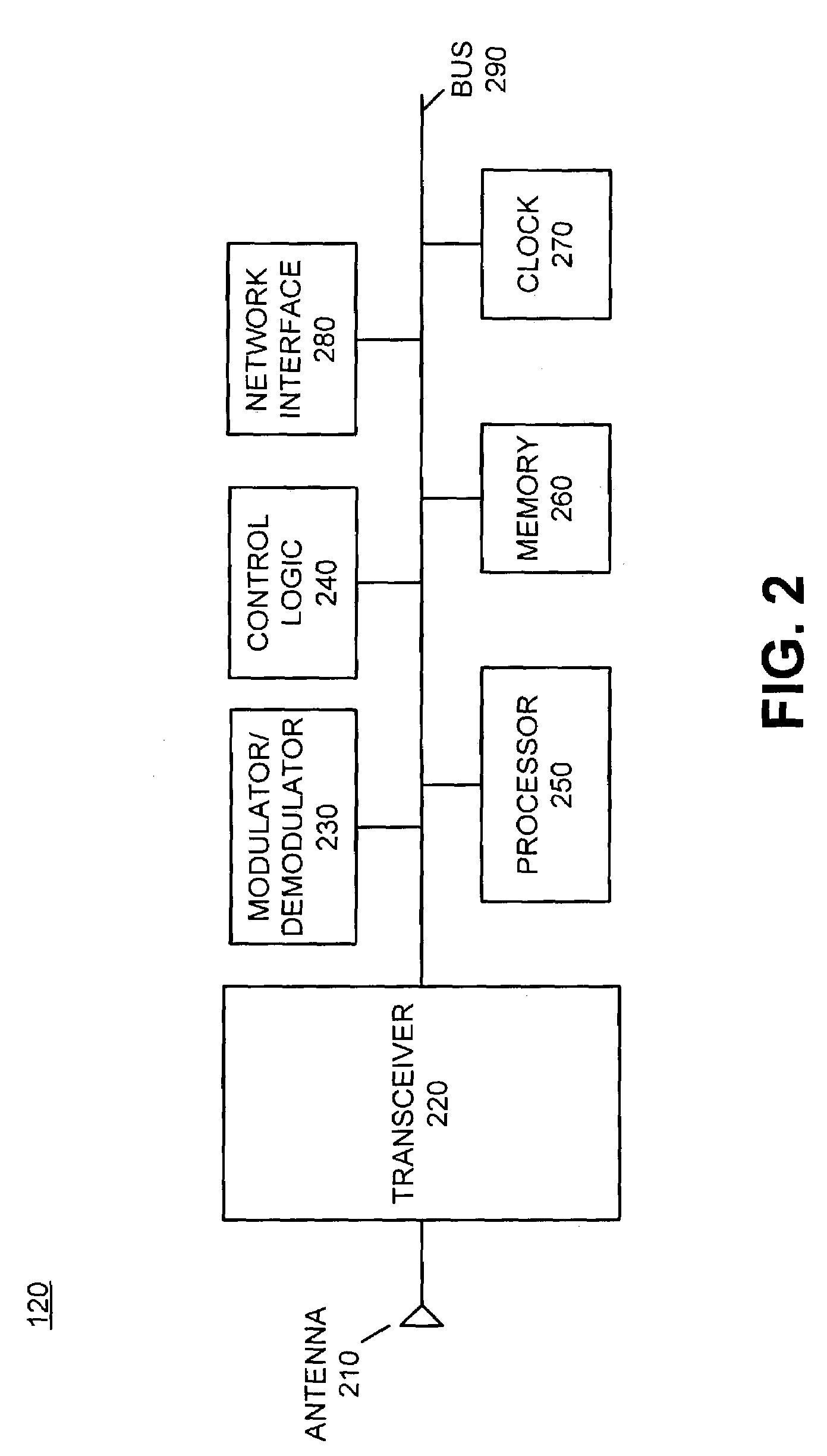
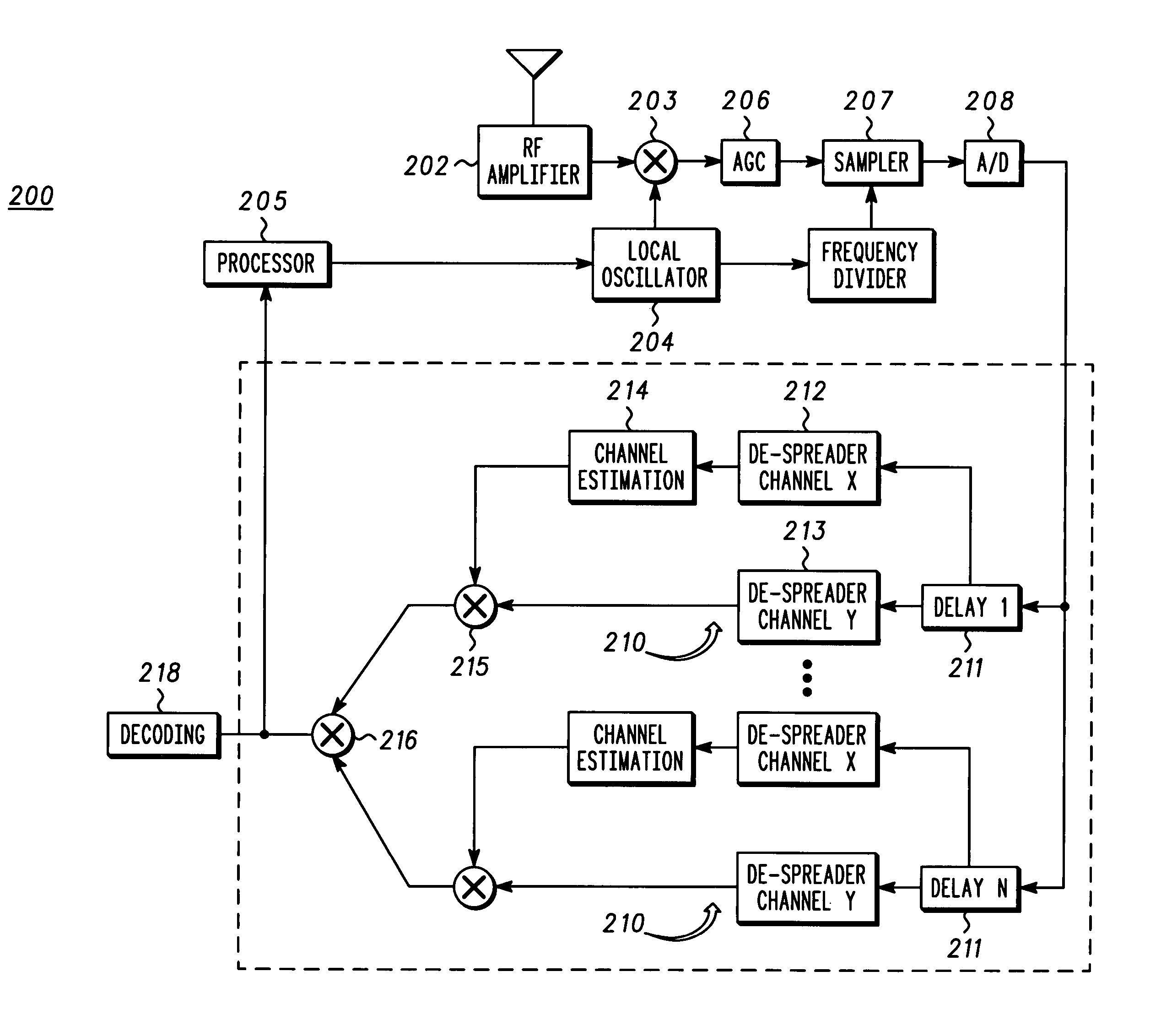
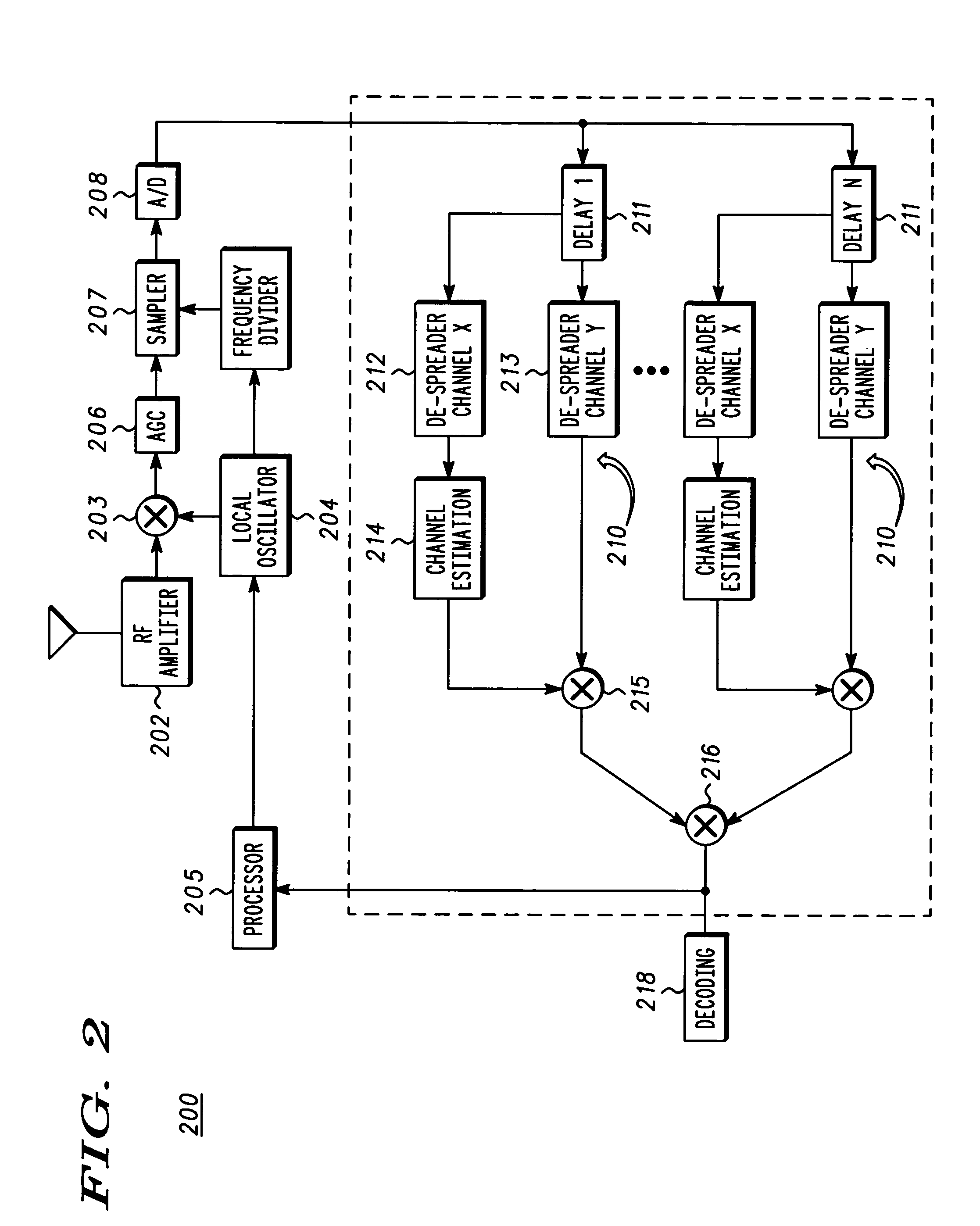
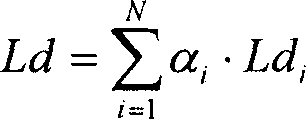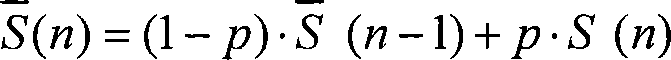Patents
Literature
143 results about "Downlink power control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
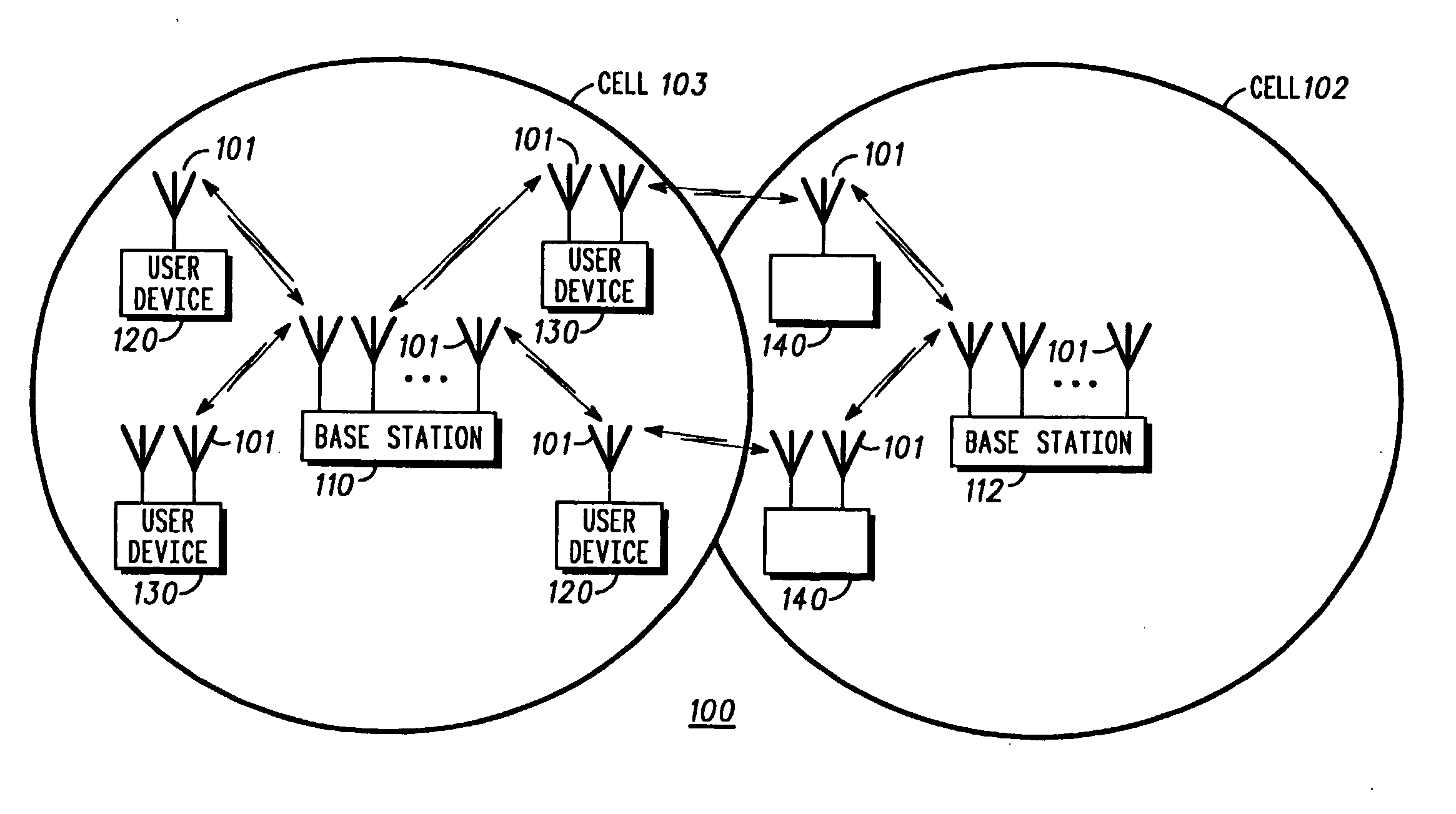
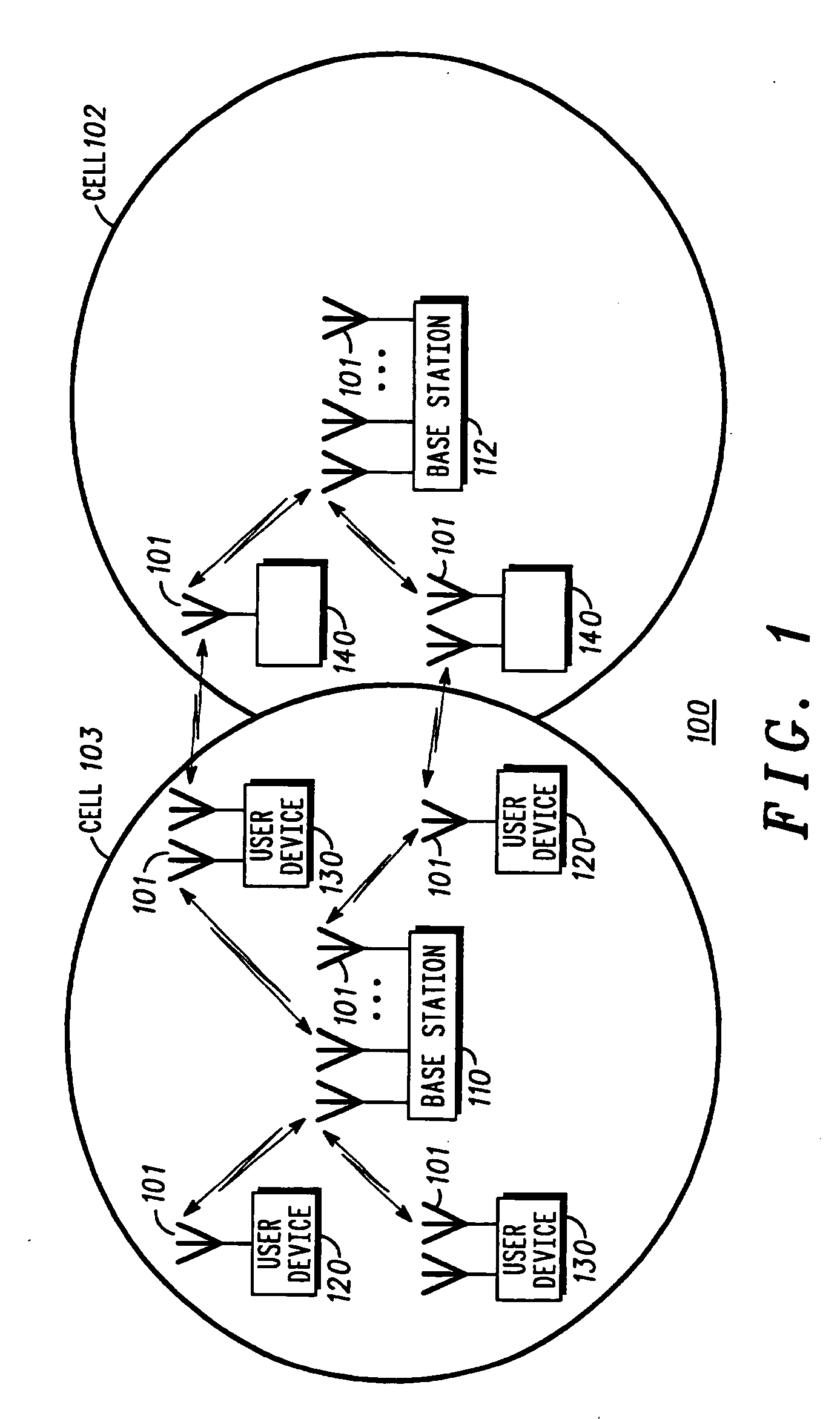
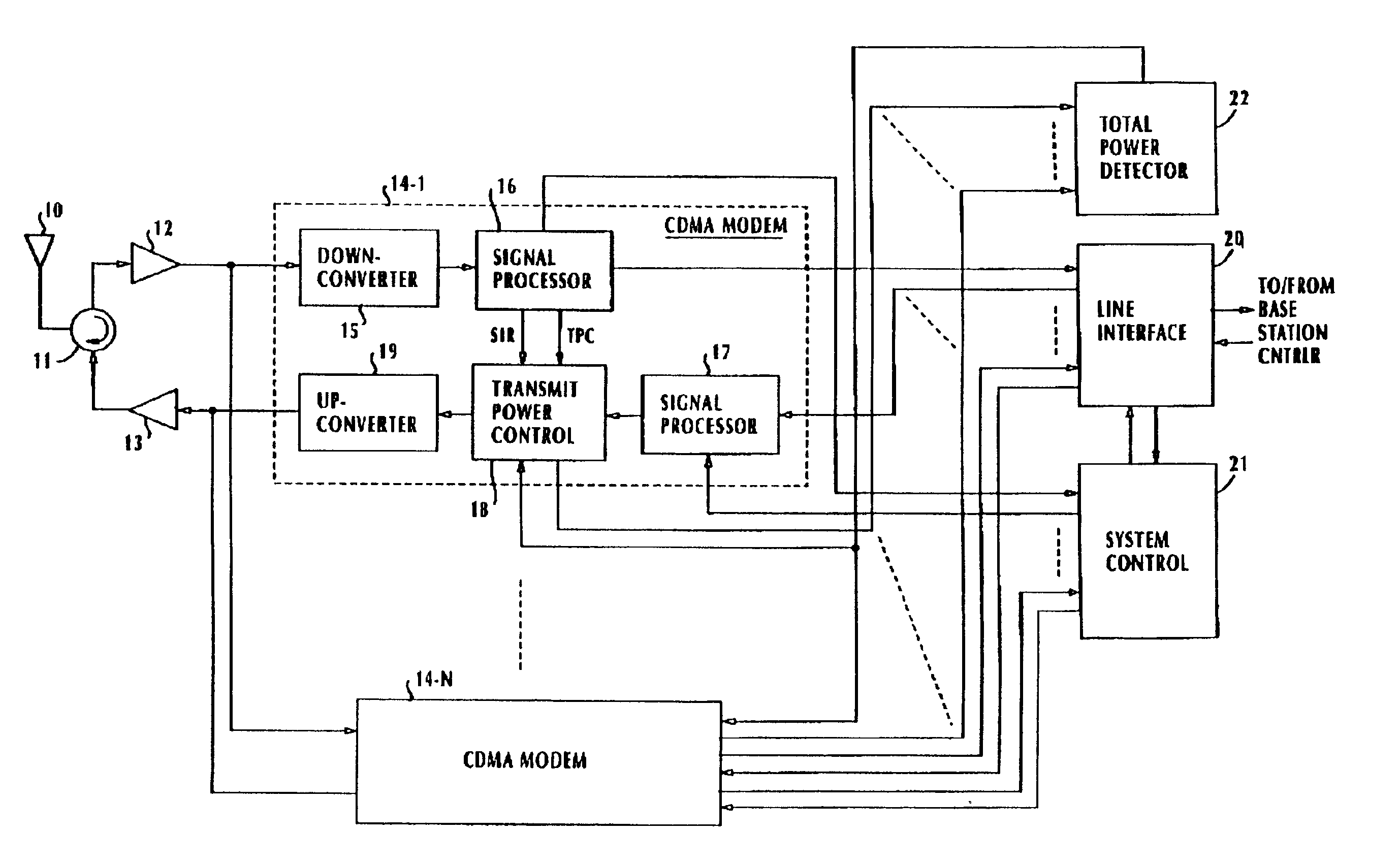
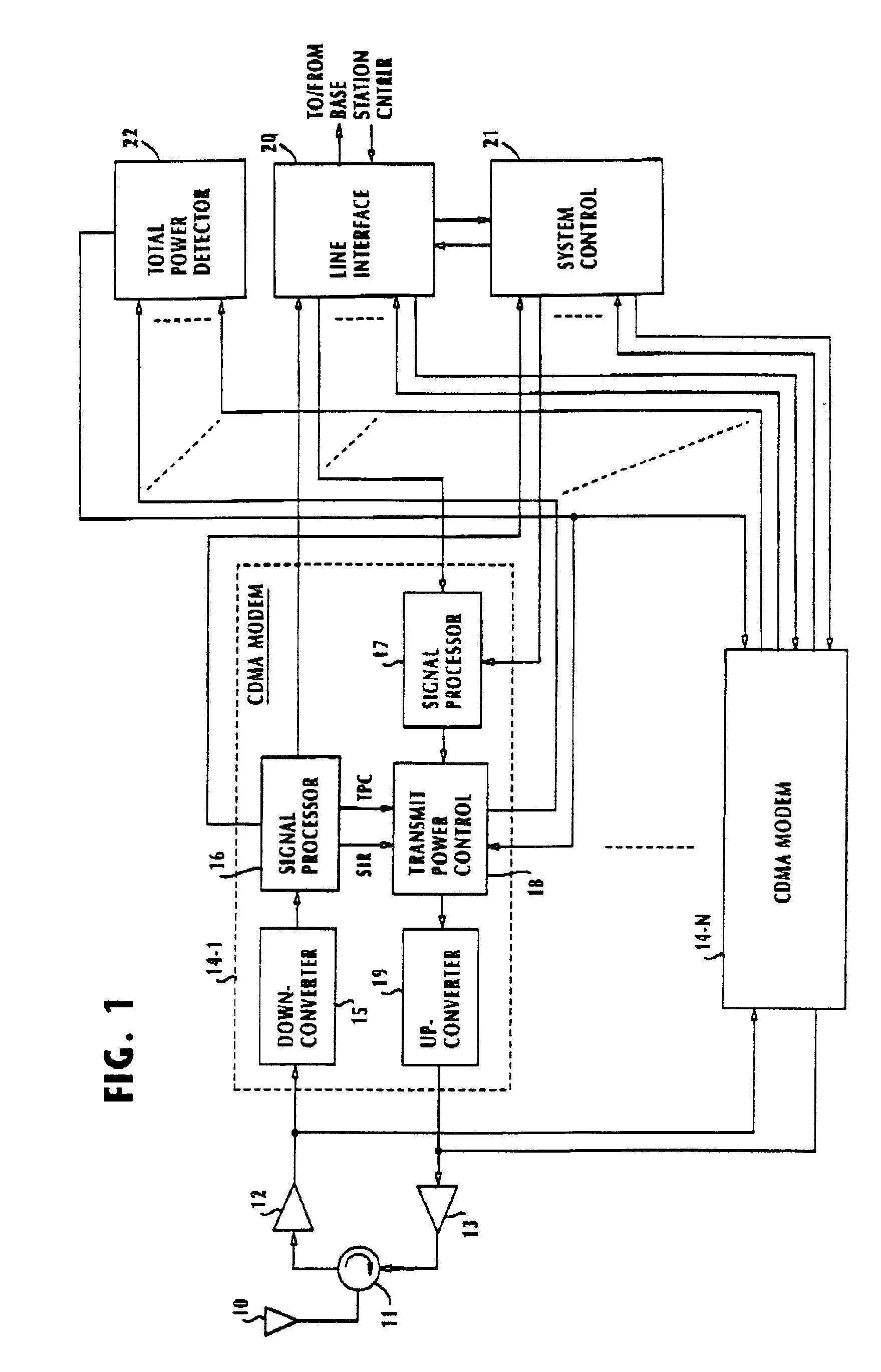
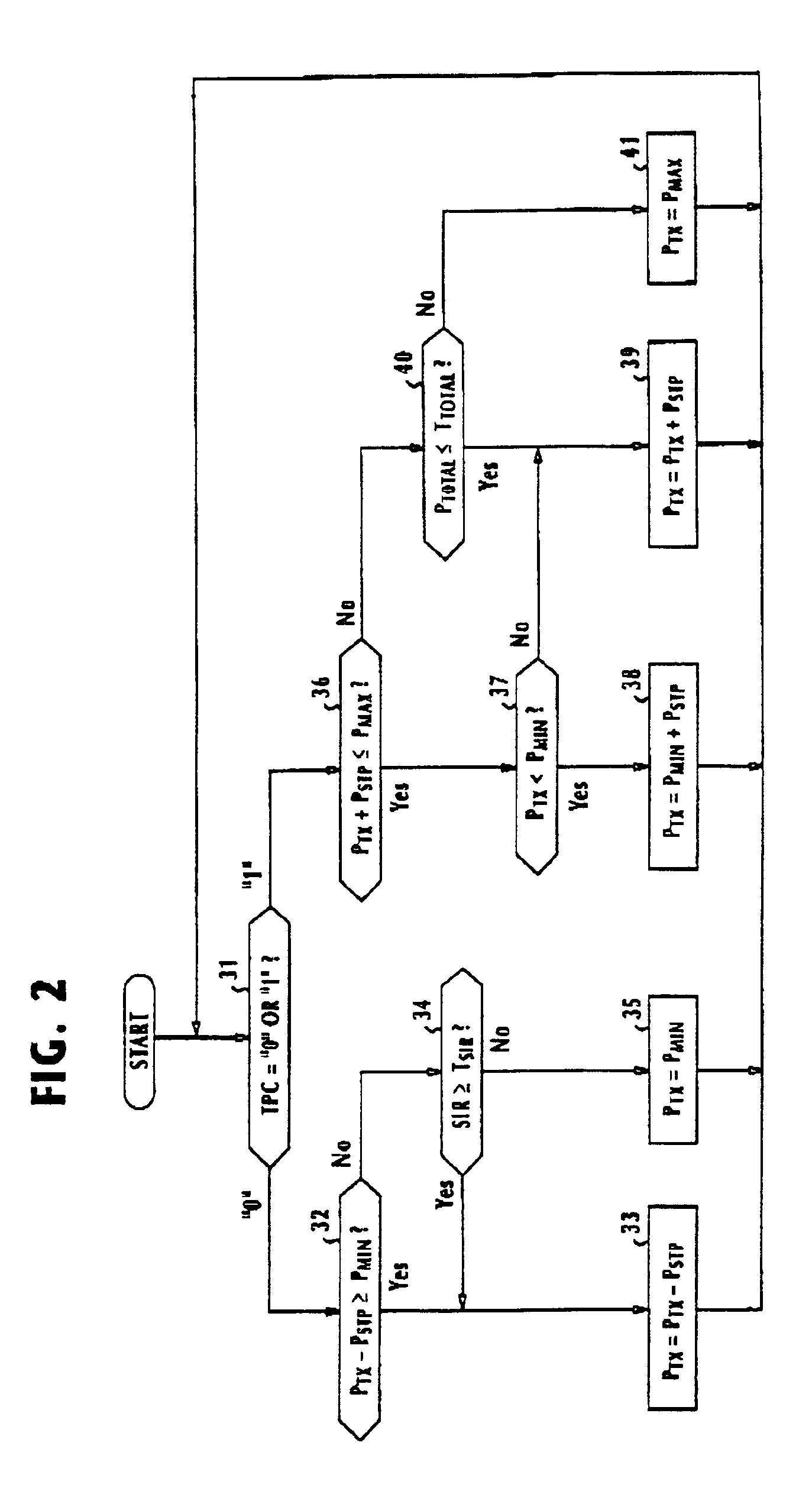
Method and apparatus for controlling transmit power of multiple channels in a CDMA communication system
ActiveUS20020009061A1Power managementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmitted powerTime-sharing
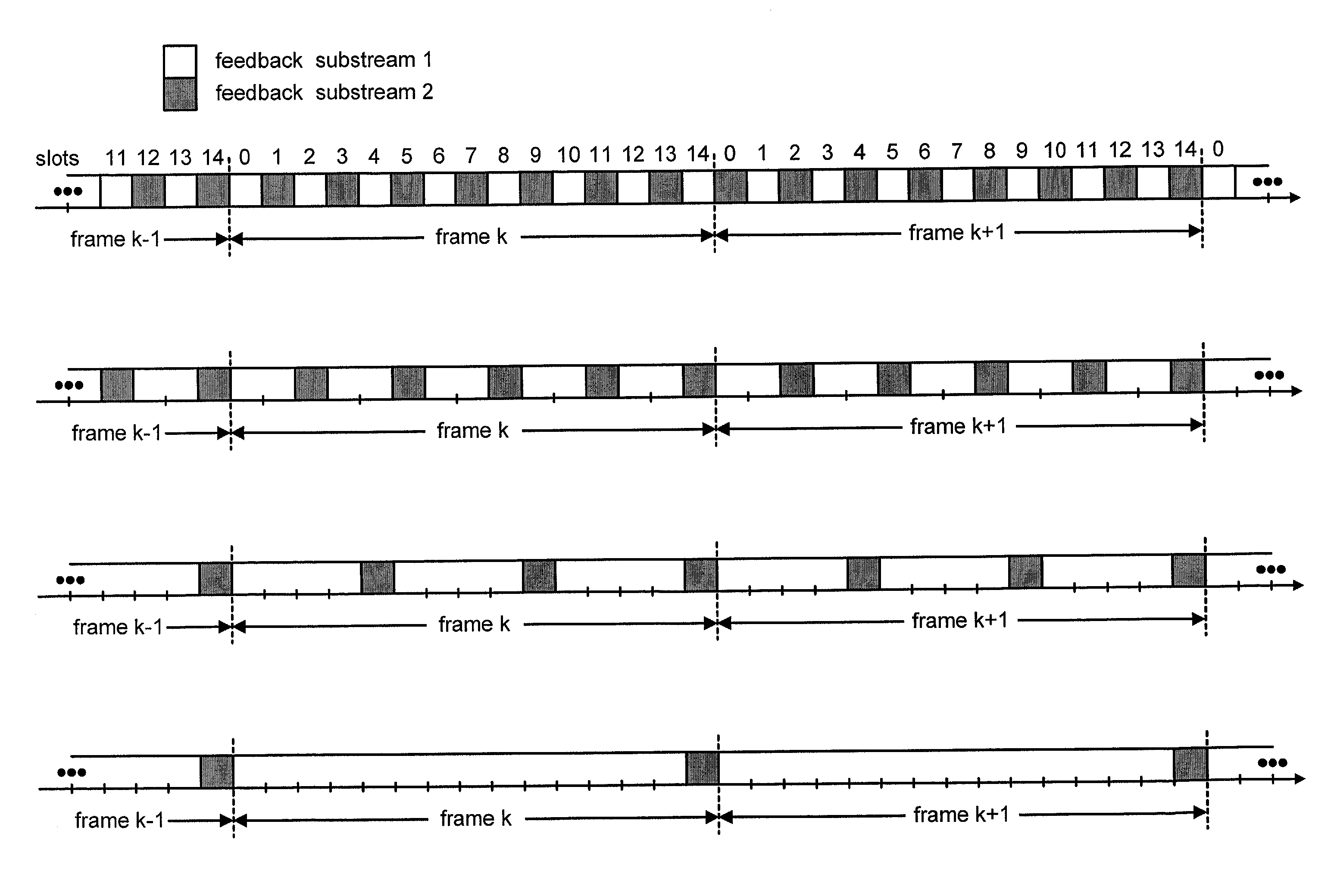
Techniques to support independent power control of multiple channels in CDMA systems (e.g., a W-CDMA system) that define a single power control feedback stream on the uplink, which is to be used for downlink power control. In one aspect, the single feedback stream is "time shared" among multiple channels requiring individual power control. Various time-sharing schemes may be used to implement multiple (substantially parallel) feedback substreams based on the single feedback stream, and different combination of feedback rates may also be achieved for the substreams. Each feedback substream may be assigned to, and used for power control of, a respective channel. In another aspect, multiple feedback substreams are implemented based on multiple fields in newly defined slot formats.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for controlling transmit power of multiple channels in a CDMA communication system
ActiveUS20050208961A1Reduce distractionsMaximize system capacityPower managementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemTransmitted power
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Methods and apparatuses for power control
InactiveUS20080316950A1Excessive signalingEnhanced signalPower managementTransmission systemsCommunications systemUplink transmission
Downlink power control commands are mapped to resources used for uplink communications within a wireless communication system. An eNode B receives communications from UEs and determines the resources used by the UEs for those transmissions on the uplink which are transmitted at non-optimum power levels. Power control messages are formulated wherein the location of the power control commands is mapped to particular resources used by the UEs for their uplink transmissions. This facilitates the eNode B to dynamically assign resources for the power control commands while permitting the UEs to decode the power control messages to adjust their power accordingly.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
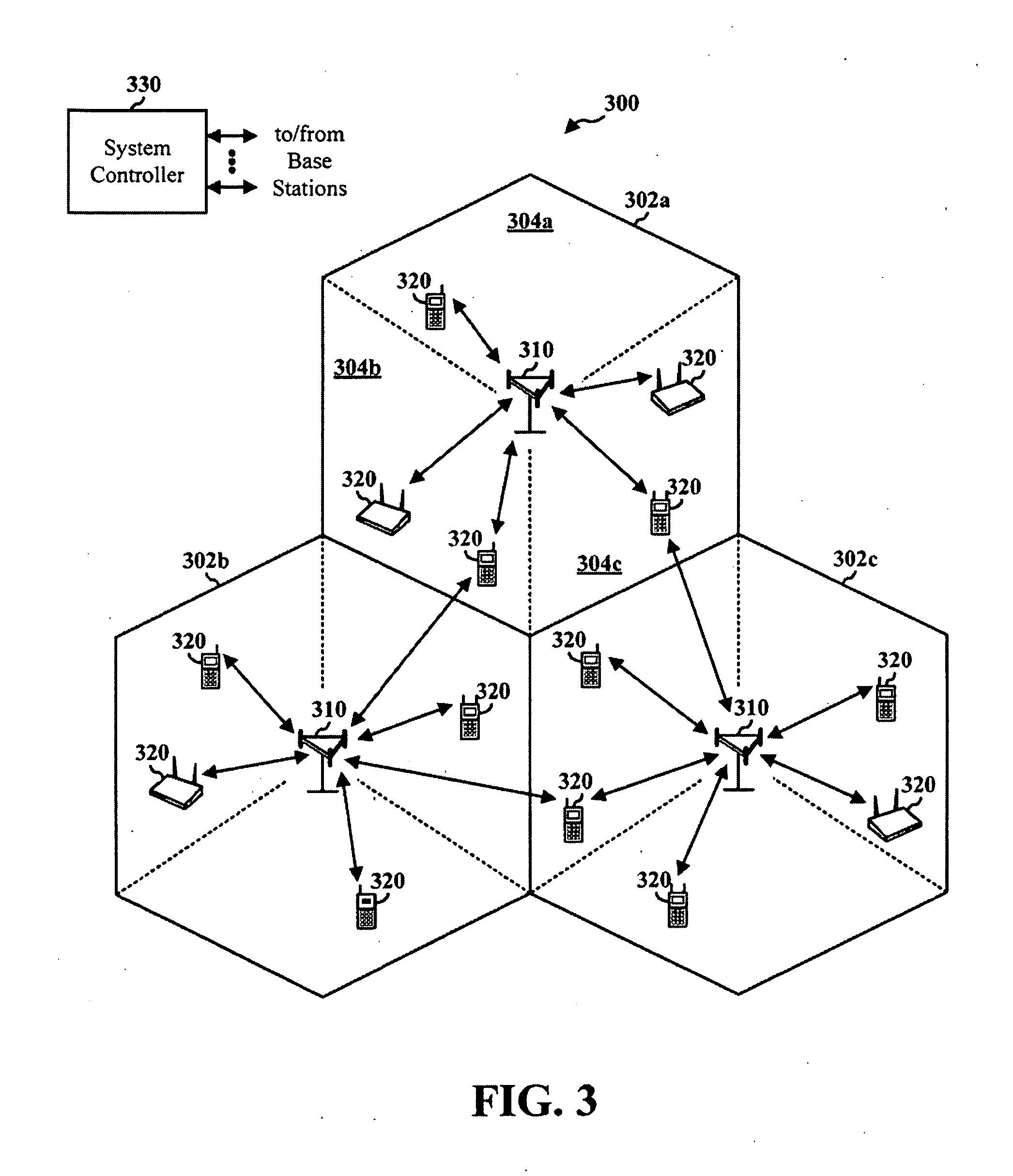
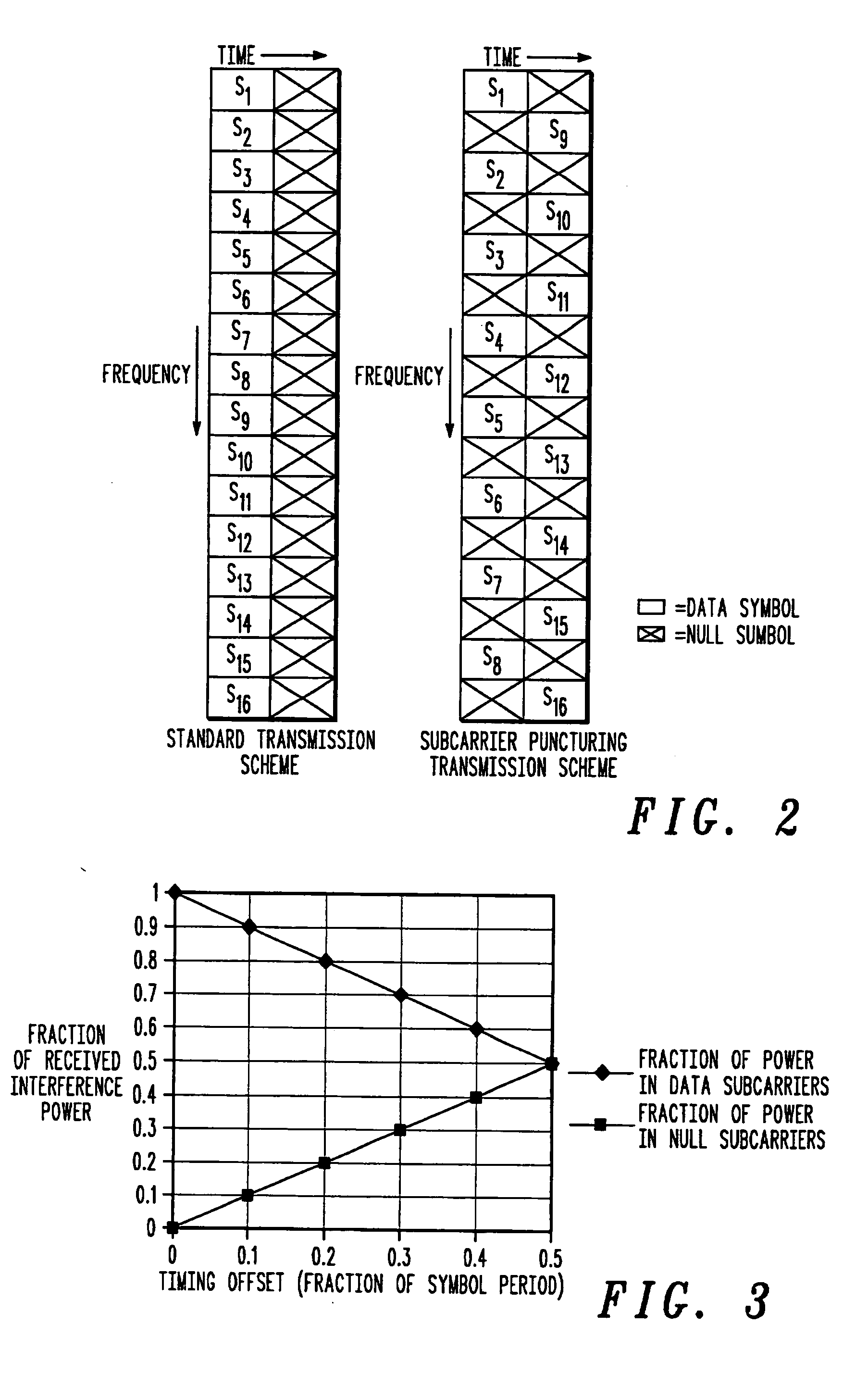
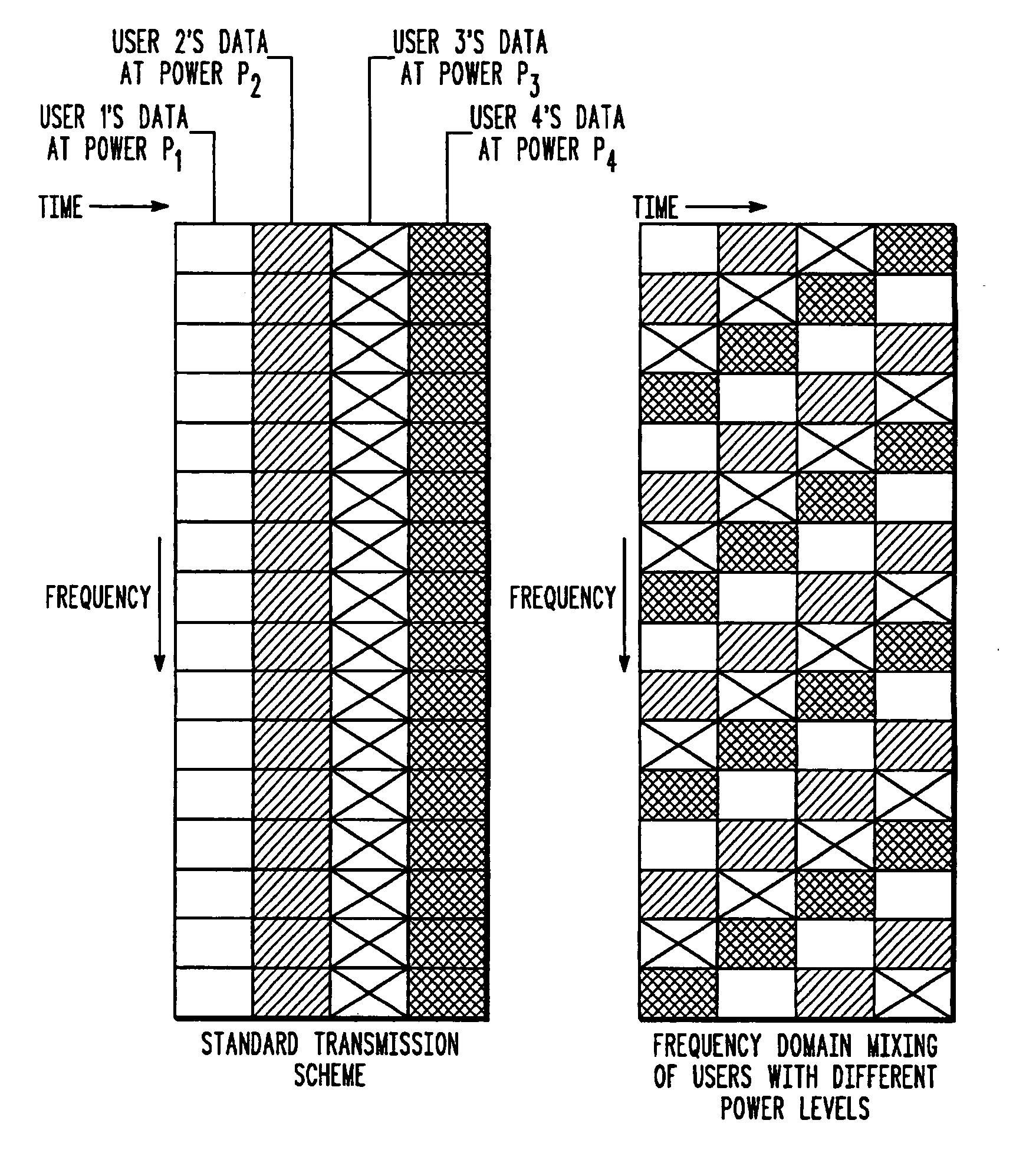
Method and system for interference averaging in a wireless communication system
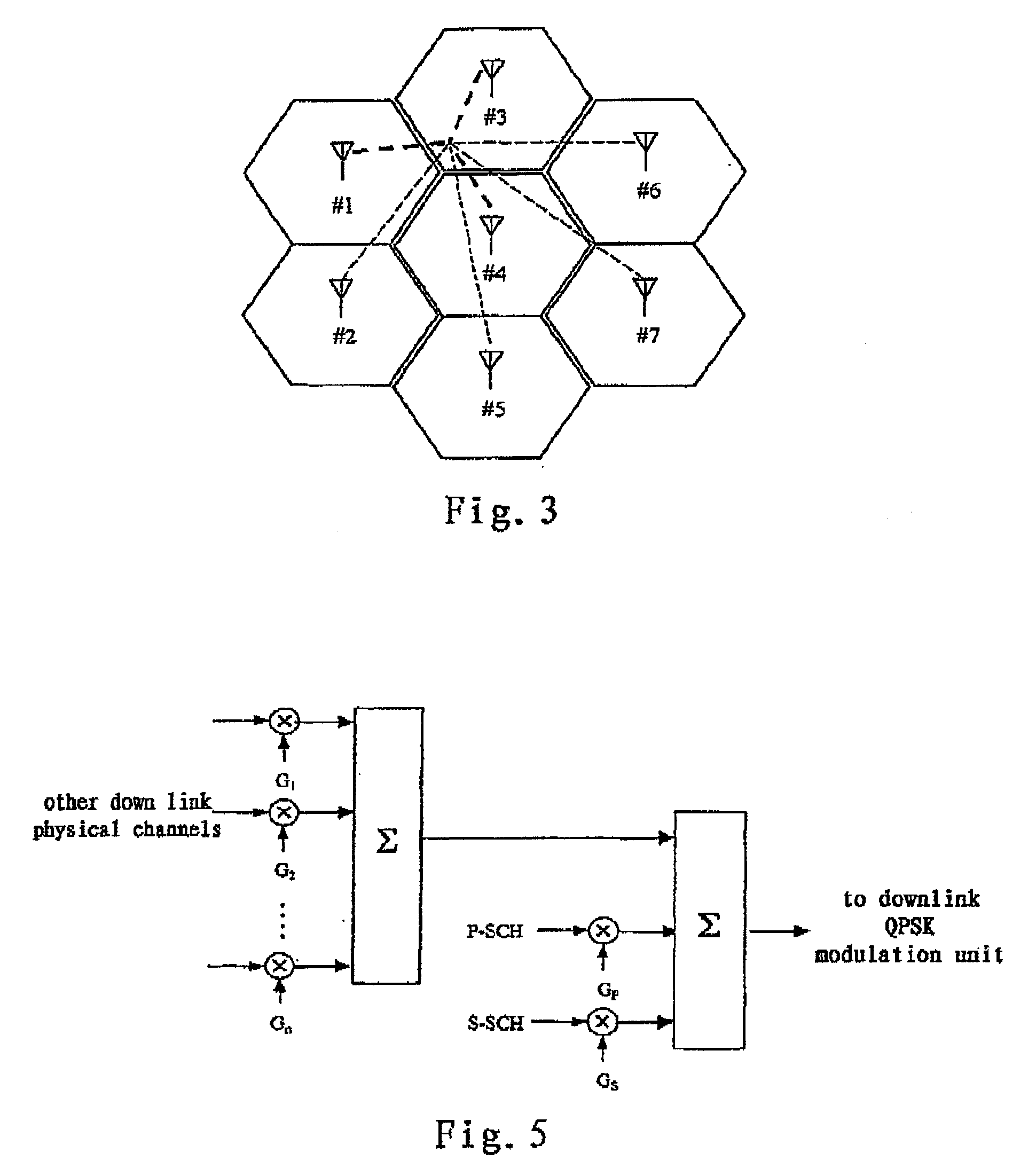
A family of methods for interference averaging in multicarrier systems, such as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems. The methods can provide interference averaging in situations where an interfering co-channel is either partially or fully loaded. For partially loaded systems, subcarrier puncturing, frequency domain repetition, time domain repetition, and hybrid time-frequency repetition schemes are provided. For systems using adaptive modulation / coding rates, lower rates and transmit power can be selected in order to perform interference averaging in time-spread and frequency-spread OFDM schemes. In systems with downlink power control, frequency domain mixing can be used to perform interference averaging.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Mobile communication apparatus with multiple transmission and reception antennas and mobile communication method therefor
