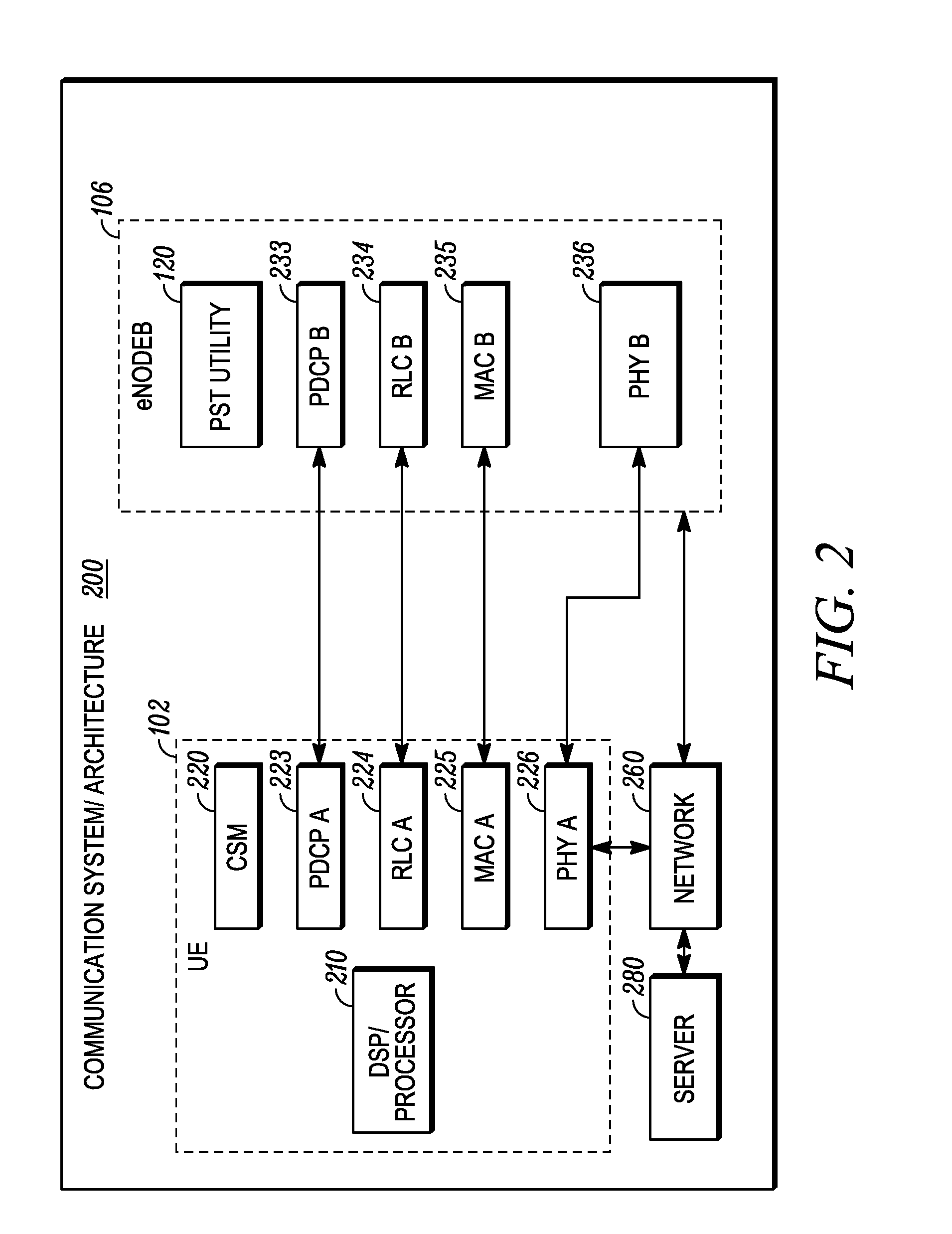
Patents
Literature
