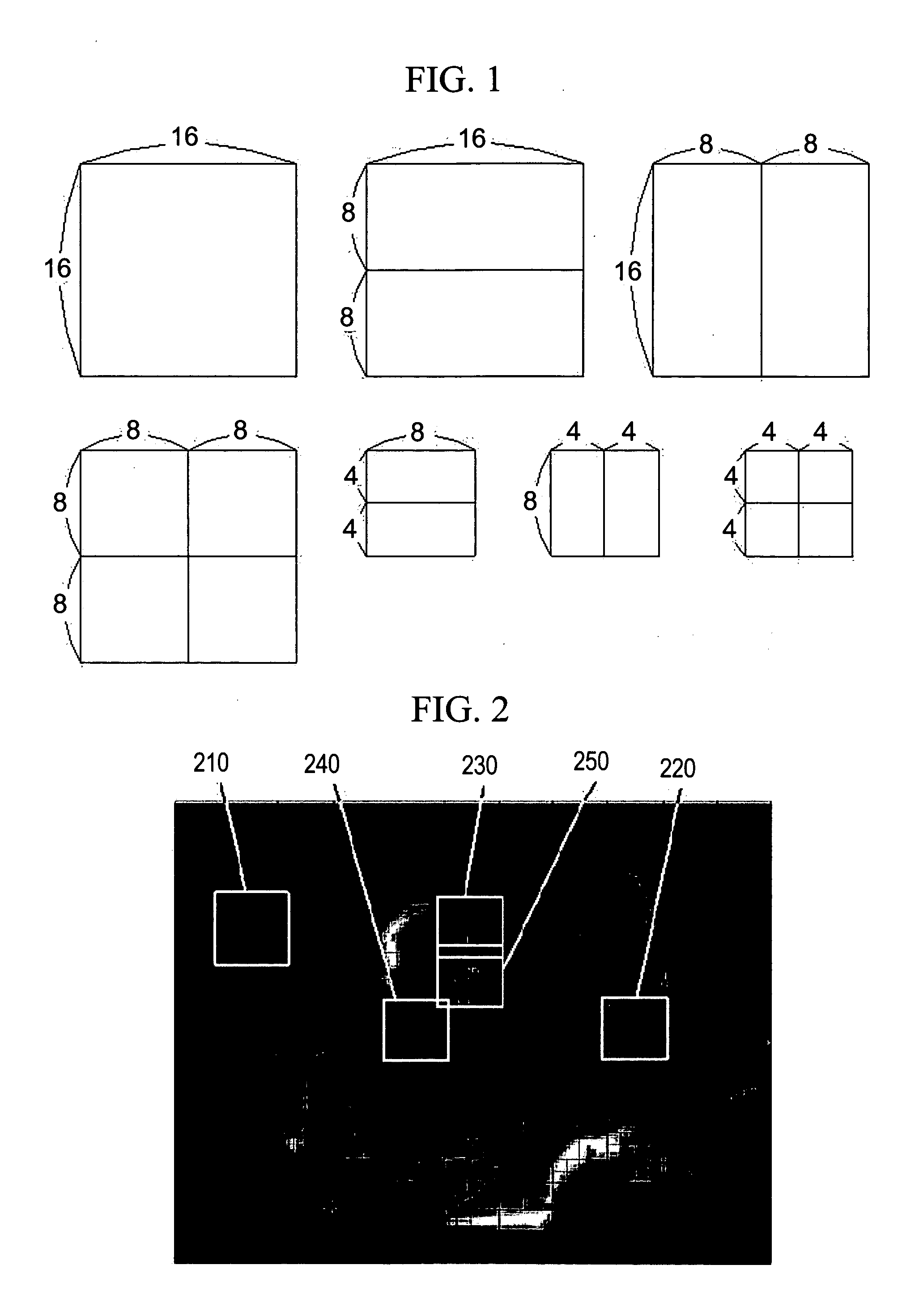
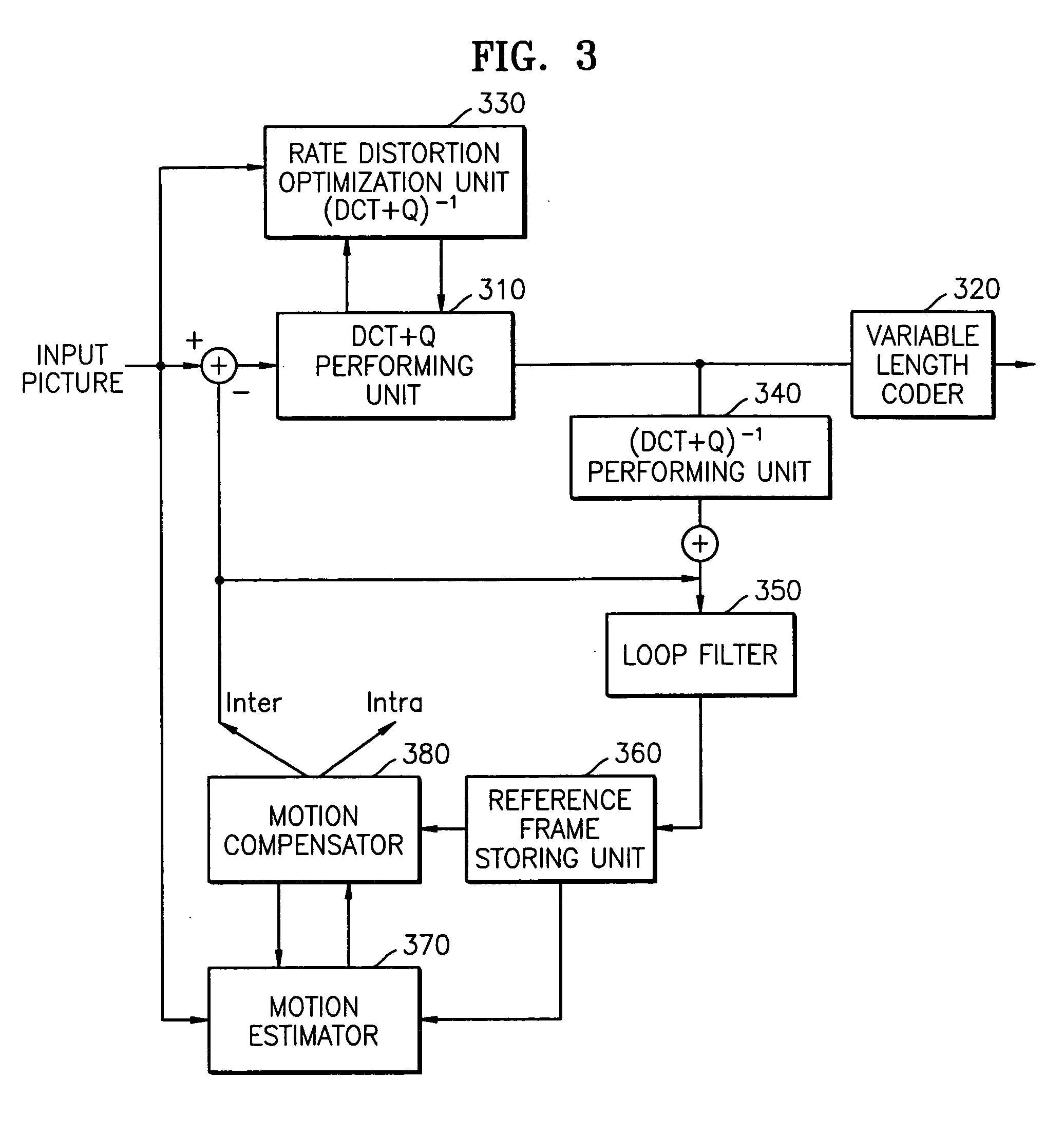
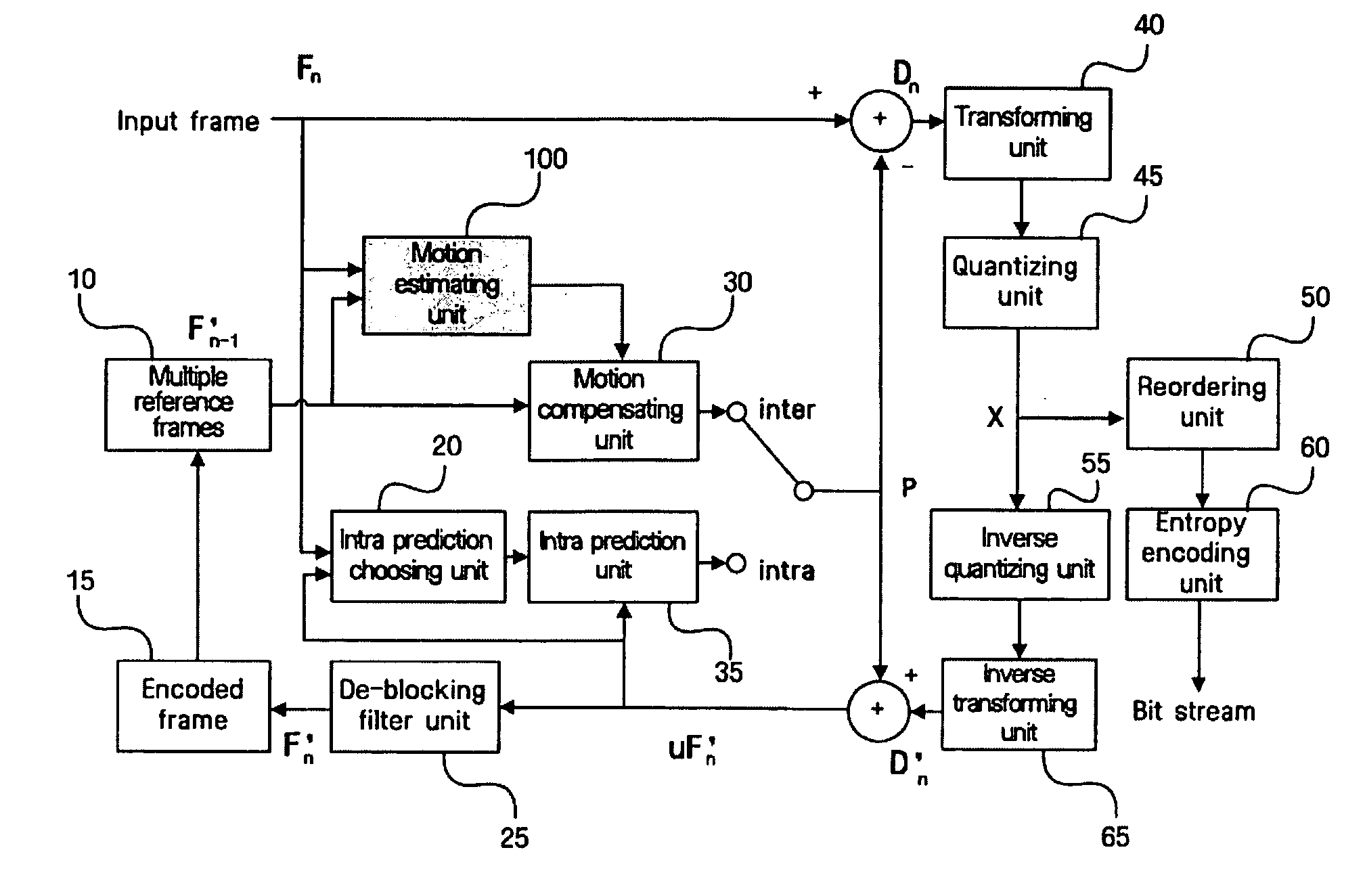
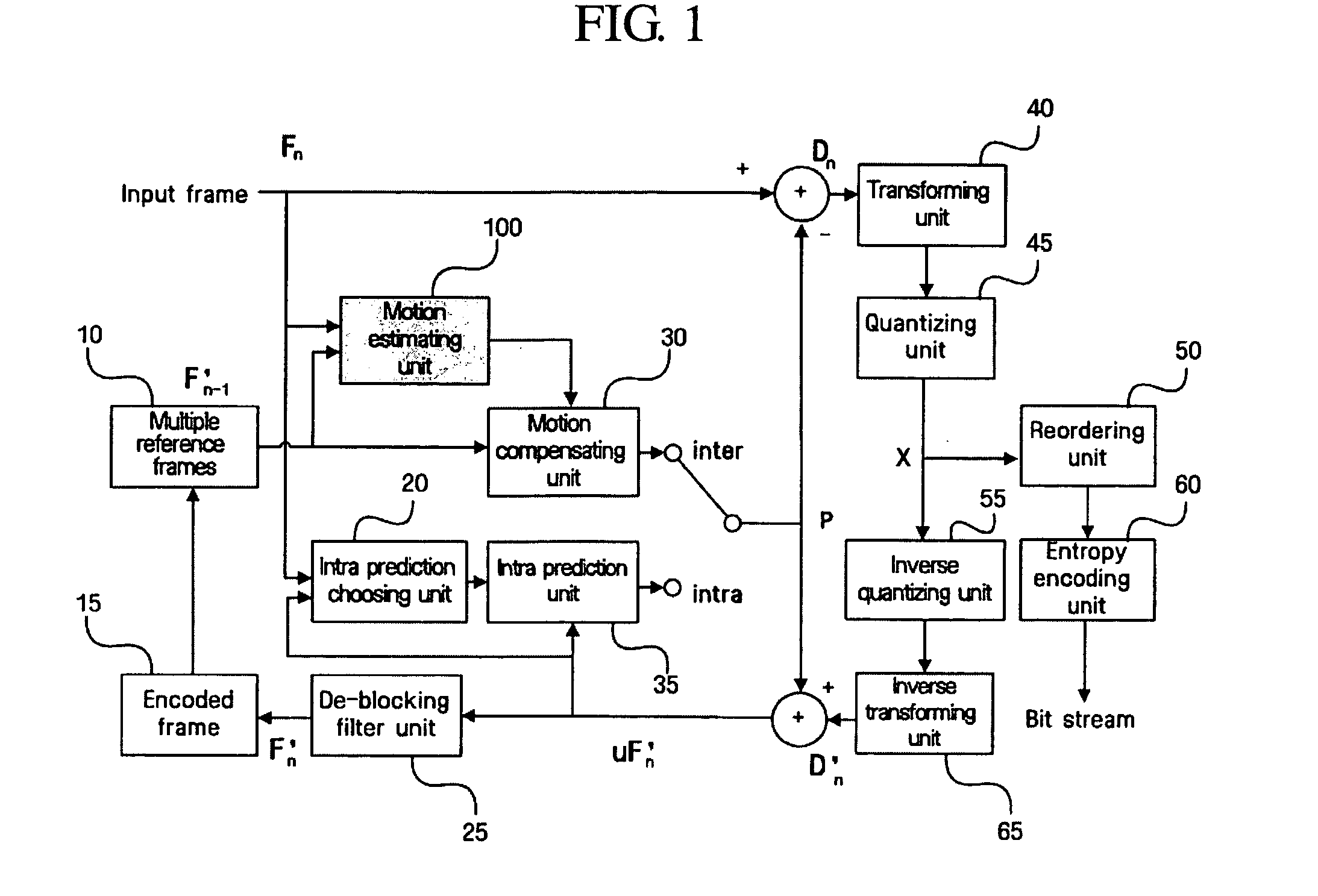
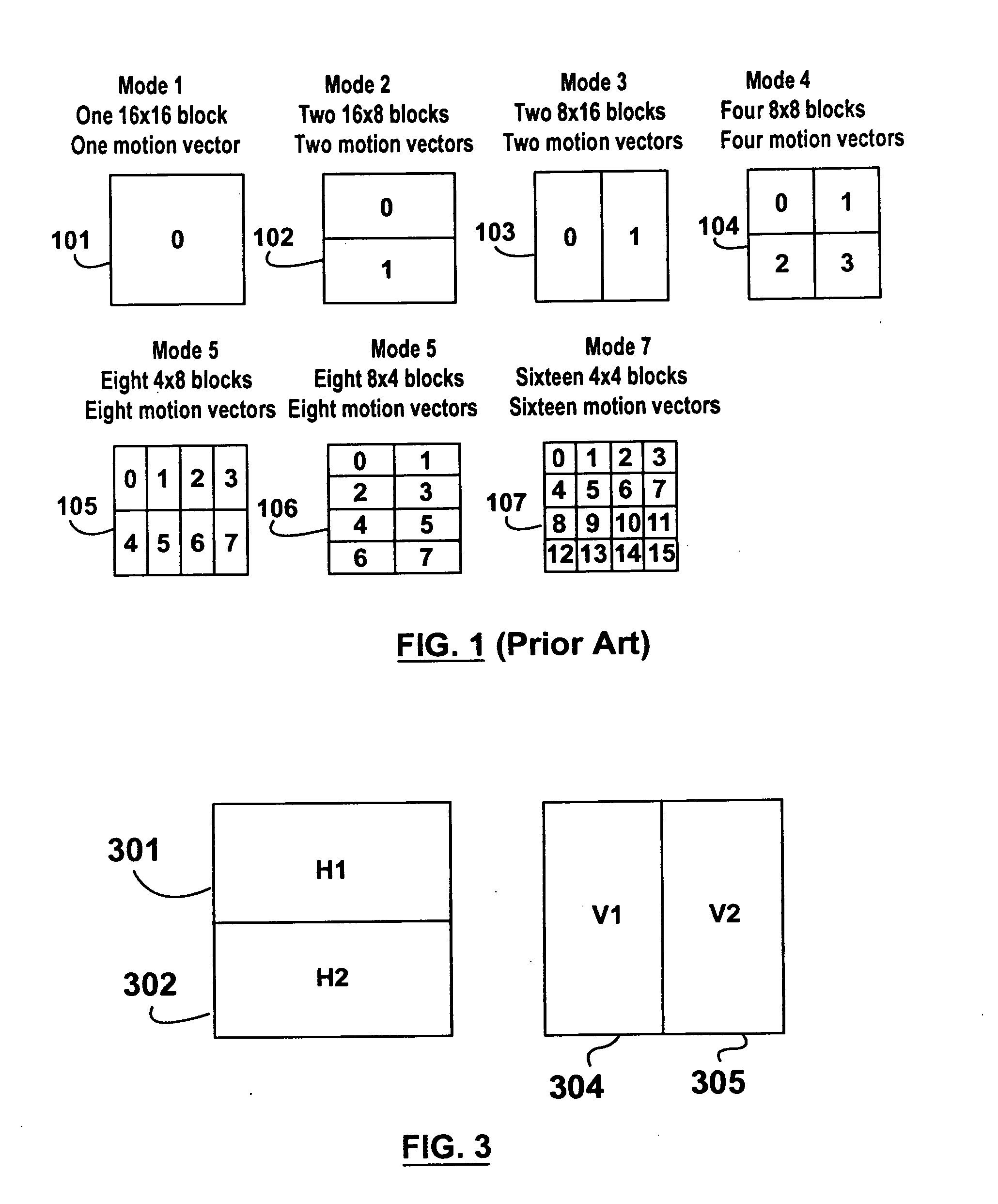
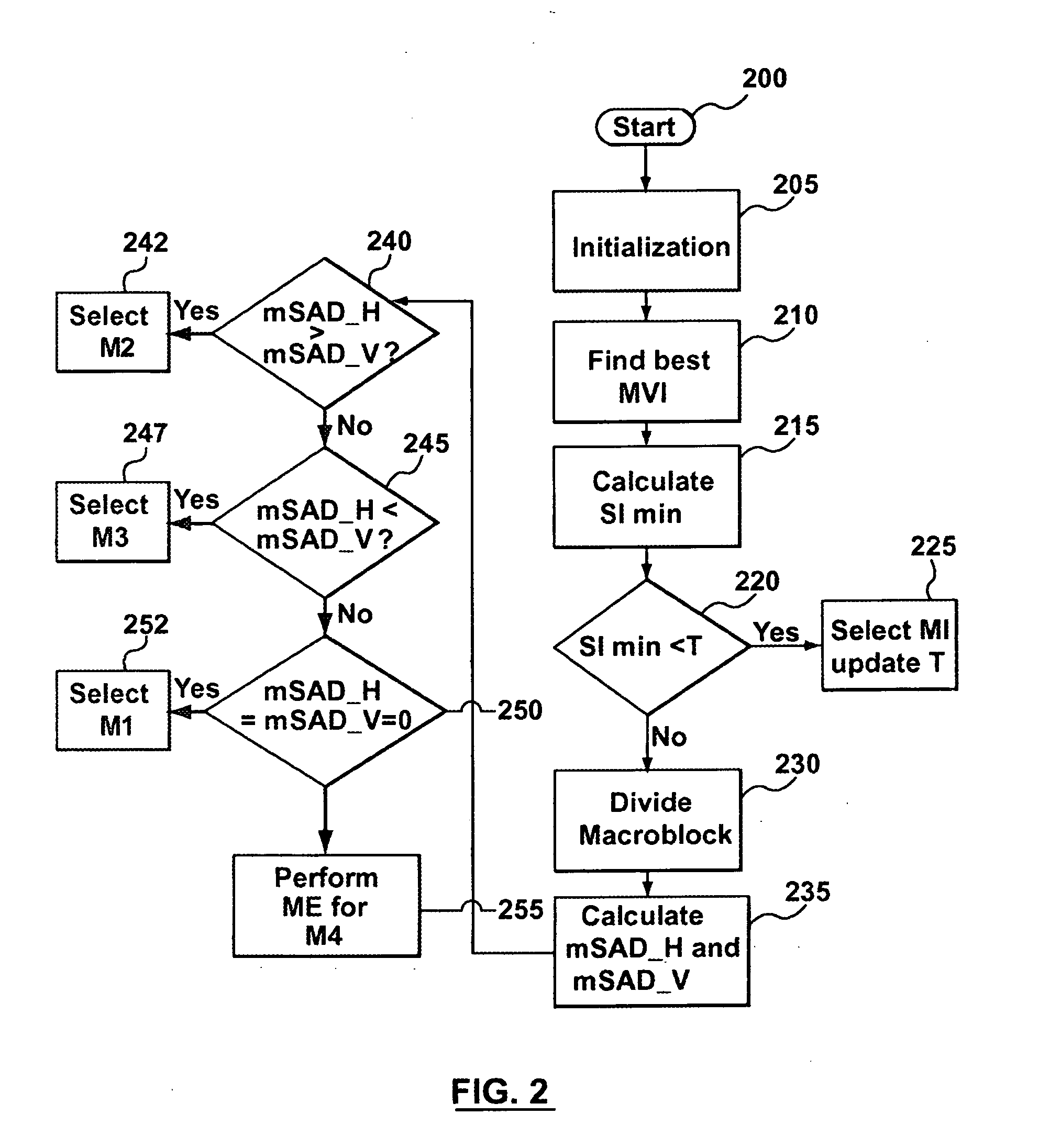
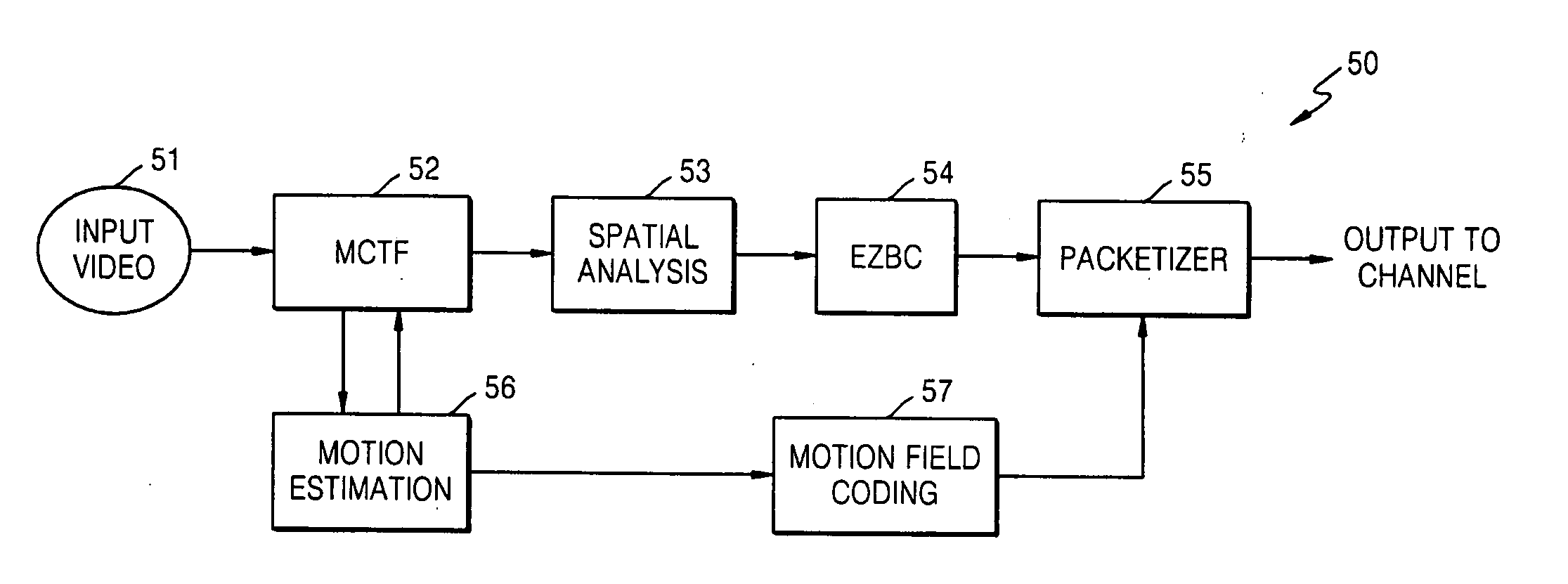
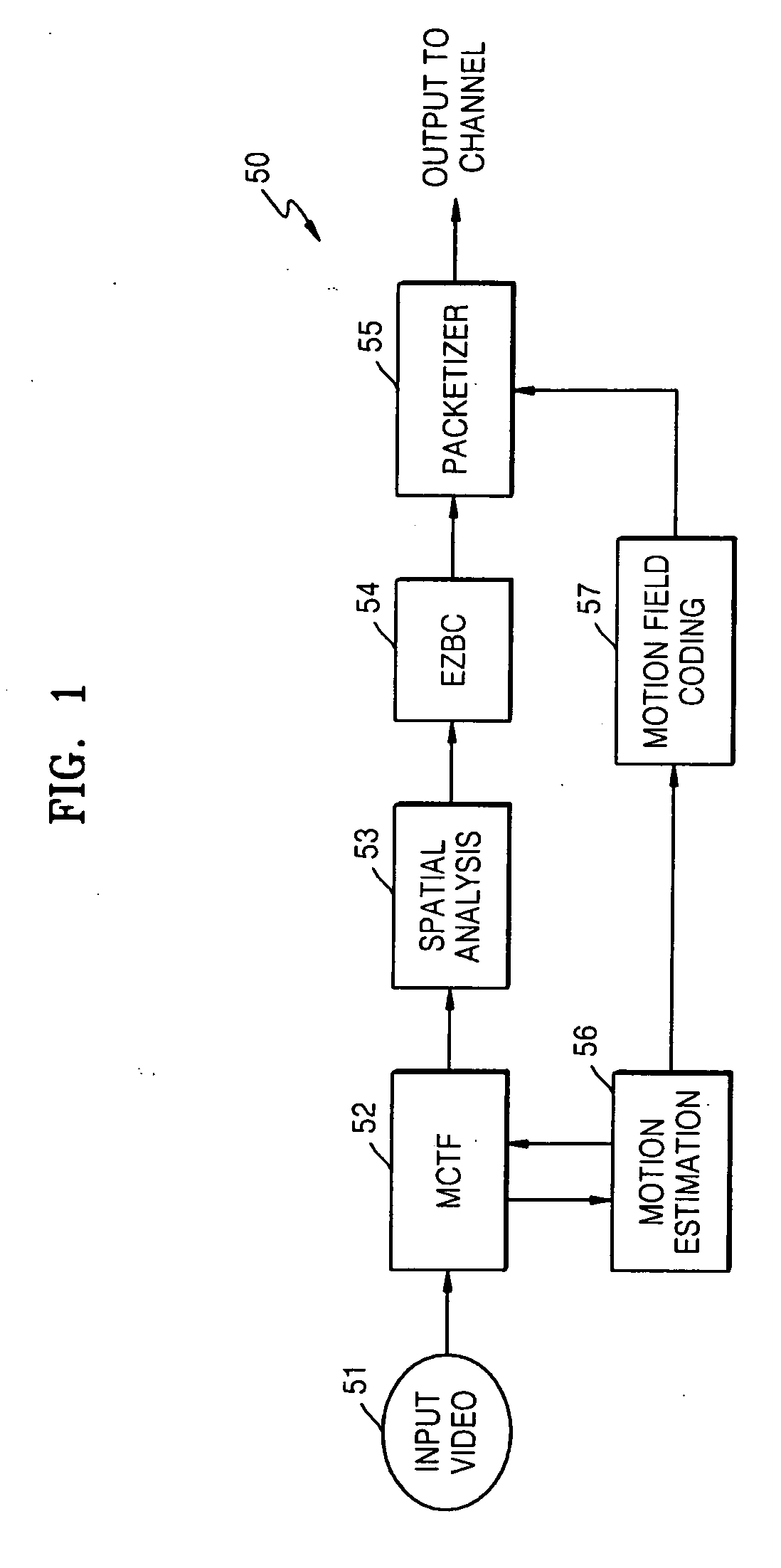
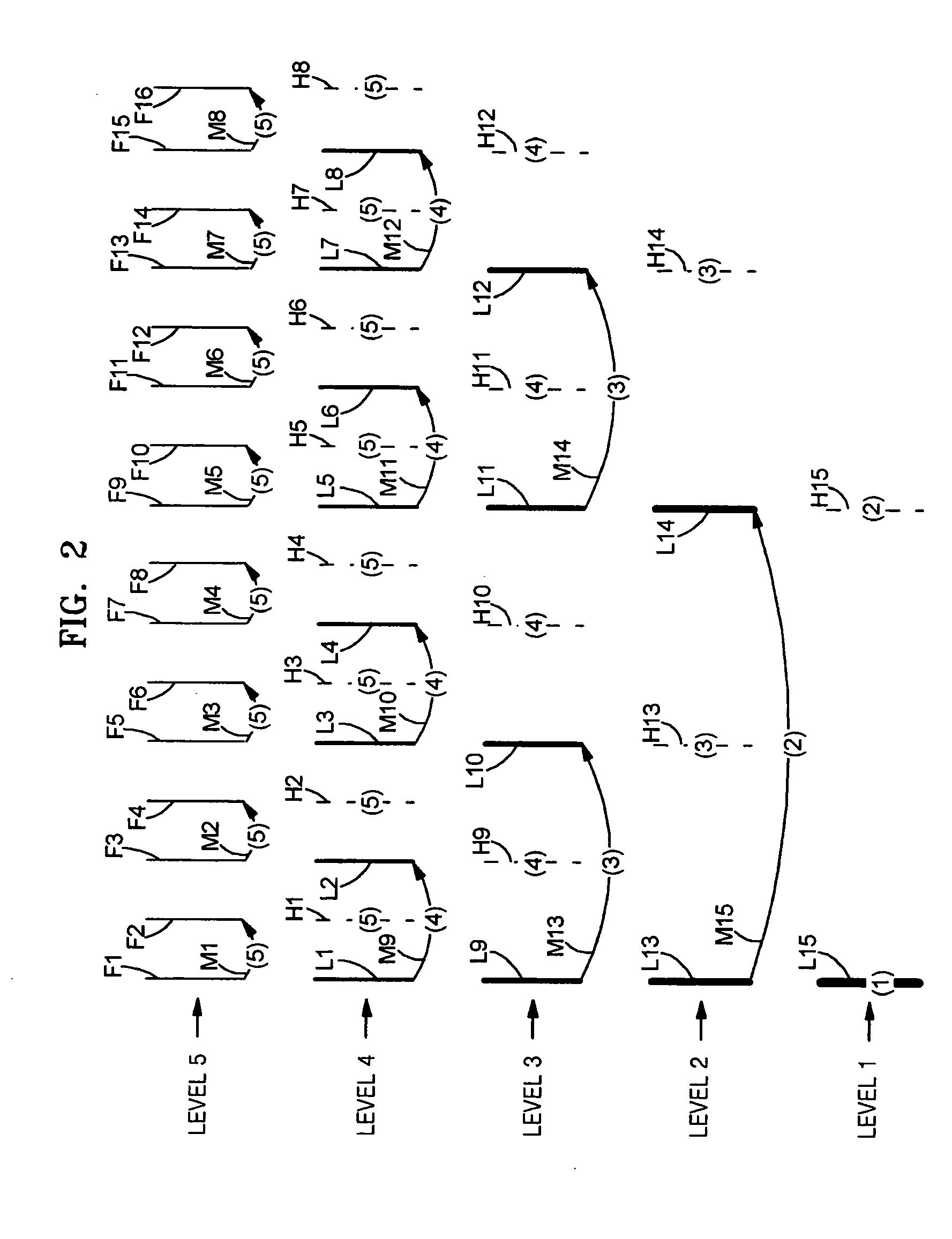
Patents
Literature
2269 results about "Motion estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
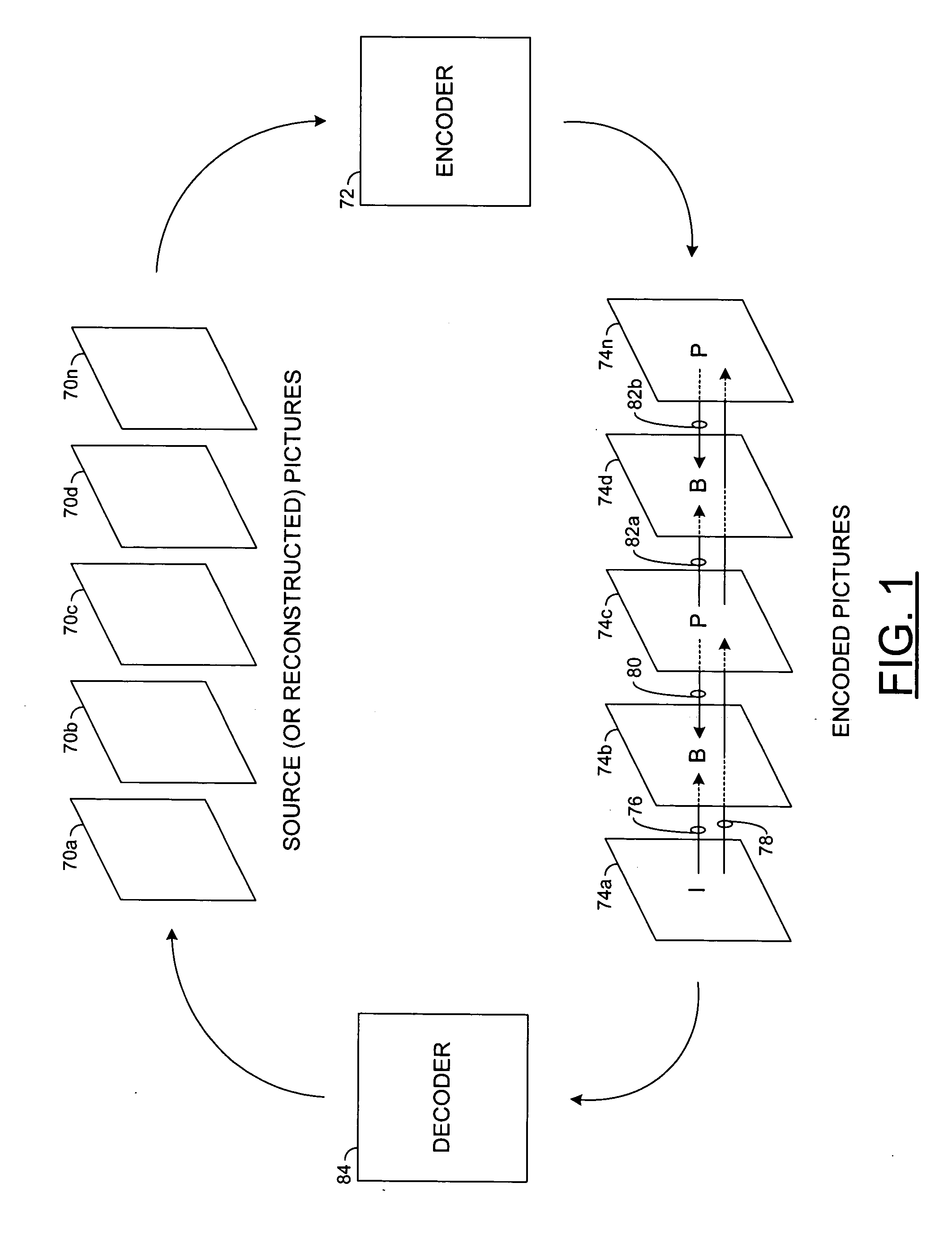
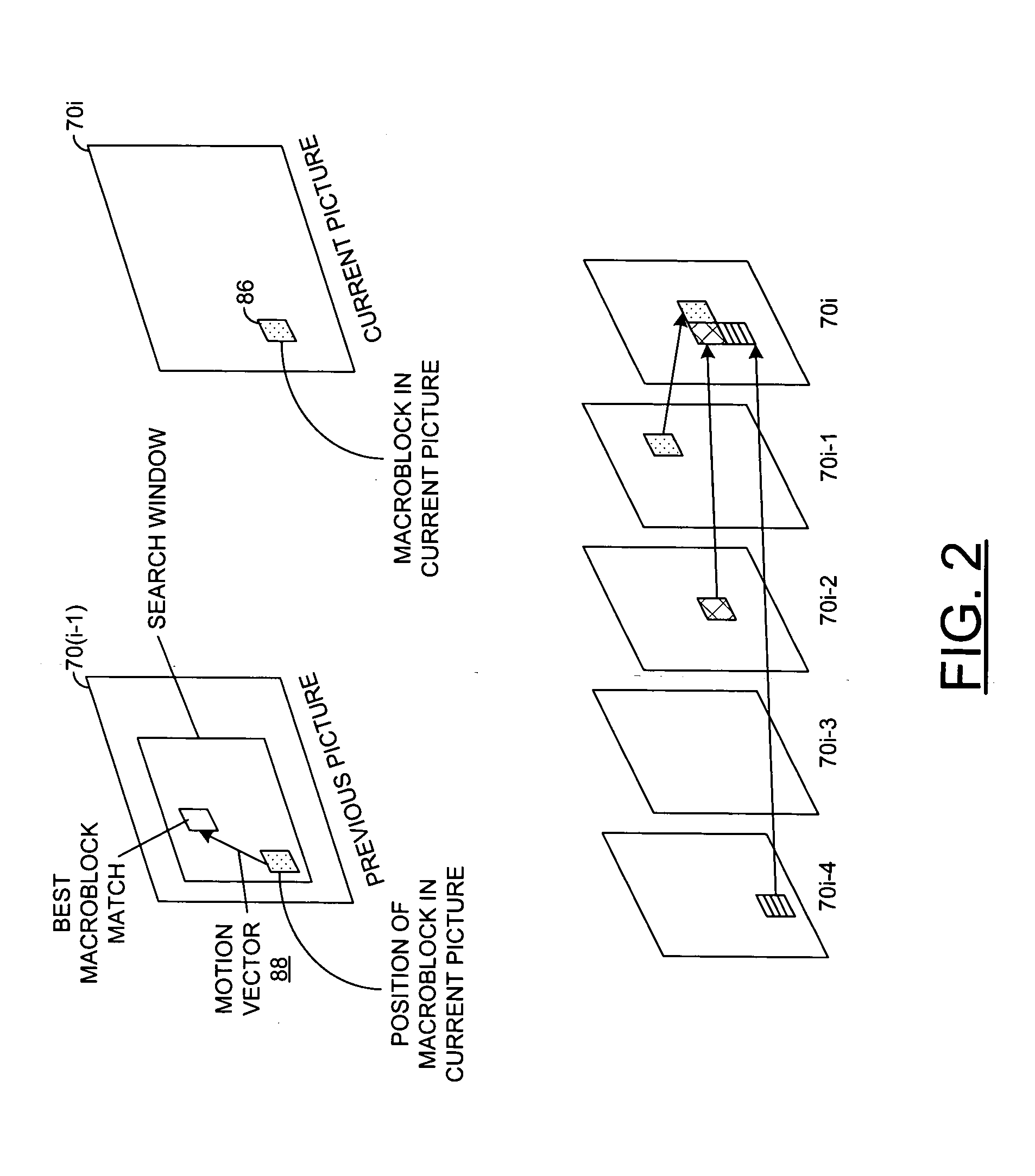
Motion estimation is the process of determining motion vectors that describe the transformation from one 2D image to another; usually from adjacent frames in a video sequence. It is an ill-posed problem as the motion is in three dimensions but the images are a projection of the 3D scene onto a 2D plane. The motion vectors may relate to the whole image (global motion estimation) or specific parts, such as rectangular blocks, arbitrary shaped patches or even per pixel. The motion vectors may be represented by a translational model or many other models that can approximate the motion of a real video camera, such as rotation and translation in all three dimensions and zoom.
