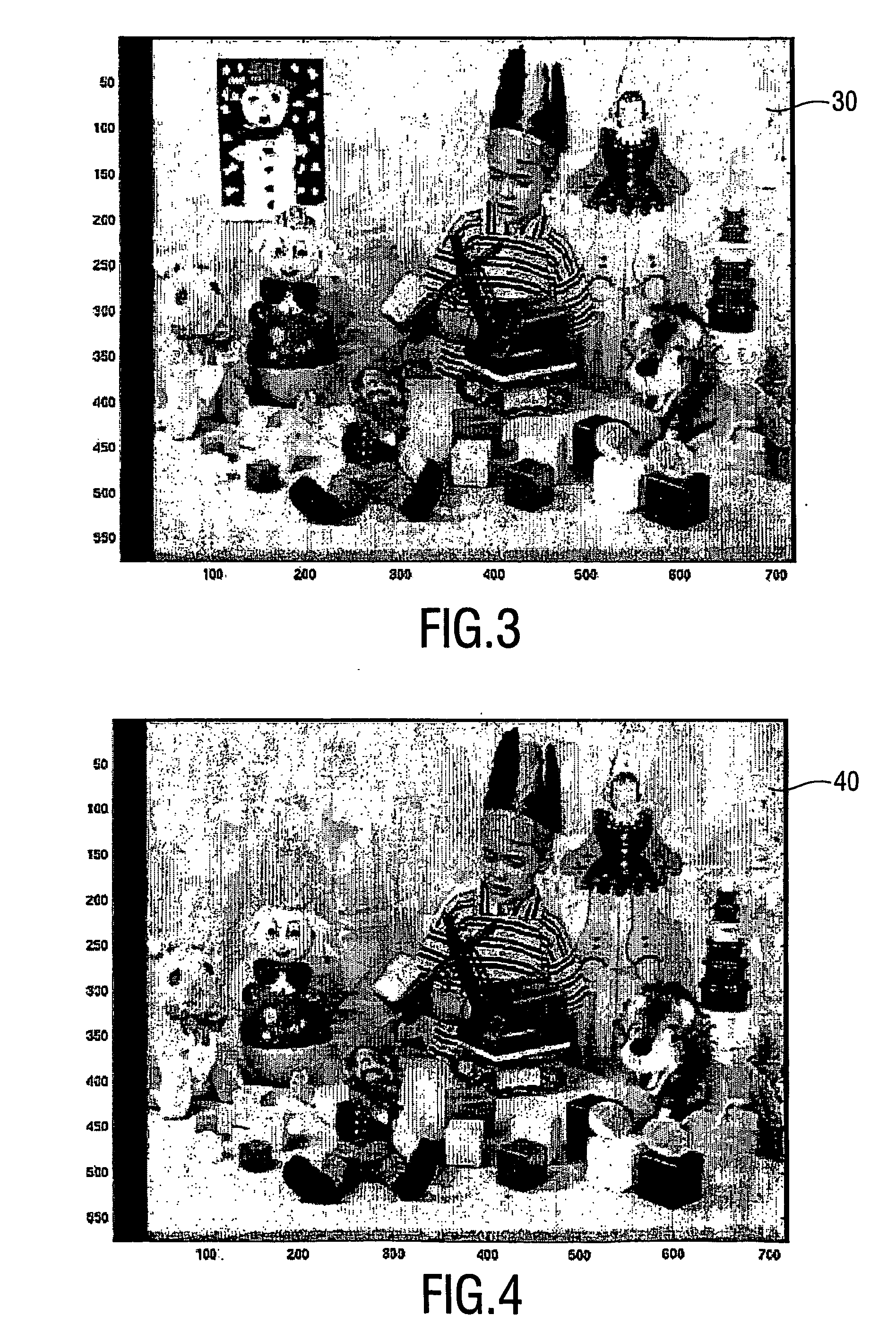
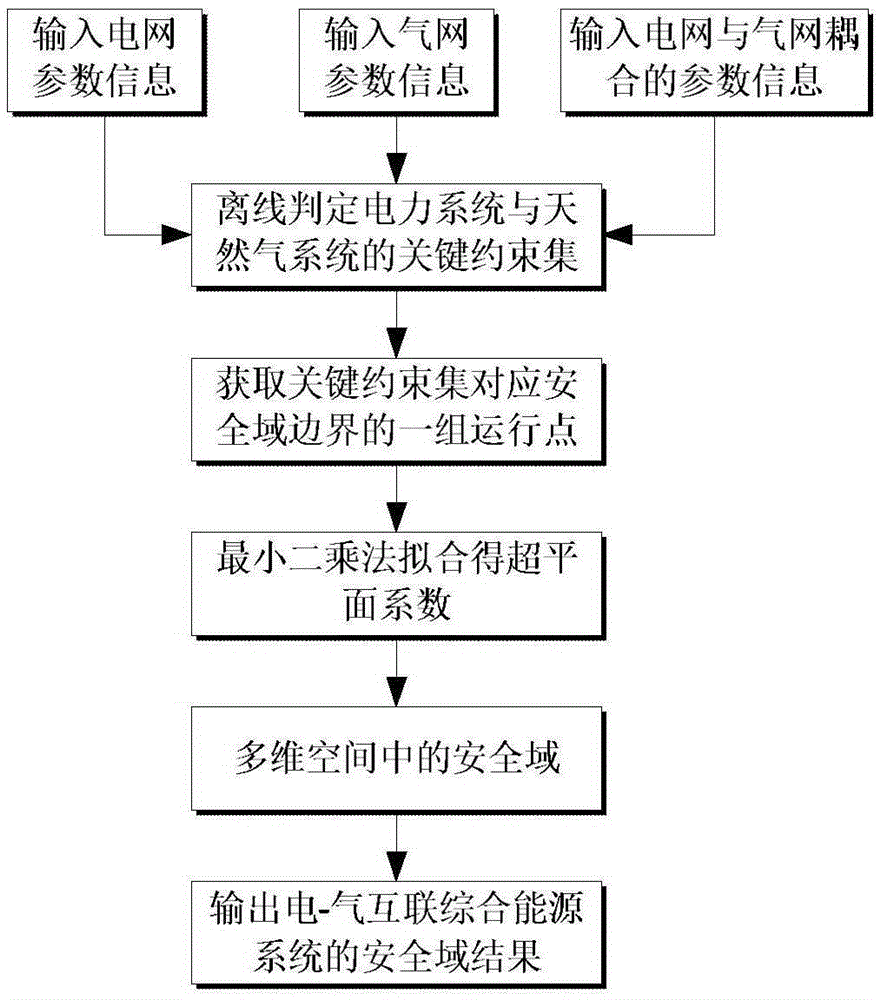
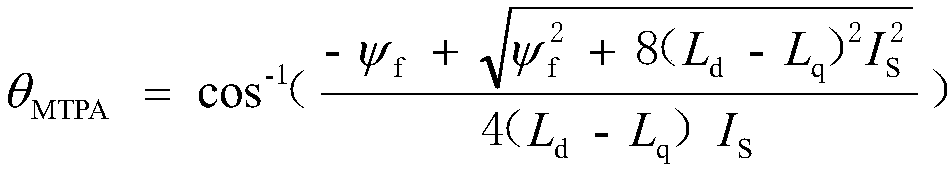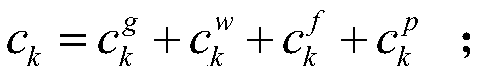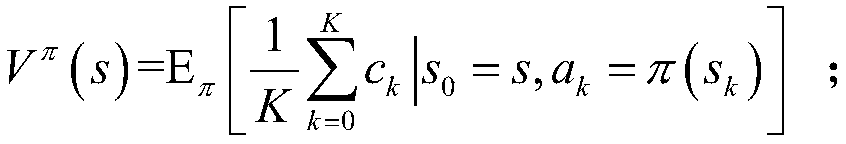Patents
Literature
596 results about "Operation point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
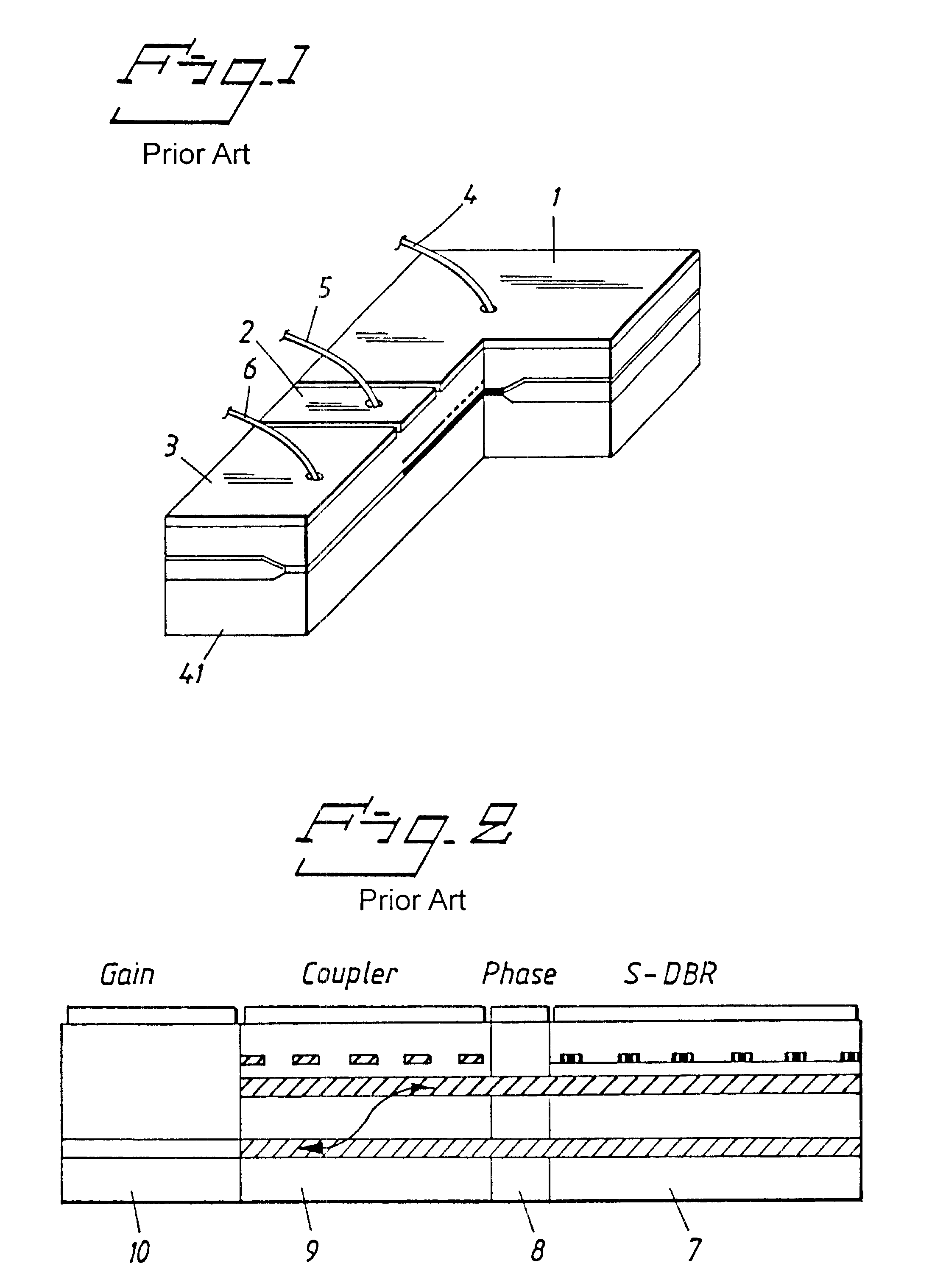
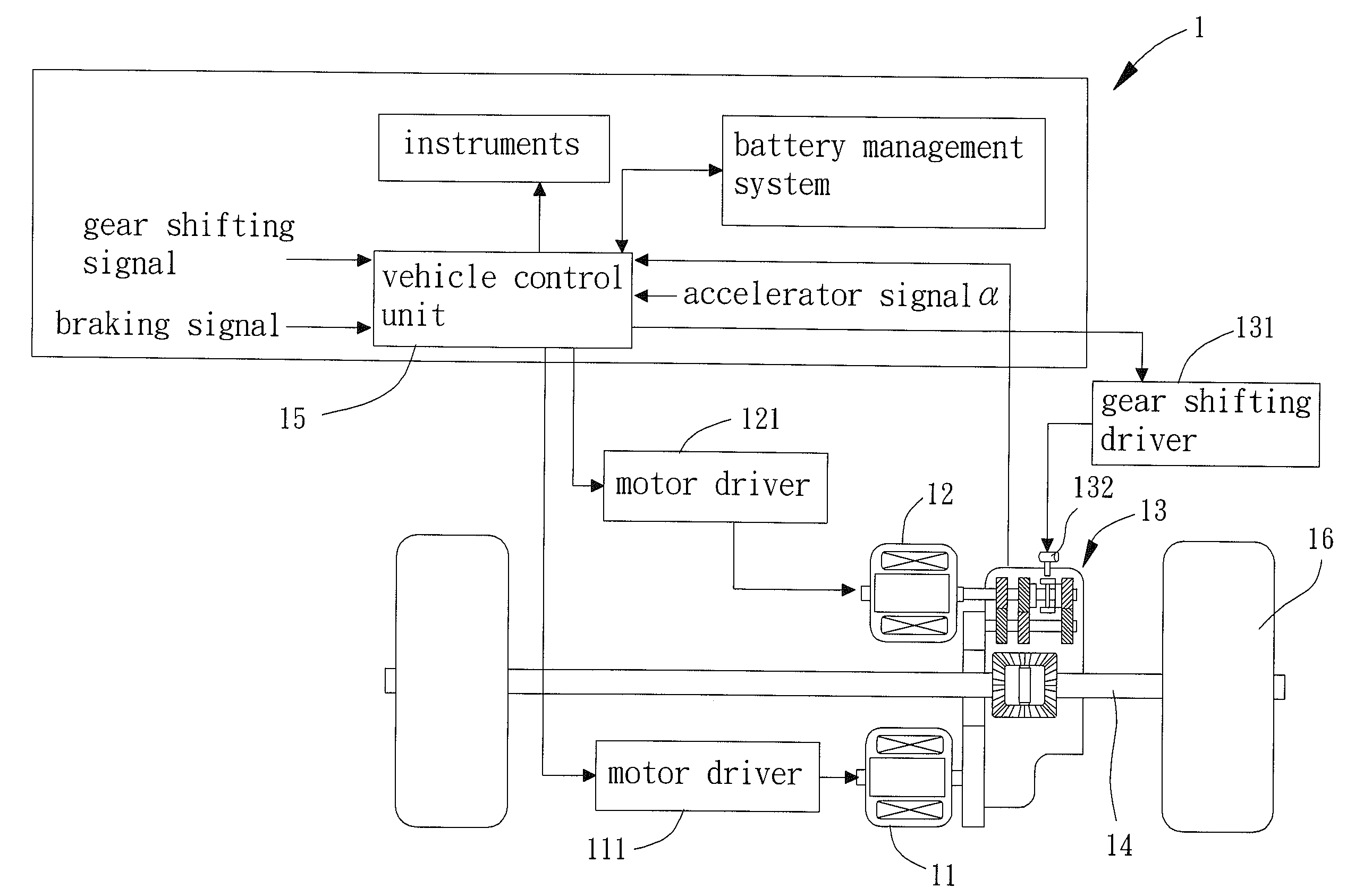
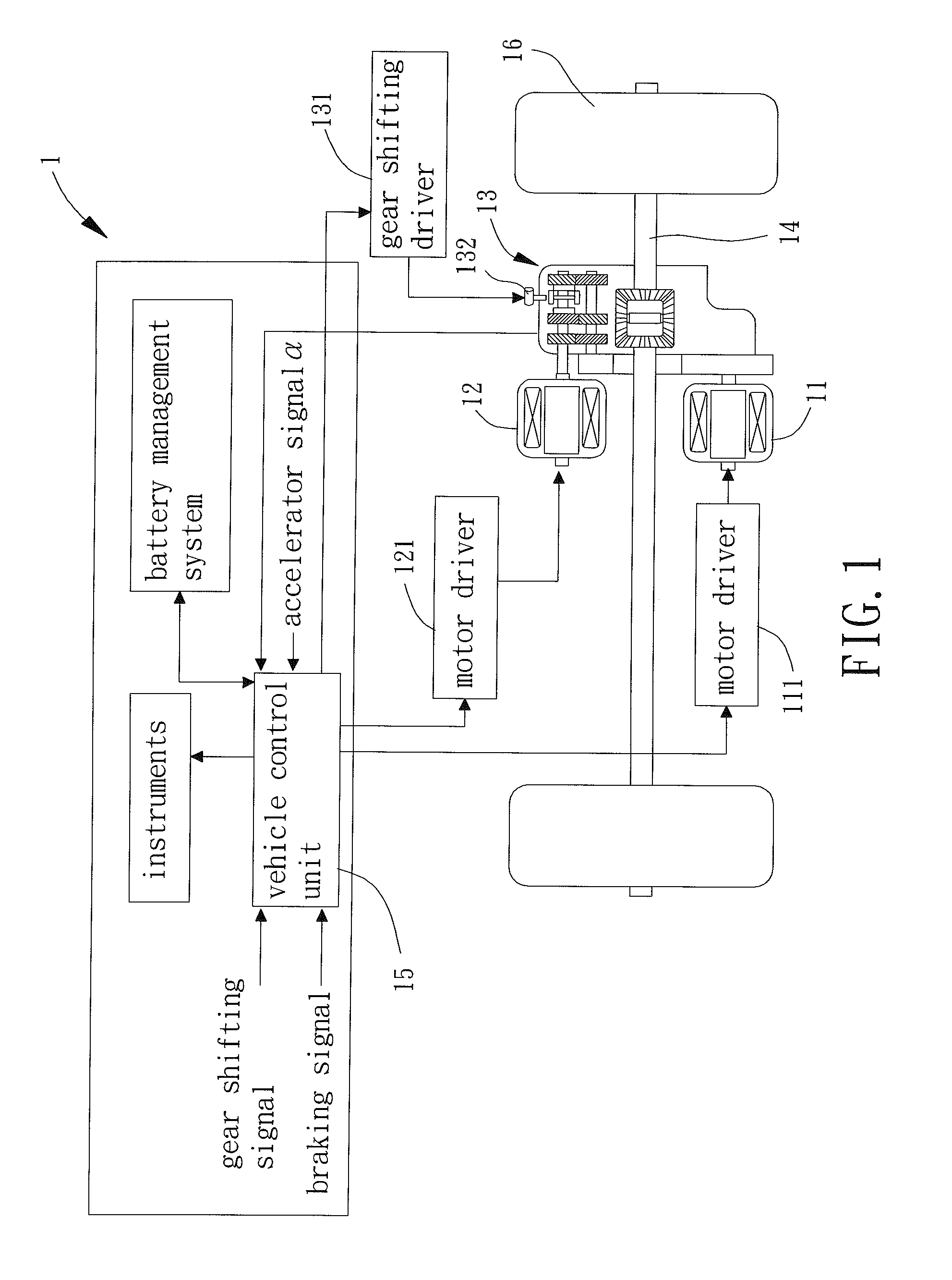
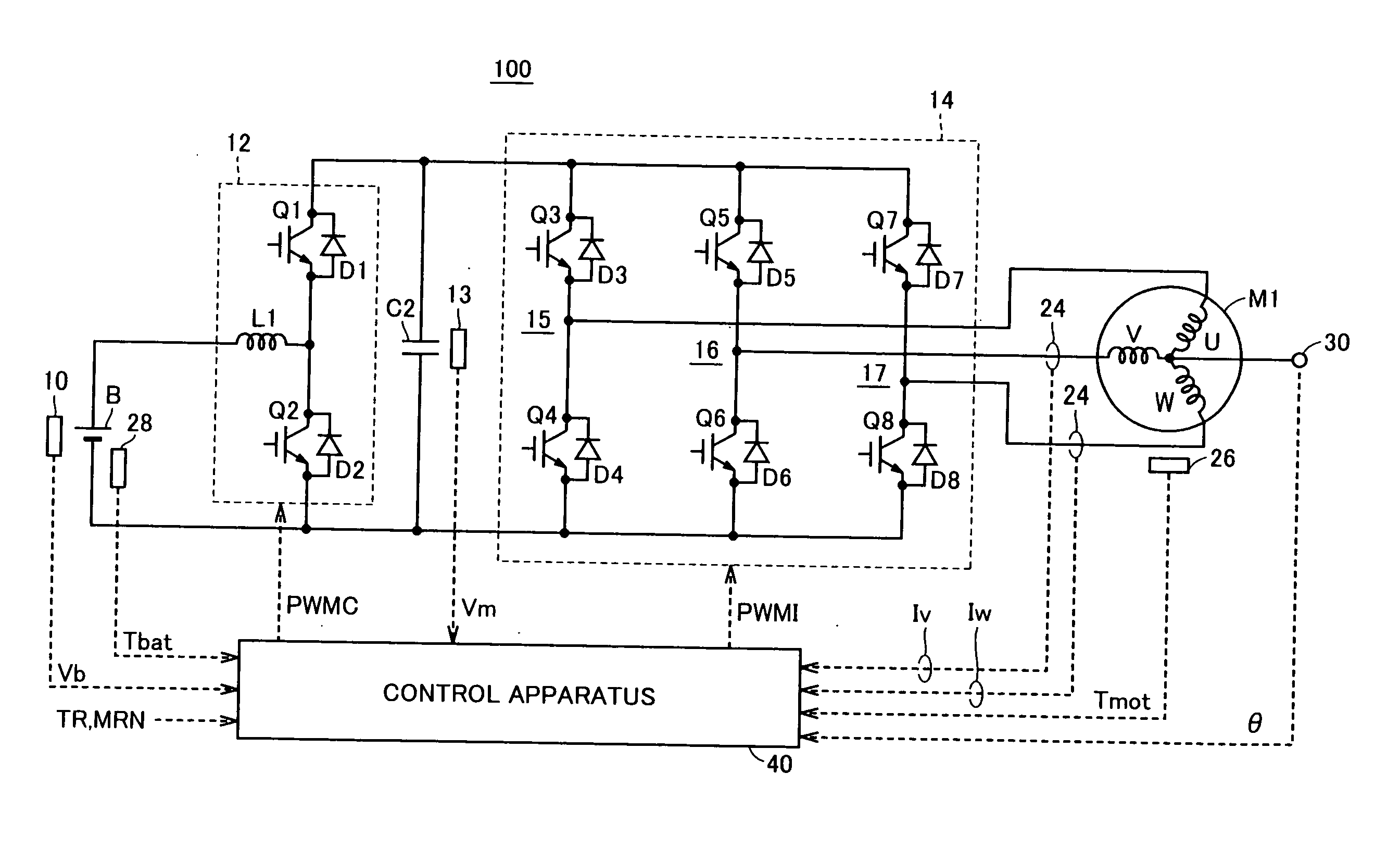
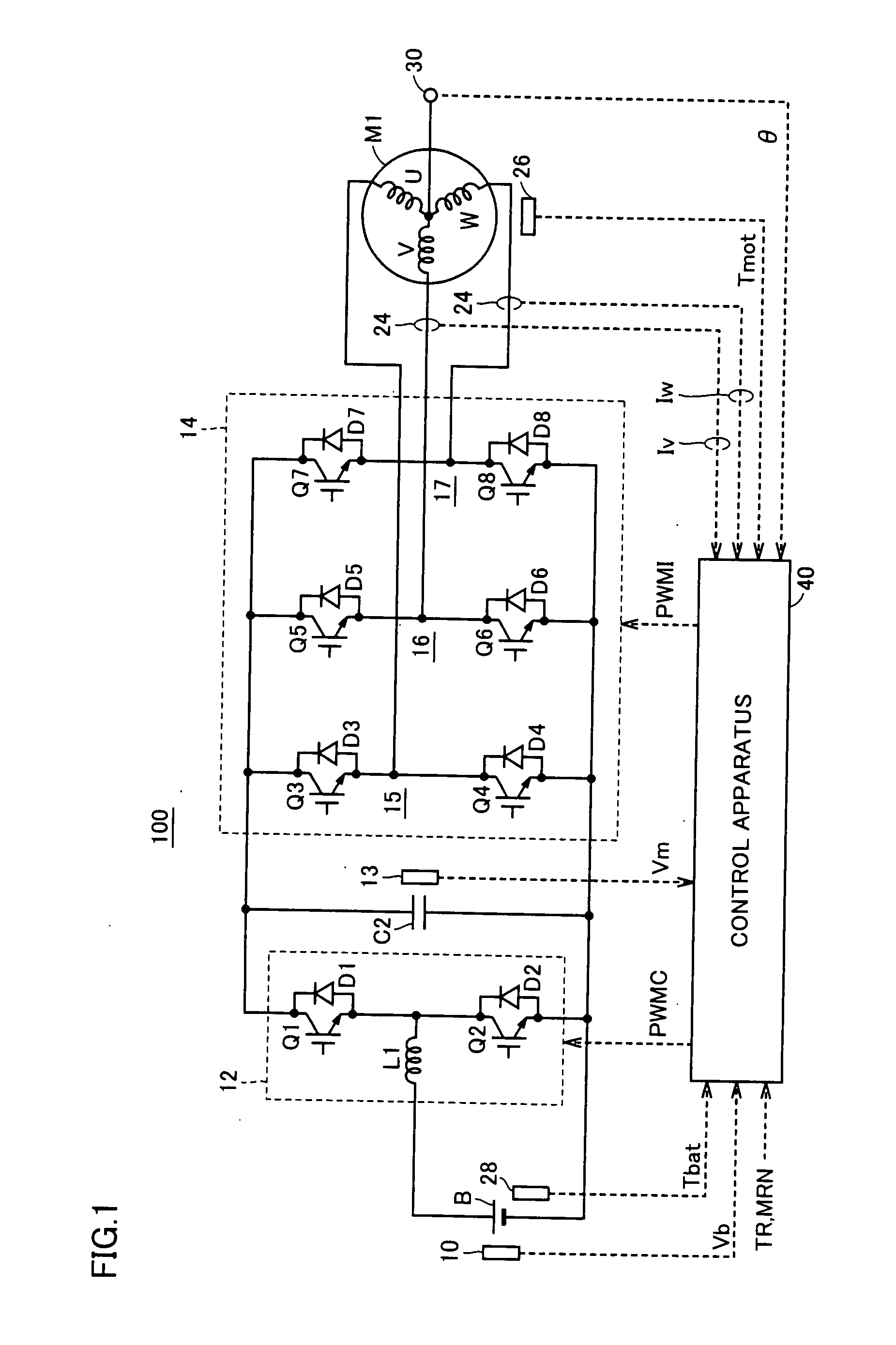
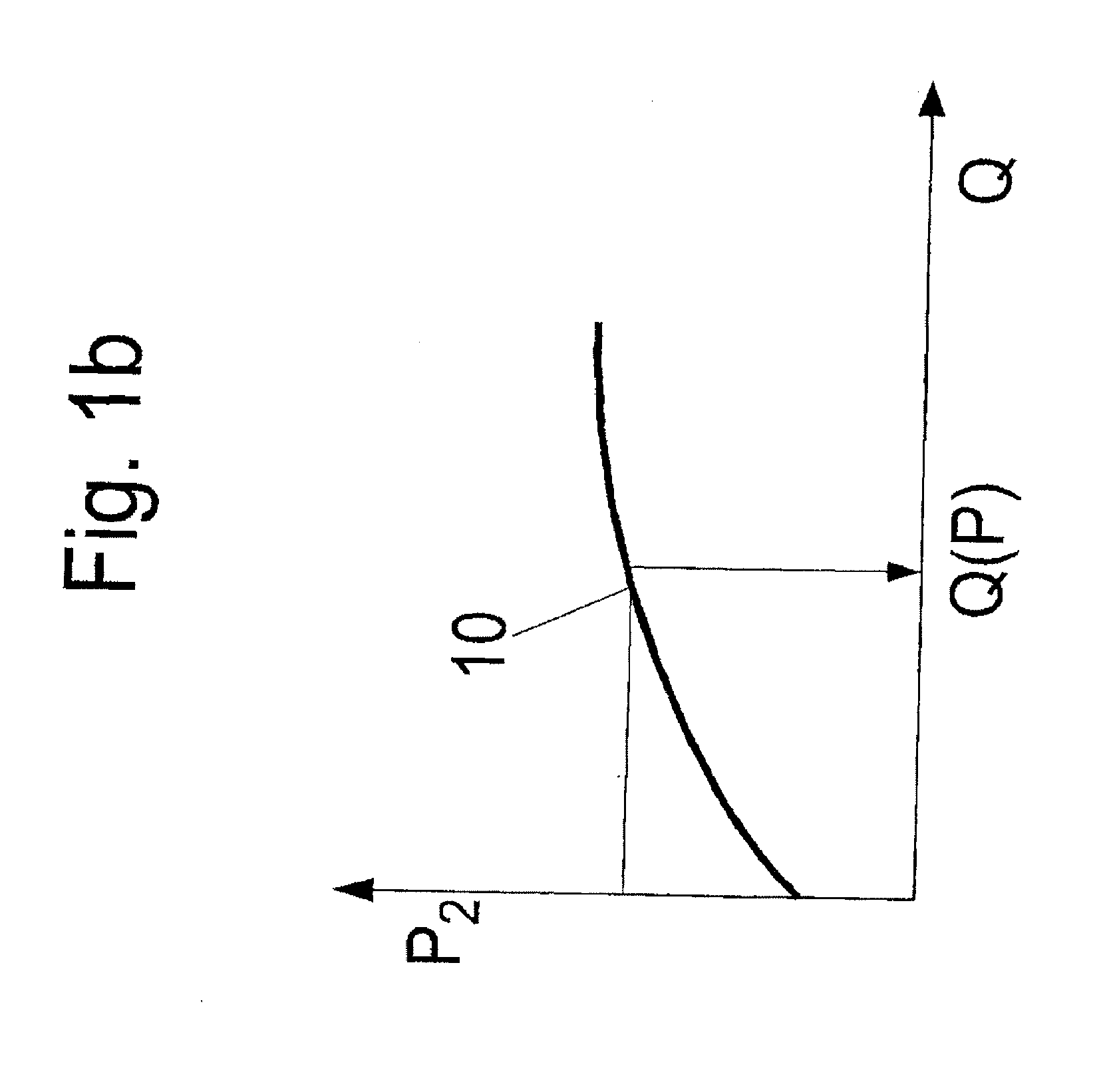
Point of Operation. The point of operation is where work is performed on the material, such as cutting, shaping, boring, or forming of stock. The power transmission apparatus is all components of the mechanical system which transmit energy to the part of the machine performing the work.
