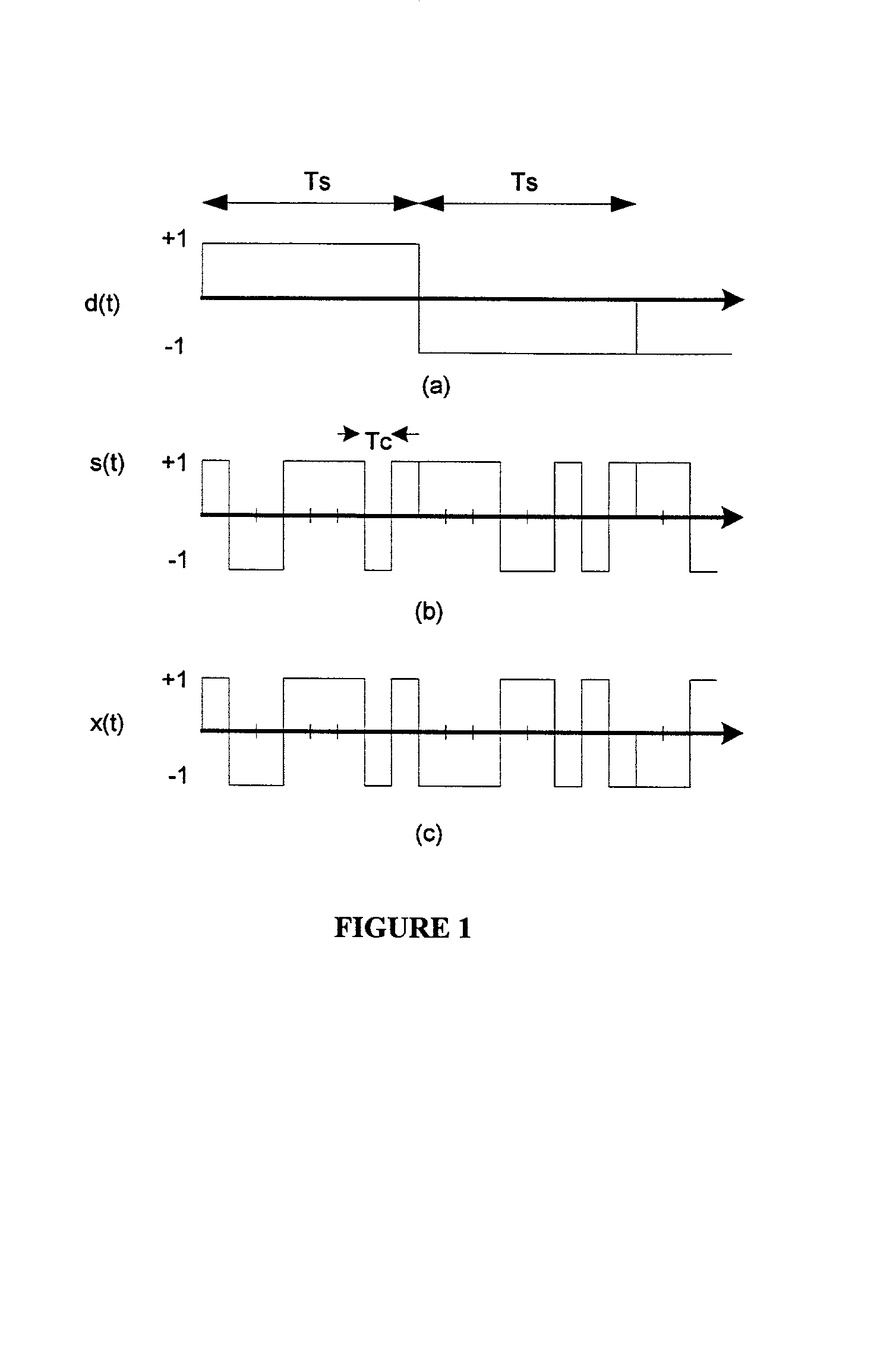
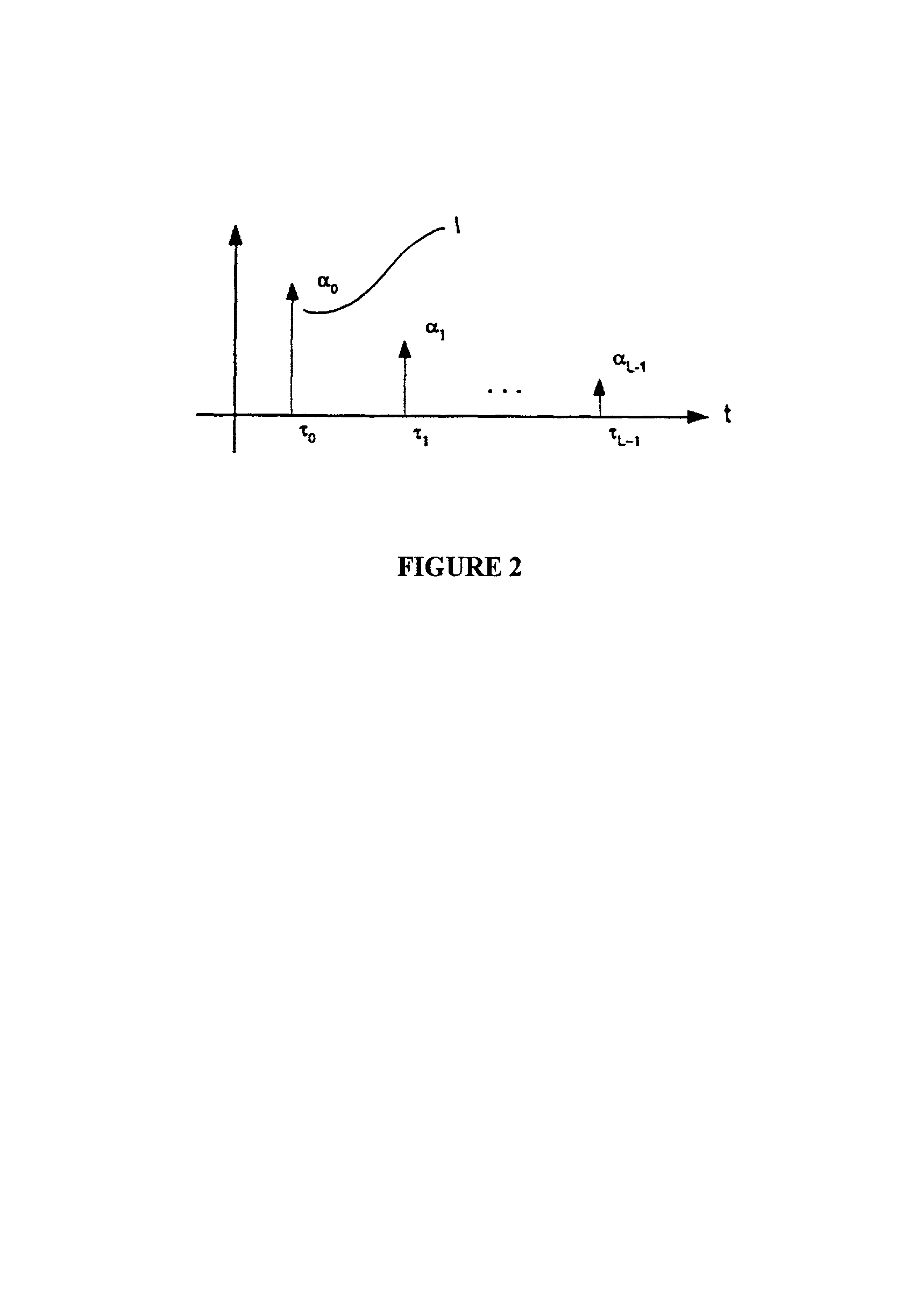
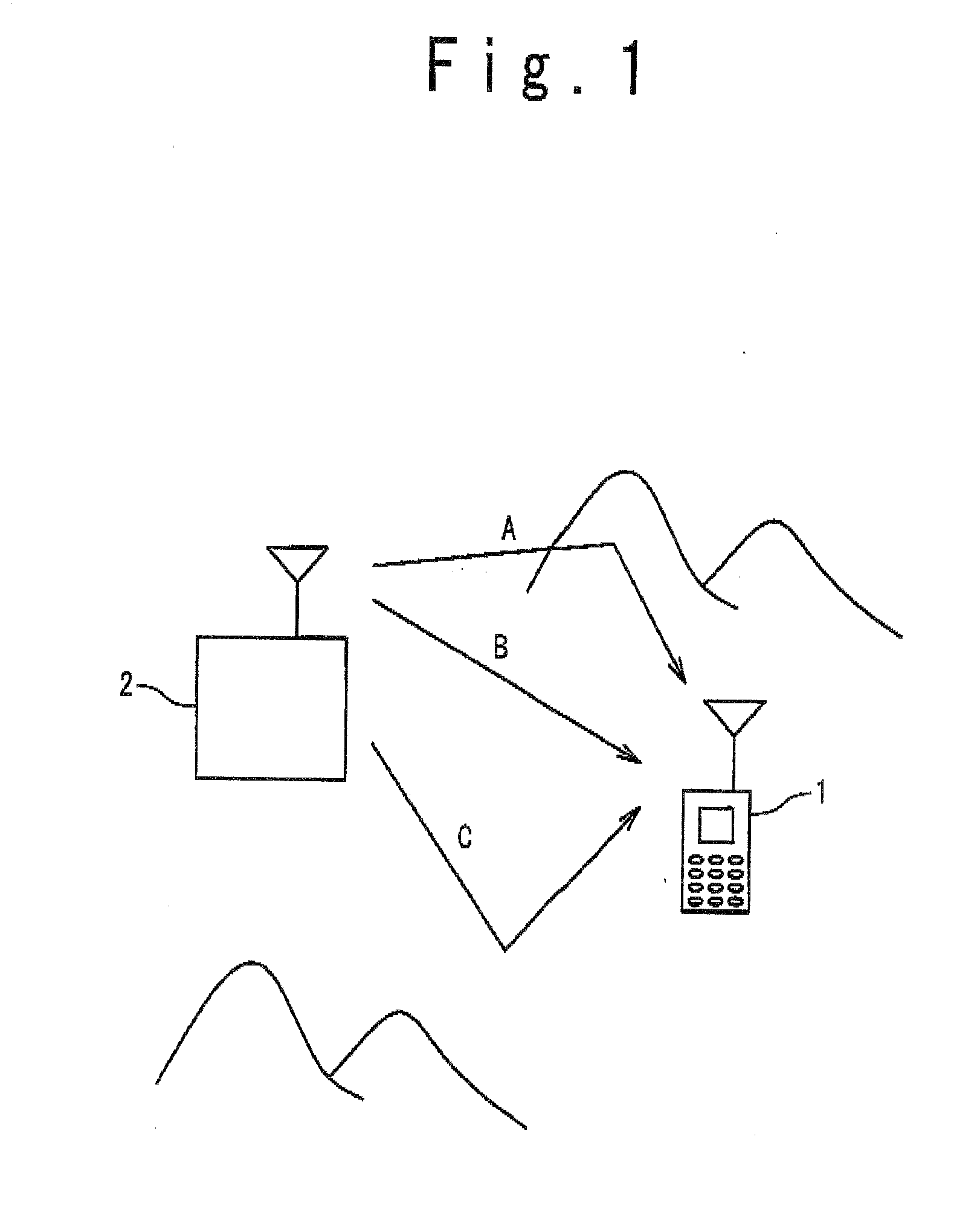
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Rake combining" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for parameter estimation in a generalized rake receiver
ActiveUS20050201447A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationCurrent channelRake combining
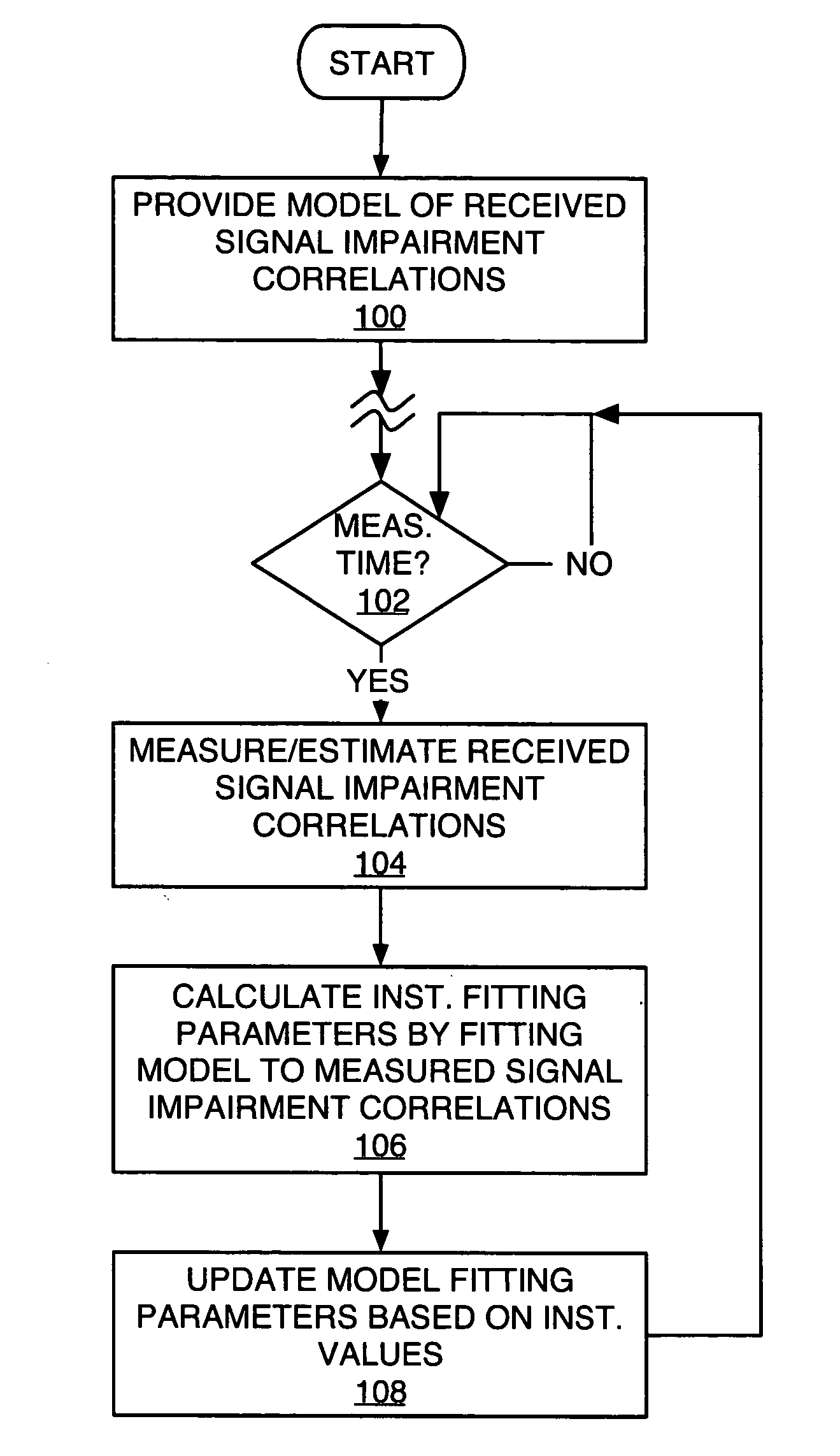
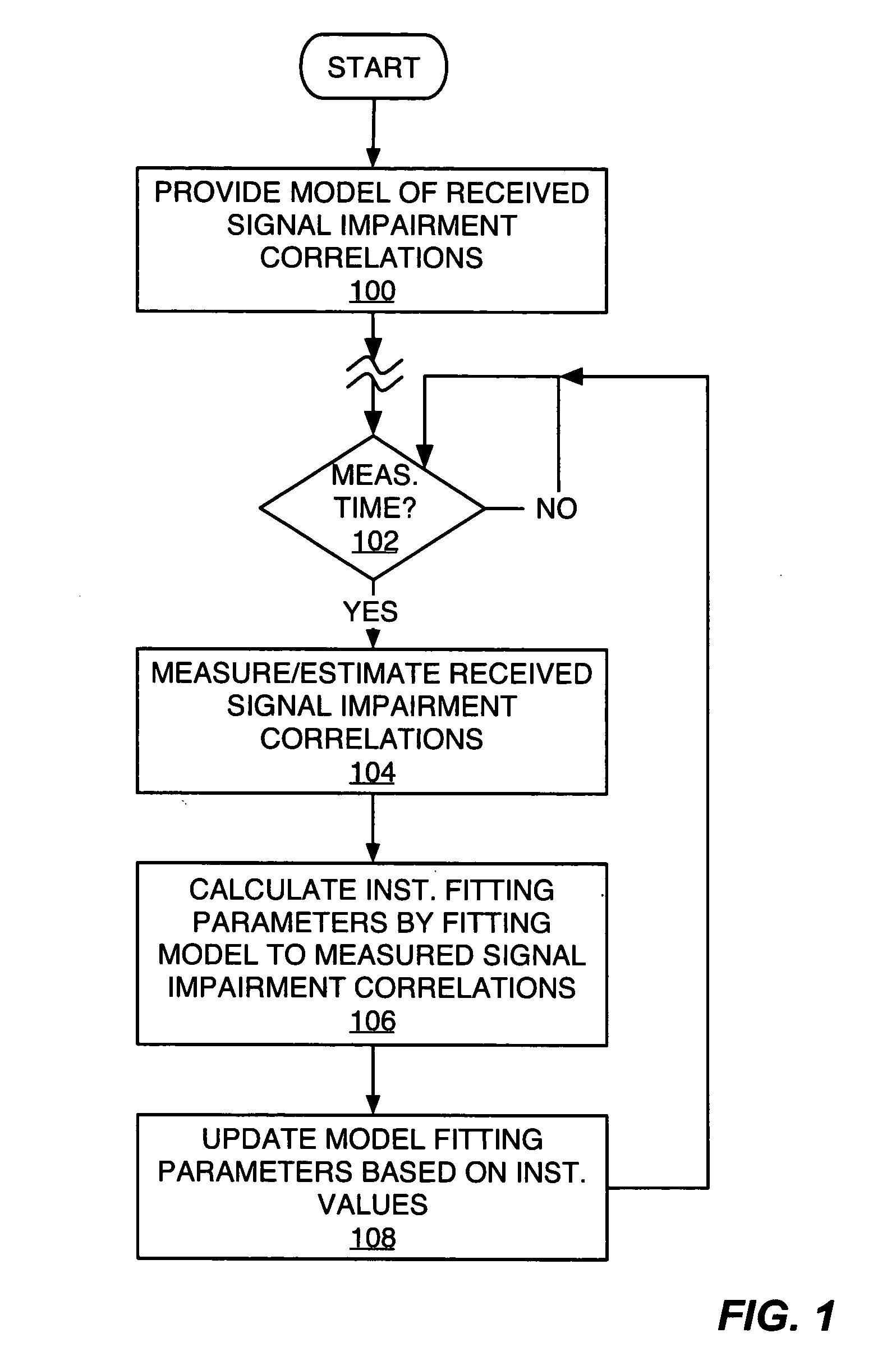
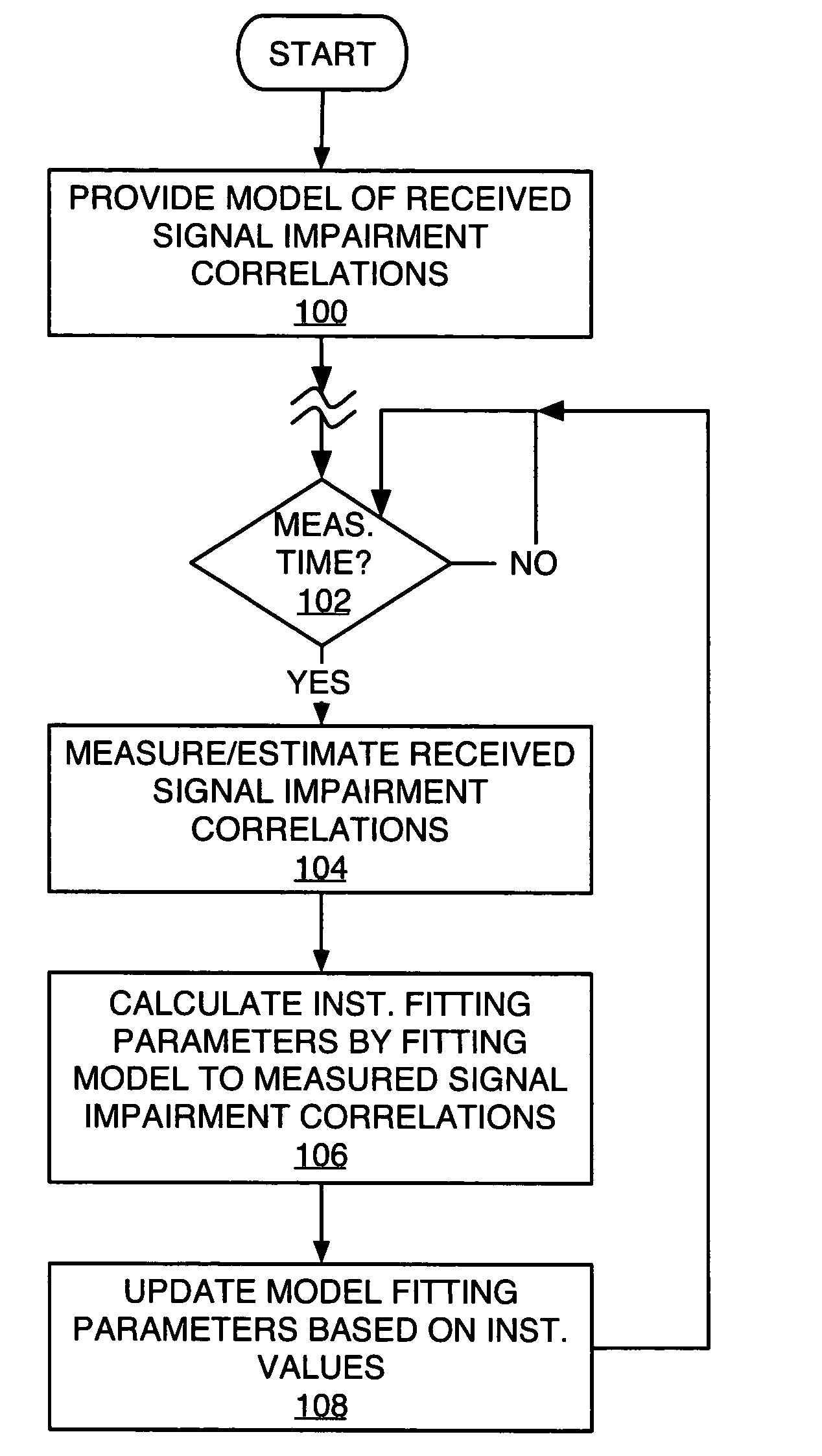
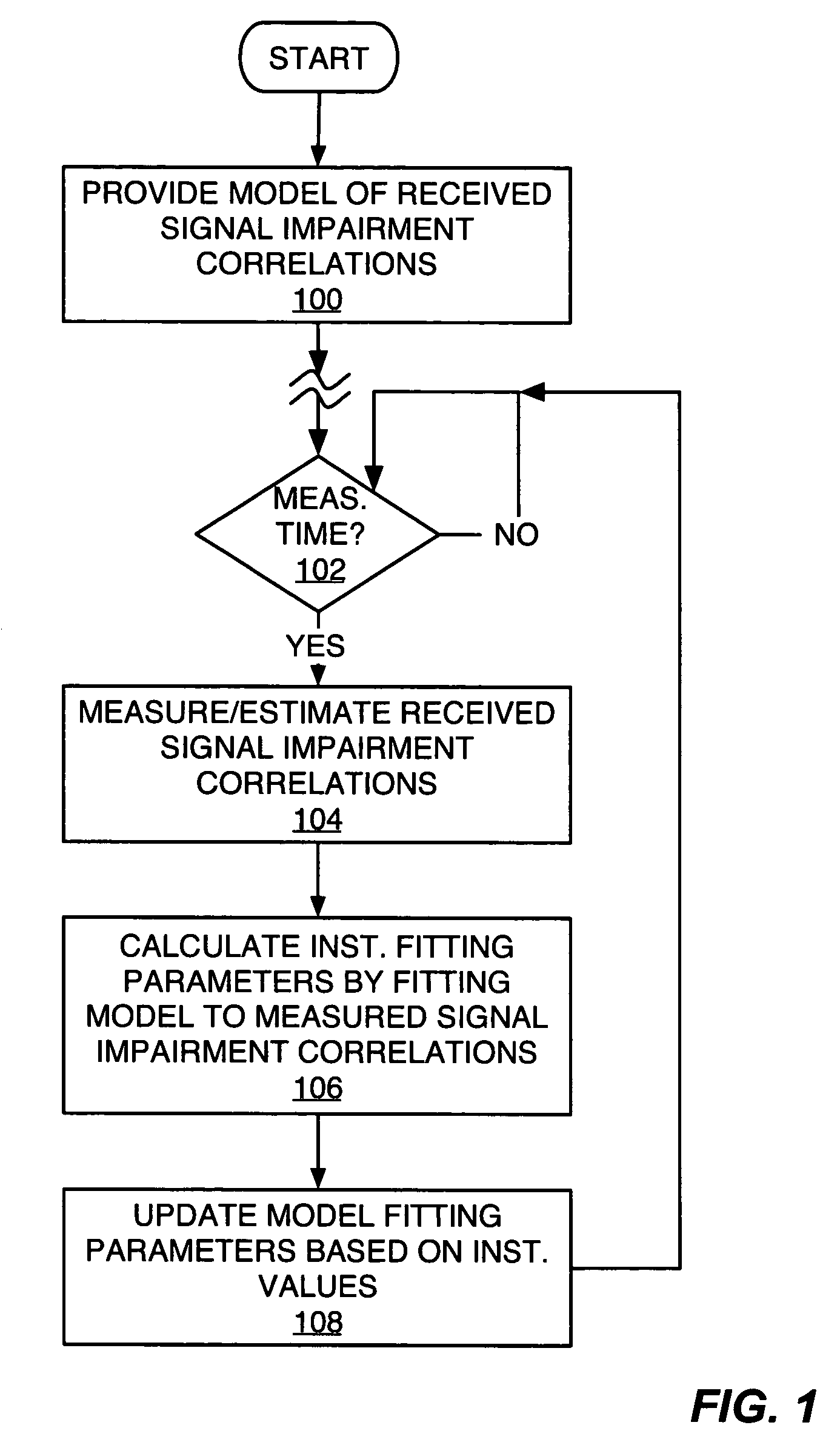
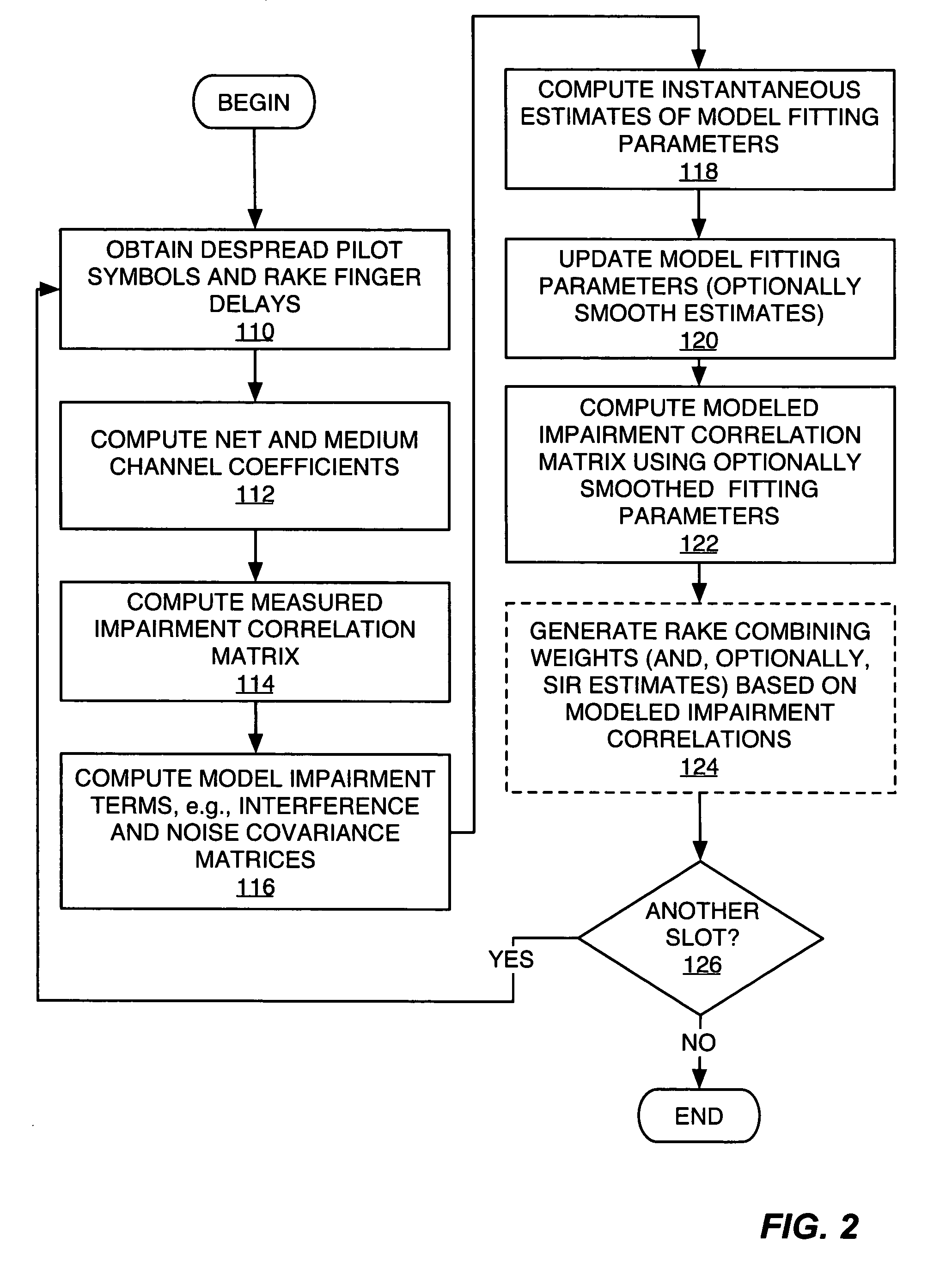
Exemplary received signal processing may be based on maintaining a model of received signal impairment correlations, wherein each term of the model is updated periodically or as needed based on measuring impairments for a received signal of interest. An exemplary model comprises an interference impairment term scaled by a first model fitting parameter, and a noise impairment term scaled by a second model fitting parameters. The model terms may be maintained based on current channel estimates and delay information and may be fitted to measured impairment by adapting the model fitting parameters based on the measured impairment. The modeled received signal impairment correlations may be used to compute RAKE combining weights for received signal processing, or to compute Signal-to-Interference (SIR) estimates. Combined or separate models may be used for multiple received signals. As such, the exemplary modeling is extended to soft handoff, multiple antennas, and other diversity situations.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
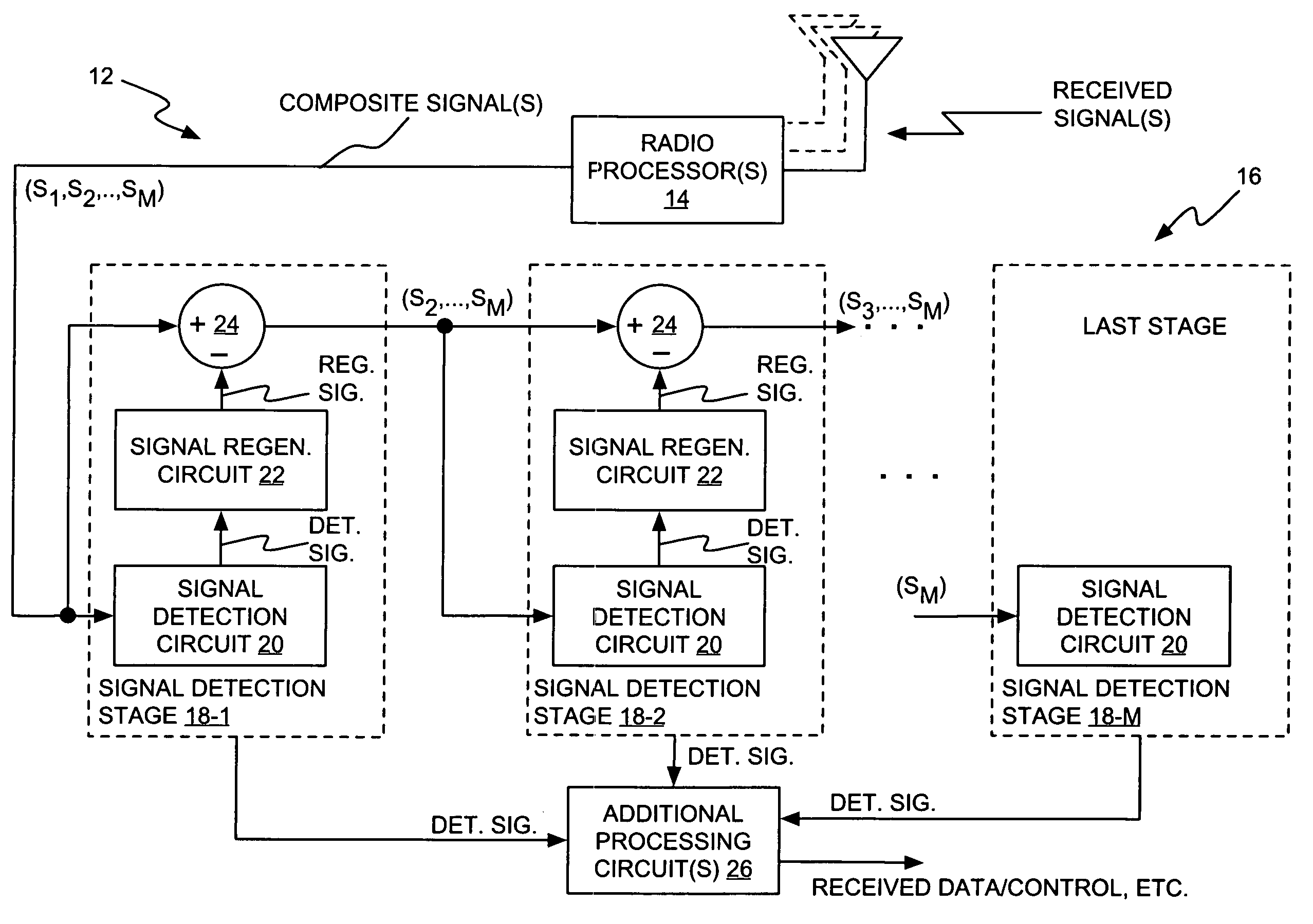
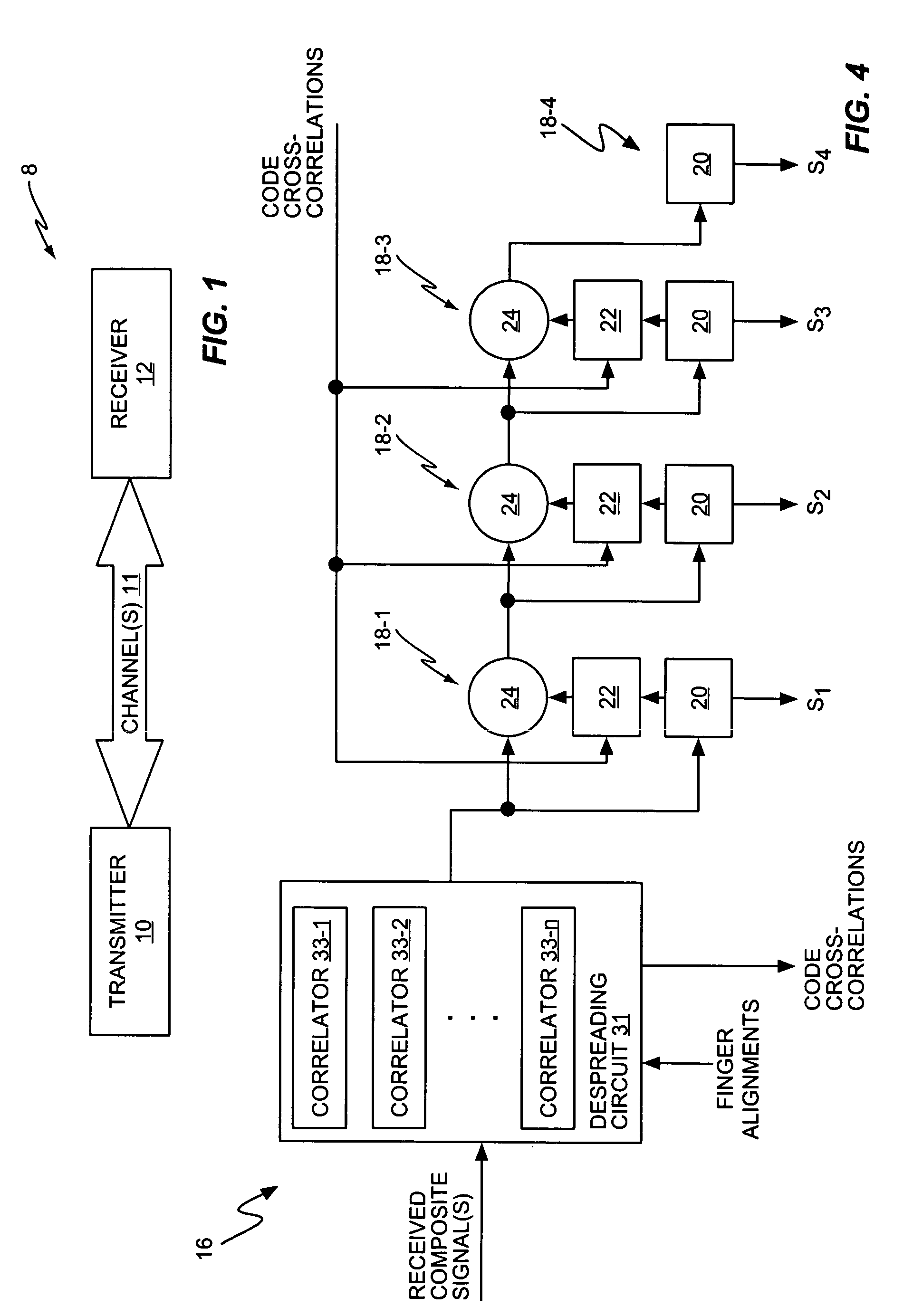
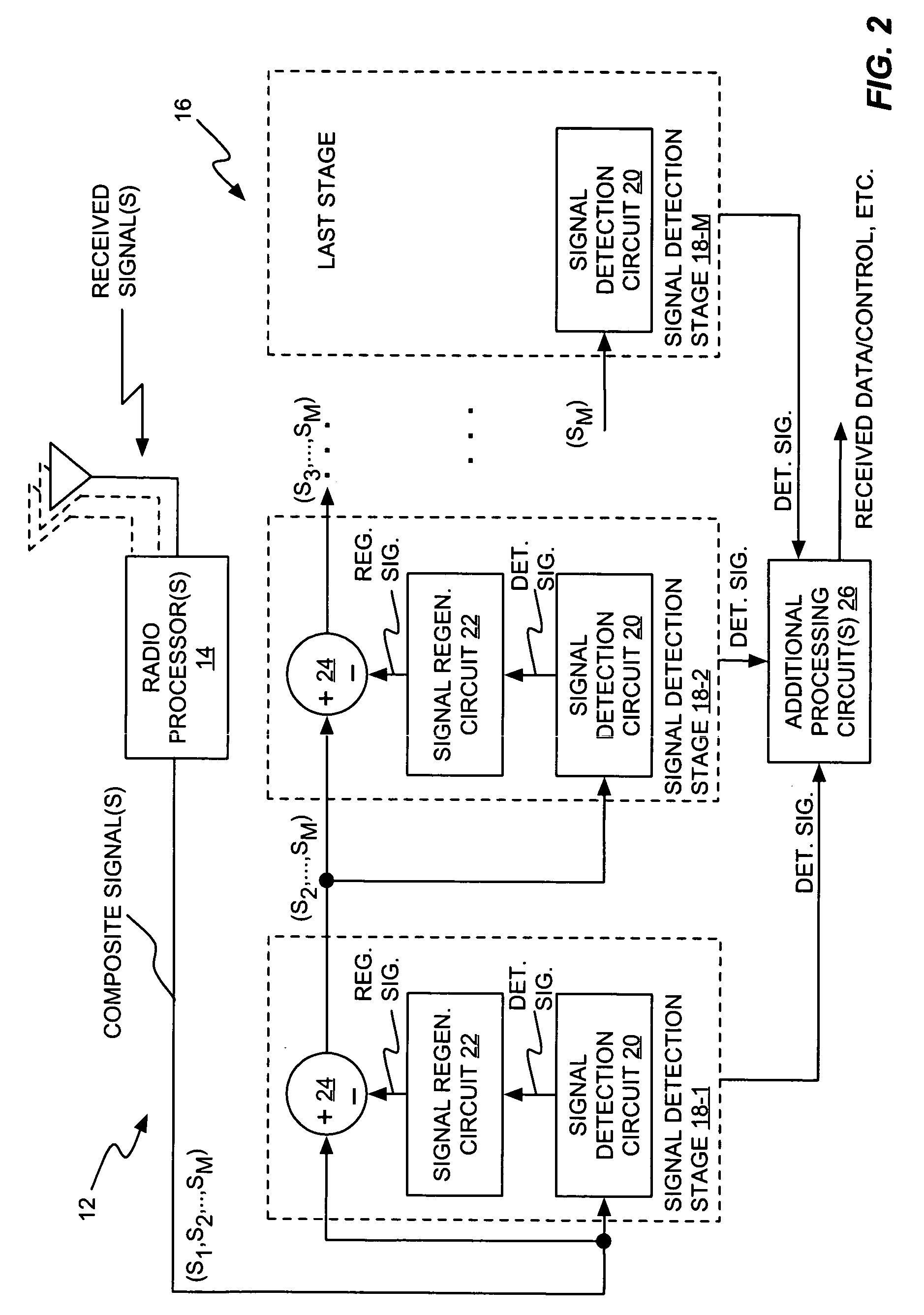
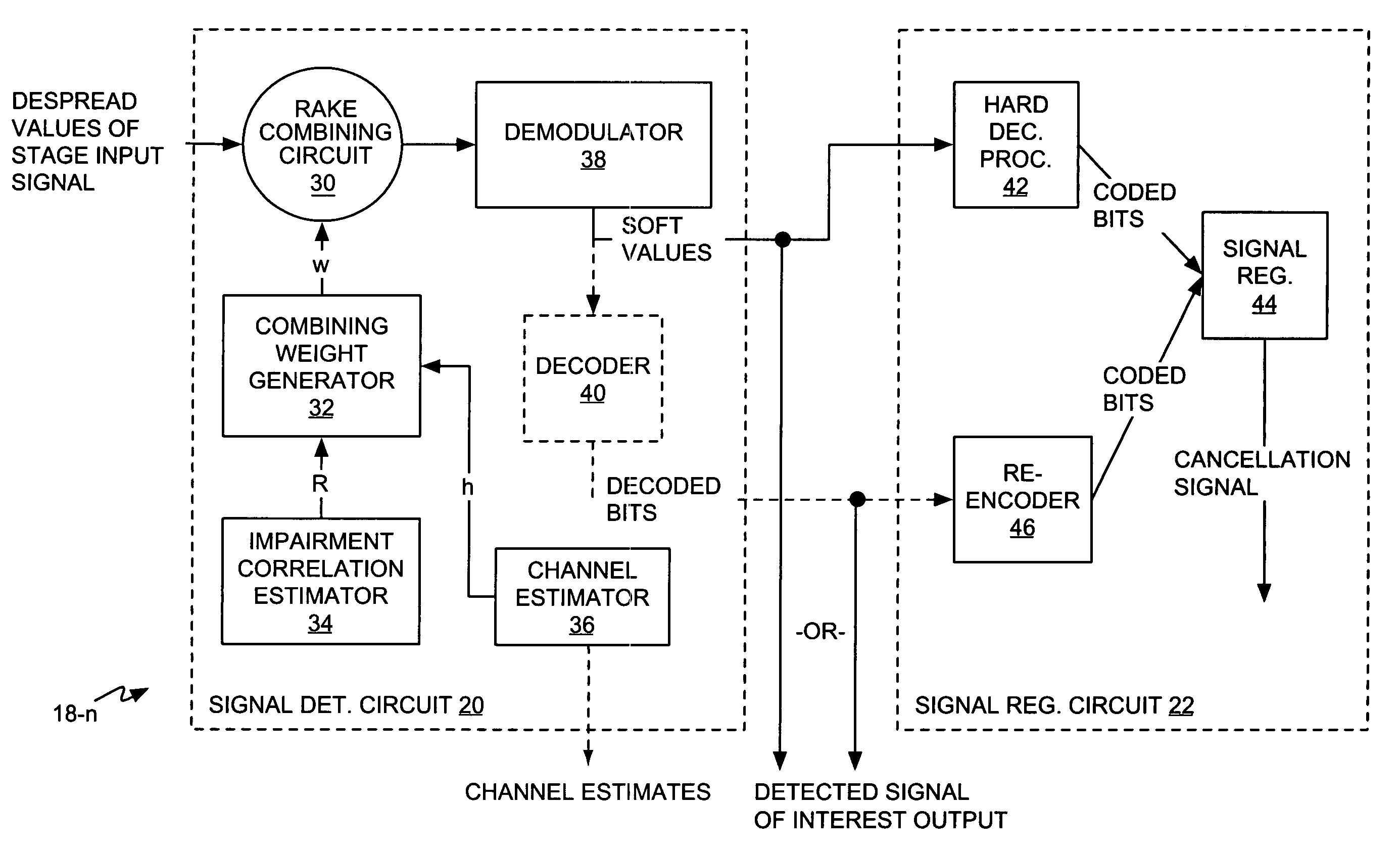
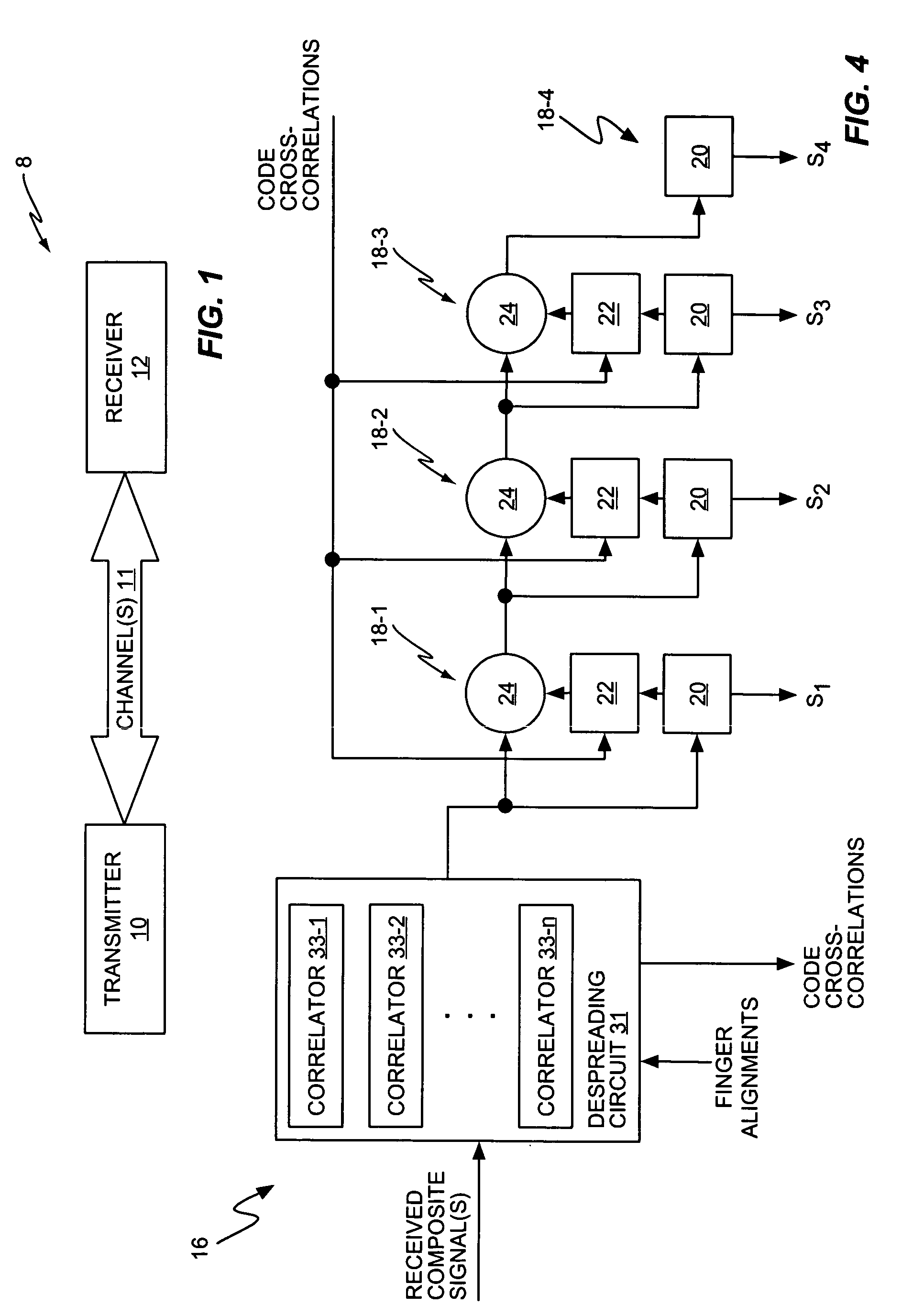
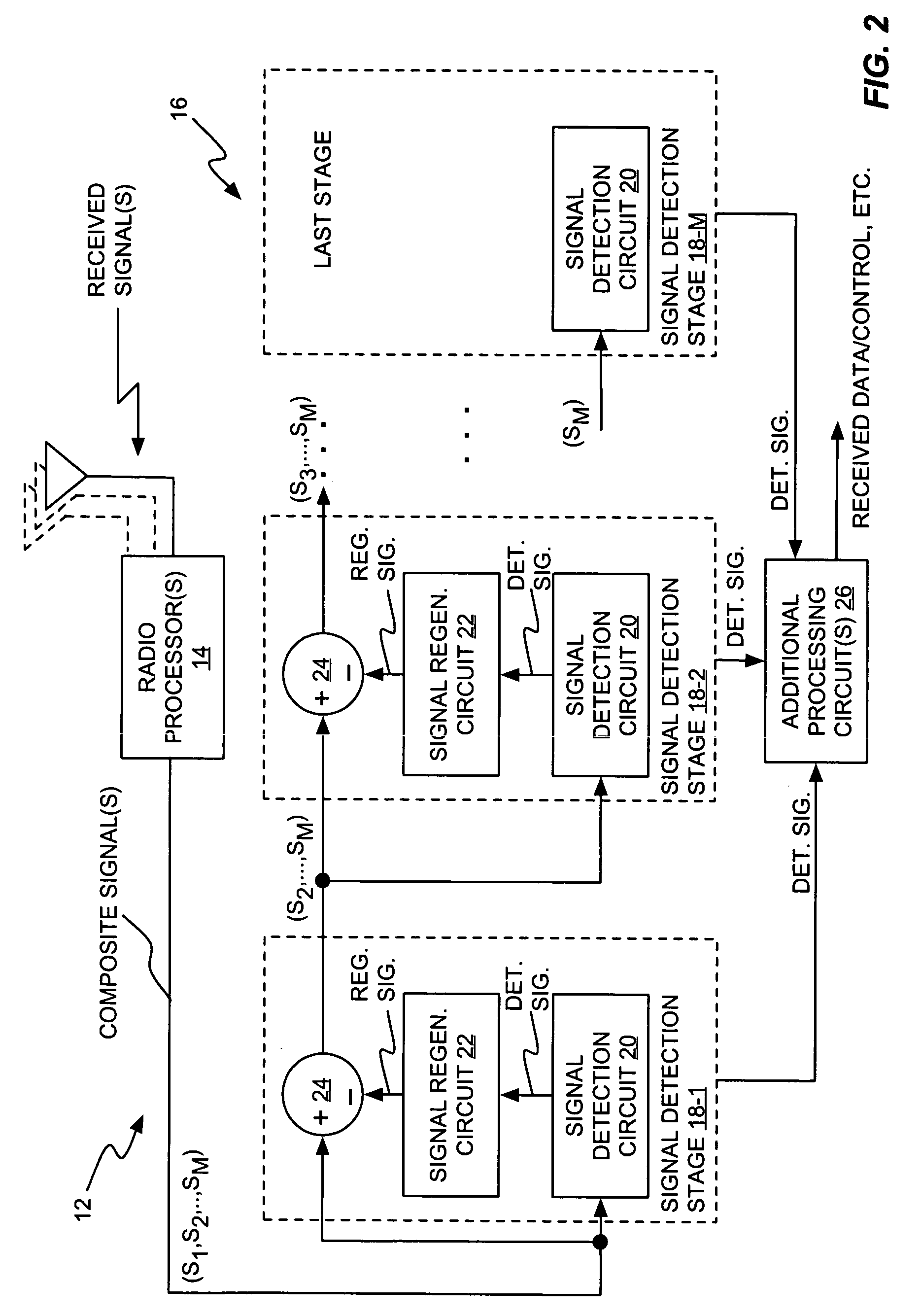
Successive interference cancellation in a generalized RAKE receiver architecture
A receiver includes a receiver circuit that decodes multiple signals of interest contained in a composite received signal. The receiver comprises a plurality of successive signal detection stages to detect respective signals contained in the composite received signal. Each detection circuit comprises at least one Generalized RAKE combining circuit and generates a detected signal at an output. Each but the last stage further comprises a signal regeneration circuit that cancels the signal of interest detected by that stage from a stage input signal provided to the next stage such that successive detection of the signals of interest benefits from cumulative cancellation of the previously detected signals.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
