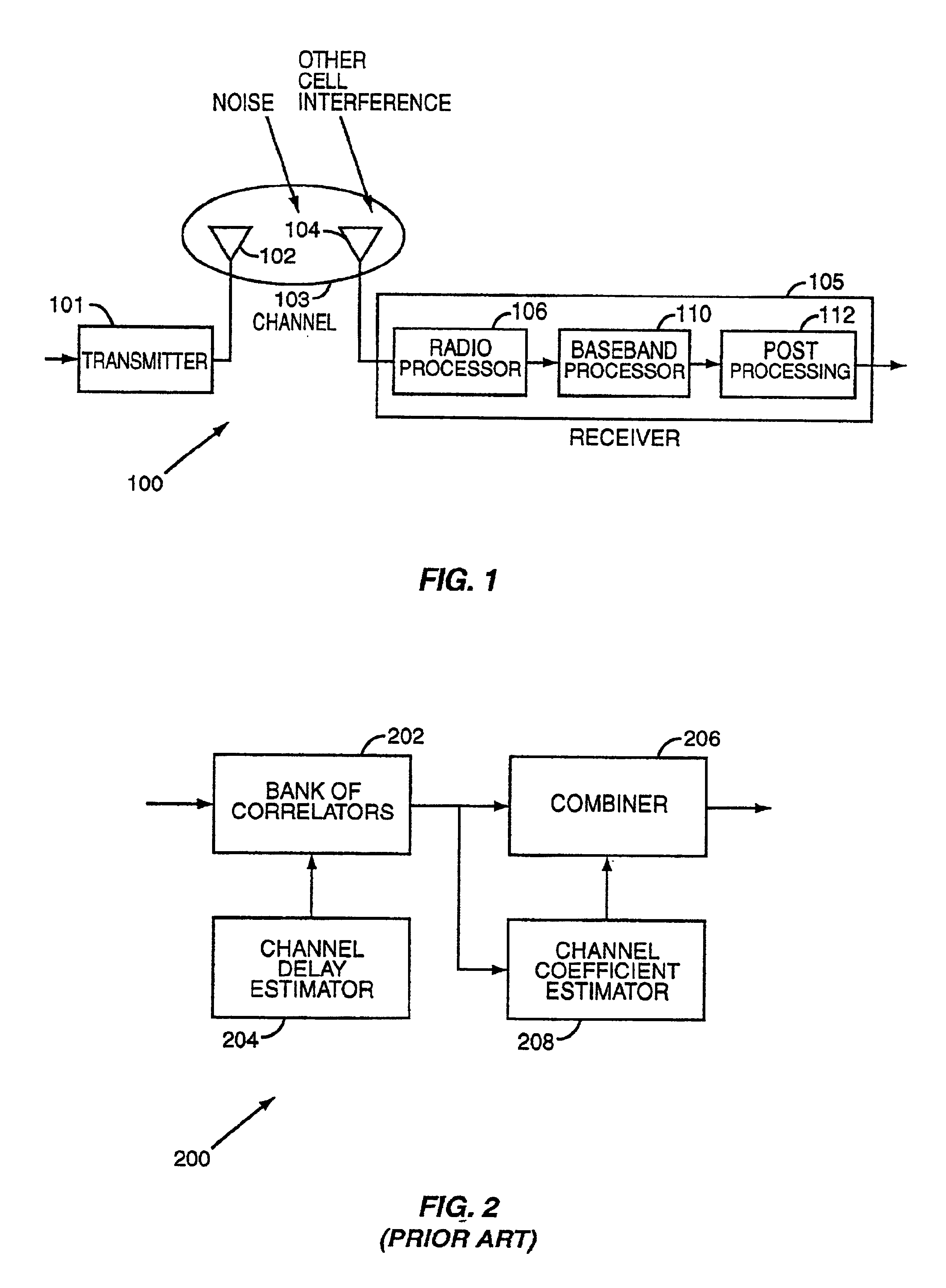
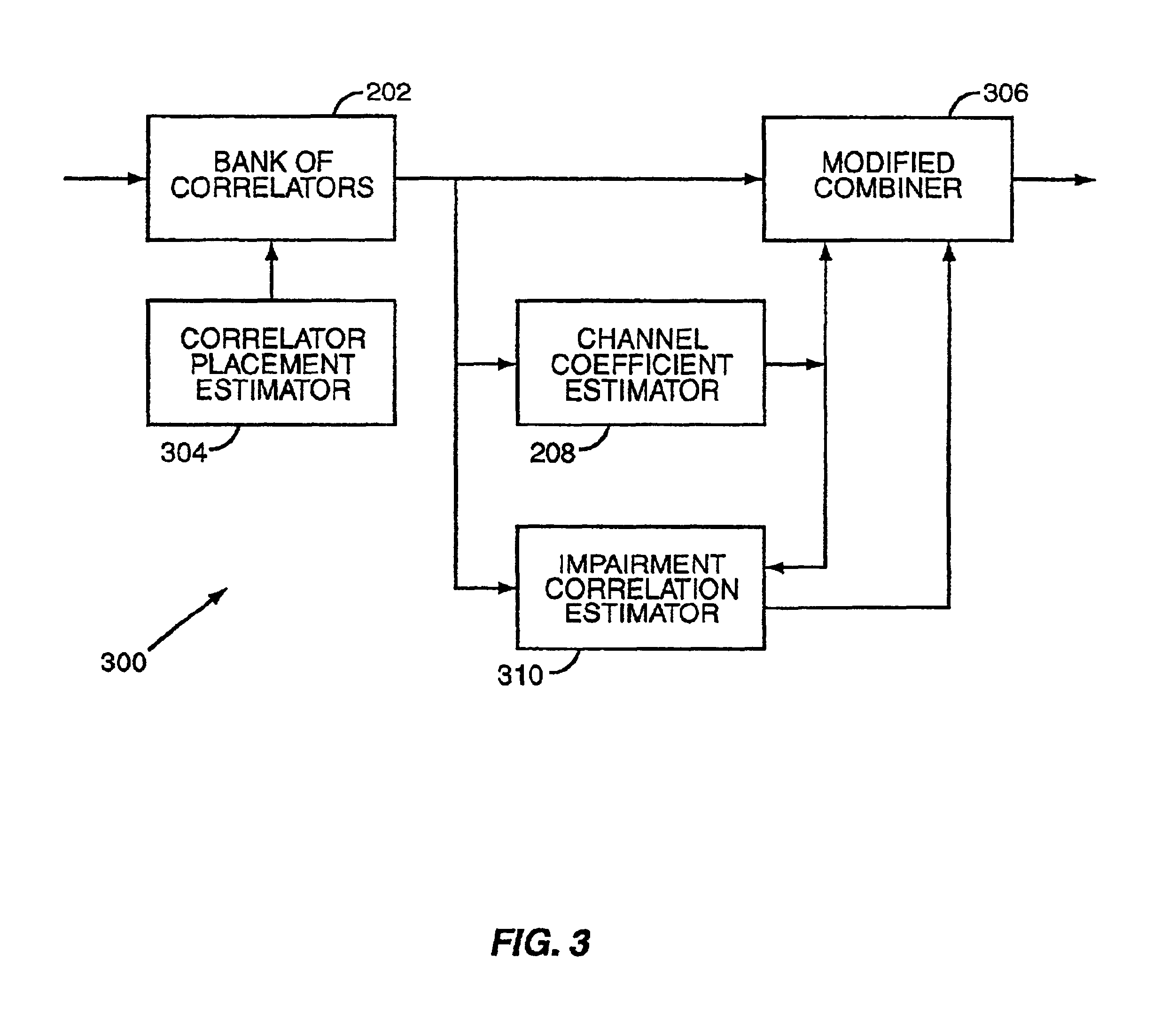
Patents
Literature
1084 results about "Interference cancelation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
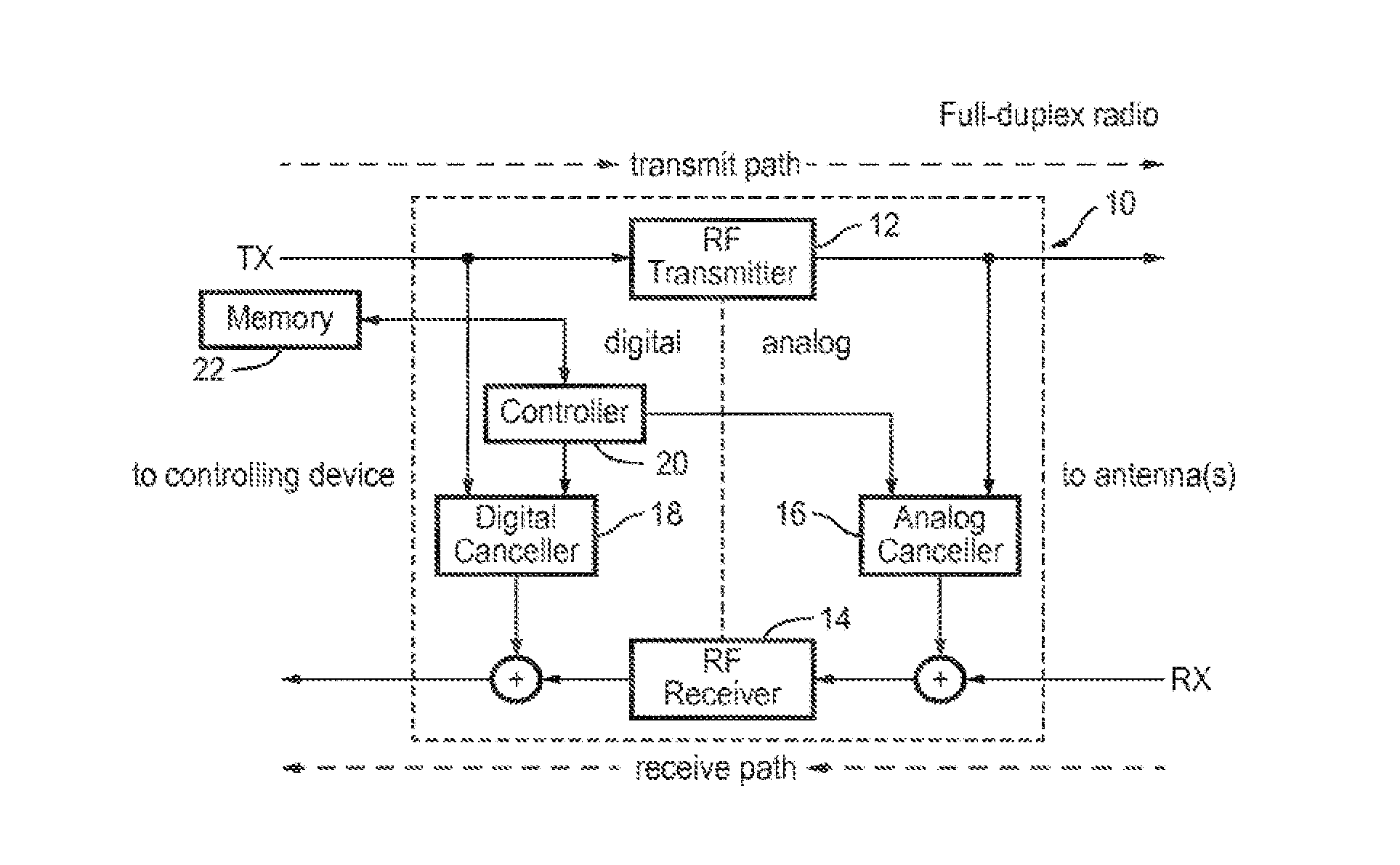
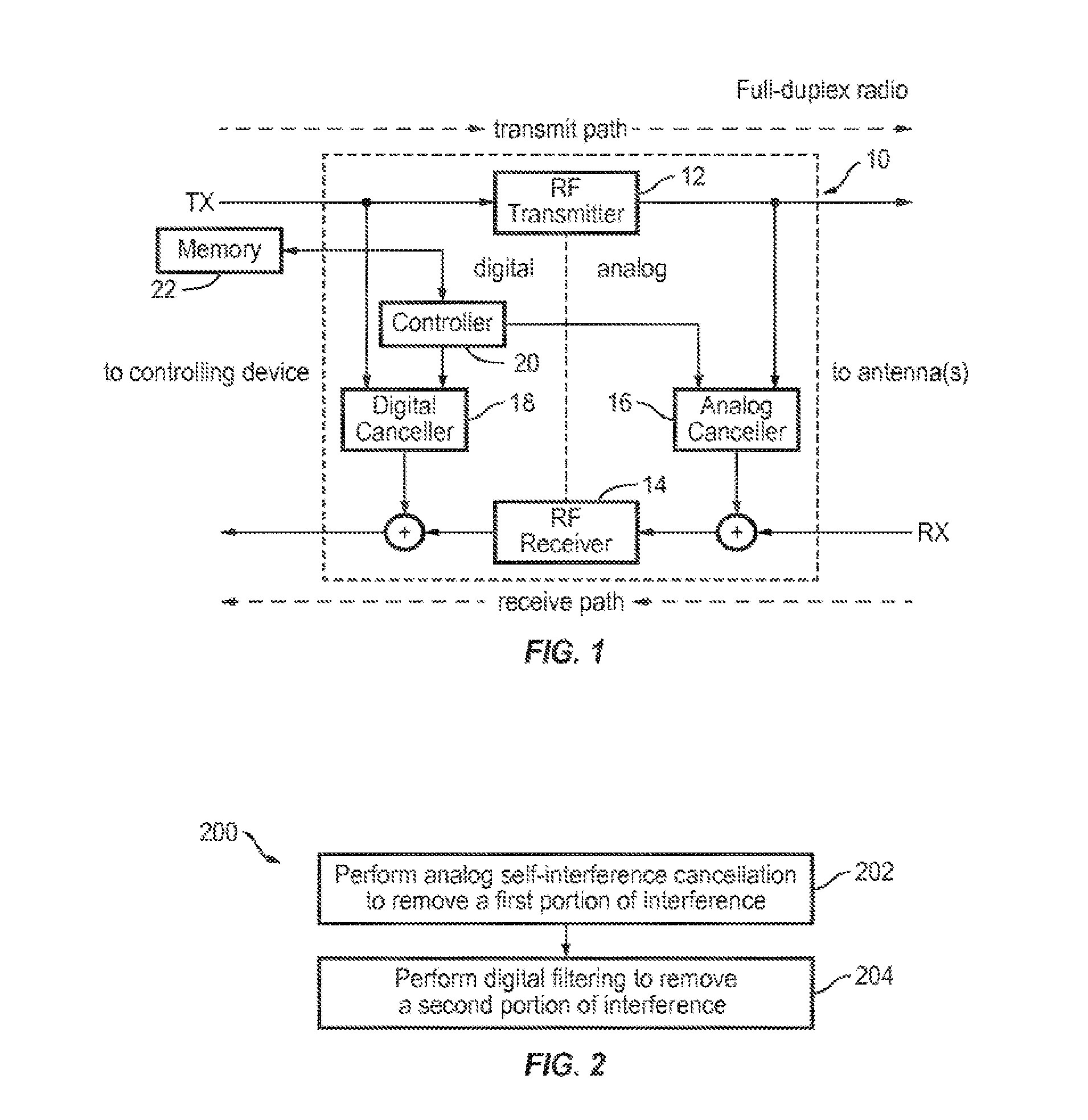
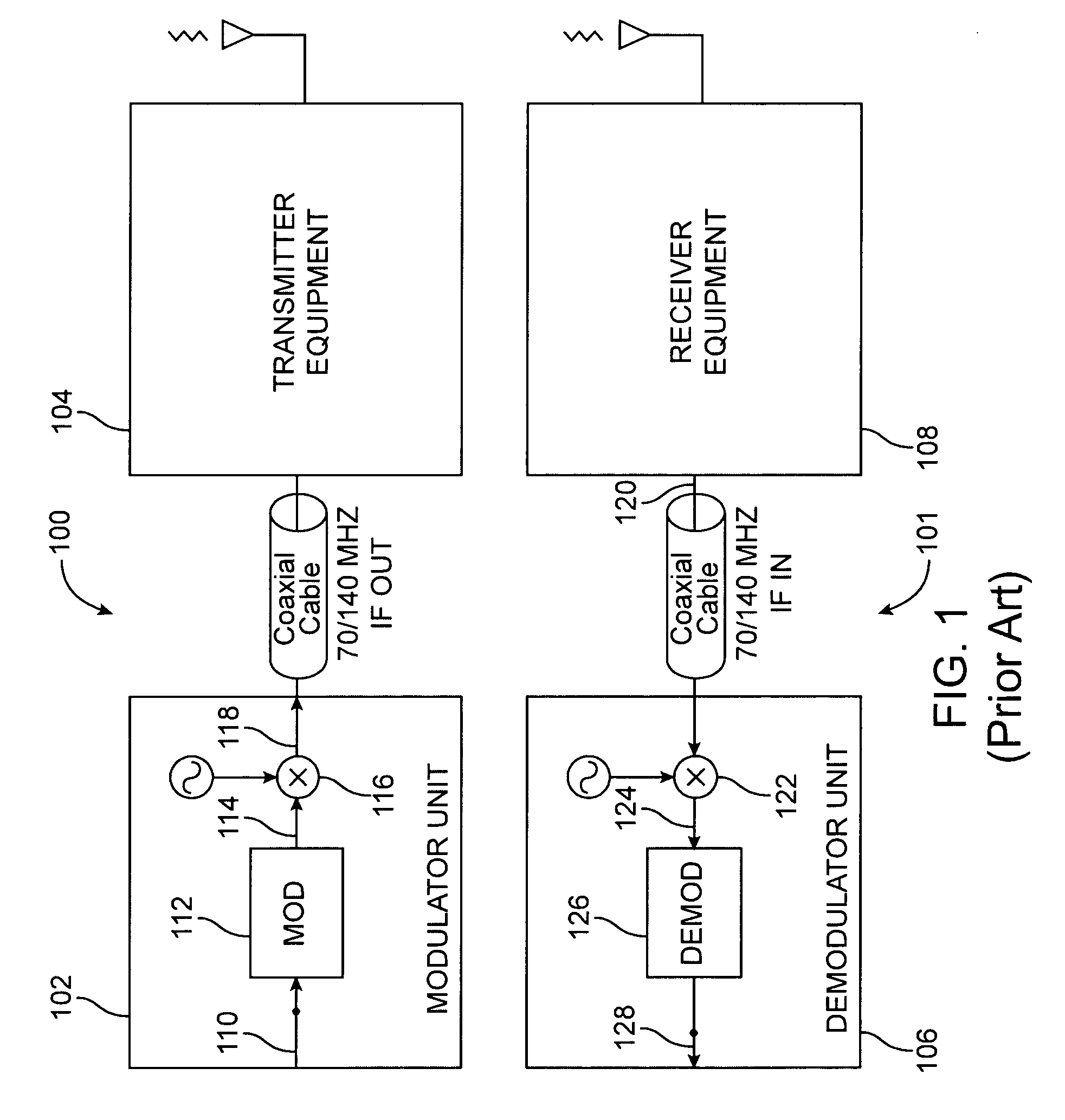
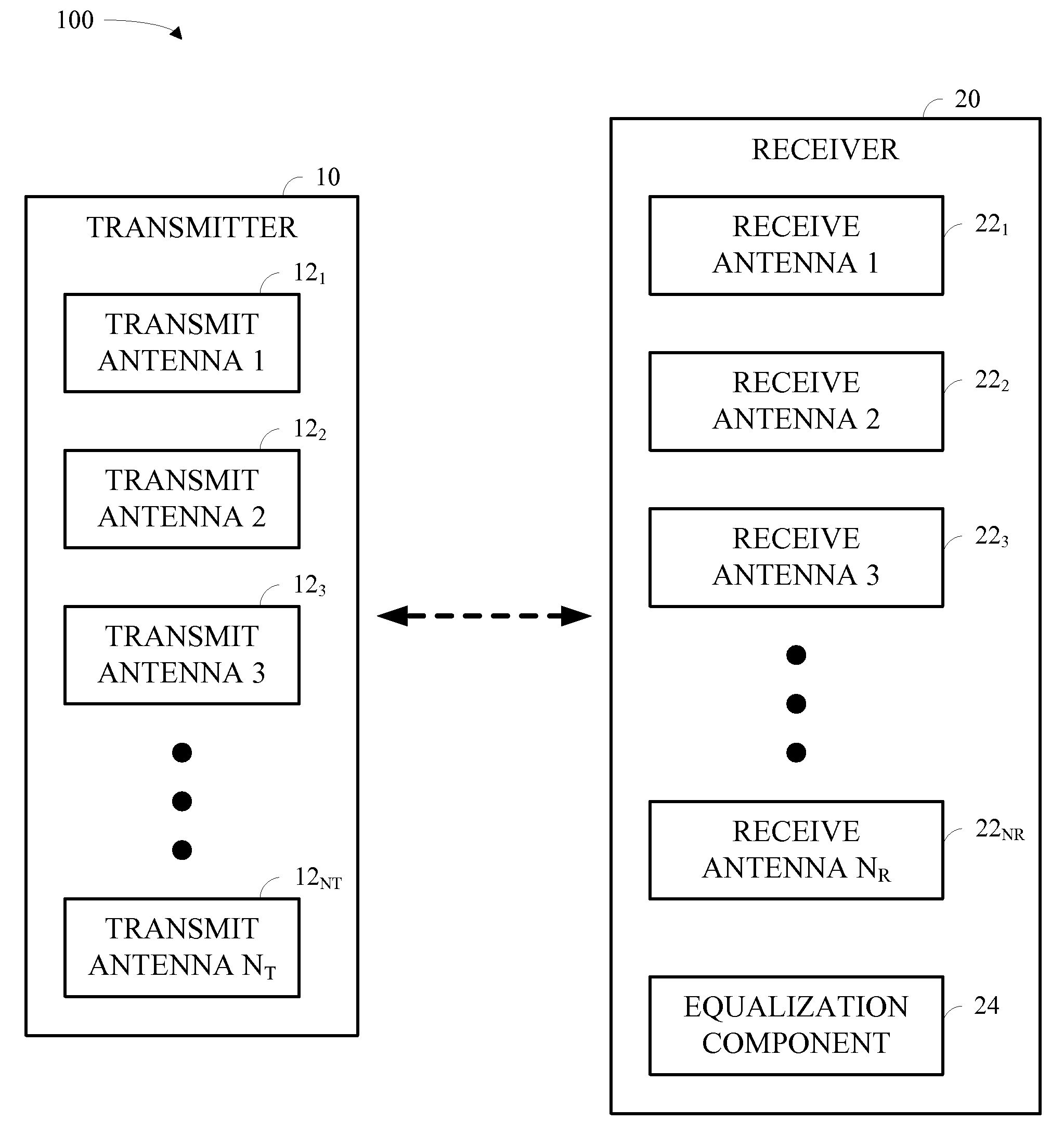
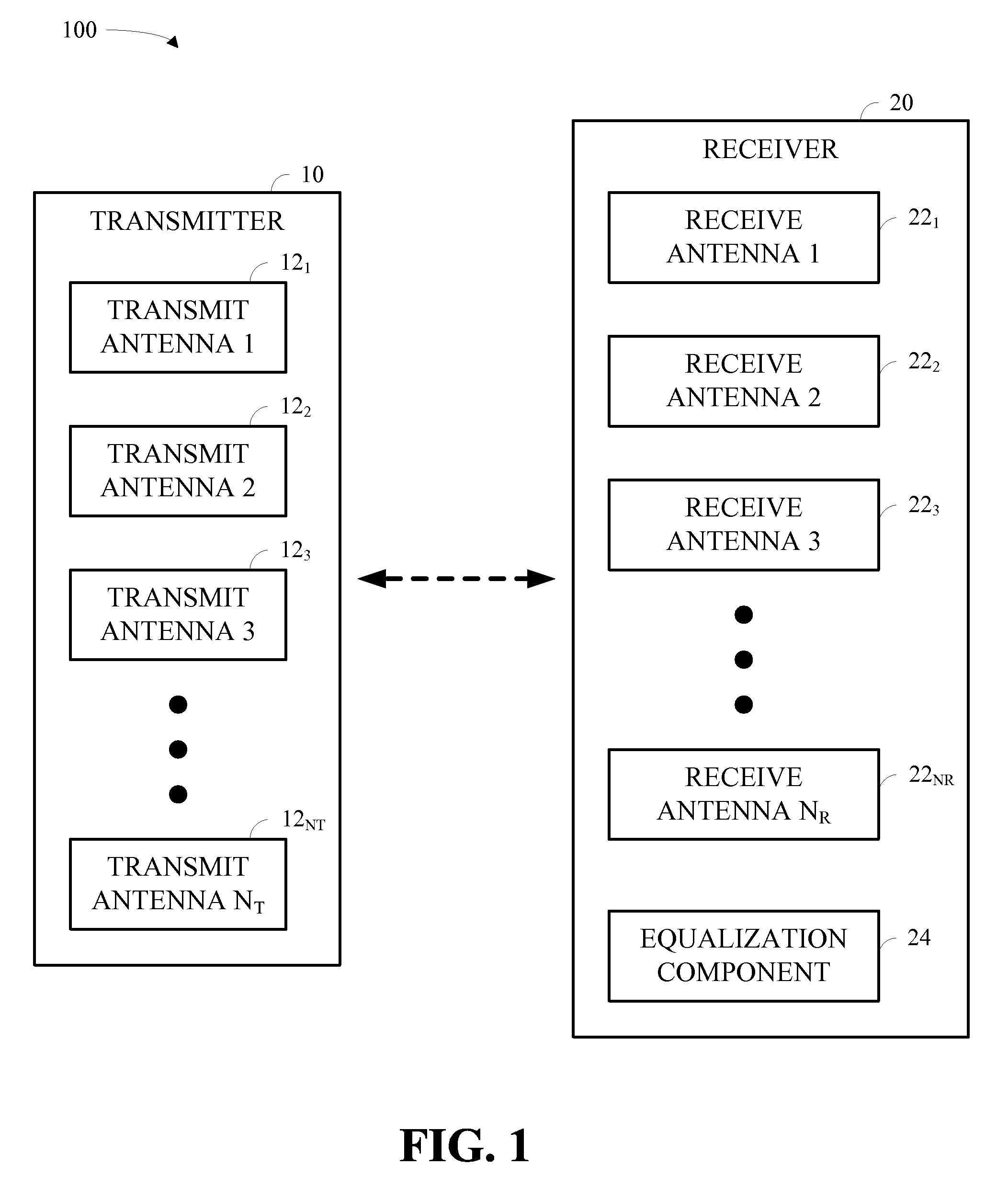
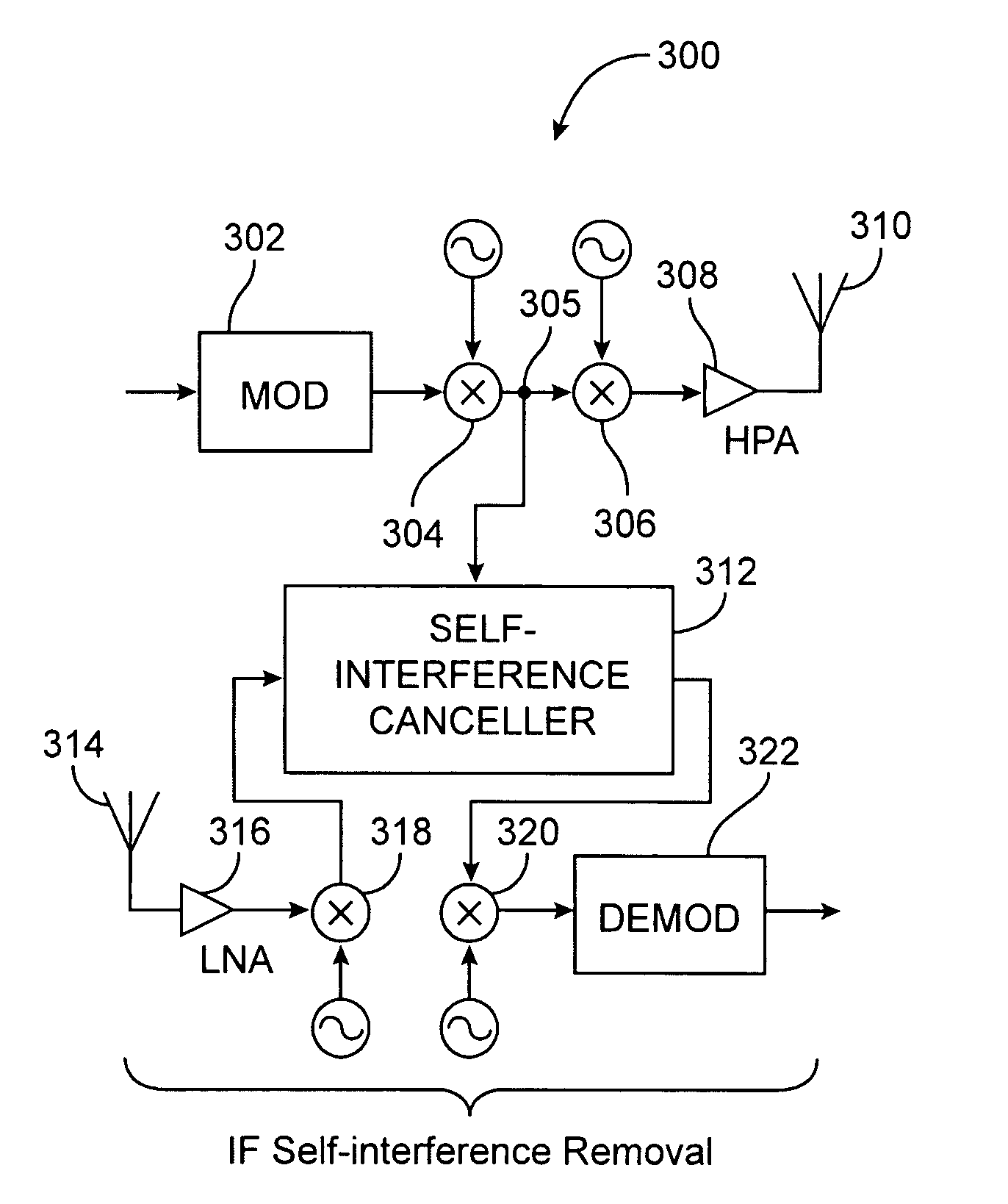
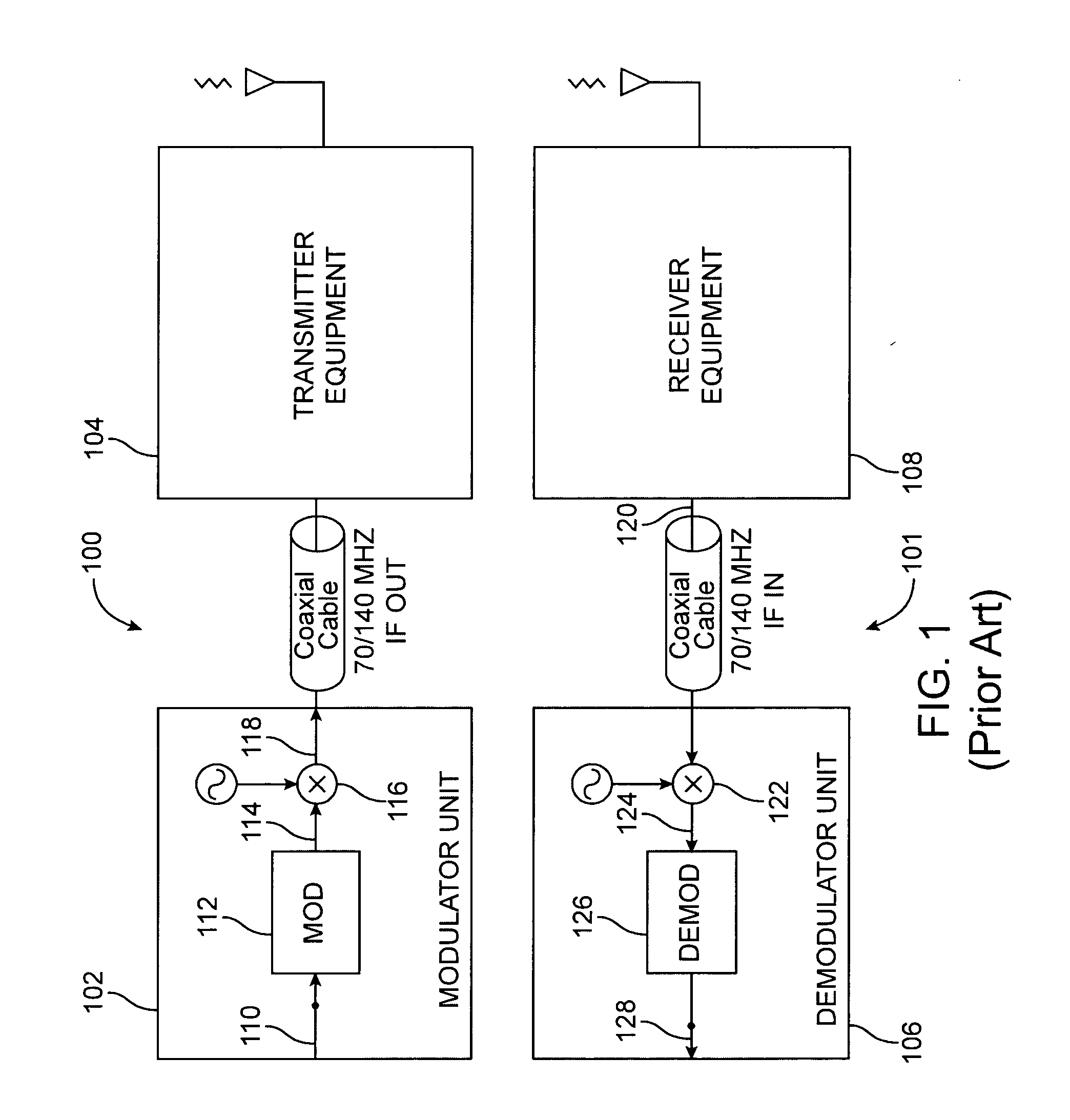
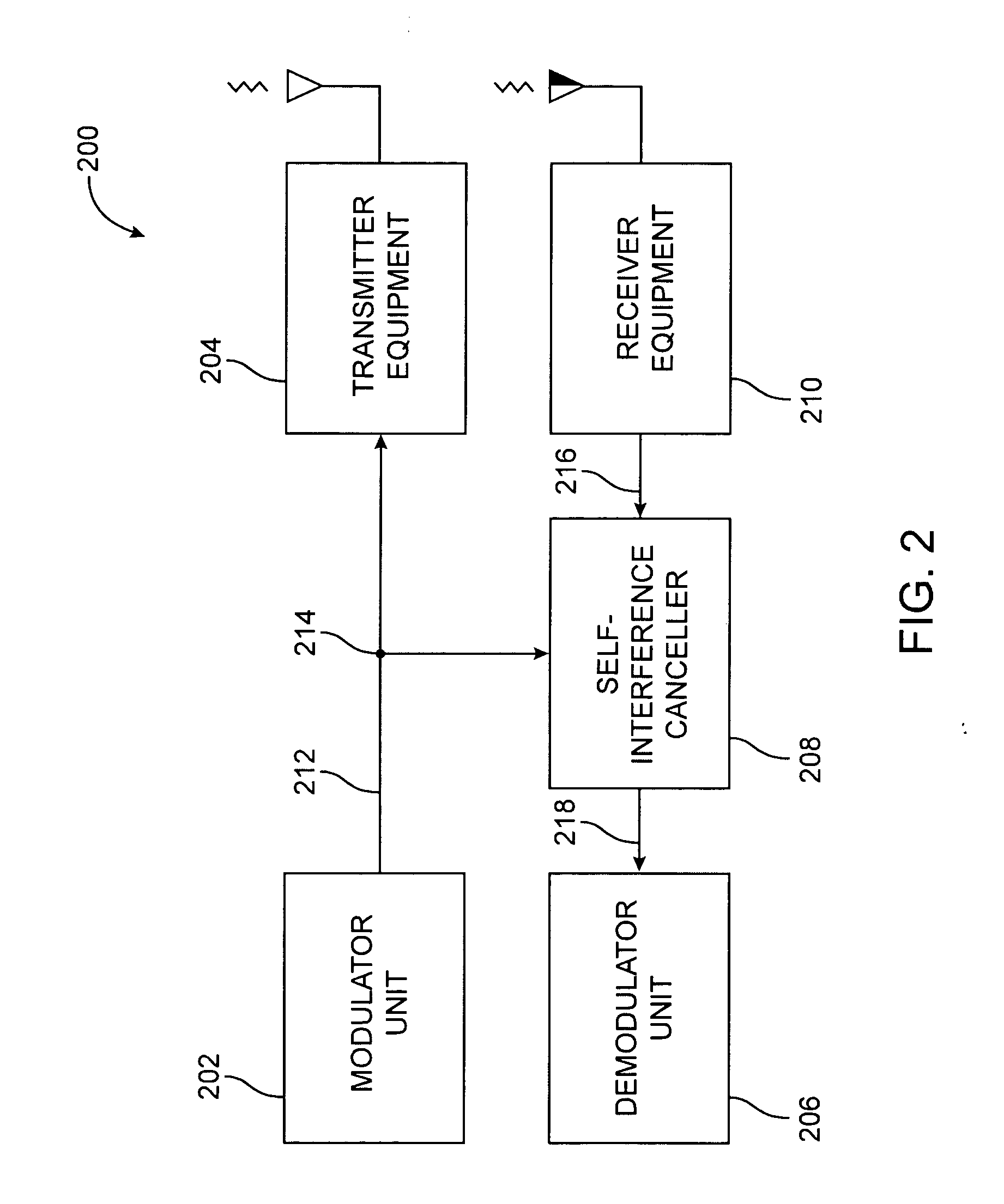
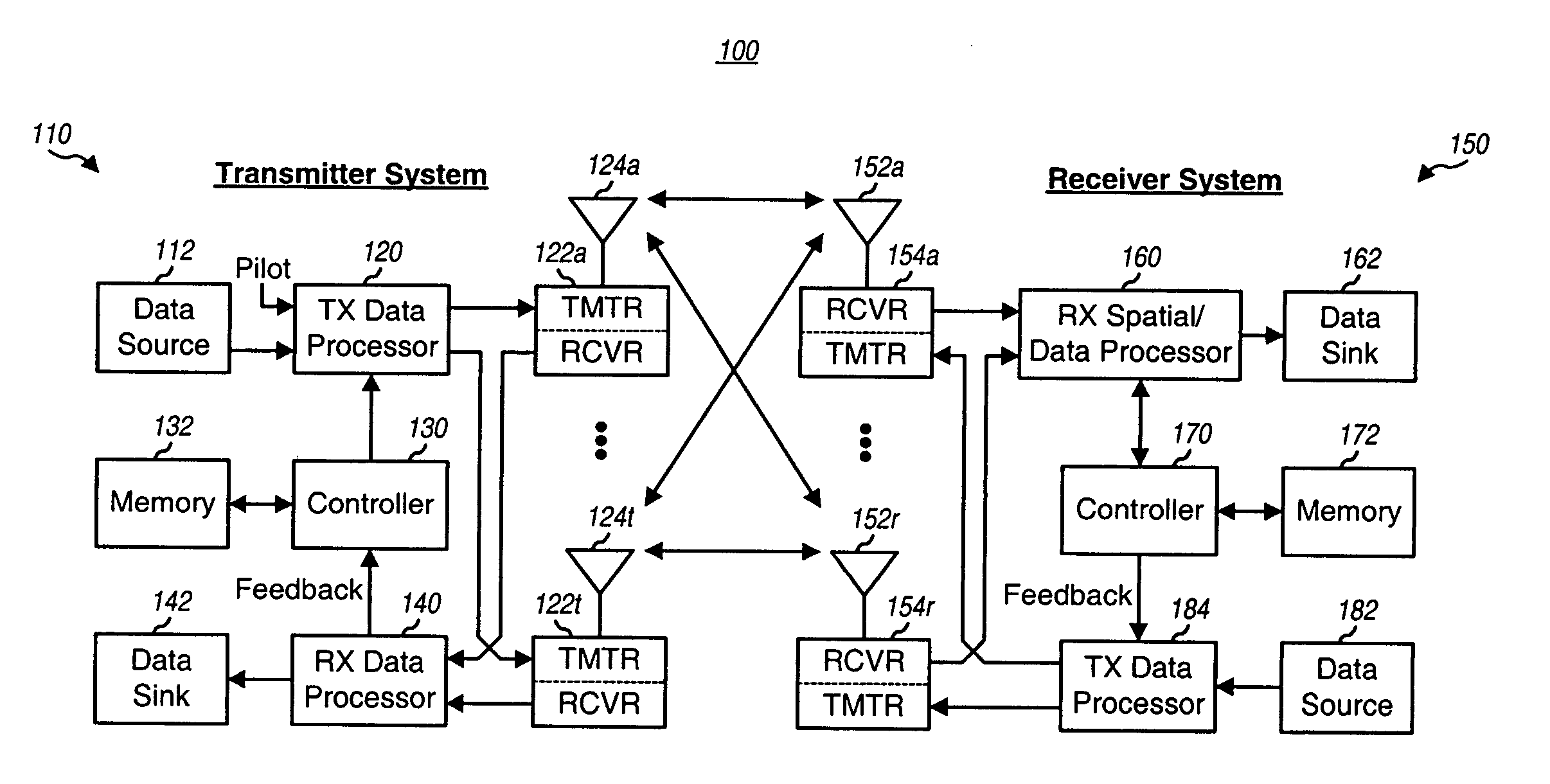
Full Duplex Wireless Transmission with Self-Interference Cancellation
ActiveUS20130301487A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSite diversitySelf interferenceWireless transmission
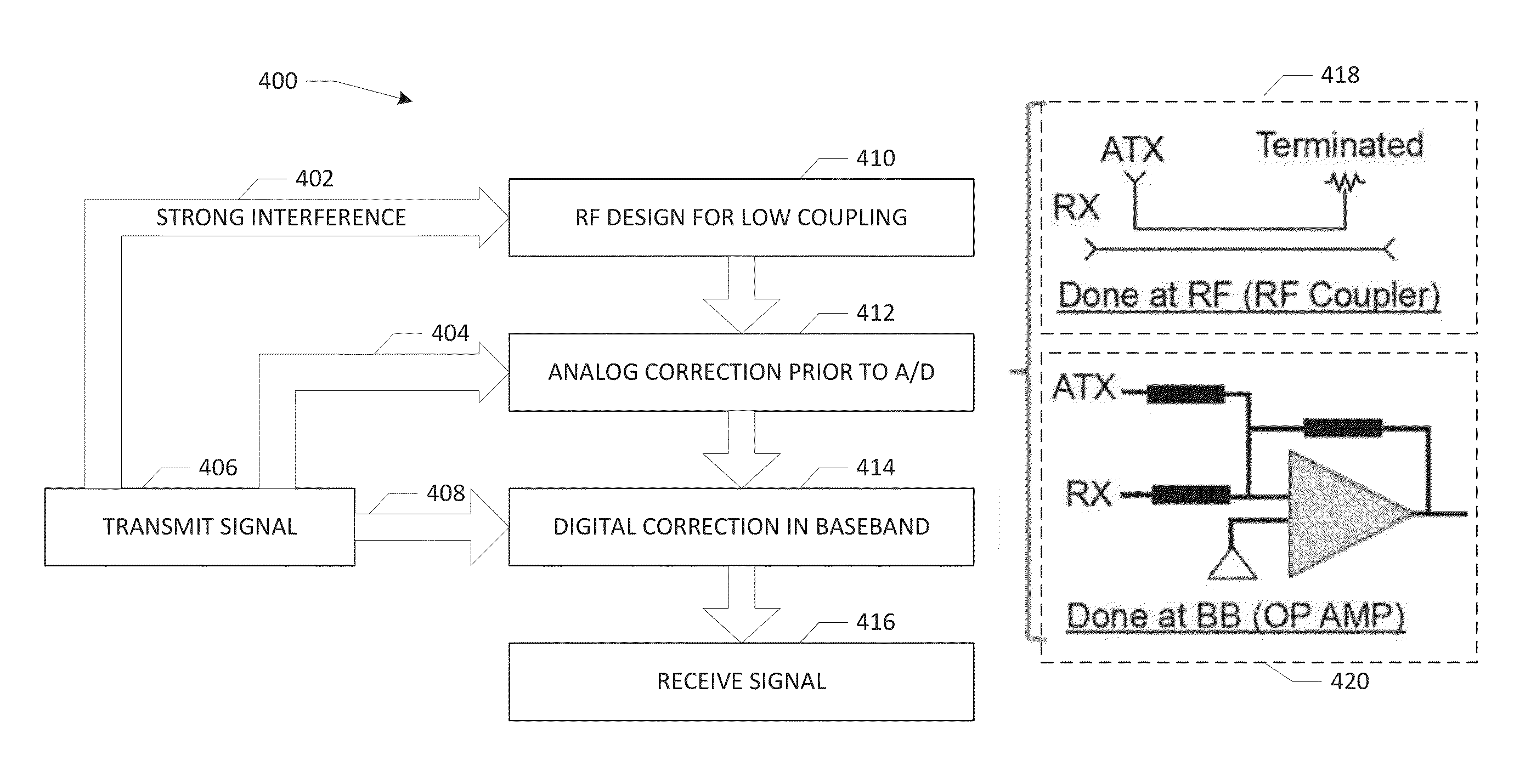
Two-way (full-duplex) wireless communications. Various embodiments measure interference channels and provide for interference cancellation in both analog and digital domains to mitigate self-interference. The system supports multiple clients wherein new clients can join the network asynchronously, and also supports Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) antennas.