ActiveUS7471963B2Minimize impactMaximize data transmission throughputPower managementEnergy efficient ICTMobile stationDownlink power control
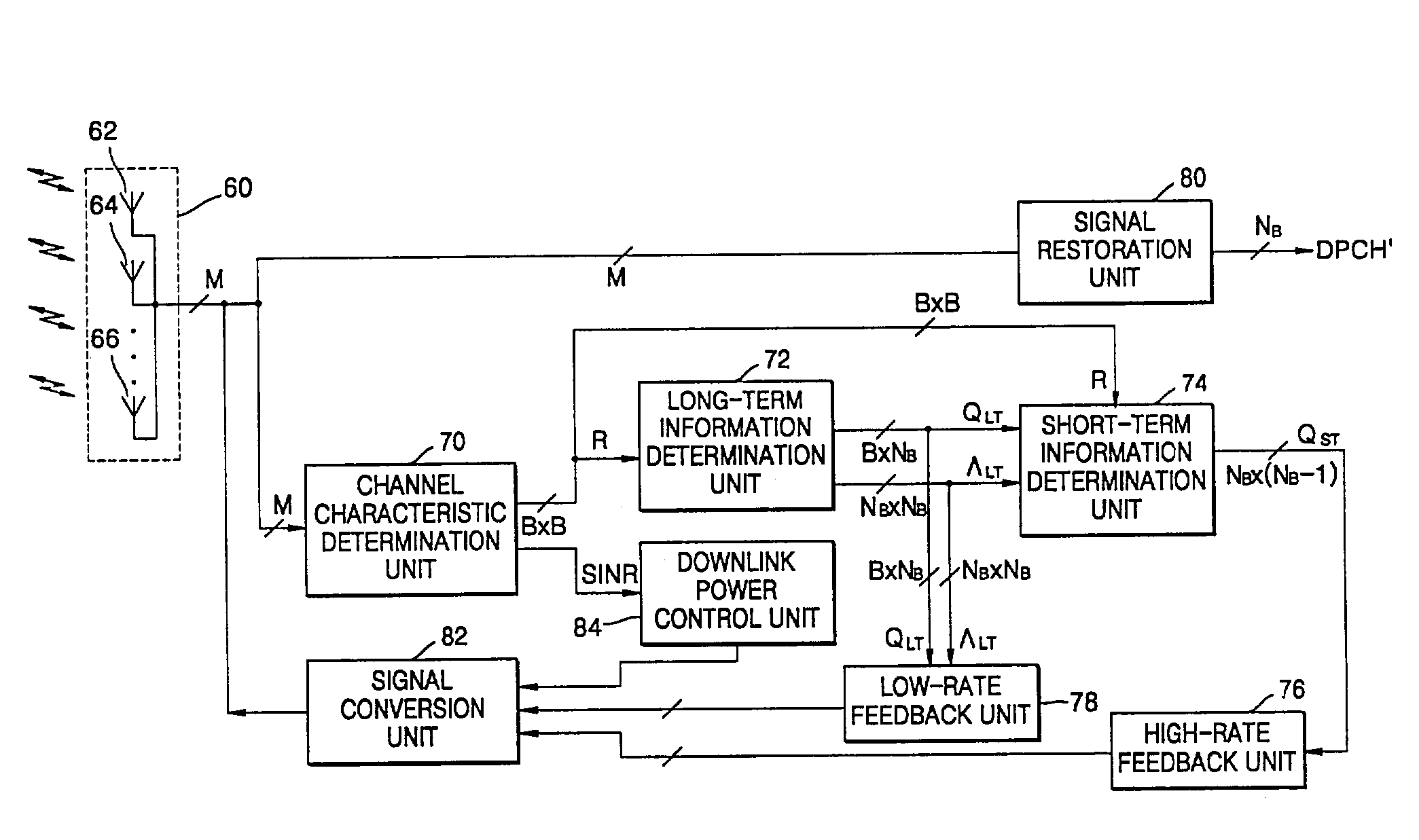
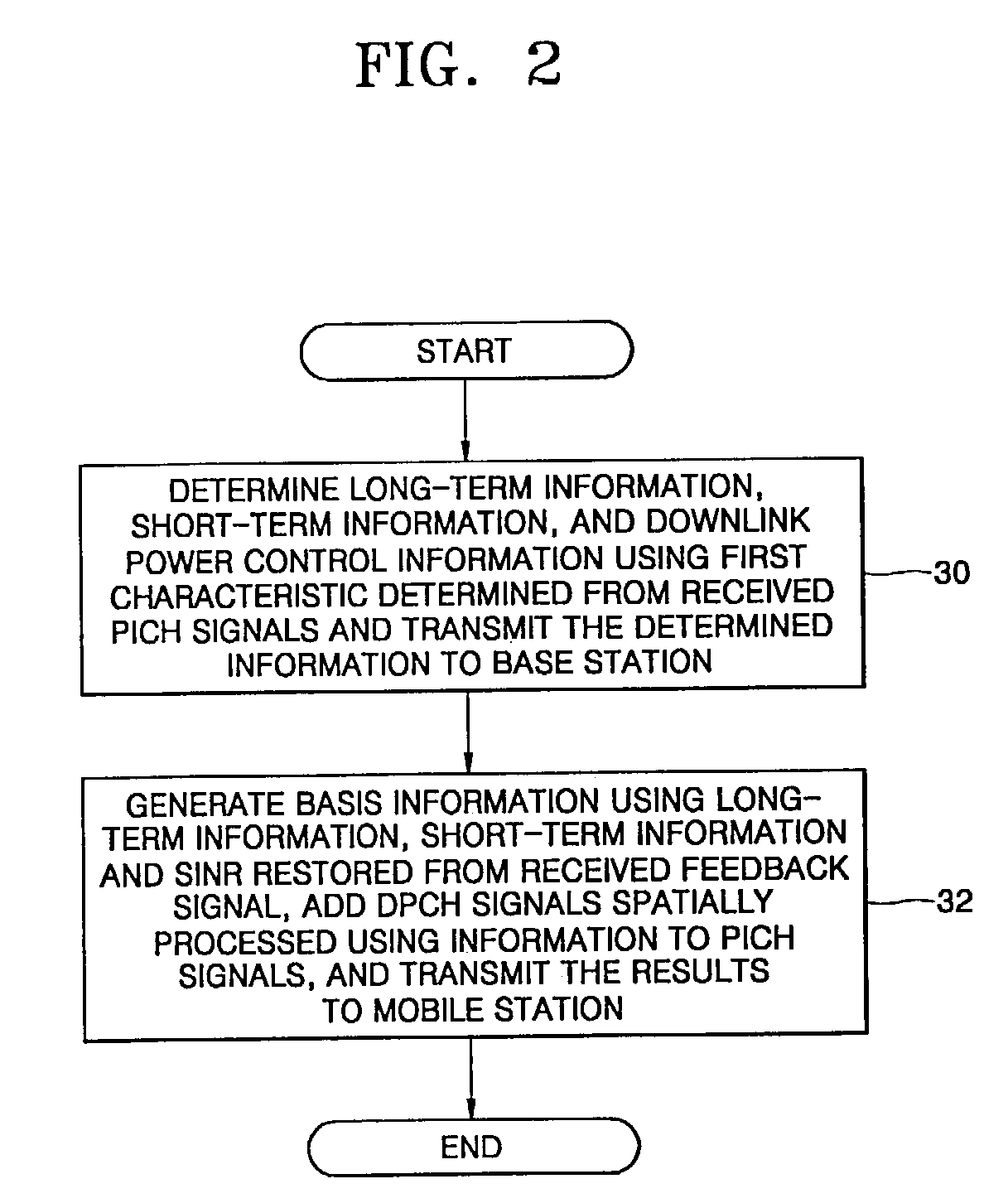
A mobile communication apparatus with multiple transmission and reception antennas and a mobile communication method therefor are provided. In the mobile communication apparatus including a base station and a mobile station, the base station with at least one transmission antenna restores long-term information, short-term information, a signal to interference and noise ratio (SINR) from a feedback signal received from the mobile station, spatially processes dedicated physical channel (DPCH) signals using basis information generated from the restored long-term information, short-term information, and SINR, and transmits the results of adding pilot channel (PICH) signals to the spatially processed results to the mobile station. The mobile station with at least one reception antenna determines a first characteristic corresponding to the channel downlink characteristic for each of the transmission and reception antennas, from the PICH signals transmitted from the base station, determines the long-term information, the short-term information, and downlink power control information including the SINR, which reflect the first characteristic, converts the determined long-term information, short-term information, and downlink power control information into the feedback signal, and transmits the feedback signal to the base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Downlink power control method for wireless packet data network
In a system having a base station transmitter for transmitting data blocks to one or more mobile stations over a radio link, a method for determining a transmit power level at which to transmit a current block. A quality measurement is received from a mobile station indicating an average radio link quality over a previous group of blocks, wherein not all of the blocks of the previous group of blocks were necessarily transmitted at the same transmit power level. A transmit power attenuation level is determined for the current block based on the quality measurement. The transmit power attenuation level is subtracted from the initial transmit power level to determine the transmit power level for the current block.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method to perform downlink power control in packet switching cellular systems with dynamic allocation of the RF channel
InactiveUS20030054850A1Minimize unsuccessfulGreat data-ratesEnergy efficient ICTPower managementAverage filterDownlink power control
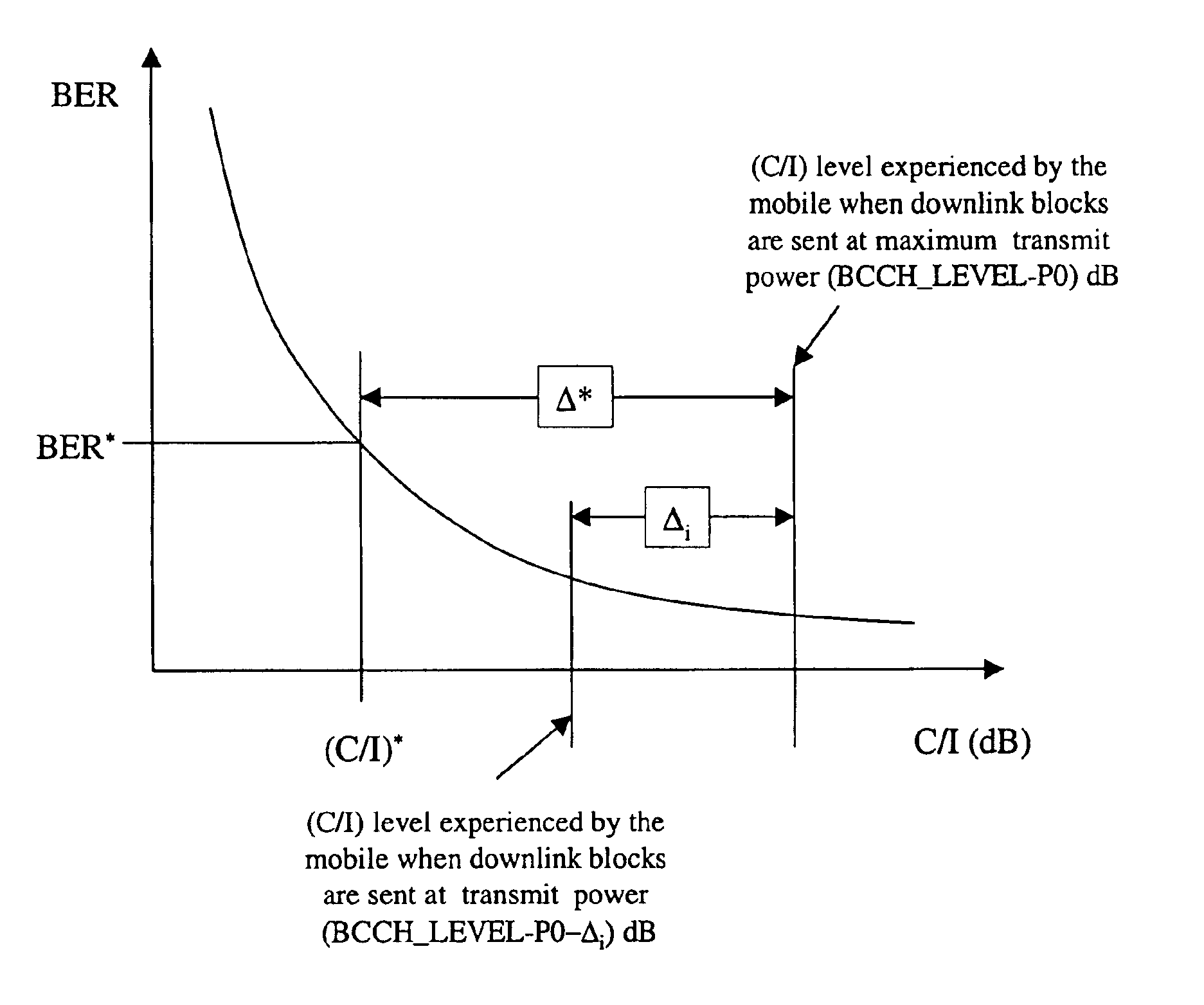
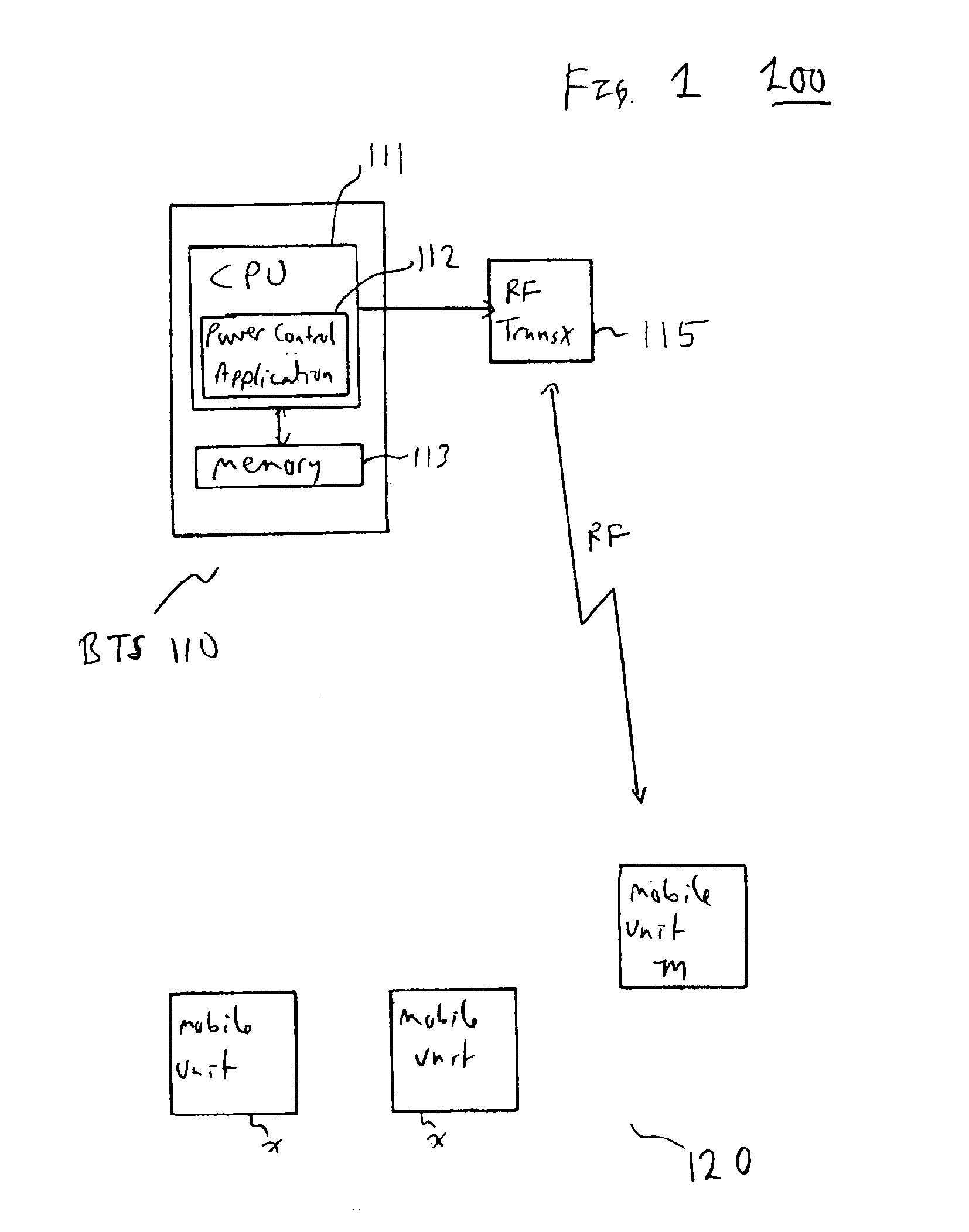
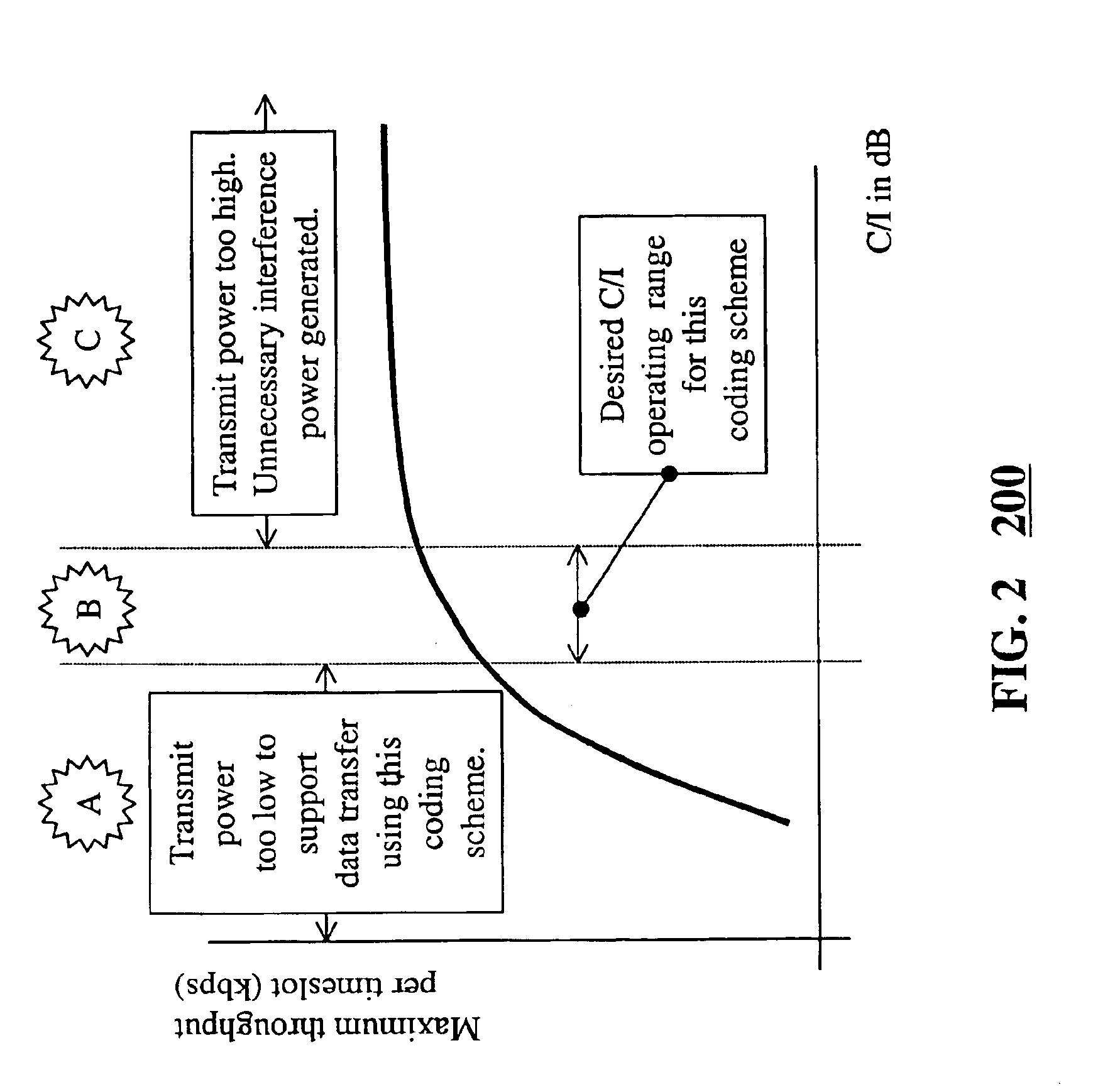
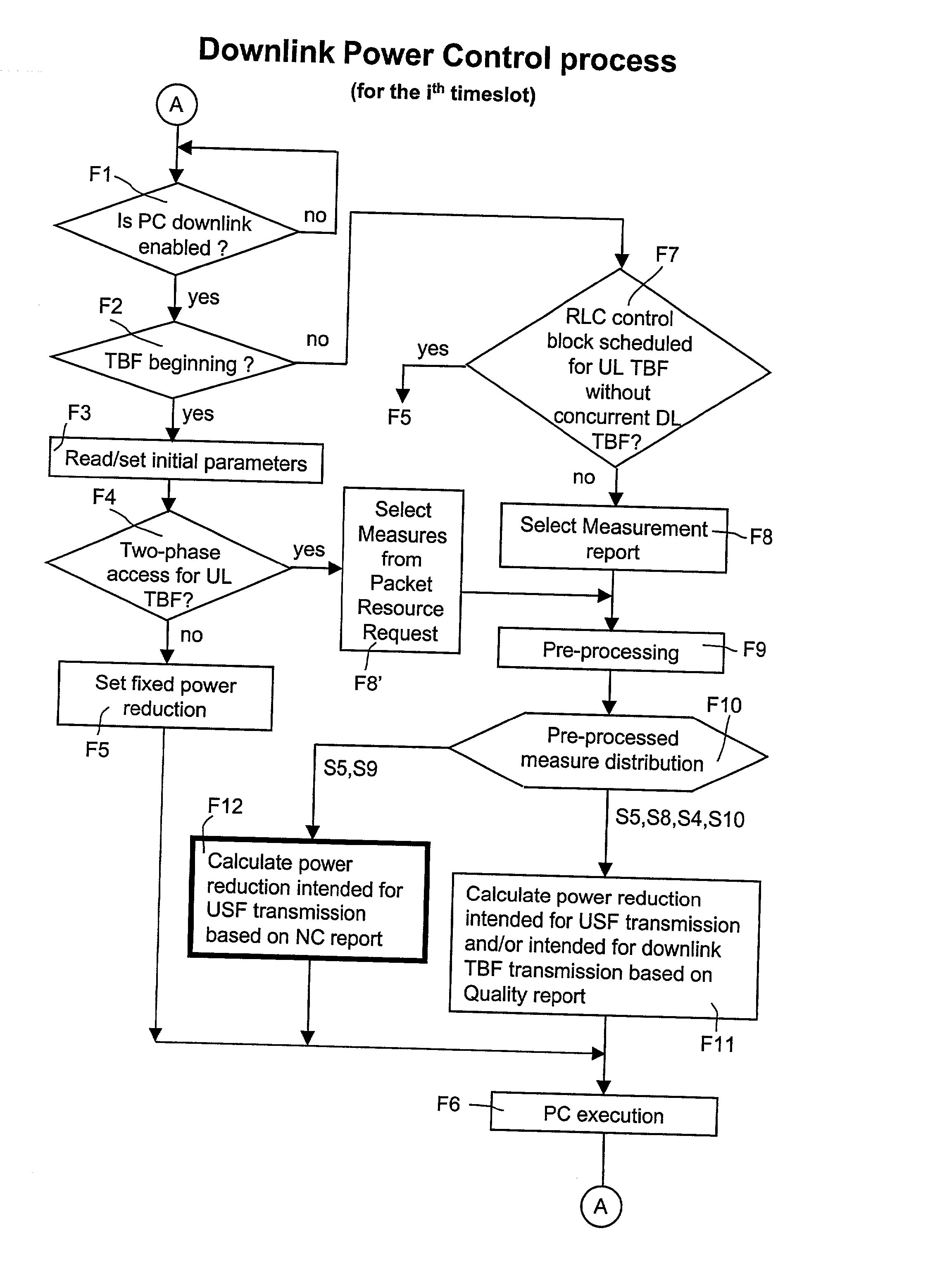
The invention discloses a method to perform downlink Power Control in packet switching cellular systems with dynamic allocation of the RF channel, such as GPRS / EGPRS. The performances concern a scenario in which a radio block transmitted from the Base Station (BTS) on a downlink channel has to be received from at least two MSs simultaneously, a first MS being the addressee of the data / control packet on the downlink TBF while the second MS being the addressee of the Uplink State Flag (USF) for scheduling transmission of the next data / control packet from an uplink TBF to an uplink shared channel. First MS transmits to the BTS a first measurement report including measures of BCCH level