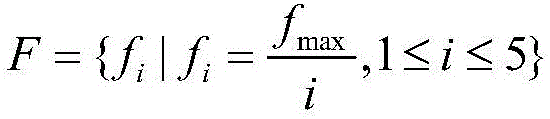Patents
Literature
49 results about "Beats per minute" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vehicle infotainment system with virtual personalization settings
InactiveUS20090164473A1Reduce distractionsScalable functionalityElectrophonic musical instrumentsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsPersonalizationDistraction
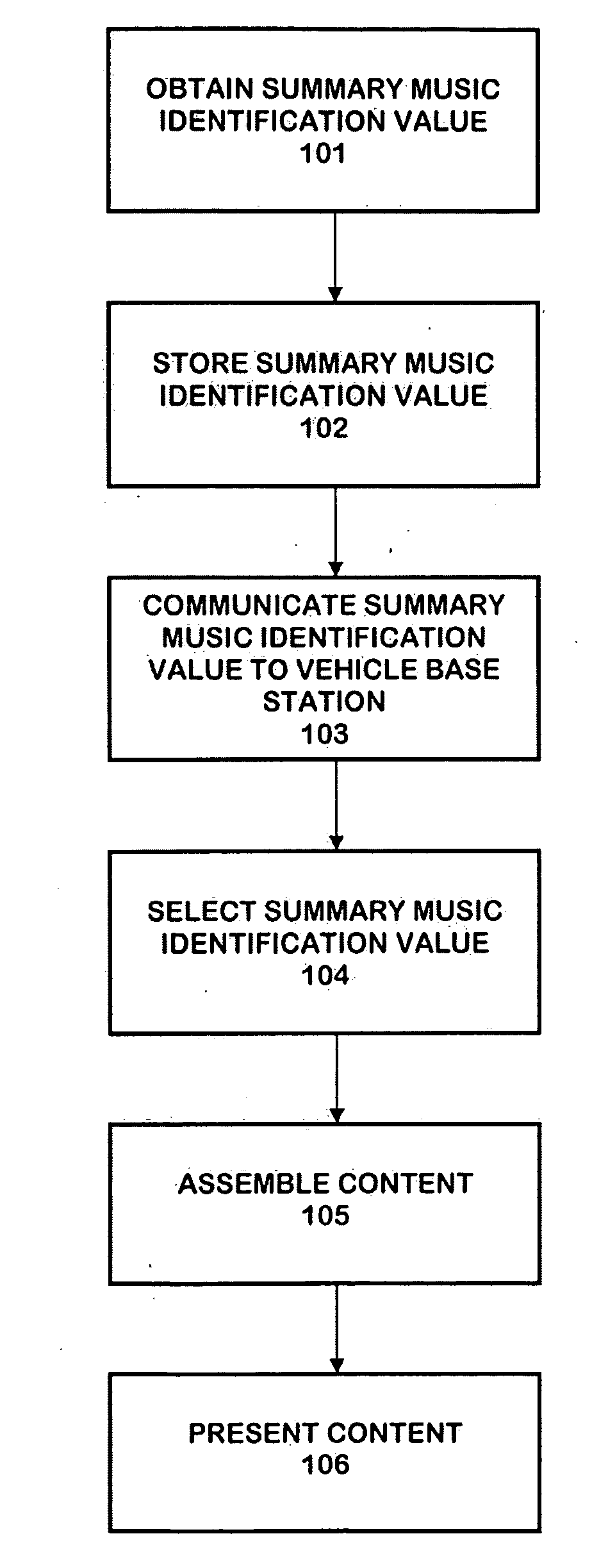
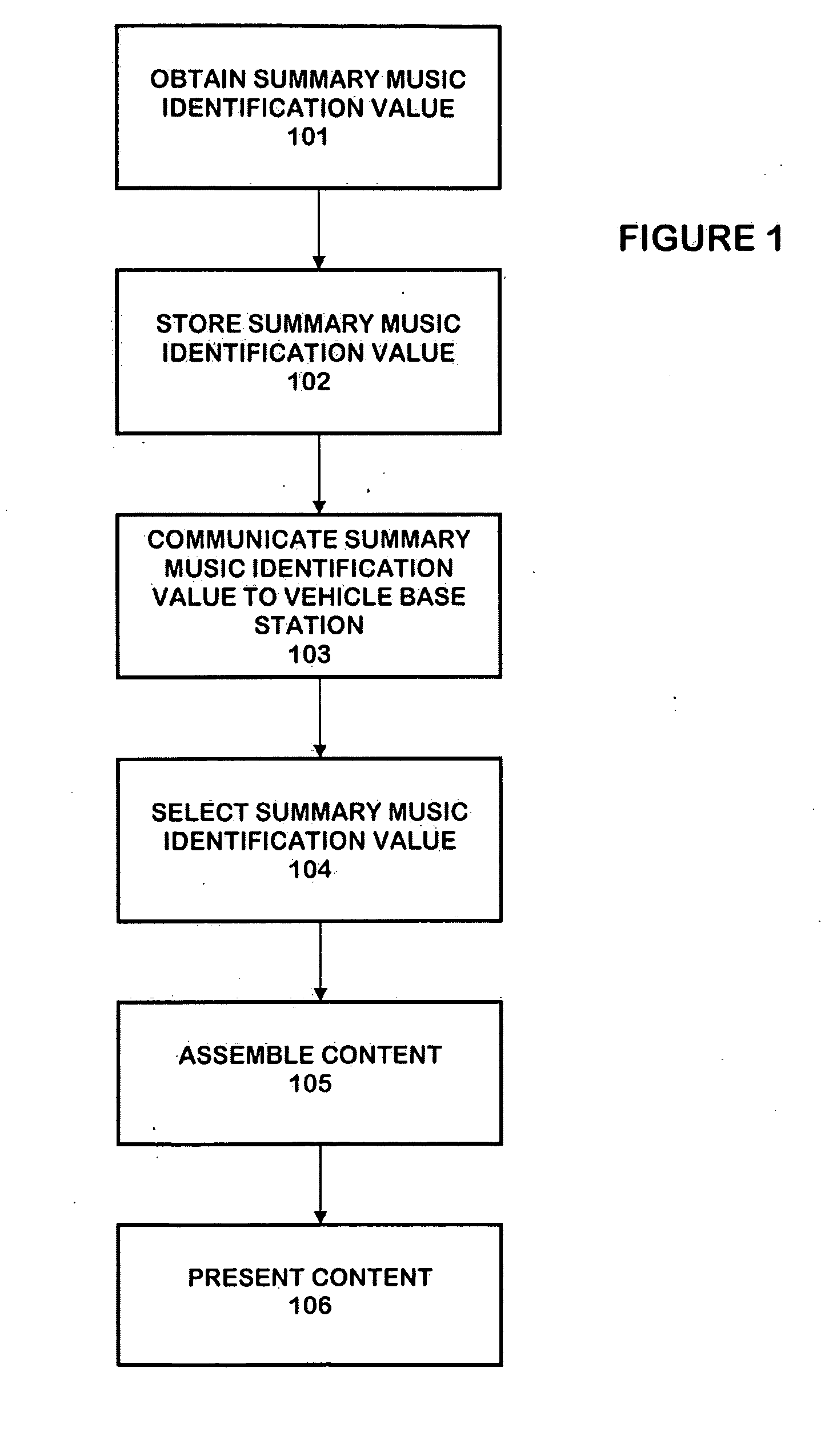
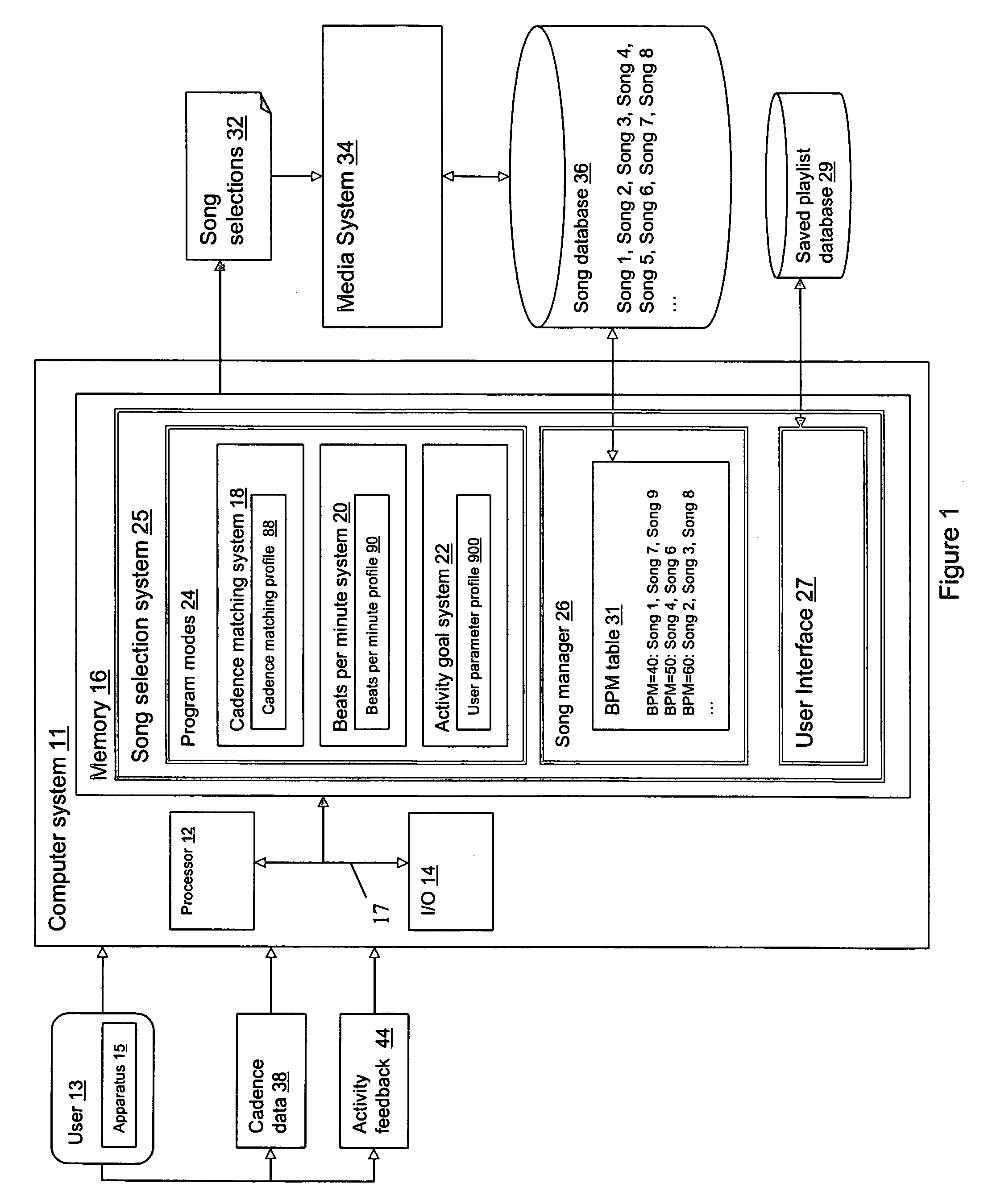
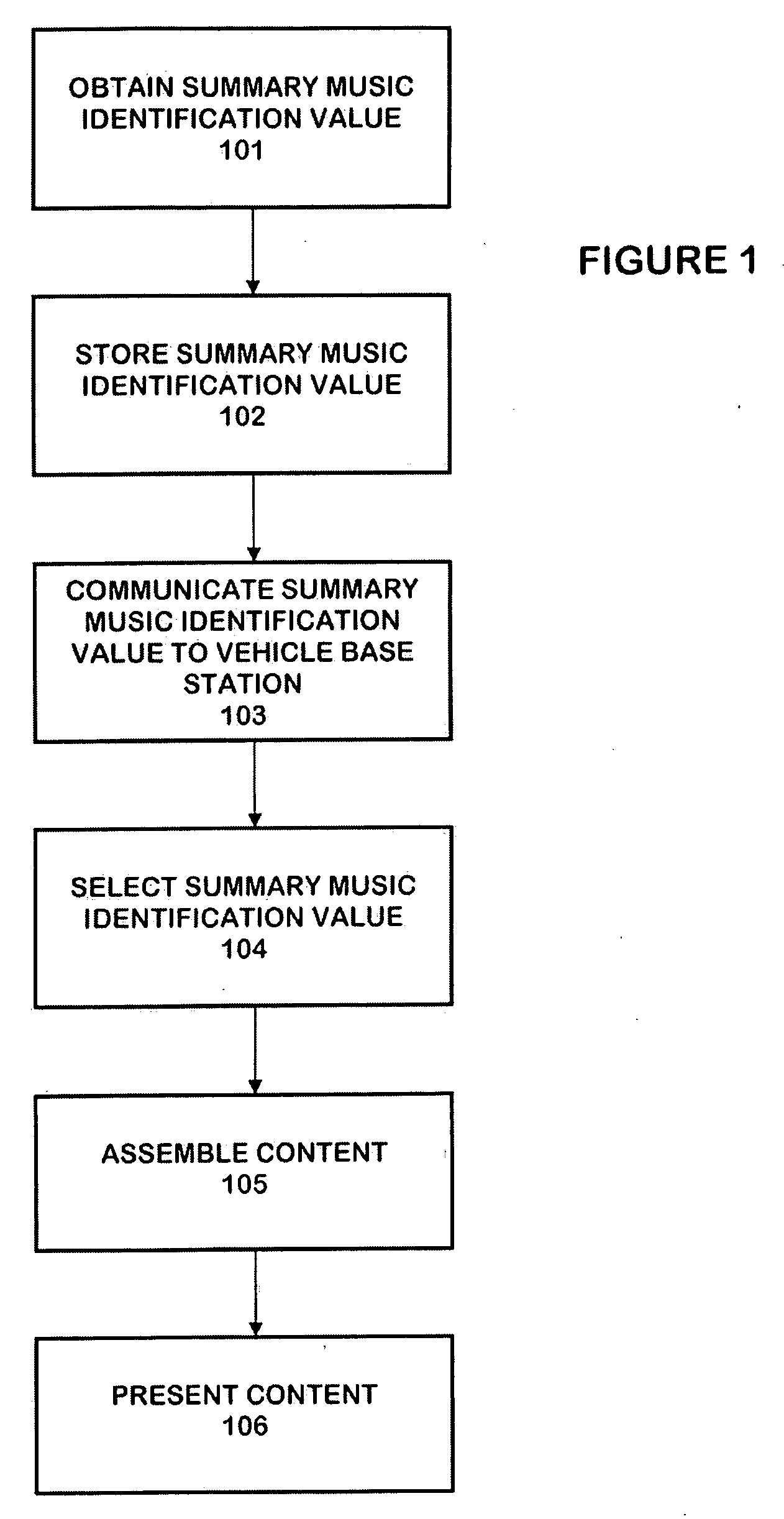
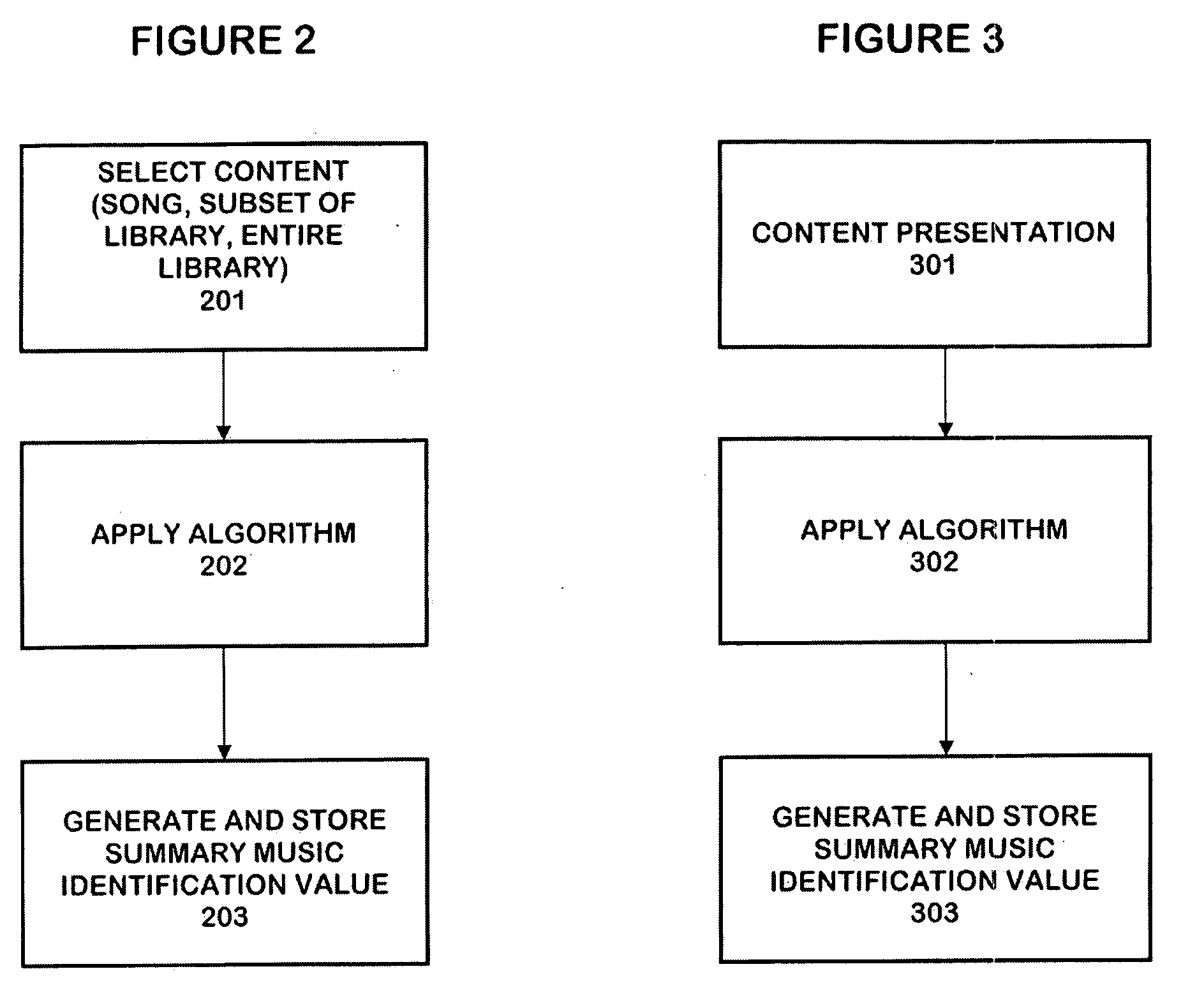
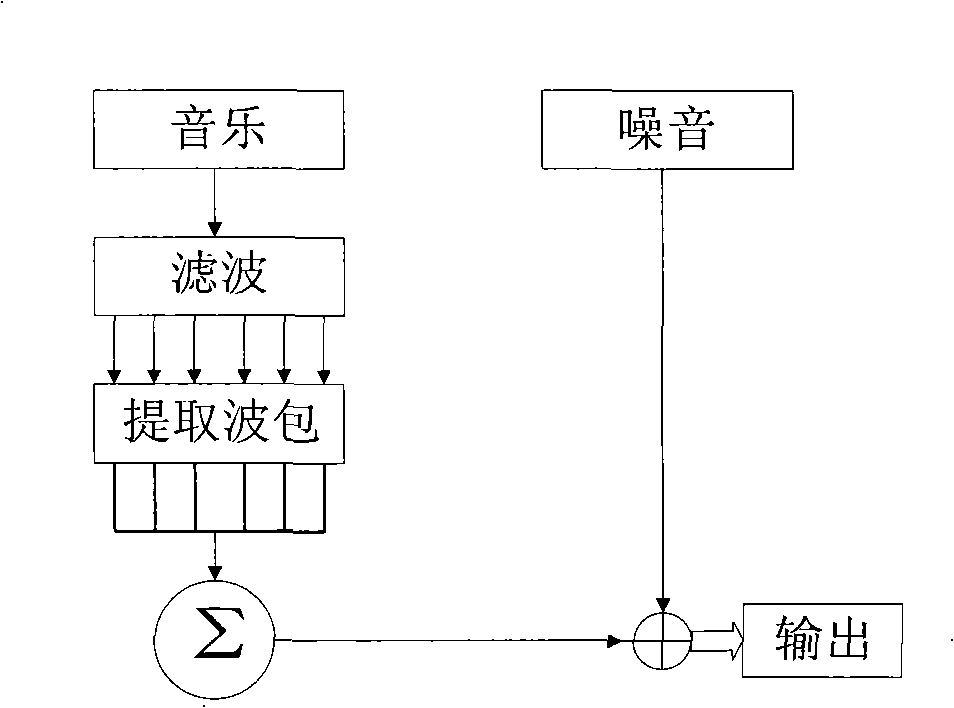
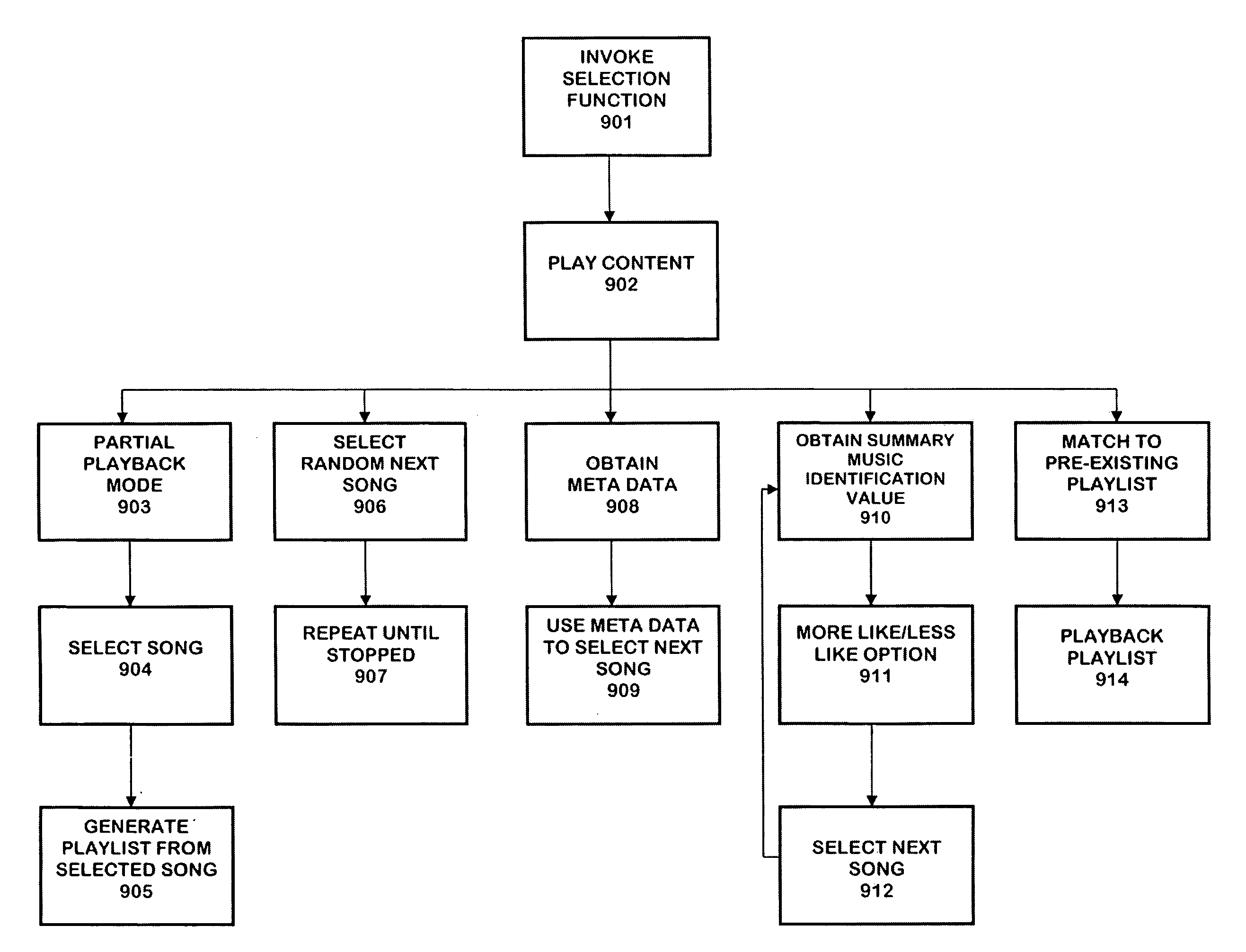
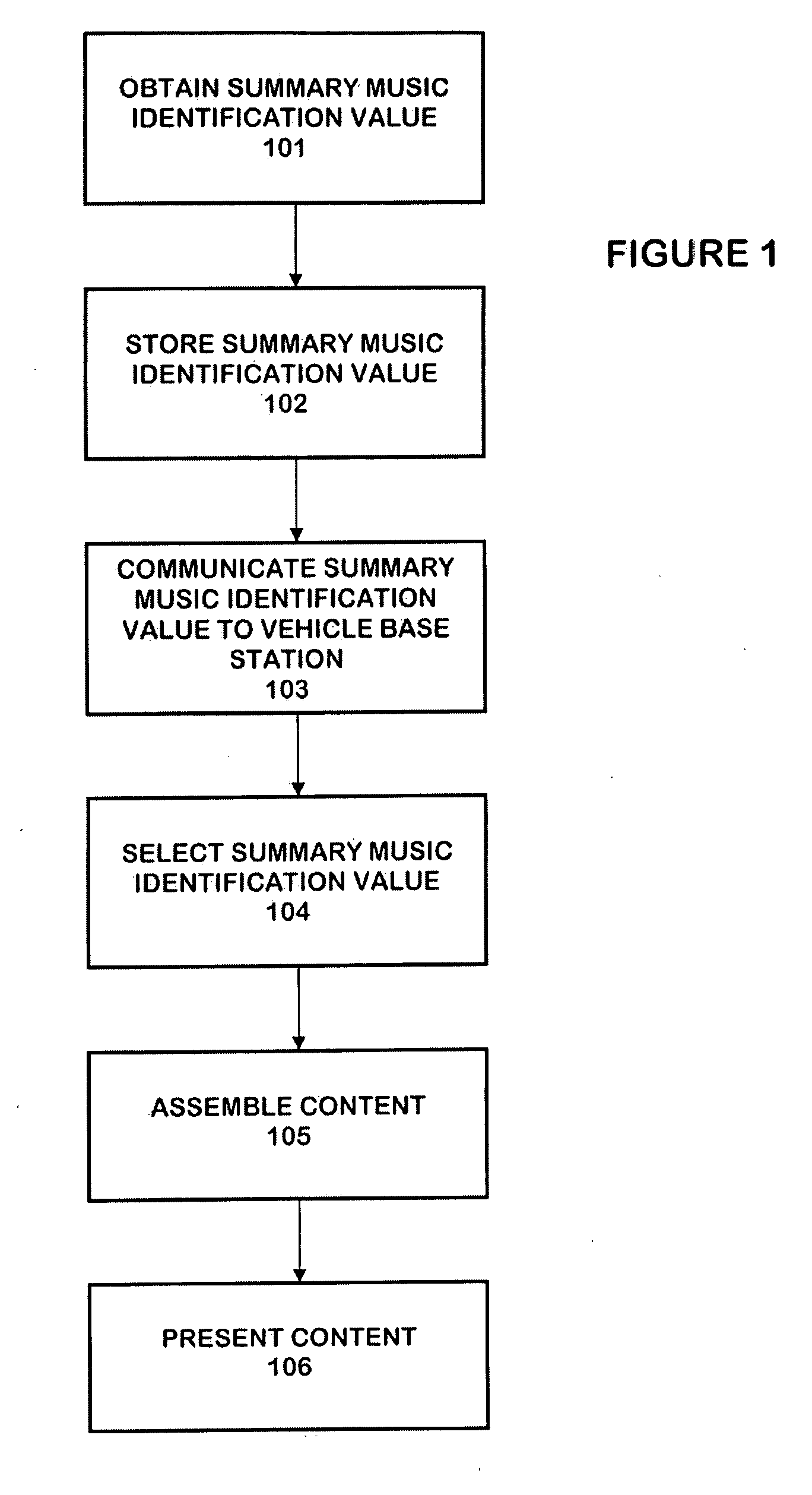
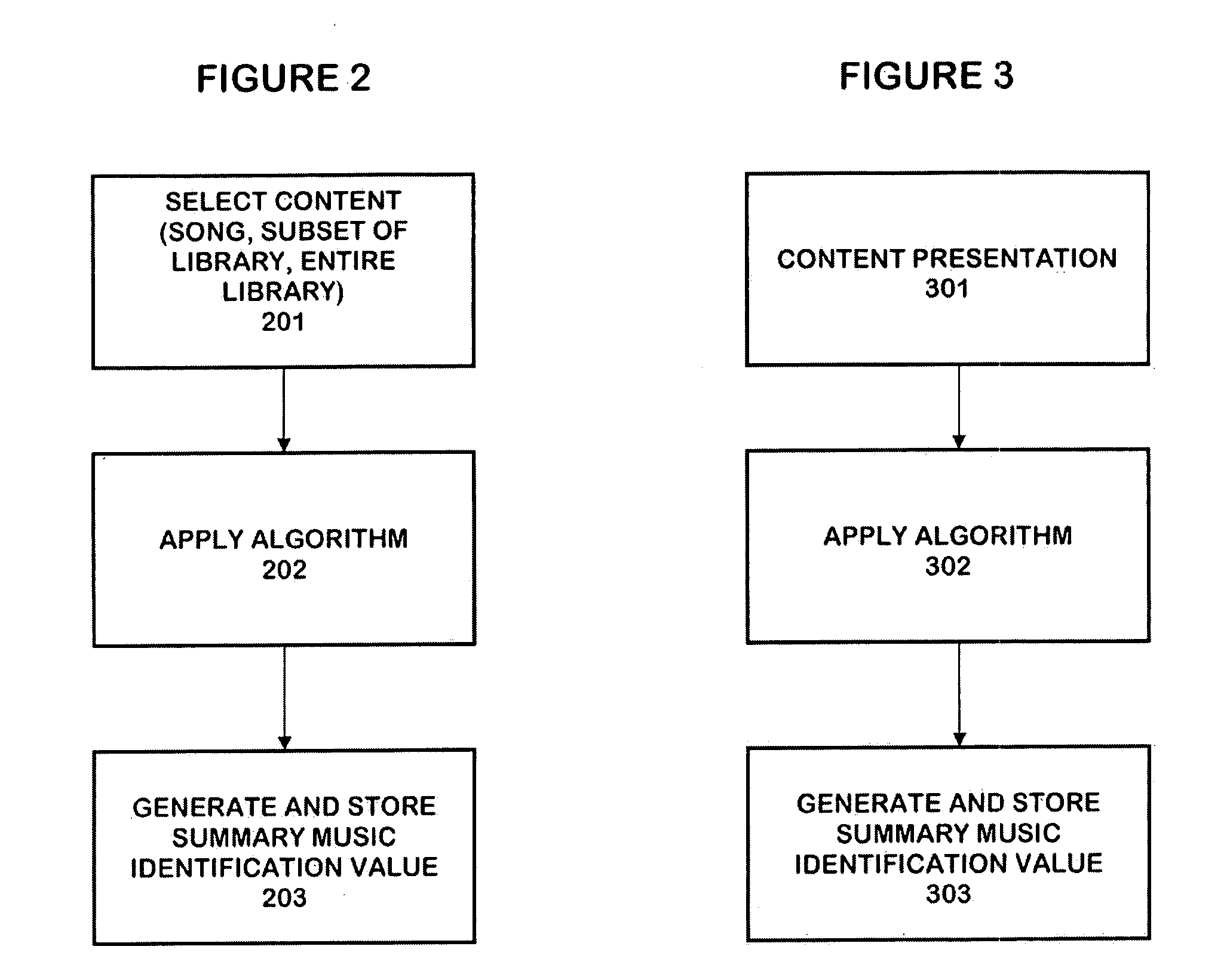
The personalized content system of the system combines a summary music identification value creation and identification algorithm that represents a mathematical summary music identification of a song, an audio file, or other relational music criteria and data (e.g. title, artist, genre, style, beats per minute, etc.) or any combination thereof. The derived value represents the musical taste or style attributes of a song or style. The analysis and generation of the summary music identification value is intended to take place while outside the vehicle where attention can be paid and vehicle distraction and safety is not an issue. A user can generate a single summary music identification value or can generate multiple summary music identification values for different criteria. In other cases, summary music identification values can be defined for genre, but with a much more personal touch possible than with fixed playlist radio stations. In another embodiment, a user can obtain and use someone else's summary music identification value (e.g. a celebrity, artist, friend, etc.) and use it with the system.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC +1
System and method for selecting music to guide a user through an activity
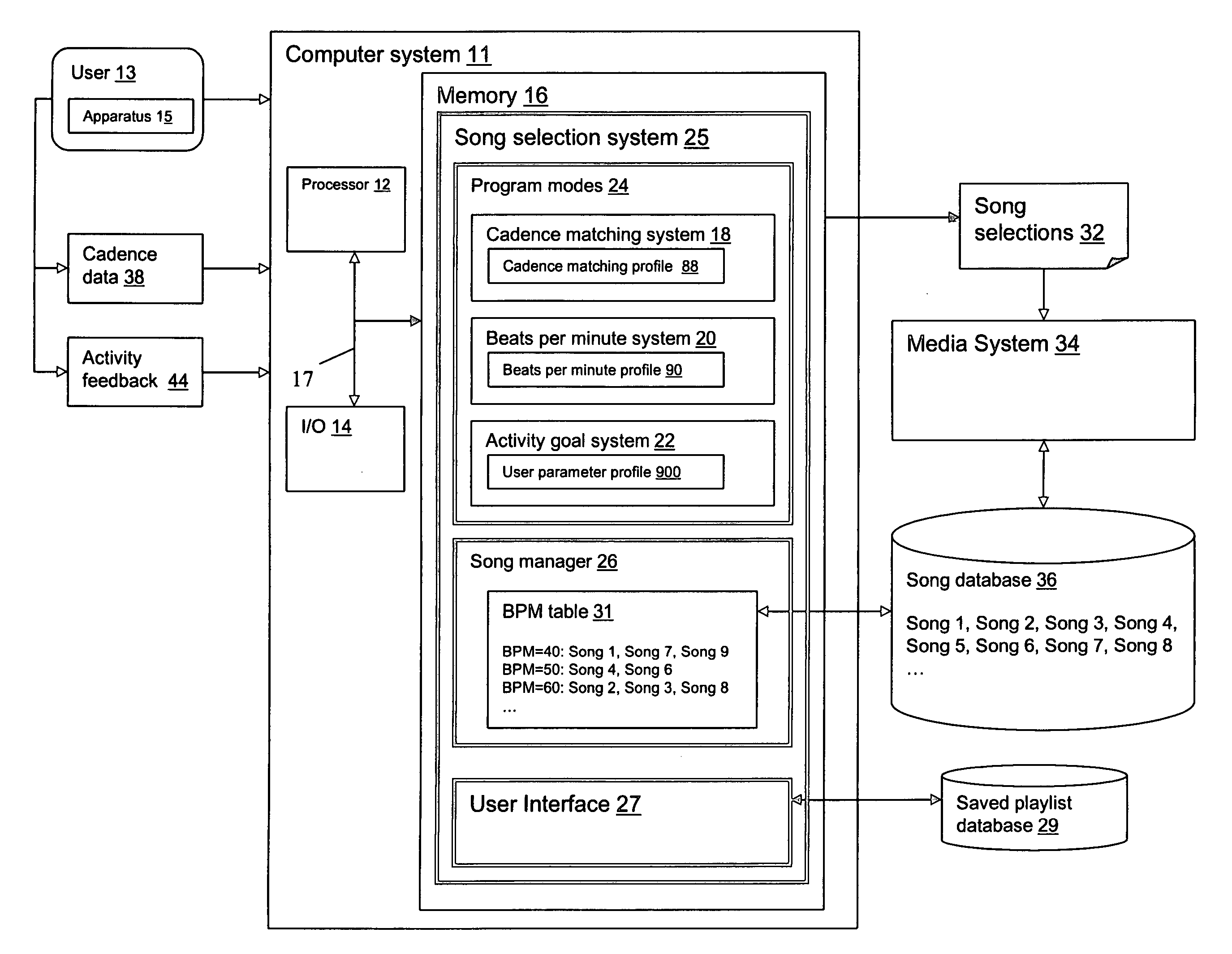
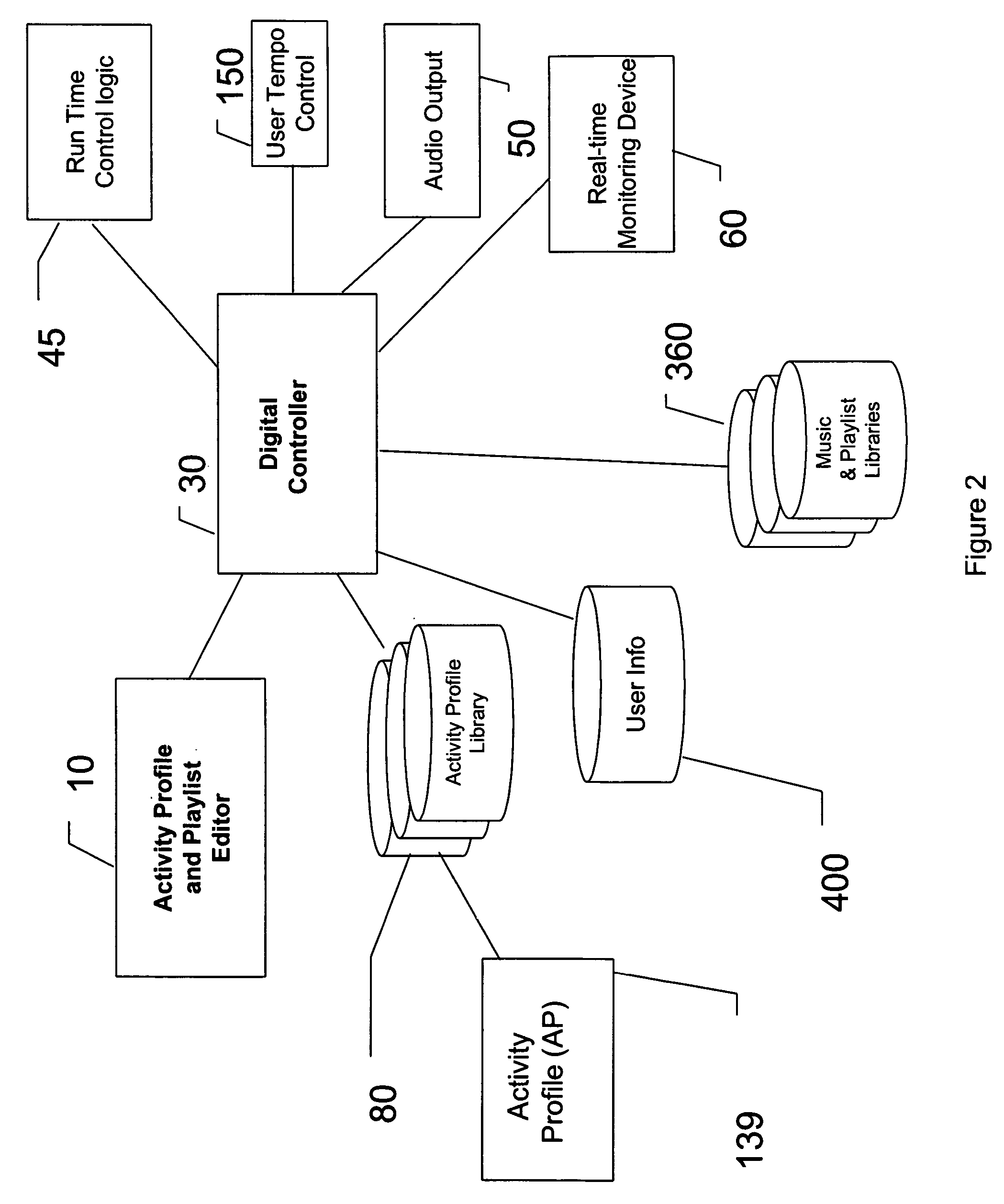
A system and method for choosing songs that can be utilized to guide a user through the performance of an activity. A system is disclosed that includes: a system for processing a beats per minute (BPM) template, wherein the BPM template defines a set of tempo values that vary; a database of songs; and a system for selecting songs from the database of songs, wherein each selected song matches an associated tempo value obtained from the BPM template.
