Patents
Literature
3253results about How to "Improve coding efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
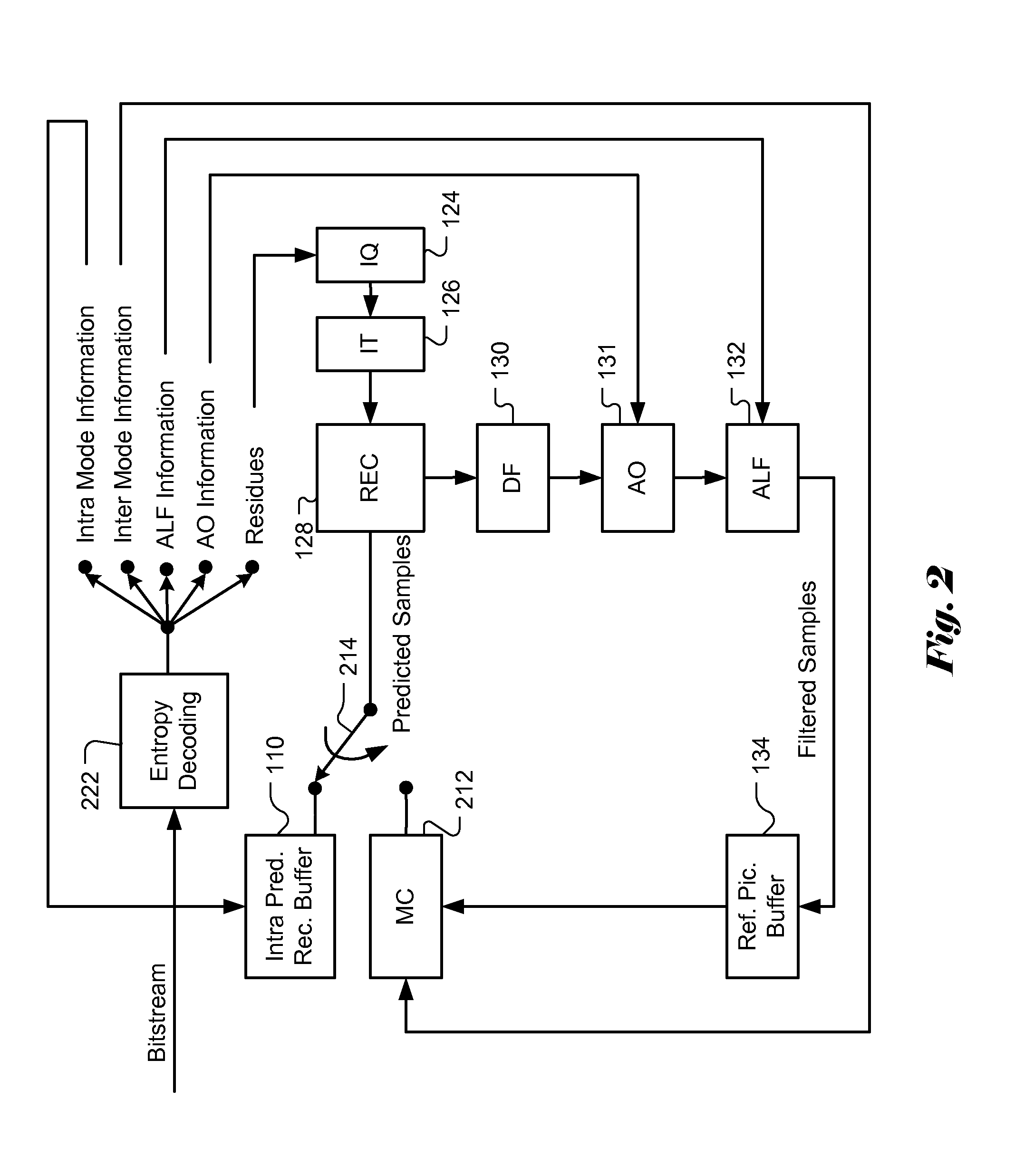
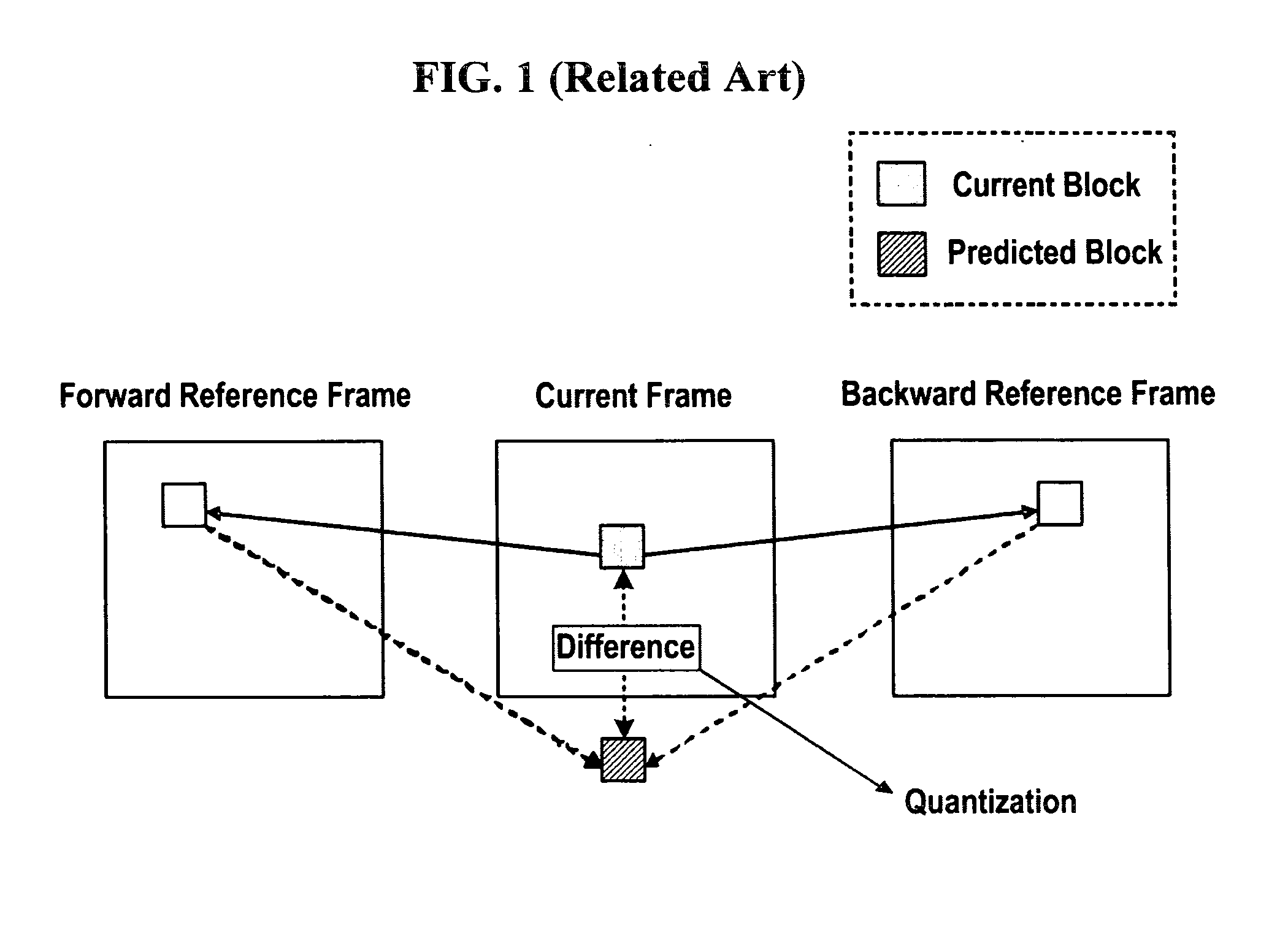
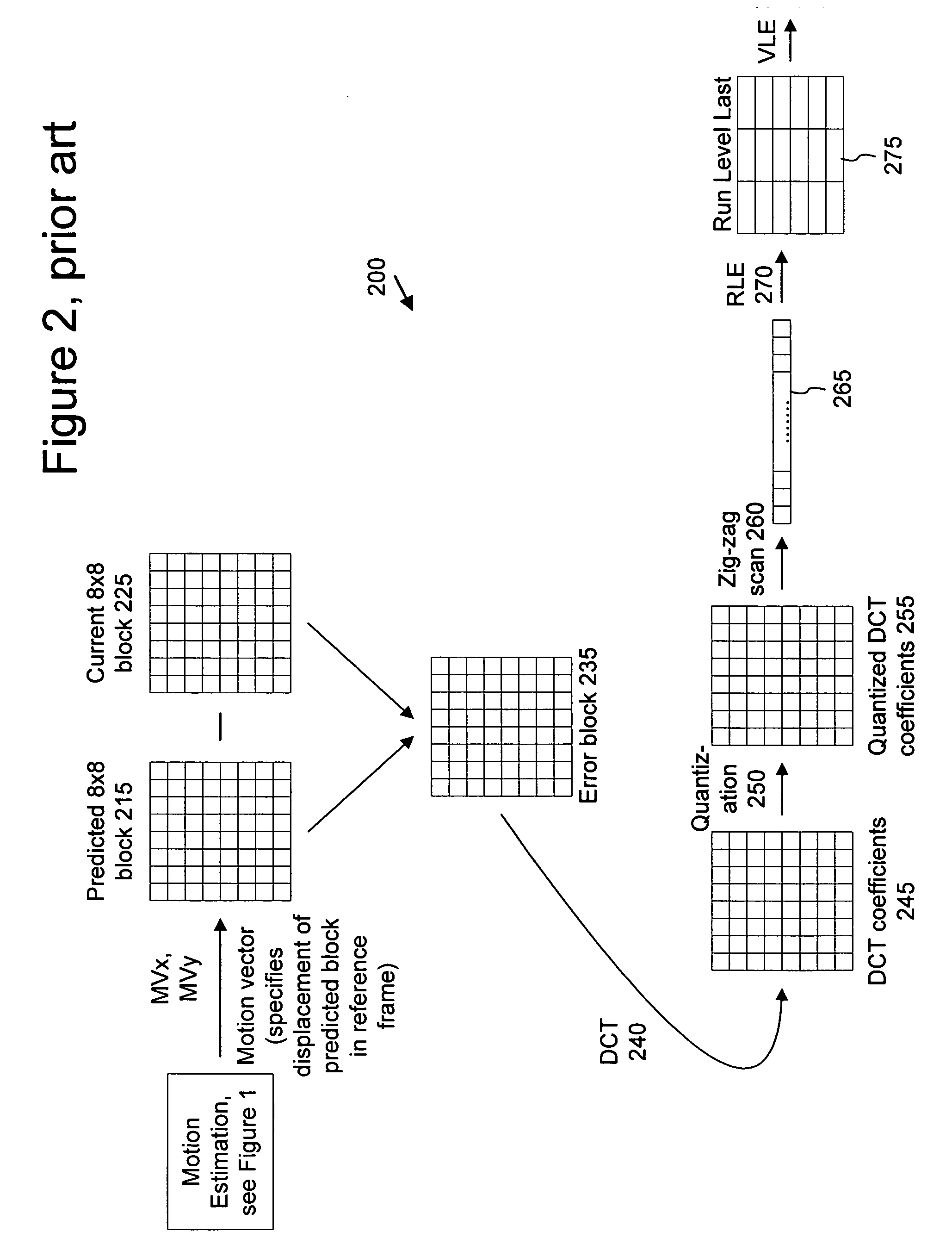
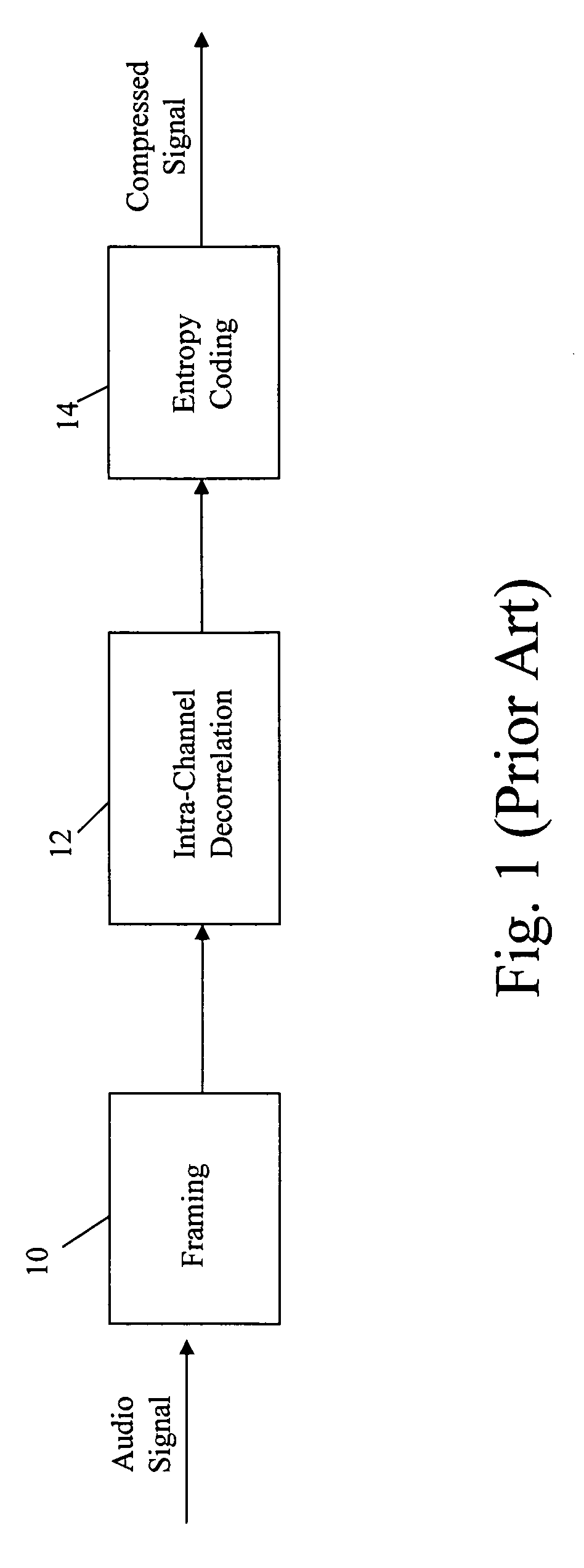
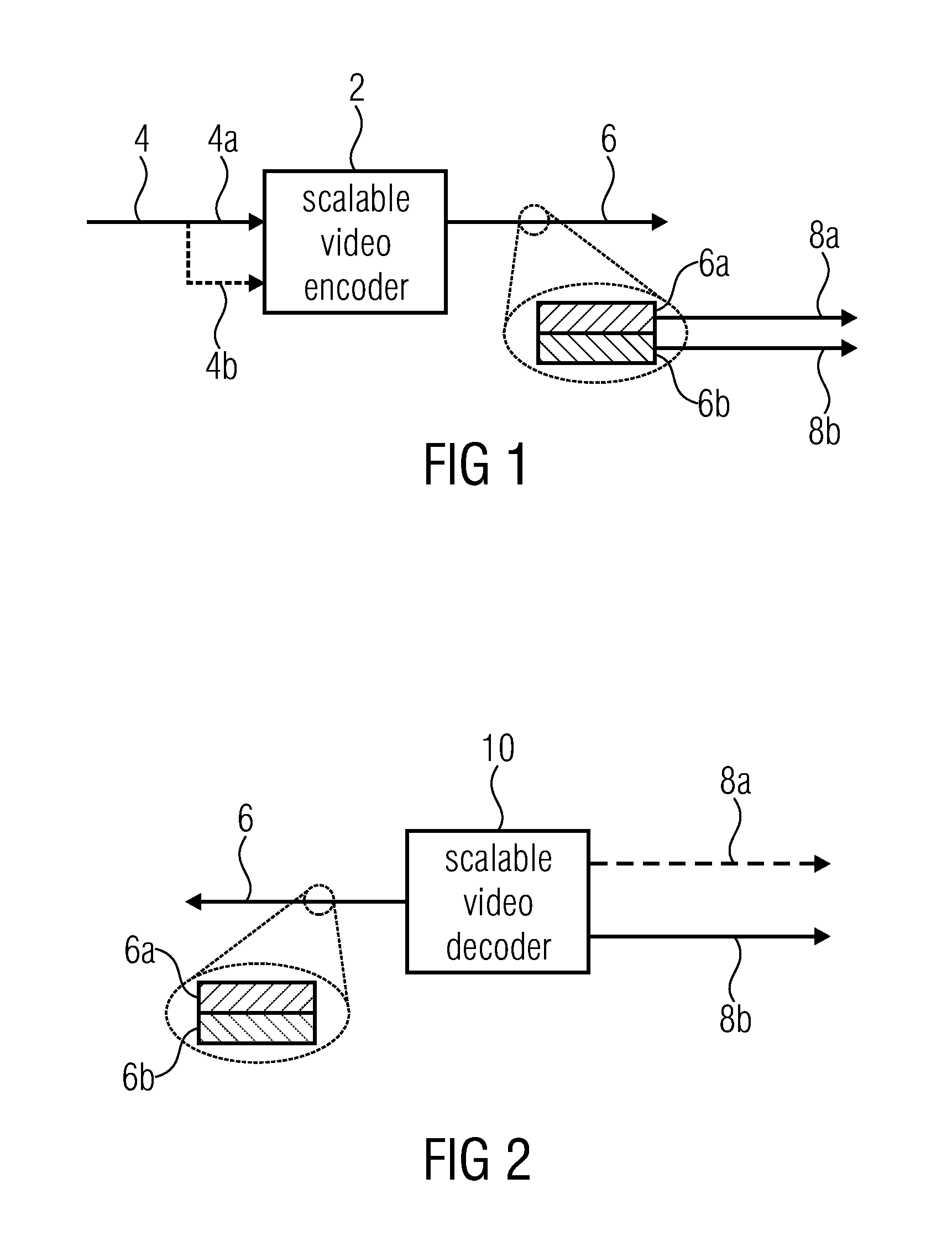
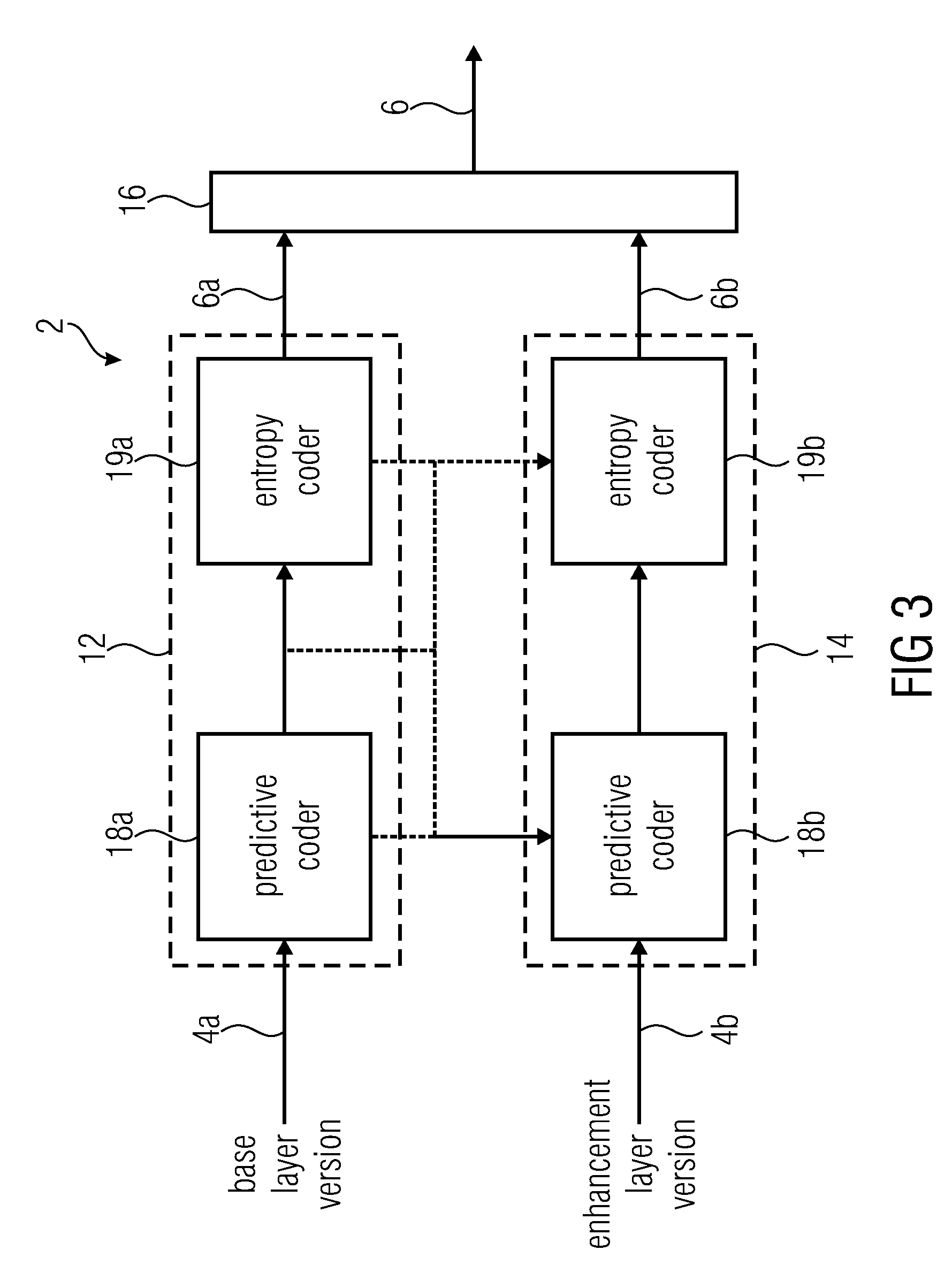
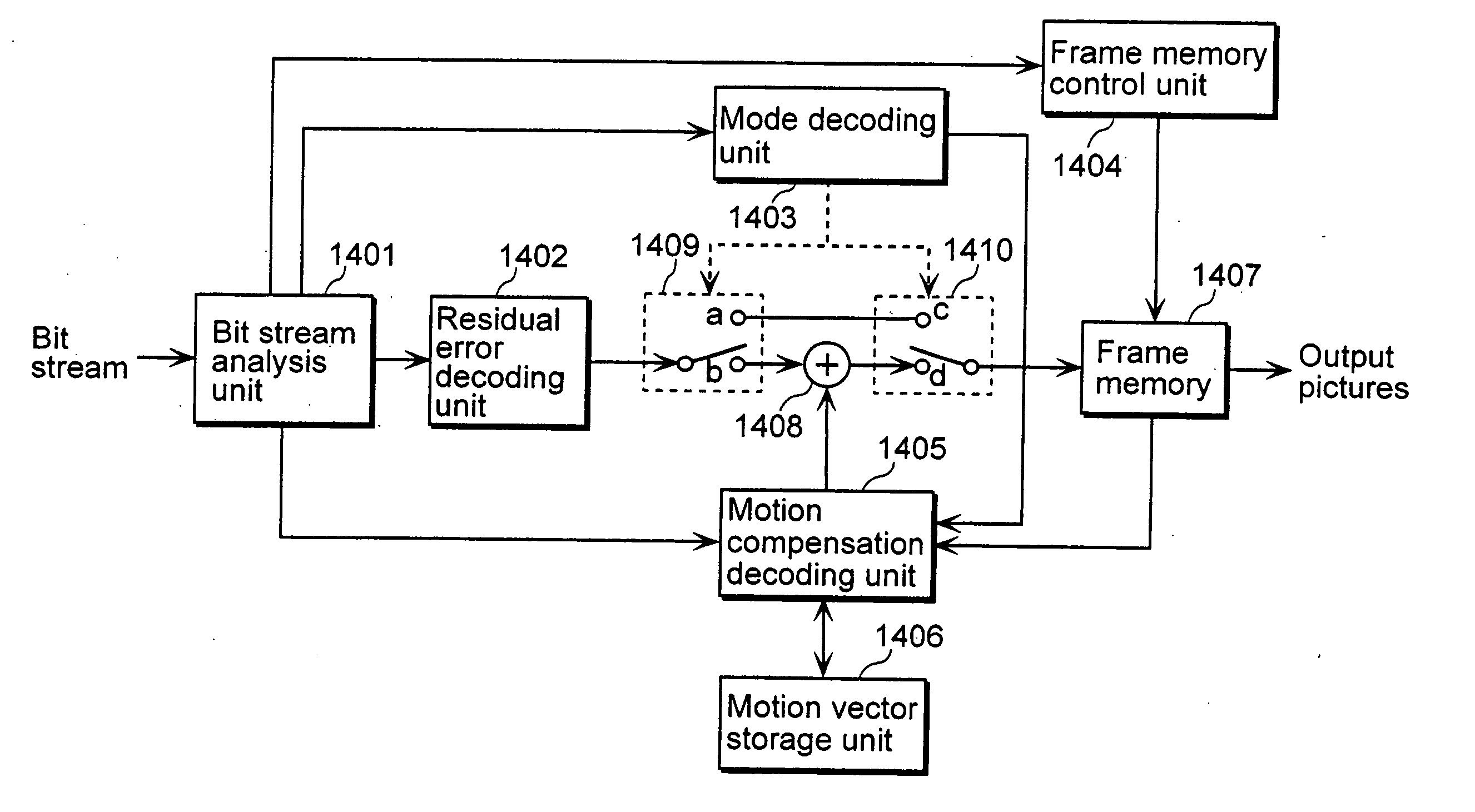
Video coding methods and apparatuses
ActiveUS7003035B2Improve efficiencyReduce amount of dataTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMacroblockVideo encoding
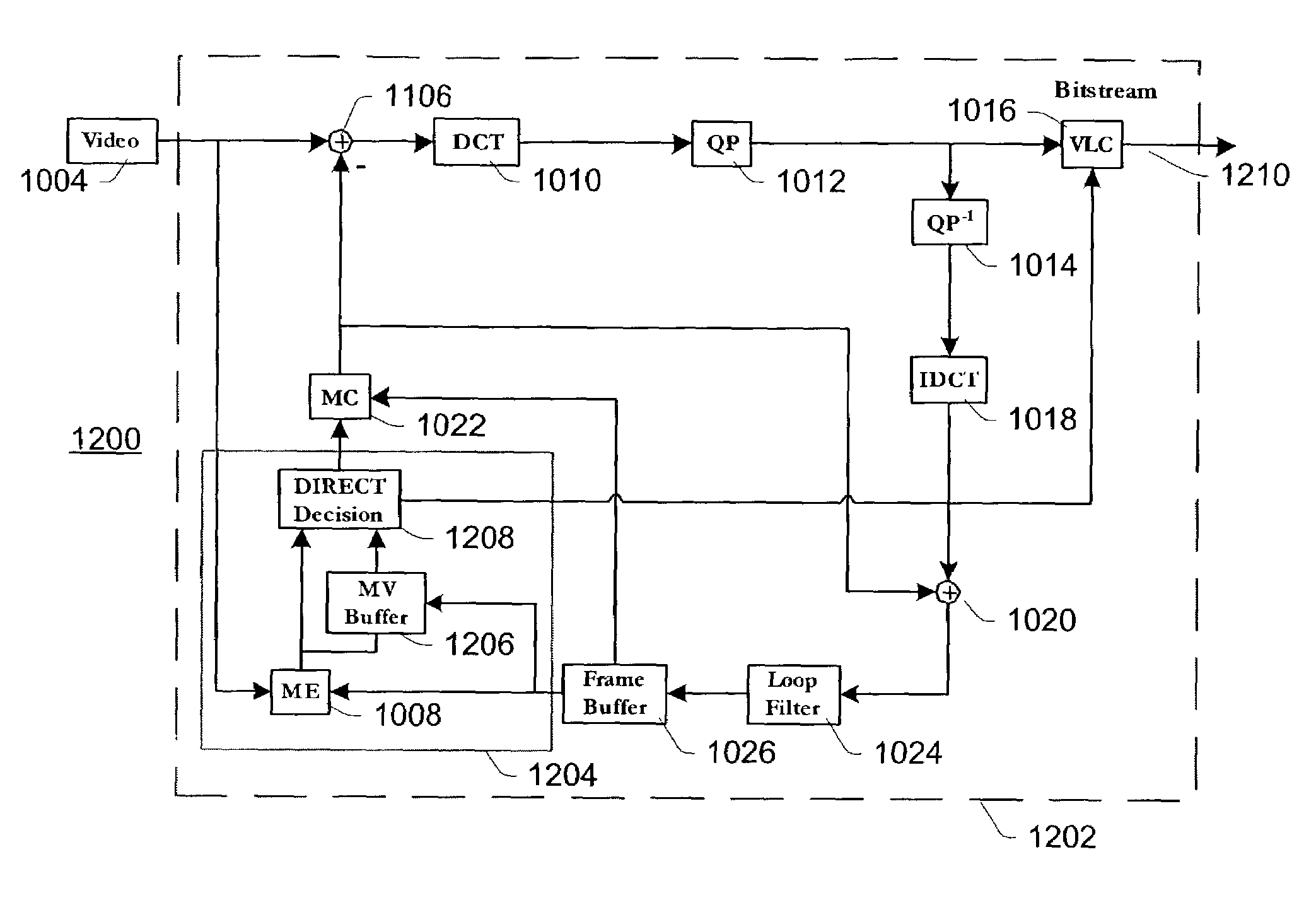
Video coding methods and apparatuses are provided that make use of various models and / or modes to significantly improve coding efficiency especially for high / complex motion sequences. The methods and apparatuses take advantage of the temporal and / or spatial correlations that may exist within portions of the frames, e.g., at the Macroblocks level, etc. The methods and apparatuses tend to significantly reduce the amount of data required for encoding motion information while retaining or even improving video image quality.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for encoding a 3D video signal, enclosed 3D video signal, method and system for decoder for a 3D video signal
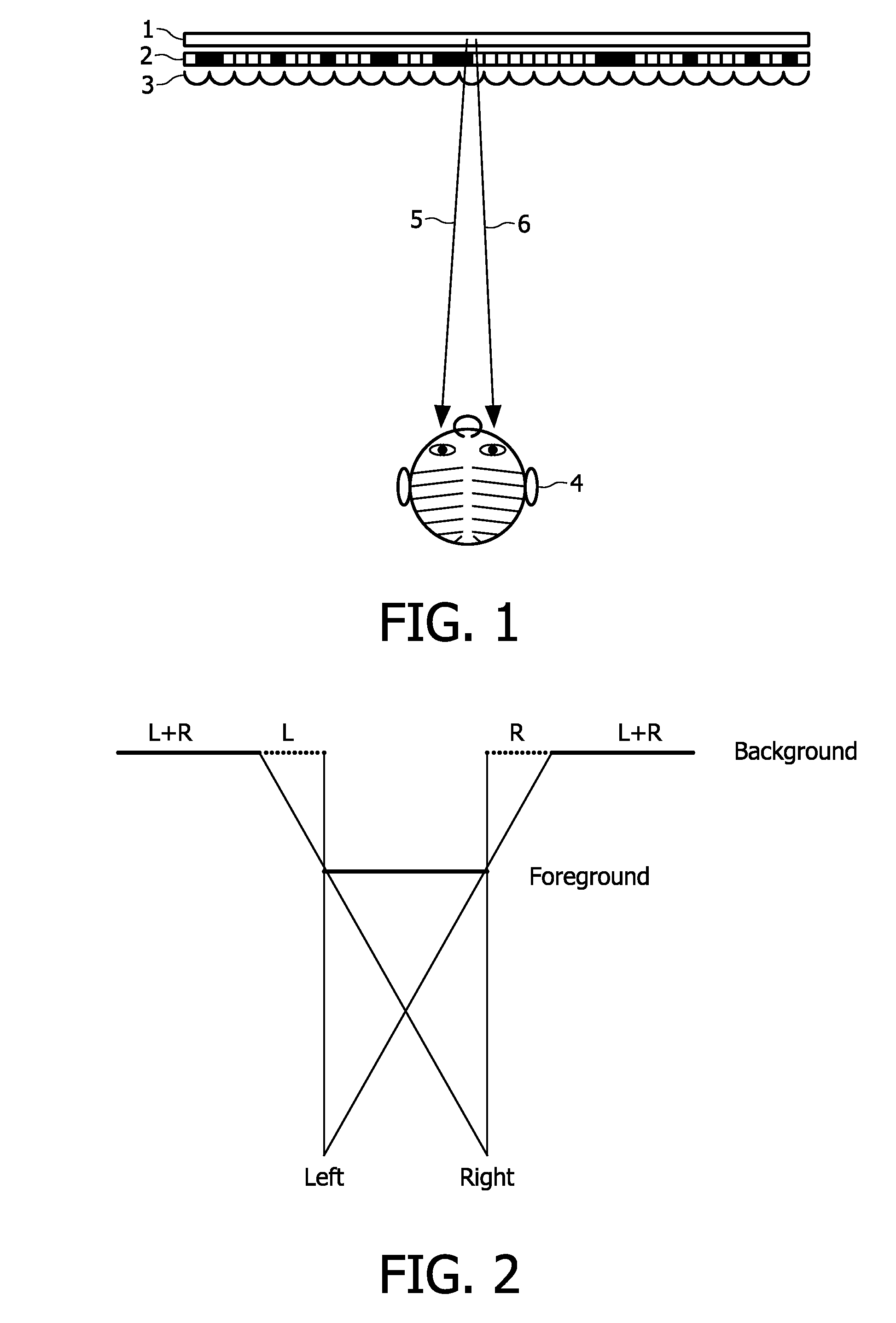
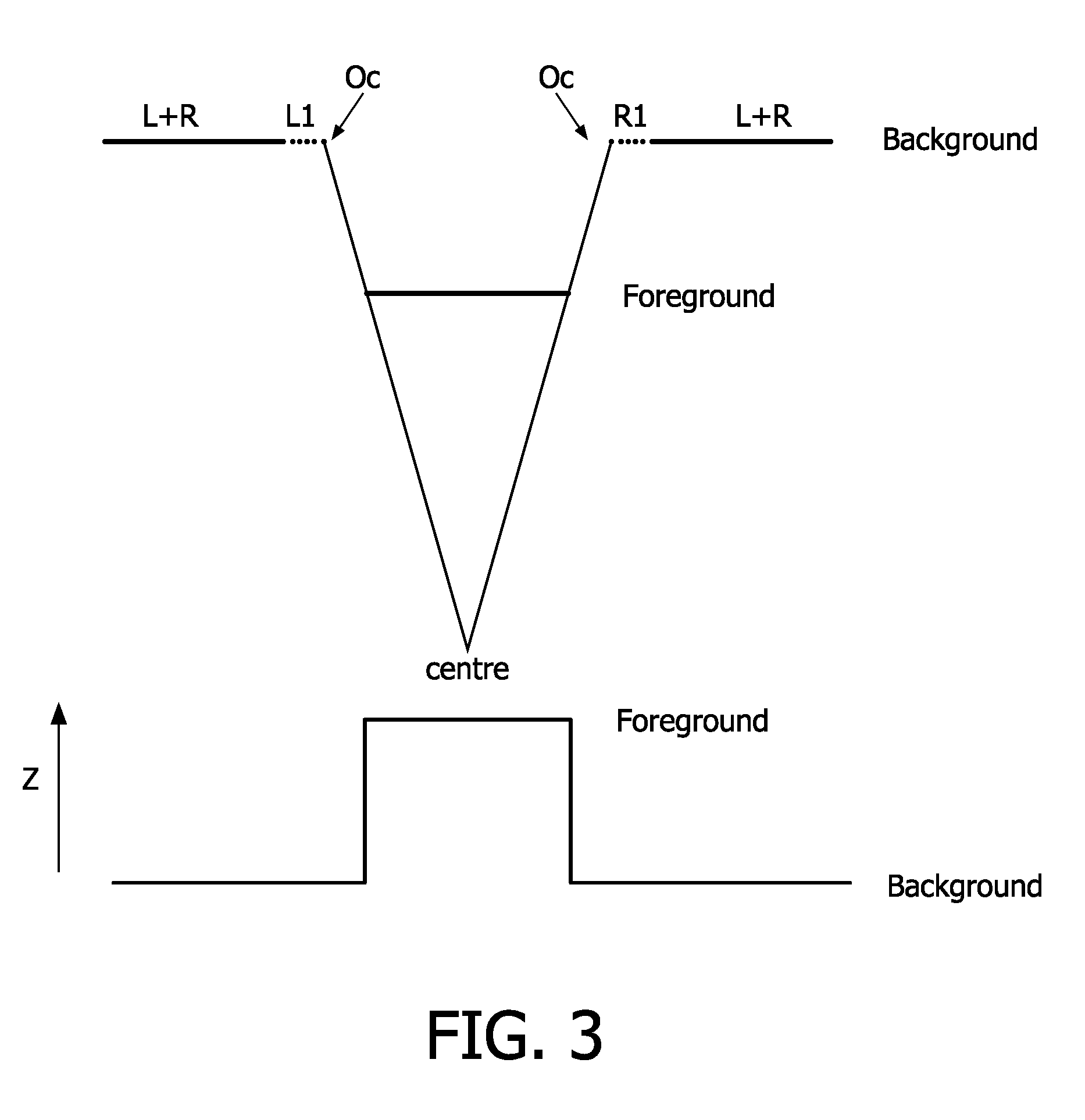
ActiveUS20100195716A1Improve coding efficiencyReduce in quantityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData streamDepth map
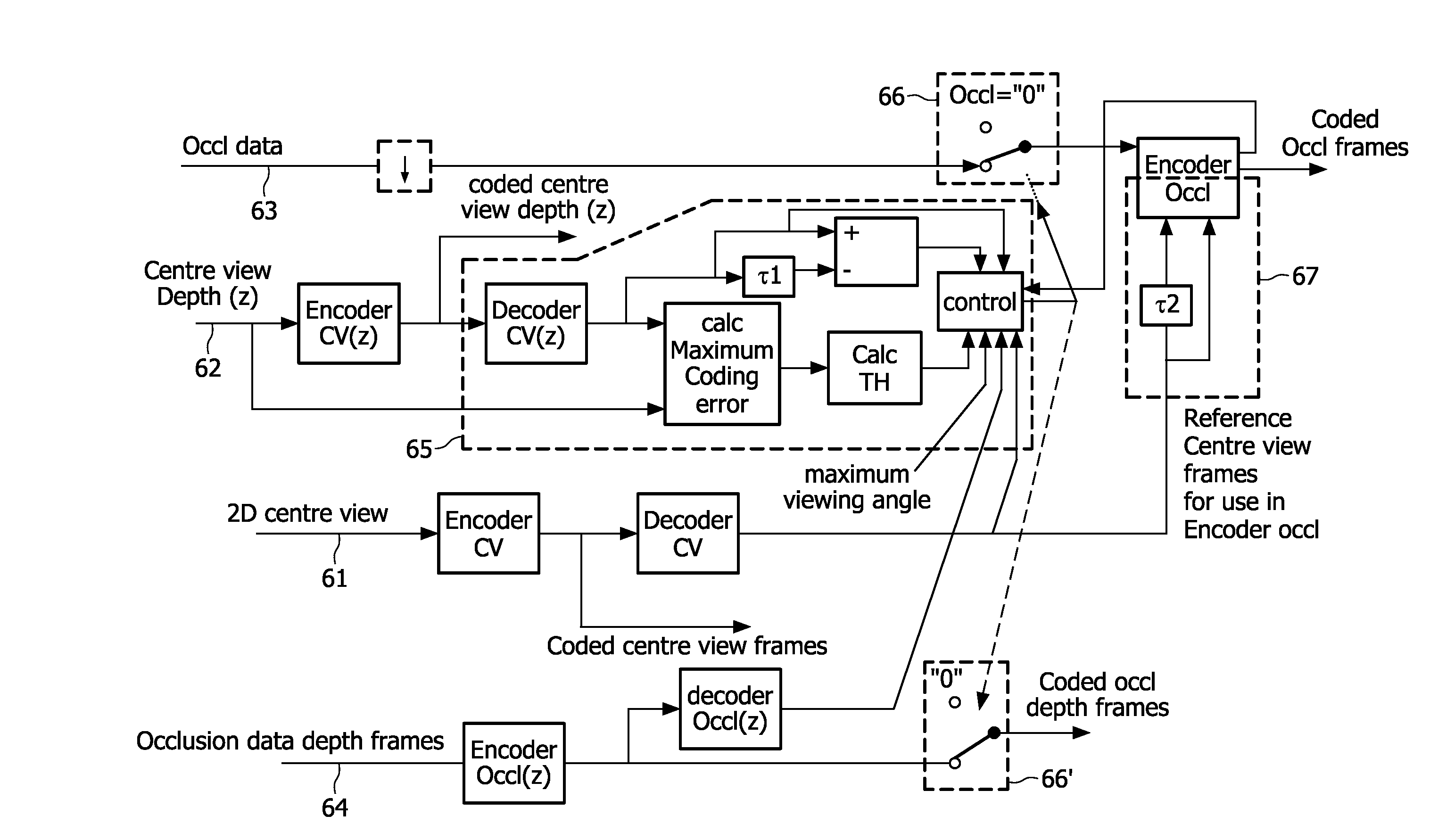
In a method for encoding and an encoder for a 3D video signal, centre view frames, a depth map for centre view frames and an occlusion data frame are encoded. On the basis of the depth map for the centre view frame a distinction is made between functional and non-functional data in an occlusion data frame. This allows a strong reduction in bits needed for the encoded occlusion data frame. In the decoder a combined data stream is made of functional data in the encoded occlusion data frames and the centre view frames. Preferably the centre view frames are used as reference frames in encoding the occlusion data frames.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
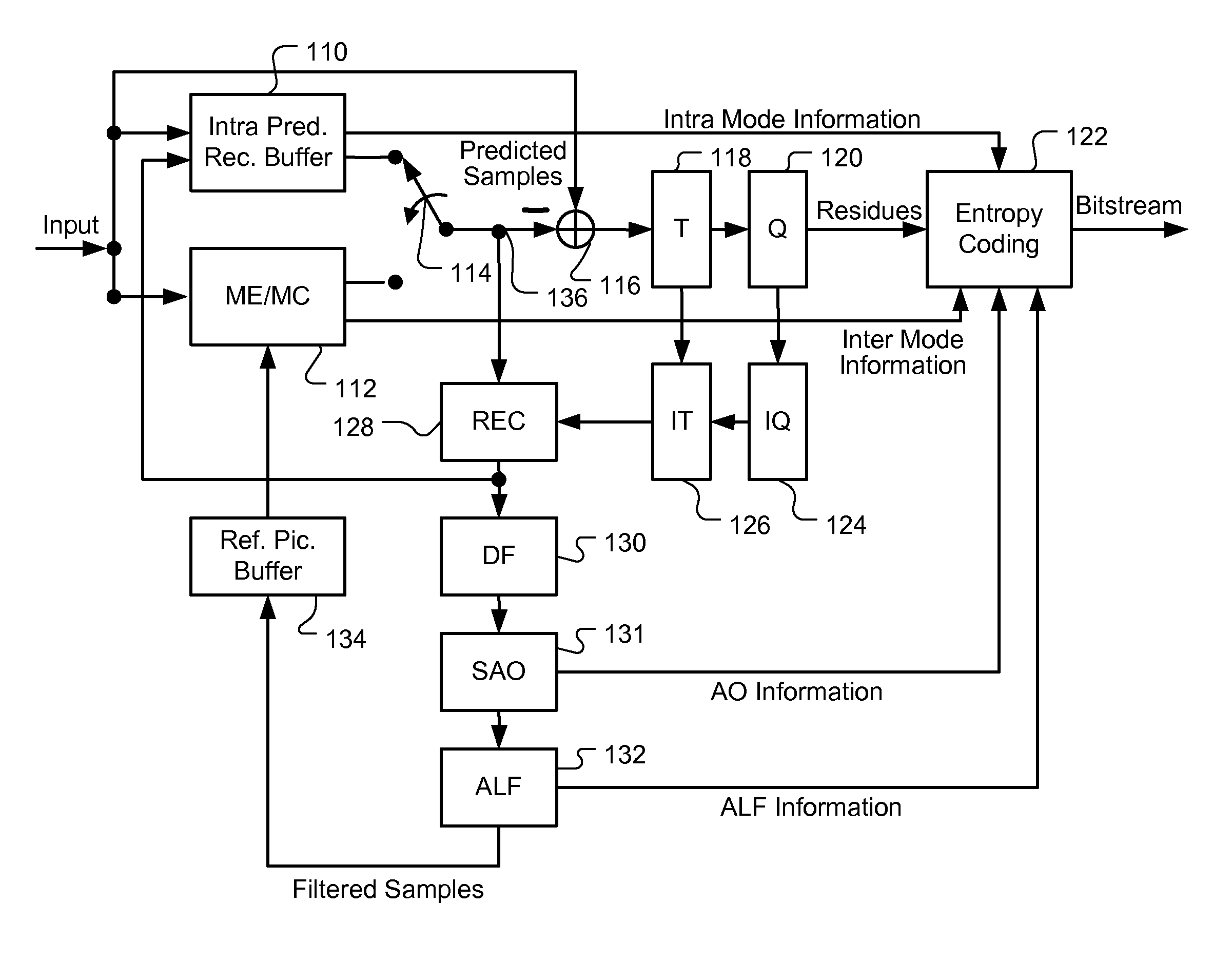
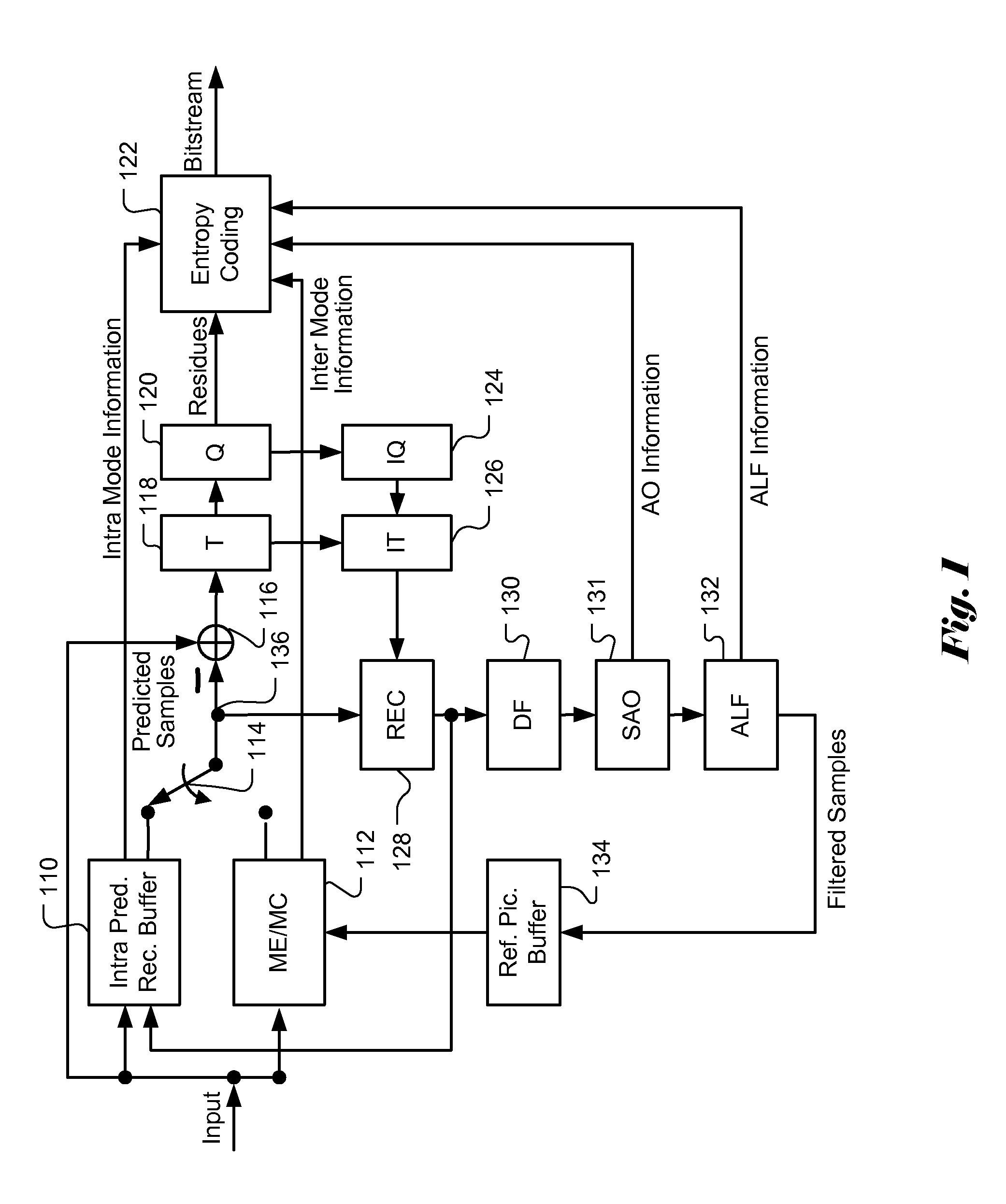
Apparatus and Method of Sample Adaptive Offset for Luma and Chroma Components
InactiveUS20120294353A1Improve coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputational scienceLoop filter
