Patents
Literature
3504 results about "Chrominance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chrominance (chroma or C for short) is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture, separately from the accompanying luma signal (or Y for short). Chrominance is usually represented as two color-difference components: U = B′ − Y′ (blue − luma) and V = R′ − Y′ (red − luma). Each of these difference components may have scale factors and offsets applied to it, as specified by the applicable video standard.
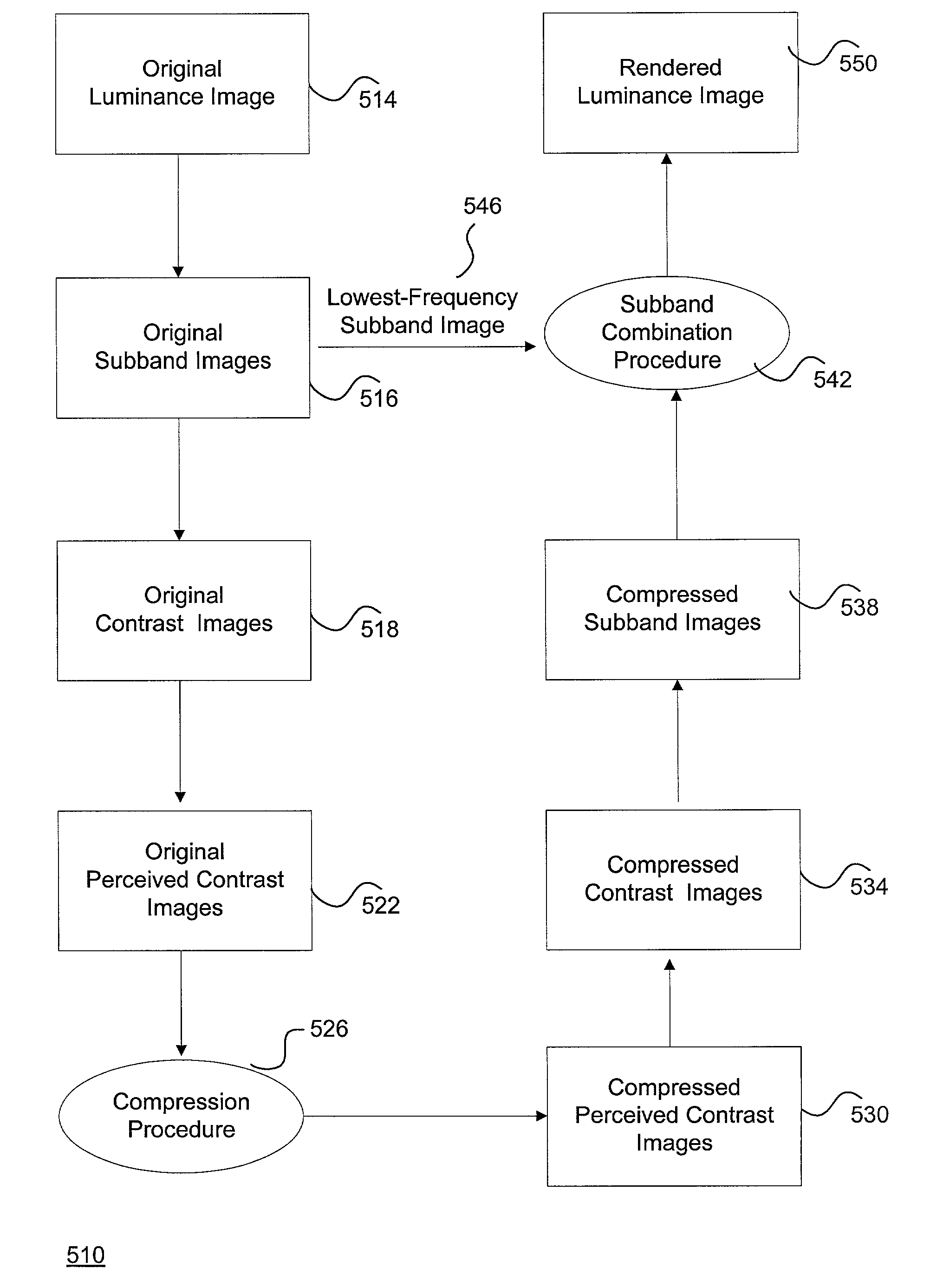
System and method for effectively rendering high dynamic range images
InactiveUS6993200B2High imagingEffectively renderingImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Image conversion
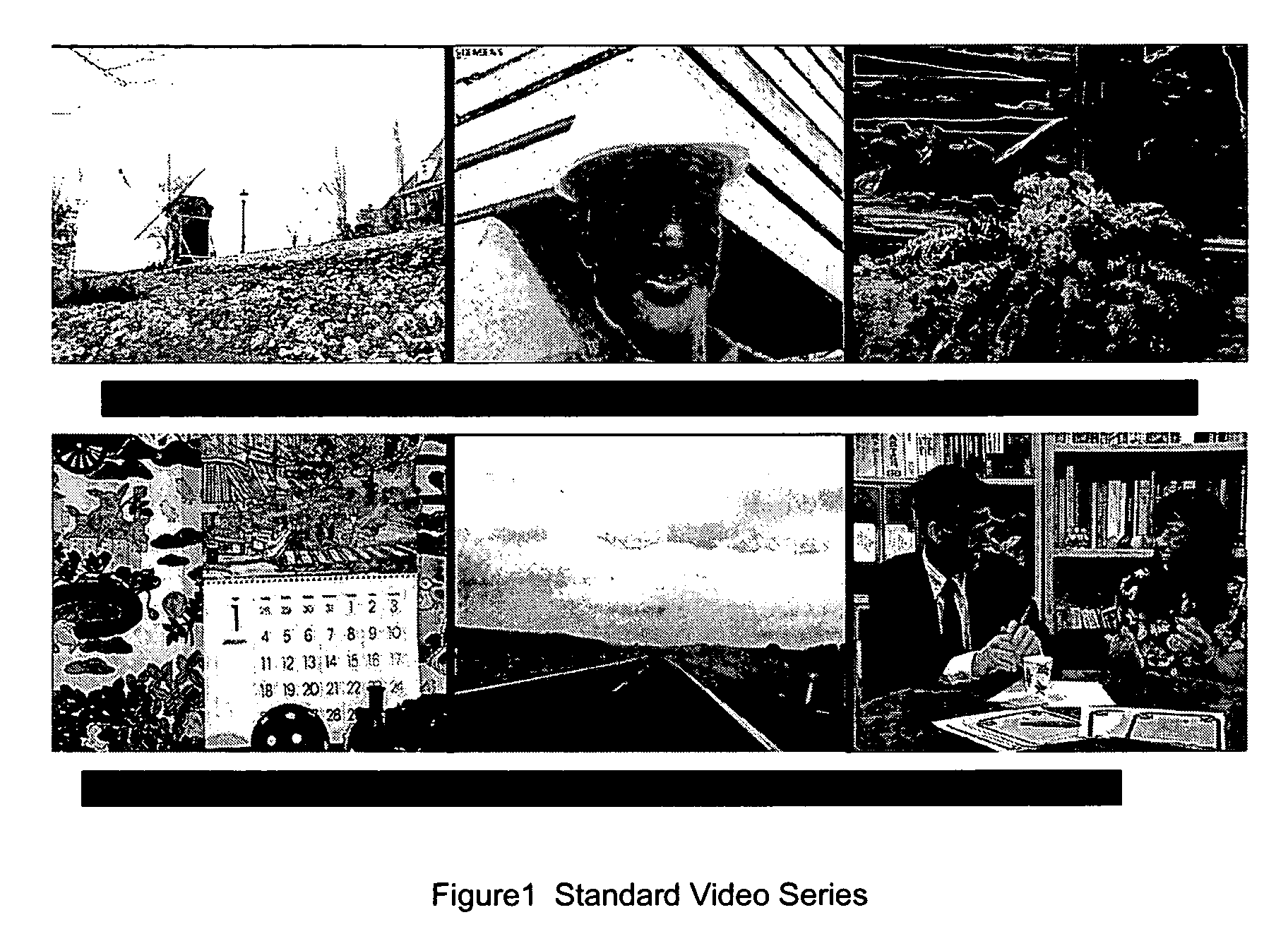
A system and method for rendering high dynamic range images includes a rendering manager that divides an original luminance image into a plurality of original subband images. The rendering manager converts the original subband images into original contrast images which are converted into original perceived contrast images. The rendering manager performs a compression procedure upon the original perceived contrast images to produce compressed perceived contrast images. The rendering manager converts the compressed perceived contrast images into compressed contrast images which are converted into compressed subband images. The rendering manager performs a subband combination procedure for combining the compressed subband images together with a lowest-frequency subband image to generate a rendered luminance image. The rendering manager may combines the rendered luminance image with corresponding chrominance information to generate a rendered composite image.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
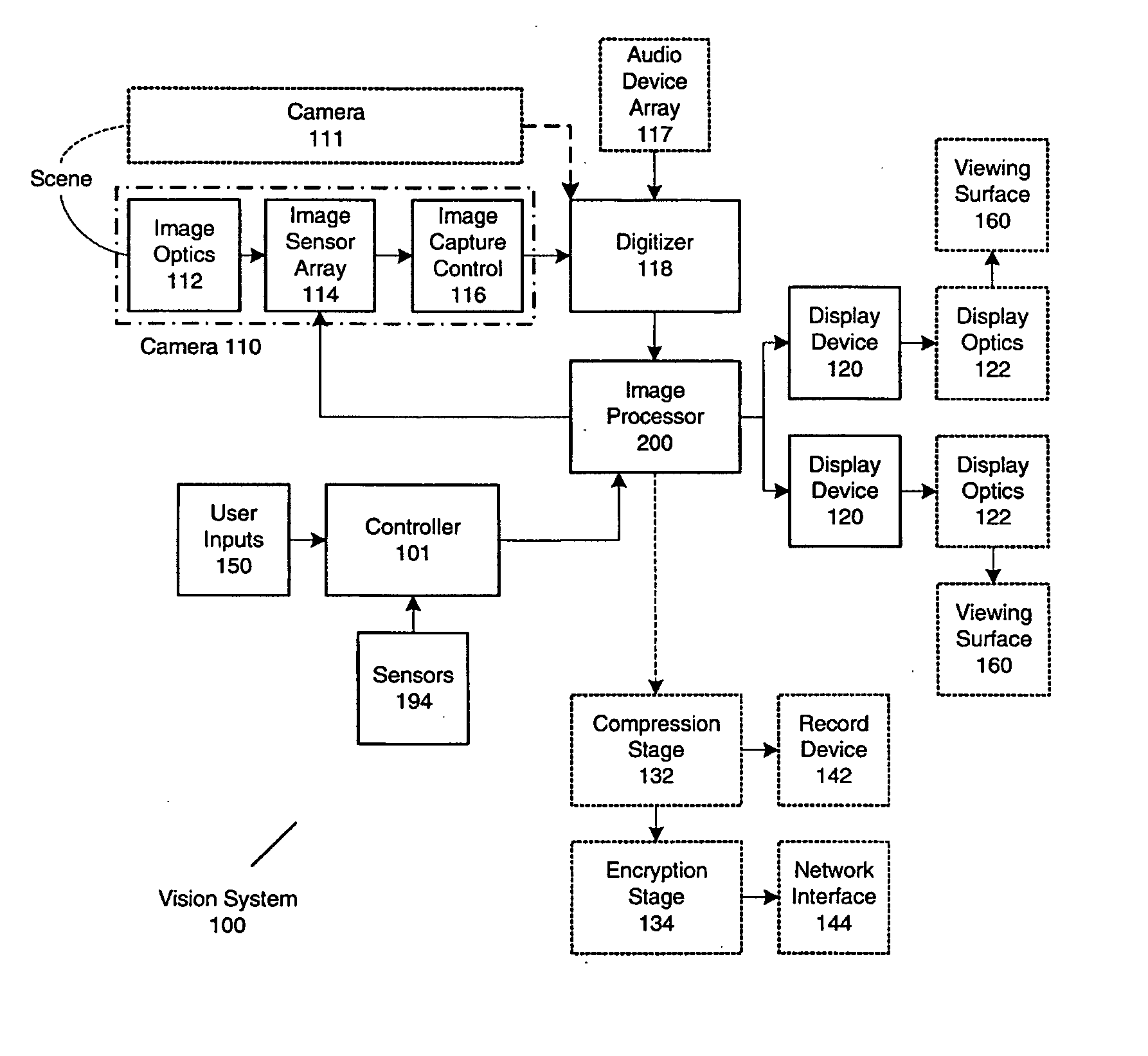
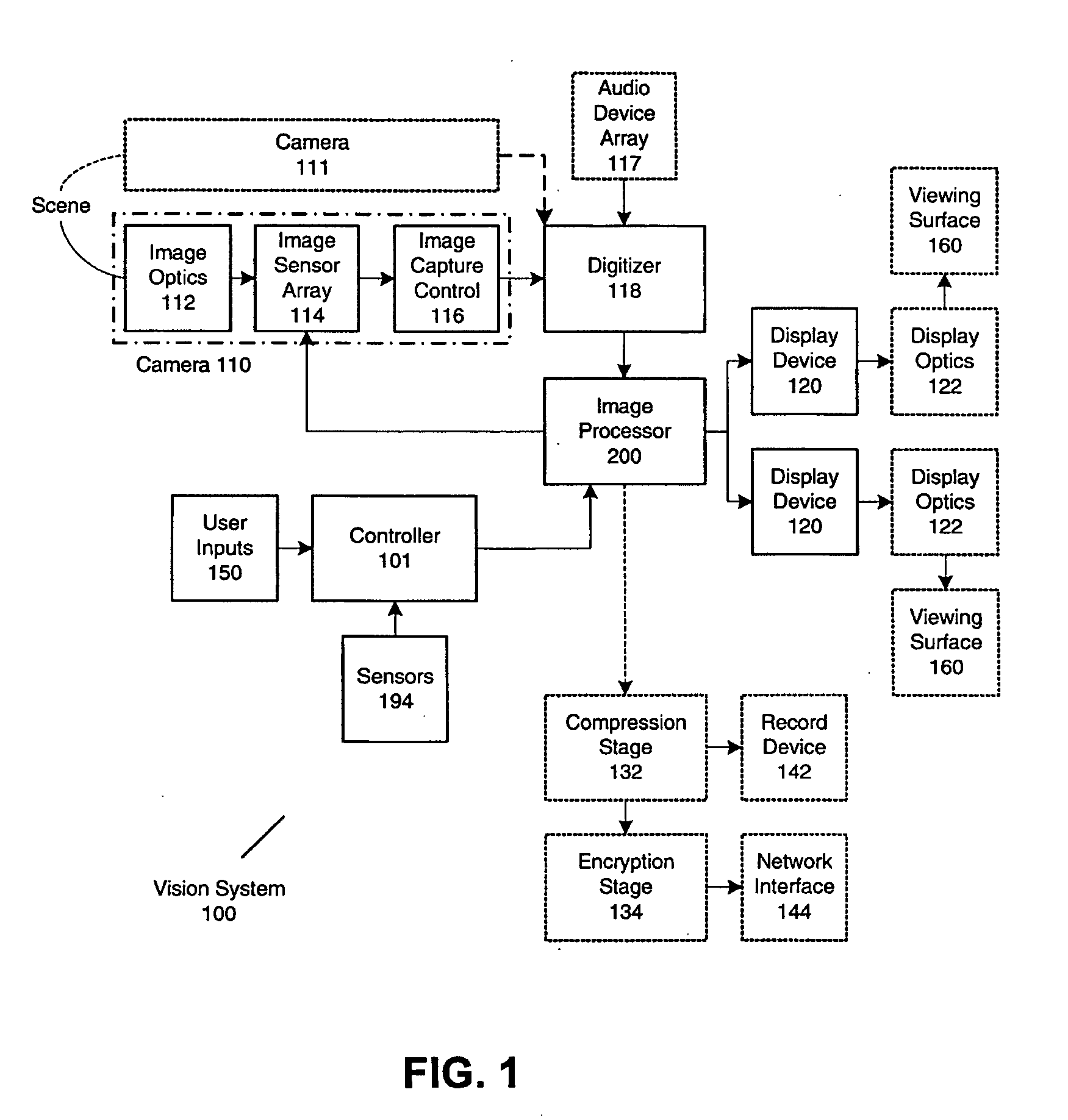
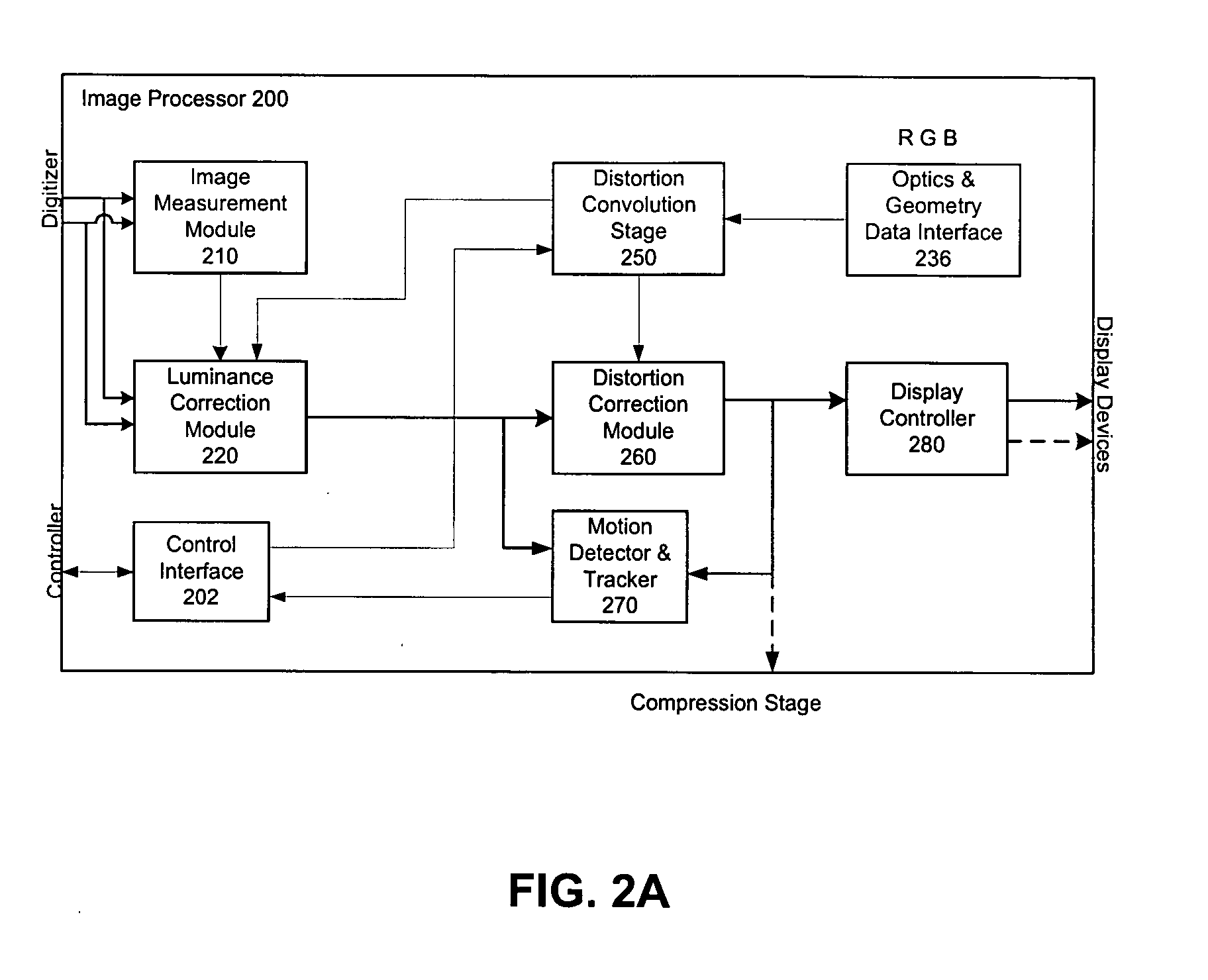
Panoramic vision system and method
ActiveUS20060017807A1Facilitate viewingZoom in on speakerTelevision system detailsTelevision conference systemsDistortion correctionProjection optics
A distortion corrected panoramic vision system and method provides a visually correct composite image acquired through wide angle optics and projected onto a viewing surface. The system uses image acquisition devices to capture a scene up to 360° or 4π steradians broad. An image processor corrects for luminance or chrominance non-uniformity and applies a spatial transform to each image frame. The spatial transform is convolved by concatenating the viewing transform, acquisition geometry and optical distortion transform, and display geometry and optical transform. The distortion corrections are applied separately for red, green, and blue components to eliminate lateral color aberrations of the optics. A display system is then used to display the resulting composite image on a display device which is then projected through the projection optics and onto a viewing surface. The resulting image is visibly distortion free and matches the characteristics of the viewing surface.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