Owner:RUN TECH
Vehicle infotainment system with personalized content
InactiveUS20080156173A1Reduce distractionsScalable functionalityElectrophonic musical instrumentsDigital data information retrievalDistractionPersonalization
The personalized content system of the system combines a summary music identification value creation and identification algorithm that represents a mathematical summary music identification of a song, an audio file, or other relational music criteria and data (e.g. title, artist, genre, style, beats per minute, etc.) or any combination thereof. The derived value represents the musical taste or style attributes of a song or style. The analysis and generation of the summary music identification value is intended to take place while outside the vehicle where attention can be paid and vehicle distraction and safety is not an issue. A user can generate a single summary music identification value or can generate multiple summary music identification values for different criteria. In other cases, summary music identification values can be defined for genre, but with a much more personal touch possible than with fixed playlist radio stations. In another embodiment, a user can obtain and use someone else's summary music identification value (e.g. a celebrity, artist, friend, etc.) and use it with the system.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Equine fitness monitoring
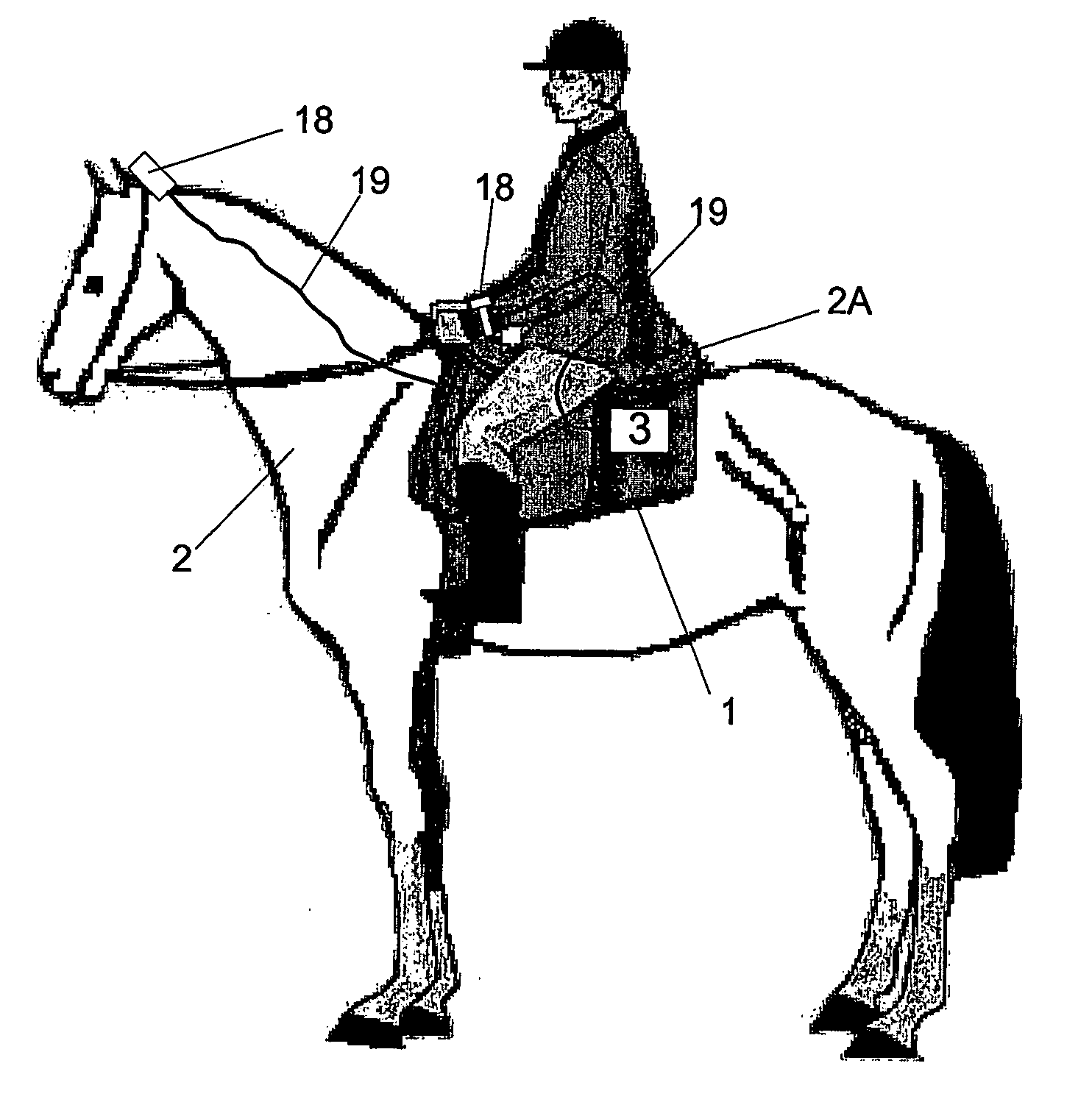
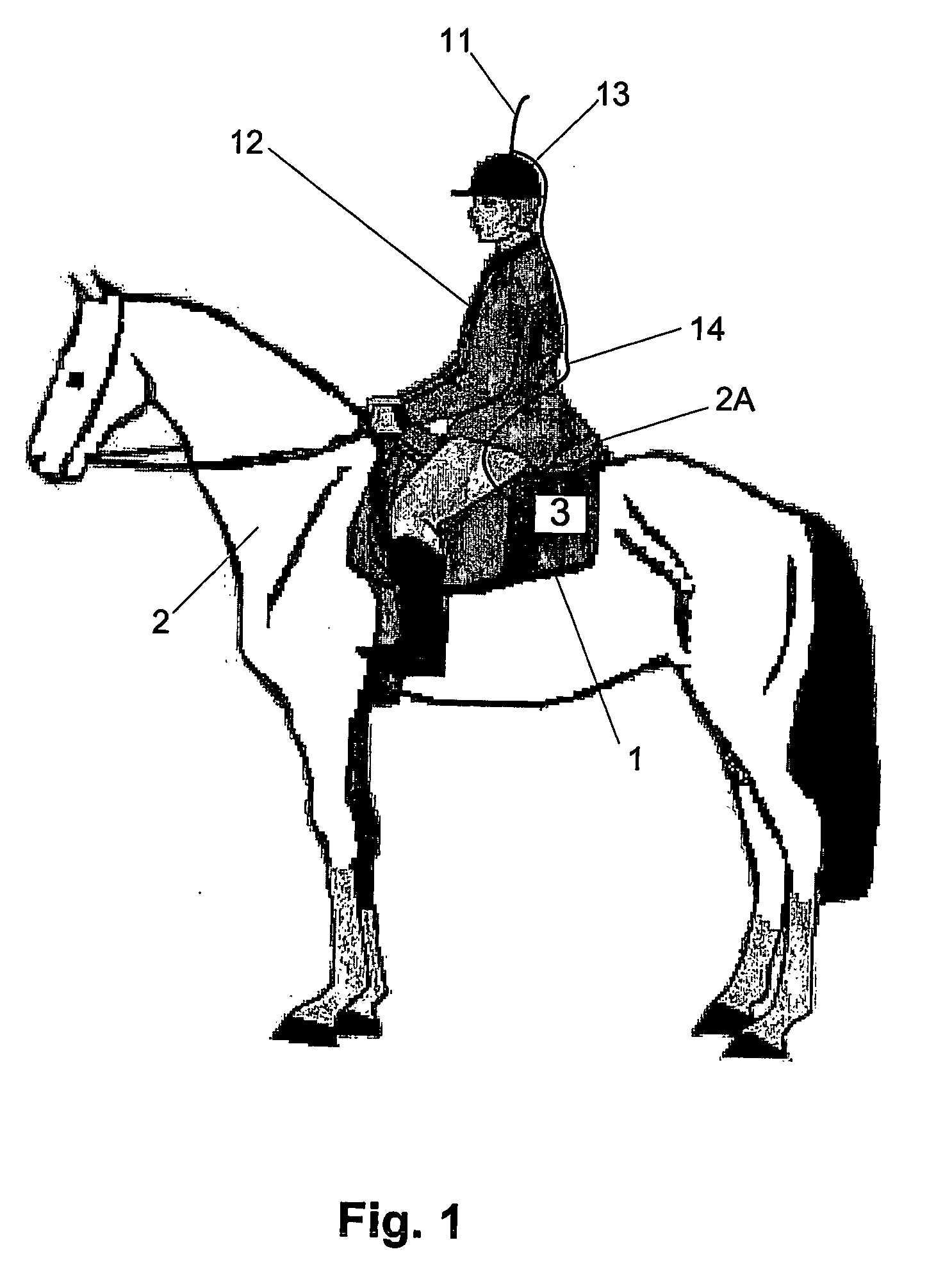
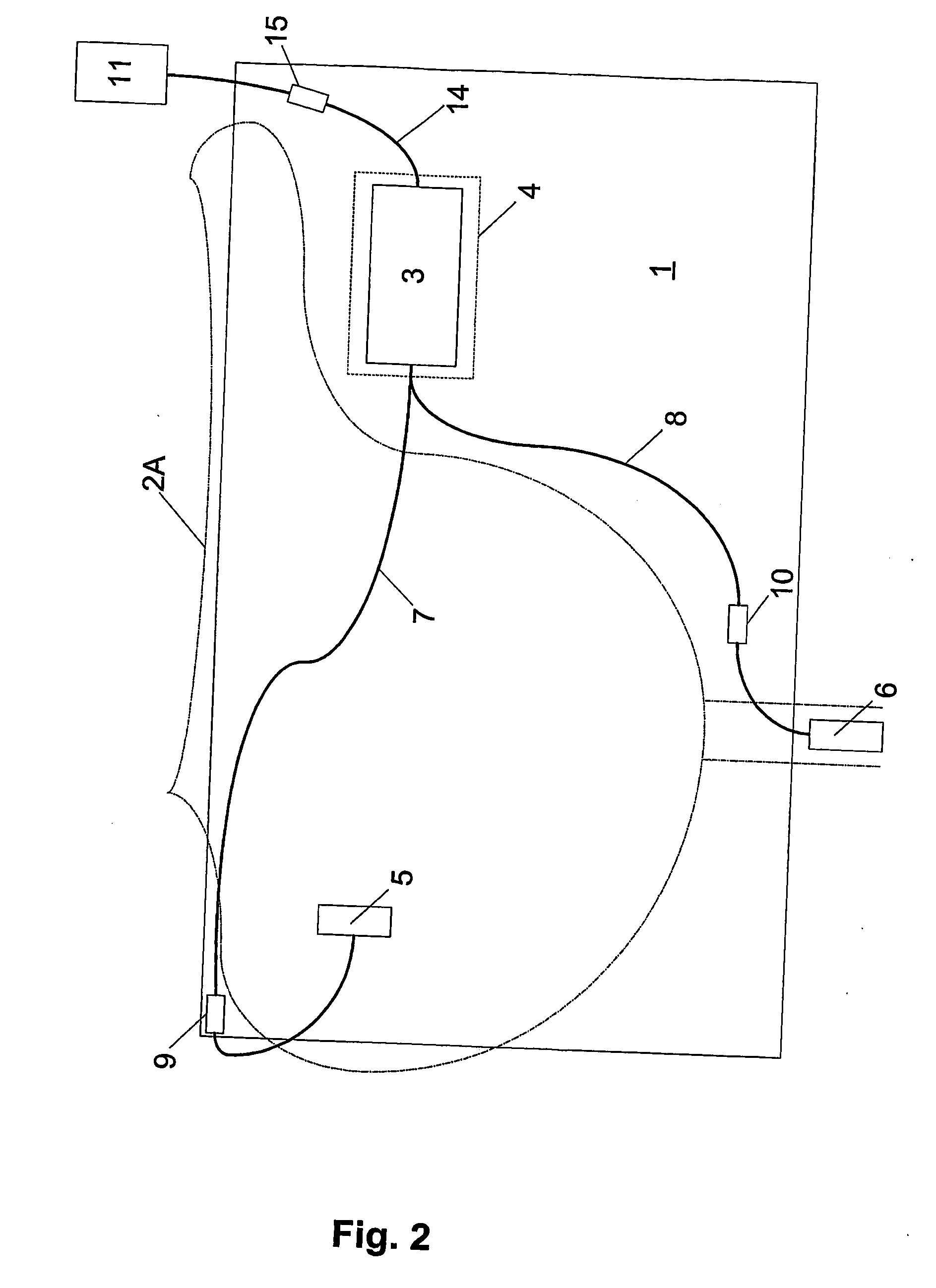
Apparatus for determining the health or fitness, under an exercise load, of an animal such a horse comprises: a first sensor (incorporated in module (3) and having electrodes (5, 6)), positioned in blanket (1) under saddle (2a) of a horse, generating physiological data, e.g. breathing or heart rate, blood pressure or flow, temperature, etc; a second sensor, also incorporated in module (3), for generating position data, e.g. a GPS sensor having antenna (11). By using an algorithm, a fitness indicator such as velocity at a heart rate of 200 beats per minute (V-200) can then be derived using data from the sensors. Lameness, disease or poor physiological potential of the animal can thus be identified.
Owner:EQUITRONIC TECH
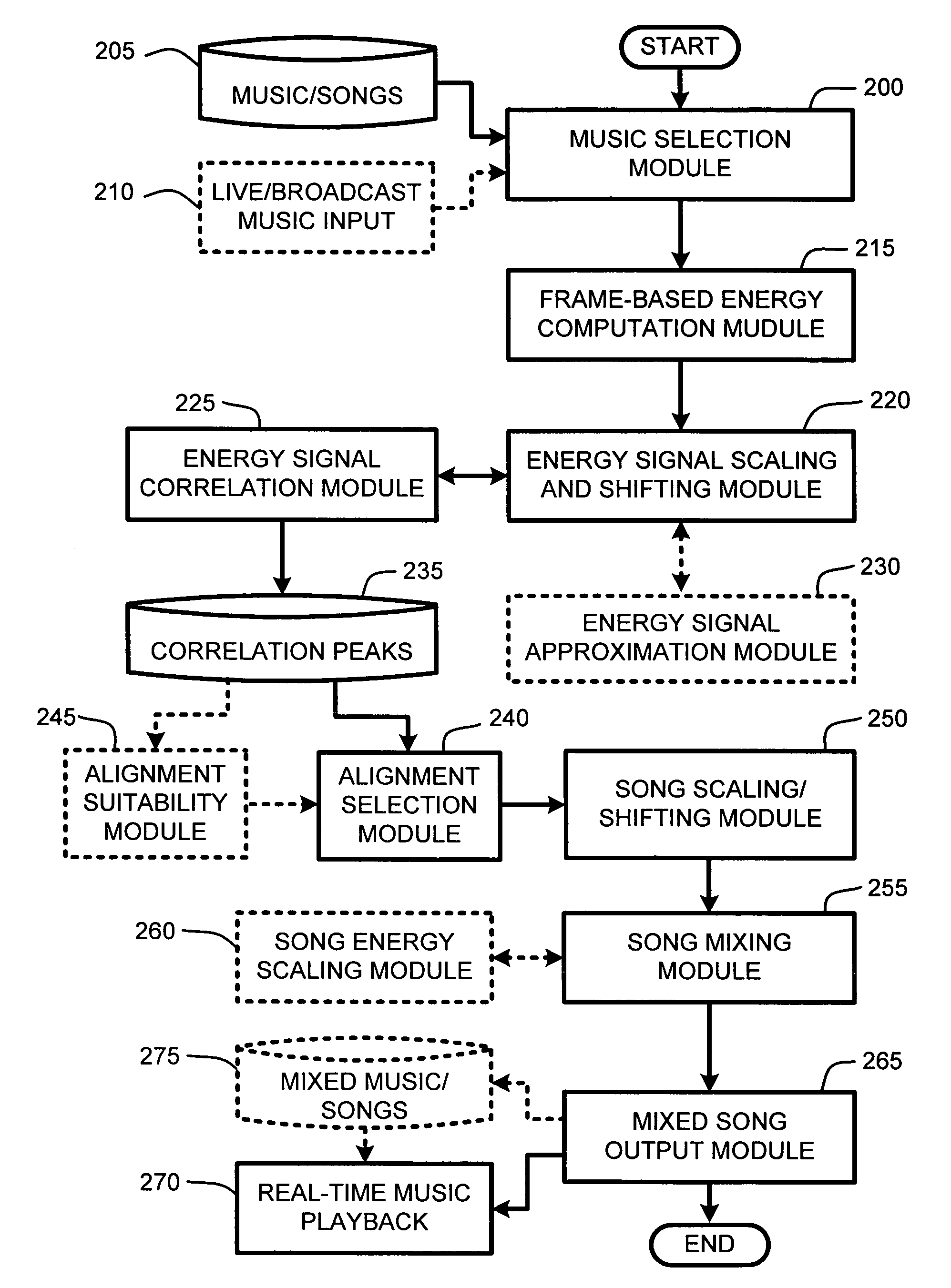
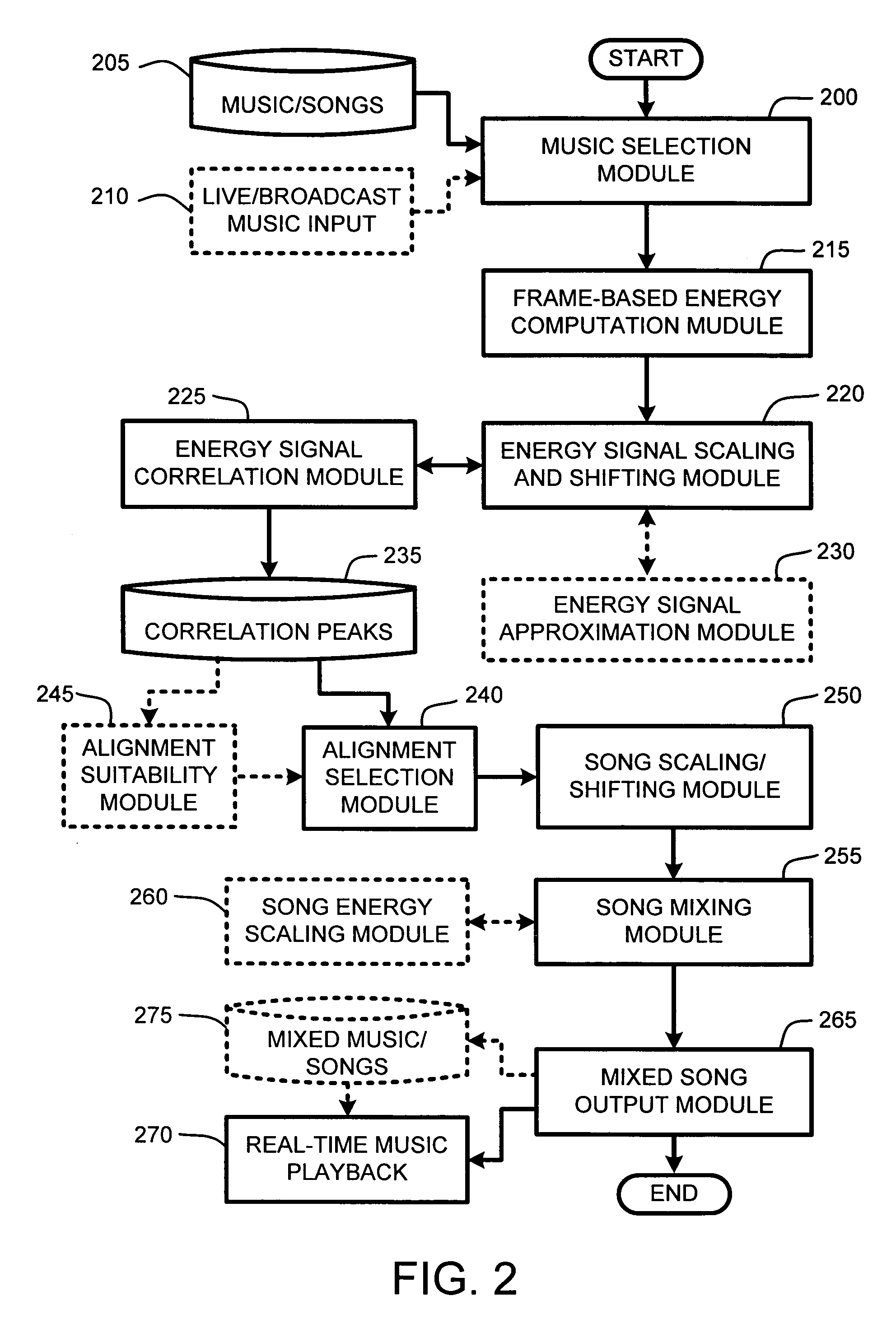
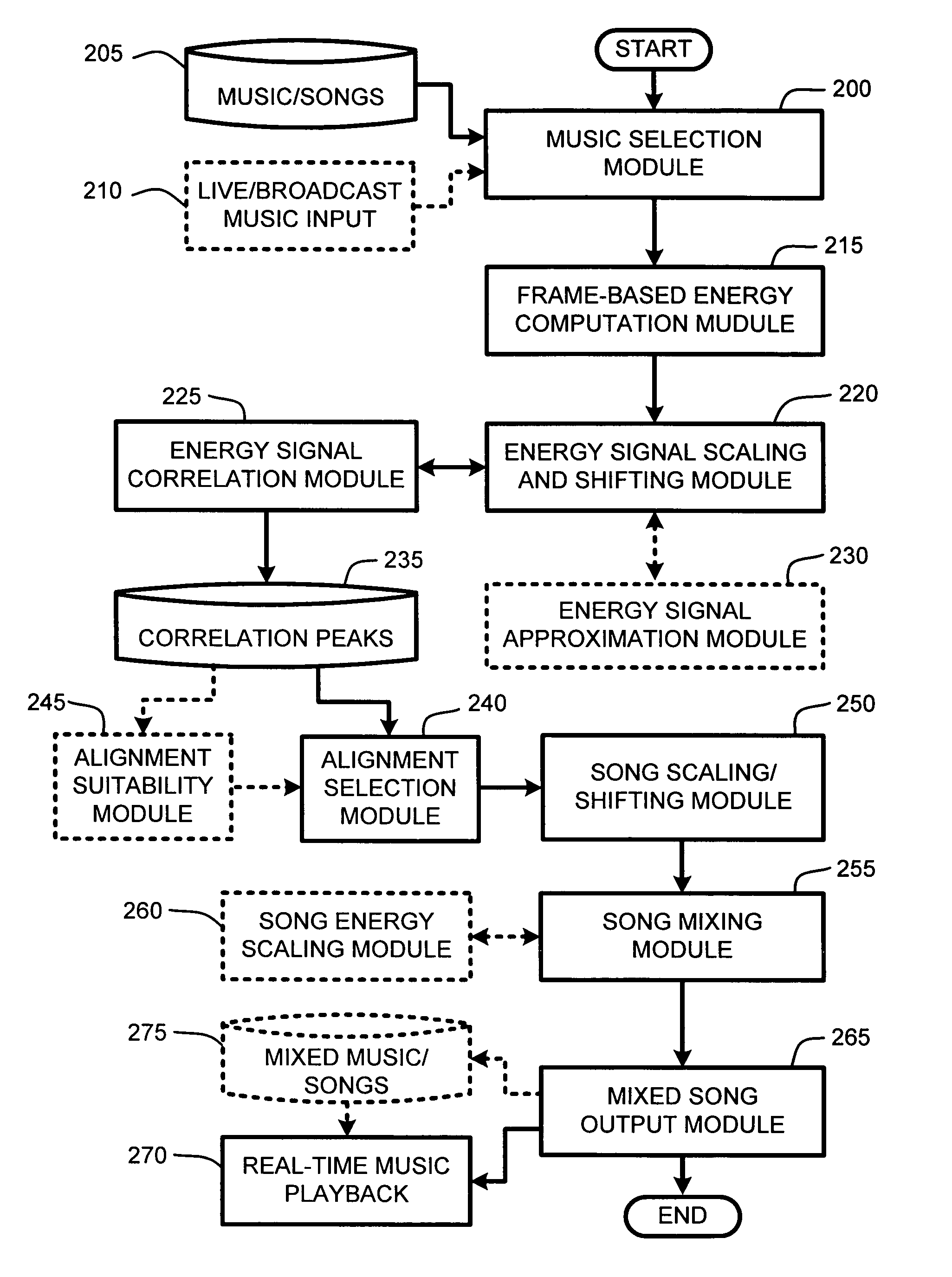
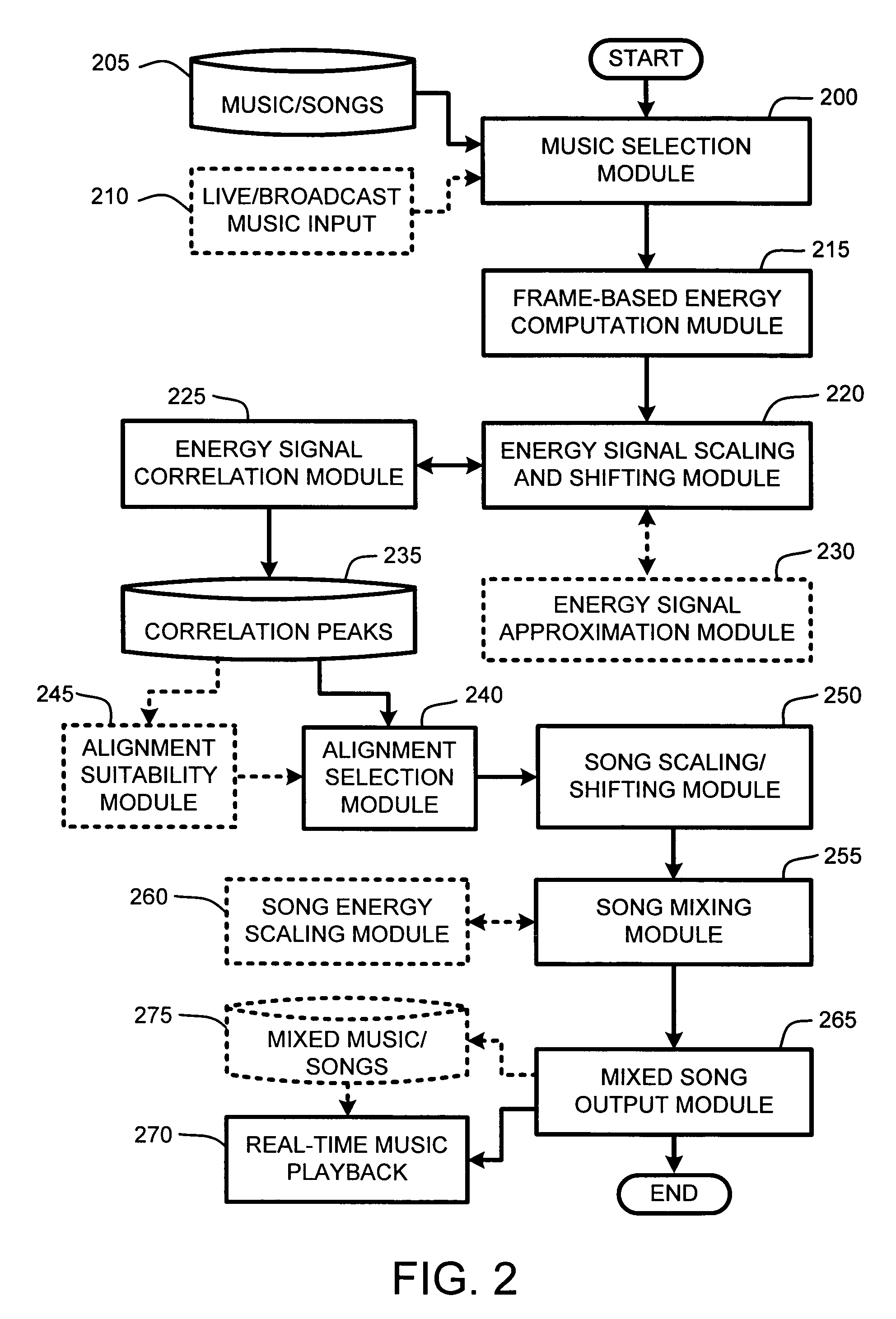
System and method for aligning and mixing songs of arbitrary genres
InactiveUS20060000344A1Reduce computational overheadIncrease rangeElectrophonic musical instrumentsFrame basedSound mixer
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
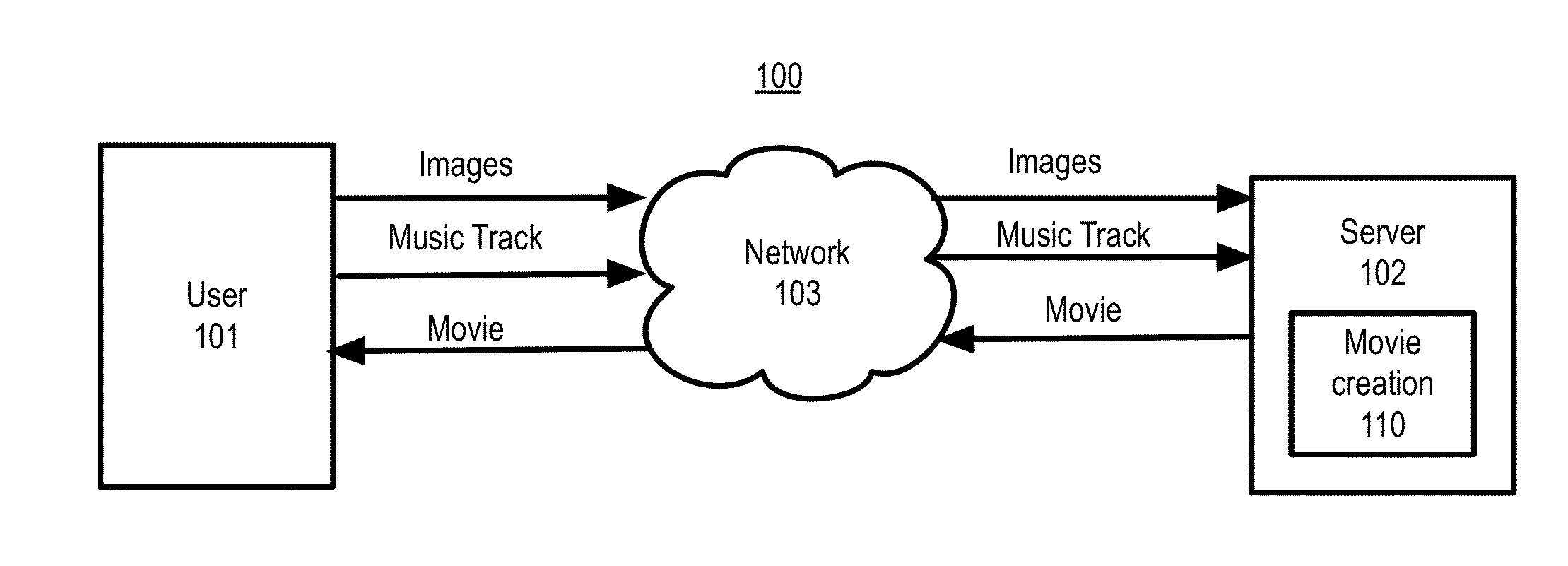
Automatic creation of movie with images synchronized to music
InactiveUS20130330062A1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsMaximum durationComputer graphics (images)
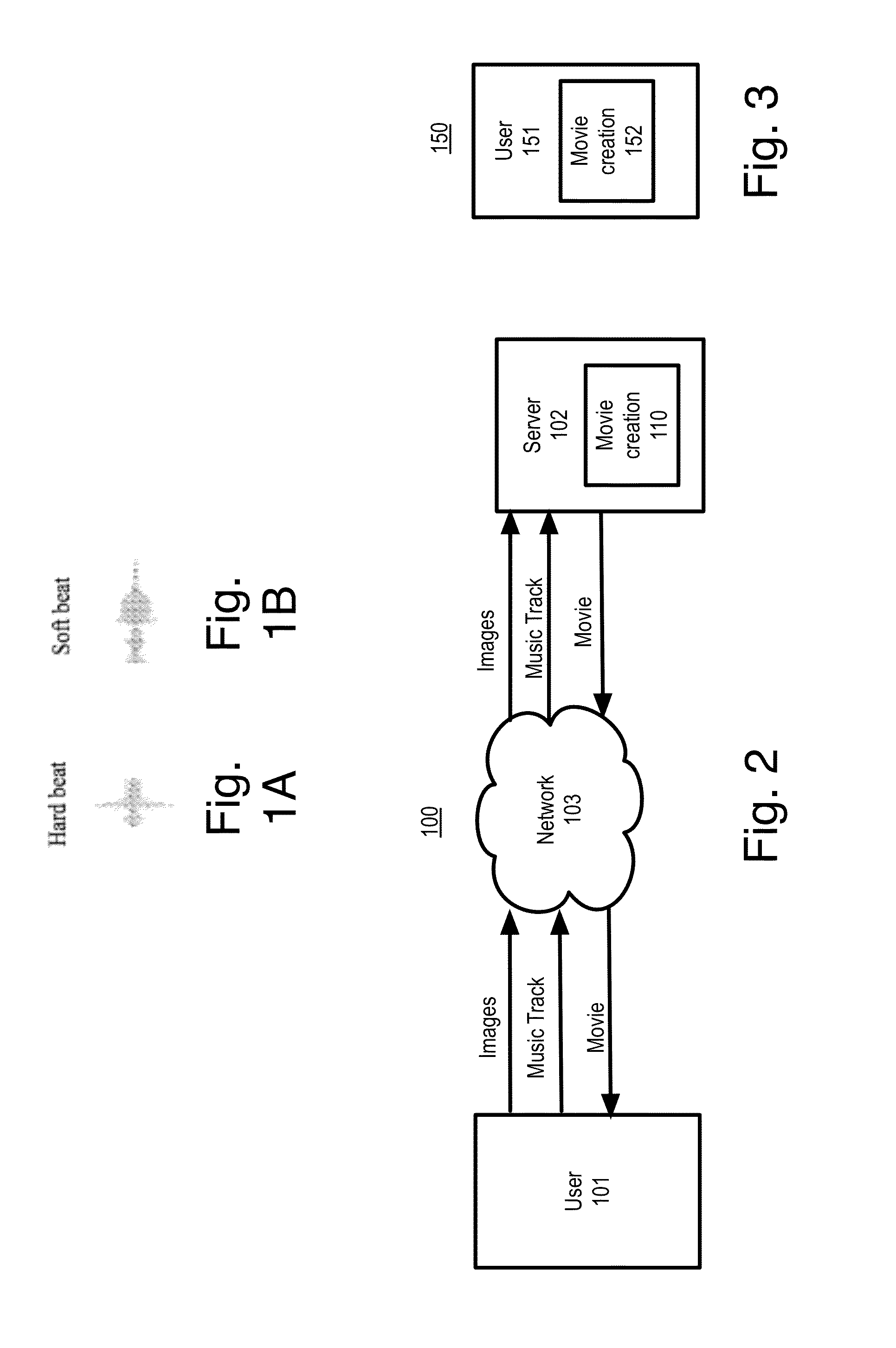
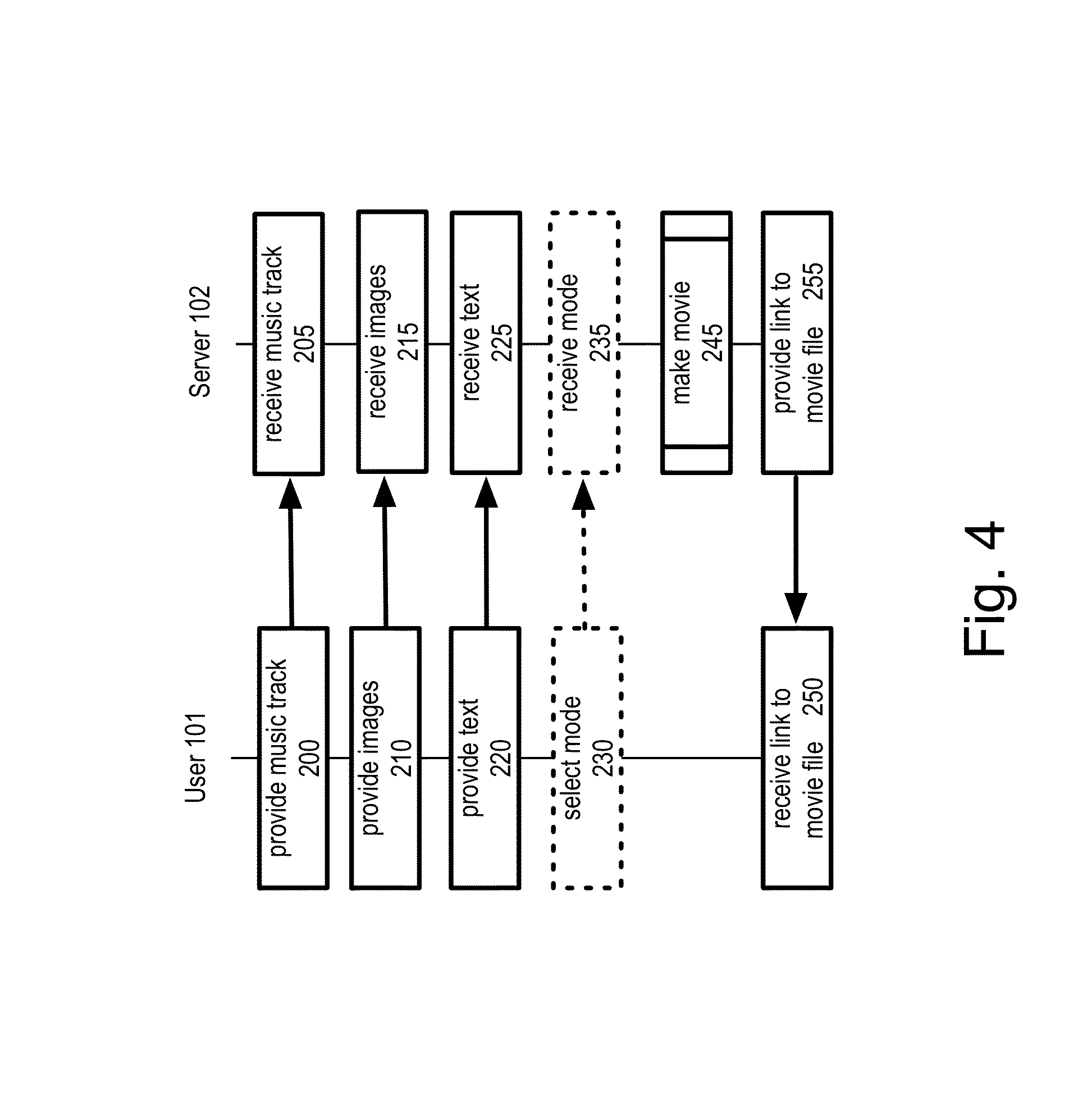
A movie is automatically created from a music track and a series of images such that placement of the images is synchronized to the music. The minimum image display time is automatically determined by the pace of the music. The pace can be determined by the beats per minute for the music. Two procedures are used for identifying beats, corresponding to hard and soft beats. The best transition points for the images in the movie are automatically determined. When the music has a relatively long quiet portion, the number of images during the quiet portion is adjusted so that each image does not exceed the maximum duration, and the duration of images during the quiet portion is approximately equal.
Owner:MYMUSAIC