Target orientation estimation using depth sensing
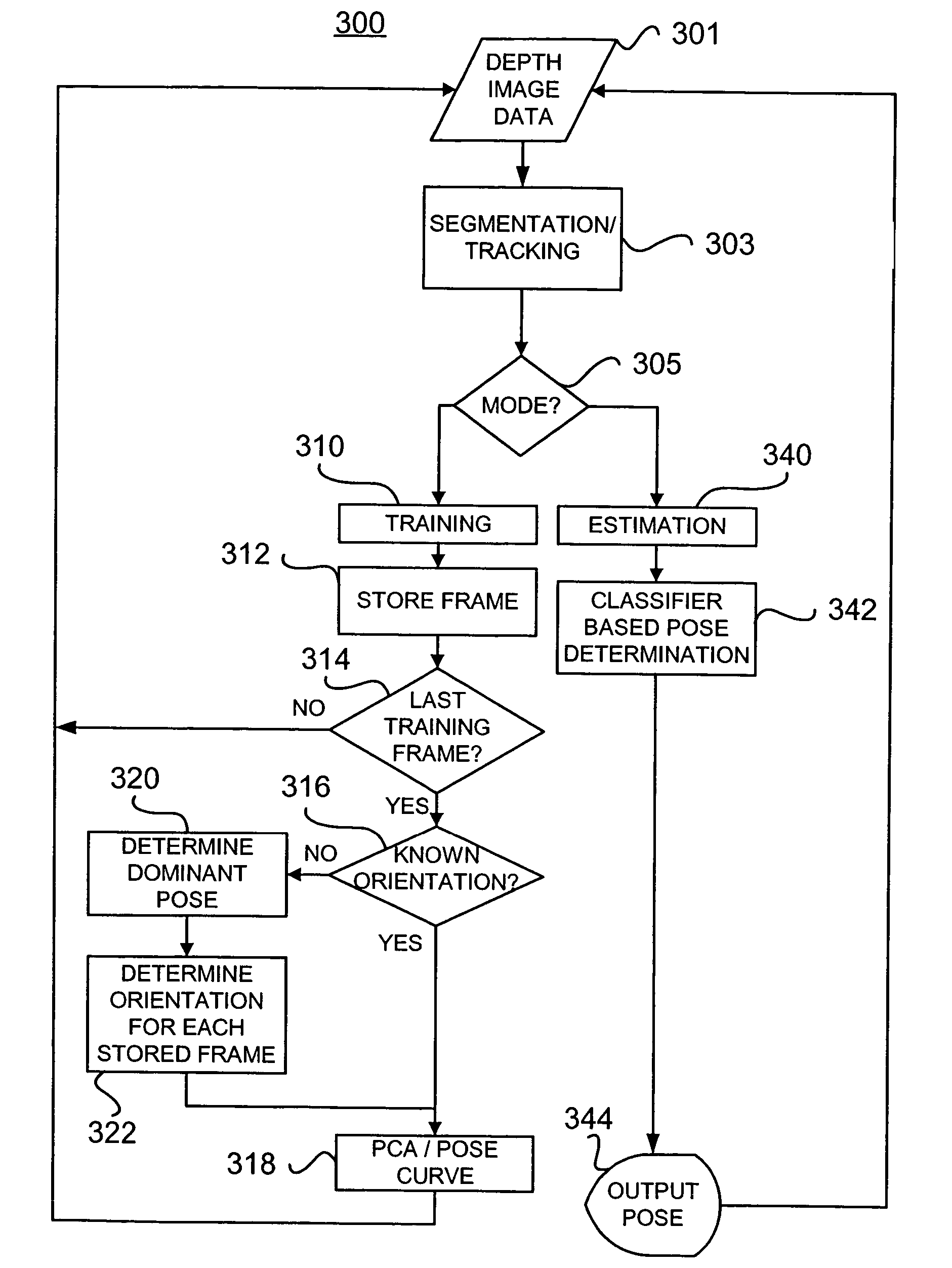
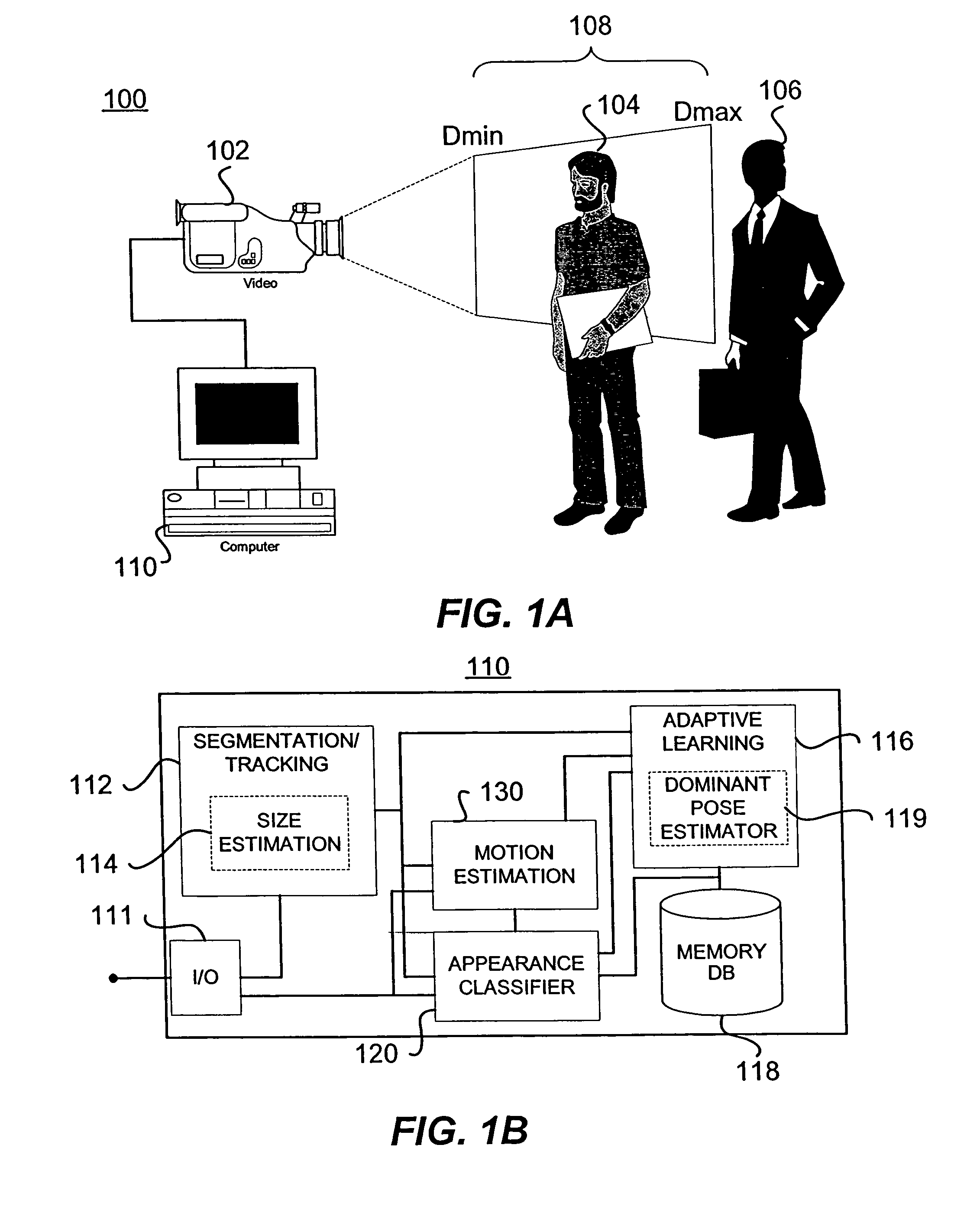
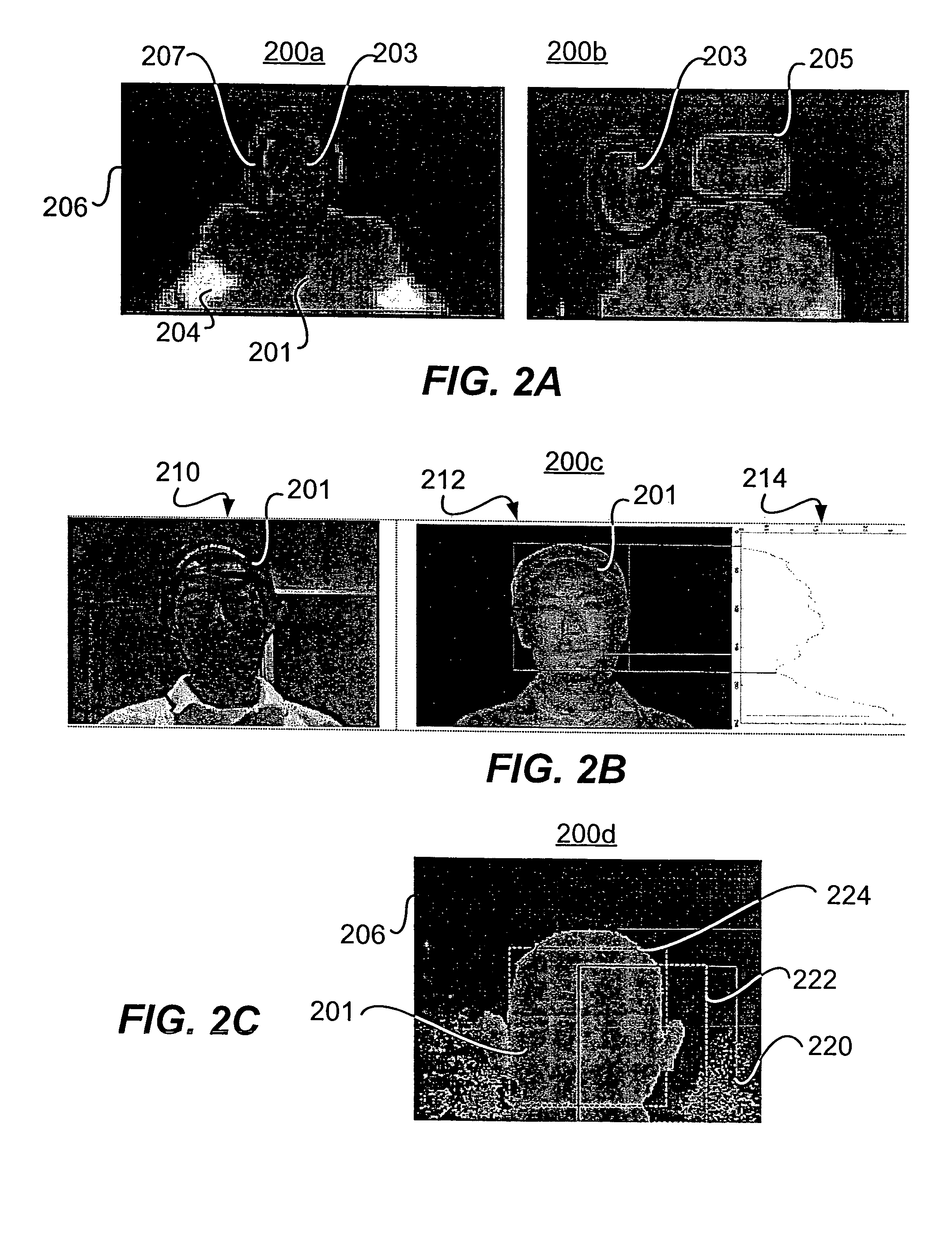
A system for estimating orientation of a target based on real-time video data uses depth data included in the video to determine the estimated orientation. The system includes a time-of-flight camera capable of depth sensing within a depth window. The camera outputs hybrid image data (color and depth). Segmentation is performed to determine the location of the target within the image. Tracking is used to follow the target location from frame to frame. During a training mode, a target-specific training image set is collected with a corresponding orientation associated with each frame. During an estimation mode, a classifier compares new images with the stored training set to determine an estimated orientation. A motion estimation approach uses an accumulated rotation / translation parameter calculation based on optical flow and depth constrains. The parameters are reset to a reference value each time the image corresponds to a dominant orientation.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
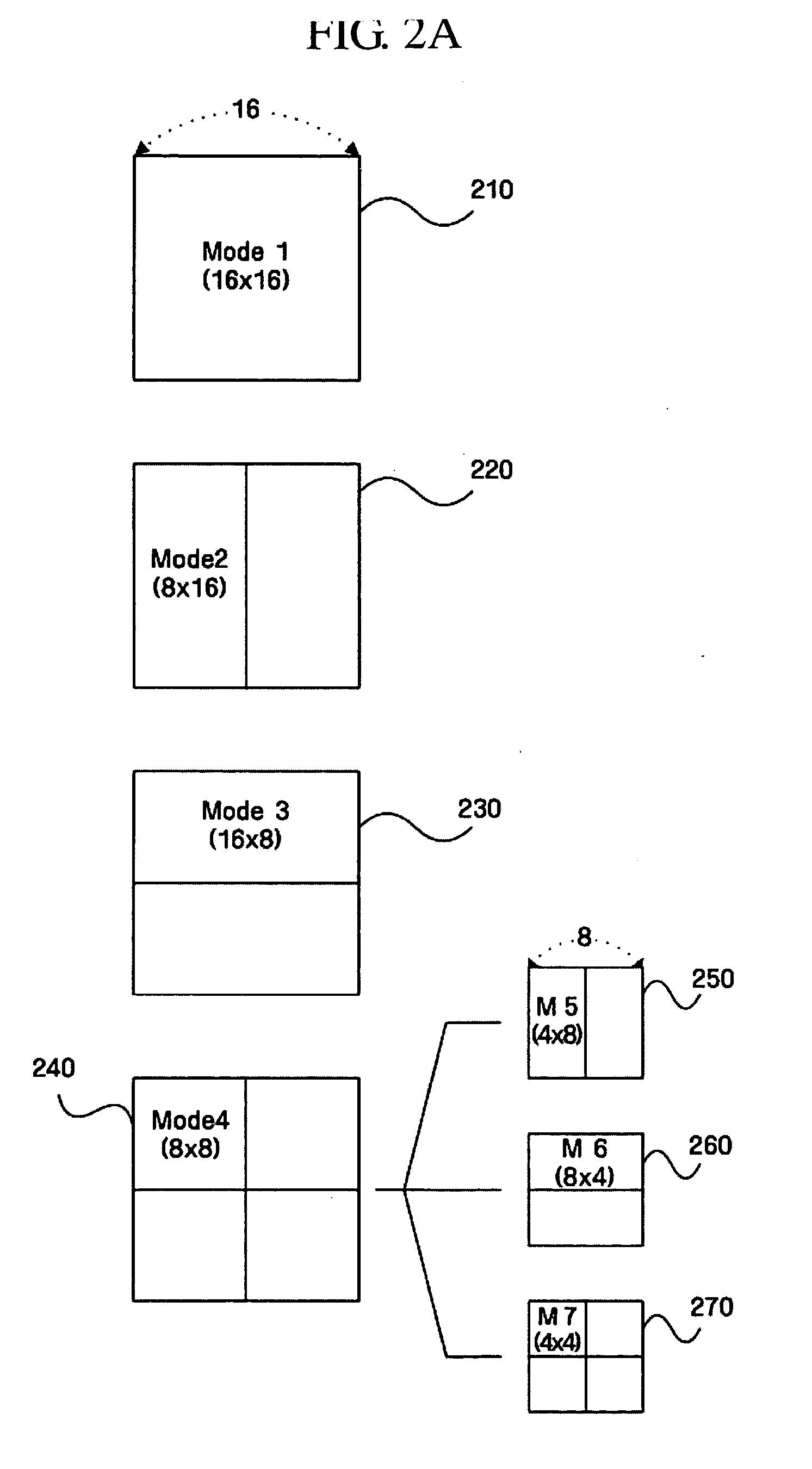
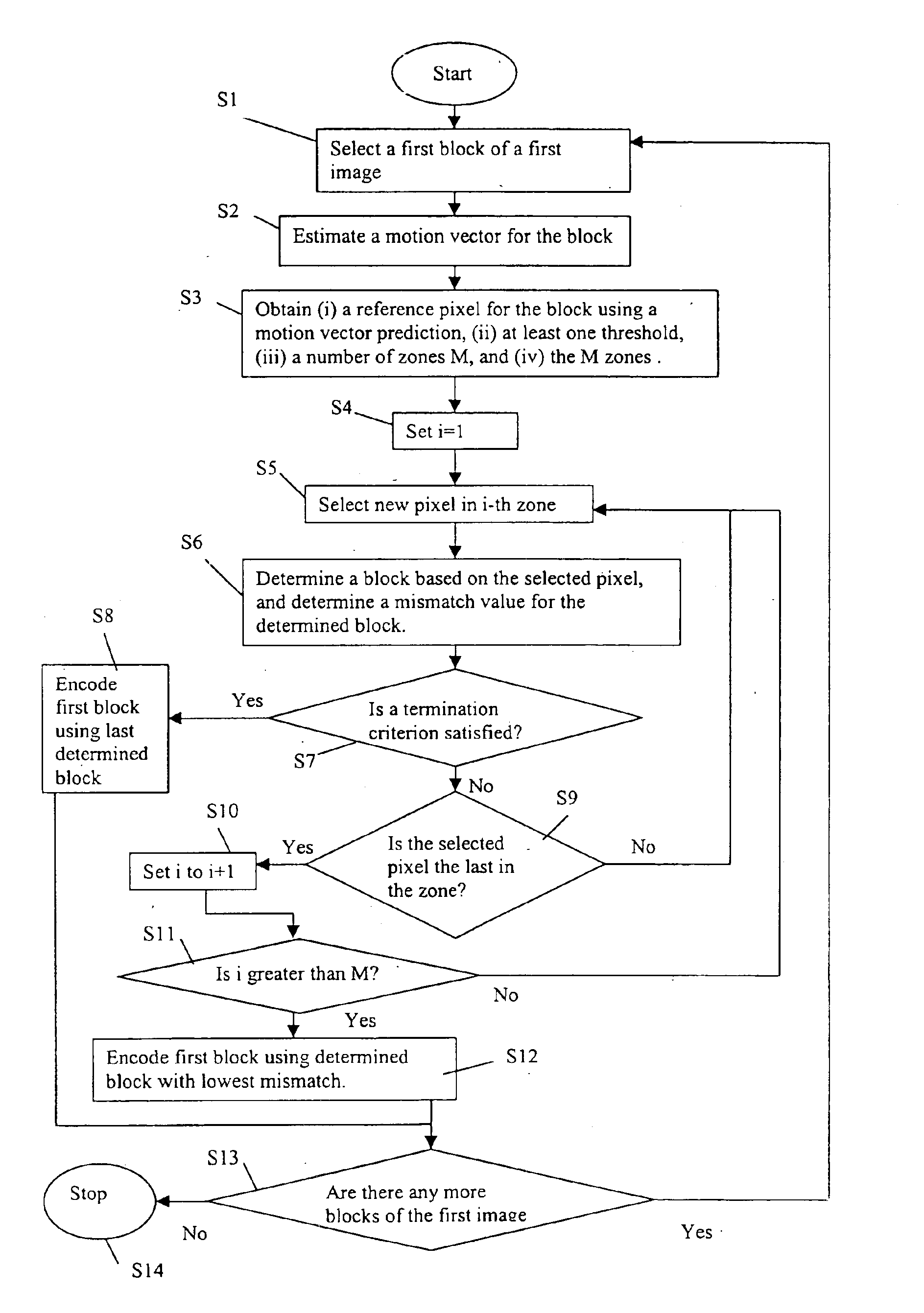
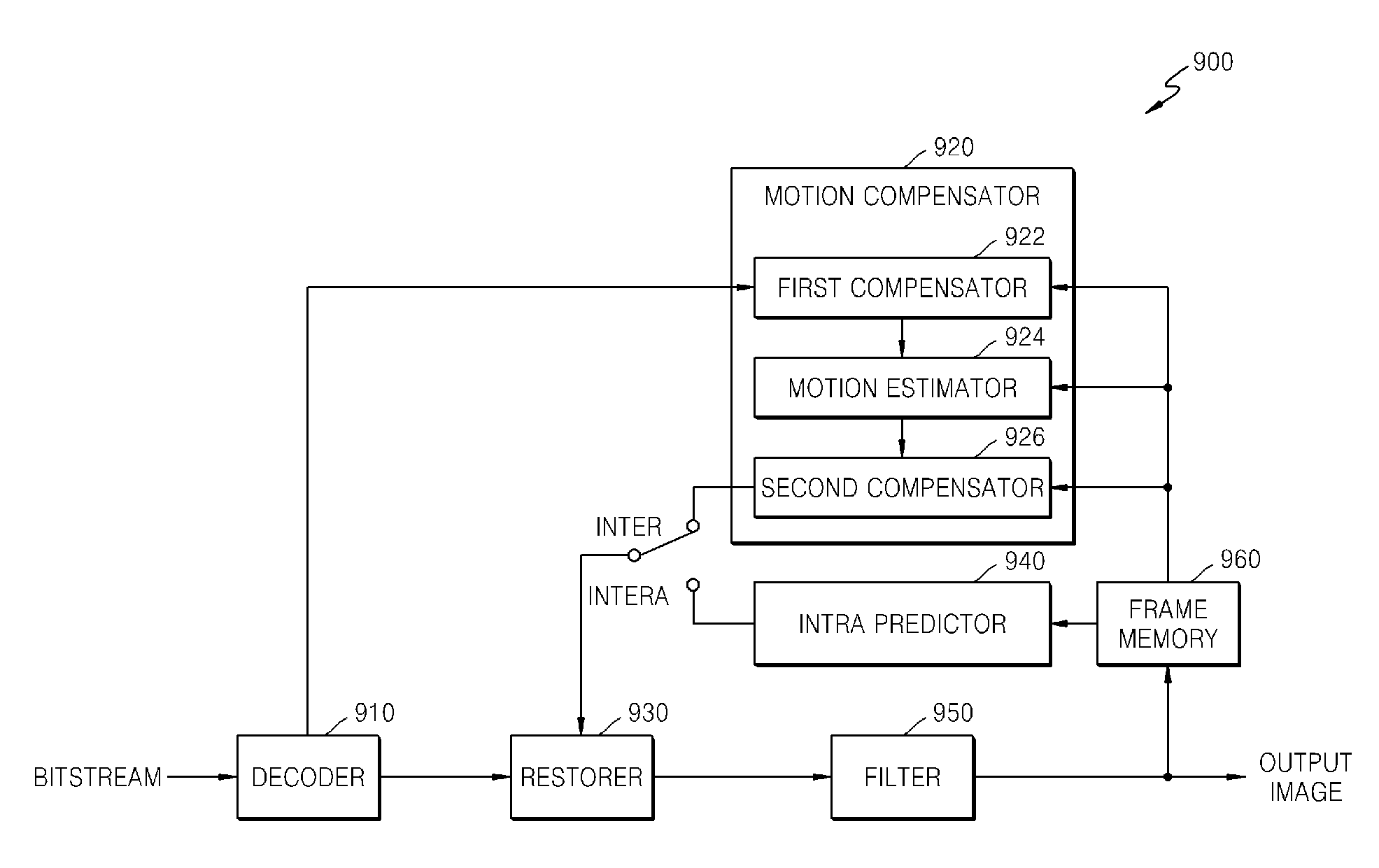
Method of encoding mode determination, method of motion estimation and encoding apparatus
InactiveUS20050135484A1Efficiently omittedQuick fixTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSpatial predictionRate distortion
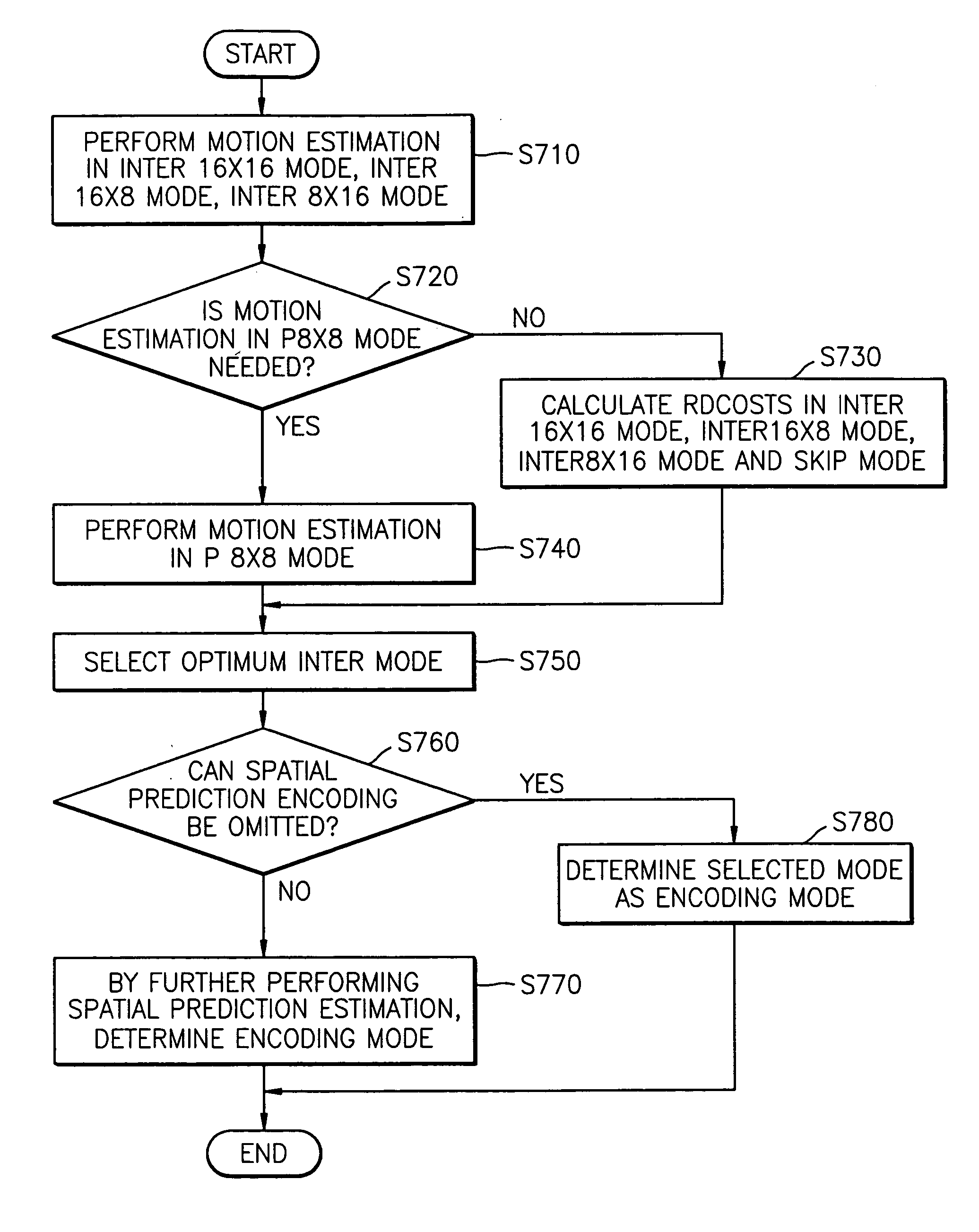
Motion estimation of a macro block in inter16×16, inter16×8, and inter8×16 modes is performed and a determination of whether to further perform motion estimation in a P8×8 mode is made. Motion estimation in P8×8 mode is either omitted or performed and one mode is determined according to a rate distortion cost of the respective modes. Spatial prediction encoding may then be performed or omitted based on comparing the rate distortion cost of the one mode with a predetermined value. Accordingly, by selectively omitting variable block motion estimation and spatial prediction encoding which are the most complicated operations in an H.264 encoder, determining an encoding mode is rapidly performed such that encoding speed increases.
