Patents
Literature
132 results about "Event synchronization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Event (synchronization primitive) In computer science, an event (also called event semaphore) is a type of synchronization mechanism that is used to indicate to waiting processes when a particular condition has become true. An event is an abstract data type with a boolean state and the following operations:
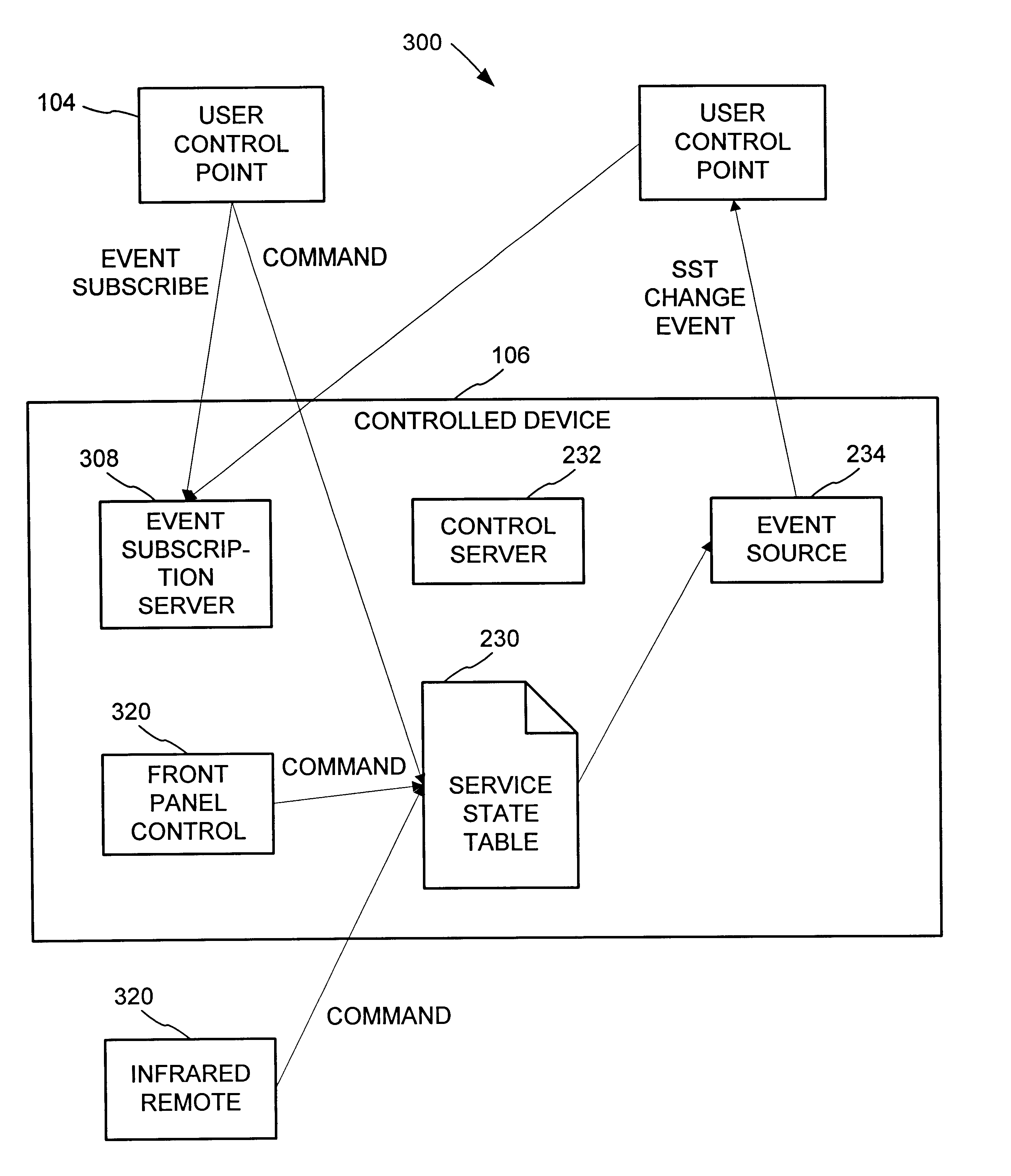
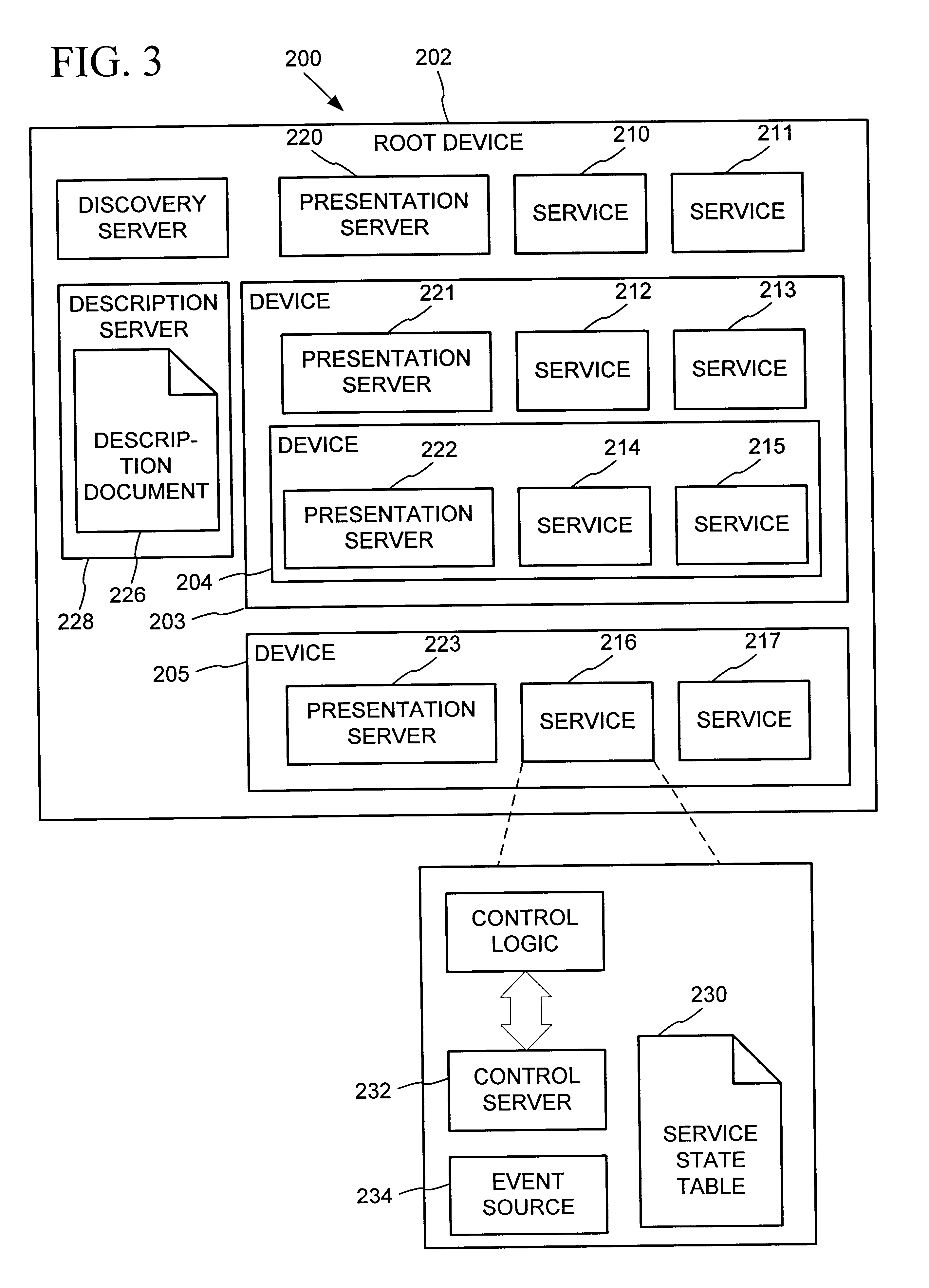
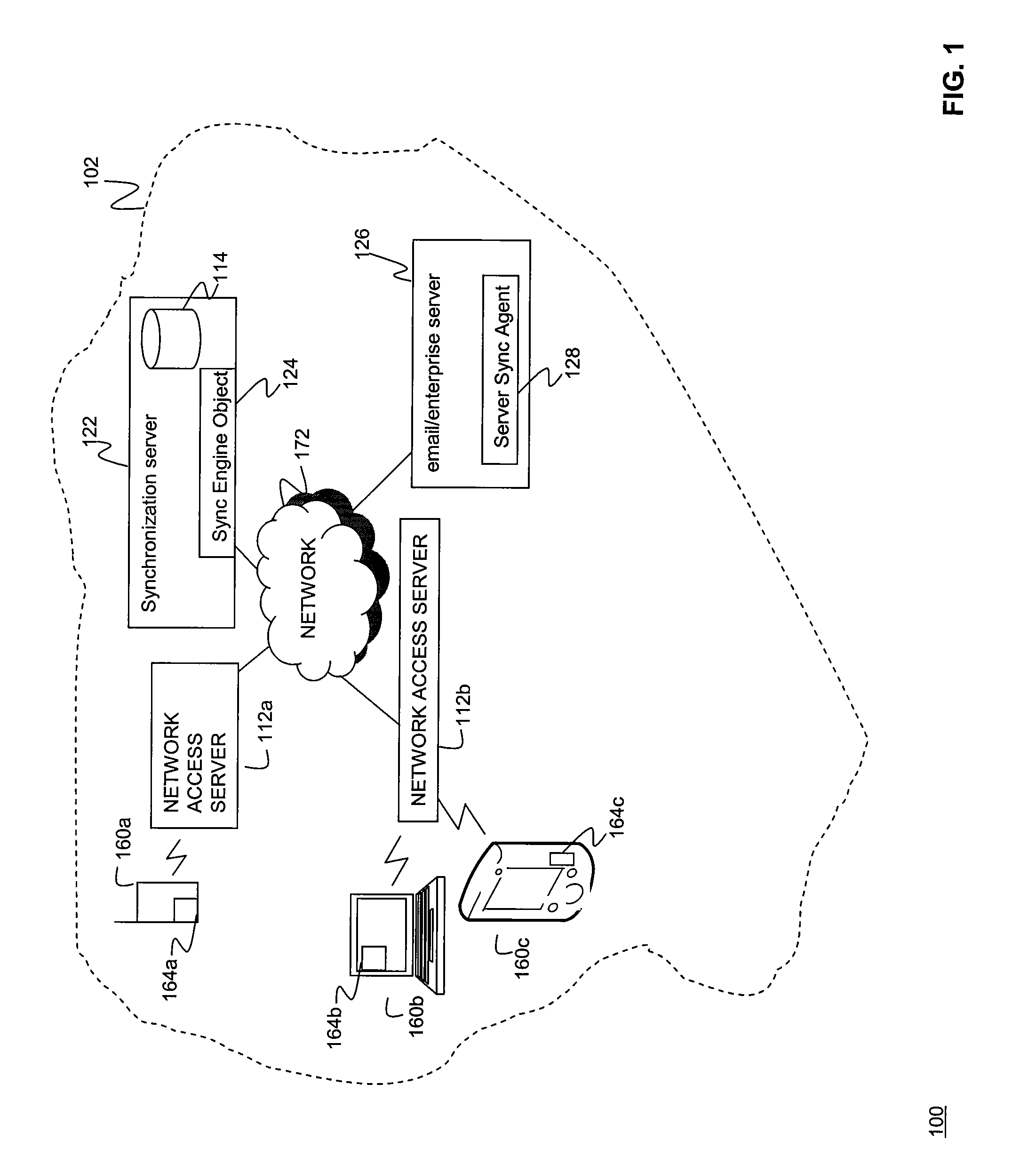
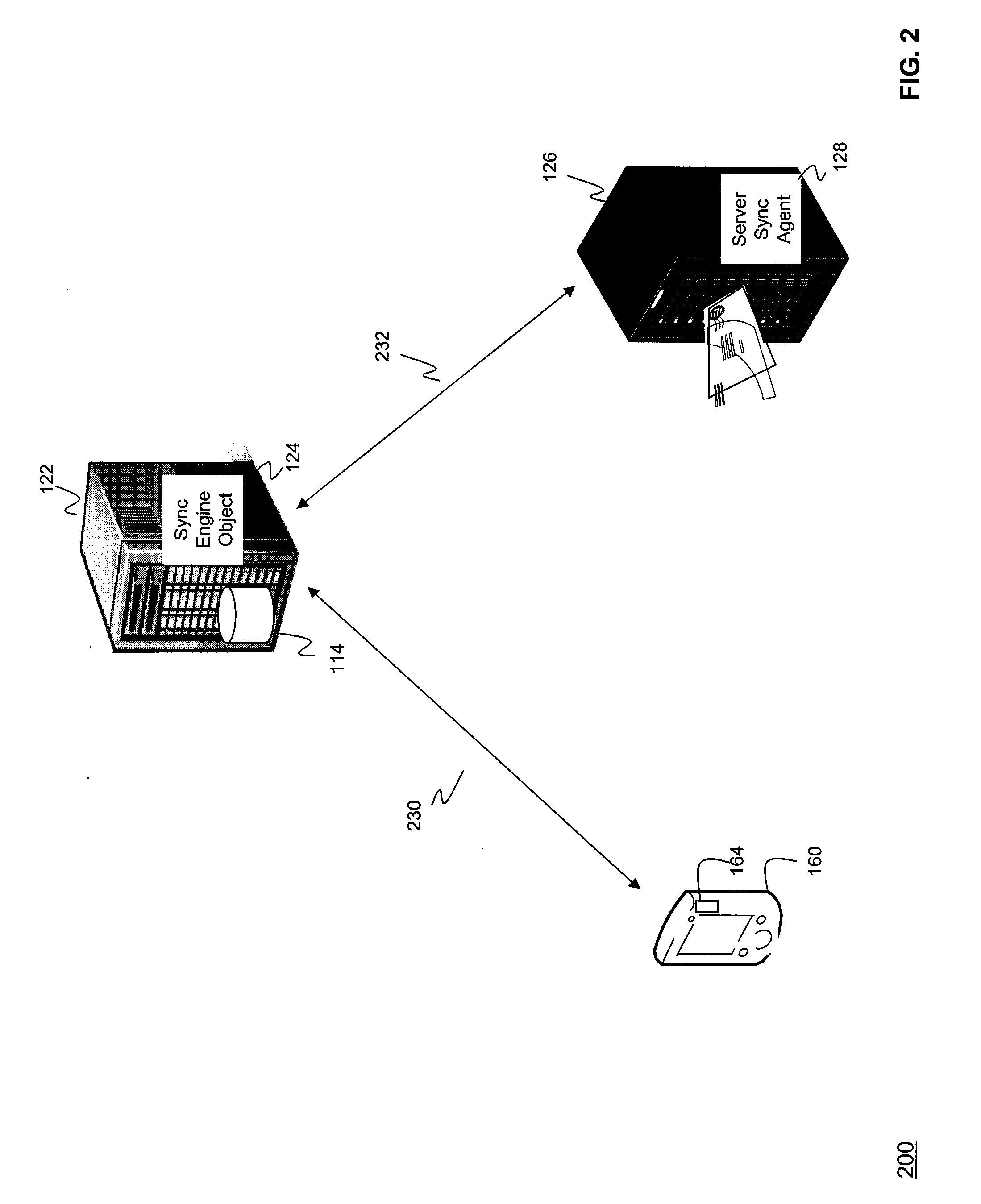
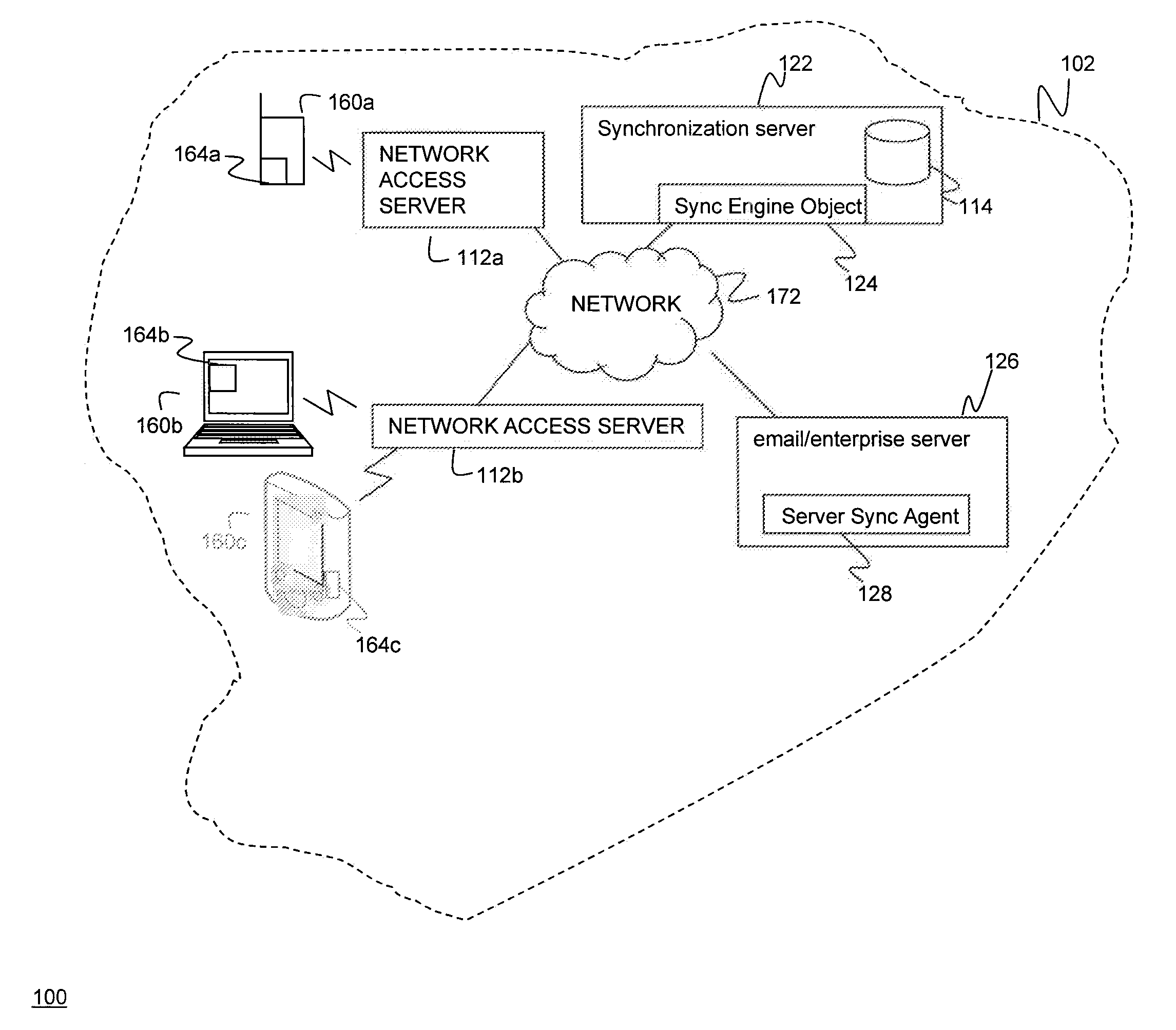
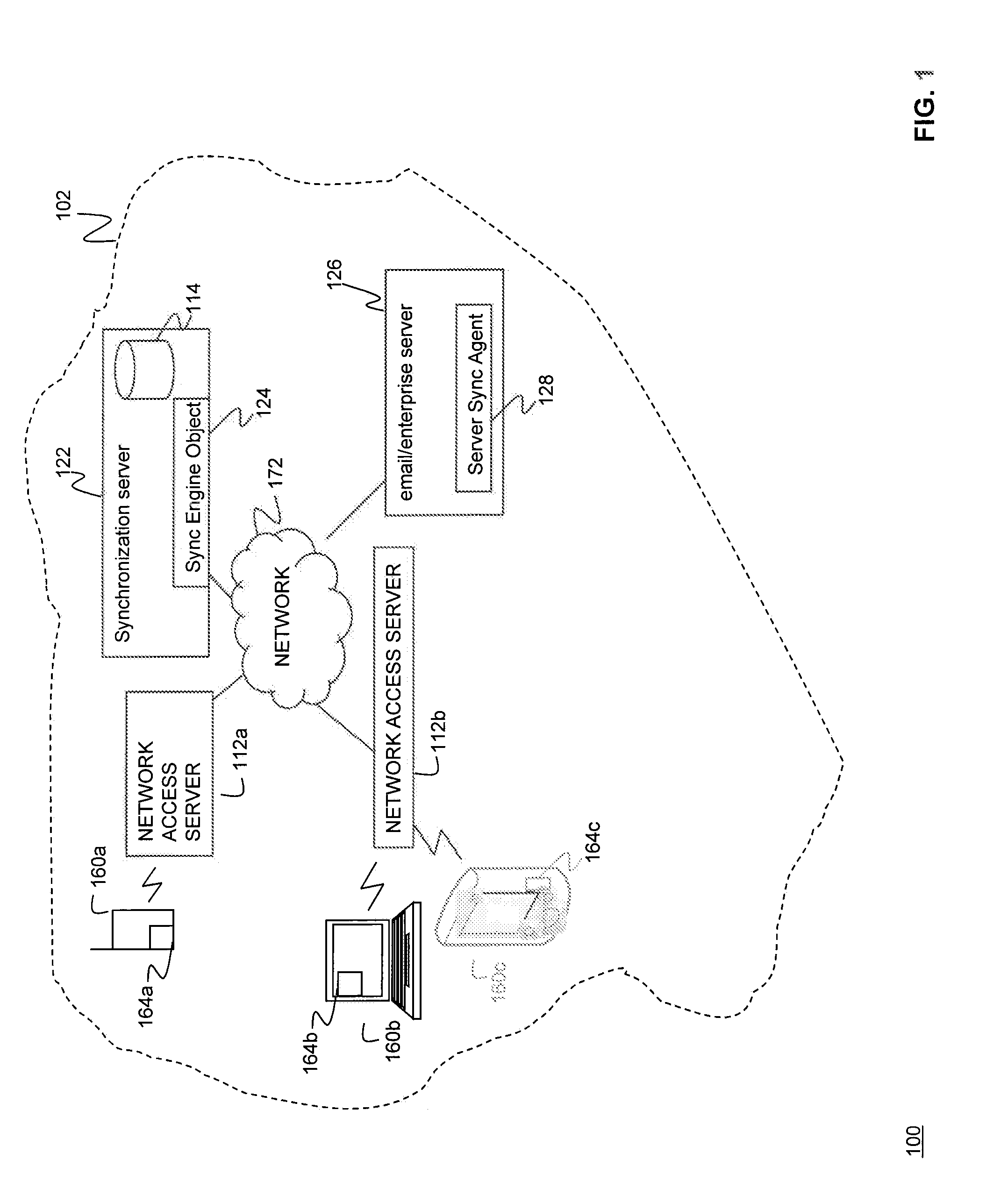
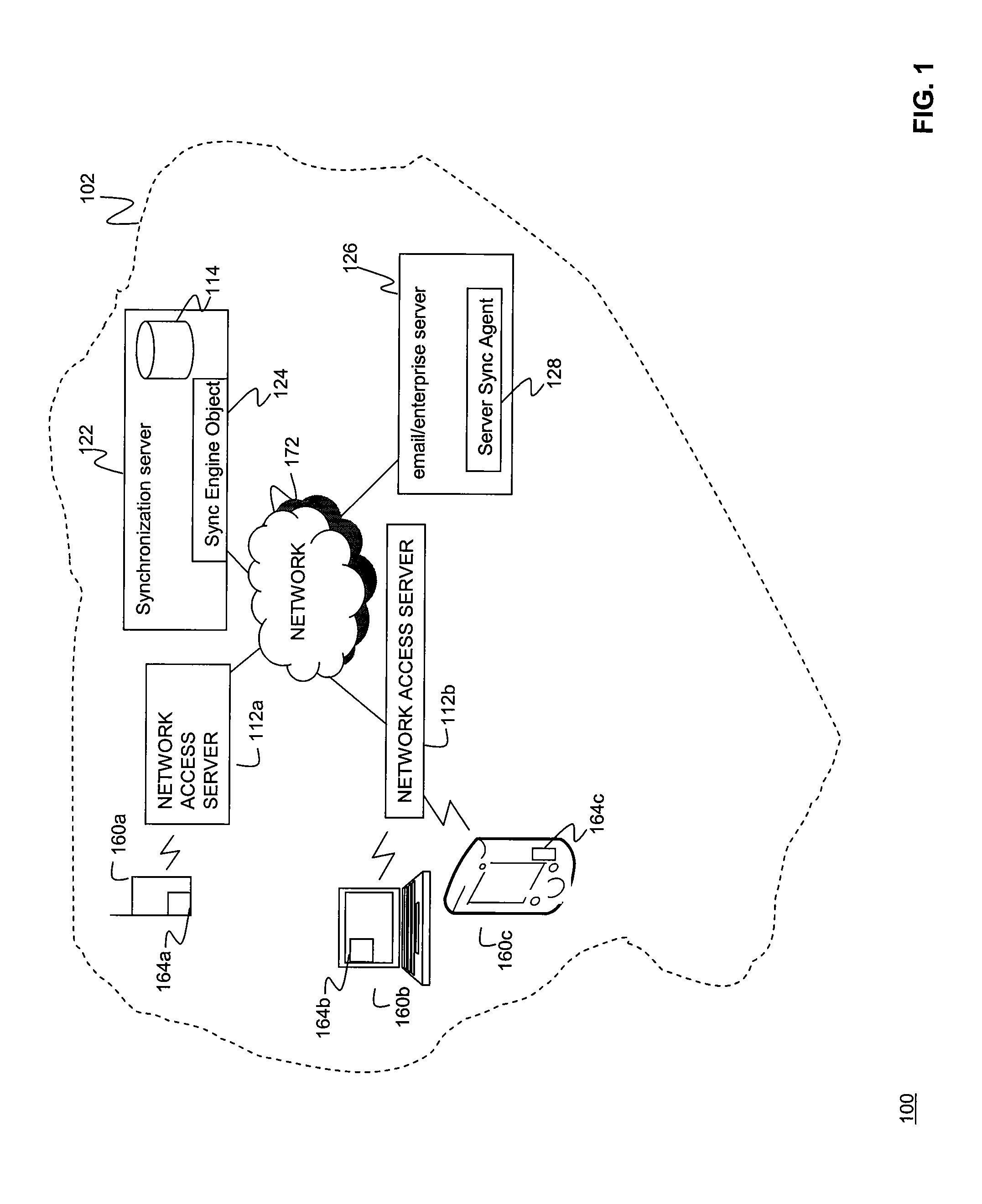
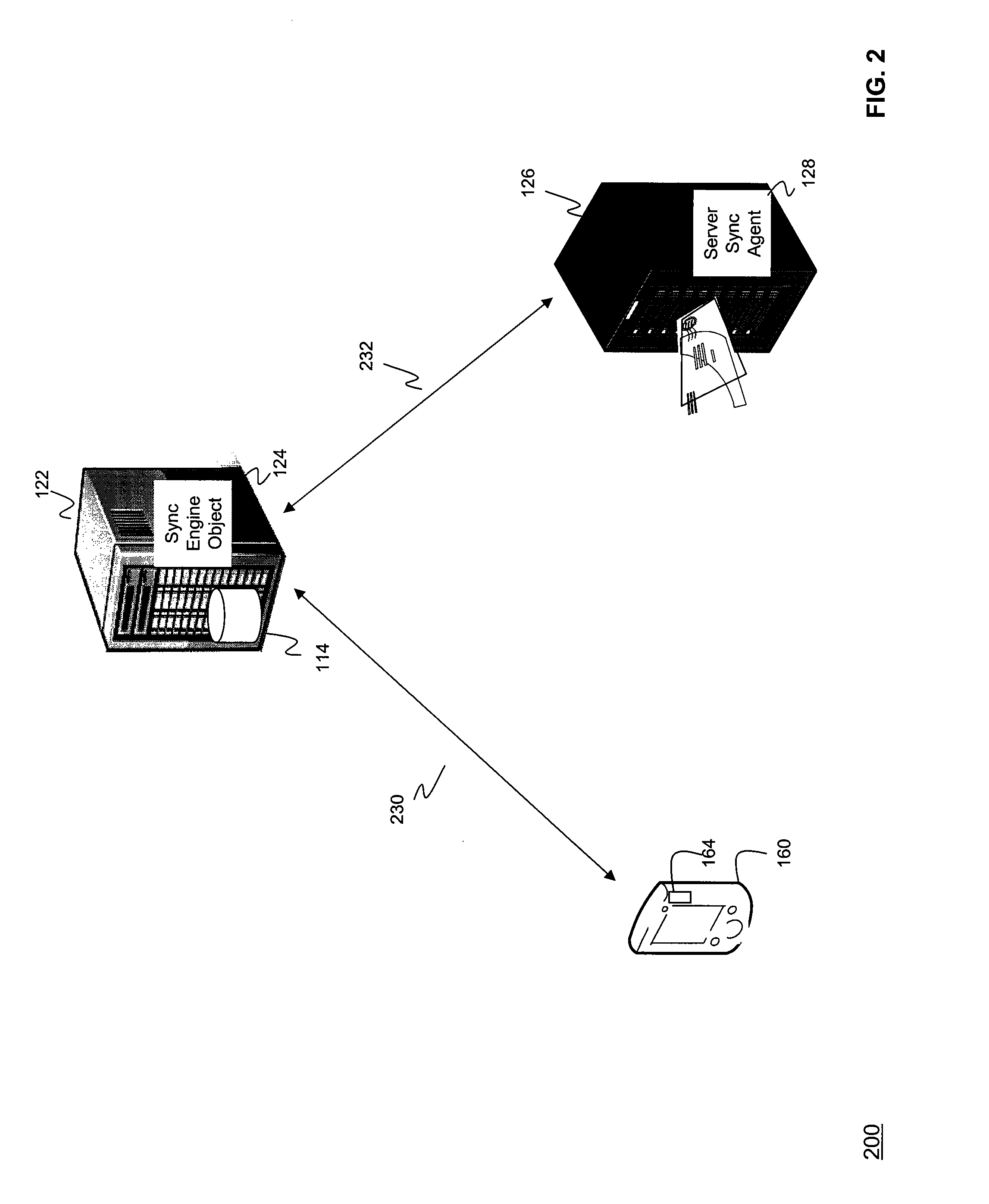
Synchronization of controlled device state using state table and eventing in data-driven remote device control model
InactiveUS6725281B1Falling in priceIncrease speedMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationEvent synchronizationEvent model
Controlled devices according to a device control model maintain a state table representative of their operational state. Devices providing a user control point interface for the controlled device obtain the state table of the controlled device, and may also obtain presentation data defining a remoted user interface of the controlled device and device control protocol data defining commands and data messaging protocol to effect control of the controlled device. These user control devices also subscribe to notifications of state table changes, which are distributed from the controlled device according to an eventing model. Accordingly, upon any change to the controlled device's operational state, the eventing model synchronizes the device's state as represented in the state table across all user control devices.
Owner:ROVI TECH CORP
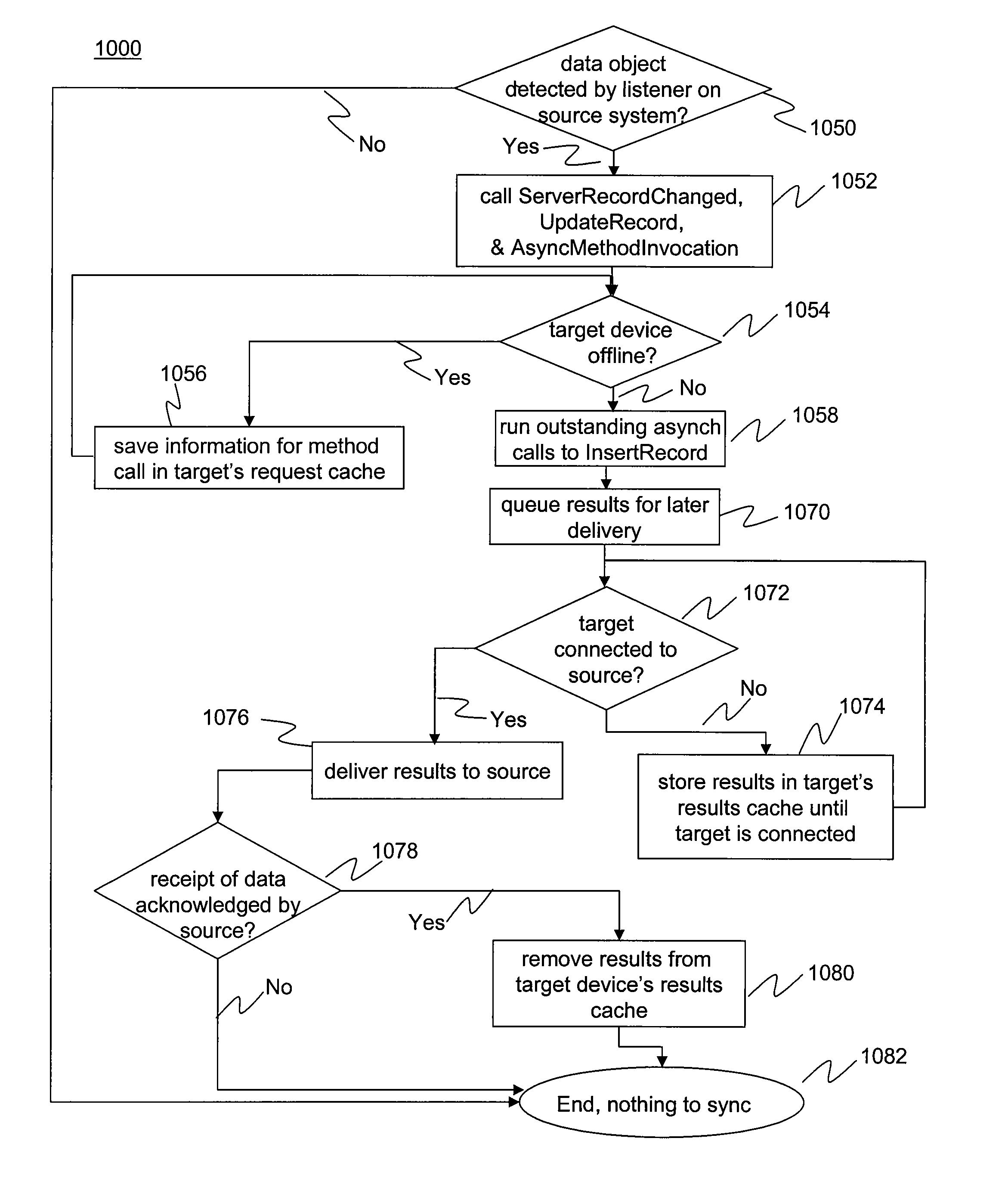
Synchronizing Events Between Mobile Devices and Servers
ActiveUS20090282125A1Natural language data processingMultiple digital computer combinationsEvent synchronizationPersonal information manager
A system, method, and computer program product for synchronizing events between a mobile device and a server are described herein. In an embodiment, the method operates by detecting events to be synchronized between a source and a target, wherein the source and target are one of either a mobile device or a server. The method comprises deducing activities that occurred in order to create the detected event, reading data records corresponding to the deduced activities, and creating packets of operations needed to recreate the deduced activities on the target. The method further comprises queuing the packets of operations and data records and receiving event synchronization results at the source after the queued packets of operations have successfully executed on the target, wherein the synchronization results include a synchronization status and a unique record identifier identifying the event. In an embodiment, personal information manager (PIM) events are synchronized.
Owner:IANYWHERE SOLUTIONS
Synchronizing Events Between Mobile Devices and Servers
ActiveUS20120066411A1Easy to completeNatural language data processingMultiple digital computer combinationsEvent synchronizationPersonal information manager
A system, method, and computer program product for synchronizing events between a mobile device and a server are described herein. In an embodiment, the method operates by detecting events to be synchronized between a source and a target, wherein the source and target are one of either a mobile device or a server. The method comprises deducing activities that occurred in order to create the detected event, reading data records corresponding to the deduced activities, and creating packets of operations needed to recreate the deduced activities on the target. The method further comprises queuing the packets of operations and data records and receiving event synchronization results at the source after the queued packets of operations have successfully executed on the target, wherein the synchronization results include a synchronization status and a unique record identifier identifying the event. In an embodiment, personal information manager (PIM) events are synchronized.
