Patents
Literature
427 results about "Rake receiver" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
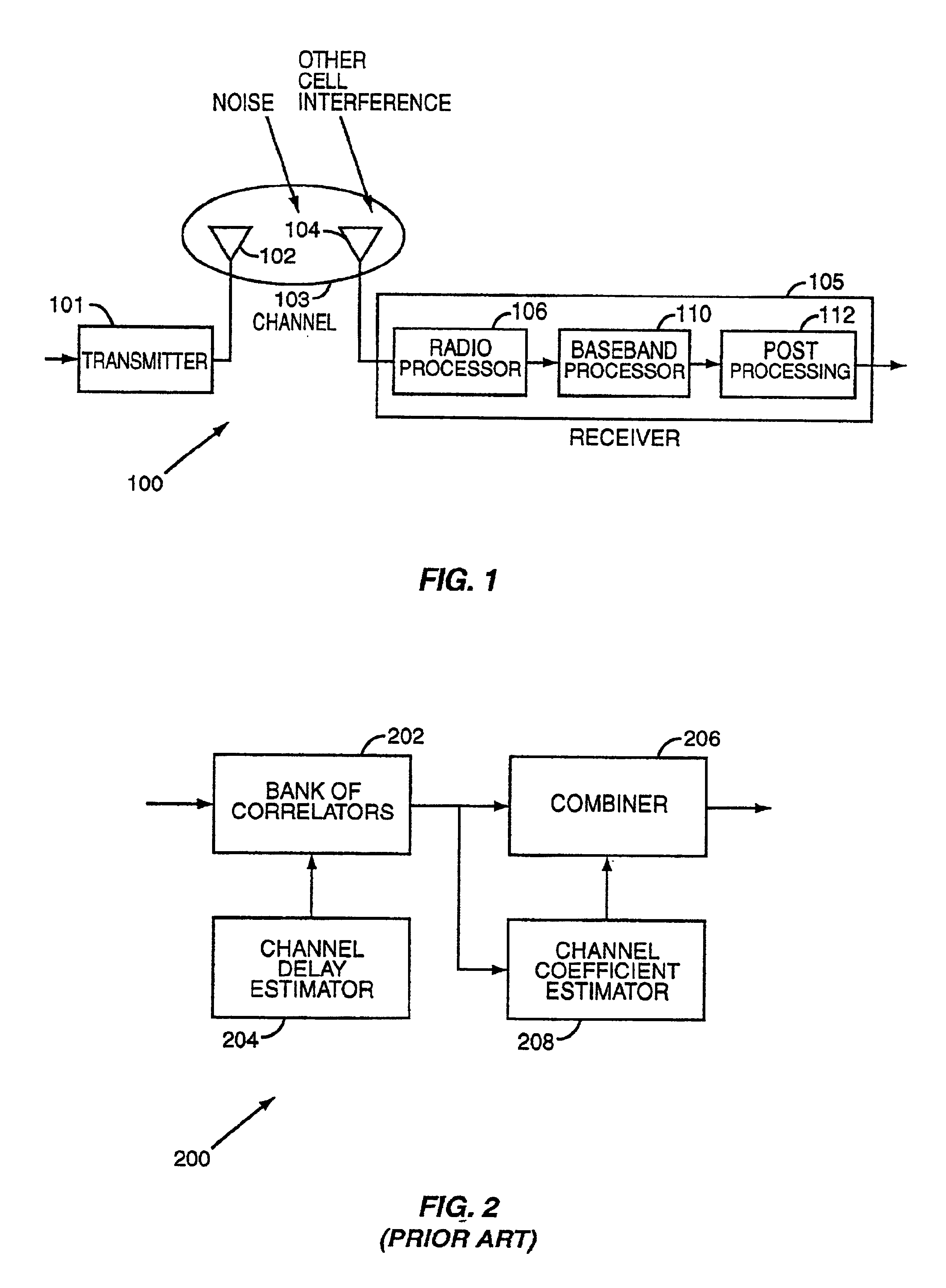
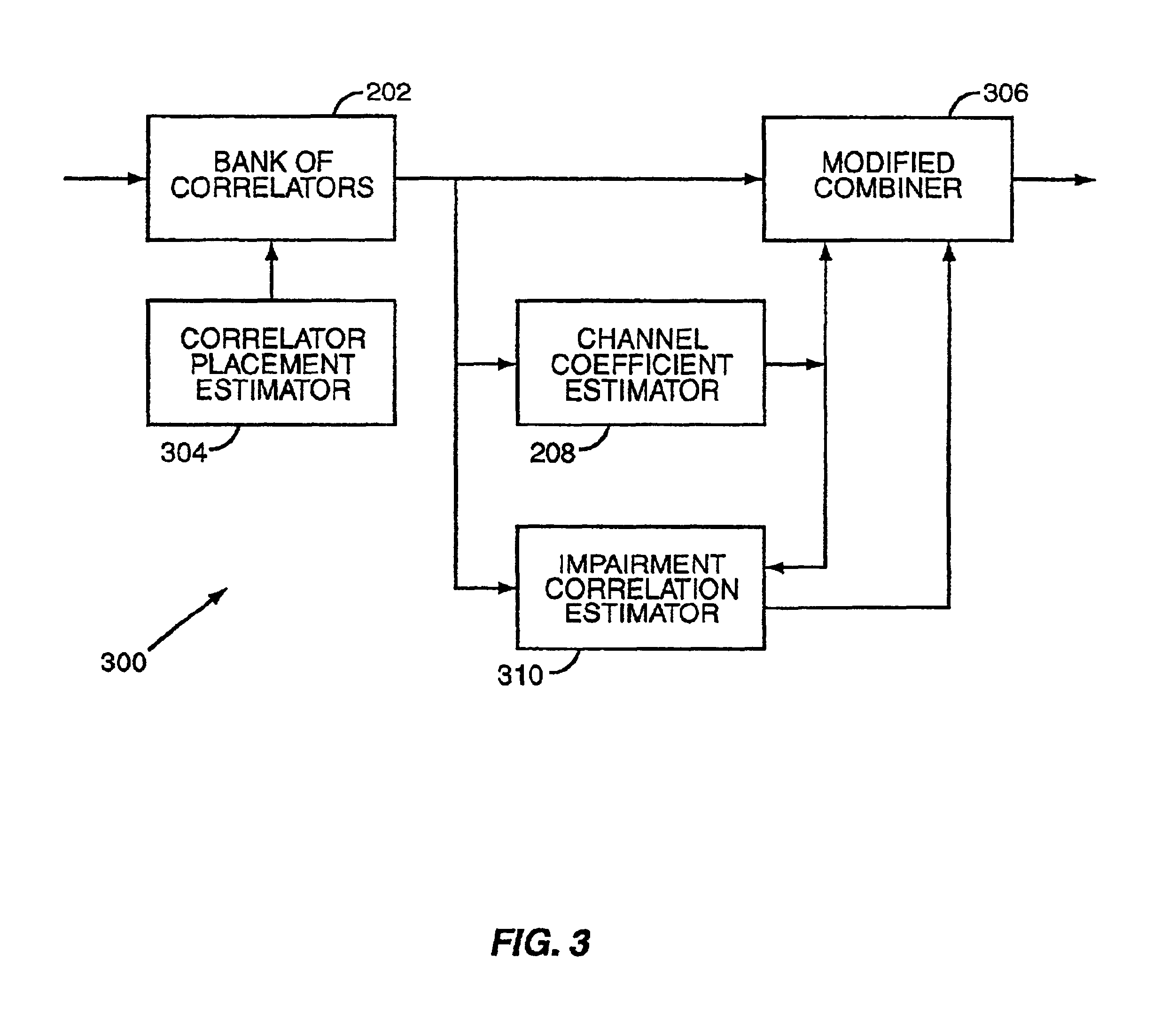
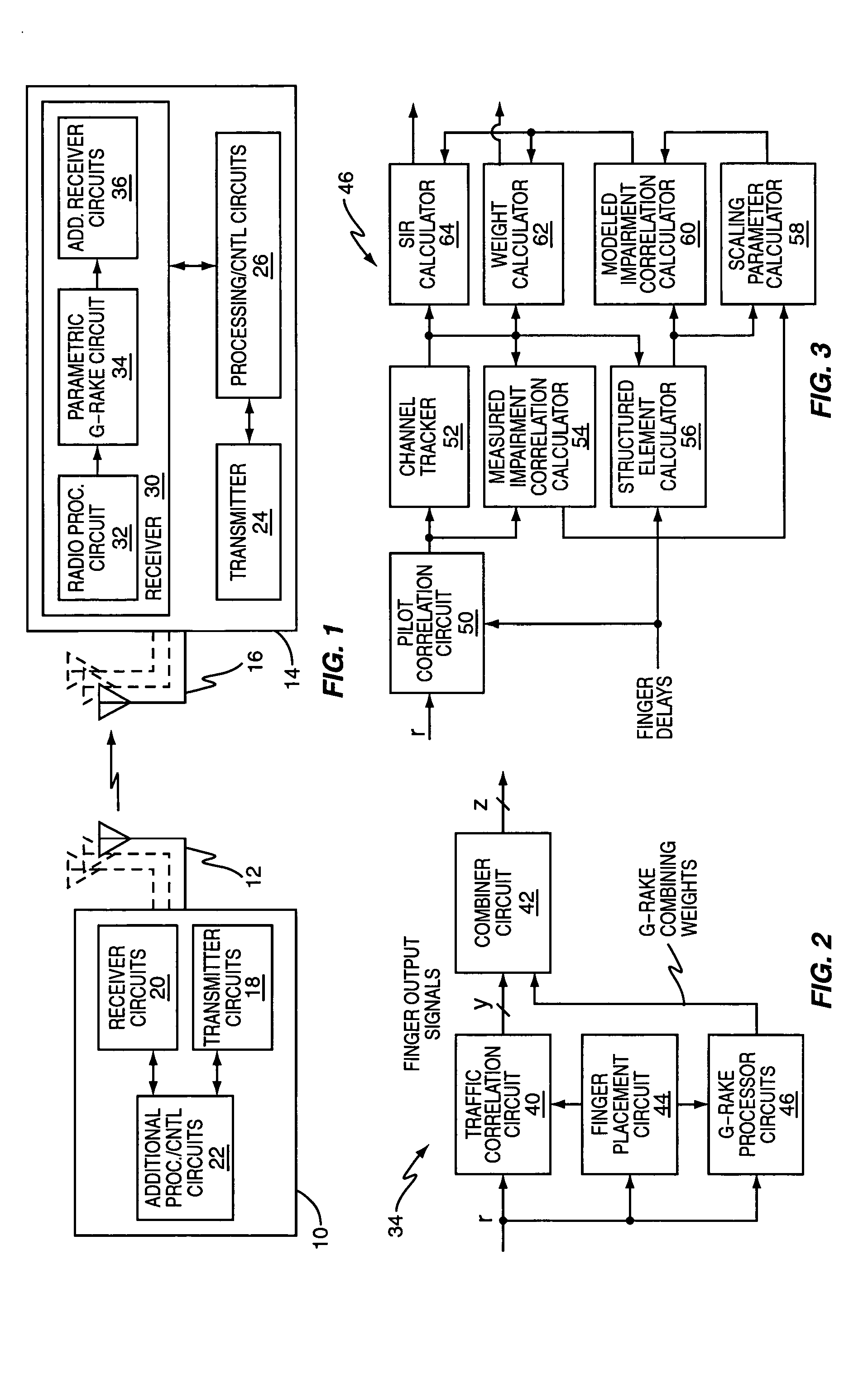
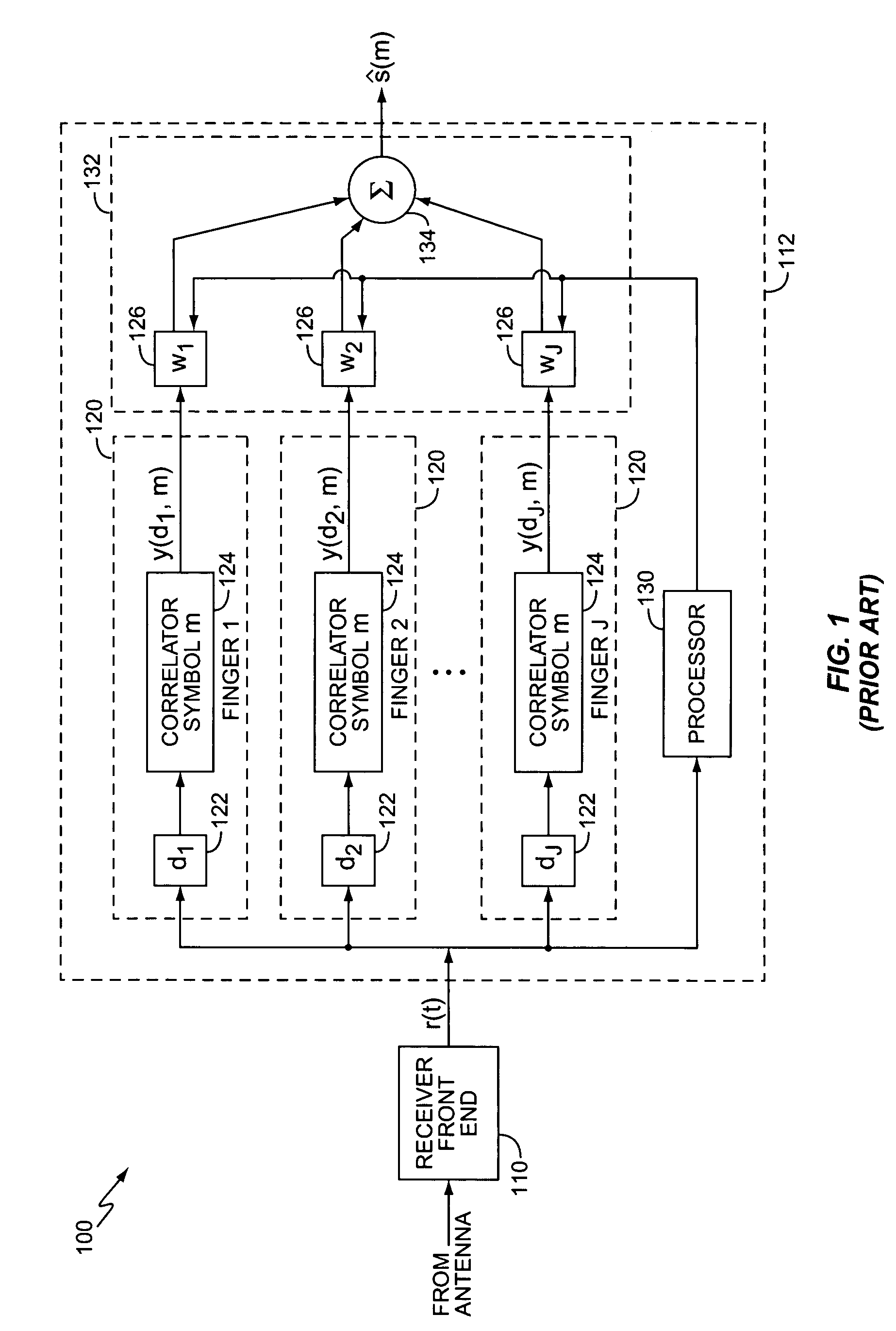
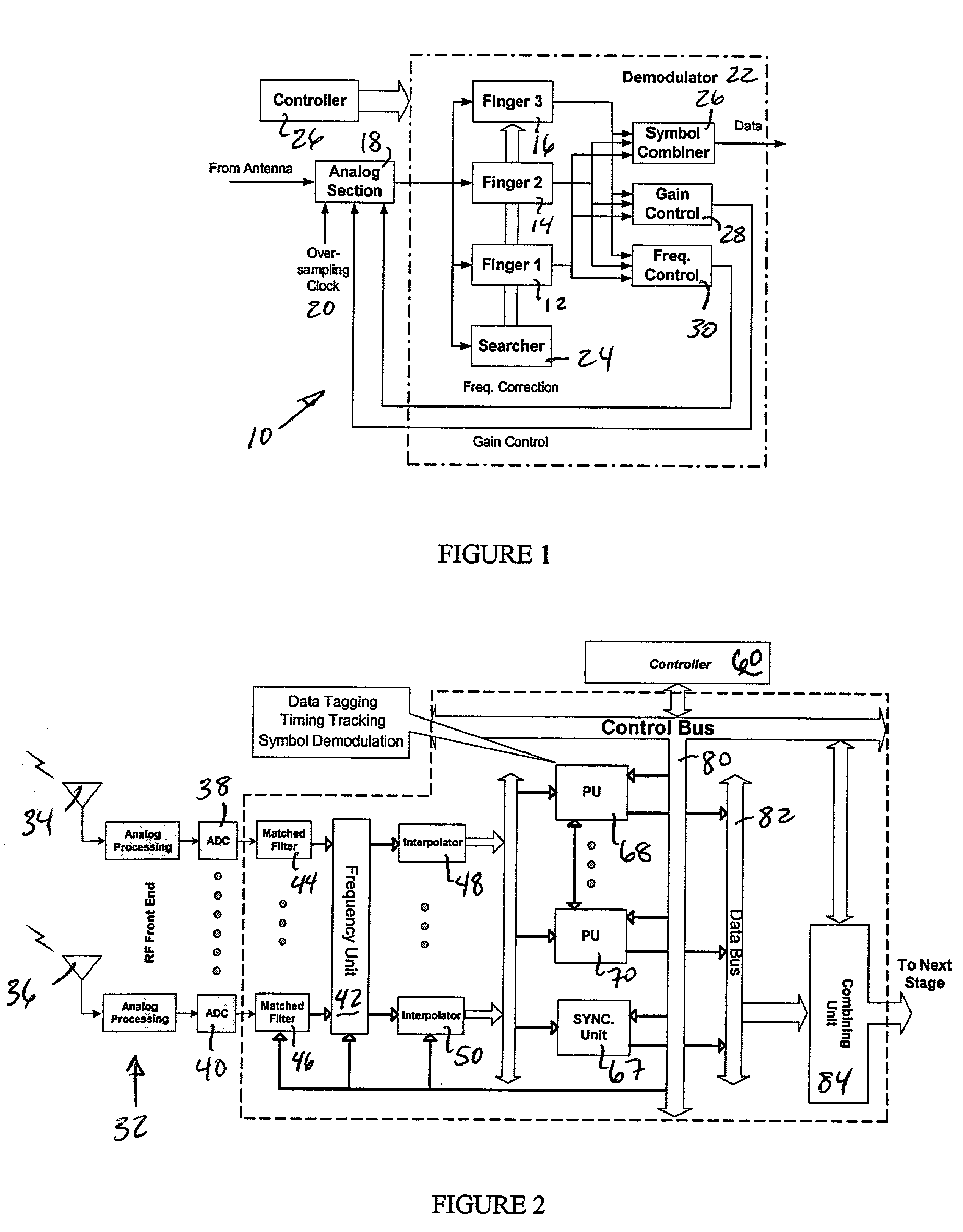
A rake receiver is a radio receiver designed to counter the effects of multipath fading. It does this by using several "sub-receivers" called fingers, that is, several correlators each assigned to a different multipath component. Each finger independently decodes a single multipath component; at a later stage the contribution of all fingers are combined in order to make the most use of the different transmission characteristics of each transmission path. This could very well result in higher signal-to-noise ratio (or Eb/N₀) in a multipath environment than in a "clean" environment.
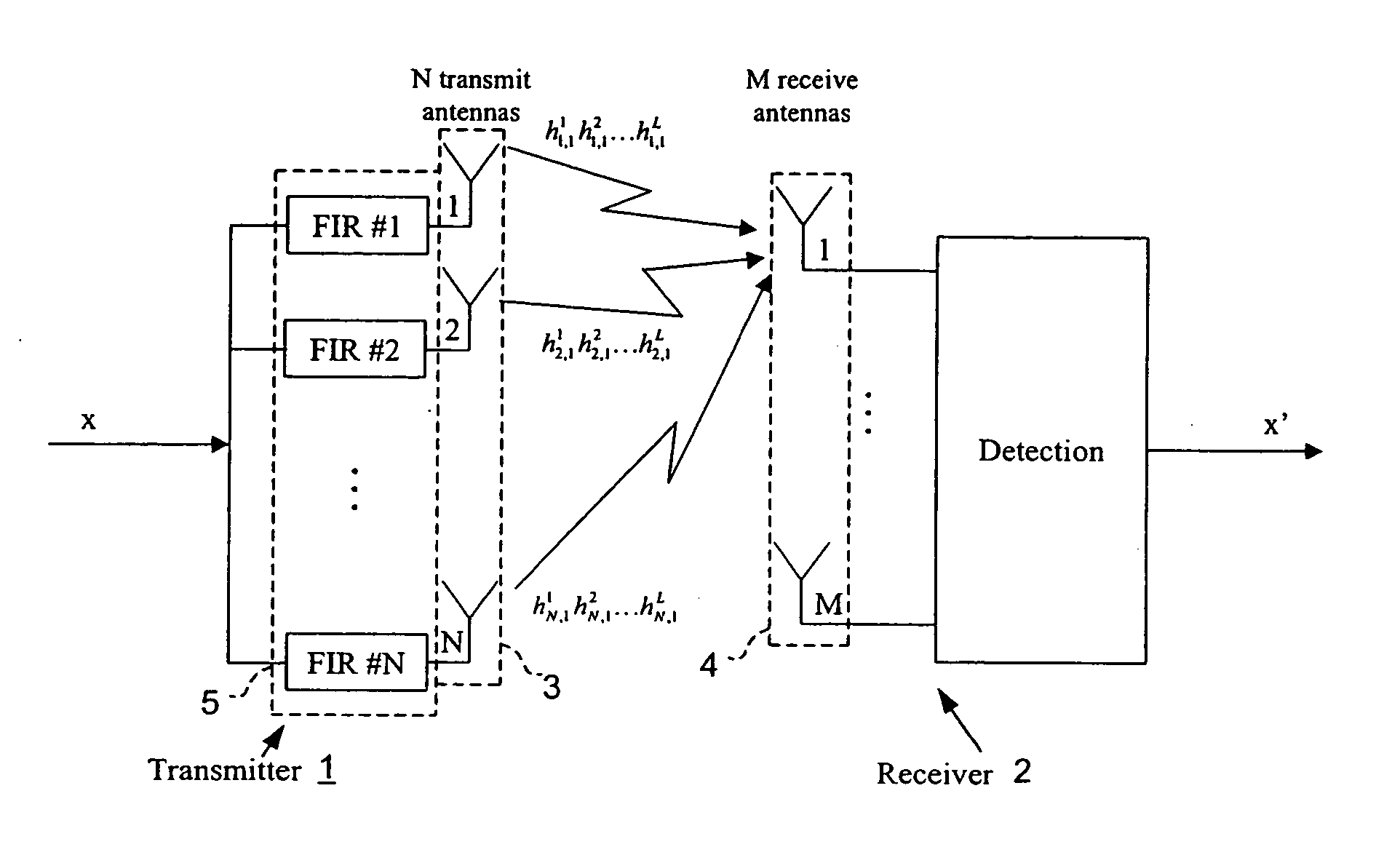
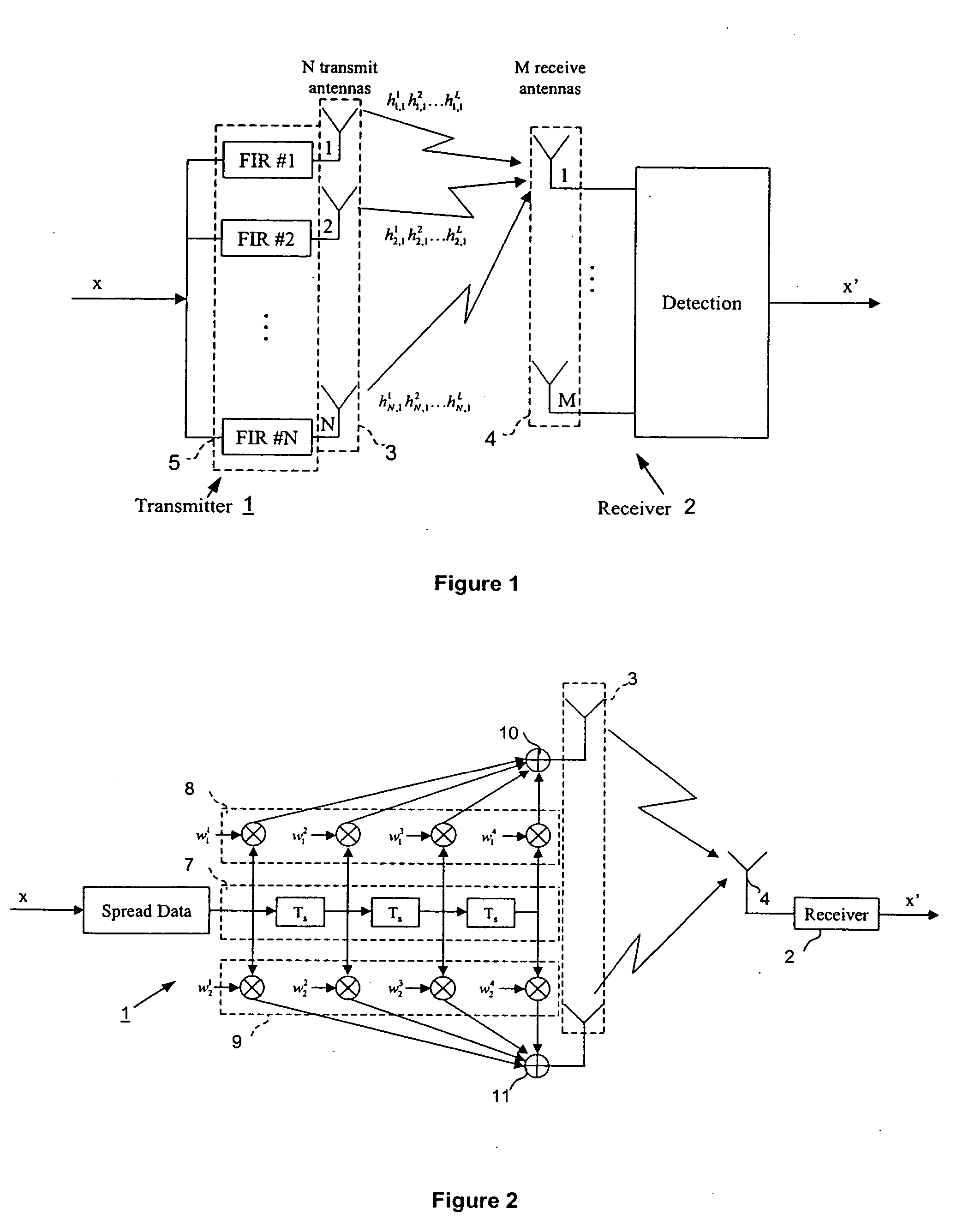
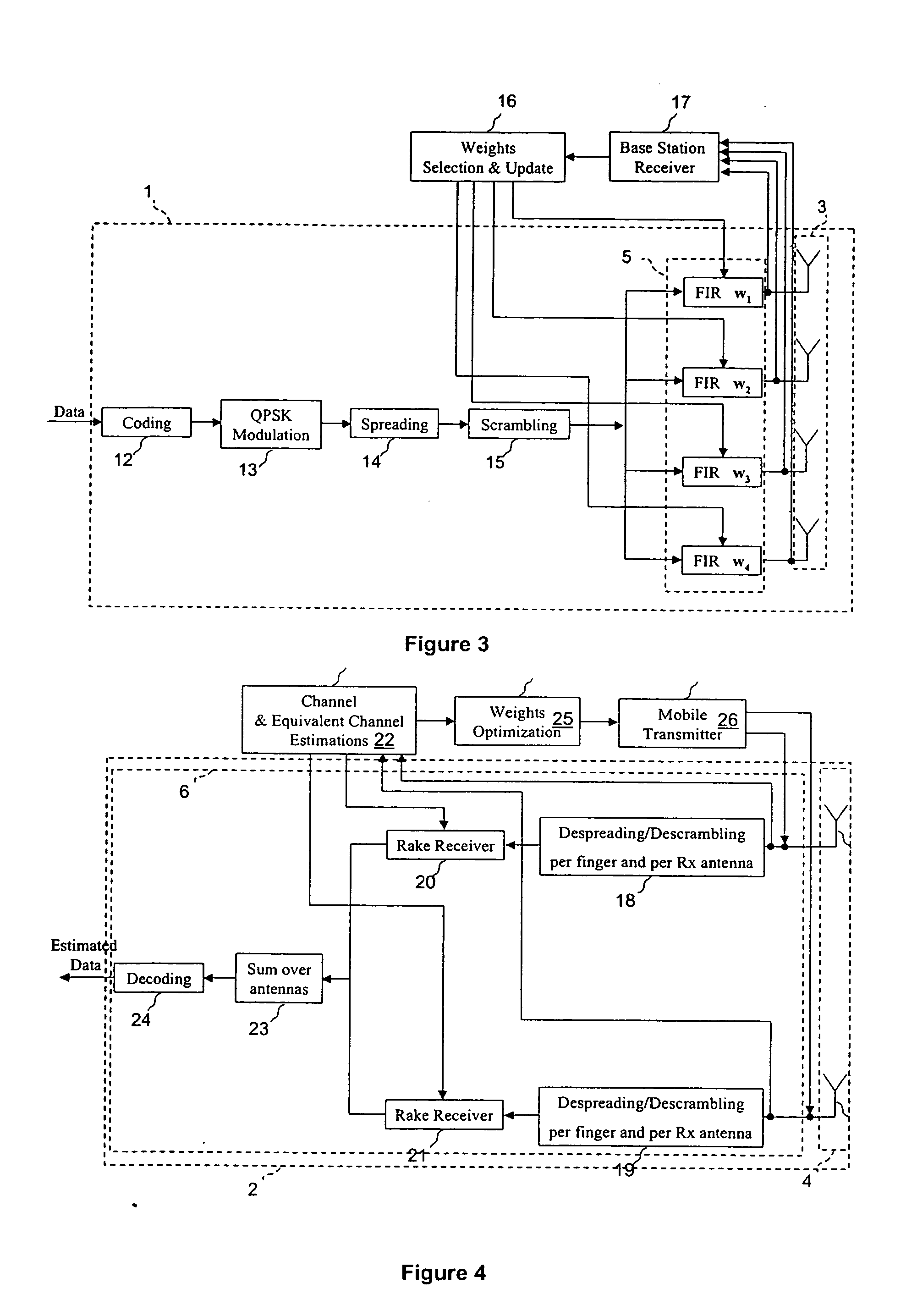
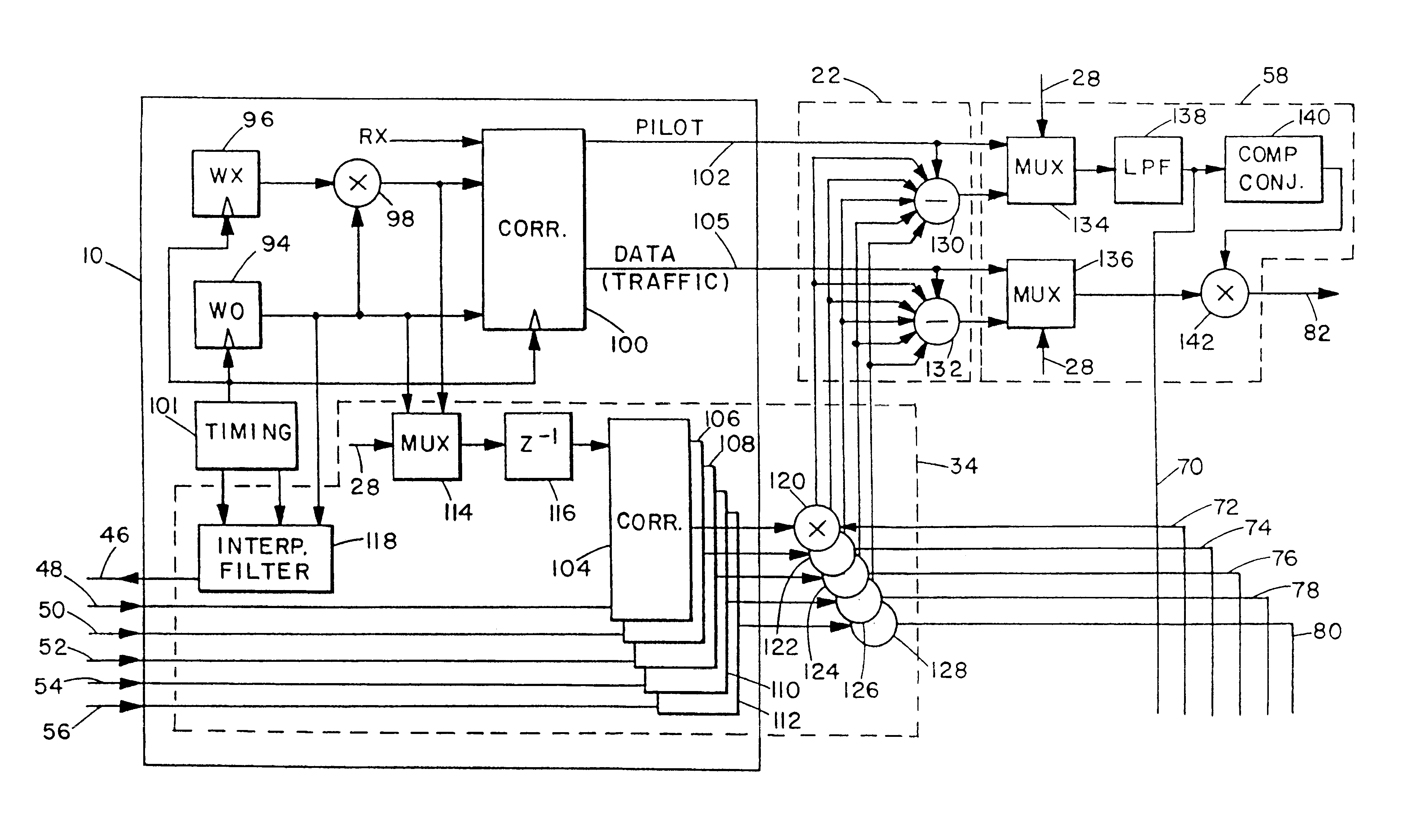
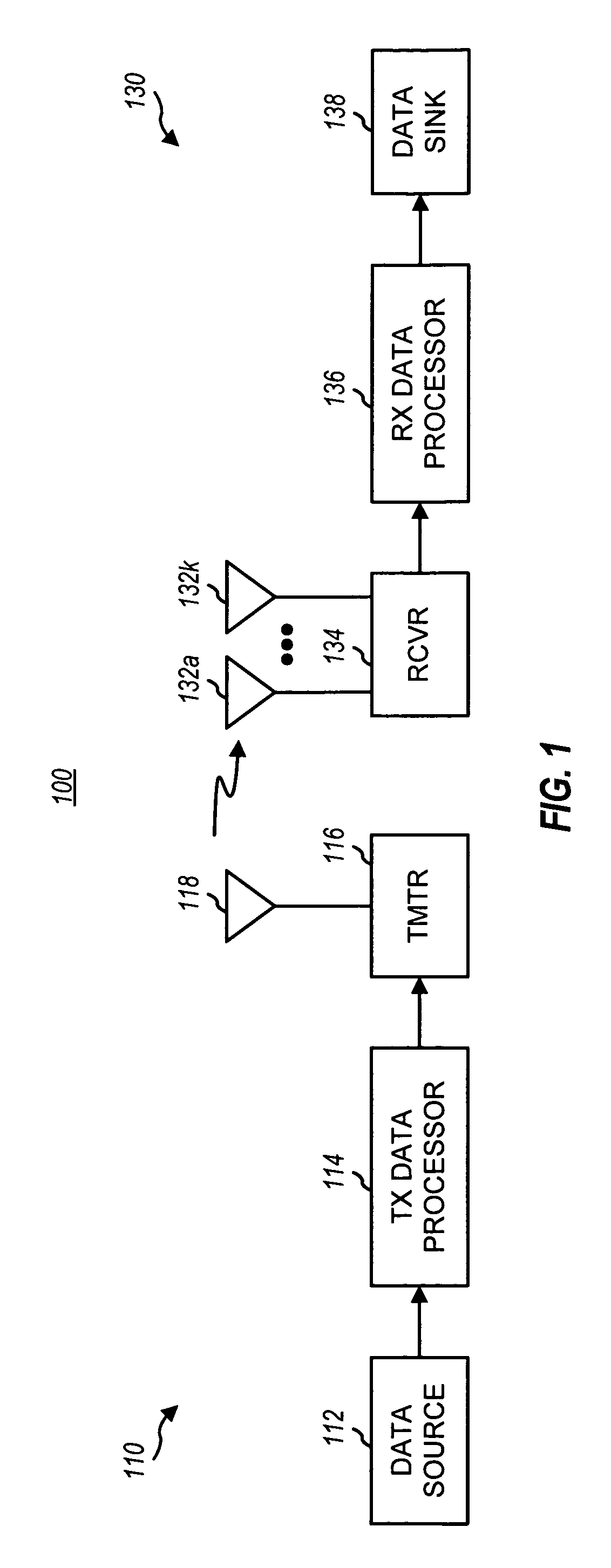
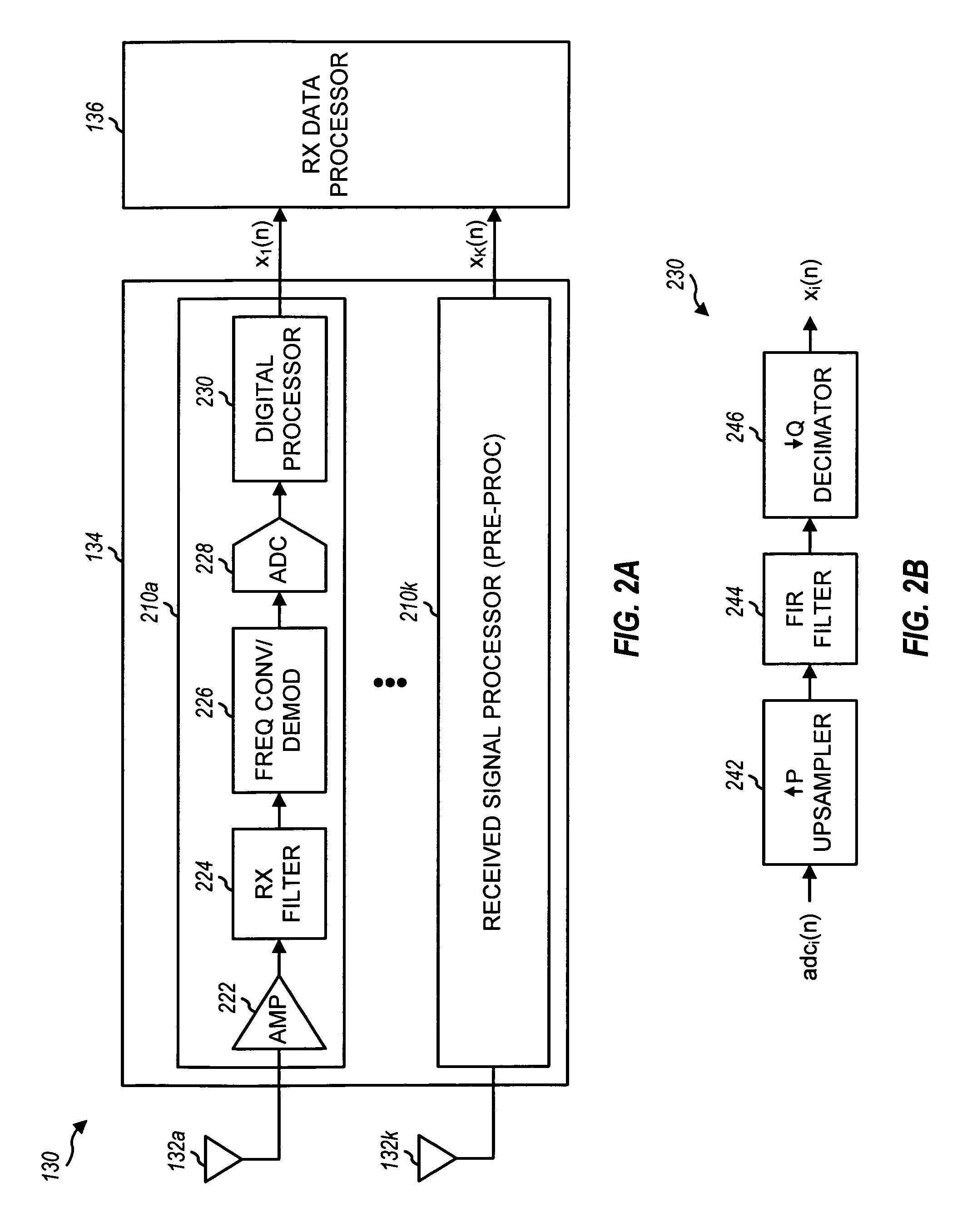
Wireless transmission using an adaptive transmit antenna array
ActiveUS20050117660A1Spatial transmit diversityBroadcast transmission systemsWireless transmissionClosed loop
Closed loop wireless communication of signals using an adaptive transmit antenna array (3), in which a plurality of copies of signals to be transmitted by the transmit antenna array (3) are produced with delays and weights (wnj) that are functions of the multi-path transmission channel characteristics (H) from the transmit antenna array (3) to a receive antenna array (4) of a receiver (2) and are combined before transmission by the transmit antenna array. The delays and weights (wnj) of the transmit copies for each transmit antenna element are functions of the respective multi-path transmission channel characteristics (hn,m=1l=1,… ,hn,m=Ml=L)from that transmit antenna element to the receive antenna array (4) ssuch that the multi-path signal components propagated to each receiver element are received with distinguishable delays according to the propagation path. The receiver (2) combines the received signal components from each receive antenna element with delays and weights (u) that are respective functions of the multi-path transmission channels. Preferably, the receiver comprises a multi-finger RAKE receiver (6) that copies the received signals from the receive antenna array with delays and weights (u) that are respective functions of the multi-path transmission channels and combines the copied received signals.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
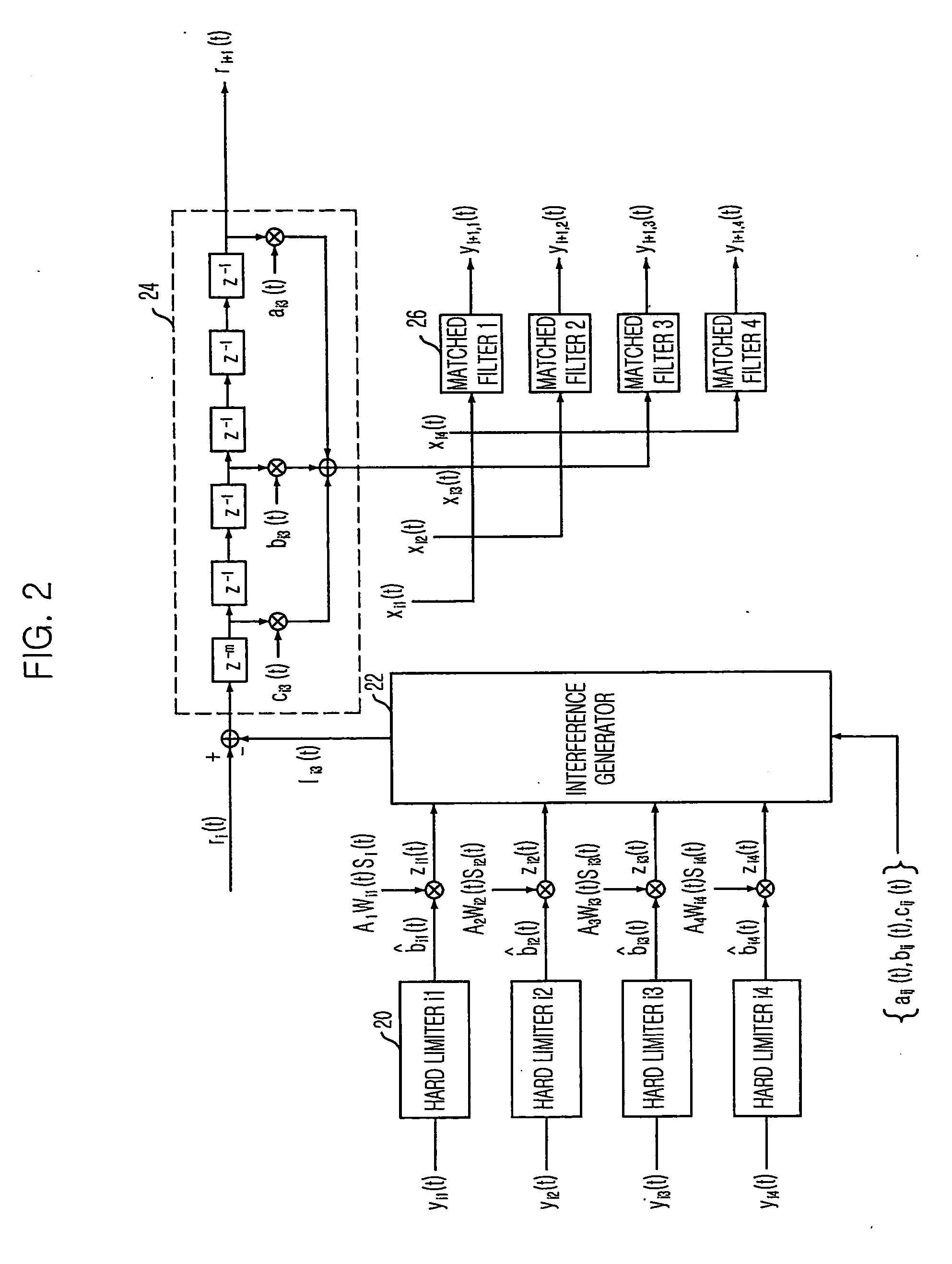
Interference suppression in a CDMA receiver
InactiveUS6570909B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultipath interferenceRake receiver
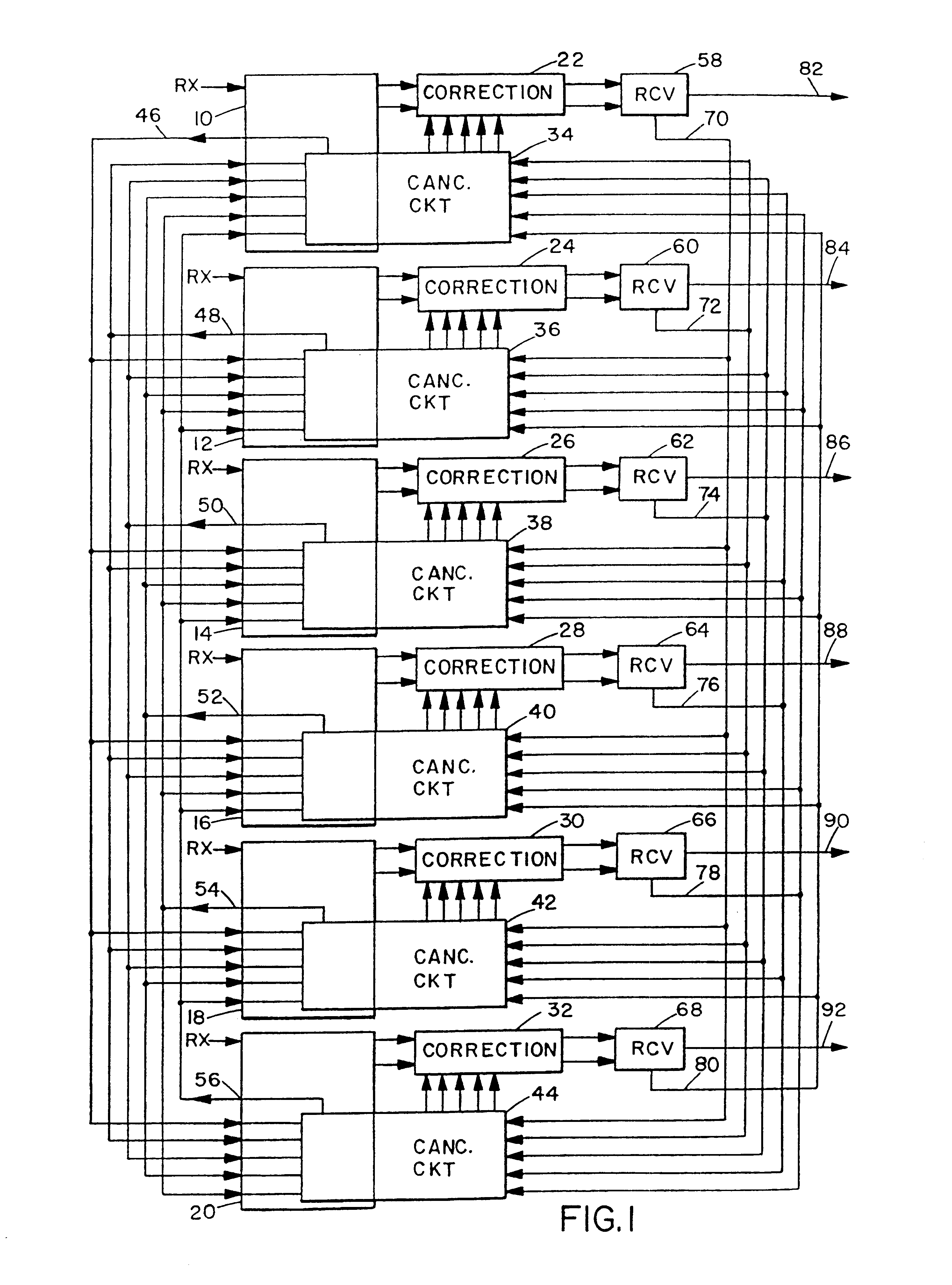
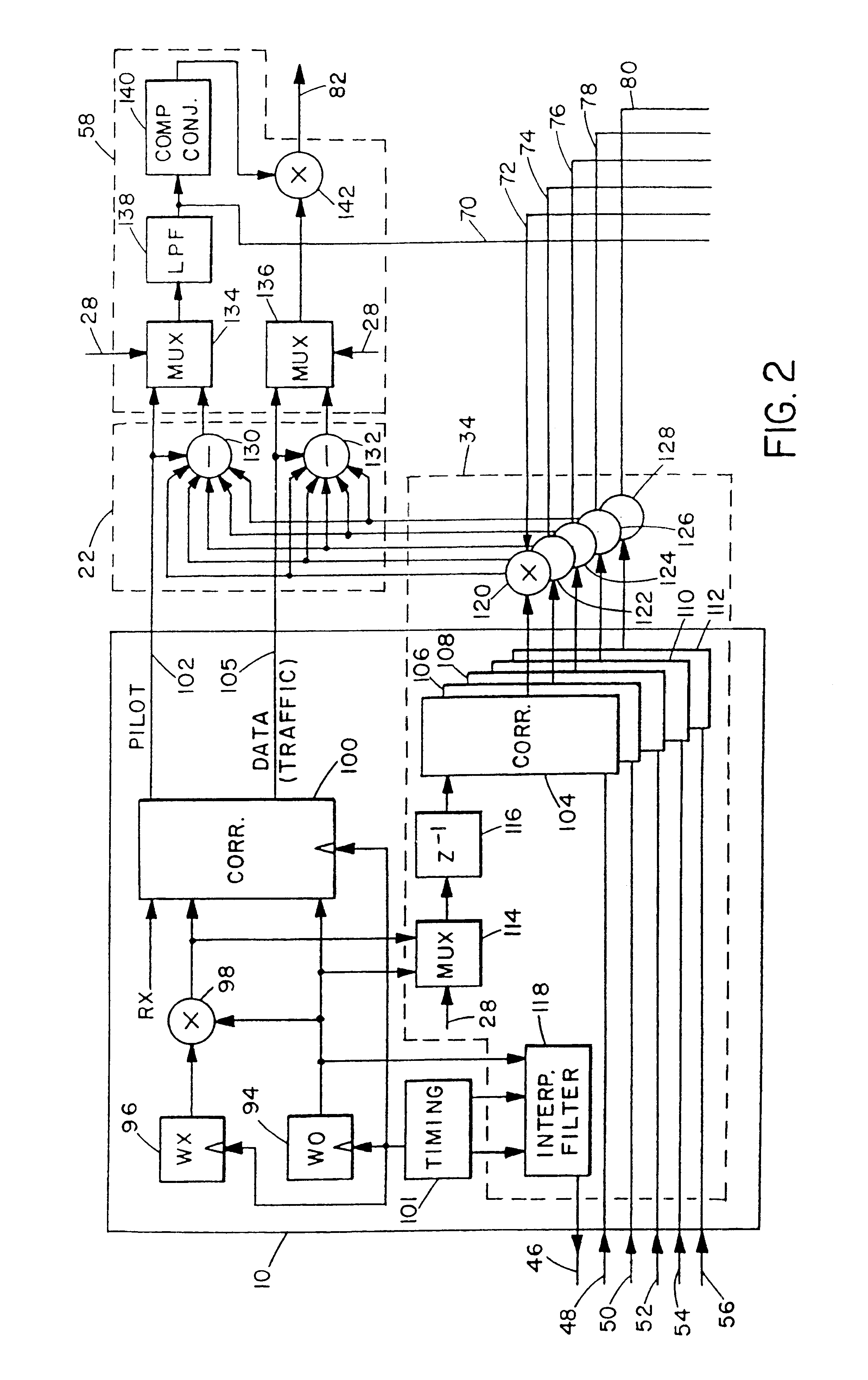
A system and method for canceling interference present in a code-division multiple access (CDMA) channel signal received at a CDMA receiver that is caused by multipath components of a transmitted pilot channel signal or by soft handoff conditions is computationally efficient because it operates at symbol rates. The channel signal from which such multipath interference is canceled can be either a traffic (data) channel or the pilot channel itself. Interference signals are produced in groups corresponding to the fingers of the CDMA rake receiver. The interference signals corresponding to each finger are used to cancel interference in the other fingers.
Owner:HMD GLOBAL
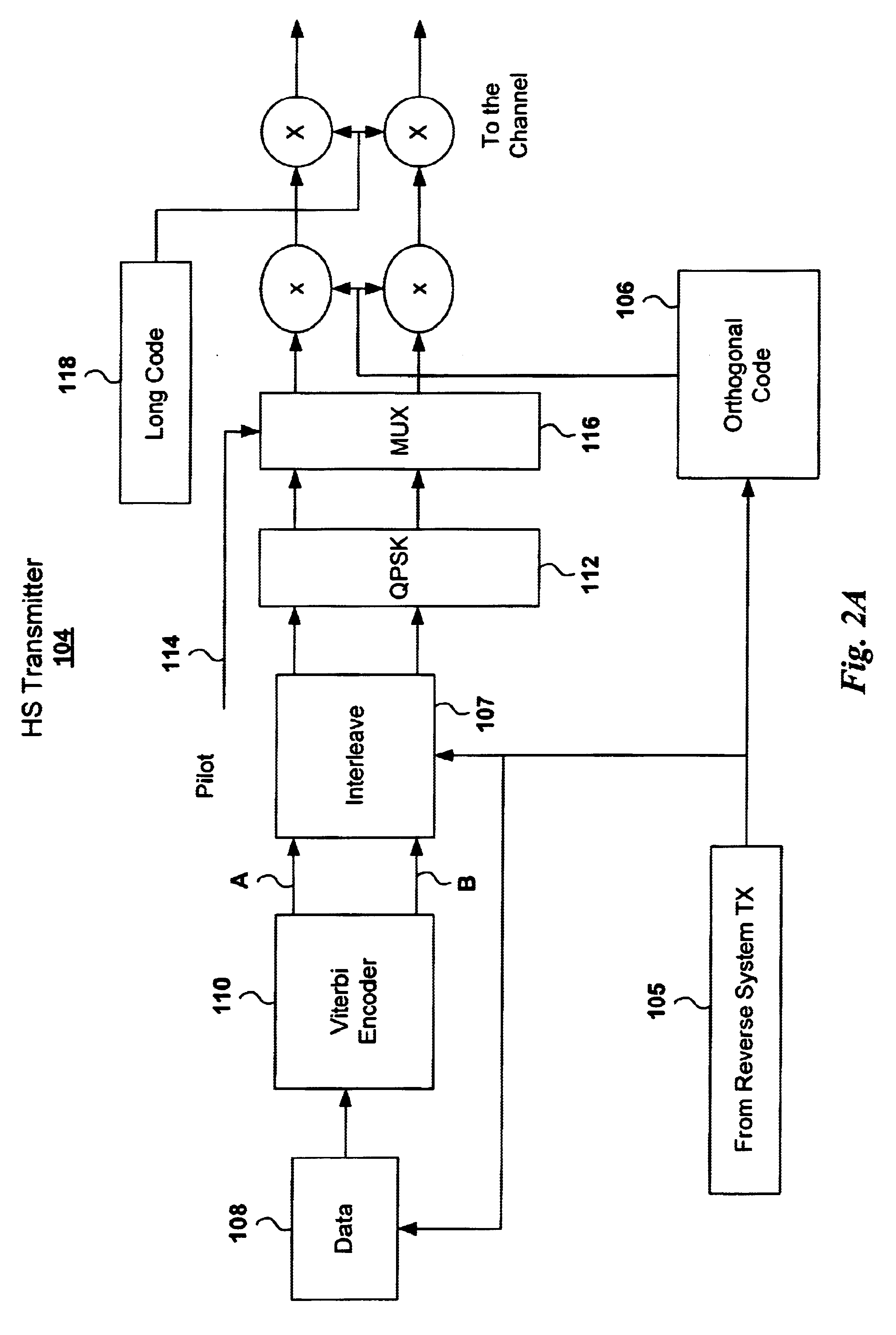
Adaptive power control based on a rake receiver configuration in wideband CDMA cellular systems (WCDMA) and methods of operation