1108 results about "Cell search" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
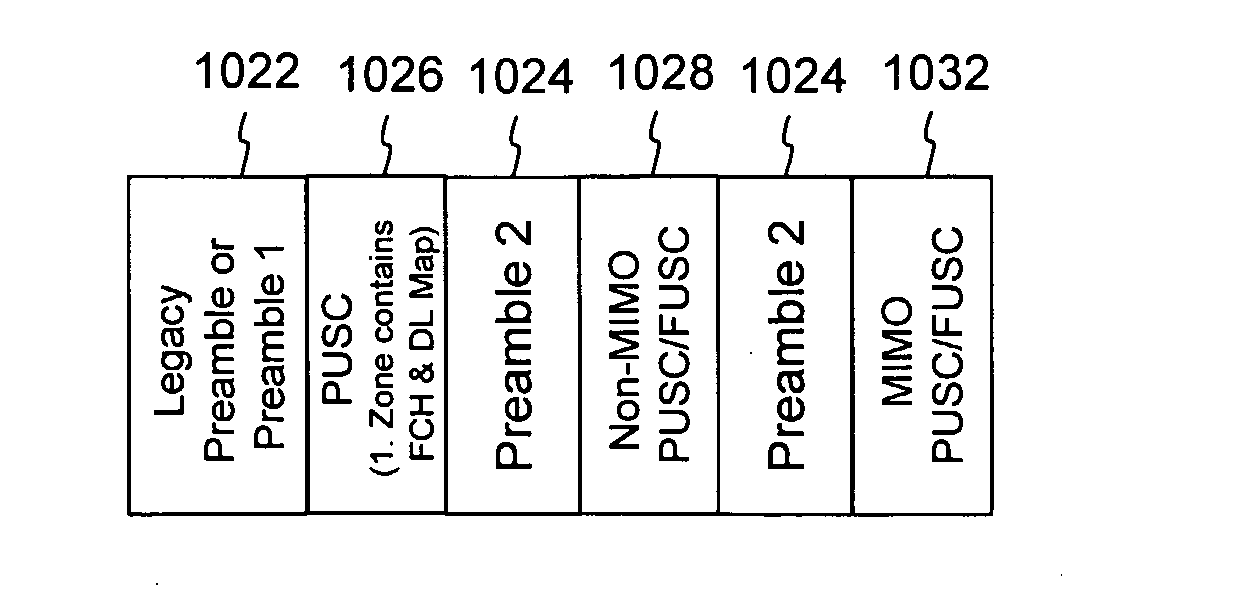