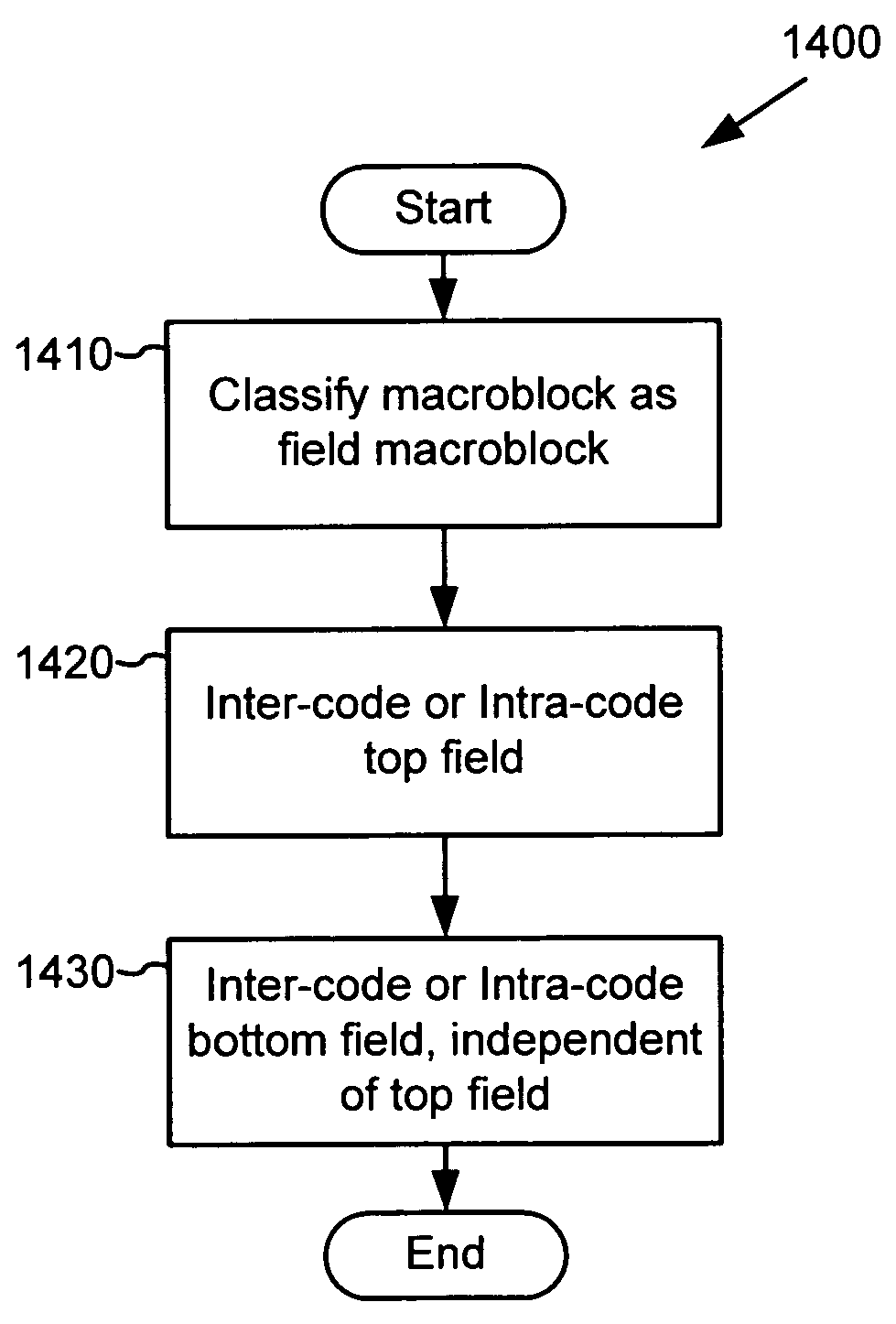
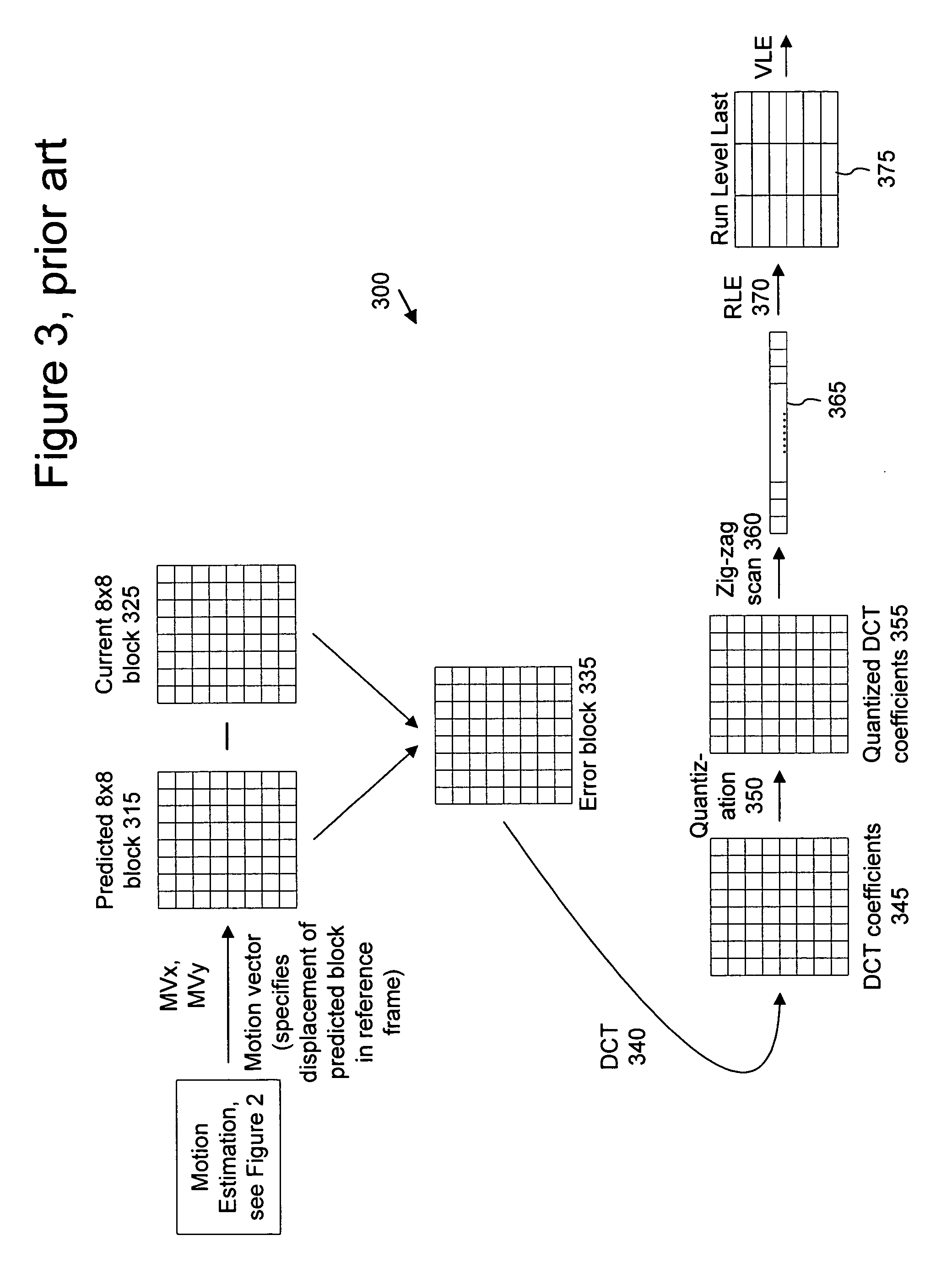
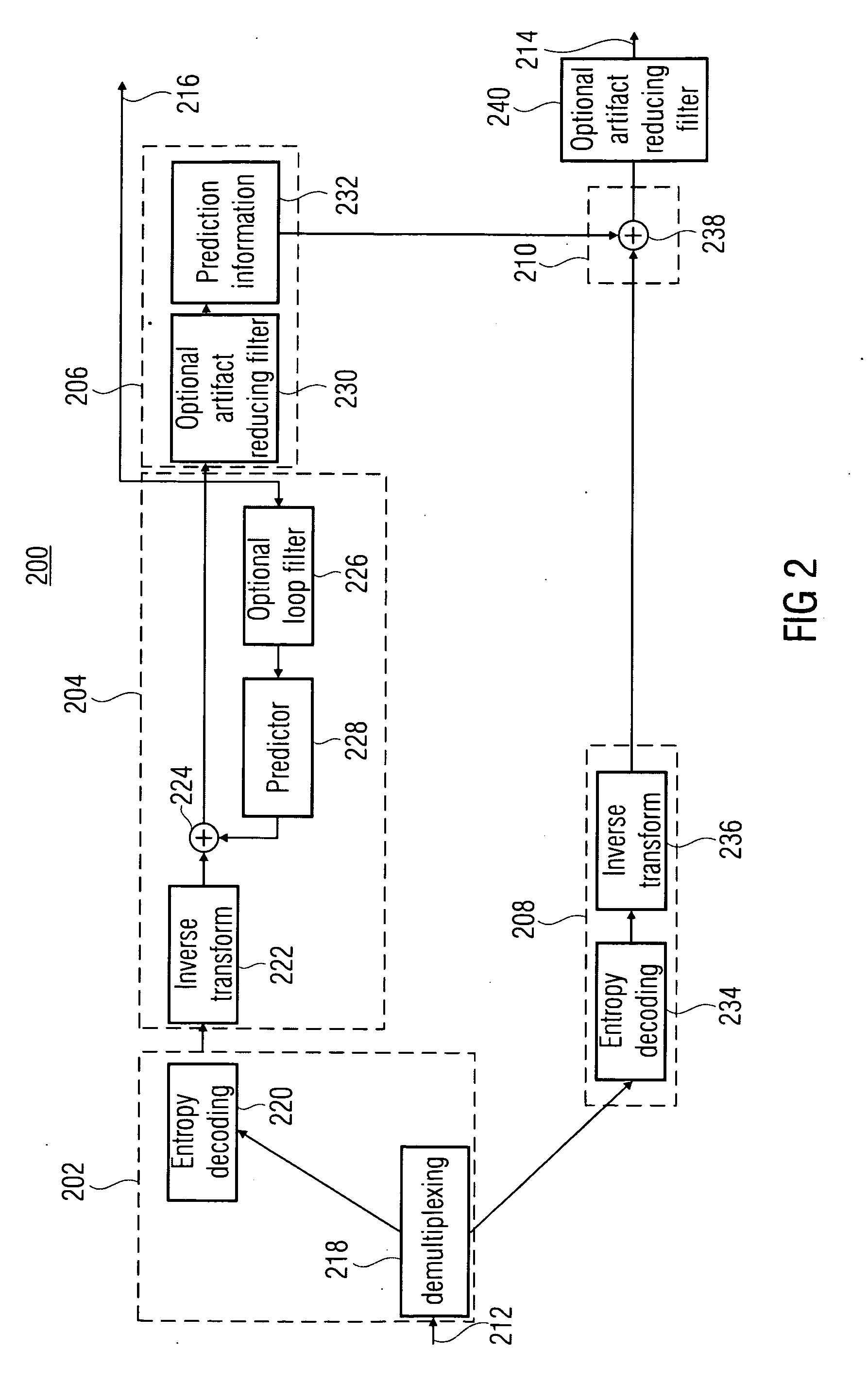
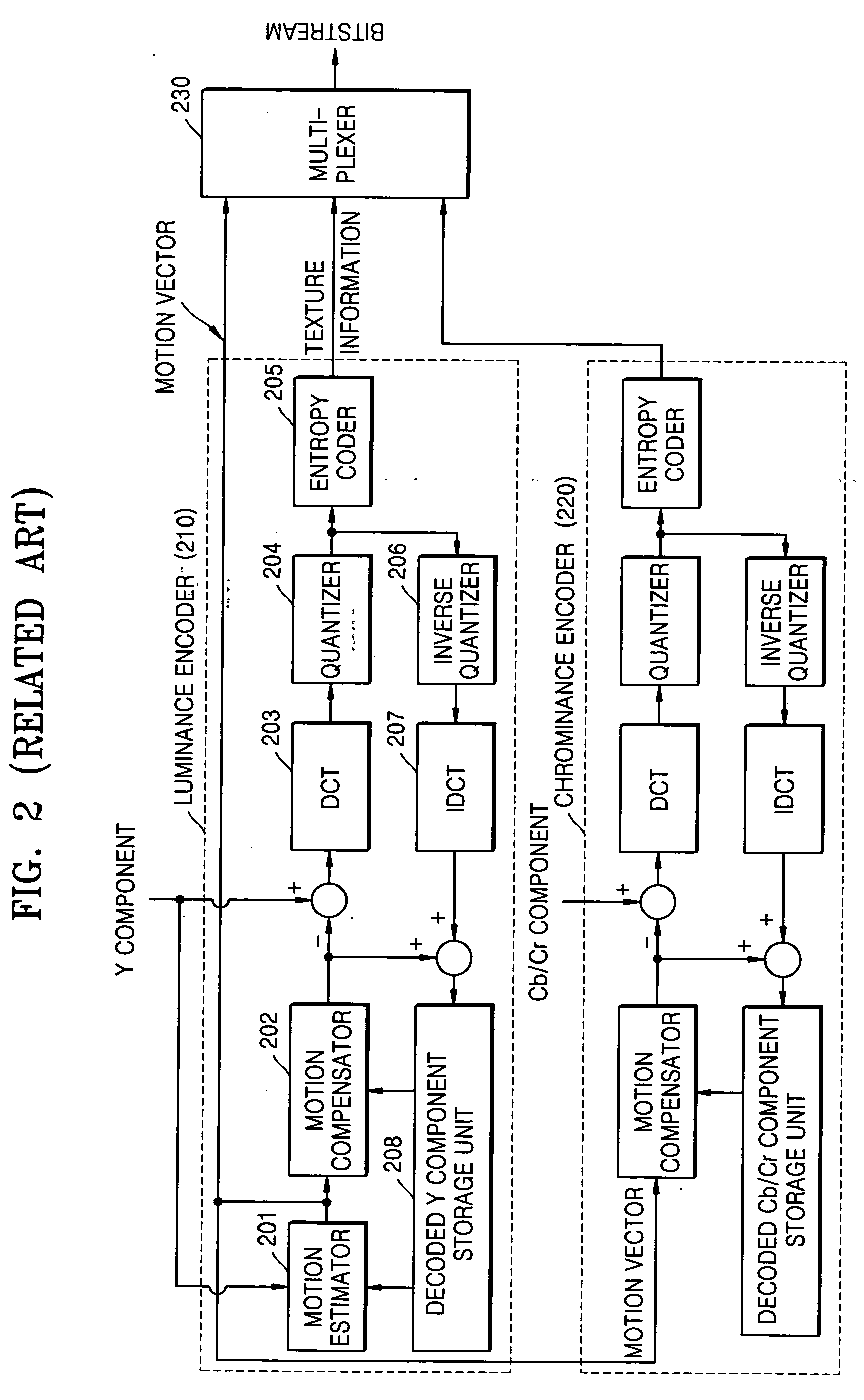
Intraframe and interframe interlace coding and decoding
ActiveUS20050013497A1Facilitate decodingCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsInterlaced videoMotion vector
Techniques and tools for encoding and decoding video images (e.g., interlaced frames) are described. For example, a video encoder or decoder processes 4:1:1 format macroblocks comprising four 8×8 luminance blocks and four 4×8 chrominance blocks. In another aspect, fields in field-coded macroblocks are coded independently of one another (e.g., by sending encoded blocks in field order). Other aspects include DC / AC prediction techniques and motion vector prediction techniques for interlaced frames.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
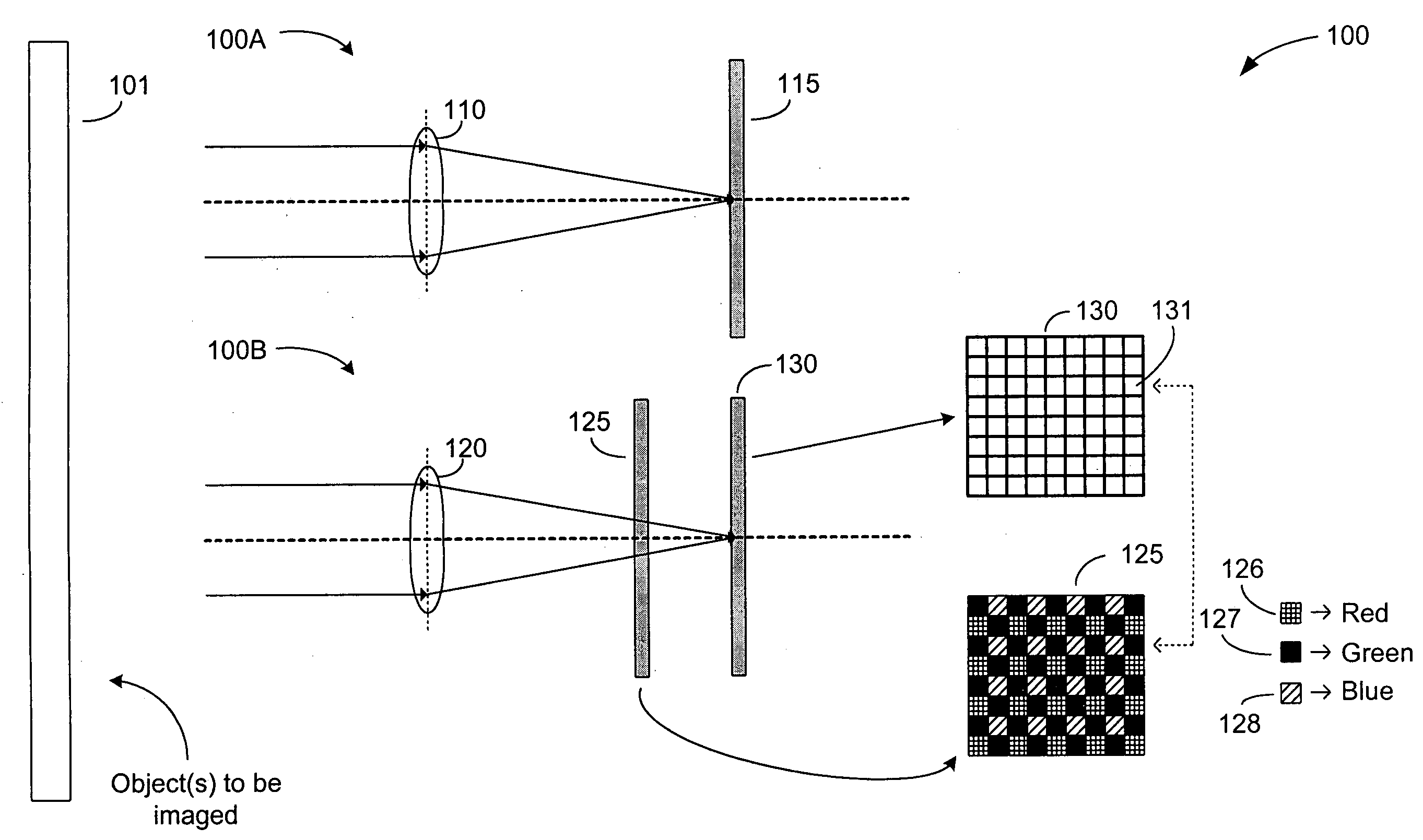
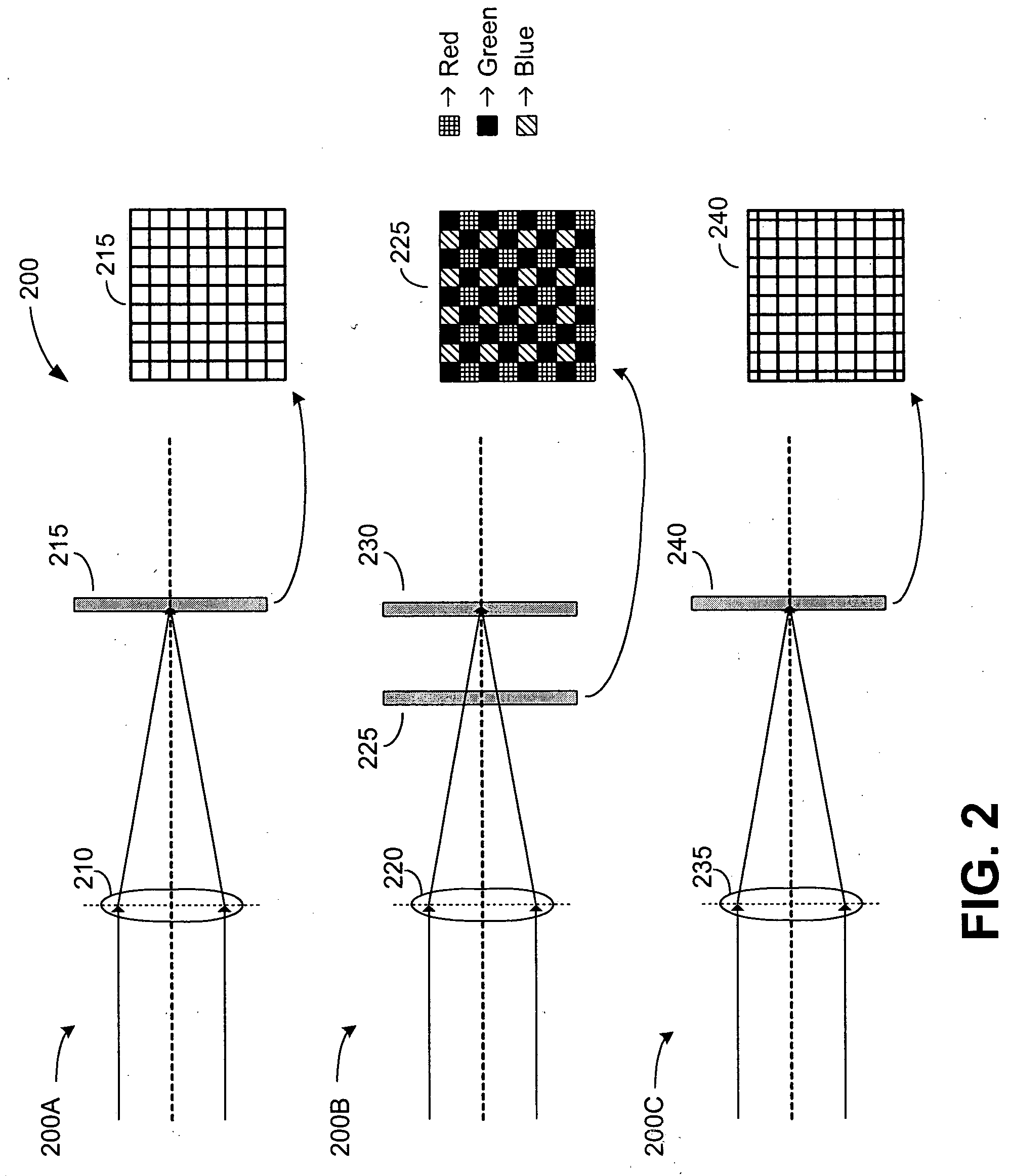
Multi-lens imaging systems and methods
ActiveUS20060125936A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsSensor arrayCamera lens
Imaging systems and methods are provided. One exemplary system incorporates multiple lenses that are individually configured to receive visible light from an object to be imaged, and to direct this light upon a corresponding sensor array. Luminance information is then derived from signals generated in one or more of the sensor arrays. When chrominance information is desired, an optical filter is interposed between a lens and the corresponding sensor array. The mosaic pattern contained in the optical filter is tailored to provide advantageous chrominance information. One or more such filters with different mosaic patterns may be employed. The luminance and chrominance information obtained from the sensor arrays are combined to generate an image of the object.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
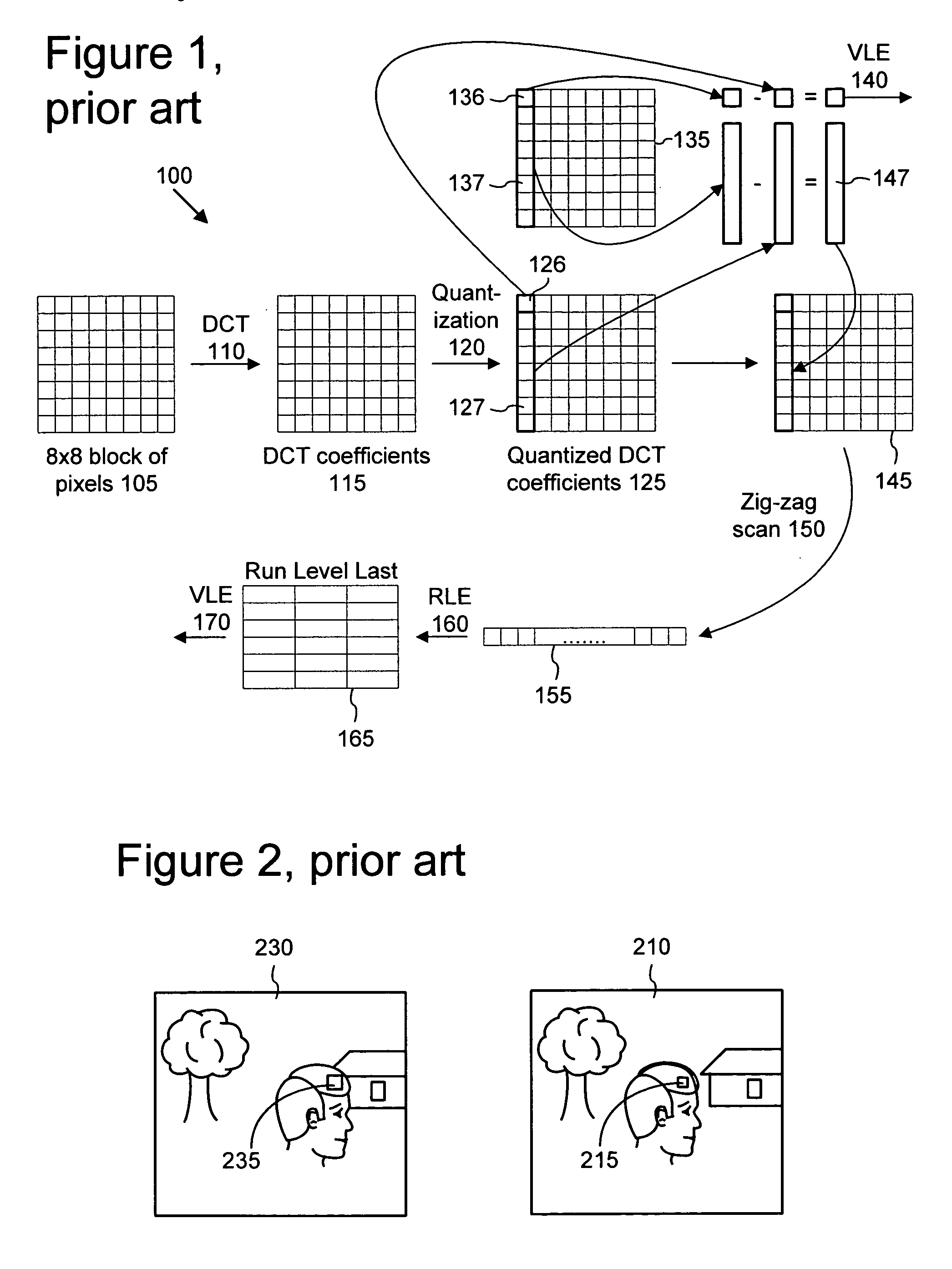
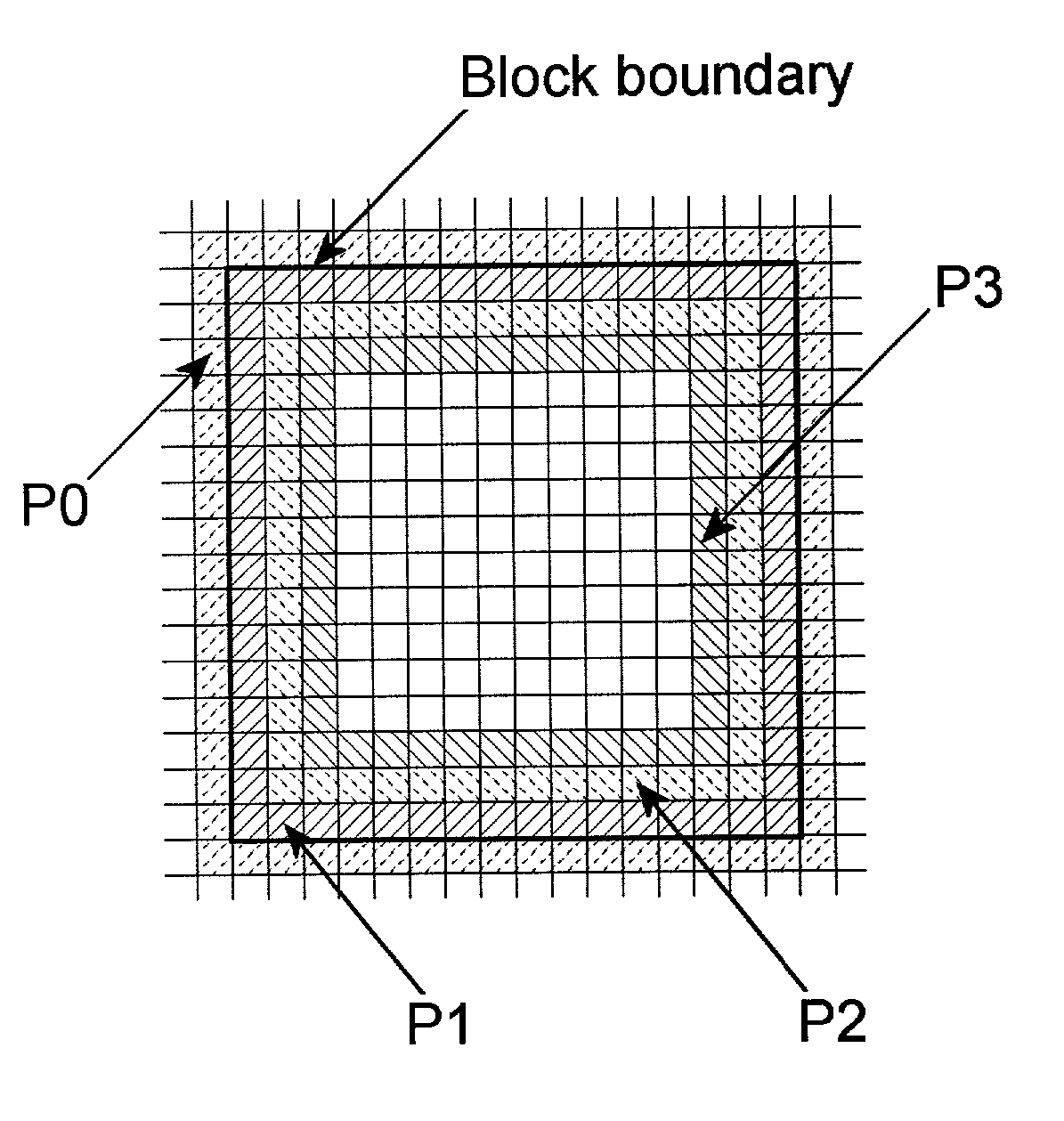
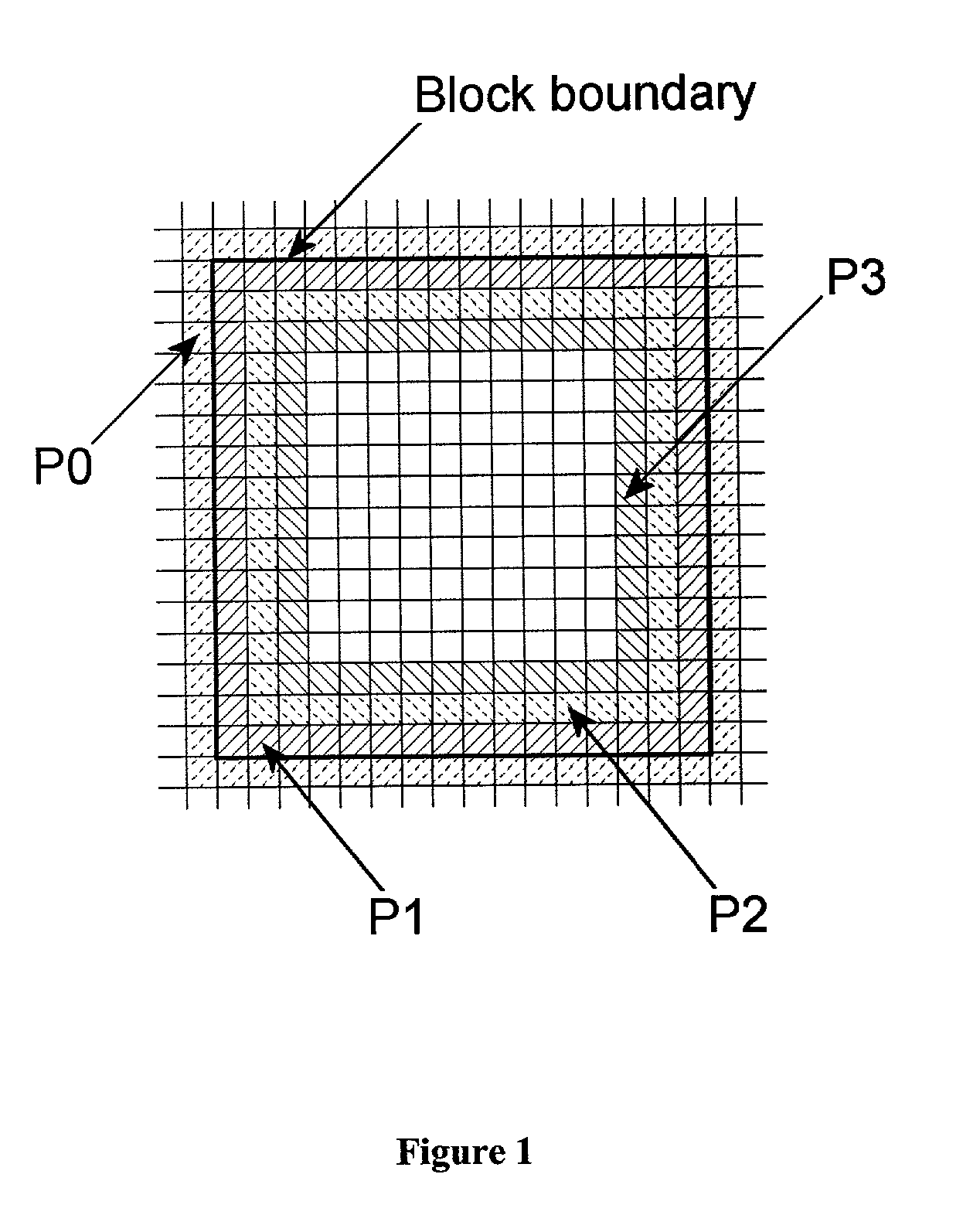
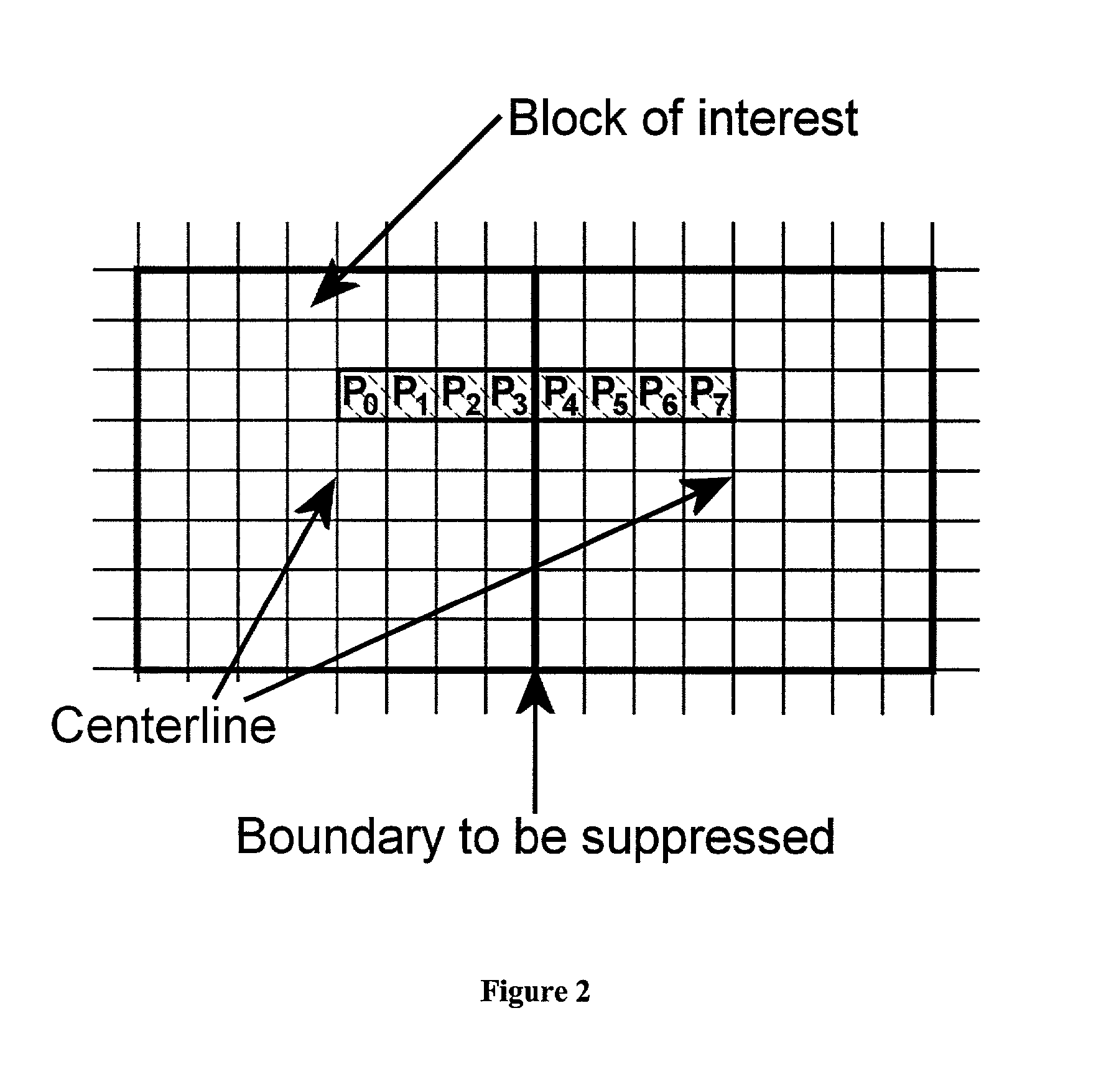
Removal of block encoding artifacts
InactiveUS7003174B2Reduce artifactsAccessImage enhancementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVisibilityPattern recognition
A method of reducing artifacts in an image previously processed by block transform encoding may comprise the steps of:determining block boundaries;determining an approximate metric of artifact visibility;optionally interpolating across block boundaries;adaptively filtering luminance;optionally adaptively filtering chrominance;adaptively adjusting local saturation variation; andadaptively simulating high spatial frequency image detail;wherein the adaptive steps are executed to an extent or in an amount depending on the metric or standard or measurement of artifact visibility.