InactiveUS6621808B1Maximizes controlMaximize throughputPower managementTransmission control/equalisingChannel powerOperational system
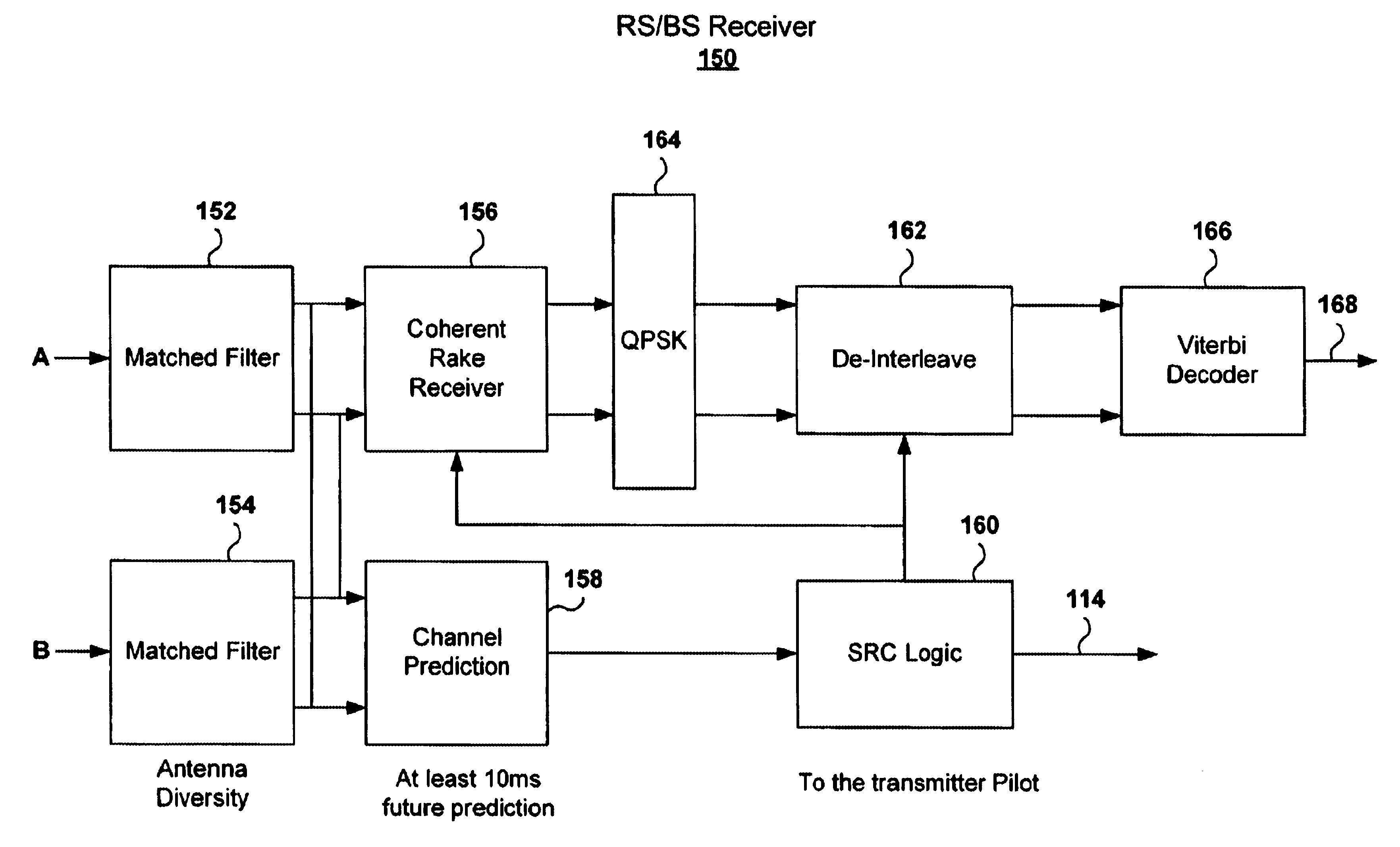
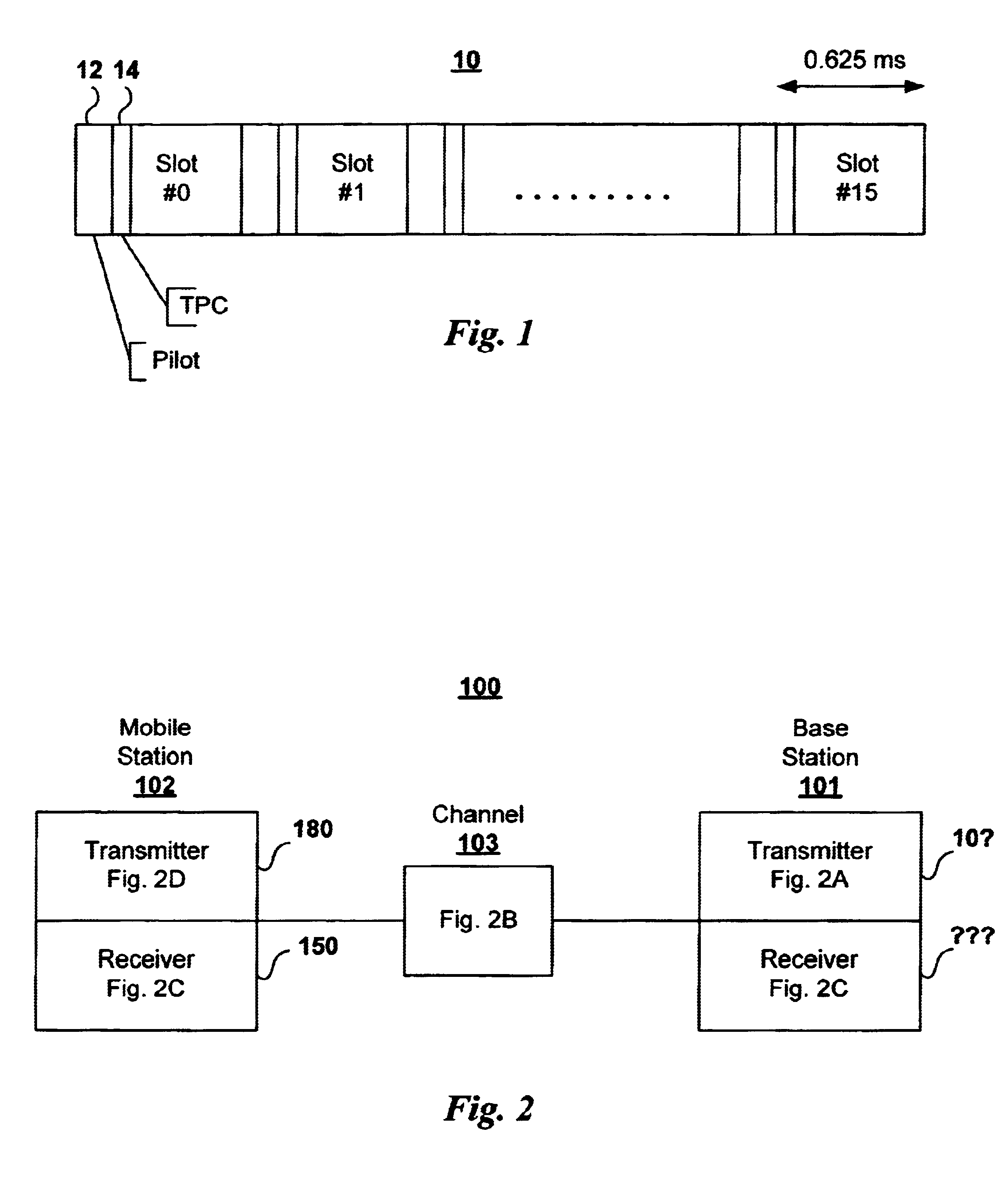
A WCDMA system includes a Base Station (BS) or forward transmitter and a pilot channel that transmits control signals between a Mobile Station (MS) and BS to reconfigure their transmitter / receiver according to the prediction of the channel power and channel power probability density function separated into three distinct equal probable regions. Data signals are encoded using a one-half Viterbi encoder and interleaved. The interleaved data bits are modulated using Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) modulation. The QPSK data is multiplexed with the pilot channel and spread by an appropriate code in an OFDM transmitter modified by a long code. Output of the transmitter may be provided to two diverse antennas for reliable communications to the receiver. Data may be received at two diverse antennas. The outputs are provided to match filters coupled to a coherent rake receiver and a channel prediction system. The future attenuation of the channel coefficients and power are determined by the prediction system for several milliseconds. The power levels of each finger in the Rake receiver can be predicted and the strongest ones used in determining the optimum transmitter power or rate control for operating the system transmitters and receivers based on computing a long range power prediction of each finger of a rake receiver.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Systems and methods for tuning an antenna configuration in a mobile communication device
InactiveUS20070042725A1Easy to receiveImprove signal qualityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsEngineeringRake receiver
A mobile communication device comprises a plurality of spatially and / or polar diverse antenna configurations. Signals received by each of the plurality of antenna configurations are combined in a combiner and passed to a rake receiver that can be configured to combine the signals received by each of the plurality of antenna configurations for further processing. The mobile communication device can comprises a signal adjusting network that can be configured to adjust the phase and / or magnitude of signals being received by one of the antennas.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Multipath interference reduction for a CDMA system
InactiveUS6865218B1Improve receiver performanceReduce multipath interferenceRadio transmissionMultipath interferenceRake receiver
A method and system reduce multipath signal interference in a CDMA receiver. The CDMA receiver including parallel first and second RAKE receivers receives a multipath signal. The first RAKE receiver includes a number of individual RAKE fingers, each operating with a defined finger delay matched to a propagation path delay. The output signal from each RAKE finger includes multipath interference. The second RAKE receiver includes a group of RAKE fingers corresponding to each RAKE finger in the first RAKE receiver. Each group of RAKE fingers is configured to produce an estimate of the multipath interference in the output signal generated by the corresponding RAKE finger in the first RAKE receiver. The estimated multipath interference signals are scaled, and then subtracted from the RAKE finger outputs from the first RAKE receiver to reduce multipath interference. Scaling coefficients are adjusted to ensure that such subtraction effectively reduces multipath interference.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
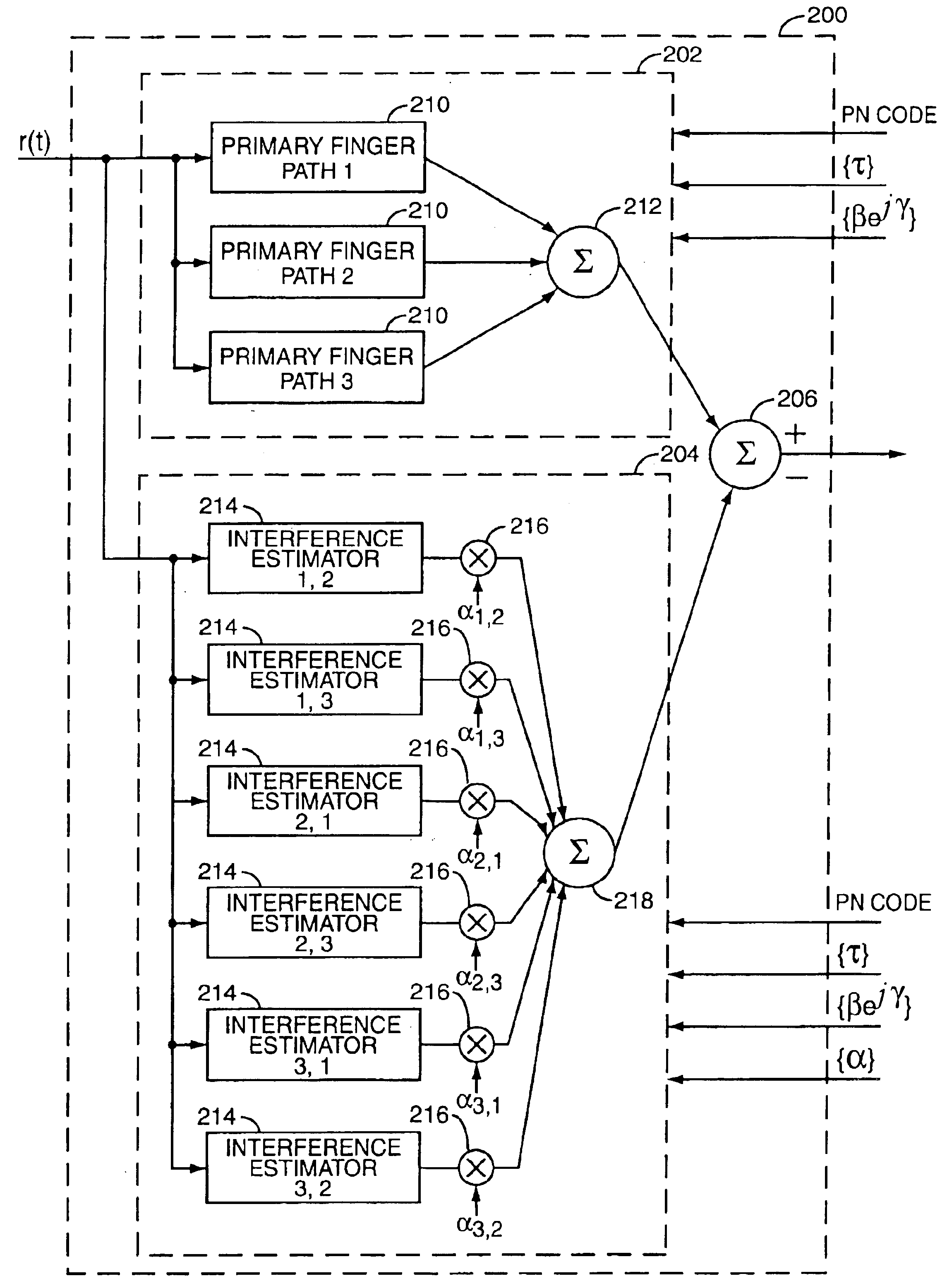
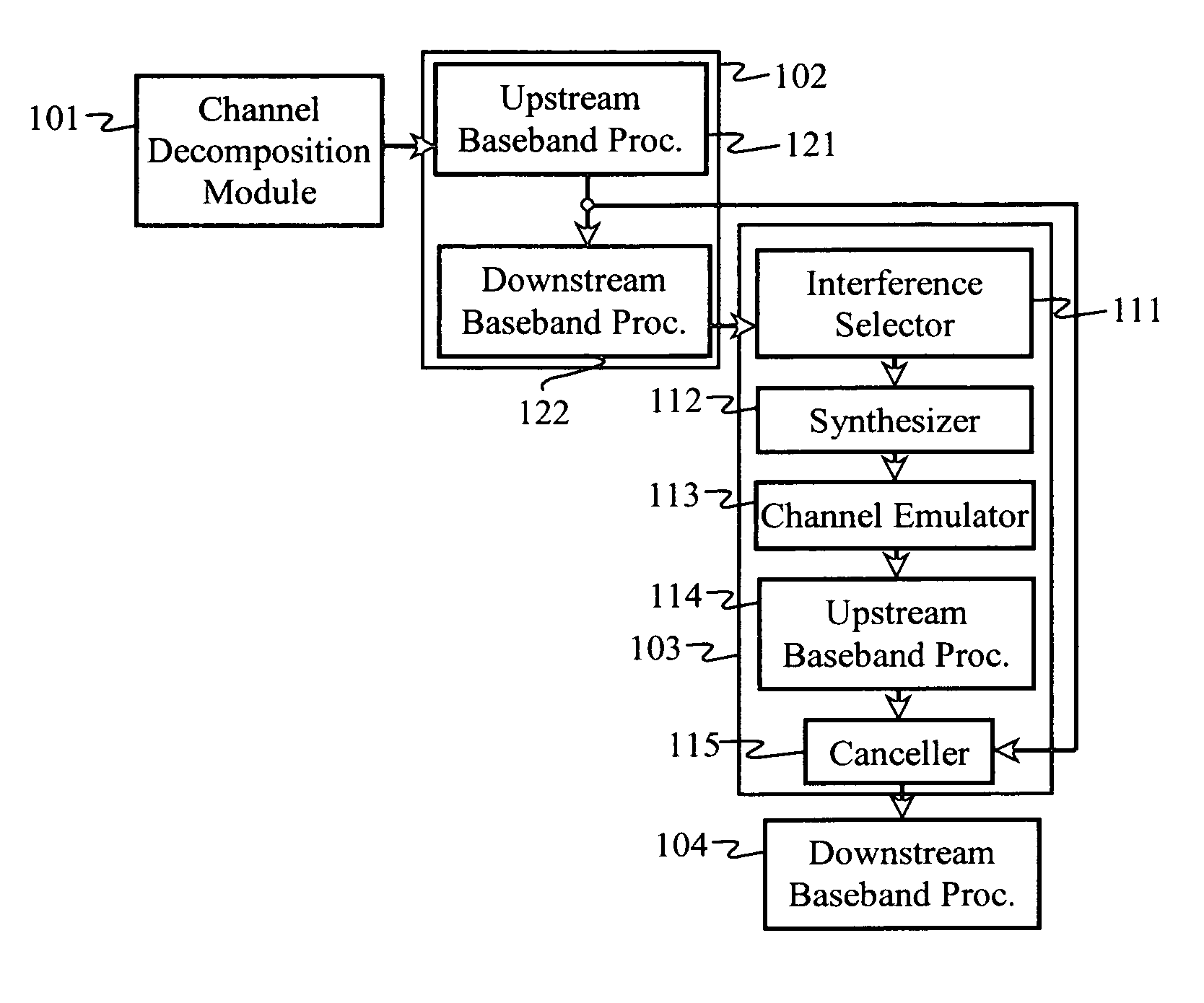
Advanced signal processors for interference cancellation in baseband receivers
