Patents
Literature
395results about How to "Accurate decoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
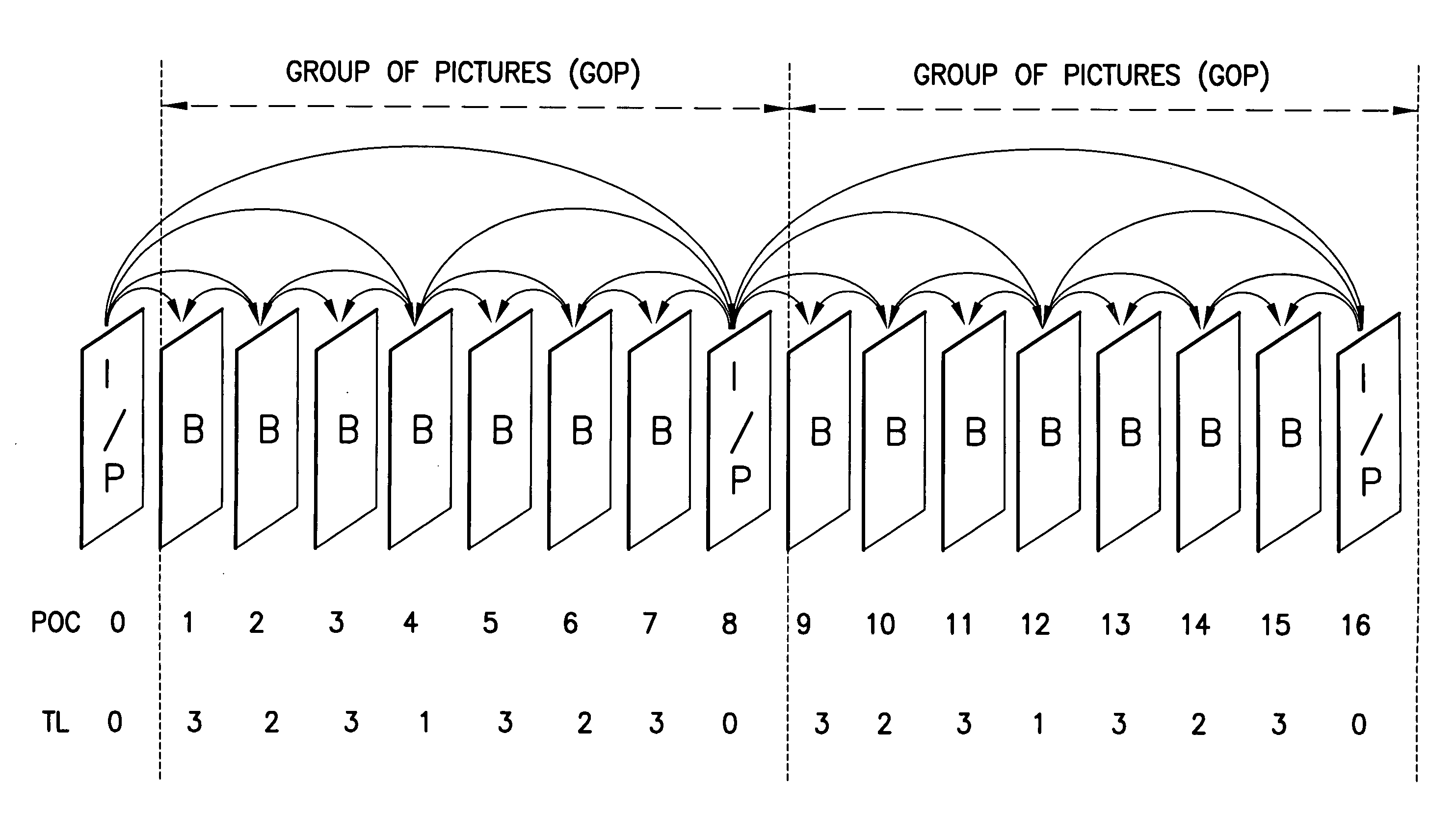
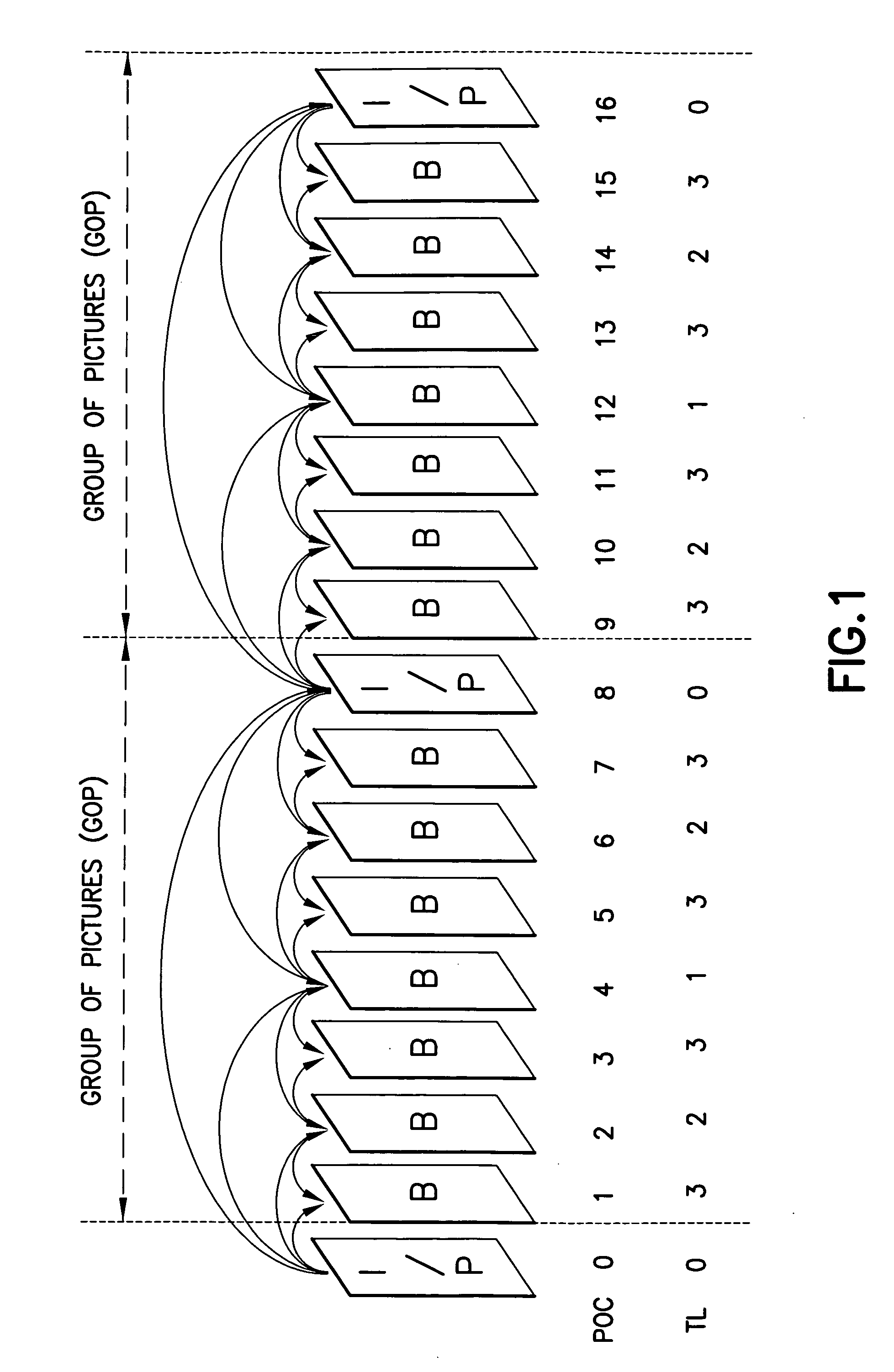
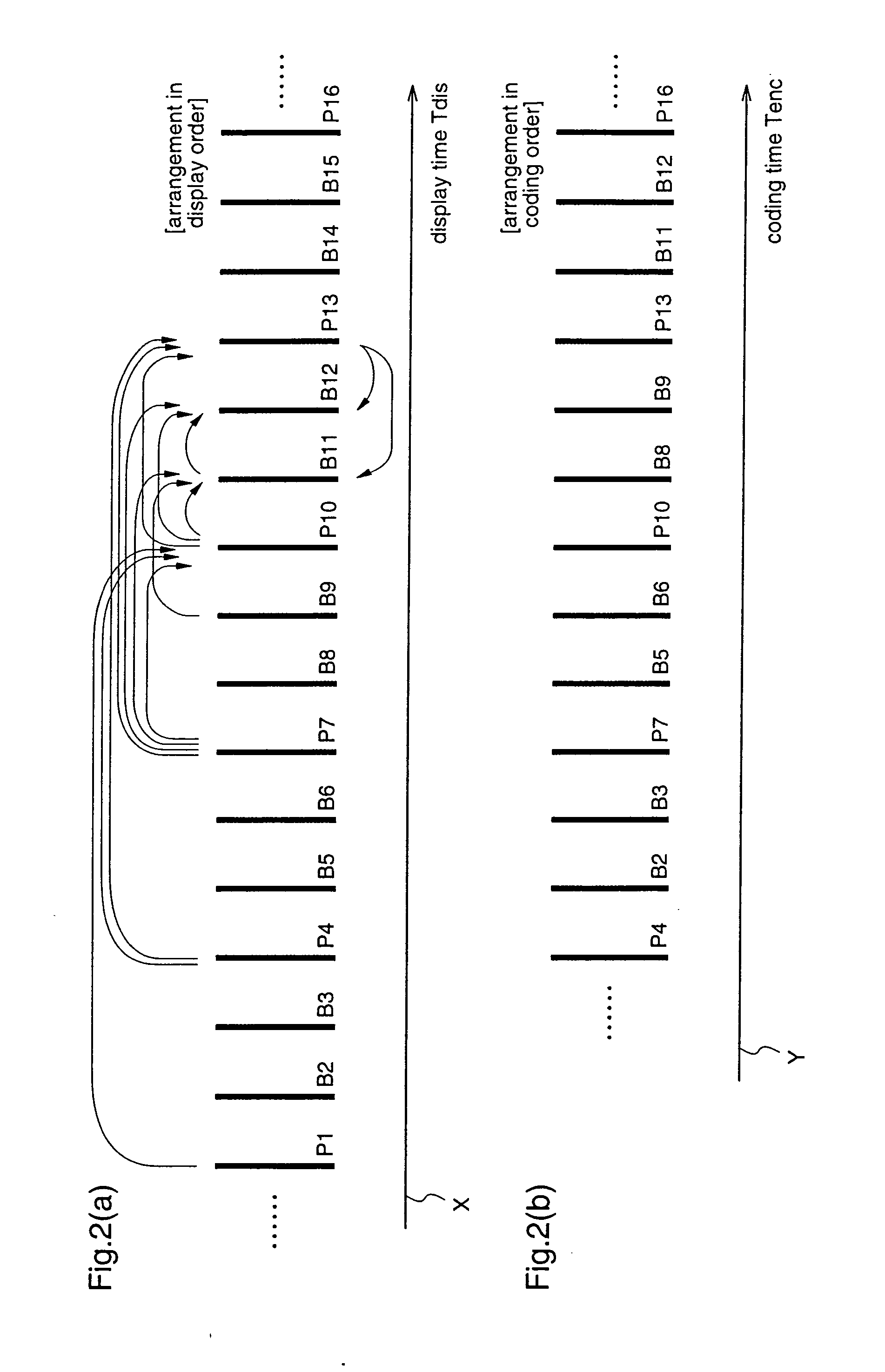
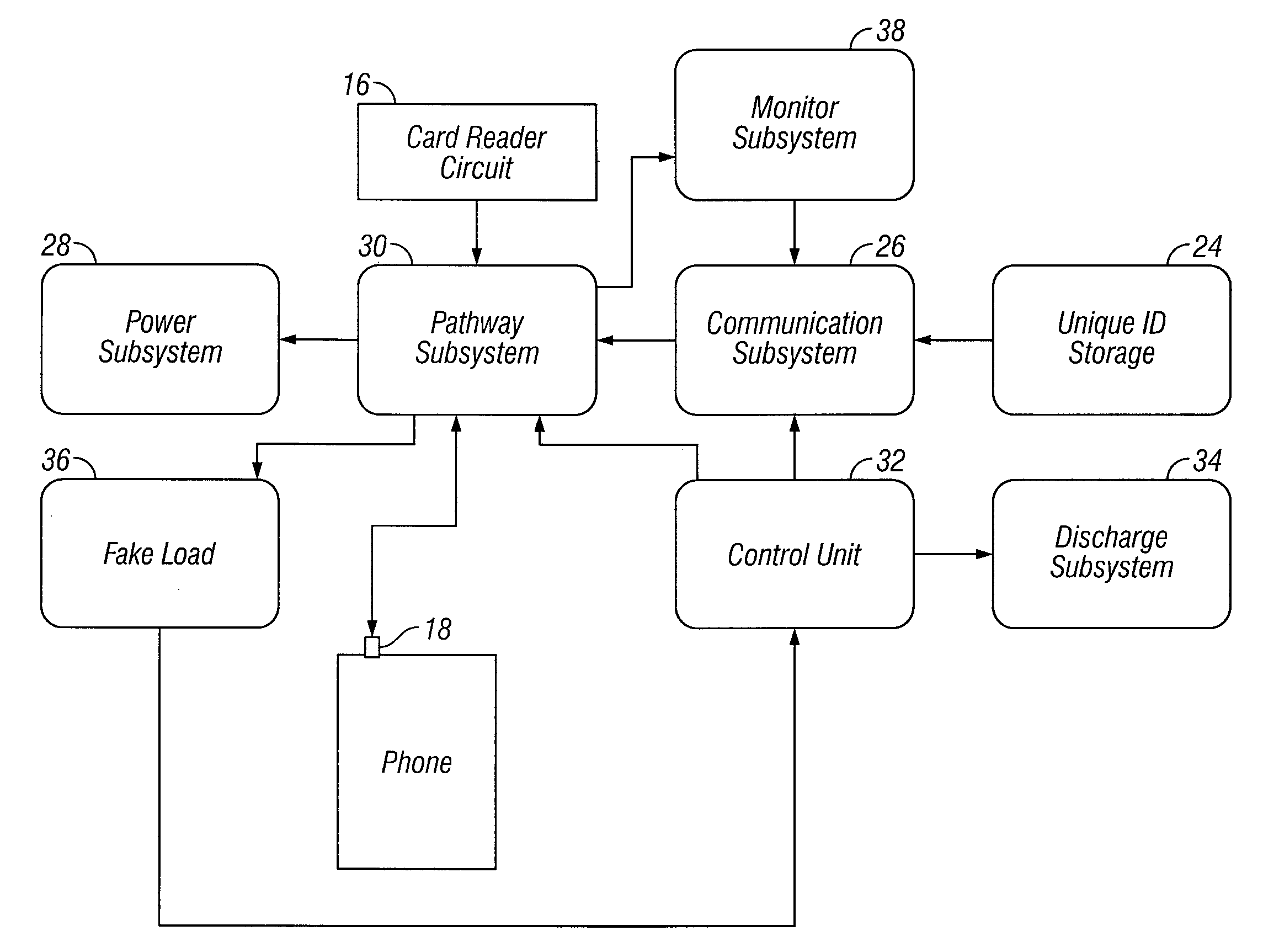
System and method for indicating temporal layer switching points
ActiveUS20090003439A1Accurately indicatedAccurate decodingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo bitstreamComputer architecture
Disclosed are a system, apparatus, computer programs and methods for indicating proper temporal layer switching points for temporal scalable coding. Various embodiments provide an apparatus and method for properly indicating temporal layer switching points in a scalable video bit stream or in a scalable video file container. Using these indications, a decoder can determine where to perform temporal layer switching, after which all of the pictures at and below the desired temporal layer can be correctly decoded.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Moving picture coding method, and moving picture decoding method
ActiveUS7310373B2Accurate decodingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDecoding methodsPattern recognition
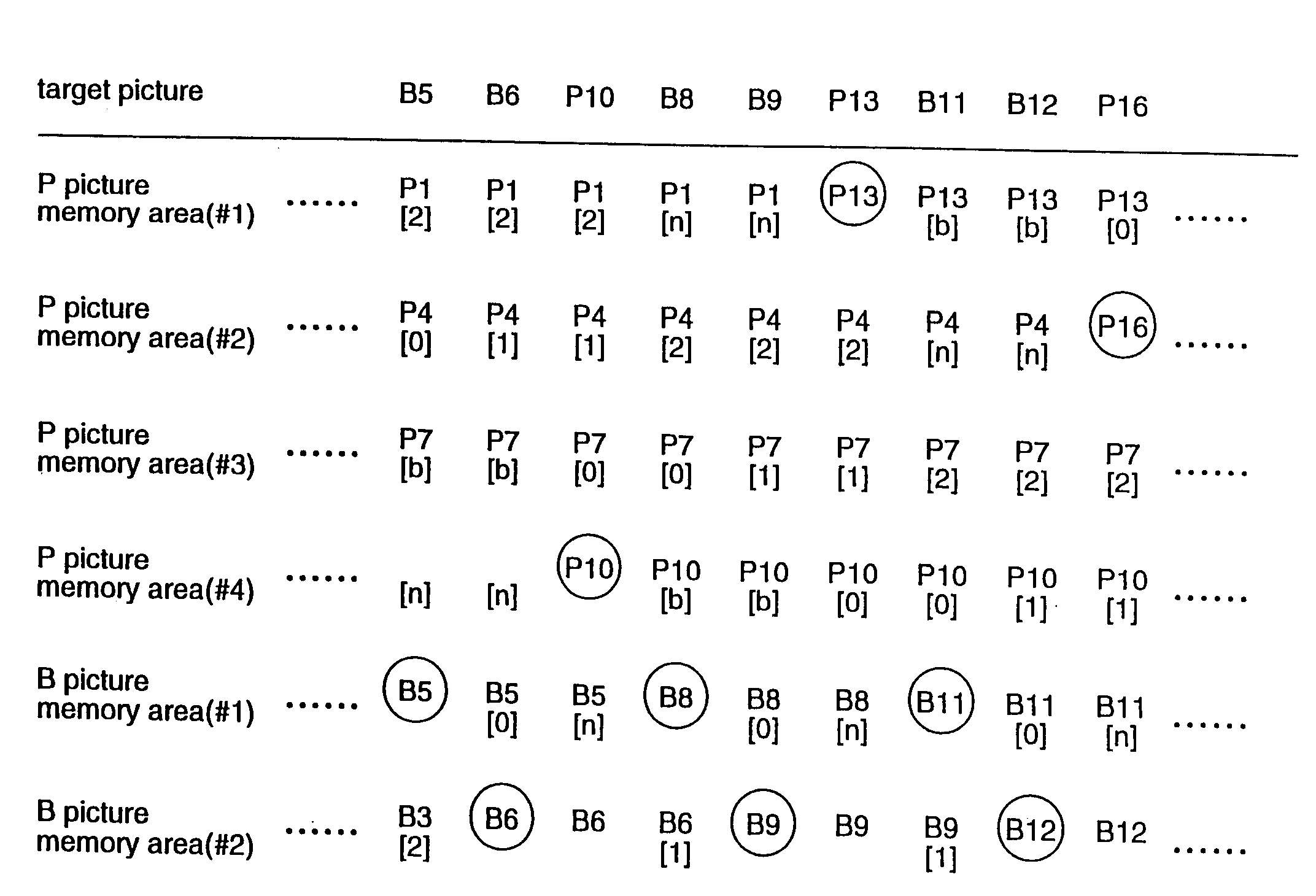
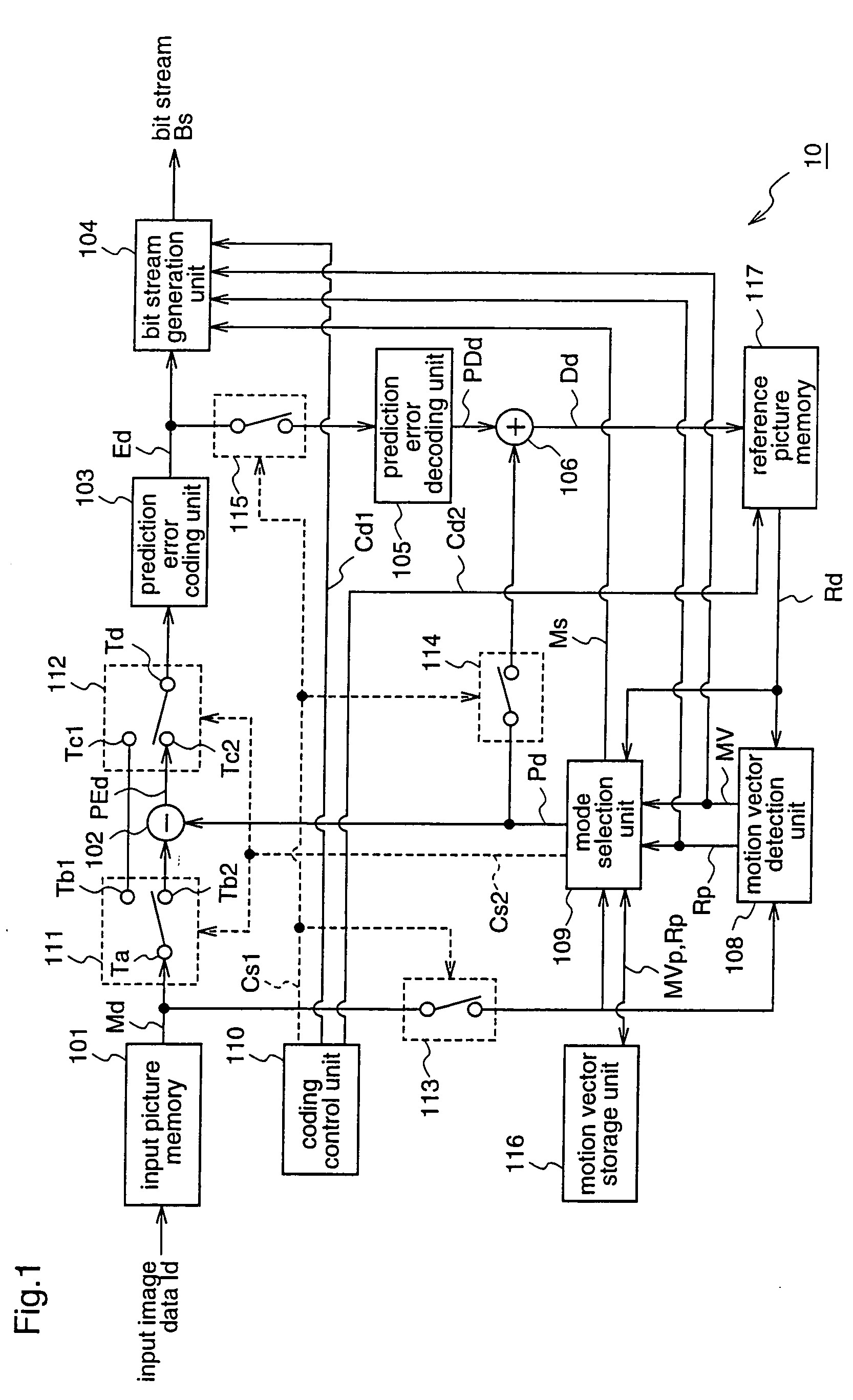
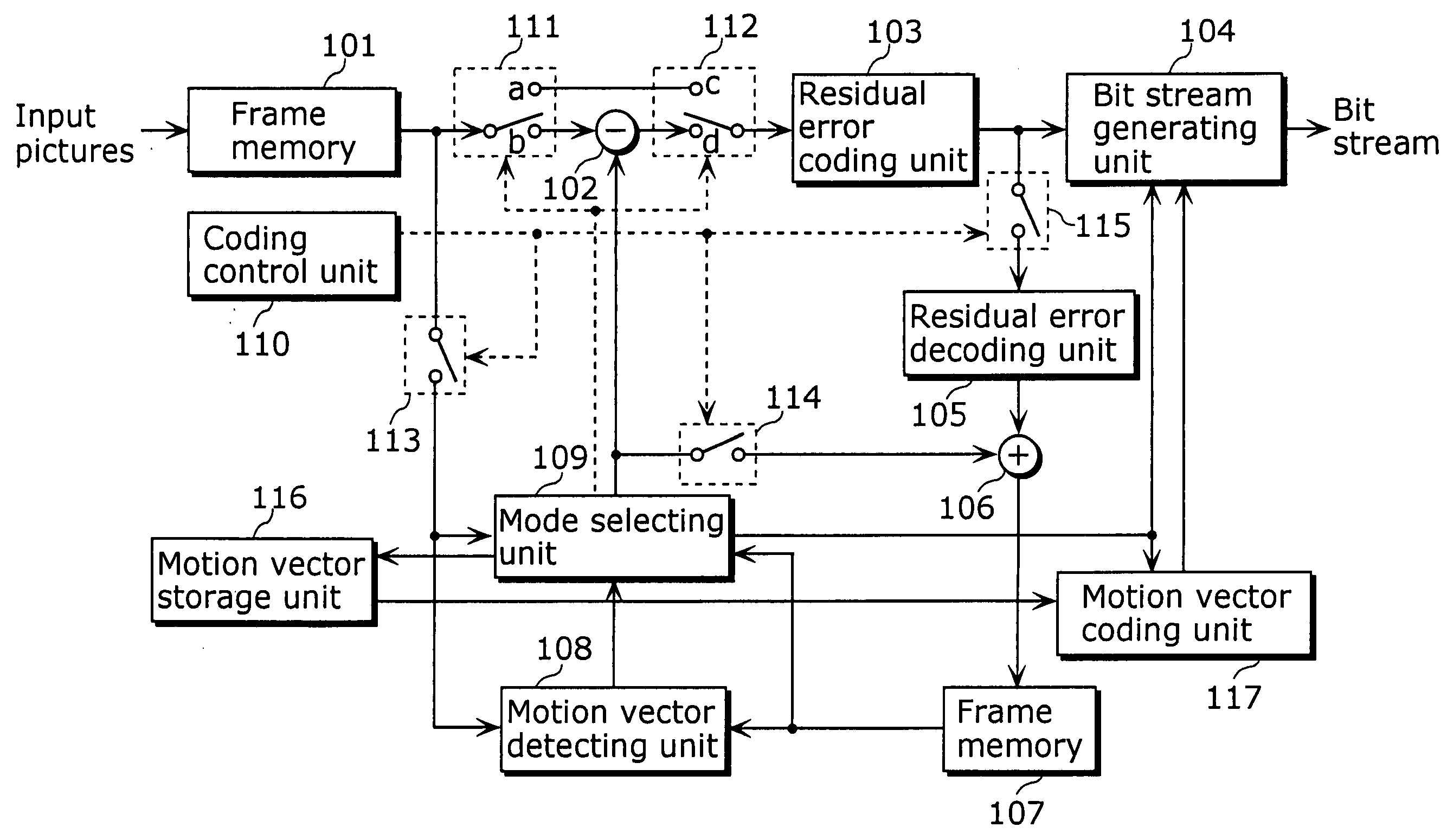
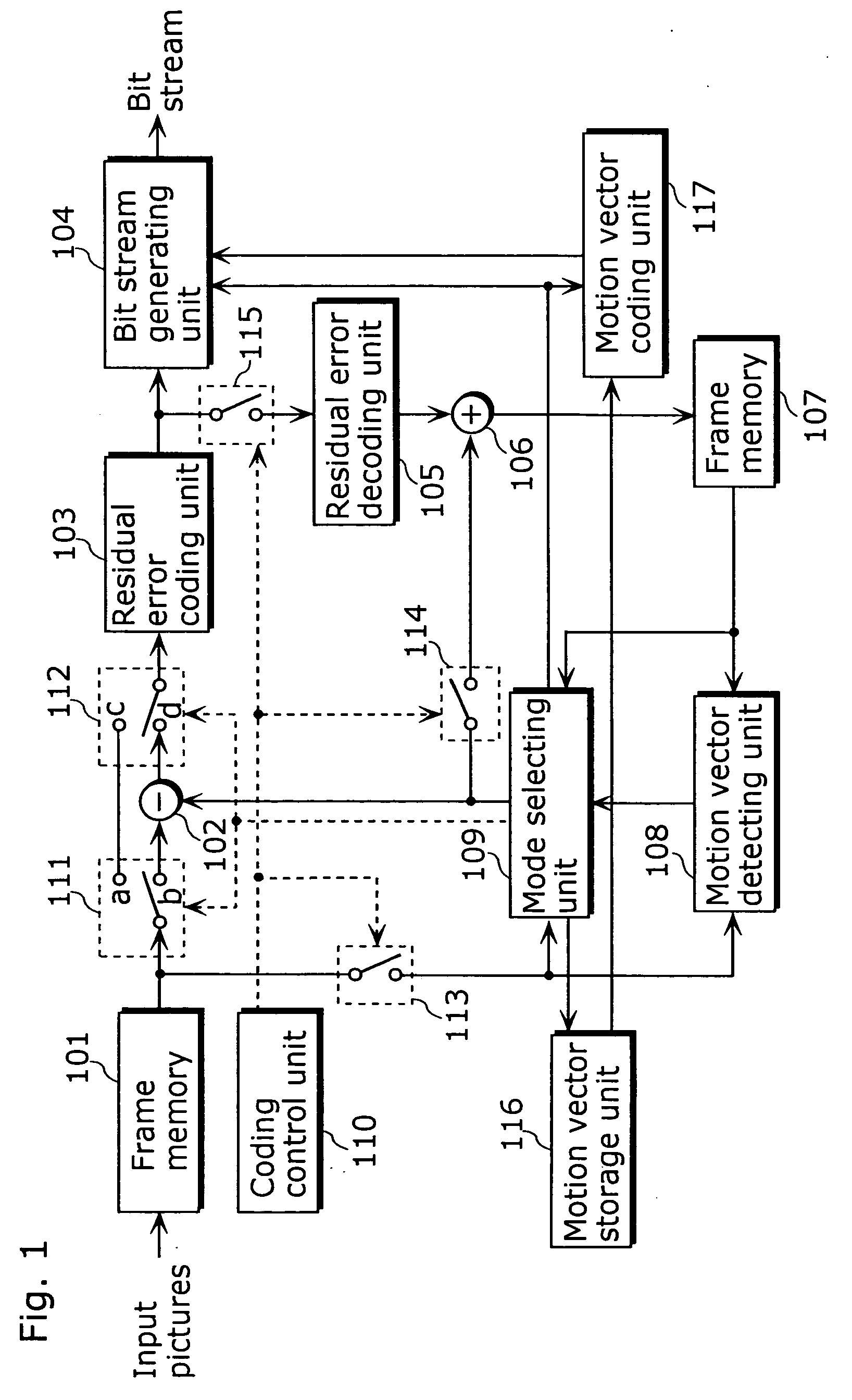
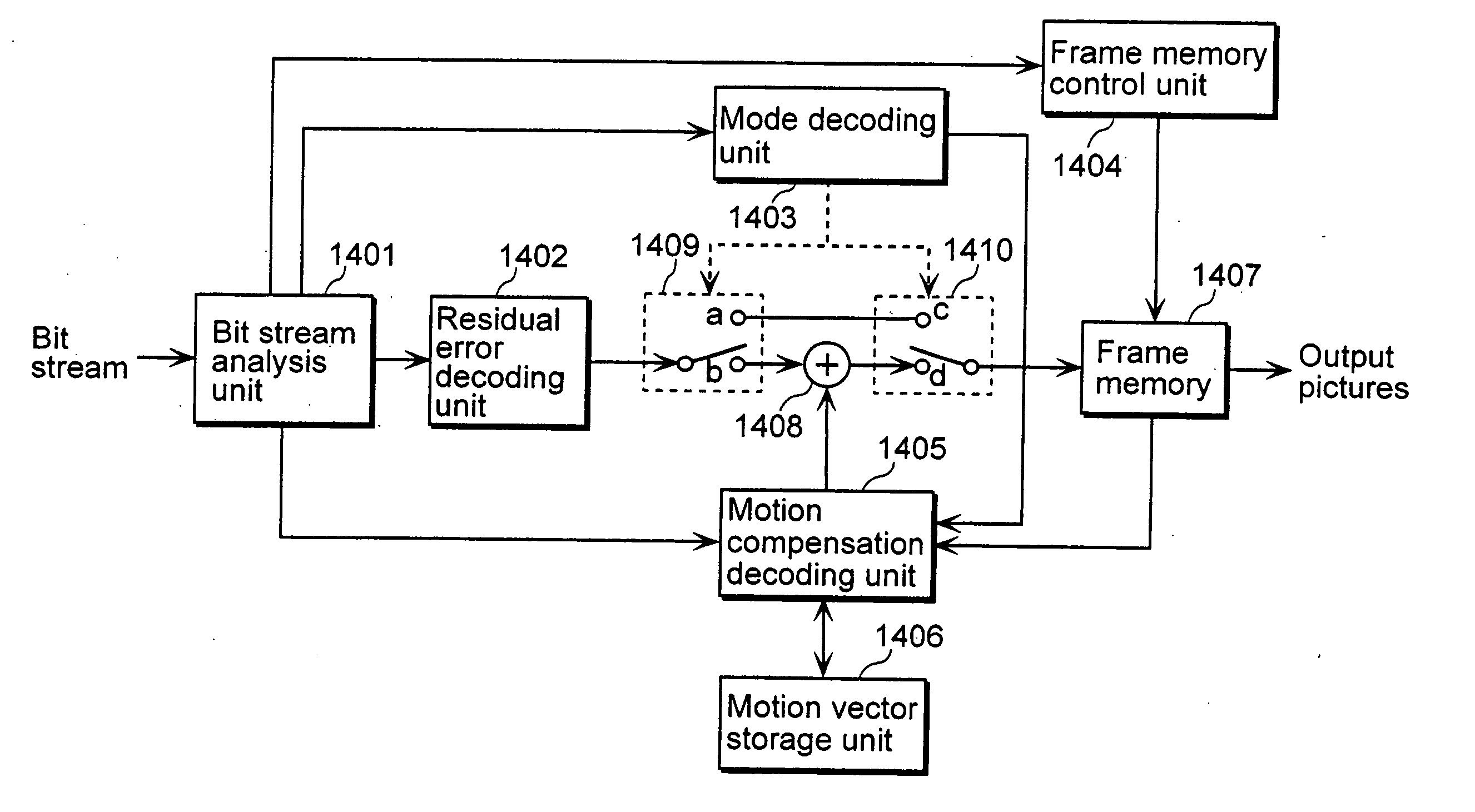
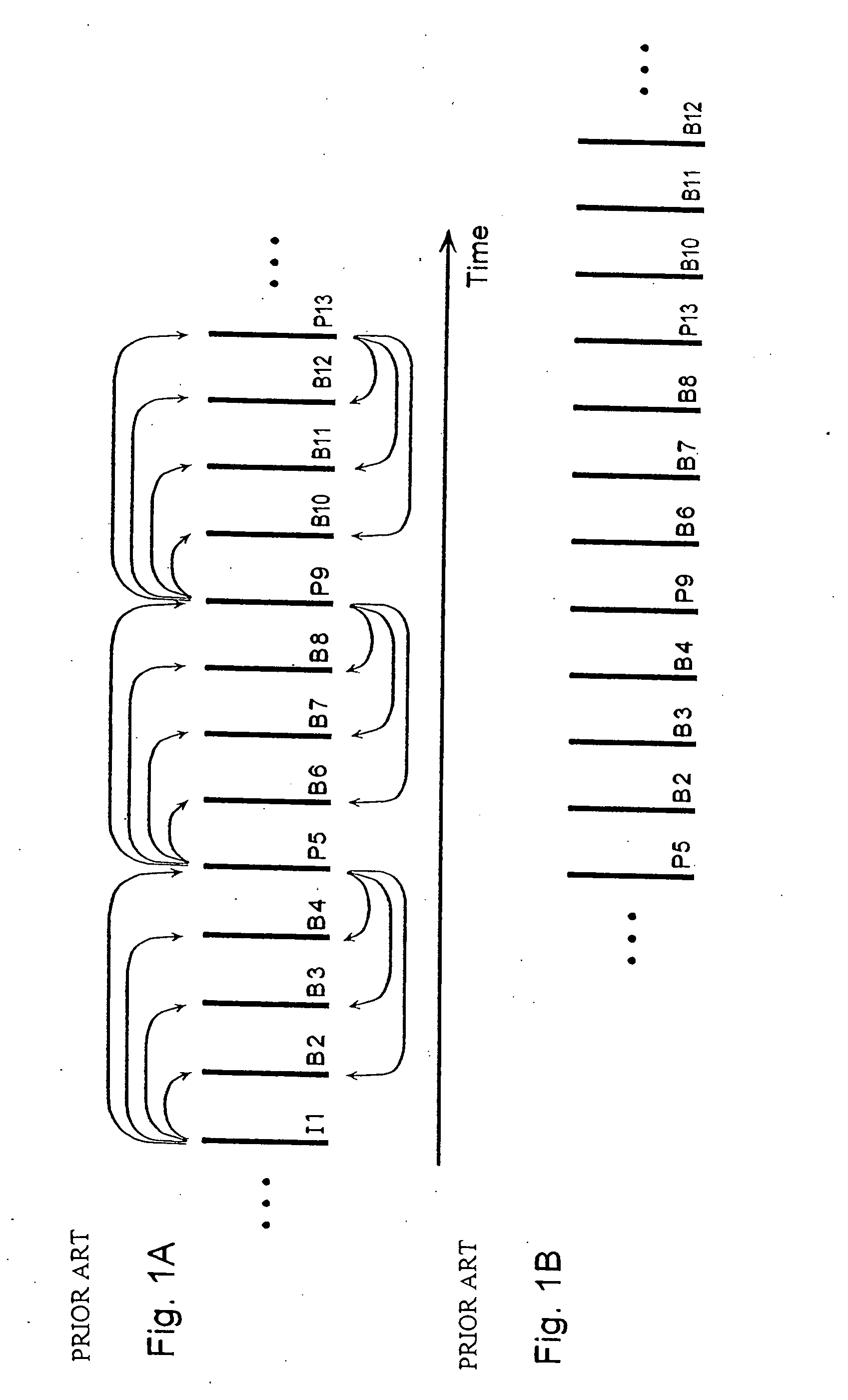
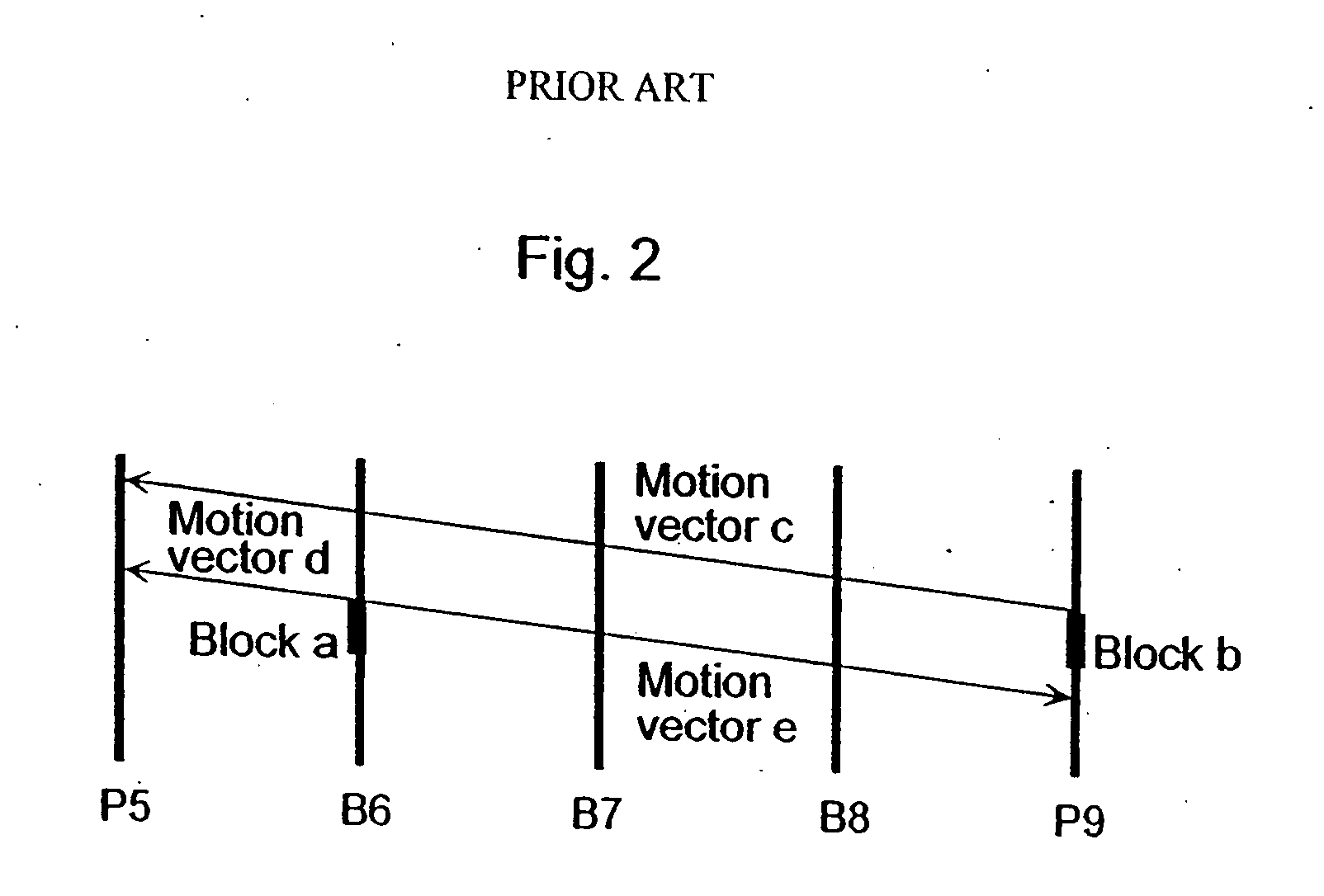
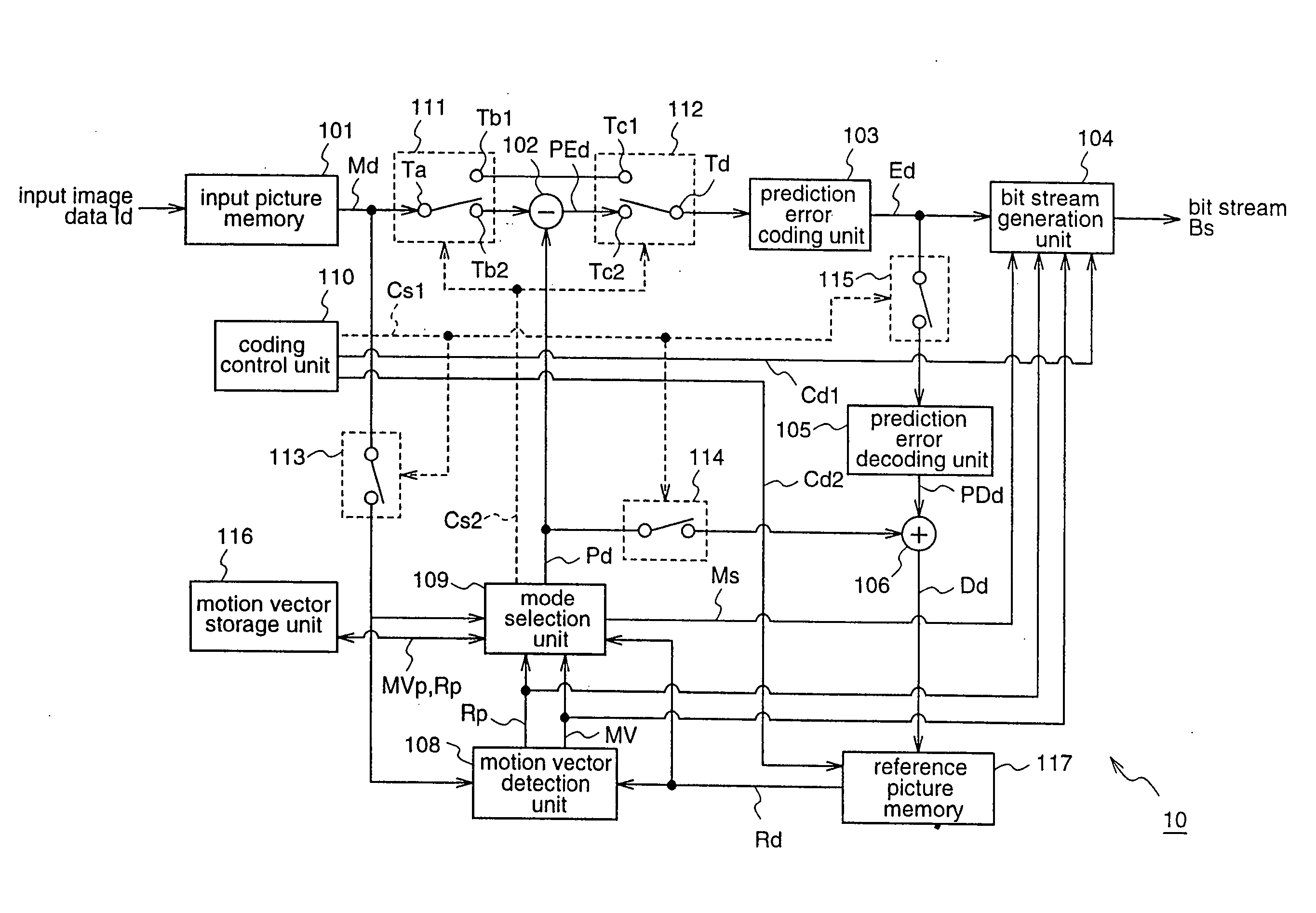
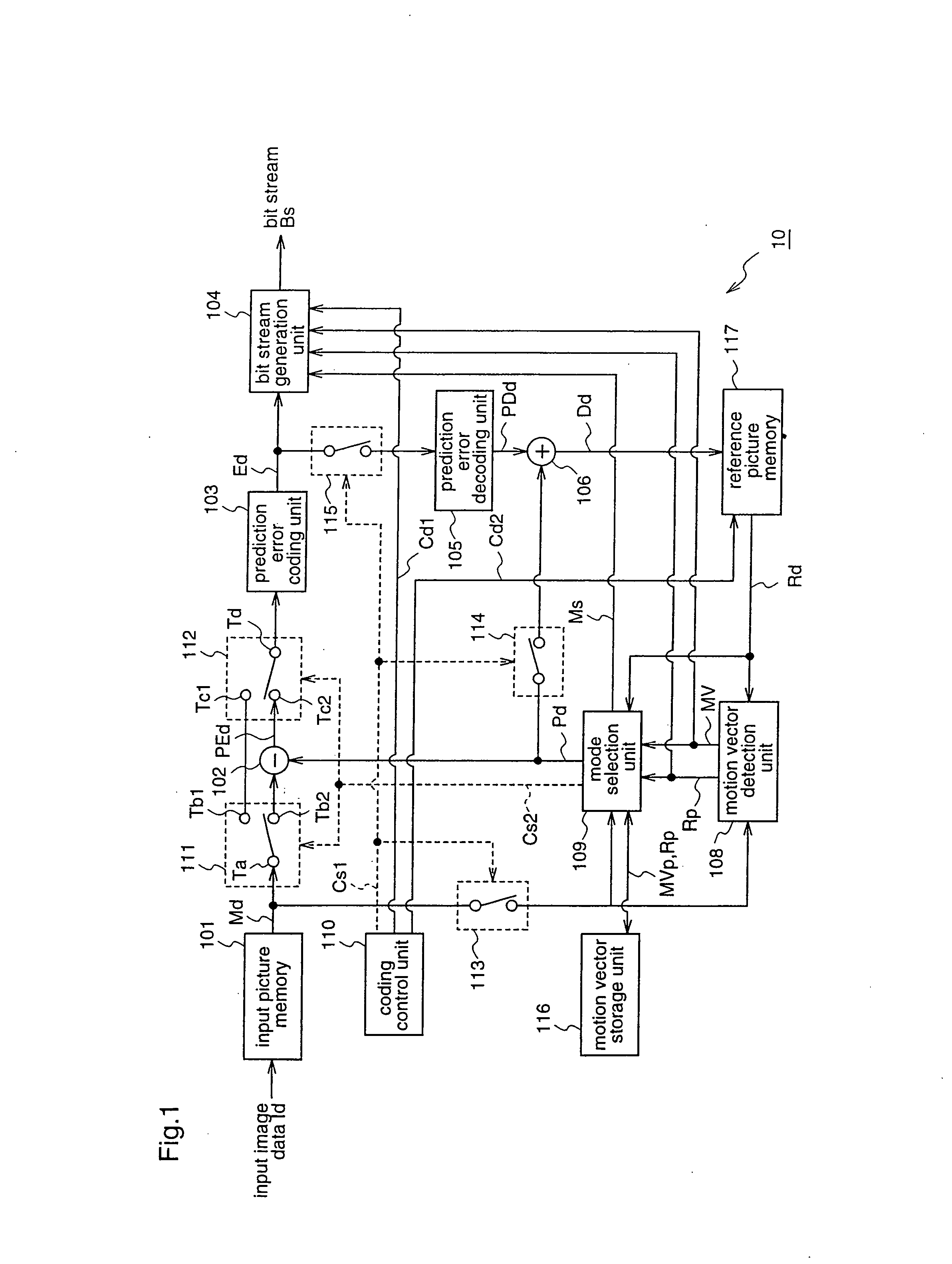
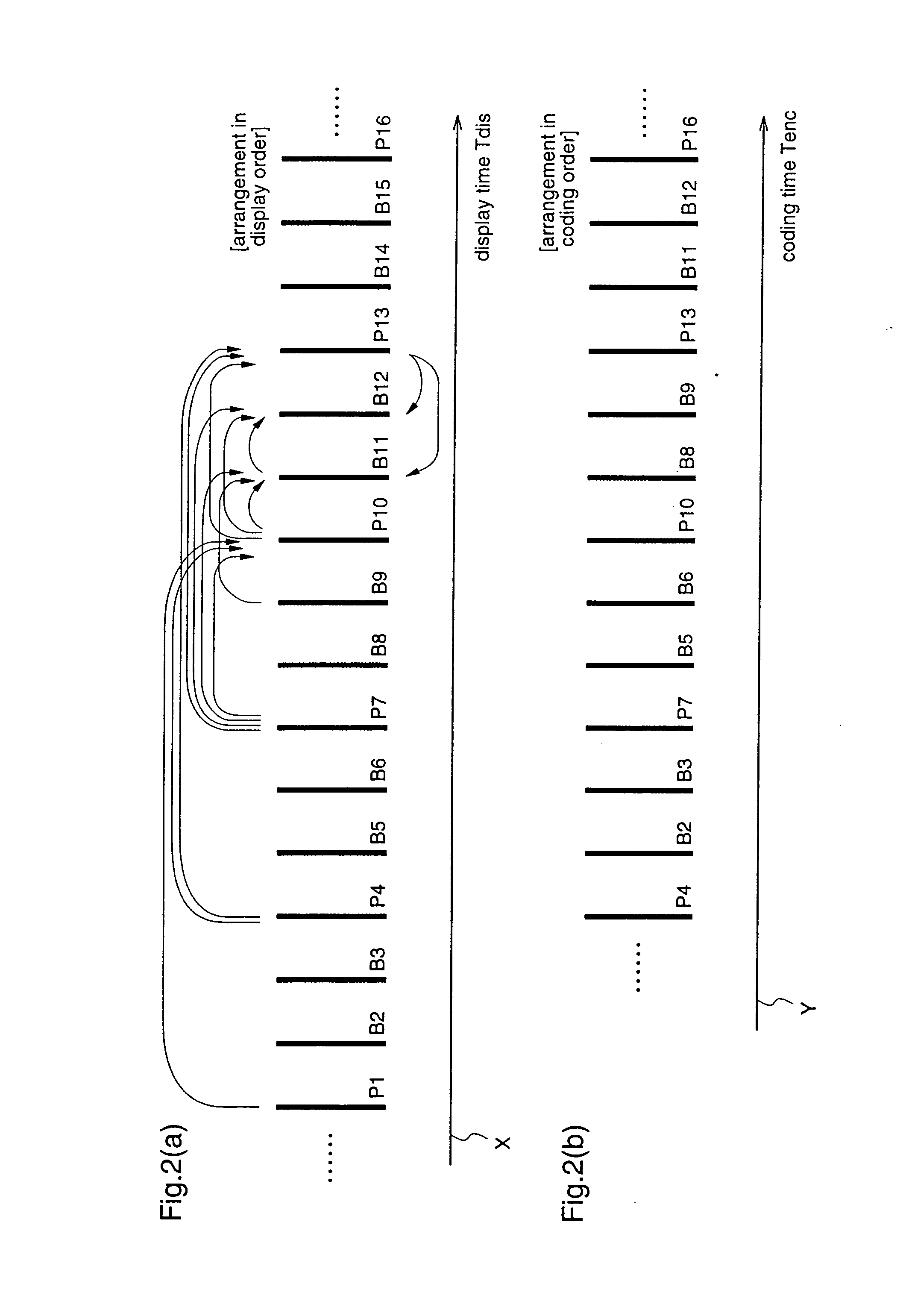
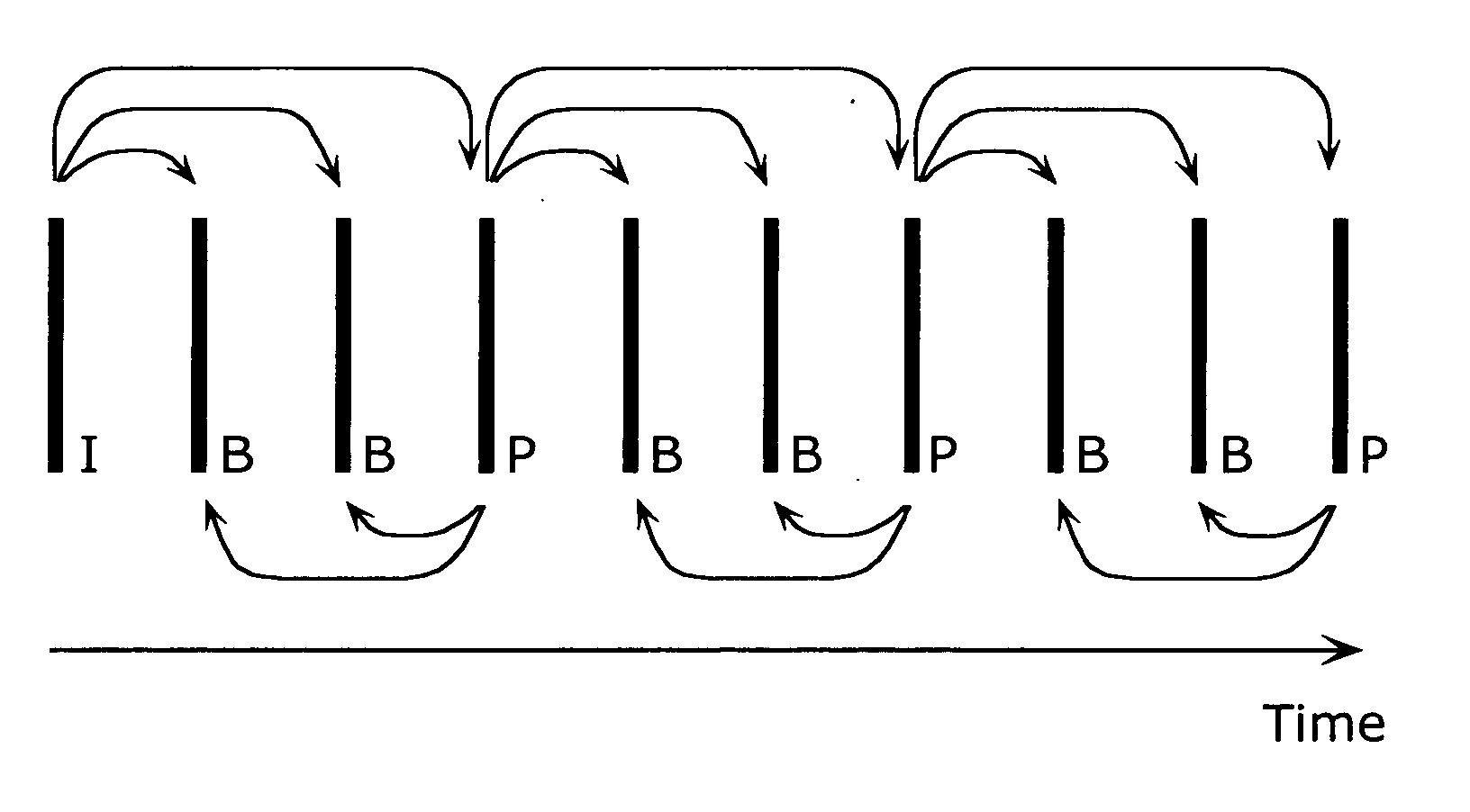
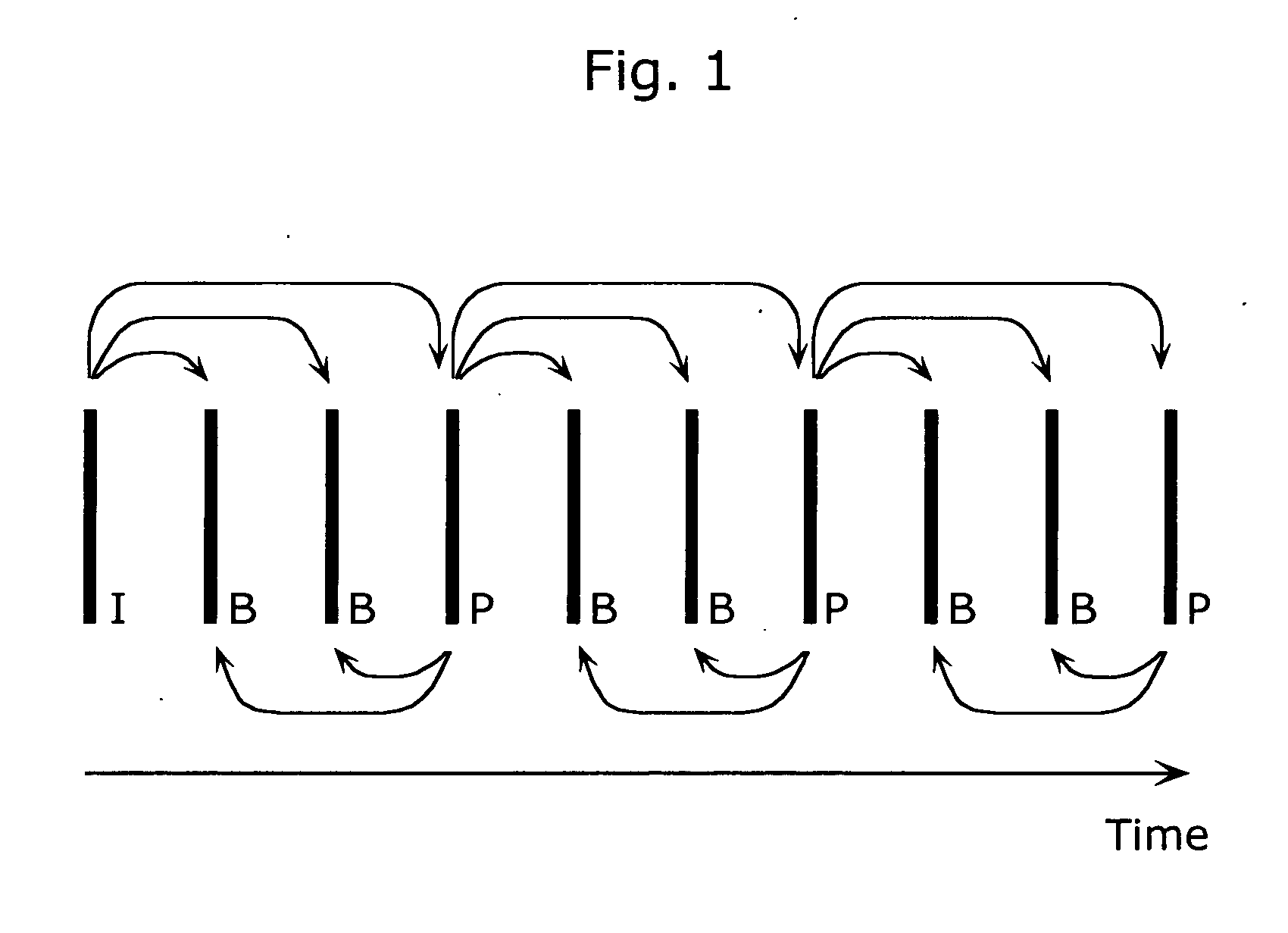
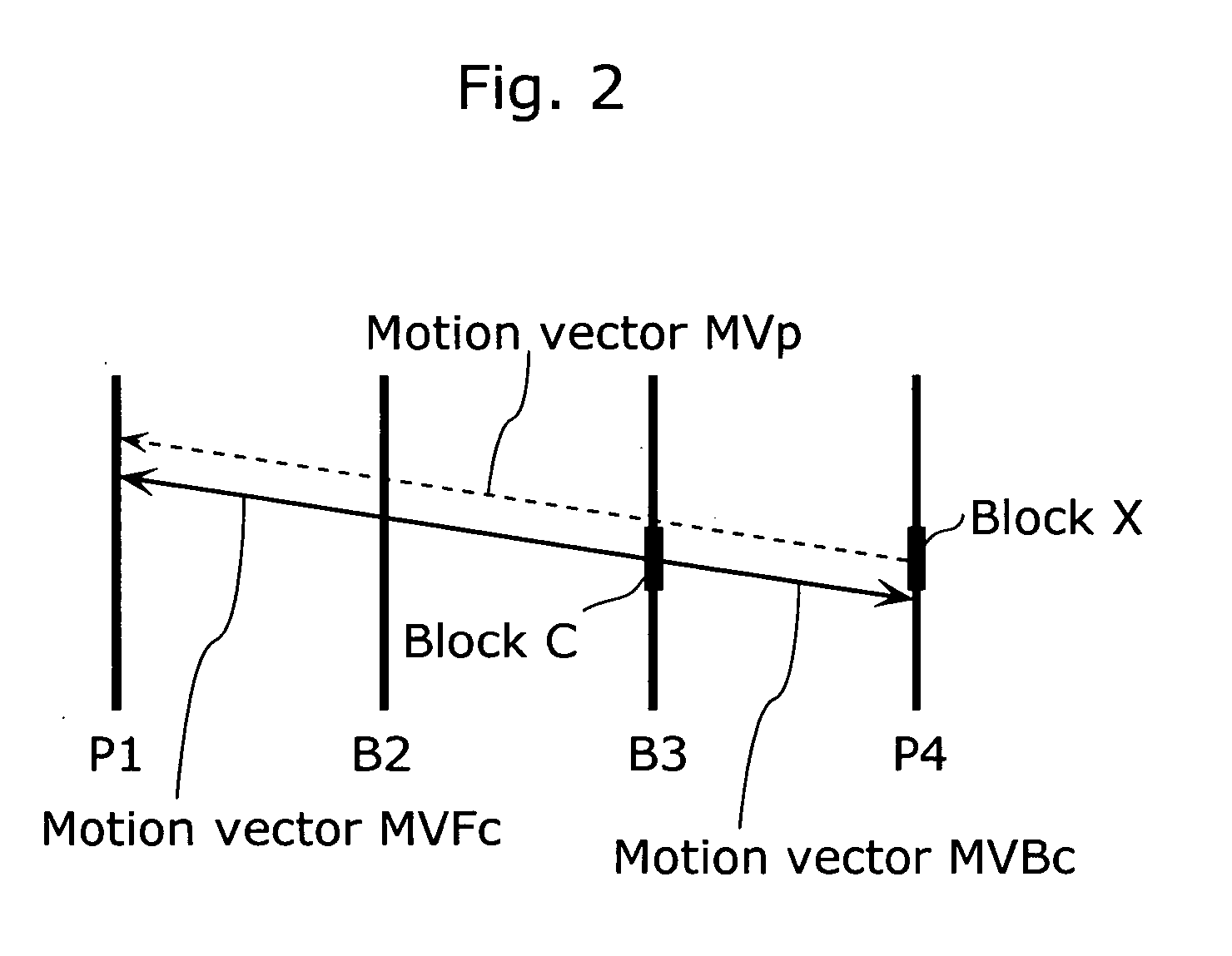
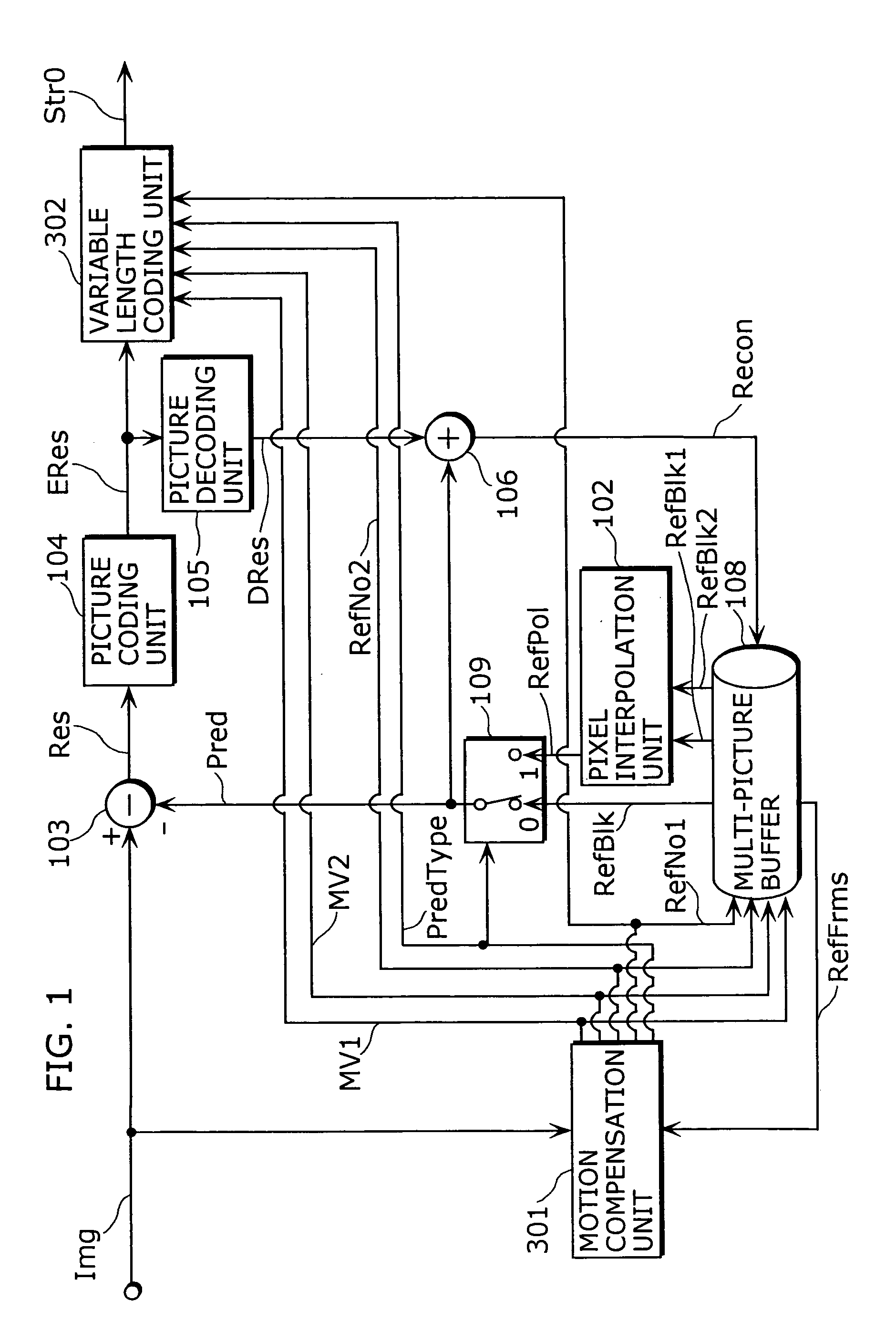
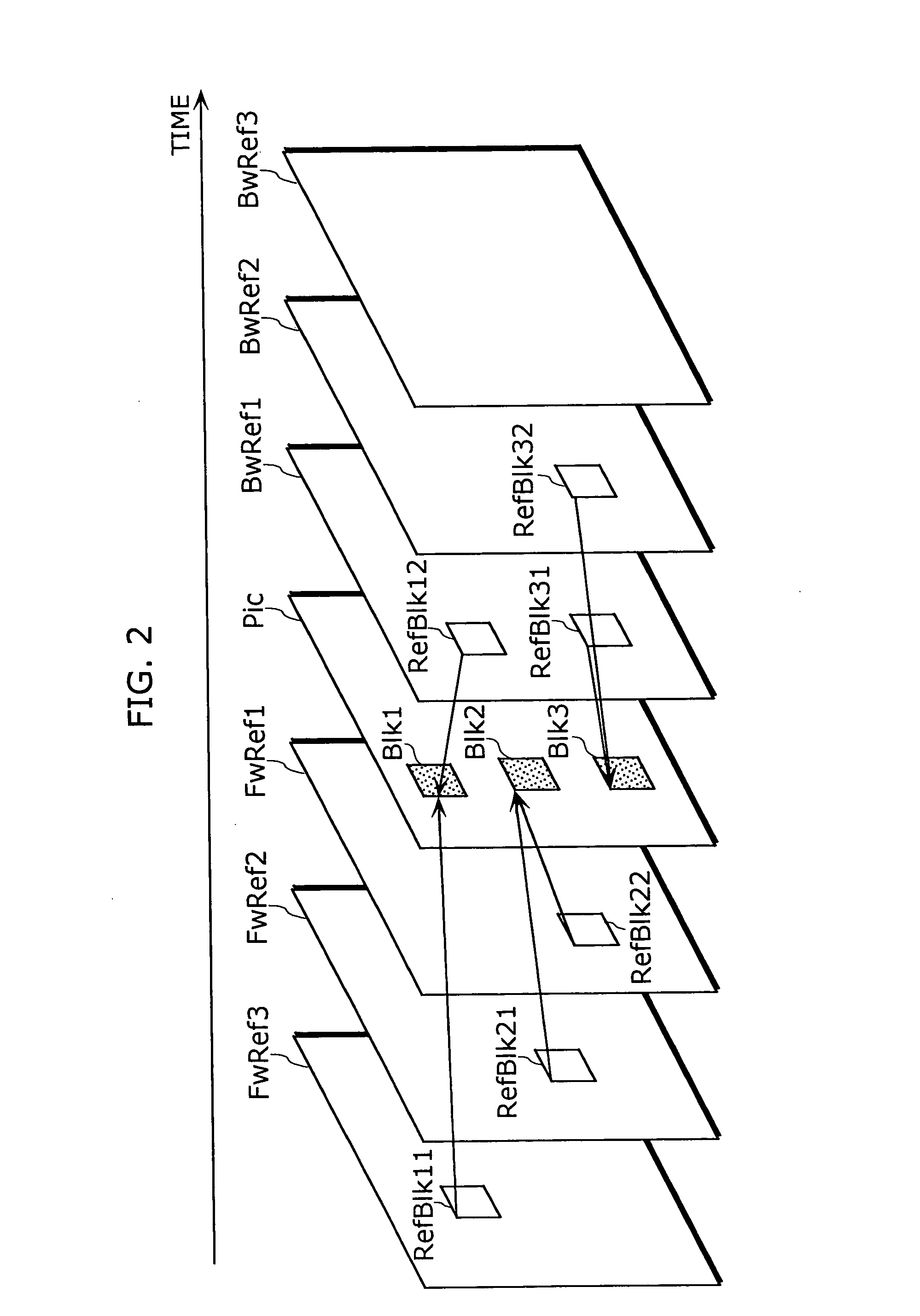
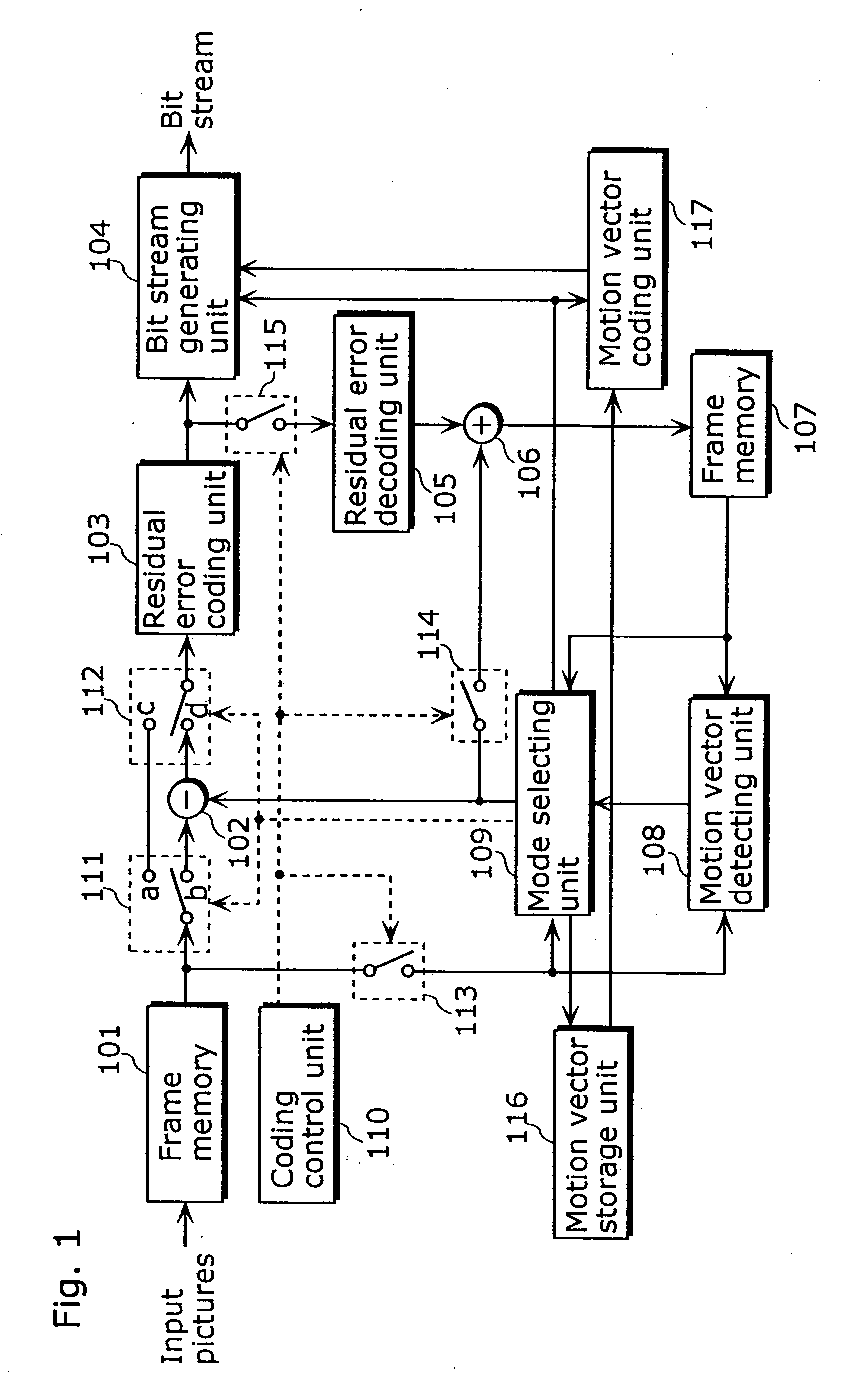
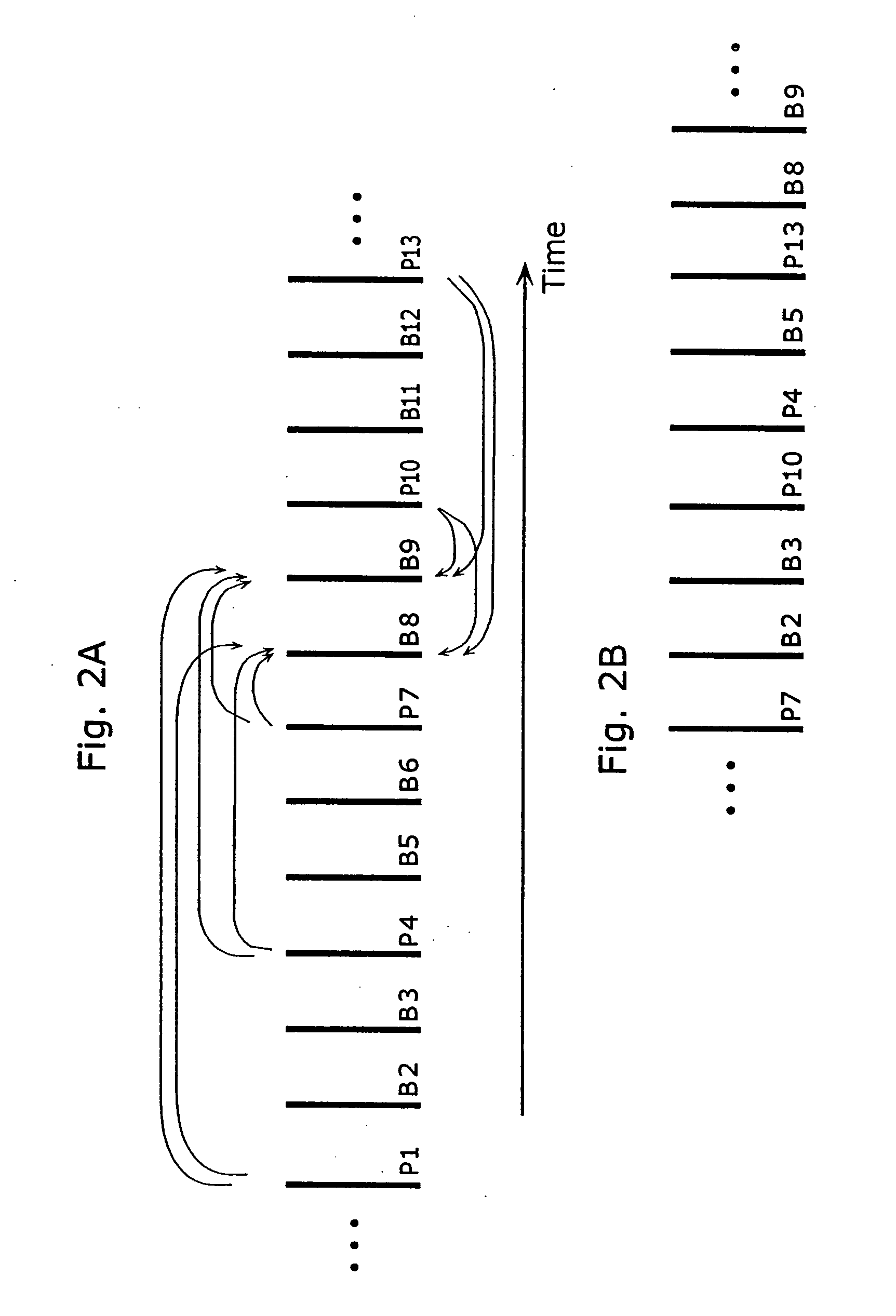