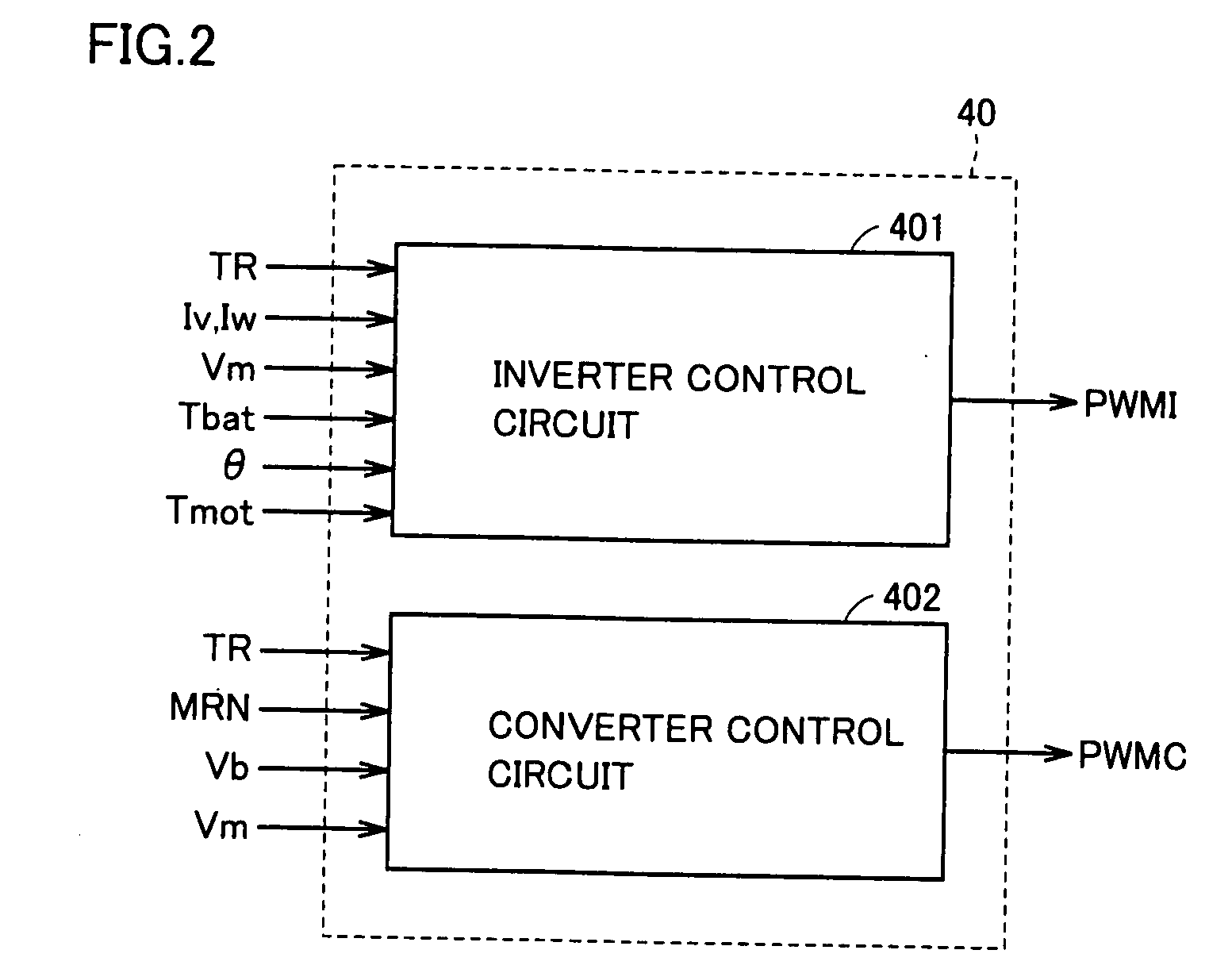
Control device
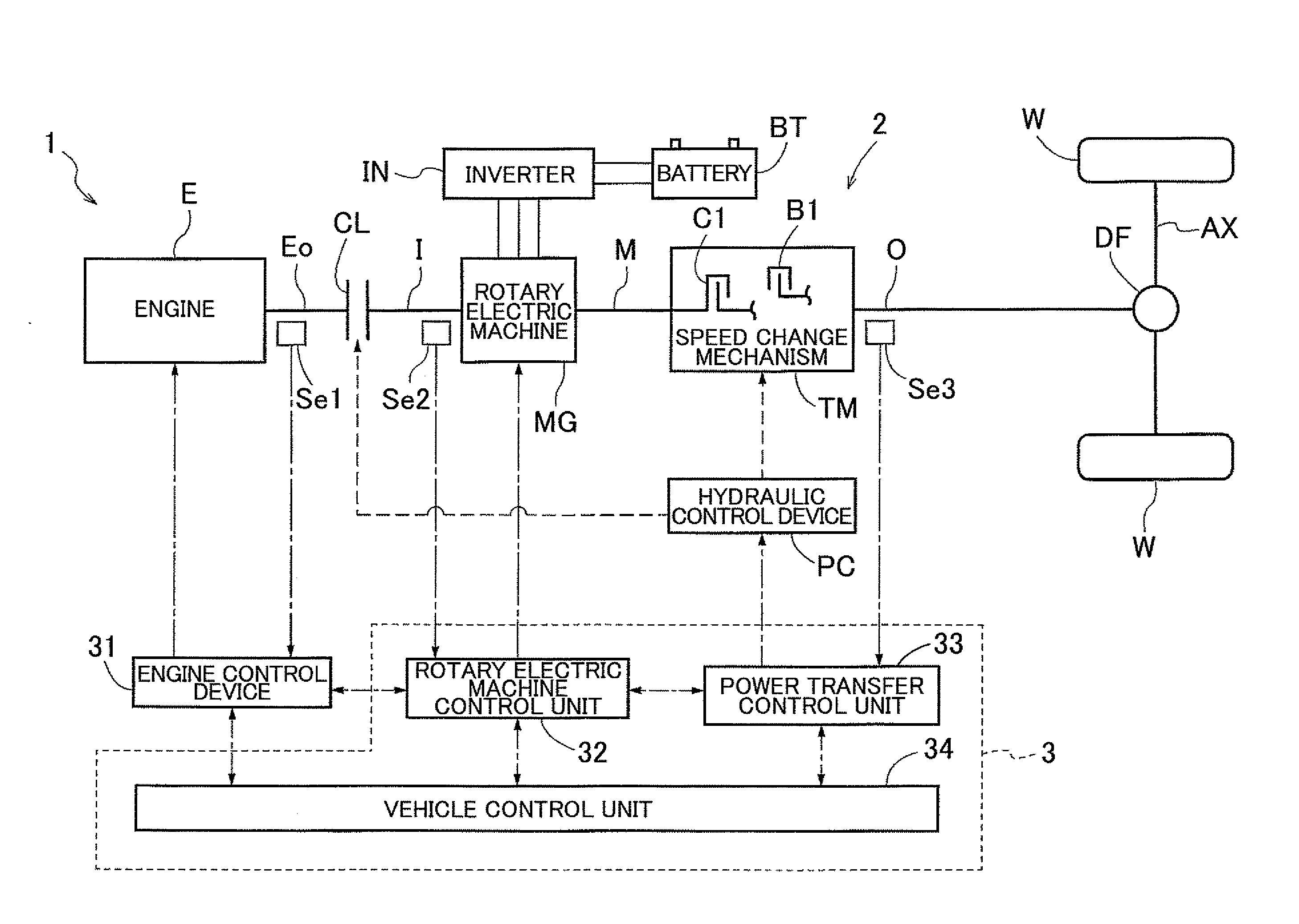
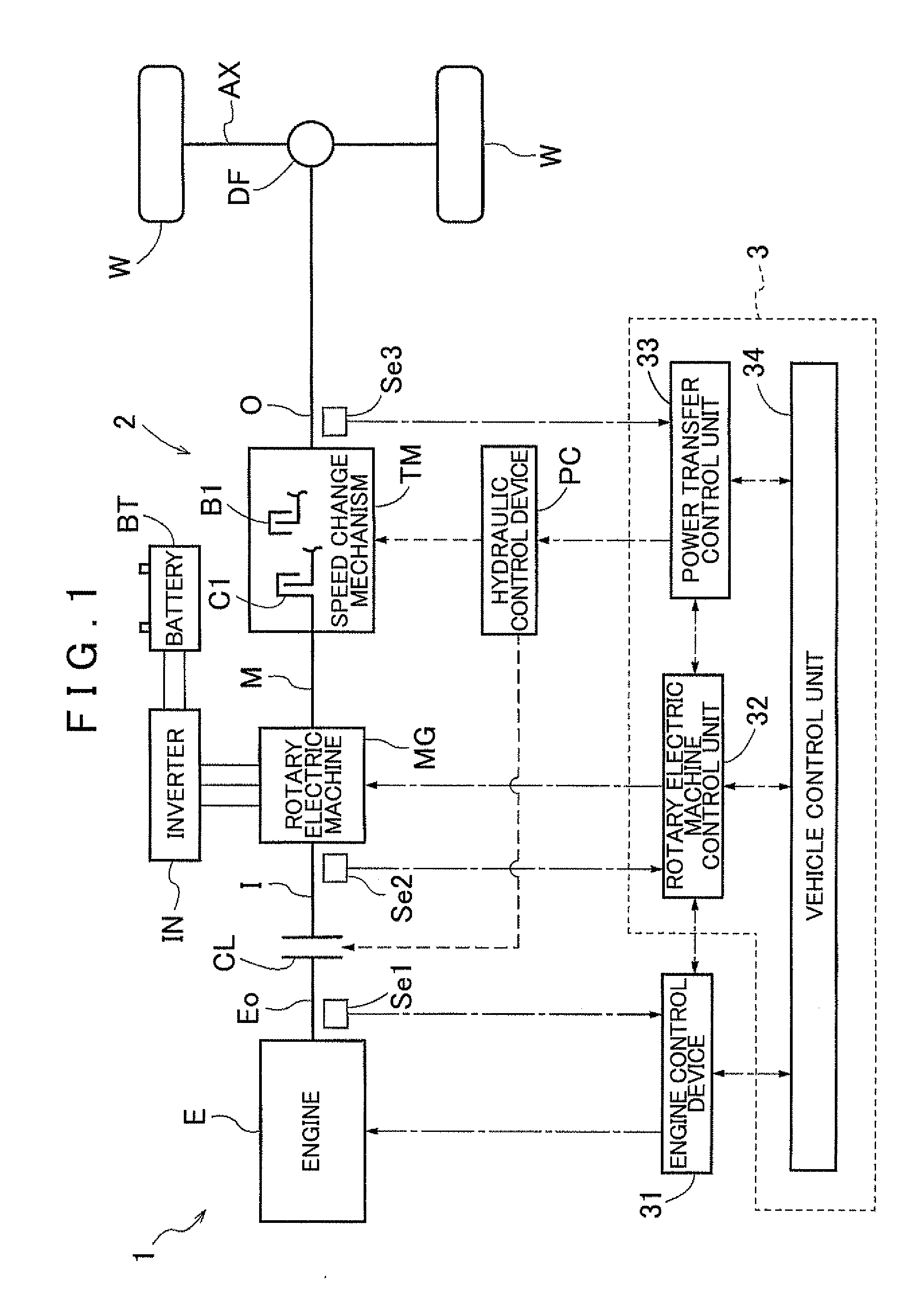
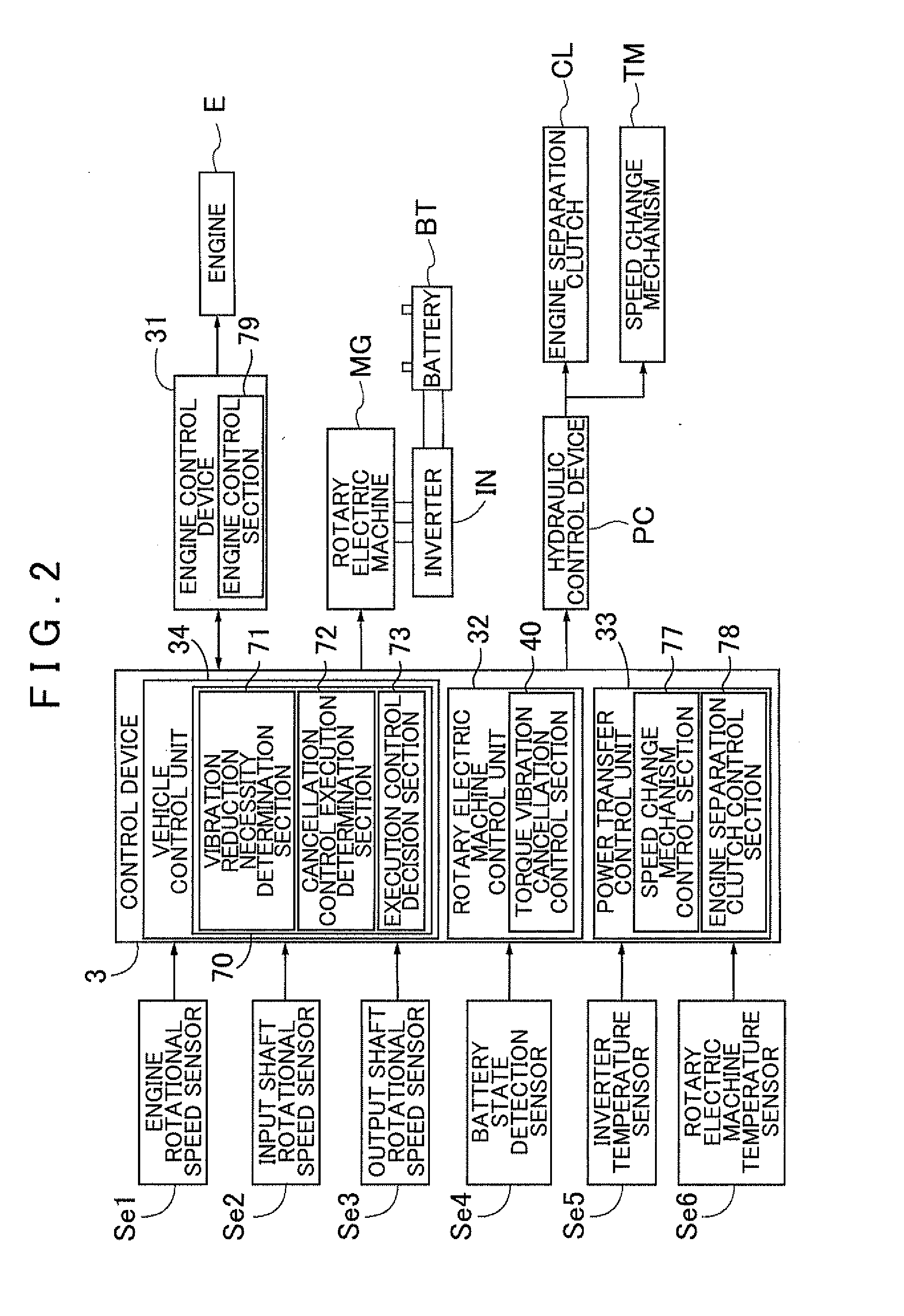
ActiveUS20120078456A1Less discomfortImprove fuel efficiencyHybrid vehiclesElectric devicesElectric machineExternal combustion engine
A control device configured with a vibration reduction necessity determination section that determines whether or not a required drive operation point falls within a reduction necessary range, which is prescribed in advance as a range in which it is necessary to reduce torque vibration transferred from the internal combustion engine to the rotary electric machine. A cancellation control execution determination section that determines whether or not torque vibration cancellation control can be executed in the case where it is determined that the required drive operation point falls within the reduction necessary range. An execution control decision section that decides to execute the torque vibration cancellation control in the case where it is determined that the torque vibration cancellation control can be executed and that decides to execute operation point change control in the case where it is determined that the torque vibration cancellation control cannot be executed.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Discardable lower layer adaptations in scalable video coding
ActiveUS20080089597A1Improve coding efficiencyAvoid spreadingCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureInter layer
A system and method for improving both coding efficiency and decoding accuracy in scalable video coding involving discardable lower layer adaptations, where applications can omit transmission of unused data for inter-layer prediction for all layers below an operation point of receivers. Indicator flags are utilized to avoid transmitting syntax elements that must be set to fixed values. In addition, padding algorithms or additional encoding constraints are applied to the encoding process.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Adaptive Joint Source and Channel Coding Scheme for H.264 Video Multicasting Over Wireless Networks
InactiveUS20100226262A1Improve system performanceImprove performancePulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionTopology informationJoint source and channel coding
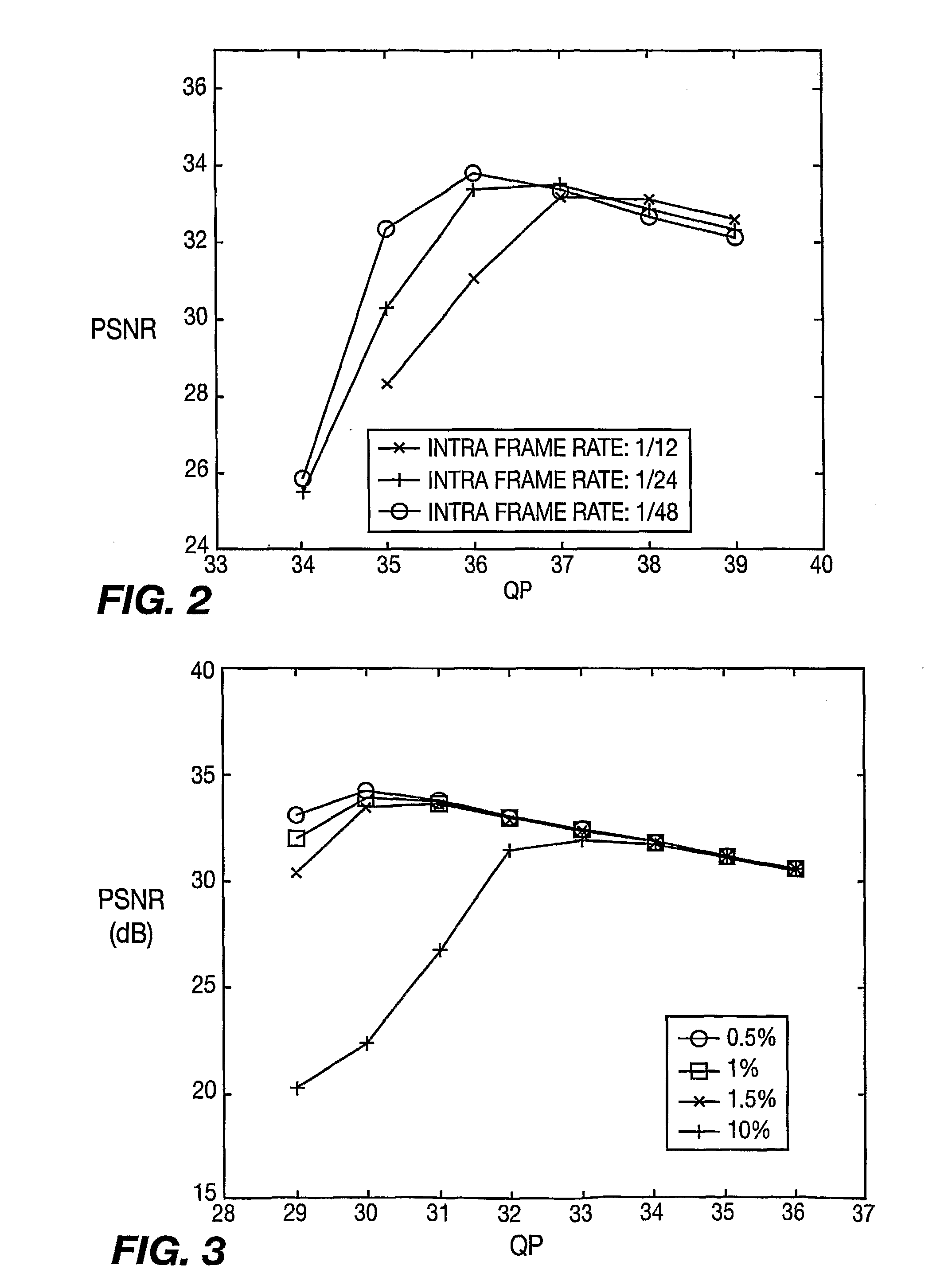
A method and apparatus for estimating packet loss rate are described including calculating a real packet loss rate in a time slot at the end of the time slot, estimating average packet loss rate for a subsequent time slot, estimating variance of packet loss rate for the subsequent time slot and estimating the packet loss rate for the subsequent time slot. A method and apparatus and also described for dynamically allocating available bandwidth for video multicast including selecting an intra-frame rate, determining a packet loss rate threshold, receiving user topology information, receiving channel conditions for each user, determining an optimal operation point for encoding and transmitting video frames in a subsequent time slot, adapting dynamically quantization parameters and a forward error correction code rate, encoding the video frames using the quantization parameters and applying forward error correction code with the forward error correction code rate to data packets of the video frames to generate forward error correction packets.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Control apparatus of hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20050103544A1Improve fuel economyReturn quicklyHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsBattery chargeElectrical battery
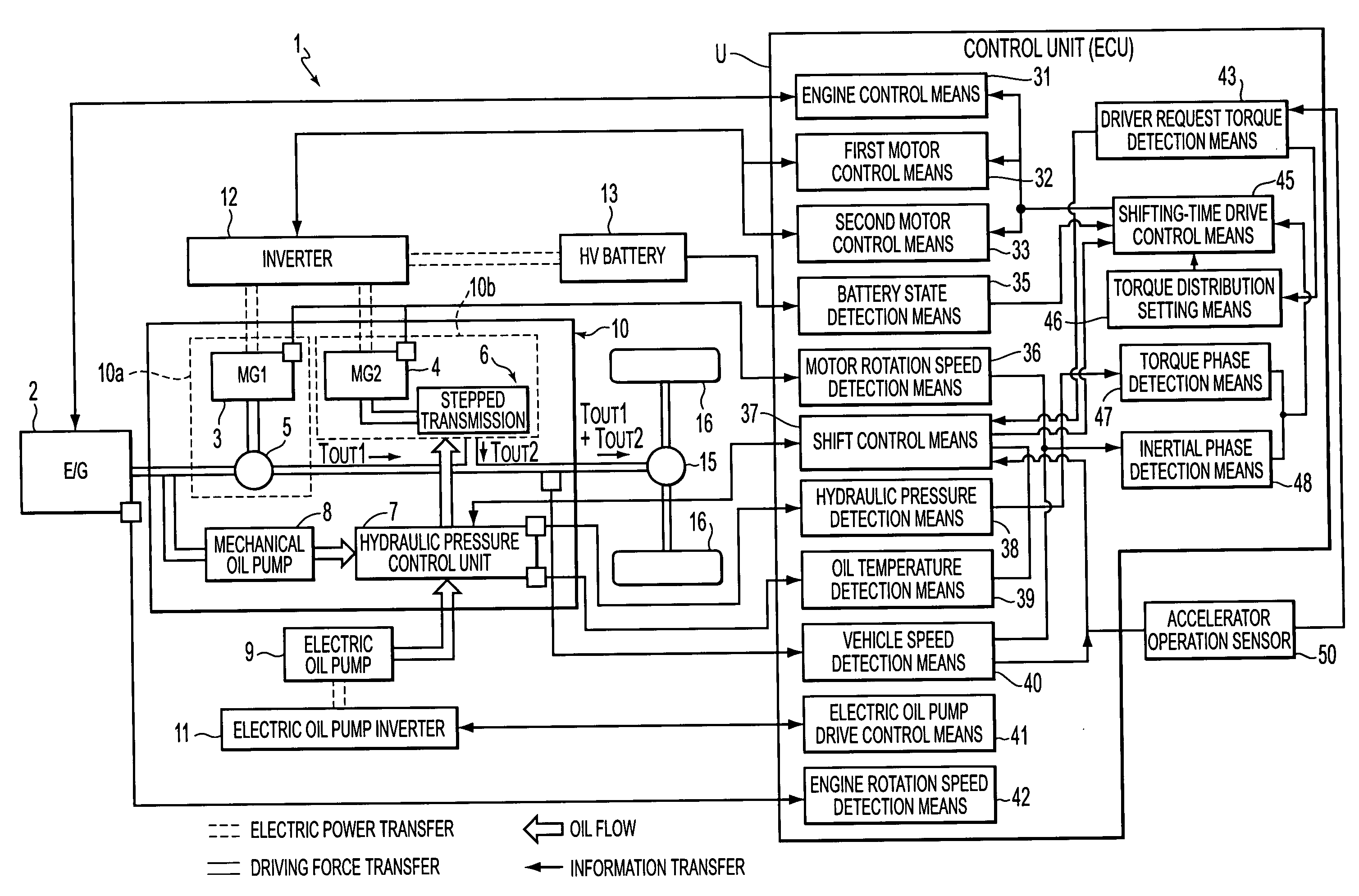
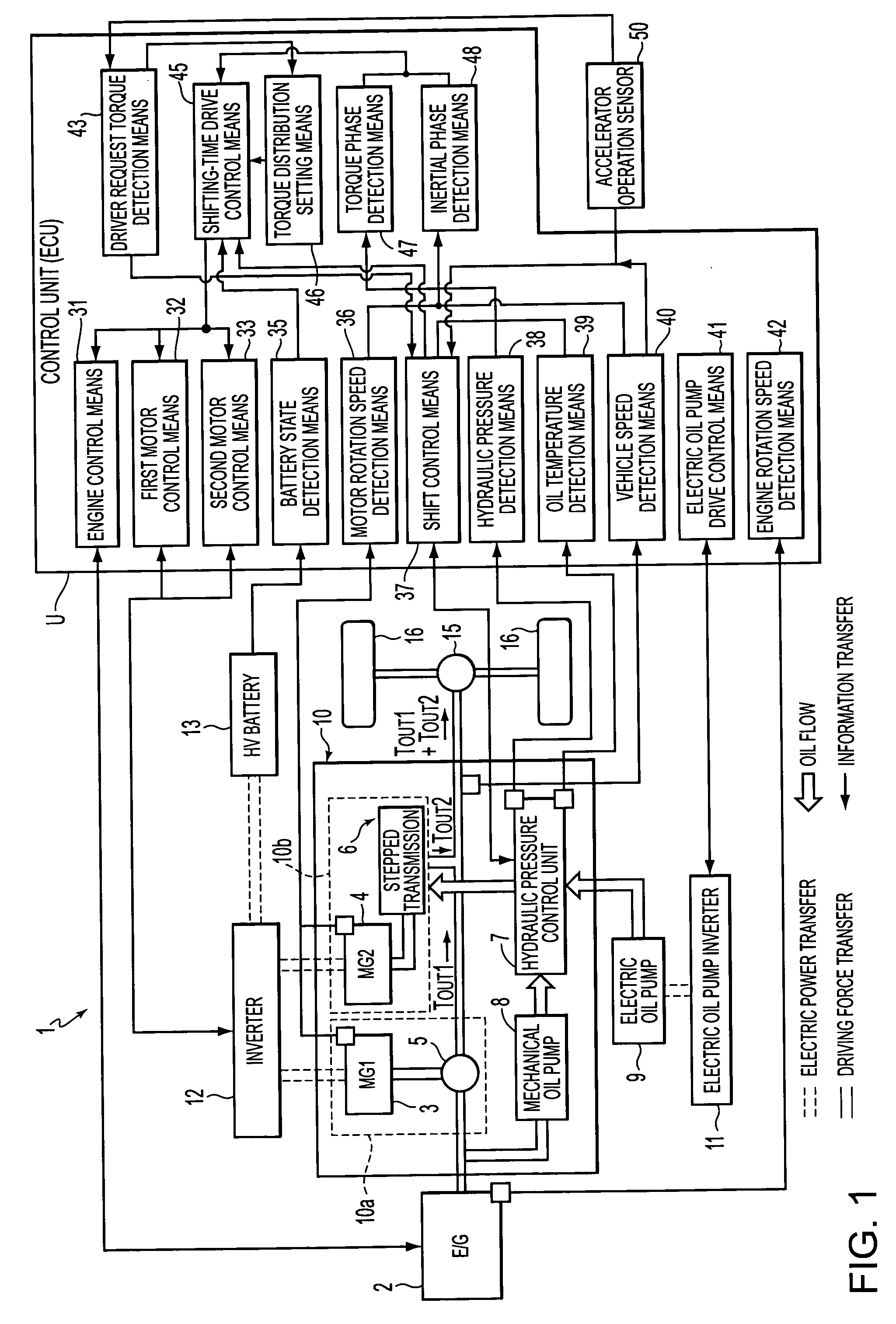
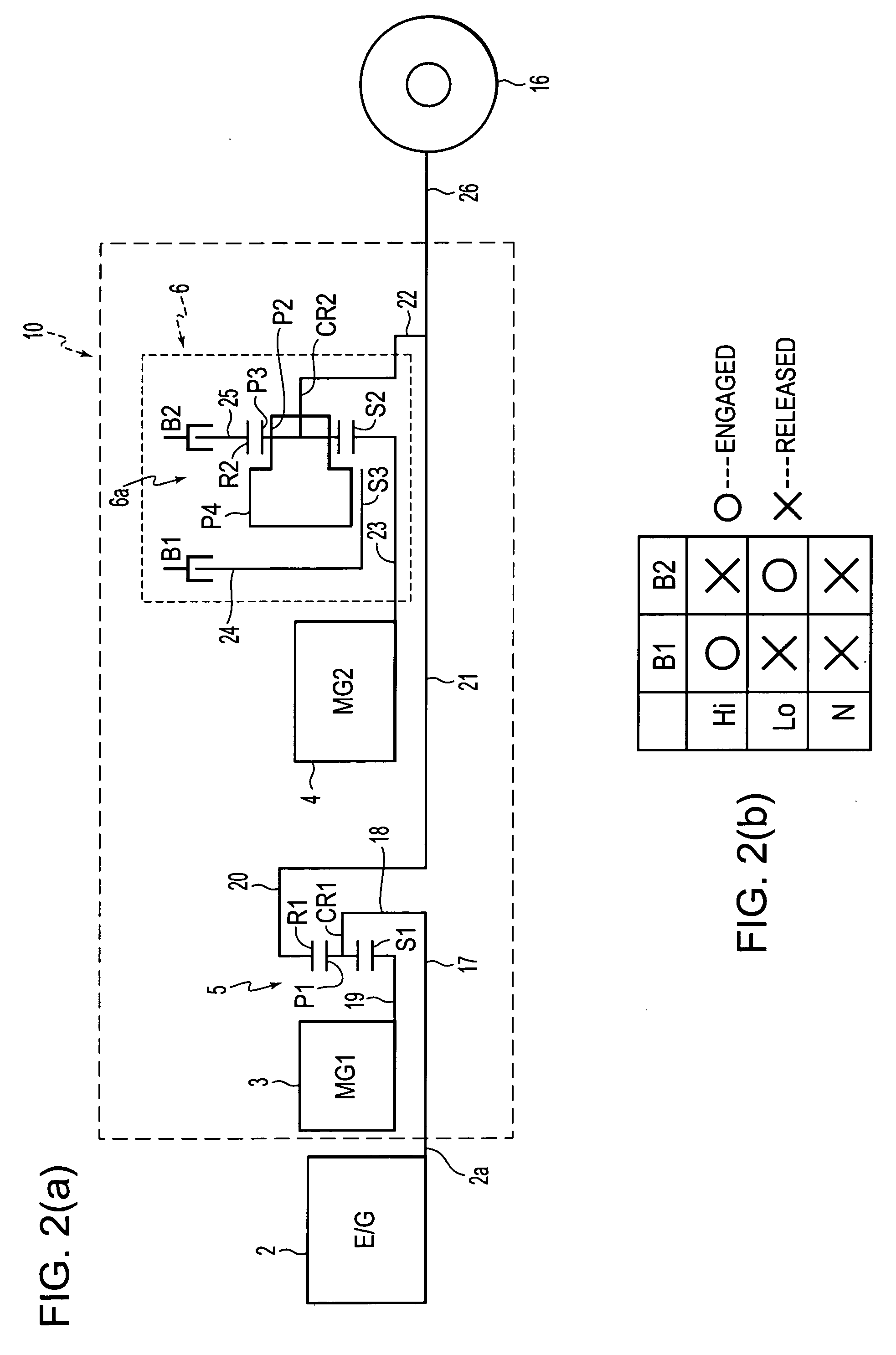
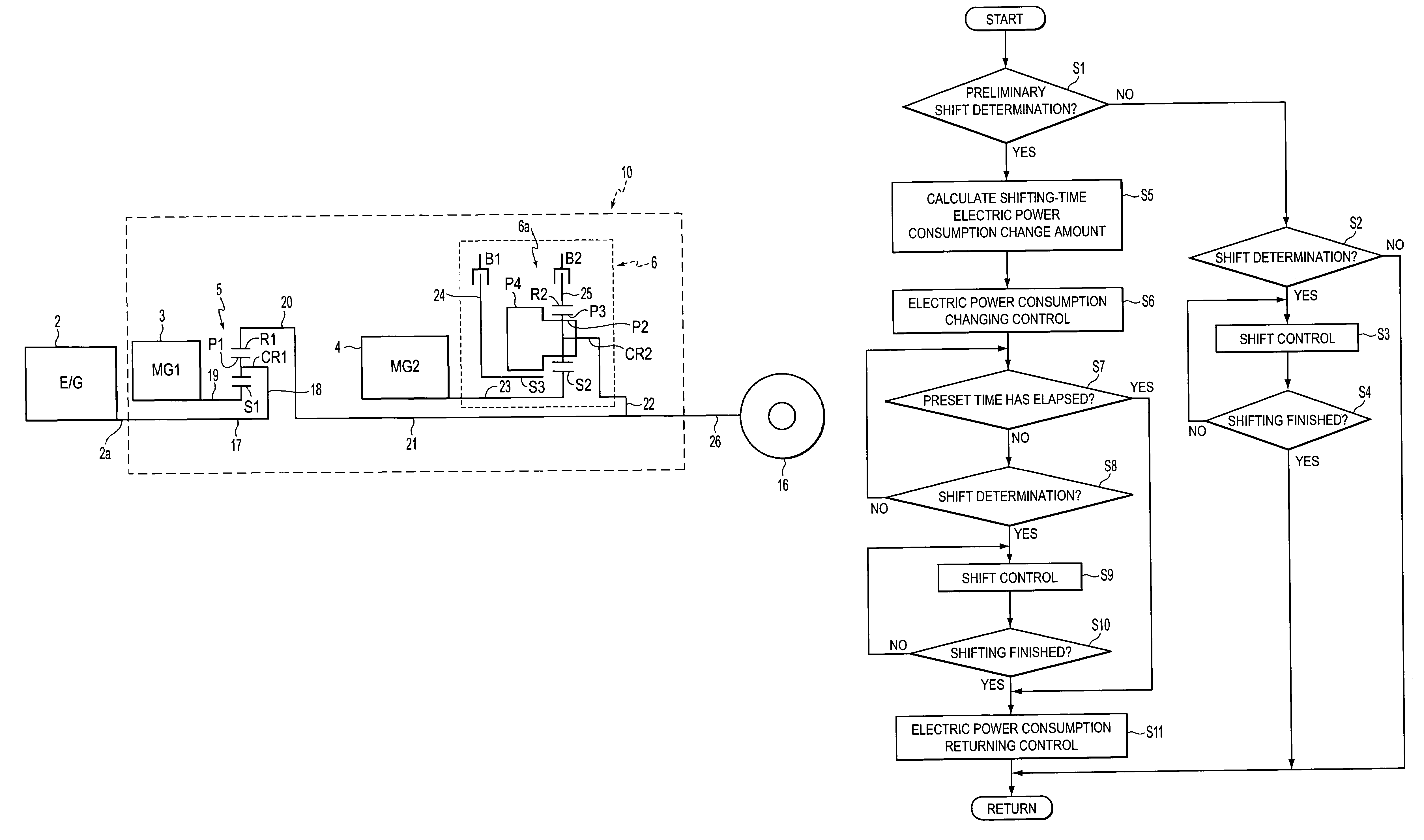
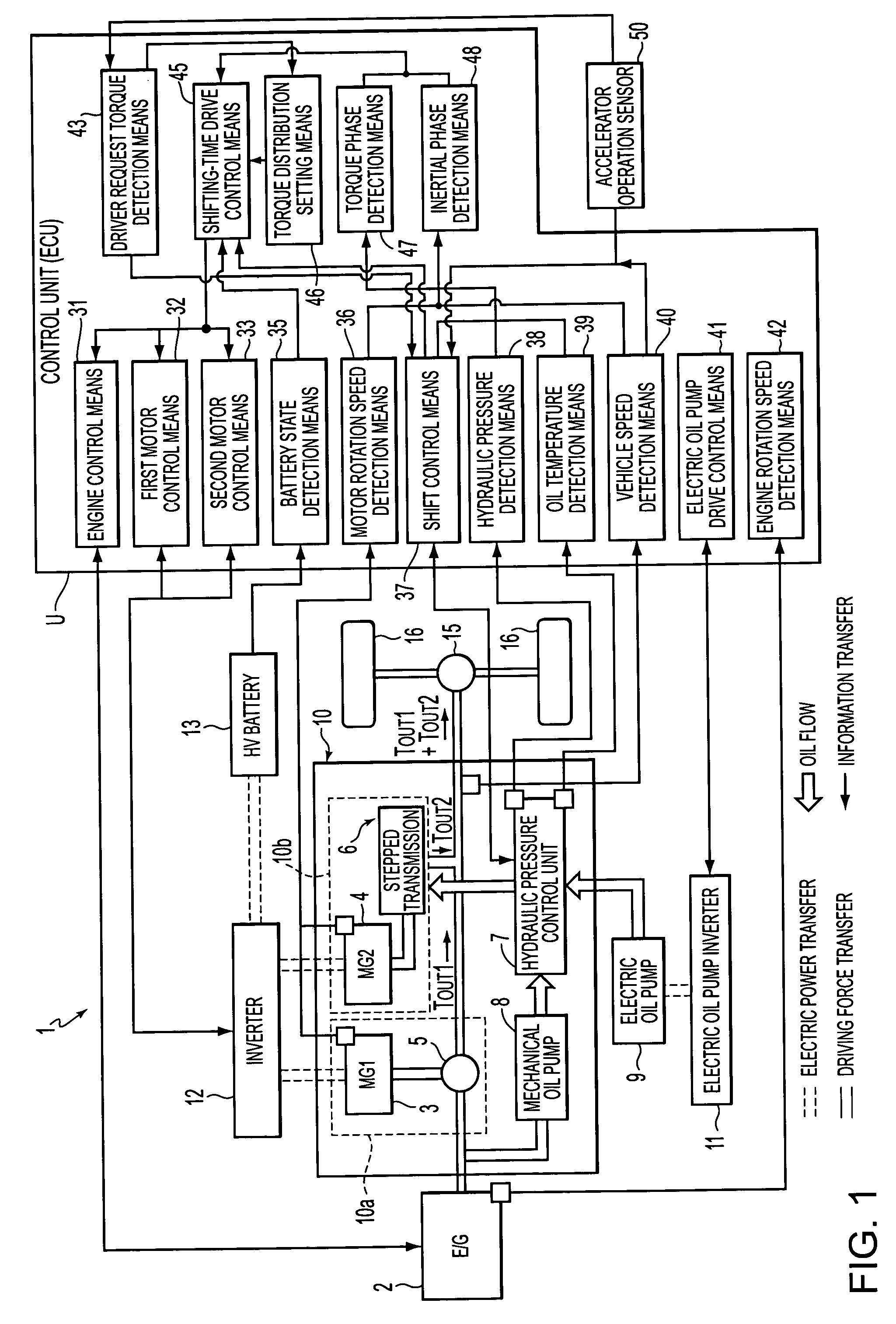
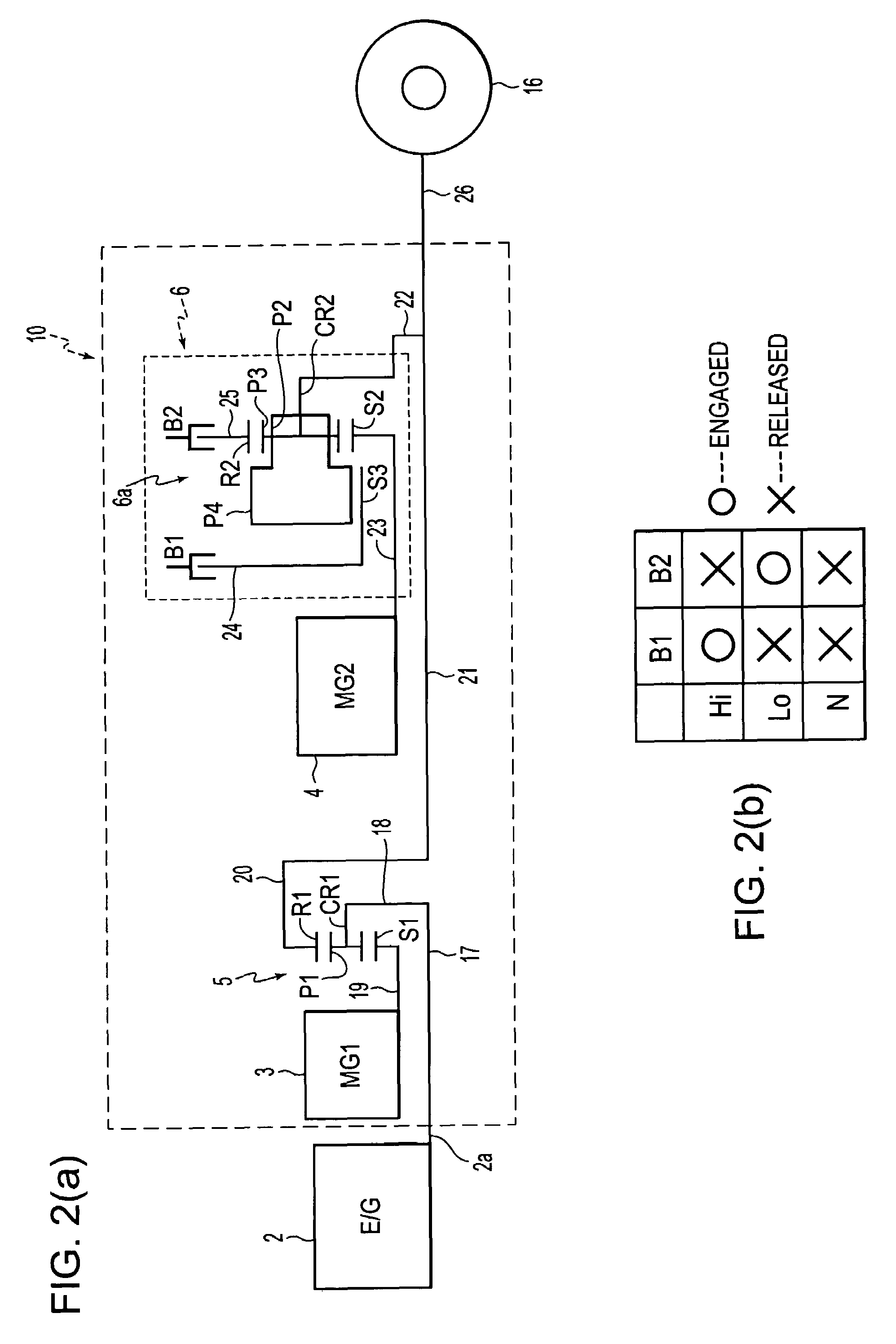