Owner:IANYWHERE SOLUTIONS
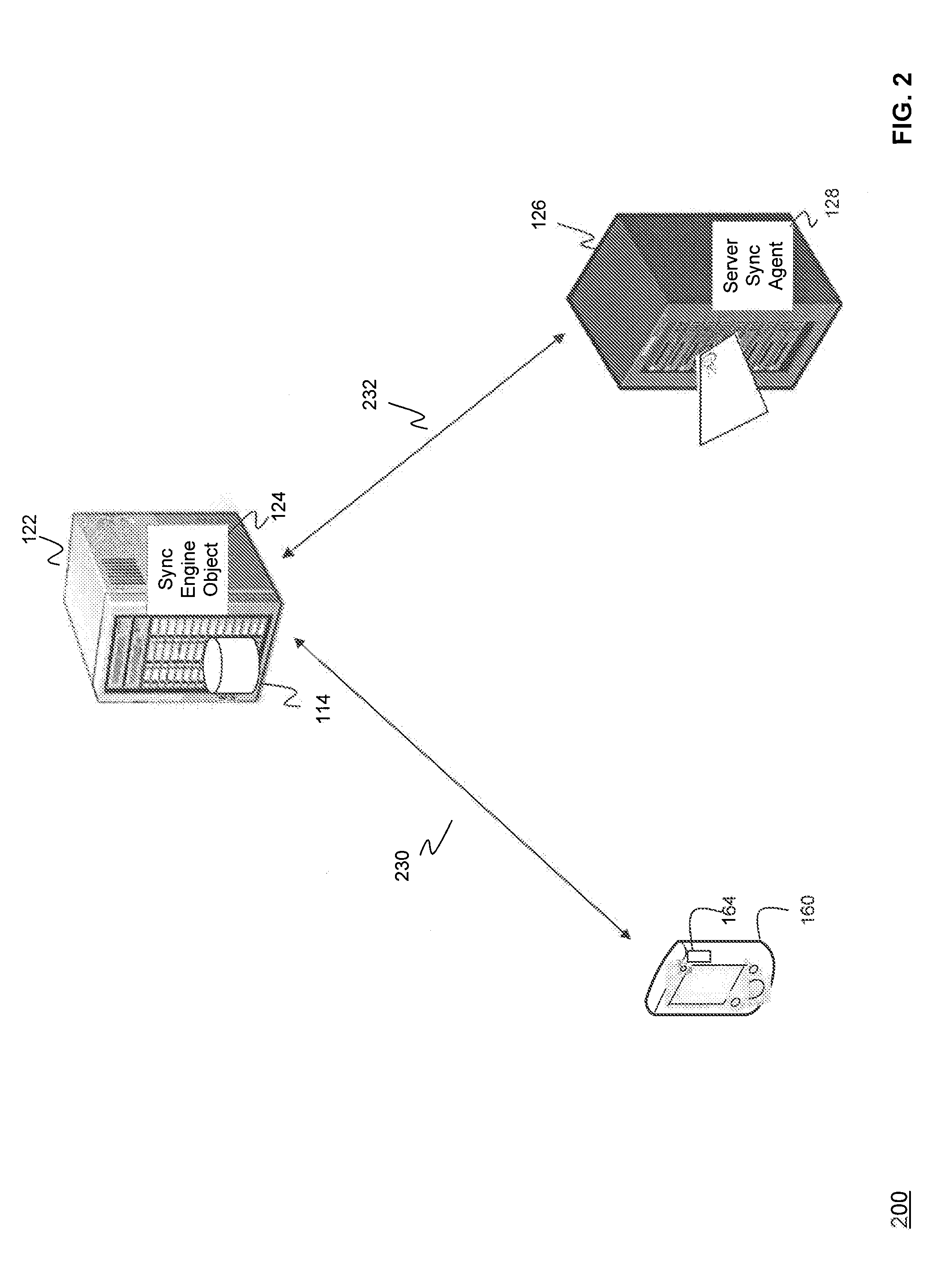
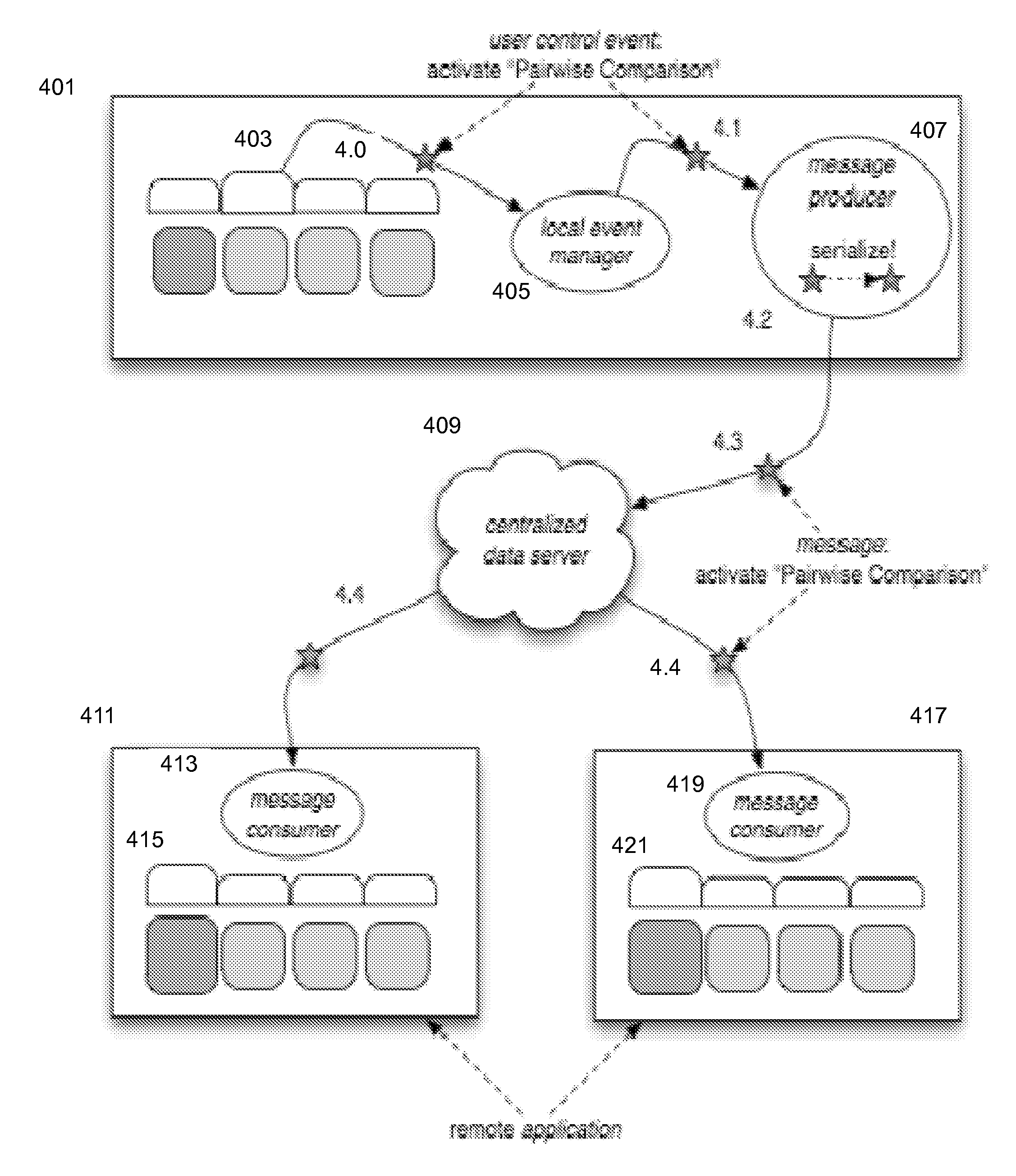
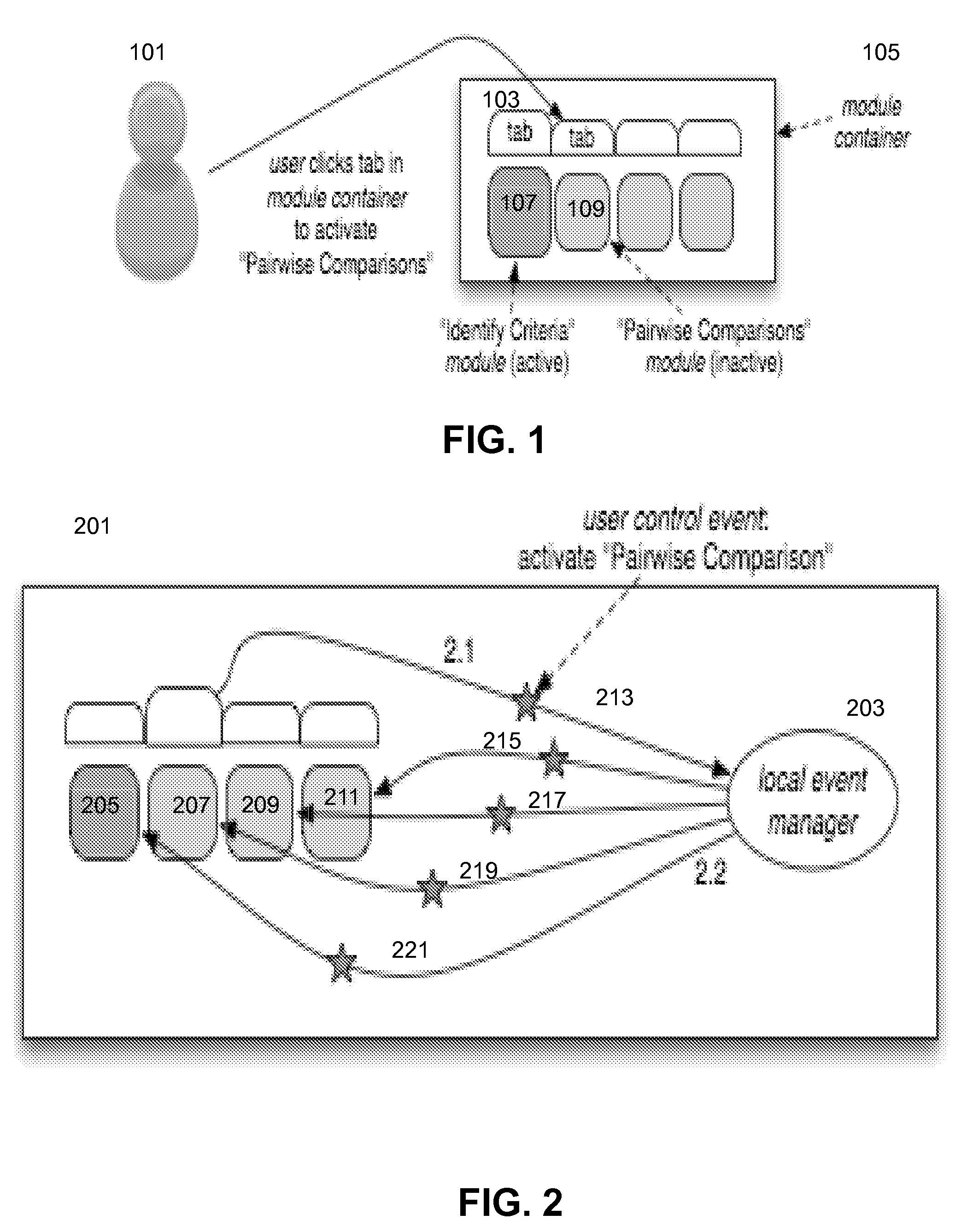
Data and event synchronization across distributed user interface modules
ActiveUS8447820B1Multiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationEvent synchronizationDistributed user interface
A computer includes, among other things, local modules contained within a module container of a same application; a message producer unit to communicate with a data server over the i / o interface; a message consumer unit configured to communicate with the data server over the i / o interface; and a local event manager unit. There is a pre-defined sequence of processing events between the local event manager unit, the local modules within the same application of the same module container, remote modules, the message producer unit, and the message consumer unit.
Owner:DECISION LENS
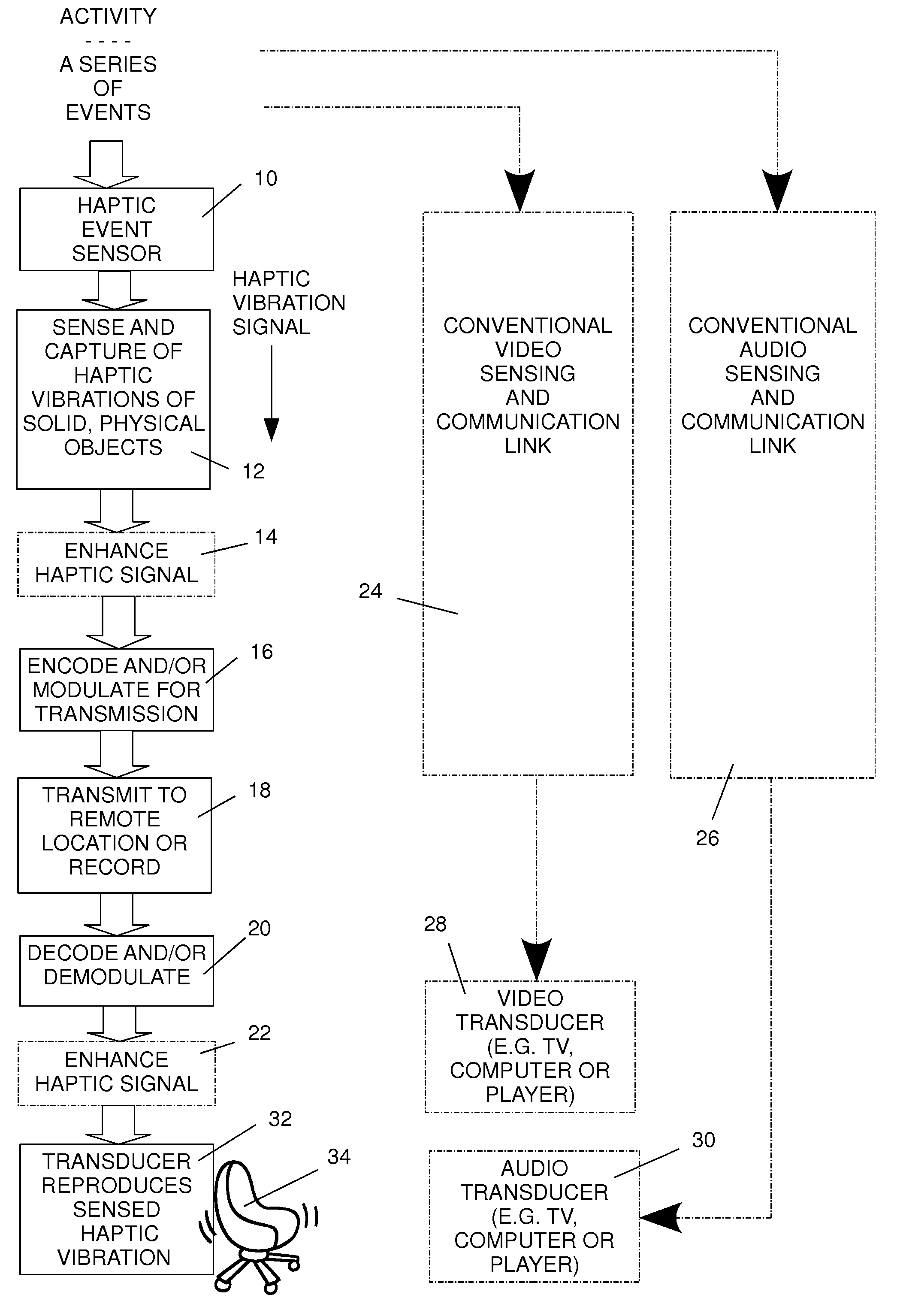
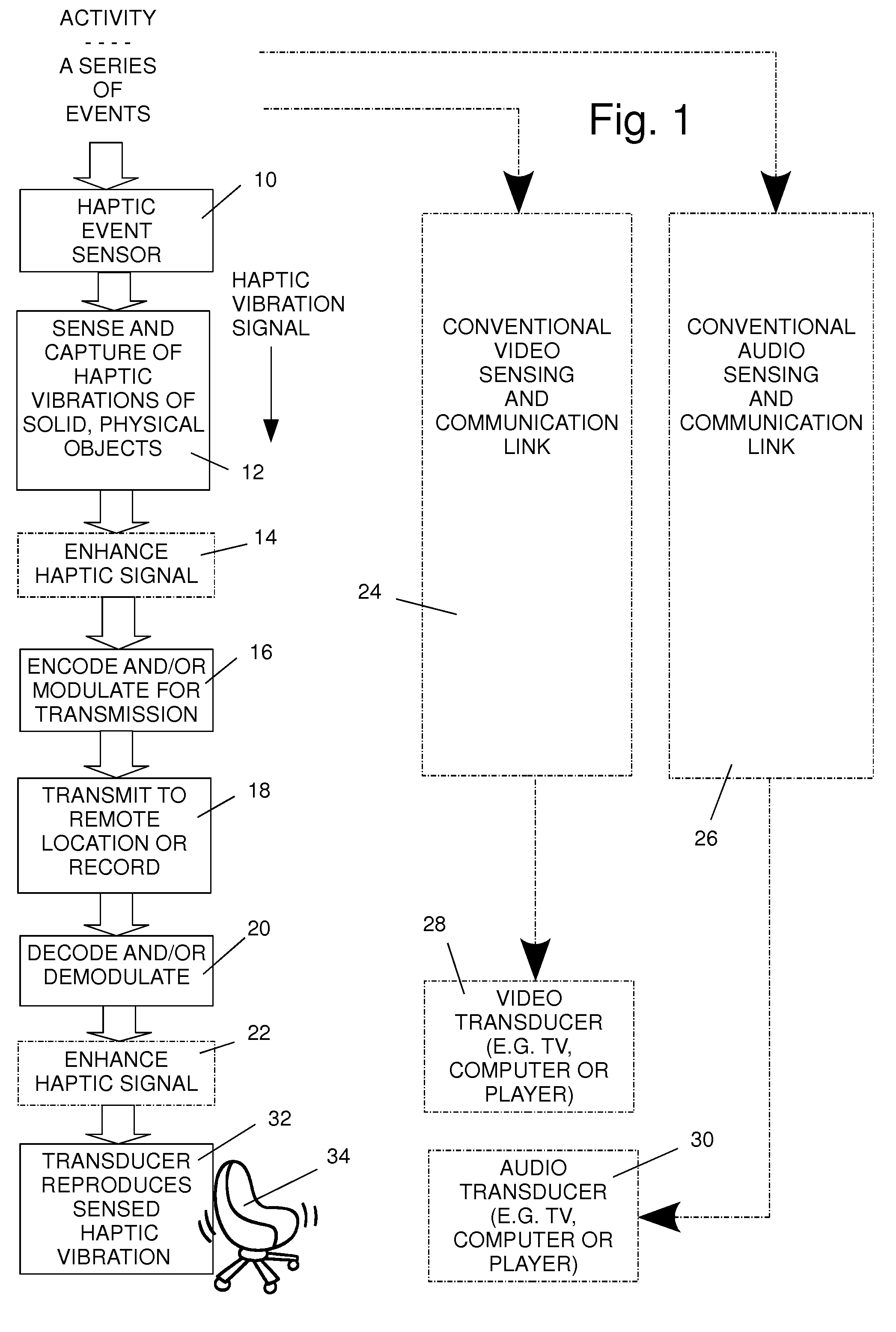
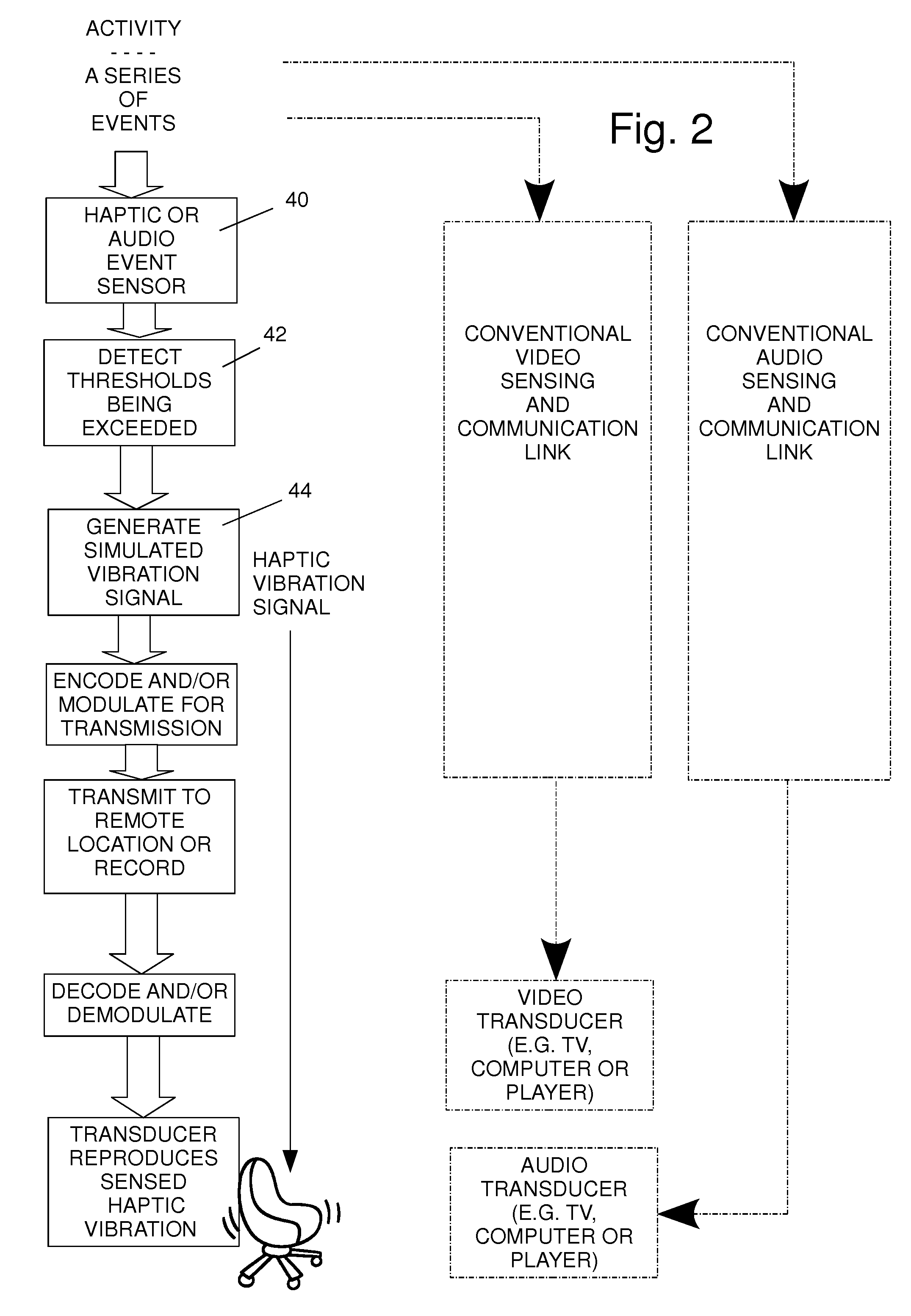
Capture and remote reproduction of haptic events in synchronous association with the video and audio capture and reproduction of those events
ActiveUS7911328B2Repeater circuitsMechanical energy handlingEvent synchronizationHuman–computer interaction
Method and apparatus for reproducing and applying reproductions of haptic vibrations that occur at a live activity to a remote video and audio viewer. In synchronism with sensing visible and audible stimuli to generate video and audio signals representing the video and audio at the activity, haptic vibrations of an object at the activity are sensed and converted to haptic vibration signals. A haptic vibration signal that is a reproduction of the sensed signal, a simulation of the haptic vibration, or an enhancement of the sensed haptic vibration signal is transmitted to a remote location or recorded. The haptic vibration signal contains information about the timing and characteristic of the sensed haptic vibrations and is recoverable separately from the visible and audible signals. At a location that is remote from the activity, that information is detected and used to generate and apply a reproduction of the sensed haptic vibration signal, in synchronism with reproduction of the sensed video signal and of the sensed audio signal, to an electromechanical transducer that is mechanically connected to a solid object in physical contact with a remote viewer.
Owner:THE GUITAMMER
Synchronizing events between mobile devices and servers
ActiveUS8019863B2Easy to completeNatural language data processingMultiple digital computer combinationsEvent synchronizationPersonal information manager
A system, method, and computer program product for synchronizing events between a mobile device and a server are described herein. In an embodiment, the method operates by detecting events to be synchronized between a source and a target, wherein the source and target are one of either a mobile device or a server. The method comprises deducing activities that occurred in order to create the detected event, reading data records corresponding to the deduced activities, and creating packets of operations needed to recreate the deduced activities on the target. The method further comprises queuing the packets of operations and data records and receiving event synchronization results at the source after the queued packets of operations have successfully executed on the target, wherein the synchronization results include a synchronization status and a unique record identifier identifying the event. In an embodiment, personal information manager (PIM) events are synchronized.
Owner:IANYWHERE SOLUTIONS
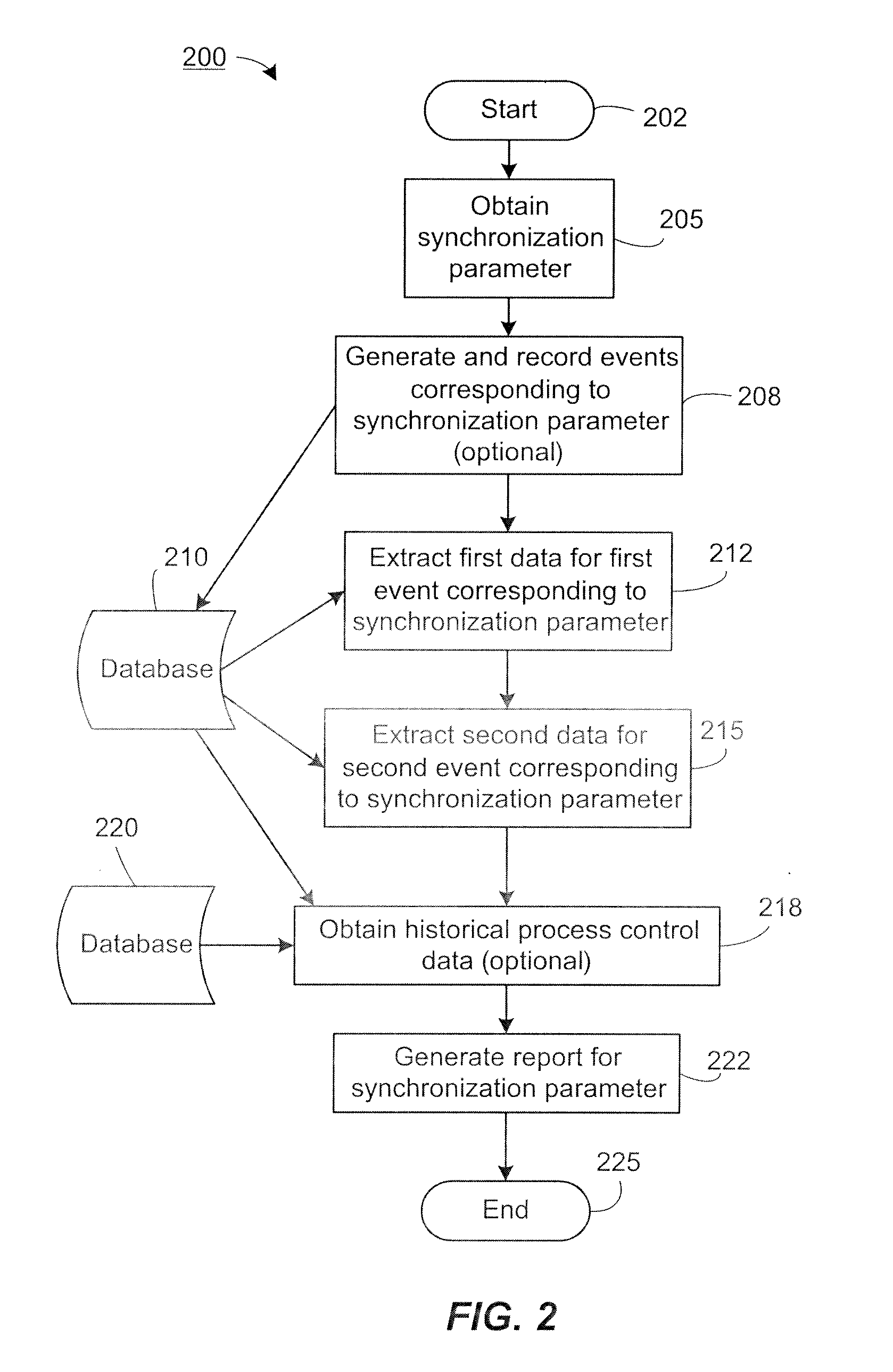
Event Synchronized Reporting in Process Control Systems
InactiveUS20100082396A1Complete banking machinesRegistering/indicating time of eventsEvent synchronizationControl system
Methods, systems, and computer-executable instructions for event synchronized reporting in an process control system are disclosed. Events may be synchronized by a synchronization parameter, whose instances of occurrence may be non-contiguous in time. Examples of synchronization parameters may include a work shift, a work group, an individual's on-duty time, a logged-on period of an individual, the execution times of a process control entity, a batch run type, and a procedure or sub-unit of a batch run. Instances of occurrence of the synchronization parameter may be recorded into a process control event database. Event synchronized reports may contain at least one synchronization value based on both the instances of occurrence of the synchronization parameter as well as historical process control data. Data from various historian databases may be accessed from process control system tools and integrated into a single report.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
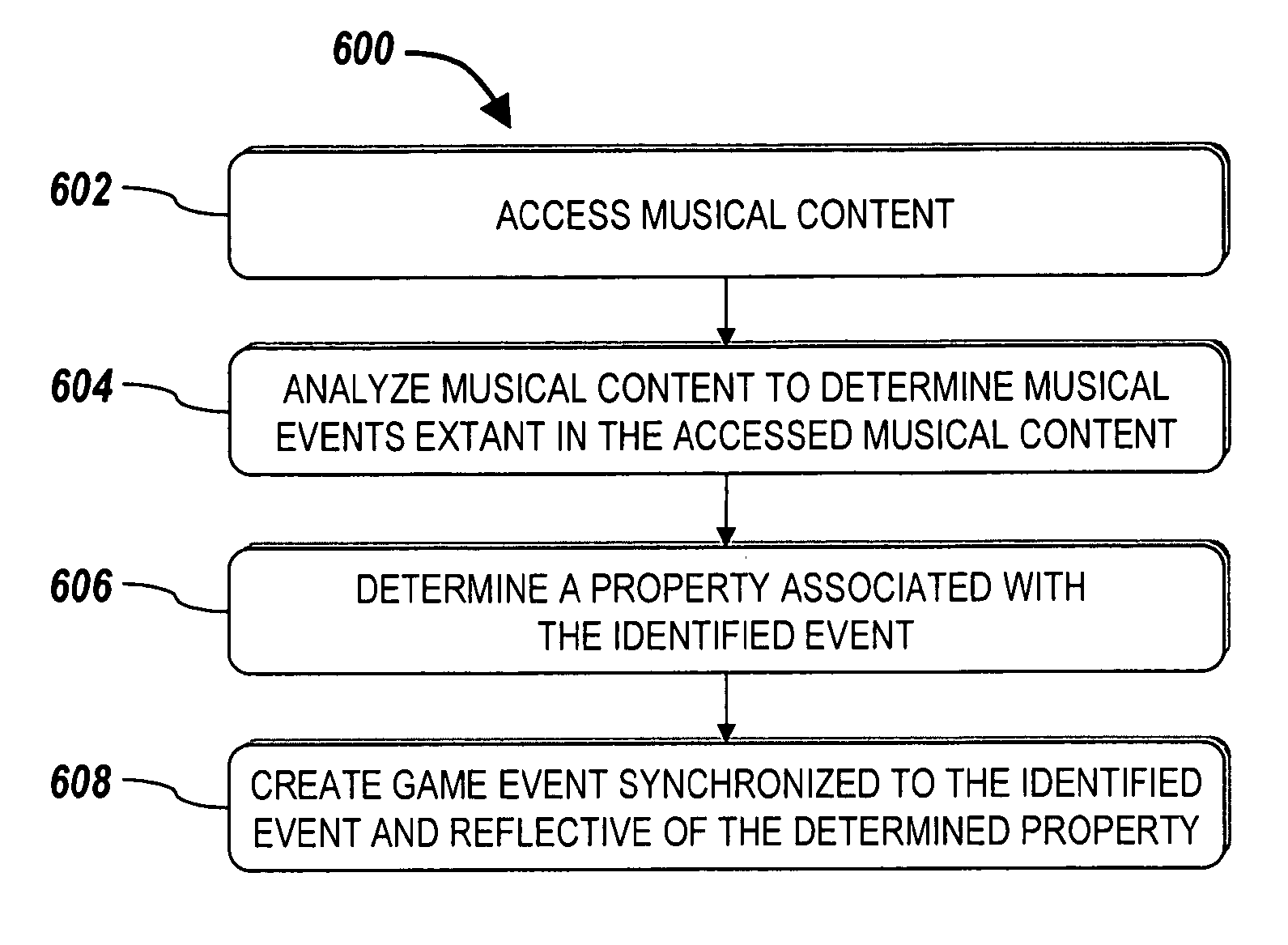
Systems and methods for generating video game content
Systems and methods for a creating a music-based video game are described as is a portable music and video device housing a memory for storing executable instructions and a processor for executing the instructions. Creating video game content using musical content supplied from a source other than the game includes analyzing musical content to identify at least one musical event extant in the musical event; determining a salient musical property associated with the at least one identified event; and creating a video game event synchronized to the at least one identified musical event and reflective of the determined salient musical property associated with the at least one identified event.