A moving picture coding apparatus (10) for performing inter-picture predictive coding on pictures constituting a moving picture is provided with a coding unit (103) for performing predictive error coding on image data; a decoding unit (105) for performing predictive error decoding on an output from the coding unit (103); a reference picture memory (117) for holding output data from the decoding unit (105); and a motion vector detection unit (108) for detecting forward and backward motion vectors on the basis of decoded image data stored in the memory (117) When coding a B picture, a picture that is timewise closest to the target picture is used as a candidate picture for forward reference, and an I or P picture that is timewise closest to the target picture is used as a candidate picture for backward reference. The moving picture coding apparatus (10) so constructed can improve coding efficiency of a B picture to be subjected to bidirectional predictive coding.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
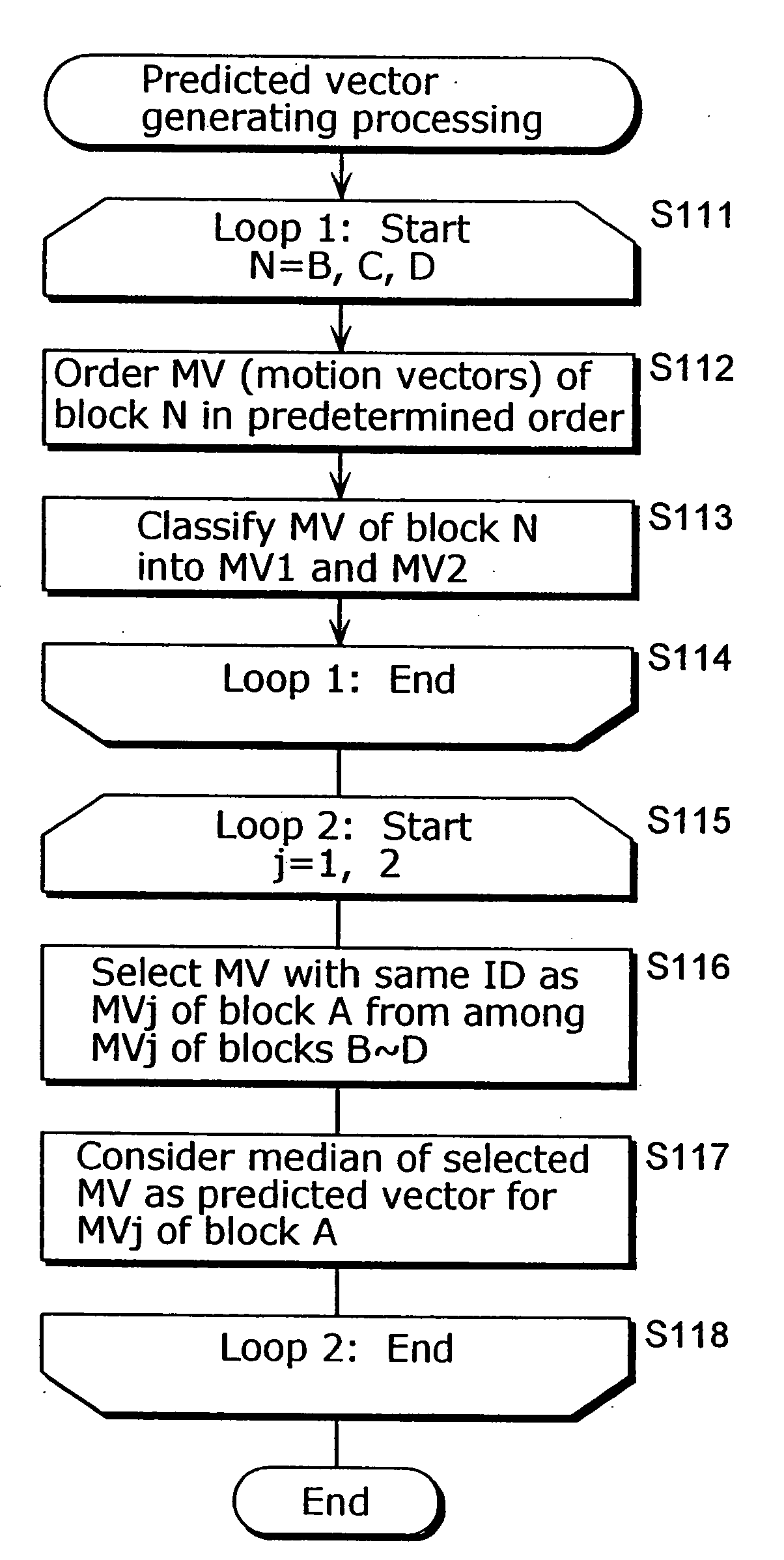
Motion vector coding method and motion vector decoding method
ActiveUS20040218674A1Improve coding efficiencyAccurate decodingPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDecoding methodsMotion vector
The present invention improves efficiency of coding motion vectors when a current block is coded using a plurality of motion vectors. A motion vector coding unit (117) codes a motion vector inputted from a motion vector detecting unit (108). A motion vector for each current block is coded based on a difference between the motion vector and a predicted vector obtained from motion vectors for previously coded neighboring blocks. The predicted vector is generated by one of the following processing: (A) the motion vectors which refer to the same picture are selected from among the motion vectors for the neighboring blocks so as to generate the predicted vector; (B) the motion vectors for the respective neighboring blocks are ordered in the predetermined order, and the motion vectors of the same order rank are selected from the ordered motion vectors so as to generate the predicted vector; and (C) the predicted vector for the second motion vector of the current block shall be the first motion vector, and if the second motion vector and the first motion vector refer to different pictures, the first motion vector is scaled according to the temporal distance between the pictures so as to generate the predicted vector.