Owner:DAEYANG FOUND SEJONG UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for motion estimation using variable block size of hierarchy structure
InactiveUS20050114093A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsMotion vectorComputer science
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for a motion estimation using a variable block size of a hierarchy structure. The method includes: calculating each of a motion vector of a desired minimum unit variable block; determining a similarity of the calculated motion vectors between the minimum unit variable blocks in a higher hierarchy including the minimum unit variable block; establishing a mode of the variable block according to the determined similarity; and deciding a motion vector with respect to the mode established variable block. The complexity of the method of compressing a motion picture of a hierarchy structure having a plurality of block sizes can be reduced by selecting a mode of the optimal block size on the basis of a motion vector with respect to the minimum unit and the cost occurred at that time without performing the motion estimation with respect to each mode each time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical see-through augmented reality modified-scale display
InactiveUS7002551B2Improve accuracyAccurate currentInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsDisplay device
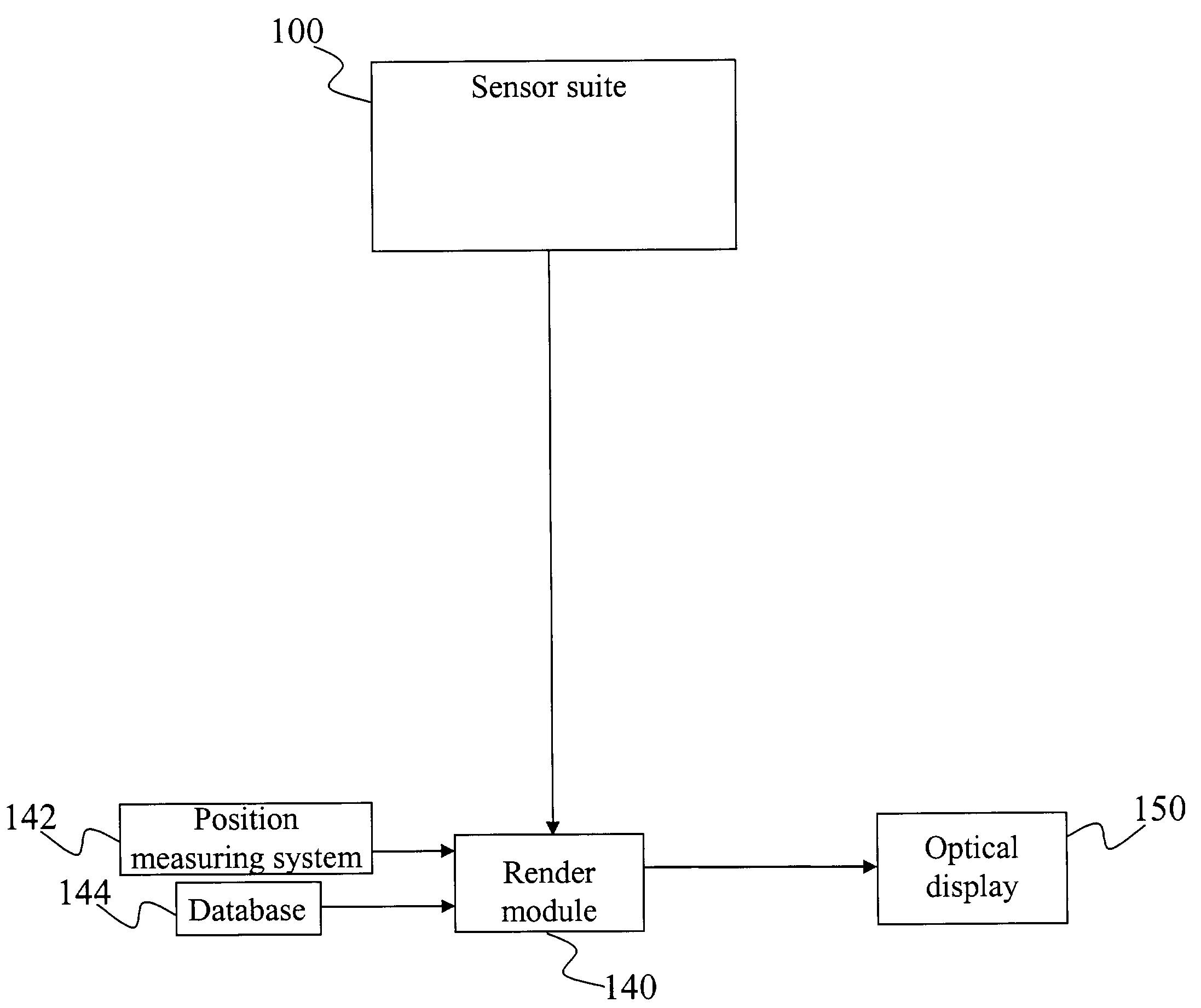
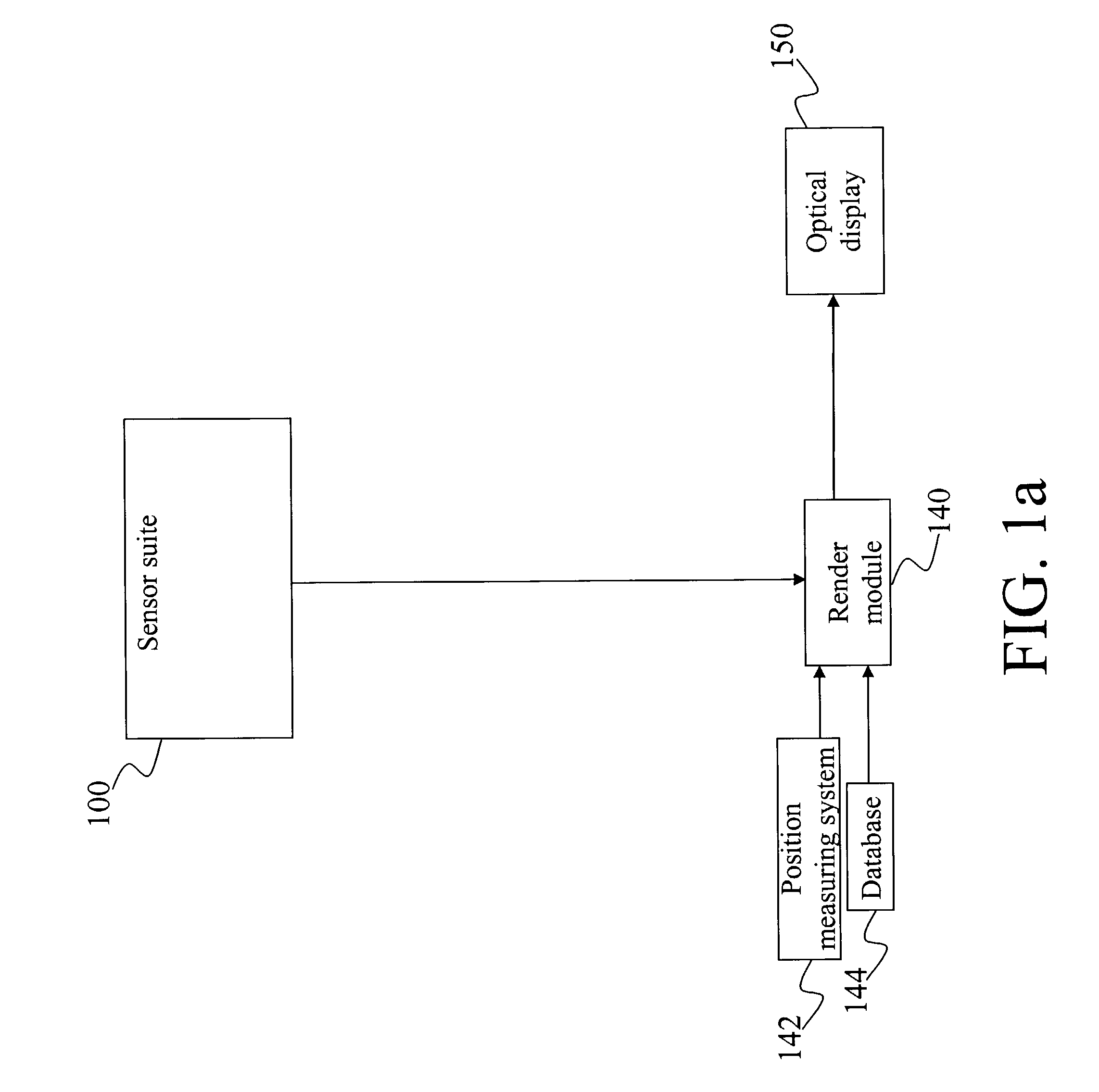
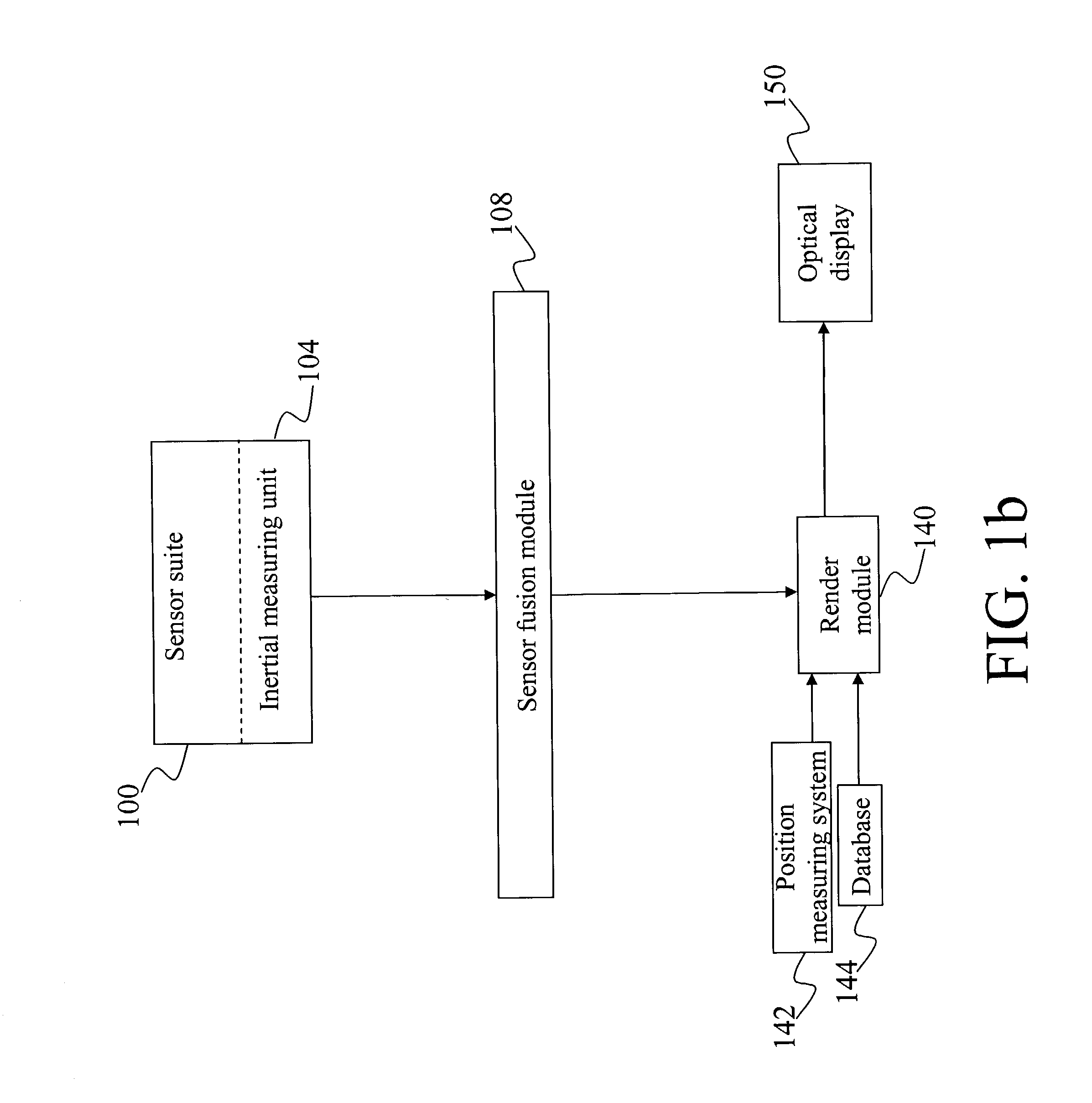
A method and system for providing an optical see-through Augmented Reality modified-scale display. This aspect includes a sensor suite 100 which includes a compass 102, an inertial measuring unit 104, and a video camera 106 for precise measurement of a user's current orientation and angular rotation rate. A sensor fusion module 108 may be included to produce a unified estimate of the user's angular rotation rate and current orientation to be provided to an orientation and rate estimate module 120. The orientation and rate estimate module 120 operates in a static or dynamic (prediction) mode. A render module 140 receives an orientation; and the render module 140 uses the orientation, a position from a position measuring system 142, and data from a database 144 to render graphic images of an object in their correct orientations and positions in an optical display 150.
Owner:HRL LAB
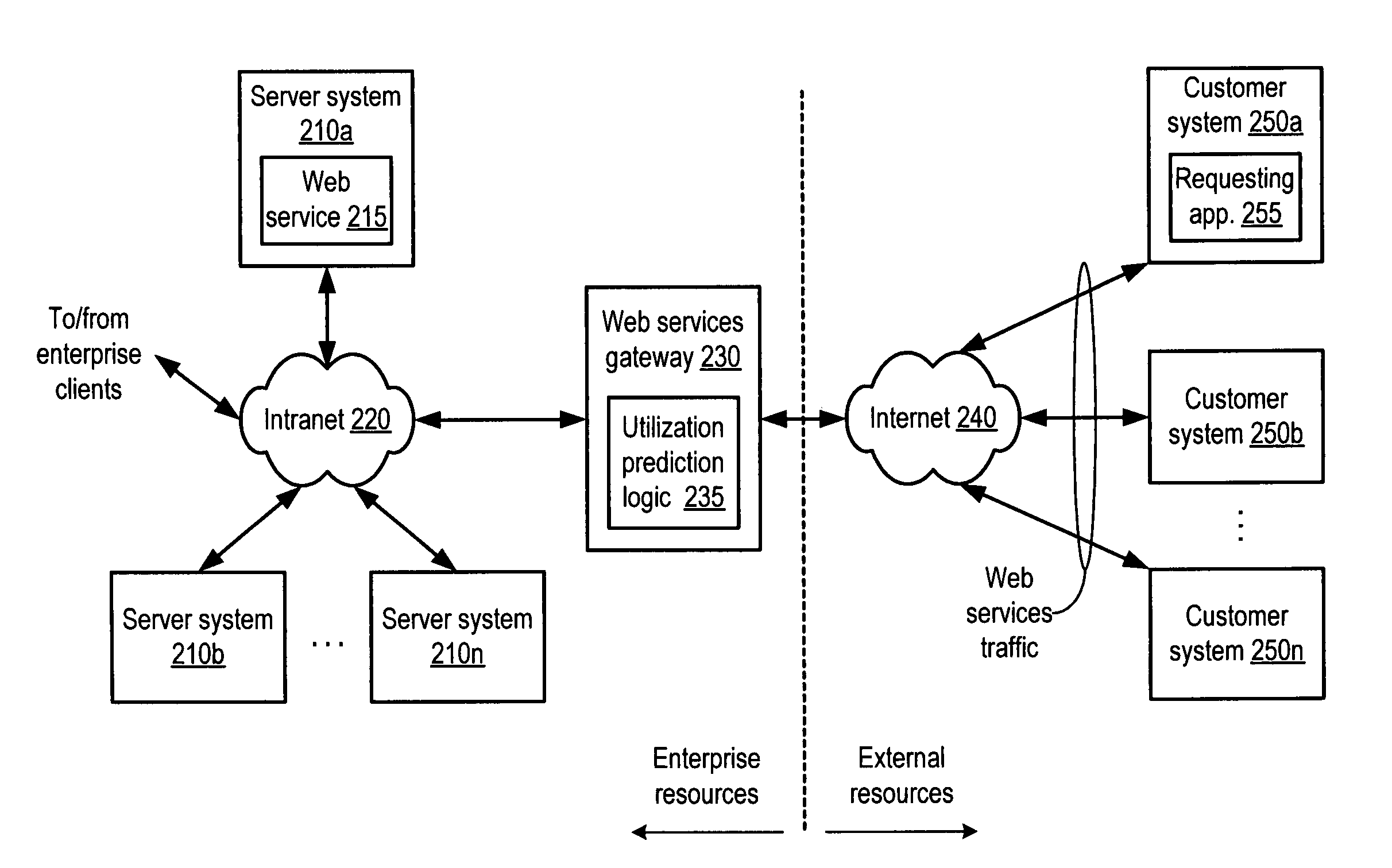
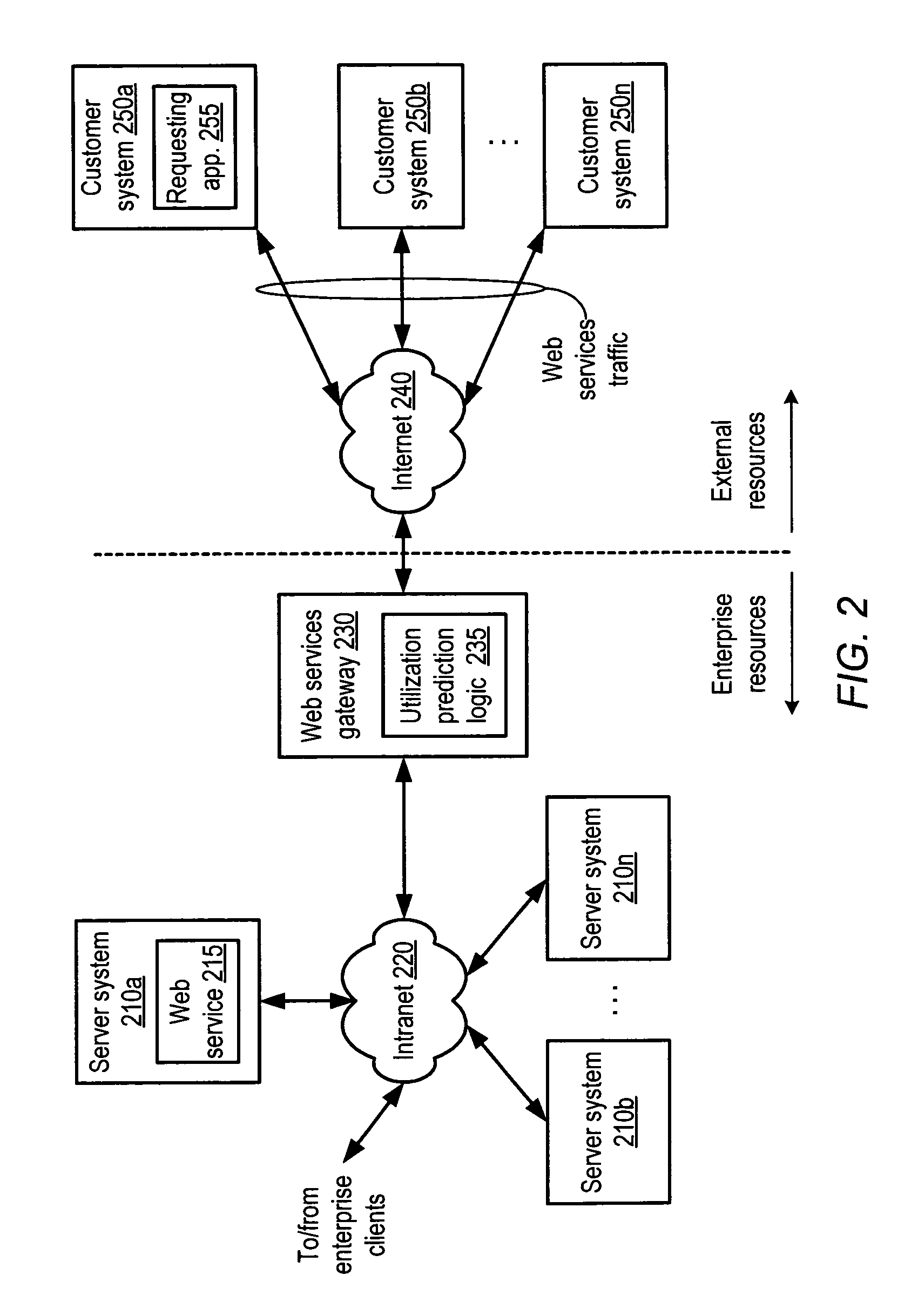
Method and system for dynamic pricing of web services utilization
A method and system for dynamic pricing of web services utilization. According to one embodiment, a method may include dynamically predicting utilization of a web services computing resource that is expected to occur during a given interval of time, and dependent upon the dynamically predicted utilization, setting a price associated with utilization of the web services computing resource occurring during the given interval of time. The method may further include providing the price to a customer.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
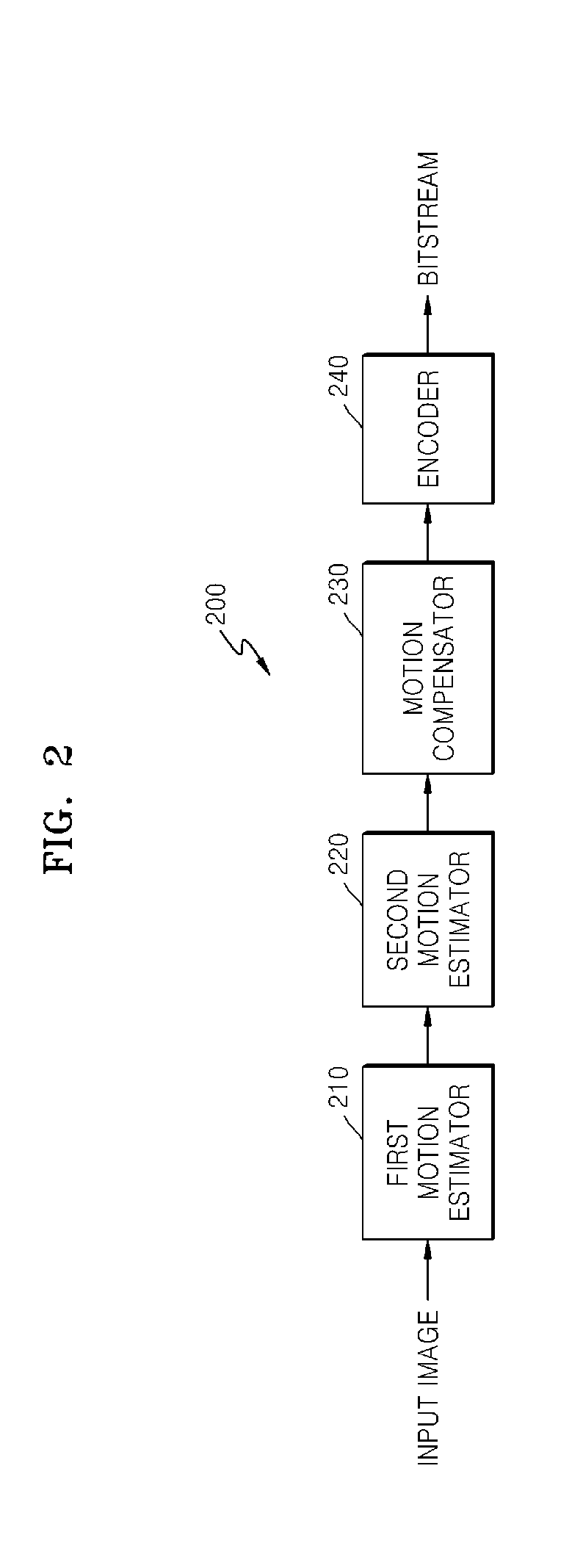
Efficient multi-block motion estimation for video compression
InactiveUS20060002474A1Reduce computing costLittle sacrificeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital signalMotion estimation
A novel method, system, and apparatus for efficient multi-block motion estimation in a digital signal compression and coding scheme. This invention selects only a few representative block sizes for motion estimation when certain favourable conditions occur, rather than using all available block sizes. This invention produces significantly reduced computational costs with virtually no sacrifice in visual quality and in bit-rate.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
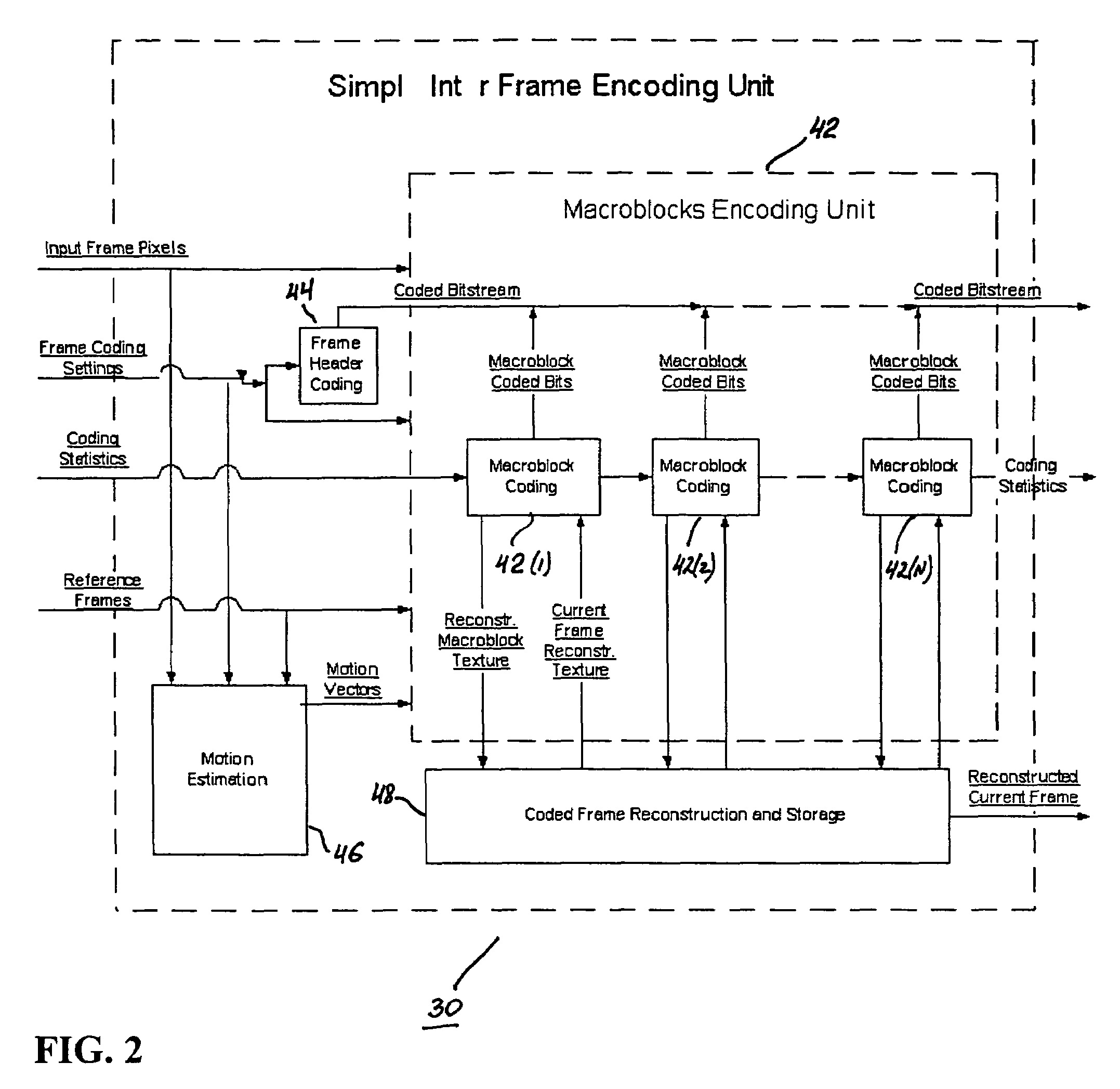
Real-time video coding/decoding
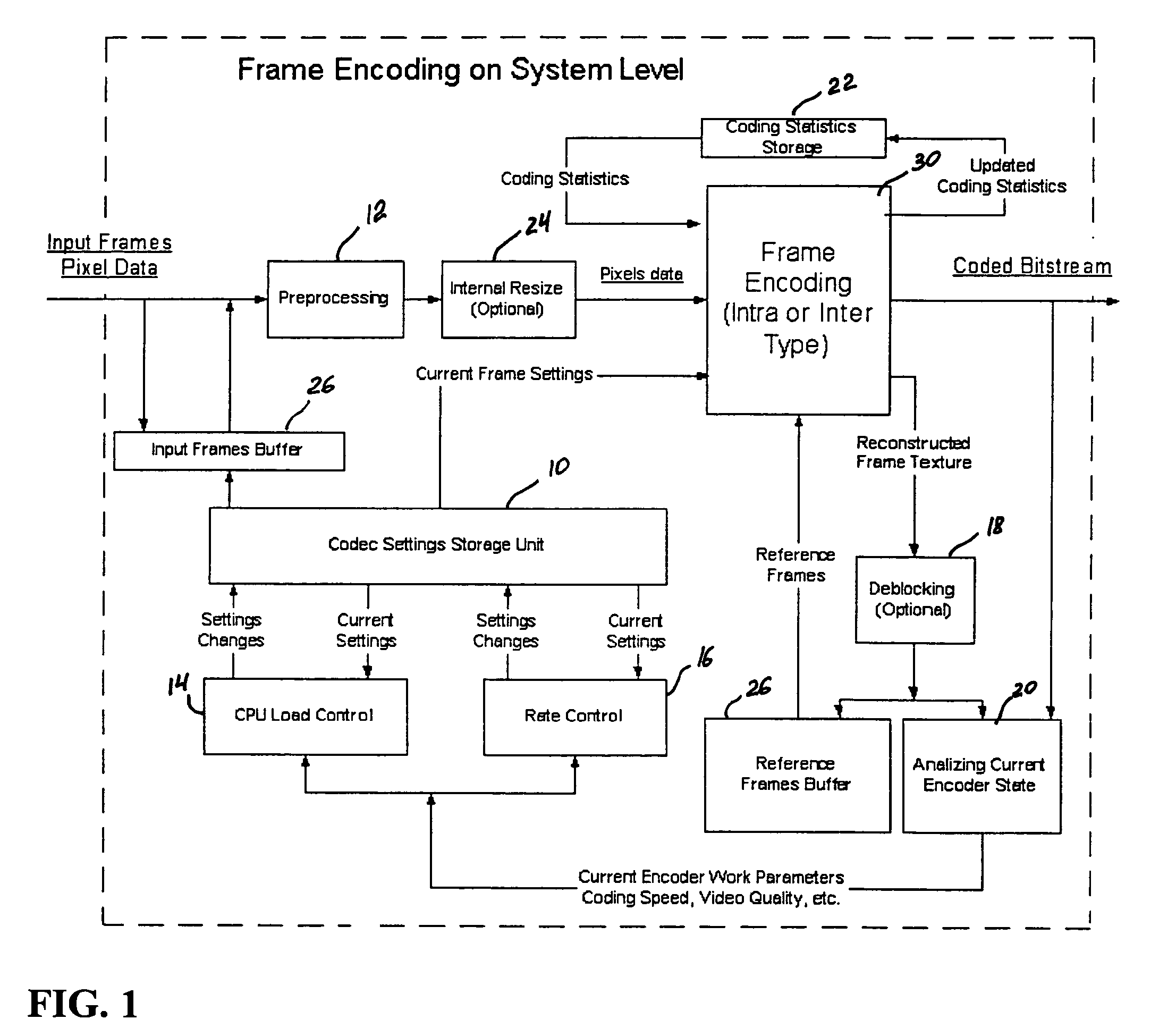
ActiveUS20050276323A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMotion vectorDownscaling
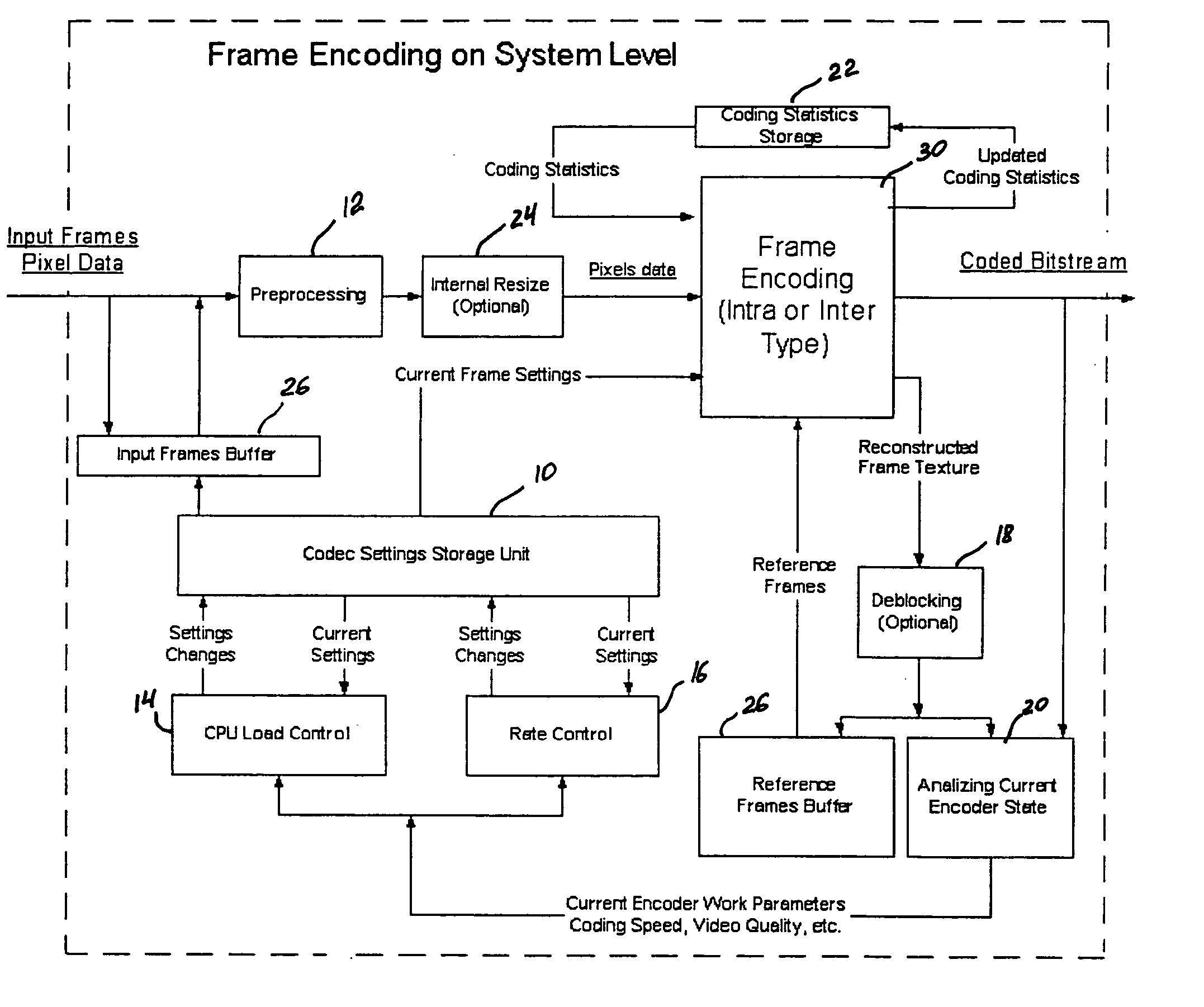
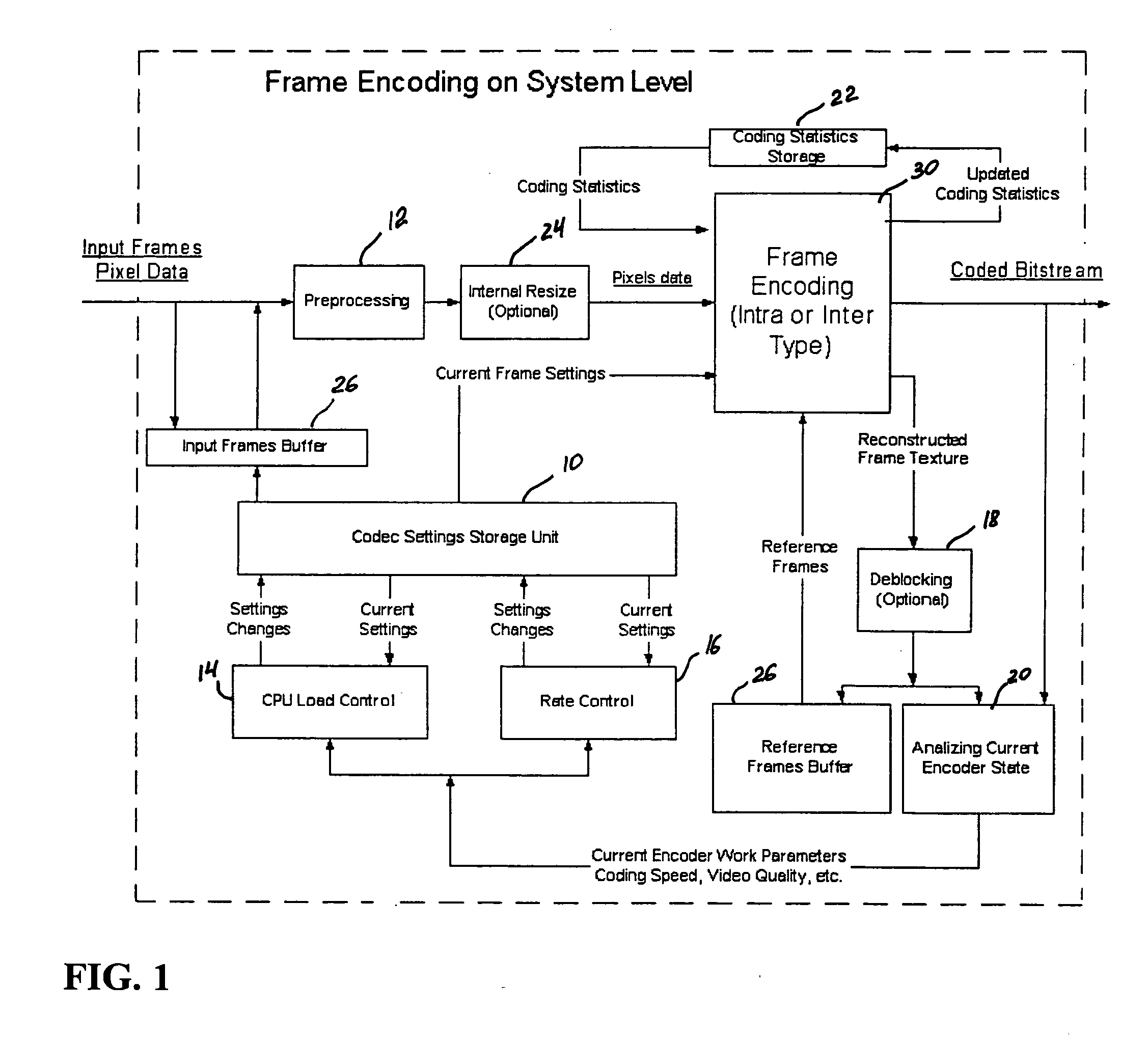
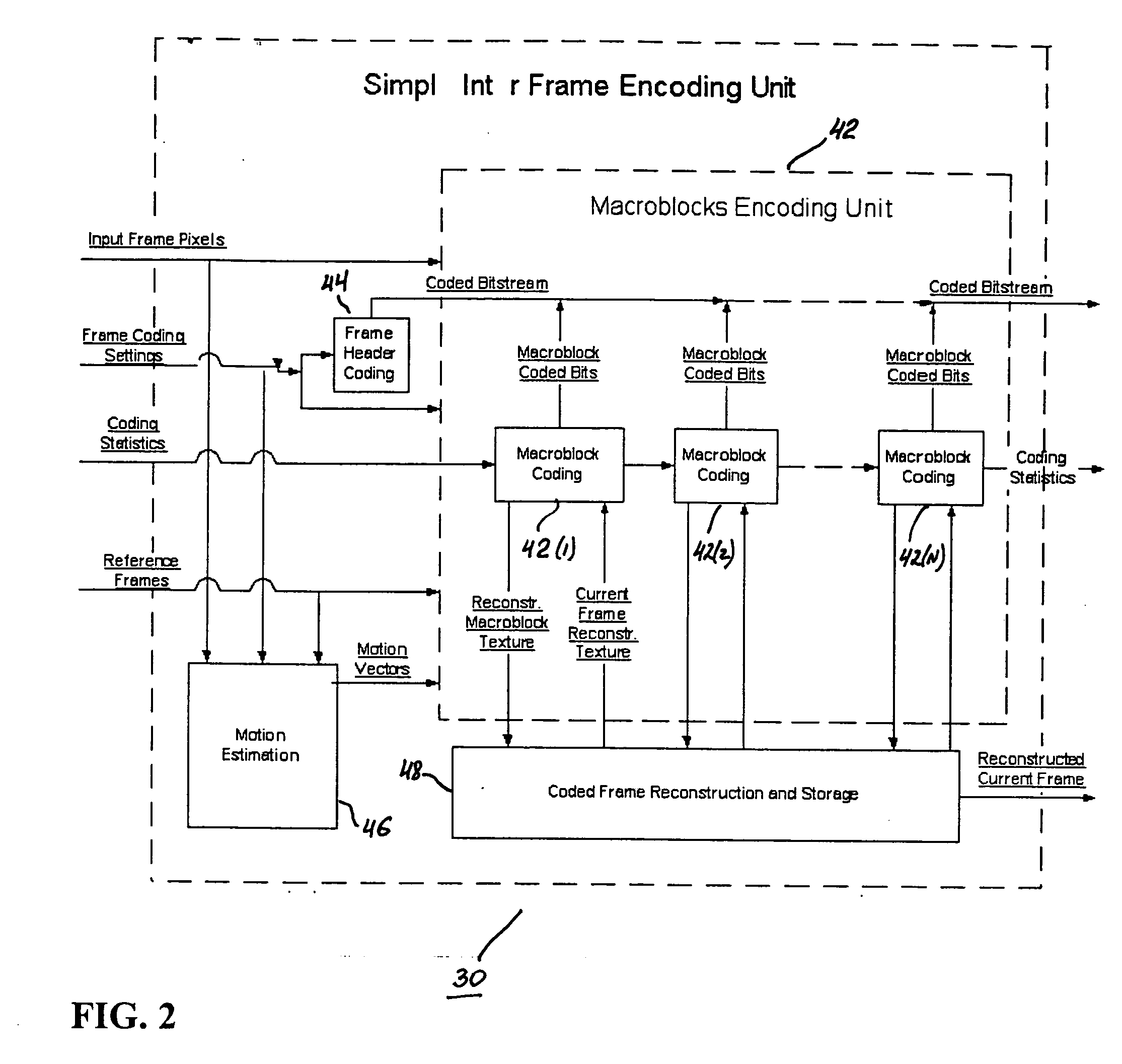
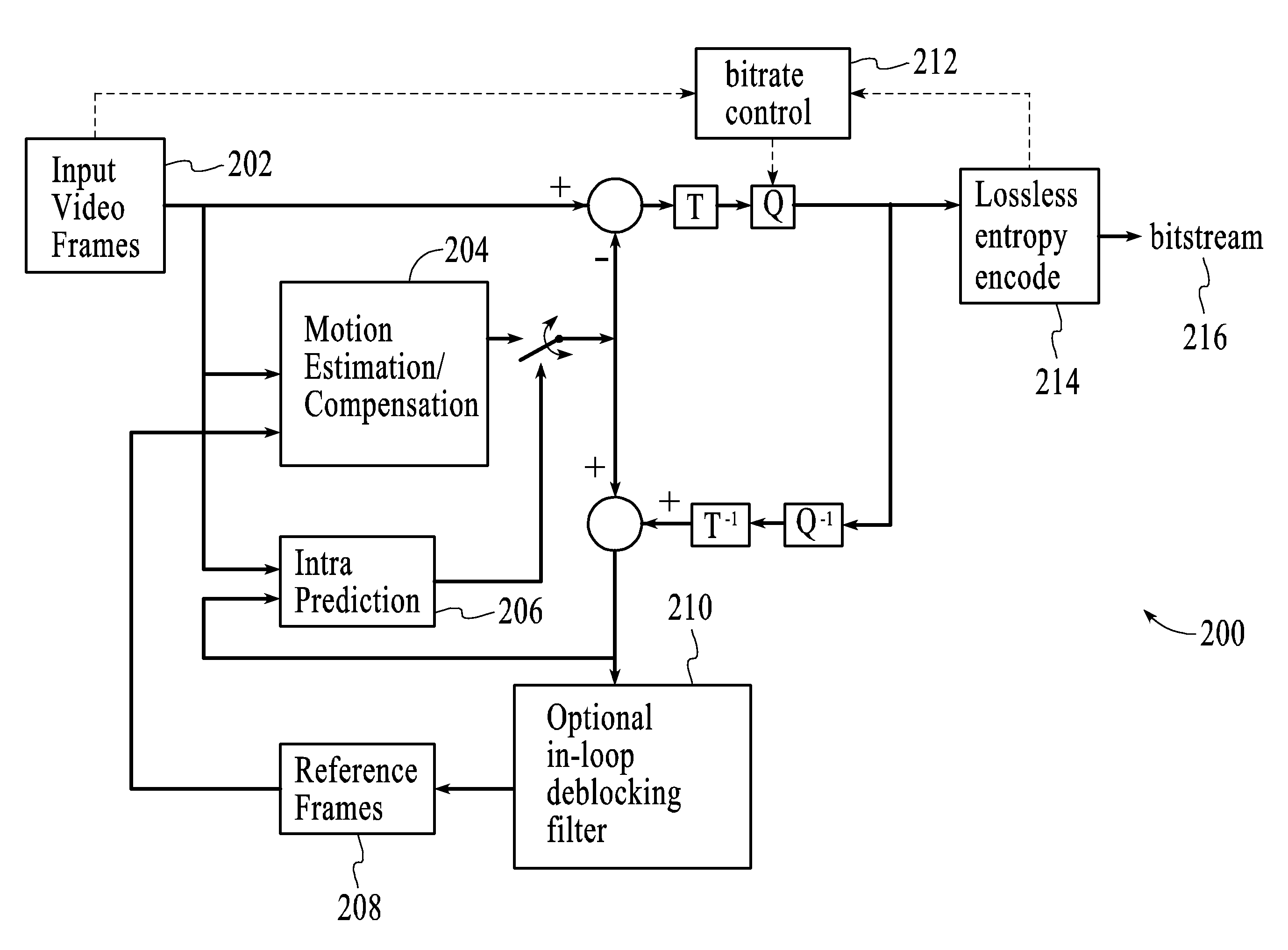
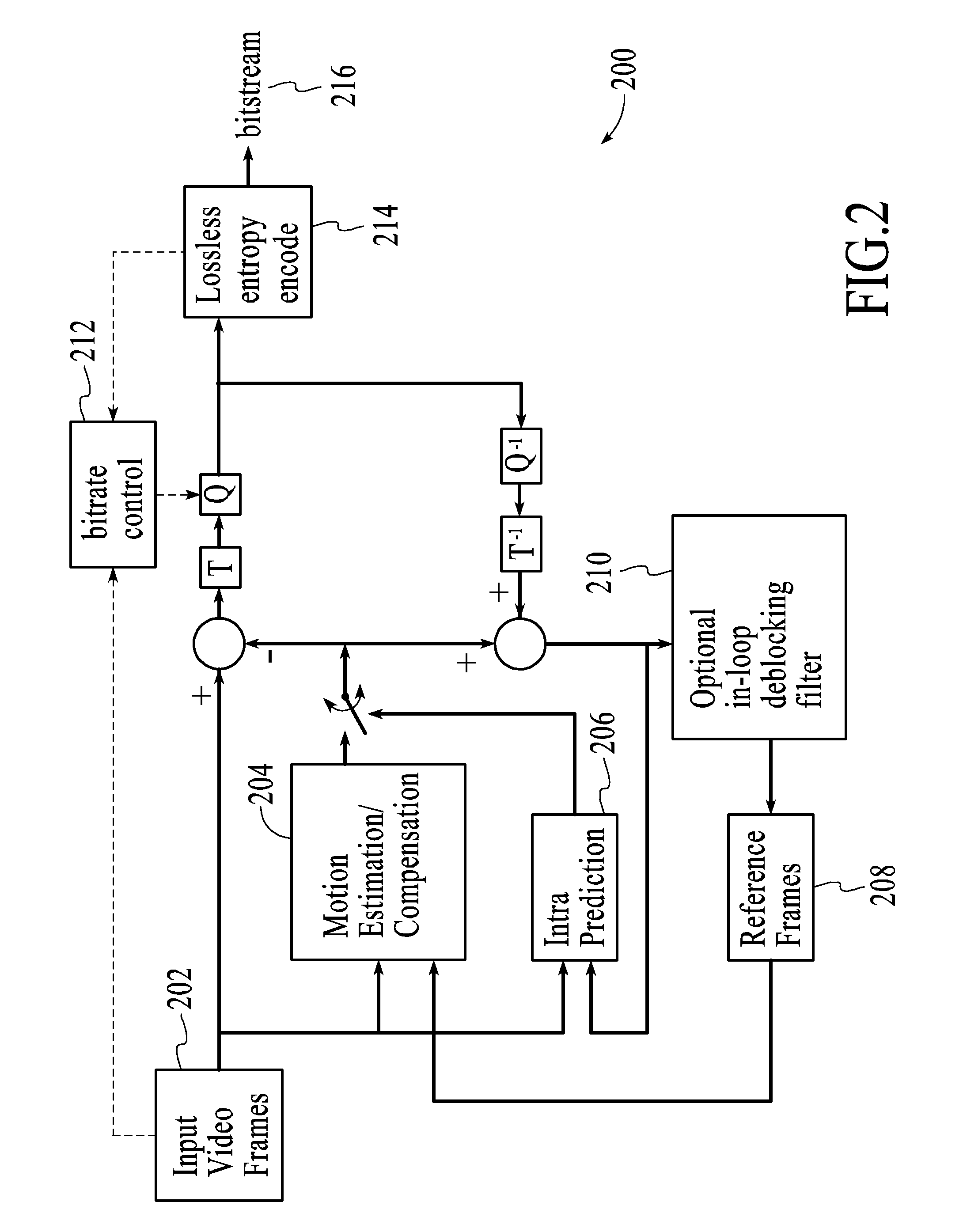
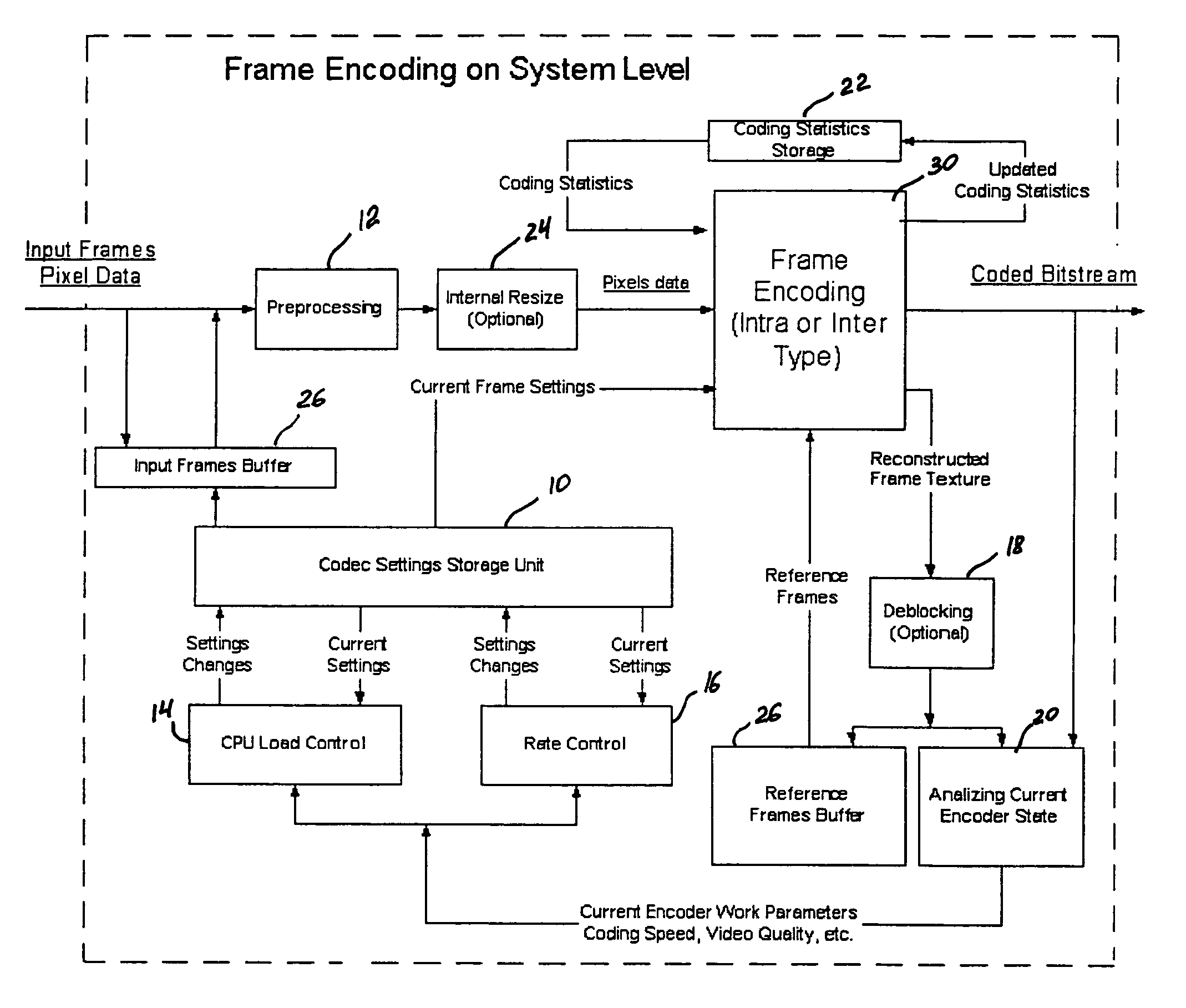
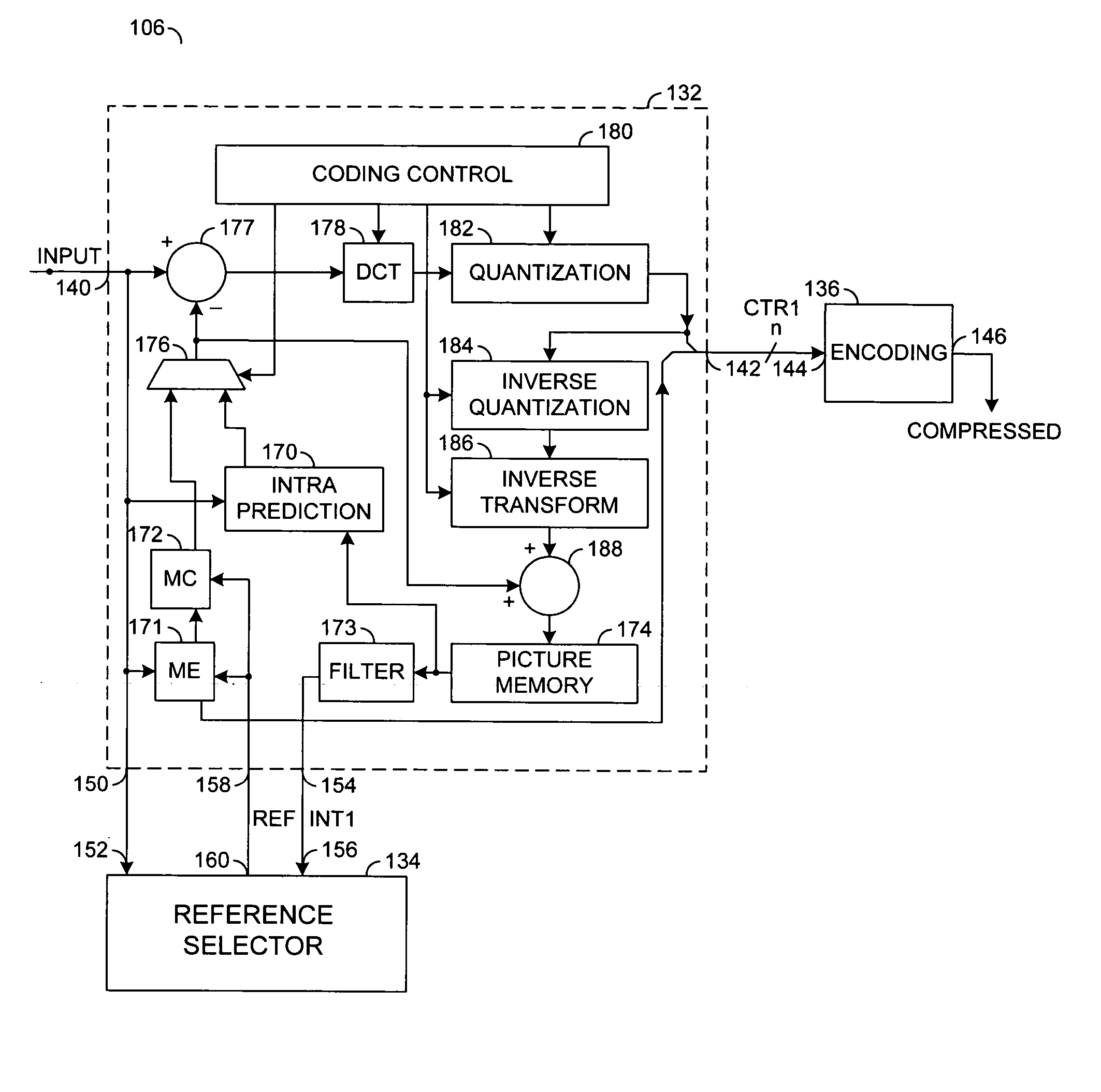
