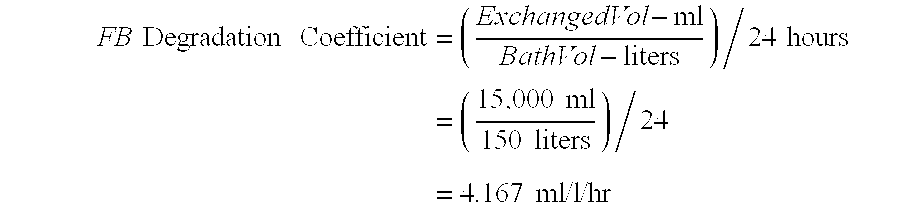Patents
Literature
173results about How to "Little overhead" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
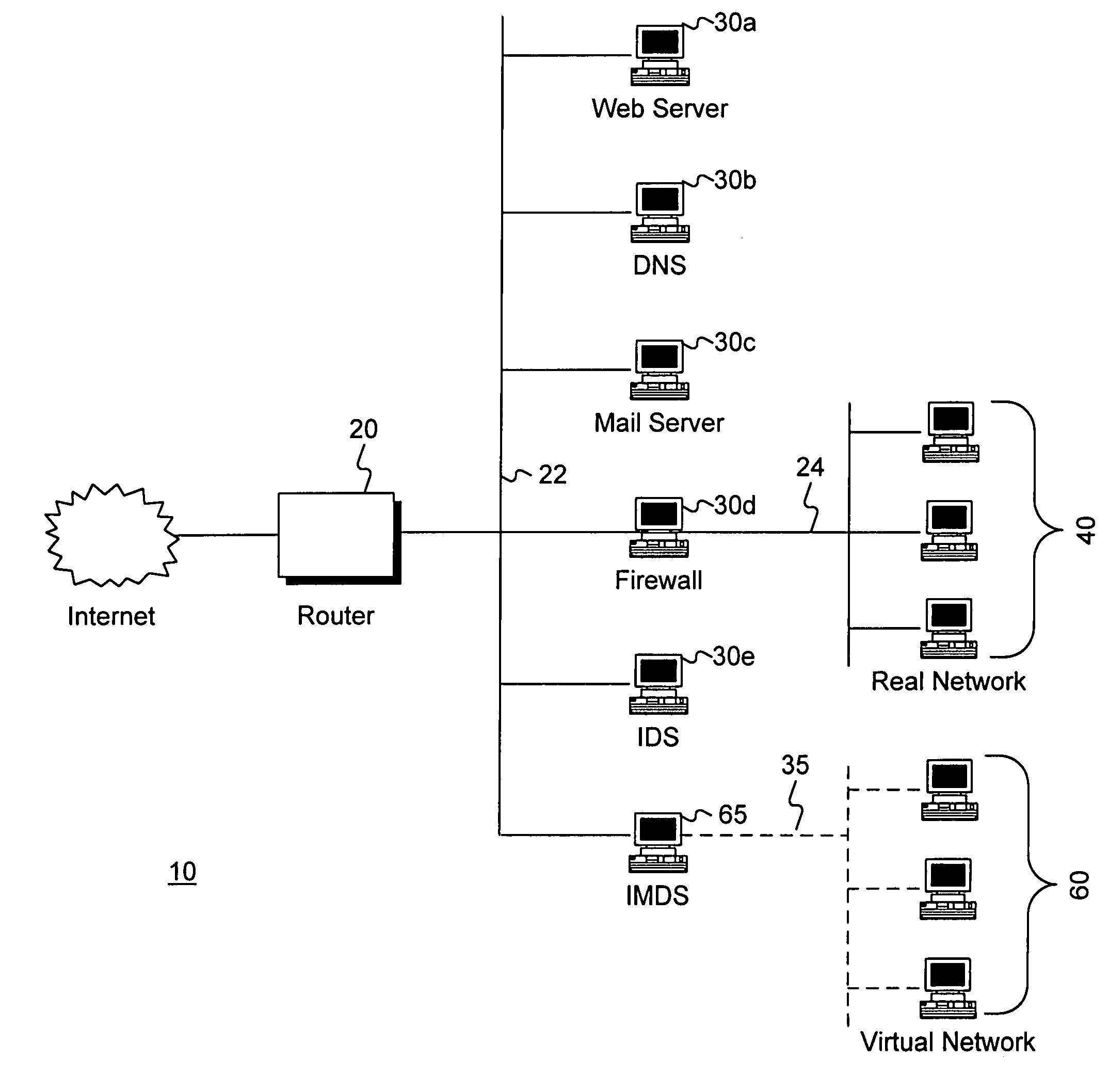
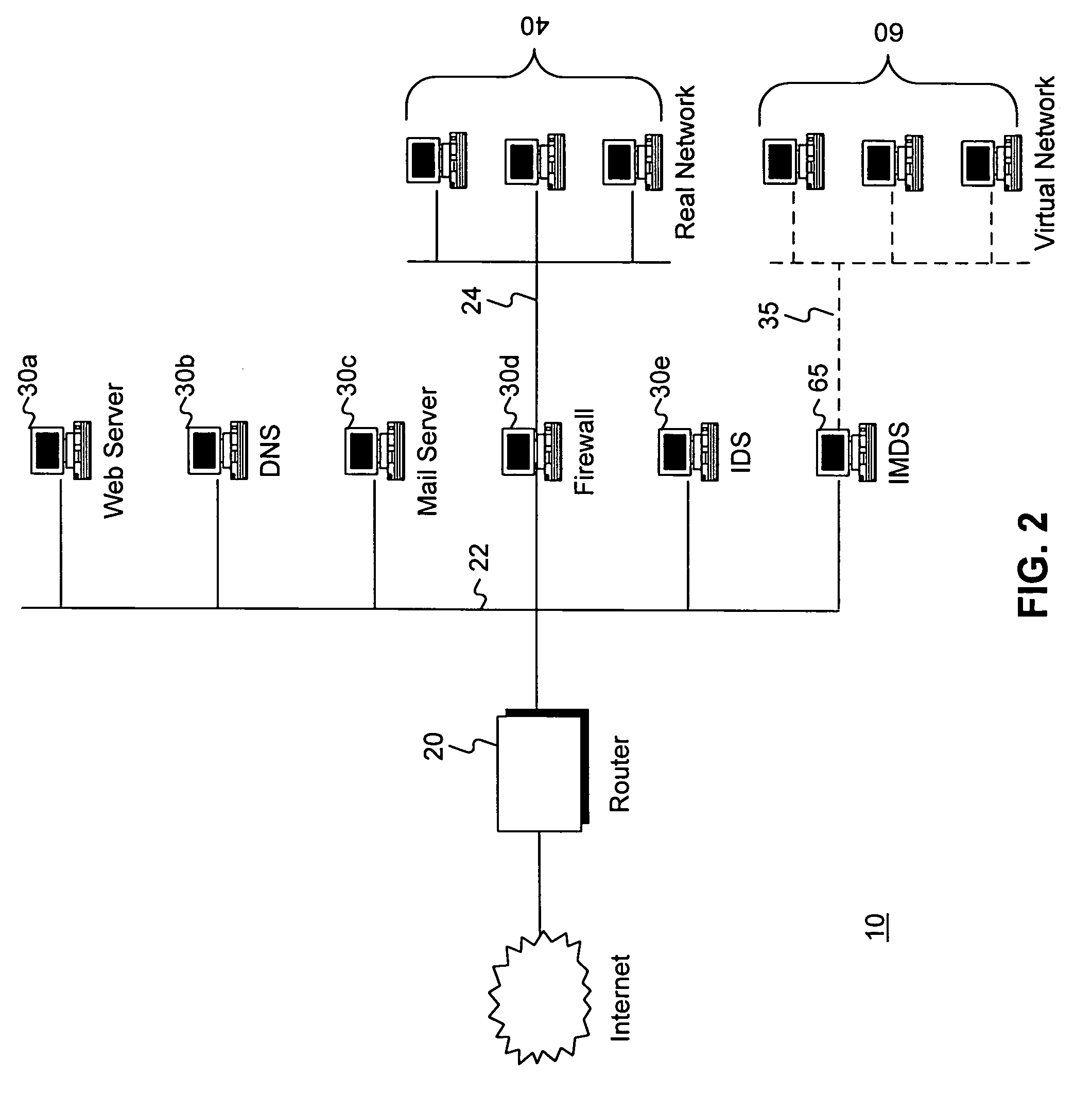
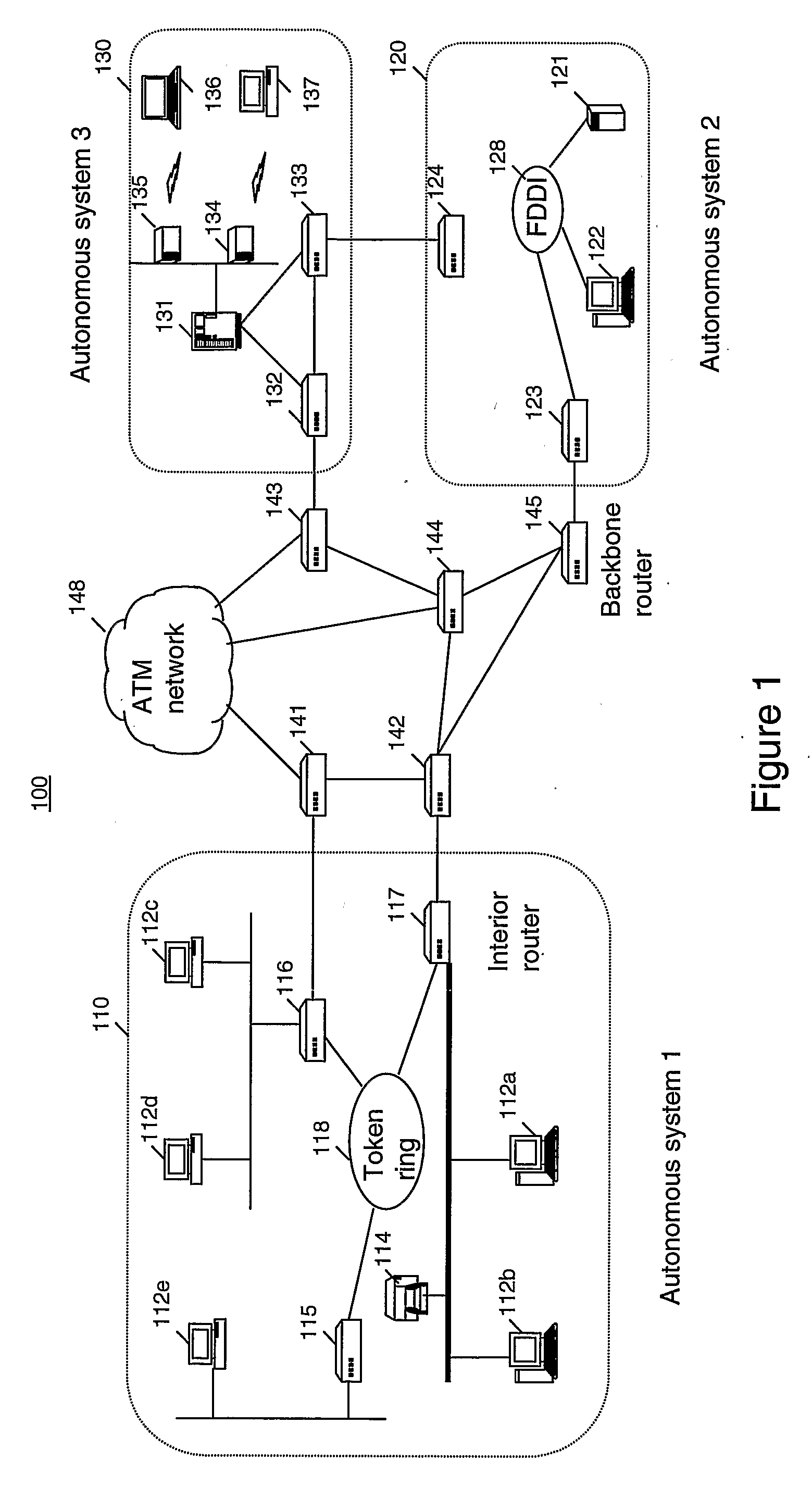
Intrusion and misuse deterrence system employing a virtual network
InactiveUS7240368B1Improve securityEasy to implementMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionIp addressBandwidth limitation
A method and apparatus is disclosed for increasing the security of computer networks through the use of an Intrusion and Misuse Deterrence System (IMDS) operating on the network. The IMDS is a system that creates a synthetic network complete with synthetic hosts and routers. It is comprised of a network server with associated application software that appears to be a legitimate portion of a real network to a network intruder. The IMDS consequently invites inquiry and entices the intruder away from the real network. Simulated services are configured to appear to be running on virtual clients with globally unique, class “C” IP addresses. Since there are no legitimate users of the virtual network simulated by the IMDS, all such activity must be inappropriate and can be treated as such. Consequently, the entire set of transactions by an intruder can be collected and identified rather than just those transactions that meet a predefined attack profile. Also, new exploits and attacks are handled just as effectively as known attacks, resulting in better identification of attack methodologies as well as the identification and analysis of new attack types. Since the IMDS only has to be concerned with the traffic going to its simulated hosts it additionally eliminates the bandwidth limitation that plagues a traditional intrusion detection system (IDS).
Owner:VERIZON SERVICES GROUP +2
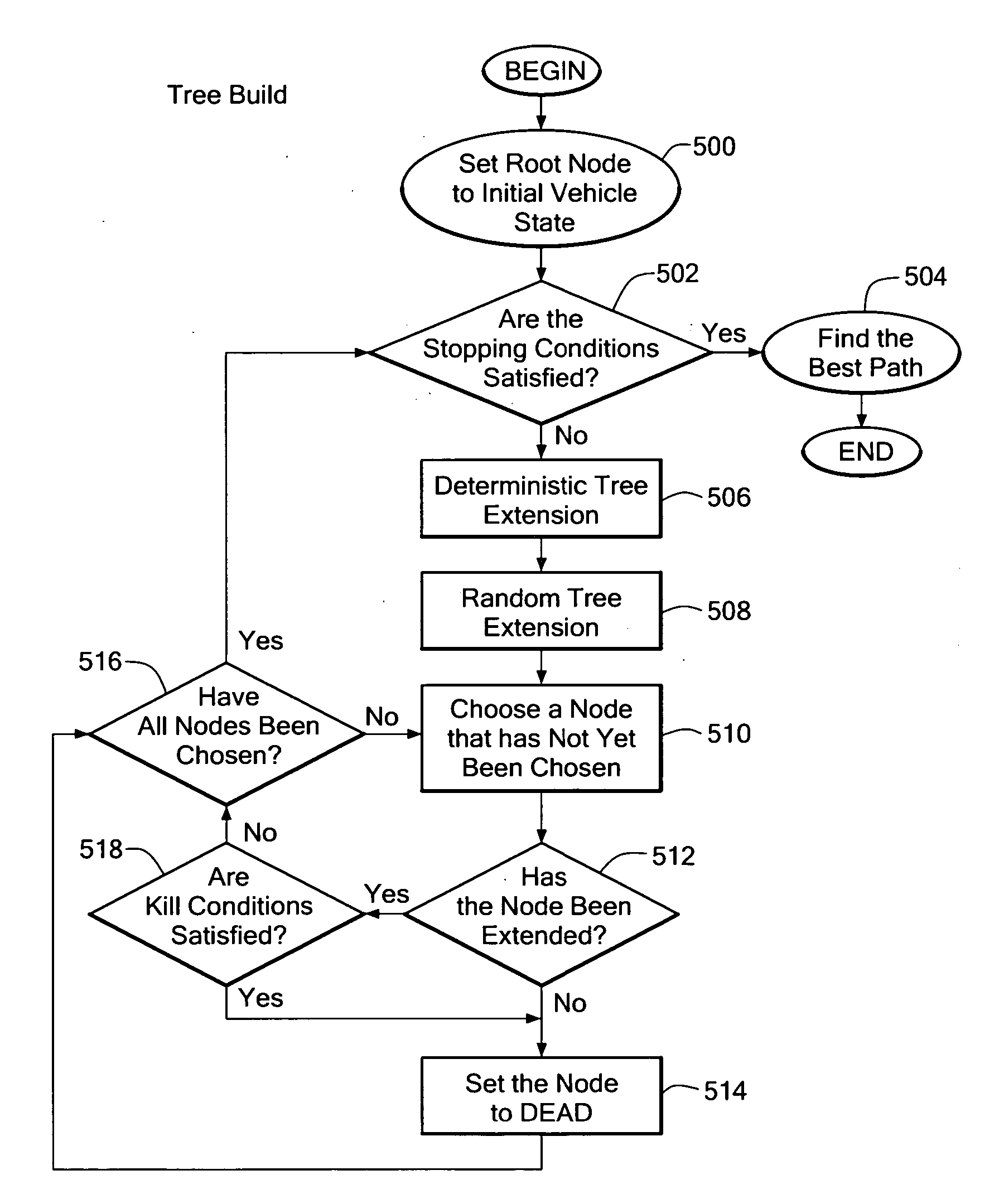
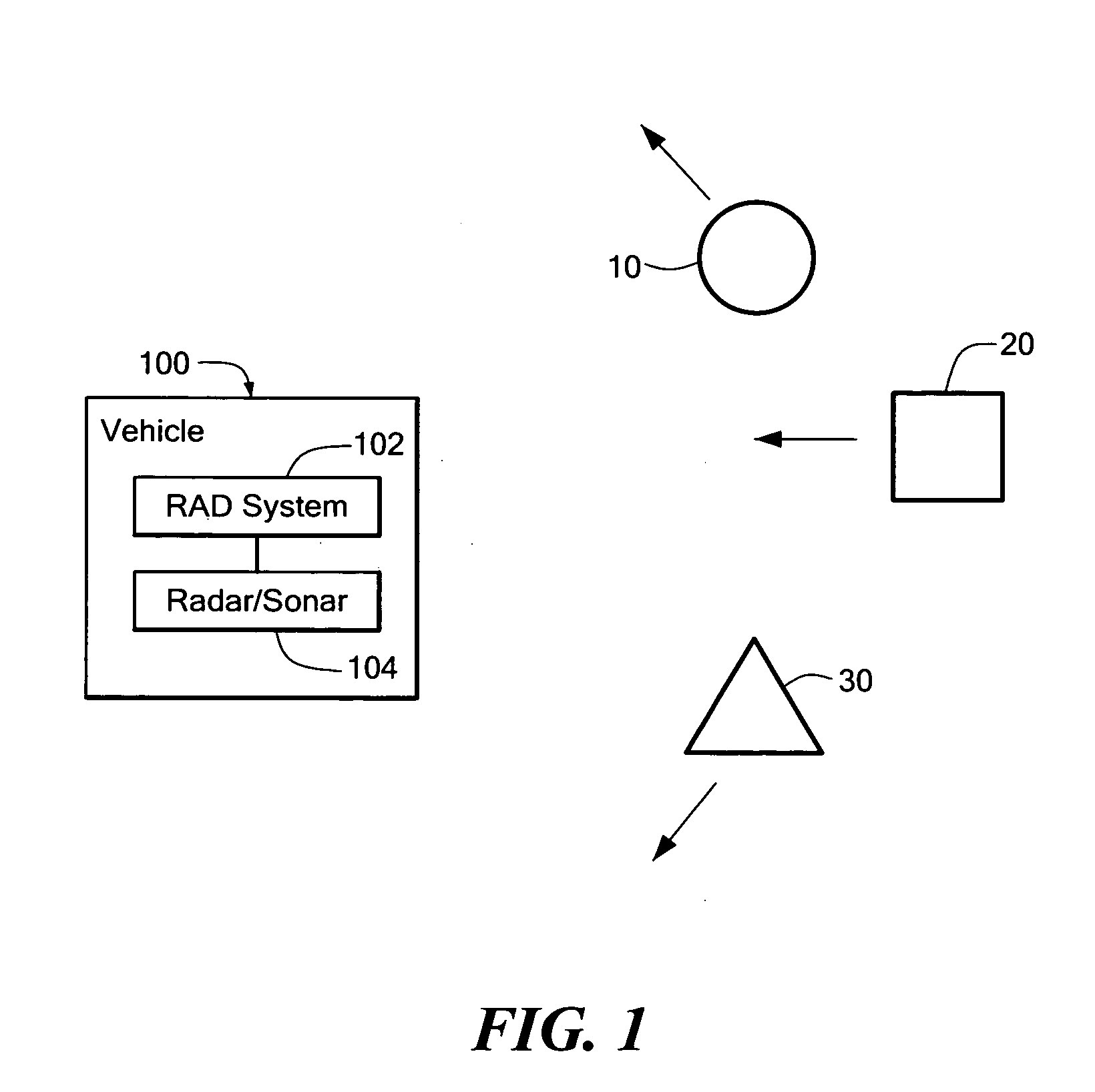
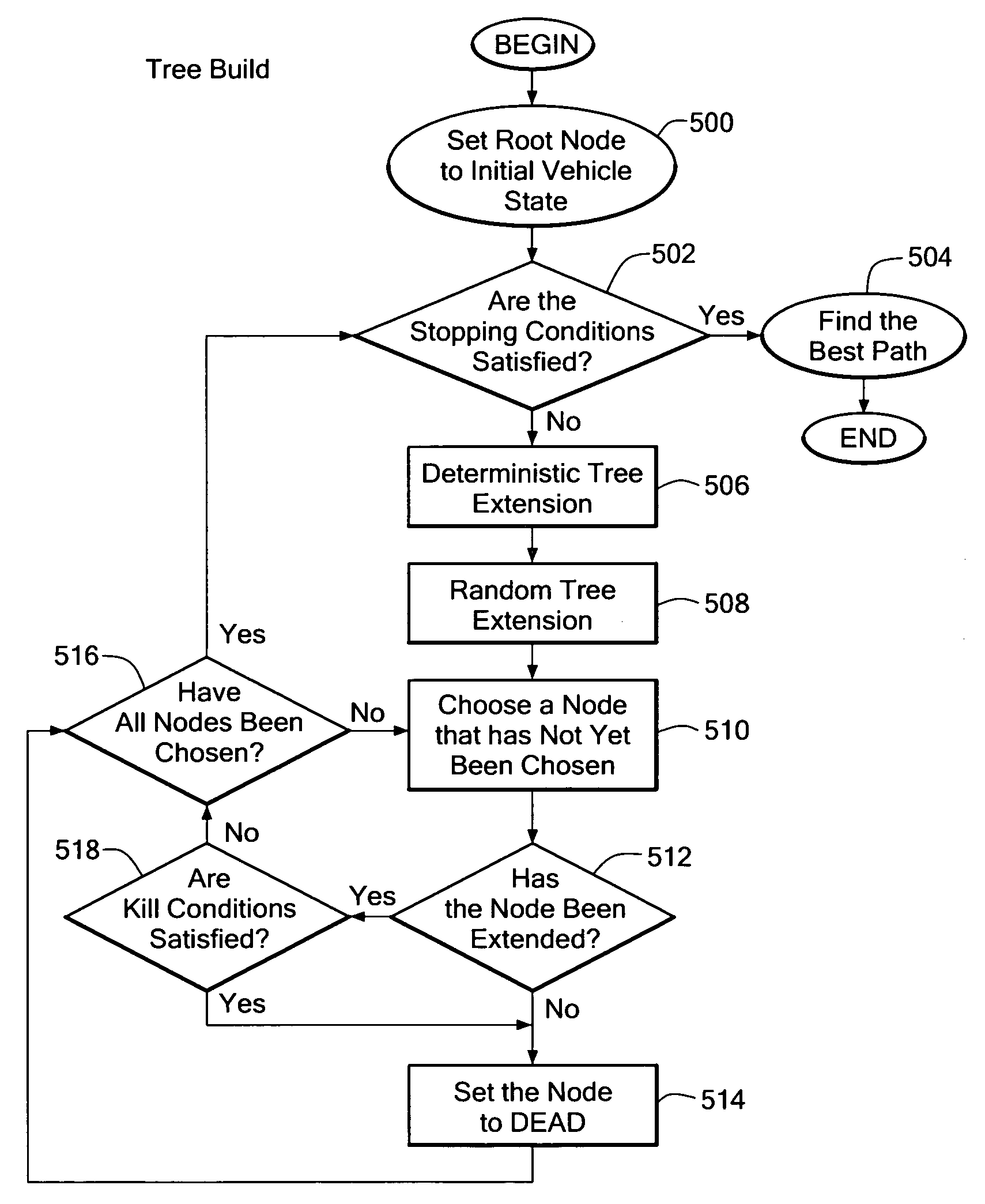
System and method for adaptive path planning
InactiveUS20050216181A1Little overheadGenerate efficientlyInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsEngineeringTime path
A path planning system and method for an object, such as a vehicle, provides a randomized adaptive path planning that handles real-time path planning for a vehicle operating under kinodynamic constraints in dynamically changing and uncertain environments with probabilistic knowledge of vehicle and obstacle movement.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
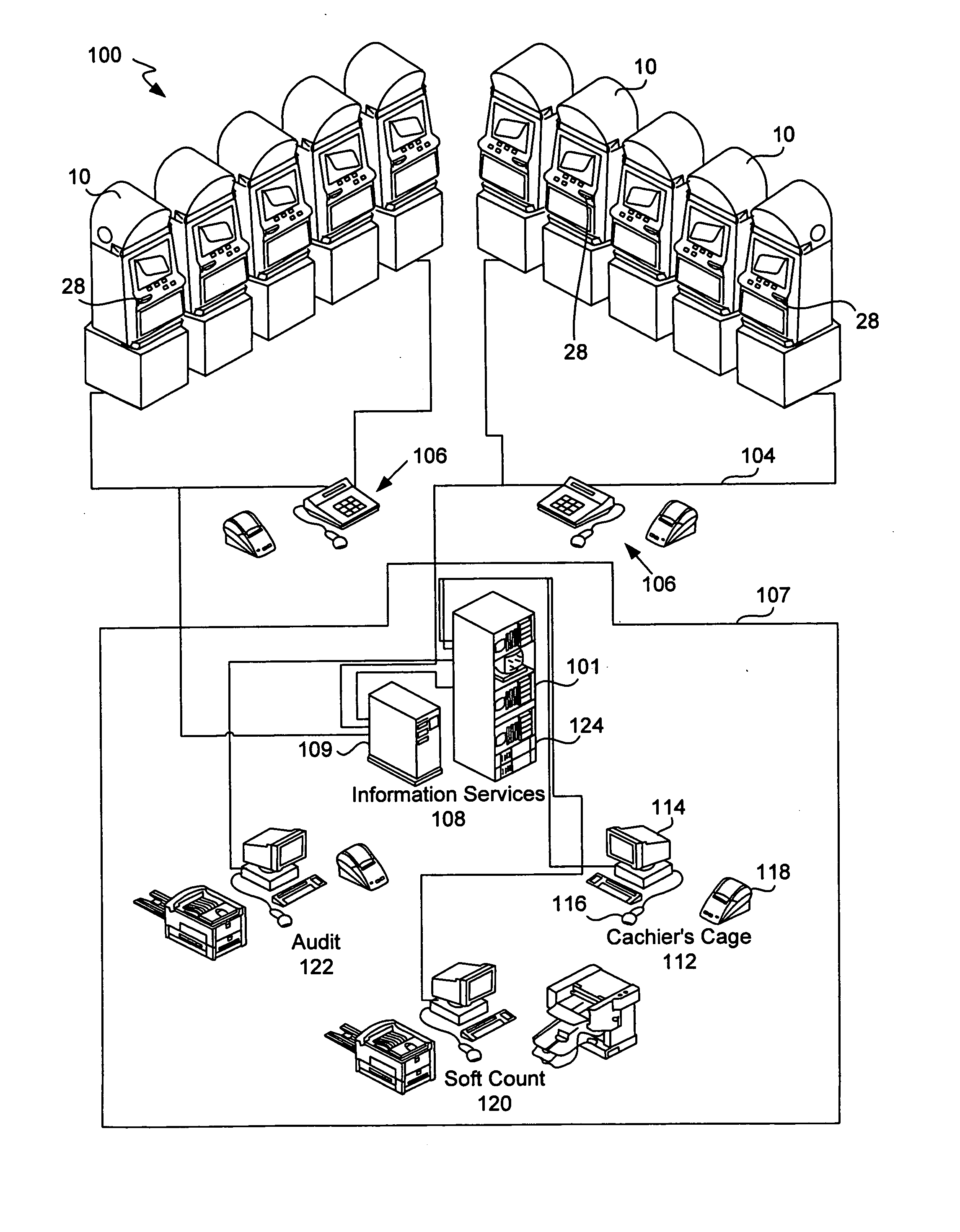
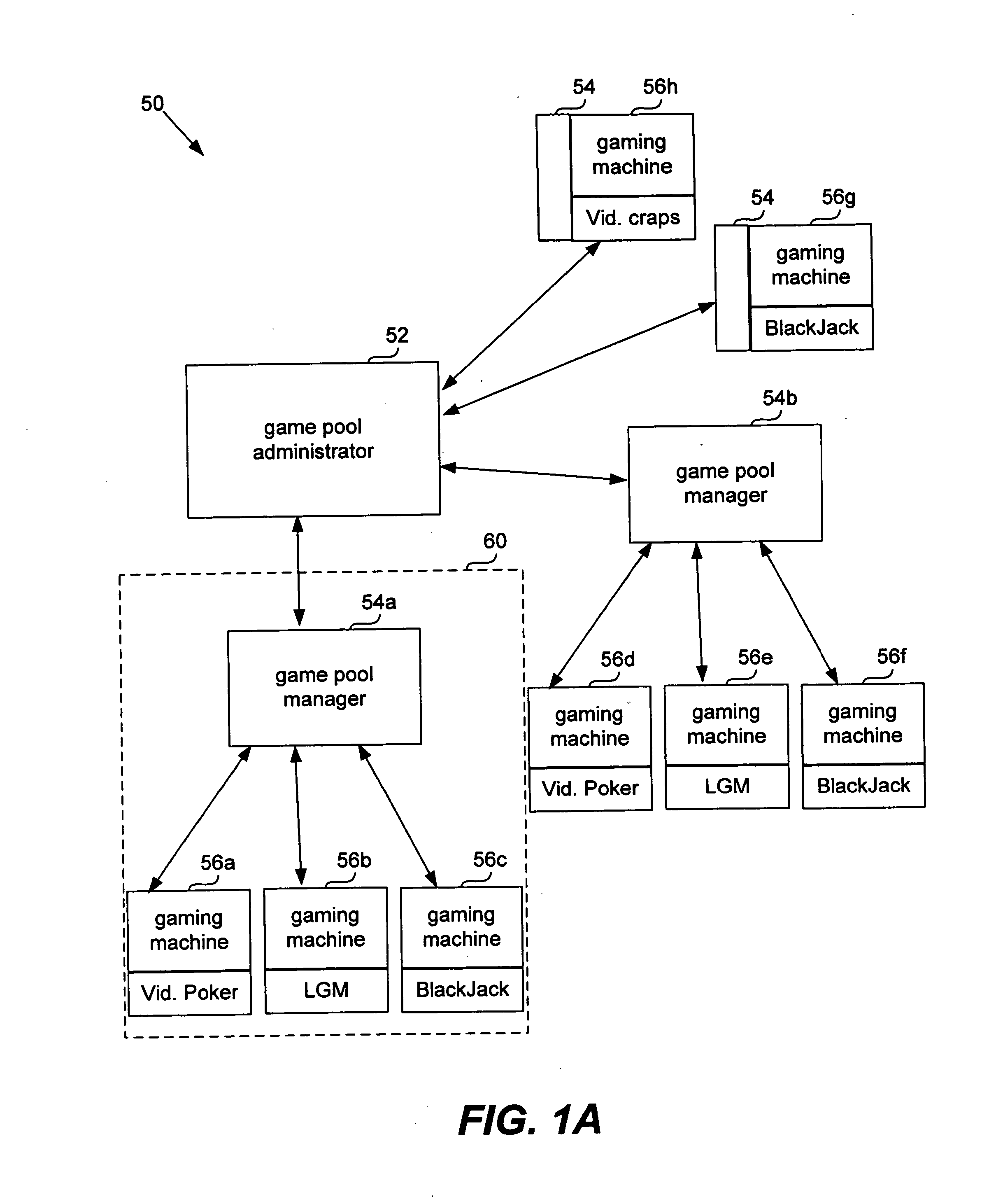
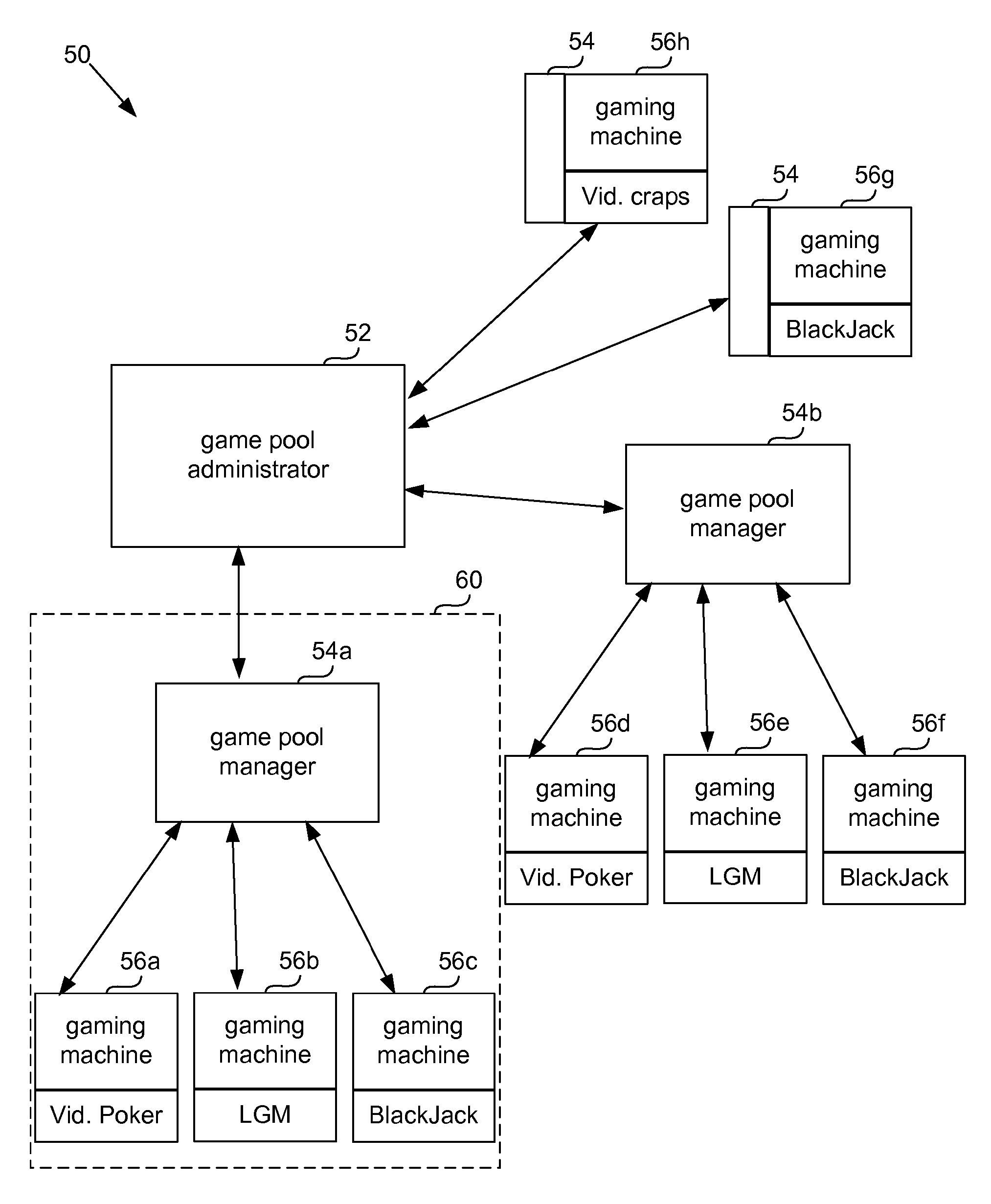
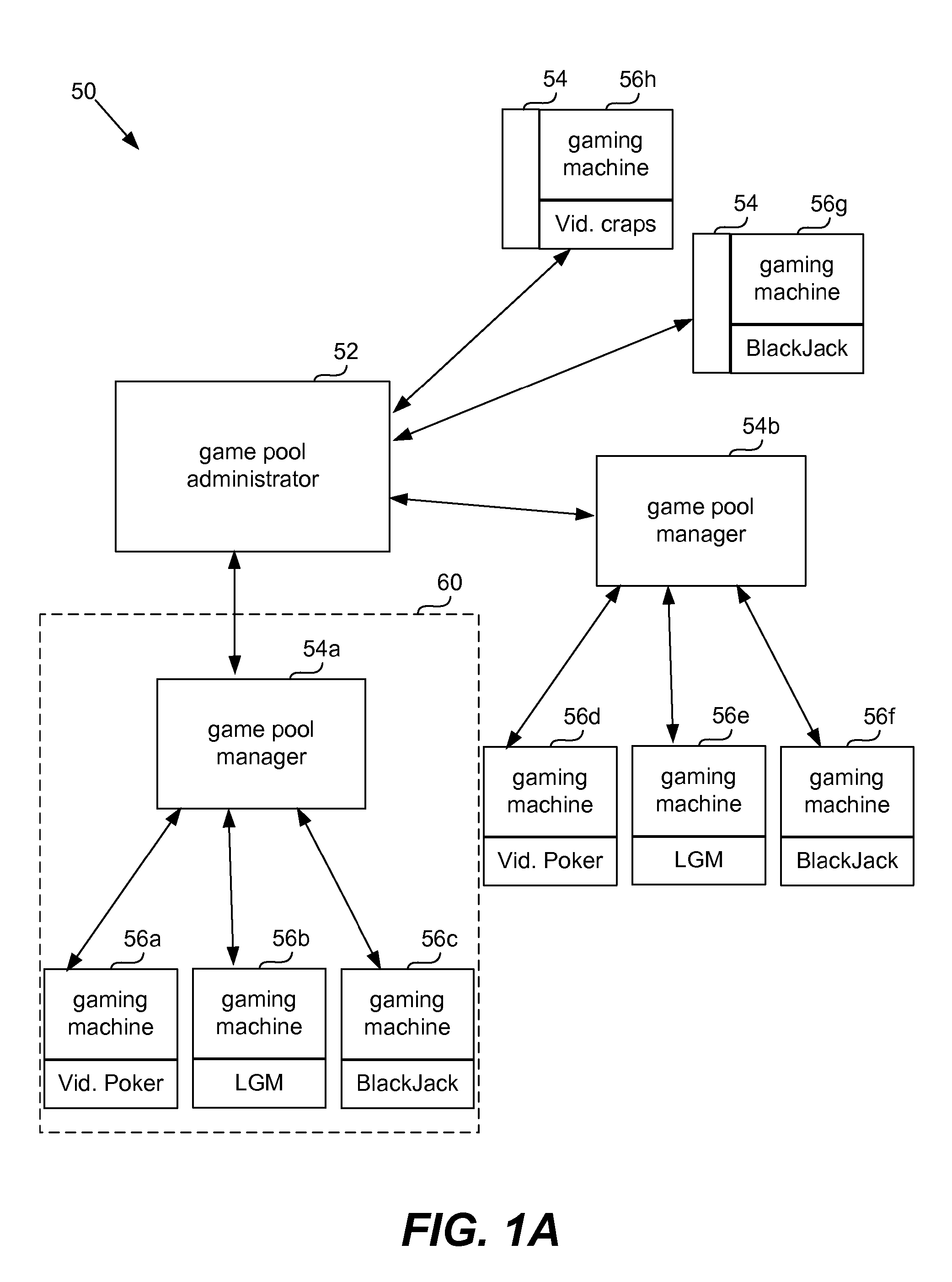
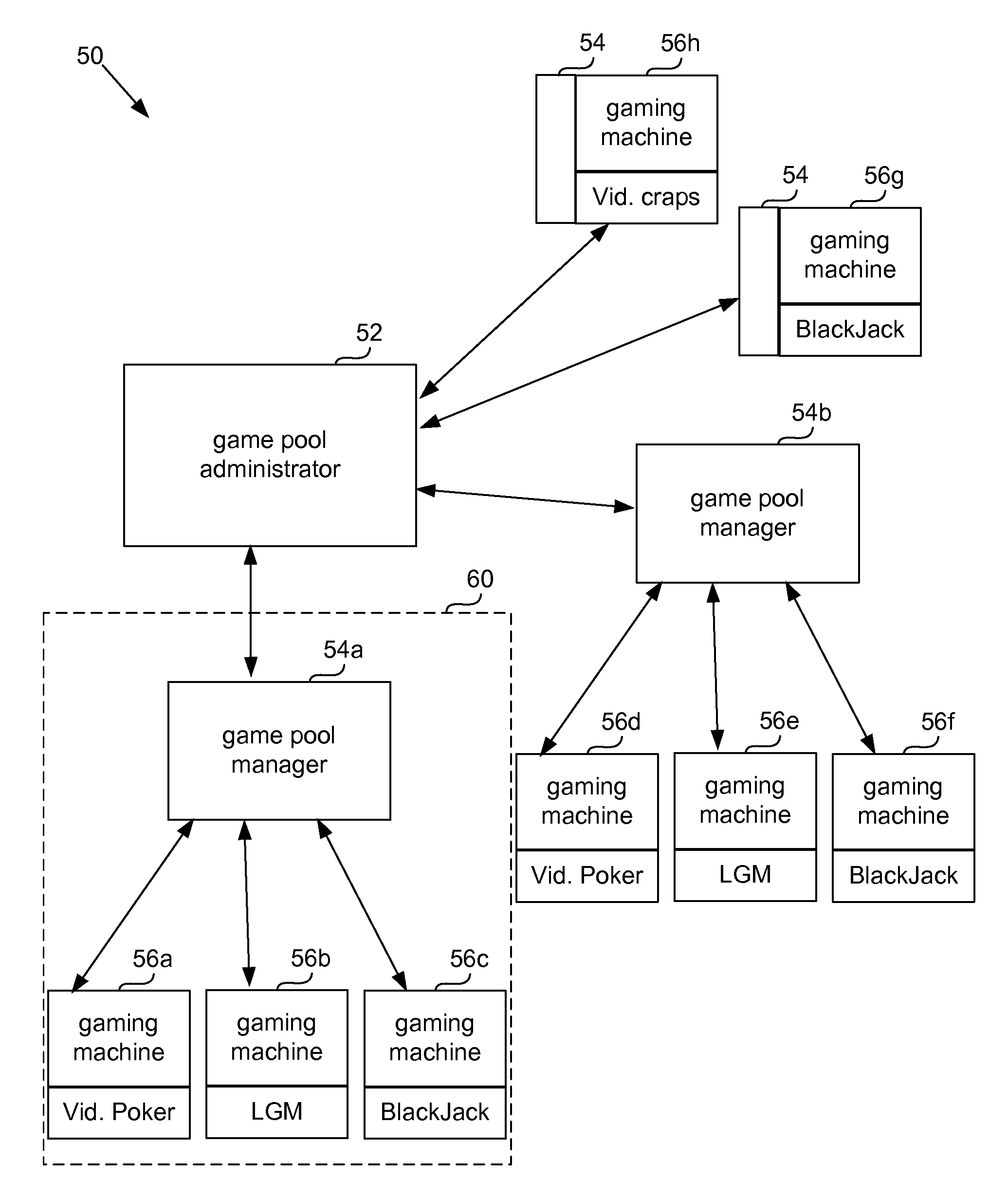
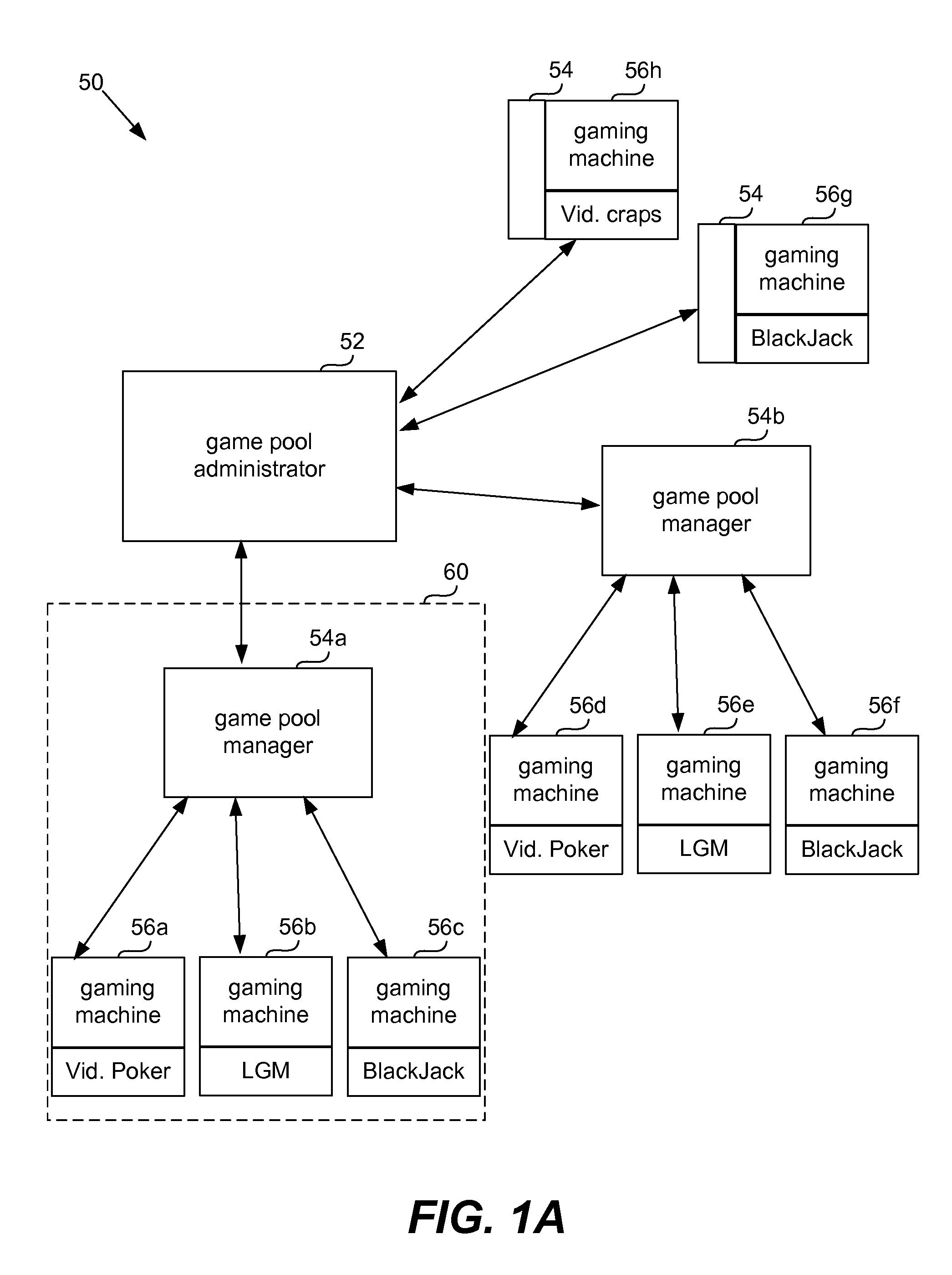
Universal progressive game pool
InactiveUS20060142079A1Significant progressQuick upgradeApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesHuman–computer interactionGame machine
The present invention provides systems and methods that allow gaming machines to participate in a progressive pool and offer a progressive award regardless of the game installed on the gaming machine. The present invention also permits gaming machine participation in a progressive pool regardless of wager amount. This permits larger progressive awards and awards that grow faster since more games and gaming machines may participate in building a progressive pool award. It also opens the attraction of a large progressive pool award to more games, gaming machines and gaming establishments.
