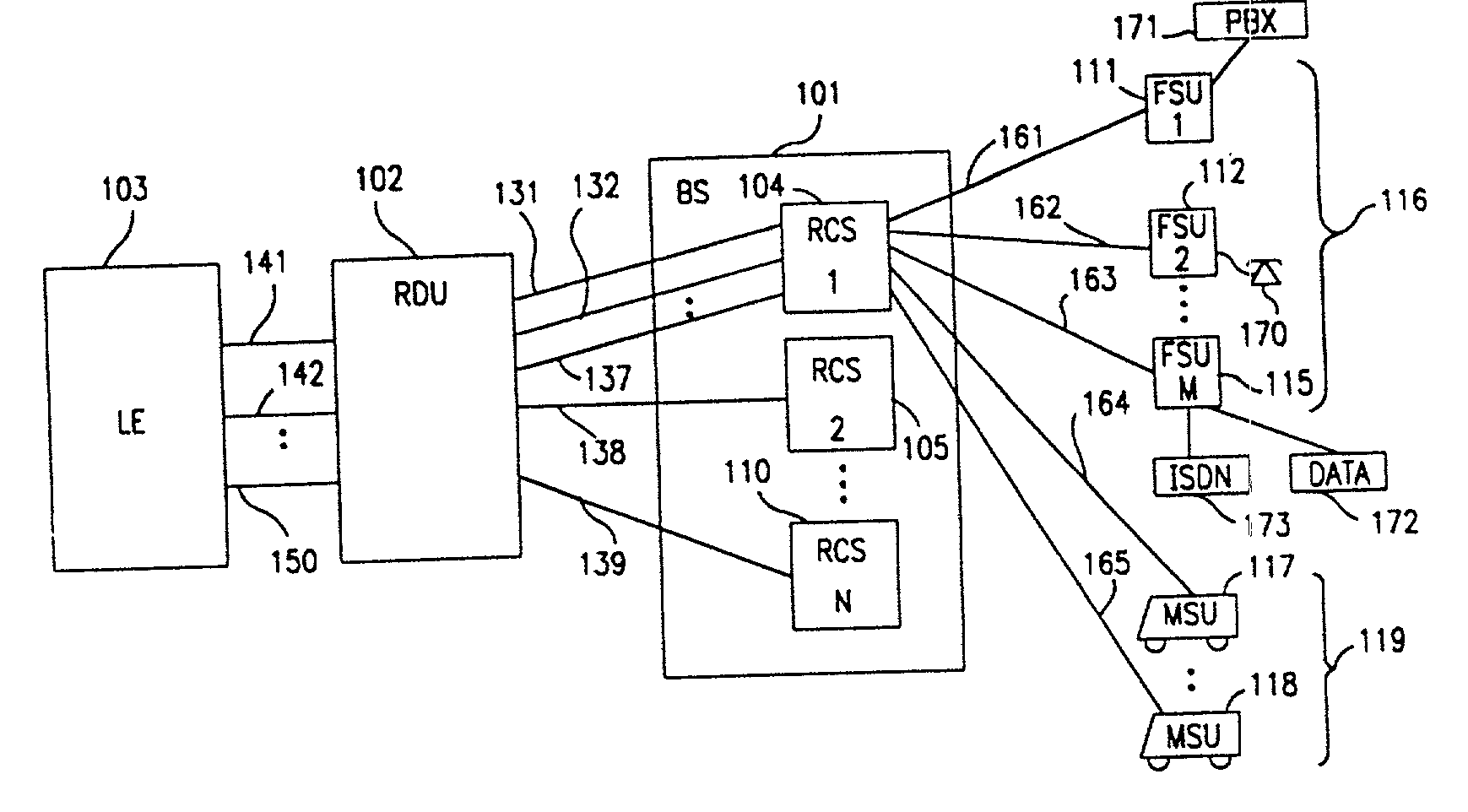
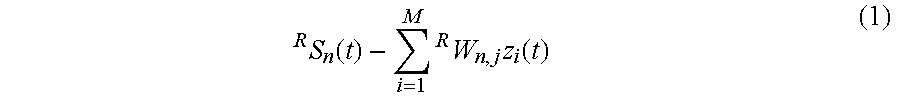Patents
Literature
836 results about "Cdma systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. It is cellular technology in which there are two main systems viz. Base Station (BS) and mobile subscribers or users. The unique codes are assigned to the users for communication with BS or NodeB.
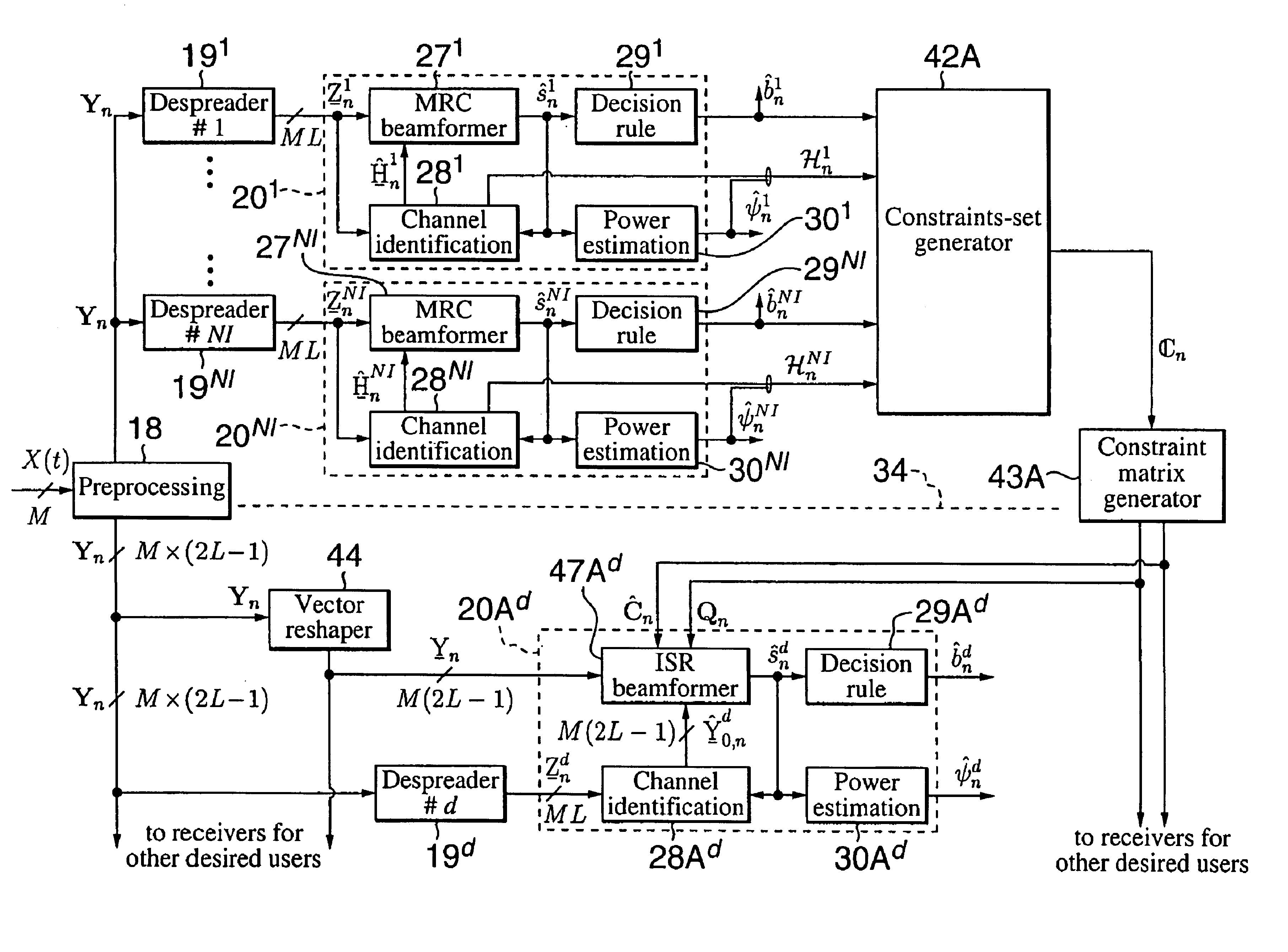
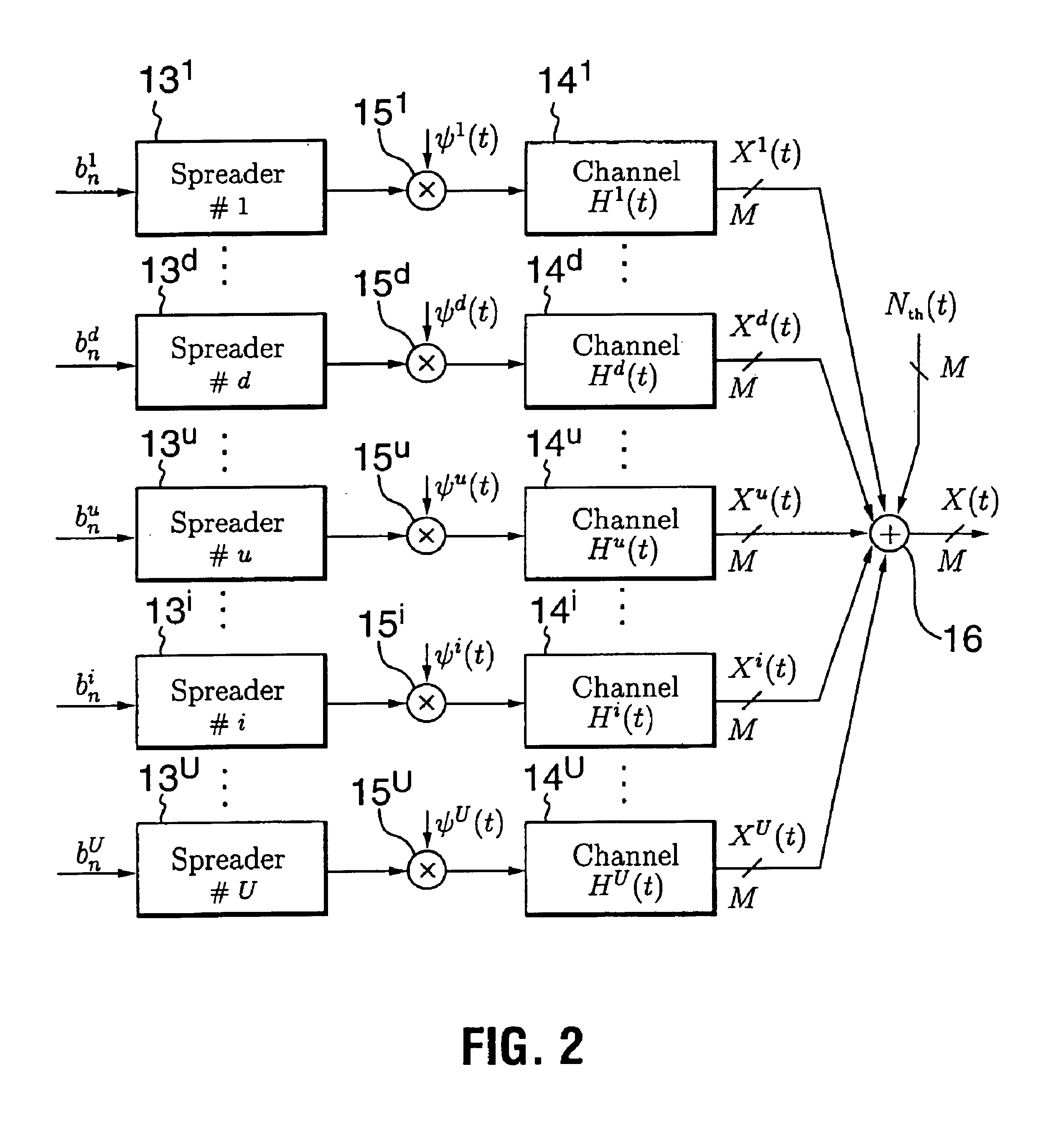
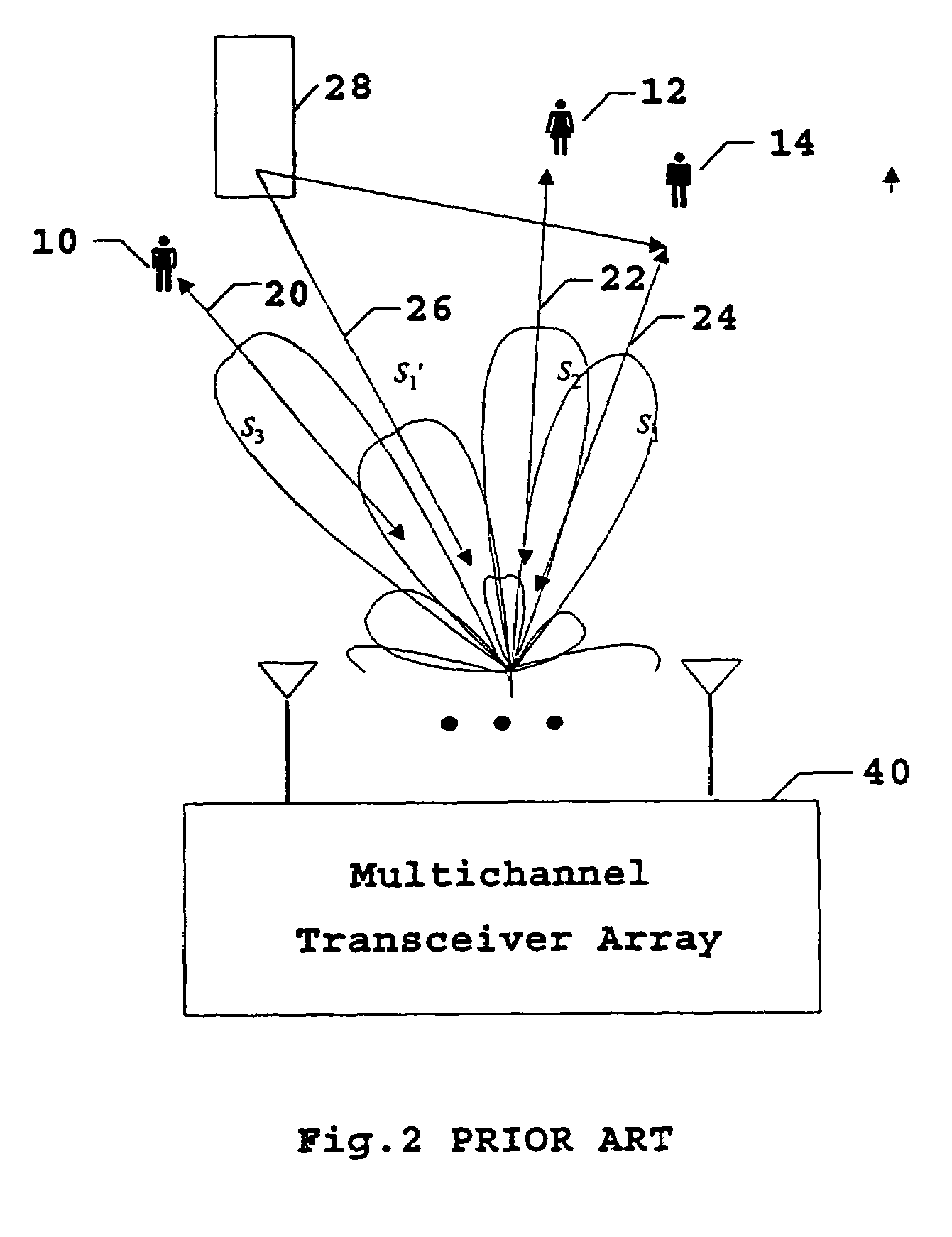
Interference suppression in CDMA systems
ActiveUS20020051433A1Improved interference suppressionSuppresses any sensitivitySpatial transmit diversityInterference (communication)Communications system
A receiver of the present invention addresses the need for improved interference suppression without the number of transmissions by the power control system being increased, and, to this end, provides a receiver for a CDMA communications system which employs interference subspace rejection to tune a substantially null response to interference components from selected signals of other user stations. Preferably, the receiver also tunes a substantially unity response for a propagation channel via which a corresponding user's signal was received. The receiver may be used in a base station or in a user / mobile station.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
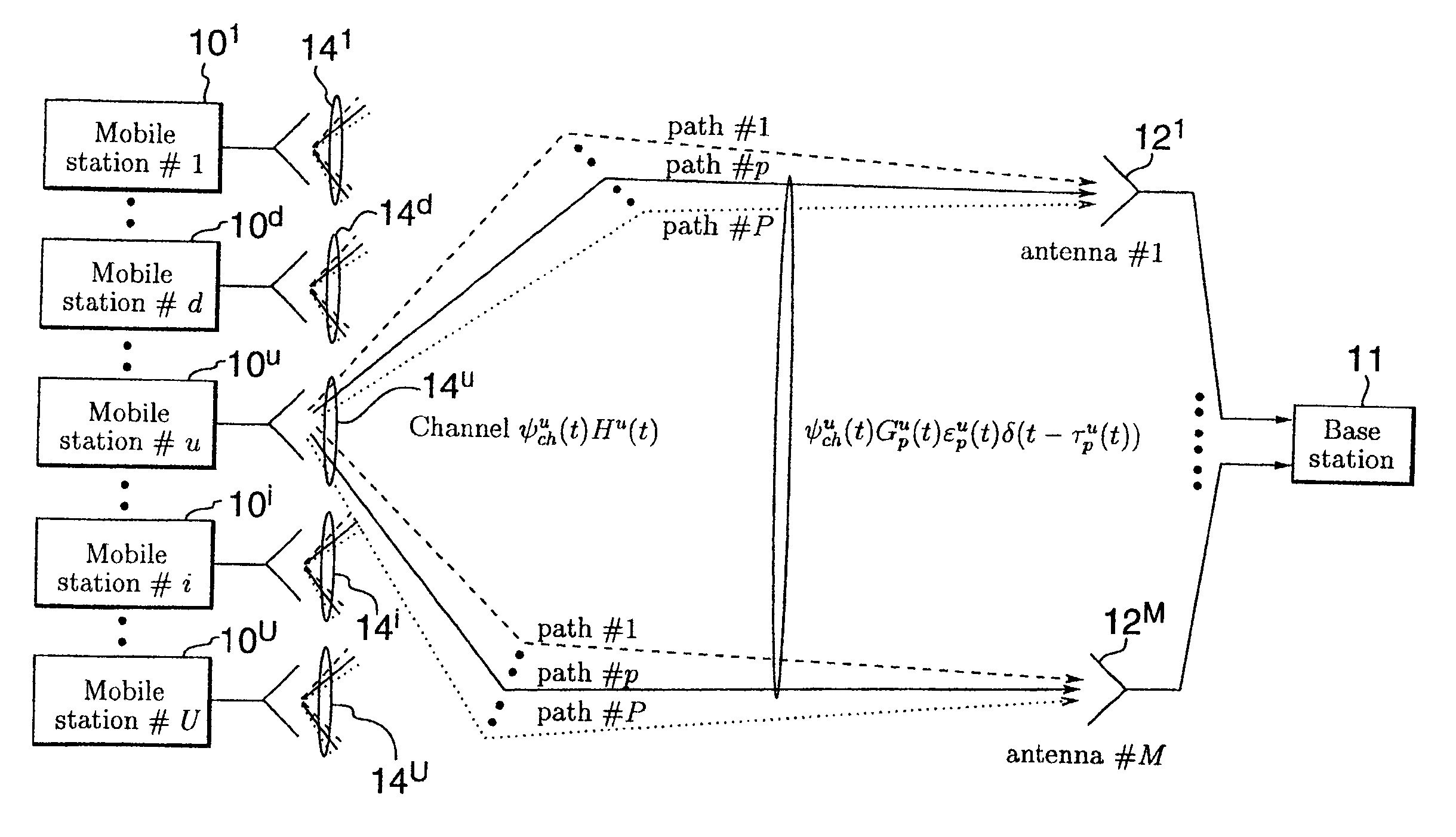
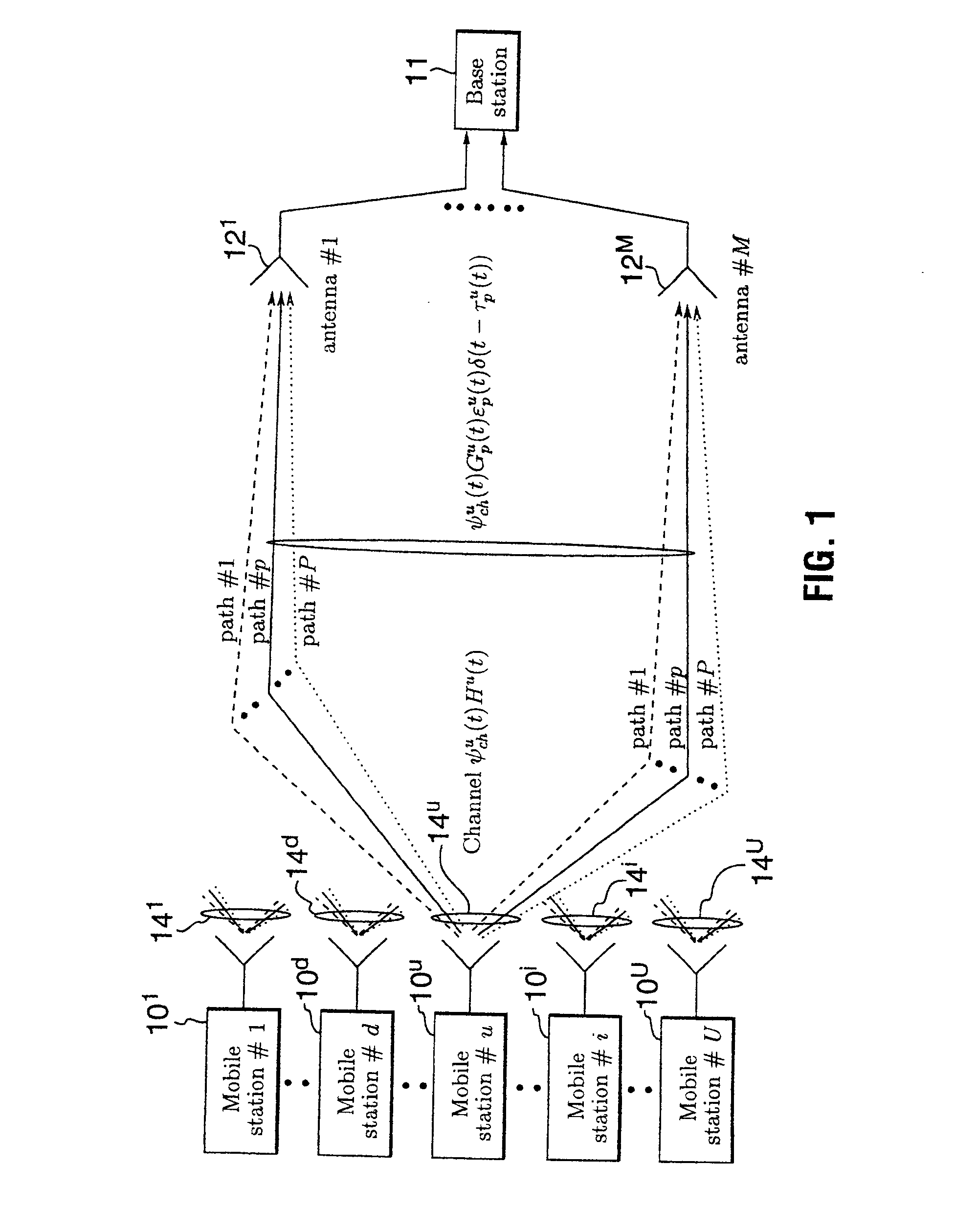
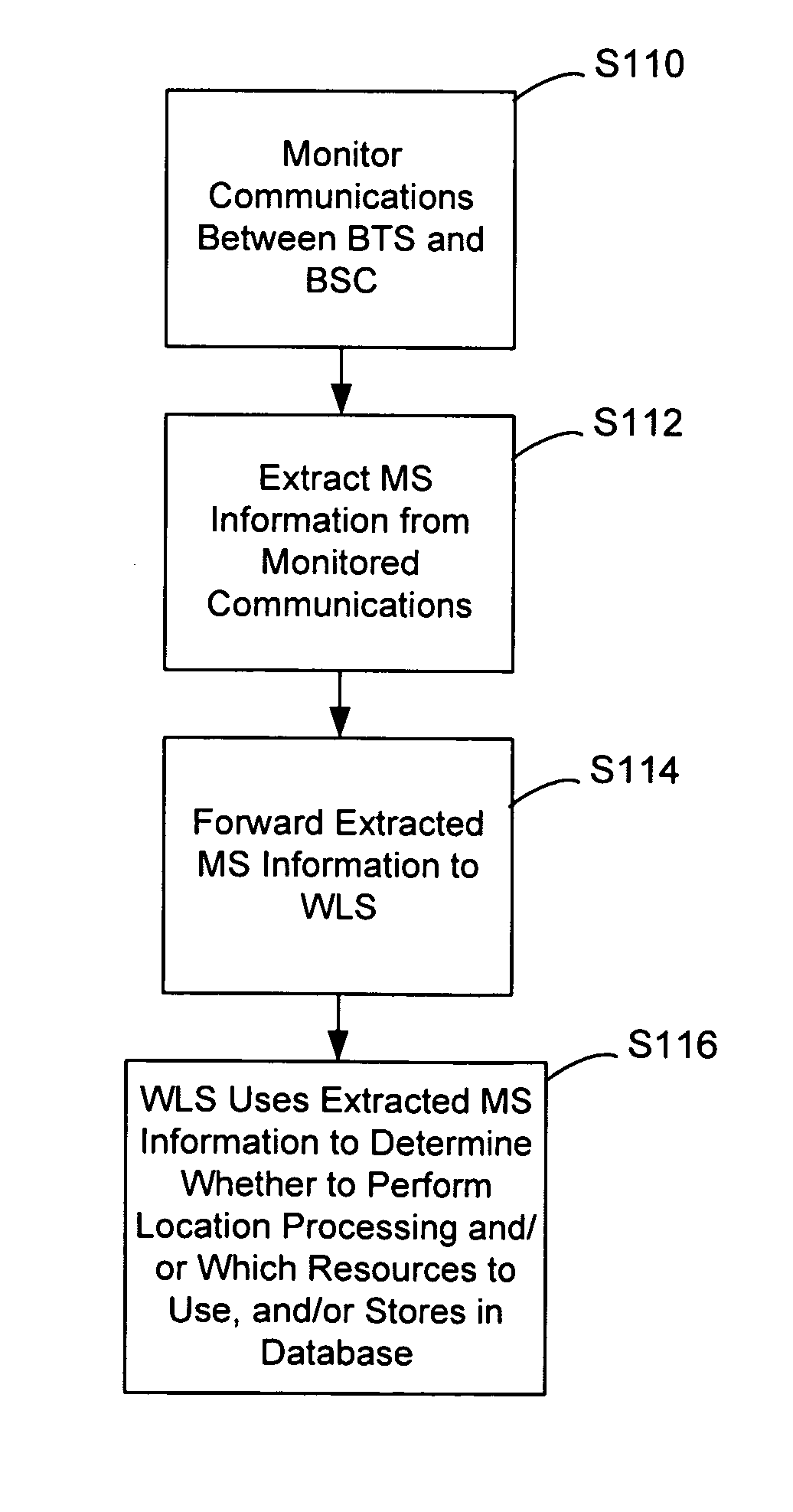
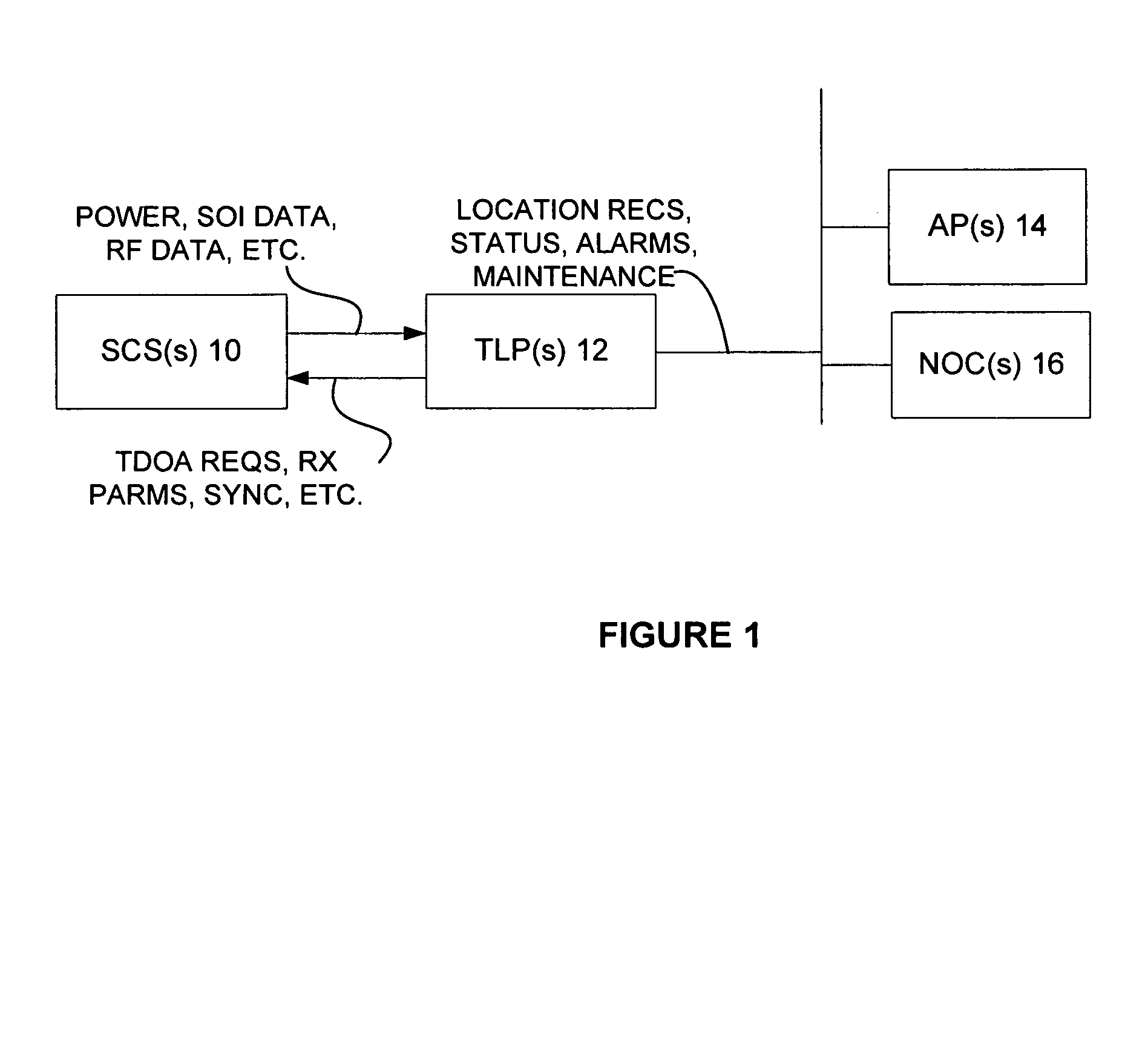
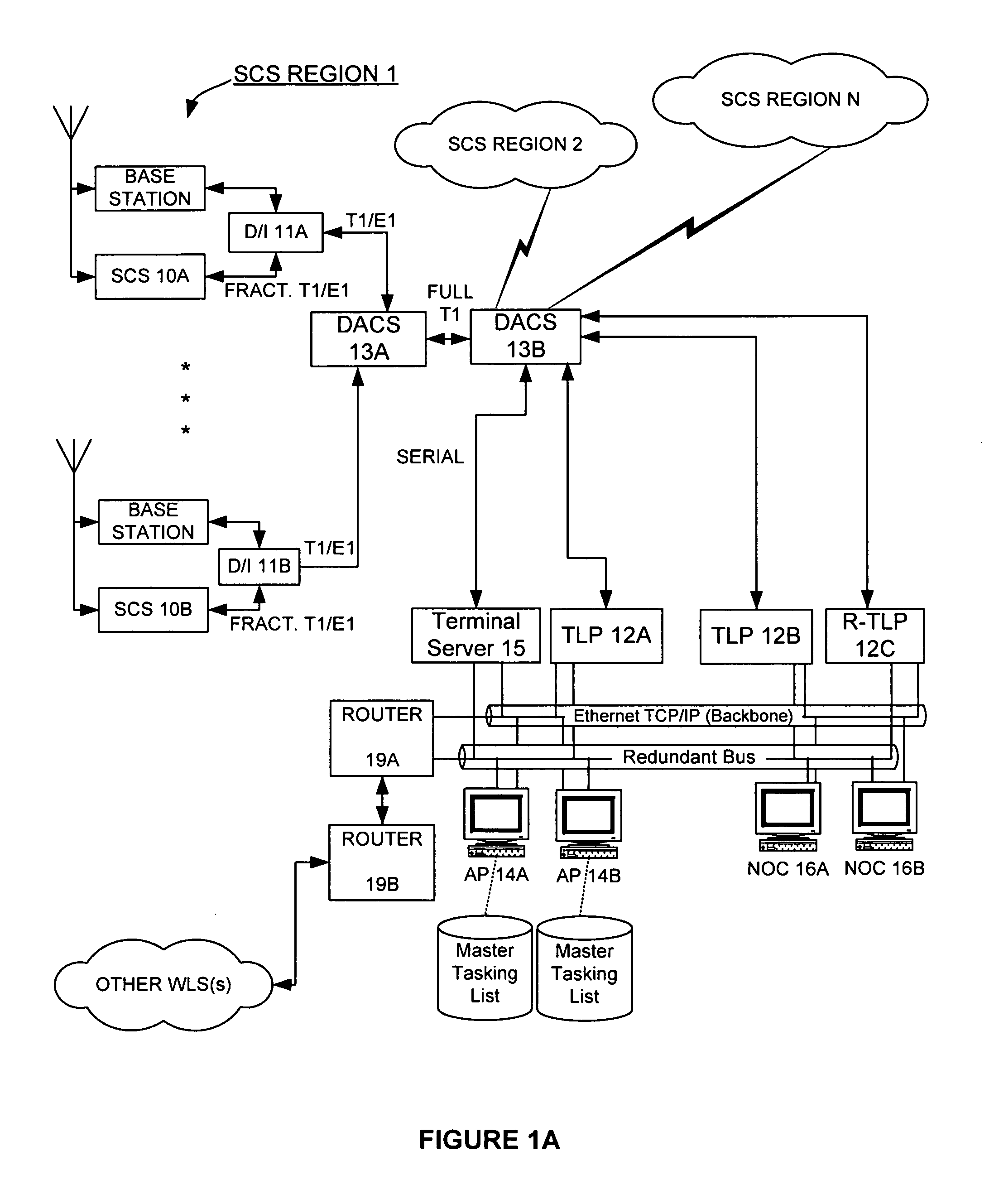
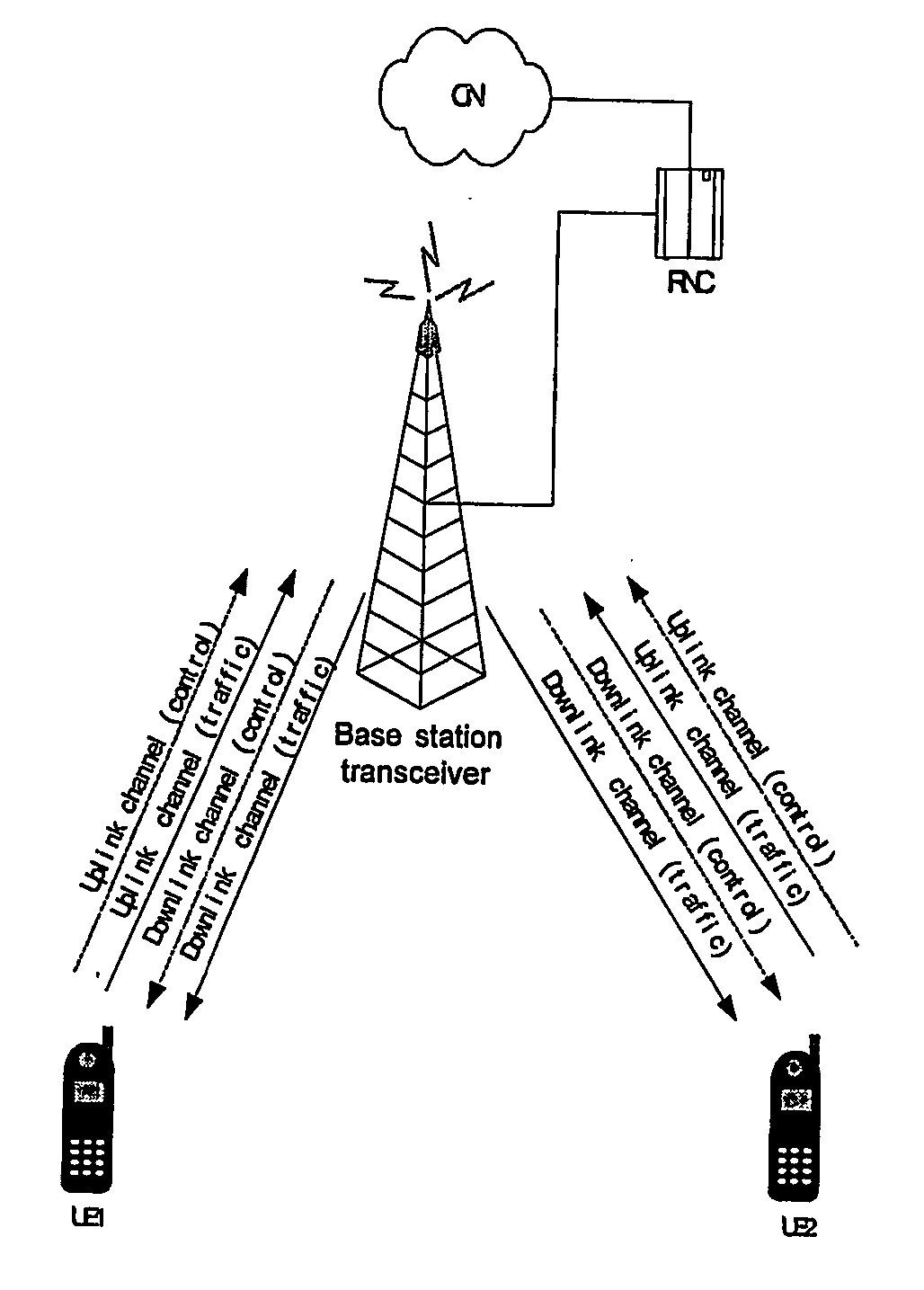
Monitoring of call information in a wireless location system
InactiveUS7167713B2Low costReduce functionEmergency connection handlingBeacon systems using radio wavesAir interfaceComputer science
In an overlay Wireless Location System, an Abis interface is monitored to obtain information used to locate GSM phones. Signaling links of the Abis interface are passively monitored to obtain certain information, such as control and traffic channel assignment, called number, and mobile identification, which is not available from the GSM air interface of the reverse channel. This approach also applies to IDEN and can include CDMA systems where the GSM architecture has been used and the system includes a separated BTS to BSC interface.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
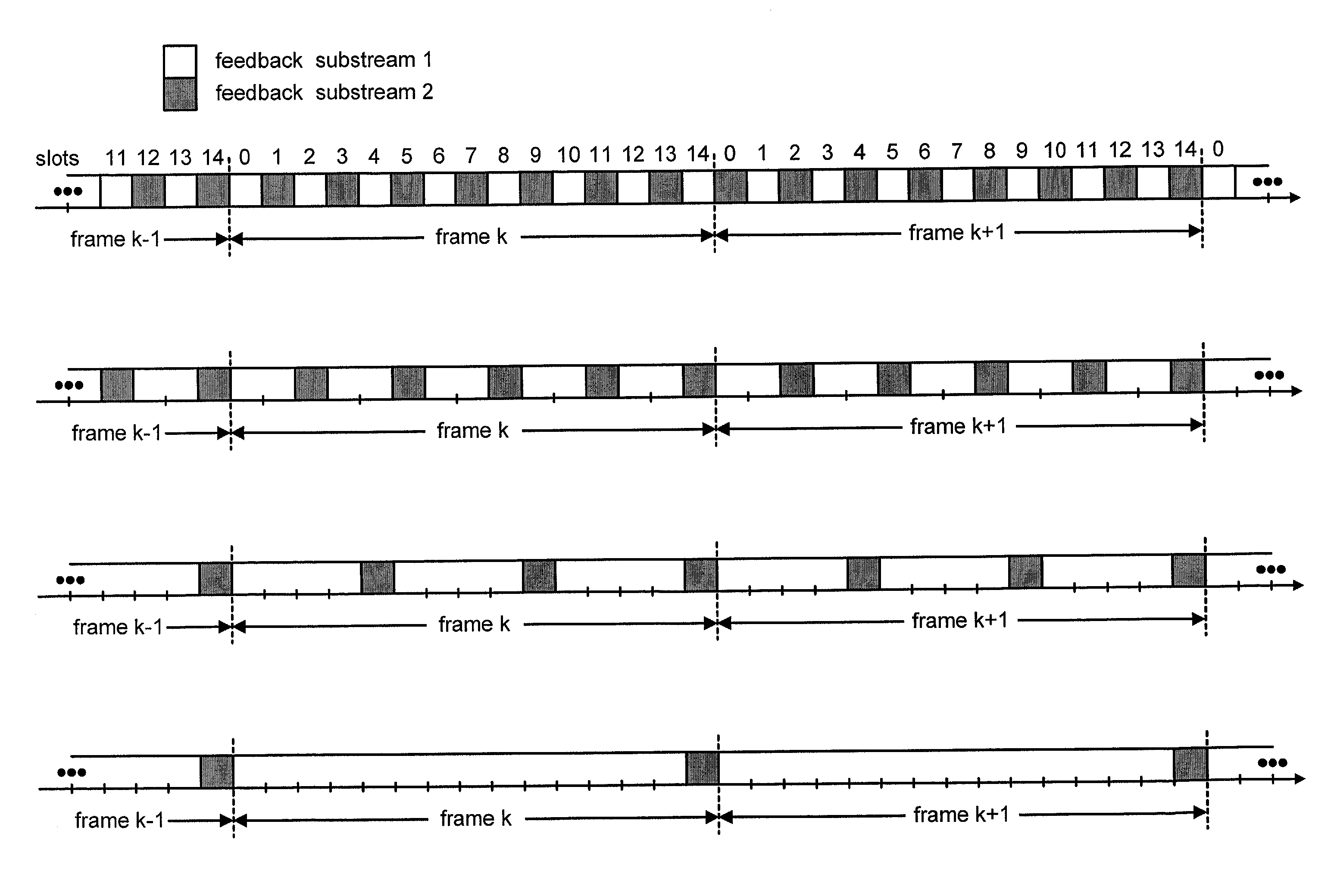
Method and apparatus for controlling transmit power of multiple channels in a CDMA communication system
ActiveUS20020009061A1Power managementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmitted powerTime-sharing
Techniques to support independent power control of multiple channels in CDMA systems (e.g., a W-CDMA system) that define a single power control feedback stream on the uplink, which is to be used for downlink power control. In one aspect, the single feedback stream is "time shared" among multiple channels requiring individual power control. Various time-sharing schemes may be used to implement multiple (substantially parallel) feedback substreams based on the single feedback stream, and different combination of feedback rates may also be achieved for the substreams. Each feedback substream may be assigned to, and used for power control of, a respective channel. In another aspect, multiple feedback substreams are implemented based on multiple fields in newly defined slot formats.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for controlling transmit power of multiple channels in a CDMA communication system
ActiveUS20050208961A1Reduce distractionsMaximize system capacityPower managementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemTransmitted power
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Monitoring of call information in a wireless location system