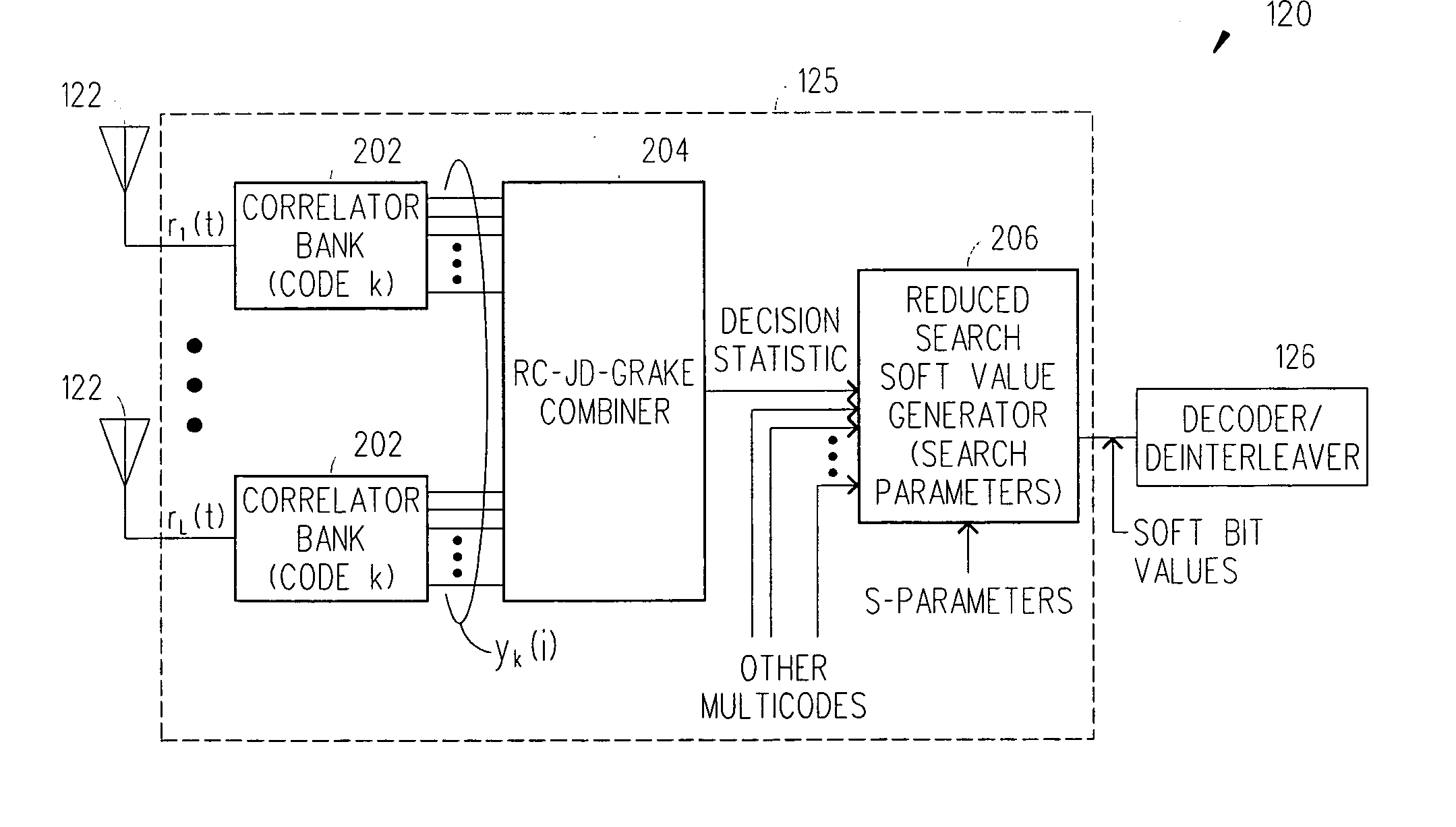
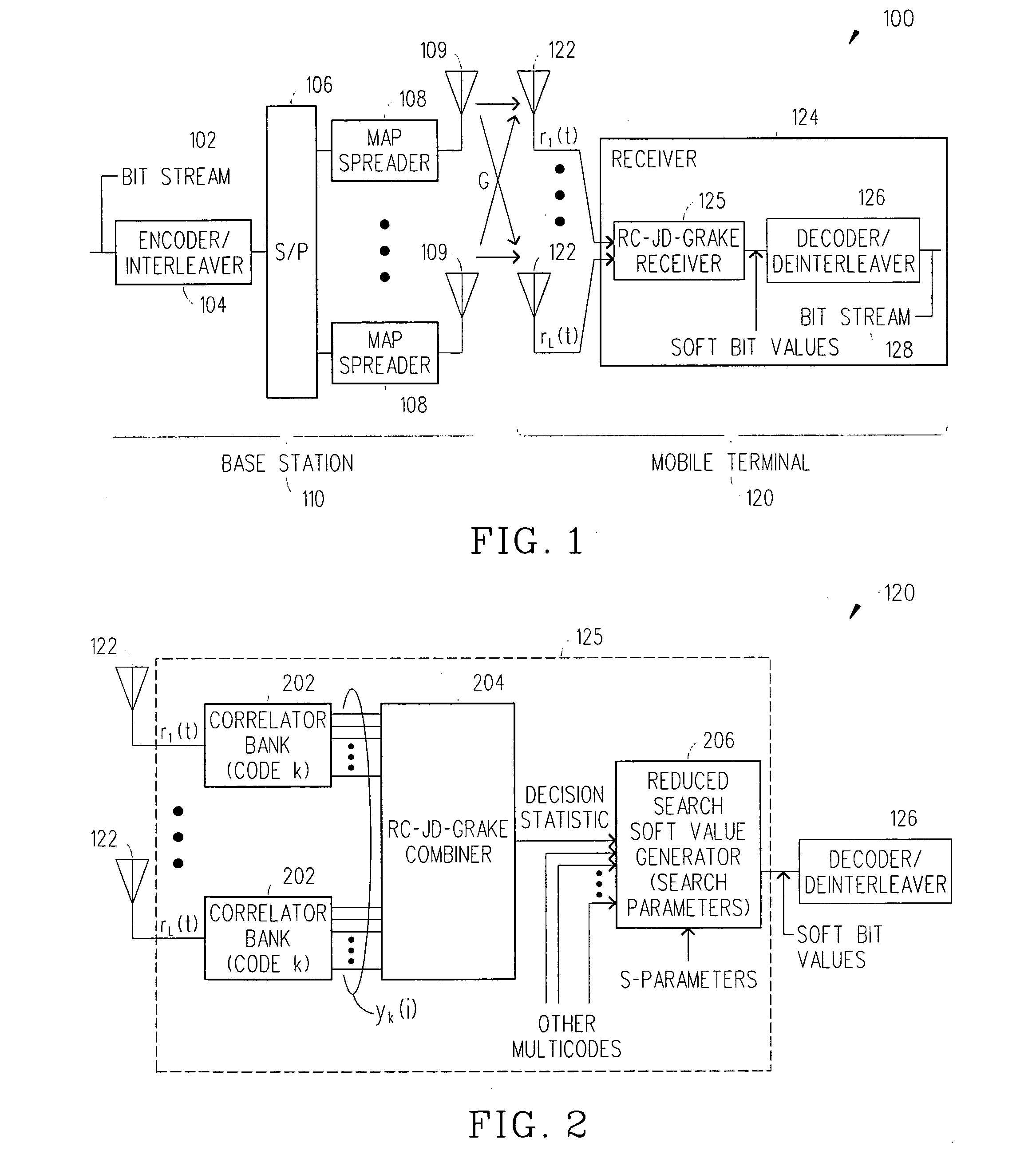
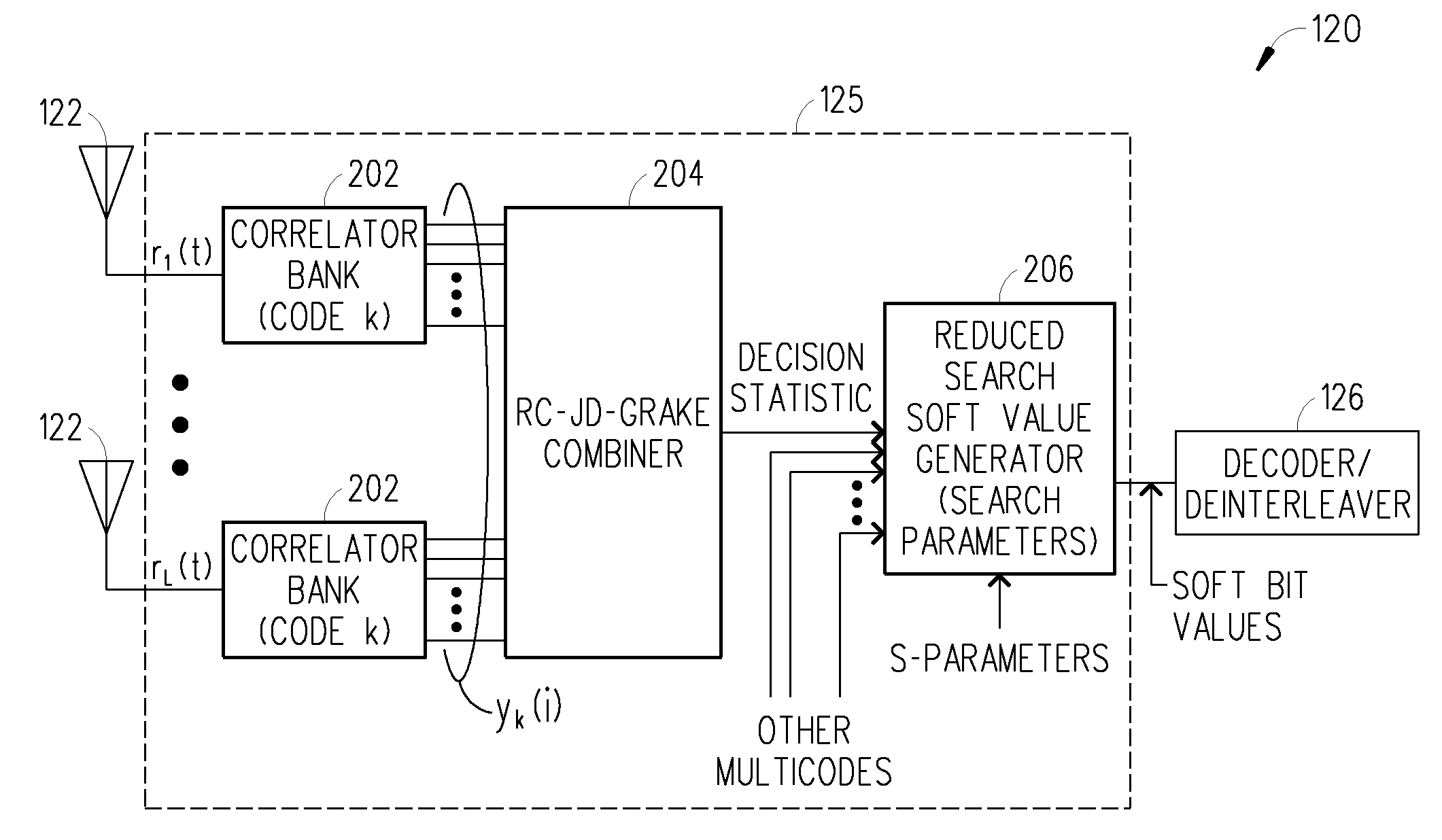
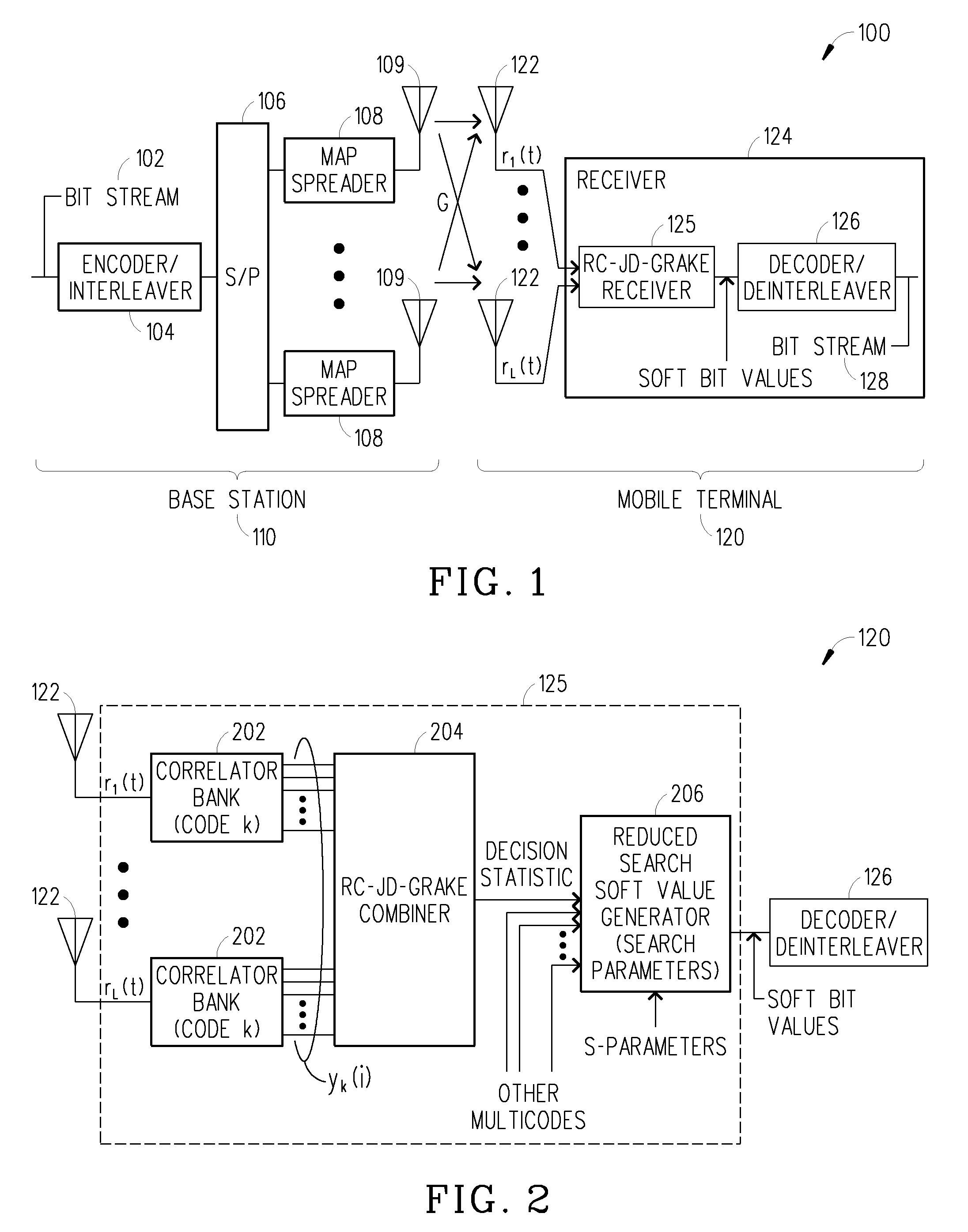
Reduced complexity soft value generation for MIMO JD-GRAKE receivers
InactiveUS20060029124A1Reduce in quantityReduce complexityDiversity/multi-antenna systemsRake combiningEngineering
A receiver includes a receiver circuit that decodes multiple signals of interest contained in a composite receive signal. The receiver comprises at least one Generalized RAKE combining circuit and a joint demodulation circuit and generates a detected signal at an output. The joint demodulation circuit contains a reduced search soft value generator circuit and generates soft bit values that represent coded bits received from the transmitter.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
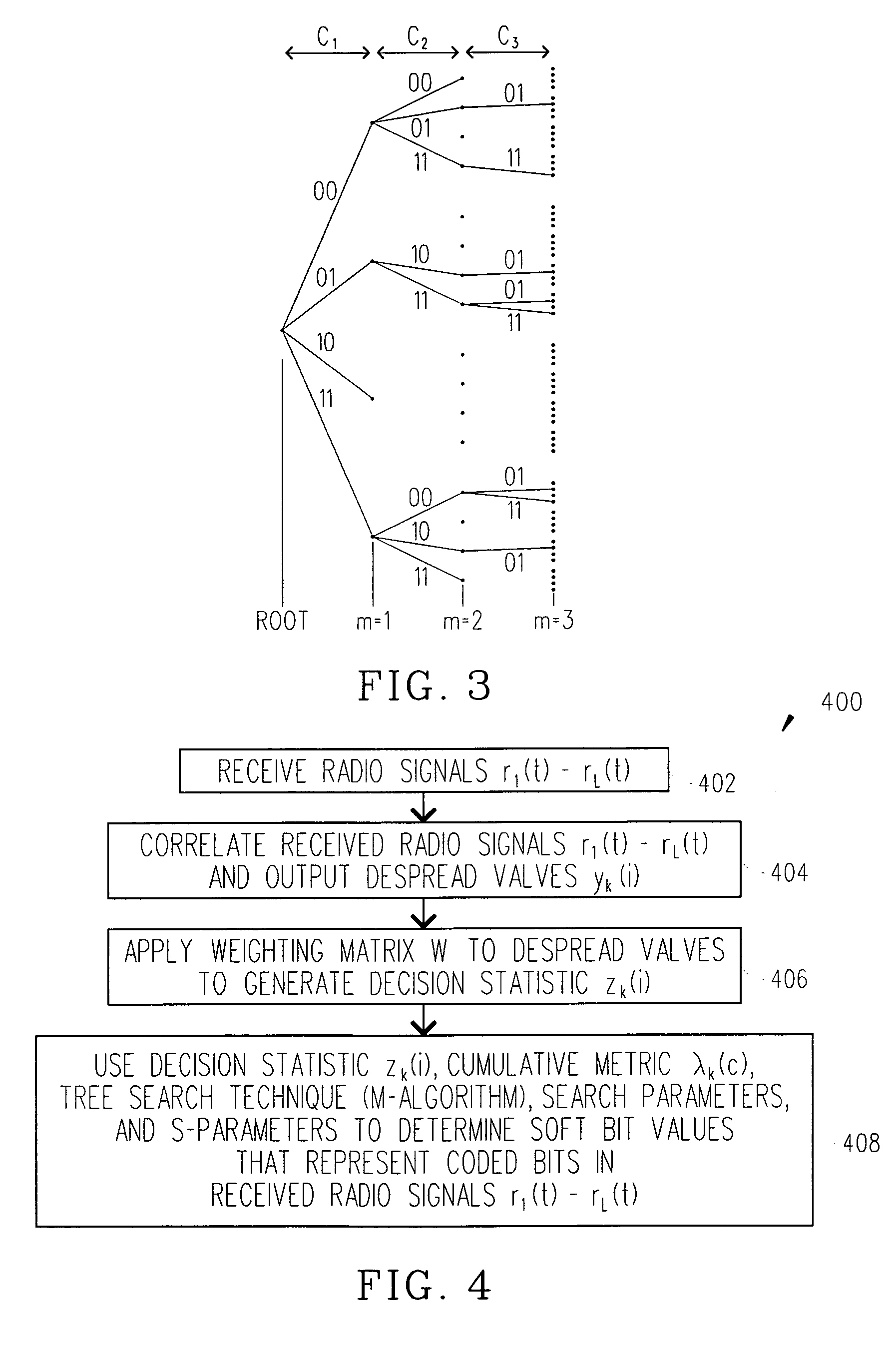
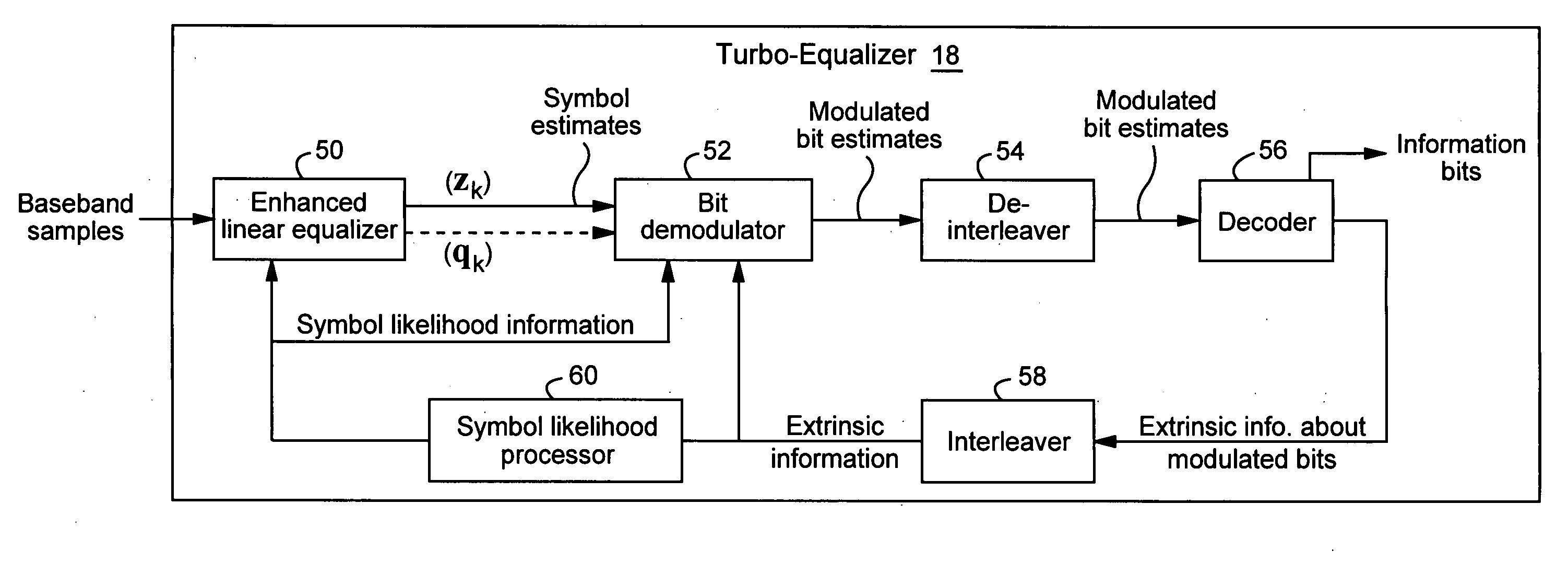
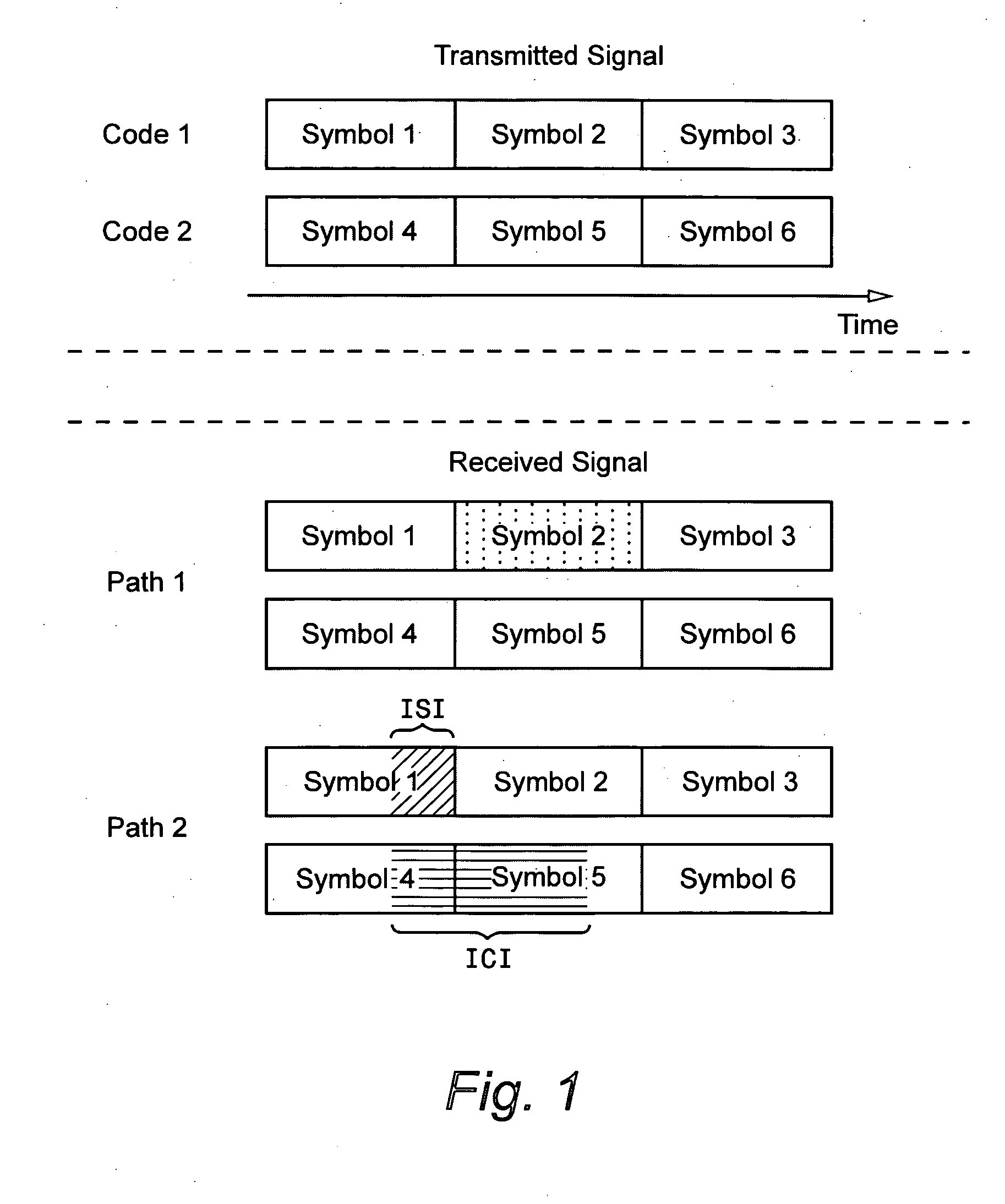
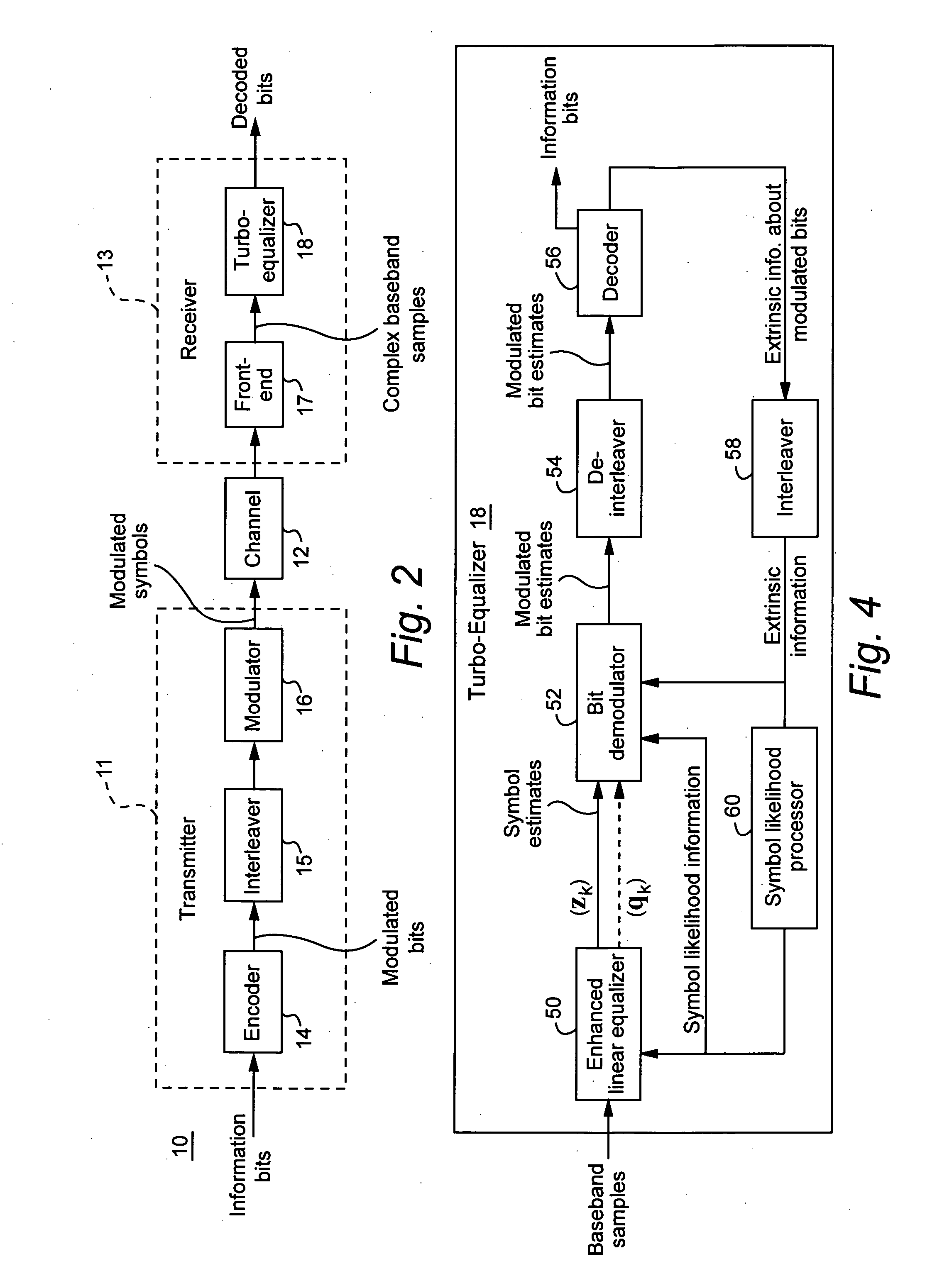
Linear turbo equalization using despread values
ActiveUS20070147481A1Suppress self-interferenceThe solution result is accurateCode conversionLine-faulsts/interference reductionSelf interferenceRake combining
A linear turbo-equalizer for use in a CDMA receiver equalizes a despread received signal (rather than the spread received signal) to suppress self-interference resulting from coupling between transmitted symbols. In an example implementation, a linear equalizer based on a generalized-Rake (G-Rake) receiver design uses decoder feedback in forming Rake combining weights as well as in forming a self-interference estimate removed from the equalizer signal provided to the decoder. Preferably, turbo de-coding is also performed. In that case, each turbo-decoder component preferably executes one pass before feeding back information to the equalizer. This ensures that the turbo-decoder does not prematurely lock onto an incorrect code word before feeding back extrinsic information to the equalizer.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Reduced complexity soft value generation for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) joint detection generalized RAKE (JD-GRAKE) receivers
InactiveUS7397843B2Reduce in quantityReduce complexityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsRake combiningEngineering
A receiver includes a receiver circuit that decodes multiple signals of interest contained in a composite receive signal. The receiver comprises at least one Generalized RAKE combining circuit and a joint demodulation circuit and generates a detected signal at an output. The joint demodulation circuit contains a reduced search soft value generator circuit and generates soft bit values that represent coded bits received from the transmitter.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Successive interference cancellation in a generalized RAKE receiver architecture