Anthropomorphic robot autonomously dancing along with rhythm
InactiveCN101524594APracticalImprove performanceSelf-moving toy figuresProduction lineHumanoid robot nao
The invention relates to an anthropomorphic robot autonomously dancing along with rhythm. The brain of the robot is provided with an embedded computer system with musical rhythm recognition capability. The embedded computer system mainly comprises a hearing subsystem, a rhythm recognition subsystem and a dancing movement combination subsystem; wherein, the hearing subsystem obtains external played music by a sensor and converts the music into digital music signals which serve as the input of the rhythm recognition subsystem; the rhythm recognition subsystem processes the digital music signals and obtains the rhythm of the music and the characters of beats which comprises beats per minute and the beginning time of beats; the dancing movement combination subsystem autonomously combines dances according to the rhythm characters obtained by the rhythm recognition subsystem; the three subsystems process in parallel in the mode of a production line to cause the robot to autonomously dance along with rhythm. The anthropomorphic robot can autonomously perform a complete set of graceful and integrated dances along with the rhythm of the music. In addition, the anthropomorphic robot has the application prospect of art, education and recreational activity.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Command interface
ActiveUS20080162147A1Reduce distractionsScalable functionalityElectrophonic musical instrumentsDigital data information retrievalPersonalizationControl system
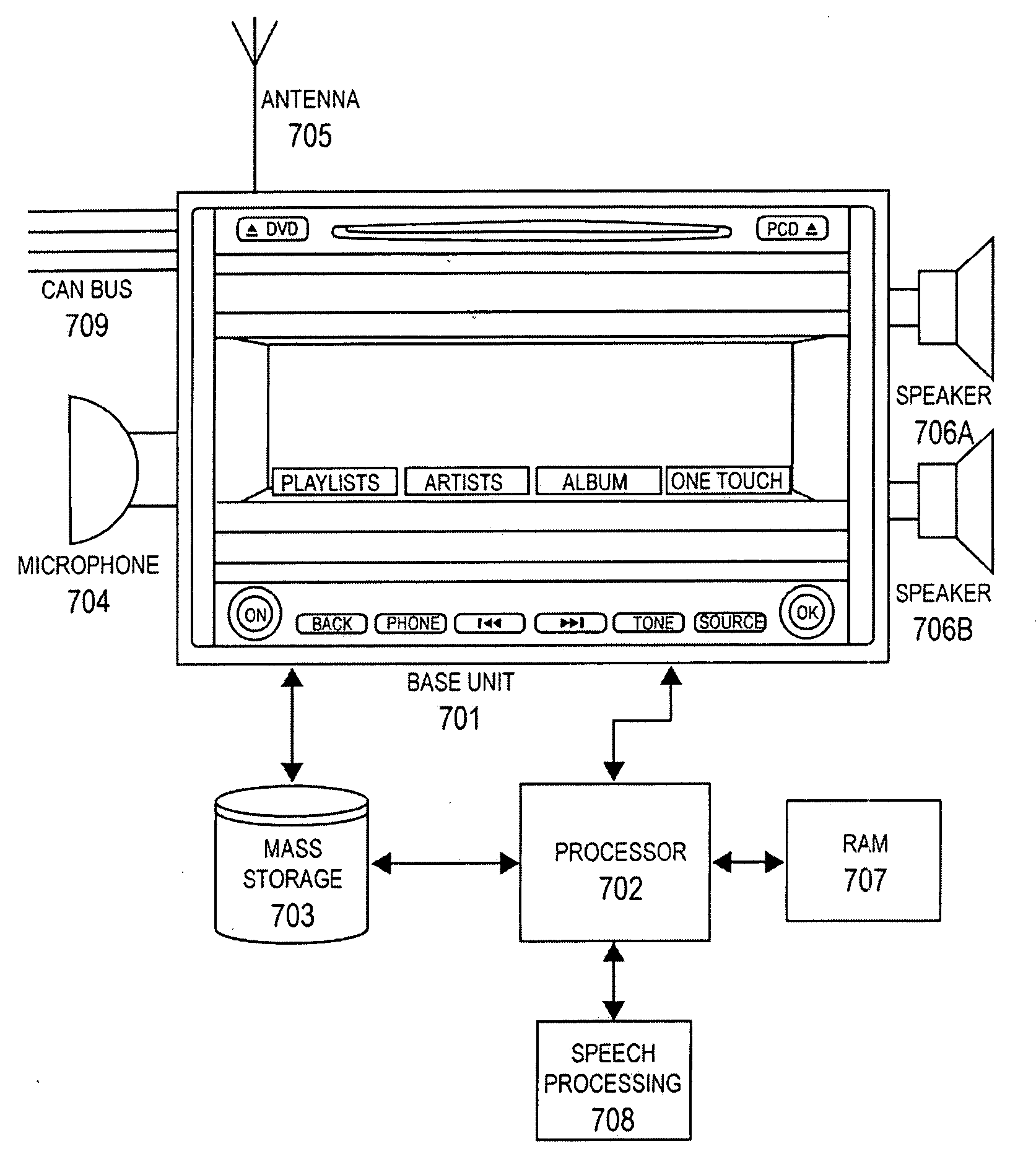
The personalized content system of the system combines a summary music identification value creation and identification algorithm that represents a mathematical summary music identification of a song, an audio file, or other relational music criteria and data (e.g title, artist, genre, style, beats per minute, etc.) or any combination thereof. The derived value represents the musical taste or style attributes of a song or style. The user can control the system by issuing one of a plurality of commands comprising artist command, song / title command, genre command, and album / filtered list command. These commands then lead to command trees that may be used in a voice controlled system, for example.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
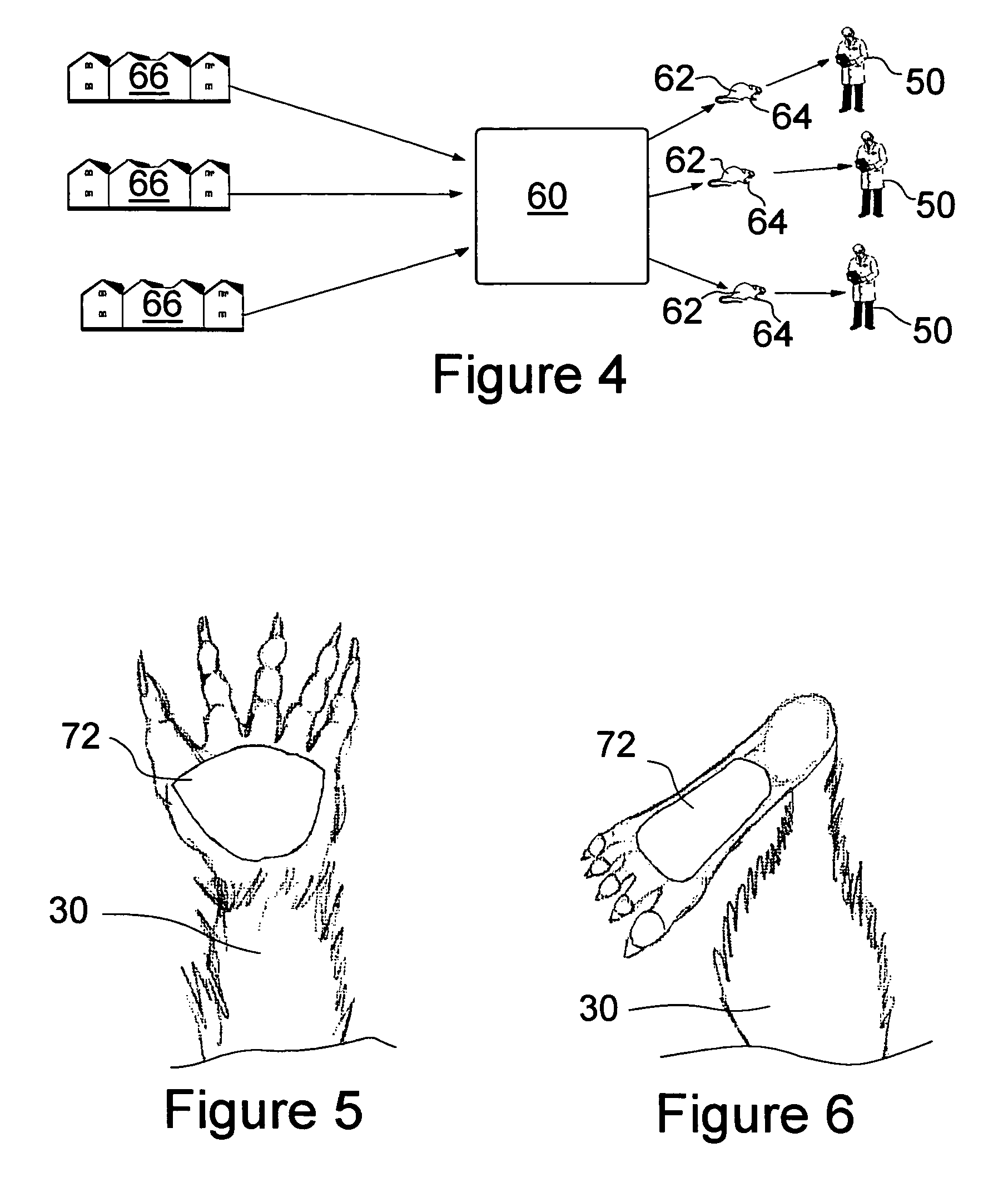
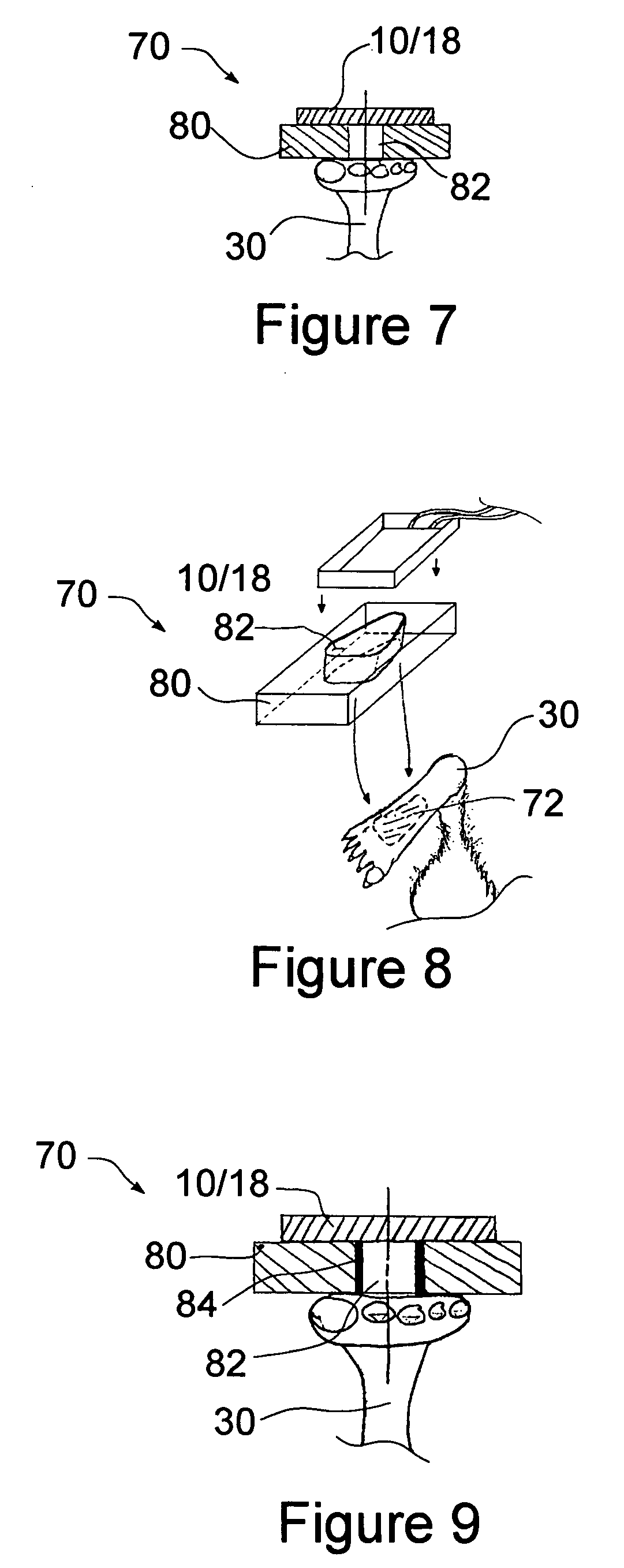
Medical devices and techniques for rodent and small mammalian based research
InactiveUS8005624B1Promote resultsReduce the effective areaBioelectric signal measurementSamplingHigh heart ratePulse oximeters
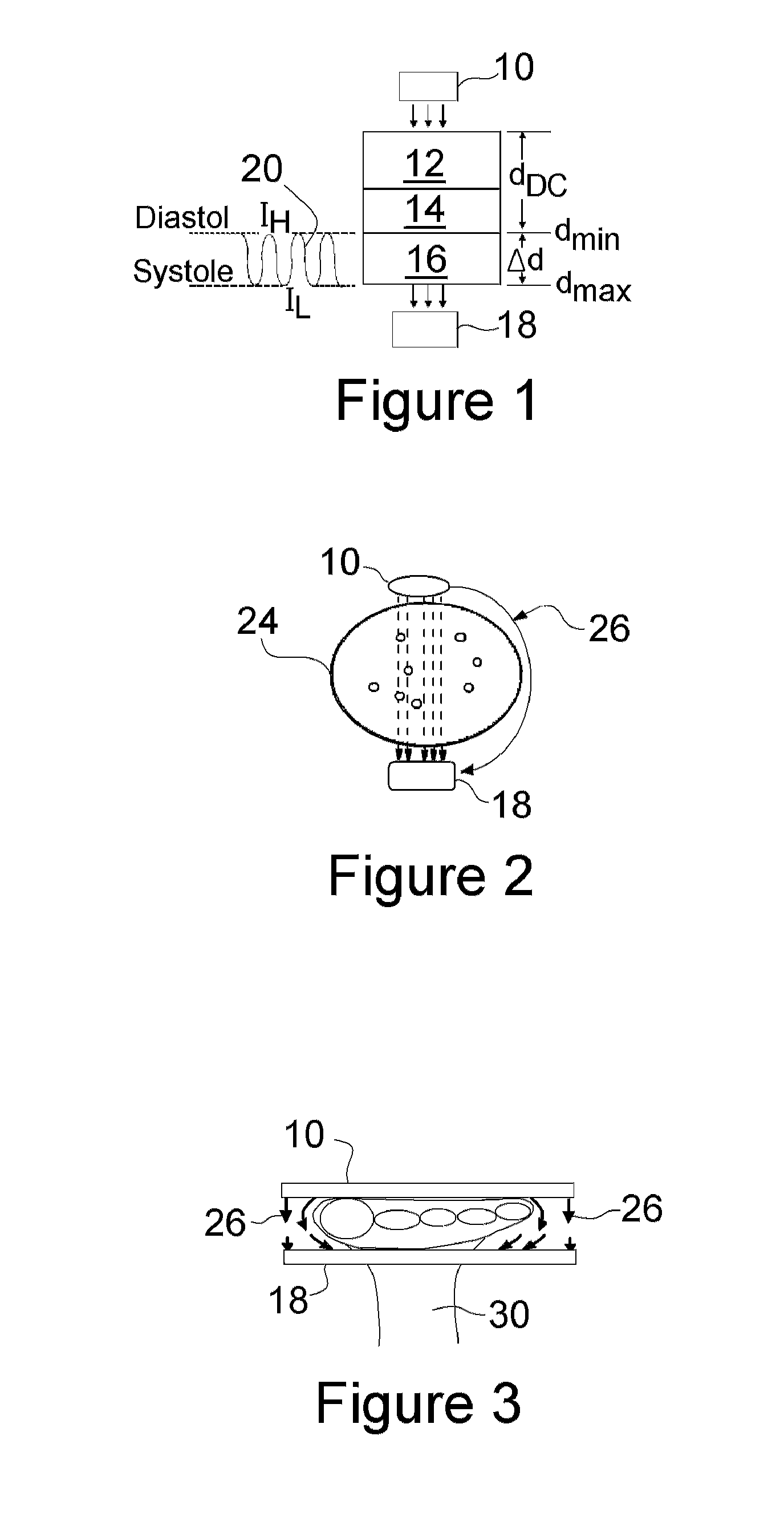
A method and system of supplying rodents, such as mice, to medical researchers pre-installs and / or embeds physiologic sensors onto or within the rodents prior to selling the modified rodents to the researchers. The specialty skills, such as small animal surgical and anesthesia skills and sensor placement and testing, are centralized in one organization rather than being spread about a collection of researchers. The subjects with preinstalled, pre-tested hardware, are sold to the researcher as needed. Communication hardware and software will be supplied for the user to convert their desktop computer into a wireless monitoring station. Additionally an external pulse oximeter for small rodents, such as mice, provides measurements on a hand or foot of the rodent with a sensor configured to avoid shunting around the rodent appendage, and configured for high heart rates (200-900 beats per minutes) of the subjects.