and interference level on all the timeslots, while the second MS transmits a NC report including measures of BCCH level only, that because detailed interference measure on the downlink channel are prevented due the absence of a concurrent downlink TBF. The measures are averaged in as many running average filters and the averages compared with target thresholds to find a first and a second power reduction intended for USF and packet transmission respectively. A final power reduction is selected from the two for the next PC execution step. Target threshold for the first MS's averaged measures is a C / I value which provides maximum achievable net throughput independently of Coding Scheme. Target threshold for the second MS depends on CS of the USF flag in a way that when the mean value of the level measures is equal to the threshold a fixed probability takes place that the USF flag is decoded with success. The network, in the capacity of the BSC and PCU, counts successfully and unsuccessfully blocks received uplink upon transmission of the scheduled USFs for that uplink TBF, being the lack of a scheduled block noticed by the network. If successfully counting reaches a fixed maximum counting before, then an increment of the first power reduction is decided, while in case the maximum unsuccessfully counting is reached before a decrement of the first power reduction is instead decided (FIG. 10).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
Downlink power control method and device applied to long term evolution (LTE) system
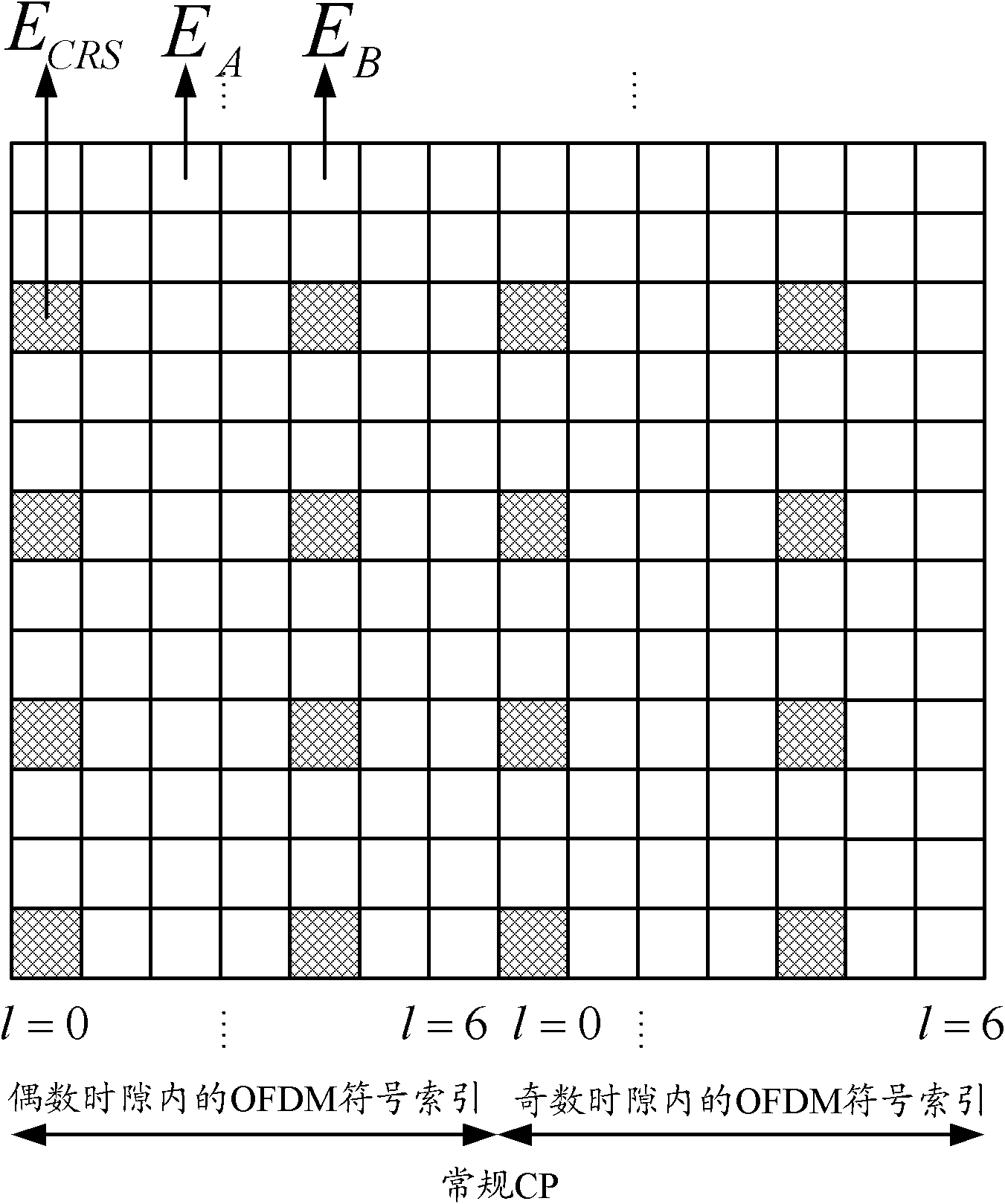
The invention discloses a downlink power control method and a downlink power control device applied to a long term evolution (LTE) system. The method comprises the following steps of: configuring an absolute power value ECRS_dBm for a resource element (RE) including a cell reference signal (CRS); configuring parameters indicating a transmission power of a same type for all downlink physical channels or downlink physical signals except the CRS according to the ECRS_dBm; and performing power control on the transmission of the downlink physical channels or the downlink physical signals according to the ECRS_dBm and the parameters indicating the transmission power. In the invention, the method for configuring the power value of the all downlink physical channels or the all downlink physical signals in the implementation of an LTE product is provided, so that the correct demodulation of receiving data by user equipment can be guaranteed, and the safety of network-side base station equipment can be guaranteed.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Downlink power control method and device
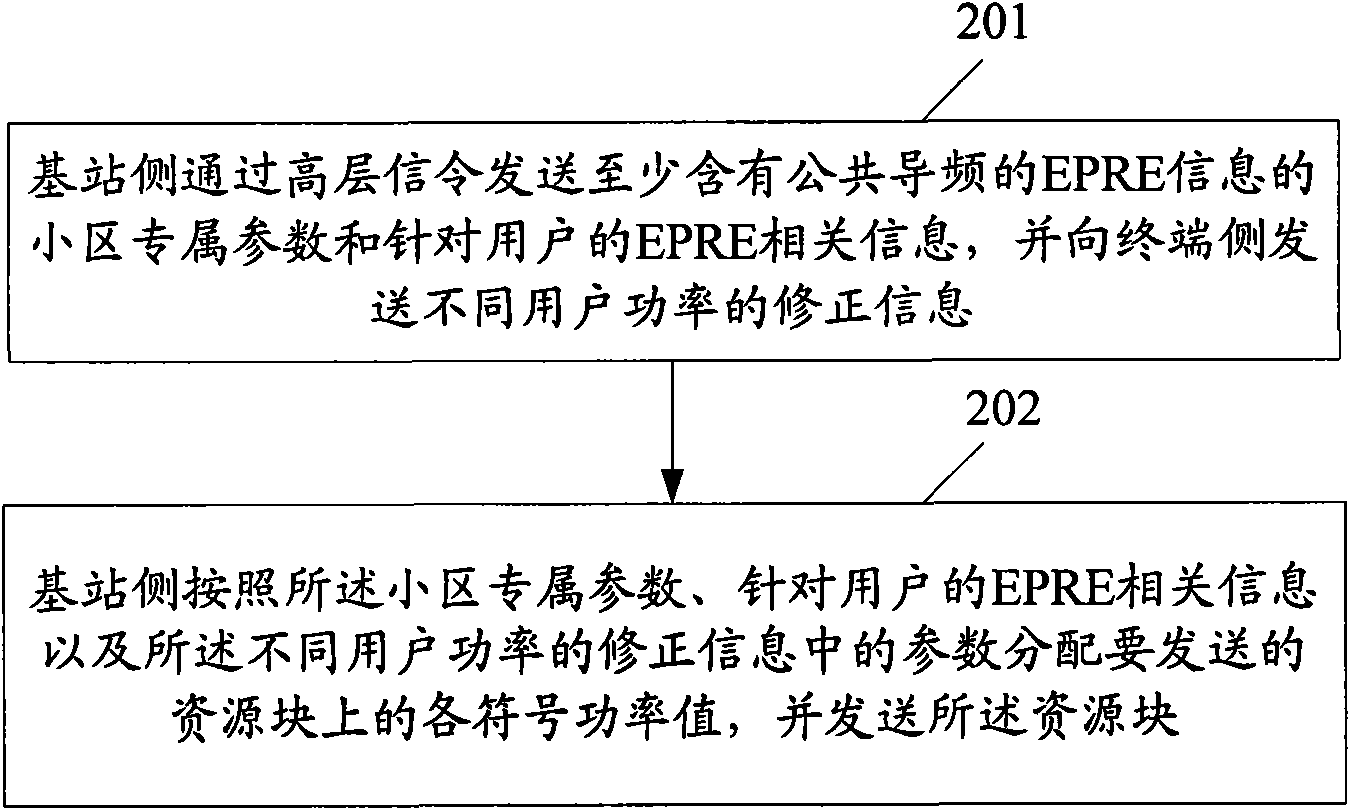
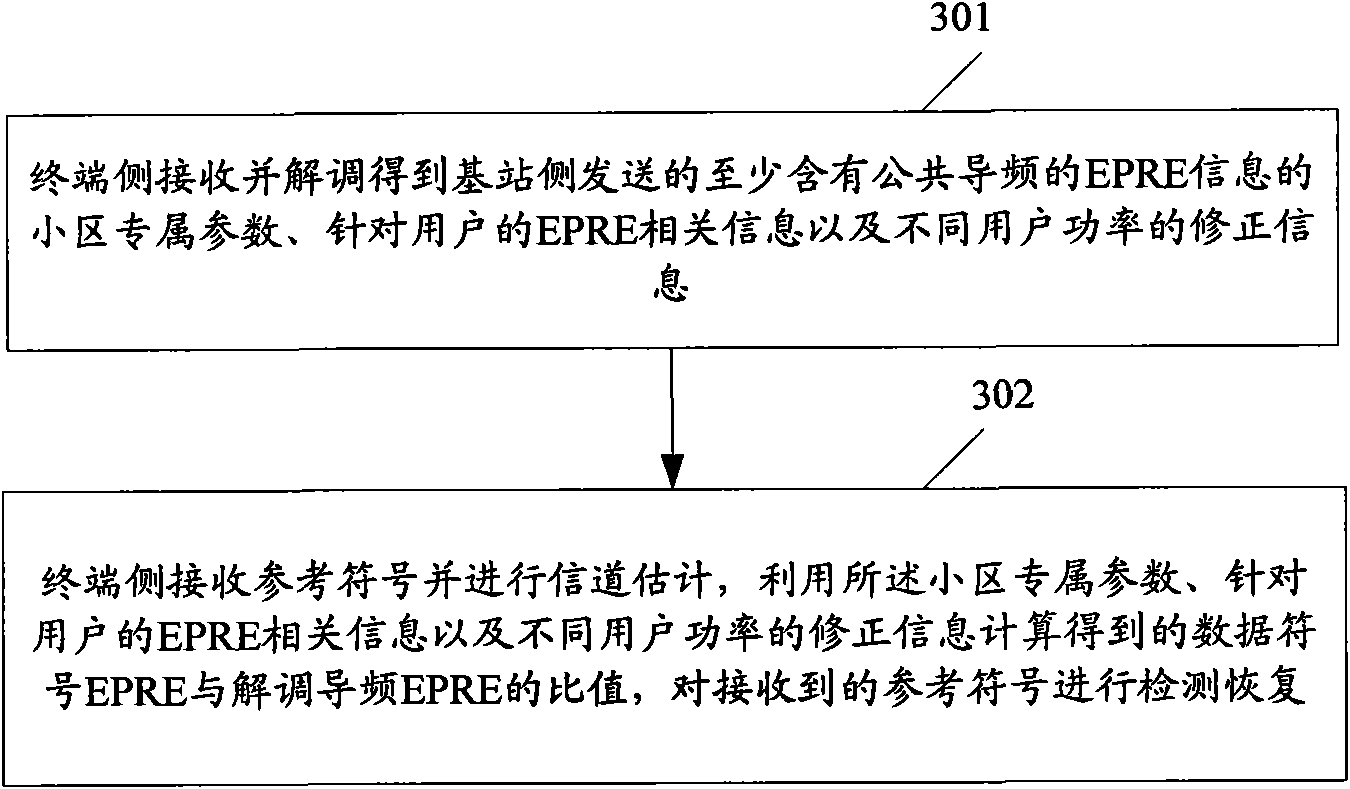
ActiveCN101888690AReduce overheadReduce complexityPower managementTransmission control/equalisingResource blockDownlink power control
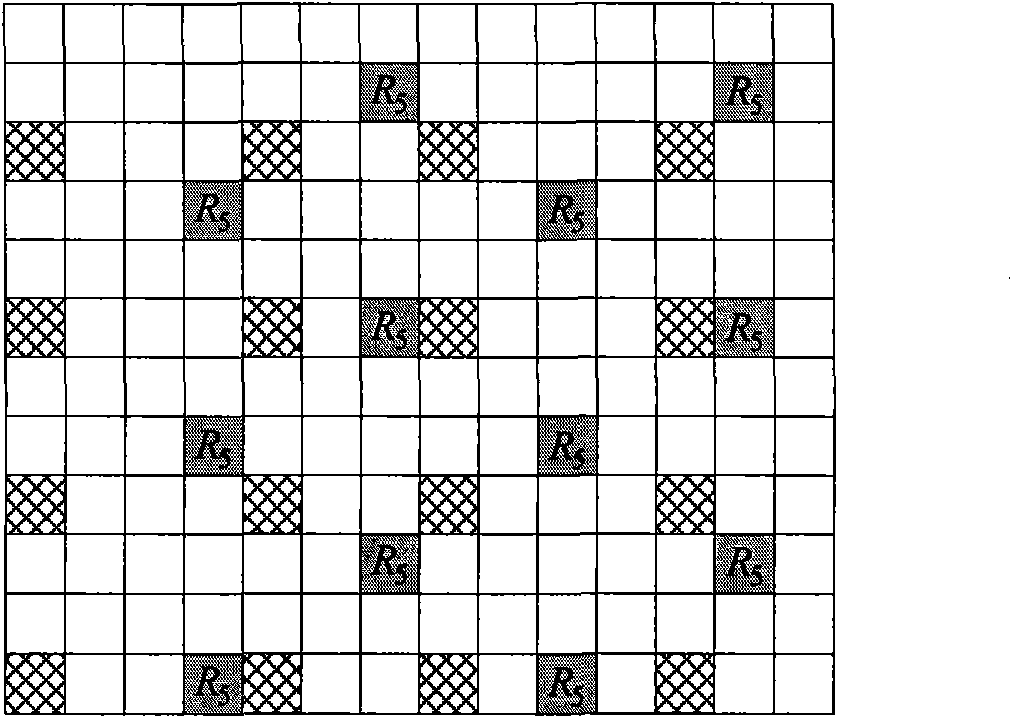
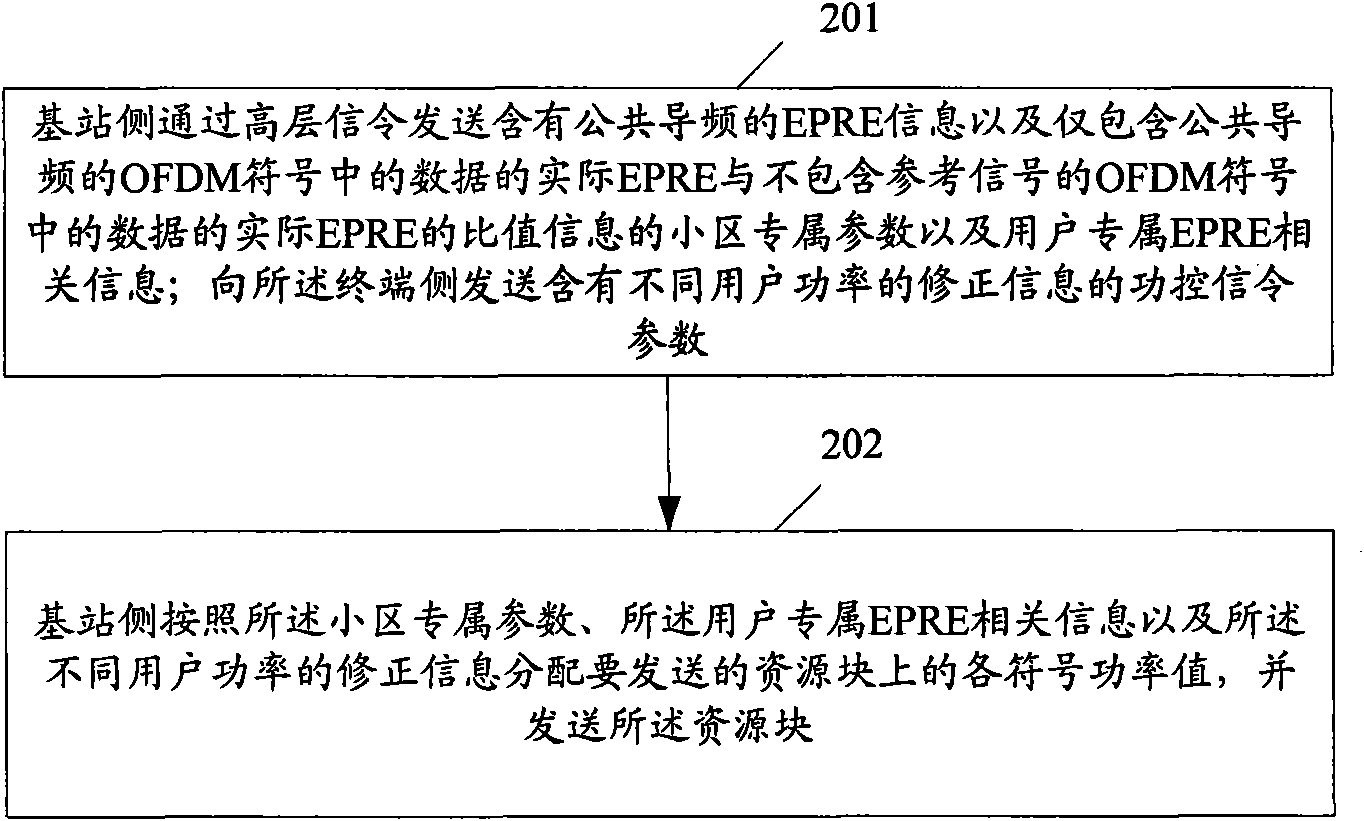
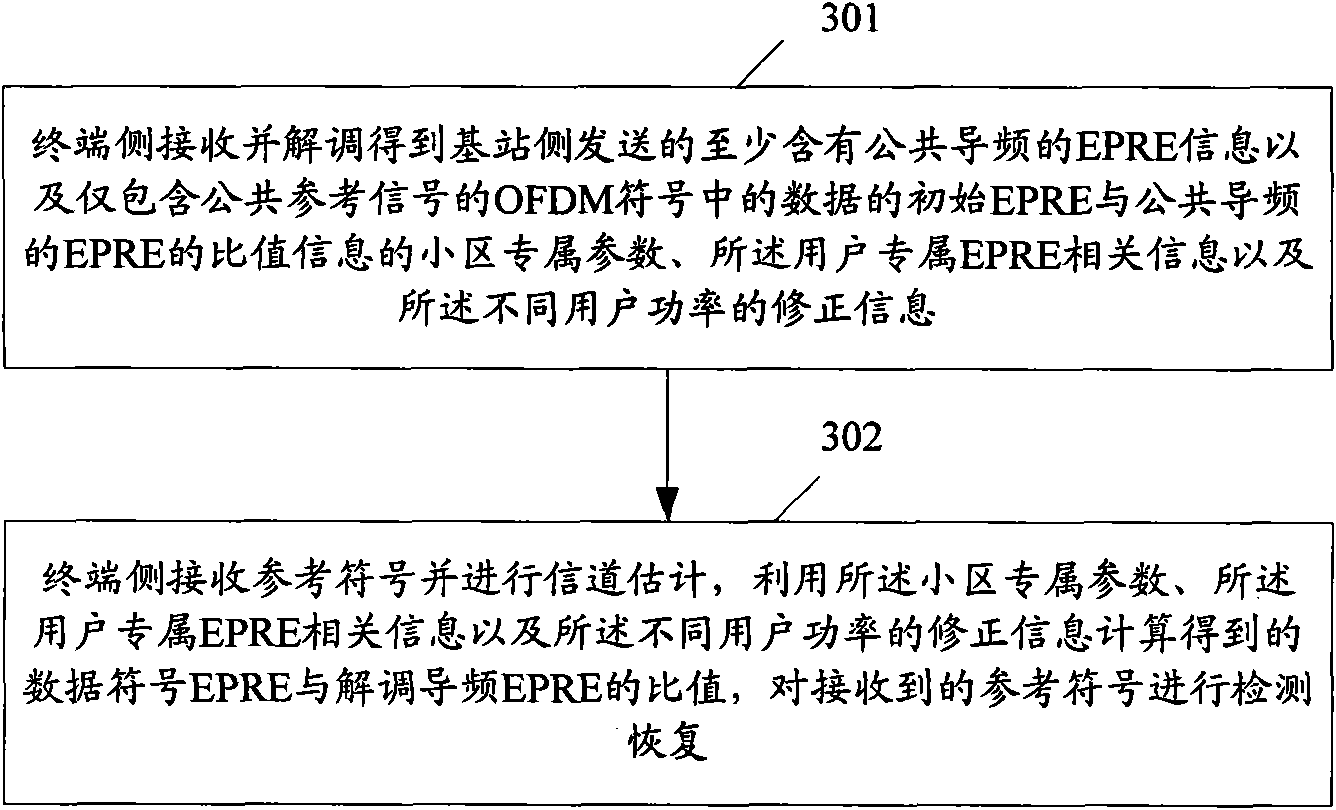
The invention discloses a downlink power control method and a downlink power control device. The method comprises the following steps that: a base station side sends EPRE information which contains common pilot frequency, the cell dedicated parameter of ratio information of real EPRE of data in an OFDM signal which only contains the common pilot frequency to real EPRE of data in an OFDM signal which does not contain a reference signal, and user dedicated EPRE related information of initial EPRE of data in the OFDM signal which does not contain the reference signal; the base station side distributes each symbol power value on a resource block to be sent according to the cell dedicated parameter, the user dedicated EPRE related information and correction information of different user power and sends the resource block; and a terminal side receives a reference symbol, performs channel estimation, and detects and recovers the received reference symbol according to the ratio of data symbol EPRE and demodulated pilot frequency EPRE which are obtained by parametric computation. The method is favorable for improving the error code performance of a system so as to increase the information throughput of the user while realizing downlink power control.