A receiver includes a receiver circuit that decodes multiple signals of interest contained in a composite received signal. The receiver comprises a plurality of successive signal detection stages to detect respective signals contained in the composite received signal. Each detection circuit comprises at least one Generalized RAKE combining circuit and generates a detected signal at an output. Each but the last stage further comprises a signal regeneration circuit that cancels the signal of interest detected by that stage from a stage input signal provided to the next stage such that successive detection of the signals of interest benefits from cumulative cancellation of the previously detected signals.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
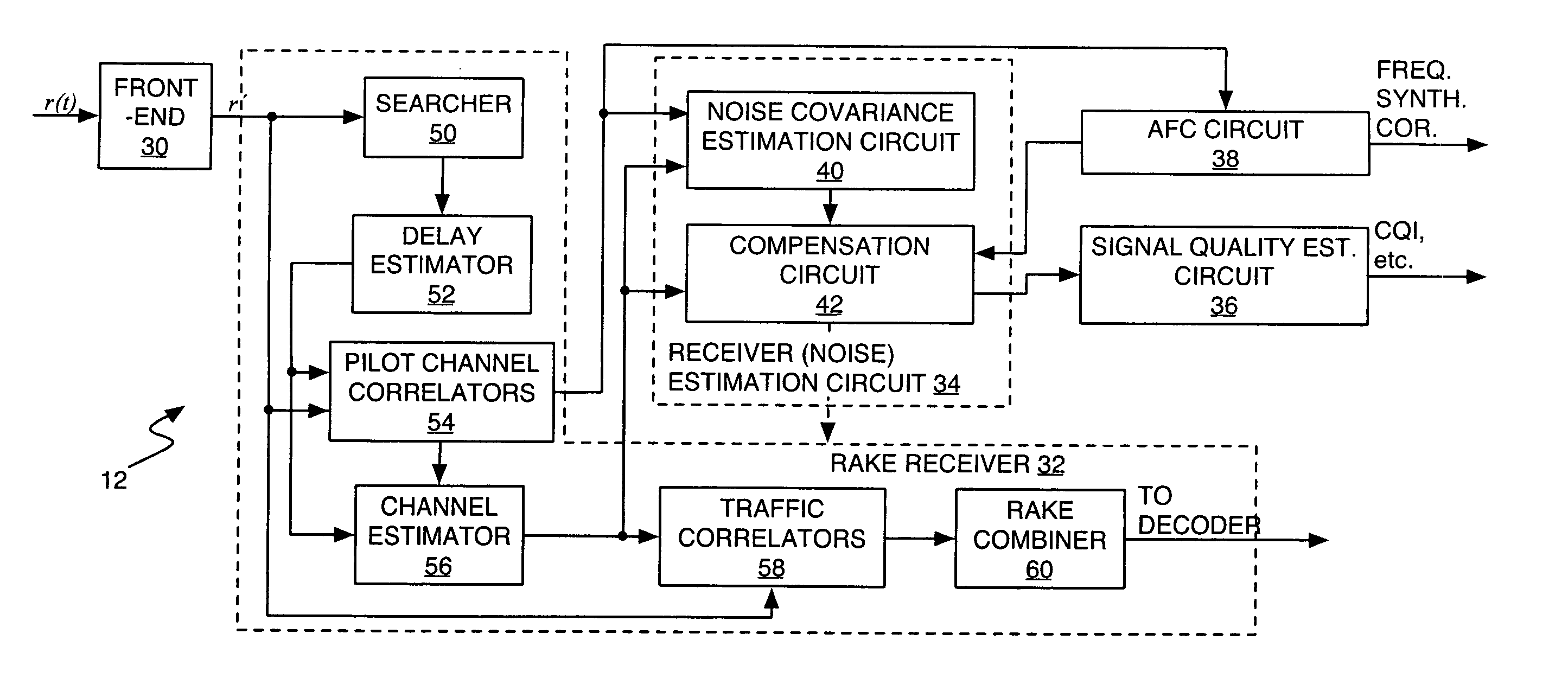
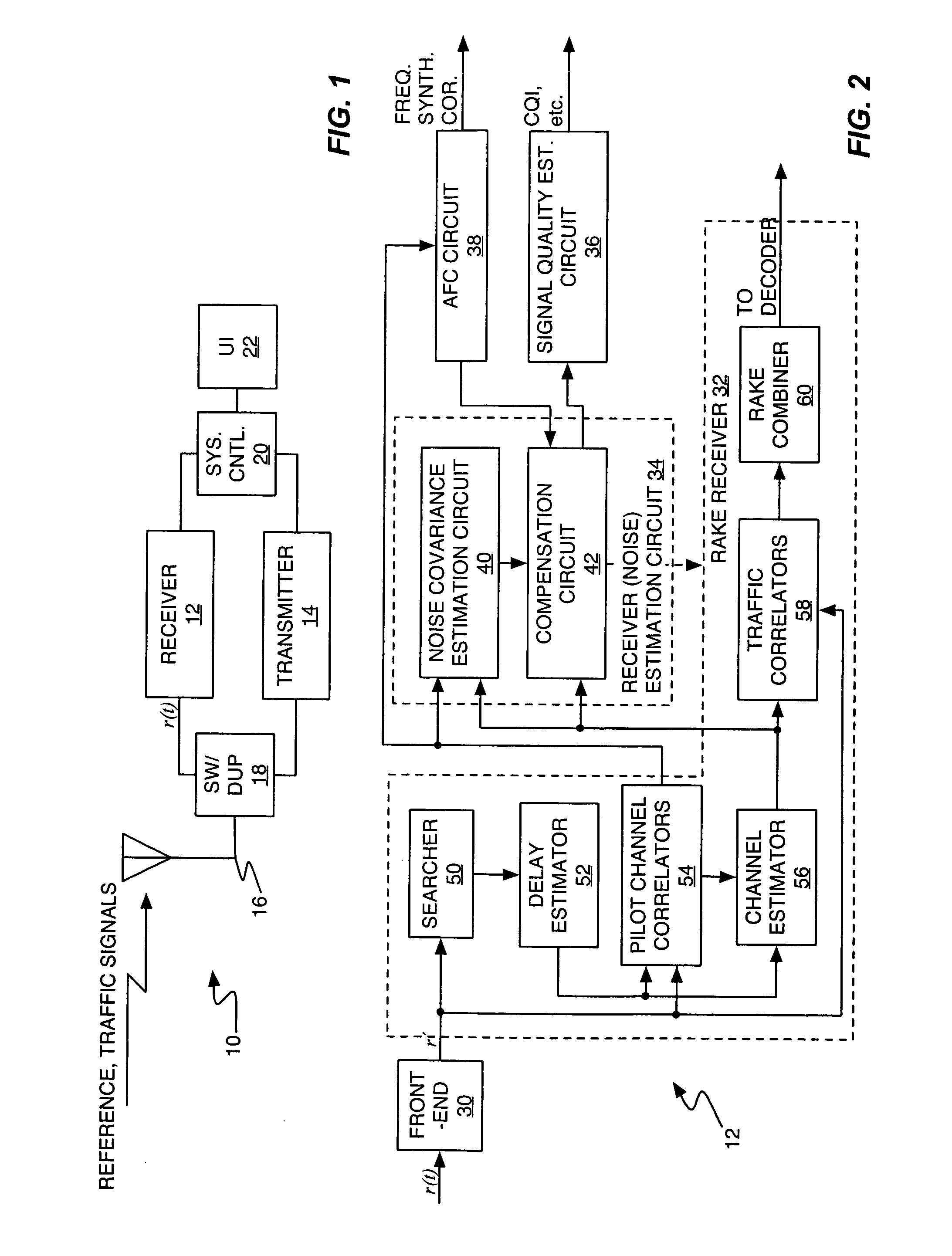
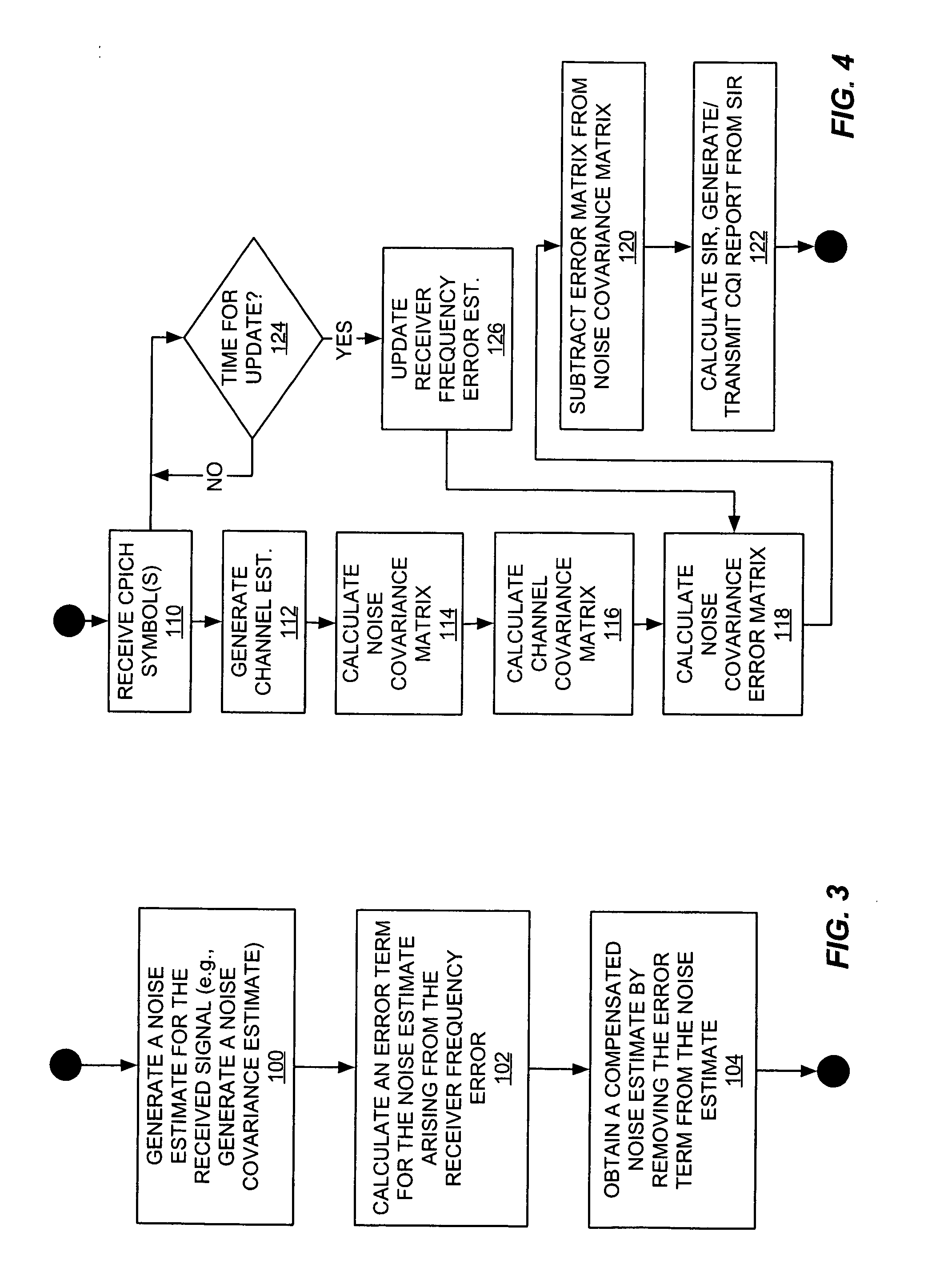
Method and apparatus to compensate for receiver frequency error in noise estimation processing
ActiveUS20050281324A1Improved noise estimationImprove accuracyError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorModulated-carrier systemsNoise estimationRake combining
A receiver circuit provides improved noise estimation processing by at least partially removing receiver frequency error bias. An initial noise estimate is compensated using an error term based on the observed receiver frequency error, and the resulting compensated noise estimate can be used to improve other signal processing in the receiver. For example, the receiver may use compensated noise estimates to generate signal quality estimates, e.g., Signal-to-Interference (SIR) estimates, having improved accuracy. Additionally, or alternatively, the receiver may use the compensated noise estimates to generate RAKE combining weights having improved noise suppression characteristics. In an exemplary embodiment, the initial noise estimate is a noise correlation matrix generated from a received reference signal, e.g., pilot symbols, and the error term is an error matrix directly generated using he observed receiver frequency error and channel estimates taken from the reference signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
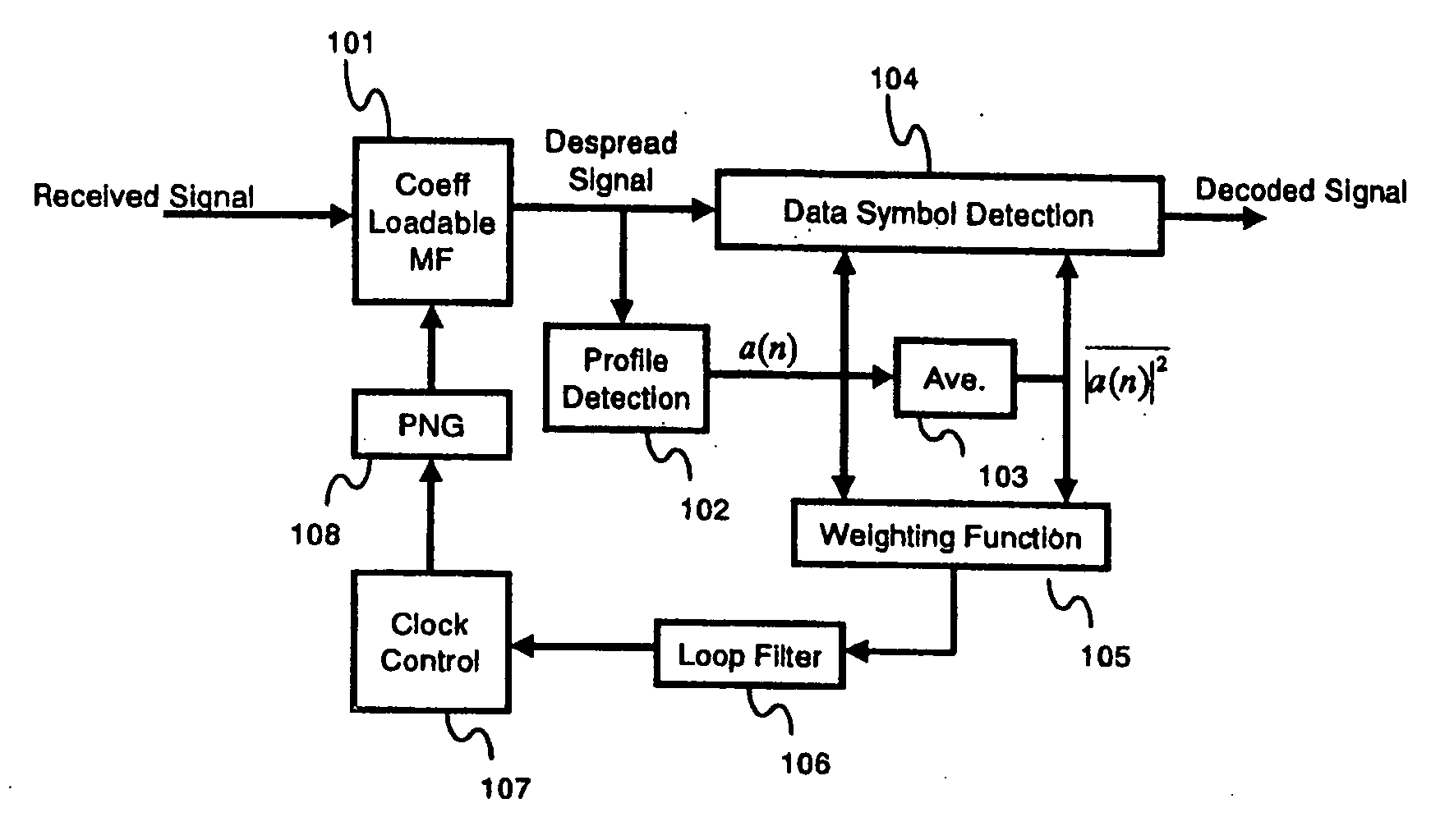
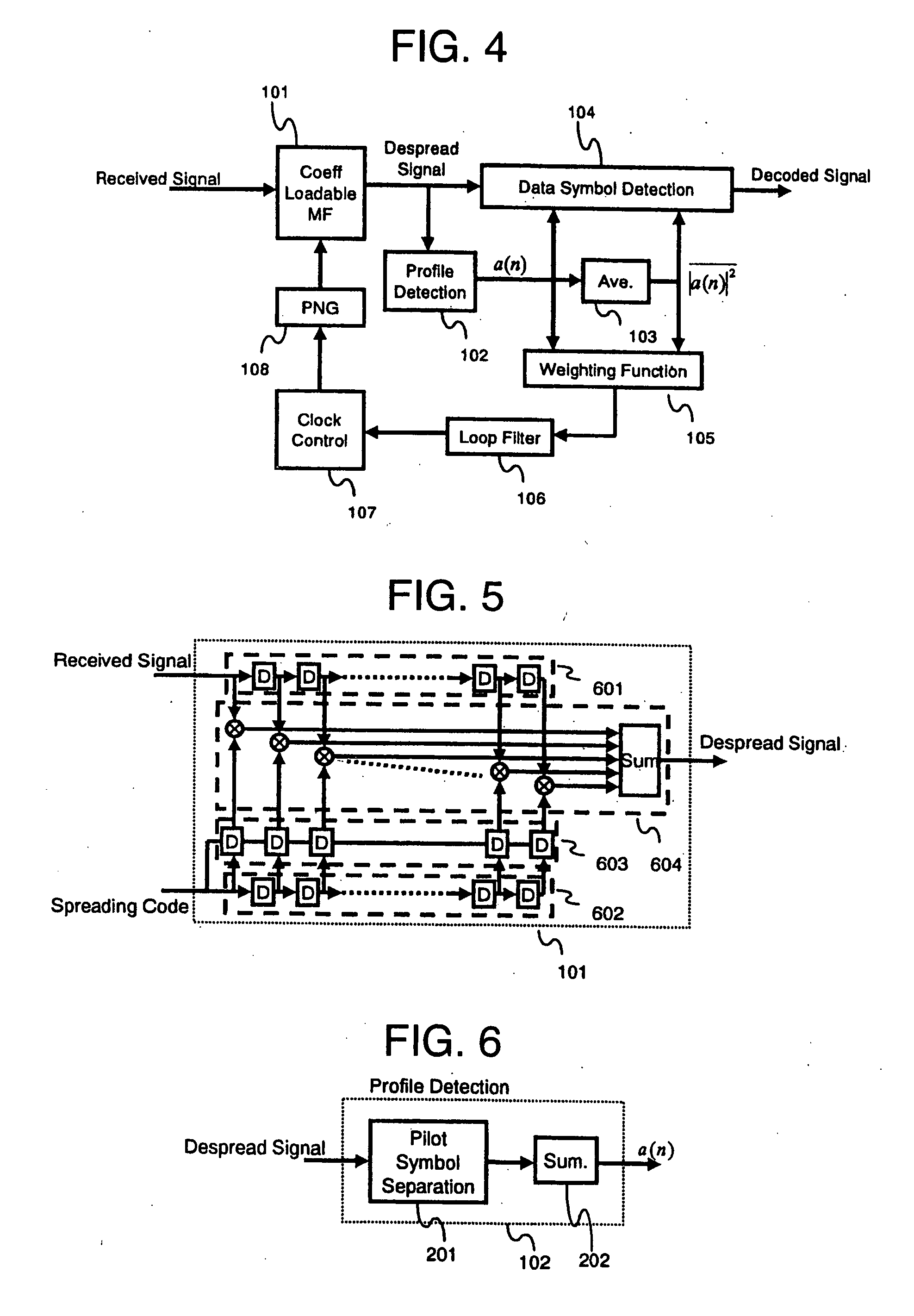
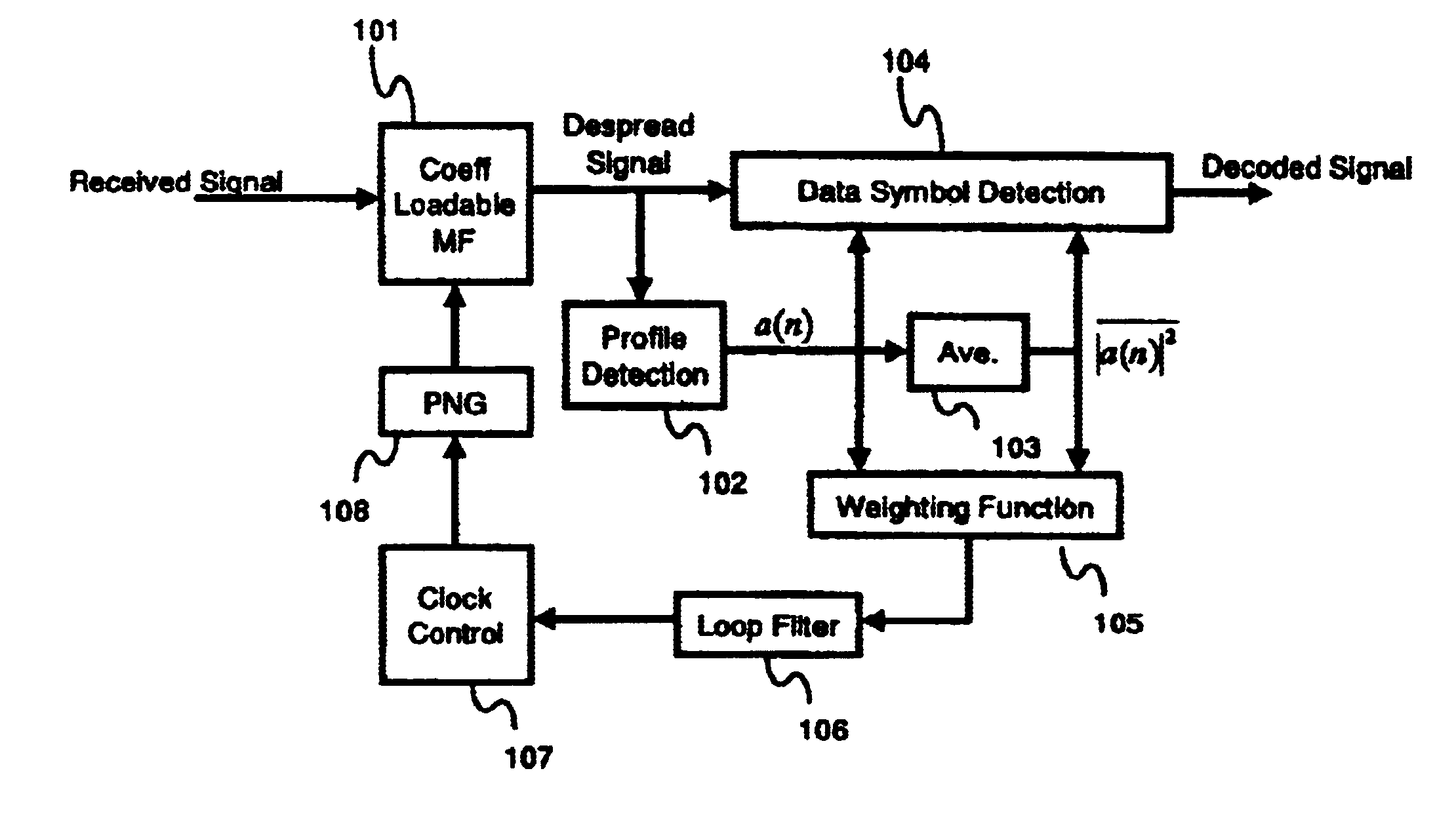
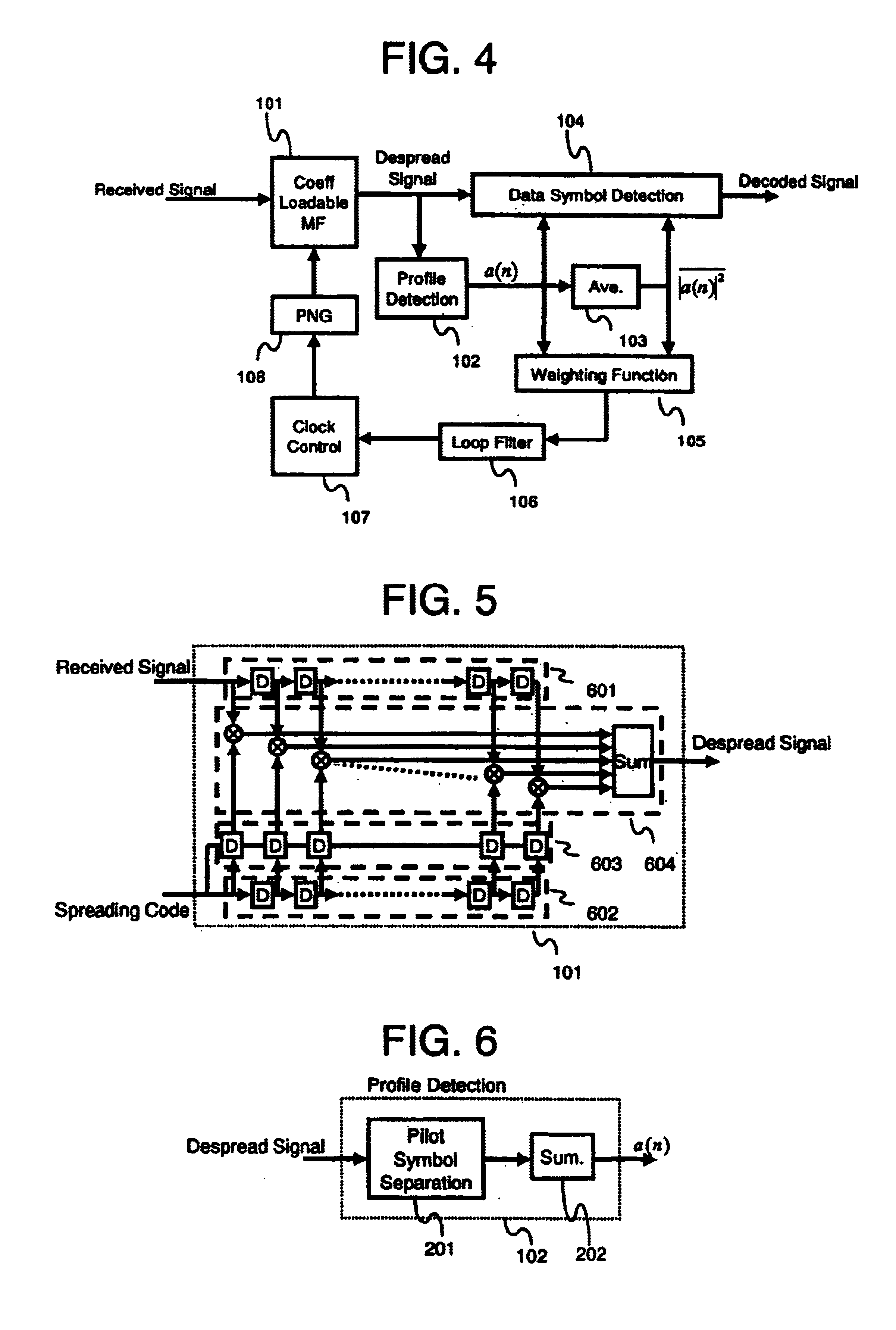
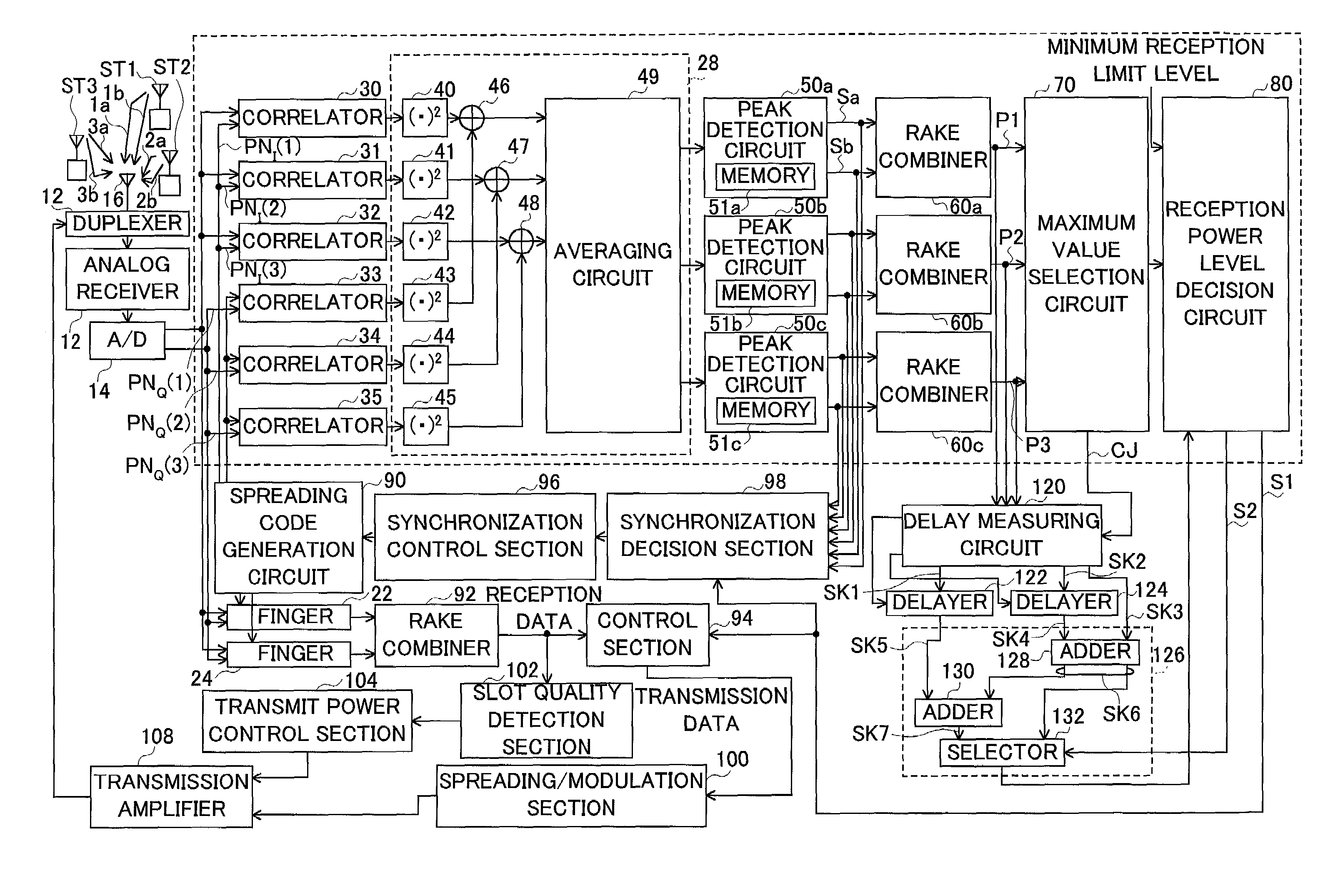
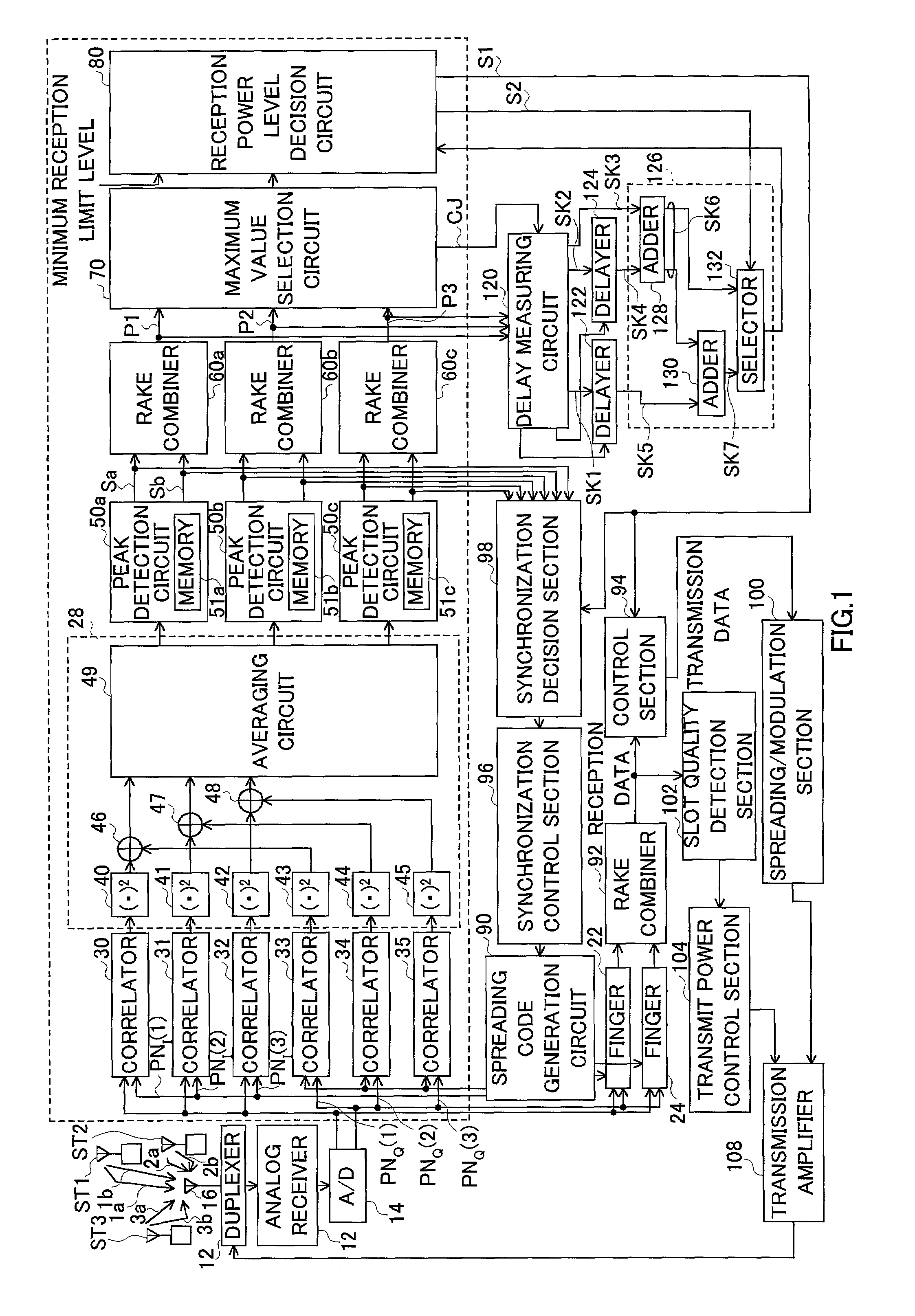