Owner:COREL CORP +1
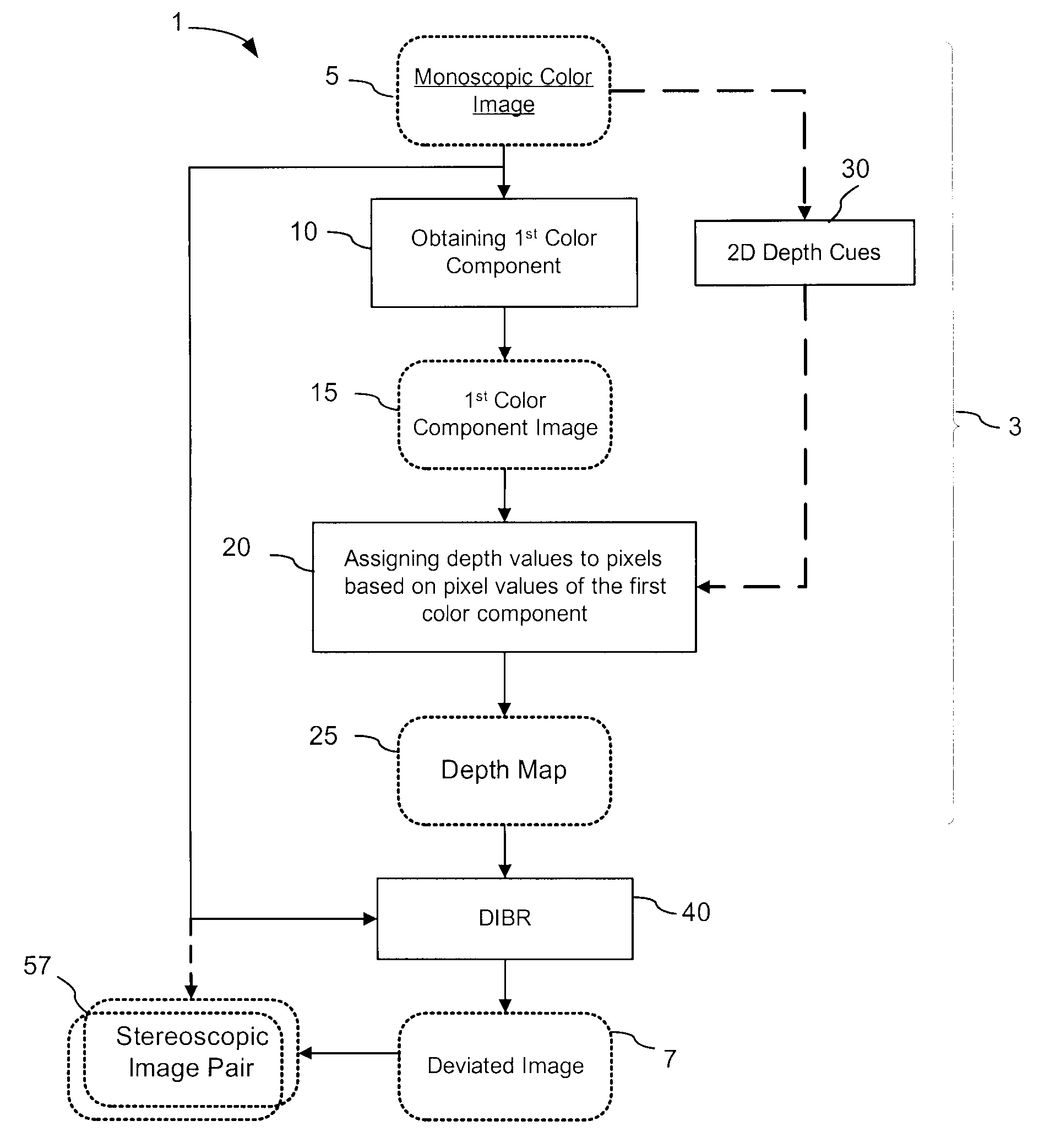
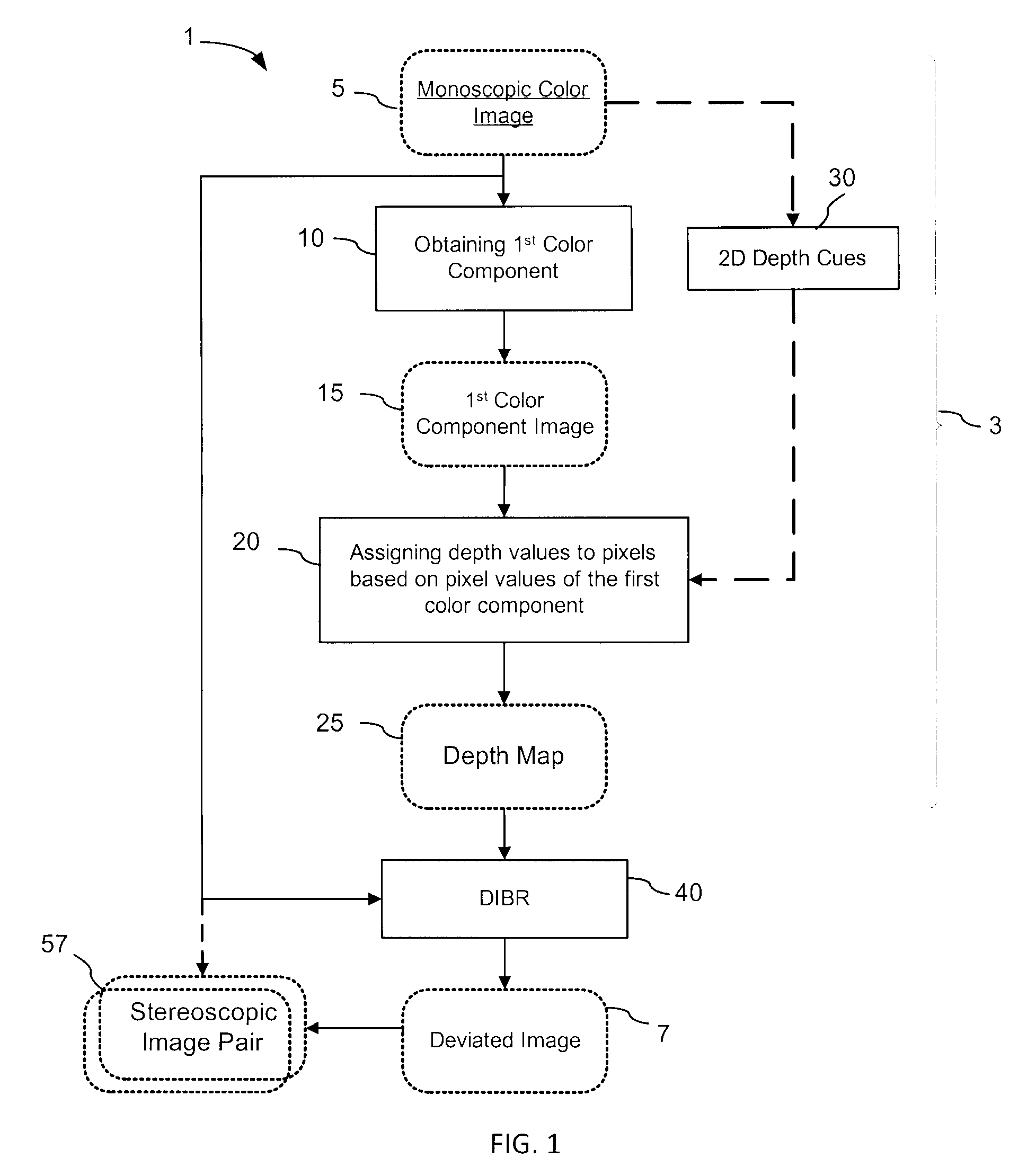
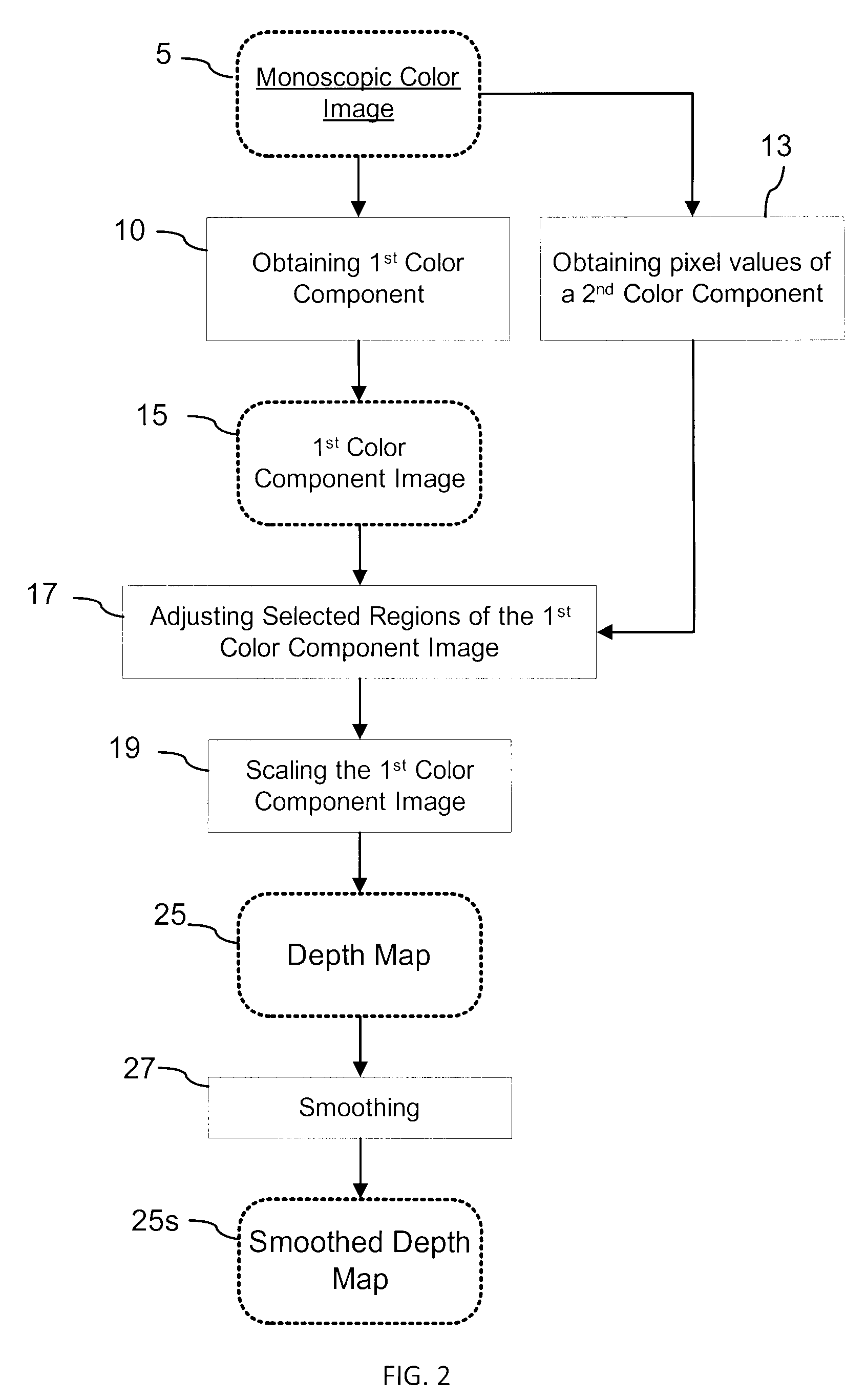
Generation of a depth map from a monoscopic color image for rendering stereoscopic still and video images
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for generating a depth map from a digital monoscopic color image. The method includes the following general steps: a) obtaining a first color component of the MCI, said first color component corresponding to partial color information of the MCI; and, b) assigning depth values to pixels of the MCI based on values of the first color component of respective pixels for forming the depth map for the MCI. In one embodiment, the depth values are generated by adjusting and / or scaling of pixel values of the Cr chroma component of the monoscopic source color image in the Y′CbCr color system.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Blending a graphic
A graphic and video are blended by controlling the relative transparency of corresponding pixels in the graphic and the video through the use of blending coefficients. One example of a blending coefficient is an alpha signal used in conjunction with a keyer. The value of a blending coefficient for a pixel in the graphic is based on the luminance and chrominance characteristics of a neighborhood of pixels in the video. Inclusions and exclusions are set up which define how the neighborhood of pixels is used to create or change a particular blending characteristic.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
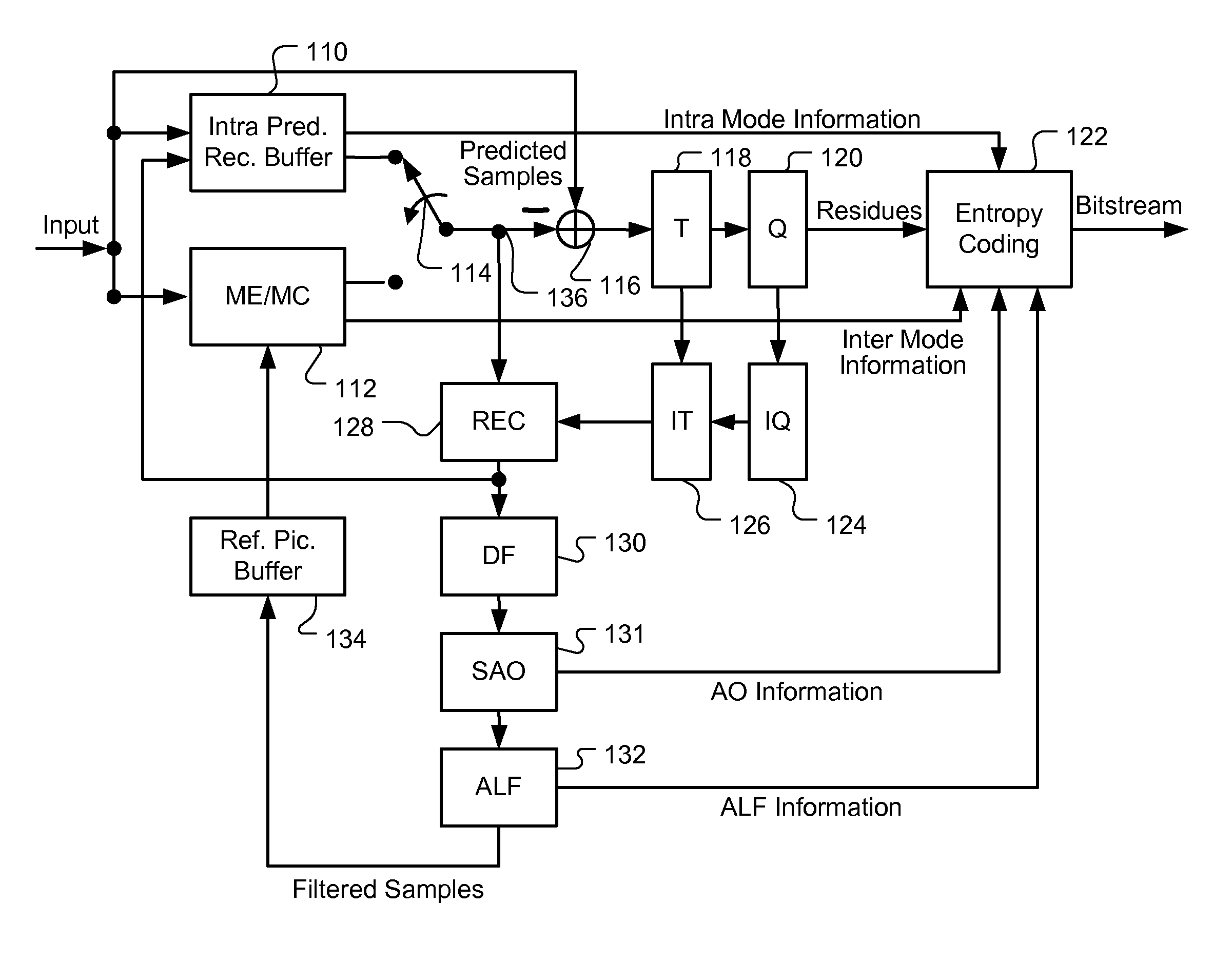
Apparatus and Method of Sample Adaptive Offset for Luma and Chroma Components
InactiveUS20120294353A1Improve coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputational scienceLoop filter
A method and apparatus for processing reconstructed video using in-loop filter in a video coding system are disclosed. The method uses chroma in-loop filter indication to indicate whether chroma components are processed by in-loop filter when the luma in-loop filter indication indicates that in-loop filter processing is applied to the luma component. An additional flag may be used to indicate whether the in-loop filter processing is applied to an entire picture using same in-loop filter information or each block of the picture using individual in-loop filter information. Various embodiments according to the present invention to increase efficiency are disclosed, wherein various aspects of in-loop filter information are taken into consideration for efficient coding such as the property of quadtree-based partition, boundary conditions of a block, in-loop filter information sharing between luma and chroma components, indexing to a set of in-loop filter information, and prediction of in-loop filter information.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
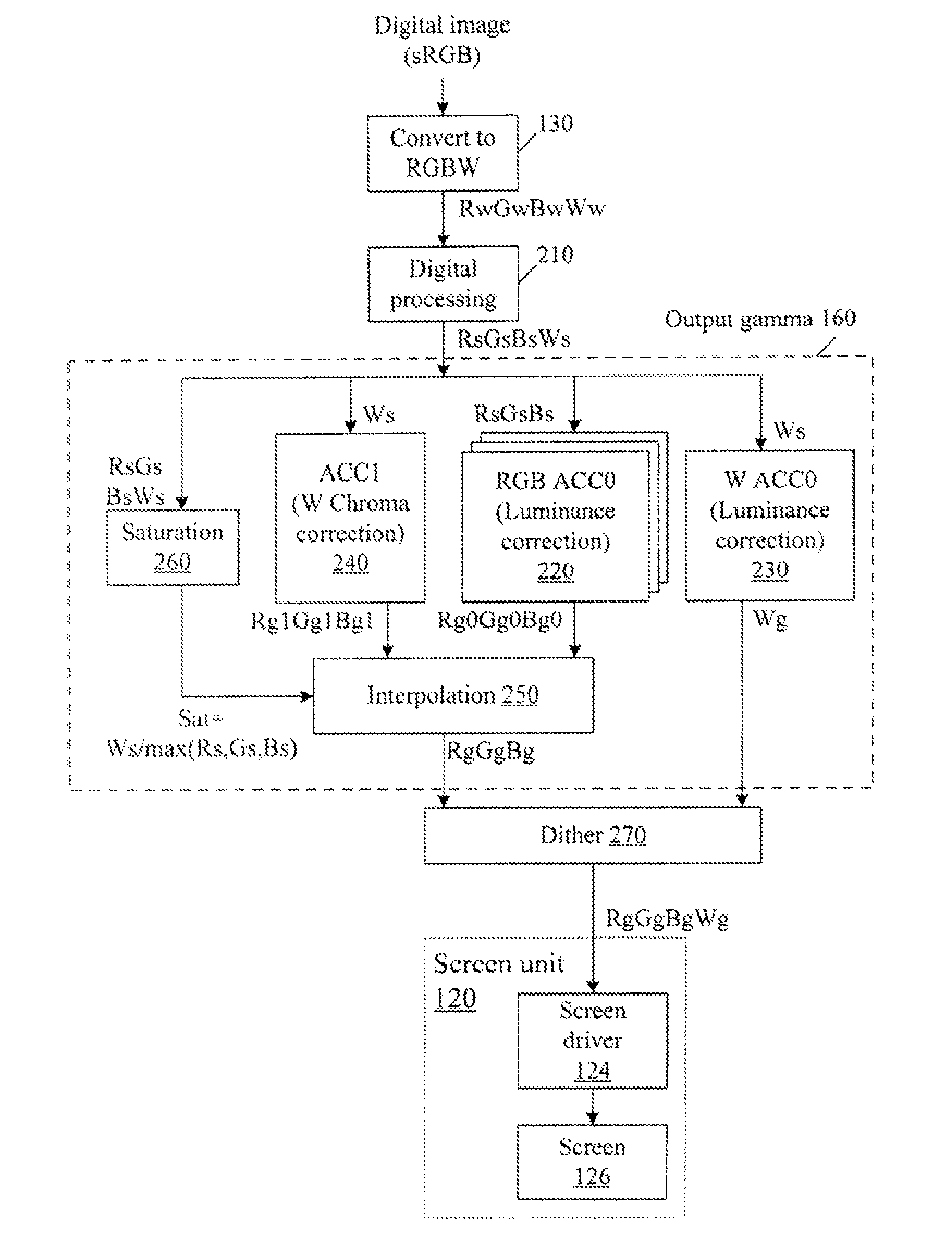
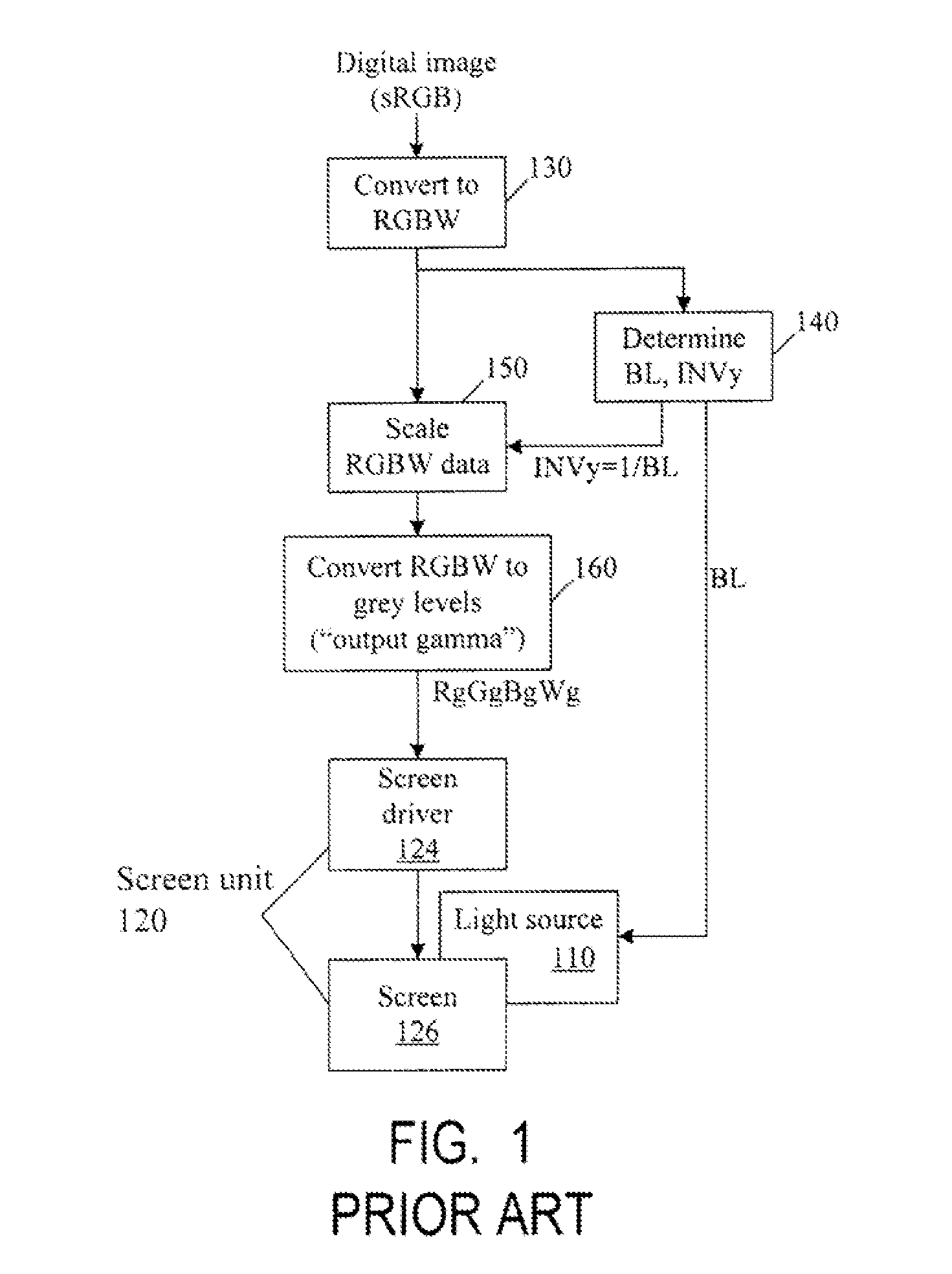
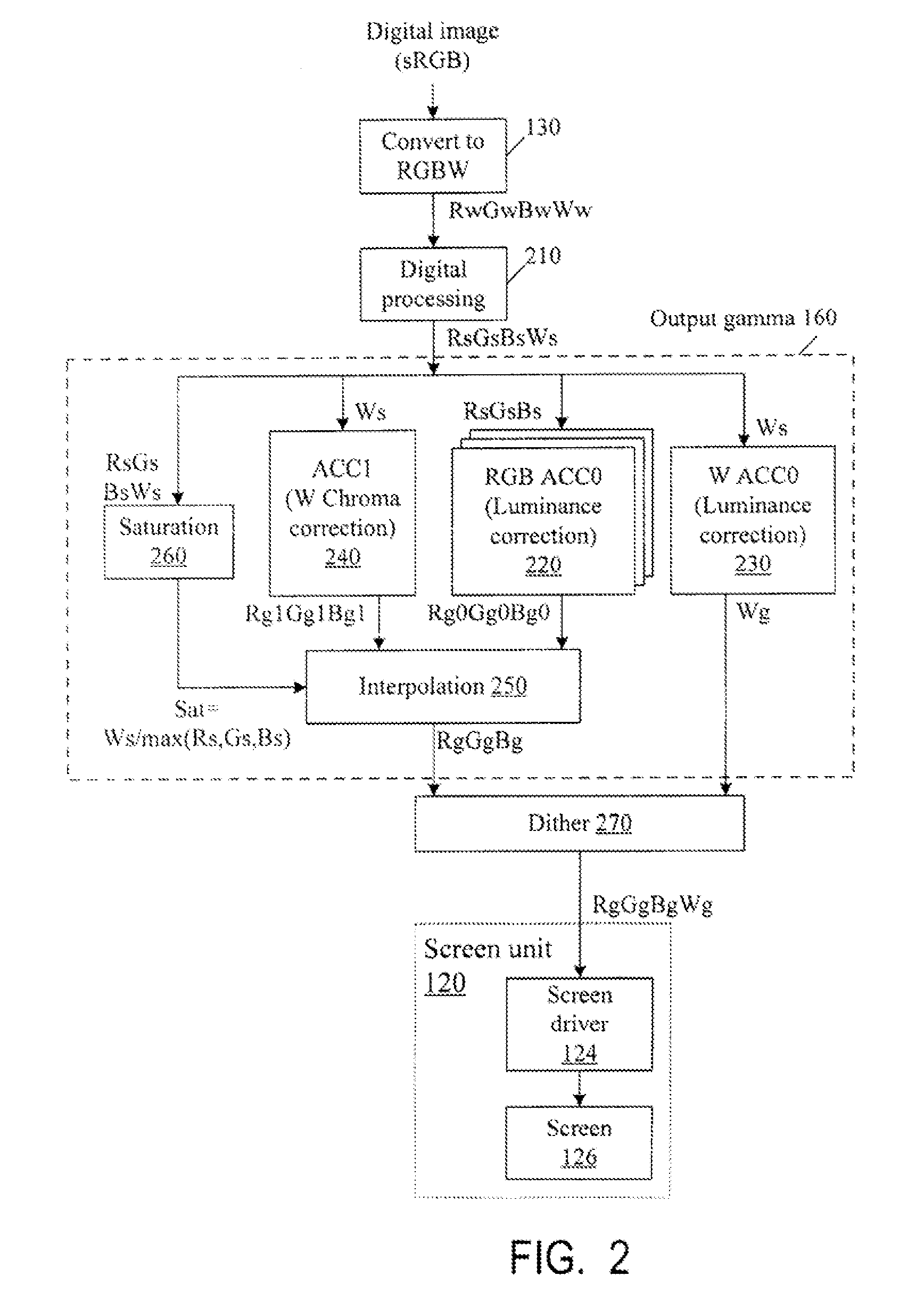
Color correction to compensate for displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics
ActiveUS20110149166A1Image degradation can be highIncrease brightnessTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor correctionDisplay device
Displays are provided with circuitry performing color correction to compensate for the displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics. Some techniques are suitable for RGBW displays and for subpixel-rendered displays. Some displays include an external light source (e.g. a backlight unit in LCDs), and the color correction is coordinated with dynamic control of the light source.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
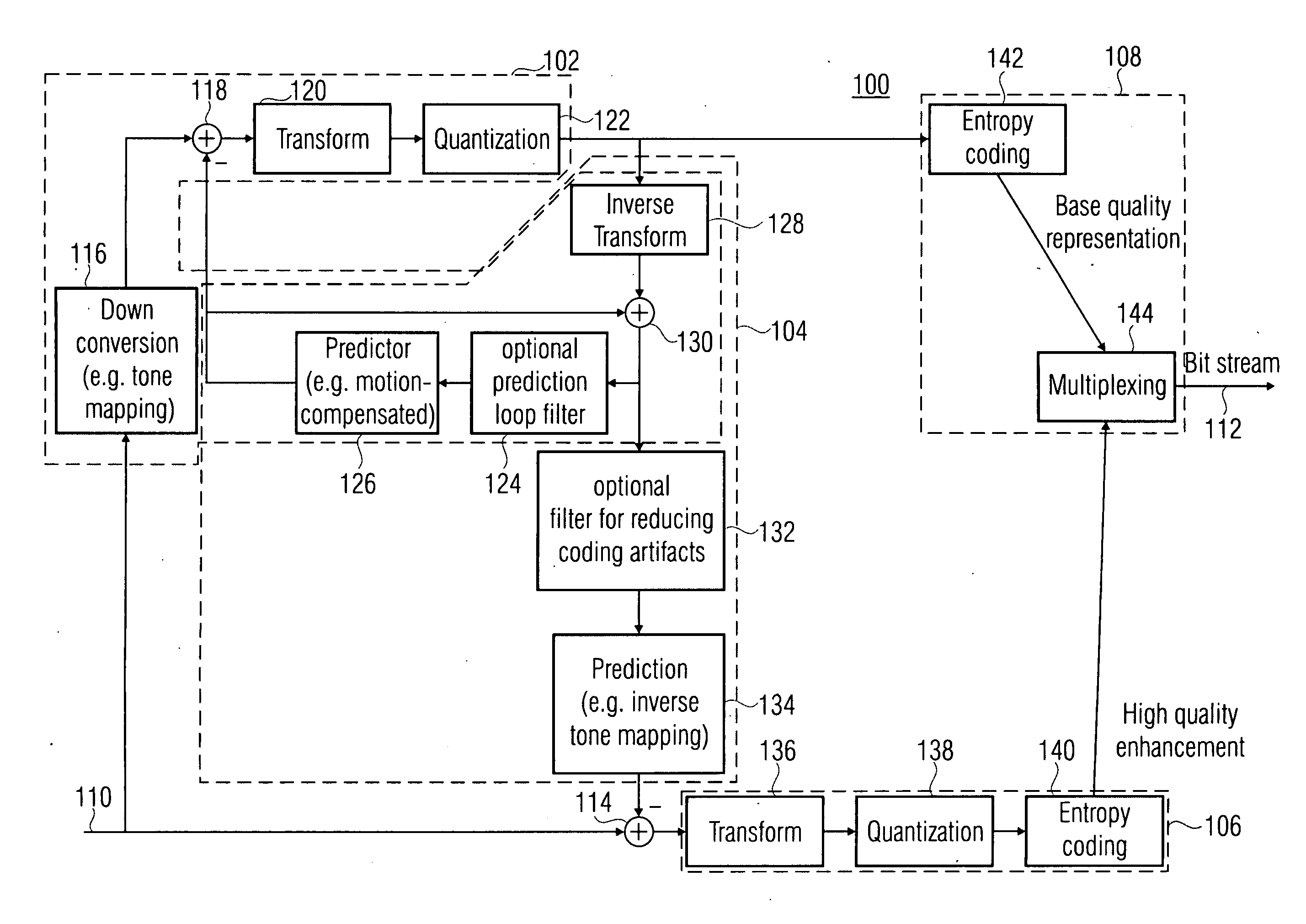
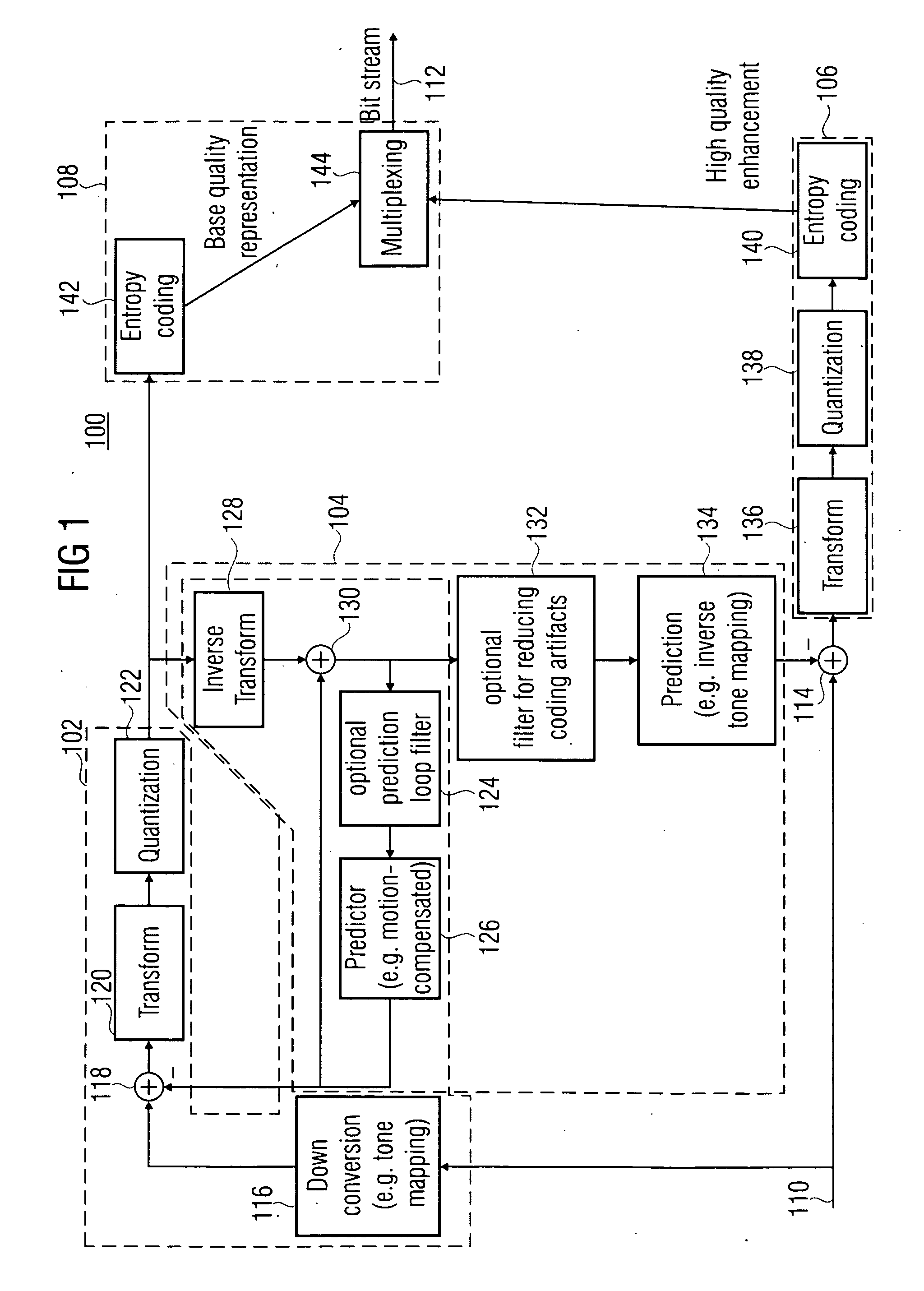
Quality scalable coding
ActiveUS20100020866A1Effective wayHigh bit-depthColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionData stream
A more efficient way of addressing different bit-depths, or different bit-depths and chroma sampling format requirements is achieved by using a low bit-depth and / or low-chroma resolution representation for providing a respective base layer data stream representing this low bit-depth and / or low-chroma resolution representation as well as for providing a higher bit-depth and / or higher chroma resolution representation so that a respective prediction residual may be encoded in order to obtain a higher bit-depth and / or higher chroma resolution representation. By this measure, an encoder is enabled to store a base-quality representation of a picture or a video sequence, which can be decoded by any legacy decoder or video decoder, together with an enhancement signal for higher bit-depth and / or reduced chroma sub-sampling, which may be ignored by legacy decoders or video decoders.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Chroma motion vector derivation for interlaced forward-predicted fields
Techniques and tools for deriving chroma motion vectors for macroblocks of interlaced forward-predicted fields are described. For example, a video encoder or decoder determines a prevailing polarity among luma motion vectors for a macroblock. The encoder or decoder then determines a chroma motion vector for the macroblock based at least in part upon one or more of the luma motion vectors having the prevailing polarity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Codec for IPTV
InactiveUS20070121728A1Easy to decodeOptimized for speedColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorSelf adaptive
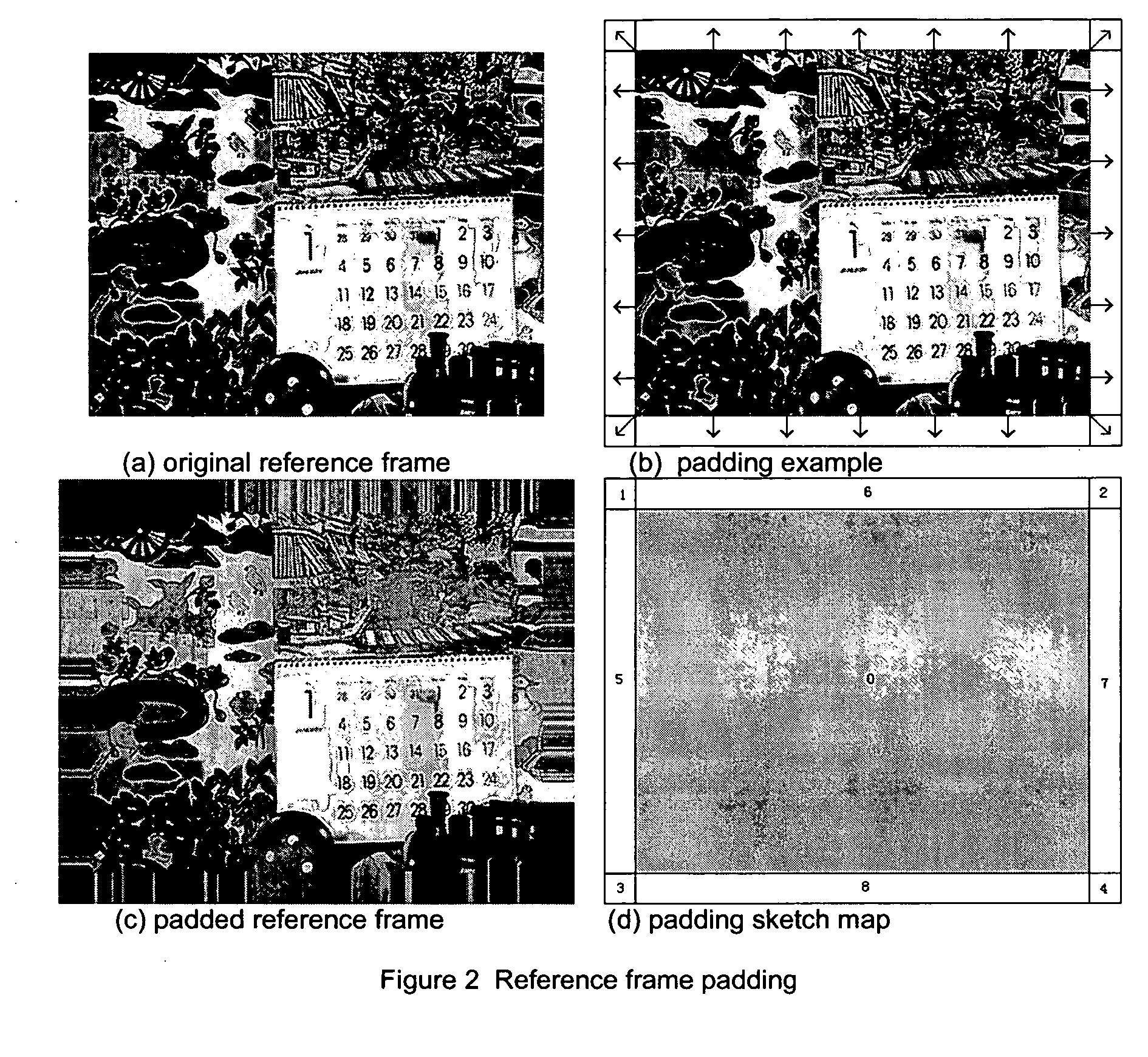
A method of optimizing decoding of MPEG4 compliant coded signals is provided, comprising: disabling processing for non-main profile sections; performing reference frame padding; performing adaptive motion compensation. The method of decoding further including performing fast IDCT wherein an IDCT process is performed on profile signals but no IDCT is performed based on whether a 4×4 block may be all zero, or only DC transform coefficient is non-zero, and including CAVLC encoding of residual data. Reference frame padding comprises compensating for motion vectors extending beyond a reference frame by adding to at least the length and width of the reference frame. Adaptive motion compensation includes original block size compensation processing for chroma up to block sizes of 16×16.