Owner:HARMONIX MUSIC SYSTEMS
Method and system for deinterleaving
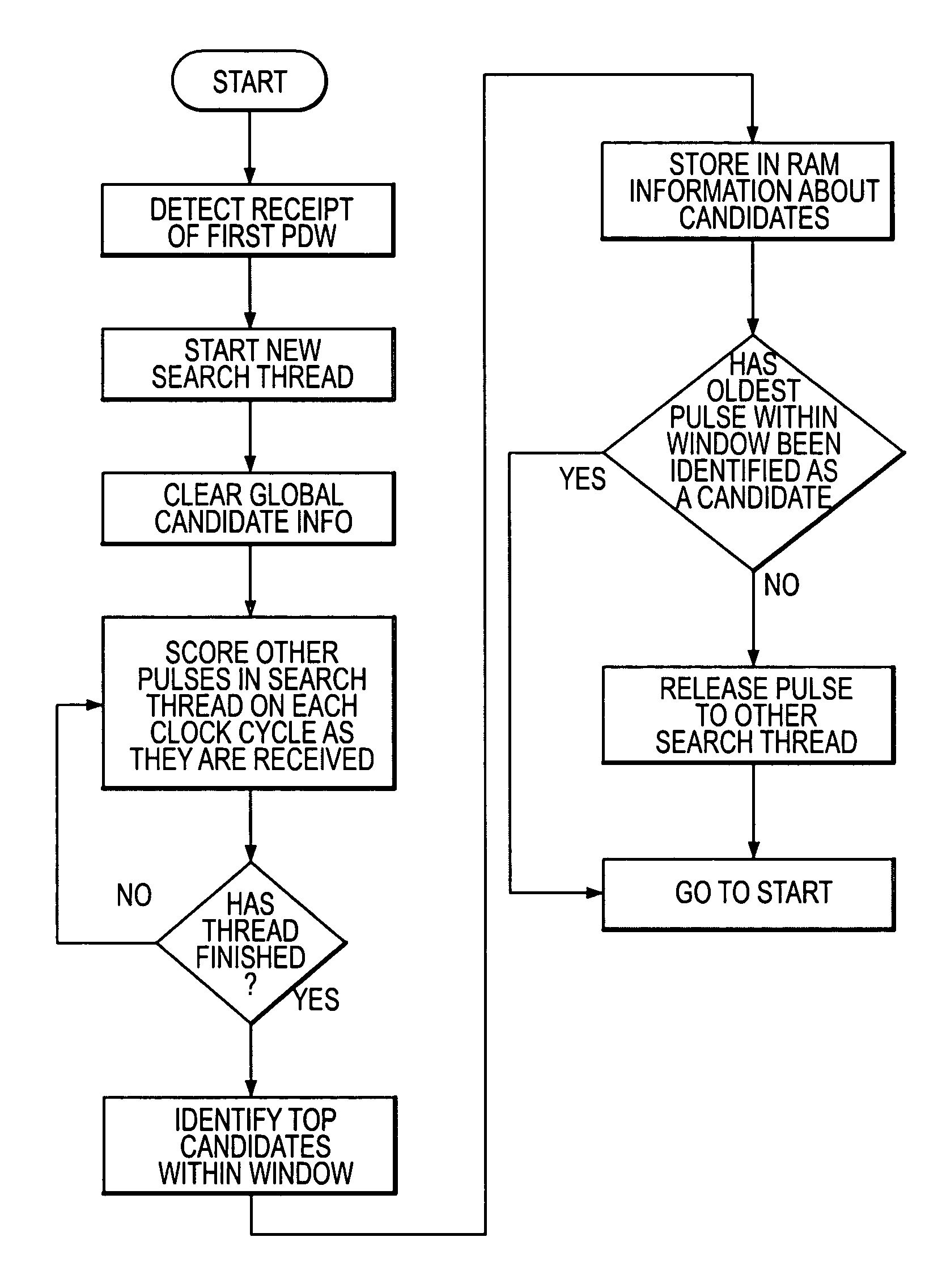
InactiveUS6985102B1Communication jammingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEvent synchronizationParallel computing
A method of deinterleaving parameter descriptor word (PDW) data includes parallel scoring of pulses in an a posteriori search for associating of pulses based on proximity within a multi-parameter problem space. The a posteriori search includes scoring an oldest pulse against all newer pulses, and then scoring a next oldest pulse against all newer pulses. The associating utilizes at least one of a plurality of parallel computation modes, parallel tasks to operate on separate data fields, and multi-threading or multitasking that can implement one of parallel and configuration-overlaid operation, synchronized by events.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
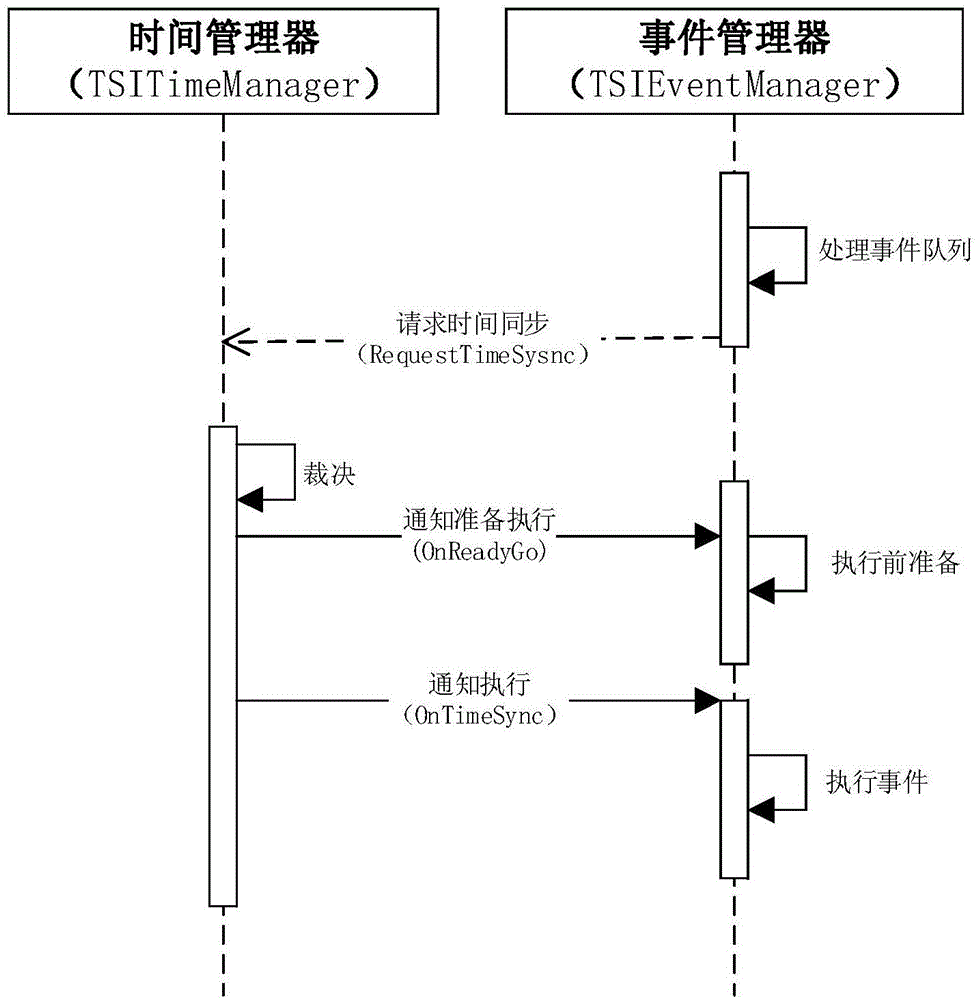
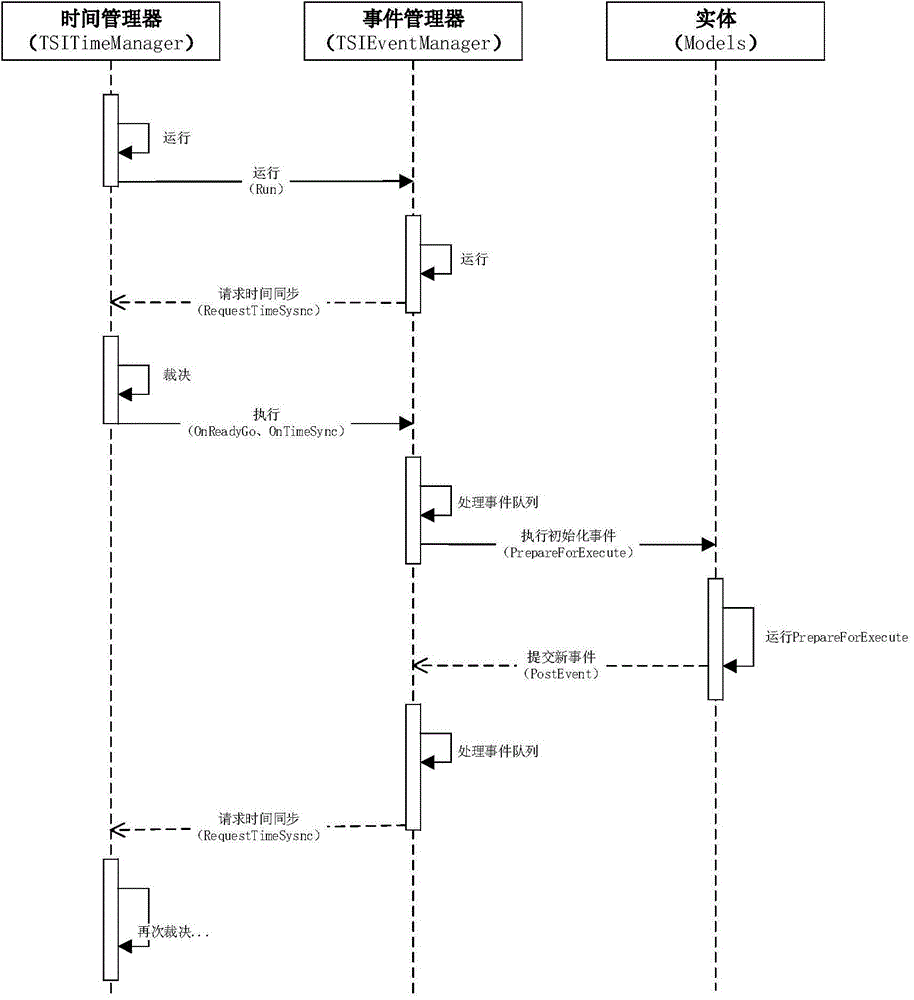
Multi-task-based discrete event parallel simulation and time synchronization method
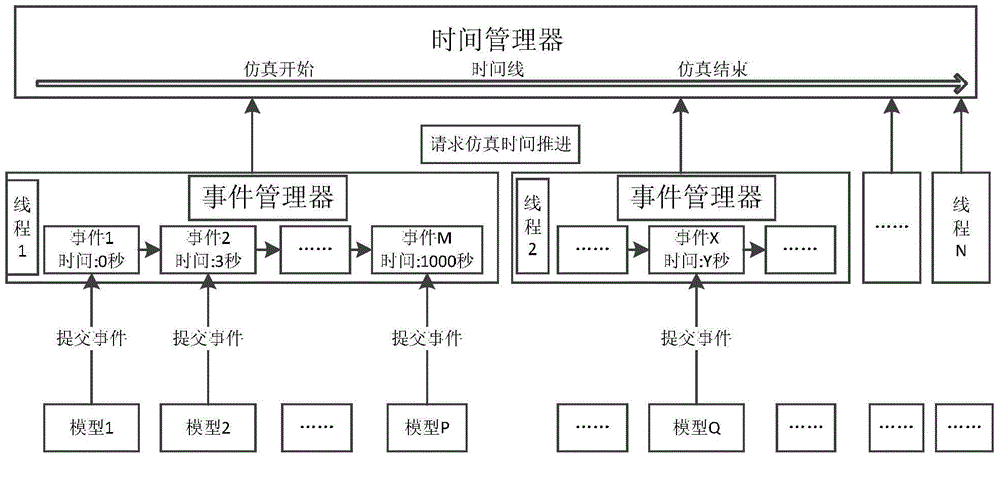
ActiveCN104866374AAvoid the disadvantage of not being able to fully utilize hardware resourcesAvoid overheadProgram initiation/switchingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEvent synchronizationTime management
Owner:BEIJING HUARU TECH
Performing seamless positioning using various location techniques
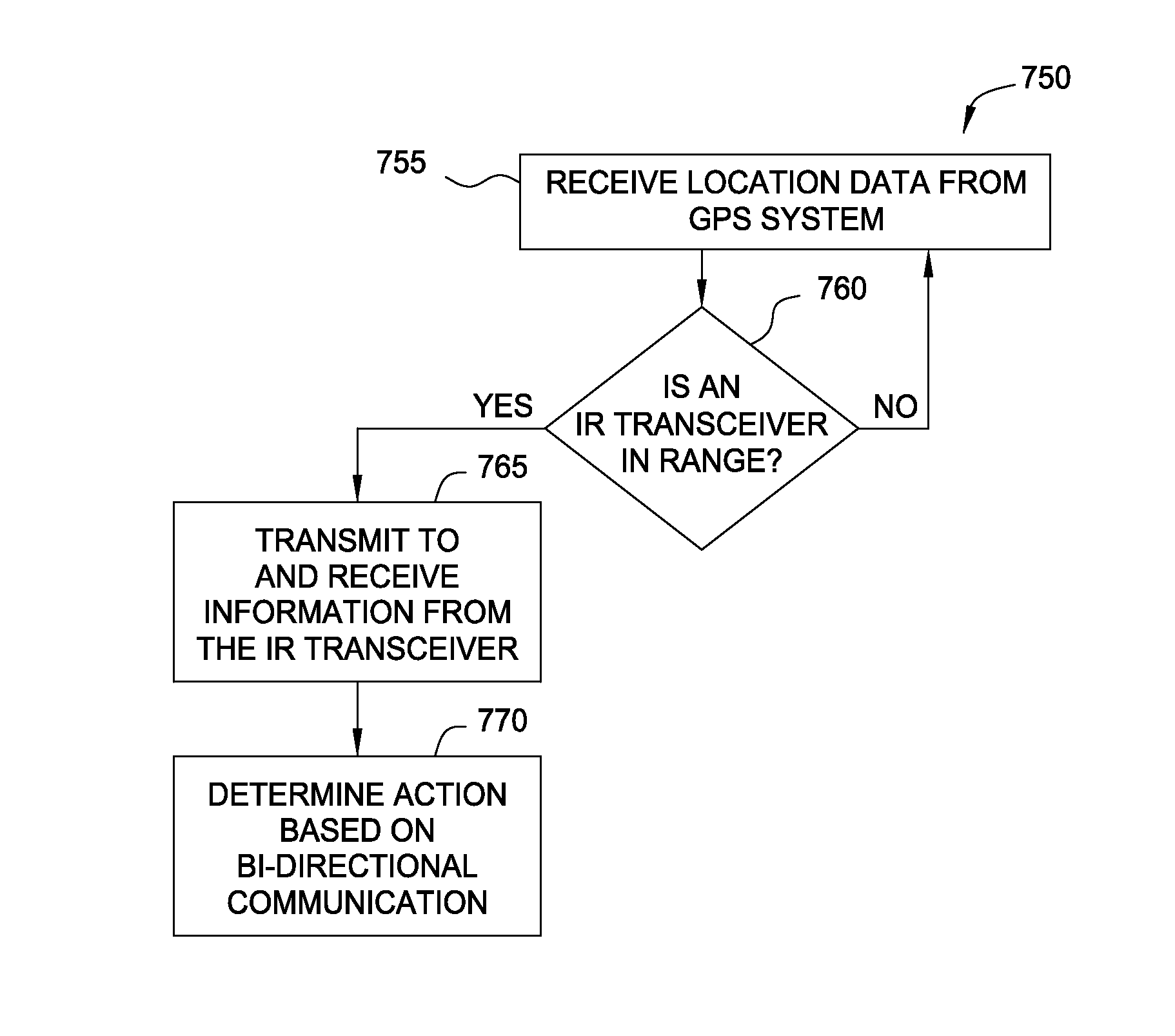
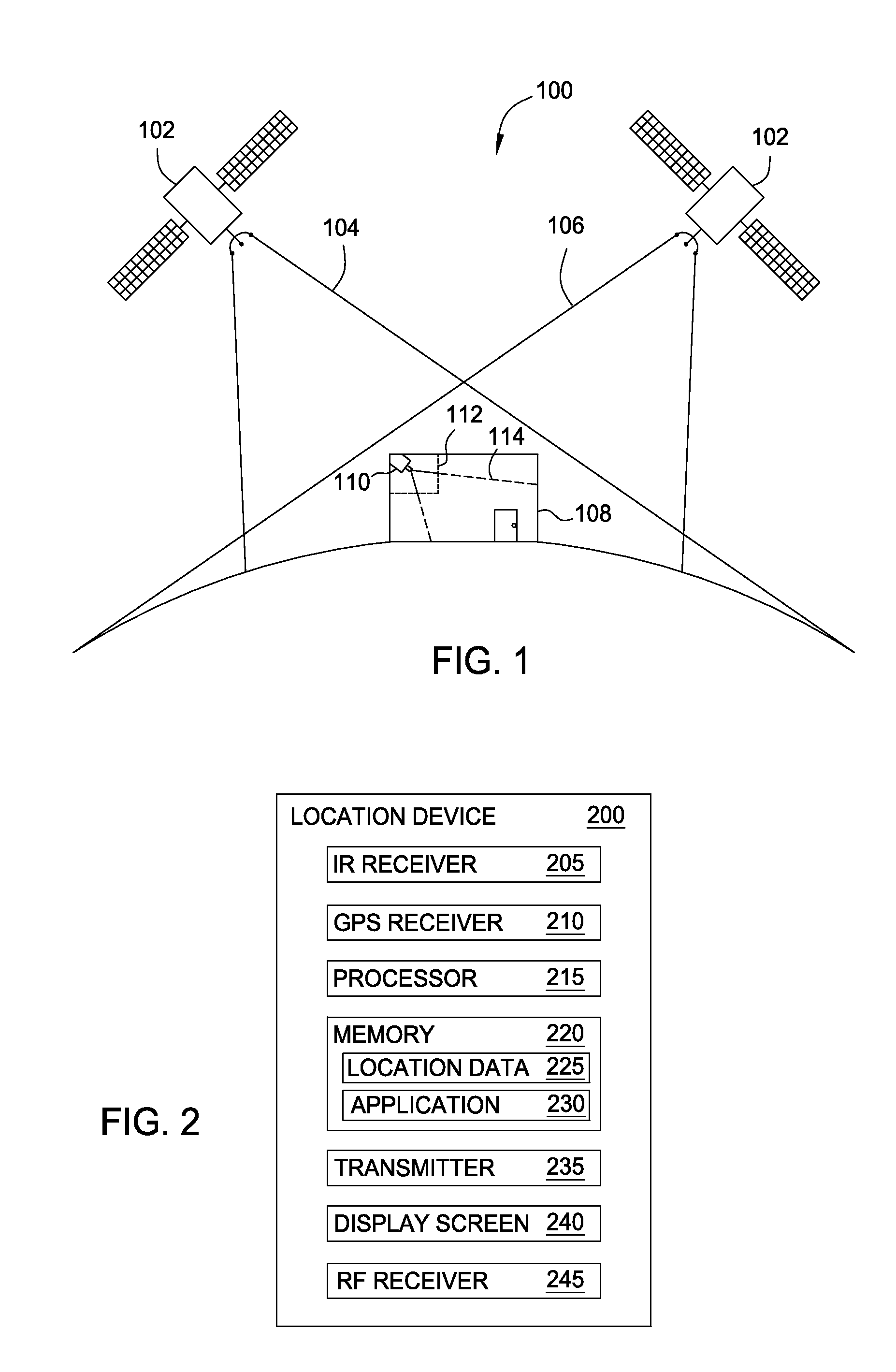
A computing device may rely on GPS and IR communication to determine its current location. The limits of GPS may prevent it from reliably providing location data to the computing device in a variety of situations such as in downtown metropolitan areas, geographic regions with thick canopies, in buildings, and the like. As a result, a second communication technique may also be used to provide location data to the computing device. For example, an IR transmitter may transmit location data to the computing device which, in turn, uses the location data to identify its current location. In addition, the computing device may receive or transmit supplemental data using the second communication technique for, e.g., synchronizing the computing device to a real-time event happening at the identified location or providing the location of the device to a central computing system.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Method and apparatus for resolving conflicts in a substrate processing system
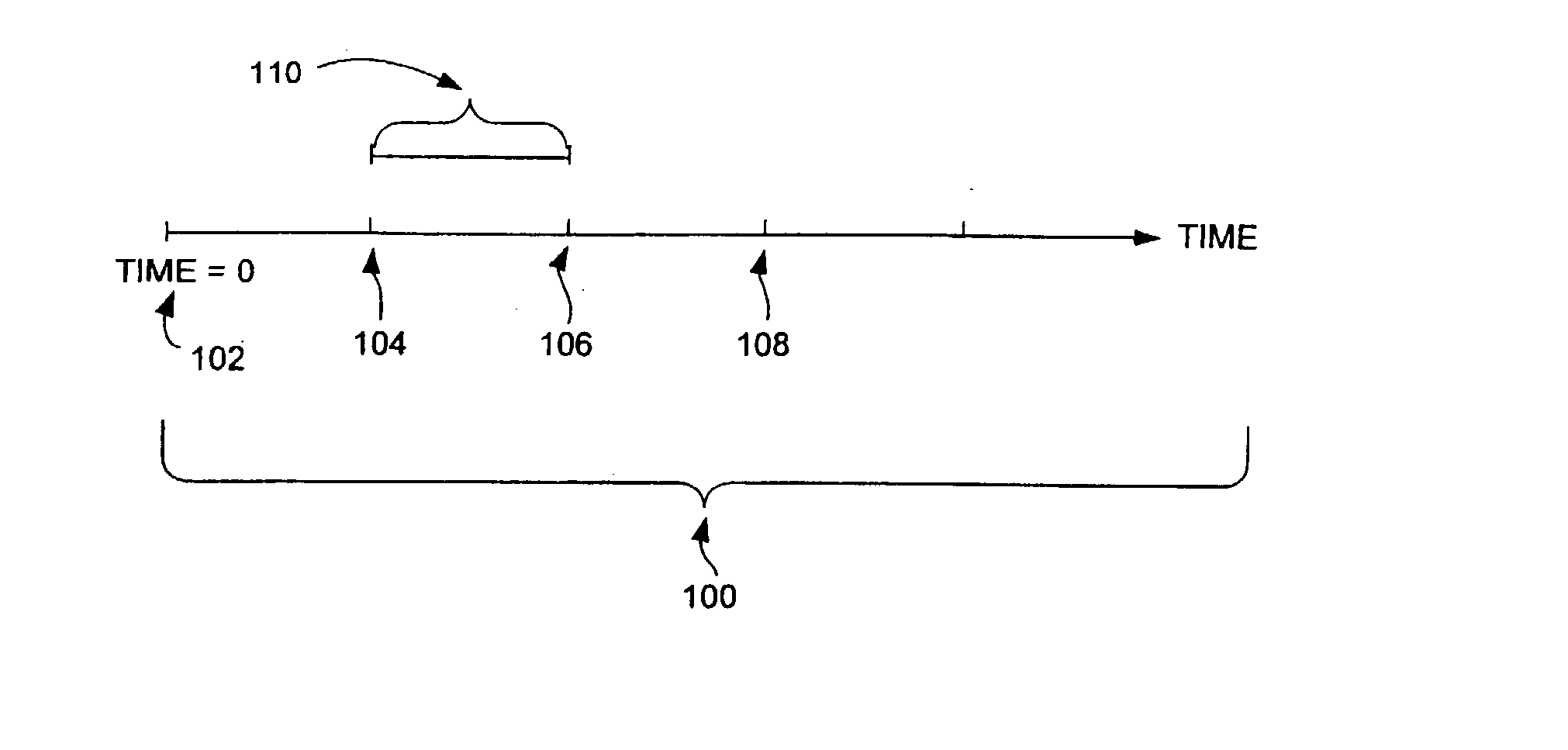
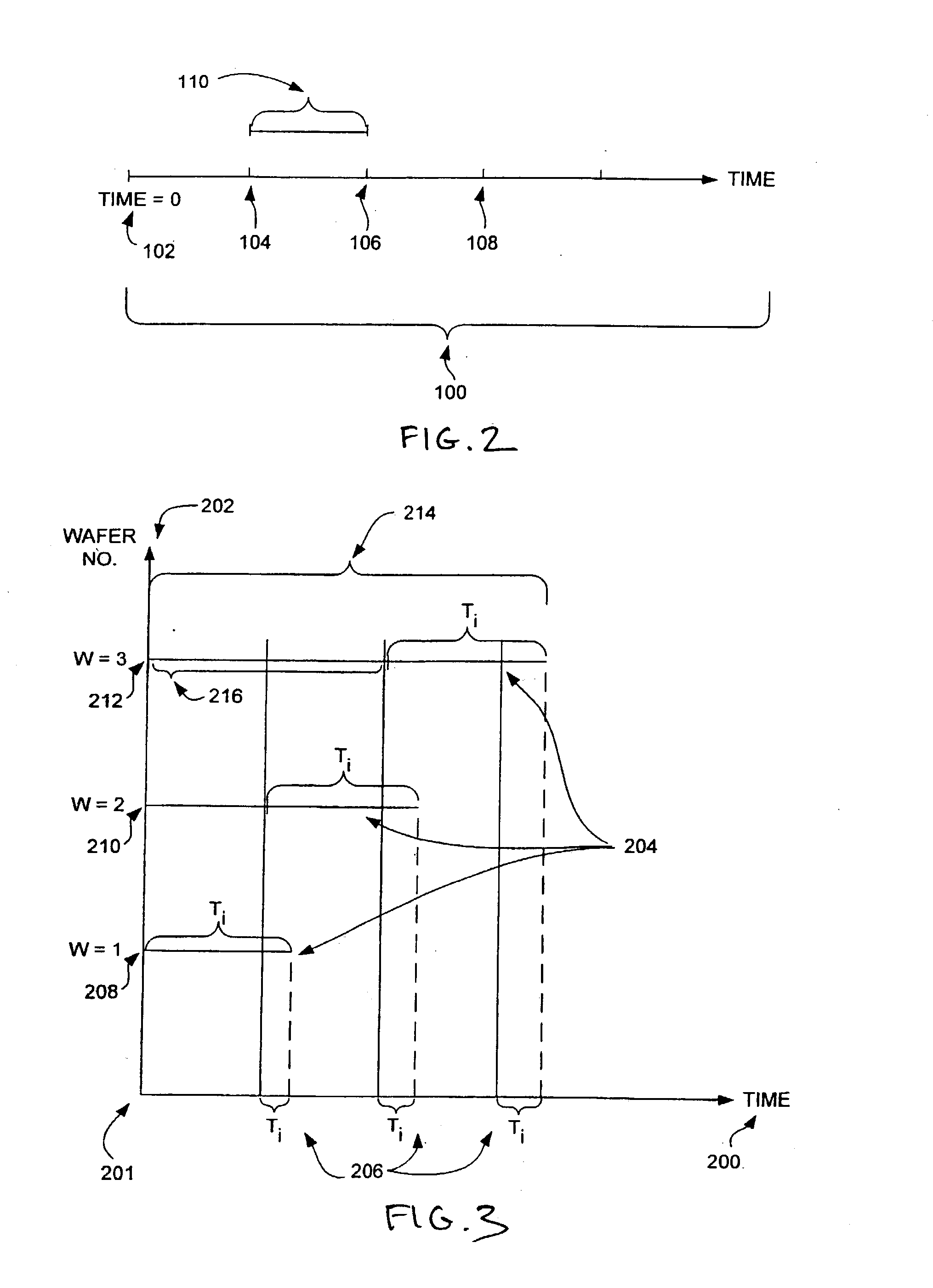
InactiveUS6768930B2Without diminishing throughputHigh and reliable throughputProgramme controlDigital data processing detailsLithographic artistEvent synchronization
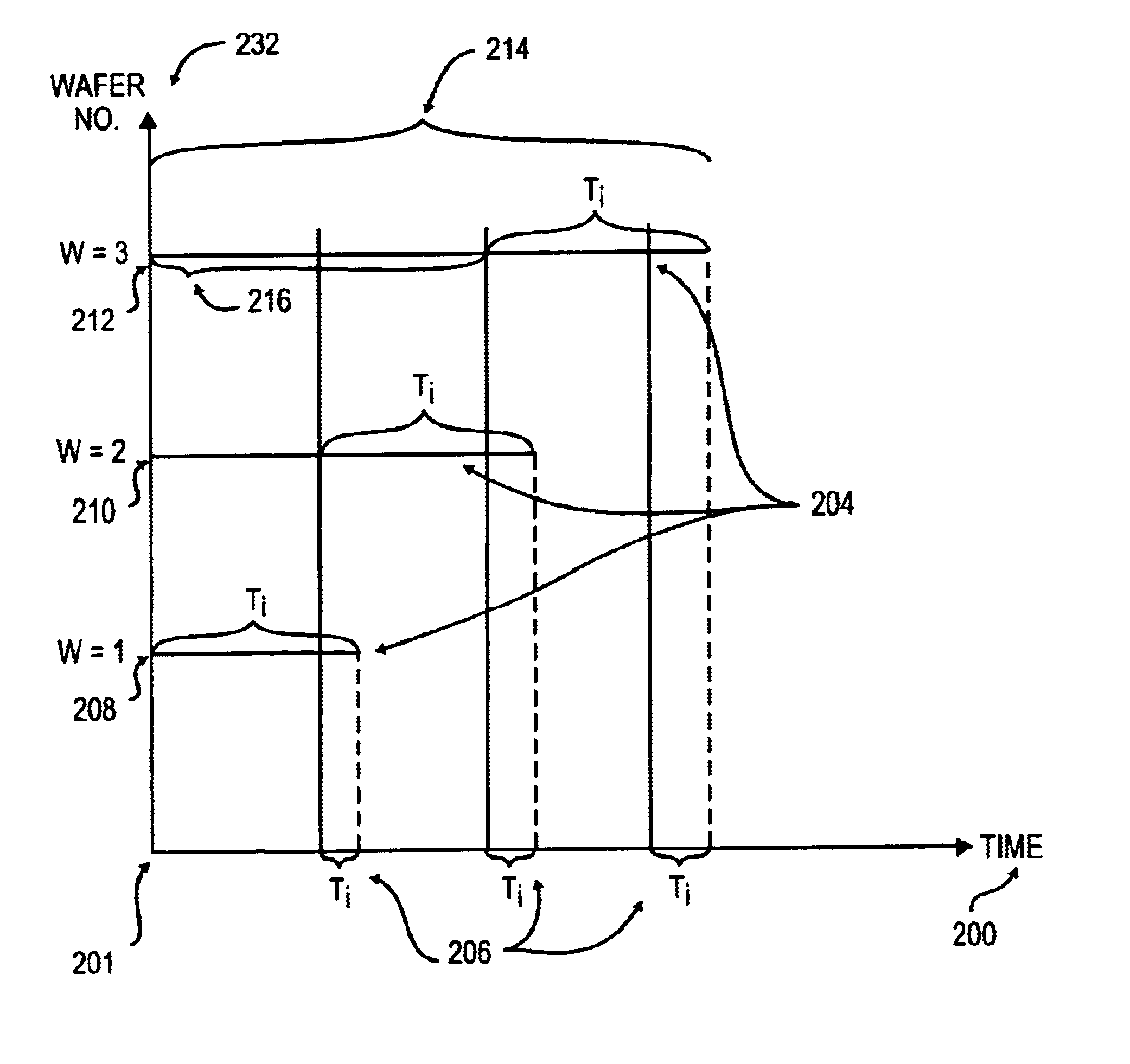
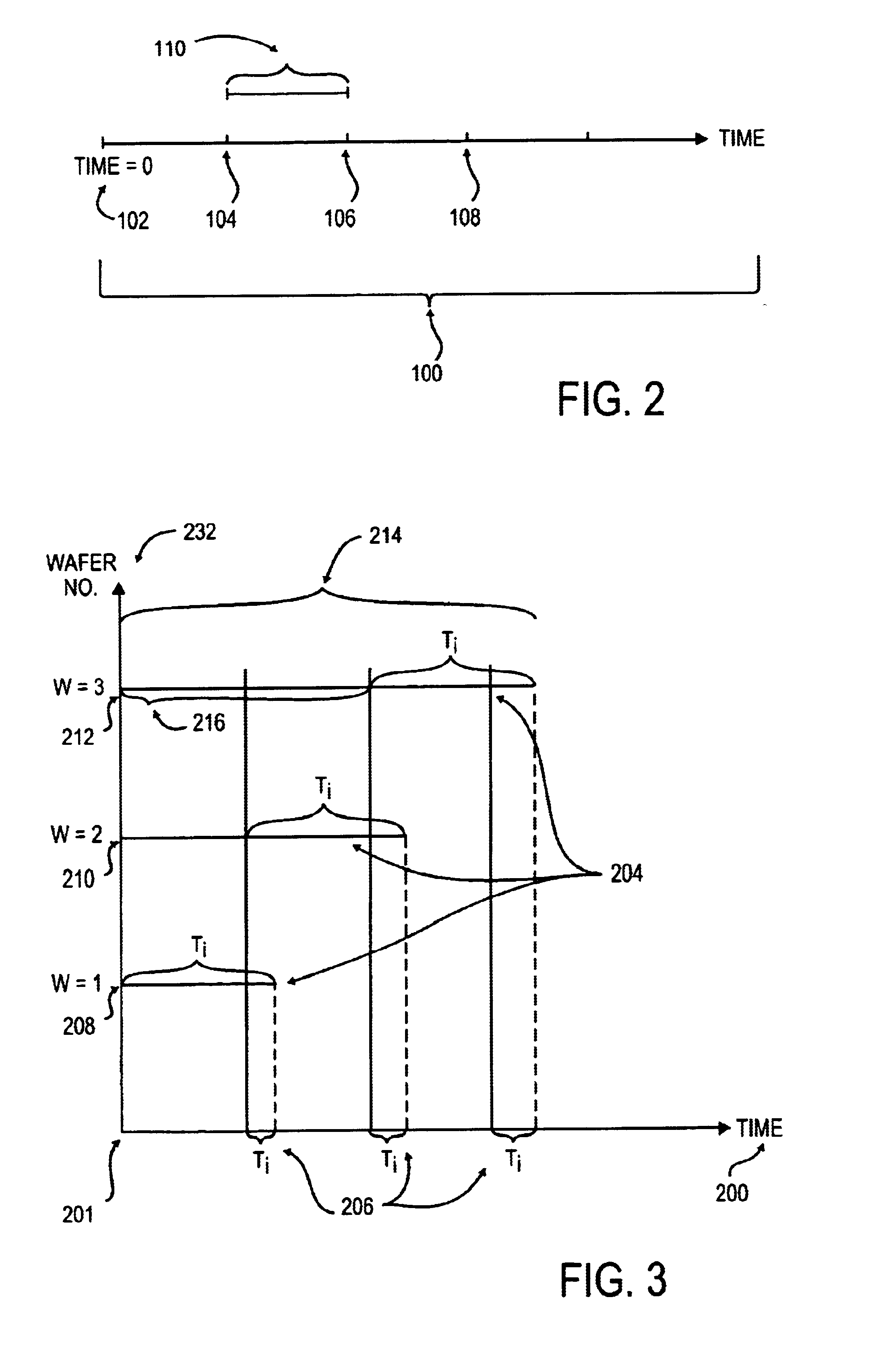
A wafer track and lithography cluster tool for performing a series of processes with a scheduler which synchronizes all events in a substrate processing system. Events in the cluster tool are scheduled to occur at regular, periodic intervals, thereby improving throughput and quality. The scheduler also eliminates conflicts for transportation resources between modules in the cluster tool. Wafers are loaded into the cluster tool at a regular interval, referred to as a sending period. All events in the system are synchronized with the sending period, and all event timings are normalized in terms of the sending period. The conflicts are resolved by selectively adding delays in modules which can tolerate them without degrading throughput or performance in the system; modules that cannot tolerate delays are exempted. The periodicity of the scheduled cluster tool enables the identification of wafers in the cluster tool. The identification of the order in which a wafer was loaded also identifies a module path followed by the wafer.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