Owner:KHANDANI AMIR KEYVAN
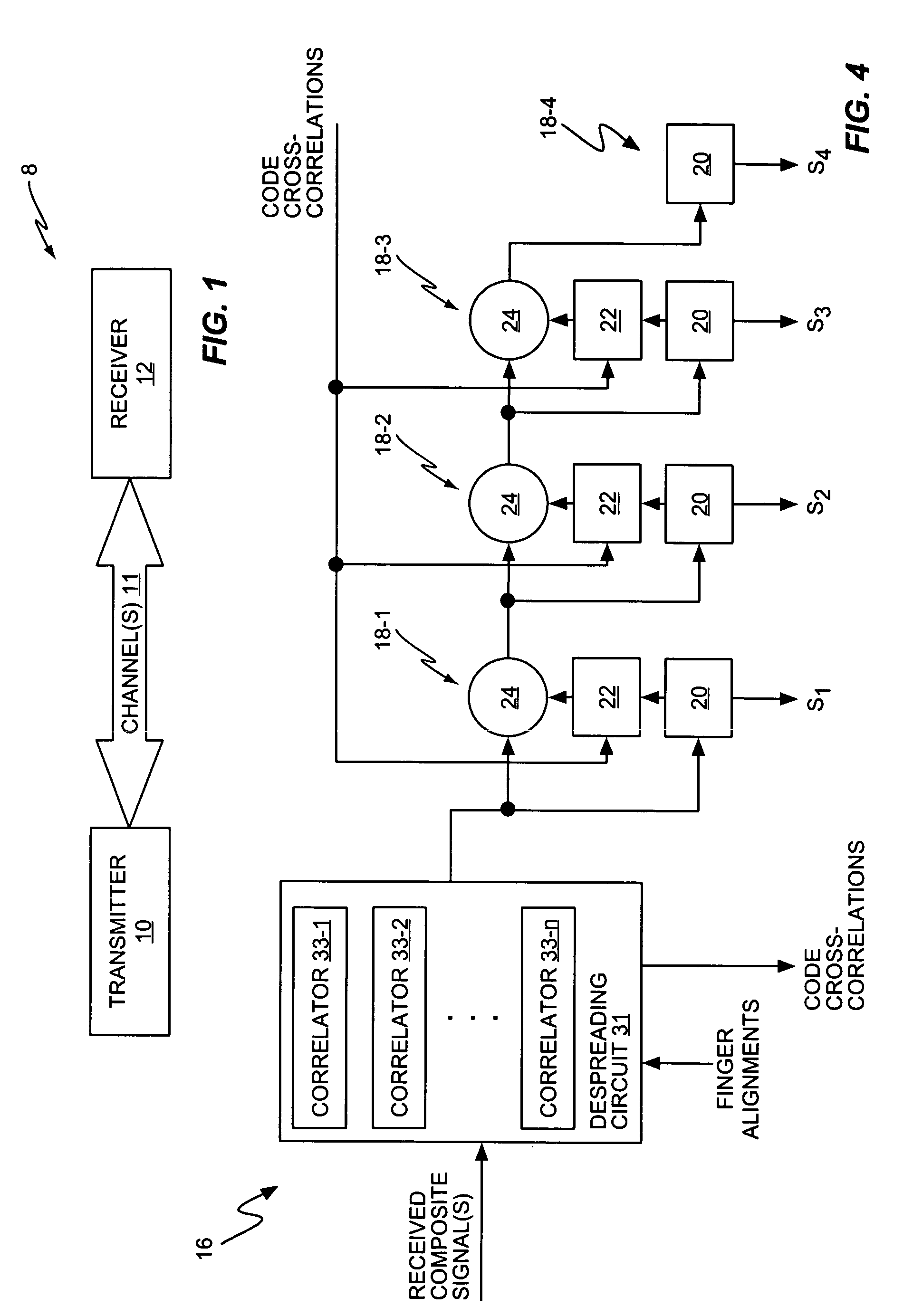
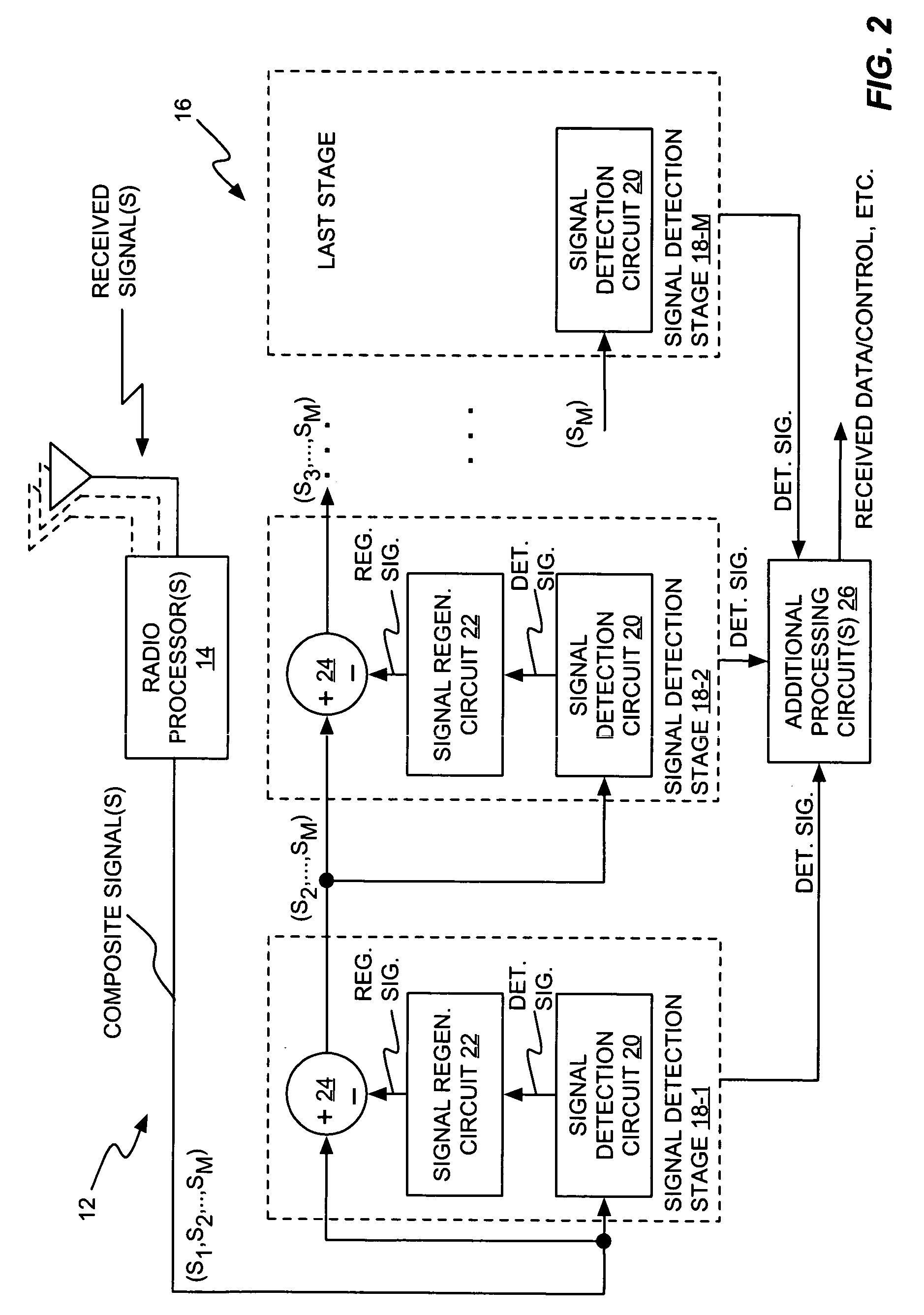
Successive interference cancellation in a generalized RAKE receiver architecture
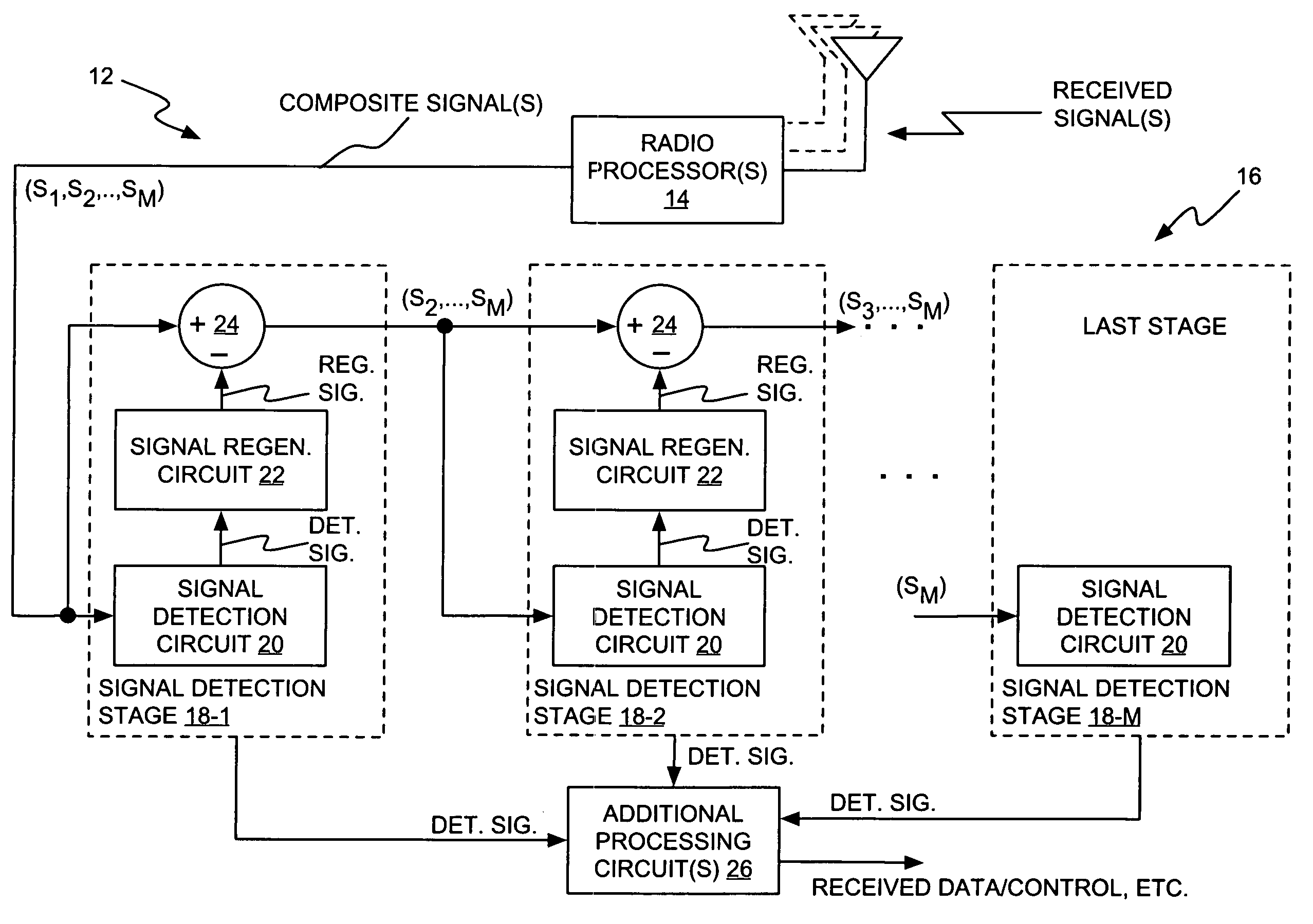
A receiver includes a receiver circuit that decodes multiple signals of interest contained in a composite received signal. The receiver comprises a plurality of successive signal detection stages to detect respective signals contained in the composite received signal. Each detection circuit comprises at least one Generalized RAKE combining circuit and generates a detected signal at an output. Each but the last stage further comprises a signal regeneration circuit that cancels the signal of interest detected by that stage from a stage input signal provided to the next stage such that successive detection of the signals of interest benefits from cumulative cancellation of the previously detected signals.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
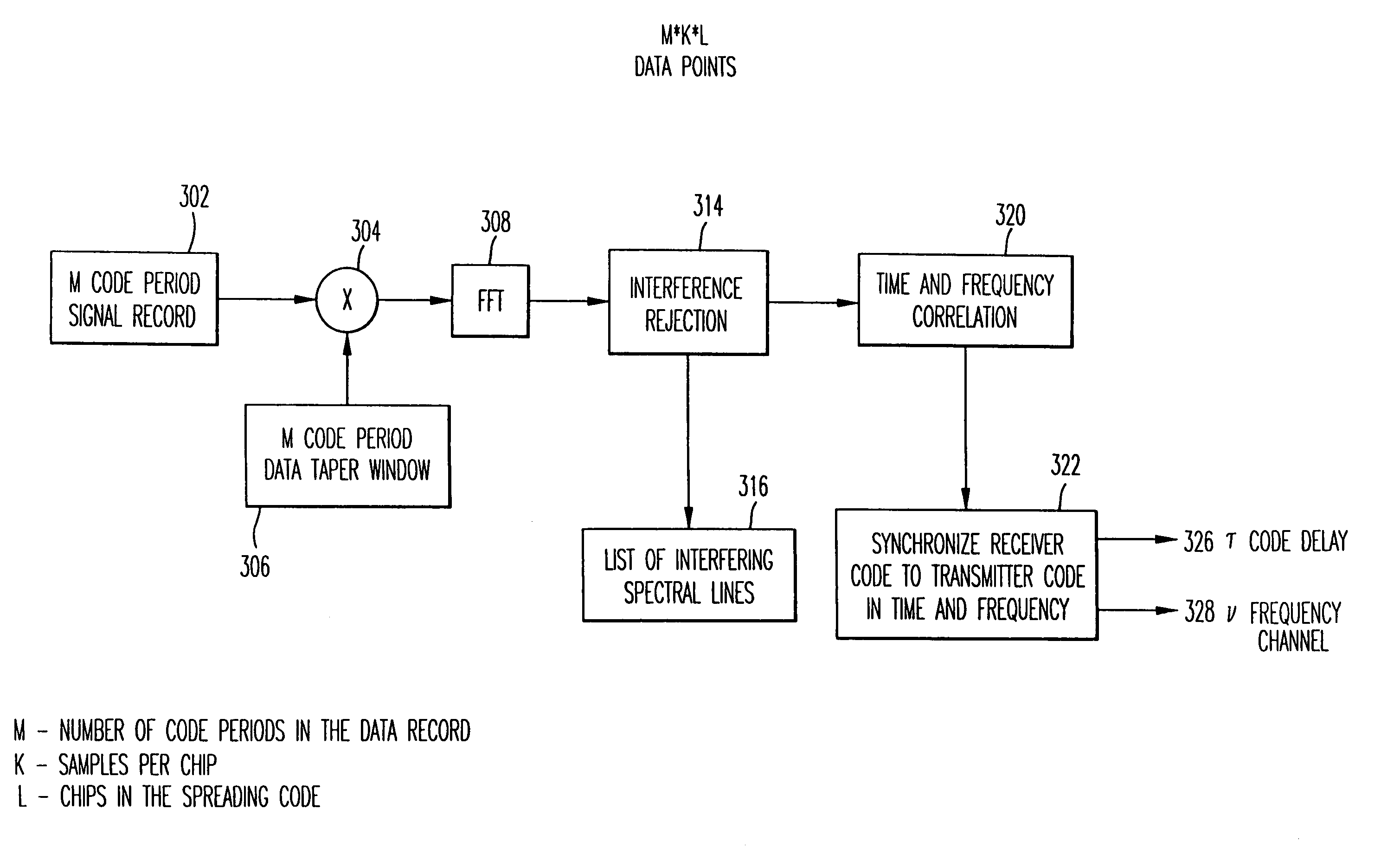
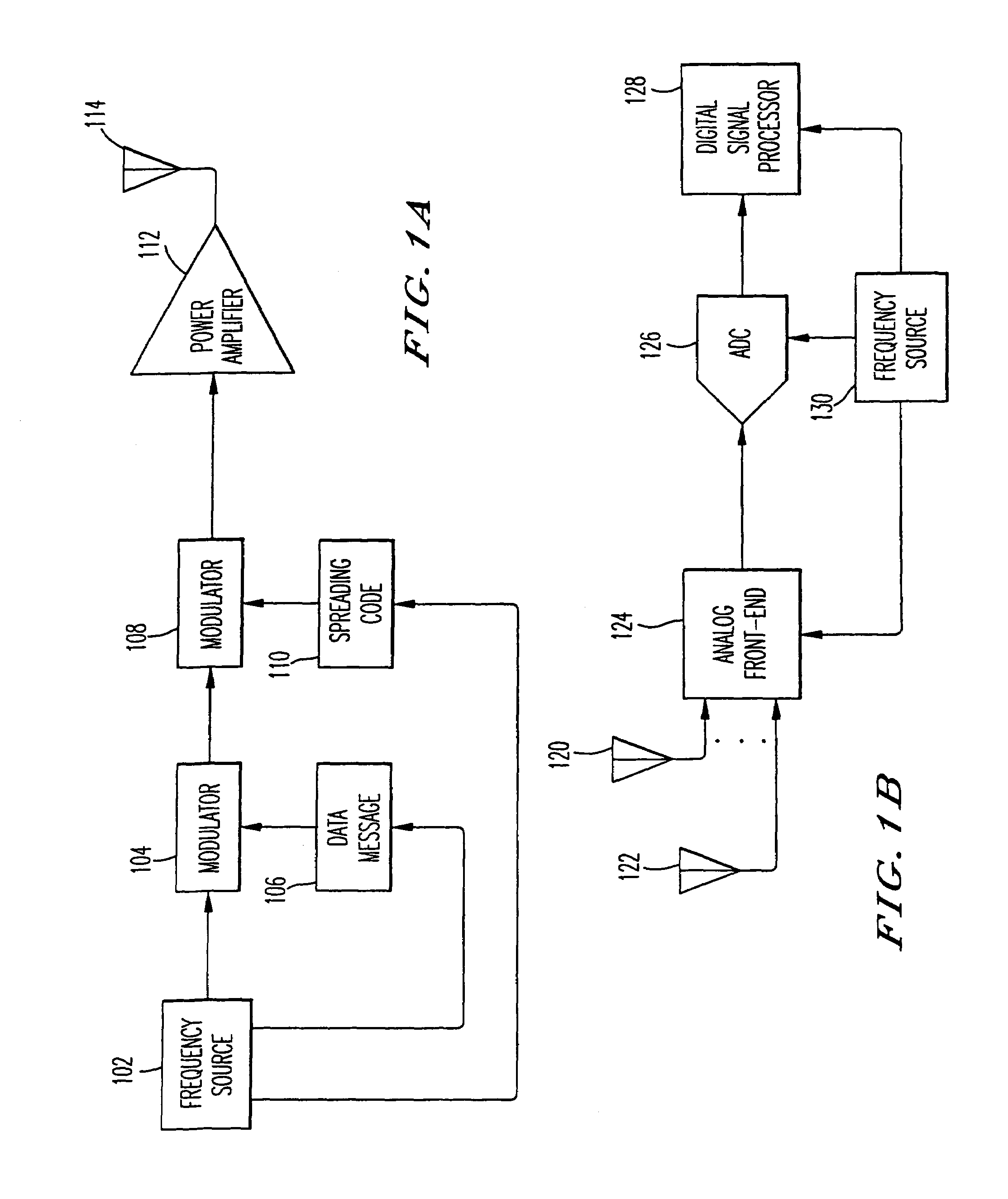
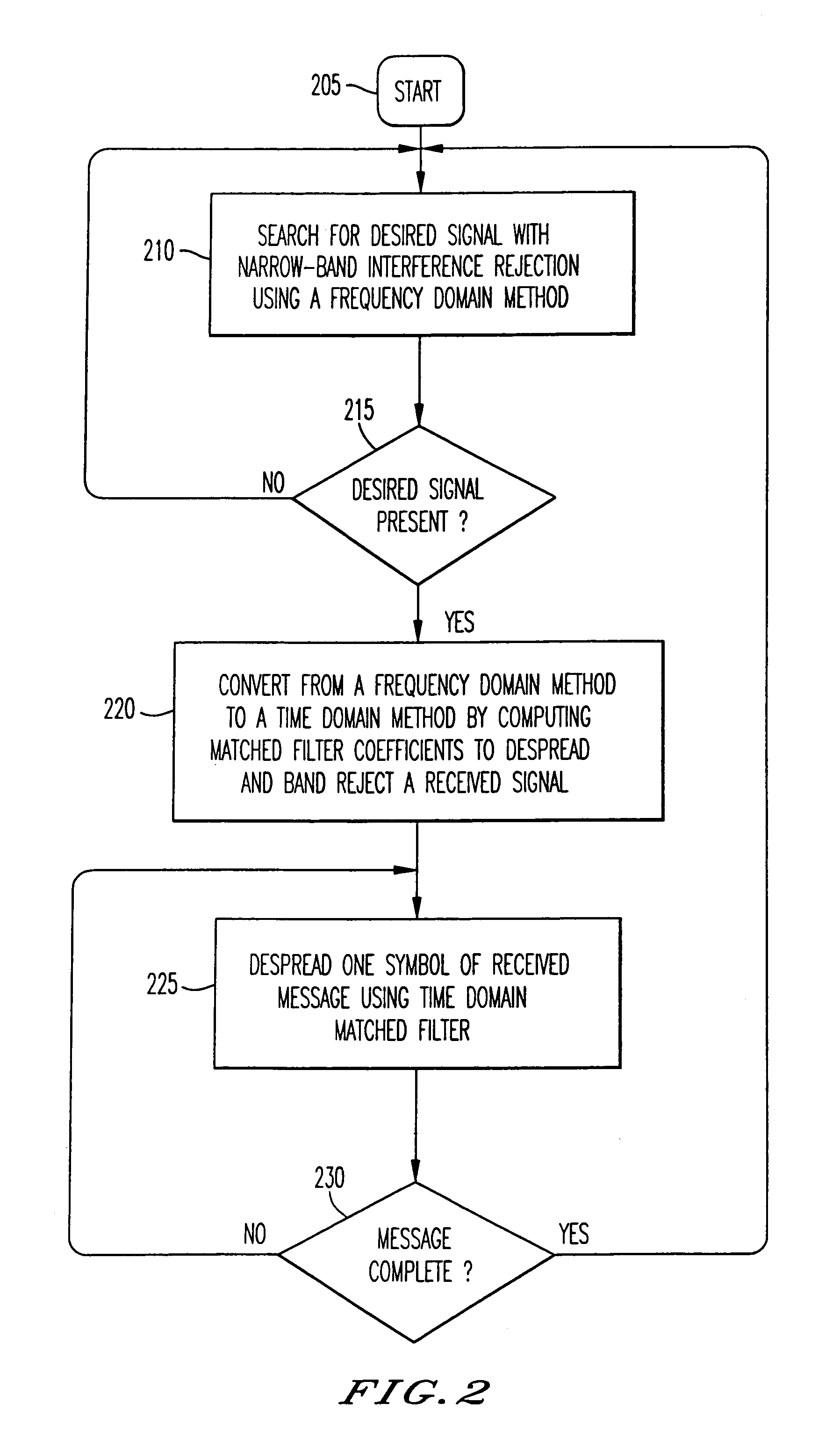
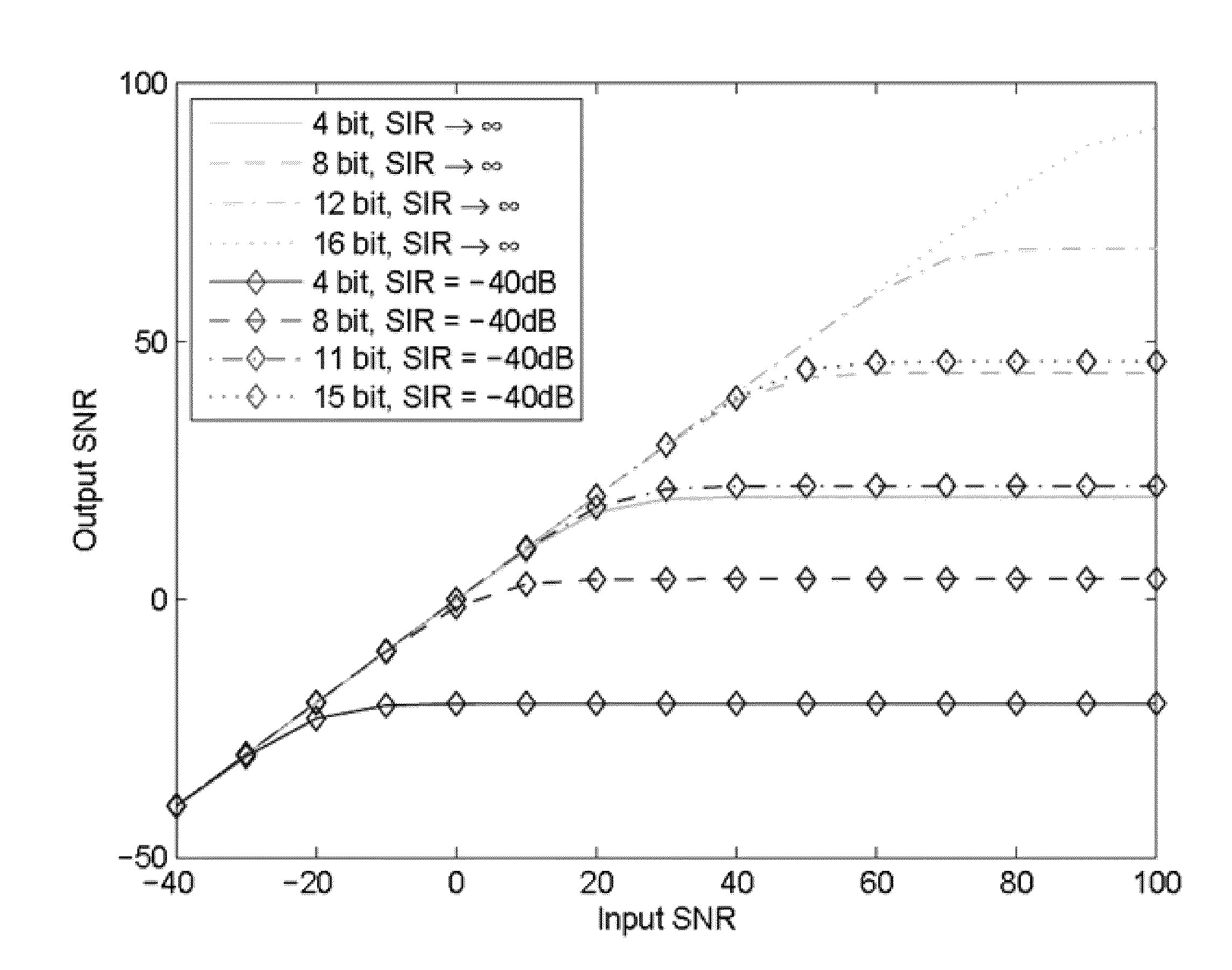
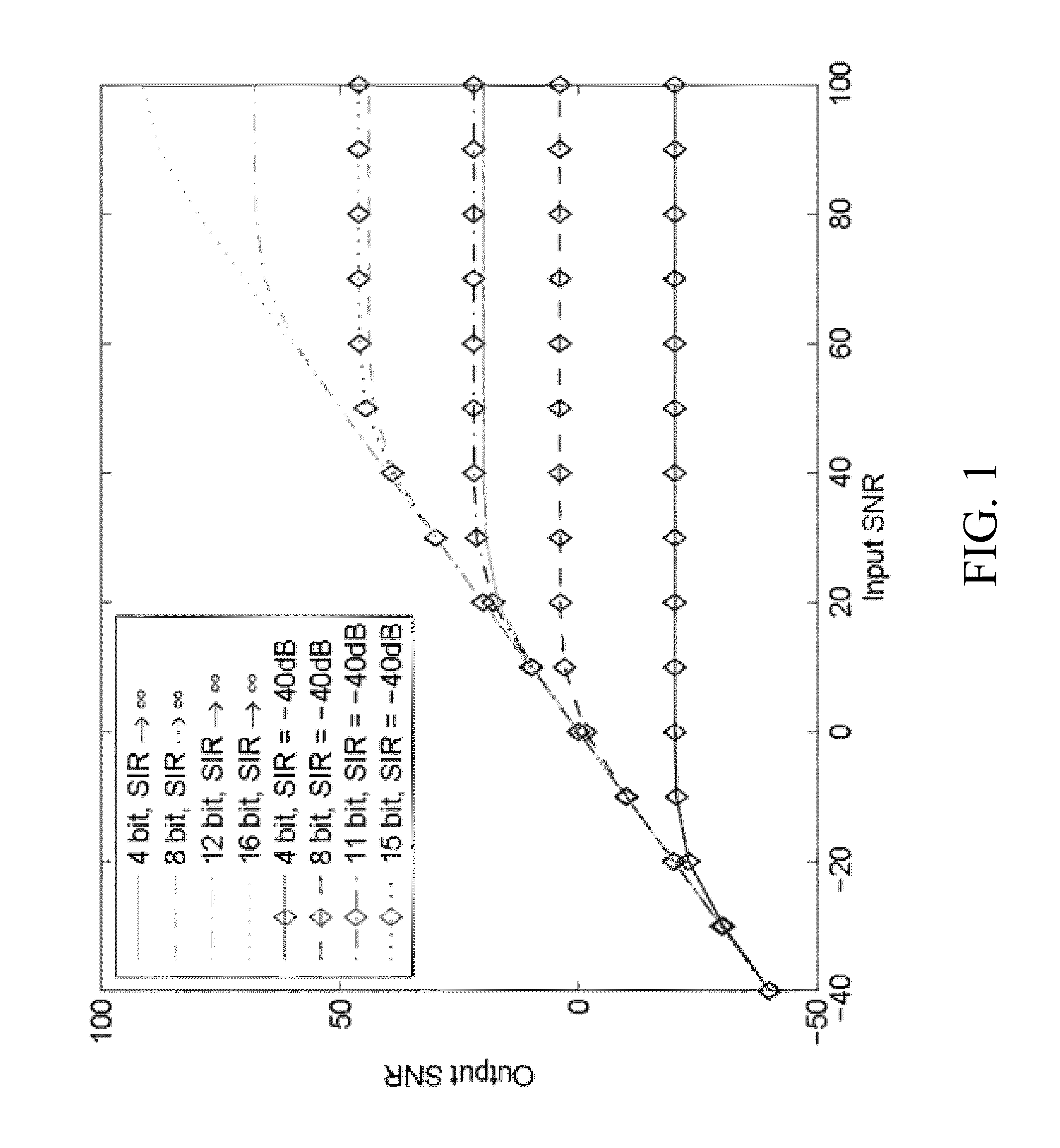
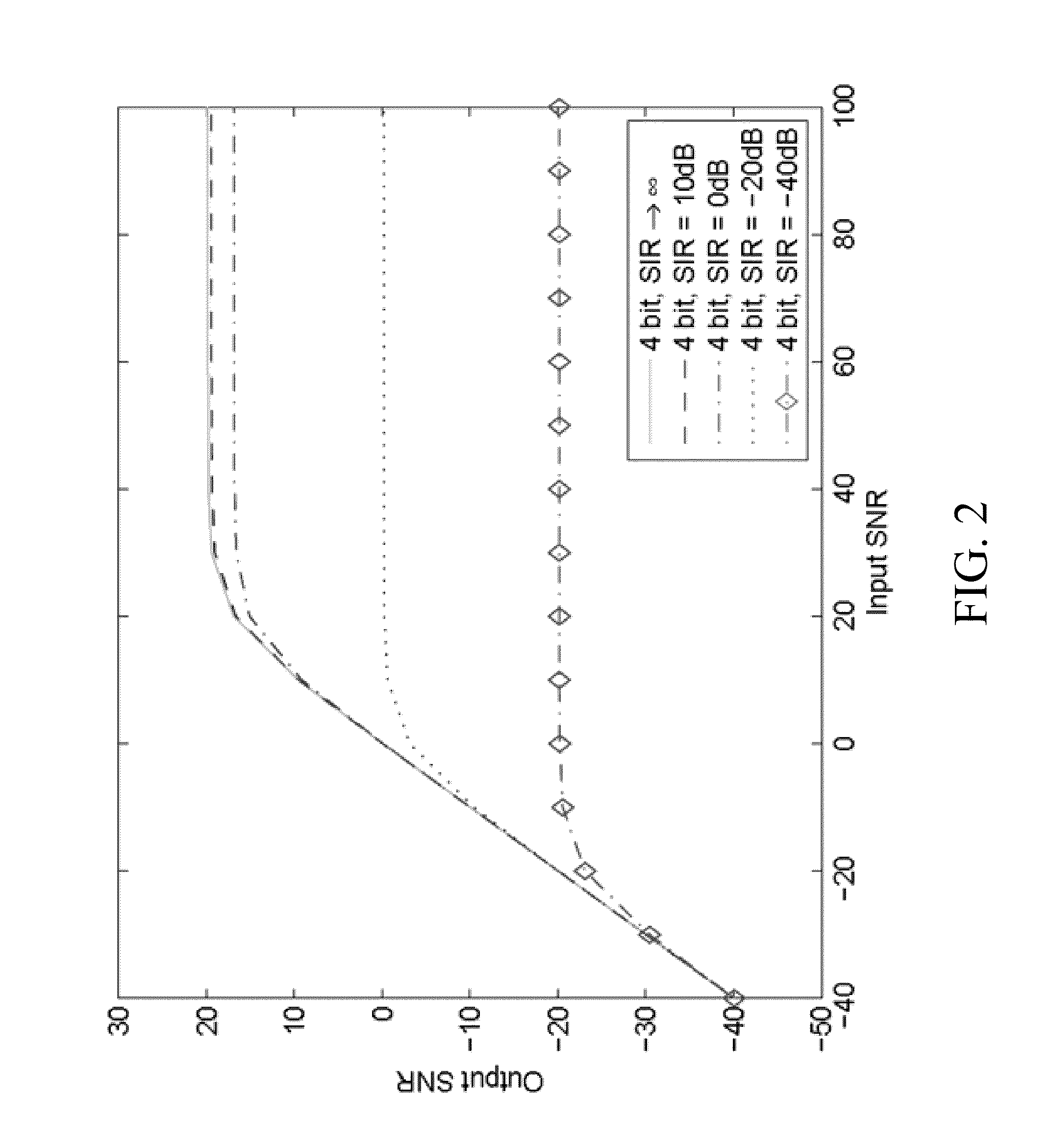
Narrow-band interference rejecting spread spectrum radio system and method
InactiveUS6975673B1Decrease requiredReduced computing resourceFrequency-modulated carrier systemsCommunication jammingTime domainDigital signal processing
A spread spectrum receiver and method having narrow-band interference rejection of narrow-band jamming signals using digital signal processing frequency domain techniques. The method performed in the receiver includes transforming the received signal to a frequency domain signal and identifying narrow-band interference components in the frequency domain signal; suppressing the identified narrow-band interference components by excising the identified narrow-band interference components from the frequency domain signal to produce an interference excised signal in the frequency domain, and storing in a memory frequencies corresponding to the identified narrow-band interference components; synchronizing a receiver code to a transmitter code in the frequency domain using the interference excised signal; generating coefficients for a time domain filter that includes notches at the frequencies corresponding to the excised narrow-band interference components and that jointly despreads and rejects narrow-band interference from the excised frequencies; applying the coefficients generated in the preceding step to the time domain filter, and despreading and filtering in real time in the time domain the received signal using the applied coefficients.