A video codec for real-time encoding / decoding of digitized video data with high compression efficiency, comprising a frame encoder receiving input frame pixels; a codec setting unit for setting and storing coding setting parameters; a CPU load controller for controlling desired frame encoding time and CPU loading; a rate controller for controlling frame size; a coding statistics memory for storing frequency tables for arithmetic coding of bitstream parameters and a reference frame buffer for storing reference frames. The frame encoder comprises a motion estimation unit, a frame head coding unit, a coded frame reconstruction and storage unit and a macroblock encoding unit. The macroblock encoding unit provides calculation of texture prediction and prediction error, transforming texture prediction error and quantization of transform coefficient, calculation of motion vector prediction and prediction error and arithmetic context modeling for motion vectors, header parameters and transform coefficients. The codec also includes a deblocking unit for processing video data to eliminate blocking effect from restored data encoded at high distortion level, which may be a part of encoder or decoder, an internal resize unit, providing matching downscaling of a frame before encoding and upscaling of decoded frame according to the coding setting parameters, and a noise suppression unit.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
Movement vector prediction method in resolution demixing technology
InactiveCN101198064AReduce bit rateHigh gain performanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationTime domainMotion vector
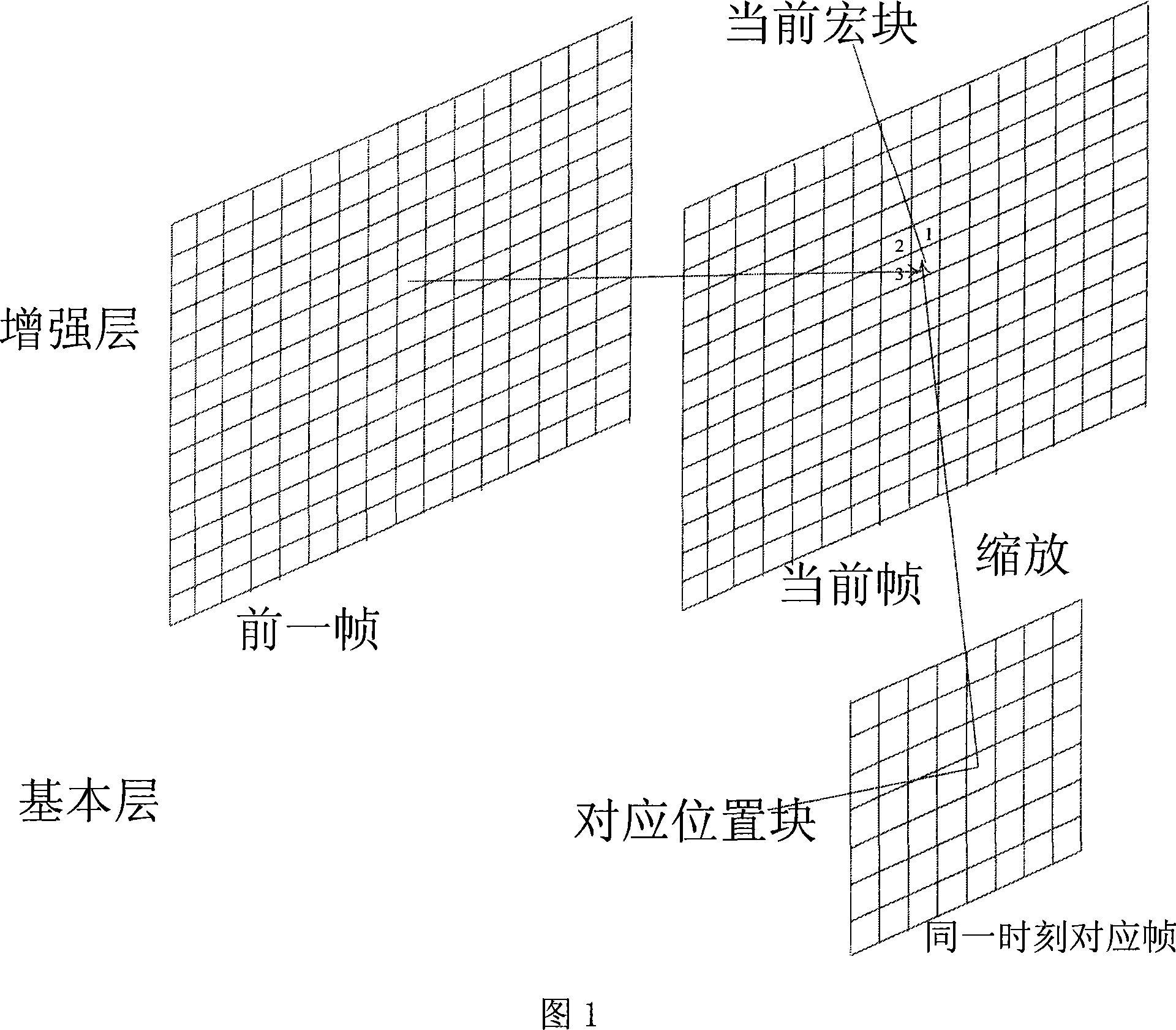
The invention discloses a motion vector forecasting method in a resolution quantizing structure, wherein, forecasting motion vectors of macro blocks in enhancement layers are acquired by utilization of relativity of motion vectors of a time domain, a space domain and an interlayer domain. The realization process is that: on the time domain, candidate motion vectors of the time domain are acquired from motion vectors of macro blocks with the same position with the prior frame; on the space domain, candidate motion vectors of the space domain are acquired from motion vectors of adjacent blocks; on the interlayer domain, candidate motion vectors of the interlayer domain are acquired from corresponding motion vectors with low space domain resolution hierarchy; candidate motion vectors with minimum motion estimation cost are selected to be forecasting motion vectors by selection among the candidate motion vectors of the time domain, the space domain and the interlayer domain. The invention has the advantages of capability of acquiring more accurate forecasting motion vectors, capability of compressing code rate of motion vectors, and obtaining of performance gain.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
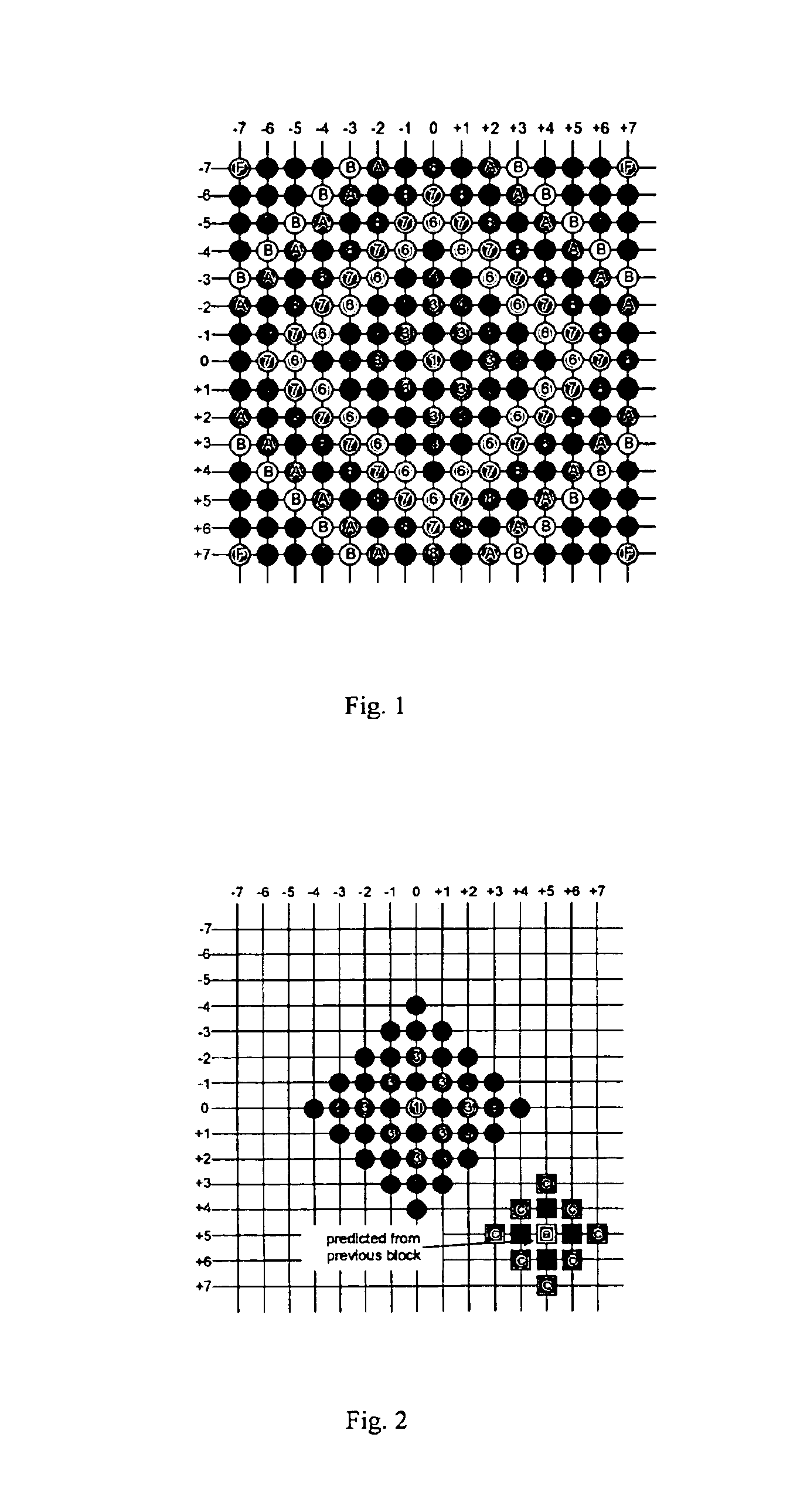
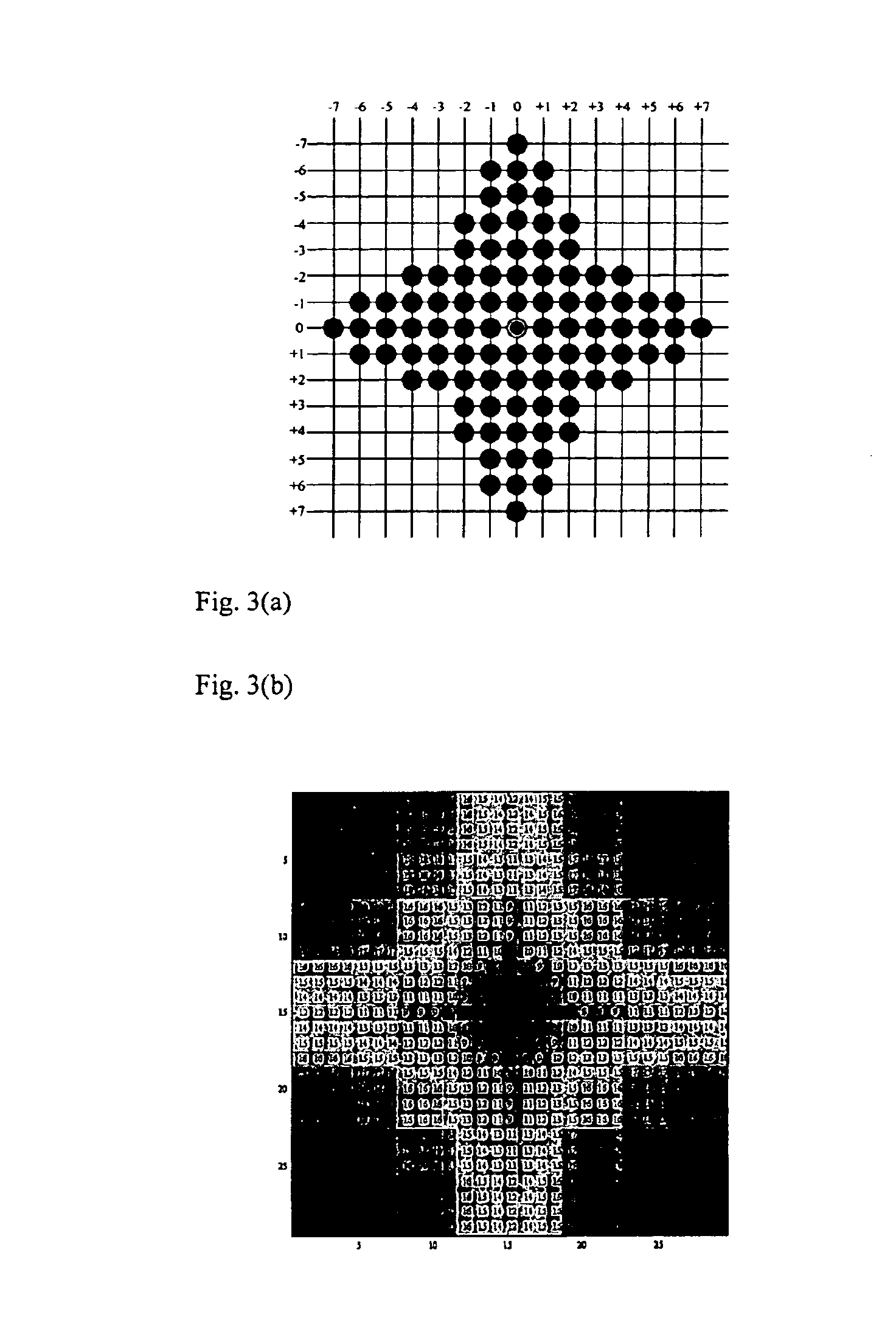
Device, method and digital video encoder for block-matching motion estimation
InactiveUS6842483B1Improve efficiencyImprove performanceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionDigital video
A device or method for video compression uses a technique in which changes in the image are encoded by motions of block of the image and signals indicating evolutions in the block. To determine the motions of the blocks of a each frame, a search is performed for a similar block of a previous frame based on points of the previous frame which are arranged in successive diamond shaped zones. The diamond shaped zones may be centred on the position of the block in previous frame, or one or more predicted motions of the block. The method terminates according to criteria defined using thresholds.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
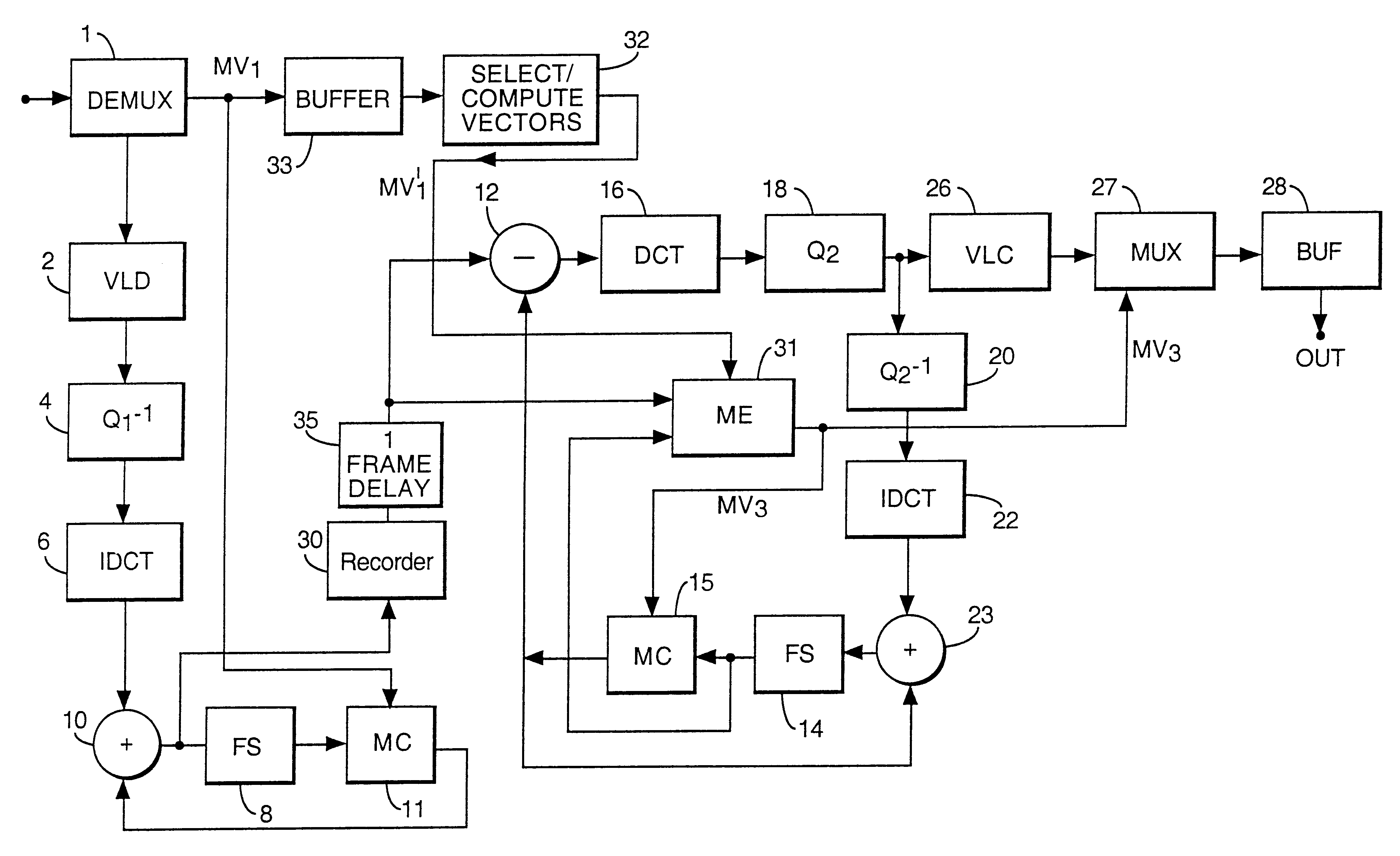
Transcoding
Transcoding is achieved by decoding a received video signal which has been coded according to a first coding scheme employing motion compensation and carries coded data and motion compensation information, and encoding the decoded according to a second coding scheme also employing motion compensation. Estimated motion vectors are generated for a current frame of the video signal, using vectors which, in the received signal, accompanying at least one other frame of the video signal. These may be used directly or used to define a search area for motion estimation.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Video/audio signal processing method and video/audio signal processing apparatus
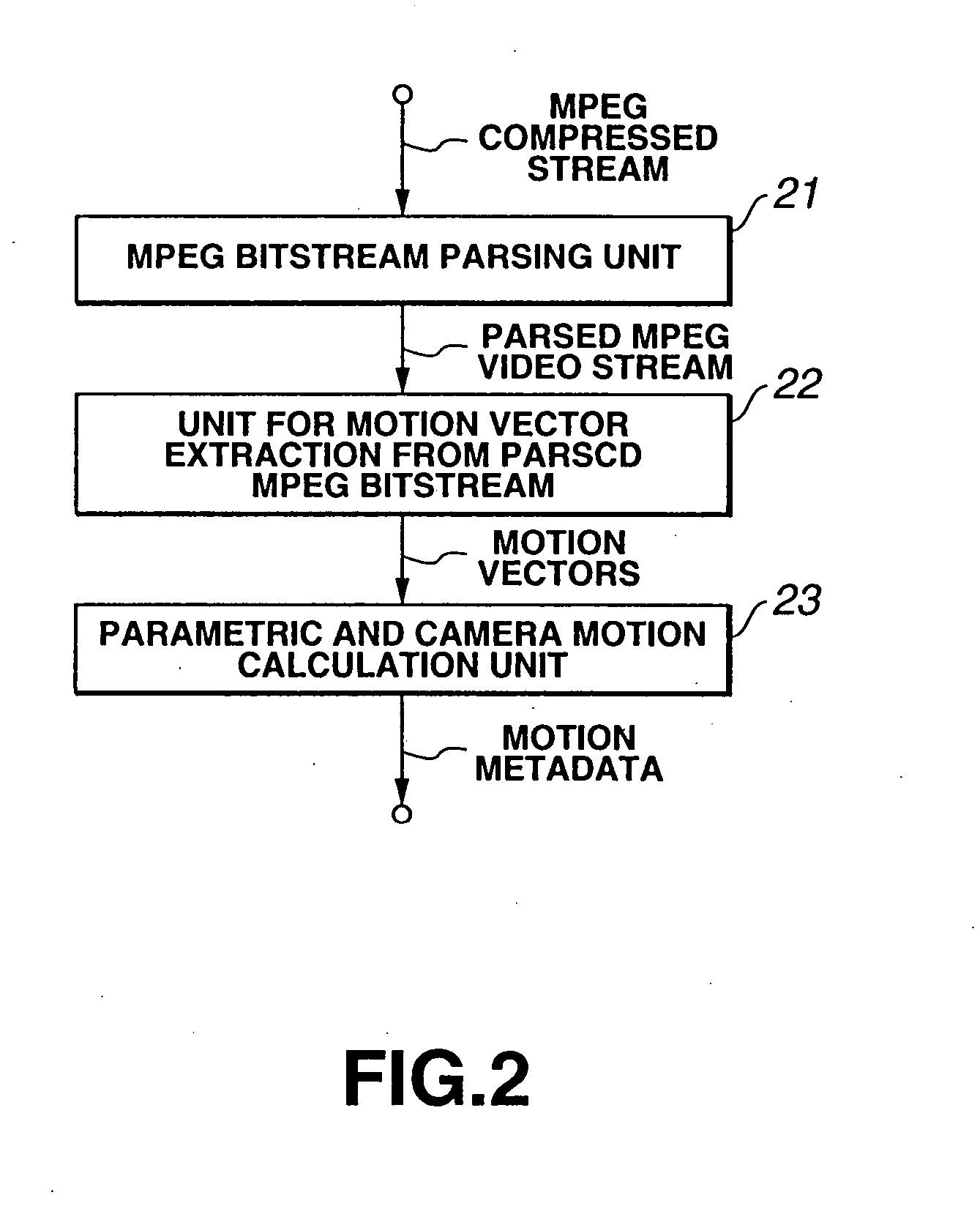
A metadata extraction unit has a feature point selection and motion estimation unit 62 for extracting at least one feature point representing characteristics of the video / audio signals in a compressed domain of the video / audio signals. Thus, reduction of time or cost for processing can be realized and it makes it possible to process effectively.