Owner:KYLINTV
Augmented Reality Simulator
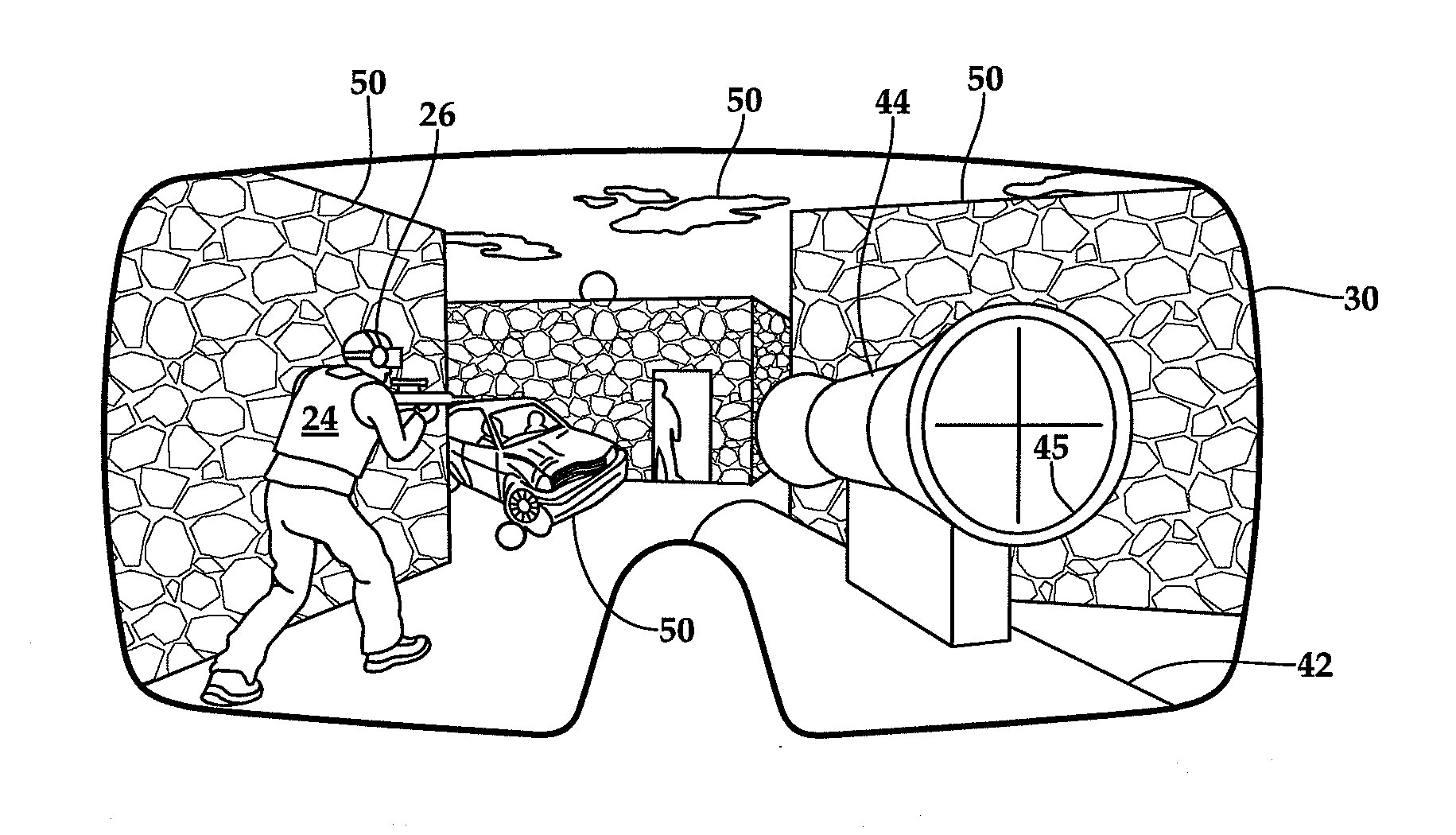
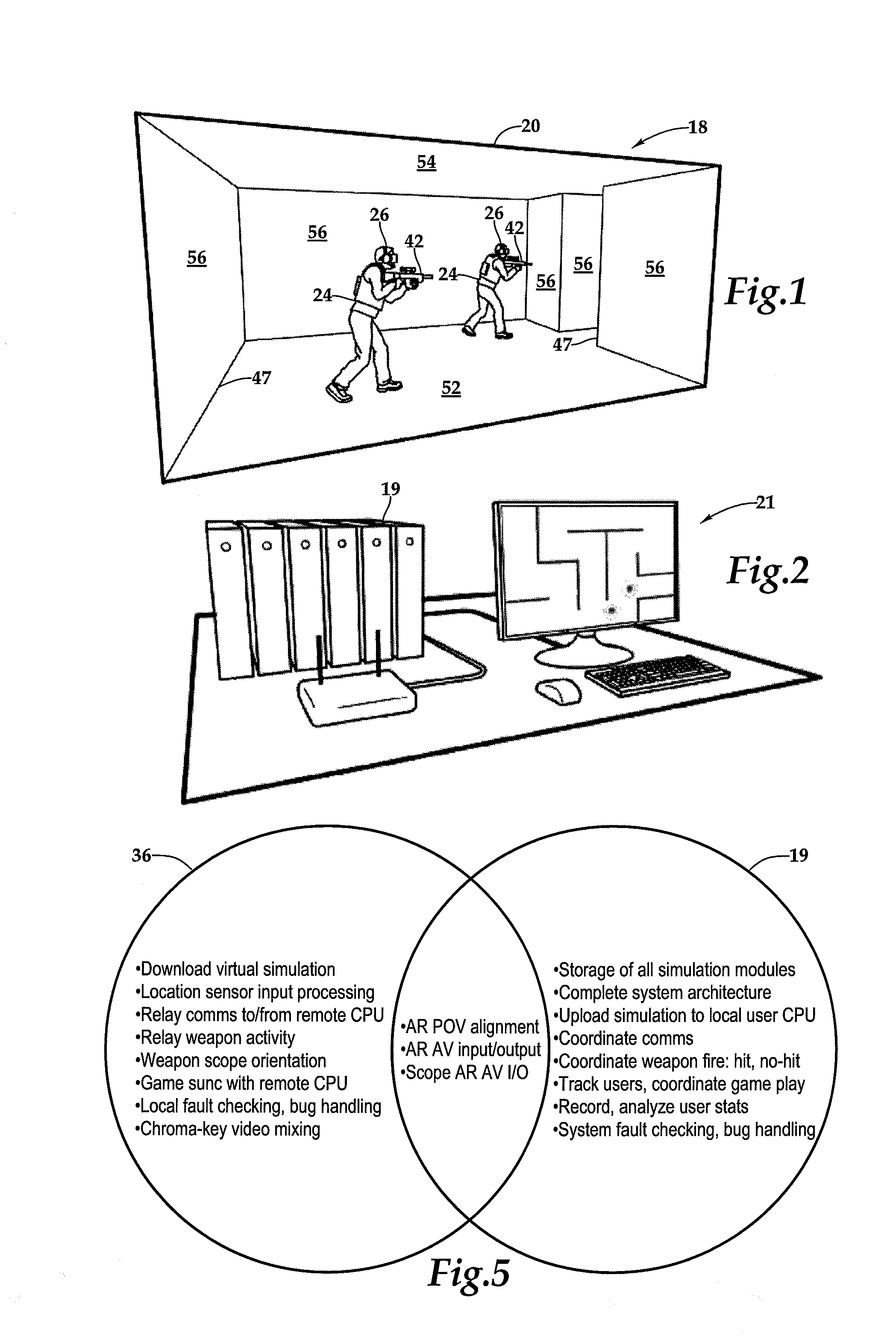
ActiveUS20150260474A1Lower latencyImprove securityInput/output for user-computer interactionCosmonautic condition simulationsDisplay deviceVideo image
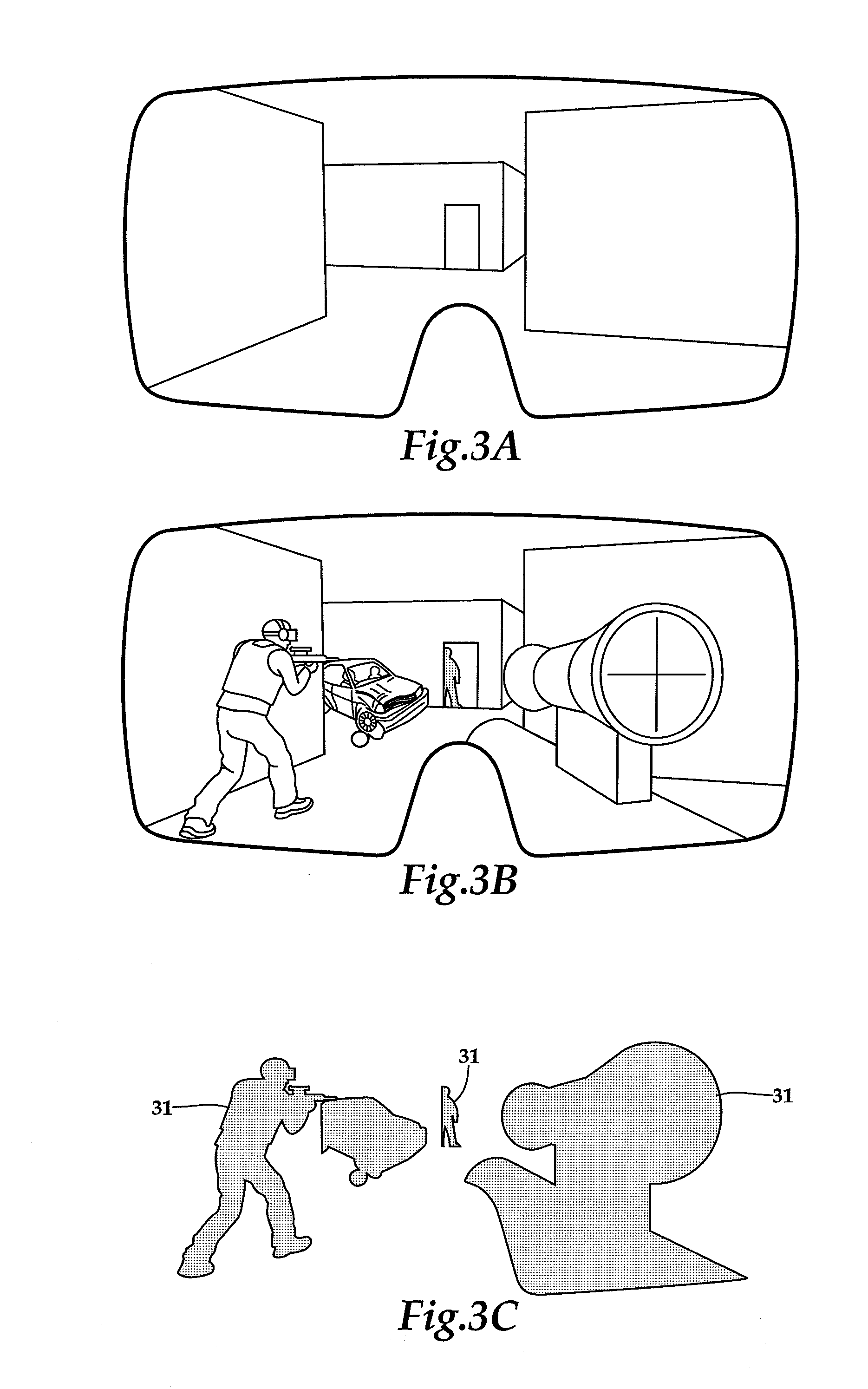
An augmented reality system in which video imagery of a physical environment is combined with video images output by a game engine by the use of a traveling matte which identifies portions of the visible physical environment by techniques such as Computer vision or chroma keying and replaces them with the video images output by the video game engine. The composited imagery of the physical environment and the video game imagery is supplied to a trainee through a headmounted display screen. Additionally, peripheral vision is preserved either by providing complete binocular display to the limits of peripheral vision, or by providing a visual path to the peripheral vision which is matched in luminance to higher resolution augmented reality images provided by the binocular displays. A software / hardware element comprised of a server control station and a controller onboard the trainee performs the modeling, scenario generation, communications, tracking, and metric generation.
Owner:LINEWEIGHT
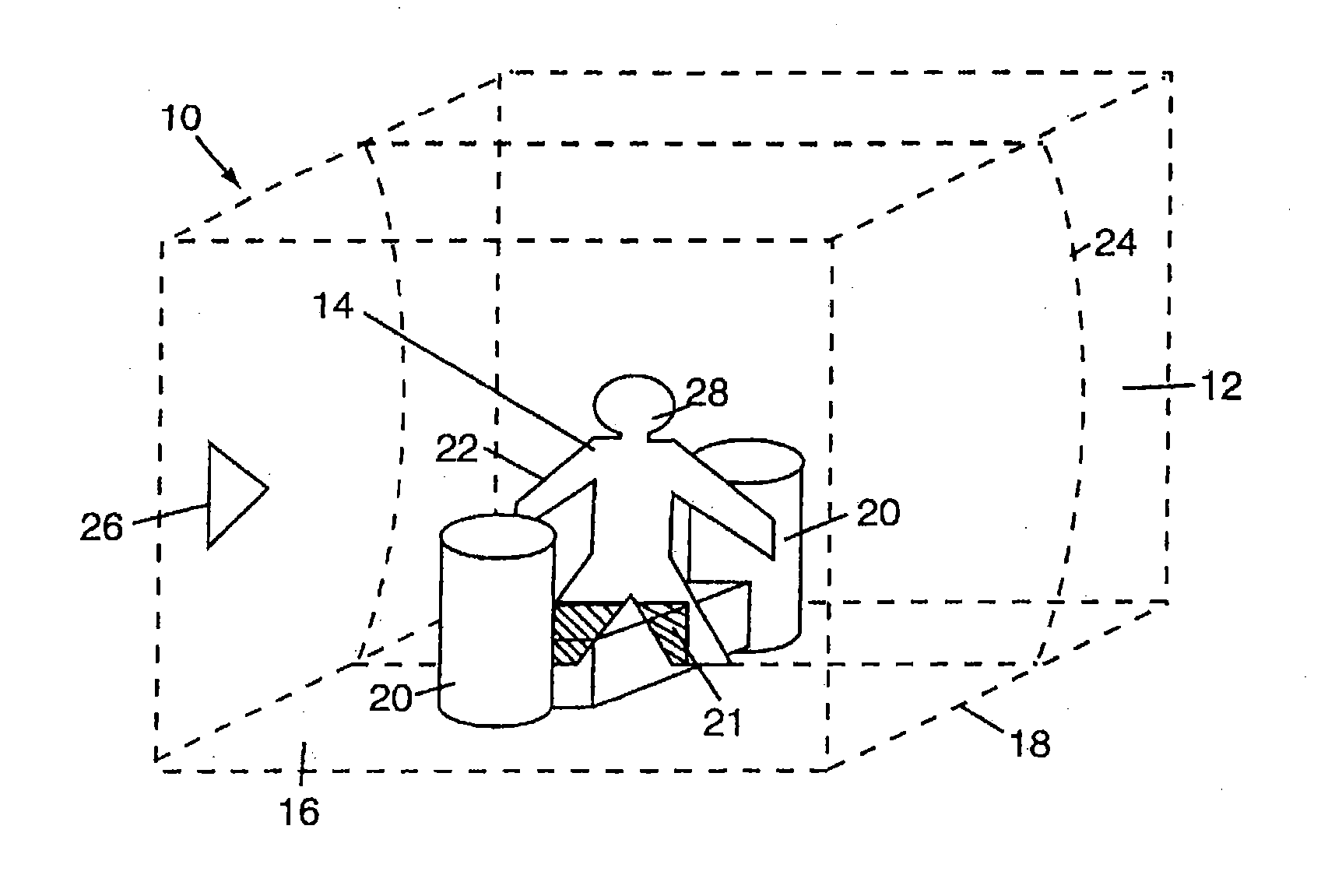
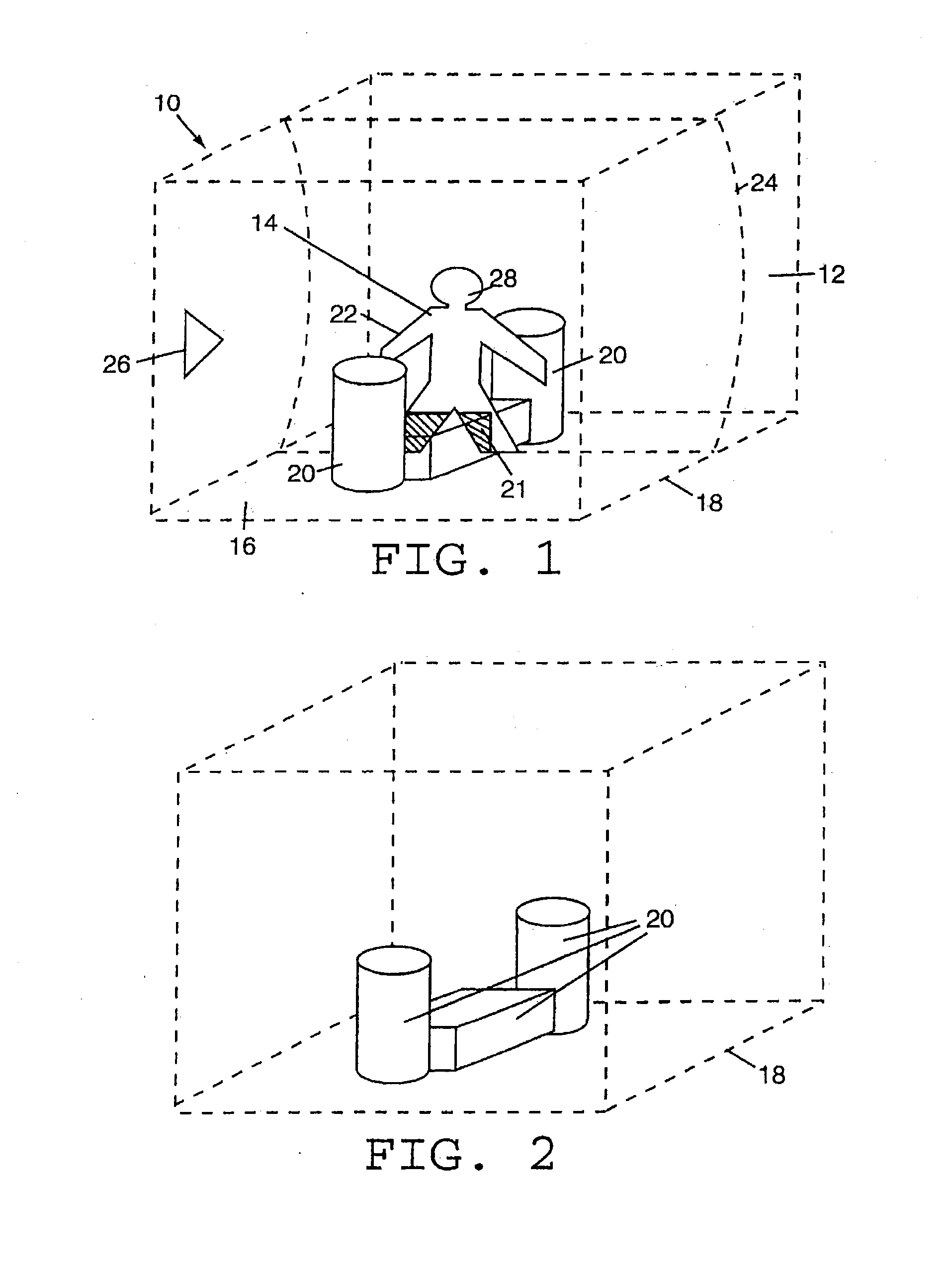
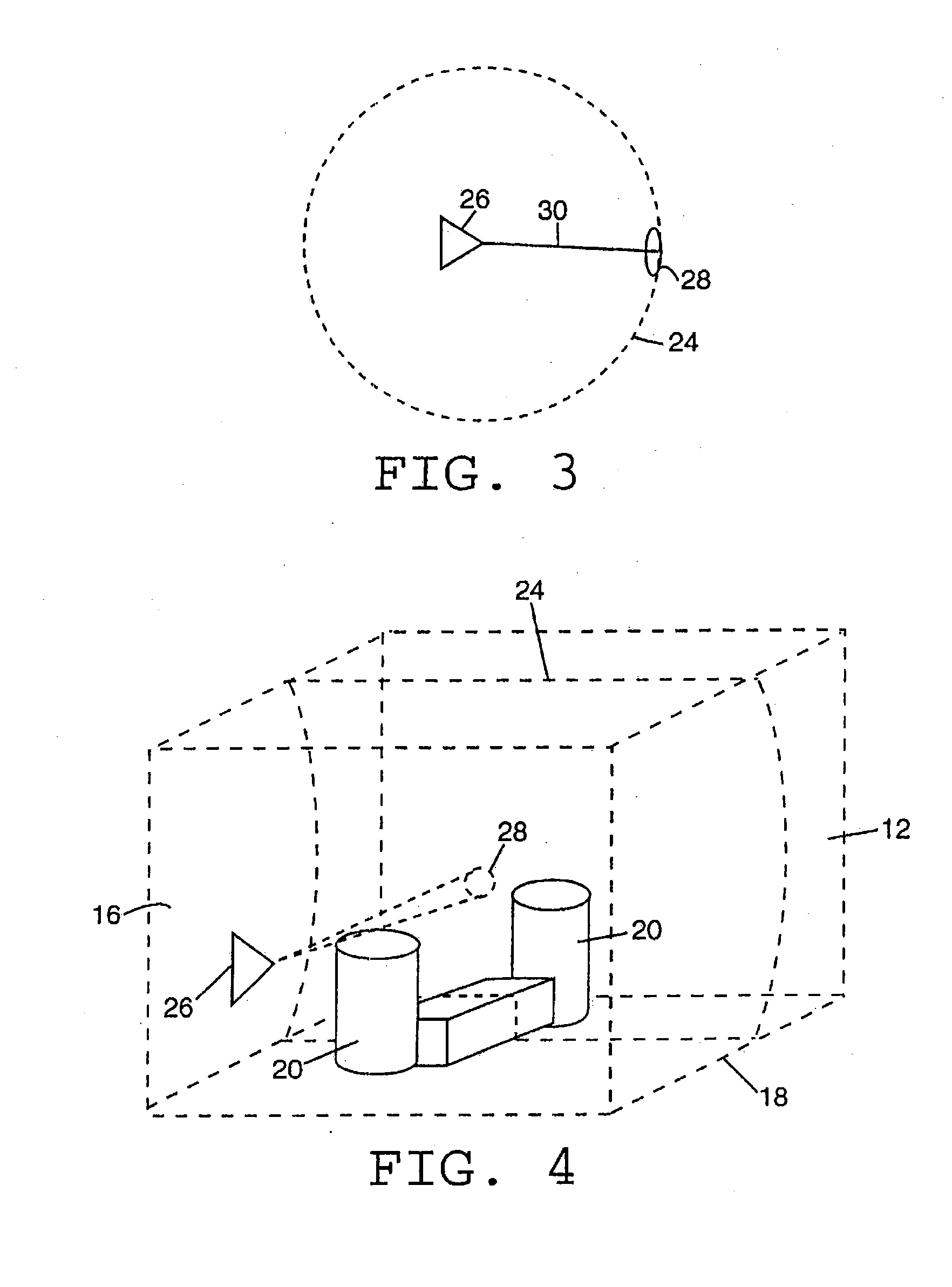
Method and system for feedback and control of a luminaire
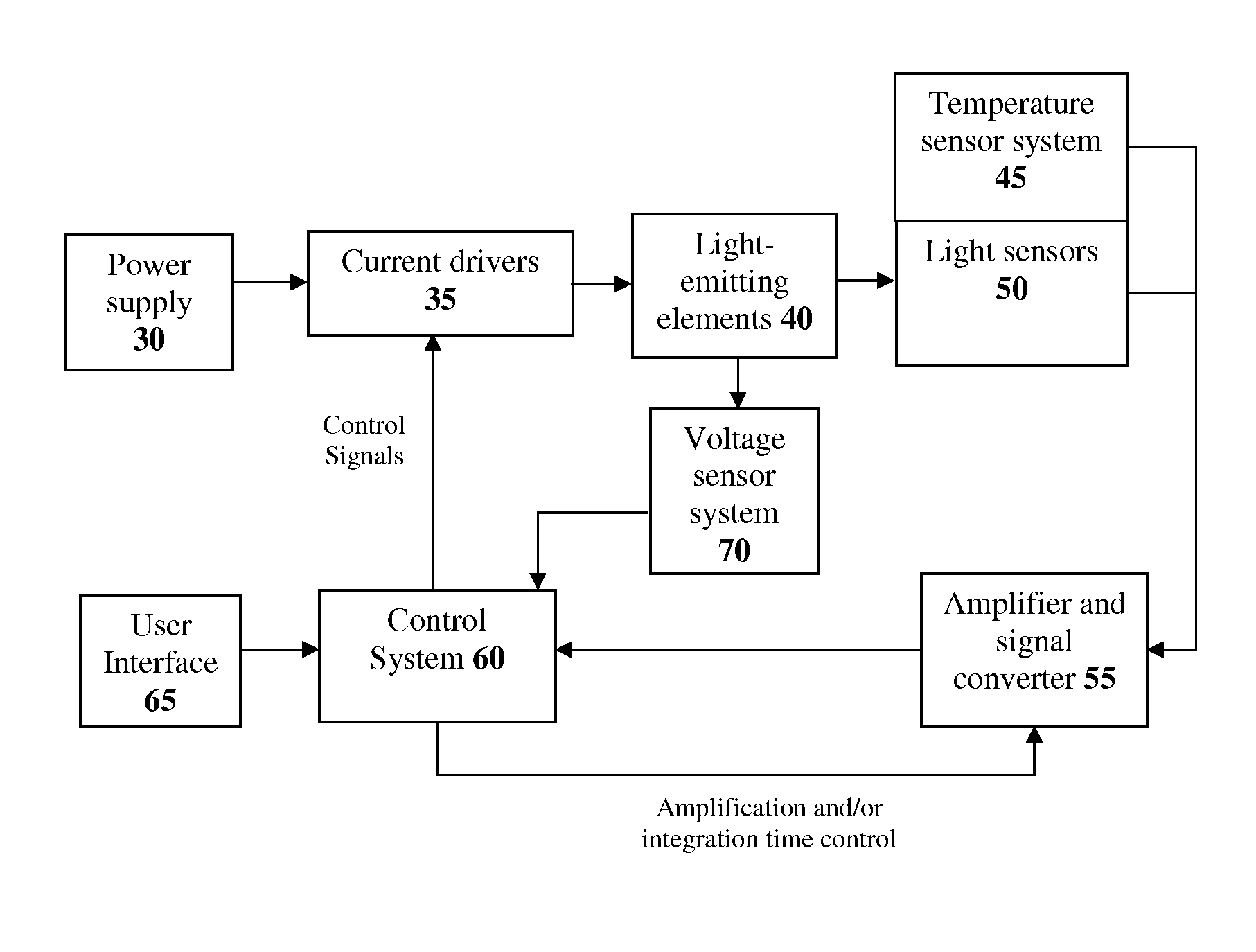
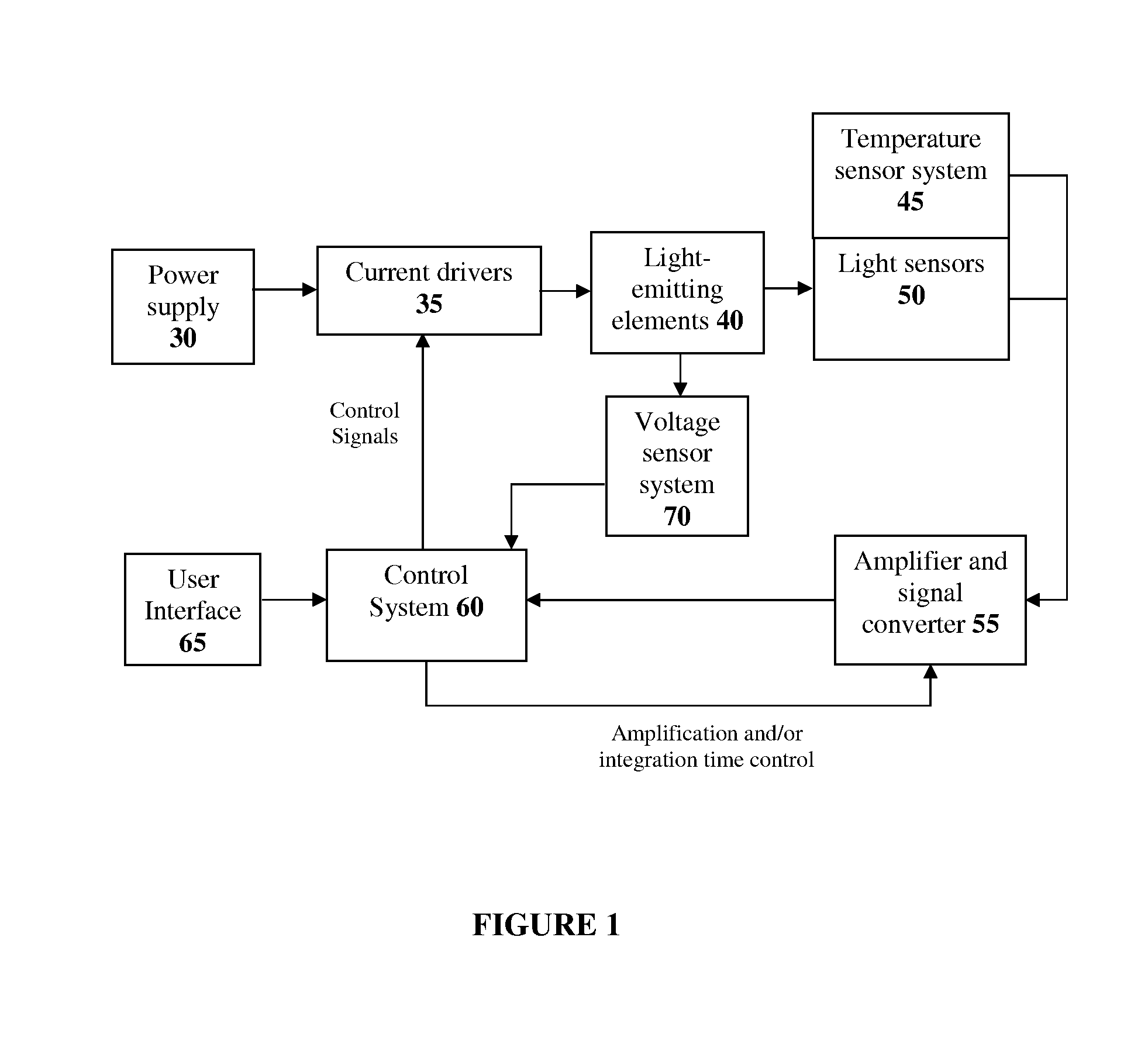
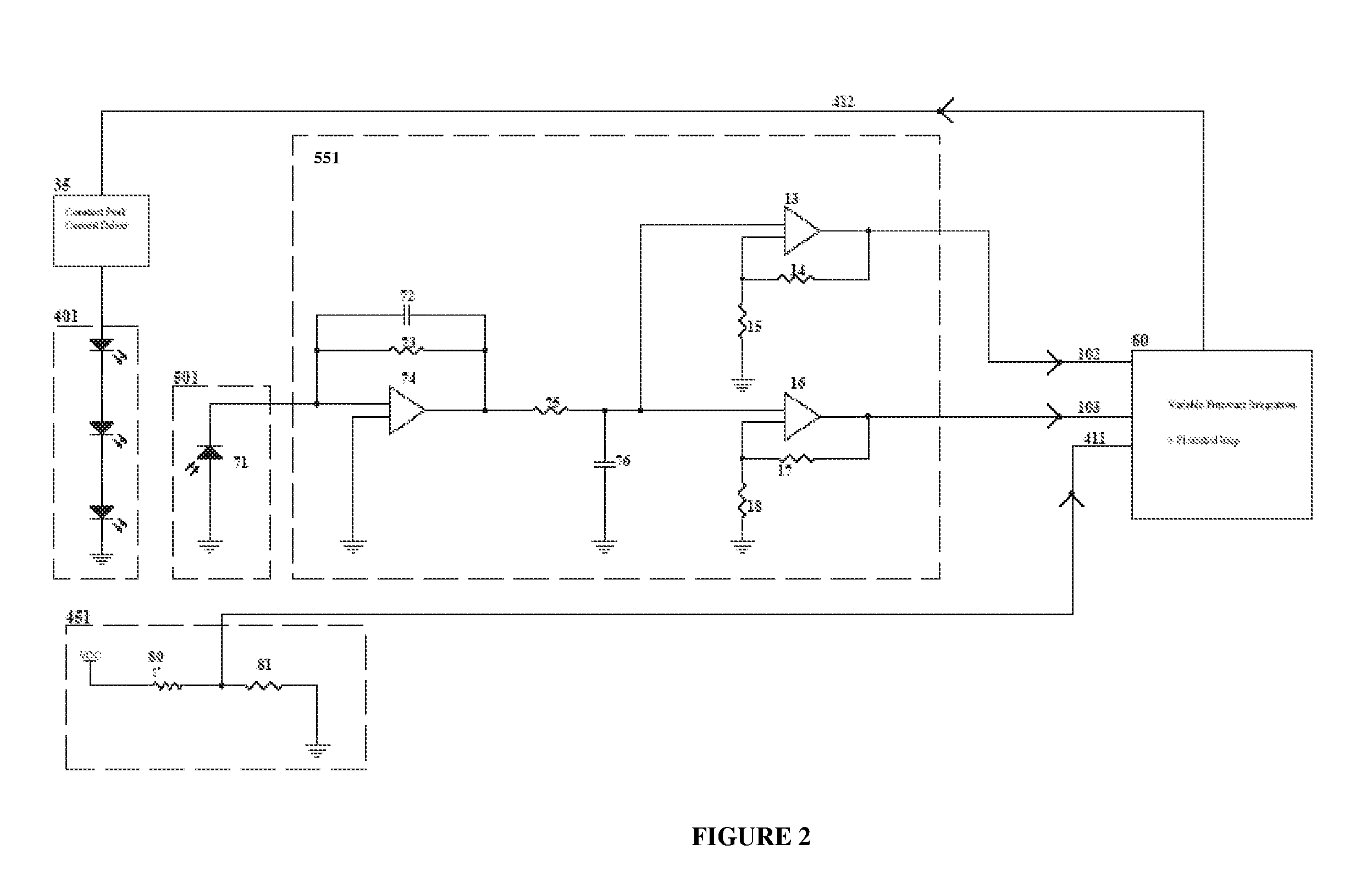
The present invention comprises a method and system for controlling the chromaticity and luminous flux output of a digitally controlled luminaire. The luminaire comprises one or more light-emitting elements and one or more light sensors which can provide optical feedback, wherein this optical feedback is filtered to remove undesired frequencies. The method and system comprises a control system which can sample the filtered signals from the light sensors according to a predetermined feedback sampling frequency scheme, wherein this scheme is specifically configured to provide sufficient iterations of the feedback loop to be performed for adjustment of the chromaticity and luminous flux output of the light-emitting elements, without perceptible visual flicker or momentary chromaticity shifts.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
System and method for object tracking
InactiveUS20050026689A1Maximizing abilityImage analysisImage data processing detailsCamera imageColor transformation
A hand-manipulated prop is picked-up via a single video camera, and the camera image is analyzed to isolate the part of the image pertaining to the object for mapping the position and orientation of the object into a three-dimensional space, wherein the three-dimensional description of the object is stored in memory and used for controlling action in a game program, such as rendering of a corresponding virtual object in a scene of a video display. Algorithms for deriving the three-dimensional descriptions for various props employ geometry processing, including area statistics, edge detection and / or color transition localization, to find the position and orientation of the prop from two-dimensional pixel data. Criteria are proposed for the selection of colors of stripes on the props which maximize separation in the two-dimensional chrominance color space, so that instead of detecting absolute colors, significant color transitions are detected. Thus, the need for calibration of the system dependent on lighting conditions which tend to affect apparent colors can be avoided.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Methods and apparatus for color uniformity
