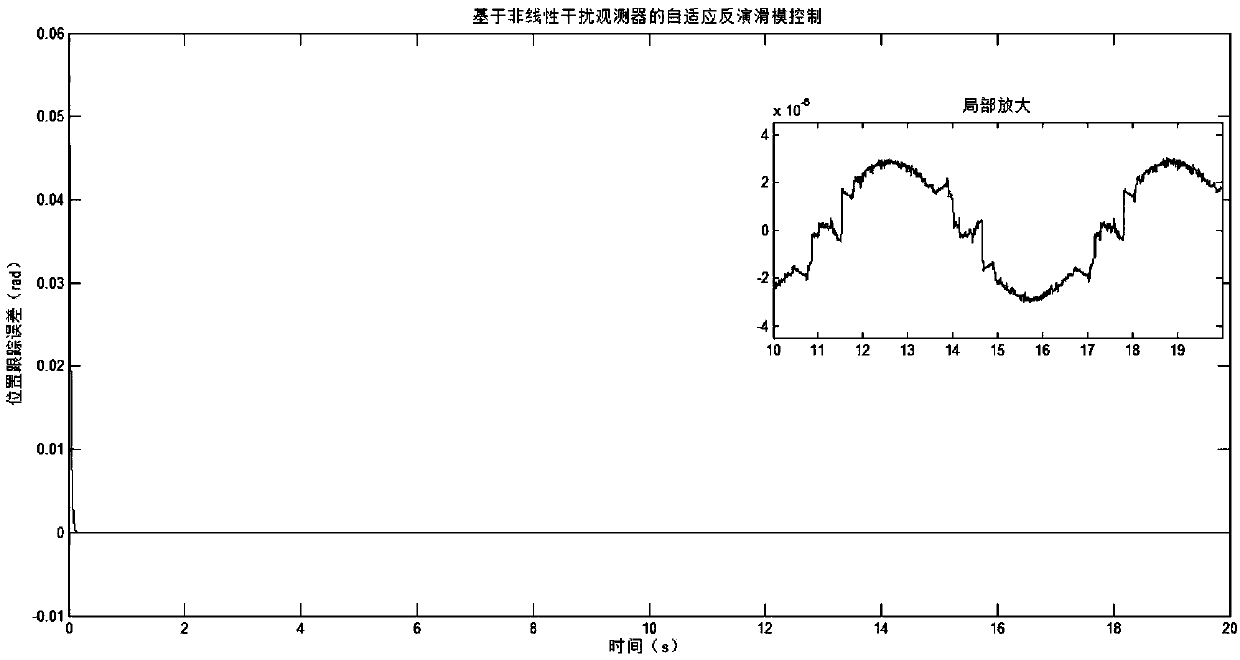
Direct-current brushless motor self-adaptive inversion slip form control method based on non-linear interference observer
ActiveCN108233781AReduce buffeting levelHigh control precisionGeneral control strategiesModelling/simulations for controlBrushless motorsDesign control
The invention discloses a direct-current brushless motor self-adaptive inversion slip form control method based on a non-linear interference observer. The non-linear interference observer is adopted for observing and compensating unmodeled dynamic and external load interference of a direct-current brushless motor. The interference-compensated