Owner:KUHN PETER M
Video encoding device
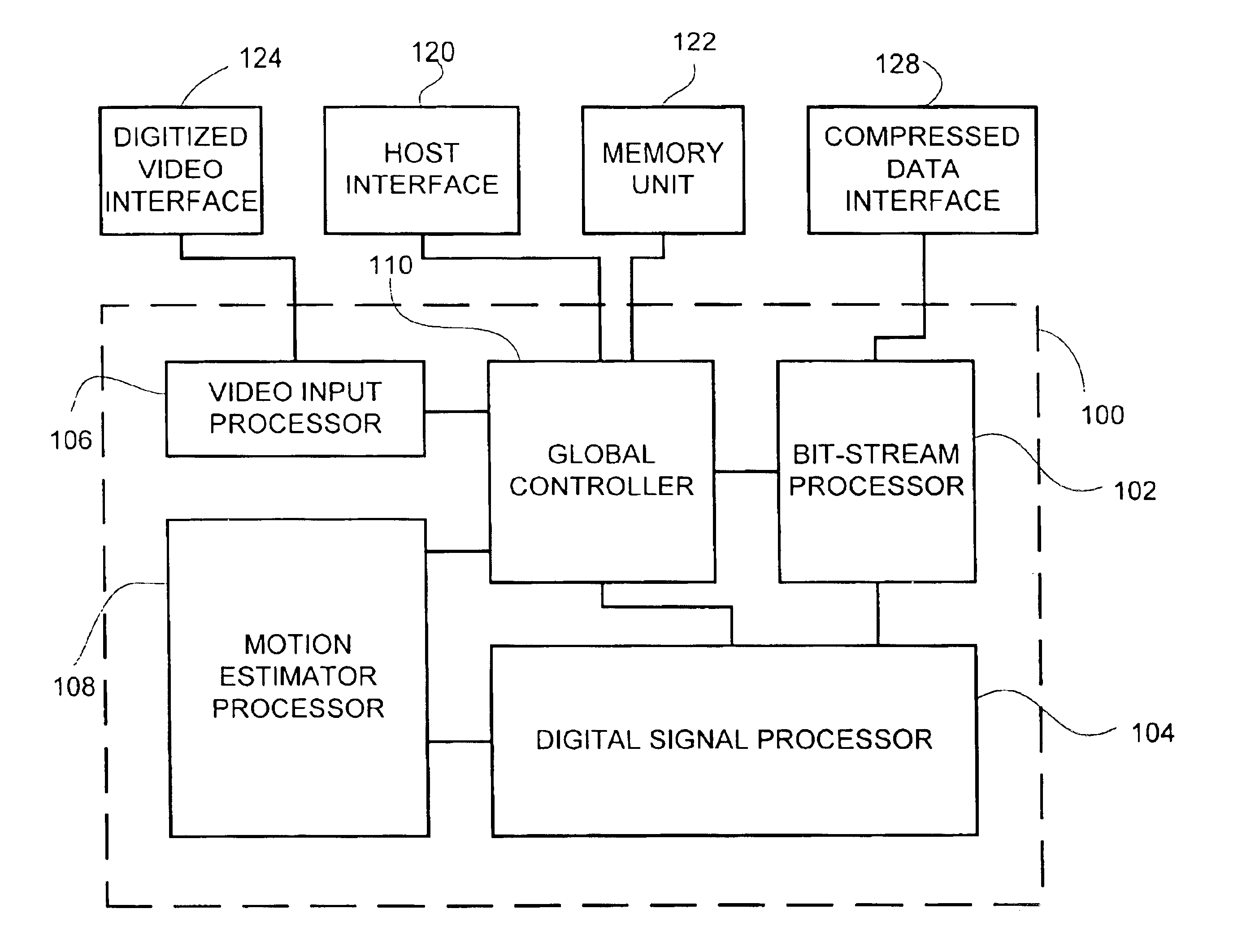
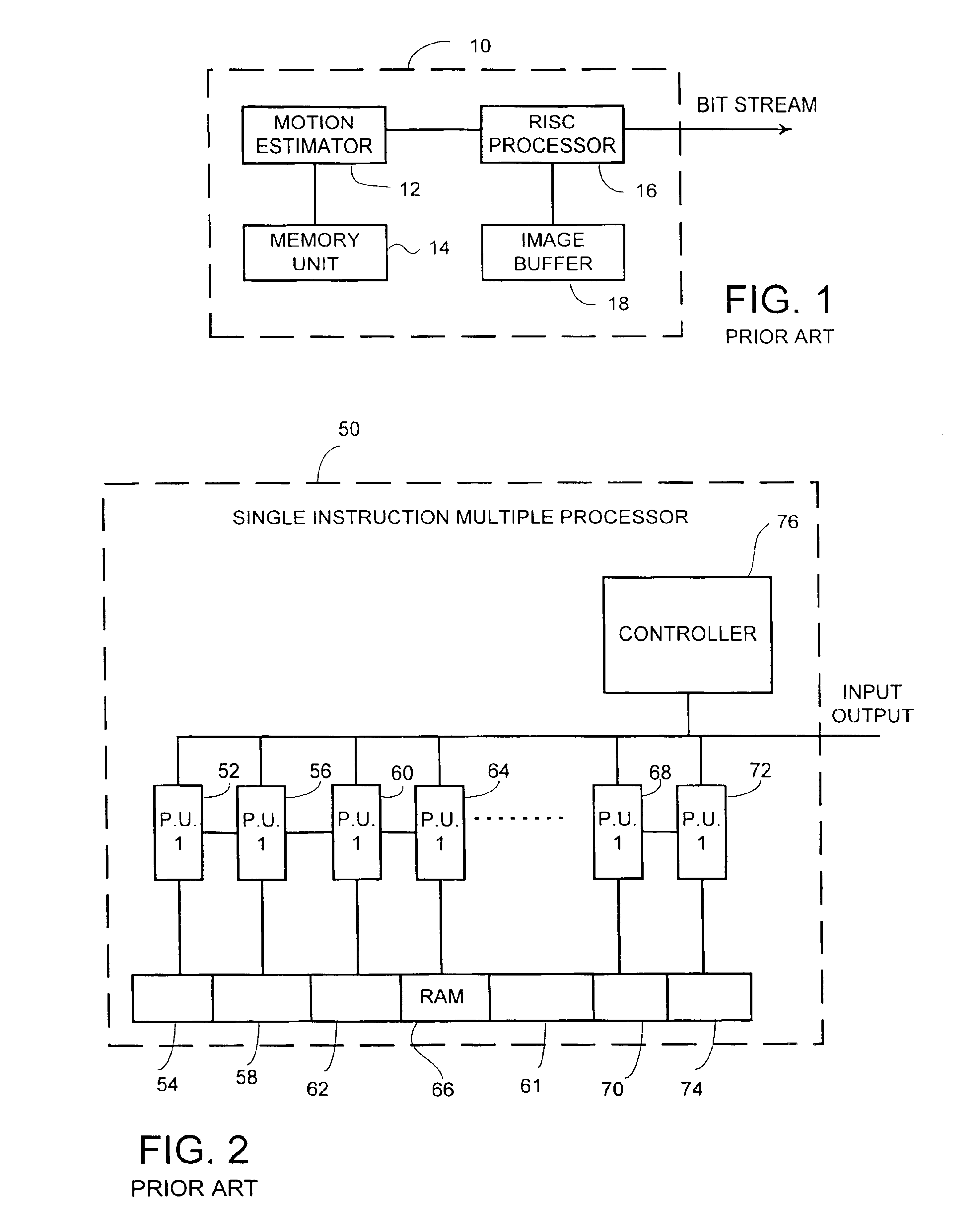
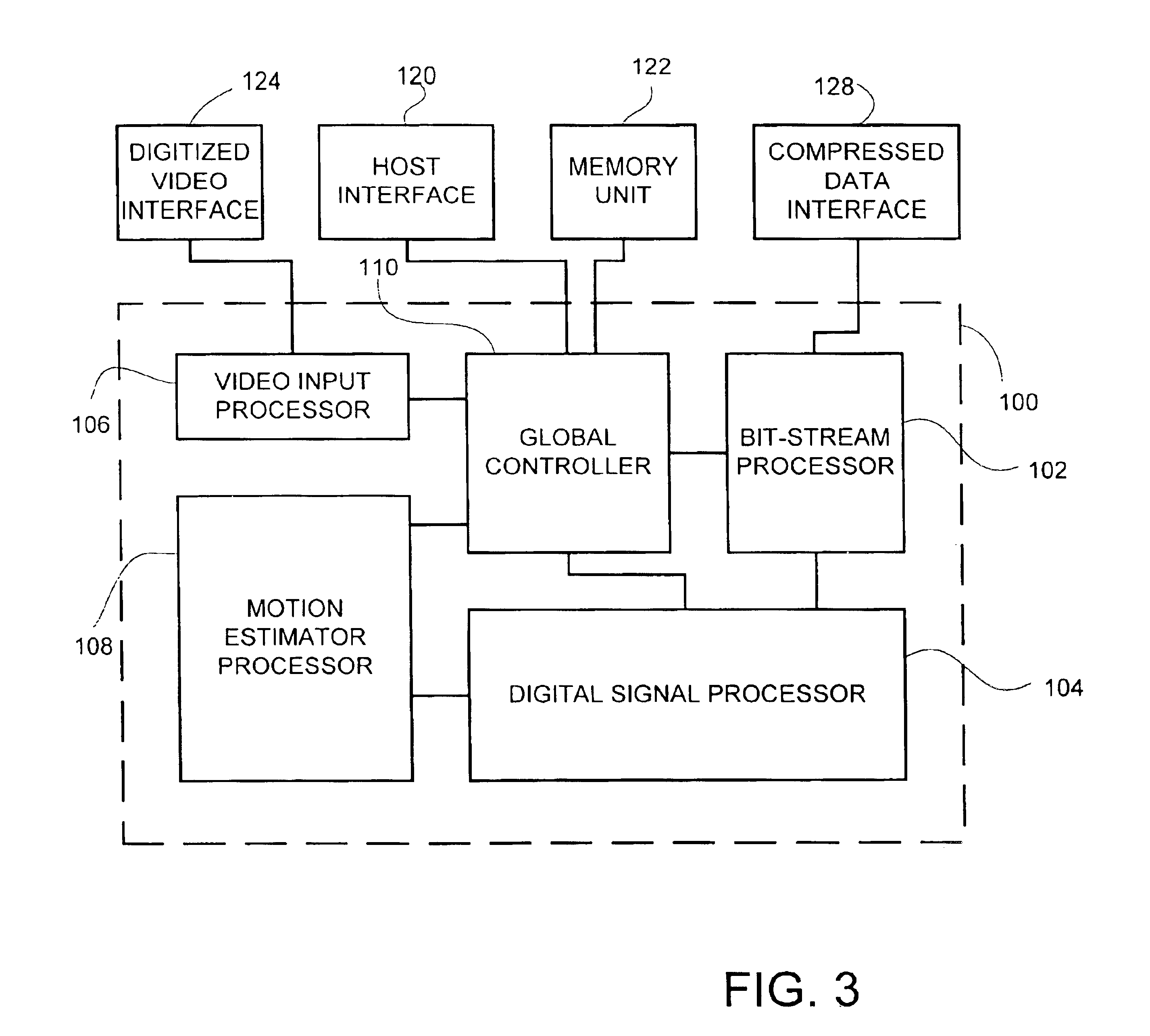
InactiveUS6847686B2Reduce selection requirementsIncrease choiceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionExternal storageVideo encoding
Video encoding device including a video input processor, for receiving said video signal, a global controller, for controlling the global operation of the video encoding device, a motion estimation processor, a digital signal processor and a bit-stream processor, wherein the global controller stores encodes commands received from a host interface thereby programming the video input processor, the motion estimation processor, the digital signal processor and the bit-stream processor, the video input processor receives and stores the video signal in an external memory unit, the motion estimation processor retrieves the video signal from the memory unit, generates motion analysis of the video signal, stores the motion analysis in the memory unit and provides the motion analysis to the digital signal processor, the digital signal processor processes the video signal according to the motion analysis, thereby producing an encoding commands sequence and encoded data, the bit-stream processor produces an encoded video signal according to the encoding command sequence and the encoded data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for scalable motion vector coding
InactiveUS20060193388A1Improve visual qualityReduce resolutionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorComputer science
A method and apparatus for scalable coding of a motion vector generated during motion estimation, in which a generated motion vector field is separated into a base layer and an enhancement layer according to pixel accuracies to obtain a layered structure for a motion vector. In addition, the motion vector field has a layered structure including a base layer composed of motion vectors of blocks larger than or equal to a predetermined size and at least one enhancement layer composed of motion vectors of blocks smaller than a predetermined size.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
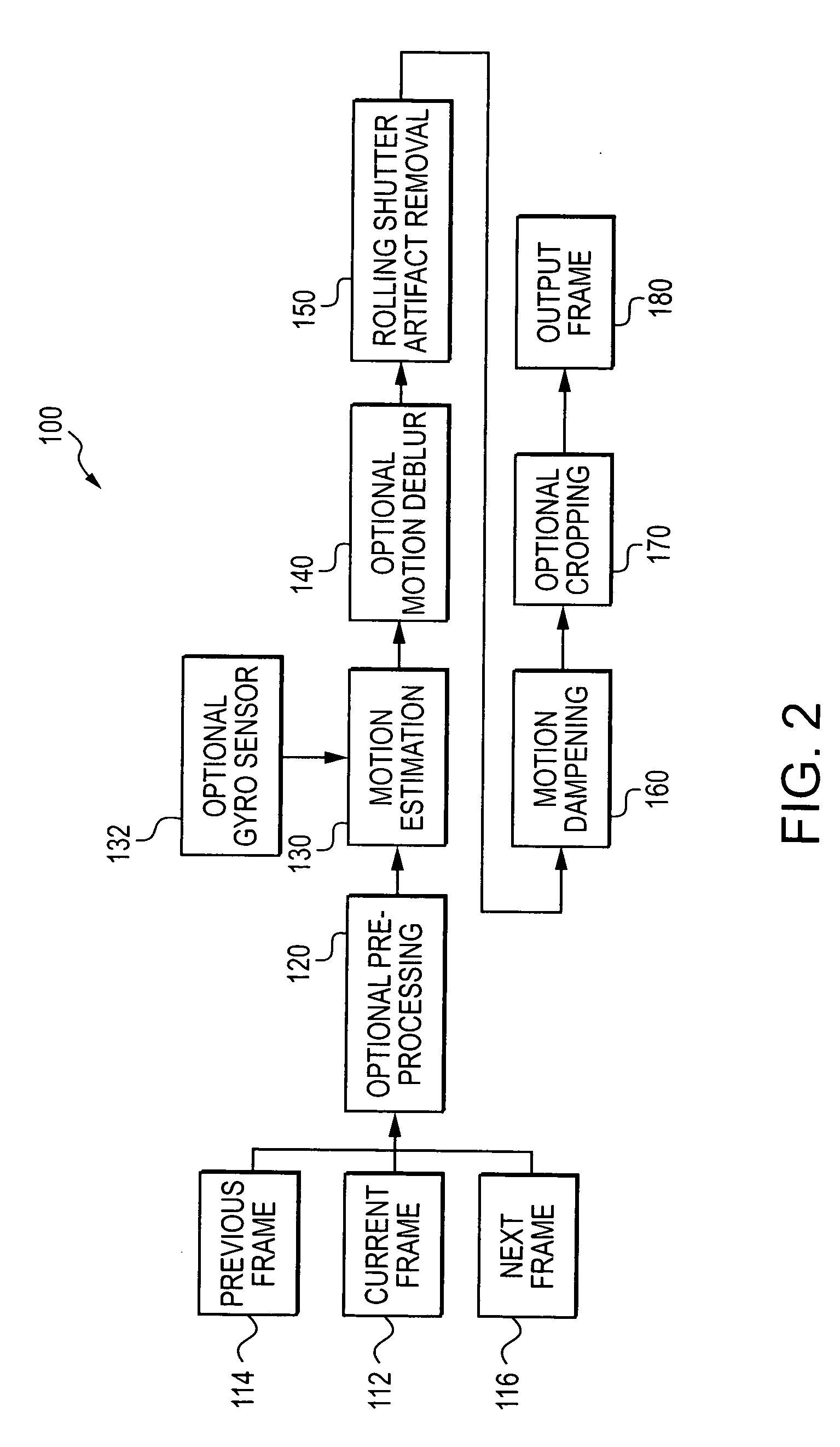
Methods and system for digitally stabilizing video captured from rolling shutter cameras
An imaging device and methods of stabilizing video captured using a rolling shutter operation. Motion estimation is used to determine a row motion vector for individual rows of a current frame of a pixel array. The row motion vectors are used to map the location of pixels in the current frame to a mapped frame representing a single acquisition time for the current frame.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
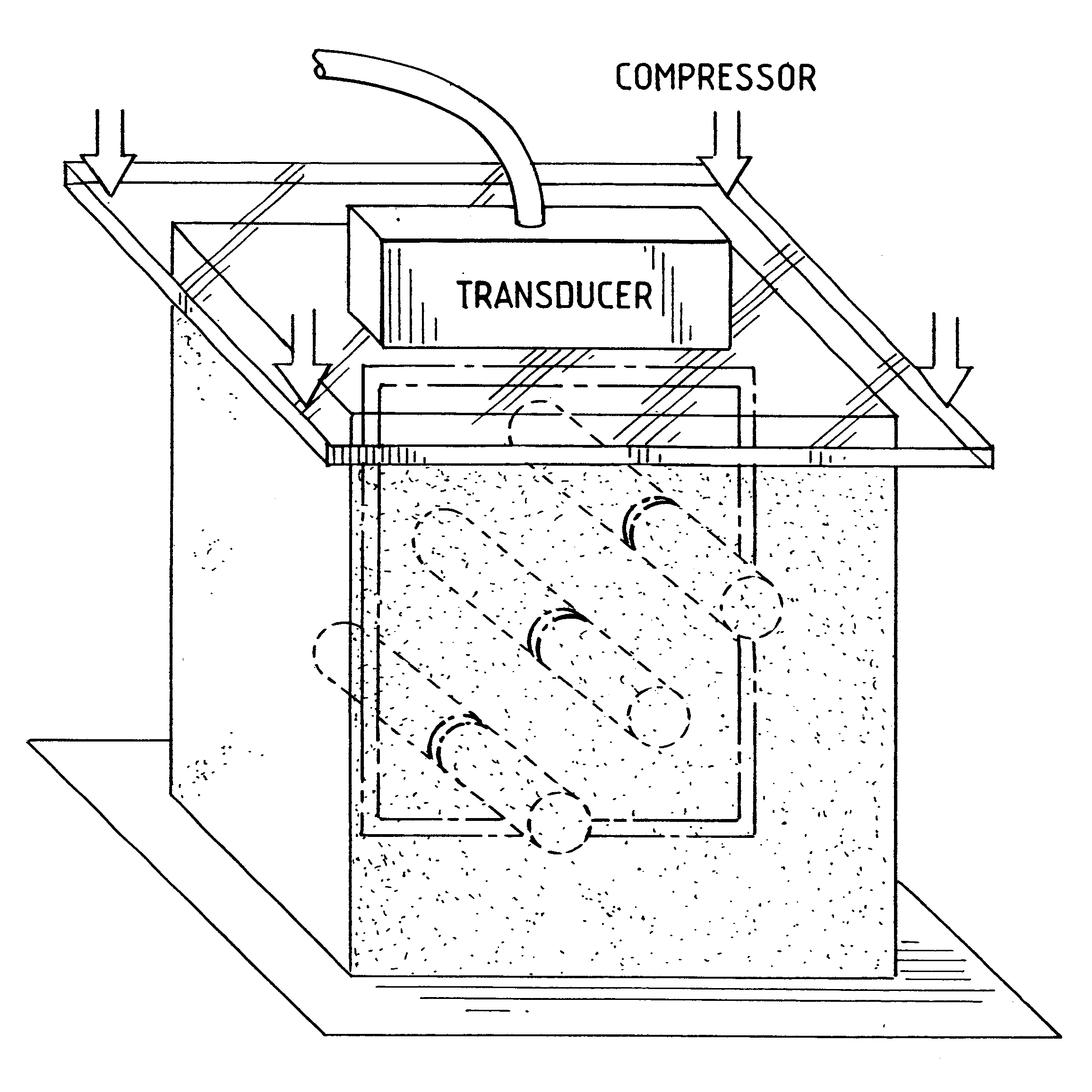
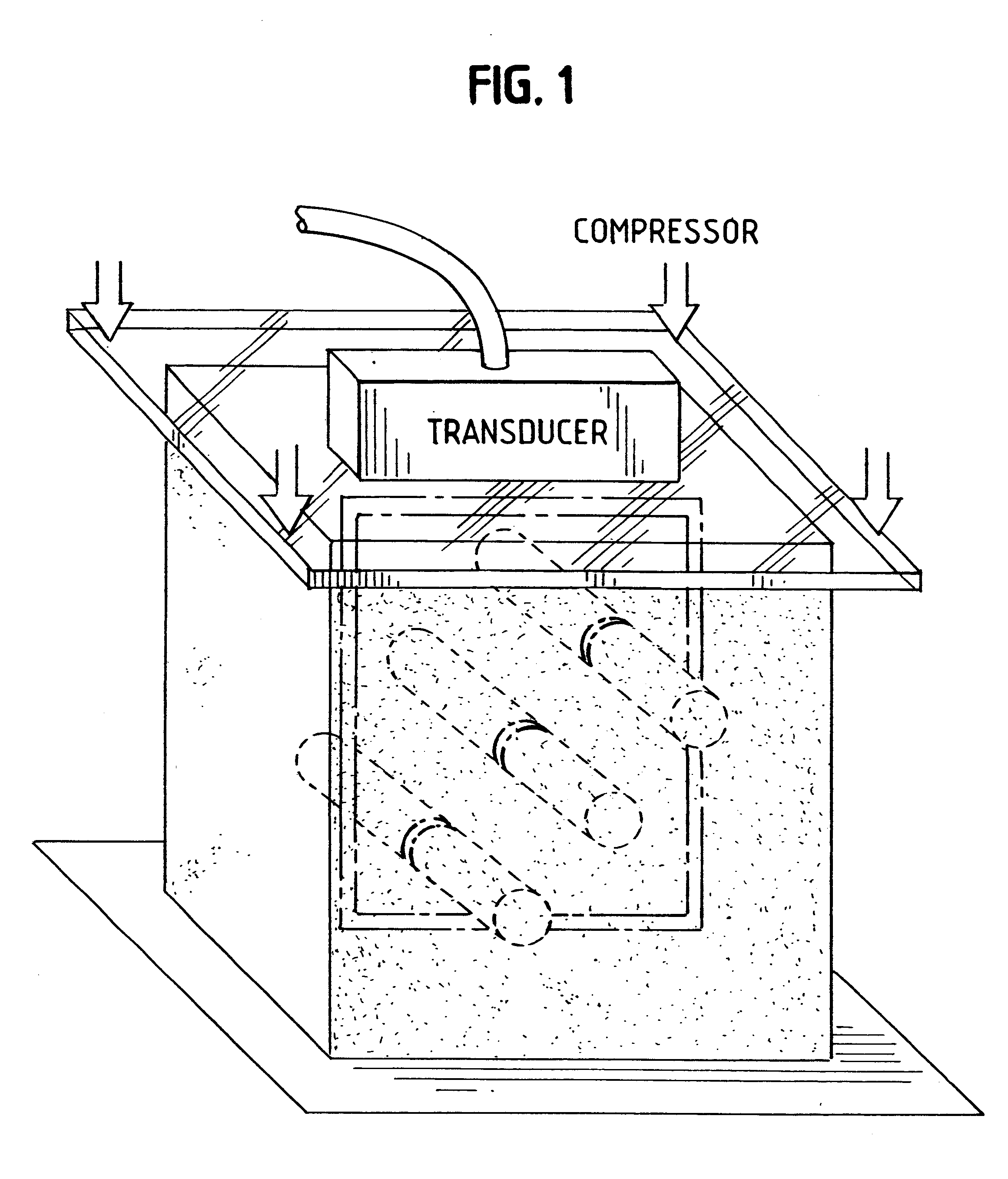
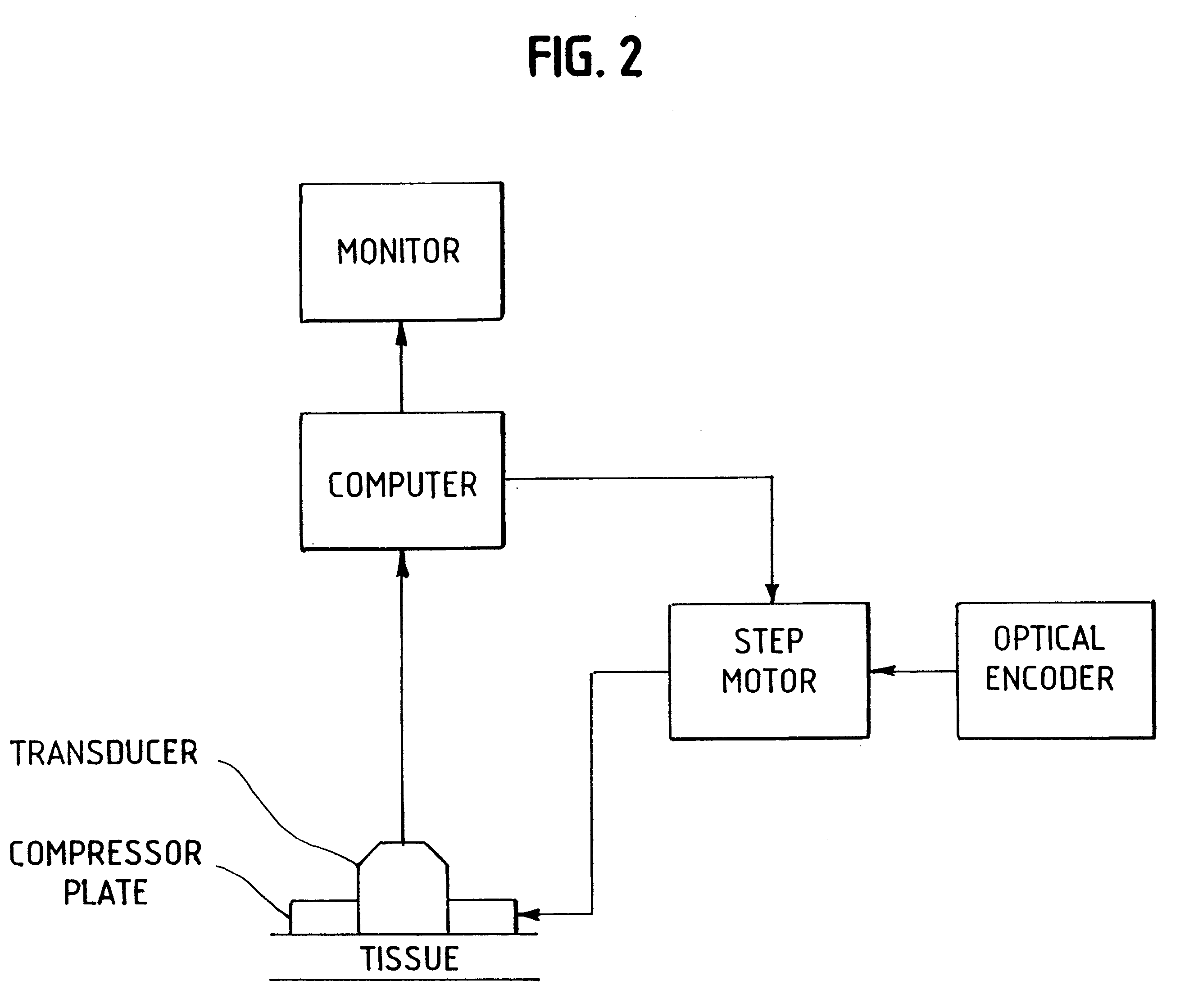
Method and apparatus for motion estimation within biological tissue
InactiveUS6277074B1Reduce noiseIncrease contrastOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostics using pressureAxial displacementData set
A method for motion estimation within biological tissue is disclosed. The method involves acoustically coupling a transducer to a target biological tissue, which transducer emits an ultrasonic signal and collects the energy back-scattered by the target issue. A first set of energy data is collected and stored, then target tissue is axially compressed and a second set of ultrasonic energy data is collected and stored. One of the first and second data sets is warped to account for the anticipated compression forming a warped data set. This warped data set is cross-correlated with the unwarped one of the first and said second data sets to obtain a fine scale displacement of said target biological tissue from the displacement estimated by the warping. This fine scale displacement is summed with the warped data set to obtain a total axial displacement. A gradient of the total axial displacement is taken and used to form a strain image. An apparatus for practicing this method is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV KANSAS MEDICAL CENT
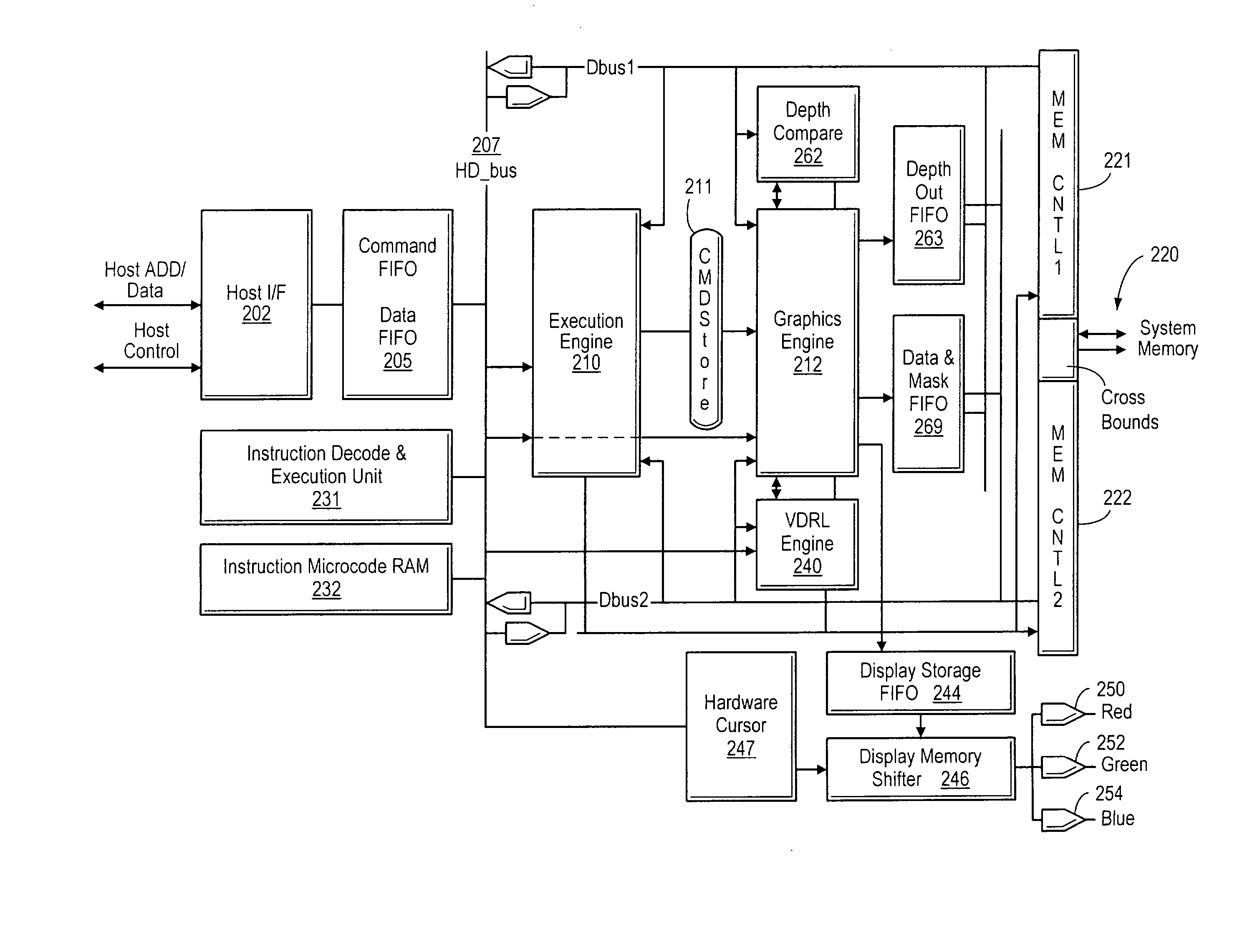
Video controller system with object display lists
InactiveUS20020145611A1Television system detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGraphicsScan line
A graphics controller which performs display list-based video refresh operations that enable objects with independent frame rates to be efficiently assembled is disclosed. The graphics controller maintains a virtual display refresh list (VDRL) comprising a plurality of pointers to scan line segments in memory. The graphics controller also creates, maintains, and deletes draw display lists (DDLs) that comprise pointers to object display list subroutines (ODLs) that independently draw objects in memory. The ODLs may allocated one or more buffers in memory into which different frames of the objects are drawn. When an ODL has completed executing, the corresponding pointer in the DDL may be updated to point to the buffer location in memory that stores the newly completed object frame. The VDRL is maintained independently (and may be doubled-buffered) and is updated using the DDLs. Motion estimation may be performed by the graphics controller using the different frames of objects that are drawn into memory by the ODLs. The different object frames may also be animated by the graphics controller once they are drawn into memory. The object frames stored in memory may be compressed to conserve memory.
