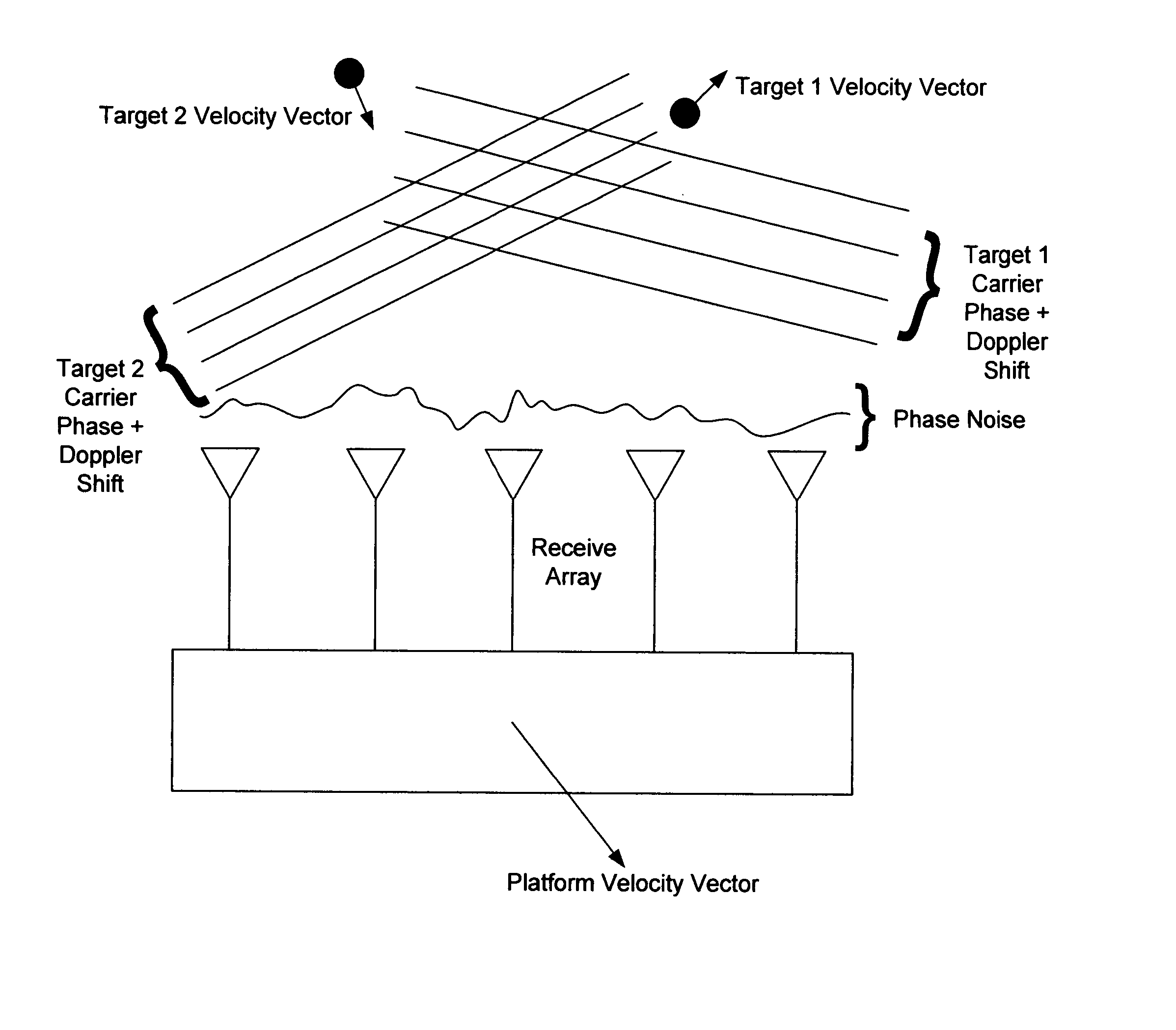
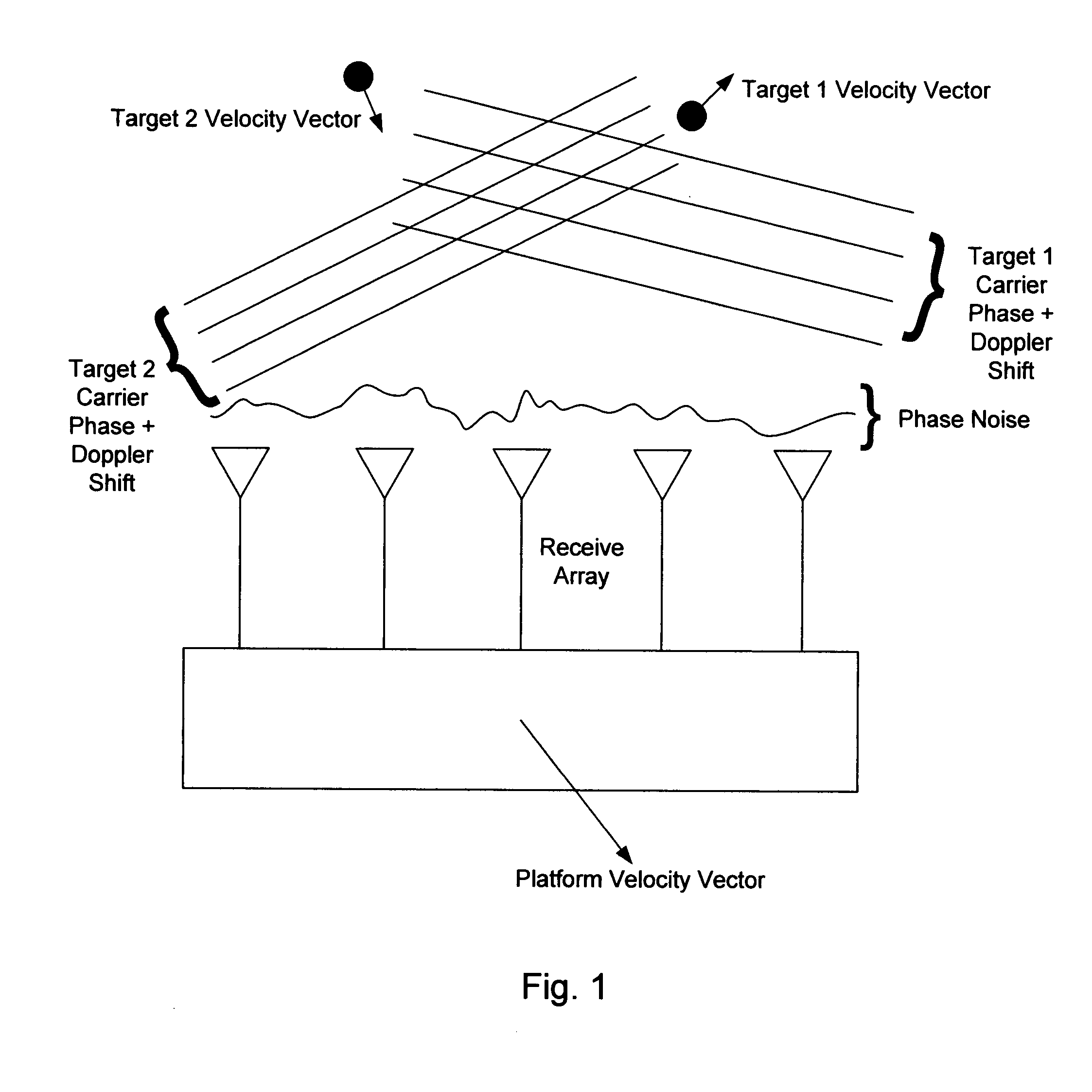
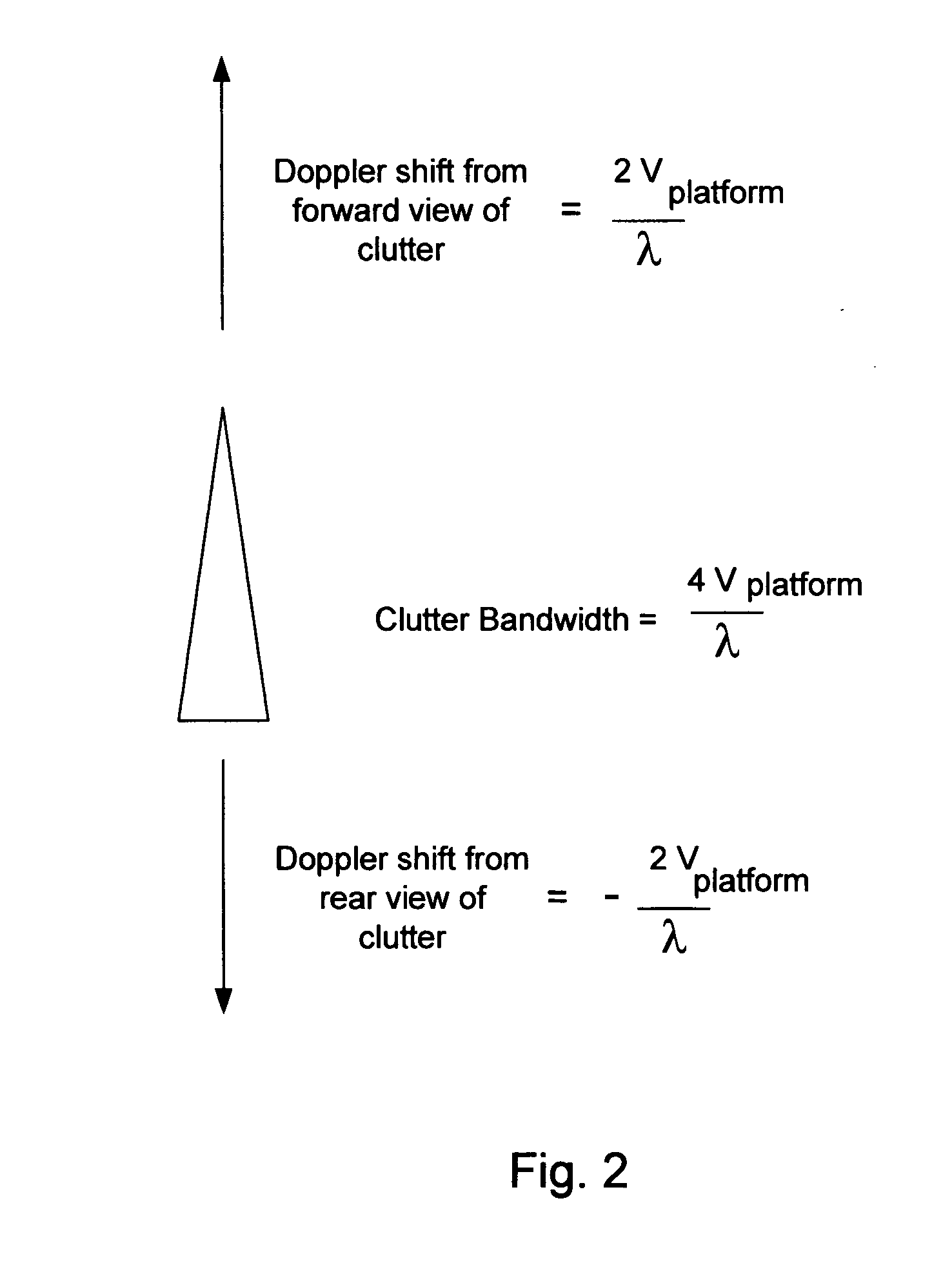
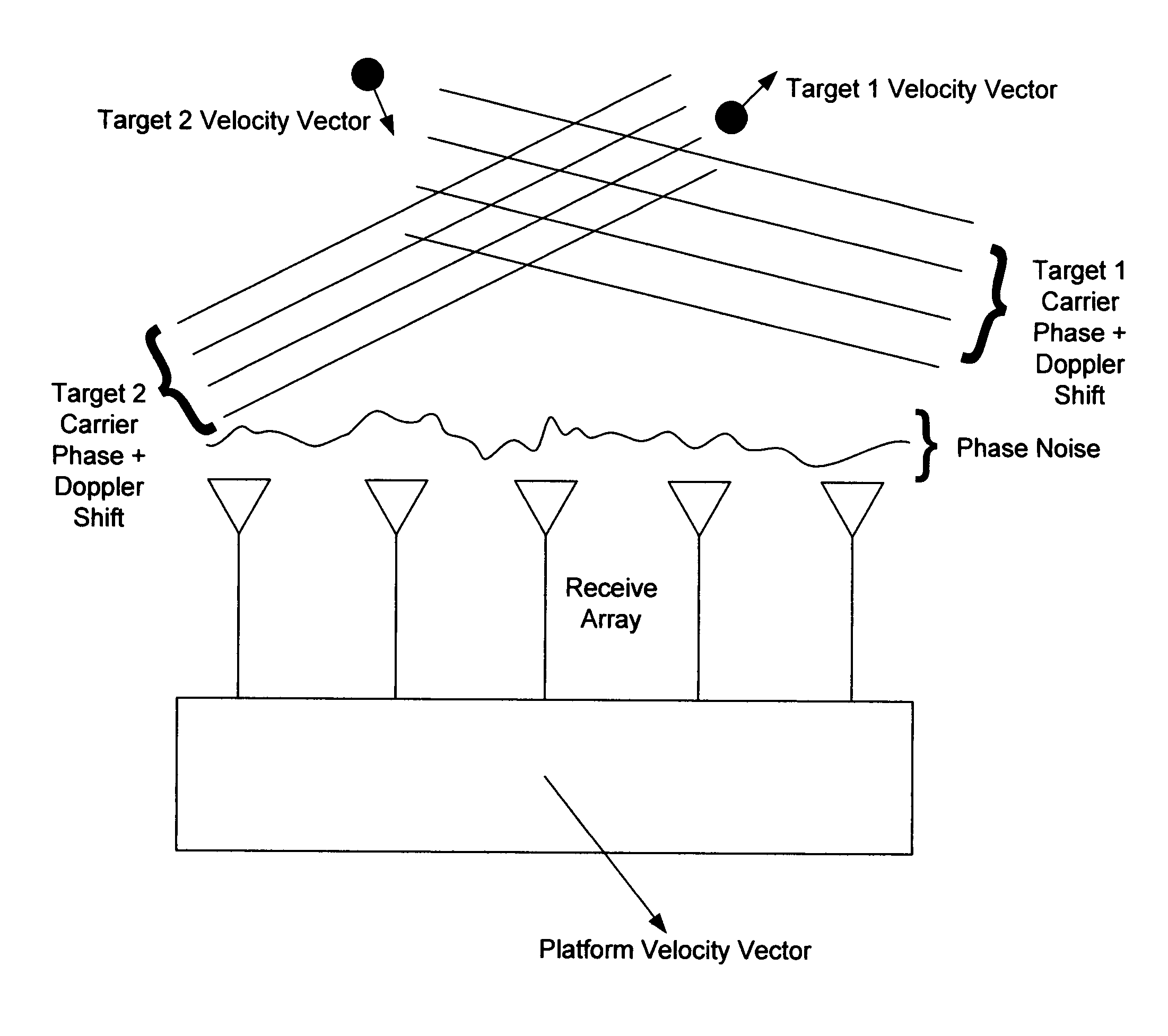
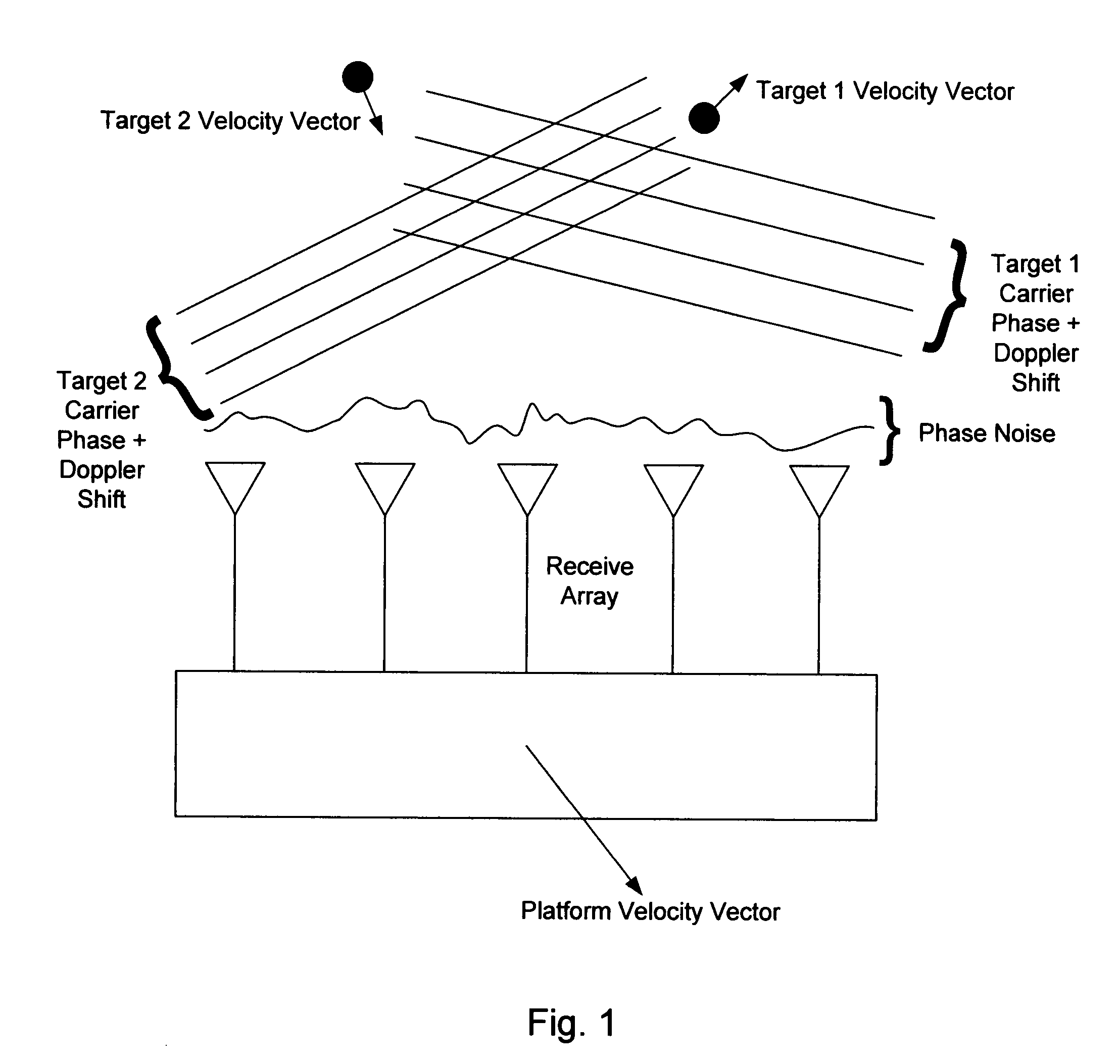
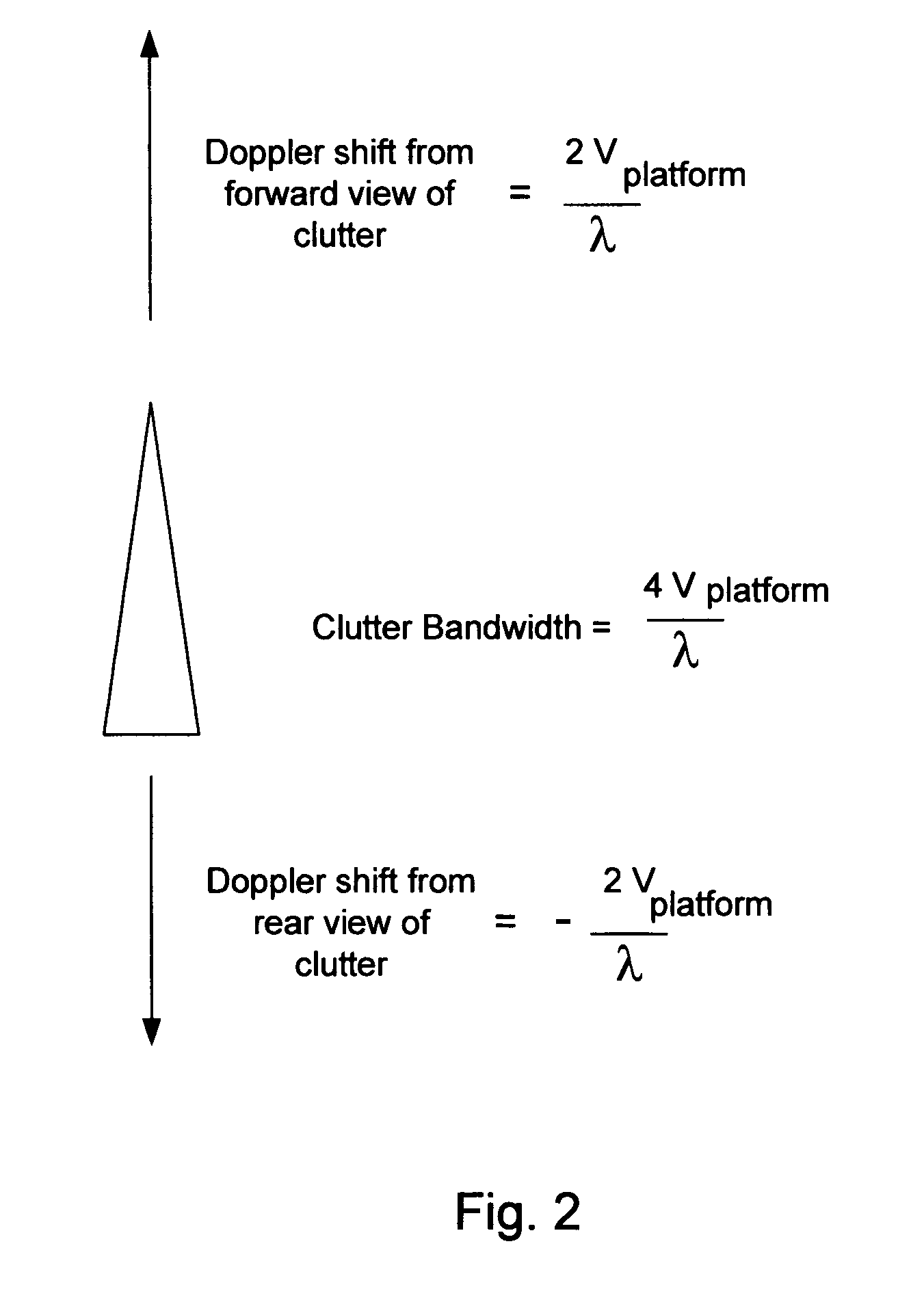
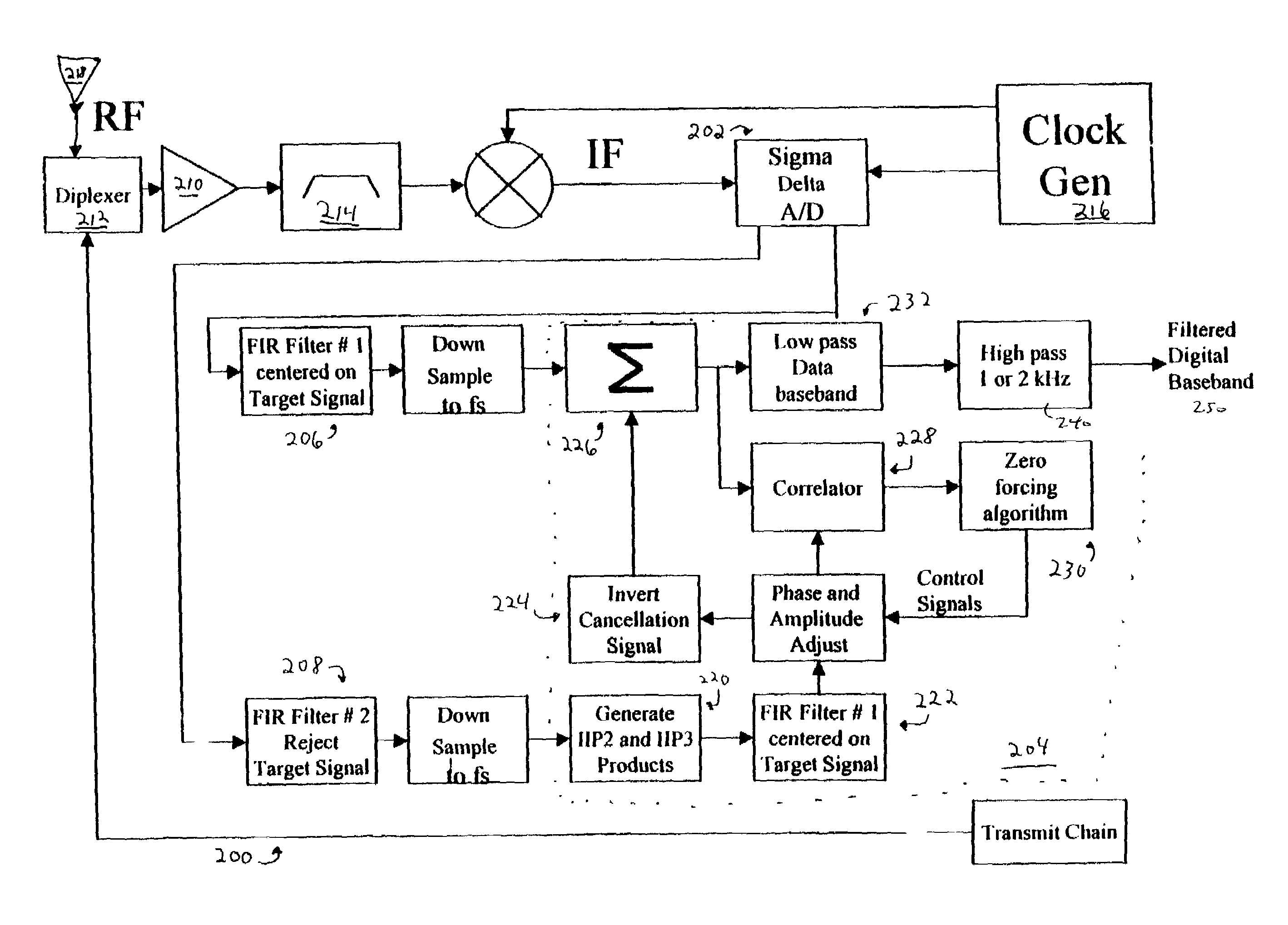
Patents
Literature
458 results about "Signal of interest" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
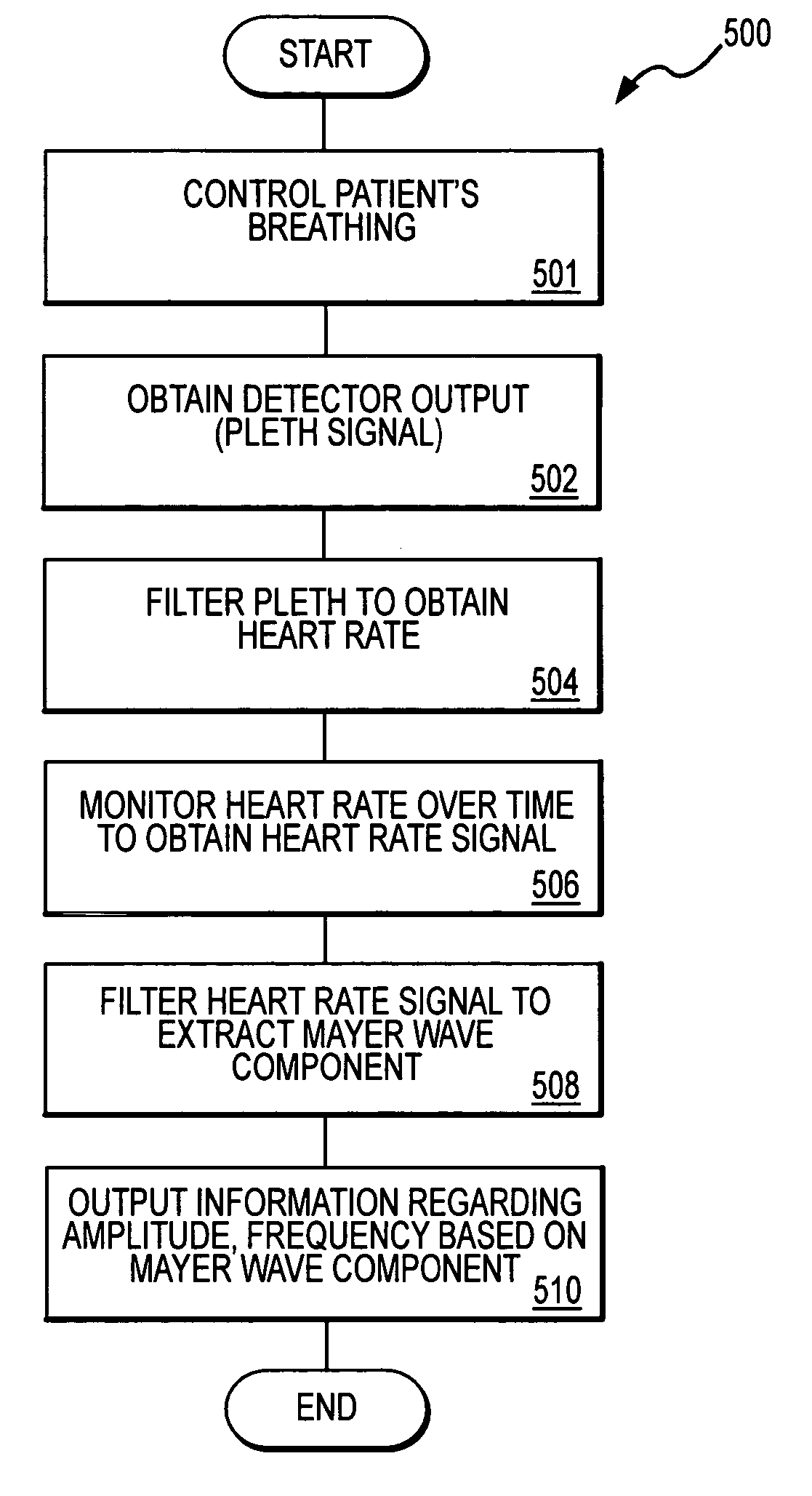
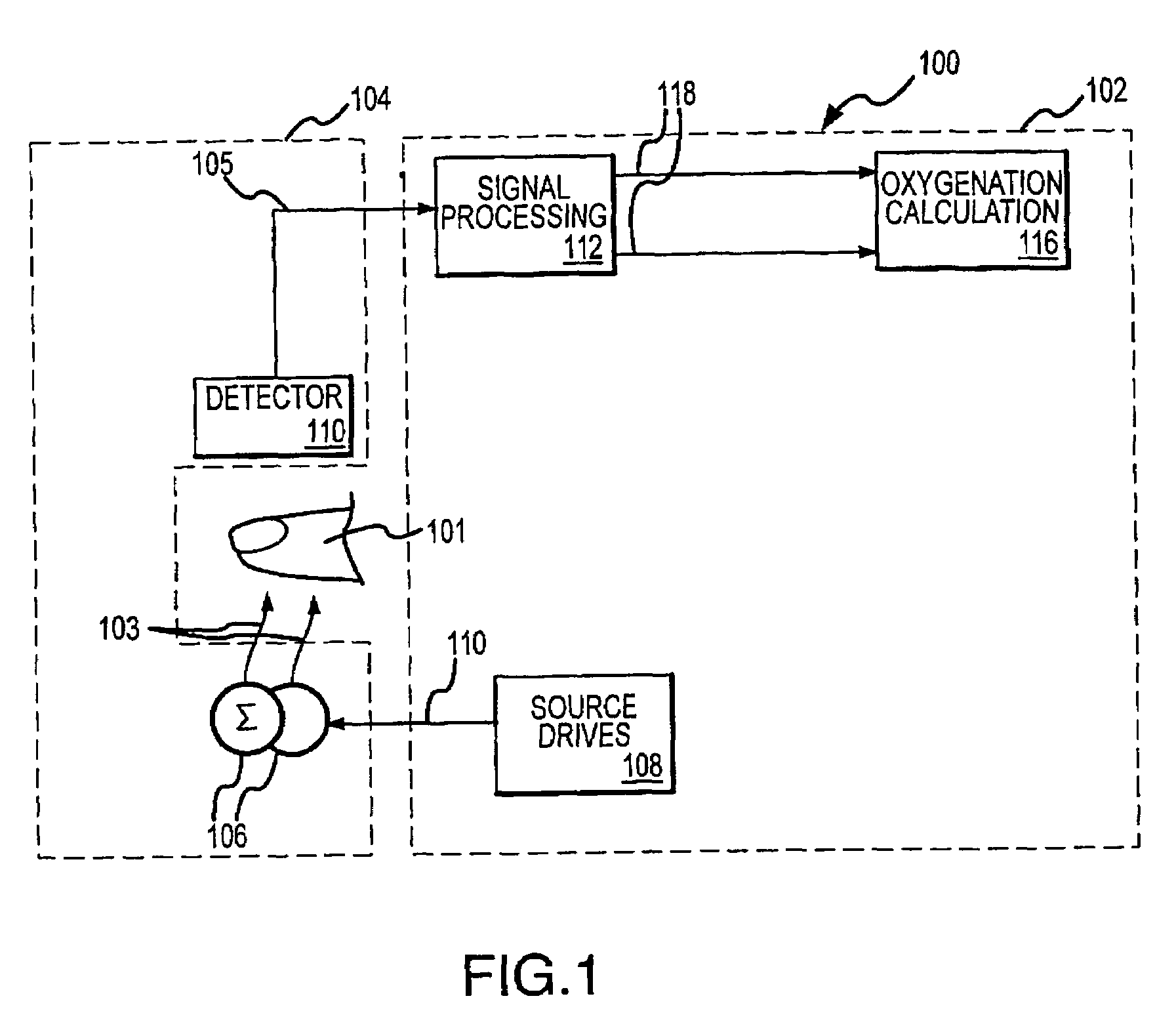
Monitoring physiological parameters based on variations in a photoplethysmographic signal
InactiveUS7001337B2Fast and robust and computationally efficientRobust processingEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterNervous systemRR interval
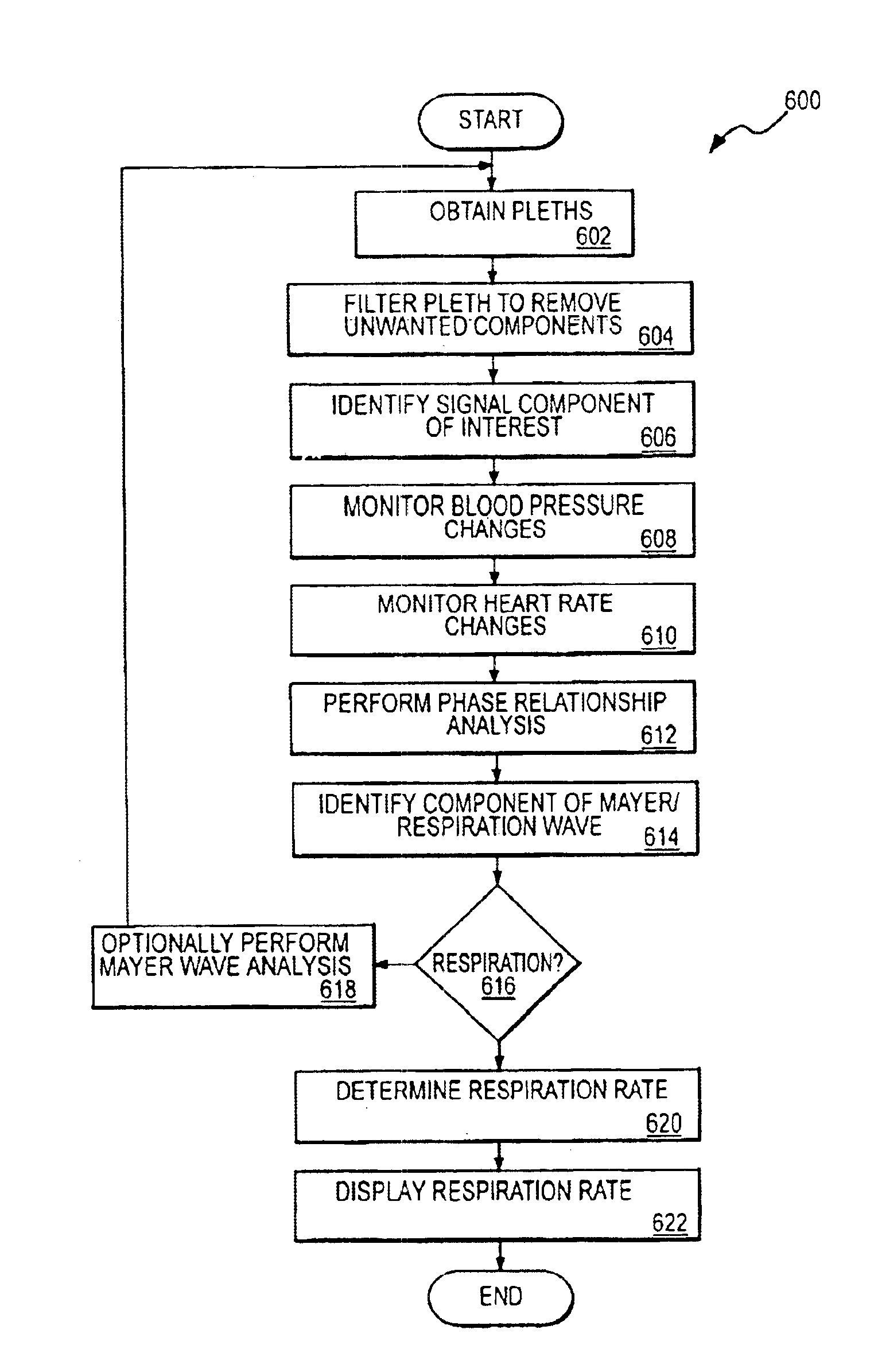
A method and apparatus are disclosed for using photoplethysmography to obtain physiological parameter information related to respiration rate, heart rate, heart rate variability, blood volume variability and / or the autonomic nervous system. In one implementation, the process involves obtaining (2502) a pleth, filtering (2504) the pleth to remove unwanted components, identifying (2506) a signal component of interest, monitoring (2508) blood pressure changes, monitoring (2510) heart rate, and performing (2512) an analysis of the blood pressure signal to the heart rate signal to identify a relationship associated with the component of interest. Based on this relationship, the component of interest may be identified (2514) as relating to the respiration or Mayer Wave. If it is related to the respiration wave (2516), a respiratory parameter such as breathing rate may be determined (2520). Otherwise, a Mayer Wave analysis (2518) may be performed to obtain parameter information related to the autonomic nervous system.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
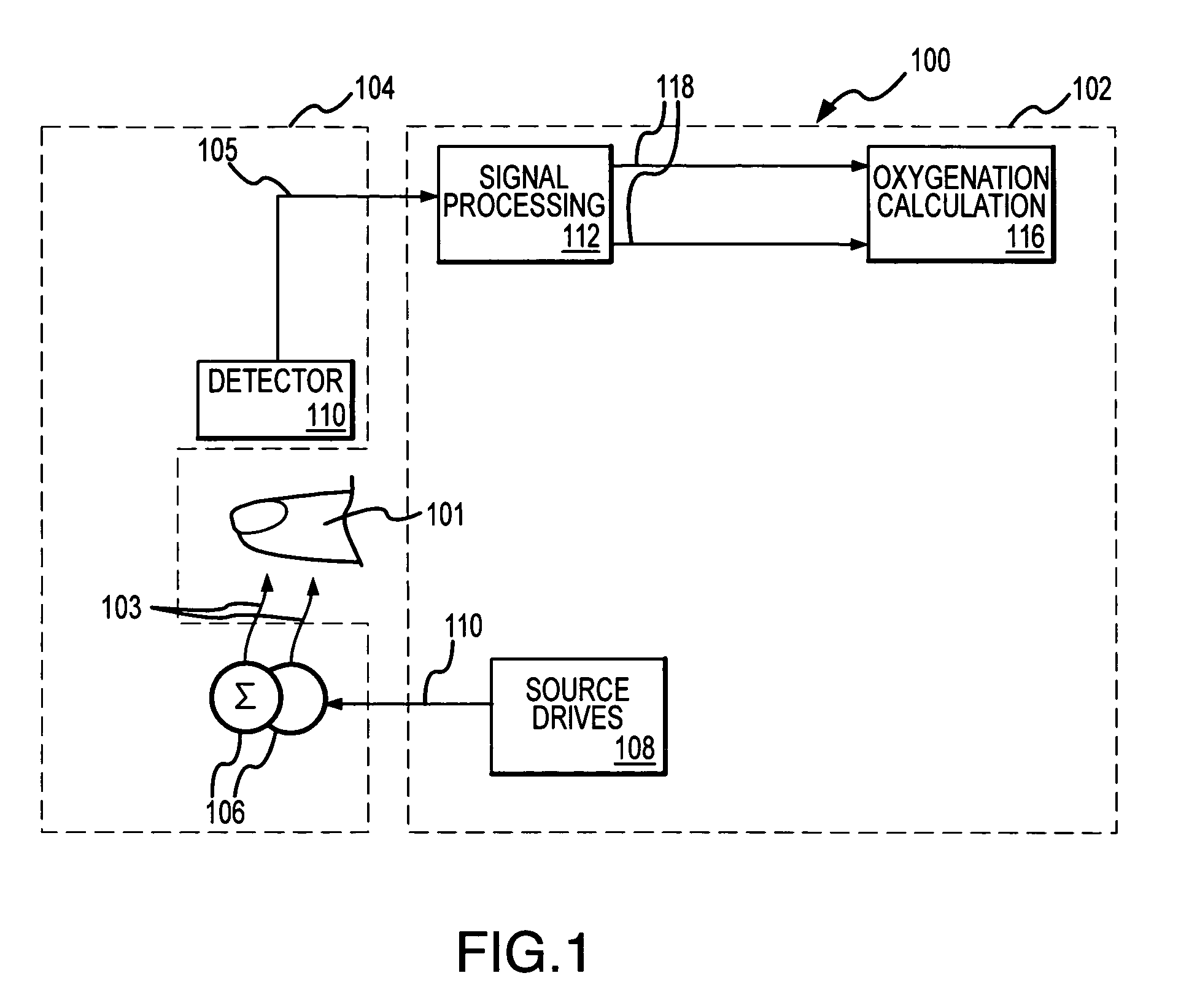
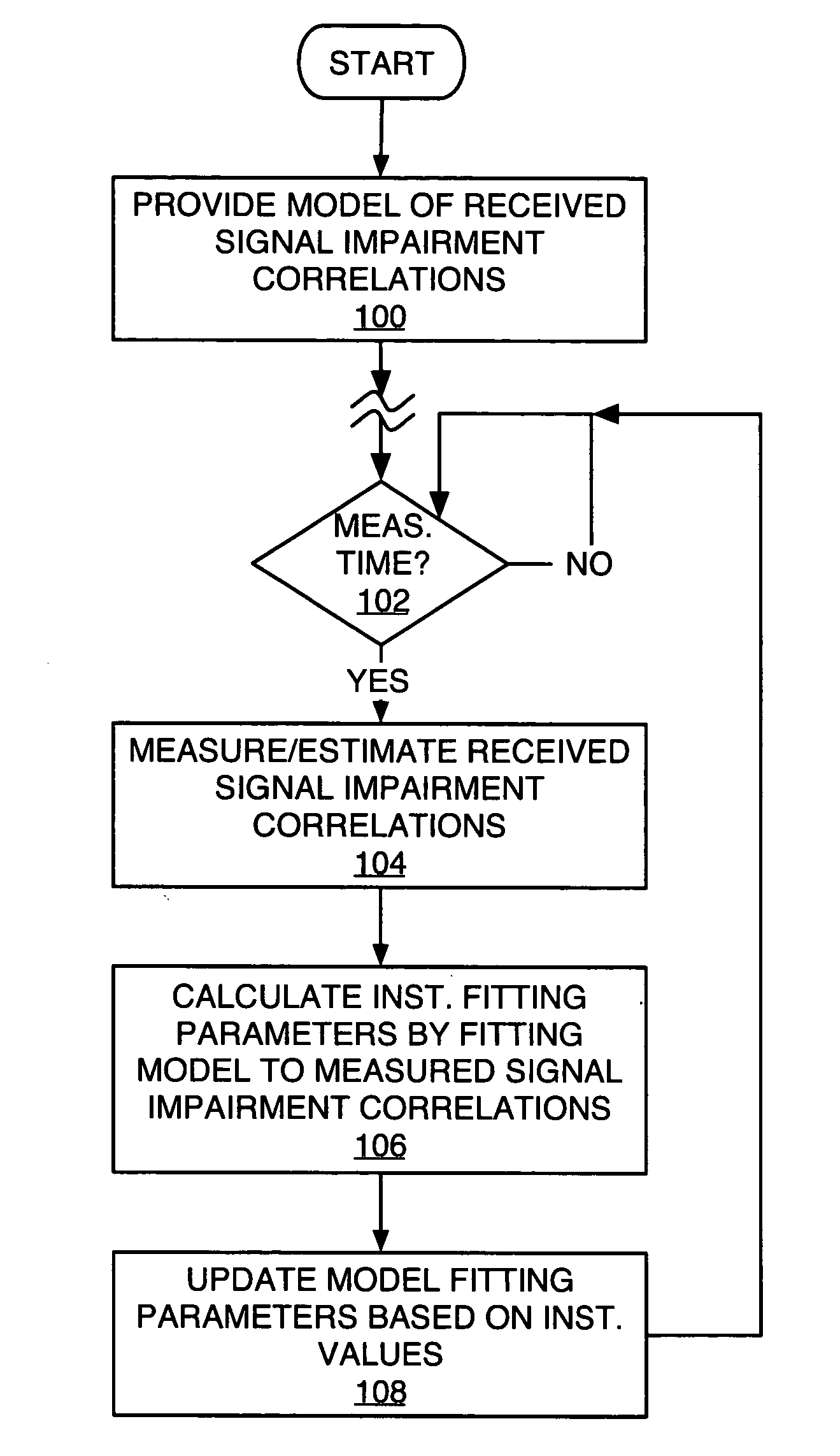
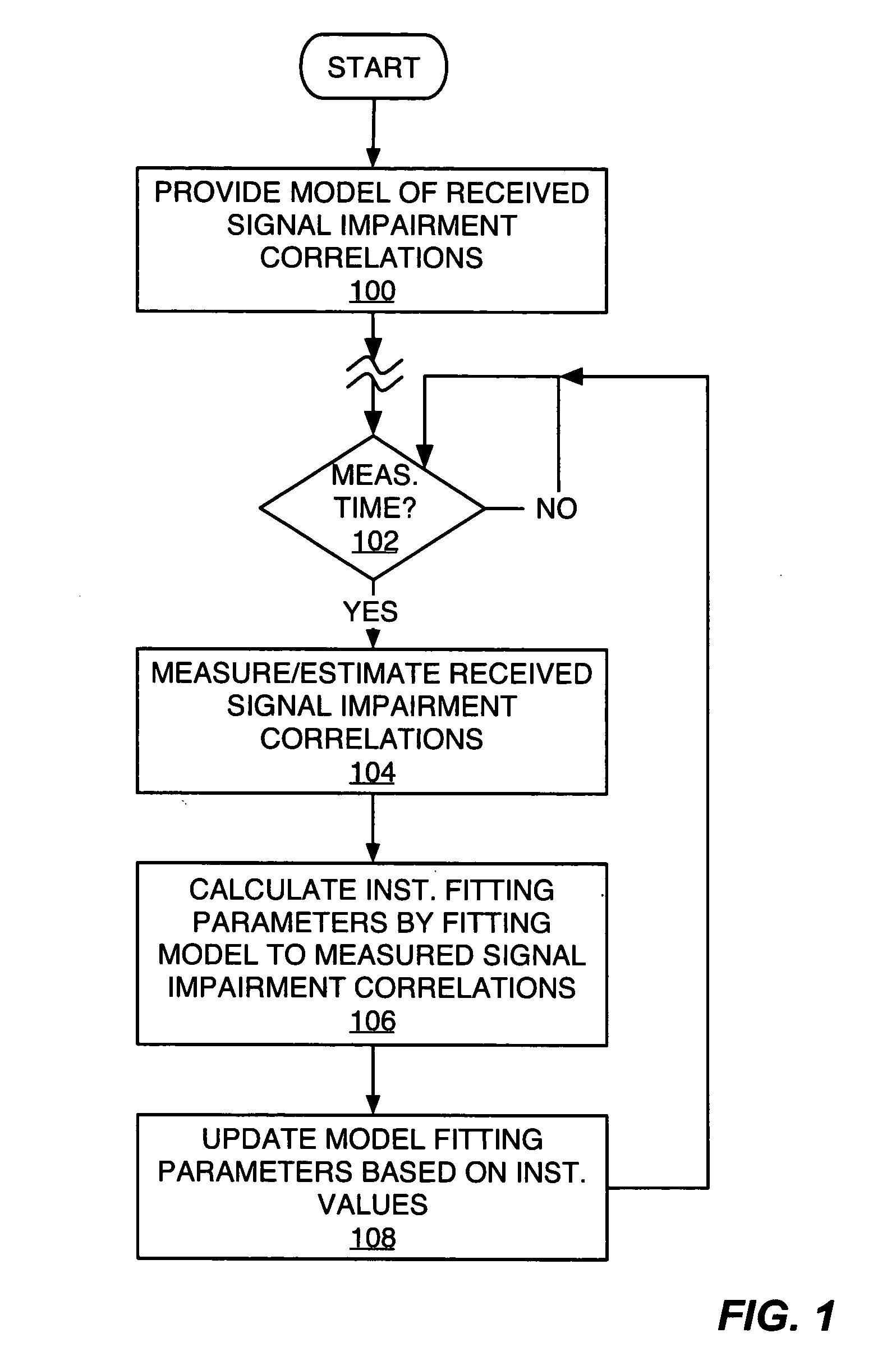
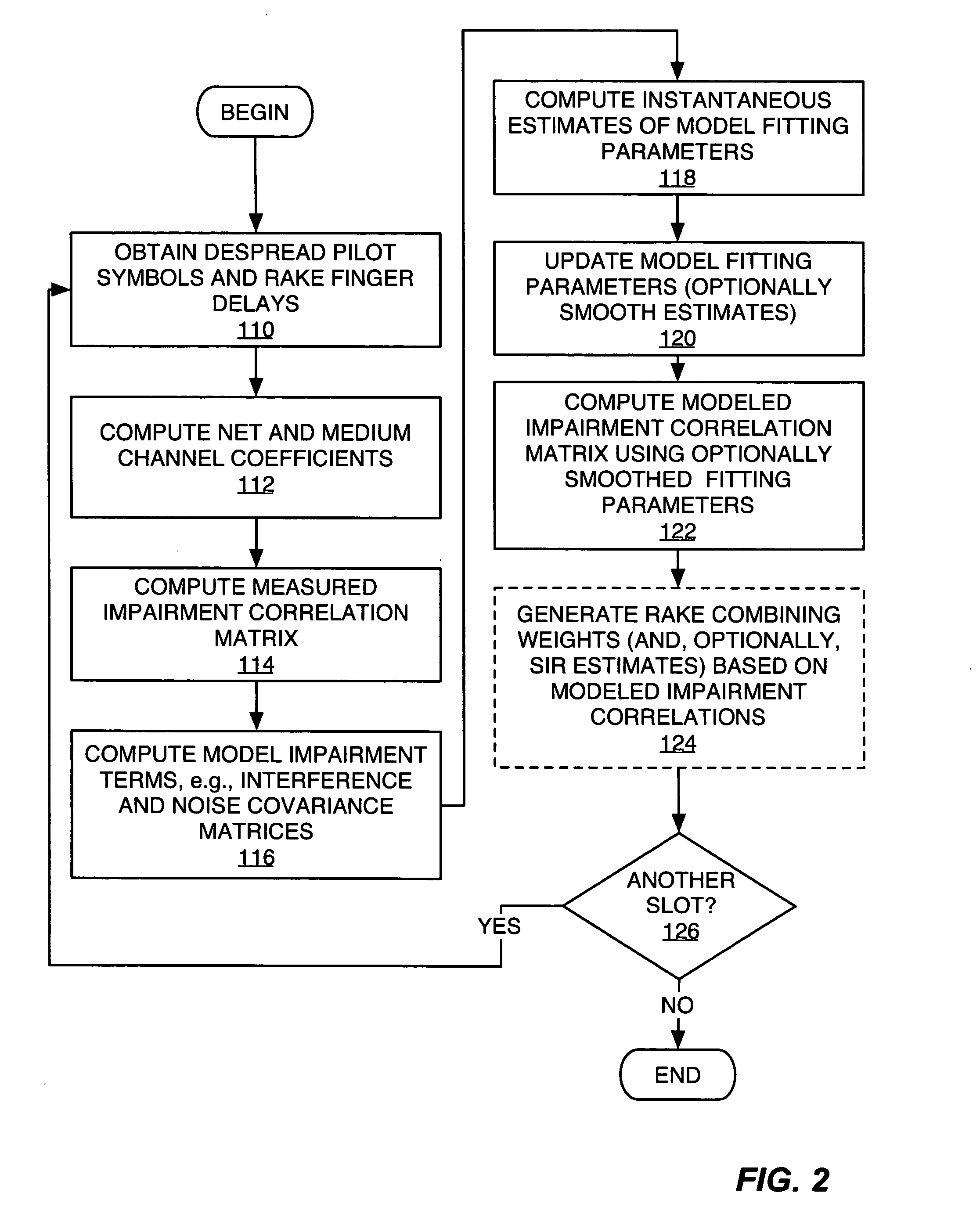
Method and apparatus for parameter estimation in a generalized rake receiver
ActiveUS20050201447A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationCurrent channelRake combining
Exemplary received signal processing may be based on maintaining a model of received signal impairment correlations, wherein each term of the model is updated periodically or as needed based on measuring impairments for a received signal of interest. An exemplary model comprises an interference impairment term scaled by a first model fitting parameter, and a noise impairment term scaled by a second model fitting parameters. The model terms may be maintained based on current channel estimates and delay information and may be fitted to measured impairment by adapting the model fitting parameters based on the measured impairment. The modeled received signal impairment correlations may be used to compute RAKE combining weights for received signal processing, or to compute Signal-to-Interference (SIR) estimates. Combined or separate models may be used for multiple received signals. As such, the exemplary modeling is extended to soft handoff, multiple antennas, and other diversity situations.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