Owner:TAGIVAN II
Inductive data and power link suitable for integration
ActiveUS20050063488A1Increase powerImproved telemetry systemElectric signal transmission systemsDiagnosticsData synchronizationTime distortion
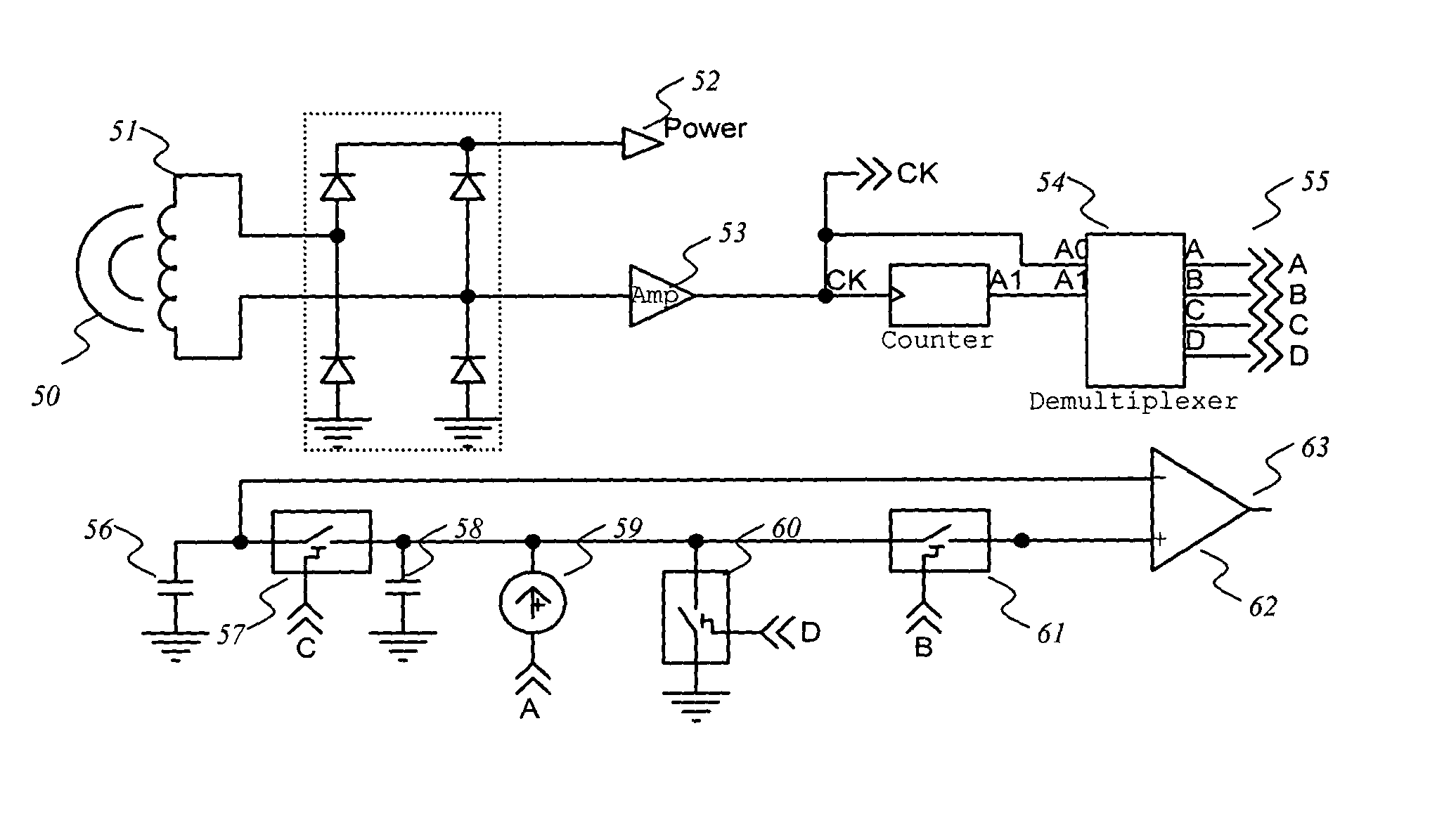
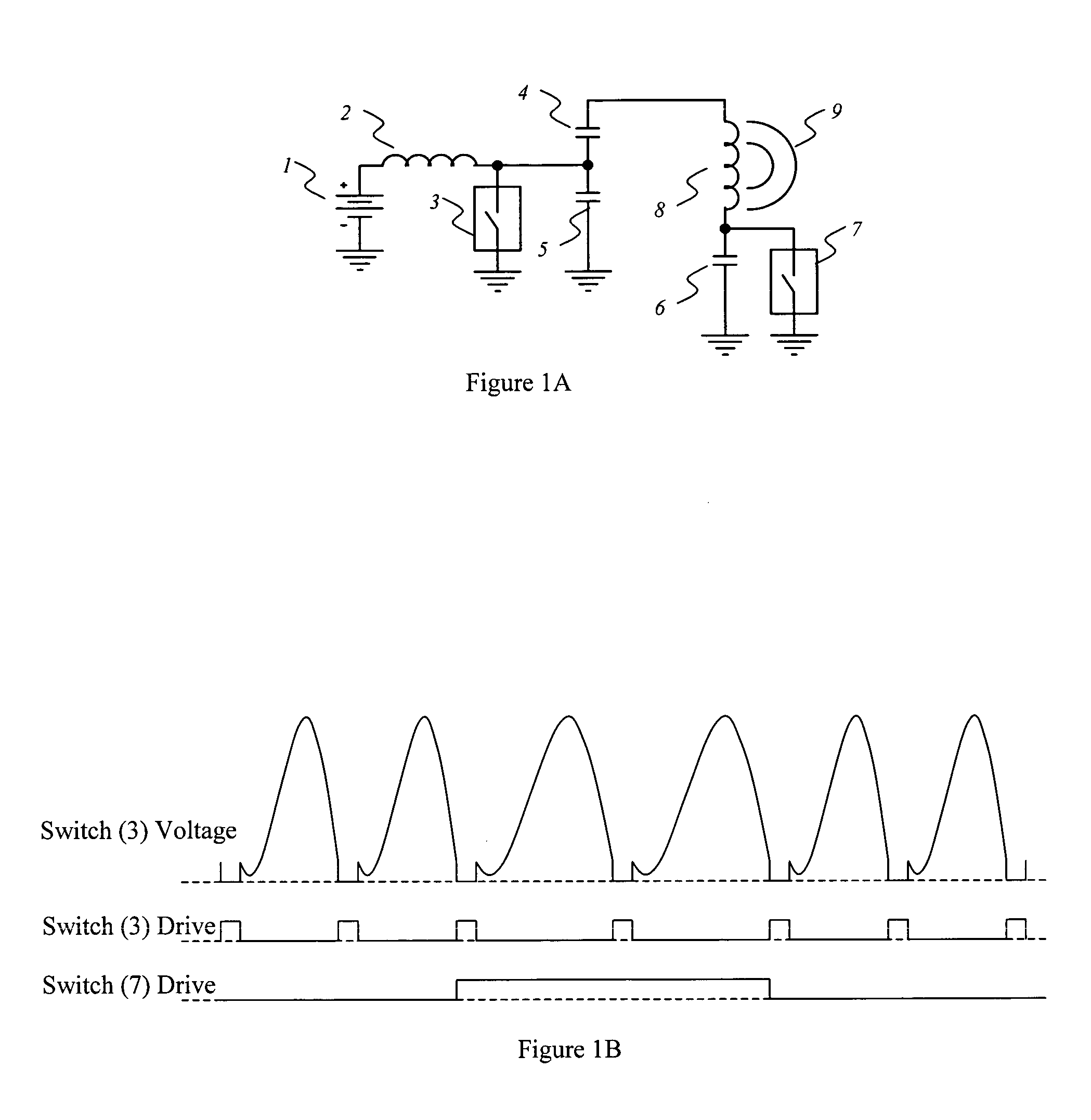
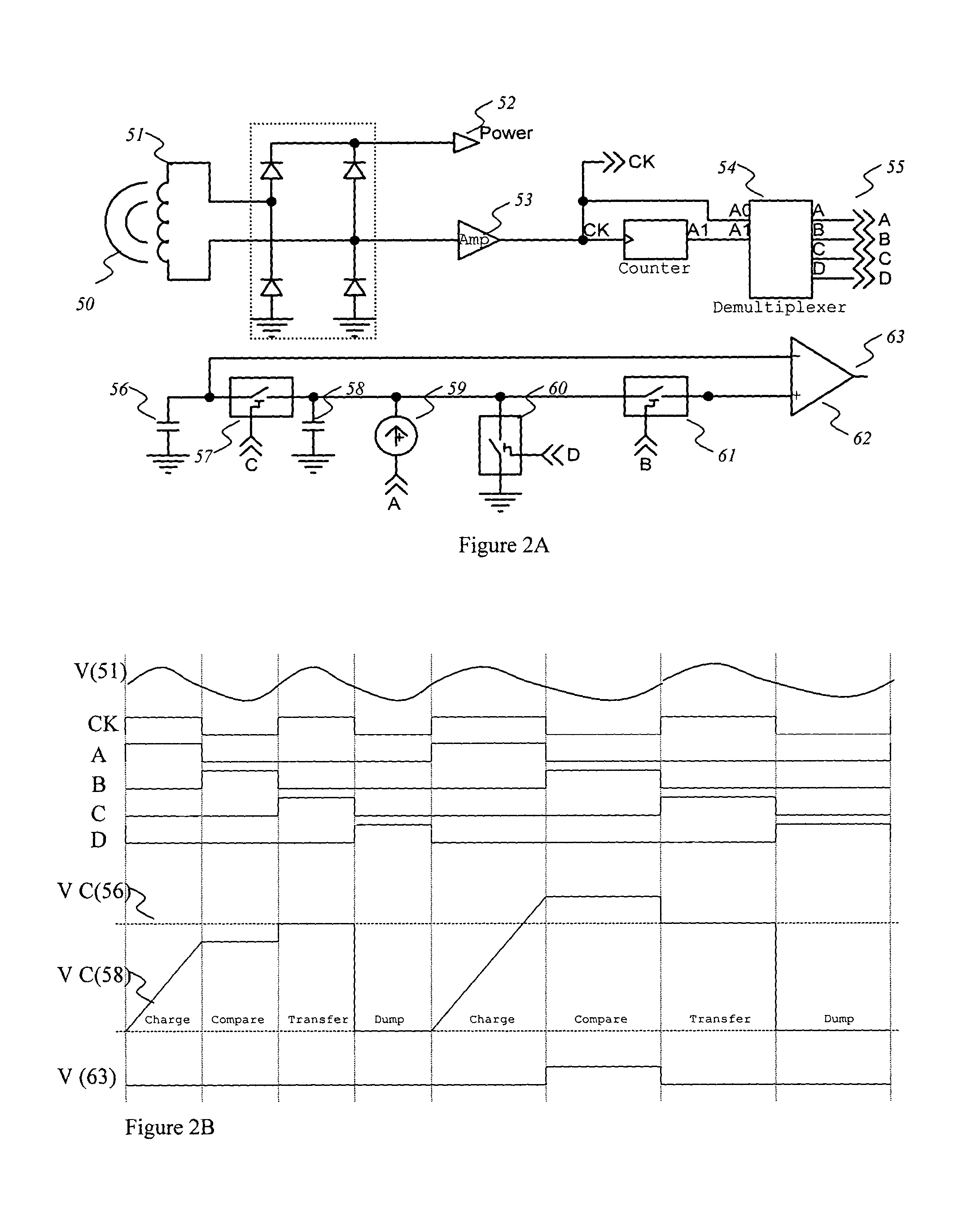
A system providing an inductive power and data link between an external transmitter and miniature internal receiver is presented. The system is suited to applications where the receiver must be of a small size and the system must consume very little power, such as an implanted biomedical device. The system is also compatible with systems where bi-directional communications are required. The novel transmitter and receiver form an improved forward data telemetry system. The transmitter consists of a Class-E converter with its optimum operating frequency being synchronously, instantaneously and efficiently altered in accordance with the data to be transmitted, thereby producing an FSK modulated magnetic field of substantially constant amplitude. The constant amplitude output allows for the continuous, data-independent transfer of power to the miniature receiver and its associated electronics. The present invention also represents an improvement over the high efficiency Class-E converters previously patented by the inventors. The receiver consists of a coil and an integrated rectifying system to recover operating power from the incident magnetic field, as well as an FSK demodulator whose operation is based on the multiphase comparison of charging times of integrated capacitors. The described FSK demodulator approach removes deleterious effects resulting from low-frequency changes in the transmitter frequency, and eliminates time distortion artifacts generated by circuit imbalances and asymmetries in the power recovery process. The combination of the transmitter and receiver improvements yields a reliable data transfer system unaffected by circuit imbalances and incidental variations in the amplitude and frequency of the magnetic field.