Owner:STARR LIFE SCI
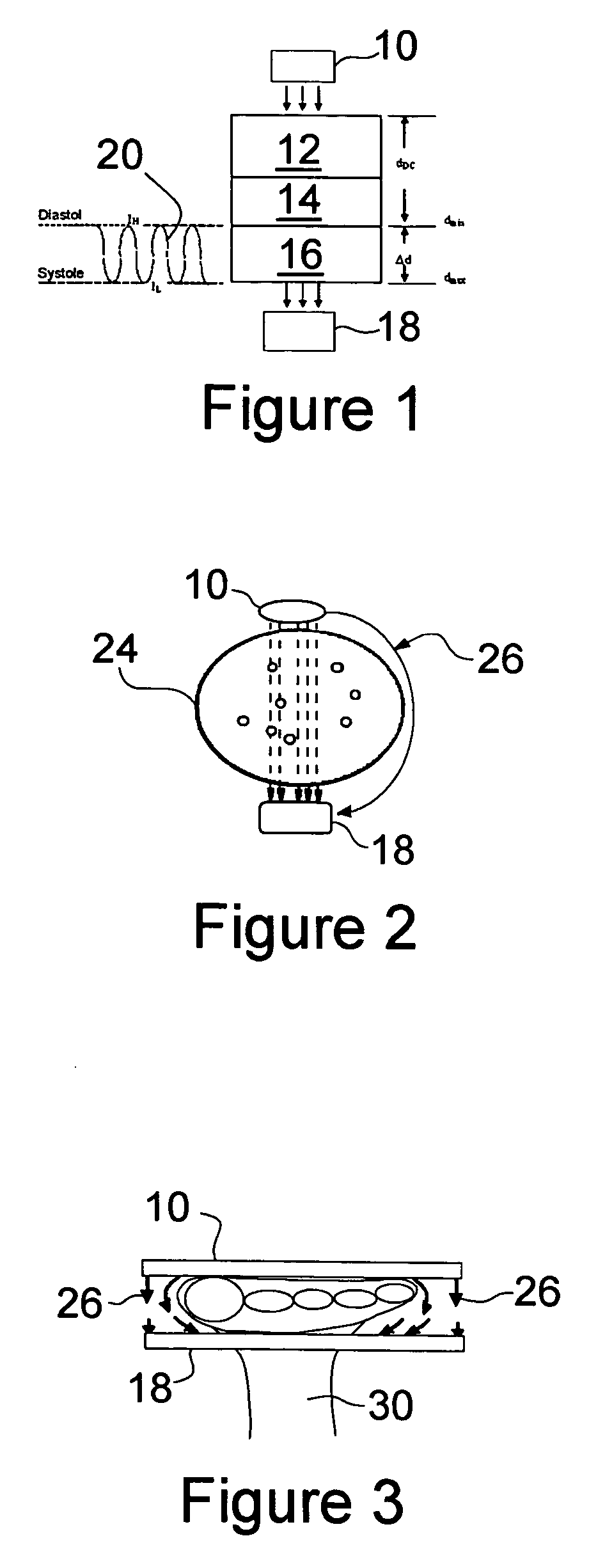
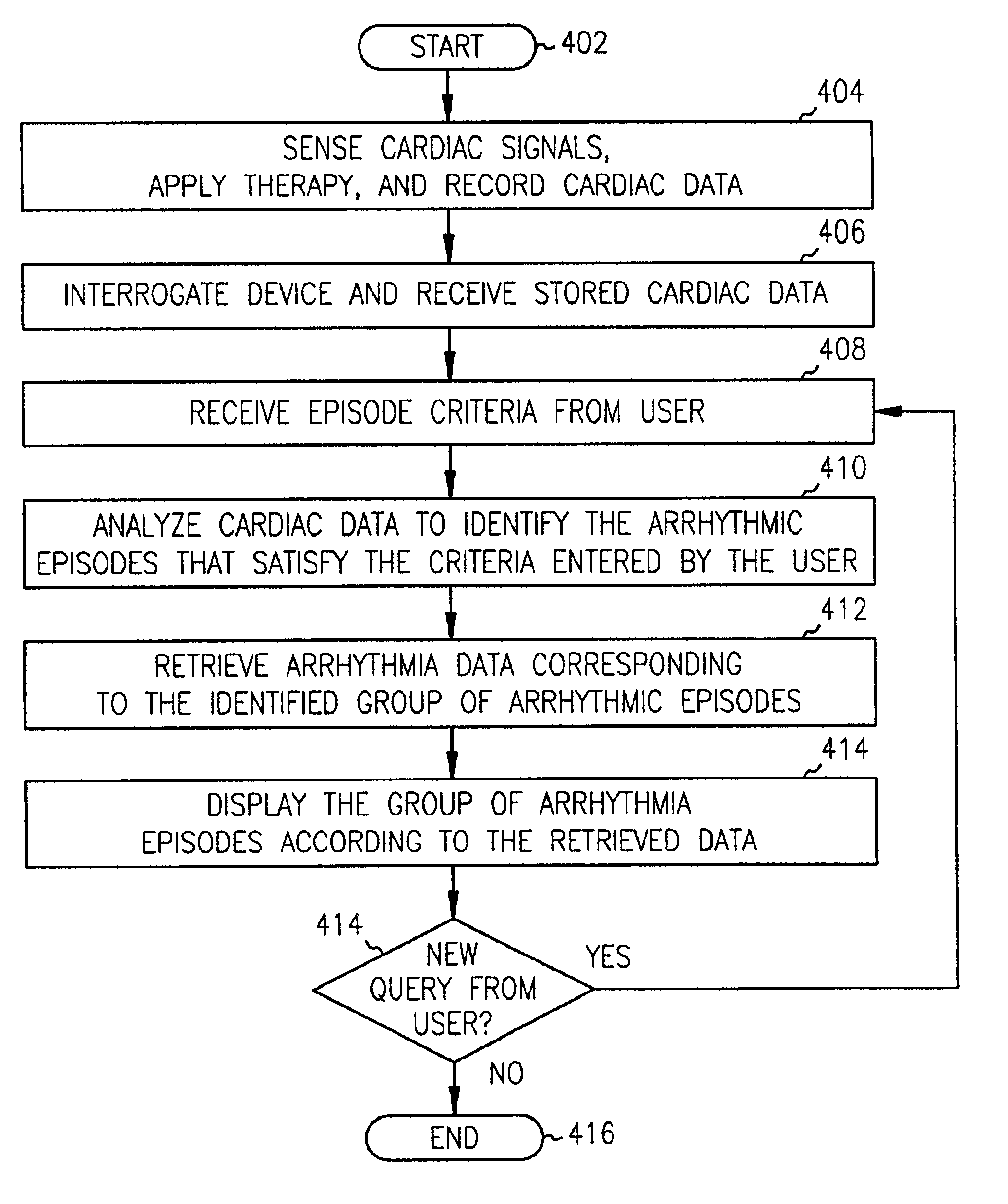
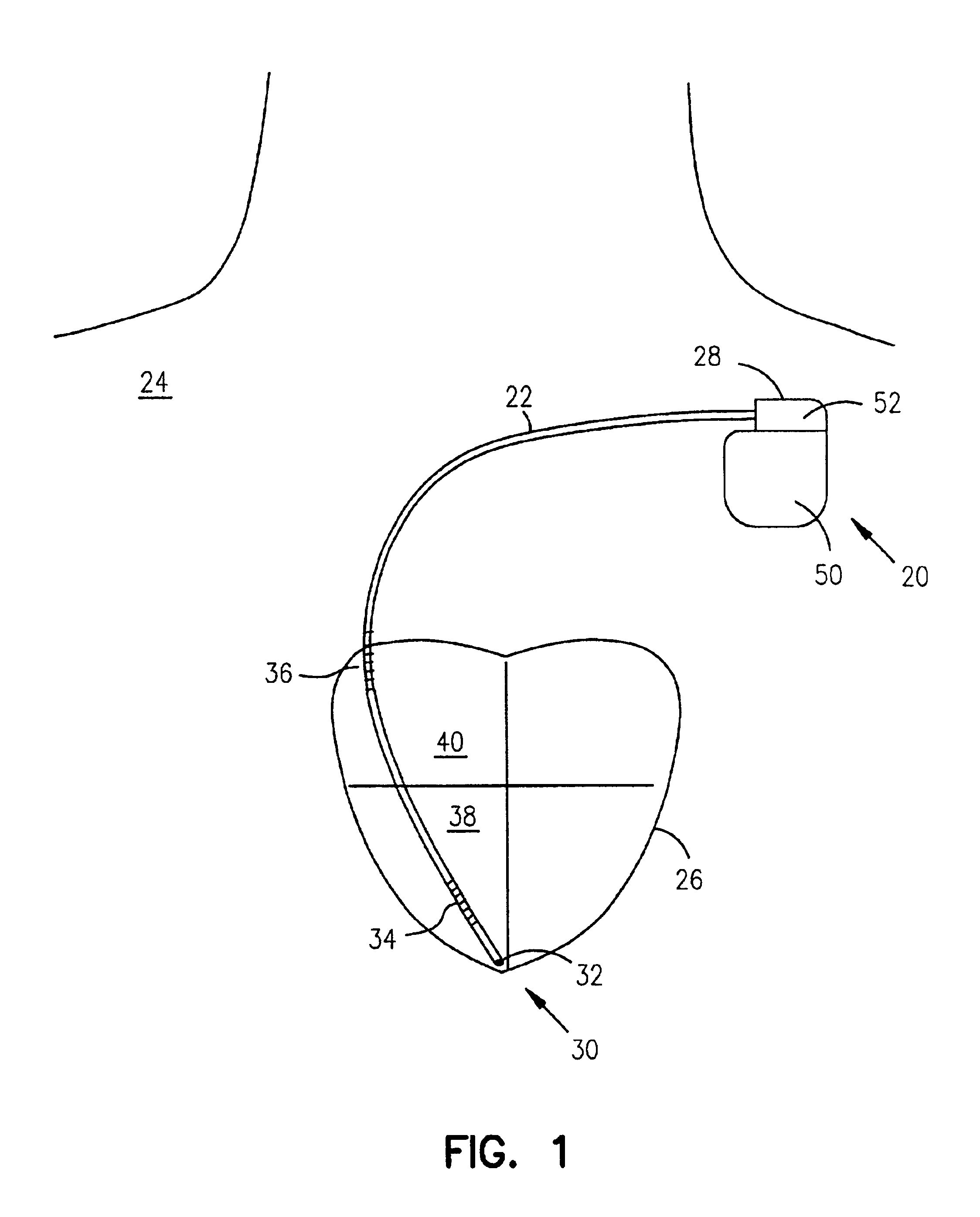
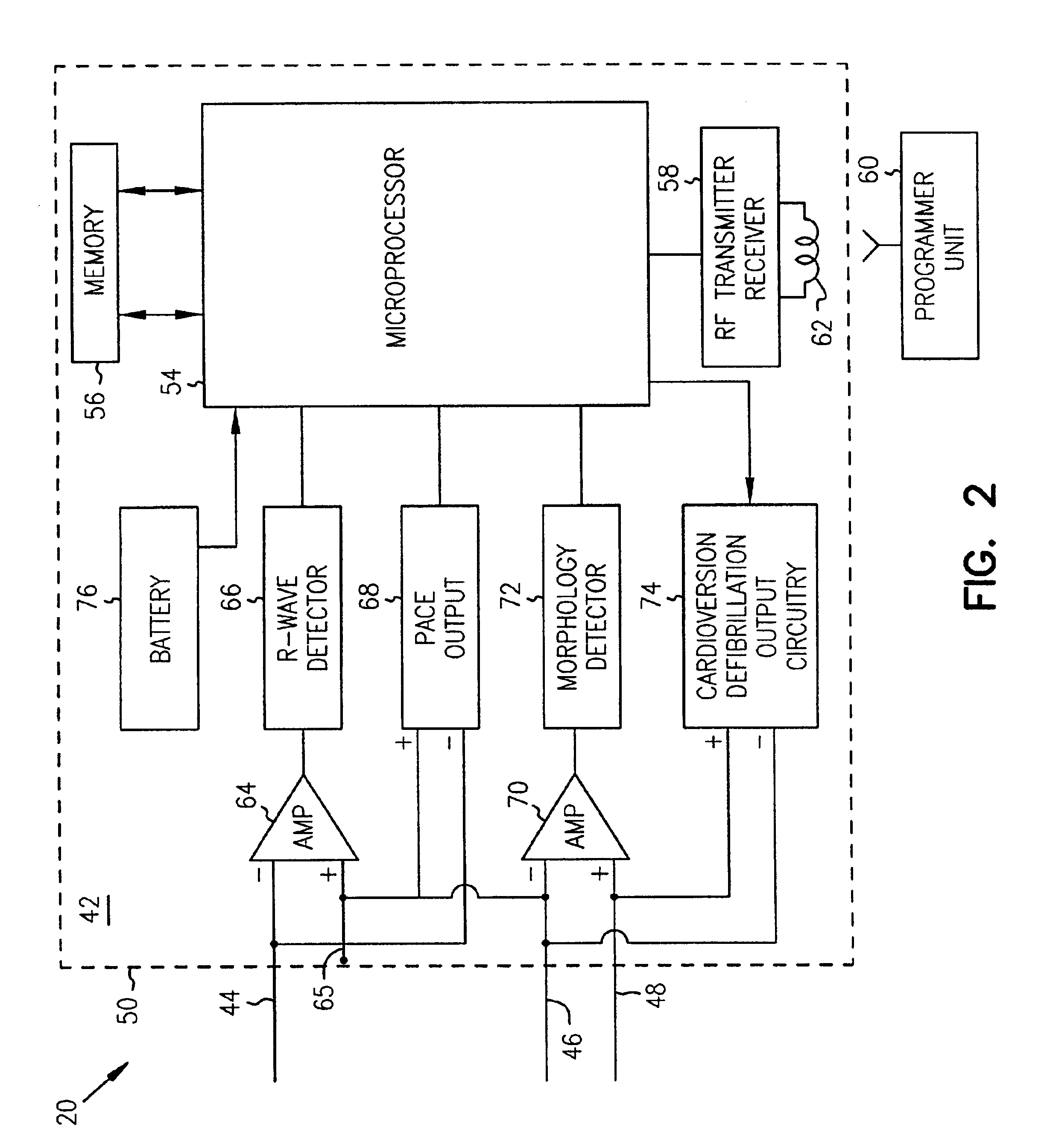
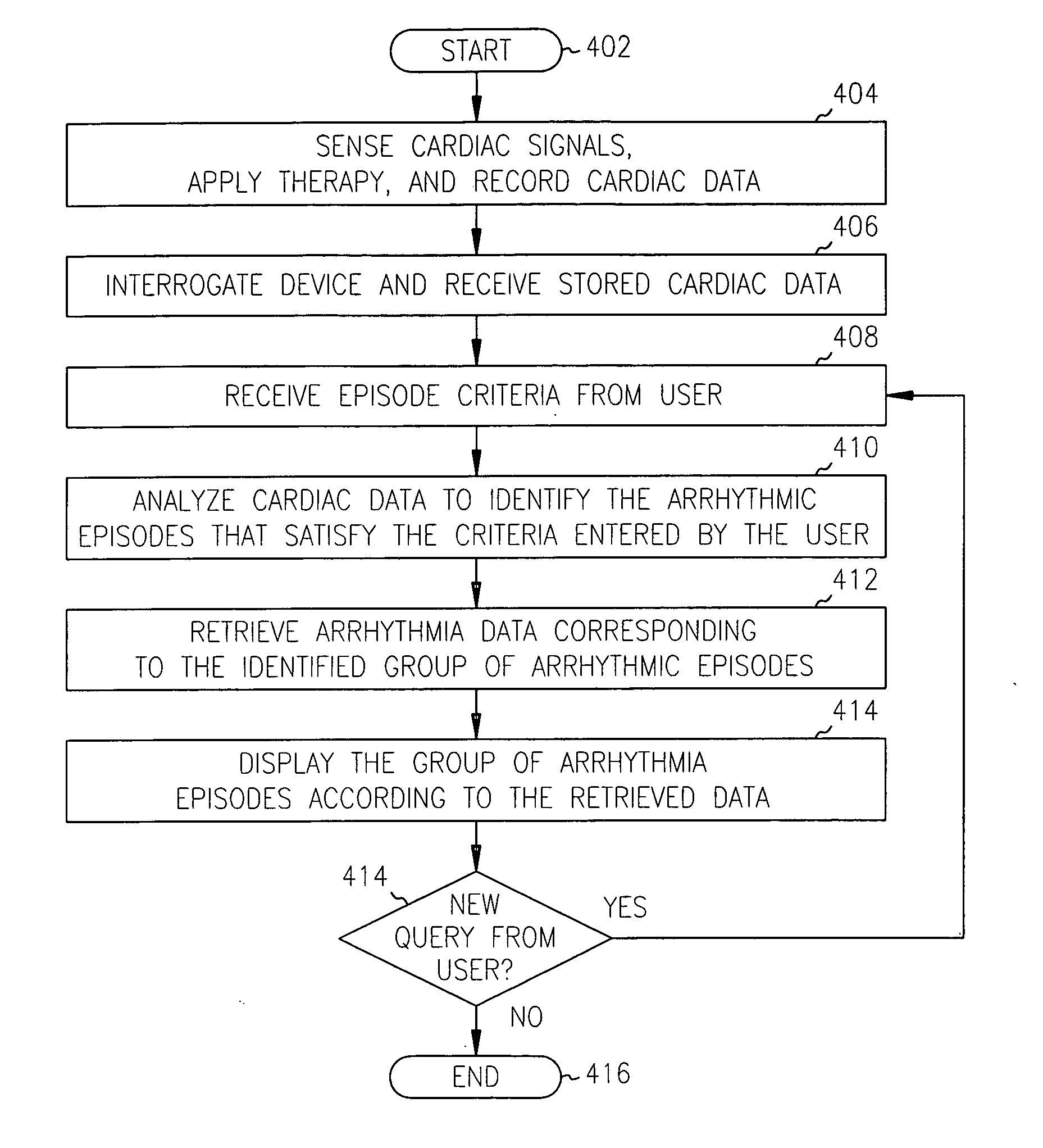
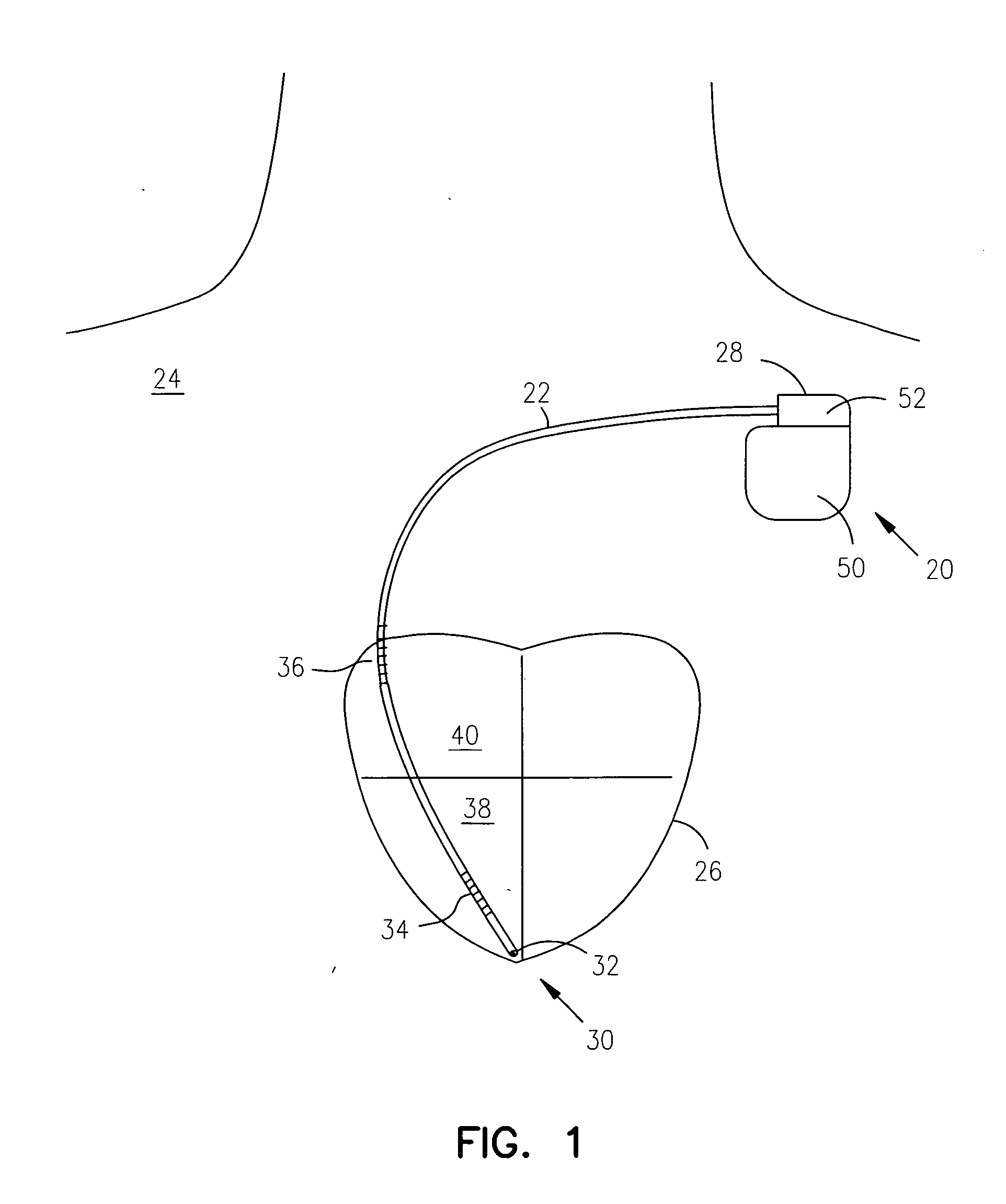
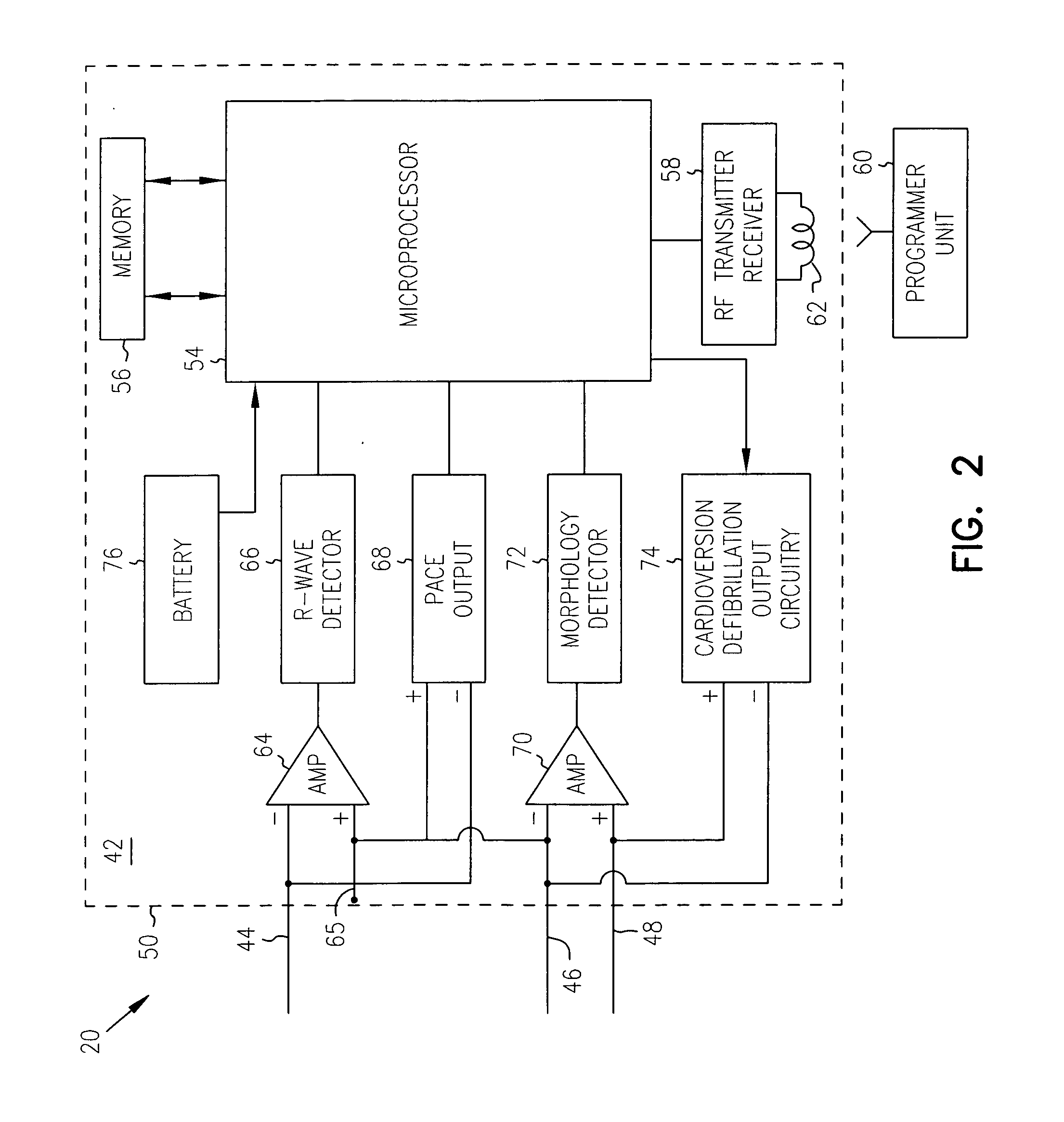
Method and system for identifying and displaying groups of cardiac arrhythmic episodes
InactiveUS6843801B2Rapid assessmentQuickly interpretElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringDisplay deviceInteractive displays
A medical device system that receives cardiac data representing a plurality of stored arrhythmic episodes, and analyzing the cardiac data to identify and display a subset of stored arrhythmic episodes as a function of user-specified episode criteria. The medical device system presents a query window on an interactive display in order to receive user-specified episode criteria via one or more input fields. The medical device displays only those episodes matching the episode criteria such as arrhythmia type, zone of detection, date of occurrence and average heart rate in beats per minute (BPM).