Owner:DIGIMEDIA TECH LLC
Multiple-Candidate Motion Estimation With Advanced Spatial Filtering of Differential Motion Vectors
InactiveUS20100166073A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorEuclidean vector
Embodiments include a motion estimation method performed in a parallel processing system that determines a list of several candidate motion vectors for a macroblock of a video image and retains them through multiple computation passes. All candidate motion vectors are used as potential neighboring predictors, so that the best combination of differential vectors rises to the top of the candidate list. Numerous combinations of differential motion vectors are considered during the process that compares motion vectors among up to eight neighboring macroblocks, instead of simply between pairs of macroblocks. The motion estimation system is configured to use a large number of compute engines, such as on a highly parallel GPU platform. This is achieved by having no dependencies between macroblocks except one per pass. This allows the number of calculations per pass to be very large.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Real-time video coding/decoding
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
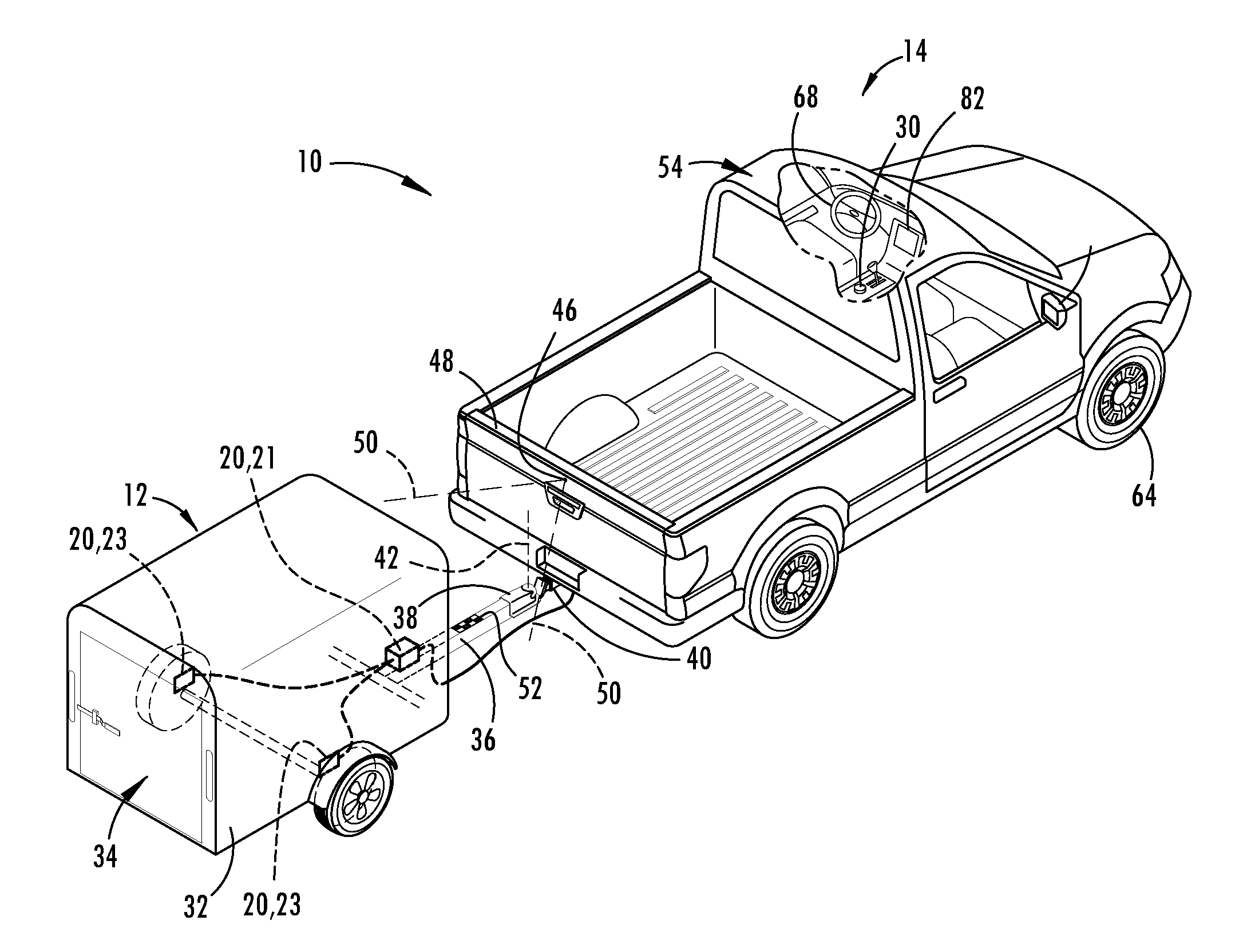
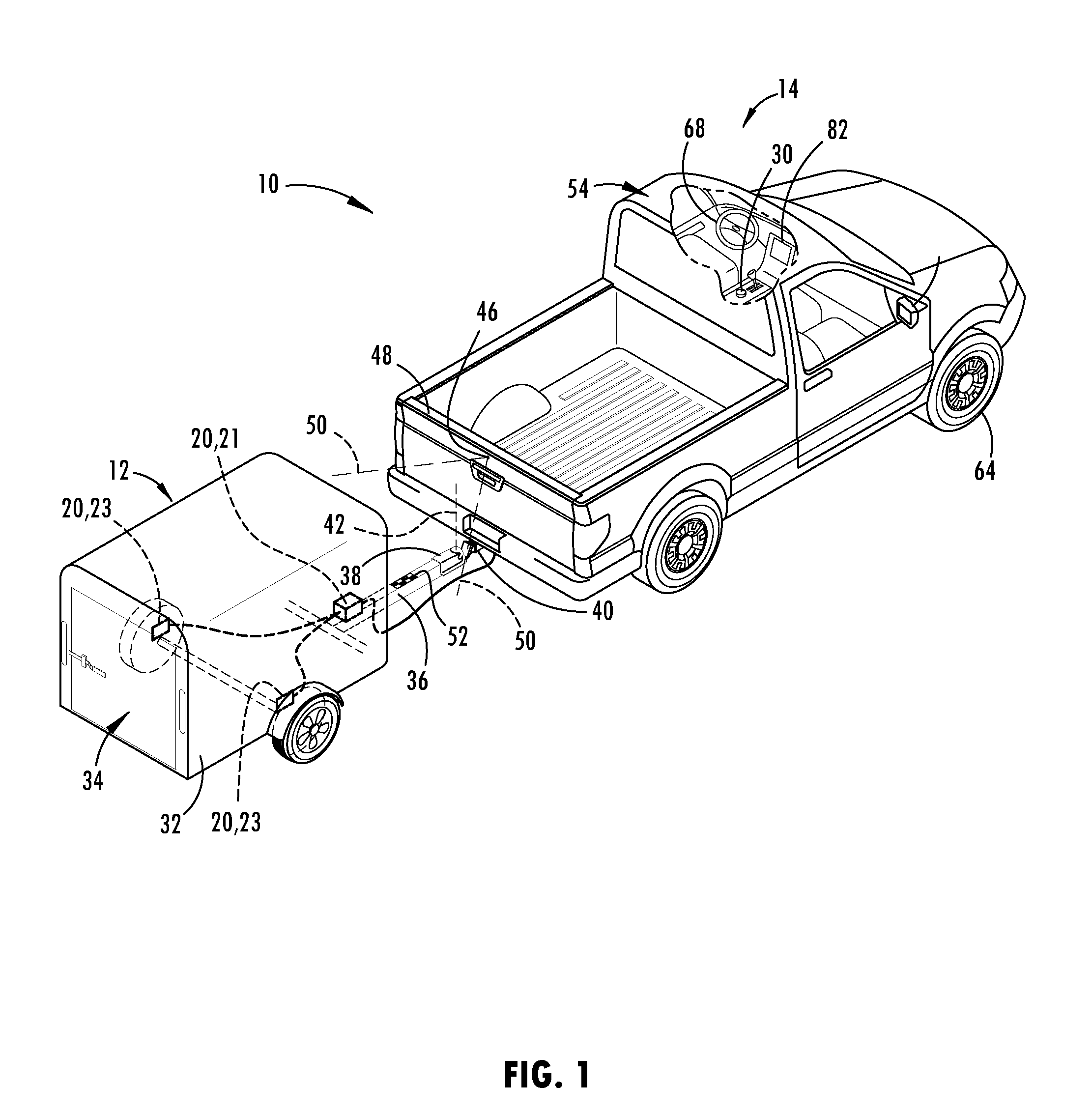
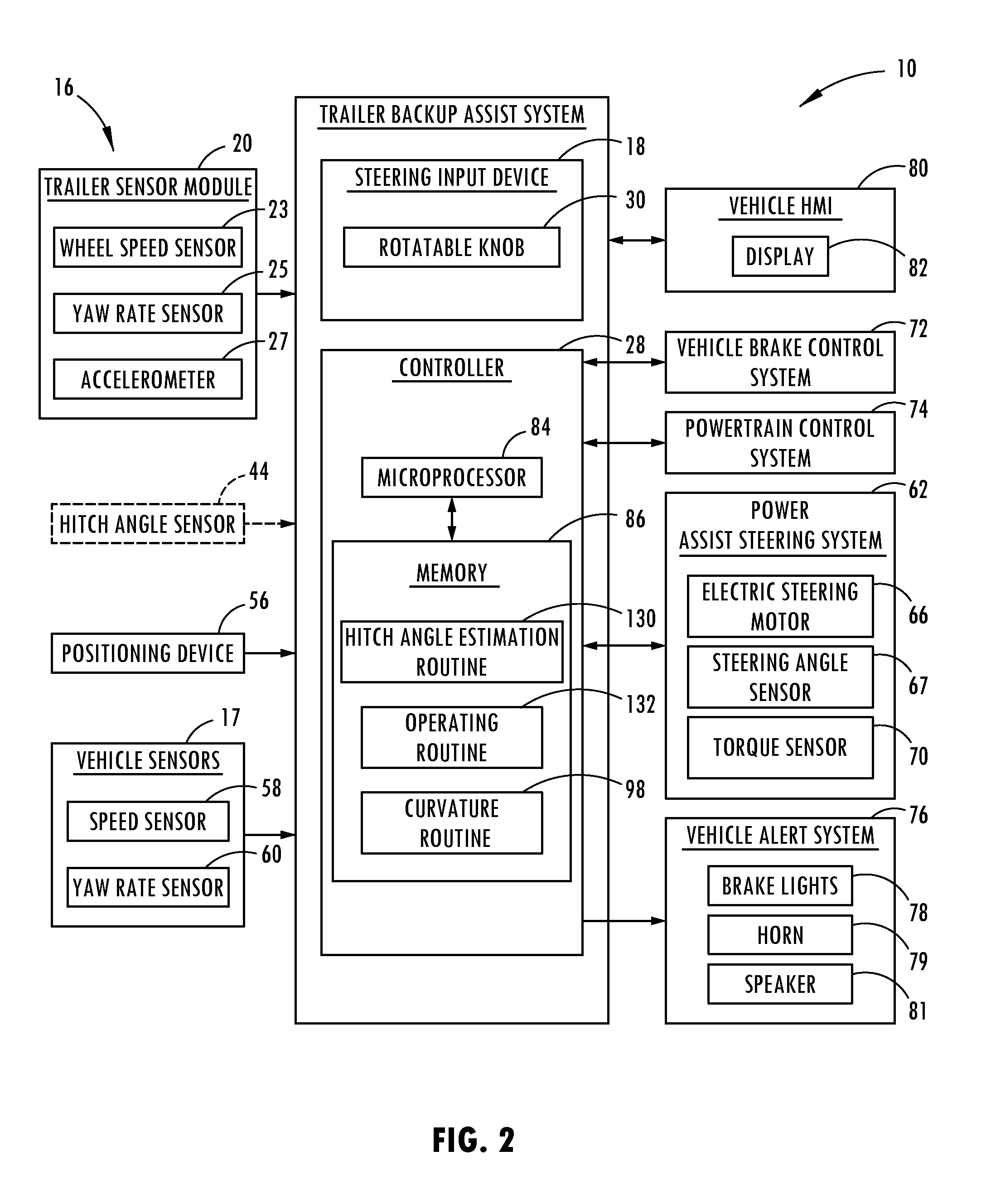
Trailer sensor module and associated method of wireless trailer identification and motion estimation
ActiveUS9315212B1Autonomous decision making processMeasurement devicesUnique identifierComputer module
A method of identifying a trailer with a vehicle includes a step of transmitting a unique identifier with a wireless transmitter attached to the trailer. The wireless transmitter may be housed as part of a sensor module with a sensor that senses a parameter of the trailer for operating a trailer backup assist system. The housing of the sensor module may be adapted to be removably attached to the trailer. The unique identifier emitted by the wireless transmitter is received with a wireless receiver on the vehicle. After the unique identifier is recognized by a controller on the vehicle, a parameter of the trailer may be accessed for autonomously guiding the trailer along a desired backing path.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
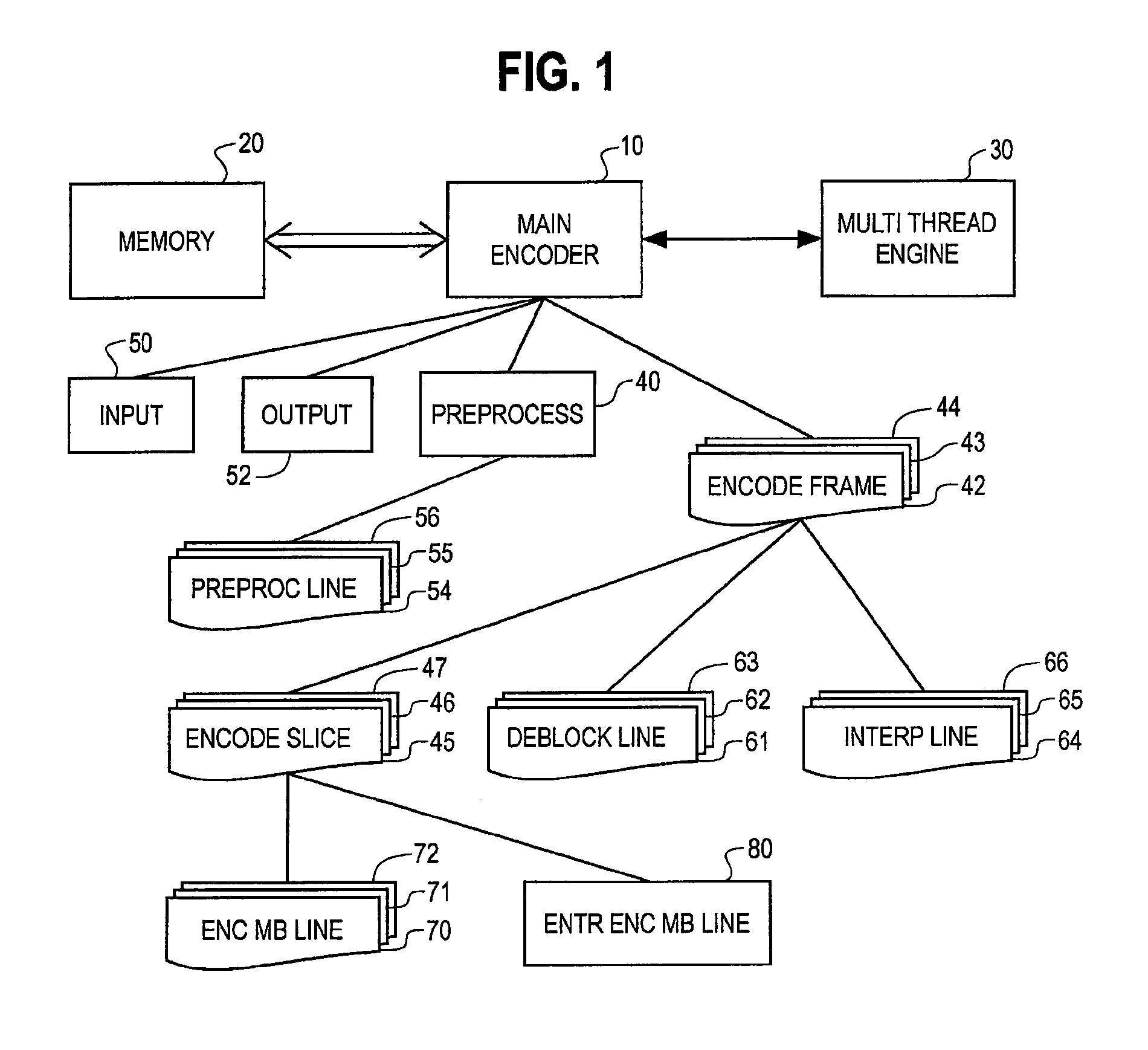
Real-time video coding/decoding
ActiveUS8023562B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureModularity
A video codec having a modular structure for encoding / decoding a digitized sequence of video frames in a multi-core system is described. The video codec comprises a memory unit; a multithreading engine. and a plurality of control and task modules organized in a tree structure, each module corresponding to a coding operation. The modules communicate with each other by control messages and shared memory. The control modules control all coding logic and workflow, and lower level task modules perform tasks and provide calculations upon receiving messages from the control task modules. The multithreading engine maintains context of each task and assigns at least one core to each task for execution. The method of coding / decoding comprises denoising, core motion estimation, distributed motion estimation, weighted texture prediction and error resilient decoding.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
Supporting region-of-interest cropping through constrained compression
InactiveUS20100232504A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
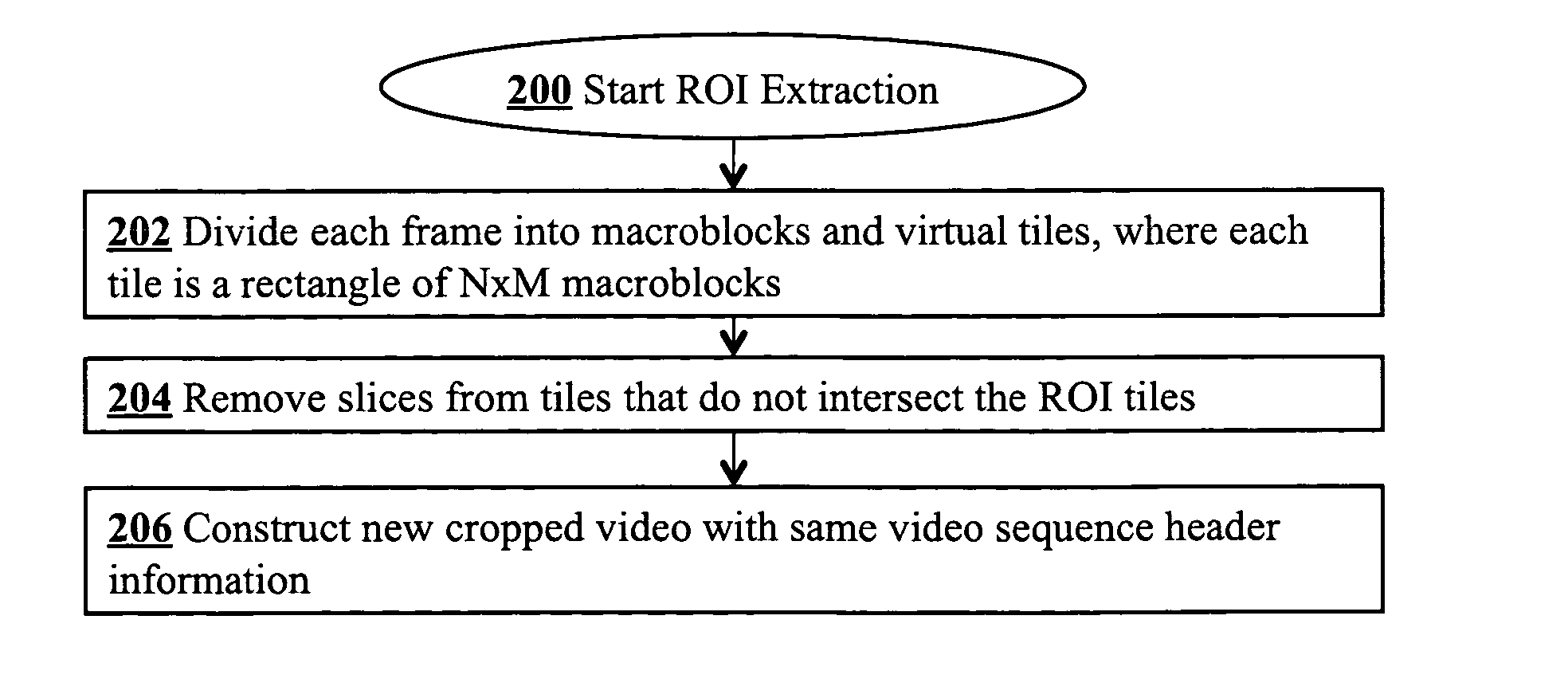
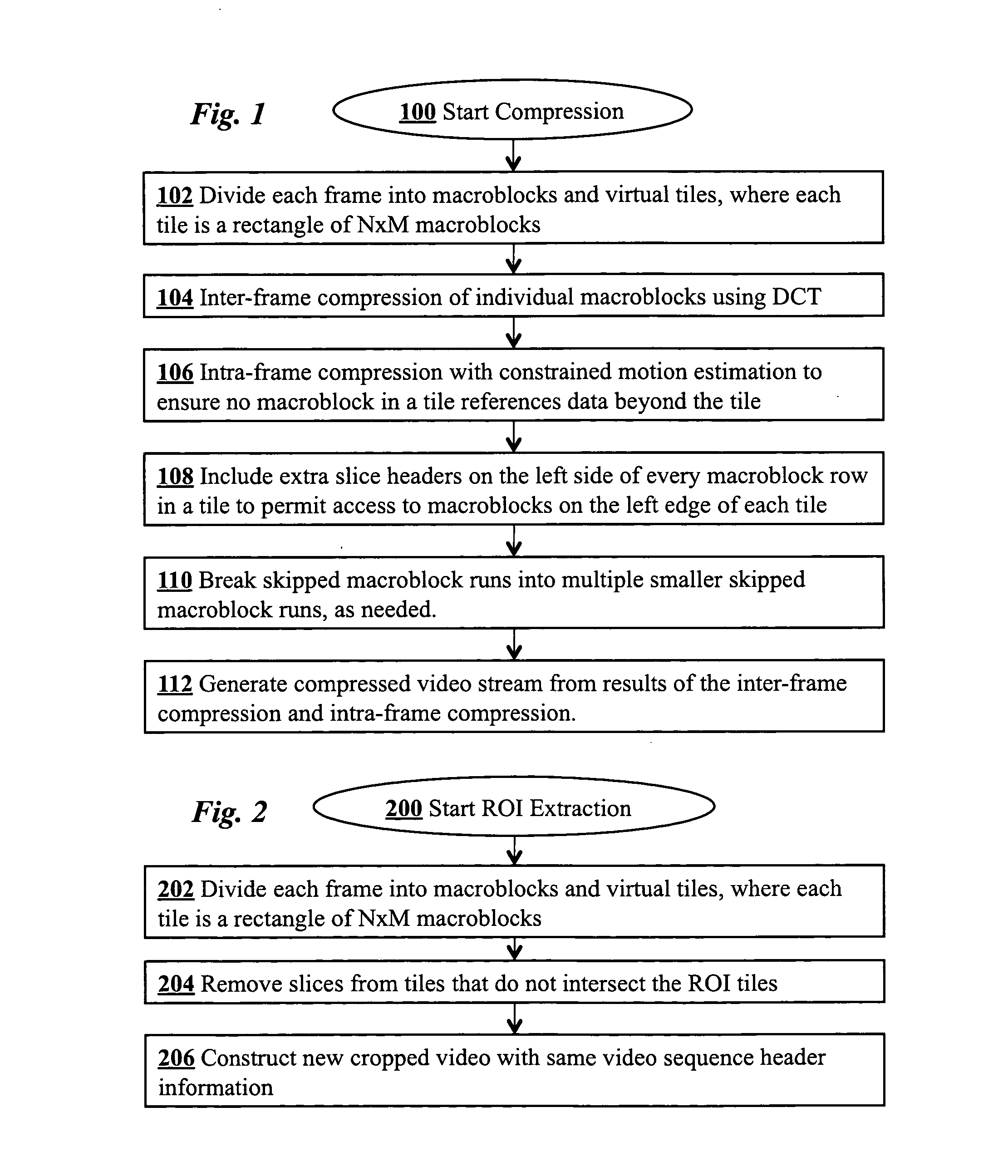
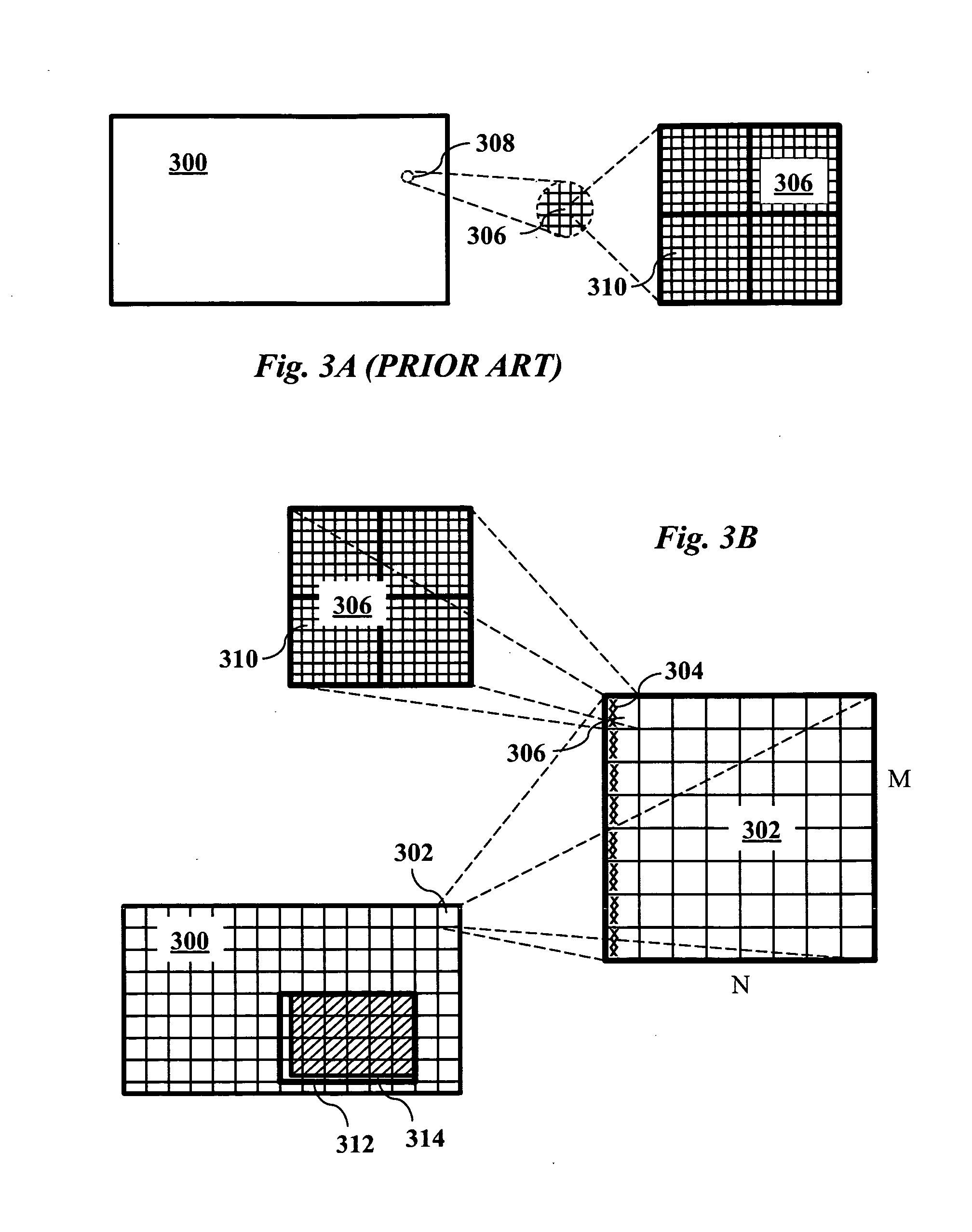
Region-of-interest cropping of high-resolution video is supported video compression and extraction methods. The compression method divides each frame into virtual tiles, each containing a rectangular array of macroblocks. Intra-frame compression uses constrained motion estimation to ensure that no macroblock references data beyond the edge of a tile. Extra slice headers are included on the left side of every macroblock row in the tiles to permit access to macroblocks on the left edge of each tile during extraction. The compression method may also include breaking skipped macroblock runs into multiple smaller skipped macroblock runs. The extraction method removes slices from virtual tiles that intersect the region-of-interest to produce cropped frames. The cropped digital video stream and the compressed digital video stream have the same video sequence header information.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV
Systems and methods for tracking objects in video sequences
InactiveUS6901110B1Reduce computational overheadPrevent steppingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMotion vectorMean difference
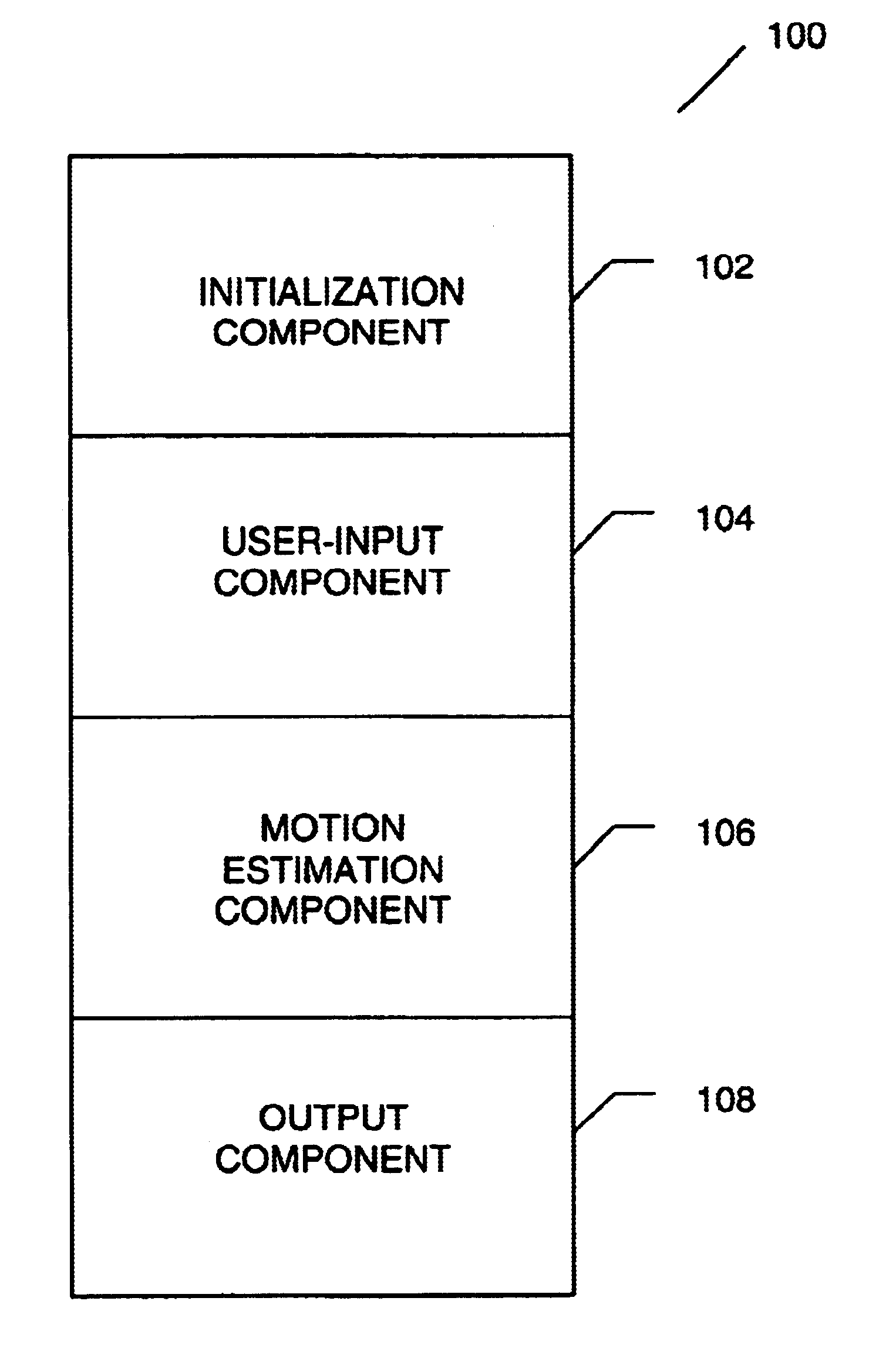
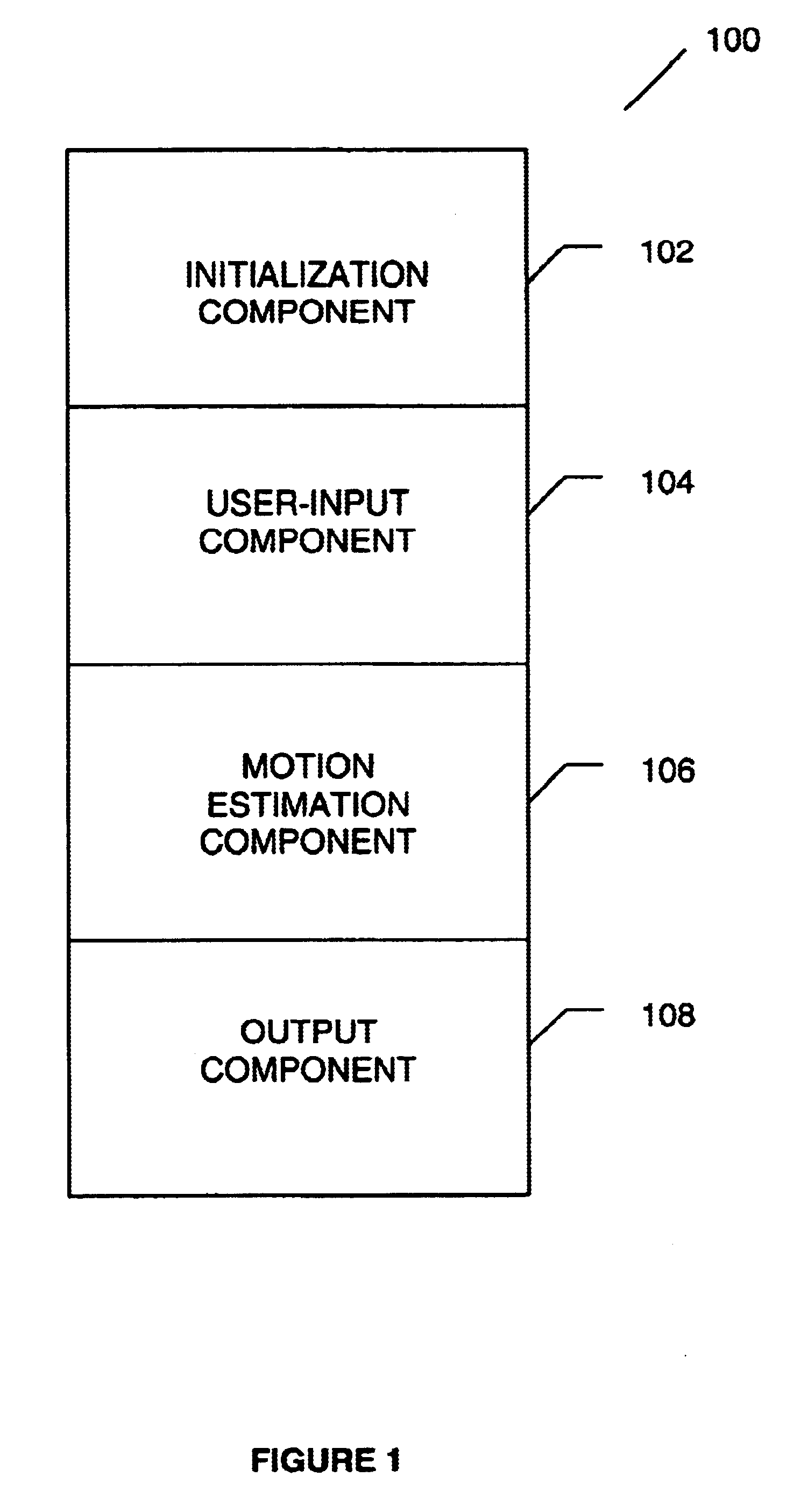
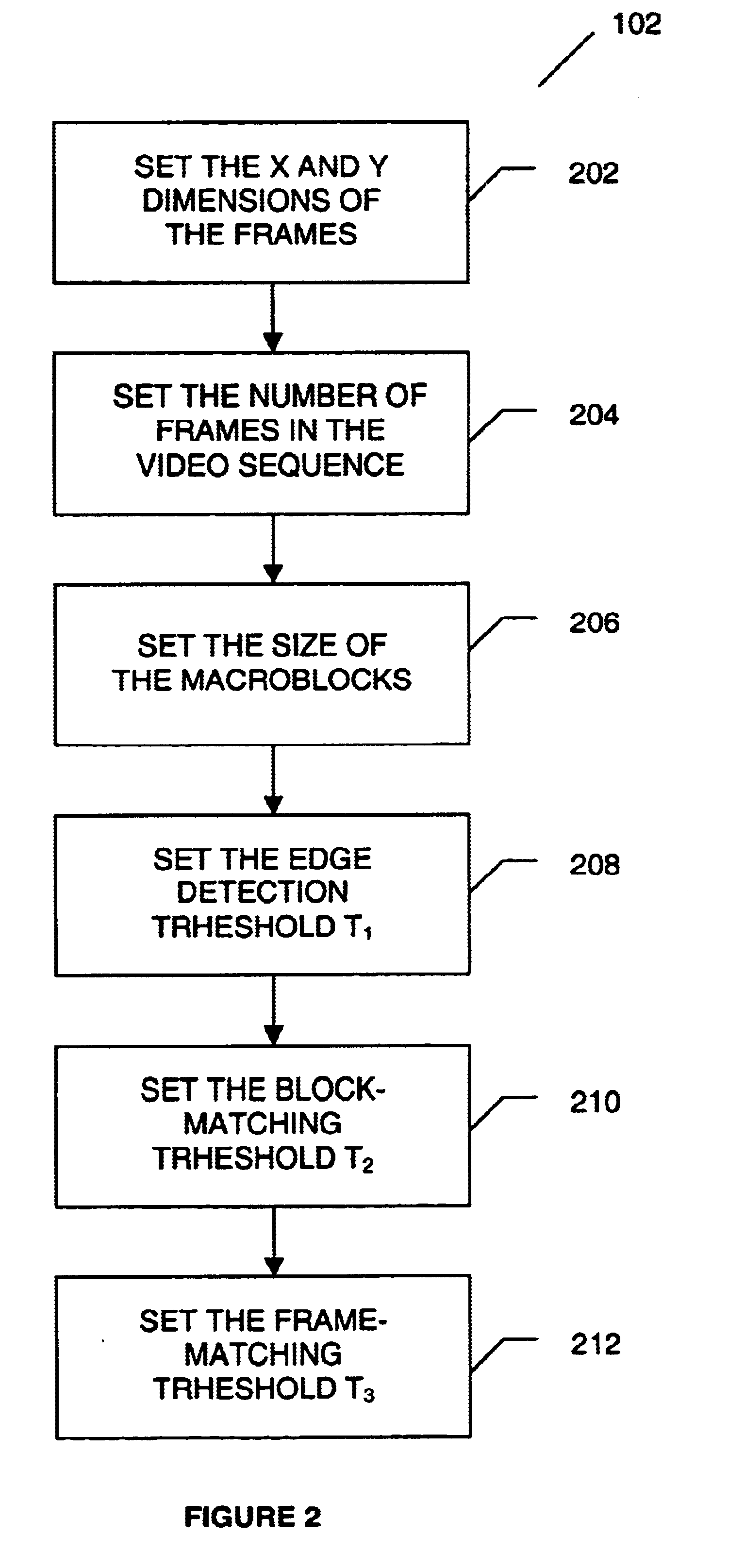
A method for tracking one or multiple objects from an input video sequence allows a user to select one or more regions that contain the object(s) of interest in the first and the last frame of their choice. An initialization component selects the current and the search frame and divides the selected region into equal sized macroblocks. An edge detection component computes the gradient of the current frame for each macroblock and a threshold component decides then which of the macroblocks contain sufficient information for tracking the desired object. A motion estimation component computes for each macroblock in the current frame its position in the search frame. The motion estimation component utilizes a search component that executes a novel search algorithm to find the best match. The mean absolute difference between two macroblocks is used as the matching criterion. The motion estimation component returns the estimated displacement vector for each block. An output component collects the motion vectors of all the predicted blocks and calculates the new position of the object in the next frame.