InactiveUS20050003831A1Low costReduce functionEmergency connection handlingBeacon systems using radio wavesAir interfaceGSM
In an overlay Wireless Location System, an Abis interface is monitored to obtain information used to locate GSM phones. Signaling links of the Abis interface are passively monitored to obtain certain information, such as control and traffic channel assignment, called number, and mobile identification, which is not available from the GSM air interface of the reverse channel. This approach also applies to IDEN and can include CDMA systems where the GSM architecture has been used and the system includes a separated BTS to BSC interface.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
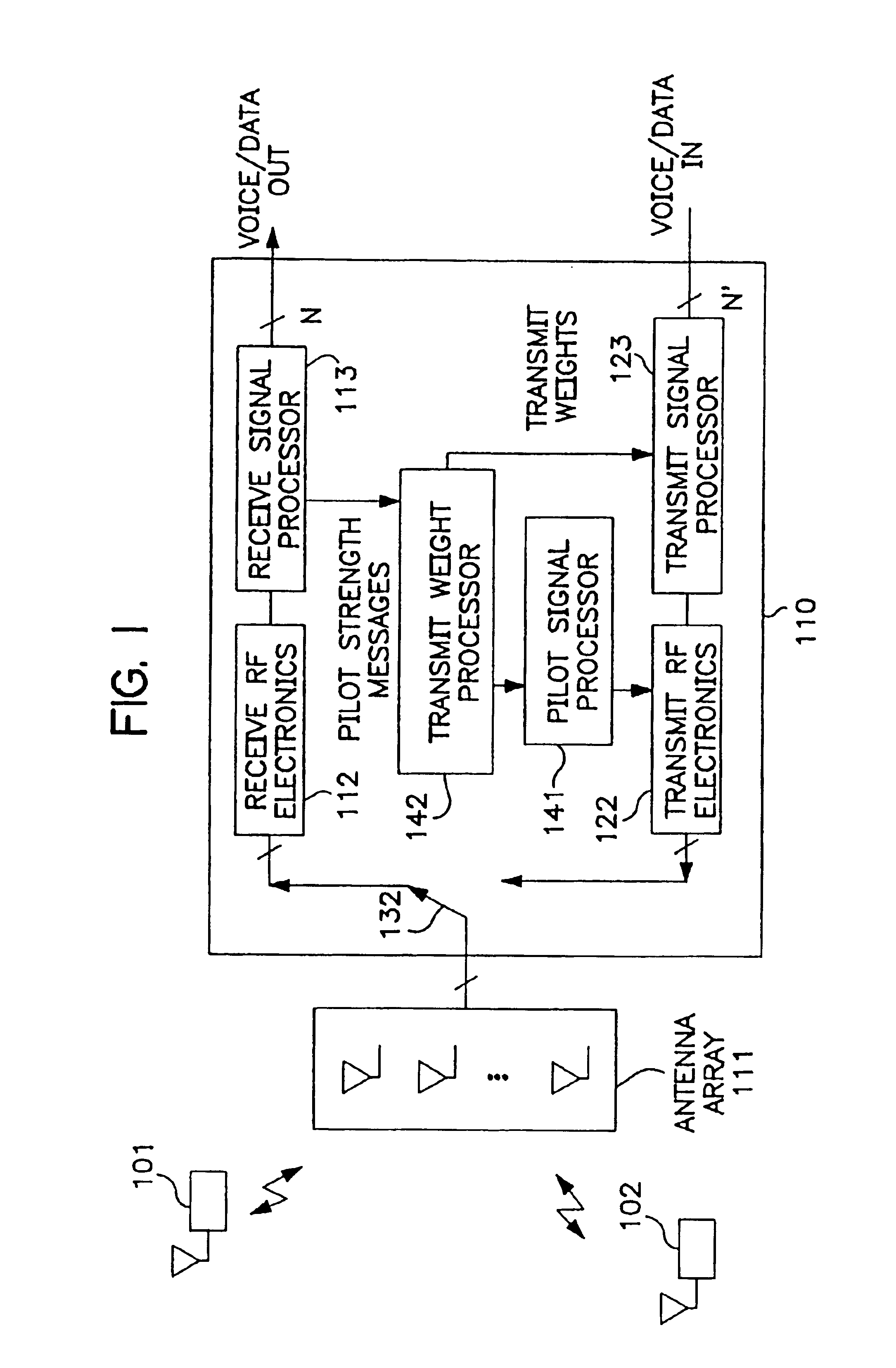
Downlink signal processing in CDMA systems utilizing arrays of antennae
InactiveUS6985466B1Spatial transmit diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCdma systemsCellular communication systems
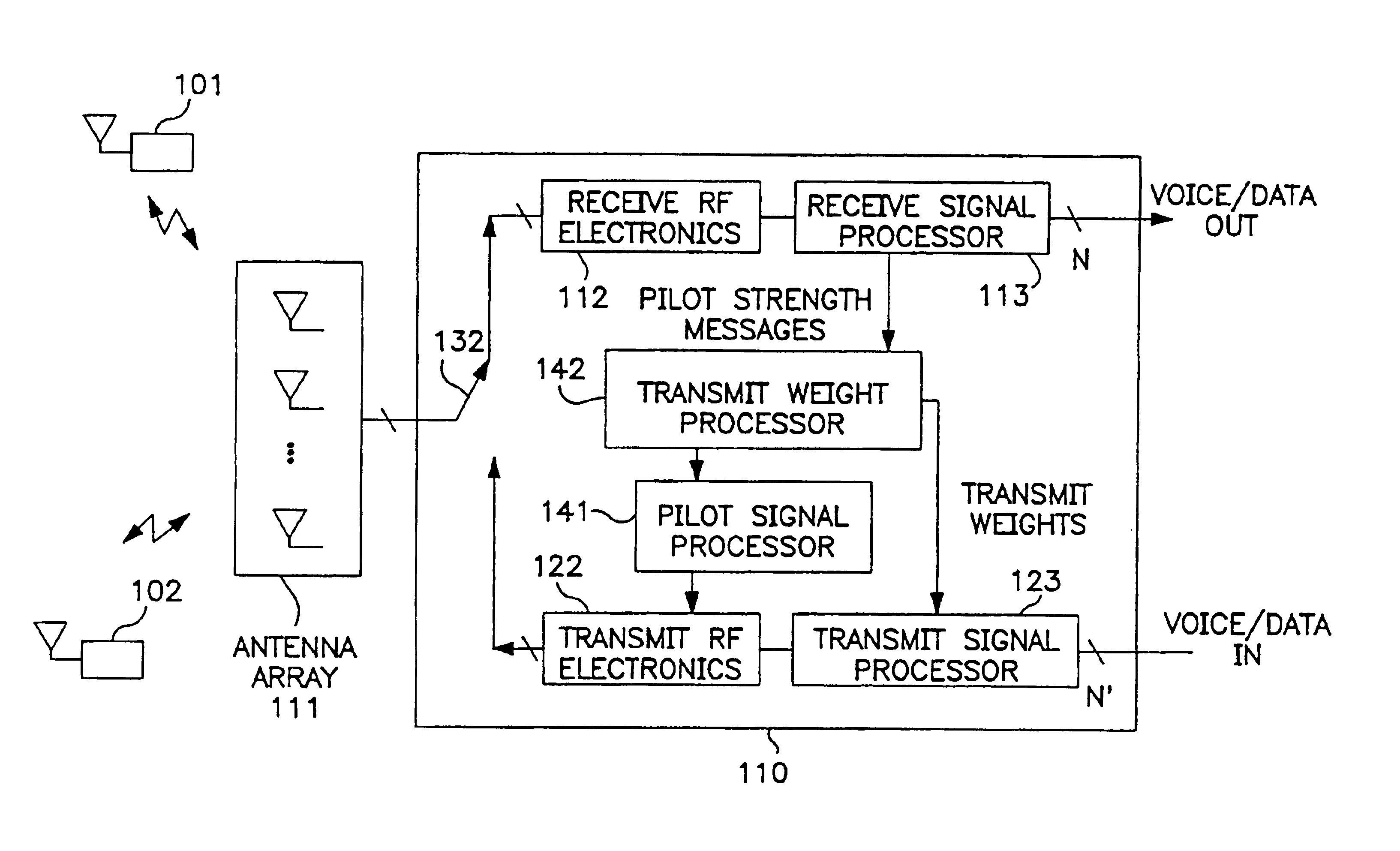
The present invention is a method for operating a base station (BS) for transmitting information to a subscriber unit (SU) in a cellular communication system. The information is included in a downlink signal sent from a signal processing circuit through an array of antennae. The processing depends on a weight set that is utilized in generating individual signals to be sent on individual antennae in the array to the SU. The weight set is determined by transmitting a plurality of pilot downlink signals from BS to the SU, each pilot downlink signal being processed with a different weight set than that used to process the other pilot downlink signals. Report signals are received for each of the pilot downlink signals and are compared to determine which weight set should be utilized. The present invention may be practiced within existing CDMA cellular standards such as the IS-95 standard.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Interference suppression in CDMA systems
InactiveUS6975666B2Suppresses any sensitivityReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversitySignal responseInterference (communication)
A receiver of the present invention addresses the need for improved interference suppression without the number of transmissions by the power control system being increased, and, to this end, provides a receiver for a CDMA communications system which employs interference subspace rejection to tune a substantially null response to interference components from selected signals of other user stations. Preferably, the receiver also tunes a substantially unity response for a propagation channel via which a corresponding user's signal was received. The receiver may be used in a base station or in a user / mobile station.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
Multipath interference reduction for a CDMA system
InactiveUS6865218B1Improve receiver performanceReduce multipath interferenceRadio transmissionMultipath interferenceRake receiver
A method and system reduce multipath signal interference in a CDMA receiver. The CDMA receiver including parallel first and second RAKE receivers receives a multipath signal. The first RAKE receiver includes a number of individual RAKE fingers, each operating with a defined finger delay matched to a propagation path delay. The output signal from each RAKE finger includes multipath interference. The second RAKE receiver includes a group of RAKE fingers corresponding to each RAKE finger in the first RAKE receiver. Each group of RAKE fingers is configured to produce an estimate of the multipath interference in the output signal generated by the corresponding RAKE finger in the first RAKE receiver. The estimated multipath interference signals are scaled, and then subtracted from the RAKE finger outputs from the first RAKE receiver to reduce multipath interference. Scaling coefficients are adjusted to ensure that such subtraction effectively reduces multipath interference.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Virtual MIMO transmitters, receivers, systems and methods