A control apparatus of a hybrid vehicle having a first drive unit, a second drive unit, a HV battery, a shift control element, a battery state detection element, and a shifting-time drive control element. Furthermore, in the control apparatus, a battery balance control element is formed by an engine control element, a first motor control element, a second motor control element and the shifting-time drive control element. If the shift control element determines there is a need for shifting carried out by a stepped transmission, the battery balance control element calculates the amount of increase / decrease in the amount of charge of the HV battery in accordance with the state of the HV battery, and changes the engine operation point on the basis of the calculated amount of increase / decrease in the battery charge, prior to the shifting.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD +1
Control apparatus of hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS7434641B2Small sizeImprove installabilityHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsBattery chargeOperation point
A control apparatus of a hybrid vehicle having a first drive unit, a second drive unit, a HV battery, a shift control element, a battery state detection element, and a shifting-time drive control element. Furthermore, in the control apparatus, a battery balance control element is formed by an engine control element, a first motor control element, a second motor control element and the shifting-time drive control element. If the shift control element determines there is a need for shifting carried out by a stepped transmission, the battery balance control element calculates the amount of increase / decrease in the amount of charge of the HV battery in accordance with the state of the HV battery, and changes the engine operation point on the basis of the calculated amount of increase / decrease in the battery charge, prior to the shifting.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD +1
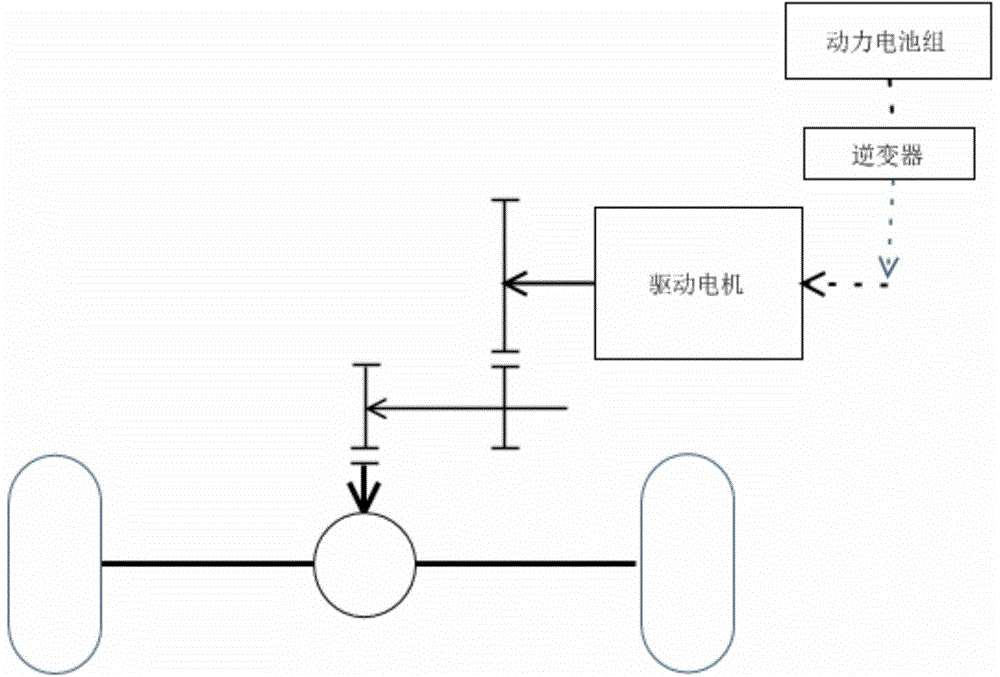
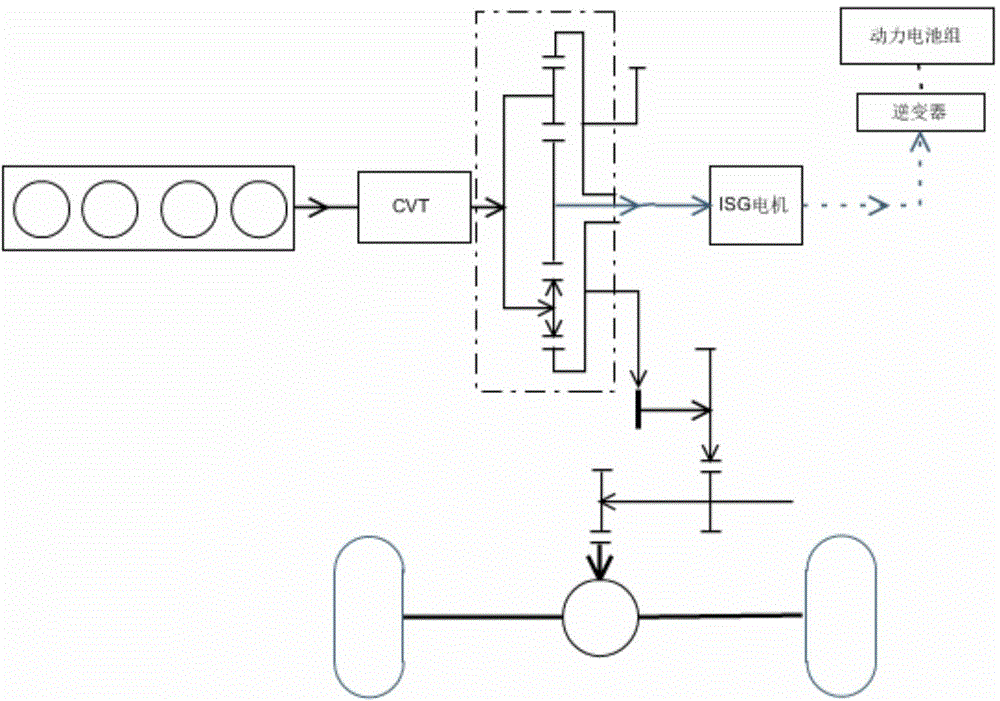
Series-parallel hybrid power automobile powertrain system and power distribution control method thereof
ActiveCN104442345AImprove powerImprove operational efficiencyGas pressure propulsion mountingPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingStarter generatorDistribution control
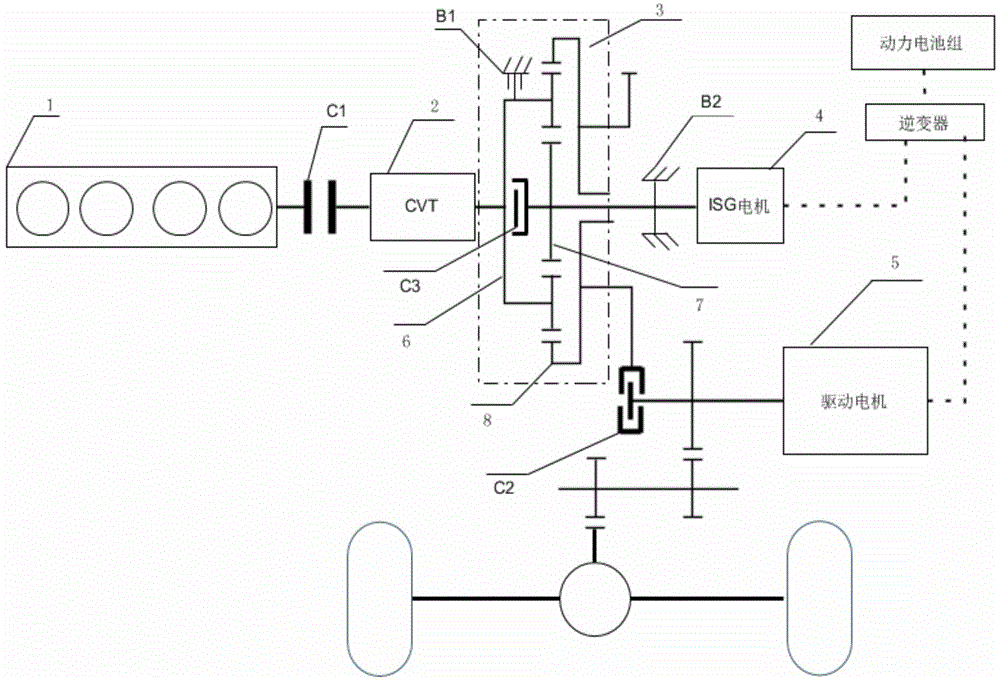
The invention discloses a series-parallel hybrid power automobile powertrain system and a power distribution control method of the series-parallel hybrid power automobile powertrain system. The powertrain system comprises an engine, an automobile integrated starter generator (ISG), a planetary gear train, a driving motor, a power battery pack, an engine clutch, an ISG brake, a planetary gear train clutch and a driving motor clutch, wherein the engine clutch, the ISG brake, the planetary gear train clutch and the driving motor clutch are controlled by a vehicle control unit. The ISG is directly integrated on a sun gear of the planetary gear train and is provided with a continuously variable transmission (CVT) and a CVT brake. By the adoption of an electric driving priority control strategy, the operation point of the engine is regulated by fully utilizing the operating characteristics of the CVT, so more automobile patterns can be selected on complex and different working conditions; besides, the driving motor and the ISG are used for coordinating operation of the engine, so that the engine operates on an optimal curve most of time; since the power performance of an automobile is optimized by coupling the rotating speed and torque, the running efficiency of the engine and the fuel economy of the whole automobile are improved remarkably, emission is reduced, and remarkable energy conservation and emission reduction effects are achieved.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
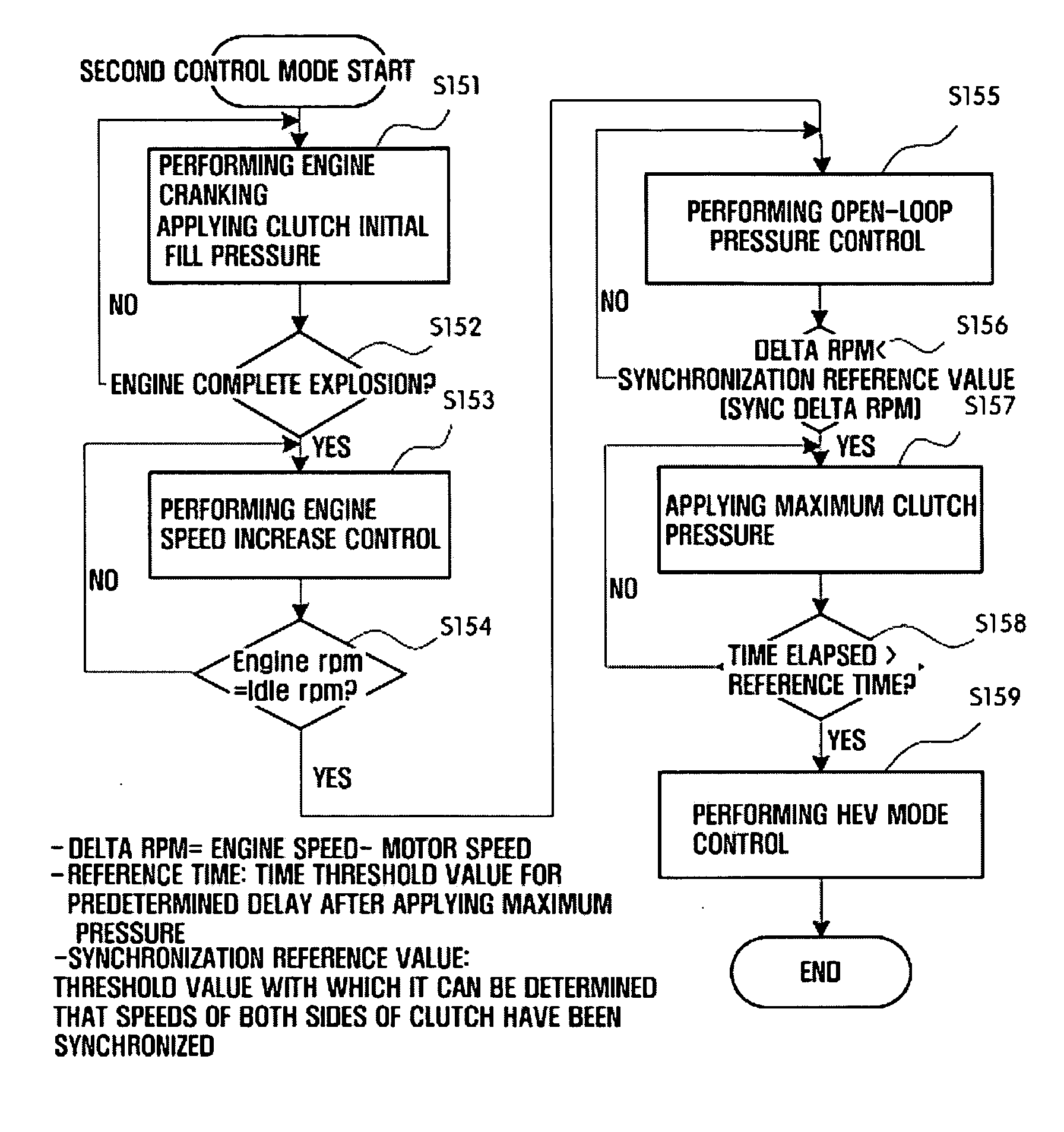
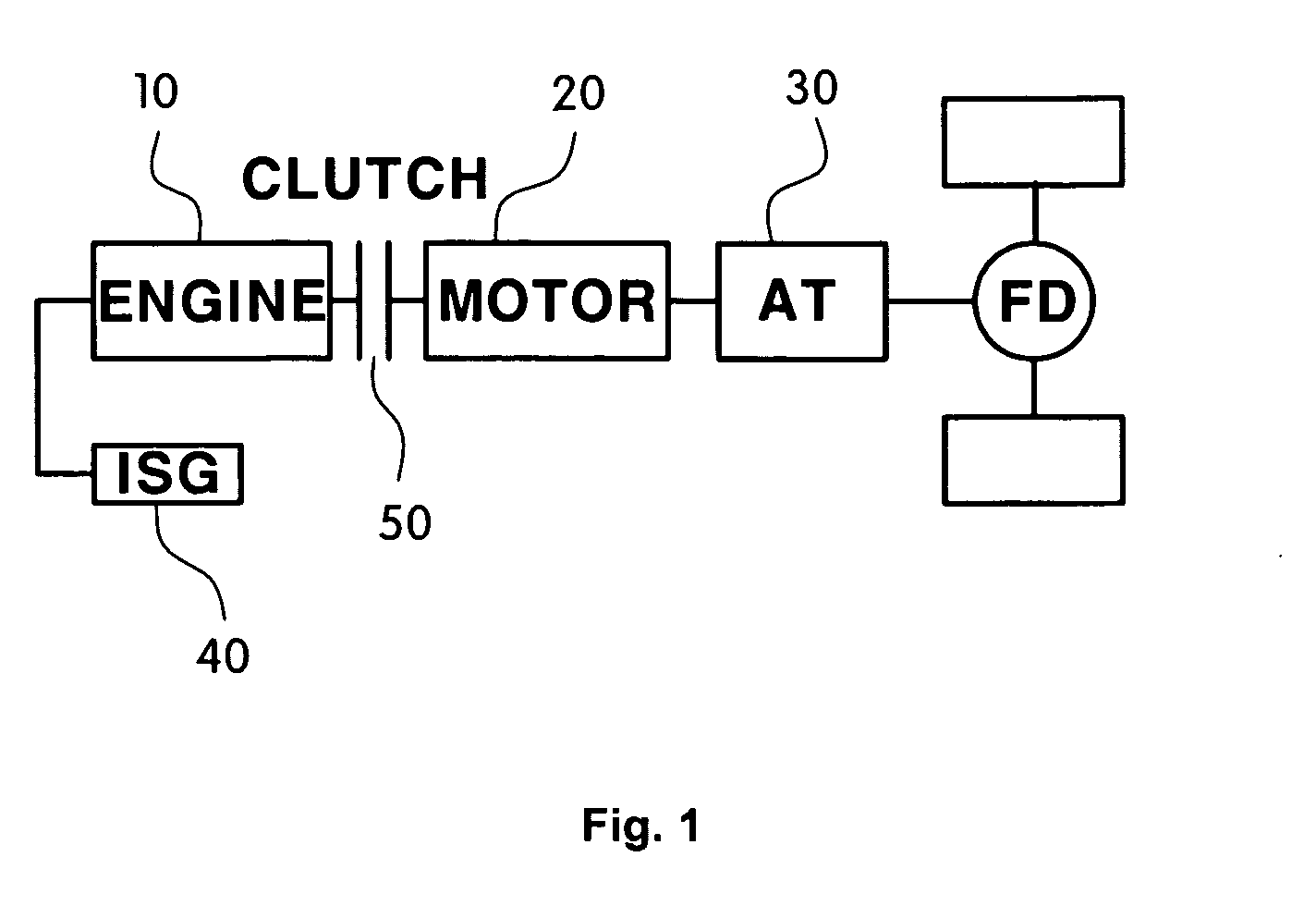
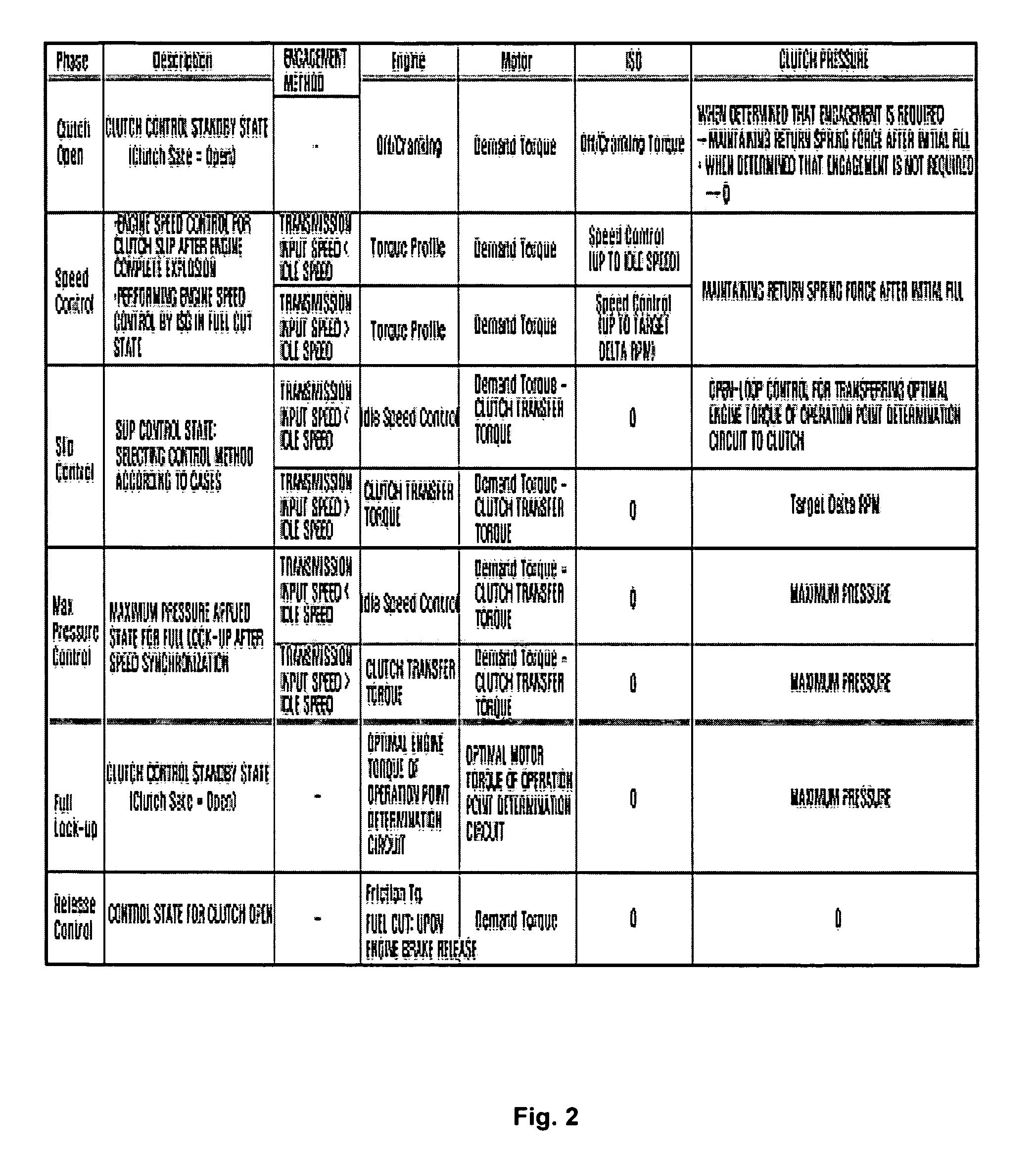
Mode change control method of hybrid vehicle