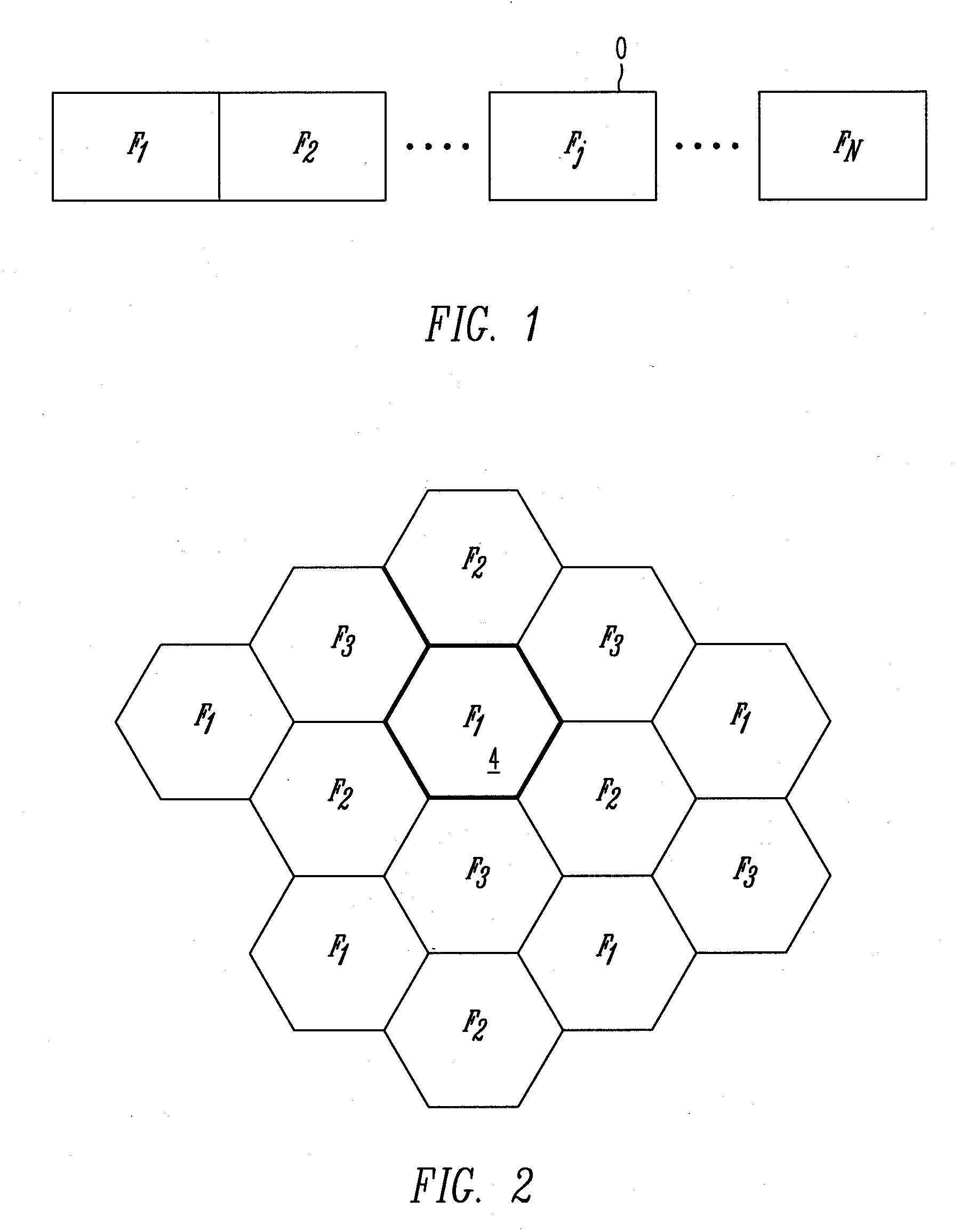