A system for doing BLAST with fewer receive antennas or even only one receiving antenna is provided. A system implementation architecture is provided together with a detailed analysis on its principle and theory behind this engineering solution to reduce the MIMO technology cost by using fewer antennas whilst achieving high spectrum efficiency. Examples are provided on how to implement this idea in a CDMA platform and in a OFDM platform. For the CDMA system, the code space is automatically doubled or tripled and therefore a significant system capacity increase is realized. For OFDM systems, the throughput is doubled similar as 2×2 blasting. The system complexity is minimum and full standards backward compatibility can be achieved.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Reuse of codes and spectrum in a CDMA system with multiple-sector cells
InactiveUS6388998B1Avoid mutual interferenceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentFrequency spectrumAntenna radiation patterns
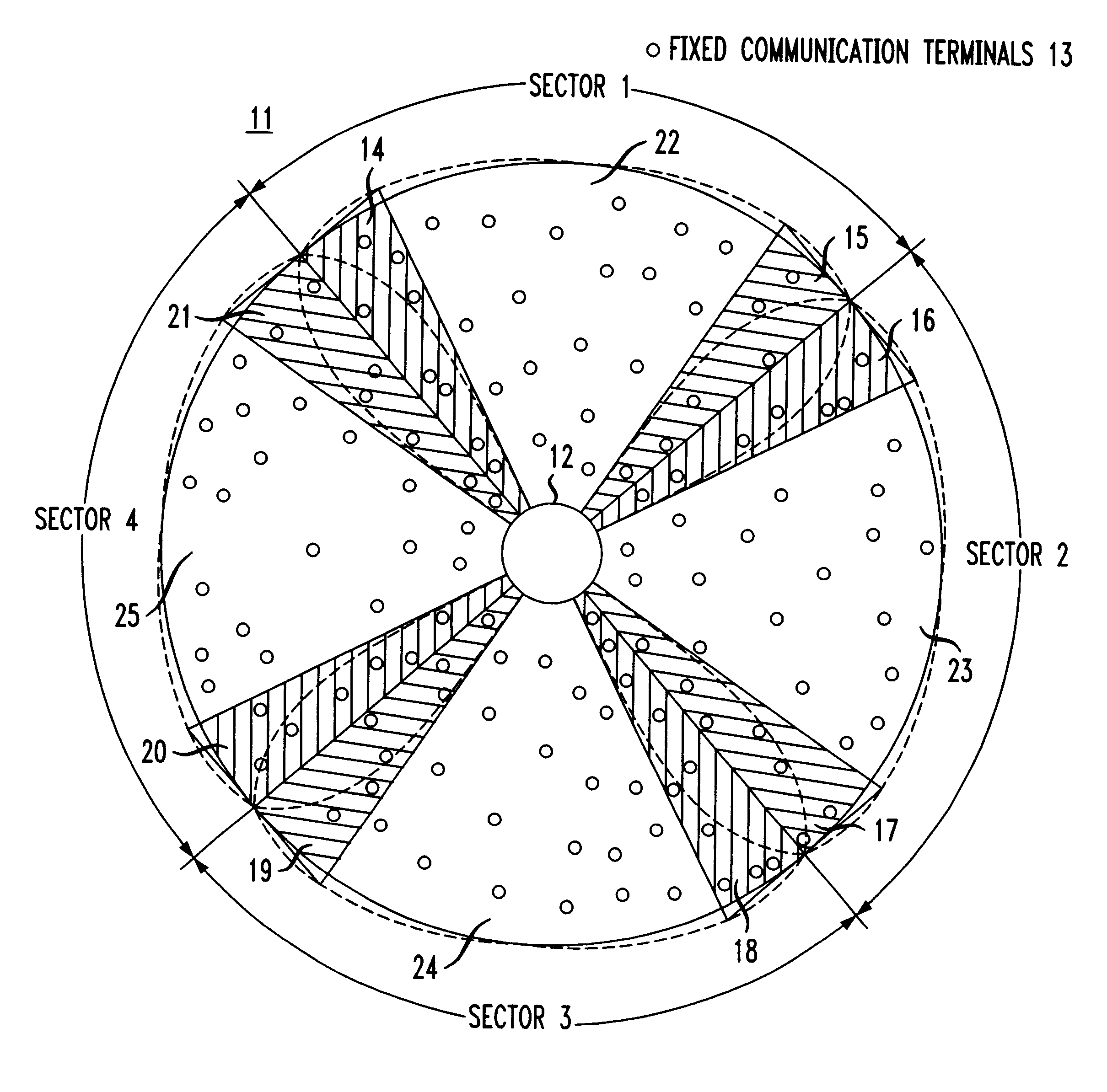
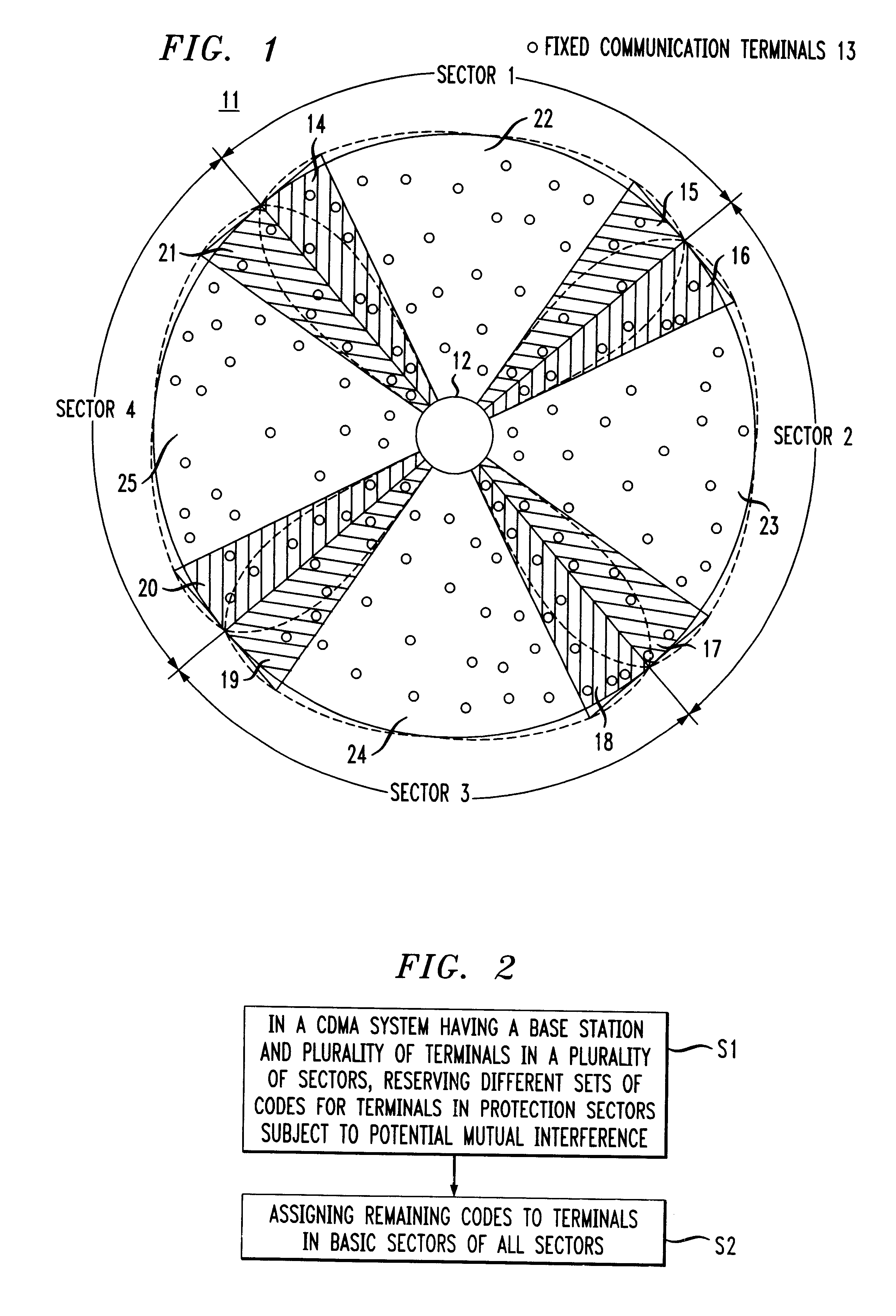
A system and a method for code division multiple access (CDMA) communication. The system includes fixed terminals communicating with a central base station. The terminals in protection sectors of each sector are configured to employ codes from different sets of codes to overcome potential mutual interference between sectors on account of antenna radiation pattern roll-off. The remaining codes, preferably the majority of the available codes, are used in any one of a plurality of basic sectors, each of which separates the protection sectors of a respective sector. For an even number of sectors in a cell, the available codes are partitioned into three groups, two for the protection sectors and one for the basic sectors. For an odd number of sectors in a cell, the available codes are partitioned into four groups, three for the protection sectors and one for the basic sectors. Protection sectors are relatively narrow but broad enough to counteract the potential mutual interference between sectors.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
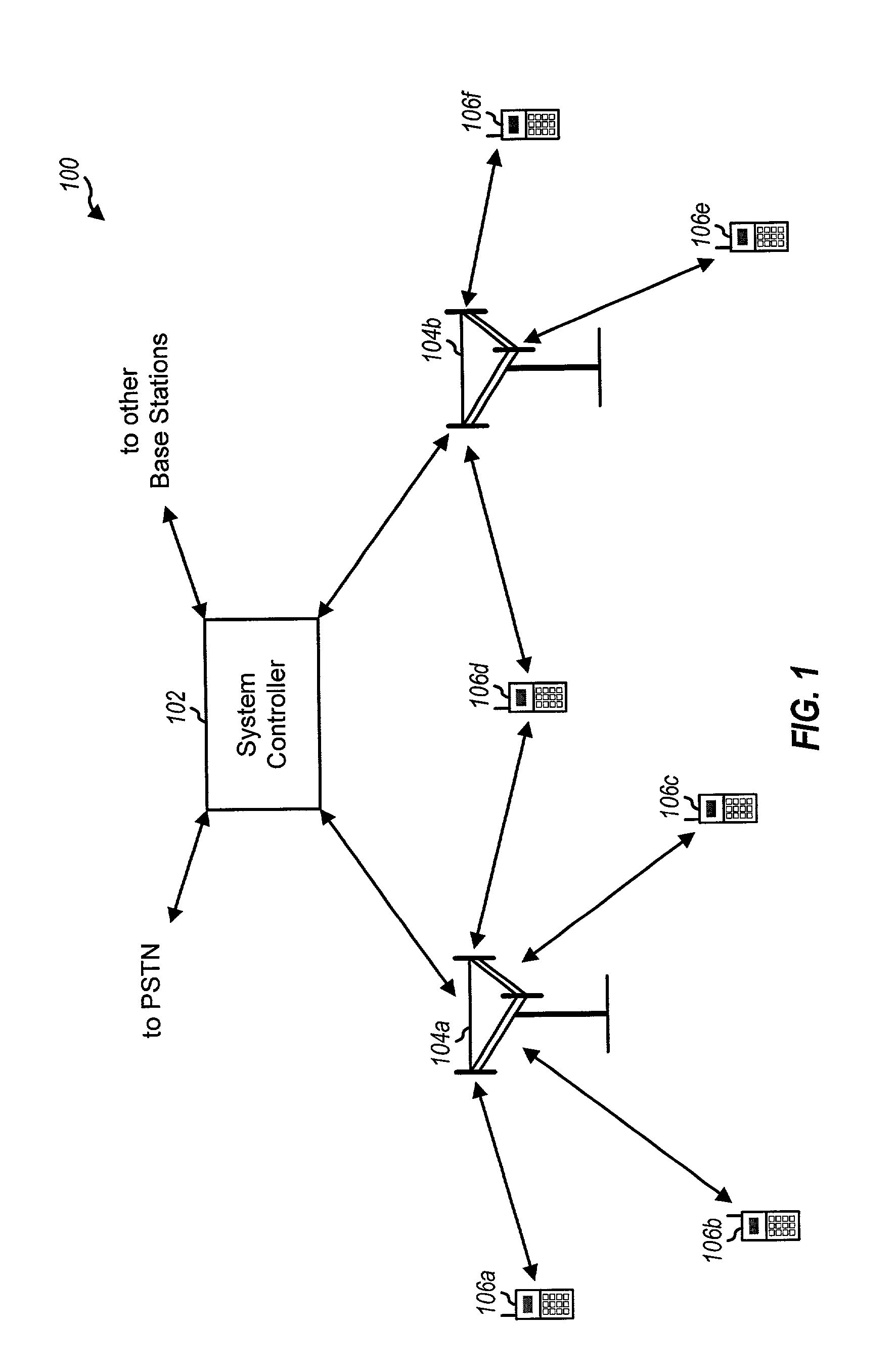
Transmission power control apparatus for a mobile communication system
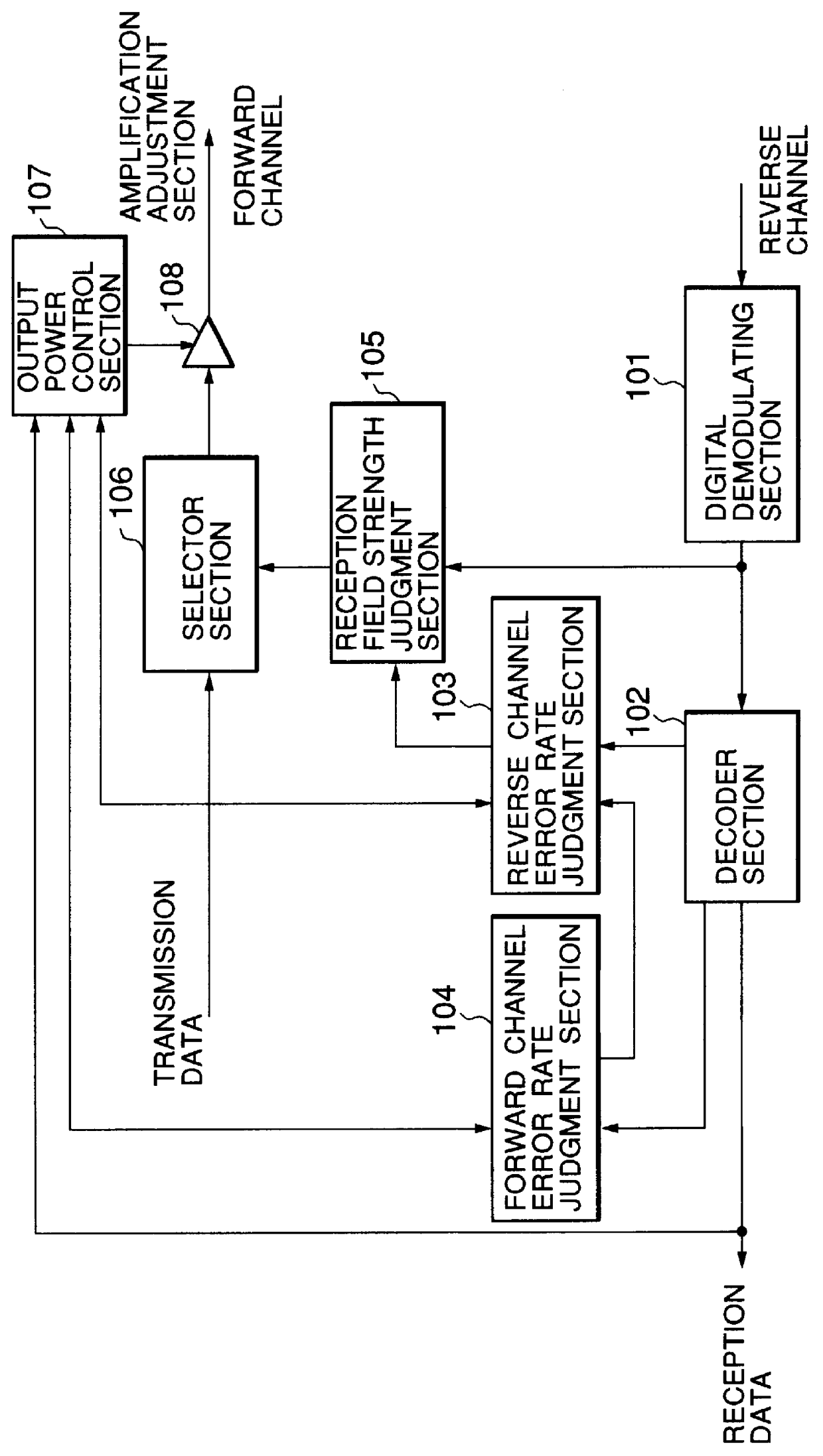
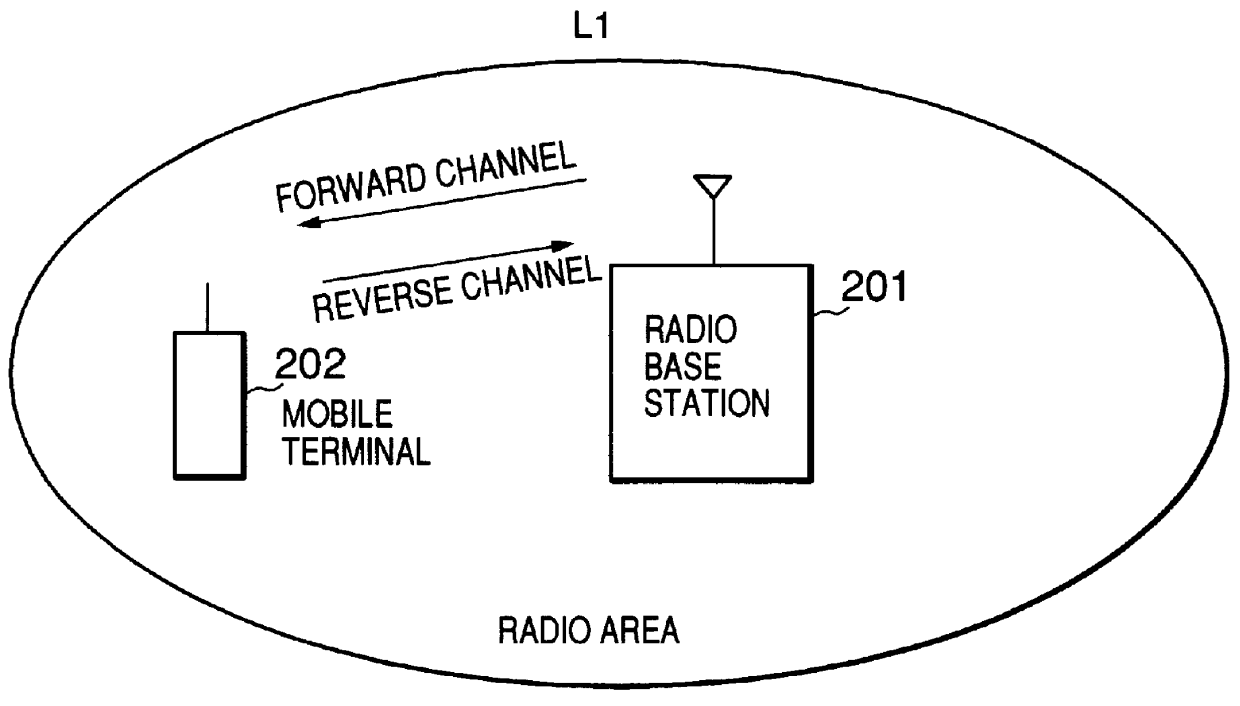
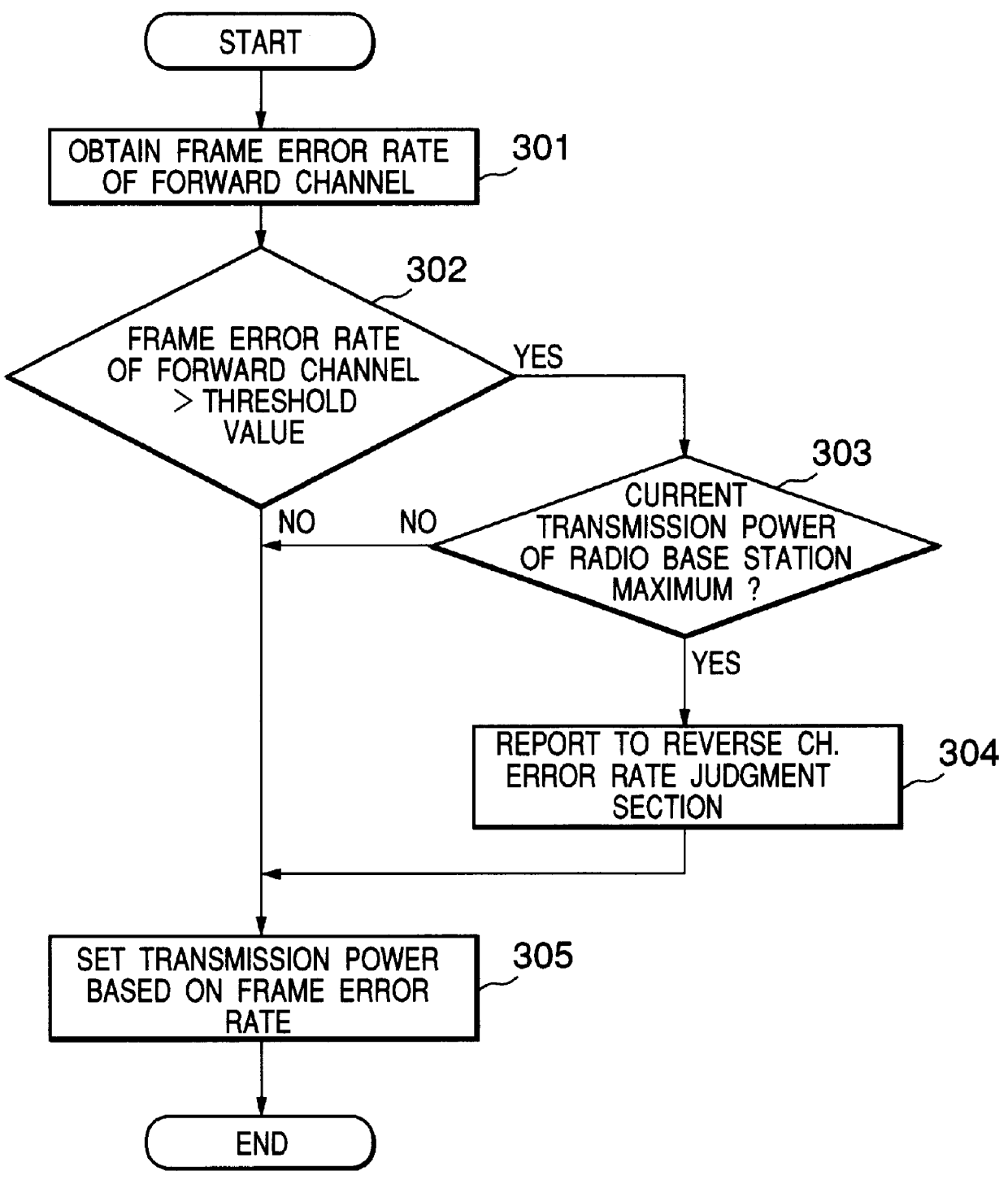
A transmission power control apparatus capable of reducing interference, in a mobile communication adopting the CDMA system, with other communications by decreasing transmission power in one direction of channel taking communication quality of other channel of direction into account is provided. A reverse channel error rate judgment section for judging a communication quality of the reverse channel by a reverse channel frame error rate detected and a forward channel error rate judgment section for judging a communication quality of the forward channel by a forward channel frame error rate reported by a mobile terminal are provided in the radio base station. The forward channel error rate judgment section, when detected, reports the state of communication degradation of own direction of channel to the reverse channel error rate judgment section which, in turn, controls to instruct the mobile terminal to decrease transmission power of the reverse channel. When communication degradation is detected by the reverse channel error rate judgment section, the state is reported to the forward channel error rate judgment section to control to decrease transmission power of the forward channel.