ActiveUS7787572B2Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionInterference cancelationInterference canceller
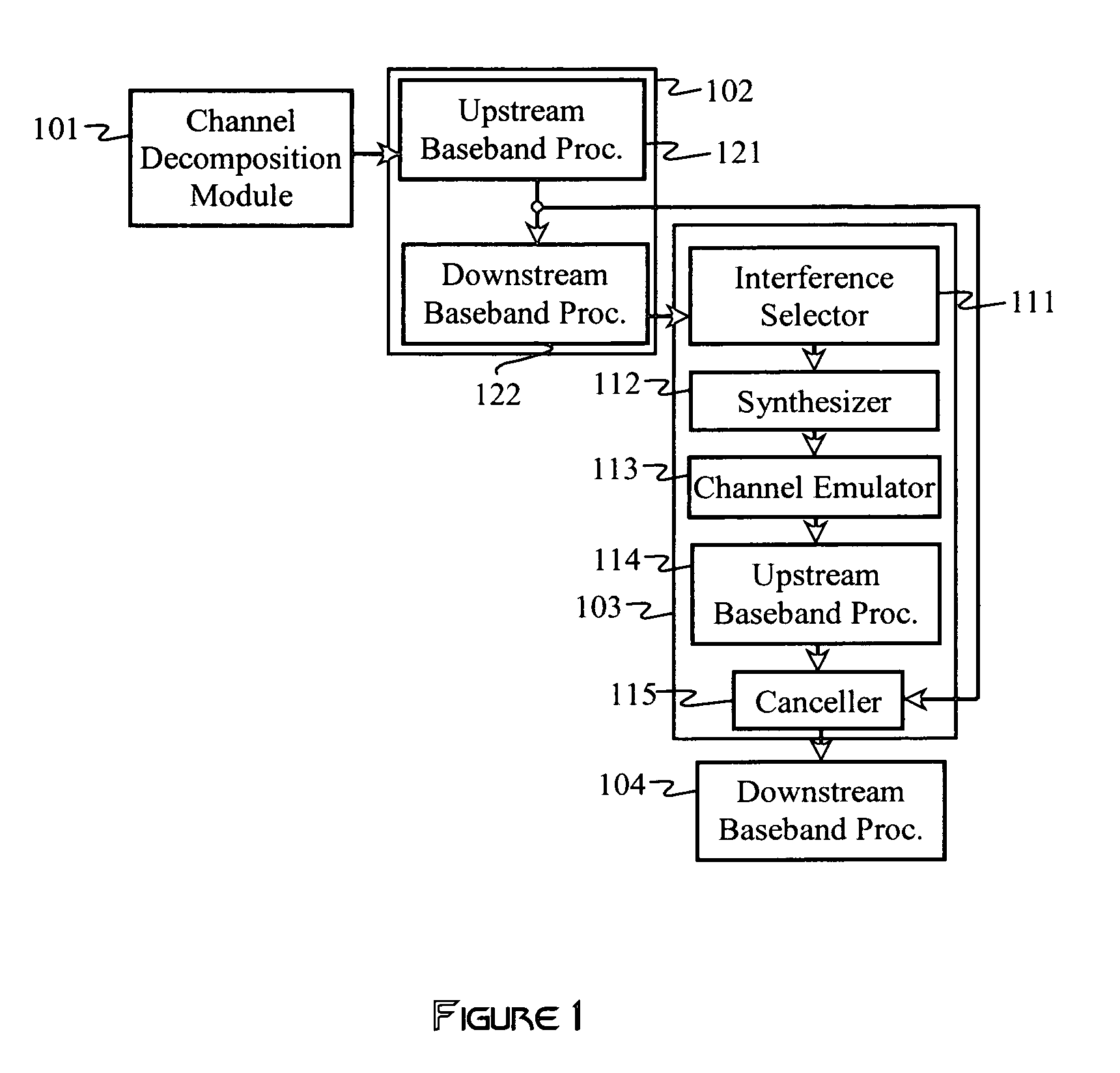
A multi-mode receiver includes a channel decomposition module (e.g., a Rake receiver) for separating a received signal into multipath components, an interference selector for selecting interfering paths and subchannels, a synthesizer for synthesizing interference signals from selected subchannel symbol estimates, and an interference canceller for cancelling selected interference in the received signal. At least one of the channel decomposition module, the synthesizer, and the interference canceller are configurable for processing multi-mode signals.
Owner:III HLDG 1
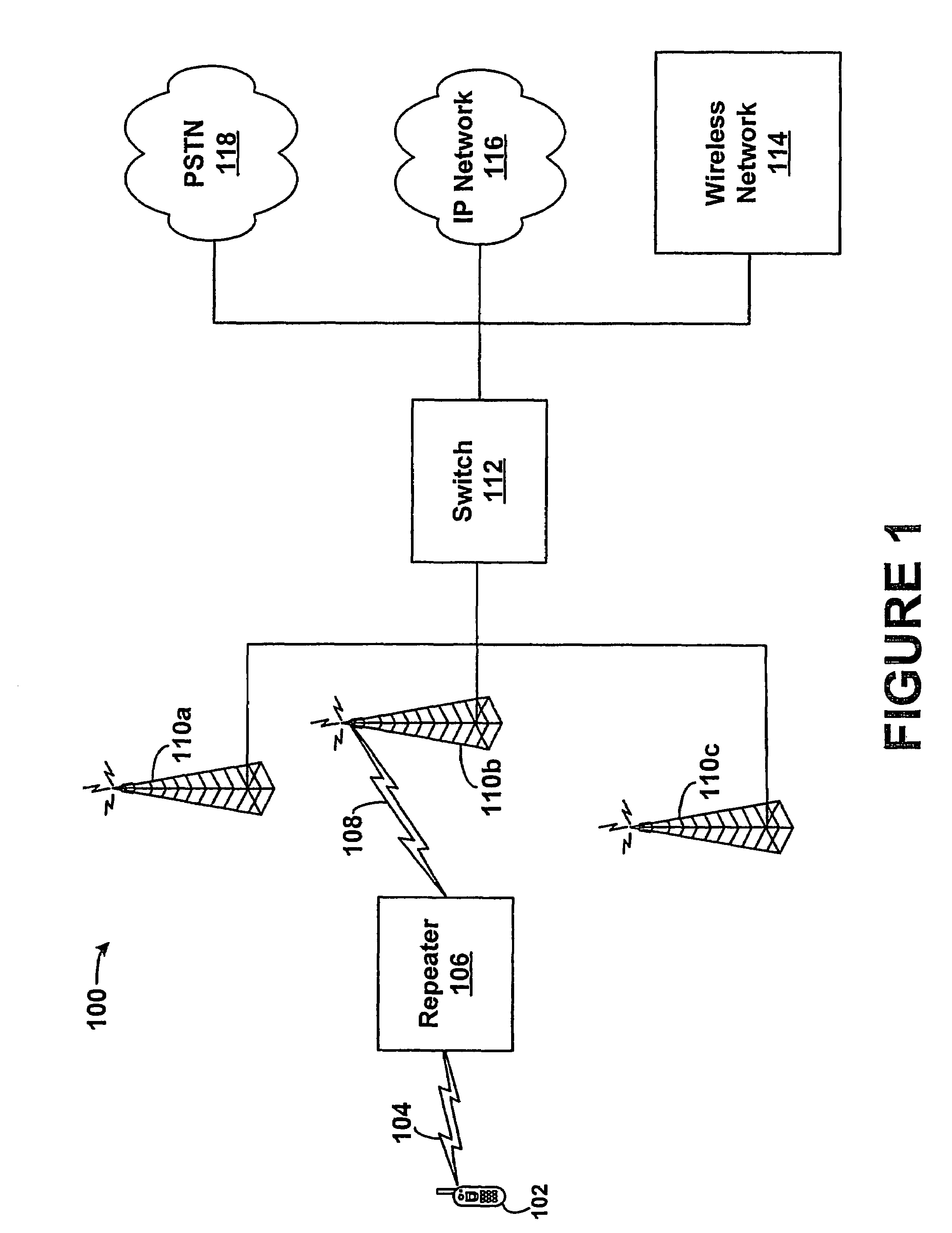
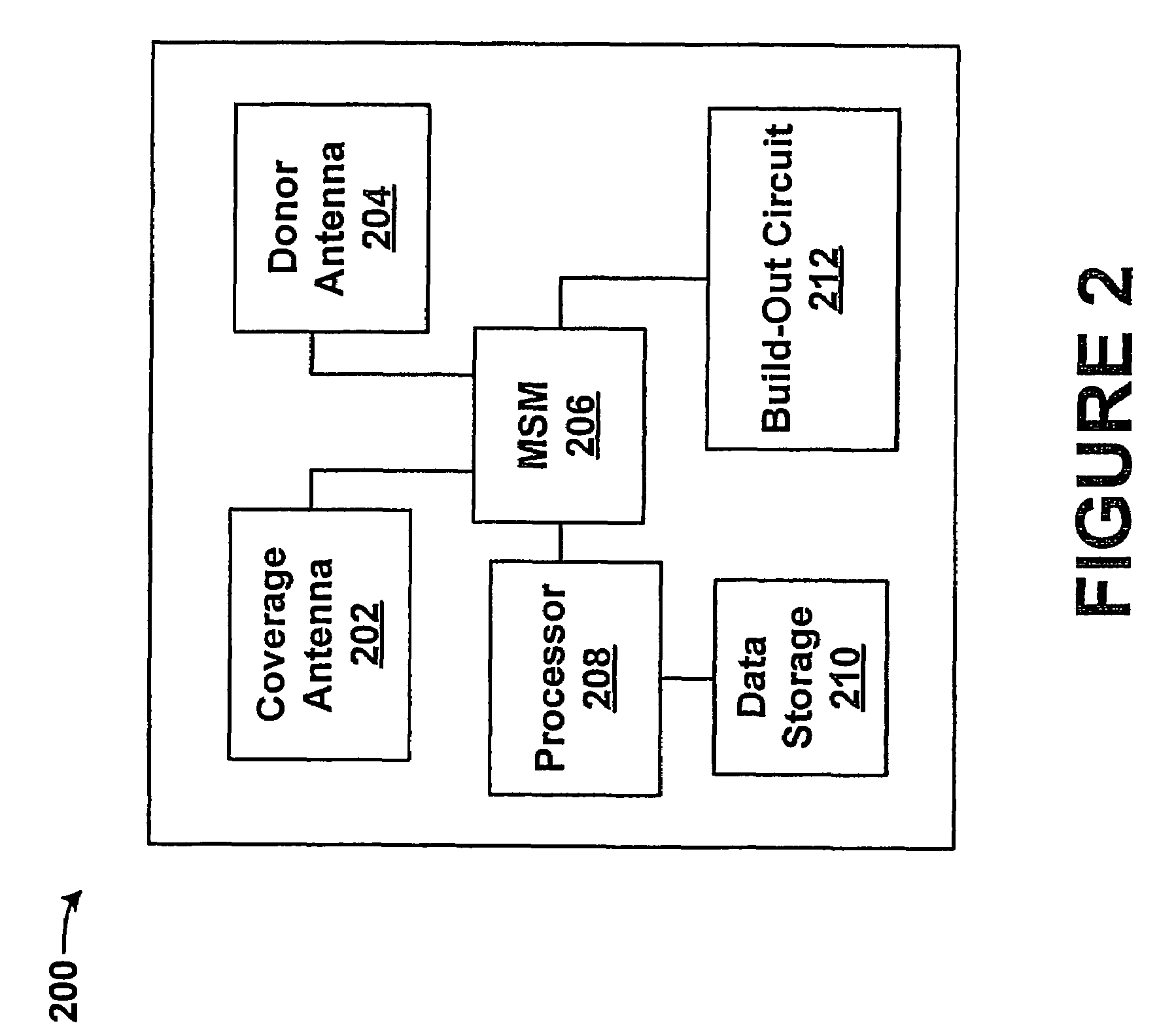
Wireless repeater and method for managing air interface communications
ActiveUS7480486B1Frequency-division multiplex detailsActive radio relay systemsModem deviceAir interface
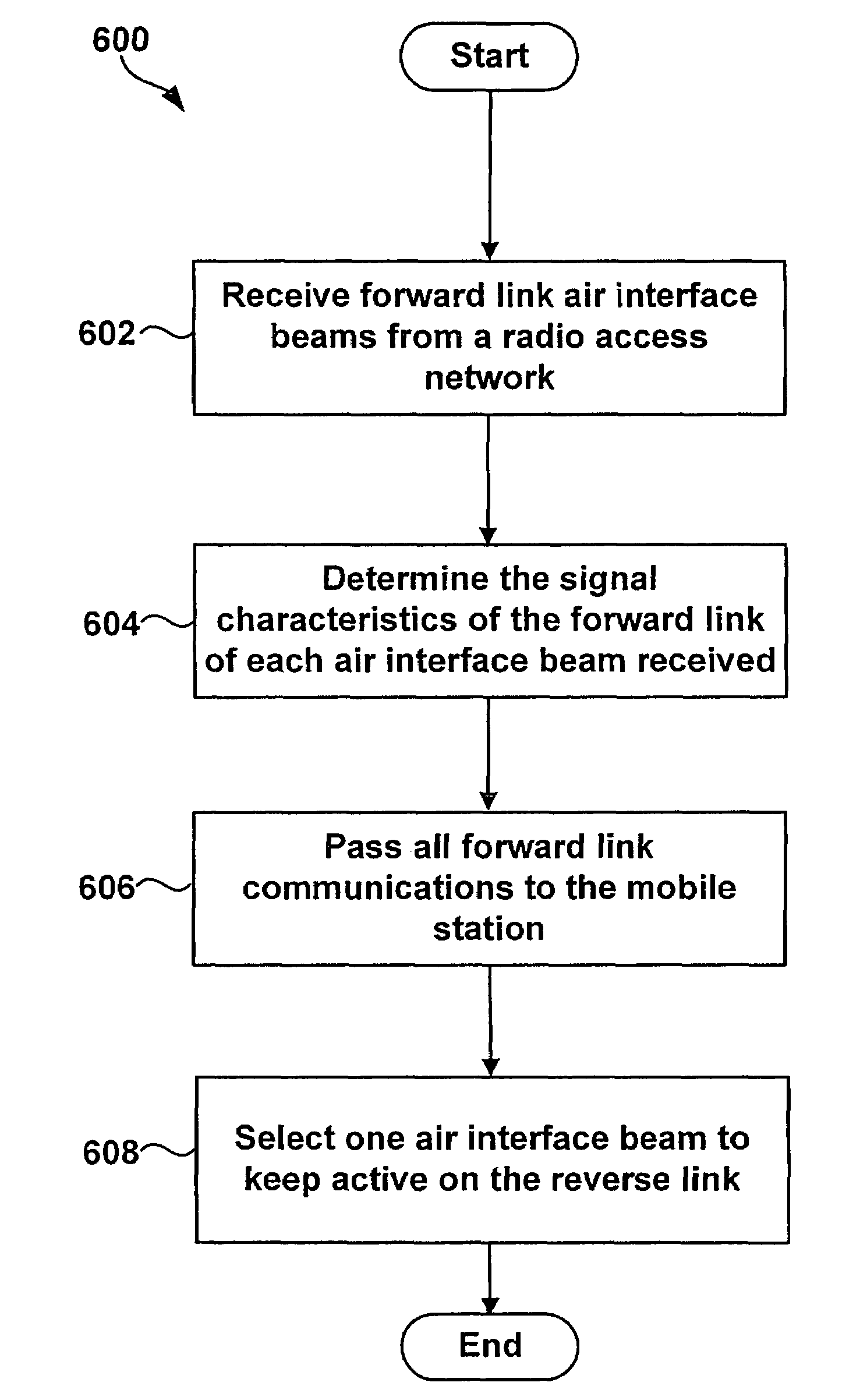
A wireless repeater and method for managing air interface communications is provided. A repeater may include a donor antenna, a coverage antenna, a mobile station modem, a processor, and data storage. The donor antenna will receive a plurality of air interface beams on the forward link from a radio access network. The coverage antenna will pass each forward link beam received to a mobile station being served by the repeater. Further, the donor antenna will pass each forward link air interface beam to the MSM, where the MSM will apply a rake receiver to identify a signal characteristic of the forward link of each beam received, and the processor will record in the data storage the signal characteristic corresponding to each beam. Given this data, the repeater will select an air interface beam with the most preferable signal characteristic, and will keep only this beam active for reverse link communications.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
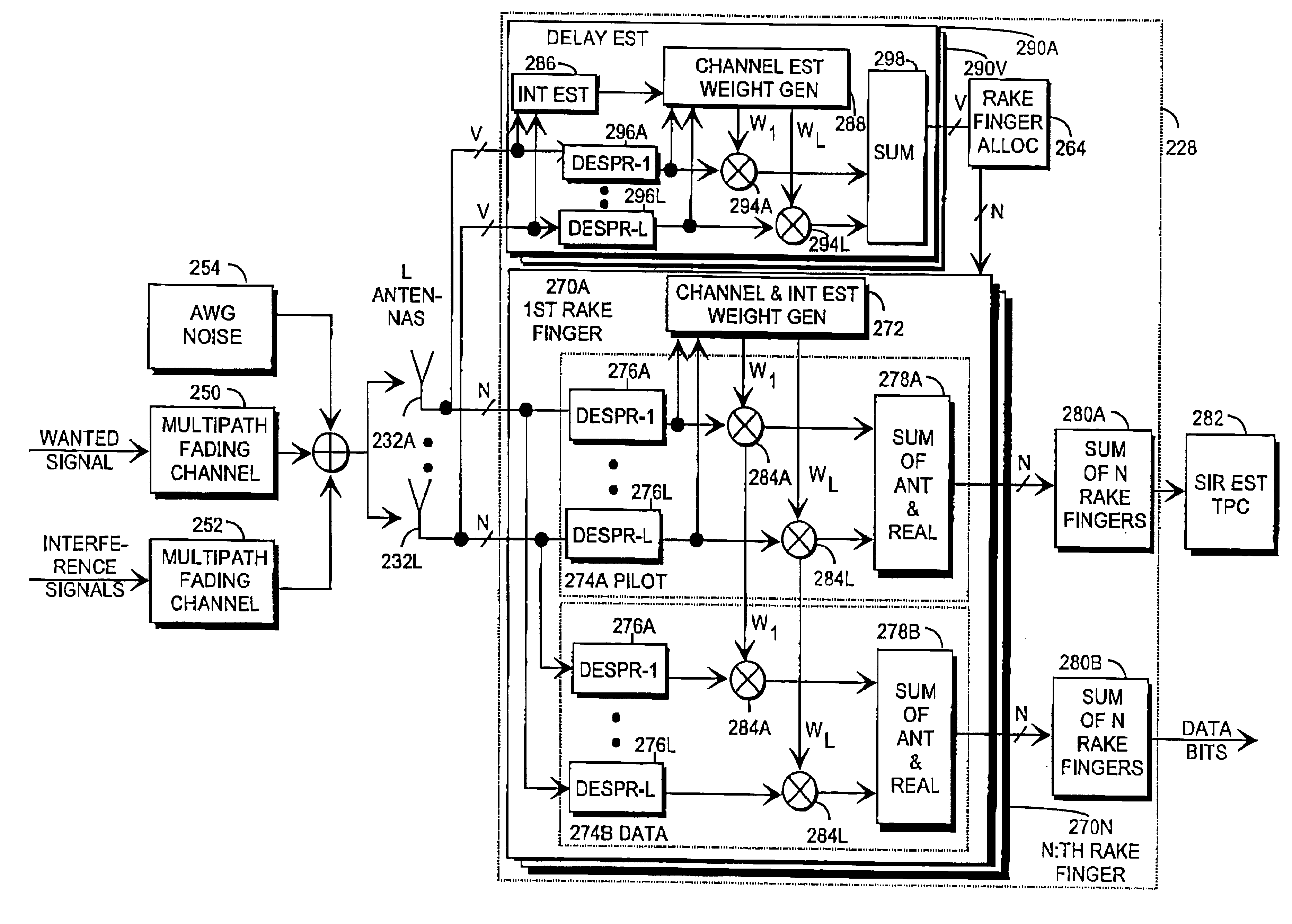
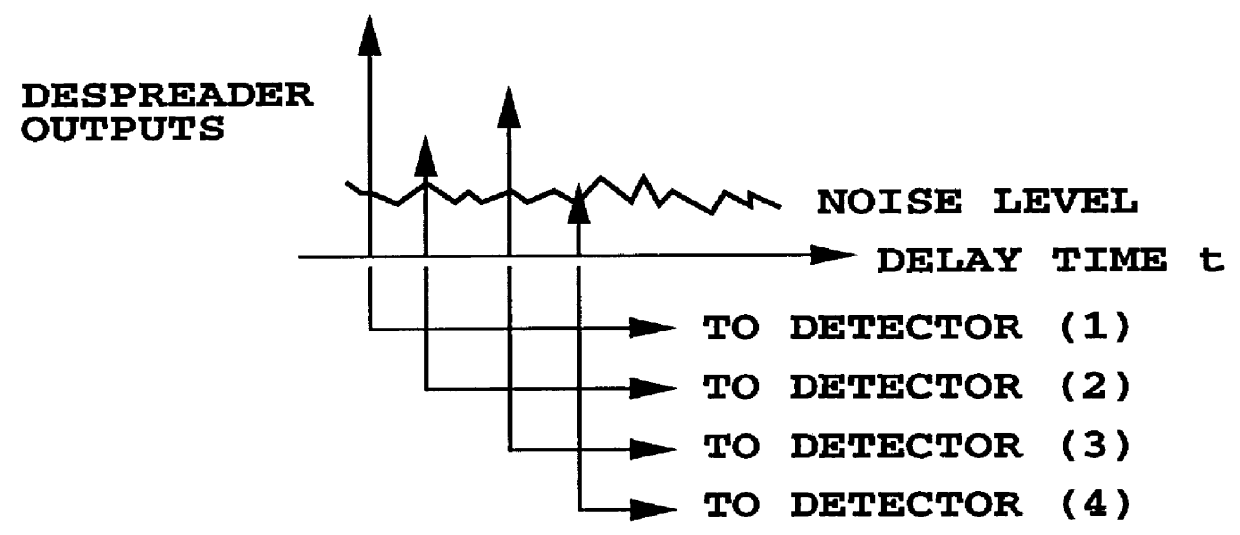
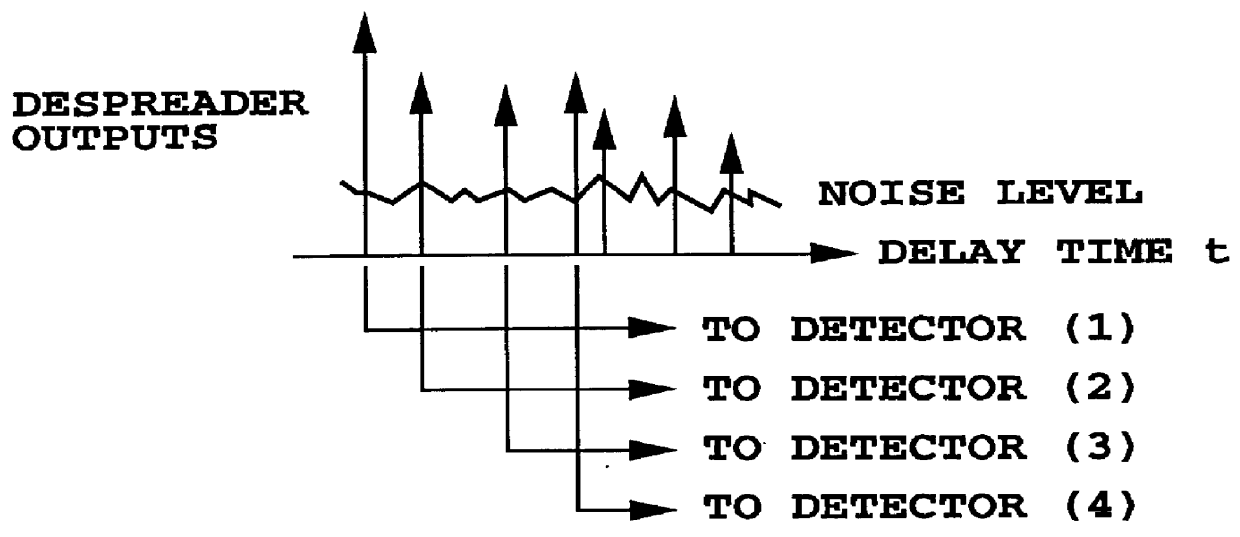
Rake receiver
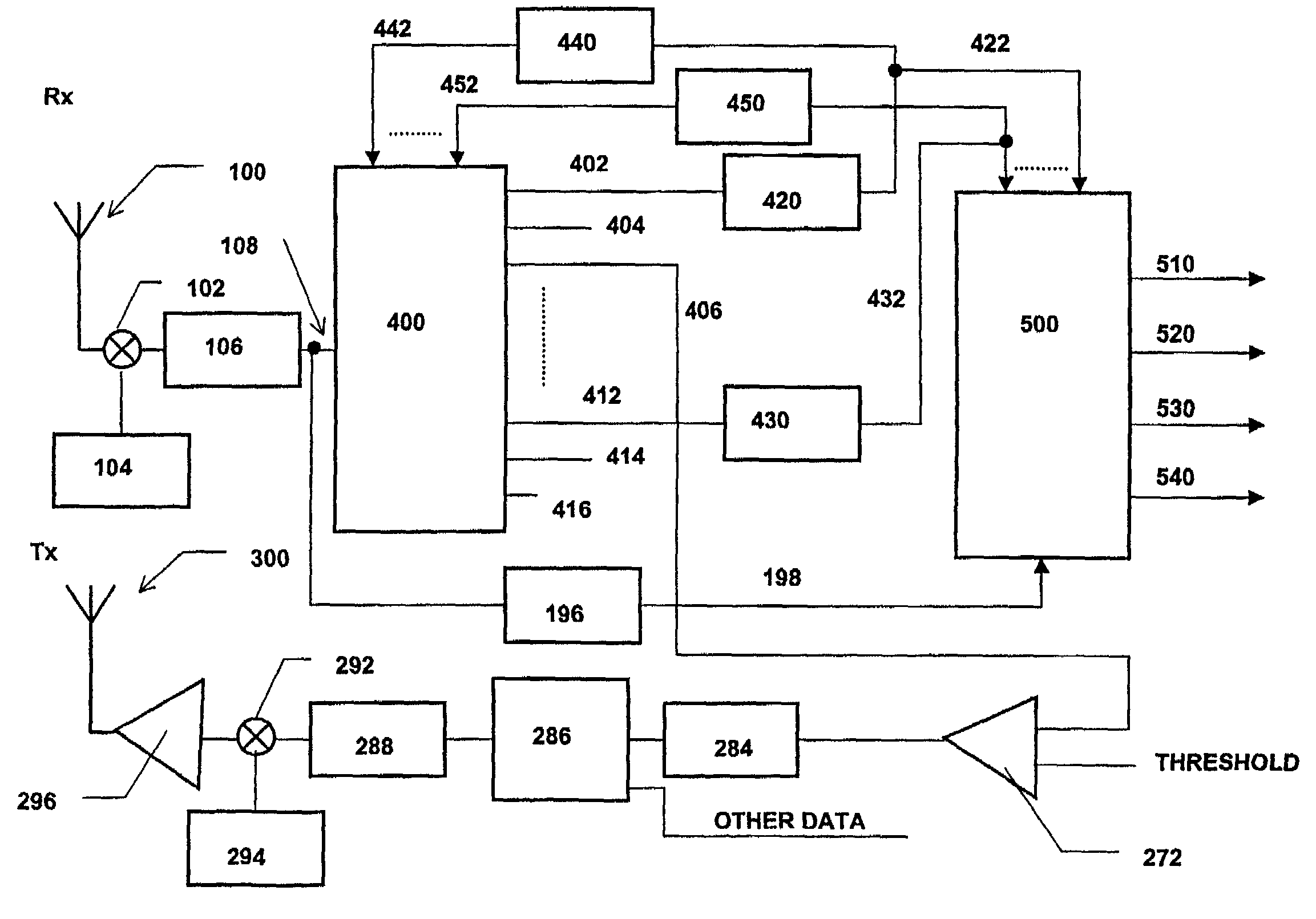
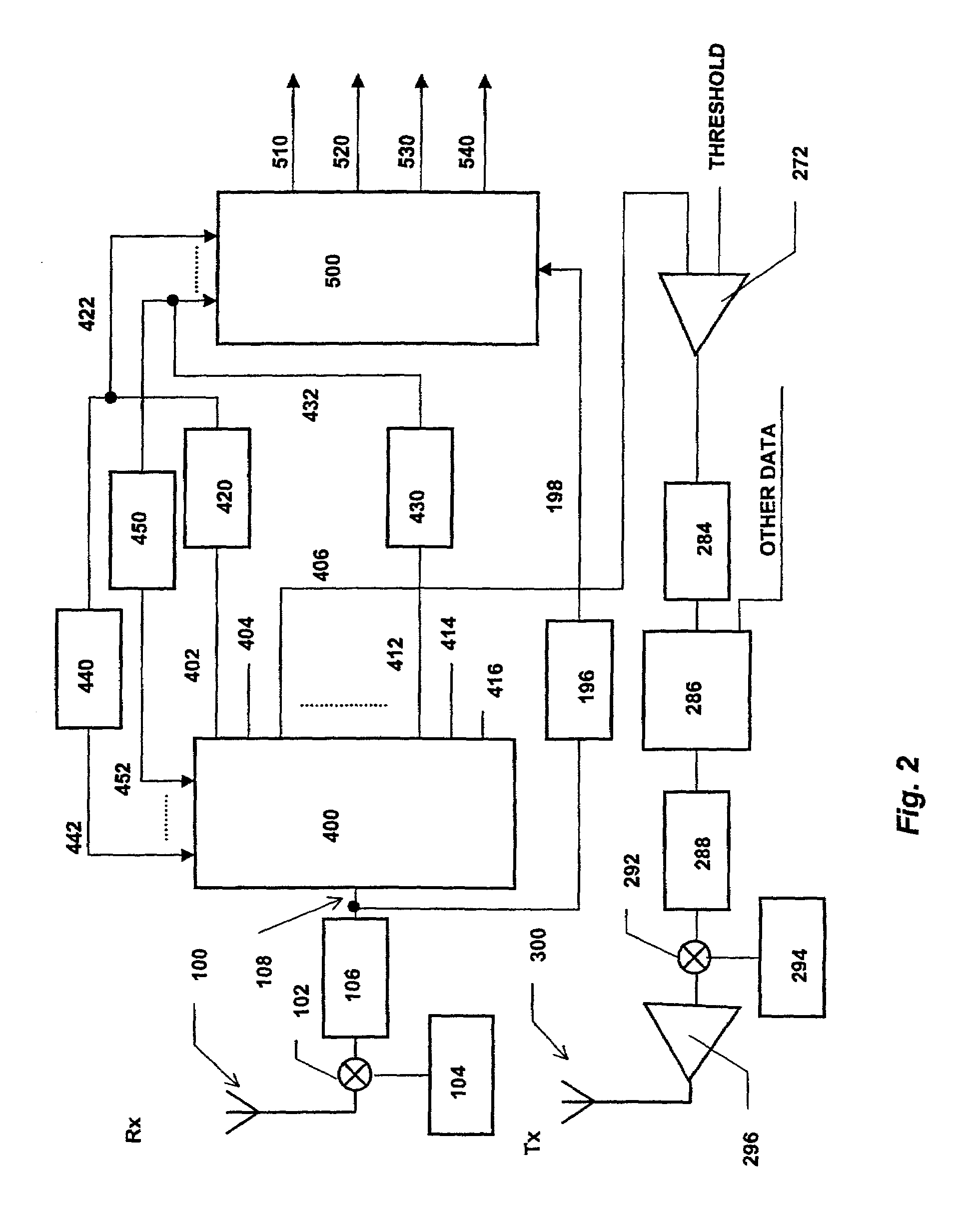
The invention relates to a Rake receiver of a CDMA system using IRC. The Rake receiver comprises at least two antenna branches, at least one Rake finger, and a delay estimator. The delay estimator comprises a despreader and an allocator for selecting at least one delay, and allocating a Rake finger for processing the signal component found by informing the Rake finger of the delay found. The delay estimator further comprises: a channel estimator, an interference estimator for generating an interference signal, a weighting coefficient part for providing each antenna branch with weighting coefficients maximizing the Signal-to-Interference-and-Noise Ratio, a multiplier for multiplying the pilot part by a weighting coefficient, and an antenna branch summer for combining the despread pilot parts, received via the separate antenna branches and multiplied by the weighting coefficient, to one combined pilot signal, on which combined pilot signal the selection is based in the allocator.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
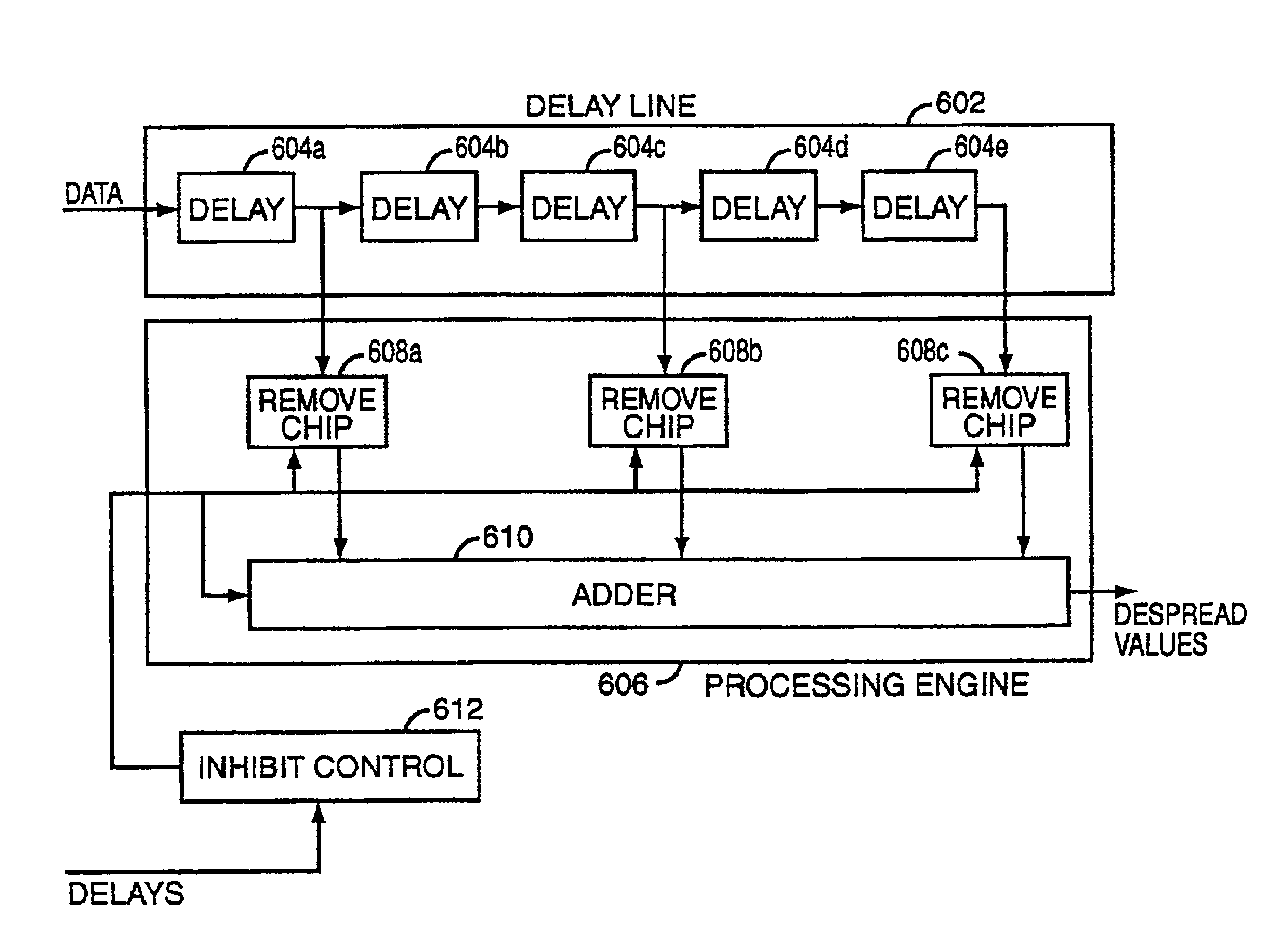
Method and apparatus for interference cancellation in a rake receiver
InactiveUS6842479B2Transmission control/equalisingAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsInterference cancelationRake receiver
Systems and methods for despreading received spread spectrum signals are described. Despreading can be performed using both channel estimates and impairment correlation estimates. Techniques for selecting delays of interest are also described, along with a despreading mechanism which saves power by operating only on delays of interest.