A method and apparatus for processing reconstructed video using in-loop filter in a video coding system are disclosed. The method uses chroma in-loop filter indication to indicate whether chroma components are processed by in-loop filter when the luma in-loop filter indication indicates that in-loop filter processing is applied to the luma component. An additional flag may be used to indicate whether the in-loop filter processing is applied to an entire picture using same in-loop filter information or each block of the picture using individual in-loop filter information. Various embodiments according to the present invention to increase efficiency are disclosed, wherein various aspects of in-loop filter information are taken into consideration for efficient coding such as the property of quadtree-based partition, boundary conditions of a block, in-loop filter information sharing between luma and chroma components, indexing to a set of in-loop filter information, and prediction of in-loop filter information.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
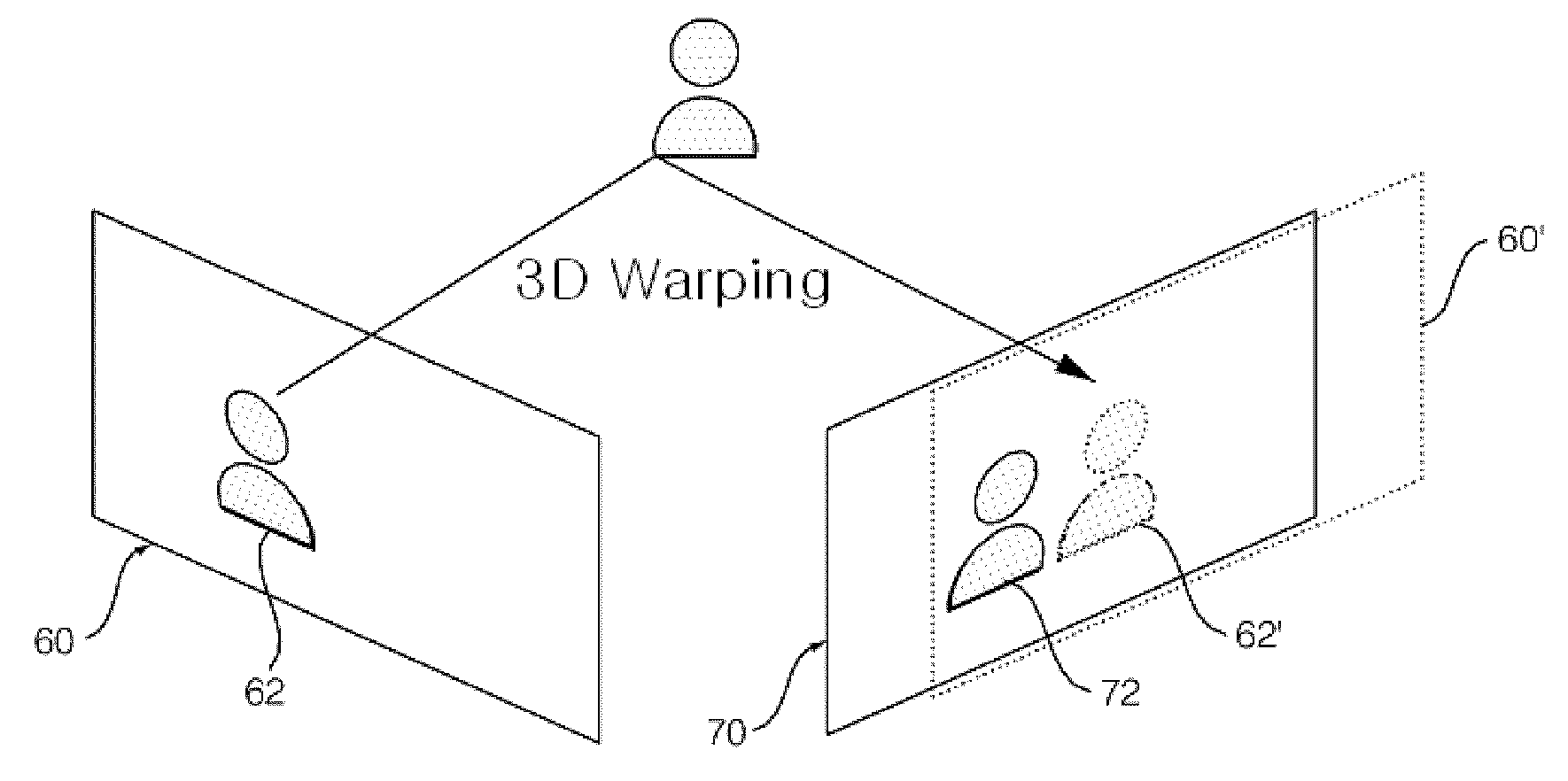
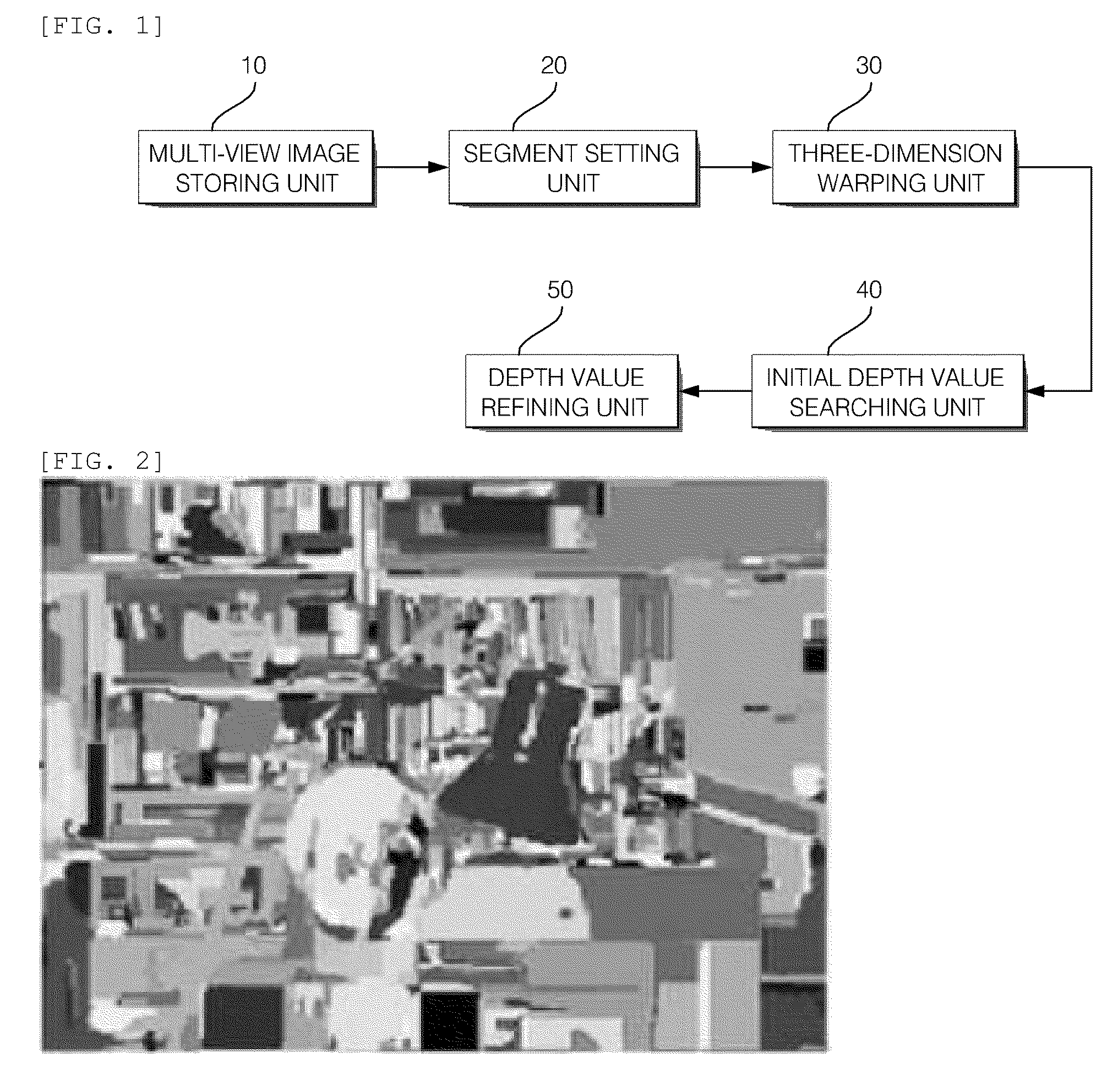
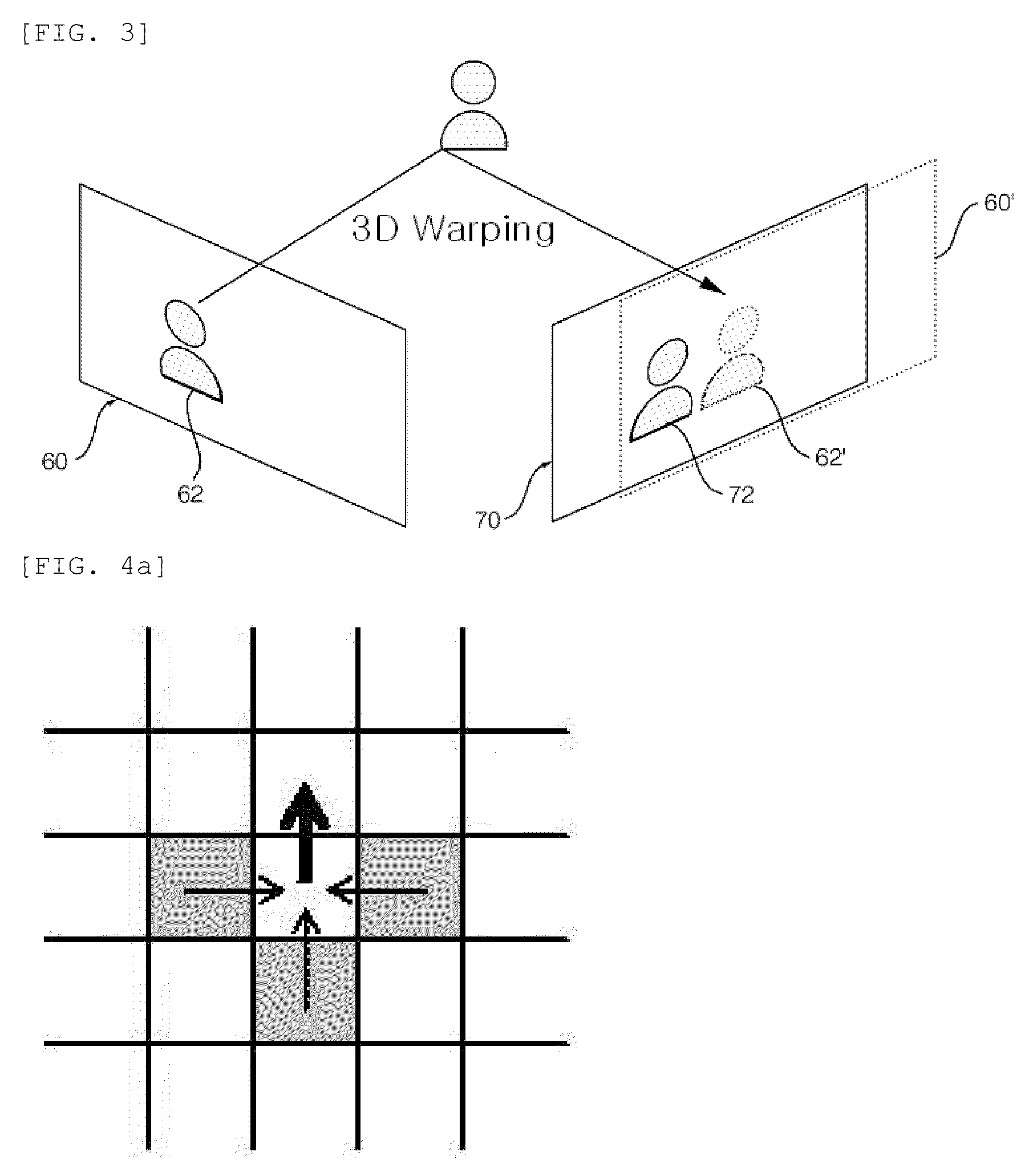
Device and method for estimatiming depth map, and method for generating intermediate image and method for encoding multi-view video using the same
InactiveUS20090129667A1Accurate depth valueRemove errorImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionBelief propagationIntermediate image
The present invention relates to a device and a method for estimating a depth map, and a method for making an intermediate image and a method for encoding multi-view video using the same. More particularly, the present invention relates to a device and a method for estimating a depth map that are capable of acquiring a depth map that reduces errors and complexity, and is resistant to external influence by dividing an area into segments on the basis of similarity, acquiring a segment-unit initial depth map by using a three-dimensional warping method and a self adaptation function to which an extended gradient map is reflected, and refining the initial depth map by performing a belief propagation method by the segment unit, and achieving smoother view conversion and improved encoding efficiency by generating an intermediate image with the depth map and utilizing the intermediate image for encoding a multi-view video, and a method for generating the intermediate image and a method for encoding the multi-view video using the same.