Owner:NEC CORP
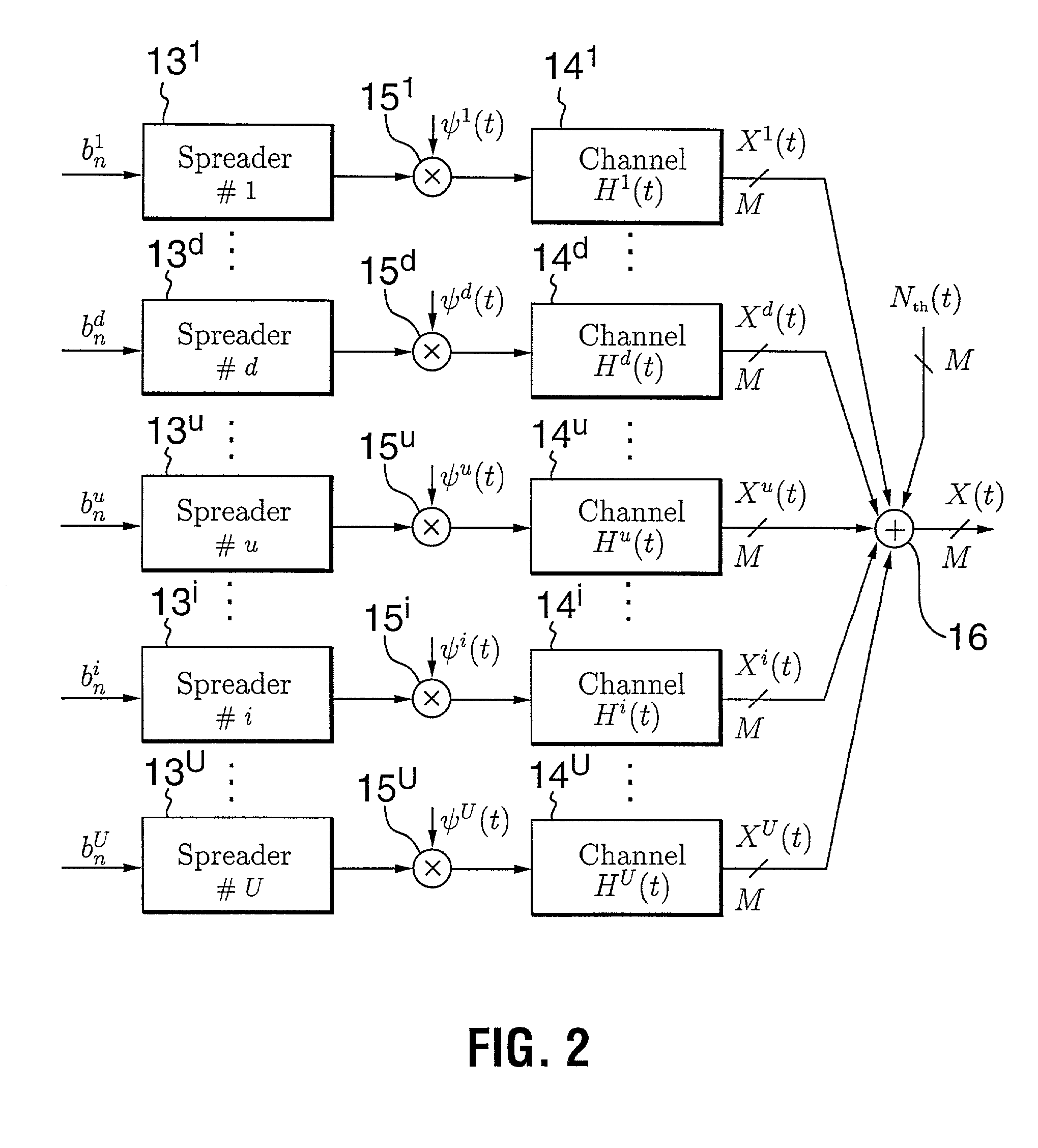
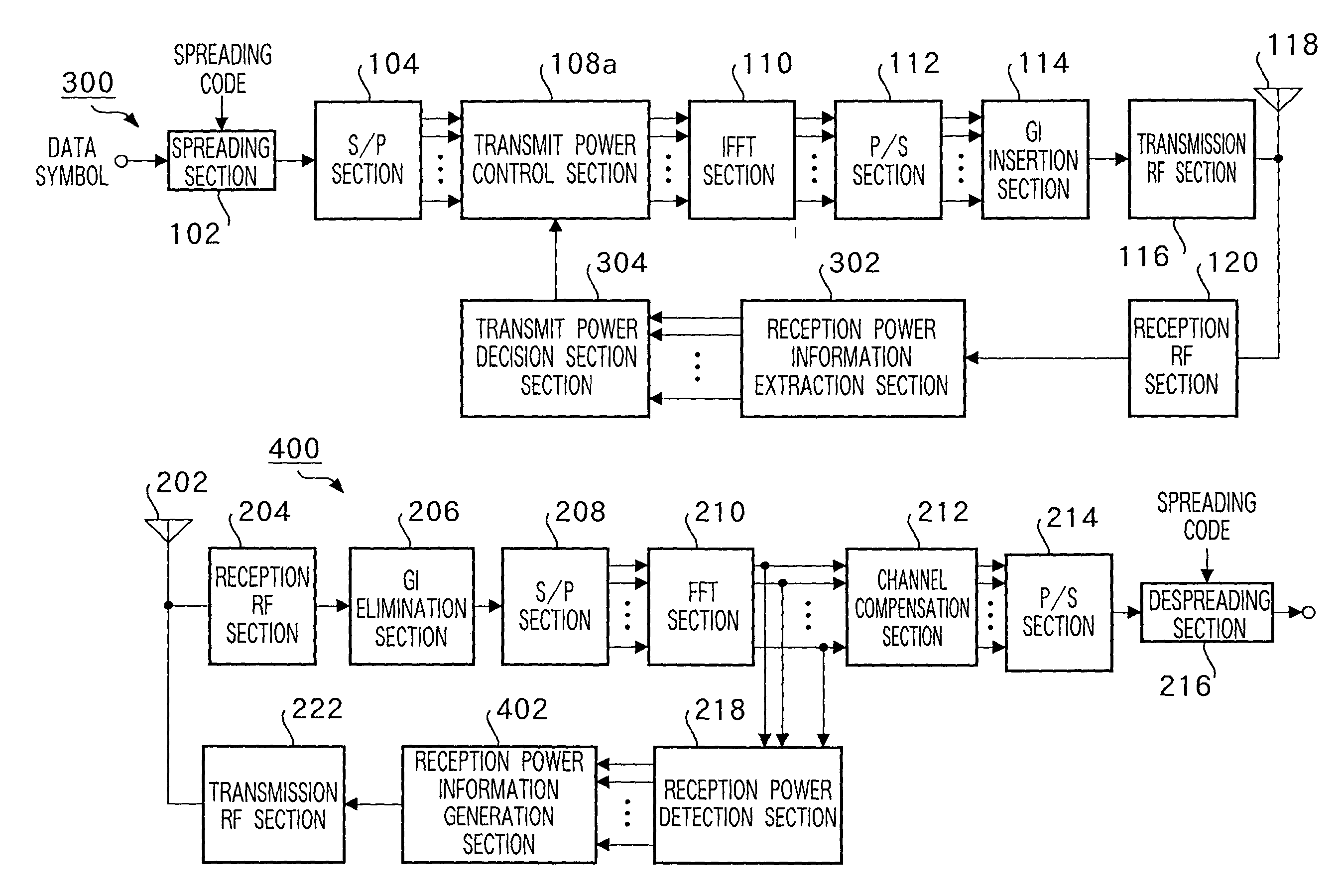
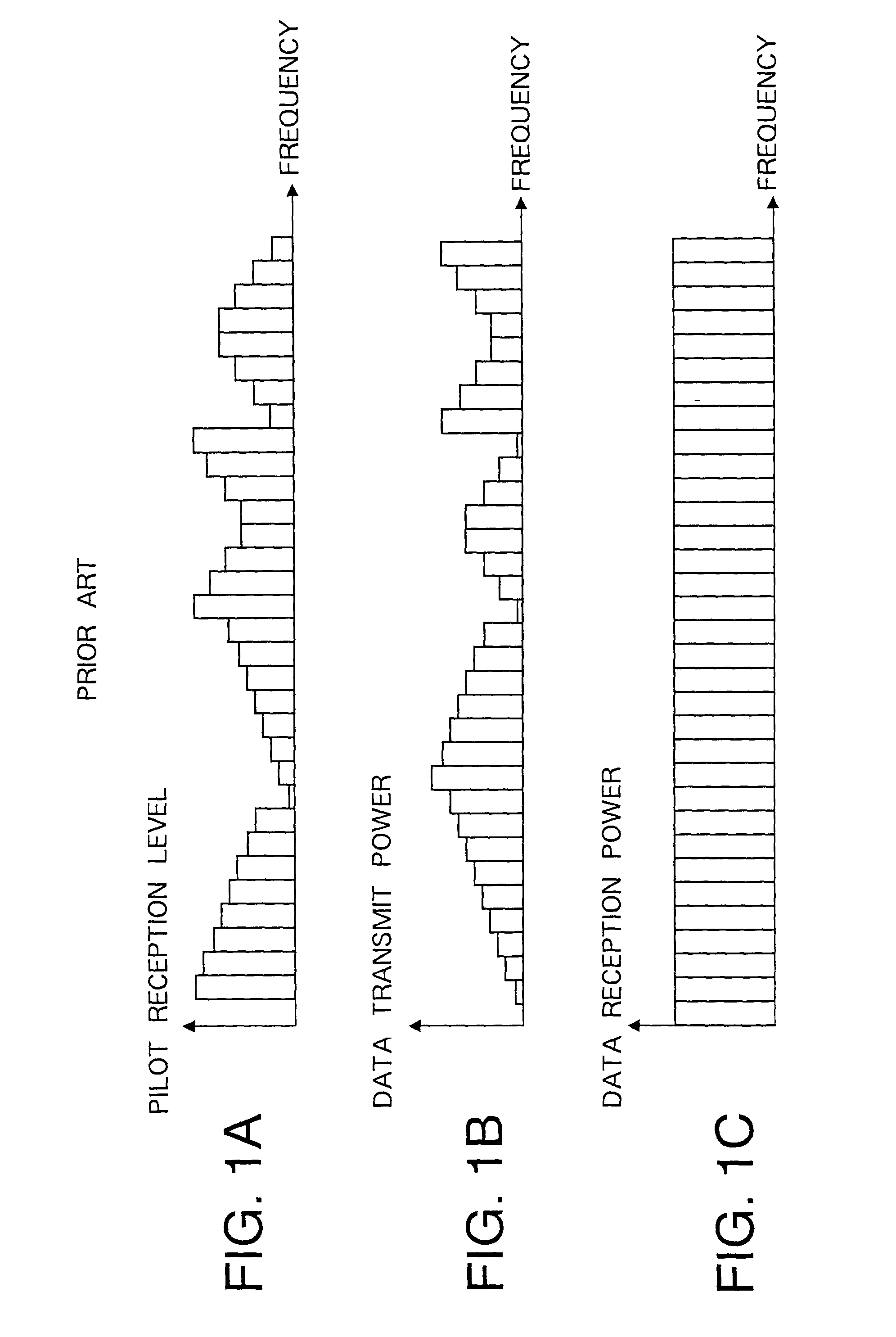
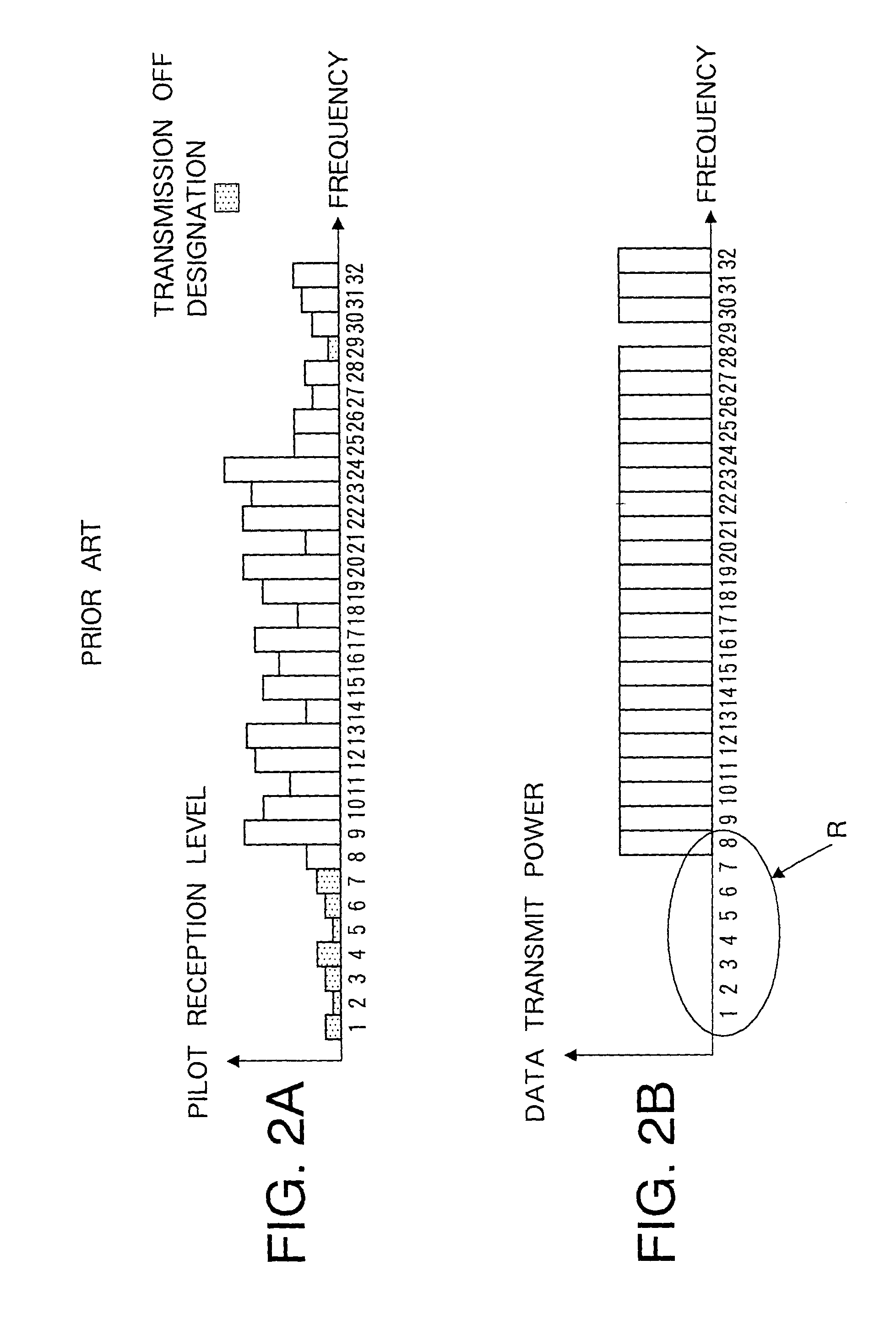
Multi-carrier transmission apparatus, multi-carrier reception apparatus, and multi-carrier radio communication method
ActiveUS7200177B2Improve information transmission efficiencyImprove reception performanceEnergy efficient ICTPower managementInformation transmissionTransmitted power
A subcarrier transmission ON / OFF control system based on an MC-CDMA system capable of improving information transmission efficiency and reception performance while keeping the number of transmission bits constant. Furthermore, a subcarrier transmit power control system based on an MC-CDMA system or OFDM system capable of improving information transmission efficiency and reception performance. The former system based on the MC-CDMA system does not carry out transmission through subcarriers of low reception quality, with no transmit power assigned (transmission OFF), assigns the corresponding transmit power to subcarriers with transmit power assigned (transmission ON) and carries out transmission (subcarrier transmission ON / OFF control) The latter system based on the MC-CDMA system or OFDM system carries out transmission according to a reception level of each subcarrier on the receiving side, with greater transmit power assigned to subcarriers with higher reception levels and smaller transmit power assigned to subcarriers with lower reception levels (subcarrier reverse transmit power control).
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
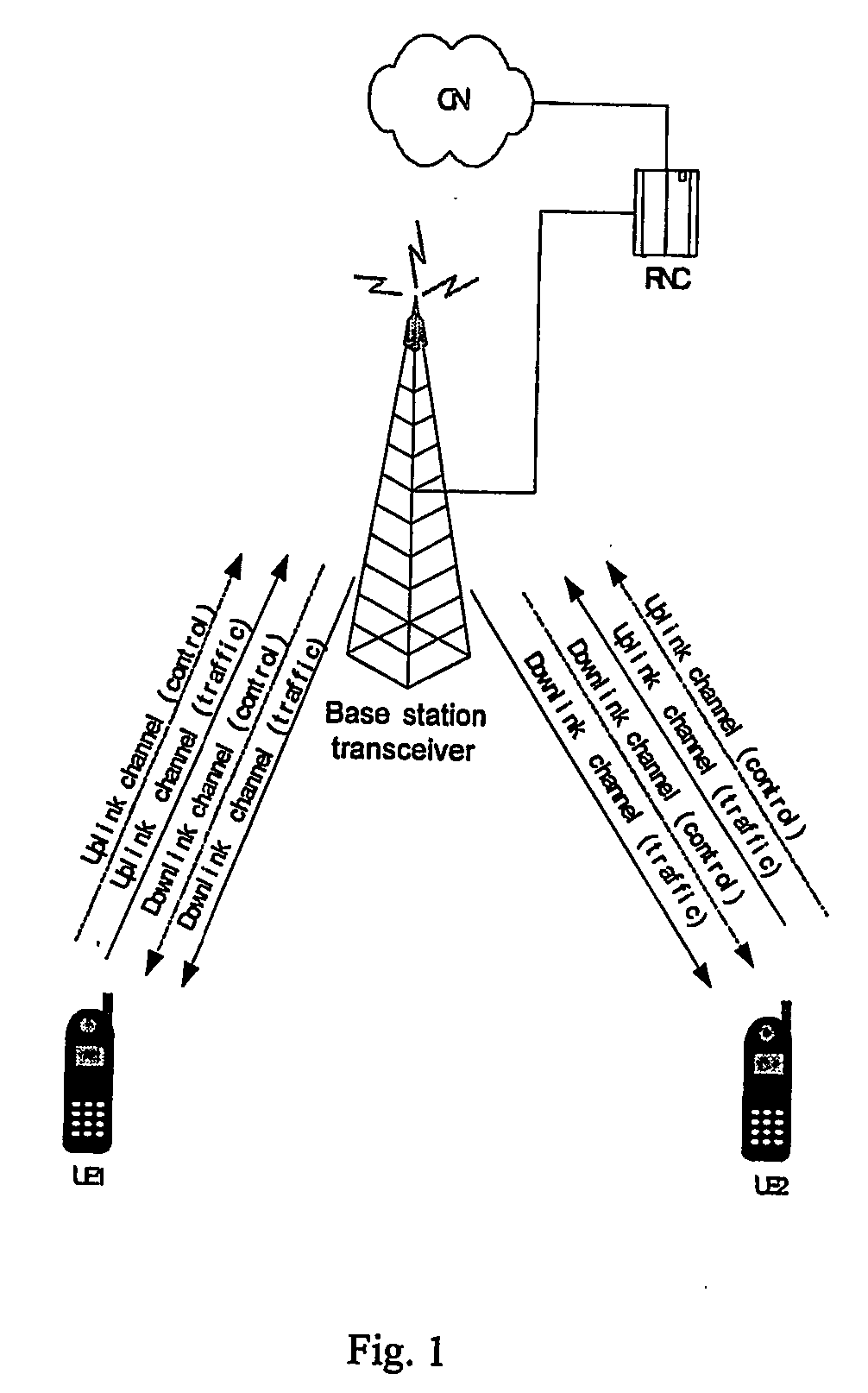
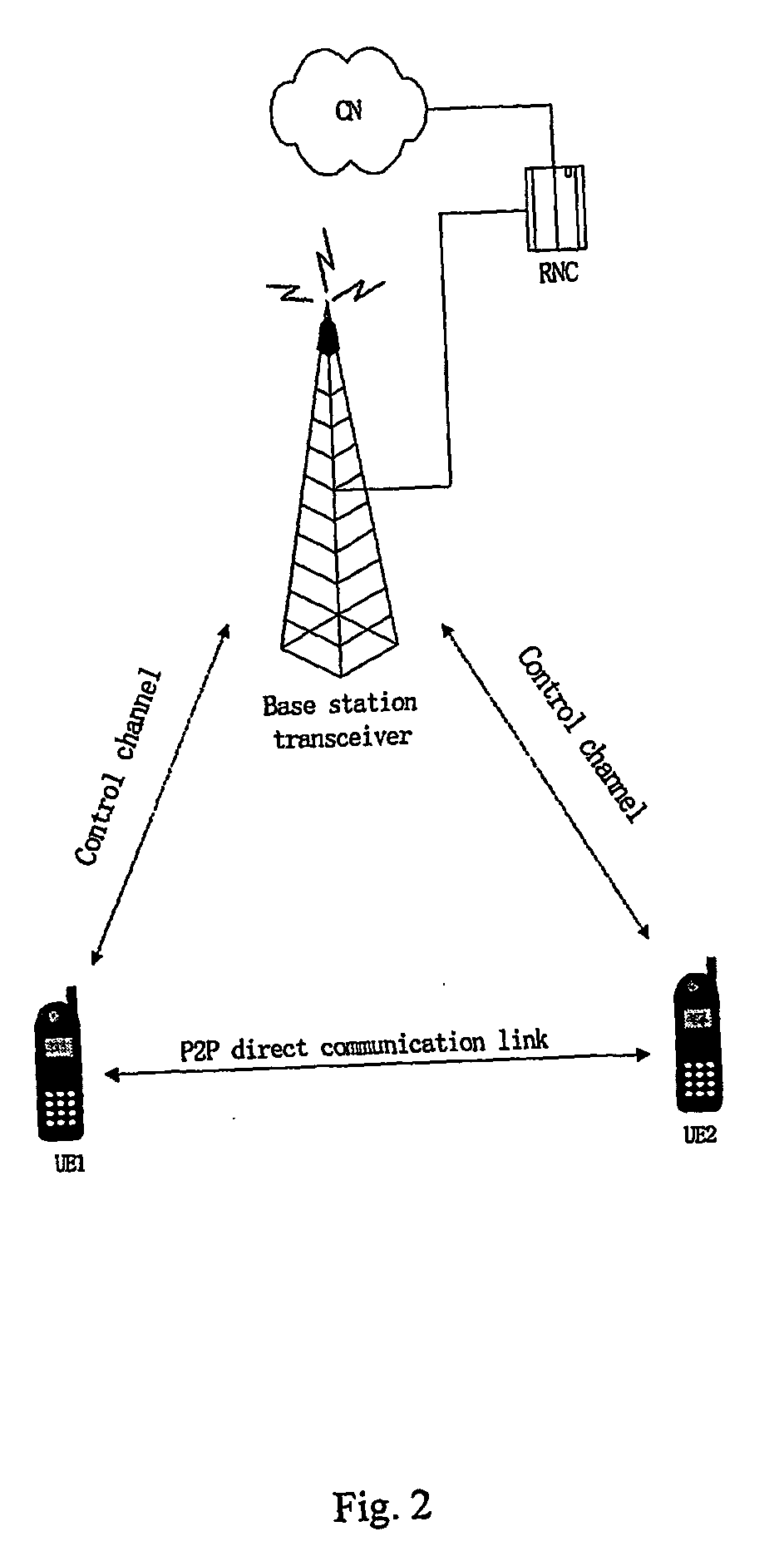
Method and apparatus for supporting direct link communication in tdd cdma system
InactiveUS20060245398A1Reduce distractionsRadio transmission for post communicationOrthogonal multiplexTelecommunicationsNetworked system
A method for supporting P2P communication between two user equipments in TDD CDMA systems, performed by user equipment, comprising: receiving signals transferred via the downlink control channel from network system; acquiring the timeslot allocation information and the spreading code allocation information of other active user equipments allocated in the specific downlink timeslot associated with the direct link used by said user equipments, according to the received signals; and synchronizing the P2P communication signals received by the user equipment and signals from network system, according to the acquired timeslot allocation information and spreading code allocation information, so as to reduce the interference caused by the downlink signals transmitted from network system to other user equipments during the P2P communication process.