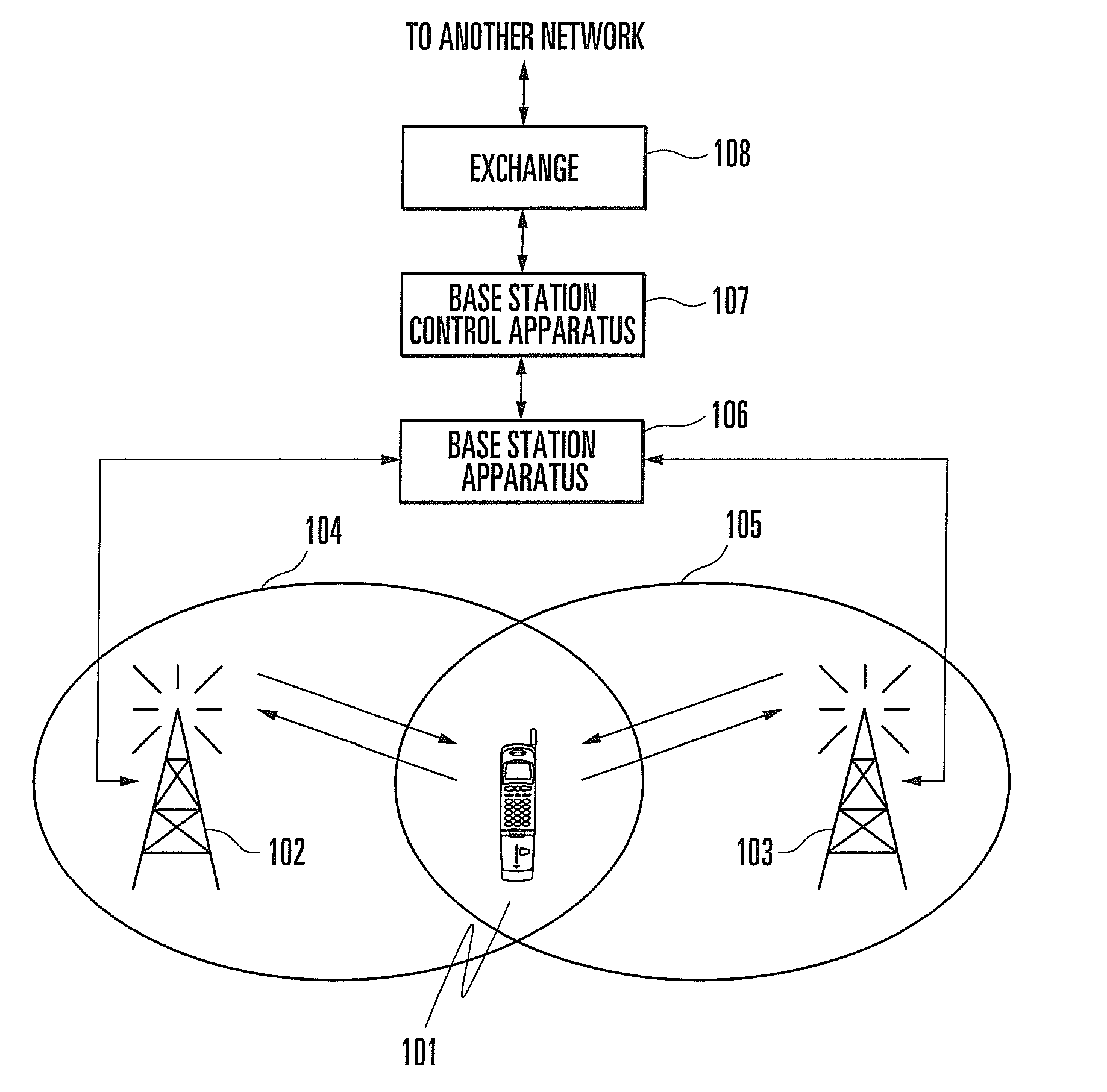
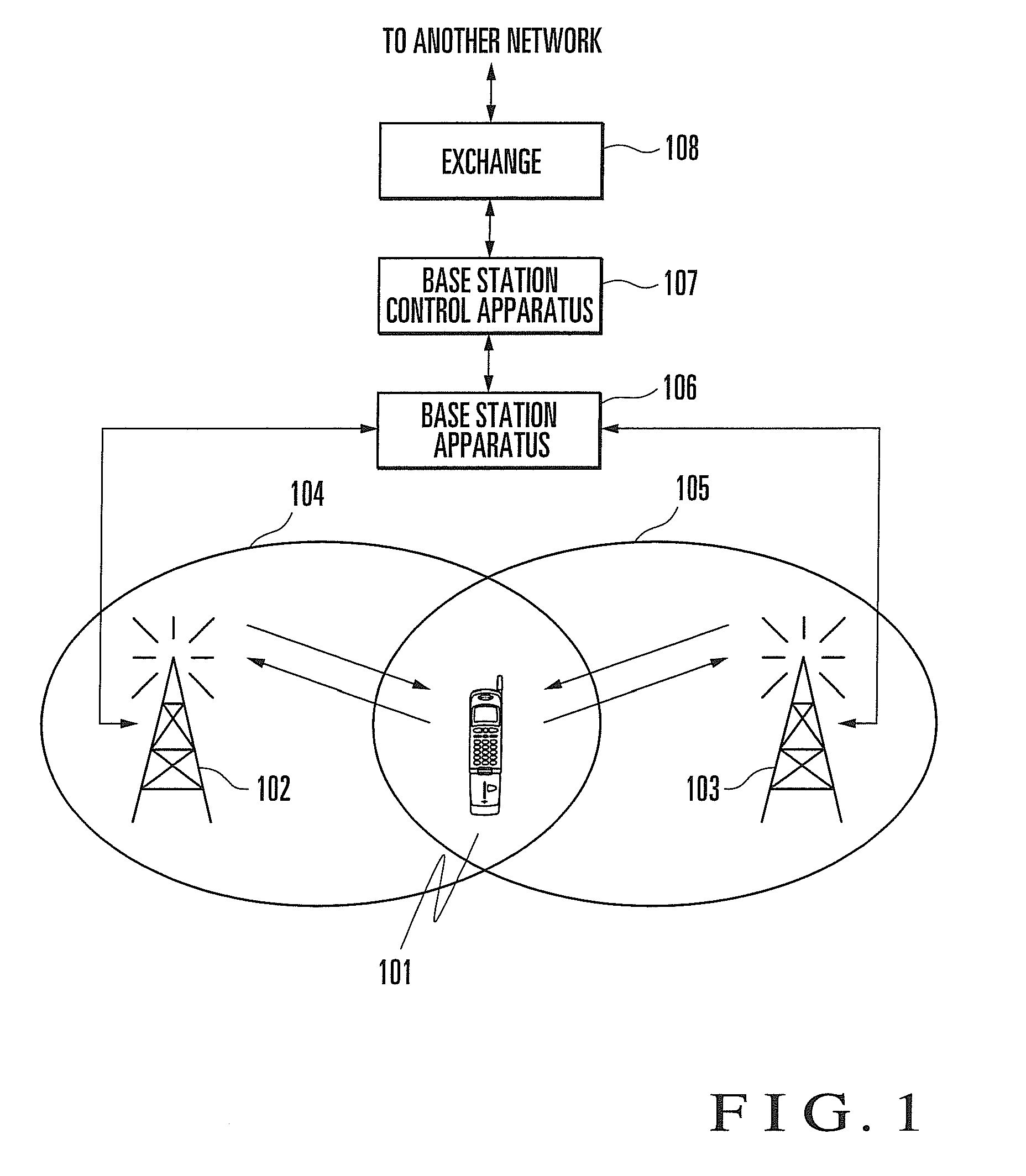
Mobile terminal, a base station, and a synchronization control method
In a mobile communication system, the tracking of synchronization is conducted in a stable state even in a multipath environment. A delay profile detector calculates a delay profile a(n) using a despread signal for each processing unit n. A delay profile averaging unit averages a(n) to produce Ave(|a(n)|<2>). A data symbol detector conducts rake combining of the despread signal using a(n) and Ave(|a(n)|<2>). According to a(n) and Ave(|a(n)|<2>, a weighting function unit calculates a representative value representing delay waves. A loop filter generates a control signal in response to the representative value. A clock controller controls a spread code generator according to the control signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
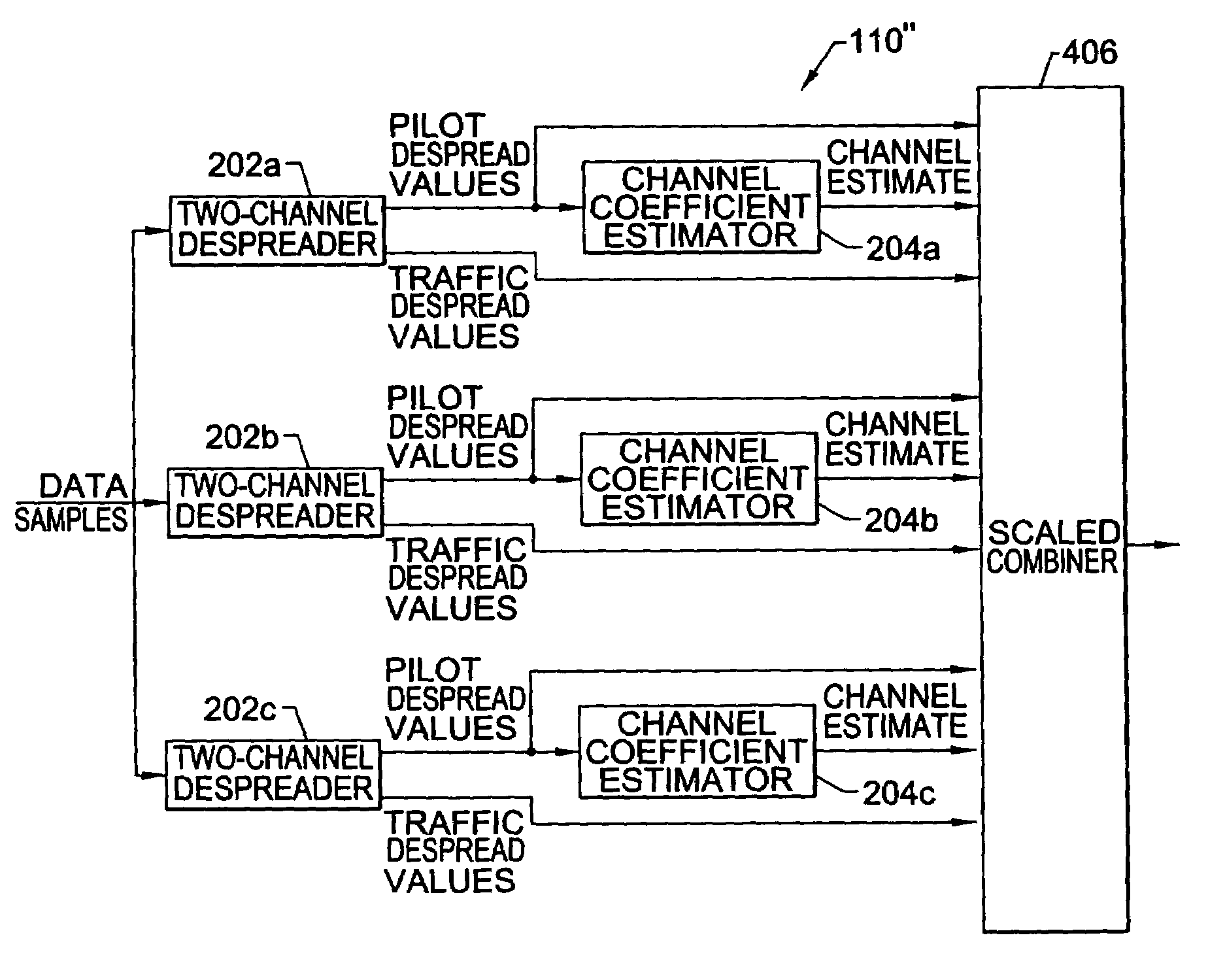
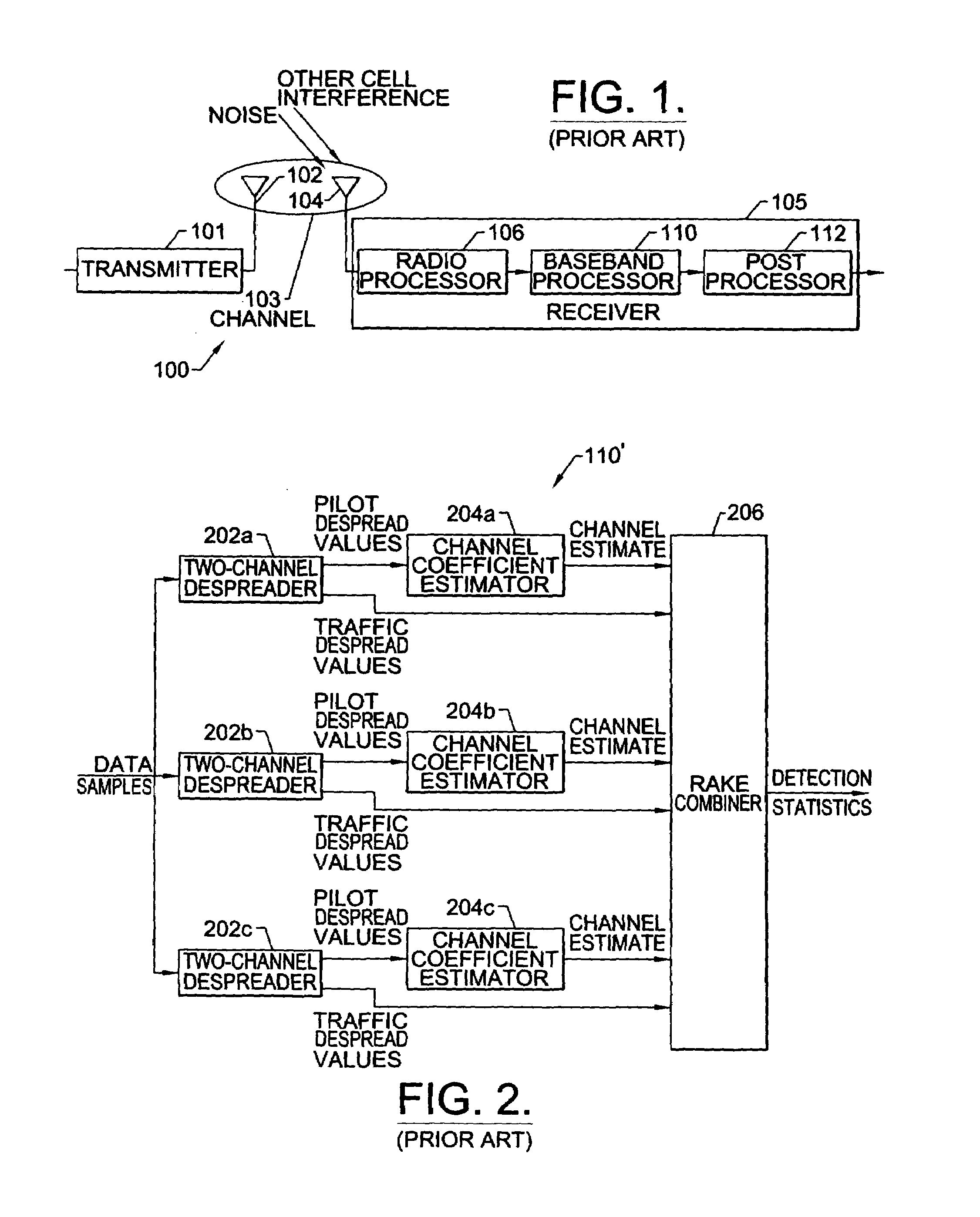
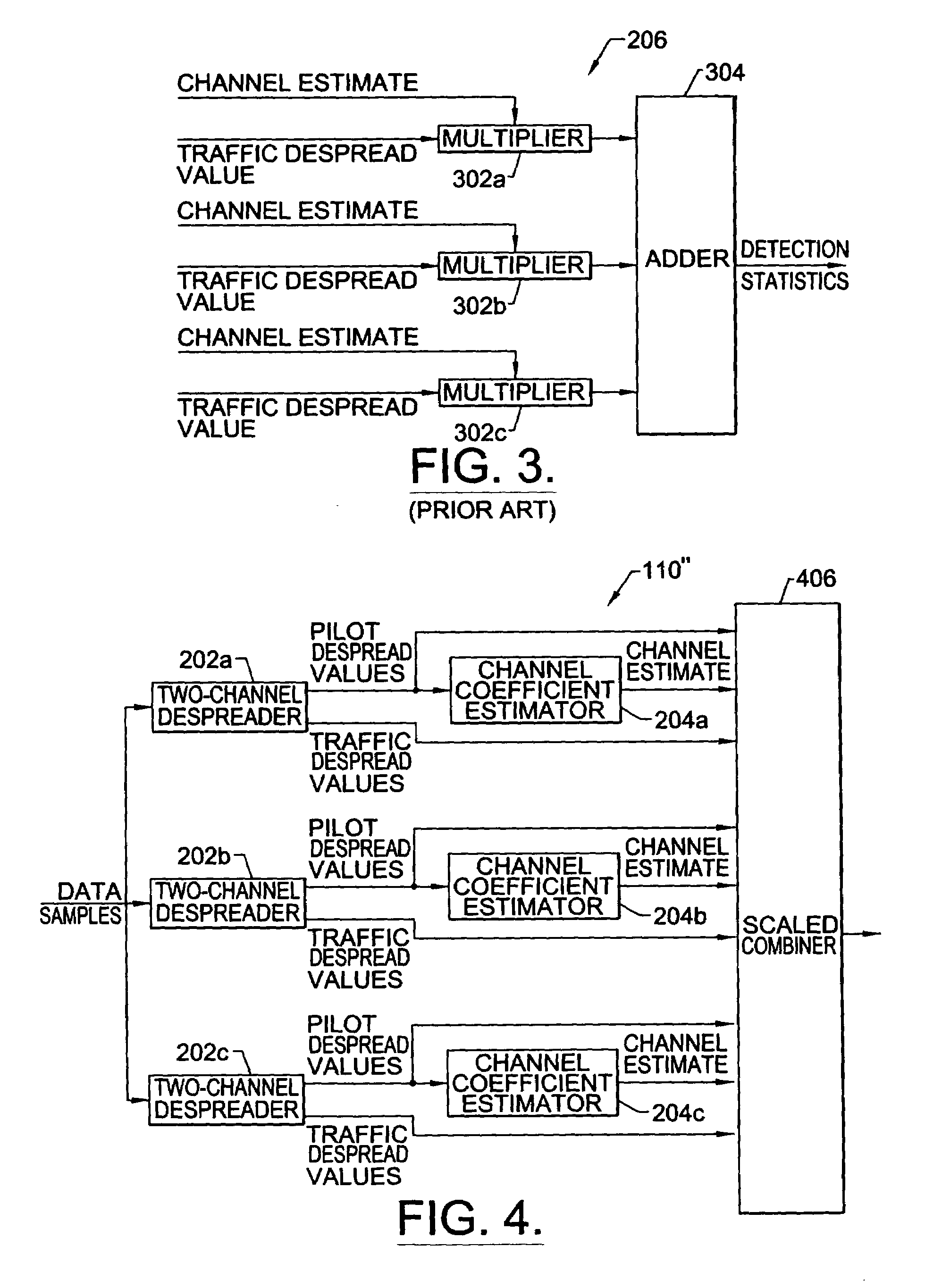
Digital receivers and receiving methods that scale for relative strengths of traffic and pilot channels during soft handoff
InactiveUS6931050B1Accurate channel estimationAccurate detectionPower managementSite diversityRake combiningTelecommunications
Digital receivers and receiving methods scale for relative strengths of traffic and pilot channels during soft handoff. In particular, spread spectrum signals are processed from traffic channels and pilot channels by receiving data samples from traffic channels and pilot channels. Detection statistics are obtained from the received data samples that correspond to information symbols while accounting for the relative strengths of the traffic channels and the pilot channels. The detection statistics are preferably obtained by performing Rake combining while accounting for the relative strengths of the traffic channels and the pilot channels.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Method for 2D antenna rake combining in a code division multiplication access system
One aspect of the present invention is a method for combining a direct sequence spread spectrum signal comprising signal components that each may be characterized by a space variable and a time variable comprising the steps of: dispreading the signal components; and determining a set of combining coefficients from the signal components using a Minimum Mean Square Error combining method that considers the space and time variables of the signal components in parallel. The Minimum Mean Square Error combining methods may utilize iterative methods such as the Least Mean Squares method or the Recursive Least Squares method.