Owner:HIGHBRIDGE PRINCIPAL STRATEGIES LLC AS COLLATERAL AGENT
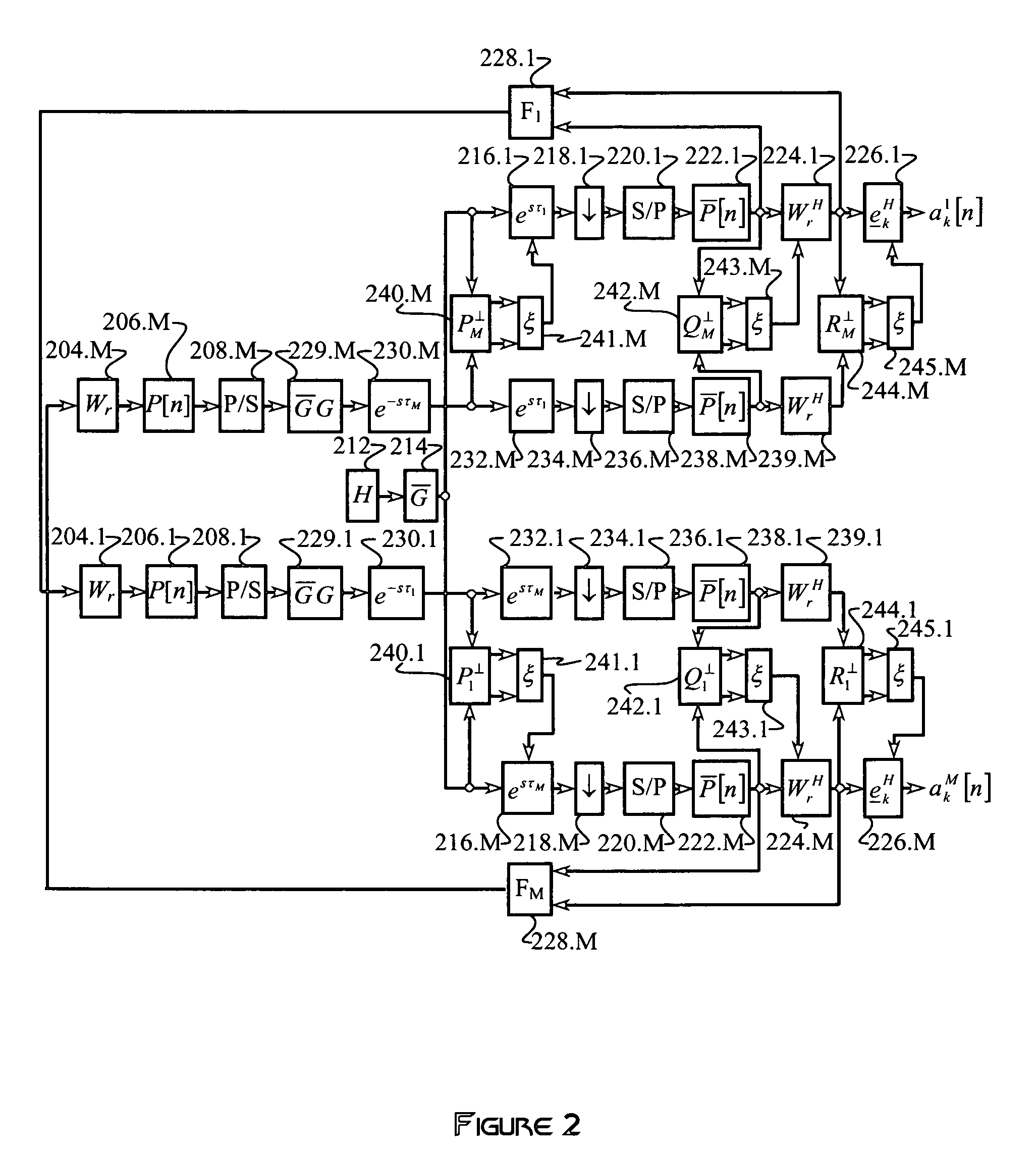
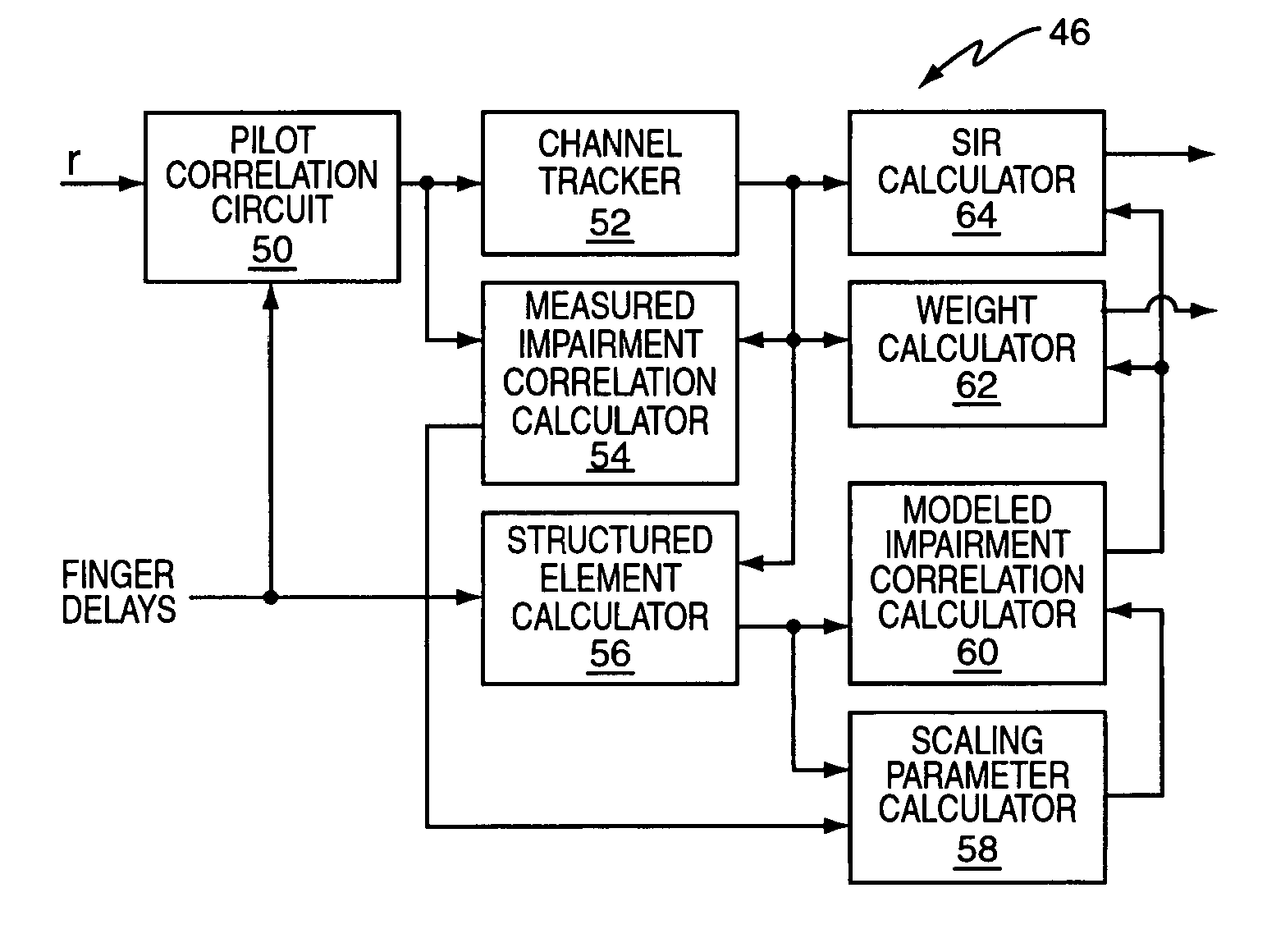
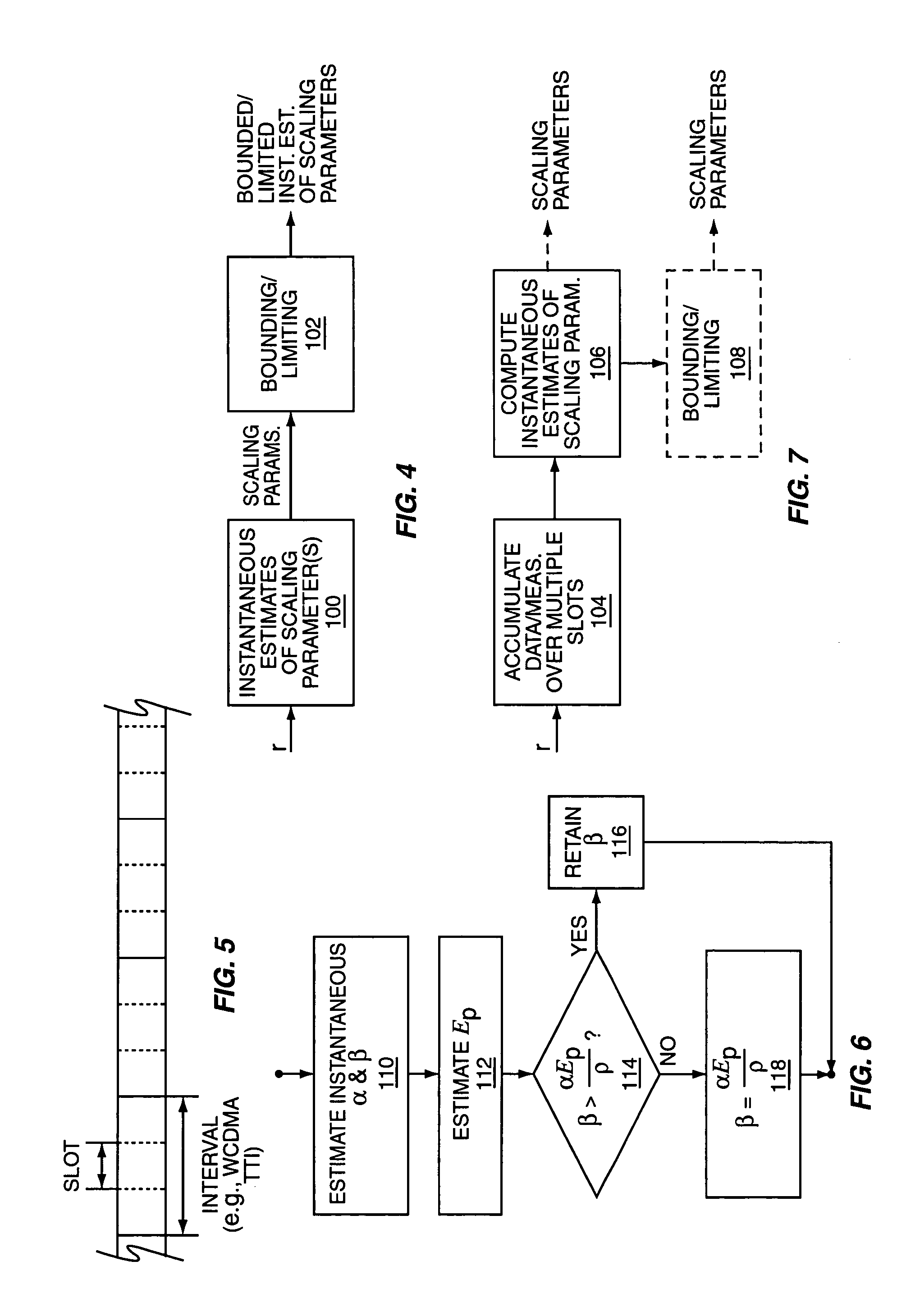
Method and apparatus for scaling parameter estimation in parametric generalized rake receivers
InactiveUS20060007990A1Spatial transmit diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverEngineering
A wireless communication receiver, such as the receiver included in a wireless communication transceiver implemented in a base station or in a mobile station of a wireless communication network, includes a parametric G-RAKE receiver circuit and a method that compute parametric scaling parameters on a per transmission interval basis. In one embodiment, measured impairment correlations are obtained for an individual transmission slot and used to estimate instantaneous values of the scaling parameters. One or both of those instantaneous values are then constrained according to one or more defined limits. In other embodiments, multiple transmission slots are used to increase the number of measurements available to estimate the scaling parameters, with parameter constraining optionally applied. Further embodiments use iterative methods and / or solve for one parameter, and use the results to obtain the other parameter(s). One or more of these embodiments can be improved through the use of error correction / detection information.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
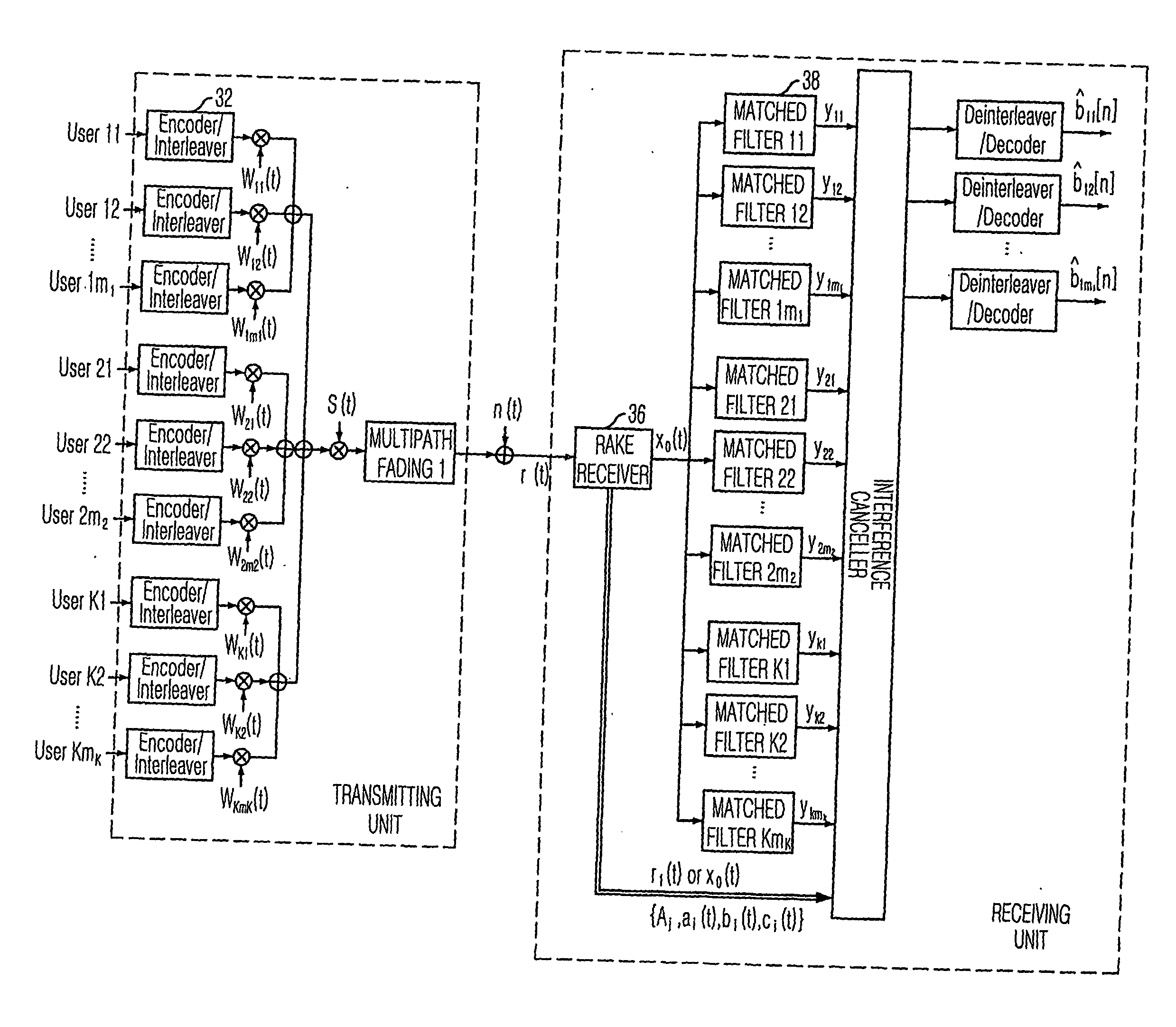
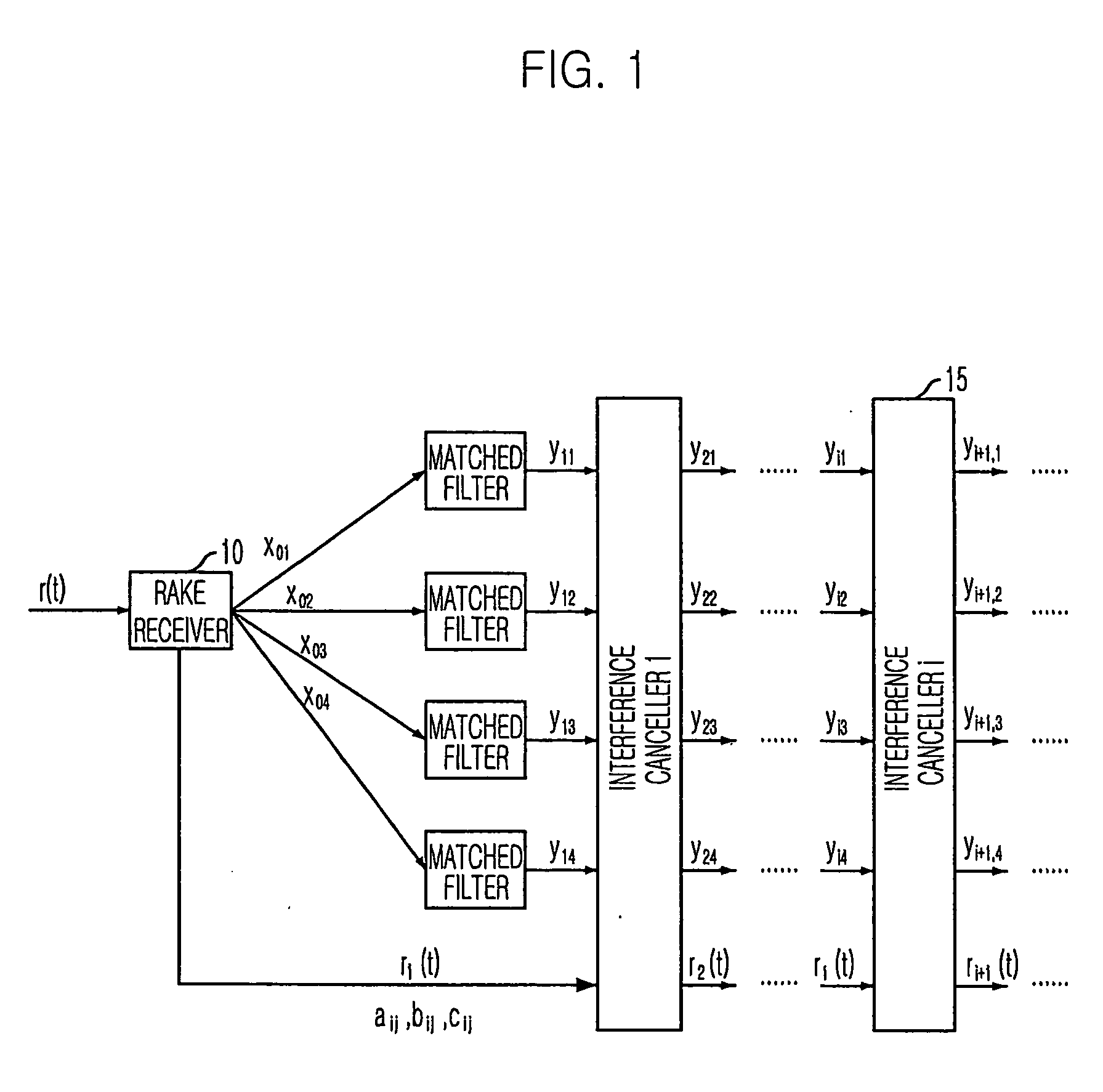
Multistage adaptive parallel interference canceller
InactiveUS20060013289A1Minimizing degradation of orthogonalityReduce circuit complexityCode division multiplexTransmissionInterference cancellerInterference elimination
A multistage adaptive parallel interference canceller is disclosed. The multistage adaptive parallel interference canceller for a downlink receiver includes: a plurality of stages of interference cancellation units. Each of interference cancellation units includes: a matched filter for matching a signal from a rake receiver each channel signal and generating a matched signal; a soft decision unit of which a slope is monotonically increased, for performing soft decision of the matched signal and generating a soft-decided signal; a weight controller for controlling the slope of the soft decision unit; a respreader for respreading the soft-decided signal based on a walsh code and a scrambling code and generating a respread signal; an interference calculator for calculating interference signals due to another user signal and multipath signals; and an interference canceller for canceling the interference signals from an input signal received in the rake receiver.