Owner:PENDRAGON WIRELESS LLC
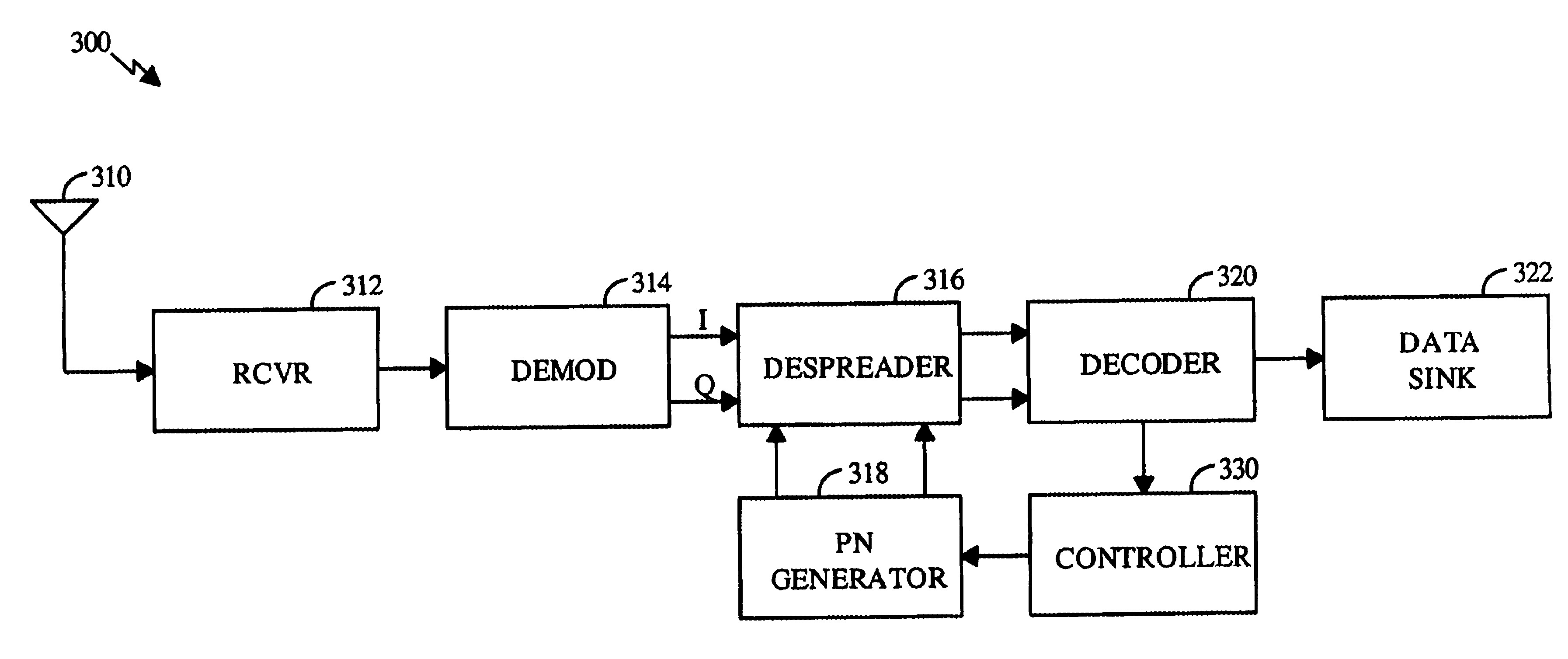
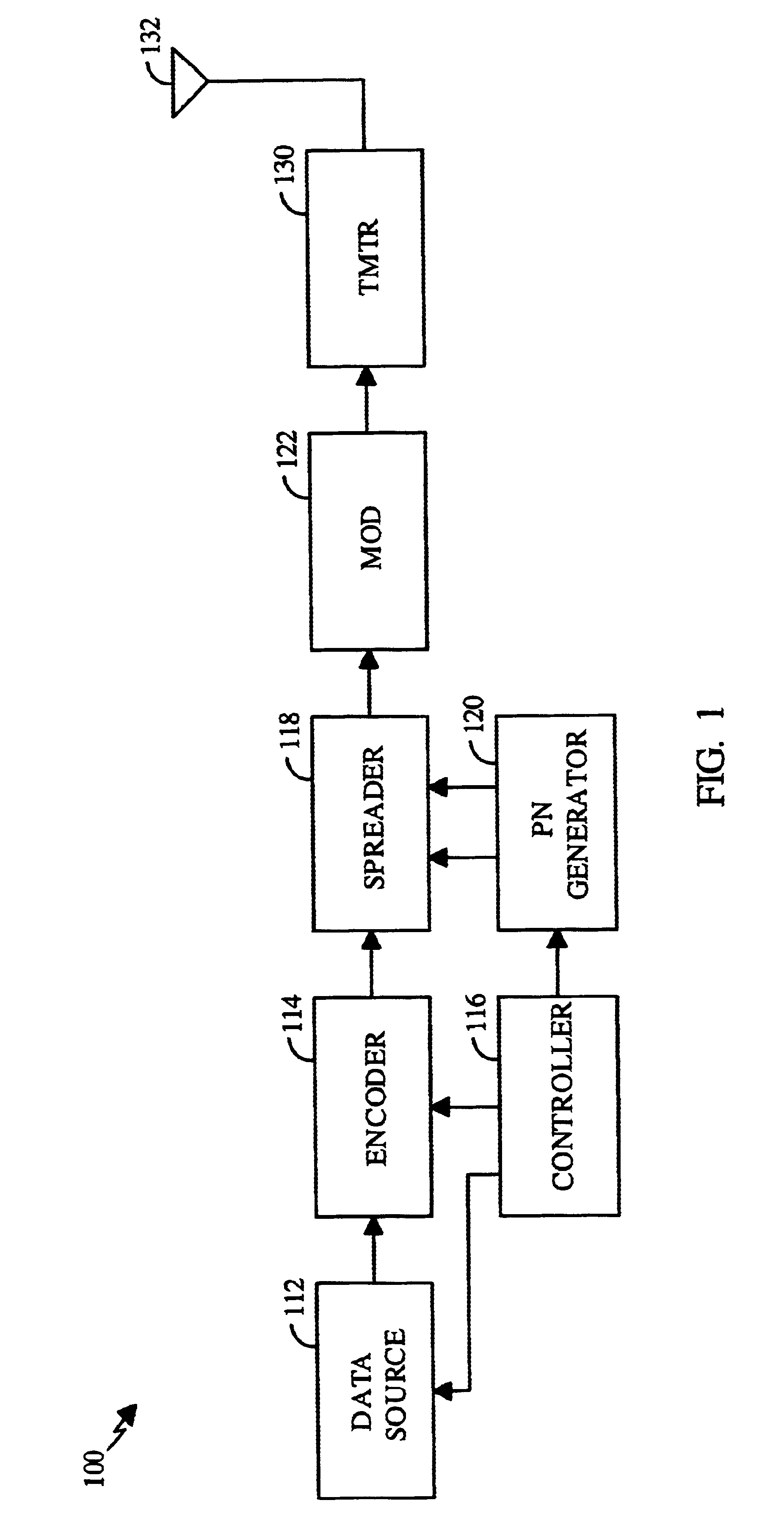
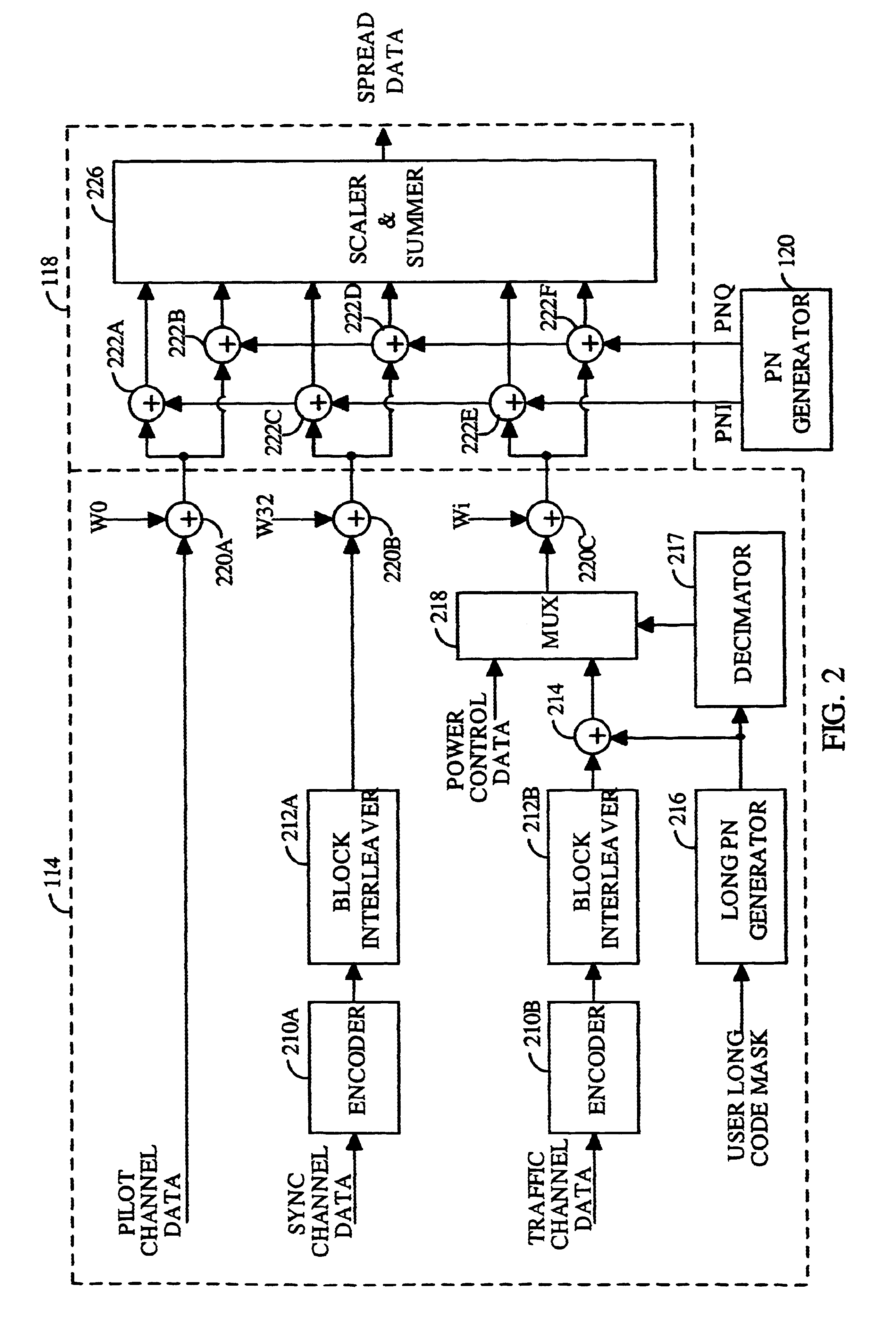
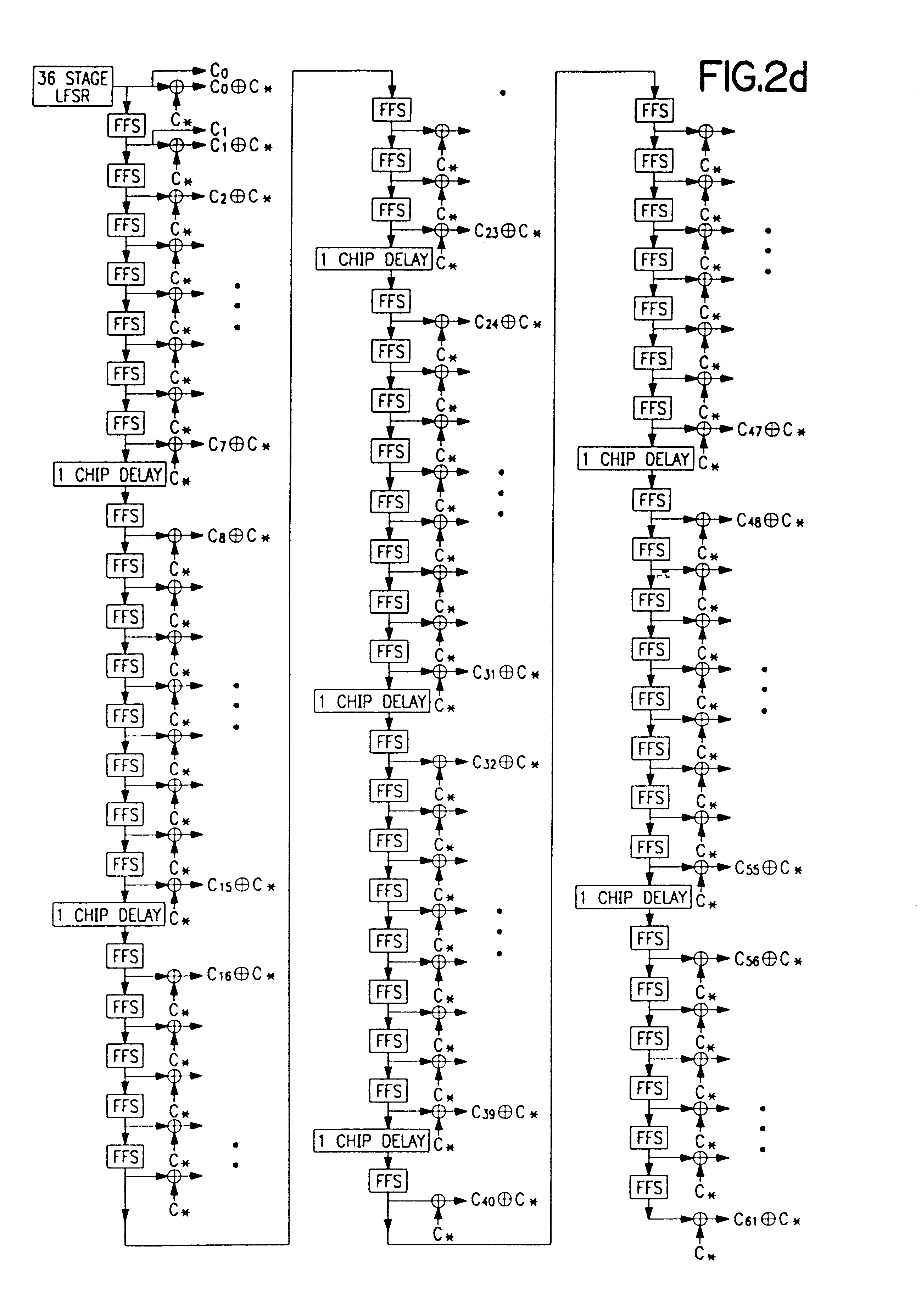
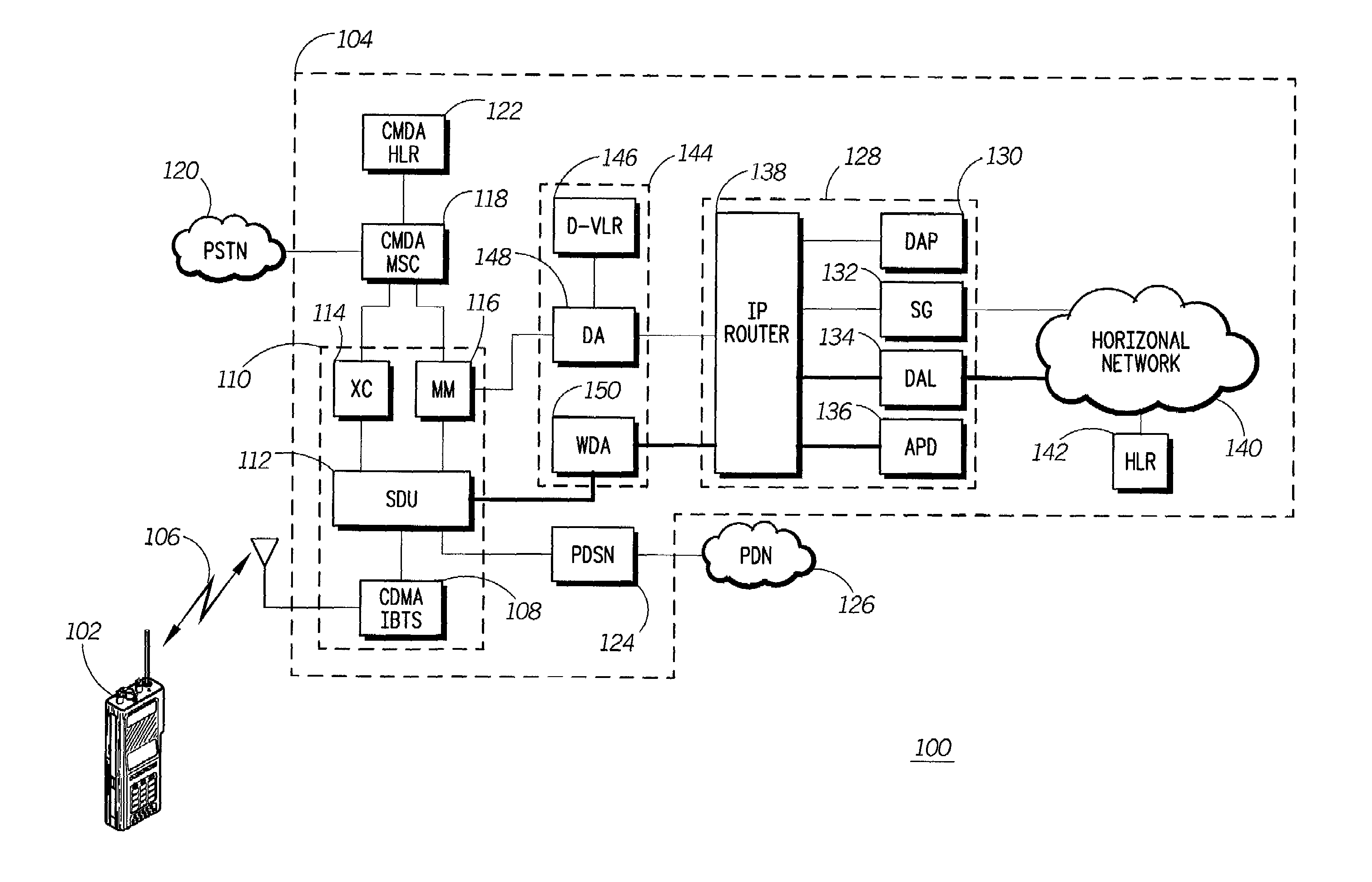
PN generators for spread spectrum communications systems
InactiveUS6661833B1Random number generatorsMultiplex code generationCommunications systemMobile station
Techniques to improve the acquisition process in a spread spectrum environment. The signals from different CDMA systems are spread with different sets of PN sequences, with the PN sequences in each set being uncorrelated to the PN sequences in the other sets. By using uncorrelated PN sequences, the likelihood of detecting a pilot signal from an undesired system is reduced or minimized, and the mean time to acquisition of the pilot signal from the desired system is improved. The mobile station can attempt to acquire the pilot signal by processing the received signal with a first set of PN sequences corresponding to a first hypothesis of the particular signal being acquired. If acquisition of the pilot signal fails, a second set of PN sequences corresponding to a second hypothesis is selected and used to process the received signal. The PN sequences in the second set are uncorrelated to the PN sequences in the first set. The PN sequences for the first set can be generated based on the characteristic polynomials defined by IS-95-A, and the PN sequences for the second set can be the reverse of the PN sequences for the first set.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
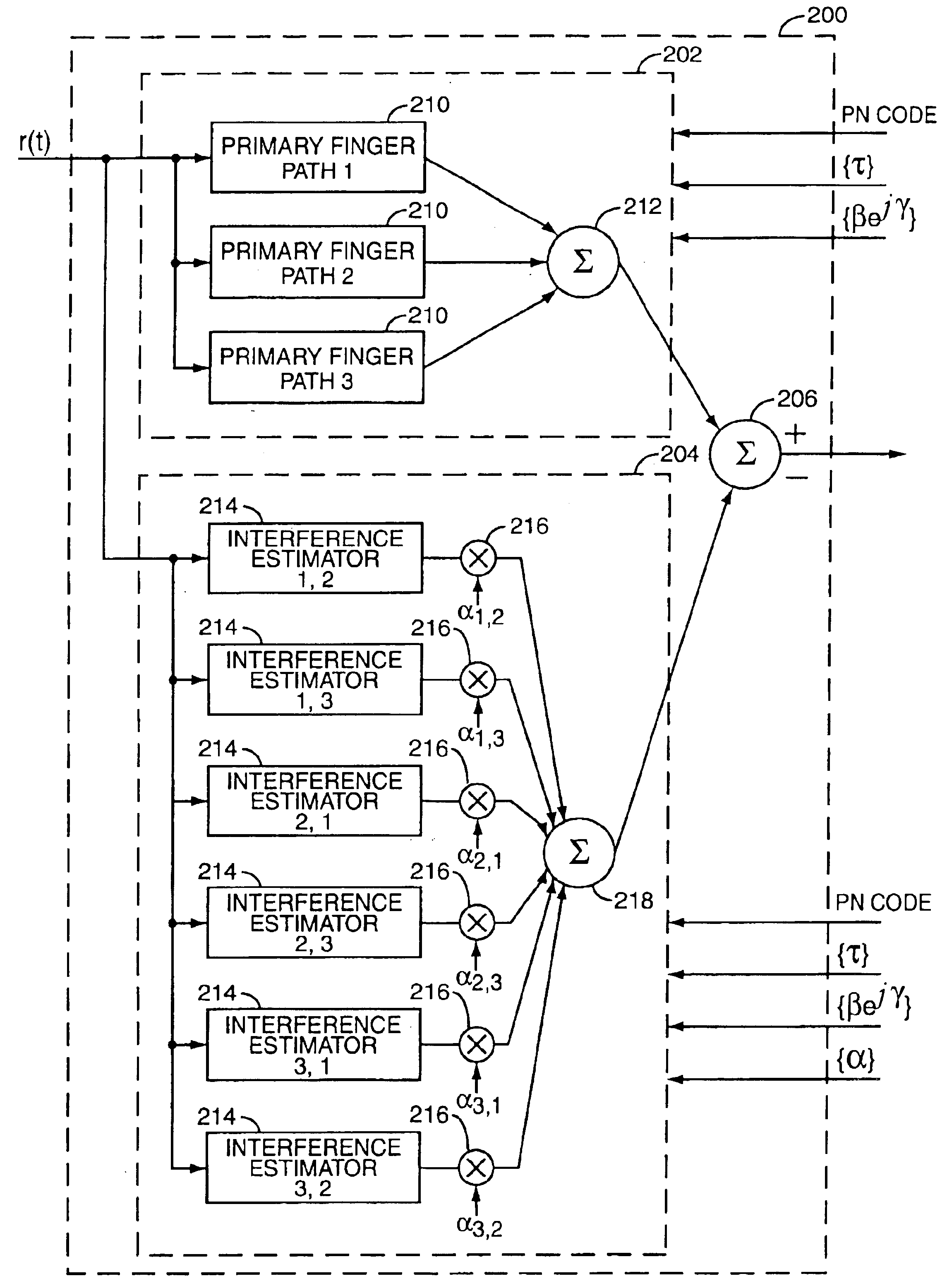
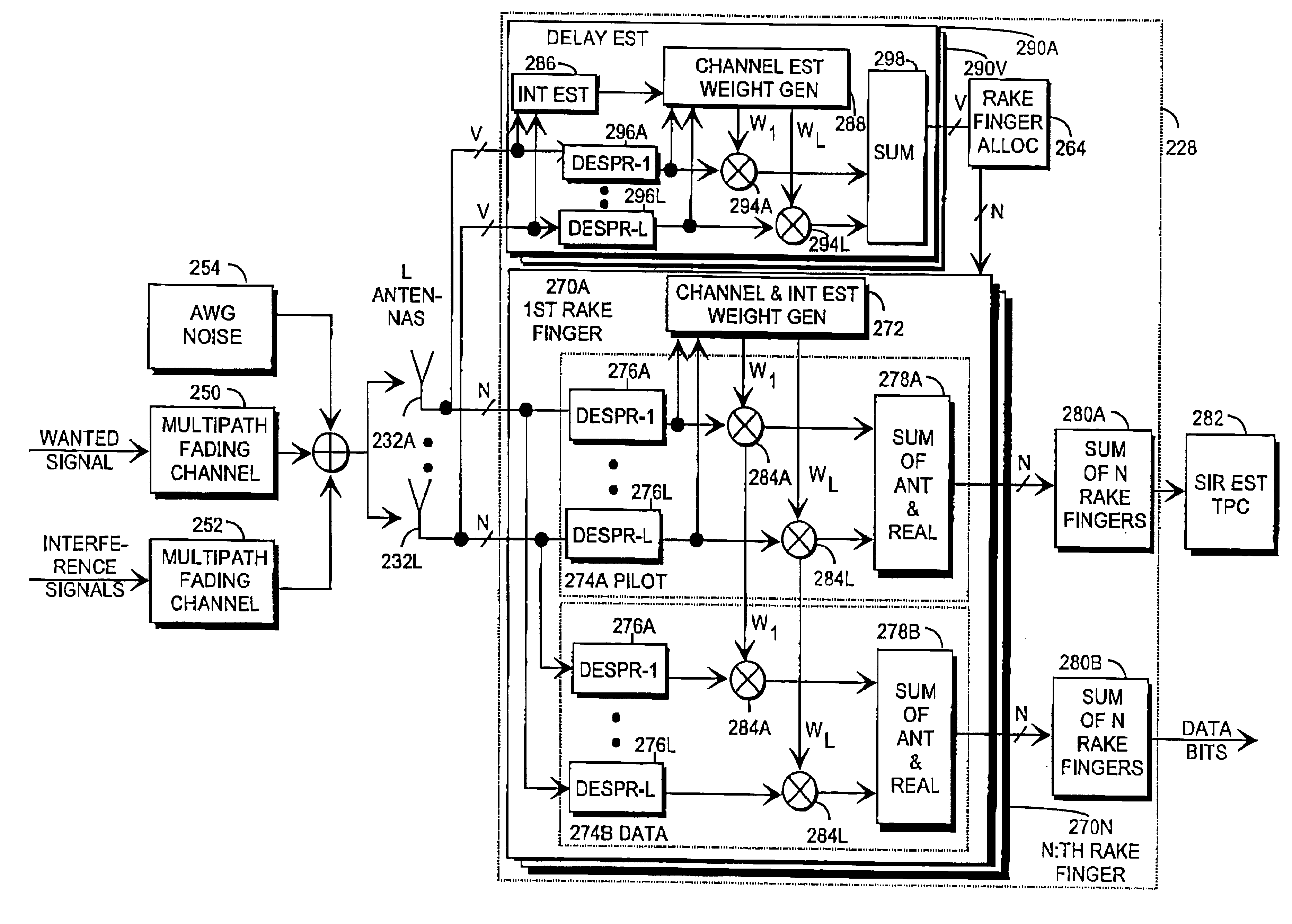
Rake receiver
The invention relates to a Rake receiver of a CDMA system using IRC. The Rake receiver comprises at least two antenna branches, at least one Rake finger, and a delay estimator. The delay estimator comprises a despreader and an allocator for selecting at least one delay, and allocating a Rake finger for processing the signal component found by informing the Rake finger of the delay found. The delay estimator further comprises: a channel estimator, an interference estimator for generating an interference signal, a weighting coefficient part for providing each antenna branch with weighting coefficients maximizing the Signal-to-Interference-and-Noise Ratio, a multiplier for multiplying the pilot part by a weighting coefficient, and an antenna branch summer for combining the despread pilot parts, received via the separate antenna branches and multiplied by the weighting coefficient, to one combined pilot signal, on which combined pilot signal the selection is based in the allocator.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Multi-carrier operation in data transmission systems
Multi-carrier point-to-multi-point CDMA system implementation reduces hardware changes in legacy single-carrier systems. The number of common downlink channels, such as timing / synchronization and paging channels, is reduced by designating an anchor carrier for transmitting these channels. Procedures for adding carriers and carrier acquisition are simplified through common carrier timing, signaling by the network to the user equipment (UE) of timing offsets and scrambling code selection, and other measures. Channel reuse is employed to minimize changes in asymmetric systems with different numbers of uplink and downlink carriers. Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) field is divided into multiple subfields to enable transmission of multiple CQIs and ACK / NACK indicators on one uplink carrier.; Joint and separate scheduling schemes are shown for concurrent scheduling of a data stream transmission to a UE via multiple downlink carriers.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for pseudo-random noise offset reuse in a multi-sector CDMA system
ActiveUS6909707B2Substation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCdma systemsSelf adaptive
A method and apparatus for reuse of pseudo-random noise (PN) offsets within a cell of a wireless communication system such as a multi-sector CDMA system. Adaptive antenna arrays are employed to form the multiple sector areas within the CDMA cell. A forward link data channel is established between a mobile unit and a base station via sectors that share or reuse comment PN offsets, thereby providing desirable transmit diversity.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Smart antenna CDMA wireless communication system
InactiveUS6980527B1Increase capacityImprove performanceSynchronisation arrangementSpatial transmit diversityFir systemDownlink beamforming
A TDD antenna array S-CDMA system for increasing the capacity and quality of a wireless communications is disclosed. By simultaneous exploiting the spatial and code diversities, high performance communications between a plurality of remote terminals and a base station is achieved without sacrificing system flexibility and robustness. The time-division-duplex mode together with the inherent interference immunity of S-CDMA signals allow the spatial diversity to be exploited using simple and robust beamforming rather than demanding nulling. Measurements from an array of receiving antennas at the base station are utilized to estimate spatial signatures, timing offsets, transmission powers and other propagation parameters associated with a plurality of S-CDMA terminals. Such information is then used for system synchronization, downlink beamforming, as well as handoff management. In an examplary embodiment, the aforementioned processing is accomplished with minimum computations, thereby allowing the disclosed system to be applicable to a rapidly varying environment. Among many other inherent benefits of the present invention are large capacity and power efficiency, strong interference / fading resistance, robustness power control, and easy hand-off.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