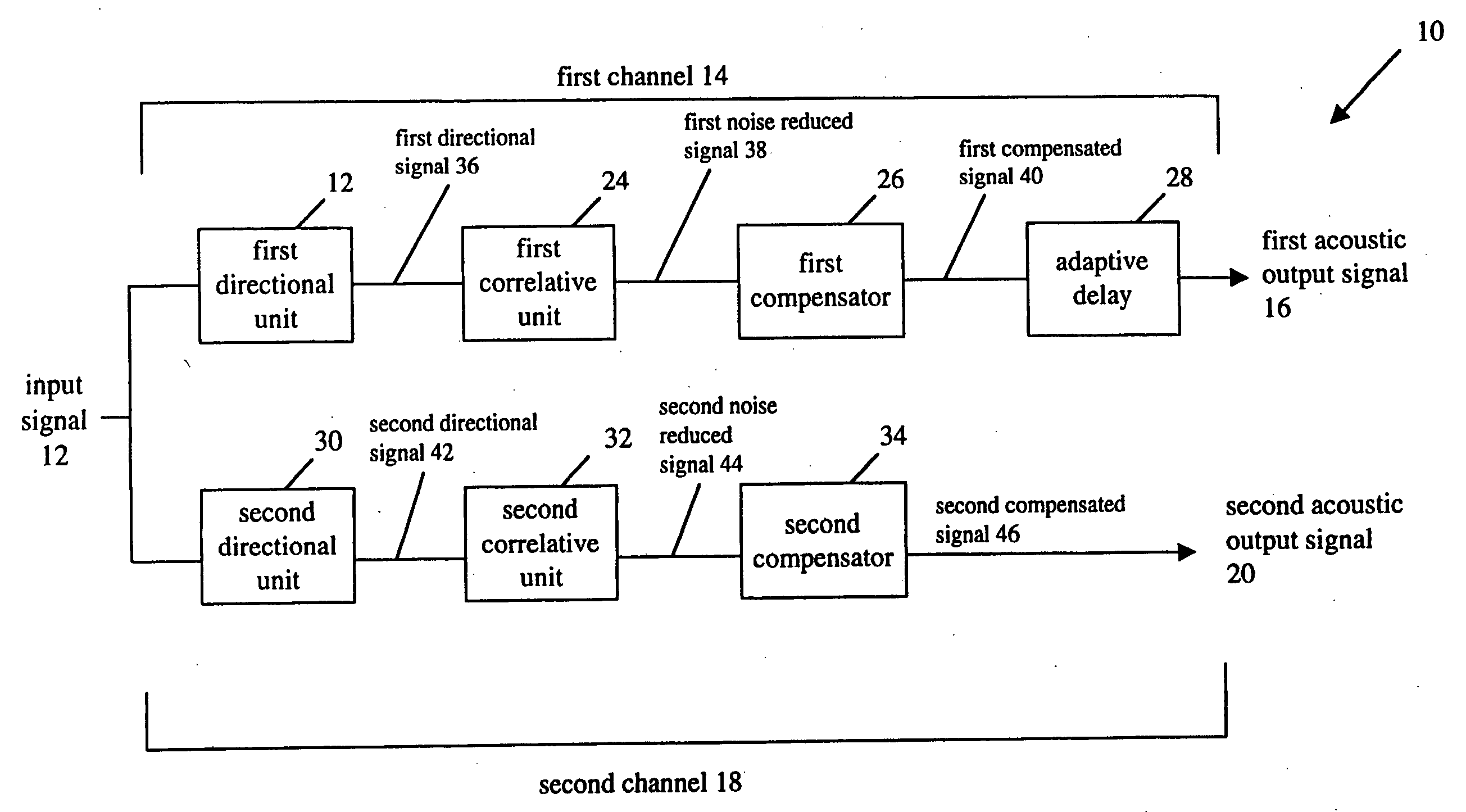
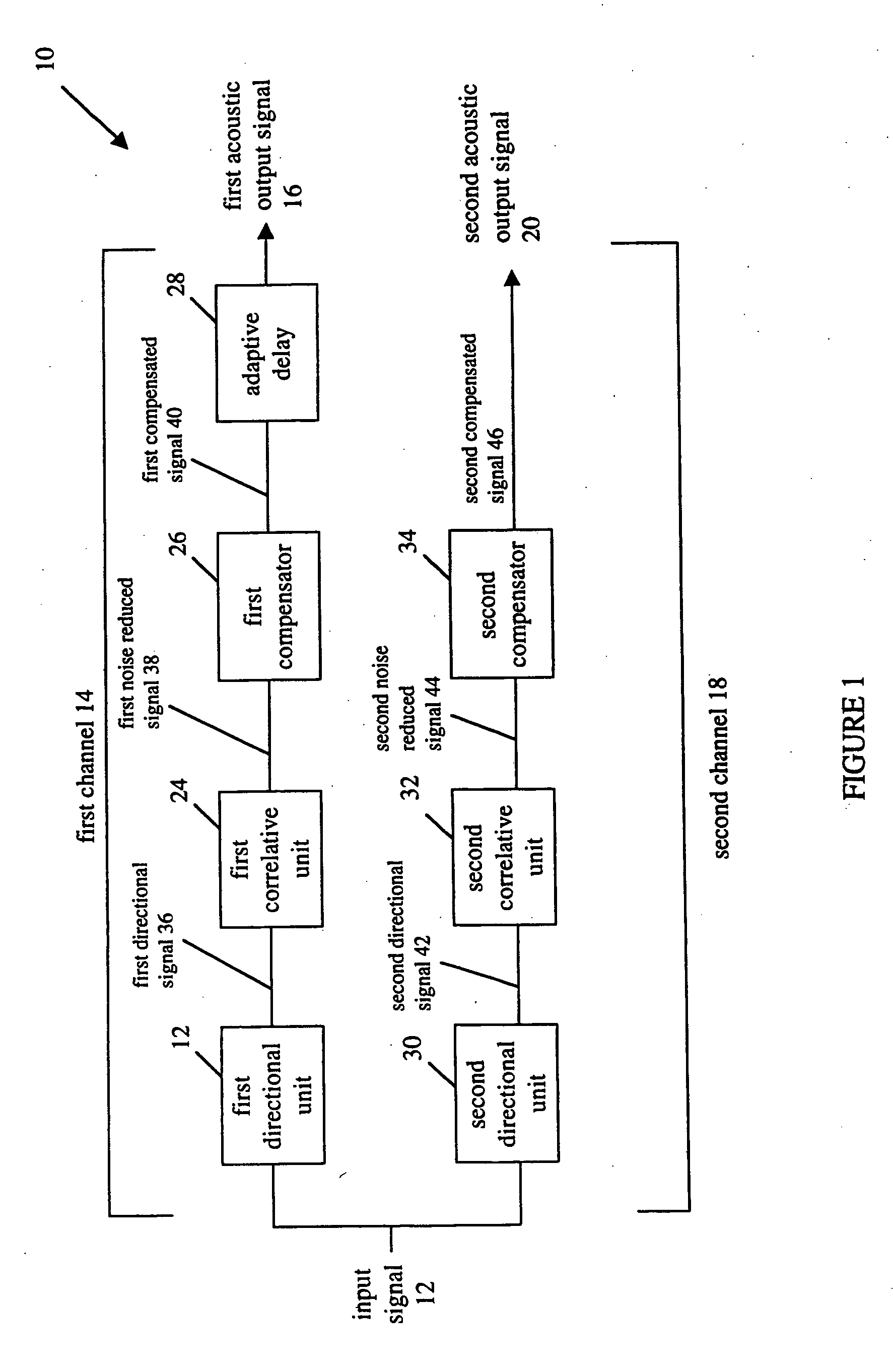
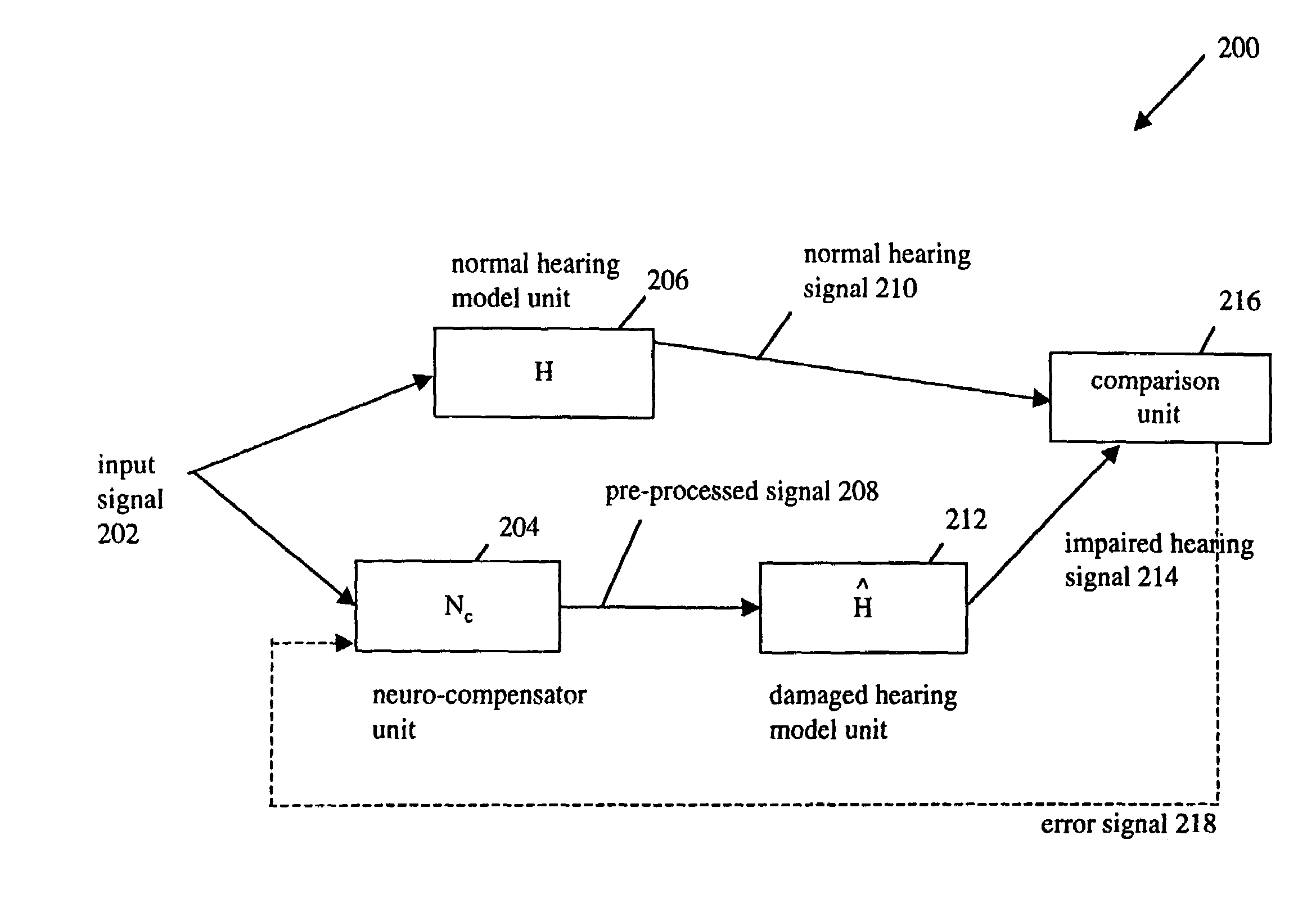
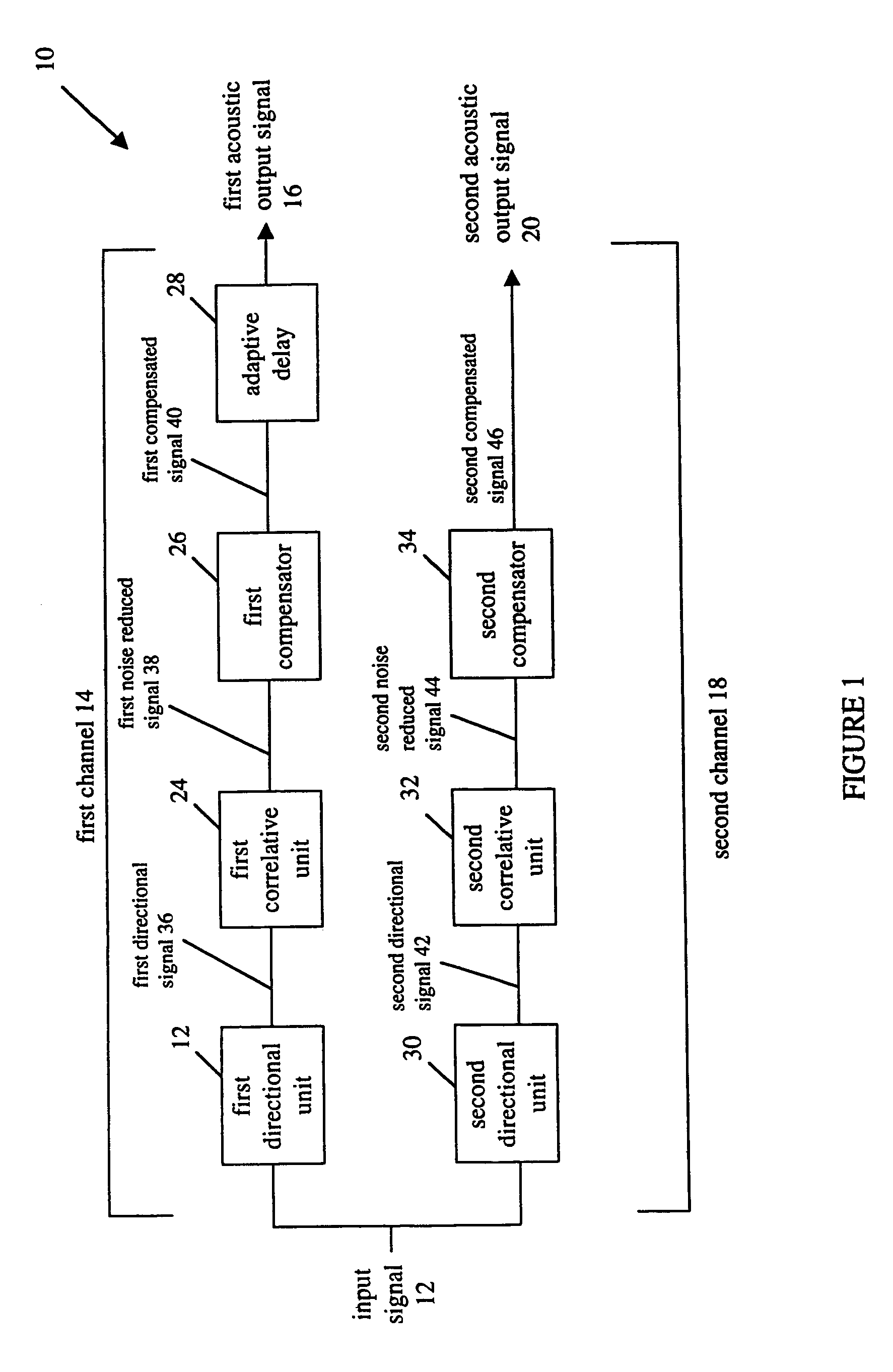
Binaural adaptive hearing aid
ActiveUS20050069162A1Restore nerve functionStereophonic systemsDeaf-aid setsSignal of interestEngineering
A system and method for processing an acoustic input signal and providing at least one output acoustic signal to a user of a hearing-aid system. The hearing-aid system includes first and second channels with one of the channels having an adaptive delay. The first channel includes a directional unit for receiving the acoustic input signal and providing a directional signal; a correlative unit for receiving the directional signal and providing a noise reduced signal by utilizing correlative measures for identifying a speech signal of interest in the directional signal; and, a compensator for receiving the noise reduced signal and providing a compensated signal for compensating for a hearing loss of the user.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
Successive interference cancellation in a generalized RAKE receiver architecture
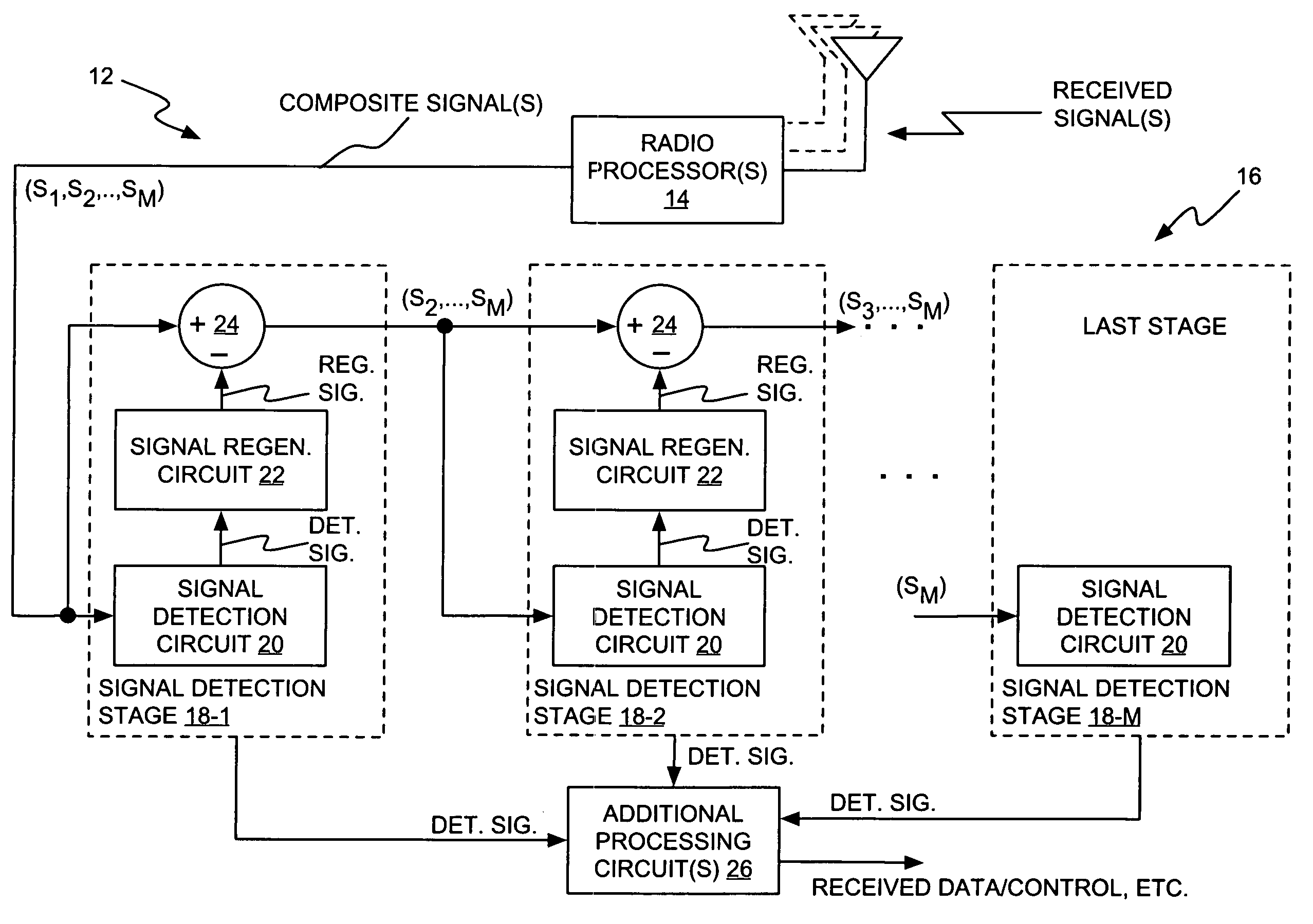
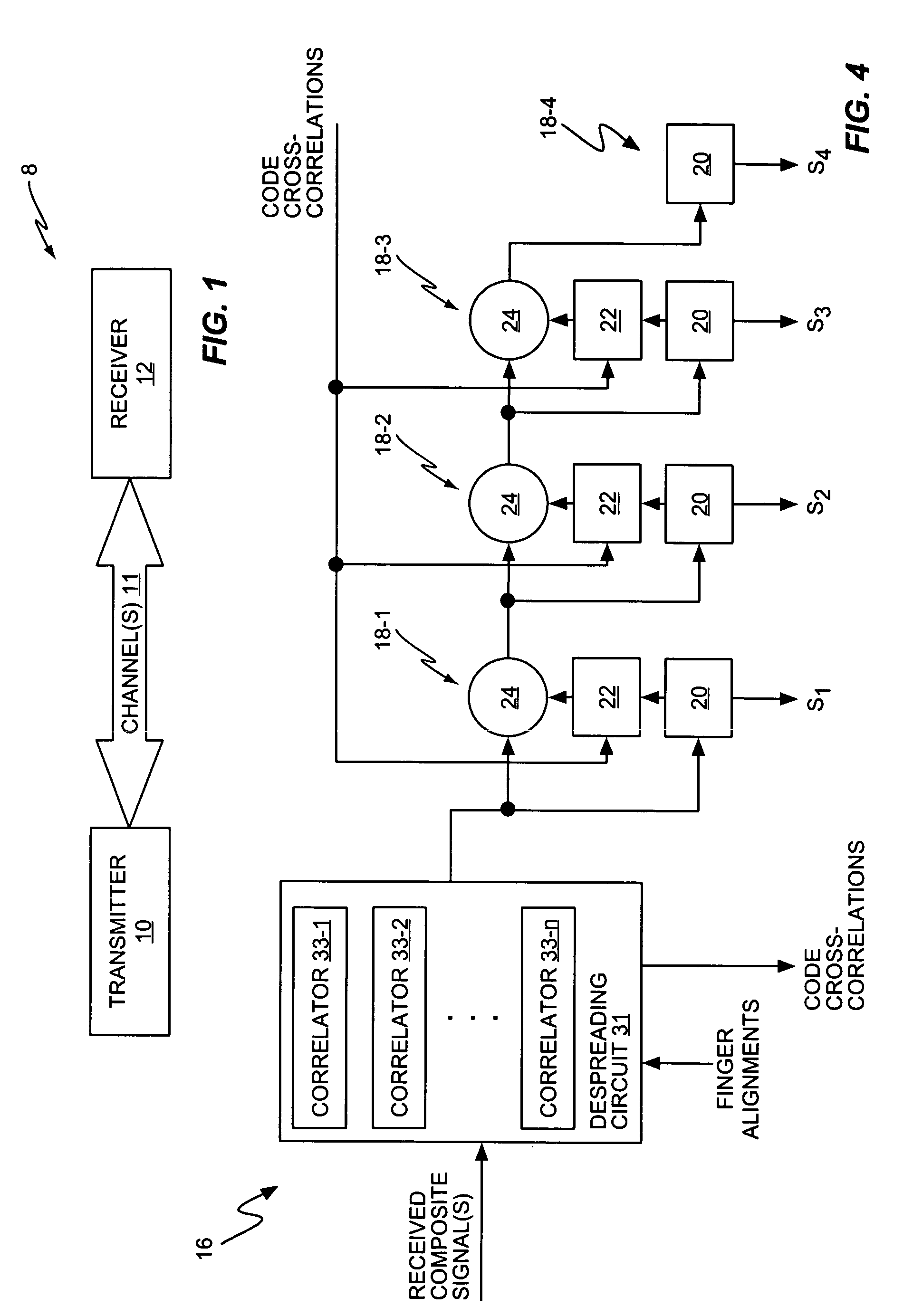
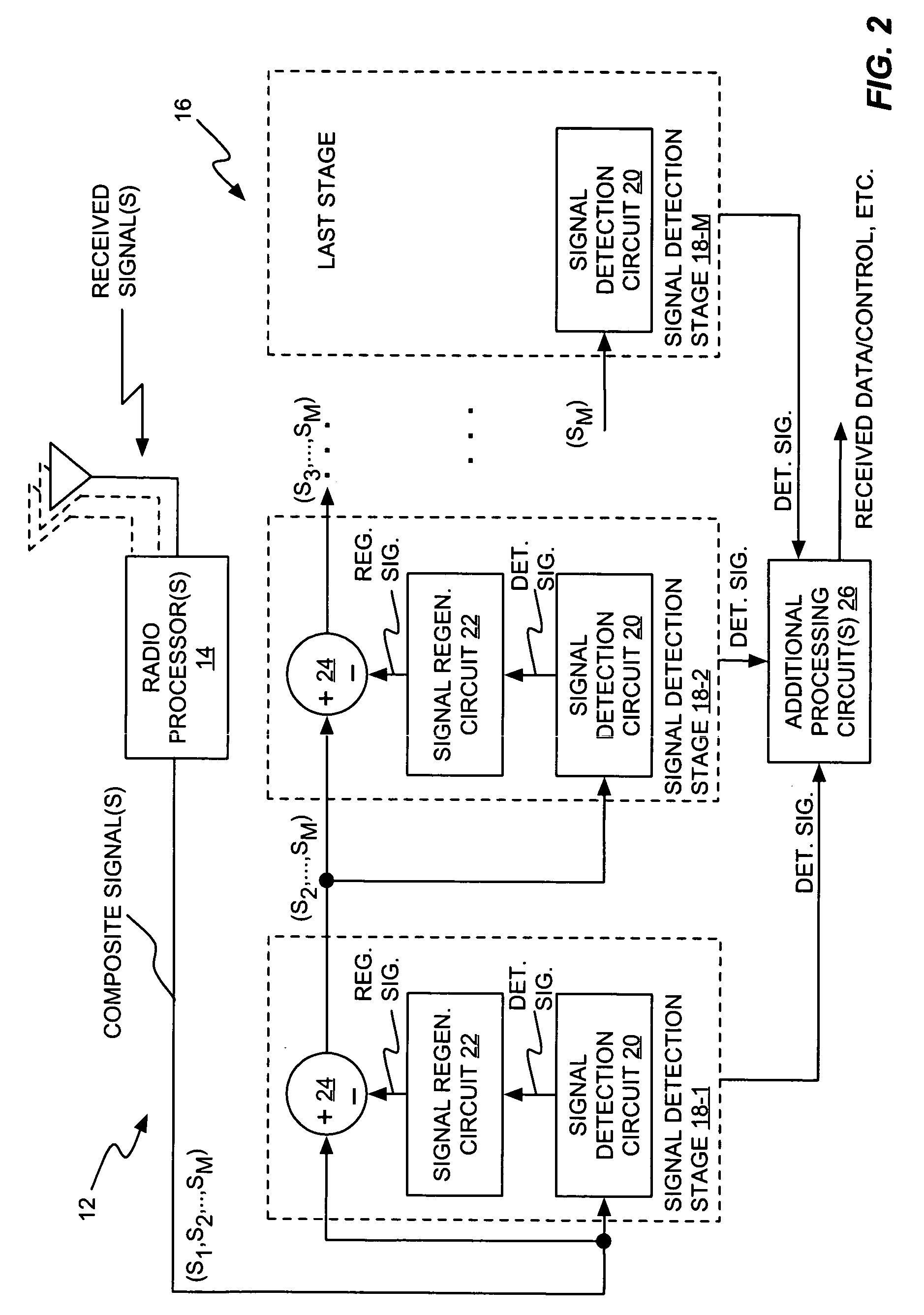
A receiver includes a receiver circuit that decodes multiple signals of interest contained in a composite received signal. The receiver comprises a plurality of successive signal detection stages to detect respective signals contained in the composite received signal. Each detection circuit comprises at least one Generalized RAKE combining circuit and generates a detected signal at an output. Each but the last stage further comprises a signal regeneration circuit that cancels the signal of interest detected by that stage from a stage input signal provided to the next stage such that successive detection of the signals of interest benefits from cumulative cancellation of the previously detected signals.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
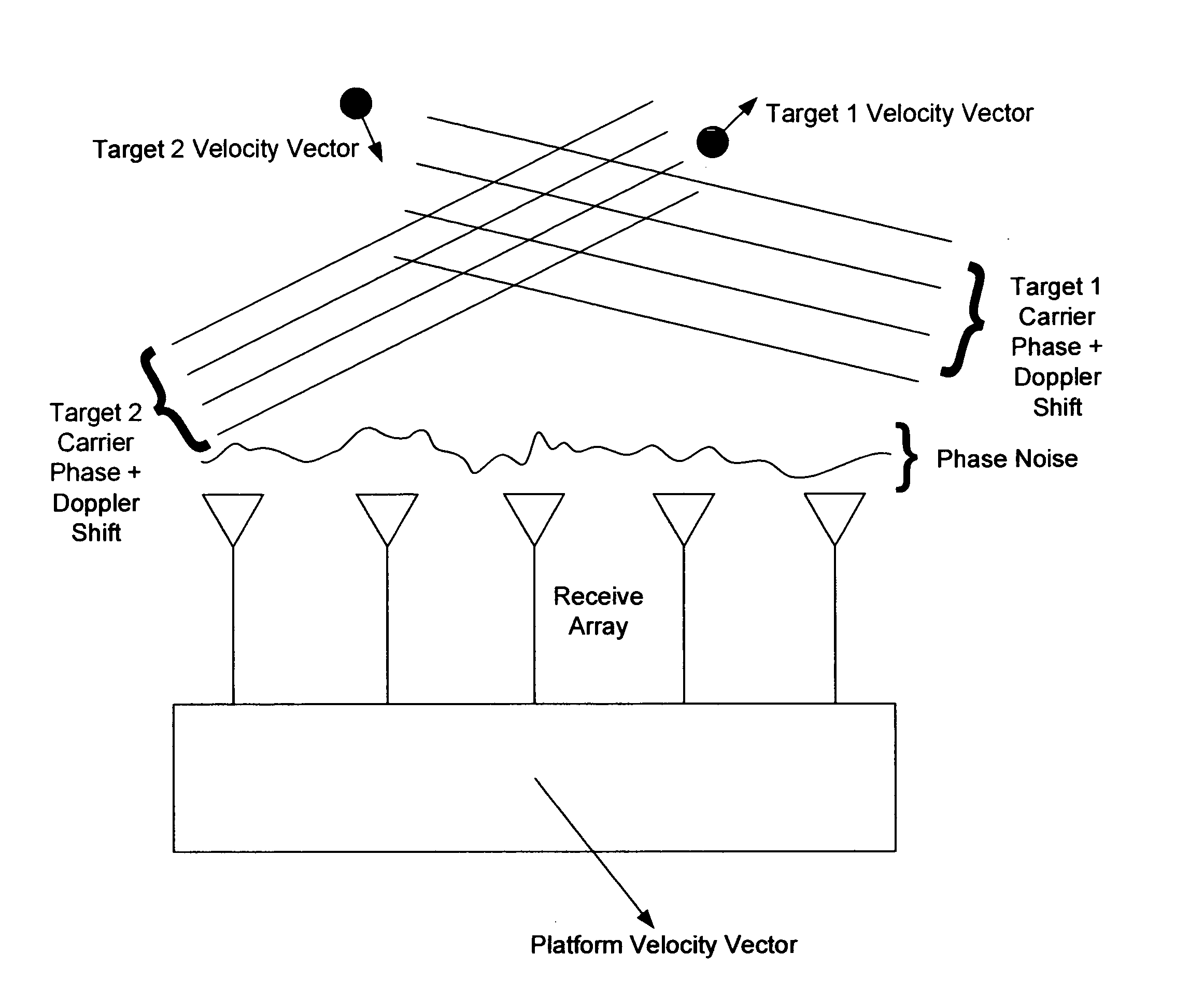
Phase arrays exploiting geometry phase and methods of creating such arrays
InactiveUS20070285315A1Reduce couplingMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeacon systemsEngineeringArray element
In the context of array sensors such as radar, sonar, and communications receiver arrays, the present invention exploits the geometry phase components of radiated wavefronts associated with the signals of interest in order to reduce the bandwidth requirements for DOA and beamforming processing. Additionally, geometry phase is exploited in order to effectively increase the resolution of an array without changing the size of its physical footprint or the number of array elements. Other embodiments of the invention include the use of virtual array elements for increase in effective array size.