Owner:SASKEN COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES
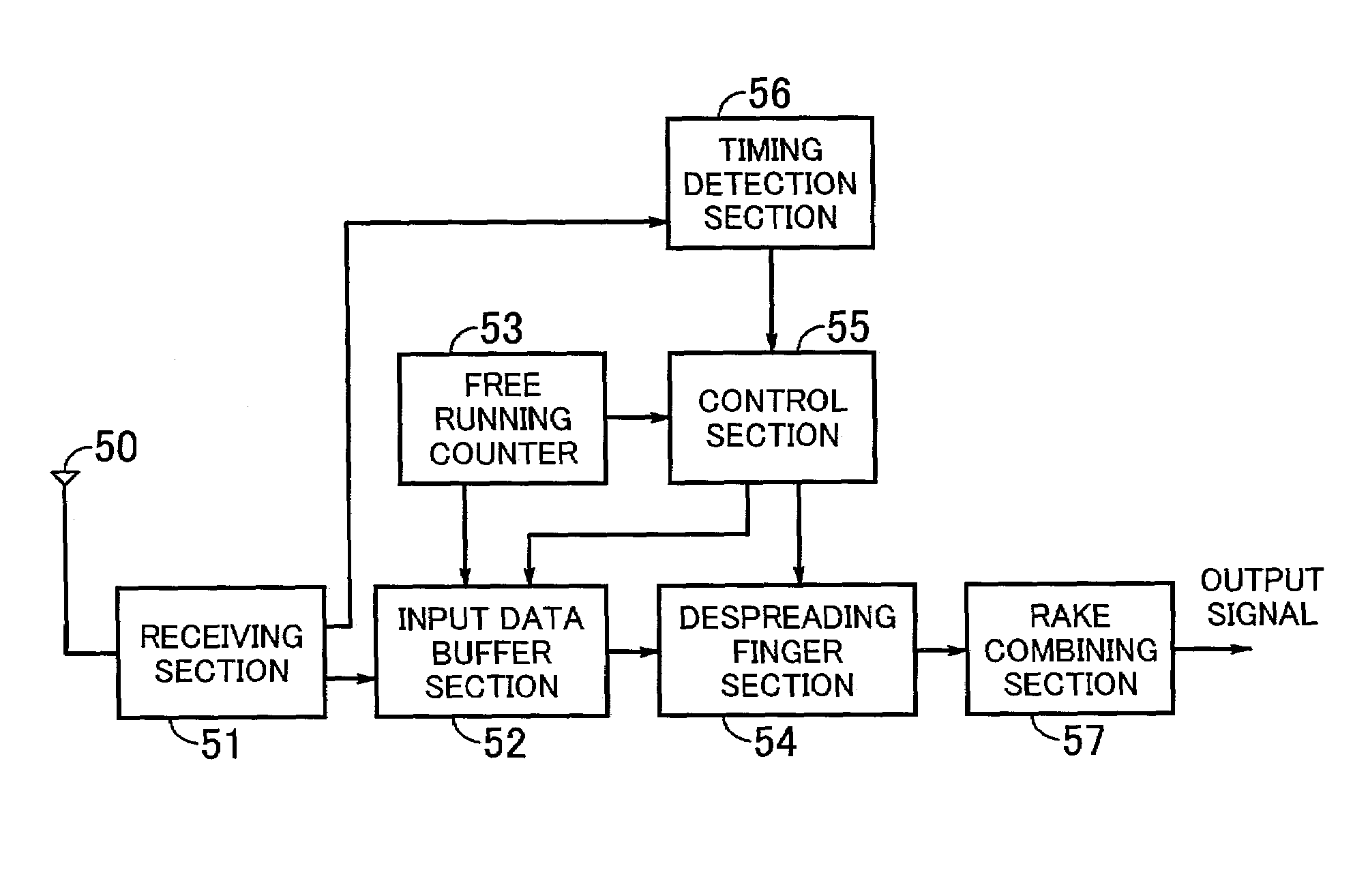
Mobile communication system using receiving apparatus and power supply control method
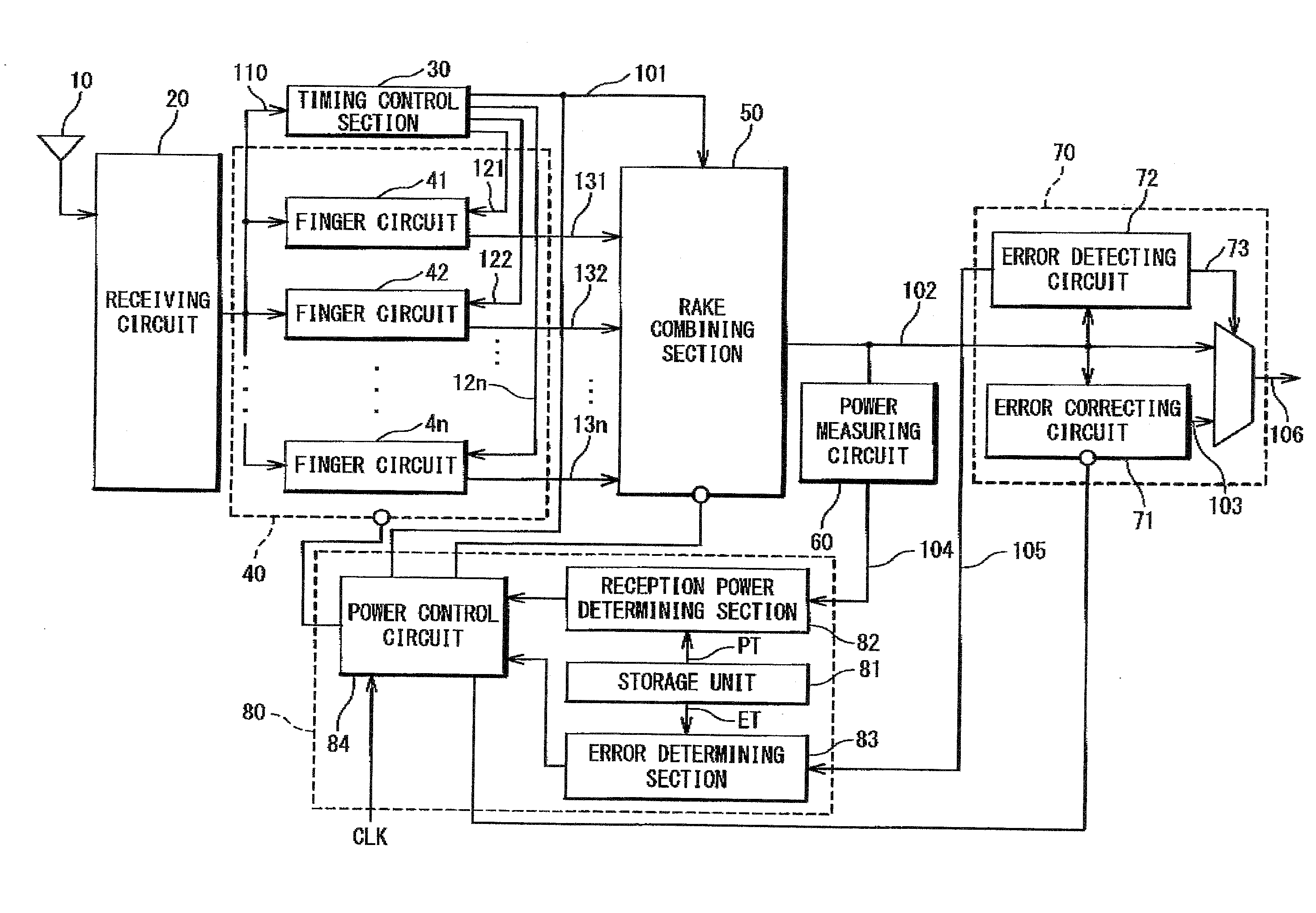
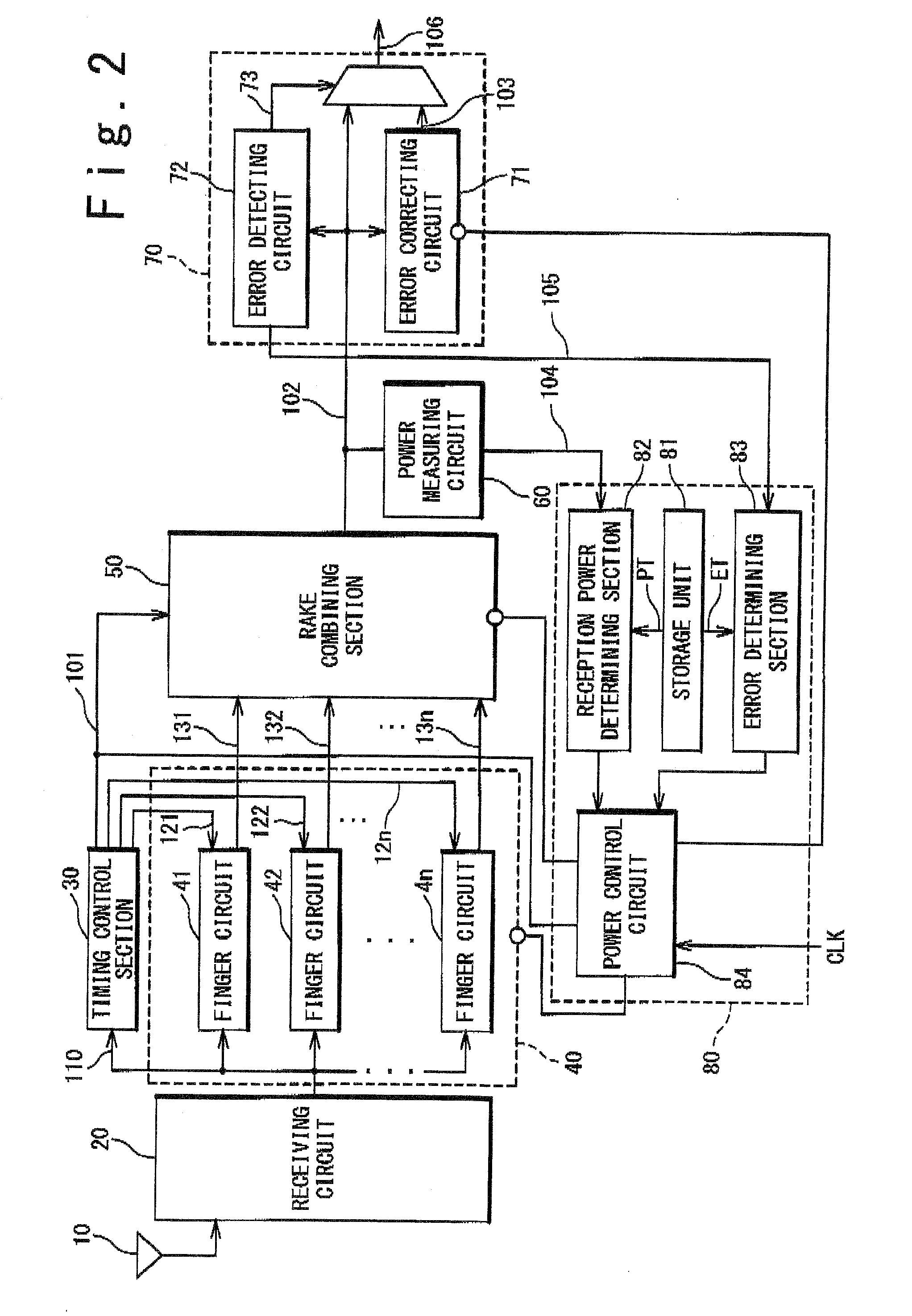
InactiveUS20080049816A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementRake combiningMobile communication systems
A receiving apparatus includes an error detecting circuit configured to detect an error of a reception signal; an error correcting circuit configured to correct the detected error of the reception signal; a power measuring circuit configured to measure a power value of the reception signal; and a power supply control section configured to control a power supply to the error correcting circuit based on the power value. The receiving apparatus further includes a receiving circuit configured to receive a radio signal; a rake finger section configured to execute a despreading process on the signal received by the receiving circuit, and a rake combining section configured to carry out a rake combination of the plurality of signals subjected to the despreading process to generate the reception signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Base station search method and mobile terminal apparatus
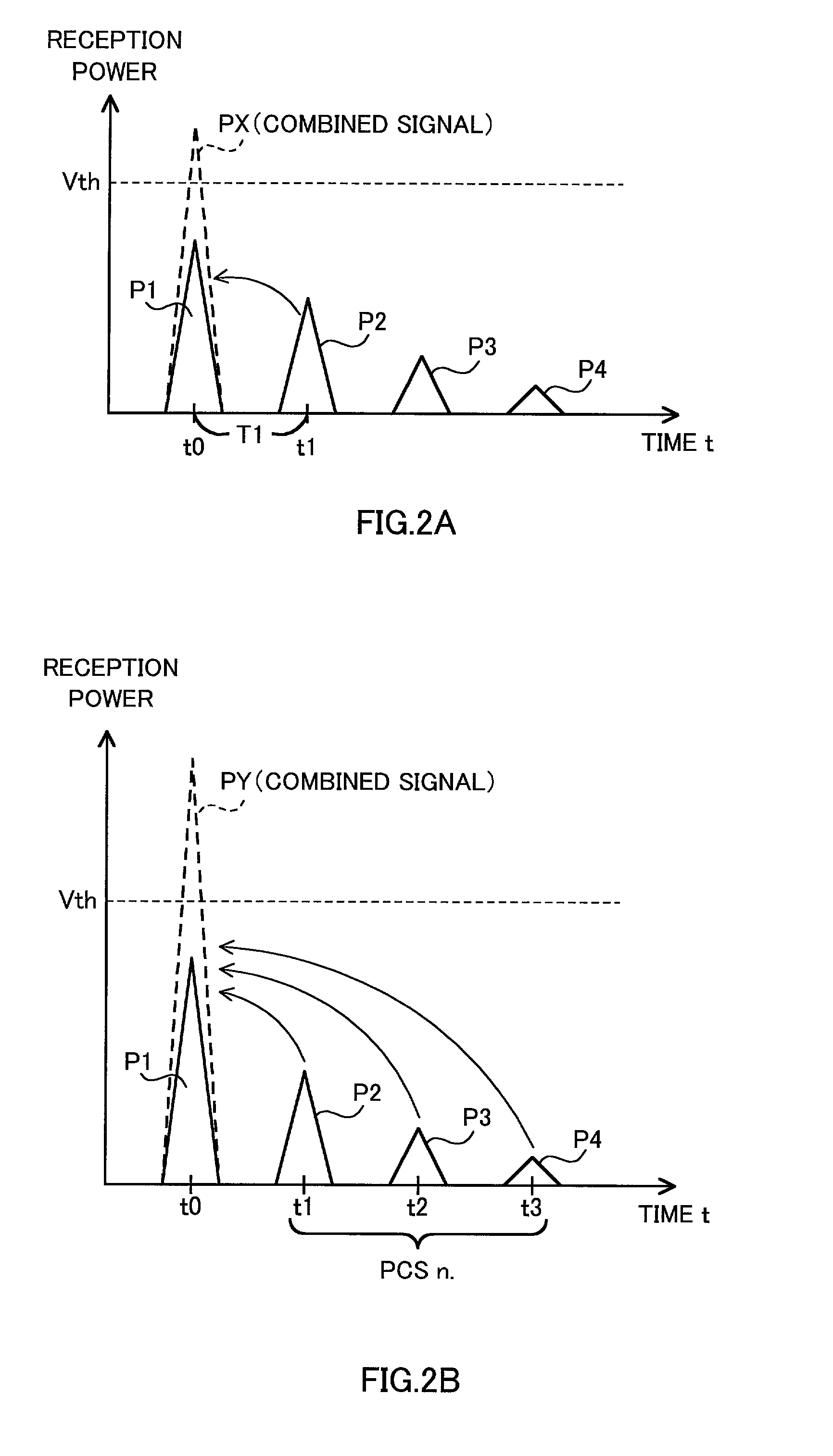
The present invention uses site diversity reception and RAKE combining reception for the method for a CDMA communication mobile terminal to carry out a cell search to search for a base station with which to communicate. Even if the reception power levels of synchronization acquisition signals sent from a plurality of base stations are lower than a predetermined threshold, in the case where the power level of a signal combining those signals is equal to or greater than the predetermined threshold, the mobile terminal continues processing of requesting position registration to any one of the plurality of base stations and thereby improves communicability.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Mobile terminal, a base station, and a synchronization control method
In a mobile communication system, the tracking of synchronization is conducted in a stable state even in a multipath environment. A delay profile detector calculates a delay profile a(n) using a despread signal for each processing unit n. A delay profile averaging unit averages a(n) to produce Ave(|a(n)|<2>). A data symbol detector conducts rake combining of the despread signal using a(n) and Ave(|a(n)|<2>). According to a(n) and Ave(|a(n)|<2>, a weighting function unit calculates a representative value representing delay waves. A loop filter generates a control signal in response to the representative value. A clock controller controls a spread code generator according to the control signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
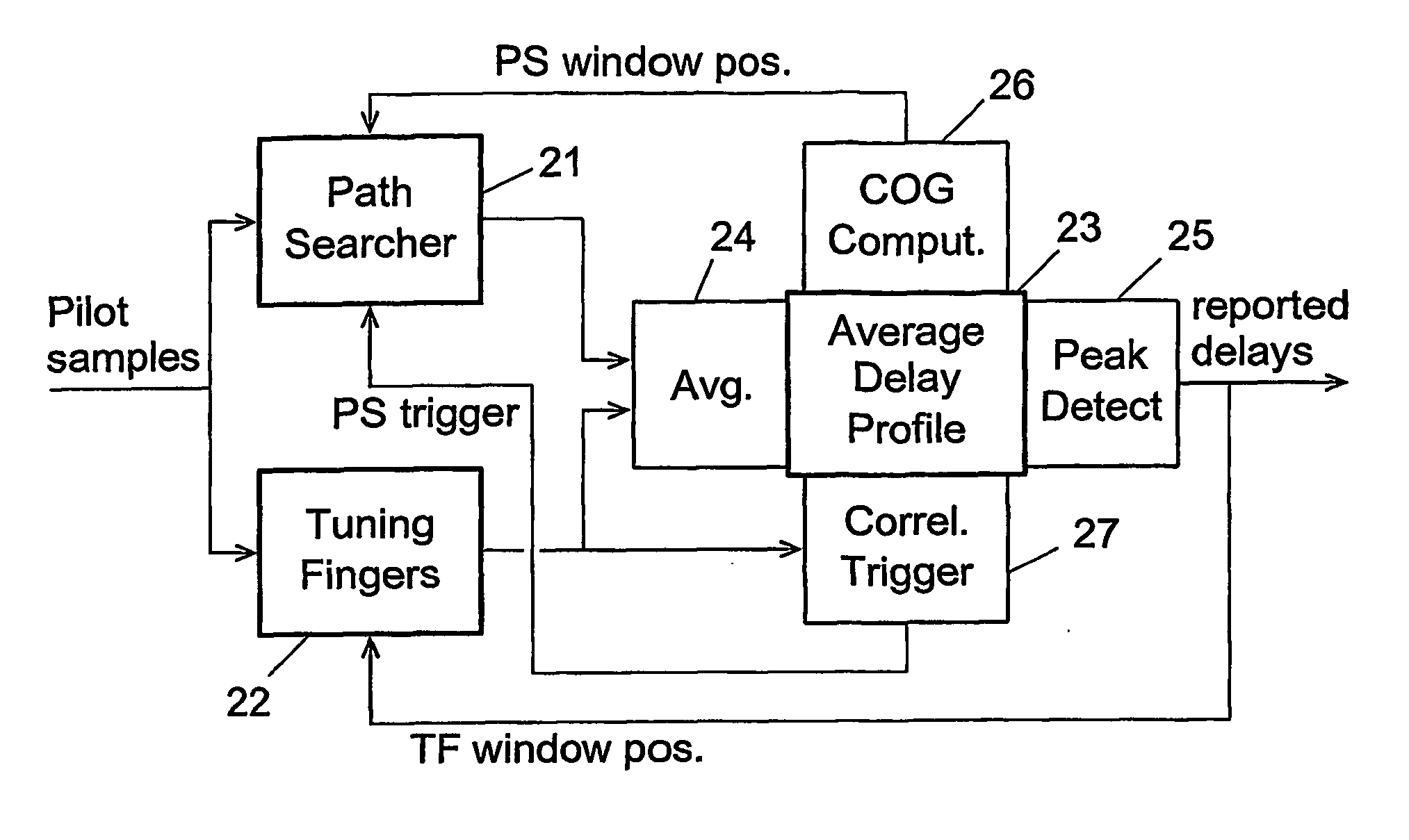
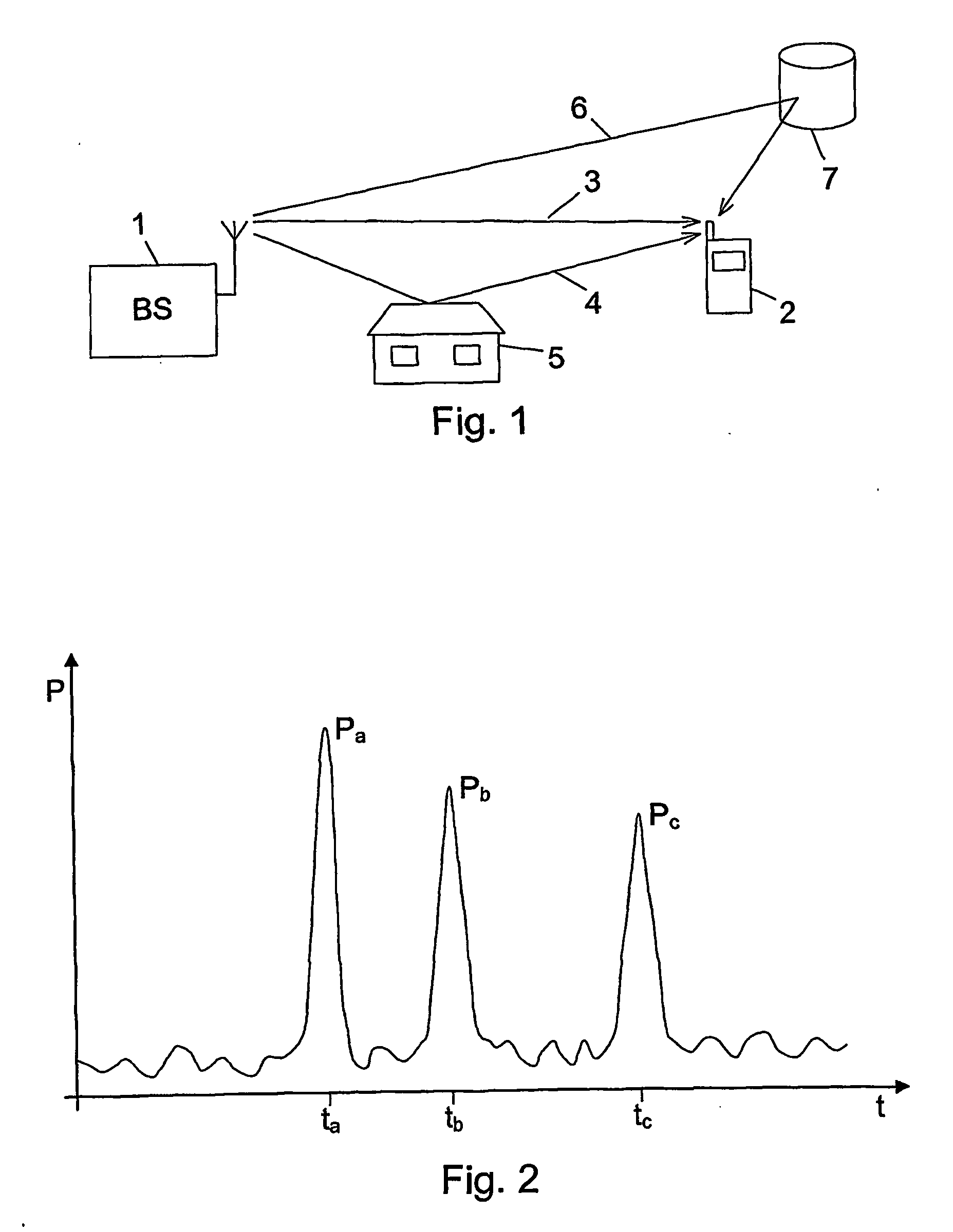
Averaging a delay profile in a limited delay range
ActiveUS20070041432A1Extensive additional storageExtensive computational resourceFrequency-modulated carrier systemsAngle demodulationRake combiningDigital radio
Multipath components of a signal transmitted through a time-varying digital radio channel are received with individual delays (τ) within a range of possible delay values. An instantaneous delay profile indicating an instantaneous magnitude (g(τ)) for each of a number of individual delays (τ) is calculated repetitively, and an averaged delay profile indicating an averaged magnitude for the individual delays is generated from a number of repetitively calculated instantaneous delay profiles. The averaged delay profile is limited to comprise only delay values in a subset (W1, W2, W3) of the range of possible delay values. The delay of each individual multipath component is estimated from the averaged delay profile; and at least some estimated delays are used for RAKE combining. In this way, the benefits of an averaged delay profile are achieved without the need for the additional storage and computational resources normally required by a general averaged delay profile image.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
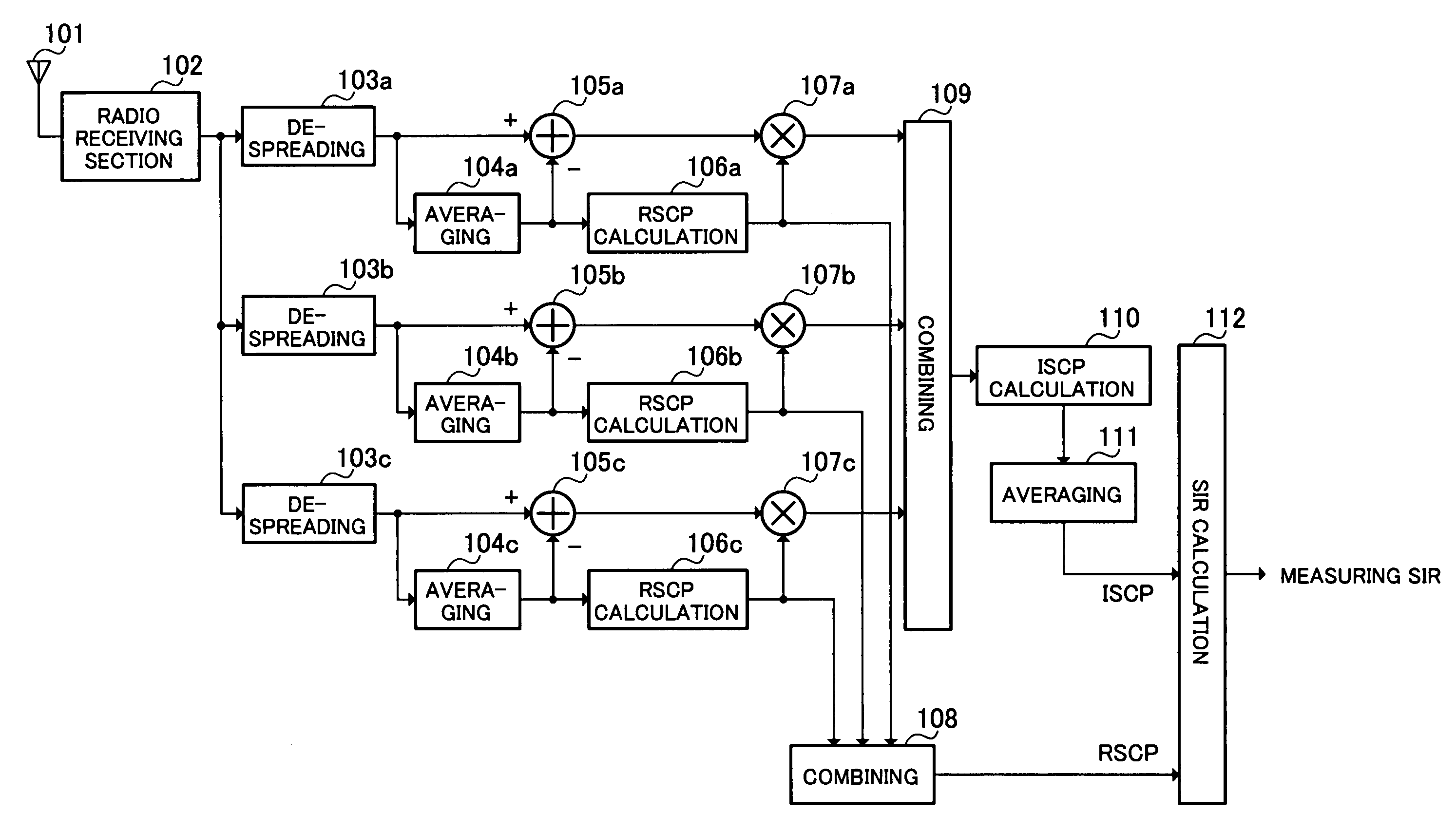
Radio reception device and sir calculation method
InactiveUS20050254563A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionRake combiningRadio reception
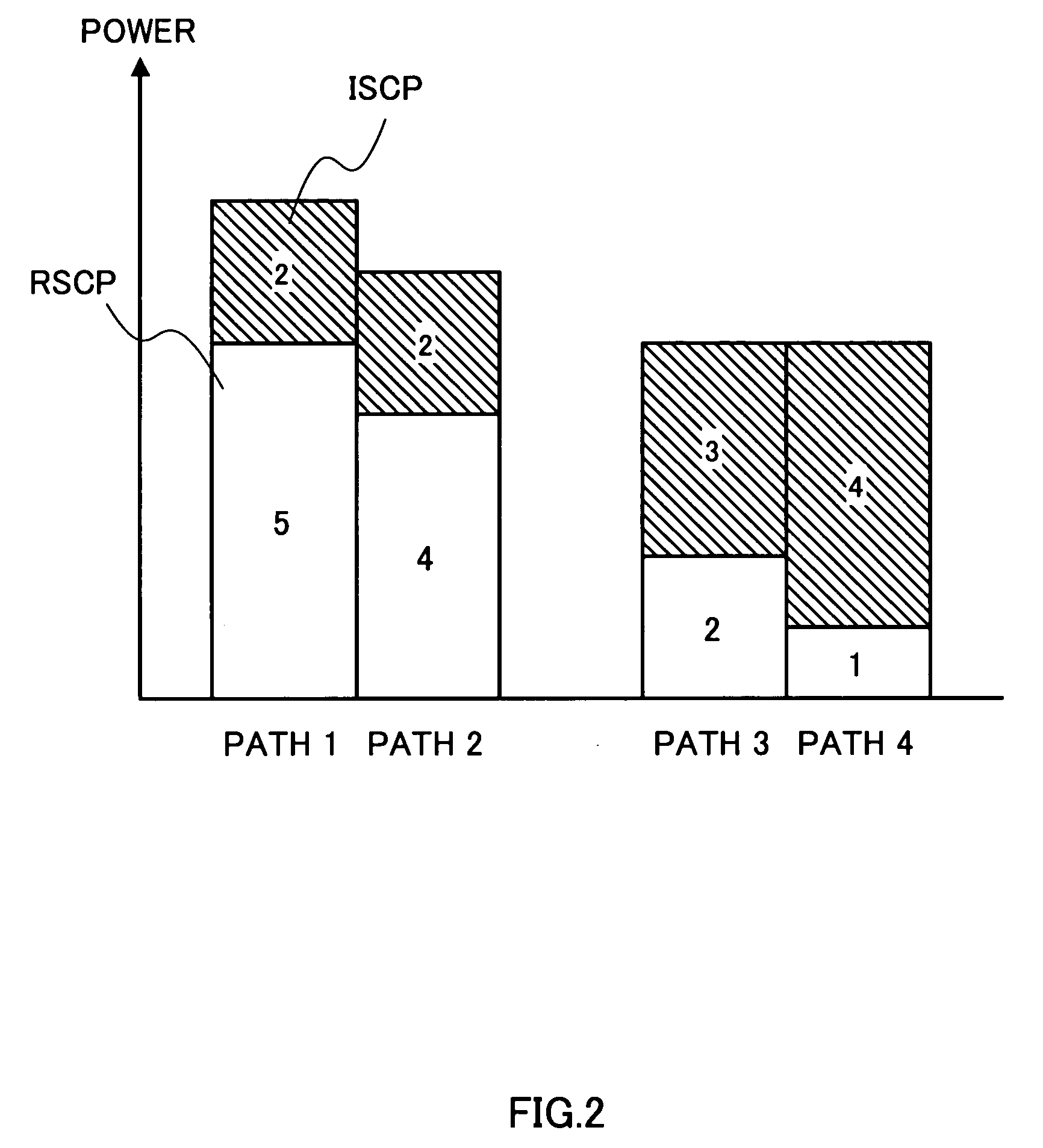
RSCP calculation sections 106a-160c calculate RSCP per path, using average signal powers. Multipliers 107a-107c multiply symbol power deviations per path and per slot by the RSCP per path, thereby weighting the deviations per path and per slot. A combining section 108 calculates a total RSCP by adding the RSCP values per path. Another combining section 109 calculates symbol power deviations per slot by adding the weighted symbol power deviations per path. An ISCP calculation section 110 calculates symbol power variance values per slot, using the symbol power deviations per slot. An averaging section 111 calculates a total ISCP by averaging the symbol power variance values across multiple slots. An SIR calculation section 112 calculates SIR from the total RSCP and the total ISCP. SIR measurement before RAKE combining can be performed with as high accuracy as SIR measurement after RAKE combining.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