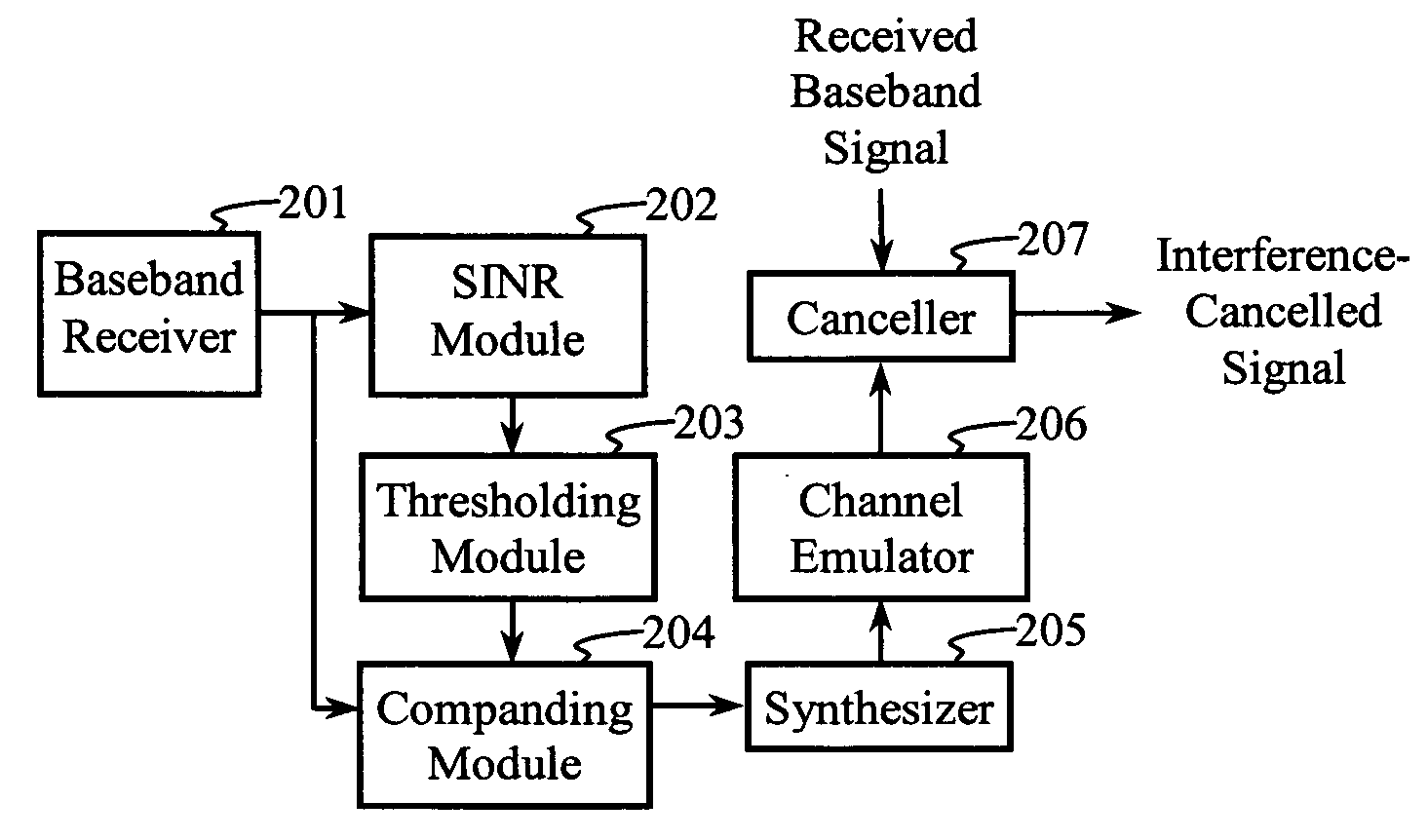
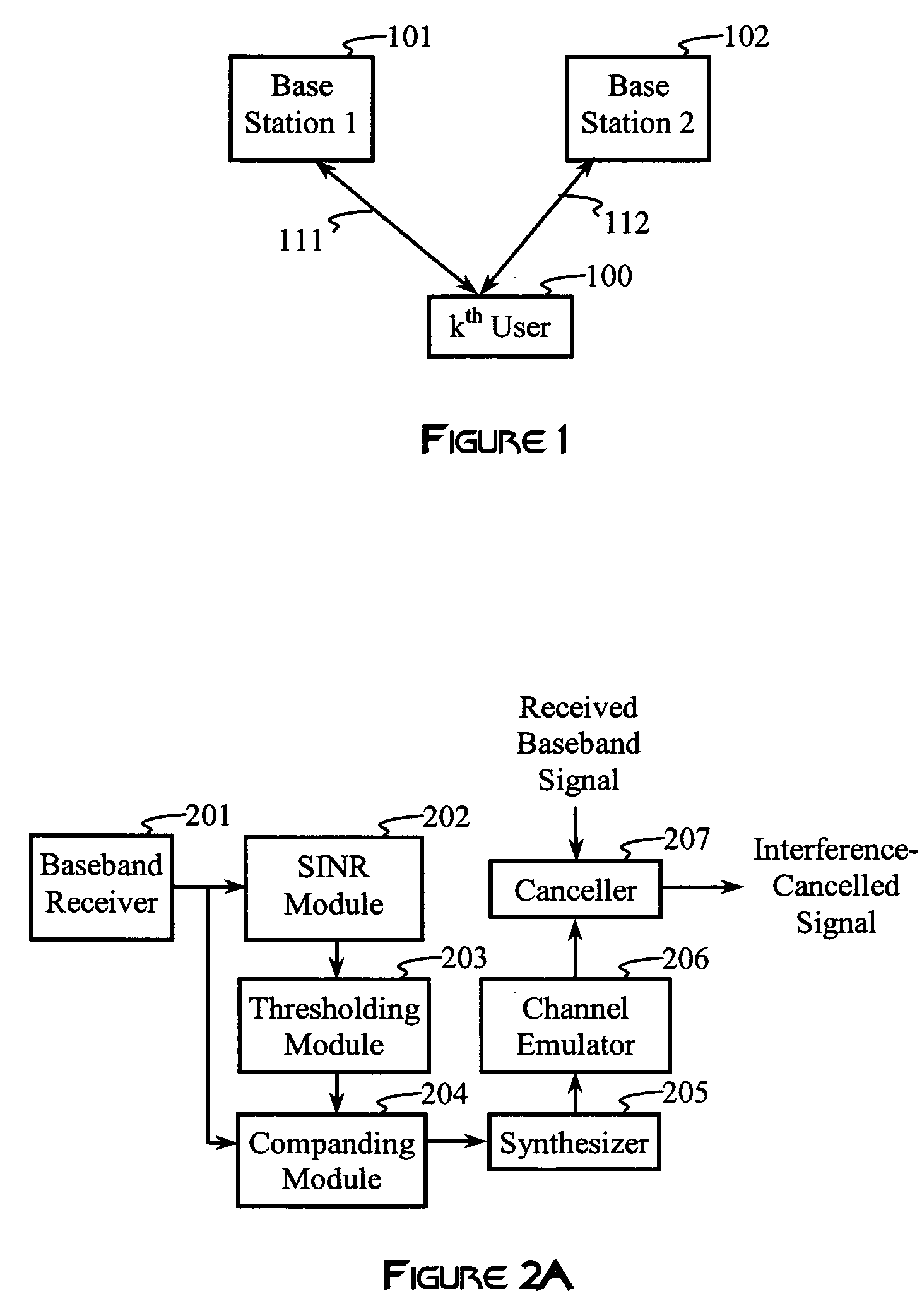
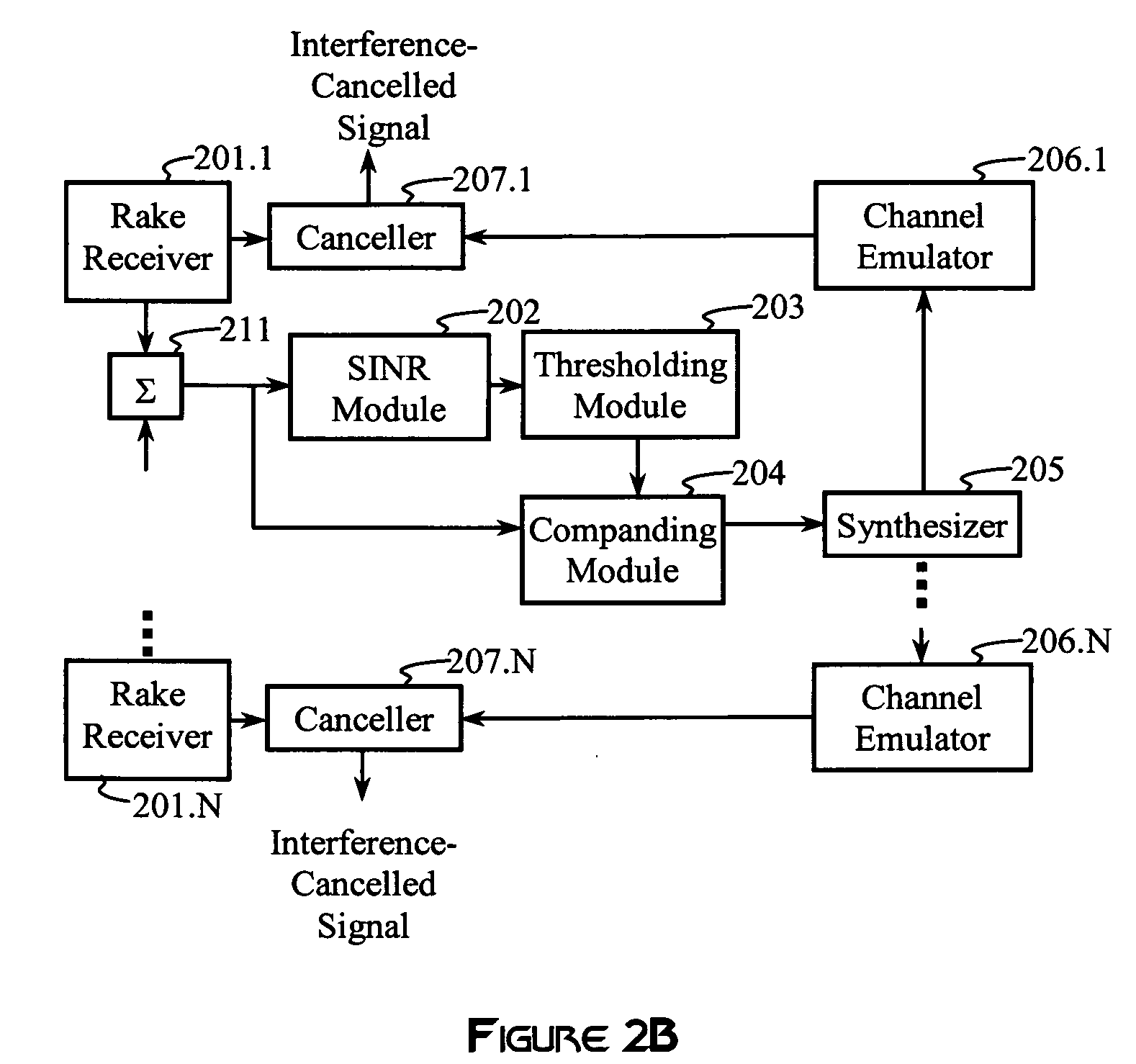
Soft weighted interference cancellation for CDMA systems
ActiveUS20060227854A1Quantity maximizationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionInterference eliminationInterference cancelation
Interference is cancelled from a baseband signal by synthesizing interference from estimated symbols in interfering subchannels. The estimated symbols are hard-coded, soft weighted, or zeroed, depending on the value of an estimated pre-processed signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio (SINR) in each subchannel in order to maximize a post-processed SINR. The estimated pre-processed SINR is obtained from averages of estimated symbol energies and estimated noise variances, or from related statistical procedures.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Method for automatic maintenance neighborlist in CDMA system
InactiveCN1434595AReduce workloadReduce overheadCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsEngineeringMobile communication systems
This invention puts forward an automatic maitaining neighborlist method in CDMA system in which, switching is an important method for guaranteeing normal talk between local area, yet, the successful switch is to configurate correct heighborlist information at the network side, actually, base station distribution information by network planning and the neighborlist got frame actual path test are not very accurate. This invented method will get the lost matched heighbor in network plan and add the local information not listed in the list reported by mobile station to the neightborlist after filtering and matching the unlisted areas.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
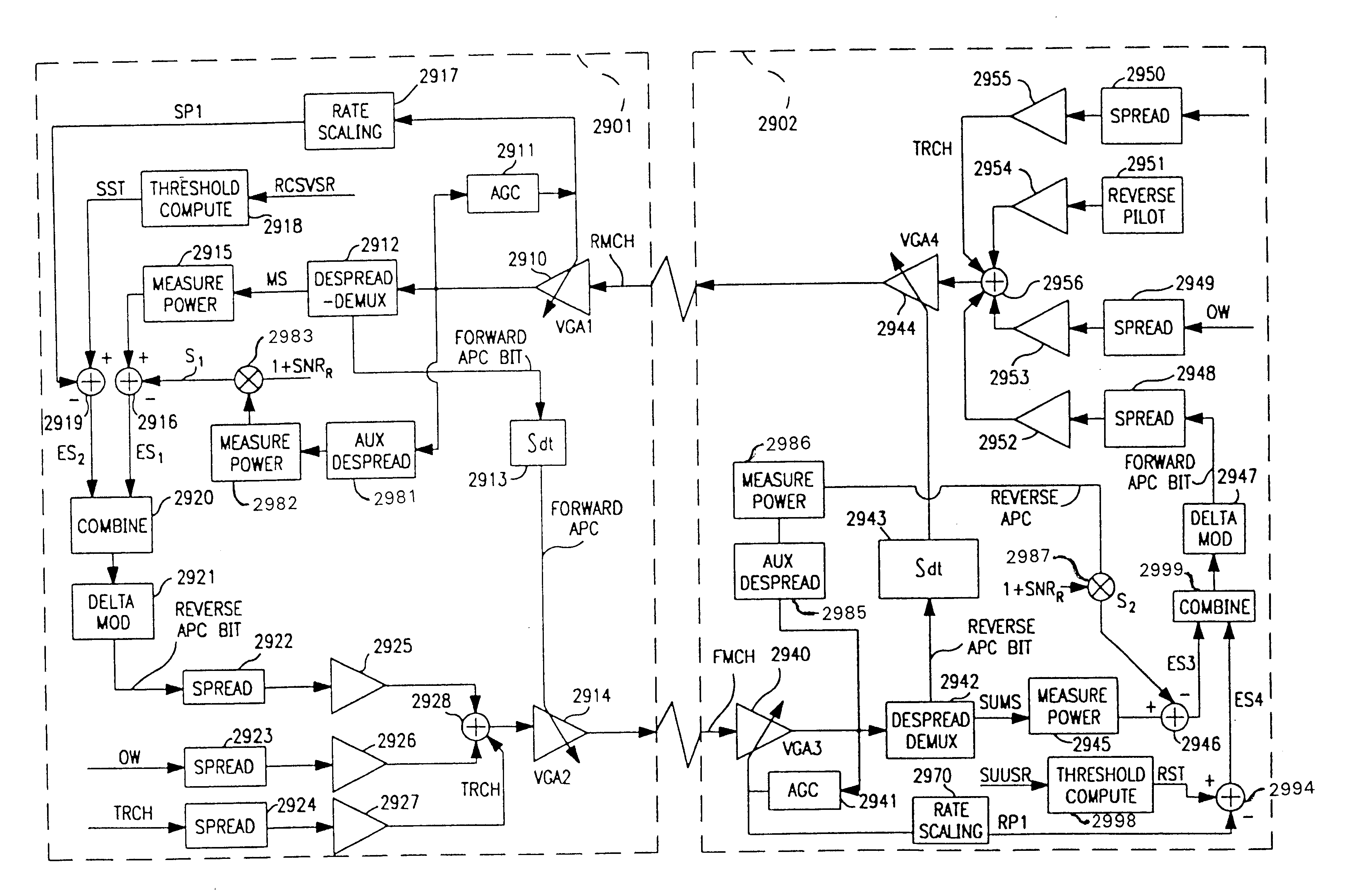
Apparatus for adaptive forward power control for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20020057659A1Easy to liftShortens channel acquisition timeError preventionRadio transmission for post communicationSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioSet point
A code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) system employing spread-spectrum modulation. The CDMA system has a base station (BS), and a plurality of subscriber units. The signals transmitted between the base station and subscriber unit use spread-spectrum modulation. The improvement apparatus for adaptive forward power control (APC) from a base station (BS) to a subscriber unit (SU), includes sending from the base station, using spread-spectrum modulation, a BS-spreading code on a forward channel. The subscriber unit despreads the BS-spreading code on the forward channel as a despread signal, determines a first power level Pd which includes power of the despread signal plus noise and a second power level PN, which includes despread-noise power. The subscriber unit determines a first error signal e1, from the first power level Pd, the second power level PN, and a required signal-to-noise ratio SNRREQ for service type, and a second error signal e2, from a measure of total received power Pr and an automatic gain control (AGC) set point Po. The subscriber unit forms a combined error signal from the first error signal e1, the second error signal e2, a first weight a1 and a second weight a2, and hard limits the combined error signal to form a single APC bit. The APC bit is transmitted to the base station. In response to the APC bit, the base station adjusts transmitter power to the subscriber unit.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Multi-carrier transmission/reception apparatus
InactiveUS7386055B2Radio resourceSuppress interferenceAssess restrictionConnection managementCarrier signalCell search
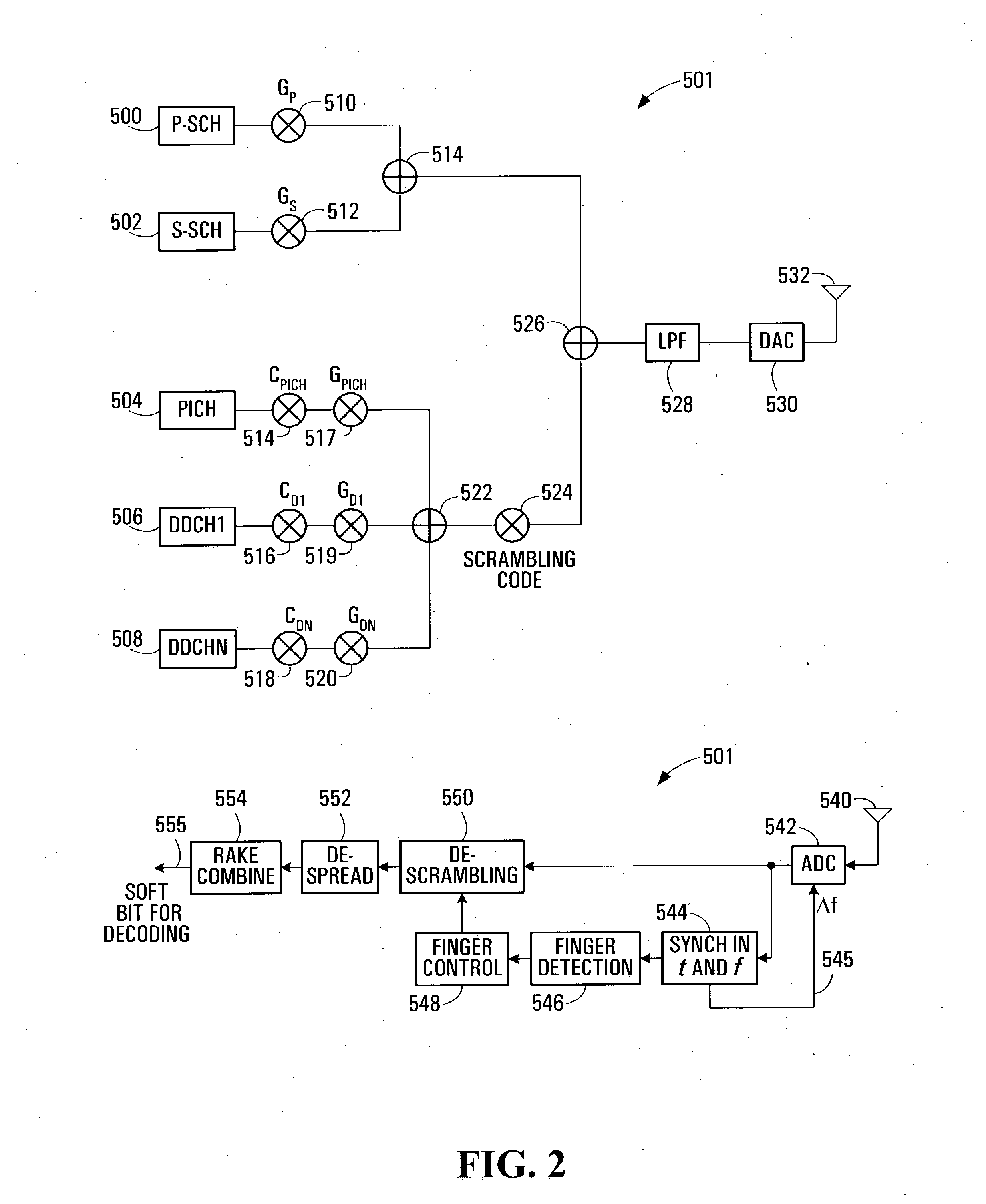
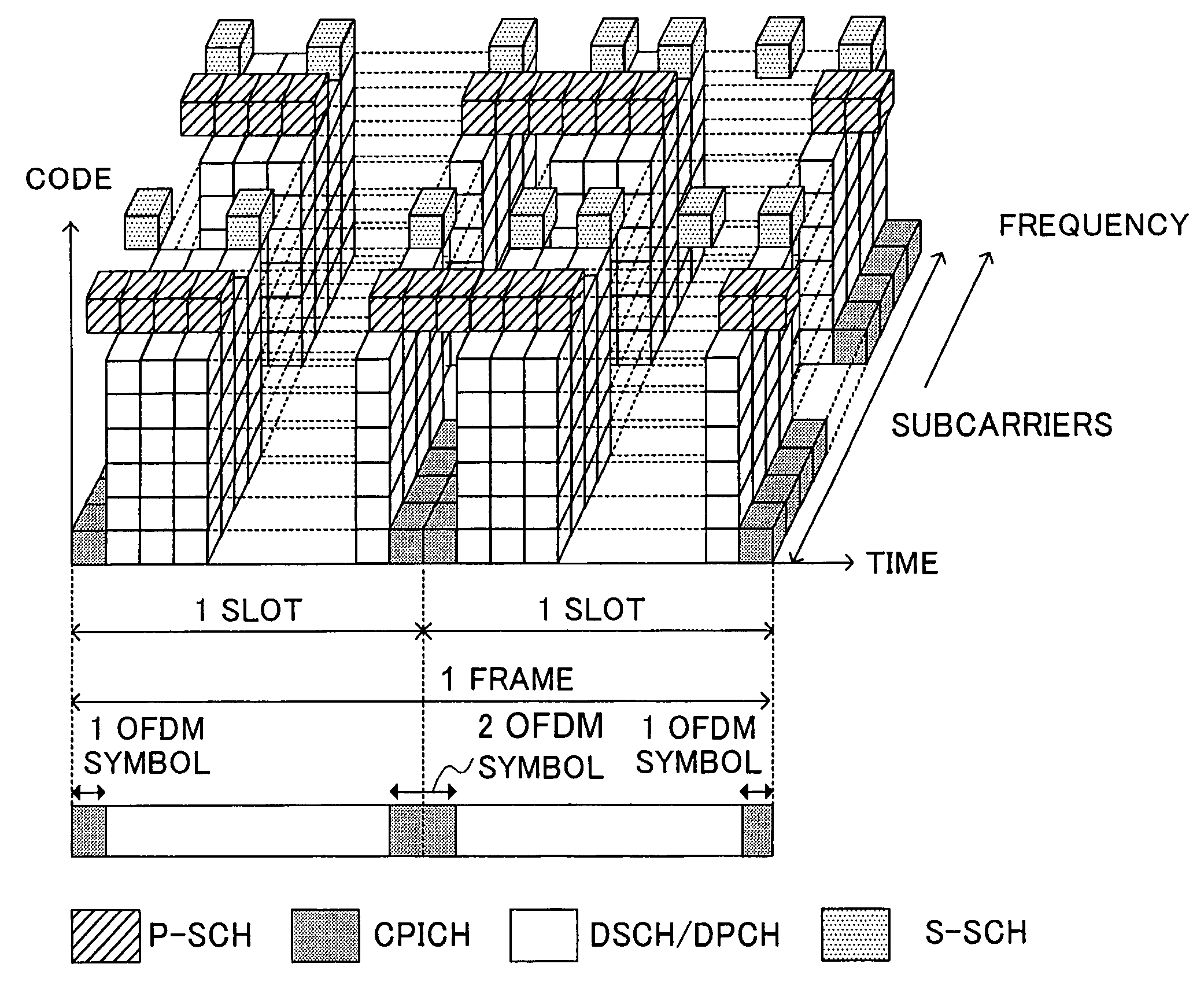
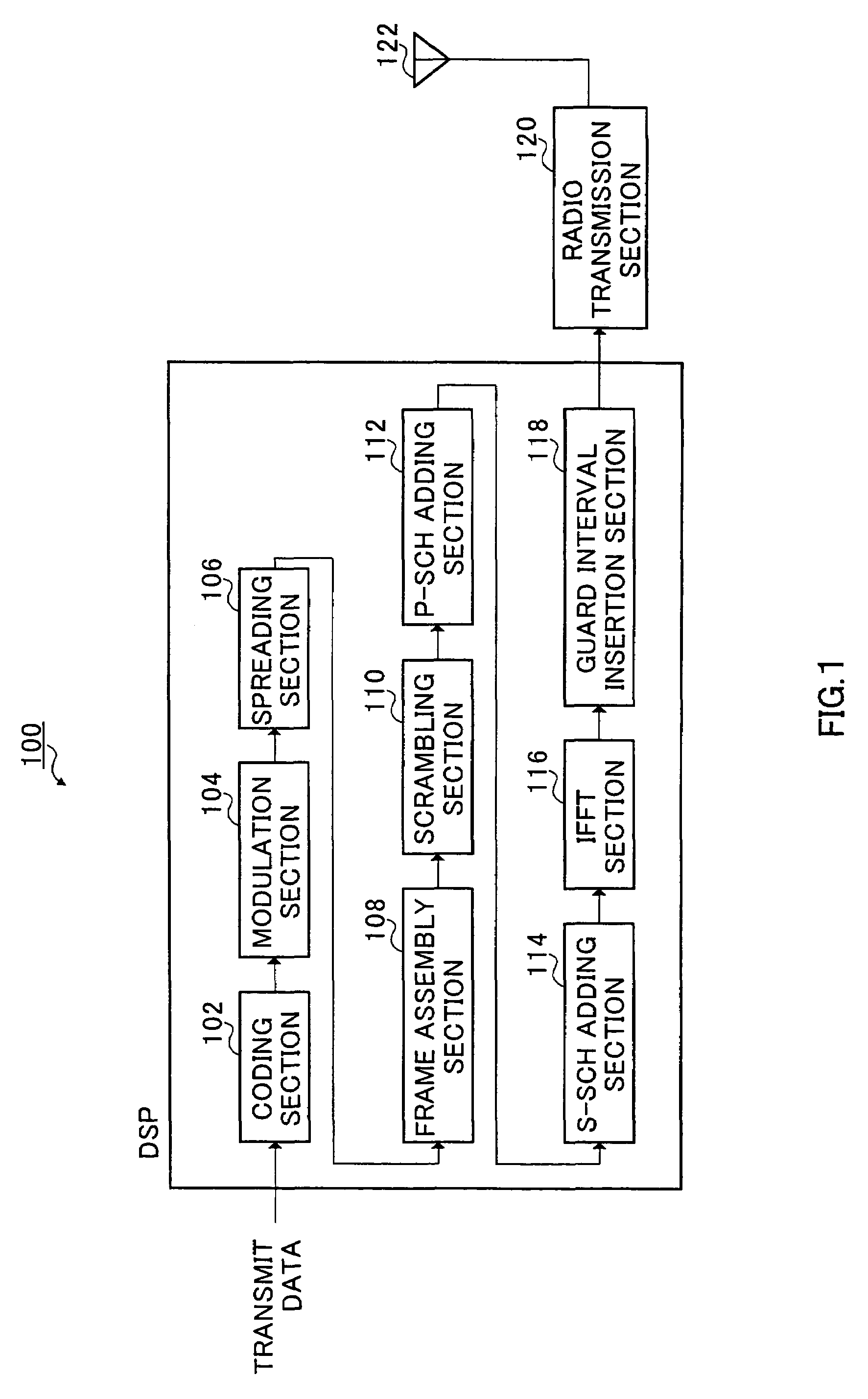
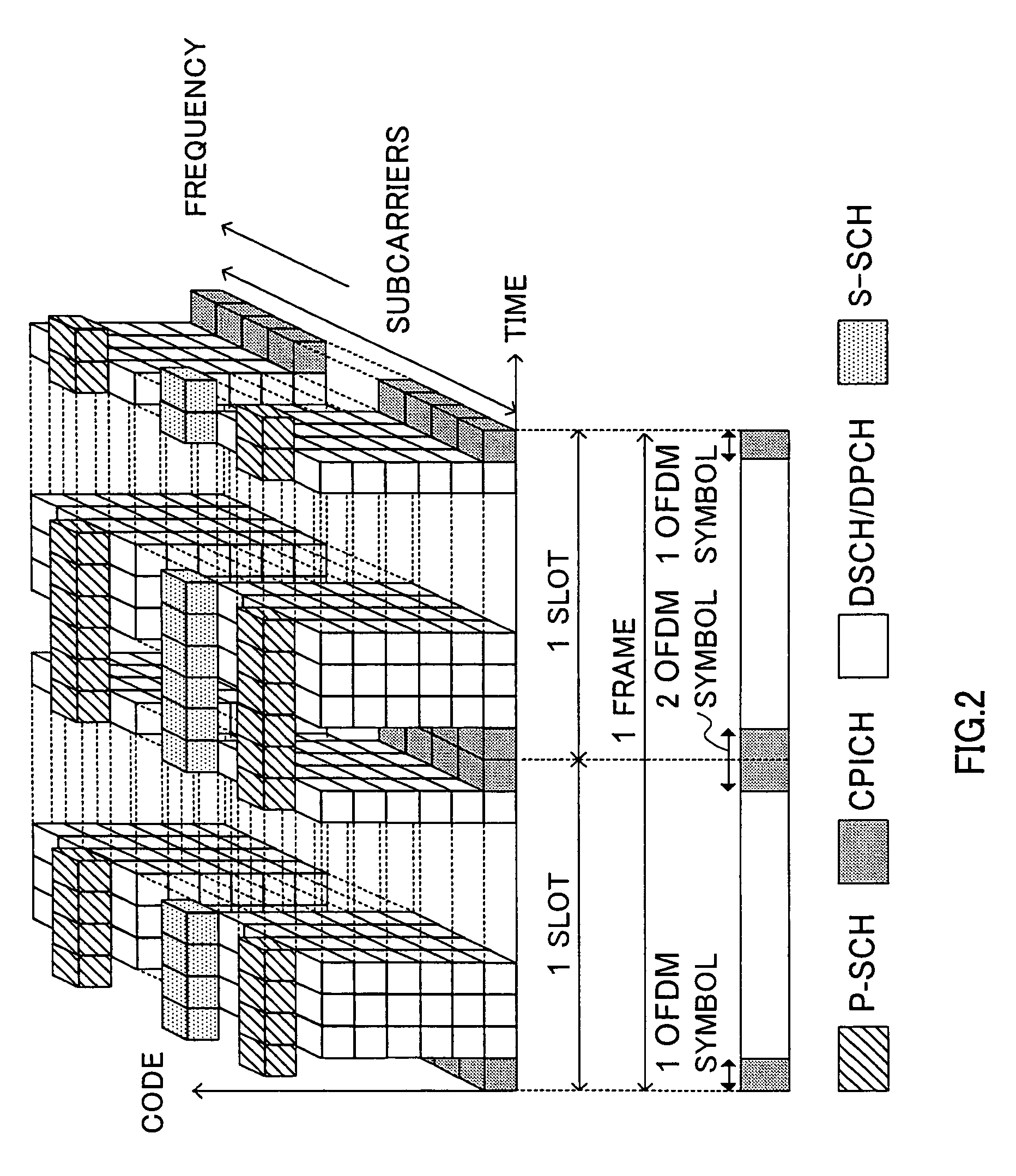
A multicarrier radio communication technology that enables radio resources to be used effectively, interference-to be suppressed, and a cell search to be performed at high speed, in a multicarrier CDMA system. In this technology, a secondary synchronization code (S-SCH signal) for identifying the group of scrambling codes divided into groups beforehand is frequency multiplexed in a plurality of subcarriers. A secondary synchronization code is coded in the time direction. Subcarriers in which a secondary synchronization code is multiplexed are mutually separated and equally spaced. The number of subcarriers in which a secondary synchronization code is multiplexed can be set to a small value with respect to the total number of subcarriers. A secondary synchronization code is an orthogonal code. On the receiving side, a cell search is carried out using such a frequency multiplexed type S-SCH.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Power control for reverse packet data channel in CDMA systems