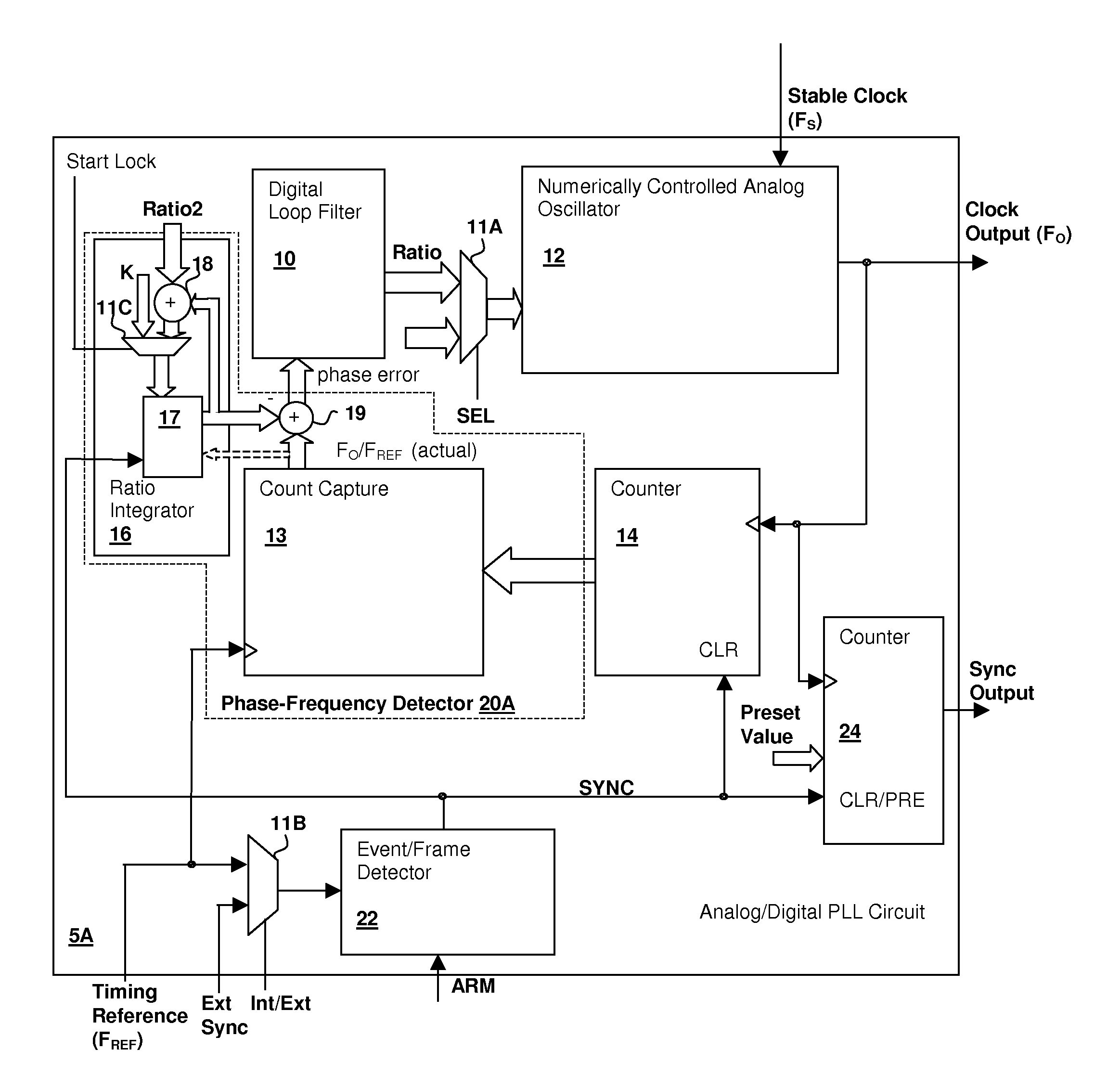
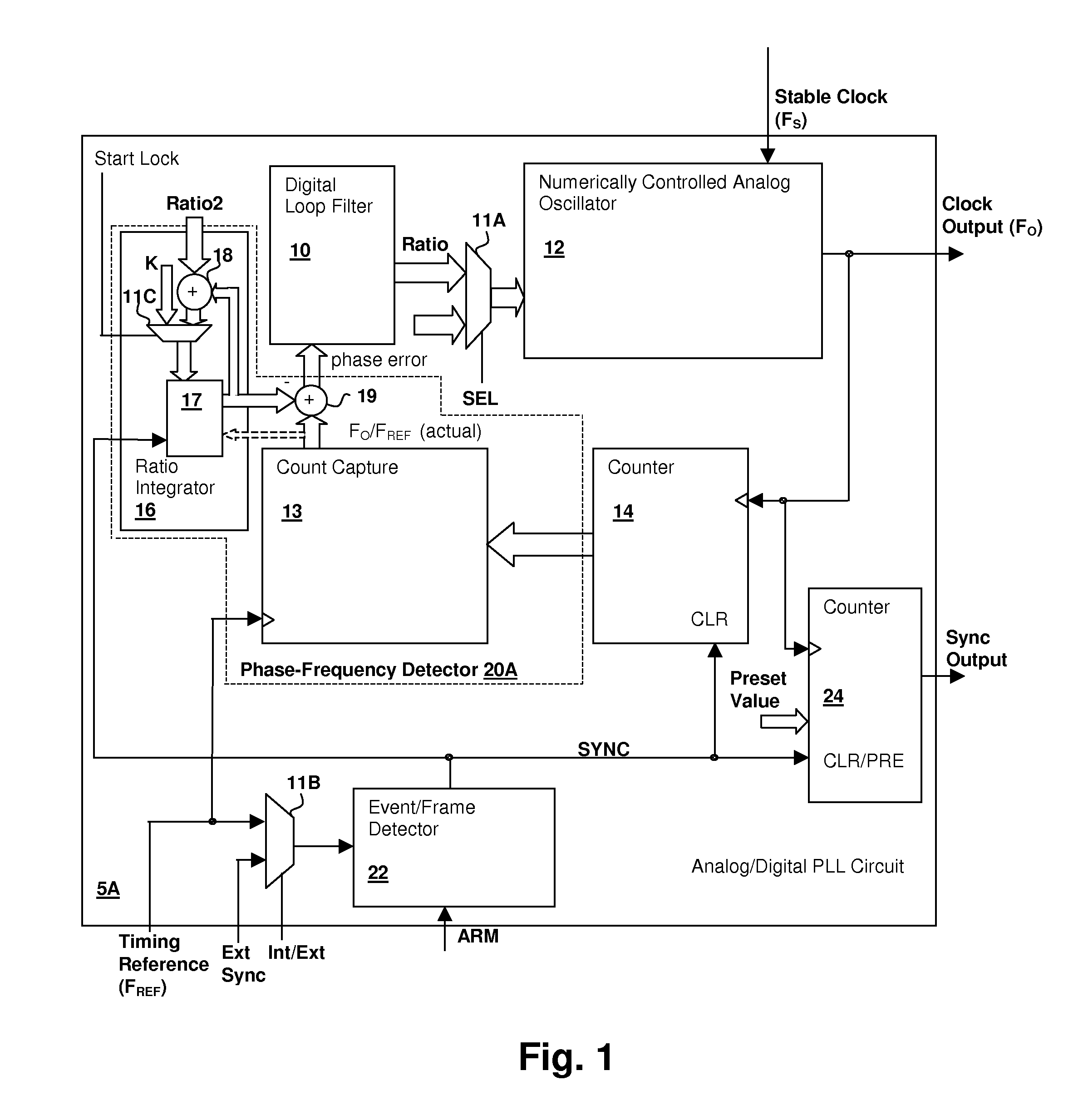
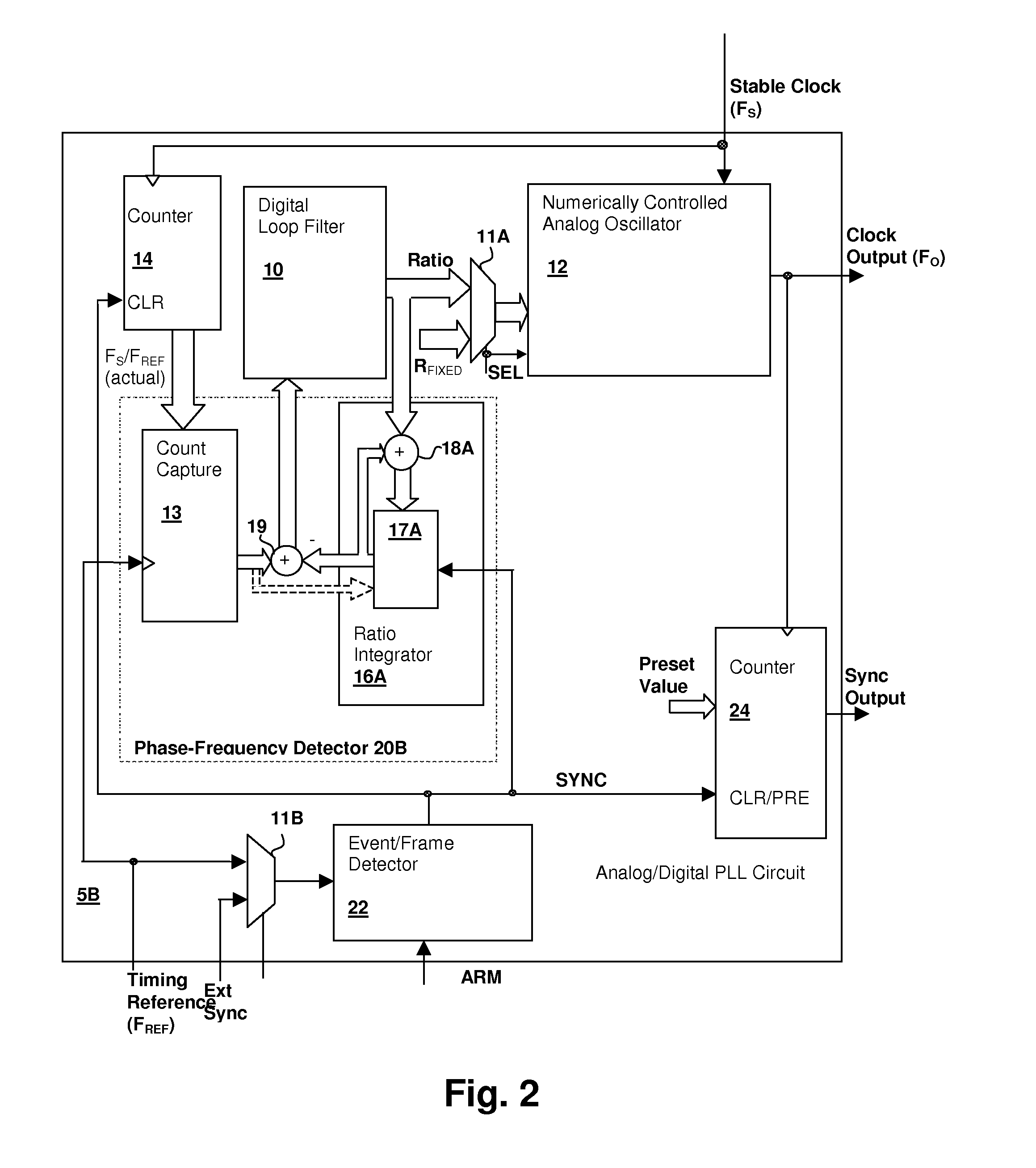
Hybrid analog/digital phase-lock loop with high-level event synchronization
ActiveUS20080075152A1Modulated-carrier systemsPulse automatic controlEvent synchronizationLow jitter
A hybrid analog / digital phase-lock loop with high-level event synchronization provides a mechanism for generating a low-jitter clock from a timing reference that has a high jitter level and synchronizing the output clock to high-level events. A numerically-controlled analog oscillator provides a clock output and a counter divides the frequency of the clock output to provide input to a digital phase-frequency detector for detecting an on-going phase-frequency difference between the timing reference and the output of the counter. A synchronization circuit detects or receives a high-level event signal, and resets the on-going phase-frequency difference and optionally the counter to synchronize the clock output with the events. The synchronization circuit may have an arming input to enable the synchronization circuit to signal a next event. Another clock output divider may be included to generate a timing reference output, and the other clock divider also reset in response to a detected event.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
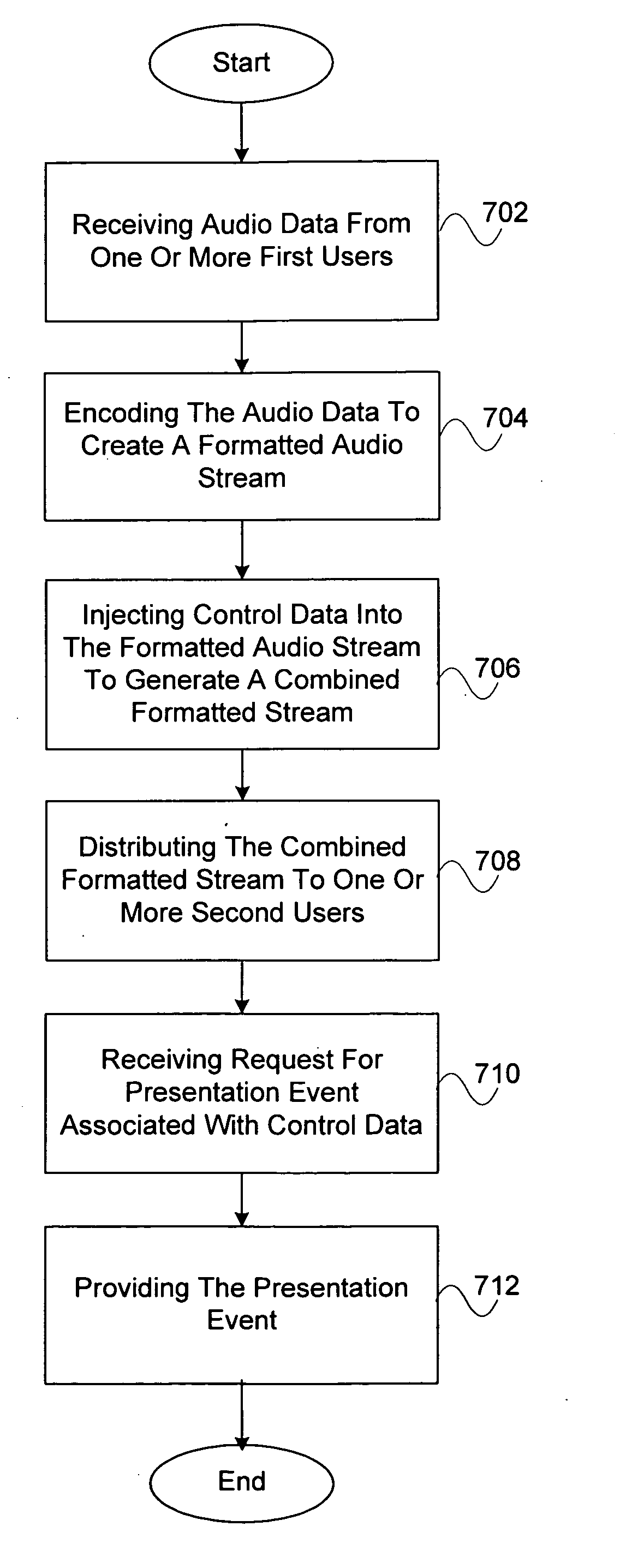
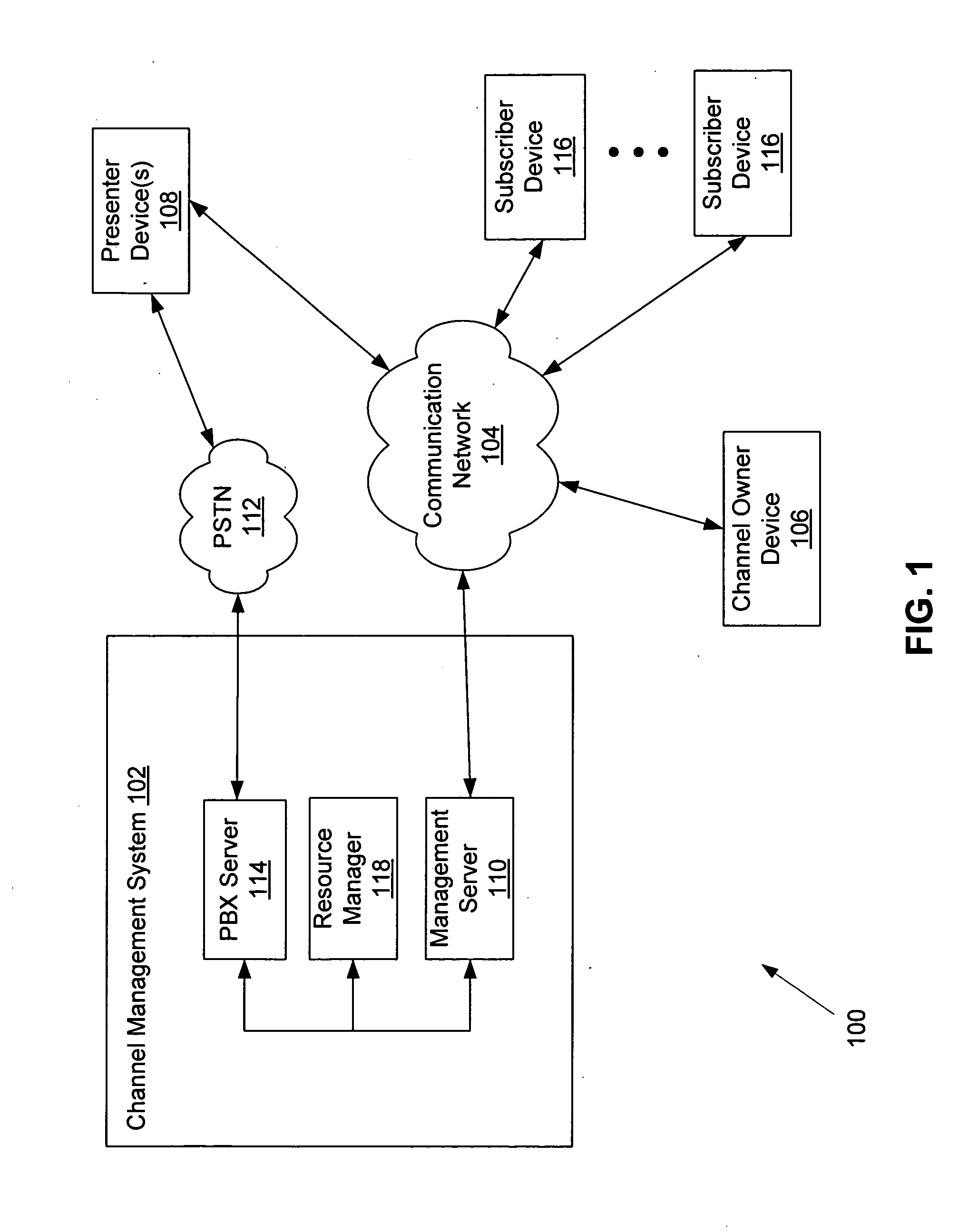
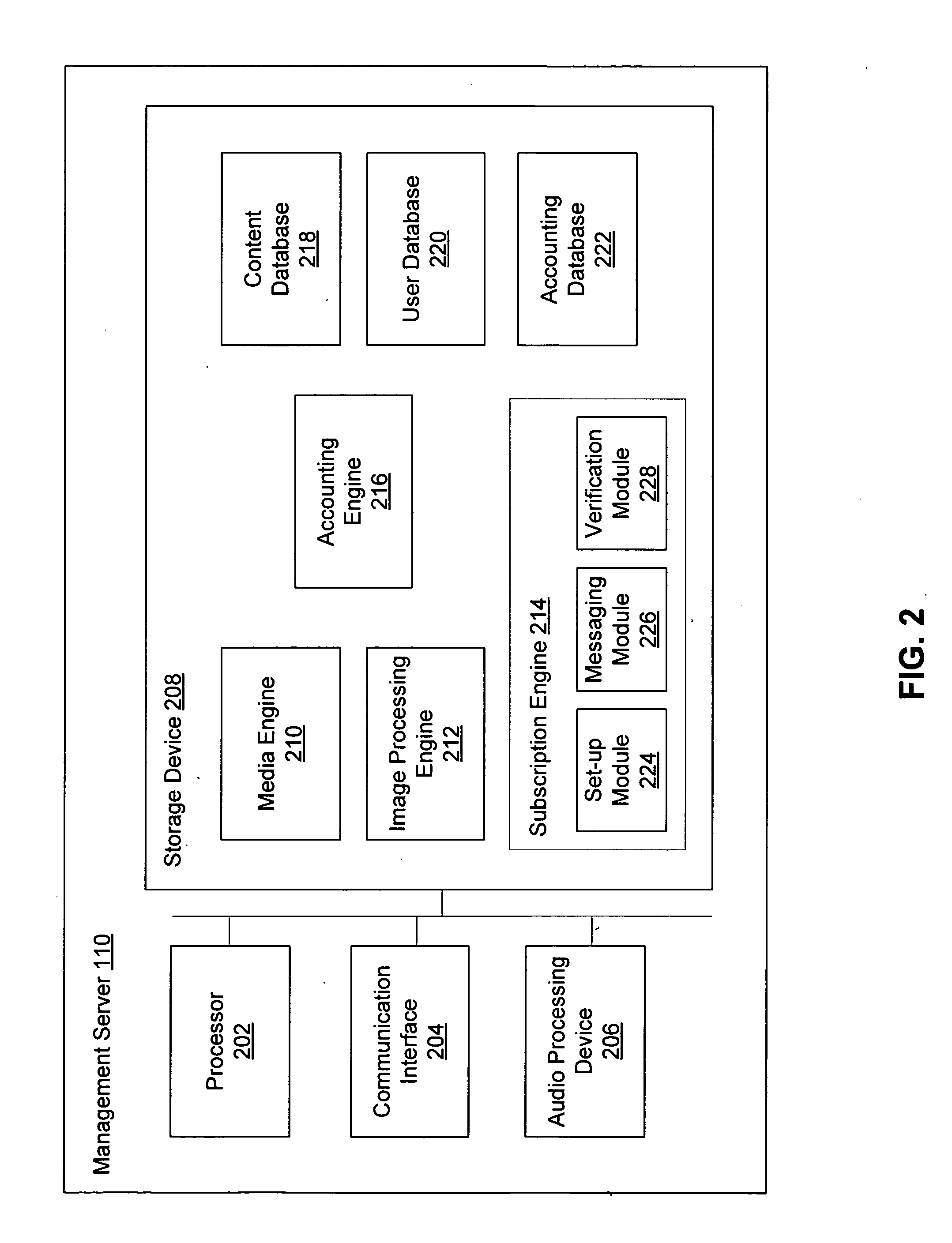
Systems and methods for integrating live audio communication in a live web event
ActiveUS20090164876A1Optimize networkTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsEvent synchronizationControl data
A system, method, and computer program for integrating live audio communication in a web event is provided. In exemplary embodiments, live audio data is received from one or more presenters. The live audio data is then encoded to create a formatted audio stream. The formatted audio stream may be synchronized with presentation events to generate the live web event by injecting control data for the presentation events. A combined formatted stream may be distributed to one or more users.
Owner:BRIGHTTALK
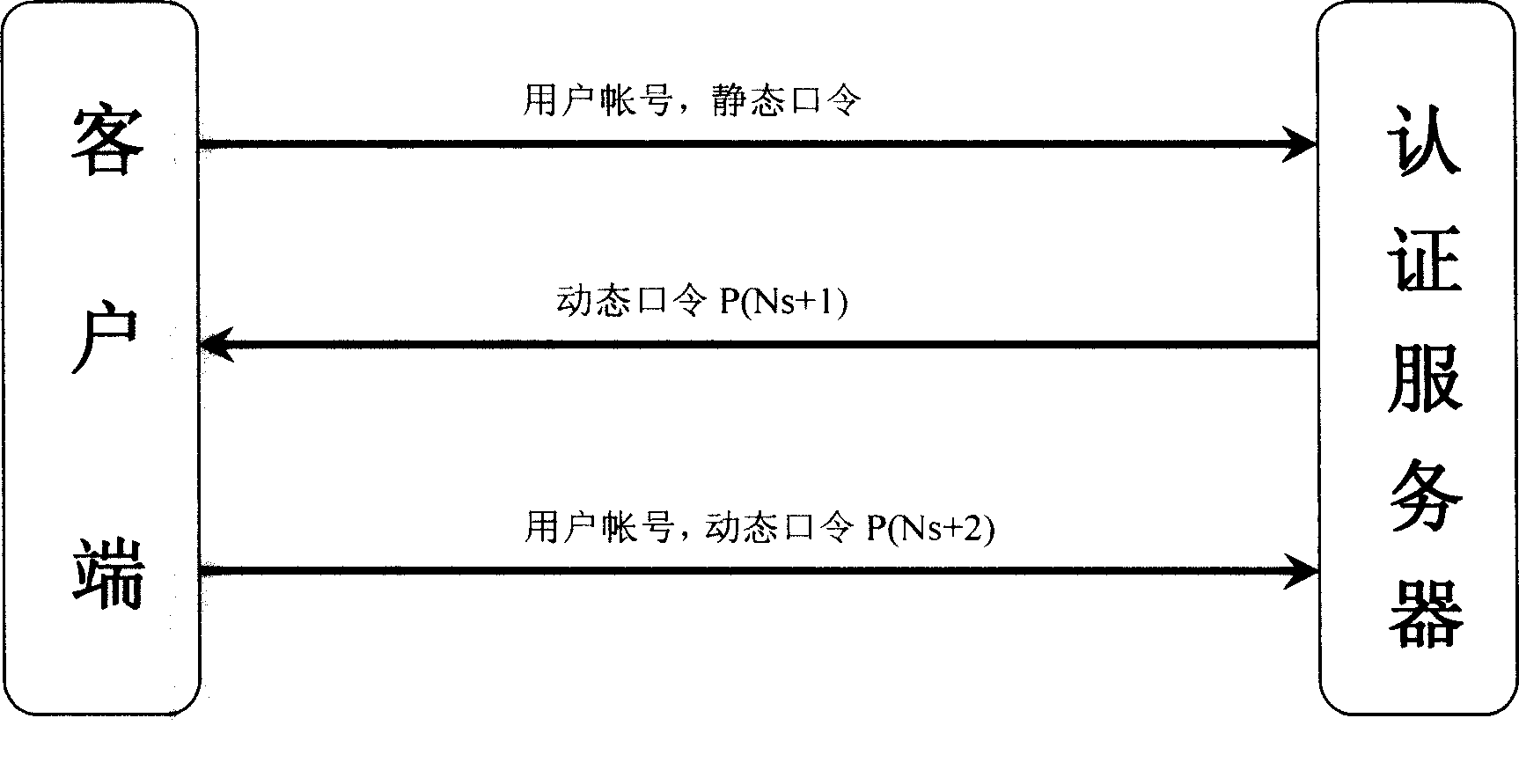
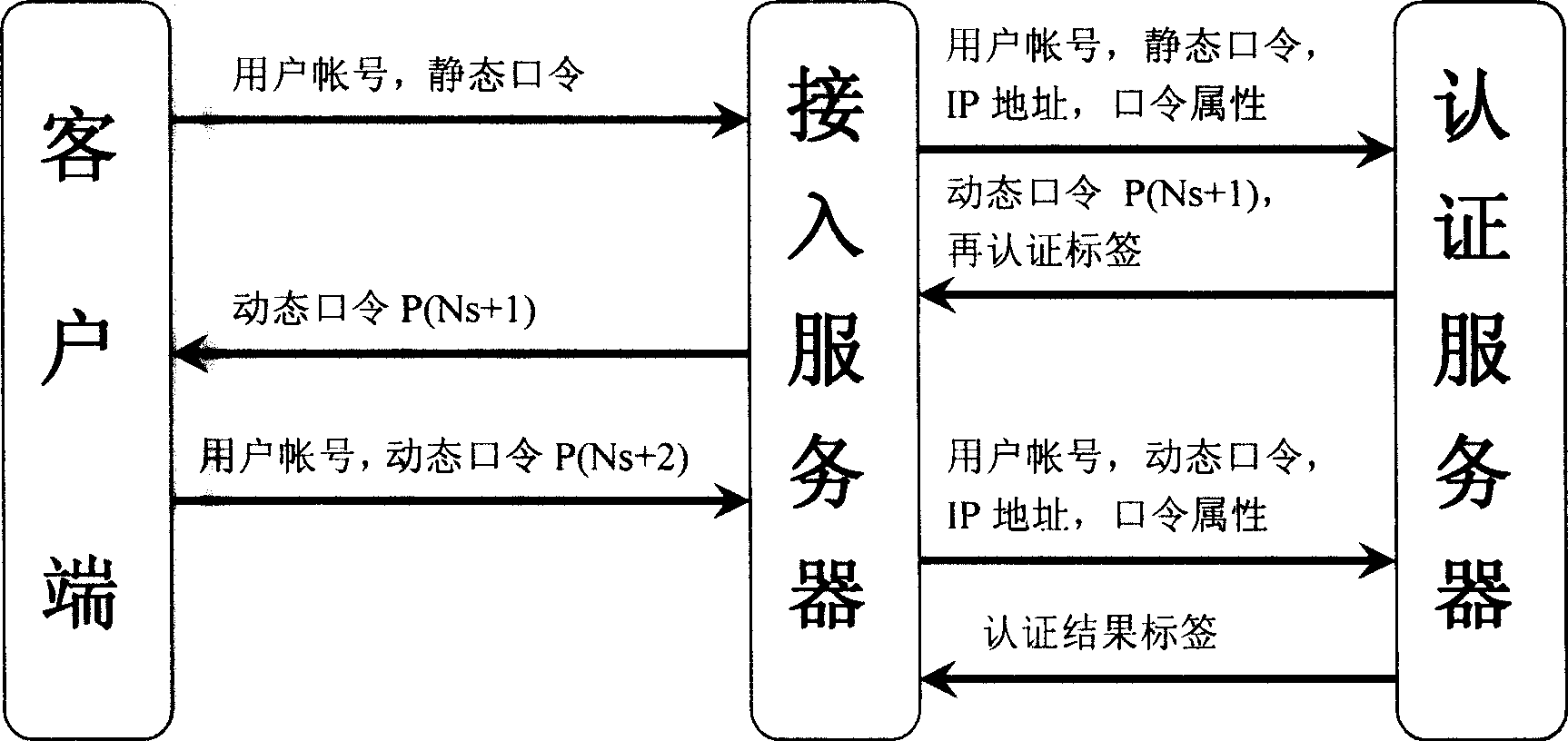
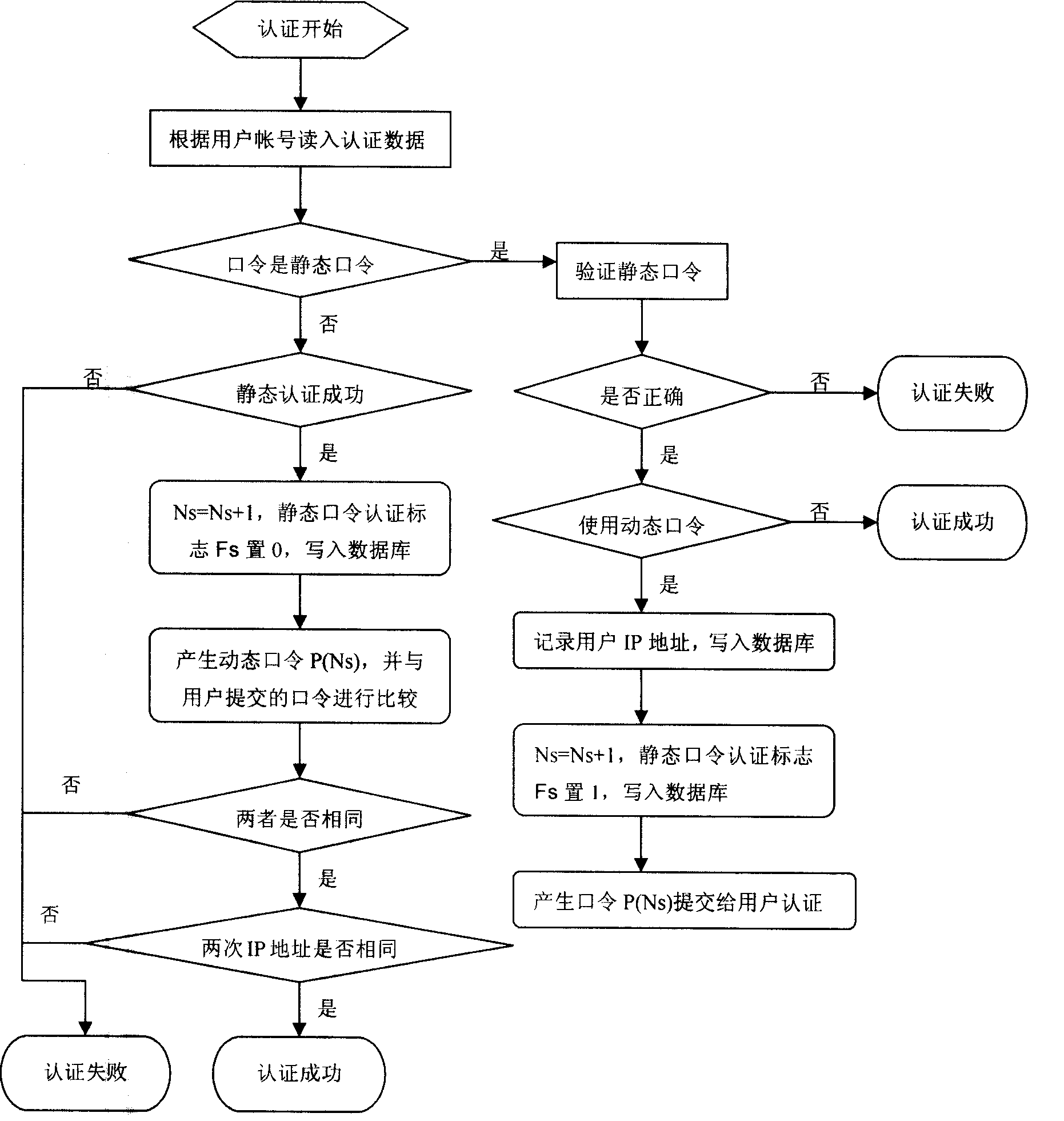
Personal identification process for dynamic cipher password bidirectional authentication based on multiple variables
The invention provides multivariable dynamic password two-way authentication based identification method technique. The core of the invention is the dynamic password generation technique adopting event synchronization, and by adopting the method in which a client end synchronizes a server end, a secure authentication flow is established. The technique not only can prevent attack by the various prior attack methods, but also is fully compatible with a prior static password authentication based network application system. The technique has the advantages of low upgrading and modifying costs of the system, short time needed for upgrading and modification of the system and unchanged use habit of a user; moreover, a user can independently determine whether the strong identity authentication method is selected to protect the security of an account number, so the method technique meets the security needs of users at different levels.