Owner:IGT
System and method of secure login on insecure systems
InactiveUS20060206919A1Little overheadEasy to addDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationKey imagesSafe system
A method for authenticating a user for use of a server computing device wherein the server computing device is connected by a network to a host device. Generating a key representation image having thereon a plurality of individual key images placed at random positions, each corresponding to a possible character value in an authentication phrase. Accepting a sequence corresponding to locations of mouse clicks representing user selections of character values in an attempted authentication phrase. Verifying that the sequence of location values corresponds to a correct authentication phrase by mapping the locations of the mouse clicks to the locations of the randomly placed key images. Alternatively, accepting a sequence corresponding to a transformation of personal identification number based on a random number and a numerical operation or selection in a matrix.
Owner:AXALTO SA
Controlling quality of service in a mobile communications system
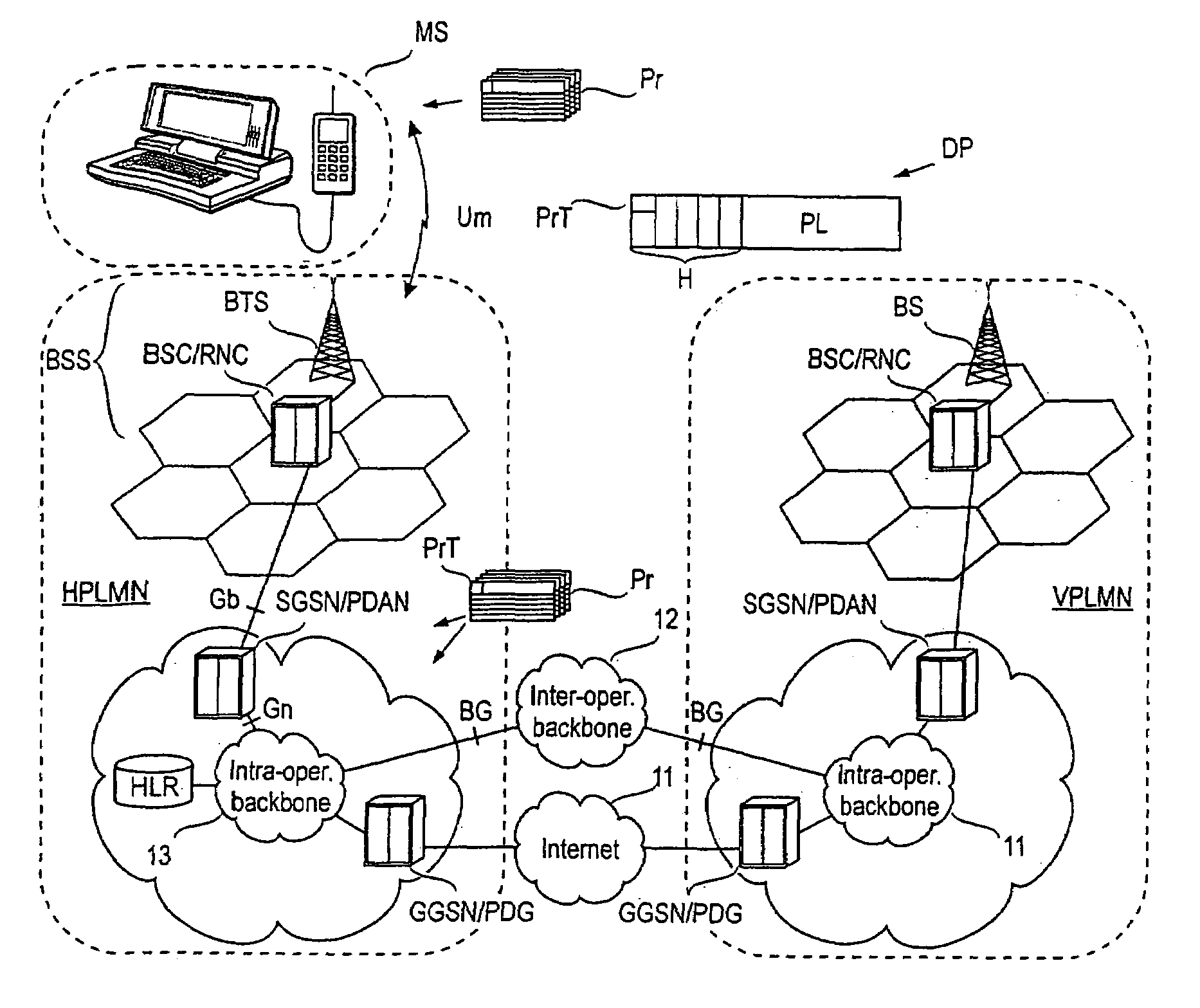
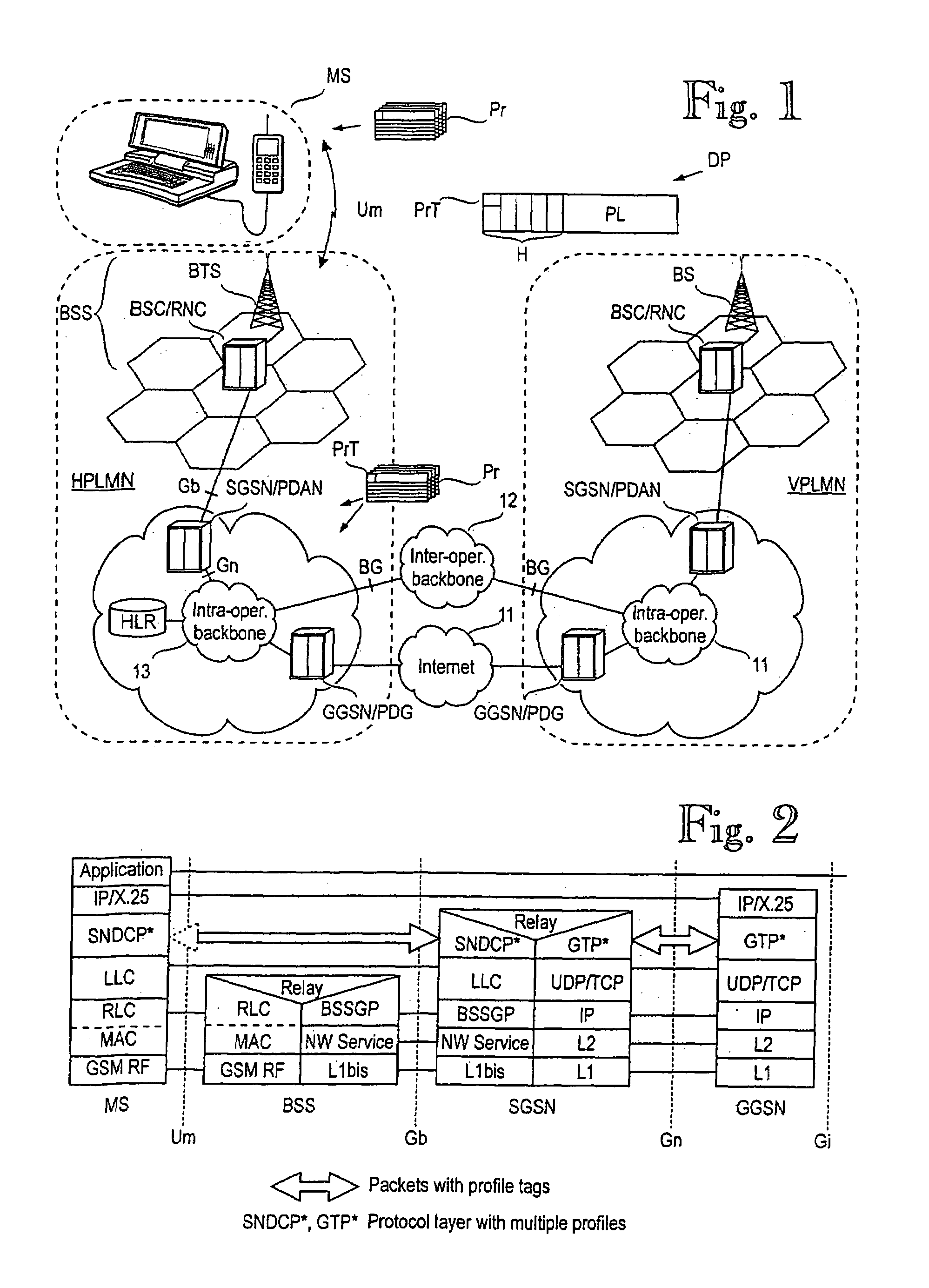
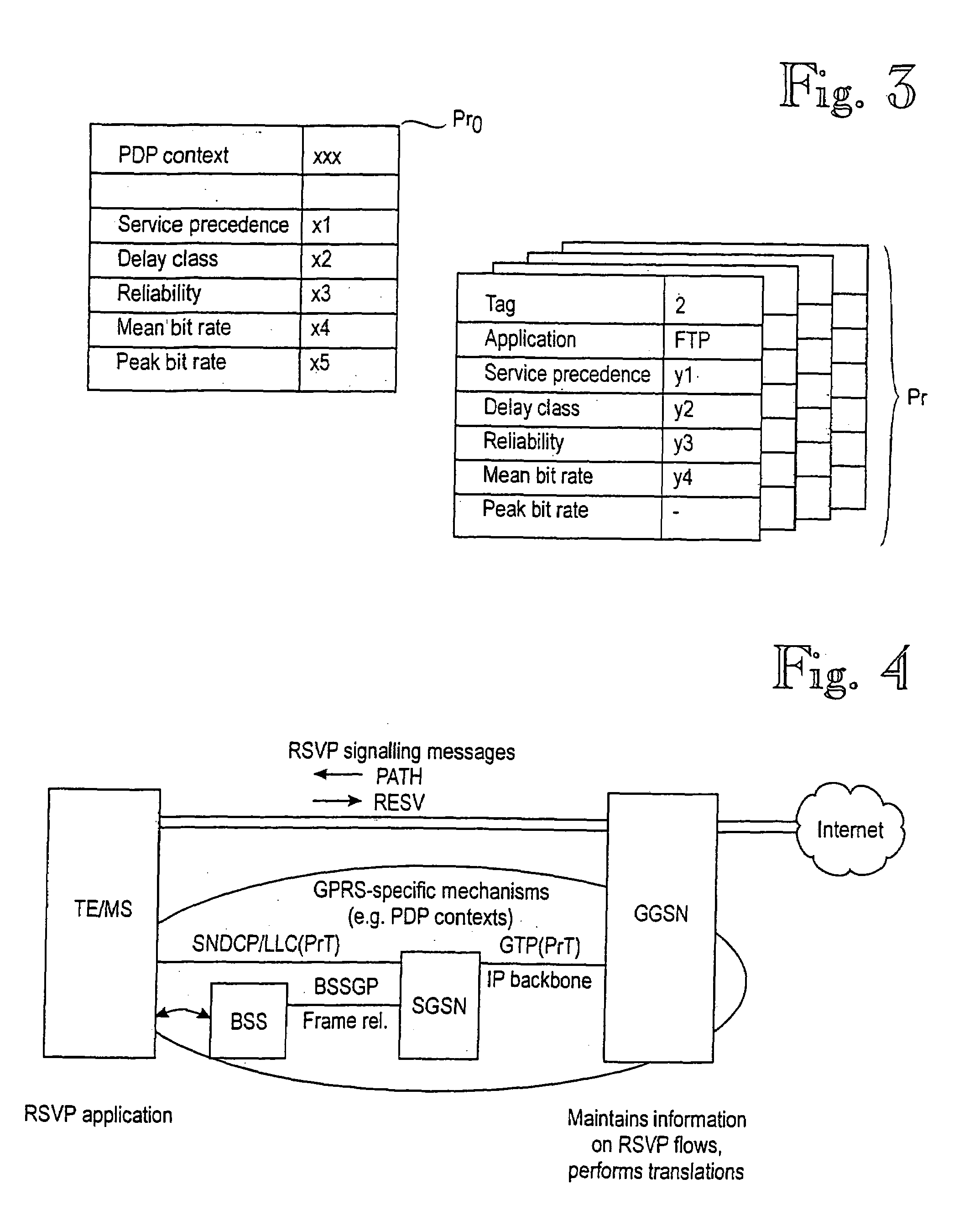
InactiveUS7023825B1Facilitates dynamic renegotiationLittle overhead into the mobile communications systemConnection managementData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceCommunications system
A method for transmitting data packets in multiple data flows to / from a mobile station in a mobile communications system. A data transmission path is formed for routing data packets. Multiple profiles are associated with the data transmission path, each profile comprising at least one quality of service parameter, or QoS parameter. Each flow or data packet is provided with a profile tag indicating one of the multiple profiles. Scheduling and policing the transmission of individual data packets is based on at least one QoS parameter of the profile indicated by the profile tag associated with the data flow in question.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
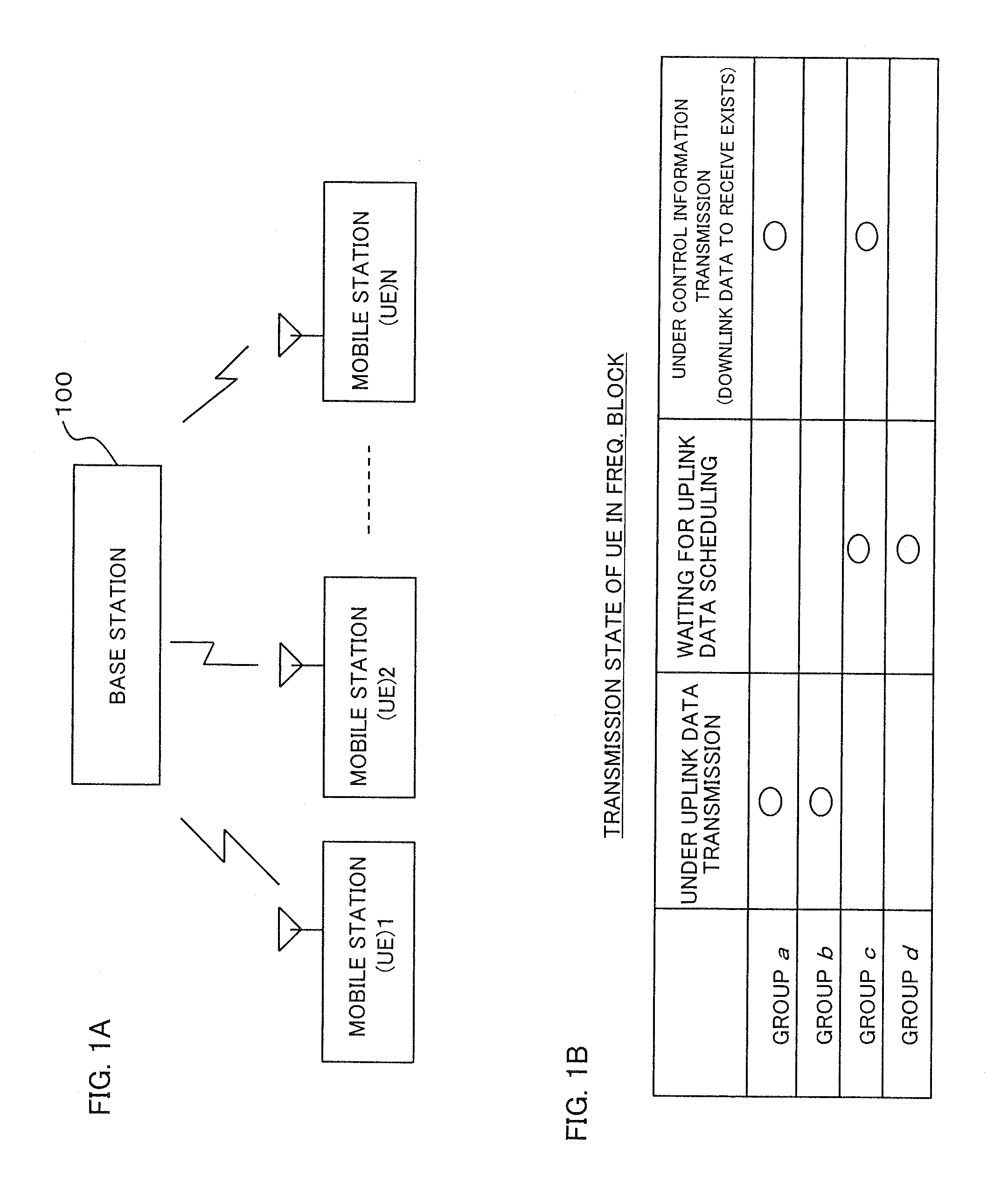
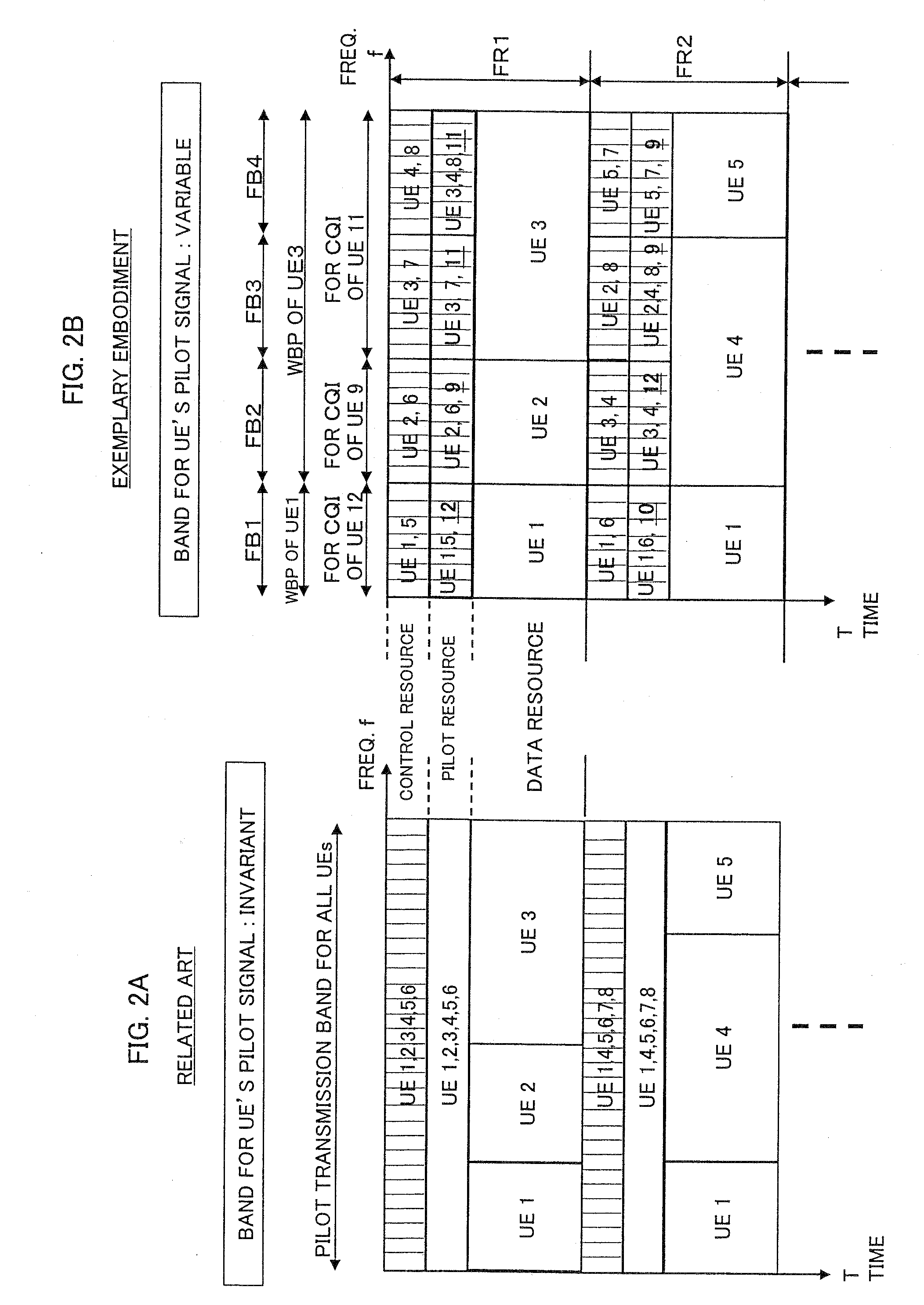
Method for measuring channel quality and base station in mobile communications system
InactiveUS20070293233A1Efficient qualityLittle overheadError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemMobile communication systems
A channel quality measurement method that accomplishes efficient channel quality measurement for each mobile station is presented. In a frequency band including a plurality of frequency blocks, a base station measures the channel quality of each of a plurality of mobile stations. With respect to each mobile station, when a pilot resource for demodulation is not allocated in at least one of the frequency blocks, the base station allocates a specific pilot resource for channel quality measurement in that frequency block. The channel quality of each mobile station in the plurality of frequency blocks is measured by using one or both of the pilot resource for demodulation and the dedicated pilot resource for channel quality measurement.