Owner:LUNA NEURO LLC
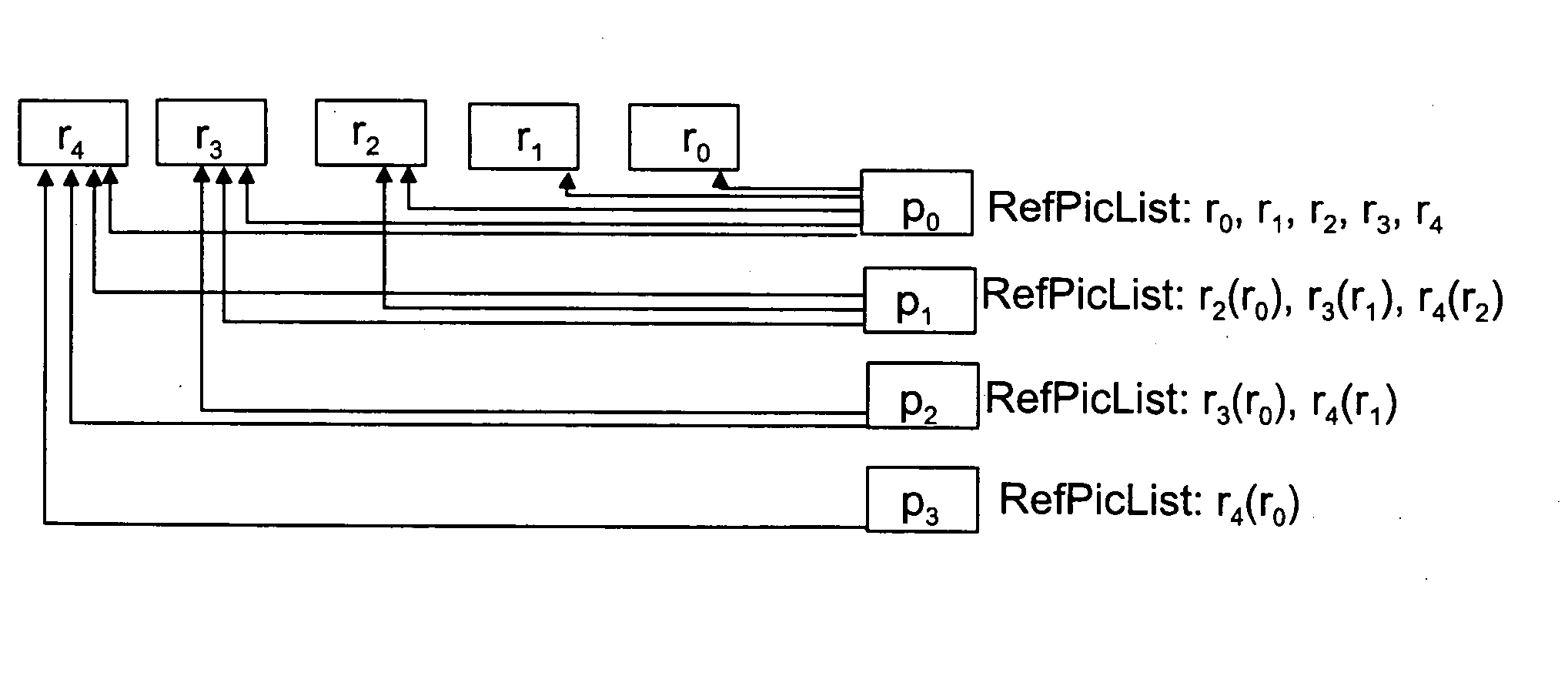
Encoding and decoding of redundant pictures
InactiveUS20050123056A1Avoid mistakesReduce frequencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo sequenceComputer science
A method of encoding video data including at least one primary picture and at least one redundant picture corresponding to the information content of the primary picture. A reference picture list of the at least one redundant picture includes multiple reference pictures. The video sequence is encoded such that a number of reference pictures are disabled from the reference picture list of the at least one redundant picture, the number being at least one, but less than the total number of the reference pictures on the reference picture list.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Moving picture coding method and moving picture decoding method for performing inter picture prediction coding and inter picture prediction decoding using previously processed pictures as reference pictures
ActiveUS20080063060A1Accurate decodingEasy to predictPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionDecoding methodsMotion vector
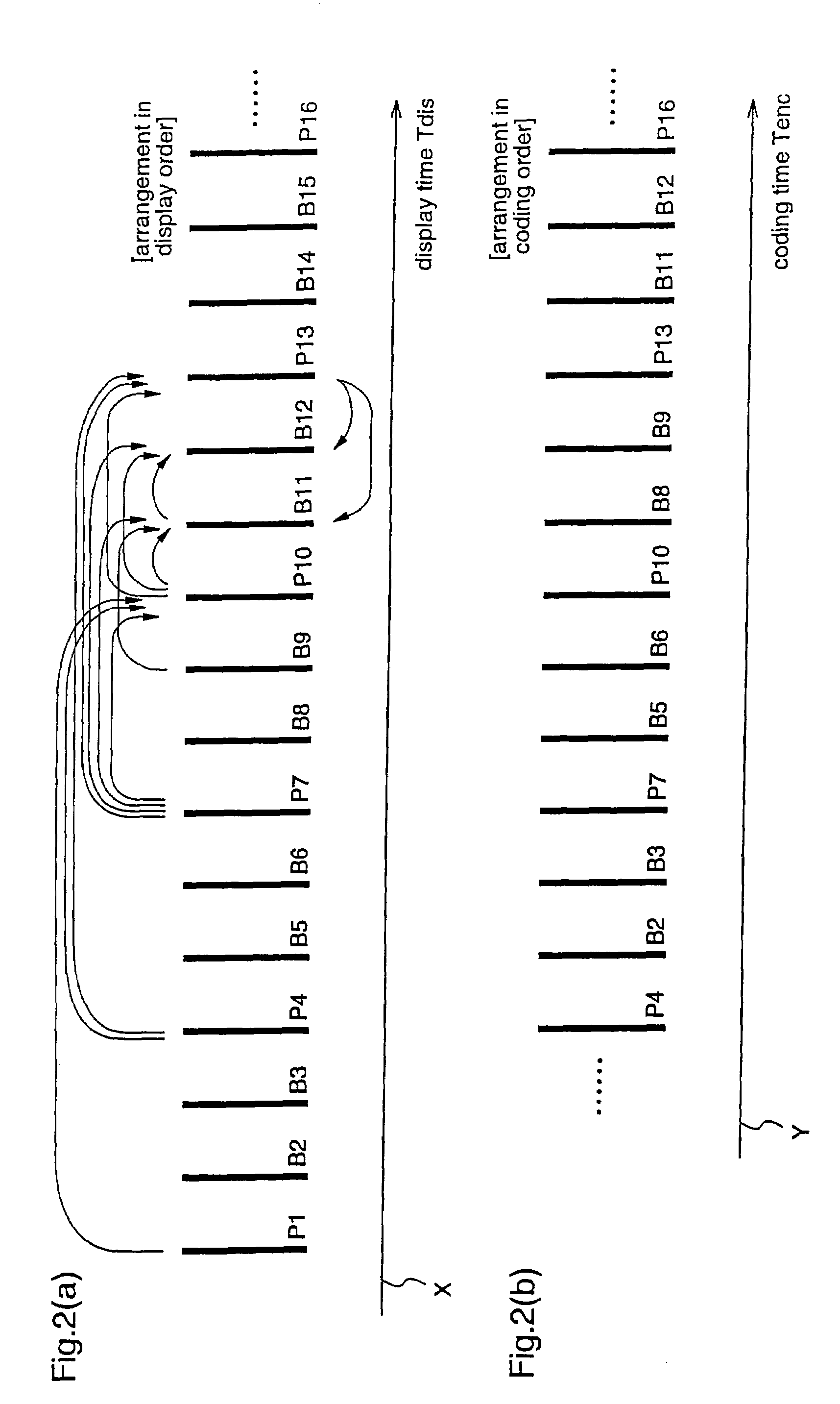
A coding control unit (110) and a mode selection unit (109) are included. The coding control unit (110) determines the coding order for a plurality of consecutive B-pictures located between I-pictures and P-pictures so that the B-picture whose temporal distance from two previously coded pictures is farthest in display order is coded by priority, so as to reorder the B-pictures in coding order. When a current block is coded in direct mode, the mode selection unit 109 scales a forward motion vector of a block which is included in a backward reference picture of a current picture and co-located with the current block, so as to generate motion vectors of the current block, if the forward motion vector has been used for coding the co-located block.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Moving picture coding method, and moving picture decoding method
ActiveUS20070041452A1Correctly decodeAccurate decodingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorBitstream
According to the present invention, a moving picture coding apparatus (70) for performing inter-picture predictive coding for pictures constituting a moving picture is provided with a coding unit (103) for performing predictive error coding for image data; a decoding unit (105) for performing predictive error decoding for an output from the coding unit (103); a reference picture memory (117) for holding output data from the decoding unit (105); and a motion vector detection unit (108) for detecting motion vectors on the basis of the decoded image data stored in the memory. When coding a B picture as a target picture, information indicating whether or not the target picture should be used as a reference picture when coding another picture is added as header information. Therefore, in a decoding apparatus for decoding a bit stream Bs outputted from the moving picture coding apparatus (70), management of a memory for holding the reference picture can be facilitated on the basis of the header information.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Discardable lower layer adaptations in scalable video coding
ActiveUS20080089597A1Improve coding efficiencyAvoid spreadingCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureInter layer
A system and method for improving both coding efficiency and decoding accuracy in scalable video coding involving discardable lower layer adaptations, where applications can omit transmission of unused data for inter-layer prediction for all layers below an operation point of receivers. Indicator flags are utilized to avoid transmitting syntax elements that must be set to fixed values. In addition, padding algorithms or additional encoding constraints are applied to the encoding process.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Apparatus and method for decoding Reed-Solomon code
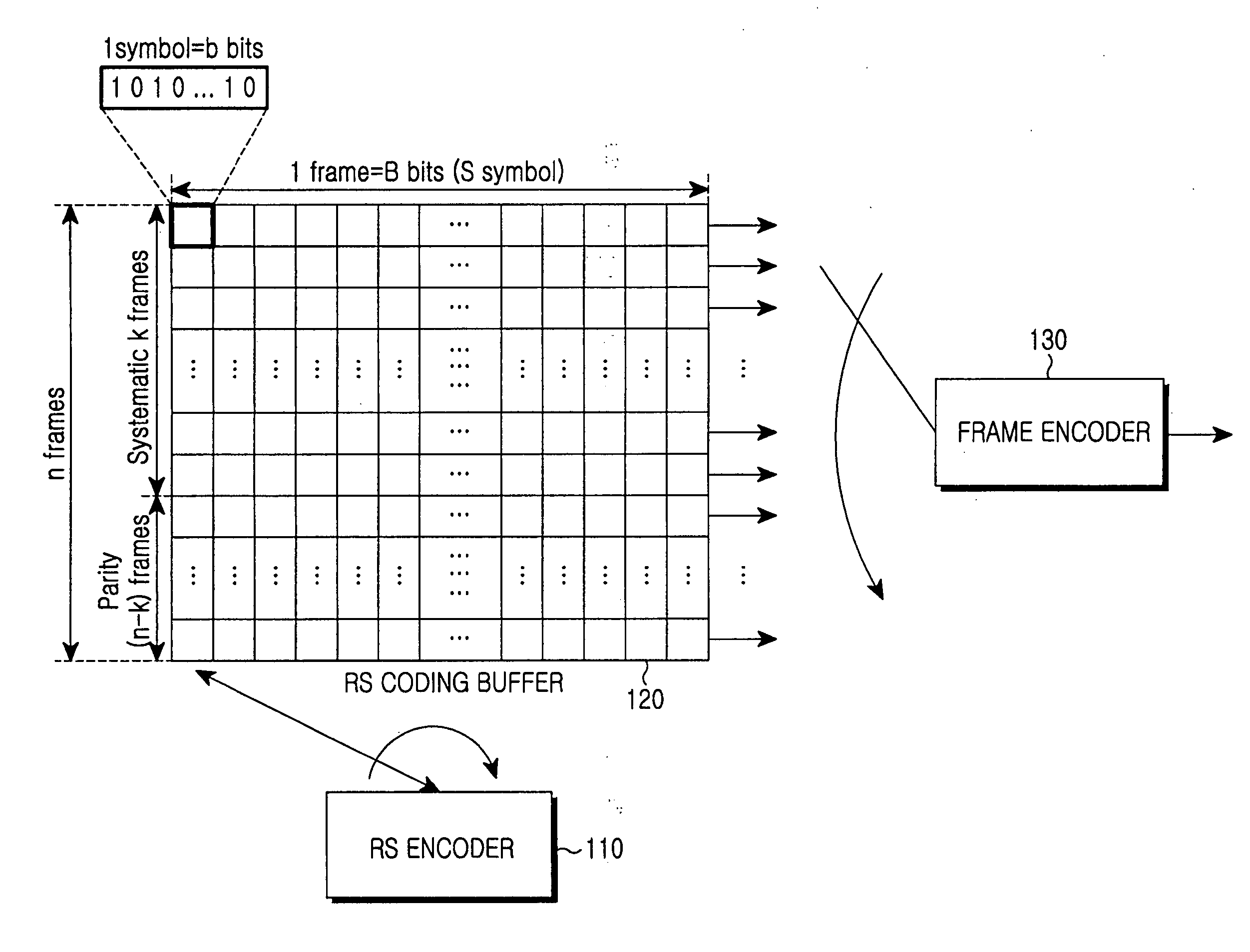
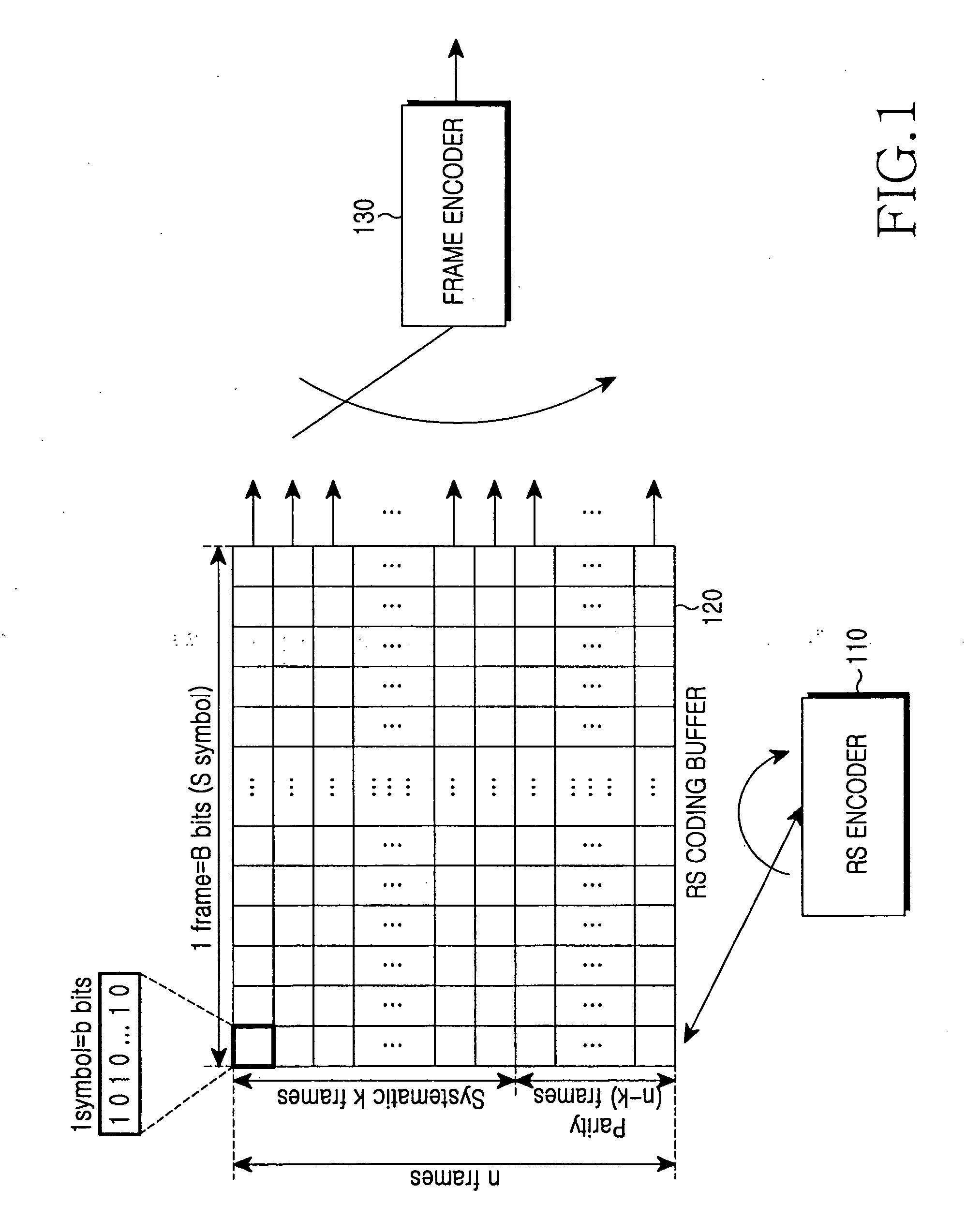
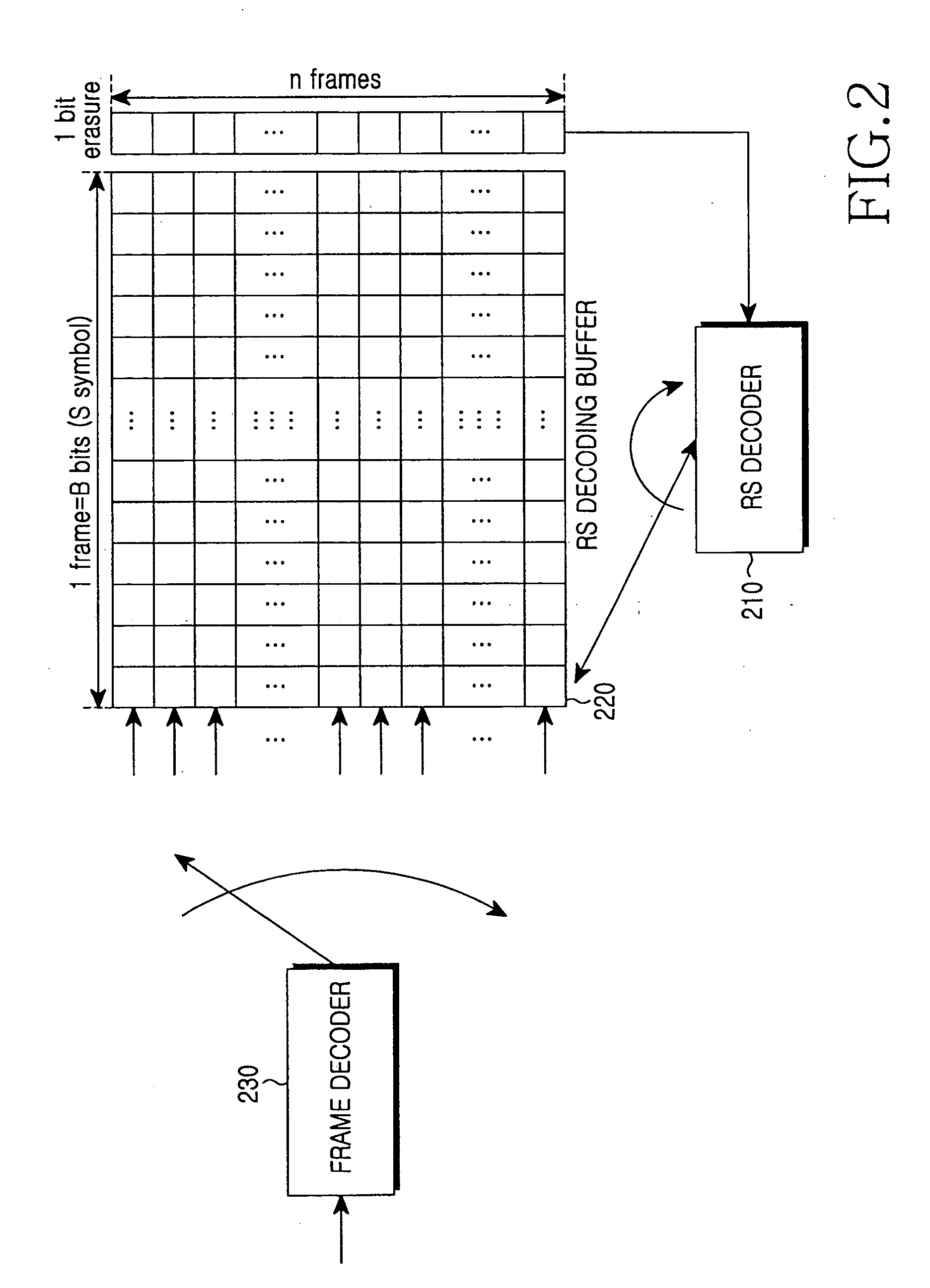
InactiveUS20060085726A1Accurate decodingImprove decoding efficiencyCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareCommunications system
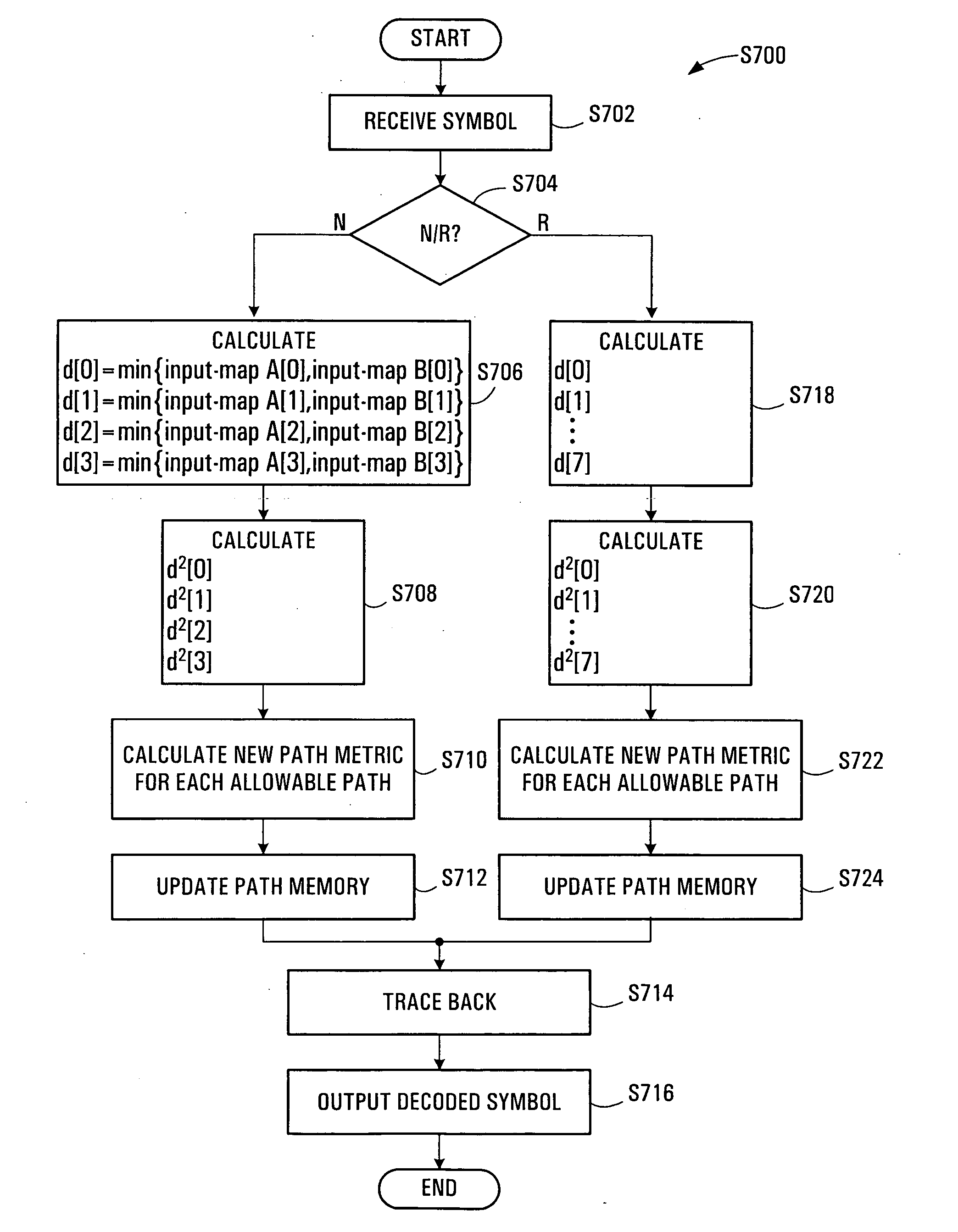
An apparatus for receiving and decoding a double-coded symbol in a communication system using a double coding scheme for encoding a Reed-Solomon (RS)-coded symbol with a predetermined scheme for communication. In the apparatus, an inner decoder receives a frame formed with the double-coded symbols, and primary-decodes the received frame. An RS decoding buffer stores an output of the inner decoder frame by frame, and an RS decoder reads symbols in the same column from symbols of a frame stored in the RS decoding buffer, performs RS decoding on the read symbols, and generates an RS decodable indicator value for each symbol. A log likelihood ratio (LLR) update unit updates an LLR value using the RS decodable indicator value, and outputs the updated LLR value to the inner decoder.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Orientation-indicating machine readable coded data
InactiveUS6929186B2Accurate decodingCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesData encodingComputer science