Owner:KT CORP +1
Method and system for context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding
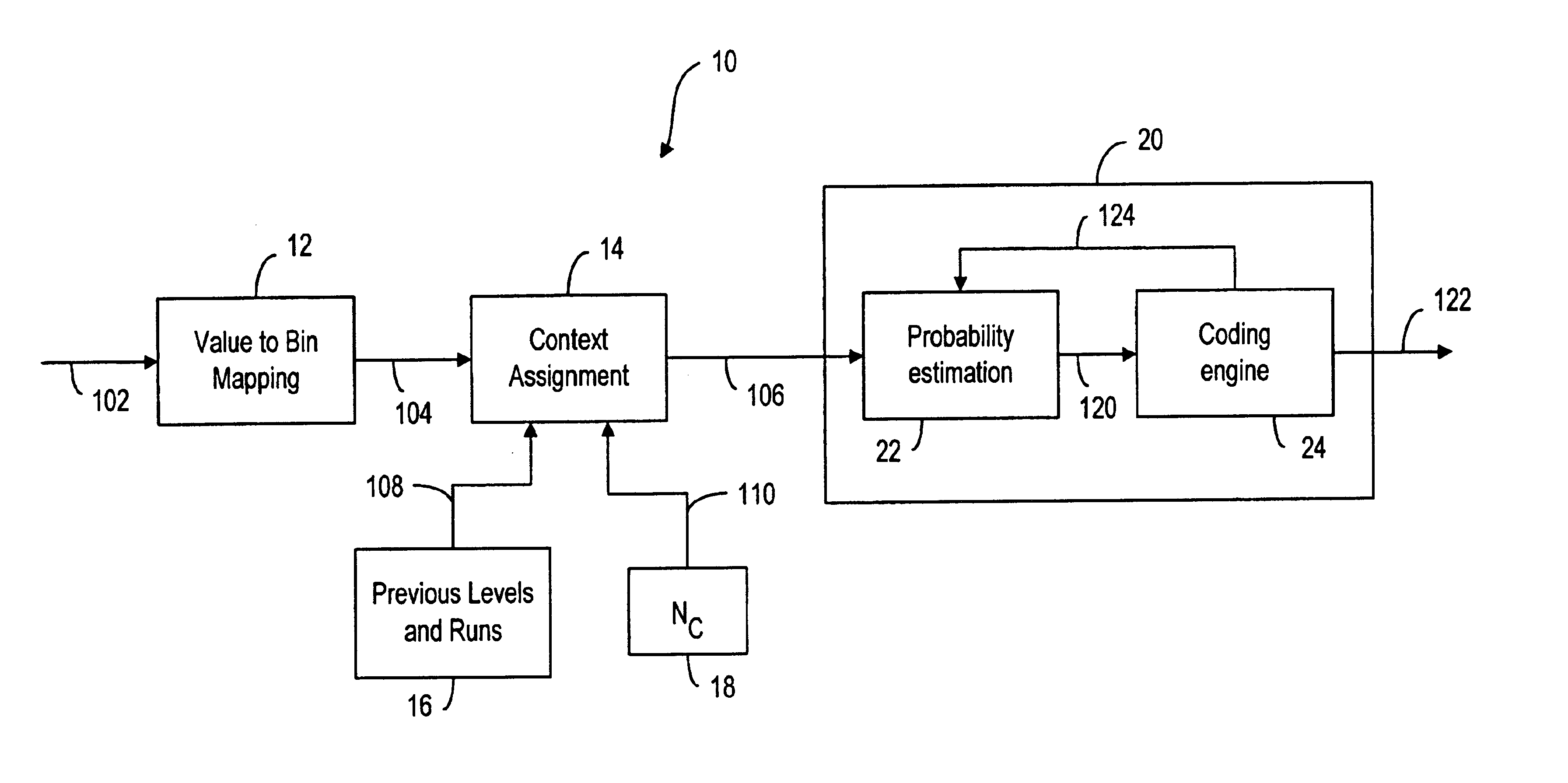
InactiveUS6856701B2Improve coding efficiencyCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionMultiple contextContext based
A method and system for image coding, wherein an image is divided into a plurality of blocks for scanning. The pixels values in the scanned block are represented by a plurality of level-run value pairs, wherein the level value is indicative of a non-zero pixel value and the run value is indicative of the number of consecutive zero pixel values preceding the non-zero pixel value. A plurality of contexts indicative of the level-run value pairs are conveyed to a decoder for allowing the decoder to reconstruct the image based on the contexts. The assignment of the contexts is also based on the level value of a preceding level-run pair. Additionally, instead of an end-of-block symbol, the number of non-zero coefficients is provided to the decoder prior to conveying the contexts thereto.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Efficient spectral envelope coding using variable time/frequency resolution and time/frequency switching
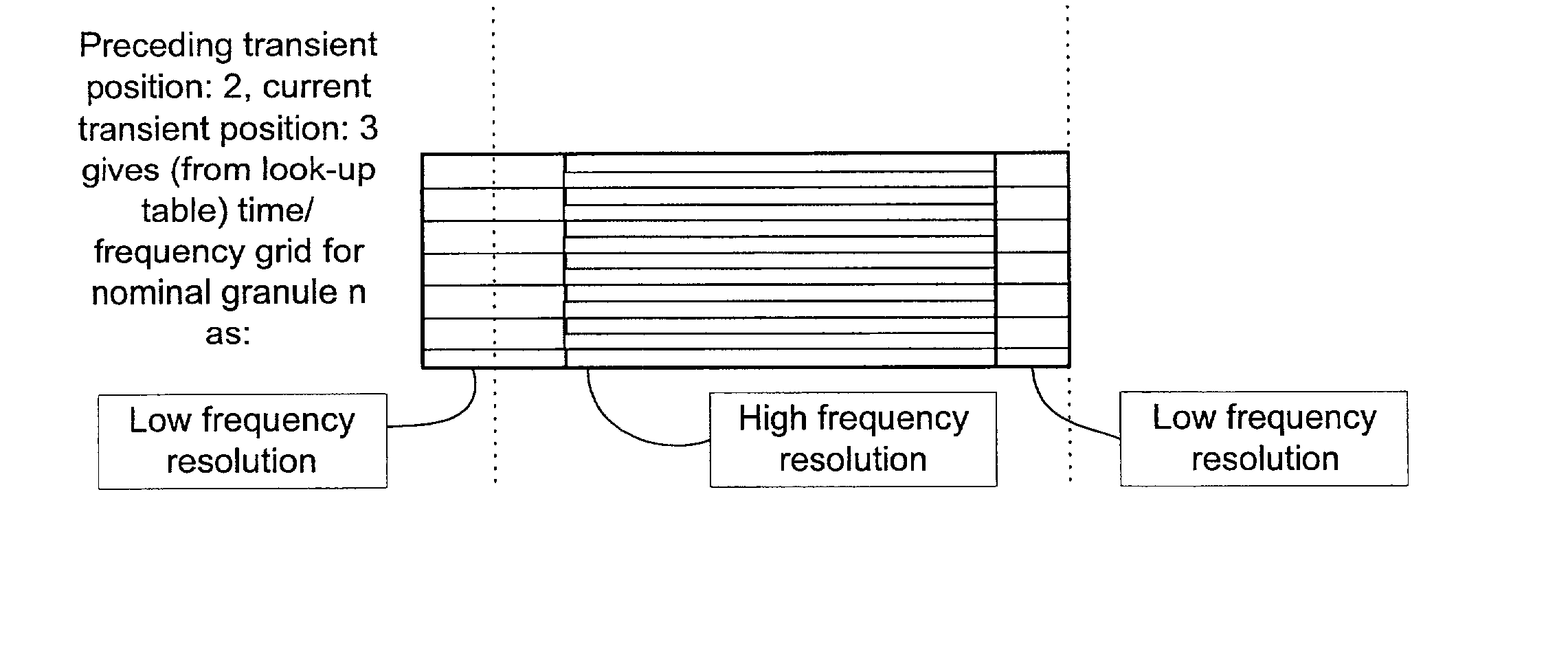
InactiveUS6978236B1Less variationImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisDigital computer detailsSpectral envelopeImage resolution
The present invention provides a new method and an apparatus for spectral envelope encoding. The invention teaches how to perform and signal compactly a time / frequency mapping of the envelope representation, and further, encode the spectral envelope data efficiently using adaptive time / frequency directional coding. The method is applicable to both natural audio coding and speech coding systems and is especially suited for coders using SBR [WO 98 / 57436] or other high frequency reconstruction methods.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
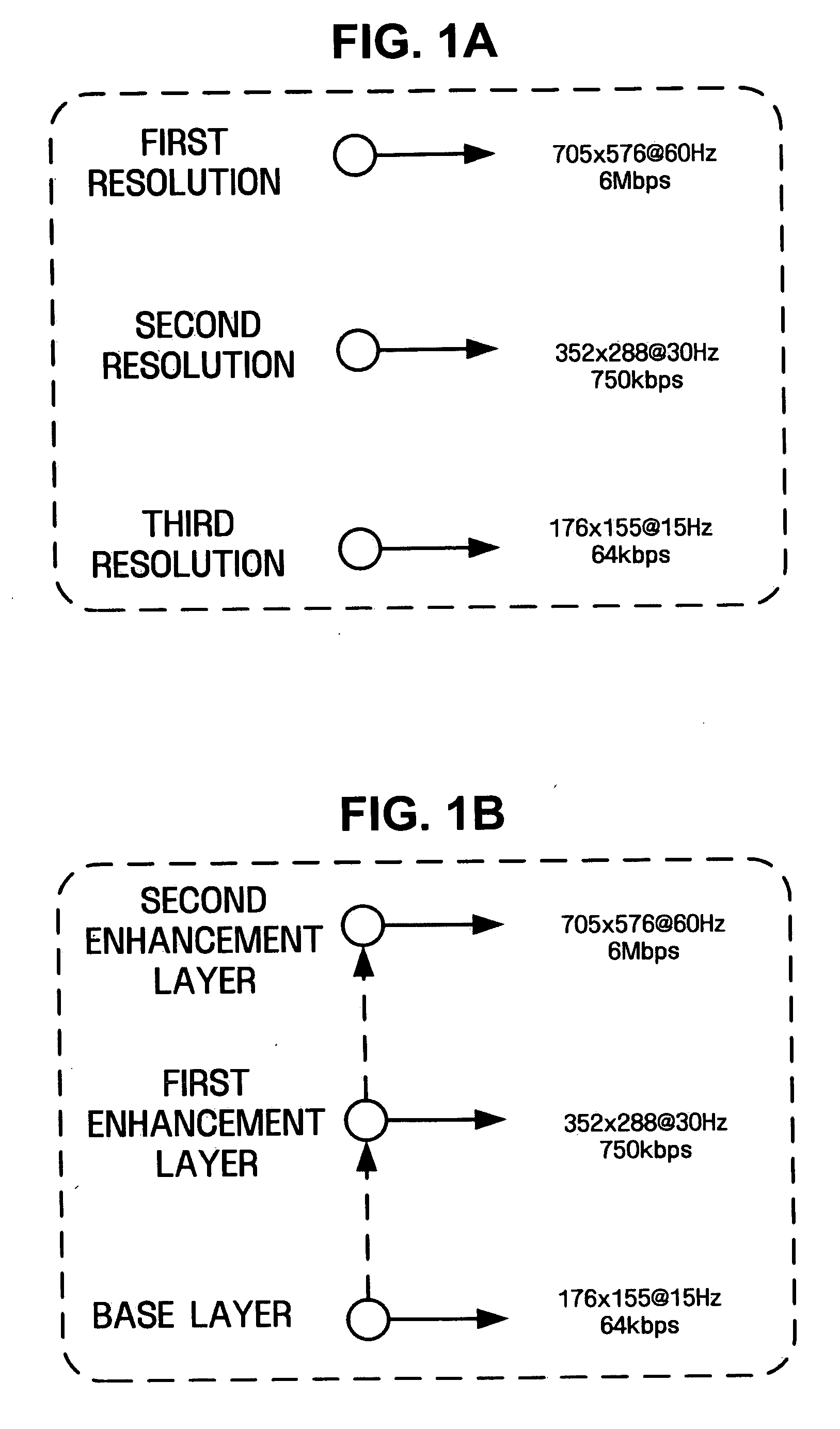
Video encoding and decoding methods and systems for video streaming service
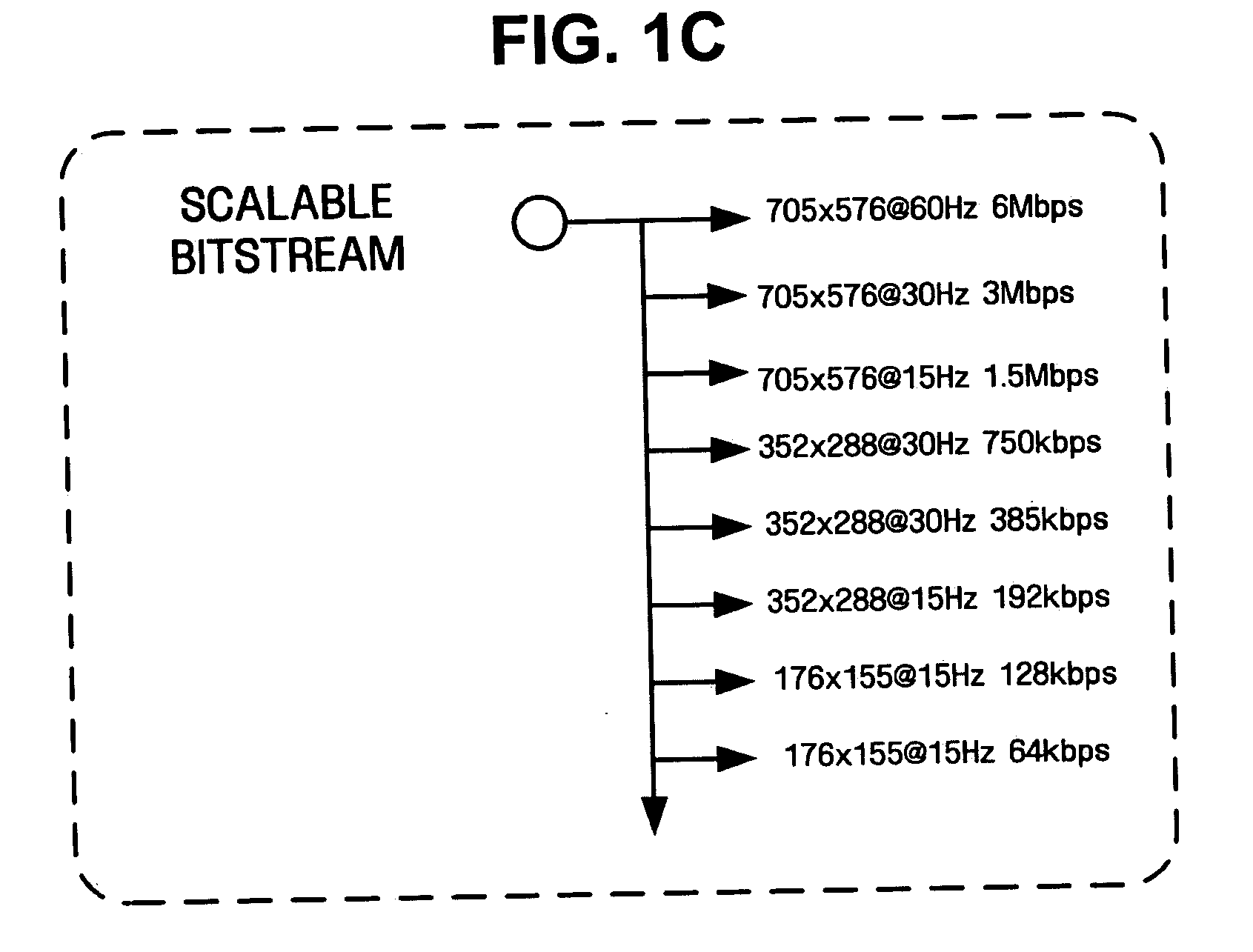
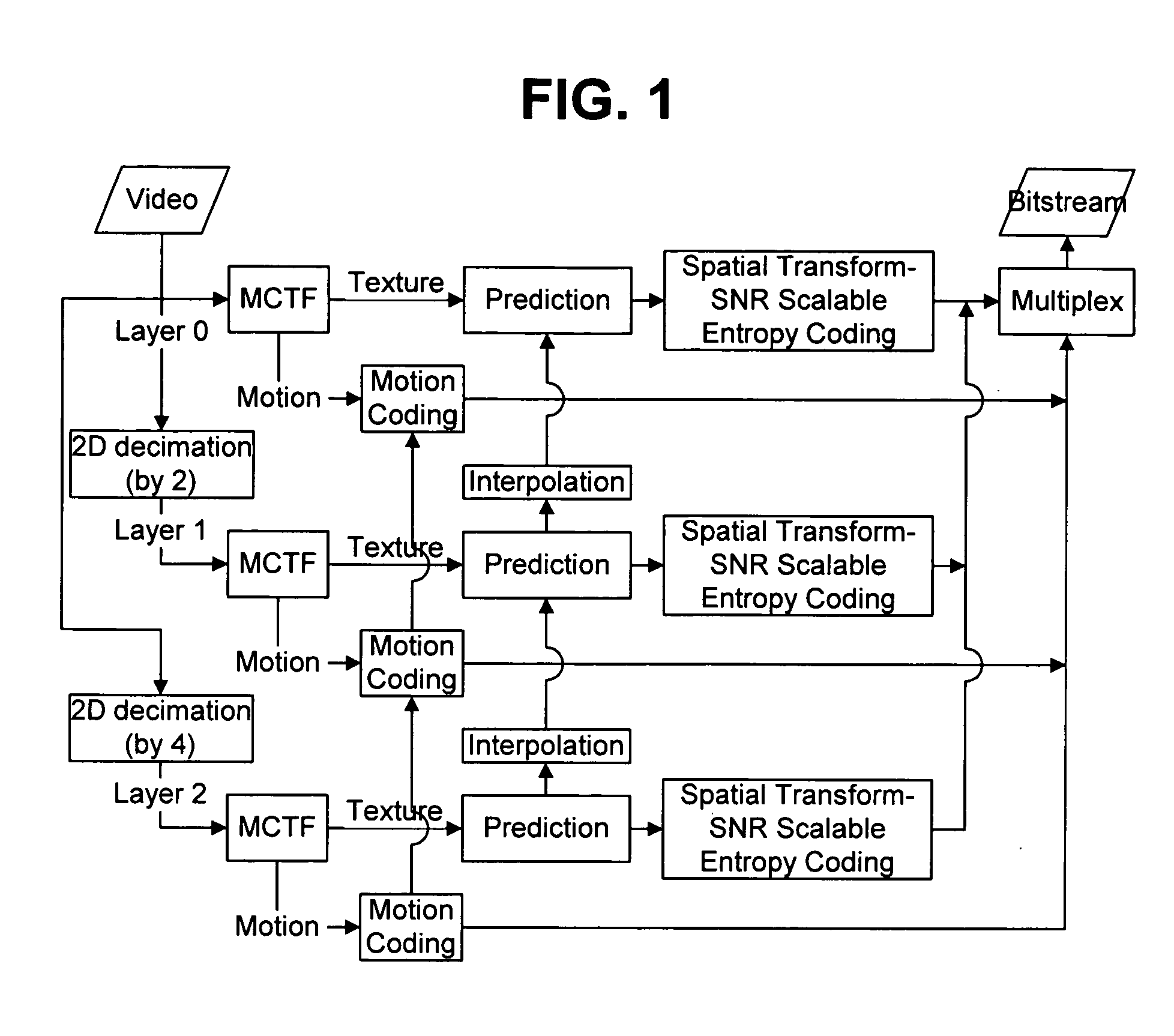
InactiveUS20050195900A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
Video encoding and decoding methods and systems for video streaming are provided. The video encoding method includes encoding first resolution frames using scalable video coding, upsampling the first resolution frames to a second resolution, and encoding second resolution frames using scalable video coding with reference to upsampled versions of the first resolution frames.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
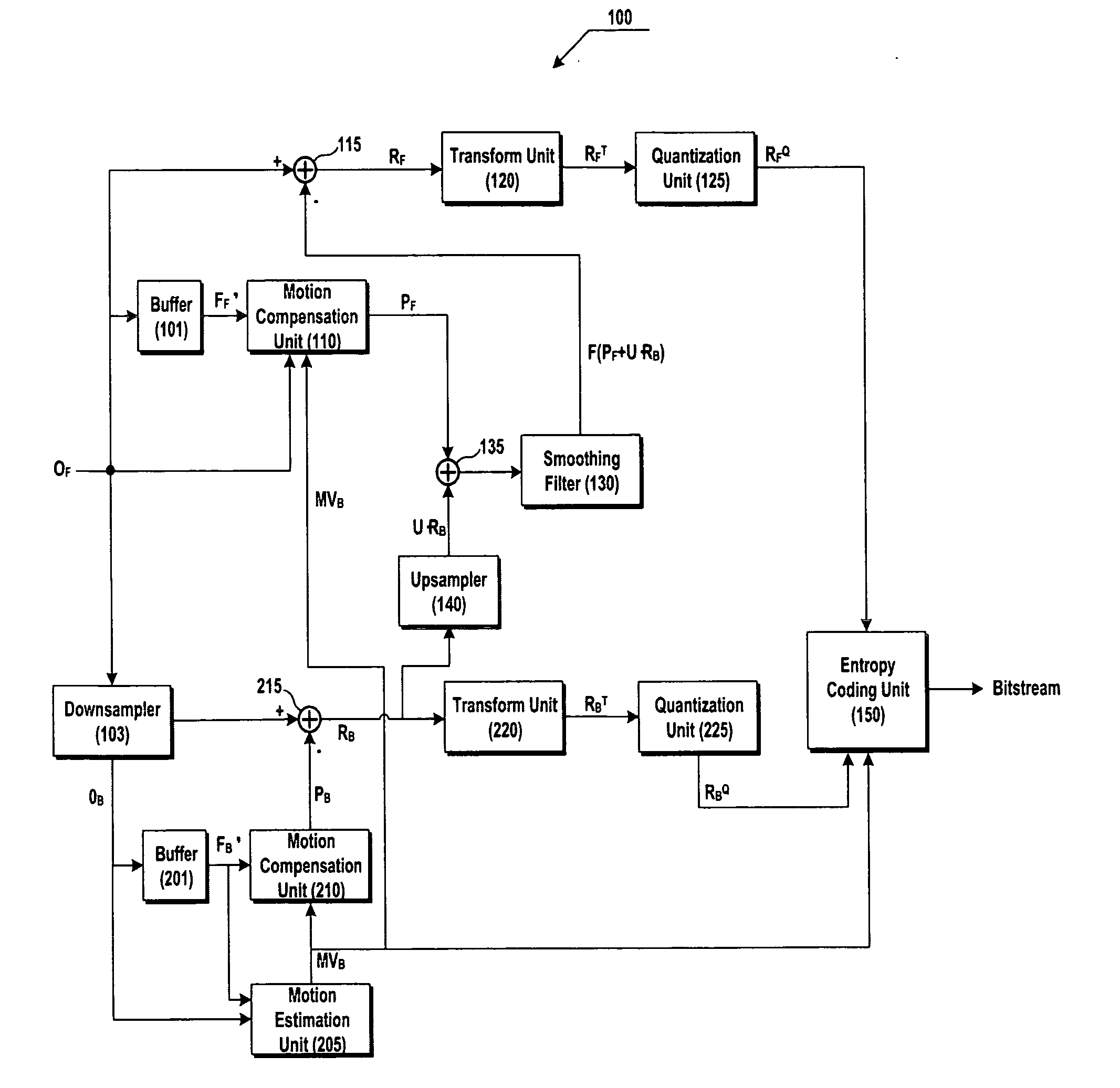
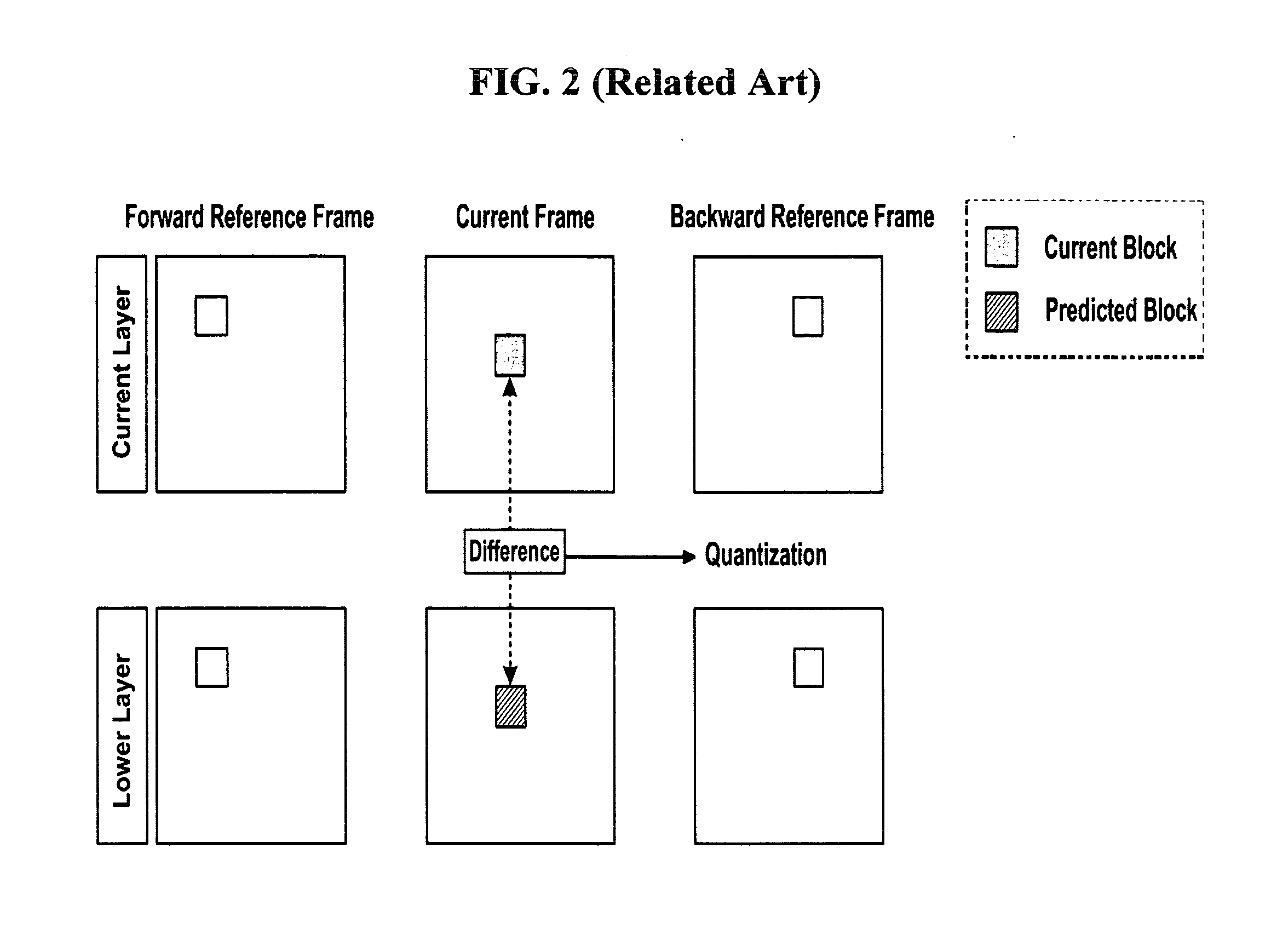
Multilayer-based video encoding/decoding method and video encoder/decoder using smoothing prediction
InactiveUS20070171969A1Improve coding efficiencyBrush bodiesPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer architectureVideo encoding
A method and apparatus for reducing block artifacts during a residual prediction in a multilayer-based video coding are disclosed. The multilayer-based video encoding method includes obtaining a difference between a predicted block for a second block of a lower layer, which corresponds to a first block included in a current layer, and the second block; adding the obtained difference to a predicted block for the first block; smoothing a third block generated as a result of the addition using a smoothing function; and encoding a difference between the first block and the smoothed third block.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
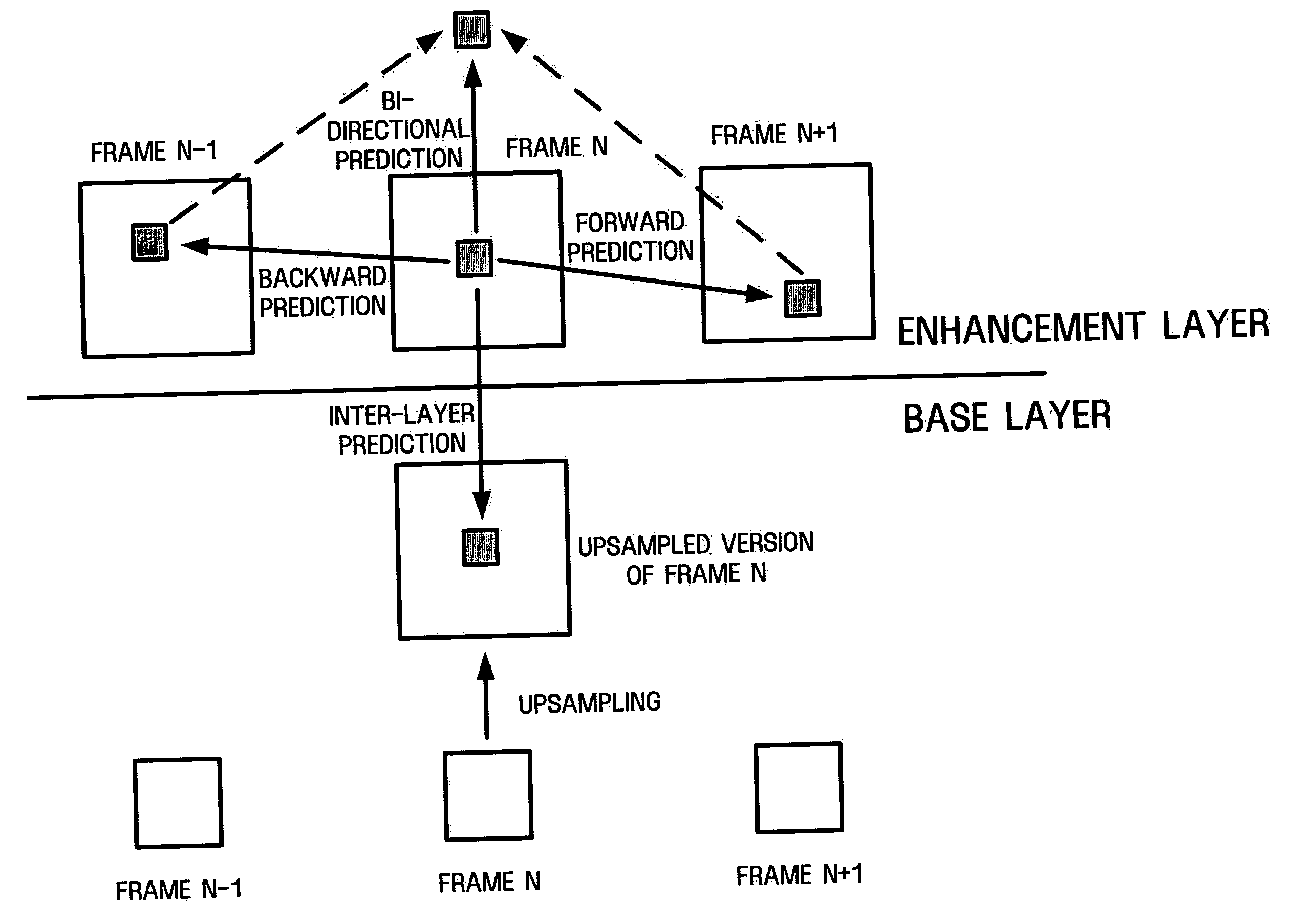
Advanced bi-directional predictive coding of interlaced video
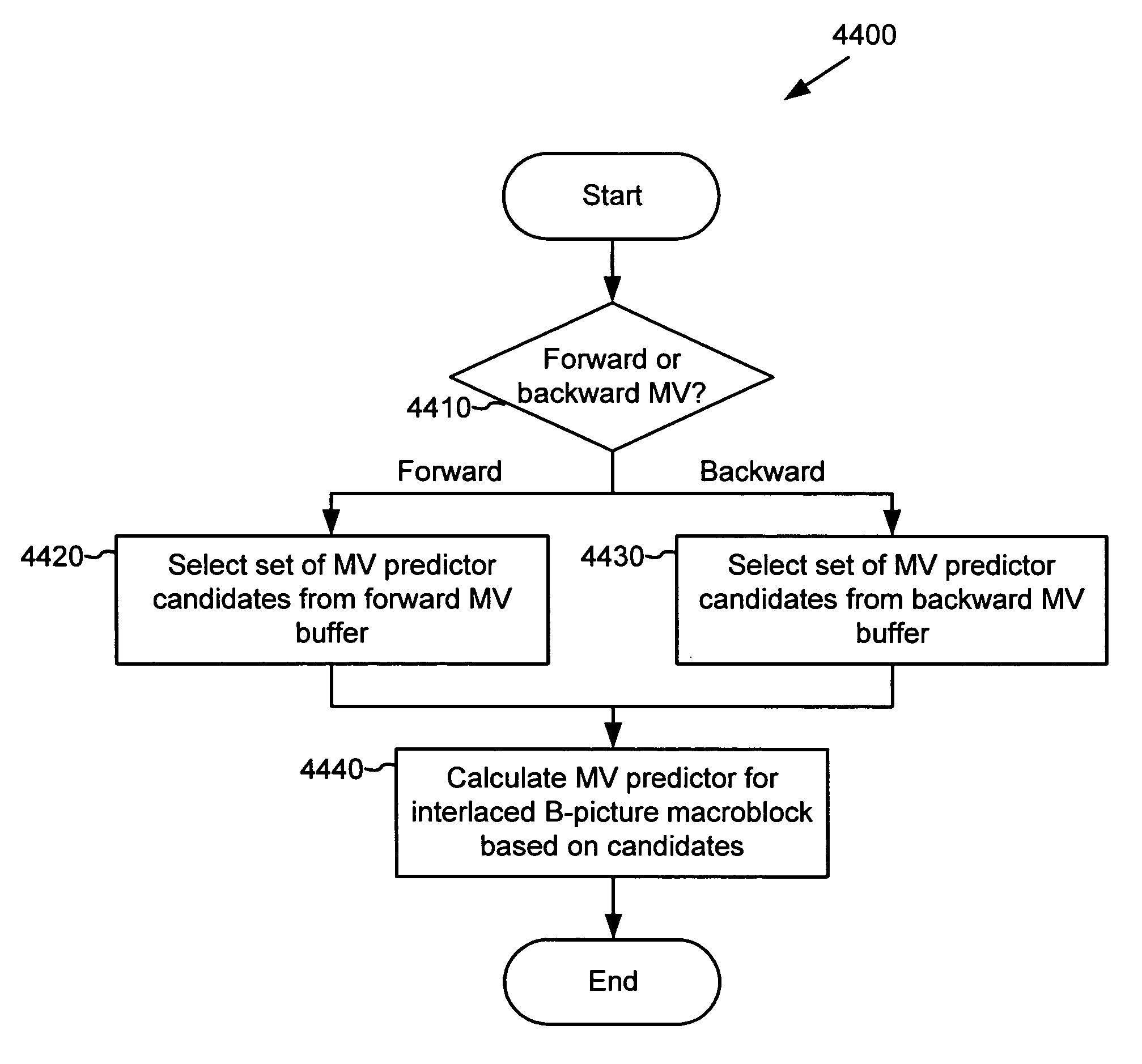
ActiveUS20050053292A1Accurate compensationReduce encoding overheadPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionInterlaced videoMotion vector
For interlaced B-fields or interlaced B-frames, forward motion vectors are predicted by an encoder / decoder using forward motion vectors from a forward motion vector buffer, and backward motion vectors are predicted using backward motion vectors from a backward motion vector buffer. The resulting motion vectors are added to the corresponding buffer. Holes in motion vector buffers can be filled in with estimated motion vector values. An encoder / decoder switches prediction modes between fields in a field-coded macroblock of an interlaced B-frame. For interlaced B-frames and interlaced B-fields, an encoder / decoder computes direct mode motion vectors. For interlaced B-fields or interlaced B-frames, an encoder / decoder uses 4 MV coding. An encoder / decoder uses “self-referencing” B-frames. An encoder sends binary information indicating whether a prediction mode is forward or not-forward for one or more macroblocks in an interlaced B-field. An encoder / decoder uses intra-coded B-fields [“BI-fields”].