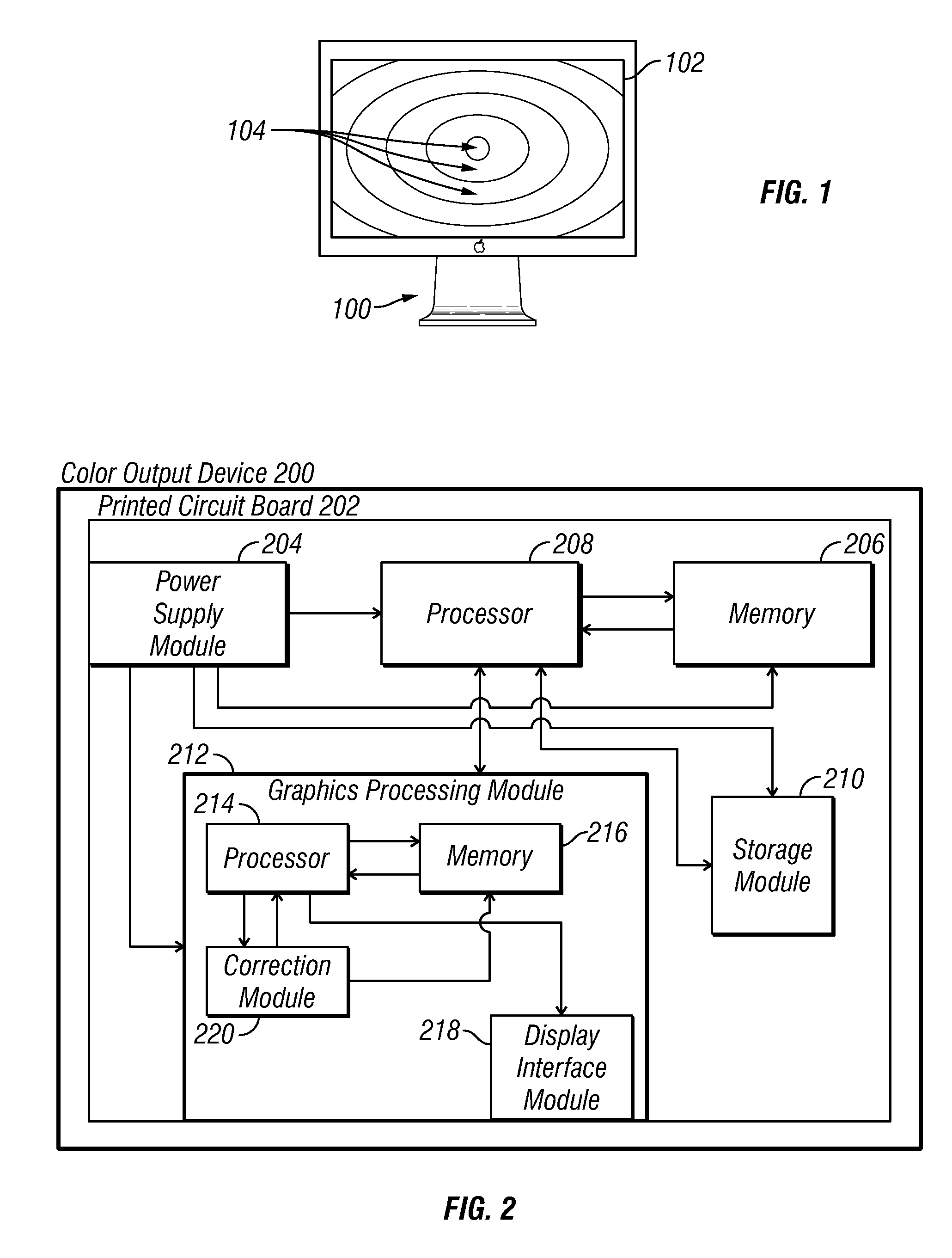
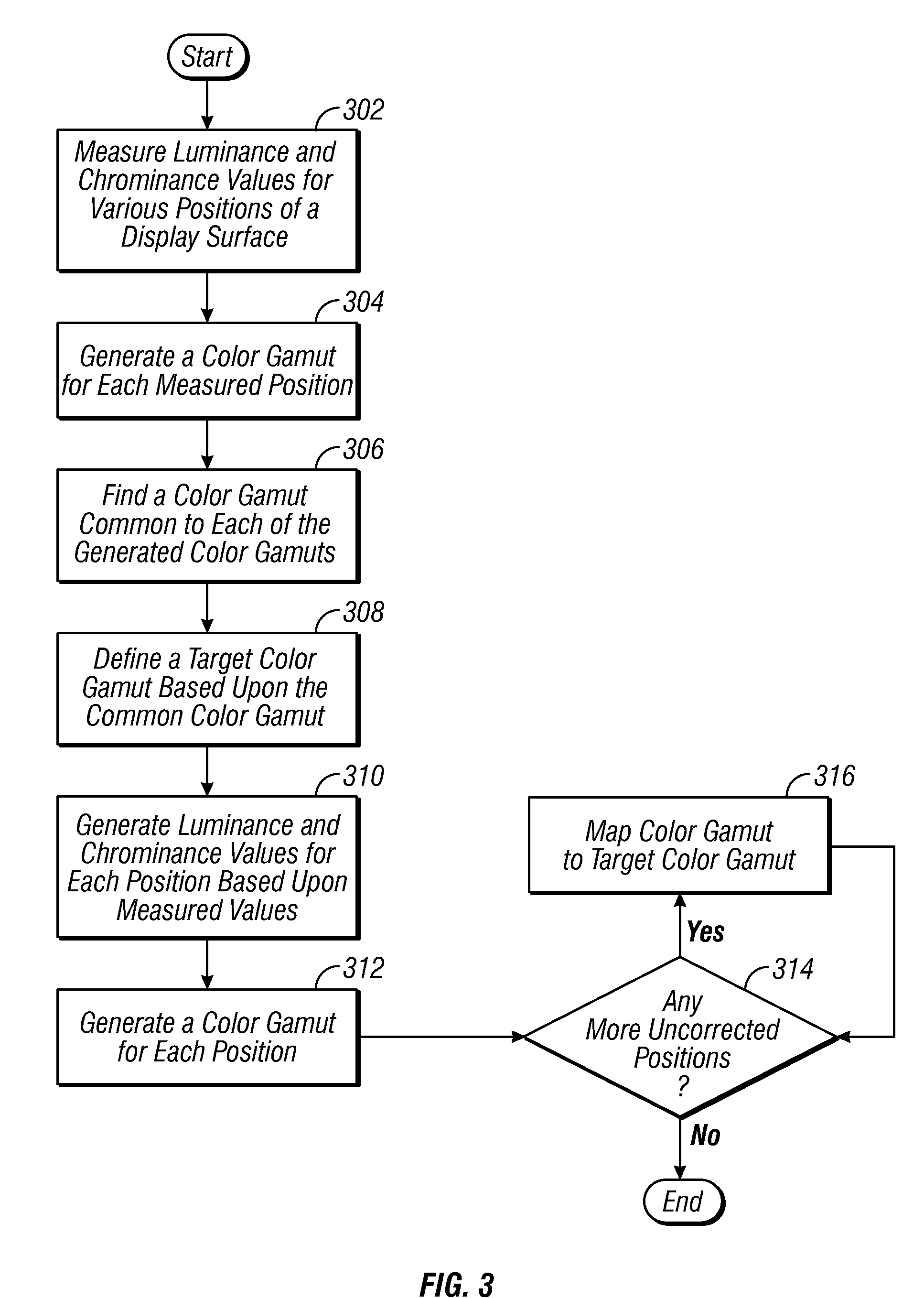
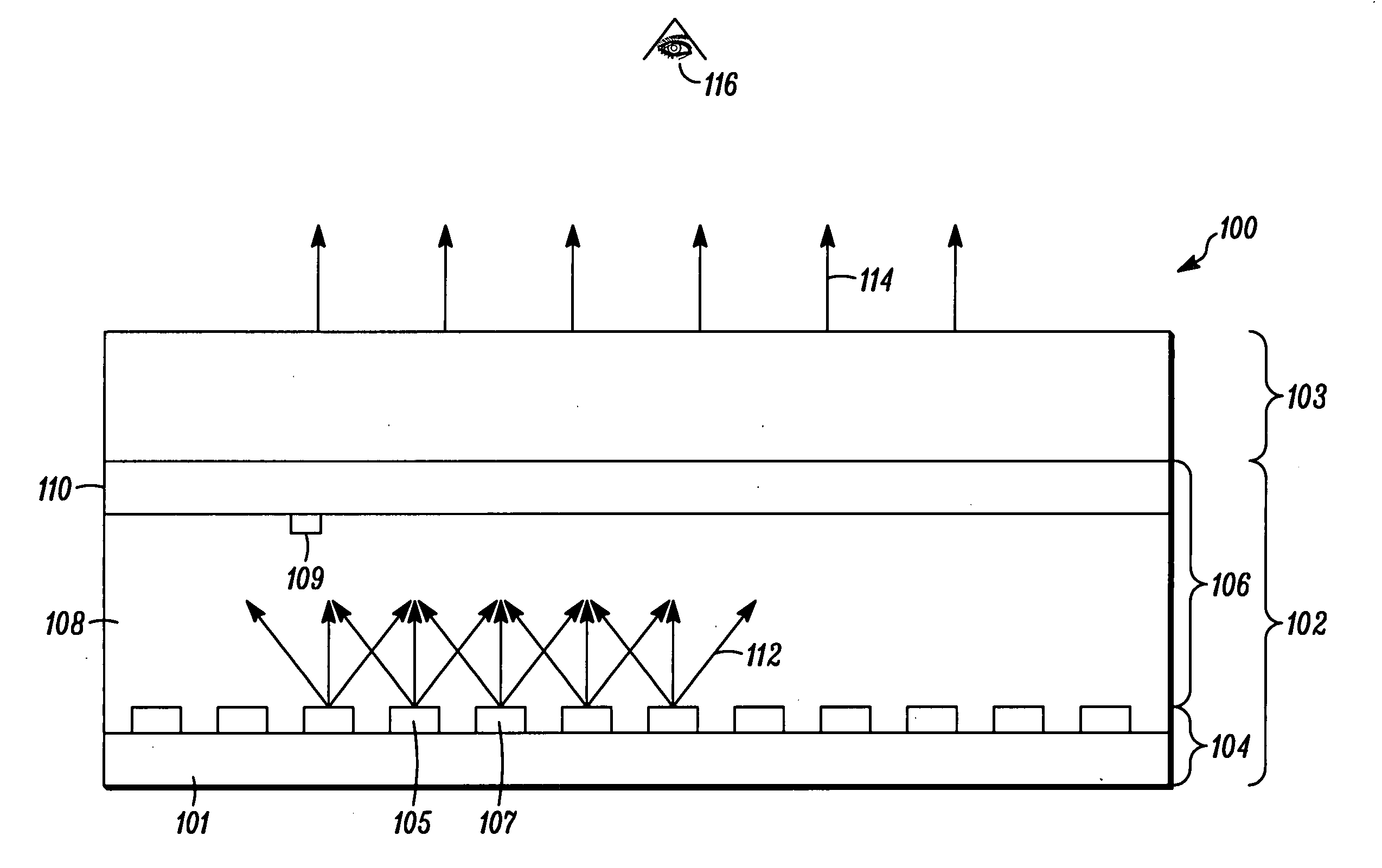
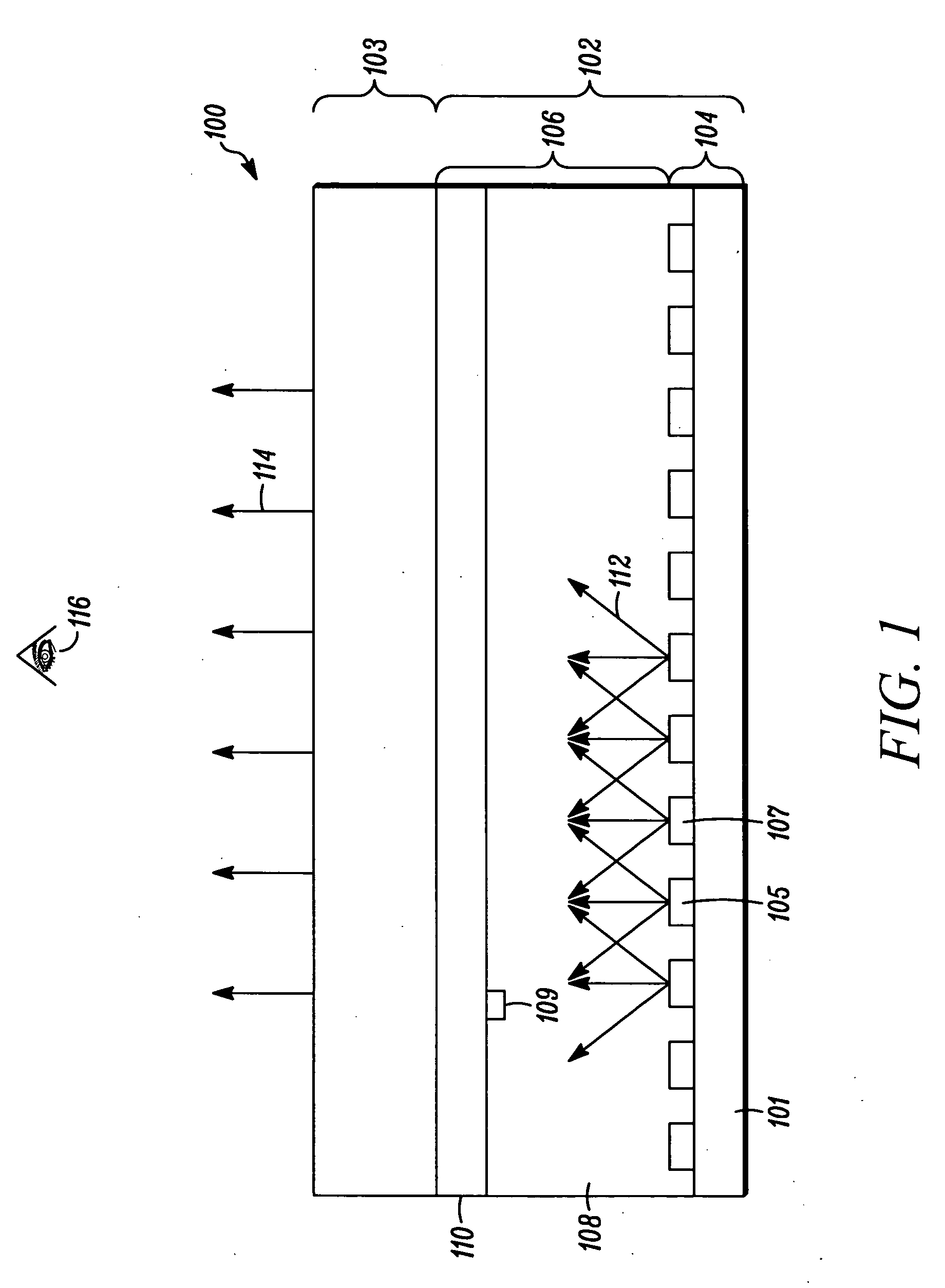
Methods and apparatus for achieving color and luminance uniformity in color output devices. In one embodiment, measurements of luminance and chrominance are taken at various regions of the display surface for a range of color inputs. Using the collected data, a color volume is formed for each of the measured regions. This color volume comprises a set of all colors producible at the measured region. The color volumes for each of the measured regions are then used to generate a common color gamut, i.e., a volume of colors that are producible in each of the measured regions. A gamut mapping can then be performed for all or a portion of the positions on the display surface to a target color gamut. Input data for the gamut mapping process may be determined by conventional interpolative techniques.
Owner:APPLE INC
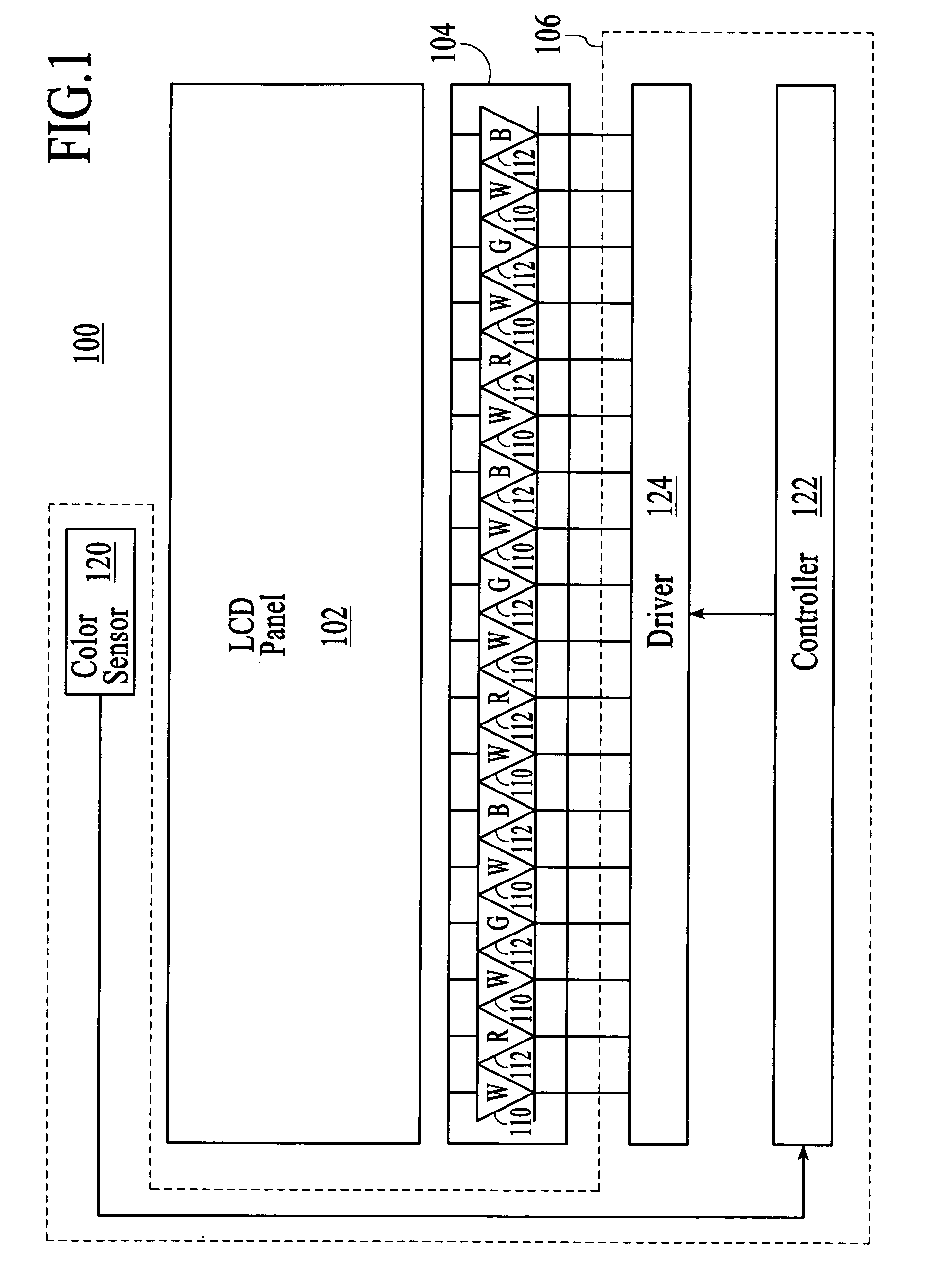
LED backlight system for LCD displays
A LCD display comprises a backlight assembly that includes a backlight substrate, one or more first white LEDs coupled to the backlight substrate and configured to produce a first light output, and one or more second white LEDs coupled to the backlight substrate and configured to produce a second light output. A light integration unit is coupled to the backlight assembly and configured to produce a combined output from the first light output and the second light output, the combined output having a desired luminance and chrominance. A LCD assembly is coupled to the light integration unit.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
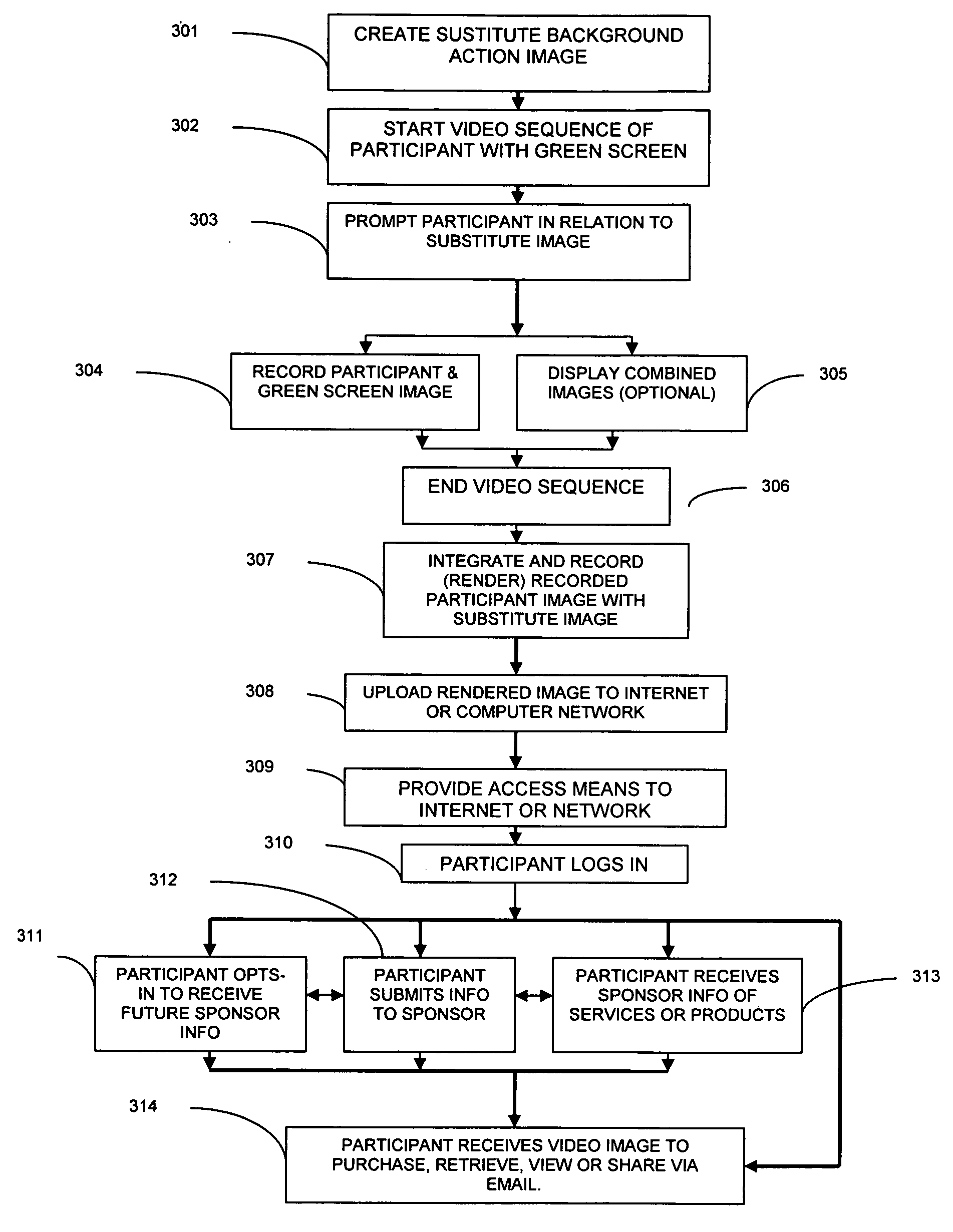
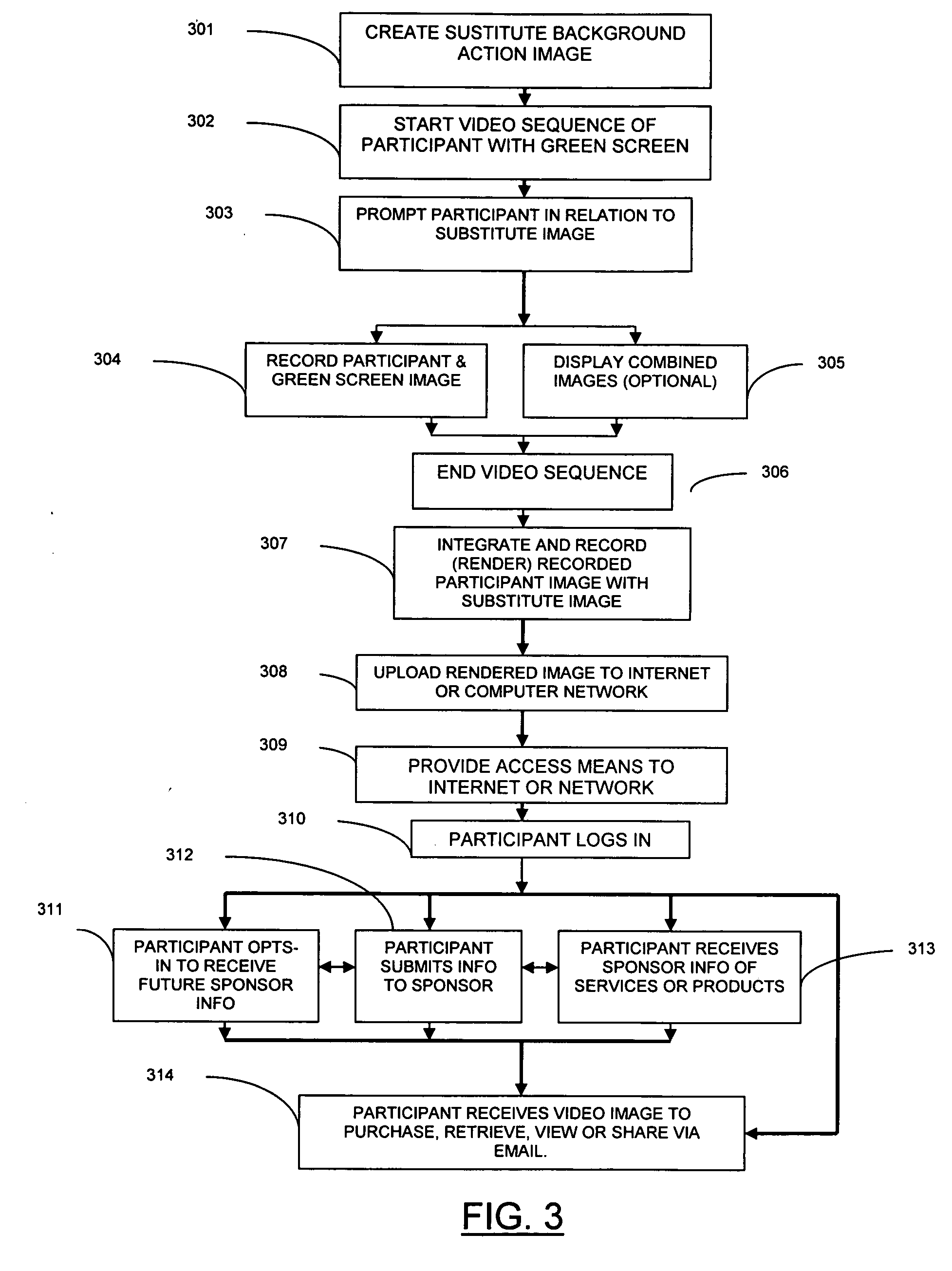
Chroma-key event photography messaging
The invention comprises an entertaining digital chroma-key video photography event (“photo event”) wherein at least one photo subject is placed in front of a green screen background. The participant is photographed while moving or speaking in response to verbal prompts or from viewing action in a simultaneously shown interactive composite of the participant with the substitute and moving background. The participant may be provided with a still photo produced from the video or photographed simultaneously with the video. The participant may view or retrieve the full video or additional still photos by logging onto an Internet website, intranet or other computer network utilizing a handheld device such as a mobile phone or personal digital assistant (PDA). The invention also comprises use of multiple substitute images wherein there may be at least a substitute background and a substitute foreground. The image of the participant appears in the resulting composite as variably being in an intermediate position, the foreground or background. The invention also comprises a method of surveying individuals. The individuals responding to survey questions may be participants of the photo event or others, e.g., the parents of adolescent children. The individual are prompted to respond in exchange for or at the time of receipt of the video or photo.