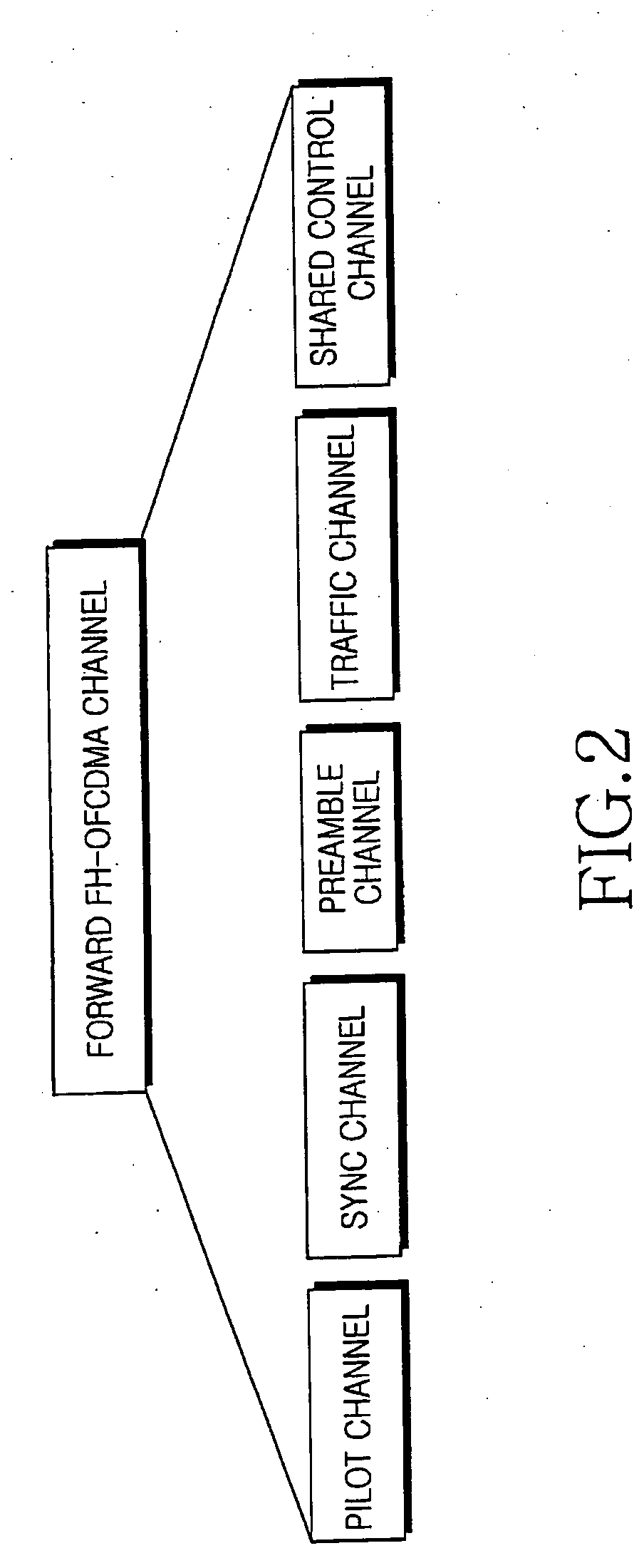
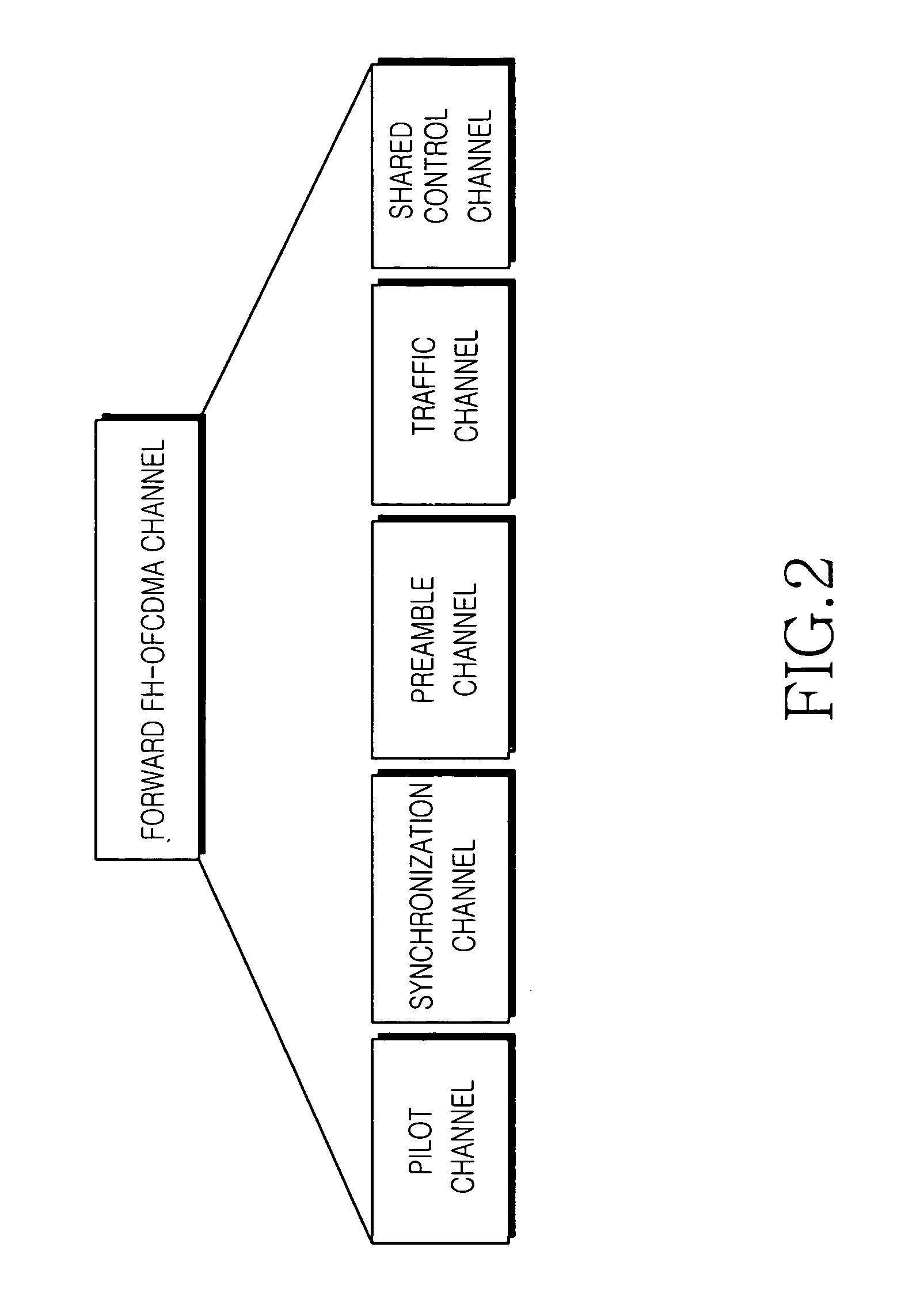