Owner:SONY CORP
Video coding
InactiveUS6208761B1Reduce in quantityEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsVideo sequenceBit plane coding
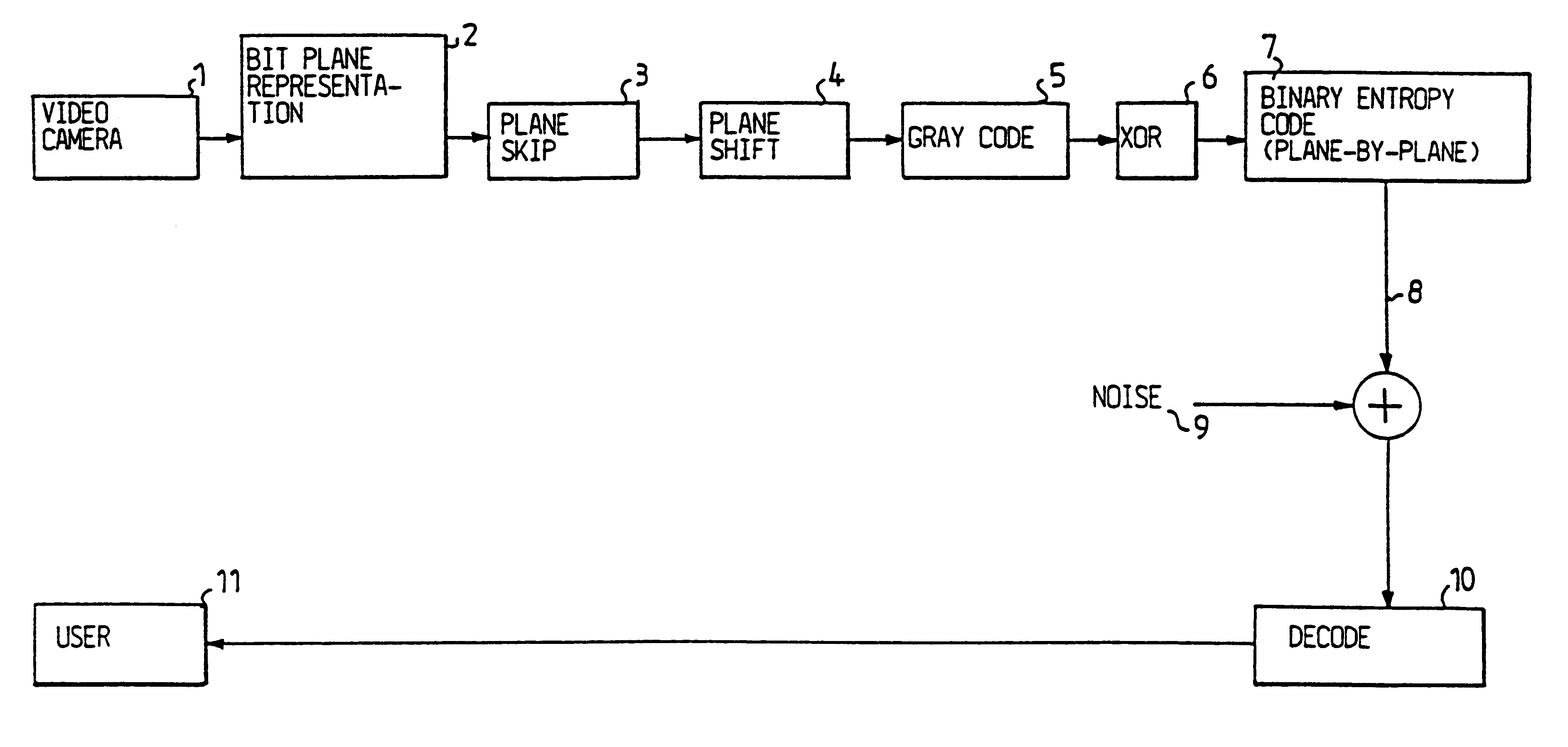
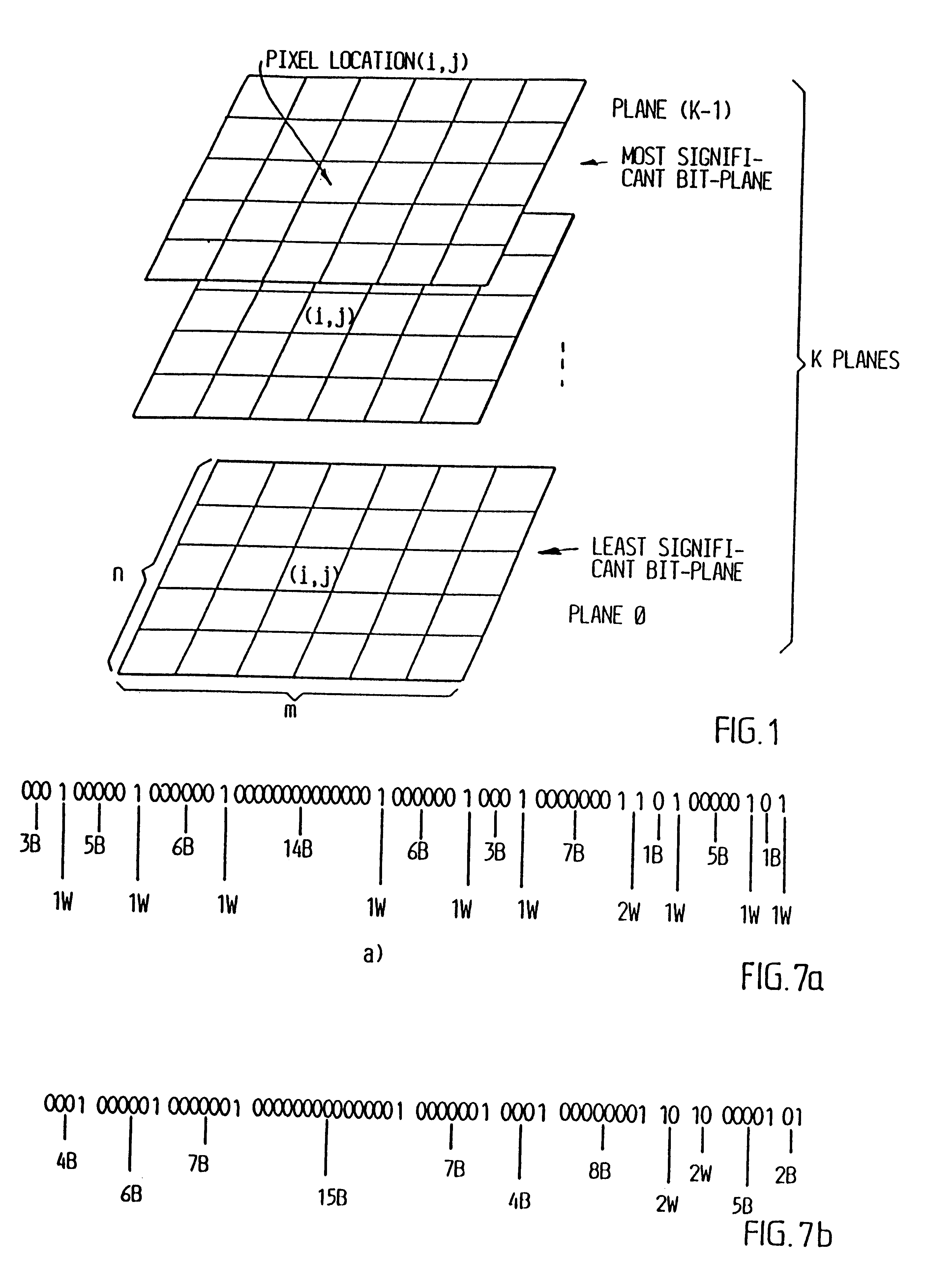
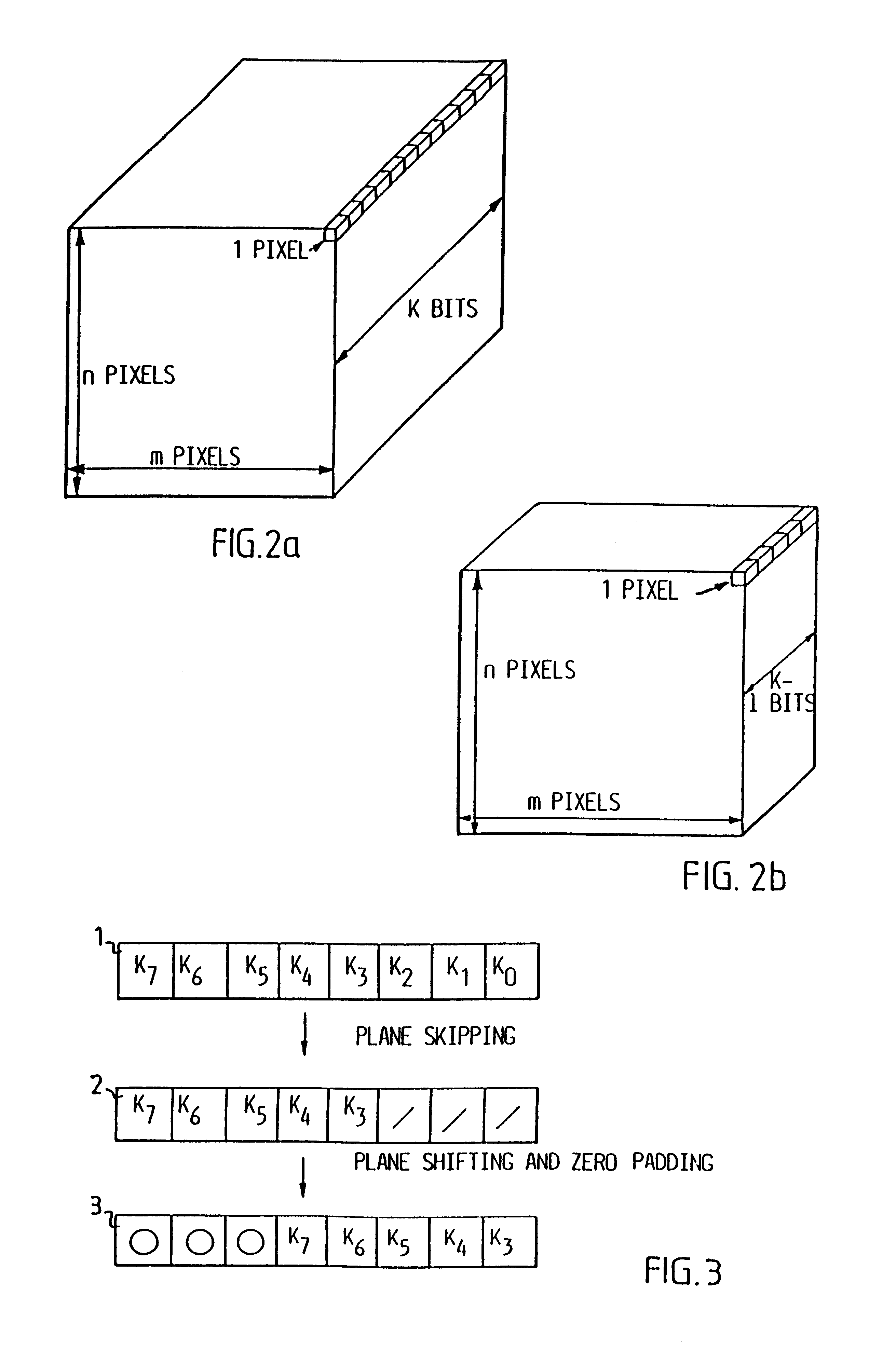
Digitalized video images are compressed in several steps in order to provide a system for transmitting moving video pictures via narrow band channels, such as the telephone network. The system is based on any extension of the bit-plane coding technique to video sequences and lossy conditions. The compression technique can also be advantageously used in a lossless compression system. The system involves the steps of bit plane representation and skipping the least significant bit plane(s), shifting the pixels, coding with a Gray code, the use of segmentation, and motion-estimation / motion compensation and application of a transmit / not transmit / motion compensate (TX / NT / MC) procedure, exploiting of the temporal redundancy of two corresponding bit planes via an XOR operation on two successive images, and a plane-by-plane application of an extended RLEID technique. The RLEID technique includes coding a run of like binary symbols with one word, the run including a transition between the penultimate and ultimate binary symbol.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
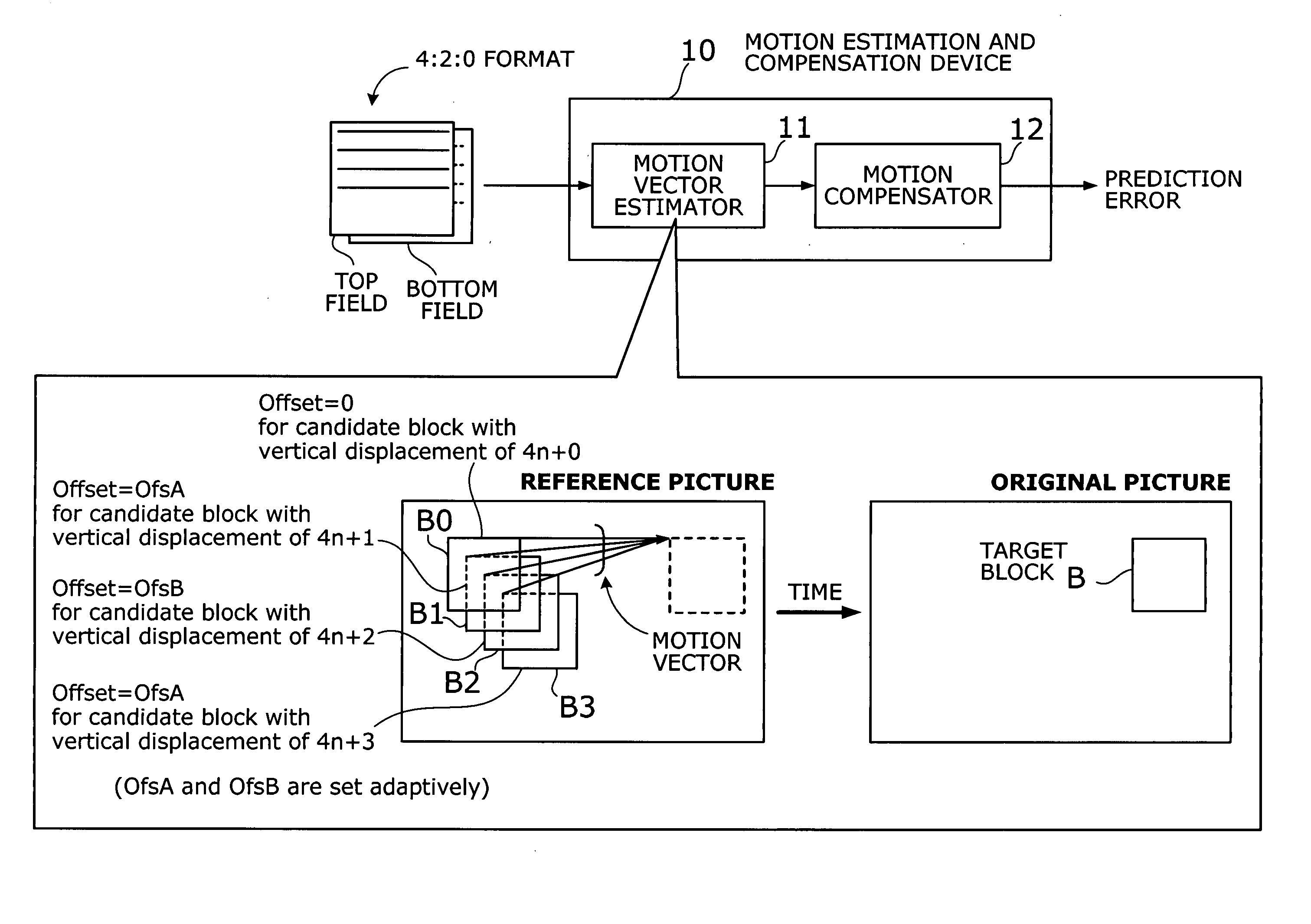
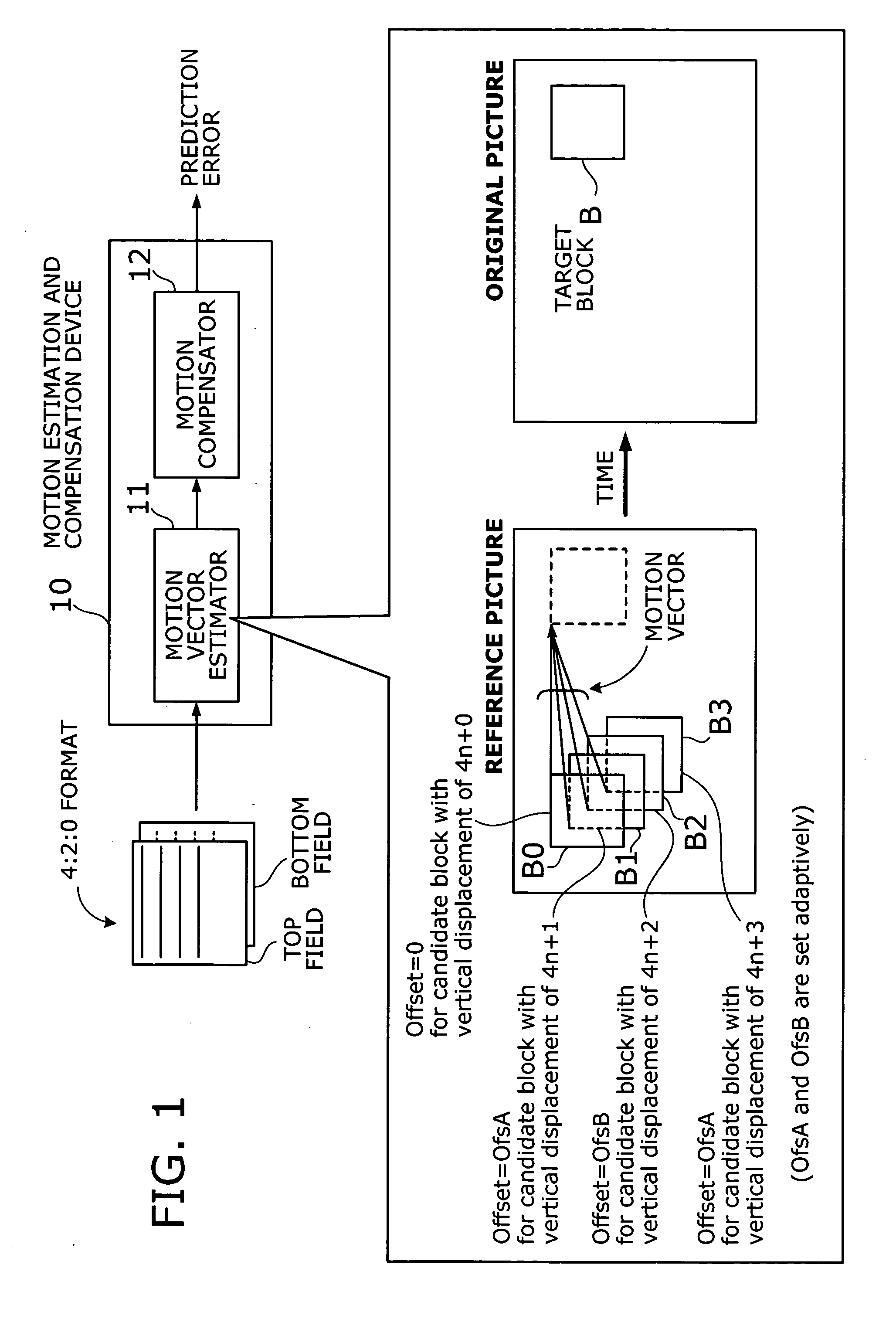
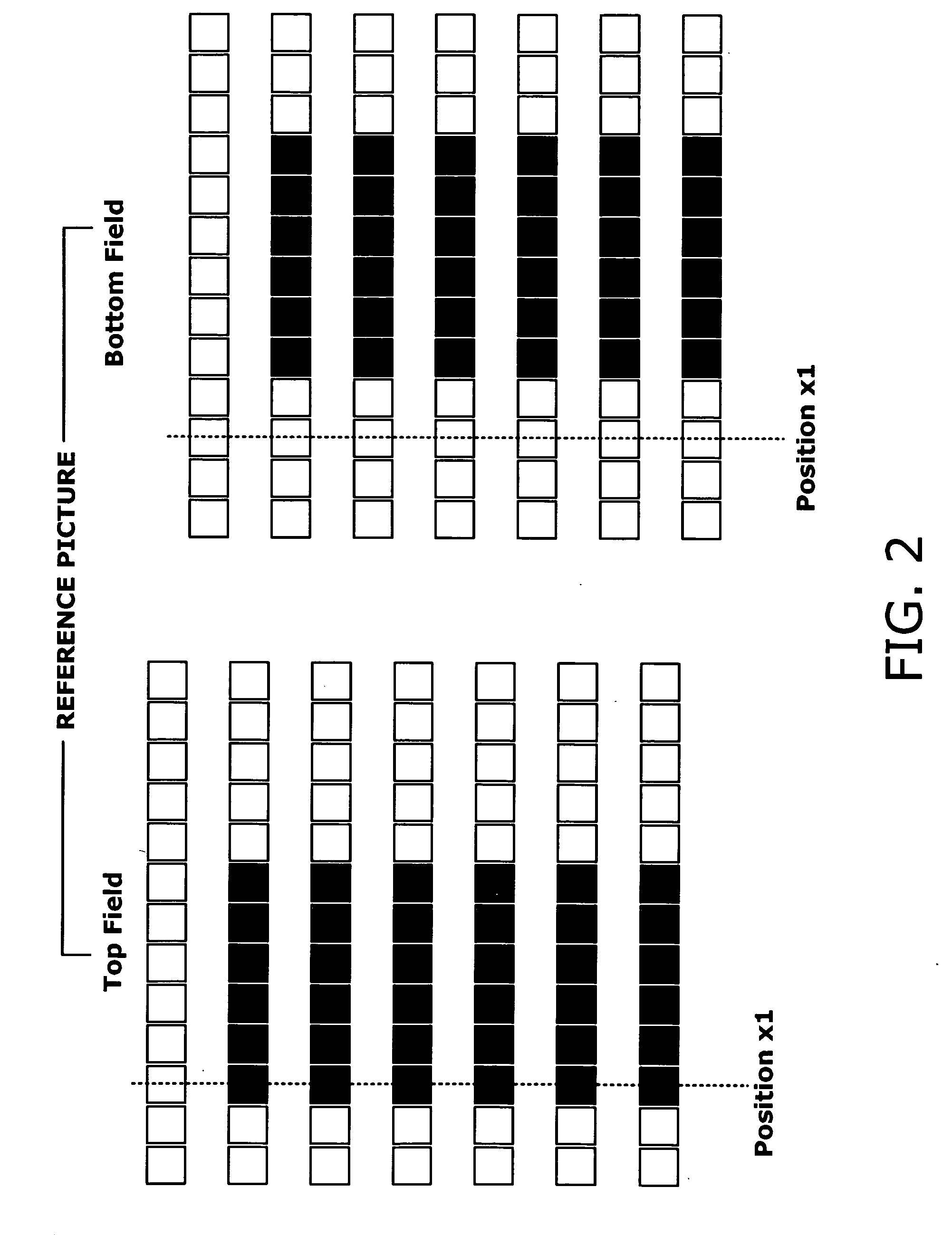
Motion estimation and compensation device with motion vector correction based on vertical component values
InactiveUS20060023788A1Color television with pulse code modulationImage analysisMotion vectorErrors and residuals
A motion estimation and compensation device that avoids discrepancies in chrominance components which could be introduced in the process of motion vector estimation. The device has a motion vector estimator for finding motion vectors in given interlace-scanning chrominance-subsampled video signals. The estimator compares each candidate block in a reference picture with a target block in an original picture by using a sum of absolute differences (SAD) in luminance as similarity metric, chooses a best matching candidate block that minimizes the SAD, and determines its displacement relative to the target block. In this process, the estimator gives the SAD of each candidate block an offset determined from the vertical component of a corresponding motion vector, so as to avoid chrominance discrepancies. A motion compensator then produces a predicted picture using such motion vectors and calculates prediction error by subtracting the predicted picture from the original picture.
Owner:FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS LTD
Method and apparatus for inter prediction encoding/decoding an image using sub-pixel motion estimation
ActiveUS20090092188A1Minimize the numberColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionPrecoding
A method of inter prediction encoding of an image, the method including: searching for a first reference block in a reference picture by using a current block, and estimating a first motion vector in a first pel unit in regards to the first reference block; estimating a second motion vector by using pixels included in a pre-encoded area adjacent to the current block, and pixels adjacent to the first reference block, and determining a second reference block based on the second motion vector; and encoding the current block based on the first motion vector and the second reference block.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
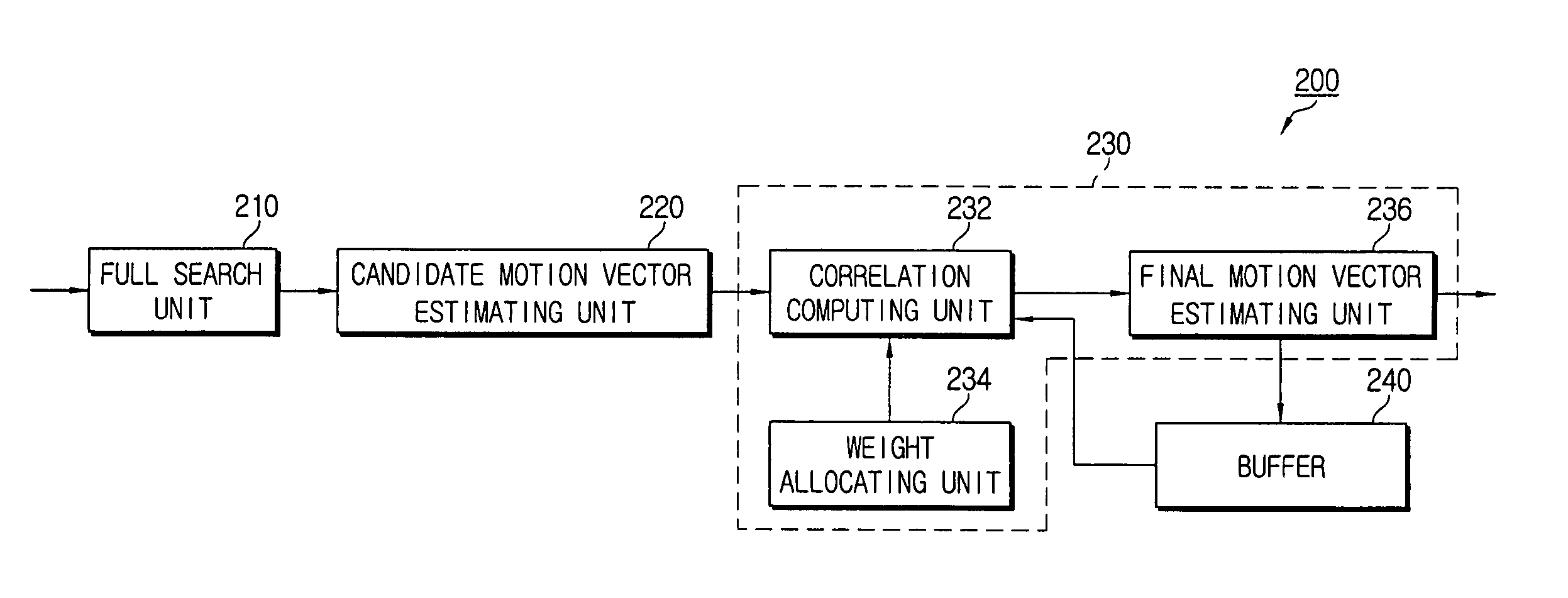
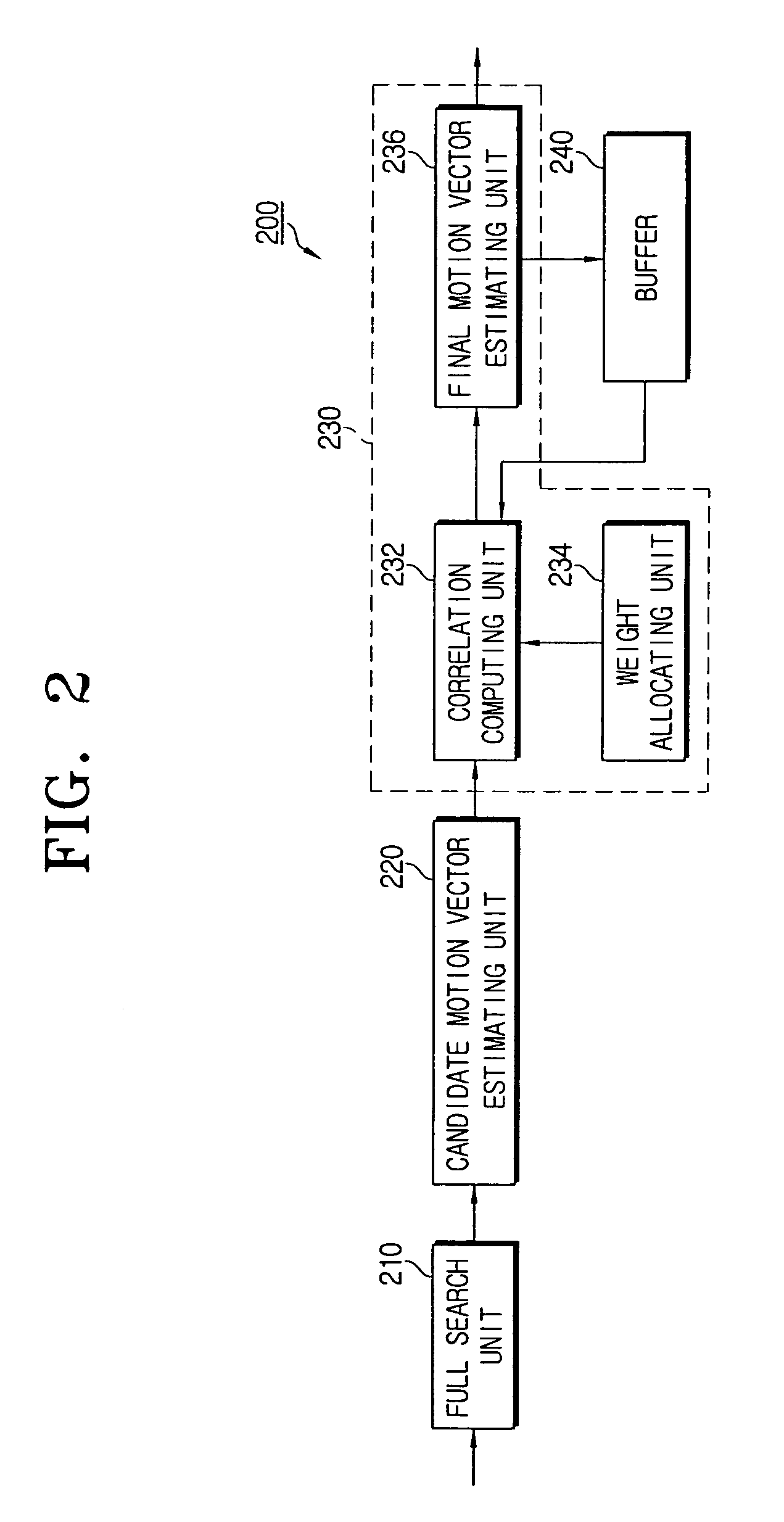
Apparatus for estimating motion considering correlation between blocks and method thereof
A motion estimation apparatus and a method considers a correlation between blocks. The motion apparatus includes a full search unit which divides a current frame / field into blocks of predetermined size and estimates an arbitrary motion vector of each block by a full search algorithm; a candidate motion vector estimating unit which computes a plurality of motion prediction error values by applying a block matching algorithm (BMA) to a current block and estimates candidate motion vectors from motion prediction error values below a predetermined threshold; a motion compensating unit which computes a correlation between respective candidate motion vectors and the motion vectors of adjacent blocks and compensates one among the candidate motion vectors to a final motion vector of the current block based on the computed correlation. By estimating motion vector of the current block in consideration of the correlation between the blocks, images free of block artifact can be provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