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Image coding method and apparatus using side matching process and image decoding method and apparatus for the same
InactiveUS20090147855A1Improve compression efficiencyEfficient motion vector informationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDecoding methodsPattern recognition
A method and apparatus for coding an image capable of performing a prediction coding process by using a correlation degree between neighboring pixels of a current block and neighboring pixels of a reference block, and an image decoding method and apparatus. In the method, reference block candidates having neighboring pixels similar to the neighboring pixels of the current block are selected, matching errors between selected reference block candidates and the current block are calculated, and a reference block candidate having the least matching error is determined to be a predicted block of the current block.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Entropy coding supporting mode switching
ActiveUS20140140400A1Increase spectral resolution of spectralImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareData stream
A decoder for decoding a data stream into which media data is coded has a mode switch configured to activate a low-complexity mode or a high-efficiency mode depending on the data stream, an entropy decoding engine configured to retrieve each symbol of a sequence of symbols by entropy decoding using a selected one of a plurality of entropy decoding schemes, a desymbolizer configured to desymbolize the sequence of symbols to obtain a sequence of syntax elements, a reconstructor configured to reconstruct the media data based on the sequence of syntax elements, selection depending on the activated low-complexity mode or the high-efficiency mode. In another aspect, a desymbolizer is configured to perform desymbolization such that the control parameter varies in accordance with the data stream at a first rate in case of the high-efficiency mode being activated and the control parameter is constant irrespective of the data stream or changes depending on the data stream, but at a second lower rate in case of the low-complexity mode being activated.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Multiple-hypothesis cross-layer prediction
InactiveUS20080089411A1Improve coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionCoding block
A system and method for predicting an inter-layer predicted slice of image data from at least two different reference layers, where the inter-layer predicted slice of image data itself resides on yet another layer, different from either of the two reference layers. At least one coded block from the inter-layer predicted slice of image data is encoded with an indication, indicating to a decoder that the at least one coded block is to be inter-layer multi-predicted from the at least two different reference layers. Identifications and corresponding prediction weights of the at least two different reference layers are also signaled to the decoder either in the coded block itself, or in the inter-layer predicted slice of image data.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
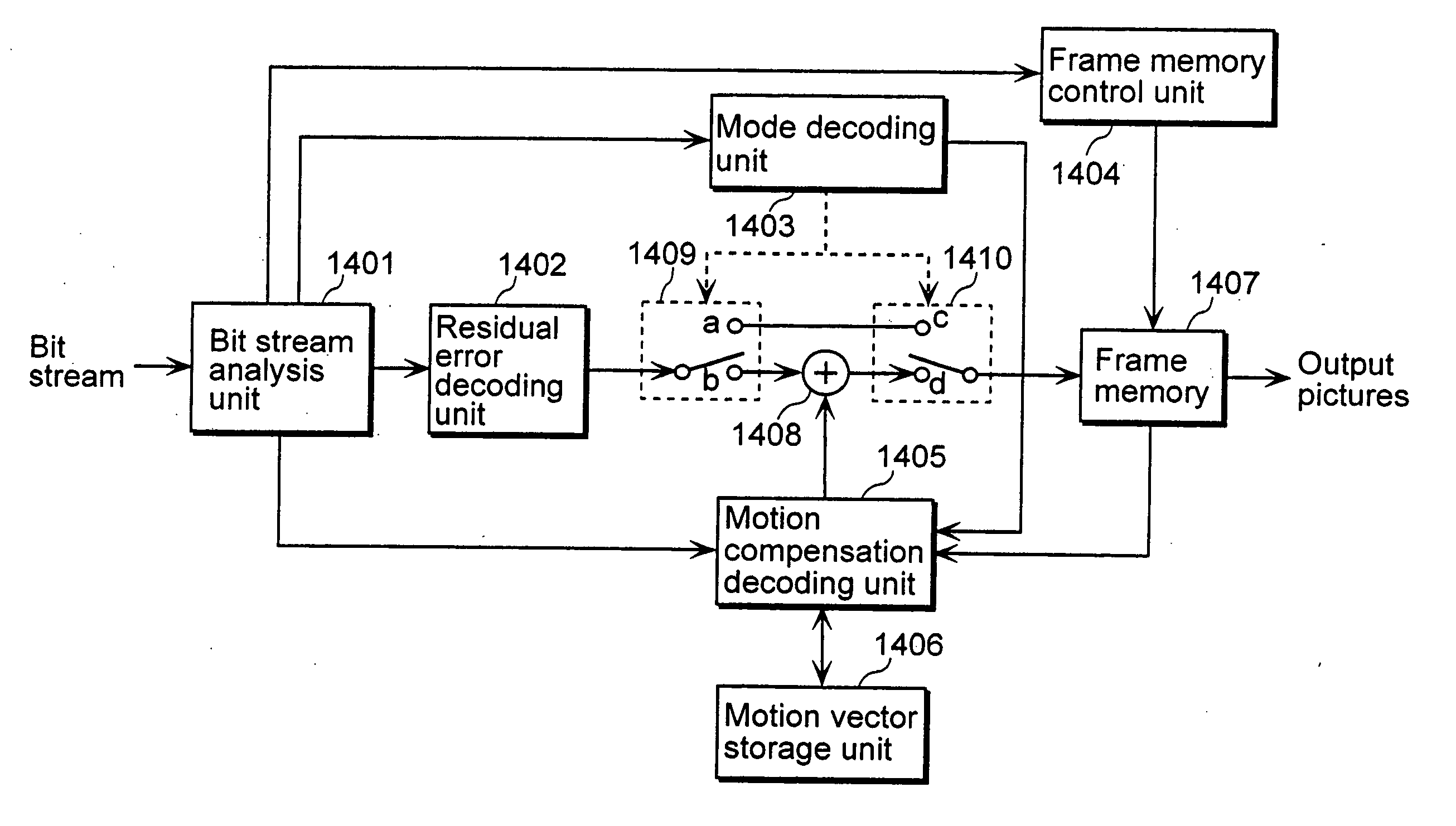
Method and device for encoding and decoding video
ActiveCN101605255AImprove coding efficiencyGuaranteed error recovery performanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationCommunications systemRecovery performance
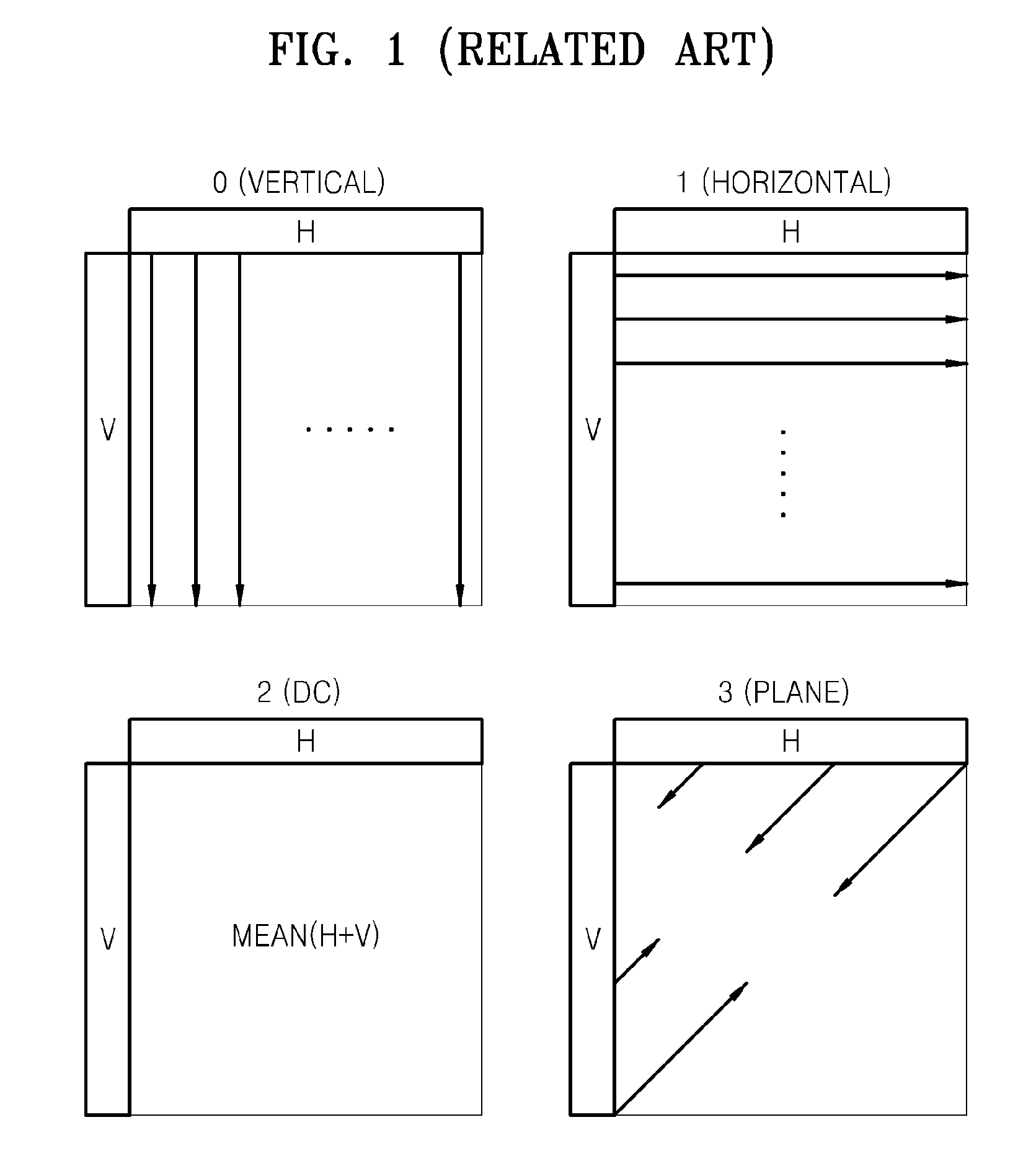
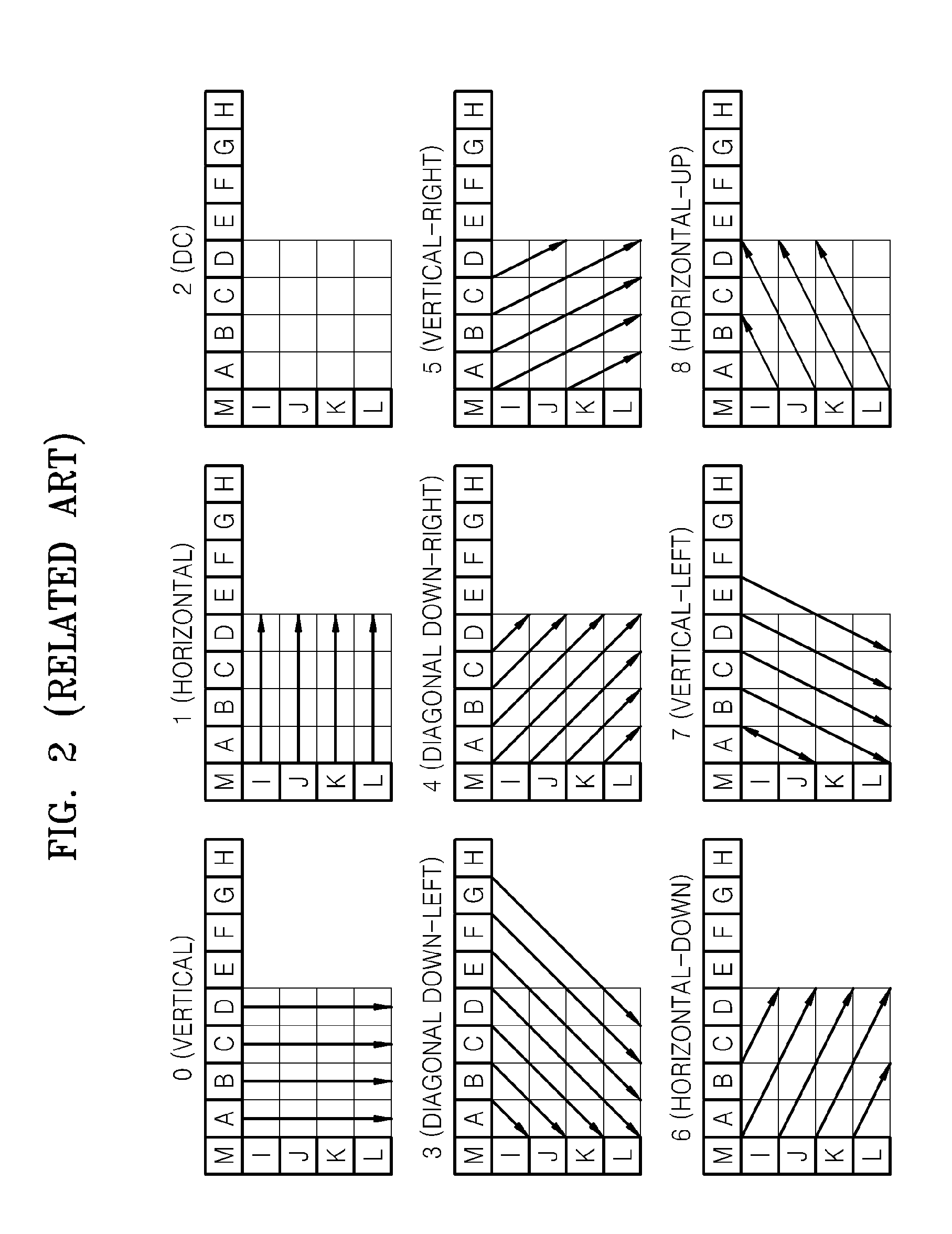
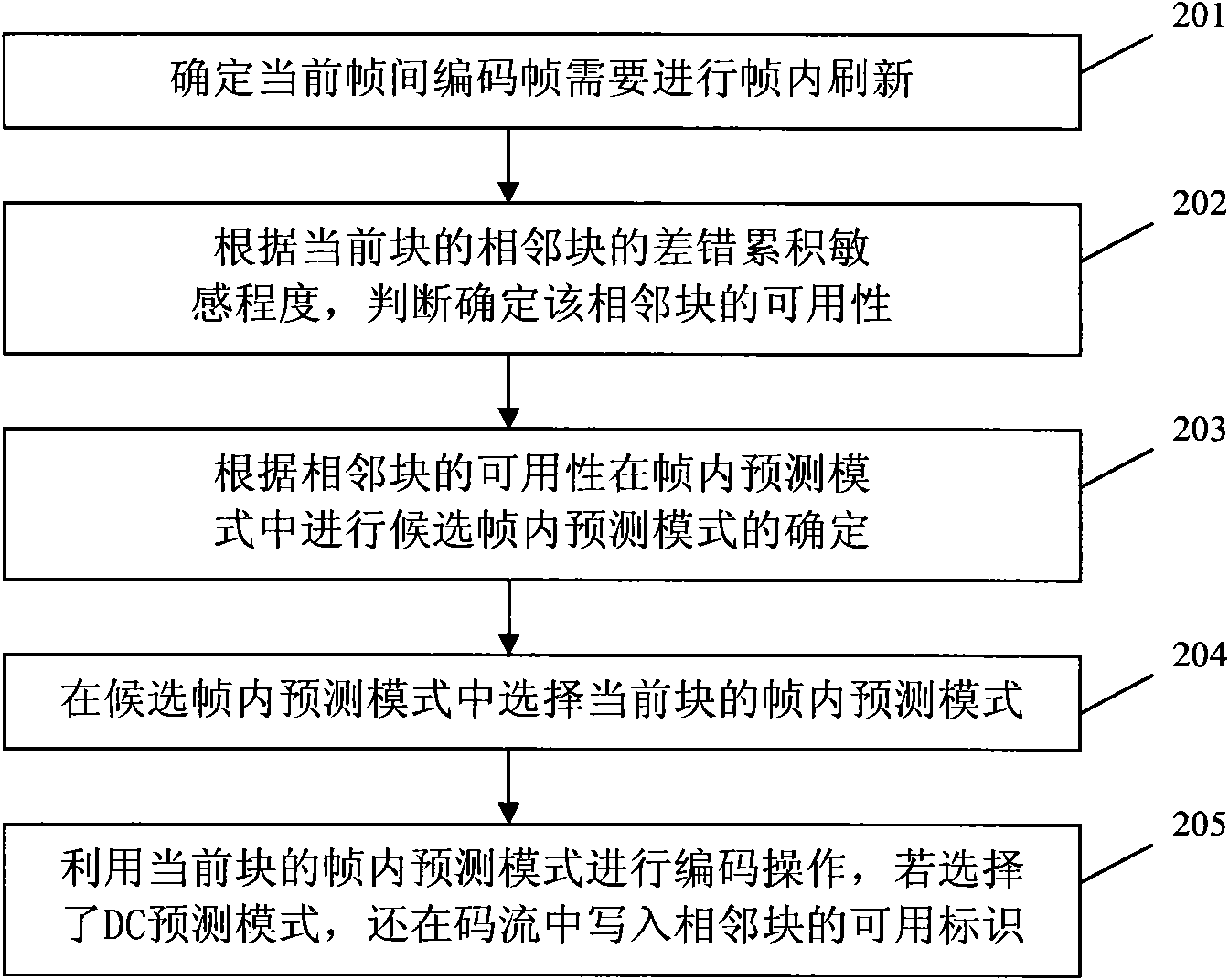
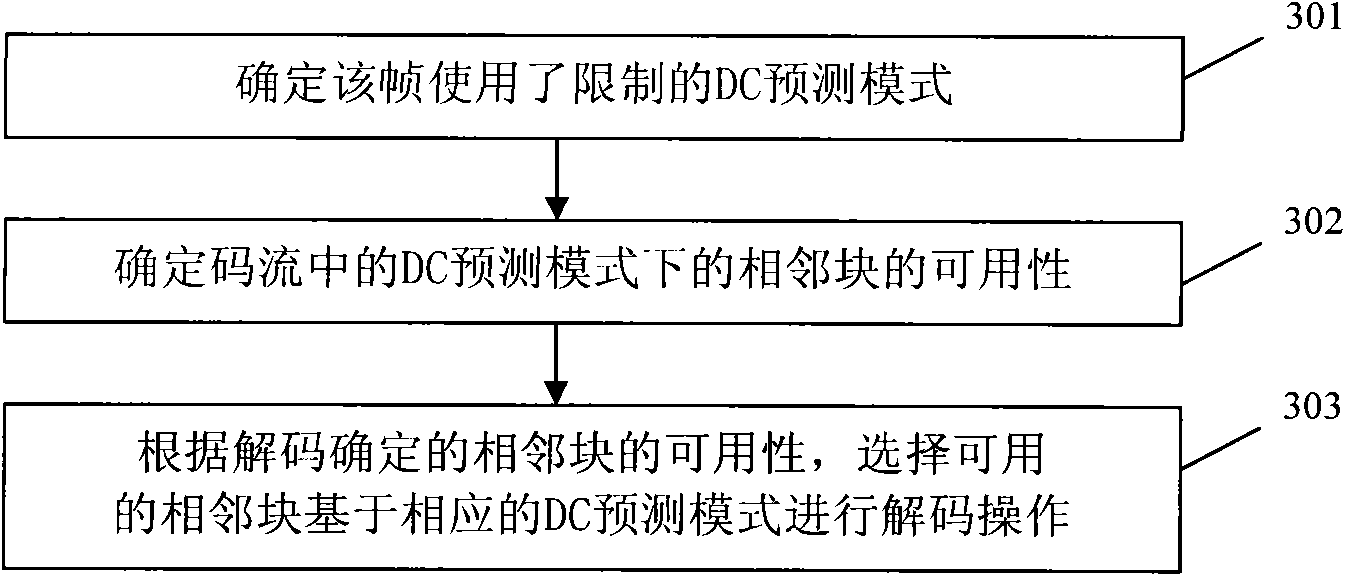
The invention discloses a method and a device for encoding and decoding a video. The method comprises the following steps: executing a selection of an intra frame predictive mode according to available adjacent blocks, writing in the available marks of each adjacent block in a code stream when the selected intra frame encoding mode is a limited DC predictive mode; thus, determining that the limited DC predictive mode is adopted for encoding by a current block at an decoding end, and then analyzing the available marks for indicating whether adjacent blocks are available, and determining available adjacent blocks according to the available marks of the adjacent blocks so as to perform decoding operation according to available adjacent blocks based on the DC predictive mode. The embodiment of the invention can set availability of left adjacent blocks and upper adjacent blocks of the DC mode when the intra frame encoding mode is the DC predictive mode, thereby ensuring the error recovery performance to improve the performance of encoding and decoding in a video communication system.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Method for scalably encoding and decoding video signal