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
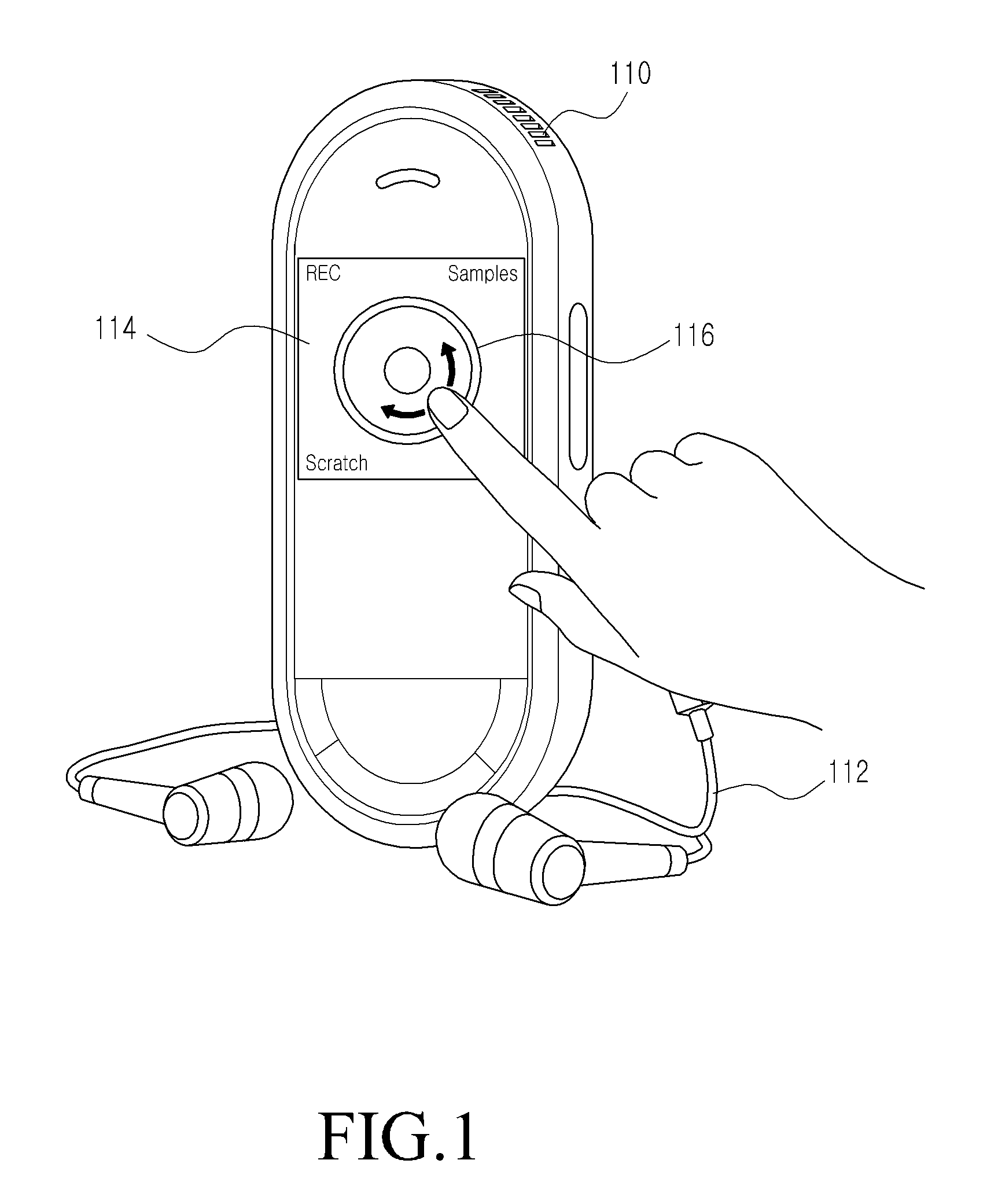
Apparatus and method for reproducing music in a portable terminal
InactiveUS20110085682A1Improve convenienceIncrease profitInput/output for user-computer interactionTransmissionComputer hardwareGraphics
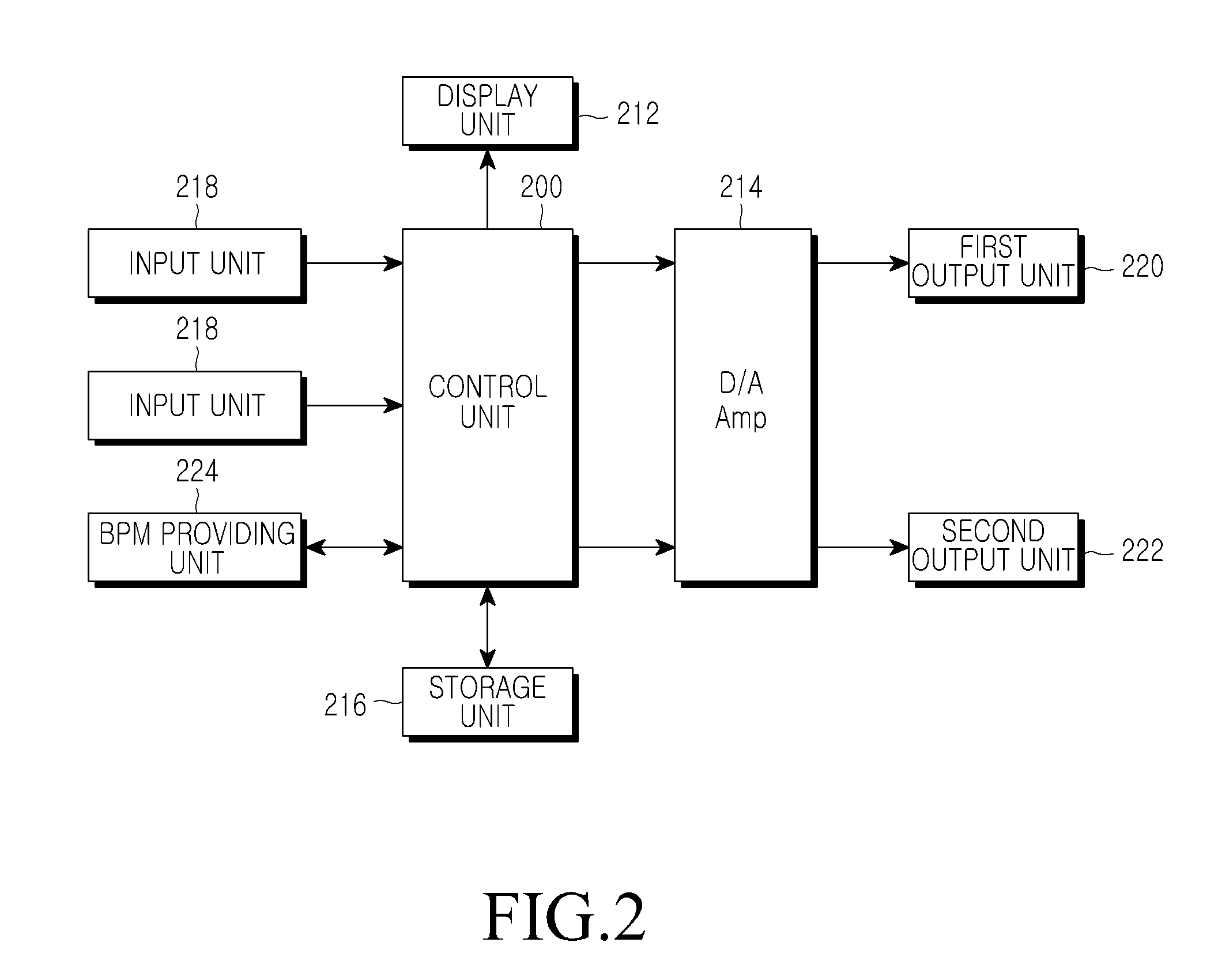
A music reproducing apparatus includes: a Graphic User Interface (GUI) providing a guide for controlling an output of a music file, a display unit for displaying the GUI, a Beats Per Minute (BPM) providing unit for converting the music file into an analog form, and for separating a specific frequency component from the converted music file of the analog form to provide BPM information of the music file, and a control unit for comparing BPM information of at least two music files with each other according to the BPM information provided from the BPM providing unit to reproduce the music file by adjusting an output frequency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device for inducing better sleep
InactiveUS20090105524A1Easy to transportEasy to combineMedical devicesSleep inducing/ending devicesSleep durationMobile device
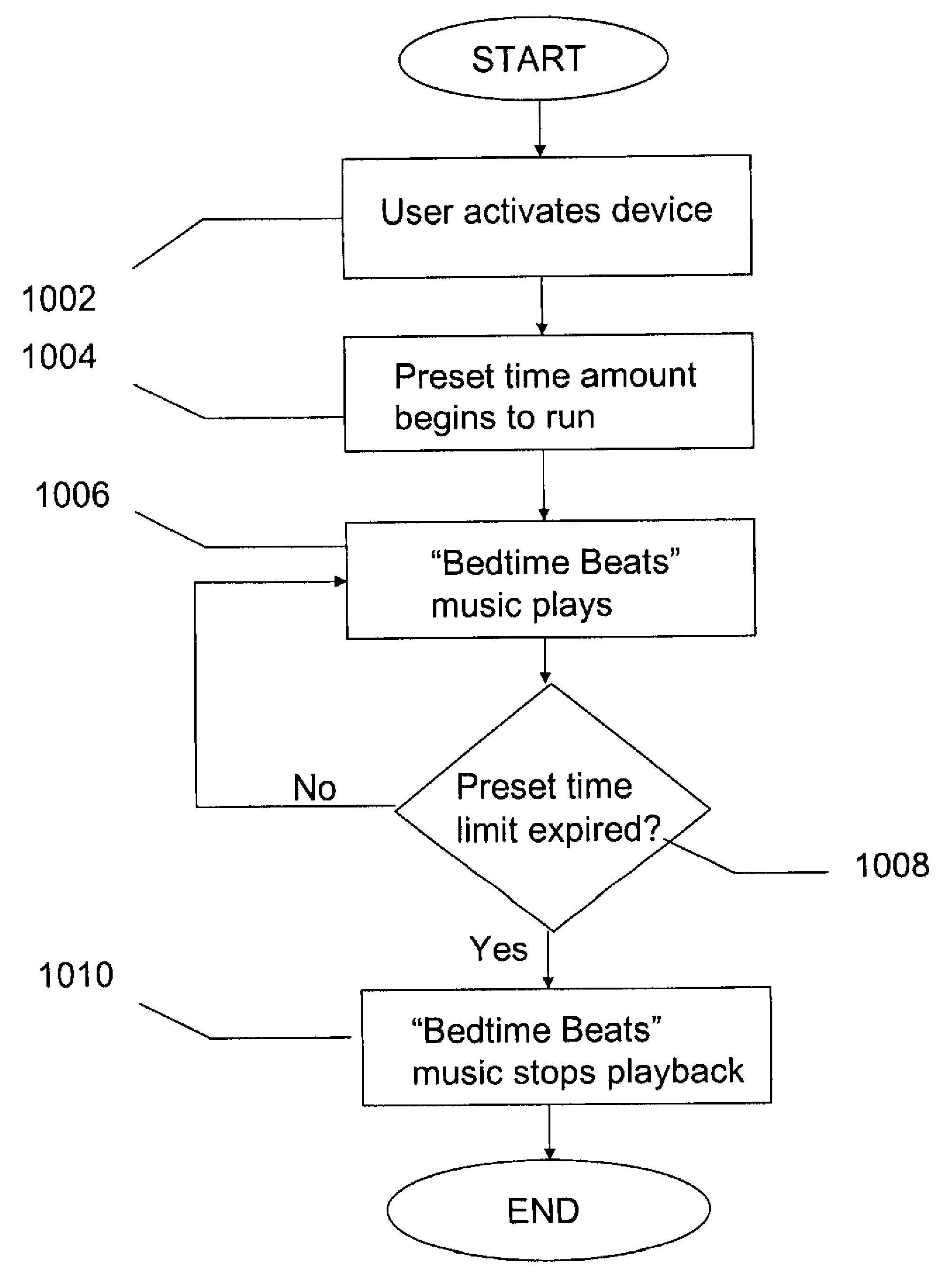
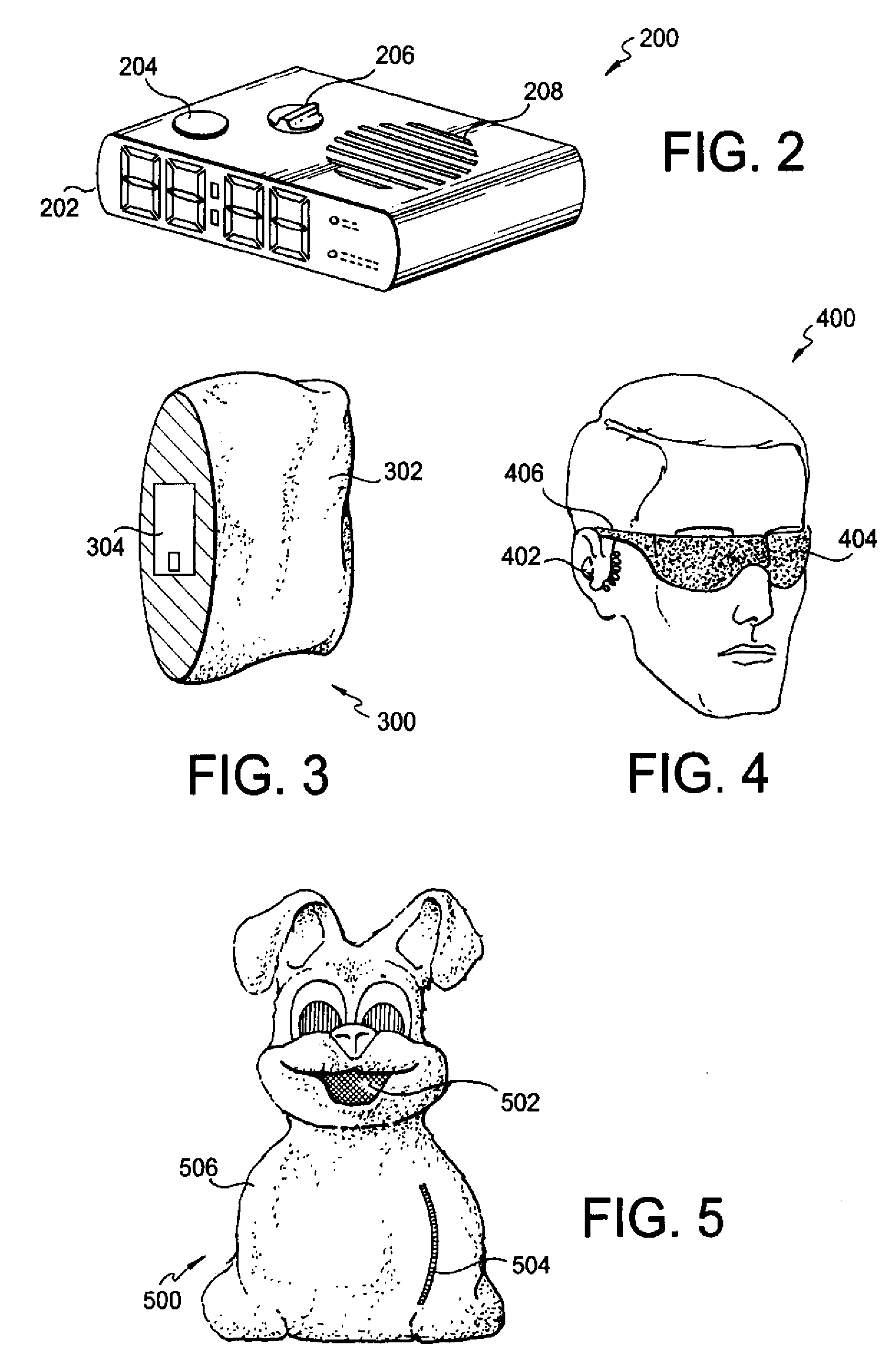
A device for inducing better sleep embedded with music having a tempo of about sixty to about eighty beats-per-minute. Listening to music with a tempo of approximately 60 to approximately 80 beats-per-minute results in significantly better sleep quality, better perceived sleep quality, longer sleep duration and greater sleep efficiency. Embodiments of the device can include, among other things, an alarm clock, a pillow, mobile, sleep mask, crib or a stuffed toy for use with children. Embodiments of the device including a travel clock, travel pillow, or mobile device allowing the device to be easily transported for purposes of inducing better sleep during travel are also contemplated.
Owner:SMASHARTS
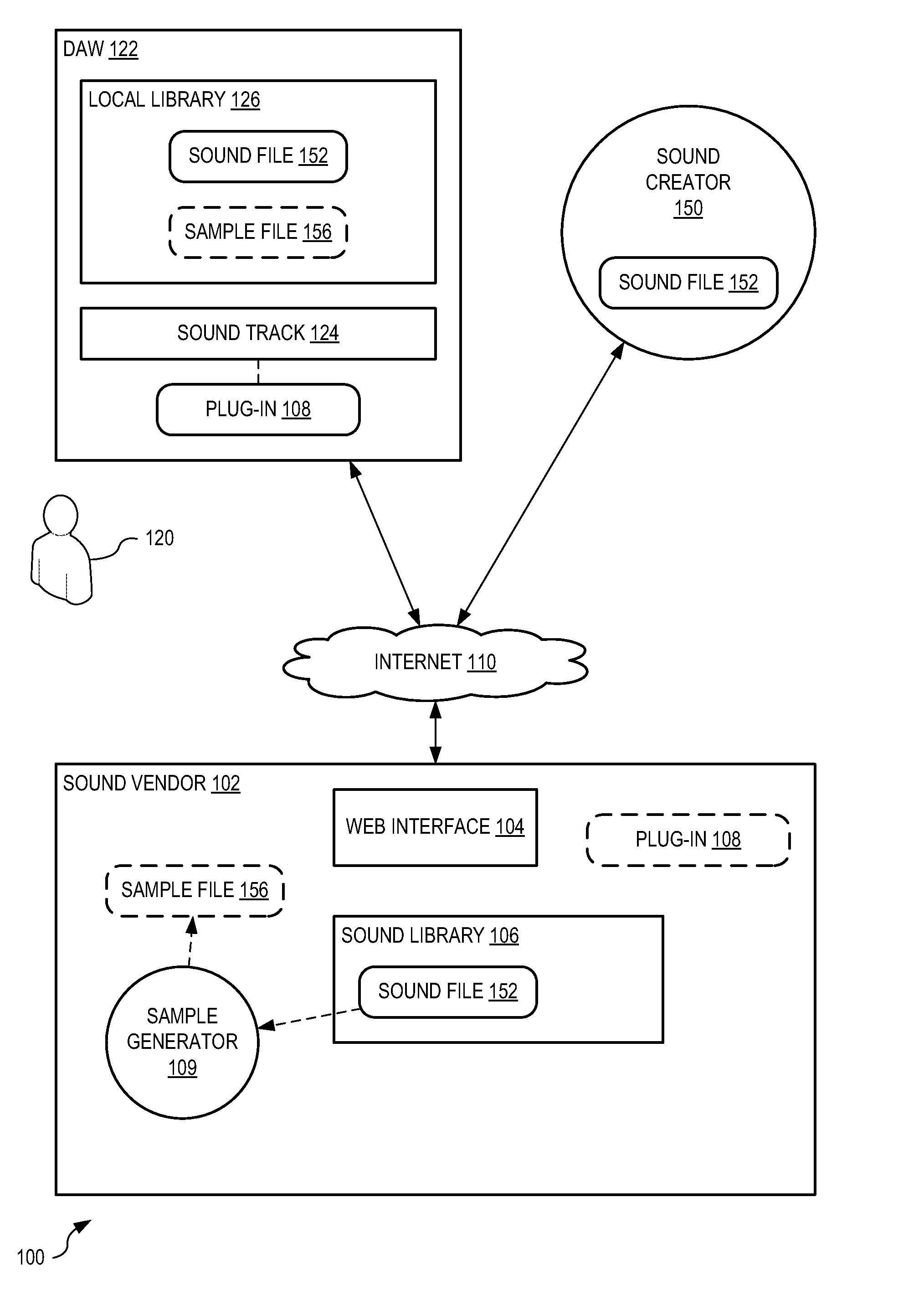
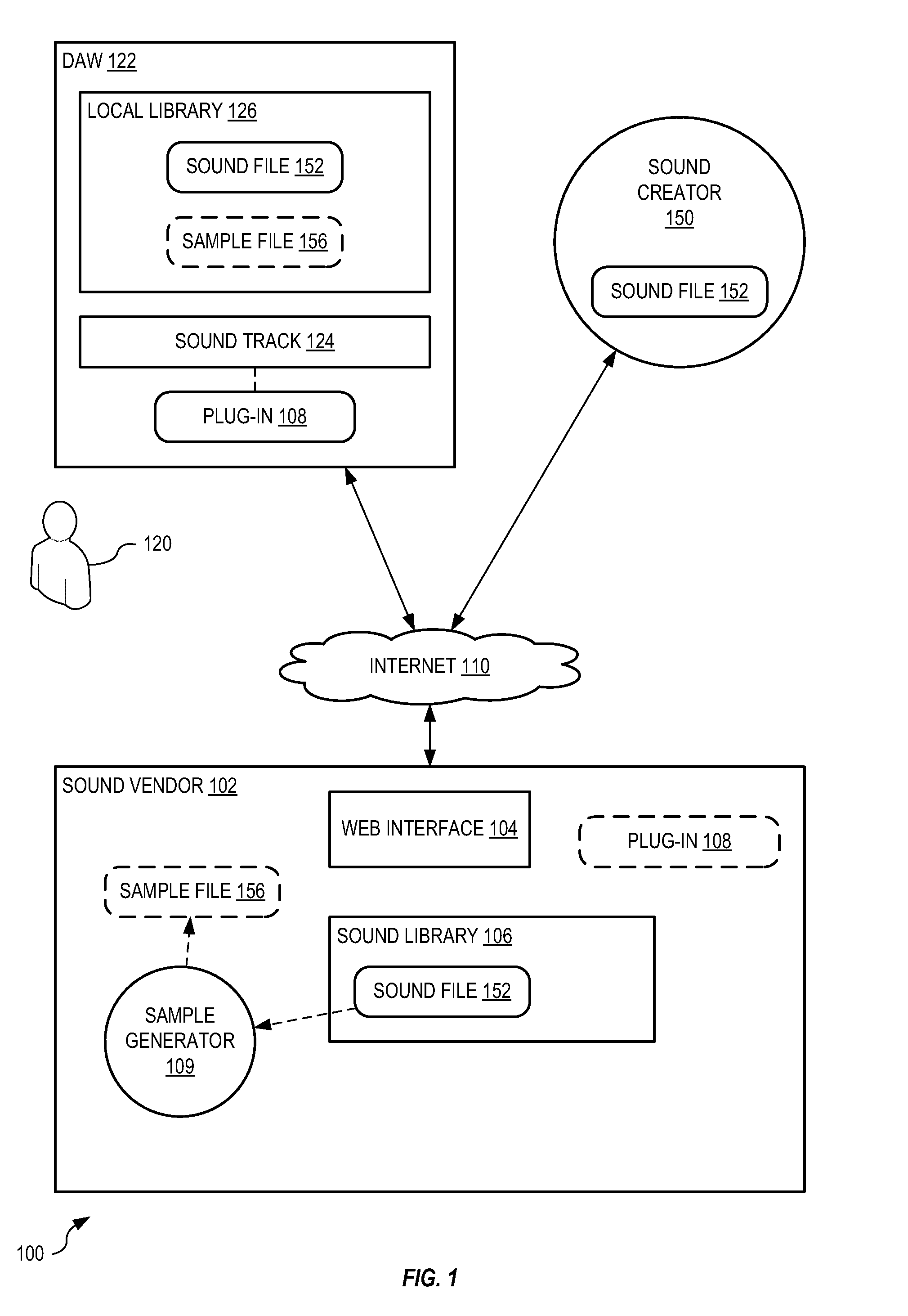
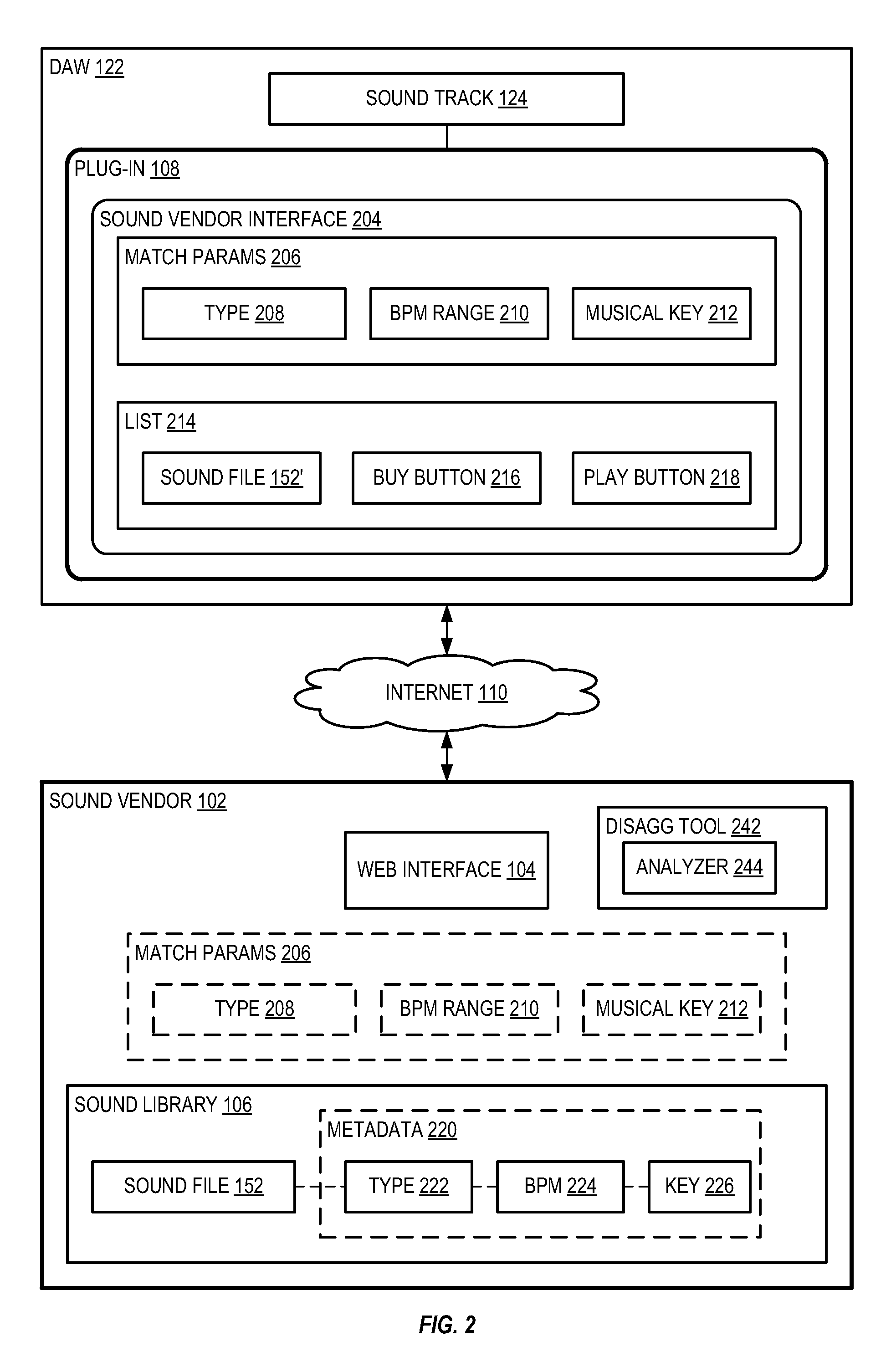
Systems and methods for selling sounds
Systems and methods sell a sound file to a user of a digital audio workstation (DAW). A sound vendor receives the sound file from a sound creator and analyzes the sound file to automatically determine a beats-per-minute value and a musical key value. The sound file is stored, in association with the beats-per-minute value and the musical key value, within a database of the sound vendor. A web interface is generated to interact with the user to receive a search request defining at least one of the beats-per-minute value and the musical key value. The sound file is selected from the database based upon the search request, a financial agreement between the user and the sound creator is completed for sale of the sound file to the user, and the sound file is sent to the DAW.