The present invention provides a mode change control method of a hybrid vehicle, which can improve driving performance and power performance and provide a more stable vehicle behavior control during a mode change from an EV mode to a HEV mode. For this purpose, a transmission input speed is compared with an engine idle speed. If the transmission input speed is lower than the engine idle speed, the pressure of a clutch is open-loop controlled so that an optimal engine torque of operation point determination circuit can be transferred to the clutch. On the other hand, if the transmission input speed is equal to or higher than the engine idle speed, the clutch pressure is feedback-controlled so that a delta RPM follows a target delta RPM profile.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
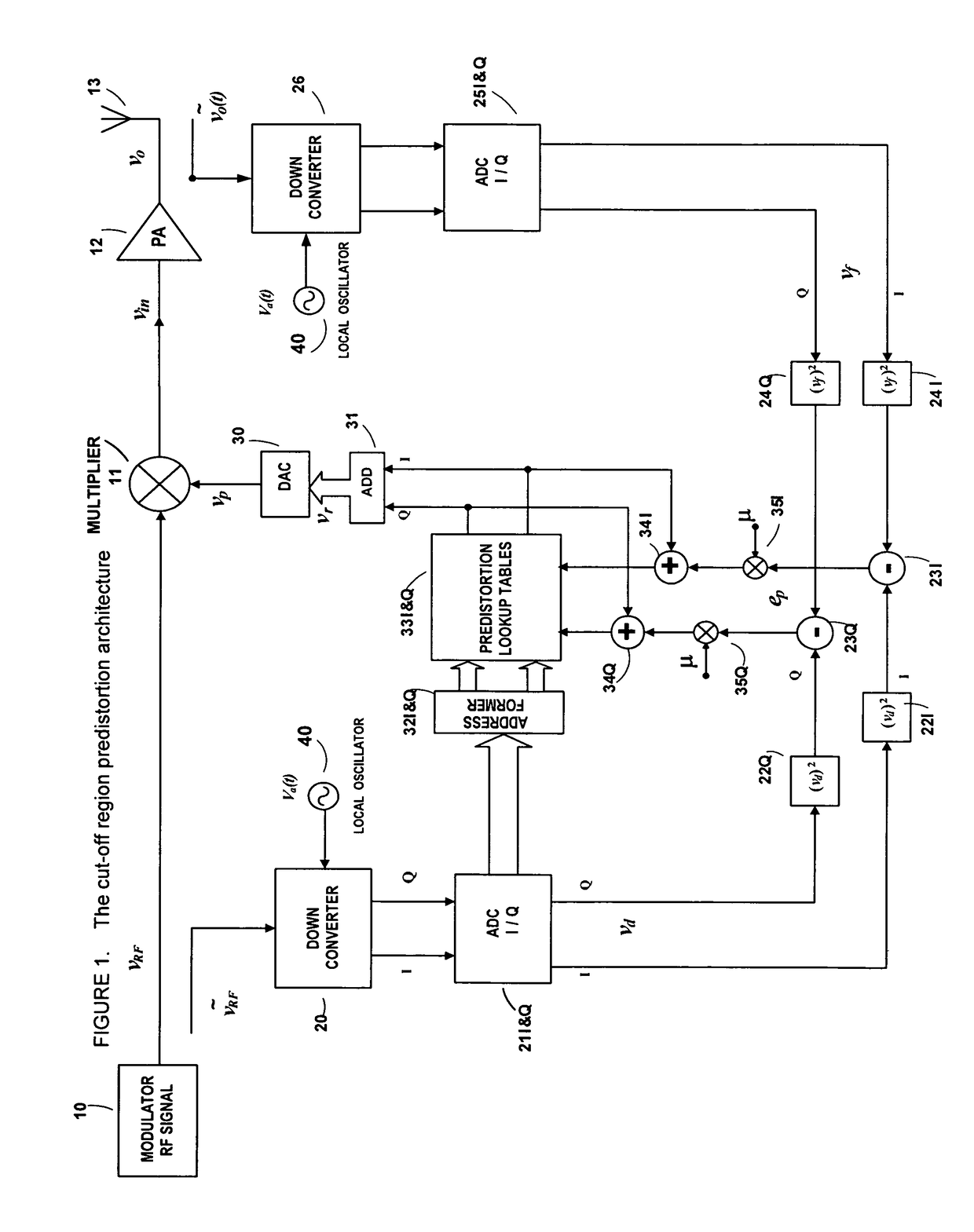
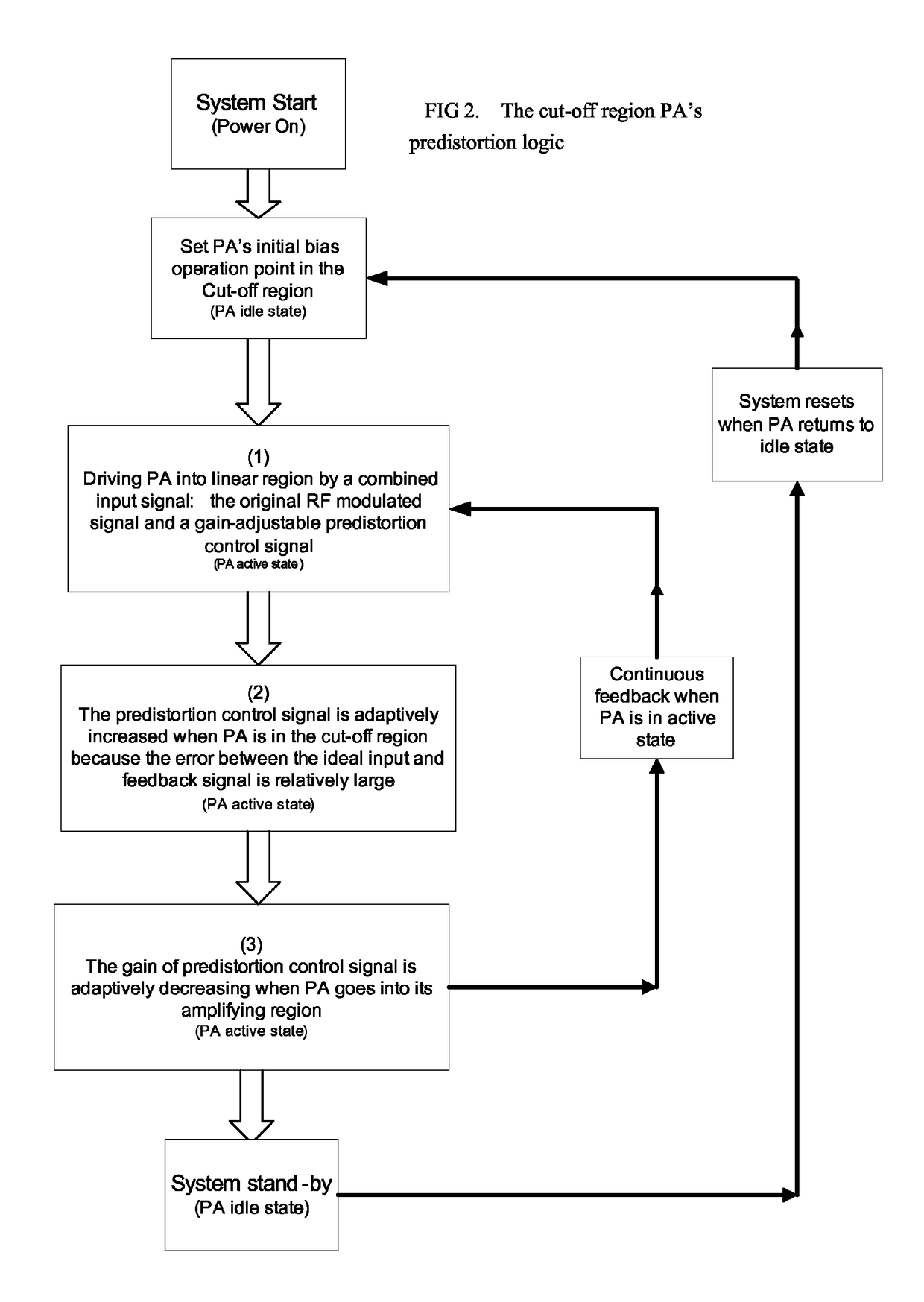
Power amplifier predistortion methods and apparatus
ActiveUS8472897B1Amplifier with control circuitsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
An embodiment of the invention is a predistortion approach to linearize a power amplifier by setting initially the static operation point of the power amplifier in the cut-off region. The architecture is based on the analog-digital combination by a multiplier and digital predistortion control circuit. The predistortion system generates an adaptive output signal to control the RF modulated signal that is the input signal of the power amplifier. The controlled and predistorted signal can contribute to drive a power amplifier with the cut-off static operation point into its amplifying region and simultaneously correct the non-linear distortion when the power amplifier operates to amplify an RF signal.
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
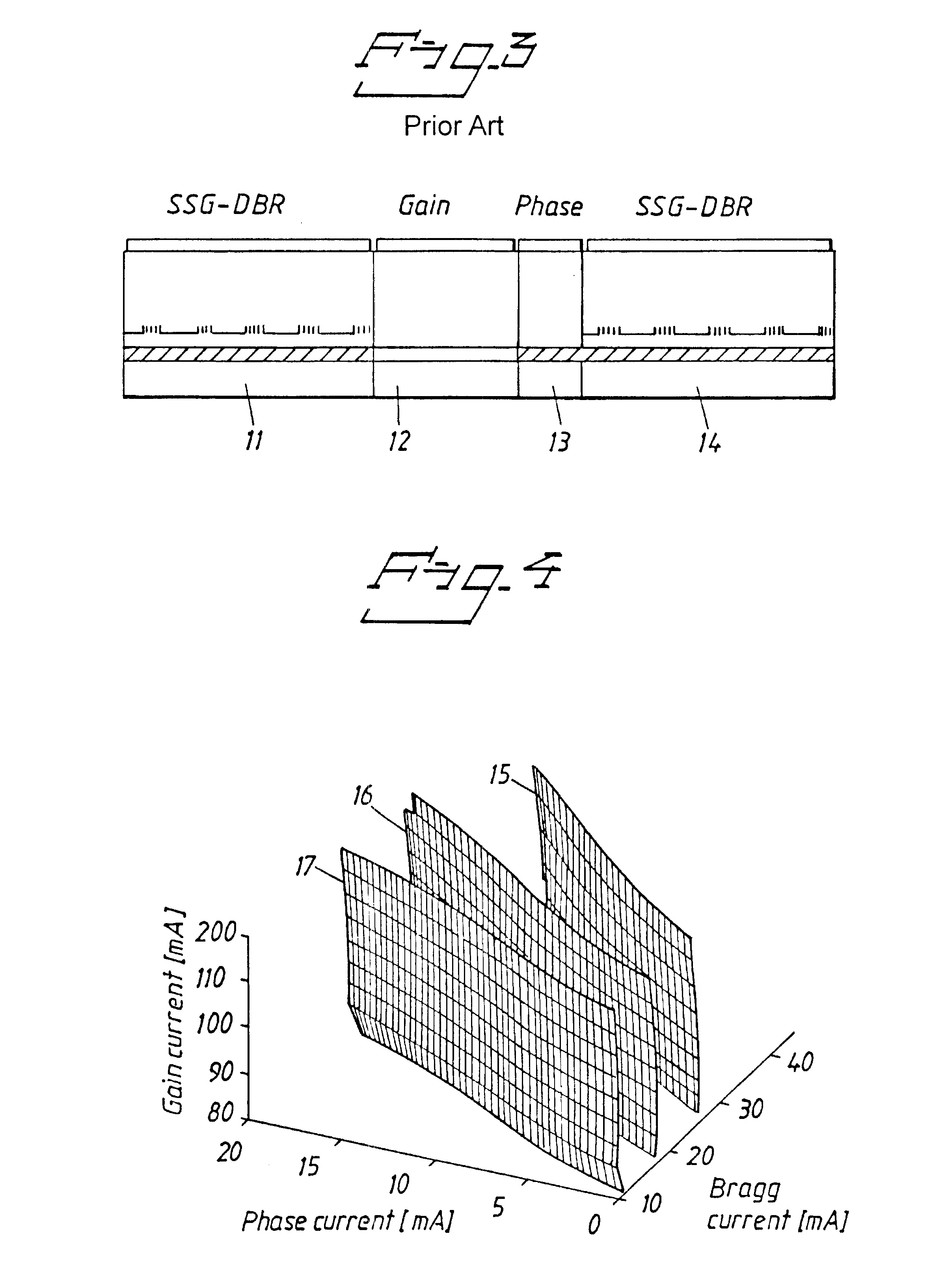
Method and apparatus for optimizing operation points of a tunable laser
A method of optimizing the operation point of a laser, including characterizing the laser and controlling the different laser sections by varying the currents injected into the respective laser sections. The method includes sensing discontinuities that occur at mode jumps in a signal by utilizing a detection device that is firmly connected to the laser. Control of the different laser sections is effected by means of a control unit. Different control current combinations and the signal delivered by the detection device are provided to the control unit, which causes the control unit to detect the mode plane of the laser. At least a part of a mode plane, or several mode planes, are stored in a memory connected with the control unit, and the control unit controls the different laser sections so that the laser will operate at the desired operation point.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
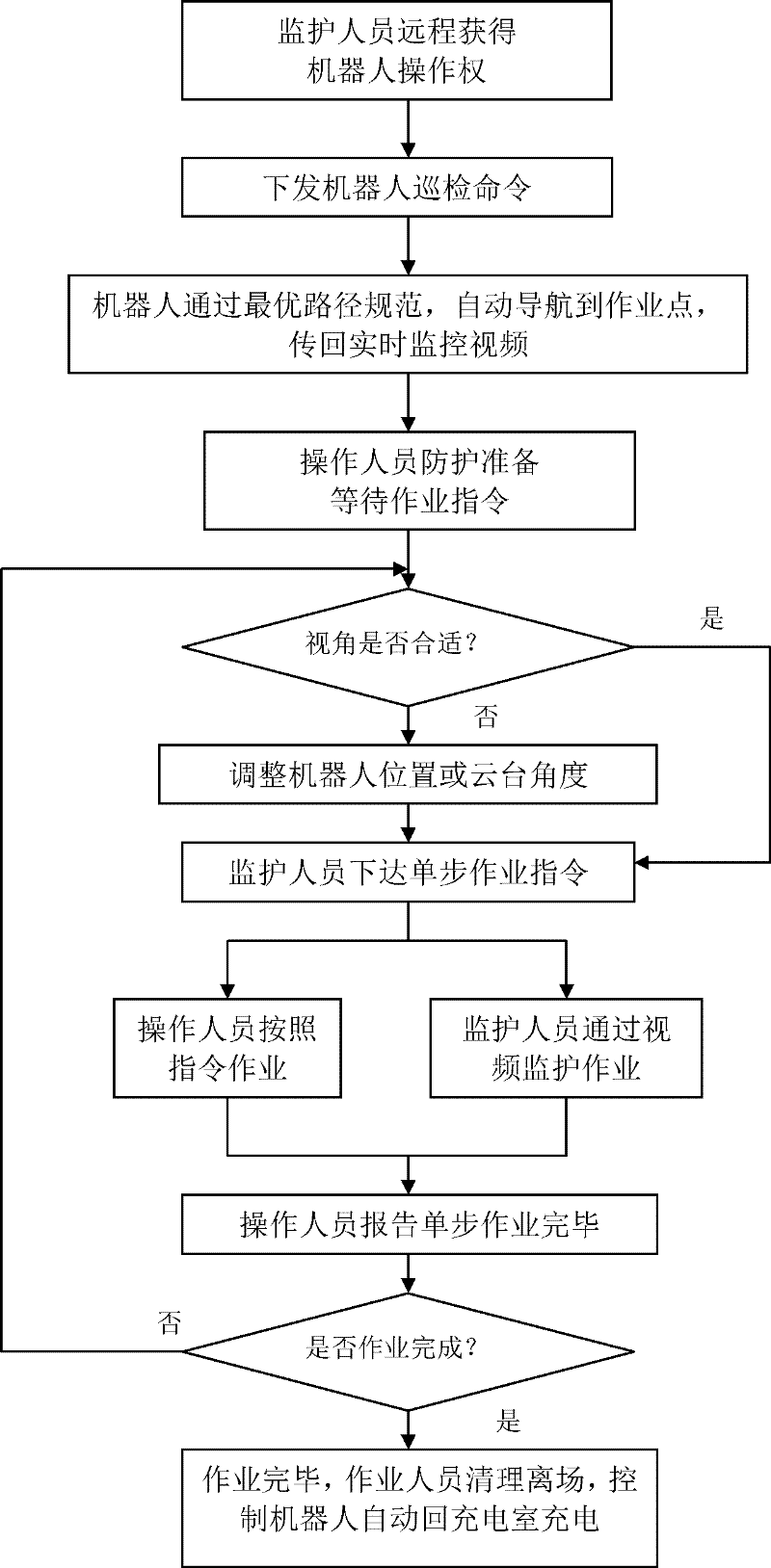
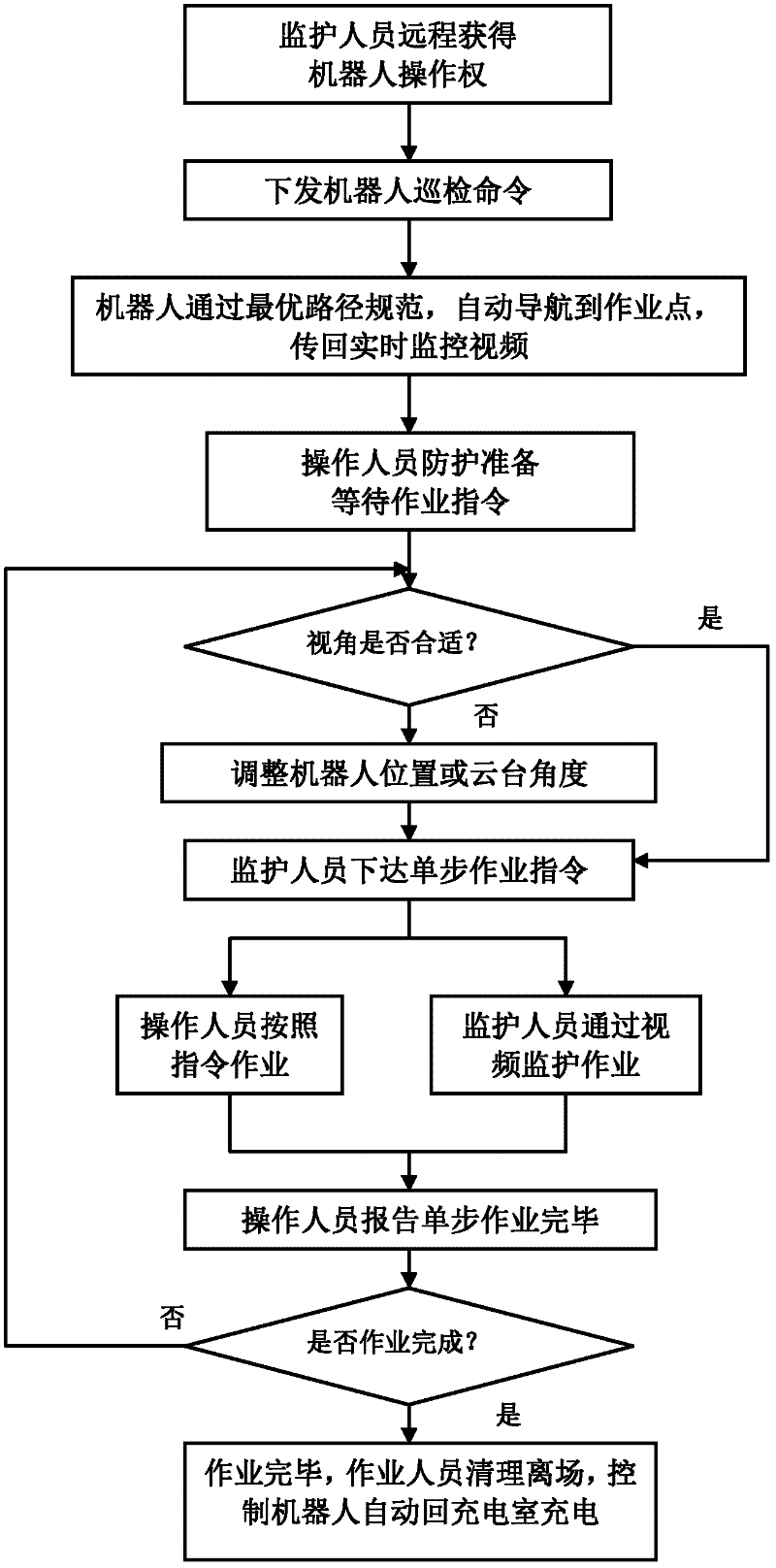
Routing inspection system based on intelligent robot of transformer station and method for monitoring operation of transformer station
InactiveCN102355052AReduce labor intensitySave operating timeCircuit arrangementsTransformerSimulation
The invention relates to a routing inspection system based on an intelligent robot of a transformer station and a method for monitoring the operation of the transformer station and can meet all-weather working requirements. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) remotely taking over the right of control of an intelligent routing inspection robot; 2) issuing an equipment detection command to the intelligent routing inspection robot of the transformer station; 3) automatically navigating the intelligent routing inspection robot to an operation point by using an optimum path specification, and sending back a real-time monitoring video; 4) after an operator is in place on the scene, waiting for an operation command; 5) issuing a single-operation instruction to the operator; 6) monitoring the operation of a scene person by using the video of the intelligent routing inspection robot; 7) remotely controlling the intelligent routing inspection robot to move to an appropriate position or adjusting a holder of the intelligent routing inspection robot to be at an appropriate angle; 8) after the operation of the steps is finished, waiting for the next operation instruction; and 9) after all operation tasks are finished, controlling the intelligent routing inspection robot to automatically move back to a charging room for charging, and finishing the operation.