Machine-readable coded data disposed on or in a substrate. The coded data includes a layout having order n rotational symmetry, formed from n identical sub-layouts rotated 1 / n revolutions apart about a center of rotation. The layout encodes a first codeword formed from a sequence of a multiple m of n first symbols, with each sub-layout defining respective positions for each of m first symbols, such that the m first symbols uniquely identify each sub-layout. Decoding the first symbols provided at one or more of the respective locations within each sub-layout is therefore indicative of the degree of rotation of the layout.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD
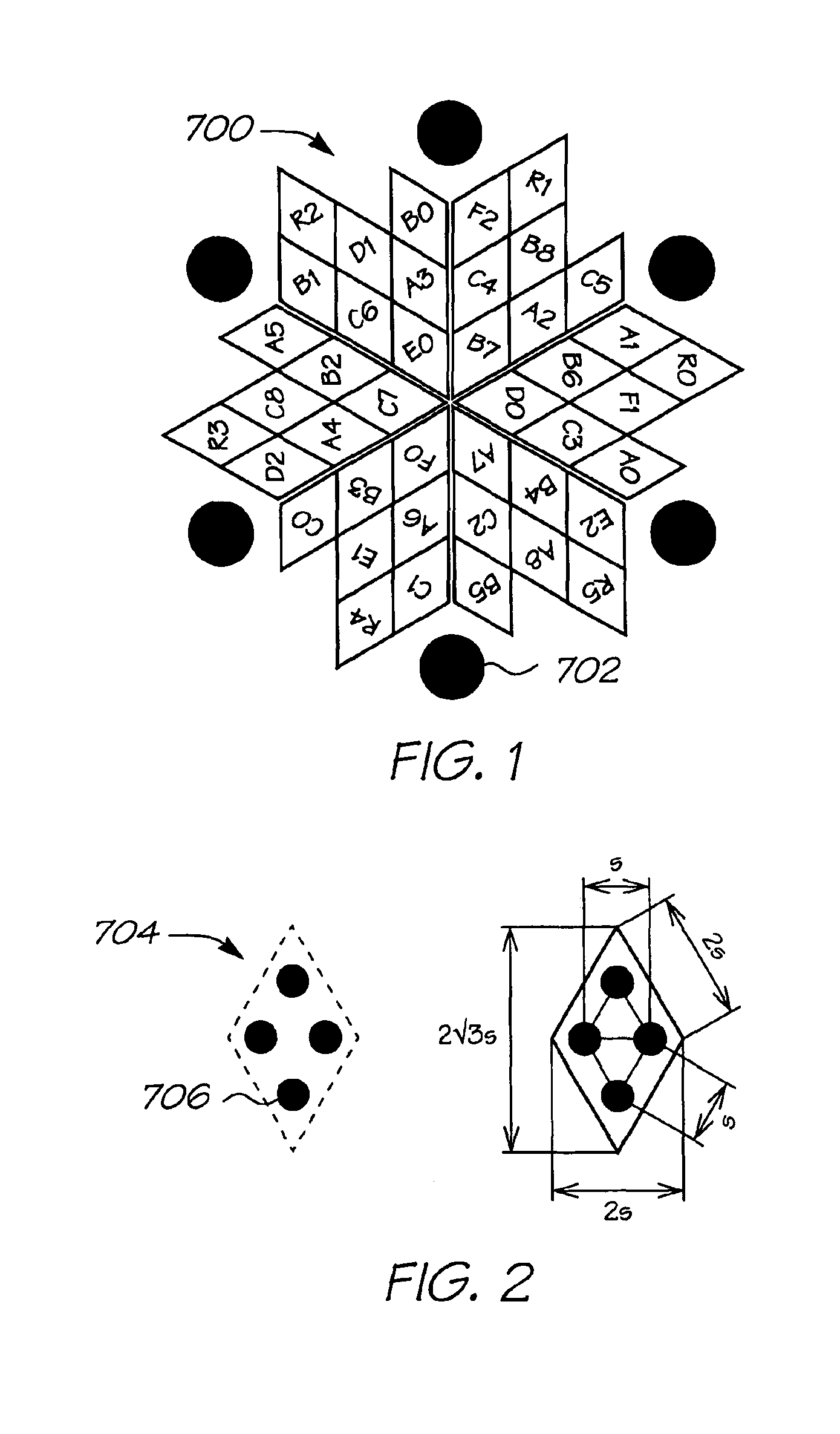
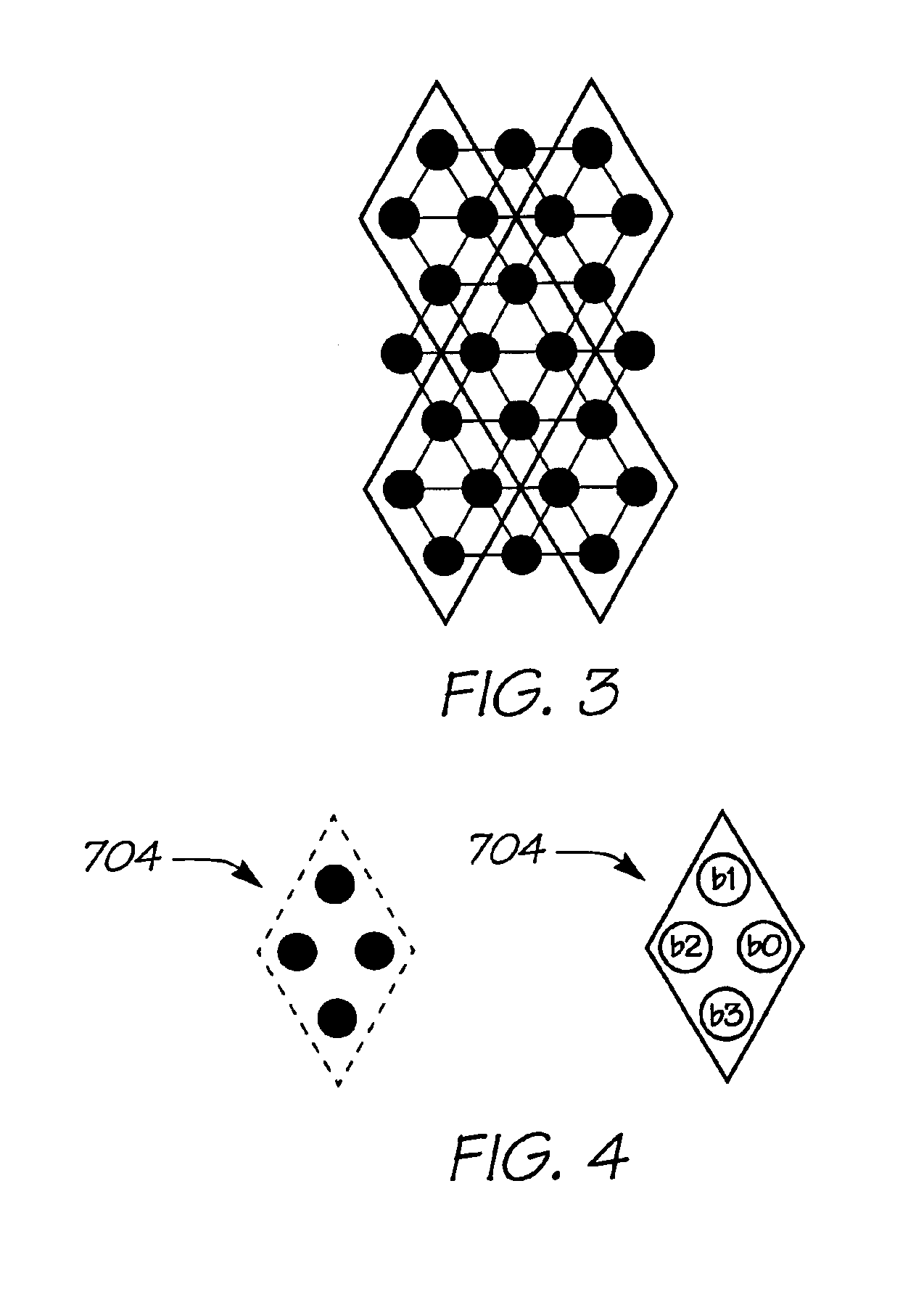
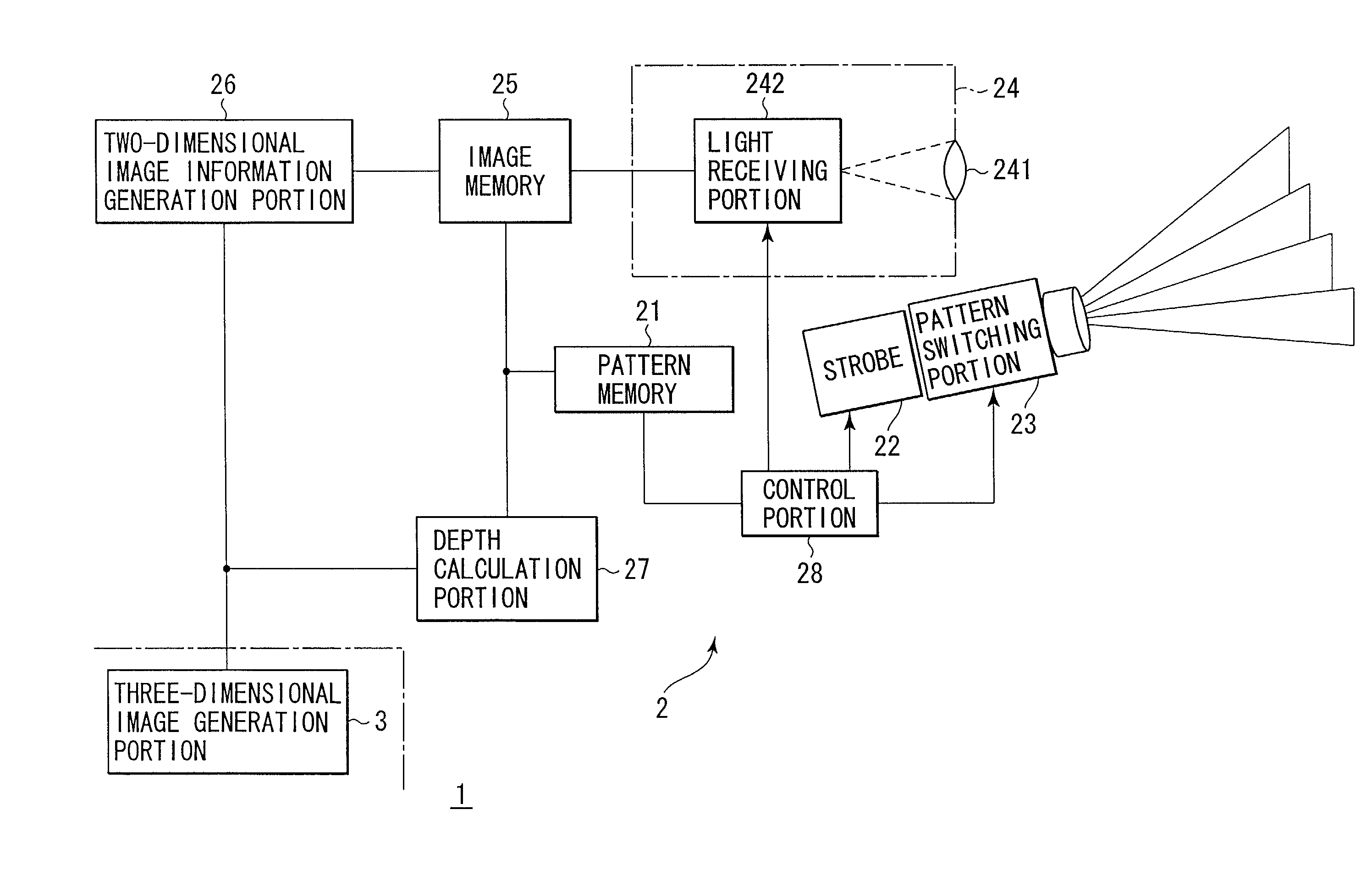
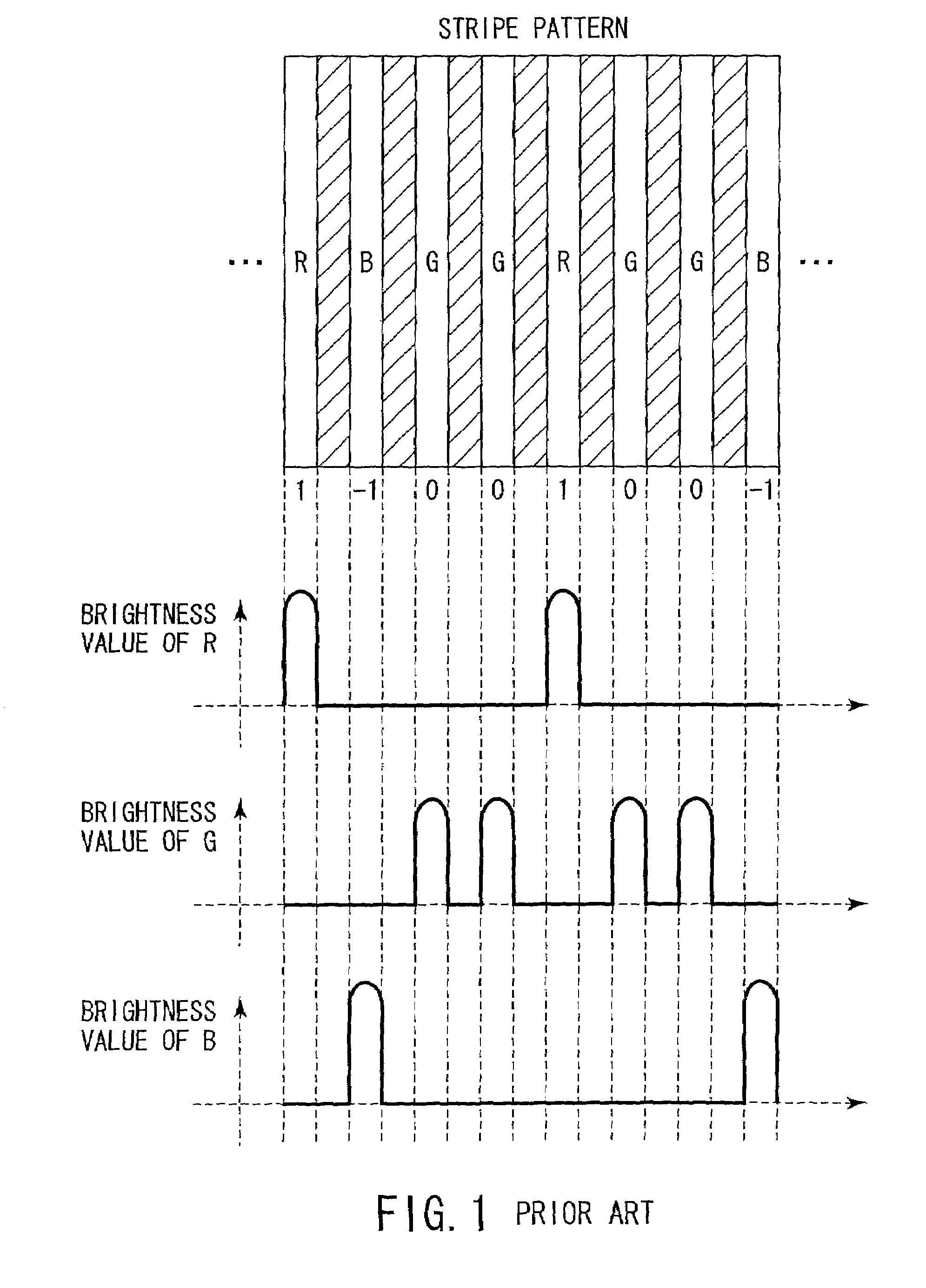
Three-dimensional information acquisition apparatus and three-dimensional information acquisition method
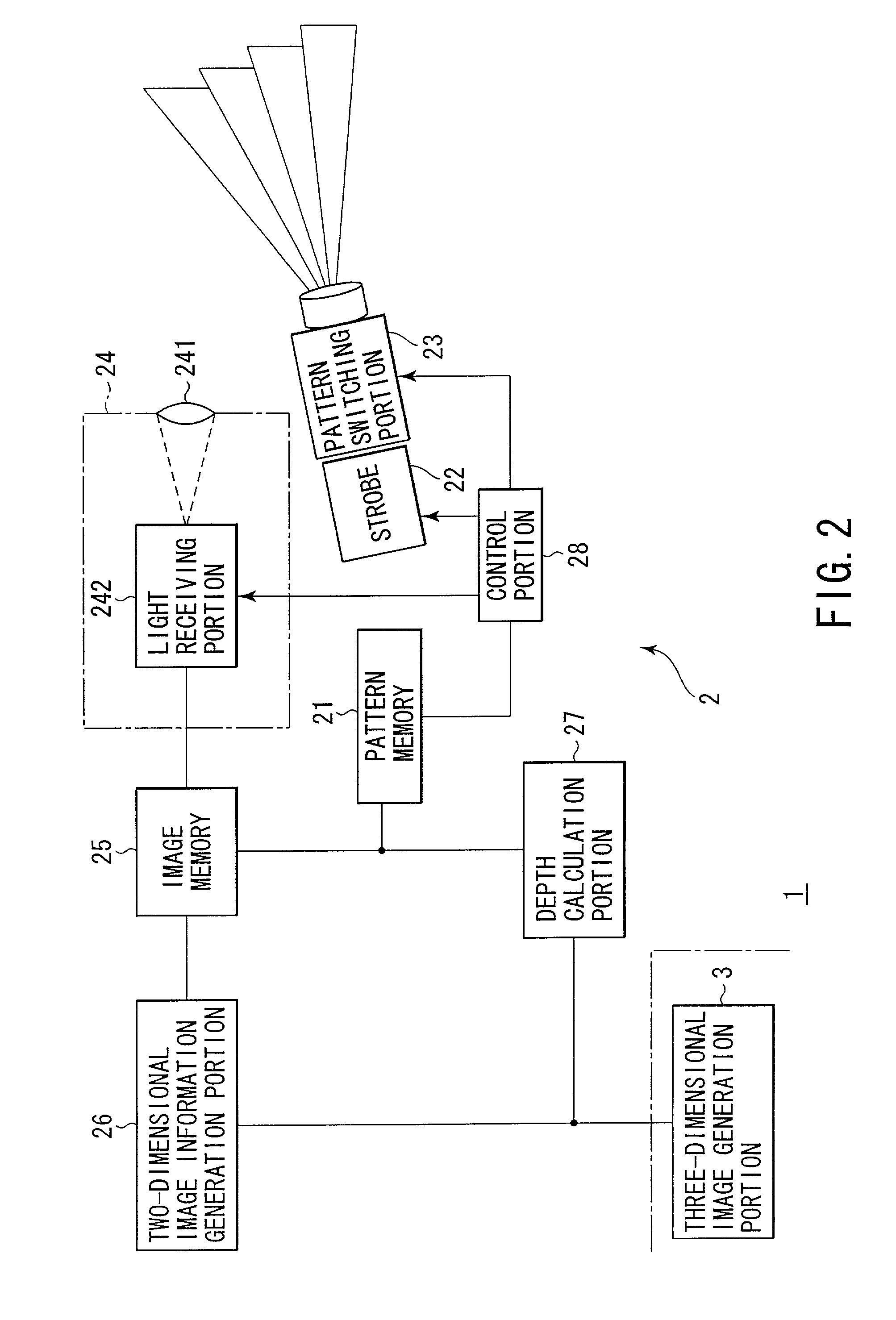
InactiveUS7092563B2Accurate decodingAvoid light transmissionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsObject basedInformation acquisition
There are performed three types of object shooting, i.e., a projection pattern shooting using a pattern including both characterization of a stripe based on a color and characterization based on a gradation of the same component, a flash shooting without a pattern and a non-flash shooting without a pattern. A two-dimensional image information generation portion corrects the influence of a surface reflectivity of an object or external light from the three types of images, and estimates a pattern structure using the characteristic based on a color with respect to an object having a white-based color or a low-saturation color and based on a gradation with respect to an object having a high-saturation color. A depth calculation portion specifies the correspondence relationship between the estimated pattern structure and information of the projected pattern, and calculates a depth of each part of the object based on a result of specification.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Encoding and decoding of audio objects
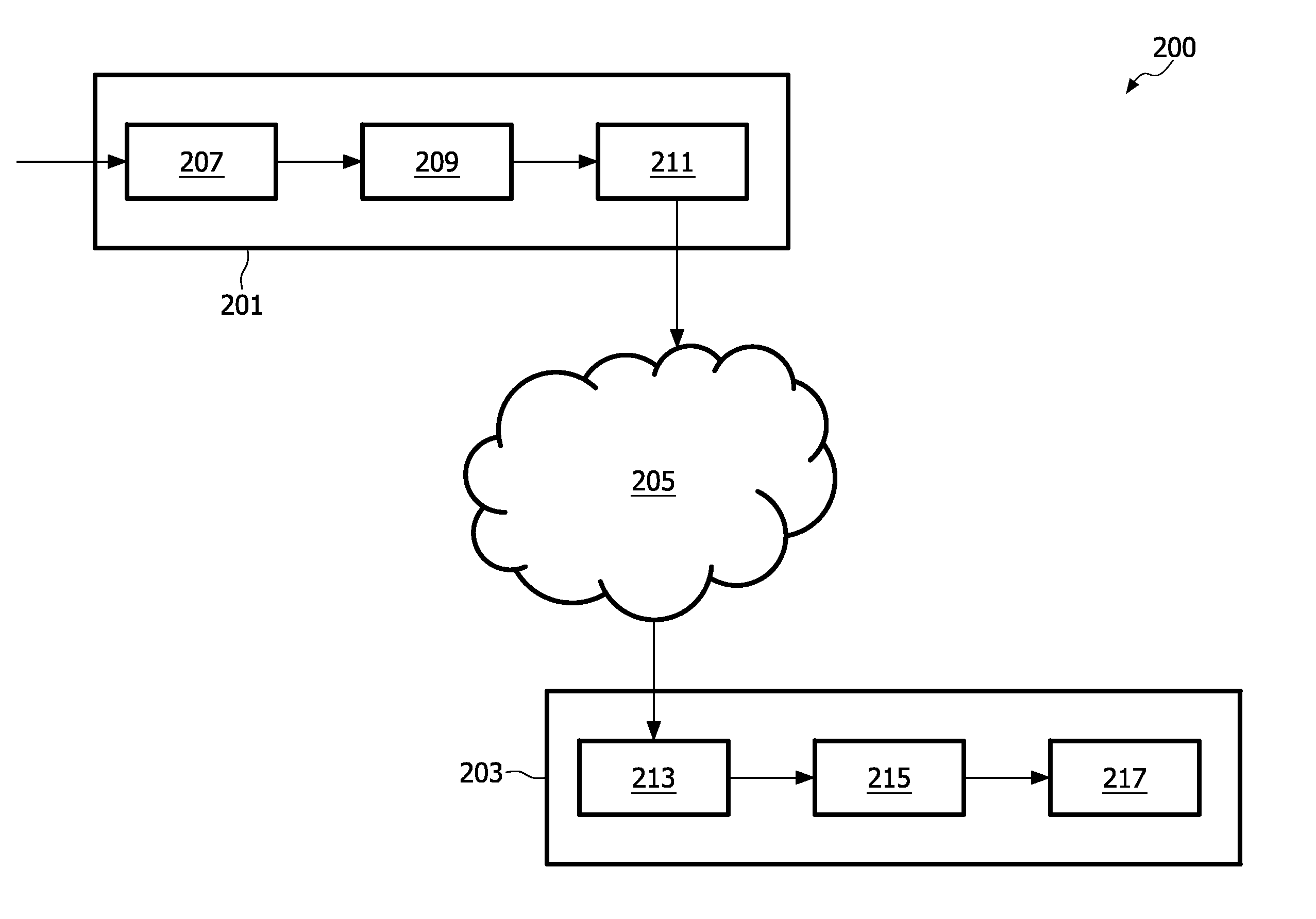
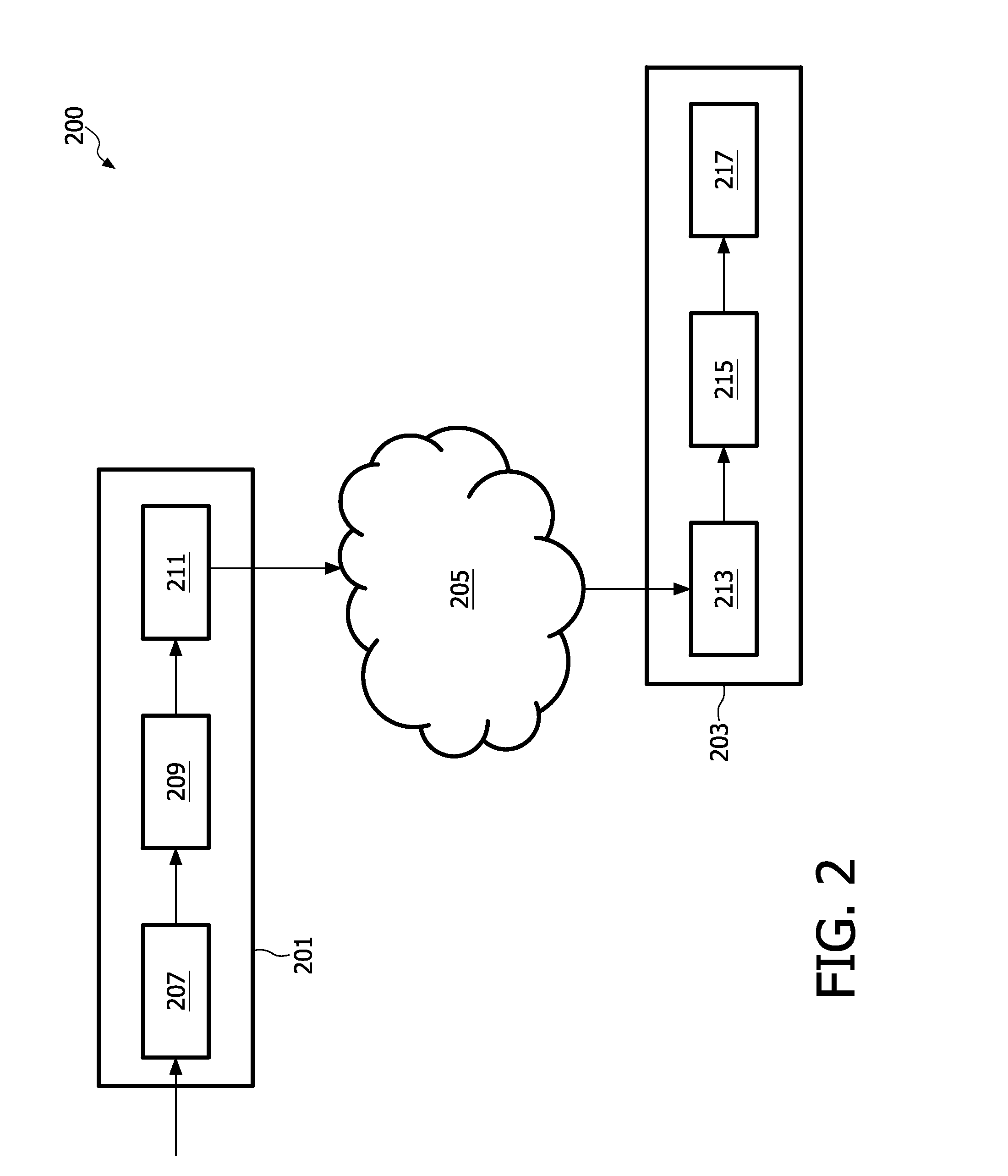
ActiveUS20090326960A1Improve operationGood serviceBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisAudio frequencyAudio signal
An audio system comprises an encoder (209) which encodes audio objects in an encoding unit (403) that generates a down-mix audio signal and parametric data representing the plurality of audio objects. The down-mix audio signal and parametric data is transmitted to a decoder (215) which comprises a decoding unit (301) which generates approximate replicas of the audio objects and a rendering unit (303) which generates an output signal from the audio objects. The decoder (215) furthermore contains a processor (501) for generating encoding modification data which is sent to the encoder (209). The encoder (209) then modifies the encoding of the audio objects, and in particular modifies the parametric data, in response to the encoding modification data. The approach allows manipulation of the audio objects to be controlled by the decoder (215) but performed fully or partly by the encoder (209). Thus, the manipulation may be performed on the actual independent audio objects rather than on approximate replicas thereby providing improved performance.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
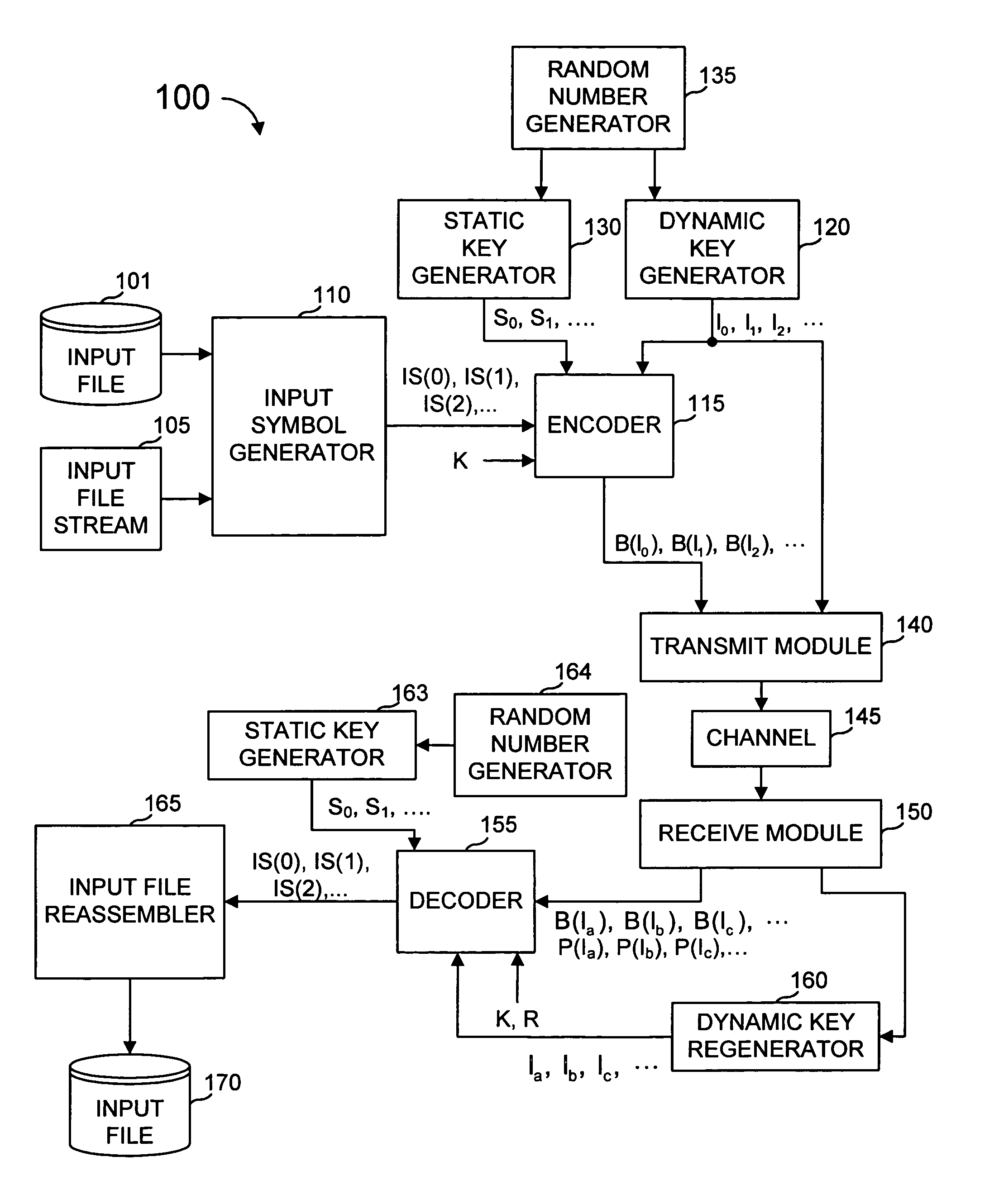
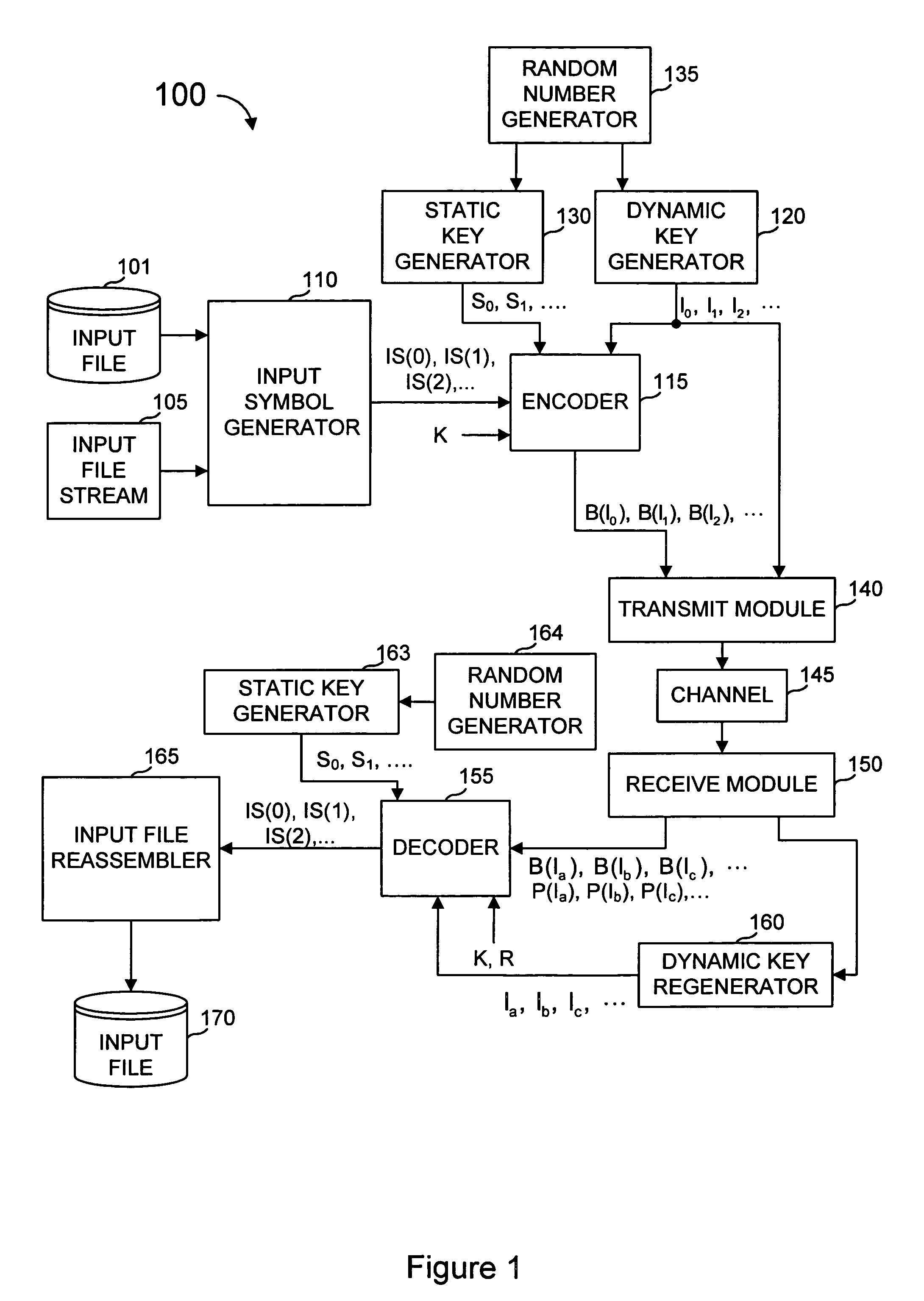
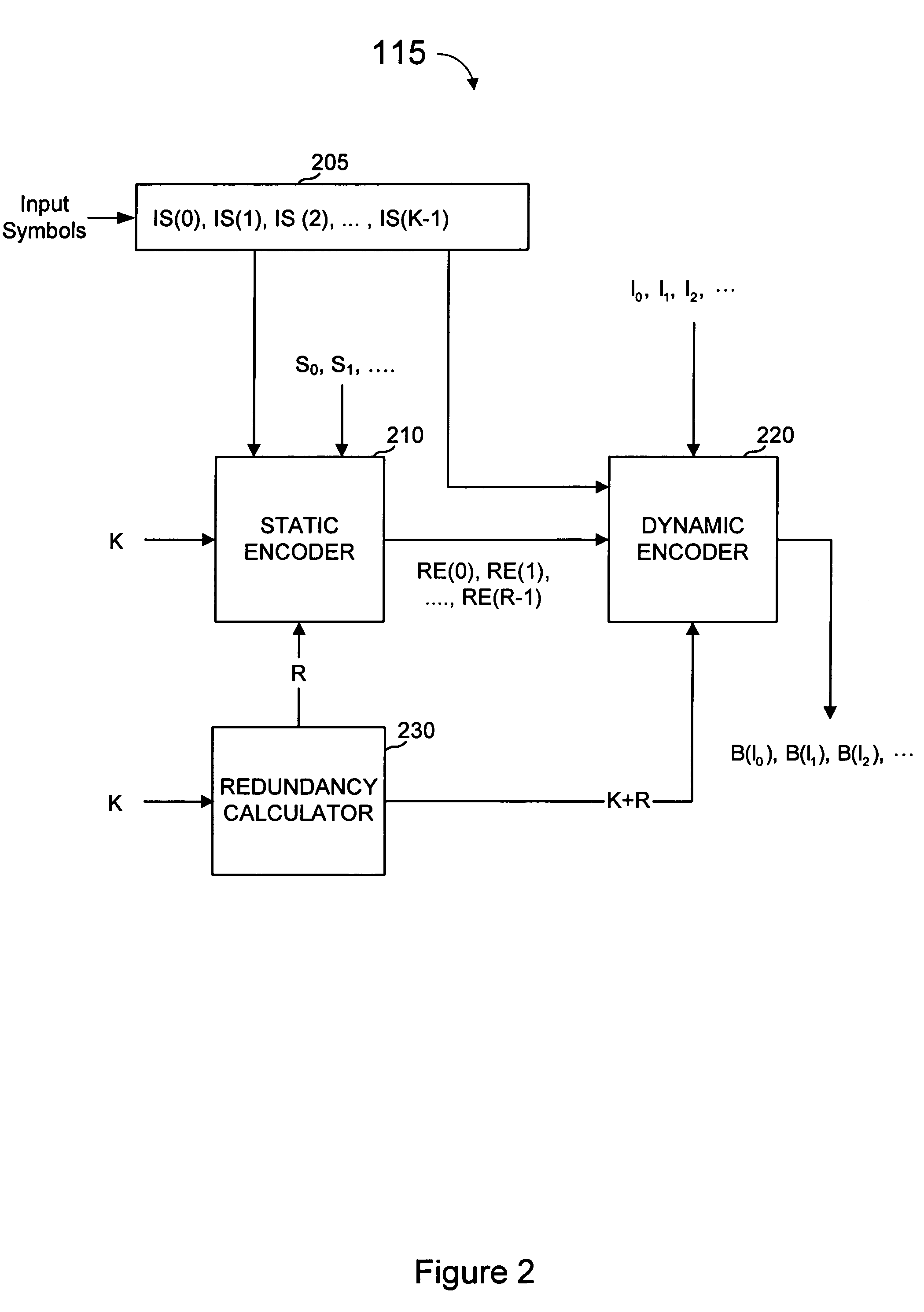
Error-correcting multi-stage code generator and decoder for communication systems having single transmitters or multiple transmitters
ActiveUS7139960B2Accurate decodingReduce expensesDigital variable displayError preventionCommunications systemComputer science
A communications system includes an encoder that produces a plurality of redundant symbols. For a given key, an output symbol is generated from a combined set of symbols including the input symbols and the redundant symbols. The output symbols are generally independent of each other, and an effectively unbounded number of output symbols can be generated, if needed. Received output symbols can provide probabilistic information for error correction. A decoder calculates check symbols from the output symbols received. For each received output symbol, the decoder updates a running total of estimated information content and, in one or more rounds, generates a probability distribution for each input symbol over all or some of possible values. This process may be repeated until, for all of the input symbols, one of the many possible values is much more probable than others, or the process may be repeated a predetermined number of rounds, or other criteria is met.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
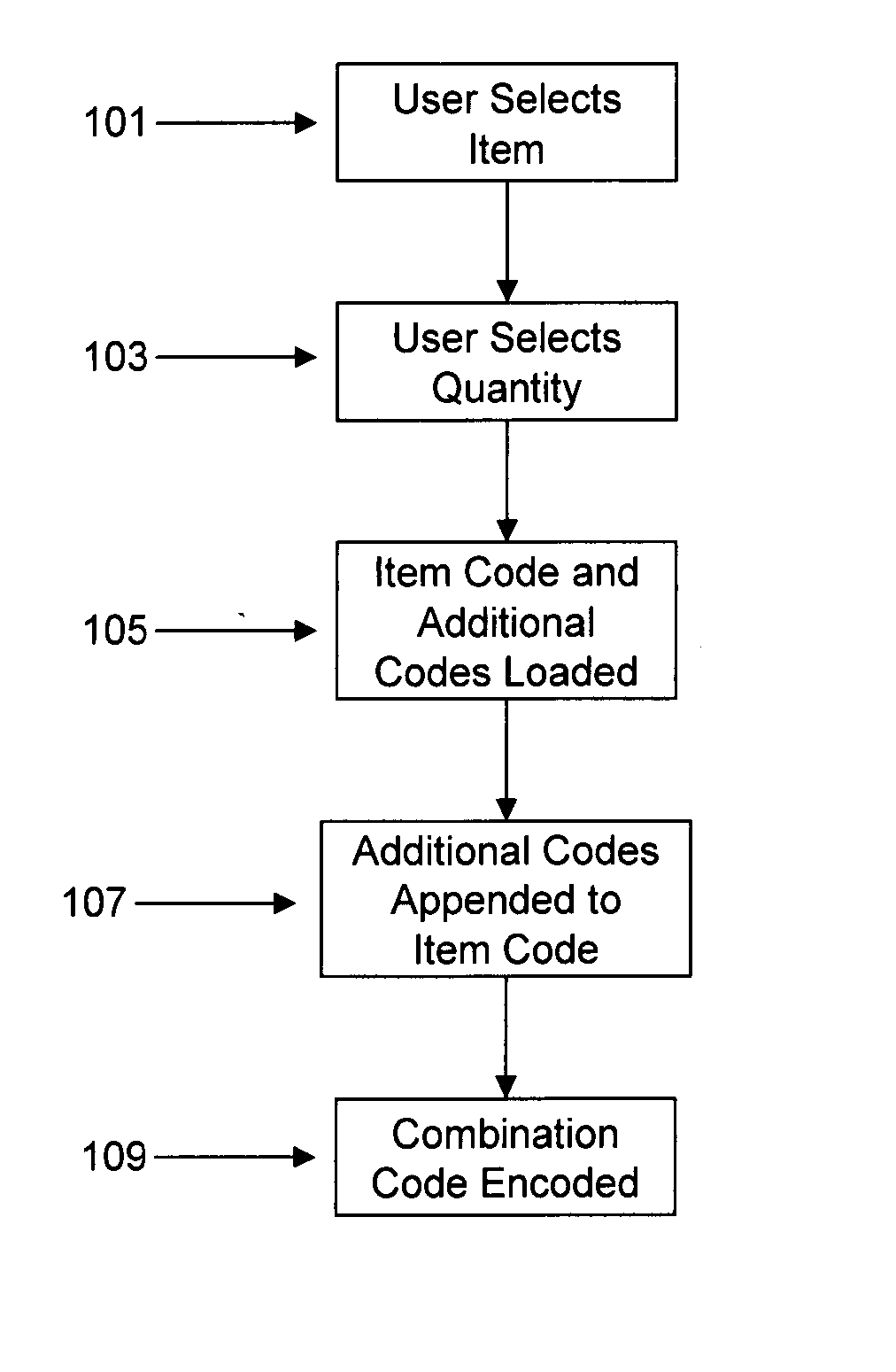
System associating sets of data into one barcode
InactiveUS20050029354A1Accurate decodingCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesSymbolic SystemsData set
The present invention discloses a system and method for encoding and decoding combination barcodes which contain two or more items of data. Generally, the device encodes a combination barcode by assembling a string of codes associated with each item of data. A barcode is then created from the string of codes by feeding it into a barcode generator. Both one and two-dimensional barcode symbologies may be utilized to create the combination barcode. To decode a combination barcode, a user first scans and uploads the combination barcode to a computer application. The application then identifies the uploaded combination barcodes utilizing a metric and separates the combination barcodes into their constituent parts.