Owner:SENSUS SPECTRUM LLC
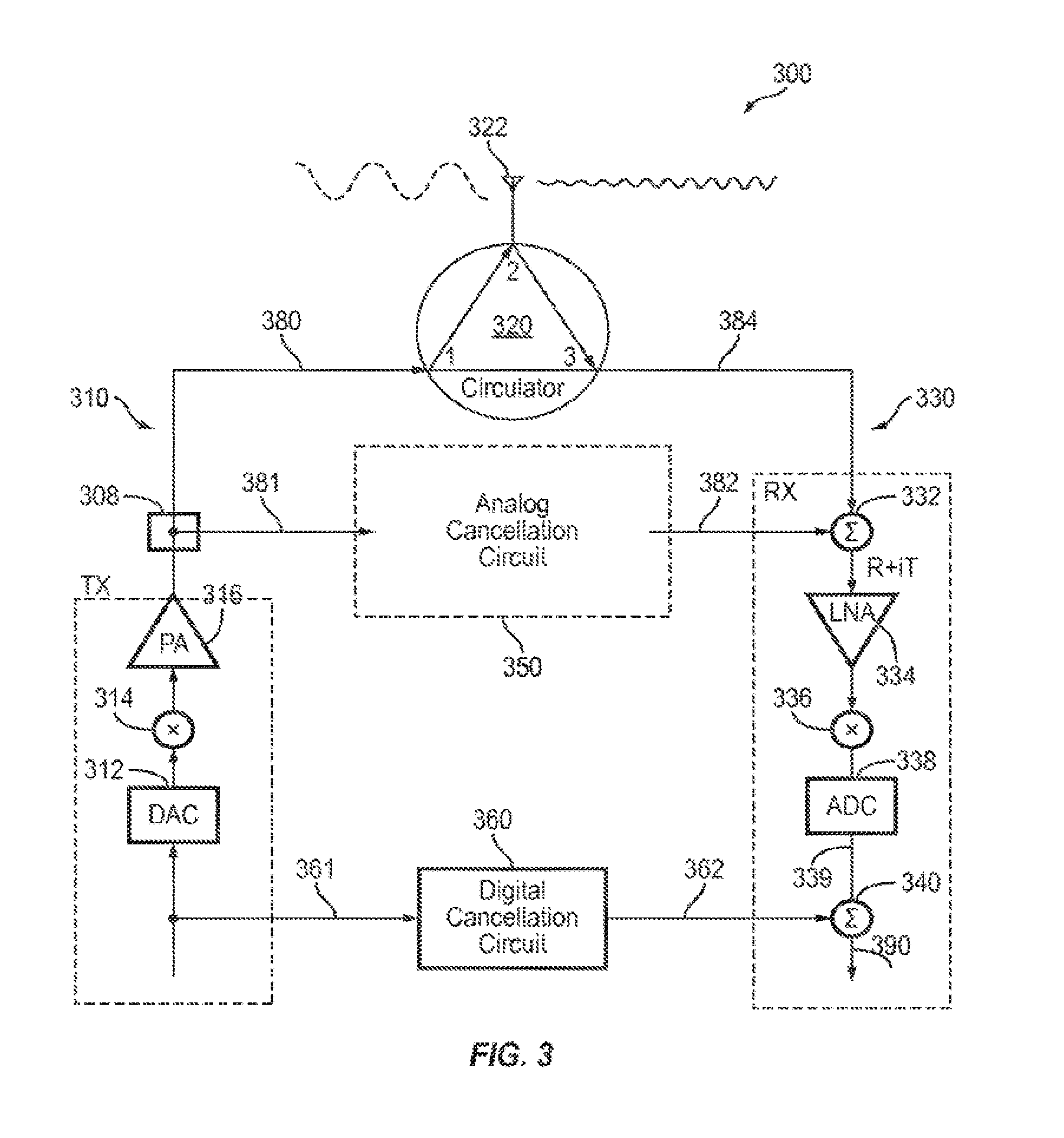
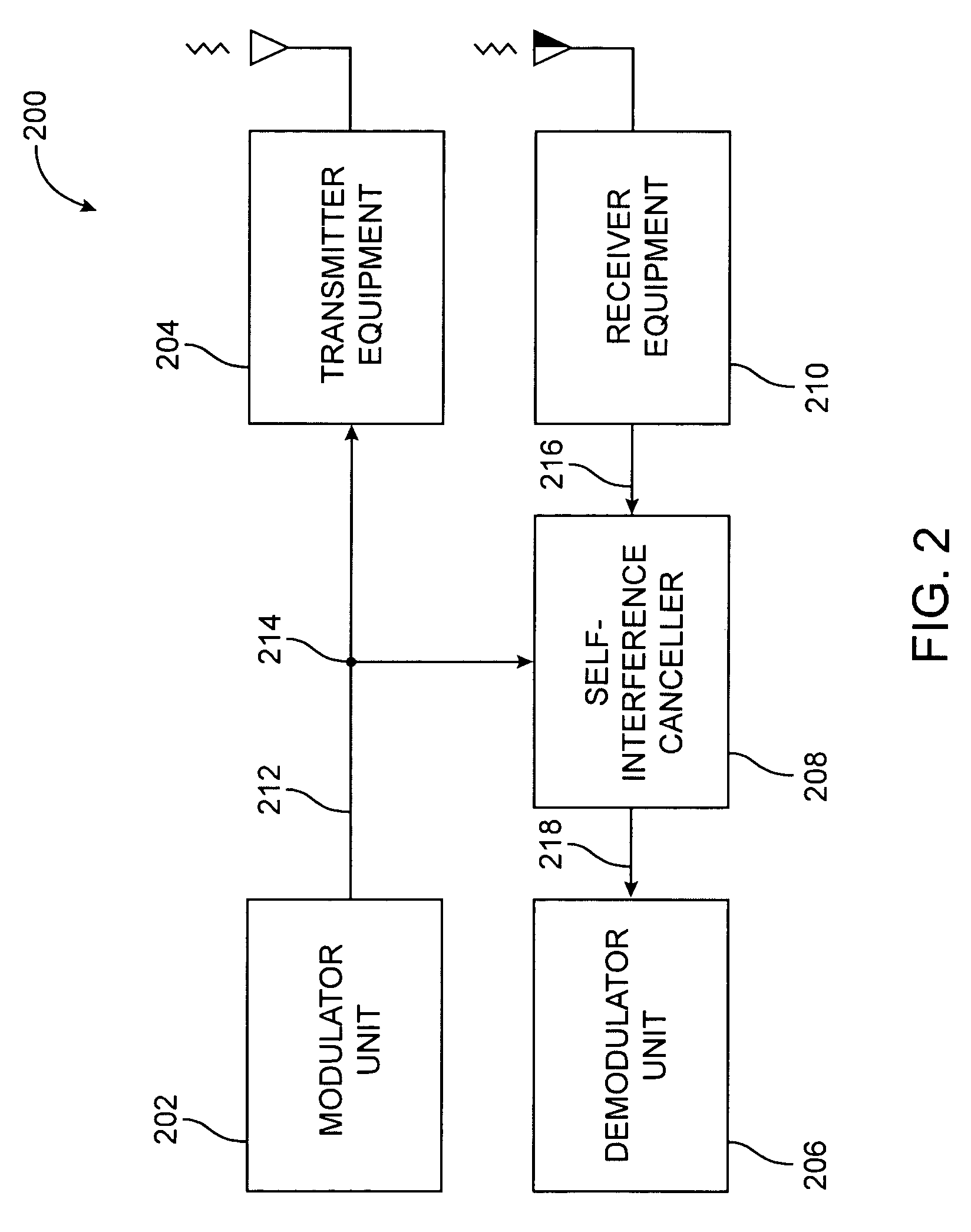
Interference Cancellation for Full-Duplex Communications
ActiveUS20130286903A1Modulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexAudio power amplifierAutomatic control
A communications apparatus used in a wireless full duplex system is disclosed. The communications apparatus includes a receiver chain connected to an antenna and an interference cancelling chain. One or more cancellation signals generated by the interference cancelling chain are fed back to the receiver chain prior to the first baseband amplifier which uses the first automatic gain control and the second automatic gain controller. Other methods and systems also are disclosed.
Owner:NEC CORP
Self-interference cancellation for MIMO radios
ActiveUS20160226653A1Spatial transmit diversityCarrier regulationSelf interferenceInterference cancelation
A MIMO wireless communication device includes, in part, a first transmit path adapted to transmit a first transmit signal from a first antenna, a second transmit path adapted to transmit a second transmit signal from a second antenna, a first receive path adapted to receive a first receive signal, an interference cancellation circuit and a controller. The cancellation circuit includes a cascaded filter structure each filter including a multitude of filter taps each including a variable element. The controller dynamically varies a value applied to each of the plurality of variable elements in accordance with frequency response characteristics of the variable element to remove a portion of a self-interference and / or cross-talk interference signal present in a signal received by the device. The device measures the frequency response characteristic of a multitude of communication channels, used in determining the values, via one or more preanible symbols that are jointly transmitted from the first transmit antenna and the second transmit antenna. A second portion of the interference signal is removed by a digital cancellation circuit using a multitude of samples of a transmitted signal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
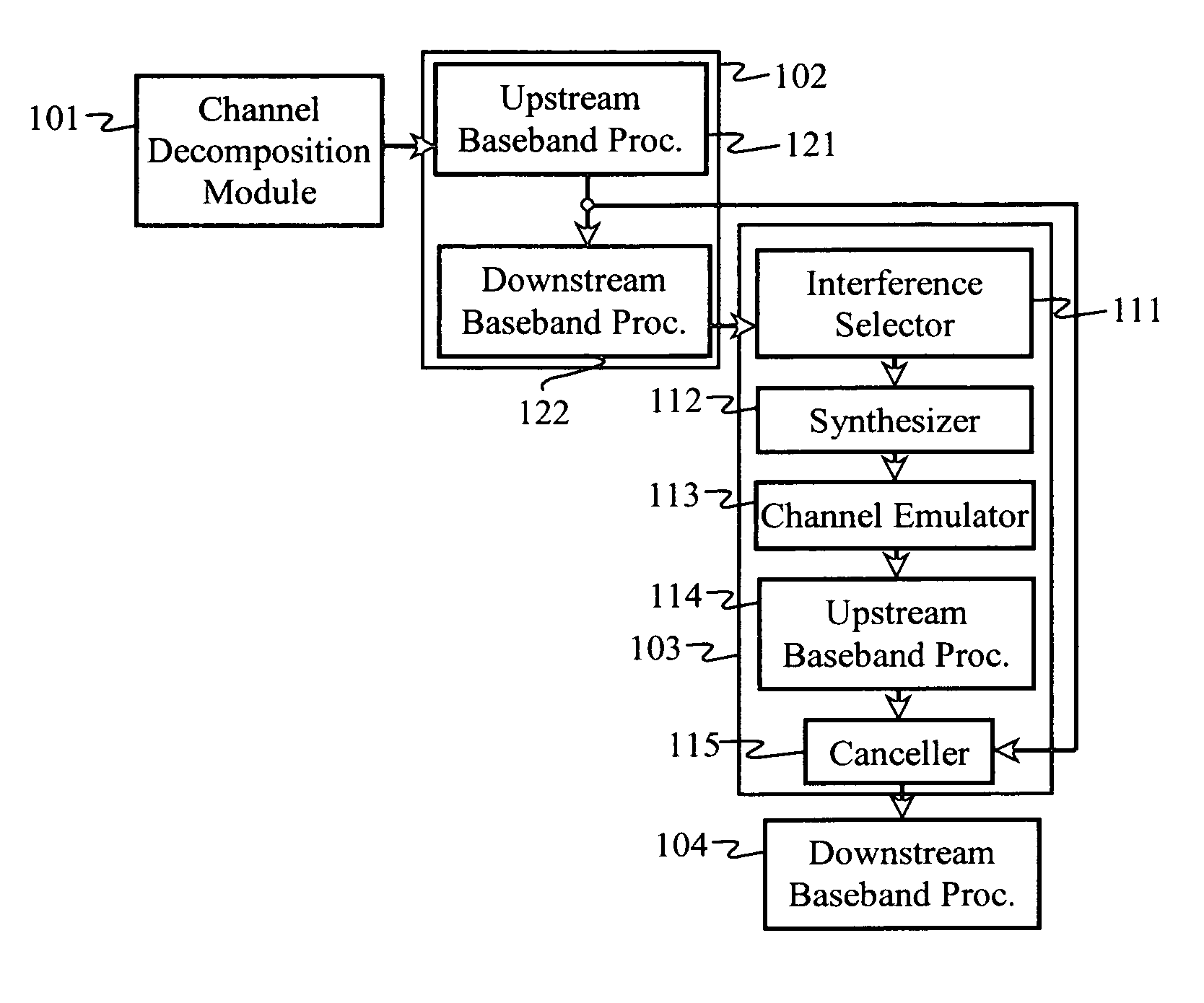
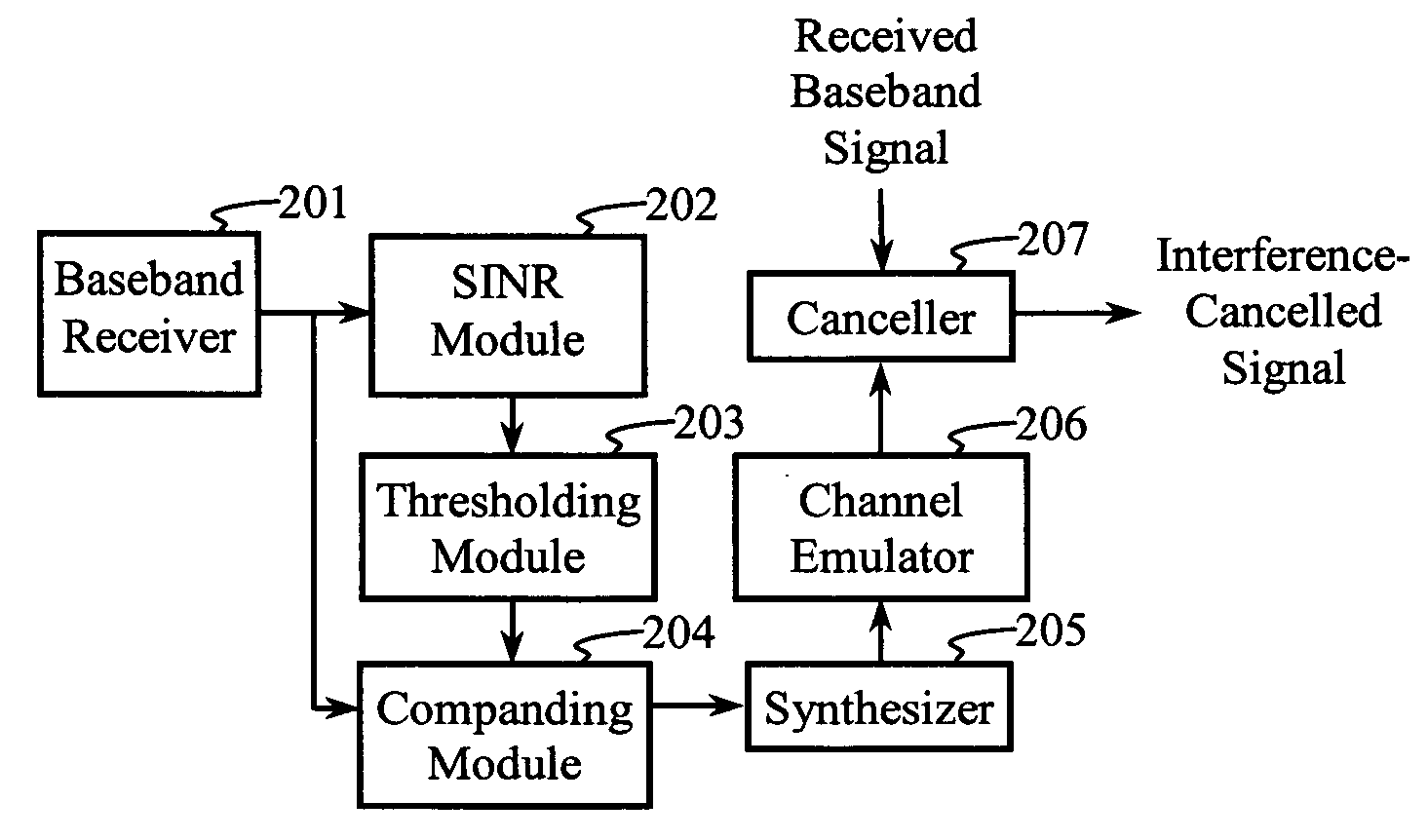
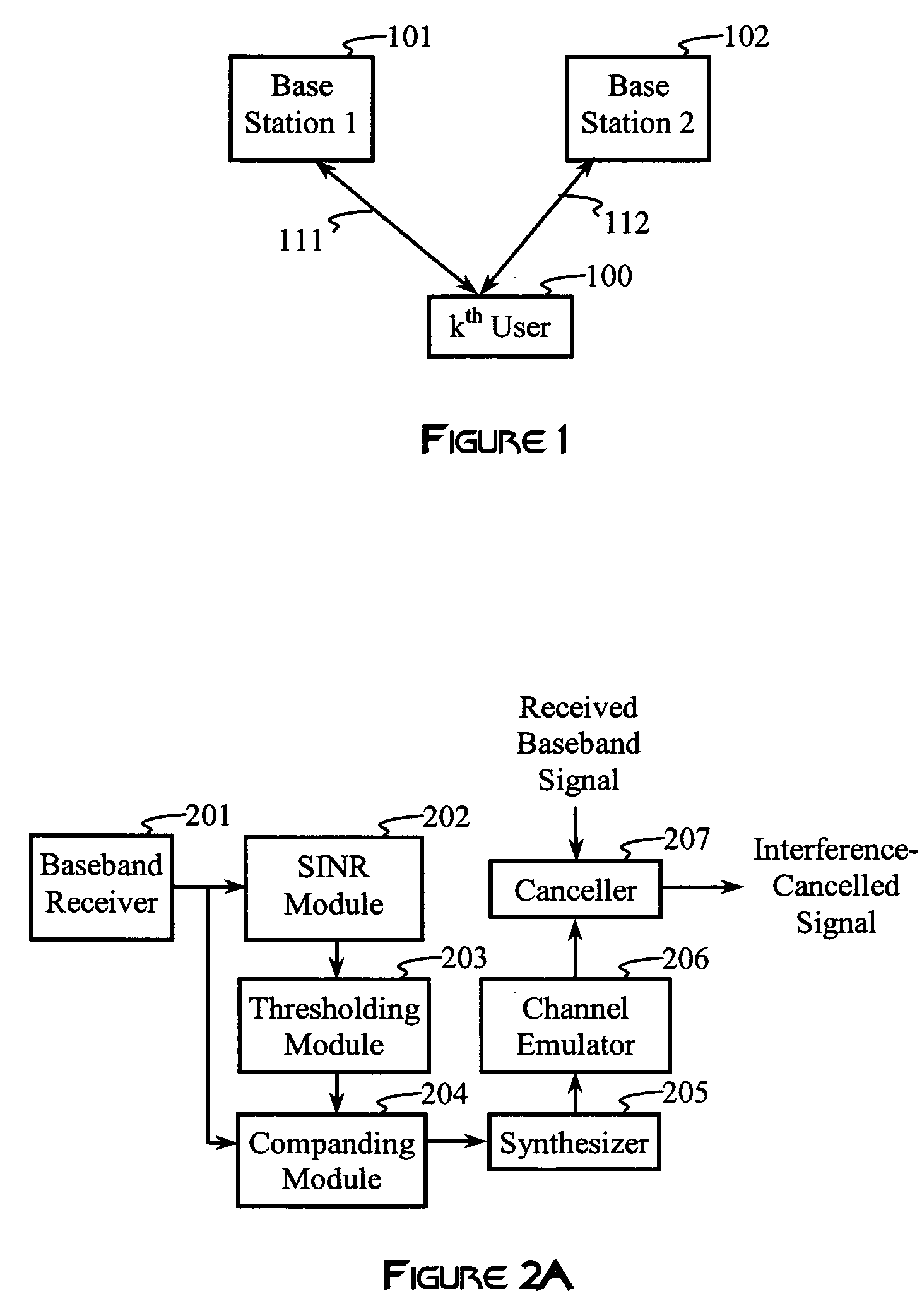
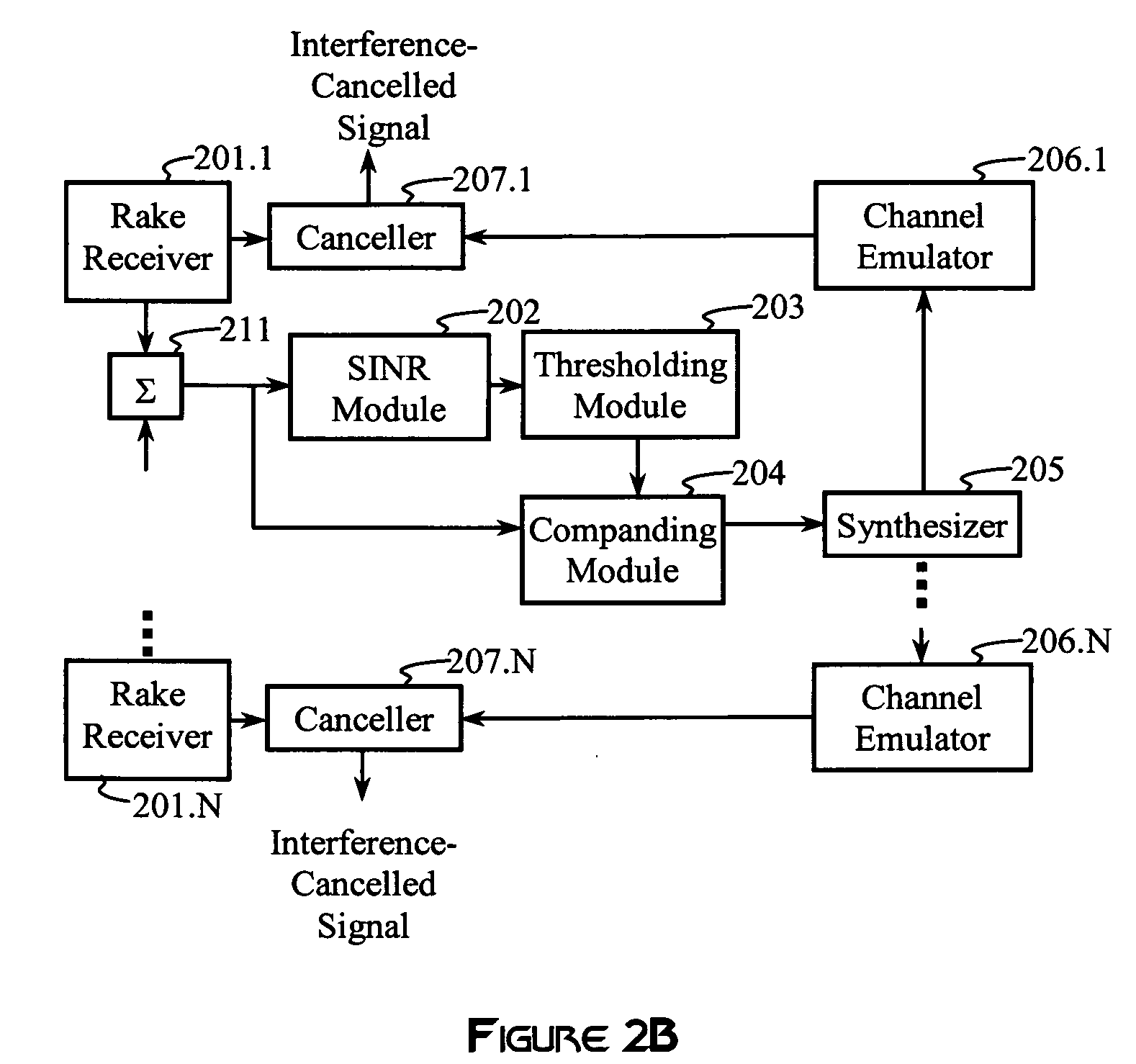
Advanced signal processors for interference cancellation in baseband receivers
ActiveUS7787572B2Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionInterference cancelationInterference canceller
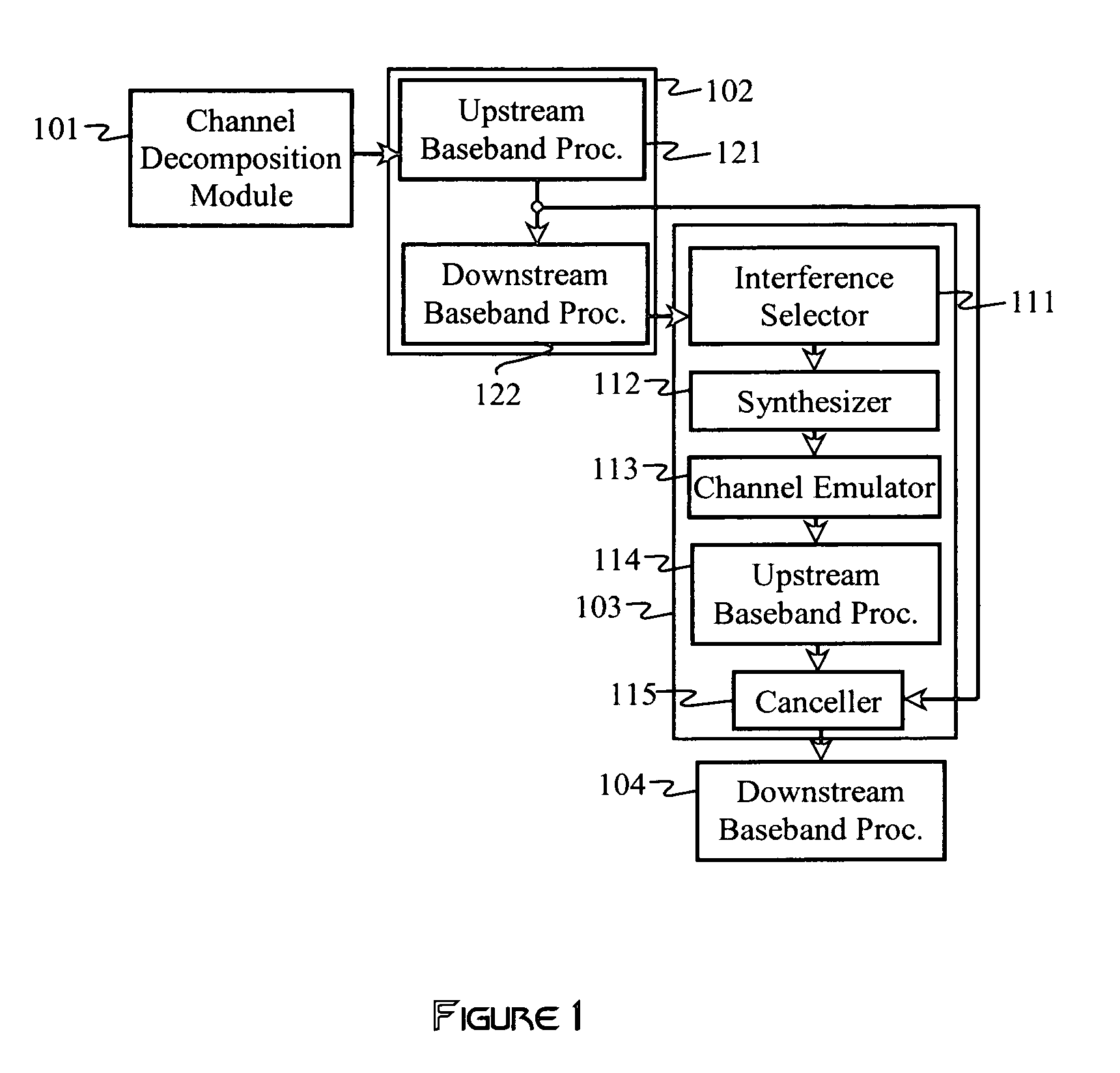
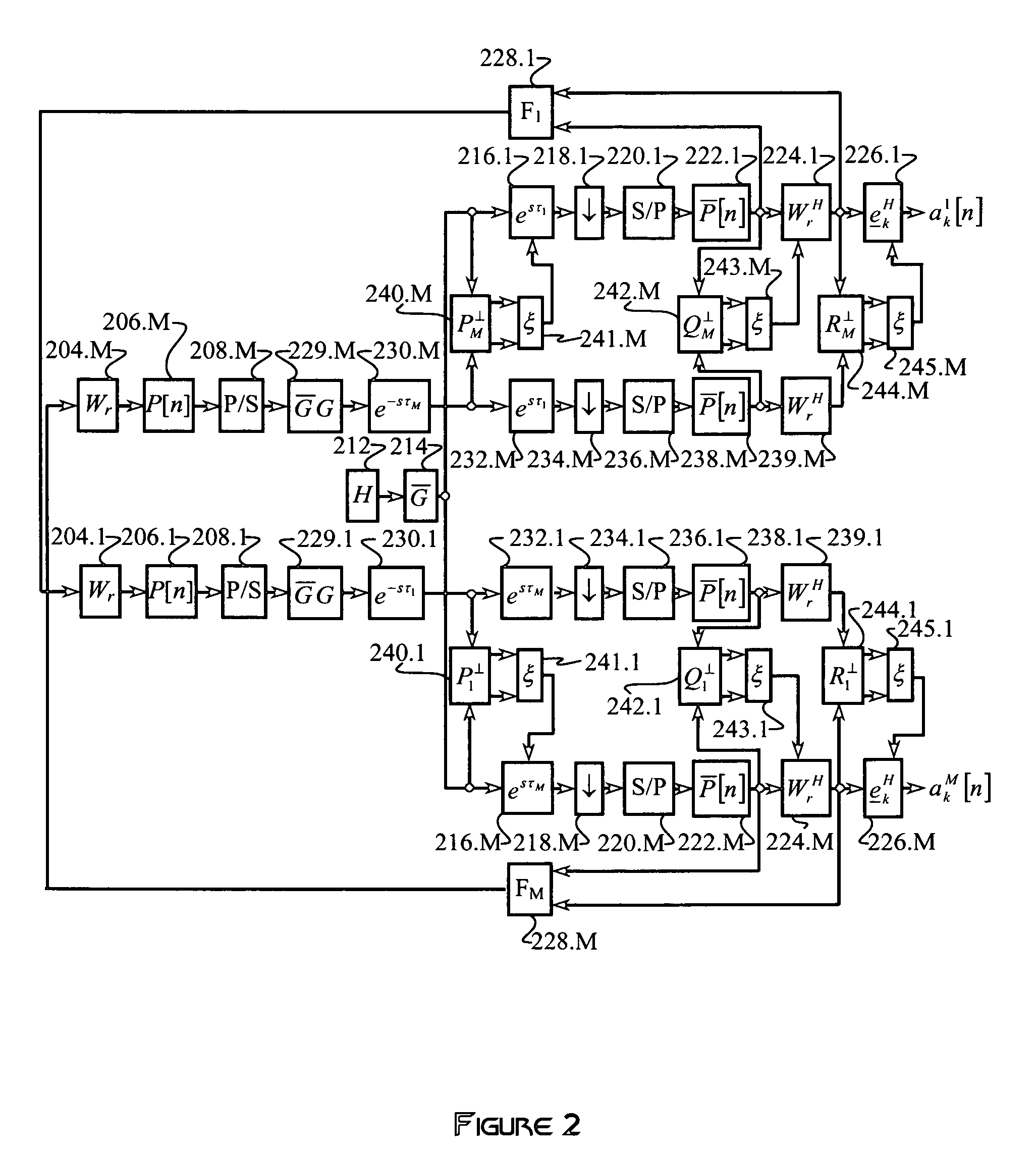
A multi-mode receiver includes a channel decomposition module (e.g., a Rake receiver) for separating a received signal into multipath components, an interference selector for selecting interfering paths and subchannels, a synthesizer for synthesizing interference signals from selected subchannel symbol estimates, and an interference canceller for cancelling selected interference in the received signal. At least one of the channel decomposition module, the synthesizer, and the interference canceller are configurable for processing multi-mode signals.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Apparatus and method for interference cancellation and synchronization maintenance over interference channel estimation in communication system based on full-duplex relay
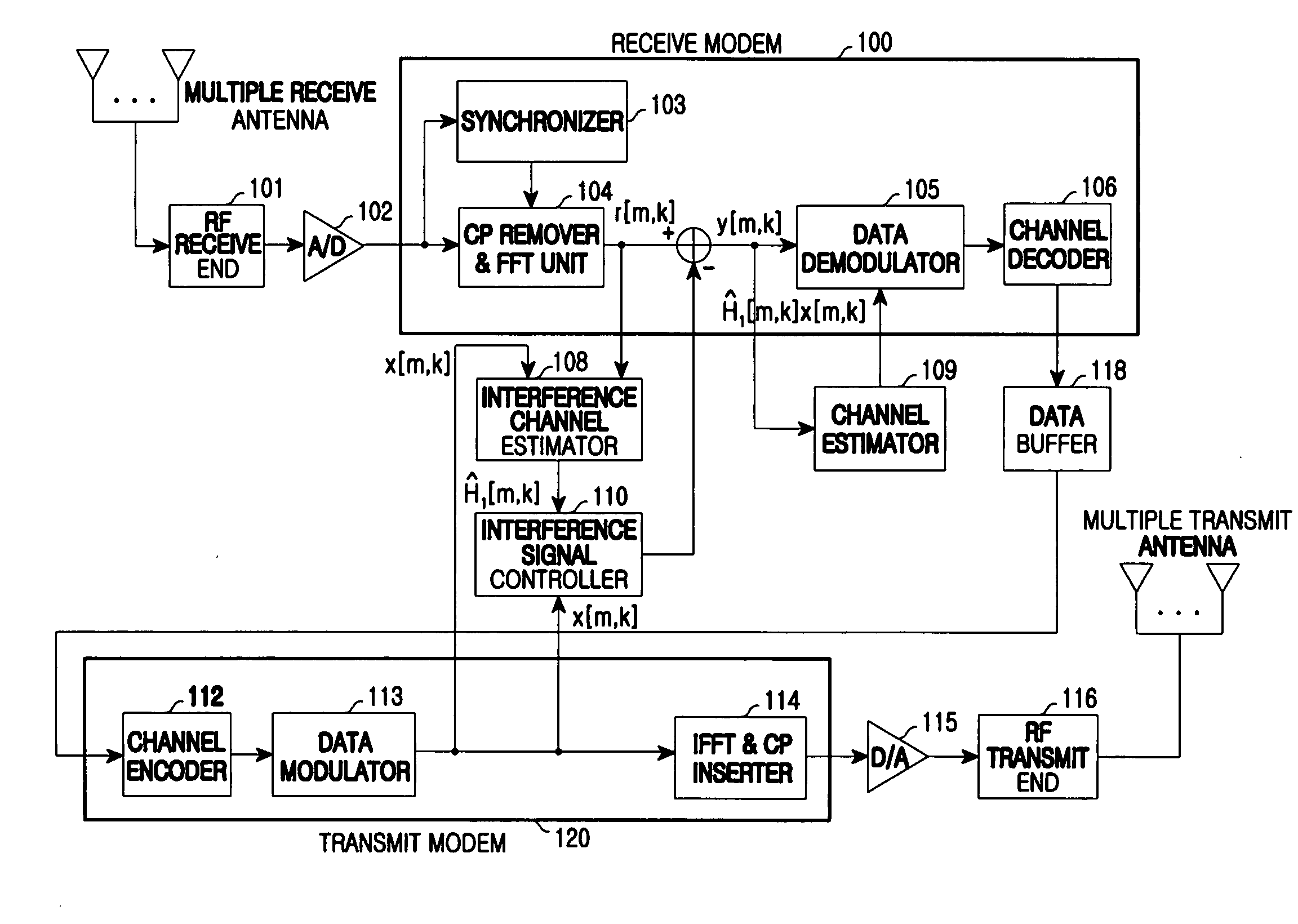
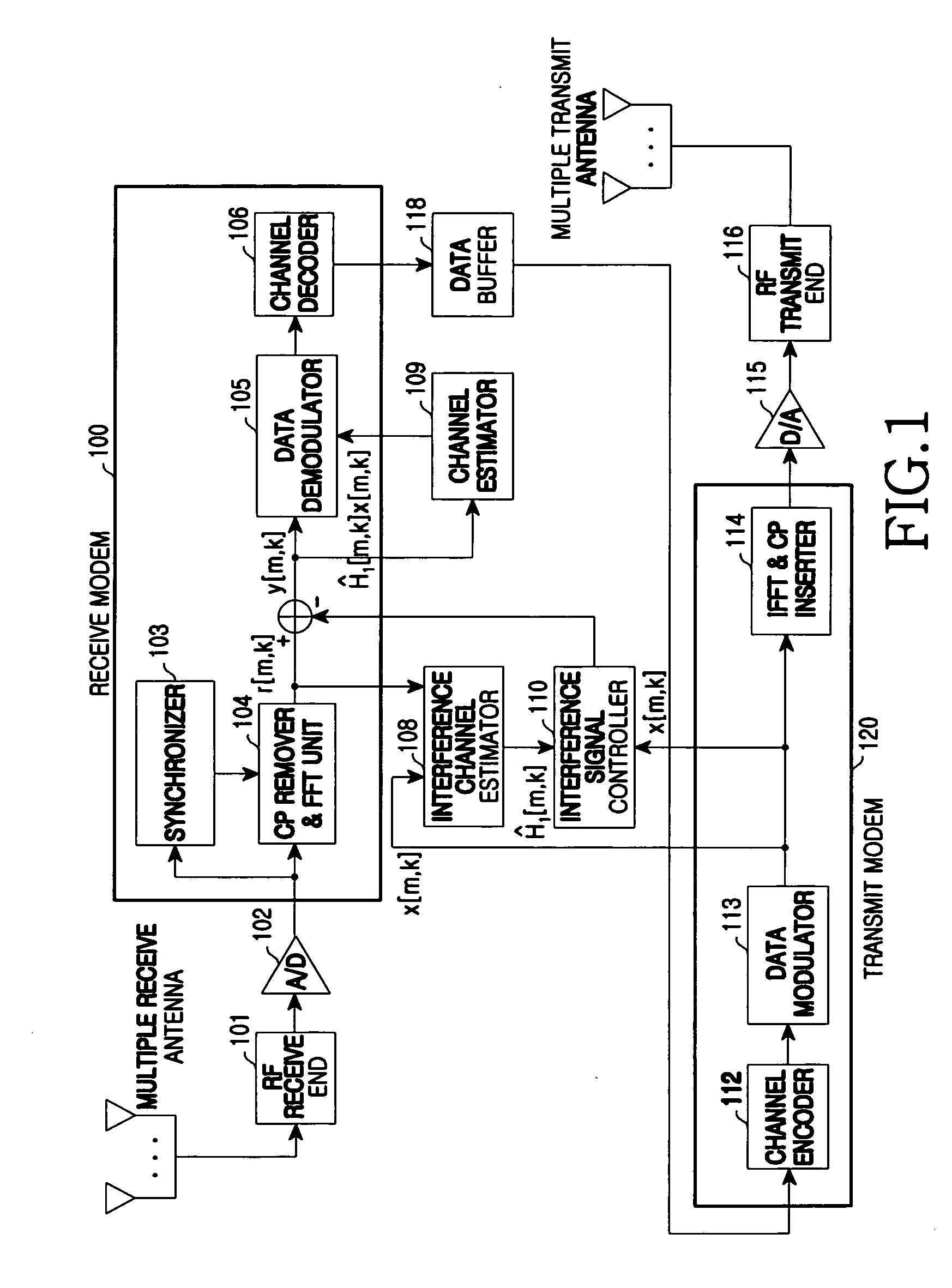
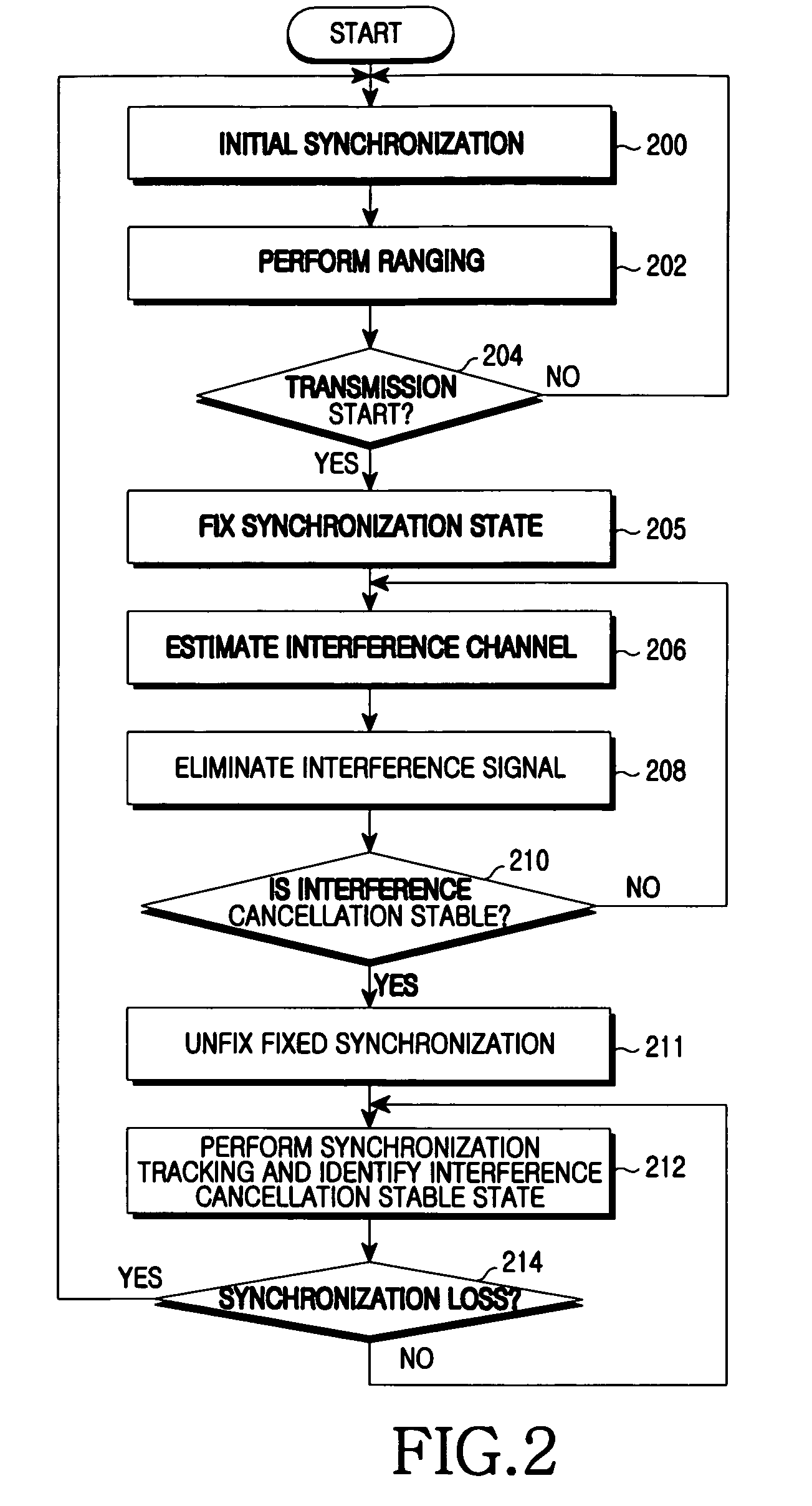
ActiveUS20090180404A1Eliminate Interfering SignalsStored dataSynchronisation arrangementFrequency-division multiplex detailsInterference eliminationInterference cancelation
An apparatus and method for interference cancellation and synchronization maintenance over interference channel estimation in a communication system are provided. An interference channel estimator fixes synchronization and estimates an interference signal. An interference signal controller eliminates the estimated interference signal from a received RF signal. A synchronization unit unfixes fixed synchronization and tracks synchronization when the interference signal cancellation is stable. A data buffer stores data from which the interference signal is canceled.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of interference cancellation in communication systems
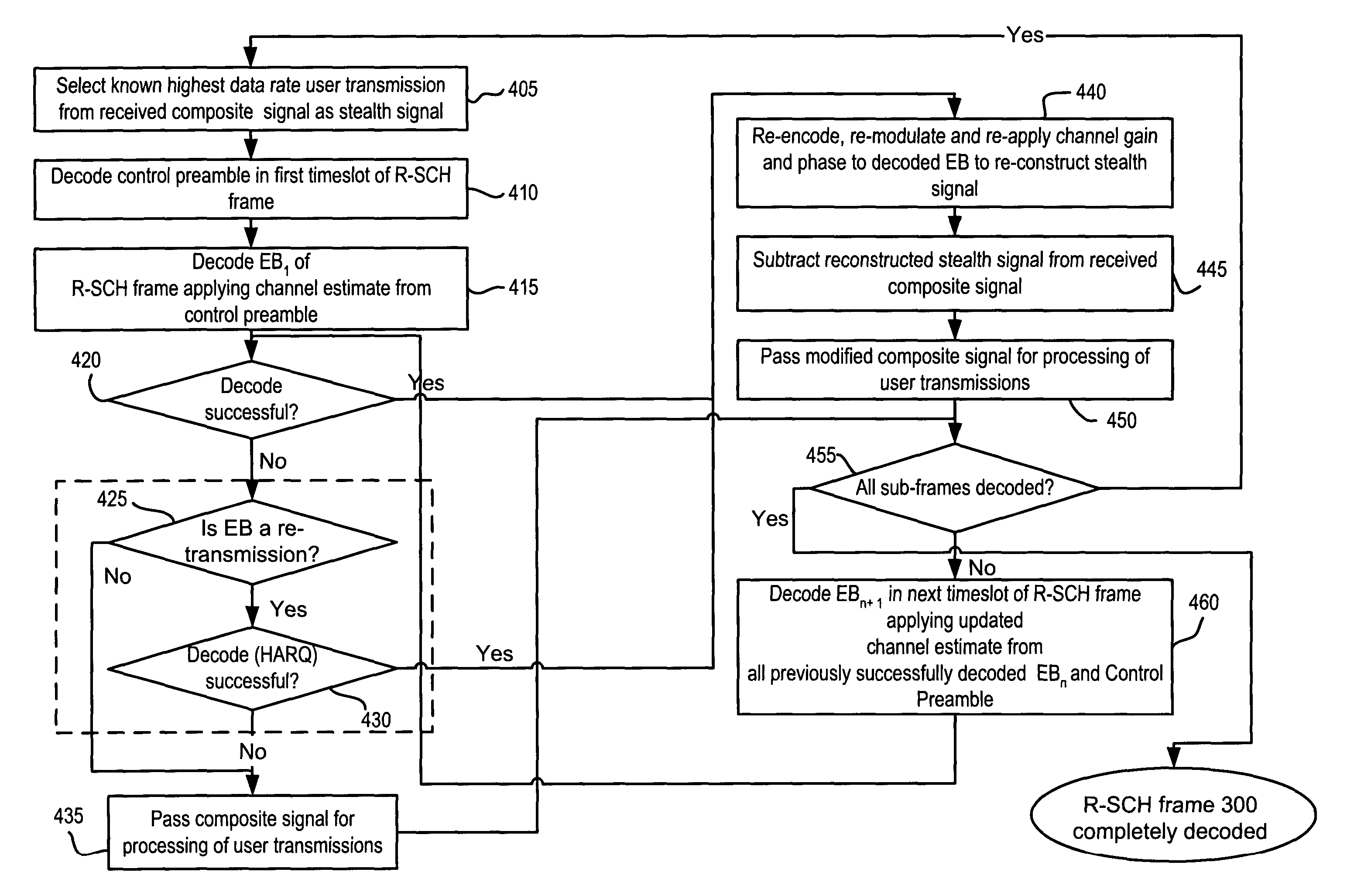
ActiveUS20040192208A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorHigh rateInterference elimination