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Methods and apparatuses for power control
InactiveUS8446849B2Enhanced signalNo wastePower managementTransmission systemsCommunications systemUplink transmission
Downlink power control commands are mapped to resources used for uplink communications within a wireless communication system. An eNode B receives communications from UEs and determines the resources used by the UEs for those transmissions on the uplink which are transmitted at non-optimum power levels. Power control messages are formulated wherein the location of the power control commands is mapped to particular resources used by the UEs for their uplink transmissions. This facilitates the eNode B to dynamically assign resources for the power control commands while permitting the UEs to decode the power control messages to adjust their power accordingly.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for estimating beacon power variations
A method for compensating for power variations in satellite communications includes measuring or estimating power variations for signals received at an earth-based terminal. The method also includes measuring or estimating changes in carrier-to-noise levels by a number of satellite terminals. The power variations may then be used to adjust the measured / estimated changes in carrier-to-noise (C / N) levels. The adjusted C / N levels may then be used to more accurately reflect actual network conditions and may be used in downlink power control related processing.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Downlink power control in wireless communications networks and methods
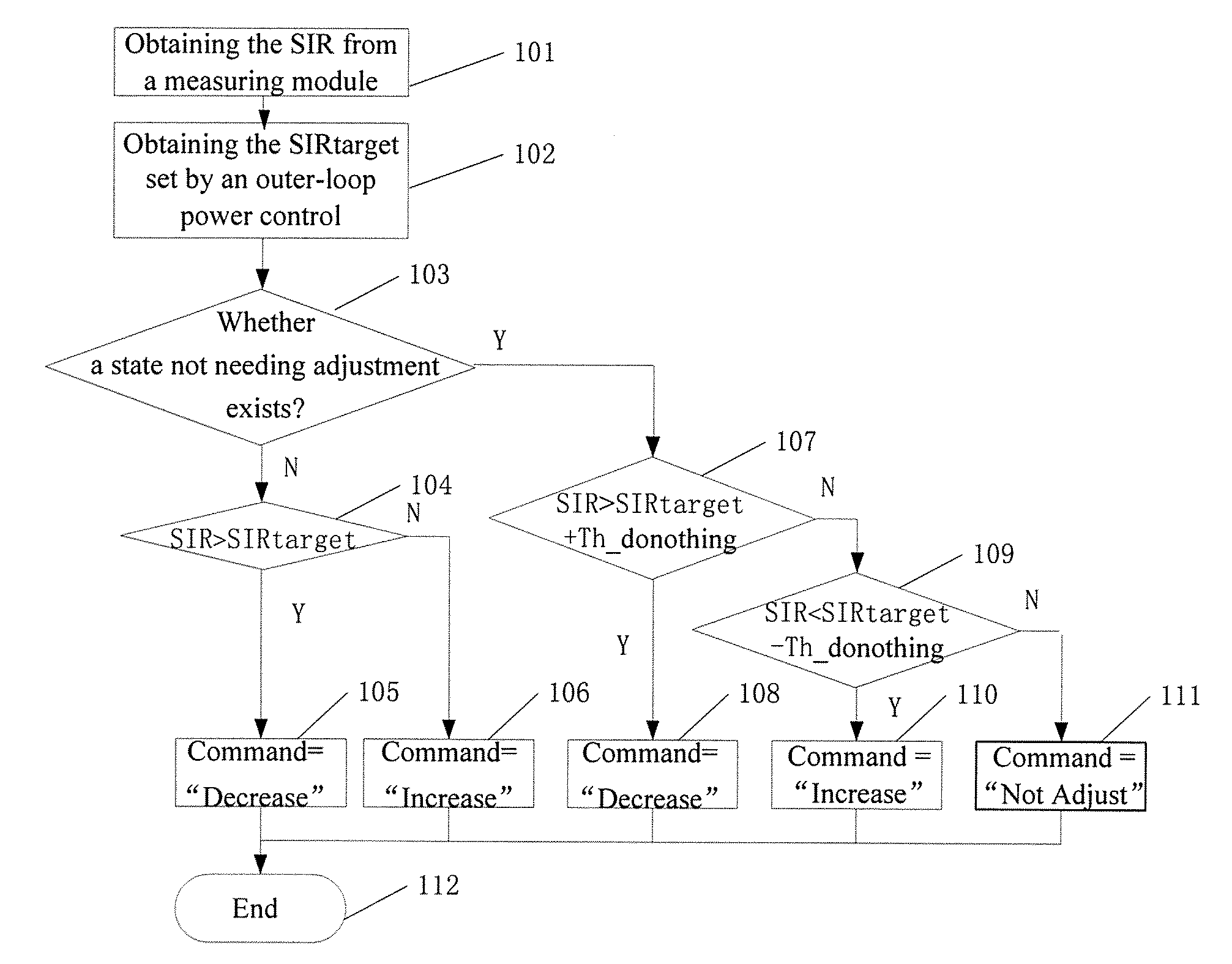
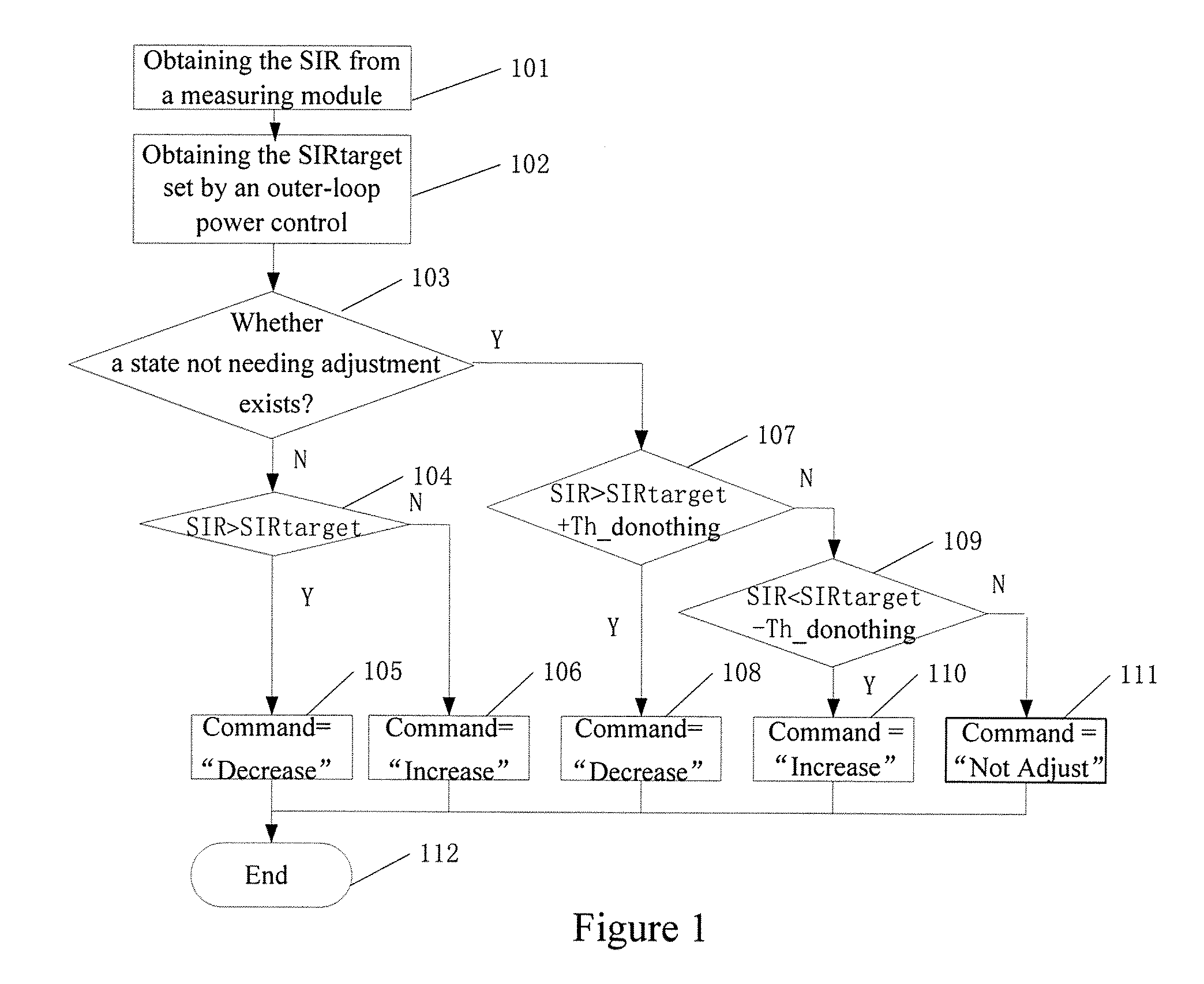
A method in a wireless communications device, for example, 3GPP W-CDMA wireless mobile user equipment, including receiving a slot-structured signal having a dedicated control channel and a dedicated data channel, estimating a first SIR (410) on the dedicated control channel, estimating a second SIR (420) on the dedicated data channel if a symbol on the dedicated data channel contains data, weighting the first and second SIR estimates (430), and summing (440) the first SIR and the second SIR estimates after weighting.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Method for determining down initial transmitting power
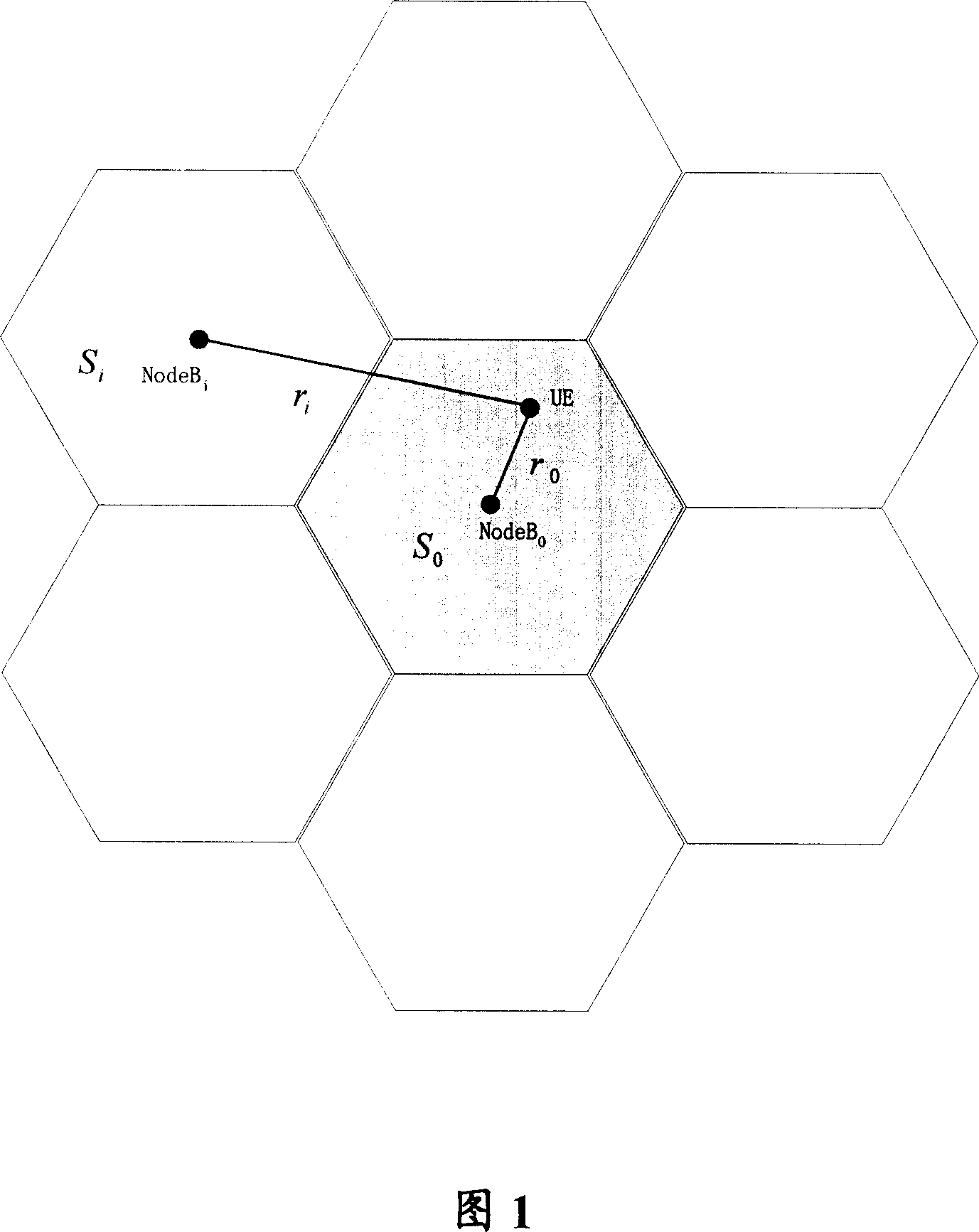
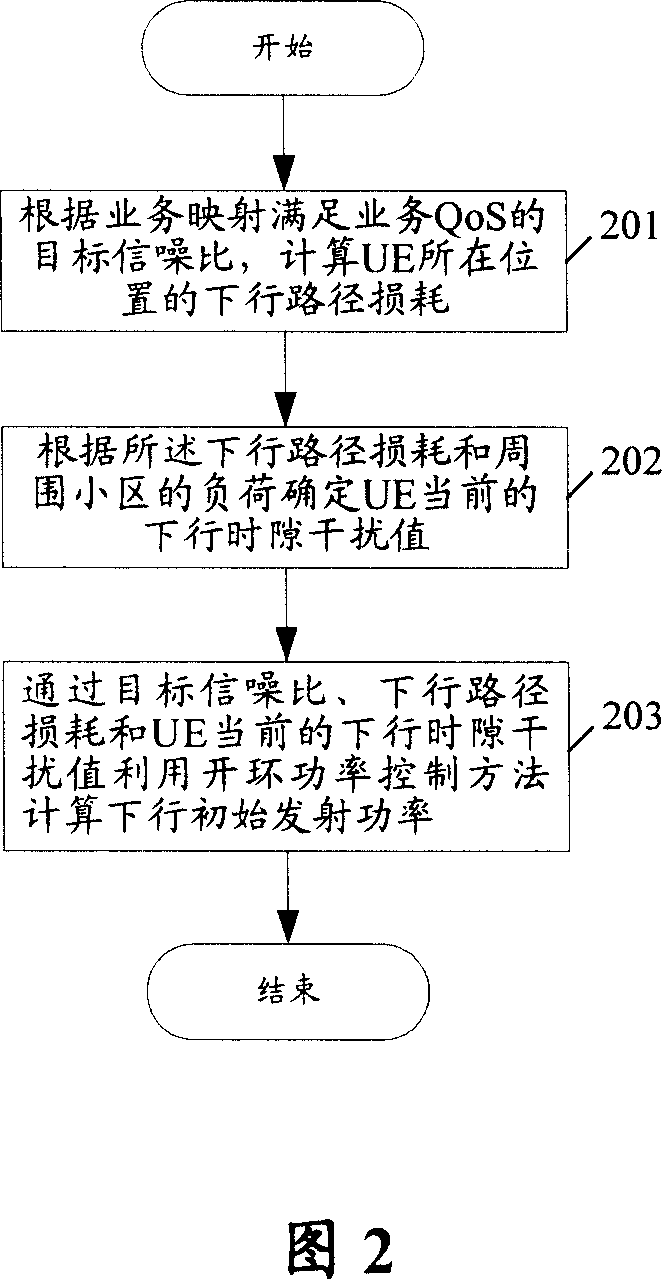
ActiveCN101075830AAvoid interferenceIncrease coverageTransmission control/equalisingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsTransmitted power
The method comprises: considering the path losses and the time slot interference when calculating the downlink initial transmitted power in order to figure out the size of downlink initial transmitted power reasonably and to avoid the influence caused by oversized transmitted power or undersized transmitted power. During the process of just establishing the physical layer or re-allocating the channel or inter-cell switchover, even if there isn't the destination time slot interference measured value reported by UE, the invention can also figure out the downlink time slot interference, and use the downlink power control to calculate the downlink initial transmitted power so as either to ensure the success ratio of access and the Quos requirement or to avoid the heavy interference to other UEs.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Method and apparatus for estimating beacon power variations