Method and system for identifying and displaying groups of cardiac arrhythmic episodes
InactiveUS20050107840A1Rapid assessmentQuickly interpretHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringDisplay deviceInteractive displays
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Musical Composition System
Owner:SULLIVAN DANIEL +5
System and method for aligning and mixing songs of arbitrary genres
InactiveUS7081582B2Reduce computational overheadIncrease rangeElectrophonic musical instrumentsFrame basedTime shifting
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
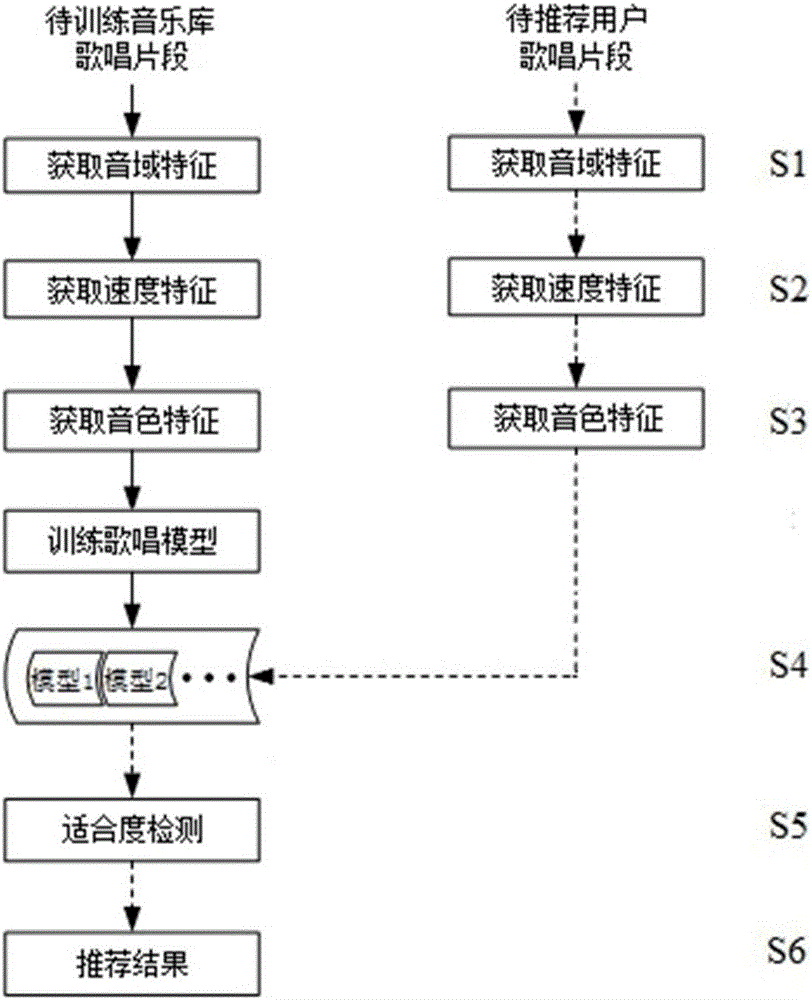
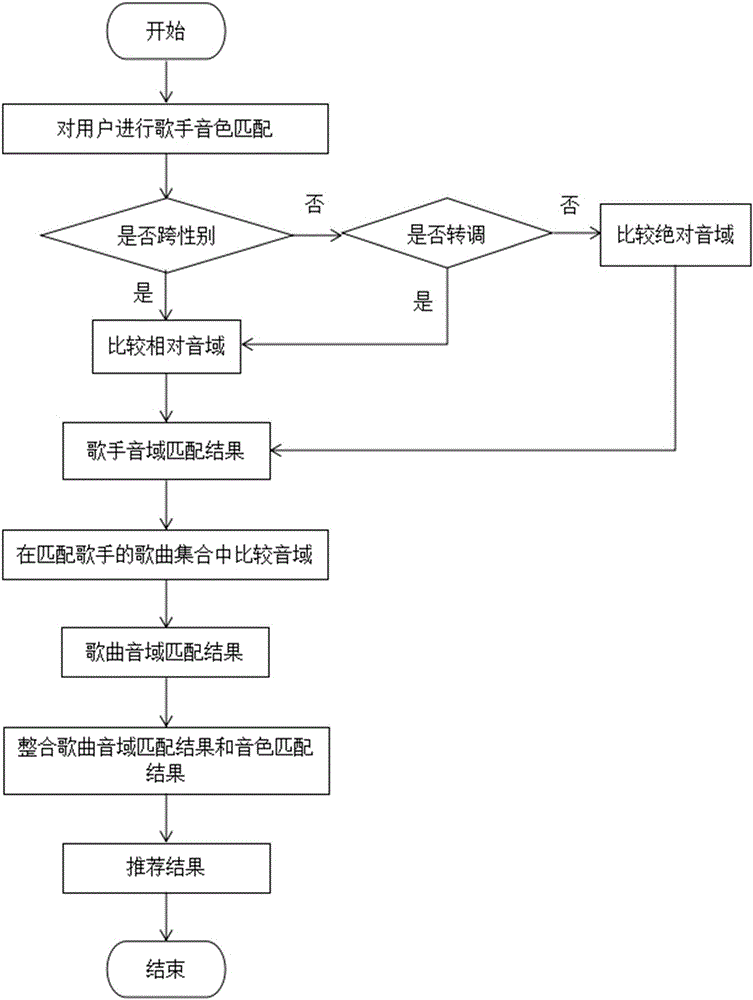
Individualized song recommending system based on vocal music characteristics
ActiveCN106095925AVerify accuracyVerify feasibilitySpecial data processing applicationsMel-frequency cepstrumPersonalization
The embodiment of the invention discloses an individualized song recommending system based on vocal music characteristics. The method includes the following steps of extracting characteristics, wherein the voice register characteristics, speed characteristics and tone characteristics of singing data are extracted, the voice register characteristics include absolute voice register and relative voice register, the speed characteristics include the number of beats per minute, and the tone characteristics include a Gaussian mixture model of Mel frequency cepstrum coefficient training; recommending songs systematically, wherein a corresponding song in a music library is found through a key sound matching algorithm according to a snatch sung by a user, and voice register conformity detection, song conformity detection and singer conformity detection are conducted. Singer recommending and song recommending are conducted according to extracted user characteristics. By means of the method, whether a current song is suitable for being sung by the user or not can be evaluated, and singers matched with the user vocal music ability and songs suitable for being sung by the user are further recommended. From the perspective of user singing, the traditional music recommending range is expanded, and higher practical value is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
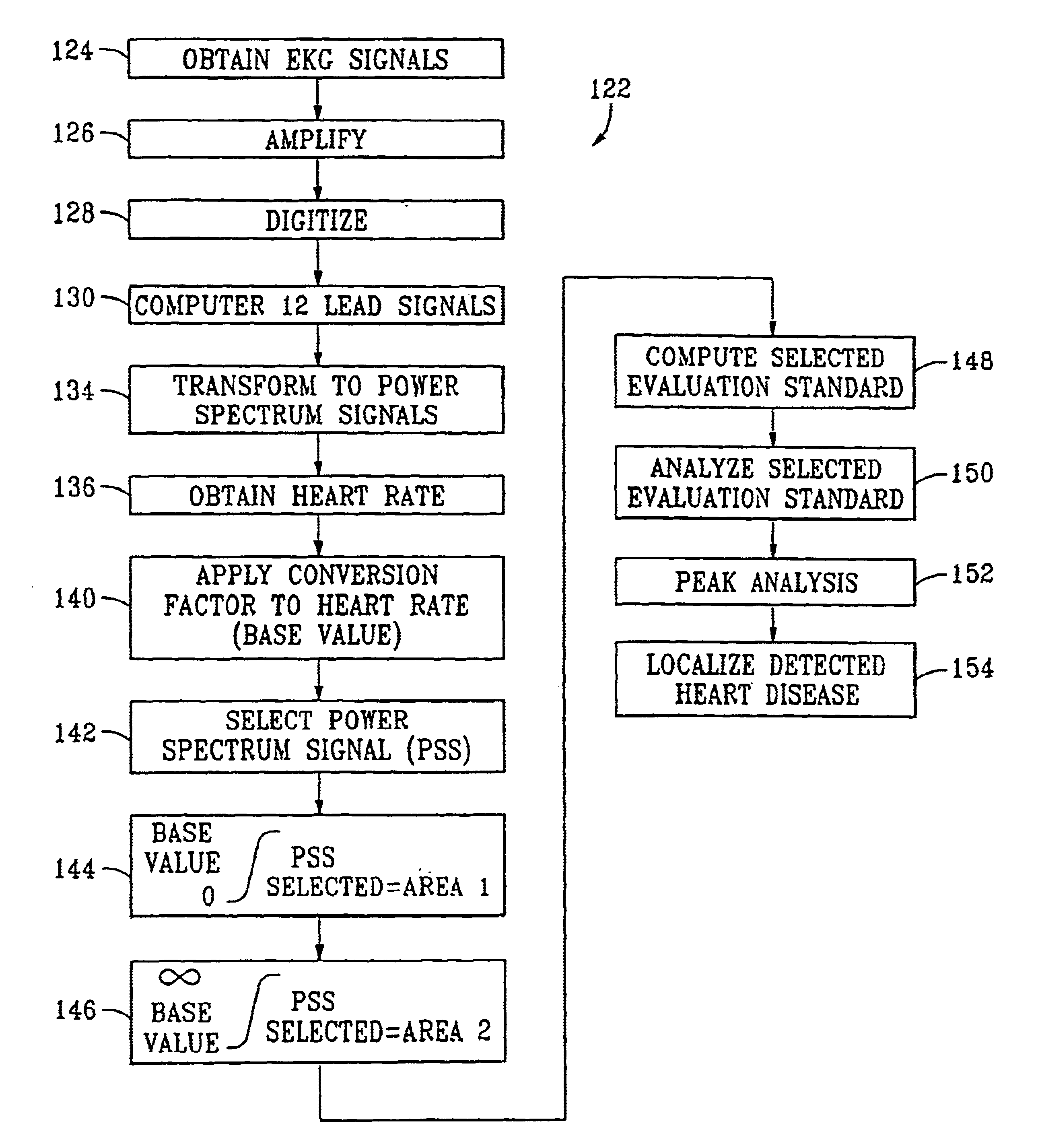
System and method for detecting and locating heart disease
Owner:FANG & QUN +1
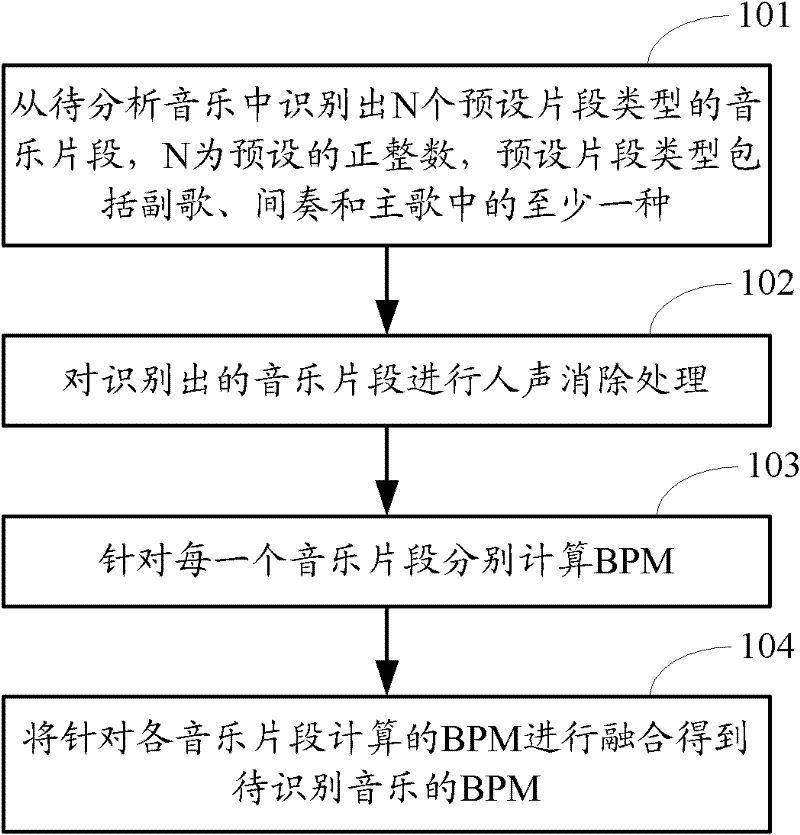
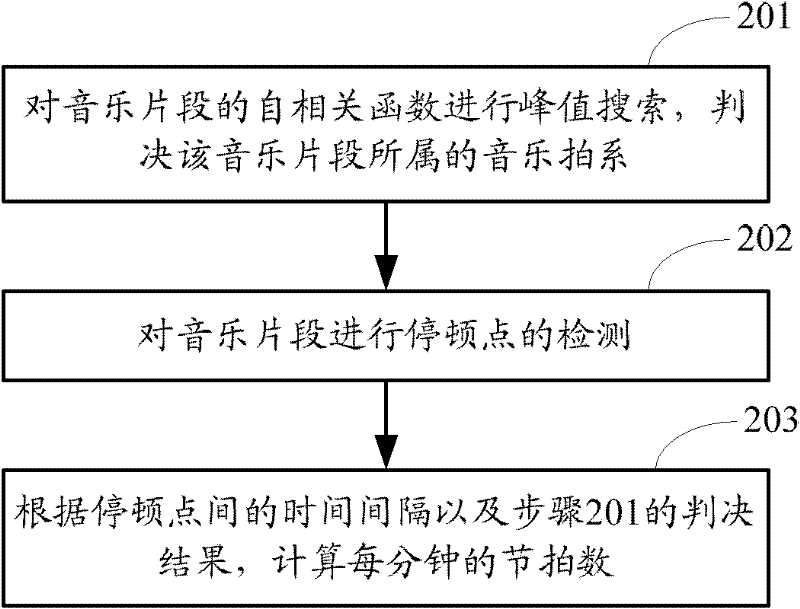
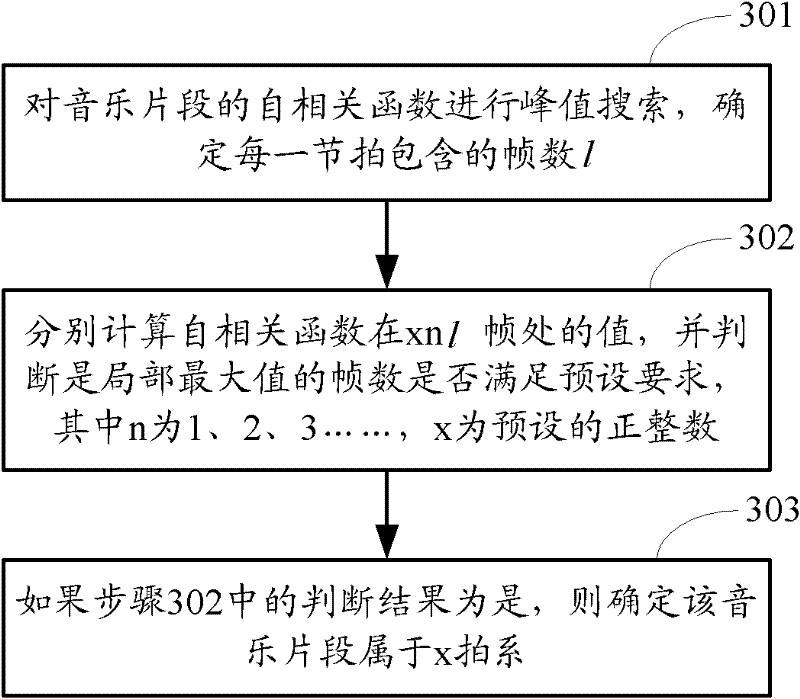
Method and device for analyzing music BPM (Beat Per Minutes)
ActiveCN102568454AImprove accuracyElectrophonic musical instrumentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
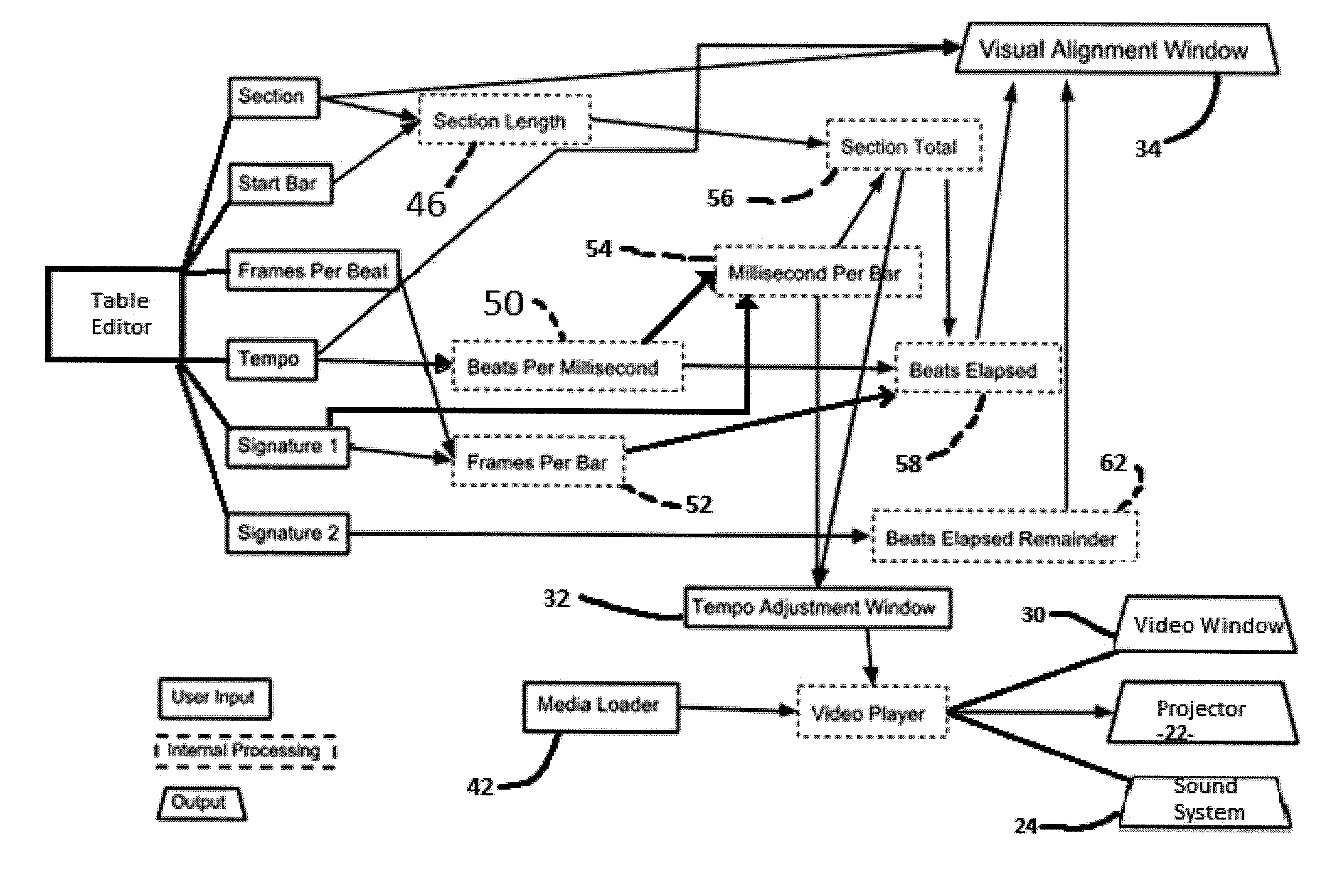
Method and Apparatus for Producing Full Synchronization of a Digital File with a Live Event
InactiveUS20140372891A1Carrier indexing/addressing/timing/synchronisingSelective content distributionEvent synchronizationUnits of measurement
A method and apparatus are provided for producing full synchronization of a digital file with a live event. Using time-based cues such as musical beats, the live event is time mapped. The video file to be synced is measured in frames per second is then translated from its frames per second original time code into the time code of the live event in beats per minute making it possible to measure the playback rate of the source media file in the same units of measurement as the live event. The result is a playback mechanism that allows for more precise real time playback rate corrections by an operator by providing a visible cue so they can better keep the source media synced with the live event, even if there are real time tempo variations in the live event.
Owner:ION CONCERT MEDIA
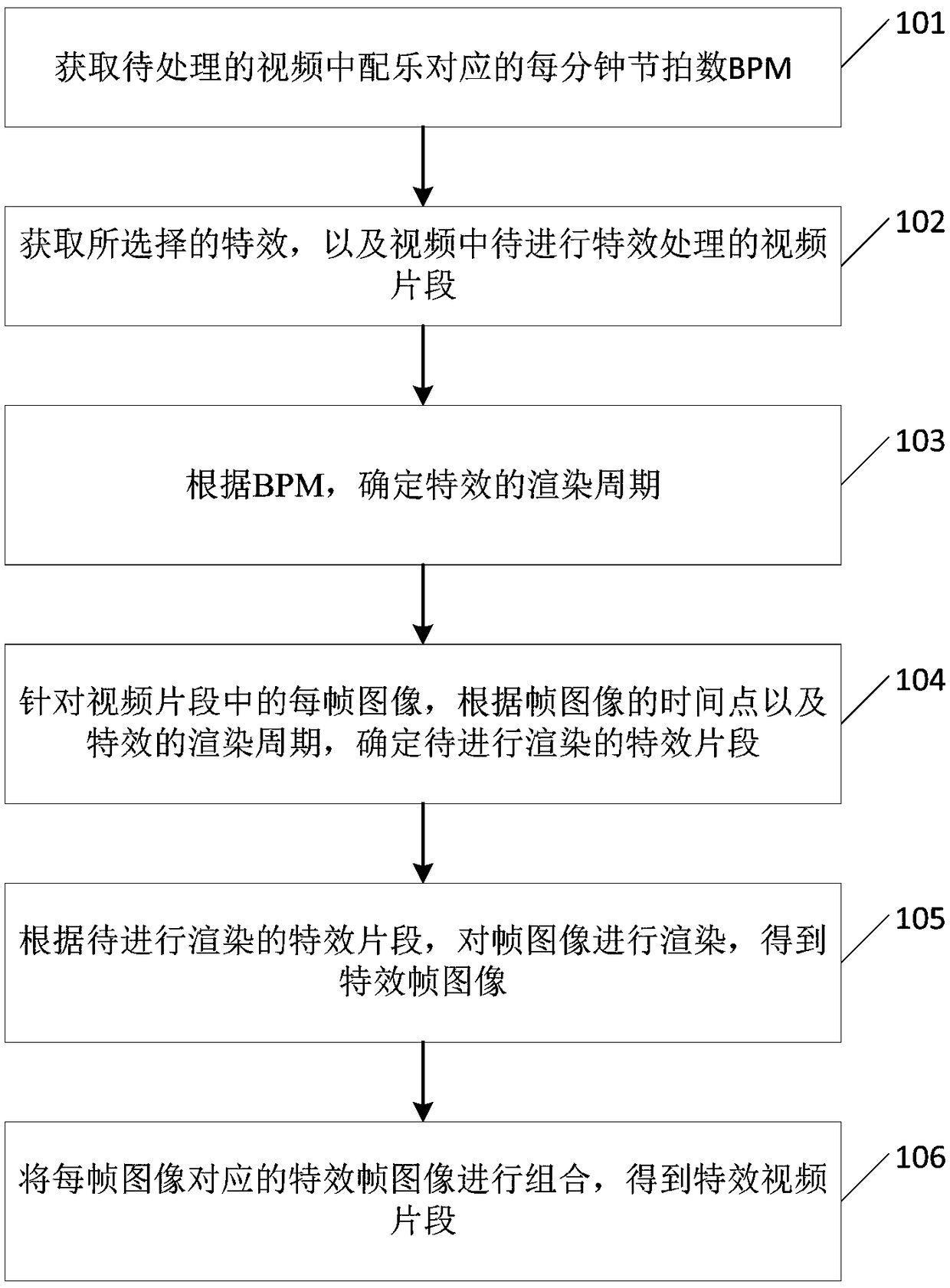
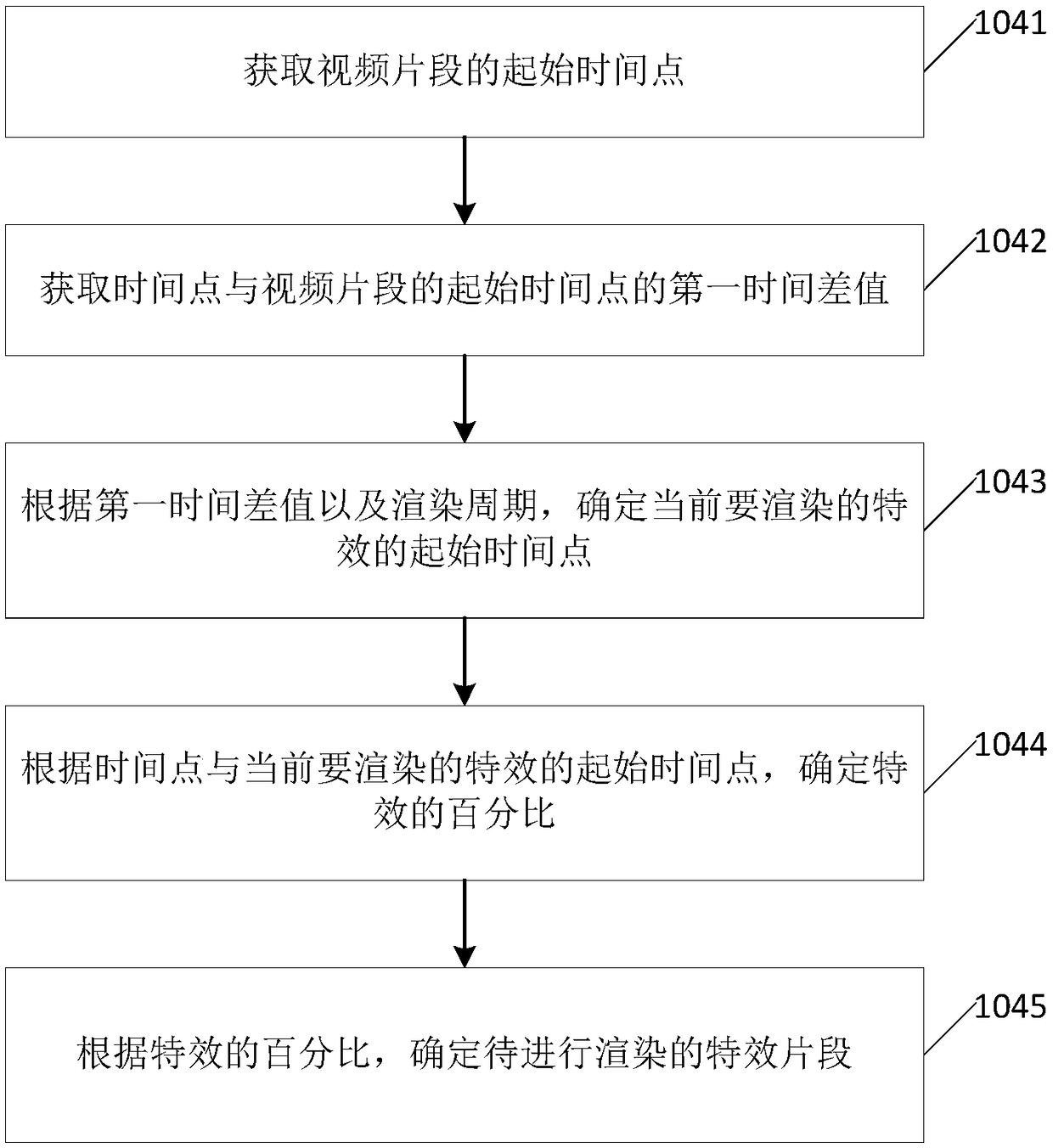
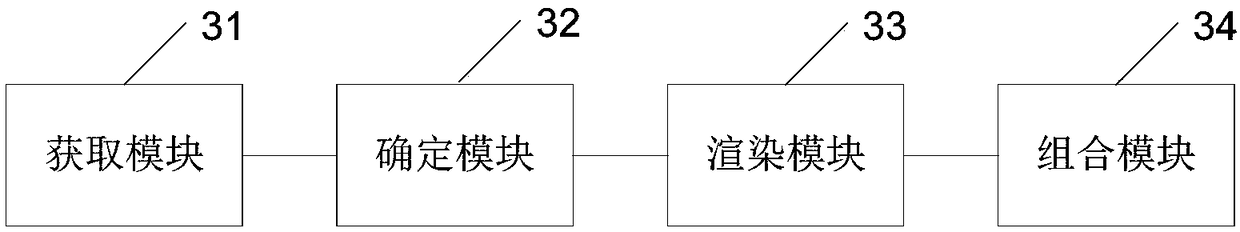
Video special effect processing method and device
ActiveCN108810597AImprove the effect of special effects processingAchieve consistencySelective content distributionComputer graphics (images)Special effects
The present invention provides a video special effect processing method and device, wherein the method comprises the following steps: acquiring beats per minute BPM corresponding to a background musicin a video to be processed; acquiring a selected special effect, and a video segment to be subjected to special effect processing in the video; determining a rendering period of the special effect according to the BPM; for each frame image in the video segment, determining the special effect segment to be rendered according to the time point of the frame image and the rendering cycle of the special effect; rendering the frame image according to the special effect segment to be rendered, and obtaining a special effect frame image; combining the special effect frame image corresponding to eachframe image to obtain a special effect video segment, thereby achieving the consistency between the special effect and the beats of the background music, ensuring the harmony between the special effect and the background music, and improving the special effect processing effect of the video.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Medical Devices and Techniques for Rodent and Small Mammalian Based Research
InactiveUS20120022351A1Promote resultsReduce the effective areaBioelectric signal measurementPerson identificationSmall animalHigh heart rate
A method and system of supplying rodents, such as mice, to medical researchers pre-installs and / or embeds physiologic sensors onto or within the rodents prior to selling the modified rodents to the researchers. The specialty skills, such as small animal surgical and anesthesia skills and sensor placement and testing, are centralized in one organization rather than being spread about a collection of researchers. The subjects with preinstalled, pre-tested hardware, are sold to the researcher as needed. Communication hardware and software will be supplied for the user to convert their desktop computer into a wireless monitoring station. Additionally an external pulse oximeter for small rodents, such as mice, provides measurements on a hand or foot of the rodent with a sensor configured to avoid shunting around the rodent appendage, and configured for high heart rates (200-900 beats per minutes) of the subjects.
Owner:STARR LIFE SCI
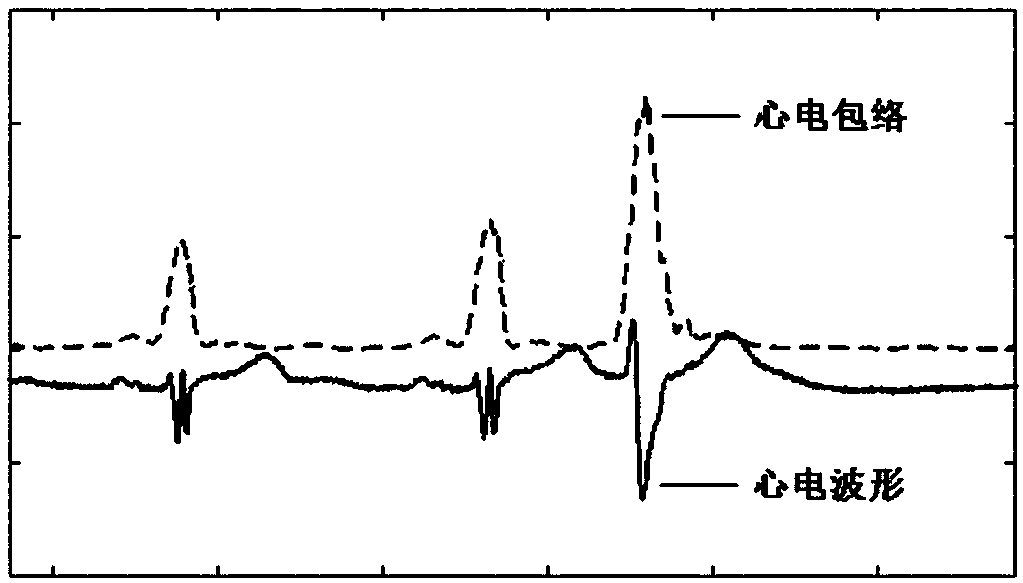
Method for detecting electrocardiogram QRS wave group and electrocardiogram analysis method thereof
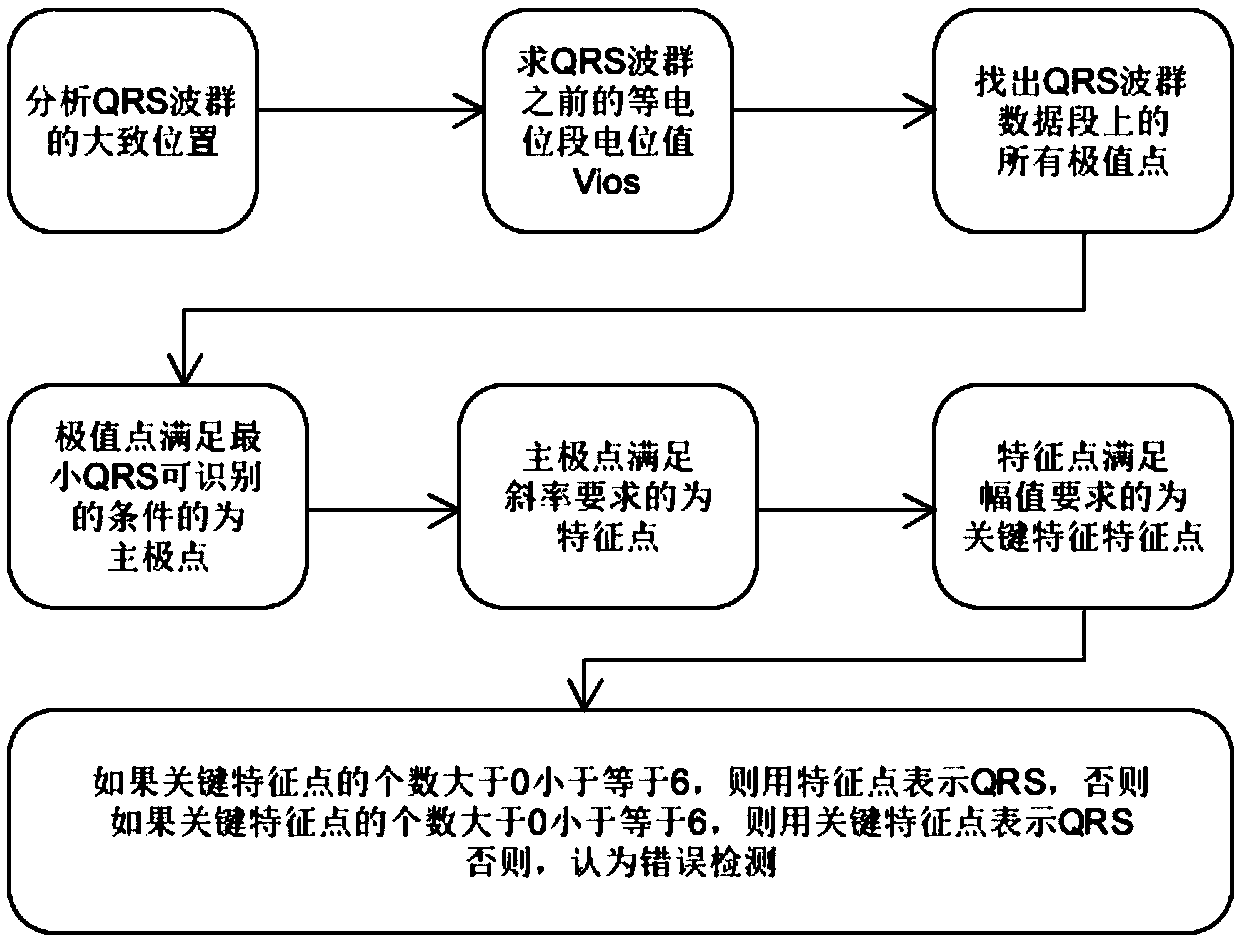
ActiveCN108814590AImprove accuracyAccurately outline the morphological featuresDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRR intervalElectrocardiogram analysis
The invention discloses a method for detecting an electrocardiogram QRS wave group. The method comprises the steps of using an extremum method to find peaks and troughs in a QRS wave, according to anextremum point found, and combining an equipotential step potential value and amplitude information to detect each sub-waveform in the QRS wave group so as to determine the time position of the QRS wave group so that QRS wave group forms can be clearly displayed and the heart rate can be calculated; the accurate detection of the QRS wave group is the basis for the automatic diagnosis of an electrocardiogram. After the detection of the QRS wave group is determined, it is possible to calculate the heart rate, that is, the number of heart beats per minute, heart rate variability and other electrocardiogram time interval measurement and amplitude measurement.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAKANG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
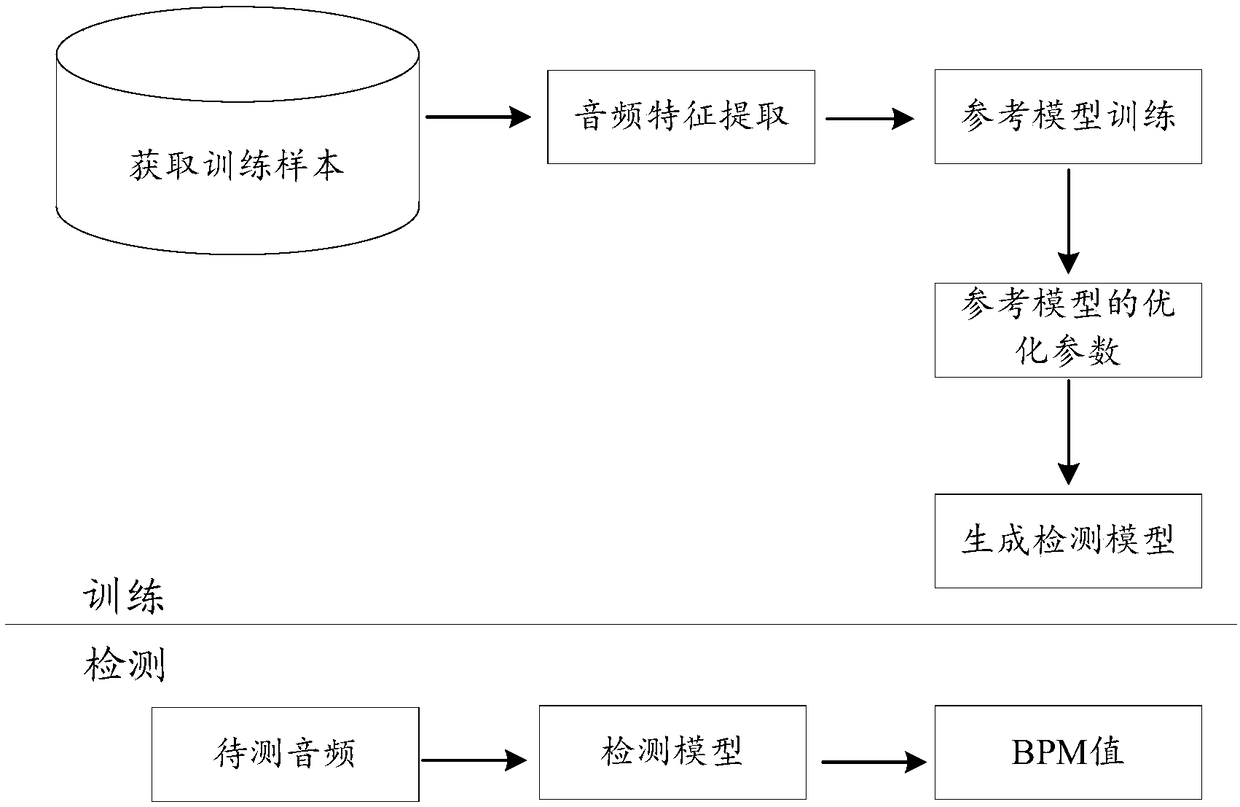
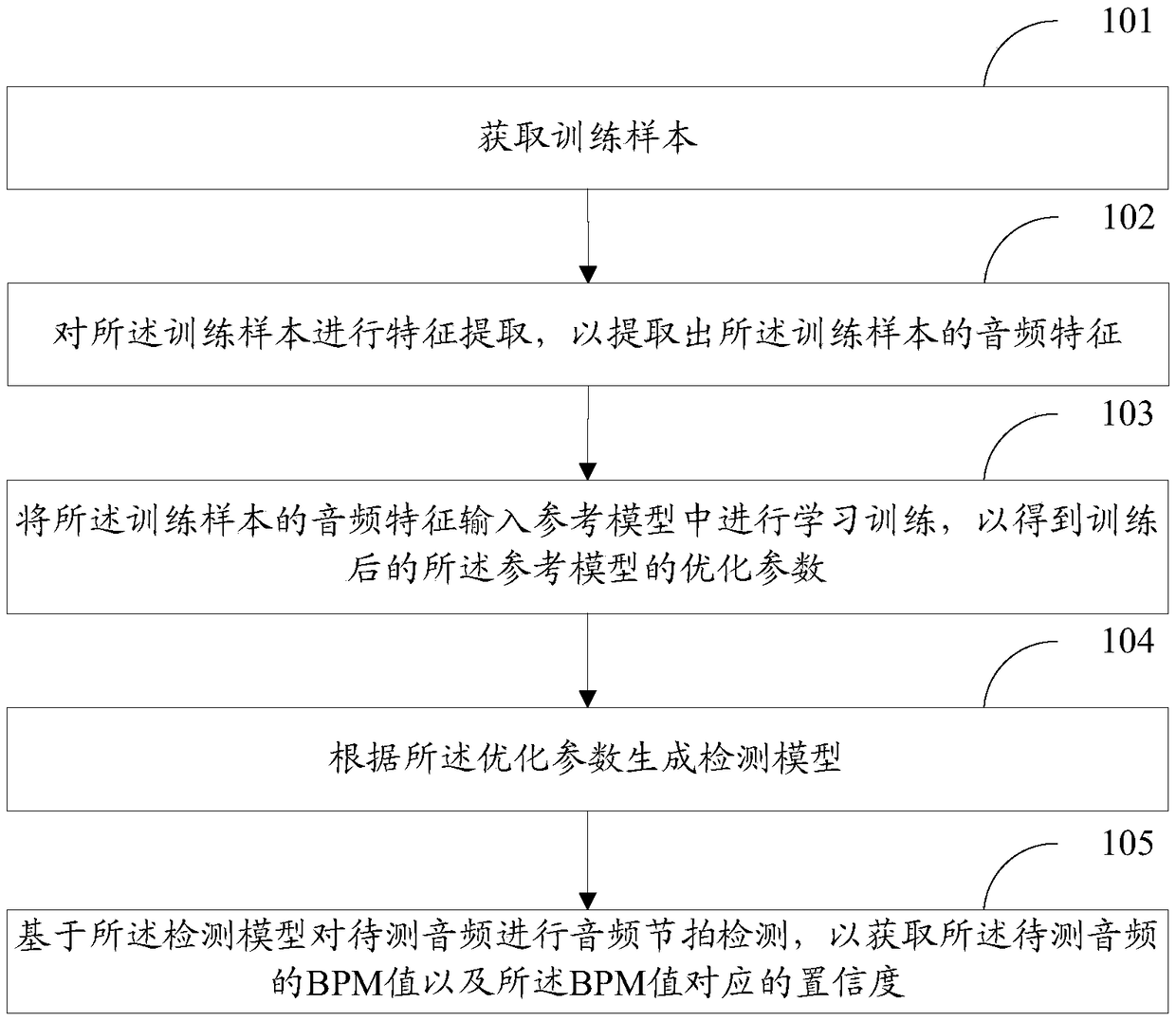
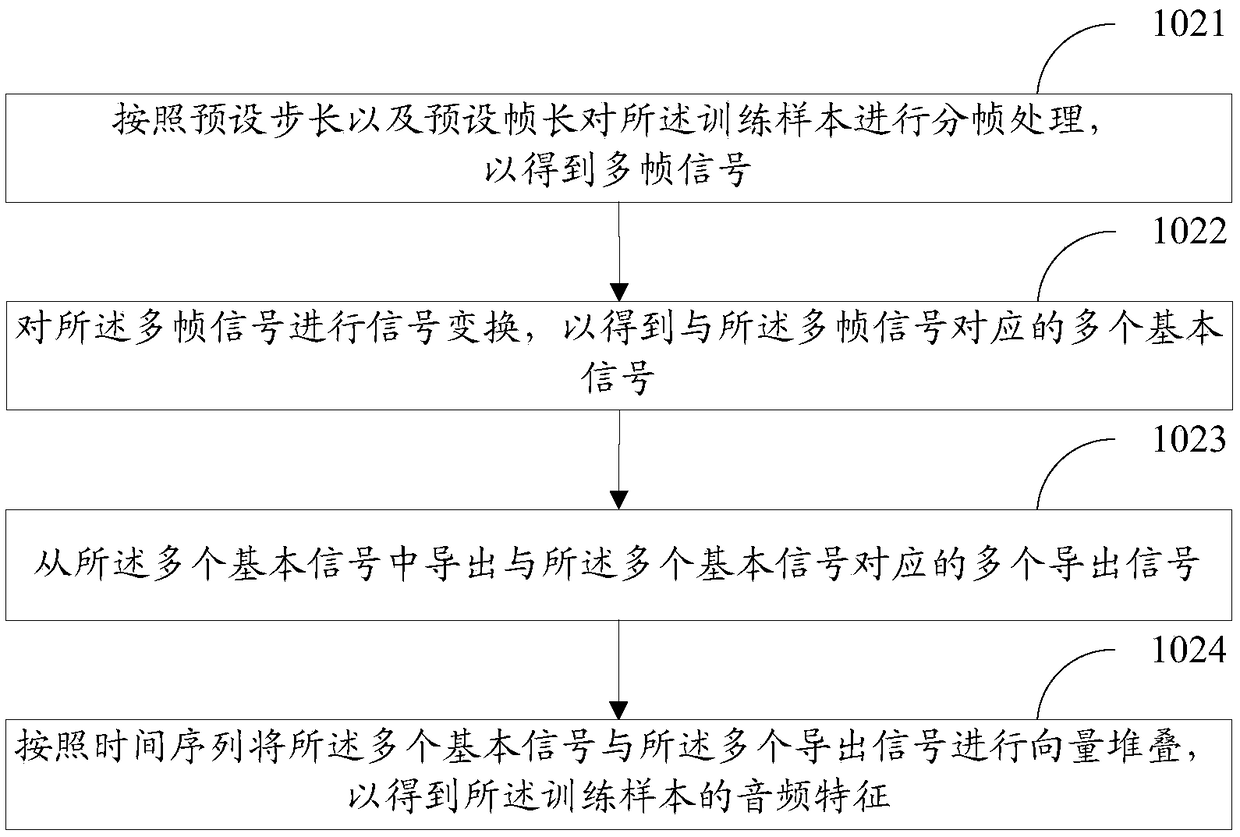
Audio beat detection method and device and storage medium
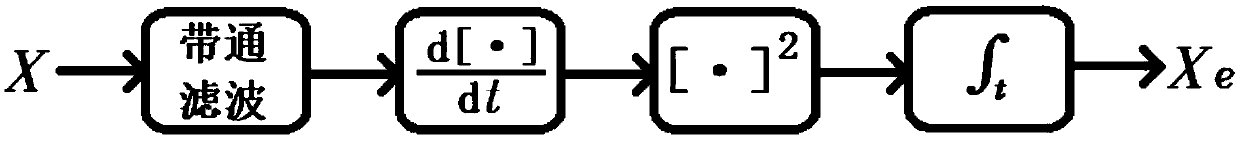
ActiveCN109256147AImprove accuracyReduce running timeElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisReference modelFeature extraction
The invention discloses an audio beat detection method and device and a storage medium. The audio beat method comprises the following steps that a training sample is obtained, characteristic extracting is carried out on the training sample to extract audio characteristics of the training sample, the audio characteristics of the training sample is input into a reference model for learning and training to obtain optimized parameters of the reference model after training, and a detection model is generated according to the optimized parameters; and then, audio beat detection is carried out on audio to be detected based on the detection model to obtain a beat per minute (BPM) value of the audio to be detected and confidence corresponding to the BPM value, so that the accuracy of audio beat detection is improved, and the running time in the detection process is shortened.