In a method of canceling interference, a base station selects a known highest data rate user transmission from a received first signal containing a group of user transmissions. The known highest rate user transmission may be configured as one or more frames, each frame including a control preamble and a plurality of encoded sub-frames. The control preamble and encoded sub-frames may be decoded, and the decoded sub-frames may be used for removing interference caused by the known highest rate user transmission to all remaining transmissions of the group.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Method and apparatus for interference cancellation
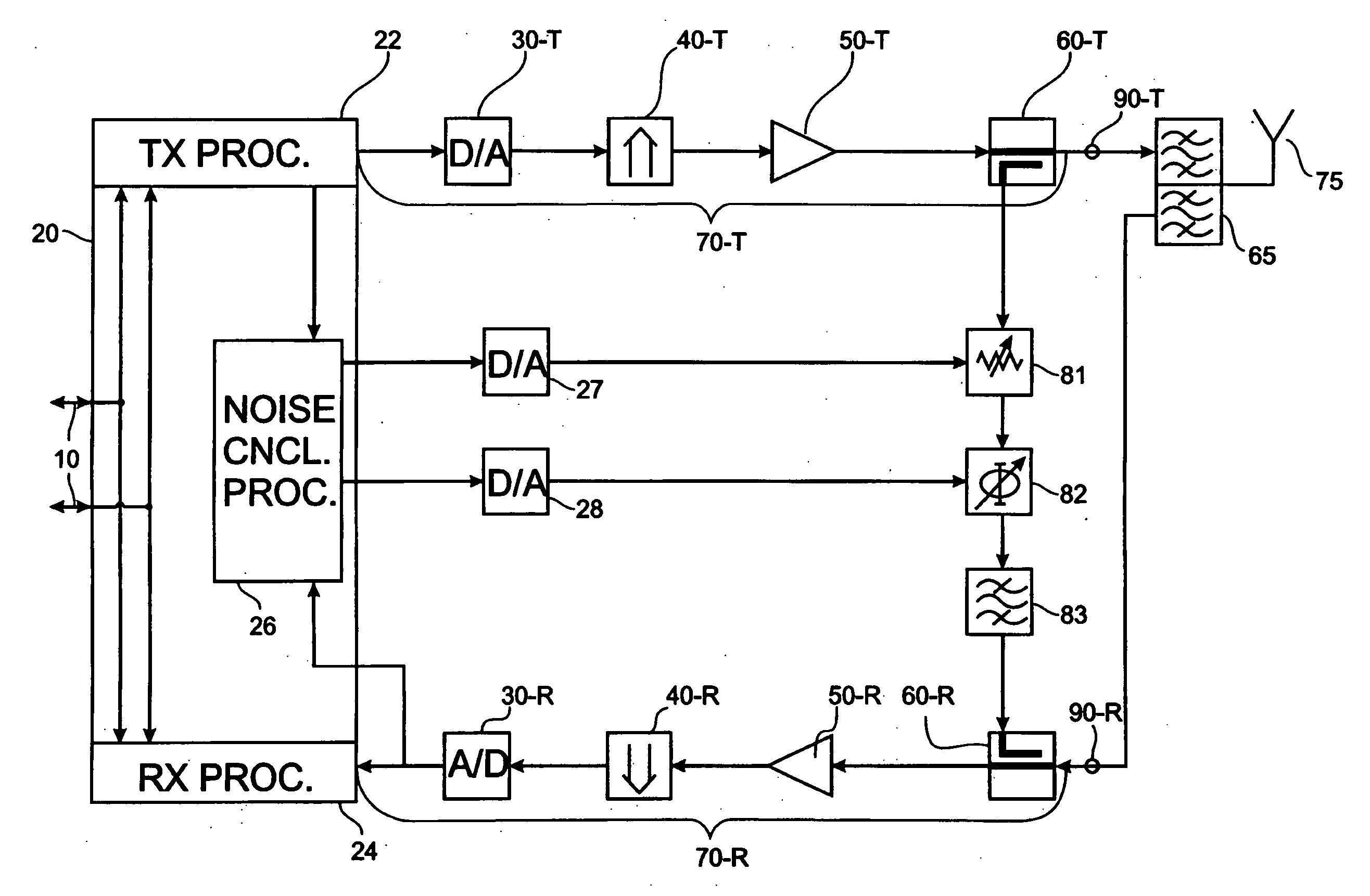
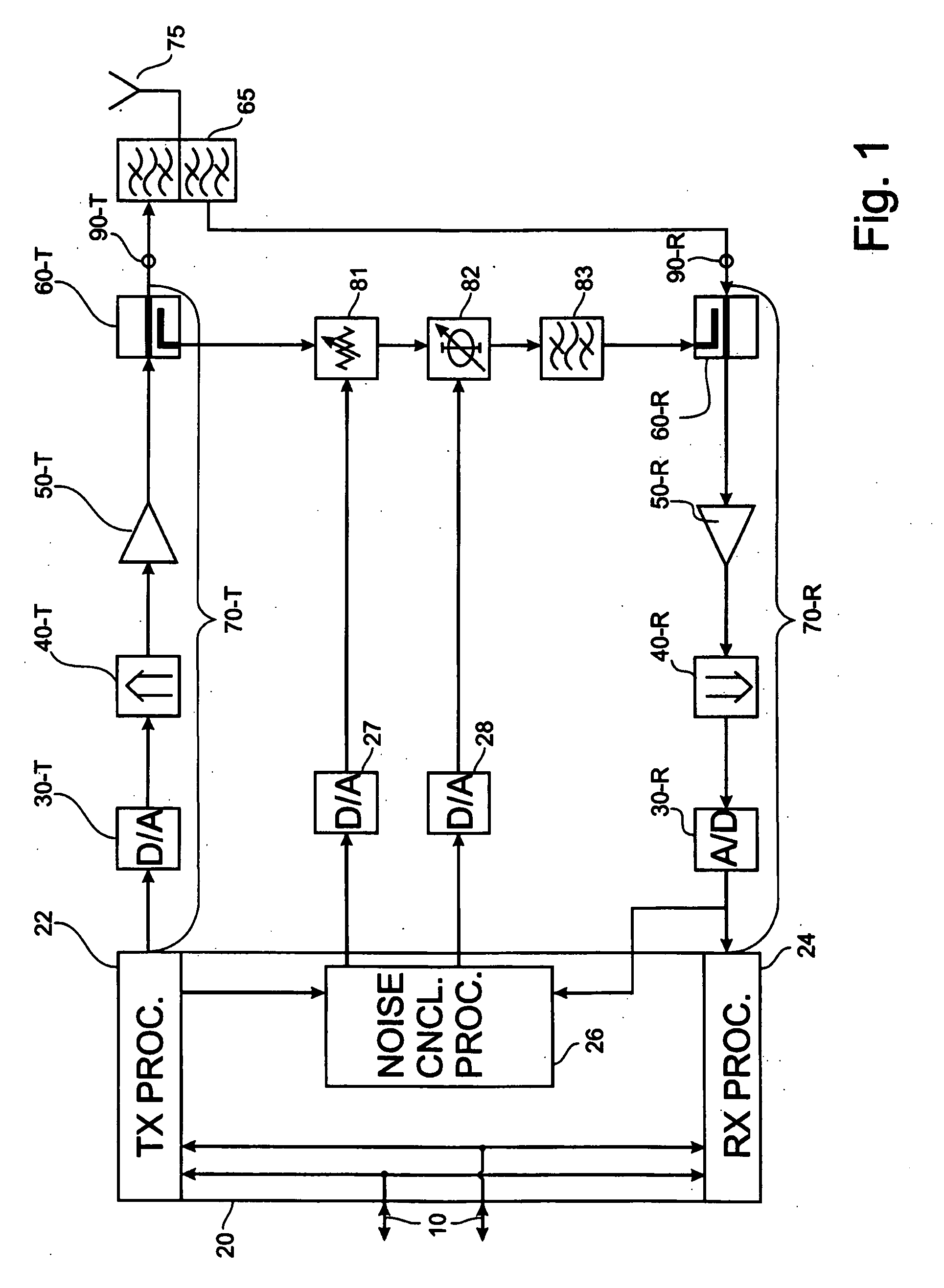
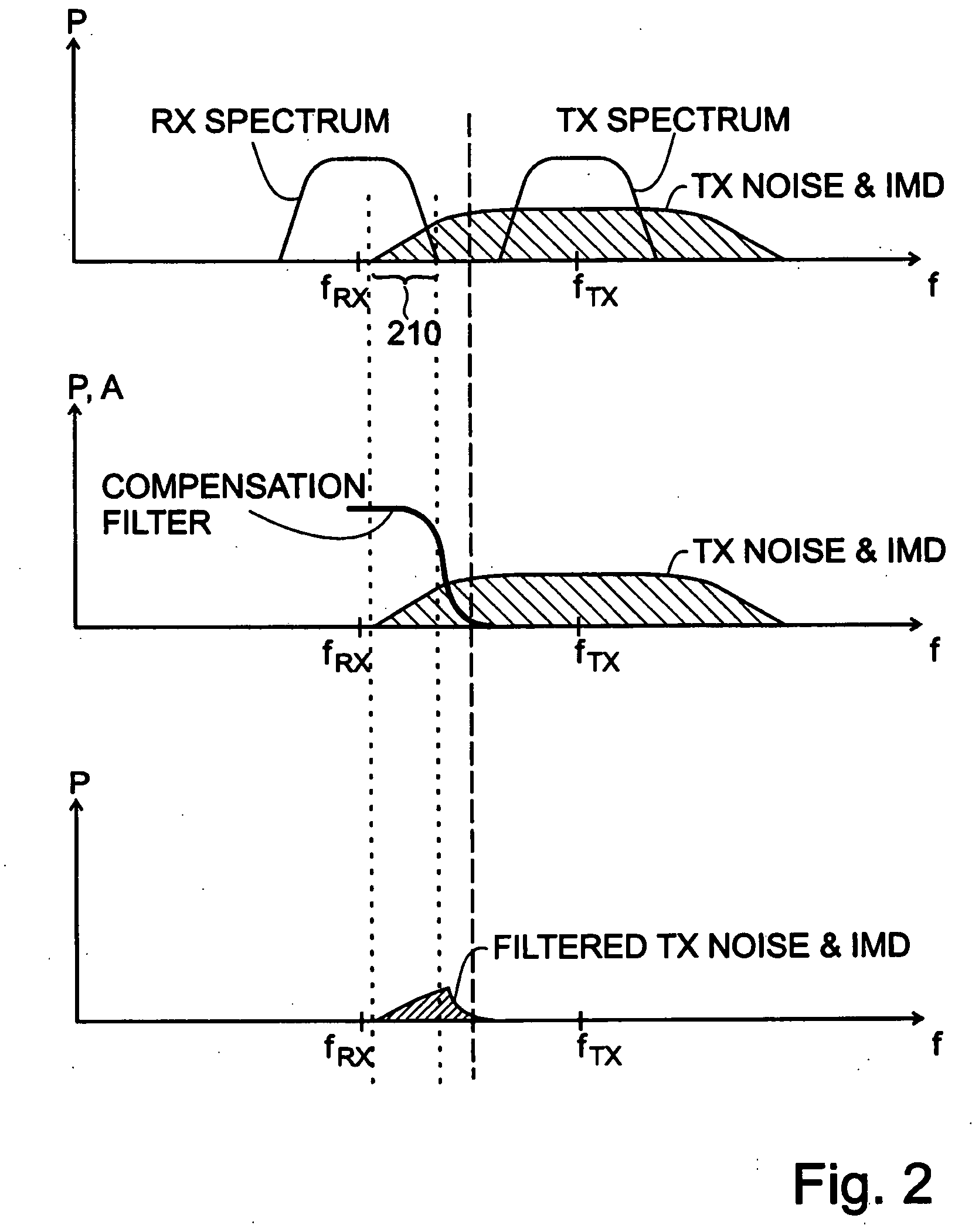
ActiveUS20100197231A1Lower performance requirementsLow costTransmission noise suppressionInterference cancellerTransceiver
An interference canceller between a transmit chain and a receive chain of a transceiver is proposed to complement the action of a diplexer, or duplex filter, that is part of the transceiver. The interference canceller comprises a transmit chain tap, a receive chain coupler for coupling an interference compensation signal into the receive chain, and an interference signal processing path between the transmit chain tap and the receive chain coupler. The interference signal processing path comprises a filter having filtering characteristics similar or corresponding to the filtering characteristic of a receive portion of said diplexer. A corresponding method for interference cancellation is also proposed. Computer-program products for the manufacture of the interference canceller and the execution of the method are also proposed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
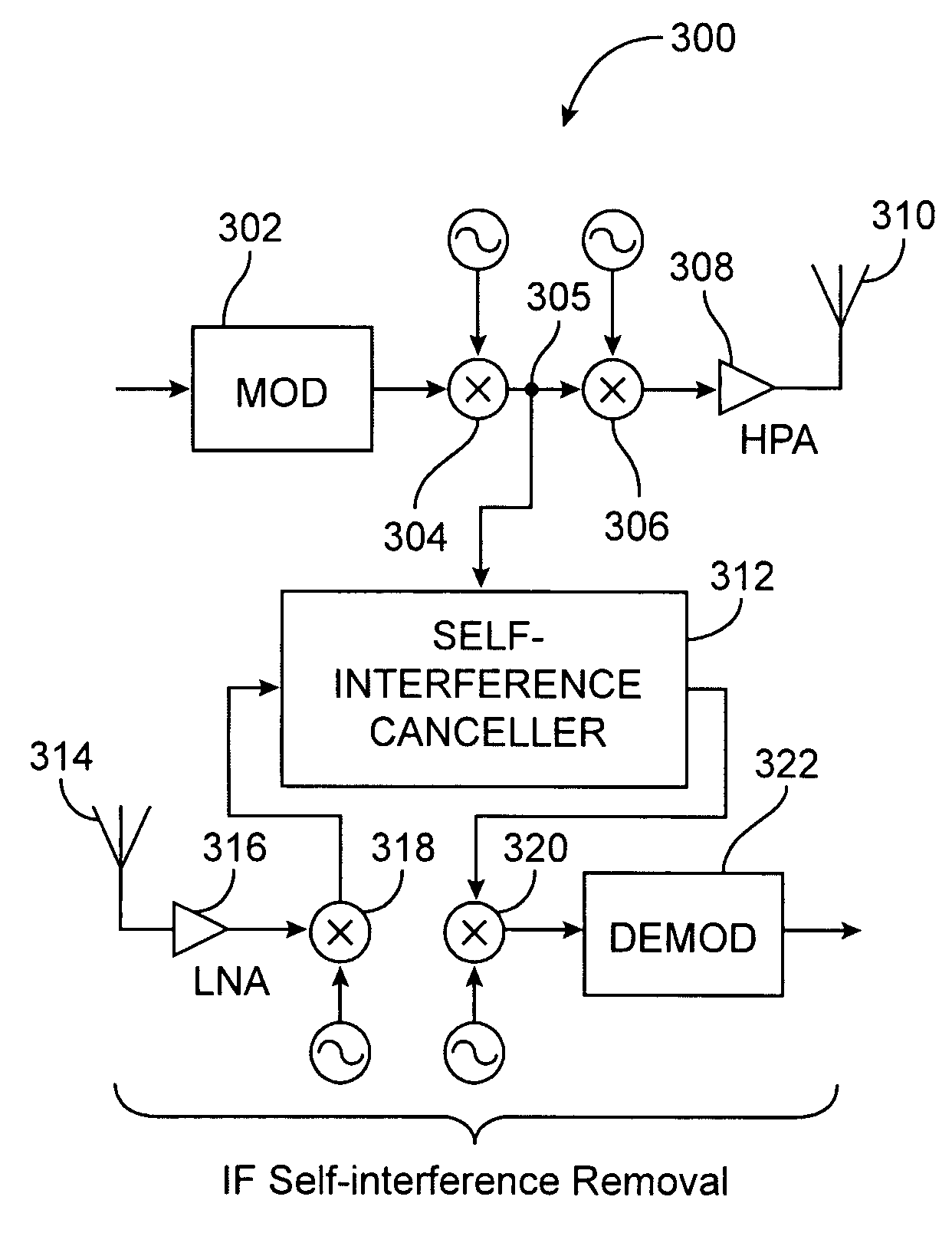
Relayed communication with versatile self-interference cancellation
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are presented for providing self-interference cancellation in two-way relayed electromagnetic communication between a first and a second device through a relay station, involving retrofitting existing equipment comprising a transmitter system and a receiver system at the first device by adding a canceler module, providing a version of a modulated near signal as a first non-baseband interface signal from the transmitter system to the canceler module, providing a version of a composite signal as a second non-baseband interface signal from the receiver system to the canceler module, generating a cancellation signal at the canceler module corresponding to a relayed version of the modulated near signal, using the first and the second non-baseband interface signals, applying the cancellation signal at the canceler module to a version of the second non-baseband interface signal, to produce a cancellation-processed signal as a third non-baseband interface signal provided to the receiver system.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Highly bandwidth-efficient communications
InactiveUS7106781B2Efficient processingEnhance signal to noise and interference ratio of signalSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
Owner:AT&T WIRELESS SERVICES
Interference cancellation method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050111405A1Increase the stationImprove abilitiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesMulti user interferenceInterference cancelation
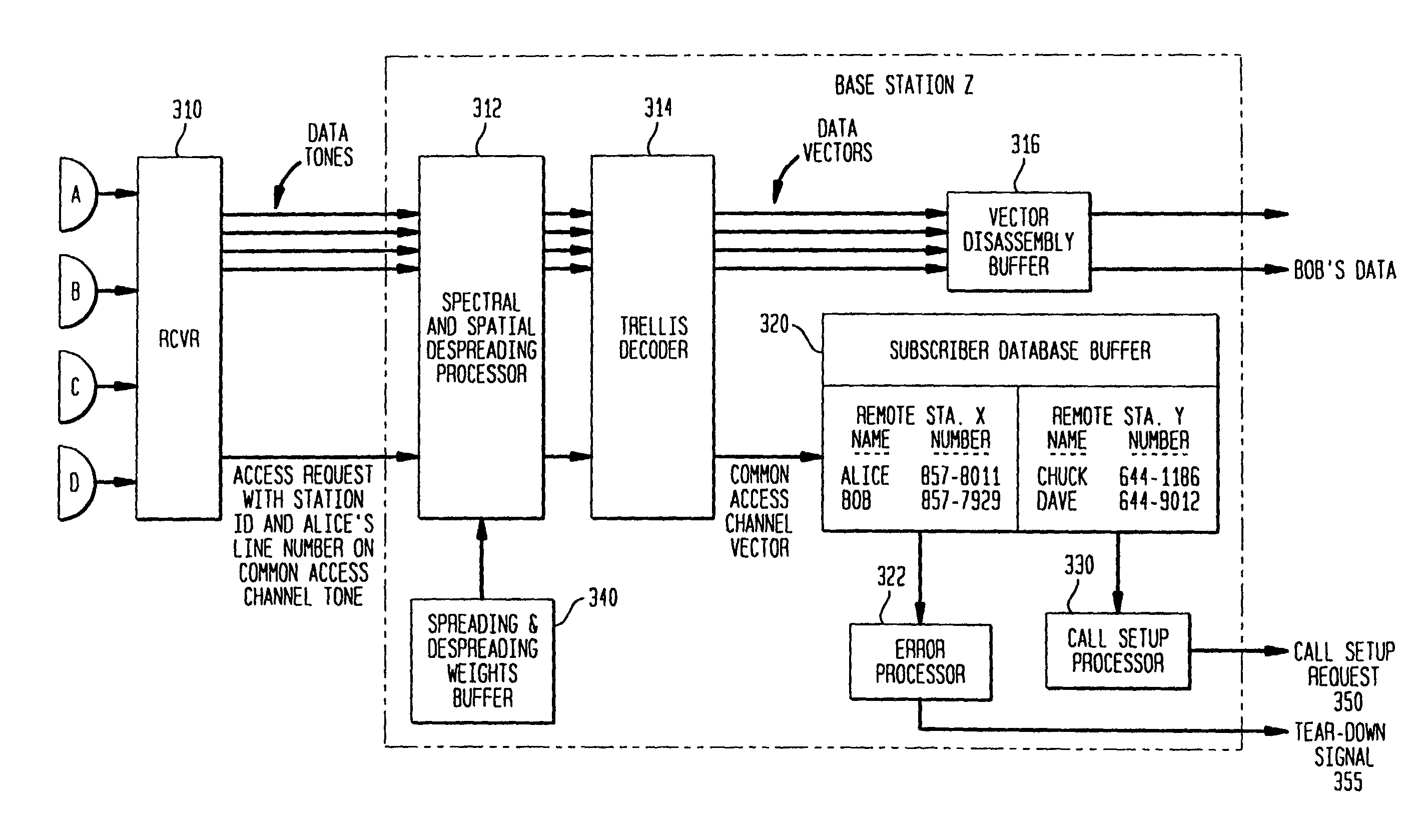
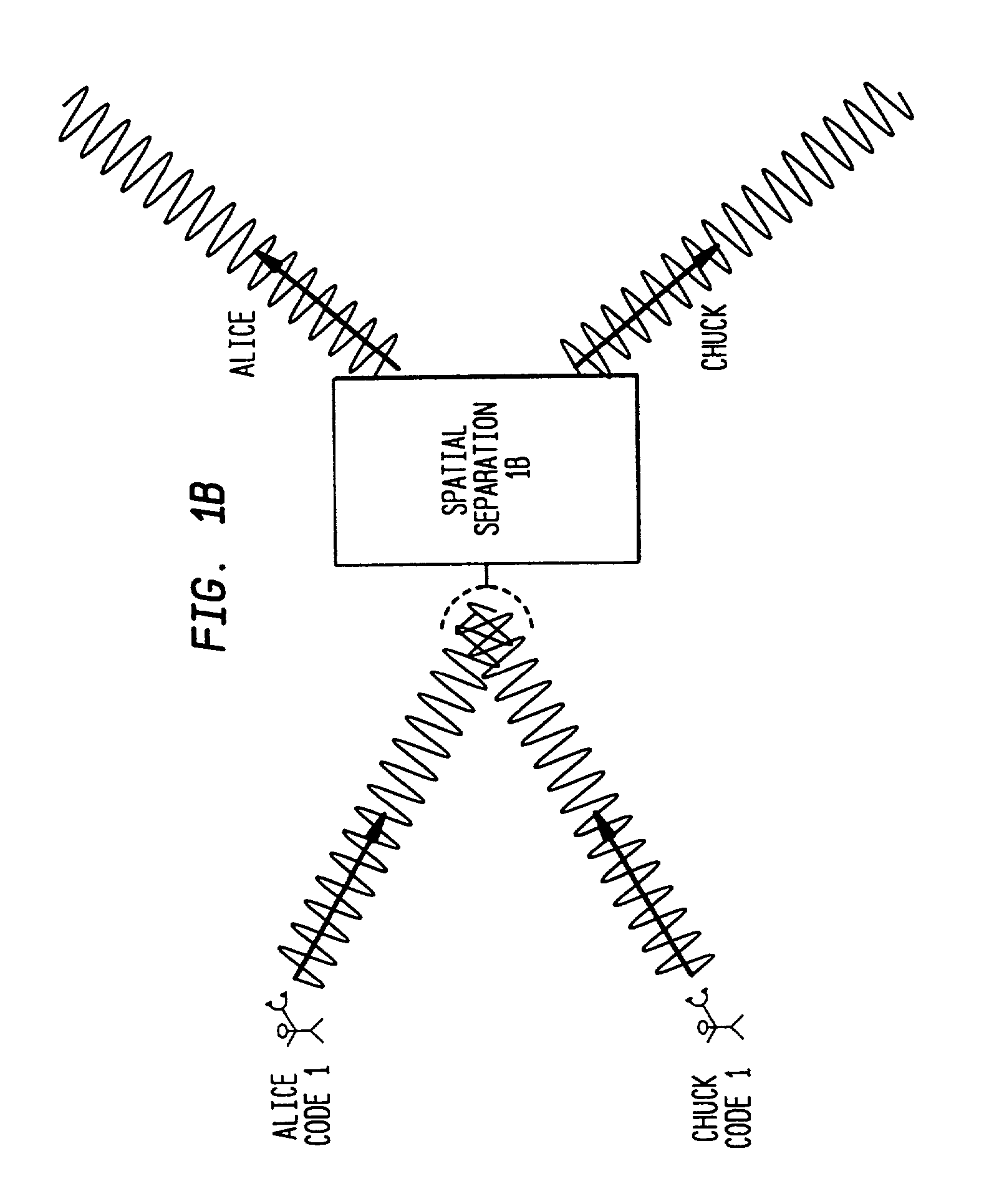
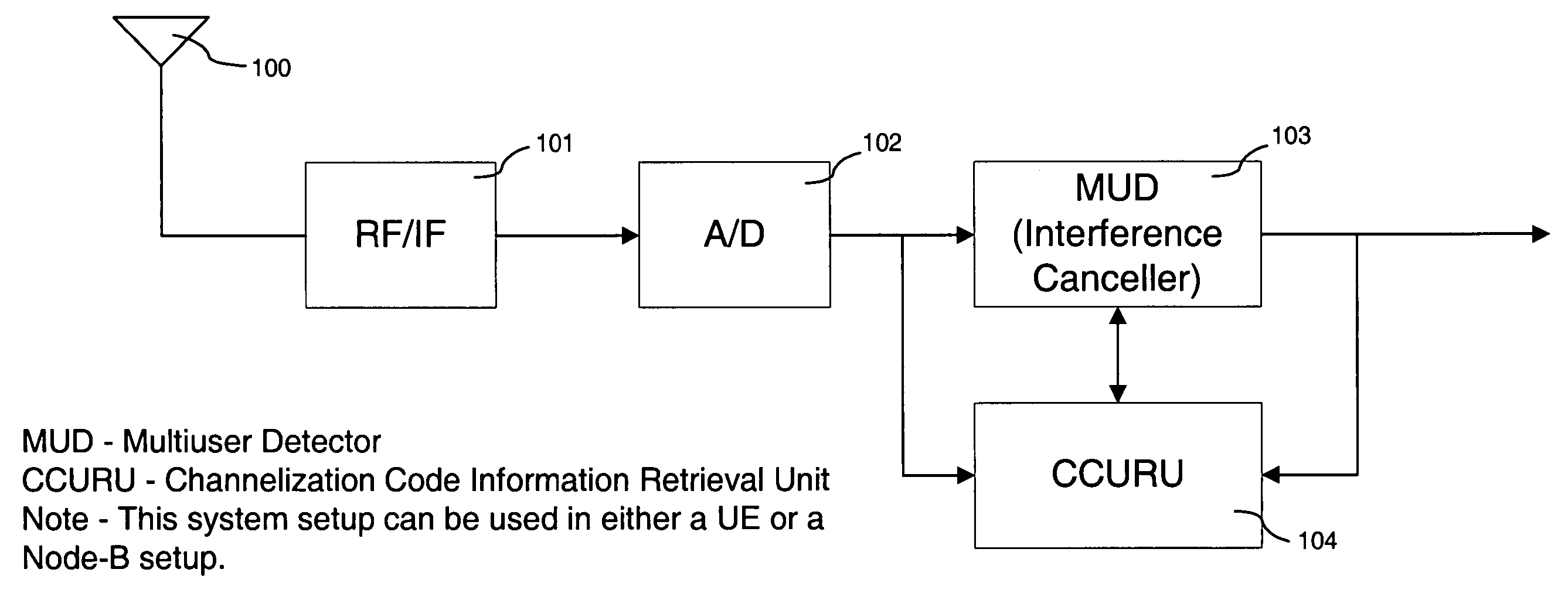
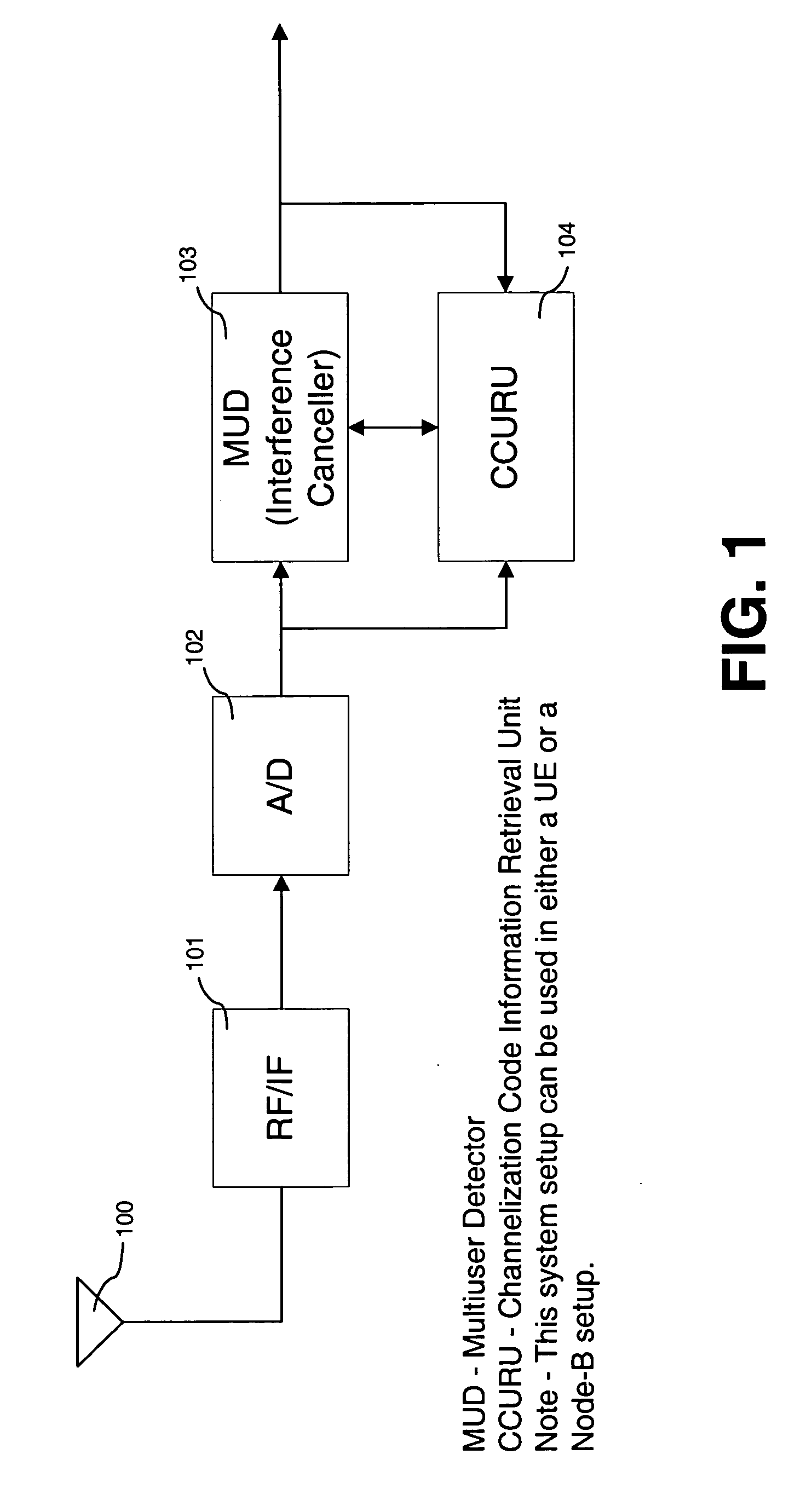
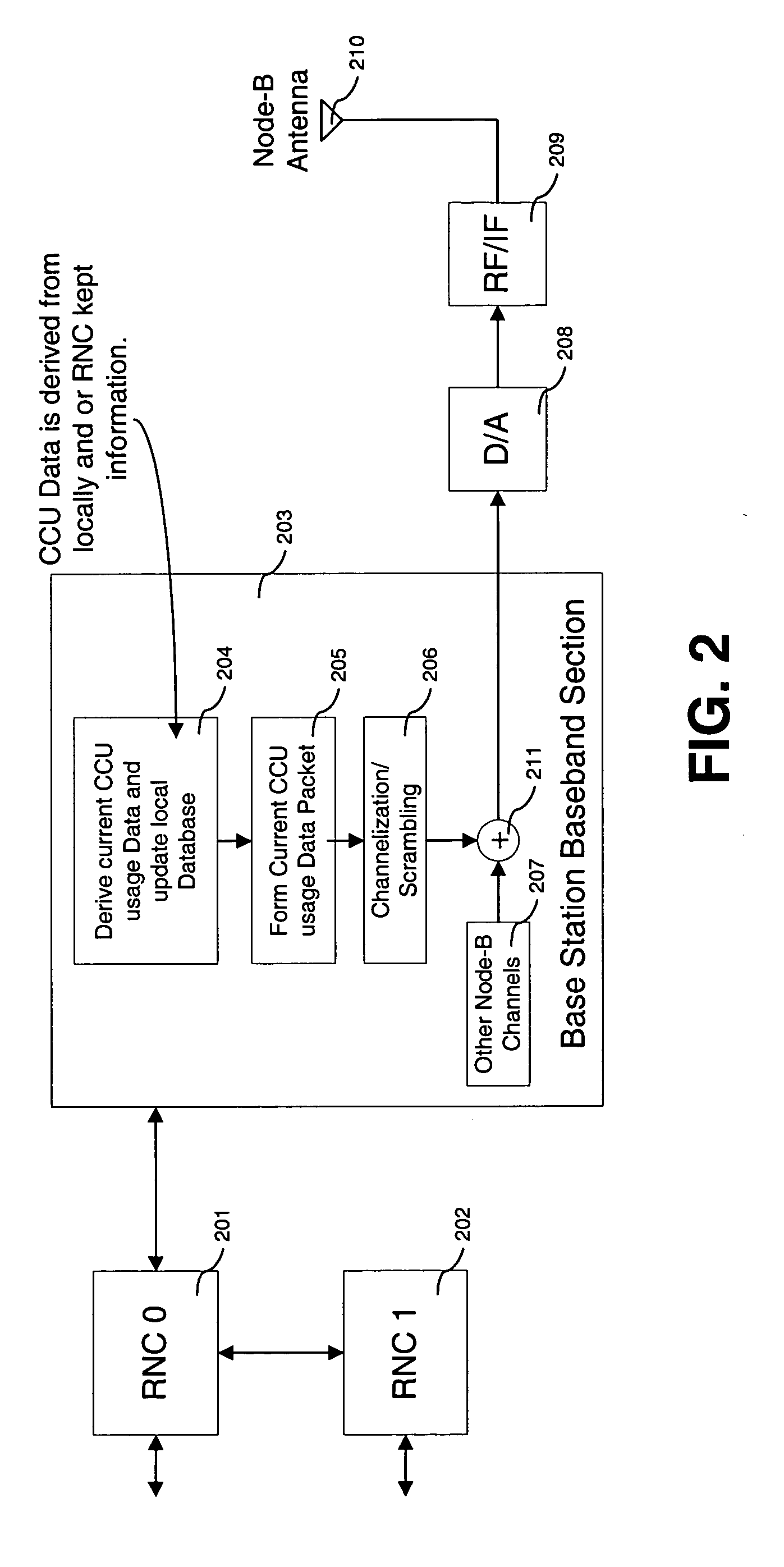
A Multi-User Detection device and method for DS-CDMA to allow enhanced signal reception under Multi-User Interference (MUI) at either the Remote Station or the Base Station is disclosed. The method includes the steps of relaying current channelization code use at Base Stations to Remote Stations operating in the vicinity of the Base Stations. This information is used by an MUD device at the Remote Station, to improve its ability to separate signals transmitted from different Base Stations. The downlink channelization code information is used to recreate the interference received by all neighboring Base Stations transmissions at the Remote Station. The same method can be applied at the Base Station side. The Uplink Channelization Code Usage information is relayed to each Base Station from its neighboring Base Stations. Recreating the total Remote Station interference at the Base Station allows a multistage interference cancellation based MUD to enhance its capability of receiving Remote Stations in its coverage area.