Owner:ALPHA PHOTOGRAPHY
System and Method for Generating Three Dimensional Presentations
A virtual three-dimensional presentation in accordance with the present invention includes three stereoscopic layers, a stereoscopic background layer, a stereoscopic video insert layer, and a stereoscopic three-dimensional foreground layer. A surface, the Z-sphere, is defined in the virtual three-dimensional space of the three-dimensional scene with reference to the aim point, the distance between the cameras, and the distance from the camera of the video scene, of a virtual stereoscopic camera looking at the three-dimensional scene being created. The separation of the virtual stereoscopic camera lens and distance to the aim point are set based on the stereoscopic cameras that are creating the video insert layer. The stereoscopic three-dimensional foreground layer scene may include a key which defines the transparency of objects in the foreground layer. The stereoscopic video insert layer may be generated by positioning a presenter, or other object, in a chroma-key set which is captured with a stereoscopic camera. The stereoscopic video insert layer may be distorted before being composited with the background and foreground such that elements of the stereoscopic video appear to move across a three-dimensional floor of the stereoscopic three-dimensional scene.
Owner:DTN LLC
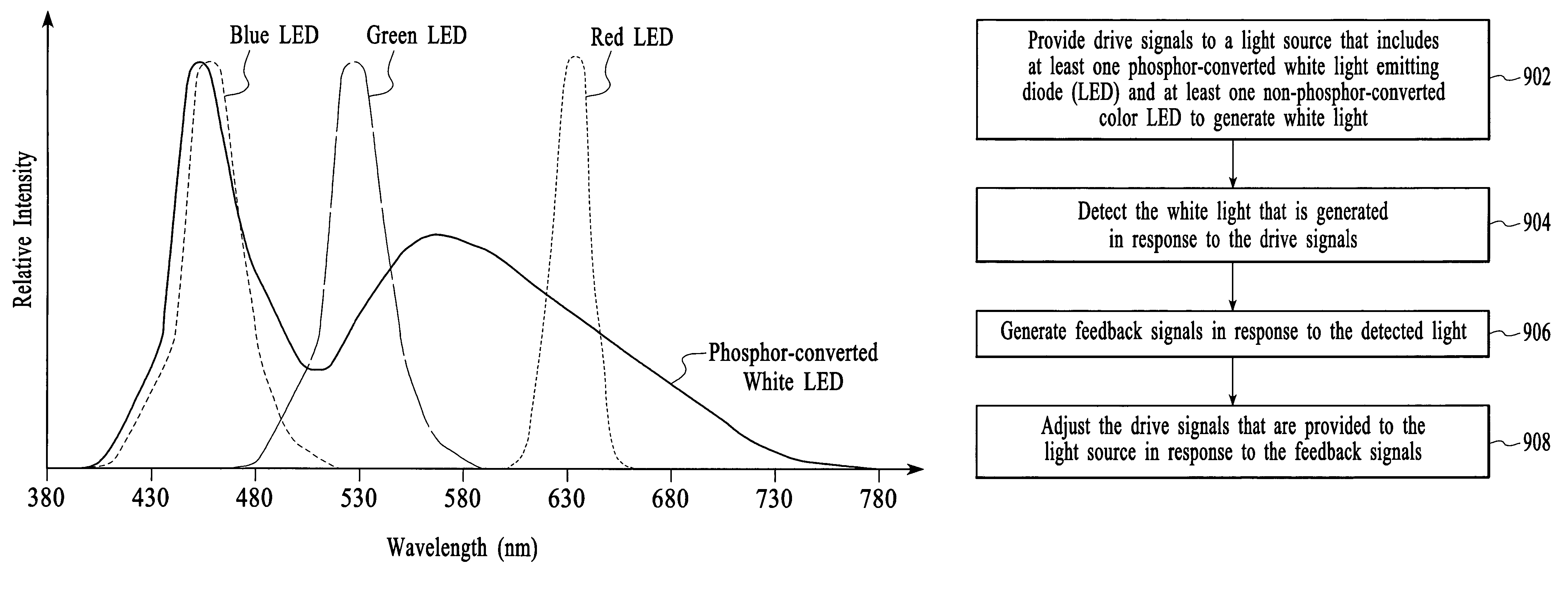
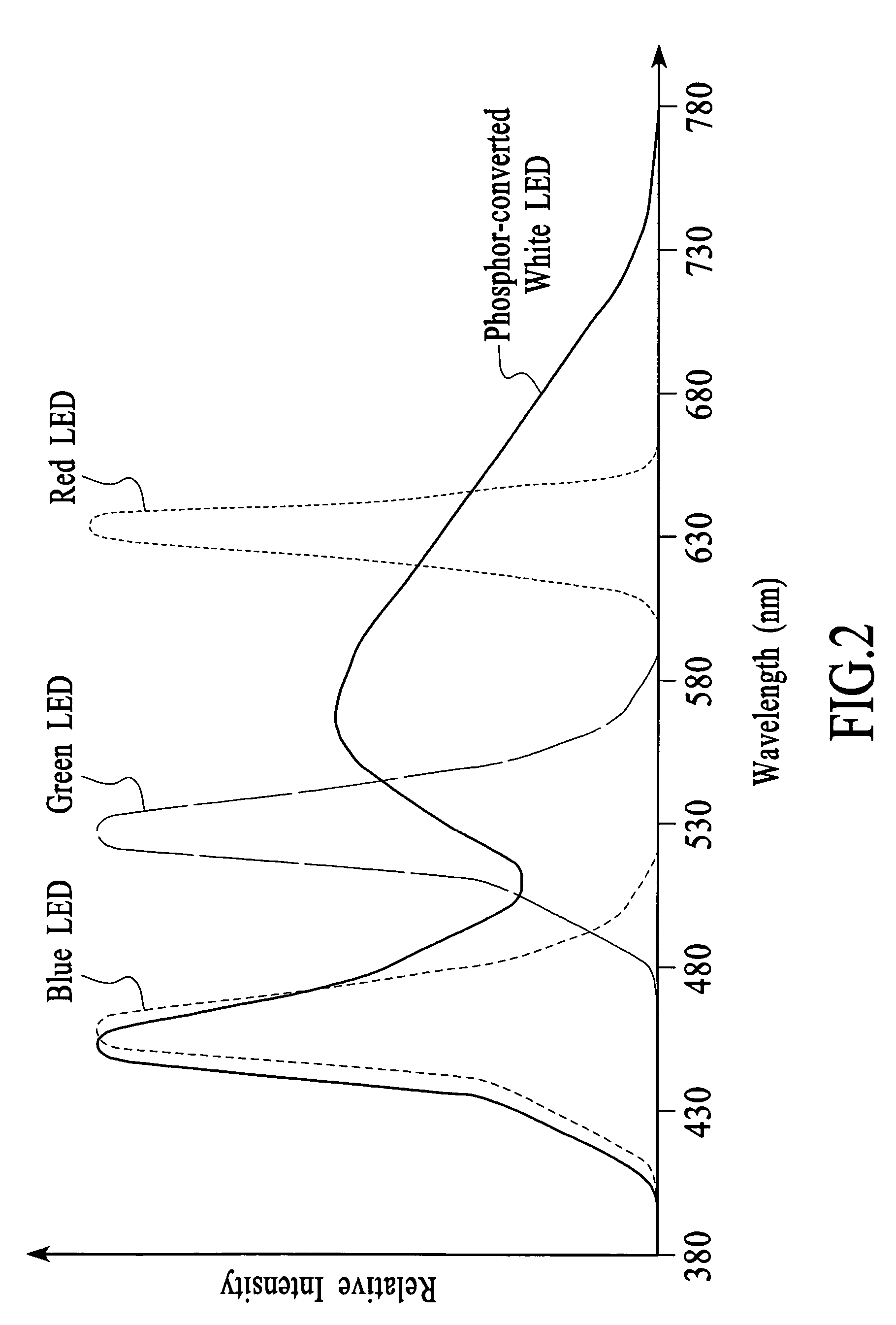
System and method for producing white light using a combination of phosphor-converted white LEDs and non-phosphor-converted color LEDs
ActiveUS7256557B2High color rendering indexWide SPDDischarge tube incandescent screensStatic indicating devicesPhosphorLightness
A system and method for generating white light involves using a combination of phosphor-converted white LEDs and non-phosphor-converted color LEDs to produce white light and adjusting the emitted light in response to feedback signals. Generating white light using a combination of phosphor-converted white LEDs and non-phosphor-converted color LEDs produces white light with an improved CRI and a wide SPD. Adjusting the emitted light in response to feedback allows luminance and chrominance characteristics of the white light to be controlled as the performance of the LEDs changes over time. The emitted light can be adjusted on a per-color basis and / or on a per-group basis, where a group of LEDs includes a combination of at least one phosphor-converted white LED and at least one non-phosphor-converted color LED.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Composition for Functional Coatings, Film Formed Therefrom and Method for Forming the Composition and the Film
InactiveUS20080311308A1Preservation deteriorateLow viscosityConductive materialPhotomechanical apparatusElectrochromismChrominance
The present invention relates to compositions for functional films, and more particularly to compositions for functional films such as a heat ray screening film compatible with hydrolic or alcoholic and anti-hydrolic resin binder, a near infrared screening film, a chrominance correcting film, a conductive film, a magnetic film, a ferromagnetic film, a dielectric film, a ferroelectric film, an electrochromic film, an electroluminescence film, an insulating film, a reflecting film, a reflection preventing film, a catalyst film, a photocatalyst film, a light selectively absorbing film, a hard film, and a heat resisting film, films formed therefrom, and a method of forming the compositions and the films.
Owner:LEE HAE WOOK
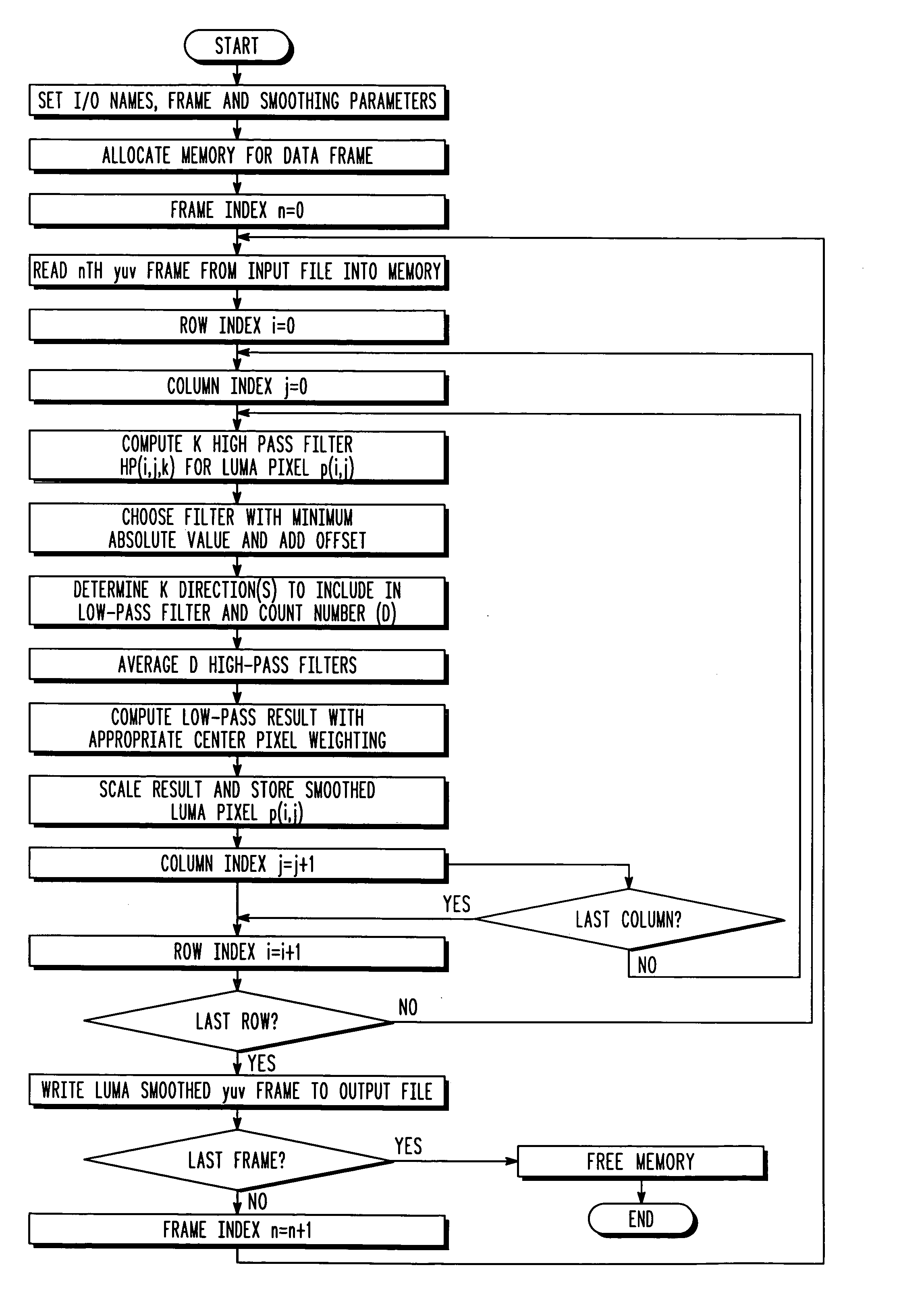
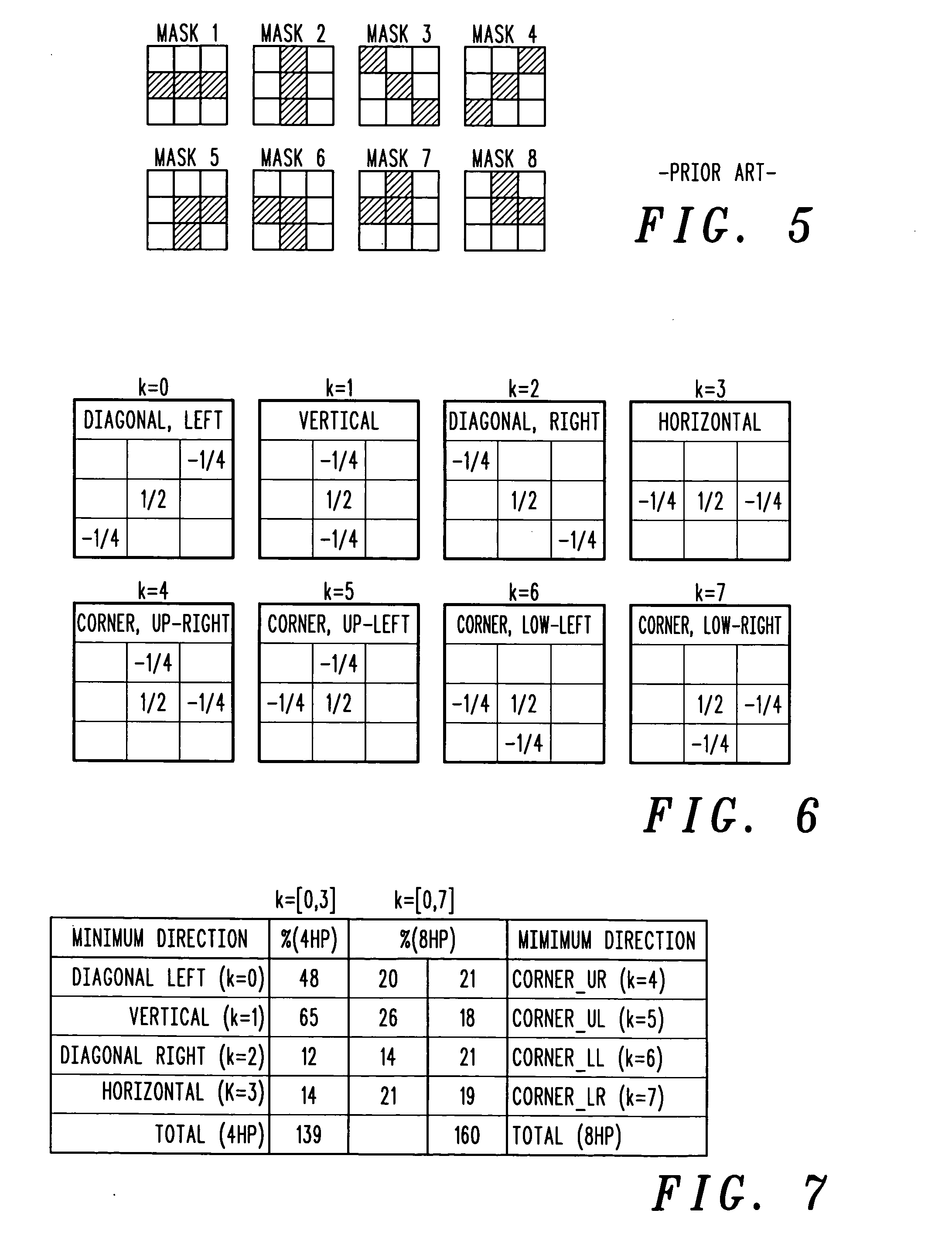
Directional spatial video noise reduction
InactiveUS20050135700A1Quality improvementLighten the computational burdenImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSpatial noise
A method of reducing spatial noise in an image. Low-pass (smoothing) filters are calculated simultaneously from three successive image rows. Three blocks (m1, m2, m3) are associated with the three successive image rows, and the blocks are processed in row-major order. This implementation is applicable to both luminance and chrominance. The number of smoothing parameters is reduced to one. The technique is applicable to both luminance and chrominance. Directional mapping is used. Extension of the technique to spatial filtering using a 5×5 neighborhood (using five successive image rows) is described. Embodiments of the method using the MMX instruction set are described.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
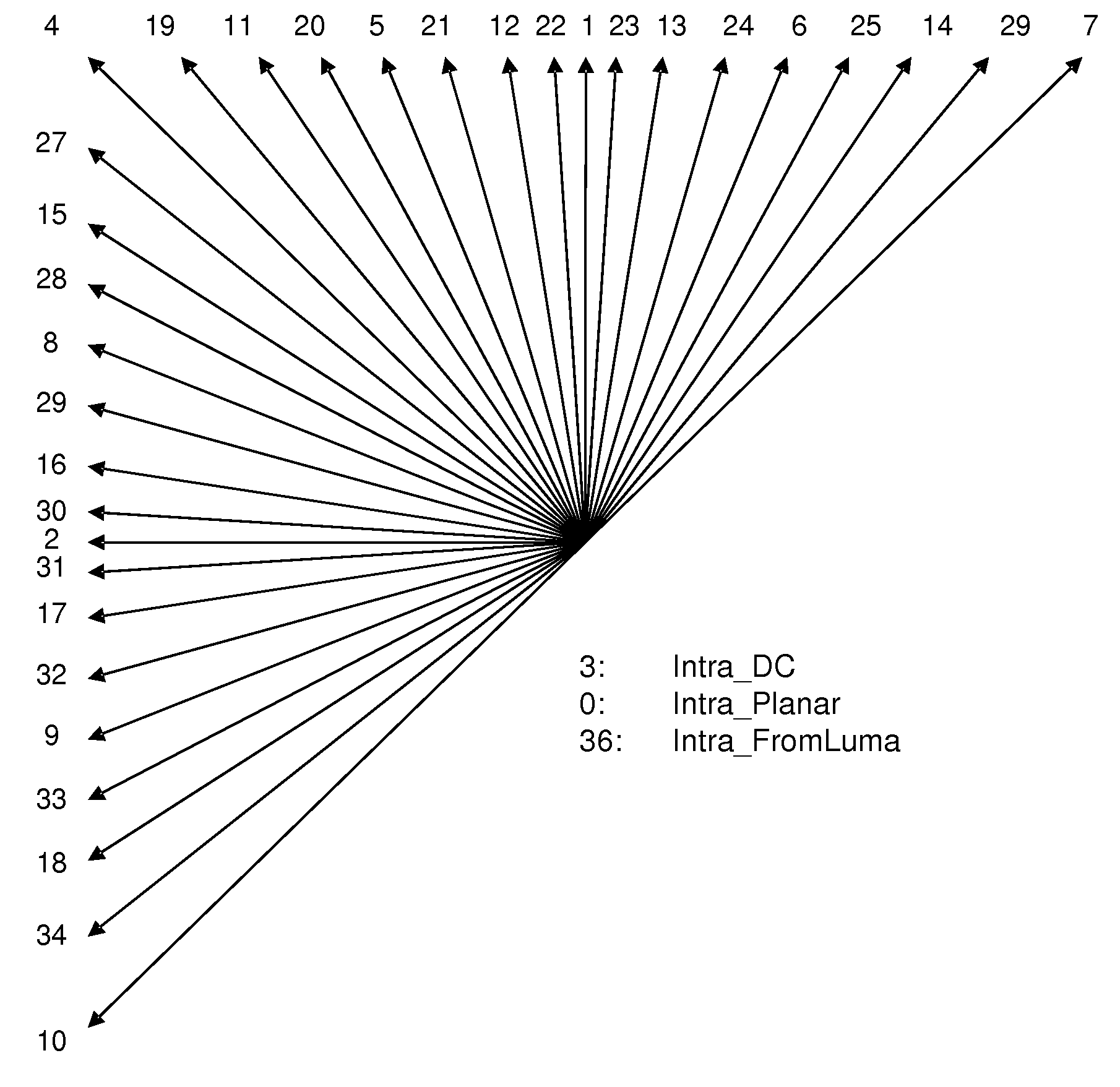
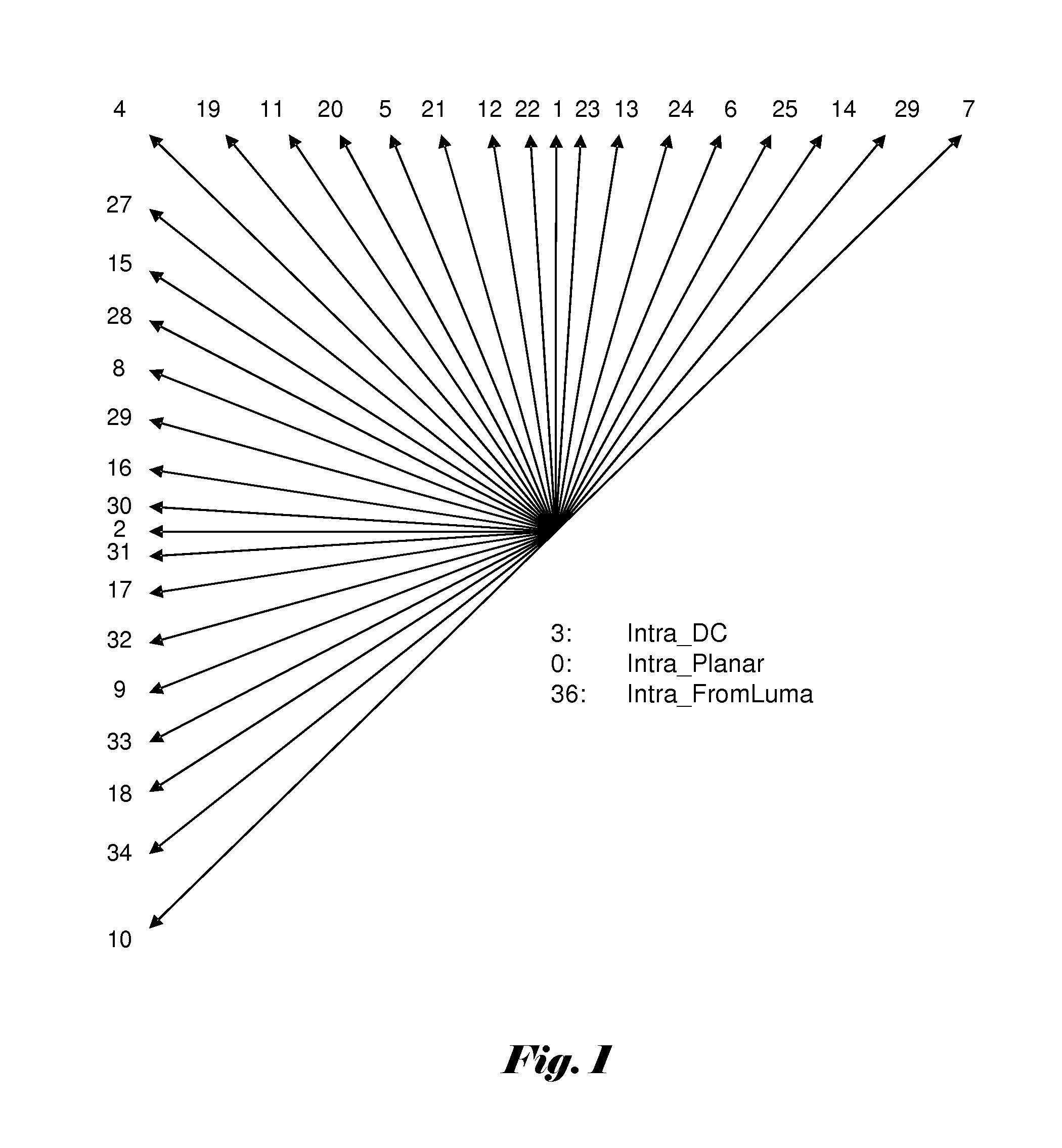
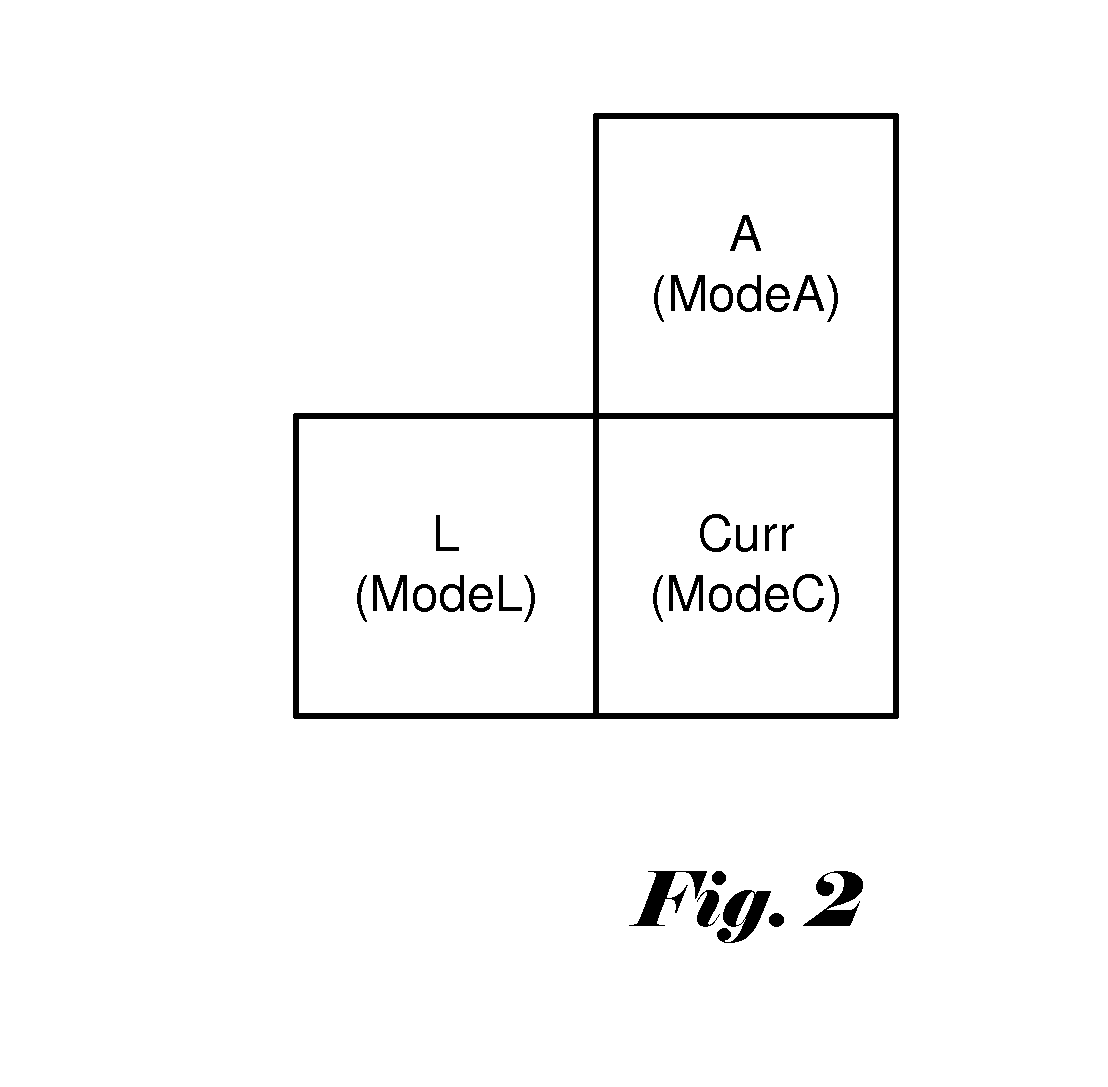
Method and apparatus for coding of intra prediction mode
ActiveUS20140086323A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesTheoretical computer scienceVariable length
Embodiments according to the present invention configure the intra prediction mode candidates into multi-level MPM sets, which comprise at least a first-level MPM set and a second-level MPM set. Encoding or decoding a current intra prediction mode is based on the multi-level MPM sets, where one syntax element of the syntax information to be generated or decoded respectively is associated with evaluating the current intra prediction mode using the first-level MPM set. A method and apparatus for spectively is associated with evaluating the current intra prediction mode using the first-level MPM set. A method and apparatus for chroma intra prediction mode encoding and decoding are also disclosed. The chroma intra prediction mode set includes a Luma-based chroma prediction Mode (LM), a Direct Mode (DM) and four other modes. The codeword set comprises variable-length codewords and fixed-length codewords, and the fixed-length codewords are longer than the variable-length codewords. The variable-length codewords are used for the DM and LM, and the fixed-length codewords are used for the four other modes.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
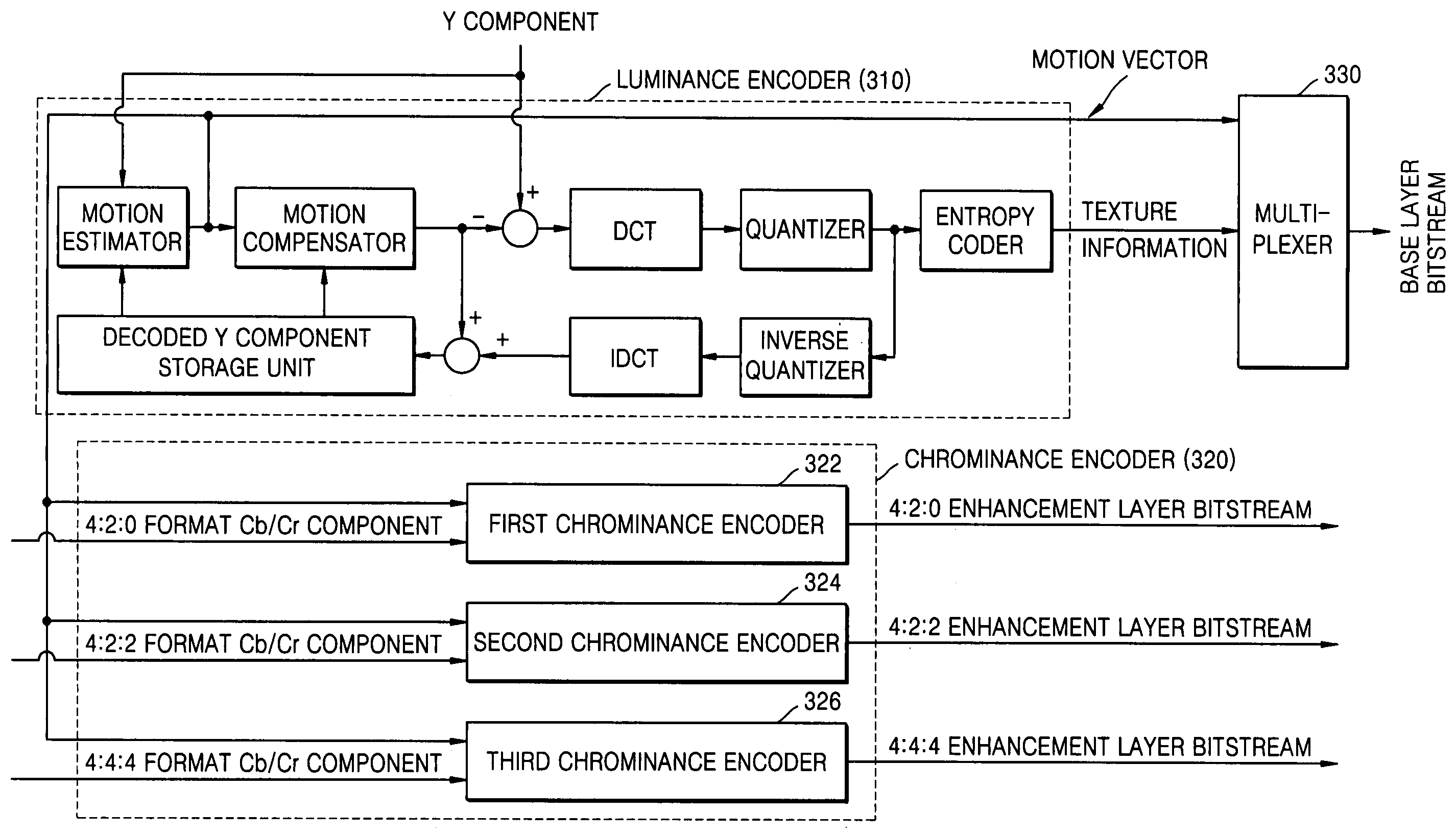
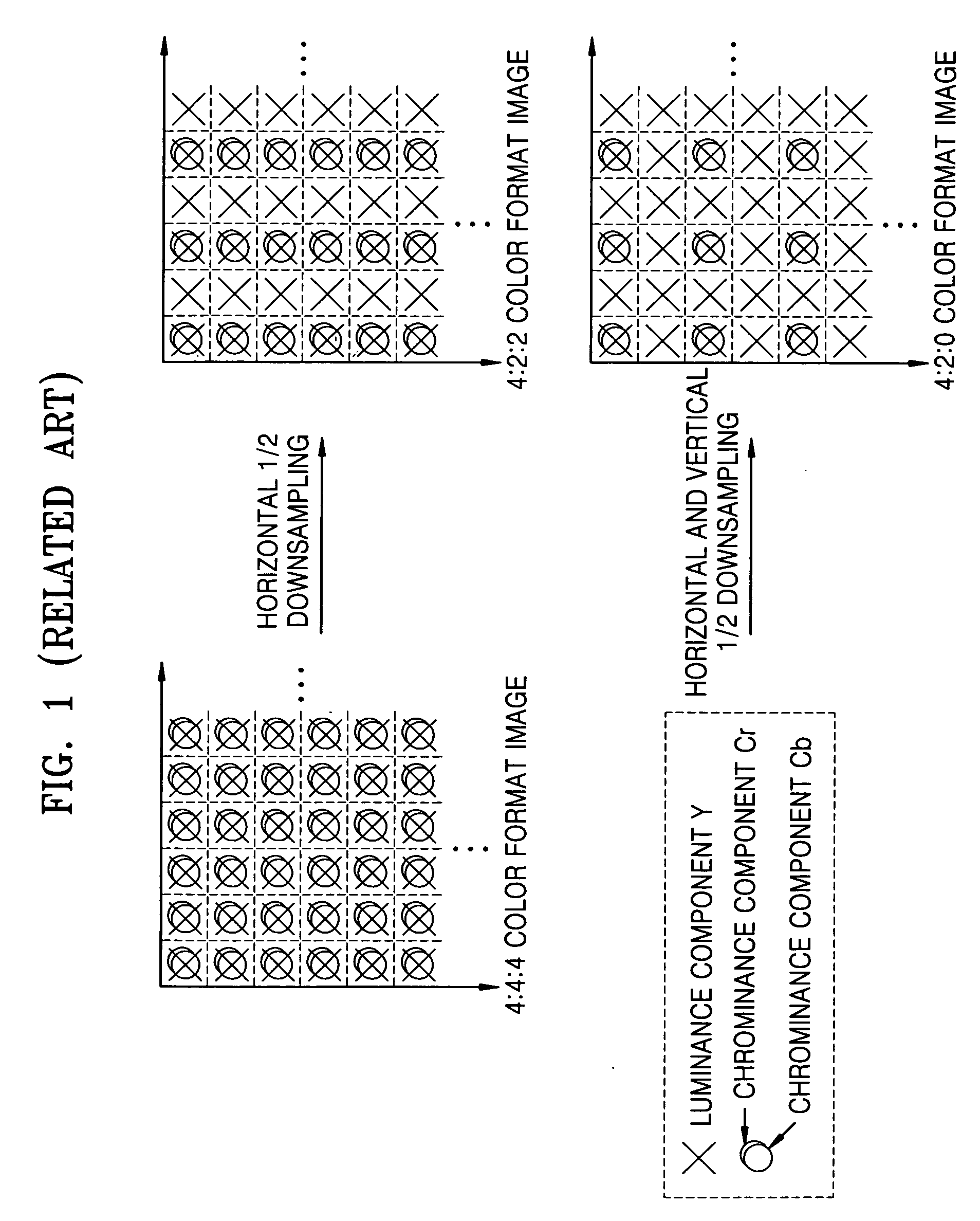
Method and apparatus for scalably encoding and decoding color video
InactiveUS20060013308A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorVideo encoding
A scalable encoding and decoding method and apparatus based on color information of moving pictures are provided. The color video encoding method comprises: generating an encoded luminance bitstream by encoding a luminance component using a motion prediction based encoding method; and generating at least one encoded chrominance bitstream by encoding at least one color format chrominance component using a motion vector generated by the motion prediction based encoding method. Using this method, storage, transmission, and reproduction of a moving picture can be efficiently performed by scalably encoding the moving picture according to a color format in which the moving picture is encoded.