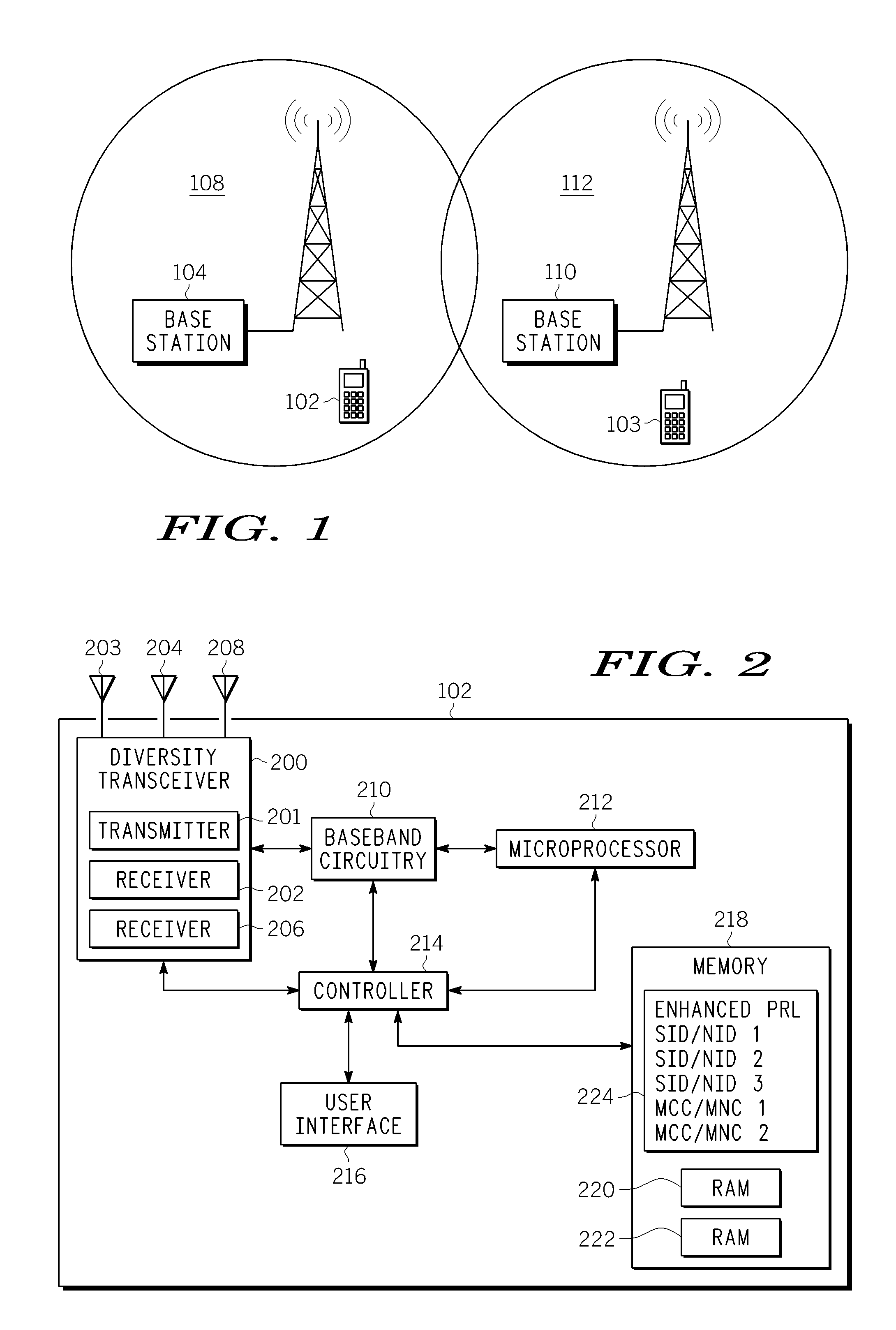