Owner:DESIGN STANDARDS CORP
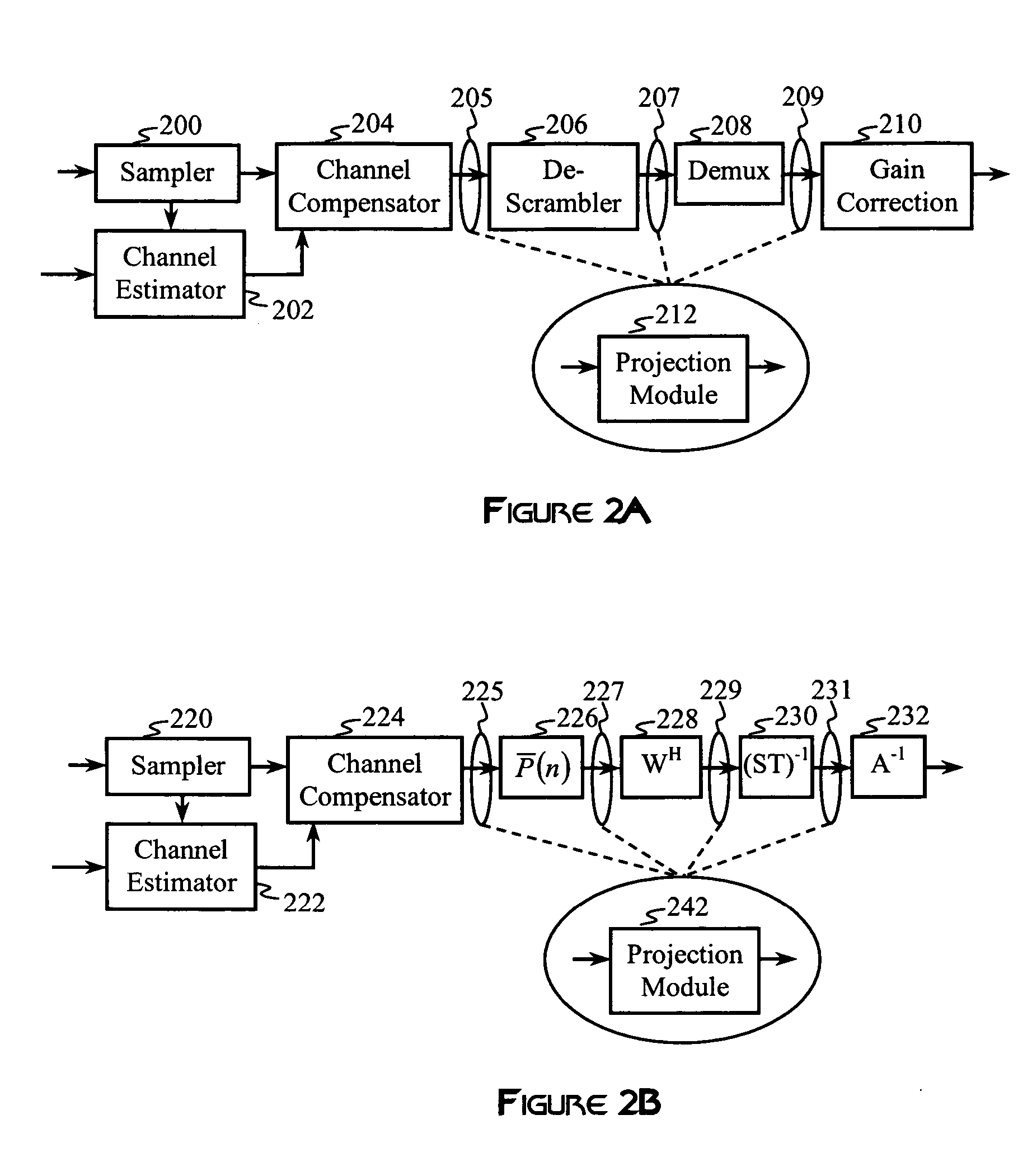
Construction of projection operators for interference cancellation
InactiveUS20050180364A1Reduce in quantityReduce complexitySecret communicationRadio transmissionTime domainTransceiver
Interference cancellation is performed in a CDMA receiver by projecting a received signal onto a subspace that is orthogonal to a signal selected for removal. An interference matrix or a combined interference vector is used to construct an interference-canceling projection operator. Confidence weights may be provided to components of the interference matrix or the interference vector based on estimation errors or relative strengths of interfering signals. Complexity reduction of the orthogonal projection operator may be achieved by providing for simplifying approximations that remove terms and operations. A linear transformation operator may be applied to the rows and / or columns of the interference matrix or the interference vector prior to construction of the orthogonal projection. Interference cancellation techniques may be configured for processing signals in a transmit-diversity system or a receive-diversity system using time and / or frequency-domain implementations and space and / or wave-number implementations of the transceiver.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Systems and methods for mitigating interference between access points
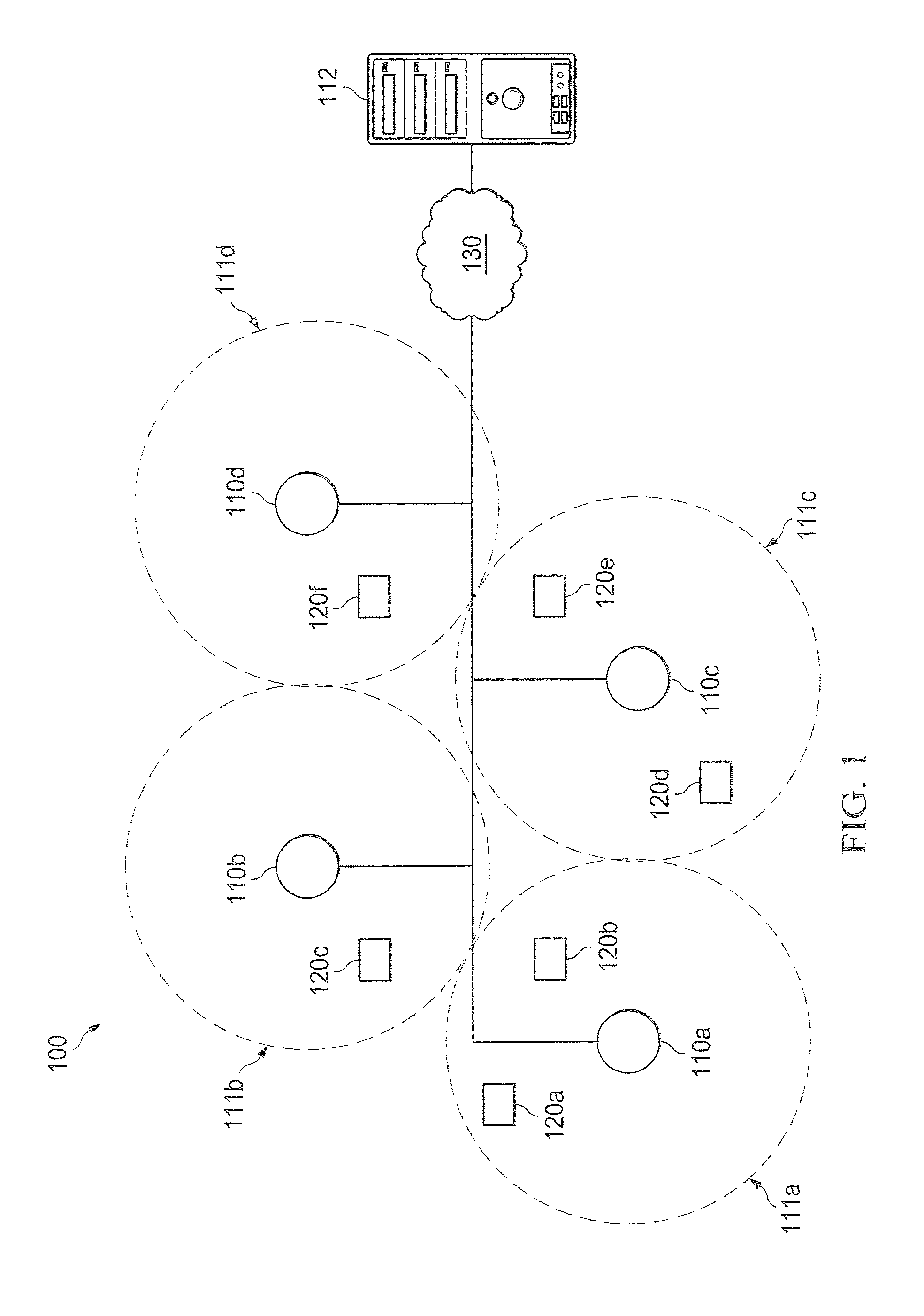
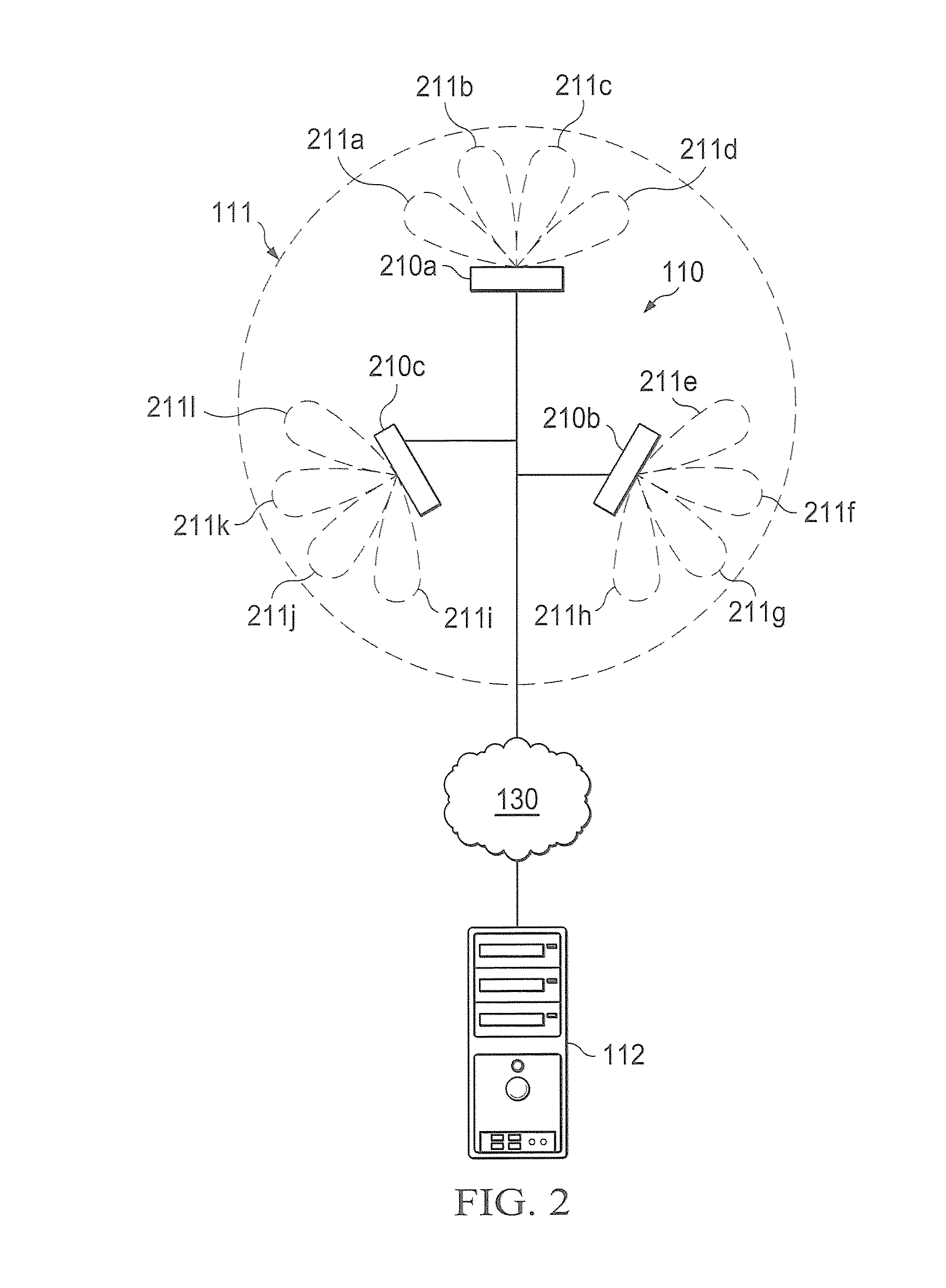
InactiveUS20110032849A1Easy to useDense reuseTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionEngineeringPoint system
Systems and methods which implement cooperative techniques at wireless network access points to provide interference mitigation are shown. Embodiments utilize cooperative antenna beam adaptation techniques wherein antenna beam selection, selective antenna beam transmission power, and / or antenna beam null selection is implemented based upon the communication environment created by a plurality of access points. Additionally or alternatively, embodiments utilize cooperative antenna beam isolation techniques wherein narrow channel filters are implemented with respect to antenna beam signals and / or shielding is provided between various antenna beams based upon the communication environment created by a plurality of access points. Embodiments additionally or alternatively utilize cooperative antenna beam coordination techniques wherein transmission and / or reception of signals is coordinated, the use of antenna beams is coordinated, and / or interference cancellation is implemented based upon the communication environment created by a plurality of access points.
Owner:FIMAX TECH
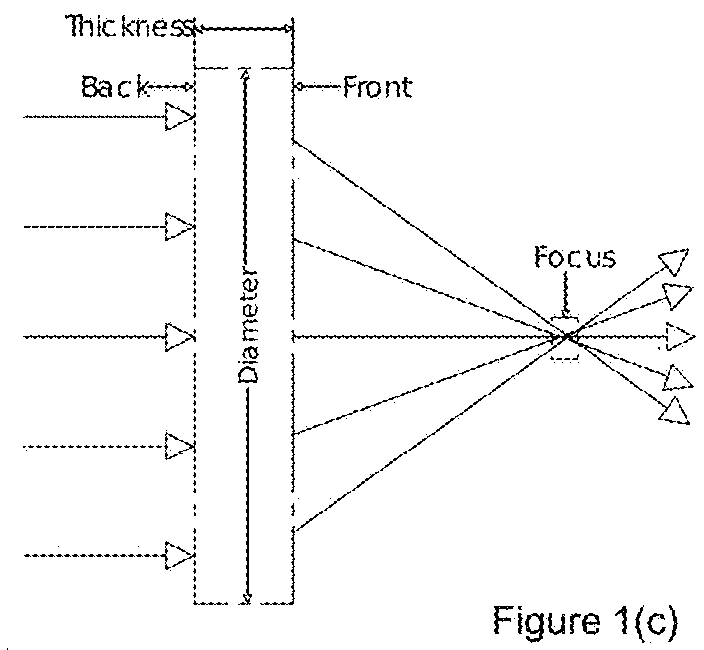
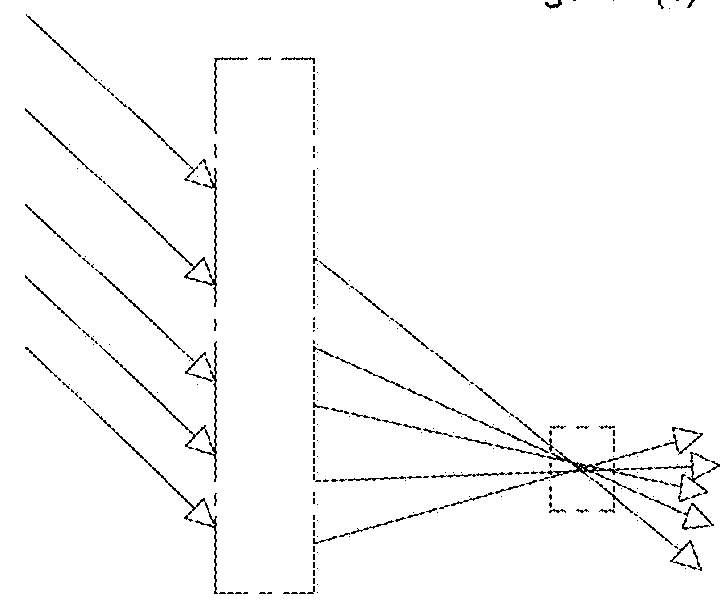
System and method for providing a compact, flat, microwave lens with wide angular field of regard and wideband operation
PendingUS20180183152A1High instantaneous bandwidthLow overall depthAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesDesign optimisation/simulationInterference (communication)Engineering
A system designs a thin and relatively flat microwave focusing lens that can produce multiple simultaneous beams, using readily-available isotropic dielectric materials, and having a gradient-index (GRIN) profile. The design optimizes the lens to achieve beam scanning and / or multiple beams over a wide field of regard (FOR) with broad bandwidth and a very short focal length compared with conventional lenses. The lens can be used individually or as an element in a more complex antenna having multiple lenses in various orientations that are independently switched, selected and / or excited simultaneously as elements in a phased array. The antenna terminal incorporates such lens into an array of lenses along with one or more feeds to produce single or multiple beams covering a broad field of regard for such applications as satellite communications on-the-move, cellular, broadband point-point or point-multipoint and other terrestrial or satellite communications systems. The lens and array design support multiple simultaneous independently steerable beams as well as null placement for interference cancellation.