Owner:北京唐桓科技发展有限公司
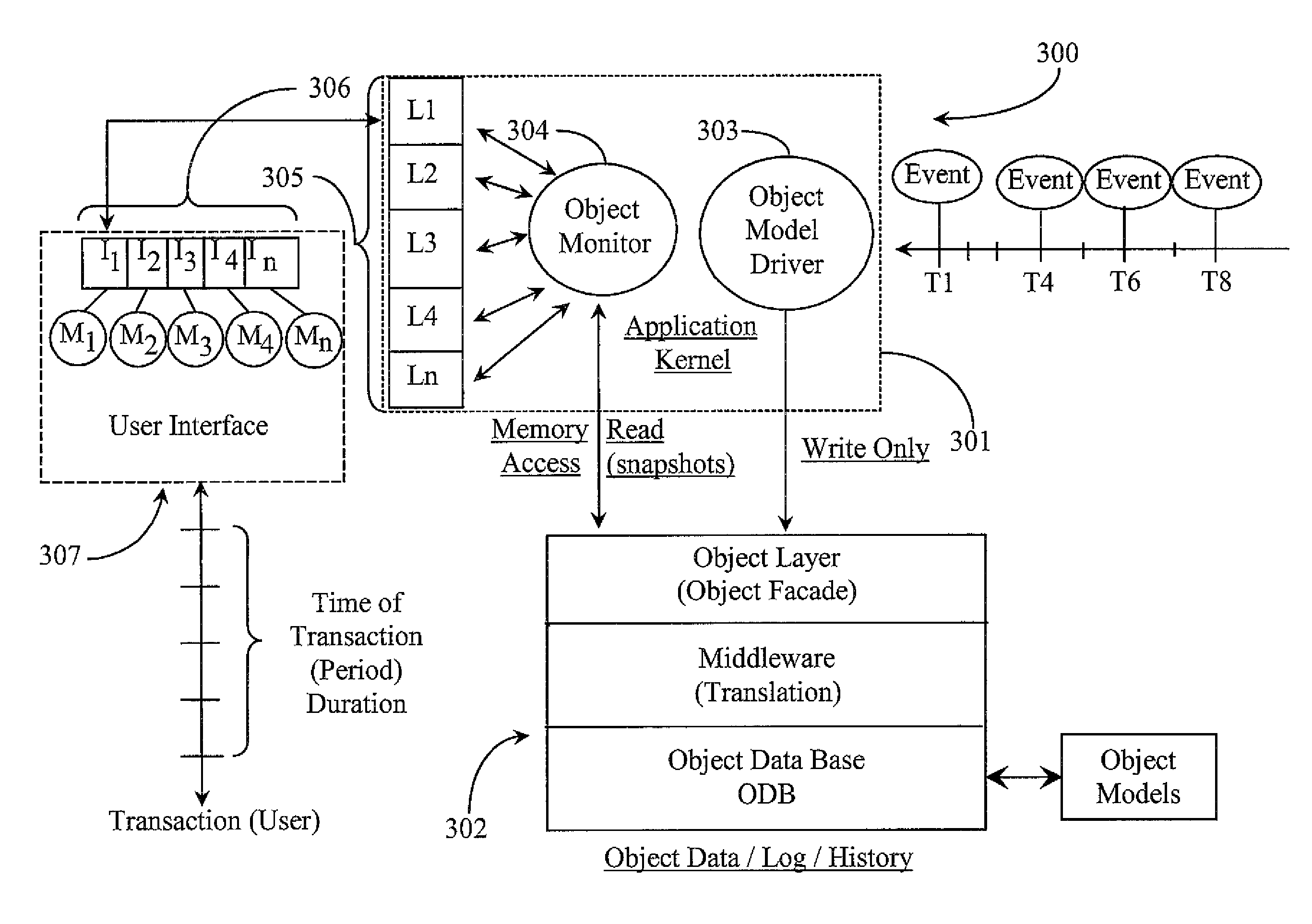
Method for improving temporal consistency and snapshot recency in a monitored real-time software-reporting-application architecture
ActiveUS7434229B2Great customizationFinanceMultiprogramming arrangementsTemporal consistencyDatabase application
An object-oriented software application is provided for receiving updates that change state of an object model and reporting those updates to requesting users. The application includes a database application for storing data; an object model driver for writing updates into the database; a notification system for notifying about the updates; and, a plurality of external monitors for reading the updates. In a preferred embodiment the object model produces multiple temporal snapshots of itself in co-currency with received events, each snapshot containing associated update information from an associated event and whereupon at the time of occurrence of each snapshot coinciding with an event the notification system notifies the appropriate external monitor or monitors, which in turn access the appropriate snapshot, performs calculations thereupon if required and renders the information accessible to the users.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORIES INC
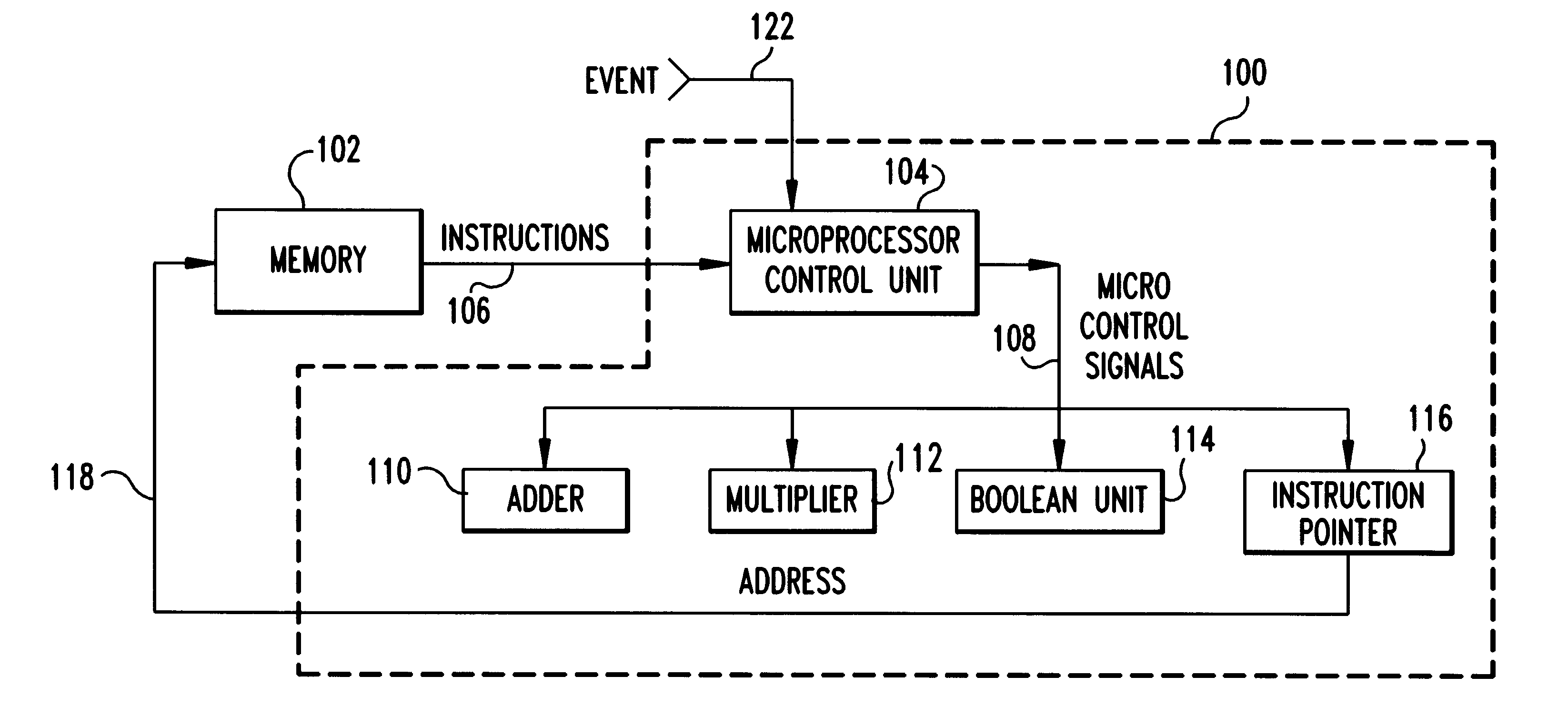
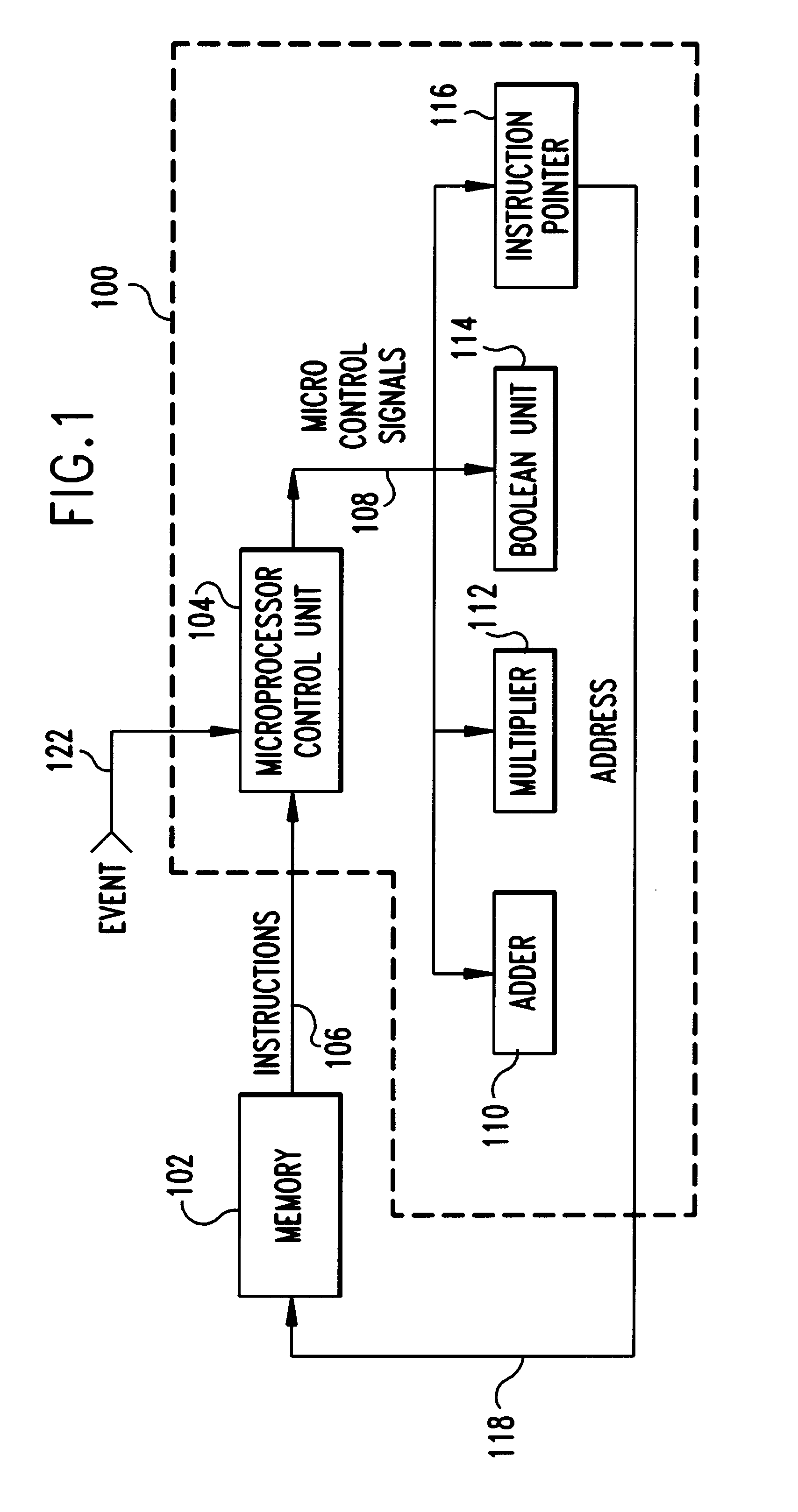
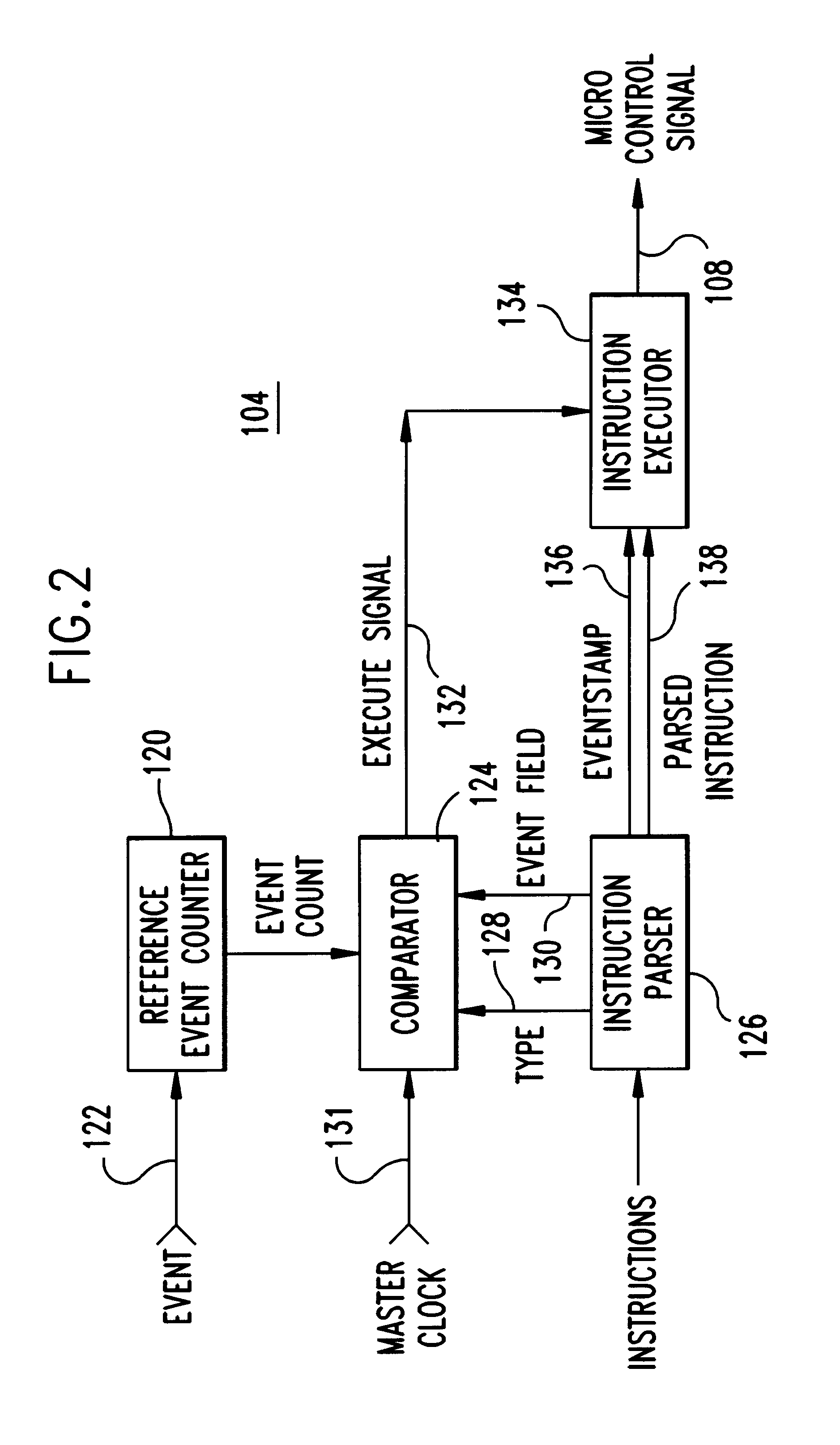
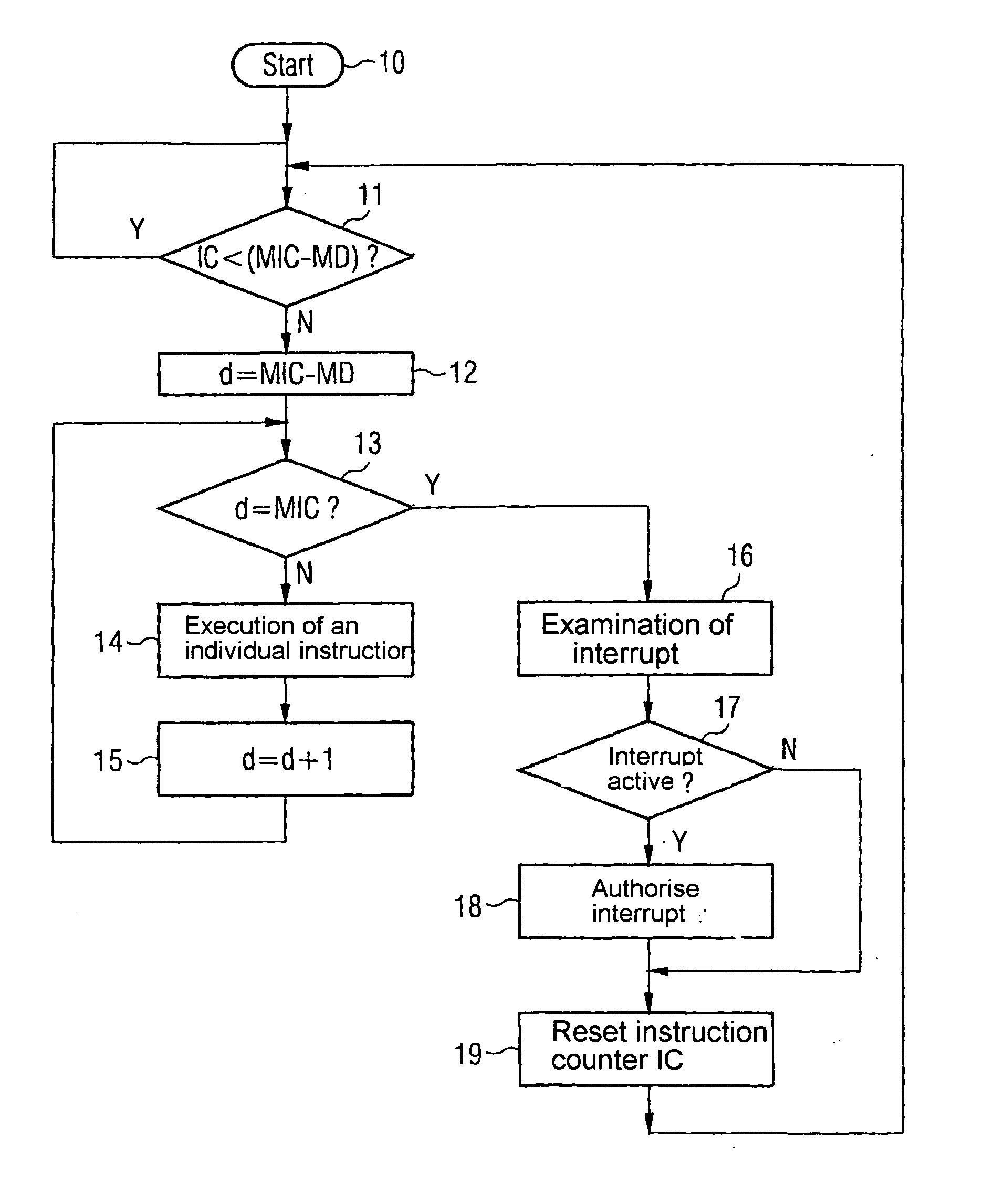
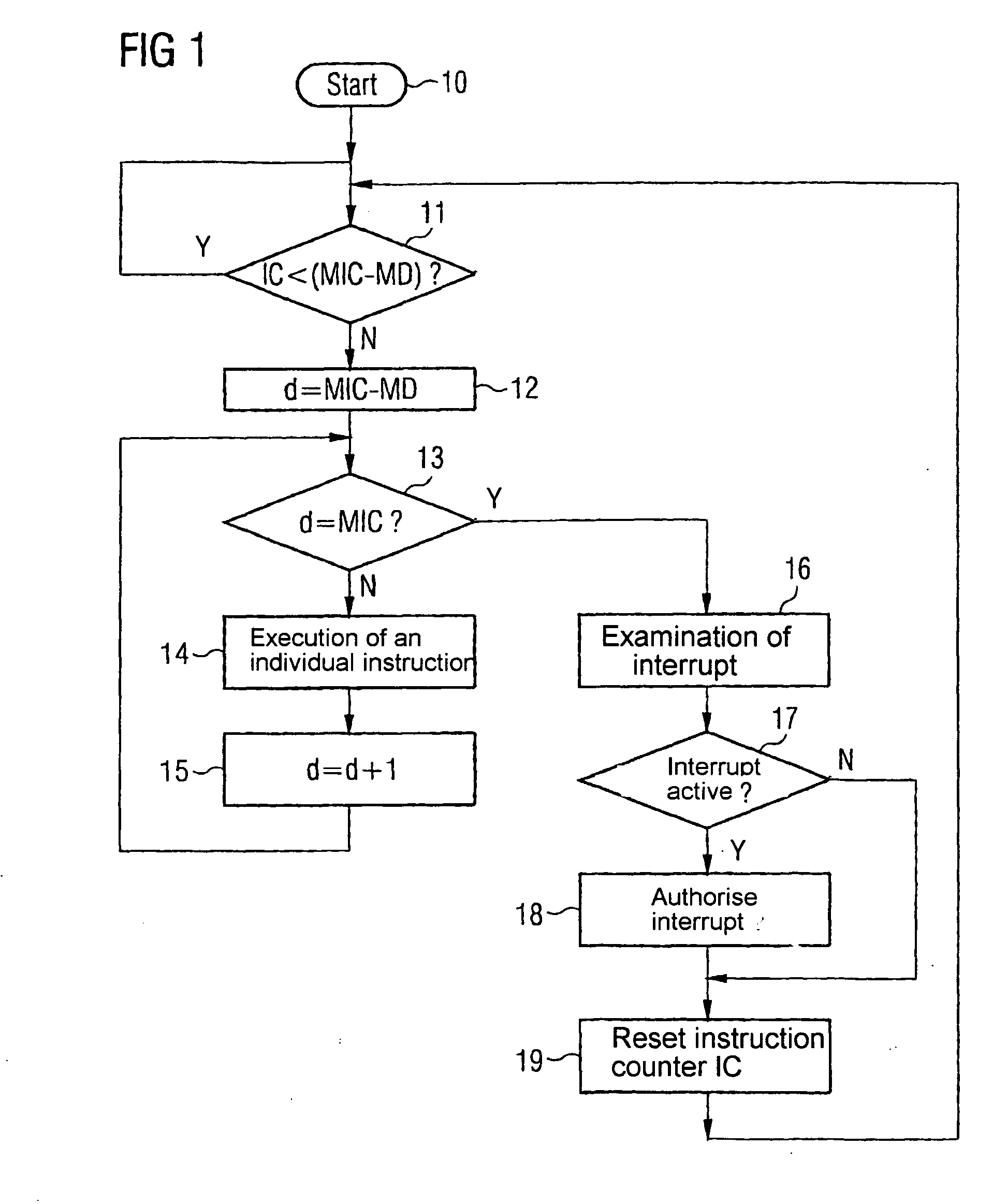
System and method for synchronizing instruction execution with external events
InactiveUS6292887B1Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationEvent synchronizationWait state
An apparatus and method of synchronizing instruction execution in the apparatus with external events. The apparatus may be a processor or microprocessor capable of executing a function specific wait state that is dependant upon a type specified by an instruction field. The processor includes an event counter that maintains an event occurrence count, an instruction parser that strips the instruction type and event count from instructions and passes the stripped information to a comparator. The comparator compares the stripped information against an event count. The instruction types include: a relative type indicating execution at some event occurrence subsequent to the present cycle; a direct type indicating an absolute event occurrence count for execution; and a event range indicating a range of event occurrences wherein execution is valid.
Owner:IBM CORP
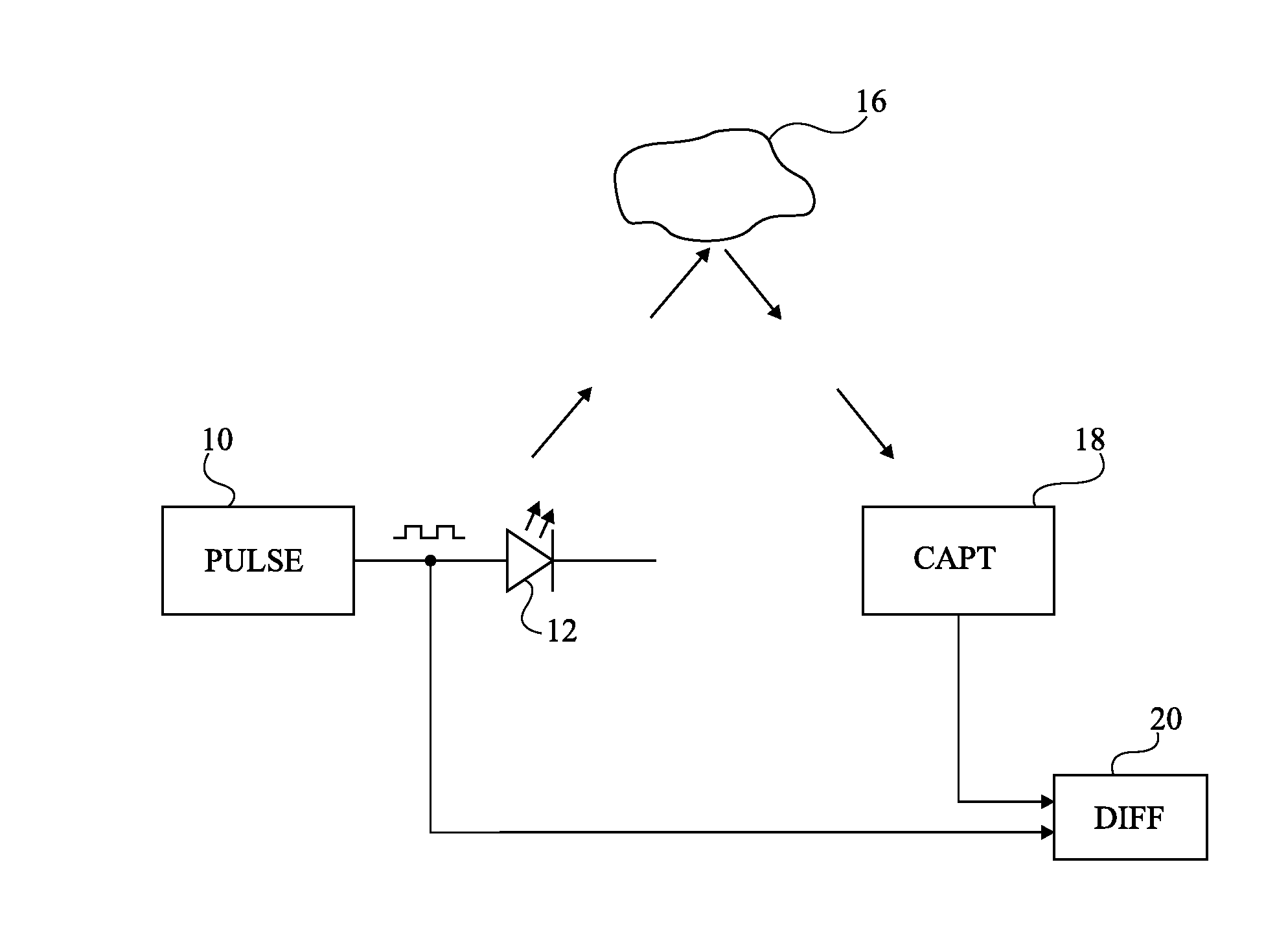
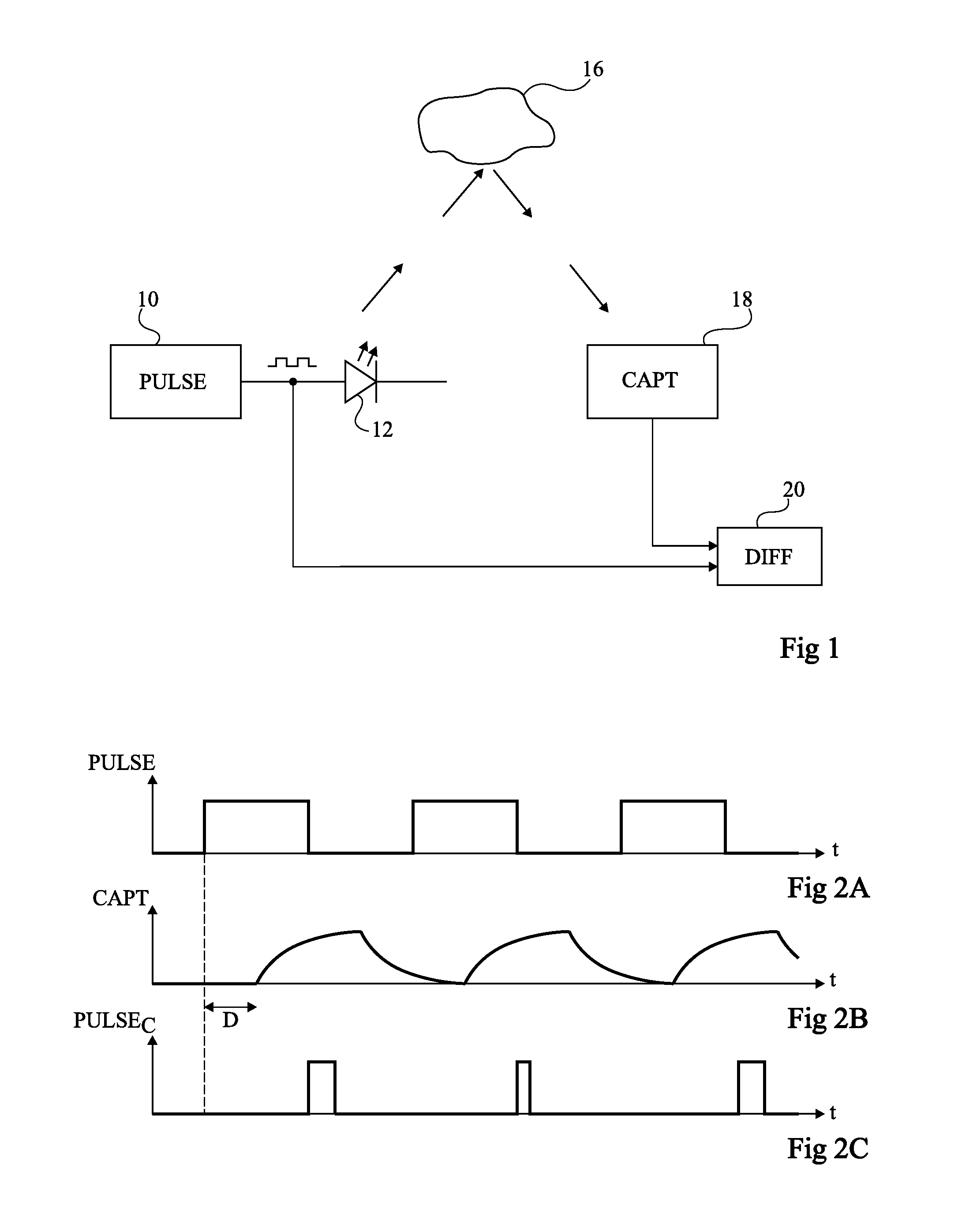
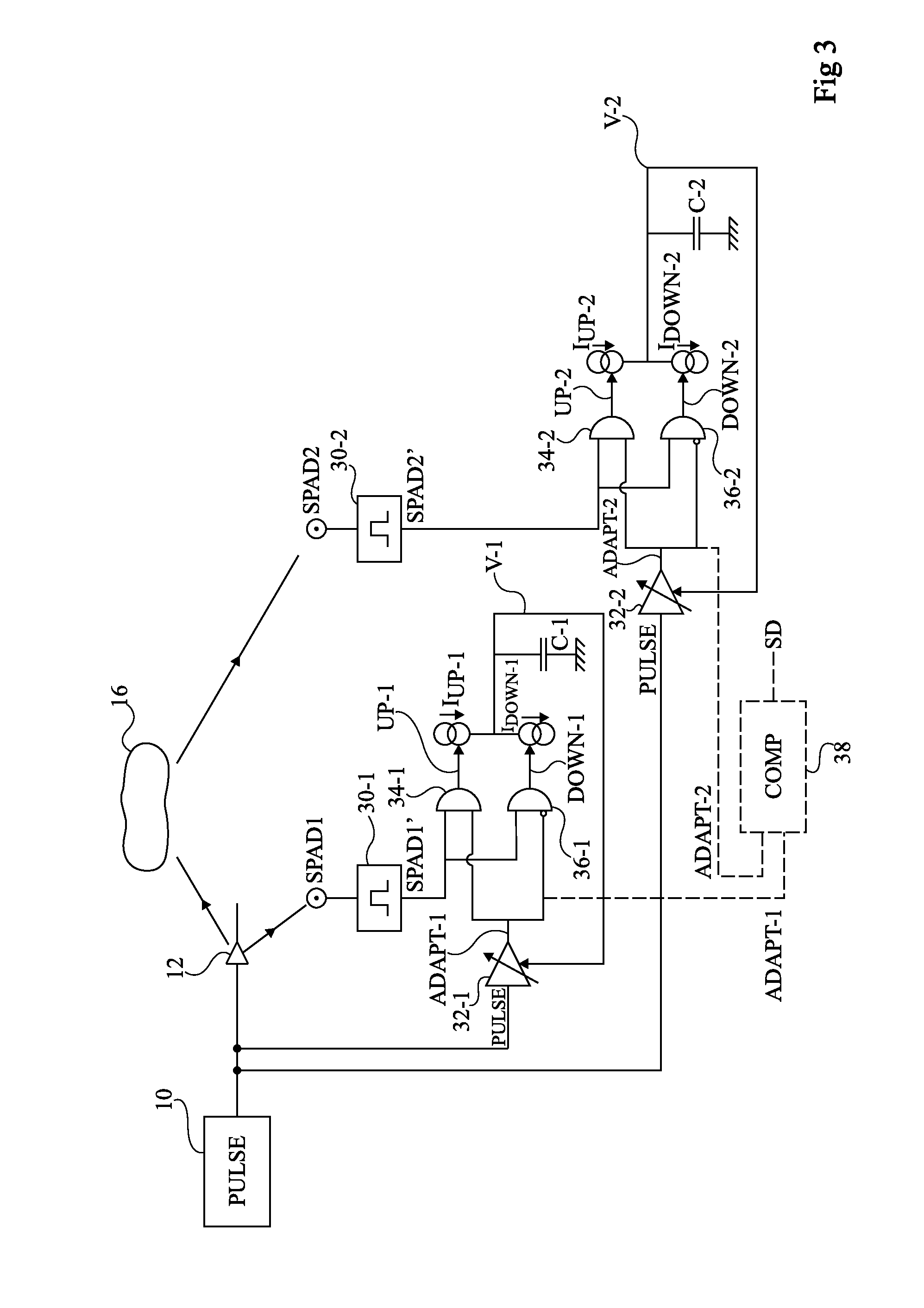
Device and Method for Determining the Distance to an Object
A method and apparatus for defining, from a first periodic signal, a second signal of same period, including the steps of: generating a third signal exhibiting detectable events; and synchronizing the second signal for each event.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (GRENOBLE 2) SAS
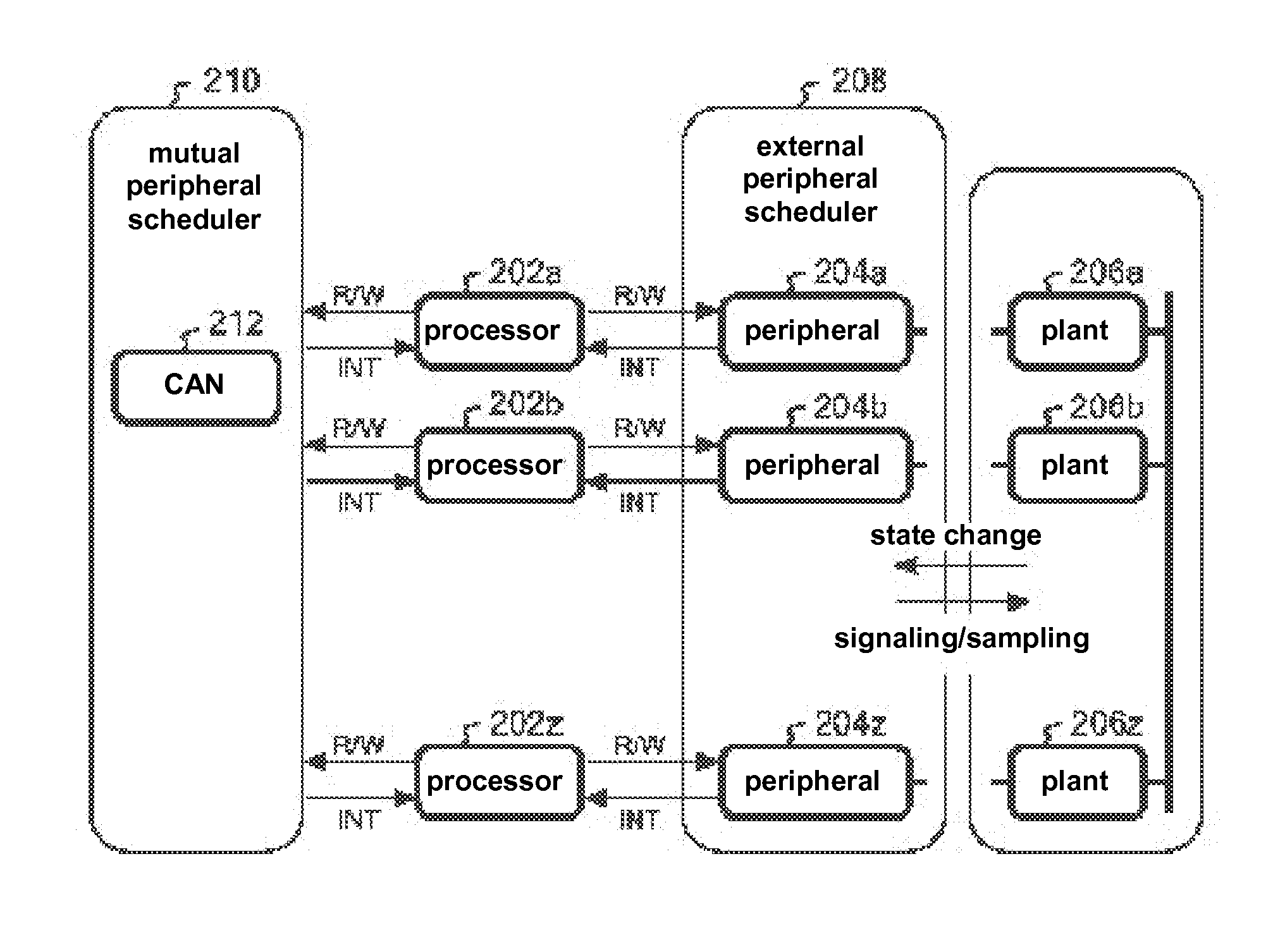
Multi-ecu simiulation by using 2-layer peripherals with look-ahead time
InactiveUS20130151220A1No overhead for avoiding deadlockFast simulationError detection/correctionSimulator controlEvent synchronizationDelayed time
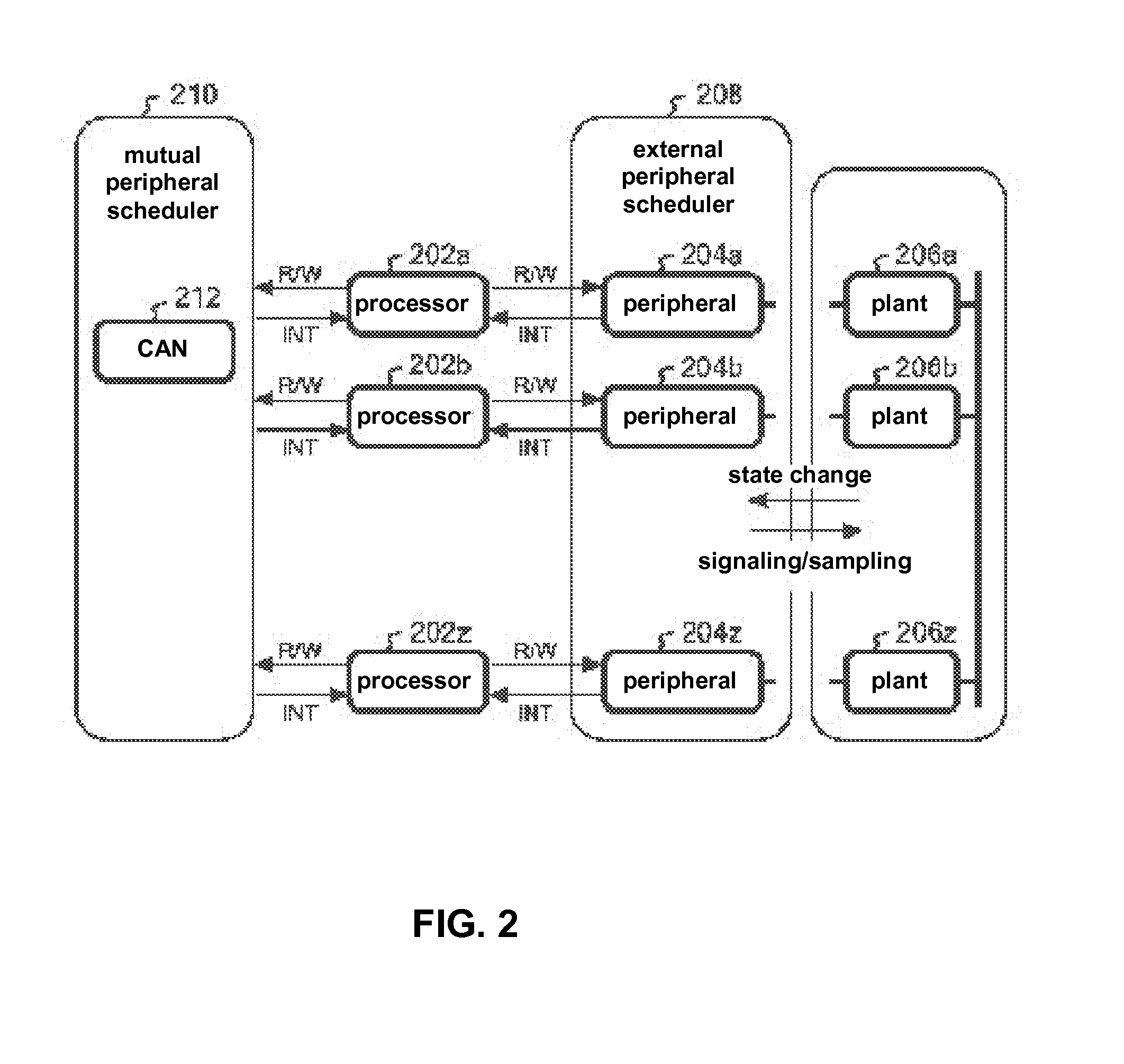
A method and system where a plurality of ECU is rapidly executed while avoiding deadlock by performing conservative event synchronization. The simulation system is provided with 4 layers, namely a processor emulator which is an ECU emulator, a plant simulator, a external peripheral scheduler, and a mutual peripheral scheduler. The external peripheral scheduler performs advanced execution of the plant simulator only during processor emulator reaction delay time (or the time until the next event). The notification to perform advanced execution of the processor emulator is provided until the actual plant simulator stop time. The mutual peripheral scheduler provides notification to the processor emulator to perform advanced execution only during communication delay timing between processor emulators (or the time until the next event). The processor emulator conservatively processes until the earliest time of the notification times. Each peripheral proceeds with processing until the earliest time of the accepted events.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for trace stream identification of multiple target processor events