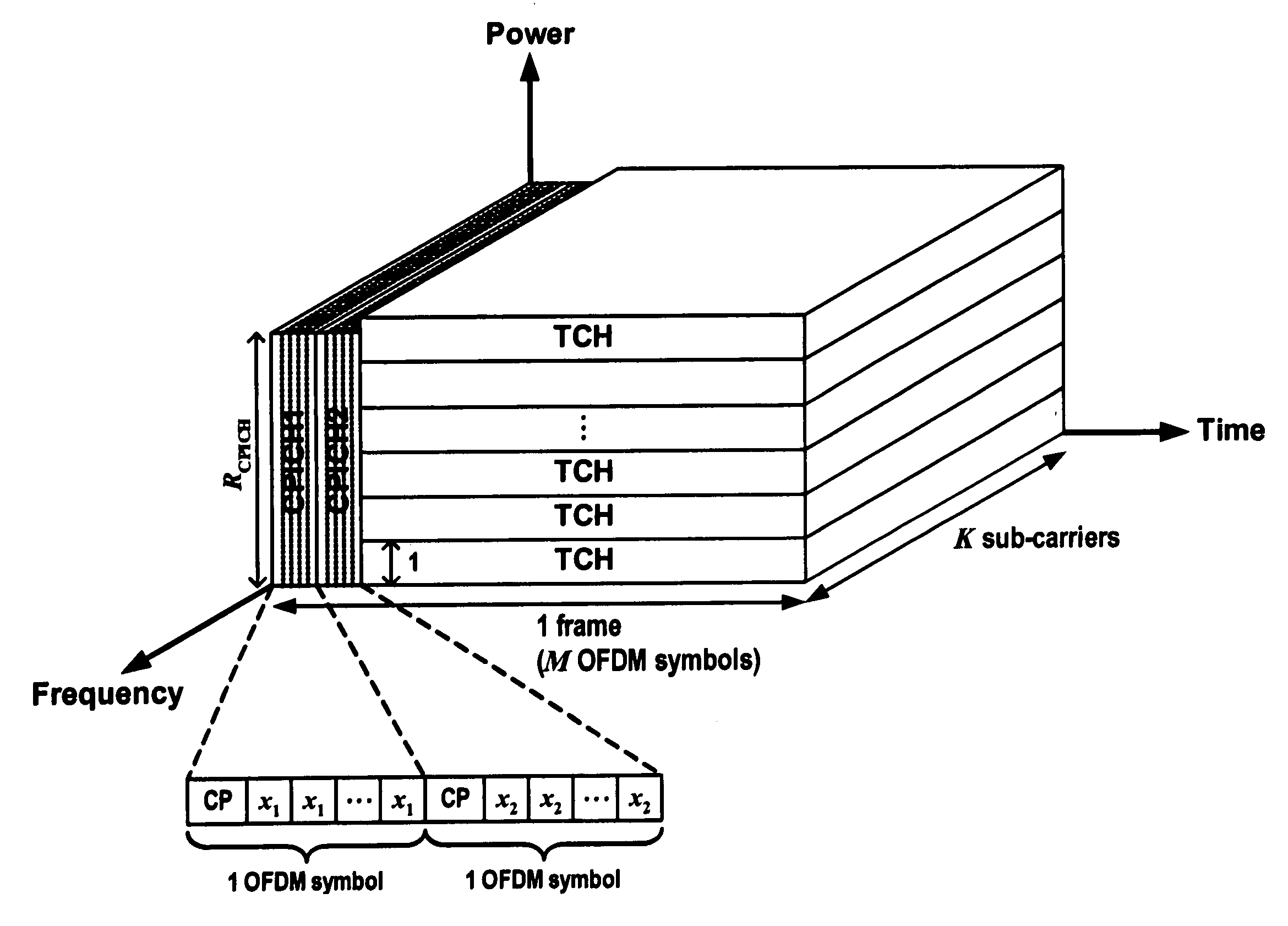
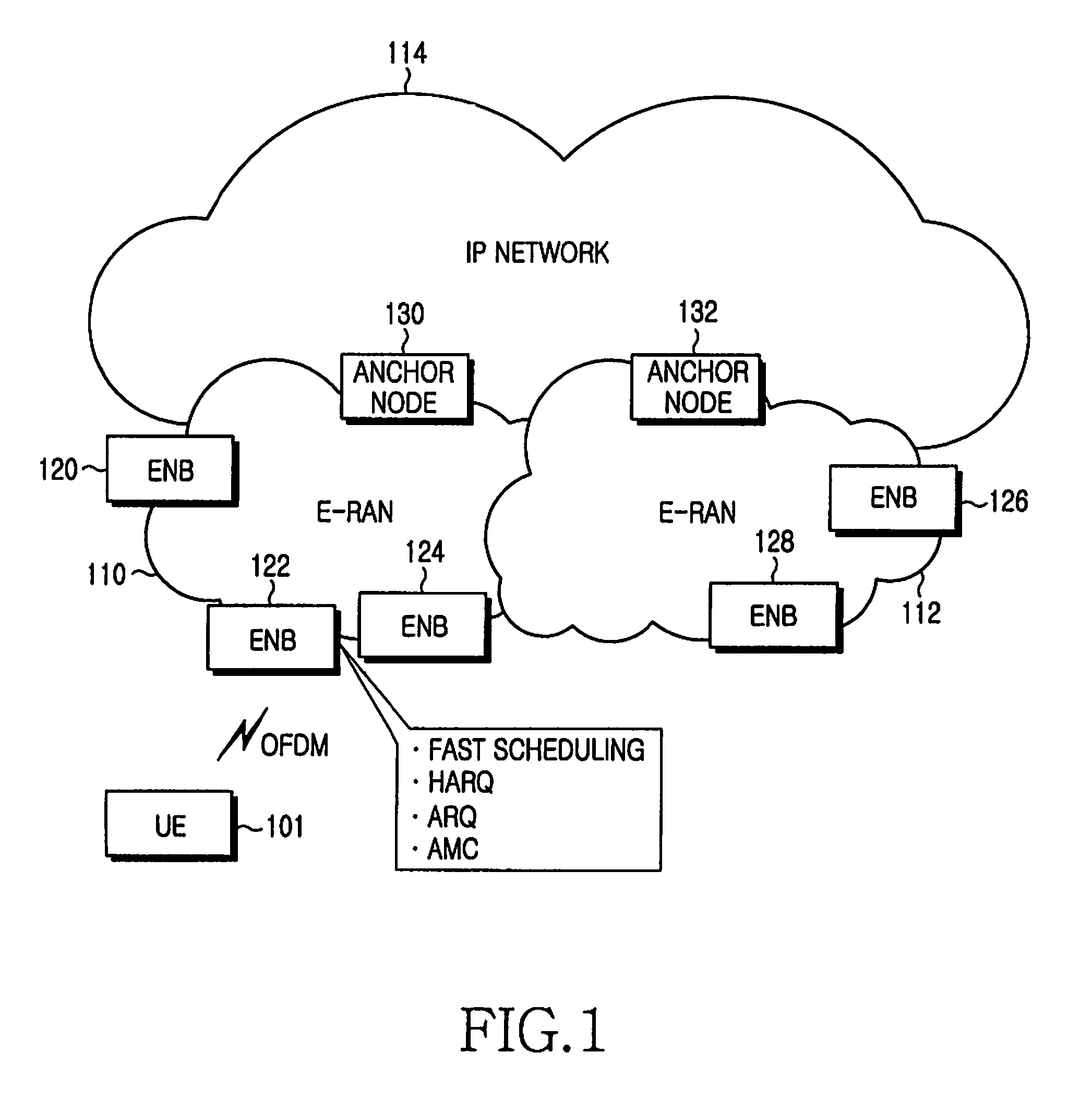