Owner:SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
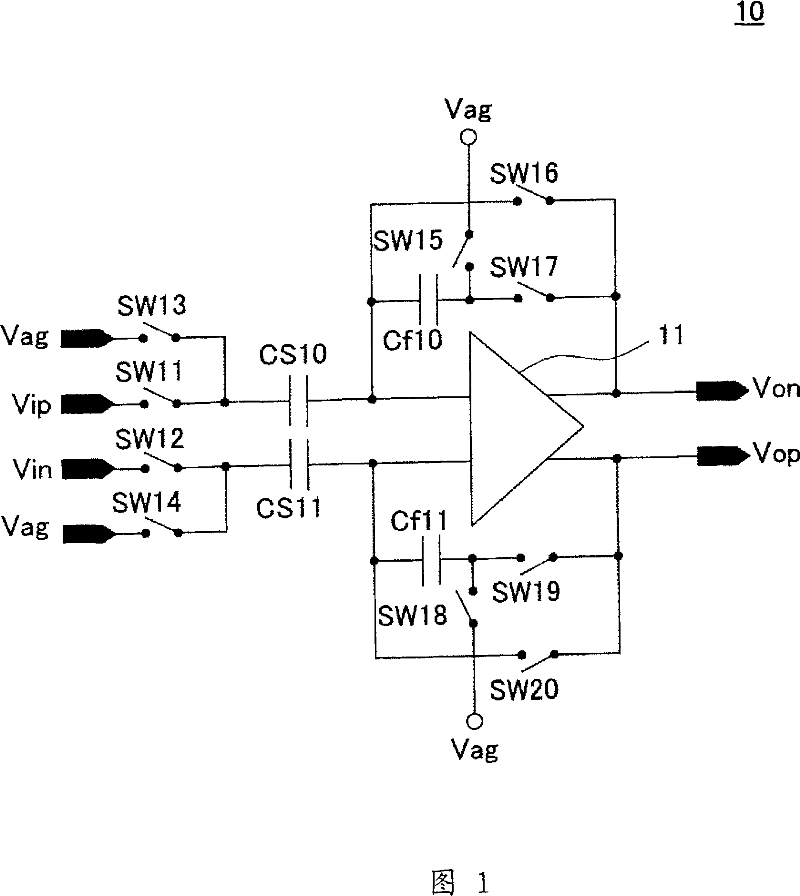
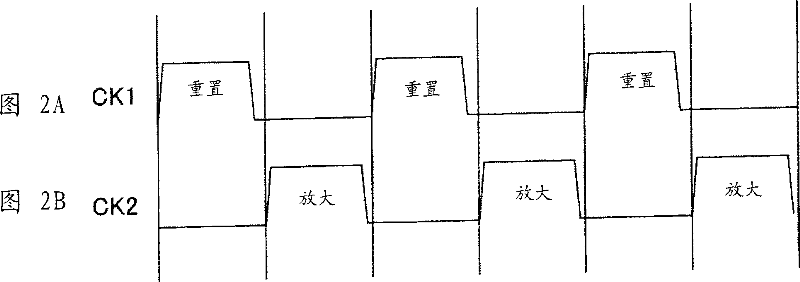
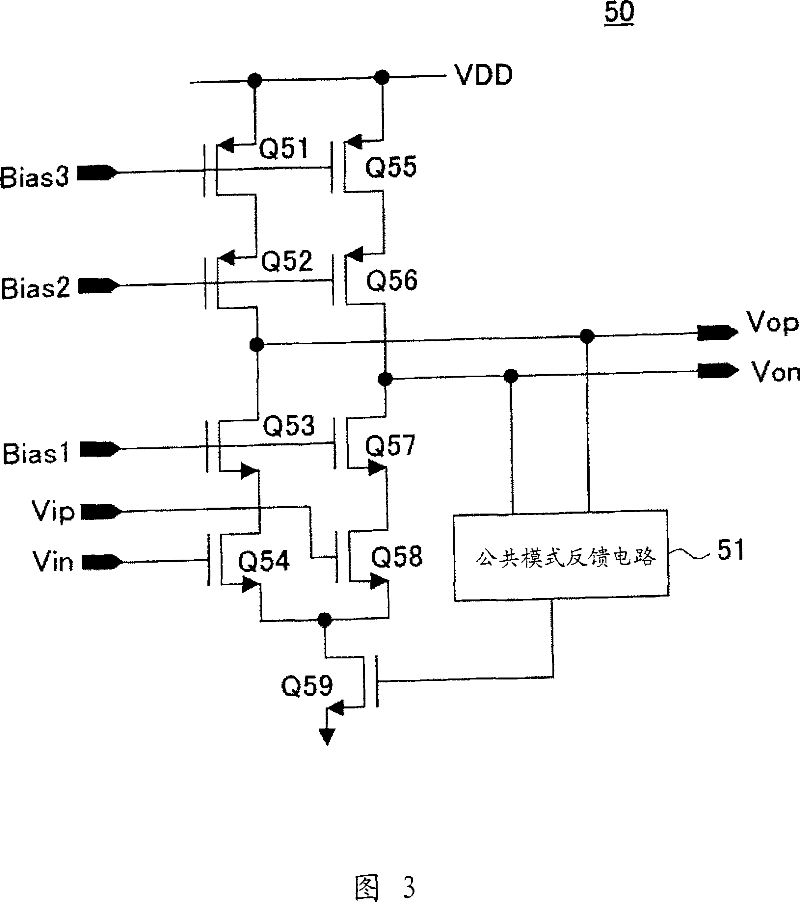
Sample hold circuit, and pipeline ad converter using the circuit
InactiveCN101040441AOperating current variableLower operating average currentElectric signal transmission systemsCharge amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A switched capacitor sample hold circuit using a source-earthed input operation amplifier. This operation circuit is provided with a feed forward circuit or a feedback circuit, which is connected with a feedback capacitor of the operation amplifier through a switch. An input common voltage or the middle point voltage of an output is detected to precharge the feedback capacitor beforehand with the difference from a reference voltage thereby to suppress fluctuations in an output operation point at the time of amplifying the operation amplifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
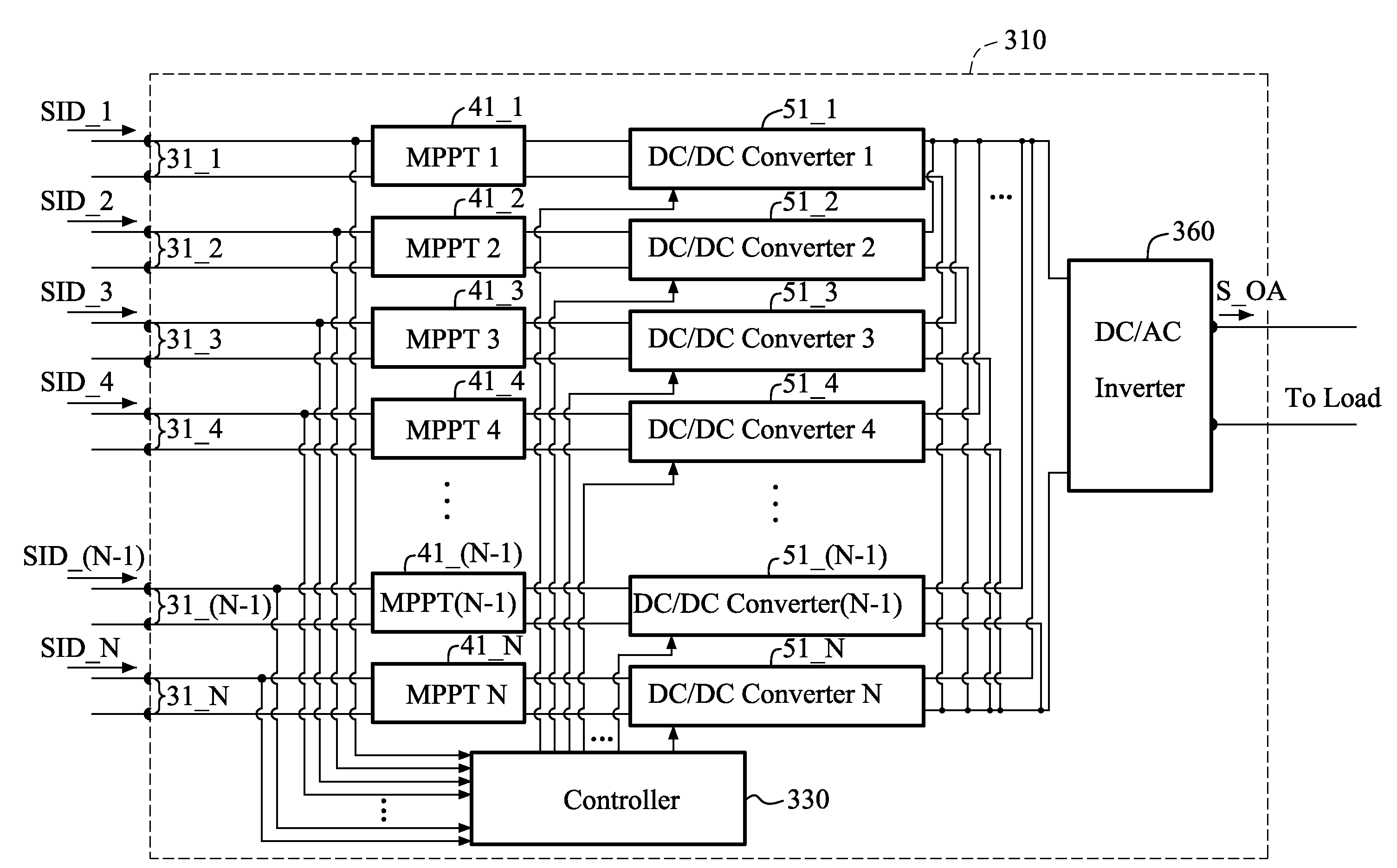
Converting device with multiple input terminals and two output terminals and photovoltaic system employing the same
InactiveUS20110115300A1Improve power efficiencyReduce complexityDc network circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationOperation pointAlternating current
A converting device with multiple input terminals and two output terminals is disclosed for converting Direct Current (DC) power from a power source to Alternating Current (AC) power. The converting device includes N pairs of input electrodes (N is an integer and N≧2), configured to receive the DC power from the power source, N maximum power point trackers, each coupled to one pair of the N pairs of input electrodes, configured to track a maximum power operation point for the DC power received from the one pair of the N pairs of input electrodes, two DC / DC converters, each coupled to one of the N maximum power point trackers, configured to convert a DC voltage received from the one of the N maximum power point trackers, a DC / AC inverter, coupled to the N DC / DC converters, configured to convert N DC voltages provided by the N DC / DC converters to an AC output signal, and a controller, coupled to the N DC / DC converters and the DC / AC inverter, configured to control the DC / DC conversion operation of the N DC / DC converters and the DC / AC conversion operation of the DC / AC inverter.
Owner:DU PONT APOLLO
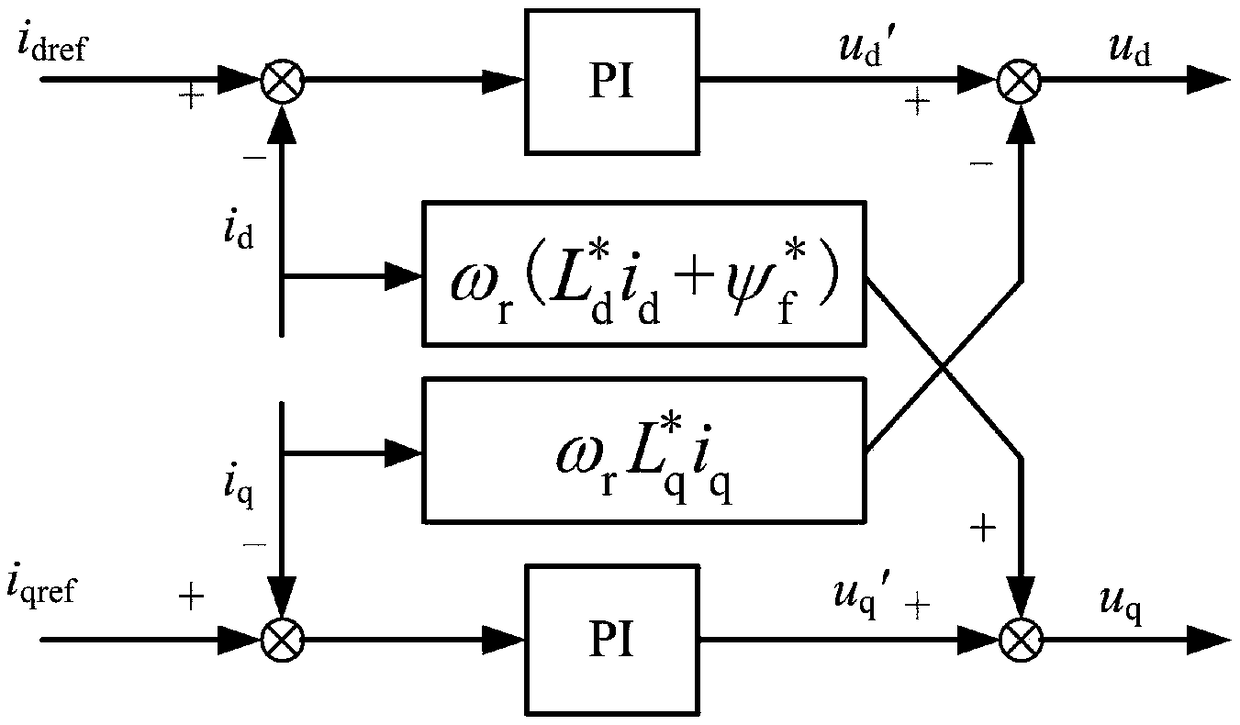
Permanent magnet synchronous motor maximum torque per ampere control method based on parameter self-correction
ActiveCN109428525AMaximum torque-to-current ratio control is preciseImprove dynamic response characteristicsElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlMaximum torqueAmpere
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor maximum torque per ampere control method based on parameter self-correction. Real-time estimation is carried out on change condition of motor parameters (permanent magnet flux linkage, d-axis inductance and q-axis inductance) through utilization of a feedforward compensation control module; further online correction is carried out on themotor parameters in a torque equation; an electromagnetic torque model comprising accurate motor parameter information is obtained; a torque to current angle change rate is directly solved through utilization of the model; further an MTPA (Maximum Torque Per Ampere) angle is computed; and precise maximum torque per ampere control is realized. When motor operation condition is changed, according to the method, the MTPA angle can be directly solved through mathematical operation, so influence of system bandwidths does not need to be taken into consideration; an algorithm simple; computing speedis fast; dynamic performance is relatively good; a motor is enabled to work at the maximum torque per ampere operation point all the time; influence of the operation condition and motor parameter change is avoided; and relatively good parameter robustness and dynamic response characteristic are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
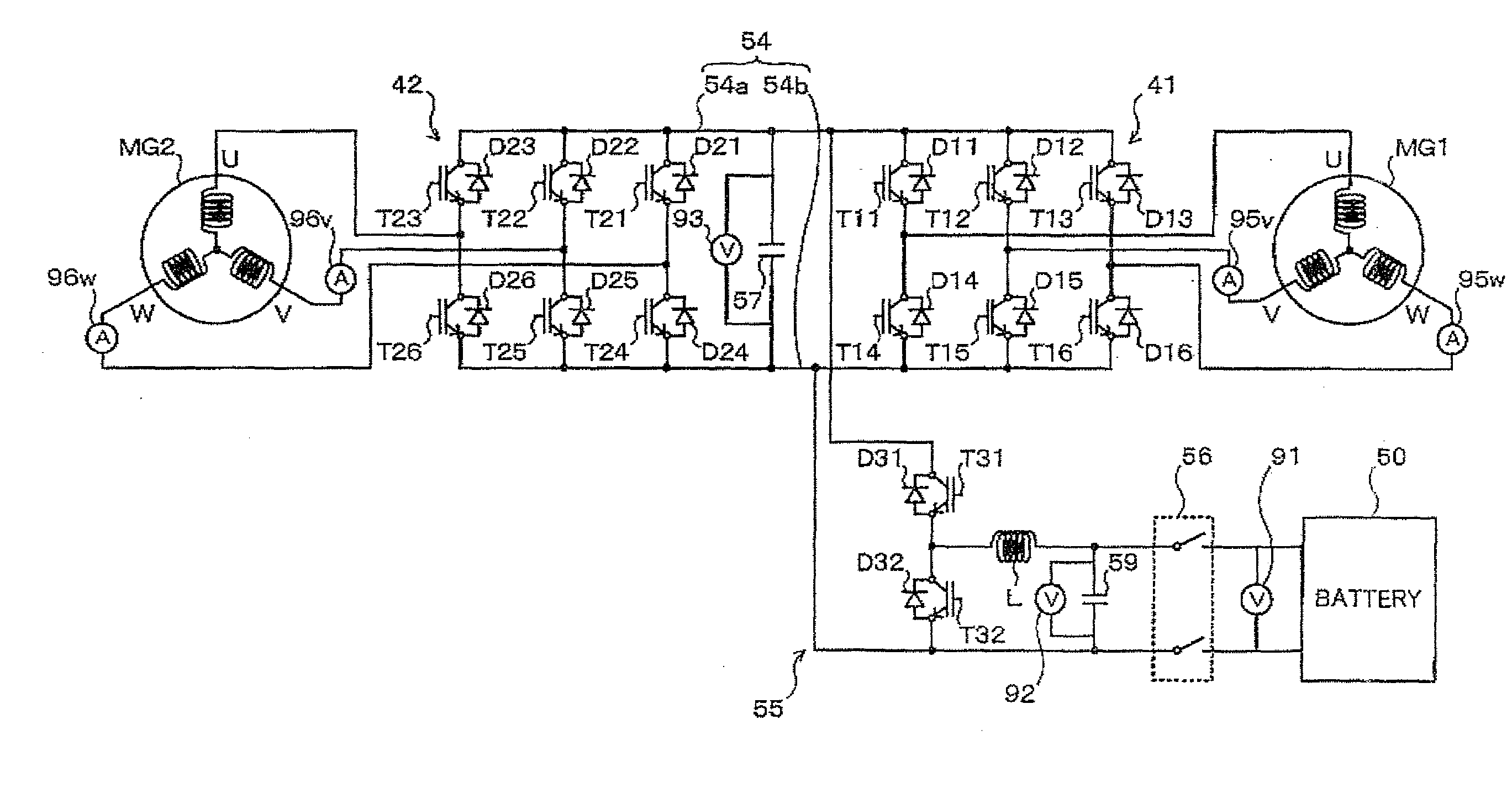
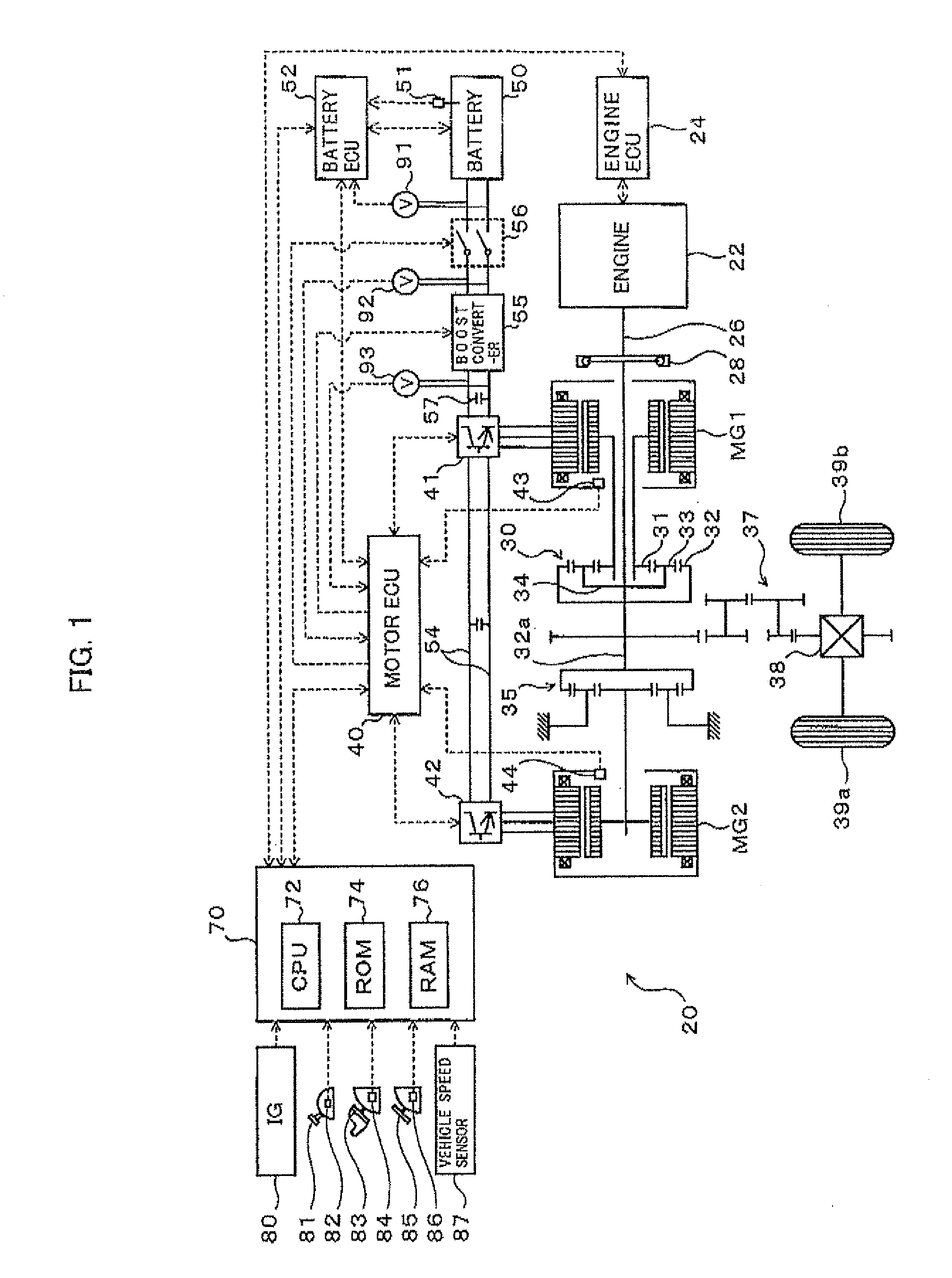
Motor drive control apparatus, vehicle with motor drive control apparatus, and motor drive control method
InactiveUS20110006723A1Improve efficiencyHybrid vehiclesSingle-phase induction motor startersOperation pointHybrid vehicle
In the hybrid vehicle, a boost converter is controlled to make a post-boost voltage or a voltage on the side of an inverter become a target post-boost voltage corresponding to a target operation point of a motor in accordance with a target post-boost voltage setting map that divides an operation region of the motor into a non-boost region and a boost region when a operation point of the motor is included in the boost region. The target post-boost voltage setting map is prepared so that the non-boost region includes a region in which a loss produced by driving the motor when not boosting the post-boost voltages becomes smaller than the loss produced when boosting the post-boost voltage and the boost region includes a region in which the loss produced when boosting the post-boost voltage becomes smaller than the loss produced when not boosting the post-boost voltage.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