motor system is characterized in that: a self-adaptiveinversion slip form is adopted for designing a controller, the stable direct-current brushless motor system is ensured. By adopting the direct-current brushless motor self-adaptive inversion slip formcontrol method, the defect that inversion control needs accurate modeling information of a controlled object and disturbance cannot be overcome in inversion sliding-mode control are solved, system robustness is improved; the unmodeled dynamic and the external load interference of the direct-current brushless motor are observed and compensated by using the non-linear interference observer, the vibration level of the inversion slip form control is lowered, and control accuracy is improved; an adaptive law is designed for upper bound of interference observing error, the upper bound of the interference observing error is estimated, the estimation value of the upper bound of the interference observing error is taken as slip form switching gain, so that the stability of the whole direct-currentbrushless motor system is ensured.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
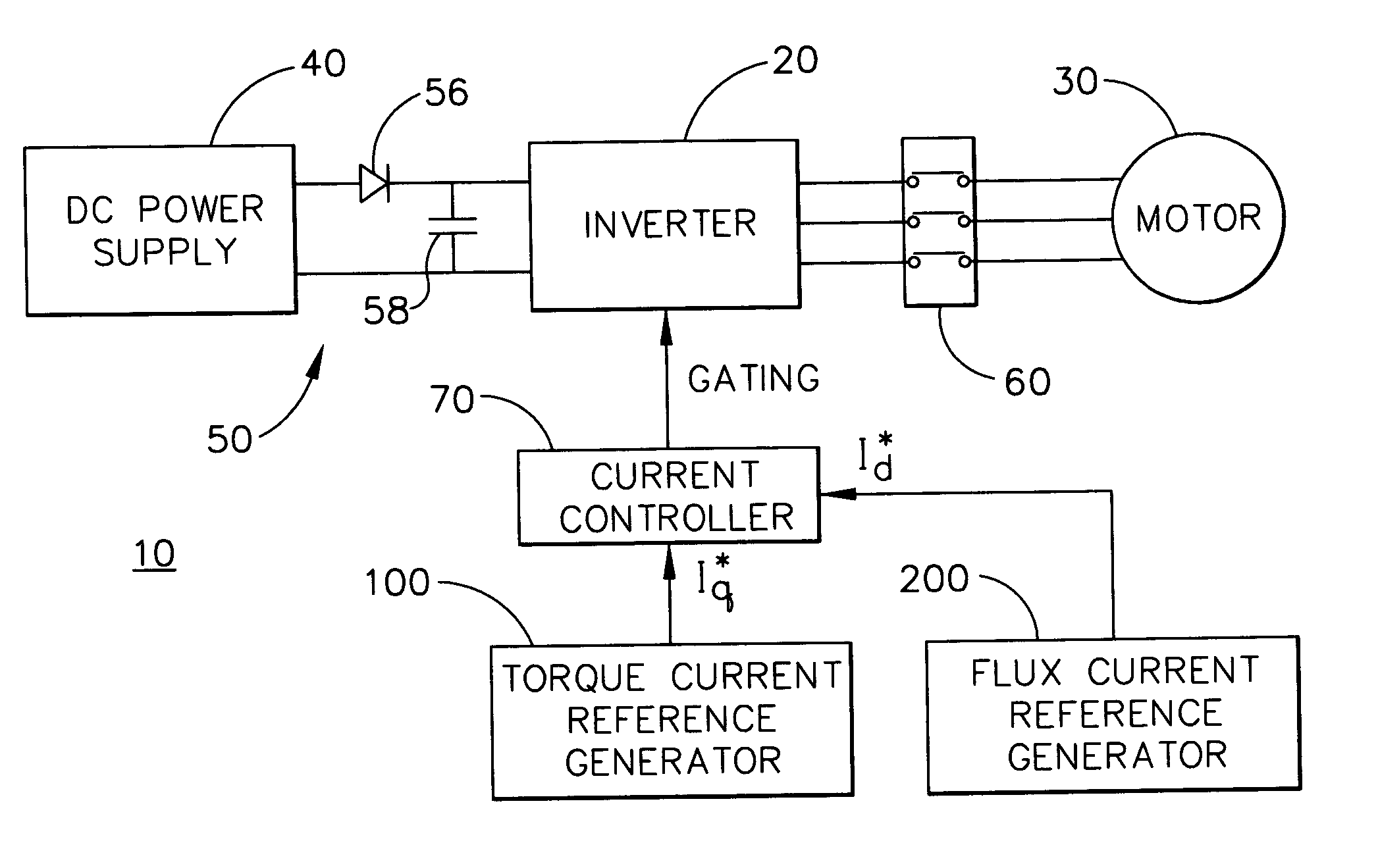
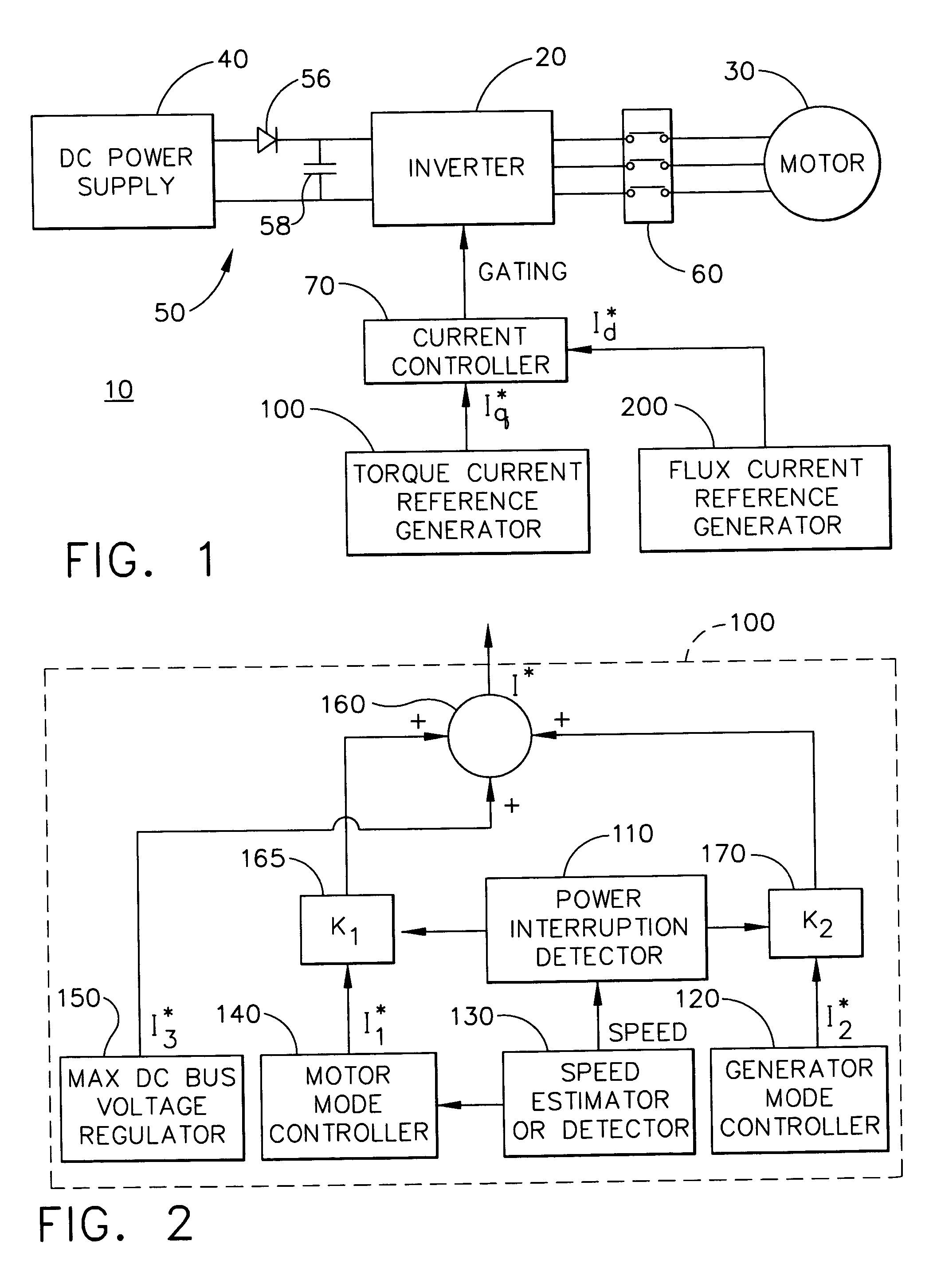
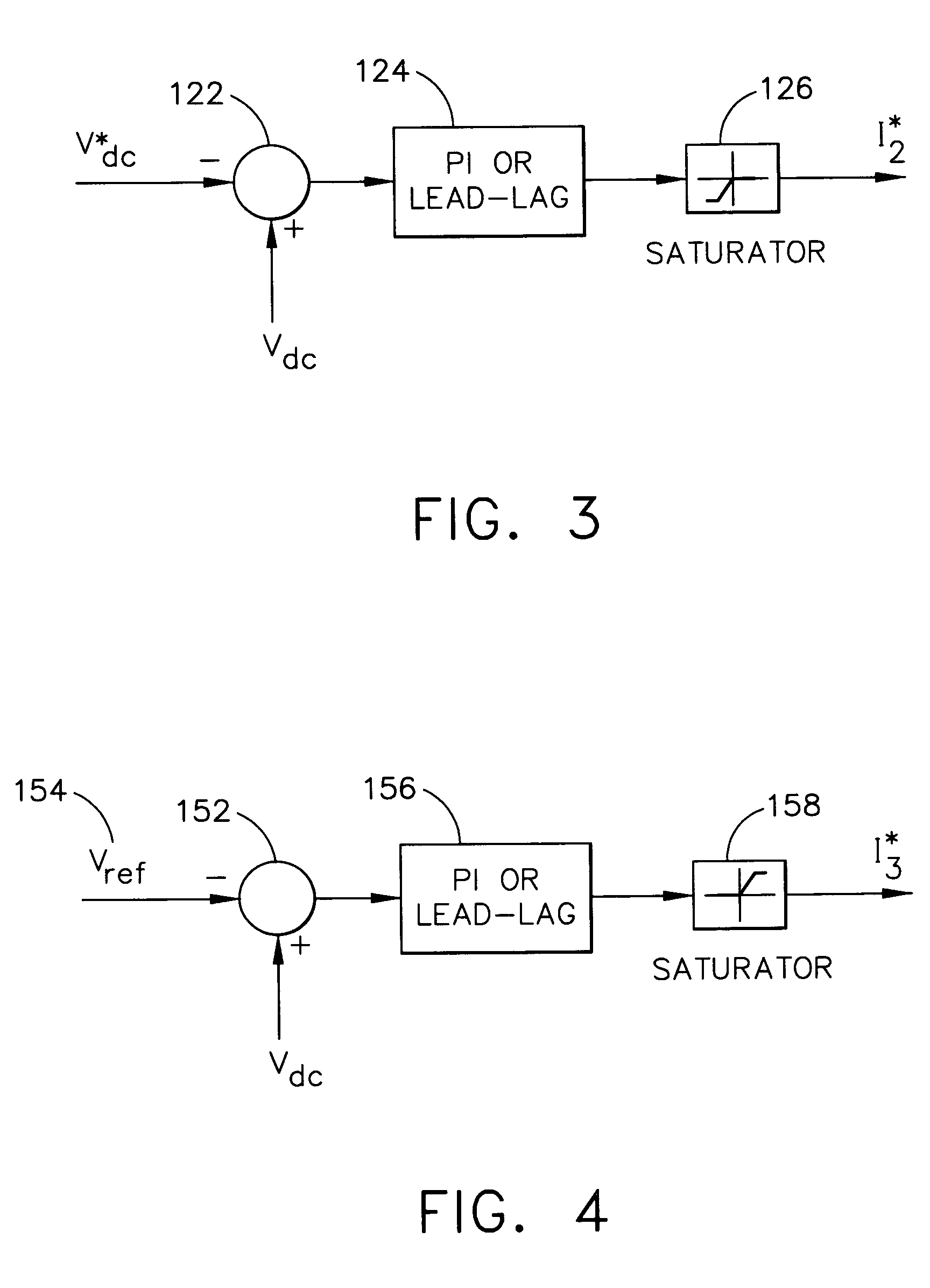