Owner:DAVIS DENNIS WILLARD +2
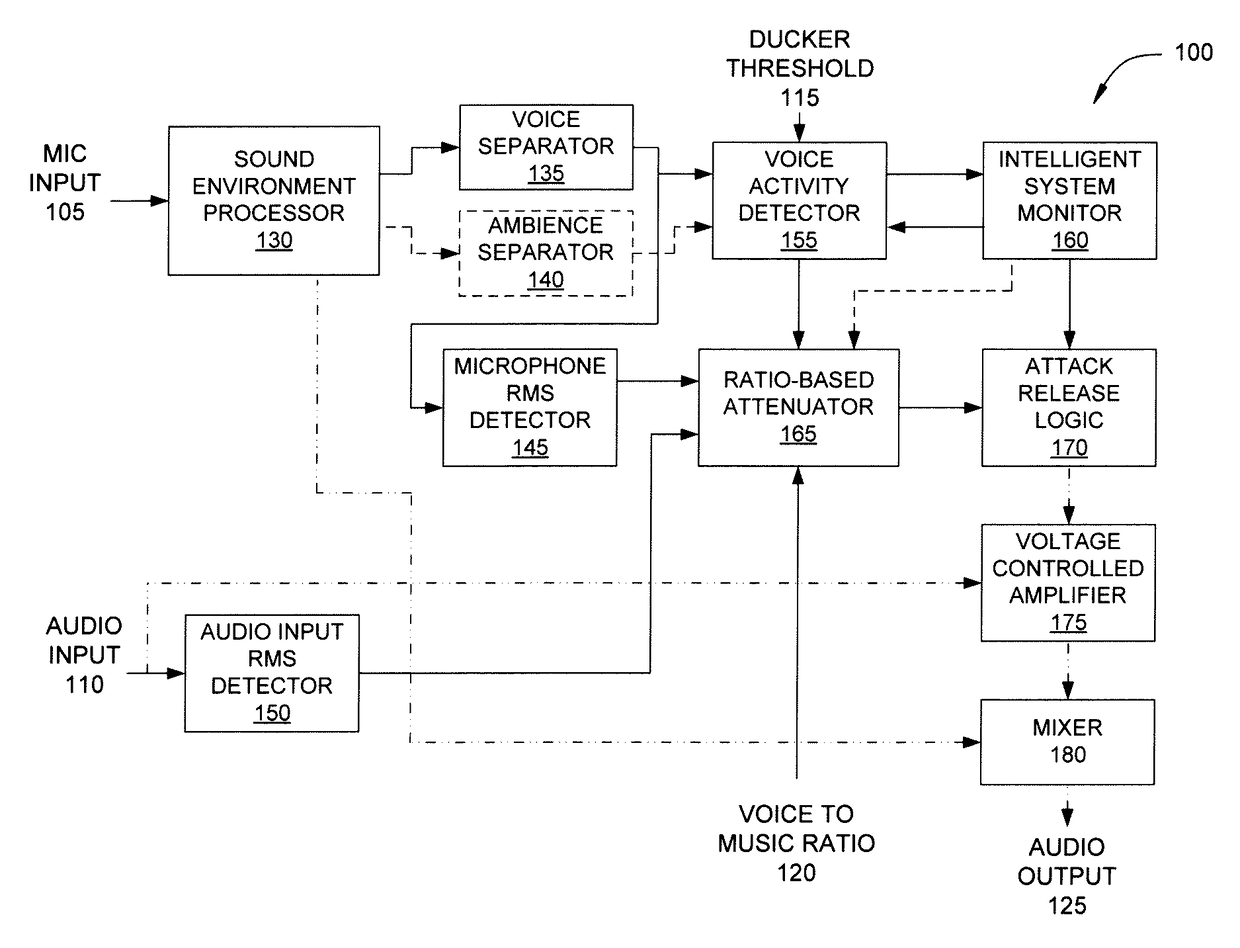
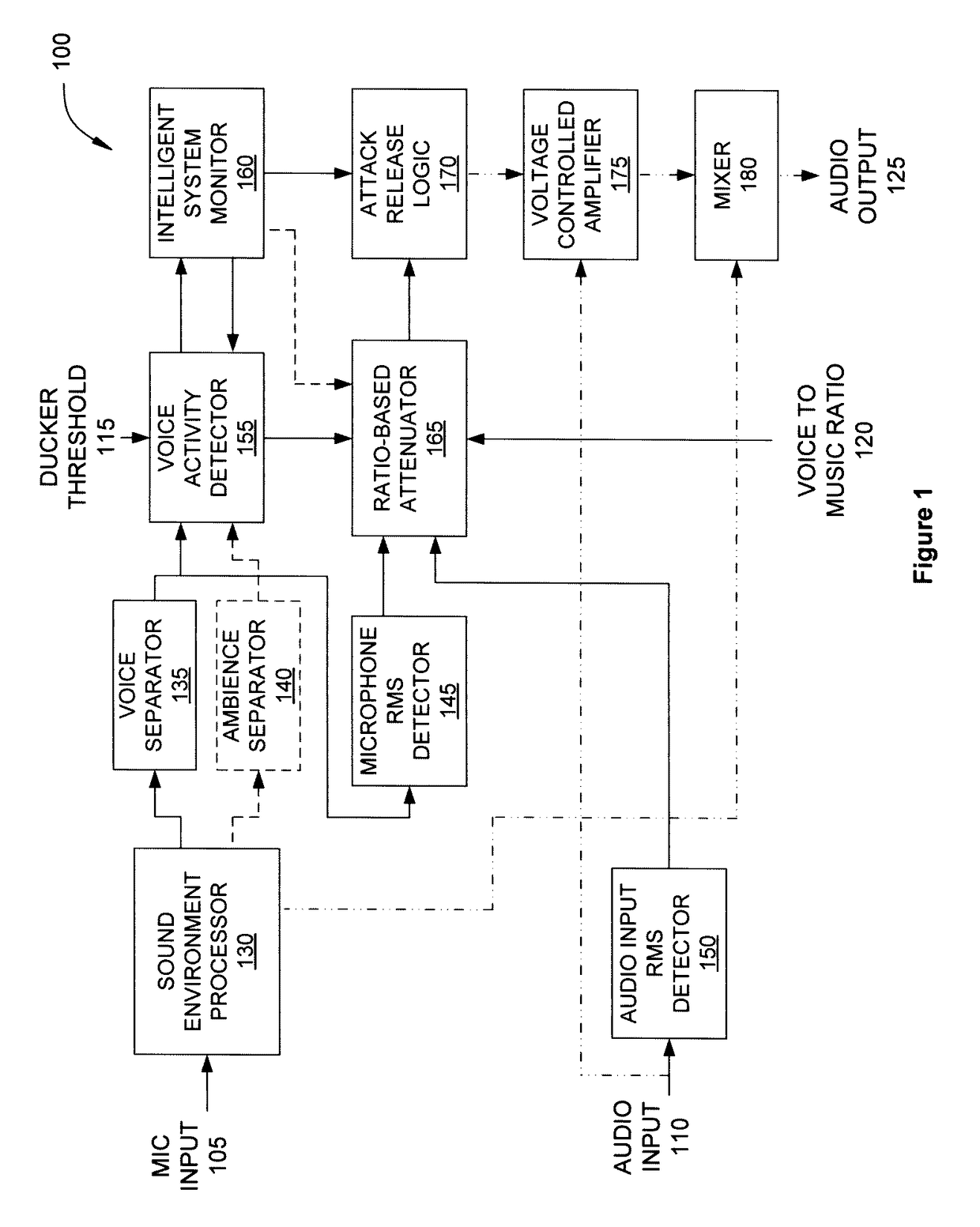
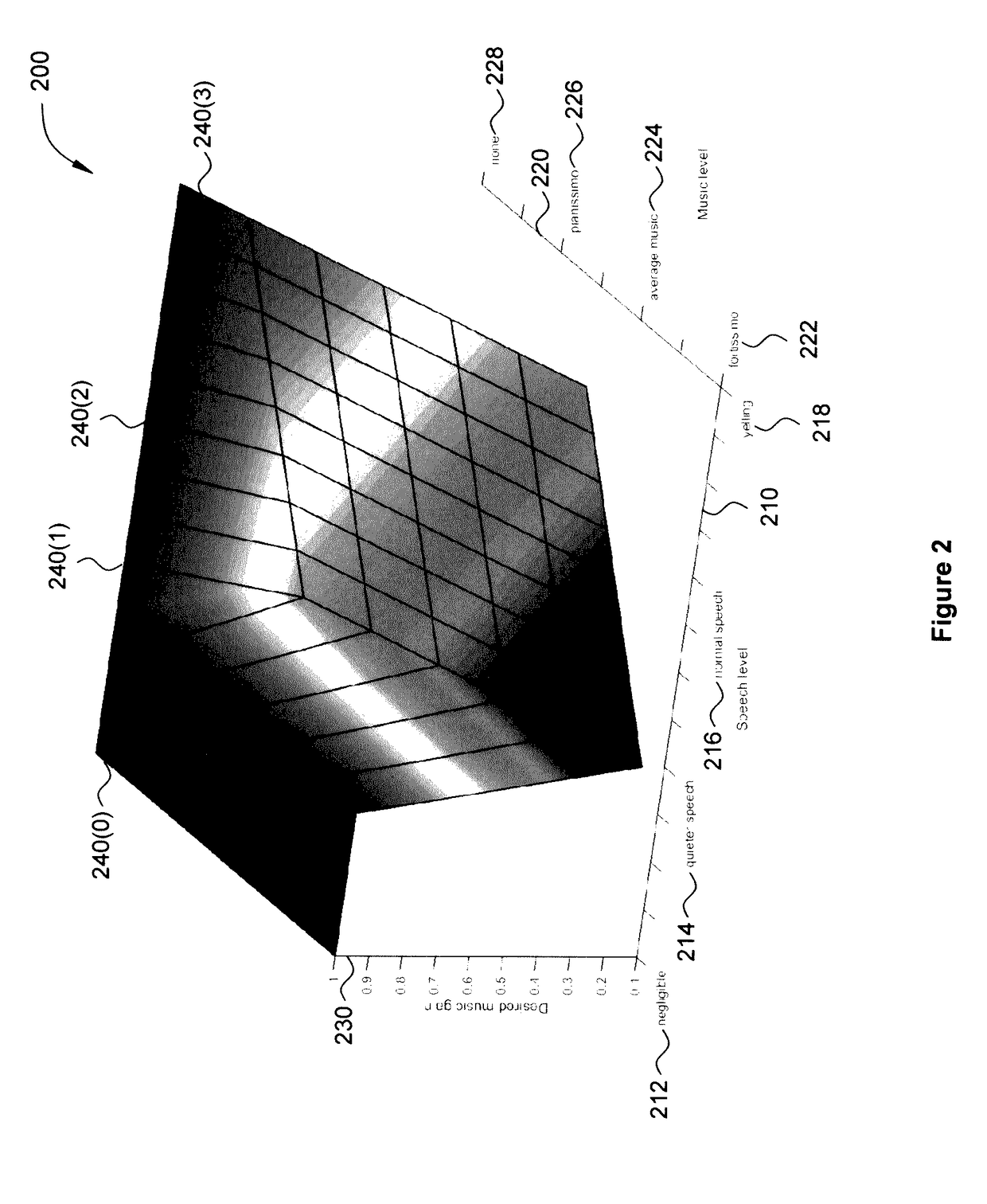
Approach for partially preserving music in the presence of intelligible speech
An audio processing system for a listening device includes an input device, a voice activity detector and a ratio-based attenuator. The input device is configured to receive a first audio signal emanating from an environment and including a signal of interest. The voice activity detector is configured to generate a control signal in response to the first audio signal. The ratio-based attenuator is configured to receive the control signal and determine whether the signal level of the first audio signal exceeds the signal level of an audio signal received from an audio playback device by at least a target difference. If so, then the audio level of the playback audio signal is maintained. Otherwise, the audio level of the playback audio signal is adjusted, where, at the adjusted value, the first signal level exceeds the playback signal level by at least the target difference.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Phased arrays exploiting geometry phase and methods of creating such arrays
InactiveUS20050195103A1Reduce couplingMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeacon systemsSonarWavefront
In the context of array sensors such as radar, sonar, and communications receiver arrays, the present invention exploits the geometry phase components of radiated wavefronts associated with the signals of interest in order to reduce the bandwidth requirements for DOA and beamforming processing. Additionally, geometry phase is exploited in order to effectively increase the resolution of an array without changing the size of its physical footprint. Other embodiments of the invention include the use of virtual array elements for increase in effective array size.
Owner:DAVIS DENNIS WILLARD +2
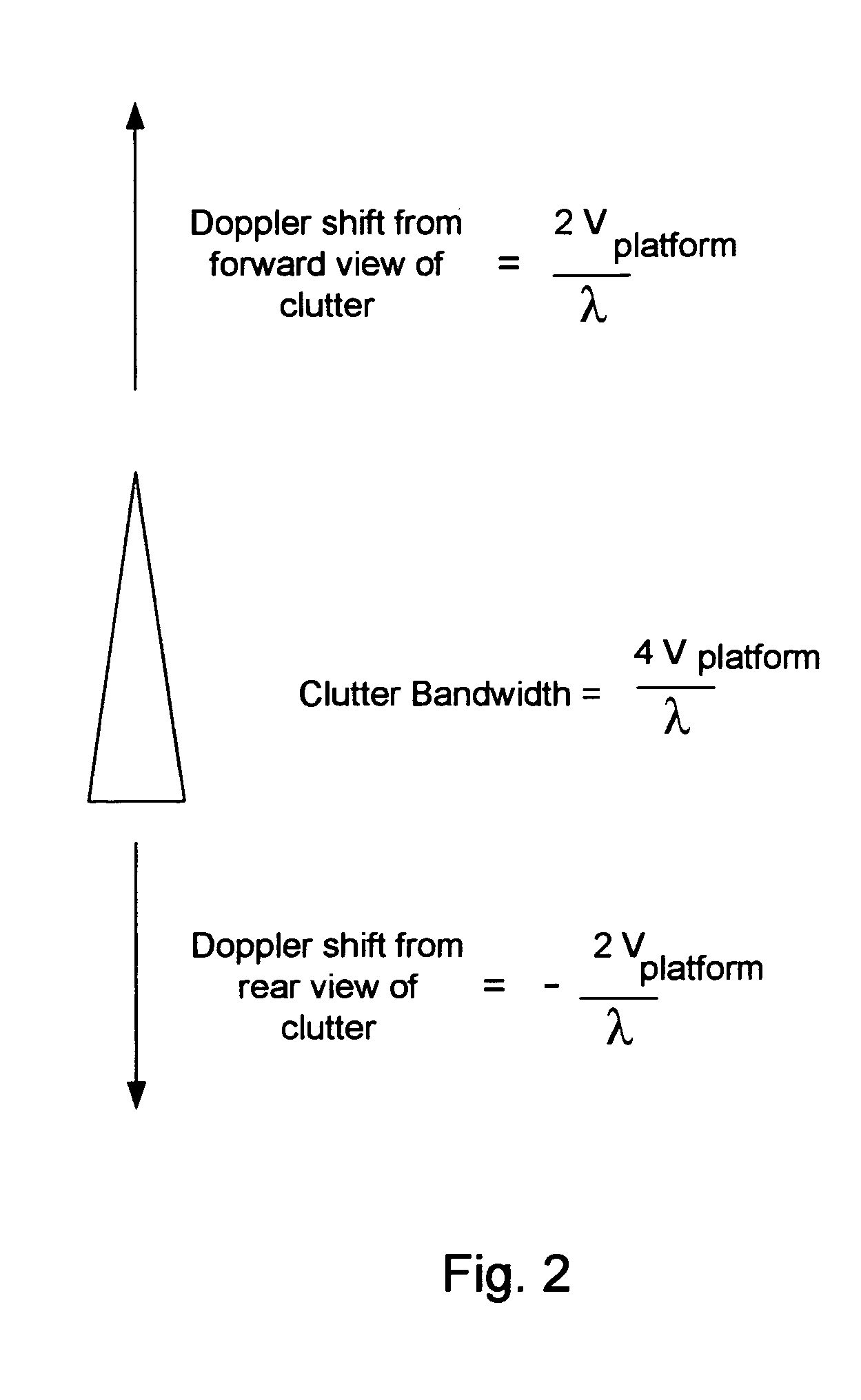
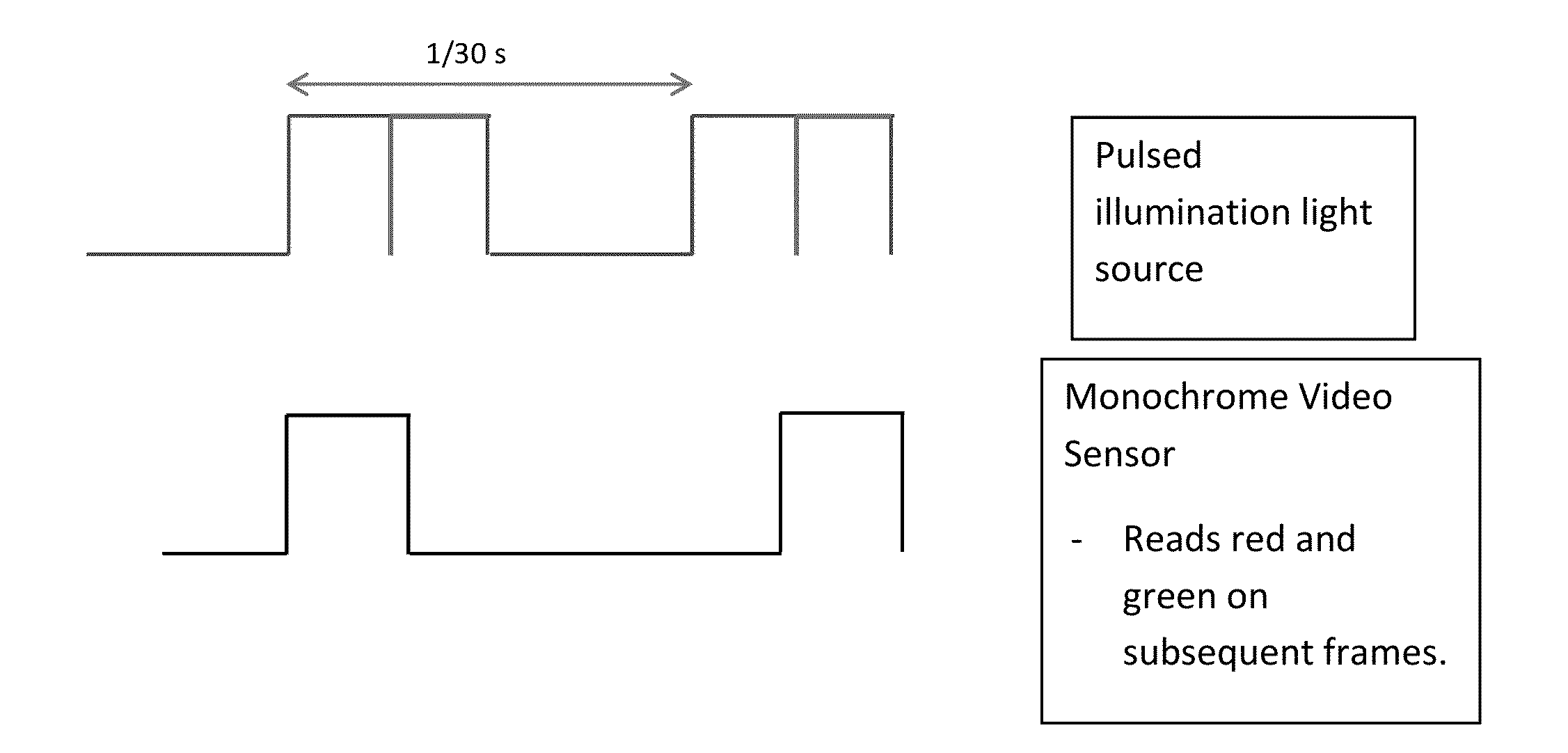
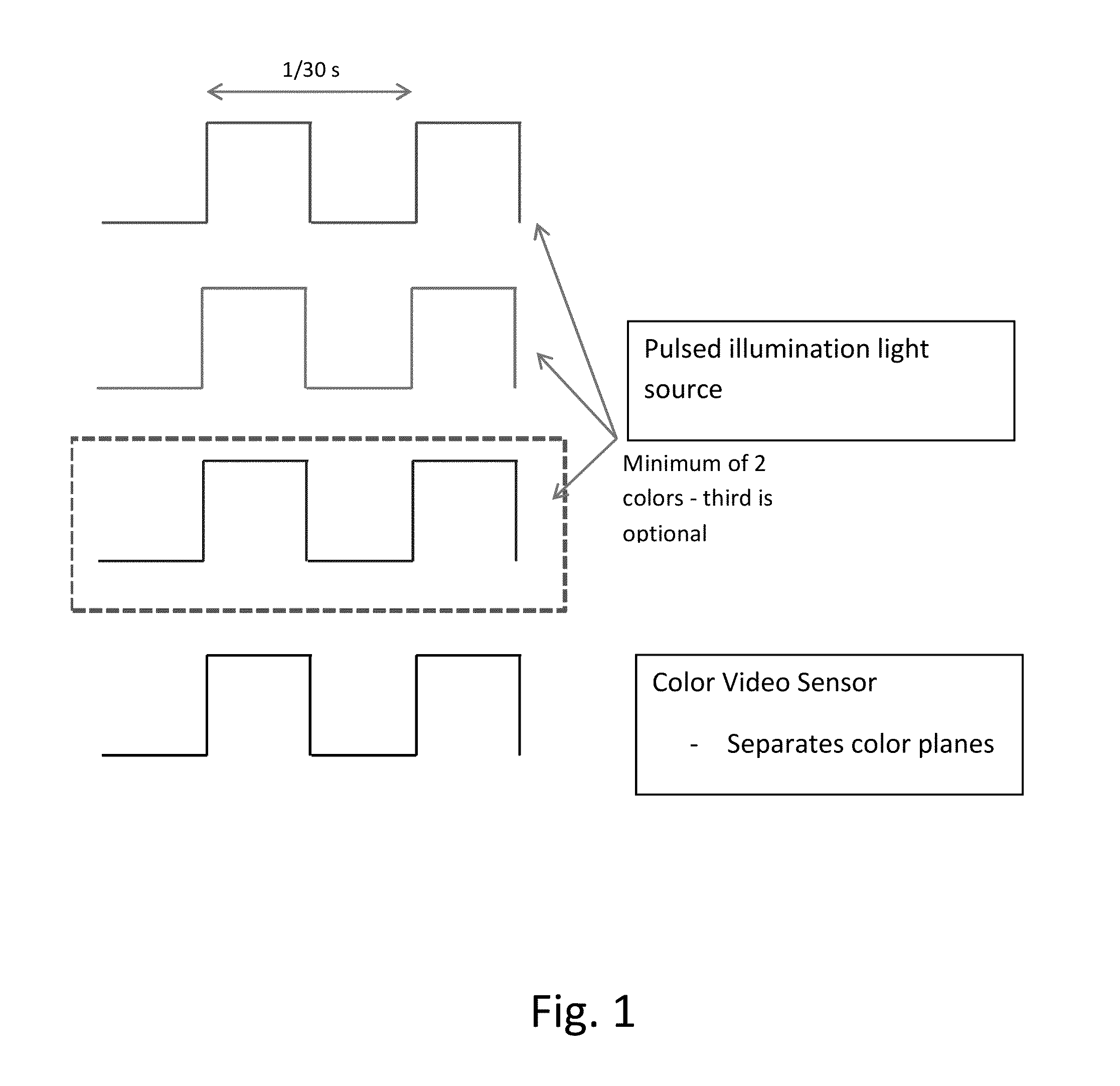
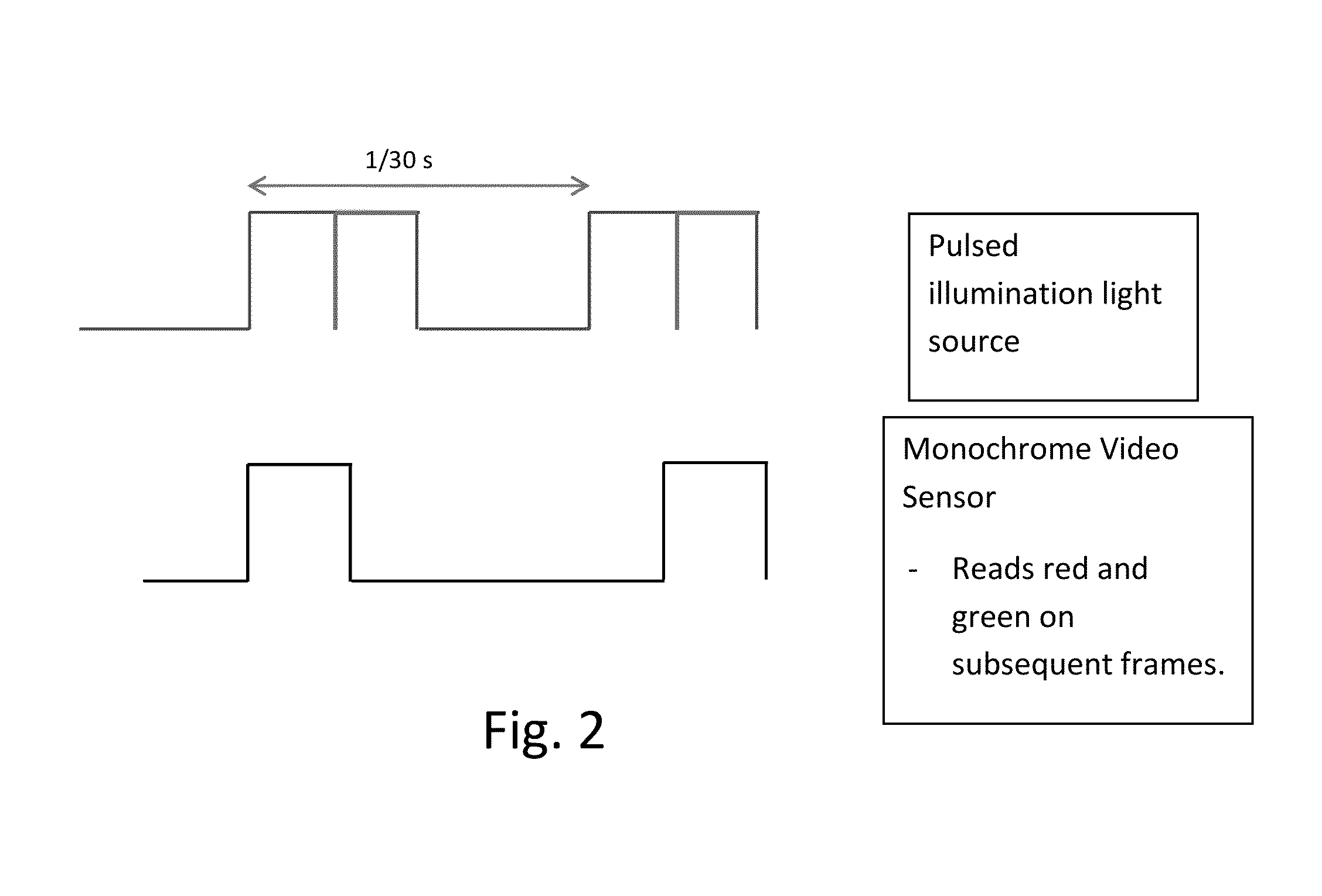
Coordinated illumination and image signal capture for enhanced signal detection
ActiveUS20130329006A1Low costLimited rangeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Signal detection and recognition employees coordinated illumination and capture of images under to facilitate extraction of a signal of interest. Pulsed illumination of different colors facilitates extraction of signals from color channels, as well as improved signal to noise ratio by combining signals of different color channels. The successive pulsing of different color illumination appears white to the user, yet facilitates signal detection, even for lower cost monochrome sensors, as in barcode scanning and other automatic identification equipment.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
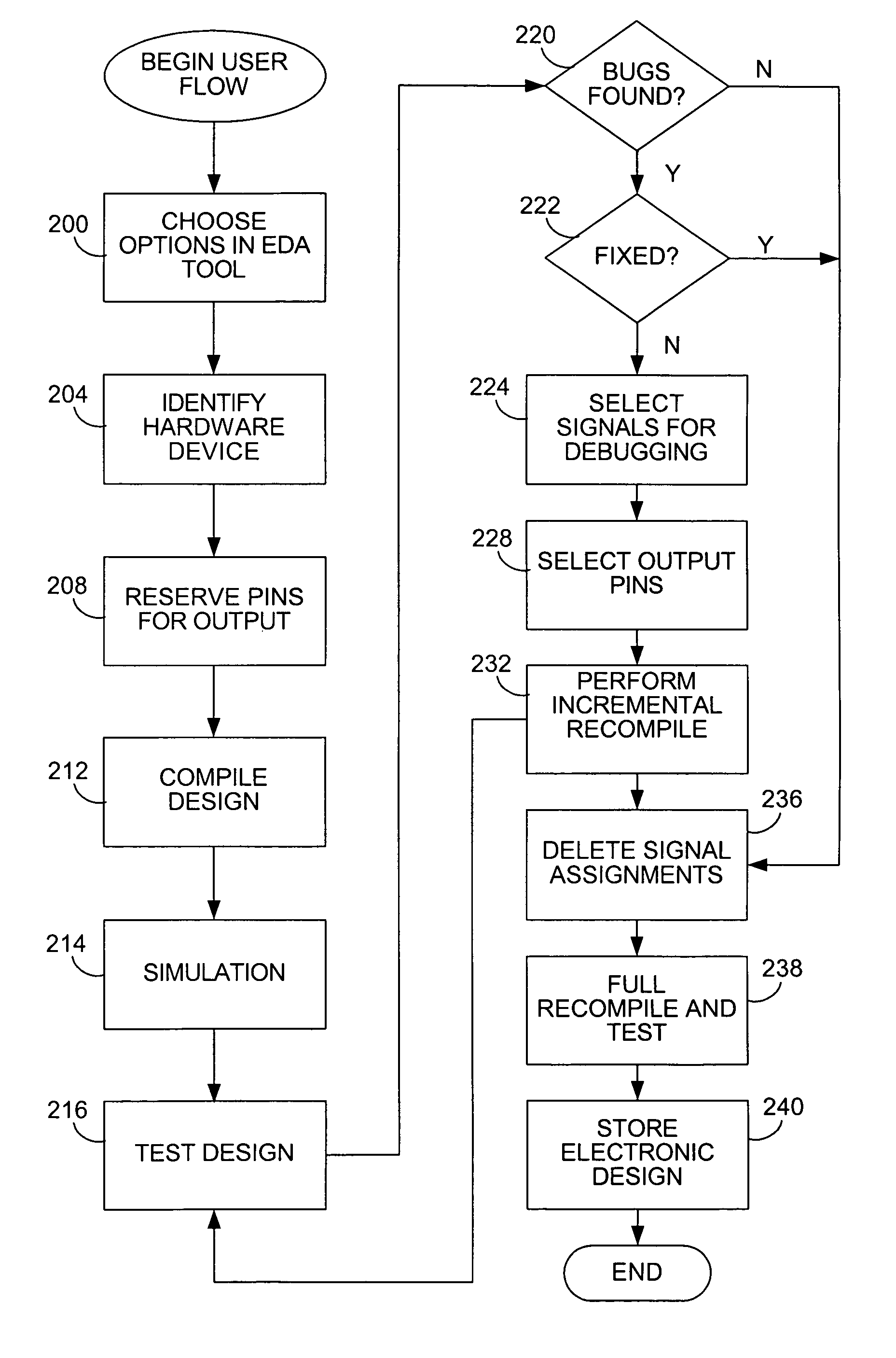
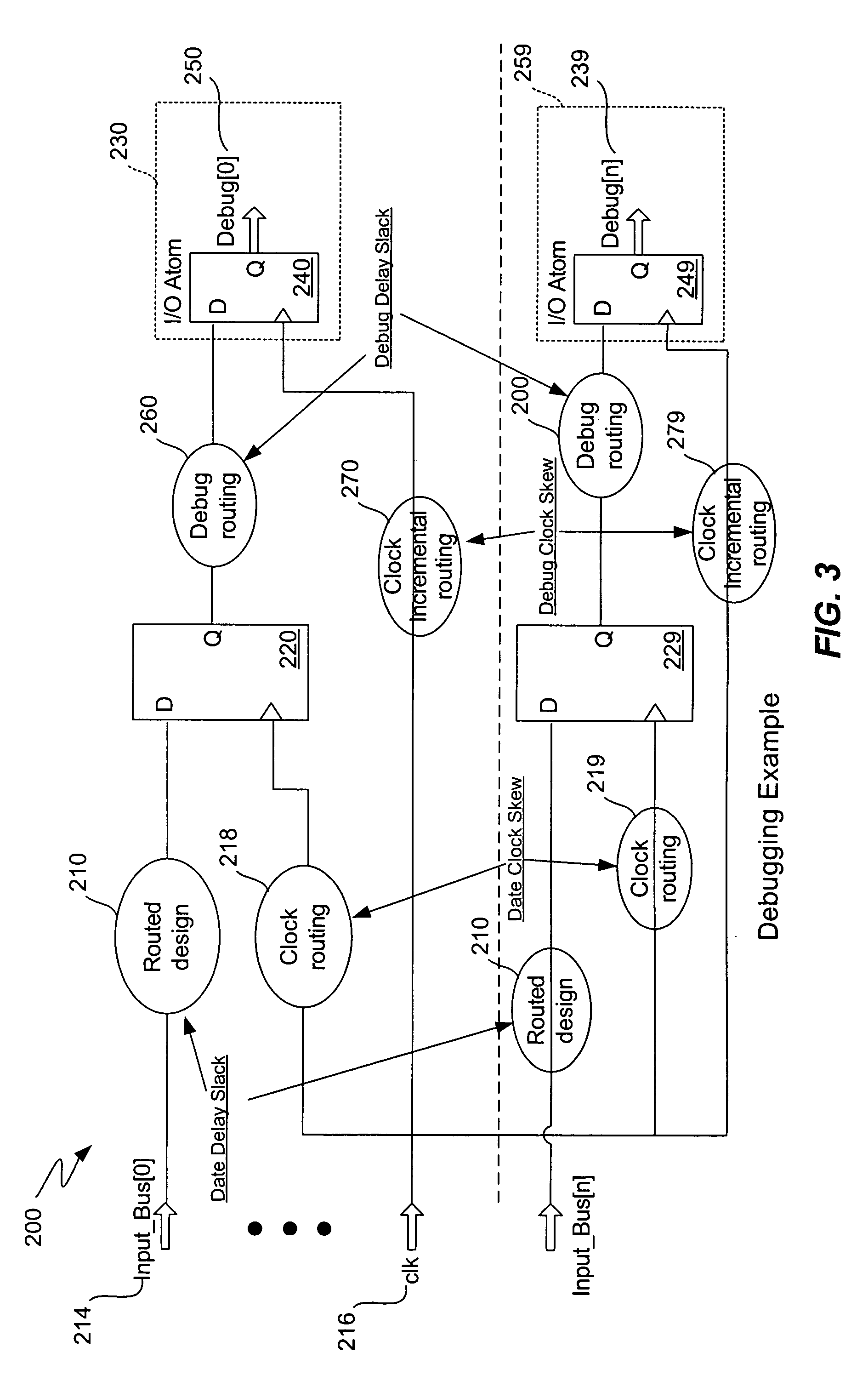
Chip debugging using incremental recompilation and register insertion
InactiveUS7206967B1Efficient solutionError detection/correctionElectrical testingComputer architectureProcessor register
While debugging, a user chooses an incremental recompile. Internal signals of interest and output pins are selected, and a number of additional registers are chosen to insert in the path of each internal signal. A clock is selected for the registers. An incremental recompile of the compiled design compiles a routing from each internal signal to an output pin via the added registers. The database building and logic synthesis stages are skipped. The post-fitting logical netlist and routing netlist are retrieved. The new registers are created and the internal signal is connected to the output pin atom in the logical netlist. The fitter places and routes the connections to create a new routing netlist and then the new routing netlist is output into a programming output file (POF) in a form suitable for programming the PLD. The original routing netlist is undisturbed. The user views the internal signals at the output pins chosen. The user may iterate through this process many times in order to debug the PLD. The debugging assignments may be deleted.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