Owner:HWANG IN KWAN
Method and apparatus for DS-CDMA interference suppression using code-specific combining
Interference, such as inter-symbol interference, from a symbol of interest in a RAKE receiver is reduced. The RAKE receiver comprises a plurality of RAKE fingers, a processor, and a combiner. The plurality of RAKE fingers despread symbols received over multiple paths of a multi-path channel. The processor determines cross-correlations between symbol waveforms from different symbols and multiple paths. The combiner combines the despread symbols using the cross-correlations to reduce interference from the symbol of interest.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
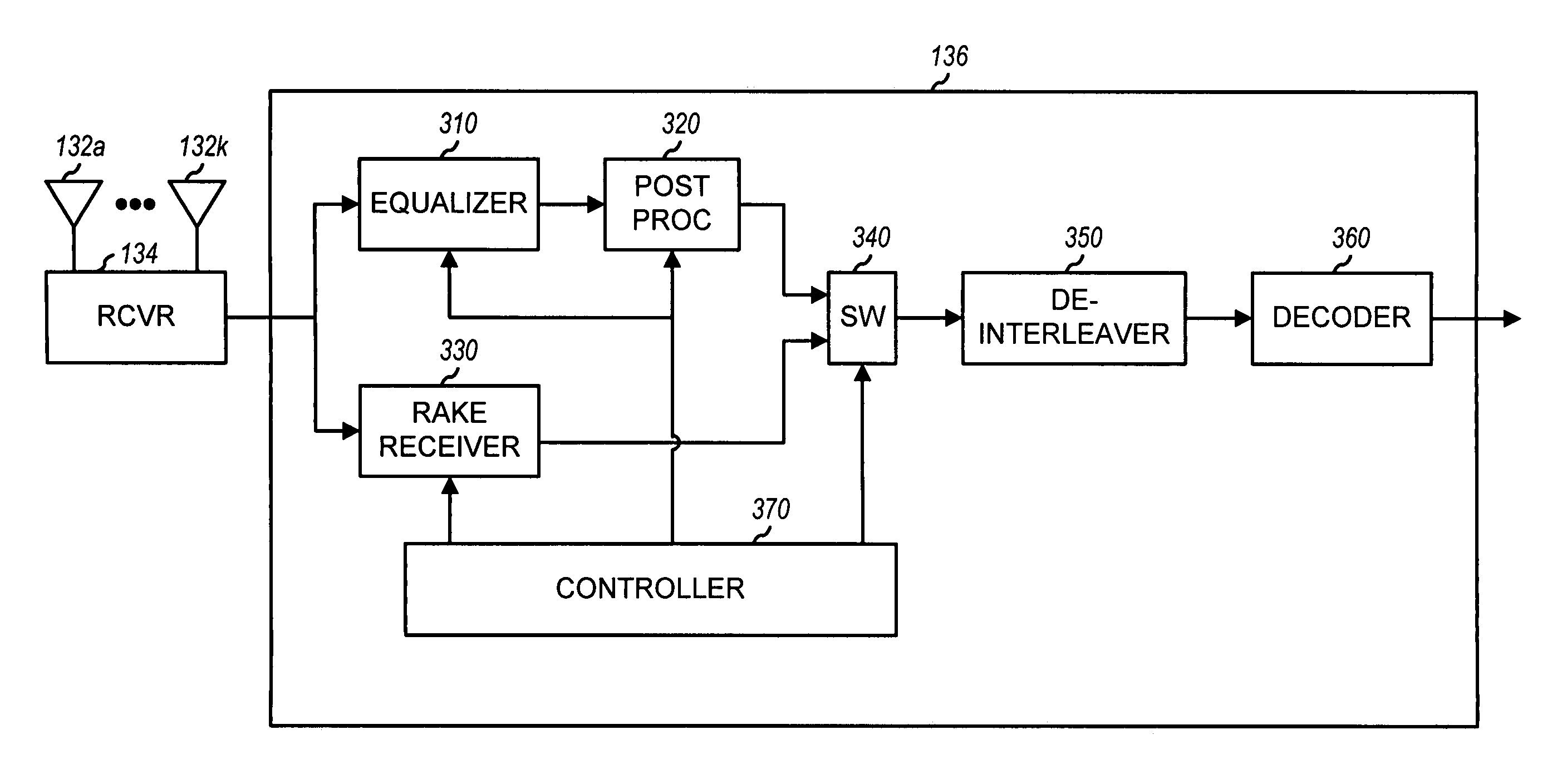
Method and apparatus for processing a modulated signal using an equalizer and a rake receiver
InactiveUS7082174B1Improve performanceImprove signal-to-noise ratioTransmission control/equlisationSpatial transmit diversitySignal qualityRake receiver
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
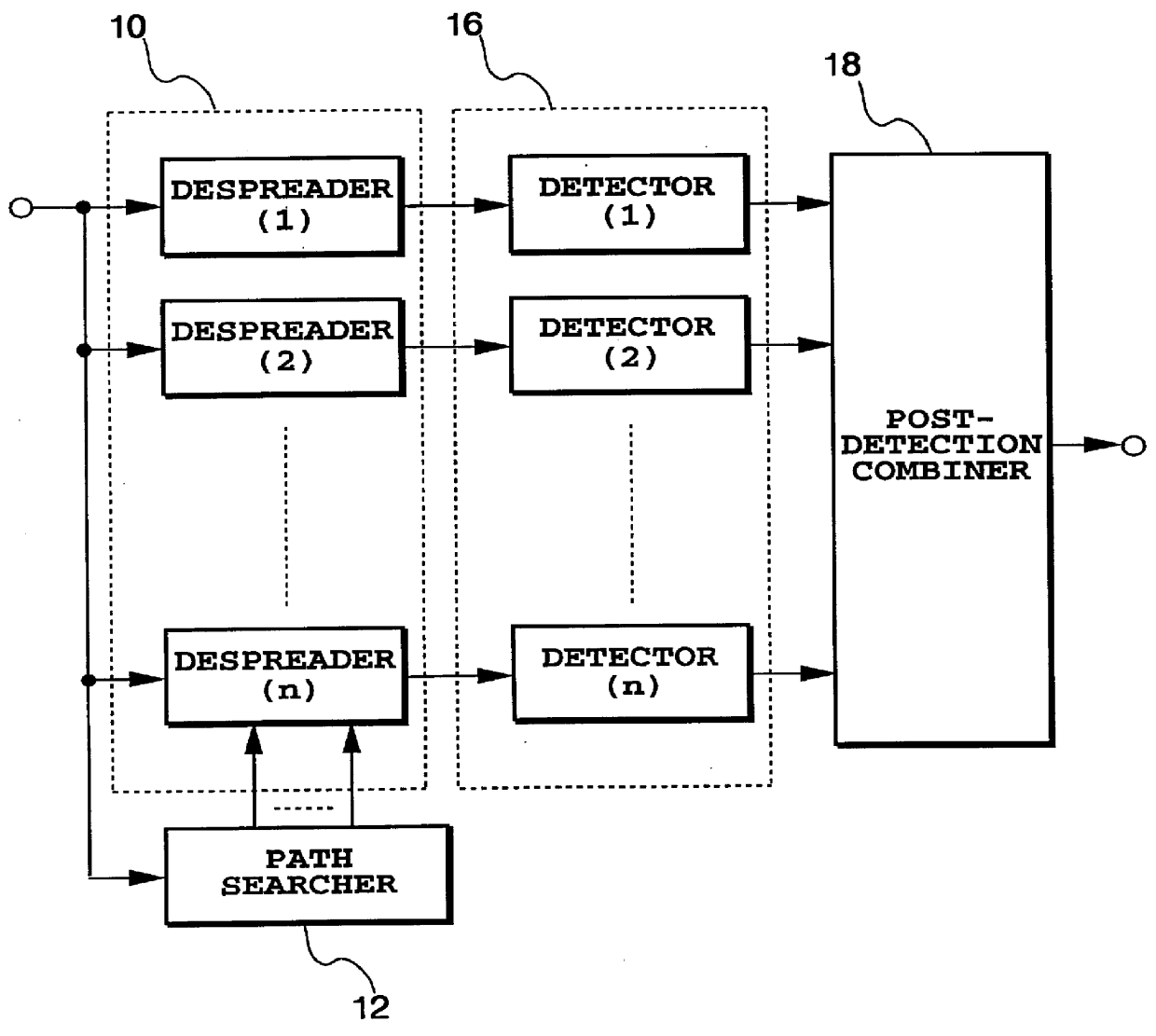
Rake receiver
A RAKE receiver which is employed in a direct sequence spread spectrum communication system, and which can effectively receive multipath signals. A path searcher measures the amplitude of each path, selects N paths with larger amplitudes in descending order of magnitude, where N is the number of despreaders, and assigns the despreaders to the selected paths to despread the signals of the paths. This assignment of the despreaders to the paths is carried out such that a path with a large amplitude and a path with a small amplitude are assigned to adjacent despreaders and are input to the same pre-detection combiner. The outputs of the despreaders are combined by the pre-detection combiners, and detected by detectors whose outputs are RAKE combined by a post-detection combiner.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
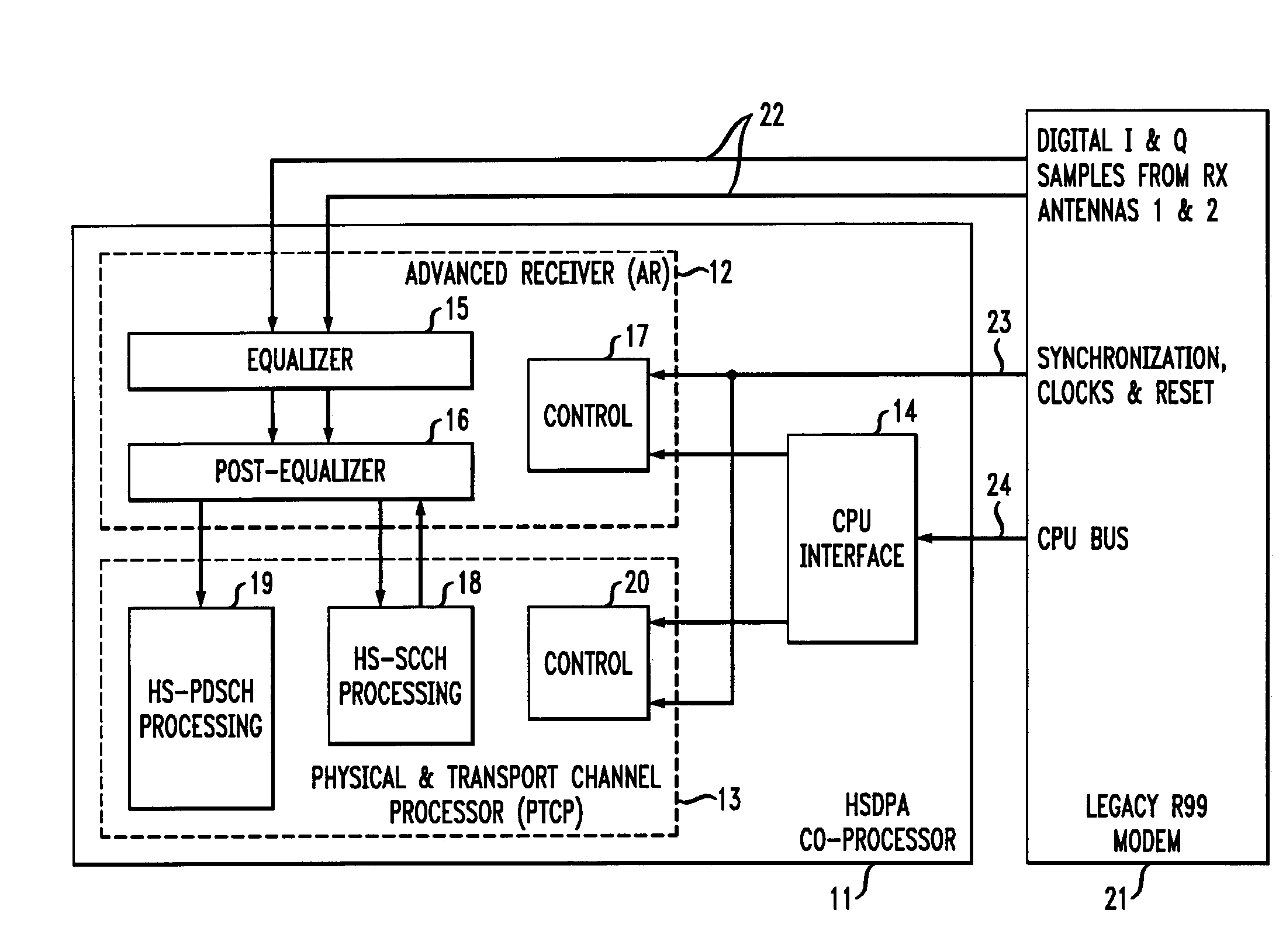
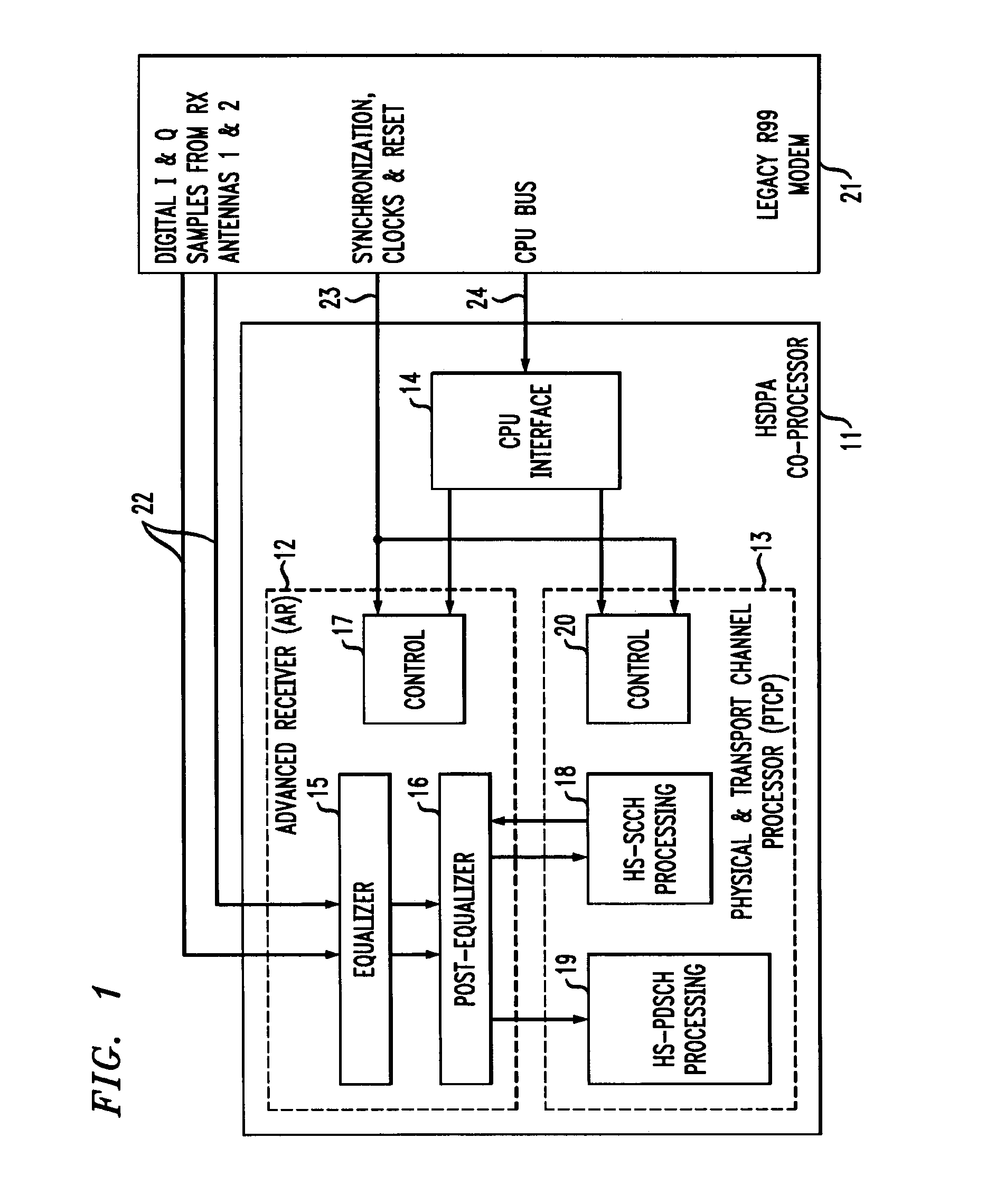
Hsdpa co-processor for mobile terminals
InactiveUS20090296798A1Improve reception performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCMOSCoprocessor
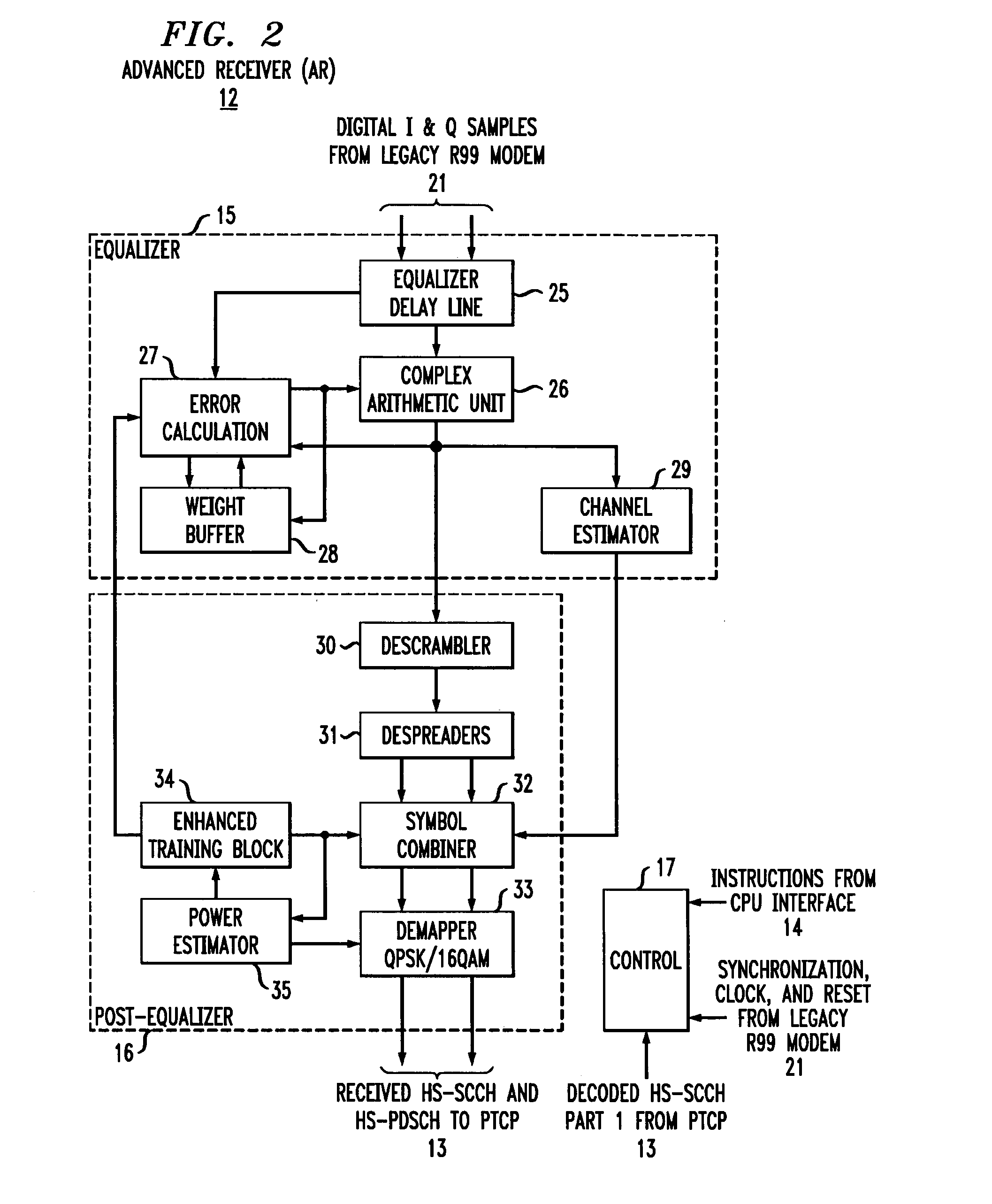
In one embodiment, an HSDPA co-processor for 3GPP Release 6 Category 8 (7.2 Mb / s) HSDPA that provides all chip-rate, symbol-rate, physical-channel, and transport-channel processing for HSDPA in 90 nm CMOS. The co-processor design is scalable to all HSDPA data rates up to 14 Mb / s. The coprocessor implements an Advanced Receiver based on an NLMS equalizer, supports RX diversity and TX diversity, and provides up to 6.4 dB better performance than a typical single-antenna rake receiver. Thus, 3GPP R6 HSDPA functionality can be added to a legacy R99 modem using an HSDPA co-processor consistent with embodiments of the present invention, at a reasonable incremental cost and power.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
Apparatus and methods for finger delay selection in RAKE receivers
InactiveUS6922434B2Facilitate canceling out known interfering signalTransmissionTelecommunicationsRake receiver
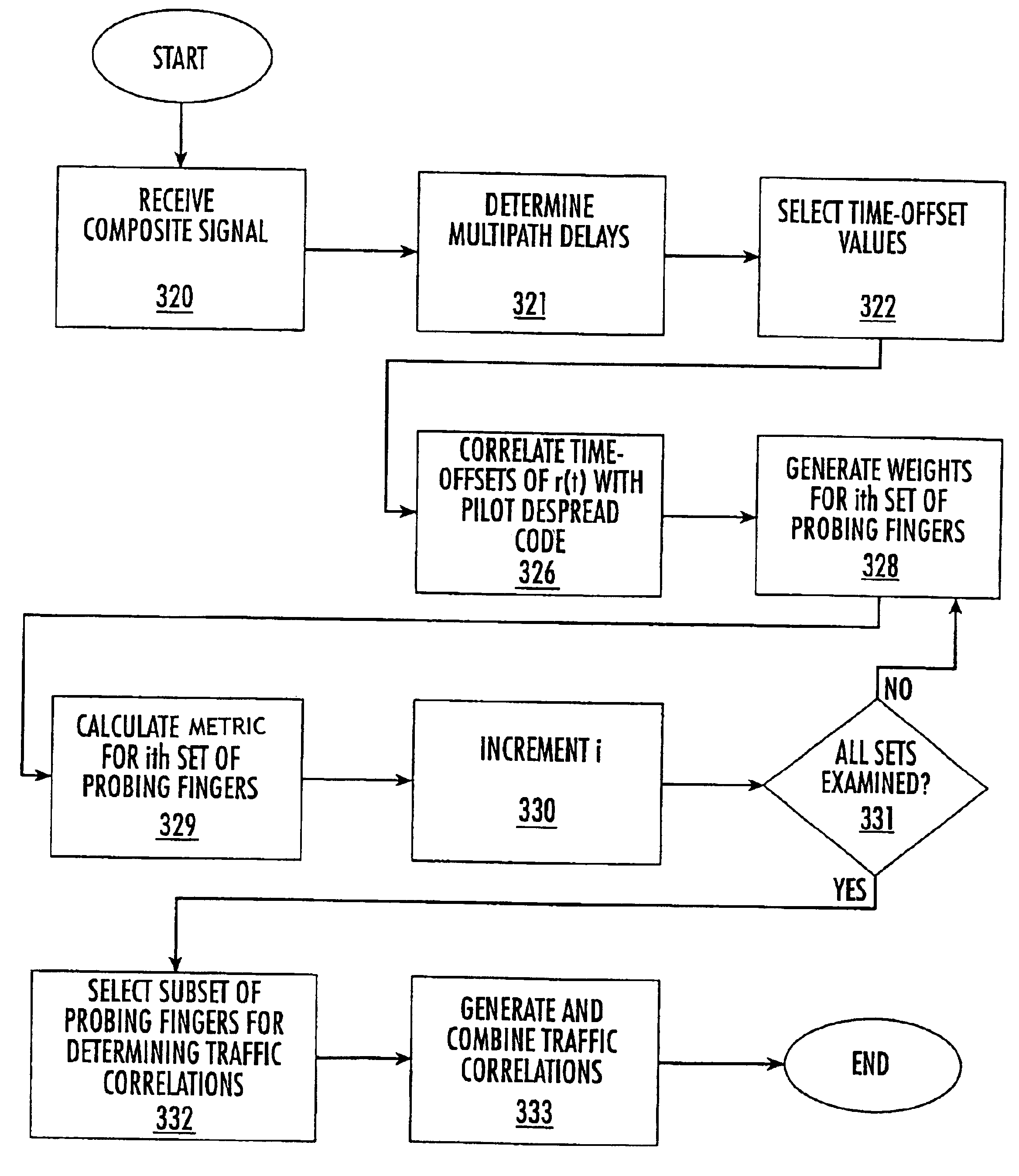
Methods of recovering information encoded in a spread spectrum signal transmitted according to a spreading sequence in a communications medium are provided in which a spread spectrum signal is received from the communications medium and correlated with a spreading sequence to produce a plurality of time-offset correlations. Some of these time-offset correlations may be designed to cancel out known interfering signals. A subset of the plurality of time-offsets may then be selected, and corresponding traffic correlations may then be combined using a weighted combination to estimate information encoded in the transmitted spread spectrum signal. Receivers for implementing these methods are also provided.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Method for compressive sensing , reconstruction, and estimation of ultra-wideband channels
InactiveUS20140140375A1Improve sparsityReasonable complexityTransmissionUltra-widebandRound complexity
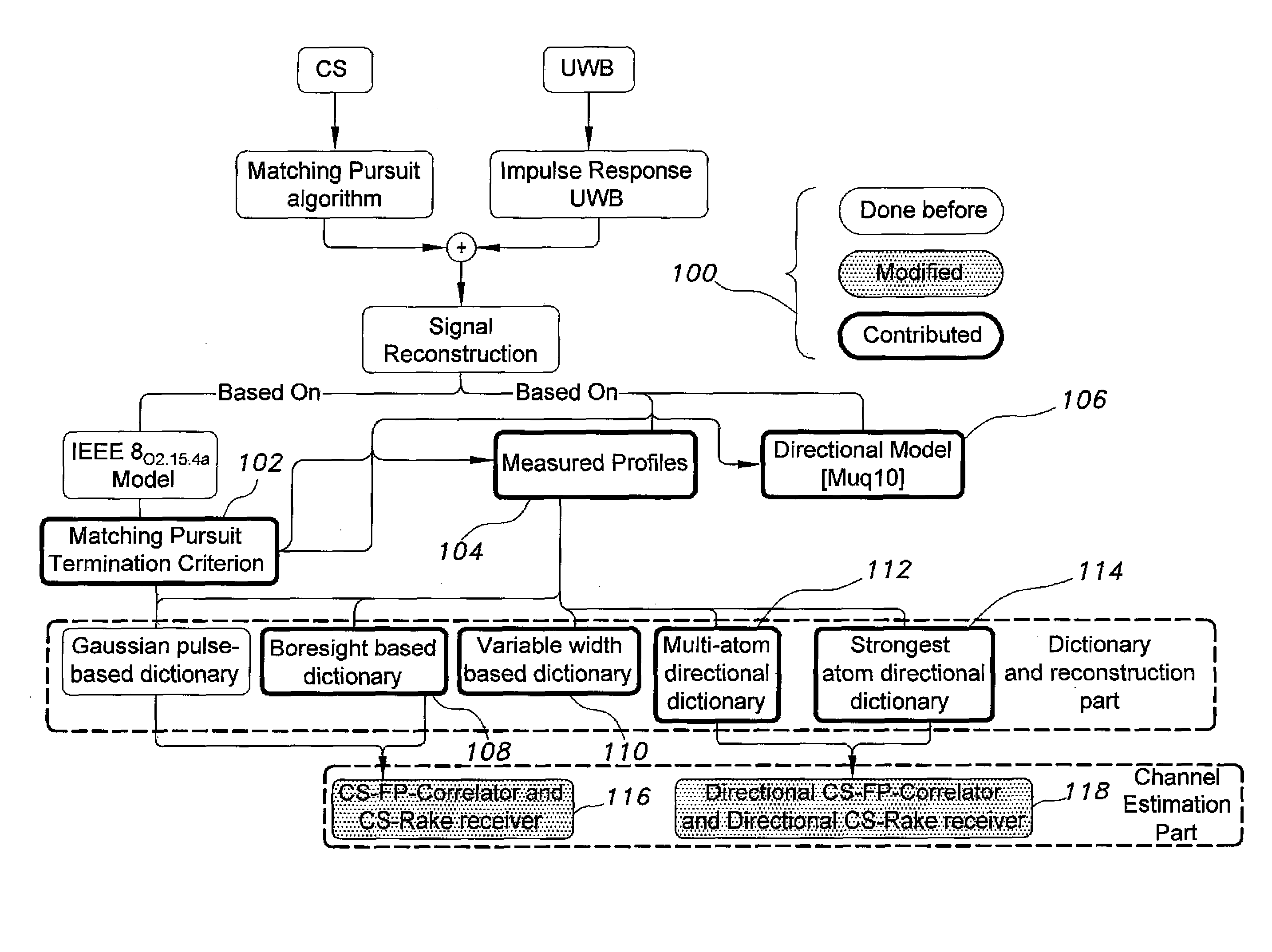
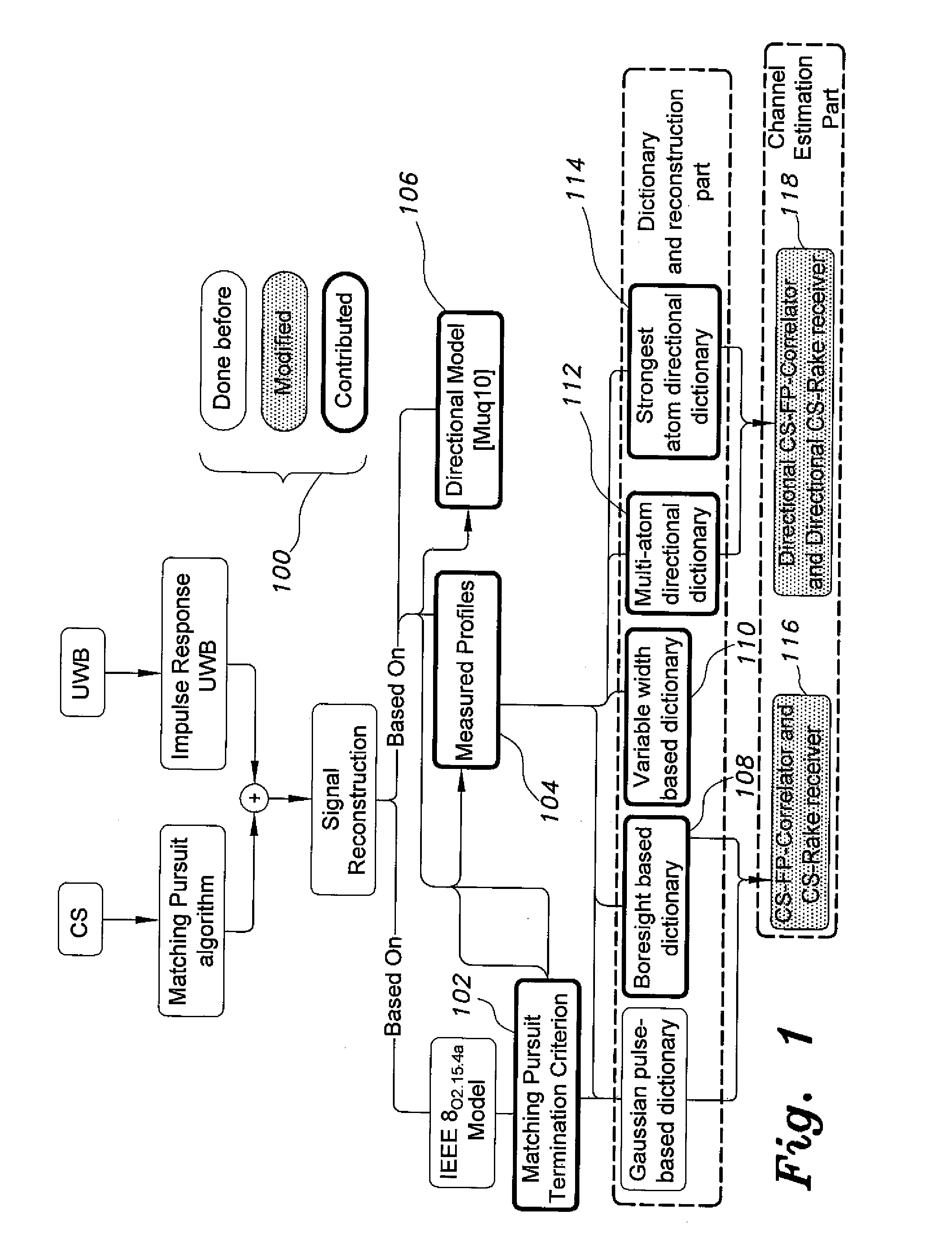
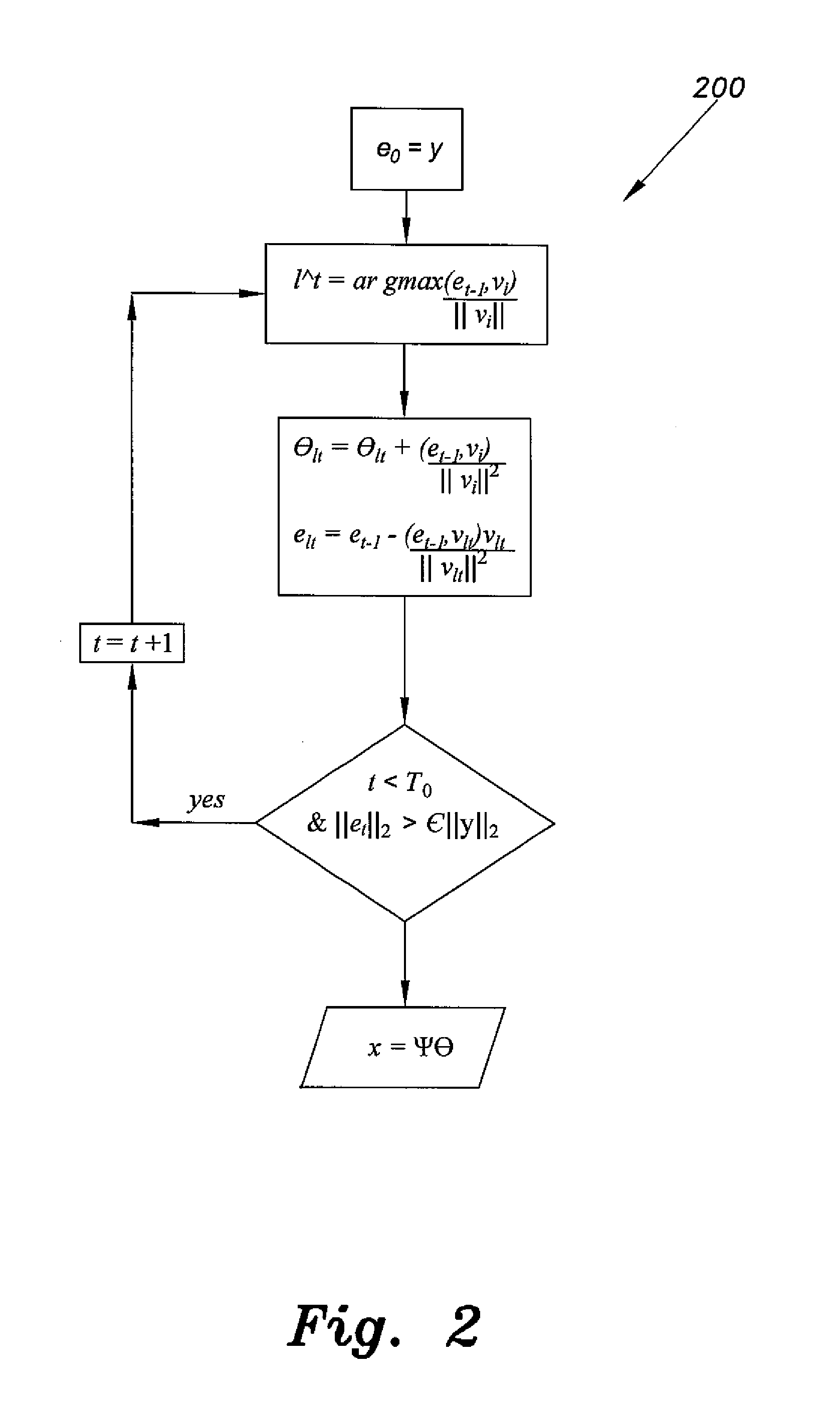
The method for compressive sensing (CS) and reconstruction of ultra-wideband (UWB) channels includes building four practically-based dictionaries related to the antenna angles of transmission and angles of arrival that enhance the sparsity of UWB signals. The dictionaries account for the practical effects of the channel, such as pulse dispersion and the unavoidable effects of the antenna. Utilizing the practically-based dictionaries CS is able to reconstruct the UWB signals more efficiently with reasonable complexity. In addition to waveform reconstruction, the dictionaries are used for channel estimation. The CS method can be used with either a single-shot full profile correlator or a Rake receiver. The Rake receiver employs CS in adjusting its parameters to take advantage of the energy available in the strongest propagation paths.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