Owner:IND ACAD COOP GRP OF SEJONG UNIV +1
Electronic device with two image sensors
An electronic device for producing an image of an object is disclosed. The electronic device may include a black-and-white camera having a first sensor area configured to receive luma data pertaining to the object. The first sensor area may correspond to a first pixel array, the luma data associated with the first pixel array. The electronic device may also include a color camera having a second sensor area configured to receive chroma data pertaining to the object. The second sensor area may correspond to a second pixel array. The chroma data may be associated with the second pixel array. The electronic device may also include first logic configured to correlate pixels in the first pixel array with locations on the second sensor area.
Owner:APPLE INC
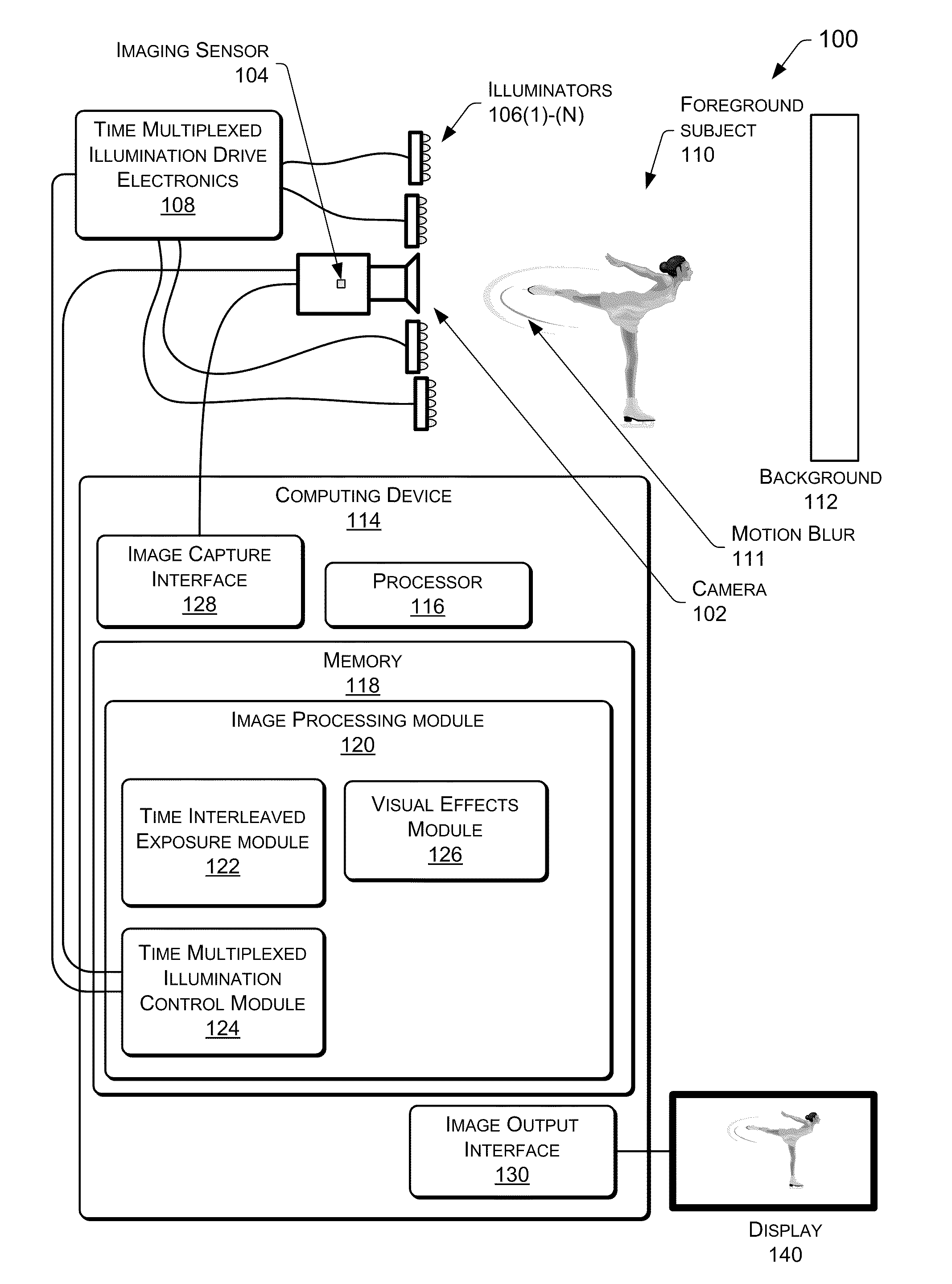
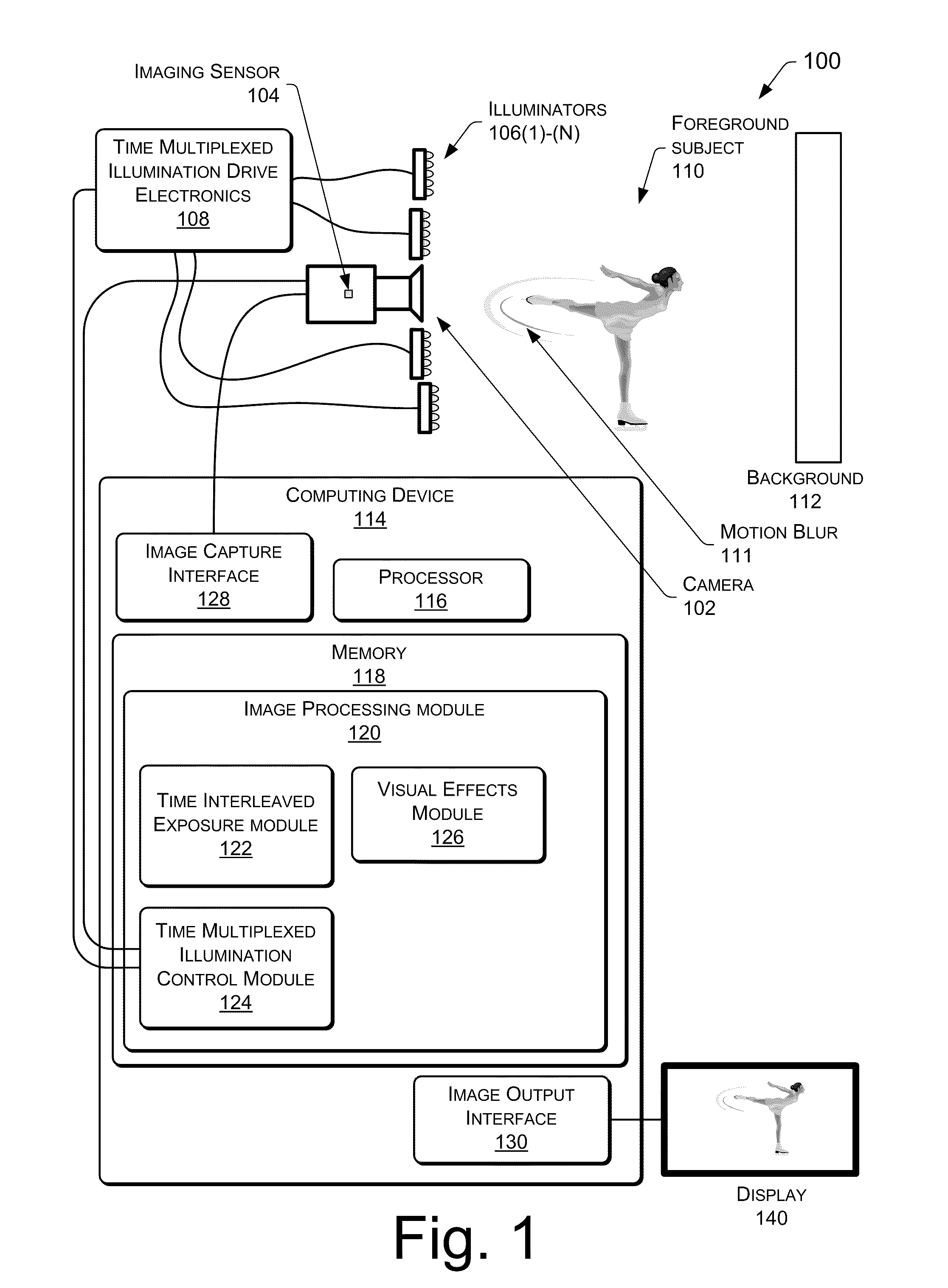
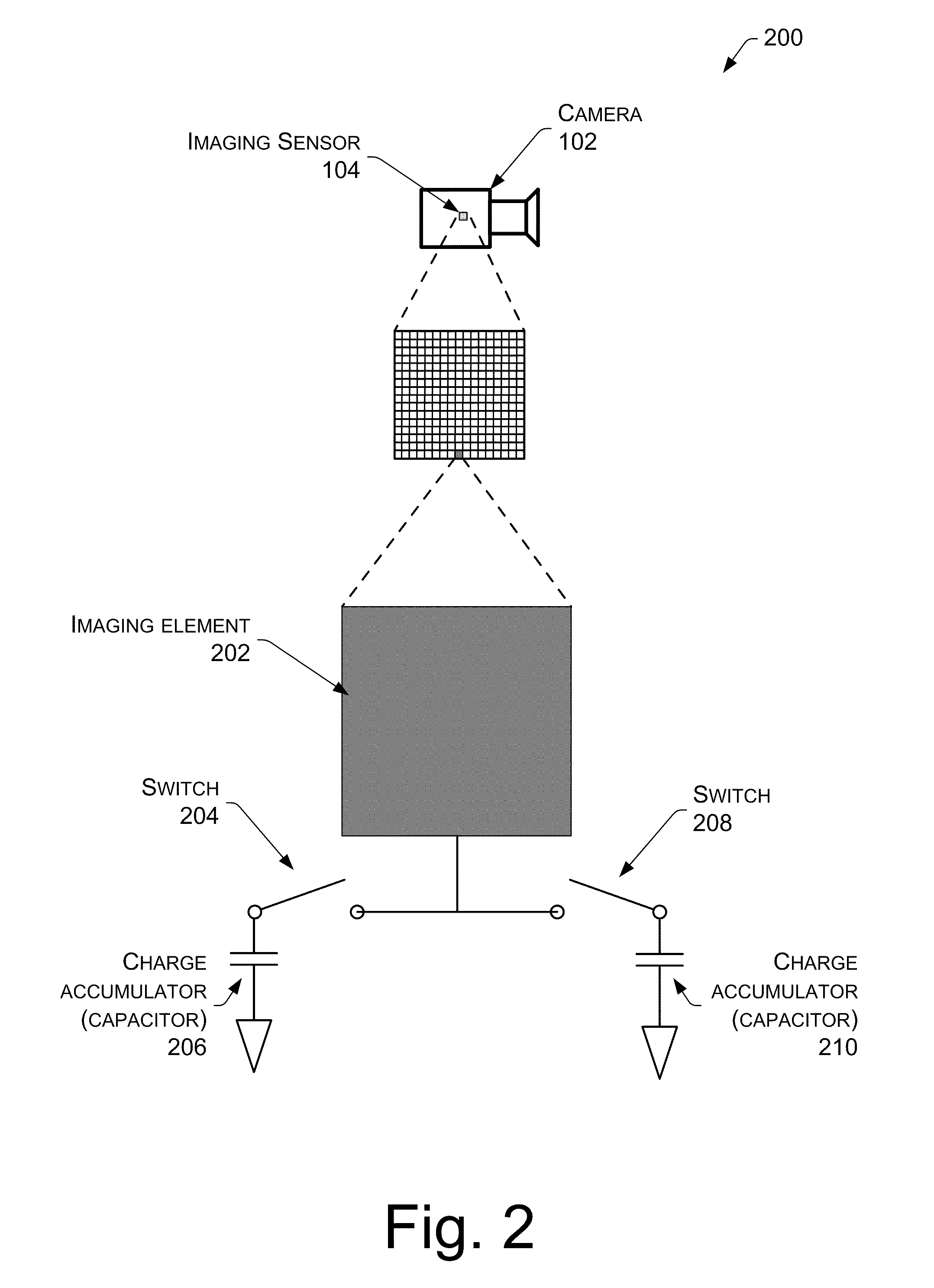
Time Interleaved Exposures And Multiplexed Illumination
InactiveUS20110242334A1Data rate outputImprove performanceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsTriangulationTime interleaved
Samples of a scene are acquired in synchronization with finely interleaved varying conditions such as lighting, aperture, focal length, and so forth. A time-varying sample at each pixel for each condition is reconstructed. Time multiplexed interleaving allows for real-time, live applications, while handling motion blur naturally. Effects such as real-time video relighting of a scene is possible. Time interleaved exposures also allow segmentation of a scene, and allows for constrained special effects such as triangulation matting using a multi-color interleaved chroma key.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
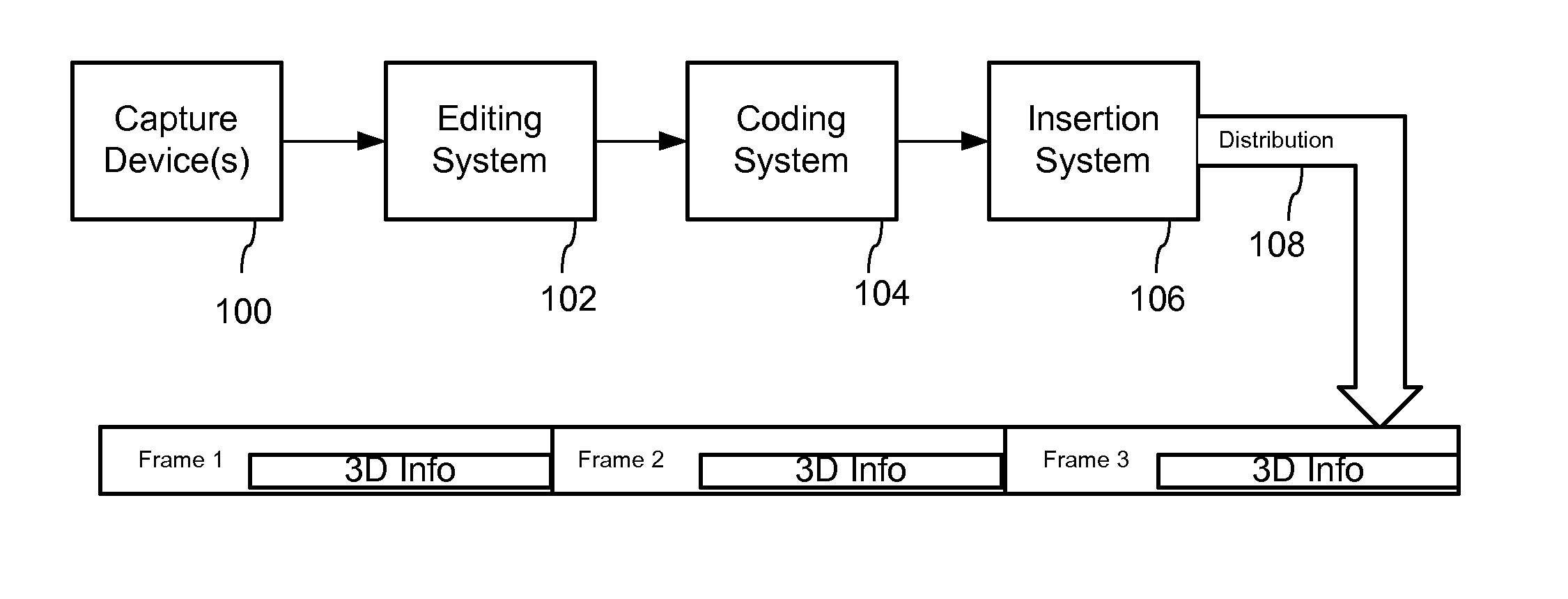
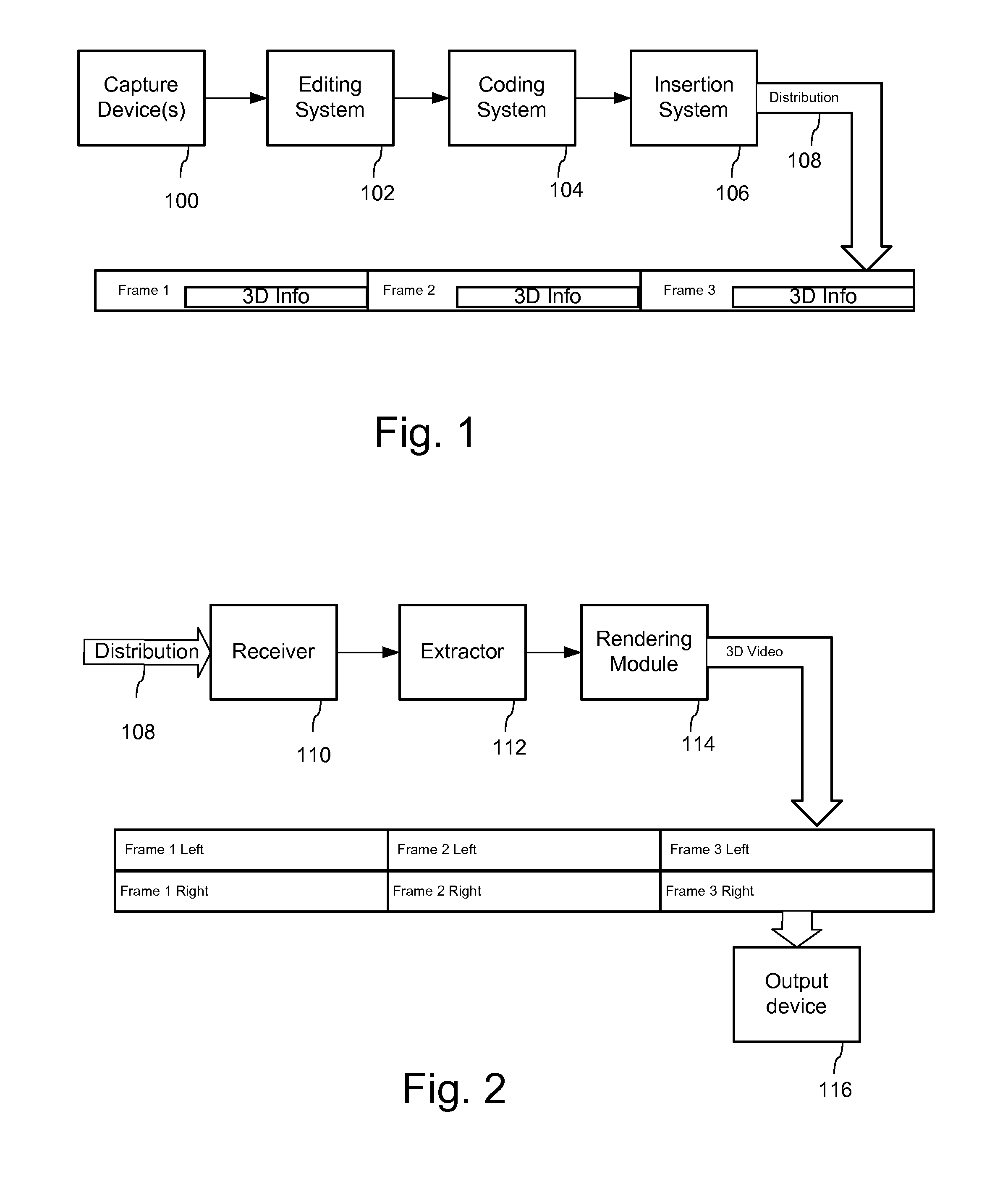
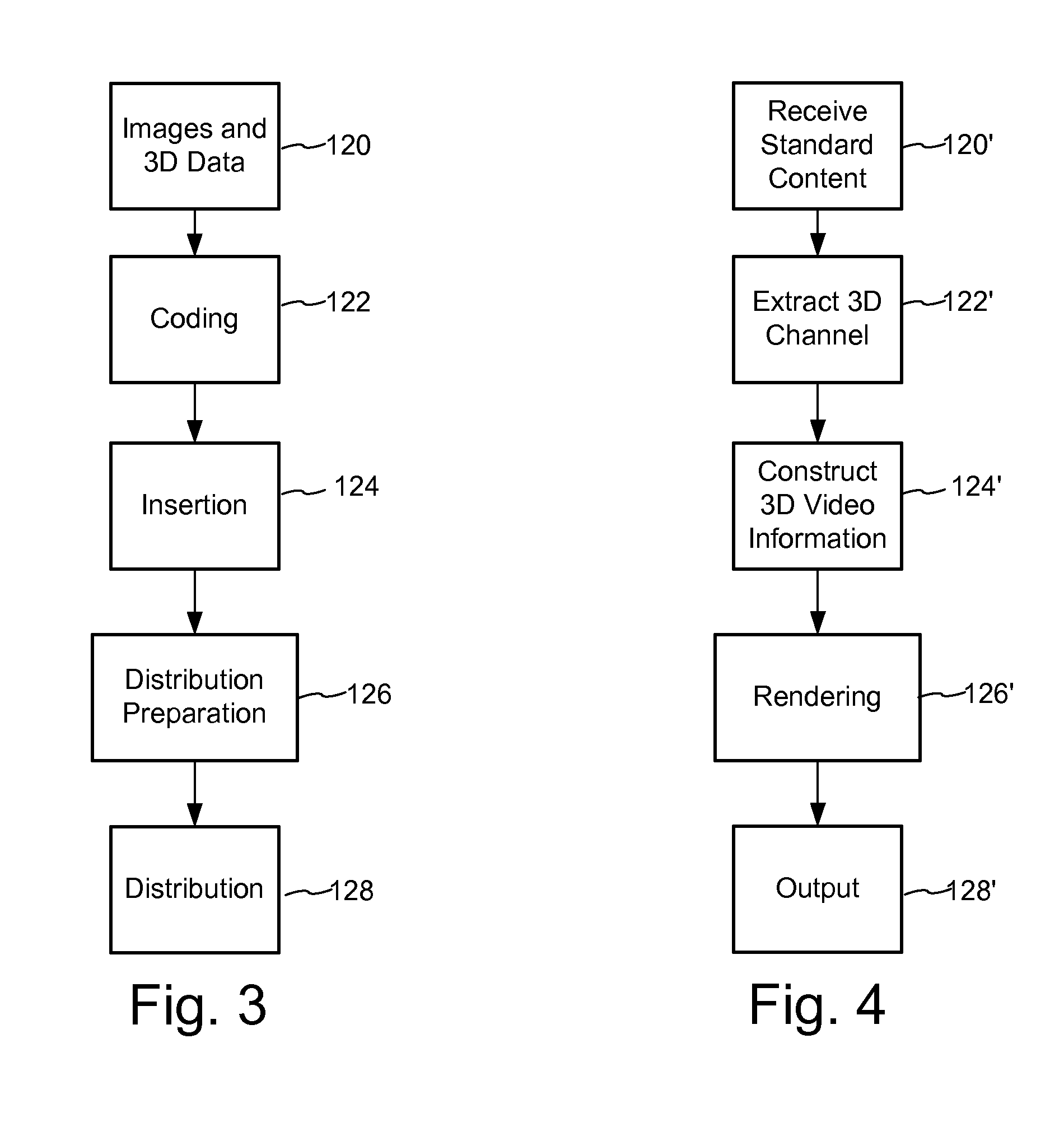
3D Data Representation, Conveyance, and Use
InactiveUS20100309287A1Efficient codingImprove experienceDigital video signal modificationSteroscopic systemsParallaxMotion vector
3D video can be transmitted in a legacy 2D video format by conveying 3rd dimension parameters within a steganographic channel of the perceptual video signal, e.g., DCT coefficients, video samples (luminance, chrominance values), etc. The 3rd dimension parameters can be coded as depth values, disparity, displacement, difference, or parallax values, including depth that is converted into X-Y shifts for adjustment to motion vectors in coded video sequence. To limit the amount of information for the steganographic channel, the 3rd dimension information can be quantized relative to the depth from viewer and other prioritization parameters that limit the need for 3rd dimension information to only aspects of the scene that are deemed important to create a desired 3D effect.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
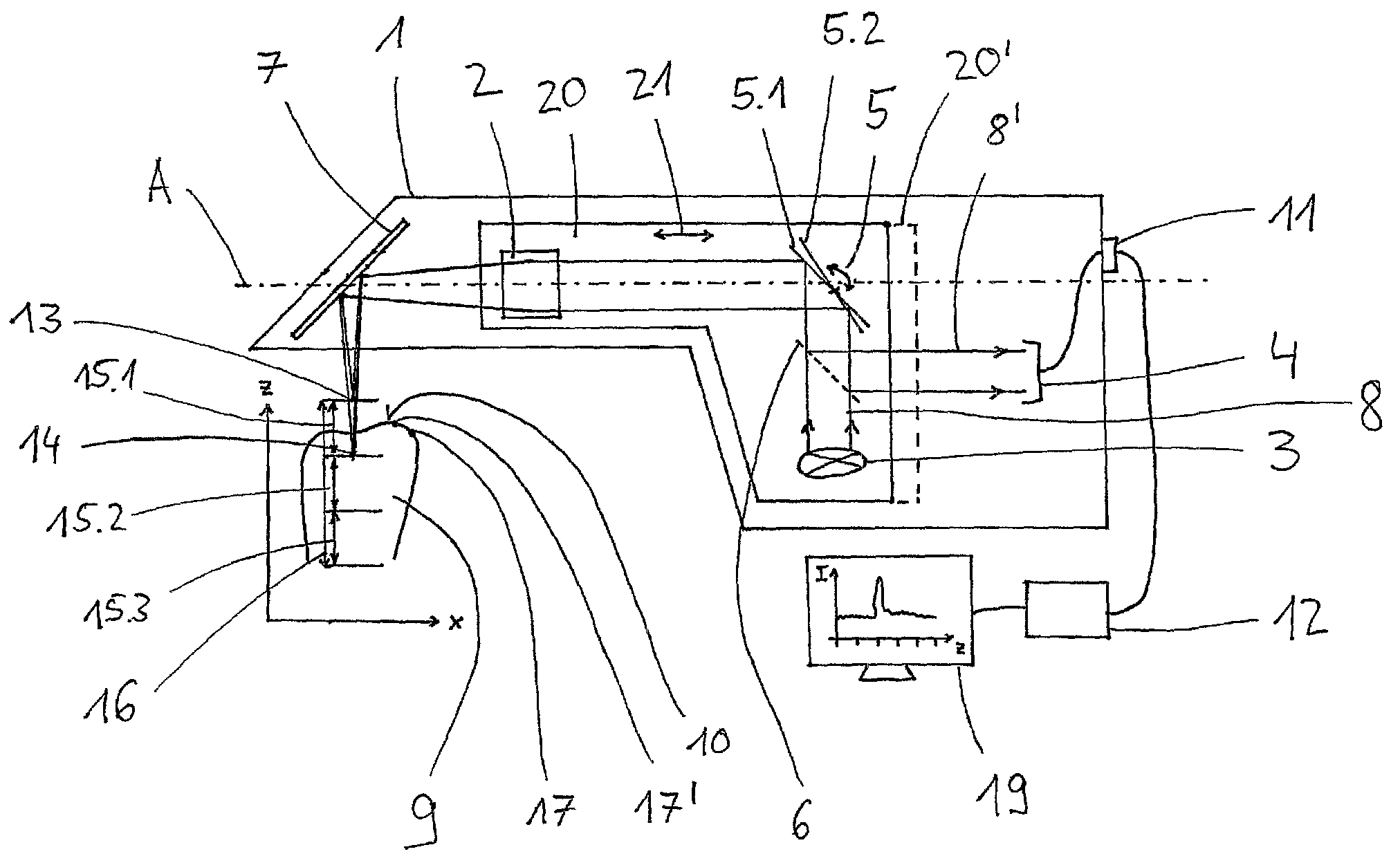
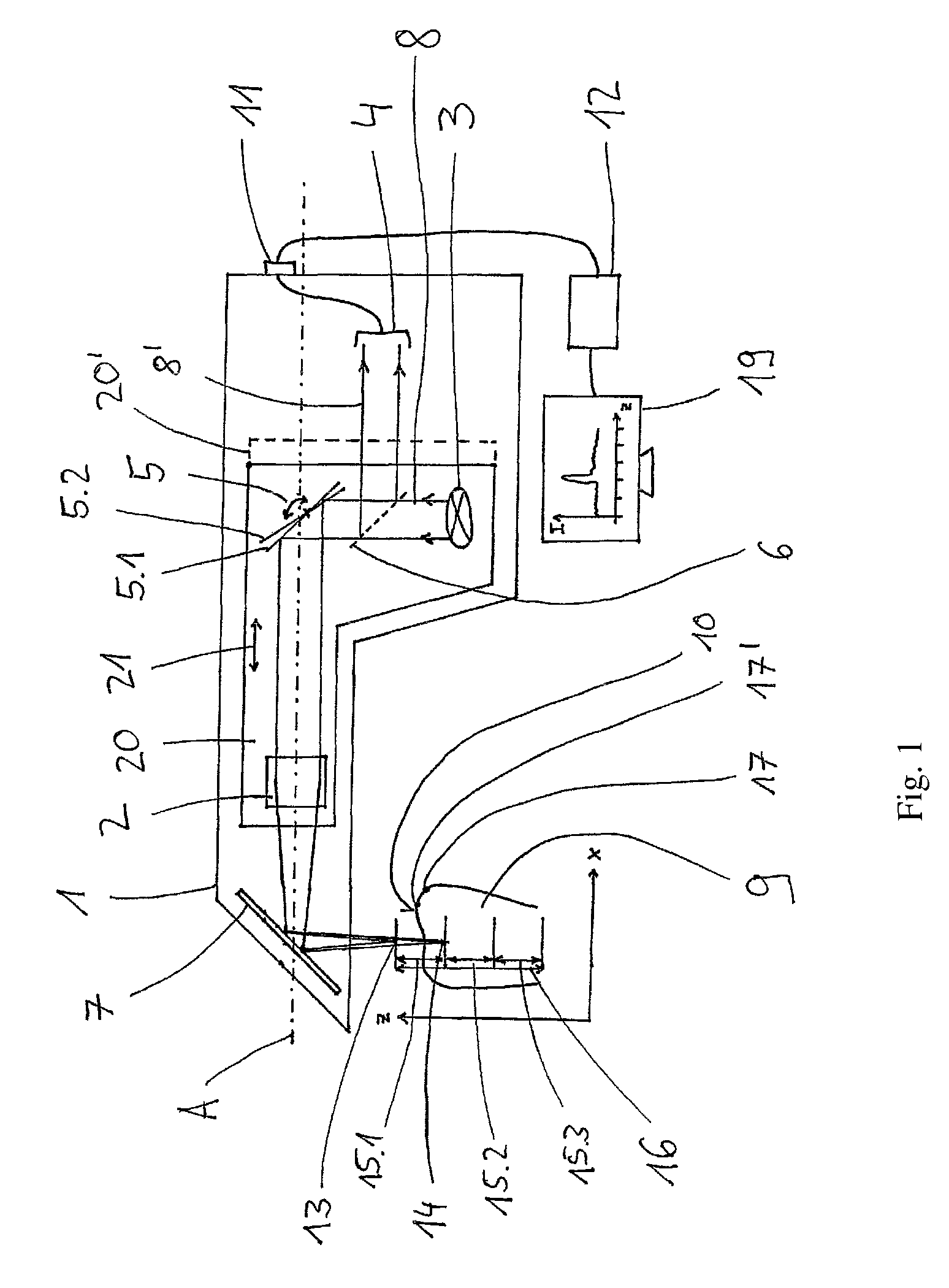
Handheld dental camera and method for carrying out optical 3D measurement