Owner:ALL SPACE NETWORKS LTD
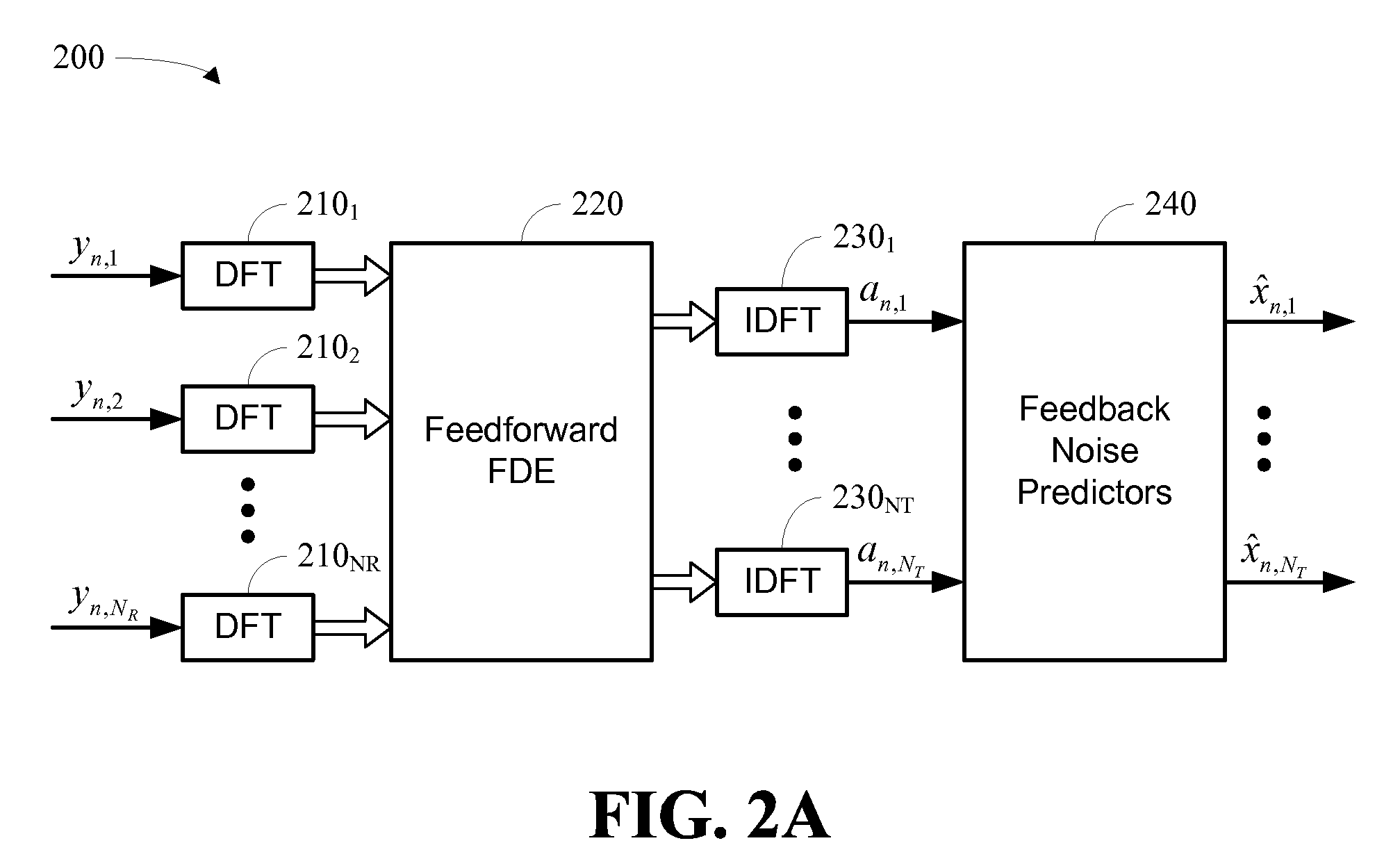
Hybrid time-frequency domain equalization over broadband multi-input multi-output channels
InactiveUS20080304558A1Good flexibilityMore reliabilityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMulti inputData stream
A system and methodology for channel equalization are provided. According to one aspect, a receiver structure for a MIMO system is provided that employs frequency domain equalization (FDE) with noise prediction (FDE-NP). The FDE-NP structure may include a feedforward linear frequency domain equalizer and a group of time domain noise predictors (NPs), which may operate by predicting a distortion corresponding to a given linearly equalized data stream based on previous distortions of all linearly equalized data streams. According to another aspect, a receiver structure for a MIMO system is provided that employs FDE-NP with successive interference cancellation (FDE-NP-SIC), which can extend the functionality of FDE-NP by ordering all linearly equalized data streams according to their minimum mean square errors (MMSEs) and detecting those streams which have a low MMSE first, thereby allowing current decisions of lower-indexed streams to be considered along with previous decisions for all data streams for noise prediction. According to a third aspect, a method for analyzing the performance of a MIMO system with equalization is provided. Pursuant to the method, a general expression of MMSE may first be derived. The MMSE expression may then be related to an error bound by applying the modified Chernoff bounding methodology in a general MIMO system. The parameters in the result may then be varied for applicability to single-input single-output (SISO), multiple-input single-output (MISO), and single-input multiple-output (SIMO) systems with receiver equalization technology.
Owner:YIM TU INVESTMENTS
Apparatus and method for interference cancellation in broadband wireless communication system
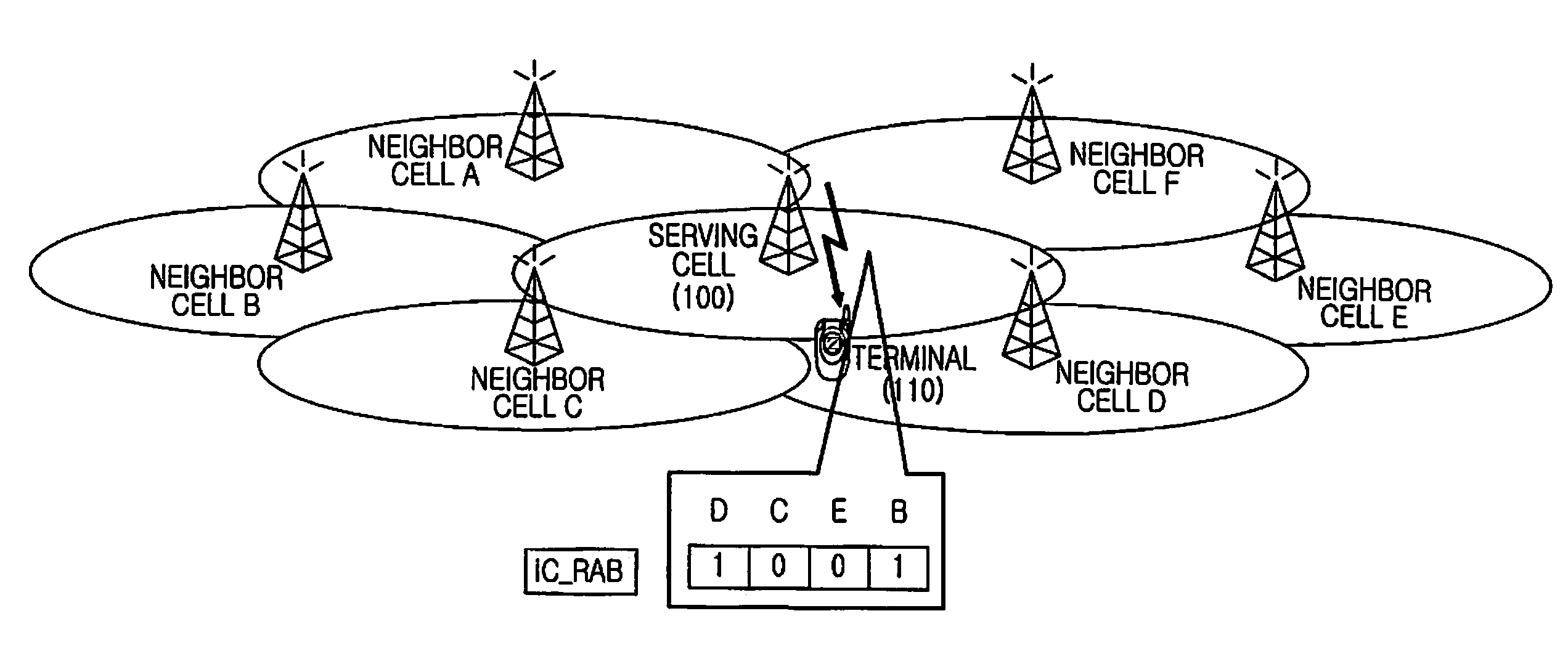
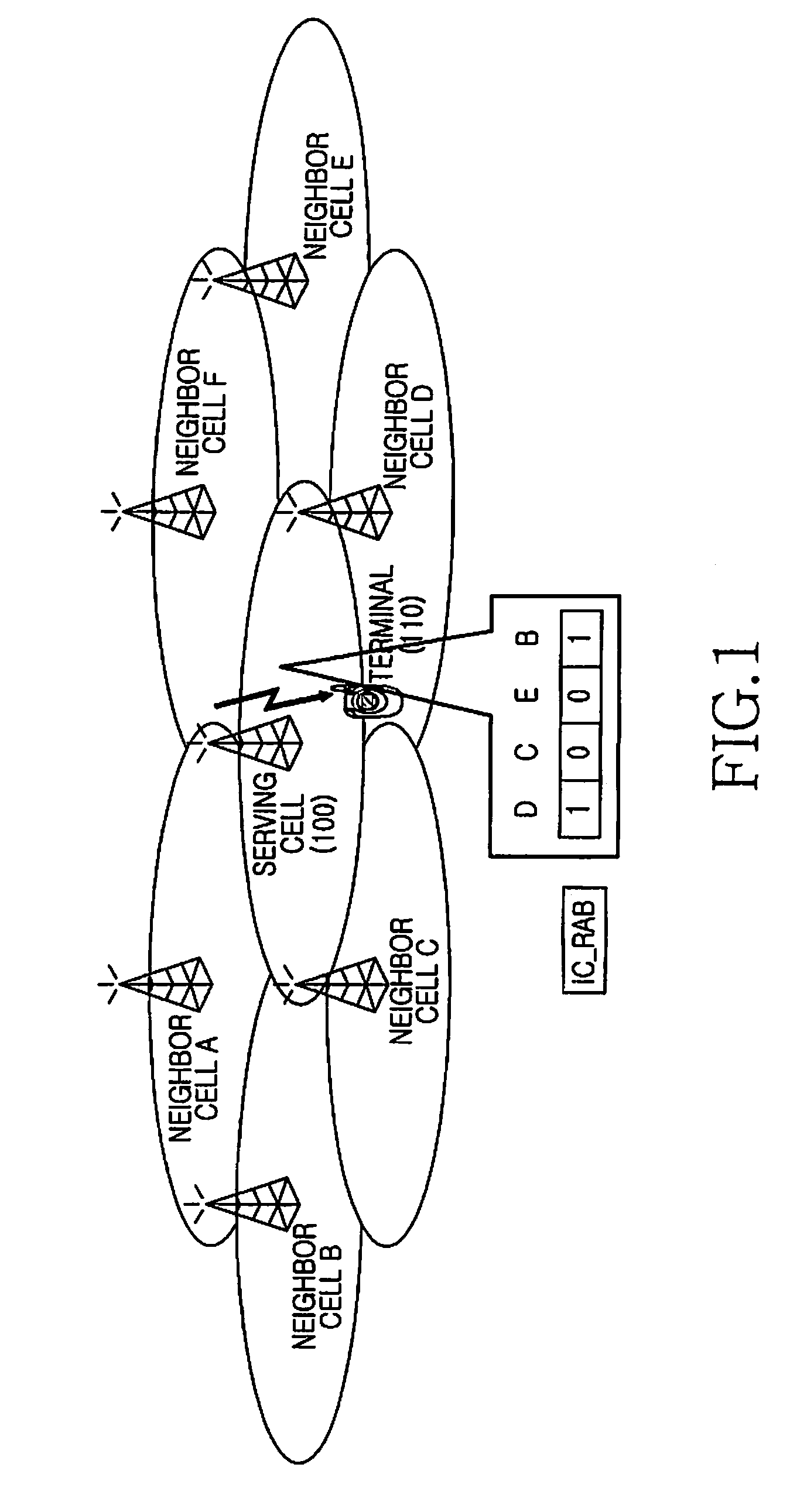
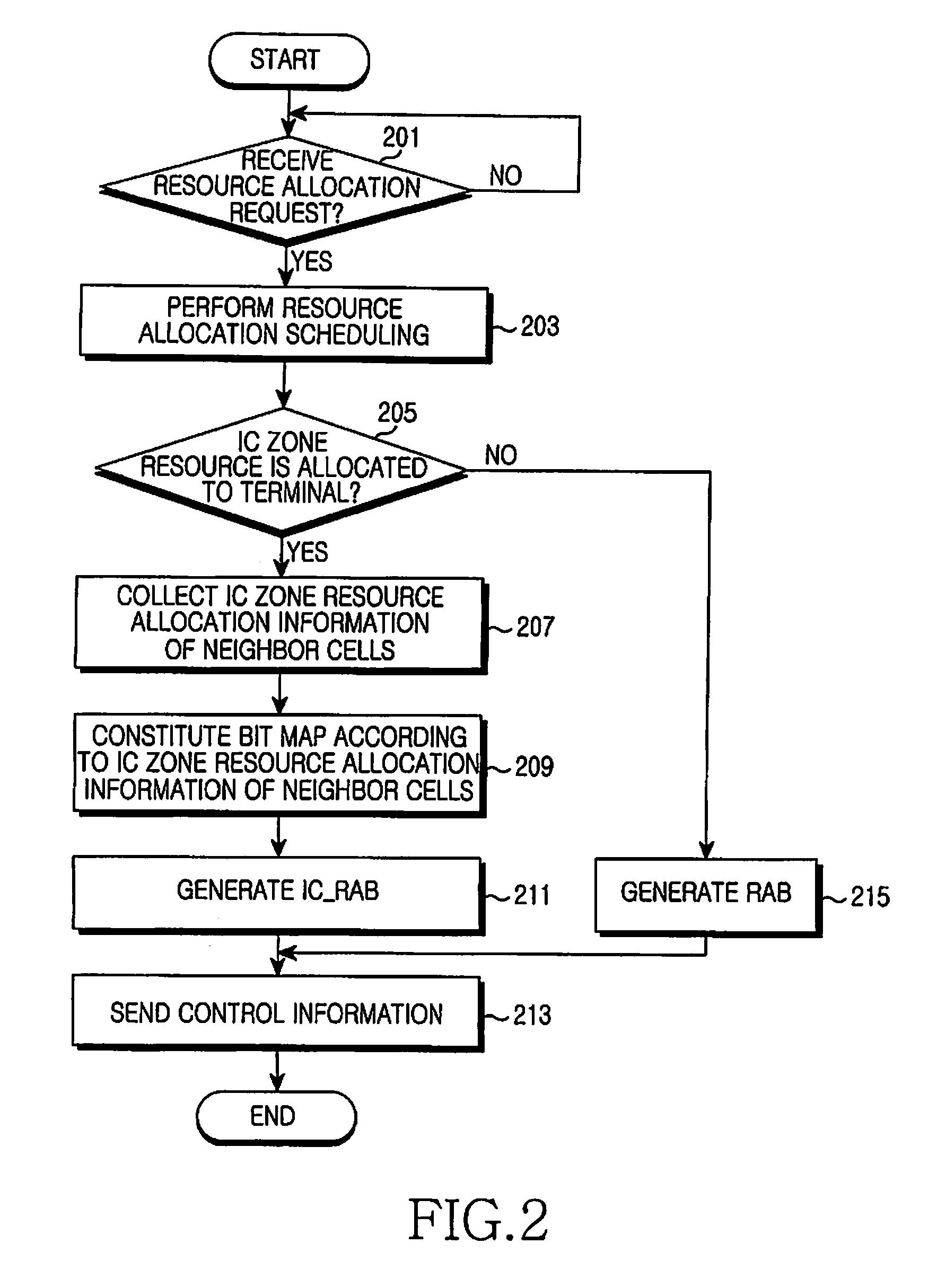
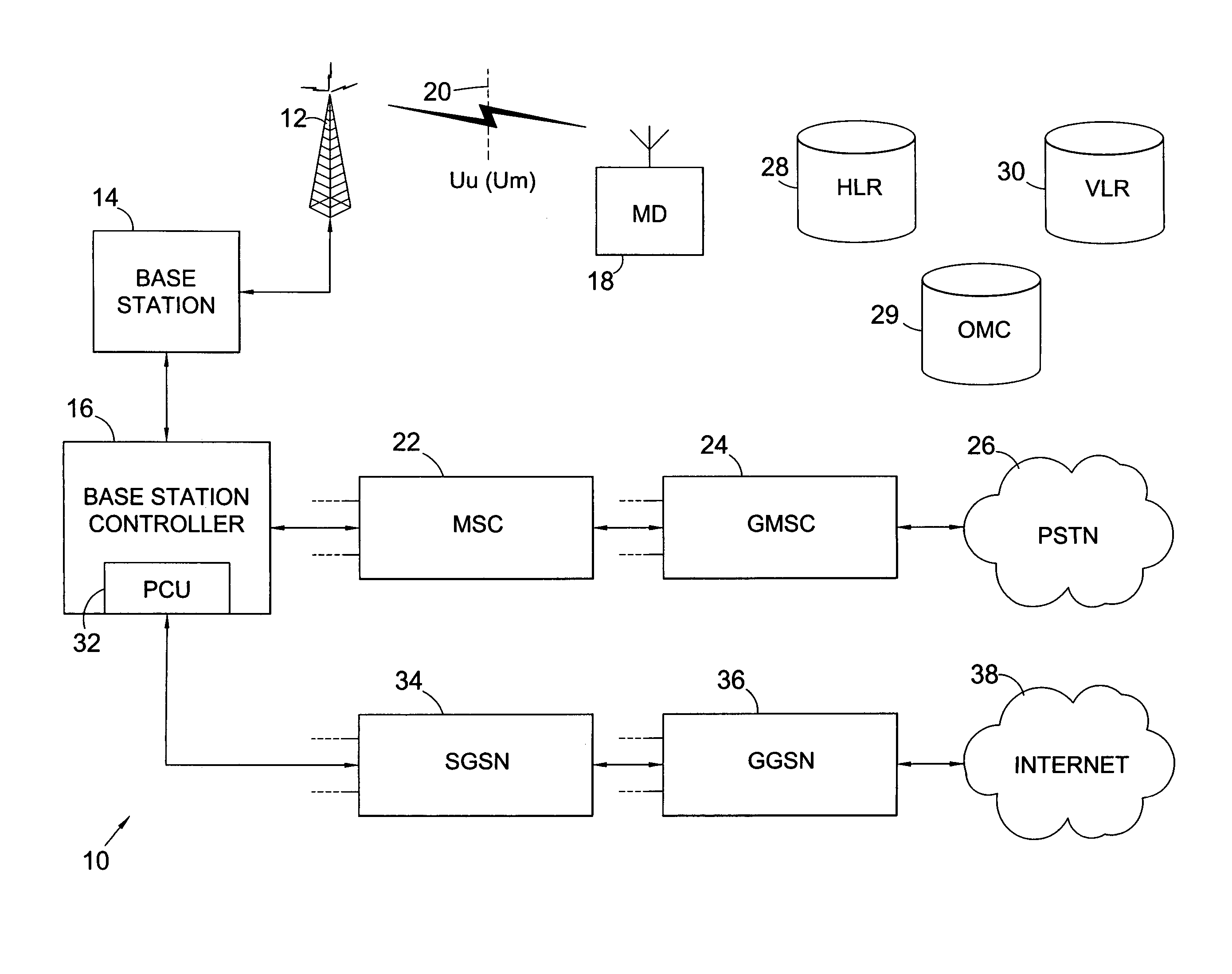
ActiveUS20080108363A1Cancel any interferenceAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemInterference elimination
An Apparatus and a method for interference cancellation in a wireless communication system are provided. When a resource of an Interference Cancellation (IC) zone is allocated to a terminal traveling in a service coverage, resource allocation information relating to an IC zone of neighbor cells is gathered. Resource allocation information is generated relating to the resource allocated to the terminal comprising resource allocation information of the IC zone of the neighbor cells. The resource allocation information relating to the resource allocated to the terminal is transmitted to the terminal. Accordingly, when the interference is present, the interference cancellation is carried out to reduce the load on the terminal and enhance the reception performance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
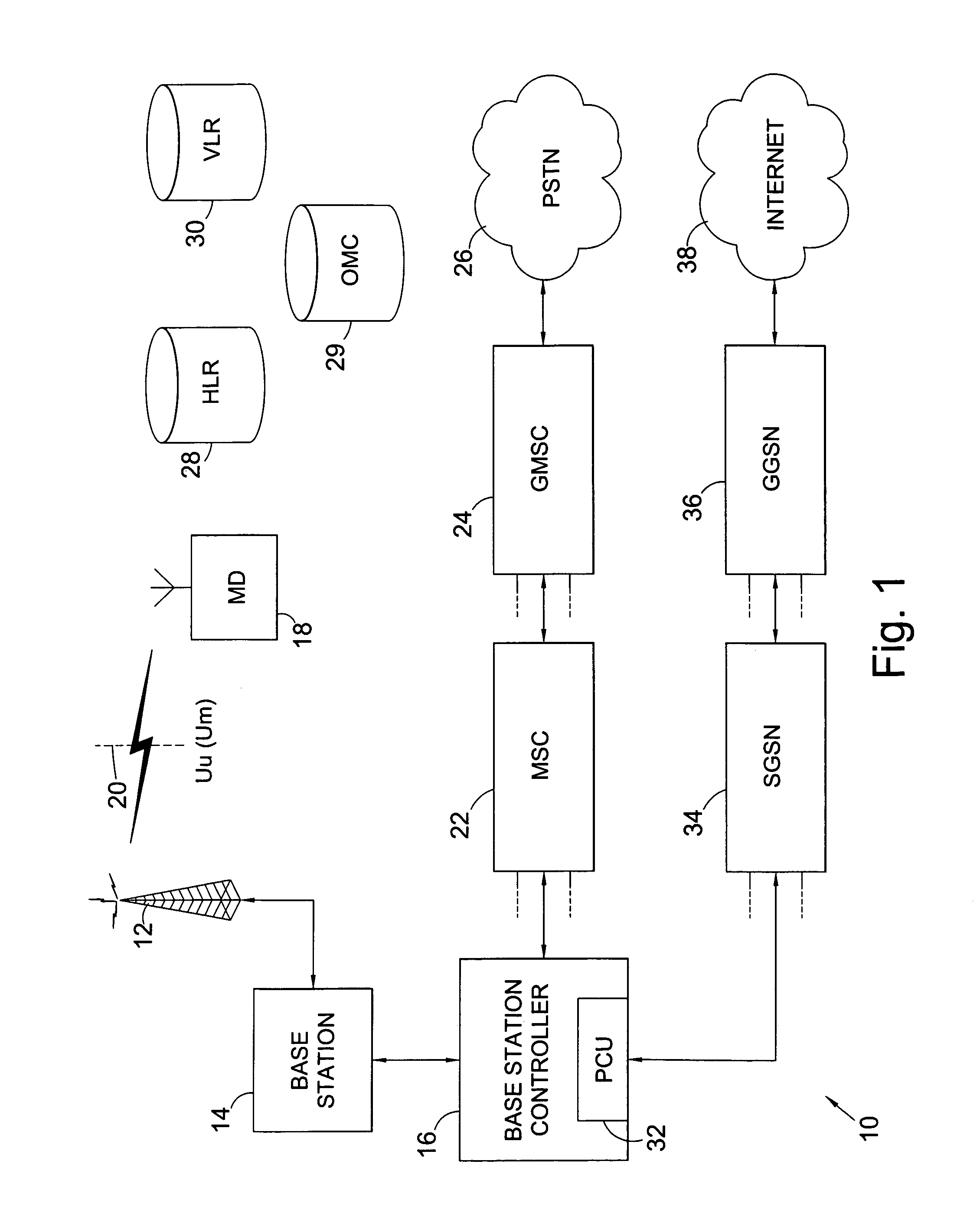
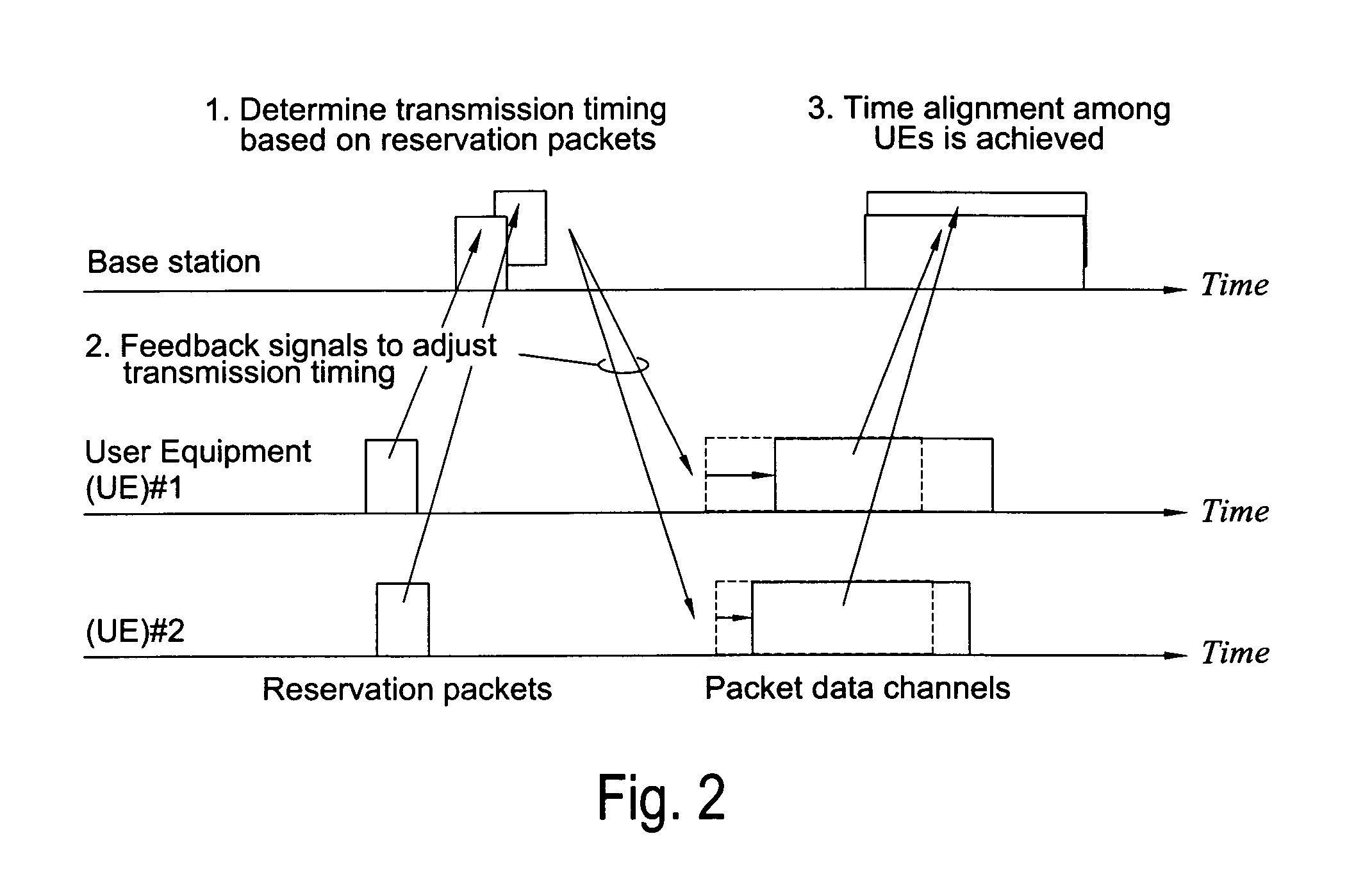
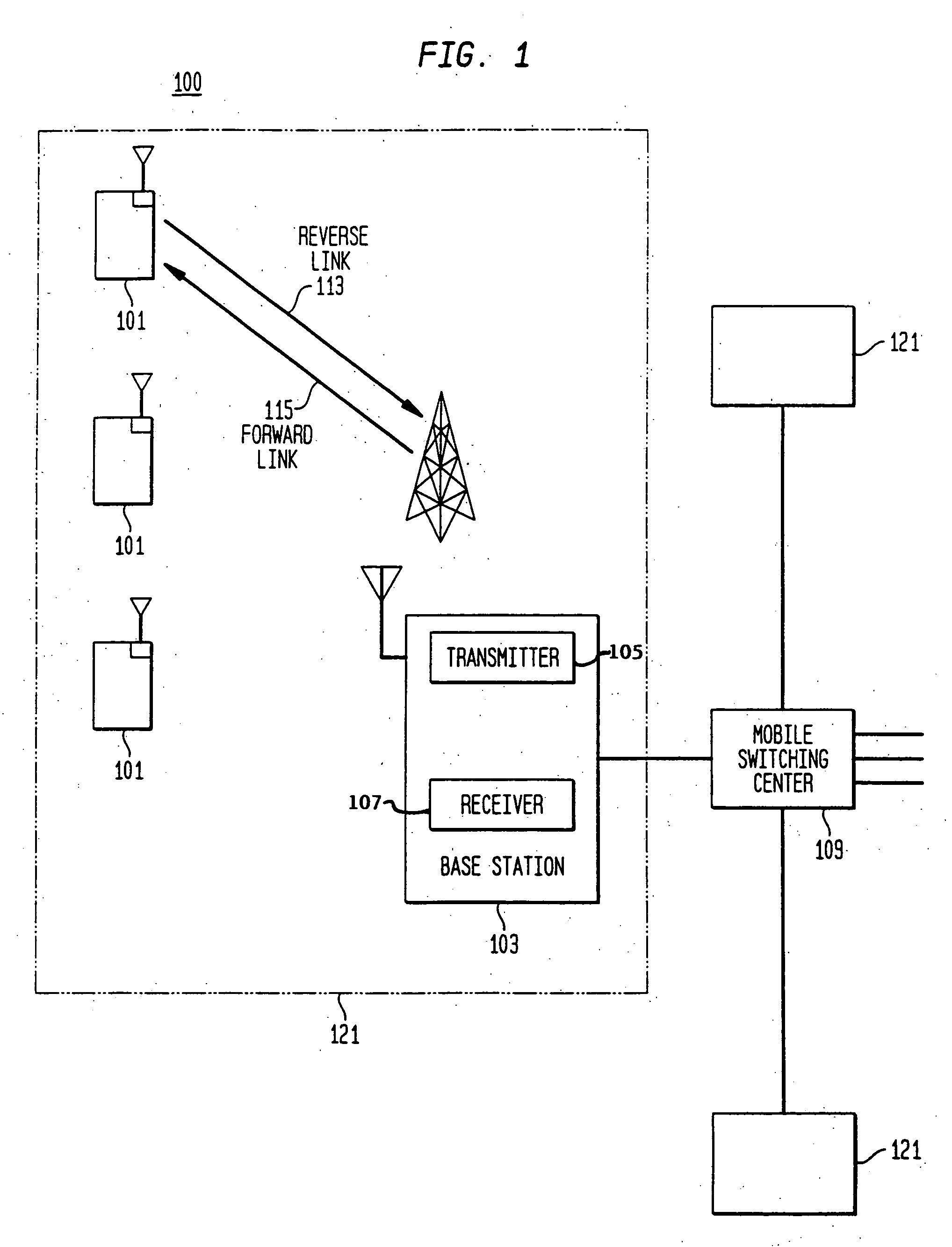
Uplink interference cancellation
InactiveUS7443829B2Reduce delaysImprove latencyTime-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInterference cancelationThird generation
The present invention provides a method of improving the performance of a CDMA based wireless network, such as a 3G cellular network for example. Interference cancellation is effectively performed earlier by using the channel request such as a reservation packet from a mobile terminal to estimate interference from that mobile on existing mobile users and interference on the mobile from existing mobile users, by determining the relative transmission timing of the new mobiles channel request compared with the transmission timings of the existing mobiles. The base station determine the cross-correlation between the codes already assigned to the existing users and the code to be allocated to the new user in order to determine an interference measure. This interference can then be cancelled from the new mobile when its data packets are received.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
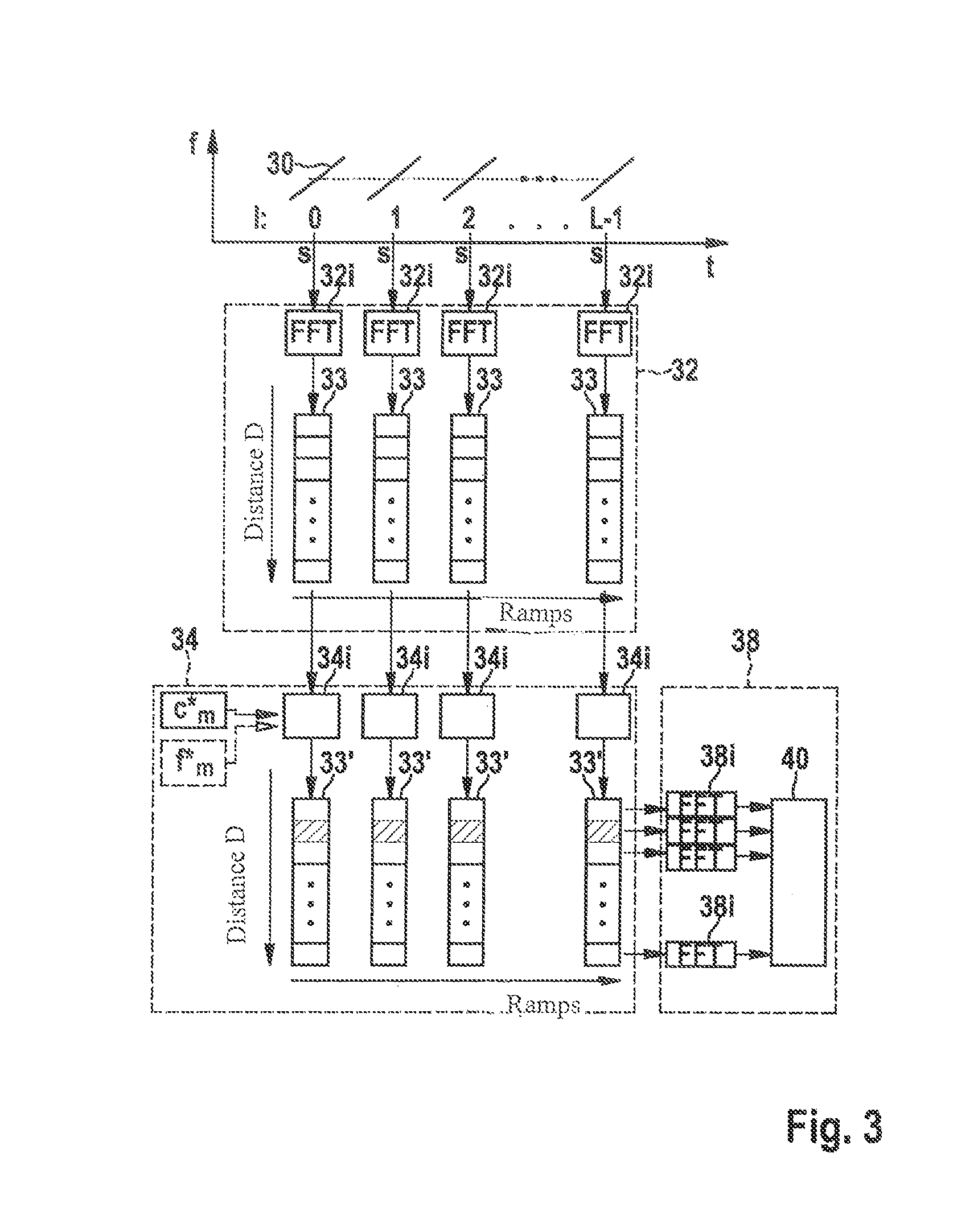
Interference cancellation in an fmcw radar
ActiveUS20160124075A1Increase the number ofIncrease probabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterference cancelationRadar systems
A radar system for transmitting a FMCW radar sensor signal encompassing a series of frequency modulation ramps and phase-modulated with a first code sequence orthogonal to a respective other code sequence with which a time-synchronized transmitted signal of another FMCW radar sensor is phase-modulated; the radar echoes are phase-demodulated with a code sequence correlating with the first code sequence; and a distance and / or a relative speed of a localized object is identified from a Fourier analysis frequency spectrum, in a first dimension over sampled radar echo values of a frequency modulation ramp, and in a second dimension over the phase-demodulated sequence of radar echoes of the ramps of the transmitted signal; and a vehicle fleet radar system having an FMCW radar sensor in which a code set satisfying a code set orthogonality condition with a code set of a radar sensor of another vehicle is used for phase modulation / demodulation.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Soft weighted interference cancellation for CDMA systems
ActiveUS20060227854A1Quantity maximizationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionInterference eliminationInterference cancelation
Interference is cancelled from a baseband signal by synthesizing interference from estimated symbols in interfering subchannels. The estimated symbols are hard-coded, soft weighted, or zeroed, depending on the value of an estimated pre-processed signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio (SINR) in each subchannel in order to maximize a post-processed SINR. The estimated pre-processed SINR is obtained from averages of estimated symbol energies and estimated noise variances, or from related statistical procedures.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Relayed communication with versatile self-interference cancellation
InactiveUS20050190870A1Error preventionRepeater/relay circuitsSelf interferenceInterference cancelation
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are presented for providing self-interference cancellation in two-way relayed electromagnetic communication between a first and a second device through a relay station, involving retrofitting existing equipment comprising a transmitter system and a receiver system at the first device by adding a canceler module, providing a version of a modulated near signal as a first non-baseband interface signal from the transmitter system to the canceler module, providing a version of a composite signal as a second non-baseband interface signal from the receiver system to the canceler module, generating a cancellation signal at the canceler module corresponding to a relayed version of the modulated near signal, using the first and the second non-baseband interface signals, applying the cancellation signal at the canceler module to a version of the second non-baseband interface signal, to produce a cancellation-processed signal as a third non-baseband interface signal provided to the receiver system.