InactiveUS20060133503A1Improve coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage resolutionAlgorithm
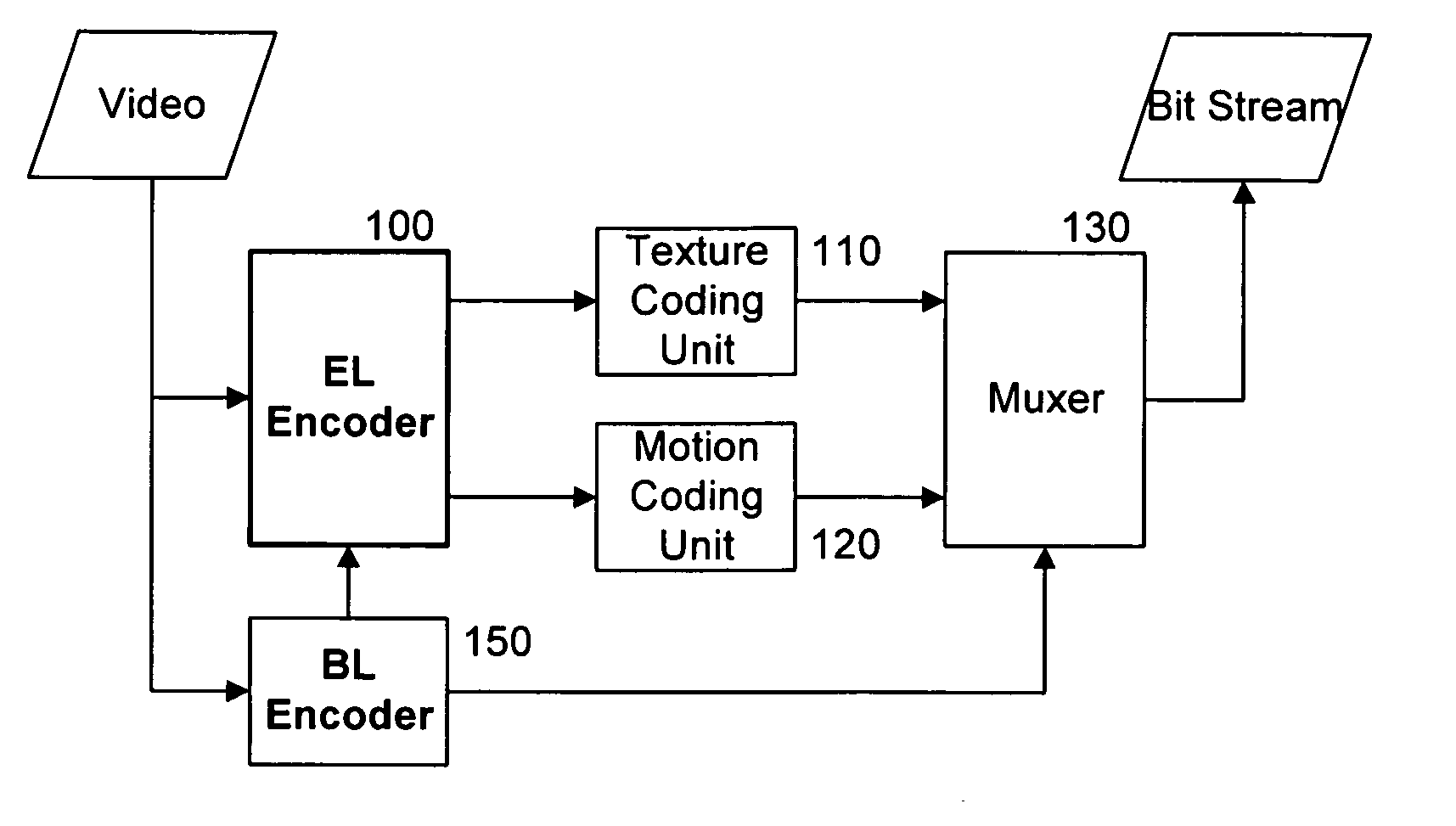
Disclosed is a method for scalably encoding and decoding a video signal. The video signal is encoded through an inter-layer prediction scheme based on a data stream of a base layer encoded with ×¼ resolution. The inter-layer prediction scheme applied between the enhanced layer and the base layer representing ×4 resolution difference includes a motion prediction scheme for predicting motion and dividing a macro block of the enhanced layer based on division information, mode information, and / or mode information of a block of the base layer. Thus, the inter-layer prediction scheme is applied between layers representing ×4 resolution difference, thereby improving a coding efficiency.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
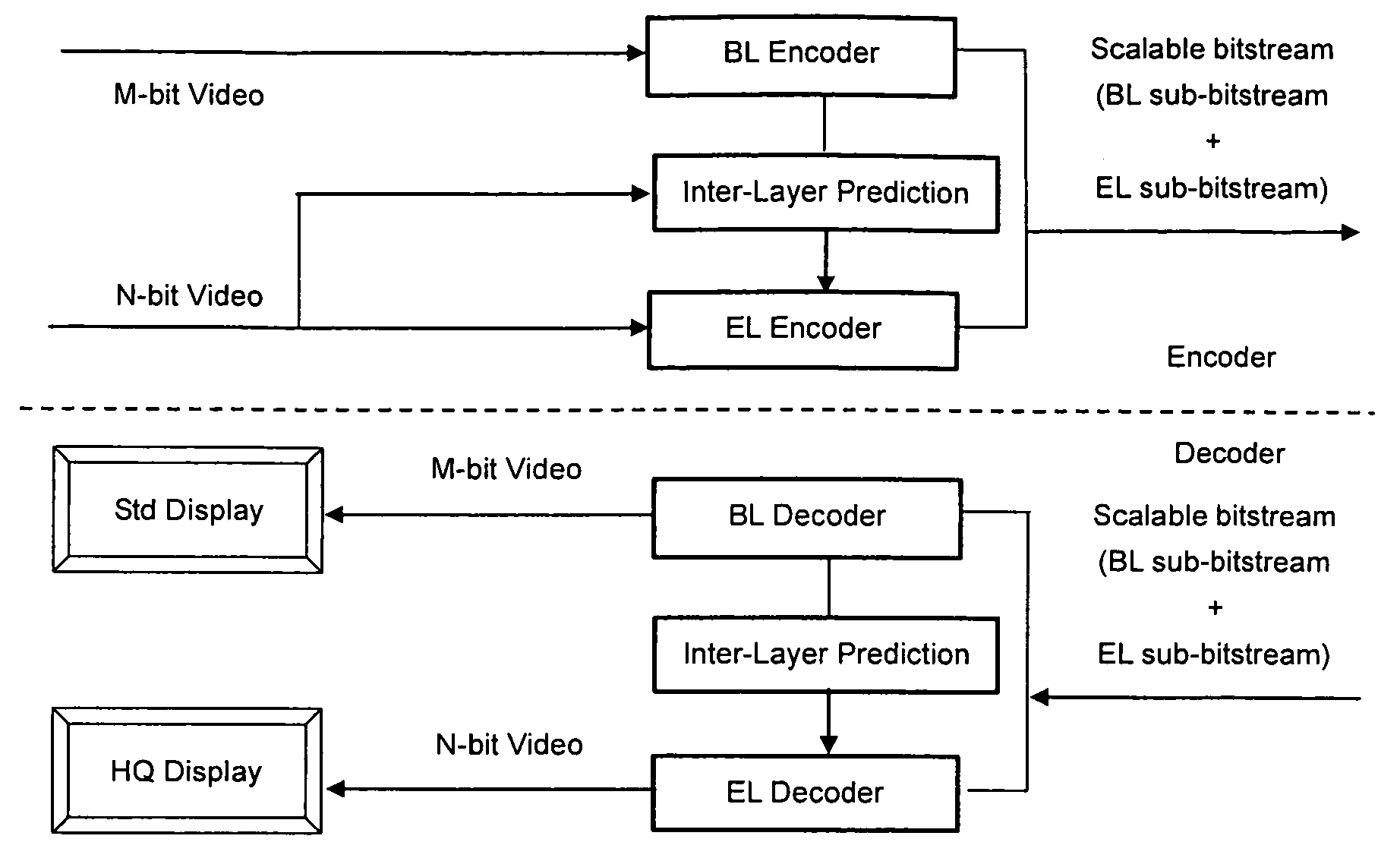
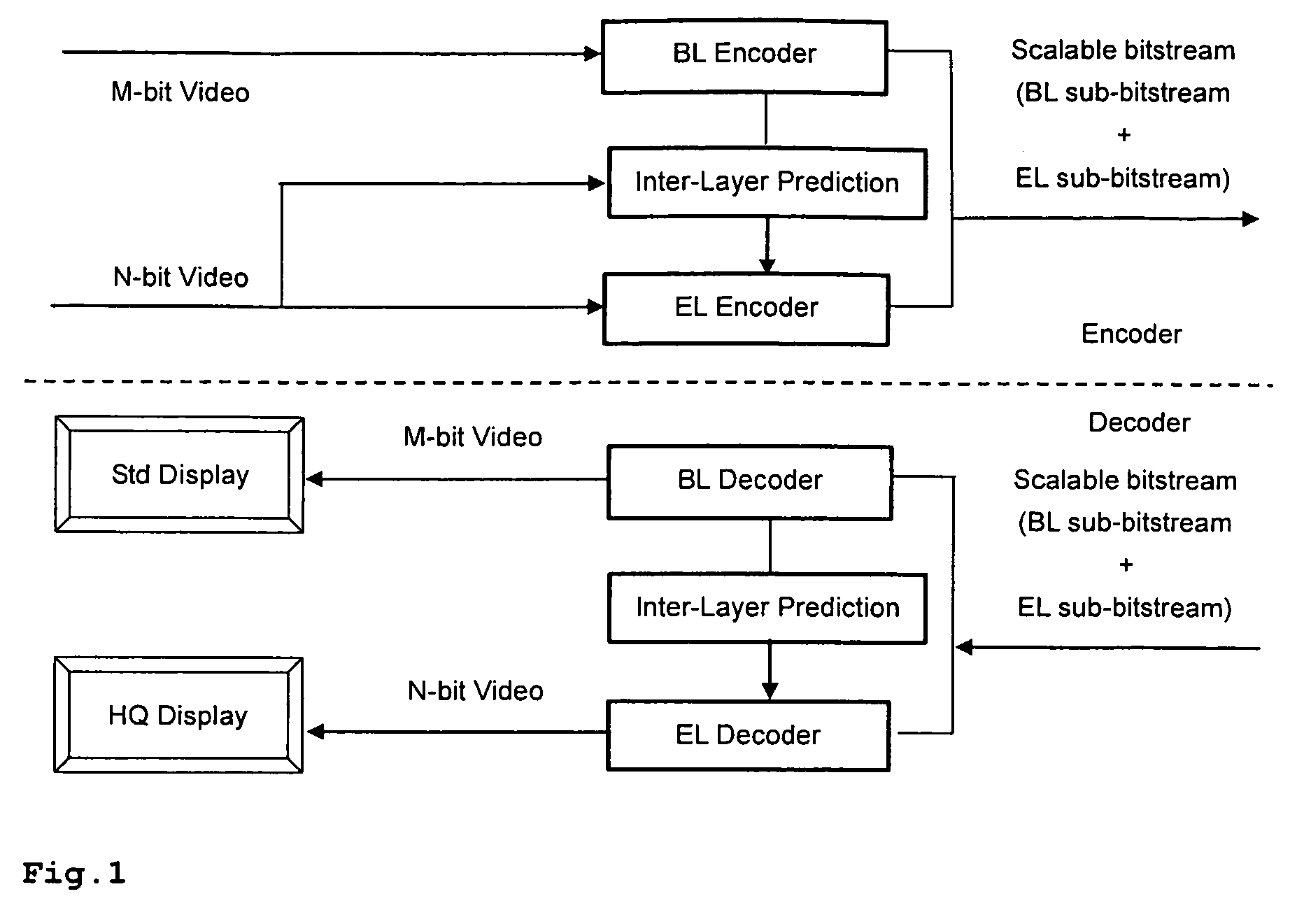
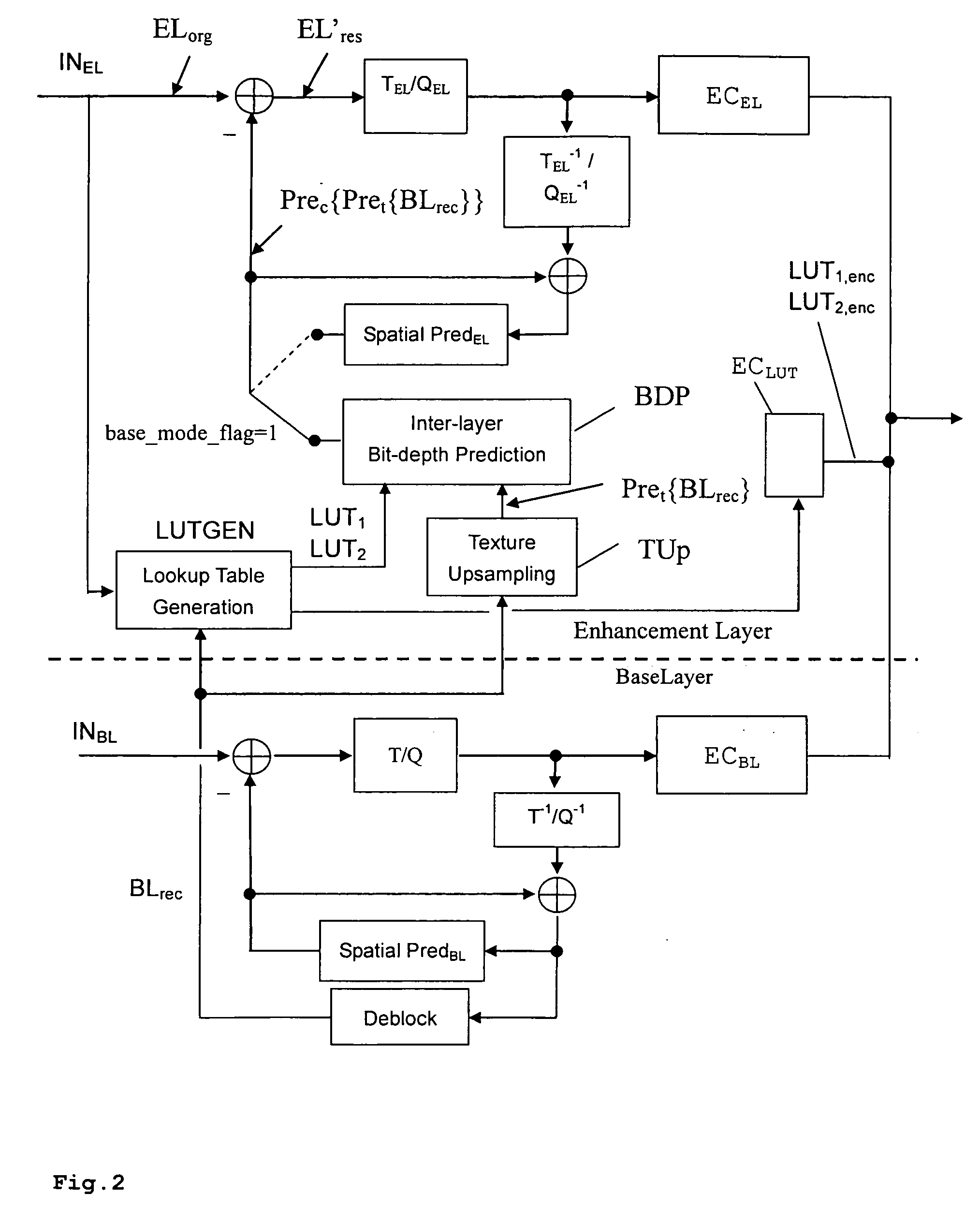
Enhancement layer residual prediction for bit depth scalability using hierarchical LUTs
ActiveUS20090110073A1Improve efficiencyReduce overheadColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionInverse tone mappingHue
A scalable video bitstream may have an H.264 / AVC compatible base layer and a scalable enhancement layer, where scalability refers to color bit-depth. According to the invention, BL information is bit-depth upsampled using separate look-up tables for inverse tone mapping on two or more hierarchy levels, such as picture level, slice level or MB level. The look-up tables are differentially encoded and included in header information. Bit-depth upsampling is a process that increases the number of values that each pixel can have, corresponding to the pixels color intensity. The upsampled base layer data are used to predict the collocated enhancement layer, based on said look-up tables. The upsampling is done at the encoder side and in the same manner at the decoder side, wherein the upsampling may refer to temporal, spatial and bit depth characteristics. Thus, the bit-depth upsampling is compatible with texture upsampling.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Image coding method and device using transform skip flag
ActiveUS20200260070A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove efficiencyDigital video signal modificationAlgorithmBitstream
A method for decoding an image according to the present document includes obtaining prediction mode information and residual related information from a bitstream, deriving prediction samples of a current block by performing prediction based on the prediction mode information, deriving residual samples of the current block based on the residual related information, and generating reconstruction samples of the current block based on the prediction samples and the residual samples, and the residual related information includes a transform skip flag based on a size of the current block and a maximum transform skip size, the transform skip flag represents whether a transform skip is applied to the current block, and information about the maximum transform skip size is obtained from the bitstream.
Owner:ROSEDALE DYNAMICS LLC
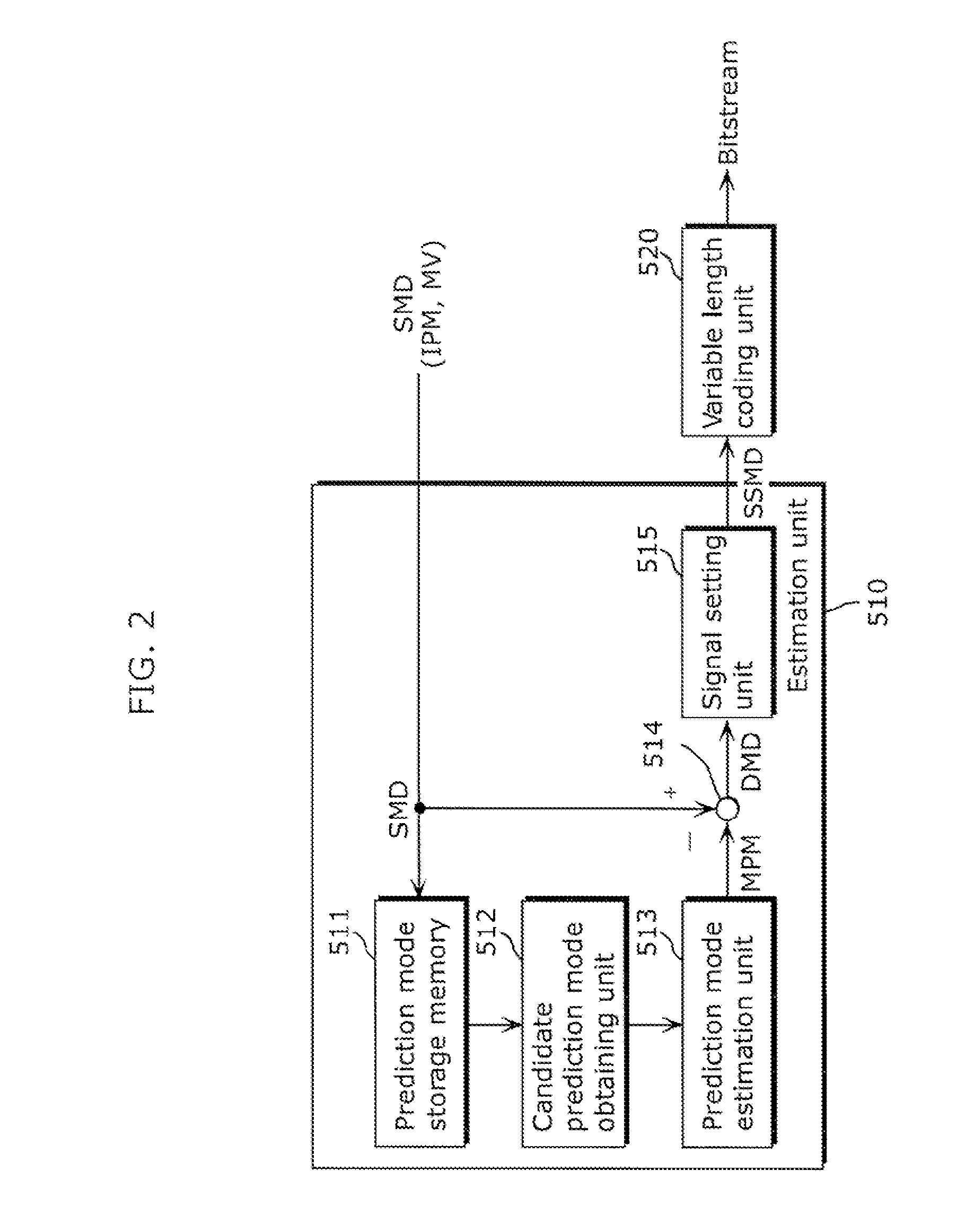
Motion vector coding method and motion vector decoding method
ActiveUS20040218674A1Improve coding efficiencyAccurate decodingPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDecoding methodsMotion vector
The present invention improves efficiency of coding motion vectors when a current block is coded using a plurality of motion vectors. A motion vector coding unit (117) codes a motion vector inputted from a motion vector detecting unit (108). A motion vector for each current block is coded based on a difference between the motion vector and a predicted vector obtained from motion vectors for previously coded neighboring blocks. The predicted vector is generated by one of the following processing: (A) the motion vectors which refer to the same picture are selected from among the motion vectors for the neighboring blocks so as to generate the predicted vector; (B) the motion vectors for the respective neighboring blocks are ordered in the predetermined order, and the motion vectors of the same order rank are selected from the ordered motion vectors so as to generate the predicted vector; and (C) the predicted vector for the second motion vector of the current block shall be the first motion vector, and if the second motion vector and the first motion vector refer to different pictures, the first motion vector is scaled according to the temporal distance between the pictures so as to generate the predicted vector.