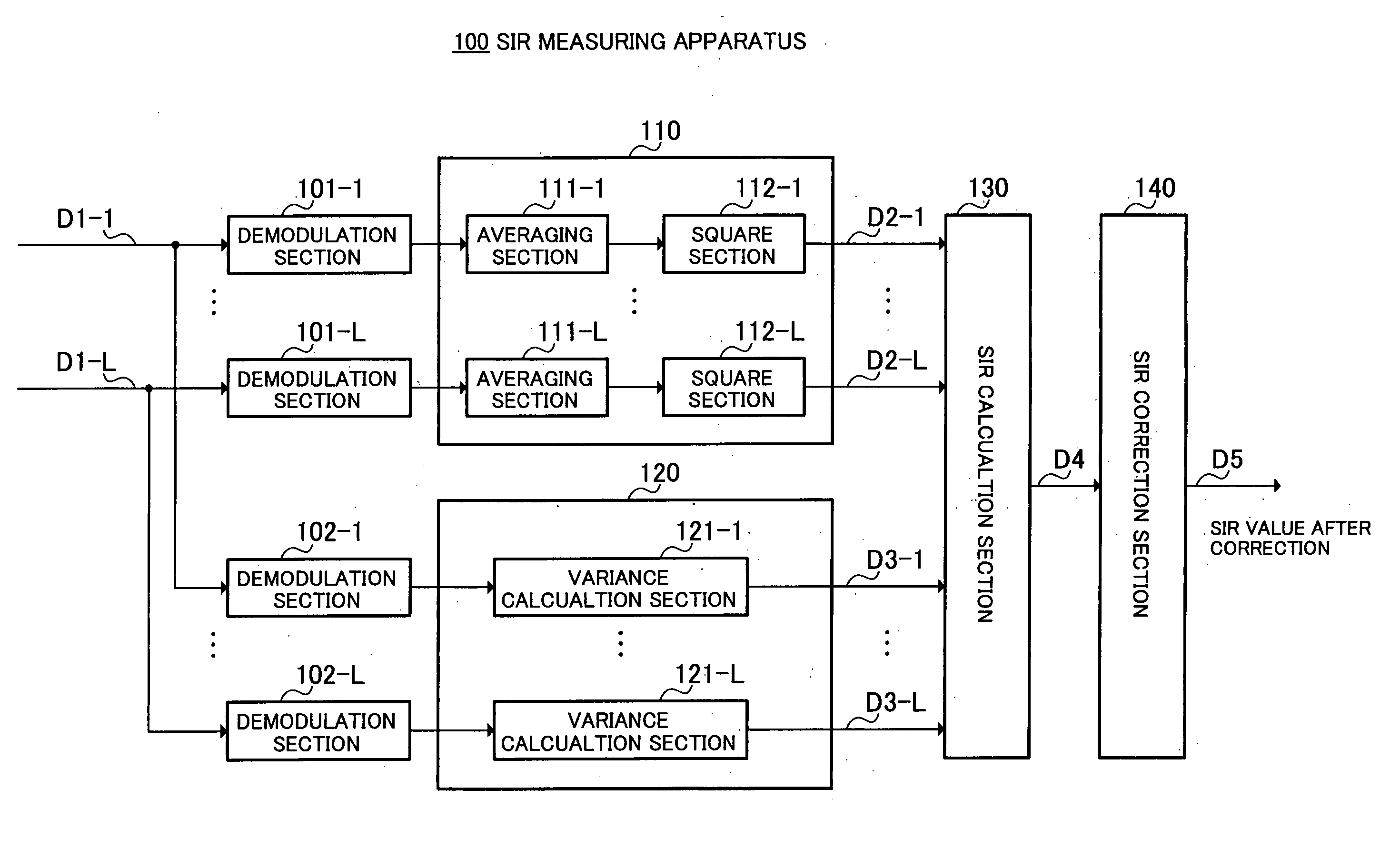
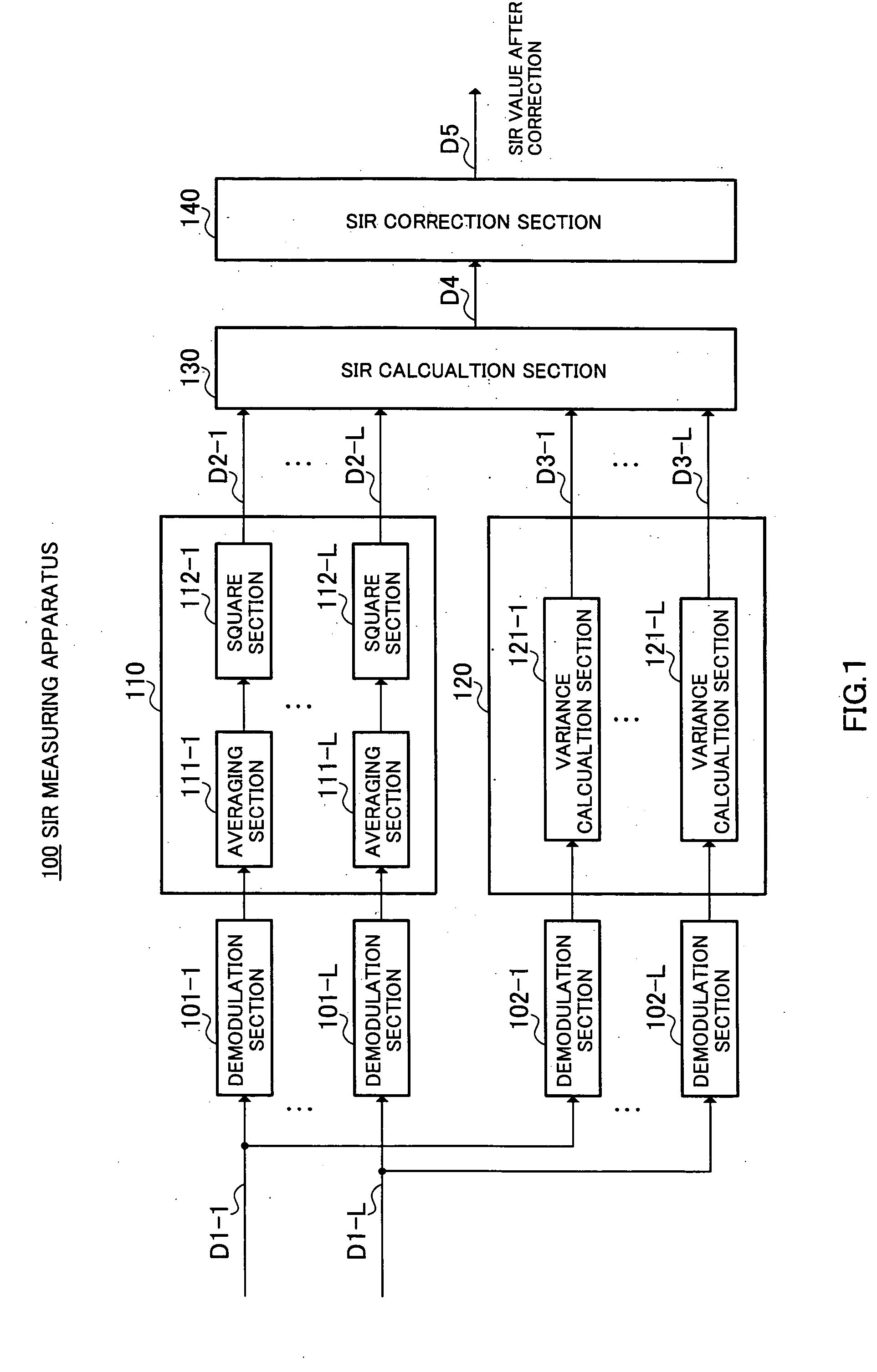
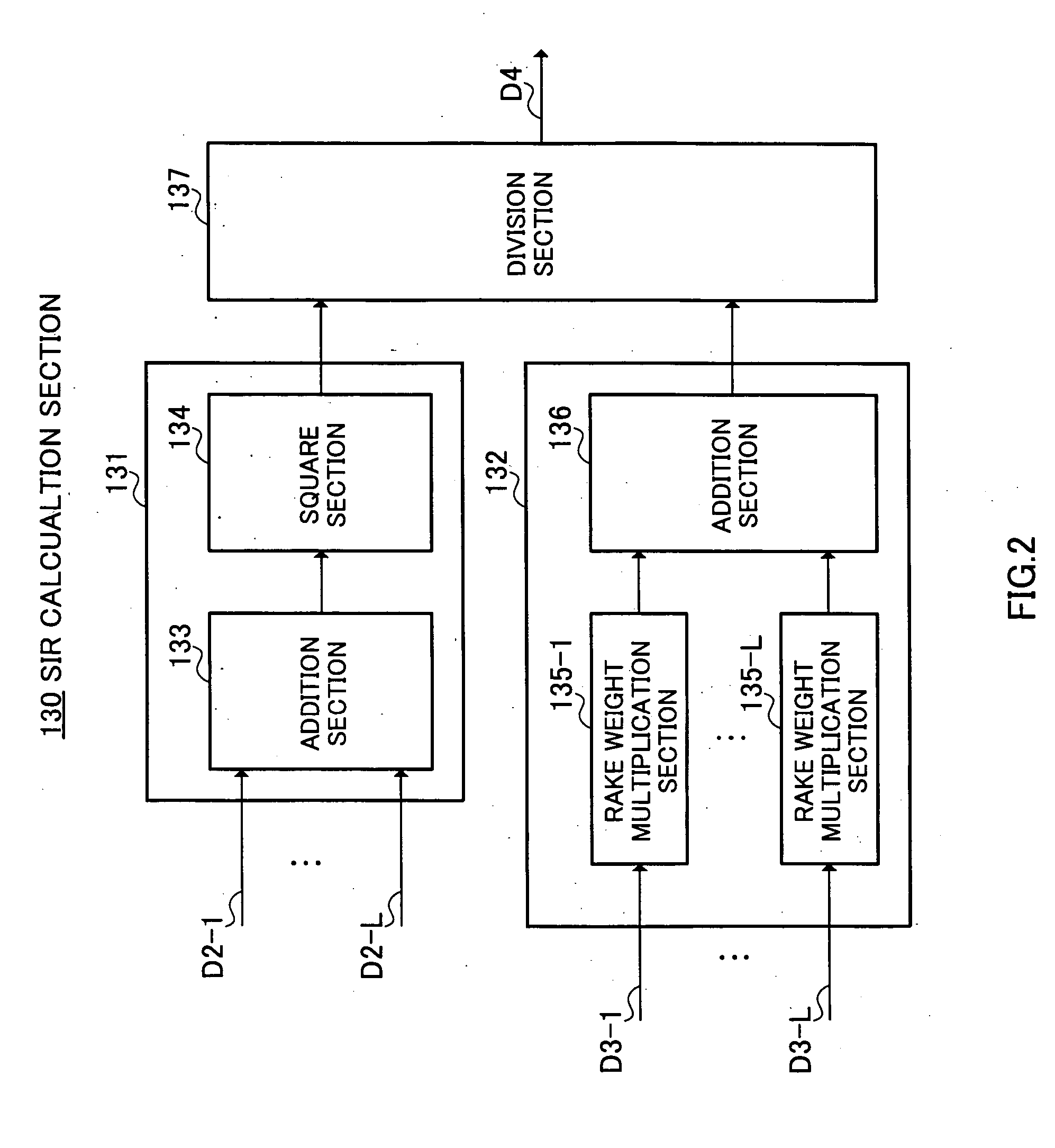
Sir measurement device and sir measurement method
An SIR calculation section 130 calculates an SIR value D4 after RAKE combining from a desired signal power value for each finger calculated by an RSCP calculation section 110 and an interference signal power value for each finger calculated by an ISCP calculation section 120. An SIR correction section 140 corrects the SIR value D4 using the number of discrete signals used to calculate RSCP, the number of discrete signals used to calculate ISCP and the number of fingers L used for RAKE combining. As a result, even when the number of discrete signals used to calculate RSCP is different from the number of discrete signals used to calculate ISCP, it is possible to realize an SIR measuring apparatus 100 capable of resolving a static error with respect to a theoretical value and realizing measurements at a high degree of accuracy and freedom.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for parameter estimation in a generalized rake receiver
ActiveUS7539240B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationRake combiningCurrent channel
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Receiver for spread spectrum communication
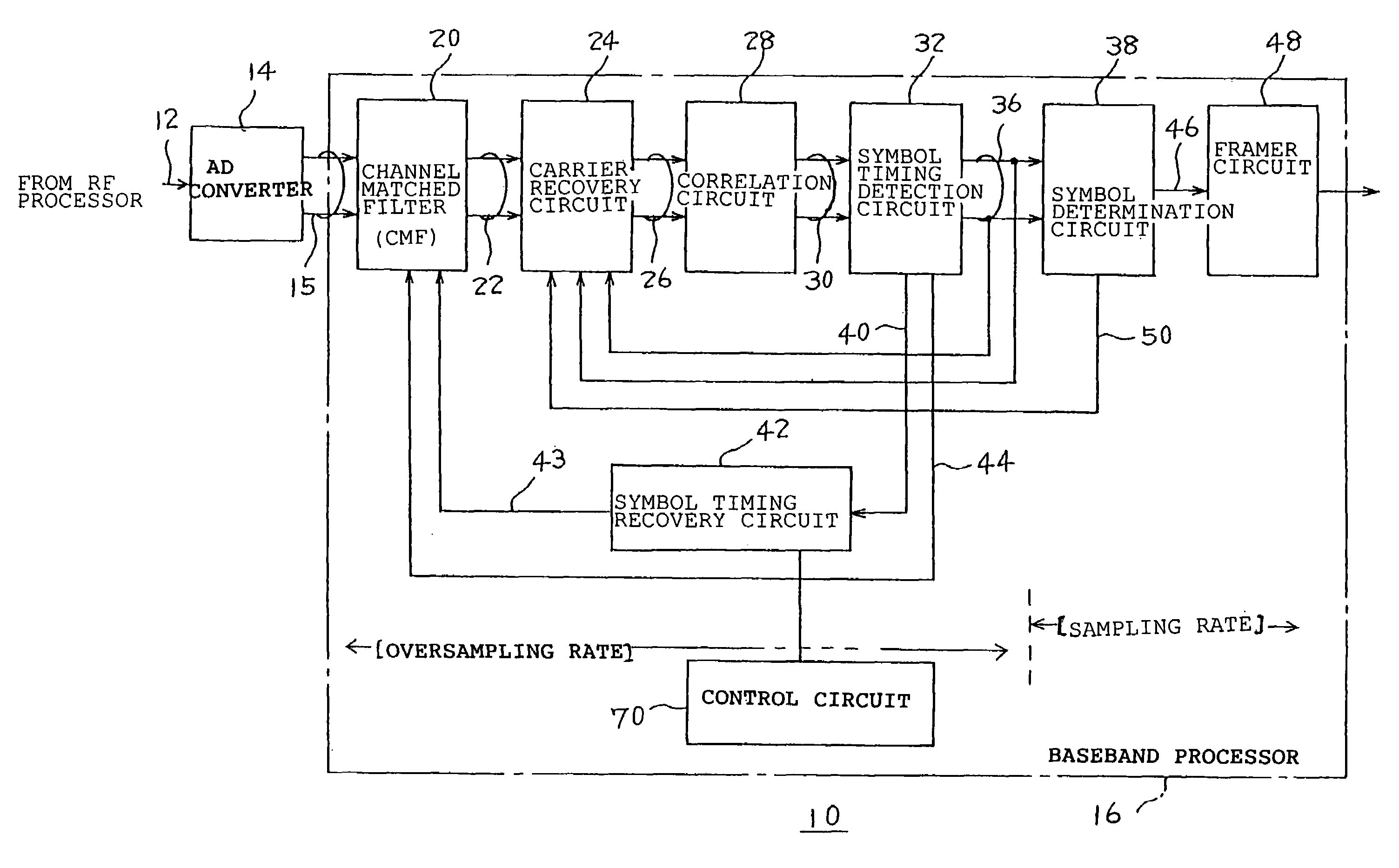
InactiveUS7349464B2Improve scaleOvercome problemsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlRake combiningMatched filter
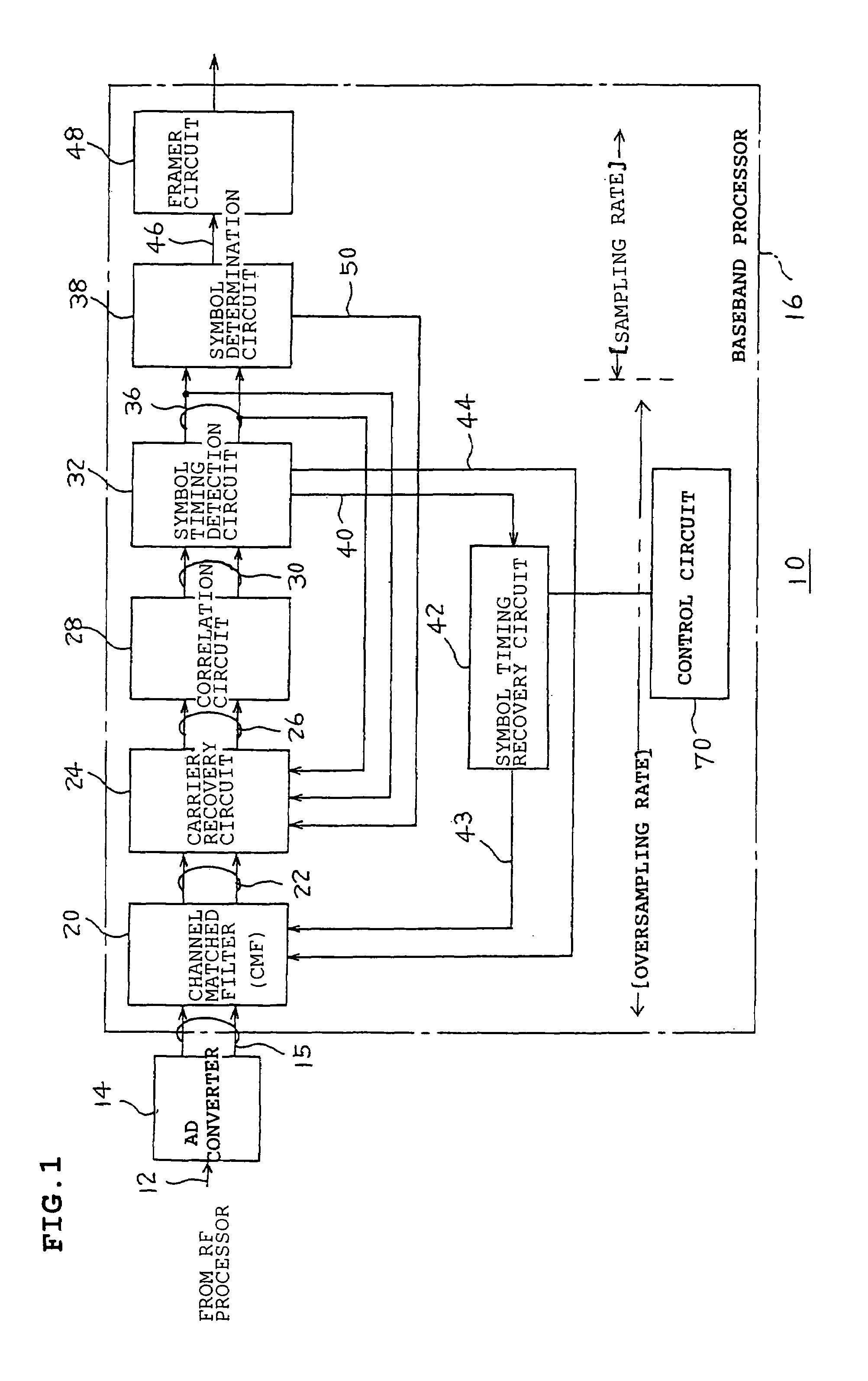
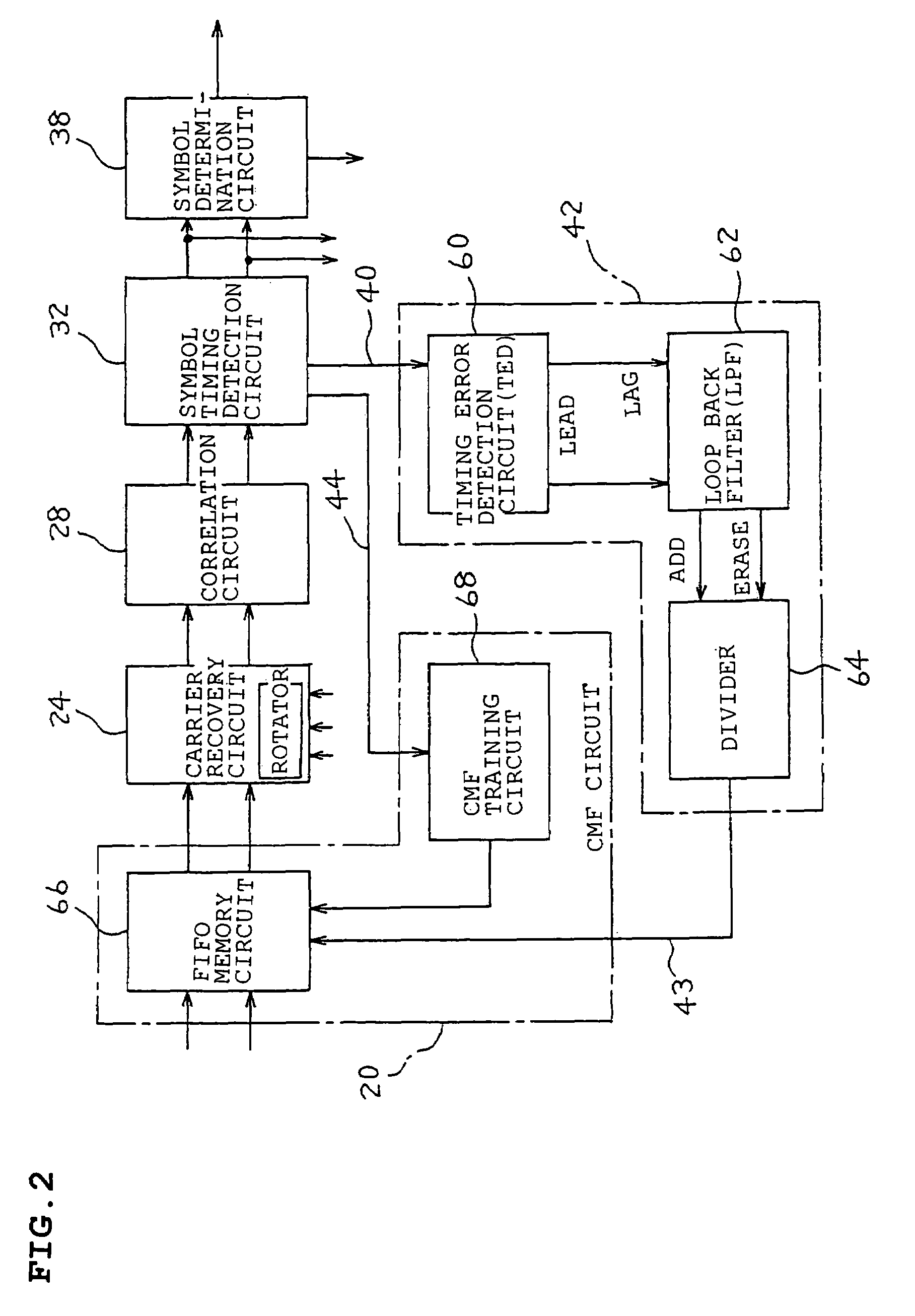
A receiver includes a channel-matched-filter for outputting a Rake-combining result from a digital spread spectrum signal; a carrier recovery circuit which removes an offset of a carrier wave from the combining result; a correlation circuit which detects correlation; a symbol timing detection circuit which extracts a symbol from the correlation; a symbol determination circuit which regenerates data from the symbol; a framer circuit which discriminates a frame configuration; and a symbol timing recovery circuit which generates a timing phase for each of symbol timings. The channel-matched-filter performs multi-phasing compensation and, in accordance with a timing phase from the symbol timing recovery circuit, performs synchronization tracking.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Path search method of spread spectrum communication system and receiver using the method
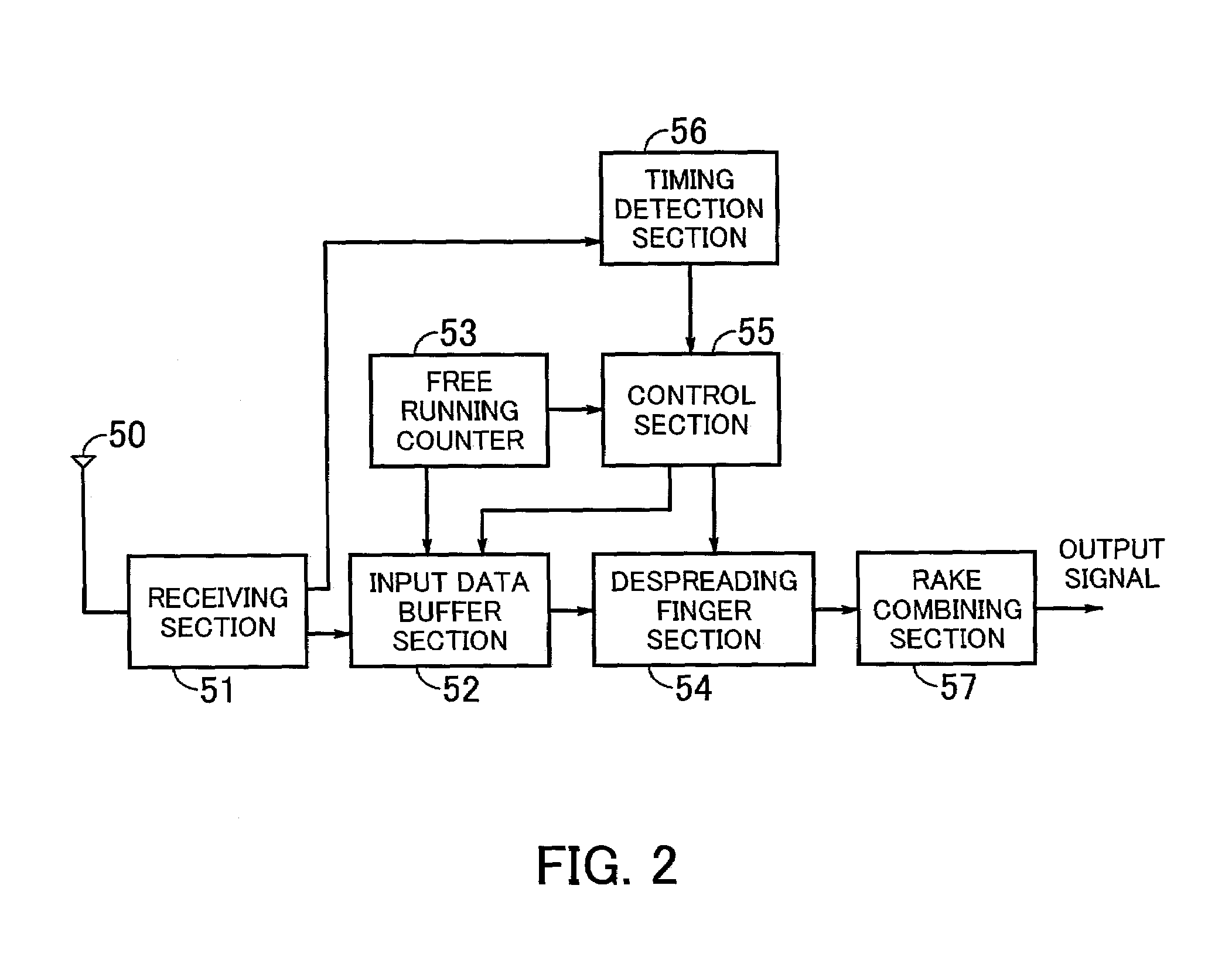
InactiveUS7072383B2Reduce power consumptionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsRake combiningMultipath component
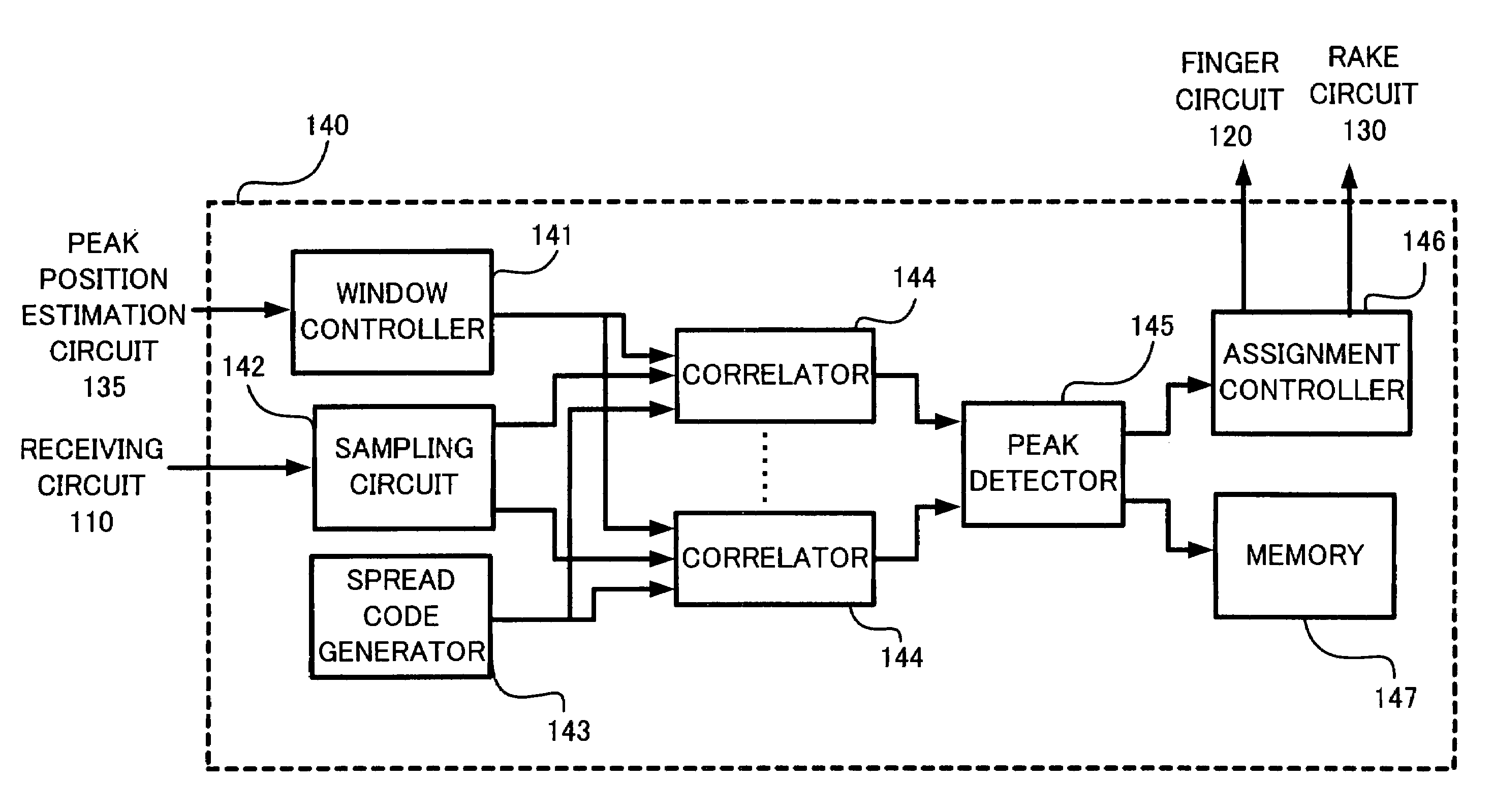
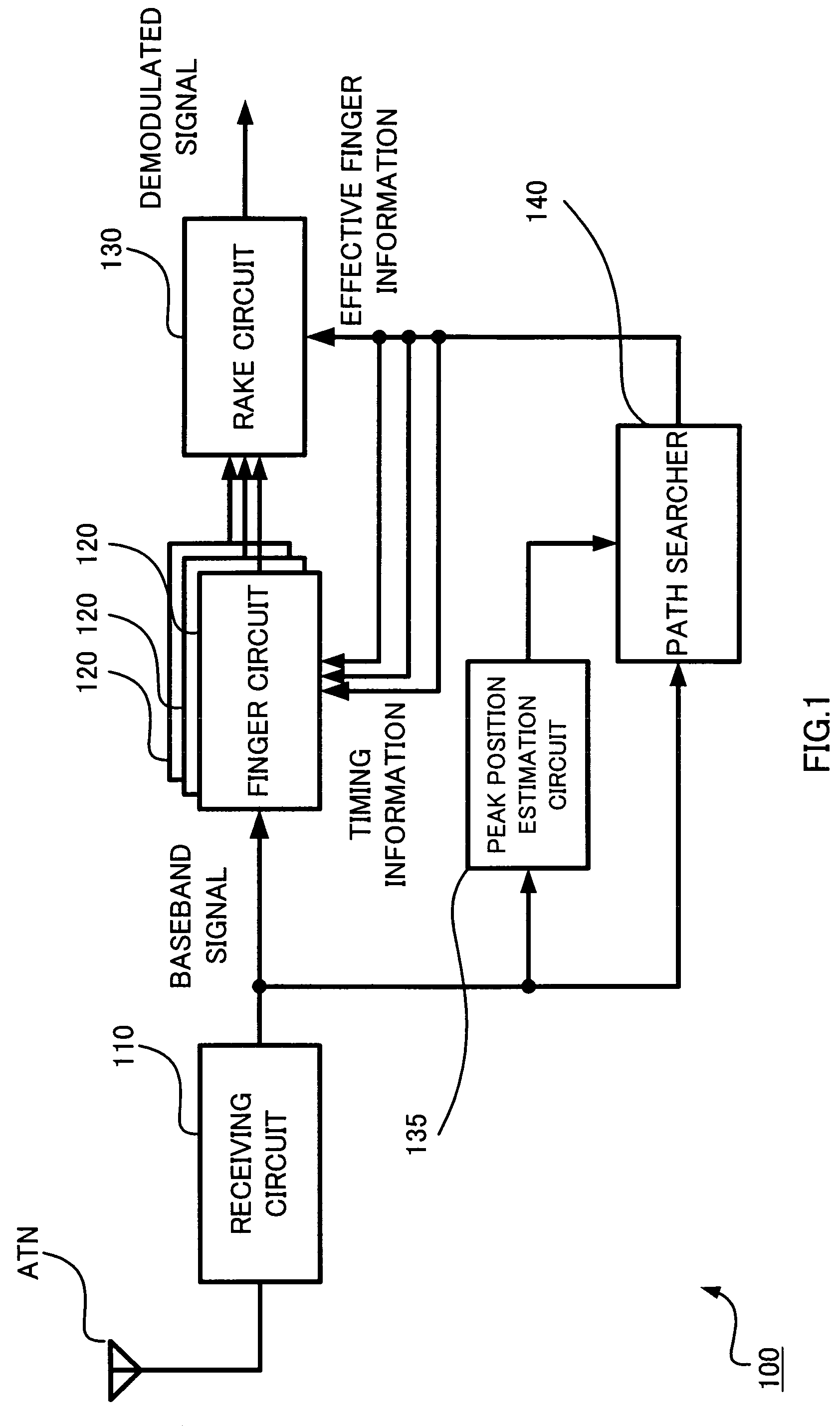
A receiver of a spread spectrum communication system comprises a plurality of despreading circuits, a rake circuit, and a path searcher. The plurality of despreading circuits despreads received signals having multipath components at predetermined timing allocated thereto. The rake circuit performs rake combining of the signals despread by despreading circuits. The path searcher forms a first window showing a part of a search range and calculates delay profile data of said received signals in said first window to search an effective path, forms at least one second window in the search range except said first window and calculates delay profile data of said received signals in said second window, and detects timing at which said received signals are despread based on calculated delay profile data to allocate the detected timing to said despreading circuits.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Frequency bias estimation equipment, method and communication device
InactiveCN101630961AImprove robustnessSuppression of noise effectsMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFrequency spectrumRake combining
The invention discloses frequency bias estimation equipment, a method and a communication device. The frequency bias estimation equipment includes a path selection module, a pre-processing module, a zero filling module, a spectrum analysis module and an interpolation module. The path selection module is used for executing channel estimation to the input signal in order to selection a plurality of paths. The pre-processing module is used for multiplying a combination signal with complex conjugate of the input signal, wherein the combination signal is obtained by rake combining the channel estimation of the selected path with input signal execution class. The zero filling module is used for filling zero on the tail of the pre-processing signal. The spectrum analysis module is used for performing spectrum analysis to the zero filled signal in order to search a plurality of peaks. The interpolation module is used for estimating frequency bias between the sending part and the receiving part by interpolation with the plurality of peaks.