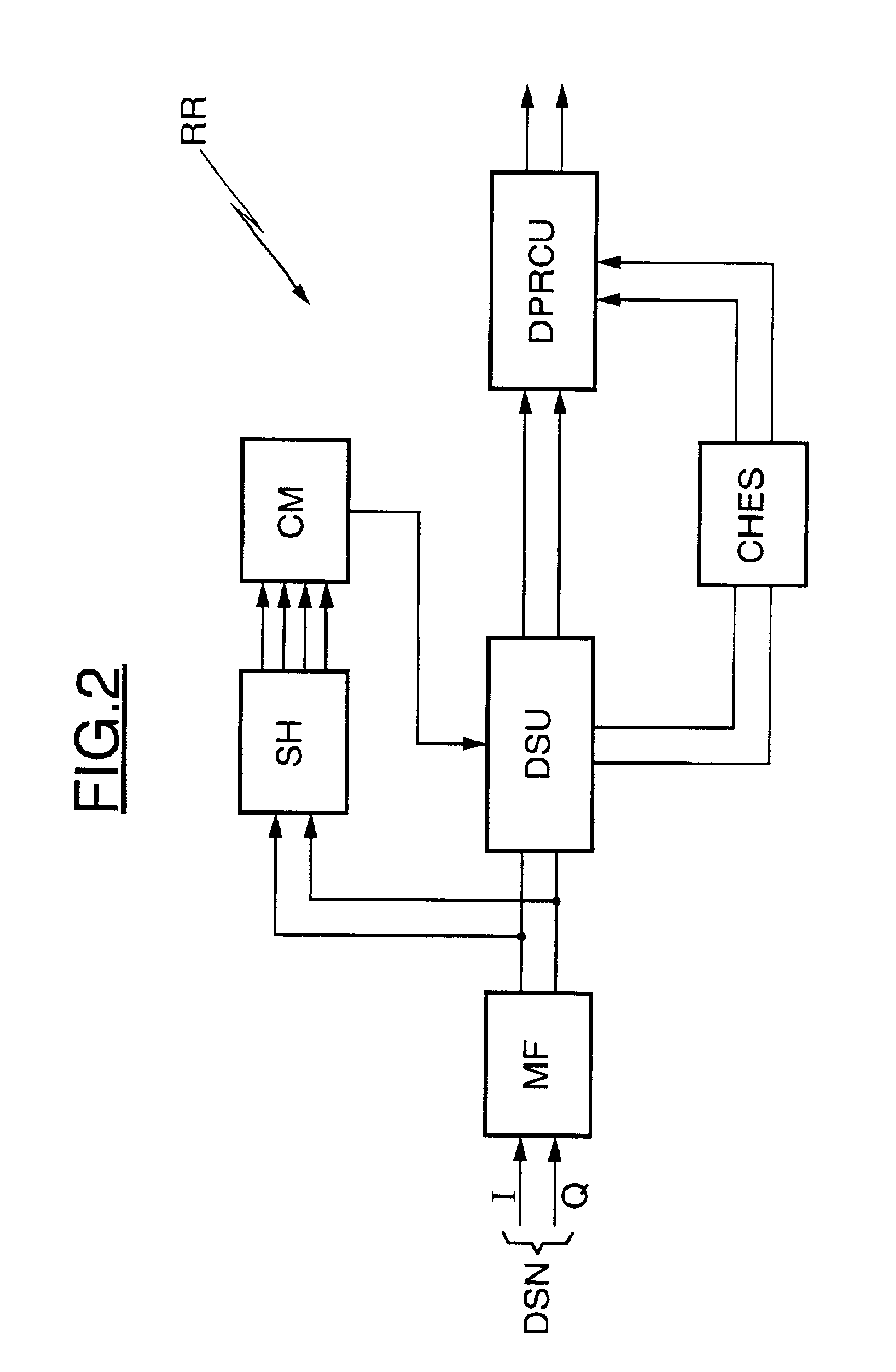
Radio receiver and channel estimator
The present invention is related to a Rake receiver (R1) for receiving a radio signal and to a searcher (S8a, S8b) for estimating the delay profile of one or more radio links. The searcher includes means for estimating delay profiles in separate windows. The searcher is arranged for being switched into a single window mode or alternatively into a multiple window mode. In single window mode the delay profiles of separate radio links are estimated in the windows, while in multiple window mode two or more windows are allocated adjacent in time for estimating the delay profile of the same radio link. Thereby, the use of the resources of the searcher can be adapted to the radio environments in which the searcher will be used. The Rake receiver comprises fingers that are grouped into two sets. Within a set of fingers the propagation paths are time aligned. The output from the two set of fingers are time aligned and then combined.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and apparatus for processing a modulated signal using an equalizer and a rake receiver
InactiveUS20060056496A1Improve performanceImprove signal-to-noise ratioMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationSignal qualityEngineering
In a method for achieving higher S / N, one or more signals are received and processed to provide one or more streams of samples. In a first processing scheme, the sample stream(s) are equalized within an equalizer to generate symbol estimates, which may be subsequently processed (e.g., despread and decovered) to provide a first stream of recovered symbols. Each sample stream is filtered with a set of coefficients and may be scaled with a scaling factor. The scaled samples for all streams are then combined to generate the symbol estimates. The sample stream(s) may also be processed by a second processing scheme with one or more rake receivers to provide a second stream of recovered symbols. The signal quality for each processing scheme can be estimated and used to select either the first or second processing scheme.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Minimizing estimation time for rake fingers with help of a speed sensor
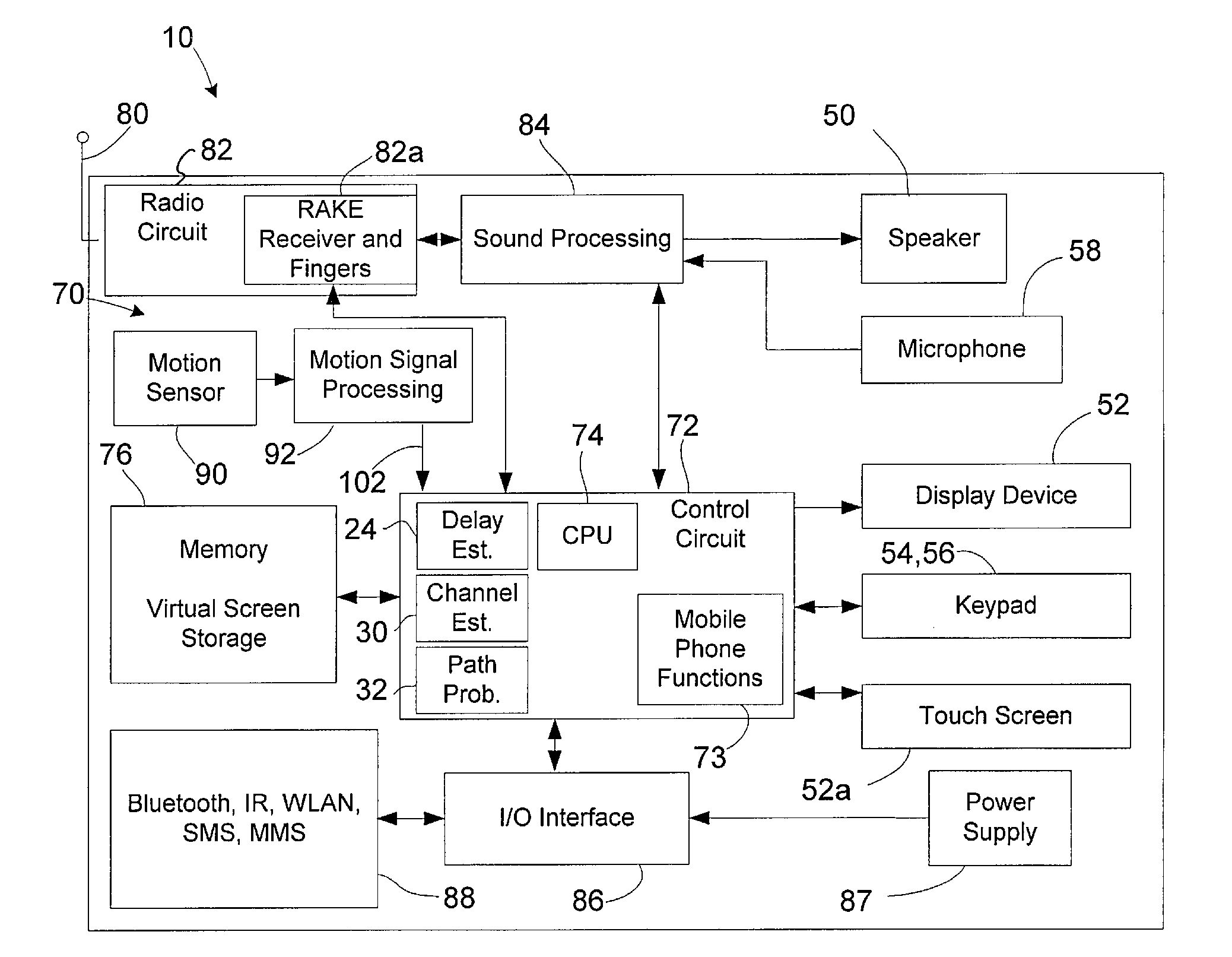
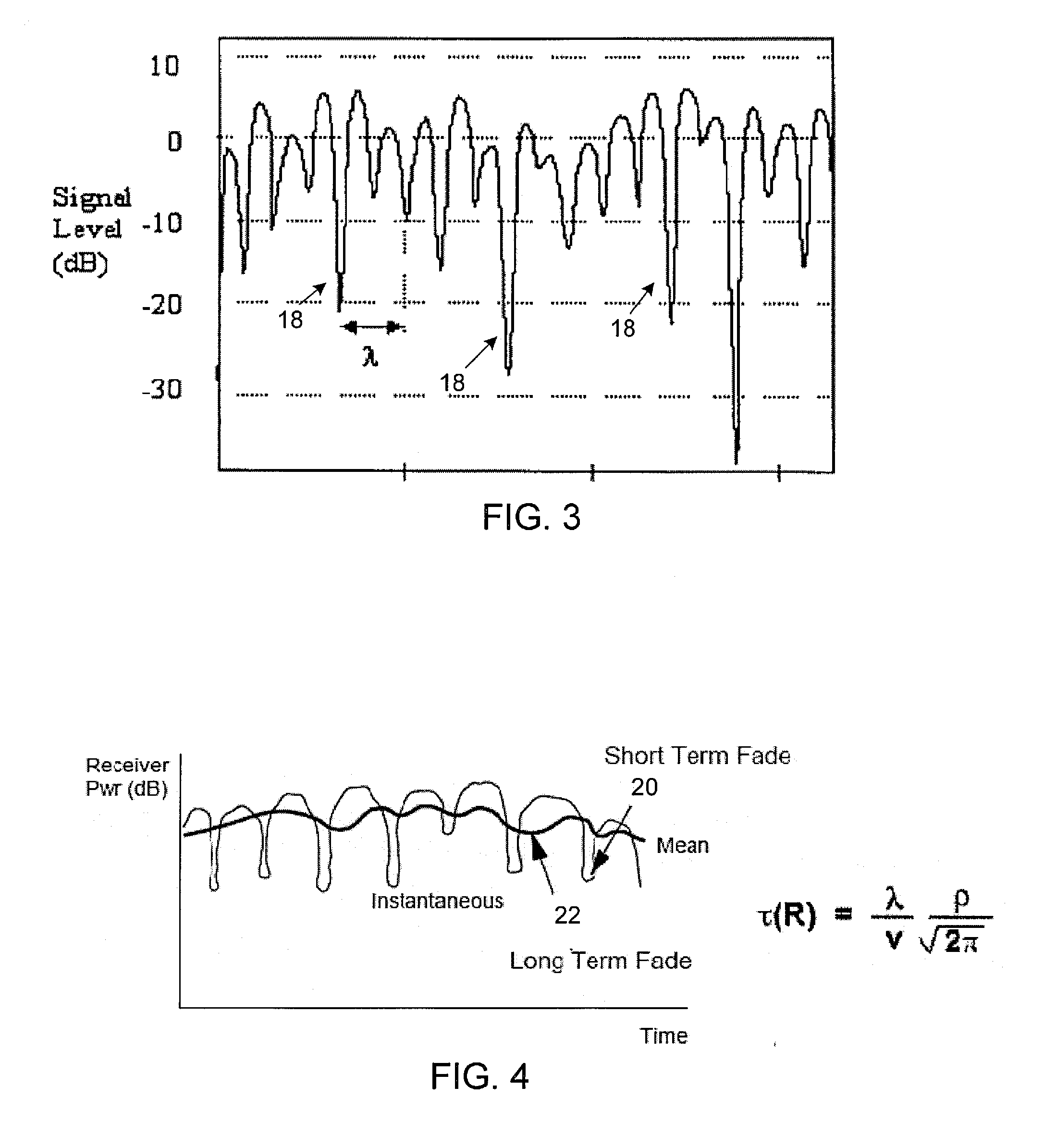
An electronic equipment includes a RAKE receiver that includes at least one finger having a settable delay, a transducer operable to provide a signal indicative of motion of the electronic equipment, and a delay estimator circuit operative to calculate a duration between fading nulls of a received signal based on the motion signal of the electronic equipment. The time delay of the at least one finger is set based on the duration between fading nulls.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Method for improved extraction in CDMA systems
InactiveUS7050481B1Overcome problemsRadio transmission for post communicationRake receiverSignal extraction
In a method for improving signal extraction in a code division multiple access (CDMA) telecommunications system, a first iteration of interference cancellation is performed on the basis of bit rates for every signal which are the same as those in a previous frame of the same signal. Filtered and down-converted signals are demodulated in Rake receivers to provide output signals corresponding to decision variables and channel estimates. The decision variables are limited and remodulated and respread prior to the signals being reconstructed using the channel estimates. The reconstructed signals are summed, and each signal is subtracted from the sum to provide an ‘interference’ signal which is then used to obtain the individual signals. Each signal is then demodulated a second time in another Rake receiver to provide a tentative DPDCH signal, a TFI signal, a TPC signal and a SNI signal. The TFI signal is processed to provide a signal indicative of the bit rate which is used to both decode the DPDCH signal providing a data output and to provide an estimate of the bit rate for a subsequent frame of the same signal.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
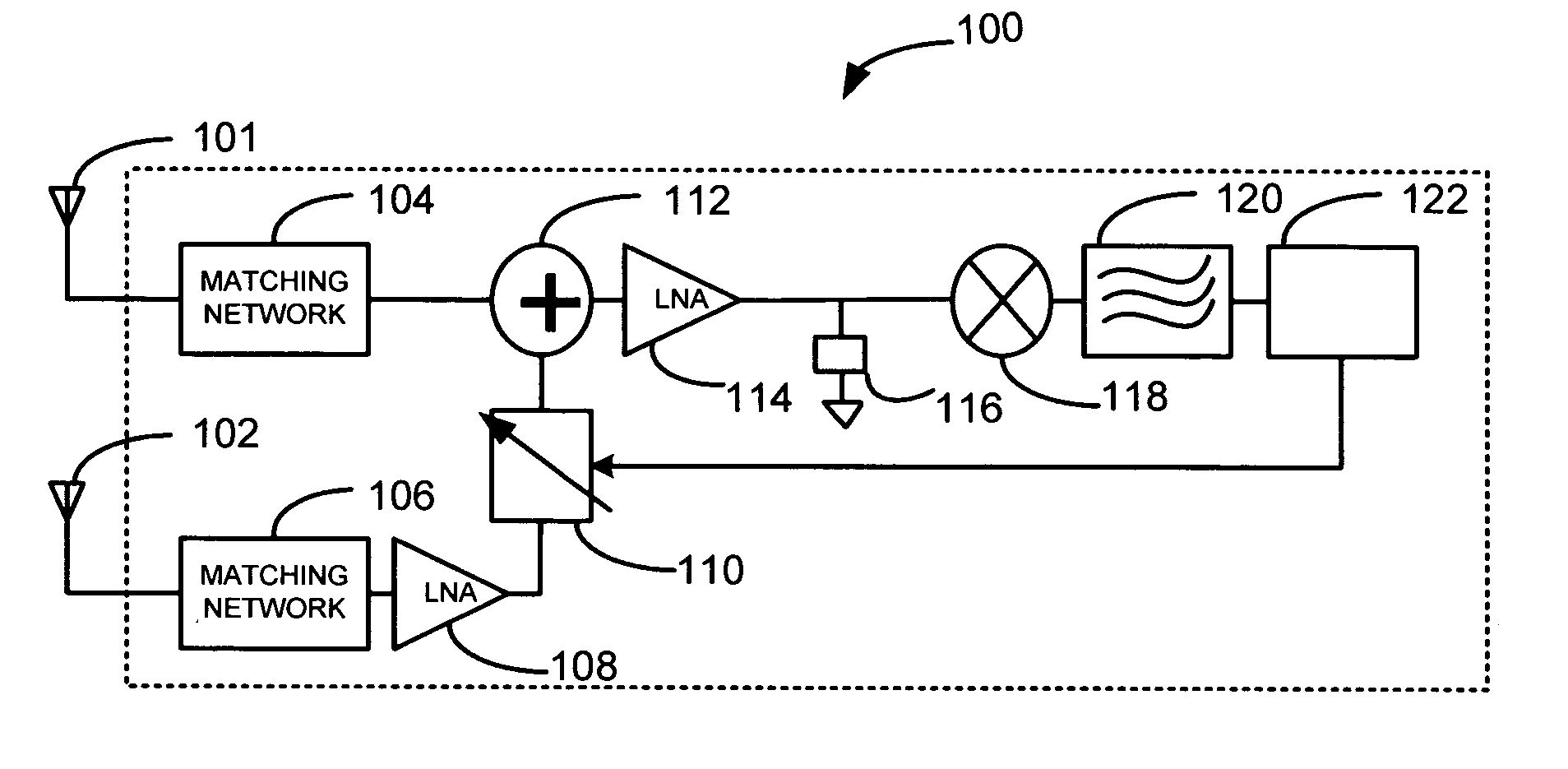
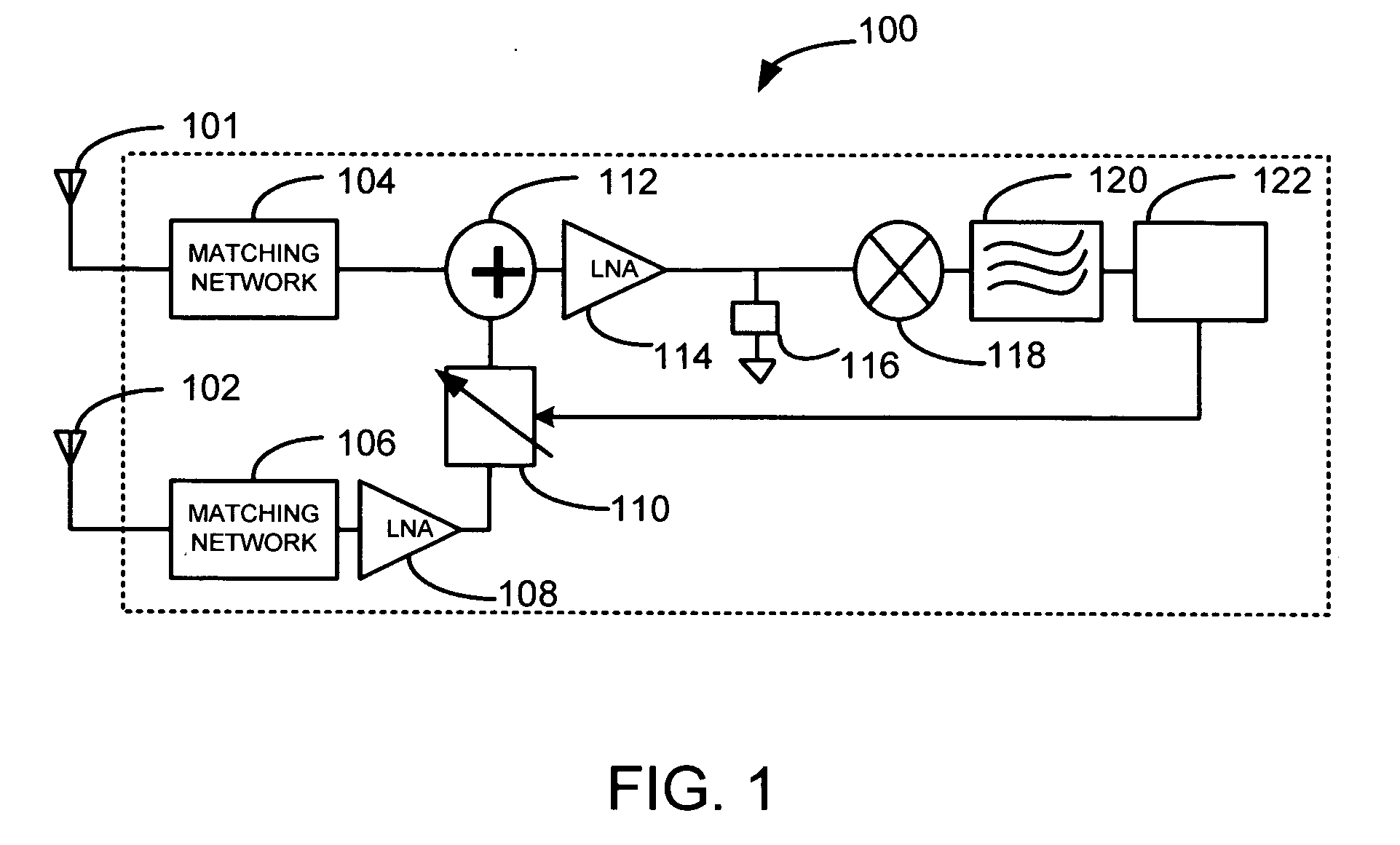
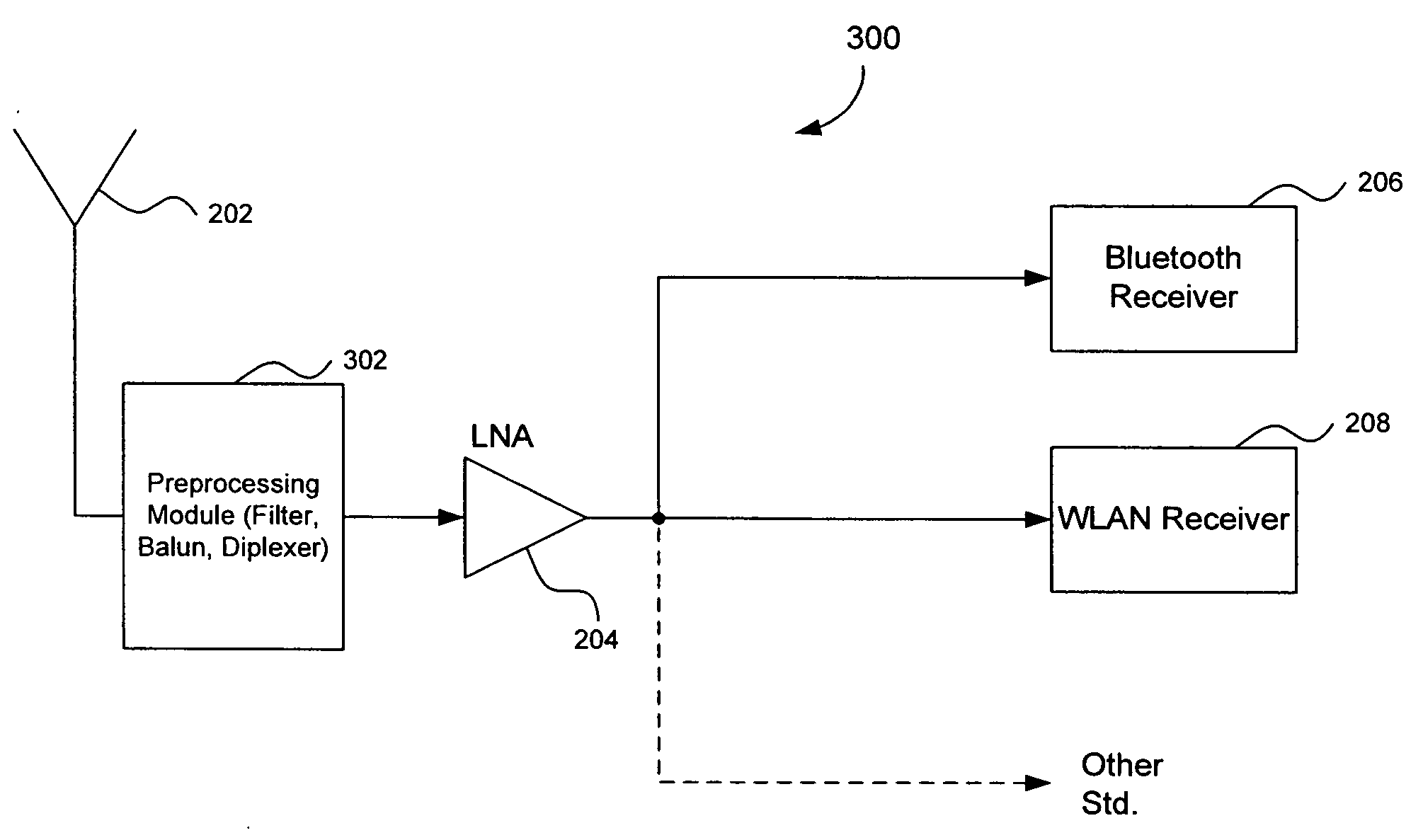
Radio receiver with shared low noise amplifier for multi-standard operation in a single antenna system
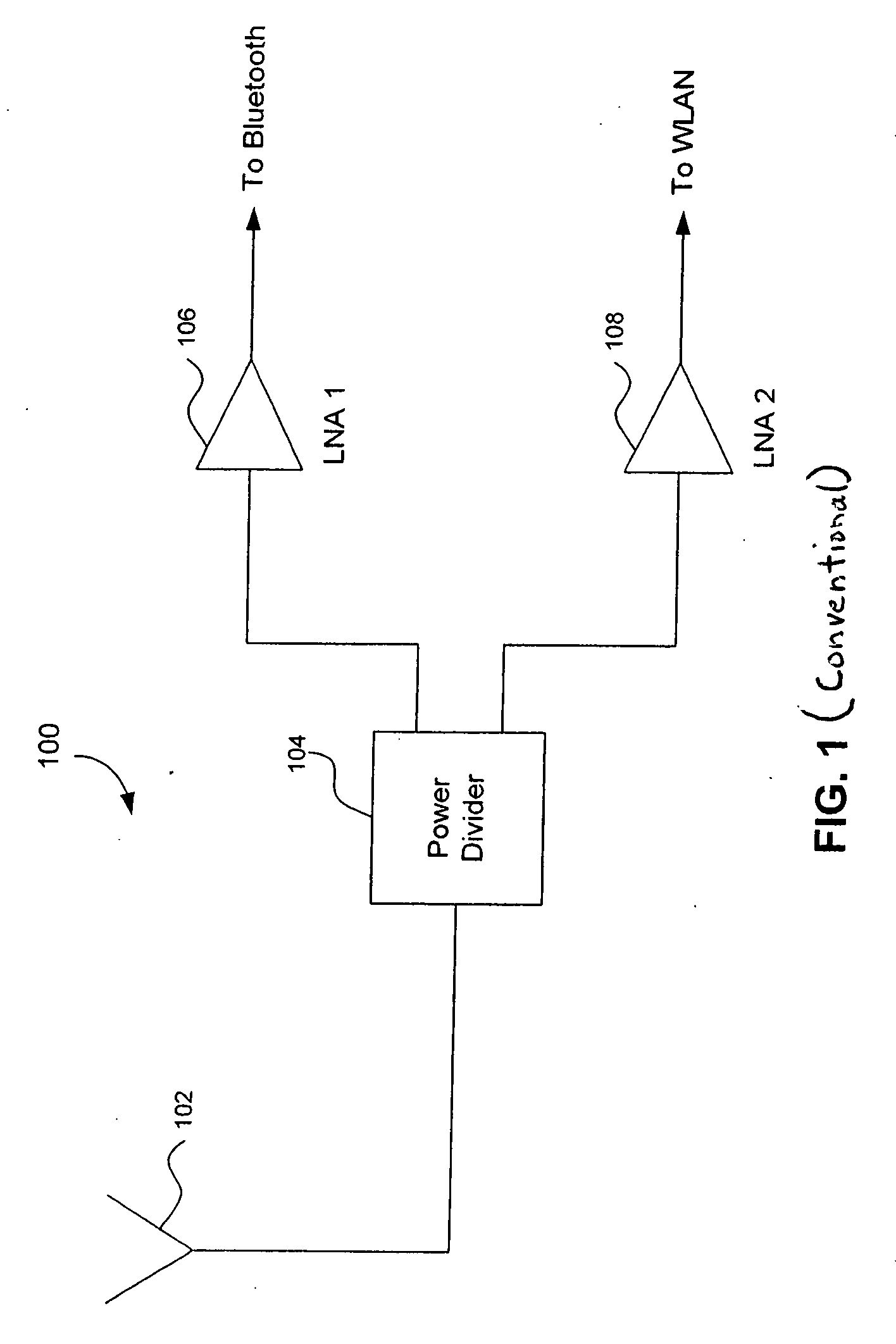
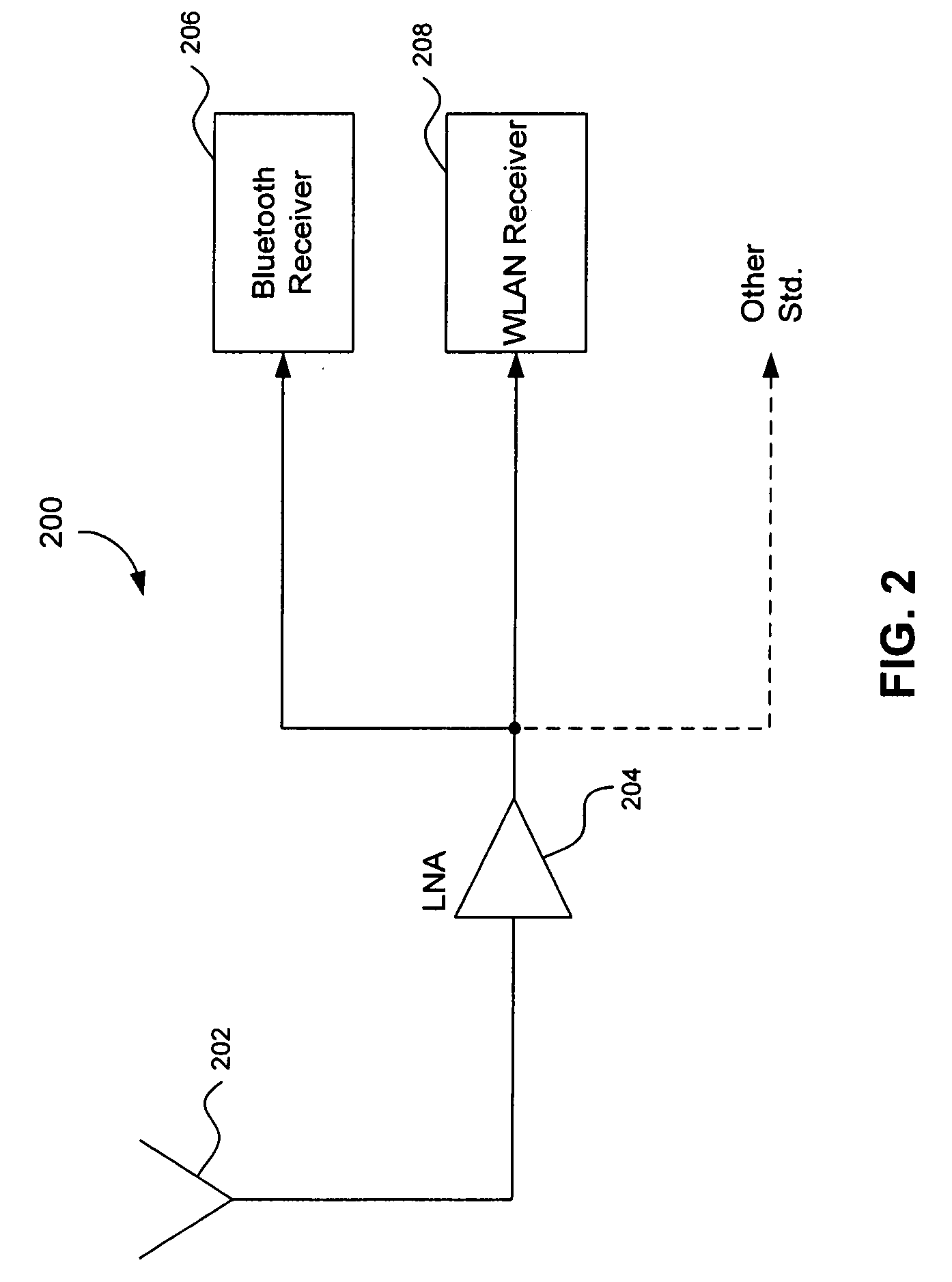
A radio receiver is described that processes multiple wireless standards using a single antenna according to embodiments of the invention. The radio receiver includes a single antenna, and a low noise amplifier that is connected to the antenna, without an intervening power divider or power splitter. The output of the low noise amplifier feeds multiple wireless receivers in a parallel arrangement that are operating according to different communications standards, including for example a Bluetooth receiver, and a WLAN 802.11 receiver. Additional wireless standards and their corresponding receivers could be added as well. The input impedance of the low noise amplifier defines the impedance seen by the antenna, regardless of which operational standard is actually in use. Since the input impedance of the low noise amplifier is substantially independent of whether the Bluetooth or WLAN paths are ON or OFF, simultaneous operation can be accomplished.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