Owner:TAGIVAN II
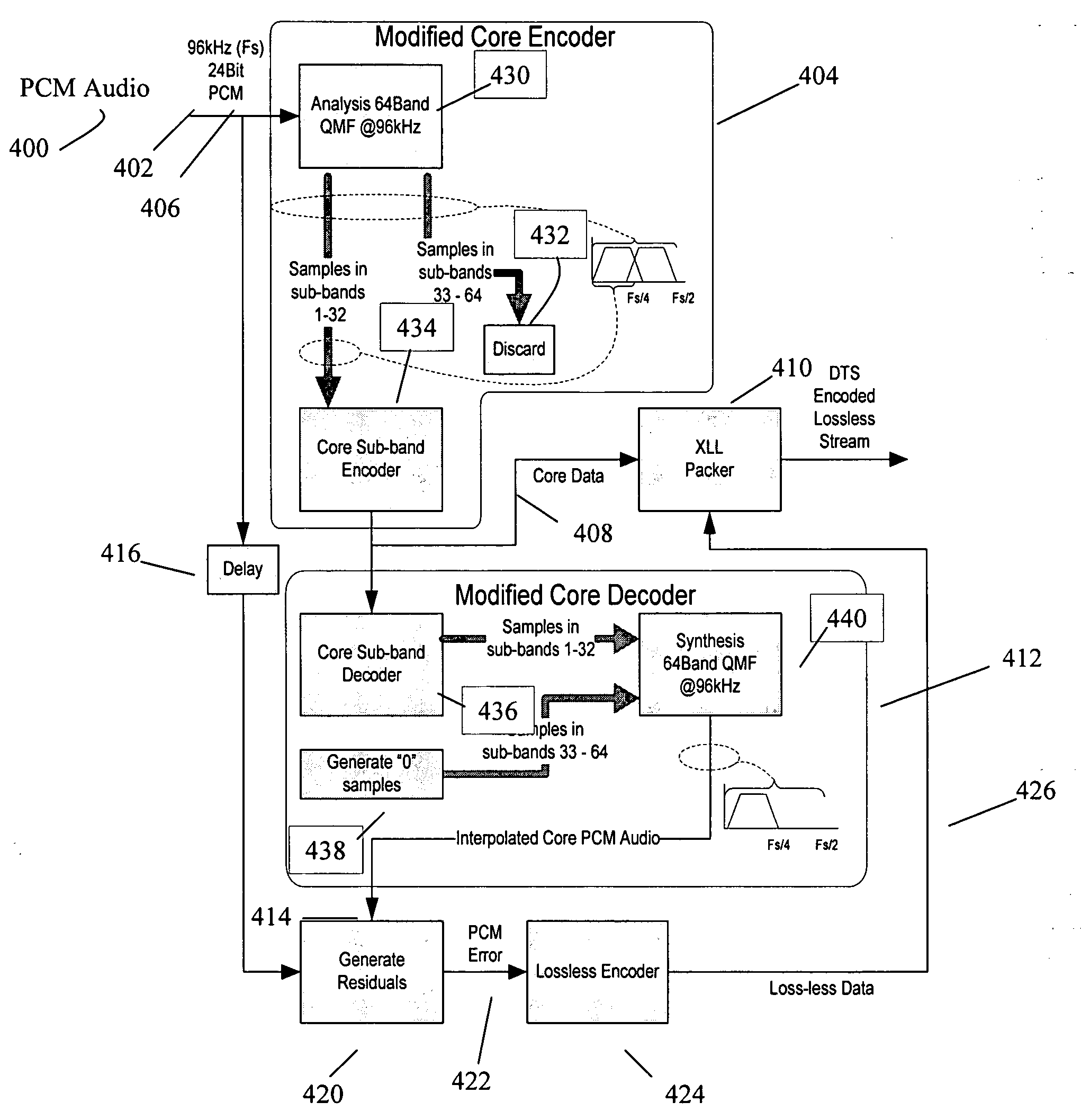
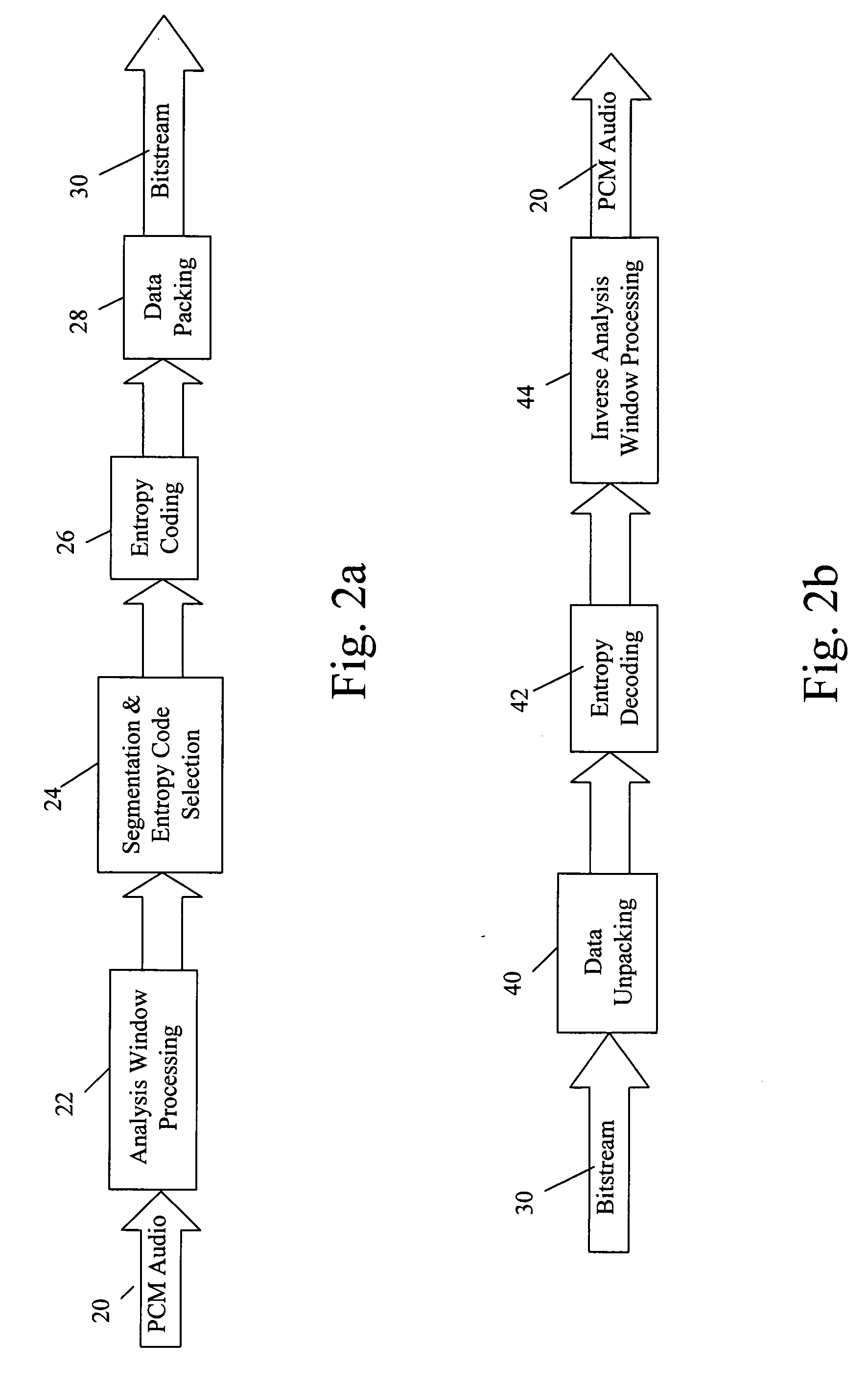
Lossless multi-channel audio codec using adaptive segmentation with random access point (RAP) and multiple prediction parameter set (MPPS) capability
ActiveUS20080215317A1Reduce transient effectsReduce encoded frame payloadBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisENCODEComputer science
A lossless audio codec encodes / decodes a lossless variable bit rate (VBR) bitstream with random access point (RAP) capability to initiate lossless decoding at a specified segment within a frame and / or multiple prediction parameter set (MPPS) capability partitioned to mitigate transient effects. This is accomplished with an adaptive segmentation technique that fixes segment start points based on constraints imposed by the existence of a desired RAP and / or detected transient in the frame and selects a optimum segment duration in each frame to reduce encoded frame payload subject to an encoded segment payload constraint. In general, the boundary constraints specify that a desired RAP or detected transient must lie within a certain number of analysis blocks of a segment start point. In an exemplary embodiment in which segments within a frame are of the same duration and a power of two of the analysis block duration, the RAP and / or transient constraints set a maximum segment duration to ensure the desired conditions. RAP and MPPS are particularly applicable to improve overall performance for longer frame durations.
Owner:DTS
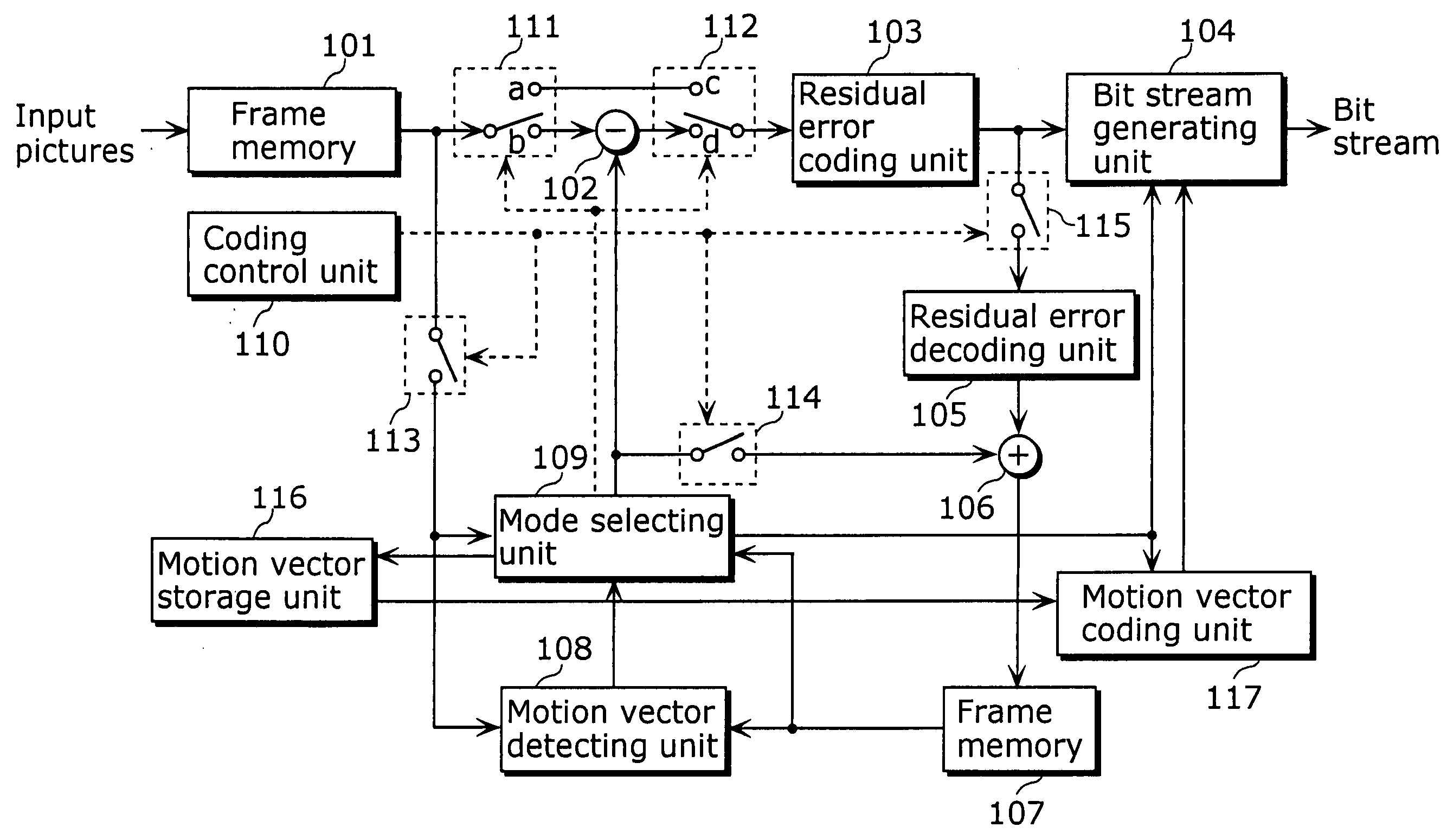
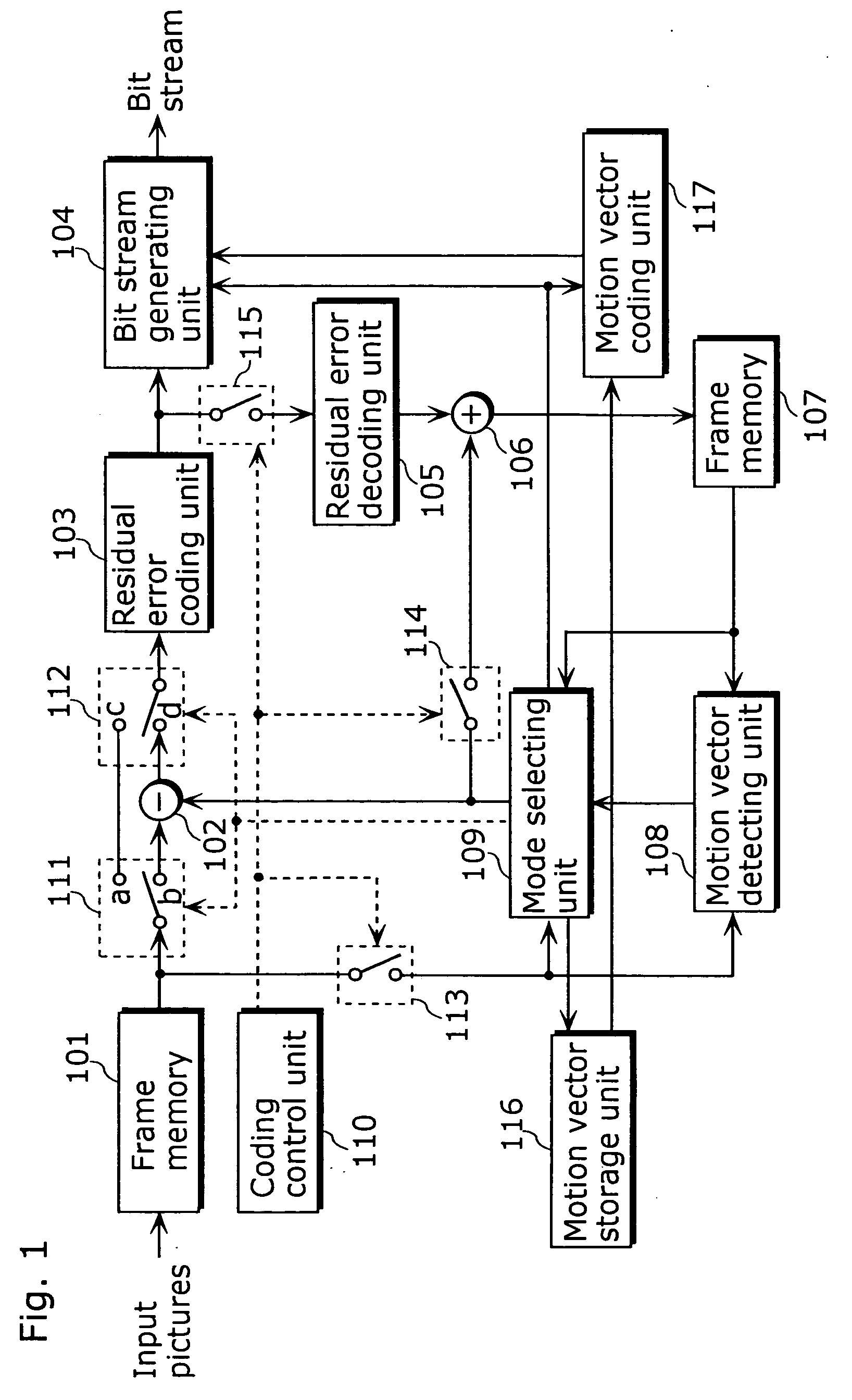
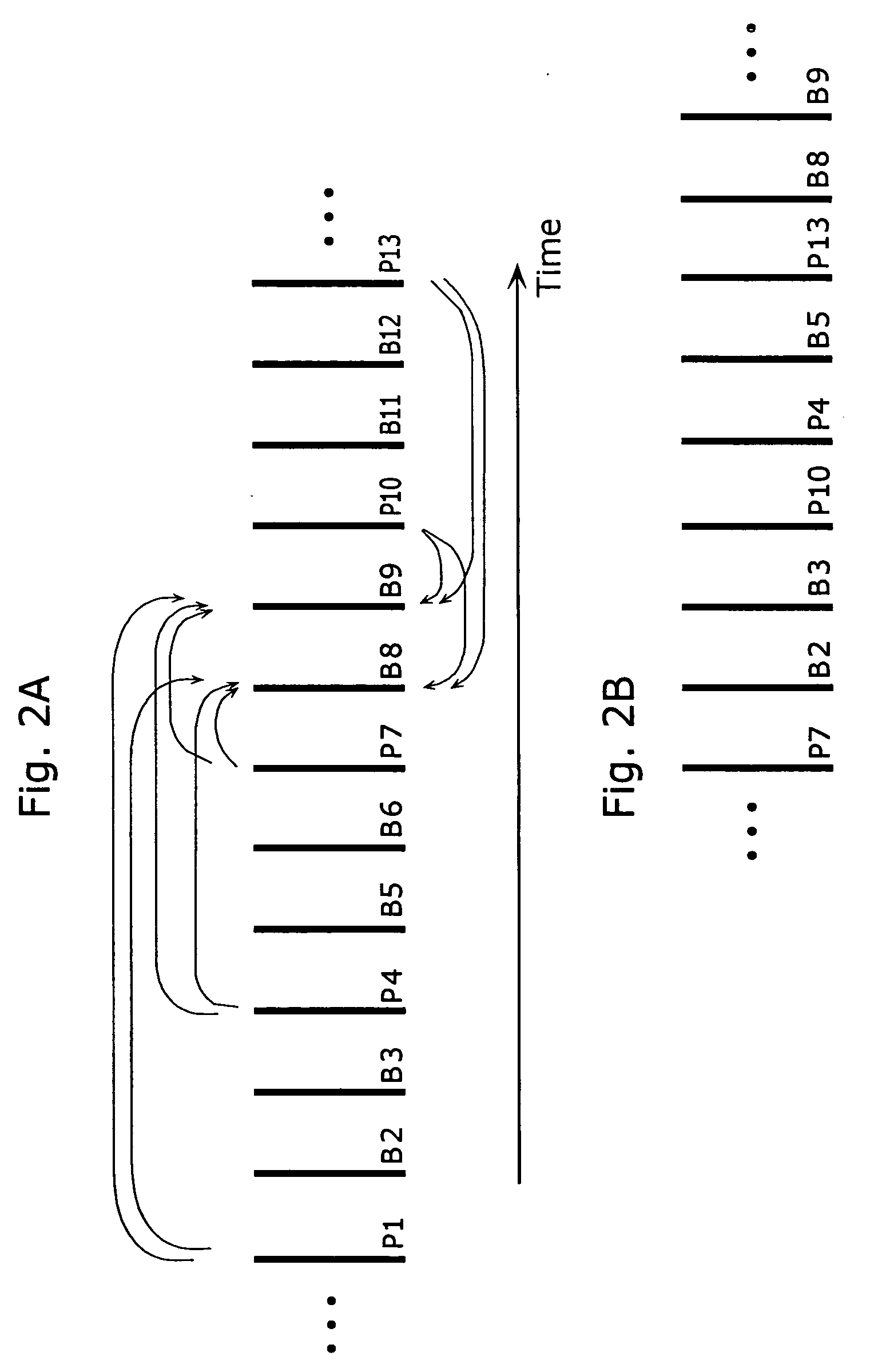
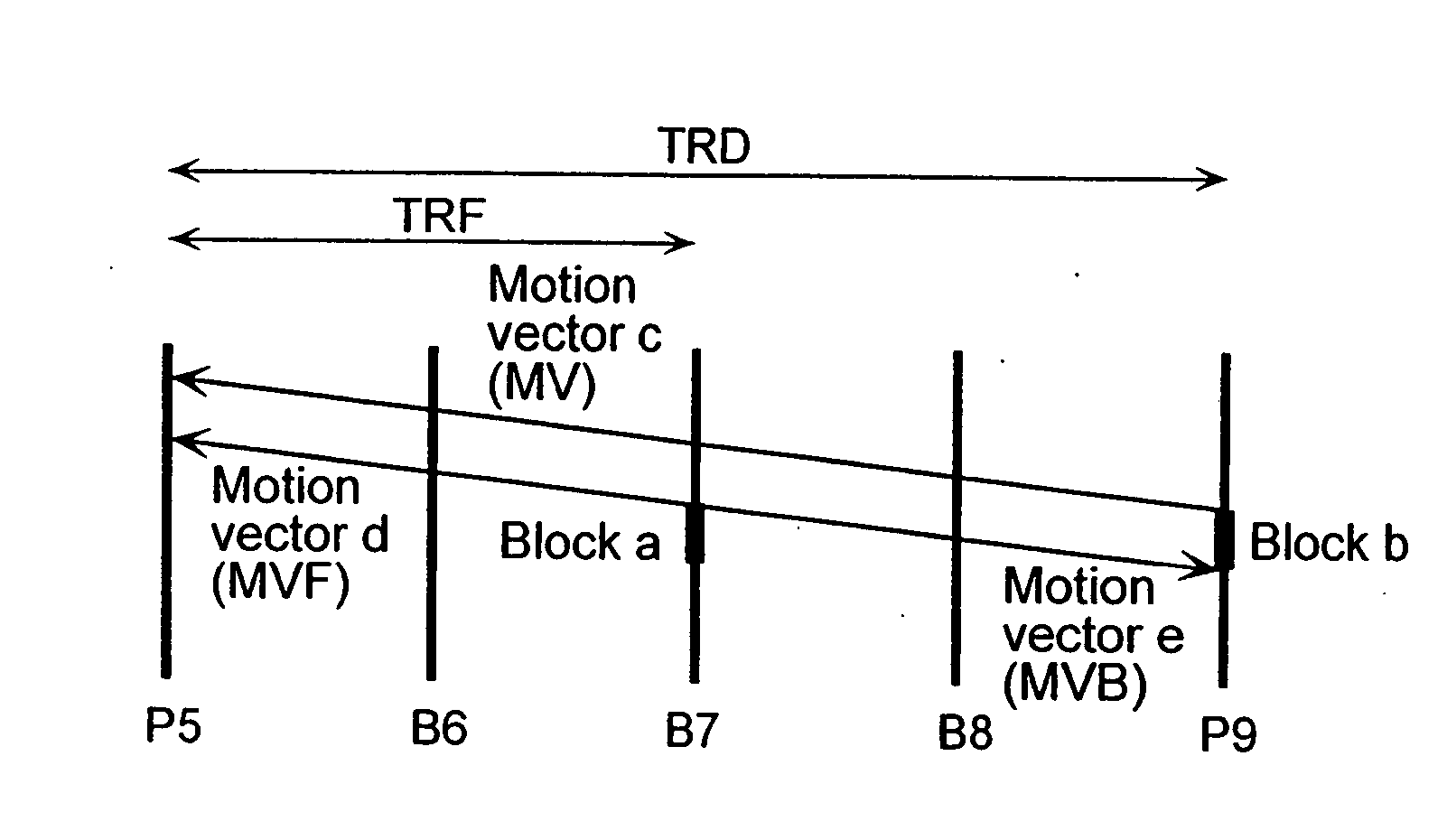
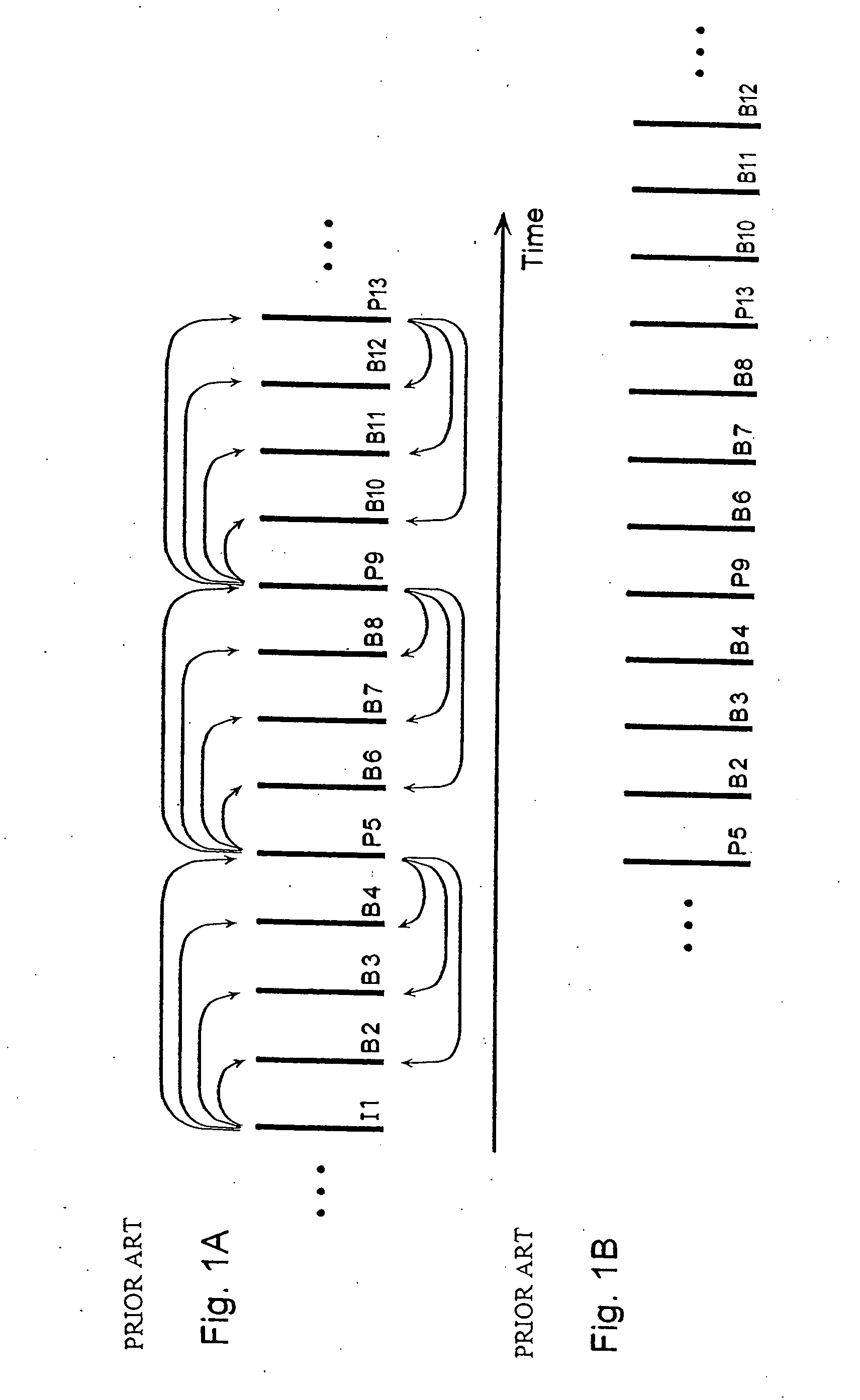
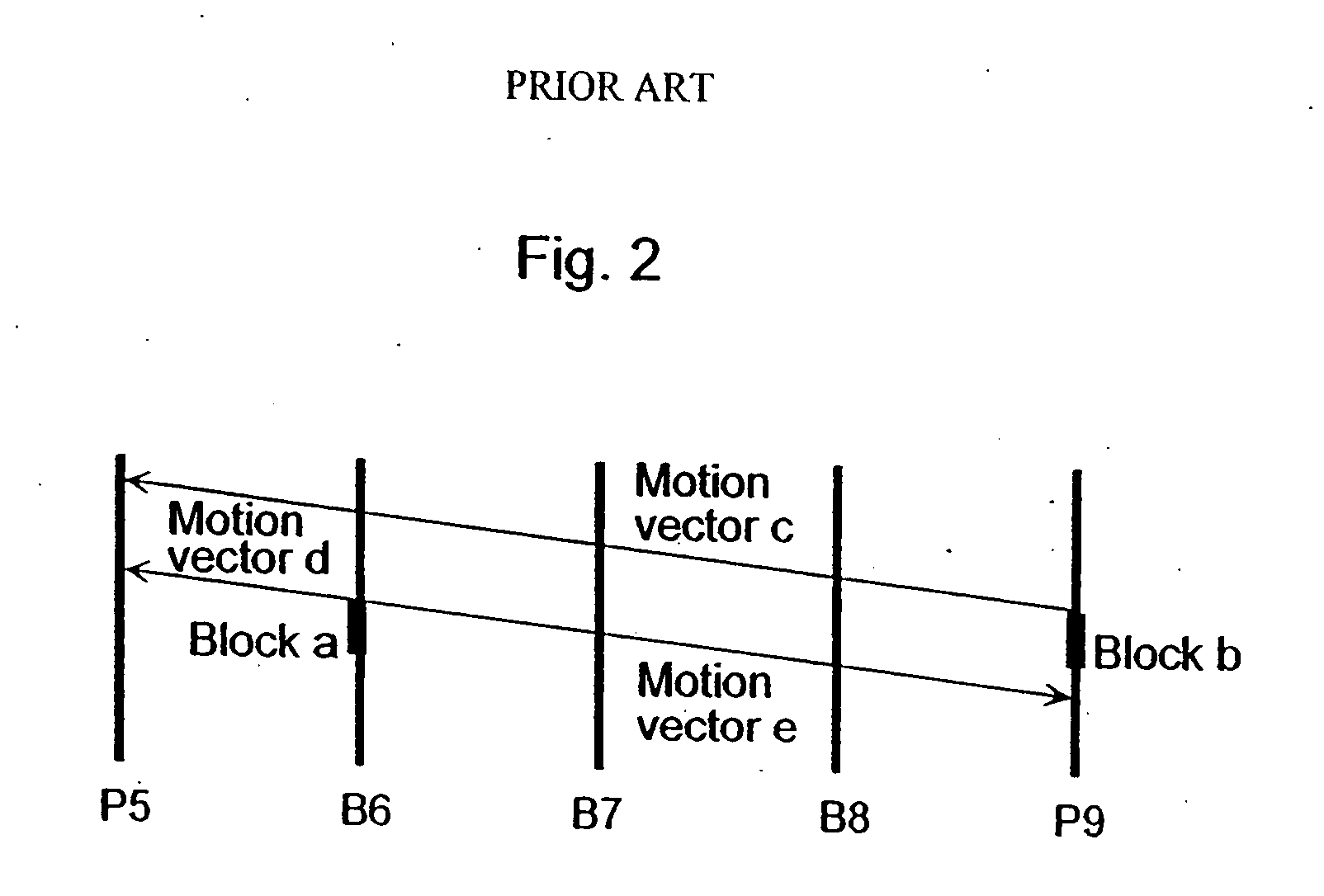
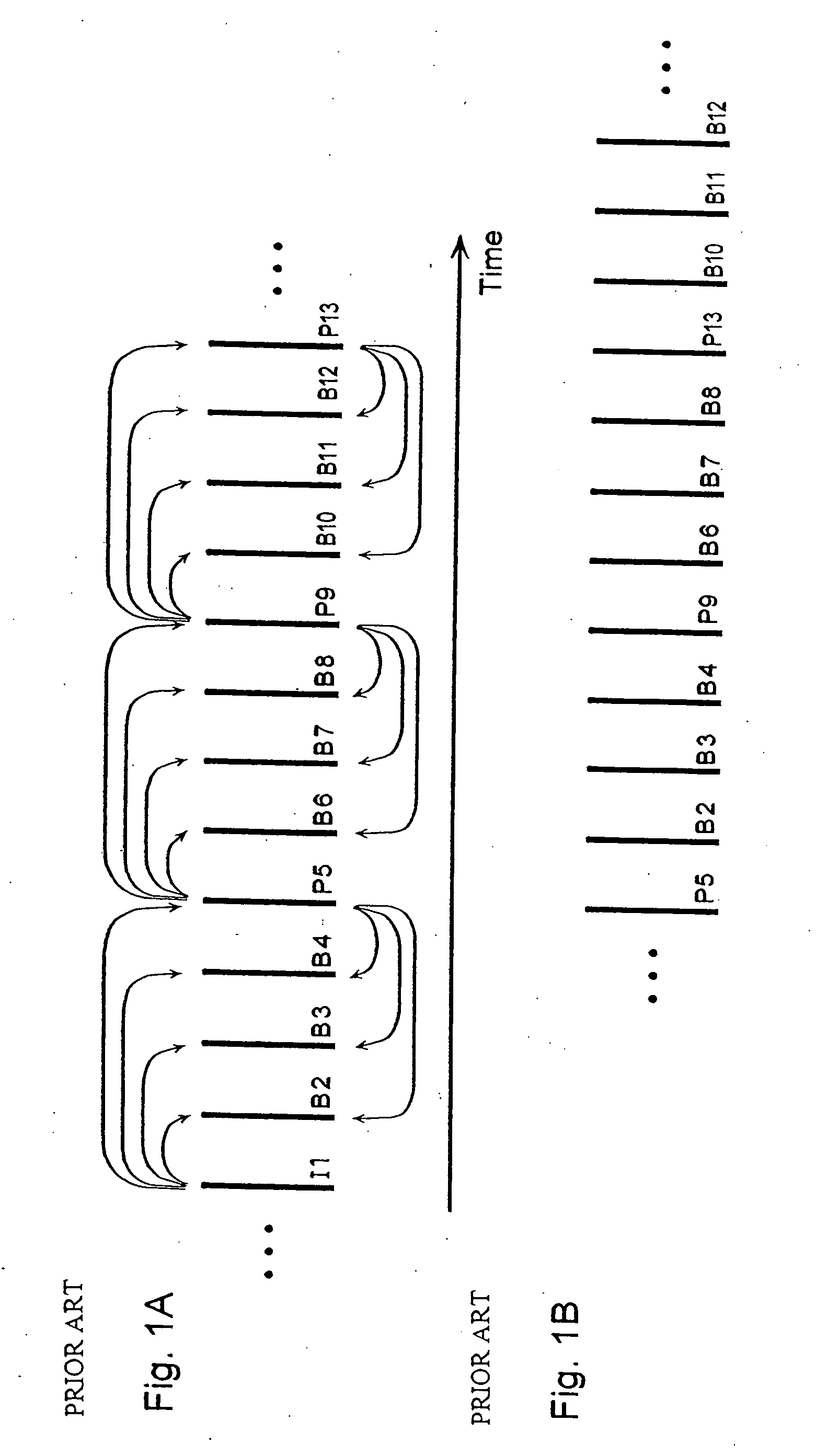
Moving picture coding method and moving picture decoding method for performing inter picture prediction coding and inter picture prediction decoding using previously processed pictures as reference pictures
ActiveUS20080069232A1Easy to predictImprove coding efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionDecoding methodsMotion vector
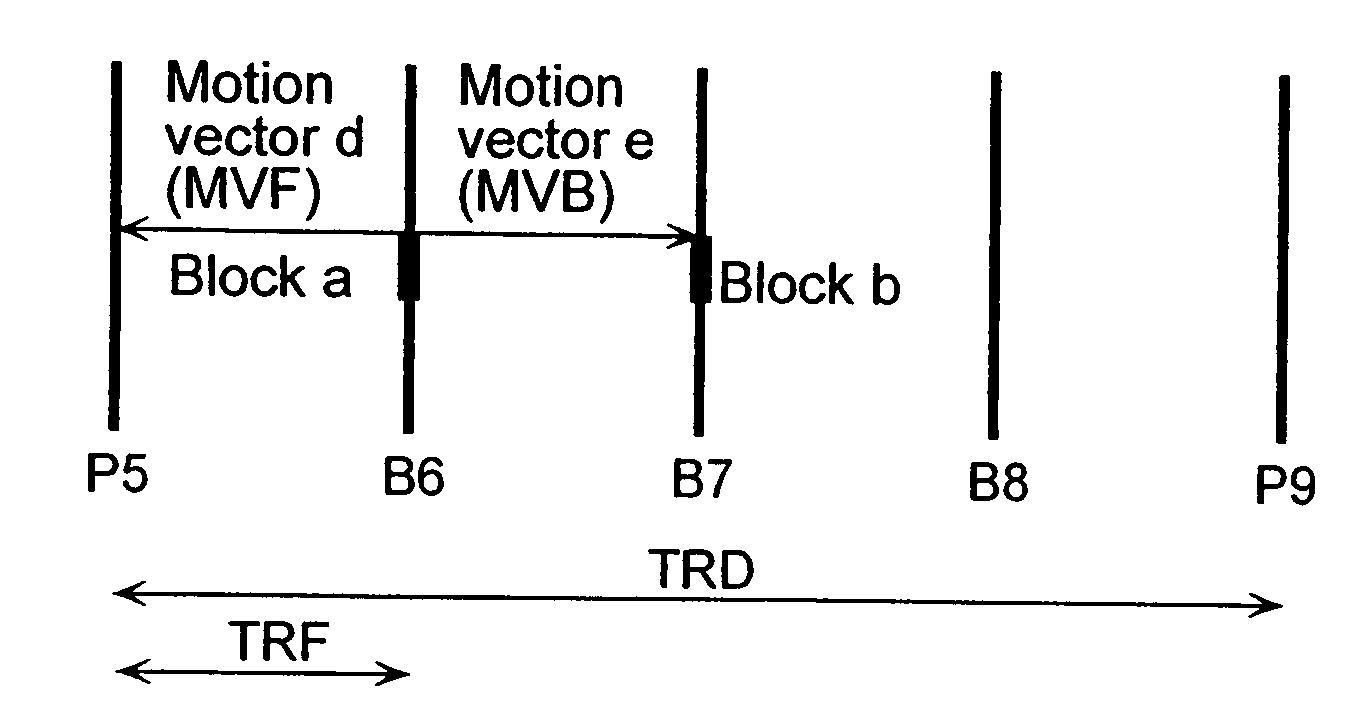
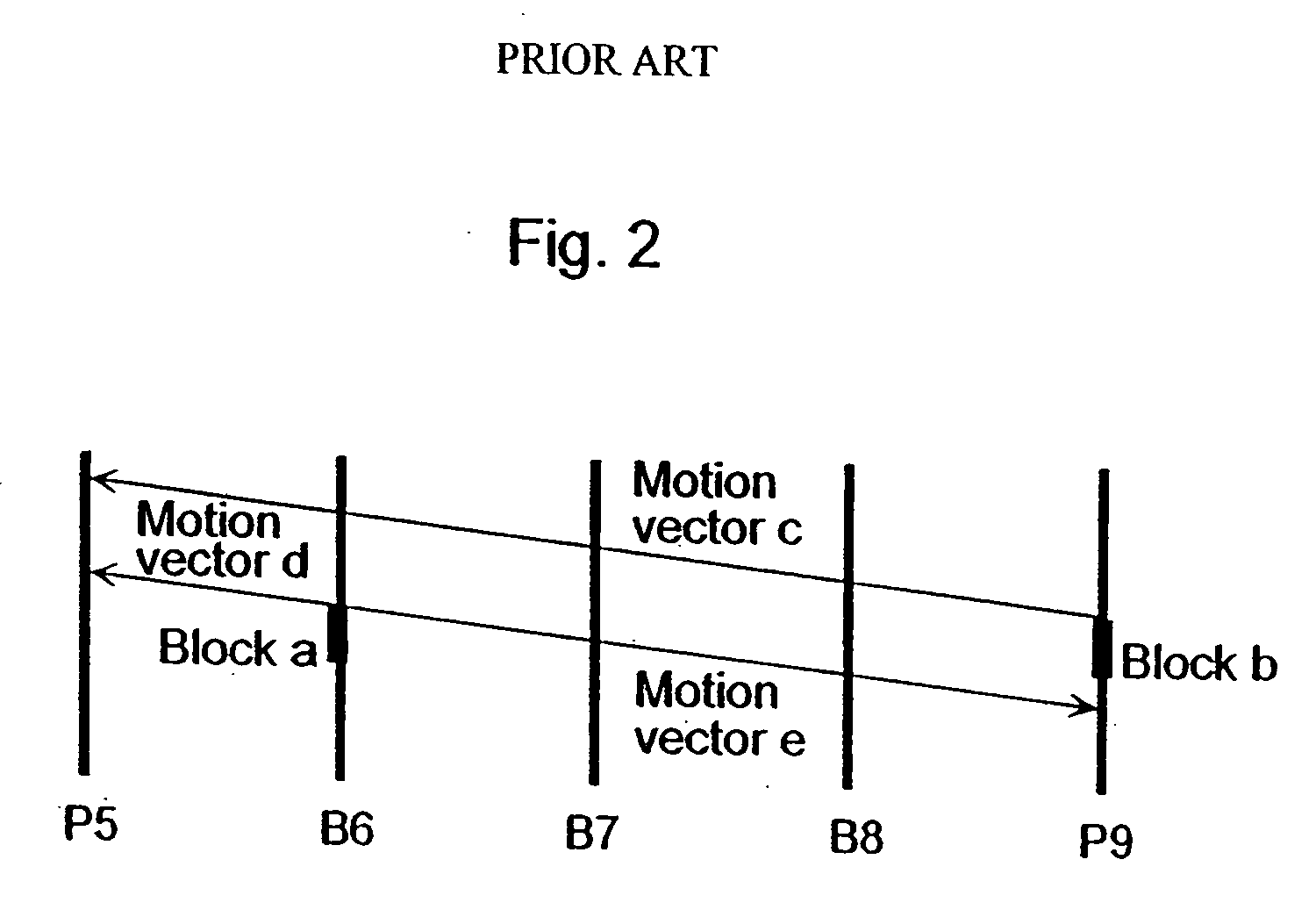
A coding control unit (110) and a mode selection unit (109) are included. The coding control unit (110) determines the coding order for a plurality of consecutive B-pictures located between I-pictures and P-pictures so that the B-picture whose temporal distance from two previously coded pictures is farthest in display order is coded by priority, so as to reorder the B-pictures in coding order. When a current block is coded in direct mode, the mode selection unit 109 scales a forward motion vector of a block which is included in a backward reference picture of a current picture and co-located with the current block, so as to generate motion vectors of the current block, if the forward motion vector has been used for coding the co-located block.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Moving Picture Coding Method And Moving Picture Decoding Method
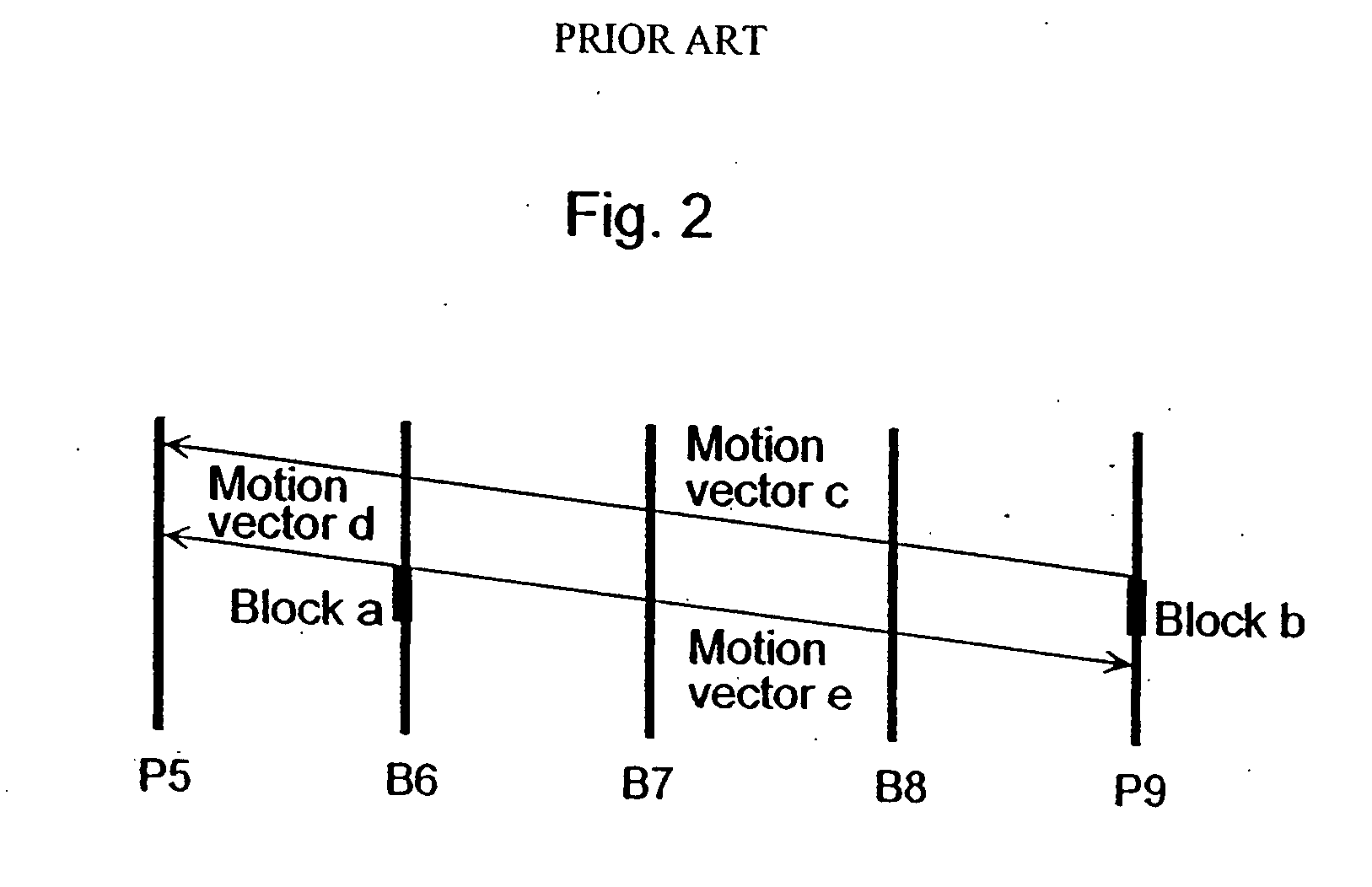
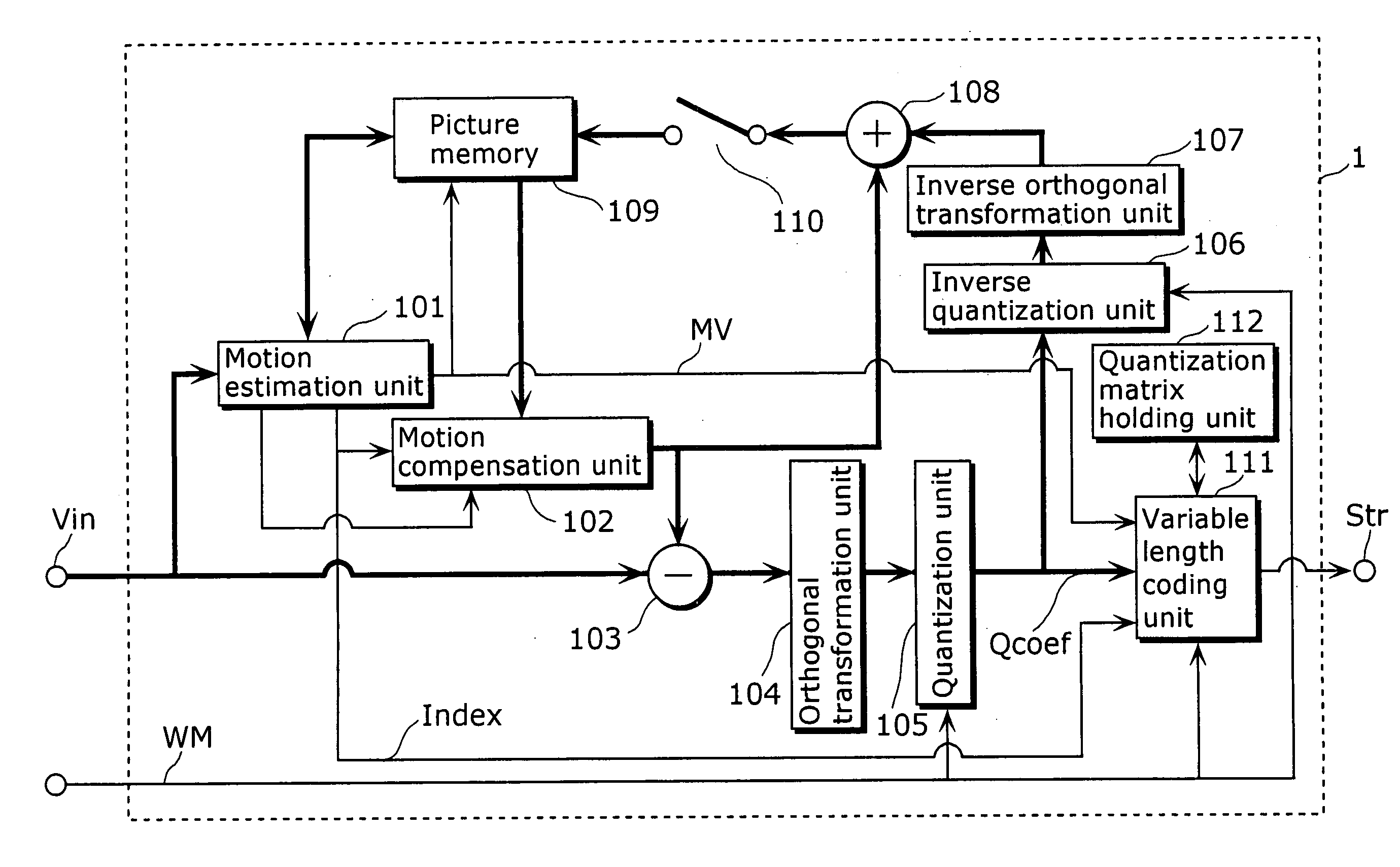
ActiveUS20080089410A1Reduce data volumeEfficient decodingPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codeQuantization matrix
A moving picture coding apparatus 1 includes: a quantization matrix holding unit (112) that holds a quantization matrix (WM) which has already been transmitted in a parameter set and a matrix ID for identifying the quantization matrix (WM), which are associated with each other; and a variable length coding unit (111) that obtains the matrix ID corresponding to the quantization matrix (WM) used for quantization from the quantization matrix holding unit (112) and places the matrix ID in a coded stream Str.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Encoding and decoding of redundant pictures
InactiveUS20050123056A1Avoid mistakesReduce frequencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo sequenceComputer science
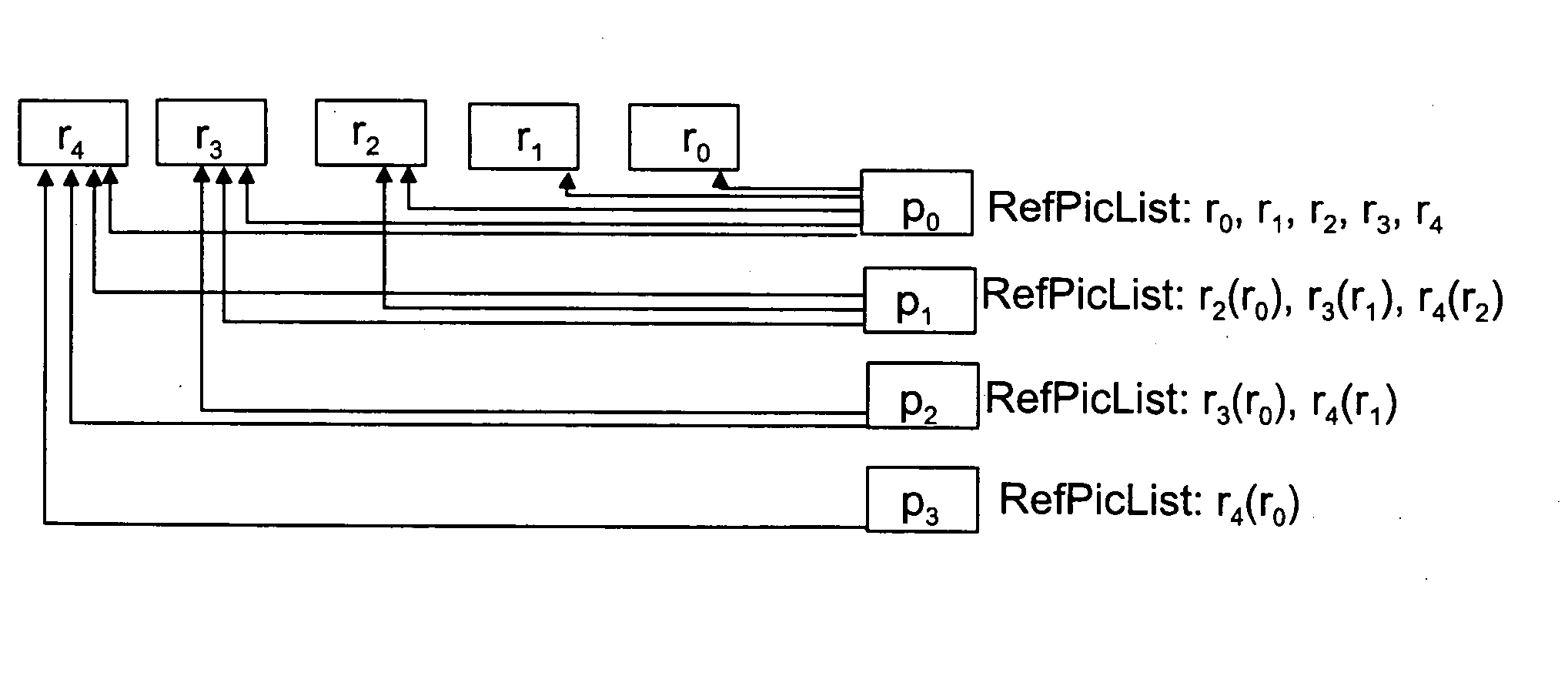
A method of encoding video data including at least one primary picture and at least one redundant picture corresponding to the information content of the primary picture. A reference picture list of the at least one redundant picture includes multiple reference pictures. The video sequence is encoded such that a number of reference pictures are disabled from the reference picture list of the at least one redundant picture, the number being at least one, but less than the total number of the reference pictures on the reference picture list.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Video coding
InactiveUS20060146934A1Increase elasticityImprove coding efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVideo encodingArtificial intelligence
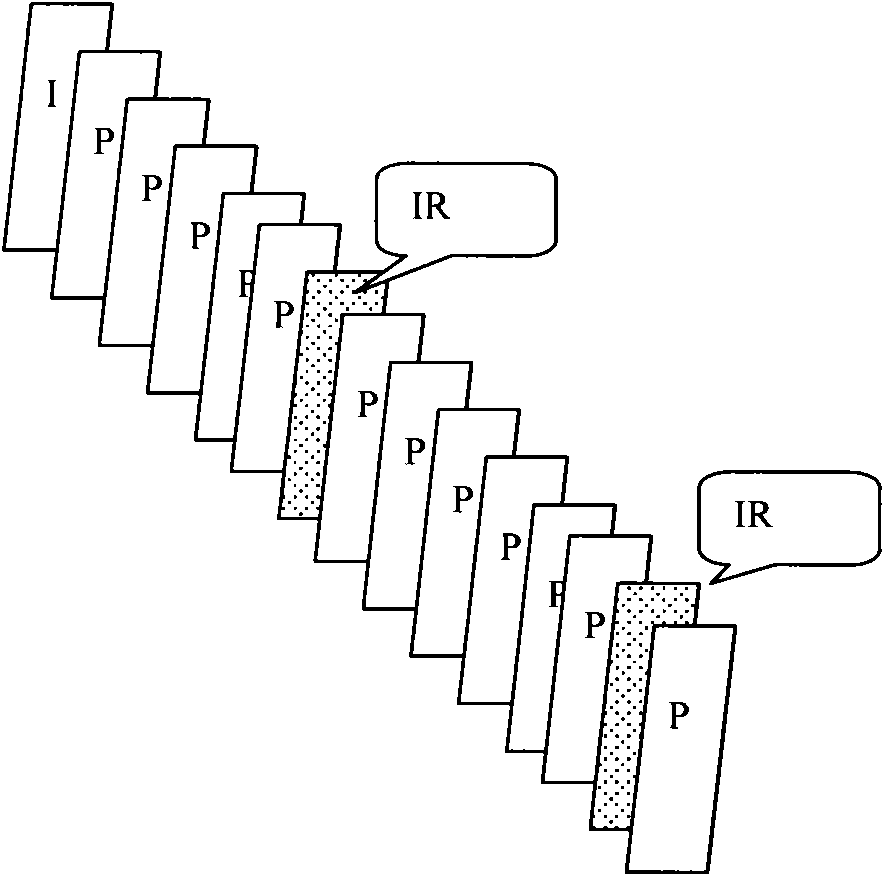
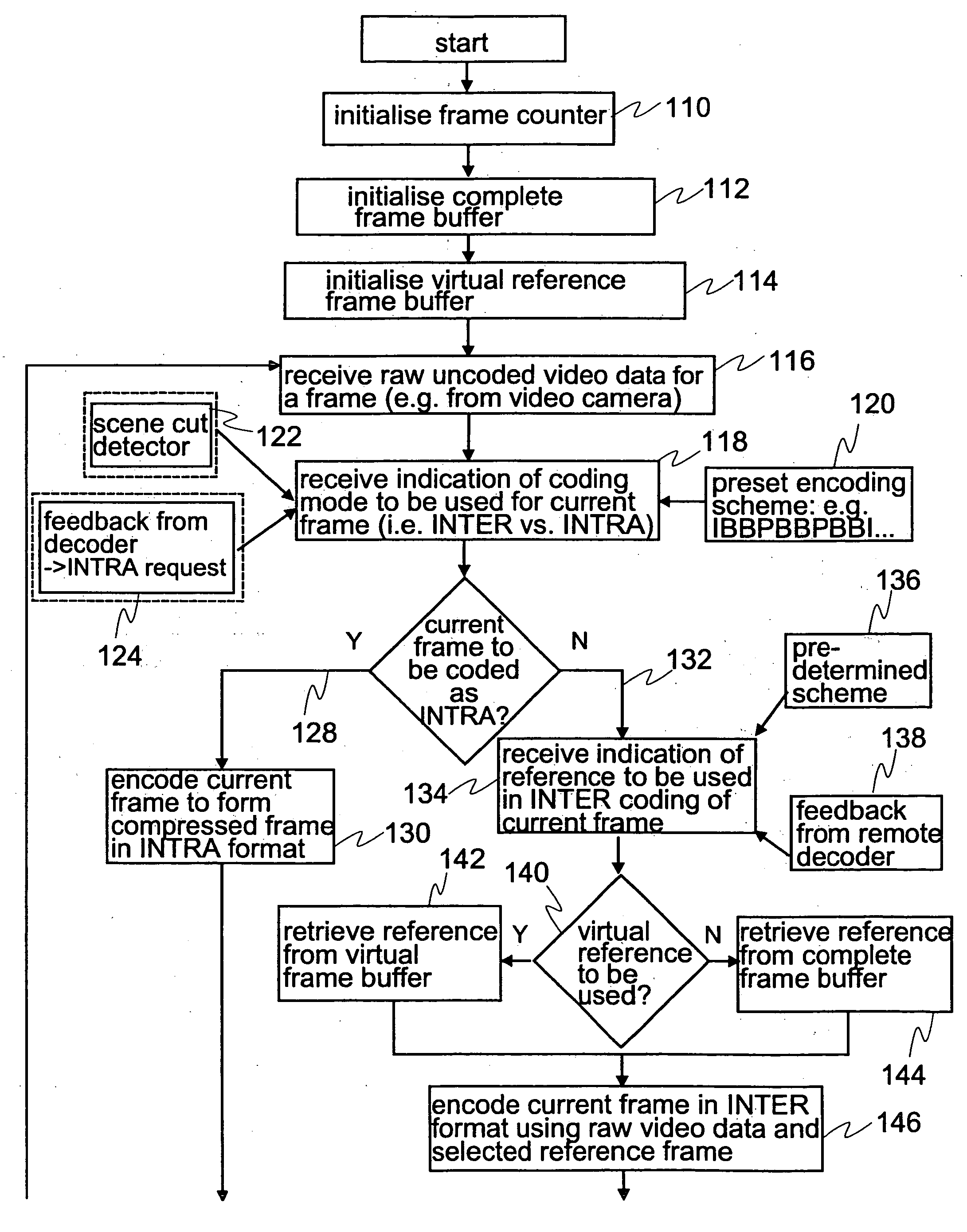