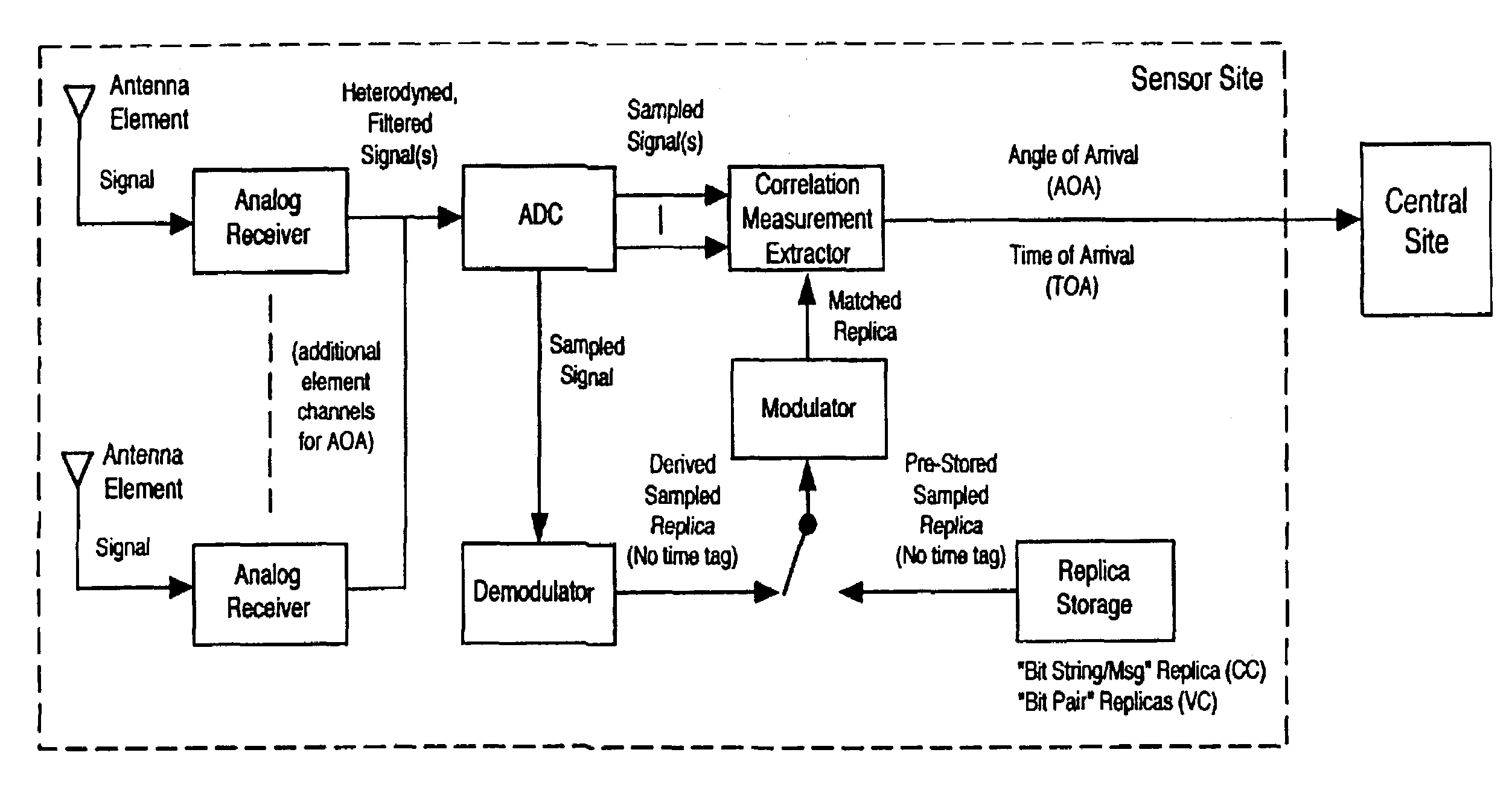
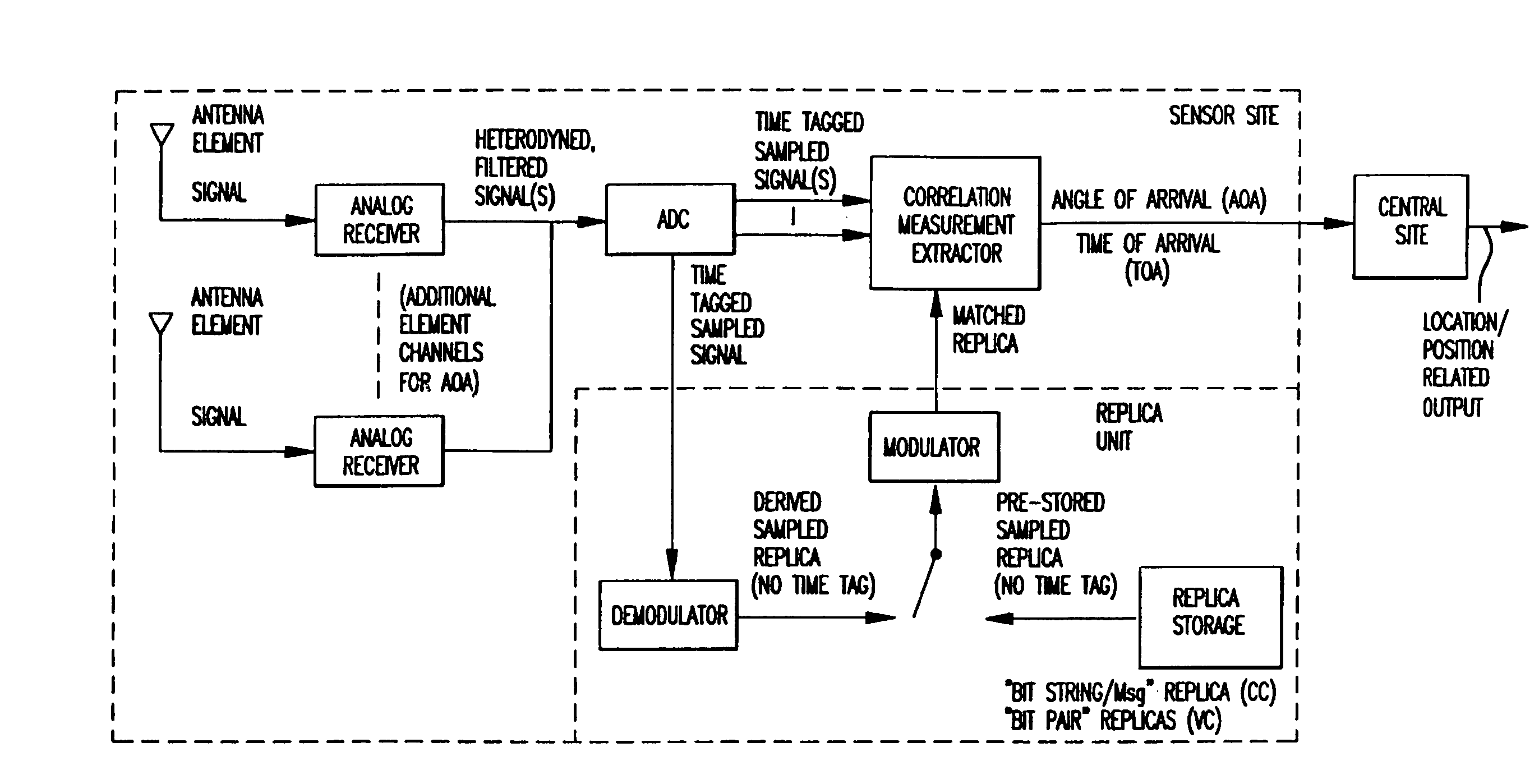
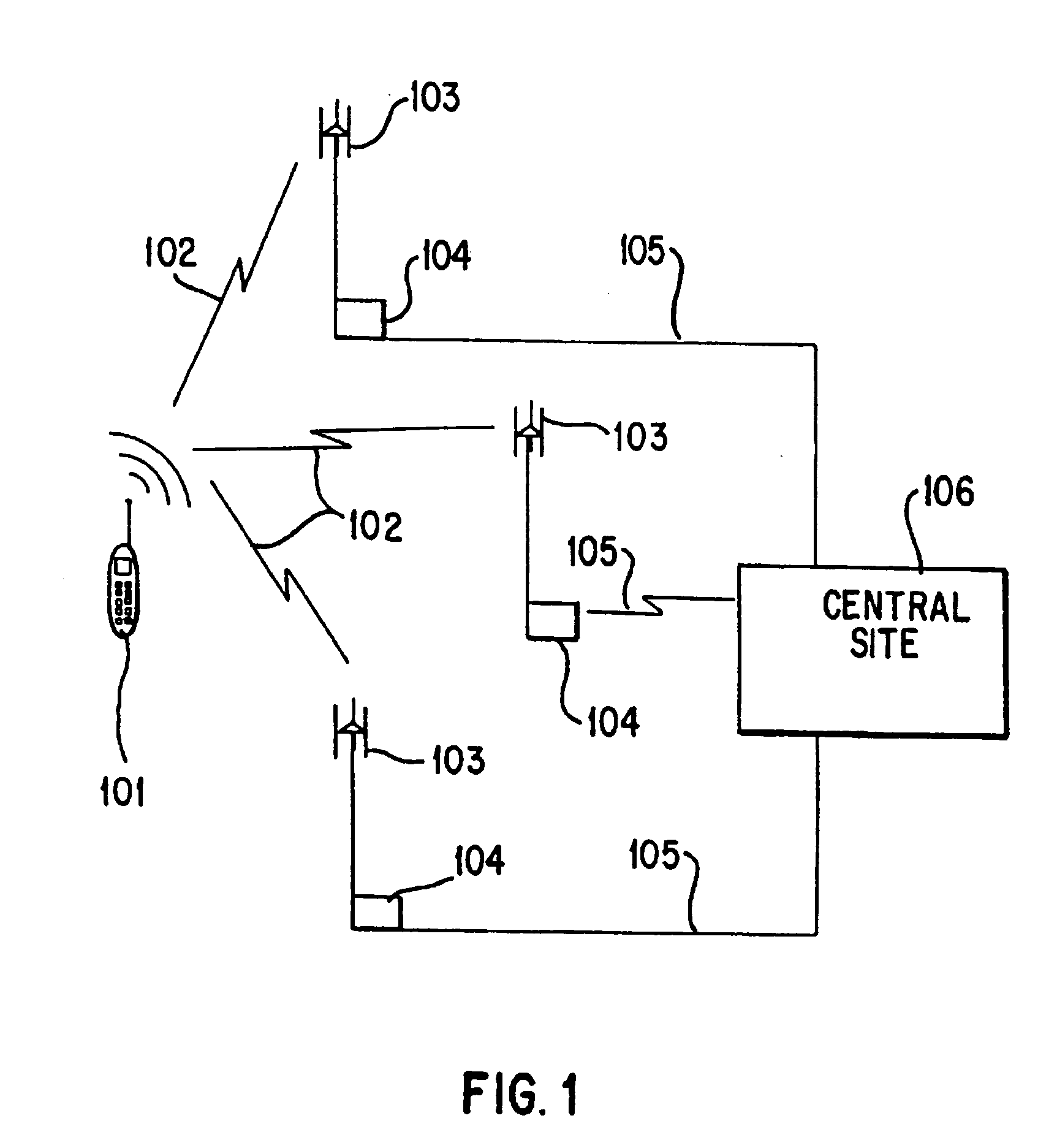
Robust, efficient, localization system
InactiveUS7340259B2Quick responseEasy to measure in real timeDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationLocalization systemCode division multiple access
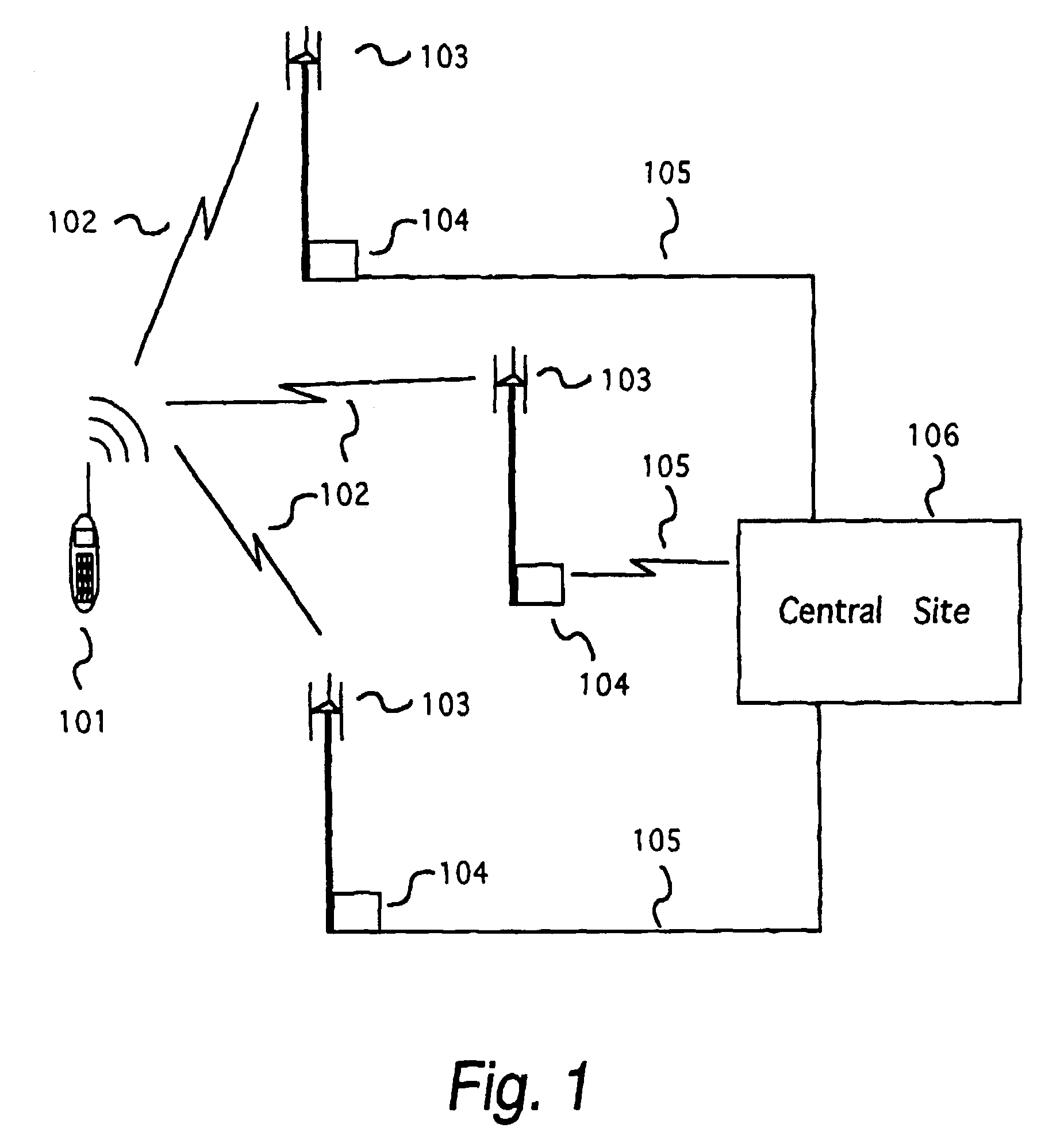
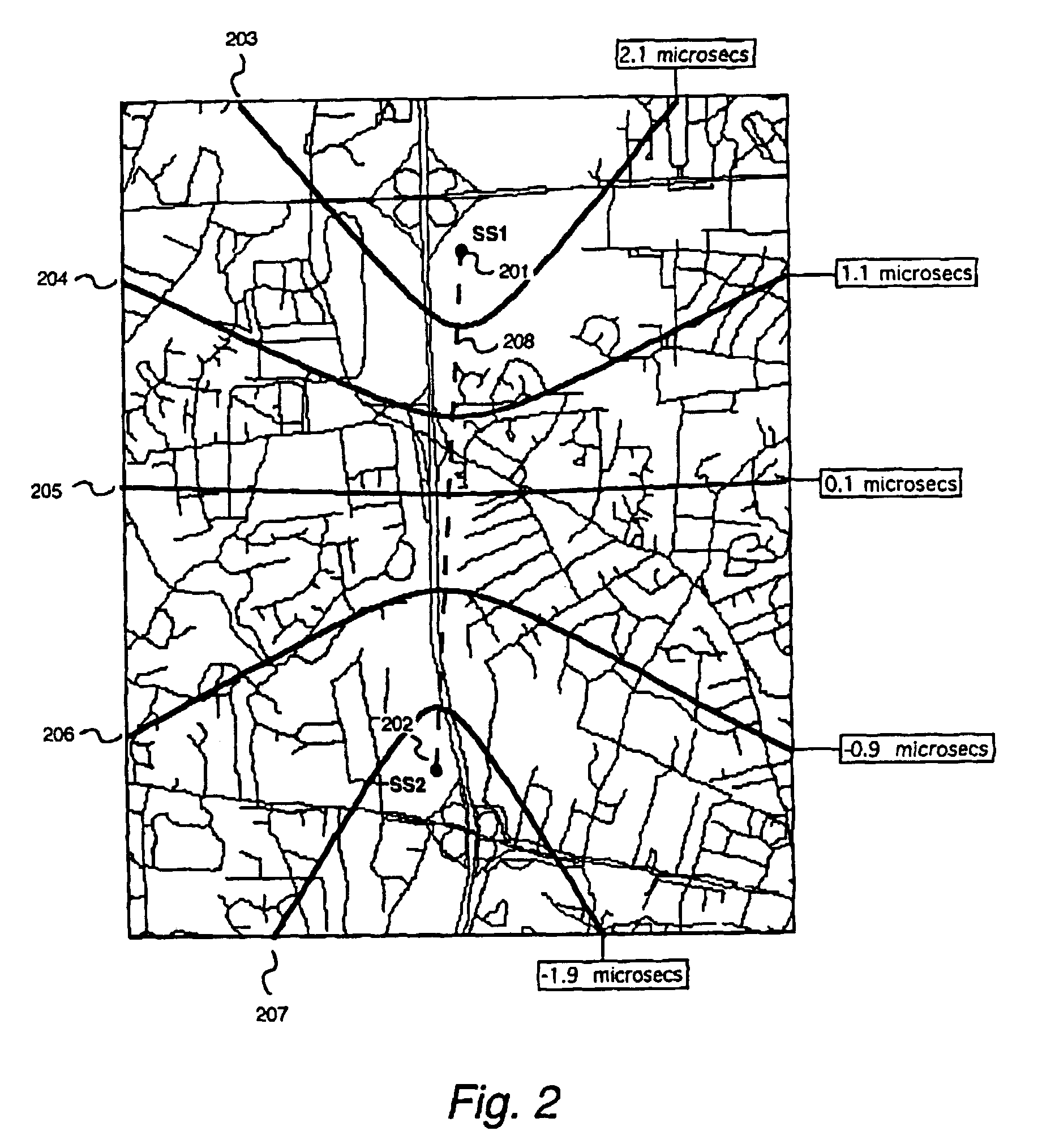
Replica correlation processing, and associated representative signal-data reduction and reconstruction techniques, are used to detect signals of interest and obtain robust measures of received-signal parameters, such as time differences of signal arrival and directional angles of arrival, that can be used to estimate the location of a cellularized-communications signal source. The new use in the present invention of signal-correlation processing for locating communications transmitters. This enables accurate and efficient extraction of parameters for a particular signal even in a frequency band that contains multiple received transmissions, such as occurs with code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) communications. Correlation processing as disclosed herein further enables extended processing integration times to facilitate the effective detection of desired communications-signal effects and replication measurement of their location-related parameters, even for the communications signals modulated to convey voice conversations or those weakened through propagation effects. Using prior, constructed, signal replicas in the correlation processing enables elimination of the inter-site communications of the signal representations that support the correlation analyses. Reduced-data representations of the modulated signals for voiced conversation, or for the variable components of data communications, are used to significantly reduce the inter-site communications that support the correlation analyses.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
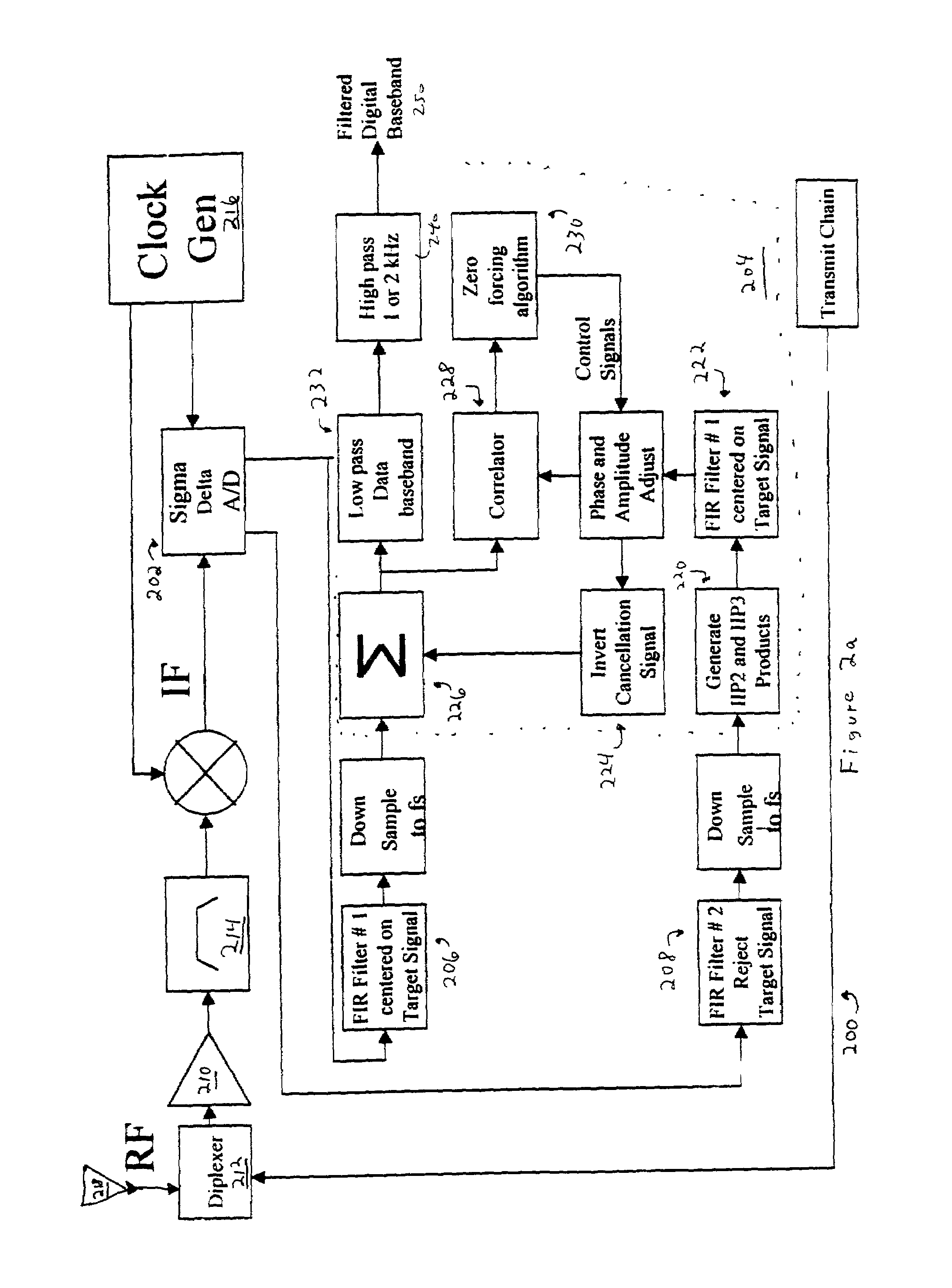
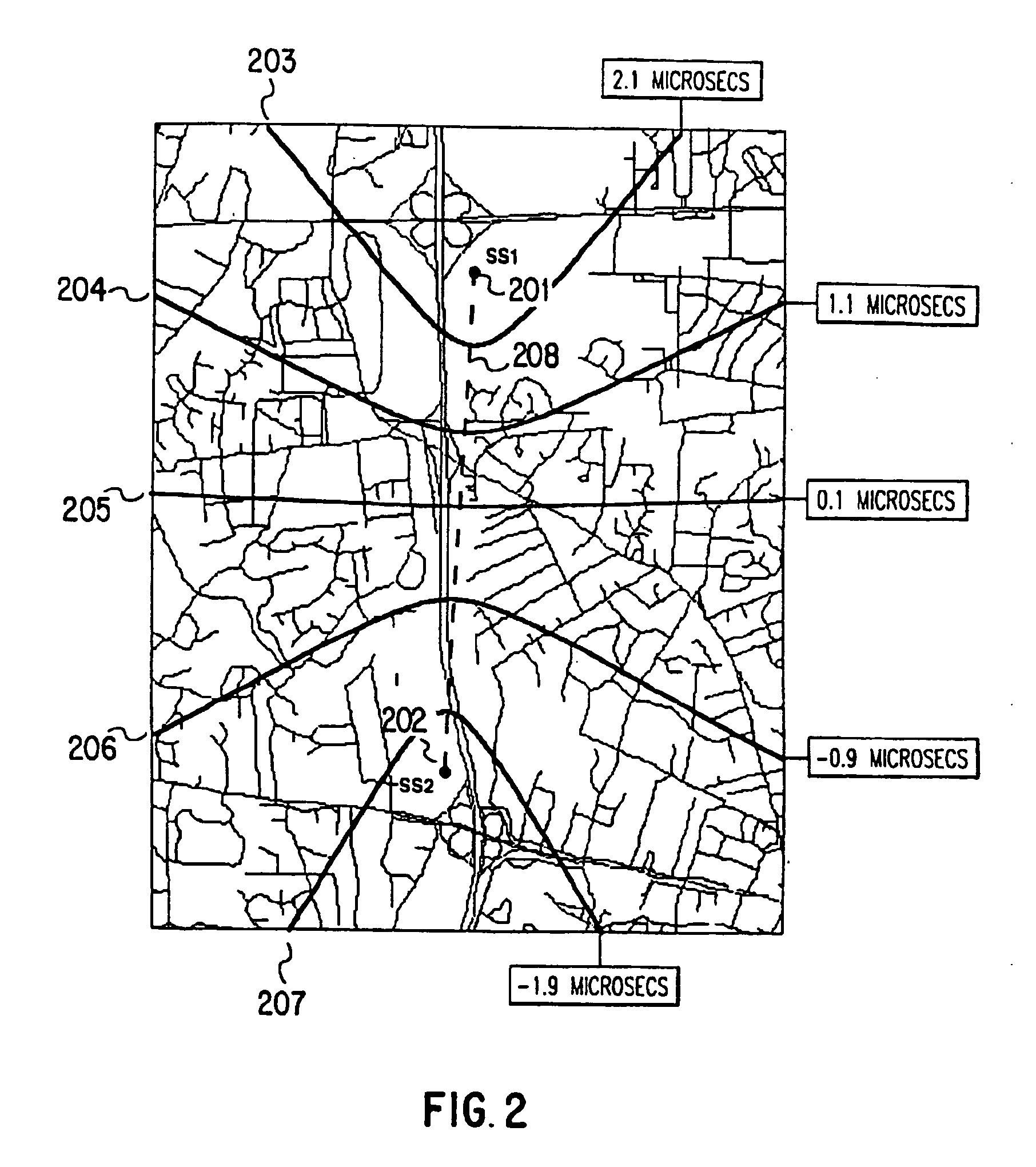
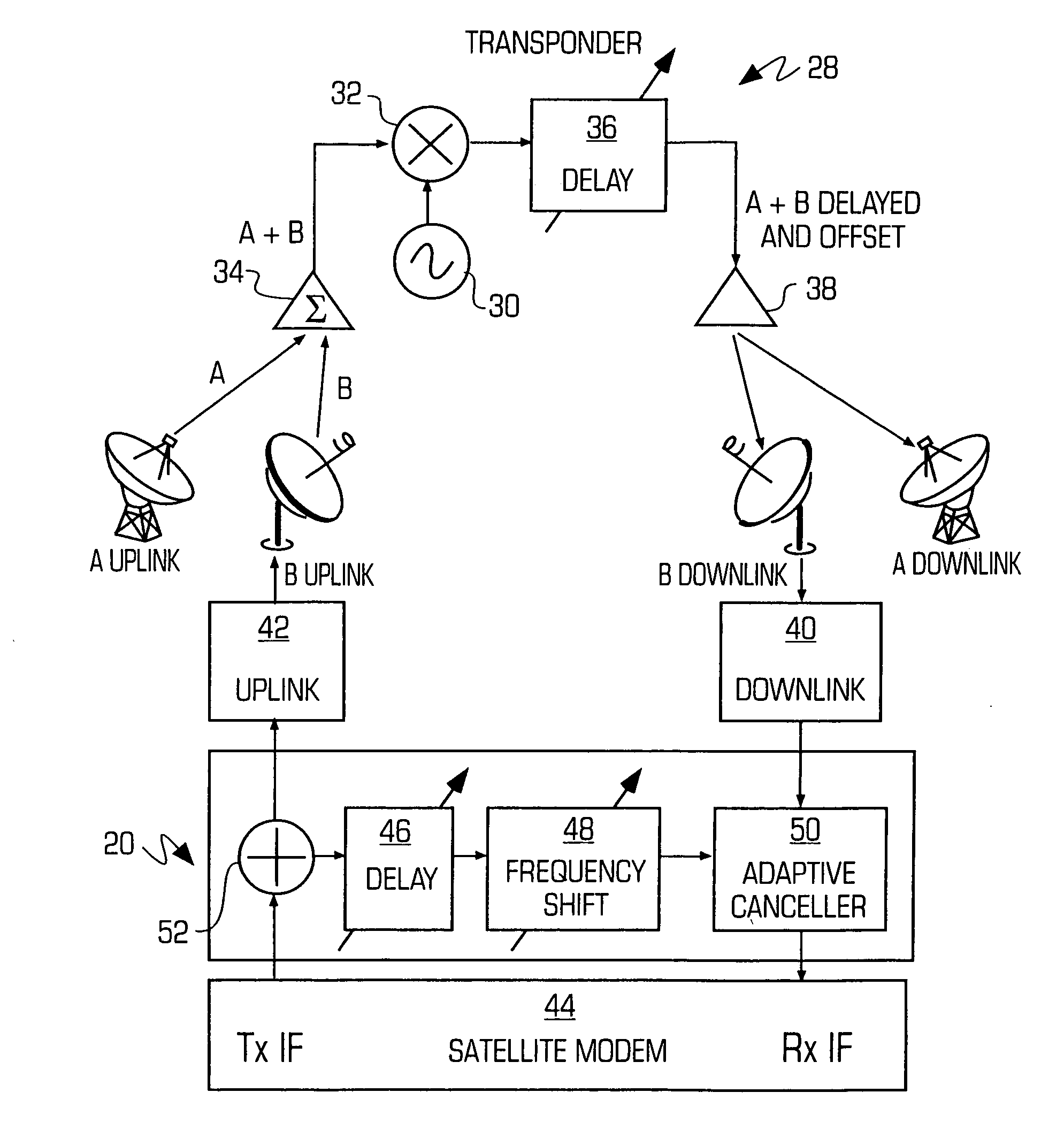
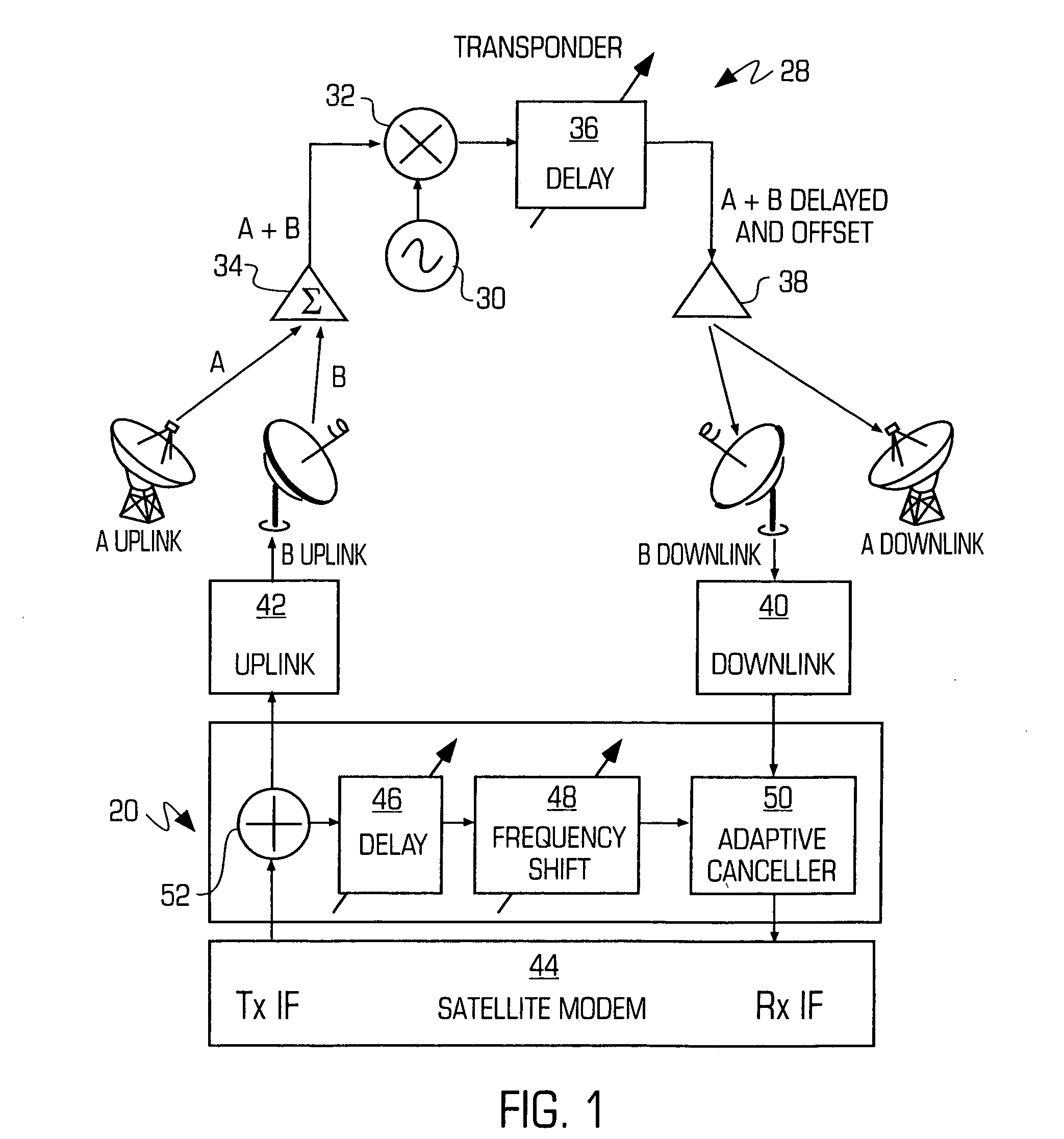
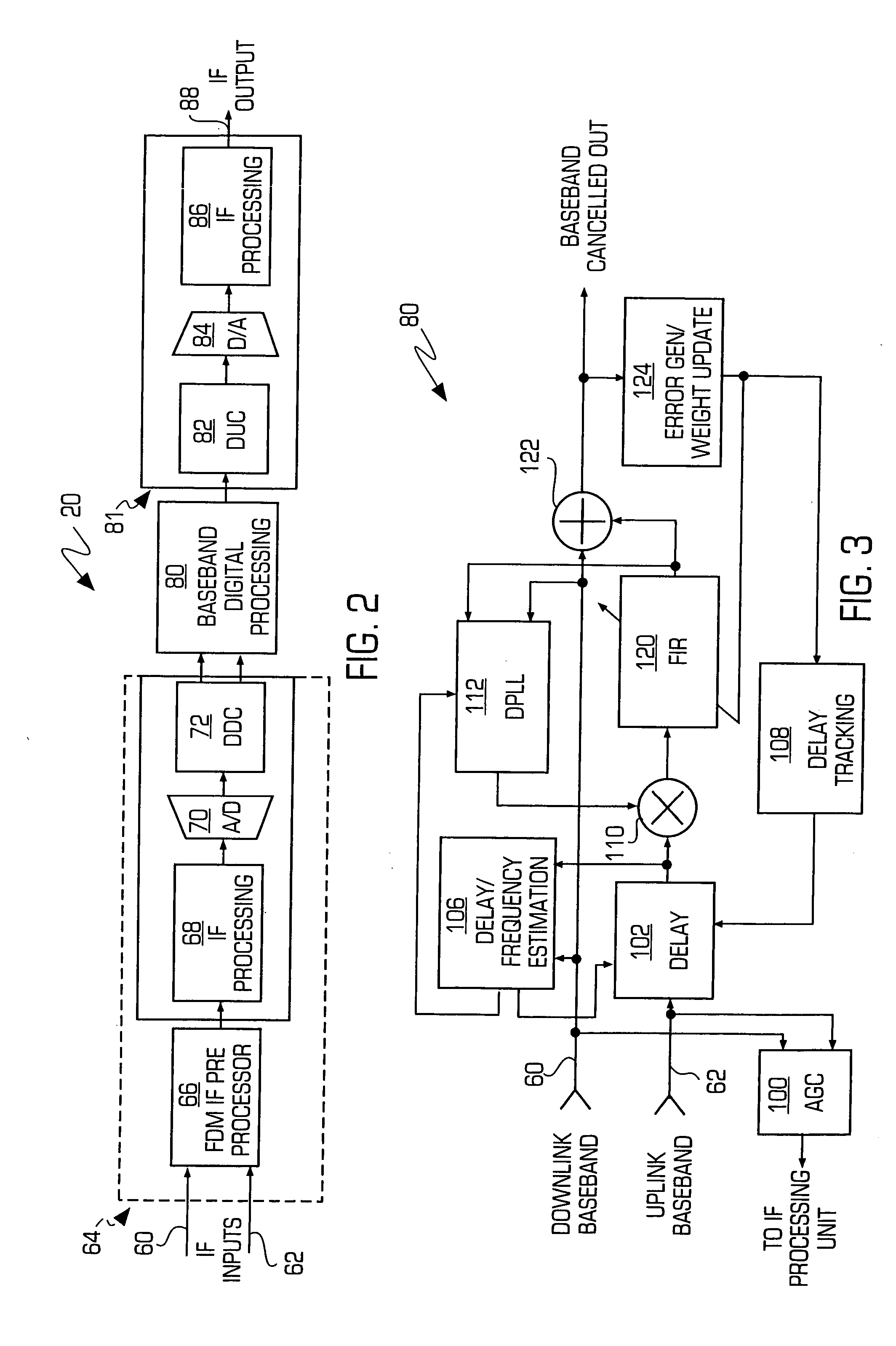
Adaptive canceller for frequency reuse systems
ActiveUS6859641B2Effective and efficient mannerEasy to useRadio transmissionTransmission noise suppressionSignal of interestSatellite
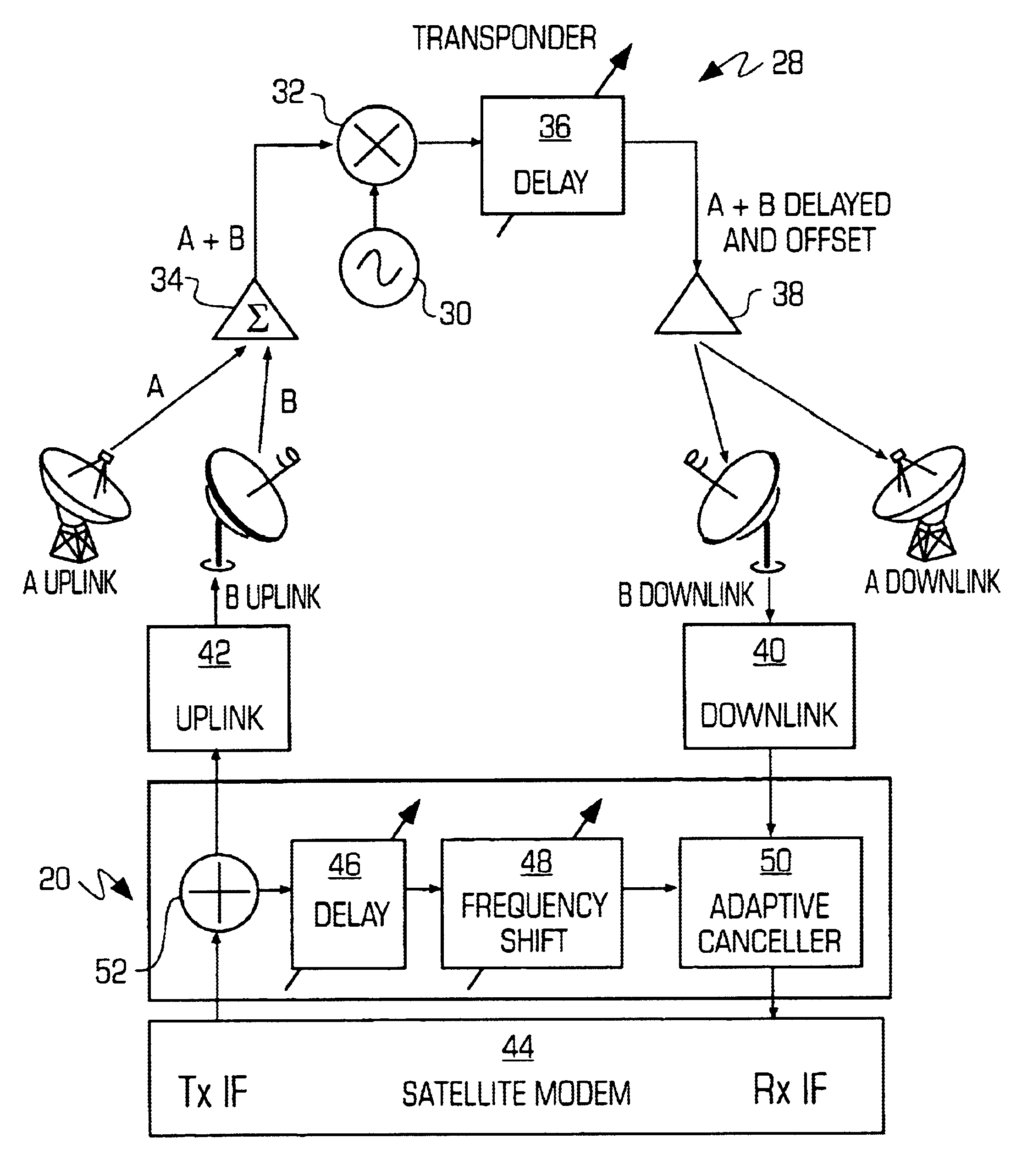
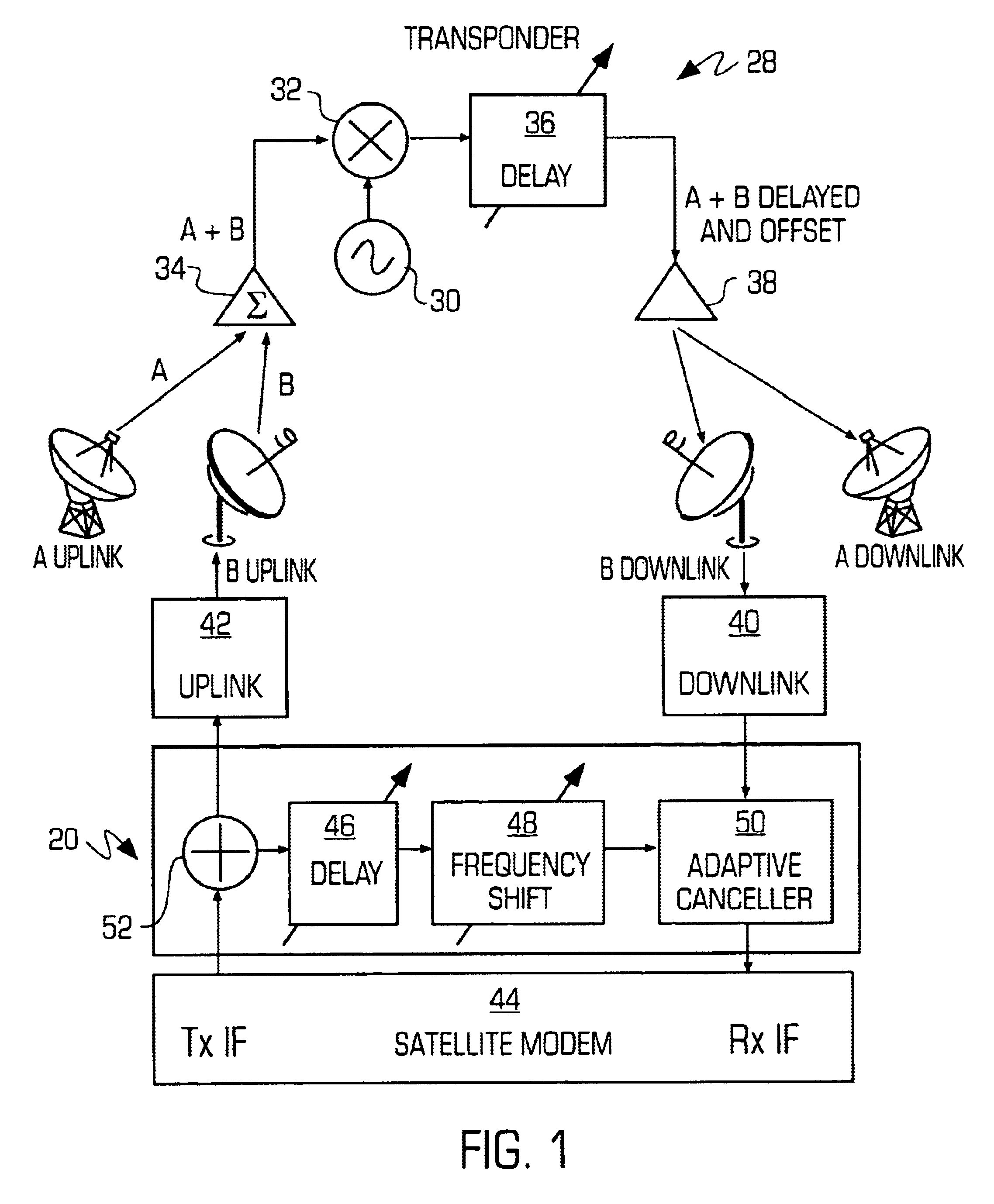
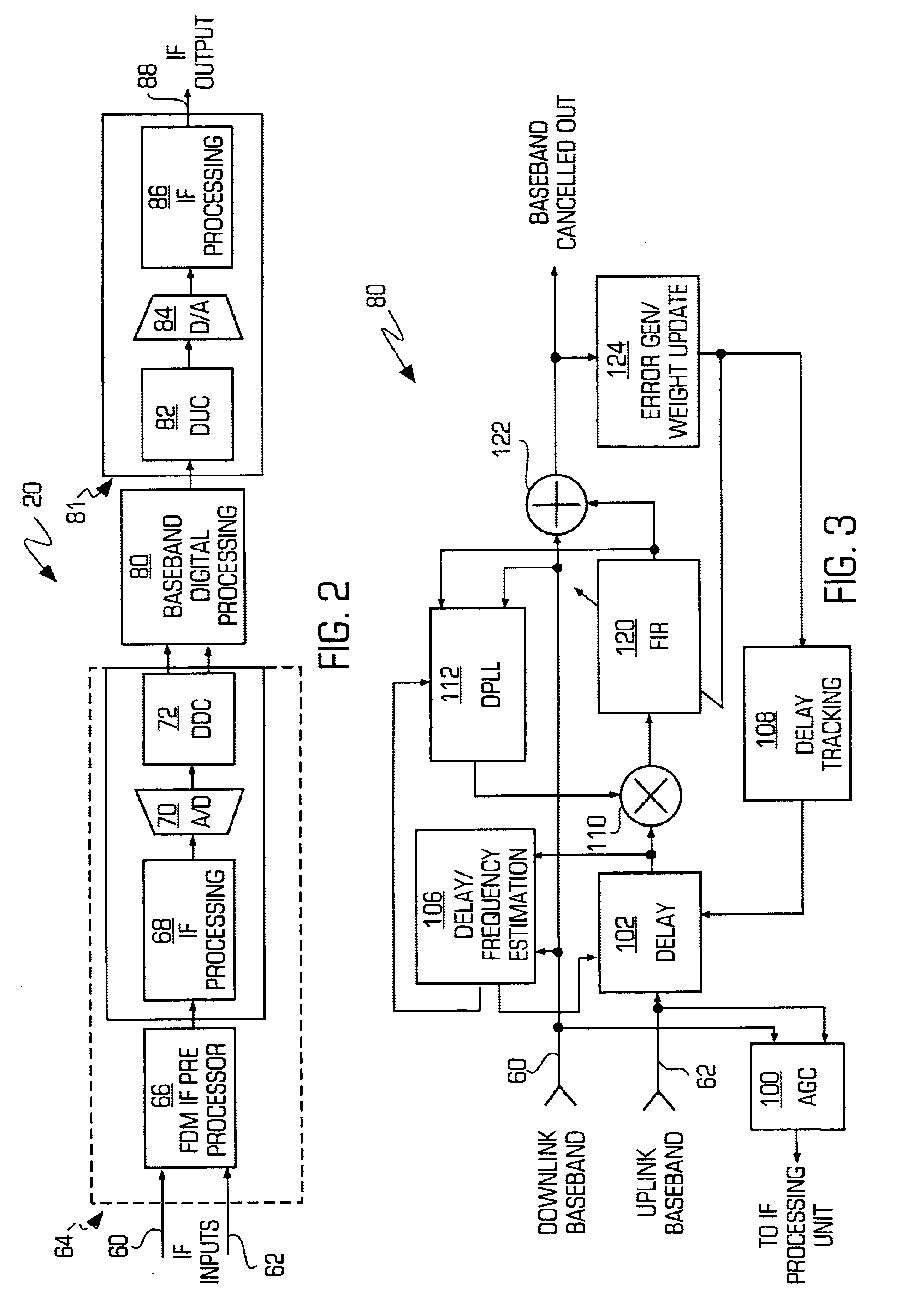
An adaptive interference canceller for canceling an interfering signal corresponding to a delayed, frequency translated, amplitude and phase offset version of a transmitted signal contained in a composite received signal relayed through a relay system such as a satellite transponder. The canceller digitally downconverts the received signal and a local replica of the transmitted signal from IF to baseband, applies a variable delay and frequency compensation to the replica as a coarse delay and frequency correction, and tracks fine delay, amplitude and phase differences using an adaptive finite impulse response filter to generate a cancellation signal corresponding to the delayed and frequency shifted version. A minimum output power process produces an error signal that drives the variable delay and adaptive filter to minimize the power in the signal of interest to maximize cancellation of the interfering signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON APPLIED SIGNAL TECH