Power converter controlling apparatus and method providing ride through capability during power interruption in a motor drive system
InactiveUS20060061320A1Maximum is limitedMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersMotor speedMotor drive
A method of controlling a power converter (20) of a motor drive system (10)controls the power converter (20) during a first operating mode by applying a current control scheme, which sets power converter commands to control torque current flowing from the power converter (20) to the motor (30) to achieve desired motor speed; and initiates a second operating mode when power supply to the power converter (20) is interrupted. The second operating mode includes controlling negative torque current between the power converter (20) and the motor (30) so that mechanical energy from the motor (30) charges an element (58) on a power supply side of the power converter (20). The first operating mode is resumed when the input power recovers. Torque current between the power converter (20) and the motor (30) is also controlled to limit a maximum transient DC bus voltage.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Motor control device
ActiveUS20170353131A1Ensure correct executionSingle motor speed/torque controlGeneral control strategiesDigital feedbackAnalog feedback
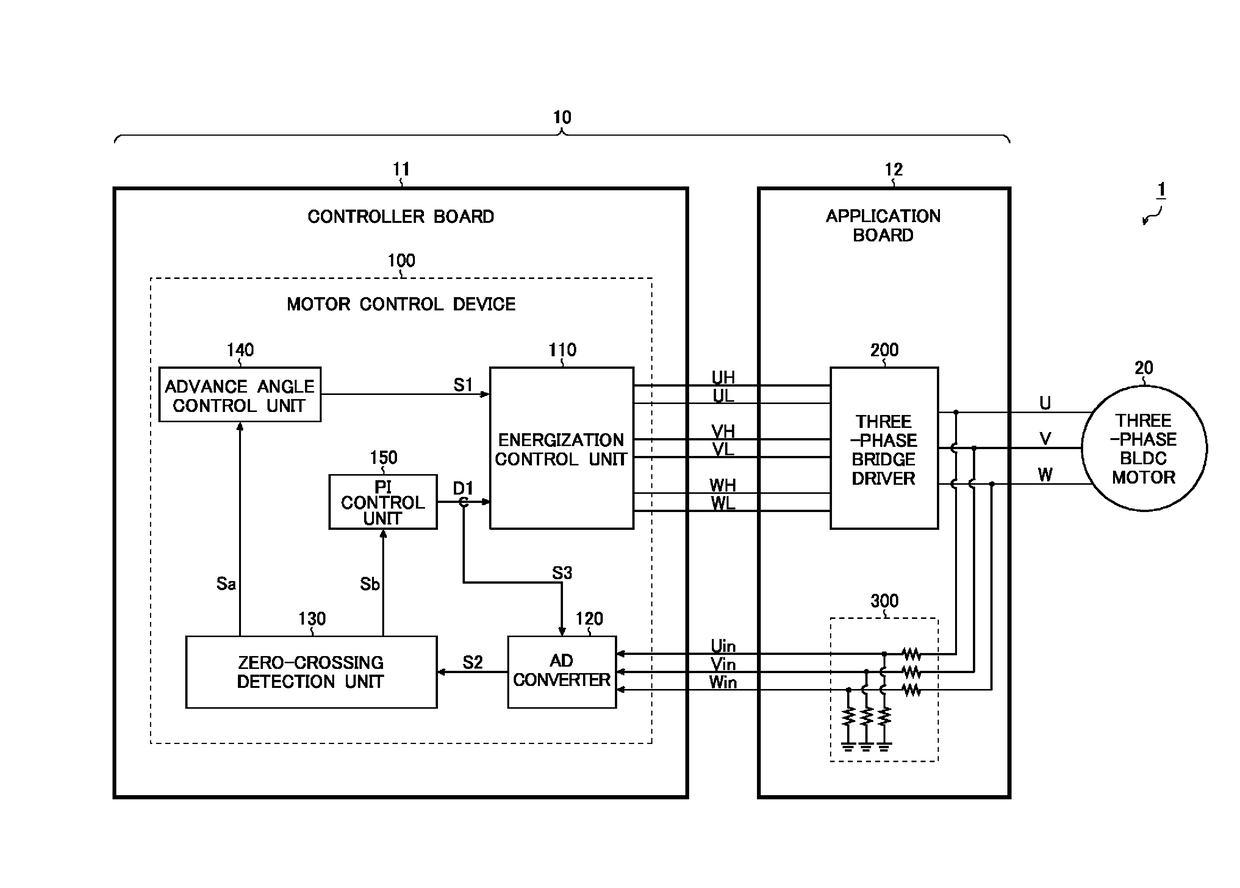