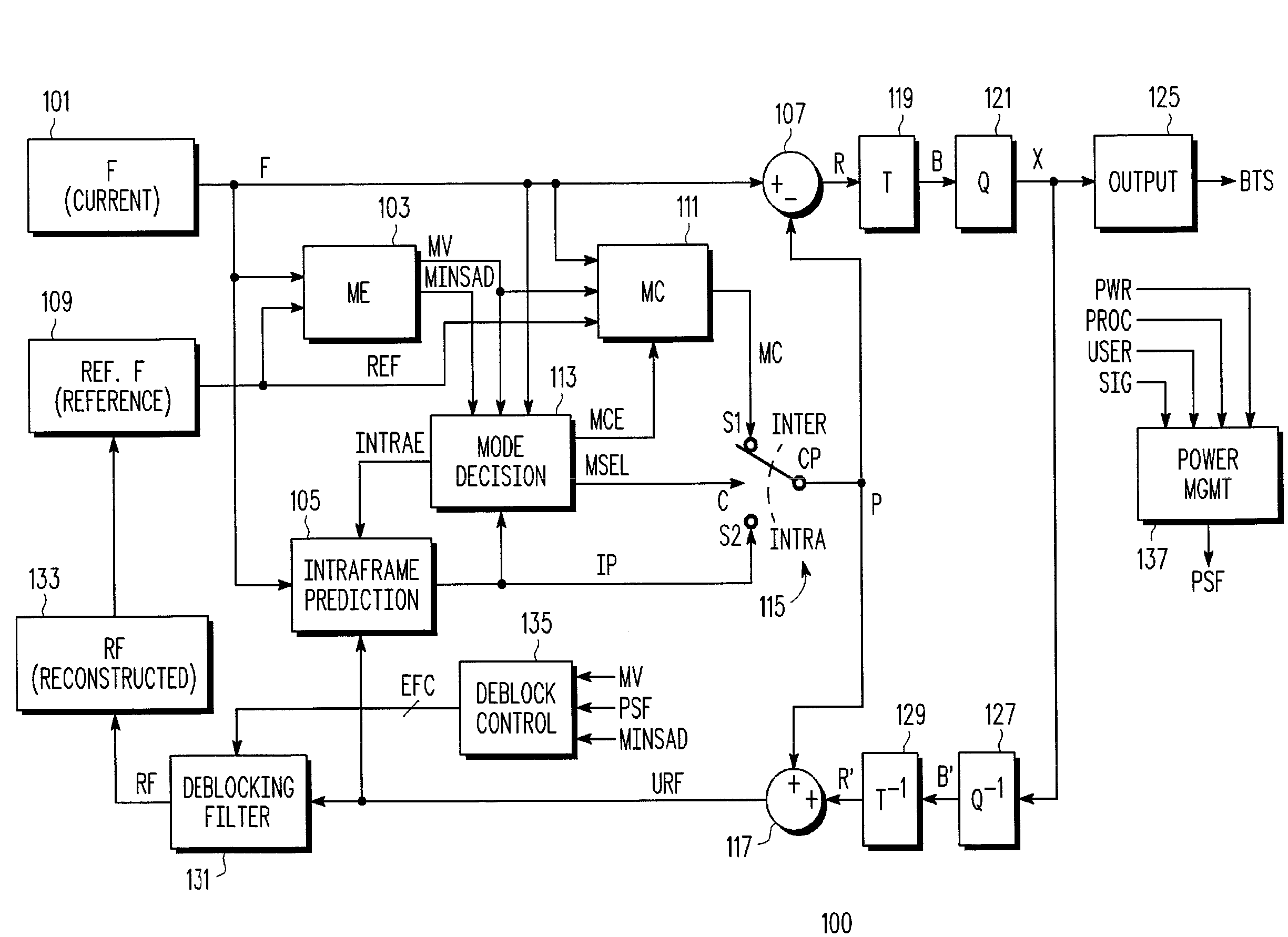
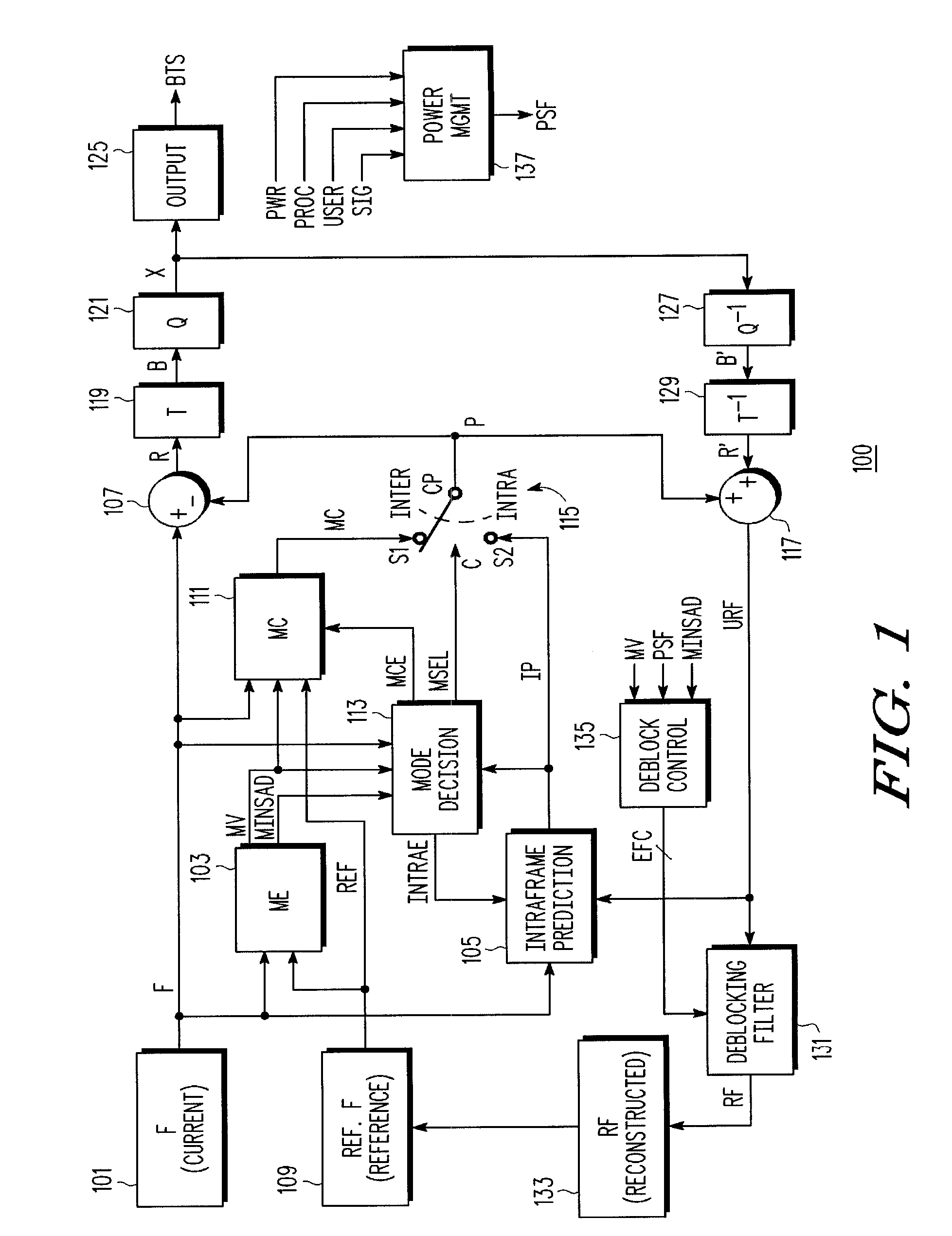
Adaptive disabling of deblock filtering based on a content characteristic of video information
ActiveUS20080137752A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionInformation processing
A method of adaptively disabling deblock filtering of video information including determining a content characteristic of the video information, and adaptively disabling deblock filtering of the video information based on the content characteristic. The content characteristic may be a content complexity, such as an average of minimum sums of absolute differences of pixel values determined during motion estimation, or the mean square error of the video information, or the number of bits used for coding the video content. The content characteristic may be other than complexity, such as motion vector information. A video information processing system including a video processing circuit which processes video information and which determines a content characteristic of the video information, and a deblocking filter circuit which adaptively disables deblock filtering of the video information based on the content characteristic.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Dynamic and predictive information system and method for shipping assets and transport
InactiveUS7385529B2Ticket-issuing apparatusDigital data processing detailsDriver/operatorElectronic communication
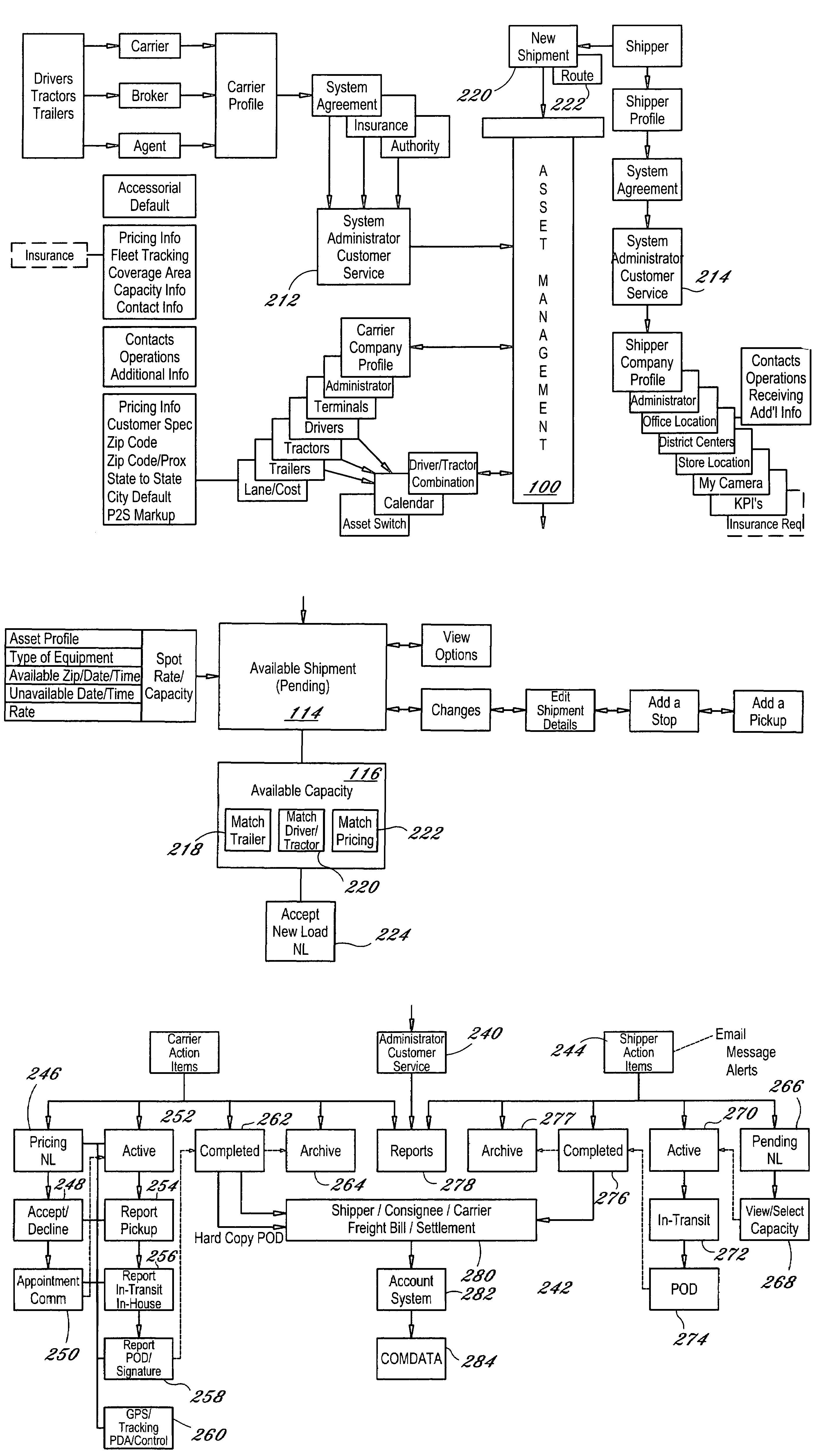
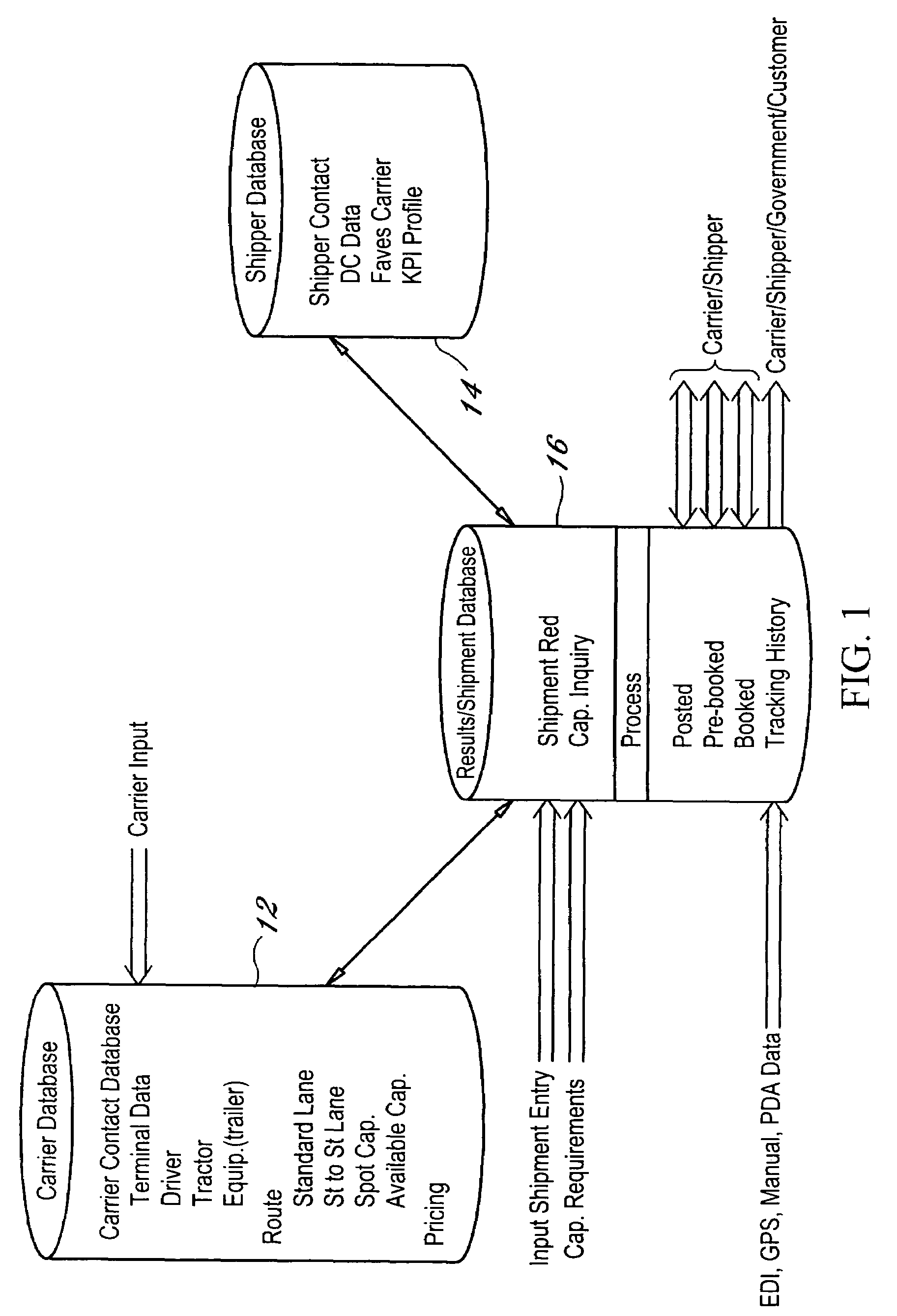
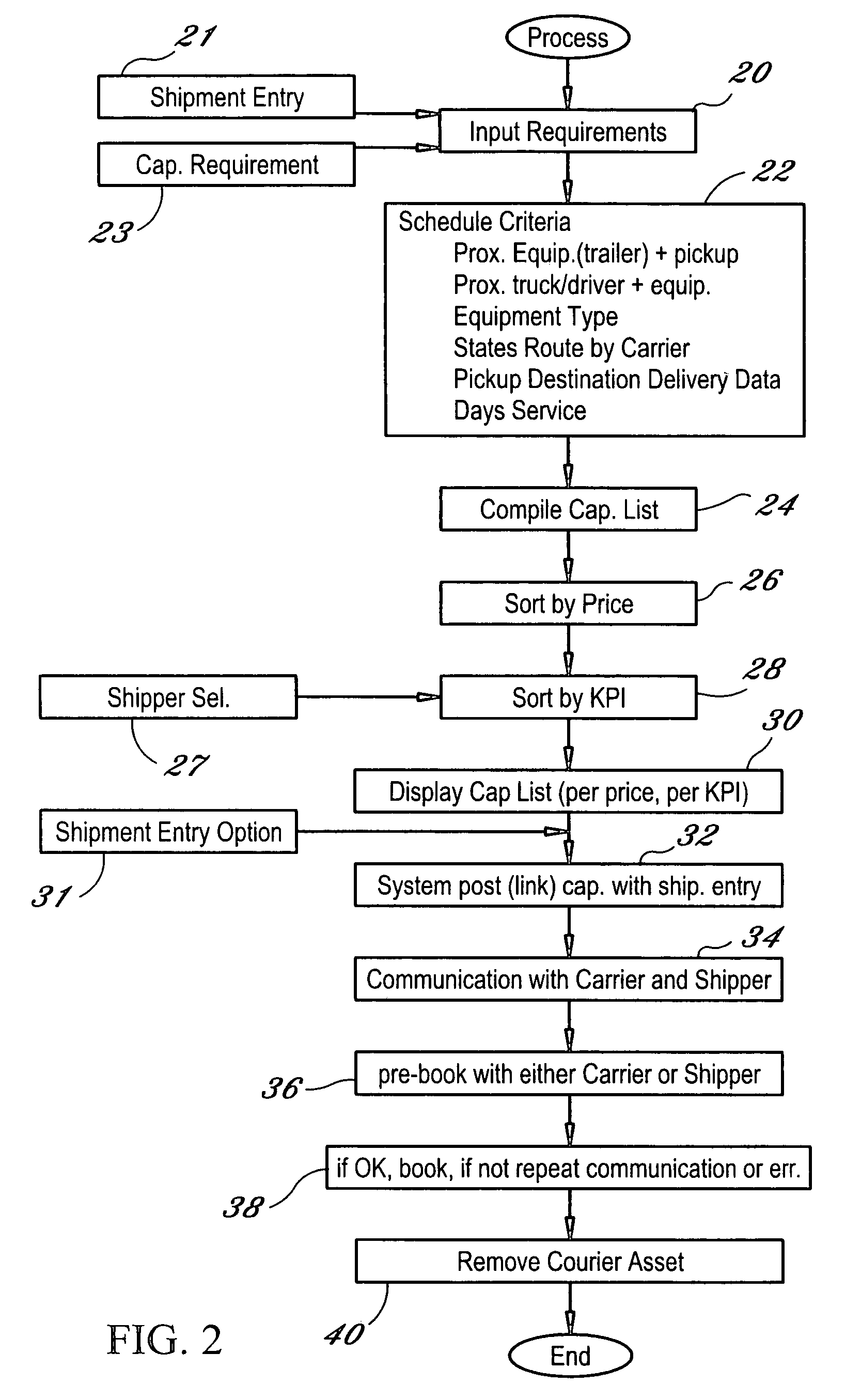
The dynamic, predictive information system and method assigns shipping assets (drivers-tractors-trailers) from carriers to transport orders by shippers. Computer databases hold shipping asset data. Specific transport orders are electronically joined to specific driver-tractor-trailer combinations. A search and sort routine produces resulting records based upon proximity, trailer type, proximity of the joined driver-trailer combination, carrier service region and pick-up and delivery date constraints. The sort is by price or performance indicators which are pre-selected shipper ranges matched to historical shipping data from carriers. The system books the carrier, the driver-tractor-trailer combination and the shipper to transport order with an electronic communications phase. In a truck lane scenario, the system joins a specific driver and a specific tractor and a non-specific trailer to a specific transport order. GPS data and electronic shipping document data from PDAs with the drivers is logged into the system and is viewable by the participants.
Owner:NUSTATE ENERGY HLDG +1
Adaptive reference picture selection based on inter-picture motion measurement
ActiveUS20050105618A1Improve compression efficiencyTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesControl signalComputer science
An apparatus comprising a first circuit and a second circuit. The first circuit may be configured to generate a control signal in response to a measurement of inter-picture motion between a current picture and a first reference picture. The second circuit may be configured to select the first reference picture or a second reference picture as a better reference picture for motion estimation in response to the control signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
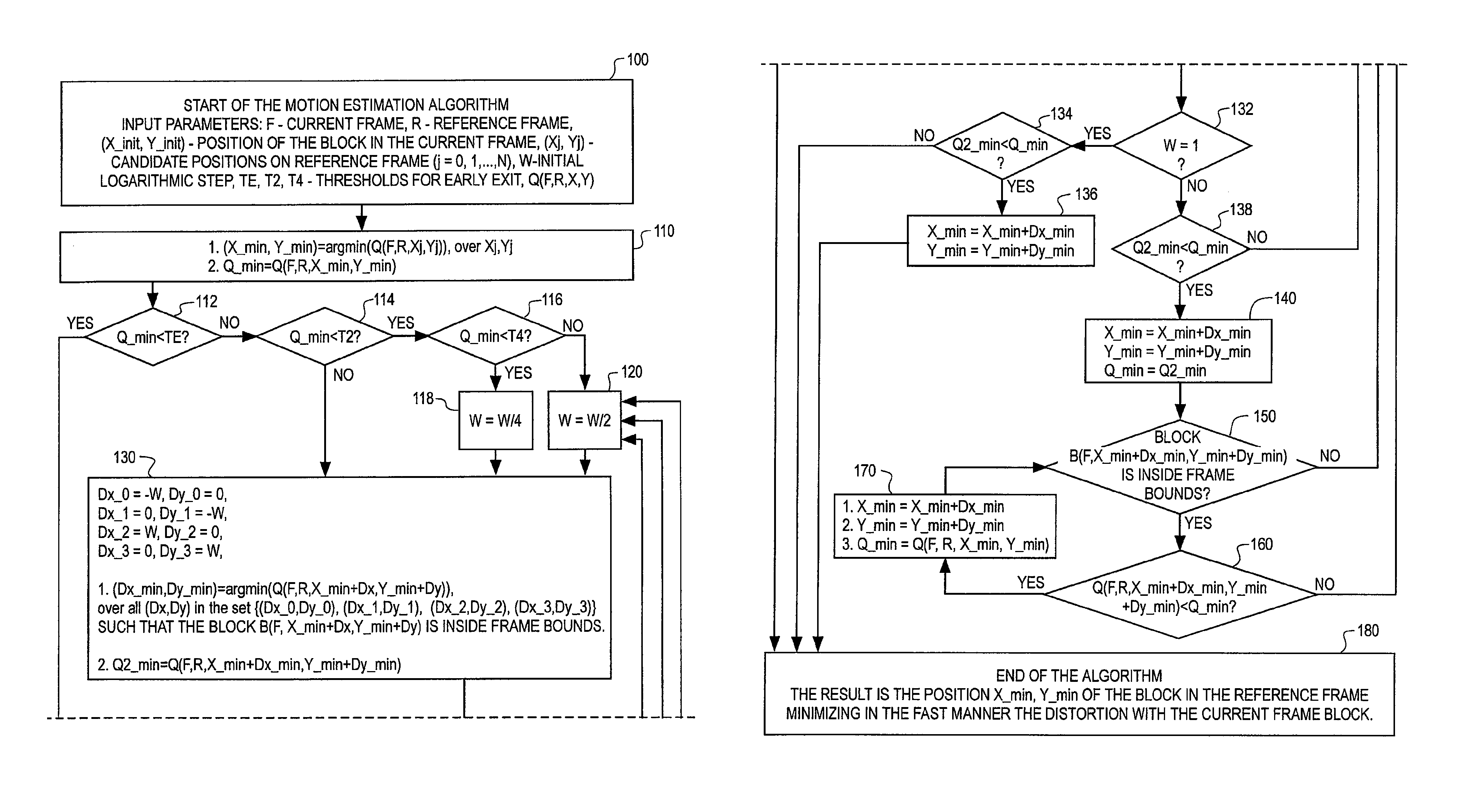
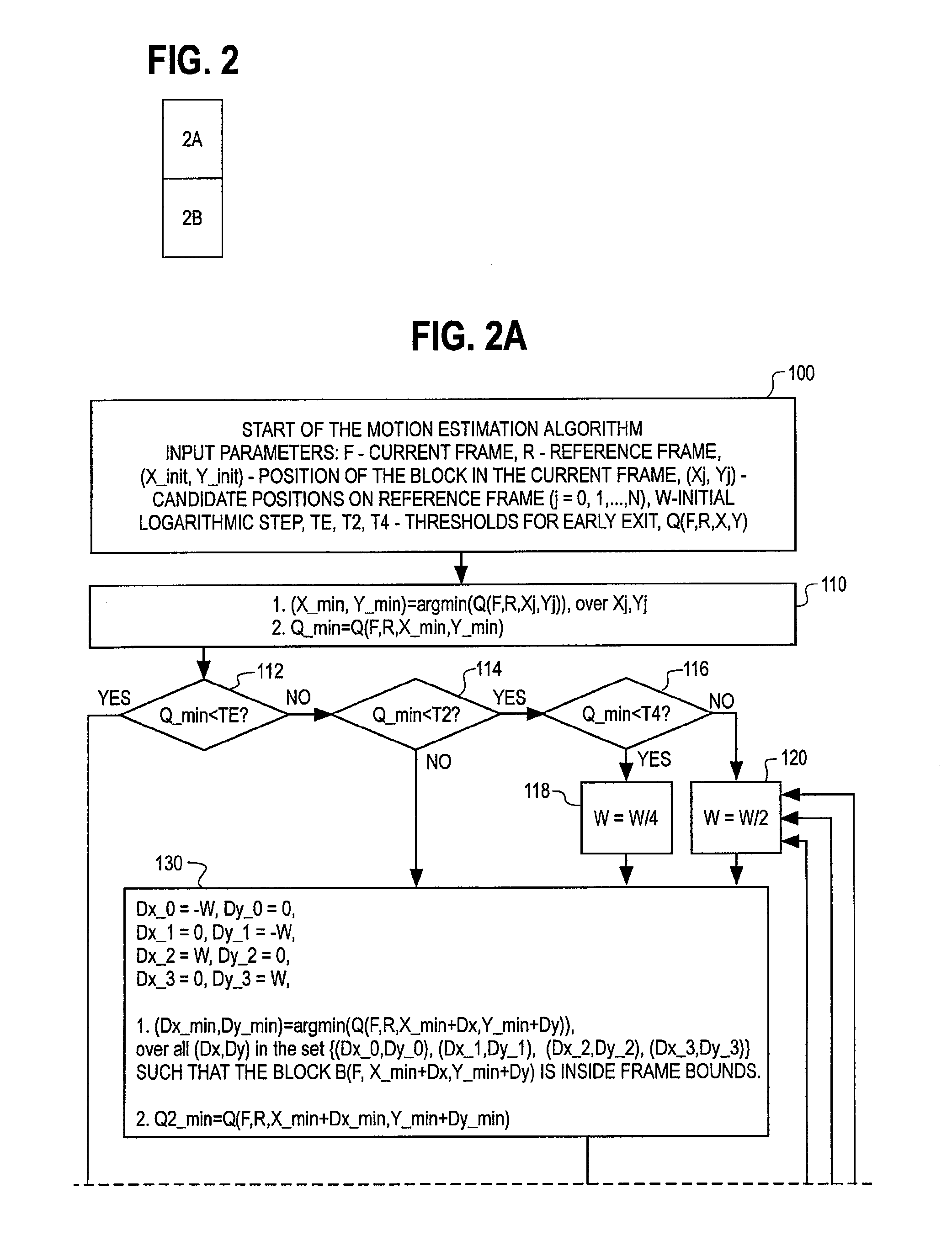
Methods for motion estimation with adaptive motion accuracy
InactiveUS6968008B1Reduce computational complexitySignificant compression gainPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionComputation complexityMotion vector
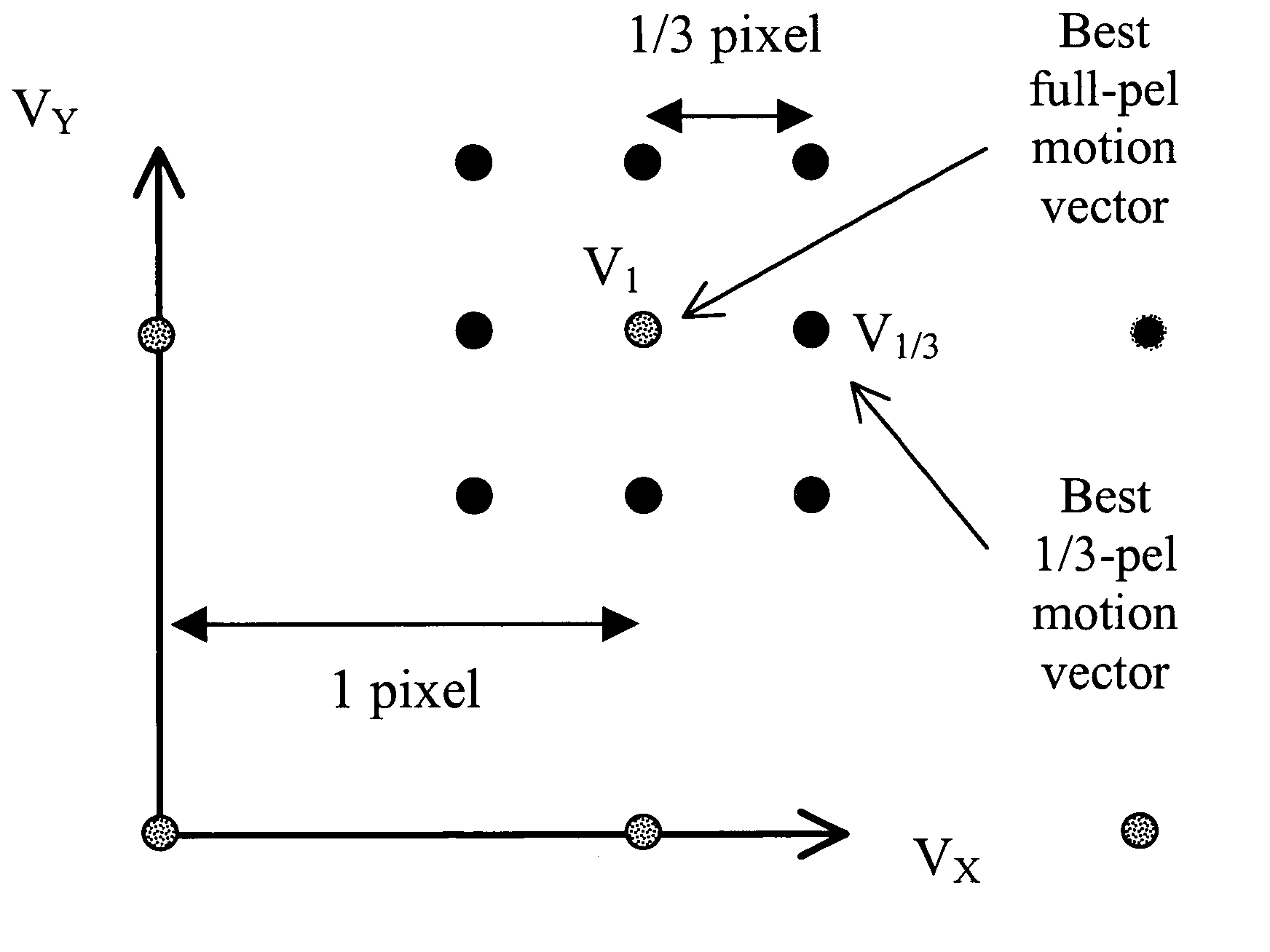
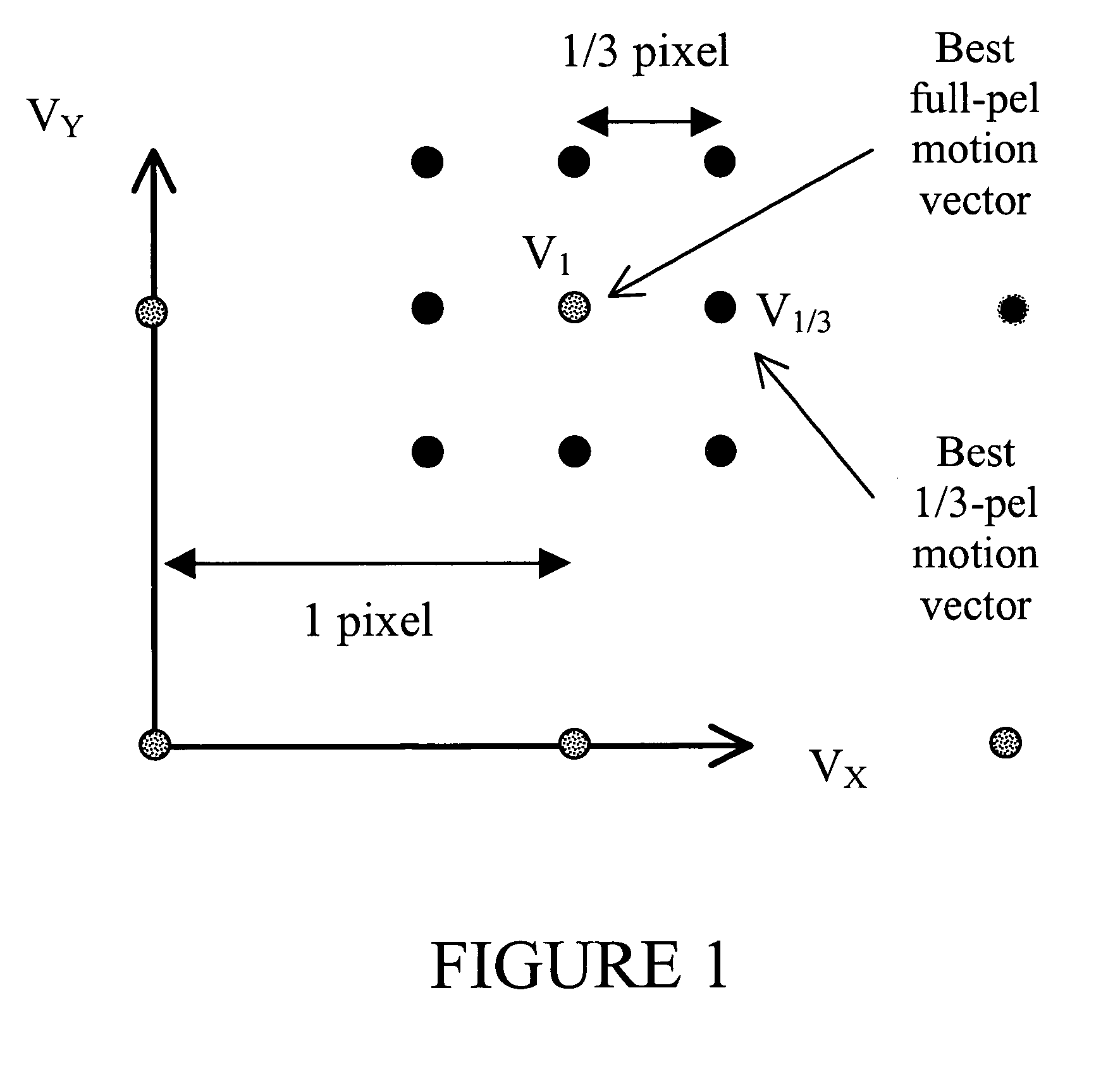
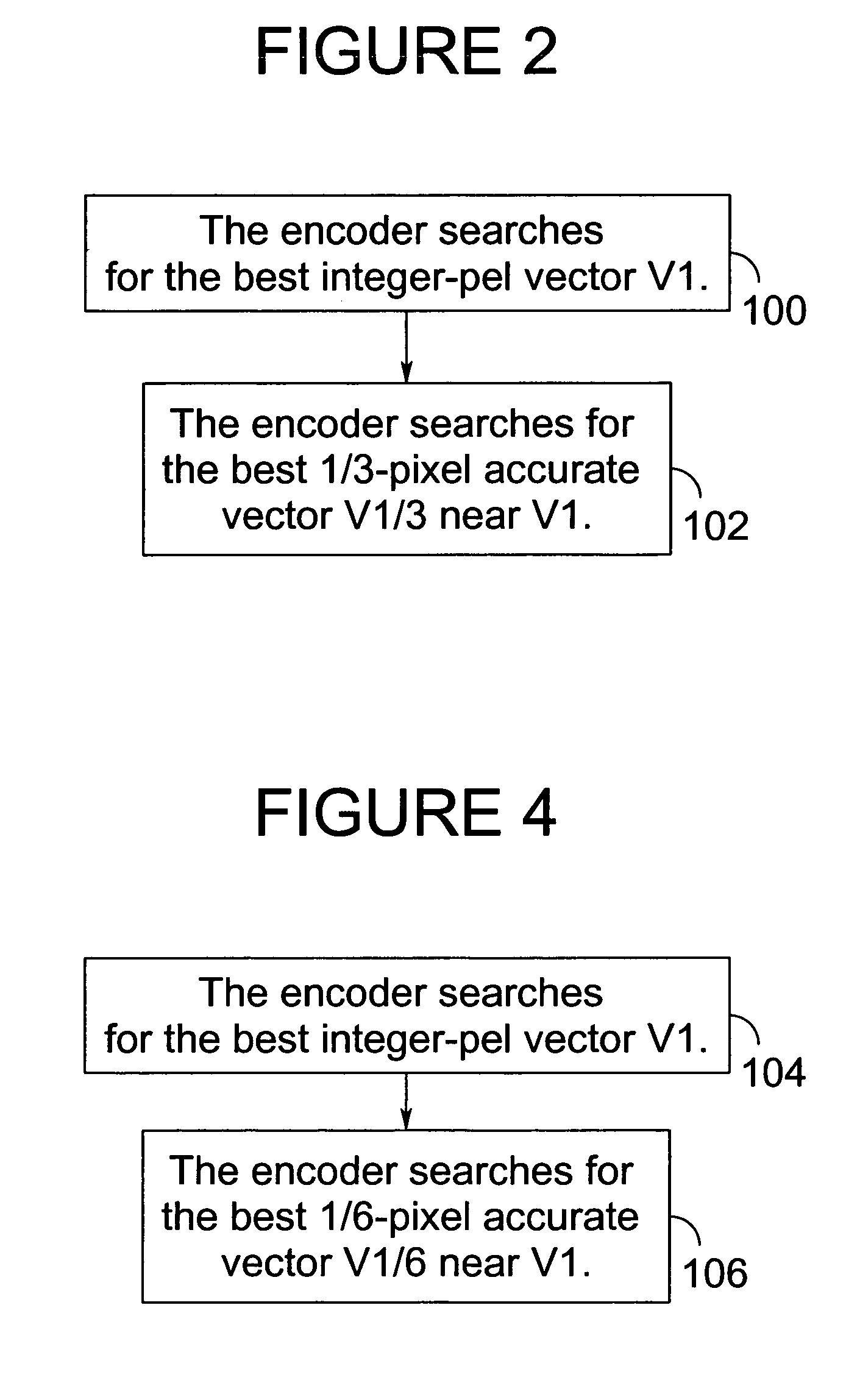
Methods for motion estimation with adaptive motion accuracy of the present invention include several techniques for computing motion vectors of high pixel accuracy with a minor increase in computation. One technique uses fast-search strategies in sub-pixel space that smartly searches for the best motion vectors. An alternate technique estimates high-accurate motion vectors using different interpolation filters at different stages in order to reduce computational complexity. Yet another technique uses rate-distortion criteria that adapts according to the different motion accuracies to determine both the best motion vectors and the best motion accuracies. Still another technique uses a VLC table that is interpreted differently at different coding units, according to the associated motion vector accuracy.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com