Owner:NEC CORP
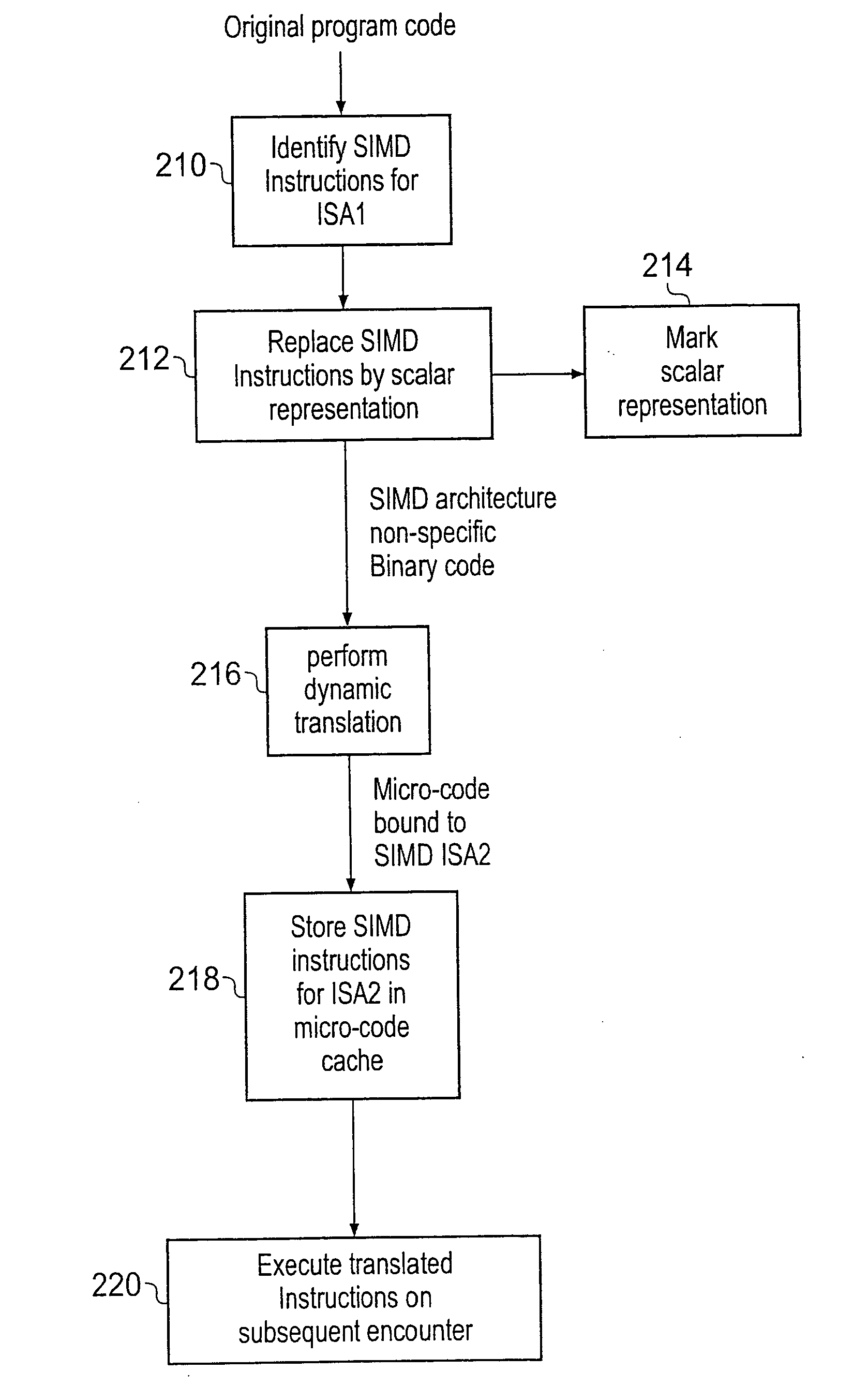
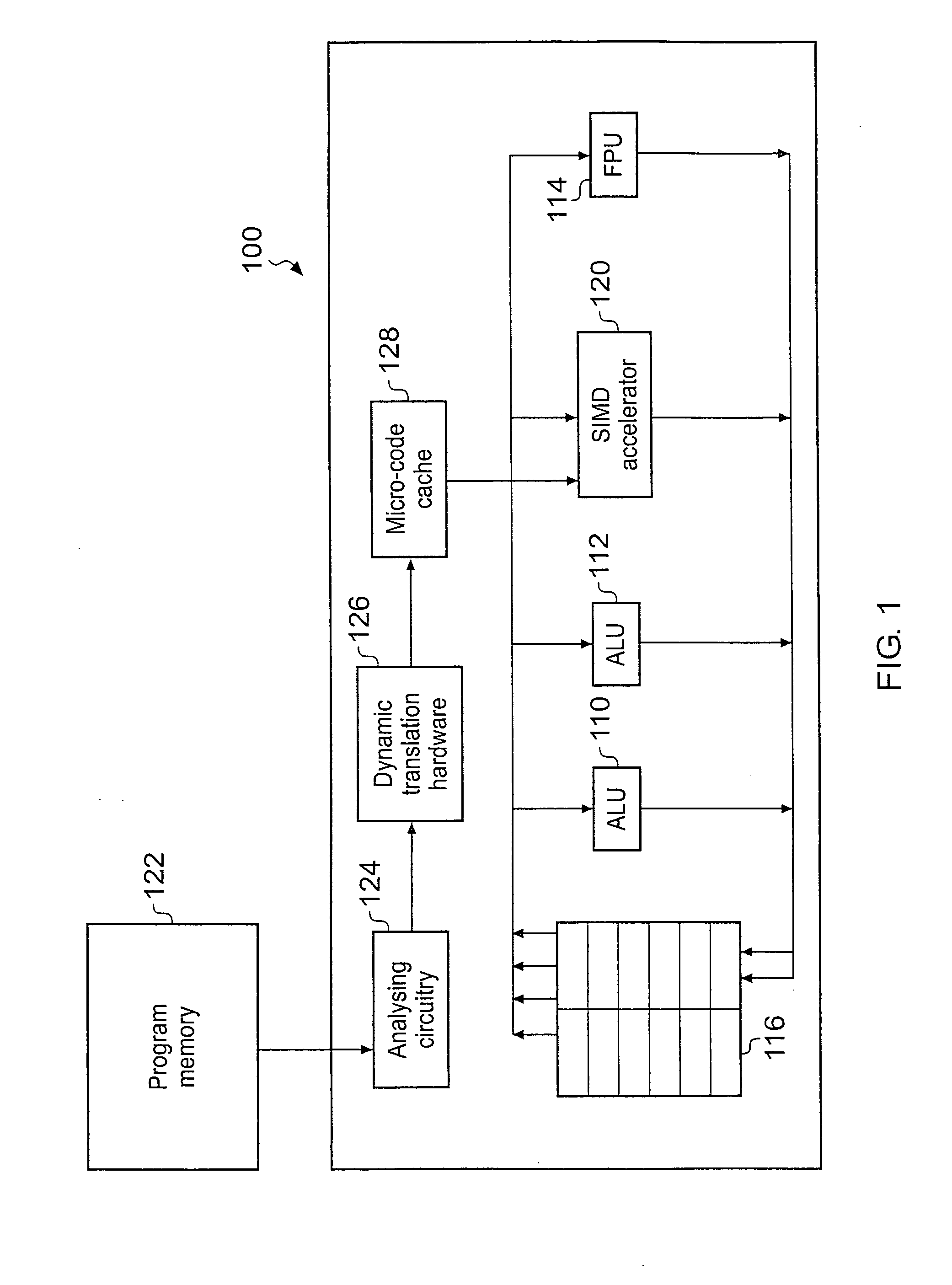
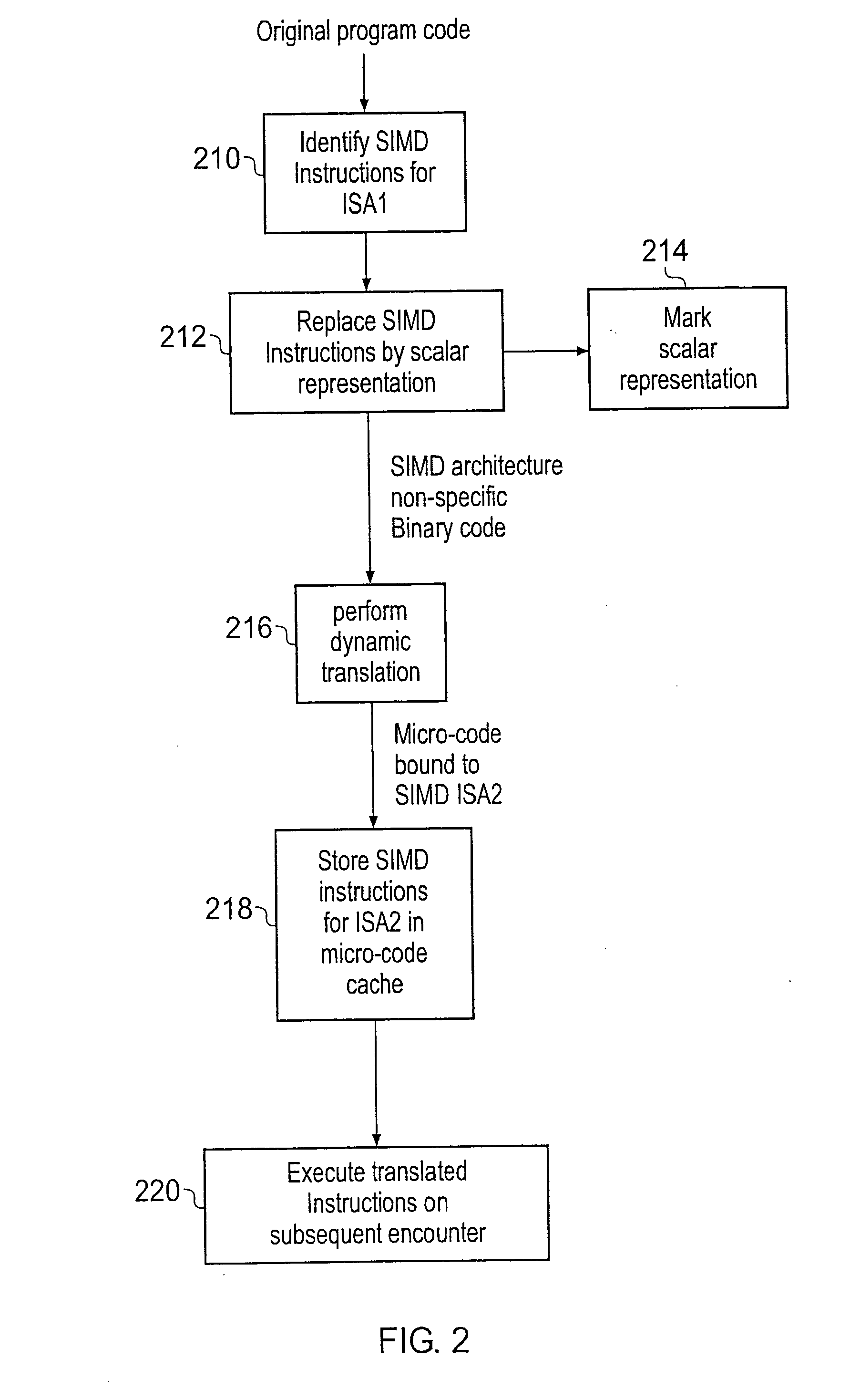
Translation of SIMD instructions in a data processing system
ActiveUS20080141012A1Little overheadEfficiently translatedDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsData processing systemInstruction set
A data processing system is provided having a processor and analysing circuitry for identifying a SIMD instruction associated with a first SIMD instruction set and replacing it by a functionally-equivalent scalar representation and marking that functionally-equivalent scalar representation. The marked functionally-equivalent scalar representation is dynamically translated using translation circuitry upon execution of the program to generate one or more corresponding translated instructions corresponding to a instruction set architecture different from the first SIMD architecture corresponding to the identified SIMD instruction.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
System and method for adaptive path planning
InactiveUS7447593B2Little overheadGenerate efficientlyInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsEngineeringTime path
A path planning system and method for an object, such as a vehicle, provides a randomized adaptive path planning that handles real-time path planning for a vehicle operating under kinodynamic constraints in dynamically changing and uncertain environments with probabilistic knowledge of vehicle and obstacle movement.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Data structure for incremental search
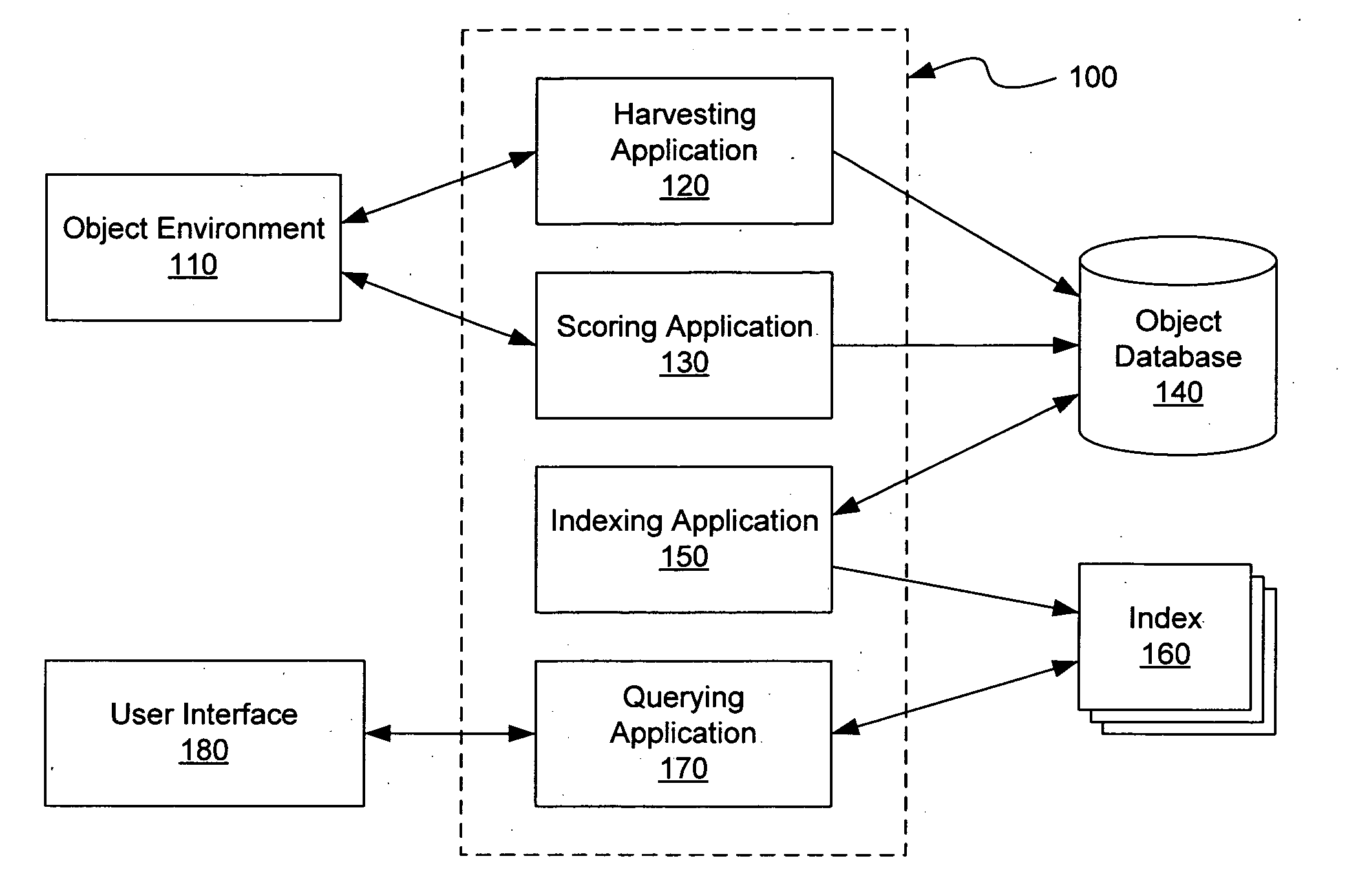
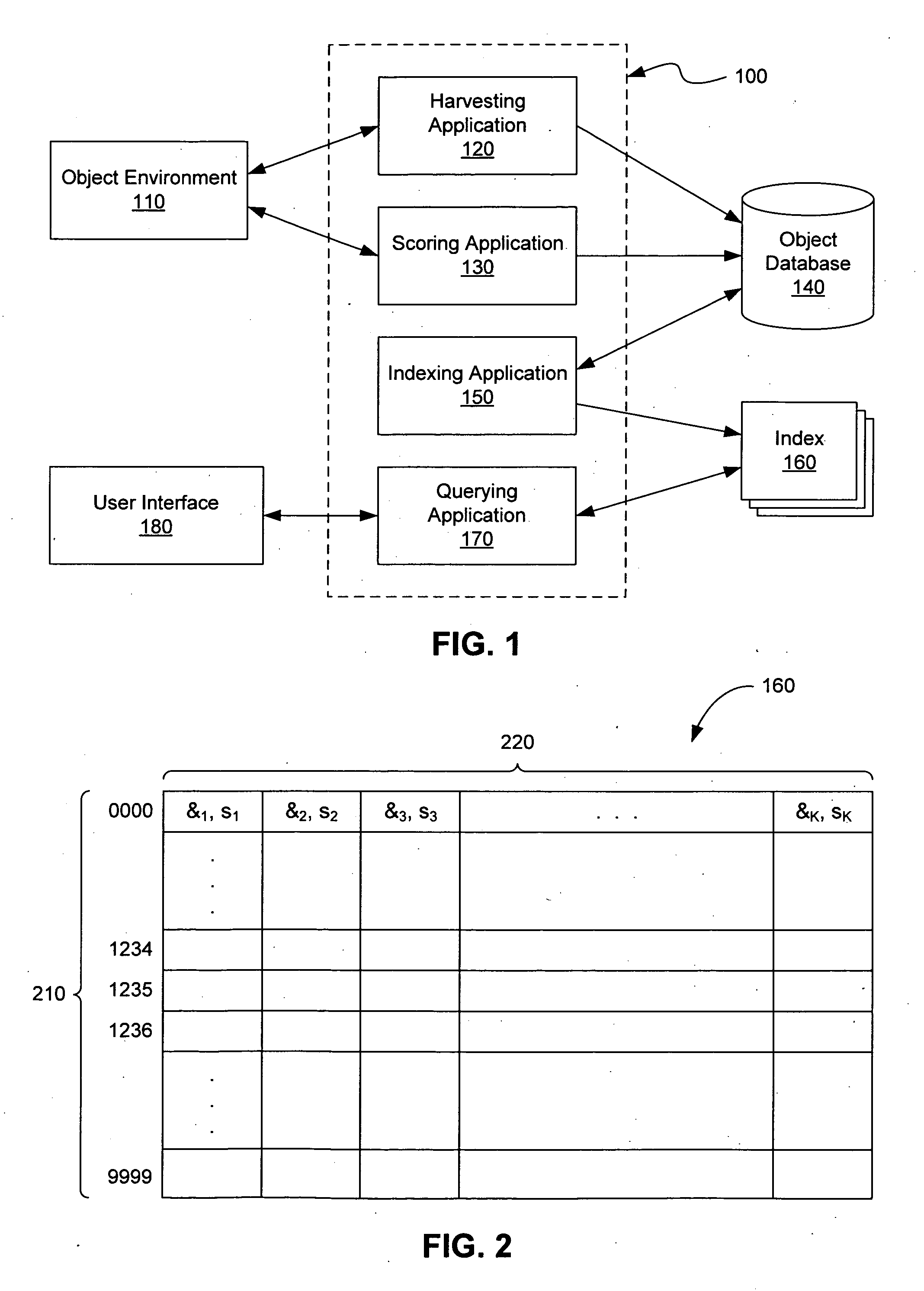
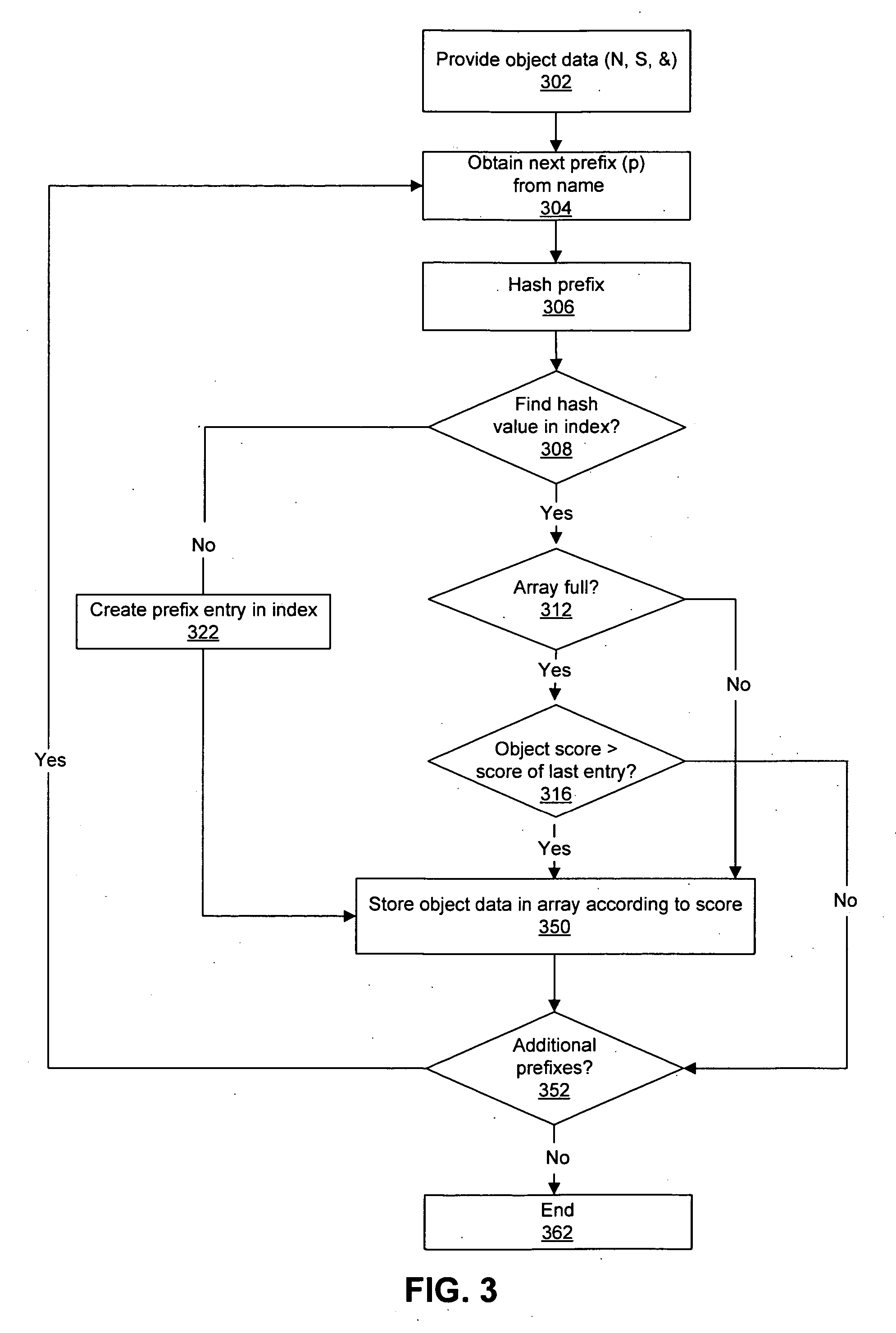
ActiveUS20070043750A1Little overheadImpact system performanceData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsHash tableFrequency of use
A system for searching an object environment includes harvesting and indexing applications to create a search database and one or more indexes into the database. A scoring application determines the relevance of the objects, and a querying application locates objects in the database according to a search term. One or more of the indexes may be implemented by a hash table or other suitable data structure, where algorithms provide for adding objects to the indexes and searching for objects in the indexes. A ranking scheme sorts searchable items according to an estimate of the frequency that the items will be used in the future. Multiple indexes enable a combined prefix title and full-text content search of the database, accessible from a single search interface.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
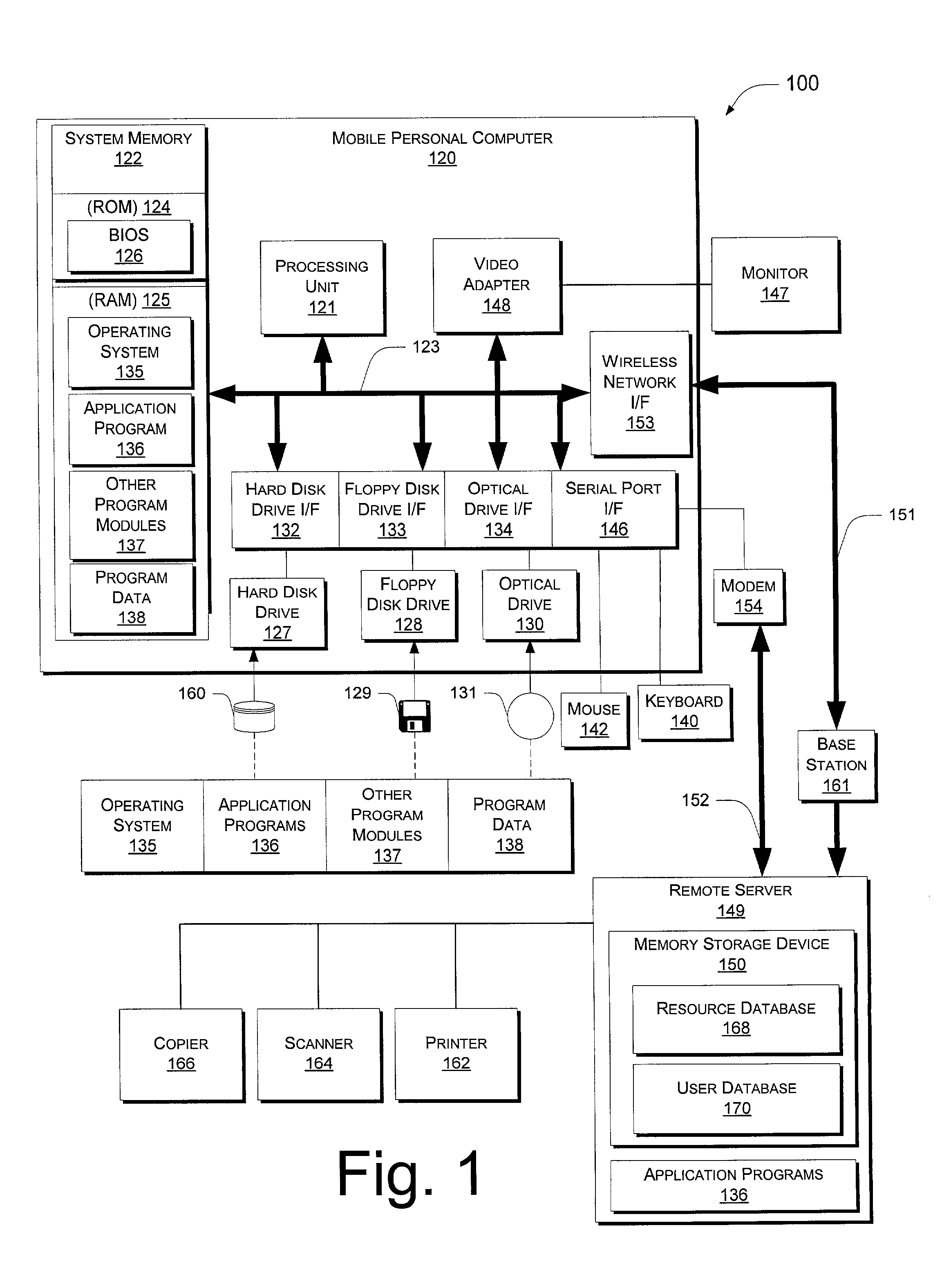
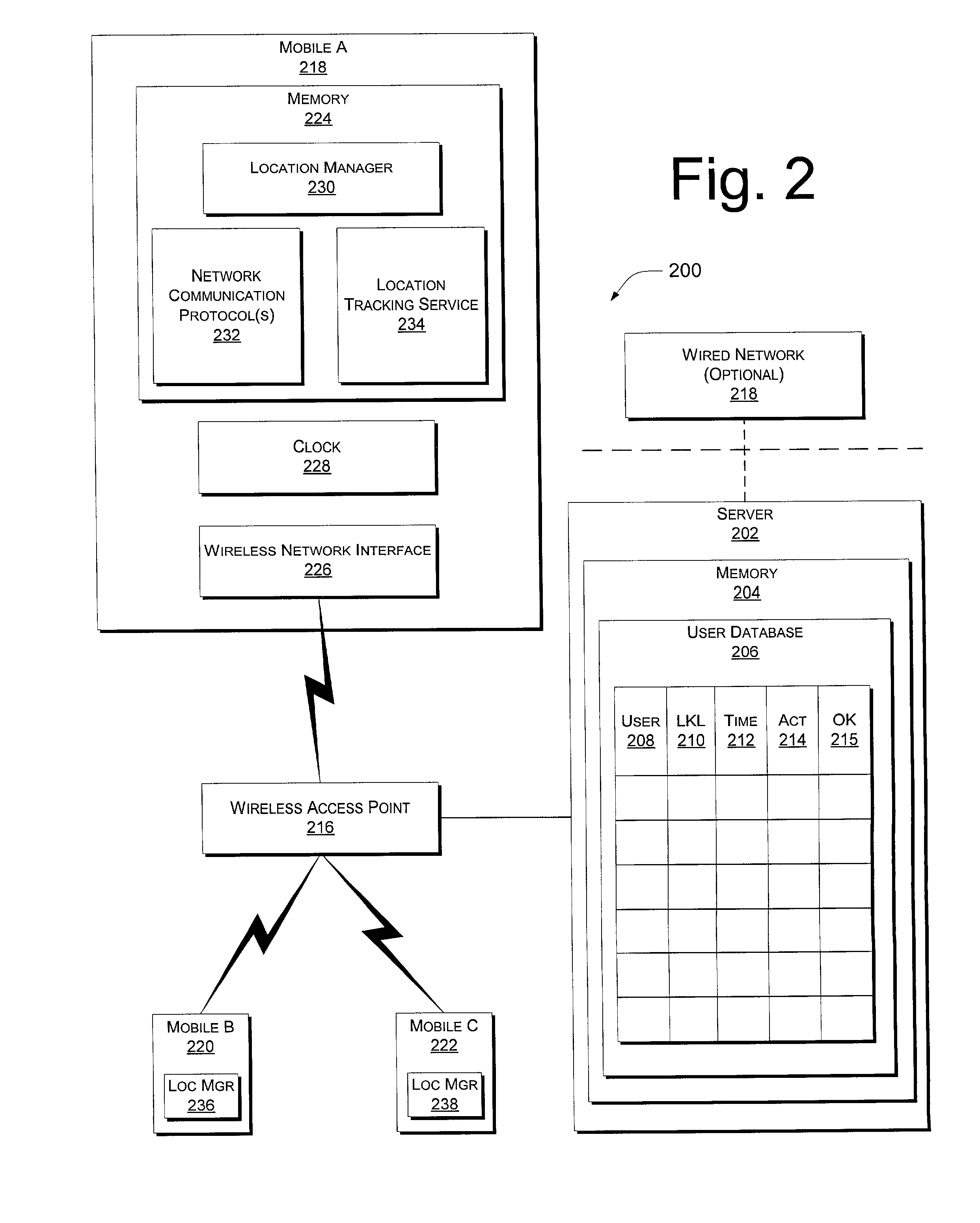
Systems and methods for locating mobile computer users in a wireless network
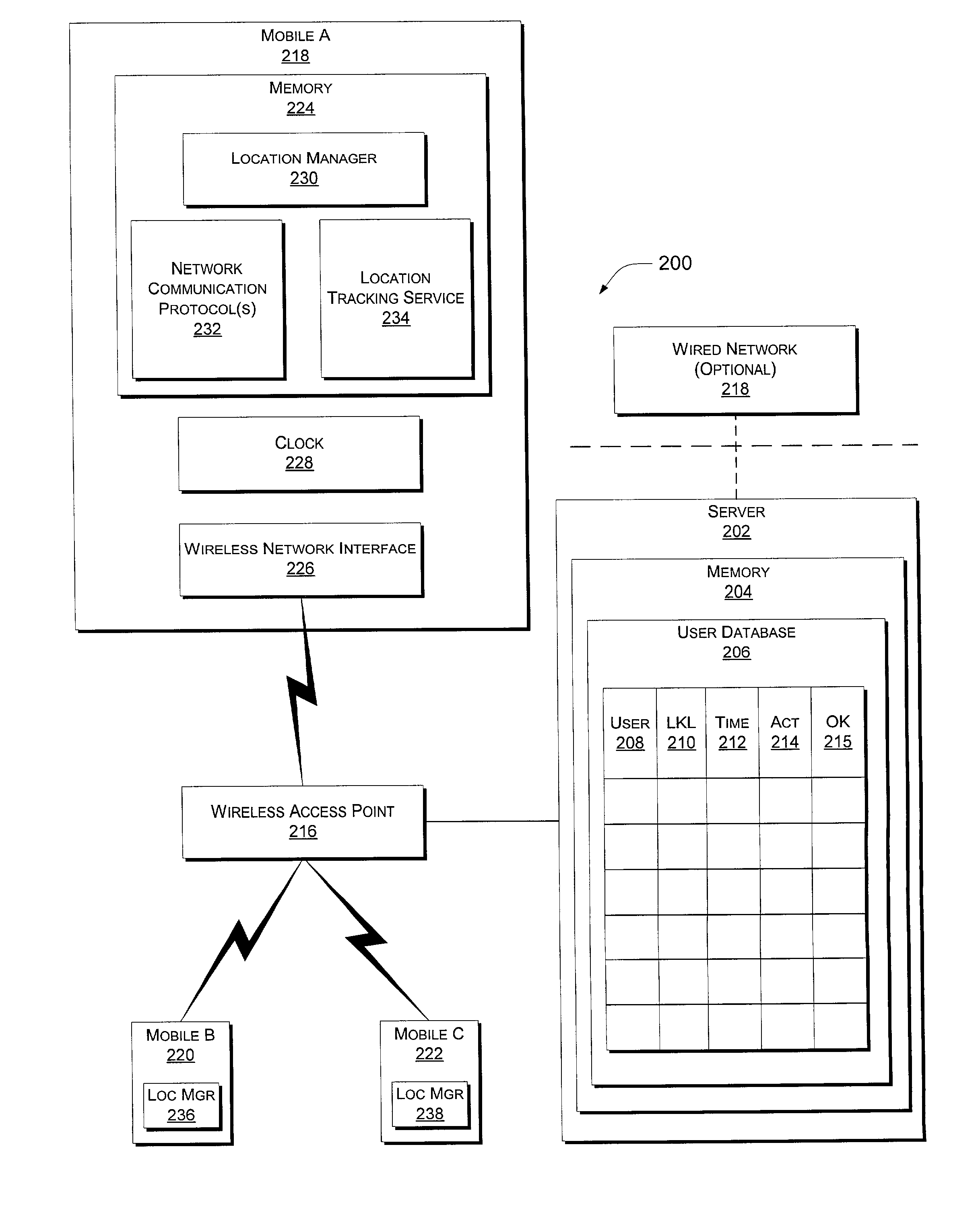
InactiveUS7133909B2Little overheadTelephonic communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer usersWireless mesh network
System and methods for locating a computer user are described wherein the computer either periodically updates a network server with its location, or updates the network server when asked by the server to do so. The network server can be a mobile computer. The user's computer determines its physical location using a location tracker service and then transmits this location information to the server, which stores it in its memory. The information stored includes the physical location of the computer, the time when the location was identified, a name identifying the user of the computer, and an indicator, which indicates whether or not the user was active on the computer during a specified time interval prior to the transmission. The location of the user is deemed to be the last known location of the computer used by the user. If the user is logged onto more than one computer, the location of the user is deemed to be the last known location of the computer that indicates the user as being active.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Universal progressive game pool
InactiveUS20080020831A1Little overheadApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesHuman–computer interactionGame machine
The present invention provides systems and methods that allow gaming machines to participate in a progressive pool and offer a progressive award regardless of the game installed on the gaming machine. The present invention also permits gaming machine participation in a progressive pool regardless of wager amount. This permits larger progressive awards and awards that grow faster since more games and gaming machines may participate in building a progressive pool award. It also opens the attraction of a large progressive pool award to more games, gaming machines and gaming establishments.