A method for encoding a video signal comprises the steps of: encoding a first complete frame by forming a bit-stream containing information for its subsequent full reconstruction (150) the information being prioritised (148) into high and low priority information; defining (160) at least one virtual frame on the basis of a version of the first complete frame constructed using the high priority information of the first complete frame in the absence of at least some of the low priority information of the first complete frame; and encoding (146) a second complete frame by forming a bit-stream containing information for its subsequent full reconstruction the information being prioritised into high and low priority information enabling the second complete frame to be fully reconstructed on the basis of the virtual frame rather than on the basis of the first complete frame. A corresponding decoding method is also described.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
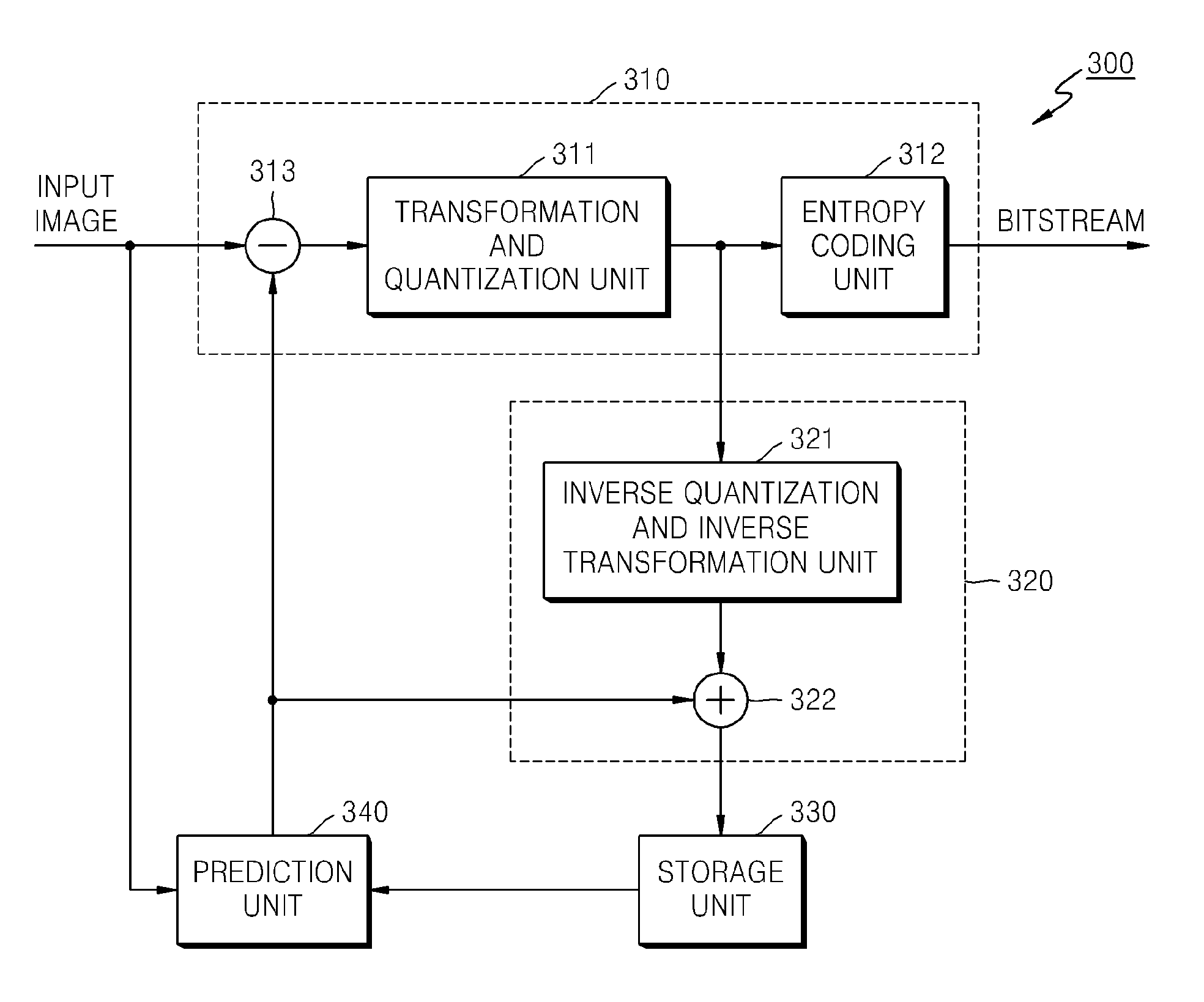
Method and apparatus for encoding video pictures, and method and apparatus for decoding video pictures
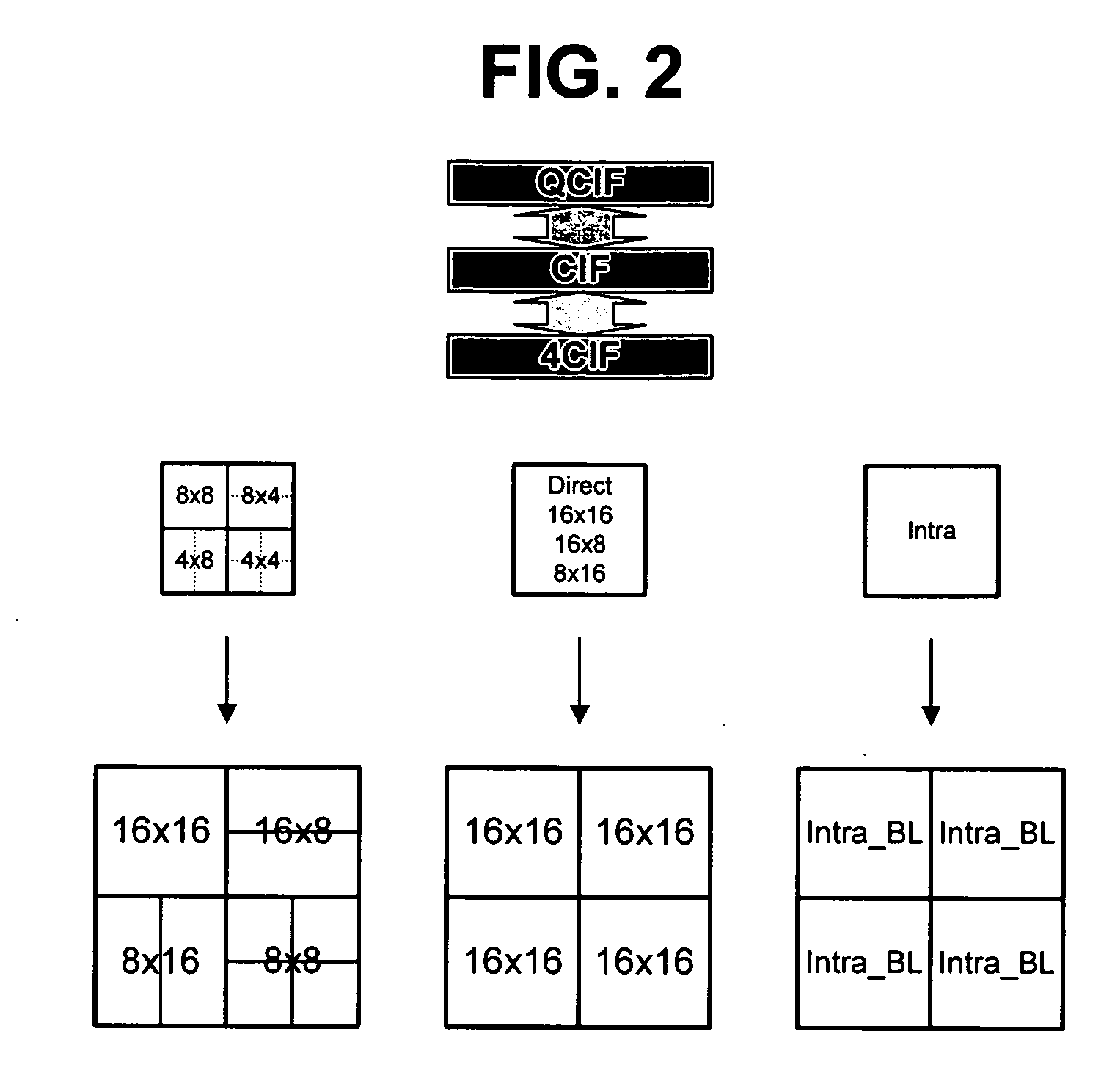
ActiveUS20060262216A1Simple methodImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage resolutionMacroblock
The H.264 standard has introduced a new coding method for intra-coded pictures, which is named “intra prediction”. The basic idea of intra prediction is to predict a block using reconstructed neighbour pixels. Thus, only the residual information needs to be encoded. Scalable video coding adds some scalable extension to H.264, in terms of spatial, temporal and SNR scalability. An improved encoding method for scalable video comprises generating from a video picture a first and a second picture with higher resolution than the first picture, wherein each macroblock in the first picture has a plurality of corresponding macroblocks in the second picture, intra-coding the first picture on macroblock level, wherein for each macroblock a prediction direction is determined, generating a first residual picture, intra-coding the second picture on macroblock level, wherein for each macroblock the prediction direction of the corresponding macroblock of the first picture is reused, and generating a second residual picture.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Encoding and decoding method, encoding device, decoding device and system for video images
ActiveCN102685504AMotion vectors are accurateImprove decoding qualityPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsComputation complexity
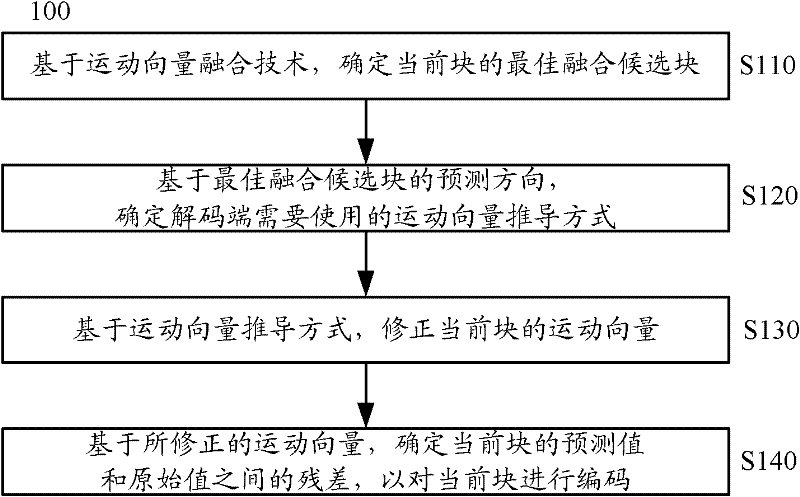
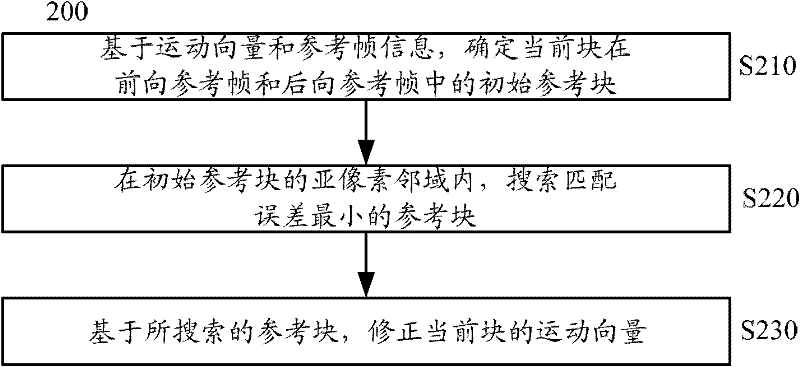
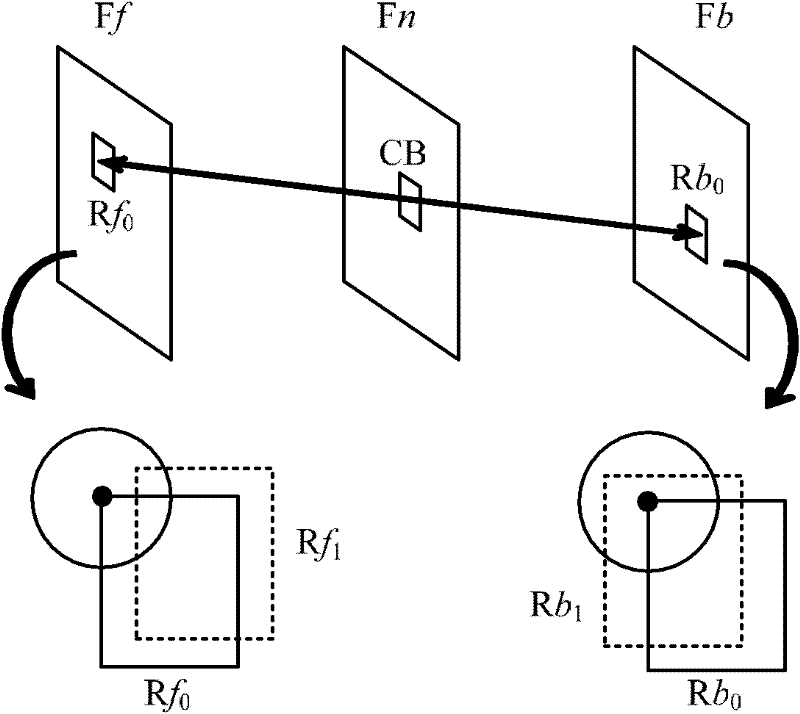
An embodiment of the invention provides an encoding method, a decoding method, an encoding device, a decoding device and a system for video images. The encoding method includes determining an optimum integration alternative block of a current block on the basis of the motion vector integration technology; determining a motion vector calculation mode required by a decoding side on the basis of the prediction direction of the optimum integral alternative block; rectifying the motion vector of the current block on the basis of the motion vector calculation mode; determining residual error between a predicted value and an original value of the current block on the basis of the rectified motion vector so as to encode the current block. According to the technical scheme in the embodiment, more accurate predicted value can be acquired through the rectified motion vector, smaller residual error is generated, encoding efficiency can be improved, increase of data bandwidth is avoided, and encoding quality can be improved while computing complexity is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Scalable video coding using derivation of subblock subdivision for prediction from base layer
ActiveUS20150195566A1Improving available qualityMotion-compensated predictionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData streamVideo encoding
Scalable video coding is rendered more efficient by deriving / selecting a subblock subdivision to be used for enhancement layer prediction, among a set of possible subblock subdivisions of an enhancement layer block by evaluating the spatial variation of the base layer coding parameters over the base layer signal. By this measure, less of the signalization overhead has to be spent on signaling this subblock subdivision within the enhancement layer data stream, if any. The subblock subdivision thus selected may be used in predictively coding / decoding the enhancement layer signal.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Image prediction method and relevant device
ActiveCN104539966AReduce computational complexityAvoid passingDigital video signal modificationComputation complexityMotion vector
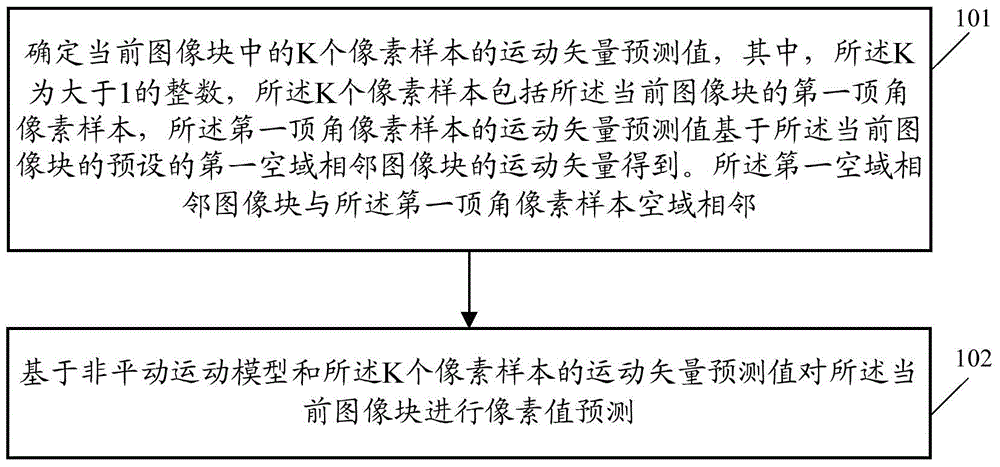