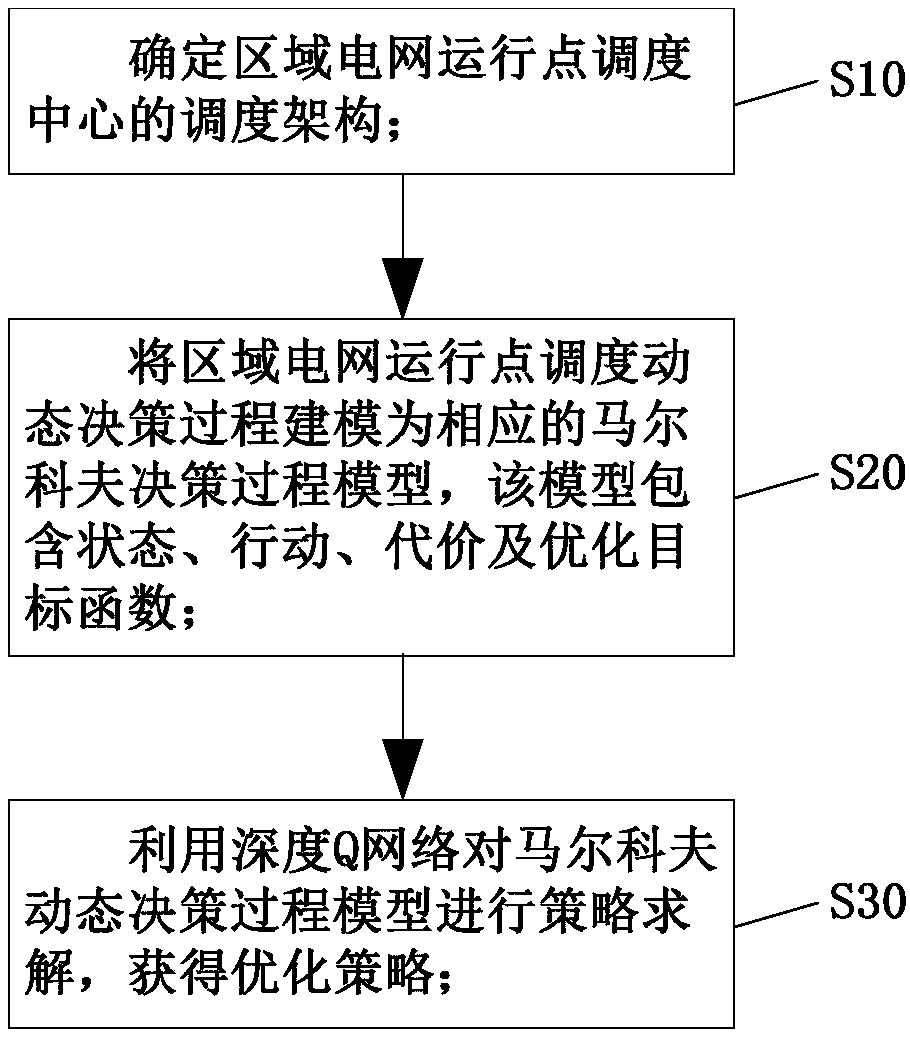
Deep Q network based regional power-grid operation point dispatching optimization method
ActiveCN108964042AImprove operational efficiencyReduce flex load requirementsLoad forecast in ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsNew energyDynamic balance
The invention provides a deep Q network based regional power-grid operation point dispatching optimization method. The method comprises the steps that a dispatching configuration of a regional power-grid operation point dispatching center is determined; a dynamic decision process for dispatching operation points of regional power grid is modeled into a corresponding Markov decision process model which comprises state, action, cost and optimization target function; the deep Q network is used to carry out strategy resolution on the Markov dynamic decision process; the operation point of the regional power grid comprises a routine thermal power set output of a next dispatching period, thermal power set output and the flexible load reduction amount; and dispatching of the operation point of the region power grid comprises, at least, that the power grid operation point in the next dispatching period is determined dynamically according to wind power and load power short-term prediction information and operation point information in the present period. Thus, effective response to randomness of the new energy output and load demands can be made, source-load interactive dispatching potential gives a full play, dynamic balance of the power of the regional power grid is maintained, and the operation efficiency of the power grid system is improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
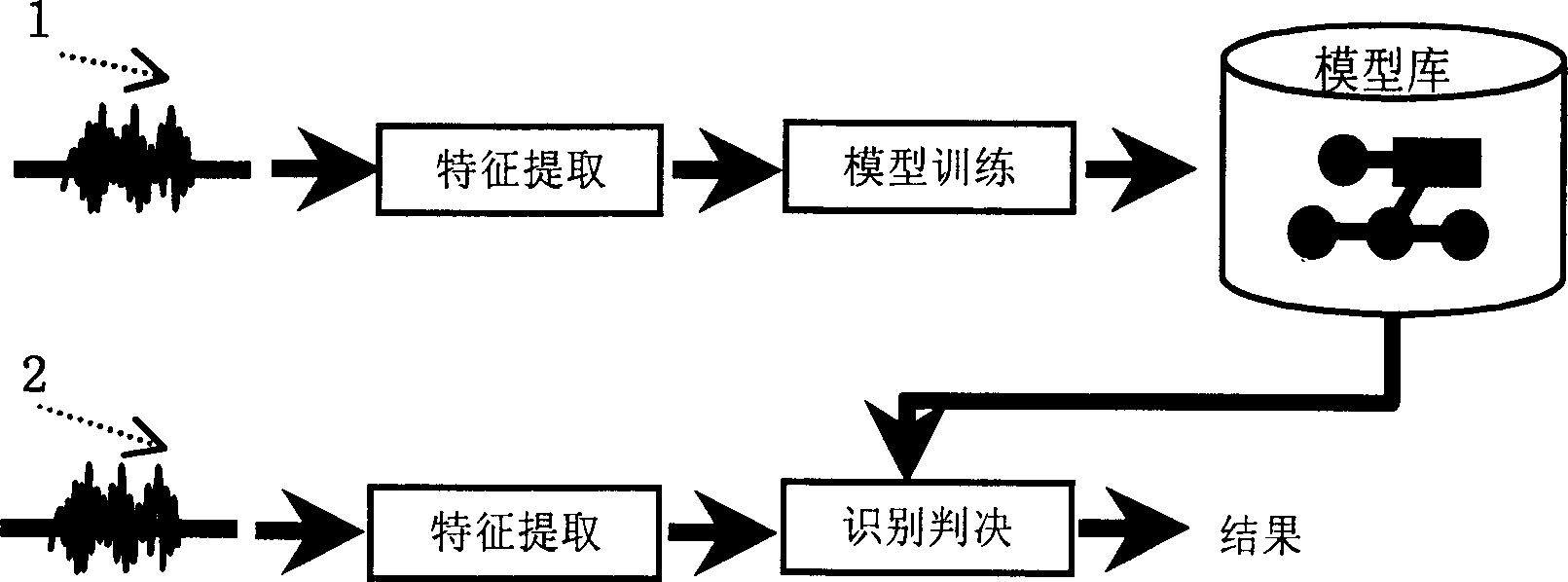
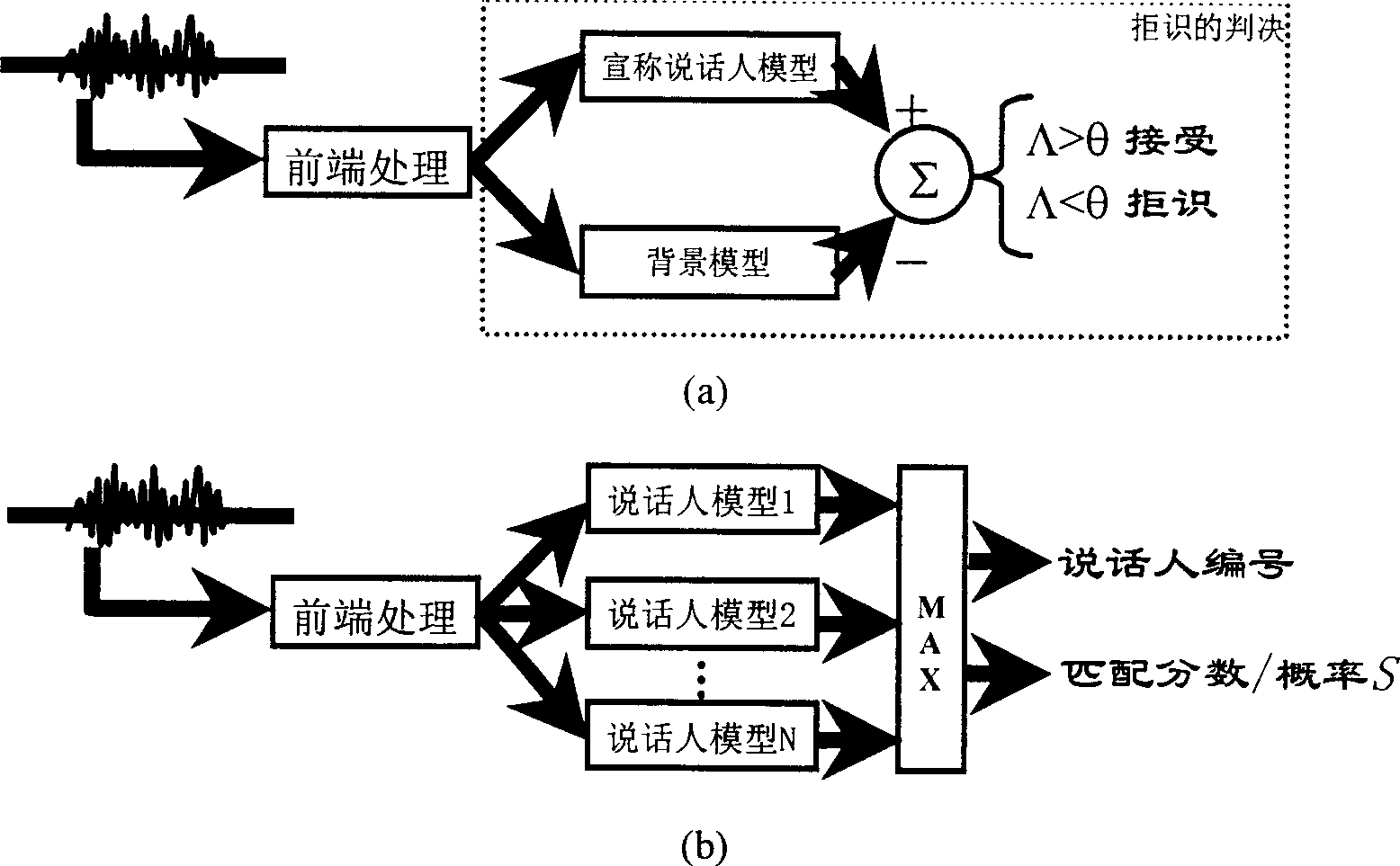
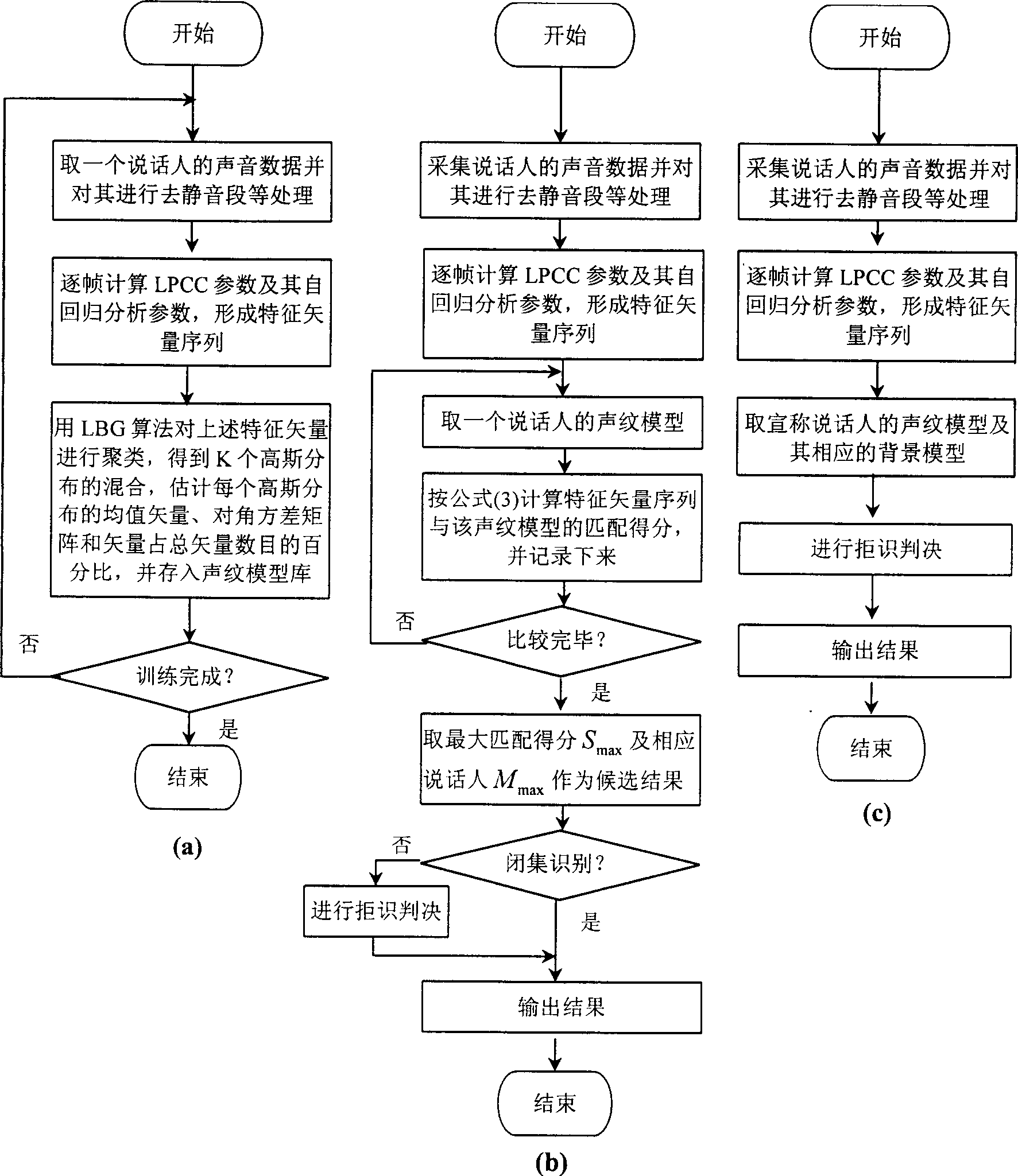
Method for recognizing voice print
InactiveCN1447278AReliable automatic estimationReliable trainingCharacter and pattern recognitionElectric/magnetic computingOperation pointLog likelihood
This invention relates to method for identifying and confirming an identity by the soundwave information of mankind including a model training method and a soundwave identification method characterizing in that every speaking person makes up of soundwave model: M=***, the character vector sequence to be identified x'={X1,...XT} matching with the speaking person soundwave model M=*** gets marks (log likelihood) as 1:s(x' / M)=***. This invention can adjust threshold value of an operation point according to different requirements to reach the highest accurate rate.
Owner:BEIJING D EAR TECH
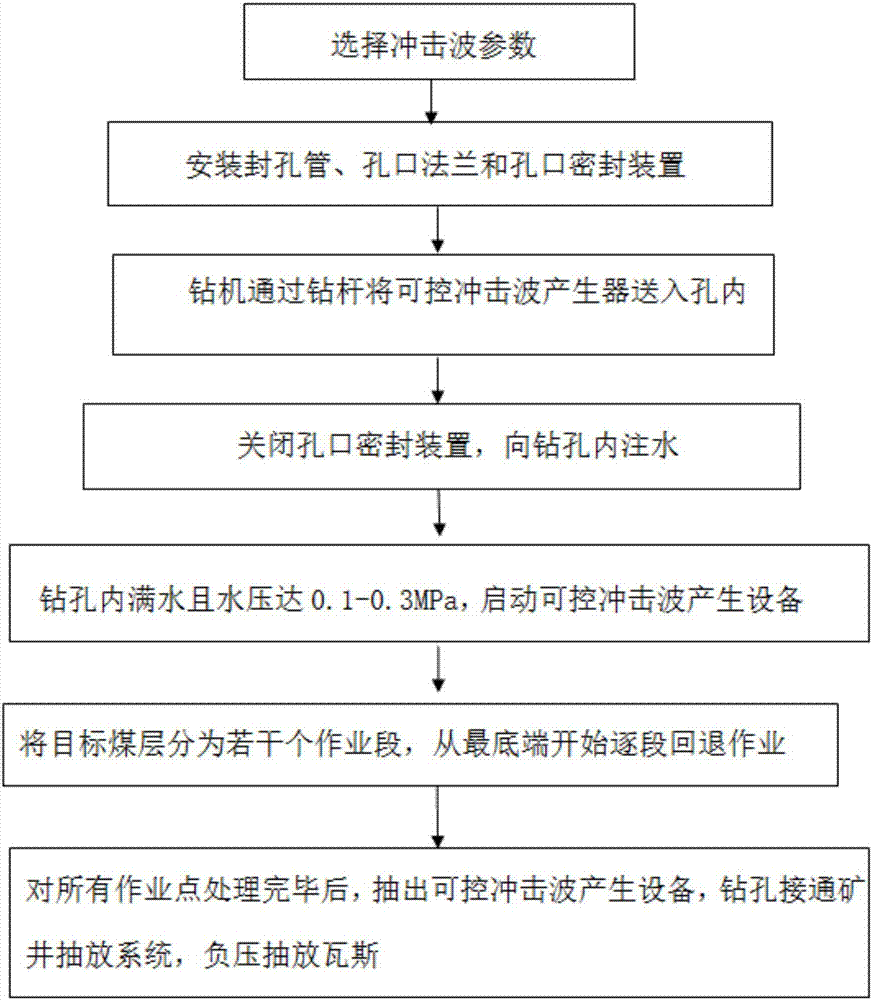
Coal mine down-hole drilling penetration improvement method based on controllable shock wave technology
InactiveCN107956505APrevent collapseAvoid the problem of rock burstFluid removalGas removalShock waveEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of energy and coal mine safety, and particularly relates to a coal mine down-hole drilling penetration improvement method based on a controllable shock wave technology. The method aims at solving the problems of high labor intensity and low safety of an existing gas treatment mode. Controllable shock wave generation equipment is pushed to the interior of a drilling hole, and after a hole opening sealing device is installed at a hole opening of the drilling hole, water is injected to the drilling hole; after the drilling hole is fully filled with the water, operation is conducted segment by segment, the middle of each operation segment is used as an operation point of shock waves, and repeated impact is conducted on each operation point multiple times. Under the effect of the injected water in the hole, the shock wave generation equipment does not need to work under the environment with explosive gas, and the shock waves are also efficiently coupled toa coal bed.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Shield machine and anterior shield system thereof
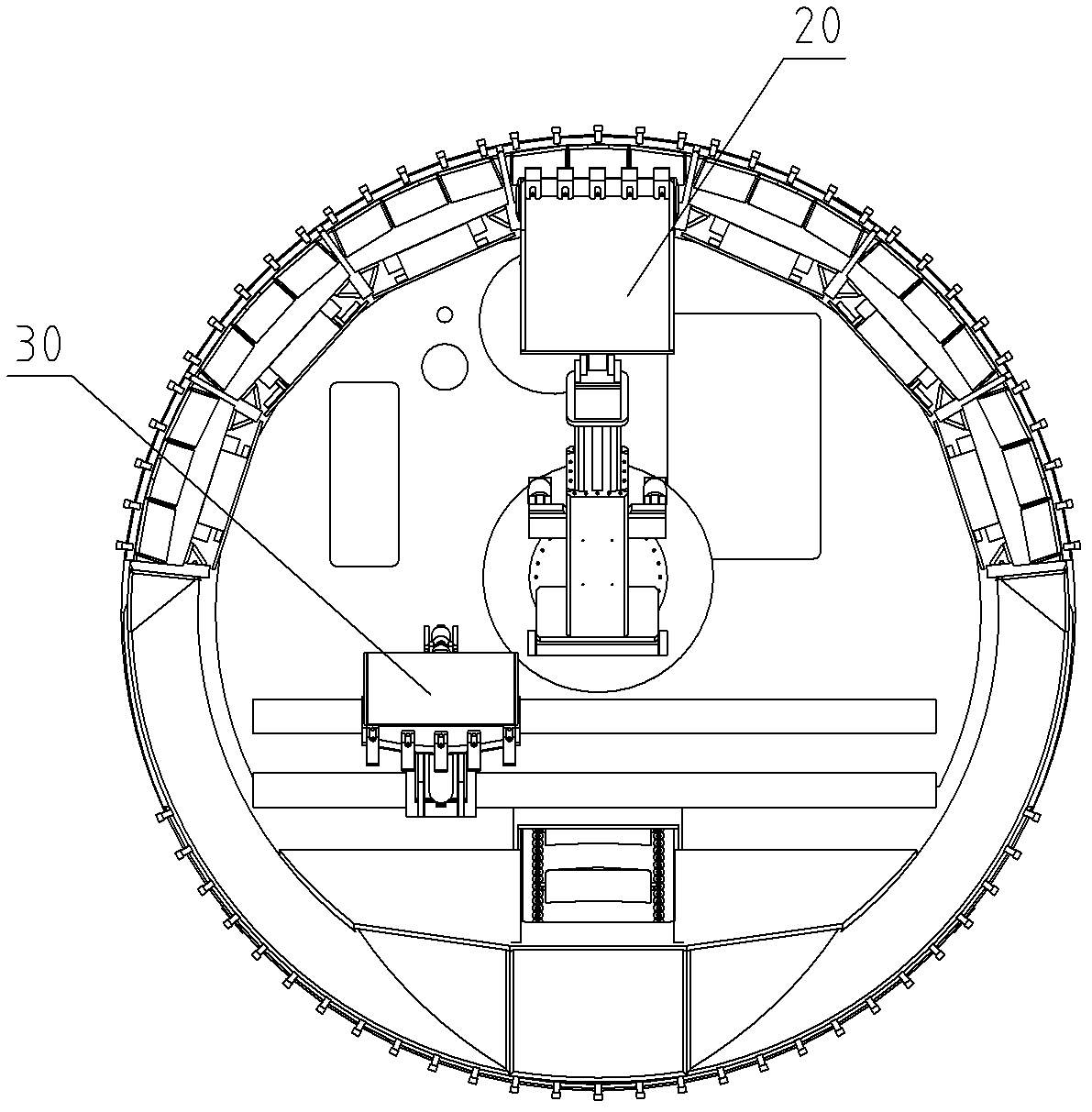
InactiveCN102305083AImprove balanceEstablish balanceUnderground chambersSoil-shifting machines/dredgersEngineeringOperation point
The invention provides a shield machine and an anterior shield system thereof. The system comprises an anterior shield body, an excavation device, a conveyor, and a partition plate, wherein the anterior shield body has a cylindrical structure; the excavation device is arranged on fixing components of the shield machine and a head of the excavation device is used for performing multi action excavation operation on different operation points on an excavation surface; and the conveyor is used for discharging dregs excavated by the head of the excavation device, a first end of the conveyor is arranged below the excavation device and a second end of the conveyor is arranged on the rear part of the first end; and the head of the excavation device and the first end of the conveyor are positioned in front of the partition plate, the second end of the conveyor is positioned on the rear part of the partition plate, and the partition plate is provided with a sealing door which can be opened and closed. The invention can avoid the mud cake agglomeration of a cutter, rolling of the shield body, improved treatment of dregs and pressurized cabin entering operation and has the advantages of quick construction progress, high stability and adaptability and the like.