Owner:TENCENT MUSIC ENTERTAINMENT TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD
Device and method for rhythm training
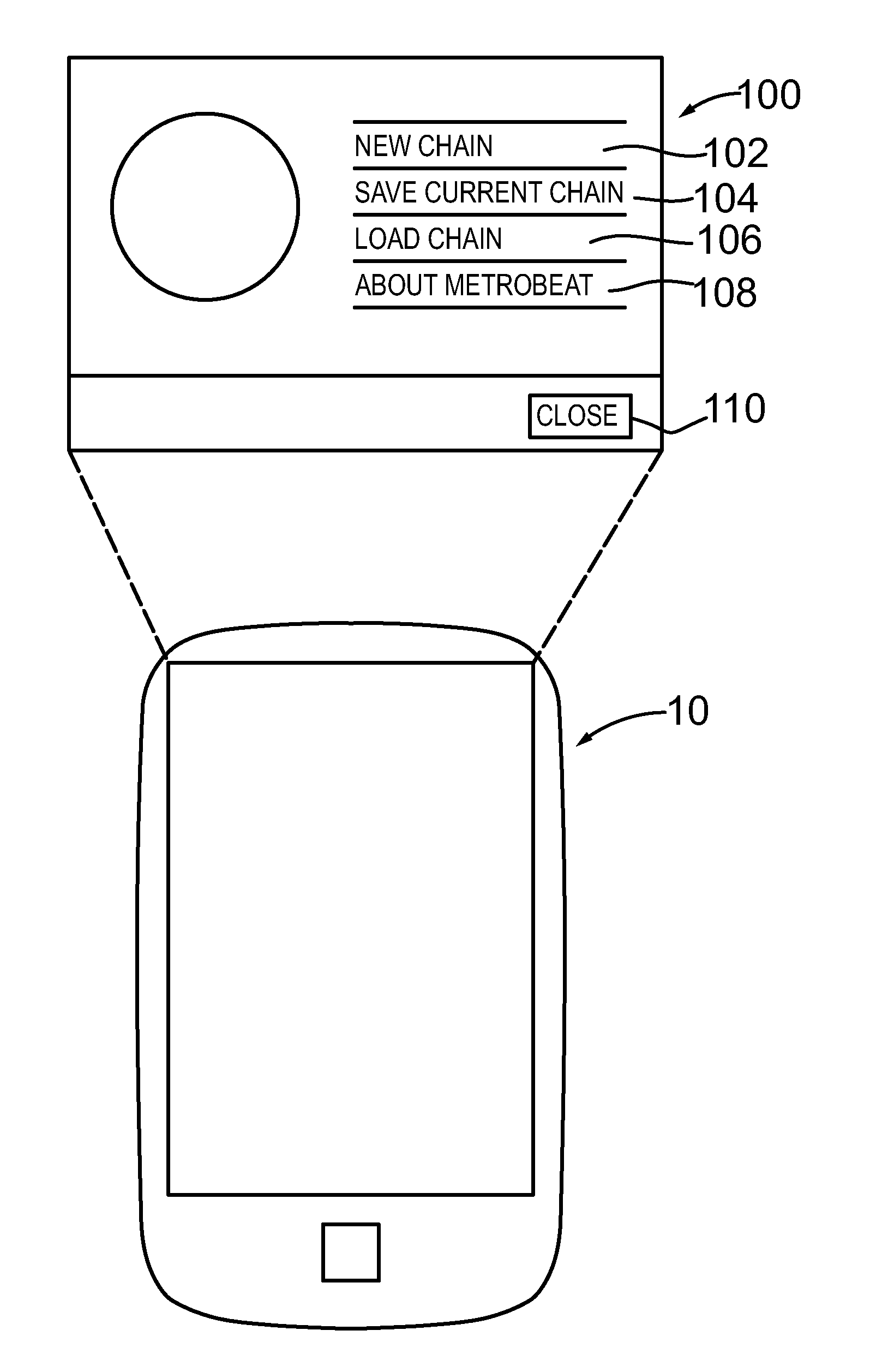
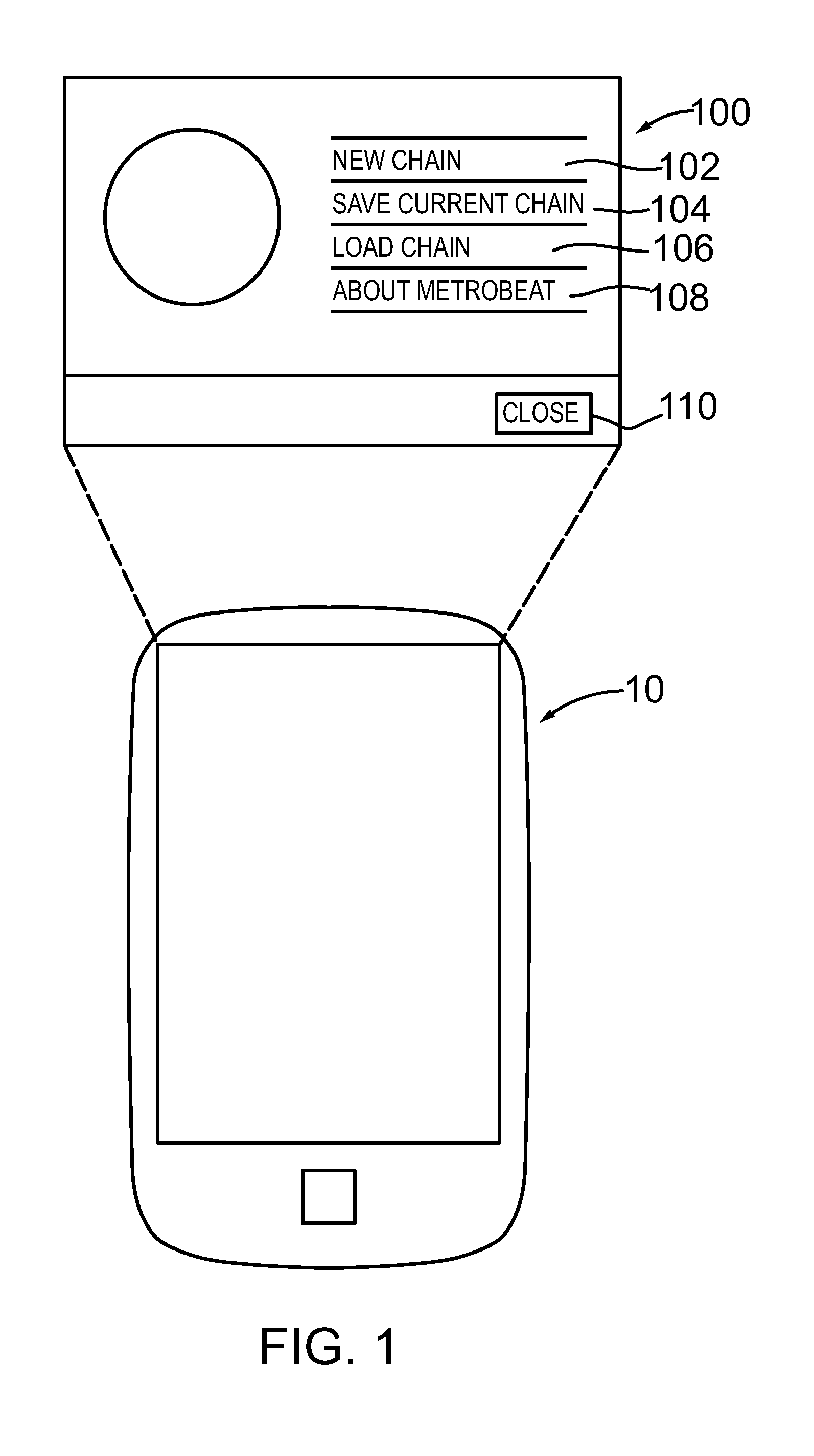
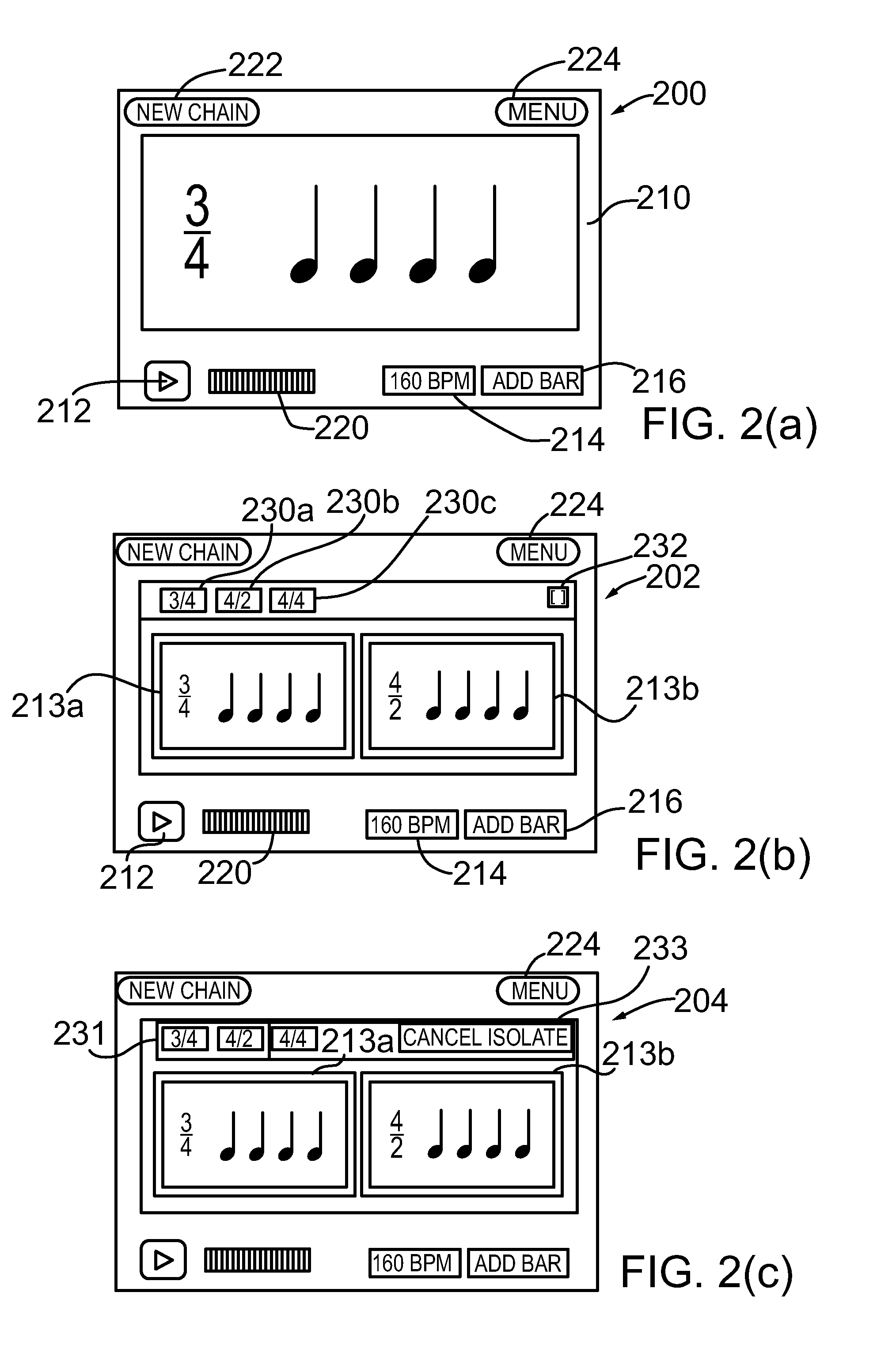
A programmable rhythm trainer configured to operate on a general purpose computing device including a handheld computing device or a mobile communication device. According to an embodiment, the programmable rhythm trainer comprises a component configured to generate a mix or chain comprising one or more bars and each the bars comprising one or more note arrangements. According to an embodiment, the programmable rhythm trainer comprises a component configured to rearrange one or more of the bars in the chain and save the rearranged chain to memory. According to an embodiment, the programmable rhythm trainer comprises a component configured to rearrange one or more of the note arrangements belonging to one of the bars. According to an embodiment, the programmable rhythm trainer comprises a component configured to set a beats-per-minute for one or more the chains in response to a user input. According to an embodiment, the programmable rhythm trainer comprises a graphical user interface and input for manipulating one or more of the notes, the note arrangements, the bars and / or the chains or mixes. According to an embodiment, the programmable rhythm trainer comprises an application or software program configured to run on computing device. According to another embodiment, the programmable rhythm trainer comprises a portable or handheld device.
Owner:SHONIKER ANDY
System for calculating the tempo of music
ActiveUS8952233B1Promote lowerReduce decreaseElectrophonic musical instrumentsAnimationDisplay device
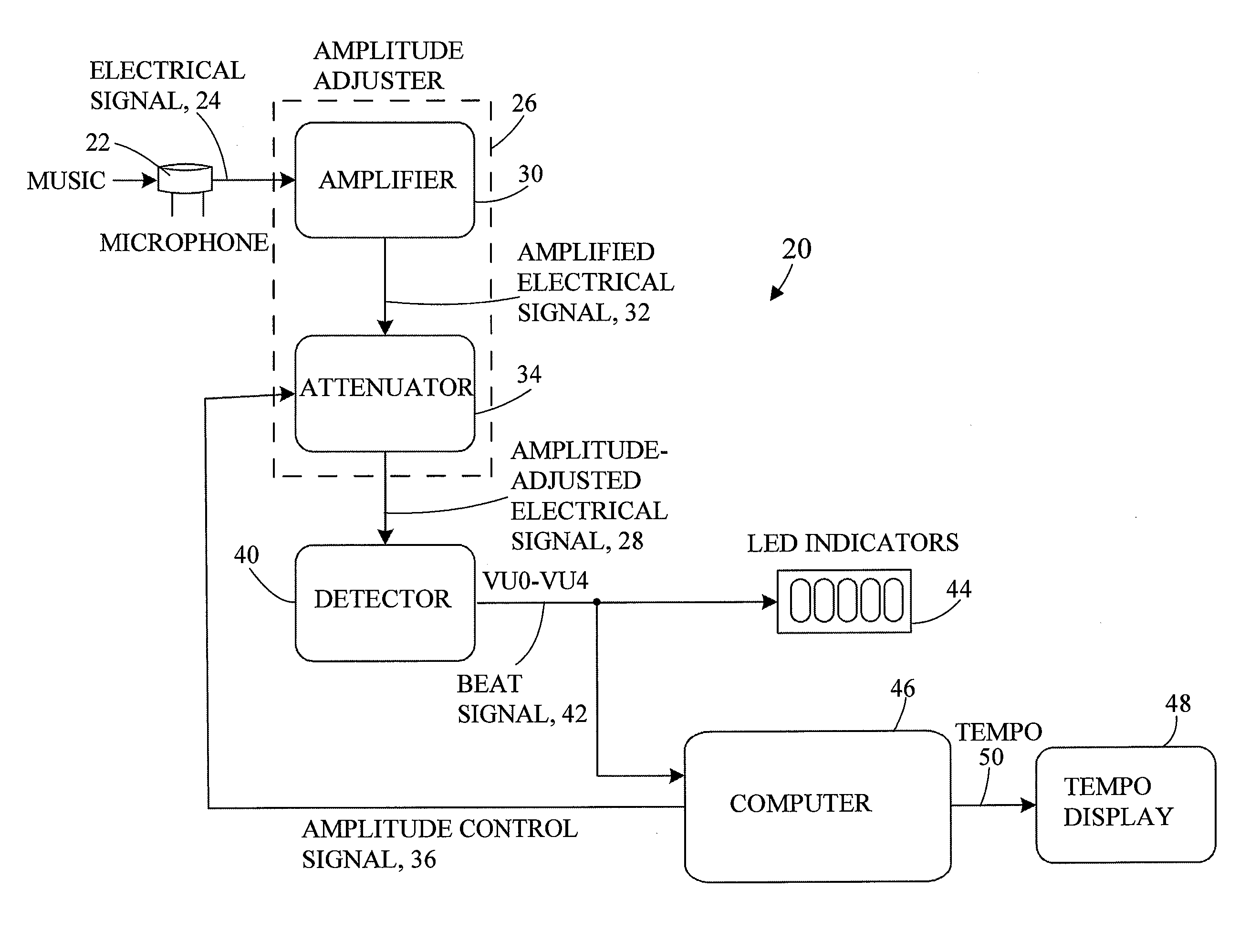
A music tempo calculation system uses a microphone to input ambient music; the input is then processed in real time to display beats per minute (BPM). Input from the microphone is decomposed by a detector into a plurality of digital signals ranging from a most sensitive signal to a least sensitive signal. A software-implemented algorithm is applied to the time between peak music values to determine tempo. BPM is then output to a display to provide feedback to performing musicians regarding tempo. The sensitivity of the detector adjusts automatically to compensate for changes in music volume. In another embodiment, the calculated tempo is used to control motors used to animate toys. Once BPM is known, the moment of an upcoming beat can be anticipated. It then becomes possible to start, stop, and reverse directions of a motor in anticipation of an upcoming beat thereby providing the appearance the animated toy is responding to music beat.
Owner:CLEVX
System and method for detecting and locating heart disease
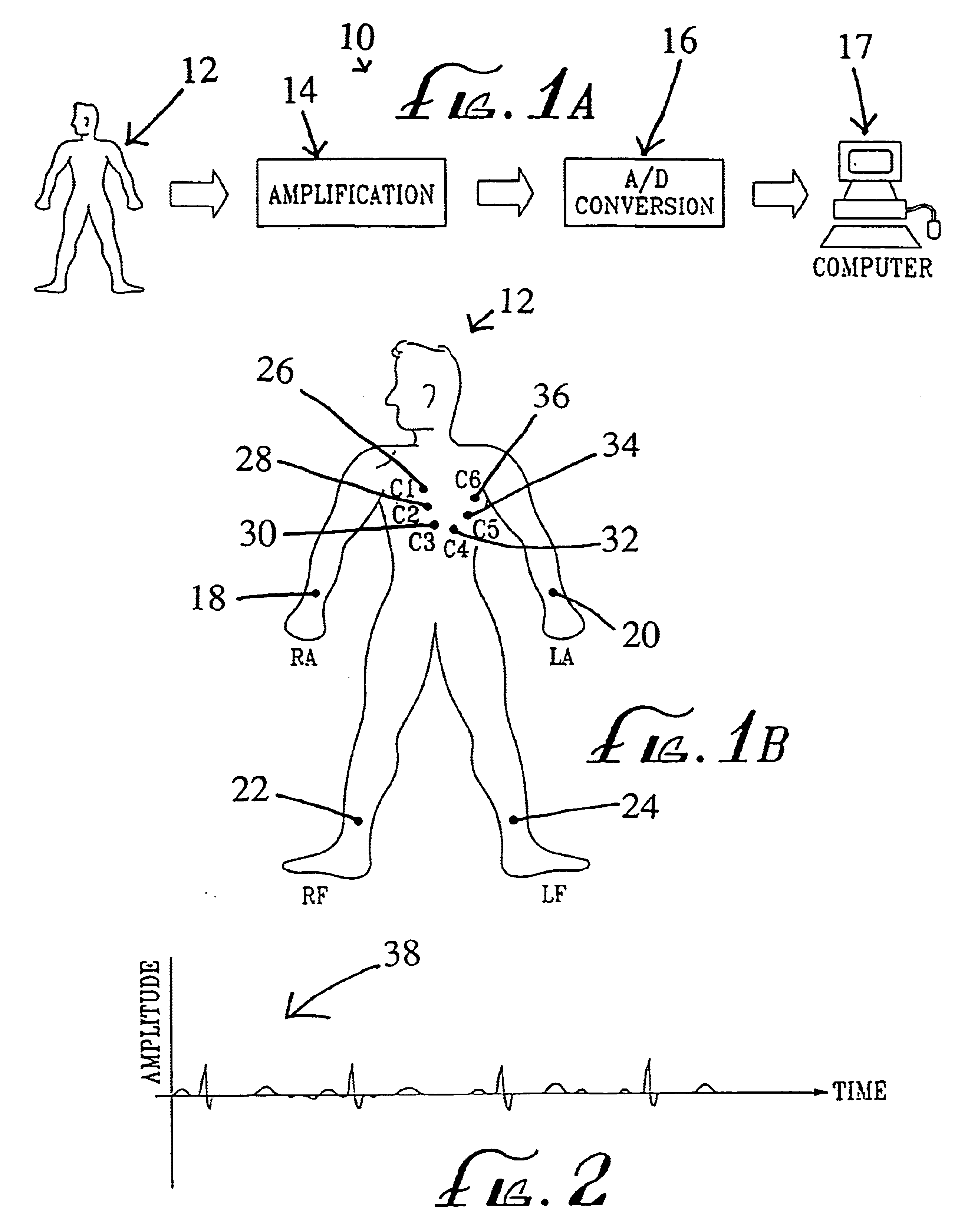
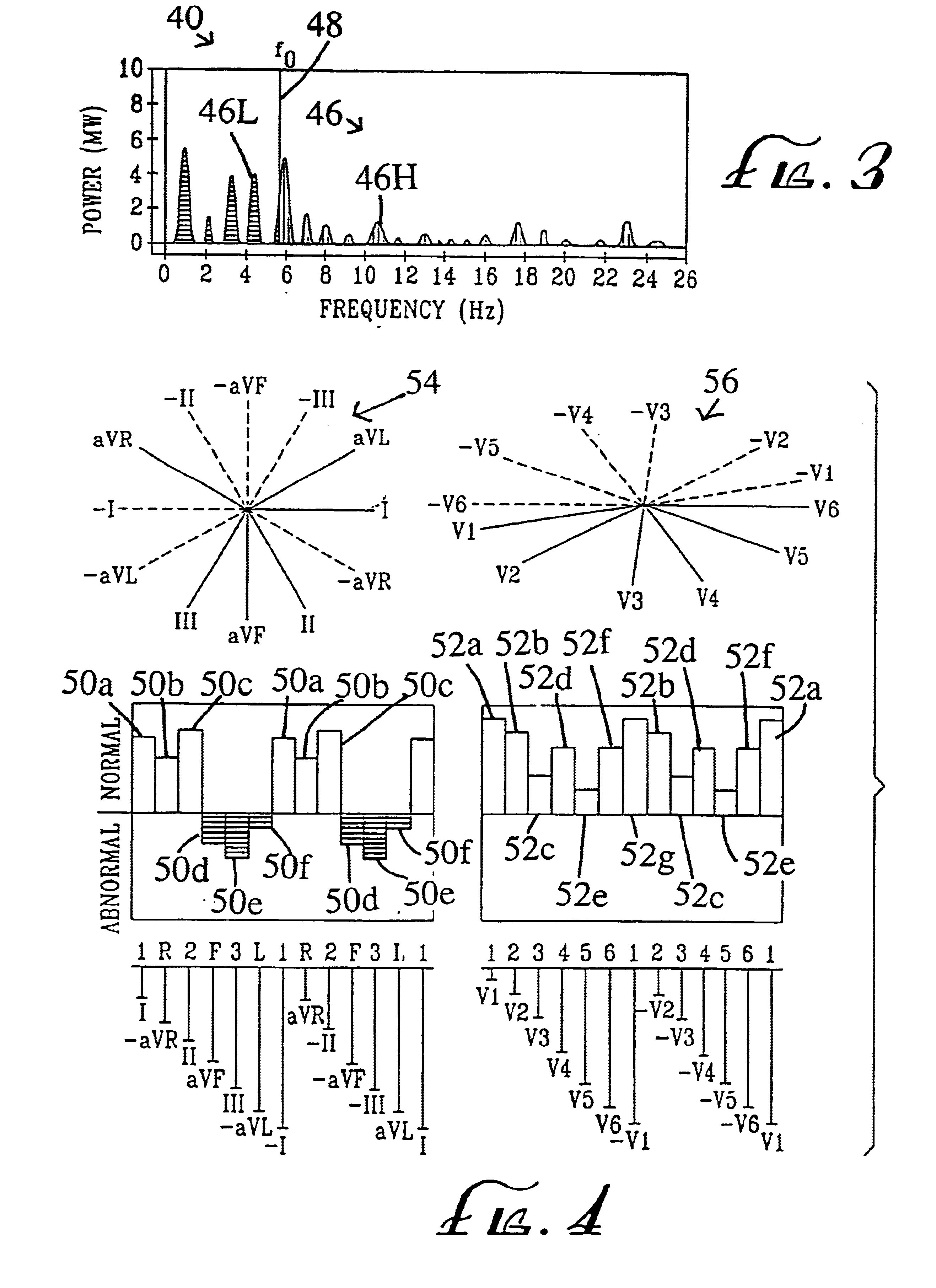
A method is delineated for detecting and locating coronary artery and heart disease comprising the steps of obtaining electrocardiograph (EKG) signals from a patient, modifying the EKG signals, and establishing a base value for use in evaluating modified EKG signals. The step of modifying includes the steps of amplifying the EKG signals, digitizing amplified EKG signals, mathematically modifying the amplified and digitized EKG signals to obtain 12 lead signals in the time domain, and converting the 12 lead signals into power spectrum signals in the frequency domain. The base value is obtained by taking a patient's resting heart rate in beats per minute, converting it to beats per second, and multiplying by a scaling quantity between approximately 3 and 7, inclusively. Then, a first area is calculated by integrating a selected one of the power spectrum signals from zero Hertz to the base value. Similarly, a second area results from integrating the selected power spectrum signal from the base value to infinity. Then, one takes the ratio of the first to second areas to obtain ail evaluation standard indicative of the patient's coronary health. Peak analysis of the power spectrum signals is also available, and a scheme for locating detected heart disease is also provided. Lastly, a system corresponding to the aforementioned methodology is shown.