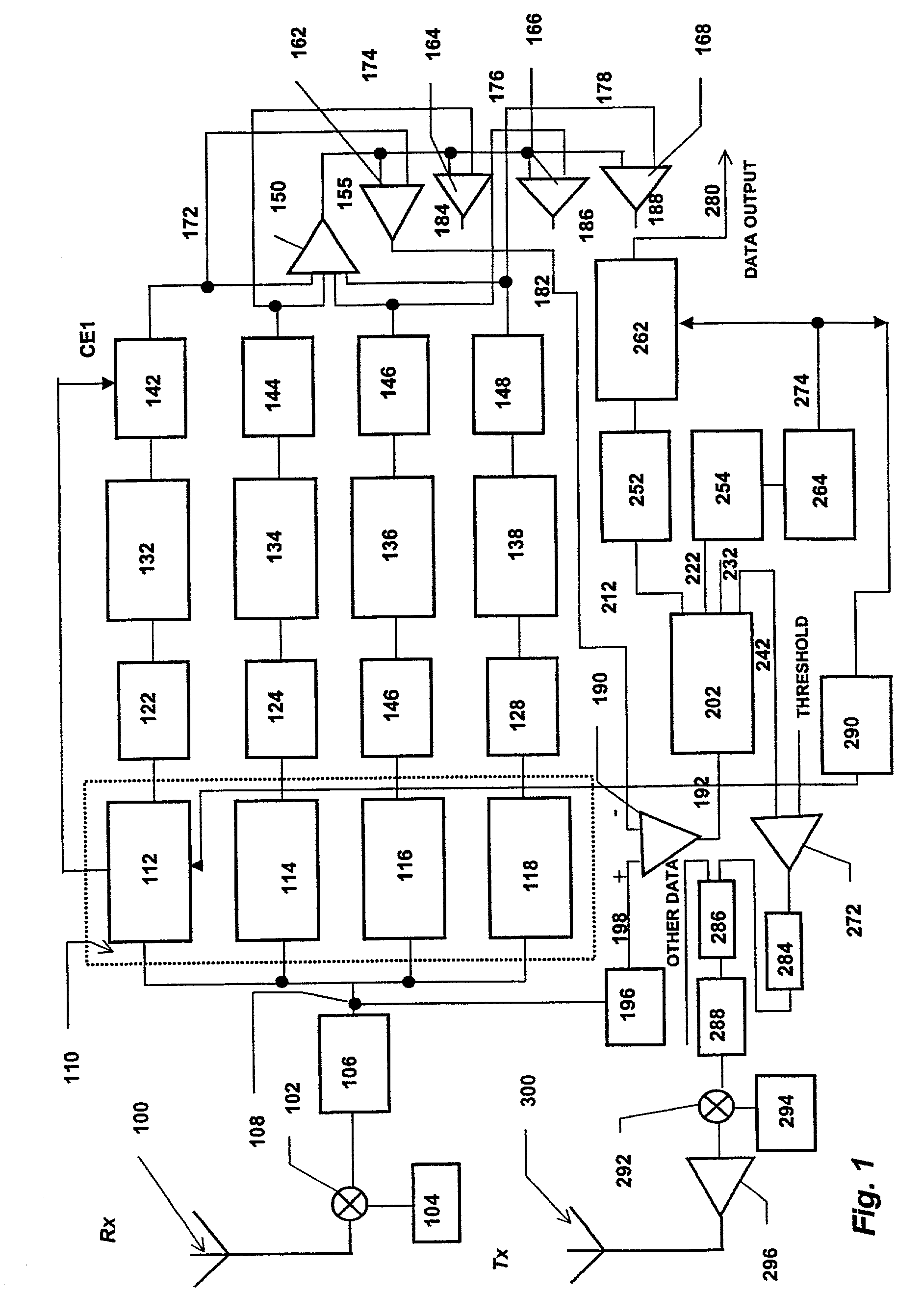
Rake receiver for a CDMA system, in particular incorporated in a cellular mobile phone
A rake receiver uses a delayed version of the received sequence and a delayed version of a scrambling code. The flexible hardware structure of the time-aligning and descrambling unit includes at least two delay chains and one multiplier. By controlling two multiplexers, the delayed versions of the received sequence can be multiplied with an arbitrary scrambling code having an arbitrary phase. During one chip period, one multiplication is performed for each path to be processed.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
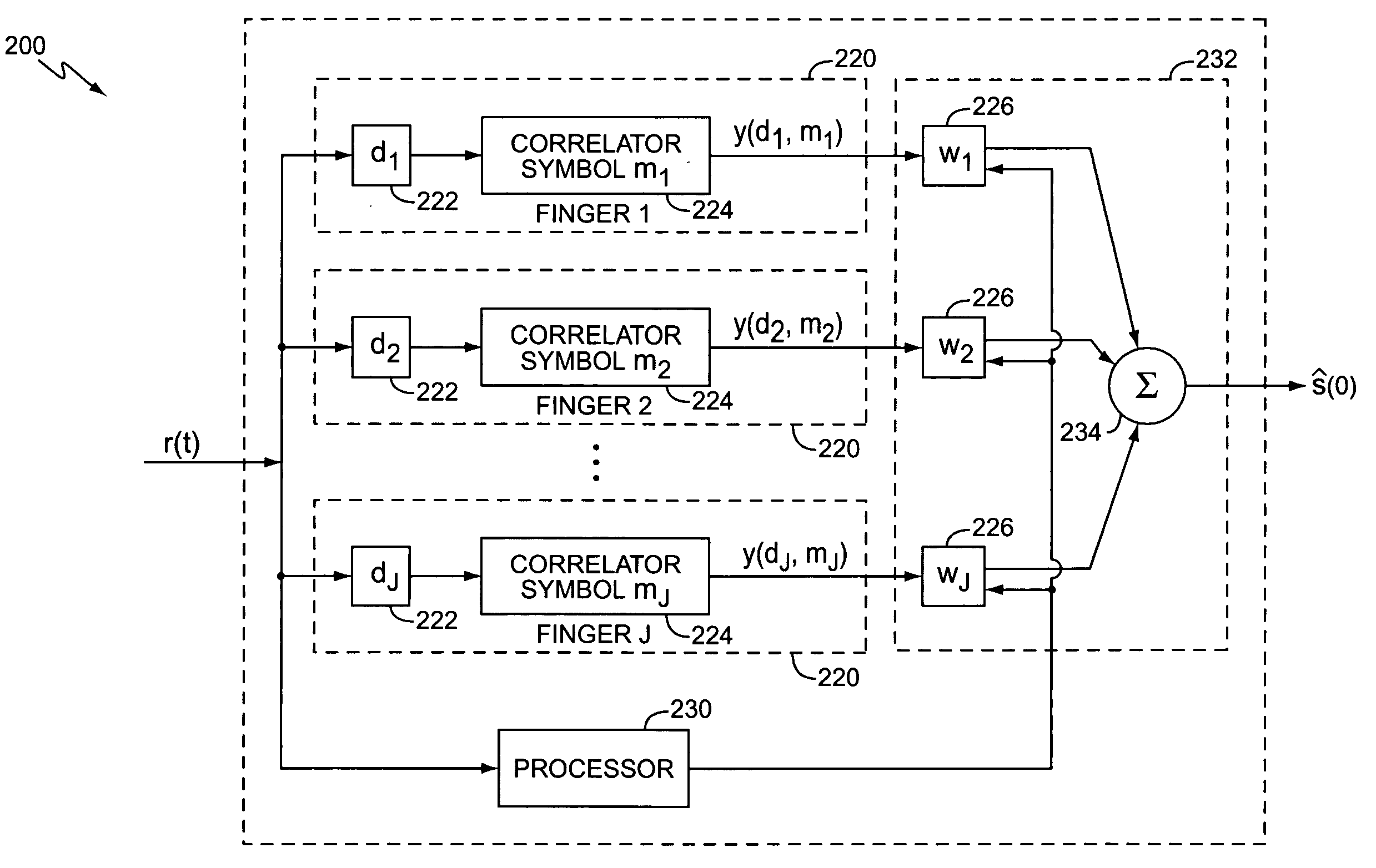
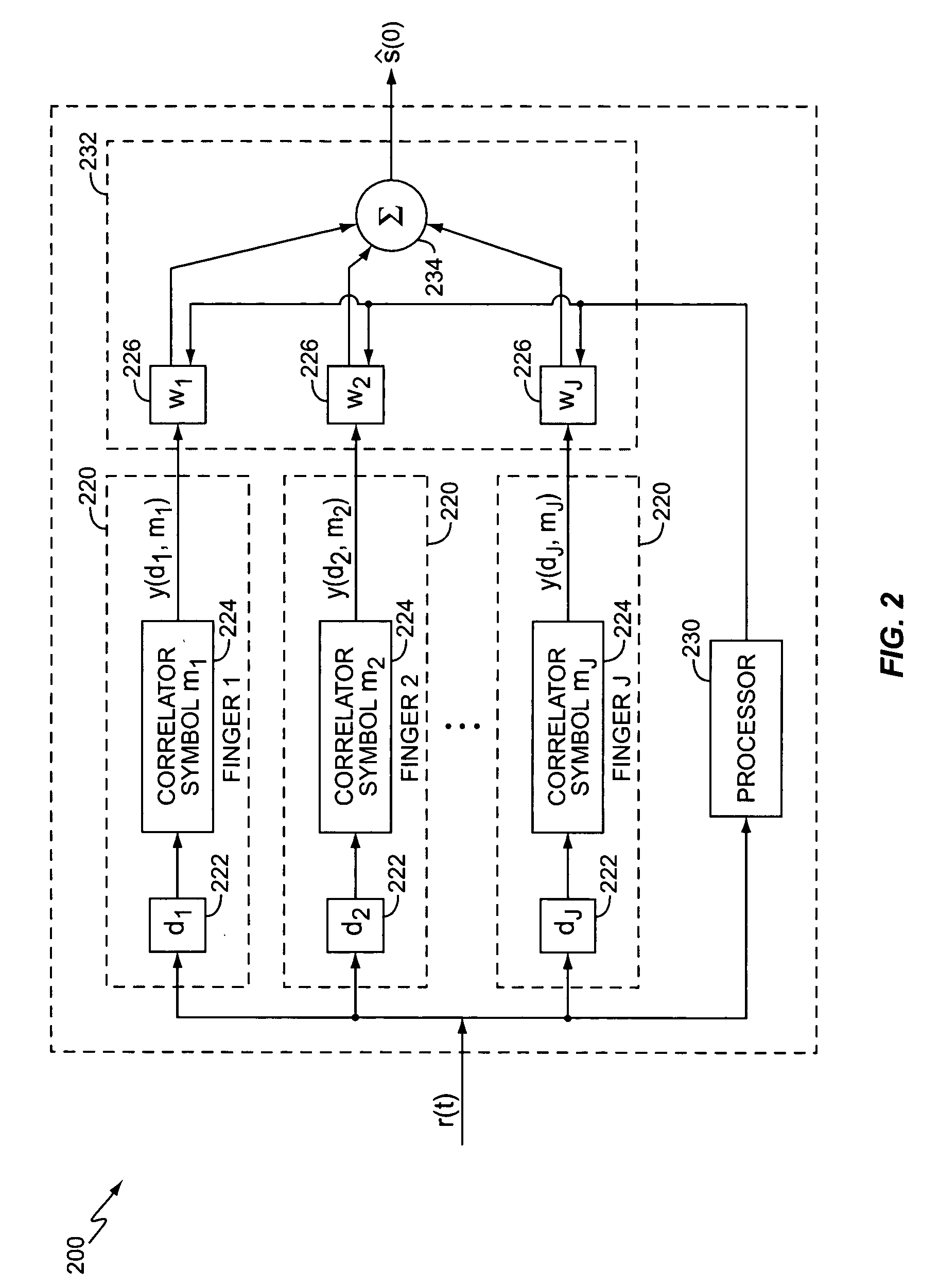
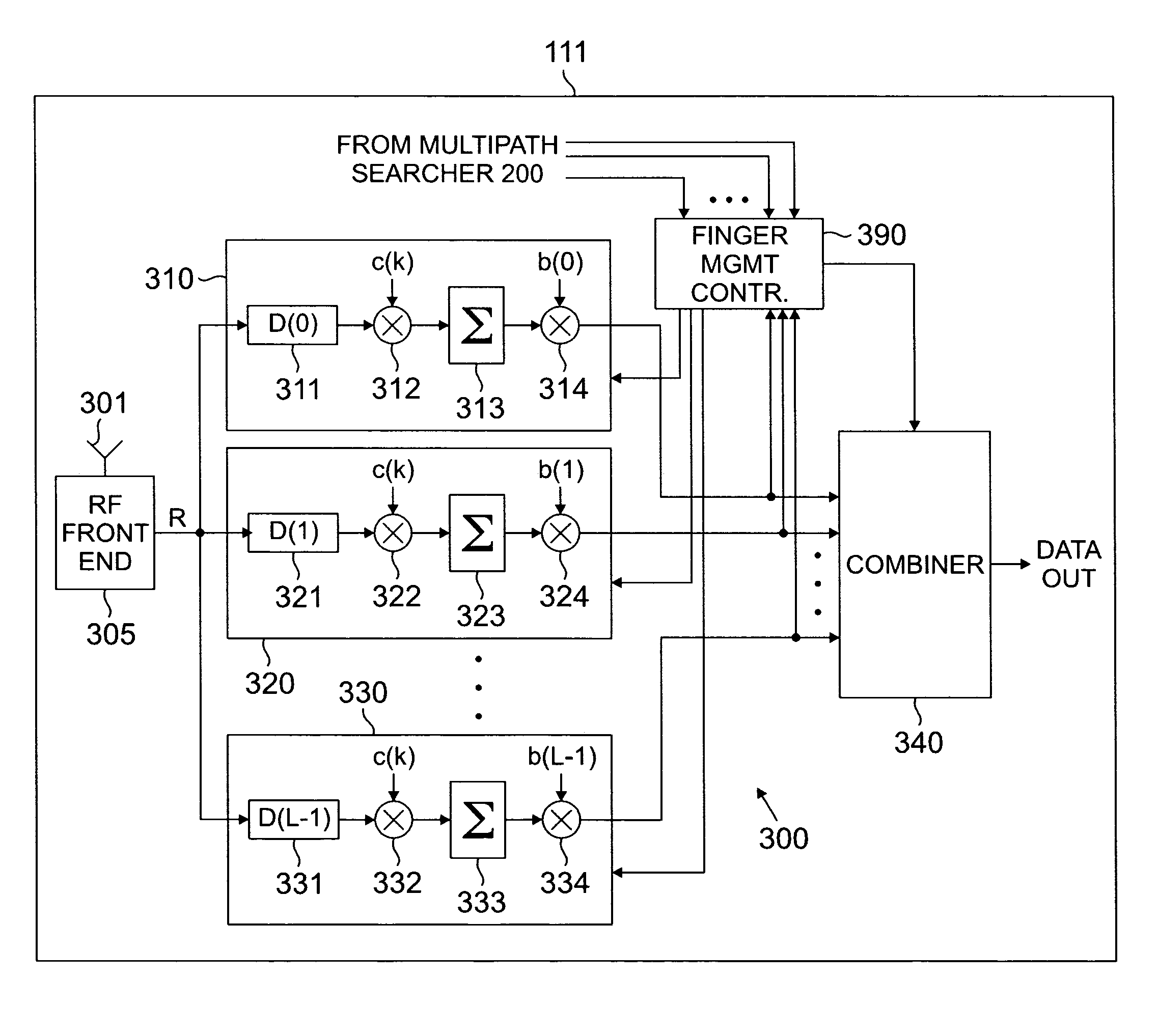
System and method for finger management in a rake receiver
In a RAKE receiver capable of detecting and combining a plurality of multipath signals, a controller for managing the assignment of the plurality of multipath signals to fingers of the RAKE receiver. The controller determines a phase difference between a selected multipath signal and a first multipath signal assigned to a first finger of the RAKE receiver and does not assign the selected multipath signal to a second finger of the RAKE receiver unless the phase difference is greater than one-half chip. If the phase difference is less that one-half chip, the controller assigns the stronger of the selected multipath signal and the first multipath signal to the first finger of the RAKE receiver. If the finger power falls below a certain threshold, the finger internal states (viz. channel estimate and delay estimate) are maintained while the output of the finger is not processed. If the finger power exceeds the threshold anytime within a specified time interval, the normal activities of the finger are restored. If the power remains lower than the threshold for that time period, the finger is deactivated.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Universal rake receiver
InactiveUS20030142726A1Spatial transmit diversityFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationModularityOperation mode
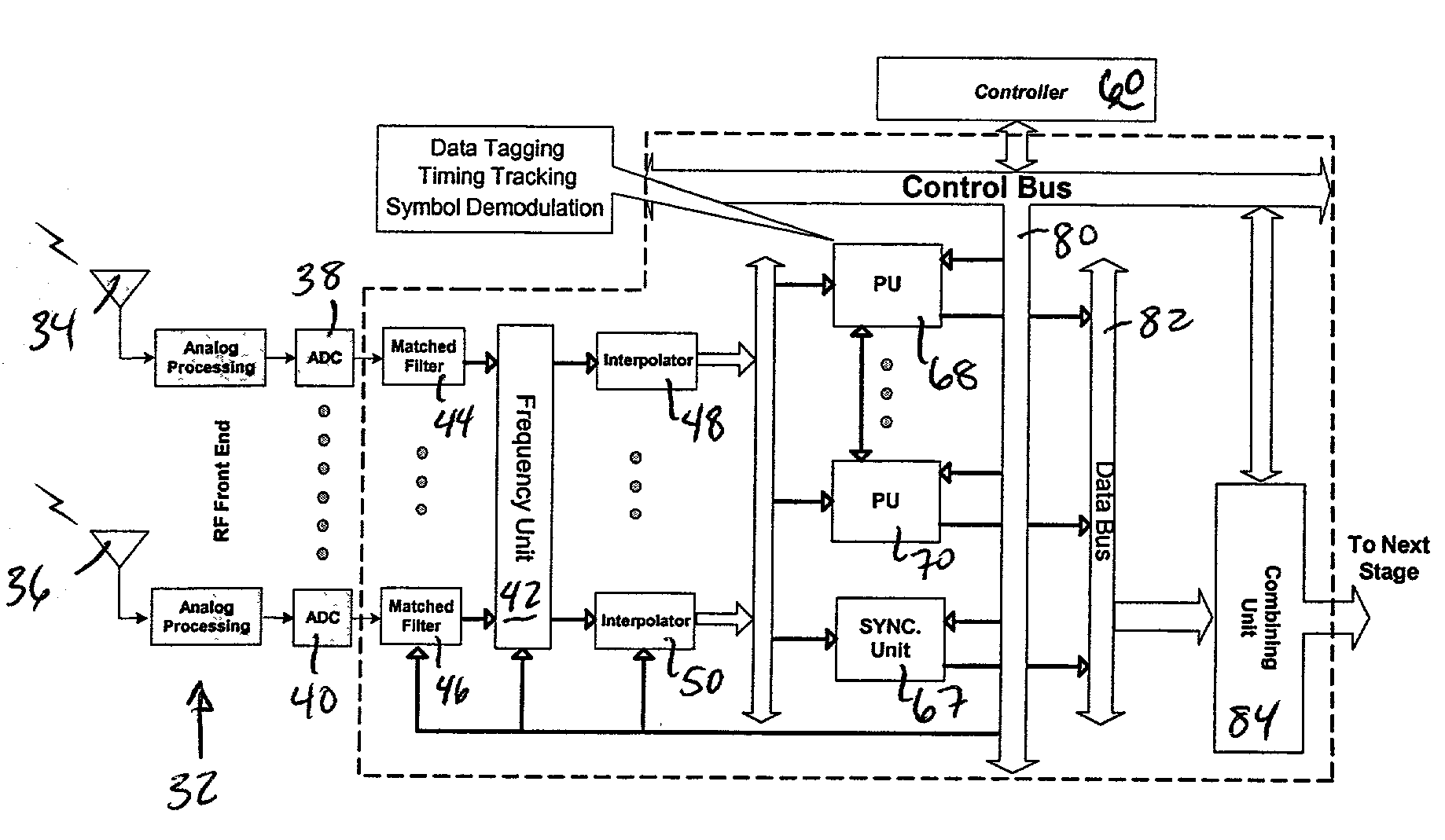
A universal rake receiver architecture includes modular independent processing units that can be flexibly programmed to support different modes of operation. The processing units are capable of performing the basic correlation calculations of DS-CDMA and each unit has an internal local memory and controller that controls its mode of operation. Each unit performs the required synchronization and demodulation operations for a multipath of a signal in the digital domain using all-digital frequency and timing correction techniques. Frequency feedback need not be supplied to the analog section of the receiver. Interpolation most preferably is used to find the optimum sampling position of each incoming chip. This independence allows the receiver to be used with one to several antennas without design modifications.
Owner:SASKEN COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES
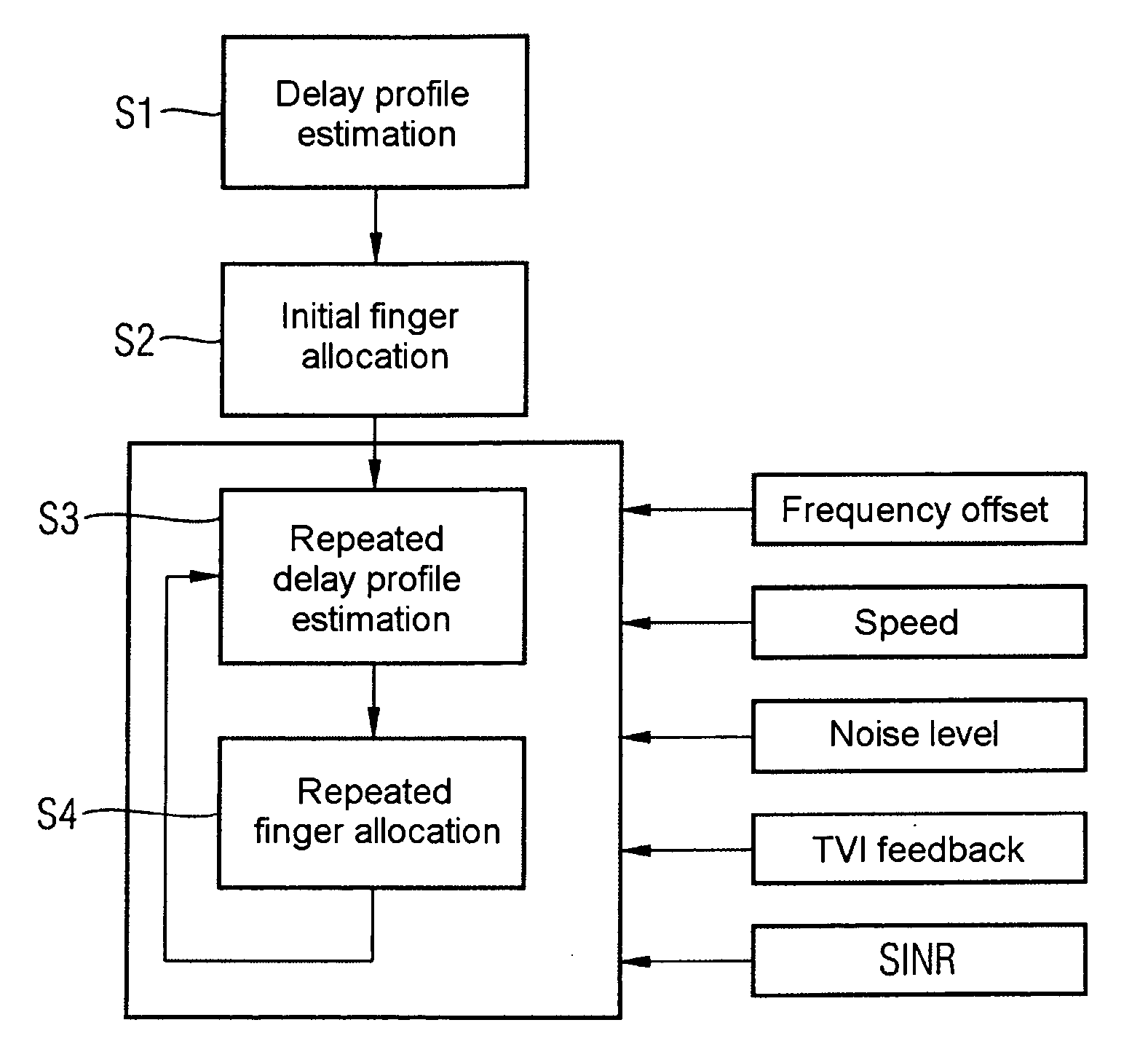
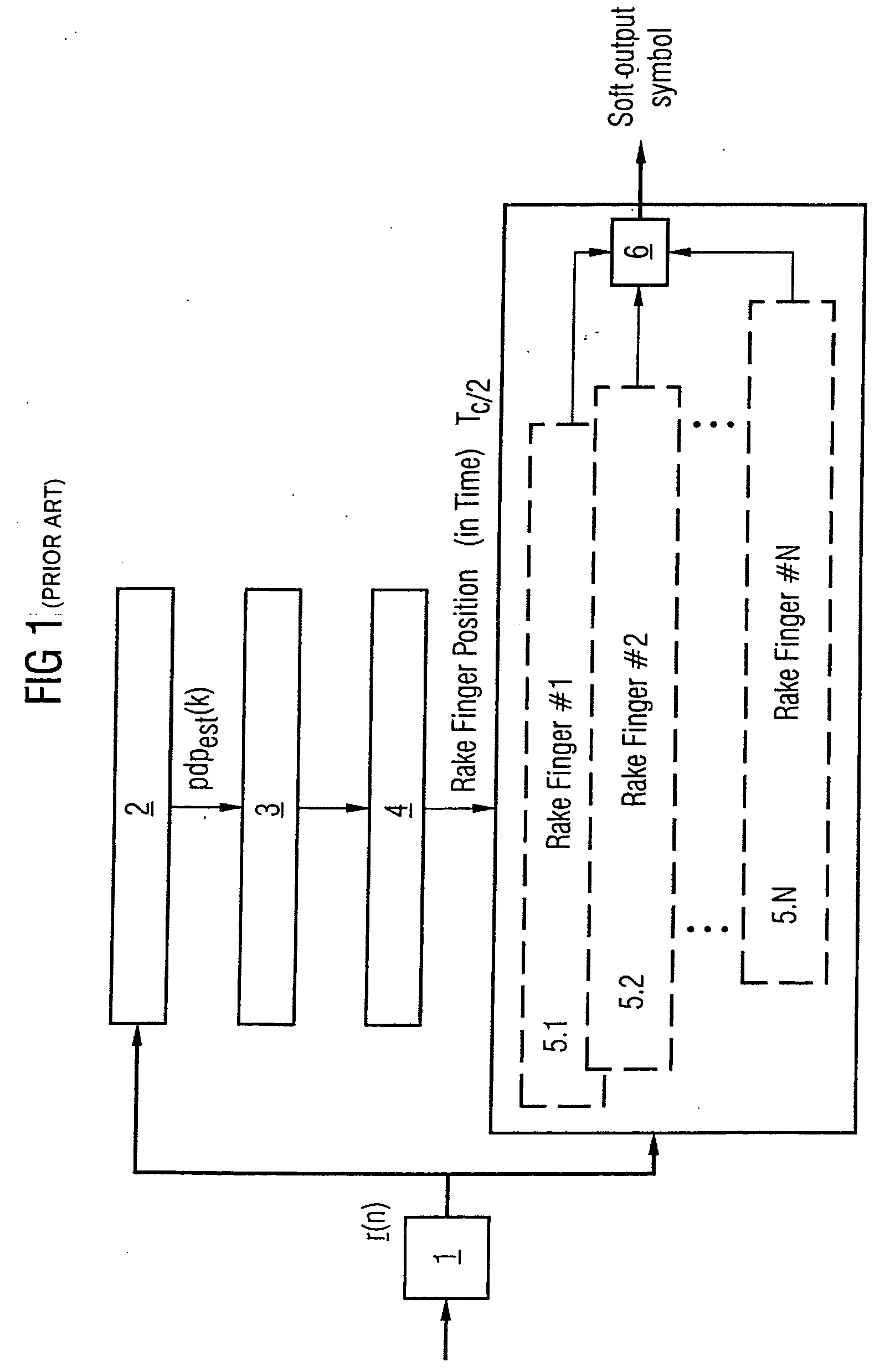
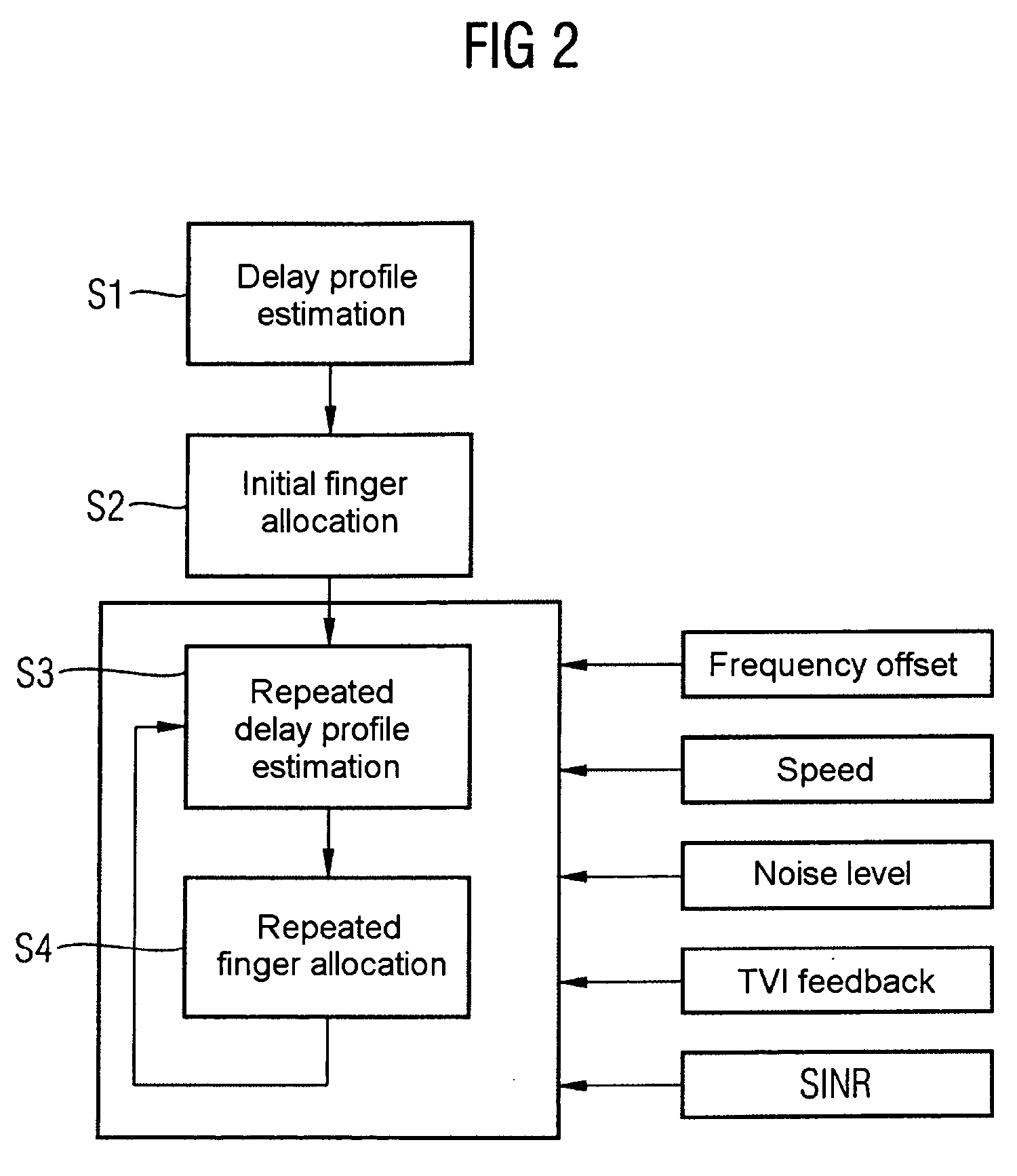
Determination and selection of transmission paths as a function of the operating situation for setting up rake fingers for rake receiver units in mobile communication terminals
ActiveUS20050111526A1MoreMore objective accuracySpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsNoise levelEngineering
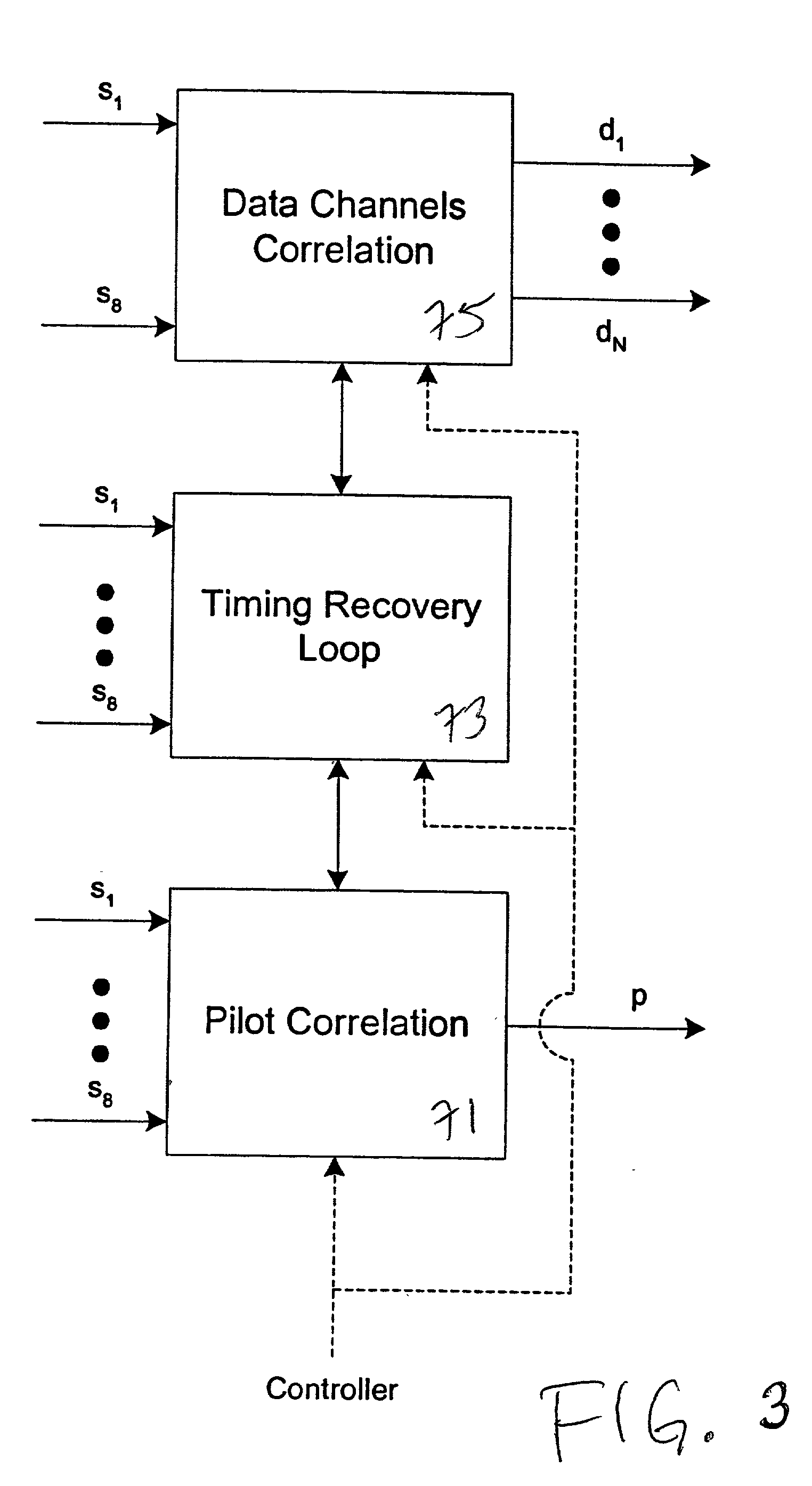
Correlations between the received signal to which pilot symbols have been applied at the transmitter end, and a correlation signal which contains the pilot symbols are carried out in the receiver in order to determine a path delay profile. Averaging processes are carried out over two or more delay profiles obtained in this way. Evaluations are carried out in one or more threshold value selection units (22.1, 22.2) on two or more averaged delay profiles with the aim of path selection. The parameters which govern the correlations and / or the averaging processes and / or the evaluations, and / or the repetition interval of these calculations are set as a function of the relative speed between the transmitter and the receiver, the frequency error between the carrier frequency of the received signal and the reference frequency that is set at the receiving end, and the noise level of the received signal. In the case of reception from two or more base stations, a final path selection is made in a finger allocation unit (40).