Owner:MARVELL TECH SHANGHAI
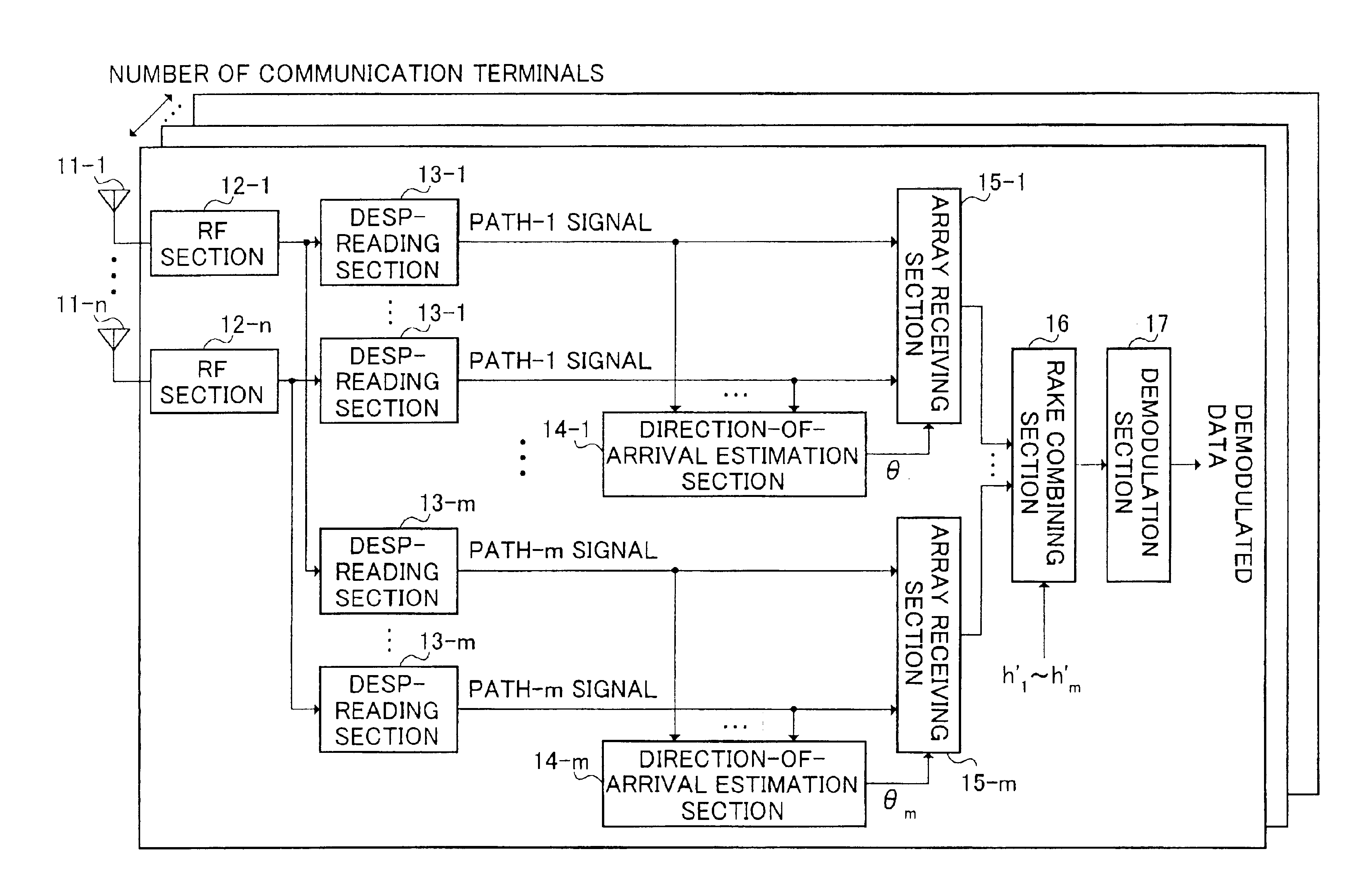
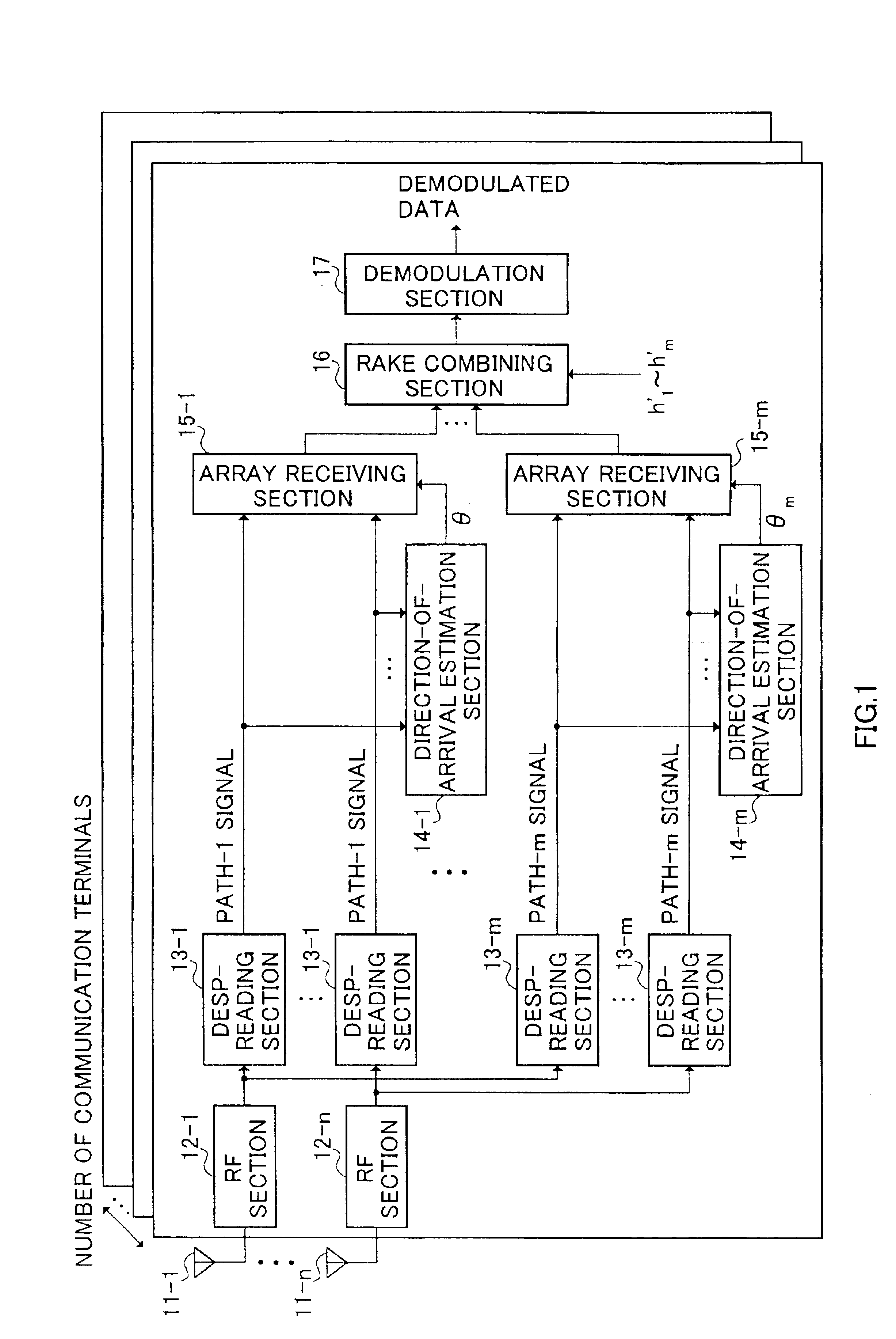
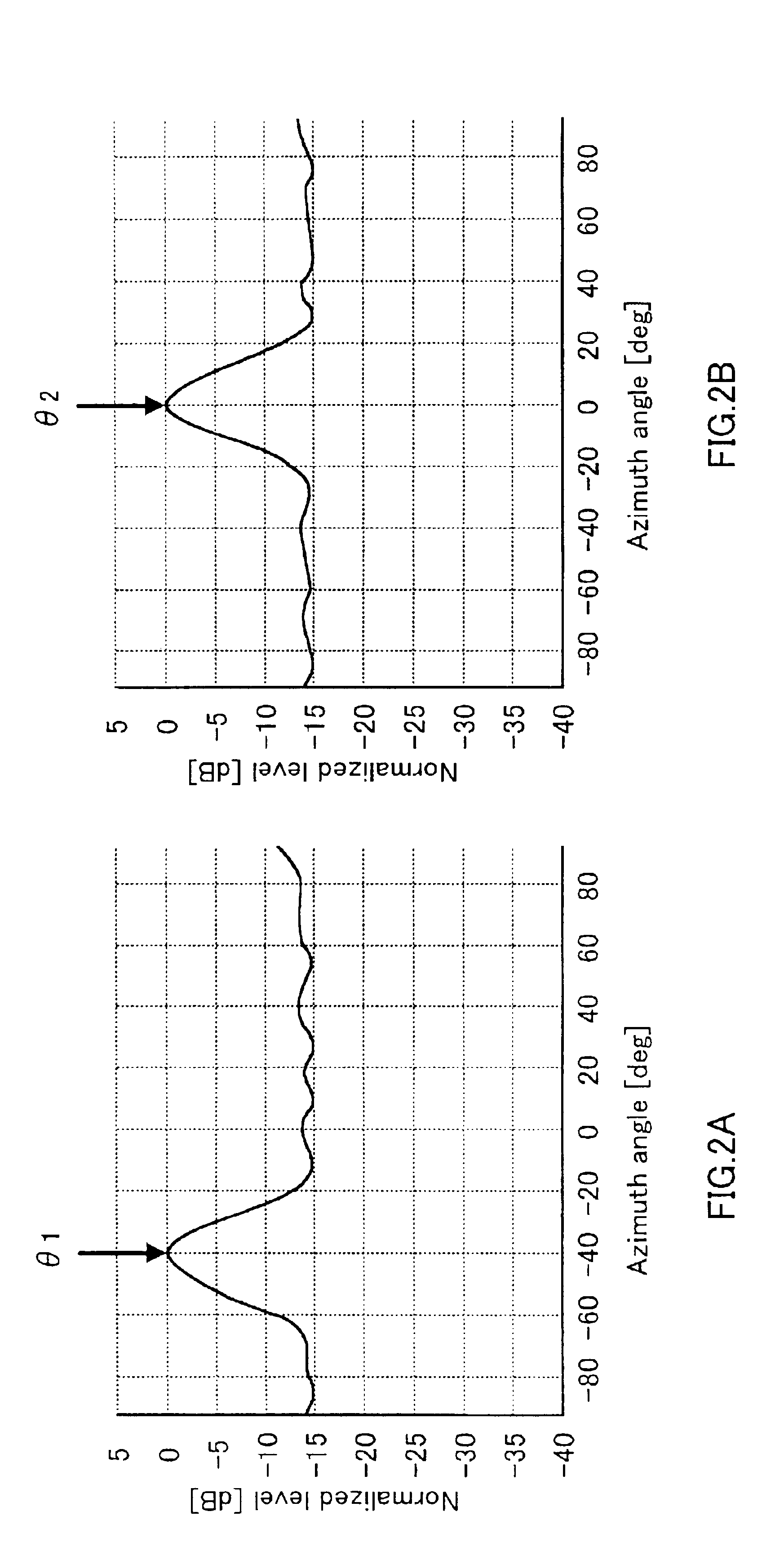
Base station apparatus and direction-of-arrival estimating method
InactiveUS7095984B2Reduce computationReduce device sizeSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityFrequency spectrumRake combining
Signals including a plurality of components representing a phase rotation between antenna elements by combining signals, which have arrived through each path of a first to an m-th paths, for every antenna are generated in RAKE combining sections 104-1 to 104-n; one angle spectrum is obtained in one direction-of-arrival estimation section 105 provided in each communication terminal, using the signals generated in the RAKE combining sections 104-1 to 104-n; and a plurality of directions-of-arrival are estimated en bloc by detecting a plurality of peak positions on the angle spectrum.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Receiving unit and semiconductor device
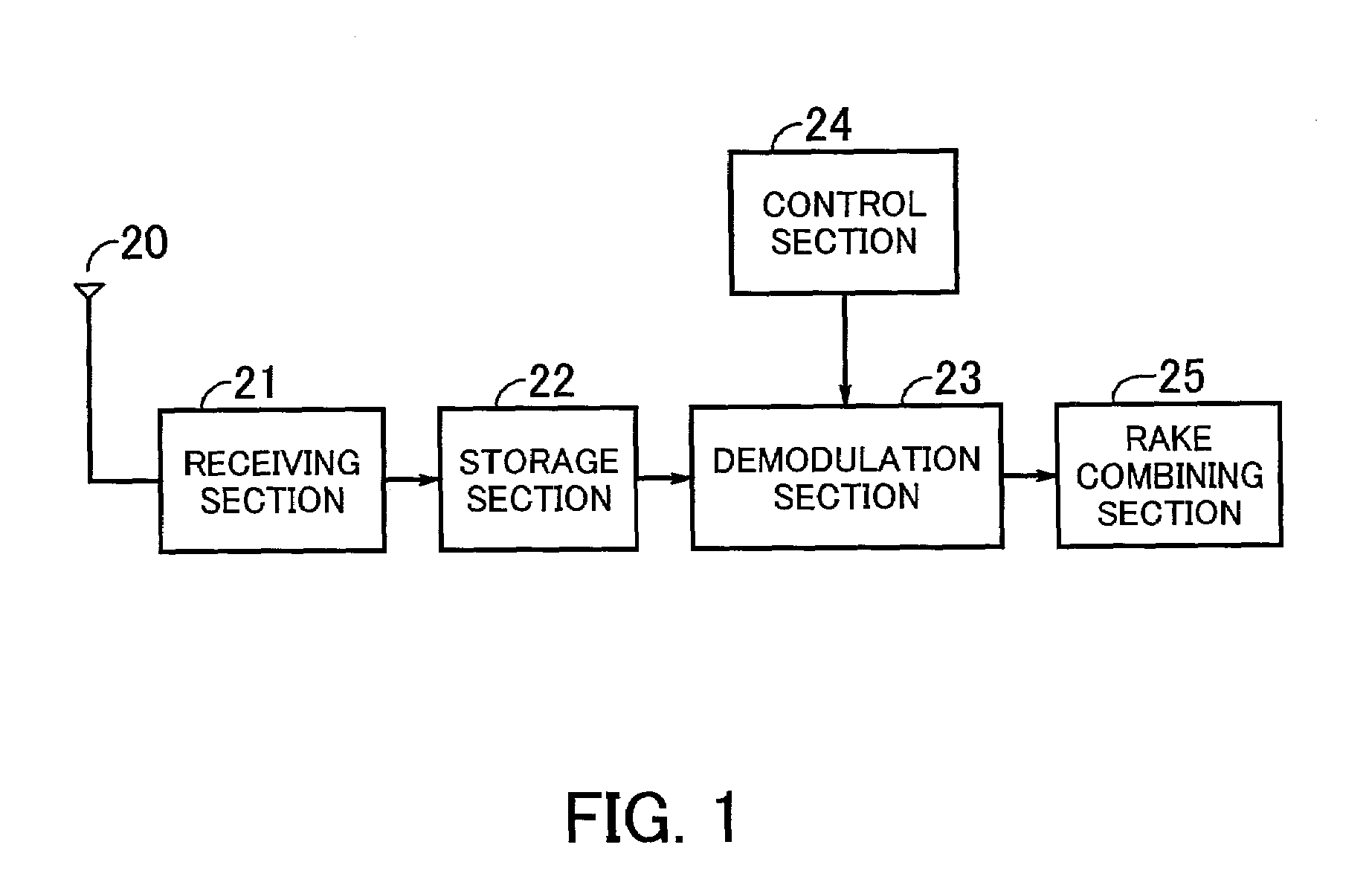
ActiveUS7035318B2Prevent scale of circuitPrevent scalingCode division multiplexRadio transmissionCdma systemsRake combining
A receiving unit for receiving a CDMA system signal having a plurality of multipath components is intended to reduce the size. A receiving section receives a CDMA system signal. A storage section stores the signal received by the receiving section. A demodulation section demodulates each of multipath components included in the received signal stored in the storage section with a despreading code. A control section controls for demodulating a plurality of the multipath components by causing the demodulation section to perform a time division multiplex process. A Rake combining section performs the maximal ratio combining of output from the demodulation section to generate a demodulated signal.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Adaptive array antenna receiving apparatus
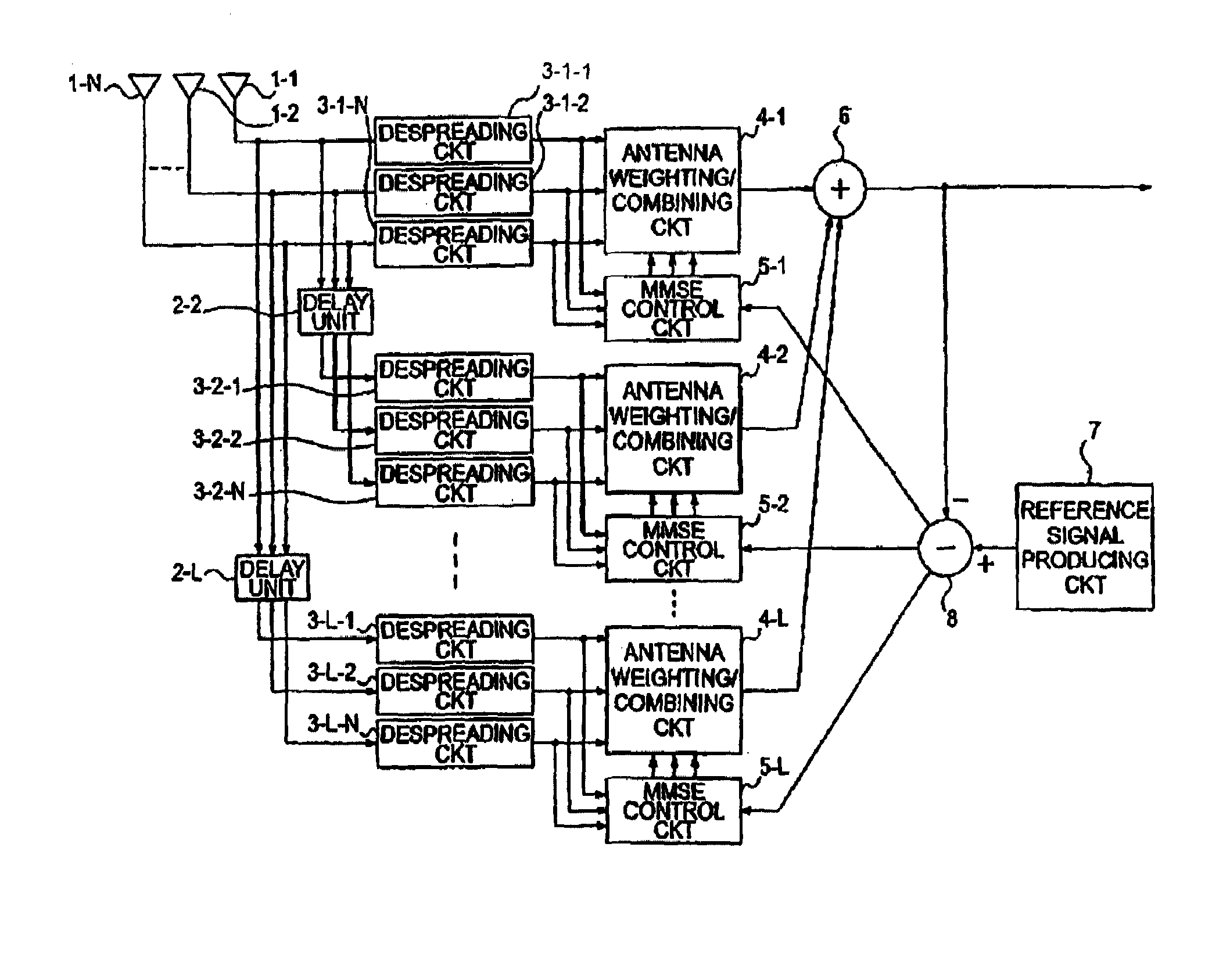
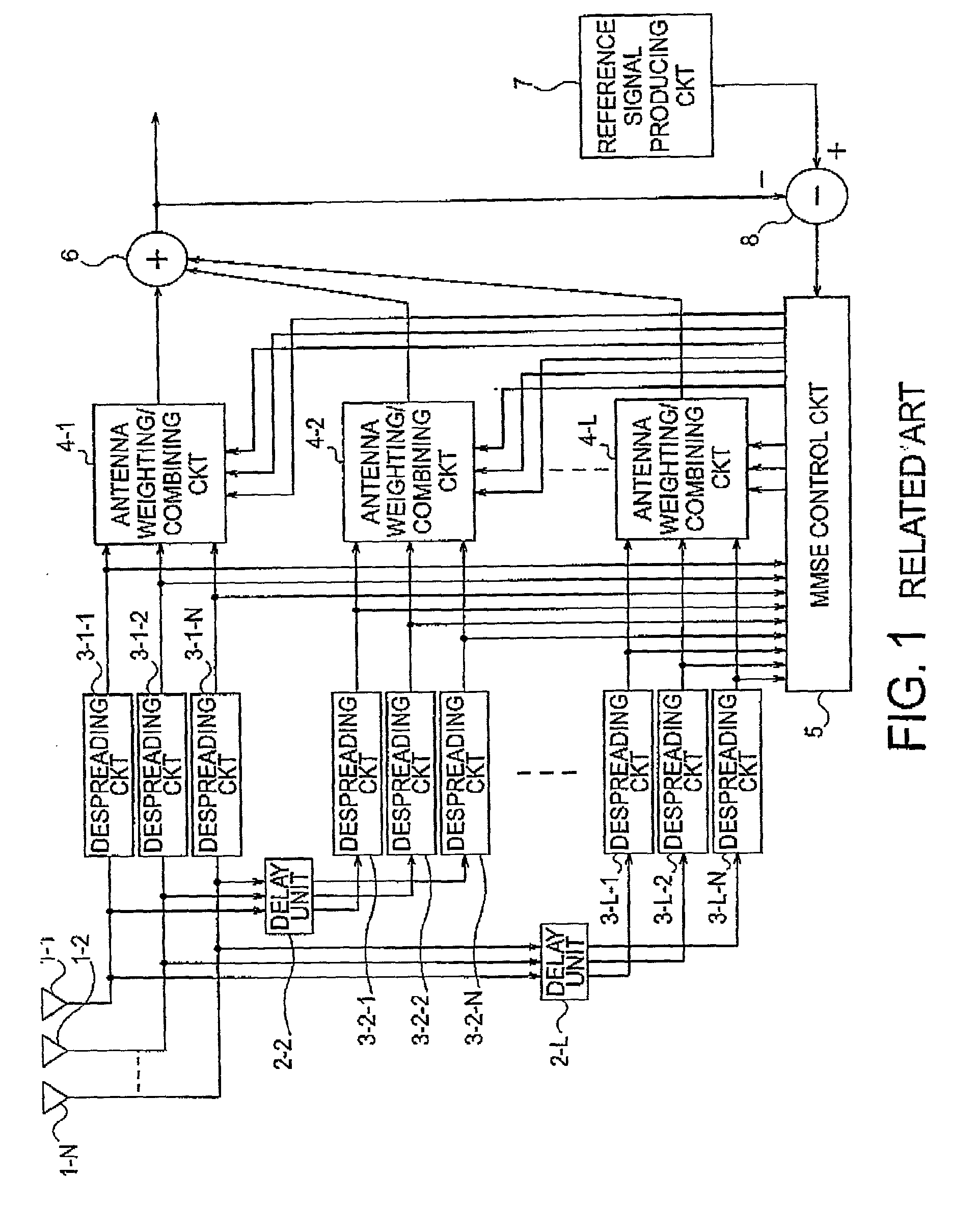
ActiveUS7221698B2Minimize mean squareReduce the amount of calculationSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityMean squareRake combining
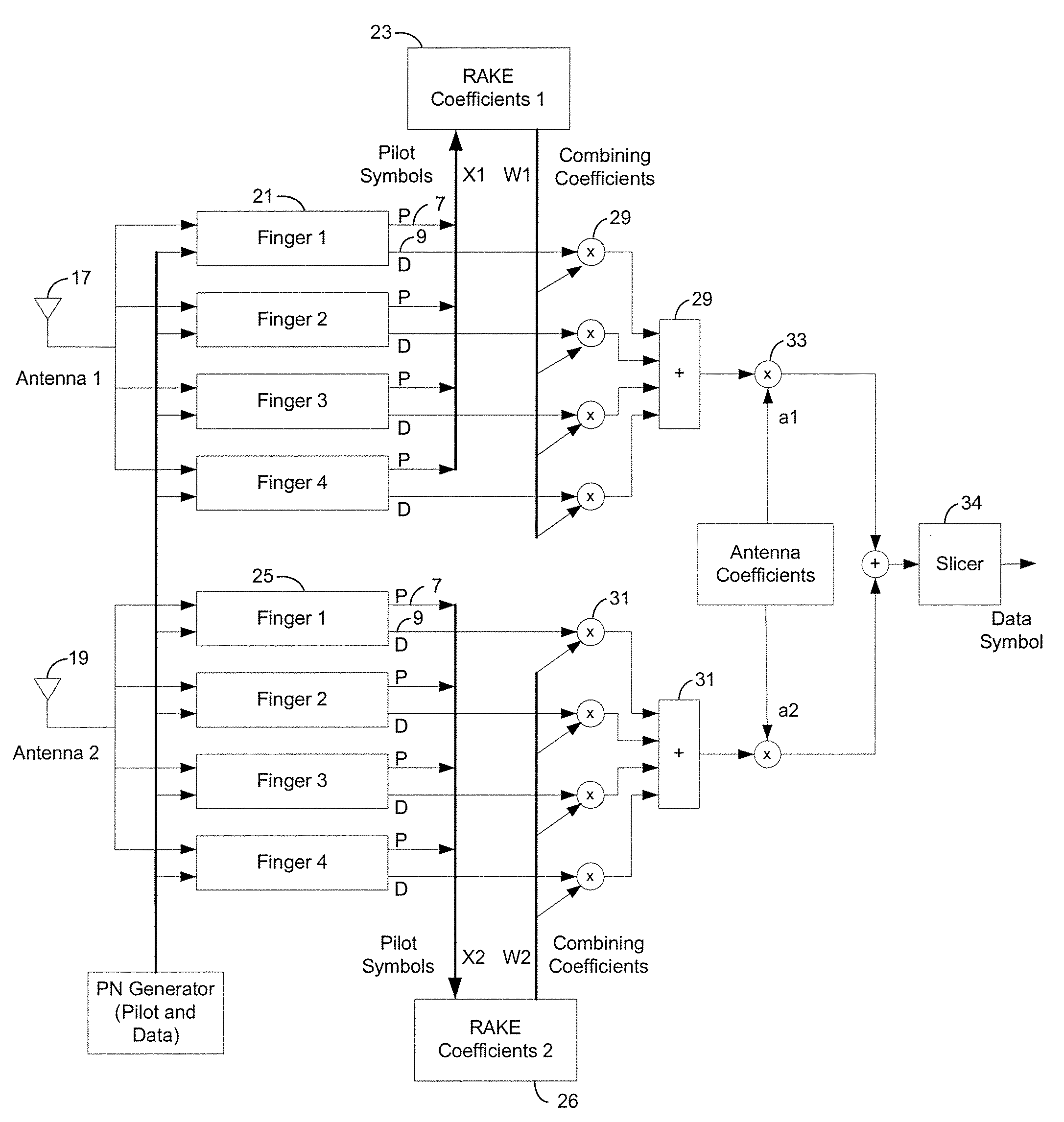
In an adaptive array antenna receiving apparatus which is used in a CDMA communication system and which includes a predetermined number L (L is an integer greater than 1) of fingers, no correlation exists between respective fingers. An adaptive update algorithm of calculating an antenna weighting factor by the use of an N-order correlation matrix independently for the respective fingers is equivalent to an adaptive update algorithm of calculating an (N×L)-order correlation matrix. In the adaptive array antenna receiving apparatus, the antenna weighting factor is controlled by the use of the adaptive update algorithm independently for the respective fingers so that a mean square of a common error signal produced by a subtractor (8) after rake combination by a rake combining circuit (6) is minimized. In this manner, the amount of calculation in the adaptive update algorithm used in all MMSE control circuits is considerably reduced proportionally from (NL)2 to N2L. As a consequence, the processing load upon the DSP can be decreased.
Owner:NEC CORP
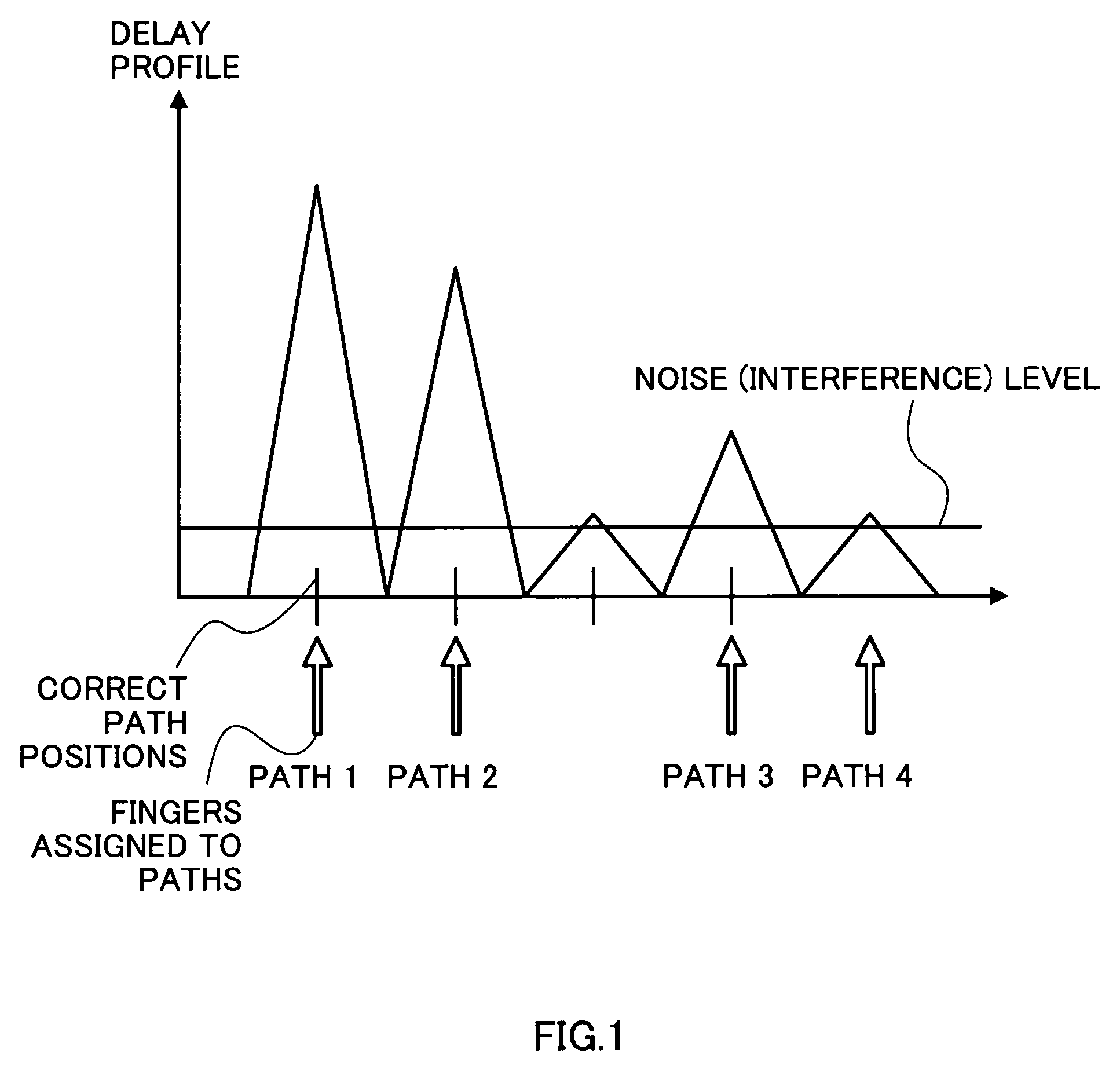
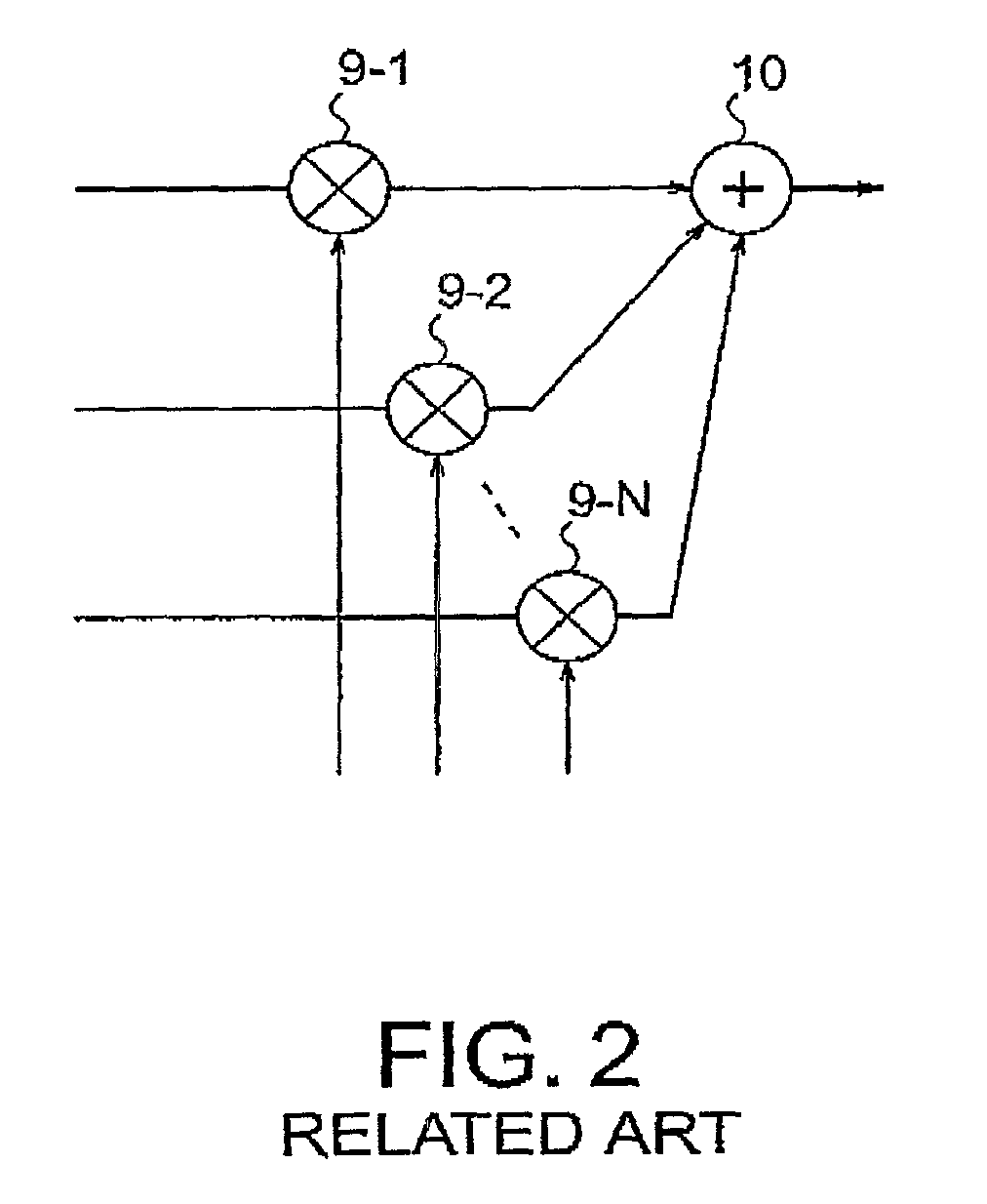
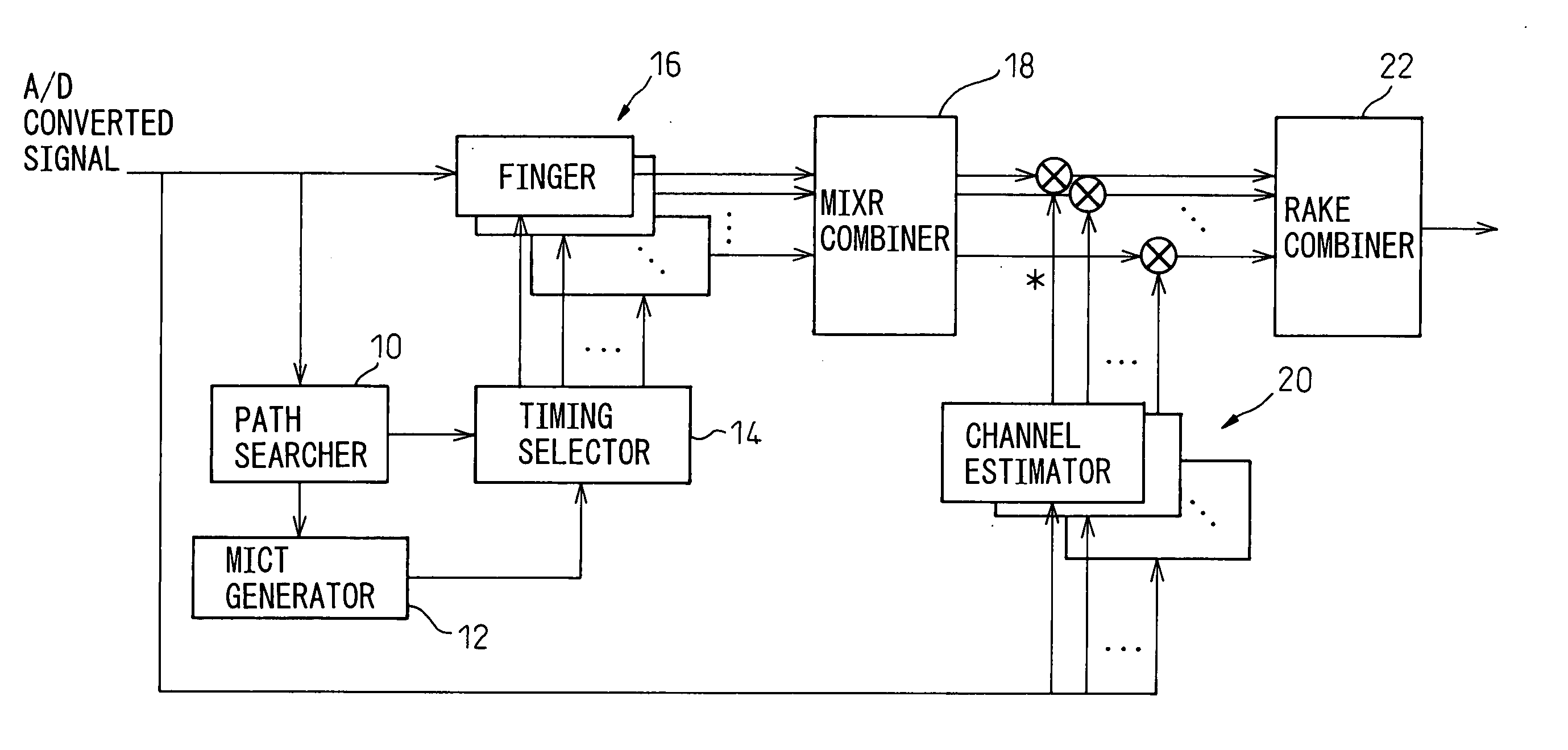
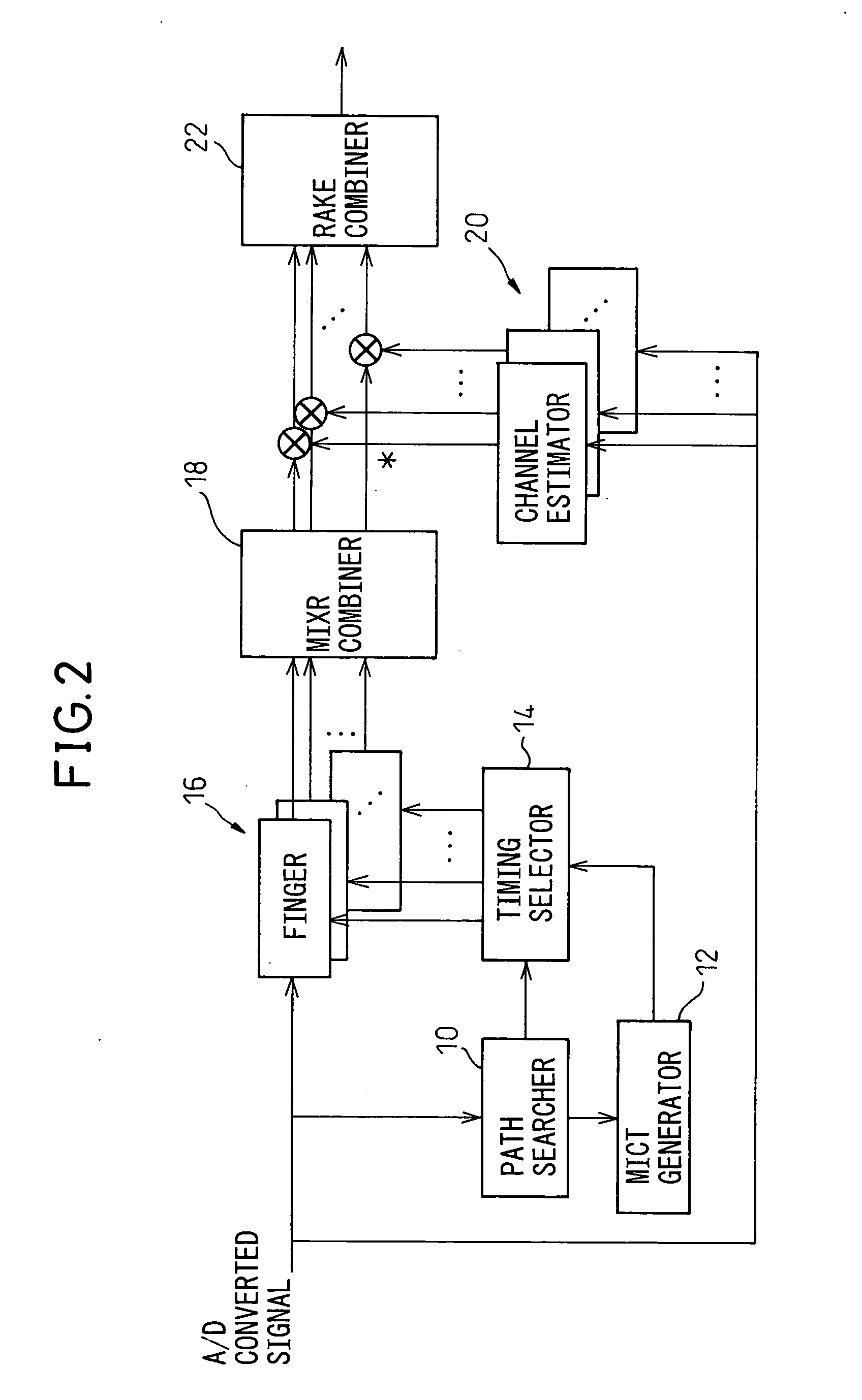
RAKE receiver having MIXR function
InactiveUS20050058183A1Quality improvementReduce in quantitySpatial transmit diversityError preventionRake combiningComputer science
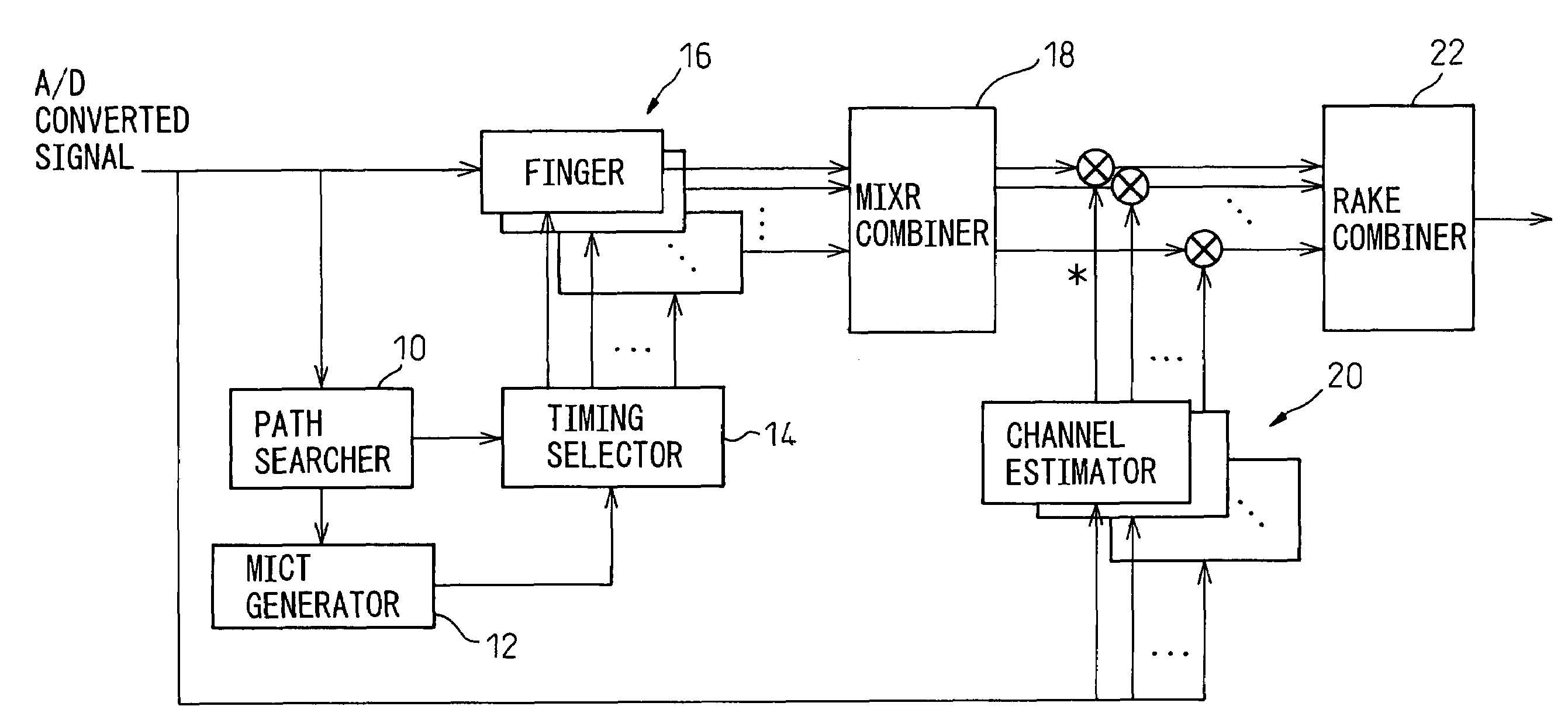
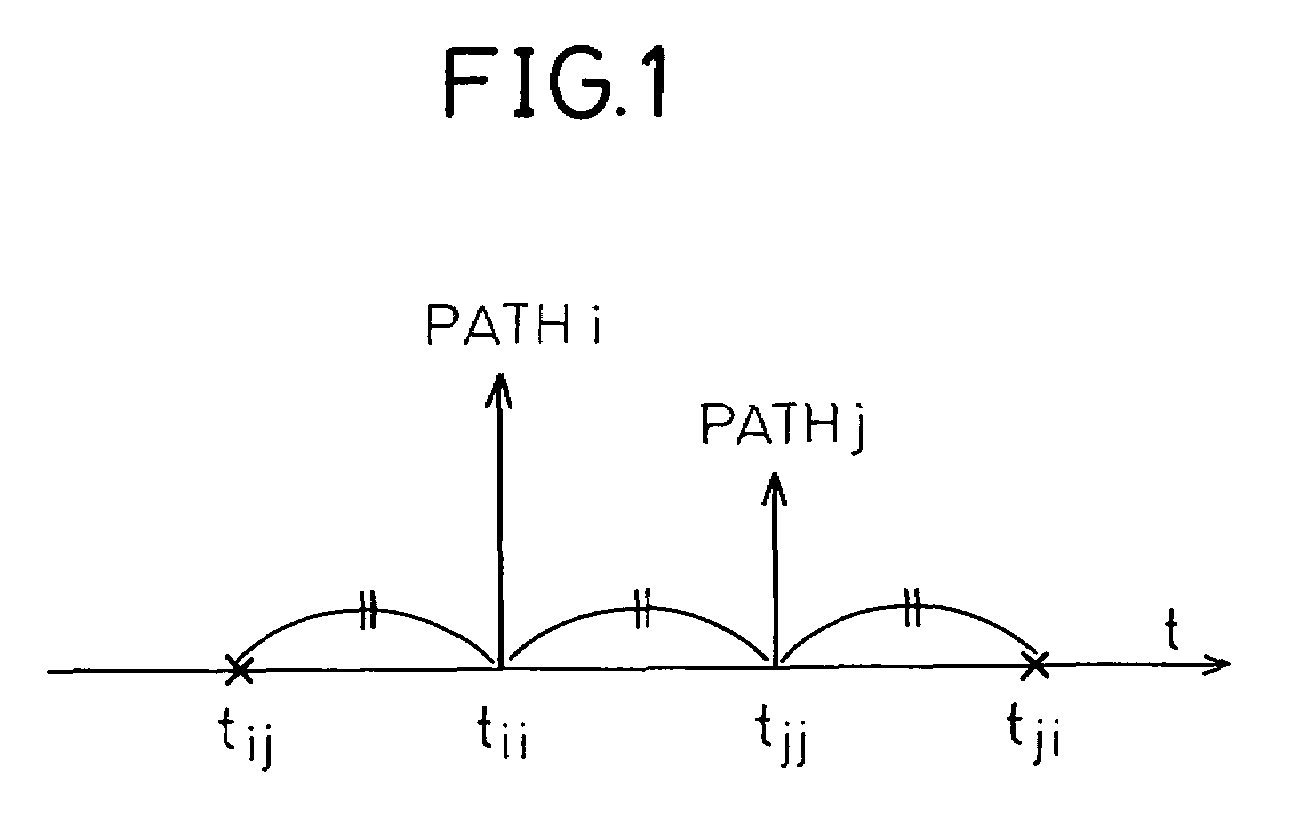
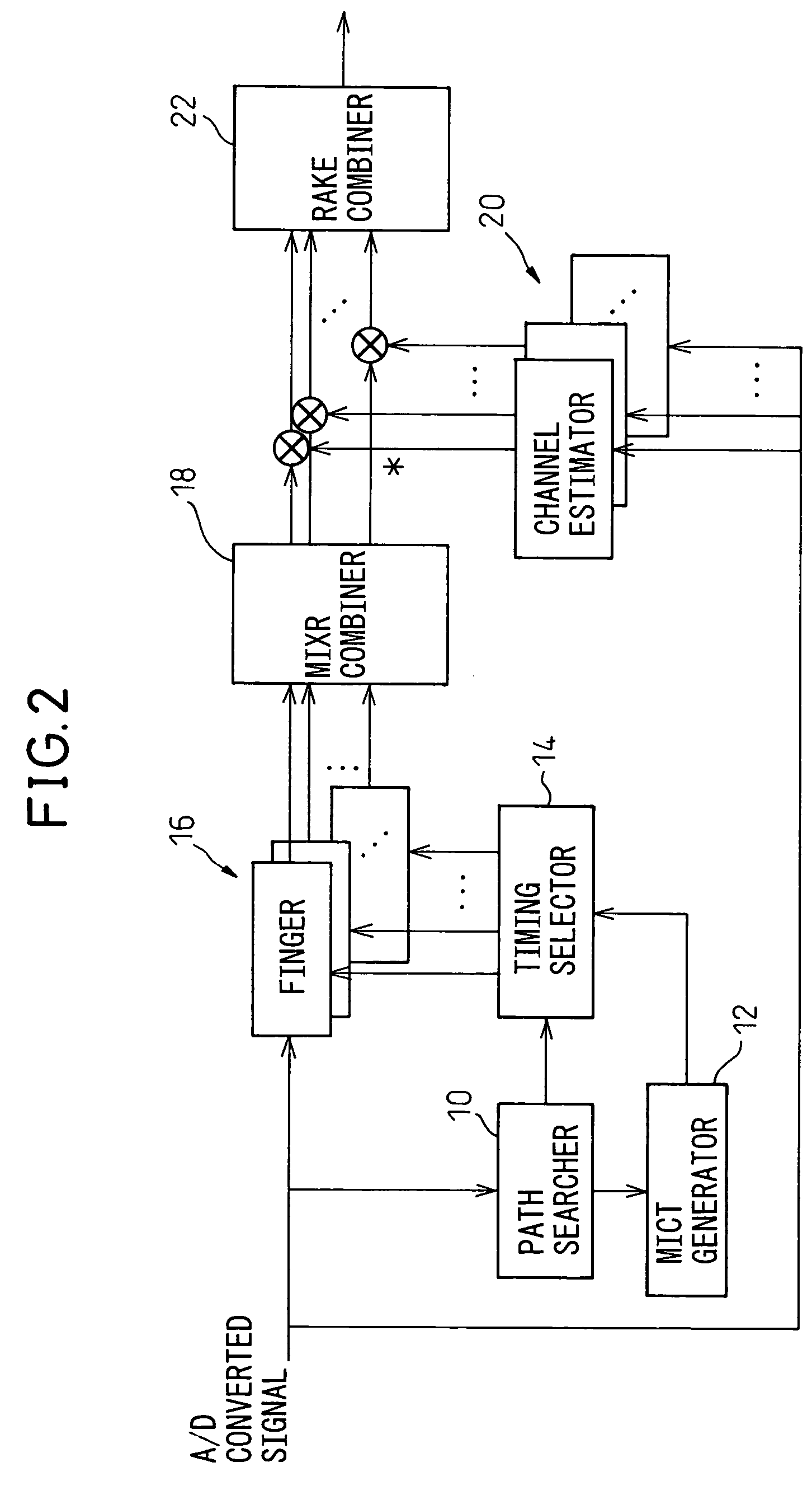
MIXR is implemented with a realistic amount of hardware even when the number of detected paths is large. From among path timings detected by a path searcher and MICTs generated based on the detected path timings, as many timings as there are fingers are selected by a timing selector and the selected timings are assigned to the fingers. When selecting the timings, the value of SNIR expected to be achieved by RAKE combining in a RAKE combiner, for example, is predicted by calculation from a received signal, and the path timing and MICT that maximize the SNIR are selected.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Base station search method and mobile terminal apparatus
ActiveUS7099667B2Improve communication environmentFacilitate communicationAssess restrictionCode division multiplexRake combiningCell search
The present invention uses site diversity reception and RAKE combining reception for the method for a CDMA communication mobile terminal to carry out a cell search to search for a base station with which to communicate. Even if the reception power levels of synchronization acquisition signals sent from a plurality of base stations are lower than a predetermined threshold, in the case where the power level of a signal combining those signals is equal to or greater than the predetermined threshold, the mobile terminal continues processing of requesting position registration to any one of the plurality of base stations and thereby improves communicability.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