A method for compensating for power variations in satellite communications includes measuring or estimating power variations for signals received at an earth-based terminal. The method also includes measuring or estimating changes in carrier-to-noise levels by a number of satellite terminals. The power variations may then be used to adjust the measured / estimated changes in carrier-to-noise (C / N) levels. The adjusted C / N levels may then be used to more accurately reflect actual network conditions and may be used in downlink power control related processing.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
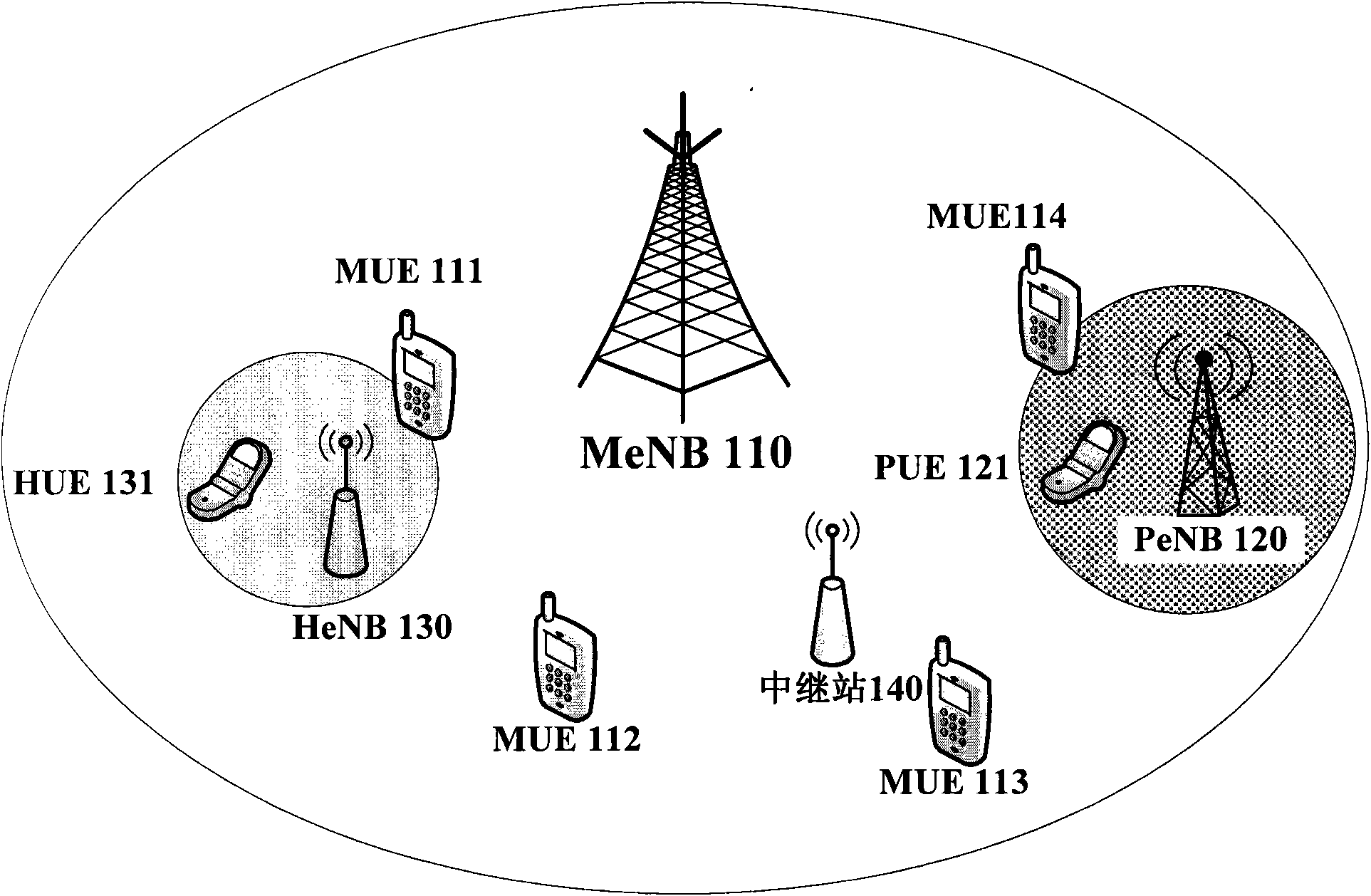
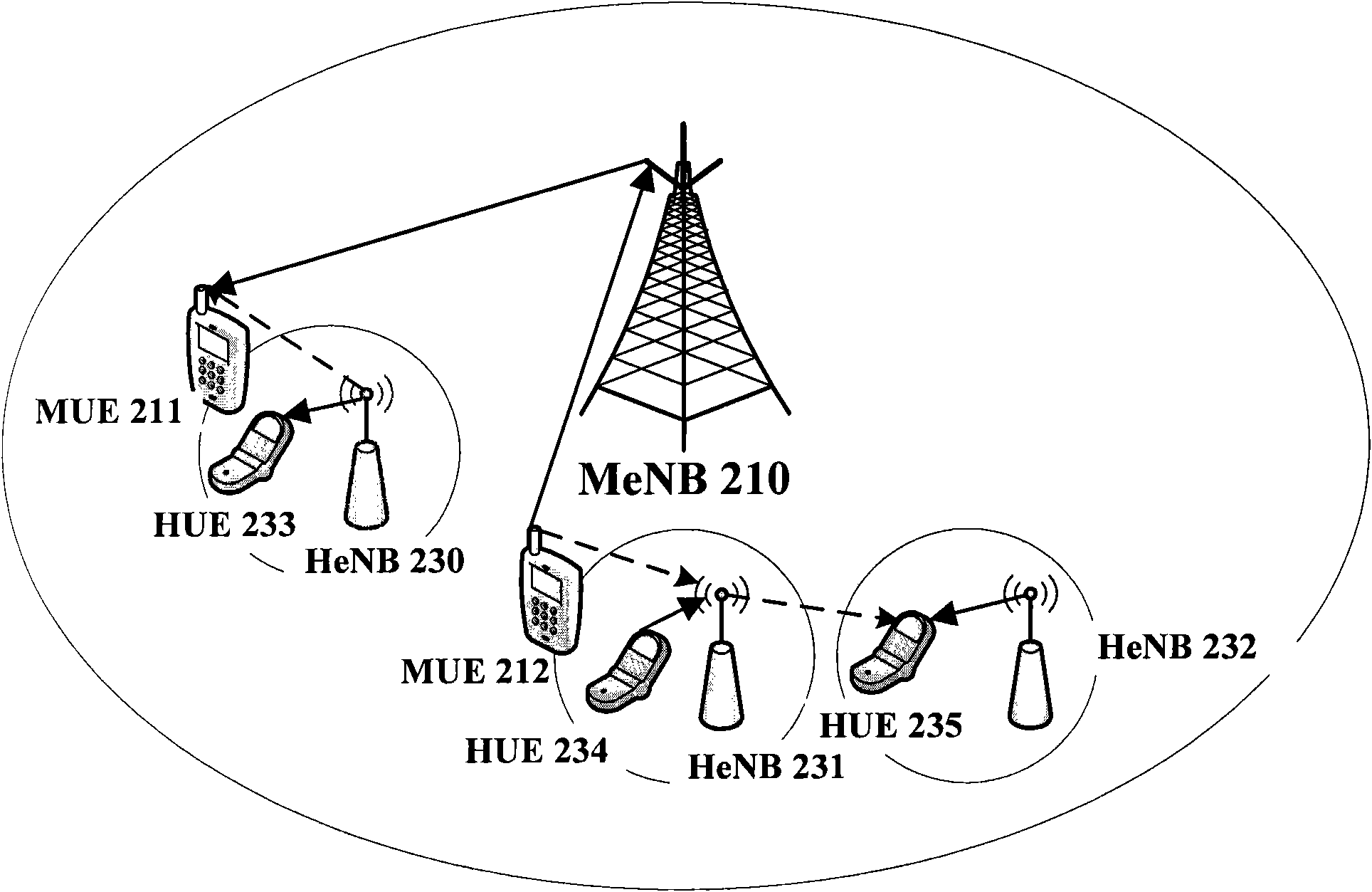
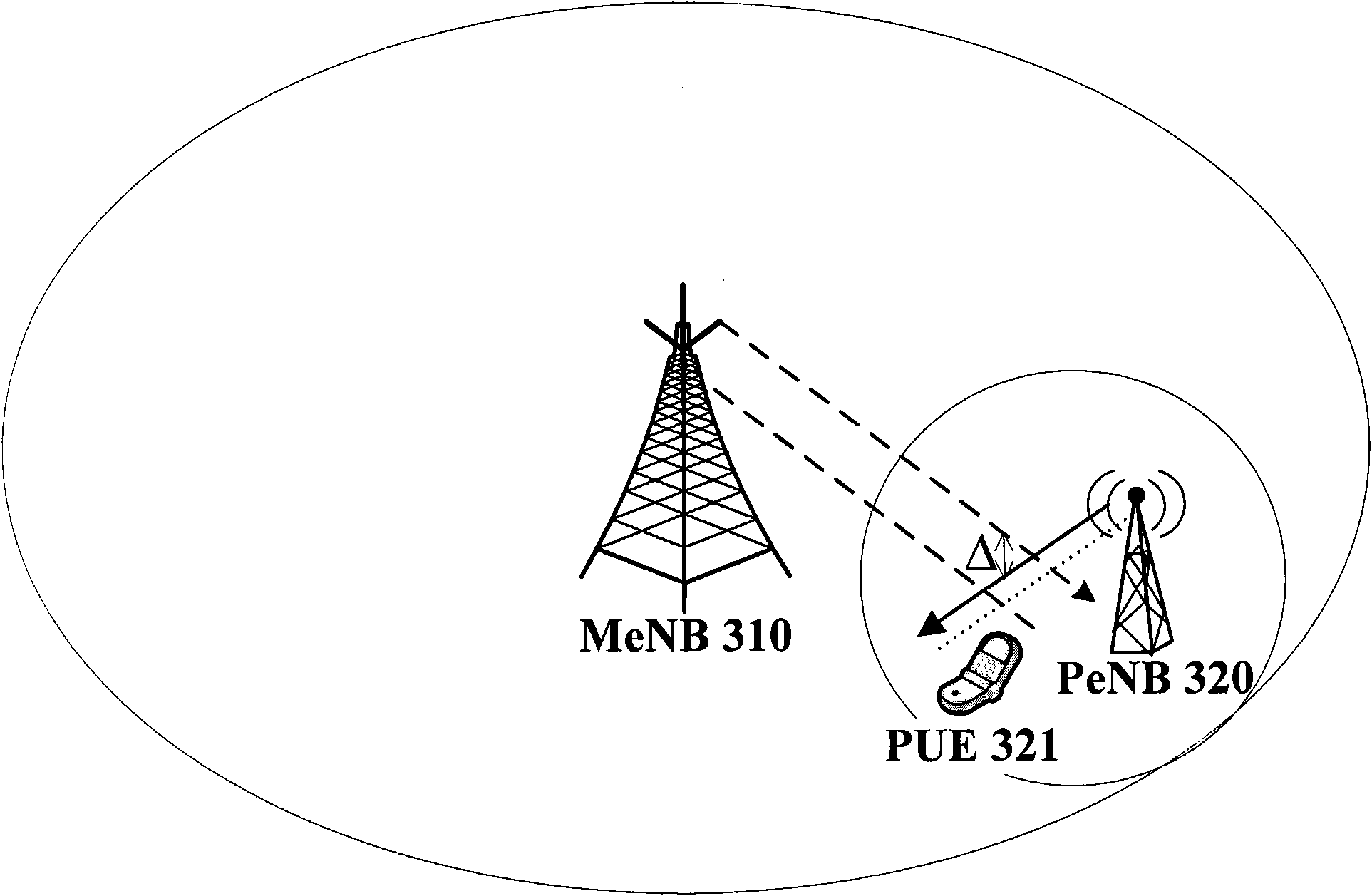
Method for enhanced inter-cell interference cancellation (eICIC) in heterogeneous network, base station and user equipment
InactiveCN102404808AInterference reduction or eliminationEfficient methodConnection managementControl channelDownlink power control
The invention discloses a method for enhanced inter-cell interference cancellation (eICIC) in a heterogeneous network, and a corresponding base station and corresponding user equipment. A macro eNodeB (MeNB) defines a signaling to inform a home eNodeB (HeNB) of an event that MeNB cell user equipment (MUE) in a connection mode enters the edge or the neighborhood of an HeNB cell; when HeNB cell user equipment (HUE) is all located at the center of the HeNB cell, the HeNB adopts downlink power control or power settings to reduce the inter-cell interference (ICI) subjected to the MUE on a control channel; the MeNB also can adopt a mechanism of being really or falsely handed over an HeNB cell aiming at that the MUE is either CSG UE (Close Subscriber Group User Equipment) or Non-CSG UE, wherein when the MeNB is falsely handed over to the HeNB cell, a mechanism that the HeNB configures the DRX (Discontinuous Reception) of the HUE can be adopted; and when the MUE in an idle mode enters the edge or the neighborhood of the HeNB cell, if the MUE dwells at the HeNB cell, the HeNB adopts different mechanisms to reduce the ICI subjected to the MUE on the basis that that the MUE is in the connection mode or the idle mode. The method has the characteristics of simplicity, flexibility, high efficiency, and easiness to implement.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method of down-chain power control in packet switching cellular system
InactiveCN1395375AAvoid uncertaintyReduce failurePower managementEnergy efficient ICTAverage filterDownlink power control
The invention discloses a method to perform downlink Power Control in packet switching cellular systems with dynamic allocation of the RF channel, such as GPRS / EGPRS. The performances concern a scenario in which a radio block transmitted from the Base Station (BTS) on a downlink channel has to be received from at least two MSs simultaneously, a first MS being the addressee of the data / control packet on the downlink TBF while the second MS being the addressee of the Uplink State Flag (USF) for scheduling transmission of the next data / control packet from an uplink TBF to an uplink shared channel. First MS transmits to the BTS a first measurement report including measures of BCCH level and interference level on all the timeslots, while the second MS transmits a NC report including measures of BCCH level only, that because detailed interference measure on the