Owner:SCANBUY
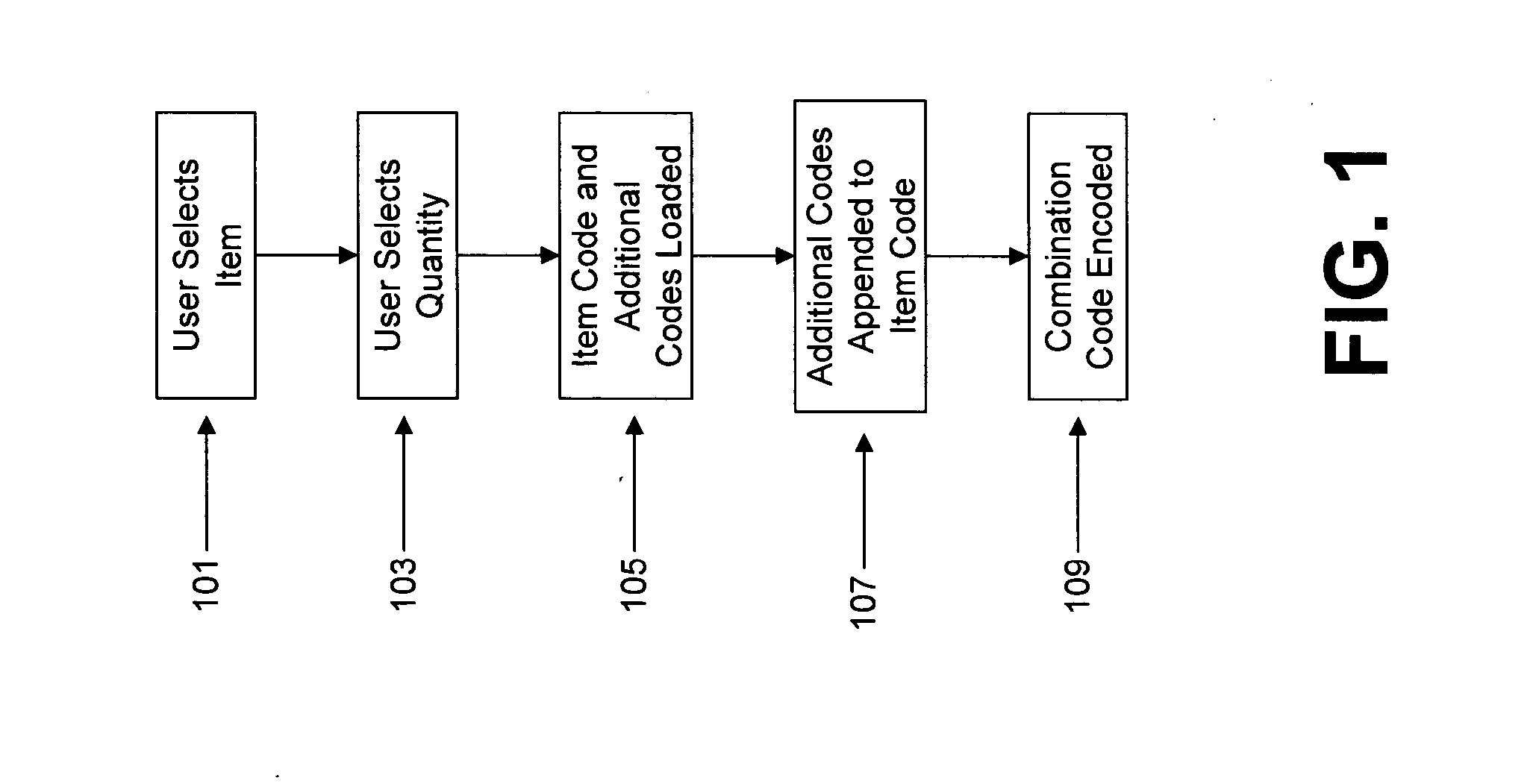
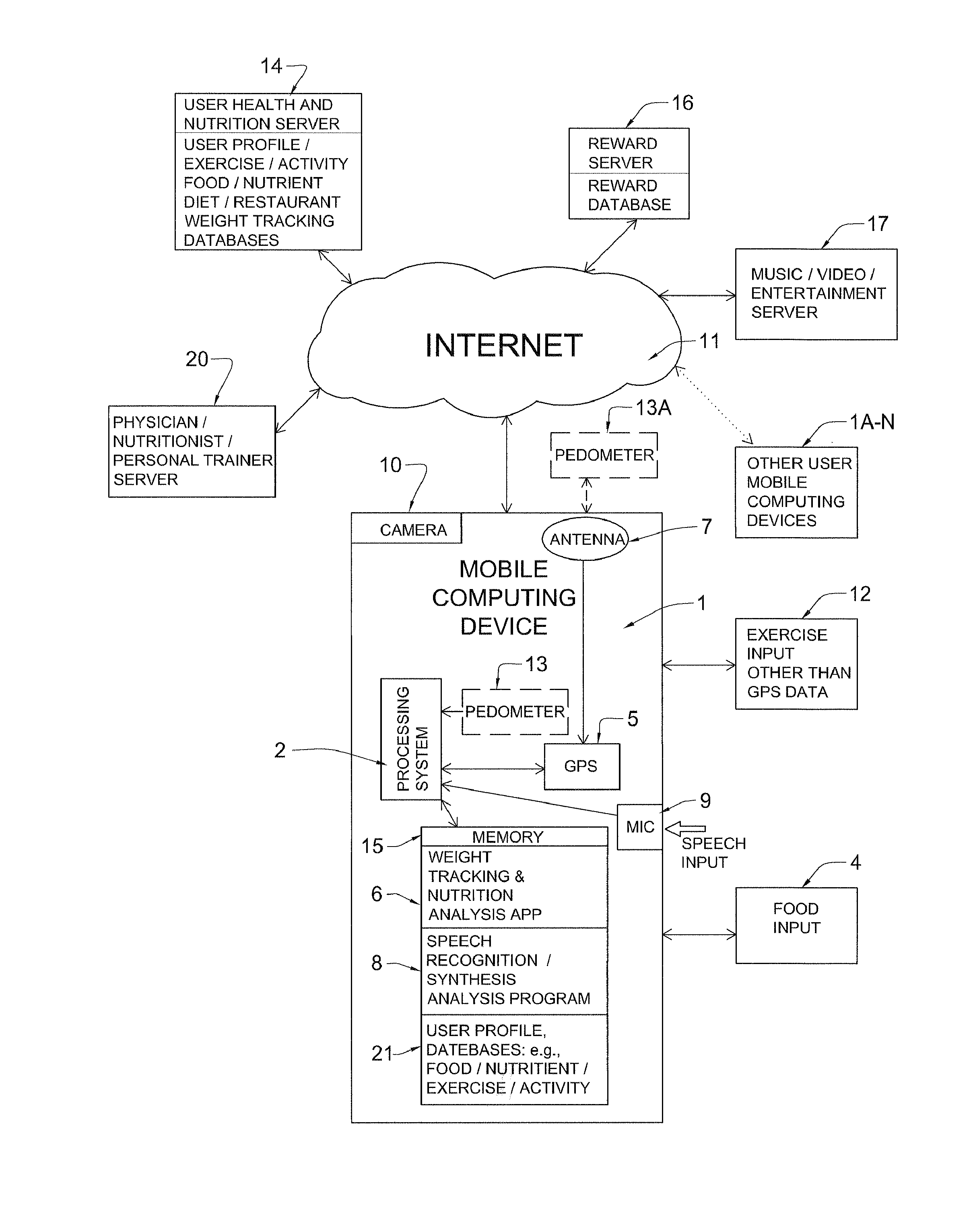
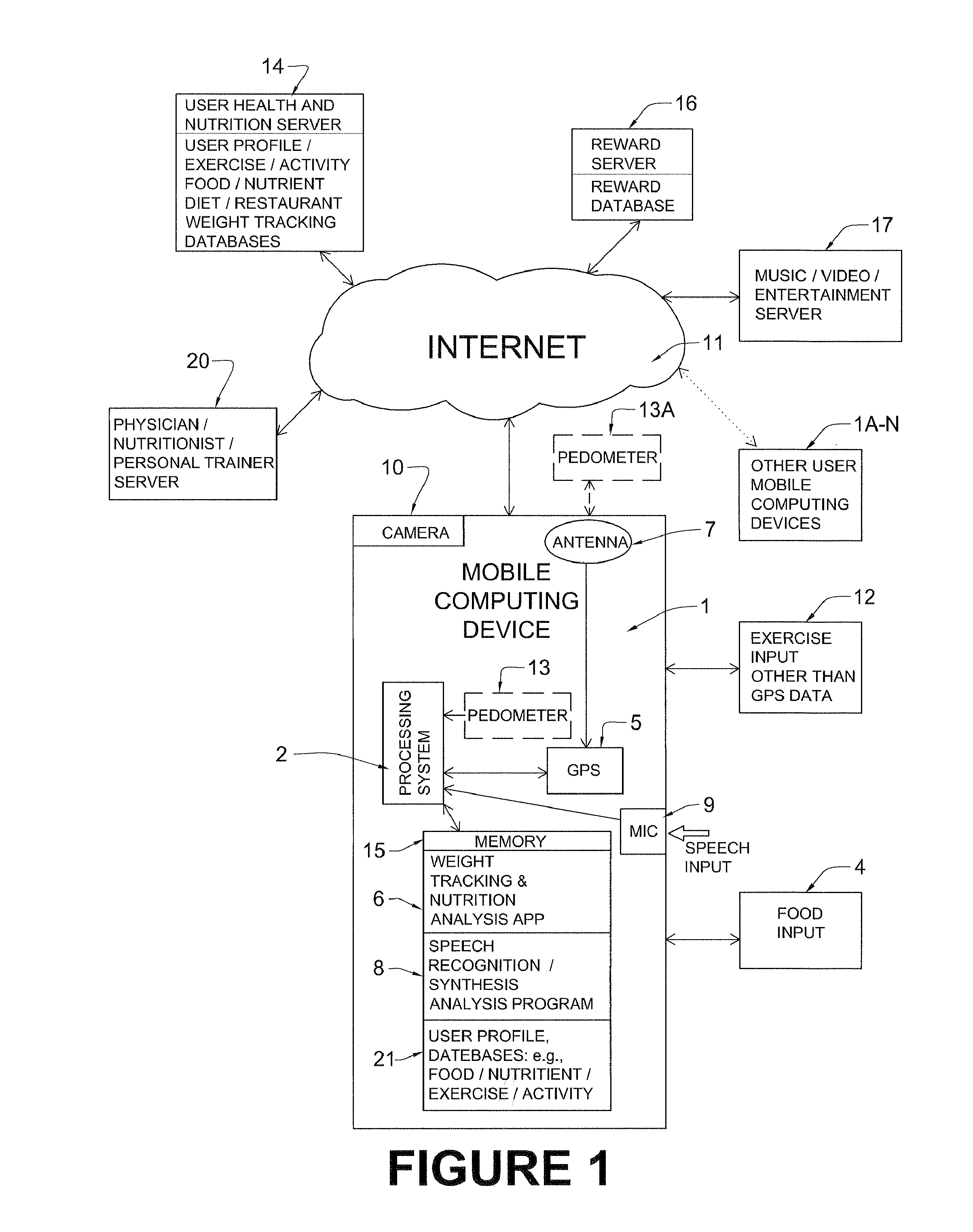
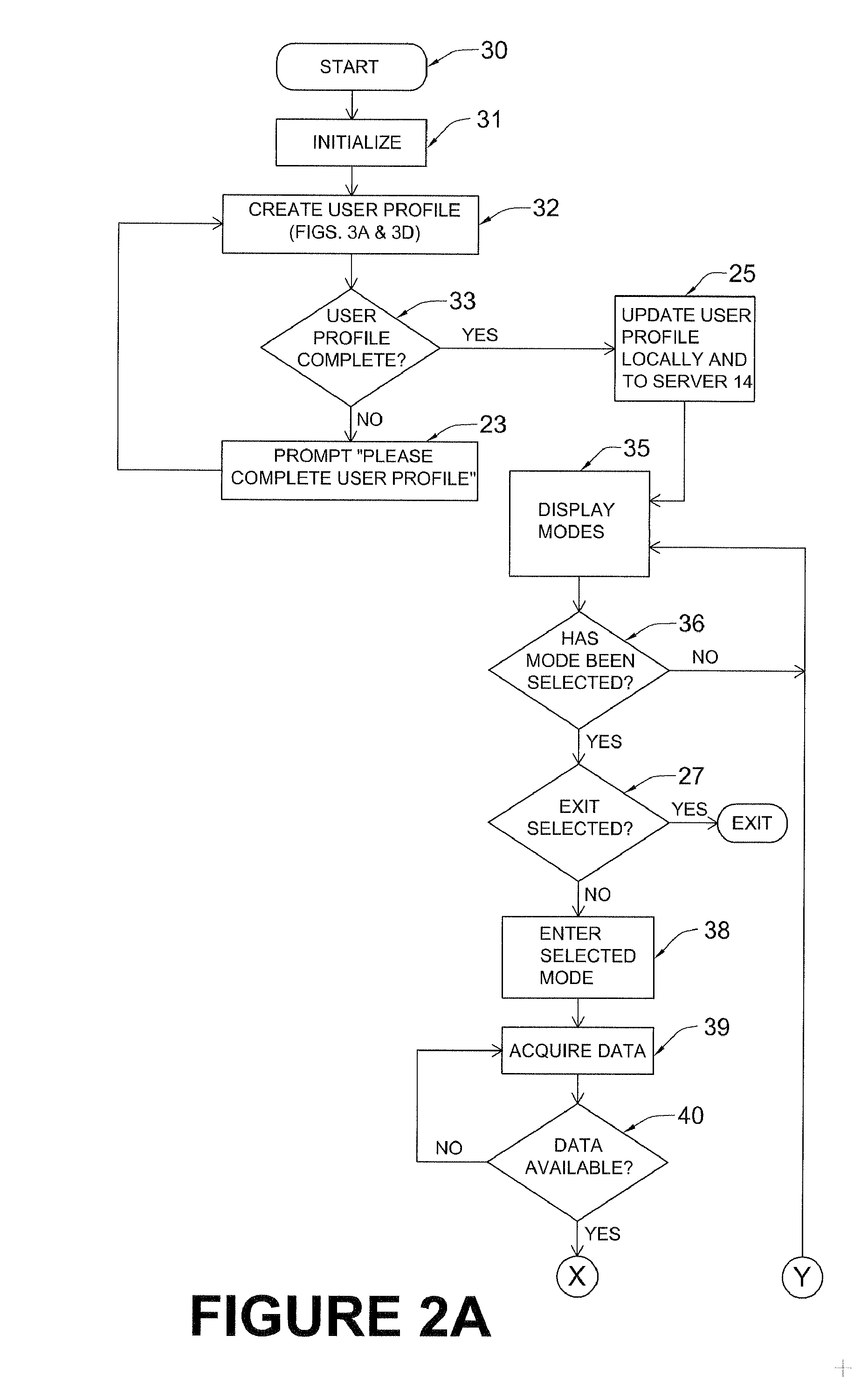
Mobile computing weight, diet, nutrition, and exercise management system with enhanced feedback and goal achieving functionality
InactiveUS20140214446A1To promote metabolismIncrease satiety, prepackaged, low and zero calorie foodsPhysical therapies and activitiesData processing applicationsNutritionSynthetic data
An illustrative mobile computing device executing weight, nutrition, health, behavior and exercise application software serves as a simulated combination personal trainer and dietician / nutritionist for the user using comprehensive databases storing personalized health, nutrition and exercise information. A mobile computing device, such as a smartphone, executing such software monitors, tracks and / or adjusts caloric intake, energy expenditure taking into account nutritional information and behavioral factors. The mobile computing device receives food consumption, exercise-related, behavior and other input using speech input and the device's GPS subsystem to ease data entry burden on users and to promote continued long-term usage. The system rewards user goal achievement in an automatic, seamless manner, through, for example, downloading music, books, or other media. In illustrative implementations, the system assists users to make healthy food and exercise choices by using a comprehensive color code system to identify good choices, bad choices and those in between.
Owner:SMARTEN LLC
Motion vector coding method and motion vector decoding method
ActiveUS20040086047A1Precise motionImprove coding efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionDecoding methodsMotion vector
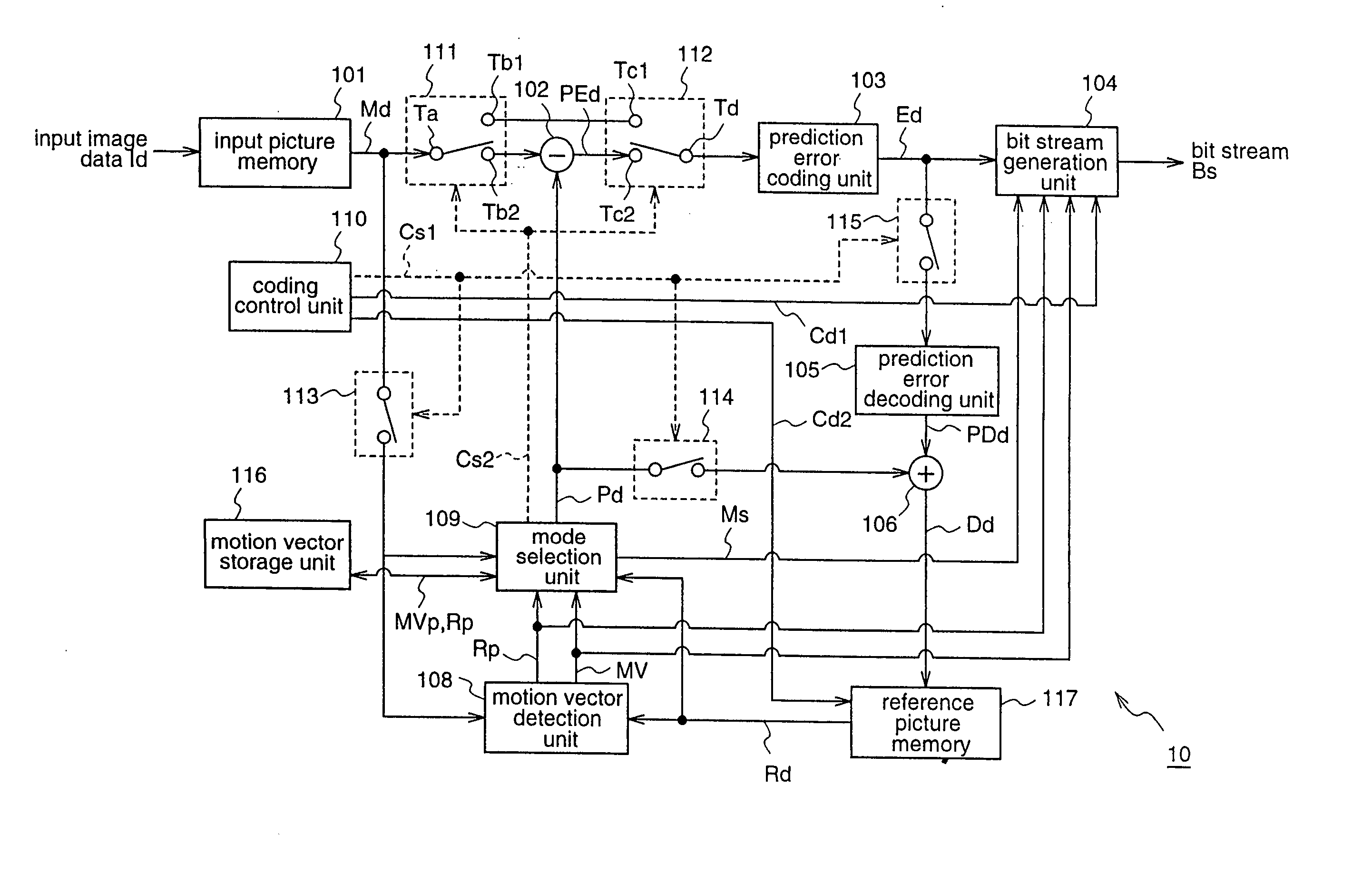
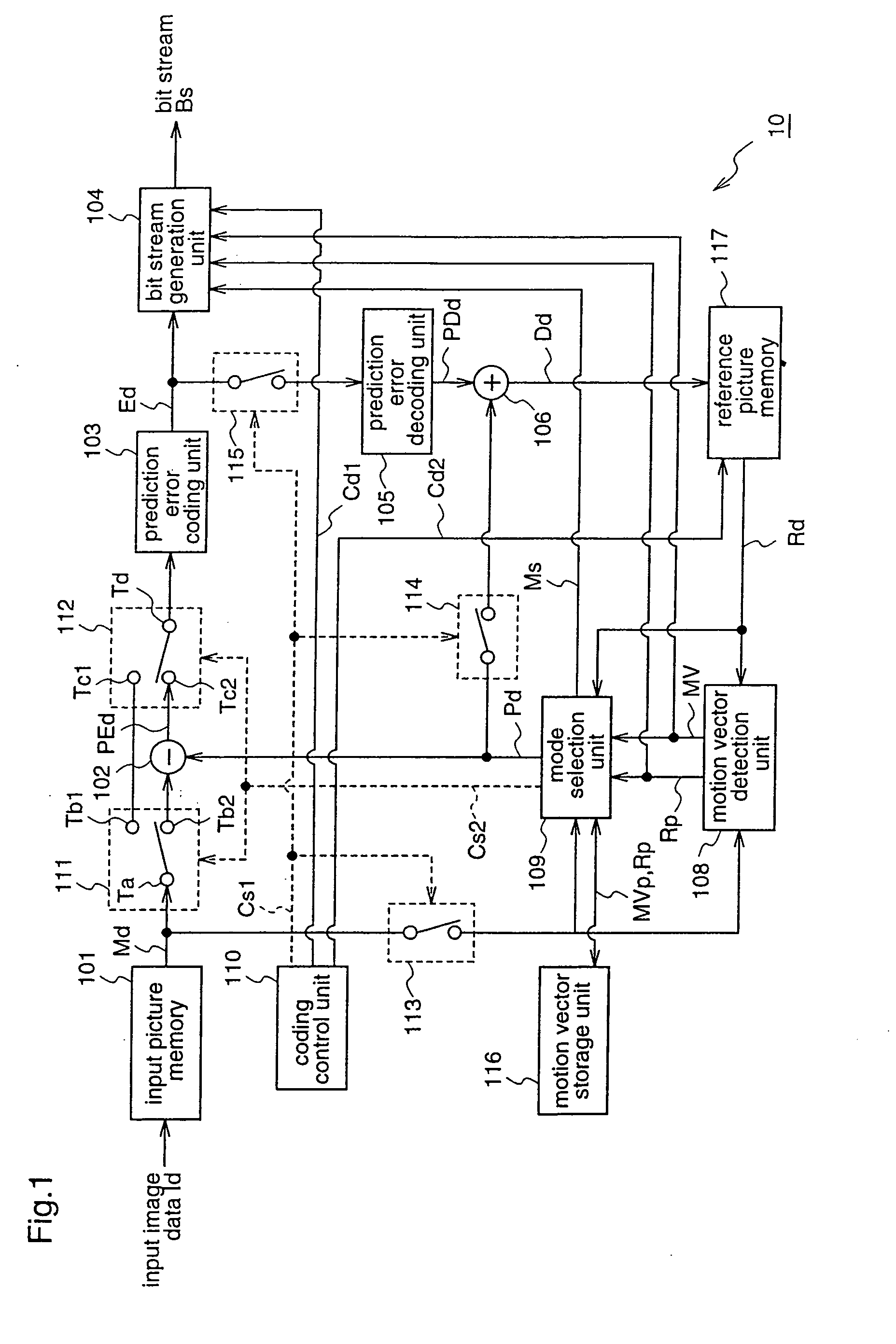
A motion vector coding unit 117 executes processing including a neighboring block specification step (S100) of specifying a neighboring block which is located in the neighborhood of a current block; a judgment step (Steps S102, S104) of judging whether or not the neighboring block has been coded using a motion vector of another block; a prediction step (S106, S108) of deriving a predictive motion vector of the current block using a motion vector calculated from the motion vector of the other block as a motion vector of the neighboring block; and a coding step (S110) of coding the motion vector of the current block using the predictive motion vector.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
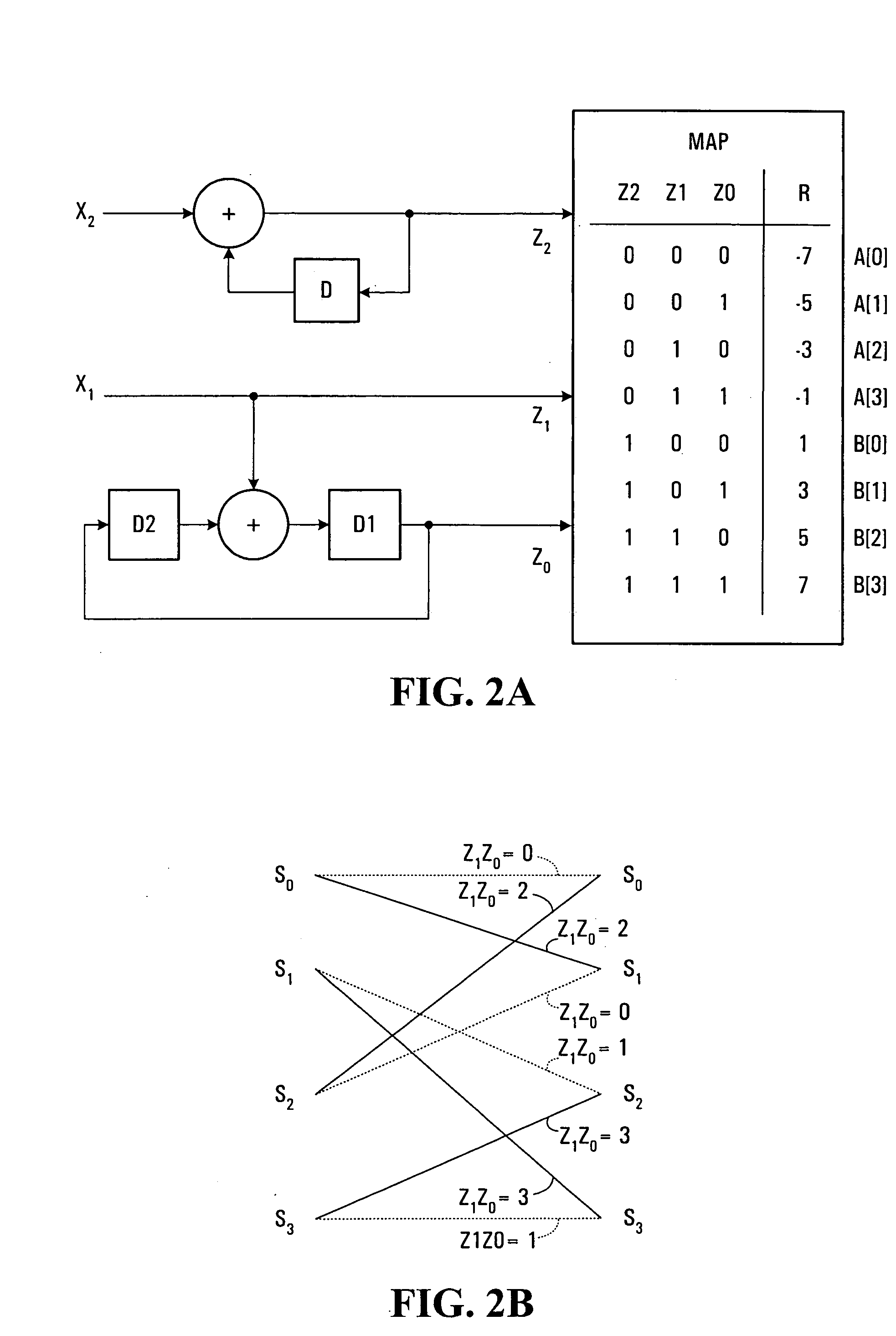
Trellis decoder for decoding data stream including symbols coded with multiple convolutional codes
InactiveUS20060088119A1Accurate decodingData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionConvolutional codeParallel computing
A trellis decoder decodes a stream of encoded symbols, including symbols of a first type (e.g. symbols encoded with a first trellis code) and symbols of a second type (e.g. encoded with a second, more robust, trellis code), without storing path indicators along a trellis for symbols of the first type. In this way, limited memory may be used to store path indicators along the trellis for symbols of the second type. This allows for more accurate decoding of the symbols of the second type. For transitions from symbols of the second type to symbols of the first type, states of the trellis decoder may be stored. In this way, paths may be traced back along the trellis for trellis decoding, without the path indicators for the symbols of the first type.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
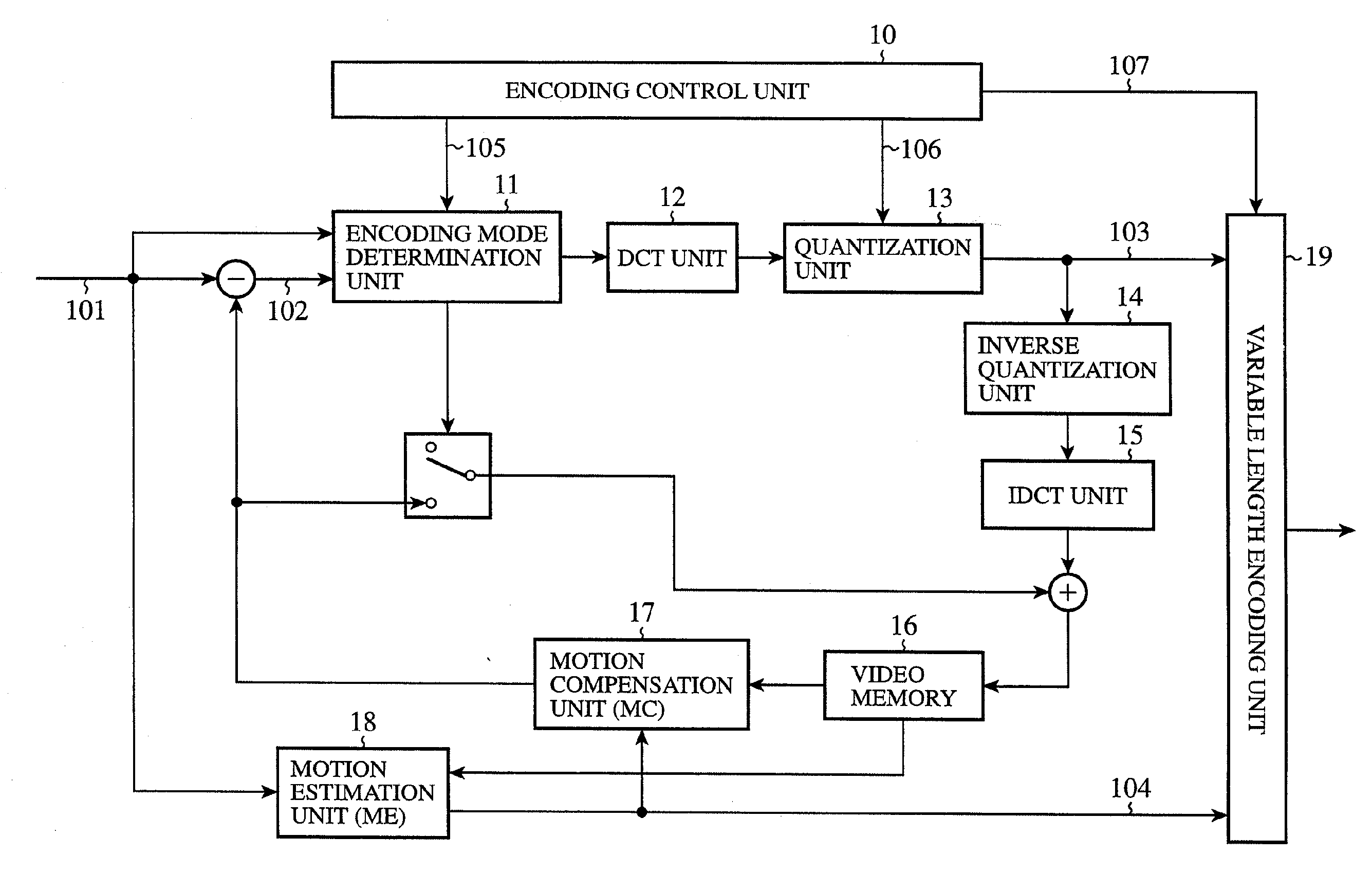
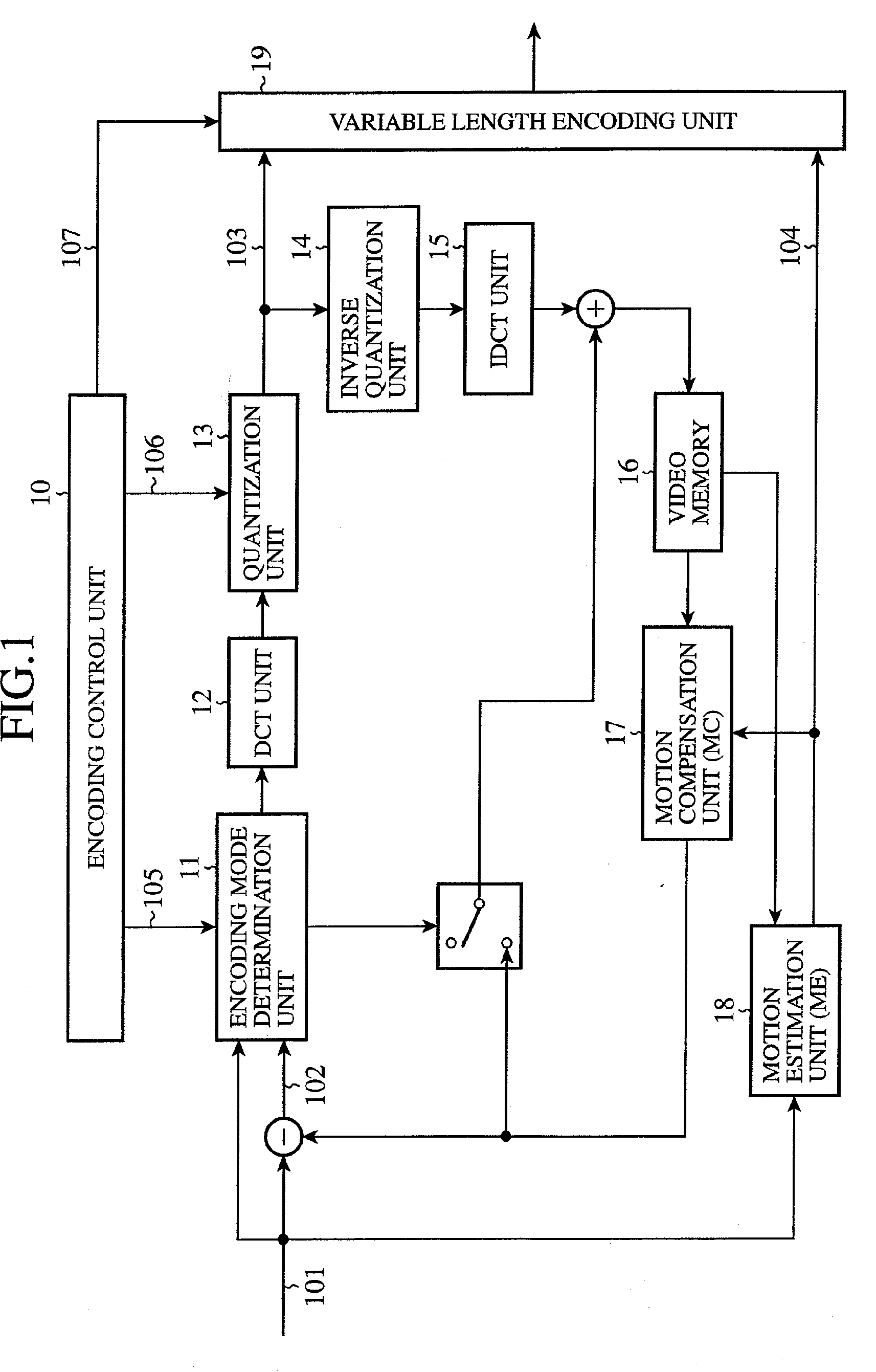
Motion picture encoding apparatus and motion picture decoding apparatus
InactiveUS20090097571A1Easy to processAccurate decodingPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionComputer graphics (images)Control unit
A motion picture encoding apparatus for encoding a motion picture signal includes a plurality of transform units for different transform schemes, and a transform scheme control unit for selecting, from the plurality of the transform units, the transform unit for the transform scheme adapted to the motion picture signal.
