Multi-task-based discrete event parallel simulation and time synchronization method
A discrete event, time synchronization technology, applied in the field of computing simulation, can solve problems such as insufficient utilization of resources, network bandwidth resources occupied by synchronization and interaction, and increased simulation running time overhead.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
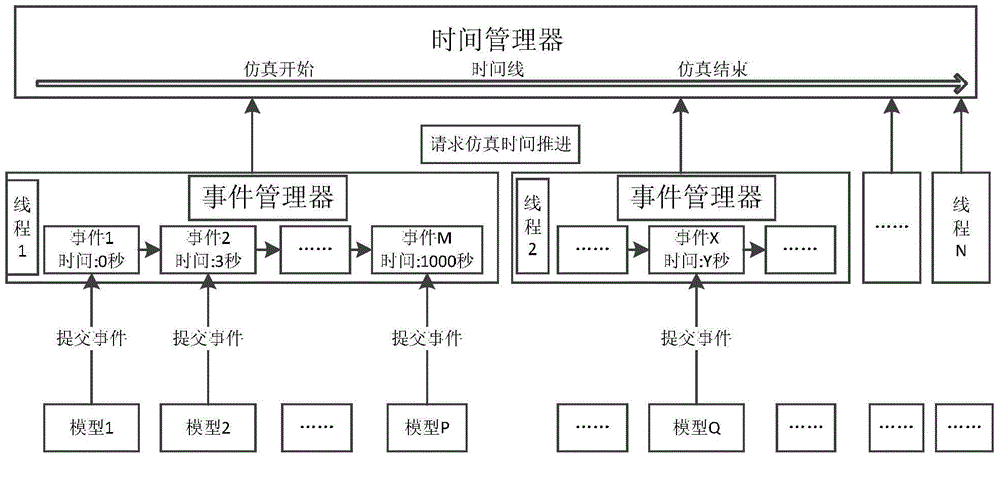
[0088] 1. Construct a large number of entities participating in the simulation into a continuous single memory image and divide it into multiple groups;
[0089] 2. Create an event queue for each group, and arrange them in order of timestamp and priority;
[0090] 3. Set a globally unique time manager to coordinate the time of each event queue;