Method for controlling a speaker array to provide spatialized, localized, and binaural virtual surround sound
ActiveUS20140064526A1Superior speaker-based binaural sound imagingExisting technologyMicrophonesTransducer detailsSource materialCommon space
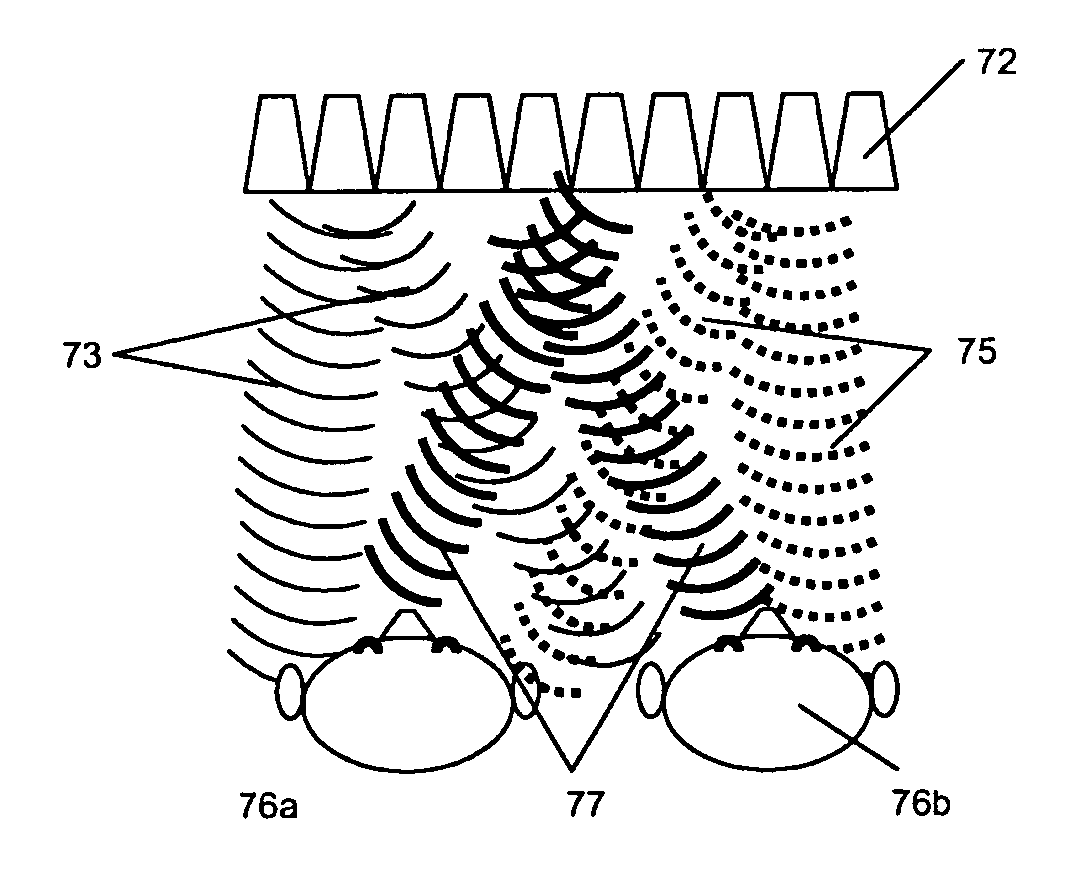
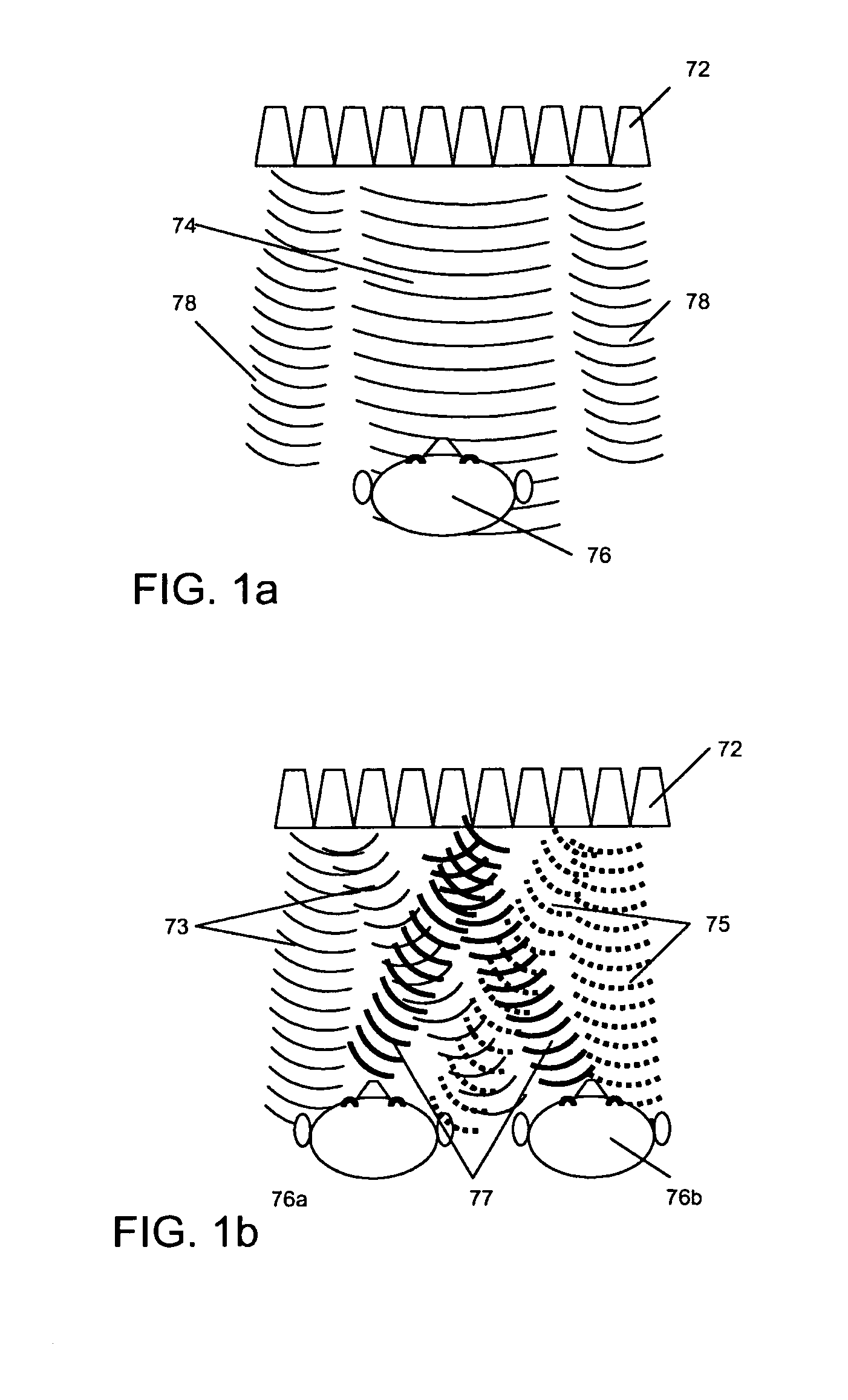
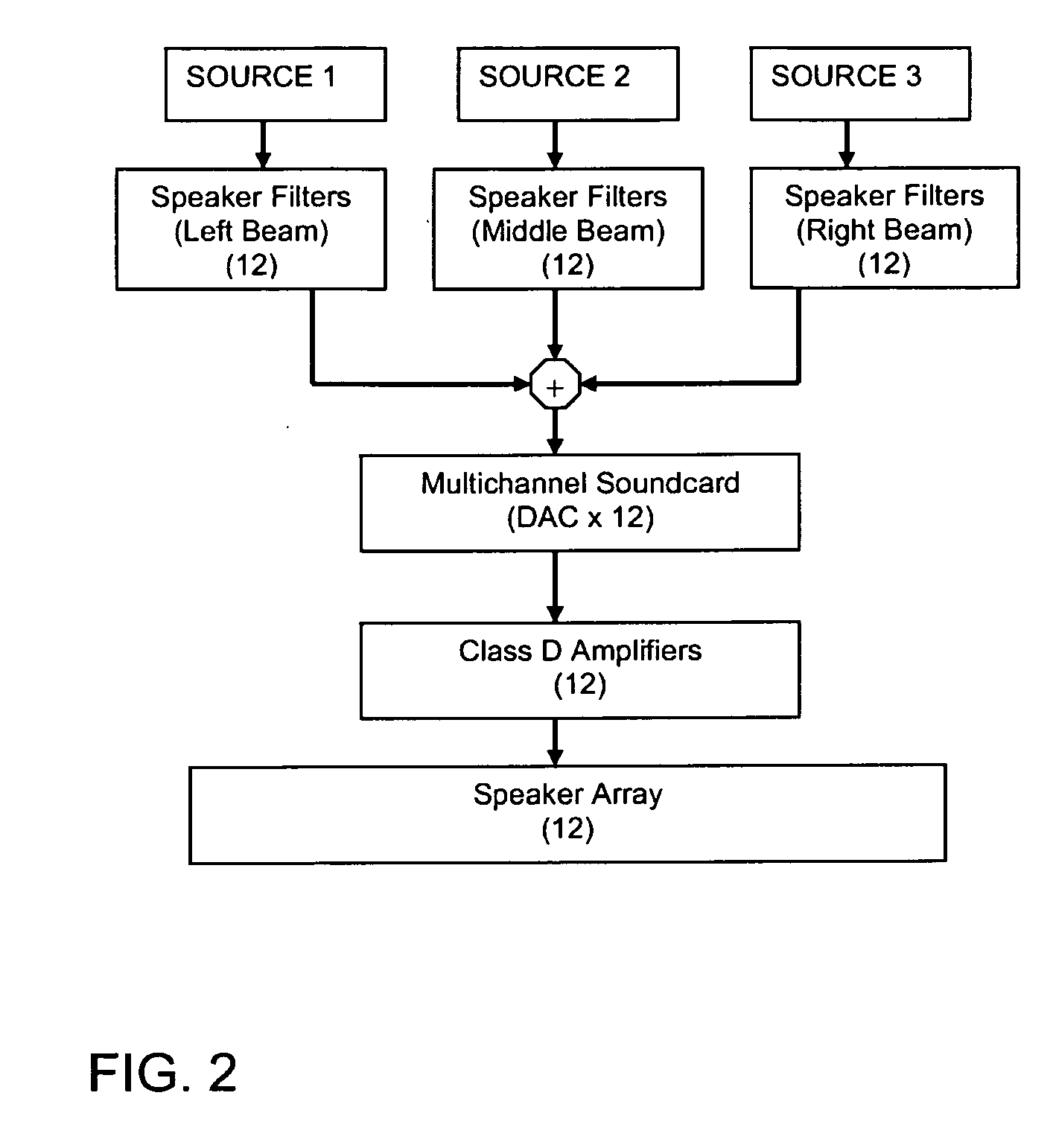
A system and method for producing a binaural and localized audio signal to a user is provided. A signal processing method is provided for delivering spatialized sound in various ways using highly optimized inverse filters to deliver narrow localized beams of sound from the included speaker array. The inventive method can be used to provide private listening areas in a public space and provide spatialization of source material for a single user to create a virtual surround sound effect. In a binaural mode, a speaker array provides two targeted beams aimed towards the primary user's ears—one discrete beam for the left ear and one discrete beam for the right ear. In a privacy mode, a privacy zone could be created in which a primary audio beam would deliver a signal of interest to the user while secondary beams would be aimed at different angles to provide a masking noise.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +2
Signal type identification
InactiveUS6904269B1Spectral/fourier analysisSimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationPattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
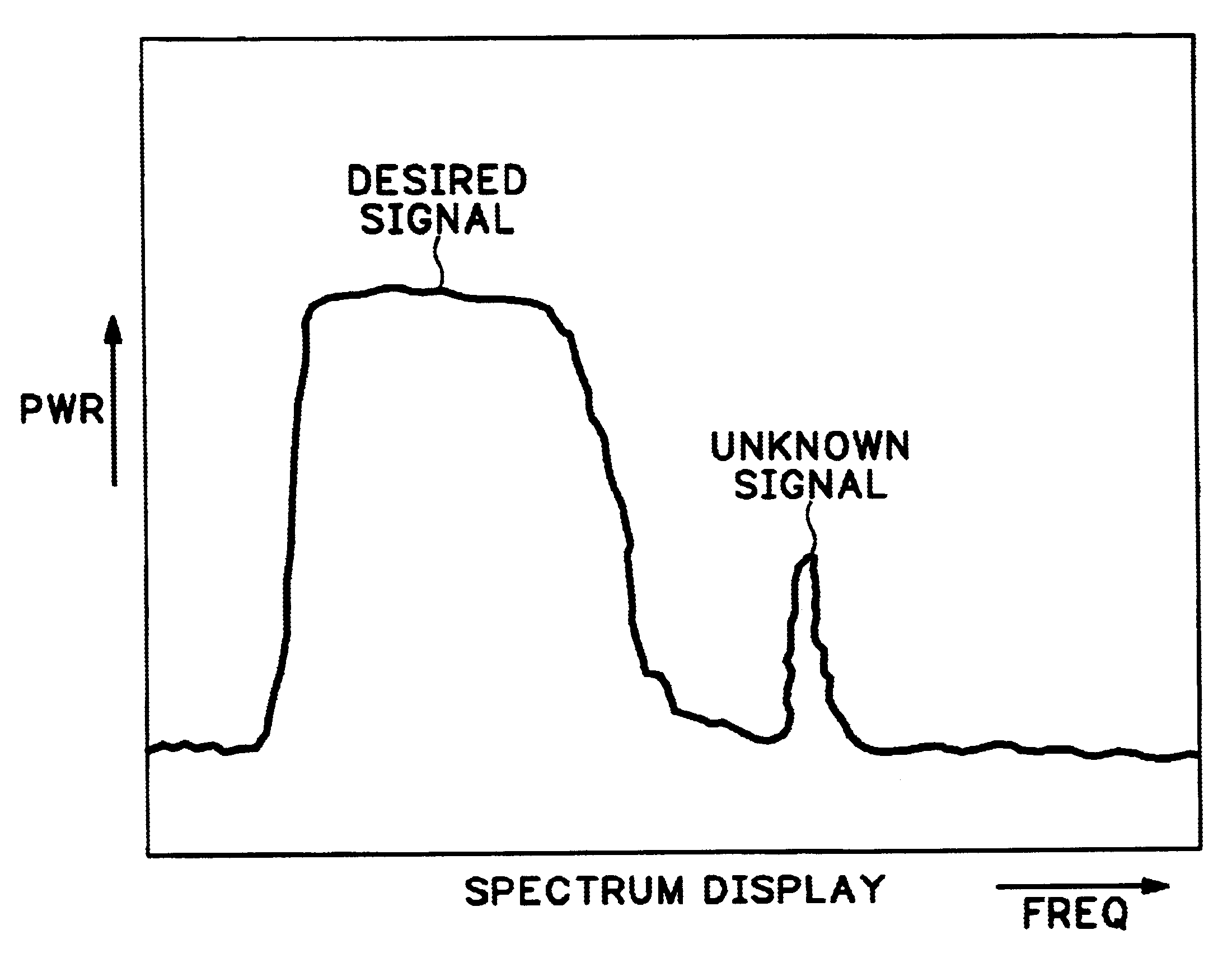
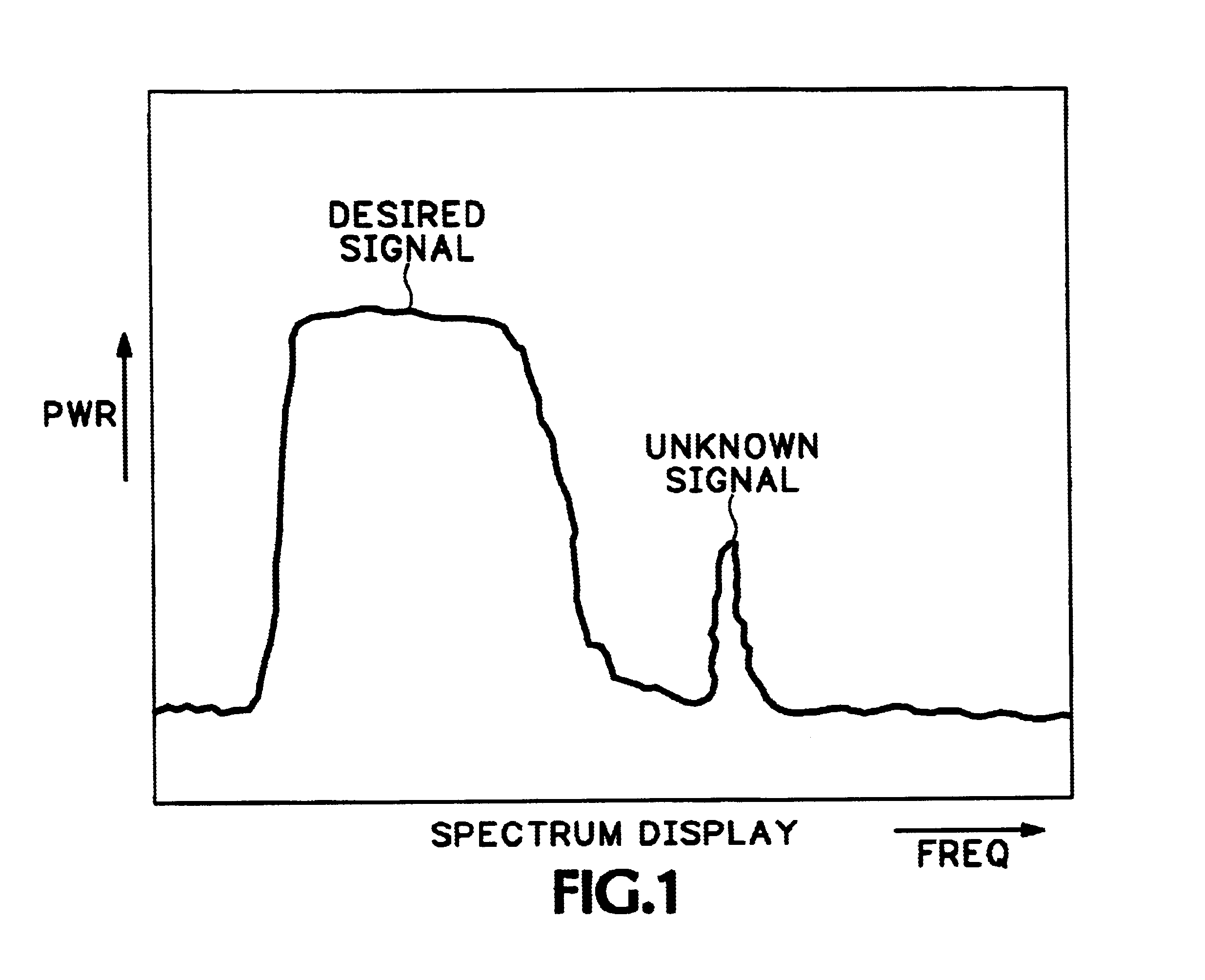
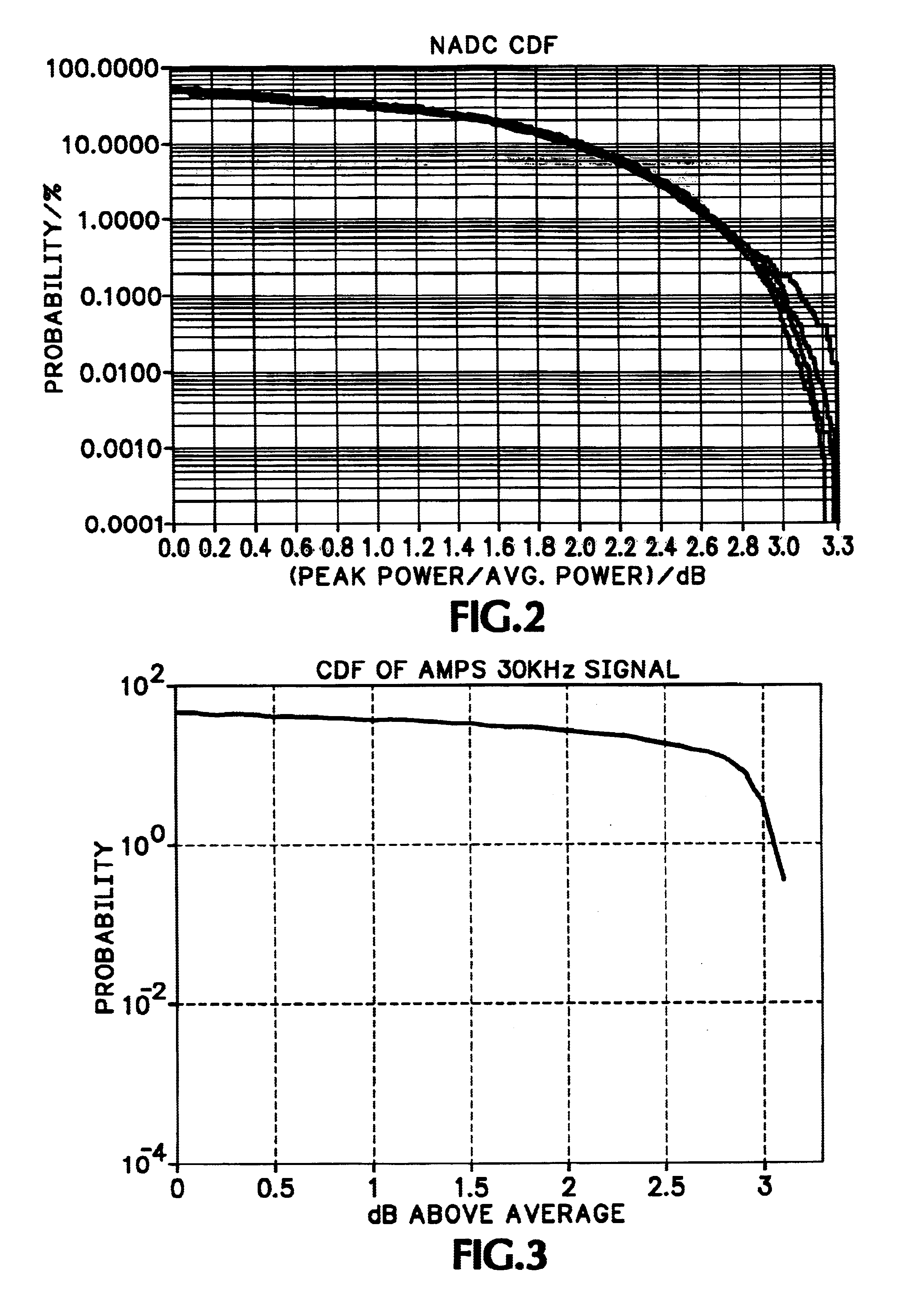
A method of identifying a signal type uses parameters of the signal as a basis for automatic identification. A signal of interest is selected from a display of a spectral waveform for a specified frequency. An occupied bandwidth for the signal of interest is estimated and, if the occupied bandwidth is common to more than one known signal type, a complementary cumulative distribution function of peak power for the signal of interest is estimated. The signal type may be identified as a function of these parameters. Additionally the frequency of the signal of interest may be compared with a database of spectral assignments for known signal types to provide further information about the signal of interest.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
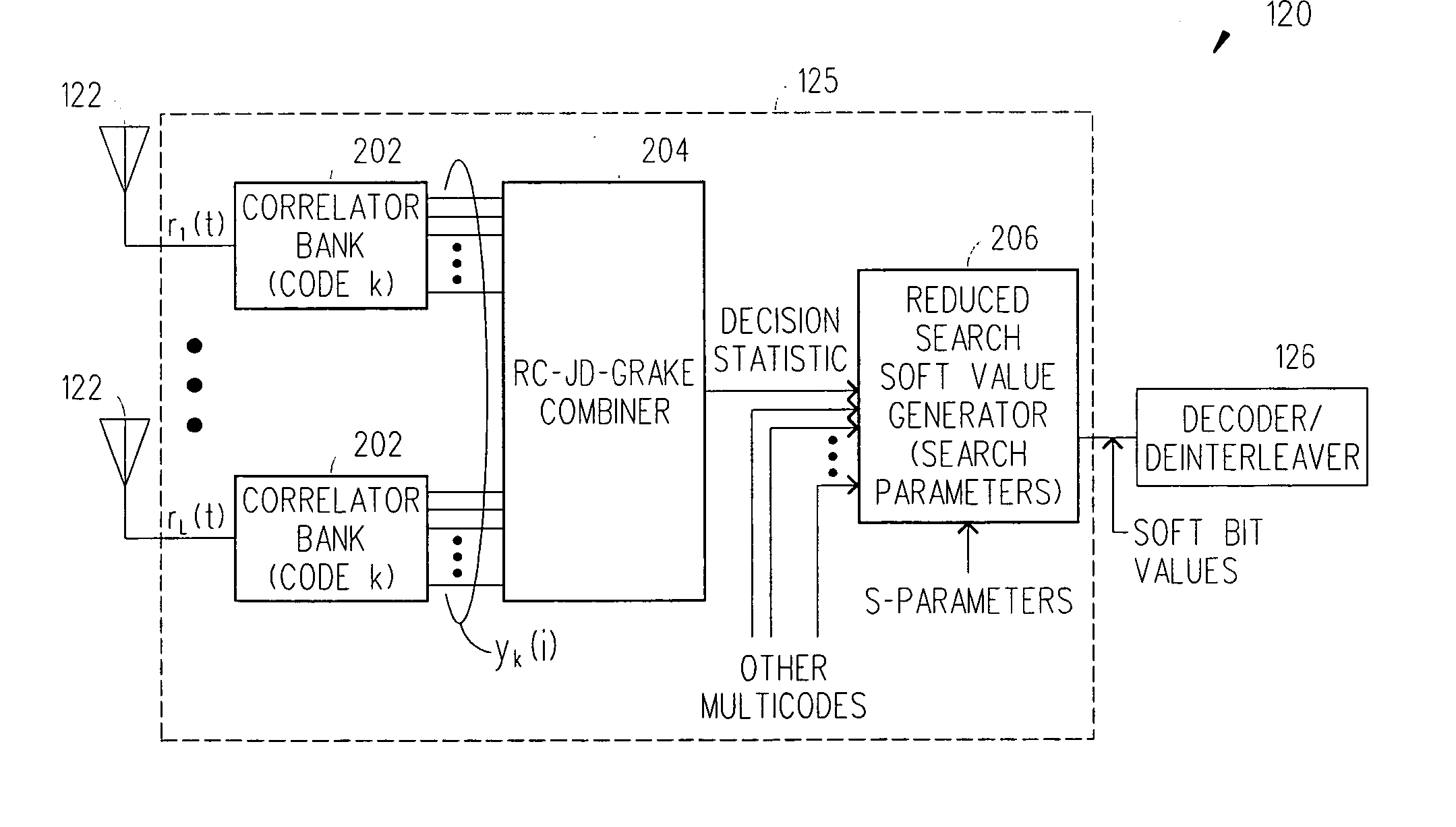
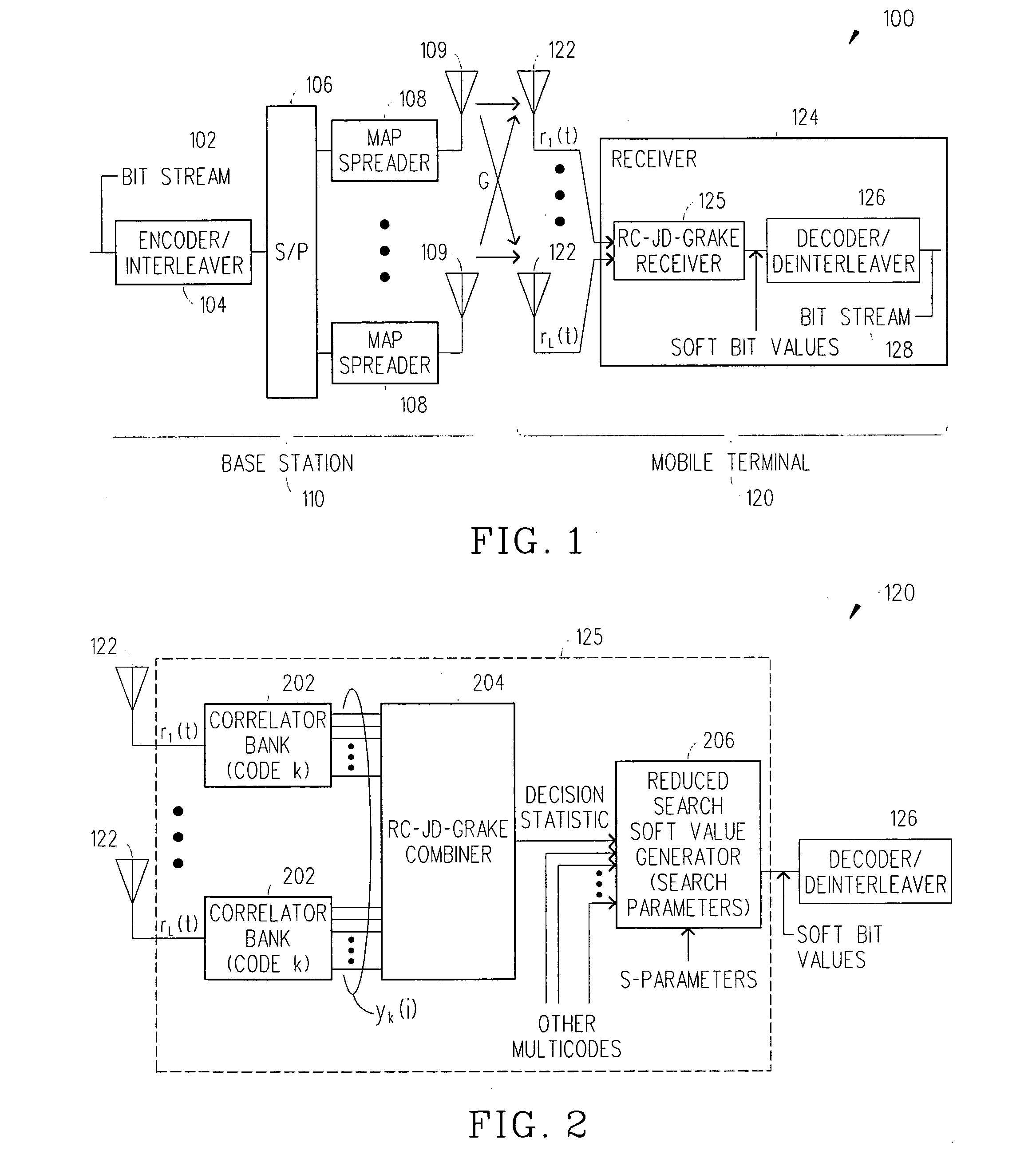
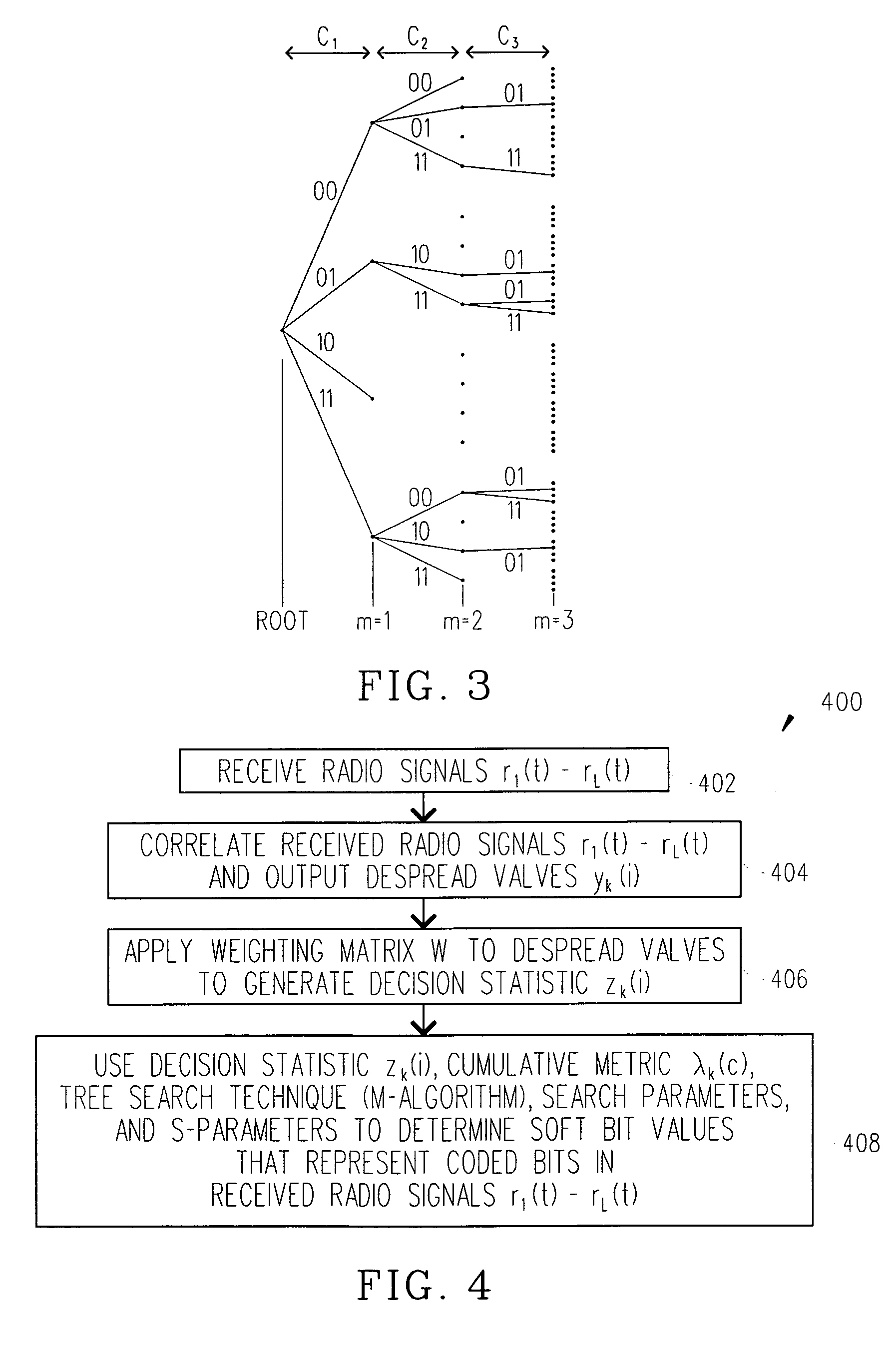
Reduced complexity soft value generation for MIMO JD-GRAKE receivers
InactiveUS20060029124A1Reduce in quantityReduce complexityDiversity/multi-antenna systemsRake combiningEngineering
A receiver includes a receiver circuit that decodes multiple signals of interest contained in a composite receive signal. The receiver comprises at least one Generalized RAKE combining circuit and a joint demodulation circuit and generates a detected signal at an output. The joint demodulation circuit contains a reduced search soft value generator circuit and generates soft bit values that represent coded bits received from the transmitter.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
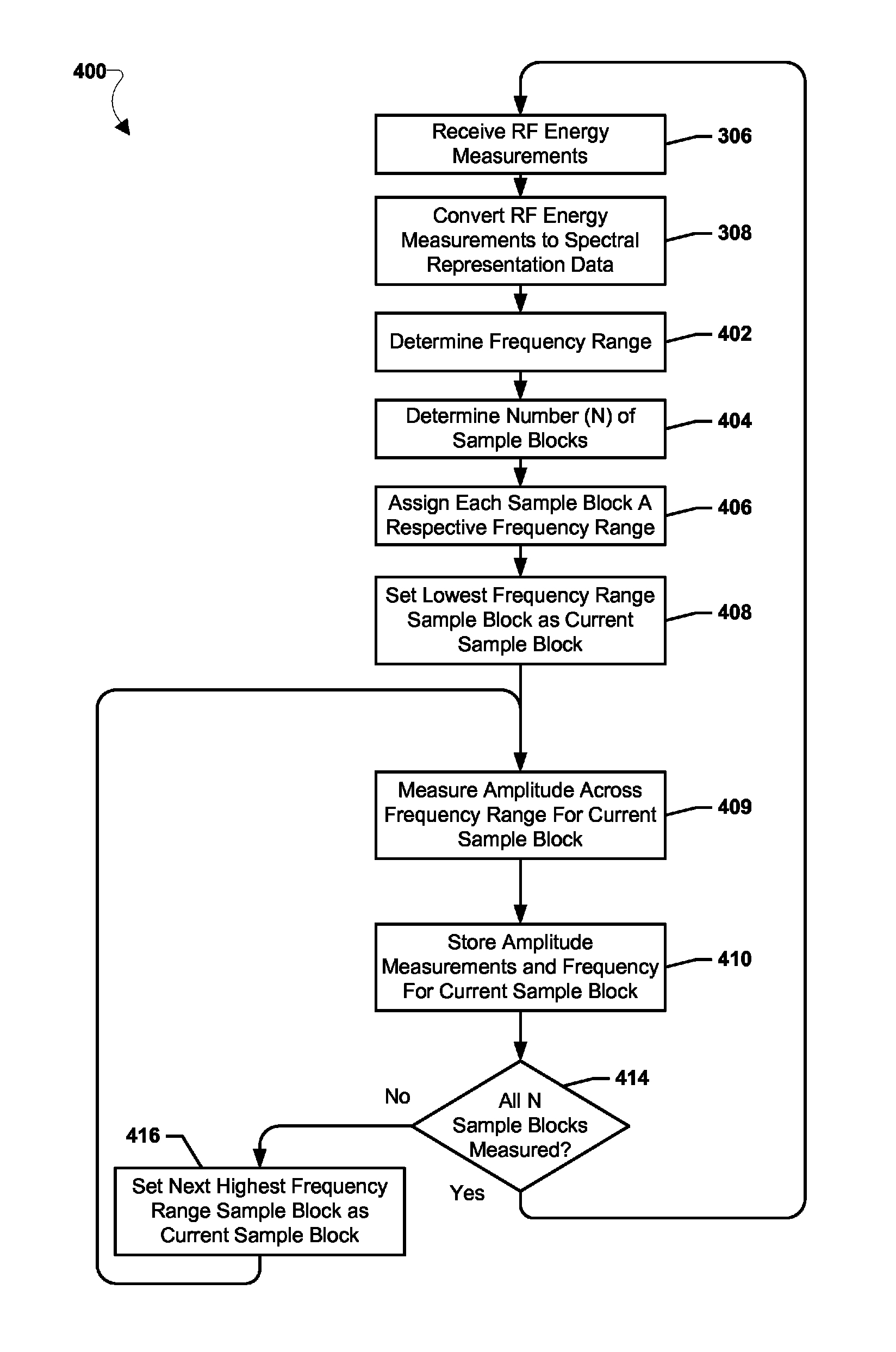
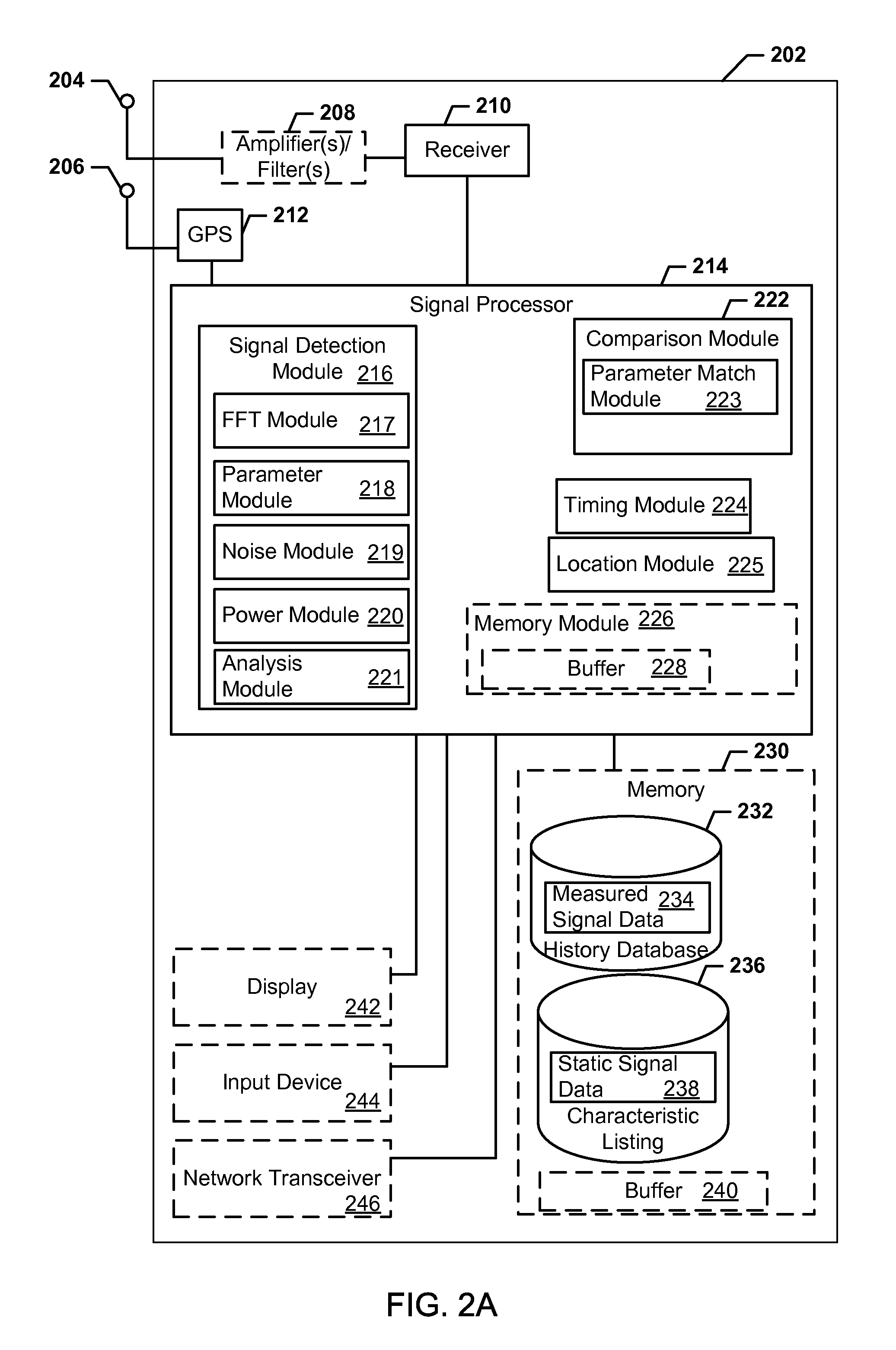
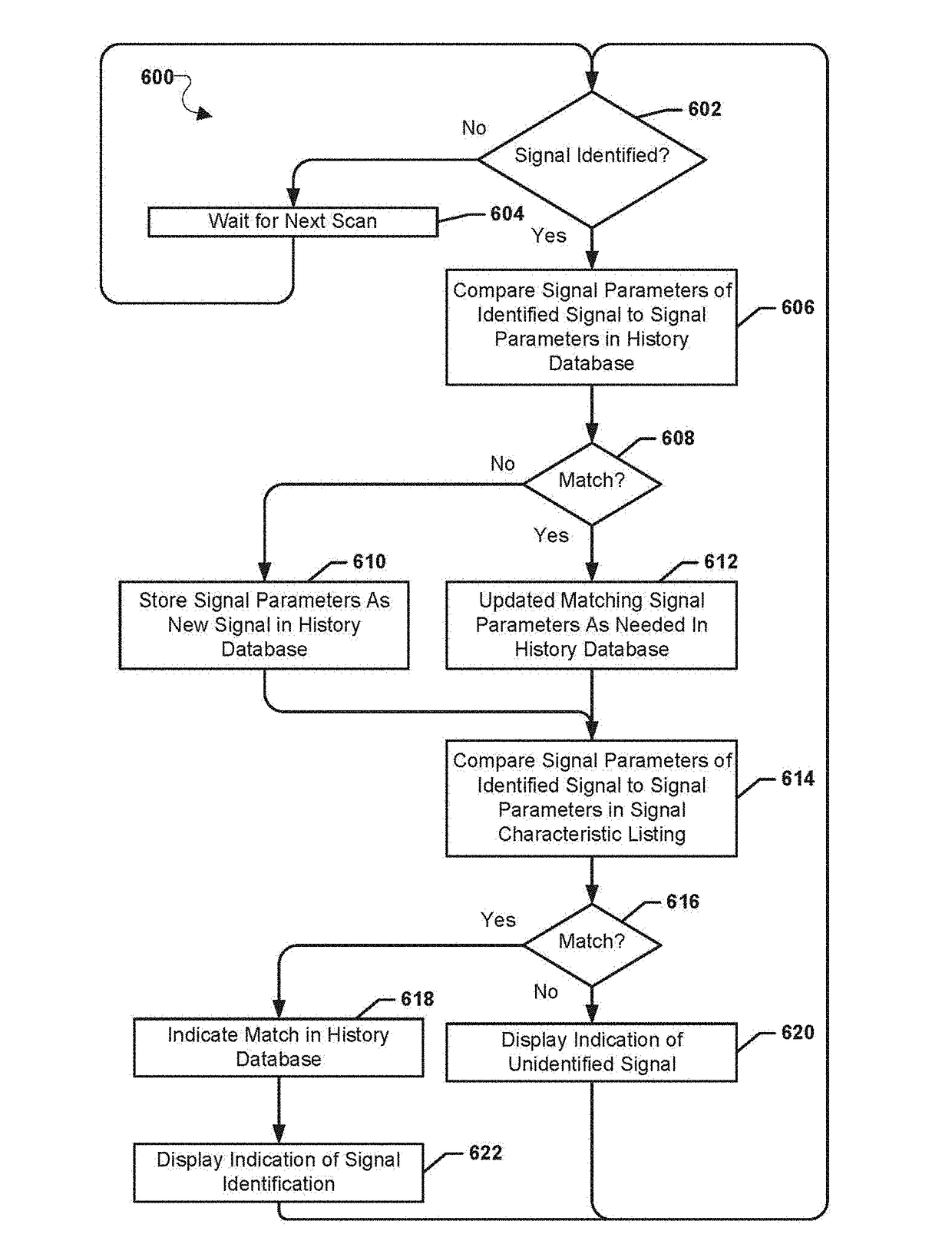
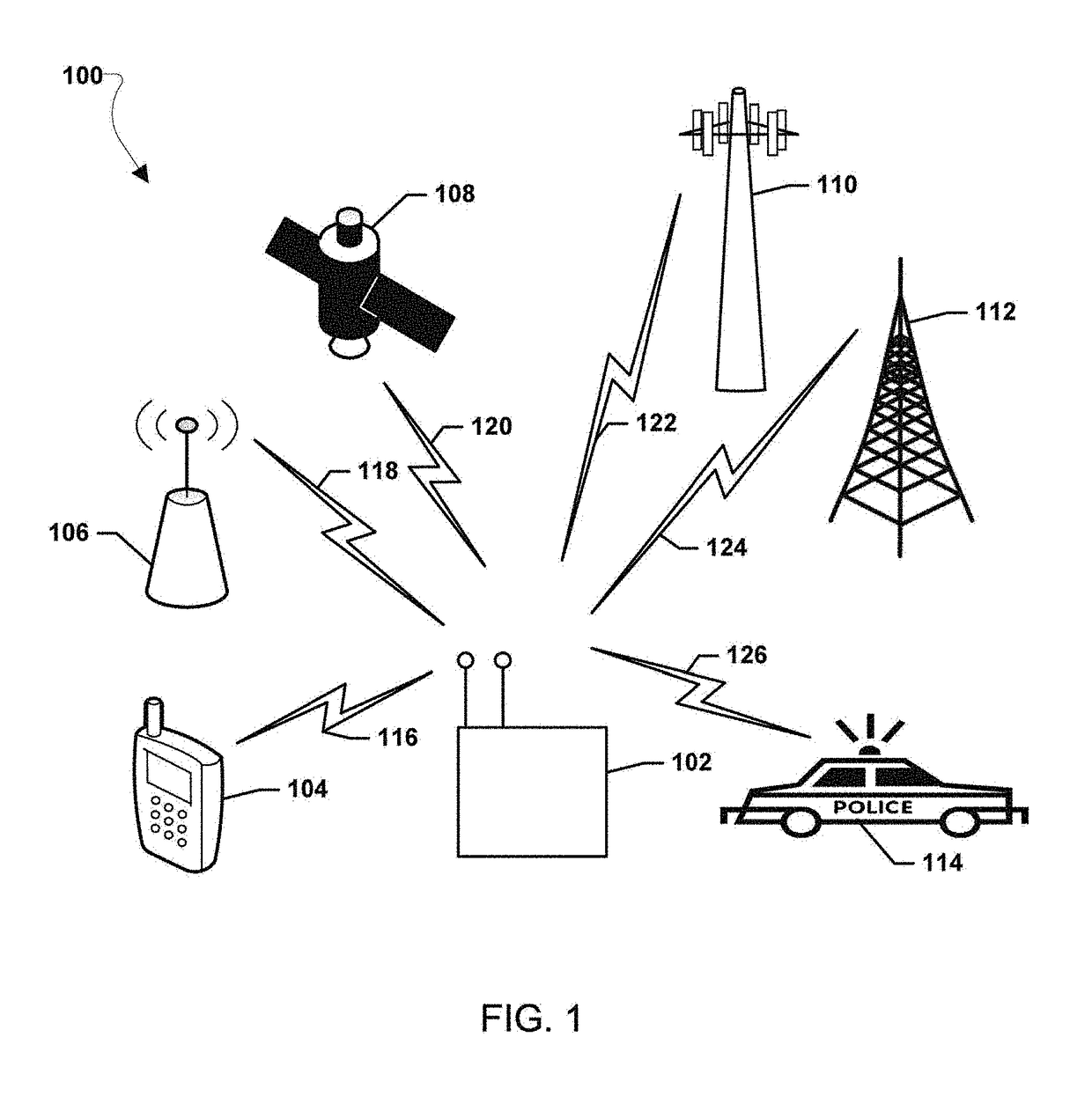
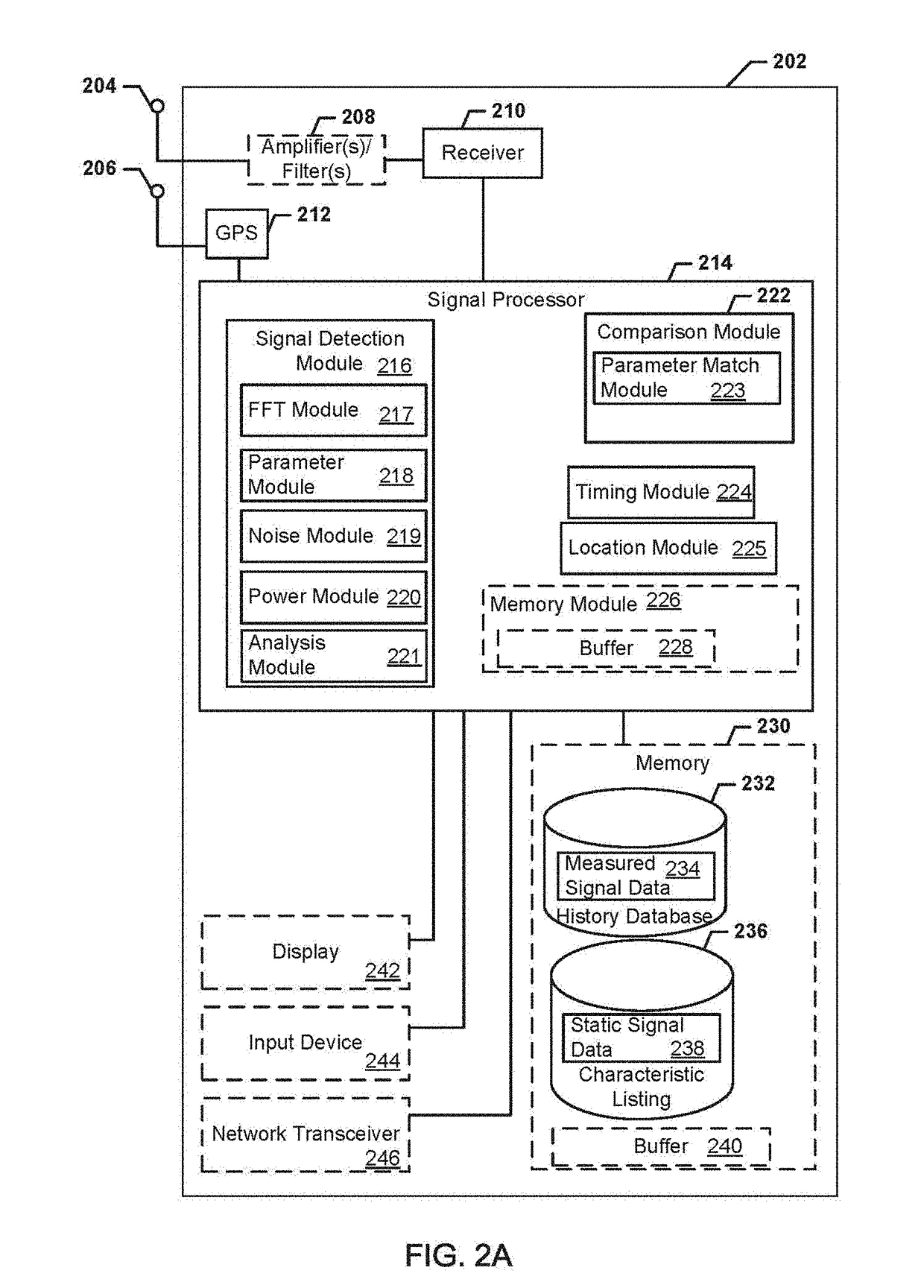
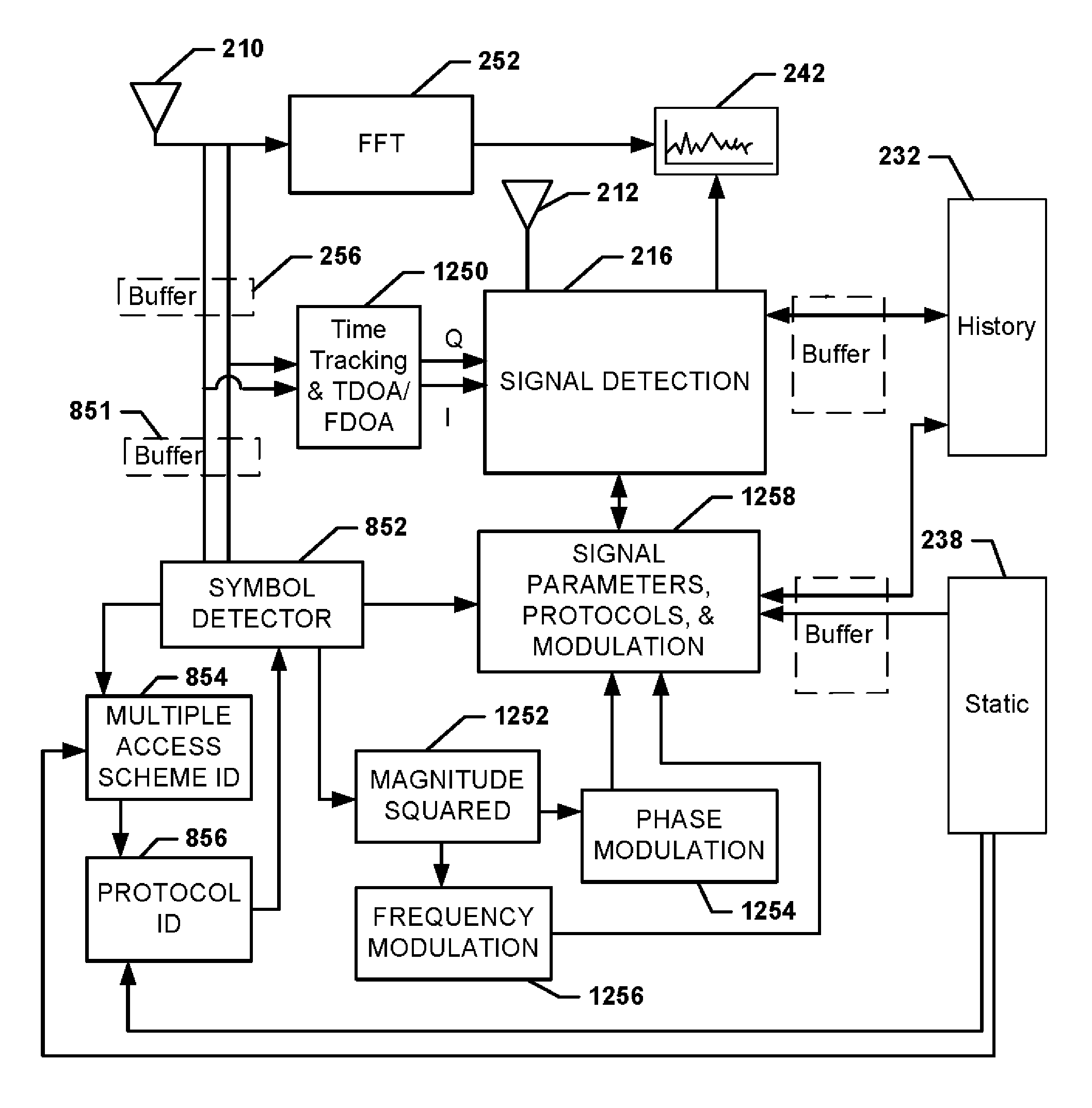
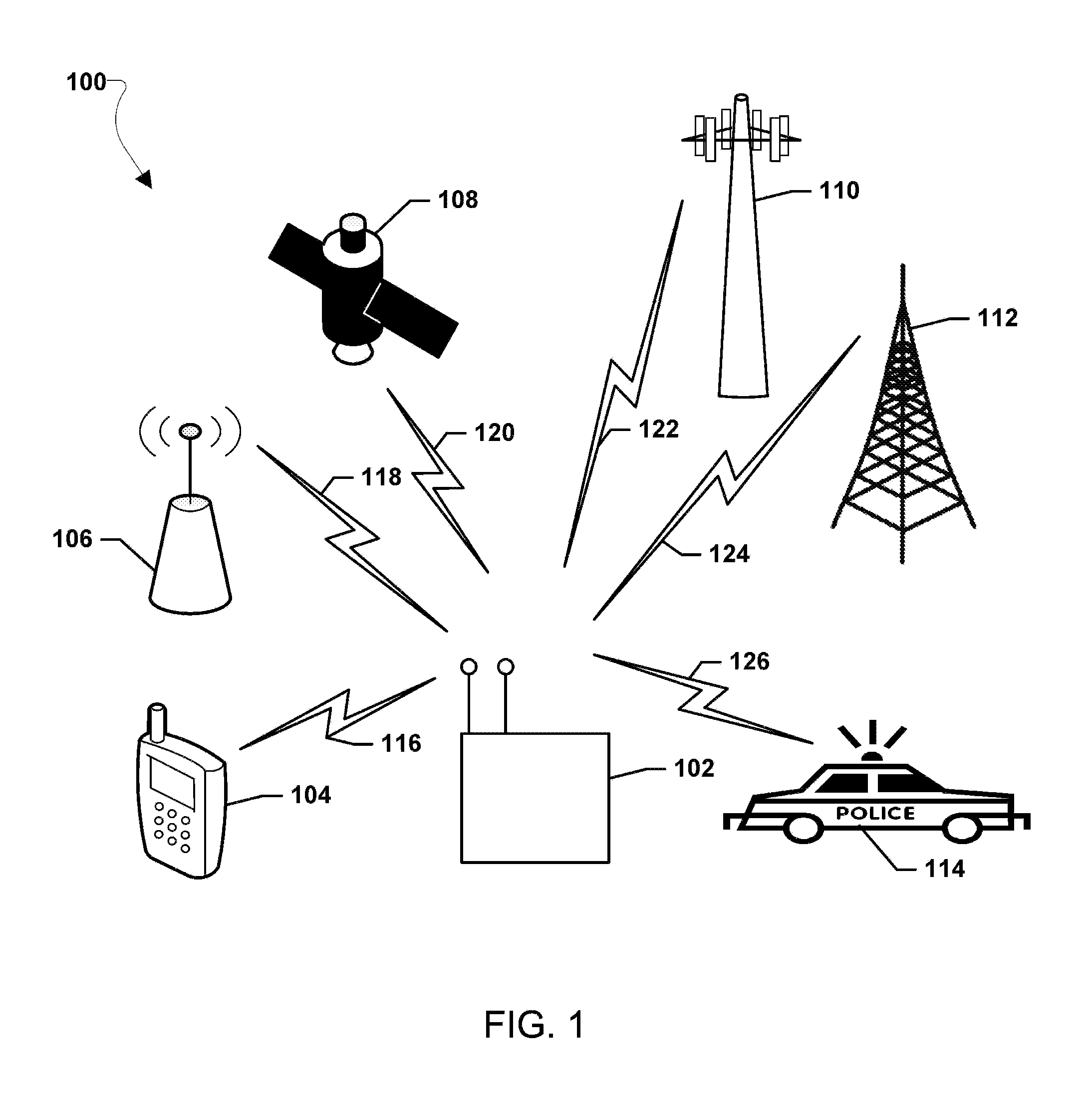
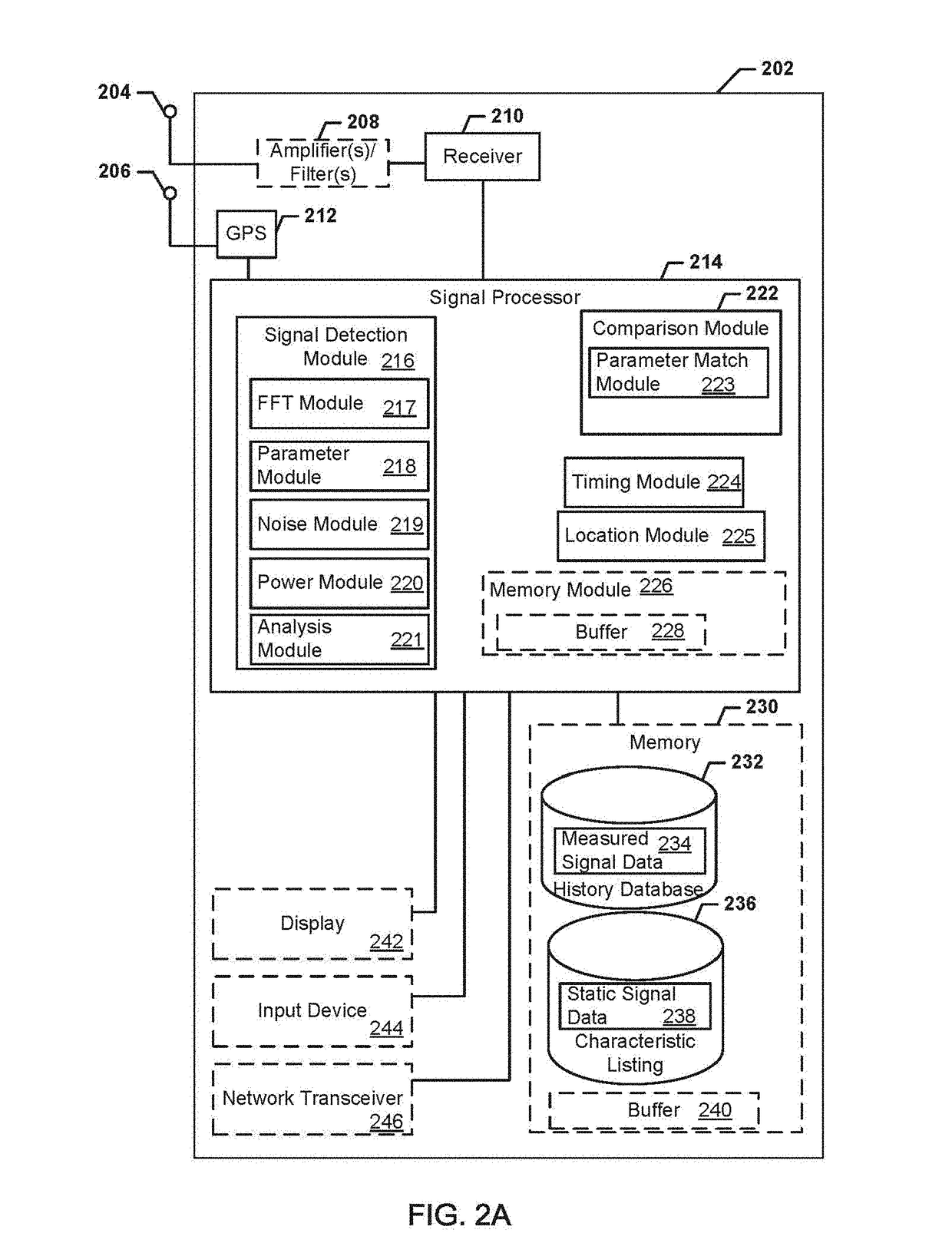
Systems, methods, and devices for electronic spectrum management