Owner:VIASAT INC
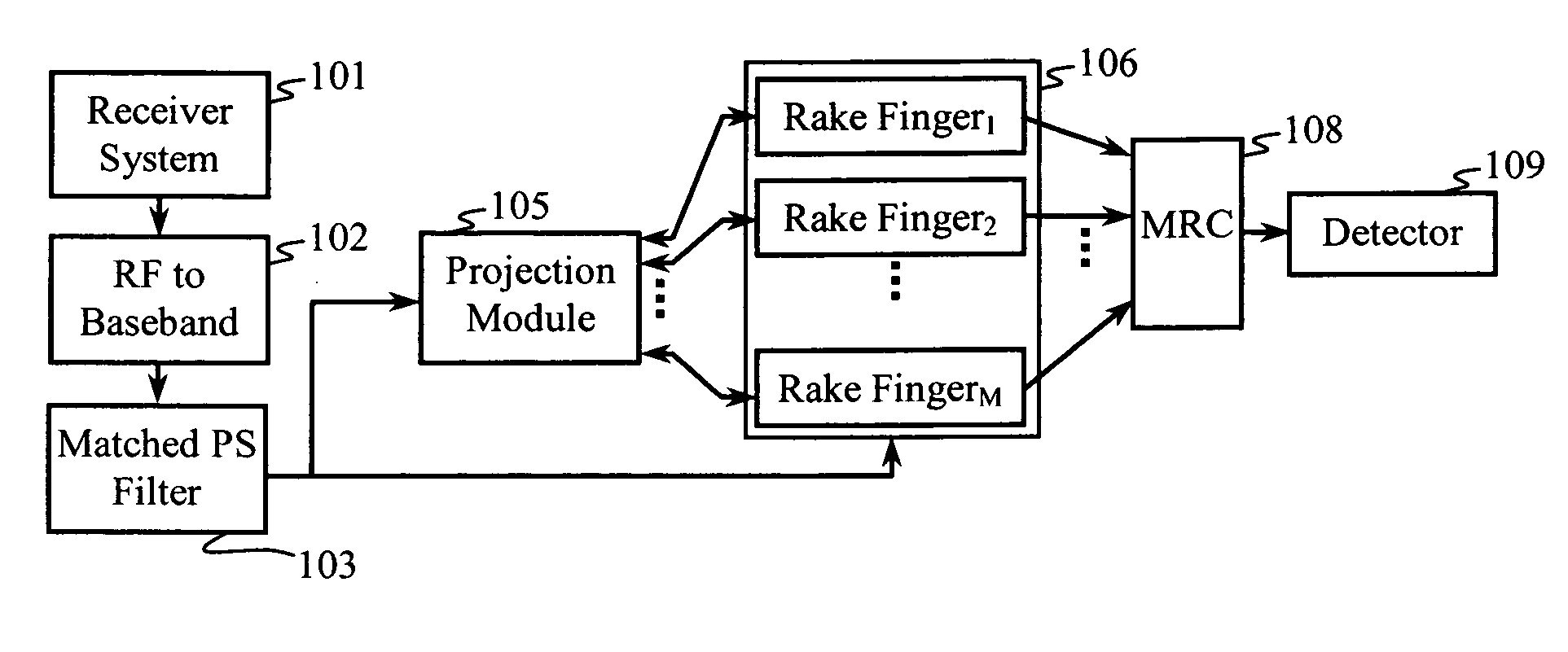
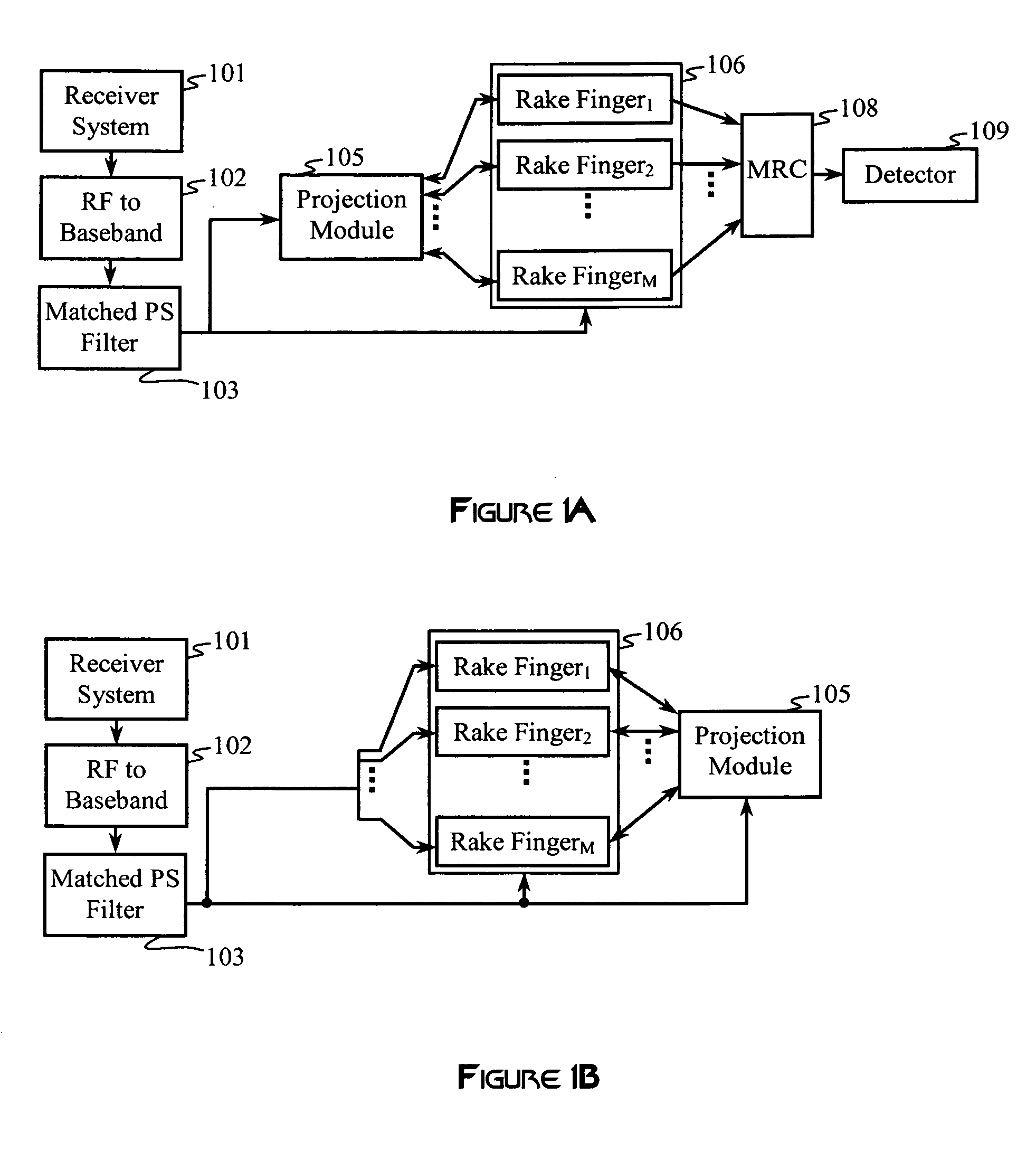
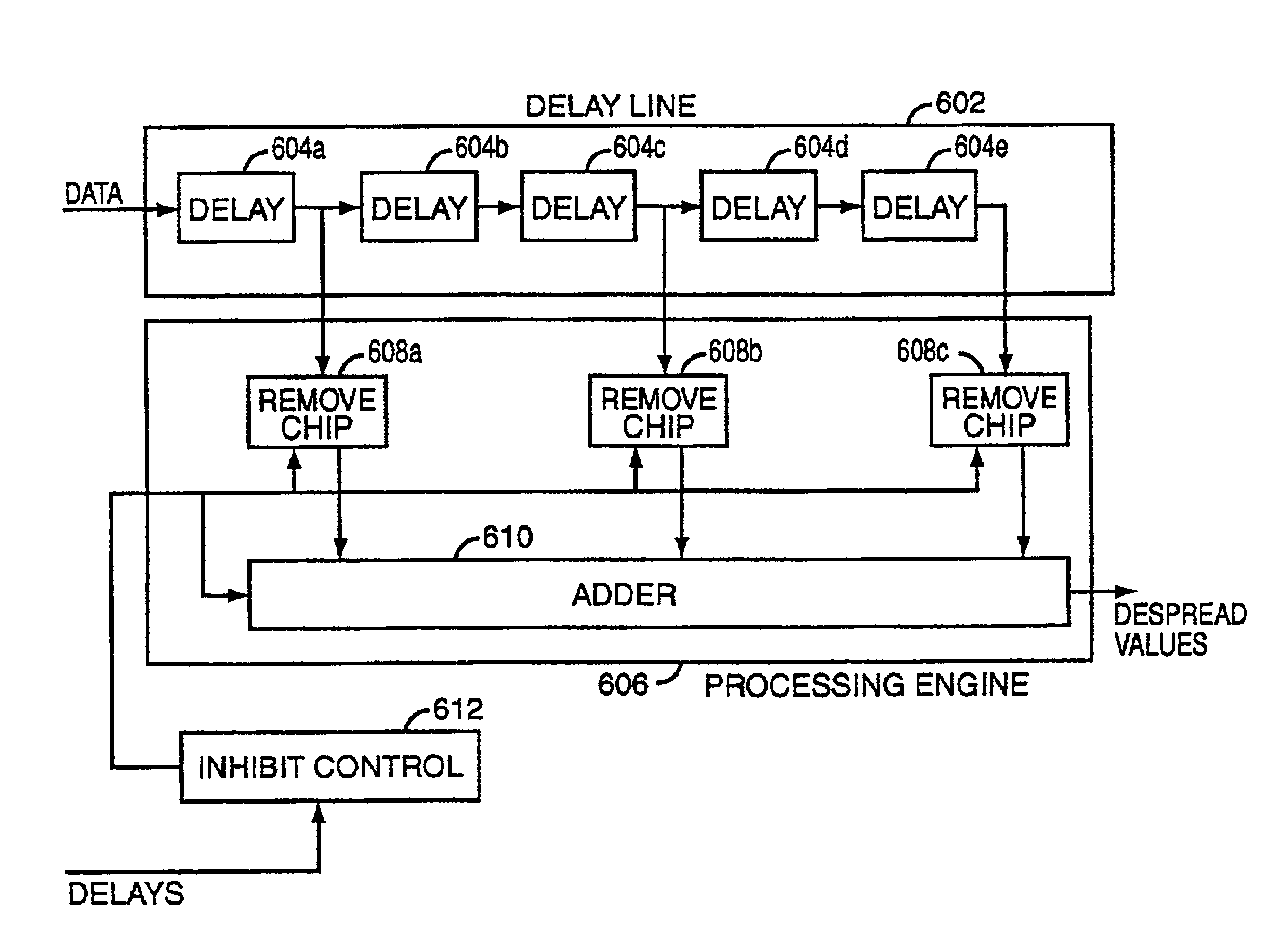
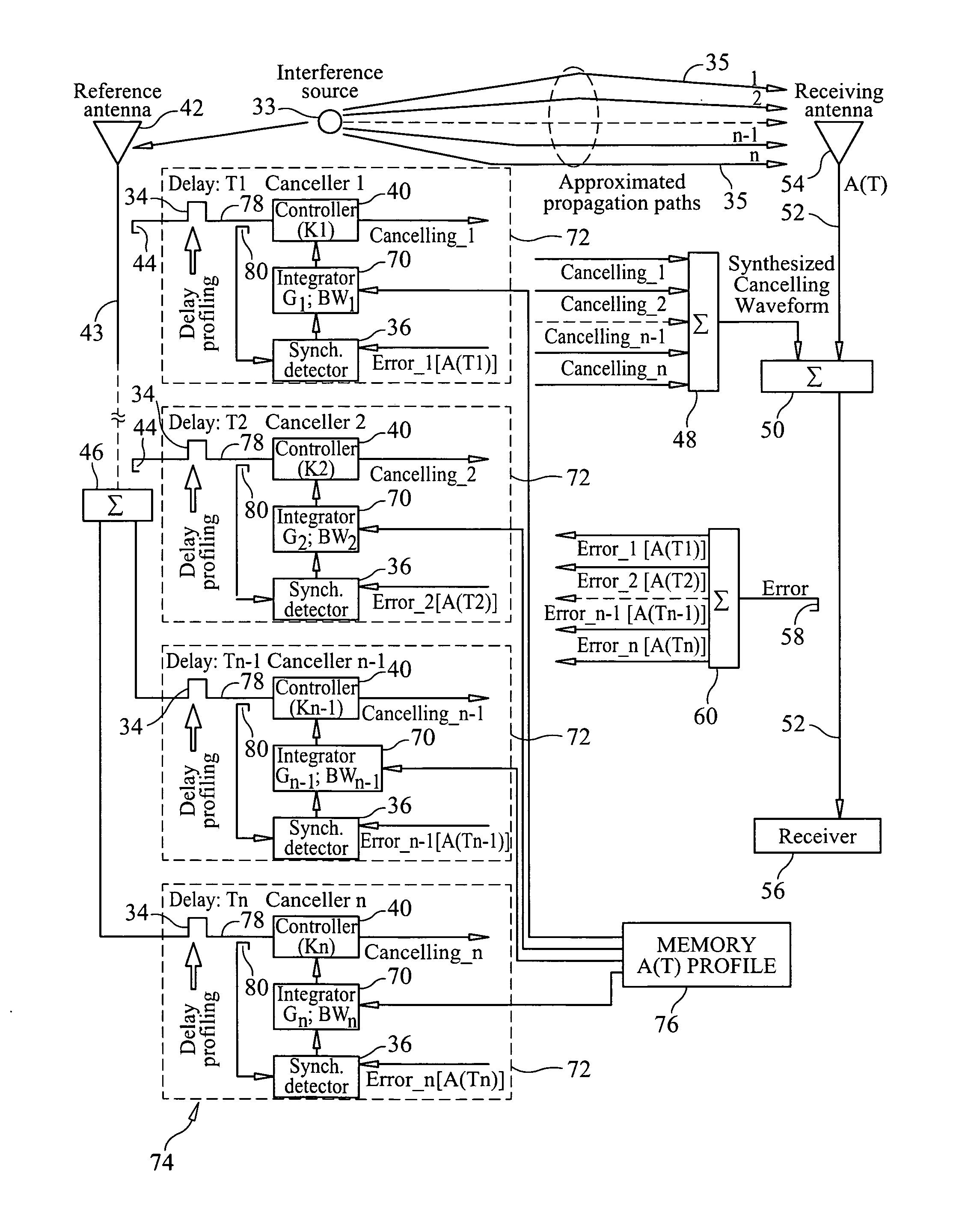
Method and apparatus for interference cancellation in a rake receiver
InactiveUS6842479B2Transmission control/equalisingAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsInterference cancelationRake receiver
Systems and methods for despreading received spread spectrum signals are described. Despreading can be performed using both channel estimates and impairment correlation estimates. Techniques for selecting delays of interest are also described, along with a despreading mechanism which saves power by operating only on delays of interest.
Owner:HIGHBRIDGE PRINCIPAL STRATEGIES LLC AS COLLATERAL AGENT
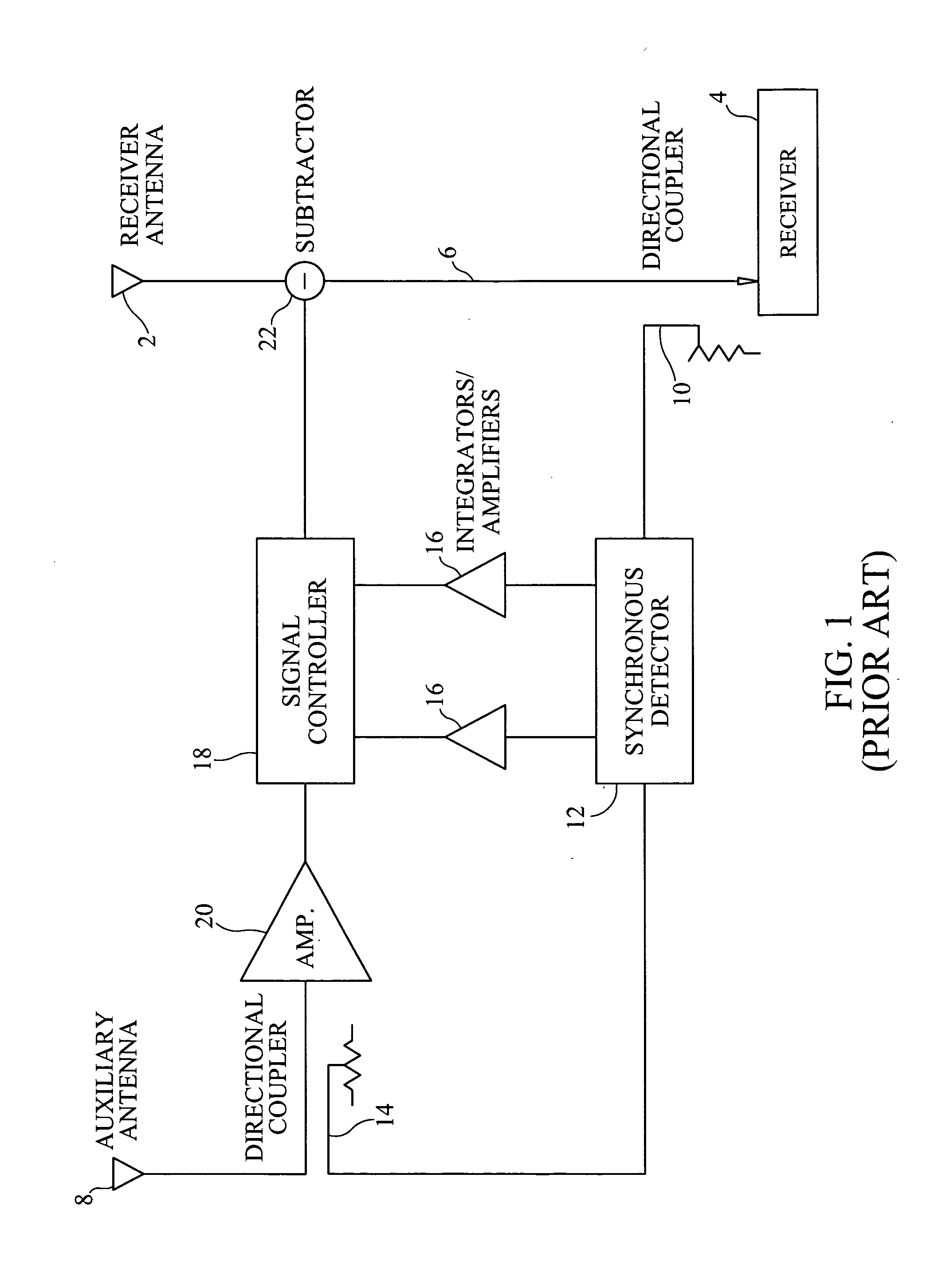
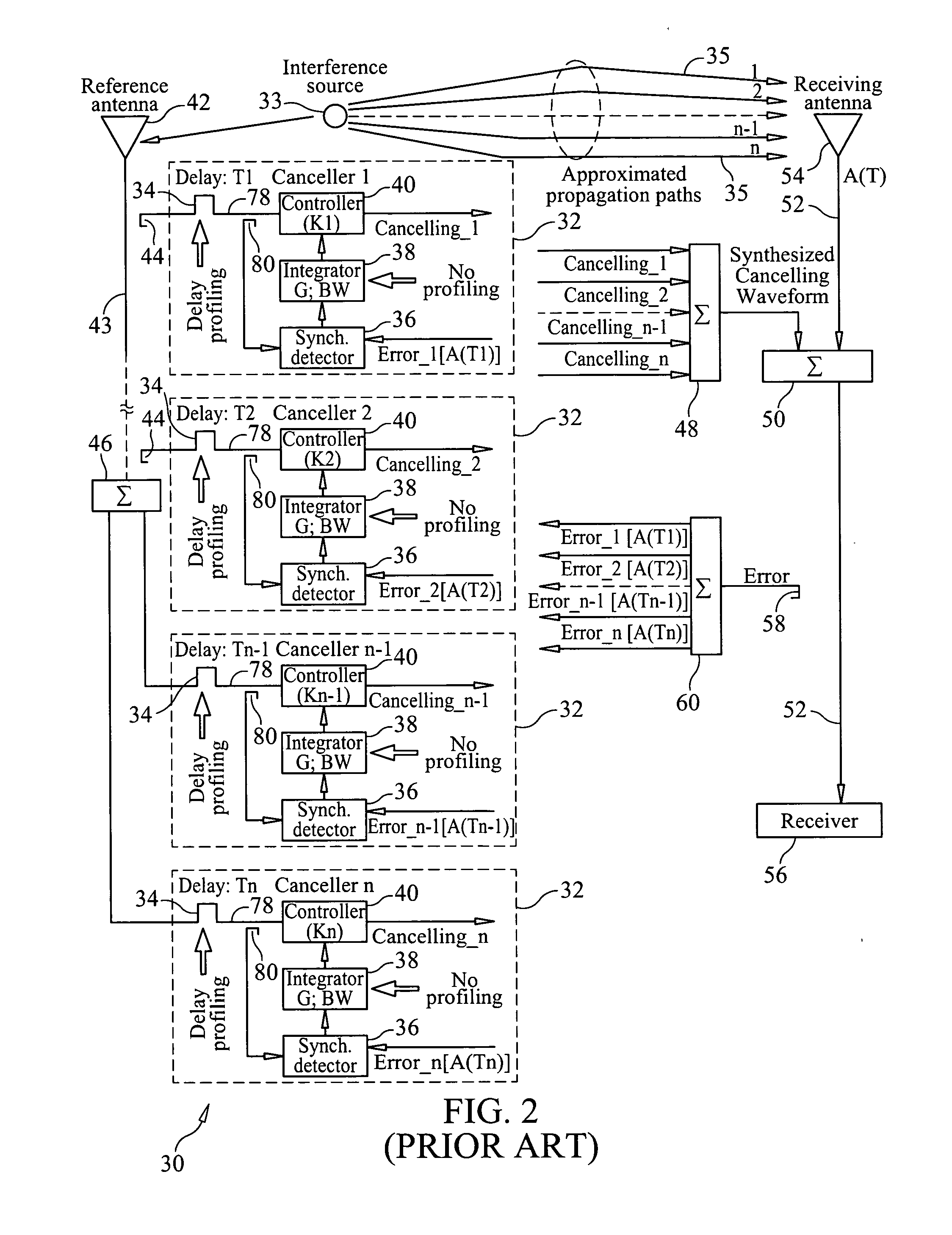
Adaptive cancellation of multi-path interferences
ActiveUS20110319044A1Minimize and eliminate signalMinimize or eliminate unwanted signals arrivingRadio transmissionIntegratorInterference canceller
A multi-path signal interference cancellation system cancels multiple time delayed signal components of a multi-path interference signal received by a receive antenna and carried on a receiver transmission line of a radio receiver system. The interference cancellation system includes a plurality of adaptive interference canceller circuits, each of which has a synchronous detector, a signal controller and an integrator as essential parts of closed control loops defined by the canceller circuits. The integrator has gain and bandwidth characteristics associated therewith which are adjustable to adjust the gain and bandwidth of each closed control loop. An intensity profile of the multi-path interference signal is generated and stored in a memory. An intensity profile signal from the memory is provided to the integrator of each adaptive interference canceller circuit to adjust the gain and bandwidth of the integrator and the loop in which it is situated to maximize the error detection residual signal-to-noise ratio of each adaptive interference canceller circuit. Each adaptive interference canceller circuit generates a cancellation signal from which a synthesized cancellation signal is generated and effectively injected onto the receiver transmission line to cancel the multiple time delayed signal components of the multi-path interference signal carried thereon so that the radio receiver of the radio receiver system only receives a desired signal.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
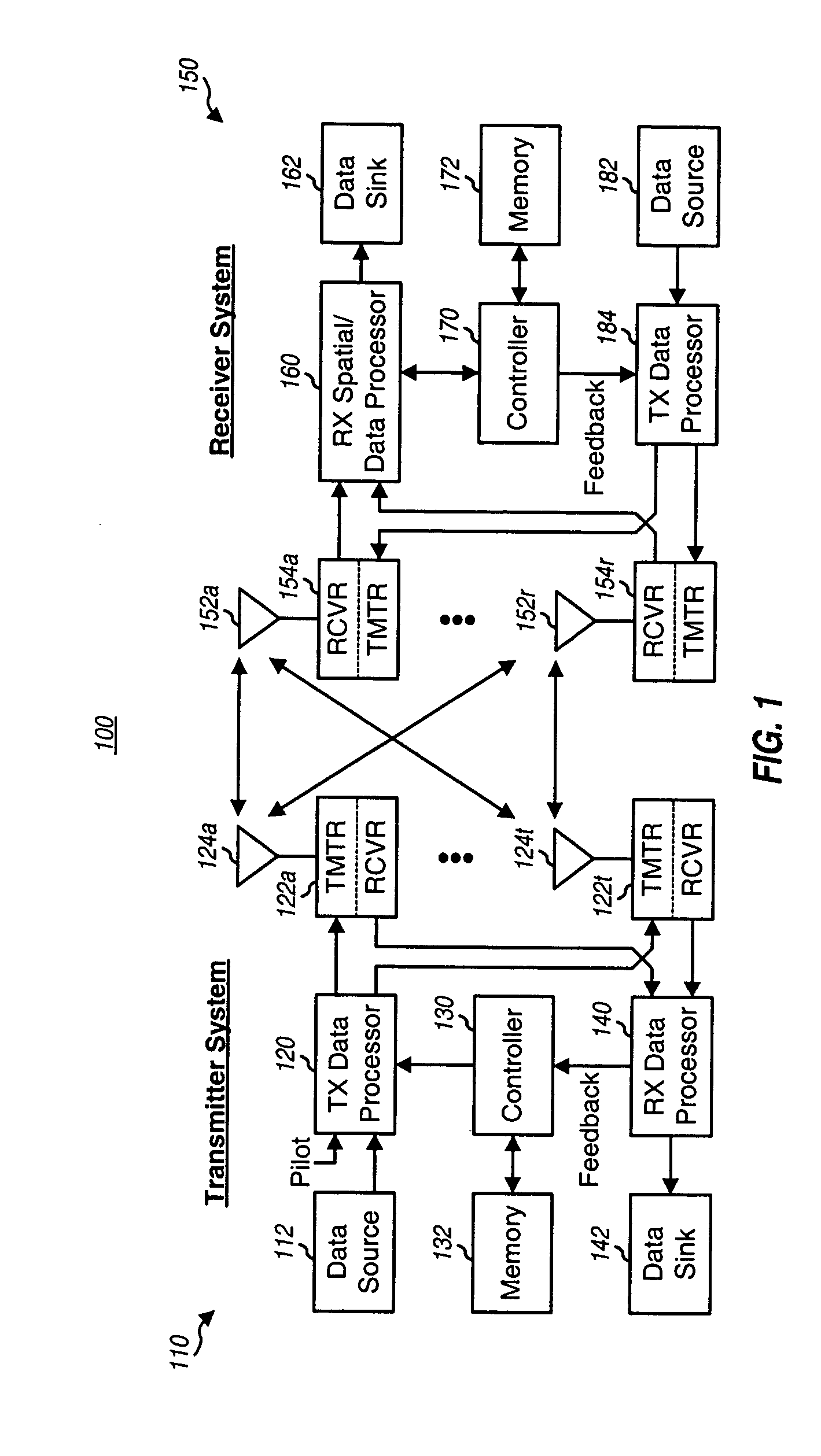
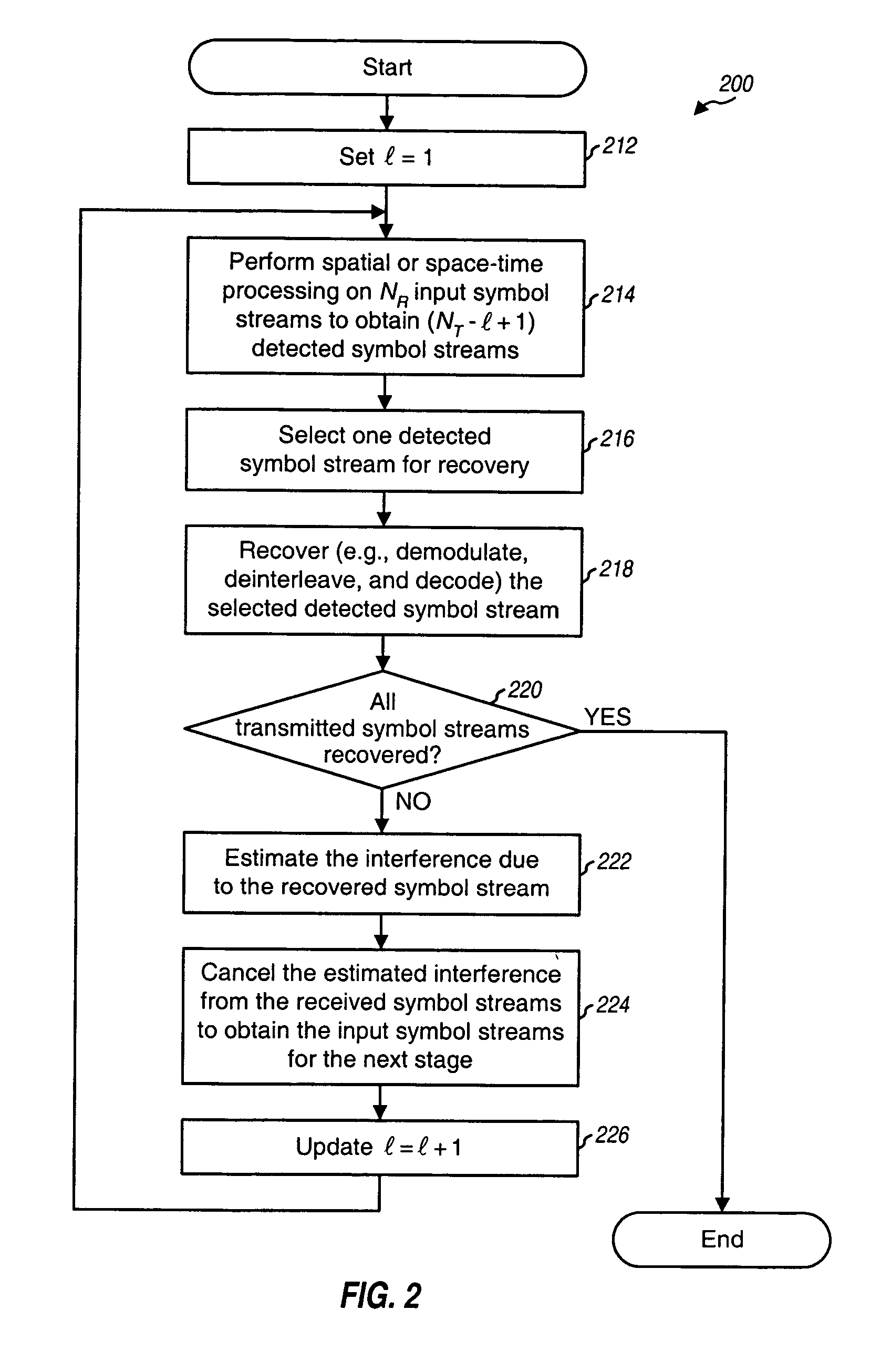
Successive interference cancellation receiver processing with selection diversity
InactiveUS20050075073A1Spatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsInterference cancelationData rate
Techniques are provided to support successive interference cancellation (SIC) receiver processing with selection diversity whereby each of NT transmit antennas may be turned on or off. One symbol stream may be transmitted from each transmit antenna. A SIC receiver recovers the transmitted symbol streams in a specific order. Up to NT! orderings are evaluated. For each ordering, NT post-detection SNRs are obtained for NT transmit antennas and used to determine NT data rates, where the data rate is zero if the post-detection SNR is worse than a minimum required SNR. An overall data rate is computed for each ordering based on the NT data rates. The ordering with the highest overall data rate is selected for use. Up to NT symbol streams are processed at the data rates for the selected ordering and transmitted. The transmitted symbol streams are recovered in accordance with the selected ordering.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and device for interference cancellation in a CDMA wireless communication system
ActiveUS7099377B2Reduce complexityError preventionSpeech analysisInterference cancelationCommunications system
The method of interference cancellation in a CDMA wireless communication system comprises receiving an incident digital signal containing a user signal transmitted on a CDMA user physical channel and an interfering signal, projecting said incident digital signal onto a projection space orthogonal to the space containing said interfering signal, filtering said projected signal with a filter matched to the CDMA user physical channel for detecting the data contained in said user signal.
Owner:MICROELECTRONIC INNOVATIONS LLC
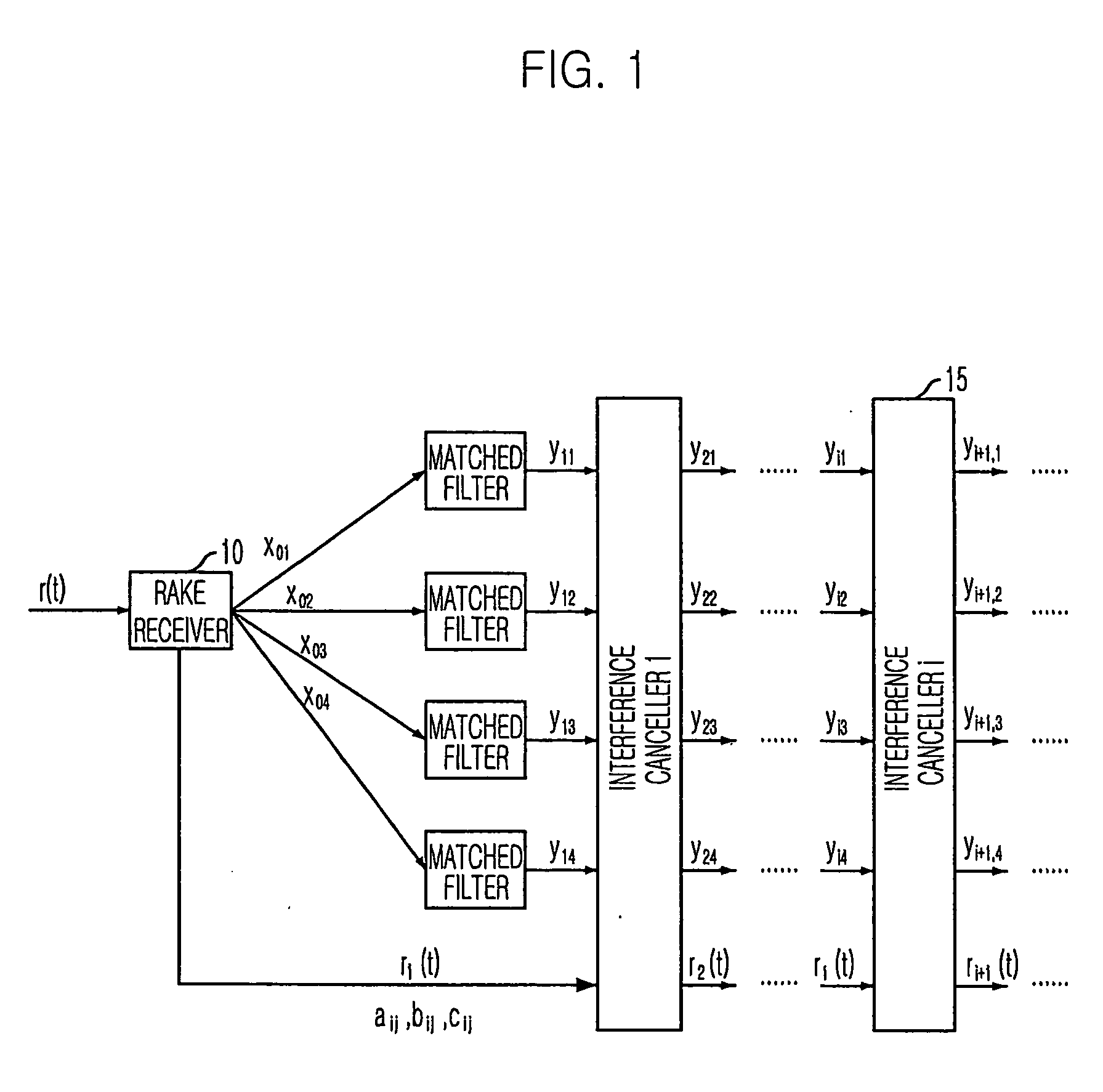
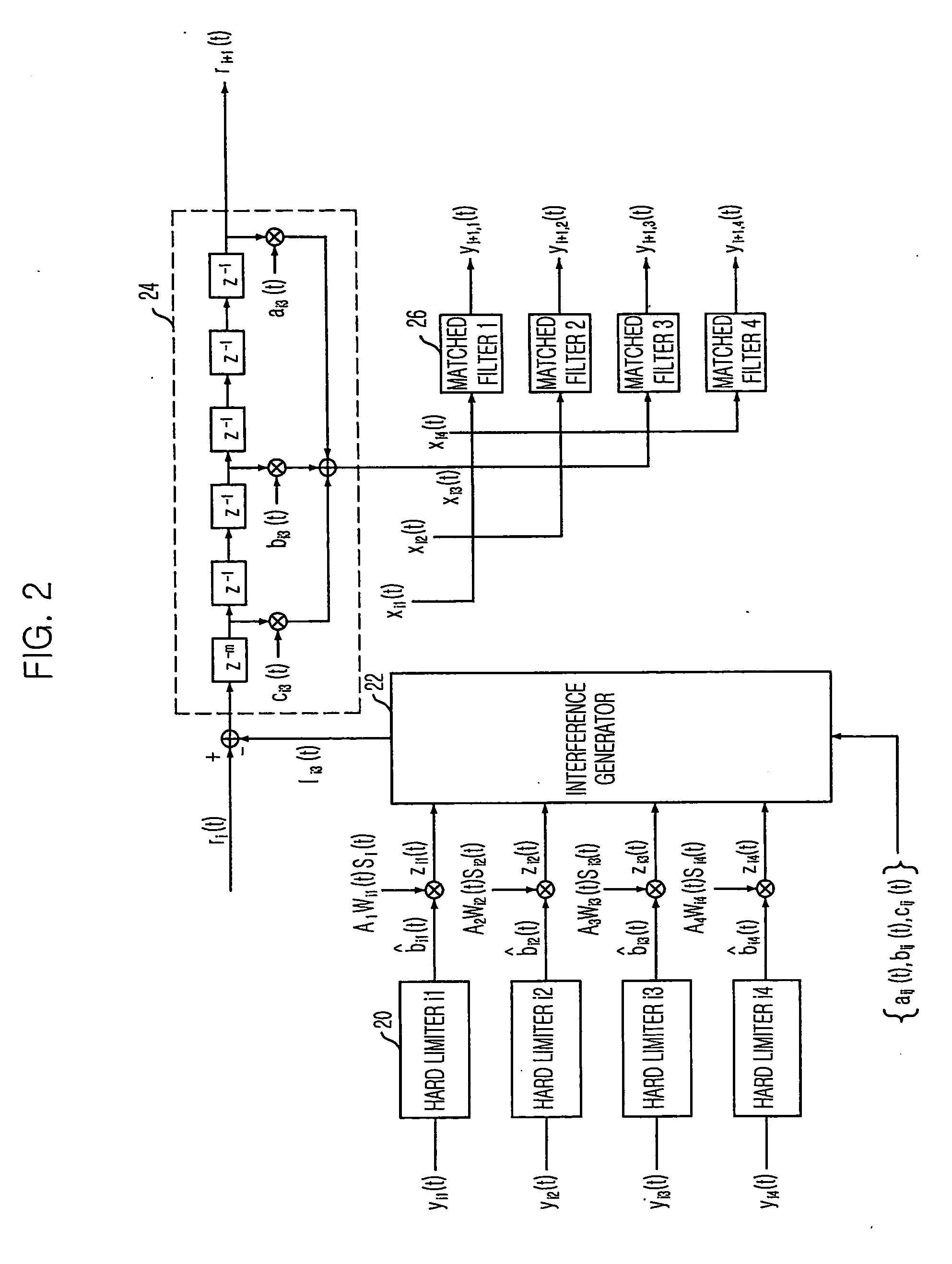
Multistage adaptive parallel interference canceller
InactiveUS20060013289A1Minimizing degradation of orthogonalityReduce circuit complexityCode division multiplexTransmissionInterference cancellerInterference elimination
A multistage adaptive parallel interference canceller is disclosed. The multistage adaptive parallel interference canceller for a downlink receiver includes: a plurality of stages of interference cancellation units. Each of interference cancellation units includes: a matched filter for matching a signal from a rake receiver each channel signal and generating a matched signal; a soft decision unit of which a slope is monotonically increased, for performing soft decision of the matched signal and generating a soft-decided signal; a weight controller for controlling the slope of the soft decision unit; a respreader for respreading the soft-decided signal based on a walsh code and a scrambling code and generating a respread signal; an interference calculator for calculating interference signals due to another user signal and multipath signals; and an interference canceller for canceling the interference signals from an input signal received in the rake receiver.