Owner:APPLE INC
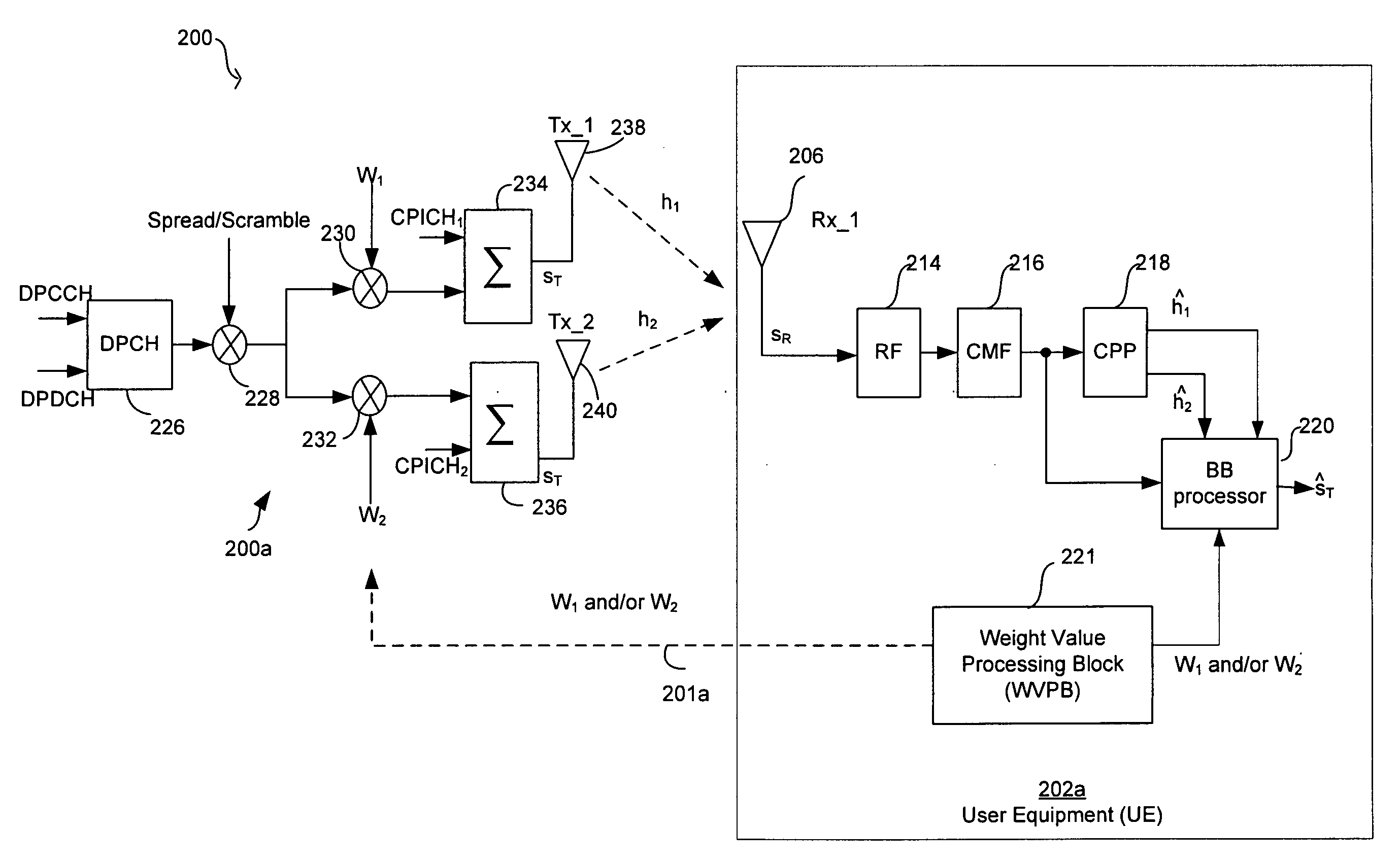
Method and apparatus to improve closed loop transmit diversity modes performance via interference suppression in a WCDMA network equipped with a rake receiver
ActiveUS20070280147A1Improve closed loop transmit diversity mode performancePolarisation/directional diversitySubstation equipmentCommunications systemSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
Methods and systems for processing signals in a wireless communication system are disclosed. Aspects of the method may include calculating at a receiver, a plurality of signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) values for a wireless signal, which is received from a transmitter, based on a corresponding plurality of weight values. A maximum one of the calculated plurality of SINR values may be determined. At least one weight value including one of the corresponding plurality of weight values may be fed back to the transmitter. The at least one weight value including one of the corresponding plurality of weight values may be associated with the determined maximum one of the calculated plurality of SINR values. The at least one weight value including one of the corresponding plurality of weight values may be communicated to the transmitter via at least one downlink communication channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for suppressing communication signal interference
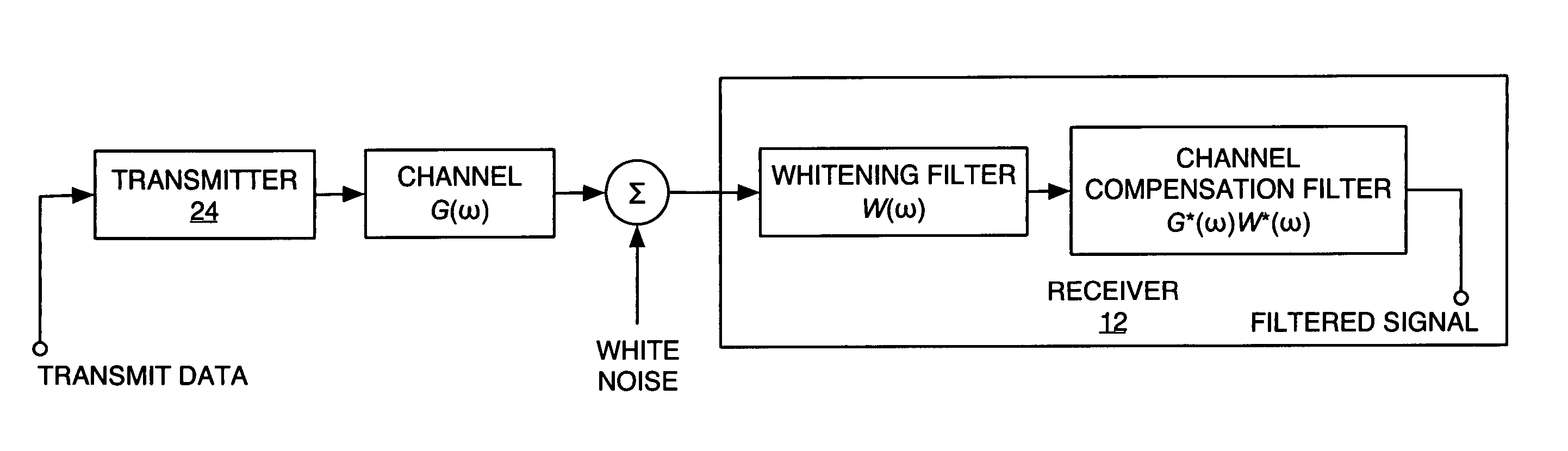
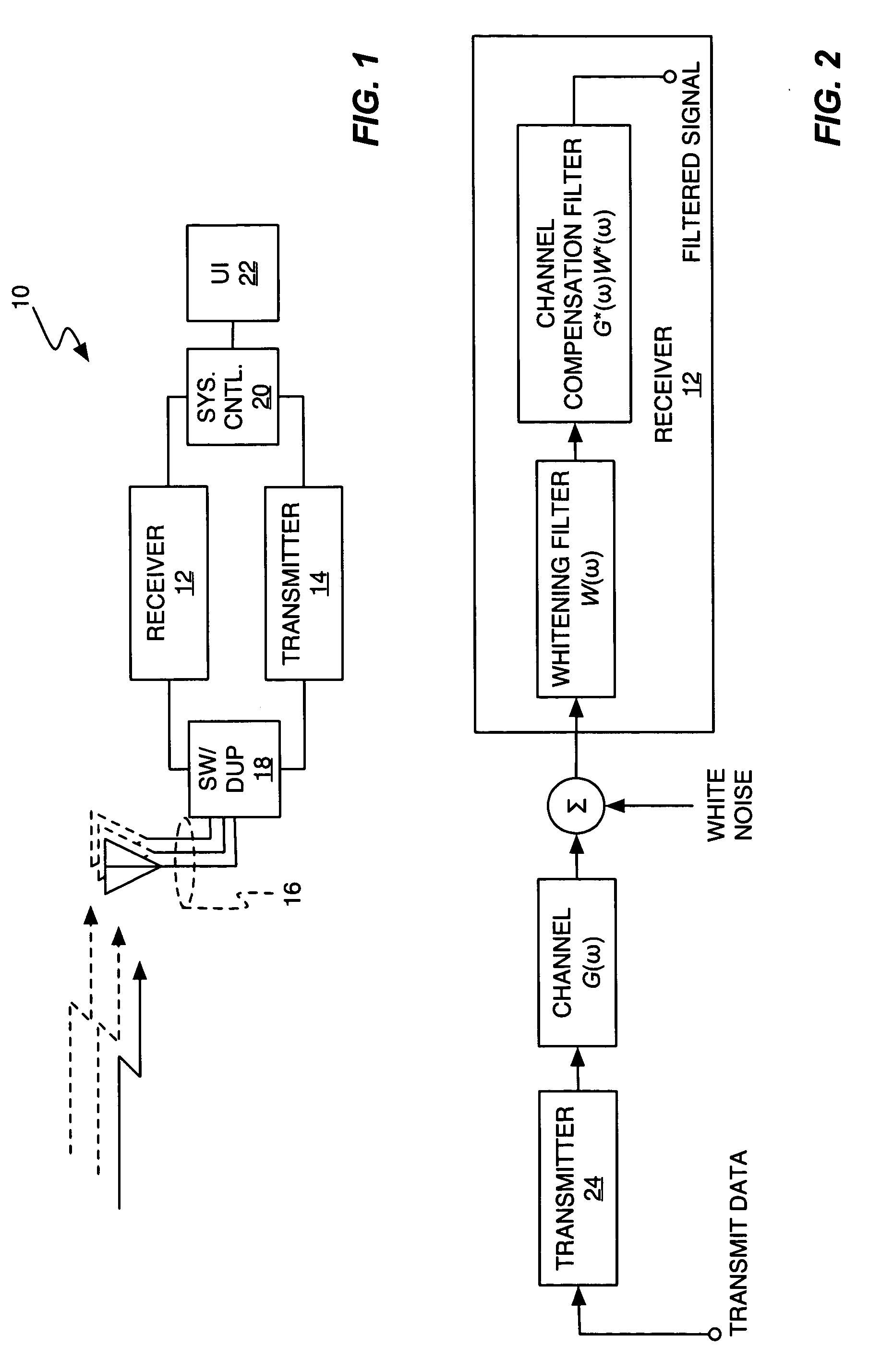
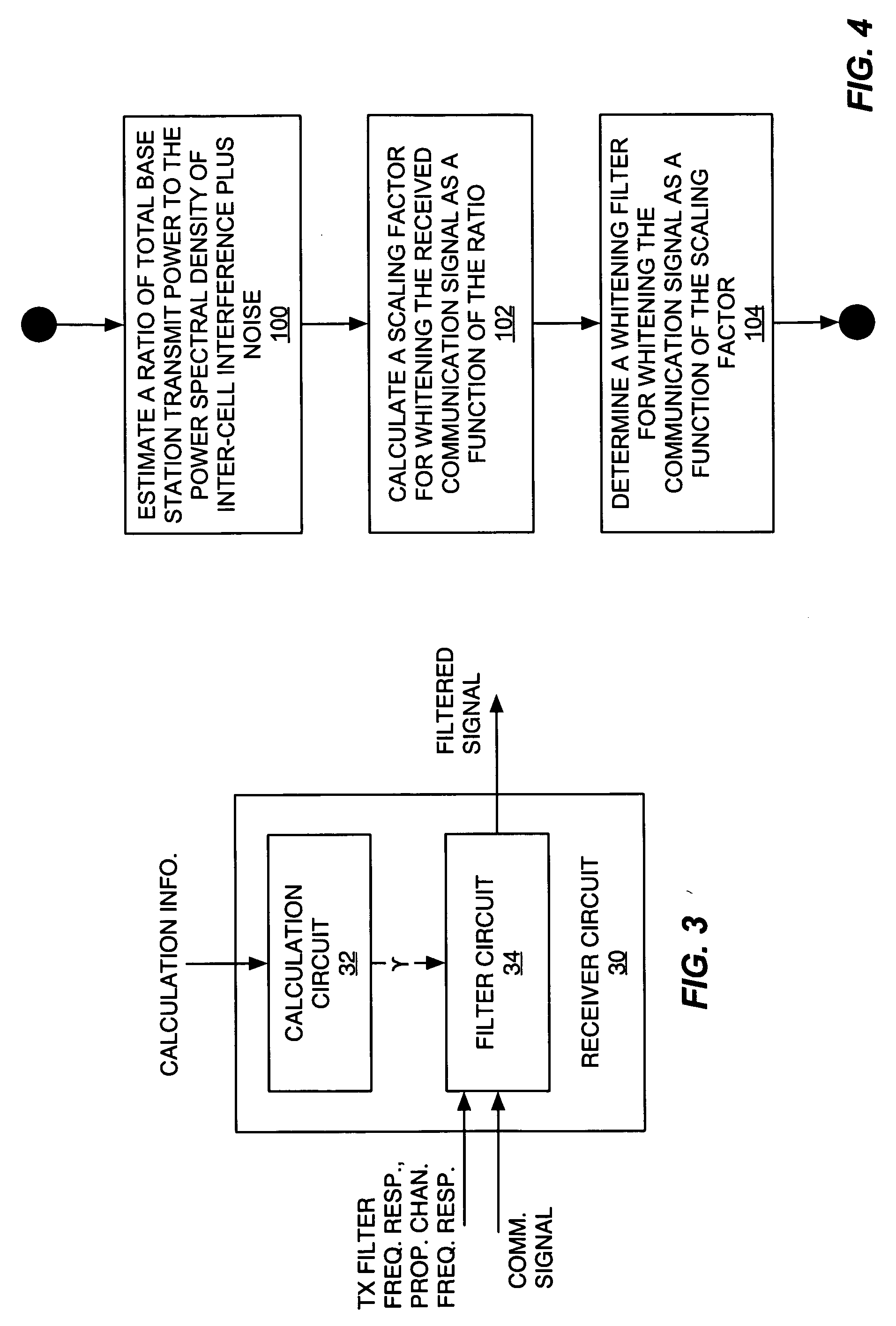
InactiveUS20060072485A1Reduce computational complexityEasy constructionError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTransmitted powerEngineering
A frequency domain representation of a whitening filter is made to depend on essentially one unknown, namely, a scaling factor that is based on an estimated ratio of total base station power to the power spectral density (PSD) of inter-cell interference plus noise. In turn, that scaling factor can be computed based on the modeling terms used in a parametric model of the impairment correlations for a received communication signal. Preferably, the model comprises an interference impairment term scaled by a first model fitting parameter, and a noise impairment term scaled by a second model fitting parameter. Further, the scaling factor can be computed by directly estimating total base station transmit power and the PSD of inter-cell interference plus noise. In any case, the whitening filter can be used in whitening a received communication signal in conjunction with channel equalization processing or RAKE receiver processing, for example.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
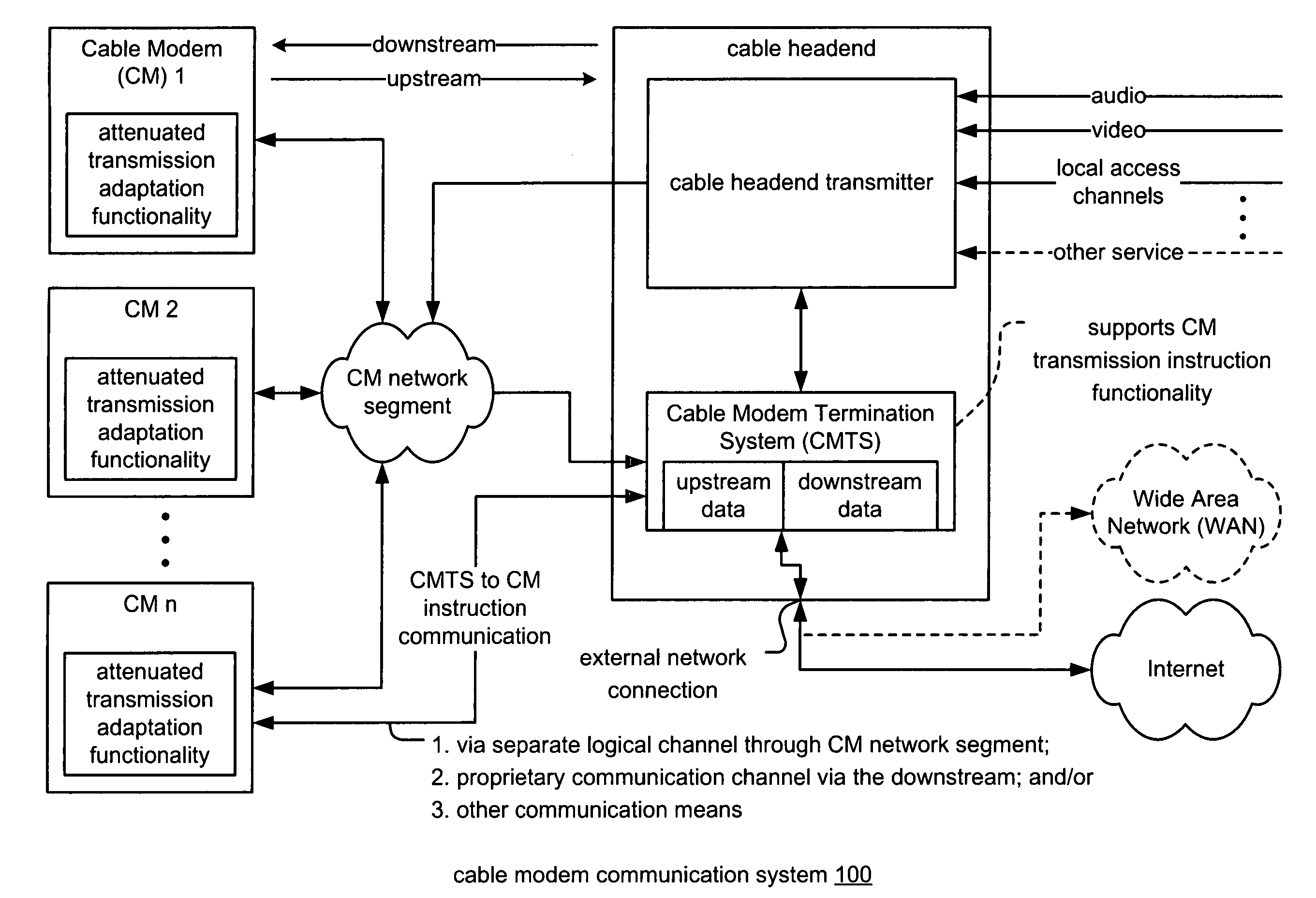
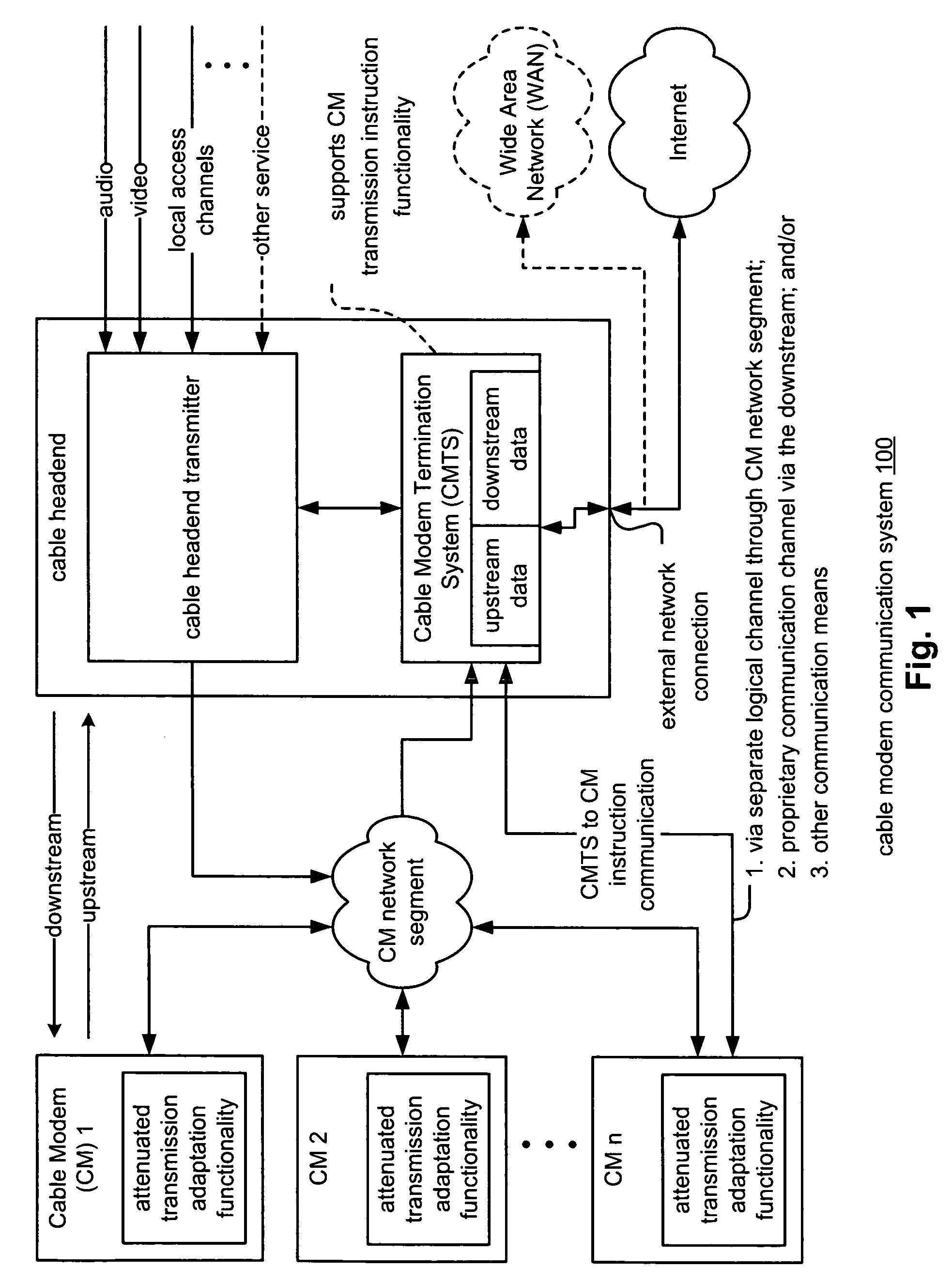
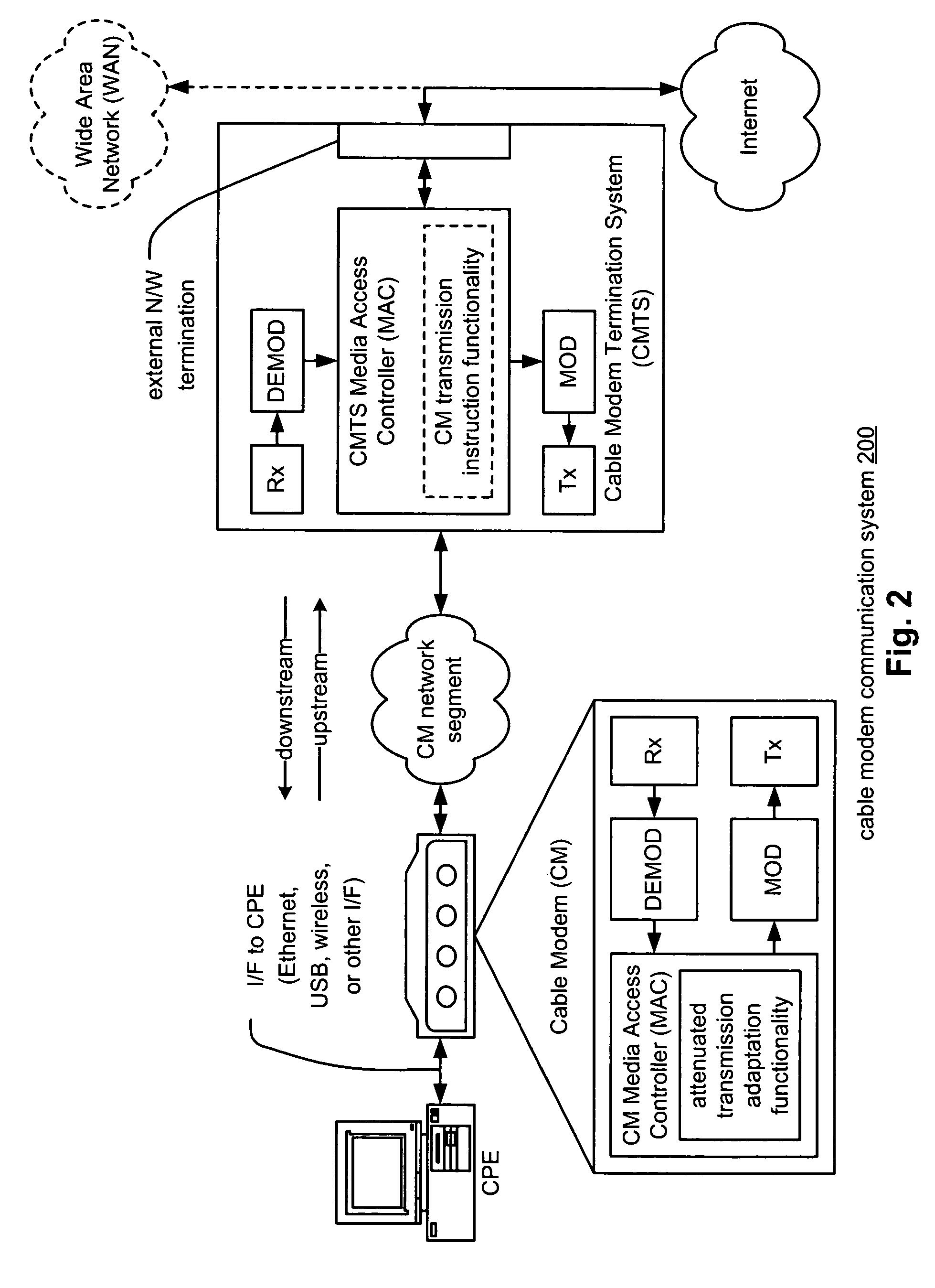
Ranging and registering cable modems under attenuated transmission conditions
InactiveUS7856049B2Analogue secracy/subscription systemsRadio transmissionModem deviceCommunications system
A cable modem communication system includes a plurality of Cable Modems (CMs), a CM network segment, and a Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS). The CMTS segregates the plurality of CMs into a first group of CMs with which standard registering and ranging operations are performed and a second group of CMs with which attenuated transmission registering and ranging operations are performed. Each CM of the first group of CMs operable to perform registering and ranging operations by transmitting a ranging burst of a first format. Each CM of the second group of CMs operable to perform registering and ranging operations by transmitting a ranging burst of a second format that differs from the ranging burst of the first format. The CMTS may include a rake receiver that receives and demodulates a plurality of multi-path copies of the ranging burst of the second format.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Apparatus and method for searching for cell and multi-path in mobile communication system
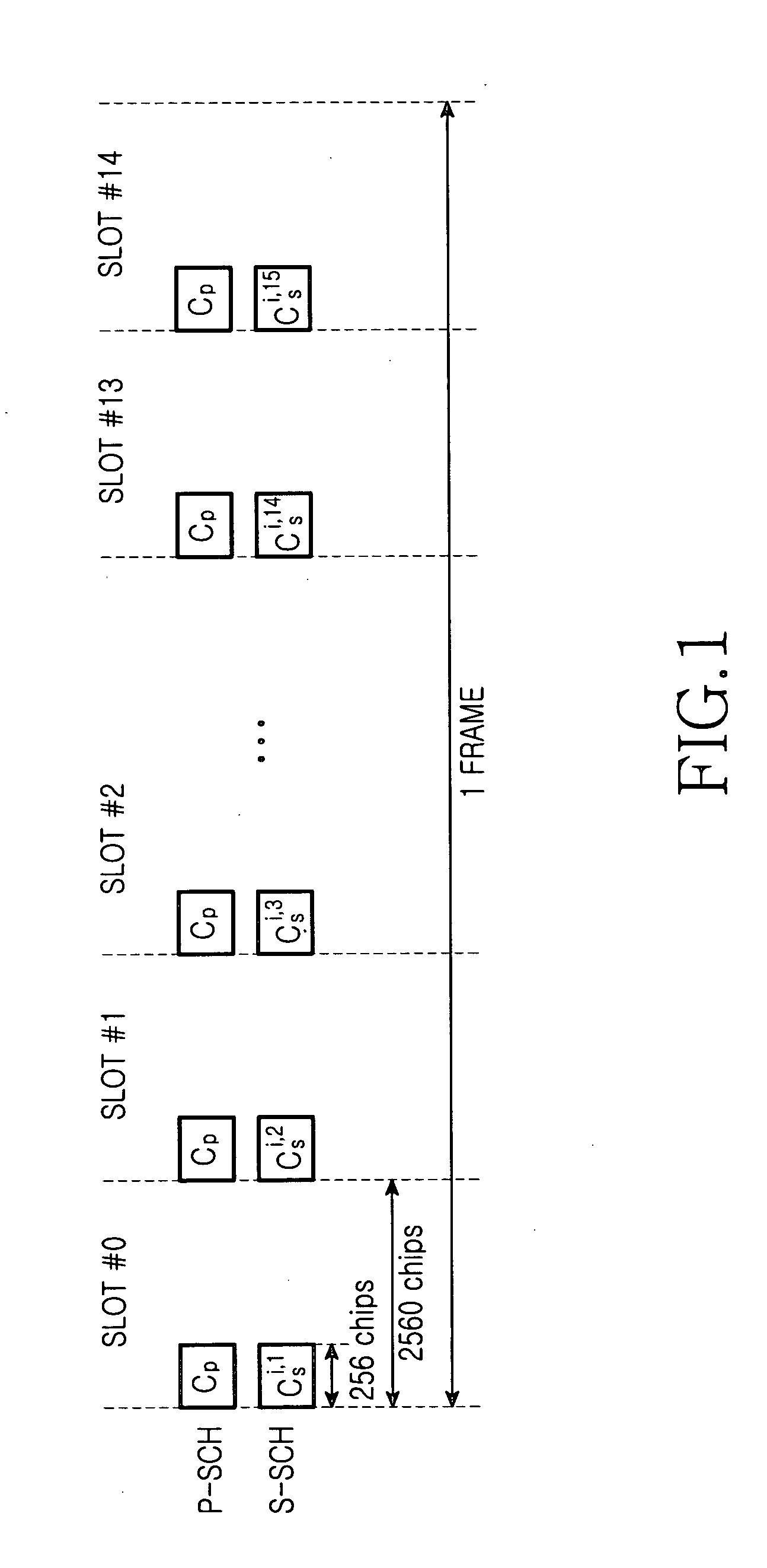
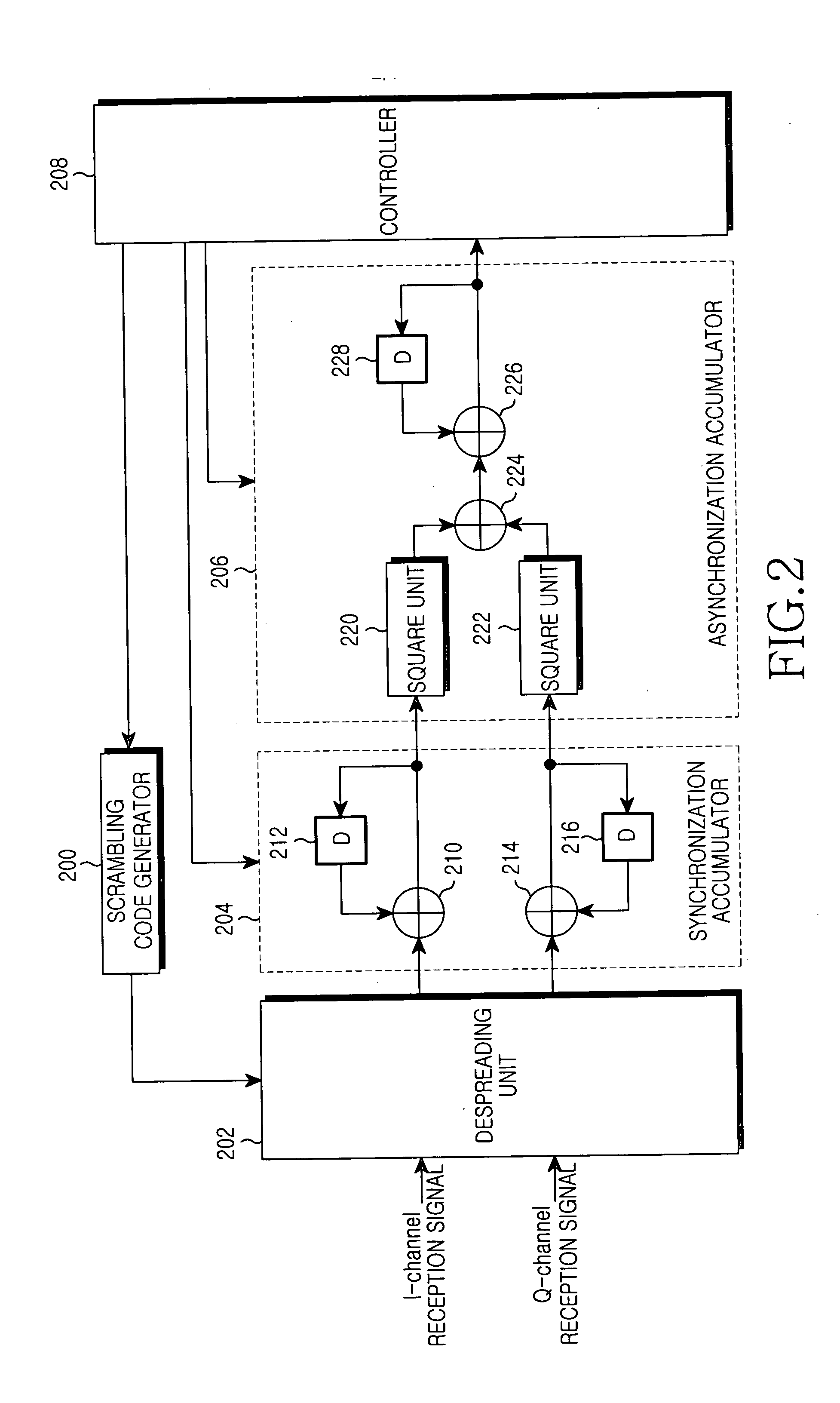
InactiveUS20050088987A1Lower the volumeReduce power consumptionAssess restrictionConnection managementTime delaysCell search
A method for performing a third cell search process or a multi-path search process to detect a scrambling code used by a Node B or in a Mobile Station by generating at least one scrambling code; determining one of first and second methods, in which the first method calculates correlation energy values of reception signals associated with at least two scrambling codes sequentially generated with predetermined time delays, and the second method sequentially generates one scrambling code with the predetermined time delays, and calculates correlation energy values of the reception signals associated with the generated scrambling codes; calculating correlation energy values of the reception signals associated with the generated scrambling codes according to the determination result; and determining a scrambling code used by the Node B or multi-paths to be assigned to individual fingers of a rake receiver using the calculated correlation energy values associated with the scrambling codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com