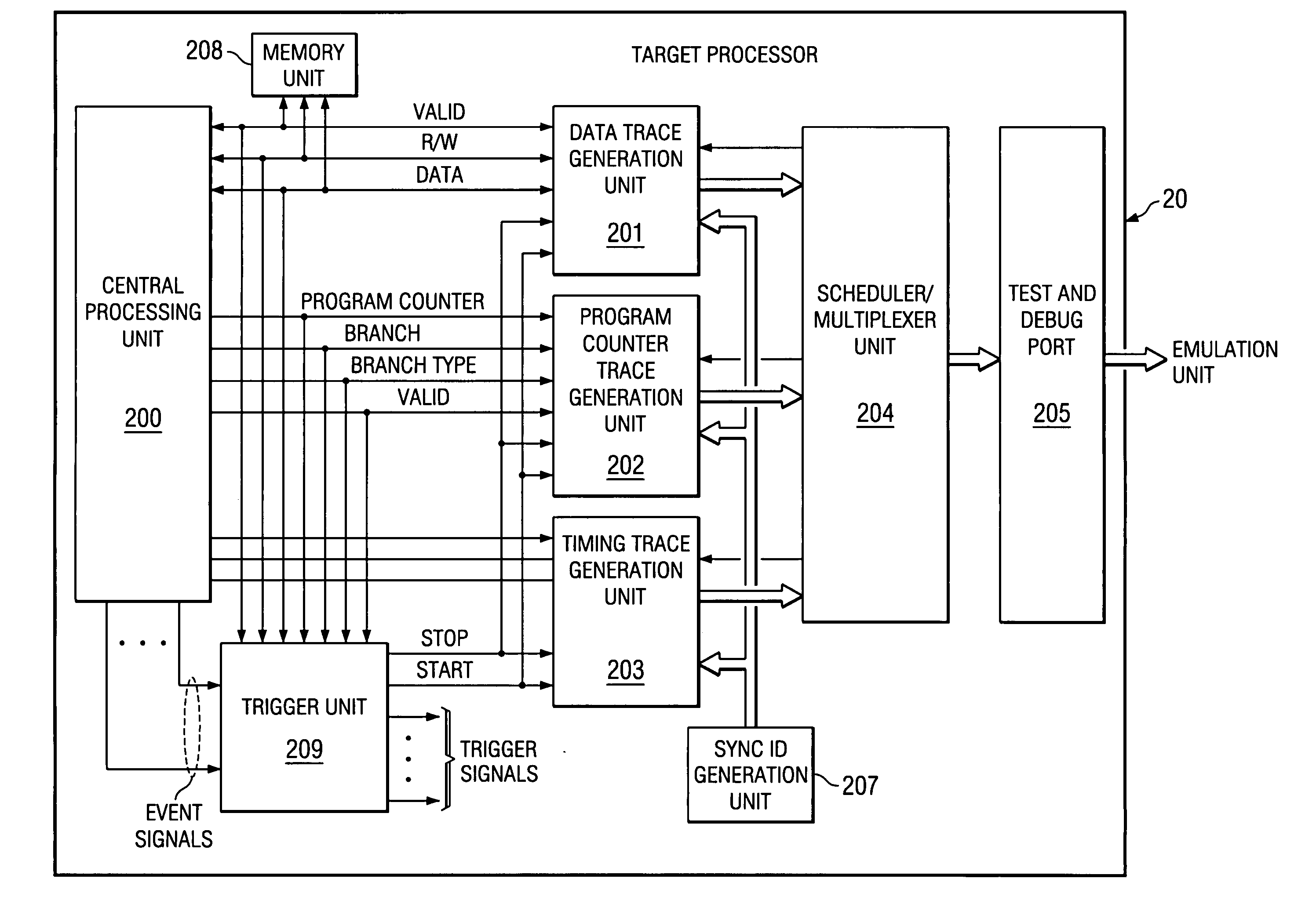
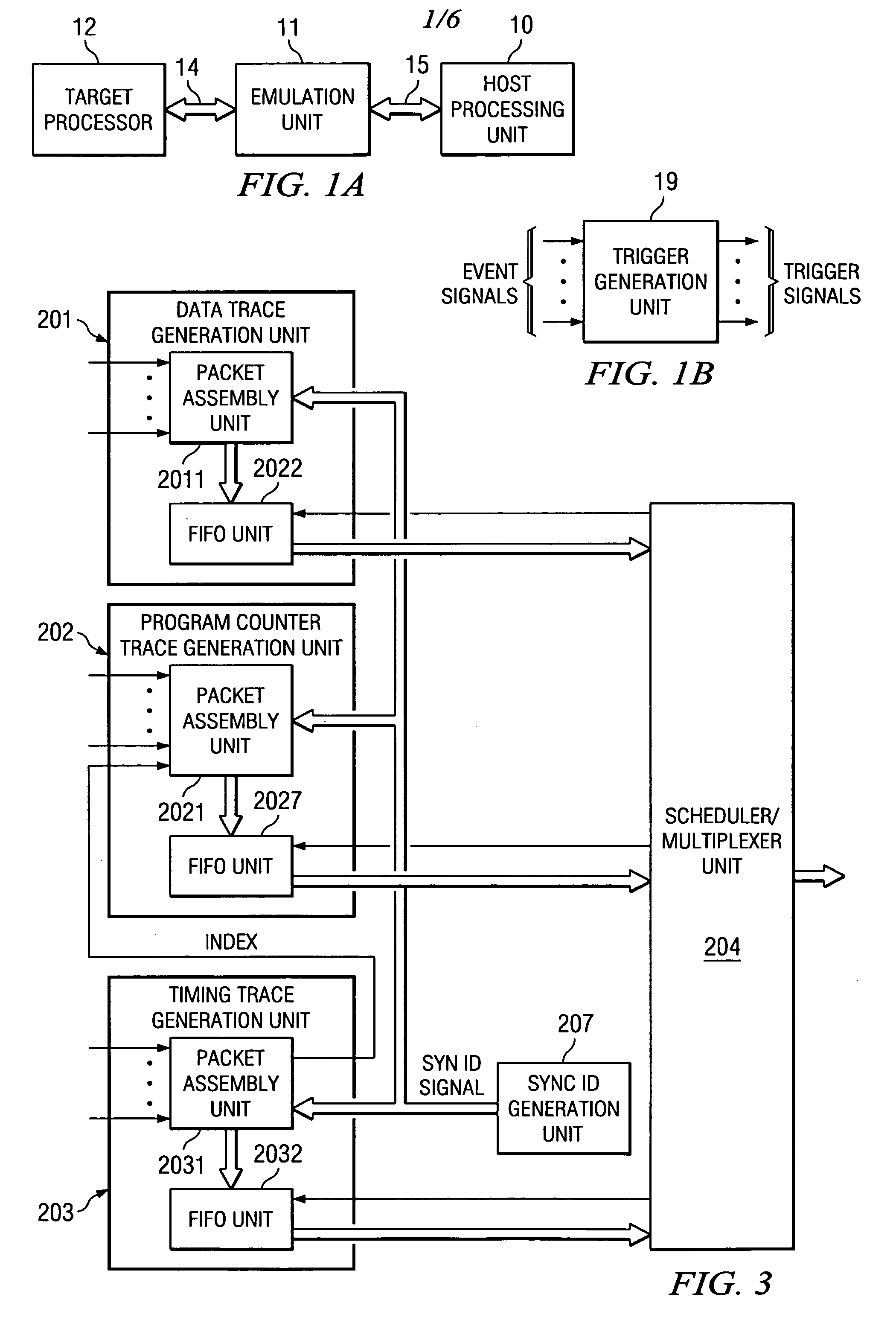
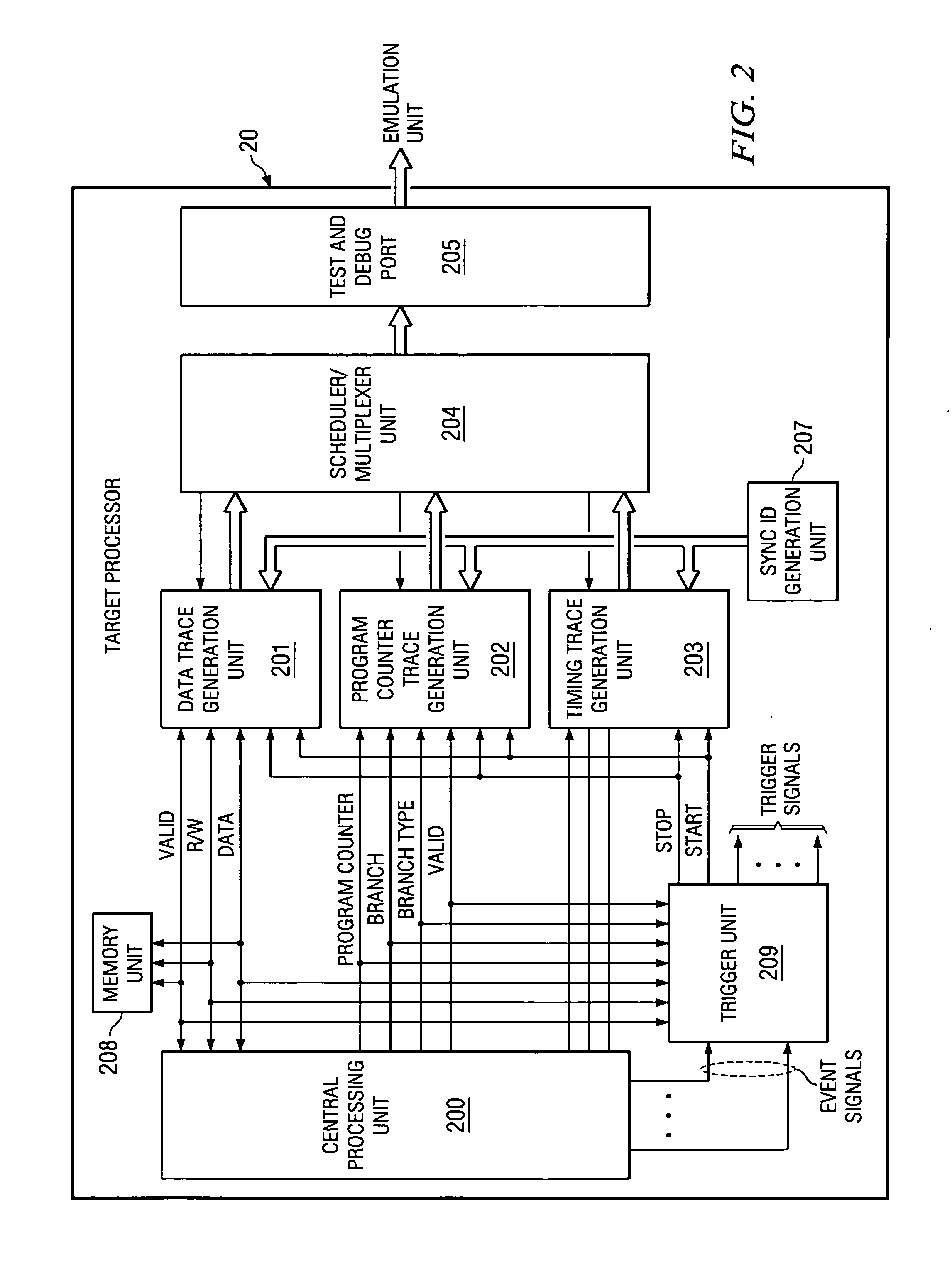
ActiveUS20040133823A1Reliability increasing modificationsError detection/correctionEvent synchronizationMulti event
When a plurality of simultaneous, preselected target processor events are detected, a multiple-event sync marker is generated that identifies the preselected events and relates the occurrence of these events to timing trace stream. The sync marker for the plurality of preselected events differs from a single event sync marker by including at least one additional packet. The additional packet includes logic signals stored at locations related to each identified event.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method for precisely synchronizing wireless events of electroencephalogram device
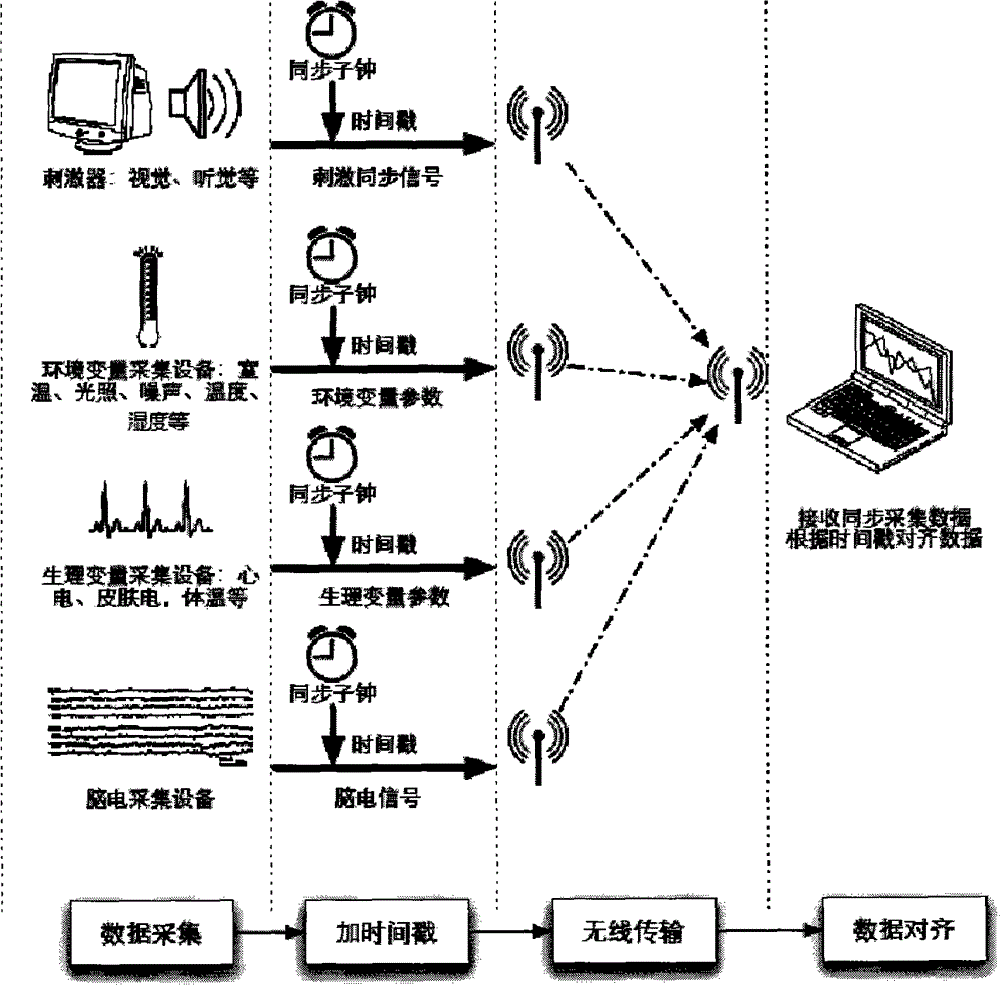
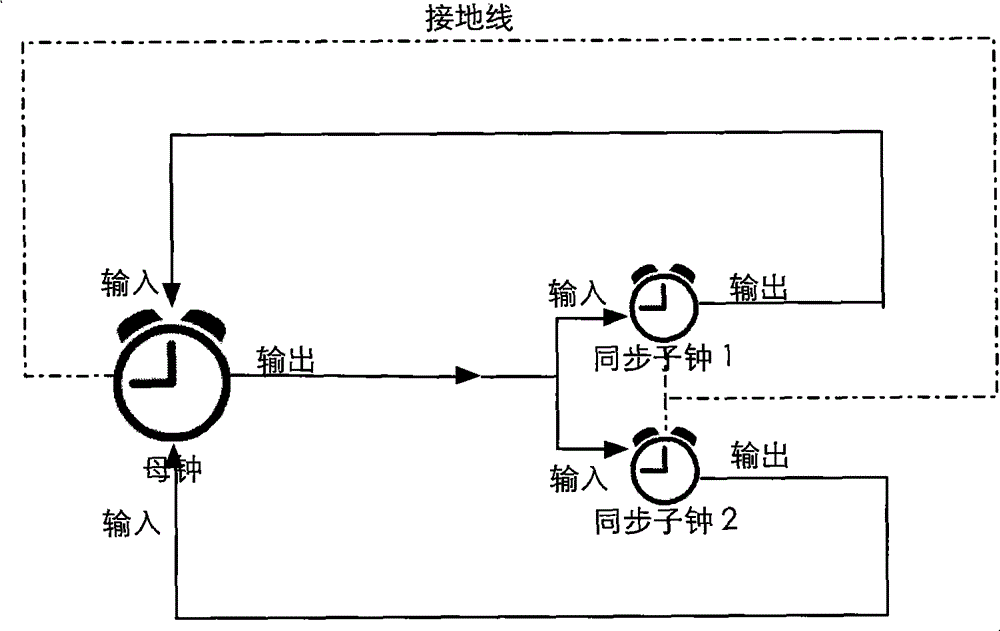
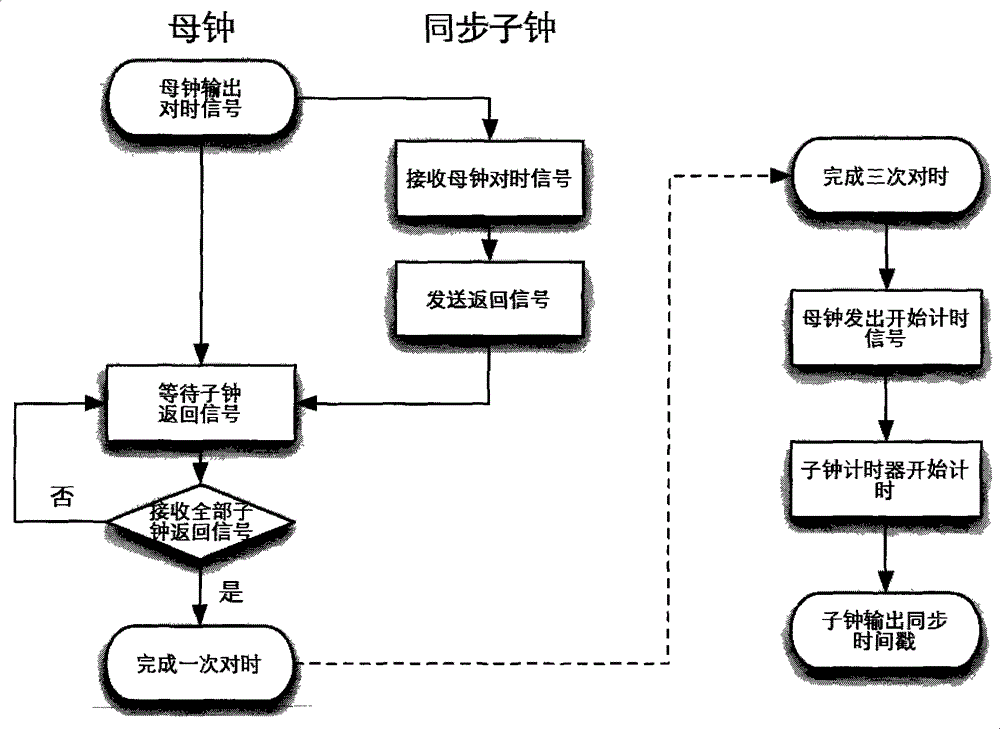
ActiveCN103607269AAchieve wireless synchronizationStimulus synchronizationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTimestampEvent synchronization
The invention provides a method for precisely synchronizing wireless events of an electroencephalogram device. Synchronous secondary clocks are added in relevant systems, three times of handshake alignment is conducted before operation of a primary clock and the secondary clocks, after operation is started, data collected by each system and timestamp read from each secondary clock are transmitted to a central processing module in a wireless mode, the central processing module conducts data alignment according to the timestamp to achieve synchronization of stimulating events, environment variables and relevant physiological parameters with electroencephalogram data, then data processing can be conducted, and intended functions are achieved.
Owner:NEURACLE TECH CHANGZHOU CO LTD
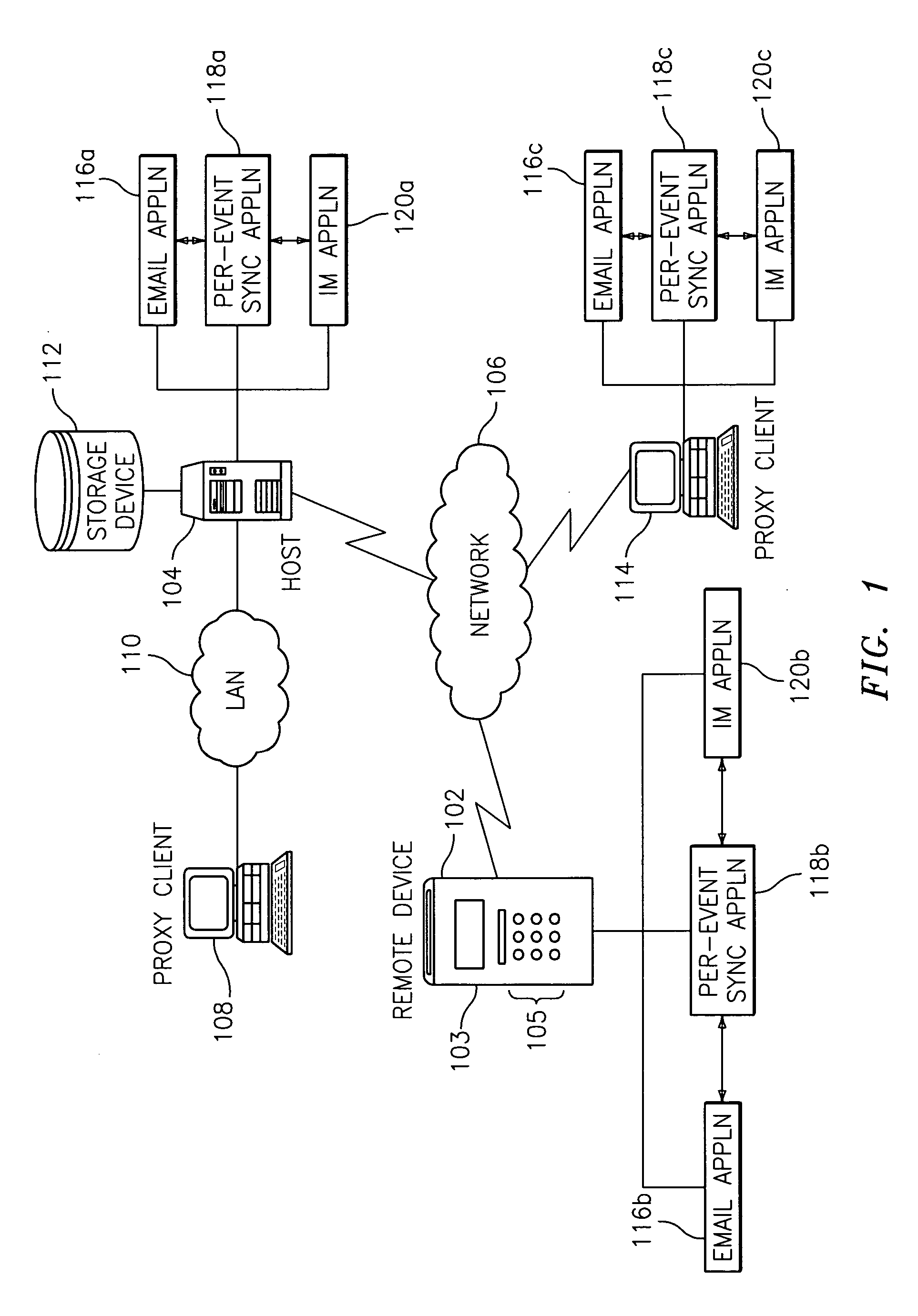
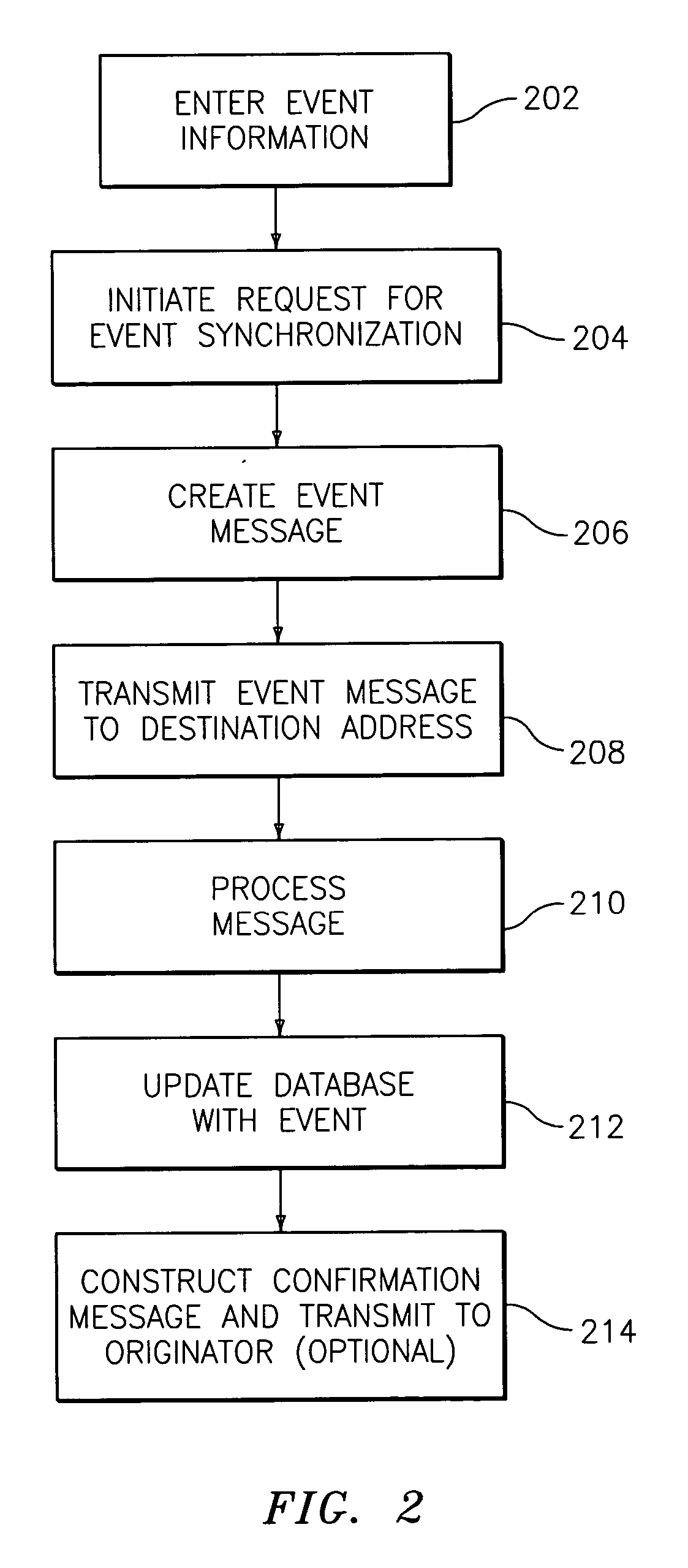
Methods, systems, and computer program products for performing per-event device synchronization
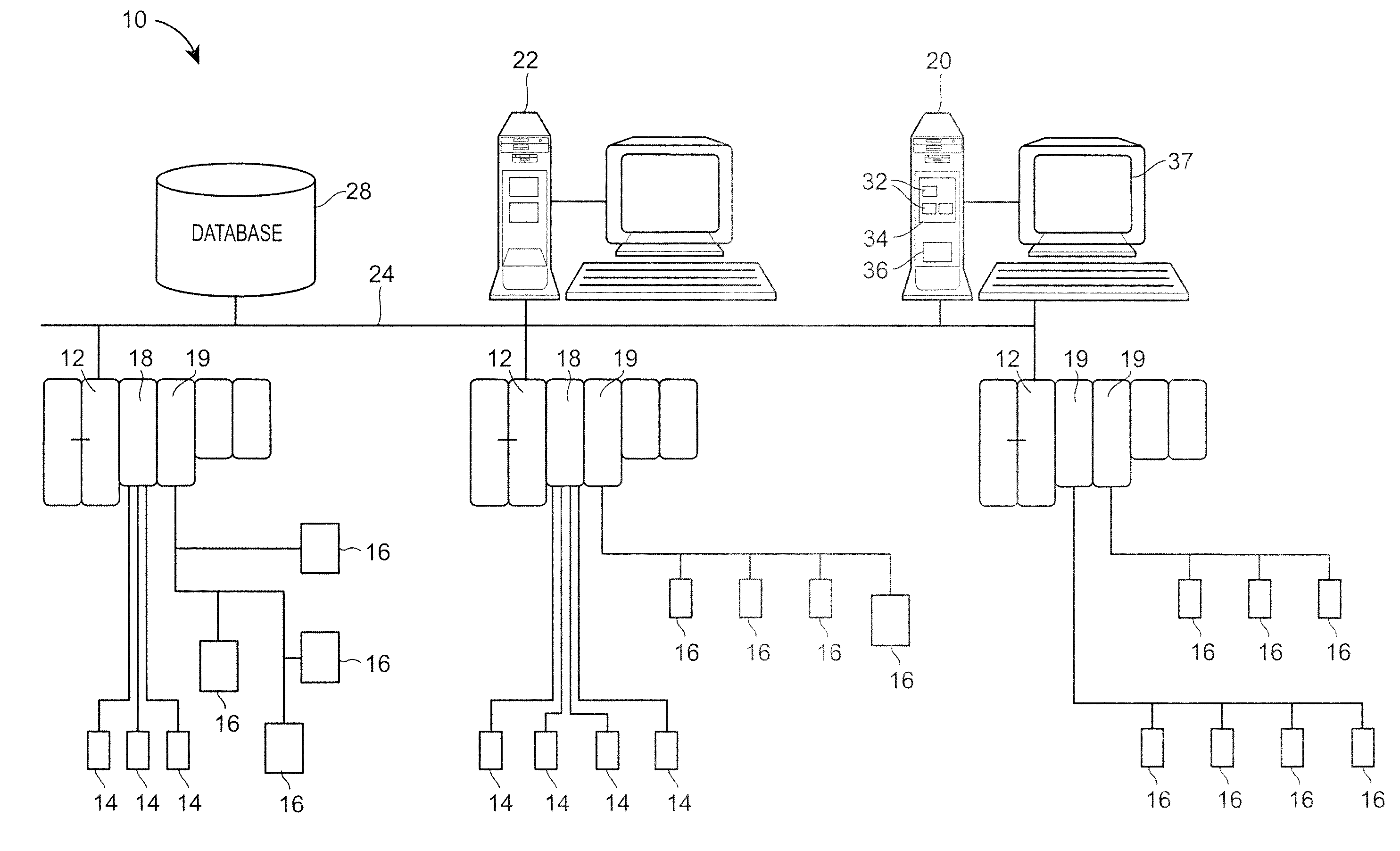
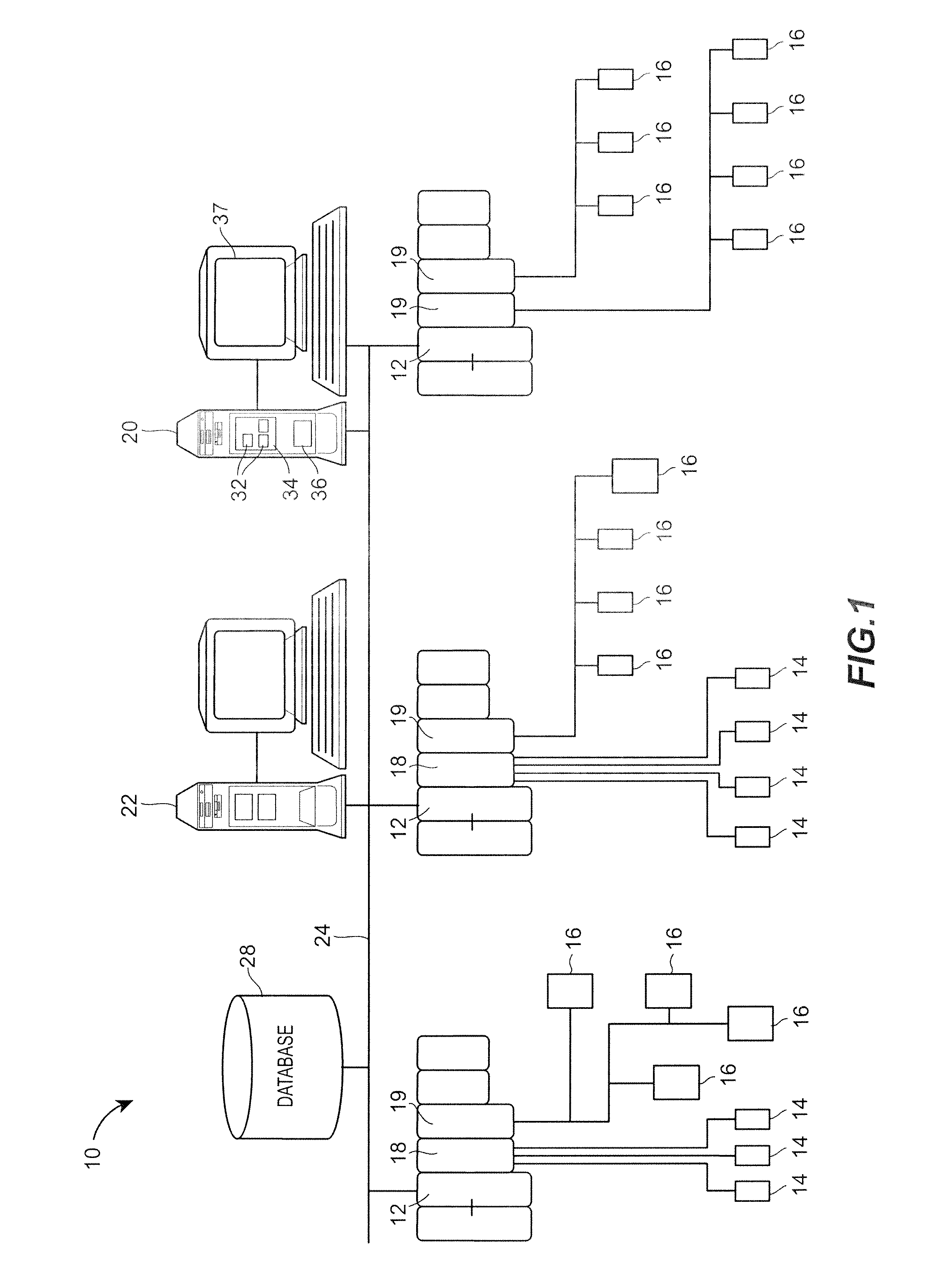
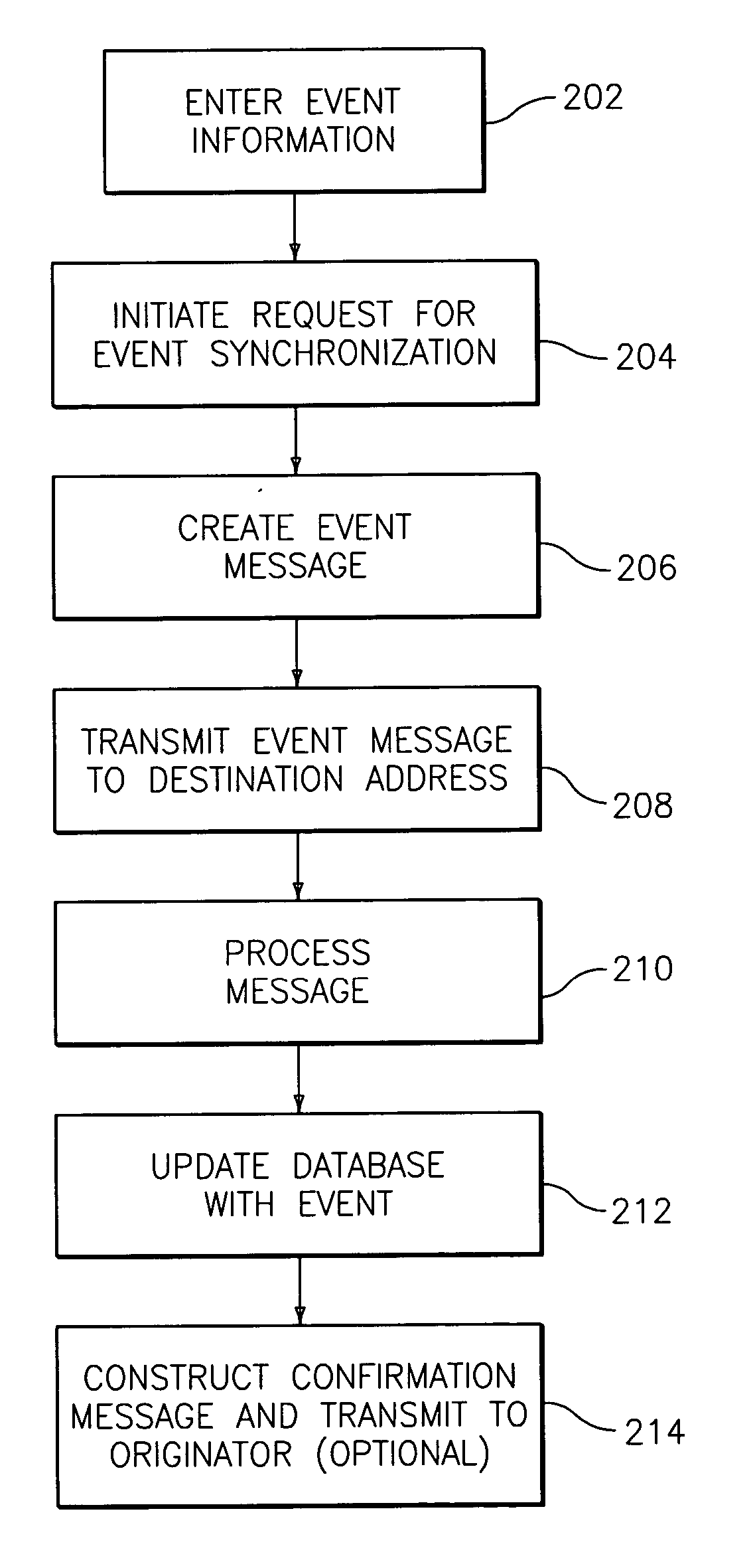
InactiveUS20060101447A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsEvent synchronizationUnique identifier
Exemplary embodiments relate to methods, systems, and computer program products for performing per-event device synchronization activities. The method includes initiating a synchronization operation in response to an entry of event information in an information management application executing on a device. The device is associated with at least one other device, which is executing another information management application. The method also includes assigning a unique identifier to the event information and generating an event message. The event message includes the unique identifier, the event information, and a destination address associated with the other device. The method further includes transmitting the event message to the destination address. Upon receiving the event message, the other device updates the other information management application with the event information via the unique identifier resulting in per-event synchronization of the device and the other device.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
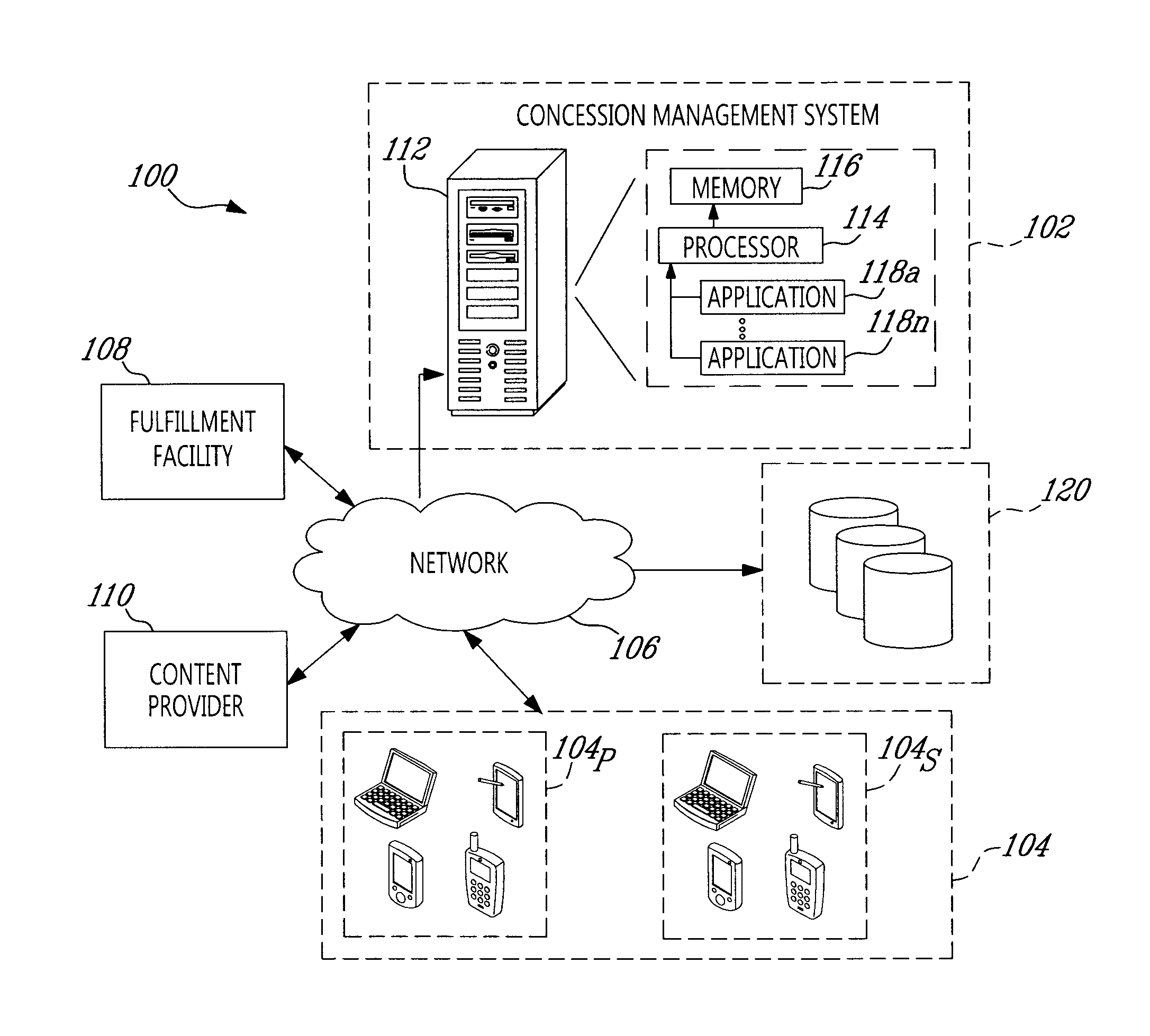
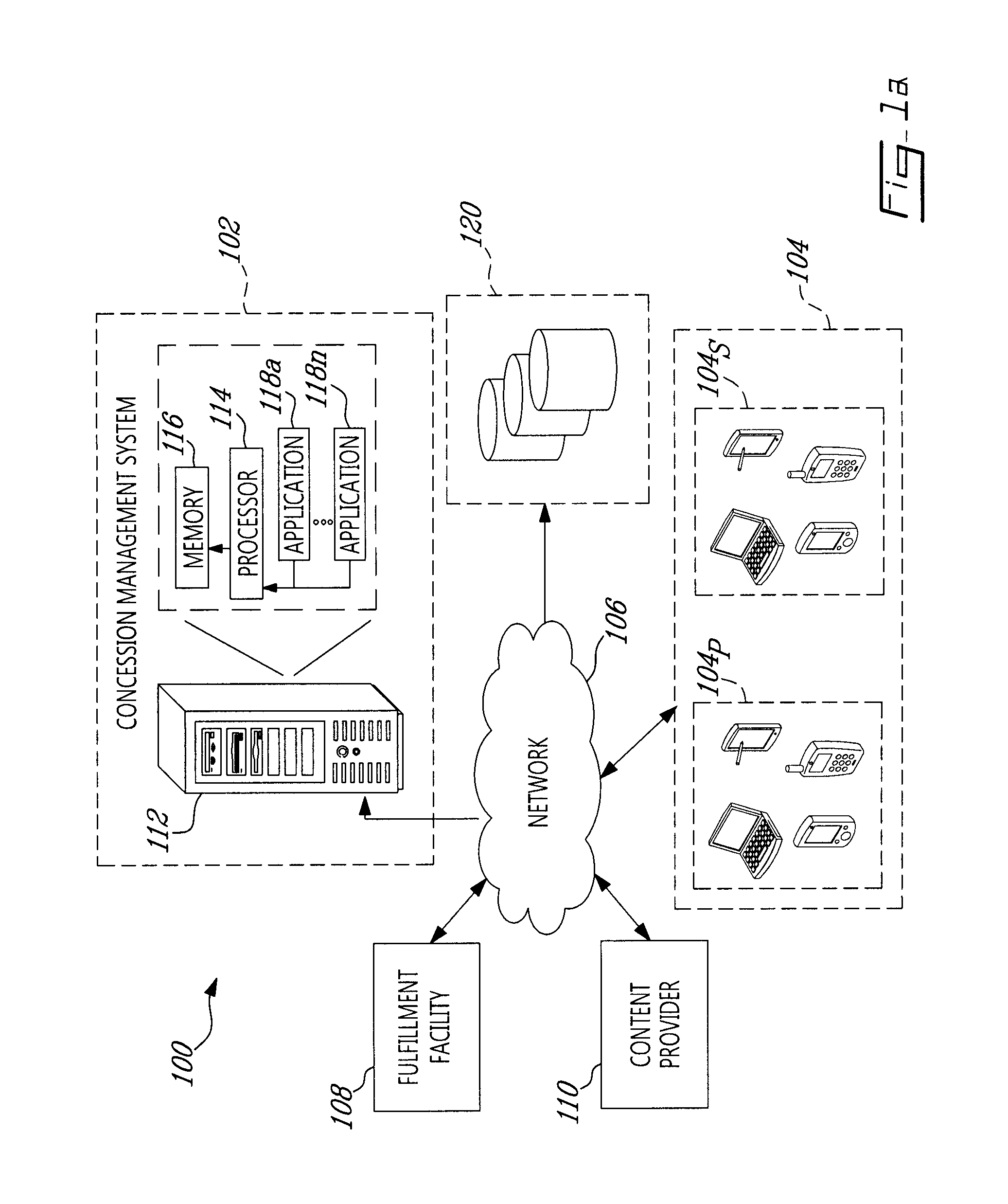
System and method for managing venue concessions