ActiveUS7299402B2Enabling detectionPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmitted powerControl signal
A method of reverse link power control for a reverse packet data channel in a wireless communication system allows a mobile station to autonomously change its data transmission rate. The mobile station transmits packet data over a reverse packet data channel having a data rate variant transmit power level that varies based on a transmit data rate on the packet data channel. The mobile station further transmits control signals over a reverse control channel associated with the reverse packet data channel. The transmit power level of the reverse control channel is such that the transmit power level does not vary with the transmit data rate on the packet data channel. The radio base station measures the strength of the received signals on the reverse control channel, compares the measured strength to a power control set point, and generates a power control signal responsive to the comparison of the control signal to the power control set point.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
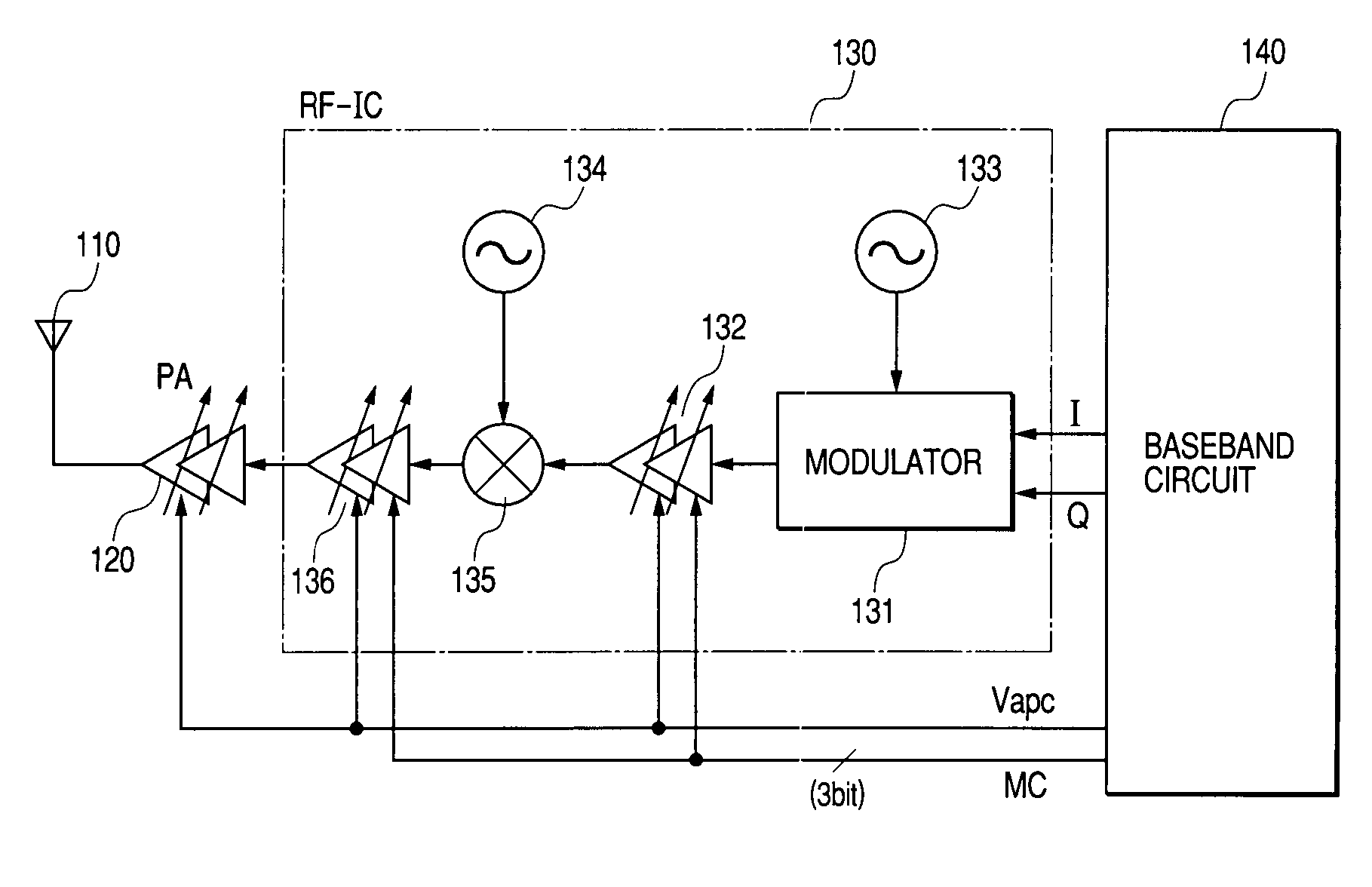
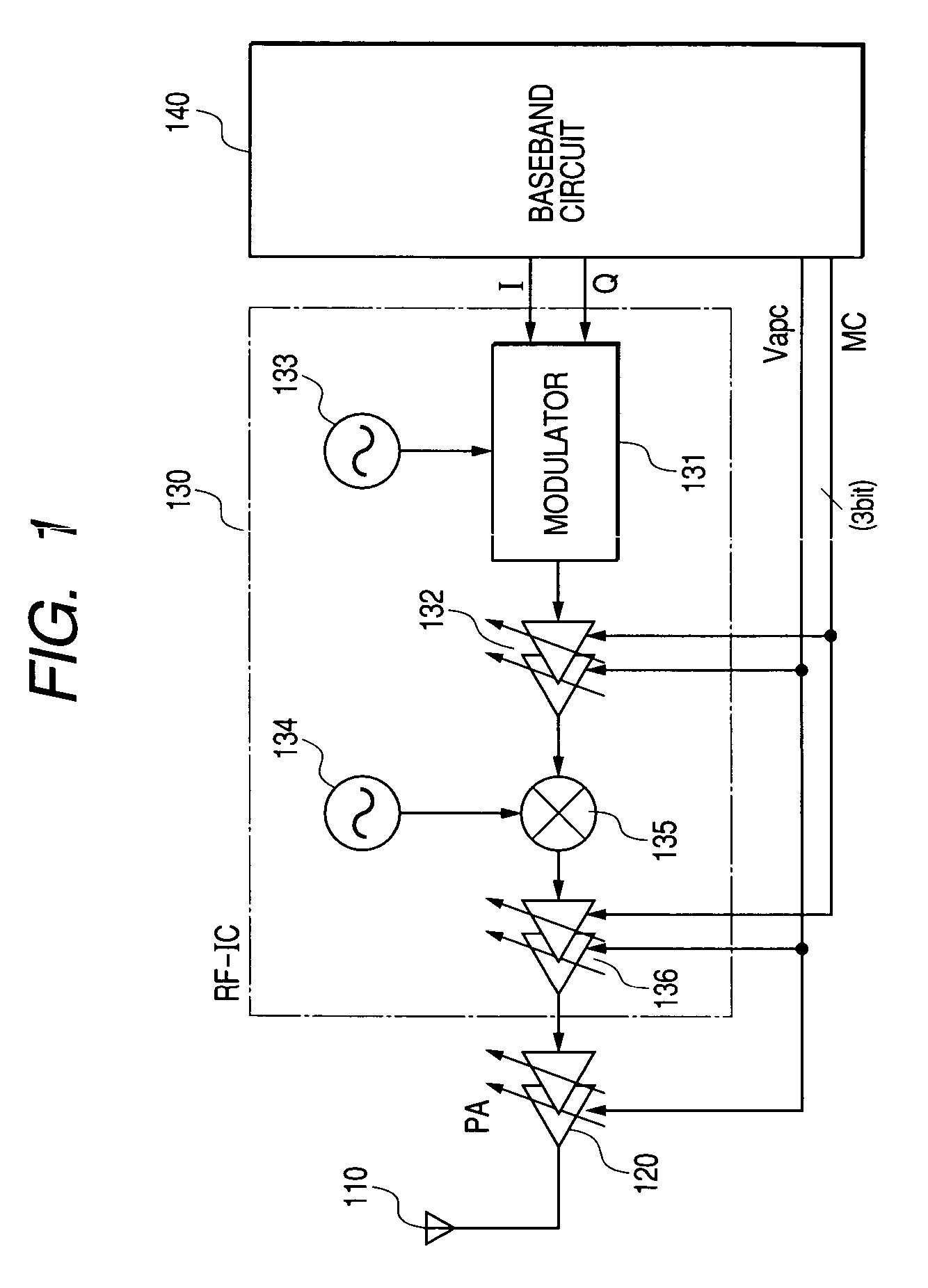
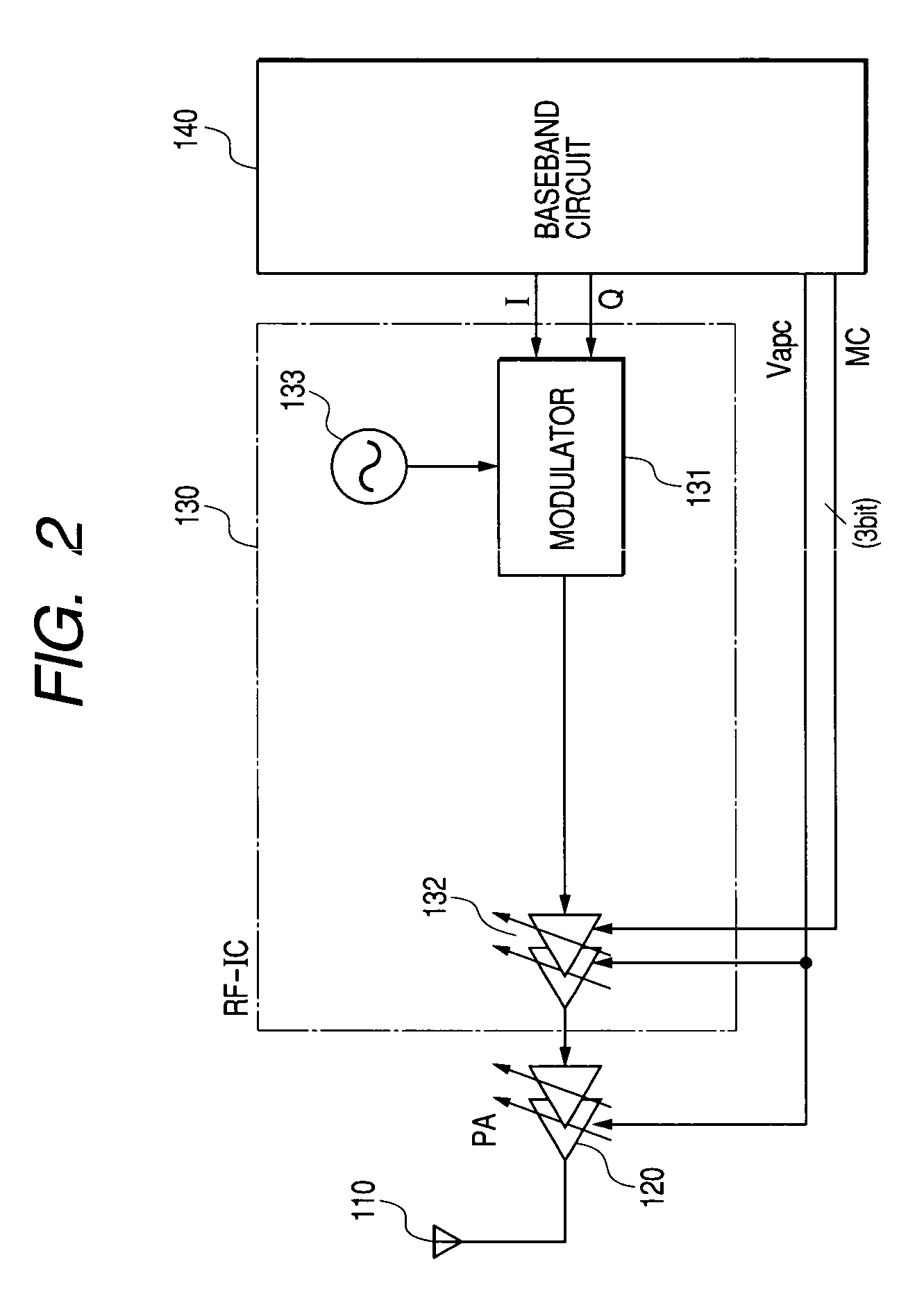
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and wireless communication system
InactiveUS7116949B2Total current dropImprove dynamic rangeResonant long antennasGain controlCurrent consumptionEngineering
The dynamic range is changed by switching a current applied to an amplifying circuit to obtain the minimum ICP required to keep linearity with the number of multiplexes even when the number of multiplexes of data is changed by switching the operation current of the amplifying circuits of the transmission system and also supplying the information about number of multiplexes of data to be transmitted to the amplifying circuits of the transmission system from the baseband circuit. Thereby, the signal can be transmitted without distortion even when the number of multiplexes increases and the current of the amplifying circuit may be reduced when the number of multiplexes is small in order to reduce the current consumption in the communication semiconductor integrated circuit device which can form a wireless communication system of the code division multiplex system such as W-CDMA system.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Frequency domain equalization in communications systems with scrambling
InactiveUS20050259757A1Transmission control/equalisingSecret communicationCdma systemsFrequency domain
A method of, and system for applying frequency-domain equalization in a DS-CDMA system, either by augmenting the transmitted data block before it is scrambled by appending a prefix and a suffix known to or knowable by the receiver or by augmenting the transmitted data block after it is scrambled but prior to transmission so that it has a scrambled cyclic prefix. In the former case, the receiver synthesizes one of the prefix, the data block, or the suffix that would have been received if the augmented transmitted data block after scrambling had had a cyclic prefix.
Owner:WI LAN INC
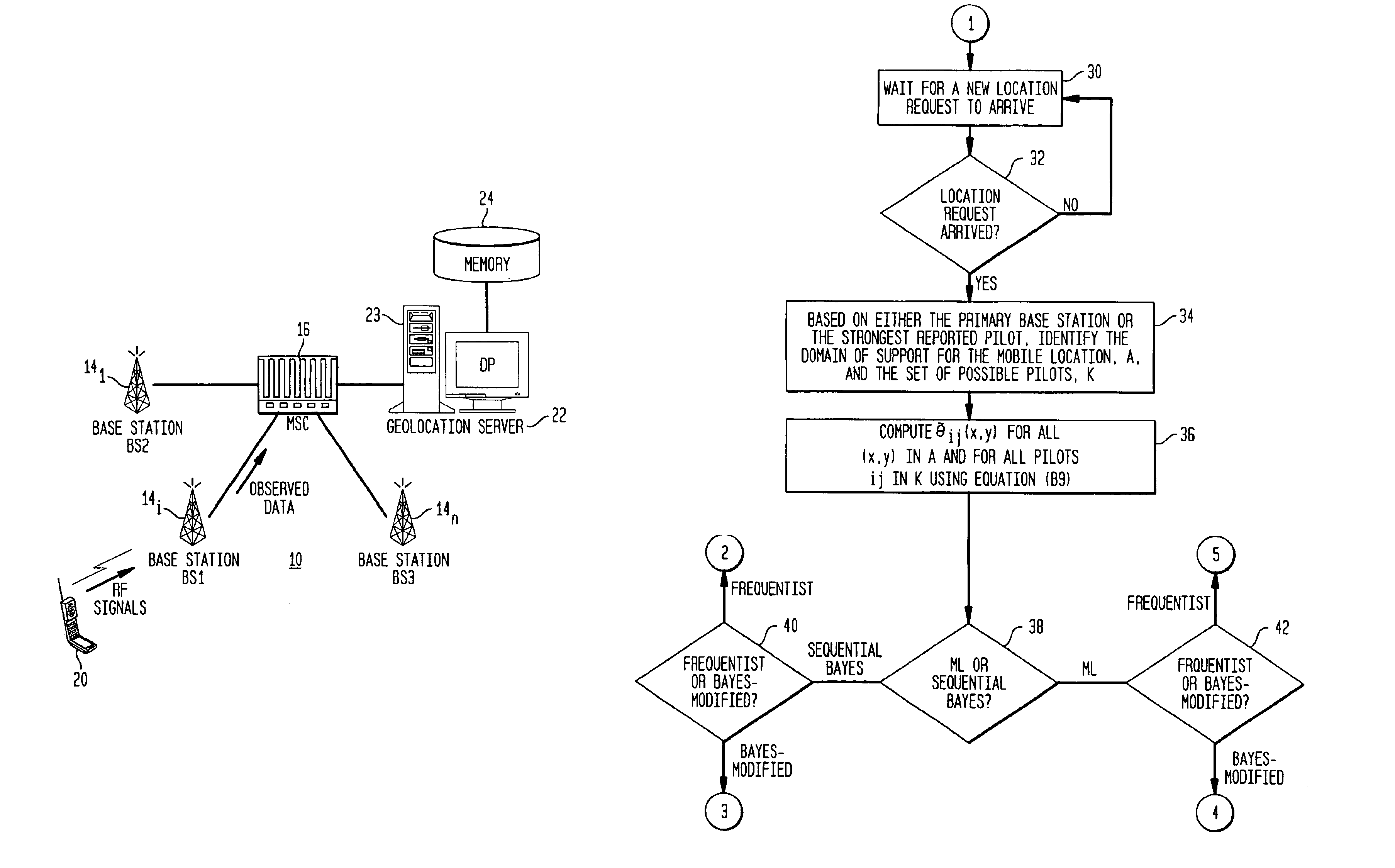
Likelihood-based geolocation prediction algorithms for CDMA systems using pilot strength measurements
InactiveUS6889053B1Maximize functionalityDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationCommunications systemPrediction algorithms
The location of a mobile wireless communication unit in the service area of a CDMA communications system is predicted utilizing two likelihood functions that define maximum likelihood estimators of the mobile unit's location, based on attribute measurements, such as but not limited to pilot signal strength, being made at the location of the mobile unit and reported back to a base station. One of the likelihood functions comprises a frequentist likelihood function and the other comprises a Bayesian-modified likelihood function. The likelihood functions are based on the assumption that there is an RF model which provides the probability a mobile unit is able to detect one or more attributes associated with an arbitrary base station, given it is located at an arbitrary location within the service area. Each of the likelihoods are also incorporated into a sequential Bayesian procedure which outputs a posterior distribution indicative of the location of the mobile unit.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Initial power control for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20050094604A1Increase profitRadio transmission for post communicationDuplex signal operationSequence signalEngineering
A code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) system employing spread-spectrum modulation. The CDMA system has a base station, and a plurality of subscriber units. The signals transmitted between the base station and subscriber unit use spread-spectrum modulation. The system and method transmits from the base station, a synchronization channel having a chip-sequence signal used by the plurality of subscriber units for synchronization. A first subscriber unit receives the synchronization channel, and determines timing from the synchronization channel. In order to initiate communications with the base station, the first subscriber unit transmits an access signal. The access signal has a plurality of power levels, which typically ramp up. The base station receives the access signal at a particular-power level. The base station then transmits to the first subscriber unit an acknowledgment signal. The first subscriber unit receives the acknowledgment signal, and transmits to the base station, a spread-spectrum signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