[0091] 4. Each event queue processes events in chronological order and advances the time;
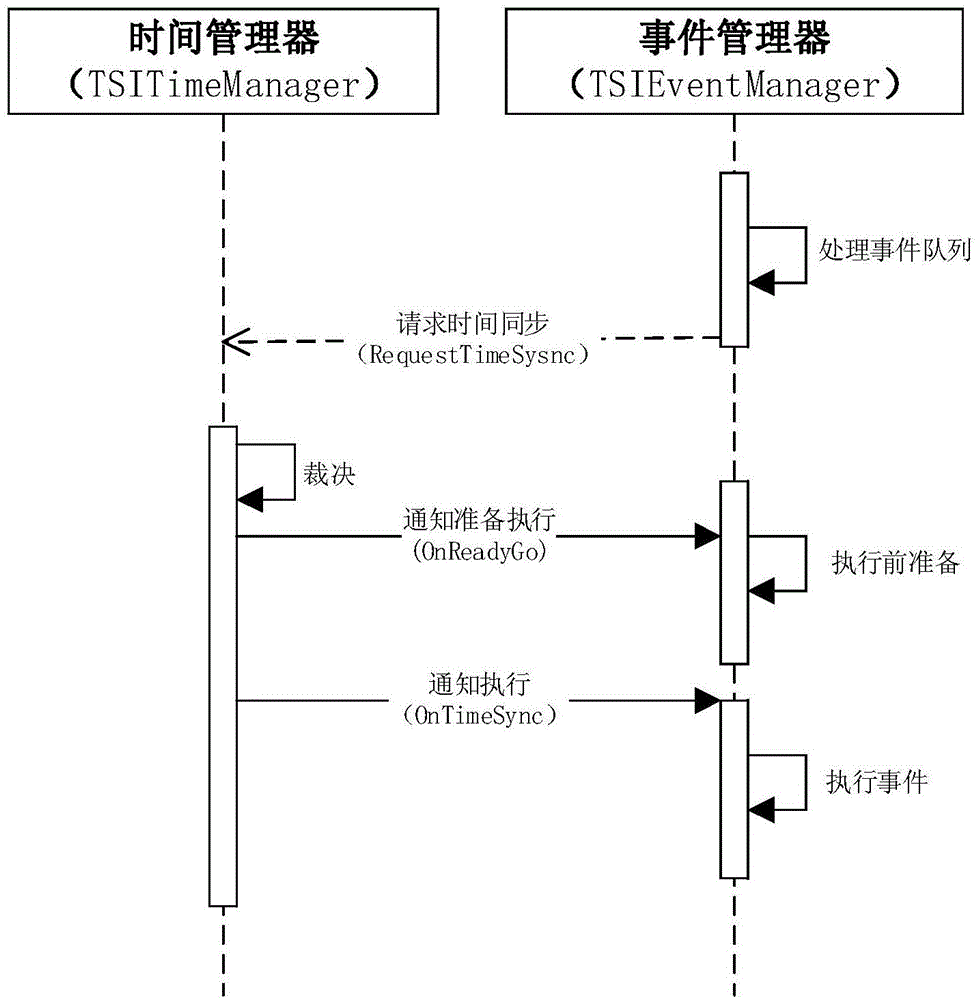
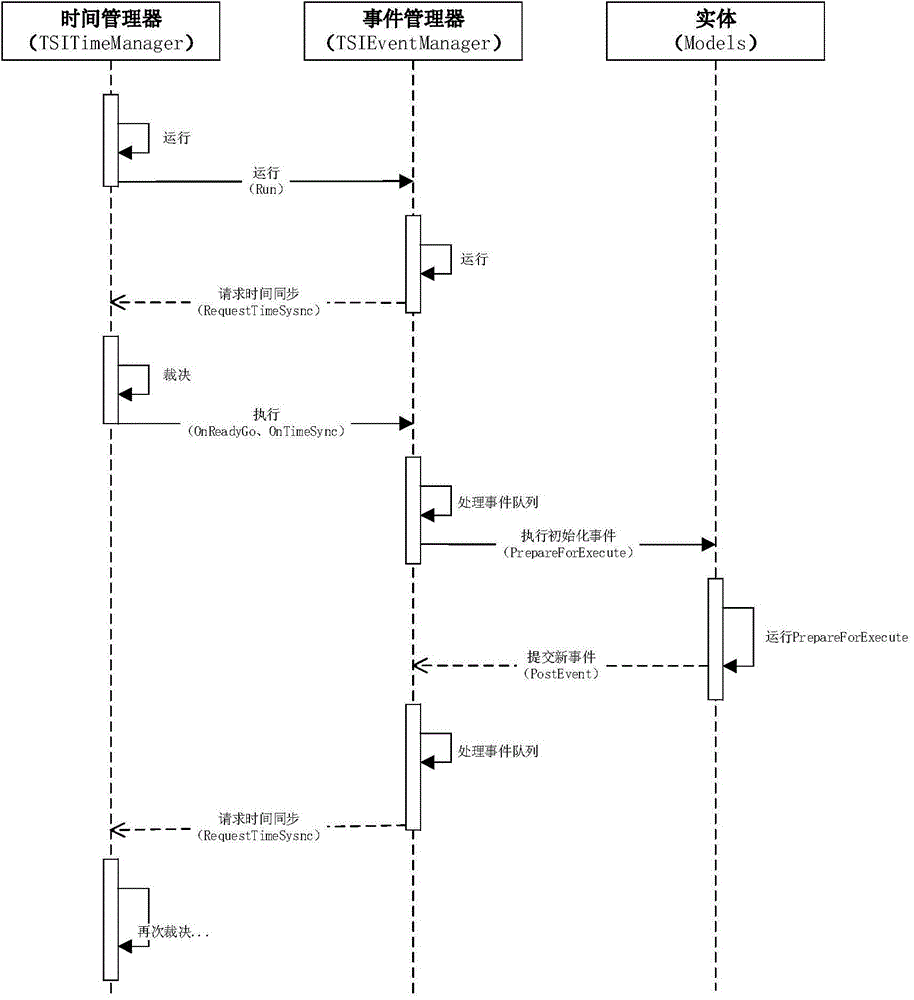
[0092] 5. When the timestamp of the next event in the event queue is greater than the current time or priority, request the time manager to advance the time;
[0093] 6. When the event queues are in the synchronous state (all are in the request advance state), the time manager scans the minimum time and highest priority that each event queue currently requires to advance, and the event manager that meets the time and priority conditions is approved, and will The current simulation time and priority is advanced to the approved time and priorit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com