There is provided a system and method for synchronizing delivery at a venue of at least one product with a live event occurring at the venue, the at least one product offered at the venue by at least one fulfillment facility. An order signal comprising order data indicative of the order for the delivery of the at least one product to a location of the venue is received. An event signal comprising event data indicative of a timing of the live event is received. It is then determined from the event data a desired delivery time at which to deliver the order to the location such that delivery of the order matches the timing of the live event. A control signal is then generated and transmitted to the at least one fulfillment facility for causing the at least one fulfillment facility to prepare and deliver the order to the location by the desired delivery time.
Owner:FANS ENTERTAINMENT
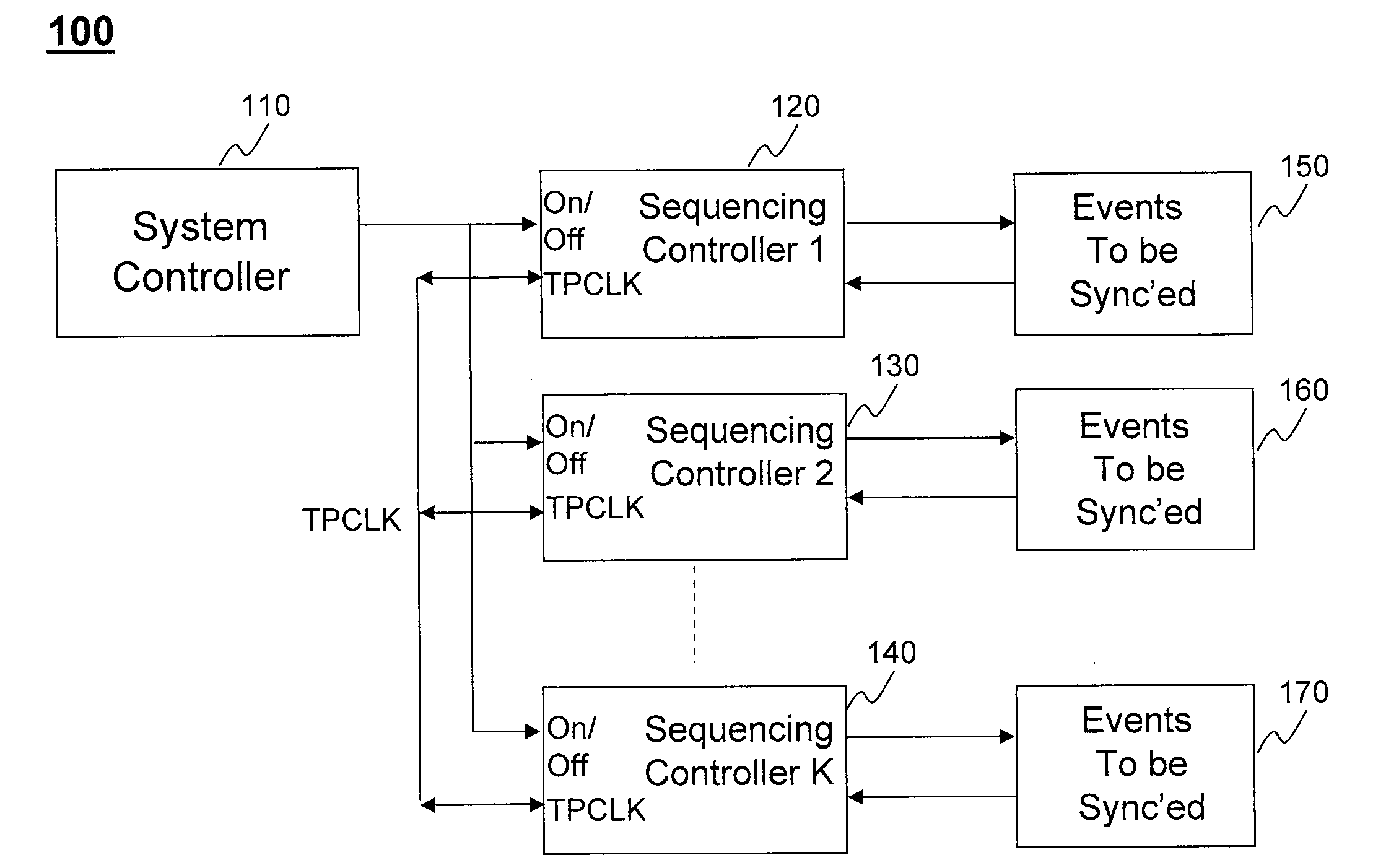
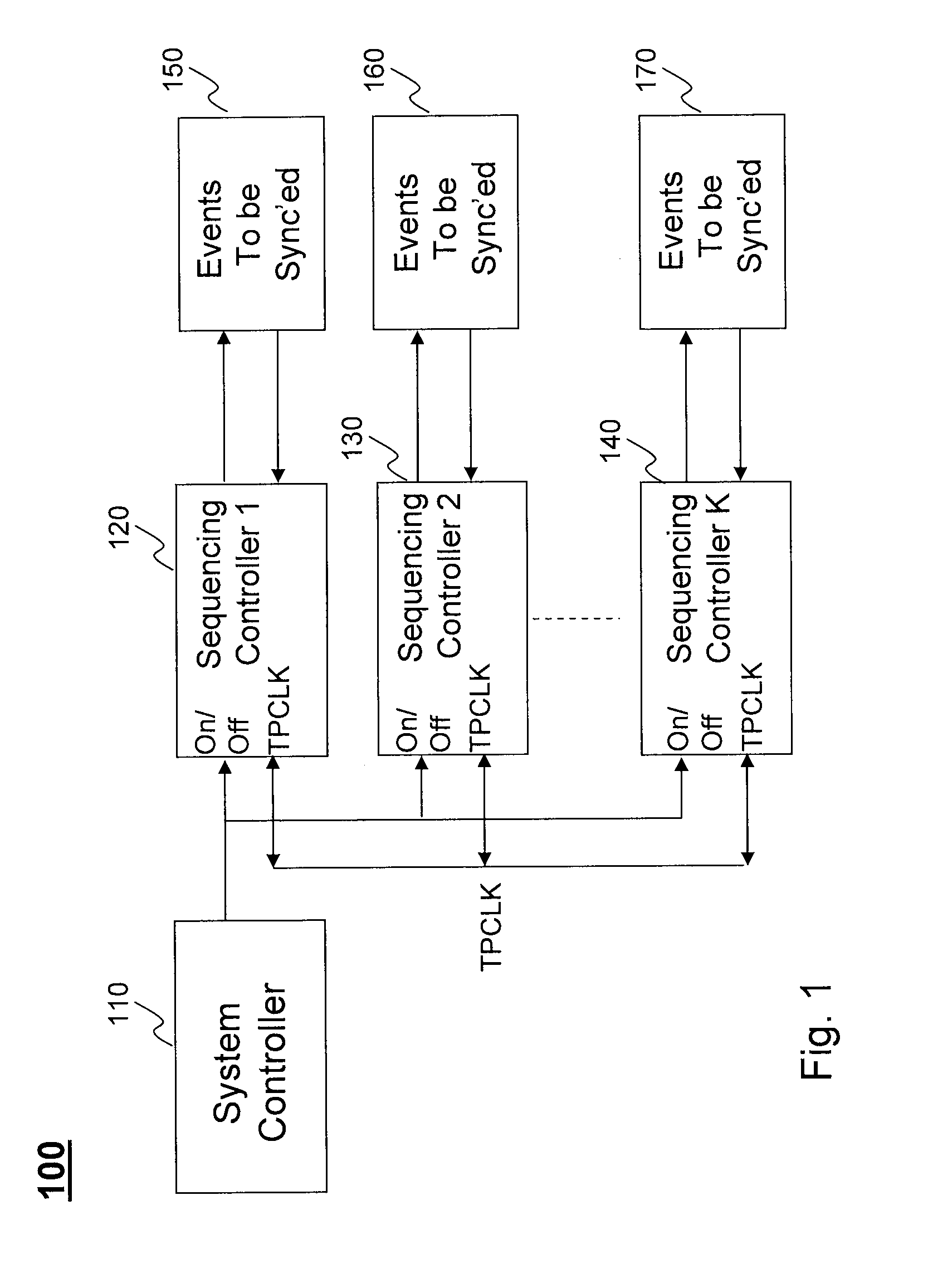
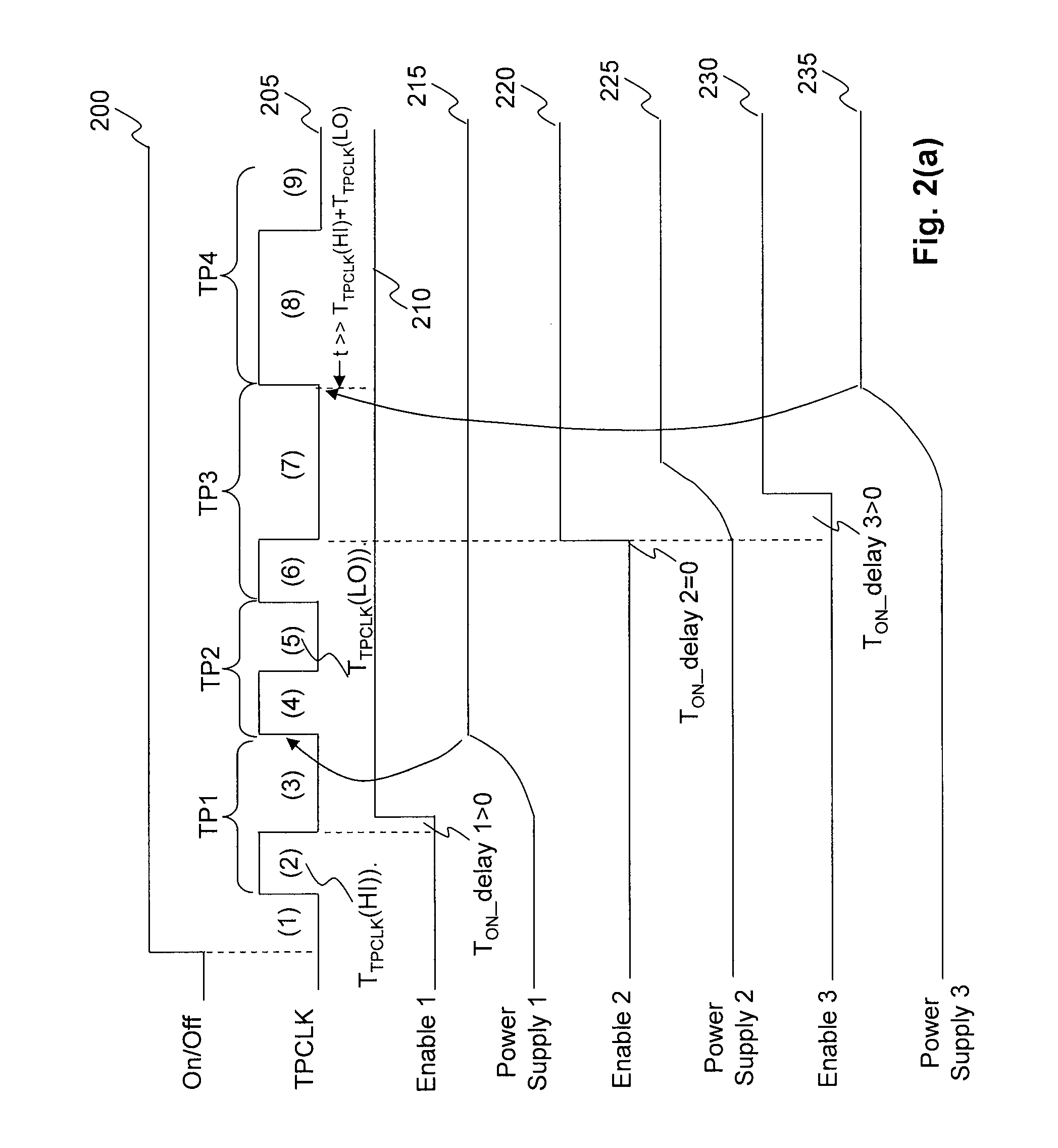
Autonomous multi-device event synchronization and sequencing technique eliminating master and slave assignments
ActiveUS20100169695A1Power supply for data processingGenerating/distributing signalsEvent synchronizationChronological time
An apparatus and method for event synchronization. One or more devices that have a plurality of events to be carried out in a scheduled order in time are connected to a single shared time position clock (TPCLK). There are one or more sequencing controllers coupled with the one or more devices and configured to control the timing of high and low states of the shared TPCLK in accordance with the scheduled order. The synchronization among the plurality of events in the scheduled order is achieved based on the high and low states of the shared TPCLK and such synchronization of the plurality of events in the scheduled order is operated without the presence of master and slave devices.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Method for synchronizing information
InactiveUS20070130223A1Database distribution/replicationSpecial data processing applicationsEvent synchronizationData store
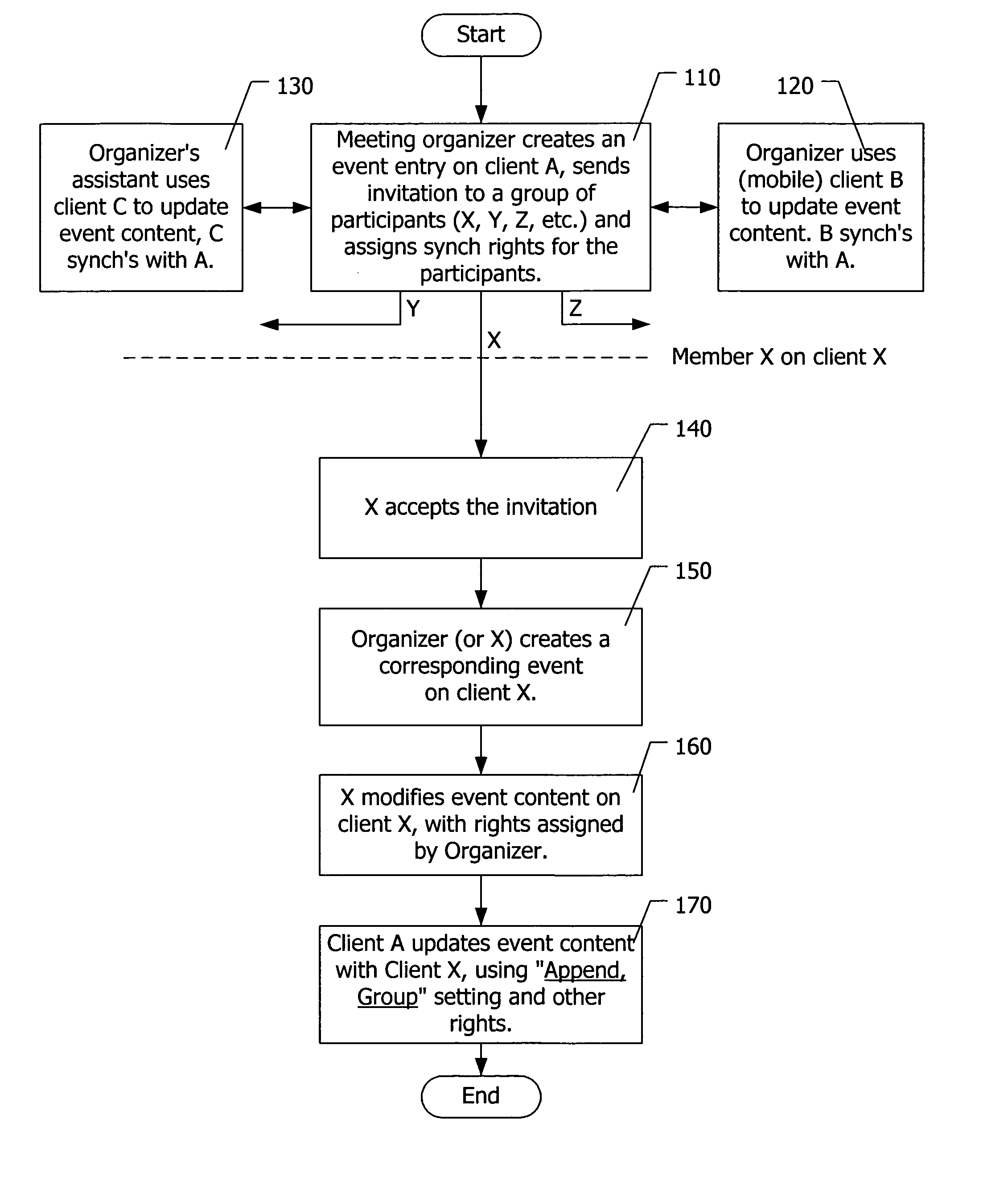
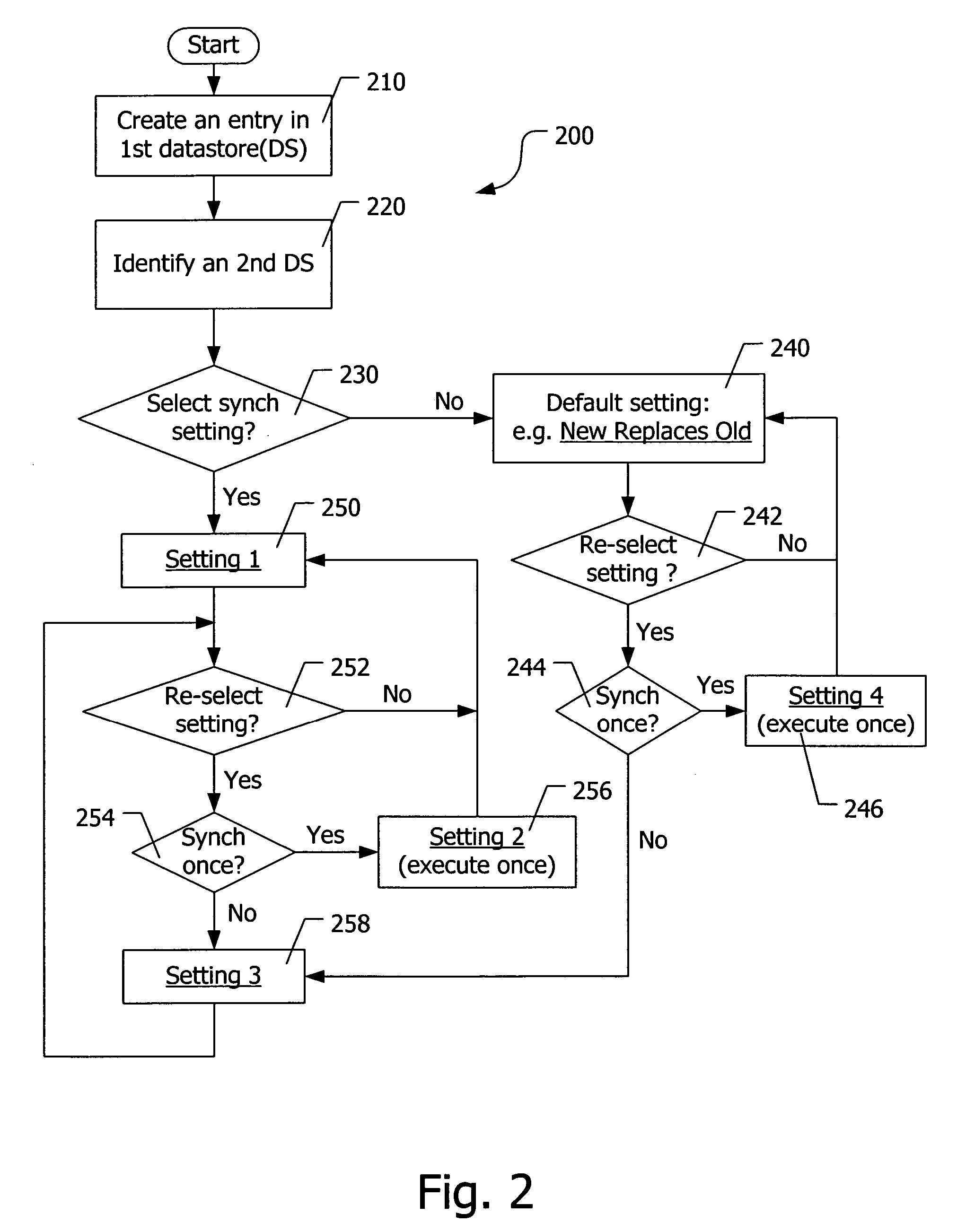
A method for synchronizing an event in a first datastore and a second datastore. The method comprises the steps of selecting a first datastore comprising a plurality of events, selecting a second datastore, and providing a synchronization setting for an event in the plurality of events so as to indicate how synchronization between the first datastore and the second datastore is to be performed with respect to the event. The synchronization setting may indicate that a corresponding event in the second datastore is to be synchronized with the event in the first datastore, or that the event in the first datastore is to be synchronized with the corresponding event in the second datastore, or the synchronization setting may indicate that the first datastore obtains from the second datastore an update to the information of the event, adds the update to the event, and synchronizes the event based on the updated event.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Open RF test pack
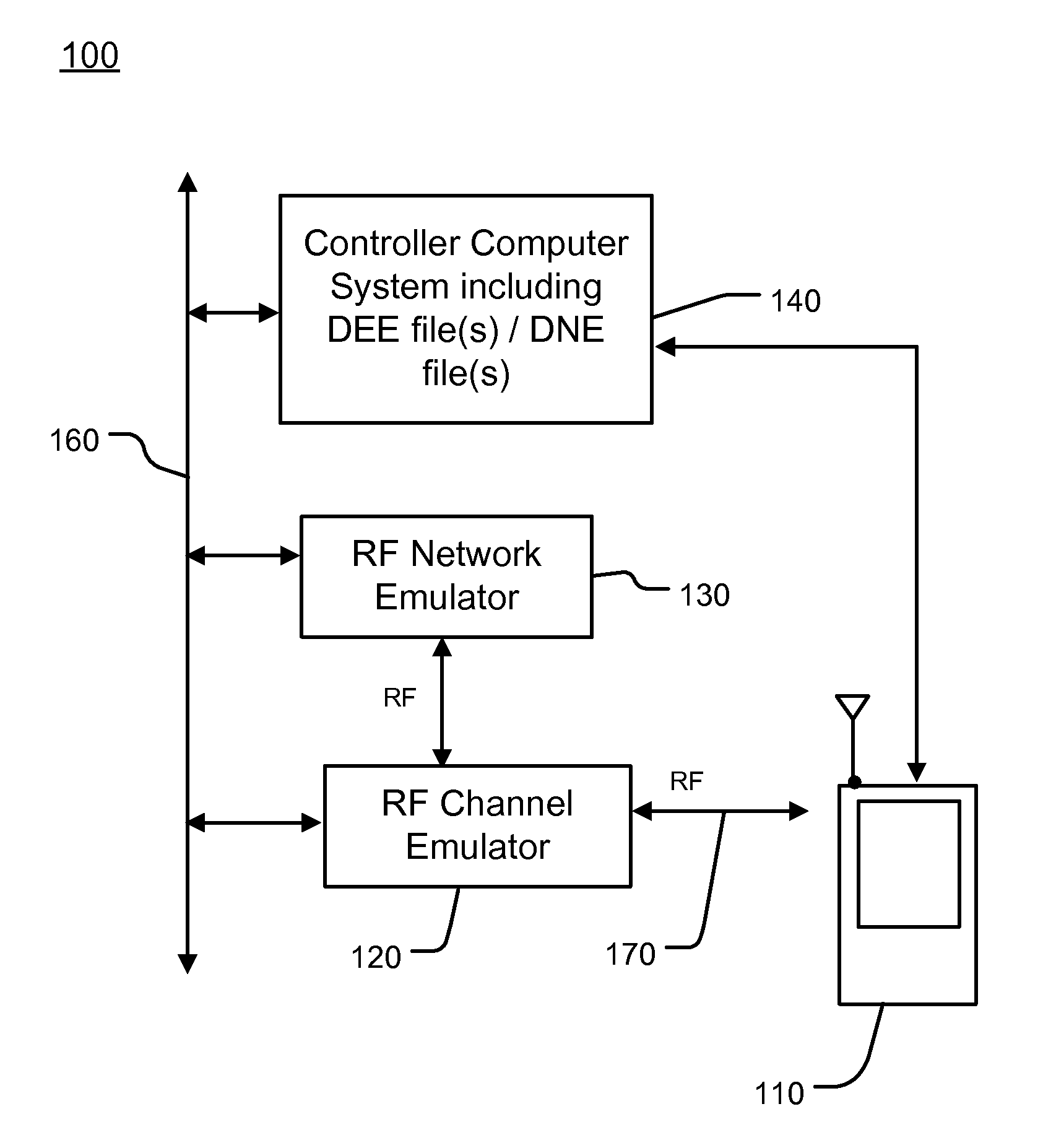
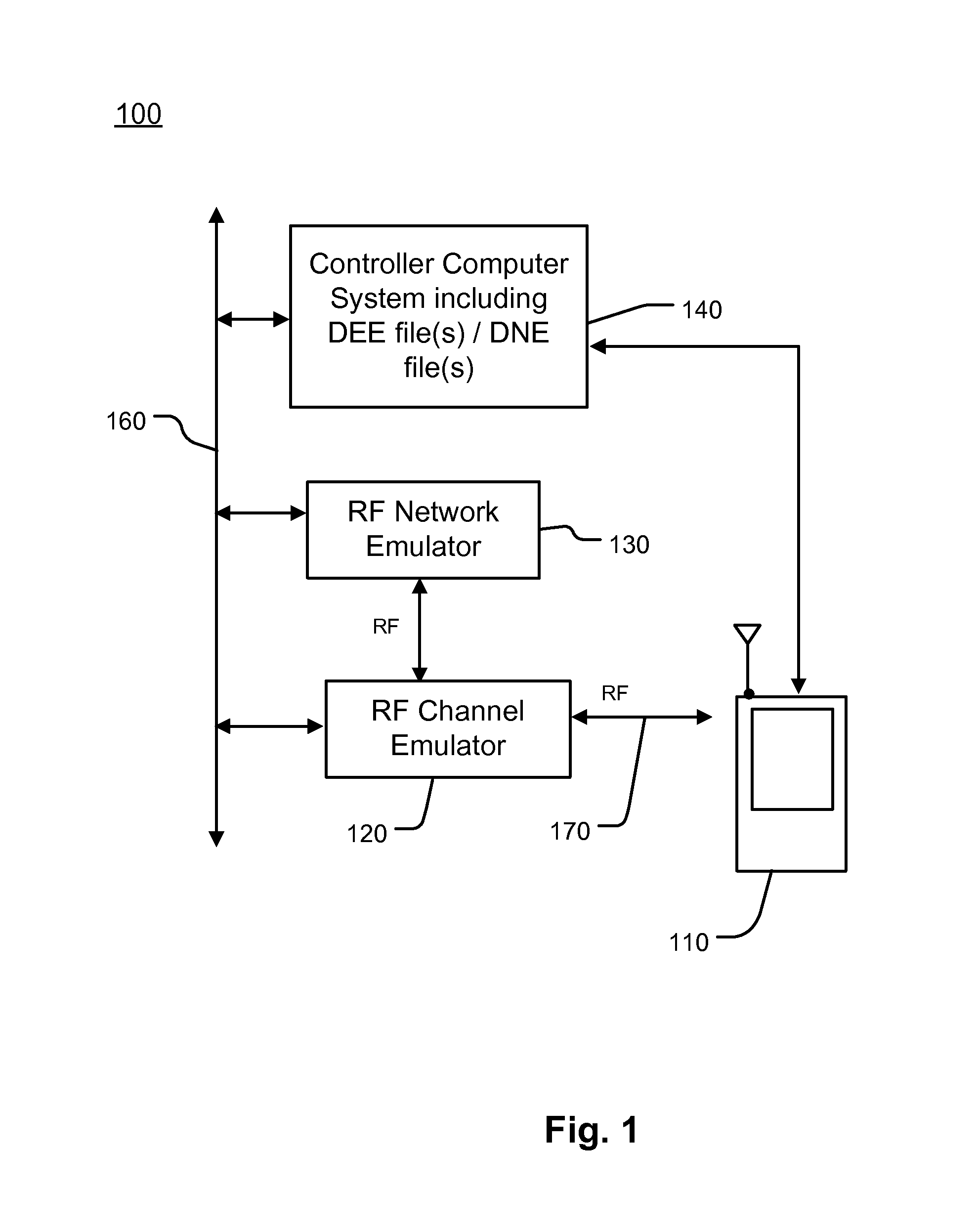
ActiveUS9069749B1Performance of wireless can be efficiently and accuratelyTime-division multiplexFunctional testingEvent synchronizationRadio channel
A channel emulator generates radio channel conditions of live cellular base station signals in a simulation of a radio environment of a fielded cellular network, based on a record of captured radio signal data of a plurality of cellular base stations in the fielded cellular network. A generates a simulation of a fielded cellular network. In one aspect, the radio channel conditions in the simulation of the radio environment are synchronized with events in the simulation of the fielded cellular network. In another aspect, an event handling state machine directs configurable events in the simulation of the fielded cellular network in response to radio channel conditions in the simulation of the radio environment.