downlink channel are prevented due the absence of a concurrent downlink TBF. The measures are averaged in as many running average filters and the averages compared with target thresholds to find a first and a second power reduction intended for USF and packet transmission respectively. A final power reduction is selected from the two for the next PC execution step. Target threshold for the first MS's averaged measures is a C / I value which provides maximum achievable net throughput independently of Coding Scheme. Target threshold for the second MS depends on CS of the USF flag in a way that when the mean value of the level measures is equal to the threshold a fixed probability takes place that the USF flag is decoded with success. The network, in the capacity of the BSC and PCU, counts successfully and unsuccessfully blocks received uplink upon transmission of the scheduled USFs for that uplink TBF, being the lack of a scheduled block noticed by the network. If successfully counting reaches a fixed maximum counting before, then an increment of the first power reduction is decided, while in case the maximum unsuccessfully counting is reached before a decrement of the first power reduction is instead decided (fig.10).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
Downlink power control method and apparatus of OFDM system
ActiveUS20130157709A1Efficient schedulingEnergy efficient ICTPower managementDownlink power controlChannel use
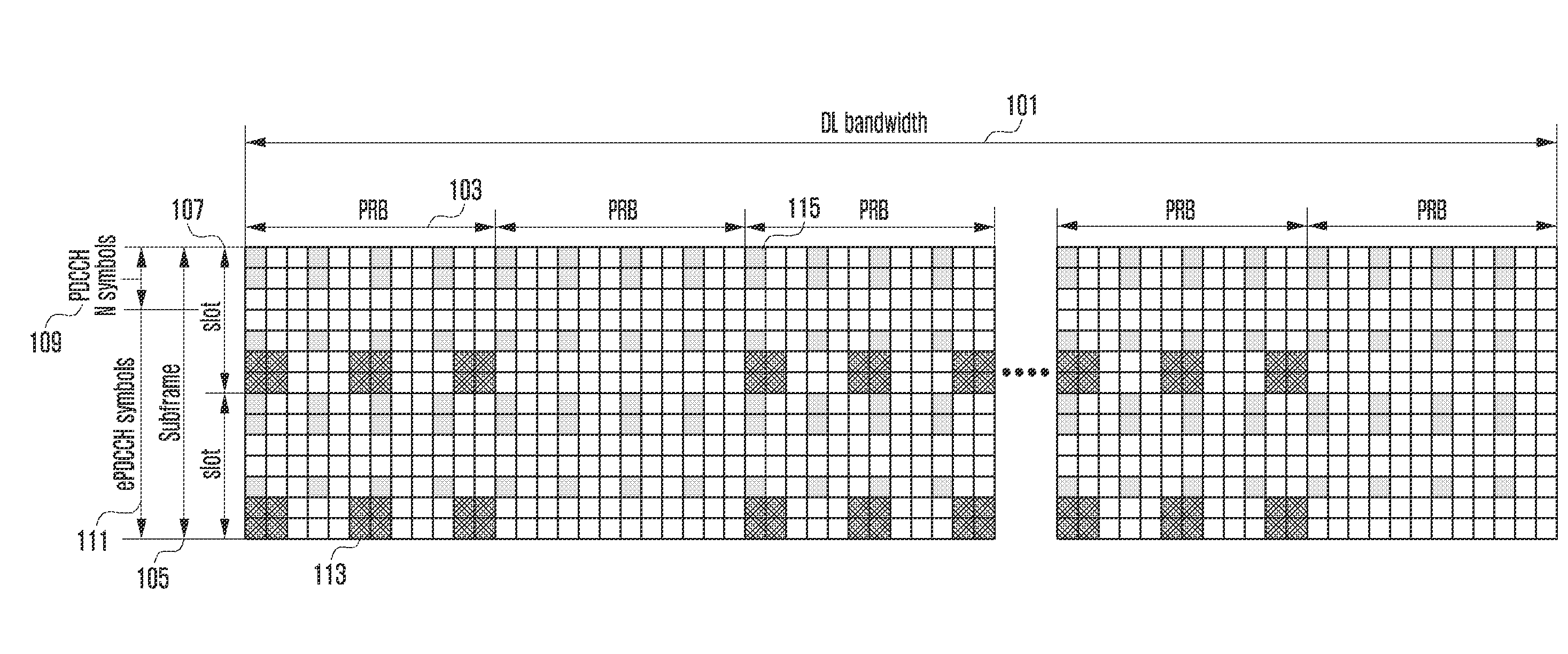
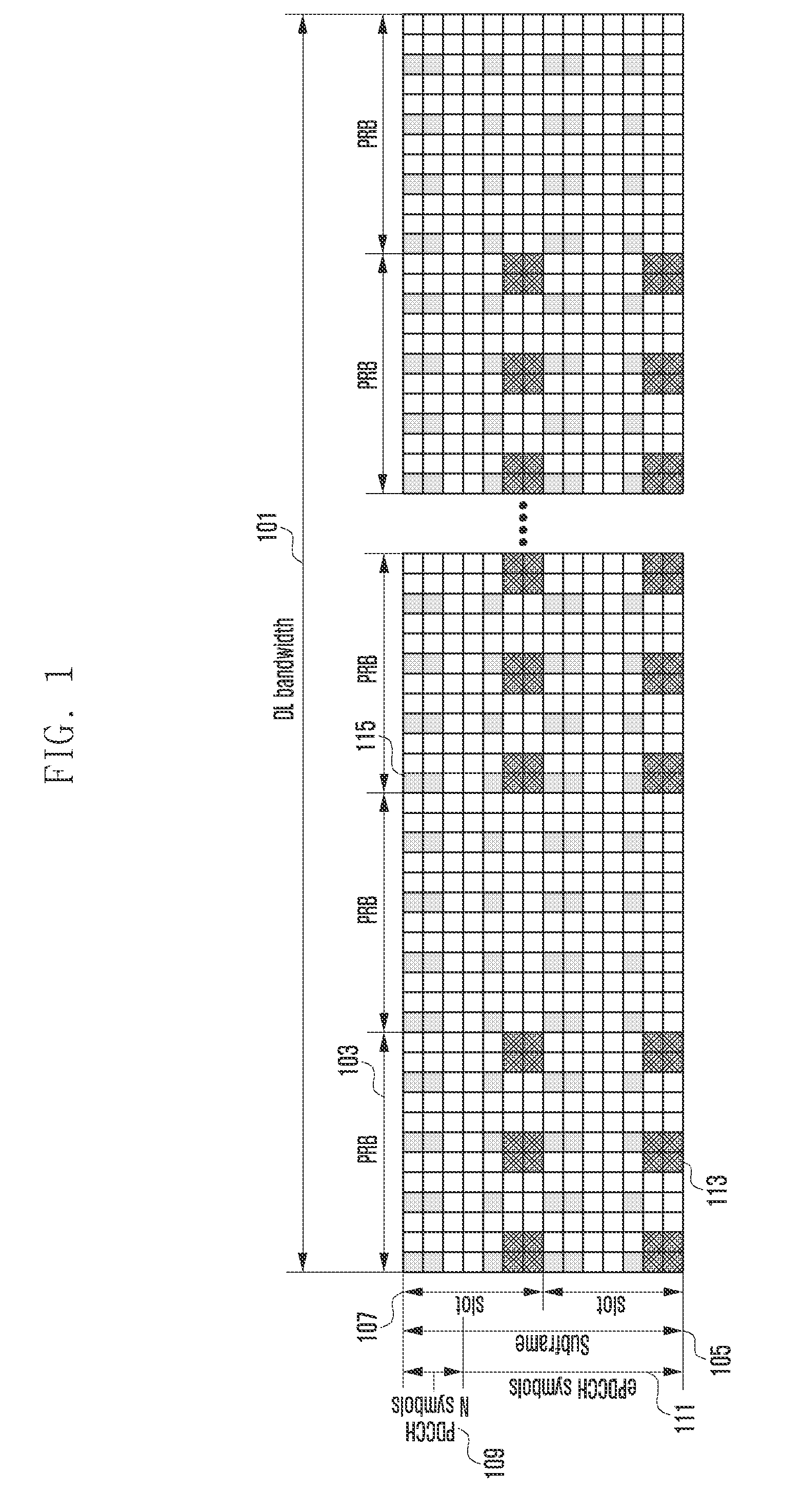
A downlink power control method and apparatus for improving downlink power efficiency gain in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system is provided. The downlink power control method includes transmitting a downlink data channel at a normal subframe according to first downlink power information for the normal subframe, and transmitting the downlink data channel at an Almost Blank Subframe (ABS) according to second downlink power information for the ABS, wherein the first downlink power information for the normal subframe and the second downlink power information for the ABS differ from each other. The downlink power control method and apparatus is capable of regulating inter-cell interference variation between contiguous symbols at a predetermined level in a subframe at a terminal of a neighbor cell and making it possible to schedule the UE receiving the low power data channel using the power ratio of the feedbacks from the UE.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
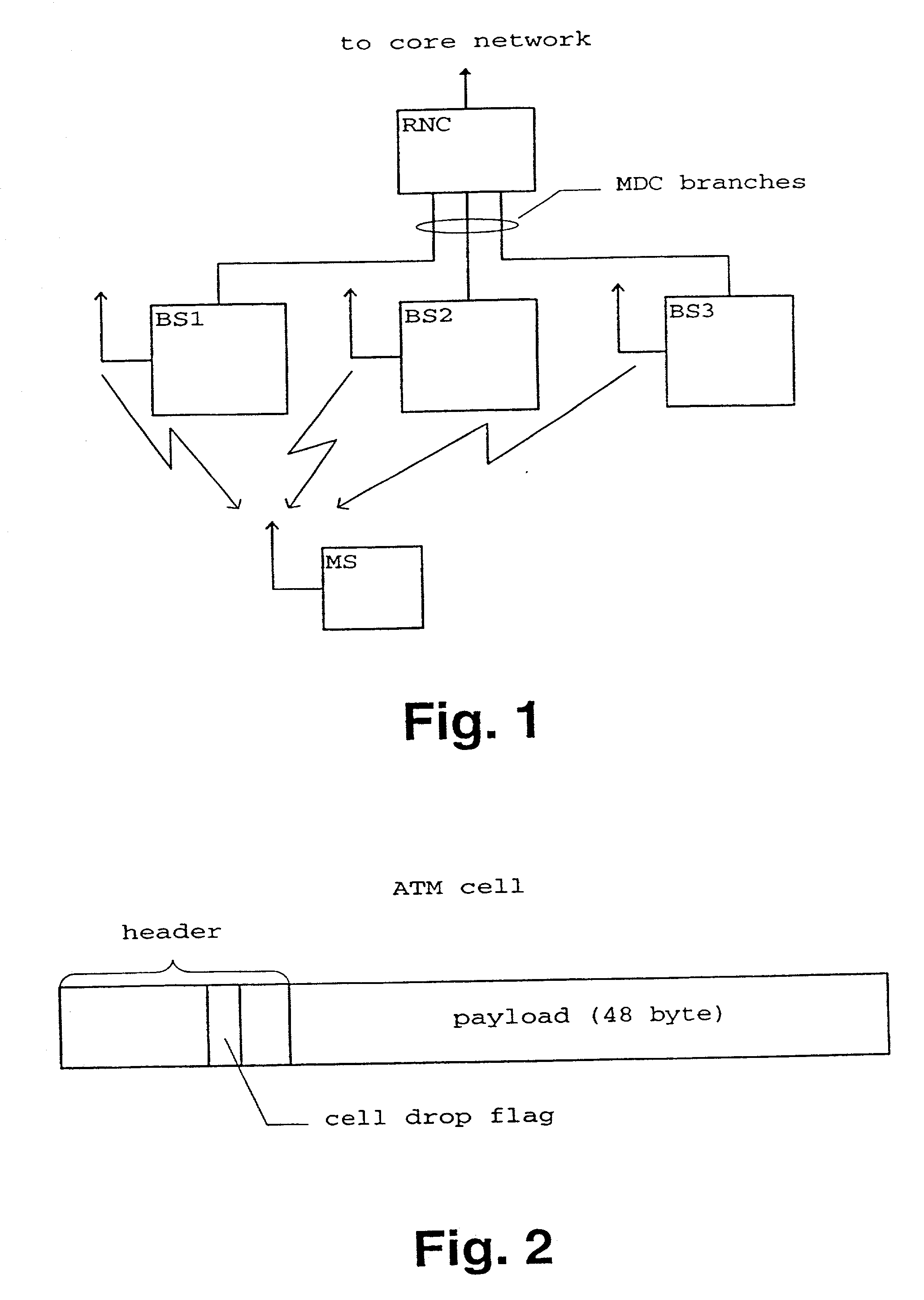
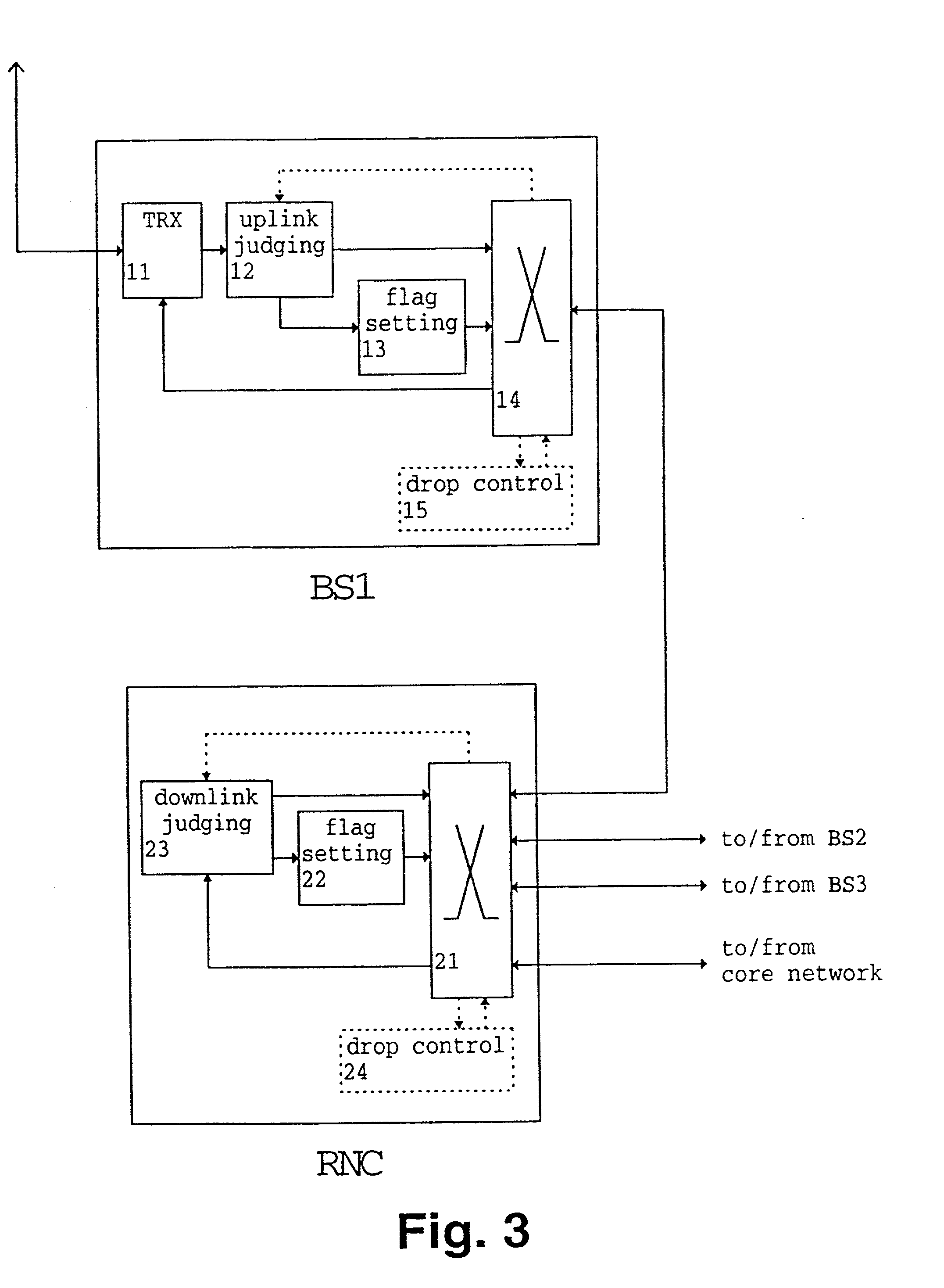
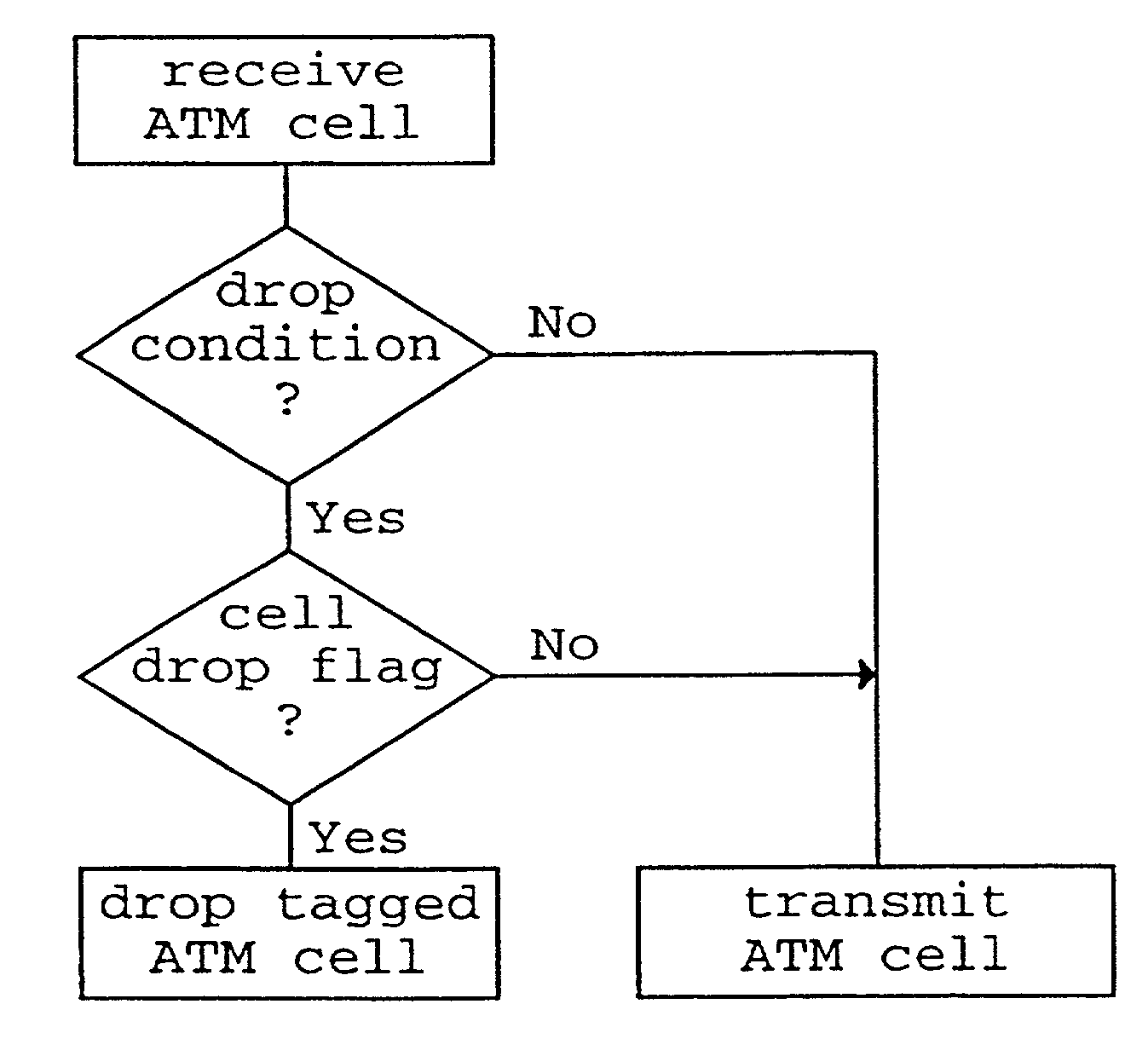
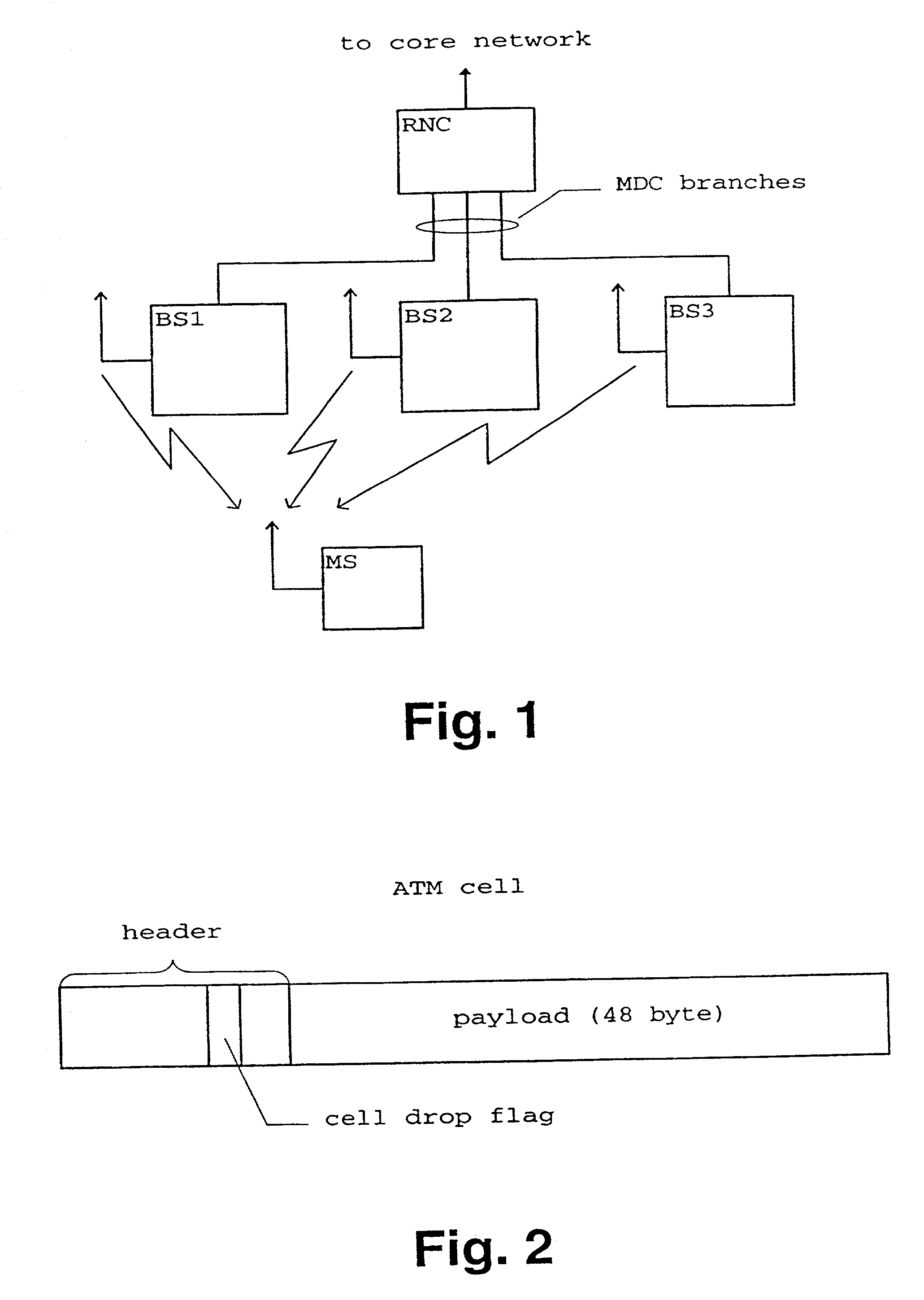
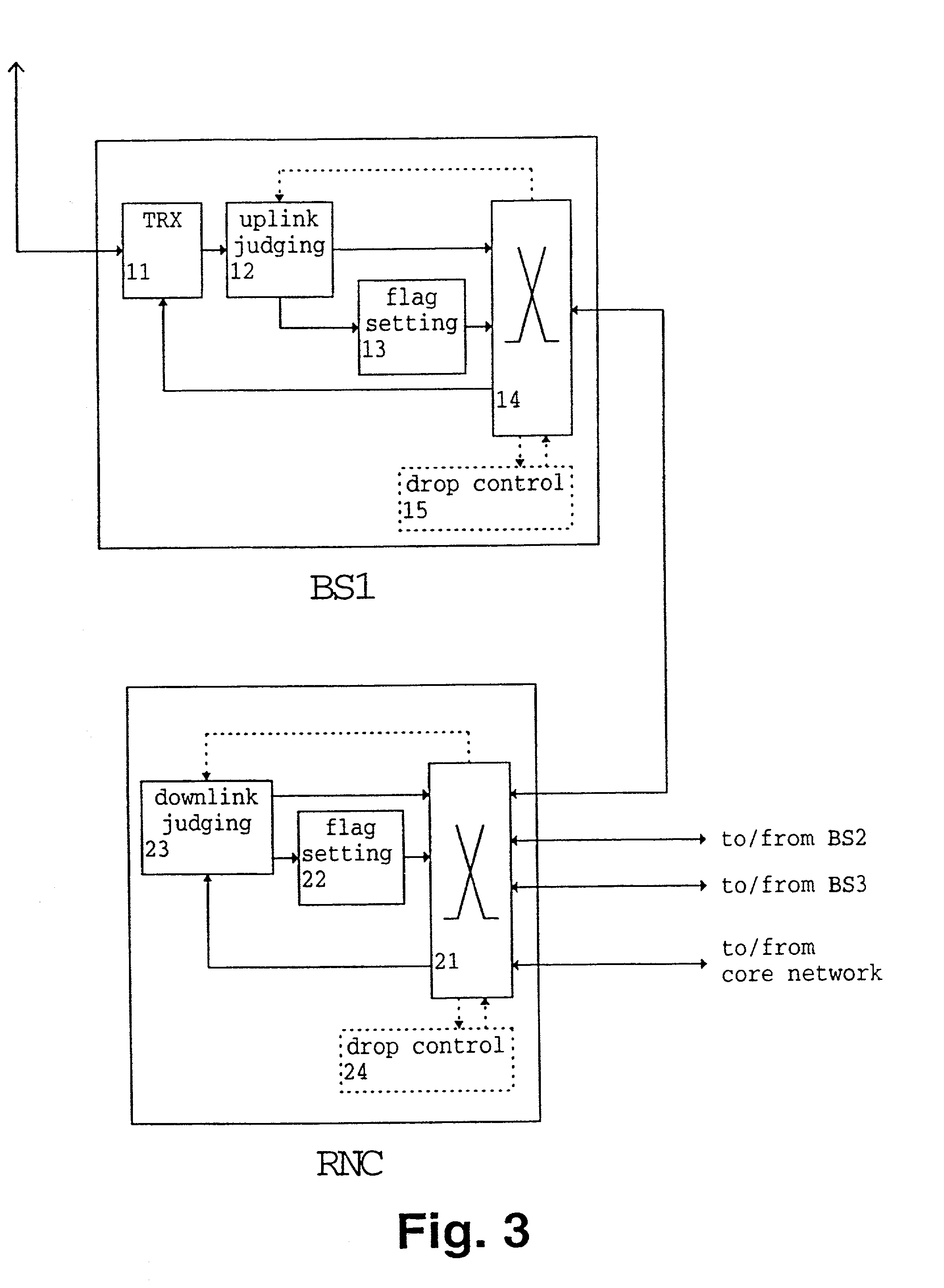
Packet transmission method and apparatus
InactiveUS20020126664A1Reduce traffic problemsReduce transmission overheadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsError checkTelecommunications network
A packet transmission method and apparatus for transmitting data packets via a telecommunication network are described, wherein the quality of a received data packet is judged and the data packet is tagged in response to the result of the quality judgment. The tagging is performed by adding a dropping information, wherein a tagged cell is dropped on the basis of the dropping information and a predetermined dropping condition such as a transmission congestion situation and / or an overuse of a contract of a particular connection. In the uplink direction, the quality judgment can be based on an error check or a comparison of a quality base likelihood parameter with a threshold value. In the downlink direction, the quality judgment can be performed on the basis of an uplink quality parameter and / or a downlink power control status. Accordingly, in case of a congestion and / or an overuse of a particular connection, low quality transmission packets are dropped first to thereby reduce traffic.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY +1