Owner:IGT
Integrated mechanism for suspension and deallocation of computational threads of execution in a processor
ActiveUS20050125795A1Valuable opcode spaceLittle overheadProgram initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringOperandProgram Thread
A yield instruction for execution in a multithreaded microprocessor is disclosed. The yield instruction includes an operand. If the operand is zero the microprocessor terminates the program thread including the yield instruction. If the operand is −1 the microprocessor unconditionally reschedules the program thread. If the operand is a positive integer the microprocessor views the operand as a bit vector specifying one or more yield qualifier inputs, such as interrupt signals, and conditionally reschedules the thread based on the qualifier inputs and bit vector values. The microprocessor also includes a mask register that specifies a bit vector of the qualifier inputs. If the operand specifies a qualifier input not also specified in the mask register, an exception to the instruction is raised. The instruction returns a value specifying the values of the qualifier inputs qualified by the mask register value.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
Coding method, decoding method, coding apparatus, decoding apparatus, image processing system, coding program, and decoding program
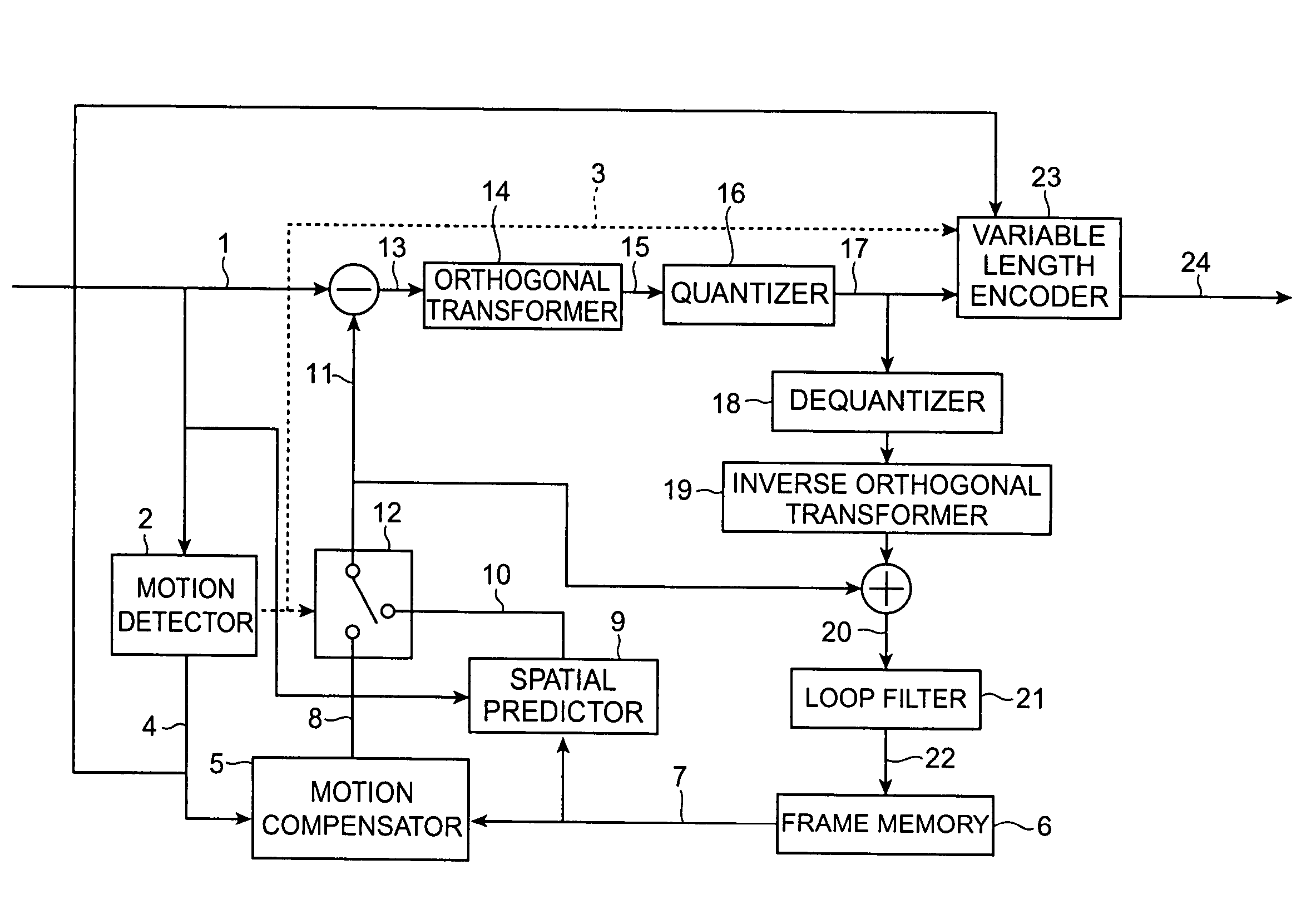
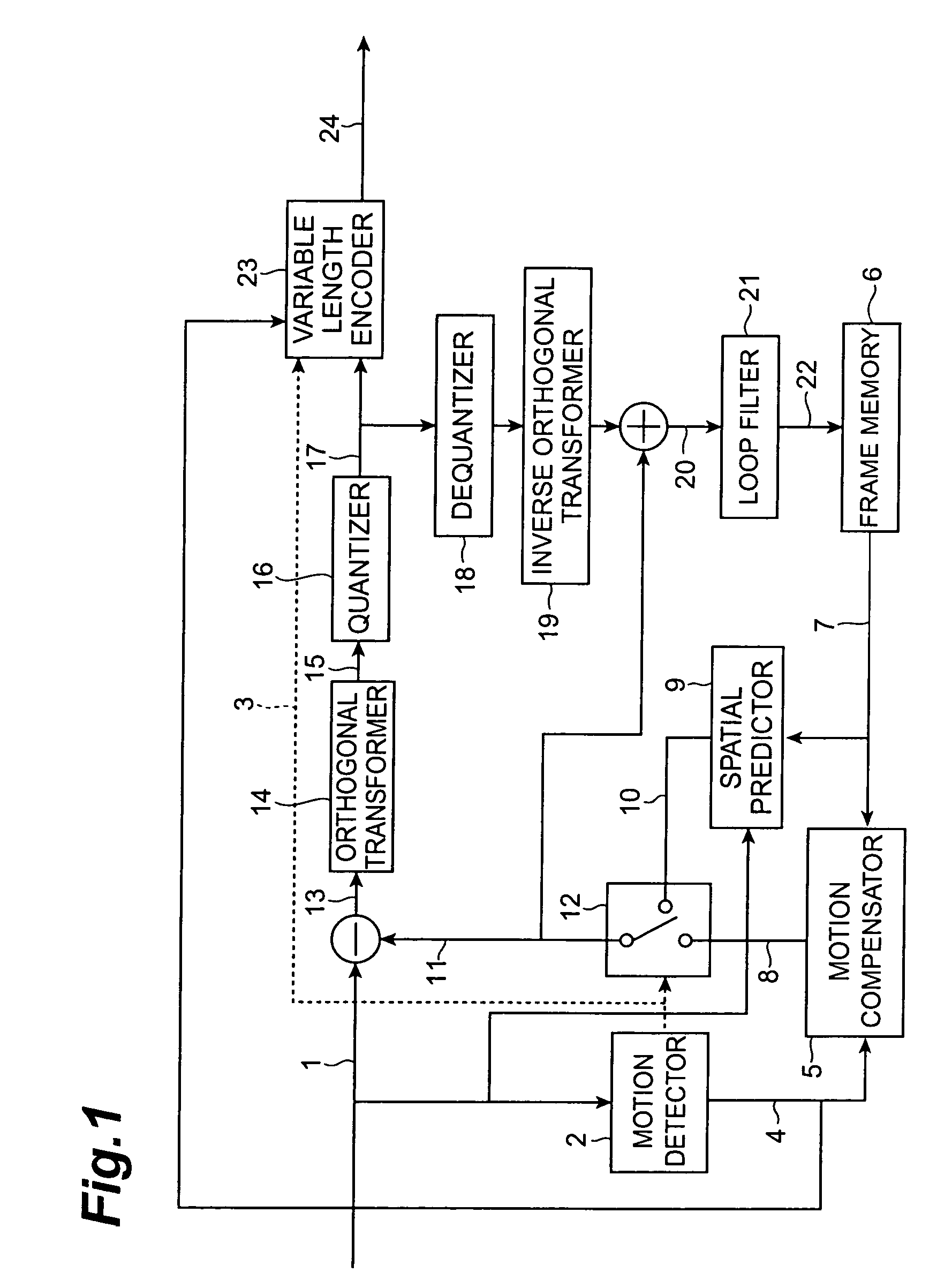
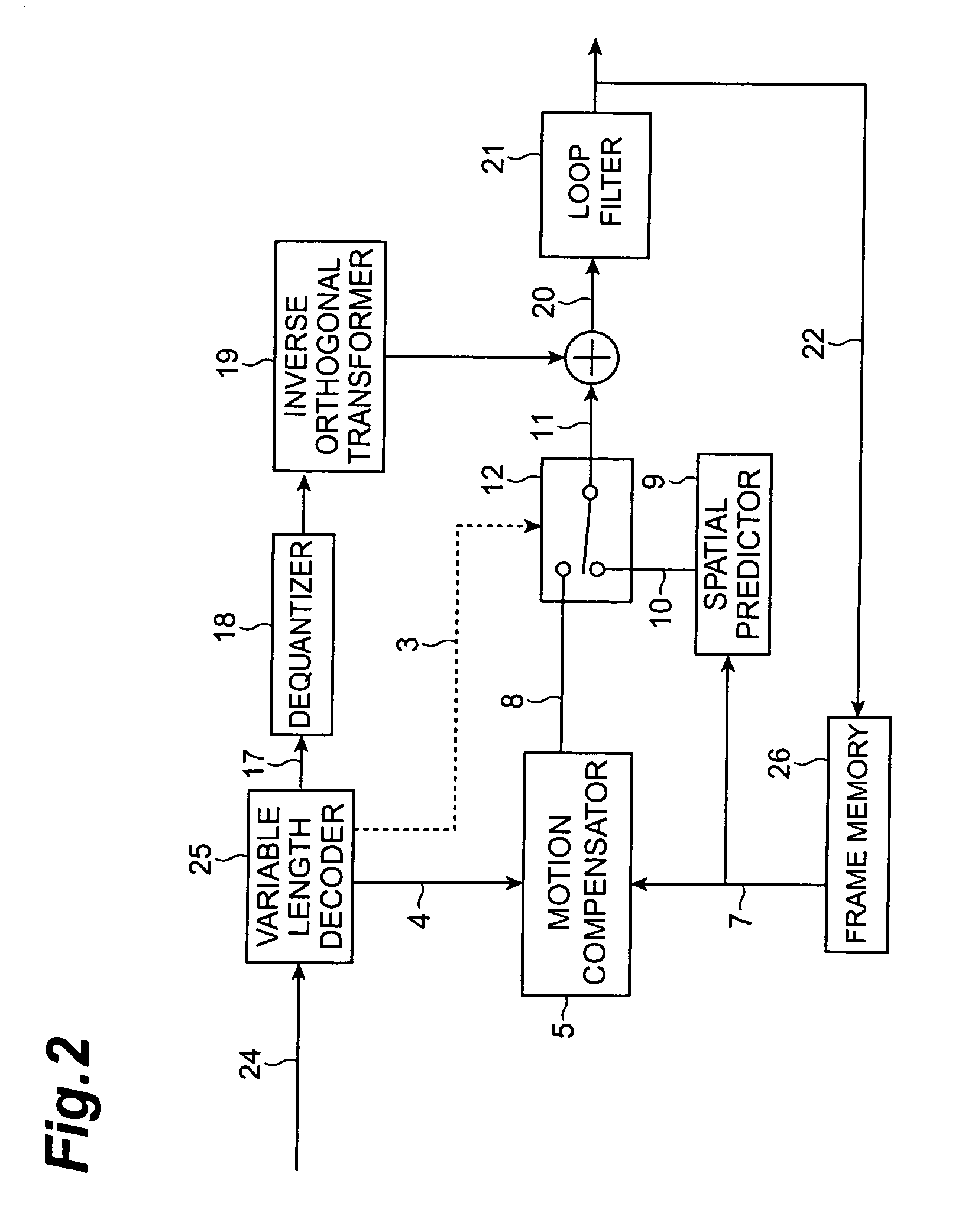
ActiveUS7643559B2Low data volumeAccurate capturePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningMotion detectorVariable length
For the purpose of coding or decoding motion information in a picture with a small overhead, a coding method of performing compression coding of a moving picture by motion compensated prediction is configured to have a motion compensated prediction step (processing by motion detector 2, motion compensator 5, spatial predictor 9, etc.) of performing the motion compensated prediction while assigning one or more motion vectors (e.g., up to two motion vectors) in units of sub-blocks obtained by sub-dividing each of macroblocks resulting from division of each frame of the moving picture; and an assignment information coding step (processing by variable length encoder 23 and others) of outputting information about an assignment situation of the one or more motion vectors to the sub-blocks in a multiplexed form on a bitstream.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method of Operating a System
ActiveUS20080031257A1Little overheadSimple introductionData switching by path configurationOperational systemRouting table
A method of operating a data network, of the type in which a number of inter-connected router devices forward received packets of data towards a destination node in accordance with a routing table associated with each router. The method comprises: receiving routing information at one of said routers, determining if the information is such that, if it were correct, it would cause the router to update its routing table in respect of one or more entries, and, if so, sending out two test packets, one of which is sent out according to the existing information contained in the routing table and the other of which is sent out according to the information which would be included in the routing table if it were up-dated in accordance with the received information; comparing the results of the two test sending; and updating the routing table to reflect the received information if the comparison indicates that the received information is correct, but otherwise ignoring the information and maintaining the routing table unchanged.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Universal progressive game pool
InactiveUS20080020830A1Little overheadApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesHuman–computer interactionIndustrial engineering
The present invention provides systems and methods that allow gaming machines to participate in a progressive pool and offer a progressive award regardless of the game installed on the gaming machine. The present invention also permits gaming machine participation in a progressive pool regardless of wager amount. This permits larger progressive awards and awards that grow faster since more games and gaming machines may participate in building a progressive pool award. It also opens the attraction of a large progressive pool award to more games, gaming machines and gaming establishments.