Owner:HWANG IN KWAN
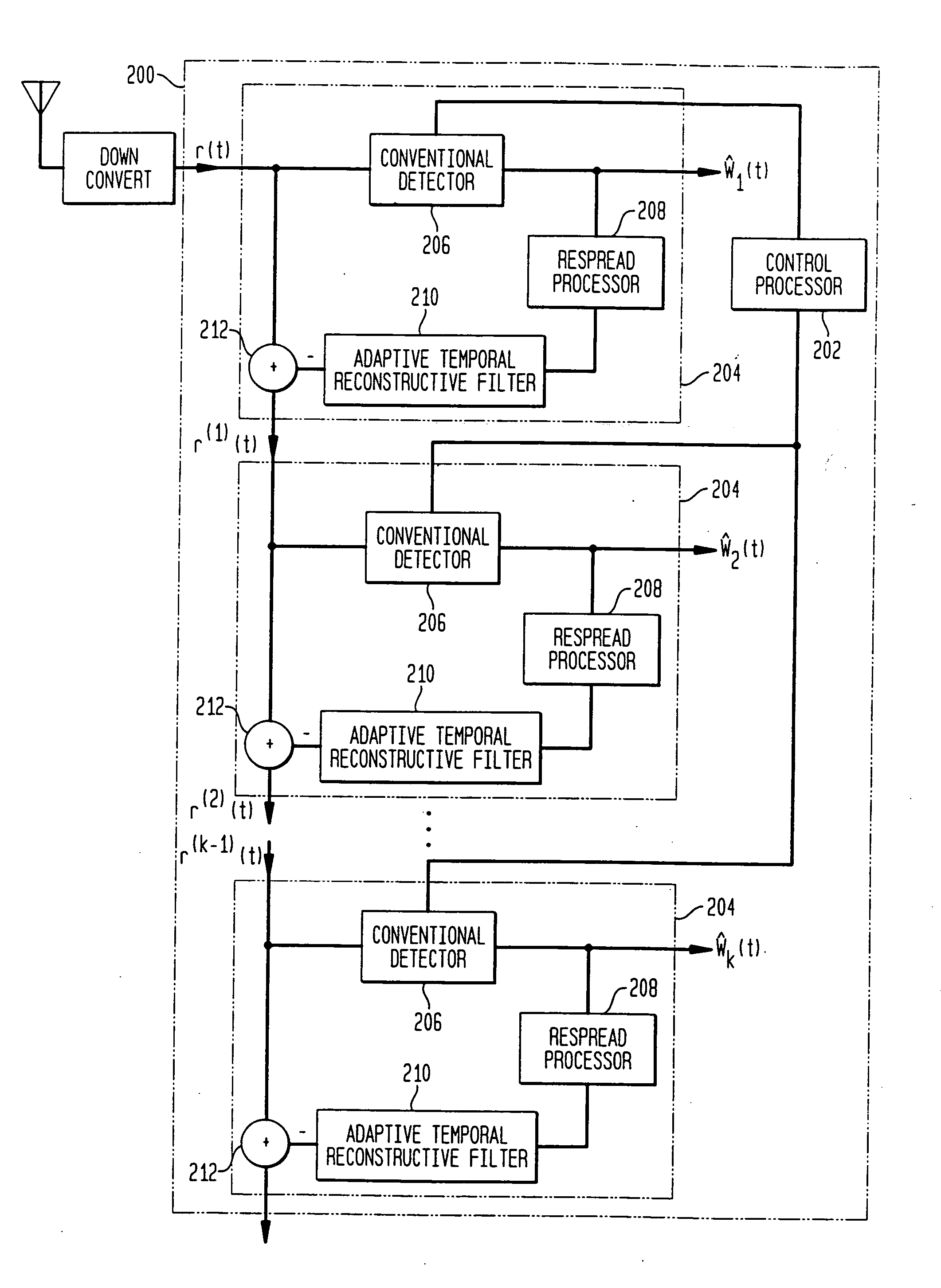
Combined adaptive spatio-temporal processing and multi-user detection for CDMA wireless systems
ActiveUS20050128985A1Reduce cancellationAccurate estimateRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesEngineeringCo-channel interference
Methods and systems in a wireless receiver for enabling the reception of input signals at varied power levels in the presence of co-channel interference utilizing combinations of space-time adaptive processing (STAP), interference cancellation multi-user detection (MUD), and combined STAP / MUD techniques. In MUD, code, timing, and possibly channel information of multiple users are jointly used to better detect each individual user. The novel combination of adaptive signal reconstruction techniques with interference cancellation MUD techniques provides accurate temporal cancellation of interference with minimal interference residuals. Additional methods and systems extend adaptive signal reconstruction techniques to take Doppler spread into account. STAP techniques permit a wireless receiver to exploit multiple antenna elements to form beams in the direction of the desired signal and nulls in the direction of the interfering signals. The combined STAP-MUD methods and systems increase the probability of successful user detection by taking advantage of the benefits of each reception method. An additional method and system utilizes STAP techniques in the case where no pilot signal is available. This method compares the outputs of various hypothesized STAP solutions.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
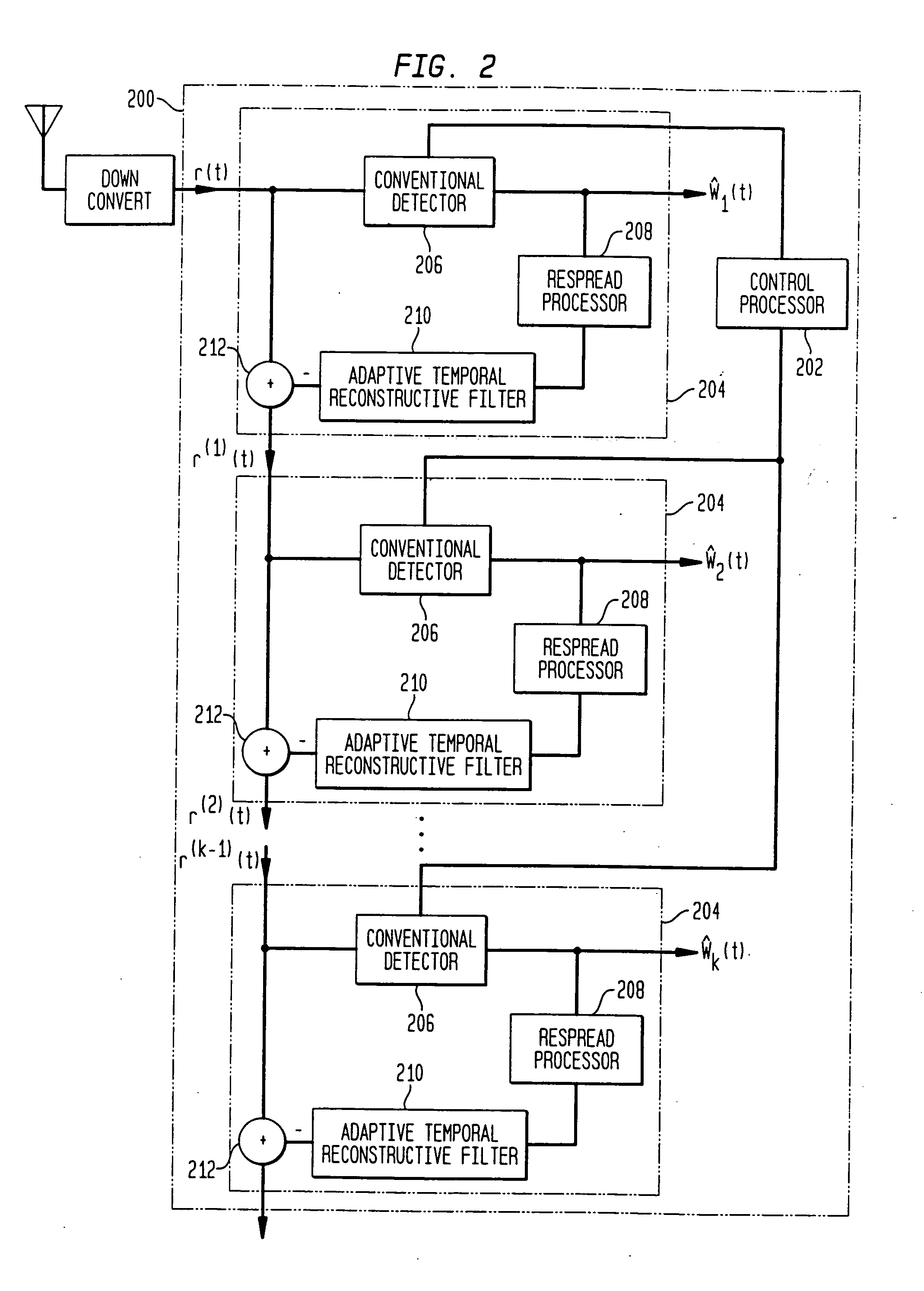
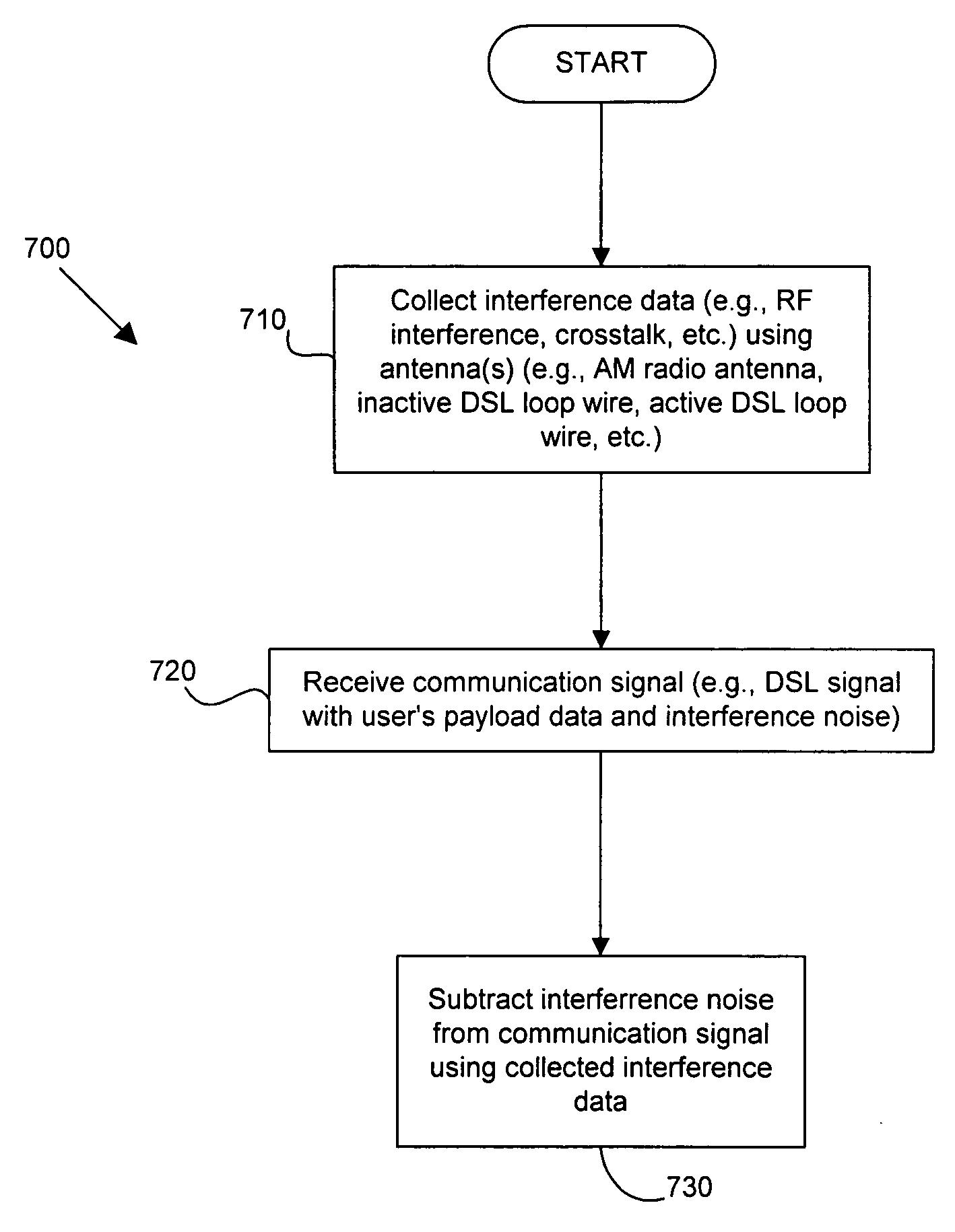
Interference cancellation system
ActiveUS20060039454A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsError preventionInterference cancelationInterference canceller
A DSL or other communication system includes a modem or other communication device having at least one antenna that is configured to collect interference data relating to interference noise affecting communication signals being received by the communication device. The interference may include RF interference, such as AM radio interference, crosstalk and other types of interference from various sources. The interference data collected by the antenna is used by an interference canceller to remove and / or cancel some or all of the interference affecting received signals. In some embodiments of the present invention, more than one antenna may be used, wherein each antenna can collect interference data pertaining to a single source of interference noise. Where a modem or other communication device is coupled to multiple telephone lines, only one of which is being used as the active DSL line, wires in the remaining telephone lines or loops can be used as antennas. Moreover, the antenna may be an antenna, per se, such as a compact AM radio antenna or any other suitable structure or device for collecting the type(s) of interference affecting signals received by the communication device.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Systems approach to interference cancellation
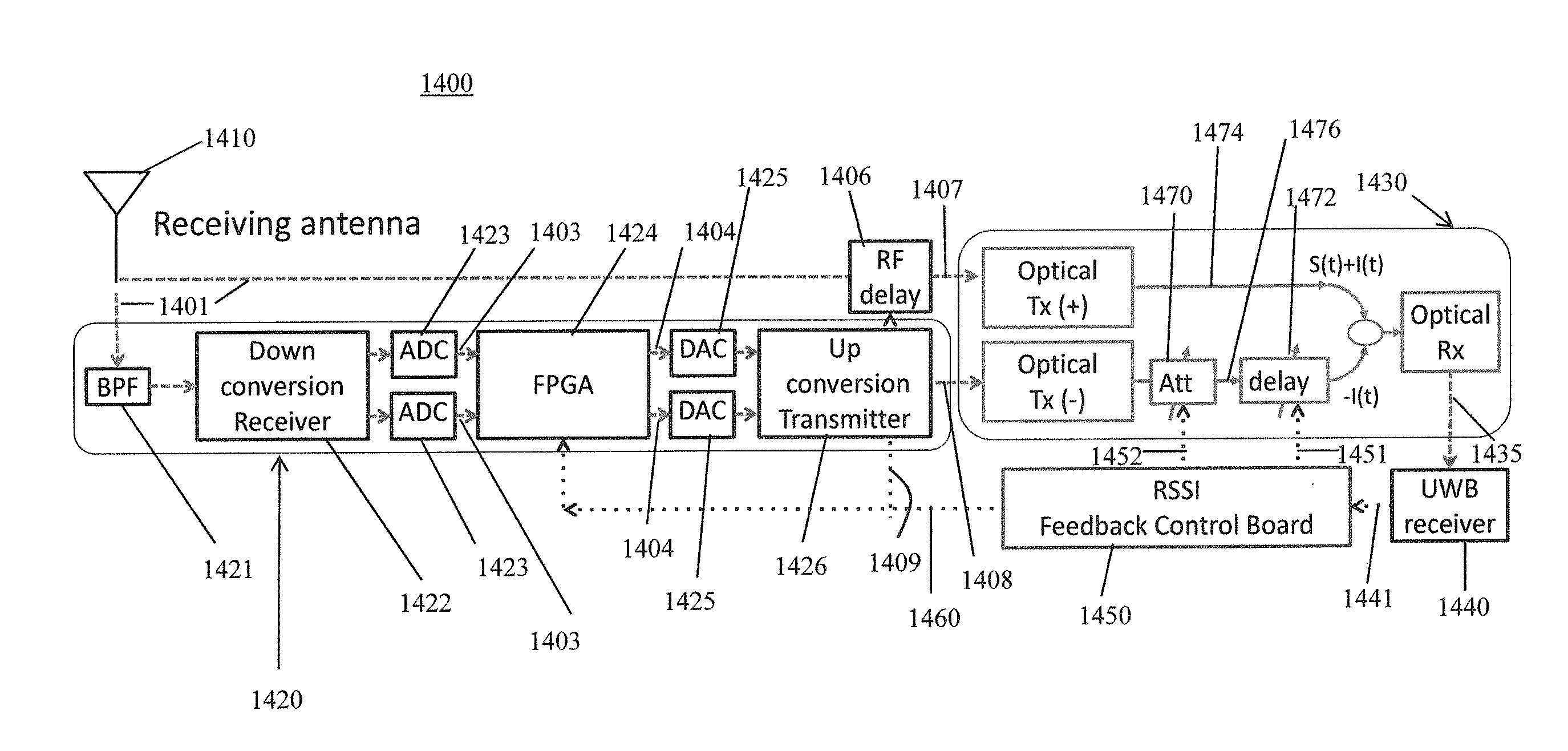
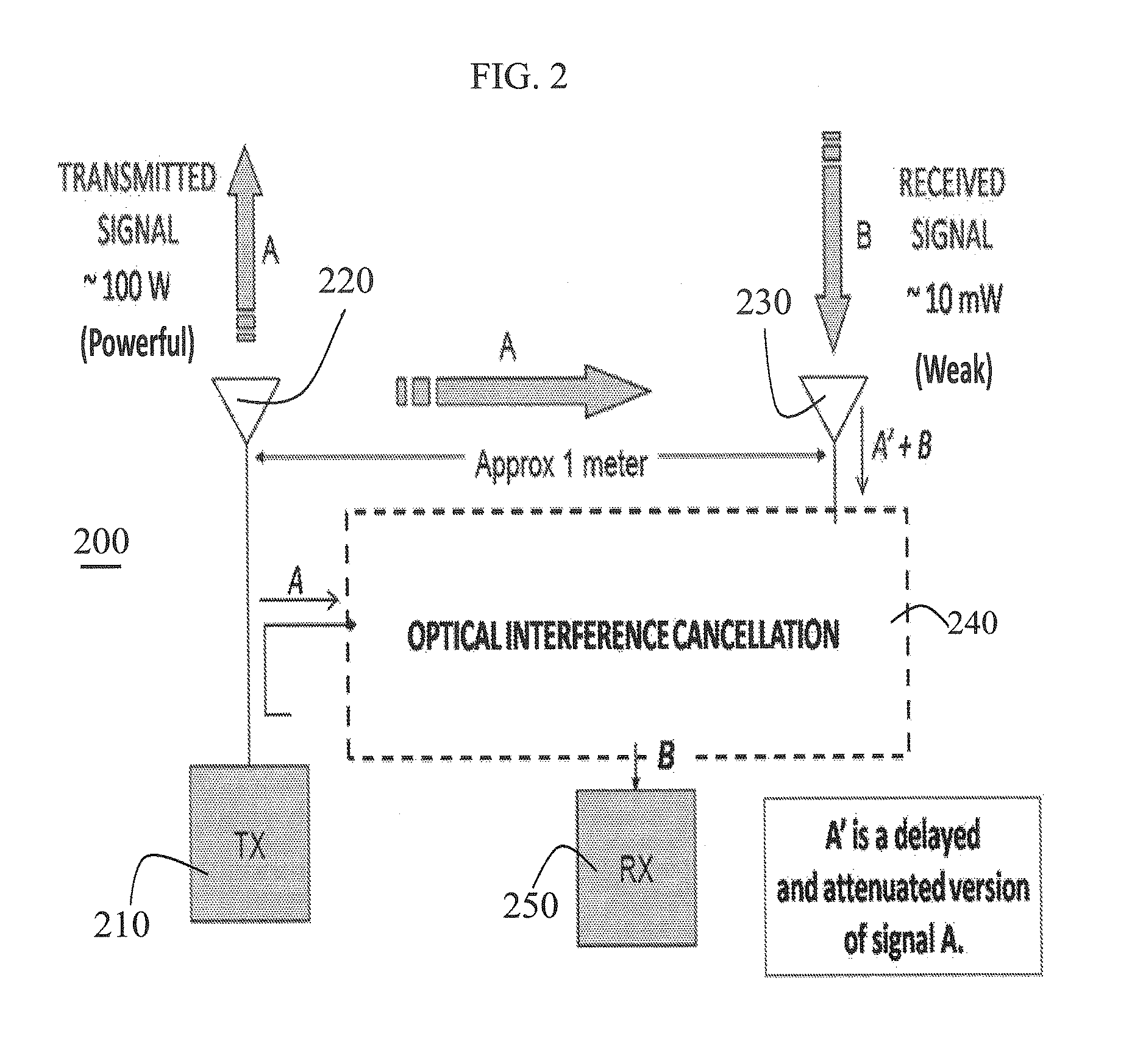
ActiveUS9571205B1Light demodulationElectromagnetic receiversInterference cancelationMultipath interference
Disclosed is a system and method of combining optical interference cancellation with other methods of interference cancellation, including electronic cancellation, digital filtering, and beam steering algorithms, to remove co-located interference, remote interference of an unknown origin, and multipath interference components created by reflections of signals both known and unknown.
Owner:BASCOM HUNTER TECH +1
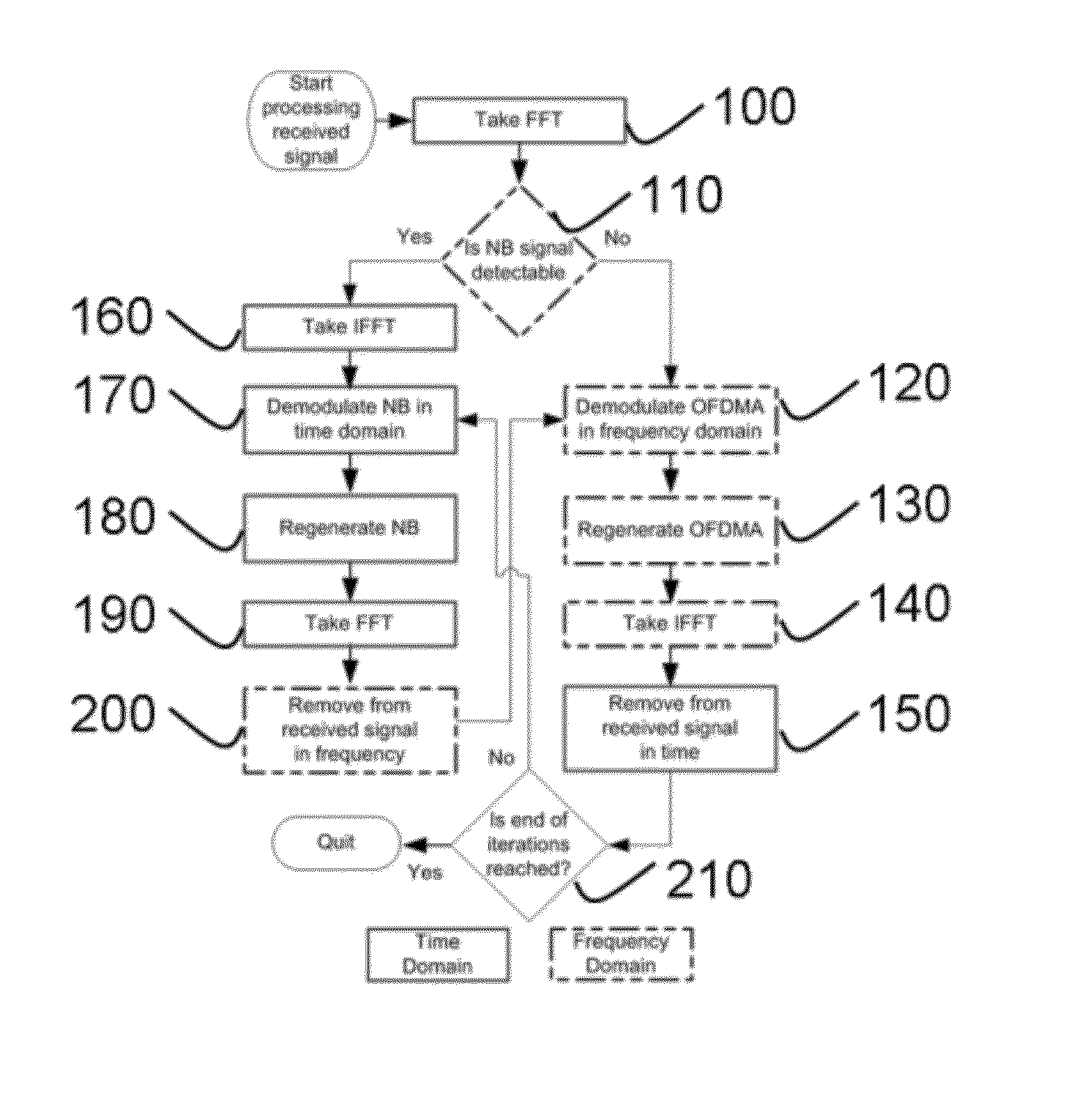
Method for iterative interference cancellation for co-channel multi-carrier and narrowband systems
ActiveUS8155595B2Improve performanceInherent signal separationError preventionTransmission path divisionChannel impulse responseCarrier signal
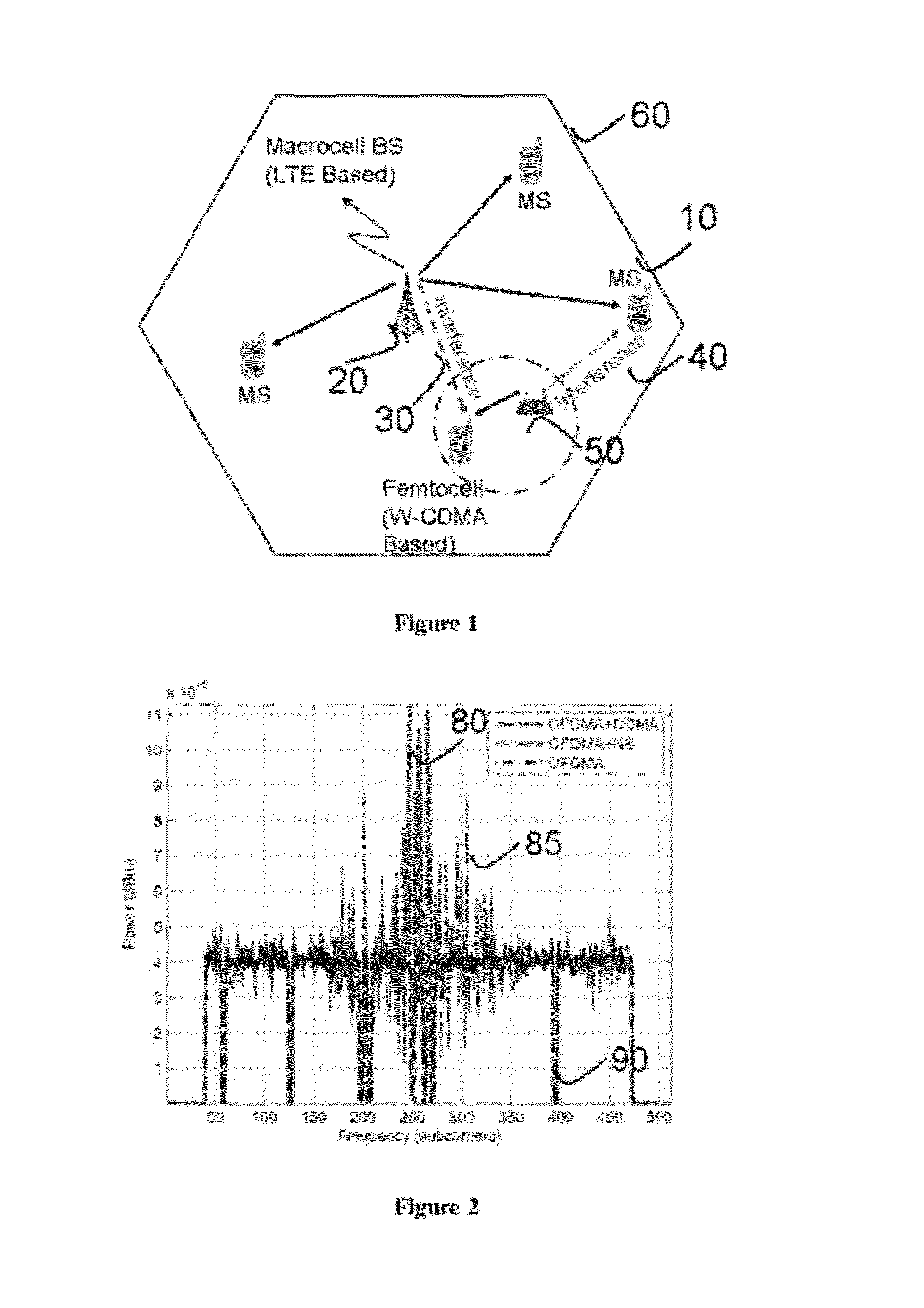
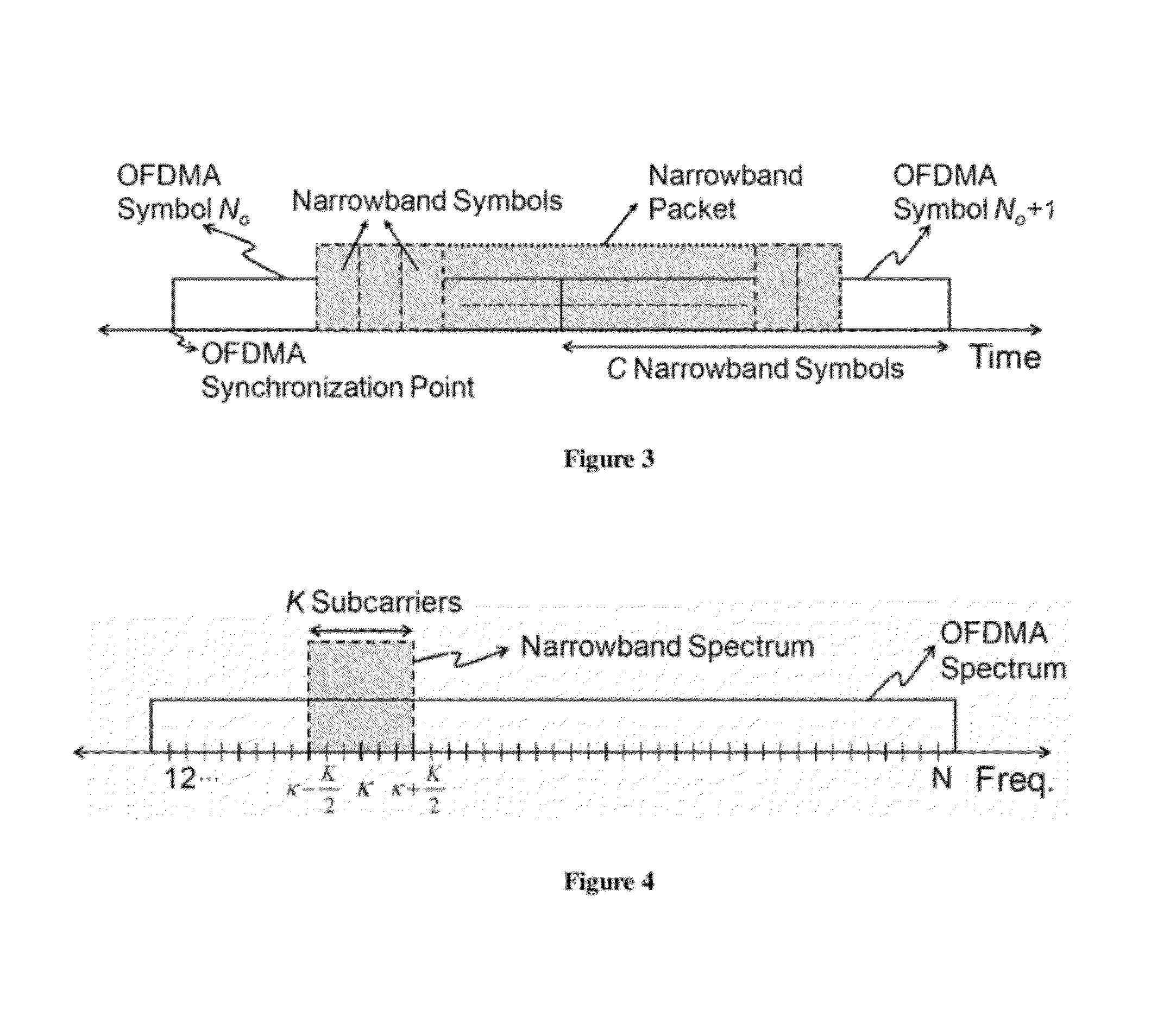
In a co-channel deployment of narrowband and multi-carrier technologies (e.g., a femtocell and a macrocell), a method provides cancelling of interference which treats the co-channel signals as desired signals and enhances each of them iteratively. At each iteration, each signal is demodulated and regenerated based on symbol decisions already made and a predetermined channel impulse response. To estimate the other (interfering) co-channel signal, the regenerated signal is subtracted from the aggregate signal. Simulations have shown that a method of the present invention can provide fundamental improvement in the performances of both interfering systems in as few as two iterations. The fundamental performance gain that can be obtained outweigh the required computational burden.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com