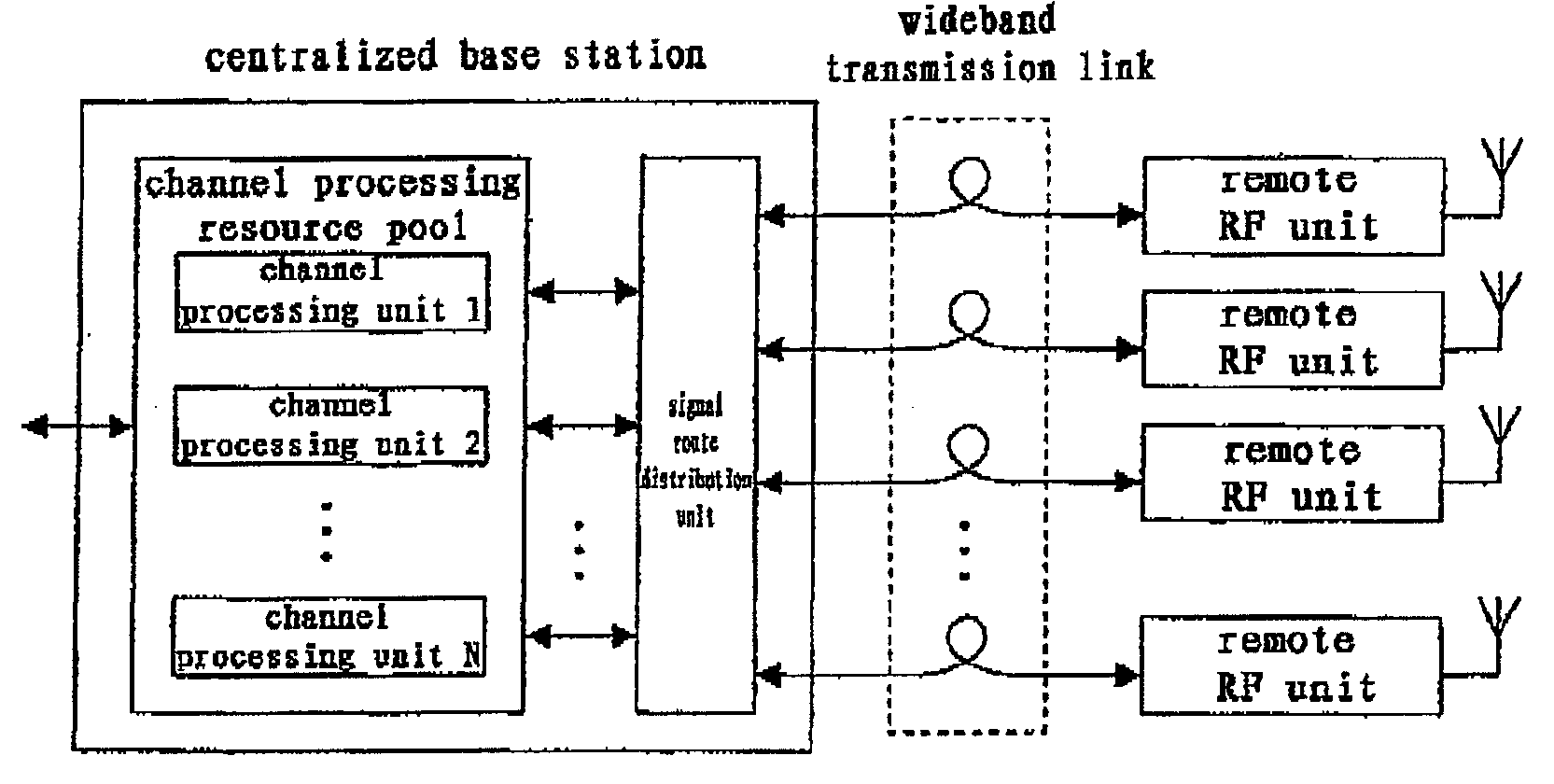
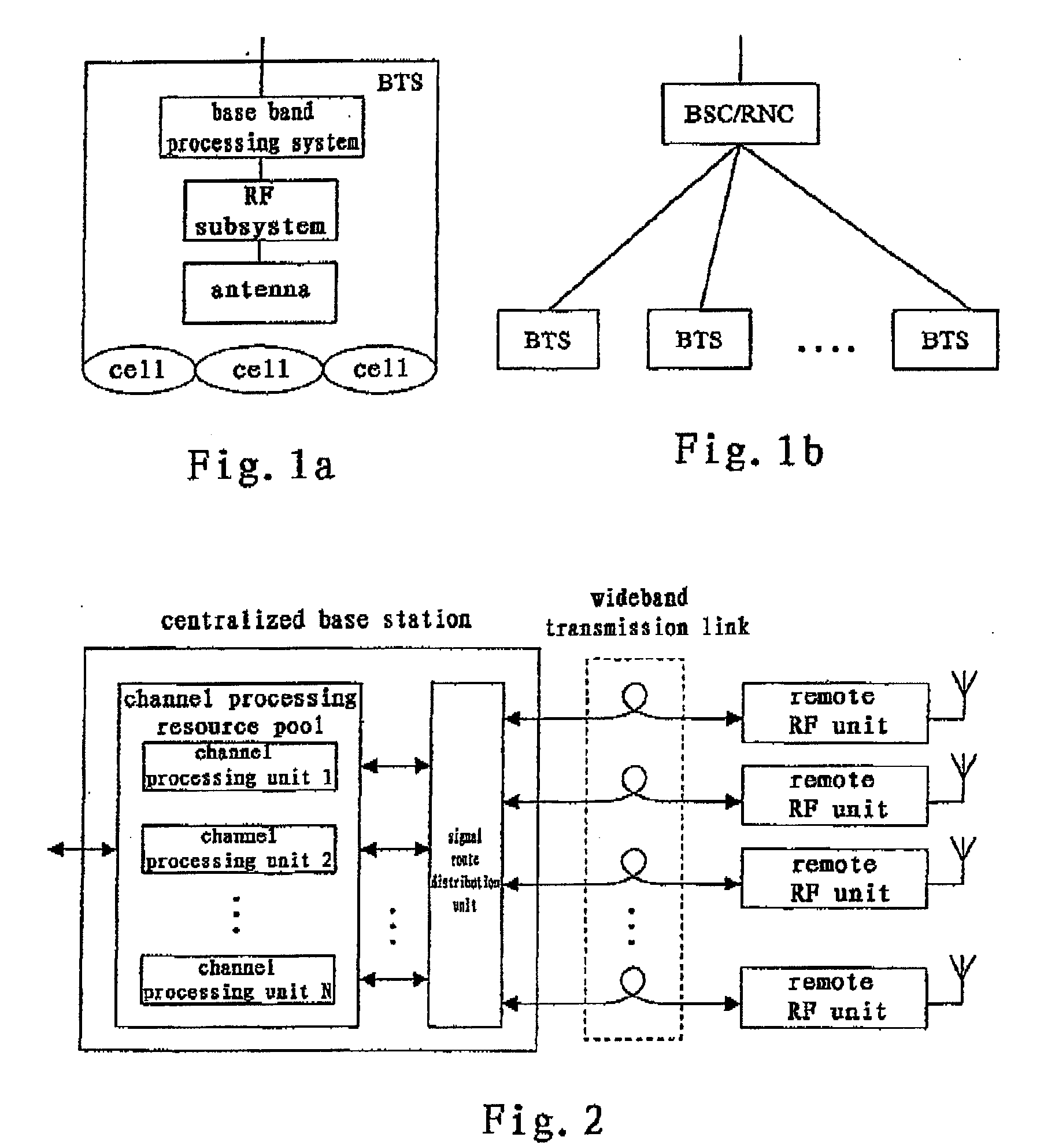
Downlink Power Control Method and Apparatus in the Distributed Antenna System
InactiveUS20080102872A1Degrade signal qualityQuality improvementEnergy efficient ICTPower managementSignal qualityDistributed antenna system
The application discloses an apparatus for controlling downlink power of the complex cell in the centralized base station system based on remote radio frequency units, said base station system having a plurality of radio frequency unit and a RAKE receiver connected to said plurality of radio frequency units, the apparatus comprising: signal quality measuring means connected to the RAKE receiver, for measuring signal quality of an uplink channel between each radio frequency unit and the same user equipment; average signal quality calculating means for calculating average signal quality of each uplink channel according to the measured signal quality; and power control means for adjusting transmission power of the downlink channel corresponding to the uplink channel according to said average signal quality, so that the transmission power of the downlink channel corresponding to the uplink channel with a lower average signal quality is relatively lower.
Owner:UTSTARCOM TELECOM CO LTD
Power control method and base station
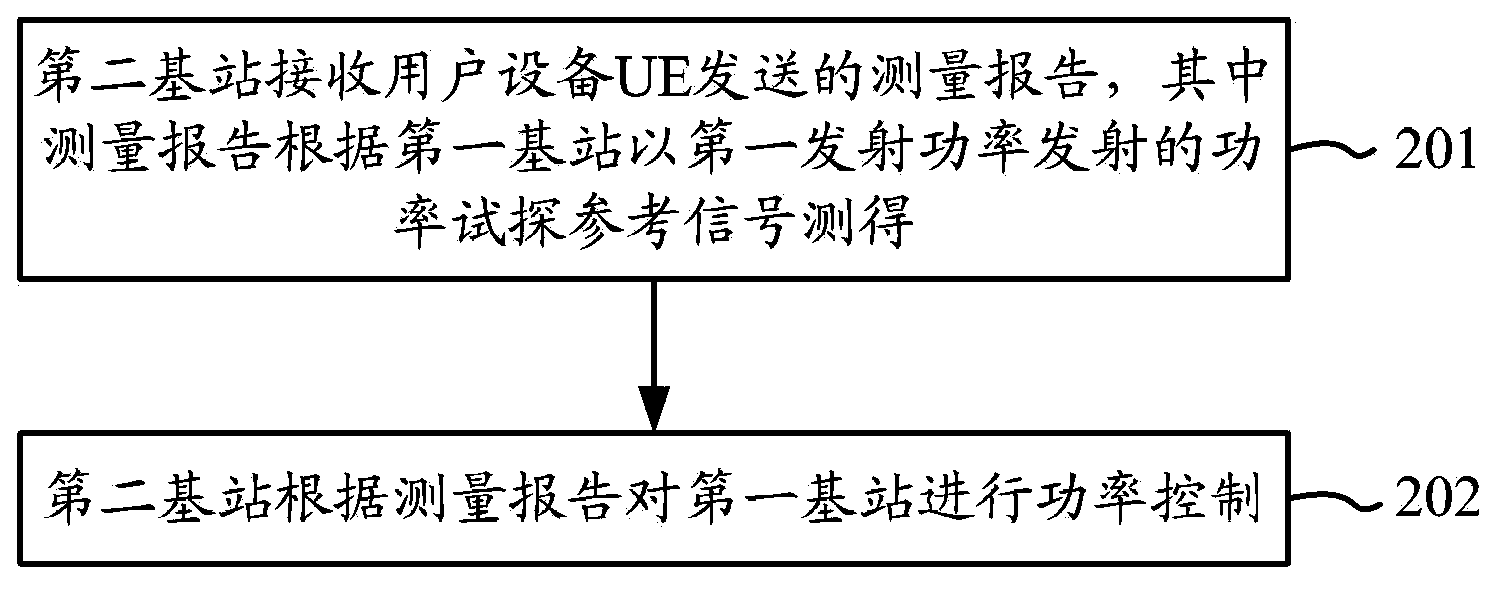
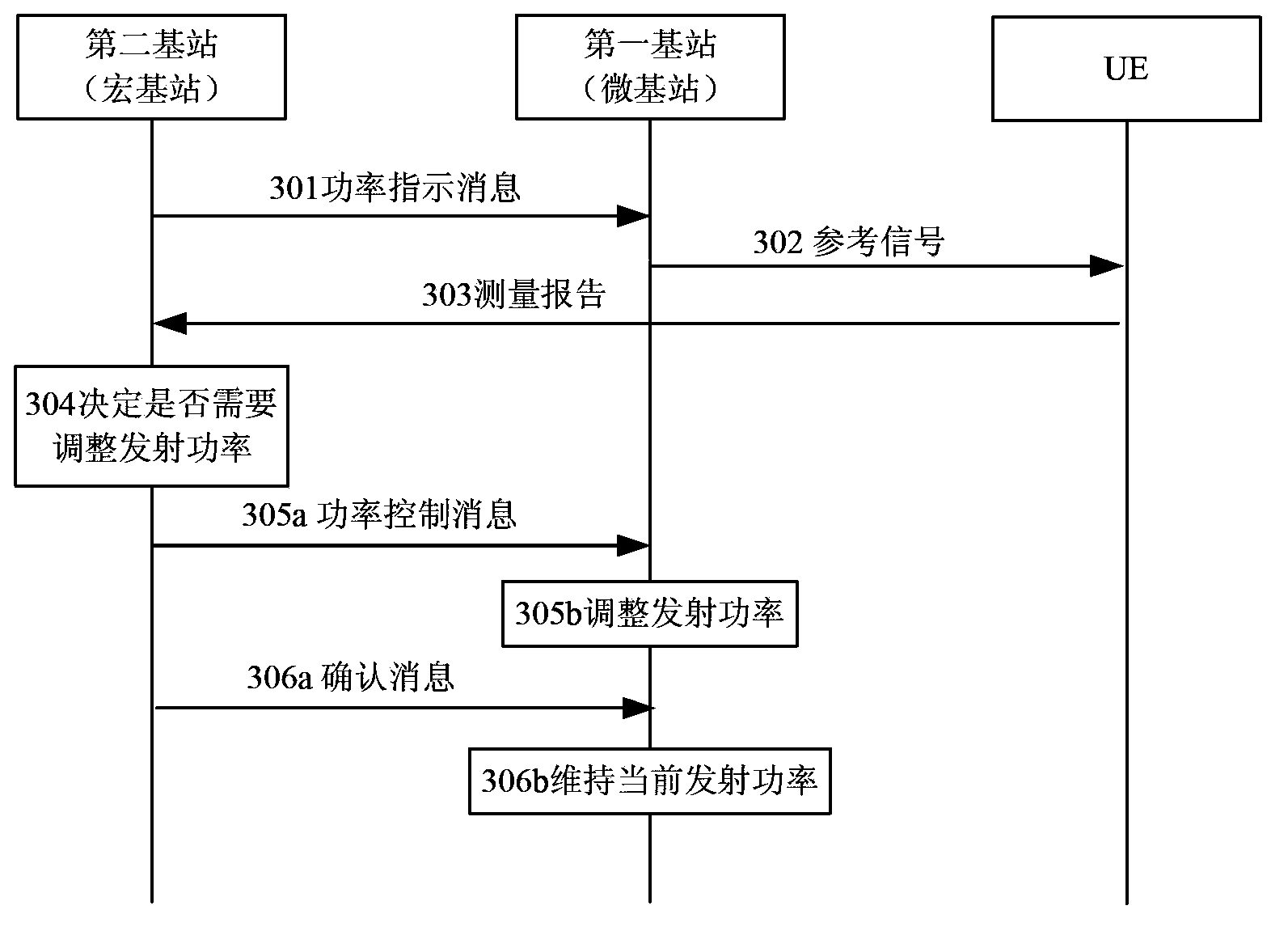
InactiveCN103916901ARealize downlink power controlPower managementMacro base stationsDownlink power control
The embodiments of the invention provide a power control method. The method comprises: a base station emitting a reference signal through first emission power; and the first base station receiving power control performed on the first emission power of the first base station by a second base station, the first base station being disposed in the coverage scope of the second base station. The embodiments of the invention further provide a base station. Single emission power is employed for trying, and a macro base station, through determining the interference bought to surrounding cells by use of the tried emission power by a micro base station, decides whether to adjust the emission power of the micro base station of maintain current emission power, such that the downlink power control of the micro base station by the macro base station is realized.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Downlink power control method and CDMA communication system incorporating the control method
InactiveUS6940839B2Full and efficient useEnergy efficient ICTError preventionLower limitTransmitted power
The transmit power of a CDMA downlink channel is controlled from a base station by receiving a command signal from a mobile station requesting it to decrease the transmit power of the downlink channel. In response, the base station decreases the transmit power if a hypothetically decremented value of the transmit power is higher than a nominal lower limit of its power control range, and further decreases the transmit power if the downlink channel still has a quality higher than a specified value at the mobile station even when the hypothetically decremented value is lower than the nominal lower limit. The base station sets the transmit power equal to the nominal lower limit if the hypothetically decremented value is lower than the nominal lower limit and the downlink channel still has a quality higher than the specified value at the mobile station.