Owner:IGT
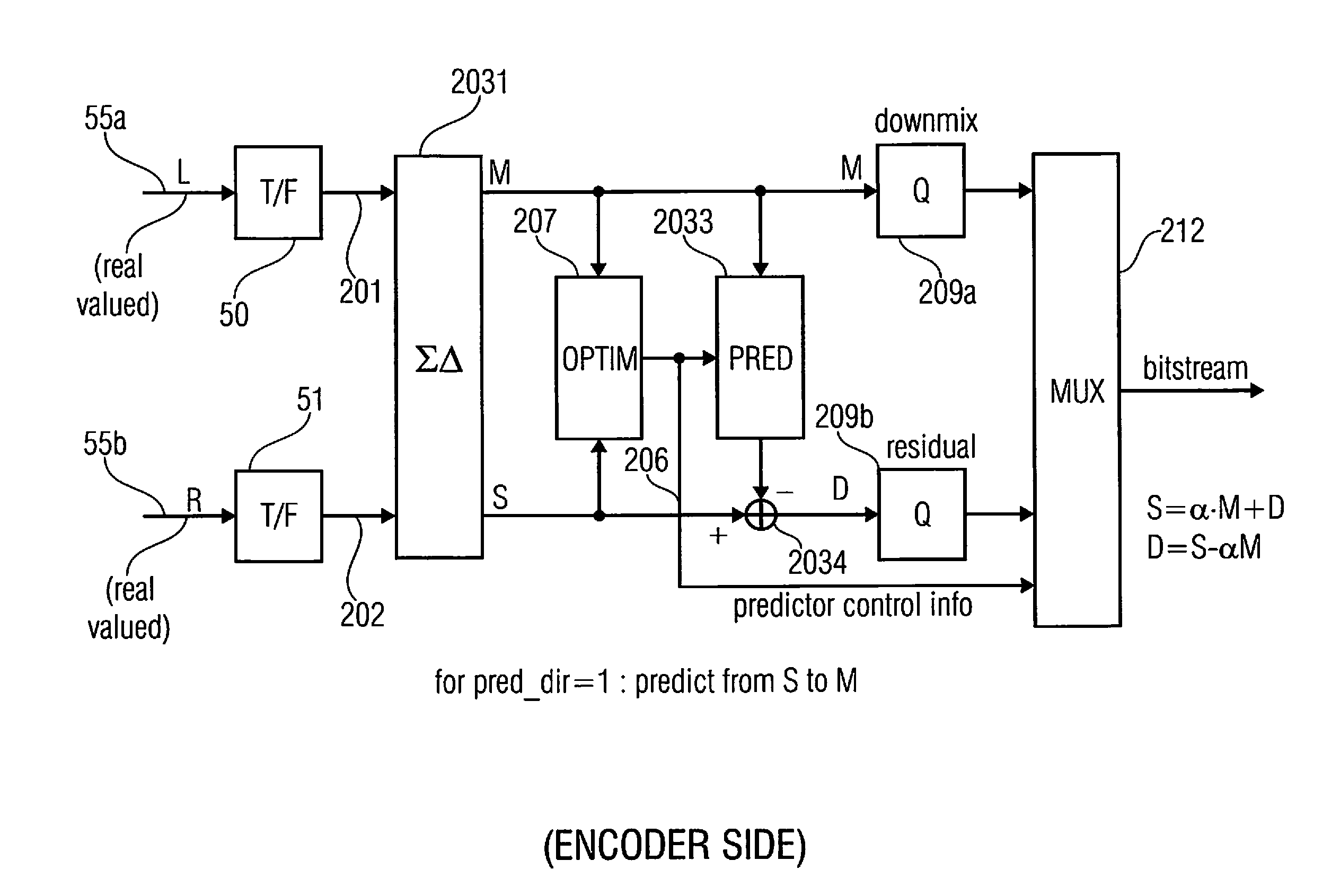
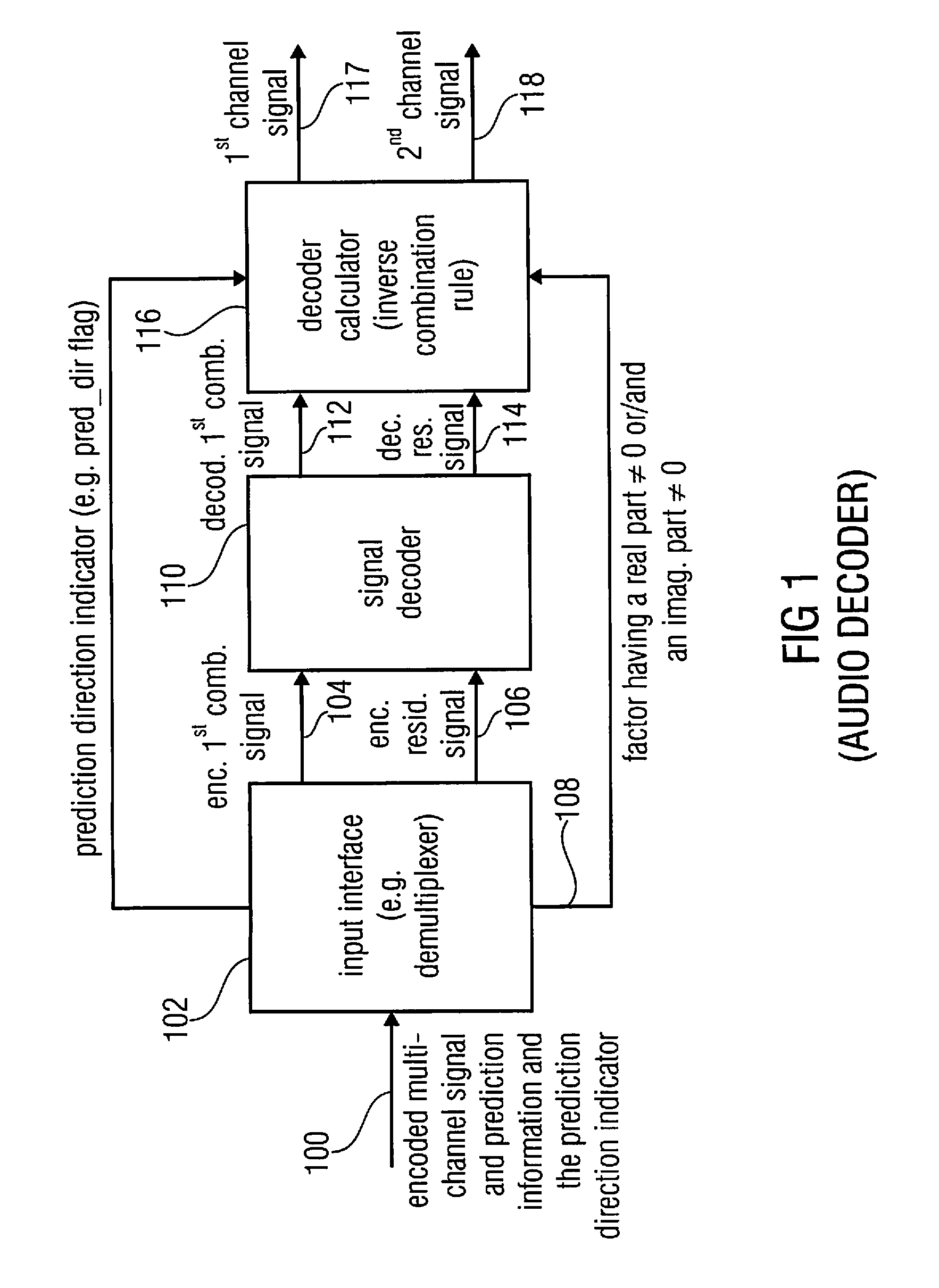
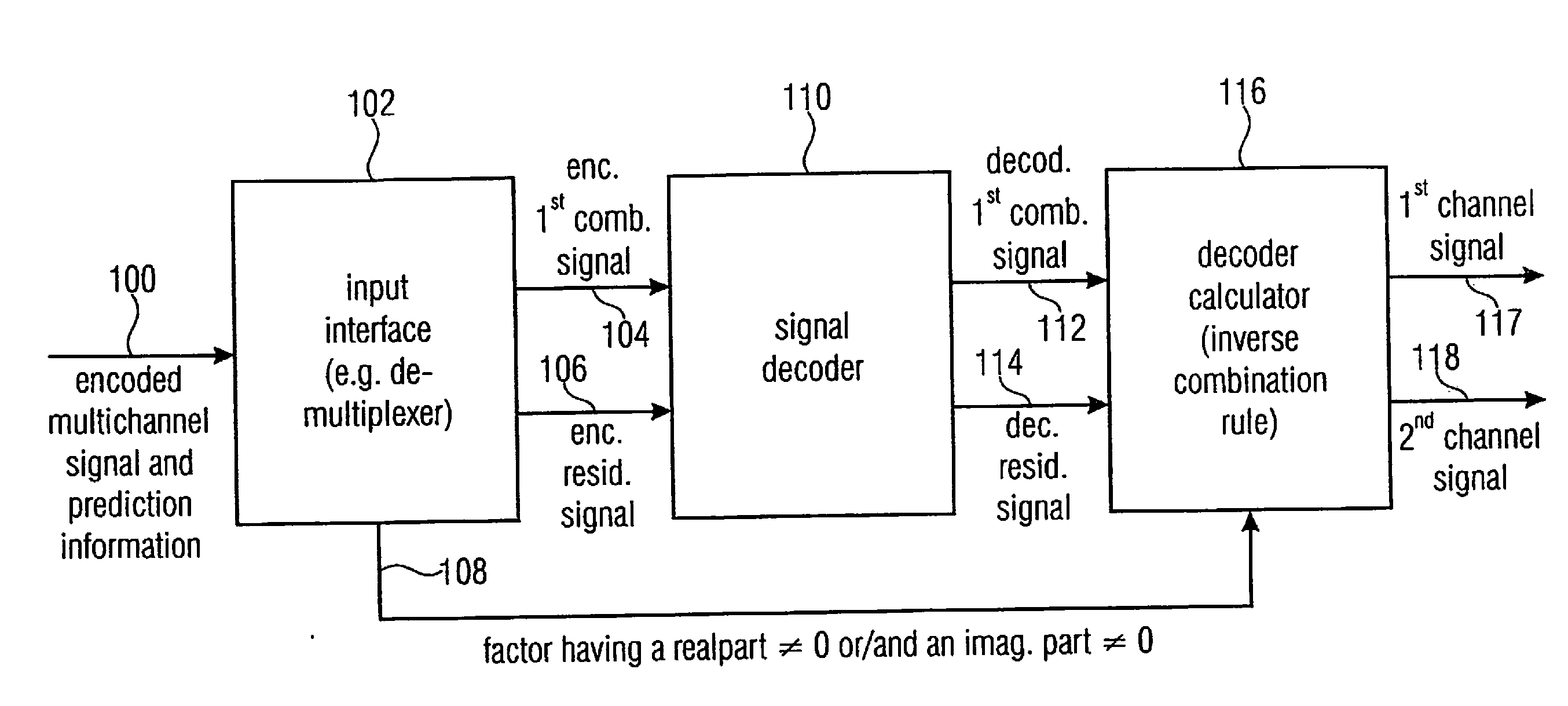
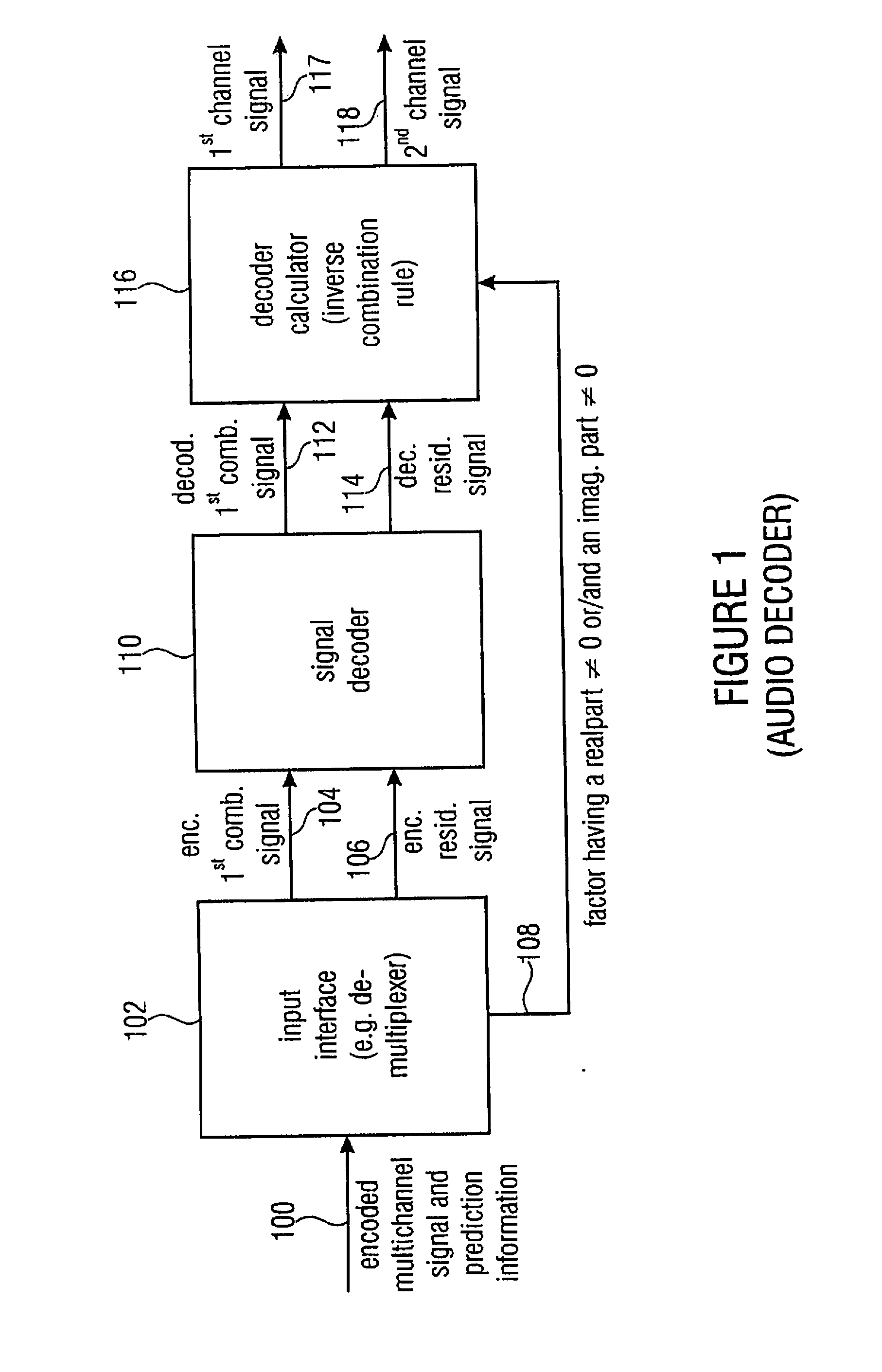
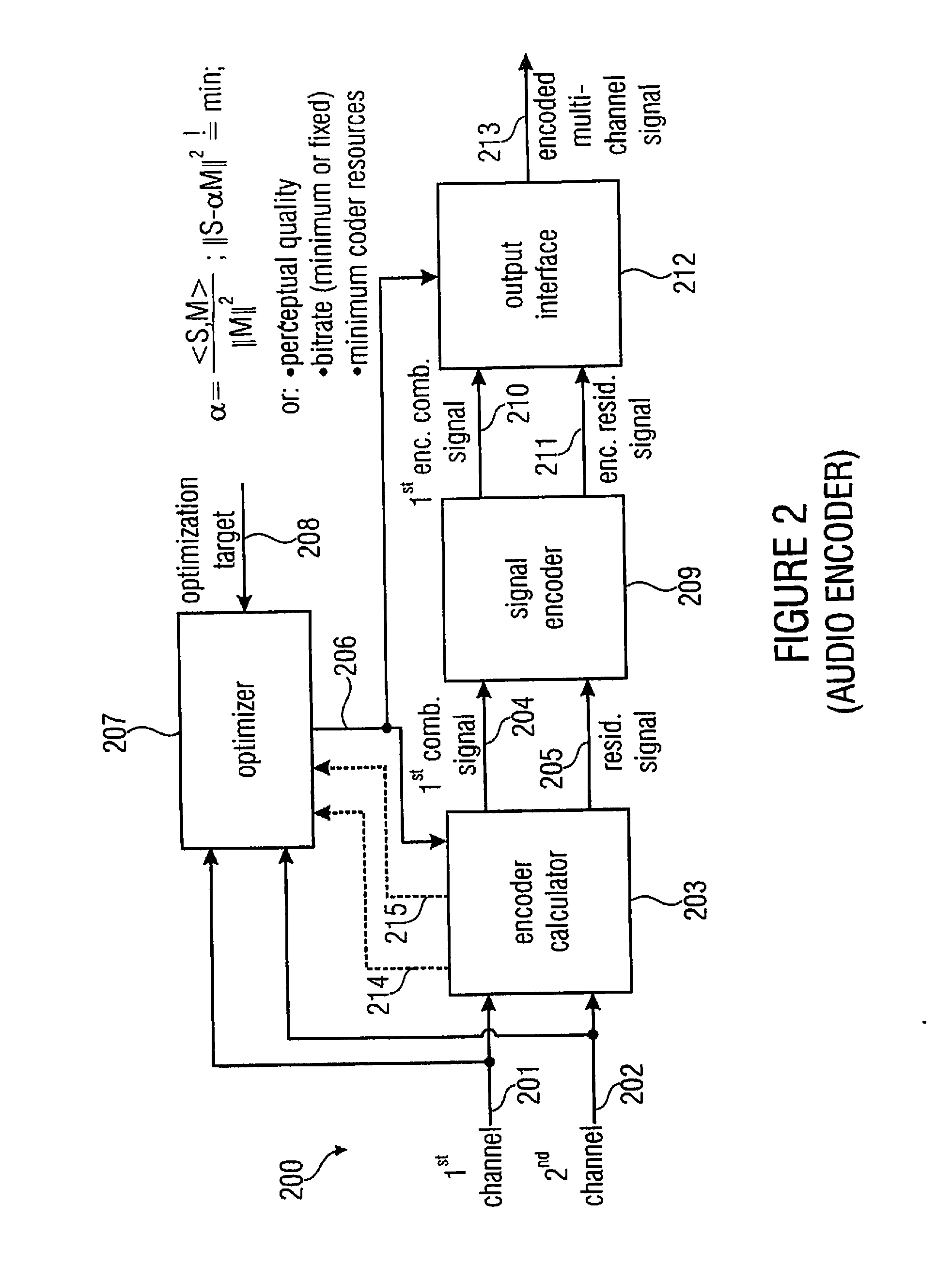
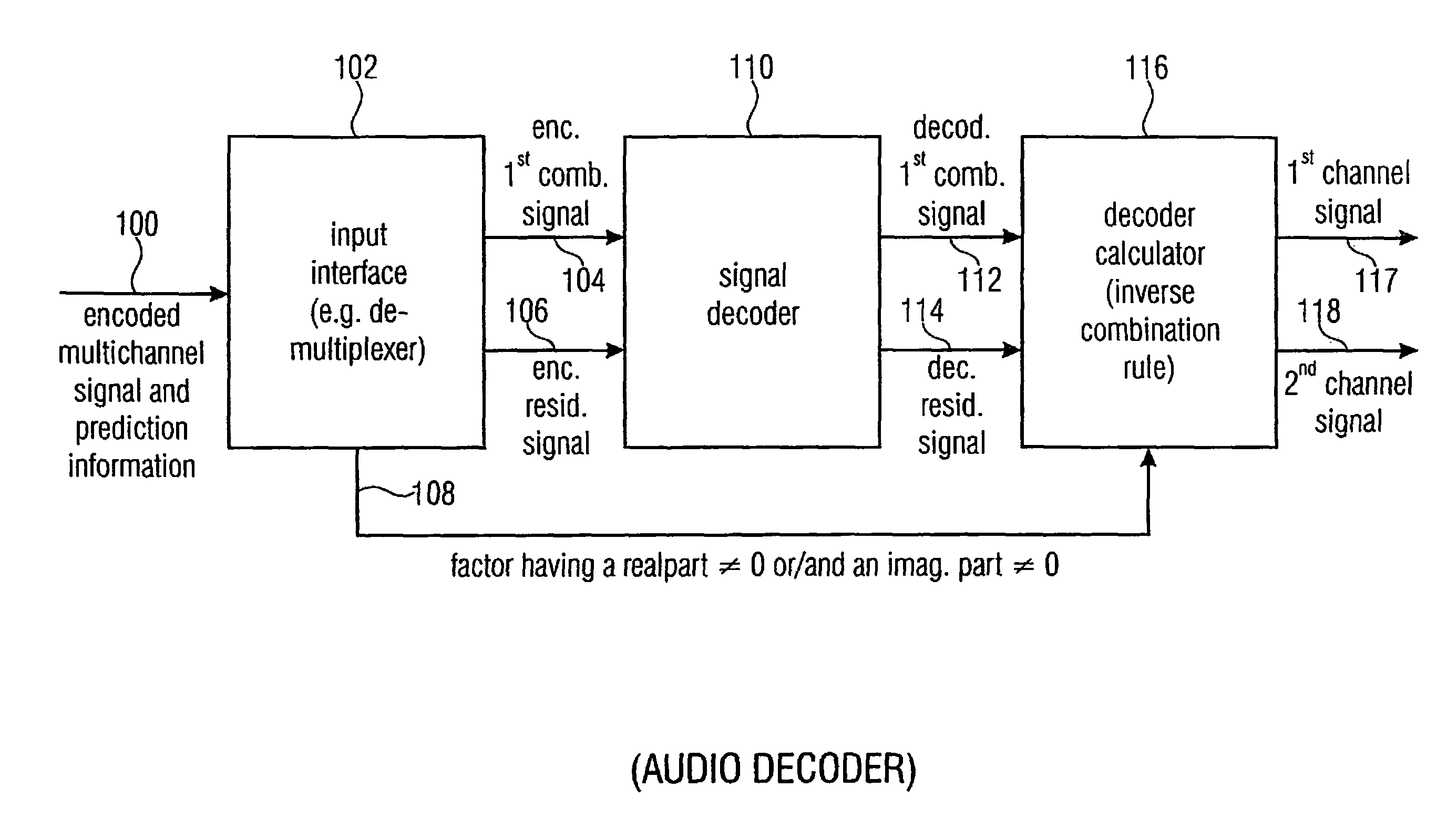
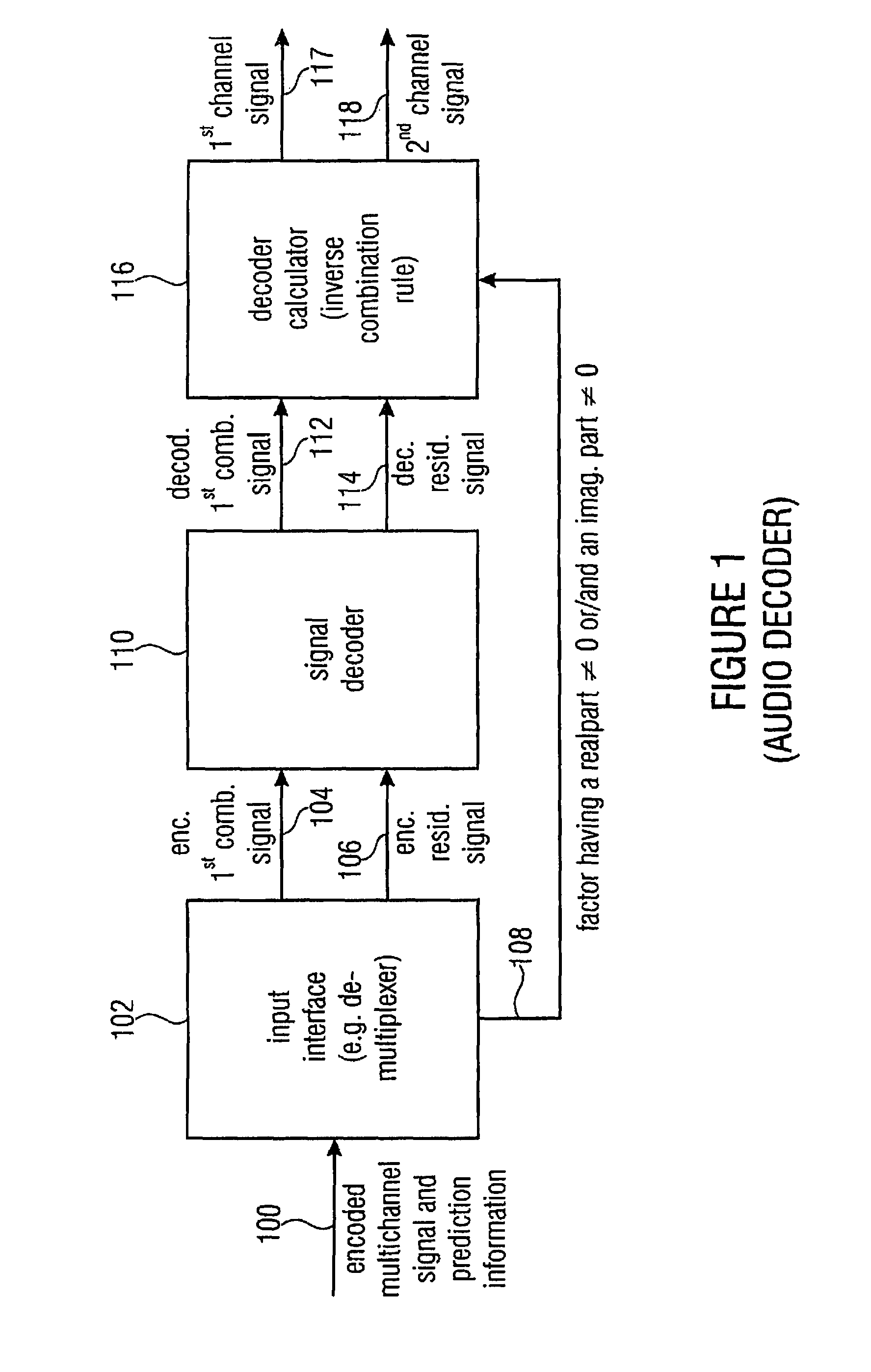
Audio or video encoder, audio or video decoder and related methods for processing multi-channel audio or video signals using a variable prediction direction
ActiveUS20130121411A1Enhanced audio and video qualityReduce bit rateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVIT signalsAudio frequency
An encoder / decoder is based on a combination of two audio or video channels to obtain a first combination signal as a mid-signal and a residual signal derivable using a predicted side signal derived from the mid-signal. A decoder uses the prediction residual signal, the first combination signal, a prediction direction indicator and prediction information to derive decoded first channel and second channel signals. A real-to-imaginary transform can be applied for estimating the imaginary part of the spectrum of the first combination signal. The prediction signal used in the derivation of the prediction residual signal, the real-valued first combination signal is multiplied by a real portion of the complex prediction information and the estimated imaginary part of the first combination signal is multiplied by an imaginary portion of the complex prediction information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
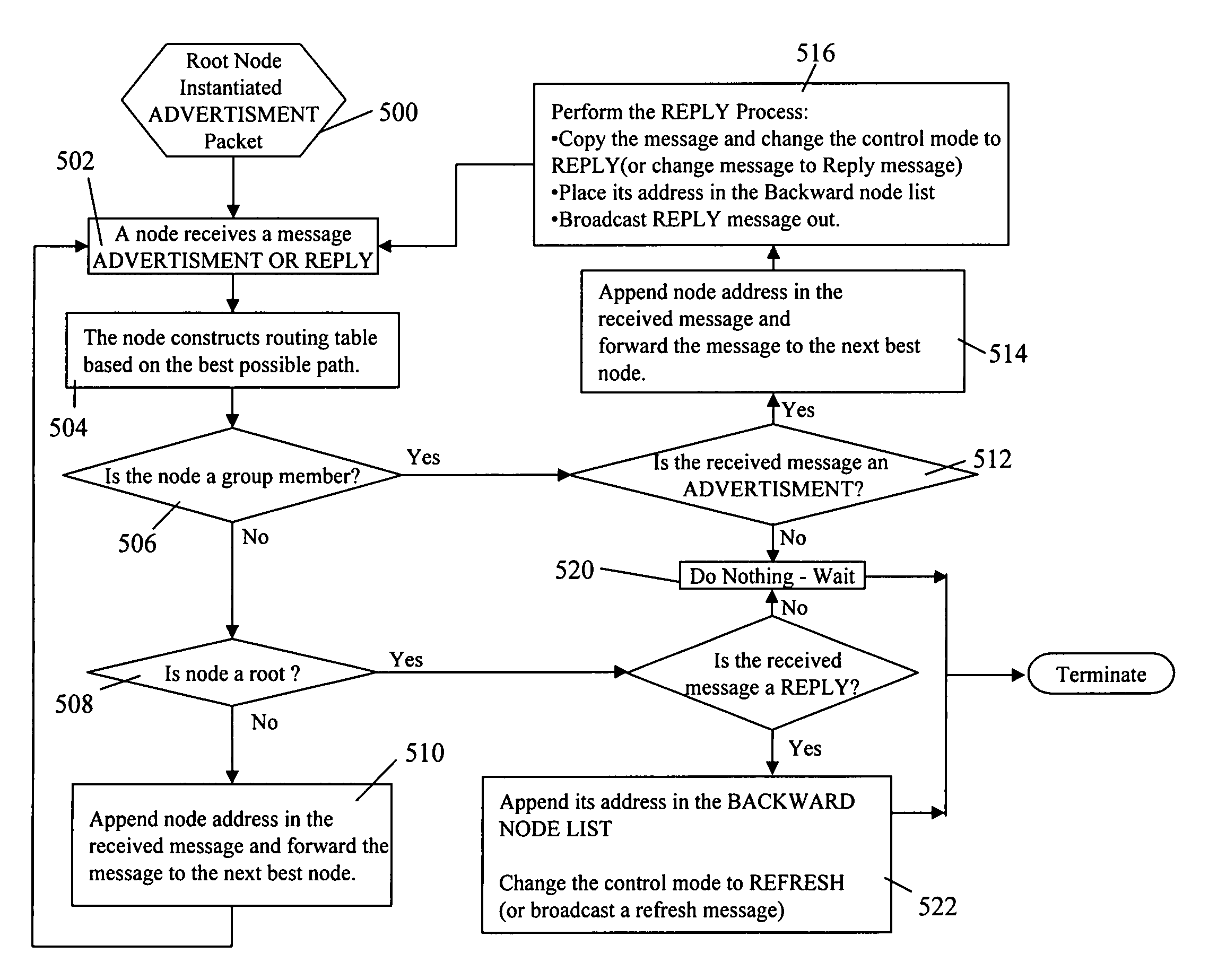
Collaborative multicast routing (CMR) for multicasting in unidirectional, hybrid, multi-tiered mobile wireless network
InactiveUS7649884B1Little overheadReduce areaData switching by path configurationWireless communicationHeterogeneous wireless networkMobile wireless
The present invention provides a scalable and reliable collaborative multicast routing for multicasting in hybrid, multi-tiered, mobile heterogeneous wireless networks. It establishes a multicast tree, maintains the established route, detects and prevents most link breakage within the multicast tree by a neighboring node or the cooperation of the neighboring node, and enables merging of partitioned multicast trees of the same multicast group by nodes that participate in one of the partitioned multicast trees. The use of local nodes to collaboratively establish, maintain, recover, and merge the hybrid, multi-tiered mobile wireless networks that use heterogeneous set of mobile wireless nodes is the fundamental basis for the collaborative multicast routing scheme of the present invention.
Owner:HRL LAB
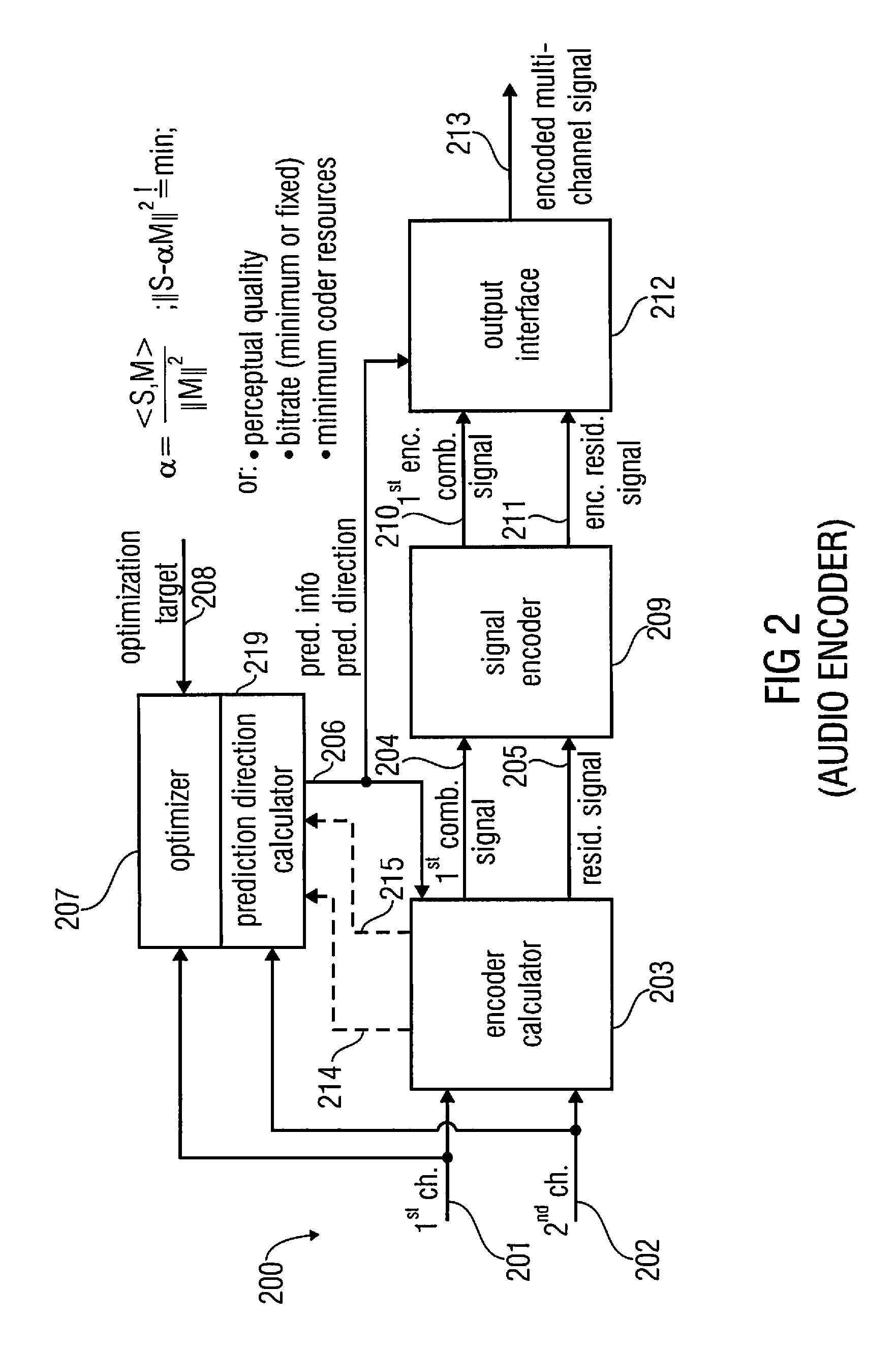
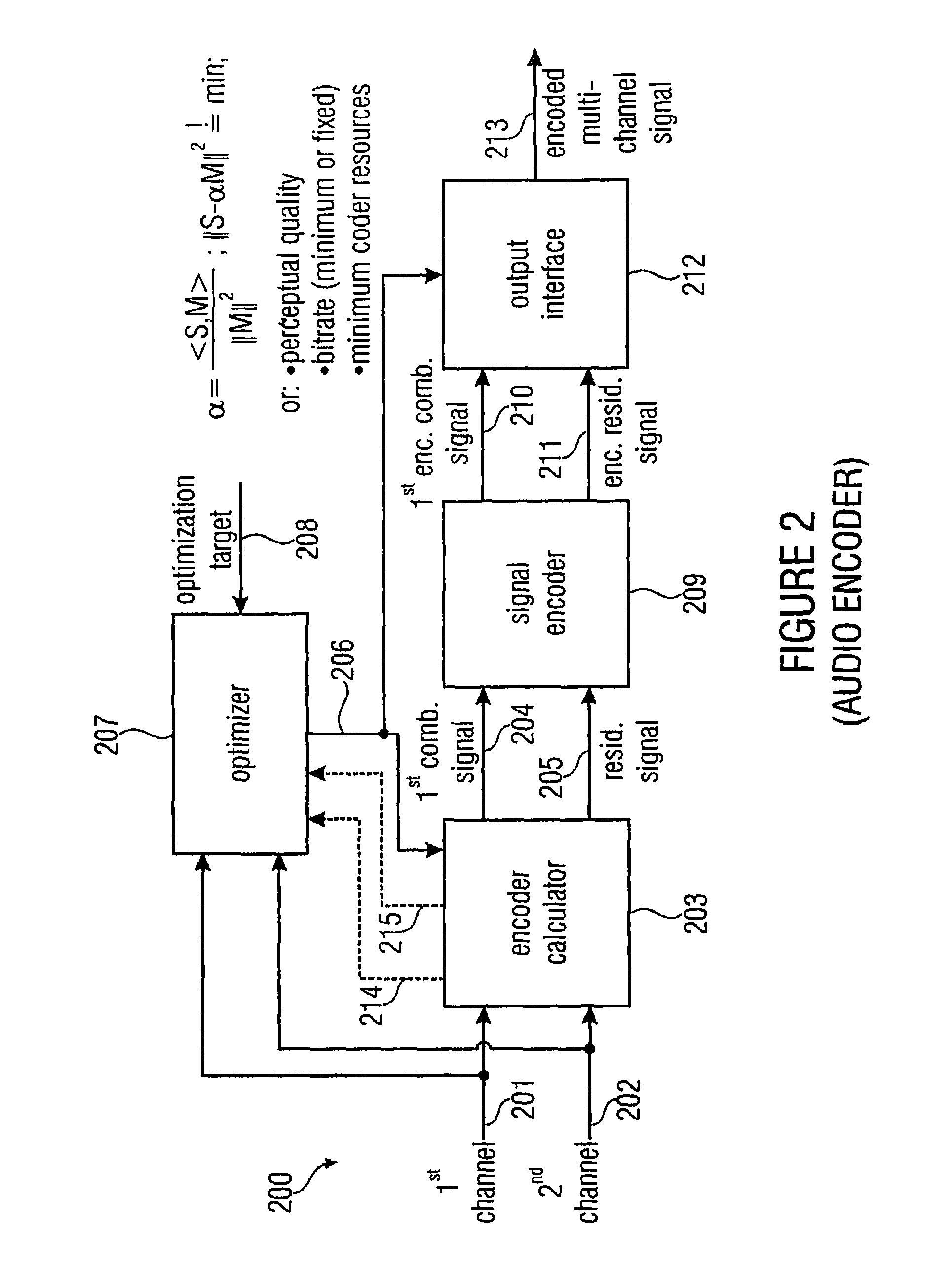
Audio encoder, audio decoder and related methods for processing multi-channel audio signals using complex prediction
ActiveUS20130030819A1Reduce complexityImprove audio qualityPulse modulation television signal transmissionSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumData stream
An encoder, based on a combination of two audio channels, obtains a first combination signal as a mid-signal and a residual signal derivable using a predicted side signal derived from the mid signal. The first combination signal and the prediction residual signal are encoded and written into a data stream together with the prediction information. A decoder generates decoded first and second channel signals using the prediction residual signal, the first combination signal and the prediction information. A real-to-imaginary transform may be applied for estimating the imaginary part of the spectrum of the first combination signal. For calculating the prediction signal used in the derivation of the prediction residual signal, the real-valued first combination signal is multiplied by a real portion of the complex prediction information and the estimated imaginary part of the first combination signal is multiplied by an imaginary portion of the complex prediction information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
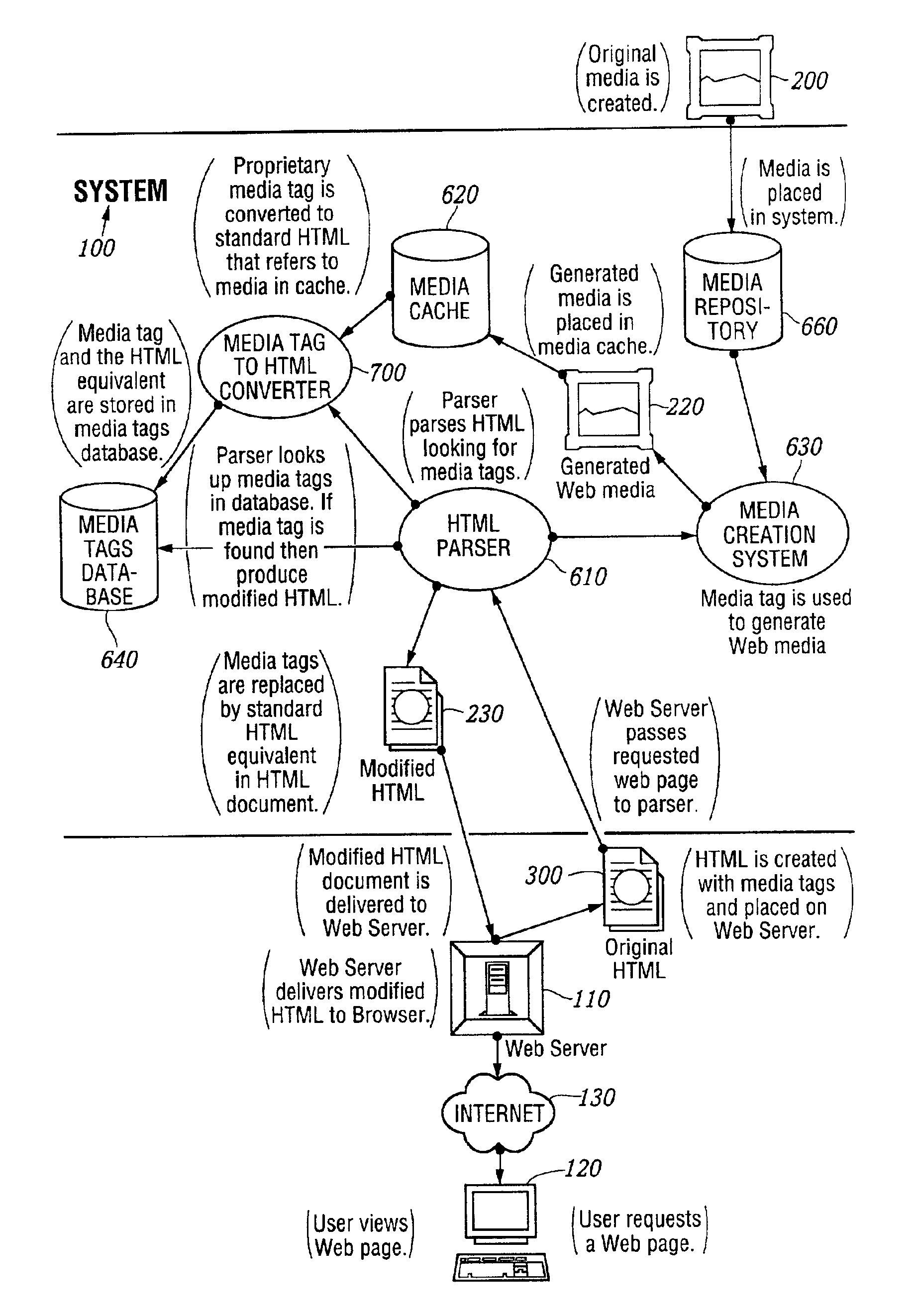
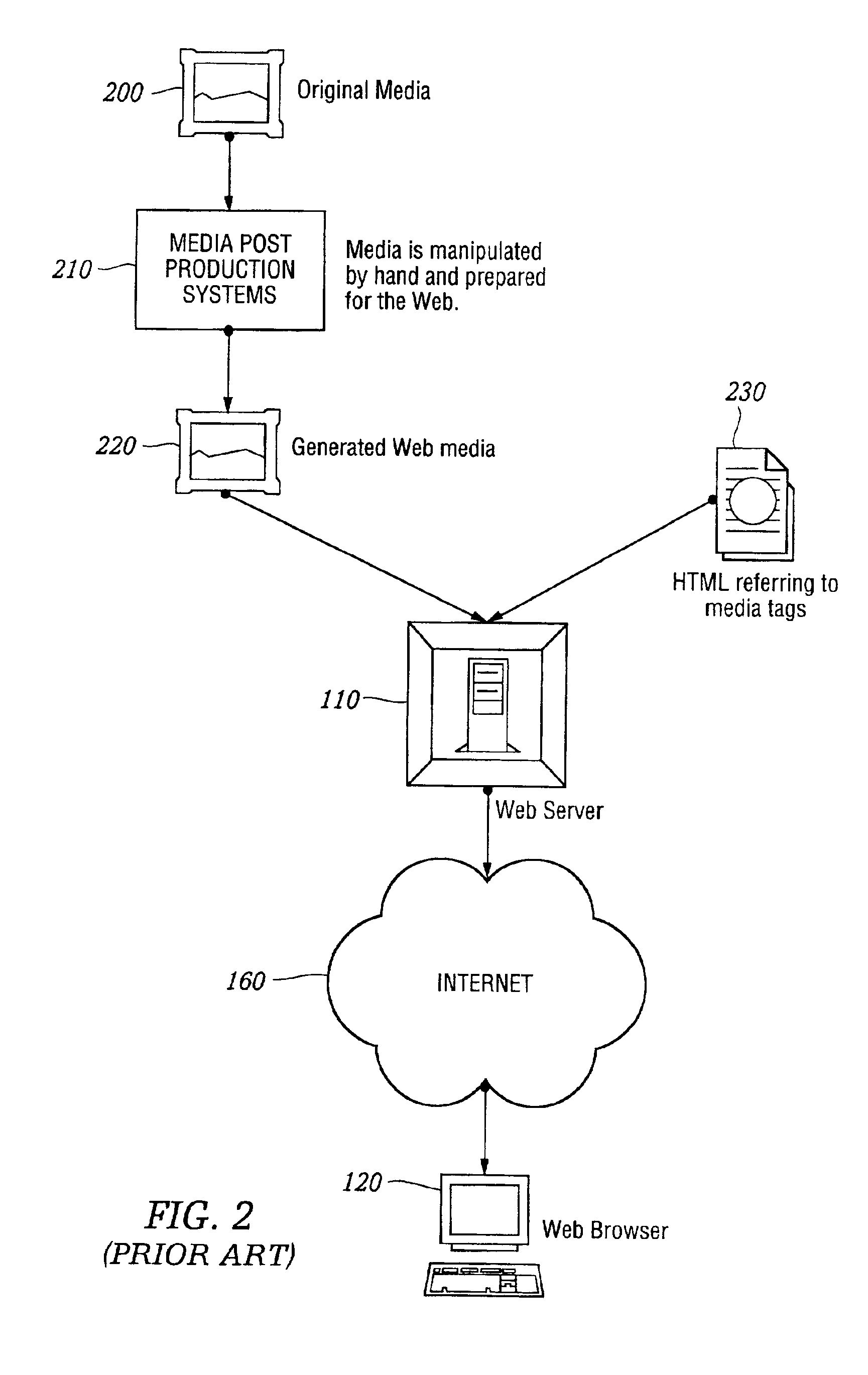
Automated media delivery system
InactiveUS6964009B2Reduce needLittle overheadDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsDocumentation procedureContent generation
An automatic graphics delivery system that operates in parallel with an existing Web site infrastructure is provided. The system streamlines the post-production process by automating the production of media through content generation procedures controlled by proprietary tags placed by an author within URLs embedded within Web documents.