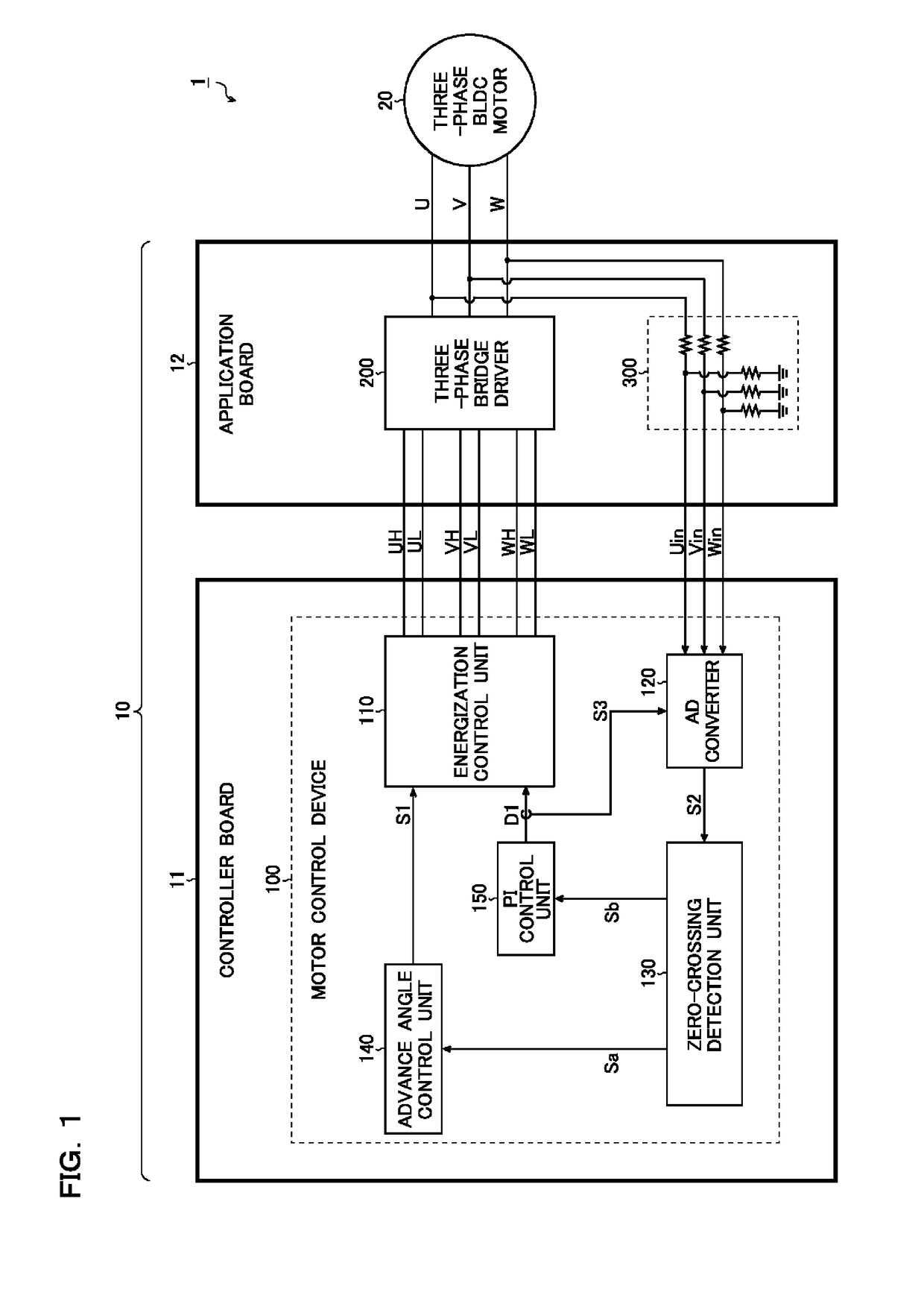
A motor control device includes an energization controller that generates energization control signals of a bridge driver, an ADC that samples and converts analog feedback voltages corresponding to output voltages of the bridge driver into digital feedback signals, and a zero-crossing detector that receives the feedback signals so as to perform zero-crossing detection for determining commutation timing and PWM duty of the energization control signal. Sampling timings of the ADC are switched to one of PWM on period and PWM off period according to the PWM duty. The energization controller PWM drives lower side