Owner:NEC CORP
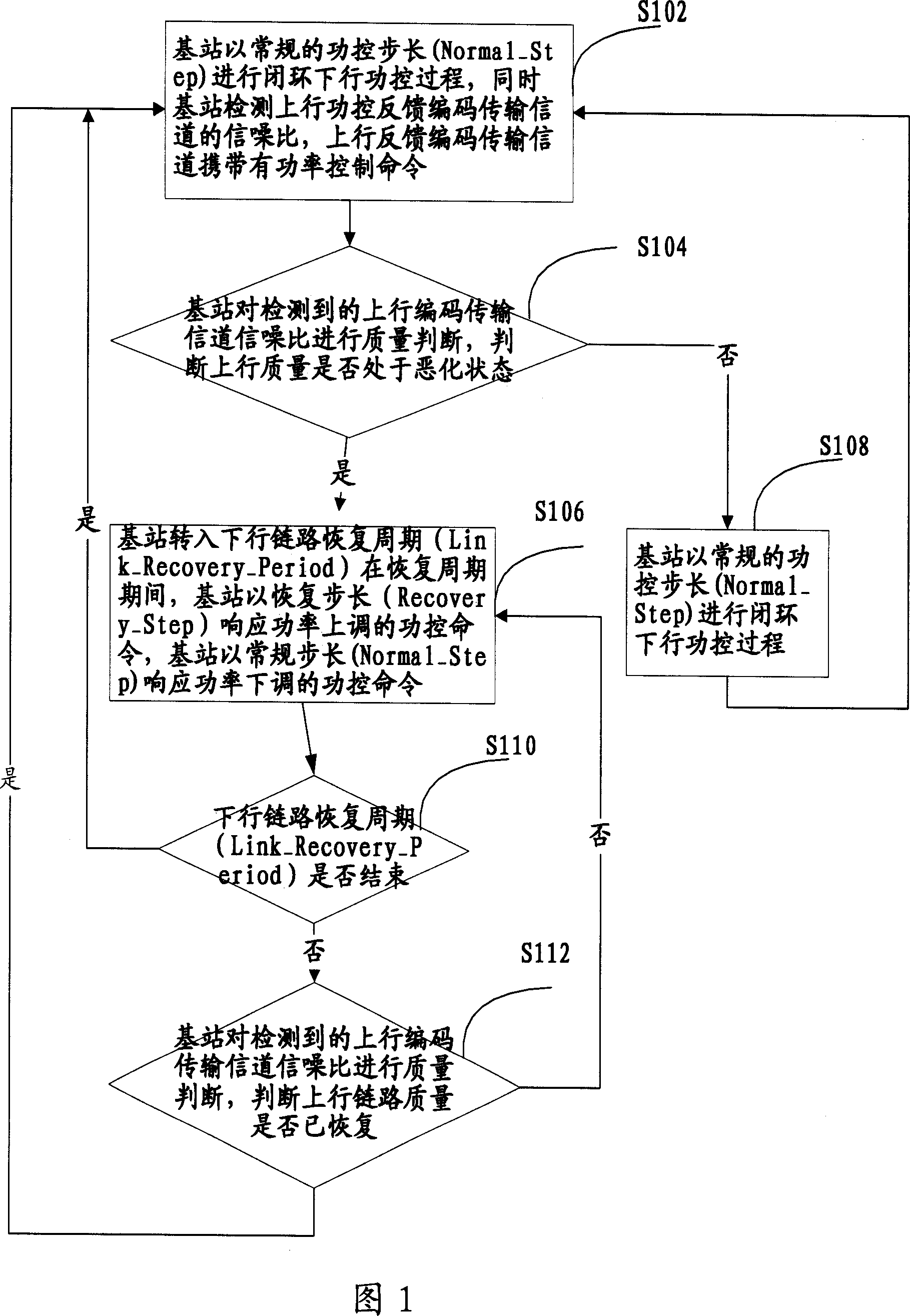
Descending power control method in TD-CDMA system
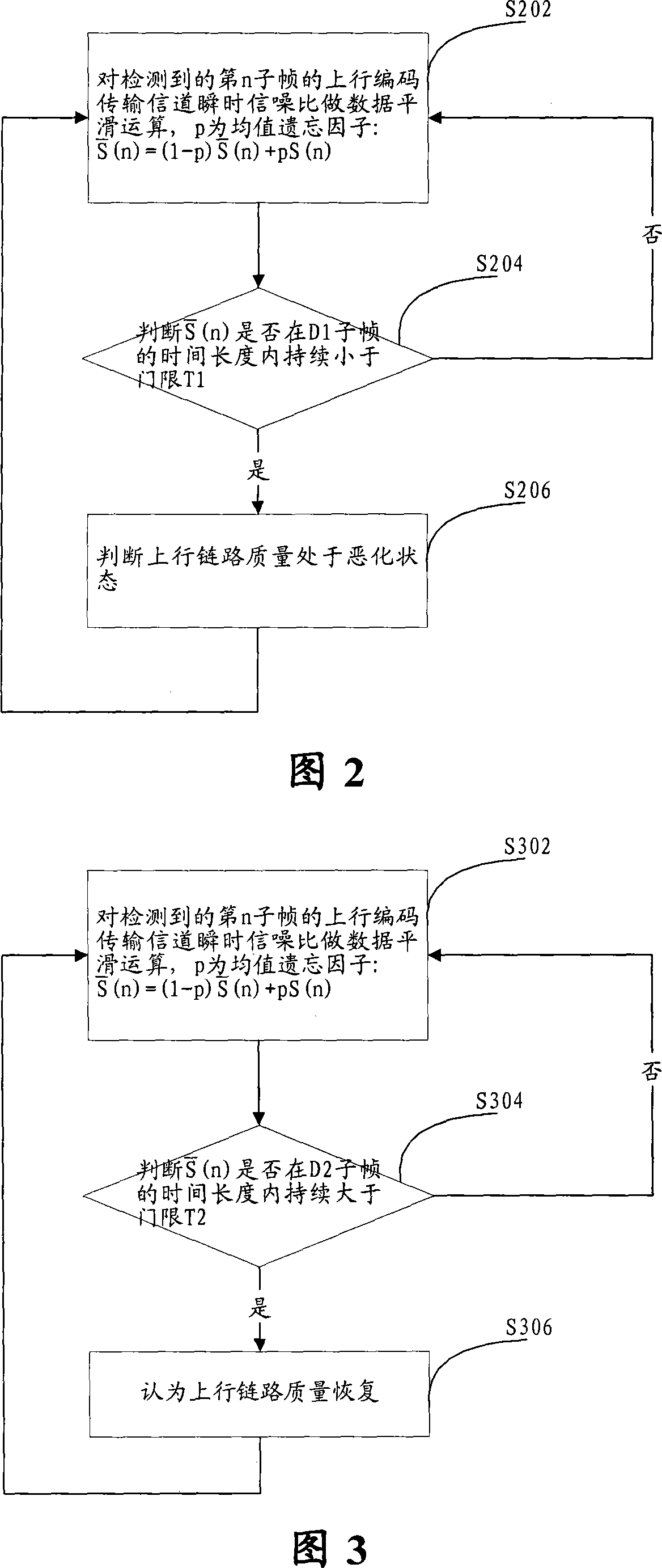
InactiveCN101132207AImprove retentionAvoid dropped callsTransmission control/equalisingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsClosed loopDownlink power control
This invention relates to a method for controlling down closed loop power in the TD-SCDMS system including: when a base station tests that the quality of the up link is at a worsen state, it turns itself to a down link resuming period to up-adjust the power control order with the resumed step length response power and down-adjust the power control order with conventional step length response power, in this way, the base station controls power of each down coding combined transmitting channel based on the down closed loop power control mode to strengthen the effect of down closed loop power control when quality of the up and down links drops at the same time.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Downlink power control method and device
The invention discloses a downlink power control method and a downlink power control device. The method comprises the following steps that: a base station side sends the cell dedicated parameter of EPRE information which at least contains common pilot frequency and user dedicated EPRE related information, and sends the correction information of different user power to a terminal side; the terminal side detects and recovers the received data from the base station side according to the cell dedicated parameter, the user dedicated EPRE related information and the correction information of different user power; and the base station side distributes each symbol power value on a resource block to be sent according to the cell dedicated parameter, the user dedicated EPRE related information and the correction information of different user power and sending the resource block. The method can well improve the error code performance and the capacity of a system.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Power Control Method for Base Station
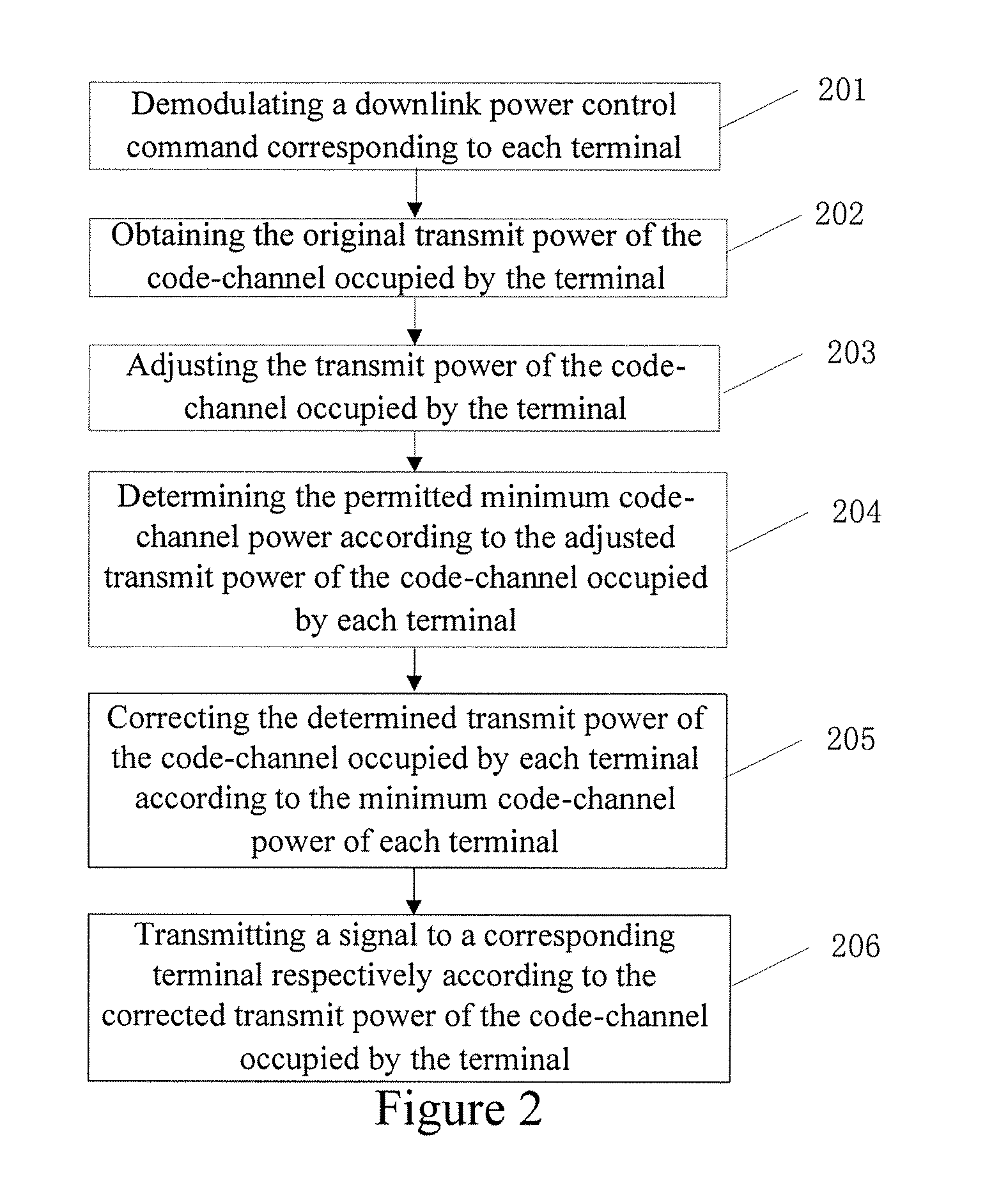
ActiveUS20080194281A1Solve the real problemIncrease system capacityPower managementResonant long antennasChannel powerEngineering
A downlink power control method for base station, includes following steps: according to the received power control command, base station obtains the transmission power of each terminal occupying code channel; according to the transmission power of each terminal occupying code channel, determines the allowable minimum code channel power of each terminal; according to the determined minimum code channel power of each terminal, amends the transmission power of each terminal occupying code channel; according to the amended transmission power of each terminal occupying code channel, sends signals to the corresponding terminal respectively. Present invention could control the difference of signal power between different users, increase the stability of wireless link, and assure the quality of system communication.
Owner:SHANGHAI ULTIMATE POWER COMM TECH
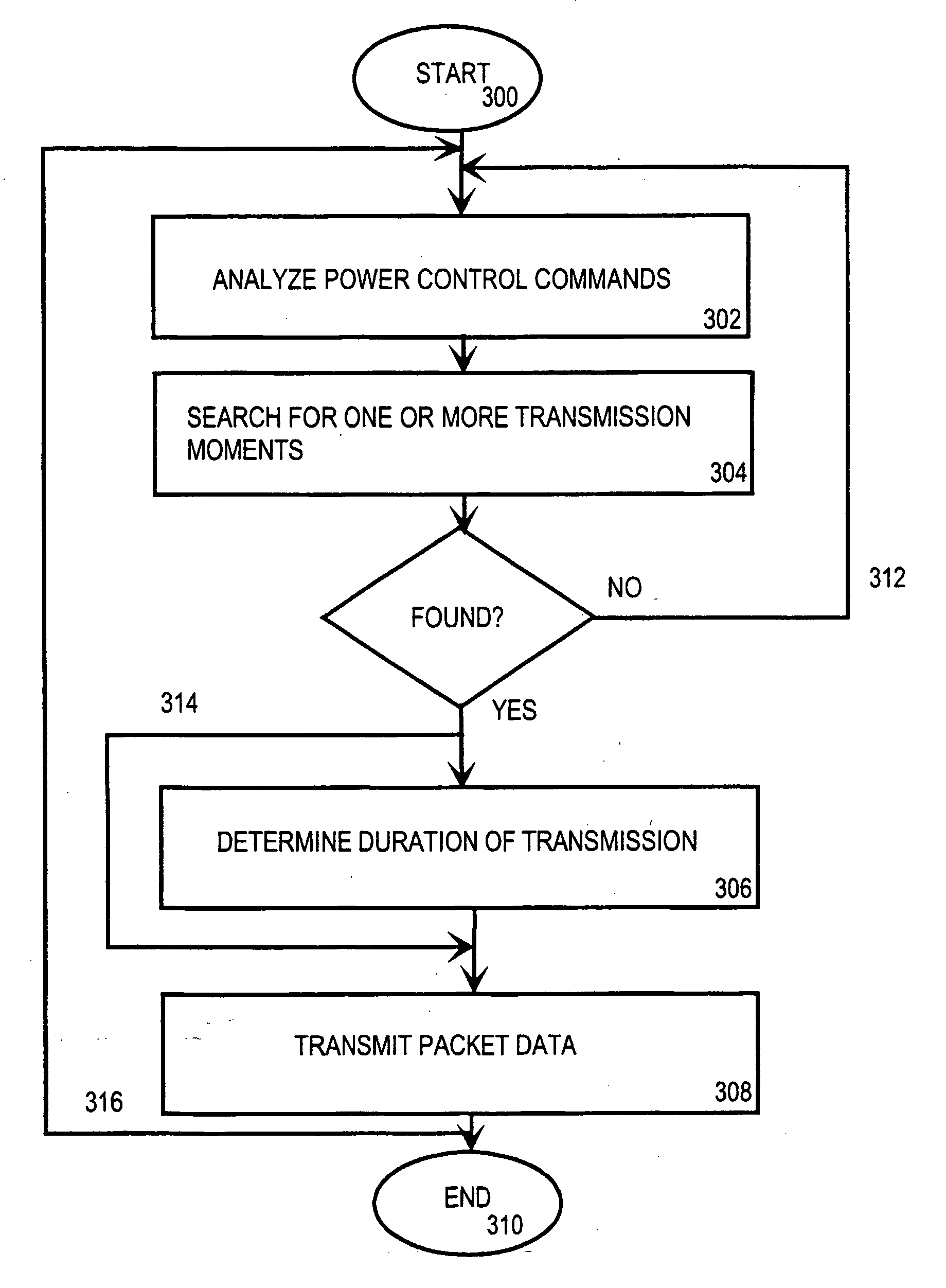
Moment decision for packet data transmission based on analysis of power control commands
InactiveUS20040190475A1Reduce transmit powerNeed lessPower managementError preventionSignal qualityEngineering
The invention relates to a method for transmitting packet data in a radio system, the radio system comprising at least one base station and at least one subscriber terminal and a downlink power control arrangement, in which power control arrangement the quality of a signal transmitted by the base station is evaluated and, on the basis of this evaluation, power control commands are transmitted to the base station. The method comprises analysing (302) the power control commands received by the base station, searching (304) for one or more transmission moments, on the basis of the analysis, that satisfy the set conditions for packet-switched data transmission, and if at least one transmission moment is found that satisfies the set conditions, transmitting (306) packet data to at least one subscriber terminal at least at one transmission moment that satisfies the set conditions.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Control method and system for uplink and downlink power
InactiveCN101079659AReduce distractionsImprove power control effectPower managementTransmission control/equalisingDownlink power controlComputer science
The invention discloses a controlling method and system of upward-downward power in the wireless communicating domain to reduce the indoor communication for outdoor interference, which comprises the following steps: calculating downward interference control threshold corresponding to calculating chamber according to the downward signal sampling data of adjacent areas; counting upward interference control threshold corresponding to calculating chamber according to the upward signal sampling data in the indoor area; judging the downward and / or downward launching power for the terminal for the terminal in the indoor area during power controlling stage; modulating the power not according to the judging result if the judging result affirms that the downward launching power of terminal at network side will be more than the downward interference control threshold; modulating the downward launching power of terminal to the downward interference control threshold; modulating the upward launching power of terminal to the upward interference control threshold if the judging result affirms that the upward launching power of terminal at network side will be more than the upward interference control threshold.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Downlink power control method and device for switching
InactiveCN101166044AAccurate receptionPower impactTransmission control/equalisingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio Network ControllerDownlink power control
This invention discloses a down-power control method and a device used in switching, in which, the method includes the following steps: 1, when it's necessary for a UE to be switched to a target area from an original area, a radio network controller computes path loss between them, 2, the controller maps the loss onto a down-power control list to get corresponding initial emission power, 3, the controller emits a switch order containing the initial emission power information to the target area.
Owner:ZTE CORP
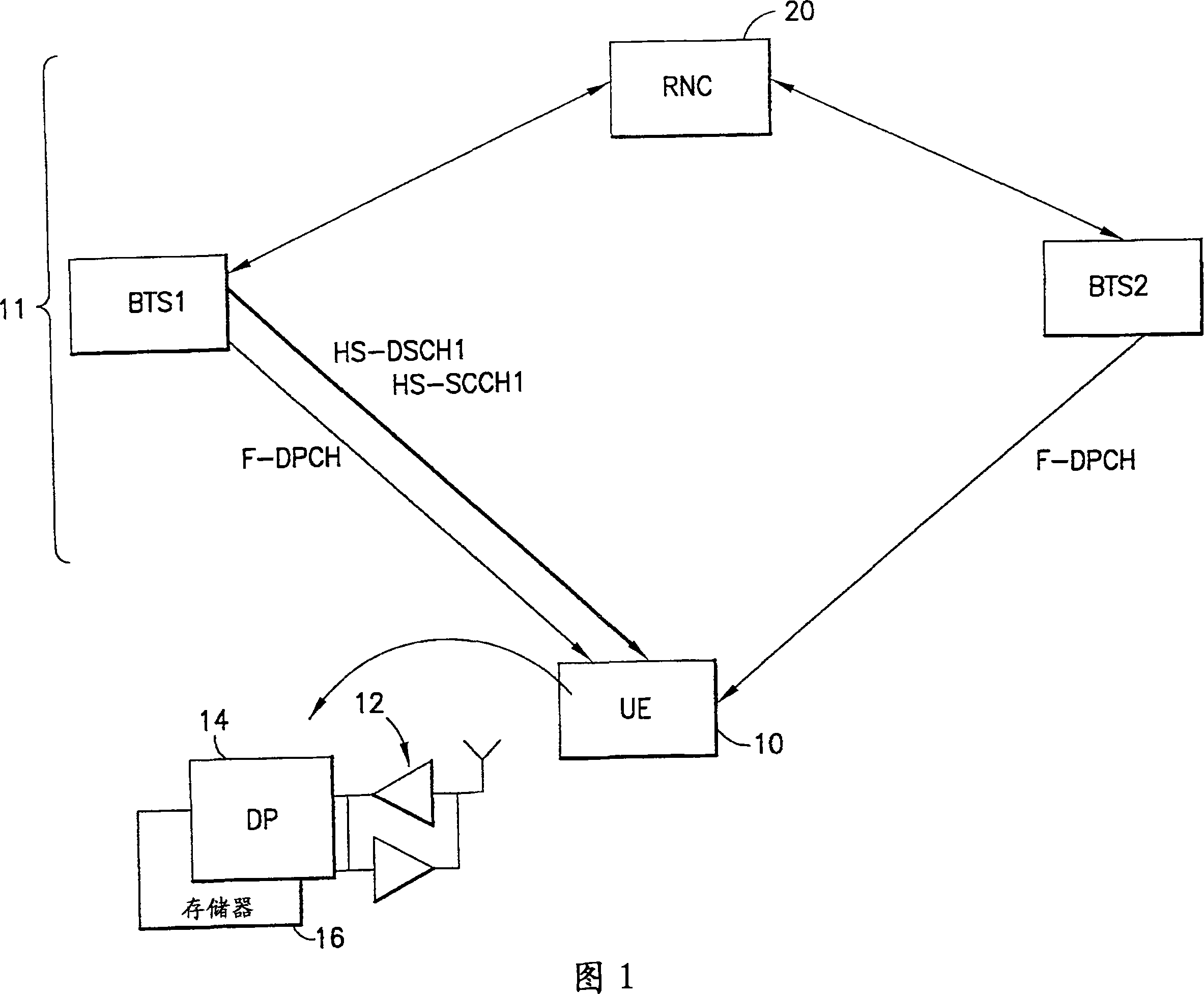
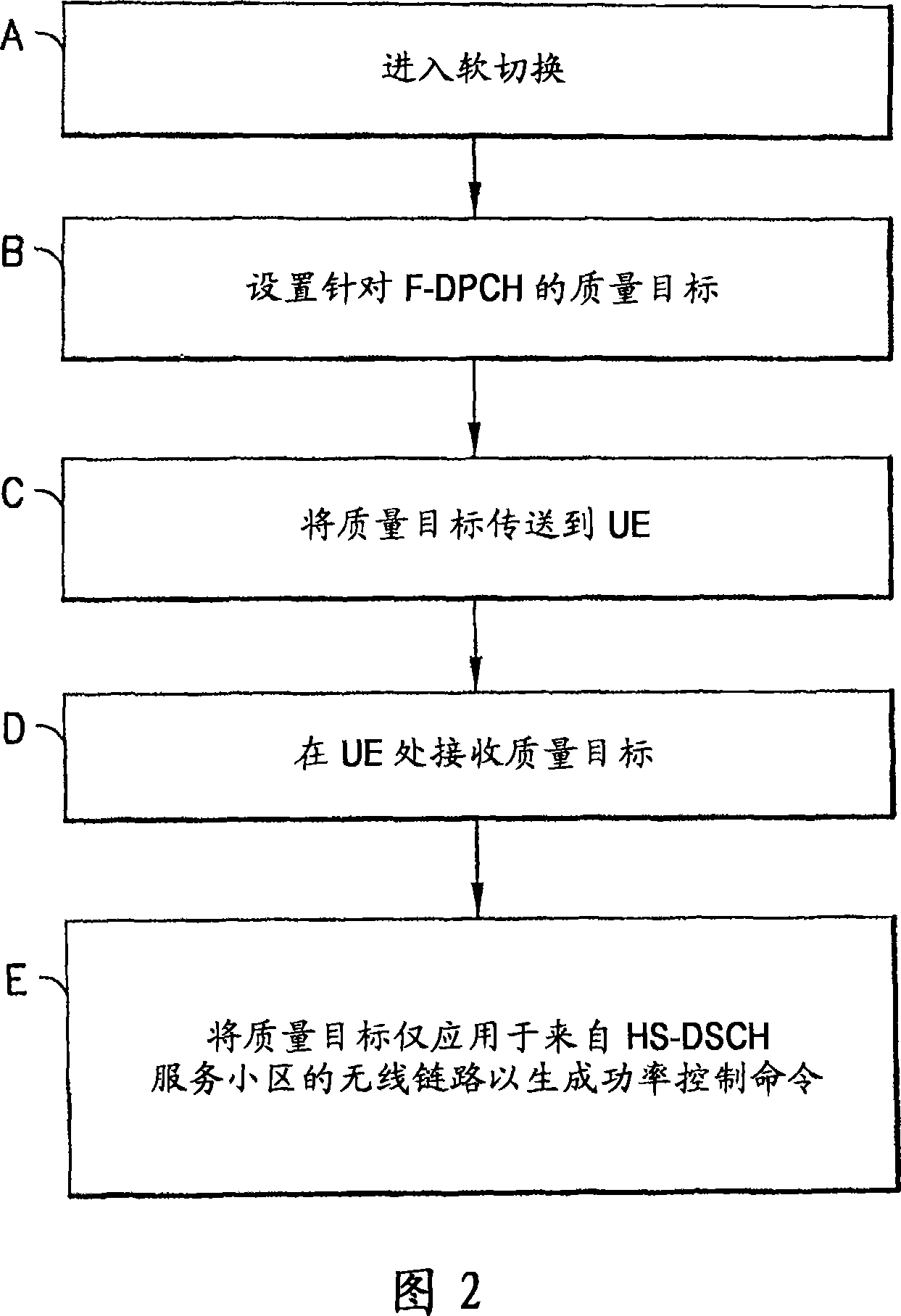
Apparatus, method and computer program providing enhanced fractional dedicated physical channel downlink power control during soft handover
ActiveCN101185257APower managementTransmission control/equalisingDownlink power controlSoft handover
A method includes establishing a first radio link with a serving network entity and a second radio link with a target network entity, commencing a soft handover from the serving network entity to the target network entity, receiving a quality target from a network comprising the serving and target network entities, and applying the quality target only to the first radio link to generate a power control command.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Packet transmission method and apparatus
InactiveUS6982957B2Reduce traffic problemsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityError check
A packet transmission method and apparatus for transmitting data packets via a telecommunication network are described, wherein the quality of a received data packet is judged and the data packet is tagged in response to the result of the quality judgment. The tagging is performed by adding a dropping information, wherein a tagged cell is dropped on the basis of the dropping information and a predetermined dropping condition such as a transmission congestion situation and / or an overuse of a contract of a particular connection. In the uplink direction, the quality judgment can be based on an error check or a comparison of a quality base likelihood parameter with a threshold value. In the downlink direction, the quality judgment can be performed on the basis of an uplink quality parameter and / or a downlink power control status. Accordingly, in case of a congestion and / or an overuse of a particular connection, low quality transmission packets are dropped first to thereby reduce traffic.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY +1
Method and system for interference averaging in a wireless communication system
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com