Owner:EQUIL IP HOLDINGS LLC +1
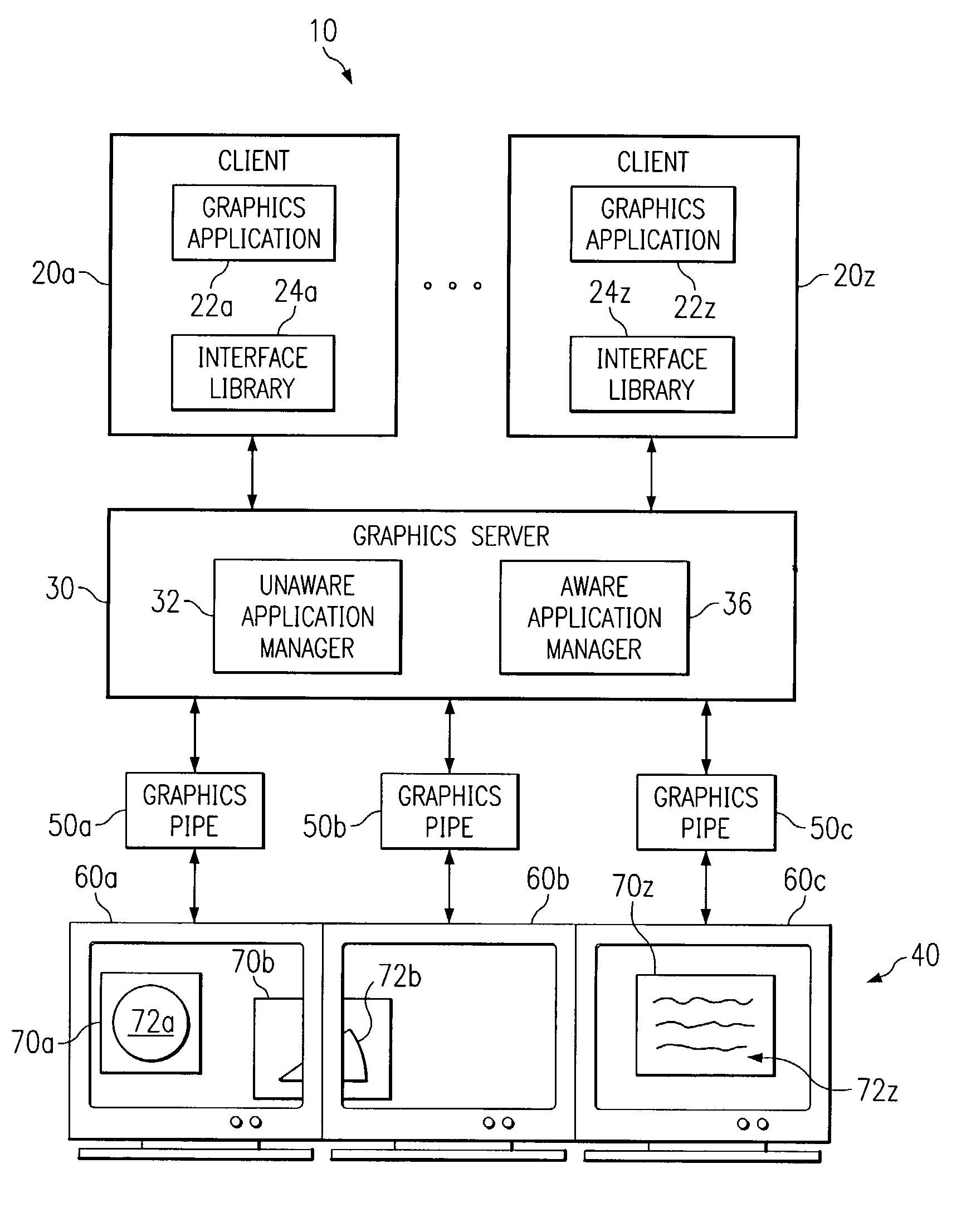
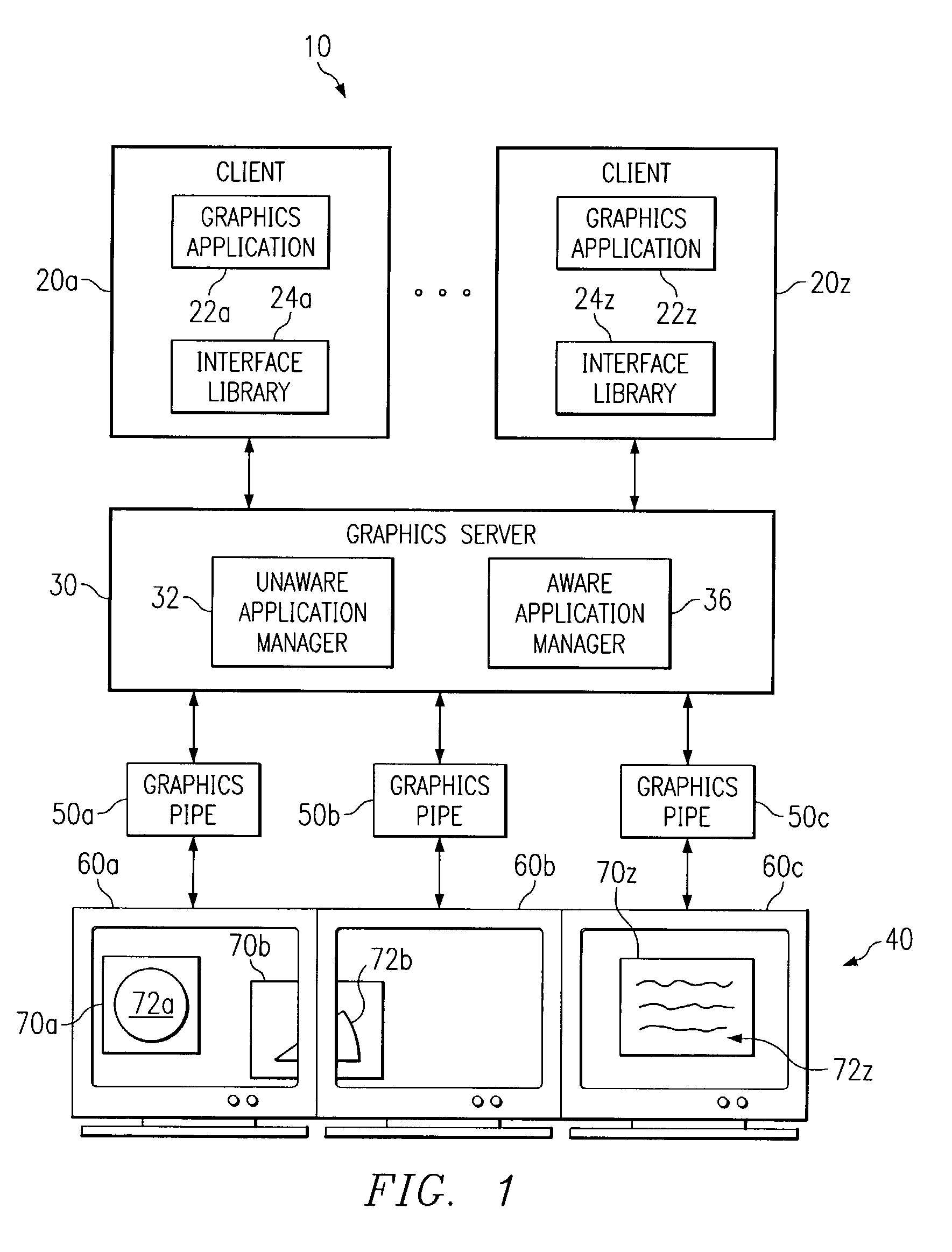
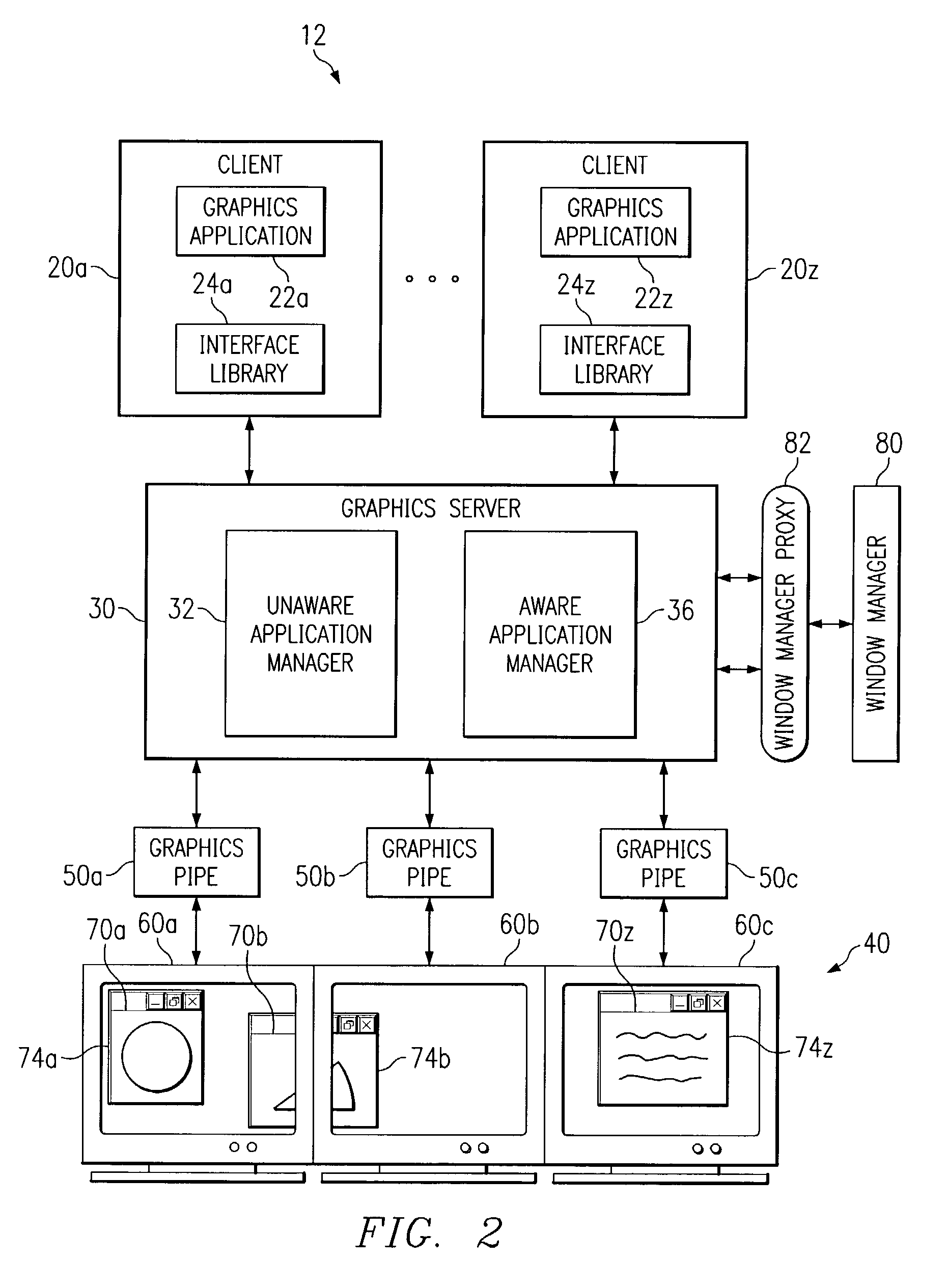
System and method for managing graphics applications
InactiveUS6982682B1Eliminate and greatly reduce disadvantageEliminate and greatly reduce and problemCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingApplication softwareGraphics
A system and method for managing graphics applications include the capability to receive graphics data from an unaware graphics application and convey the graphics data to at least one of a plurality of graphics pipes having different display directions. The system and method further include the capability to modify the graphics data to account for non-planar display of the graphics data.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
Audio encoder, audio decoder and related methods for processing multi-channel audio signals using complex prediction
ActiveUS8655670B2Quality improvementLittle overheadPulse modulation television signal transmissionSpeech analysisData streamFrequency spectrum
An encoder, based on a combination of two audio channels, obtains a first combination signal as a mid-signal and a residual signal derivable using a predicted side signal derived from the mid signal. The first combination signal and the prediction residual signal are encoded and written into a data stream together with the prediction information. A decoder generates decoded first and second channel signals using the prediction residual signal, the first combination signal and the prediction information. A real-to-imaginary transform may be applied for estimating the imaginary part of the spectrum of the first combination signal. For calculating the prediction signal used in the derivation of the prediction residual signal, the real-valued first combination signal is multiplied by a real portion of the complex prediction information and the estimated imaginary part of the first combination signal is multiplied by an imaginary portion of the complex prediction information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
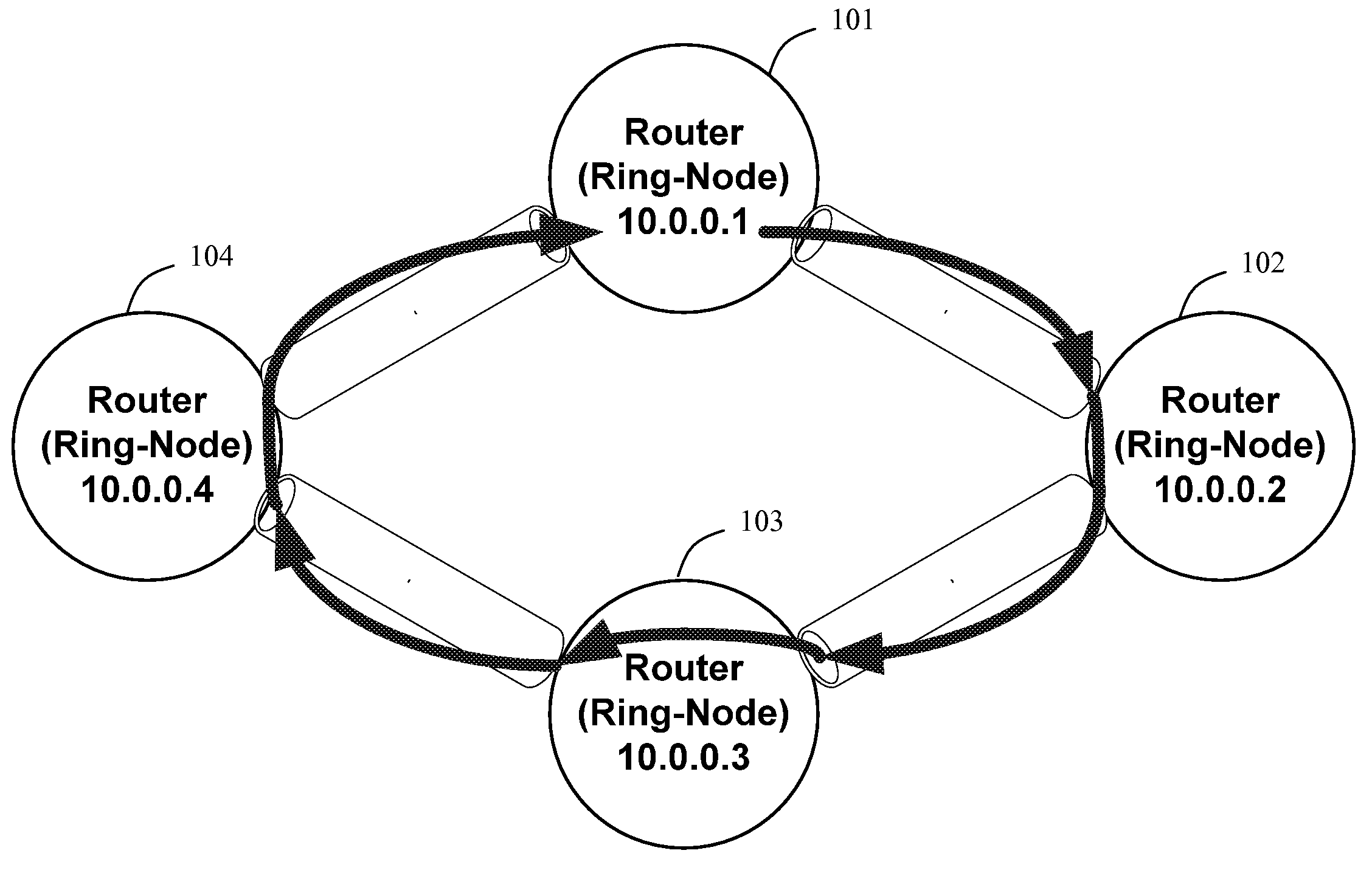
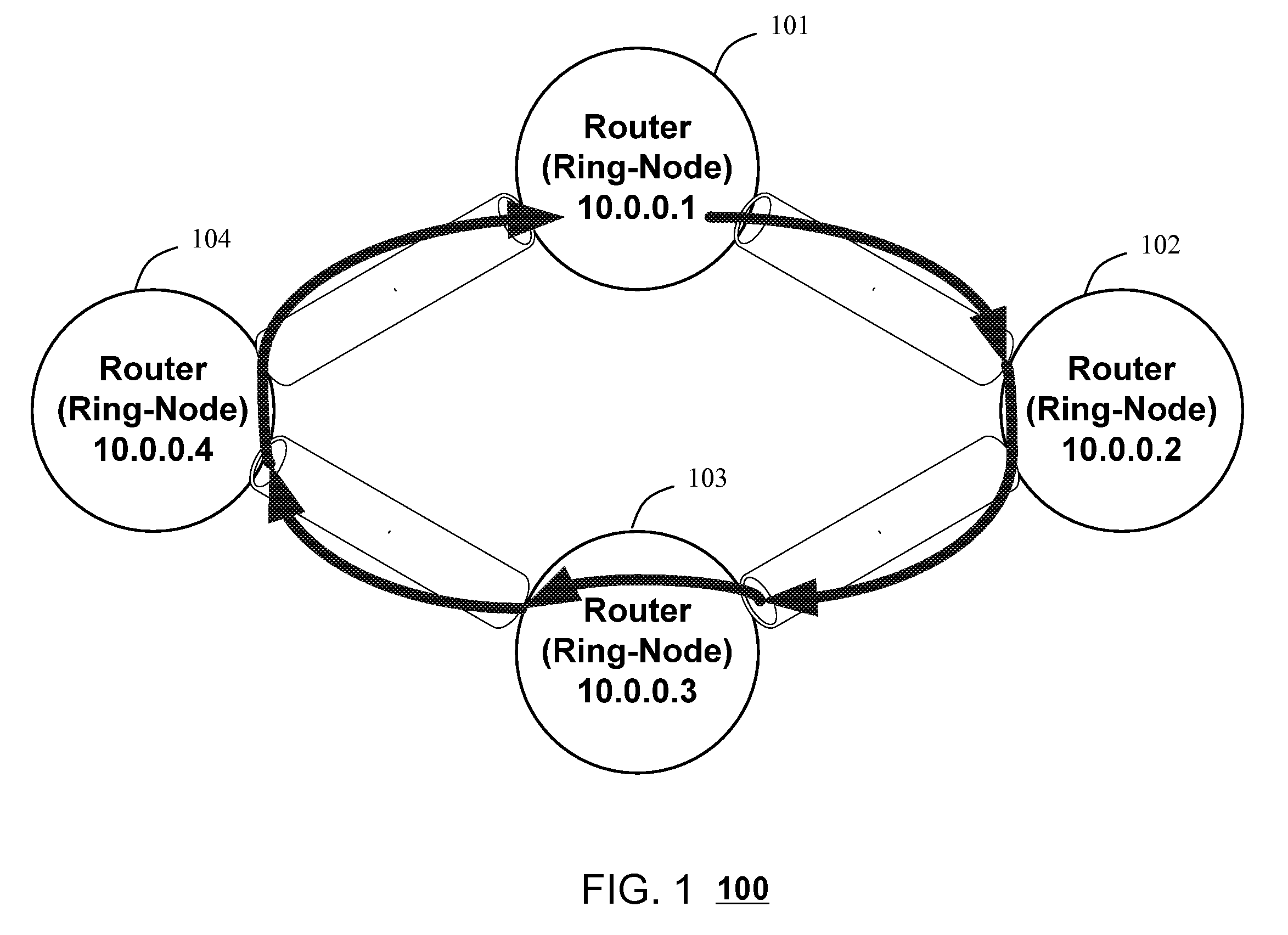
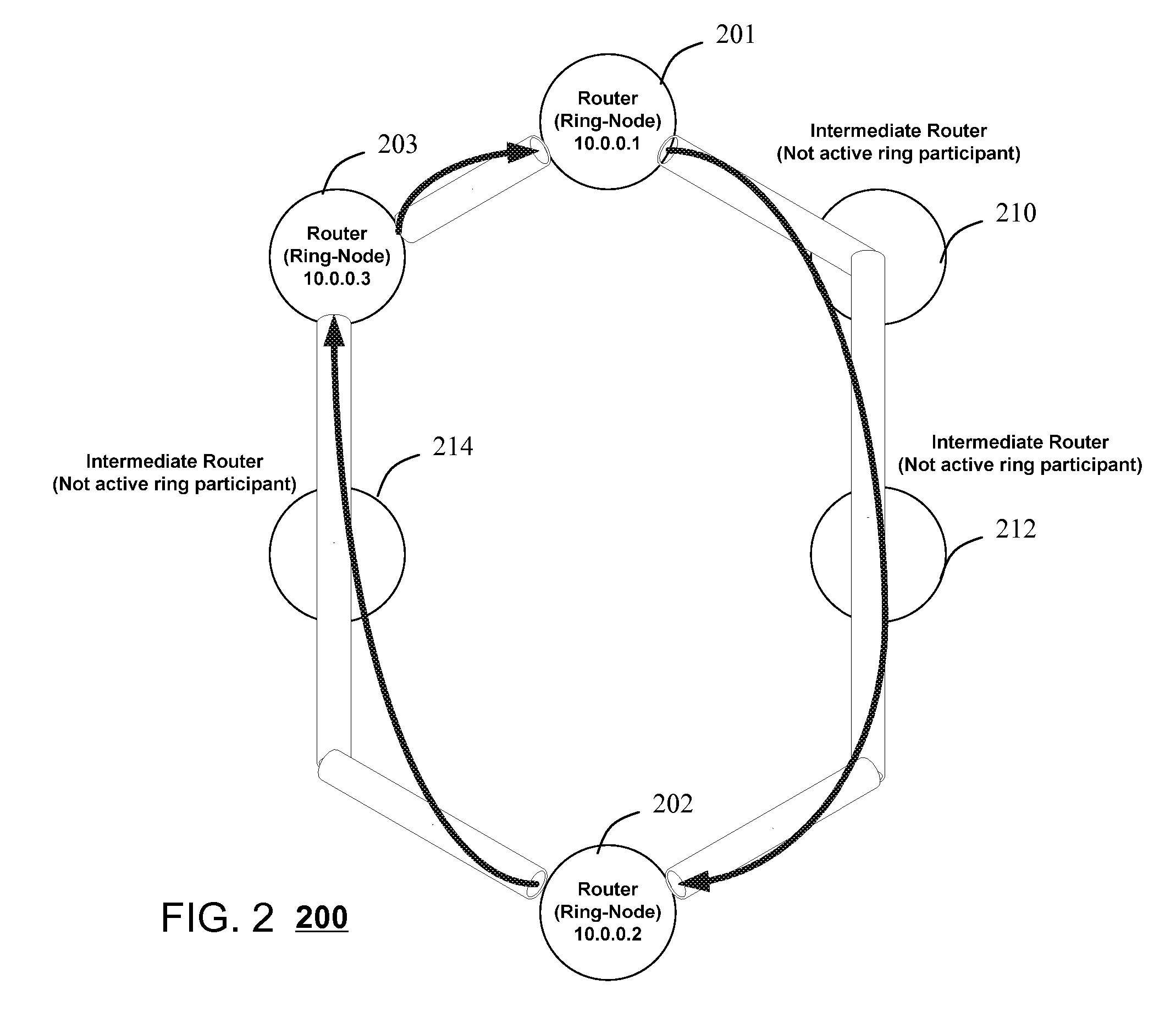
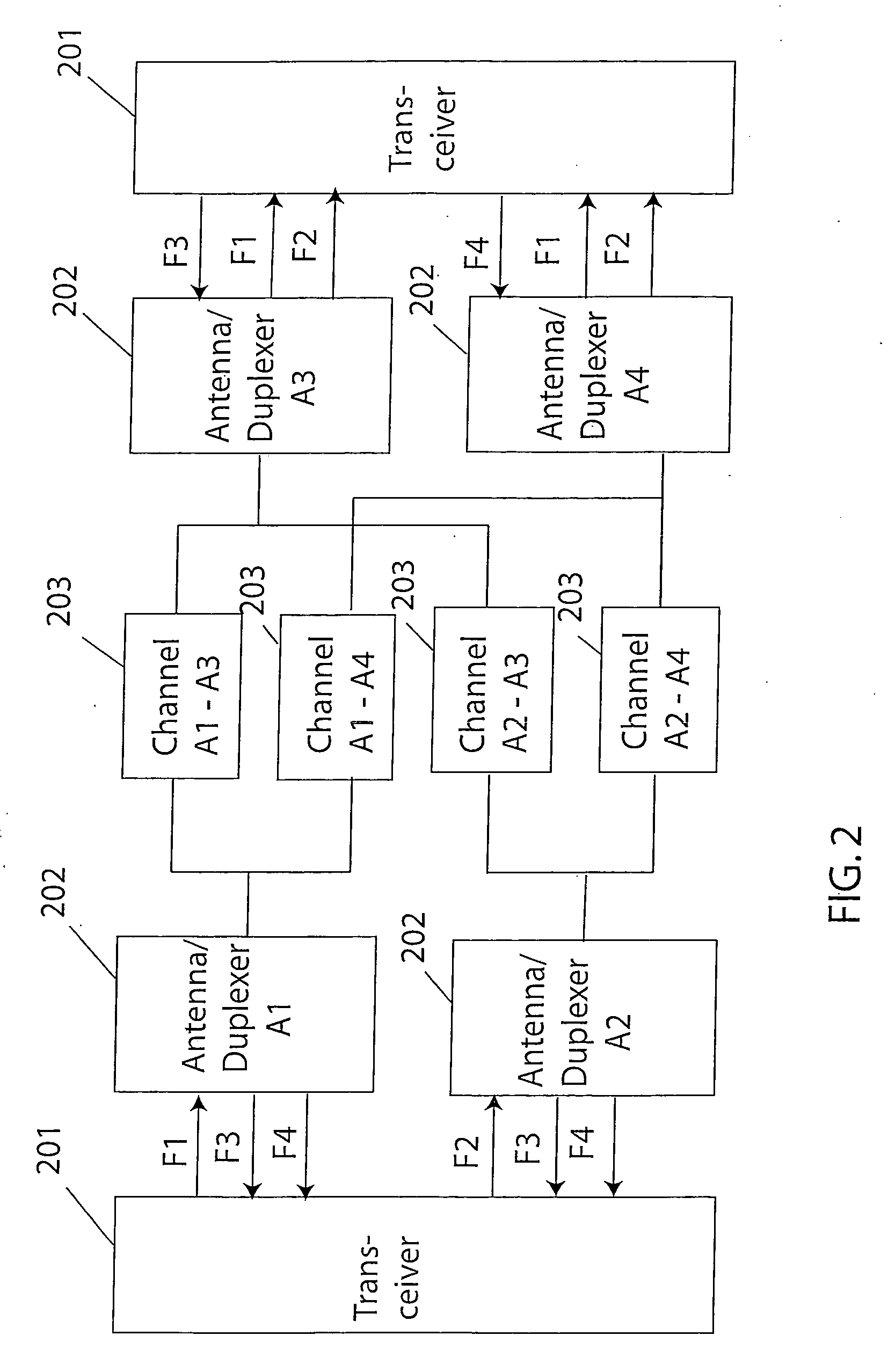
Resilient IP ring protocol and architecture
InactiveUS20070237072A1Little overheadError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemTransceiver
A system and method are disclosed for a resilient IP ring protocol. A system that incorporates teachings of the present disclosure may include, for example, a communication device using a resilient internet protocol (IP) ring protocol, including a controller (602) that manages operations of a transceiver (620) for exchanging messages in a communication system with adjacent ring nodes in a communication ring architecture (300). The controller can be programmed to use sub-second level signaling between adjacent ring nodes to determine when adjacent ring nodes have failed and enable failure options upon detection of an adjacent ring-node failure. Additional embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
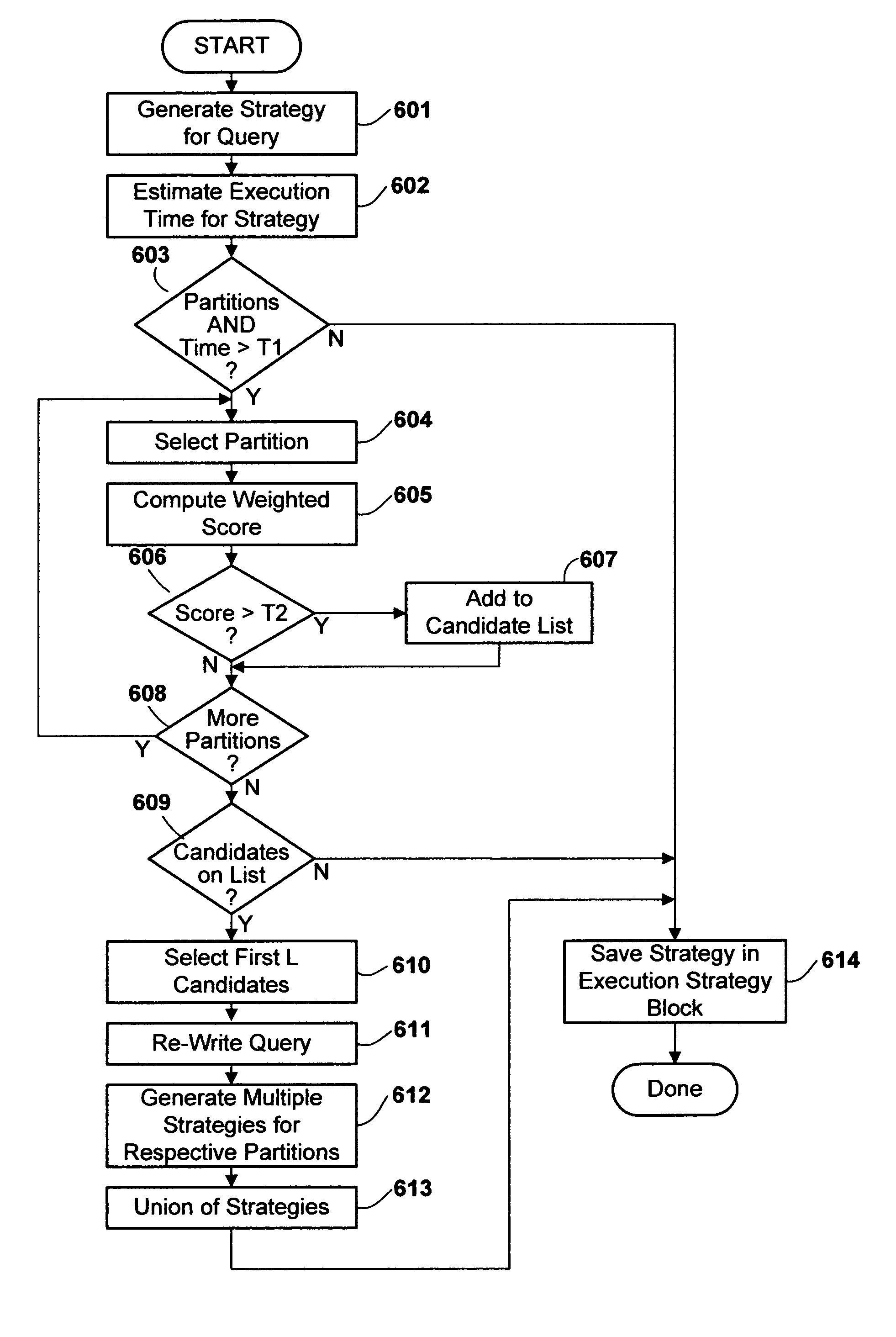
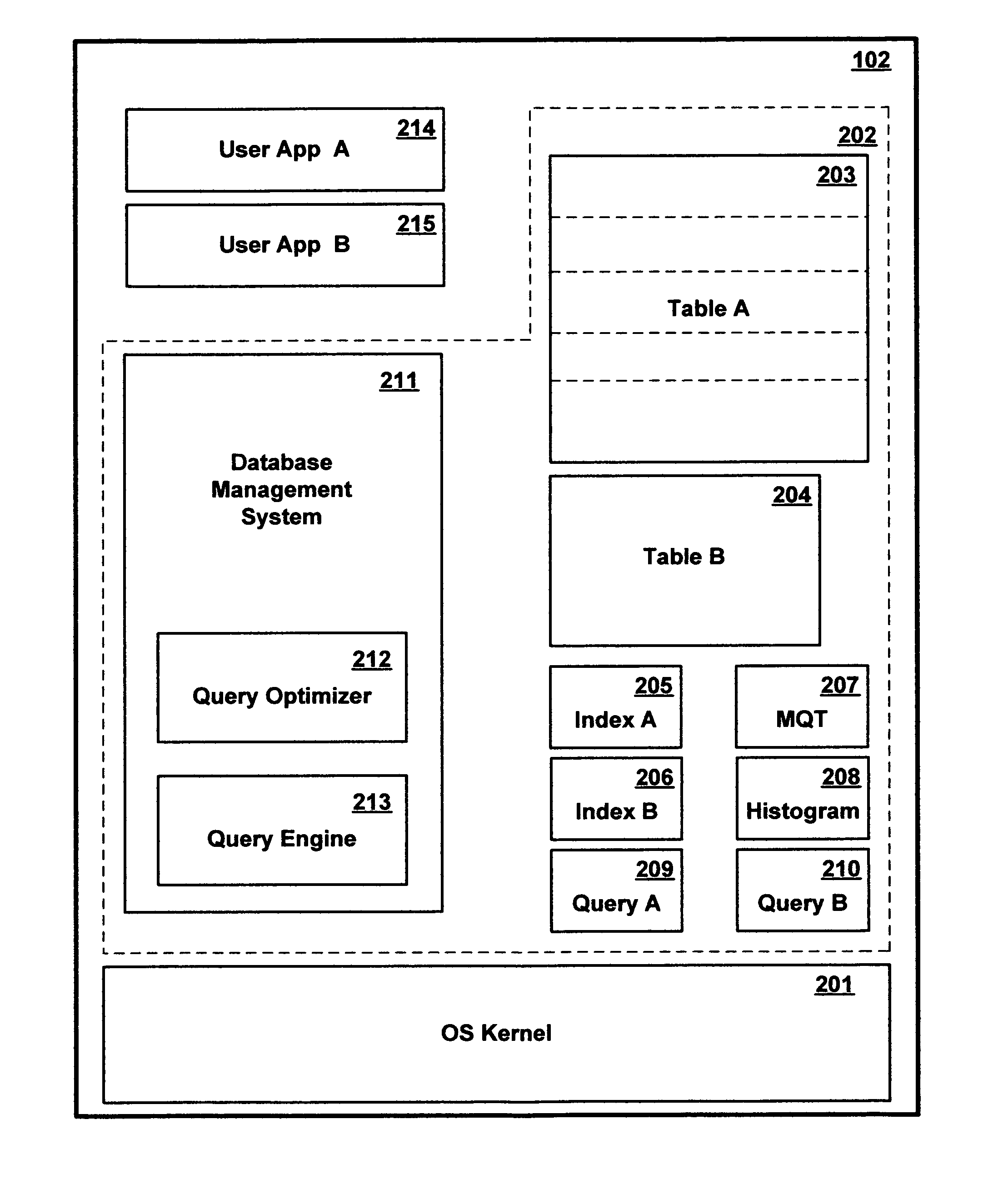
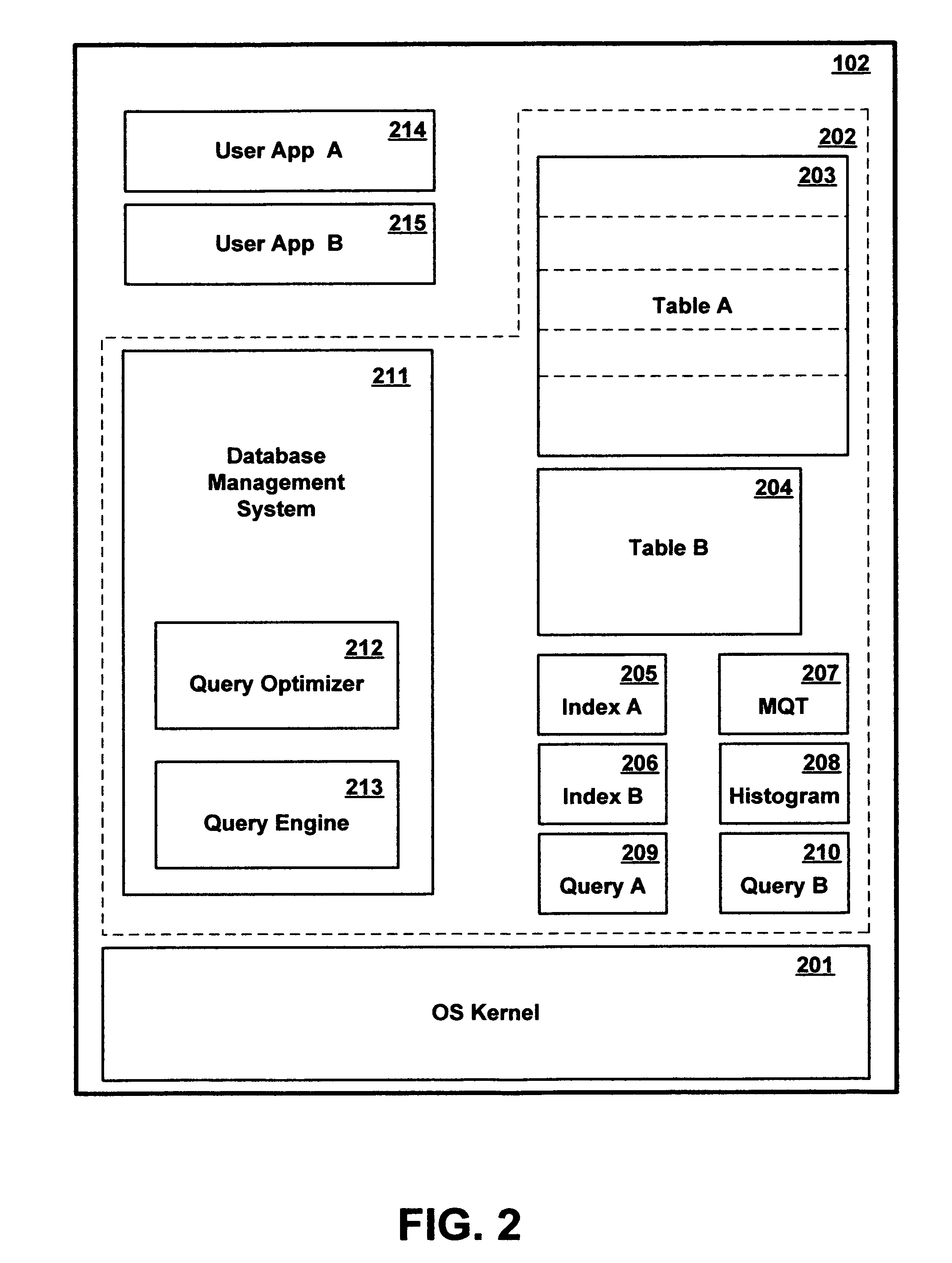