A handheld dental camera performs three-dimensional, optical measurements. The camera includes a light source that emits an illuminating beam, a scanning unit, a color sensor, and a deflector. The scanning unit focuses the illuminating beam onto a surface of an object to be measured. The surface of the object reflects the illuminating beam and forms a monitoring beam, which is detected by the color sensor. Focal points of wavelengths of the illuminating beam form chromatic depth measurement ranges. The scanning unit stepwise displaces the chromatic depth measurement ranges by a step width smaller than or equal to a length of each chromatic depth measurement range, so that a first chromatic depth measurement range in a first end position of the scanning unit and a second chromatic depth measurement range in a second end position are precisely adjoined in a direction of a measurement depth, or are partially overlapped.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
Motion estimation and compensation device with motion vector correction based on vertical component values
InactiveUS20060023788A1Color television with pulse code modulationImage analysisMotion vectorErrors and residuals
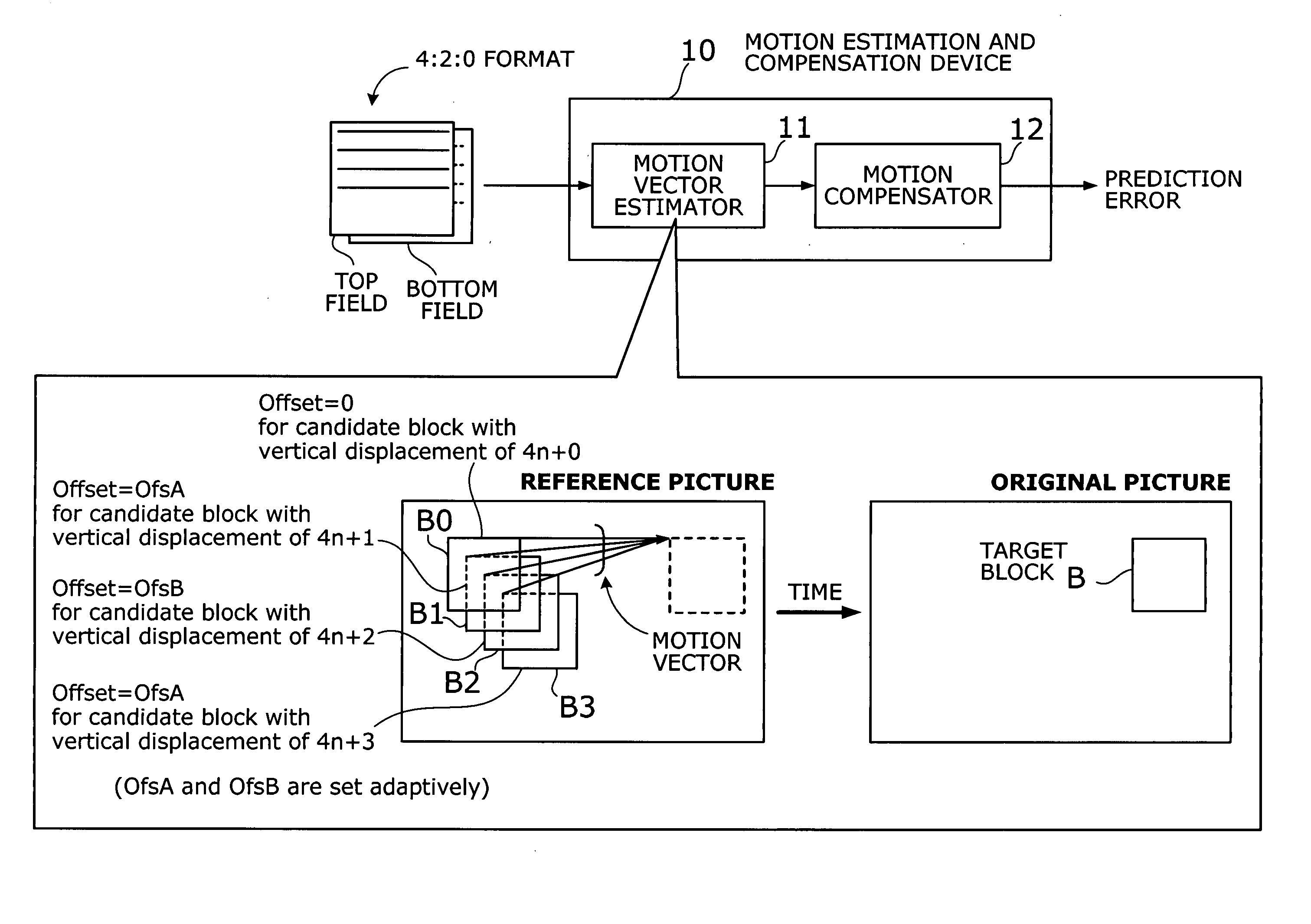
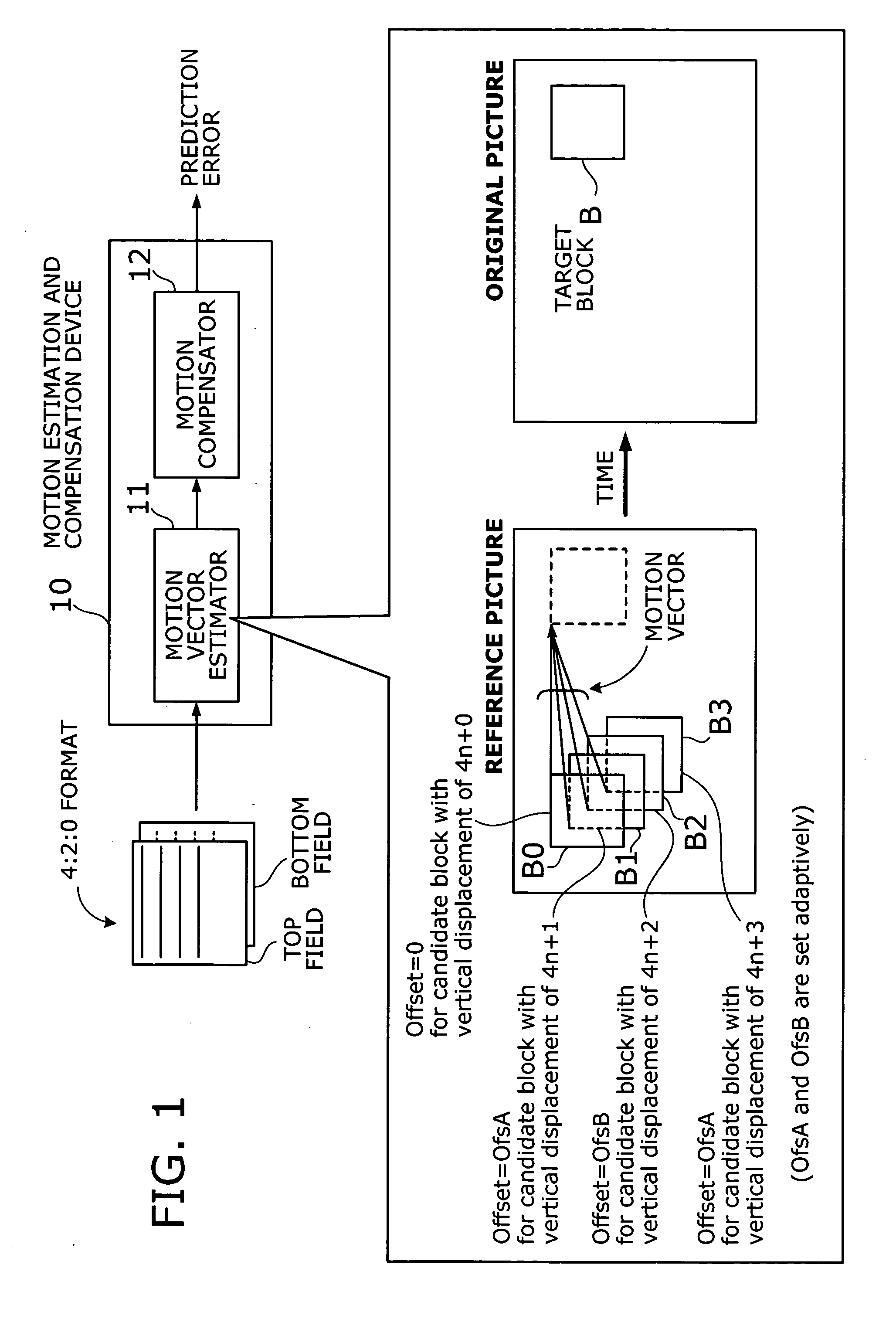
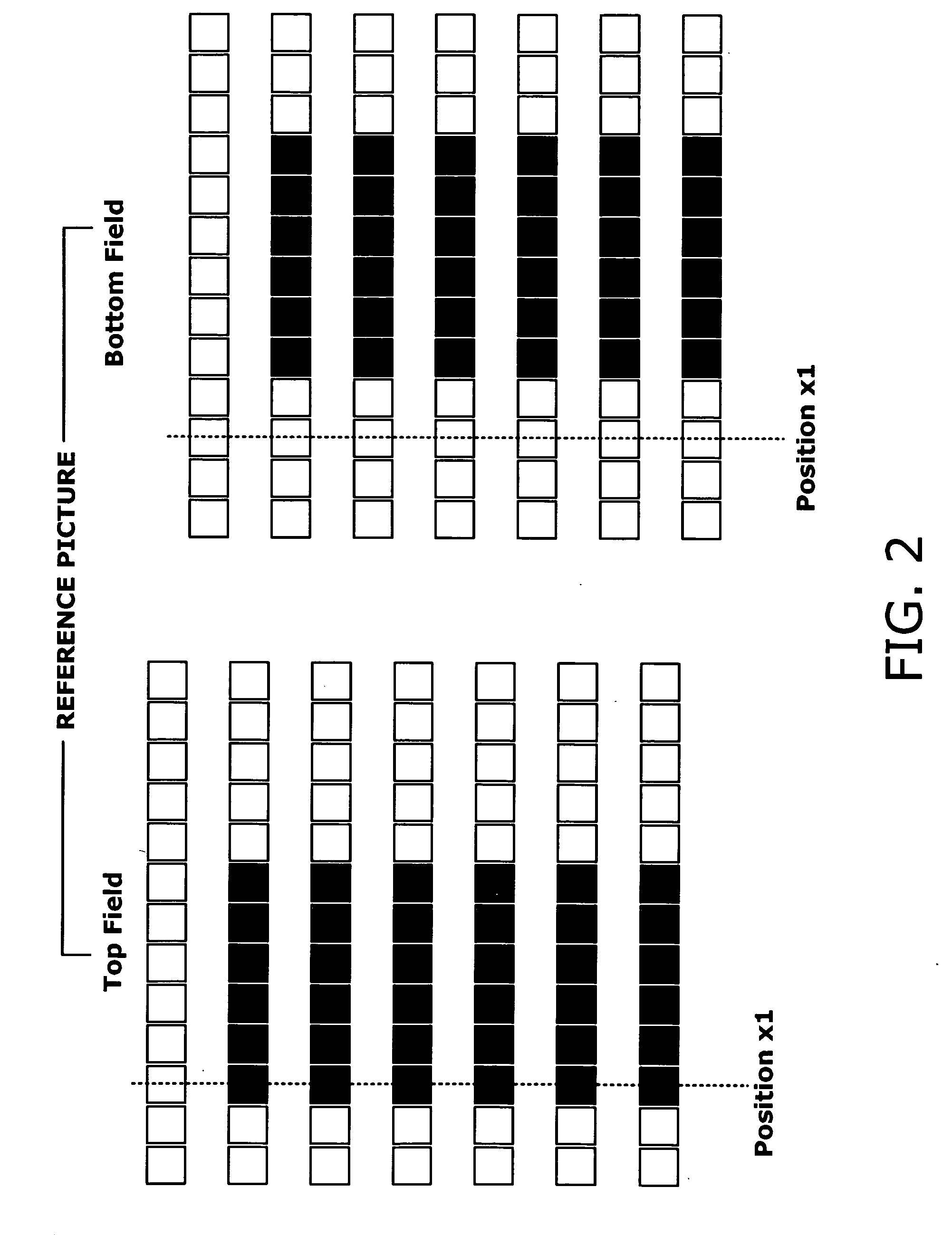
A motion estimation and compensation device that avoids discrepancies in chrominance components which could be introduced in the process of motion vector estimation. The device has a motion vector estimator for finding motion vectors in given interlace-scanning chrominance-subsampled video signals. The estimator compares each candidate block in a reference picture with a target block in an original picture by using a sum of absolute differences (SAD) in luminance as similarity metric, chooses a best matching candidate block that minimizes the SAD, and determines its displacement relative to the target block. In this process, the estimator gives the SAD of each candidate block an offset determined from the vertical component of a corresponding motion vector, so as to avoid chrominance discrepancies. A motion compensator then produces a predicted picture using such motion vectors and calculates prediction error by subtracting the predicted picture from the original picture.
Owner:FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS LTD
Digital image system and method for implementing an adaptive demosaicing method
InactiveUS7088392B2Reduce imbalanceAdaptive smoothingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionSharpening
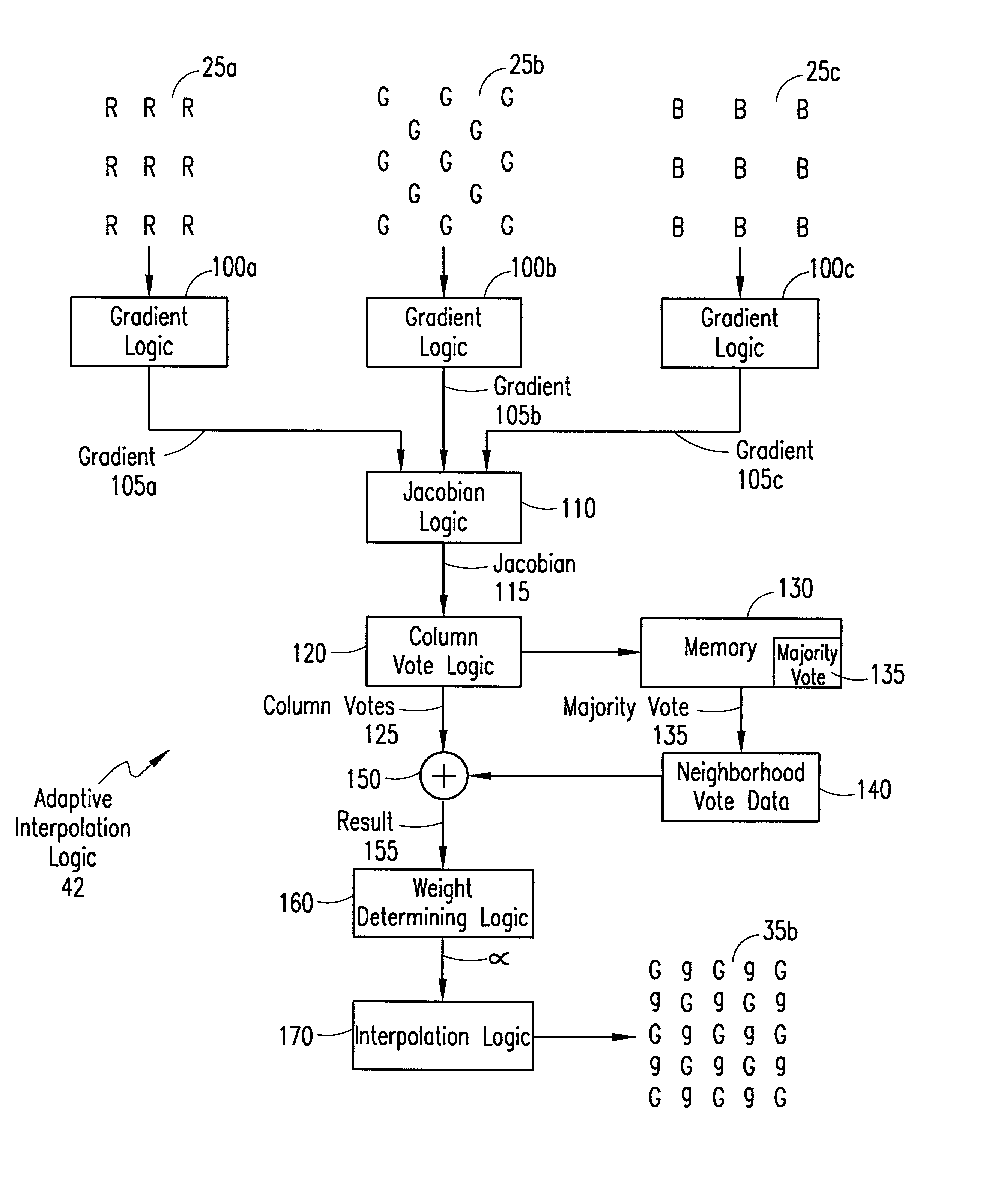
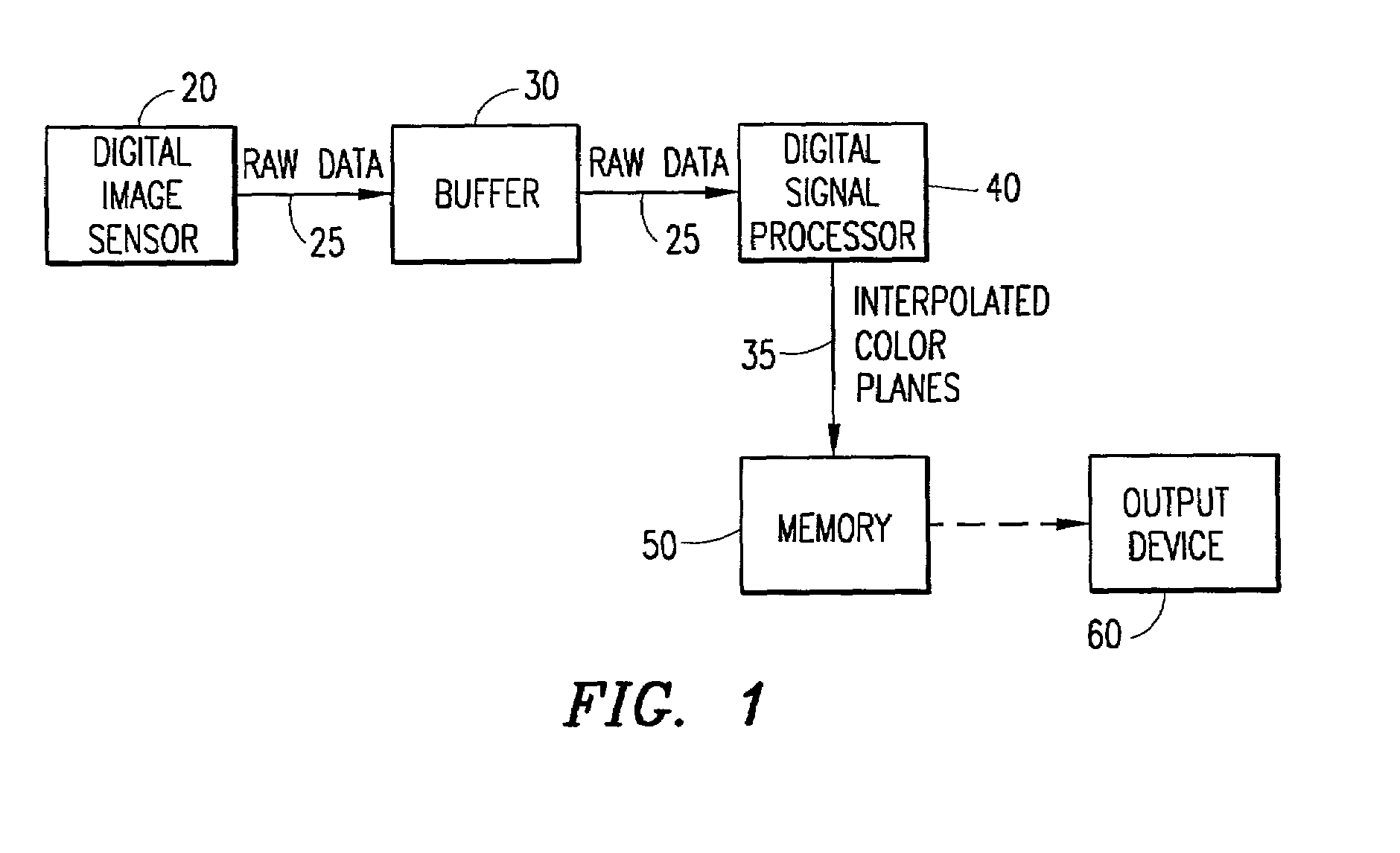
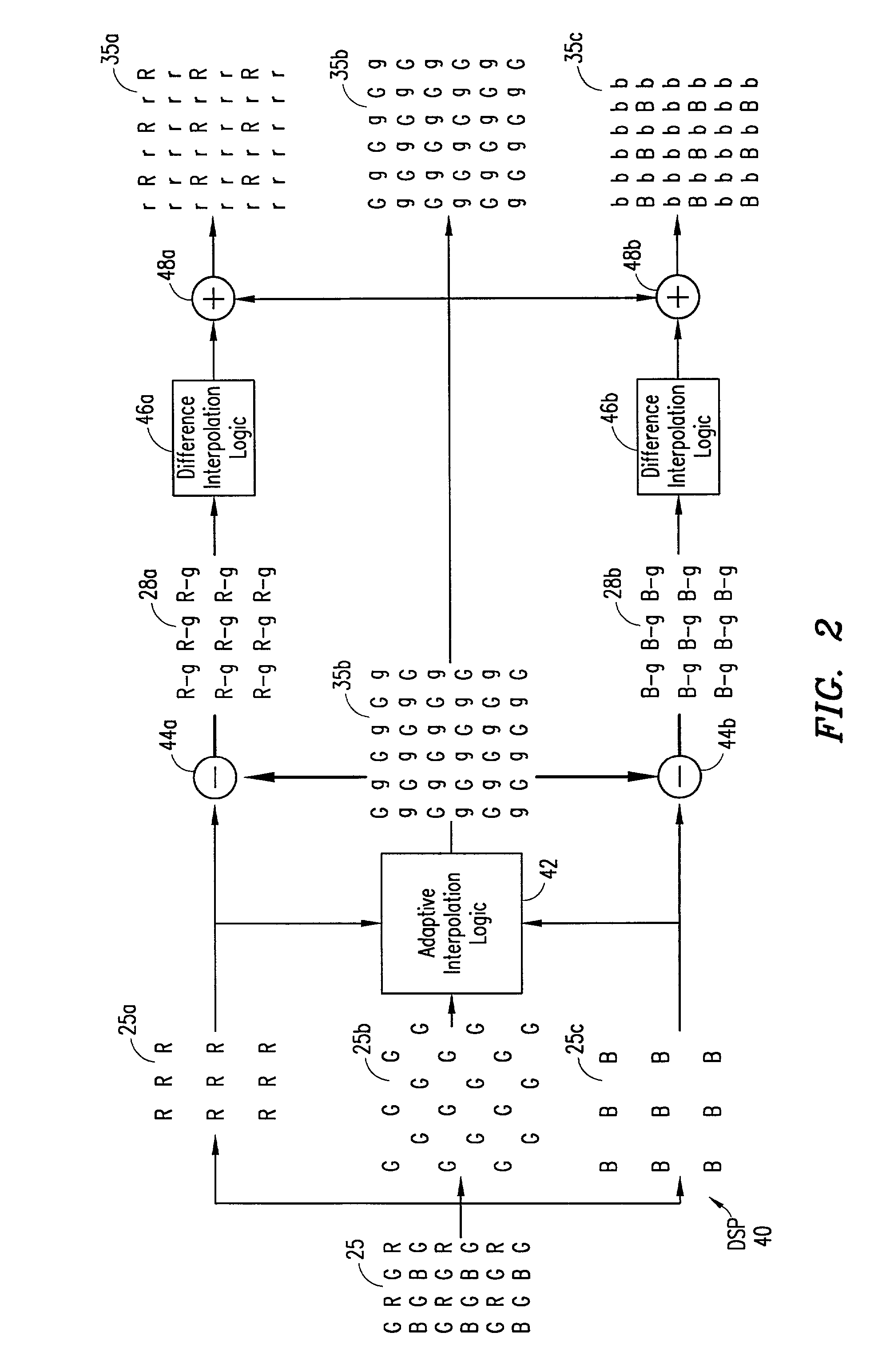
An adaptive demosaicing method interpolates images based on color edge detection and neighborhood voting. The adaptive demosaicing algorithm uses a voting scheme to determine the direction of interpolation at each missing luminance pixel location. Each color plane votes either horizontal or vertical based on a comparison between the horizontal and vertical components of the degree of change (i.e., gradient, Laplacian or other measure of the degree of change) in that color plane. Votes are counted from the neighborhood pixels as well as from measurements taken at the pixel location itself. Once the luminance plane is fully interpolated, the chrominance planes are filled in by simple bilinear or median interpolation of difference chrominance values. Enhancements to the adaptive demosaicing algorithm permit adaptive smoothing and sharpening.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com