Owner:YAMADA YOSHIHISA +3
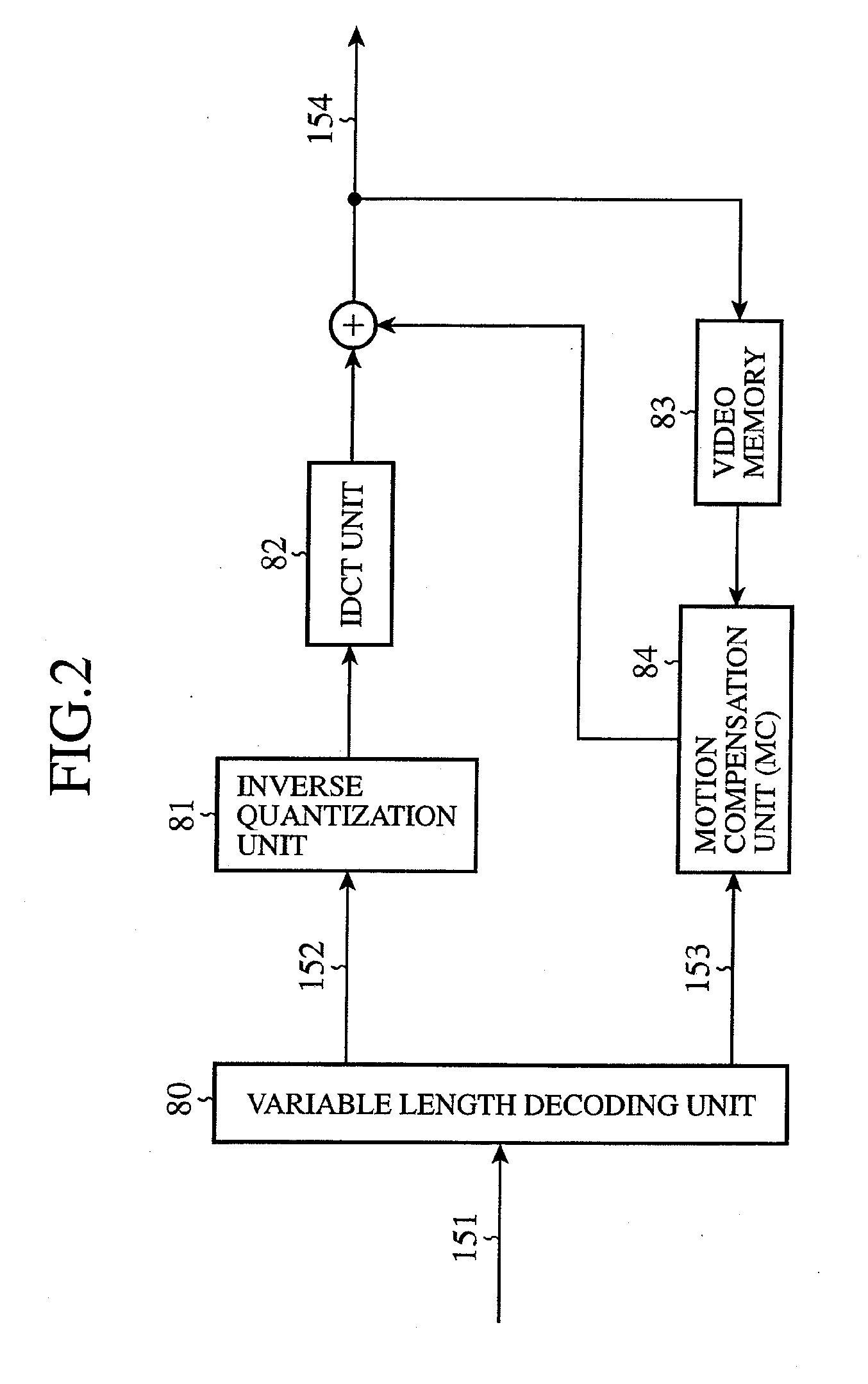
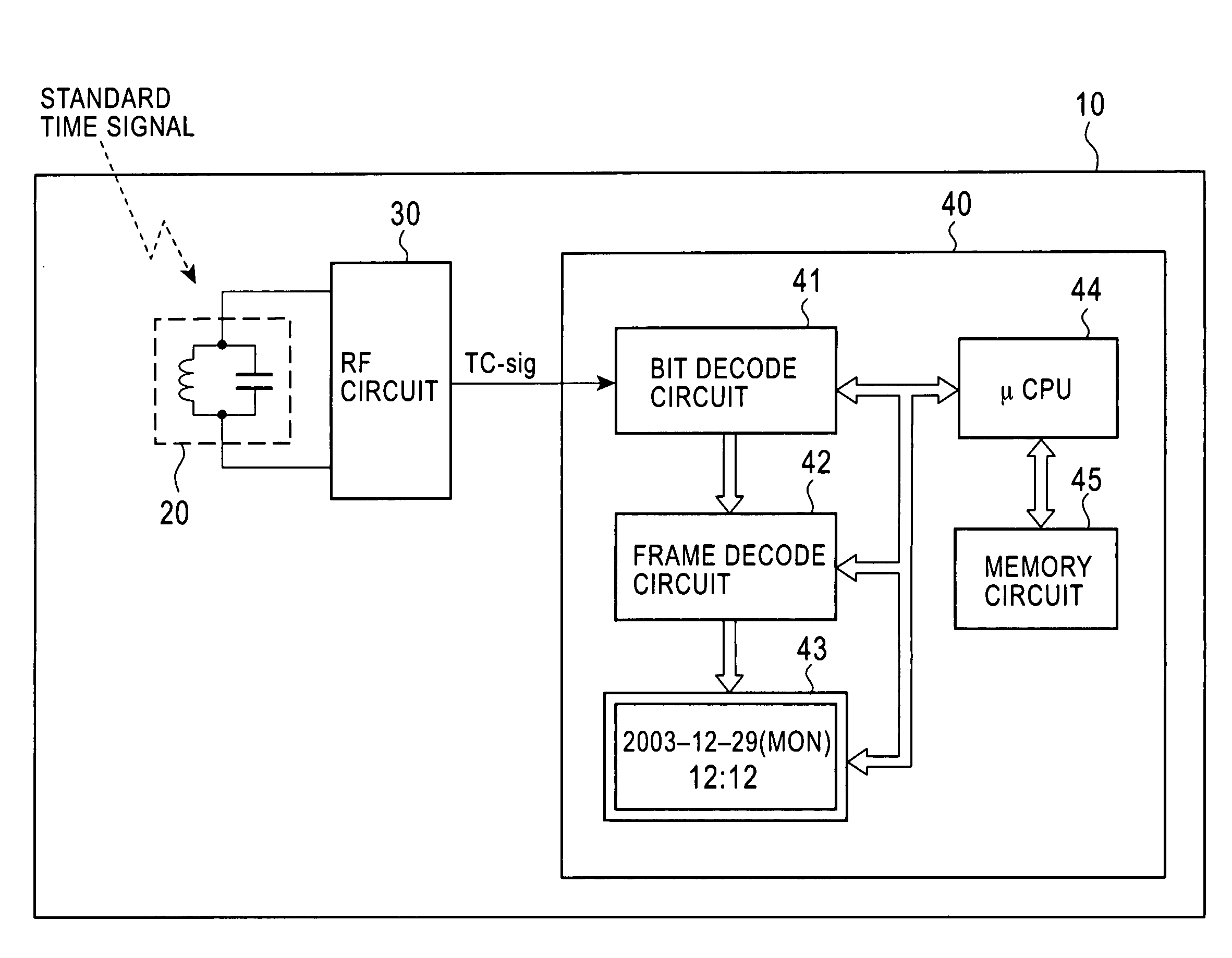
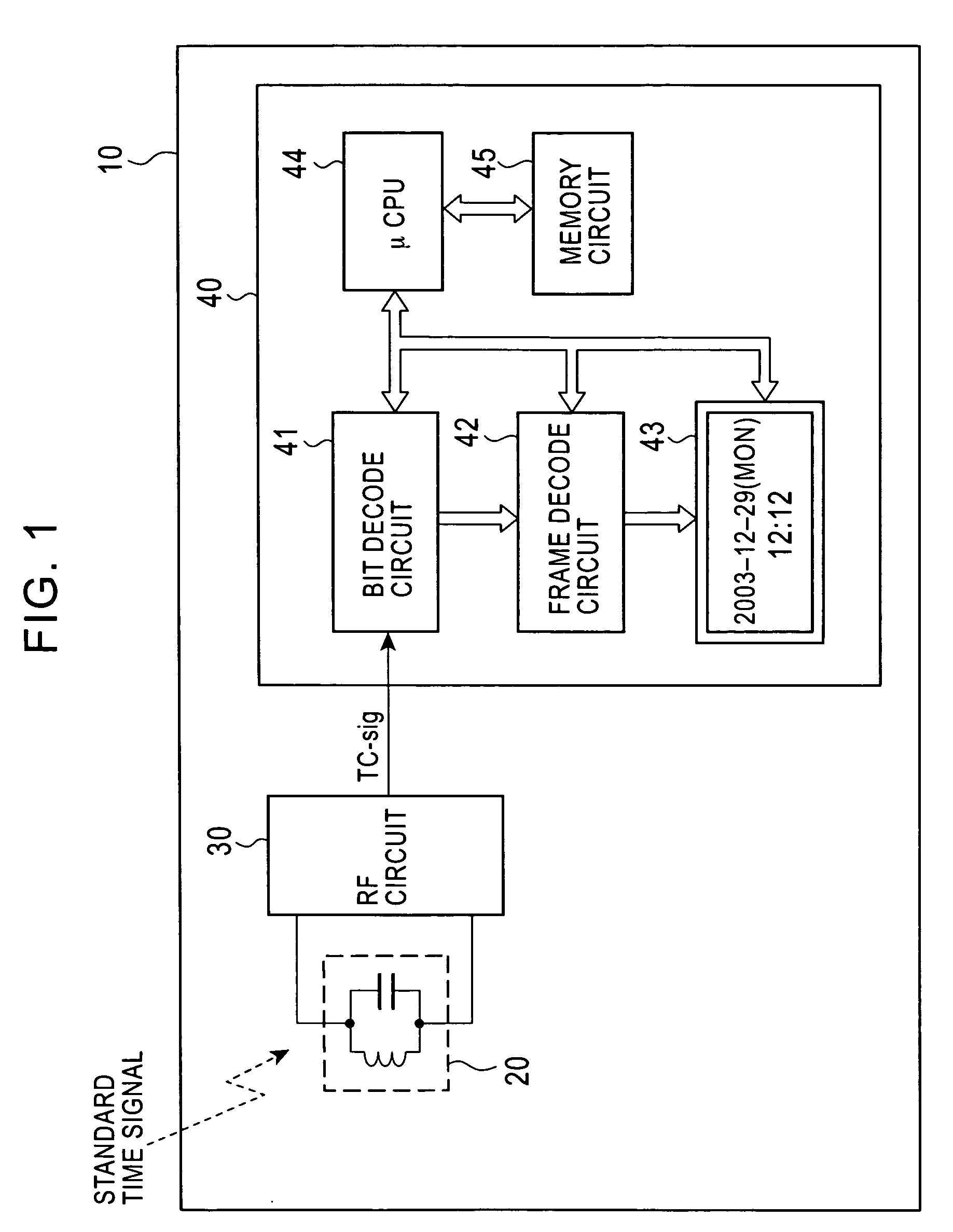
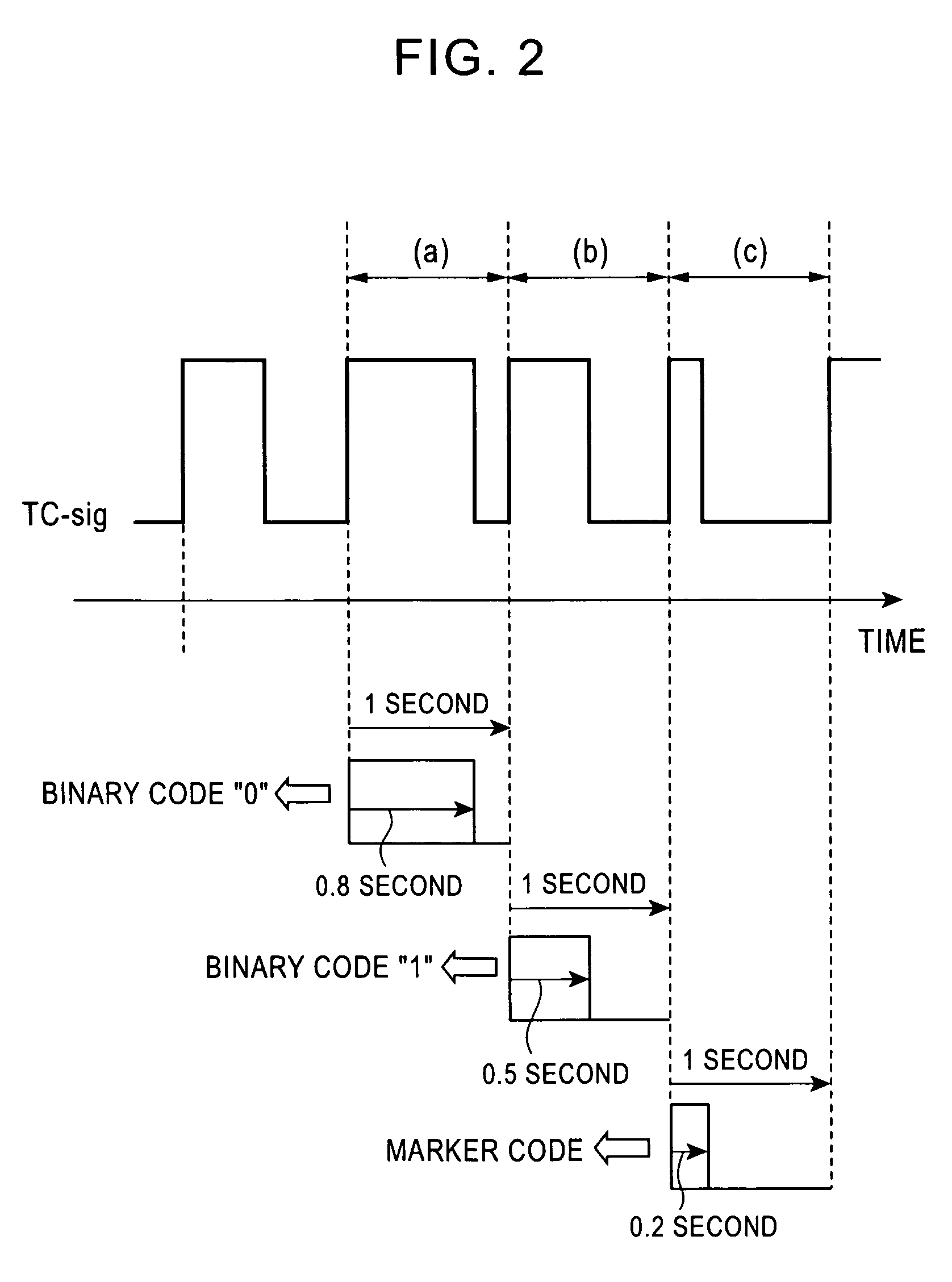
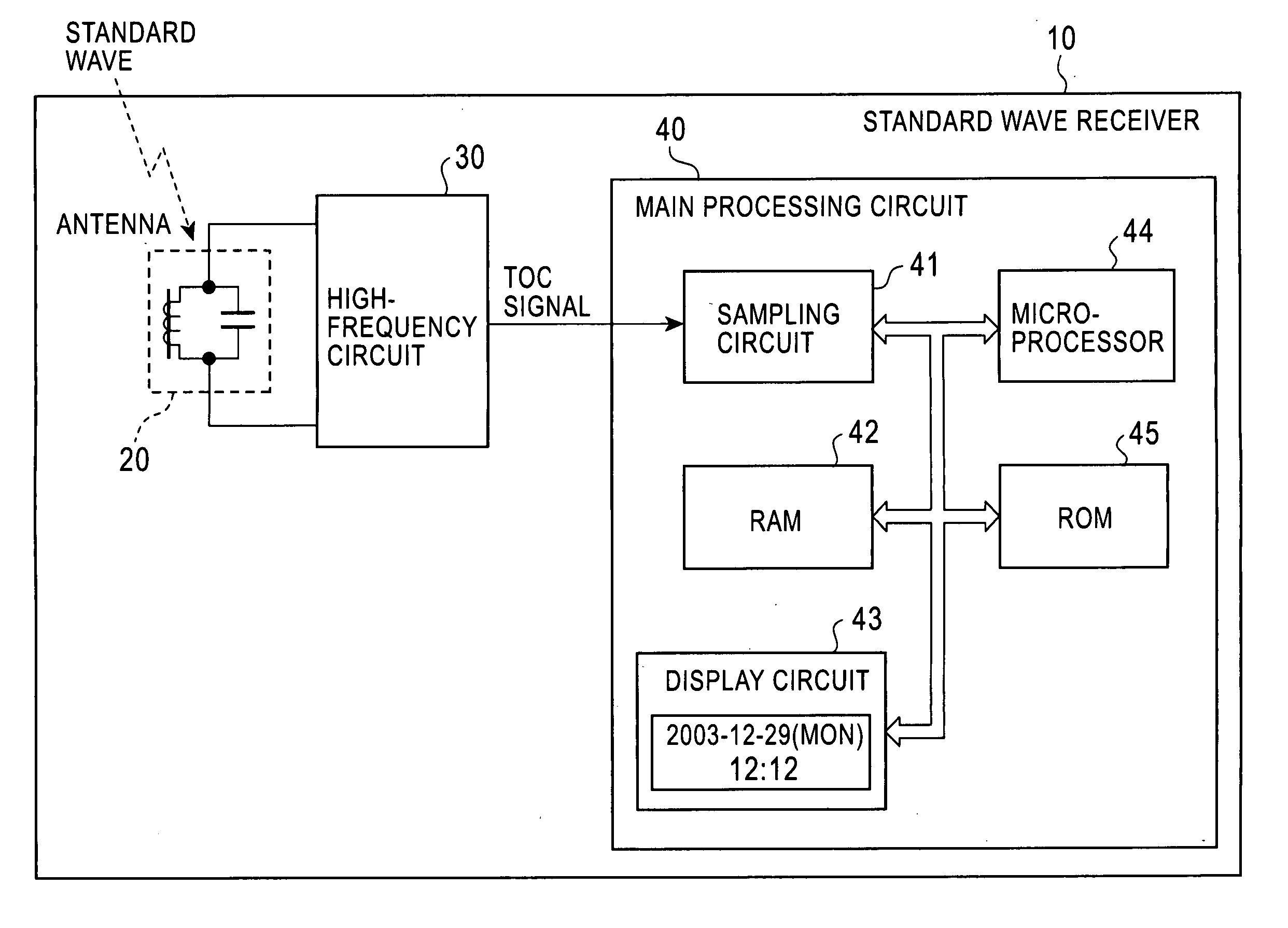
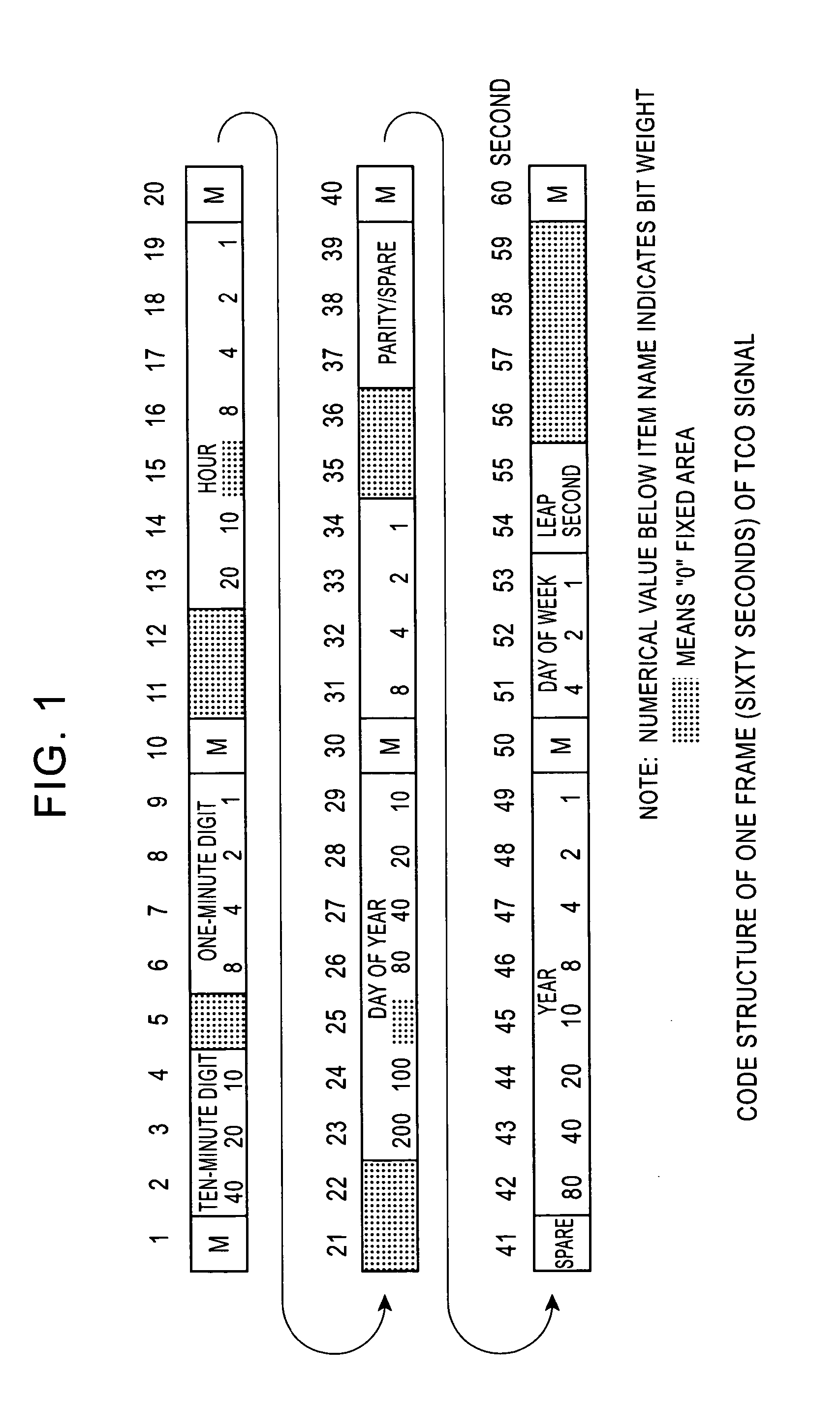
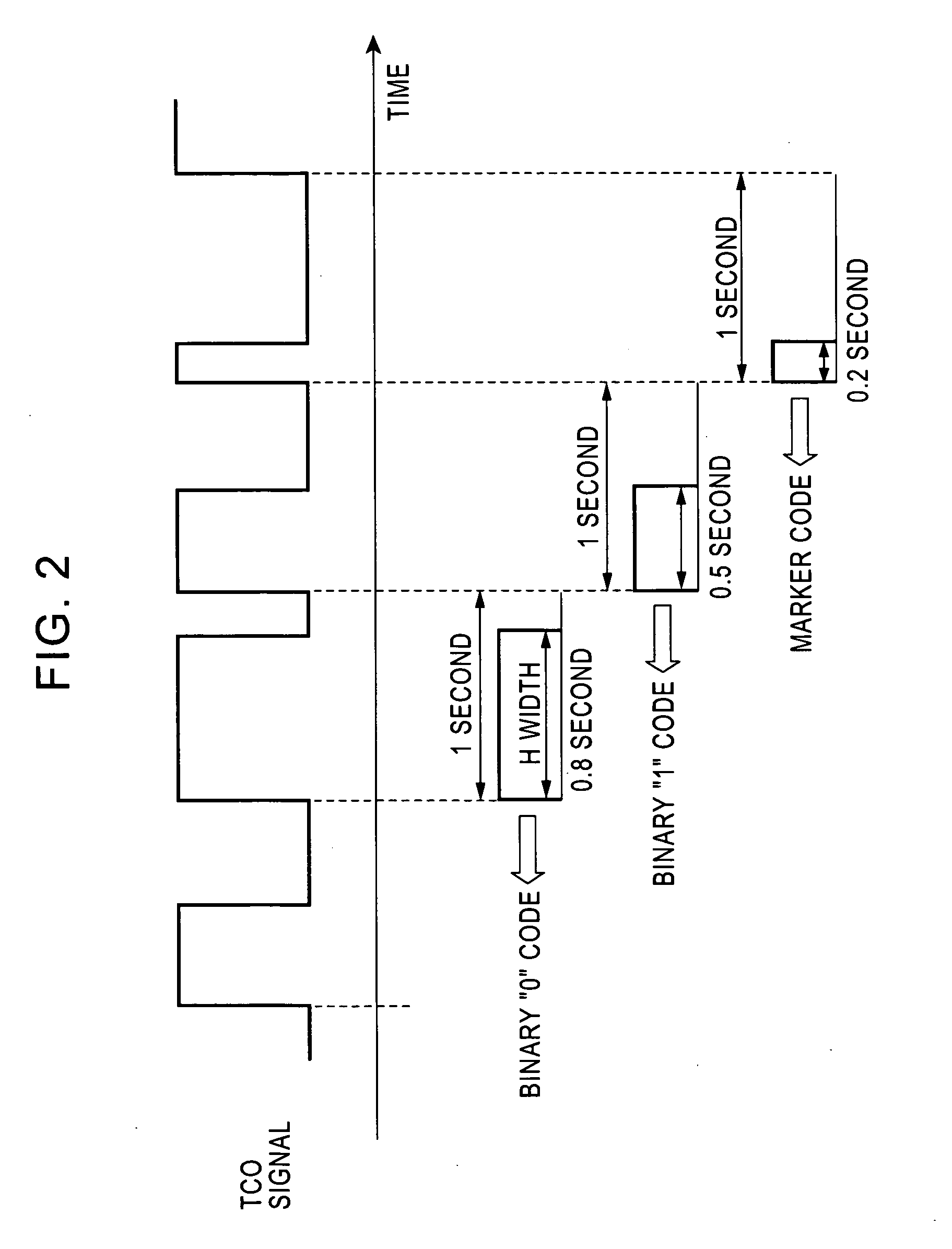
Standard time signal receiving time device and decoding method of time code signal
InactiveUS20050195690A1Accurate decodingSimple arithmetic processingSetting time indicationRadio-controlled time-piecesDecoding methodsComputer science
In a radio controlled clock and a decoding method of a time code signal, the time code signal can be accurately decoded irrespective of the mixture of noises and the deterioration of a radio wave signal receiving situation, and arithmetic processing is simple. A standard time signal is received and the time code signal superposed on this standard time signal is sampled at an interval of 50 ms and is stored to a memory. The stored sampling data are formed as a list in a data group every one second (20 samples). The plurality of data groups formed as a list are added every each sampling point, and a point for maximizing an increase change of the adding result is set to a synchronizing point of the sampling. Further, the correlation of the sampling data group and a code template pattern is calculated and a code shown by the sampling data group is judged.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
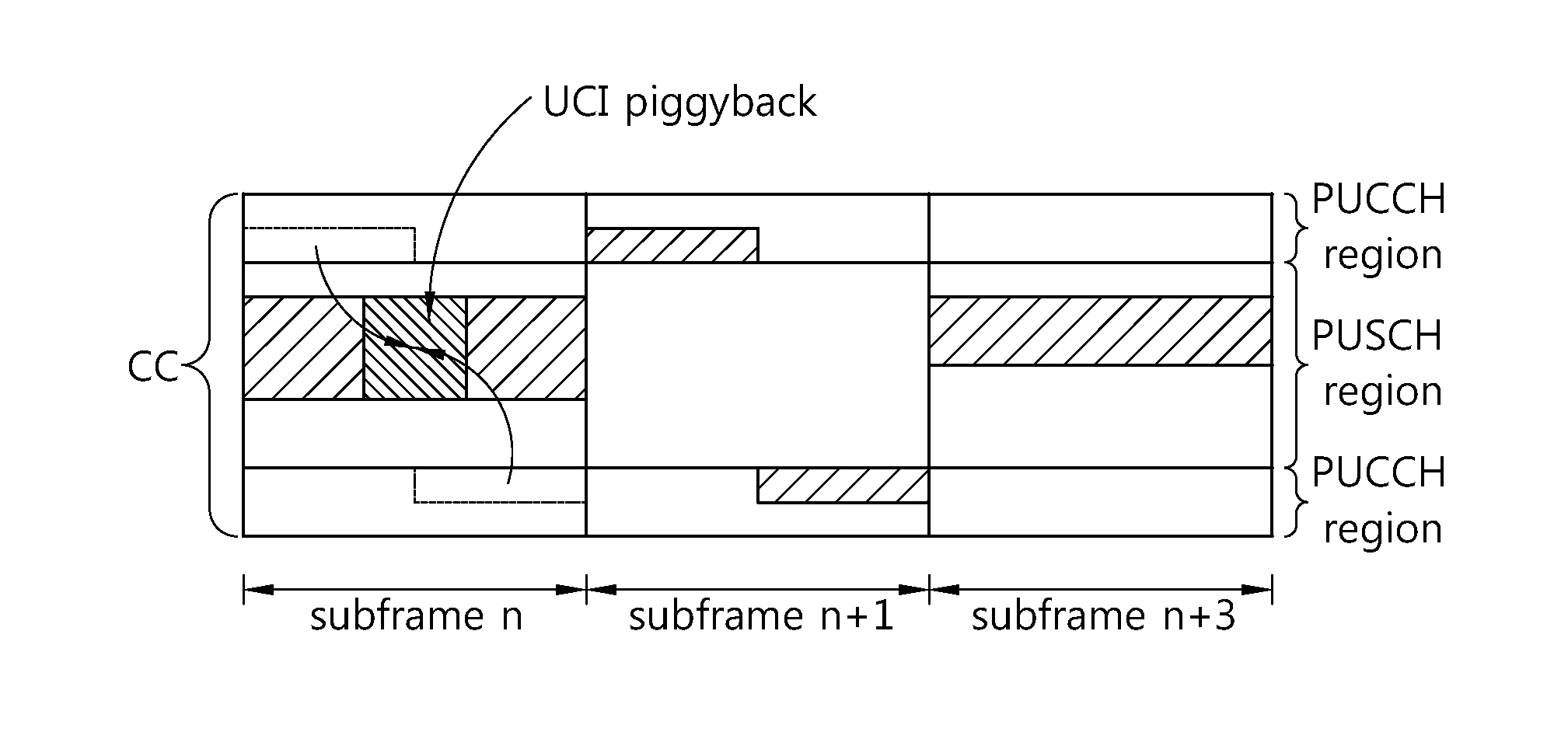
Method and apparatus for transmitting channel status information in carrier aggregation system
ActiveUS20130250903A1Accurate decodingNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionChannel state informationCarrier signal
Provided is a channel status information (CSI) transmission method performed by a user equipment in a carrier aggregation system. The method includes: allocating a plurality of serving cells; configuring a subframe predetermined to transmit CSI for a single serving cell among the allocated plurality of serving cells; and if uplink data transmission via a physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH) region exists in the configured subframe and if the single serving cell is deactivated, transmitting deactivation confirmation information for indicating that the single serving cell is deactivated via the PUSCH region together with the uplink data.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
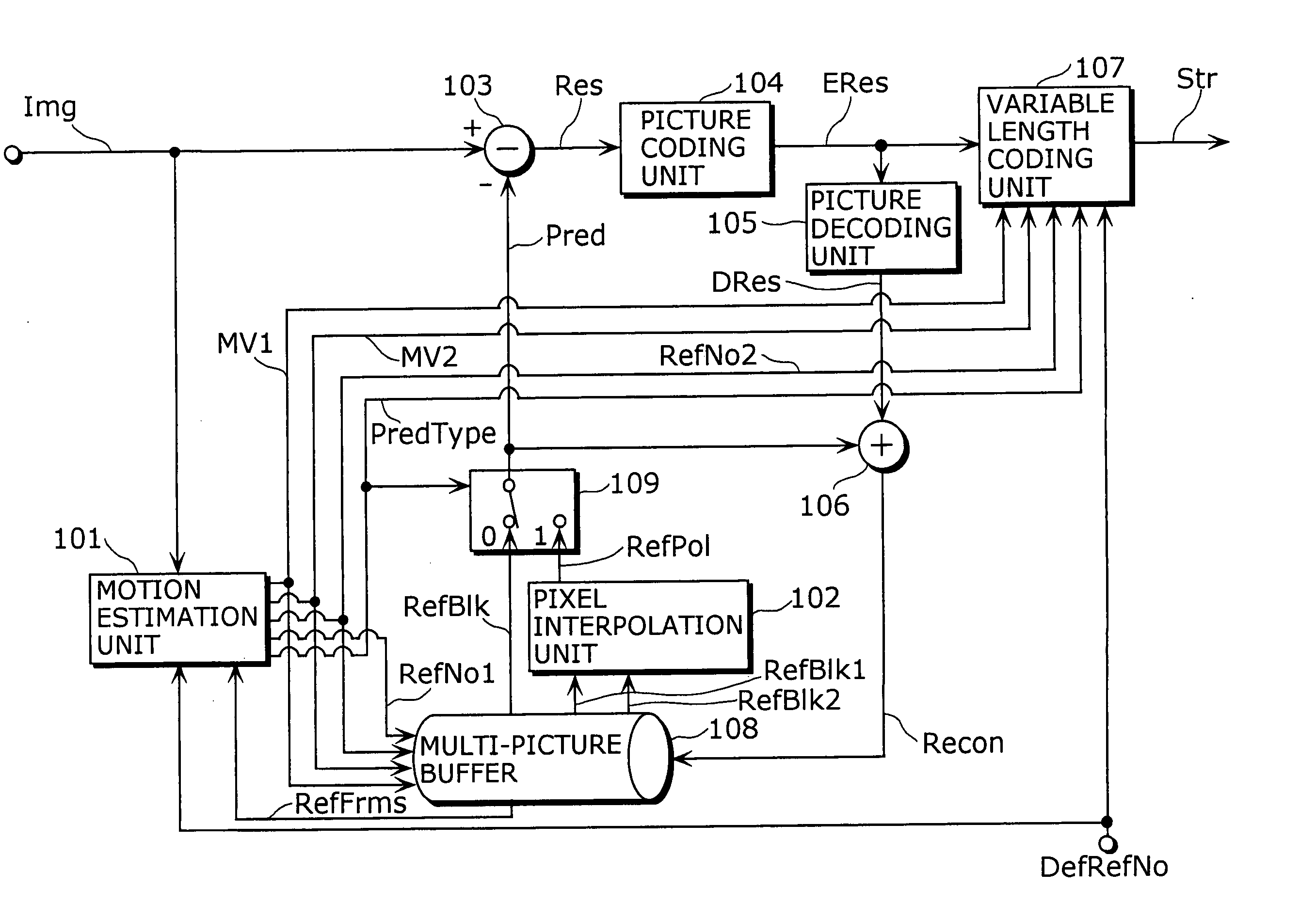
Moving picture coding method and a moving picture decoding method
ActiveUS20040146105A1Valid encodingReduce processing burdenColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVariable-length codePattern recognition
A moving picture coding apparatus includes a motion estimation unit (101) for performing motion estimation by fixing the one of two reference pictures as a reference picture indicated by an inputted default reference picture number DefRefNo and a variable length coding unit (107) for performing variable length coding on coded residual data ERes, a prediction type PredType, a reference picture number RefNo2 and motion vectors MV1, MV2 on a block-by-block basis, and outputting them as coded moving picture data Str.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Moving picture coding method, and moving picture decoding method
ActiveUS20070041451A1Correctly decodeAccurate decodingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorBitstream
According to the present invention, a moving picture coding apparatus (70) for performing inter-picture predictive coding for pictures constituting a moving picture is provided with a coding unit (103) for performing predictive error coding for image data; a decoding unit (105) for performing predictive error decoding for an output from the coding unit (103); a reference picture memory (117) for holding output data from the decoding unit (105); and a motion vector detection unit (108) for detecting motion vectors on the basis of the decoded image data stored in the memory. When coding a B picture as a target picture, information indicating whether or not the target picture should be used as a reference picture when coding another picture is added as header information. Therefore, in a decoding apparatus for decoding a bit stream Bs outputted from the moving picture coding apparatus (70), management of a memory for holding the reference picture can be facilitated on the basis of the header information.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
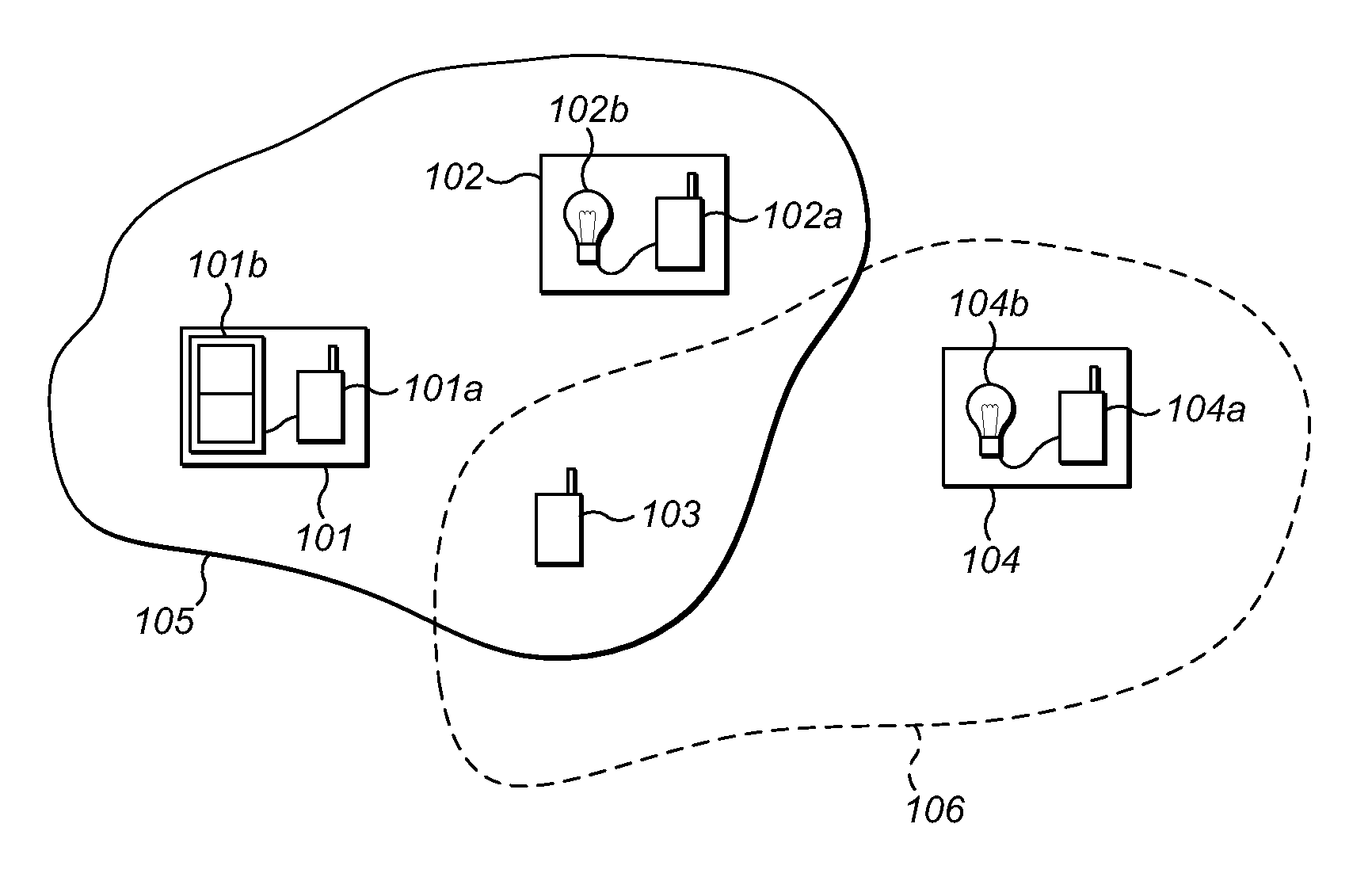
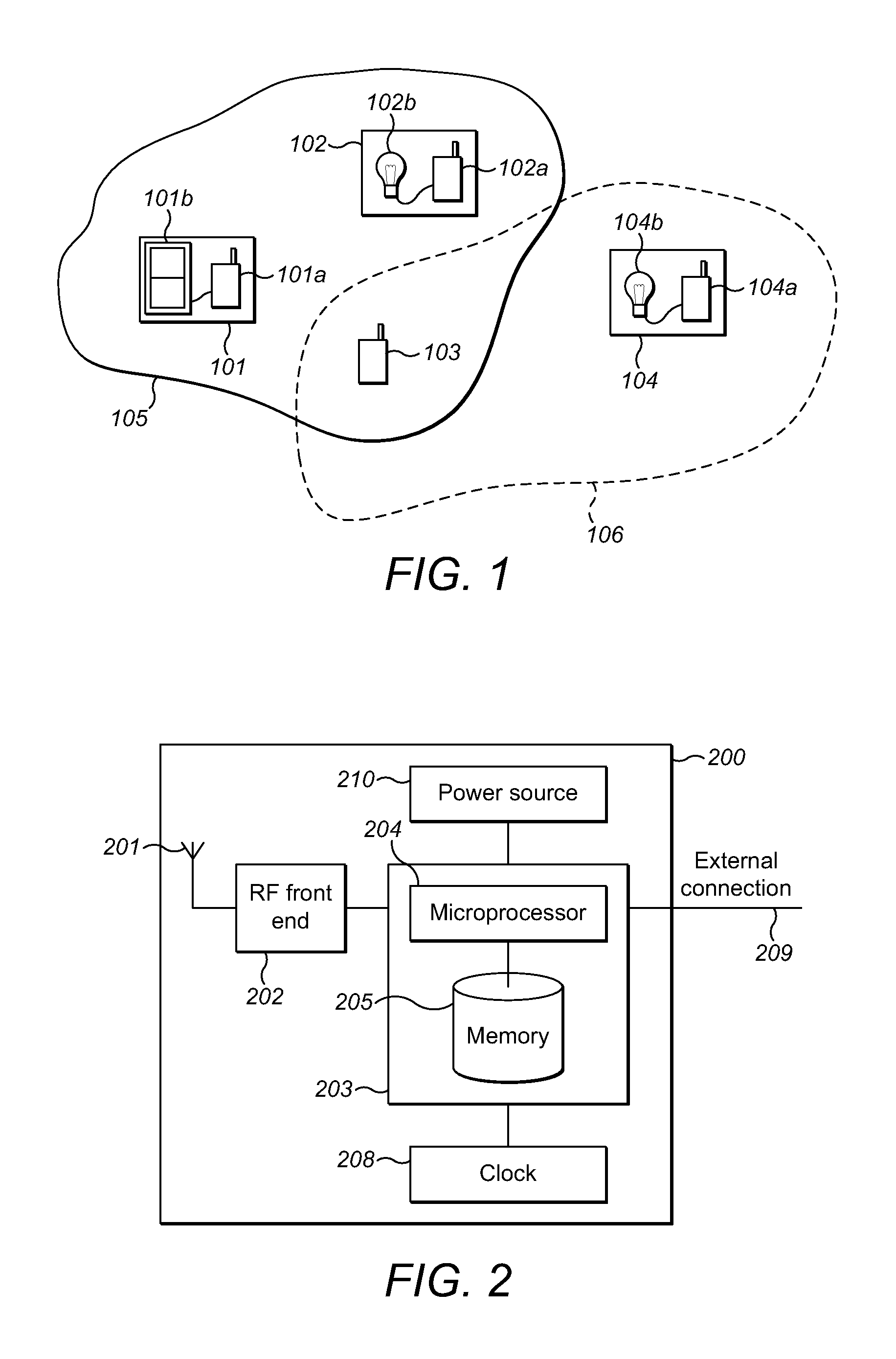
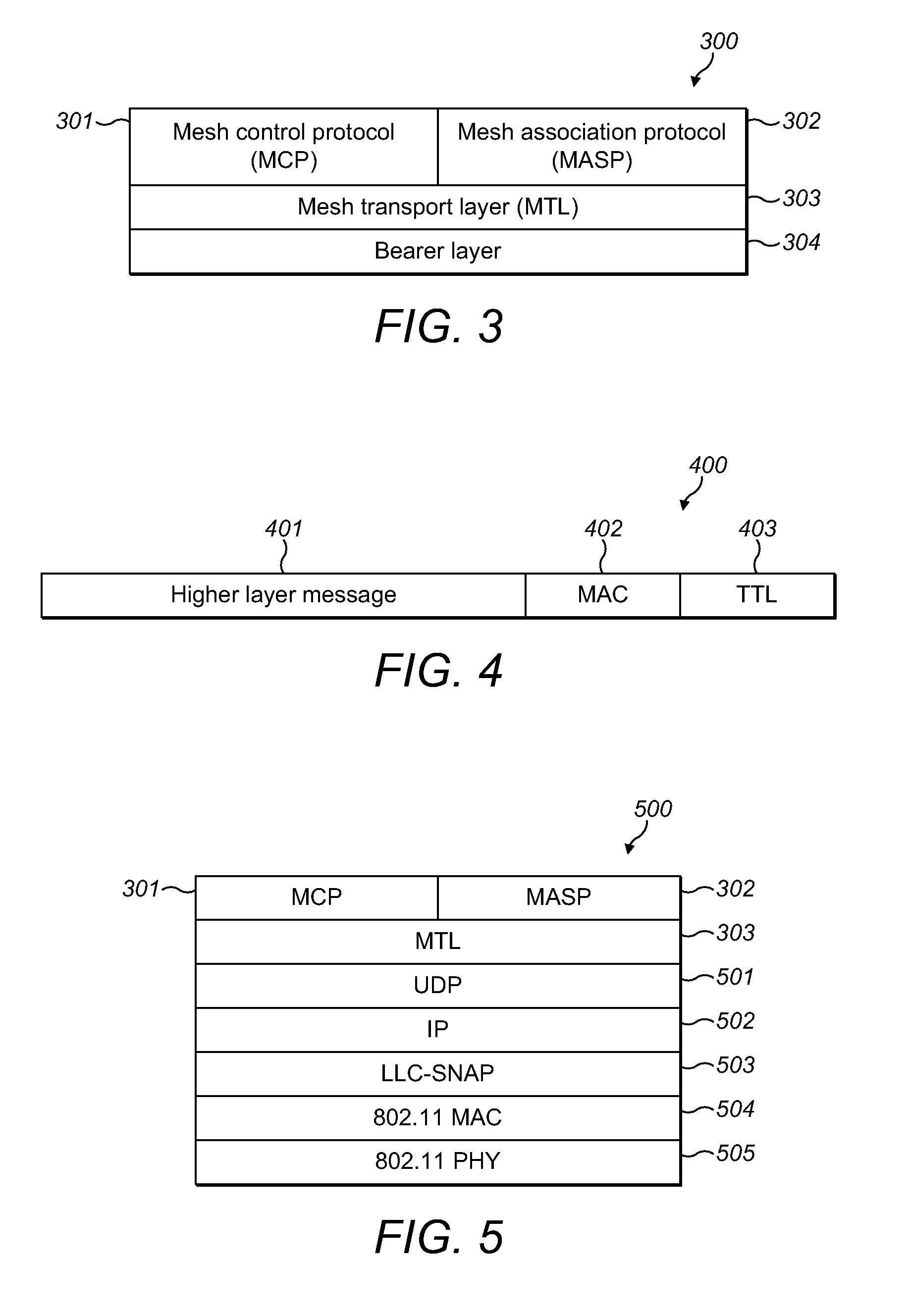
Communicating data over a mesh network
InactiveUS20150245351A1Accurate decodingNetwork topologiesBroadcast transmission systemsNetwork Communication ProtocolsNetwork data
A wireless communications device capable of operating according to a WLAN communications protocol, and capable of communicating in a mesh network. The wireless communications device may be configured to generate a mesh network data packet. The device may encapsulate the mesh network data packet in a WLAN data frame. The data frame may be constructed such that it is capable of being received and accurately decoded by WLAN-capable devices with which the wireless communications device has not established a WLAN communications connection. The device may then transmit the WLAN data frame.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECH INT
Standard wave receiver and time code decoding method
InactiveUS20060050824A1Accurate decodingTime-pieces with integrated devicesSetting time indicationConvolutionAlgorithm
A standard wave receiver and a time code decoding method, which receive a standard wave including a time code signal, in which one frame including plural time codes is repeated, and decode the time codes, are provided. The time code signal is sampled over a period, in which a plurality of the frames continue, and sampled value sequences including plural sampled values generated in time series are accumulated. The sampled value sequences are convolutionally added every predicted period of a marker code indicating a leading position of the frame to generate an added value sequence and a position of the marker code is determined on the basis of the added value sequence. Positions of the respective plural time codes are determined in accordance with the determined position of the marker code and, for each of the time codes, partial sampled value sequences, which corresponds to a position of the time code and is expected to take an identical value, is extracted out of the sampled value sequences, the partial sampled value sequences are convolutionally added to generate an added value sequence, and a value of the time code is determined on the basis of the added value. This makes it possible to decode a time code signal precisely even under an inferior reception environment.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