Method and apparatus for dynamically associating different query execution strategies with selective portions of a database table
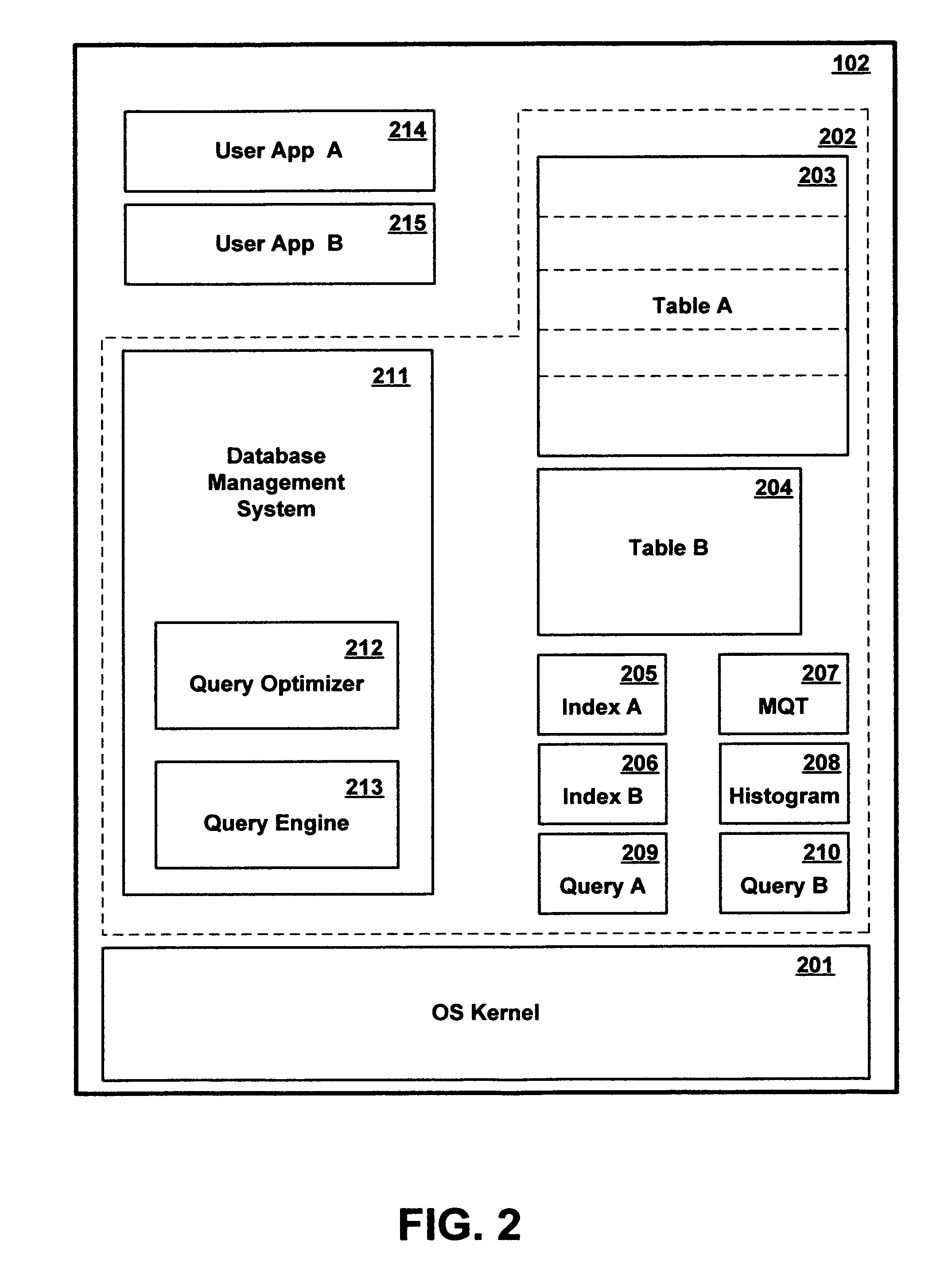
InactiveUS8386463B2Little overheadAvoid overheadDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDatabase queryTable (database)
A query facility for database queries dynamically determines whether selective portions of a database table are likely to benefit from separate query execution strategies, and constructs an appropriate separate execution strategies accordingly. Preferably, the database contains at least one relatively large table comprising multiple partitions, each sharing the definitional structure of the table and containing a different respective discrete subset of the table records. The query facility compares metadata for different partitions to determine whether sufficiently large differences exist among the partitions, and in appropriate cases selects one or more partitions for separate execution strategies. Preferably, partitions are ranked for separate evaluation using a weighting formula which takes into account: (a) the number of indexes for the partition, (b) recency of change activity, and (c) the size of the partition.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Multicast data services and broadcast signal markup stream for interactive broadcast systems
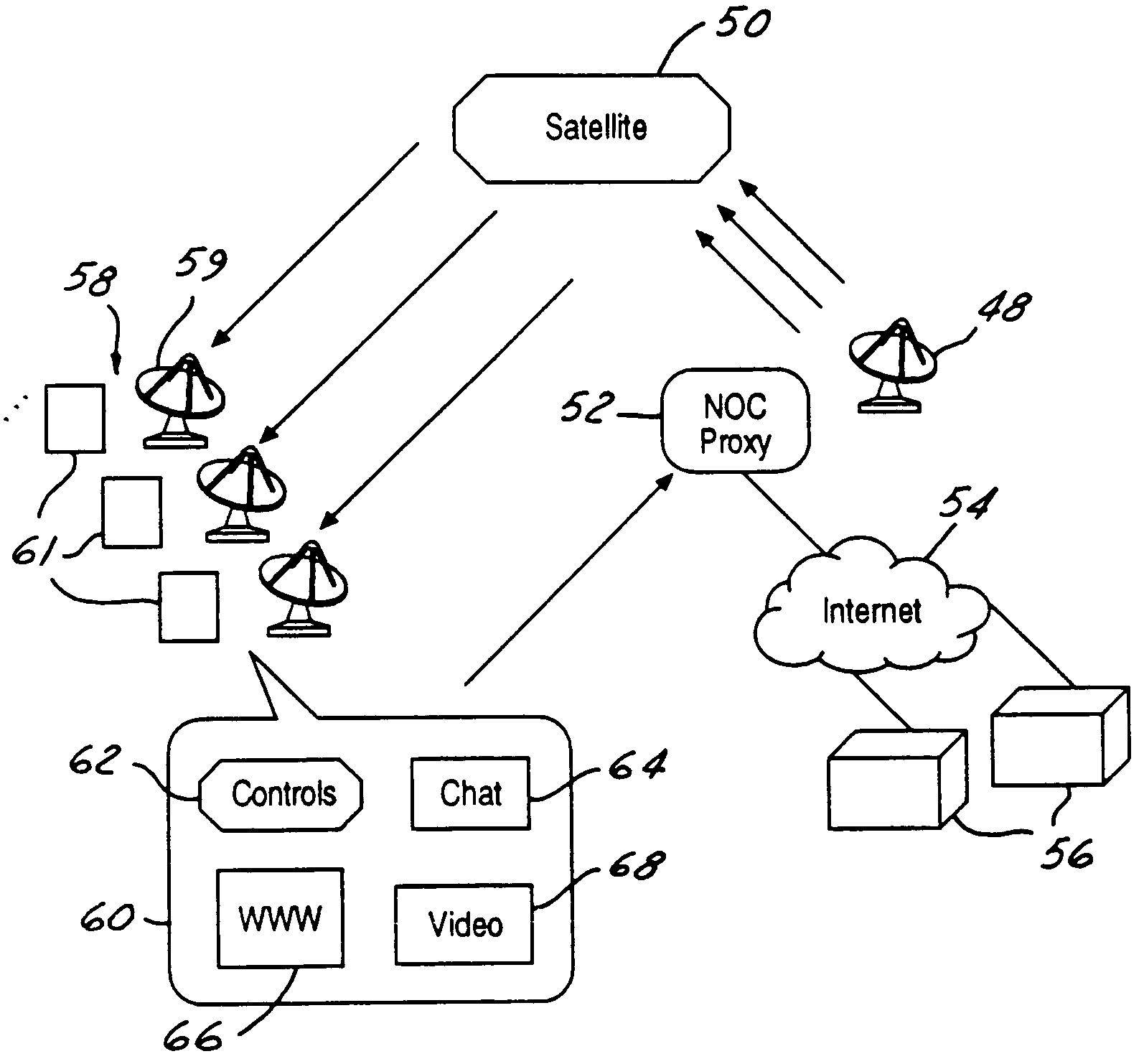
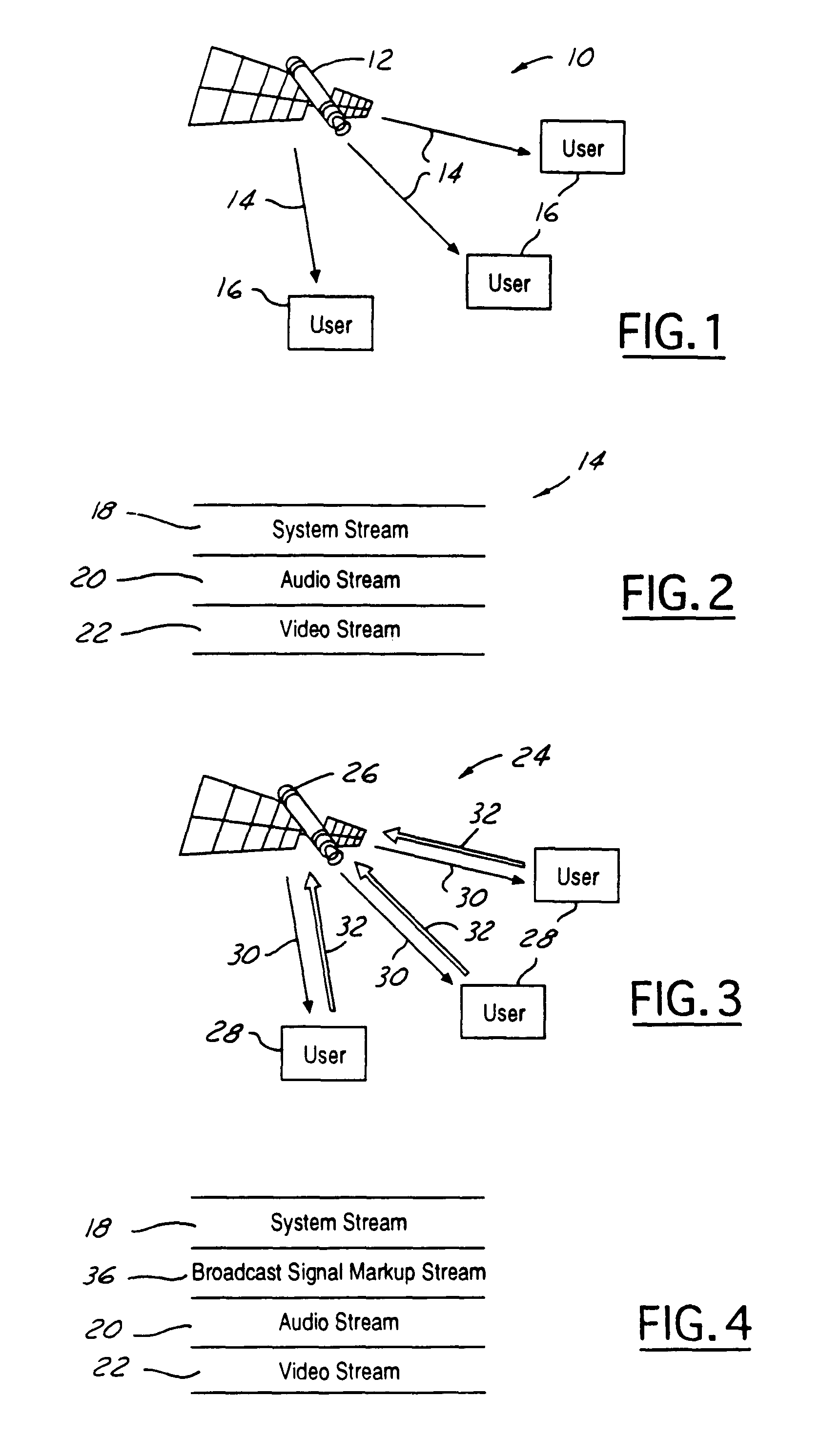
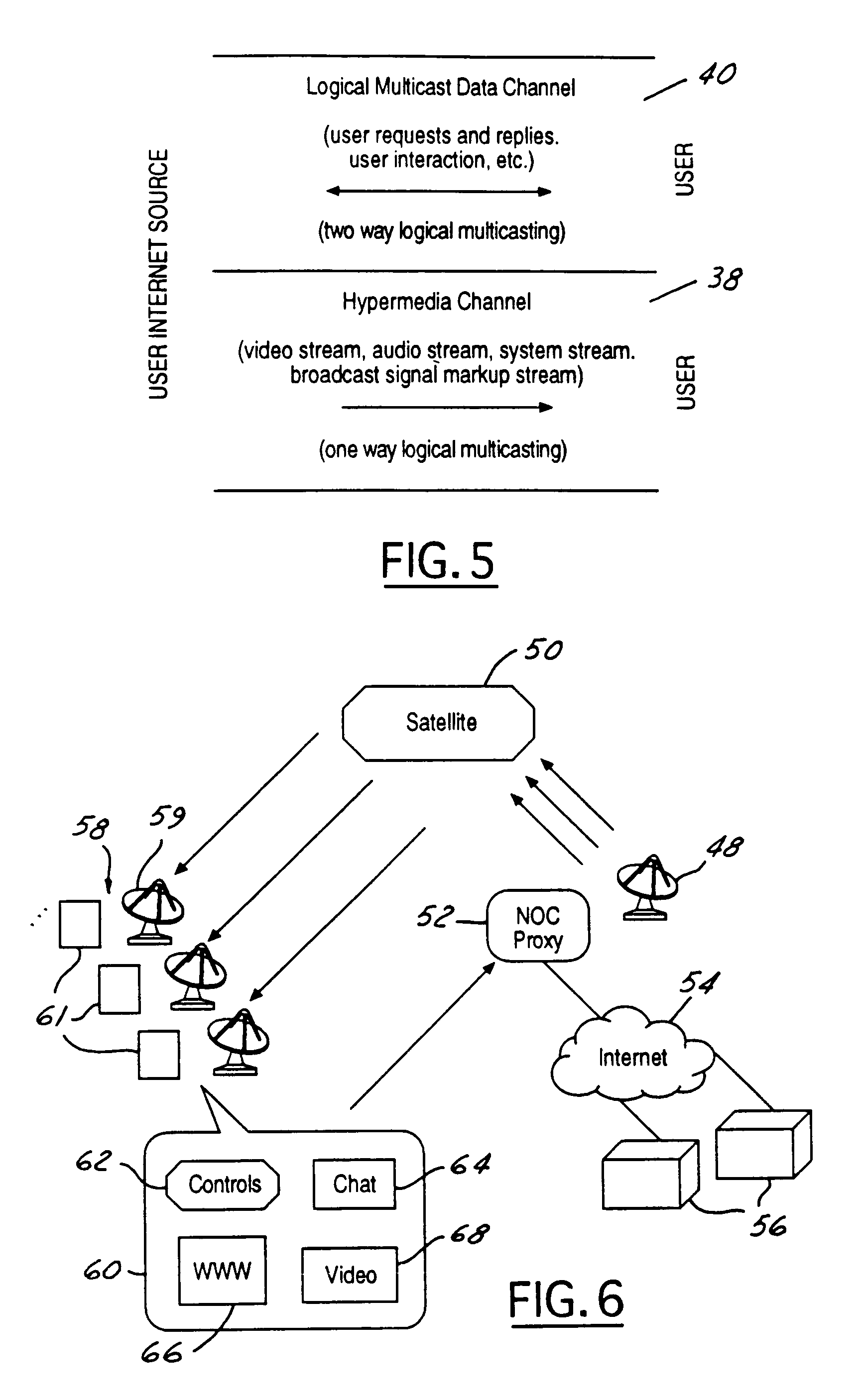
InactiveUS7861275B1High degreeLittle overheadPulse modulation television signal transmissionGHz frequency transmissionSpeech soundKeyword search
A system and method for producing and receiving interactive broadcasting having a broadcast signal with a hypermedia channel and a logical multicast data channel. The logical multicast data channel has a broadcast signal markup stream (BSMS). The system users have a receiver with an interactivity module and a communication module. The BSMS allows user selectable objects to be displayed to users of the system. BSMS objects can be generated by combining speech recognition, language (and optionally video) processing, and keyword searches. By selecting objects various information relating to those objects may be displayed to users. A portion of the logical multicast channel may be employed to provide interactivity between users. A variation eliminates the BSMS either by employing a markup stream server to provide access links or by generating link content directly in the receiver by the same process.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
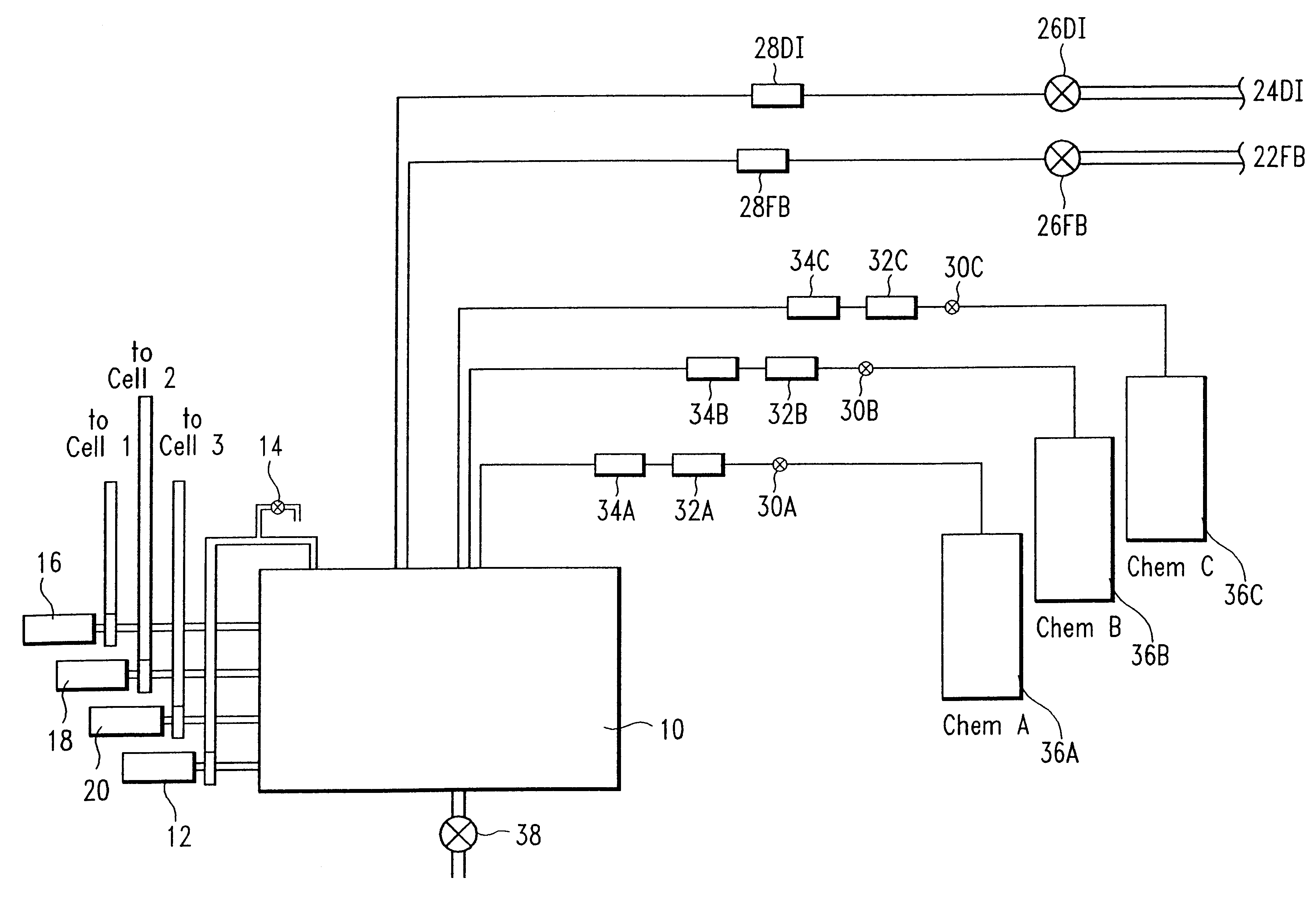
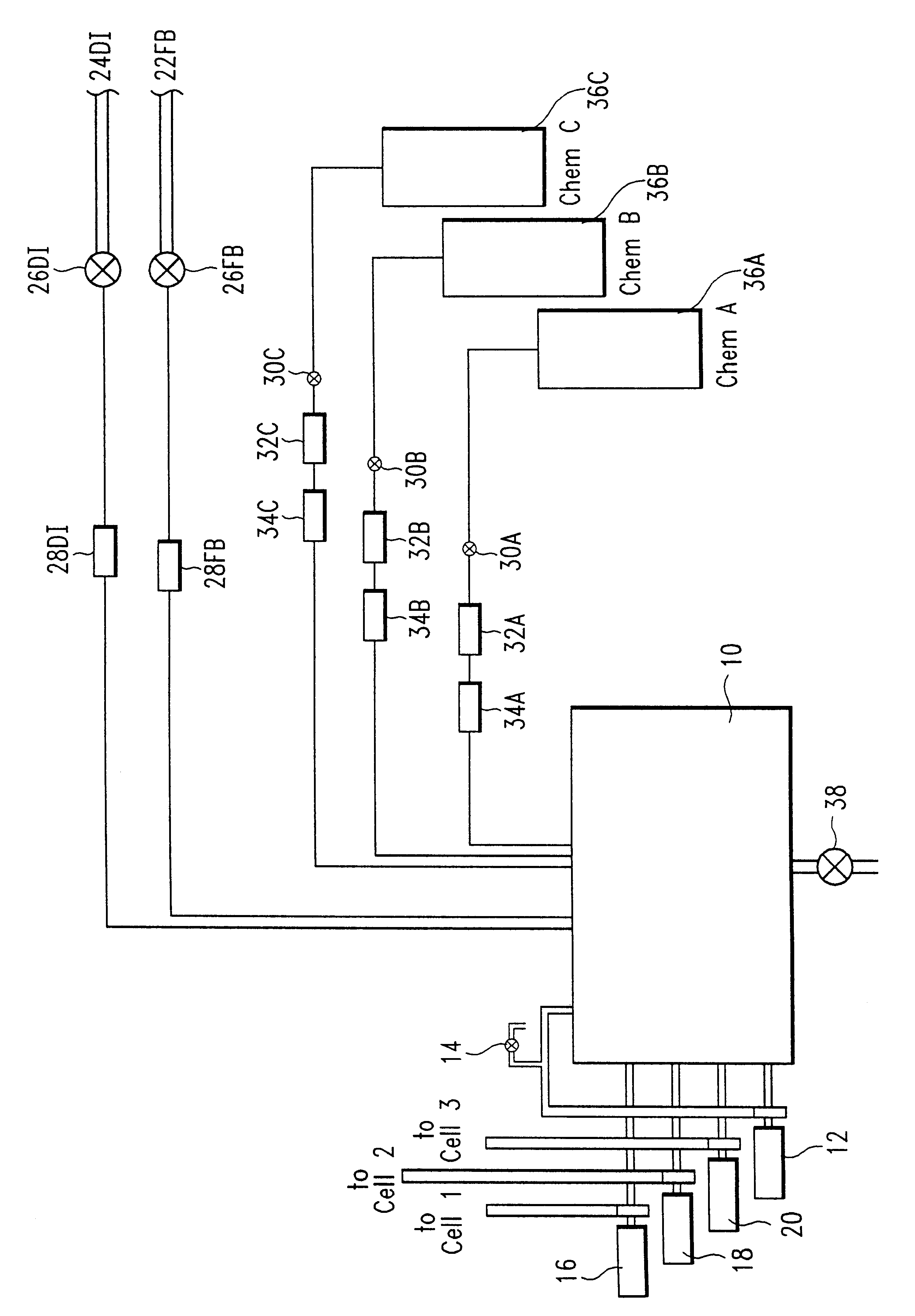
Method of controlling chemical bath composition in a manufacturing environment
InactiveUS6471845B1Little overheadPrecise controlCellsRatio controlProcess engineeringChemical composition
A method for controlling the composition of a chemical bath in which predictive dosing is used to account for changes in the composition of the bath in which the operating characteristics of the process are partitioned into a plurality of operating modes and the consumption or generation of materials related to the process are determined empirically and additions of material are made as appropriate.