Owner:BEIJING SANY HEAVY MASCH CO LTD
Control method for maximum power point tracking (MPPT) of photovoltaic array
ActiveCN102624285AAmplified volatilitySolve the large power lossPhotovoltaic energy generationLight radiation electric generatorOperation pointEngineering
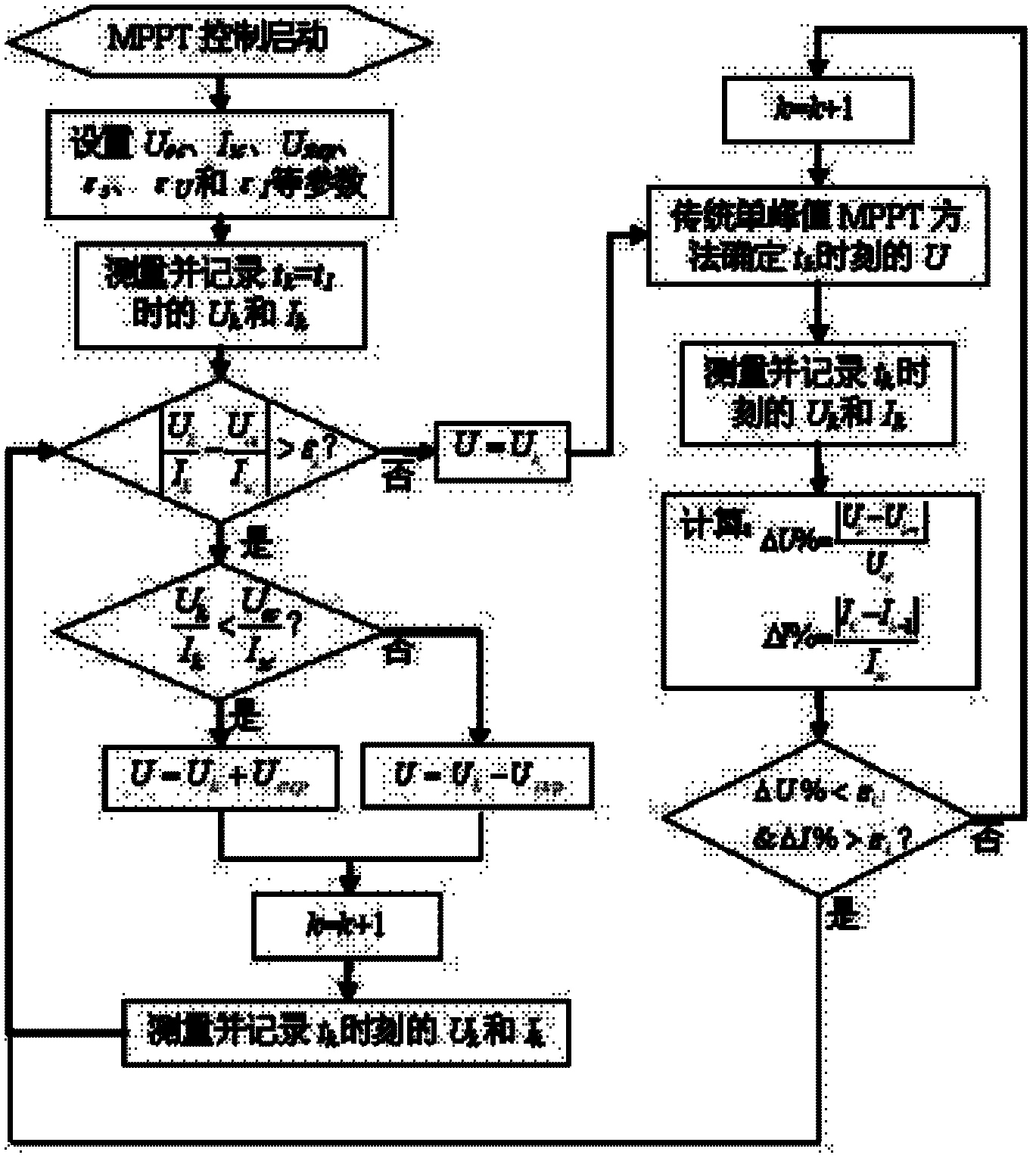
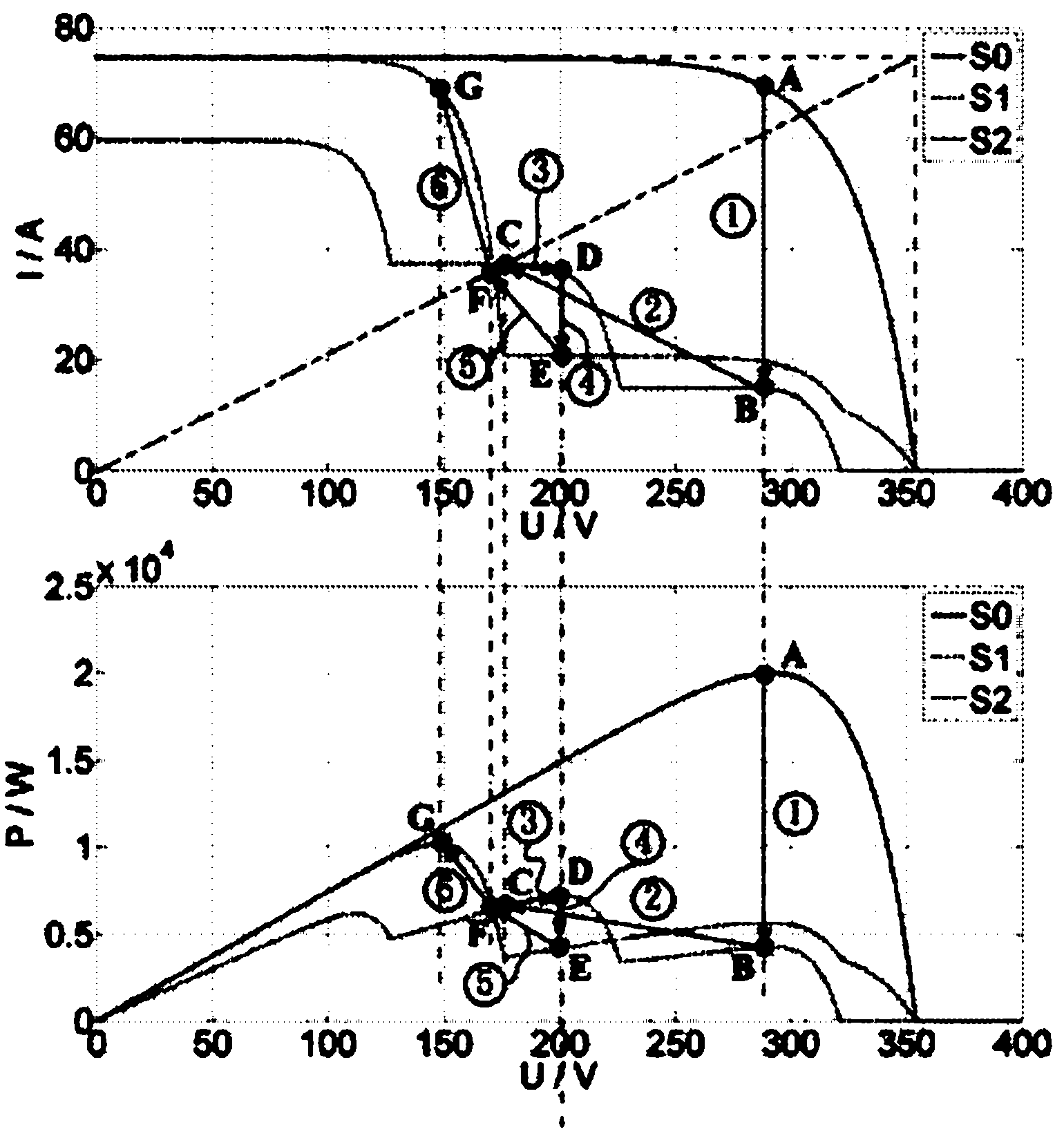
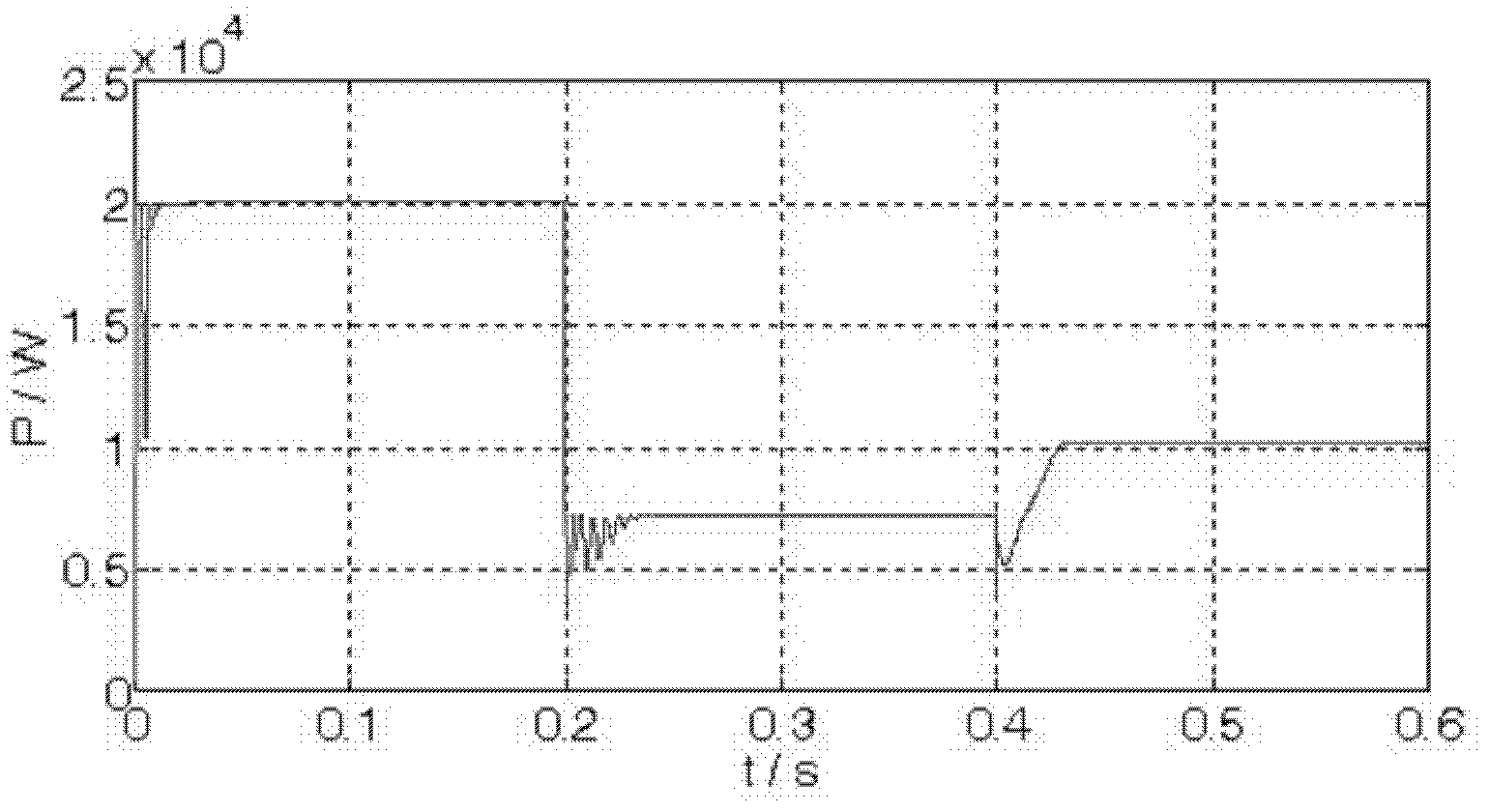
The invention discloses a control method for the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) of a photovoltaic power system. For the control method, on the basis of the traditional MPPT method, a judgement basis for the output characteristic change of the photovoltaic array is added, and a control strategy for the MPPT after the output characteristic change is improved. When the output characteristics of the photovoltaic array are remarkably changed due to a shadow or an assembly fault and the like, an operation point (U, I) on the I-U output characteristic curve of the photovoltaic array is rapidly adjusted to a straight line for connecting the origin of coordinates with a point (Uoc, Isc), and then tracking is performed to the maximum power point of the photovoltaic array starting from the operation point by using the traditional MPPT method. With the adoption of the control method for the MPPT of the photovoltaic power system disclosed by the invention, tracking can be rapidly and accurately performed to a global maximum power point on a multimodal output P-U characteristic curve of the photovoltaic array, and the fluctuation on the output power of the photovoltaic array due to the MPPT method during the tracking process is slight, so that the control method for the MPPT of the photovoltaic power system is good in application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
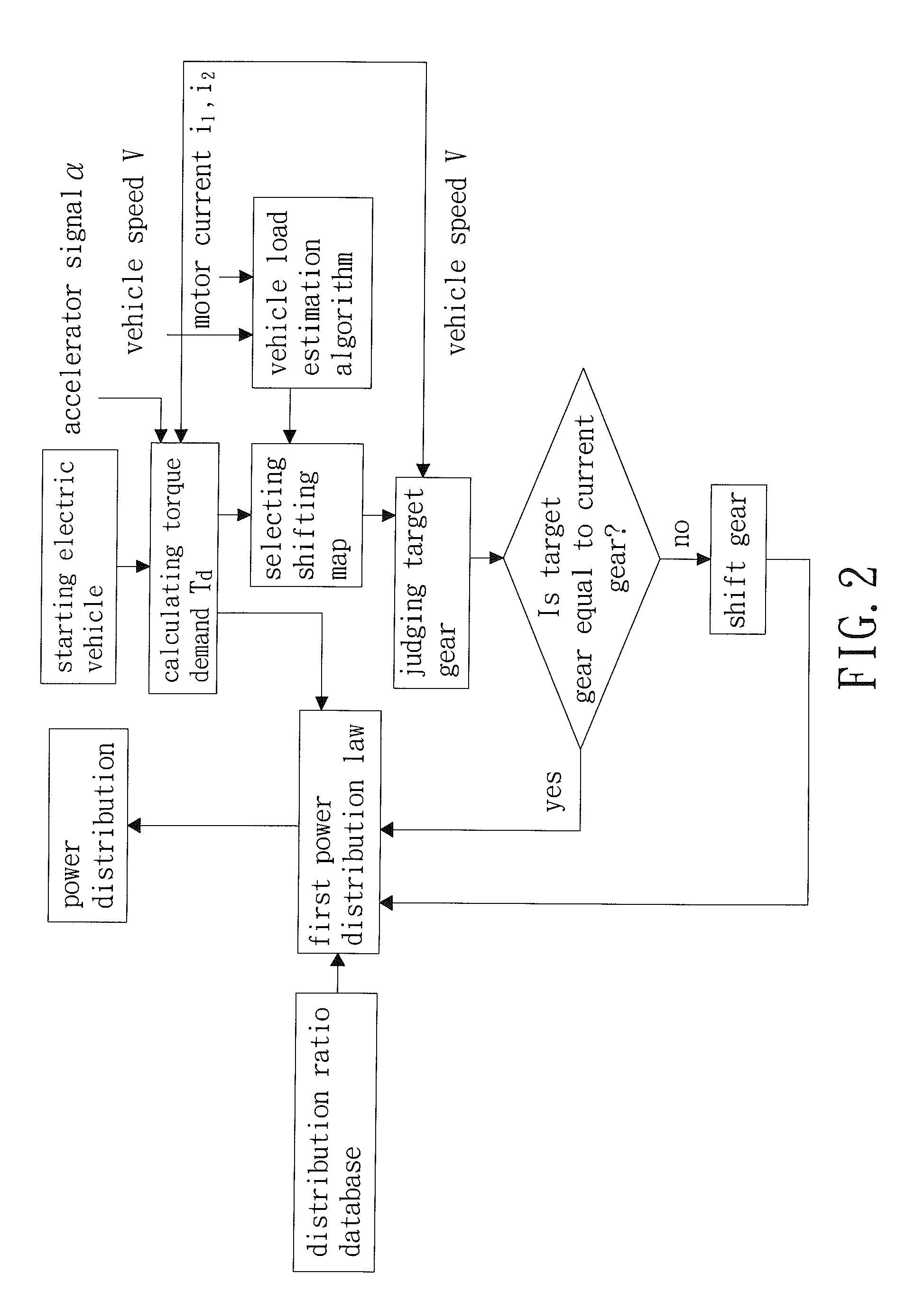
Power Distribution Method for Electric Vehicle Driven by Two Power Sources
InactiveUS20150057866A1Operation efficiency can be improvedReduce energy consumptionDigital data processing detailsElectric propulsion mountingDistribution methodOperation point
A power distribution method for electric vehicle driven by two power sources includes executing a first power distribution law by a vehicle control unit, wherein the first power distribution law sets a distribution ratio according to a vehicle speed of the electric vehicle, a torque demand, and a current gear of a transmission. The powers outputted by first and second motors are adjusted according to the distribution ratio such that the first and second motors can operate at the most efficient operation points to increase the operational efficiency of the electric vehicle driven by two power sources.
Owner:NAT PINGTUNG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device for feeding electrical energy from an energy source
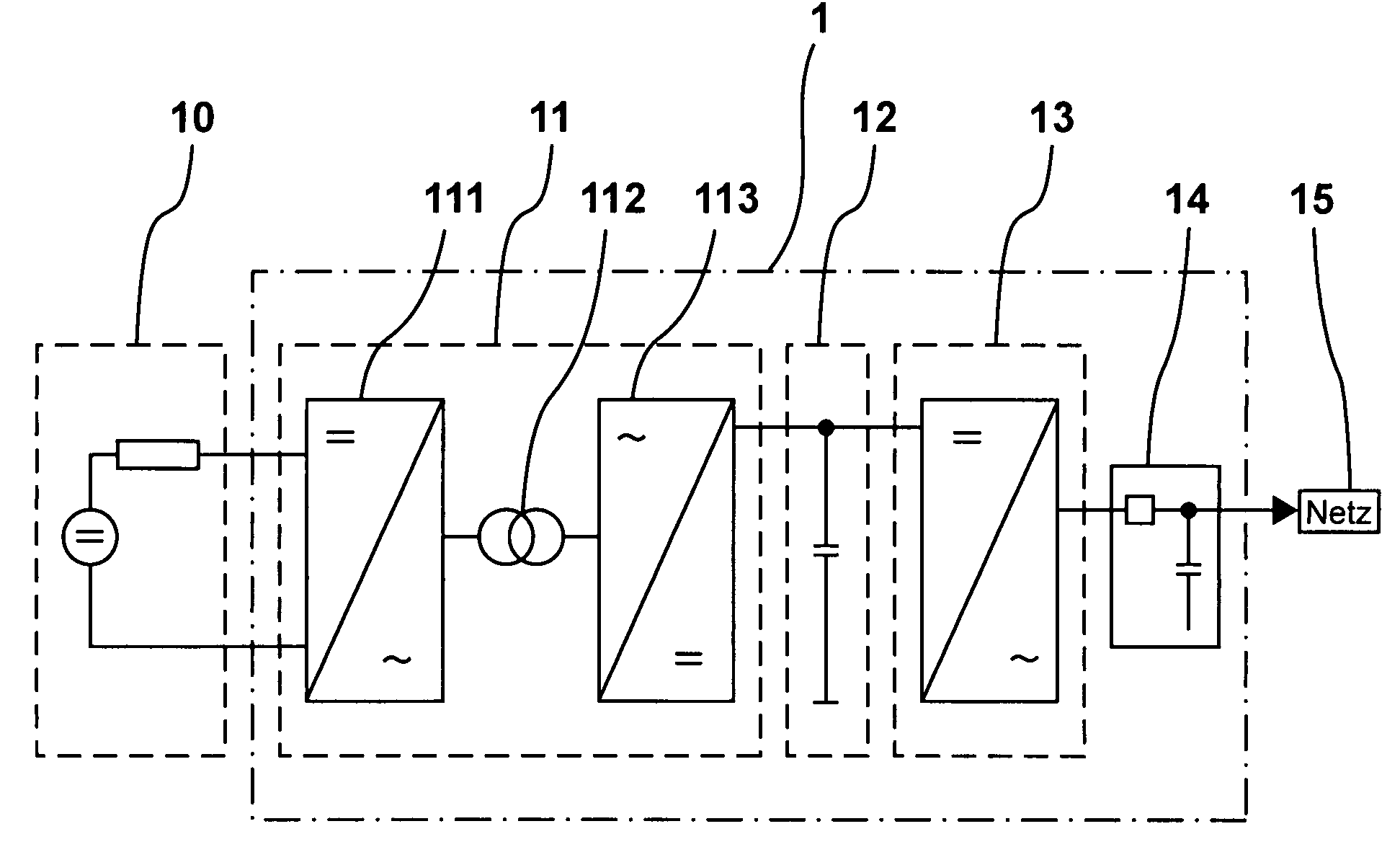
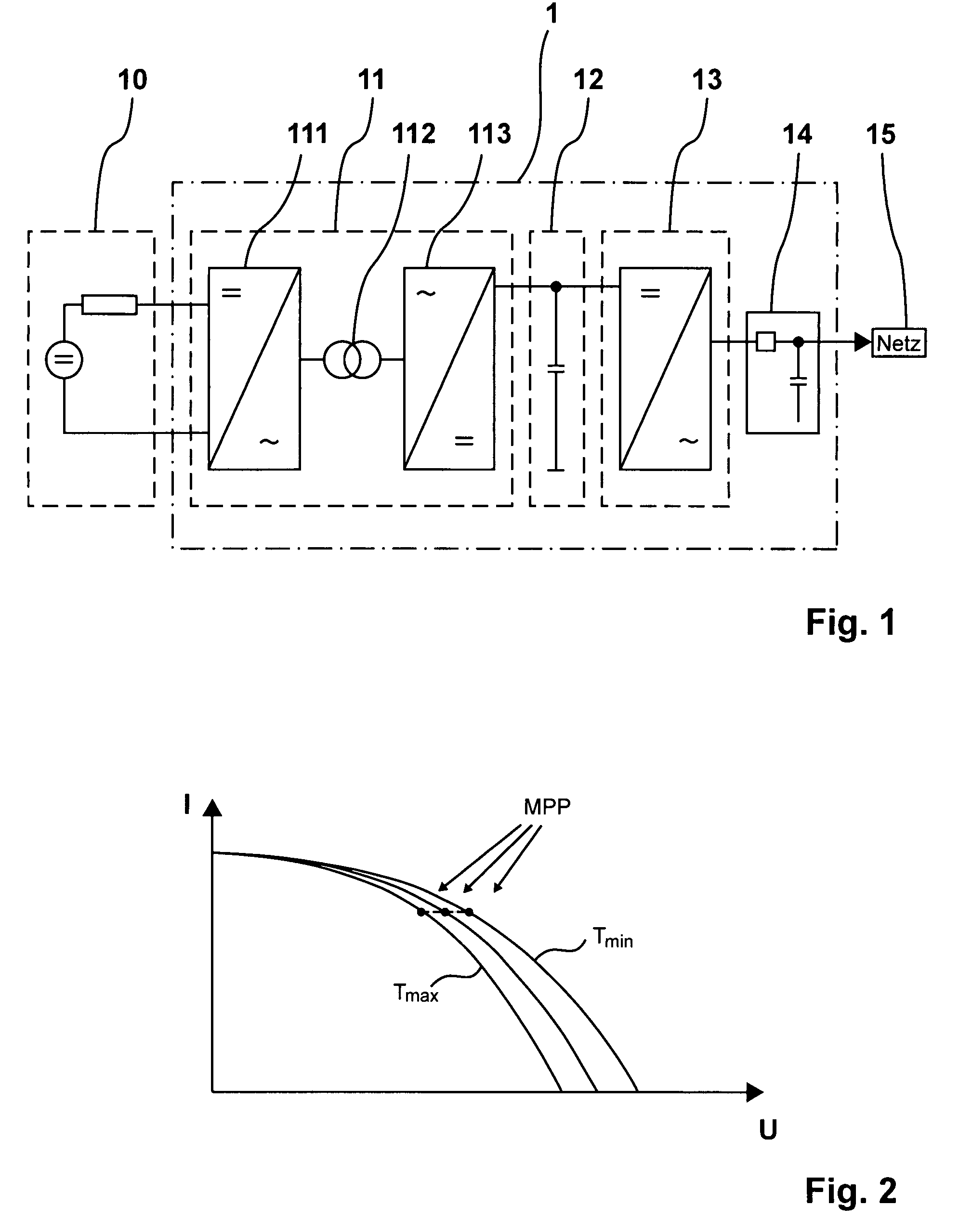
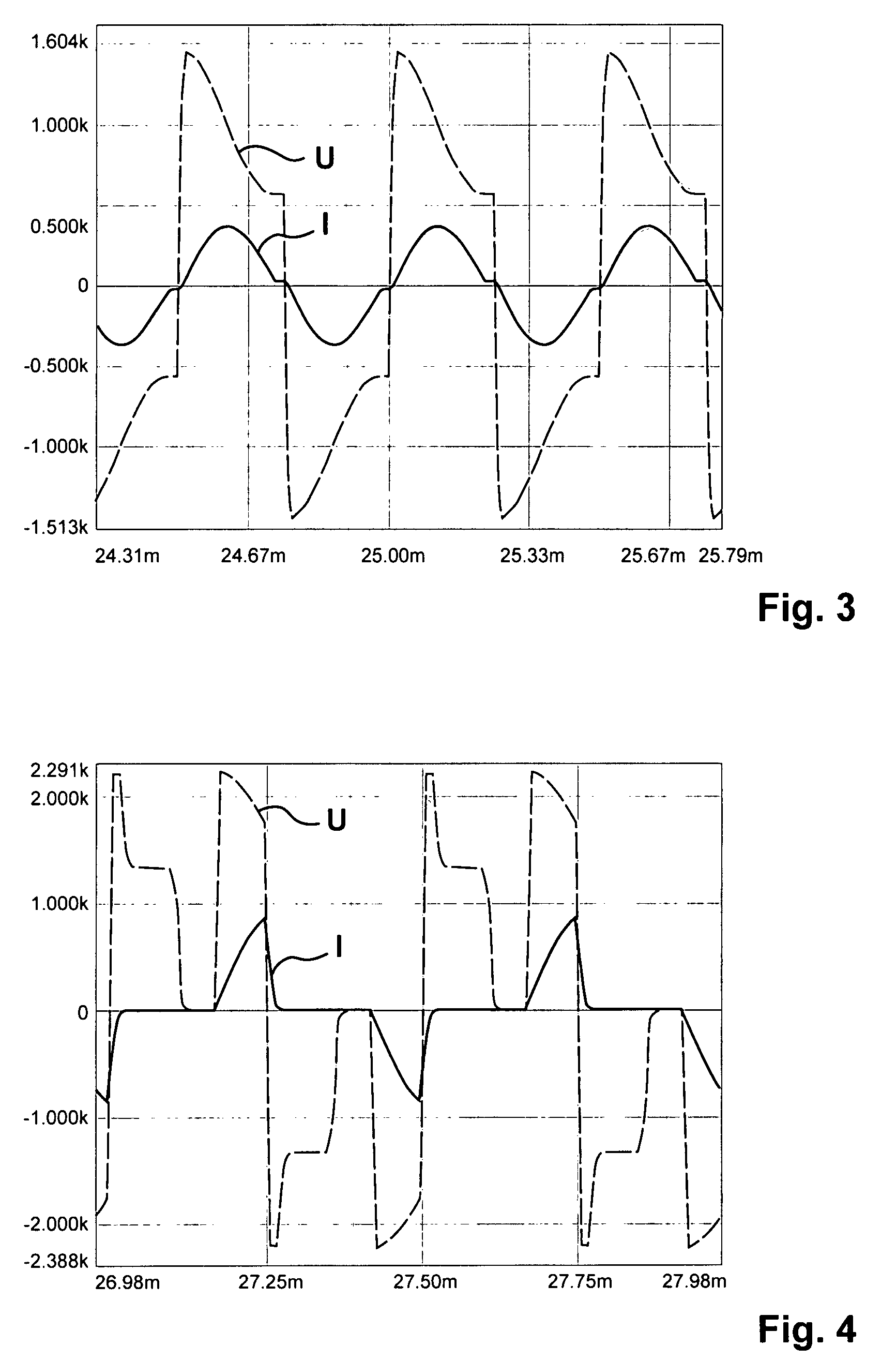
InactiveUS7672149B2Improve efficiencyLow costDc network circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionResonant inverterEngineering
A device (1) for feeding electrical energy from an energy source with variable source voltage into an electric power supply network (15), said device (1) including a transformer (112) for galvanic isolation, a resonant inverter (11) with semi-conductor switches (a-d; A, B), one or several resonant capacitors (17; 18, 19; 20, 21) and one rectifier (113), is intended to provide high efficiency and have galvanic isolation. This is achieved in that the resonant inverter (11) is operated in the full resonant mode if the operating voltage is in an operation point (MPP) and in the hard-switching mode if the voltages exceed the operation point (MPP).
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
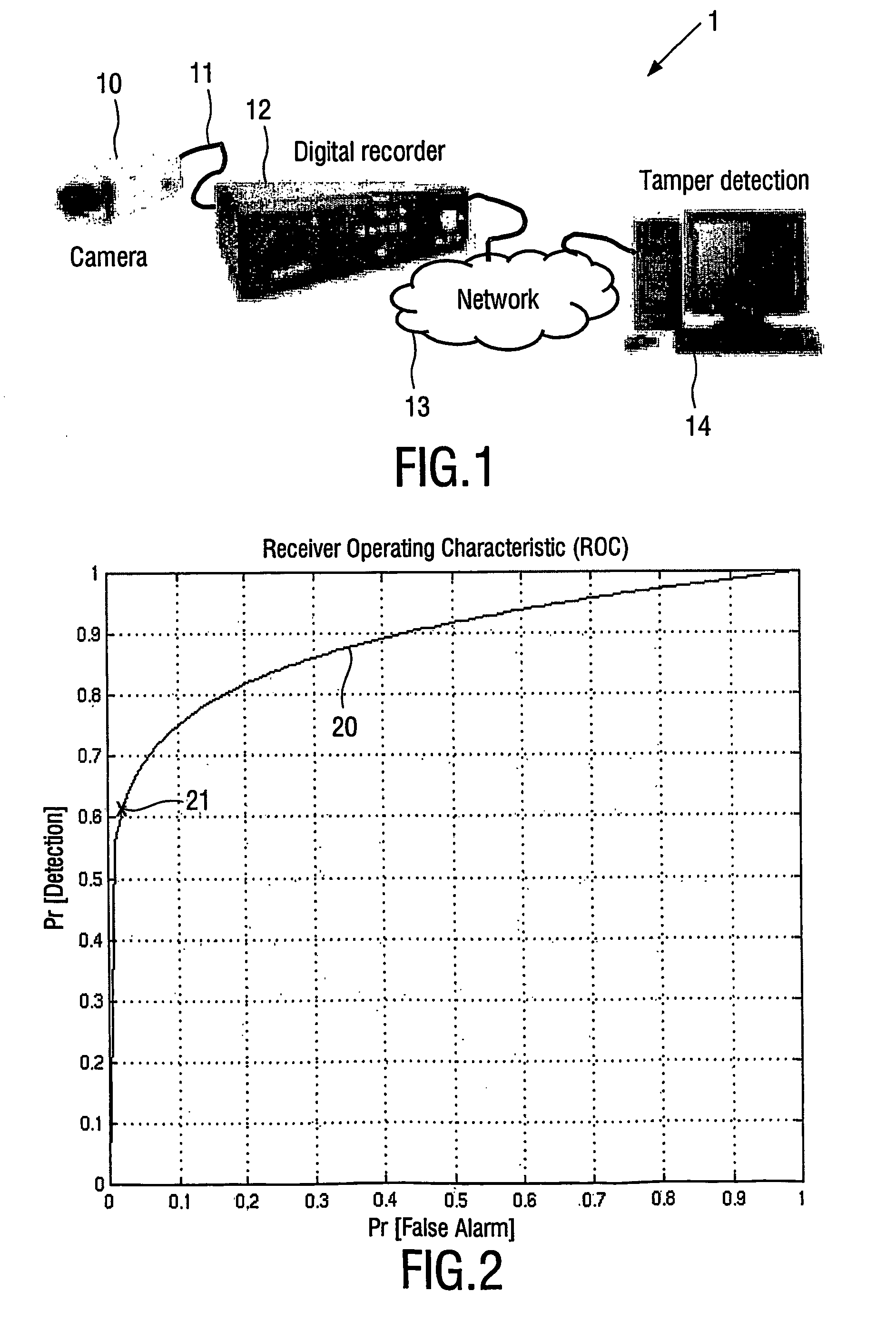
Localisation of image tampering
InactiveUS20060020830A1Reduce probabilityUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringReceiver operating characteristicOperation point
A method and device (8) for verifying the authenticity of media content is provided. According to an embodiment accurate tampering location for digital image authentication is provided. Typically, a suspect image is divided into blocks. For each block, an authentication bit is generated by computing a property of the image content and then thresholding said property to give a ‘0’ or ‘1’. The authentication bits of the suspect image are compared with those of the original image. If there is a mismatch, and the content has indeed been tampered, tampering is detected. A mismatch due to allowable operations, such as e.g. compression, is called a false alarm, which should be avoided. A so-called ROC curve (Receiver Operating Characteristic) gives the relation between detection probability and false alarm probability. Preferably, the threshold used to determine the authentication bits represents an operation point on the ROC curve. In accordance with an embodiment of the invention, an operation point corresponding to a low false alarm probability is initially chosen. In order to more precisely identify a tampered image area, the authentication decisions are repeated for neighbouring blocks, using a different operation point. This continues until no further tampered blocks are found. Thus improved tampering localisation is provided, being valuable e.g. to authenticate images captured by e.g. a security camera, and localise any tampered areas, whereby the value of these images is increased as e.g. evidence in a court of law.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
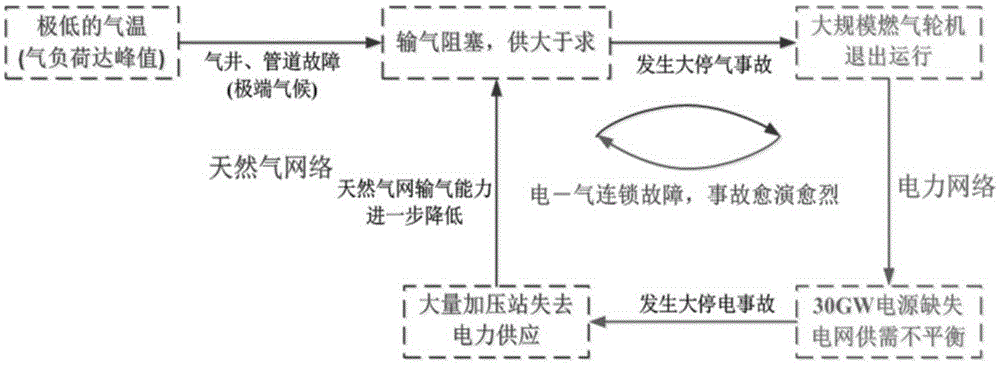
Analysis method for steady-state security region of electric-pneumatic interconnected integrated energy system
ActiveCN105356447AData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsOperation schedulingSteady state security
The invention discloses an analysis method for a steady-state security region of an electric-pneumatic interconnected integrated energy system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, building a steady-state energy flow model of the electric-pneumatic interconnected integrated energy system; secondly, proposing the concept of the steady-state security region of the electric-pneumatic interconnected integrated energy system by referring to a definition and a model of the steady-state security region of a power system; thirdly, obtaining a group of boundary operation points on the boundary of the security region through repeated energy flow calculation; and finally, obtaining the steady-state security region of the electric-pneumatic interconnected integrated energy system on the basis of linear hyperplane fitting. The security region model disclosed by the invention provides a theoretical basis for real-time operation scheduling and online security evaluation of the electric-pneumatic interconnected integrated energy system.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Secondary Battery Control Apparatus and Secondary Battery Control Method
InactiveUS20080143281A1Energy loss is increased and reducedTemperature can be quickly and easilySingle motor speed/torque controlTemperatue controlElectrical resistance and conductanceInternal resistance
When it is determined that a battery temperature is lower than a threshold value, an inverter control circuit alternately switches an operation point of an AC motor between an optimum operation point and a motor loss increase point. At the motor loss increase point, an increase in the amplitude of the motor current increases copper loss occurring in the three-phase coil of the AC motor. On the other hand, at the optimum operation point, a reduction in the amplitude of the motor current reduces copper loss. Corresponding to the cyclical increase / reduction in the copper loss, the battery is cyclically charged / discharged by the electric power corresponding to the copper loss. The change in the battery current occurred by the charge / discharge causes the internal resistance to generate heat, whereby the temperature of the battery is increased. The foregoing temperature increase operation is prohibited when the motor temperature exceeds an allowable temperature with which the operation efficiency of the AC motor is ensured.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for controlling stroke lengthening of serially connected pluggable electric vehicle
ActiveCN101979265ASave layout spaceMeet electricity demandBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerElectricityComputer module
The invention provides a method for controlling stroke lengthening of a serially connected pluggable electric vehicle. The system adopted by the method consists of an engine, a control unit EMS of the engine, a generator, a controller IPU of the generator and a whole vehicle controller HCU. The controlling method comprises the following steps of: (1) setting starting conditions of a stroke lengthening module; (2) starting the stroke lengthening module; and (3) controlling operation of the stroke lengthening module. In the method, a small starting motor which starts the engine can be saved, the engine can be directly started by the generator with high efficiency so as to reduce cost and save arrangement space of parts and components, simultaneously a command is sent to the IPU through the HCU to ensure the generator starts the engine, so that the success rate of one-time start is higher, and the starting effect and the communication command are simpler compared with those obtained whenthe small starting motor starts the engine. Meanwhile, in the method, several operation points with better economy can be selected on an external characteristic curve of the engine so as to reduce energy consumption and meet the requirement of electricity utilization of the whole vehicle.