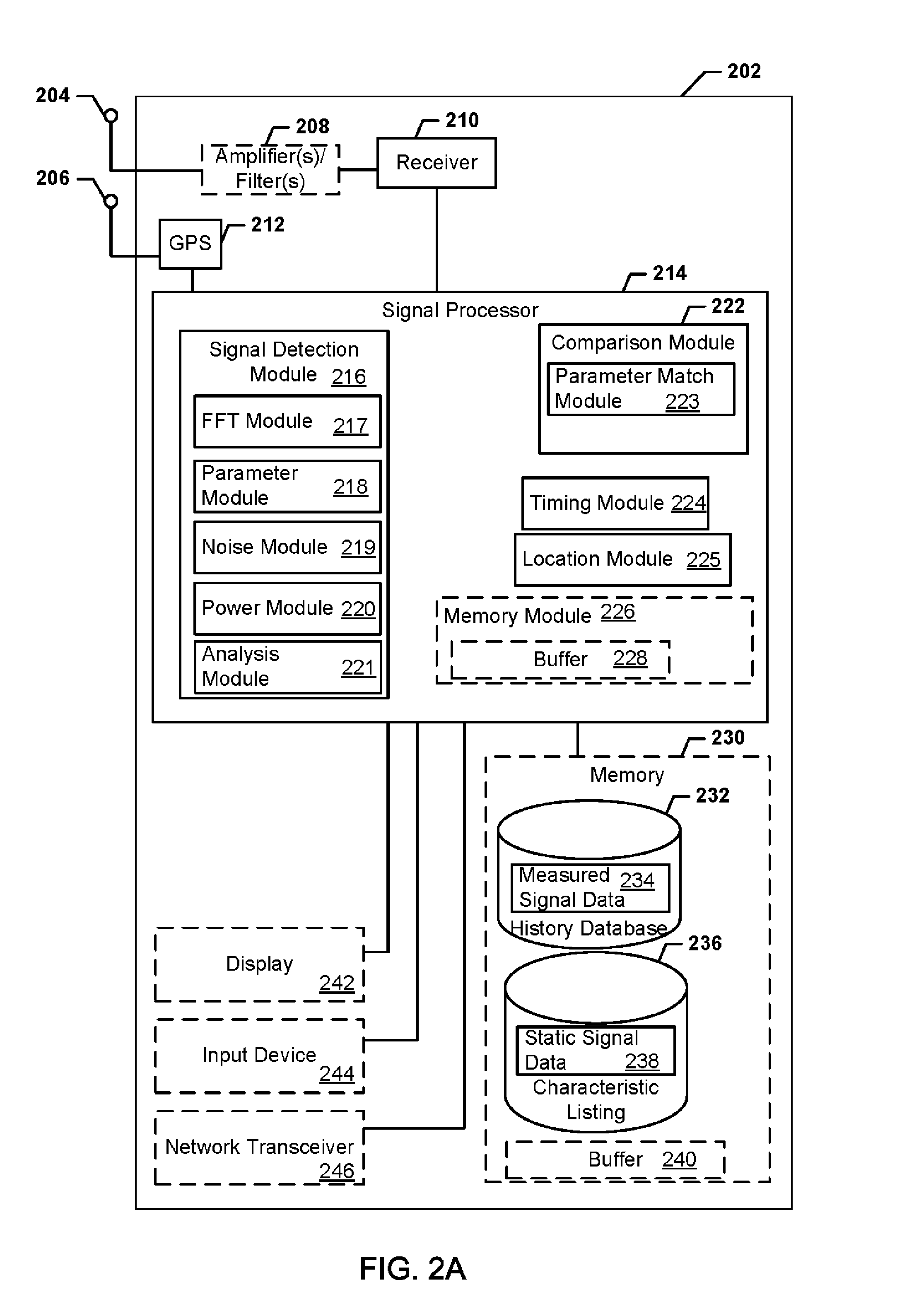
ActiveUS8780968B1Receivers monitoringLine-transmission monitoring/testingFrequency spectrumSignal of interest
Systems, methods, and devices enable spectrum management by identifying, classifying, and cataloging signals of interest based on radio frequency measurements. In an embodiment, signals and the parameters of the signals may be identified and indications of available frequencies may be presented to a user. In another embodiment, the protocols of signals may also be identified. In a further embodiment, the modulation of signals, data types carried by the signals, and estimated signal origins may be identified.
Owner:DIGITAL GLOBAL SYST INC
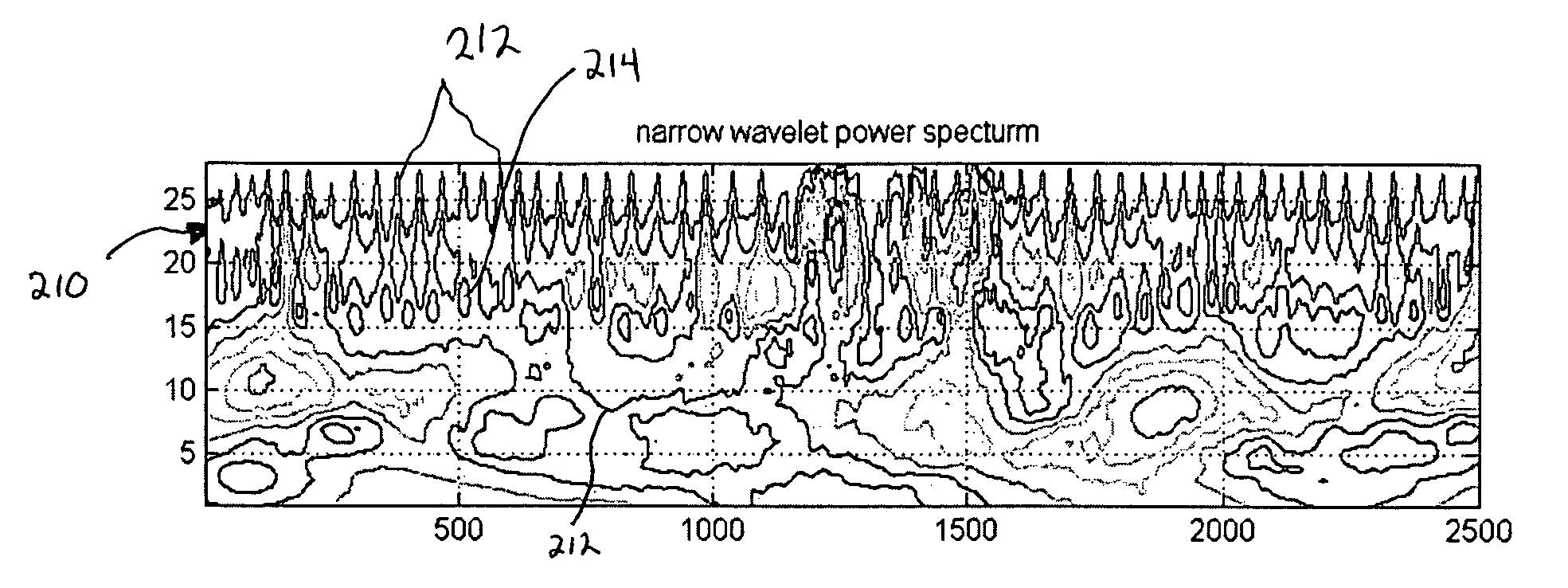
Wavelet transform of a plethysmographic signal
ActiveUS7515949B2Enhanced identification and isolationEfficient separationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsAnalyteEngineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Phase arrays exploiting geometry phase and methods of creating such arrays
InactiveUS7714782B2Multi-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeacon systemsEngineeringArray element
Owner:DAVIS DENNIS WILLARD +2
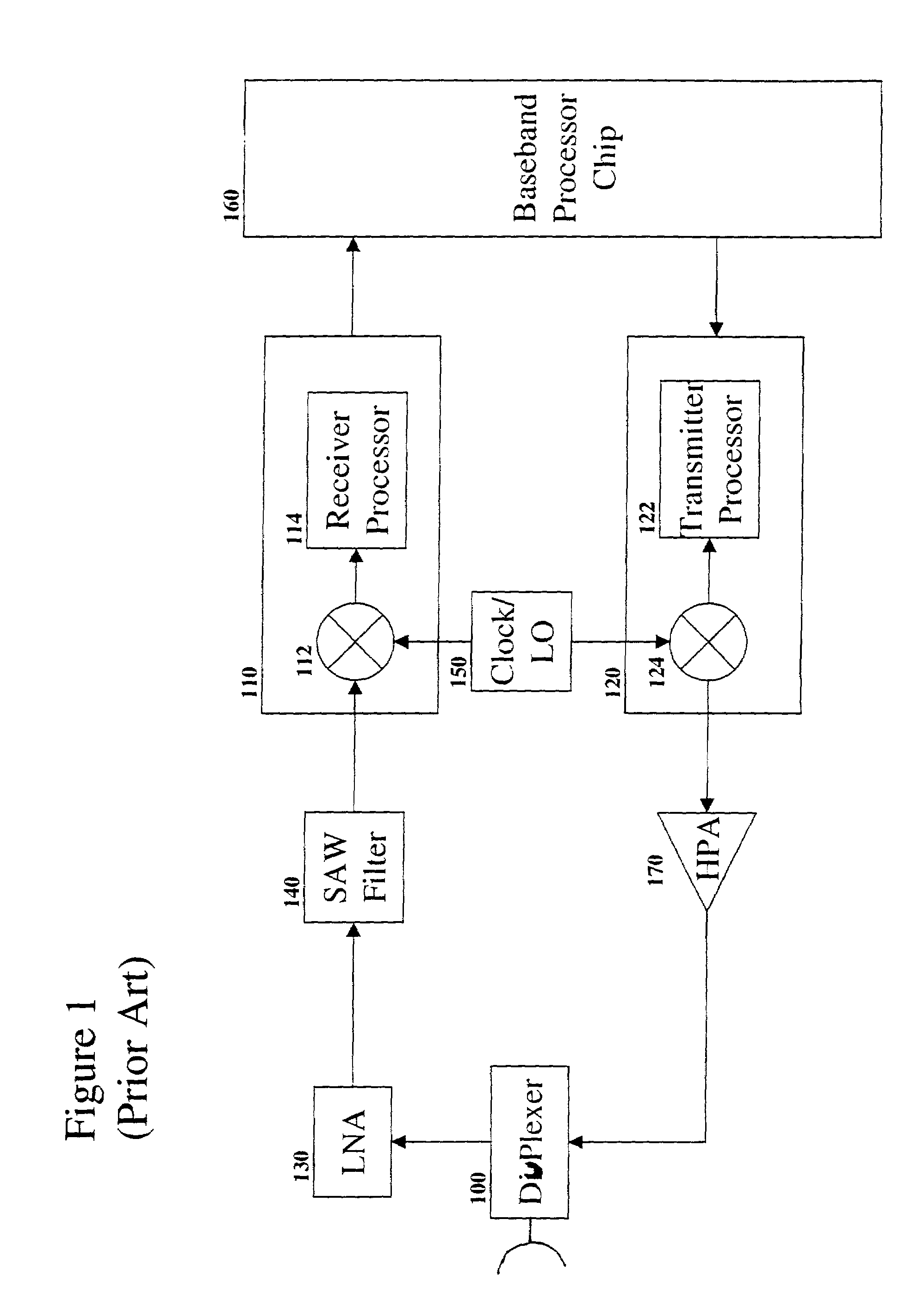
Radio receiver
Various apparatuses and methods are described to reduce interference in signals subject to intermodulation products and high power narrow band interfering signals on lower power wideband signals. Apparatuses and methods described herein also provide the capability for supporting multi-standards, multi-modes and multi-bands in wireless and wired applications with a single receiver or a receiver with minor variations. The receiver described herein samples the entire band in which there can be signals of interest or signals that can generate interference. All of these signals are sampled in one bit stream and the bit stream is processed to isolate signals of interest and interfering signals. The isolated interfering signals are then cancelled out of the signals of interest.
Owner:SMITH FRANCIS J
Robust, Efficient, Localization System
InactiveUS20080161015A1Faster routingConvenient and effective detectionDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationLocalization systemCode division multiple access
Replica correlation processing, and associated representative signal-data reduction and reconstruction techniques, are used to detect signals of interest and obtain robust measures of received-signal parameters, such as time differences of signal arrival and directional angles of arrival, that can be used to estimate the location of a cellularized-communications signal source. The new use in the present invention of signal-correlation processing for locating communications transmitters. This enables accurate and efficient extraction of parameters for a particular signal even in a frequency band that contains multiple received transmissions, such as occurs with code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) communications. Correlation processing as disclosed herein further enables extended processing integration times to facilitate the effective detection of desired communications-signal effects and replication measurement of their location-related parameters, even for the communications signals modulated to convey voice conversations or those weakened through propagation effects. Using prior, constructed, signal replicas in the correlation processing enables elimination of the inter-site communications of the signal representations that support the correlation analyses. Reduced-data representations of the modulated signals for voiced conversation, or for the variable components of data communications, are used to significantly reduce the inter-site communications that support the correlation analyses.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