Owner:IBM CORP
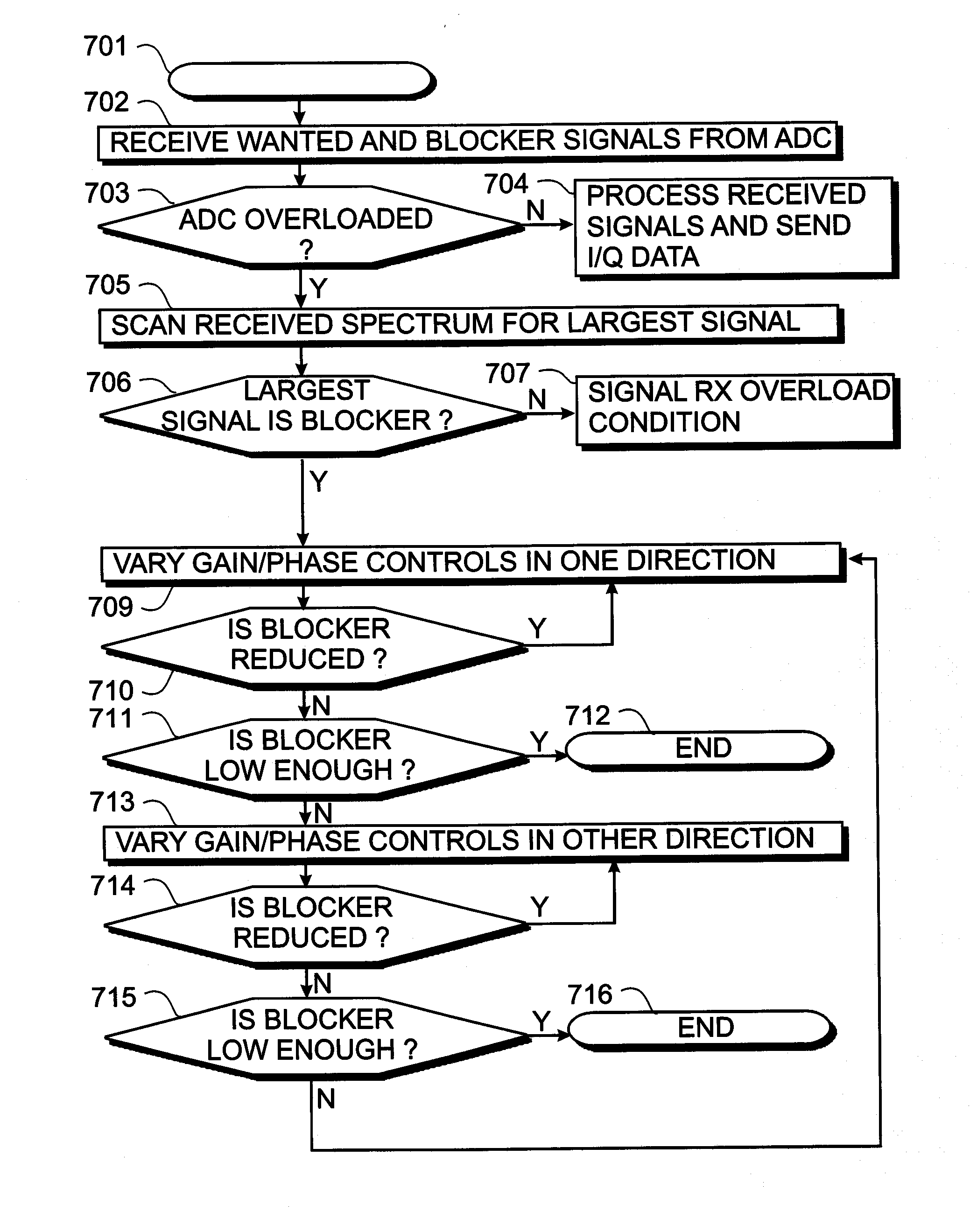
Mismatched delay based interference cancellation device and method
InactiveUS20110065408A1Reduce Interfering SignalsPrevents excessive intermodulationTransmissionInterference cancelationSignal cancellation
An interference signal cancellation device comprises a signal splitter, a delay element and a signal combiner. The signal splitter distributes a disturbed signal to a first signal path and a second signal path. The delay element is situated in at least one of the first signal path and the second signal path for introducing a relative delay between a first signal in the first signal path and a second signal in the second signal path. The signal combiner combines the first signal and the second signal. An interference signal within the disturbed signal is substantially reduced within the signal combiner. A method for interference signal cancellation is also proposed. Furthermore, a computer program product with instructions for the manufacture and a computer program product enabling a processor to carry out the method for interference signal cancellation are also proposed.
Owner:UBIDYNE
Access control for packet-oriented networks
InactiveUS20080198744A1Efficient methodAvoid disadvantagesError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityNetwork output
The invention relates to a method for access control to a packet-oriented network. An admissibility check for a group of packets is carried out by means of a threshold value for the traffic volume between the network input node and the network output node for the flow. The transmission of the groups of data packets is not permitted when an authorisation of the transmission would lead to traffic volume exceeding the threshold value. A relationship between the threshold values and the traffic volume in partials stretches or links may be formulated by means of the proportional traffic volume over the individual partial stretches. Using the capacities of the links the threshold values for pairs of input and output nodes can be fixed such that no overload occurs on the individual links. Within the above method a flexible reaction to the drop-out of links can be achieved by means of a resetting of the threshold values. Furthermore the inclusion of other conditions is possible, for example relating to the capacity of interfaces to other networks or special demands on transmission of prioritised traffic.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
System and method for creating an application-consistent remote copy of data using remote mirroring
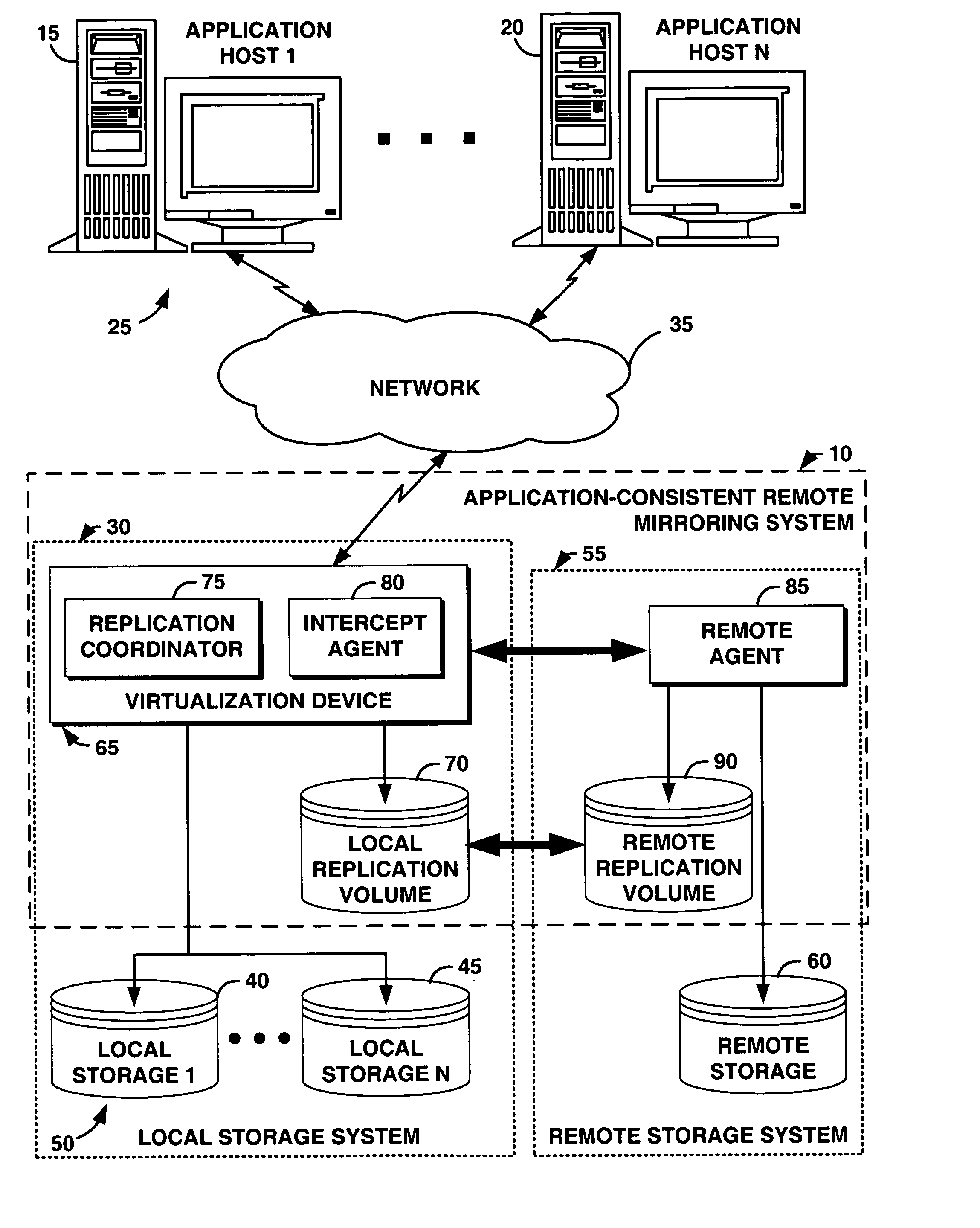
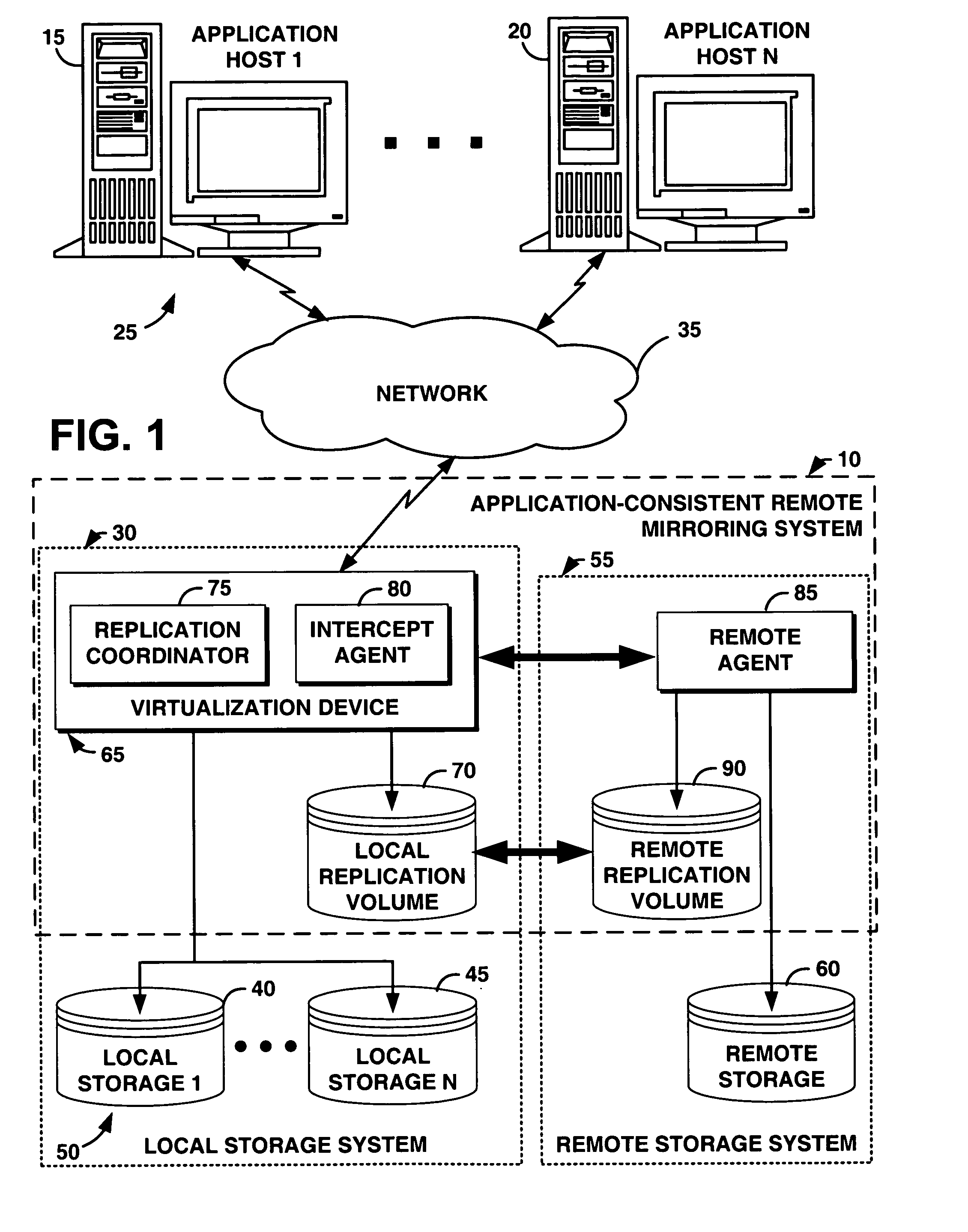
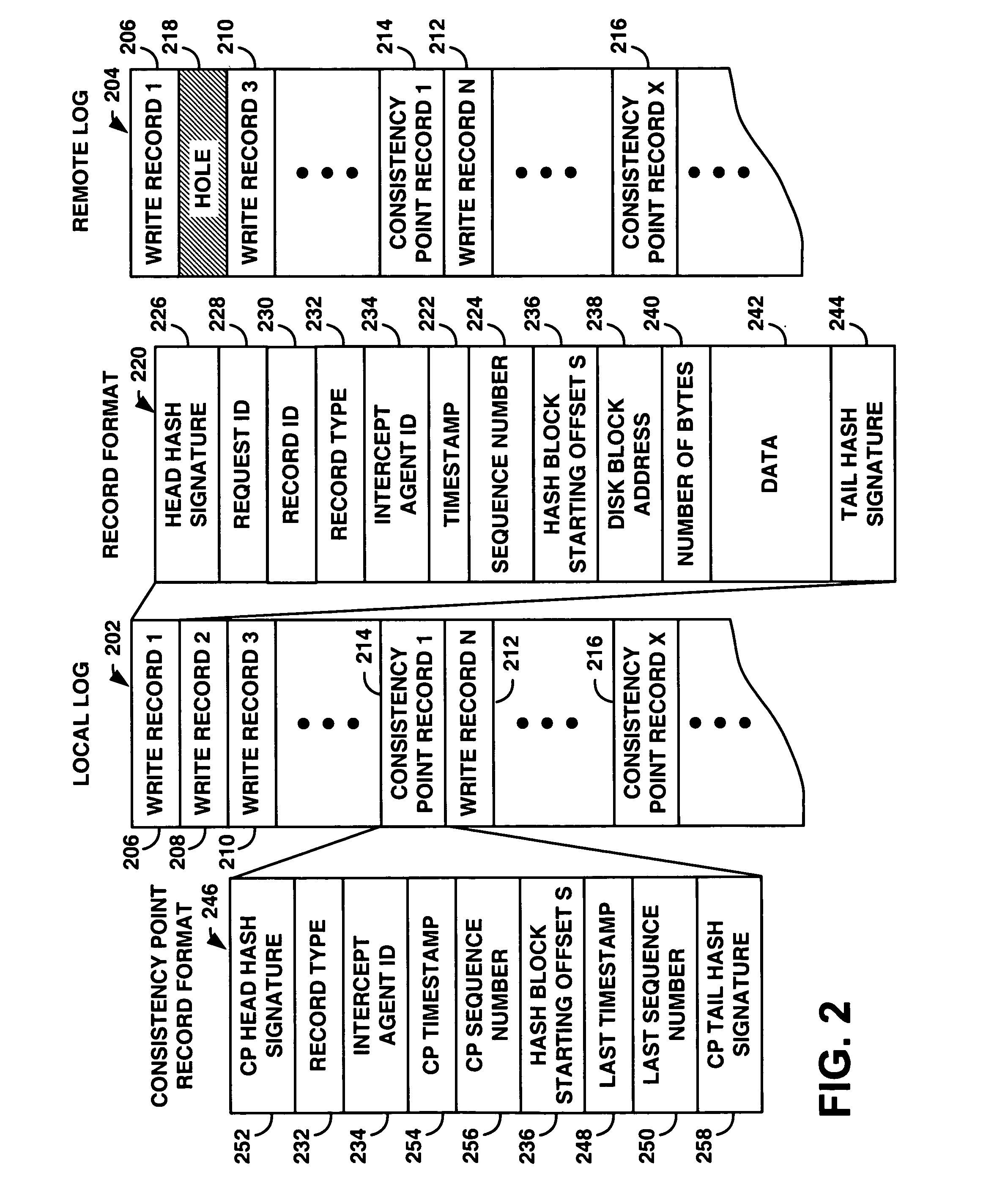
InactiveUS20070022144A1Easy to createEnsure consistencyData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsVirtualizationDisk layout
An application consistent data protection system provides application-assist and replication-technology neutral mirroring that ensures that a remote data copy is application-consistent. The system comprises a coordination protocol to coordinate application hosts across heterogeneous hosts and heterogeneous storage devices. The system utilizes a disk layout and data record format that enables use of an underlying replication ability of a storage device, minimizing development cost and utilizing customer investment. The system comprises on-demand consistency point initiation to minimize performance impact and maximize system resource usage. The system can be applied to both synchronous and asynchronous mirroring and can be incorporated into any virtualization device.
Owner:IBM CORP
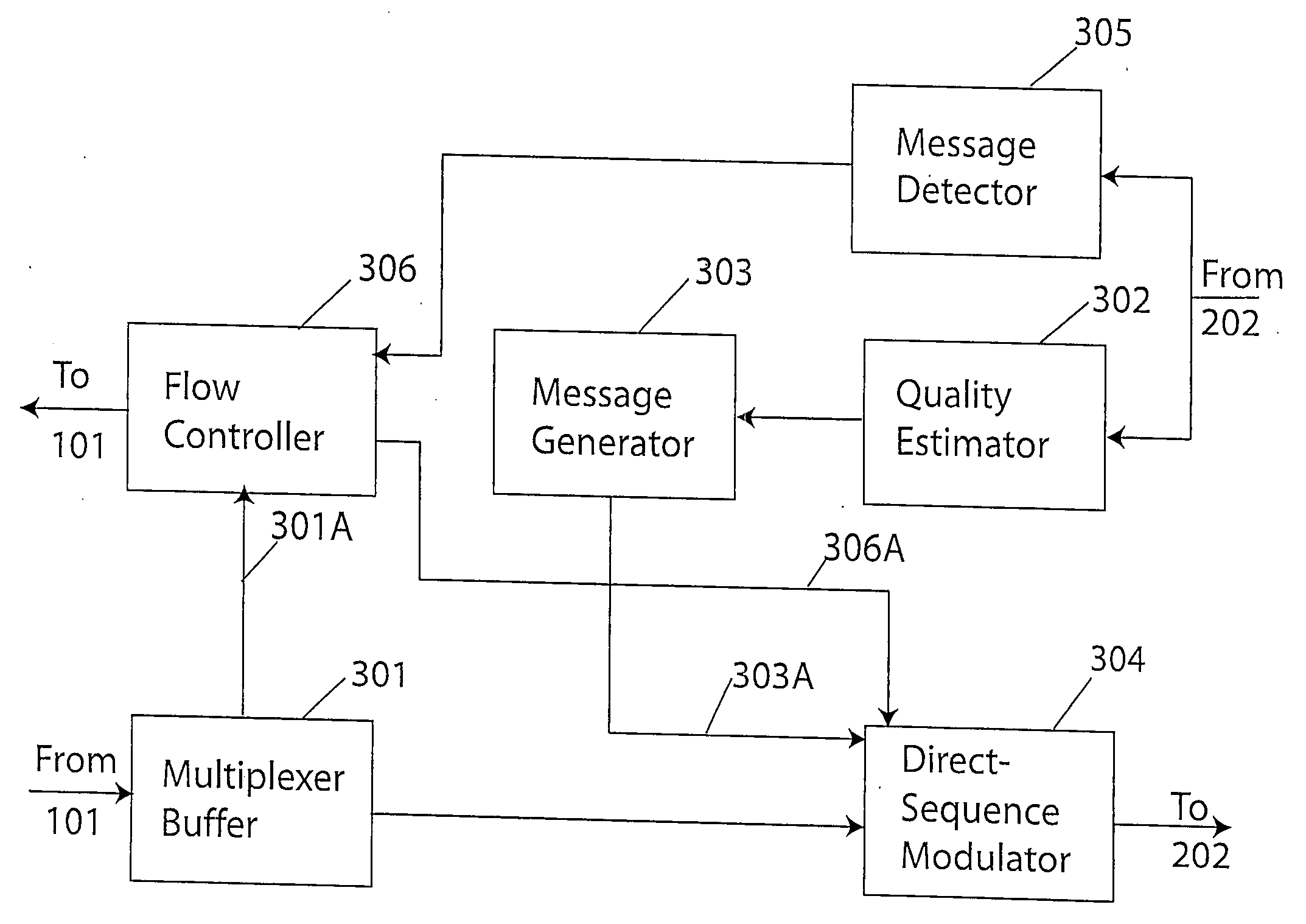
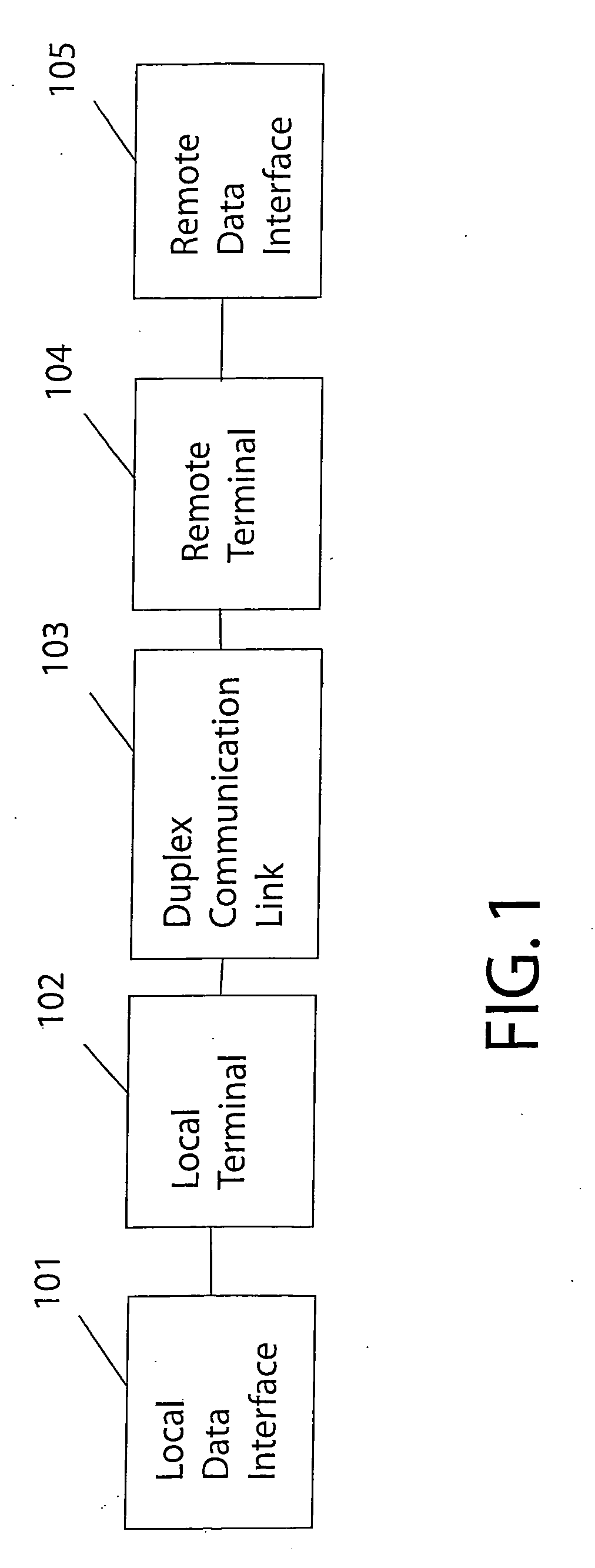
Technique for adaptive data rate communication over fading dispersive channels
ActiveUS20070147251A1Increase capacityMitigate mutual interferenceTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsIndependent dataWave band
In a duplex radio link wherein digital data information from a data interface is transmitted from a local terminal to a remote terminal over fading dispersive channels, a method and transceiver are described that provide for transmission at an adaptive data rate. The transmission is at a constant symbol rate so that the signal bandwidth can be fixed and at the remote terminal receiver the input sampling rate can be fixed. The digital data information is transmitted over a constant data rate interval in accordance with a selected data rate mode that is a function of direct sequence spreading gain, error correction code rate, and signal constellation type. The data rate is adapted by selecting a data rate mode that is a function of the arrival rate of data packets from the data interface and a link quality measure fed back from the remote terminal. The data packet arrival rate is controlled as a function of the link quality measure and the current data packet arrival rate. In systems with multiple transmit diversity channels, independent data is sent over each of the transmit diversity channels. The adaptive data rate technique utilizes both orthogonal transmit diversities such as frequency and troposcatter polarization diversity as well as nonorthogonal transmit diversities in a Multiple-input Multiple-Output (MIMO) configuration. A single antenna troposcatter link using angle diversity and adaptation of data rate by feedback communications is described. In an idealized feedback communication example, the single antenna system in a Ku-band application is shown to have 15.5 times the data rate capability of a conventional two-antenna system at S-band.
Owner:MONSEN PETER
Method and apparatus for dynamically associating different query execution strategies with selective portions of a database table
InactiveUS20070016558A1Little overheadAvoid overheadDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDatabase queryMetadata
A query facility for database queries dynamically determines whether selective portions of a database table are likely to benefit from separate query execution strategies, and constructs an appropriate separate execution strategies accordingly. Preferably, the database contains at least one relatively large table comprising multiple partitions, each sharing the definitional structure of the table and containing a different respective discrete subset of the table records. The query facility compares metadata for different partitions to determine whether sufficiently large differences exist among the partitions, and in appropriate cases selects one or more partitions for separate execution strategies. Preferably, partitions are ranked for separate evaluation using a weighting formula which takes into account: (a) the number of indexes for the partition, (b) recency of change activity, and (c) the size of the partition.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com