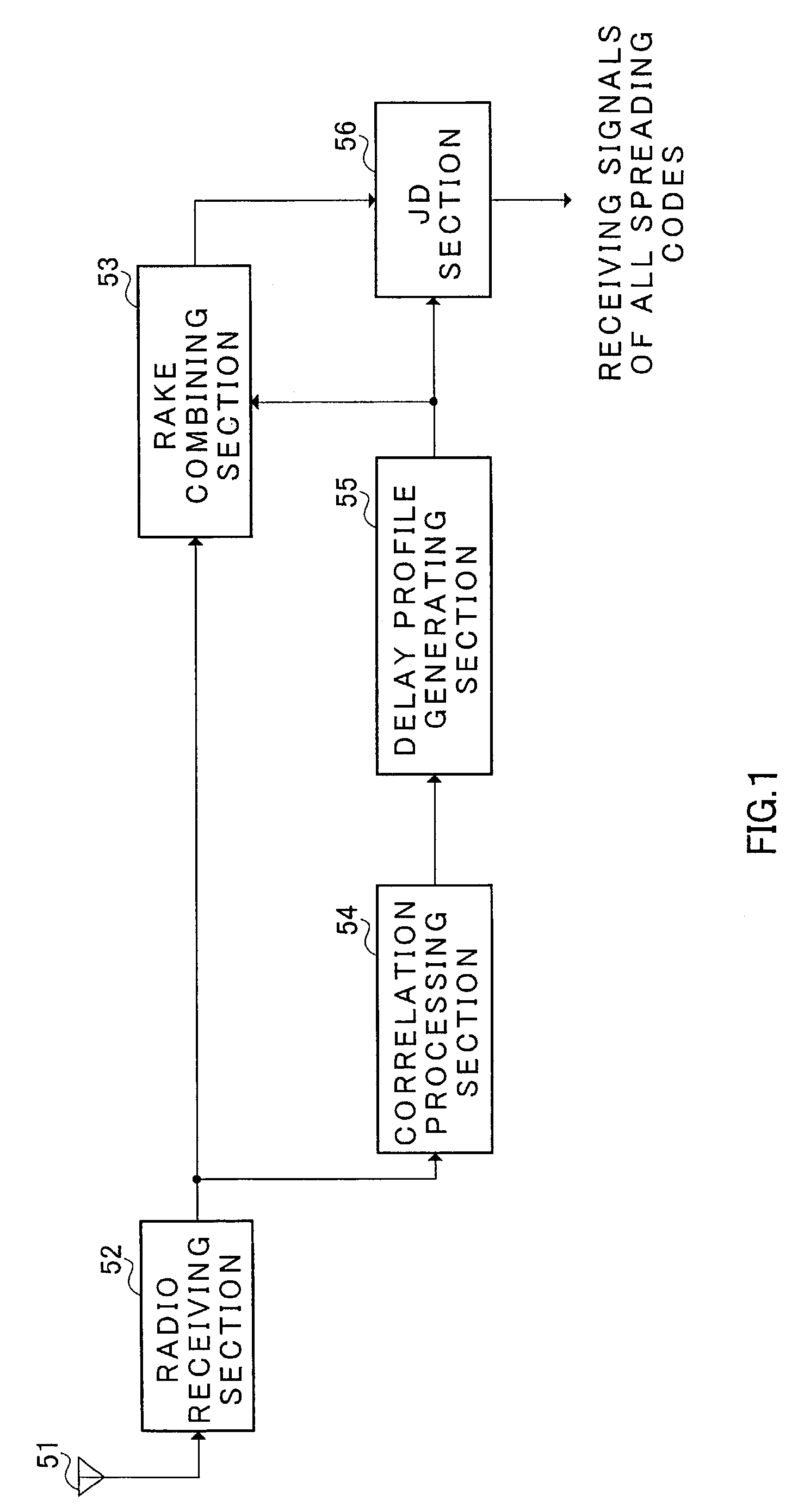
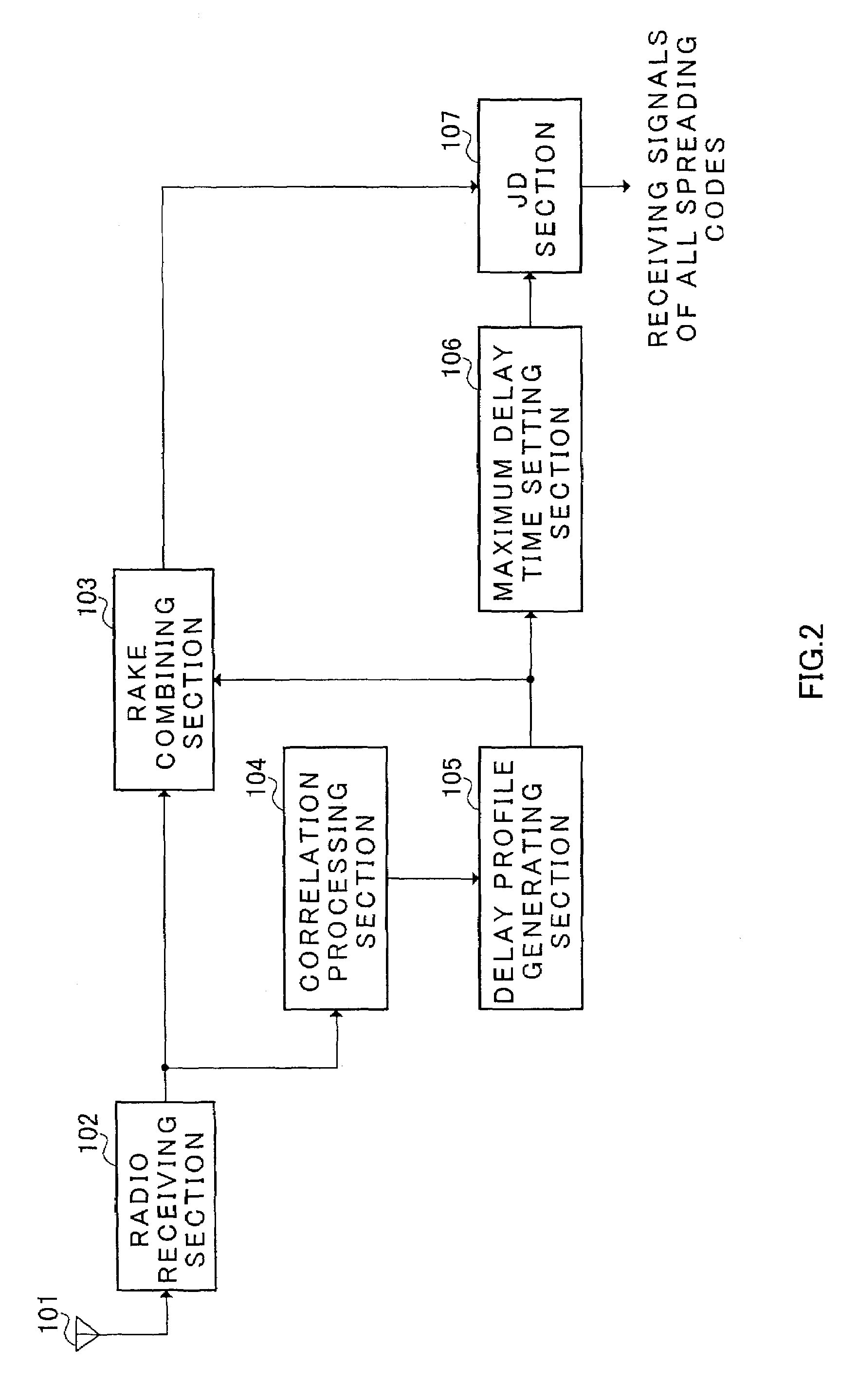
Radio receiving apparatus and radio receiving method
InactiveUS7167505B2Inhibit deteriorationImprove performanceError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionDelay spreadRake combining
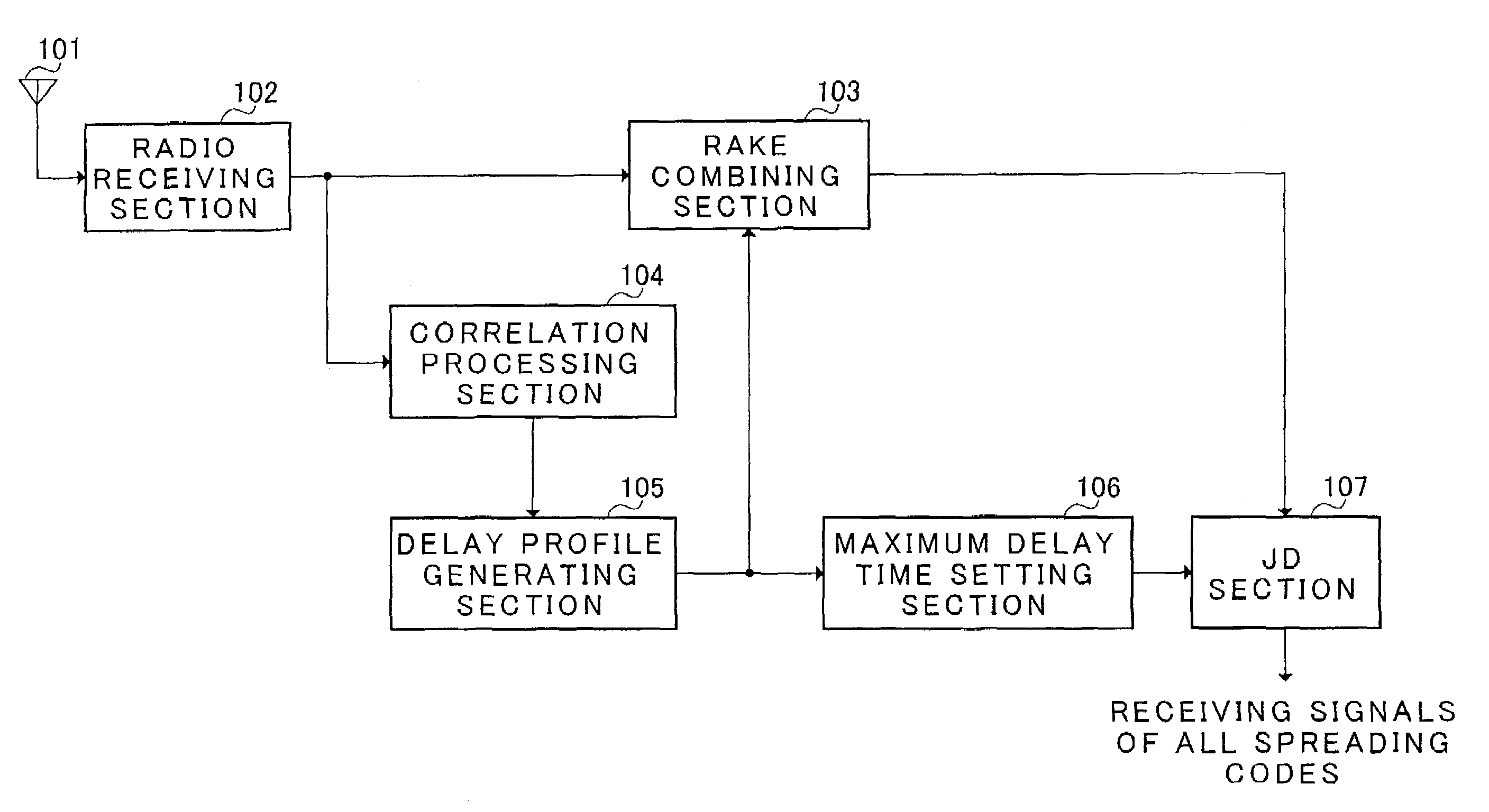
In maximum delay time setting section 106, a delay time width W′ used for cancelling the interference is set using the delay profile. In the present embodiment, delay spread is calculated and a delay wave included in the delay spread is set as W′. First, the delay spread is calculated in delay spread calculating section 1061 of maximum delay time setting section 106. That is to say, the standard deviation of the delay profile is calculated. The calculated delay spread is outputted to maximum delay time determining section 1062. The maximum delay time (window width) W′ is determined in maximum delay time determining section 1062 based on the delay spread. Therefore, the delay wave included in the maximum delay time which is determined by such a way is set to be an object of interference cancellation in joint detection. Thus, besides interference cancellation performance, optimization of calculation scale can be planned without losing performance of RAKE combining.
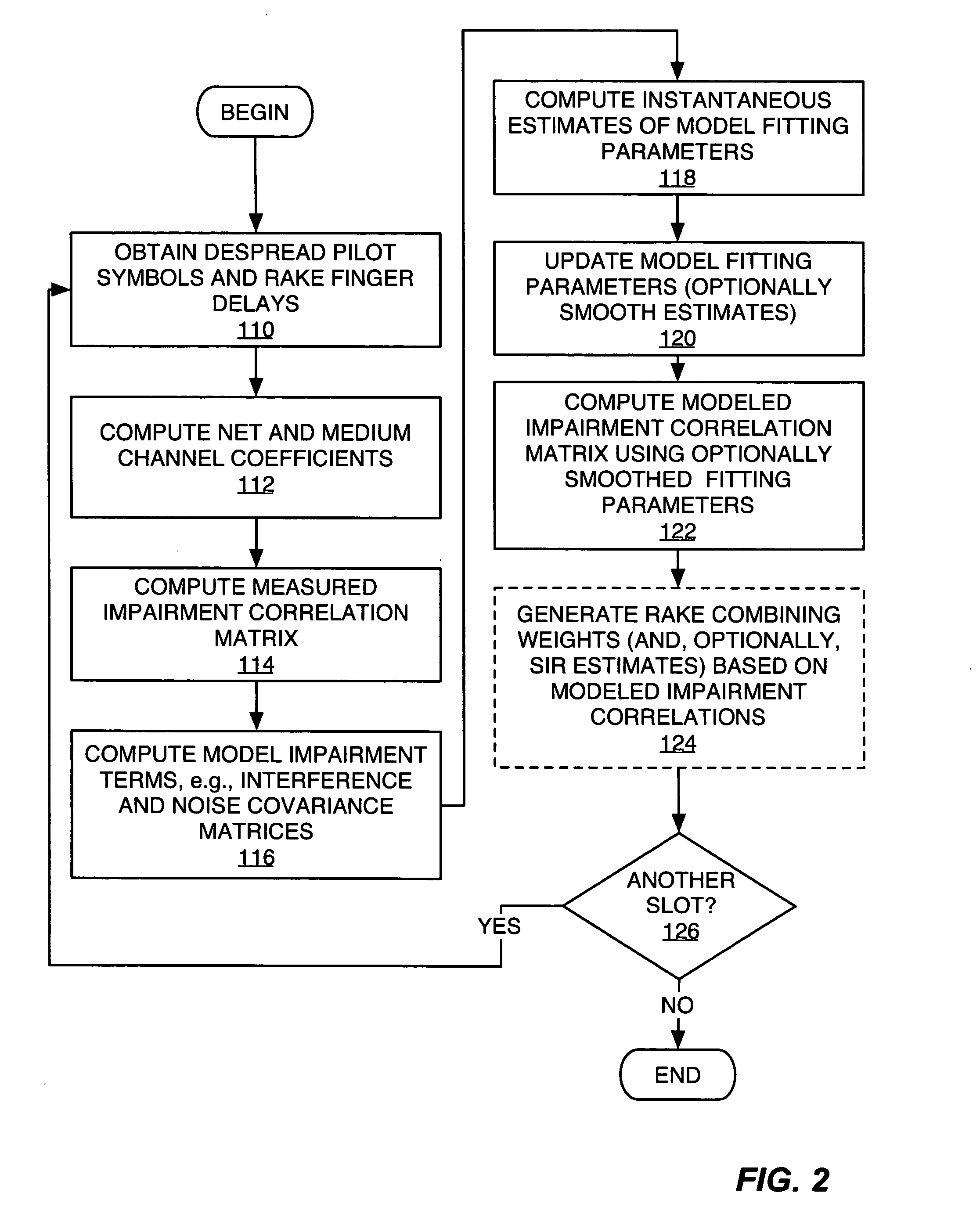
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
Wireless Diversity Reception Apparatus and Reception Method
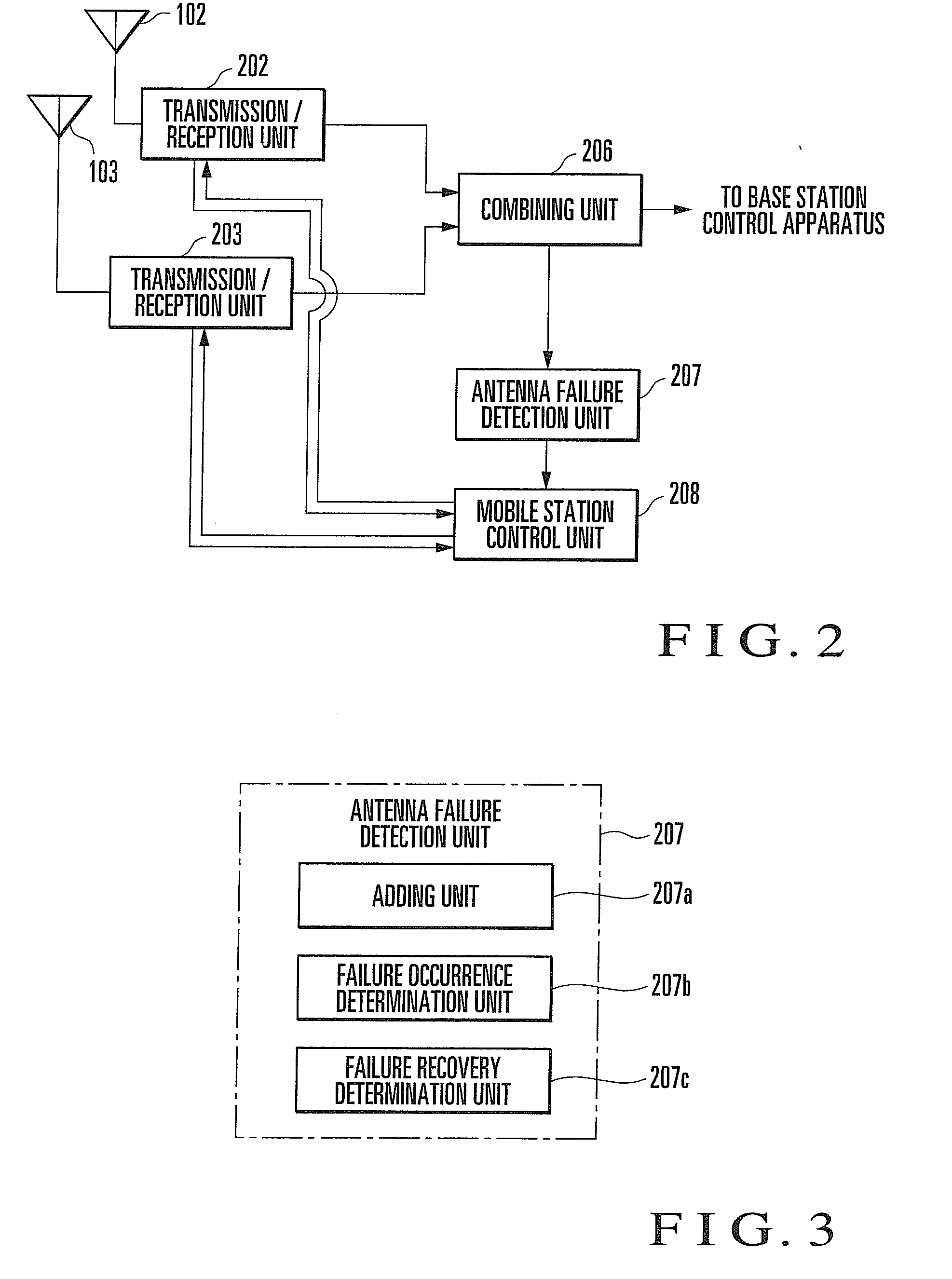
InactiveUS20090117894A1Efficient executionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementRake combiningMobile station
In a wireless diversity reception apparatus, a combining unit RAKE-combines signals of multipaths transmitted from a mobile station and received by a plurality of antennas. An antenna failure detection unit detects an antenna failure based on selection result information representing paths used for RAKE combining. A mobile station control unit calculates the total reception power value of a cell in accordance with an antenna failure detection state and outputs power control information to make the total reception power value of the cell match a target total reception power value. A transmission unit transmits the power control information to the mobile station to perform transmission power control of the mobile station. A wireless diversity reception method is also disclosed.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for 2D antenna rake combining in a code division multiplication access system
One aspect of the present invention is a method for combining a direct sequence spread spectrum signal comprising signal components that each may be characterized with a space variable and a time variable comprising the steps of: despreading said signal components; and determining a set of combining coefficients from said signal components using a Minimum Mean Square Error combining method that considers said space and time variables of the signal components in parallel. The Minimum Mean Square Error combining methods may utilize iterative methods such as the Least Mean Squares method or the Recursive Least Squares method.
Owner:SASKEN COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES
CDMA receiving apparatus and method
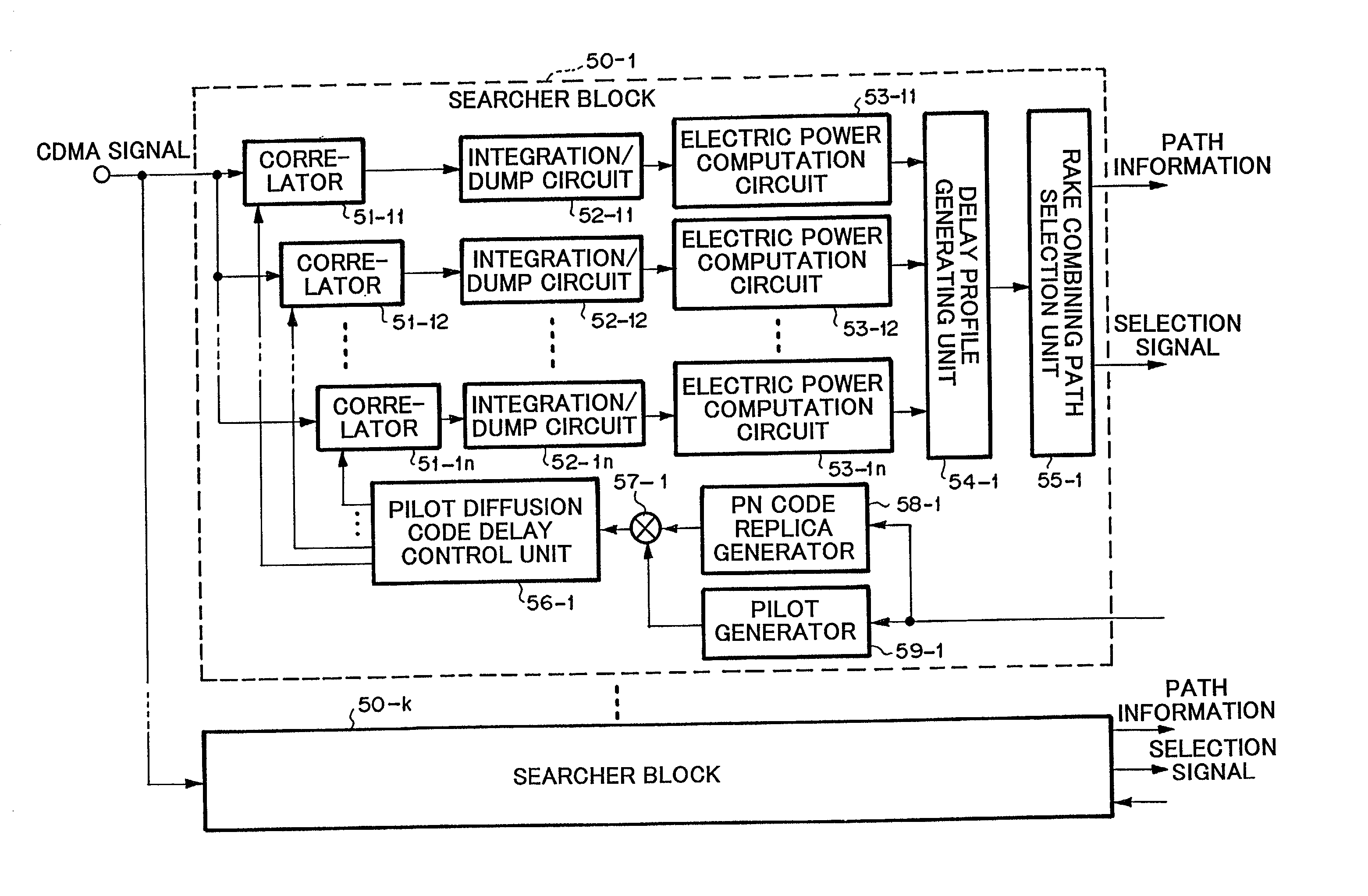
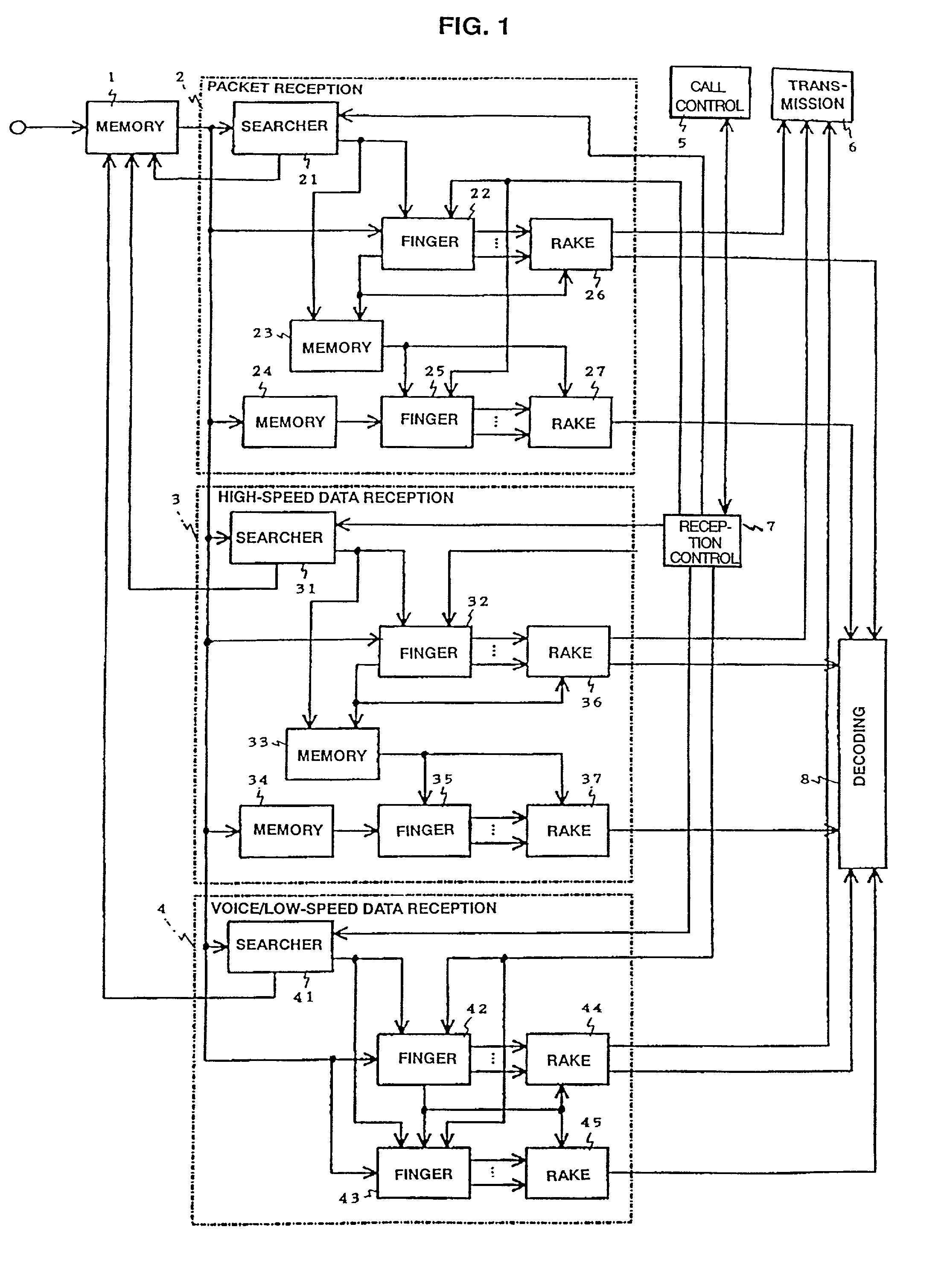
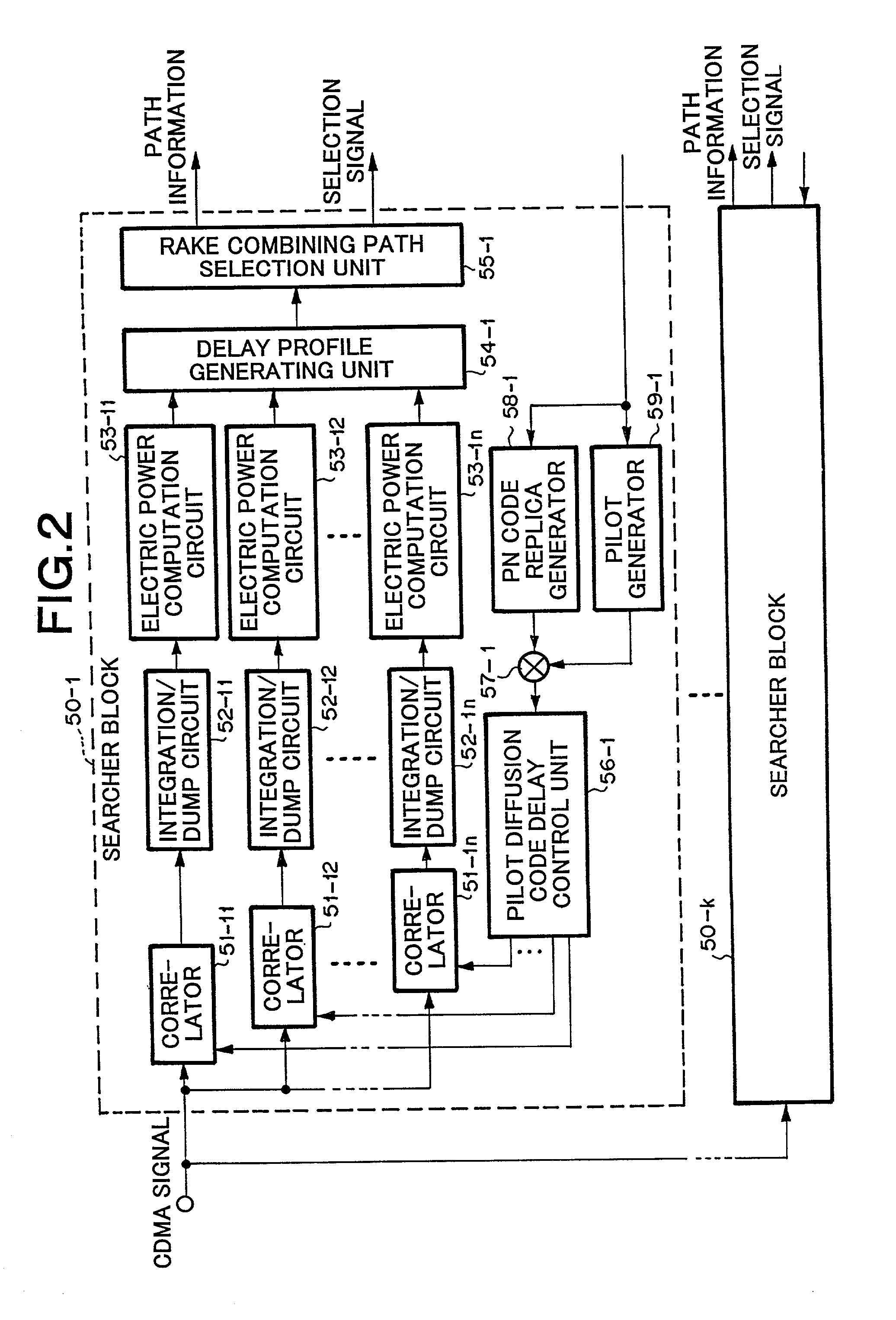
The present invention provides a CDMA receiving apparatus capable of corresponding to the service types of data and system conditions flexibly and efficiently, so as to achieve such processing for electric power control, diversity control and the like, requested to have real-time property. A CDMA signal inputted into a memory is searched by searcher units of each reception processing block. Voice data and low-speed data are demodulated immediately by a finger unit for data field and a finger unit for control field, and combined by RAKE-combining units. Data fields of packet data and high-speed data are accumulated in memories for data field and demodulated by finger units for data field successively based on path information stored in memories for path information.
Owner:NEC CORP
RAKE receiver having MIXR function
InactiveUS7305022B2Reduce in quantityReduce power consumptionSpatial transmit diversityError preventionRake combiningComputer science
MIXR is implemented with a realistic amount of hardware even when the number of detected paths is large. From among path timings detected by a path searcher and MICTs generated based on the detected path timings, as many timings as there are fingers are selected by a timing selector and the selected timings are assigned to the fingers. When selecting the timings, the value of SNIR expected to be achieved by RAKE combining in a RAKE combiner, for example, is predicted by calculation from a received signal, and the path timing and MICT that maximize the SNIR are selected.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com