Owner:CHONGQING CHANGAN AUTOMOBILE CO LTD +1
Method and Apparatus for Determining an Operating Point of a Work Machine
ActiveUS20120111114A1Reduce spendingImprove accuracyVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMotor driveOperating point
Method and apparatus for determining an operating point of a work machine and / or asynchronous motor driving the same, the operating point being characterized by the power consumed by and / or output rate of the machine, in which one or more operating point-dependent measurement variables of the machine are detected by sensors, and the measured values are evaluated and / or stored during operation of the machine. The operating point is determined without using electric measurement variables of the motor by determining a frequency linearly proportional to the fundamental tone of the machine through signal analysis, especially frequency analysis of a measured mechanical variable selected from pressure, differential pressure, power, vibration, and solid-borne or air-borne sound. From this, the rotational speed of the driving machine is determined, and the operating point characterized by the power consumed by and / or output rate of the machine is determined utilizing the rotational speed / torque relationship of the motor.
Owner:KSB AG
Fabricated scaffold and using method thereof
InactiveCN101844612AImprove utilizationShorten the timeDry-dockingSlipwaysWork patternGeneral assembly
The invention discloses a fabricated scaffold and a using method thereof. The fabricated scaffold comprises a plurality of fixing parts, bearing parts and a plurality of scaffold platforms, wherein the plurality of fixing parts are vertical to a mounting surface; one bearing part is arranged on each fixing part; and the plurality of scaffold platforms are paved between two or among more than two bearing parts. The using method thereof comprises the following steps of: a ship segment stage, namely vertically and fixedly arranging the plurality of fixing parts on the mounting surface at preset intervals; and a general assembly and carrying phase, namely arranging one bearing part on each fixing part and arranging one scaffold platform on the adjacent bearing part. In the invention, a conventional operating mode that a tubular scaffold is needed to be erected in a whole cabin space so as to help a worker reach a higher operation point is changed, a method for extendedly arranging the scaffold clung to the mounting surface is adopted so as to release most of the space in the cabin, shorten the construction period, improve the use ratio of a dock, and reduce the hazard index of workersbelow the scaffold; and the fabricated scaffold has very obvious effect on backing construction in the ship building.
Owner:SHANGHAI WAIGAOQIAO SHIP BUILDING CO LTD
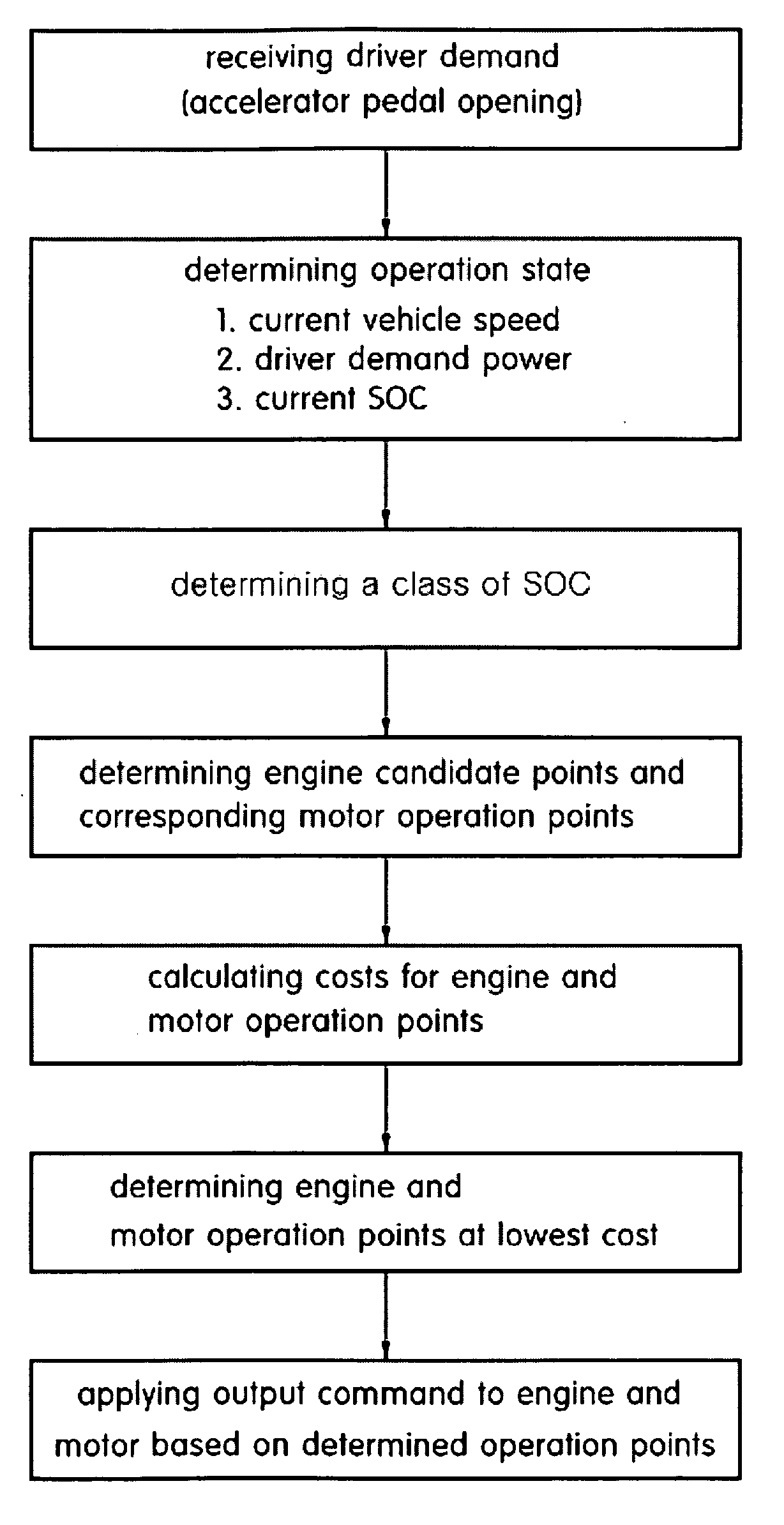
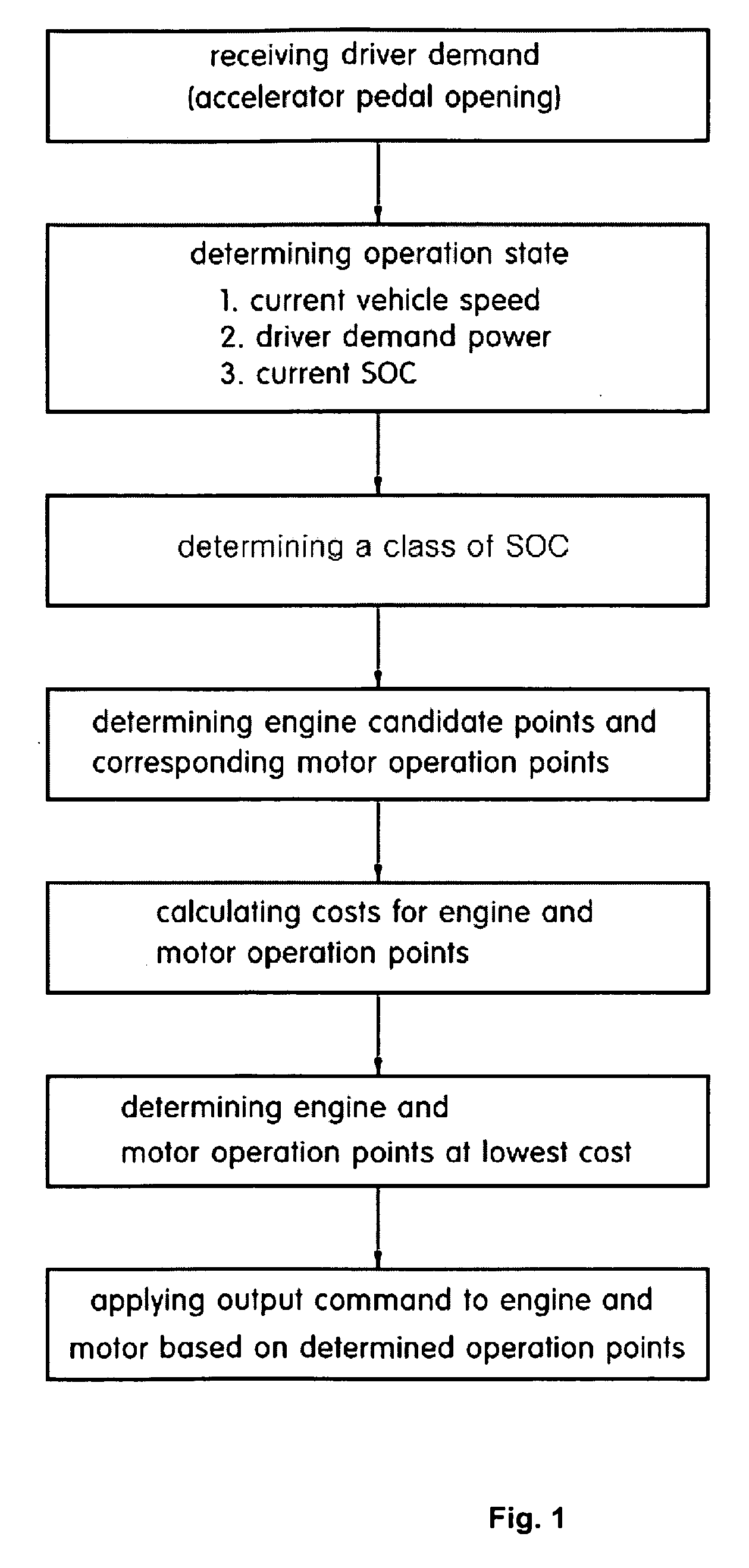
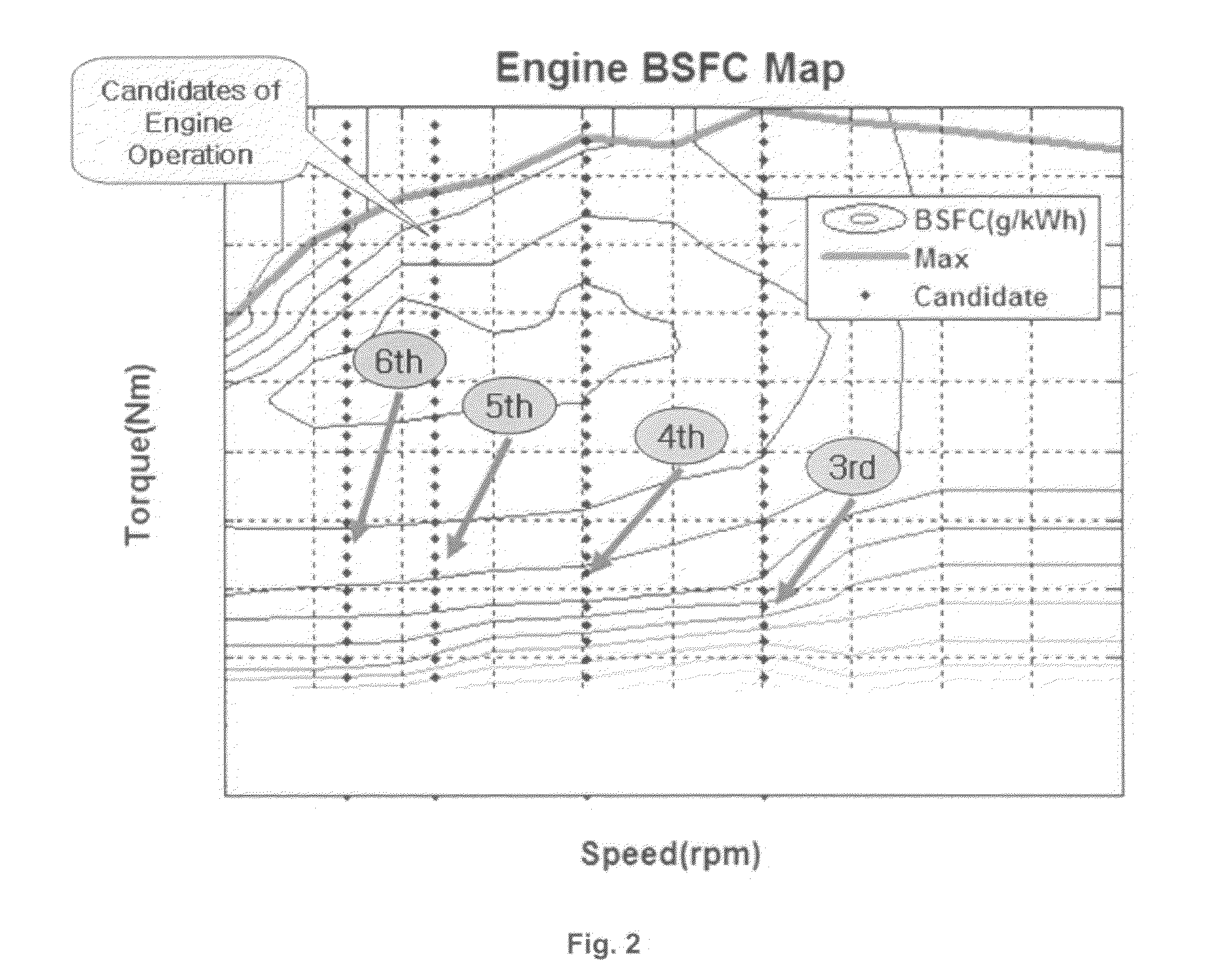
Method for determining optimal operation point with respect to state of charge in hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20090157244A1Improve fuel efficiencyHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsConversion factorFuel efficiency
The present invention provides a method for determining an optimal operation point with respect to SOC in a hybrid electric vehicle, in which, as a conversion factor (fuel equivalent factor) that can quantitatively compare the amount of fuel consumed by an engine with electrical energy consumed by a motor, a factor for obtaining a desired final SOC with respect to an initial SOC is determined, and an optimal operation state based on a current SOC of the hybrid electric vehicle is determined using the factor, thus improving fuel efficiency of the hybrid electric vehicle.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
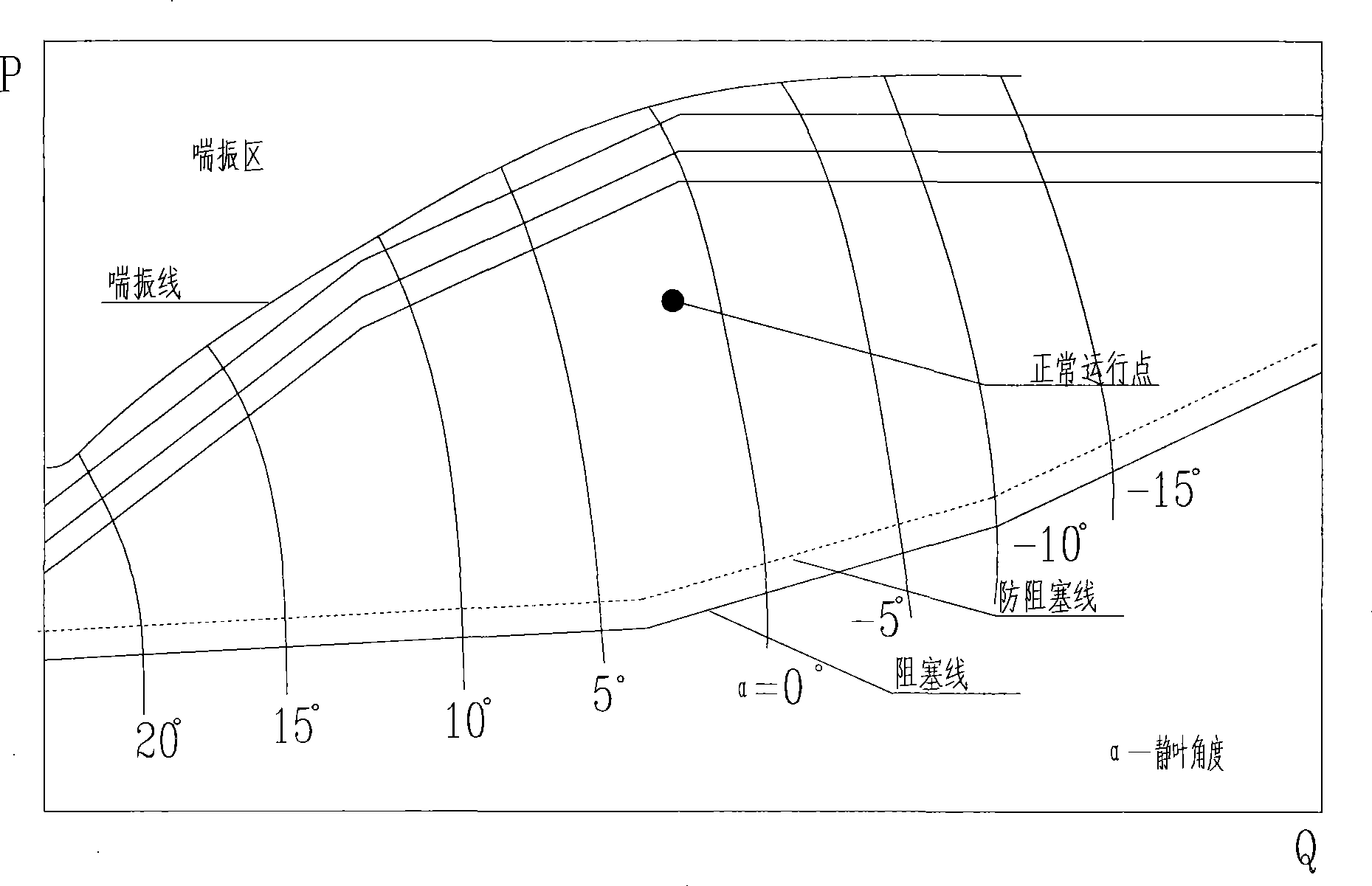
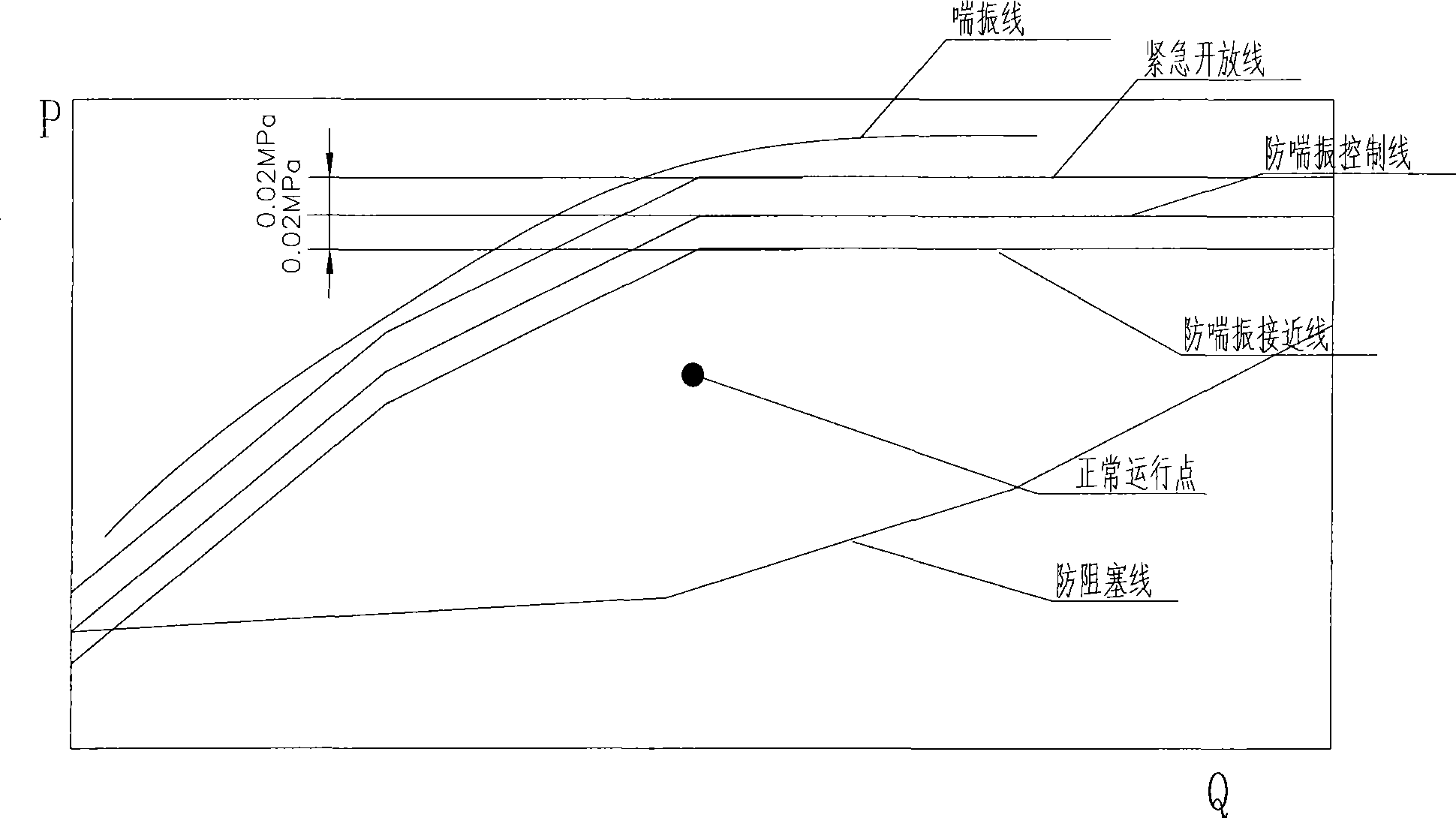
Device and method for controlling anti-surging of a blast blower
ActiveCN101545495AGuaranteed safe operationAnti-surge control implementationPump componentsPump controlStandard stateControl signal
The invention discloses a device for controlling anti-surging of a blast blower, which comprises a sensor module, a standard flow conversion module, a dynamic anti-surging control module, an anti-surging adjuster and an execution mechanism. The invention also discloses a method for controlling the anti-surging, which comprises the following steps: step one, measuring temperature and pressure of an inlet and pressure of an outlet; step two, converting flow of the inlet into the flow in a standard state; step three, calculating a dynamic anti-surging control curve according to the temperature and the pressure of the inlet and a static anti-surging control curve; step four, finding out anti-surging control pressure corresponding to the converted flow in the standard state according to the dynamic anti-surging control curve, and outputting an anti-surging control signal when the pressure of the outlet is equal to or larger than the anti-surging control pressure; and step five, controlling a normal operation point of the operation of the blast blower according to the anti-surging control signal. The method establishes the dynamic anti-surging control curve and realizes the anti-surging control under different ambient temperatures and pressure states.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAOSIGHT SOFTWARE CO LTD
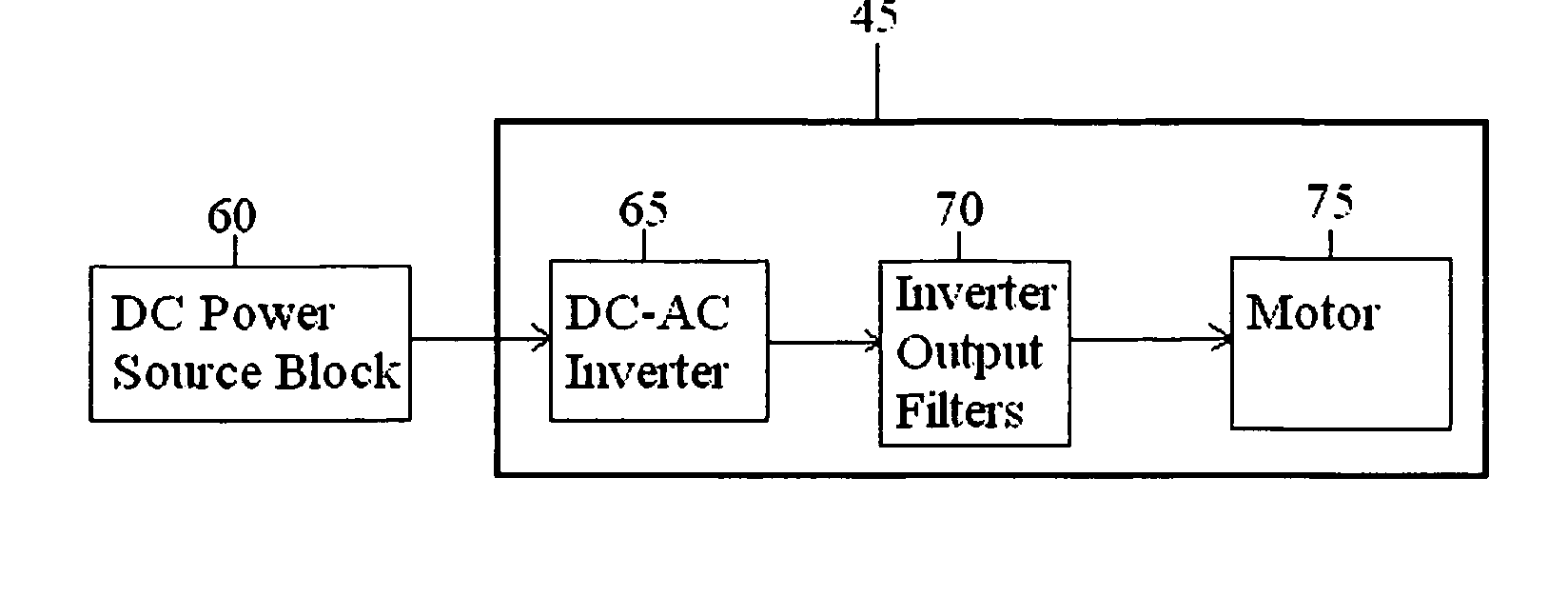
High power density/limited DC link voltage synchronous motor drive
InactiveUS20060113952A1Improve performanceMinimise currentElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlSynchronous motorMotor drive
A method and an apparatus optimize performance of a motor drive system. The method according to one embodiment comprises: selecting a property for a rated operation point; selecting inverter system characteristics and motor characteristics such that a motor drive system including an inverter system having the selected inverter system characteristics operatively connected to a motor having the selected motor characteristics will have a rated operation point exhibiting the property; providing an inverter system having the selected inverter system characteristics; operatively connecting a motor having the selected motor characteristics to the inverter system; and minimizing current of the motor drive system including the motor operatively connected to the inverter system in entire operating range of the motor drive system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com