The embodiment of the invention discloses an image prediction method and a relevant device. The image prediction method comprises the following steps: determining the motion vector predictors of K pixel samples in a current image block, wherein K is an integer greater than 1, the K pixel samples comprise a first vertex angle pixel sample of the current image block, the motion vector predictor of the first vertex angle pixel sample is obtained on the basis of the motion vector of a preset first spatial domain adjacent image block of the current image block, and the first spatial domain adjacent image block is adjacent to a first vertex angle pixel sample spatial domain; and predicting the pixel value of the current image block on the basis of a non-translational motion model and the motion vector predictors of the K pixel samples. According to the scheme in the embodiment of the invention, the computation complexity of image prediction based on the non-translational motion model is lowered.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Moving picture coding method and moving picture decoding method for performing inter picture prediction coding and inter picture prediction decoding using previously processed pictures as reference pictures
InactiveUS20080069231A1Easy to predictImprove coding efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionDecoding methodsMotion vector
A coding control unit (110) and a mode selection unit (109) are included. The coding control unit (110) determines the coding order for a plurality of consecutive B-pictures located between I-pictures and P-pictures so that the B-picture whose temporal distance from two previously coded pictures is farthest in display order is coded by priority, so as to reorder the B-pictures in coding order. When a current block is coded in direct mode, the mode selection unit 109 scales a forward motion vector of a block which is included in a backward reference picture of a current picture and co-located with the current block, so as to generate motion vectors of the current block, if the forward motion vector has been used for coding the co-located block.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Moving picture coding method and moving picture decoding method for performing inter picture prediction coding and inter picture prediction decoding using previously processed pictures as reference pictures
ActiveUS20080063060A1Accurate decodingEasy to predictPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionDecoding methodsMotion vector
A coding control unit (110) and a mode selection unit (109) are included. The coding control unit (110) determines the coding order for a plurality of consecutive B-pictures located between I-pictures and P-pictures so that the B-picture whose temporal distance from two previously coded pictures is farthest in display order is coded by priority, so as to reorder the B-pictures in coding order. When a current block is coded in direct mode, the mode selection unit 109 scales a forward motion vector of a block which is included in a backward reference picture of a current picture and co-located with the current block, so as to generate motion vectors of the current block, if the forward motion vector has been used for coding the co-located block.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Image coding method and image decoding method
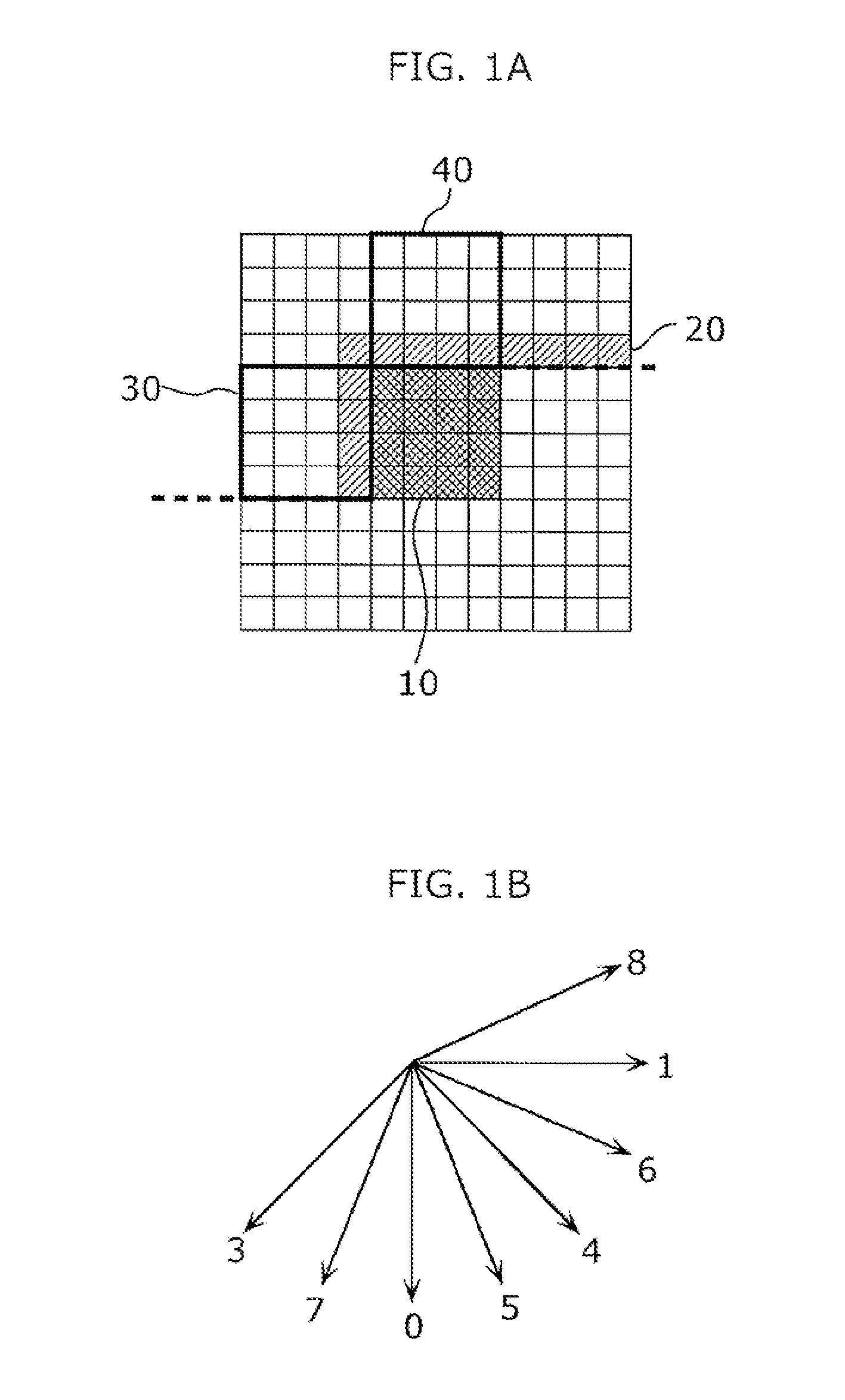
InactiveUS20120020580A1Increase in amount of computationCod efficiency be improveCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationImage codeImaging data
In order to achieve higher coding efficiency, suppress coding artifacts, and not to need a large computing amount, an image and video data are coded. Provided is an image coding method of coding image data on a block-by-block basis, and the method includes: coding a current block according to a prediction based on a selected prediction mode (S101); determining an estimated prediction mode from among candidate prediction modes; and outputting the coded current block and mode information for reconstructing the selected prediction mode (S108). The determining includes: detecting an edge (S103); reducing the candidate prediction modes in number based on the detected edge (S105); determining the estimated prediction mode from among the candidate prediction modes reduced in number (S106); and generating the mode information based on the estimated prediction mode and the selected prediction mode (S107).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Moving picture coding method and moving picture decoding method for performing inter picture prediction coding and inter picture prediction decoding using previously processed pictures as reference pictures
InactiveUS20080063061A1Accurate decodingEasy to predictPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionDecoding methodsMotion vector
A coding control unit (110) and a mode selection unit (109) are included. The coding control unit (110) determines the coding order for a plurality of consecutive B-pictures located between I-pictures and P-pictures so that the B-picture whose temporal distance from two previously coded pictures is farthest in display order is coded by priority, so as to reorder the B-pictures in coding order. When a current block is coded in direct mode, the mode selection unit 109 scales a forward motion vector of a block which is included in a backward reference picture of a current picture and co-located with the current block, so as to generate motion vectors of the current block, if the forward motion vector has been used for coding the co-located block.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com