Adaptive canceller for frequency reuse systems
InactiveUS20050159128A1Easy to useHighly effectiveRadio transmissionTransmission noise suppressionFinite impulse responseAdaptive filter
An adaptive interference canceller for canceling an interfering signal corresponding to a delayed, frequency translated, amplitude and phase offset version of a transmitted signal contained in a composite received signal relayed through a relay system such as a satellite transponder. The canceller digitally downconverts the received signal and a local replica of the transmitted signal from IF to baseband, applies a variable delay and frequency compensation to the replica as a coarse delay and frequency correction, and tracks fine delay, amplitude and phase differences using an adaptive finite impulse response filter to generate a cancellation signal corresponding to the delayed and frequency shifted version. A minimum output power process produces an error signal that drives the variable delay and adaptive filter to minimize the power in the signal of interest to maximize cancellation of the interfering signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON APPLIED SIGNAL TECH
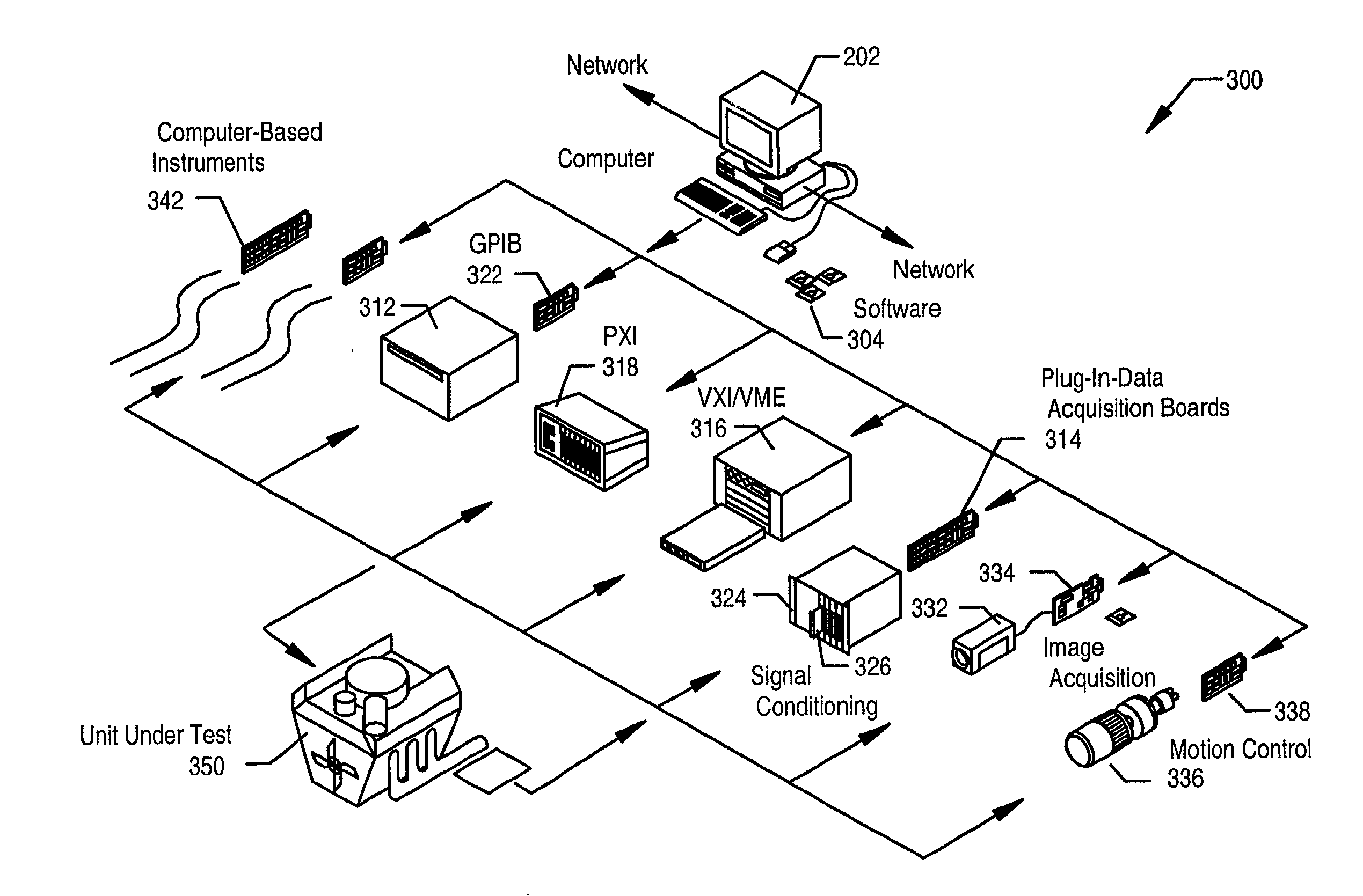
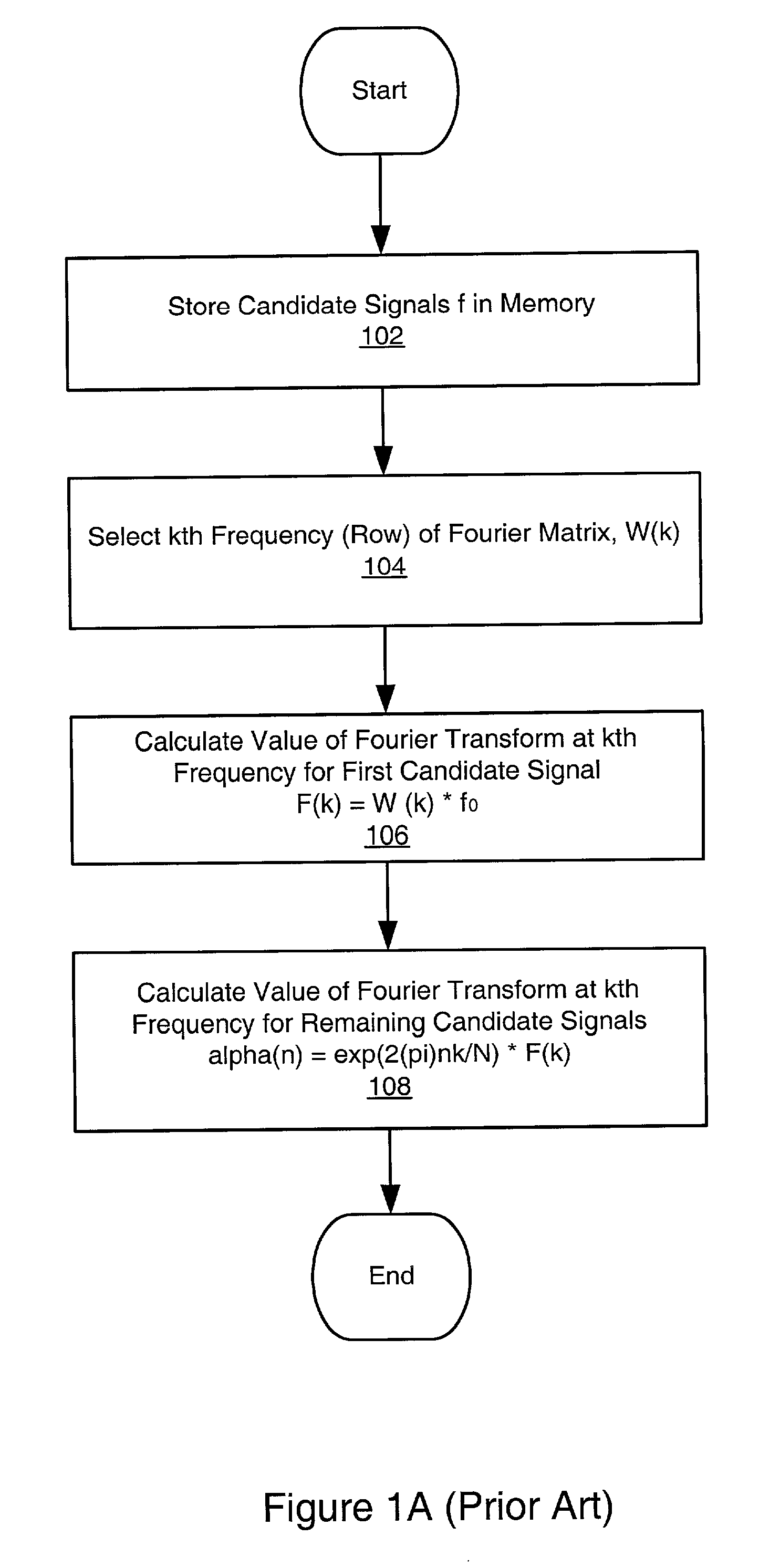
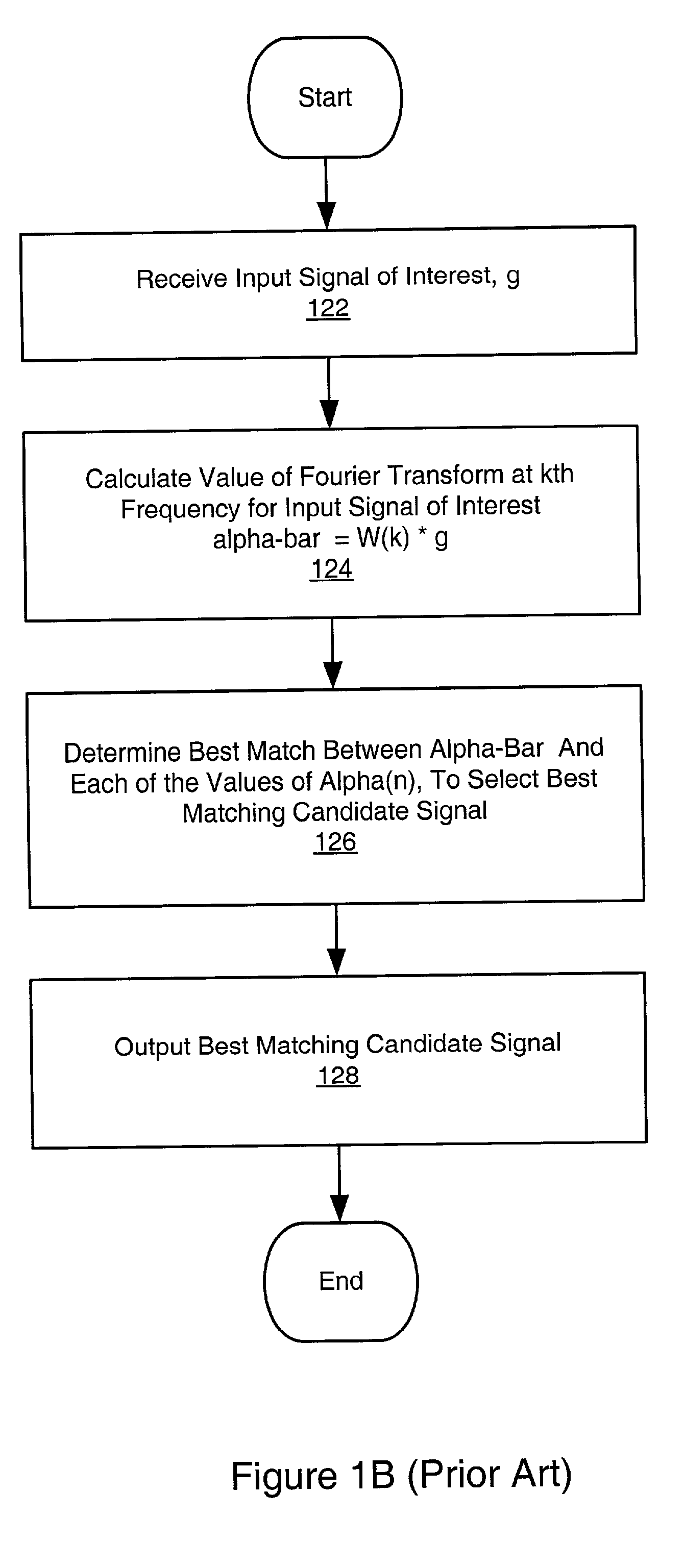
System and method for signal matching and characterization
InactiveUS20020150298A1Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSignal of interestComputer science
A system and method for selecting a best match of a received input signal from a set of candidate signals, wherein two or more of the candidate signals are uncorrelated. In a preprocessing phase a unified signal transform (UST) is determined from the candidate signals. The UST converts each candidate signal to a generalized frequency domain. The UST is applied at a generalized frequency to each candidate signal to calculate corresponding generalized frequency component values (GFCVs) for each candidate signal. At runtime, the input signal of interest is received, and the UST is applied at the generalized frequency to the input signal of interest to calculate a corresponding GFCV. The best match is determined between the GFCV of the input signal of interest and the GFCVs of each of the set of candidate signals. Finally, information indicating the best match candidate signal from the set of candidate signals is output.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Systems, methods, and devices for electronic spectrum management
ActiveUS20170243139A1Receivers monitoringNetwork traffic/resource managementTerrainRadio frequency energy
Devices and methods enable optimizing a signal of interest based on identifying and analyzing the signal of interest based on radio frequency energy measurements. Signal data is compared with stored data to identify the signal of interest. Signal degradation data is calculated based on noise figure parameters, hardware parameters and environment parameters. The signal of interest is optimized based on the signal degradation data. Terrain data may also be used for optimizing the signal of interest.
Owner:DIGITAL GLOBAL SYST INC
Systems, methods, and devices for electronic spectrum management
Systems, methods, and devices enable spectrum management by identifying, classifying, and cataloging signals of interest based on radio frequency measurements. In an embodiment, signals and the parameters of the signals may be identified and indications of available frequencies may be presented to a user. In another embodiment, the protocols of signals may also be identified. In a further embodiment, the modulation of signals, data types carried by the signals, and estimated signal origins may be identified.