System and method to view crash dump information using a 2-d barcode
InactiveUS20100325490A1Accurate decodingAvoid excessive errorFault responseGraphicsRelevant information
In some embodiments, the invention involves a system and method for the generation and use of a compact crash dump that can be viewed and / or captured as a two-dimensional (2-D) high contrast graphical barcode. When an error is detected, machine context and other relevant information is formatted for entry to a barcode generator unit. The a barcode generator unit received formatted text or codes, and outputs a 2-D barcode for visible capture. The barcode image is ultimately transformed into an electronic image which may be sent to an error reporting site, or individual. The error reporting site uses a decoding unit to decode the high contrast graphical image of the 2-D barcode. The resulting decoded information provides an analyst, or automated system with information relevant to debugging the error. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:ANVIN H PETER +1
Signal transmission method for estimating phase noise in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20190081844A1Accurately decodedMinimize overheadSpatial transmit diversityTransmission path divisionData channelBase station
Disclosed are a signal transmission method and a base station, the method: generating a PCRS used in order to remove phase noise from a downlink signal; mapping the PCRS at predetermined intervals on a region, in which a data channel is mapped, in a downlink resource region; and transmitting the PCRS to a terminal.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Quantization-Based Data Embedding in Mapped Data
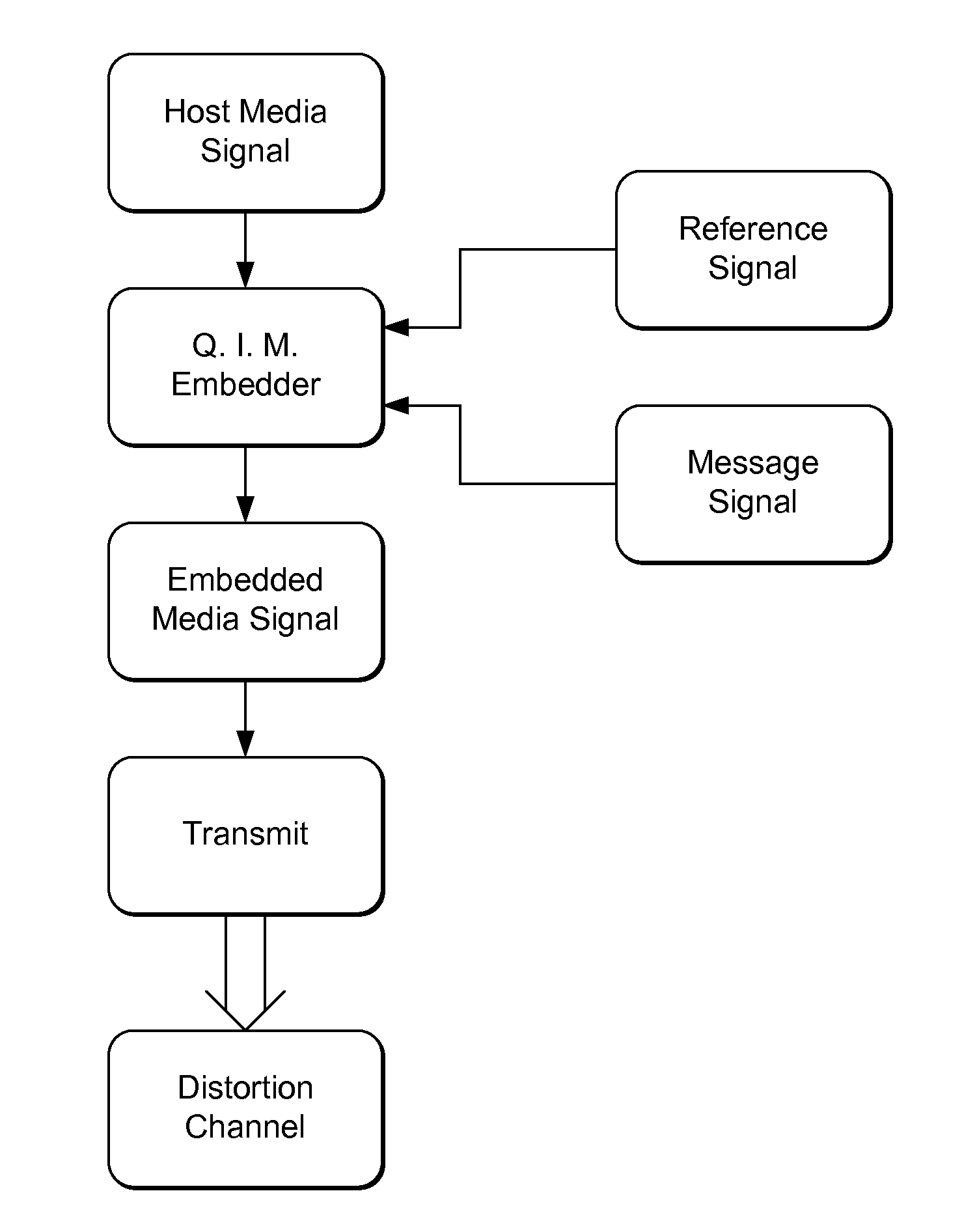
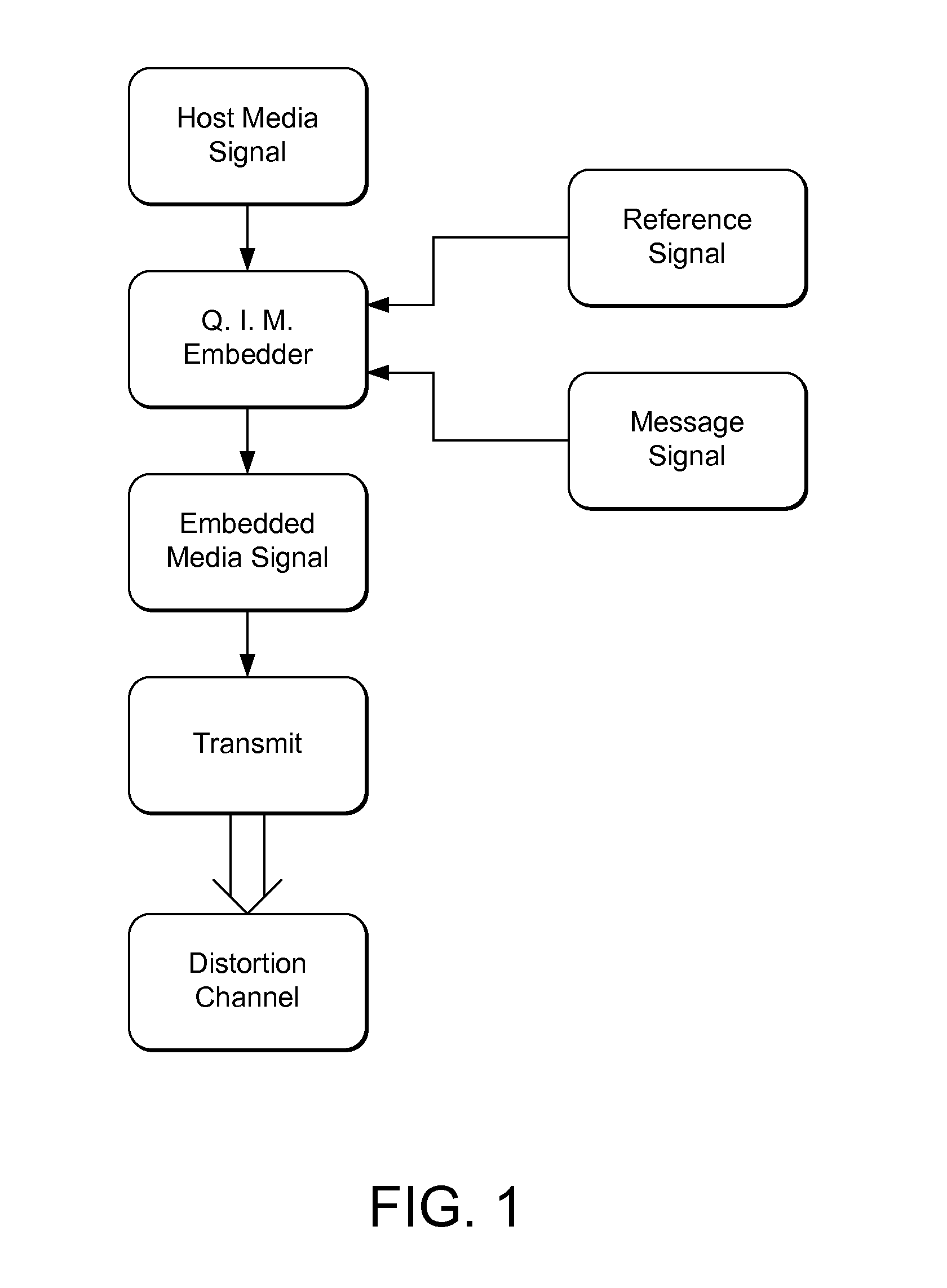
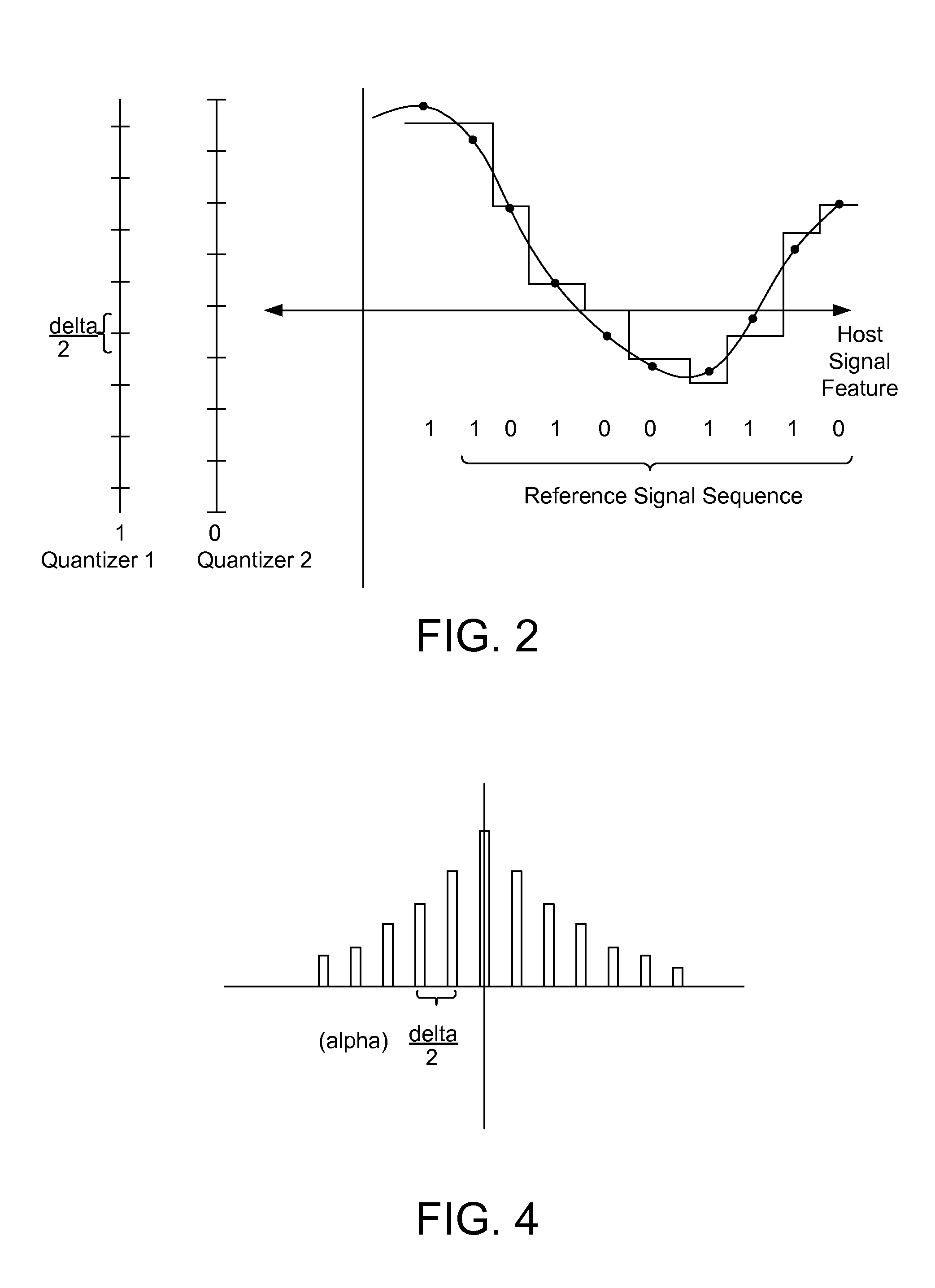
InactiveUS20110044494A1Reduce errorsReduce the impactSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmDistortion
Novel methods and systems for quantization based data embedding and reading in host signals, such as image, audio and video signals. To embed auxiliary data in a host signal, an embedder maps the host signal from a first domain into a mapped signal in a second domain. The embedder performs quantization based embedding of auxiliary data into the host signal using quantizers. The quantizers are adapted such that the relationship between corresponding quantizers in the first and second domains satisfies a predetermined constraint. The mapping improves the robustness of the data embedding method by increasing the chances that the embedded data can be recovered by an auxiliary data reader after modifications. A related embedding method projects the mapped signal unto a vector, and specifically, a pseudorandom vector. It performs quantization based embedding on the projected signal. The use of this projection provides added robustness of the embedded data to noise and other forms of distortion.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Systems and methods for financial transaction through miniaturized card with ASIC
ActiveUS9016572B2Improve reliabilityMore accurate card swipesFinancePayment architectureElectricityFinancial transaction
Owner:BLOCK INC
Motion vector coding and decoding methods
ActiveUS20080063077A1Improve coding efficiencyAccurate decodingPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDecoding methodsMotion vector
A motion vector coding method and apparatus that improves efficiency of coding motion vectors when a current block is coded using a plurality of motion vectors. The apparatus includes a motion vector coding unit that codes a motion vector inputted from a motion vector detecting unit. A motion vector for each current block is coded based on a difference between the motion vector and a predicted vector obtained from motion vectors for previously coded neighboring blocks. The predicted vector is generated by one of the following processes: (A) the motion vectors which refer to the same picture are selected from among the motion vectors for the neighboring blocks so as to generate the predicted vector; (B) the motion vectors for the respective neighboring blocks are ordered in the predetermined order, and the motion vectors of the same order rank are selected from the ordered motion vectors so as to generate the predicted vector; and (C) the predicted vector for the second motion vector of the current block shall be the first motion vector, and if the second motion vector and the first motion vector refer to different pictures, the first motion vector is scaled according to the temporal distance between the pictures so as to generate the predicted vector.
Owner:TAGIVAN II
Access channel structure for wireless communication system
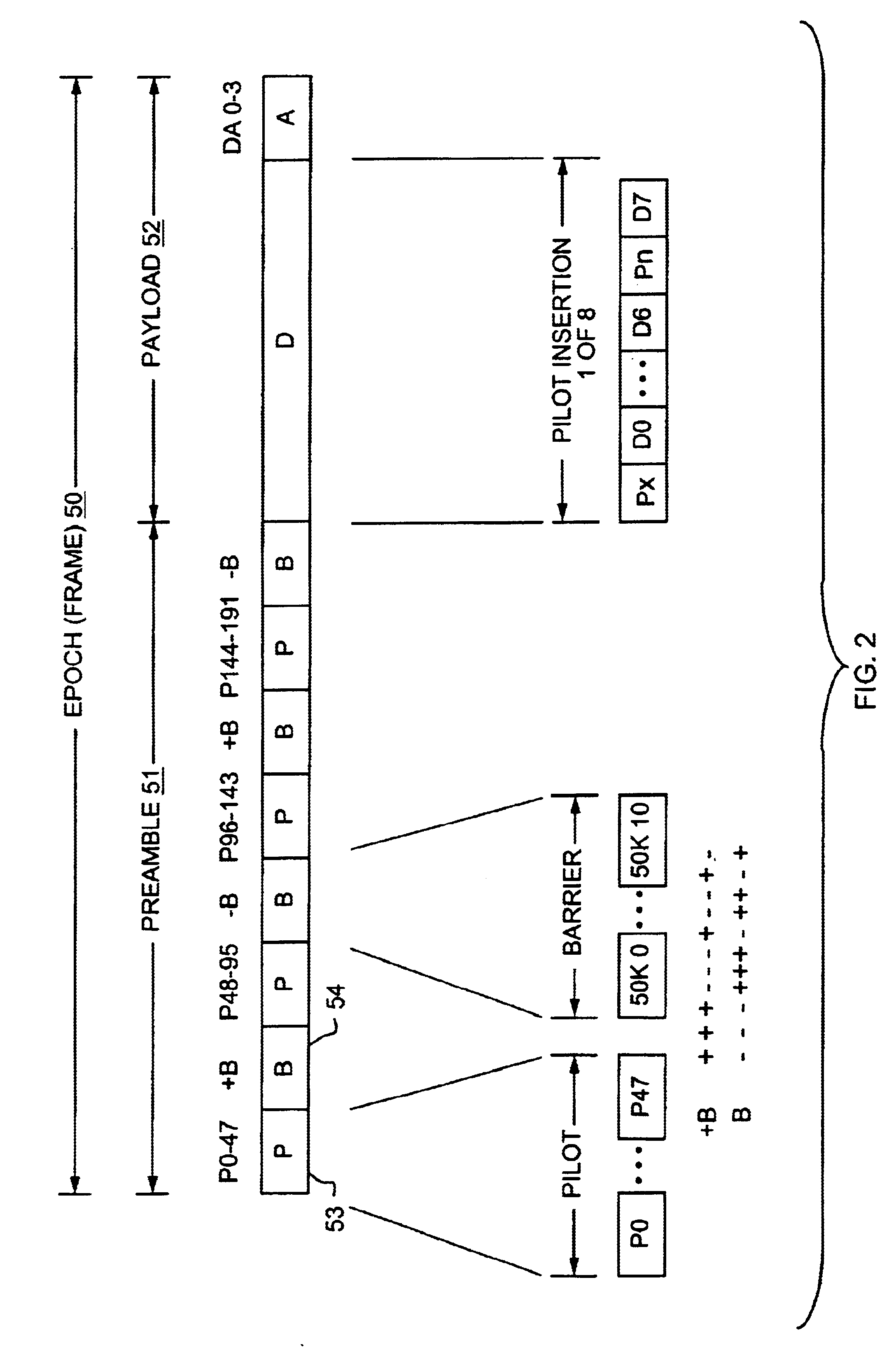
InactiveUS6904079B2Undo effectEasy to optimizeTransmission control/equlisationFrequency-division multiplex detailsPreambleWireless communication systems
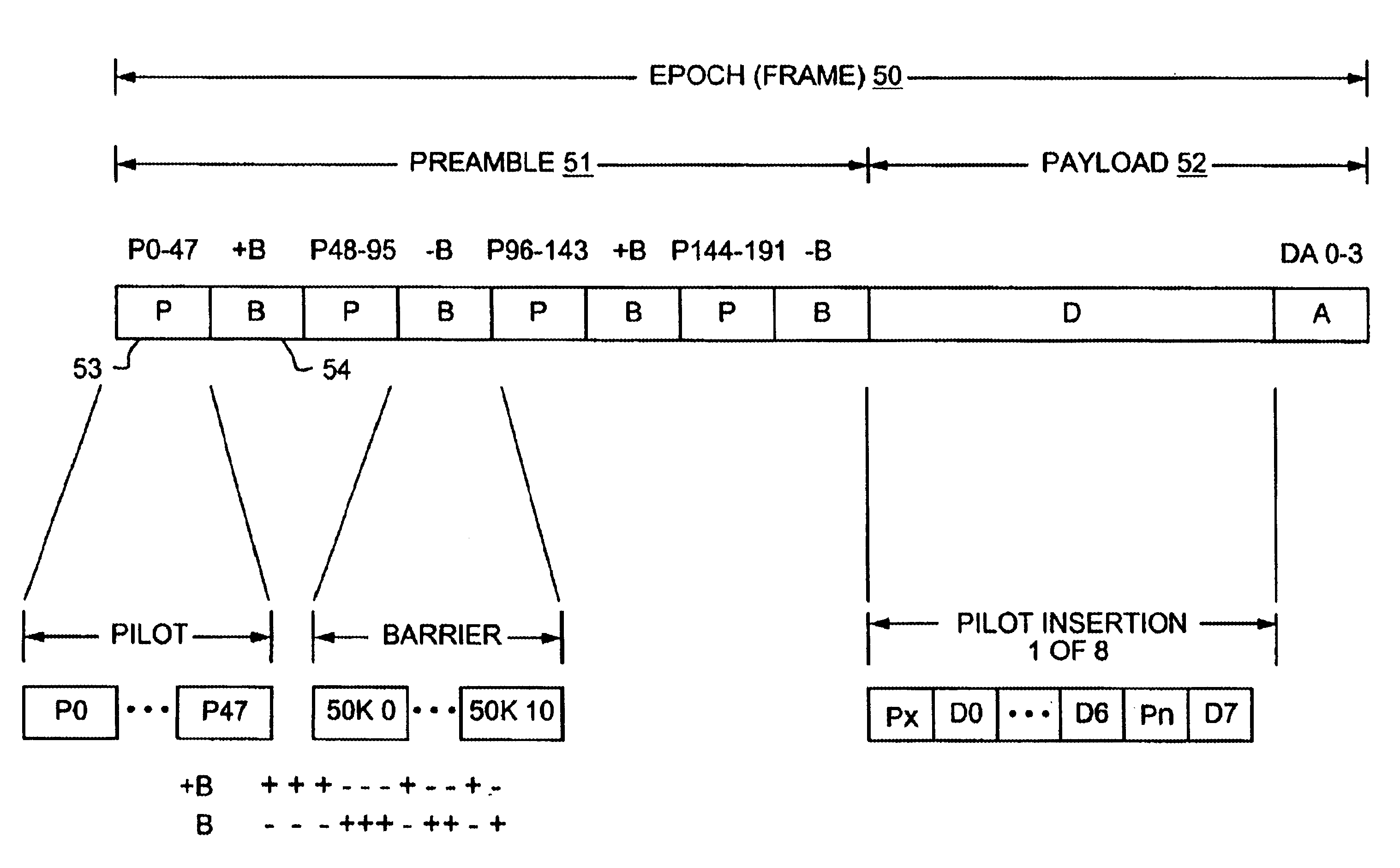
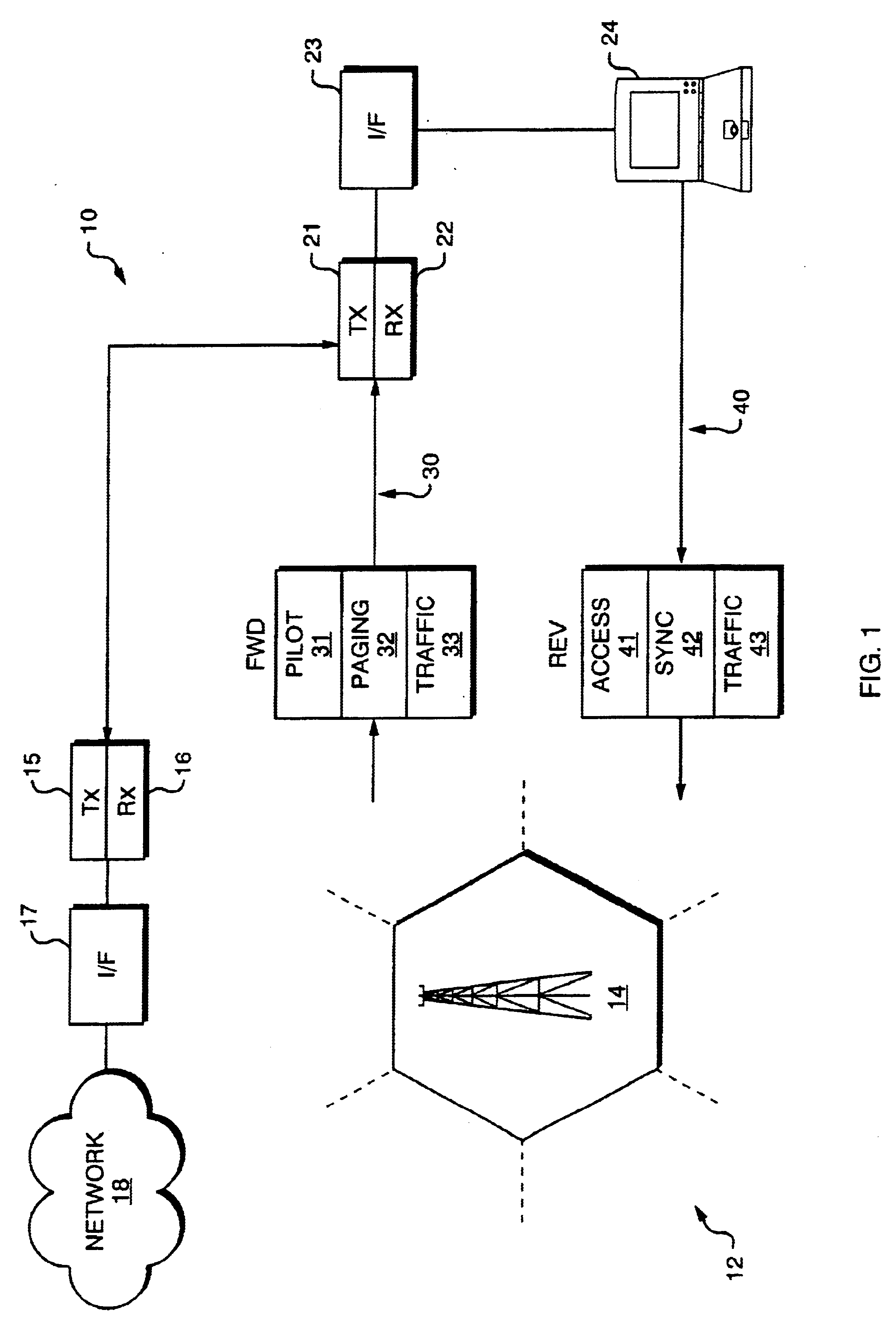
A technique for efficient implementation of pilot signals on a reverse link in a wireless communication system. An access channel is defined for the reverse link such that within each frame, or epoch, a portion is dedicated to sending only pilot symbols. Another portion of the frame is reserved for sending mostly data symbols; however, within this second portion of the frame, additional pilot symbols are interleaved among the data symbols. The pilot symbol or preamble portion of the access channel frame allows for efficient acquisition of the access signal at the base station, while providing a timing reference for determining the effects of multipath fading. In particular, a pilot correlation filter provides a phase estimate from the pilot symbols in the preamble portion, which is then used to decode the data symbols in the payload portion. An access acquisition portion of the receiver uses the phase estimates provided by the pilot correlation filter to process the output of a data symbol correlation filter. The additional pilot symbols embedded in the payload portion are used in a cross product operation to further resolve the effects of multipath fading.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com