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
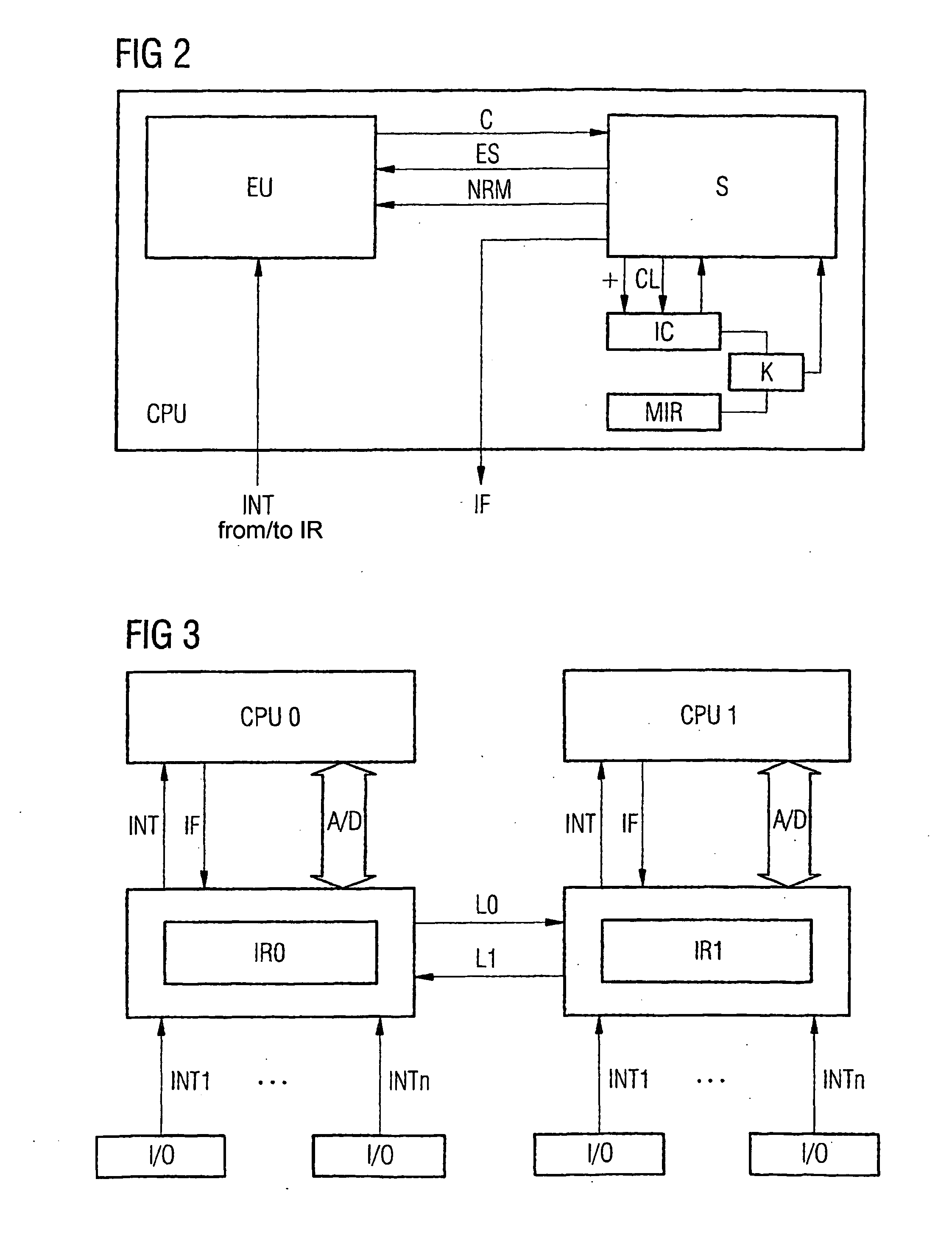
Method for event synchronisation, especially for processors of fault-tolerant systems
InactiveUS20050229035A1Allow usePossible to useRedundant hardware error correctionEvent synchronizationIdentical stimulus
Redundant systems are often provided with identically mounted processor boards which function according to a lockstep operation. The basic condition for the implementation of a lockstep system is the deterministic behaviour of all of the constituents contained in the board, such as CPUs, chip sets, main memory etc. According to the invention, deterministic behaviour signifies that said constituents supply identical results at identical times, in an error-free case, when the constituents receive identical stimuli at identical times. Deterministic behaviour also presupposes the use of interfaces in clock-controlled synchronism. Asynchronous interfaces cause a certain temporal indeterminacy in the system in many cases, whereby the entire synchronised behaviour of the system cannot be maintained. In order to thus be able to carry out a lockstep operation, the invention relates to a method for the synchronisation of external events which are supplied to a processor (CPU) and influence the same. The external events are intermediately stored accordingly and the processors are presented at identical points in the execution of commands. Problems which are created by the capacity of modern processors to execute commands in parallel are avoided by the fact that the parallel execution of the processors is stopped before the desired point in the command execution is reached and said point is then reached exactly in the single step mode.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
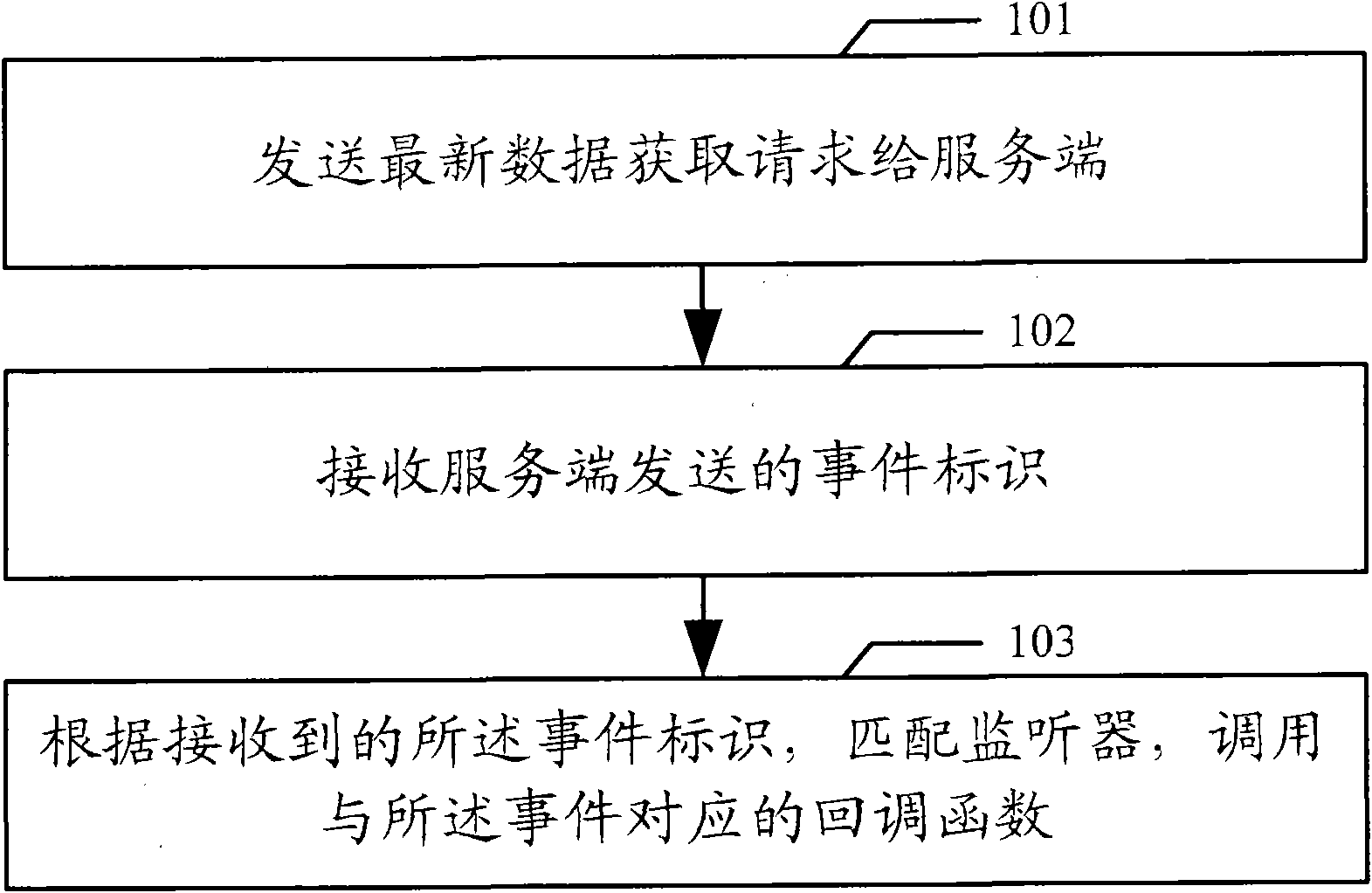
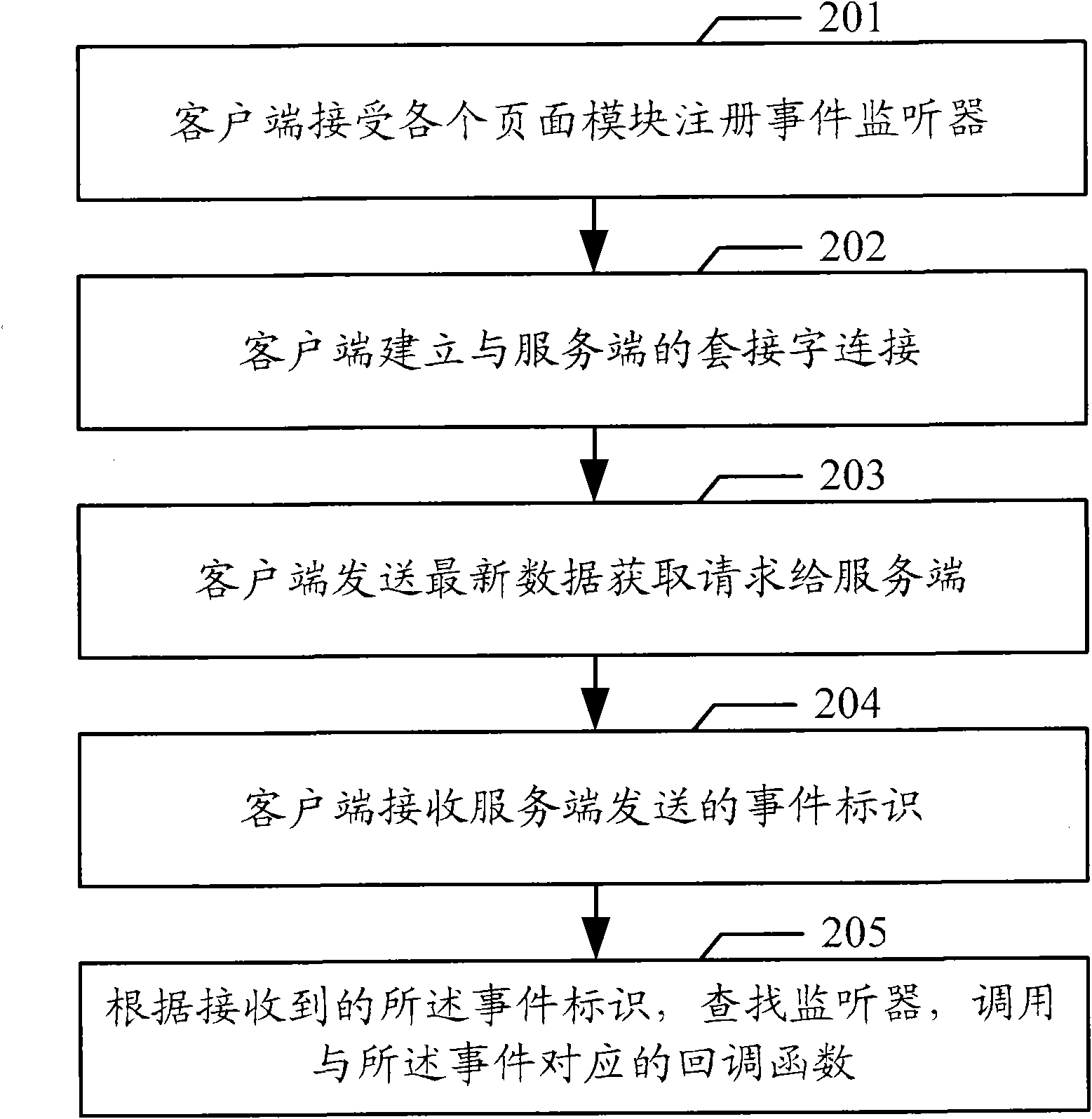
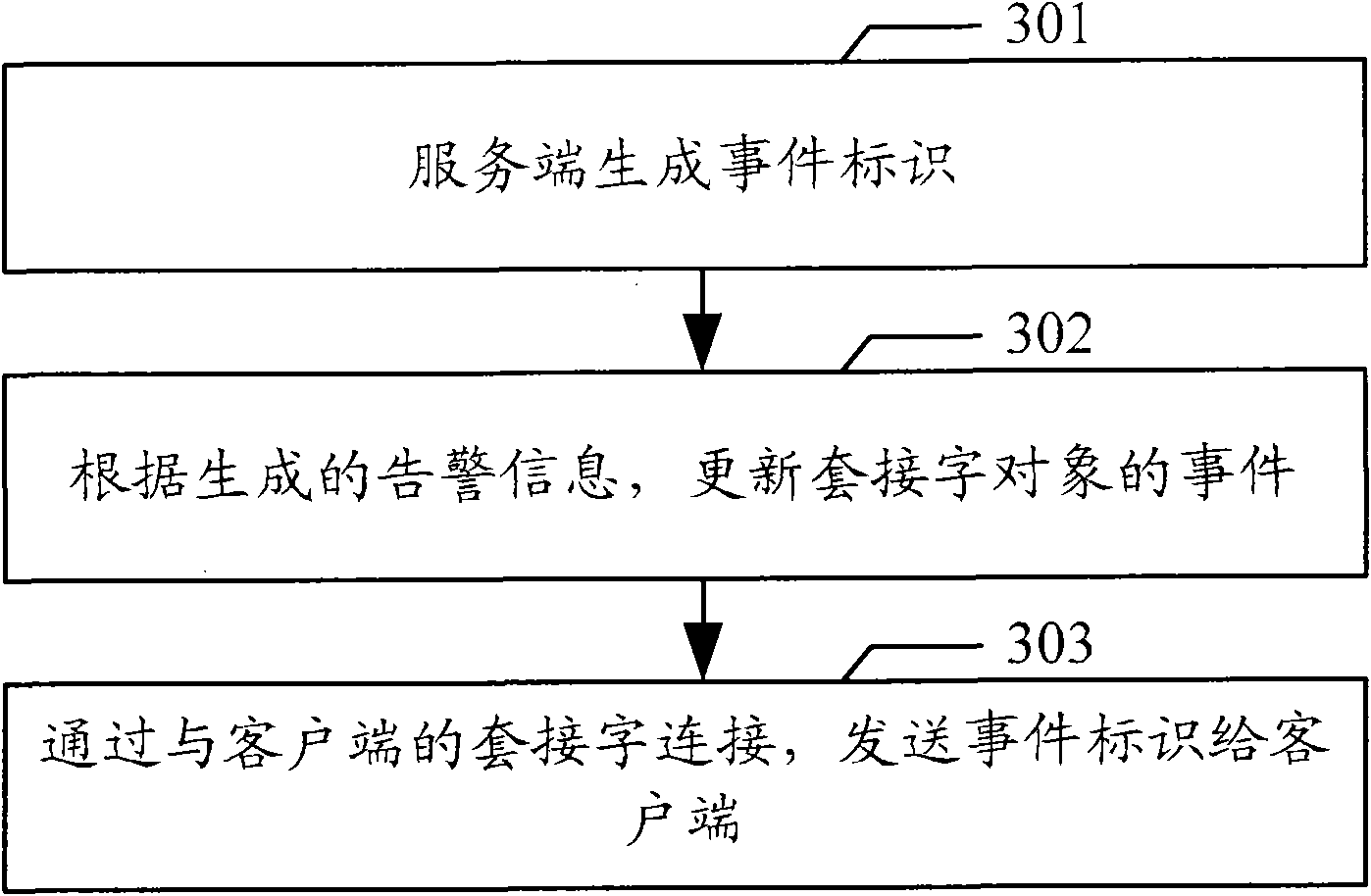
Event synchronization method, system, client and server
InactiveCN102215243AAvoid experienceImprove efficiencyTransmissionEvent synchronizationData acquisition
The invention discloses an event synchronization method, an event synchronization system, a client and a server. The embodiment of the invention comprises the following steps of: transmitting a latest data acquisition request; receiving an event identifier from the server by socket connection with the server; and matching a monitor for monitoring an event of the event identifier according to the received event identifier, calling a callback function corresponding to the event, and executing a synchronization operation indicated by the callback function. The embodiment of the invention can timely return corresponding data to the client, improves the efficiency of the client and the server because the client is not required to set a timer to periodically repeatedly transmit requests to the server, and avoids user experiences with unfinished long connection loading and influence on the displaying of a browser of the client.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for resolving conflicts in a substrate processing system
InactiveUS20030154001A1Without diminishing throughputHigh and reliable throughputProgramme controlDigital data processing detailsLithographic artistEvent synchronization
A wafer track and lithography cluster tool for performing a series of processes with a scheduler which synchronizes all events in a substrate processing system. Events in the cluster tool are scheduled to occur at regular, periodic intervals, thereby improving throughput and quality. The scheduler also eliminates conflicts for transportation resources between modules in the cluster tool. Wafers are loaded into the cluster tool at a regular interval, referred to as a sending period. All events in the system are synchronized with the sending period, and all event timings are normalized in terms of the sending period. The conflicts are resolved by selectively adding delays in modules which can tolerate them without degrading throughput or performance in the system; modules that cannot tolerate delays are exempted. The periodicity of the scheduled cluster tool enables the identification of wafers in the cluster tool. The identification of the order in which a wafer was loaded also identifies a module path followed by the wafer.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Method and apparatus for wireless intersystem handover
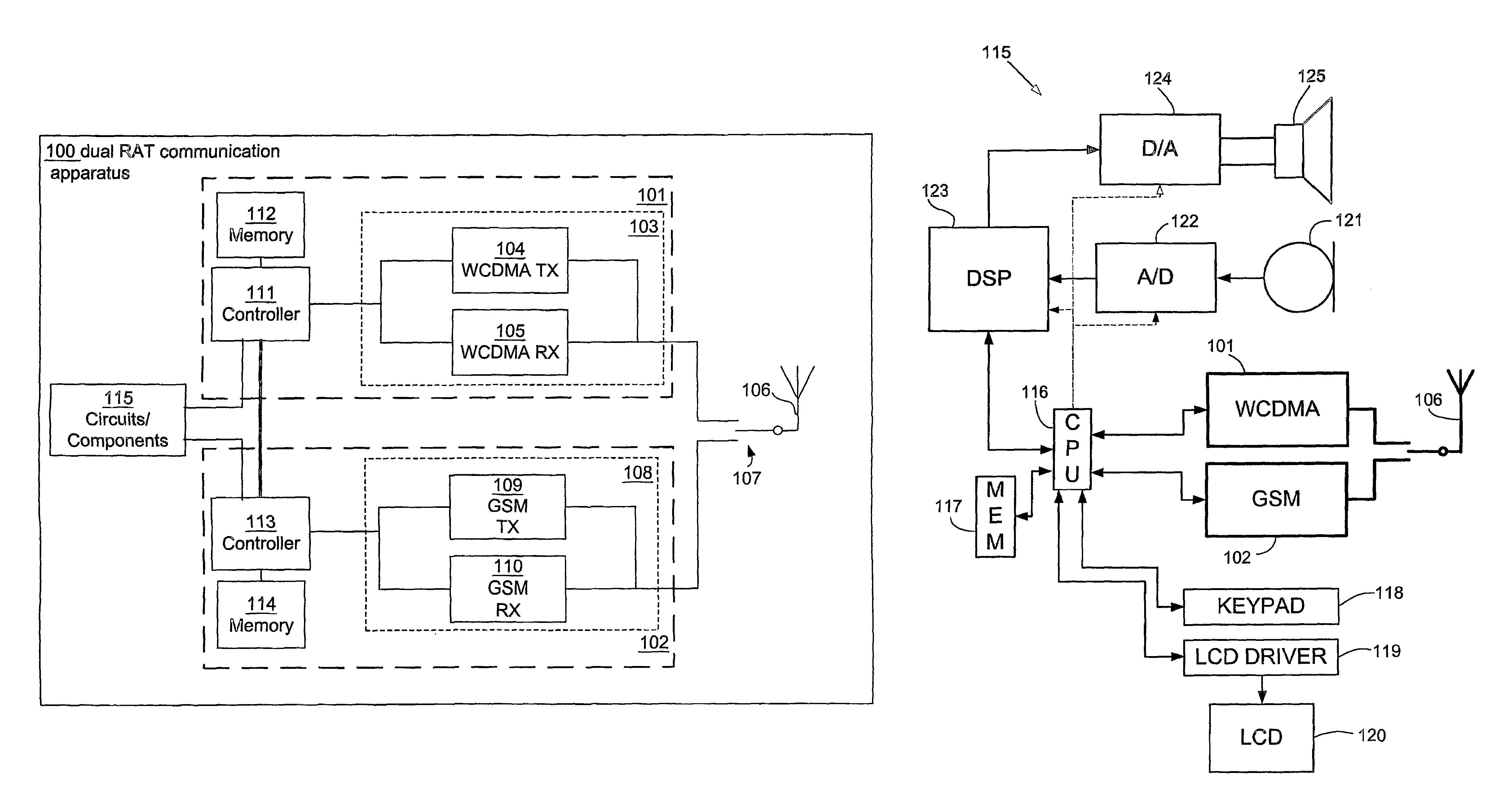
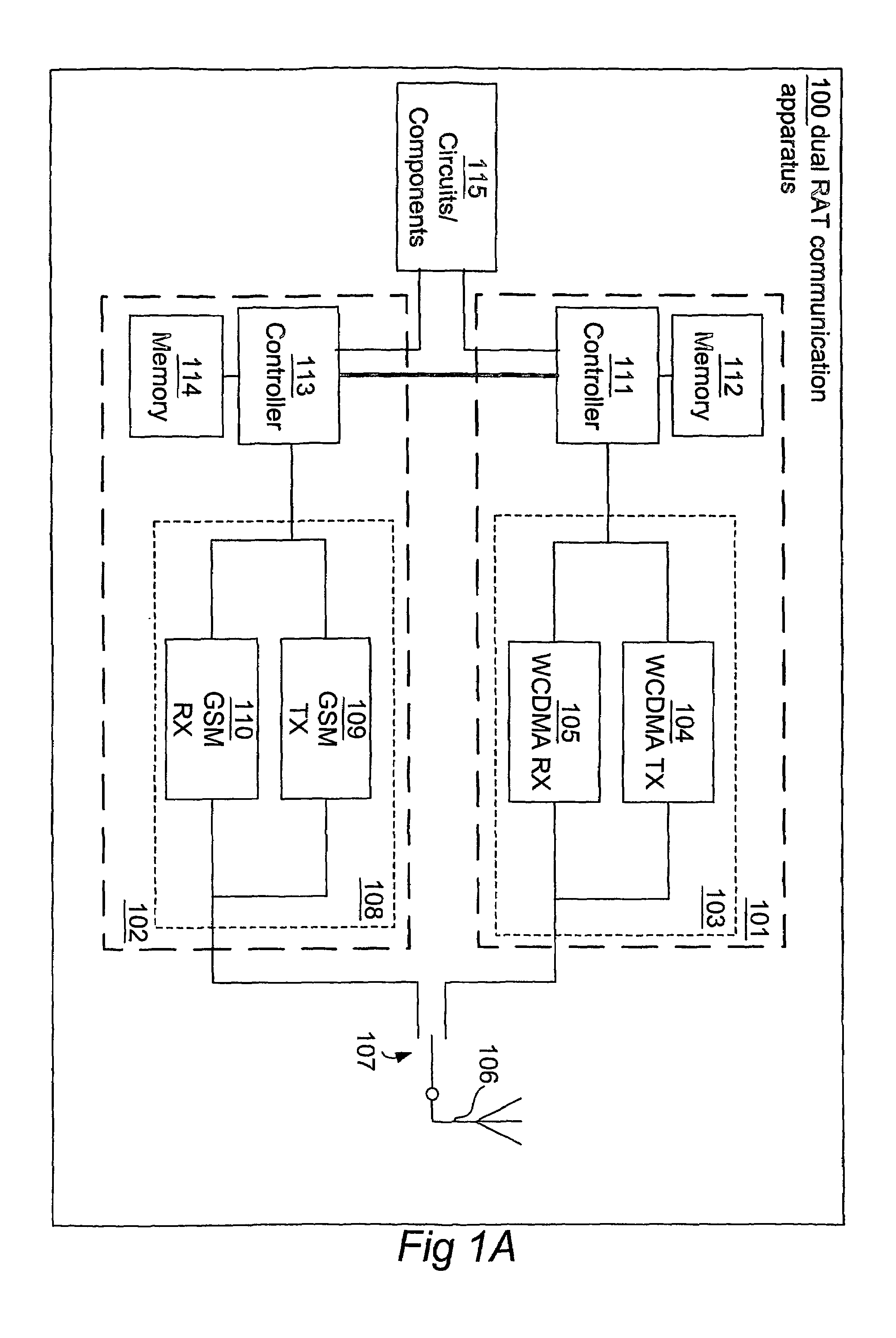
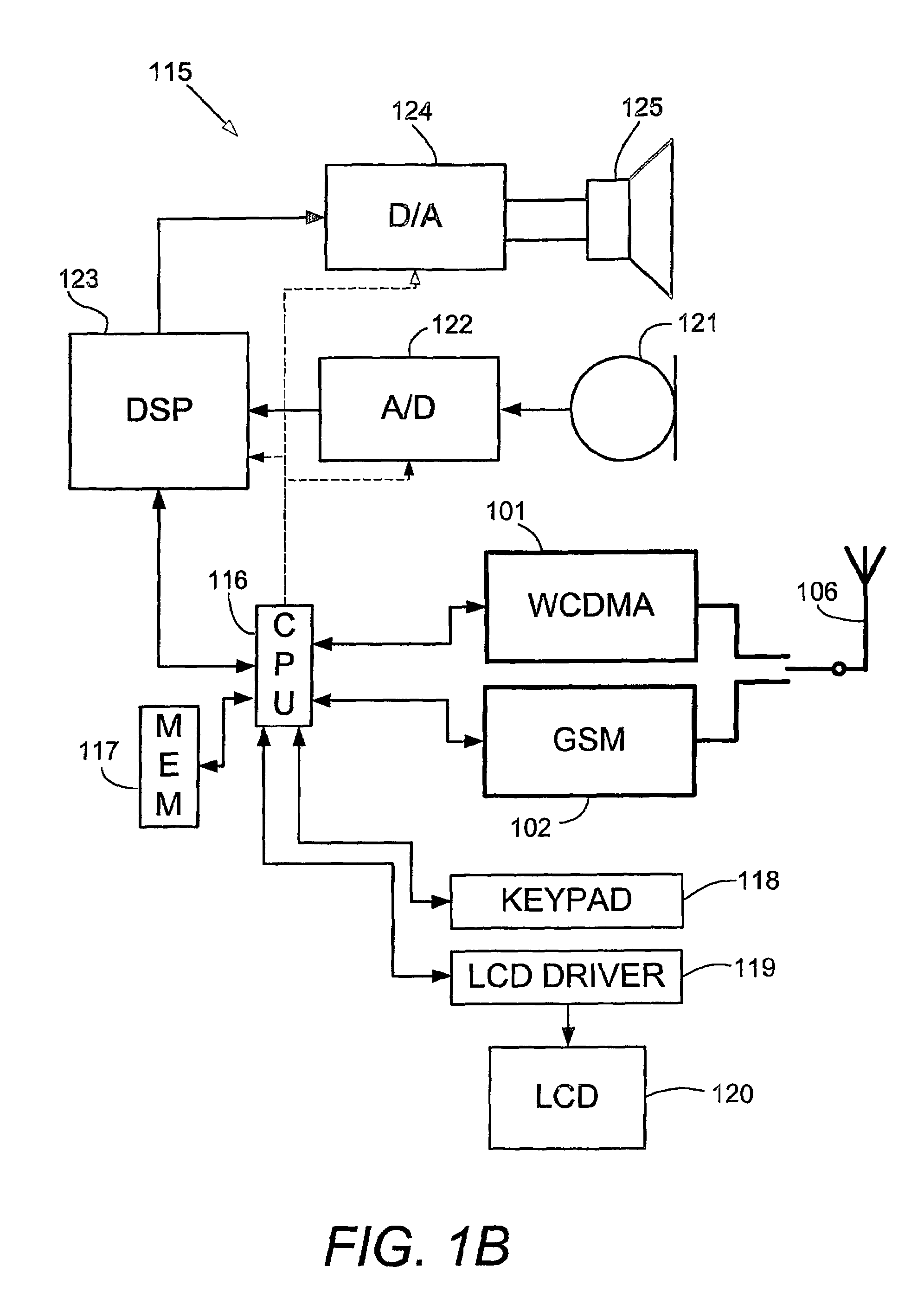
ActiveUS7626956B2Reduce complexitySynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesRadio access technologyEvent synchronization
A method and apparatus for measurement event synchronization of a portable radio communication apparatus providing multiple radio access technologies, wherein an idle gap is identified between transceiver activities of a first radio access technology device, and an execute signal is sent to a second radio access technology device for initiating inter radio access technology measurements of the second radio access technology device, to be performed during the gap.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com