Owner:DIGITAL GLOBAL SYST INC
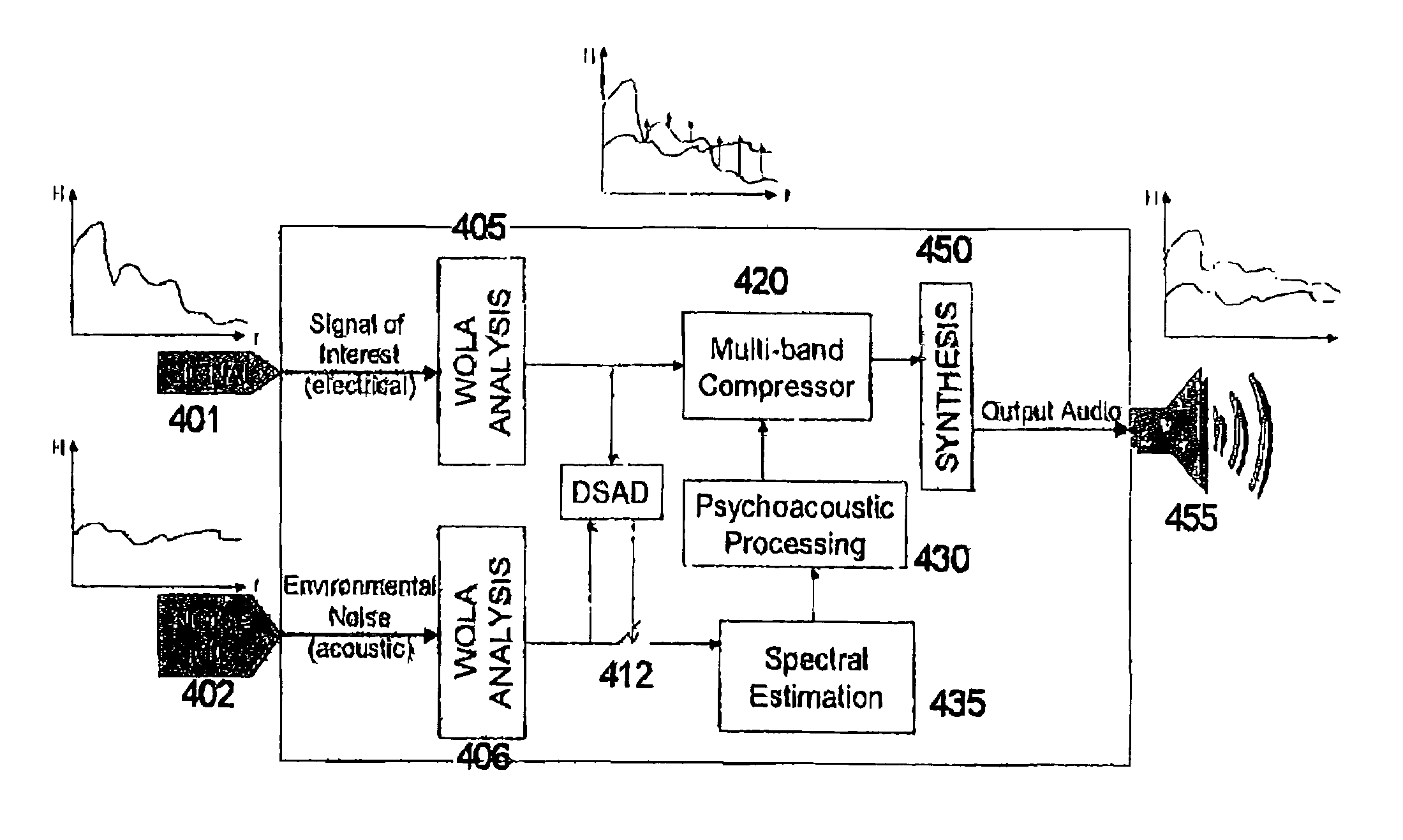
Sound intelligibility enhancement using a psychoacoustic model and an oversampled filterbank
InactiveUS7050966B2Improve signal qualityImproving signal signal intelligibilityEar treatmentNoise generationSignal of interestEngineering
A system and method of improving signal intelligibility over an interference signal is provided. The system includes a psychoacoustic professor having a psychoacoustic model wherein the level of a signal-of-interest is improved so as to be audible above noise and so as not to exceed a predetermined maximum output level. The system can be combined with active noise cancellation.
Owner:HIMPP
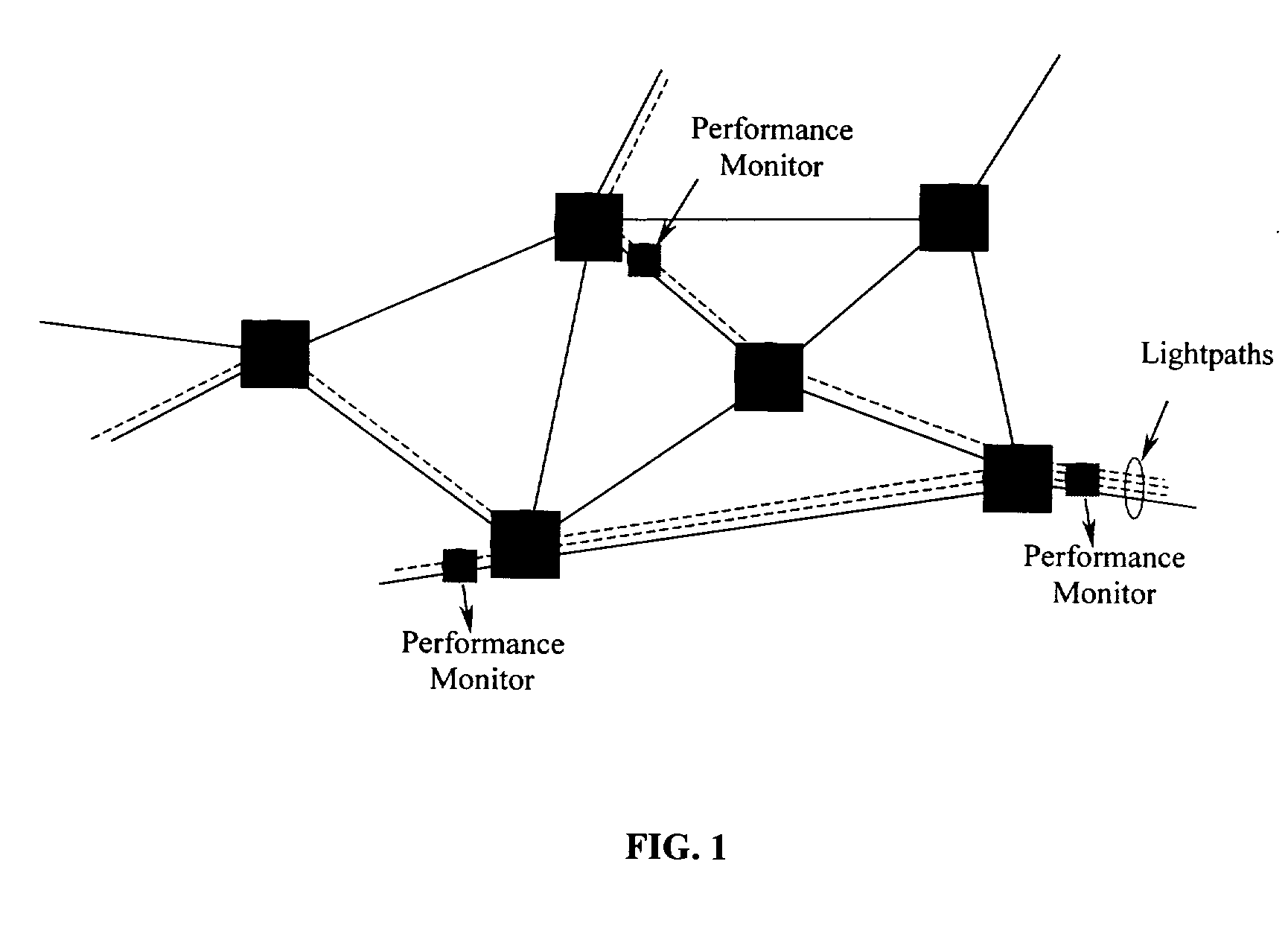
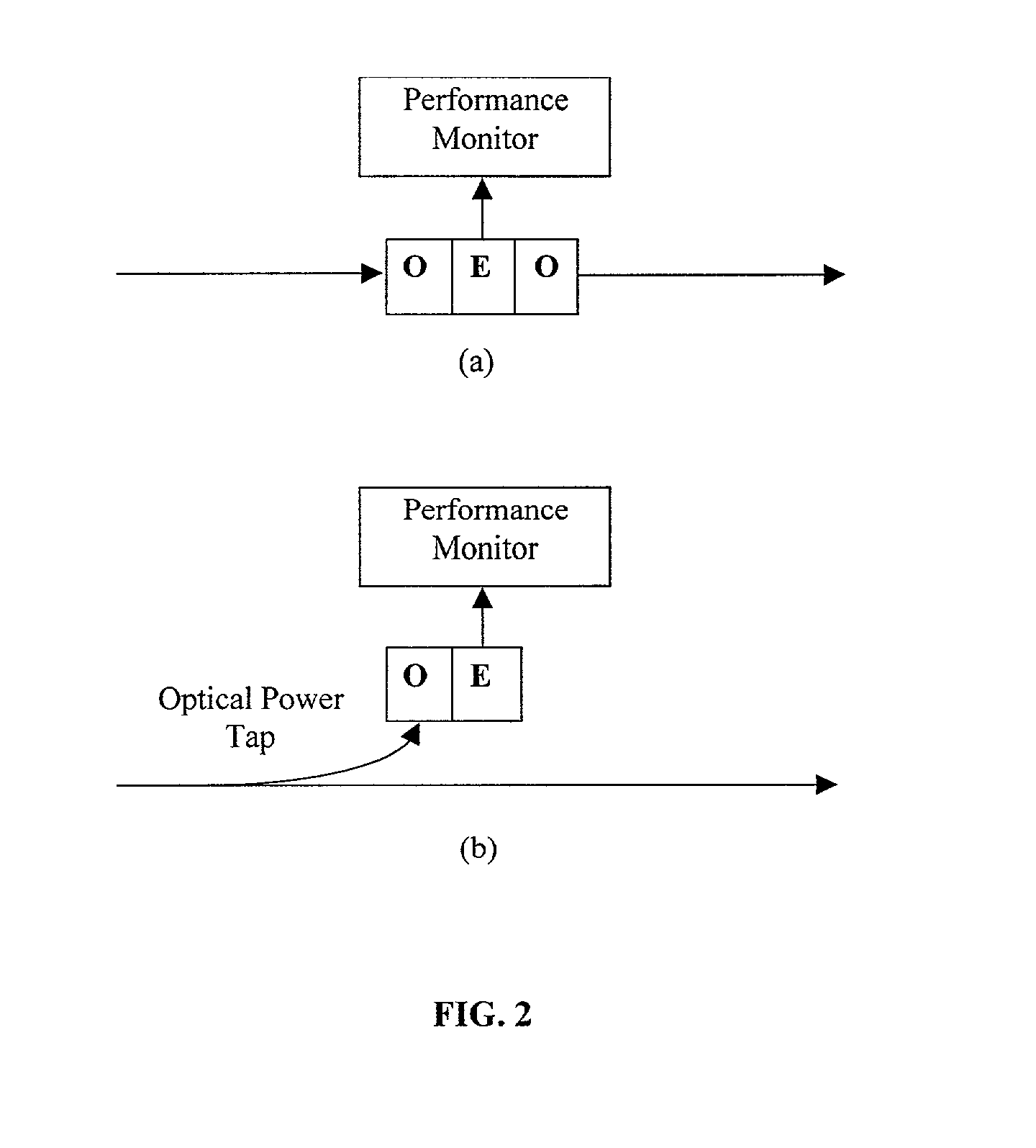
Methods for monitoring performance in optical networks
InactiveUS20020044322A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringFiber chromatic dispersionCarrier signal
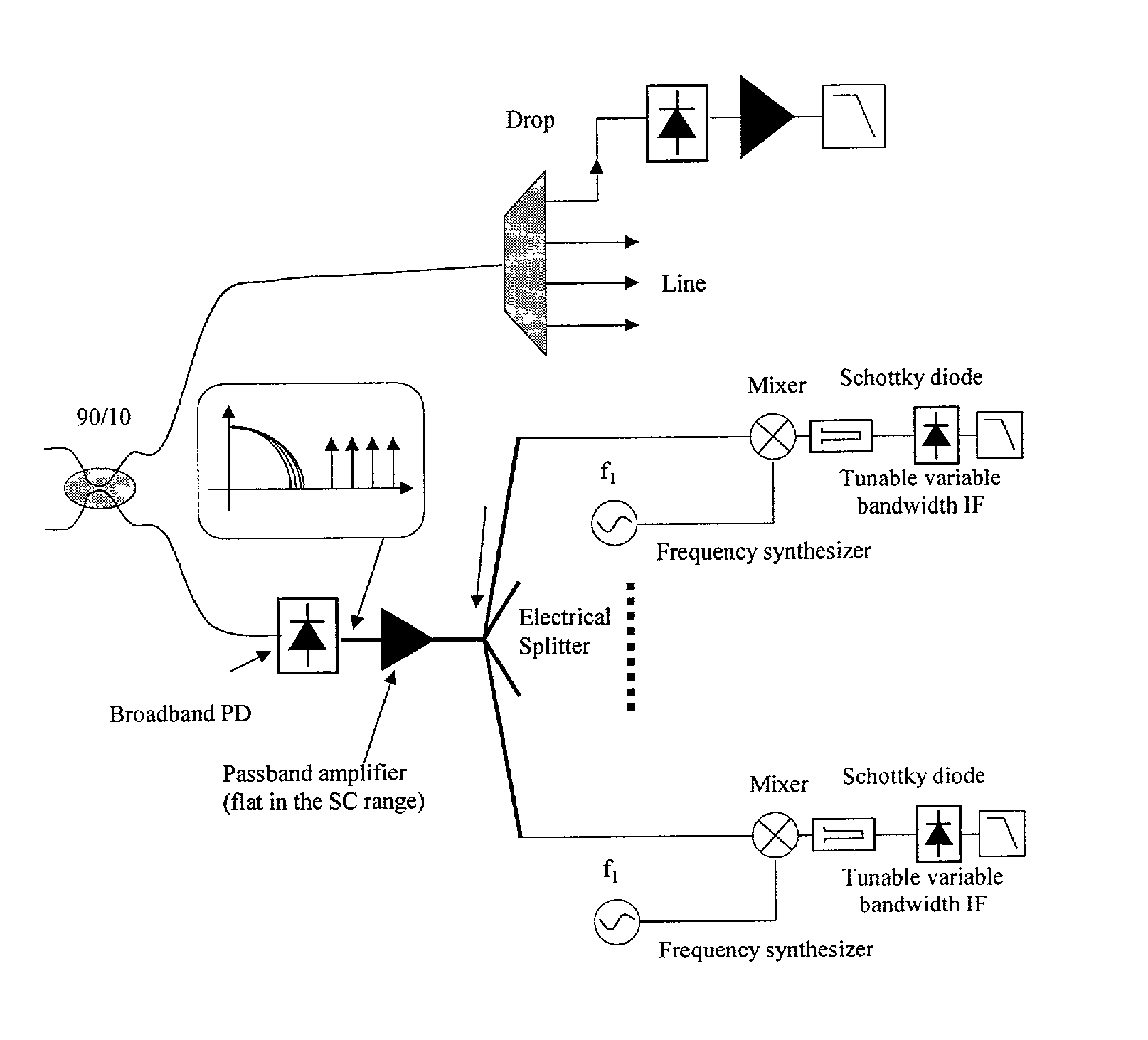
A suite of optical performance monitoring (OPM) methods, based on optical subcarrier multiplexing, are described by the invention. The strength of this approach lies in the simplicity of double sideband subcarrier signals and the fact that these signals travel the complete optical path with the baseband signal of interest. The subcarrier signals can be recovered using techniques described in the application and are immune to fiber dispersion induced fading.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
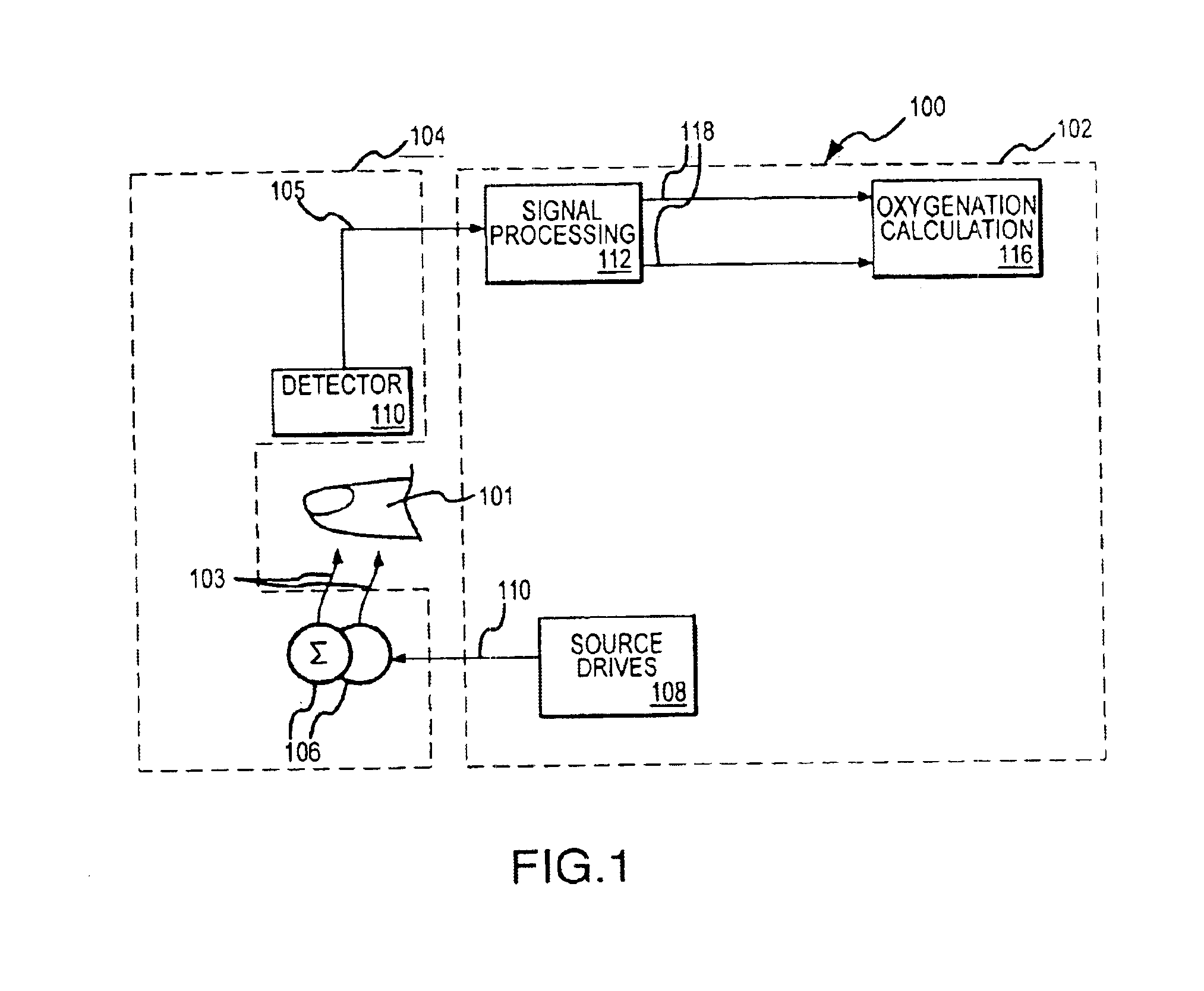
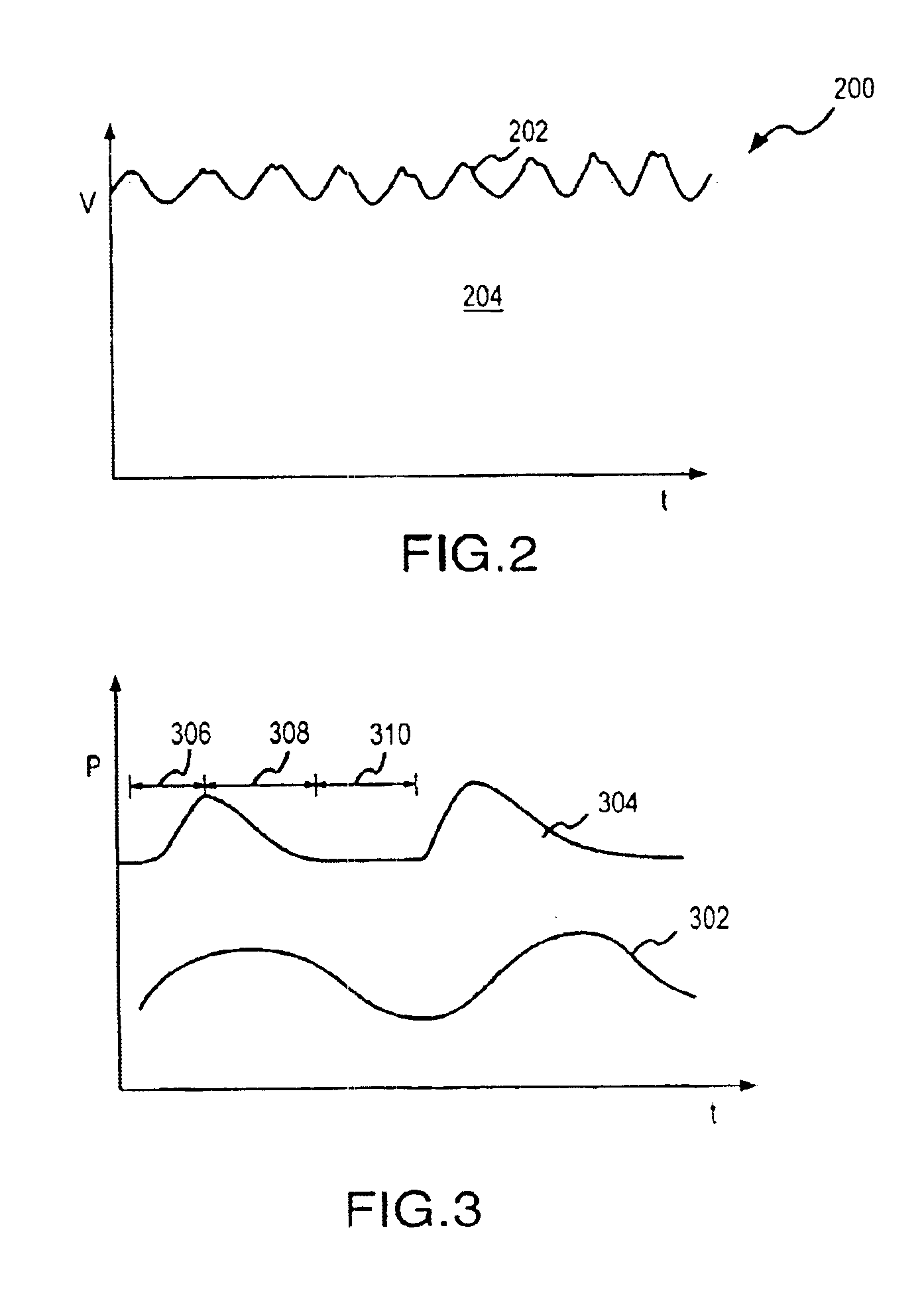
Monitoring physiological parameters based on variations in a photoplethysmographic baseline signal
InactiveUS6896661B2Function increaseReduce the amount requiredCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationNervous systemMedicine
A method and apparatus are disclosed for using photoplethysmography to obtain physiological parameter information related to respiration or the autonomic nervous system. In one implementation, the process involves obtaining (602) a pleth, filtering (604) the pleth to remove unwanted components, identifying (606) a signal component of interest based on the filtered signal, monitoring (608) blood pressure changes, monitoring (610) heart rate, and performing (612) an analysis of the blood pressure signal to the heart rate signal to identify a phase relationship associated with the component of interest. Based on this phase relationship, the component of interest may be identified (614) as relating to the respiration or Mayer Wave. If it is related to the respiration wave (616), a respiratory parameter such as breathing rate may be determined (620). Otherwise, a Mayer Wave analysis (618) may be performed to obtain parameter information related to the autonomic nervous system.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
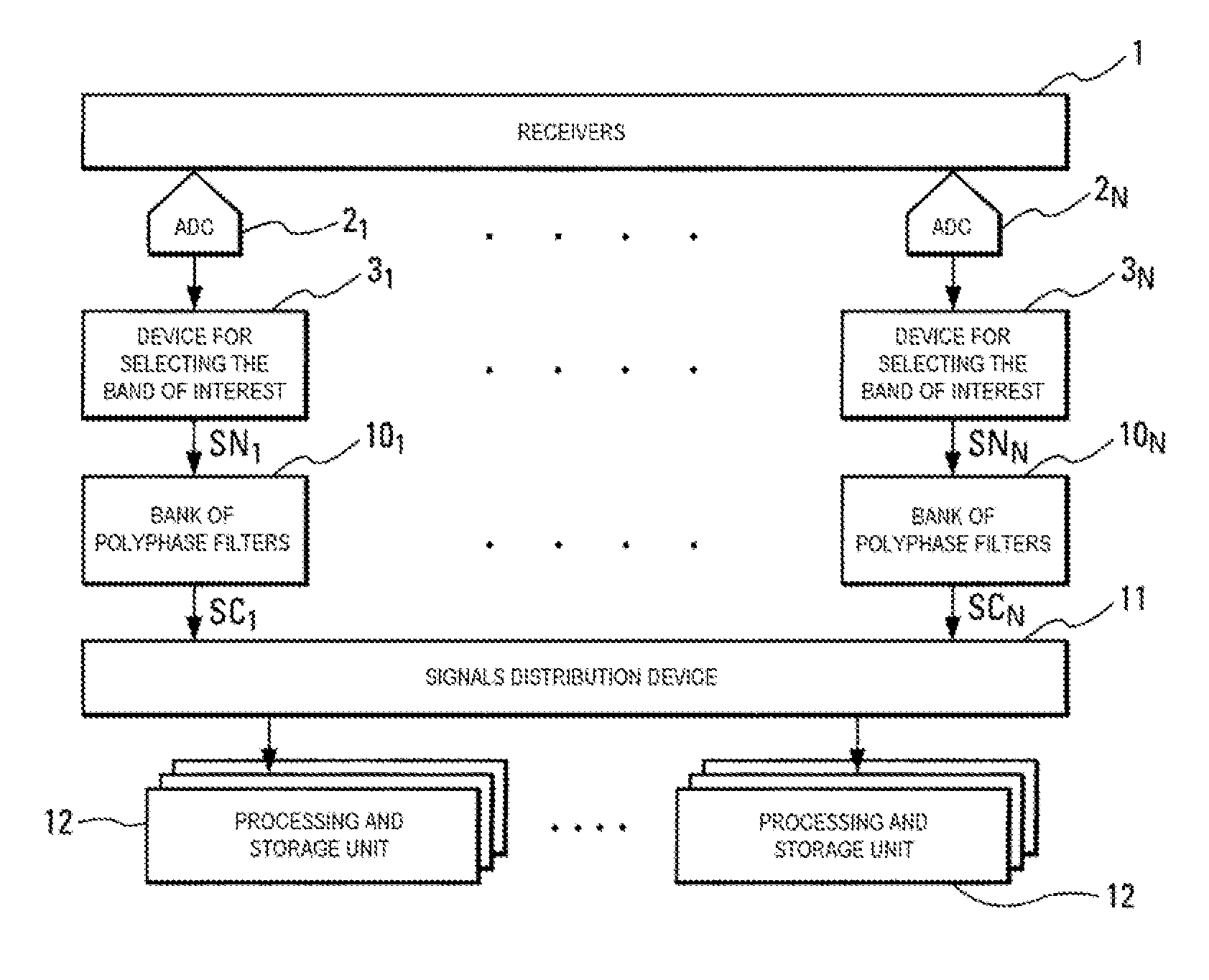
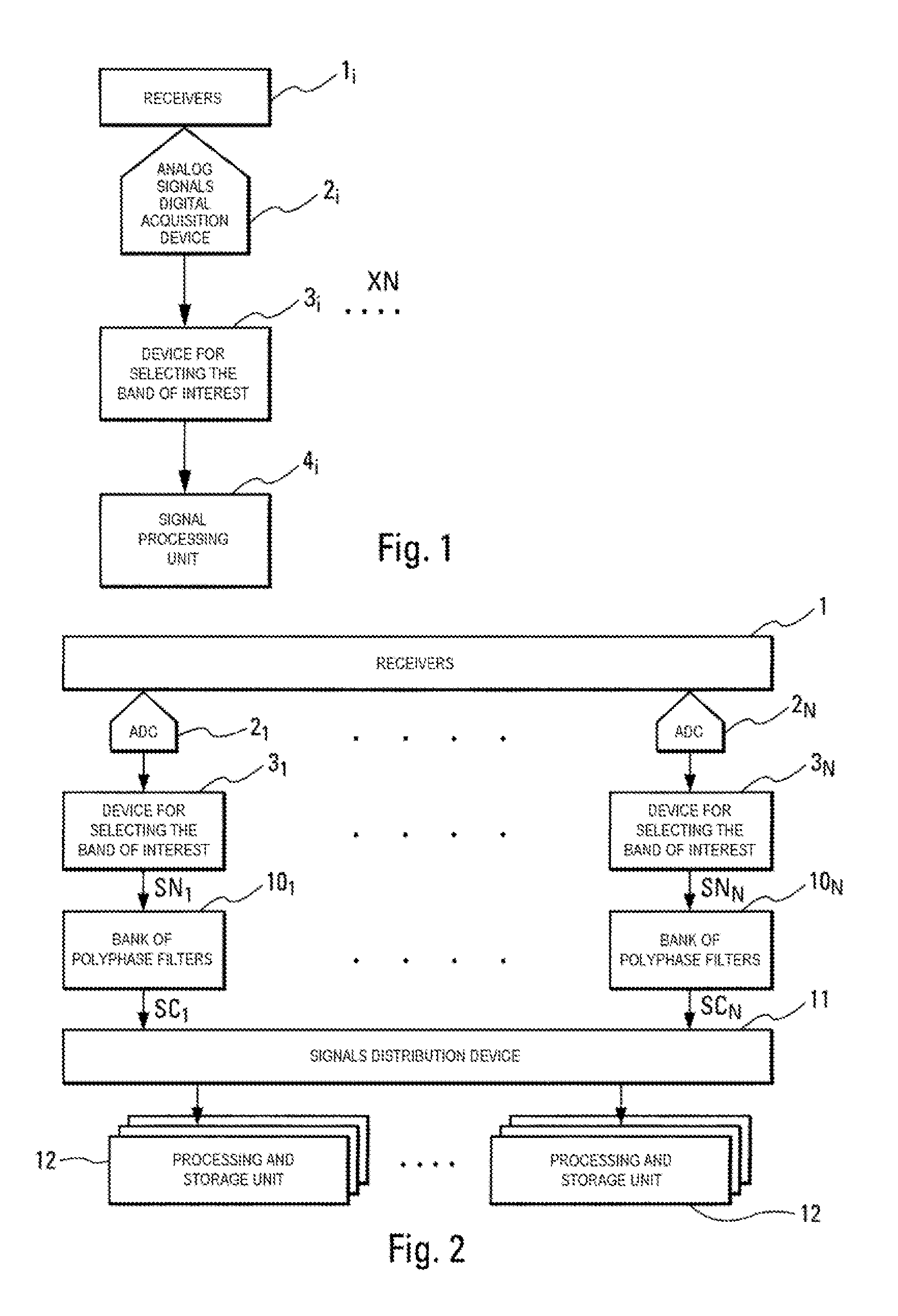
System for extraction and analysis of significant radioelectric signals
Embodiments of the invention relate to a system for extracting and analyzing radioelectric signals of interest. It includes an integer number N of channels. Each channel Vi includes a receiver linked to an analog signals digital acquisition device delivering a digital signal SNi. Each channel Vi includes a bank of polyphase filters, extracting digital signals SEi from the digital signal SNi. The digital signals SEi each have a smaller frequency bandwidth than that of the digital signal SNi. The system includes at least one extracted digital signals distribution device suitable for receiving the digital signals SEi and distributing SEi to one or more processing and storage units. The processing and storage units are suitable for the analysis, characterization and storage of the digital signals received. Embodiments of the invention apply to the system for the radio-monitoring of radioelectric emissions in real time or in deferred time.
Owner:THALES SA
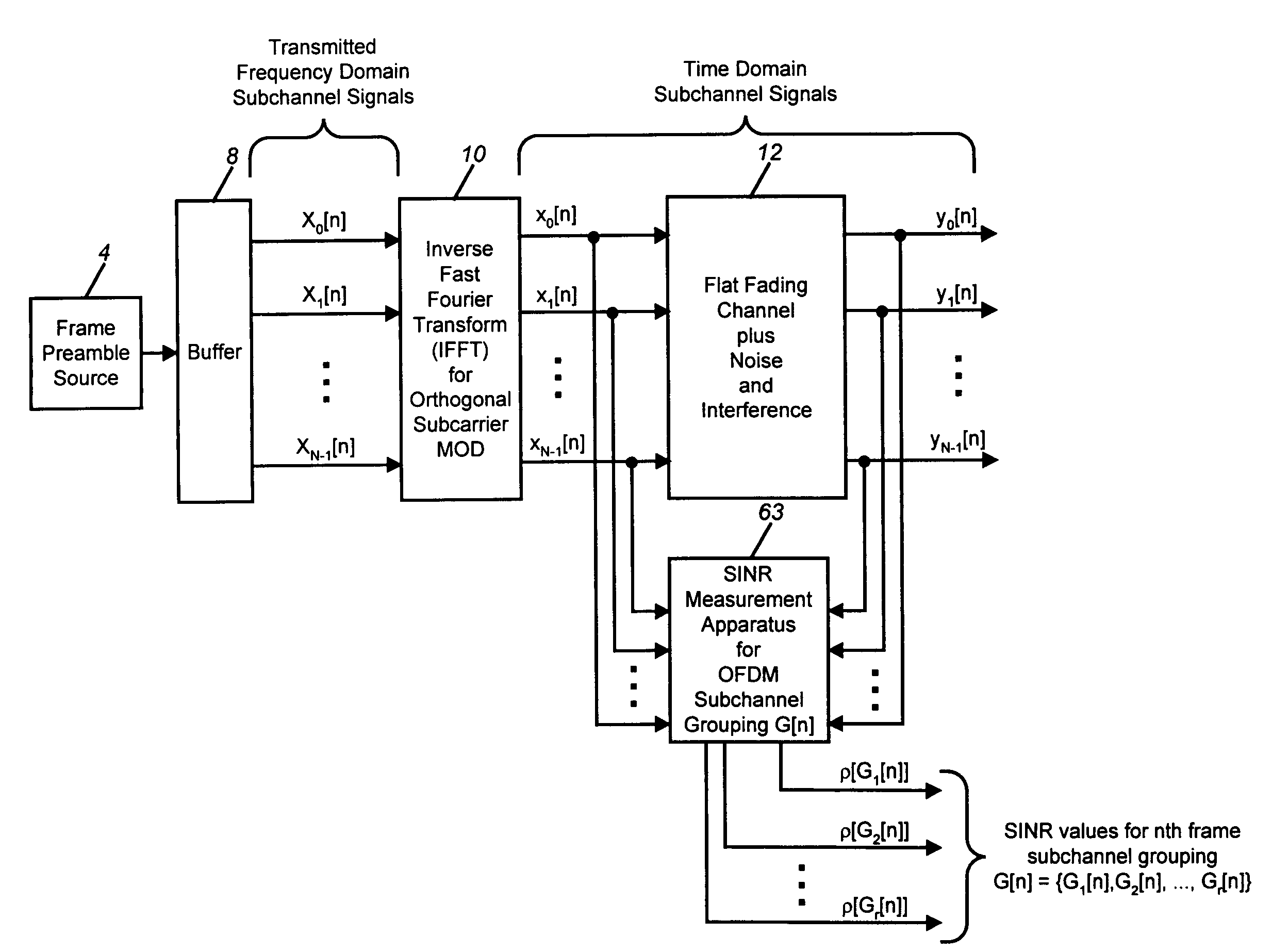
SINR measurement method for OFDM communications systems
ActiveUS7260054B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplexEngineeringMulti carrier
A signal to interference-plus-noise power ratio (SINR) measurement method for wireless communications systems which employ orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) for multicarrier data transmission is disclosed. Fast-Fourier transform (FFT)-based SINR measurements can be computed on frame-by-frame or greater interval for individual or groupings of subchannel signals. Given a known transmitted time-domain OFDM frame preamble, and the corresponding channel and interference-plus-noise (IPN) corrupted received time-domain frame preamble, the disclosed method first computes the power spectral densities of the received signal of interest and of a received unwanted interference-plus-noise signal. The FFT-computed power spectral densities are then used to compute average received signal and received IPN power measurements for specified individual or groupings of OFDM subchannel signals. The power measurements are then frame-averaged using a recursive exponential smoothing method. The frame-averaged signal and IPN power measurements are then used to form quantized measurements of SINR for the specified OFDM subchannel signals of the received frame.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Binaural adaptive hearing aid
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
Systems, methods, and devices for electronic spectrum management for identifying signal-emitting devices
ActiveUS20170250766A1Receivers monitoringSpectral gaps assessmentFrequency spectrumSignal of interest
Apparatus and methods for identifying a wireless signal-emitting device are disclosed. The apparatus is configured to sense and measure wireless communication signals from signal-emitting devices in a spectrum. The apparatus is operable to automatically detect a signal of interest from the wireless signal-emitting device and create a signal profile of the signal of interest; compare the signal profile with stored device signal profiles for identification of the wireless signal-emitting device; and calculate signal degradation data for the signal of interest based on information associated with the signal of interest in a static database including noise figure parameters of a wireless signal-emitting device outputting the signal of interest. The signal profile of the signal of interest, profile comparison result, and signal degradation data are stored in the apparatus.
Owner:DIGITAL GLOBAL SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com