Owner:FANG DAN OUN +1
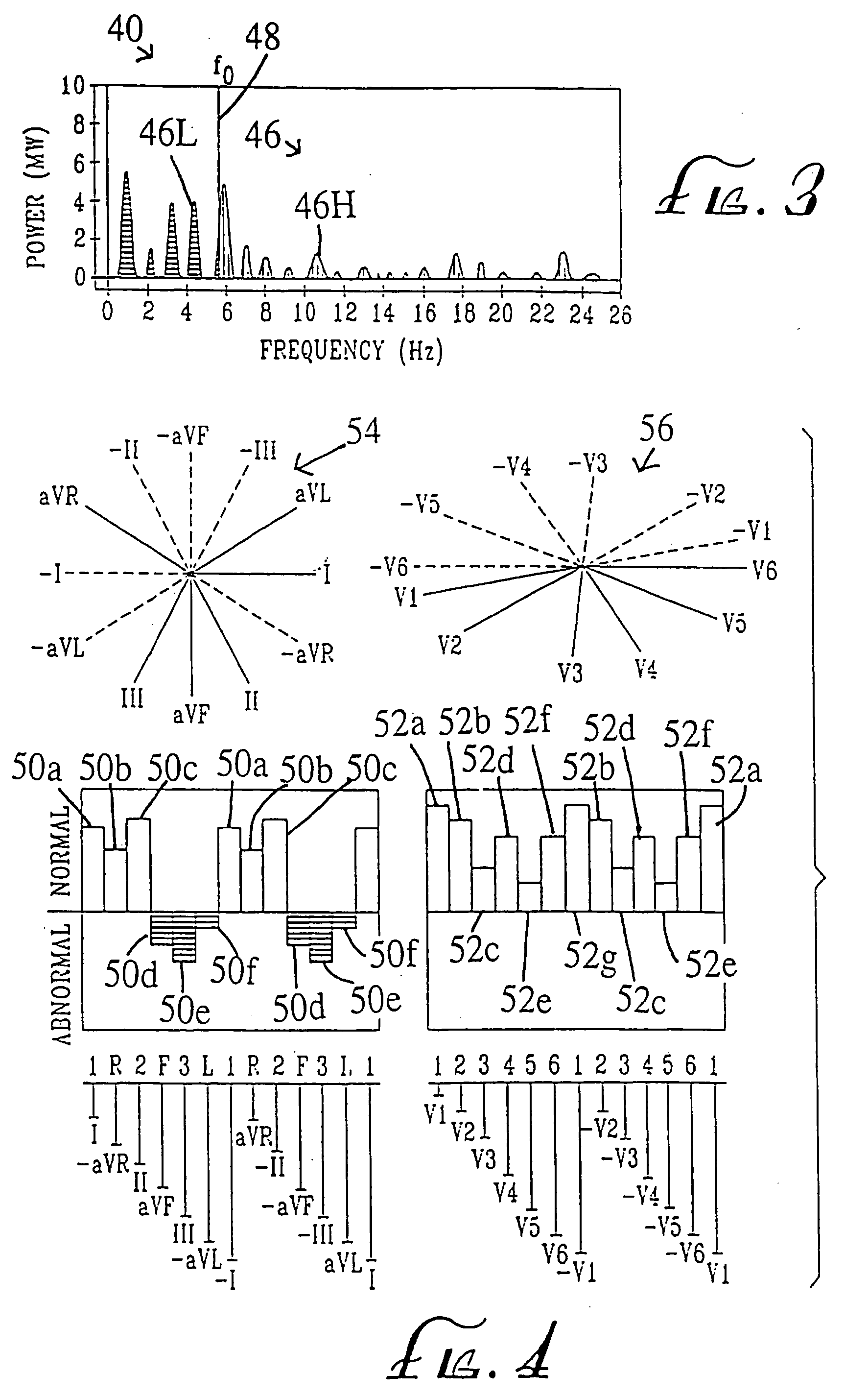
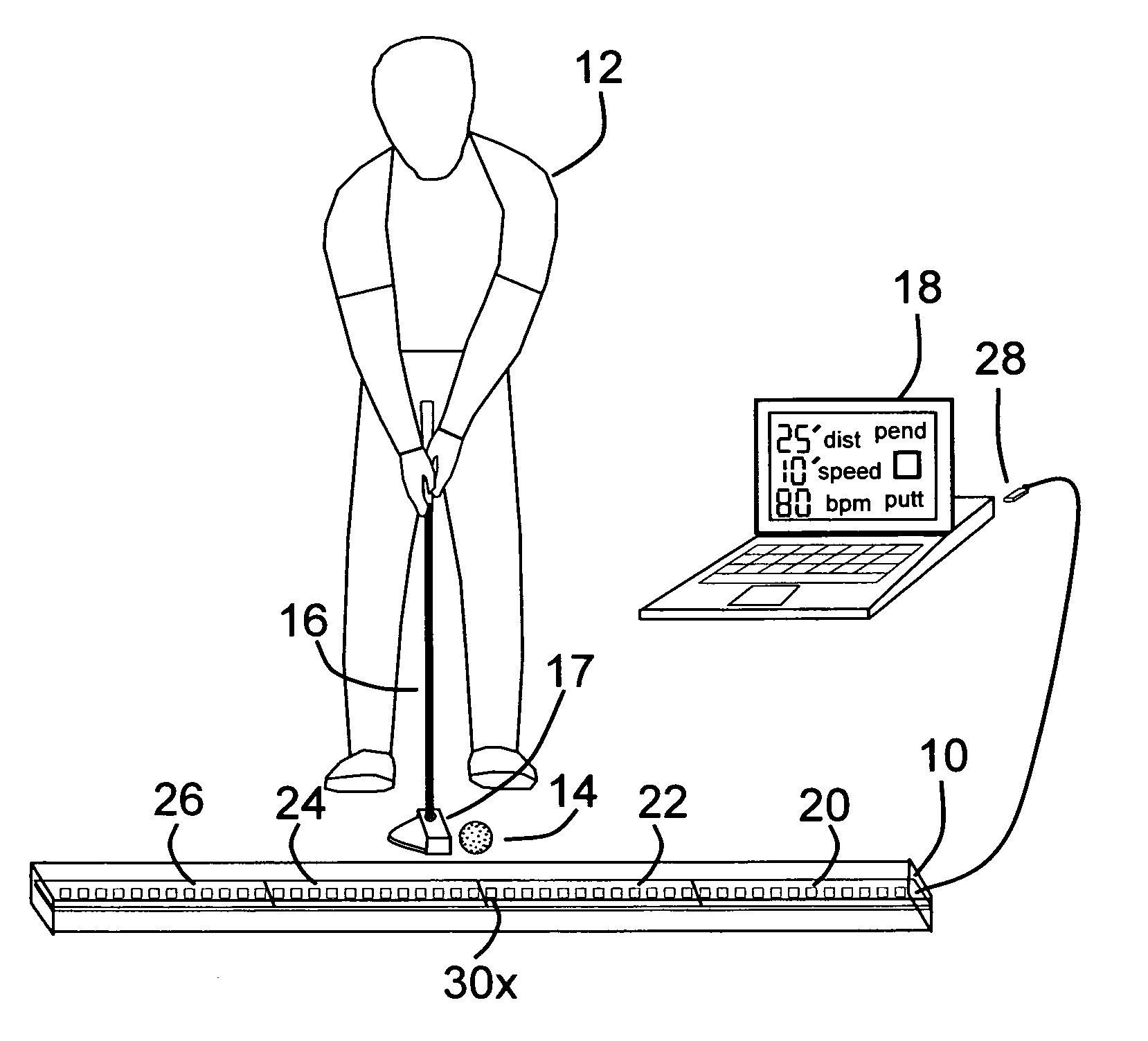
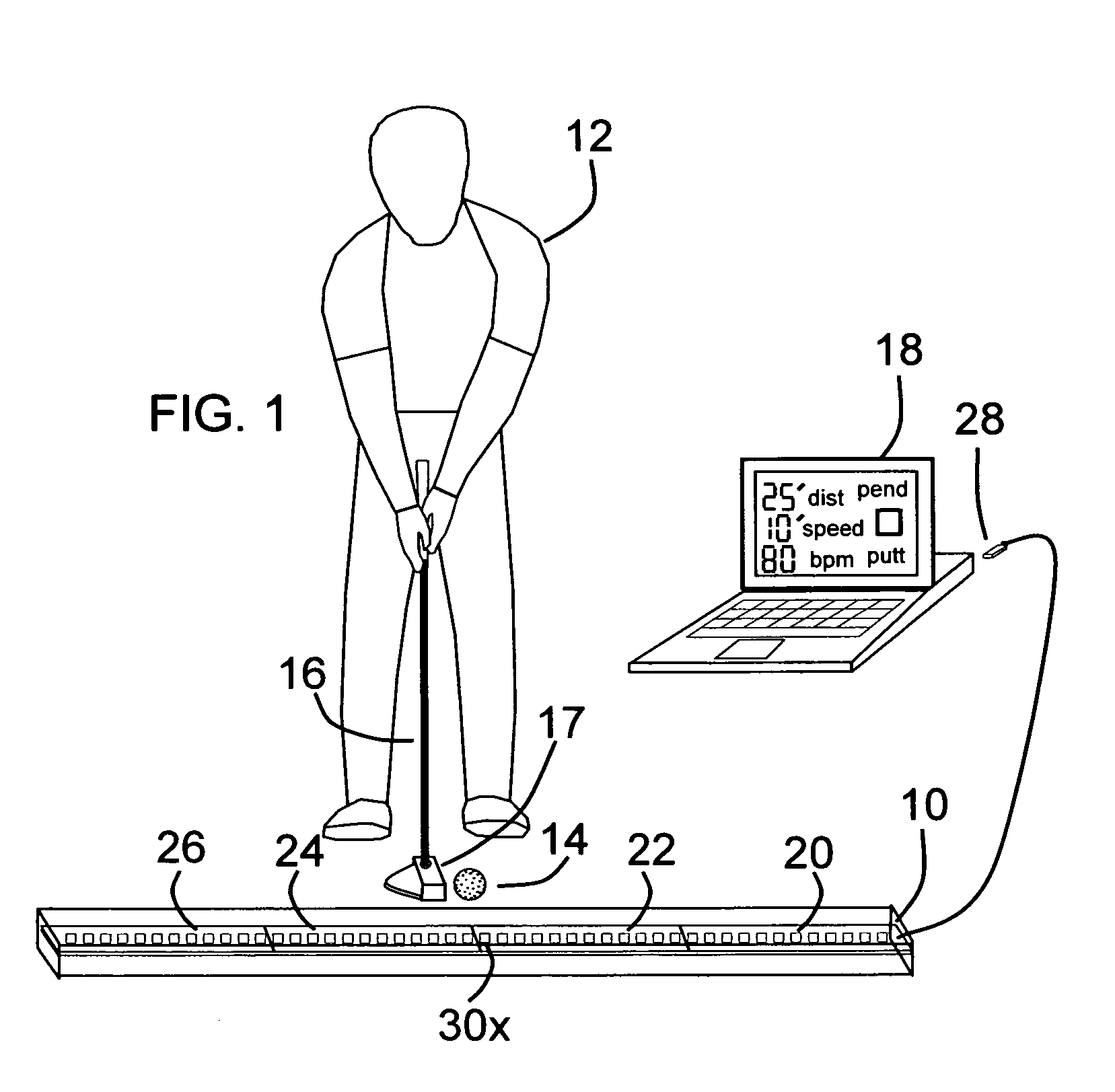
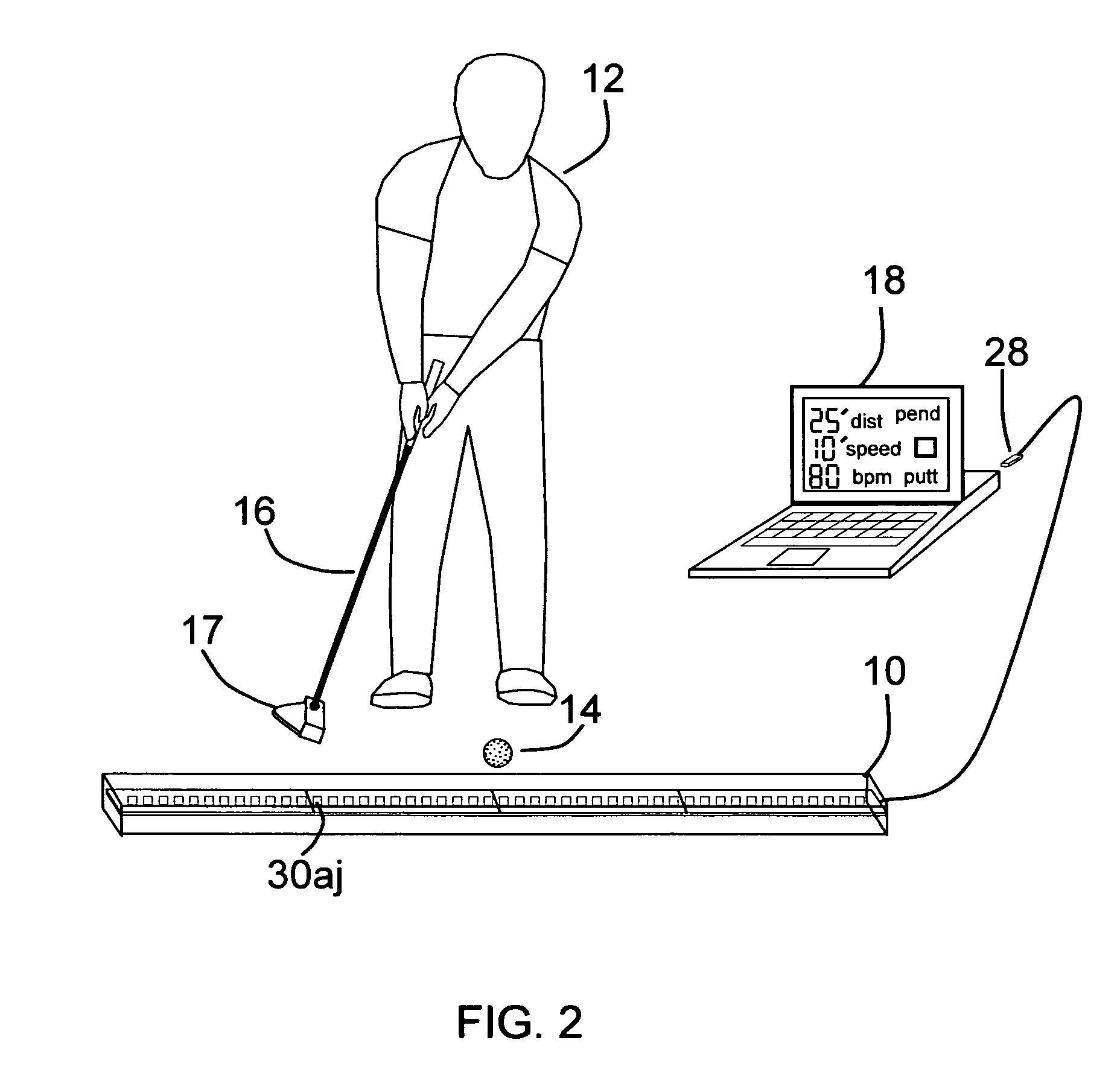
Pendulum putting stroke training aid
An apparatus for indicating the proper pendulum putting stroke to a golfer with An elongated display device that is positioned on a floor parallel to the stroke path of the practicing golfer, A display device containing multiple microcontroller module sections, each containing visual indicators spaced uniformly along the length of the sections, Each section being responsive to commands from a peripheral computing device to turn on a specific visual indicator, a peripheral computing device such as a personal computer running a computer program which calculates the putting stroke based on desired distance, green speed, and the golfer's personal rhythm rate in beats per minute, A peripheral computing device that after calculating the putting stroke time-position data, commands the display device to turn on and off consecutive visual indicators at a predefined time in such a way as to display a putting stroke path, and show the golfer the proper time-space dynamics to strike a golf ball a desired distance.
Owner:MCCONNELL WILLIAM DEAN
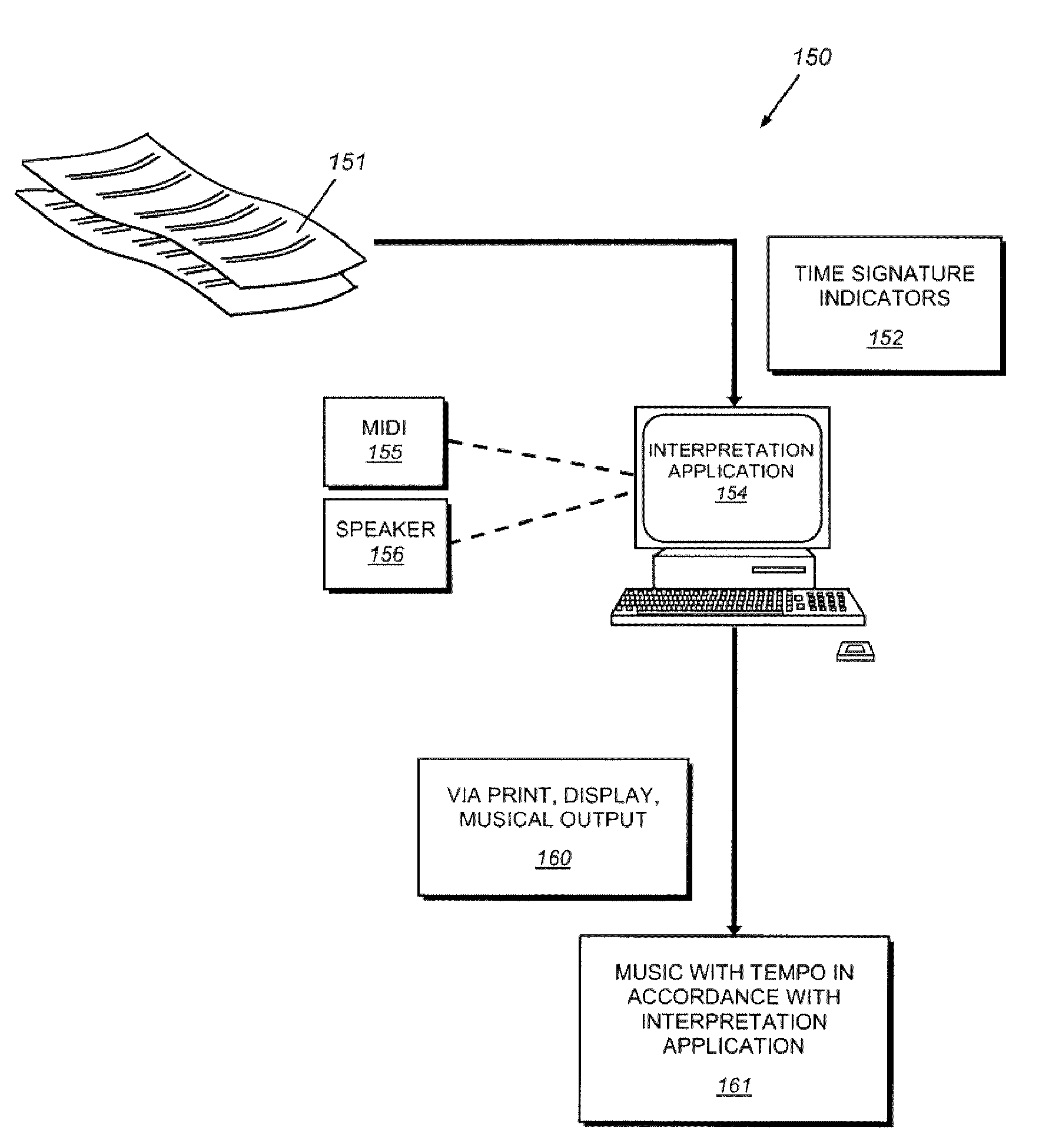
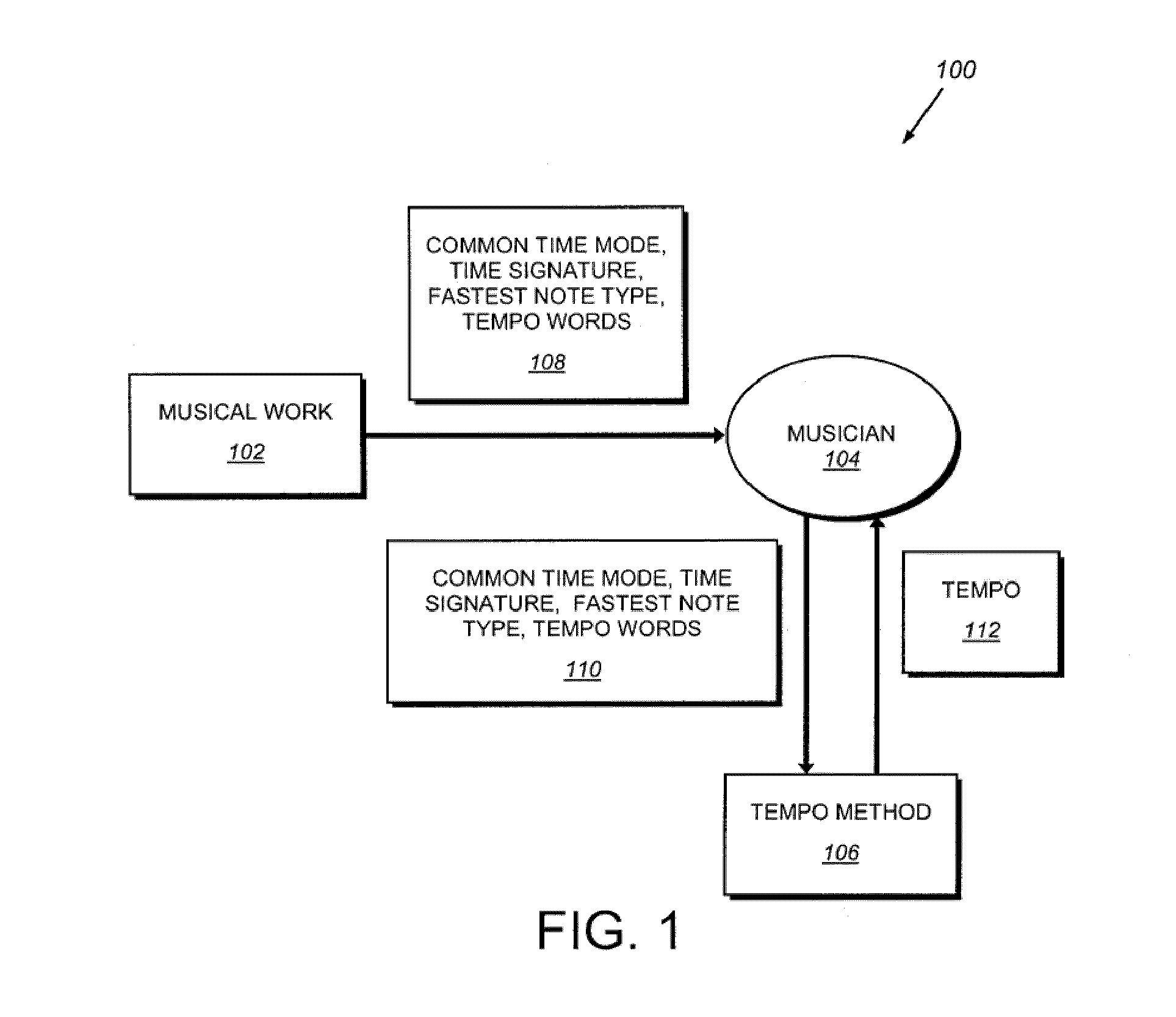
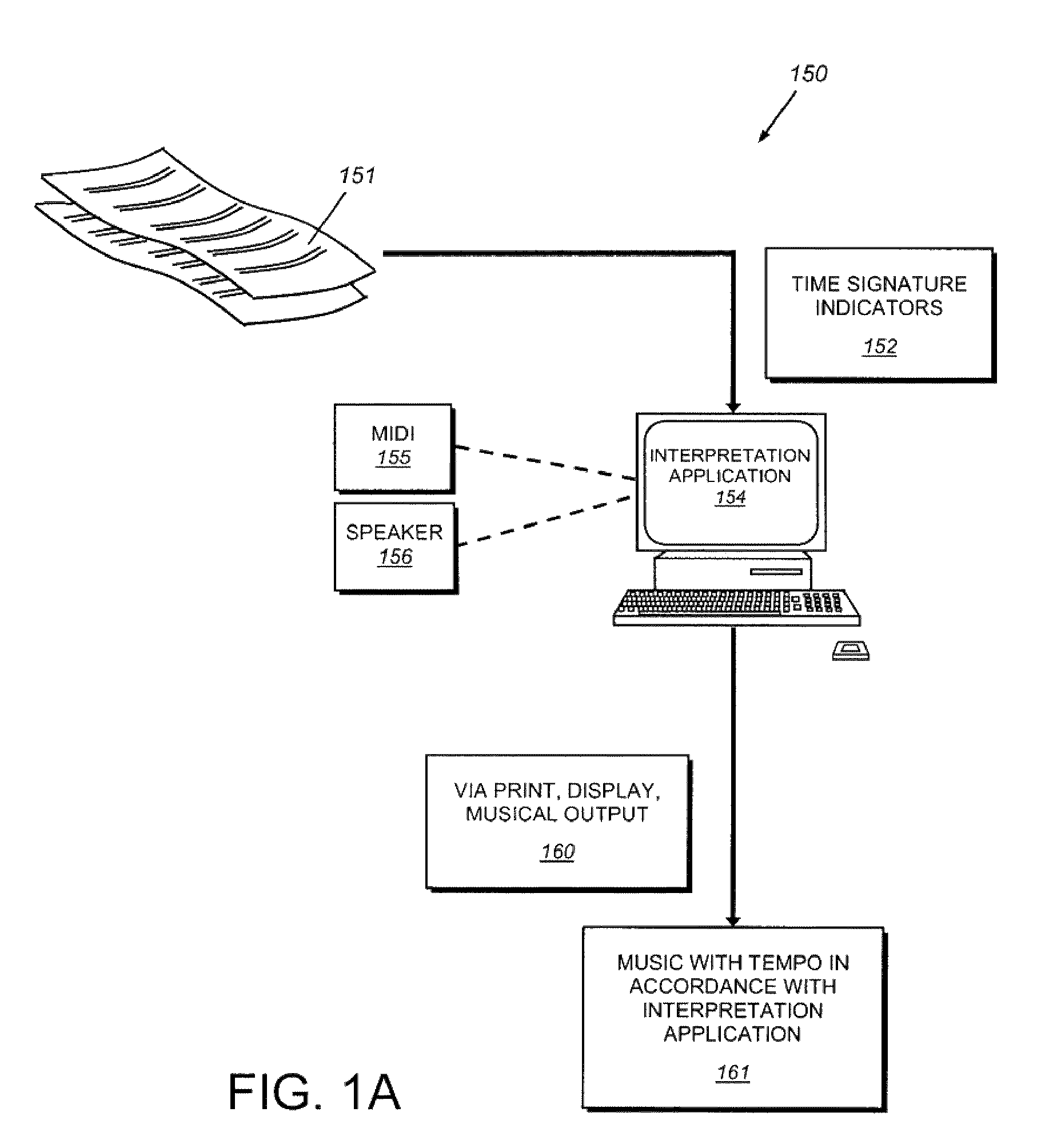
System and method for determining tempo in early music and for playing instruments in accordance with the same
A system and method for determining the appropriate tempo for early music, which may have originally lacked metronome-based time values, and for playing musical instruments according to the same. One example of such early music is the various piano works of Johann Sebastian Bach. The appropriate tempo is determined according to a number of indicators or parameters within the music score including the common time mode, the time signature, the fastest note type, and the absence or presence of any tempo words. Tempos are based around a common time beat value of 71 beats per minute and a cut-time beat value of 80. Other beats are derived using the parameters based on either of these two base values. An electronic device and / or software application may be provided for determining the appropriate tempo according to the illustrative system and displaying it according to an audio and / or visual queue.
Owner:KENNEY LESLIE M
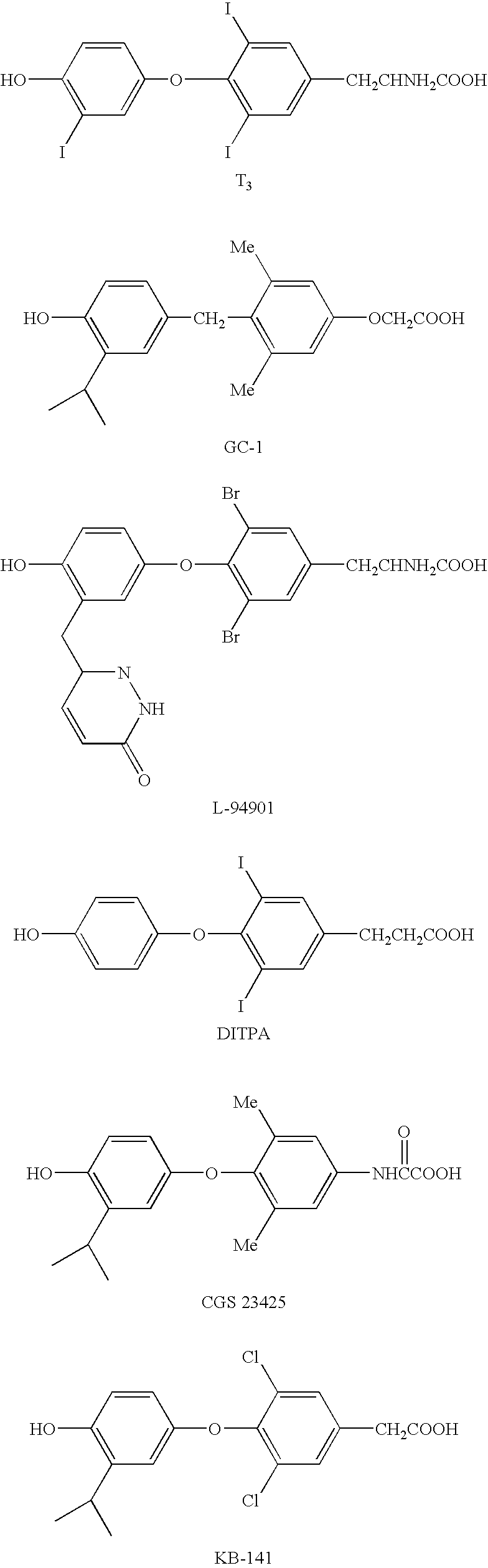
Method to treat chronic heart failure and/or elevated cholesterol levels
A method for treating a patient having congestive heart failure by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a thyroid hormone analog sufficient to produce an increase in cardiac index of at least 15% while increasing heart rate no more than 10 beats per minute.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com