switches of the bridge driver, and the sampling timings of the ADC are set to the PWM off period. The ADC performs an ADC process of the feedback voltage both in the PWM on period and in the PWM off period, and the zero-crossing detector adopts one of ADC results according to the PWM duty.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Method and system for motor control with delay compensation
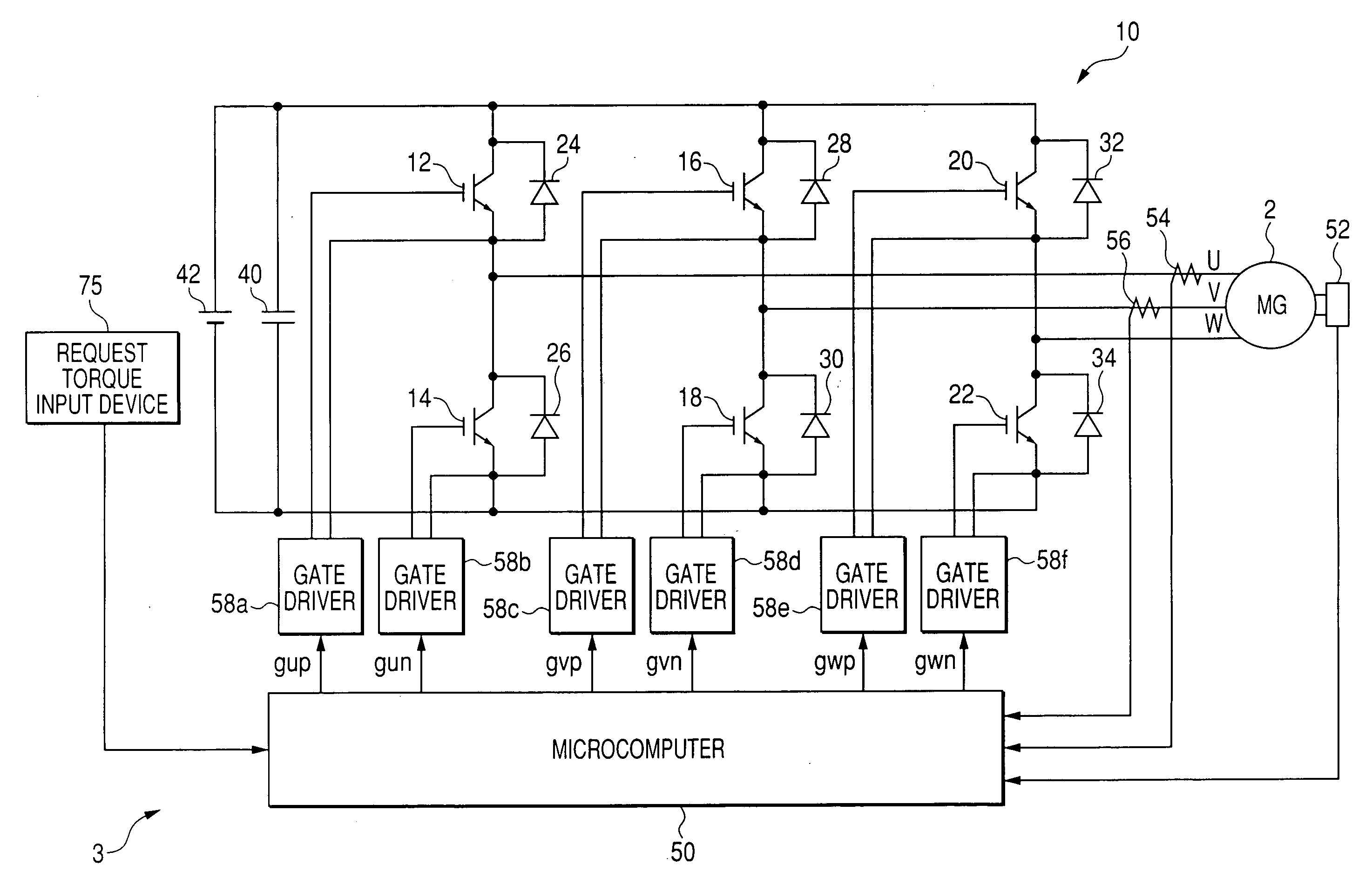
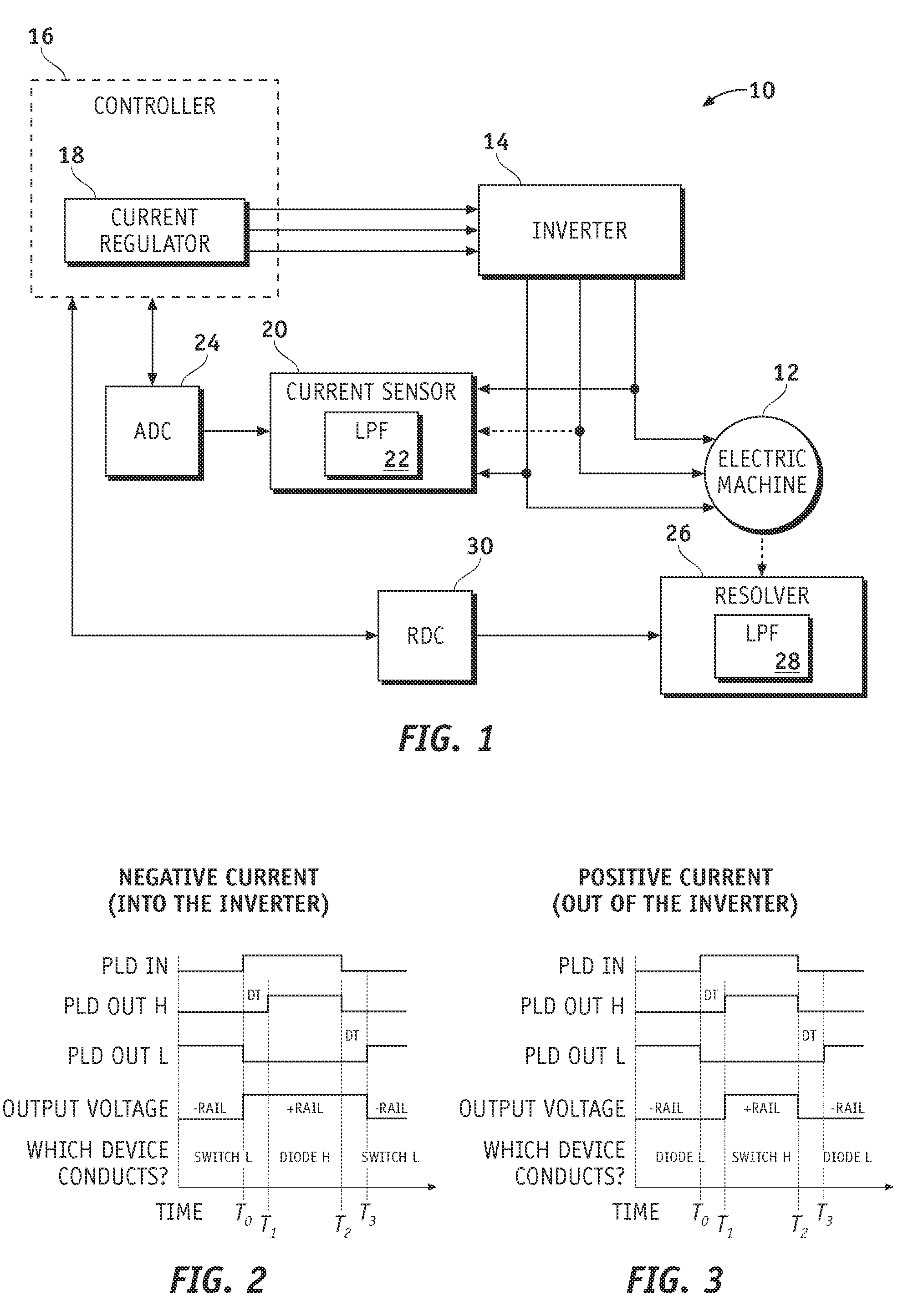
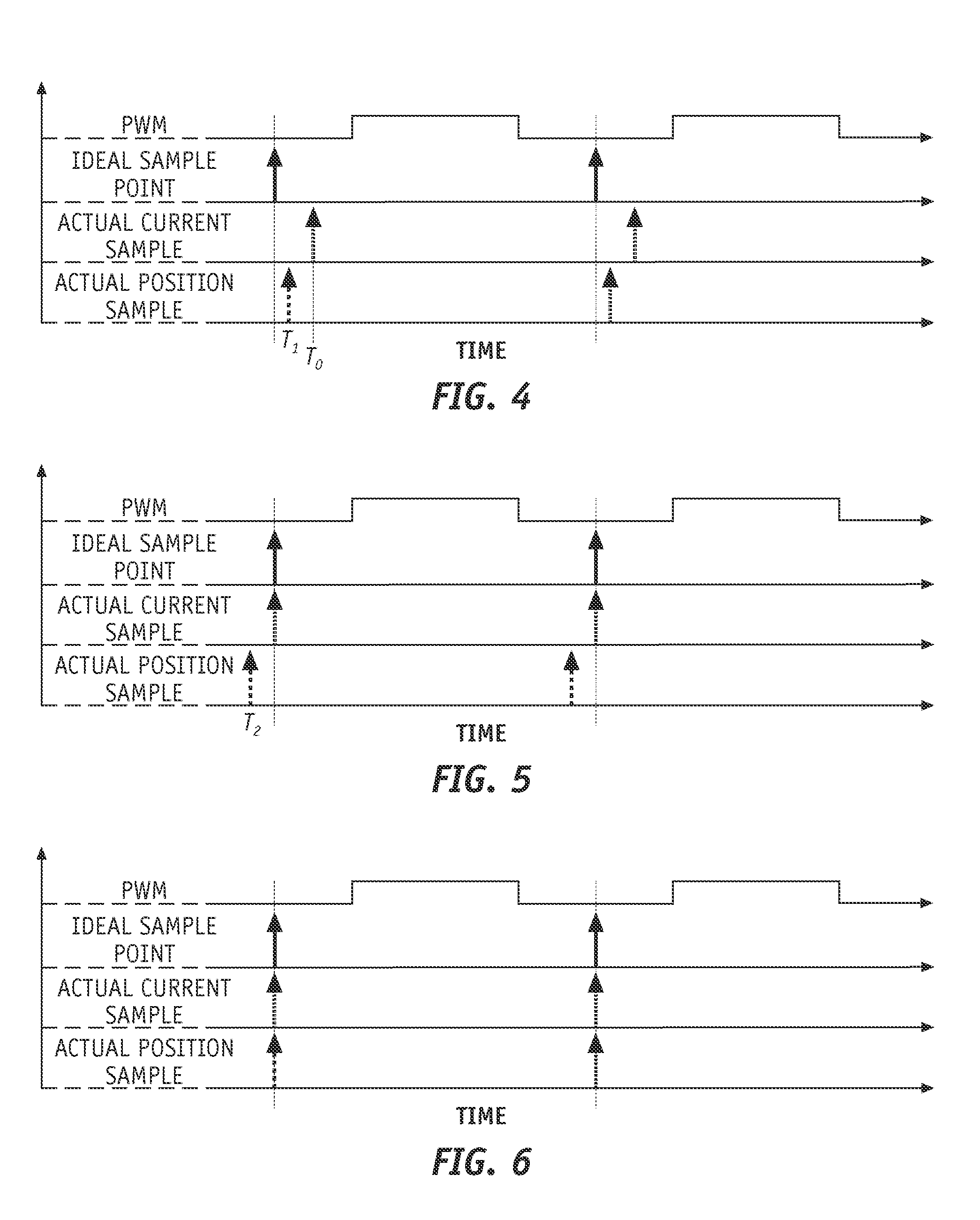
ActiveUS20080272732A1Improve controllabilityImprove stabilityDC motor speed/torque controlGeneral control strategiesElectric machineControl signal
Methods and systems are provided for controlling an electric machine via an inverter while compensating for one or more hardware delays. The method includes receiving a control signal, producing a first sampling signal based on the control signal, and adjusting the sampling signal to compensate for a first delay of the one or more hardware delays. The inverter is operable to produce a voltage signal based on the control signal, and the electric machine is operable to produce a current based on the voltage signal. A sampling of the current is performed based on the first sampling signal.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com