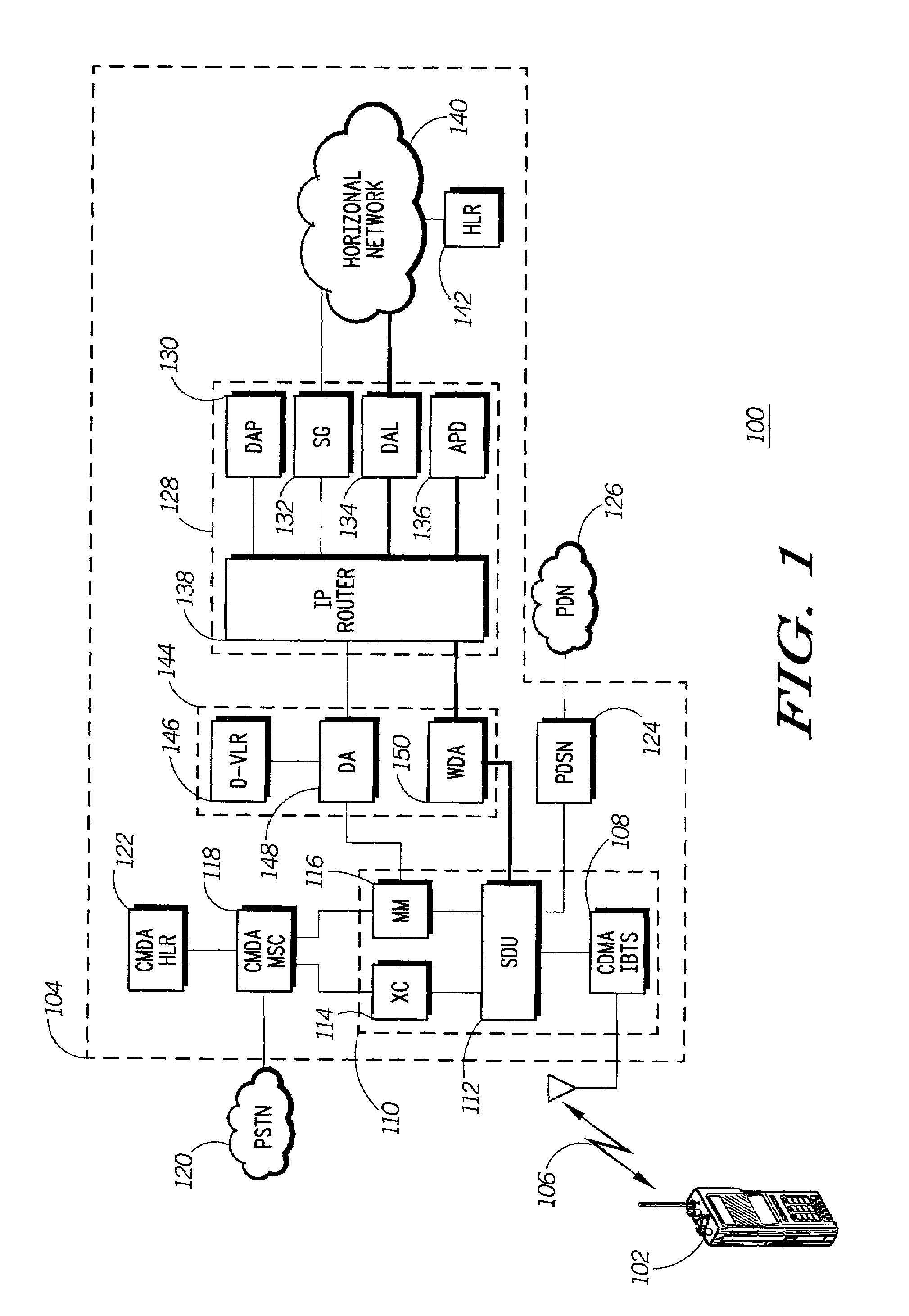
Data session setup system for wireless network
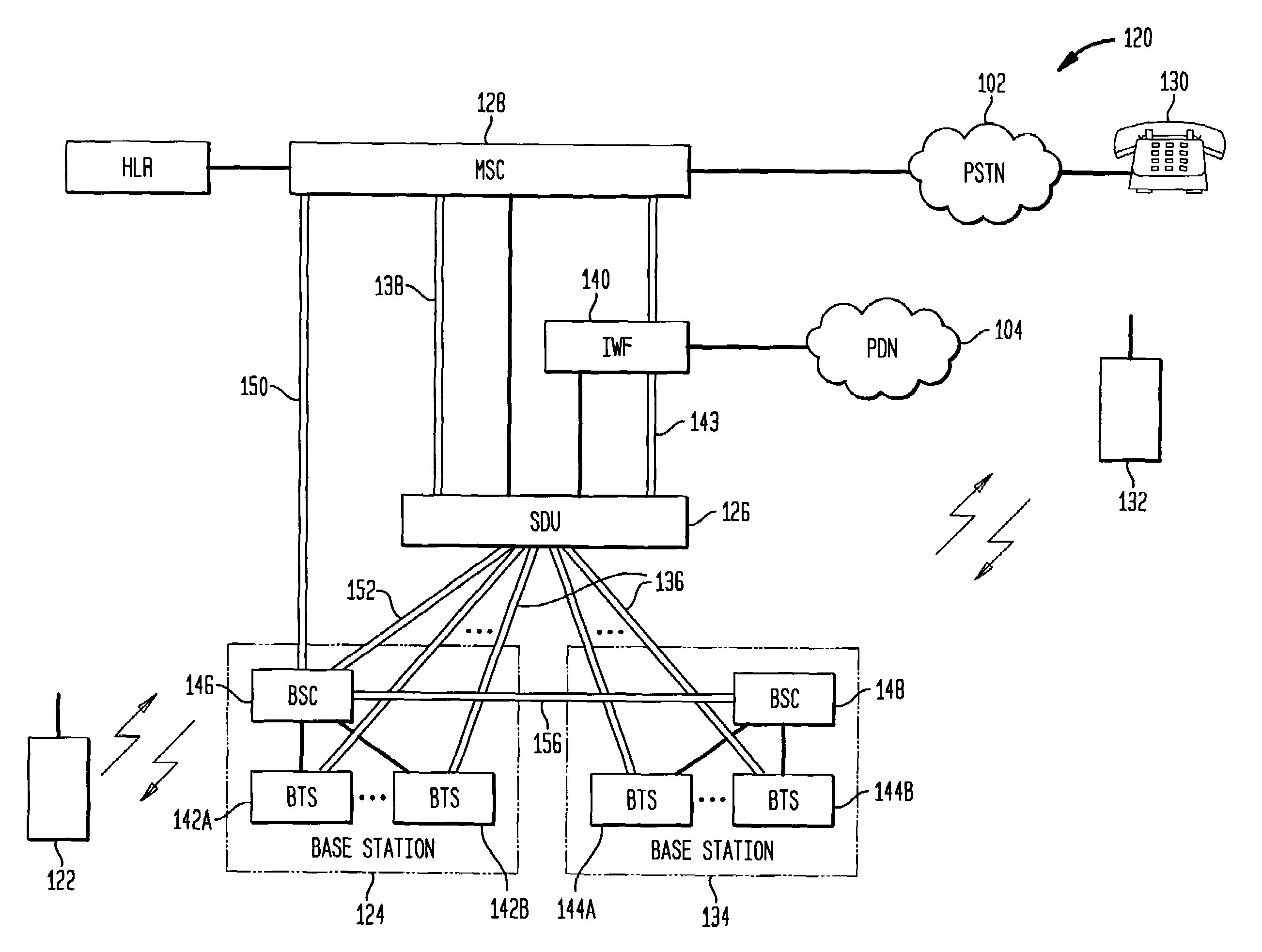
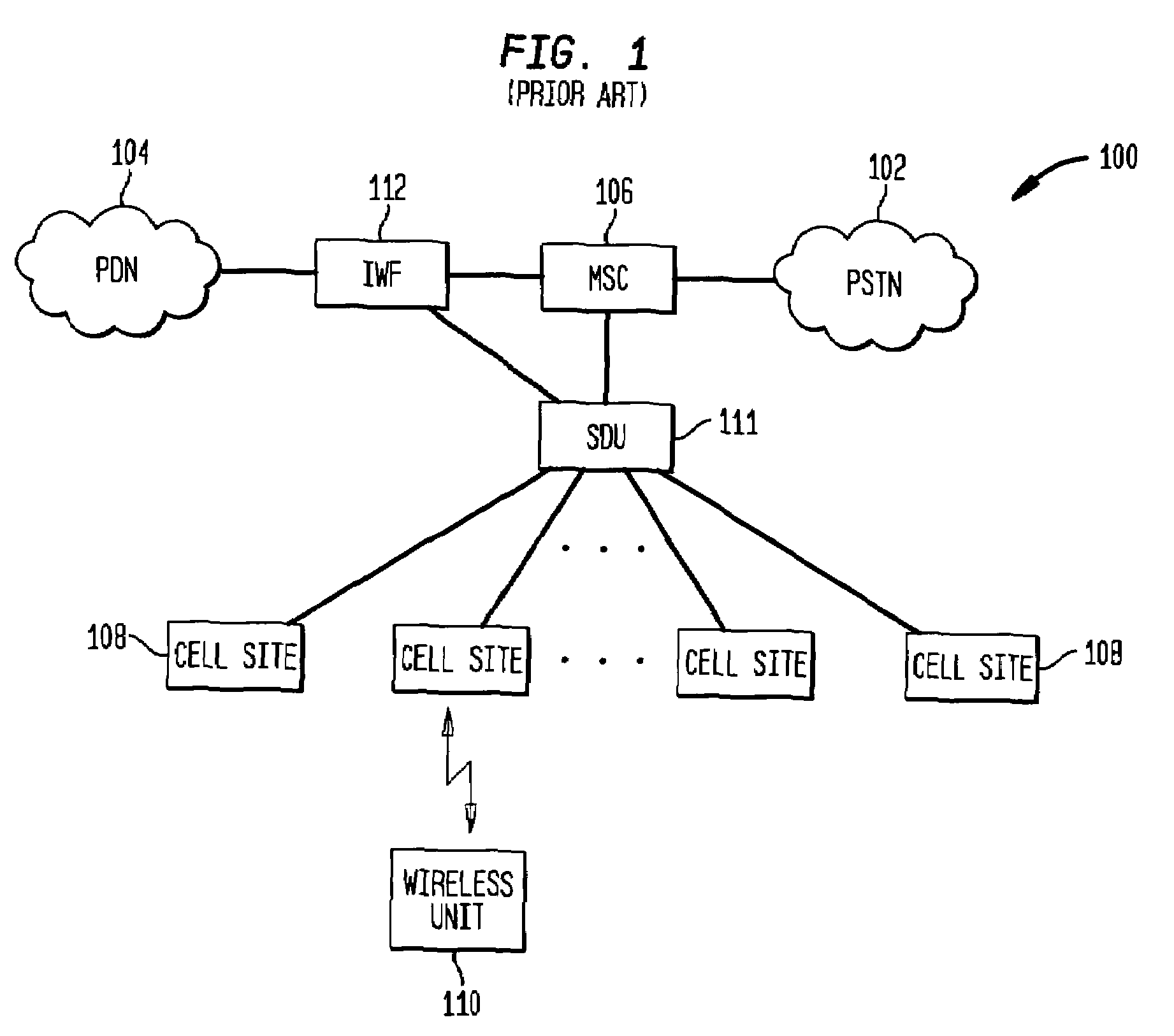
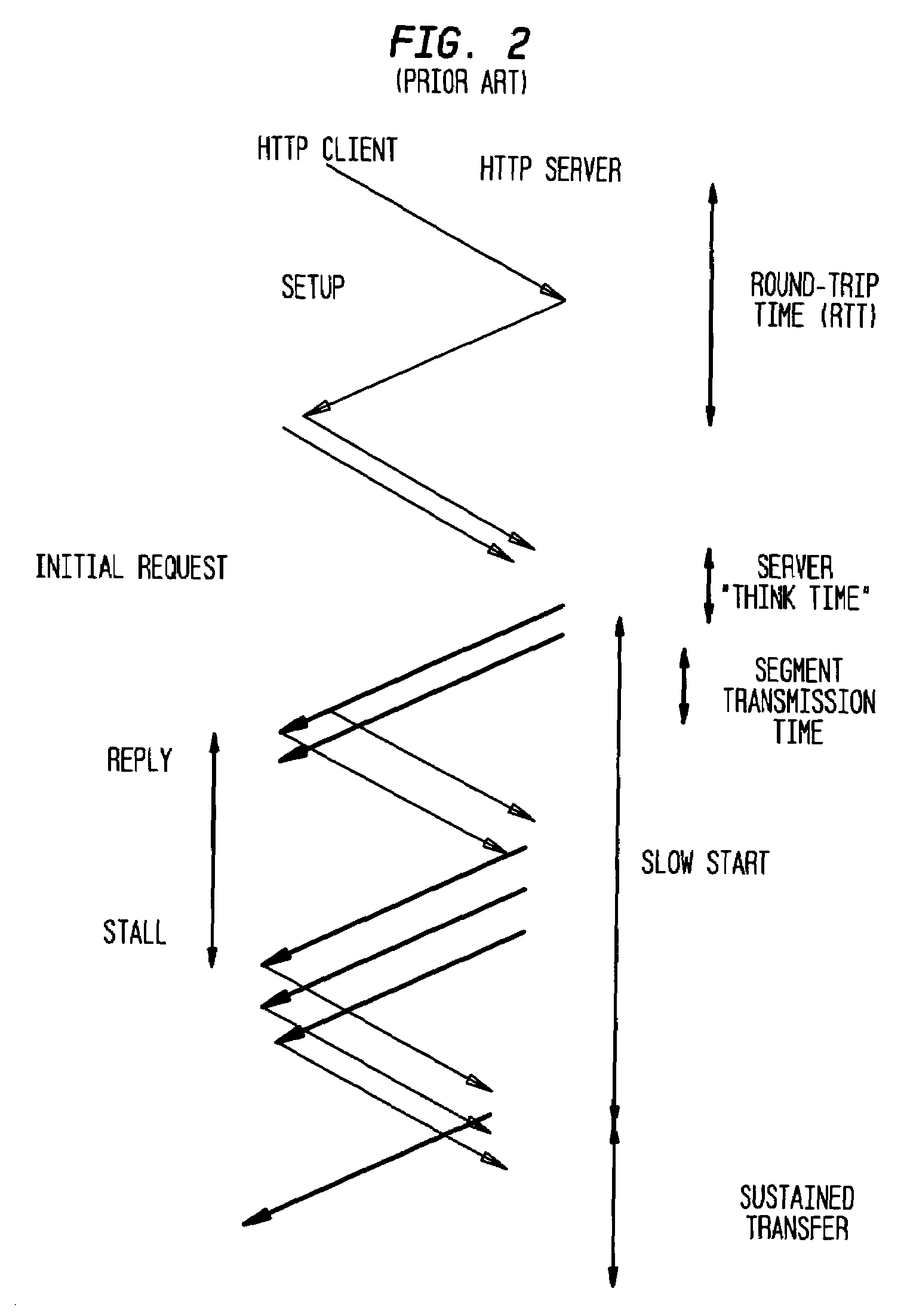
InactiveUS7218630B1Avoid delayIncrease data rateConnection managementSubstation equipmentTraffic capacityCommunications system
A wireless communication system uses a circuit switched link between a wireless unit and a base station to establish a data session with a network device in a packet data network. After the data session is established, the data session can proceed using a packet switched link between the wireless unit and the base station. By using the circuit switched link to send data session setup packets, the system avoids the delay associated with requesting and being allocated wireless resources in sending the setup packets using the packet switched link. Decreasing the delay associated with setting up the data session improves the data rate and throughput between the wireless communications system and the packet data network. For example, in an exemplary CDMA system, a circuit switched link is established to carry primary traffic (such as voice) and secondary traffic. The setup packets for the data session can be directly sent as secondary traffic on the circuit switched link, thereby avoiding the delay associated with sending the setup packets over a packet switched link. In this way, the round trip time (RTT) associated with setting up the data session can be reduced to improve the overall data rate and throughput through the wireless network to the packet data network.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Apparatus for adaptive reverse power control for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS6940840B2Increase profitRadio transmission for post communicationLink quality based transmission modificationSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioAutomatic gain control
A code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) system employing spread-spectrum modulation. The CDMA system has a base station (BS), and a plurality of subscriber units. The signals transmitted between the base station and subscriber unit use spread-spectrum modulation. The improvement method for adaptive reverse power control (APC) from a subscriber unit (SU) to a base station (BS), comprises the steps of sending from the subscriber unit, using spread-spectrum modulation, a SU-spreading code on a reverse channel. The base station despreads the SU-spreading code on the reverse channel as a despread signal, determines a first power level Pd which includes power of the despread signal plus noise and a second power level PN, which includes despread-noise power. The base station determines a first error signal e1, from the first power level Pd, the second power level PN, and a required signal-to-noise ratio SNRREQ for service type, and a second error signal e2, from a measure of total received power Prt at the base station, and an automatic gain control (AGC) set point Po. The base station forms a combined error signal from the first error signal e1, the second error signal e2, a first weight a1, and a second weight a2, and hard limits the combined error signal to form a single APC bit. The APC bit is transmitted to the subscriber unit. In response to the APC bit, the subscriber adjusts transmitter power to the base station.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
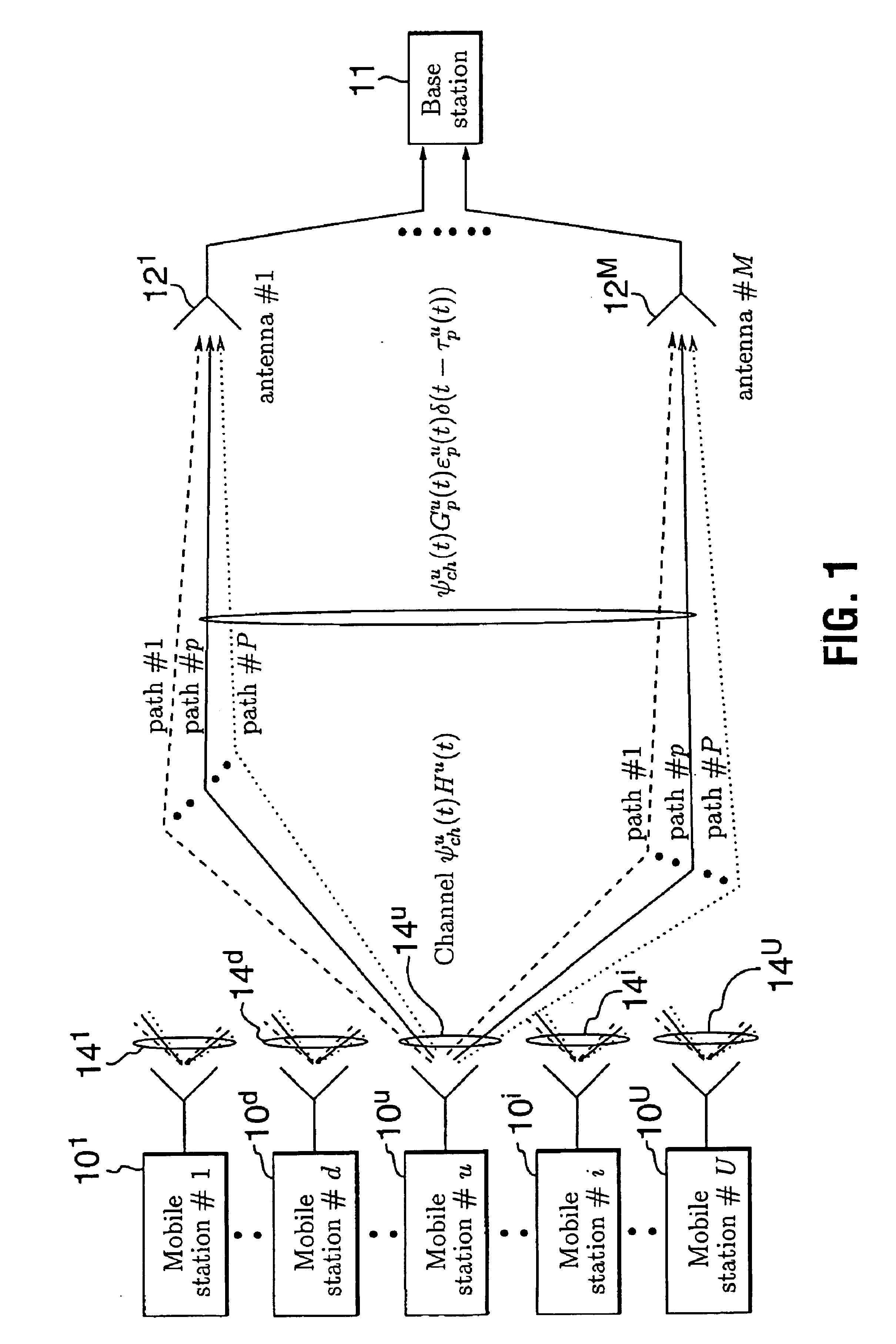
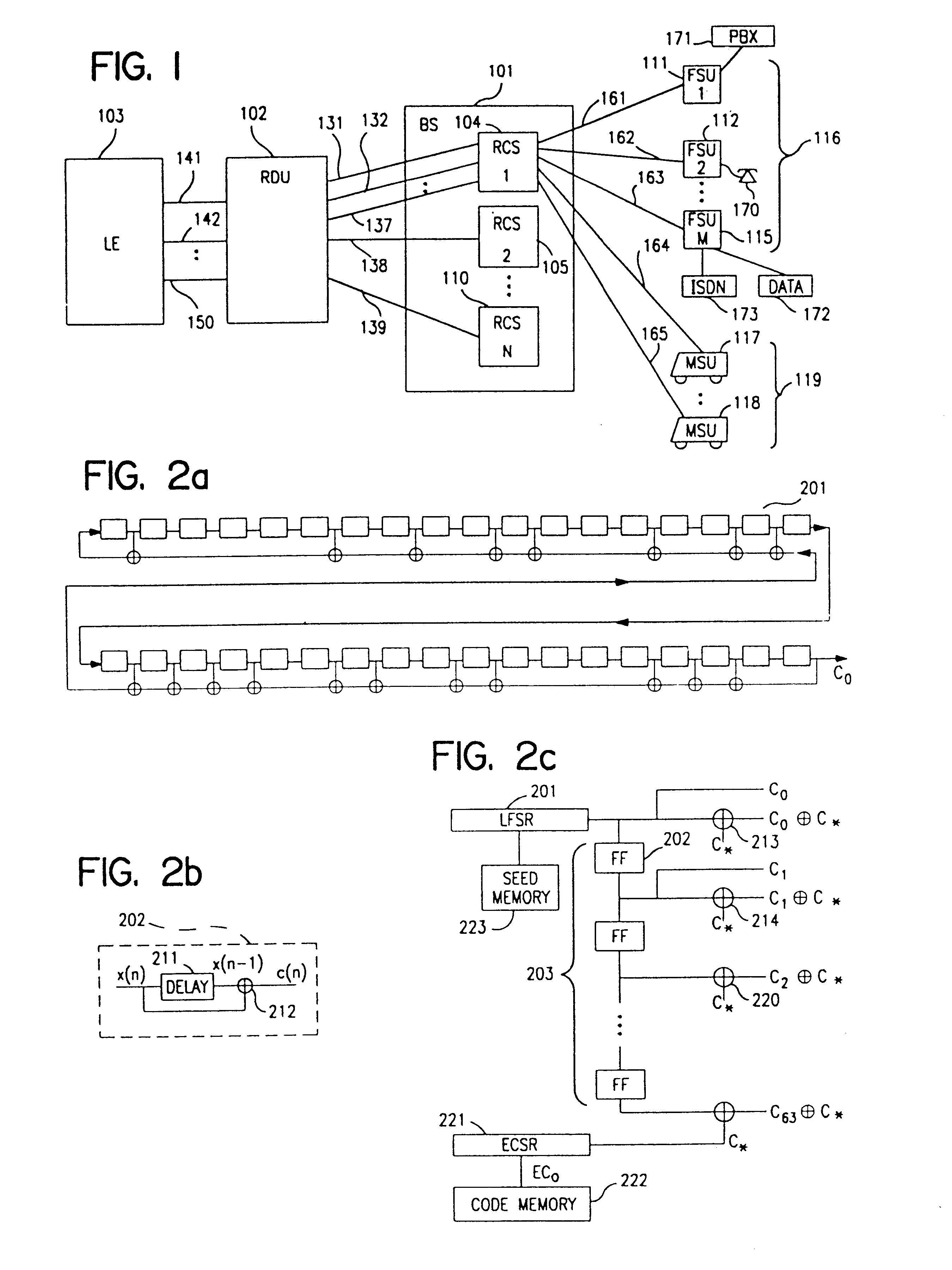
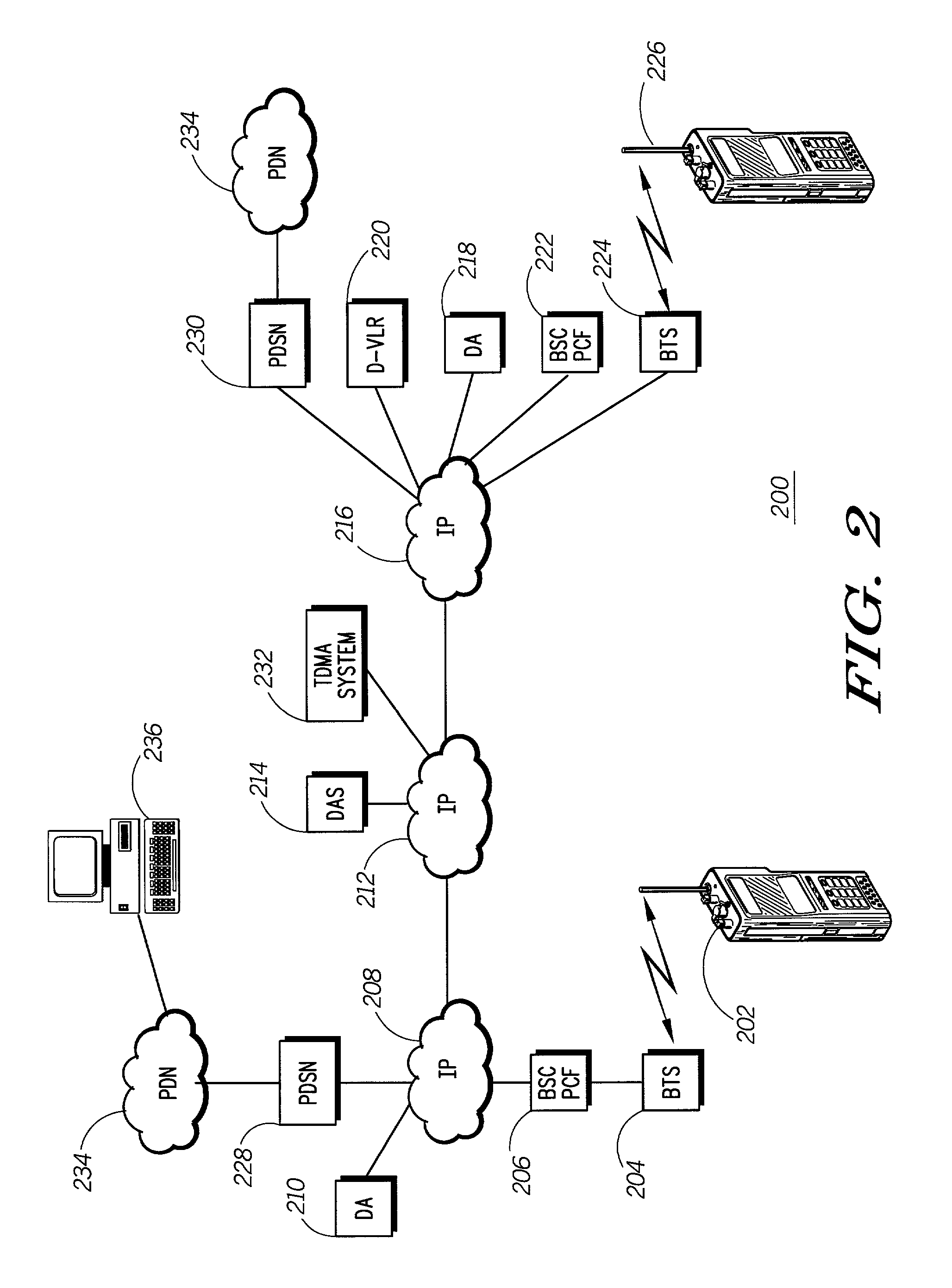
Dispatch call origination and set up in a CDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS7099291B2Reduce delaysNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexCommunications systemRadio access network
In a CDMA wireless communication system (200) a dispatch call can be established between two CDMA mobile stations (202, 226), or between other mobile stations and the CDMA mobile station, or between a CDMA mobile station and a computer (236) located outside of the wireless system. To reduce the delay normally association with call set up in a CDMA system, a dispatch processing network (128, 144) is provided in addition to a telephony switch (118). Dispatch calls and call set up requests are routed to the dispatch processing network from the radio access network (110) which includes base stations (204, 206). Once a dispatch call request is made, while the dispatch processing network begins setting up a traffic channel for the originating mobile communication device, the target is also paged, and upon responding, set up on a traffic channel. The concurrence of establishing radio links with the target and originating communication devices substantially reduces dispatch call set up time.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com