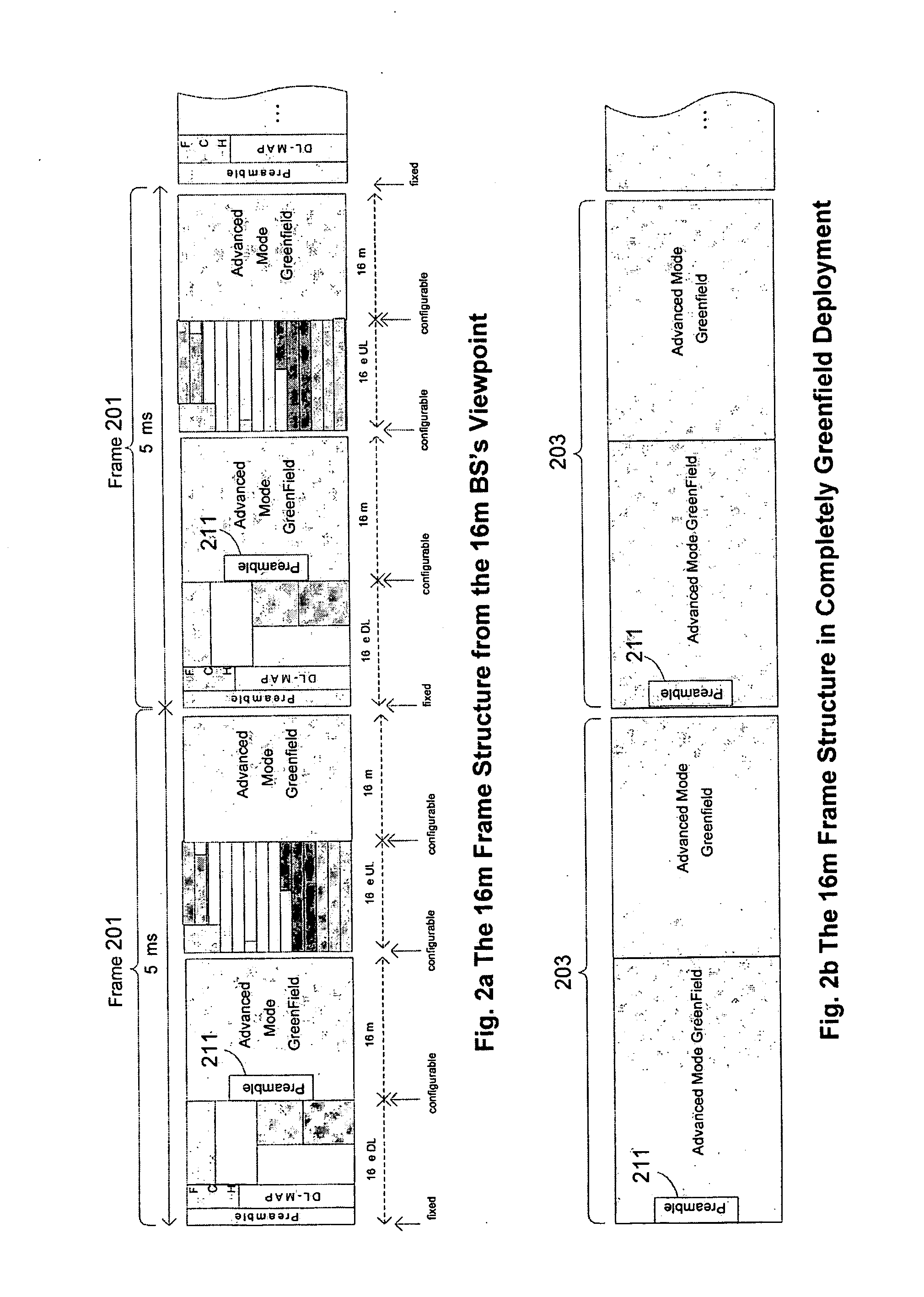
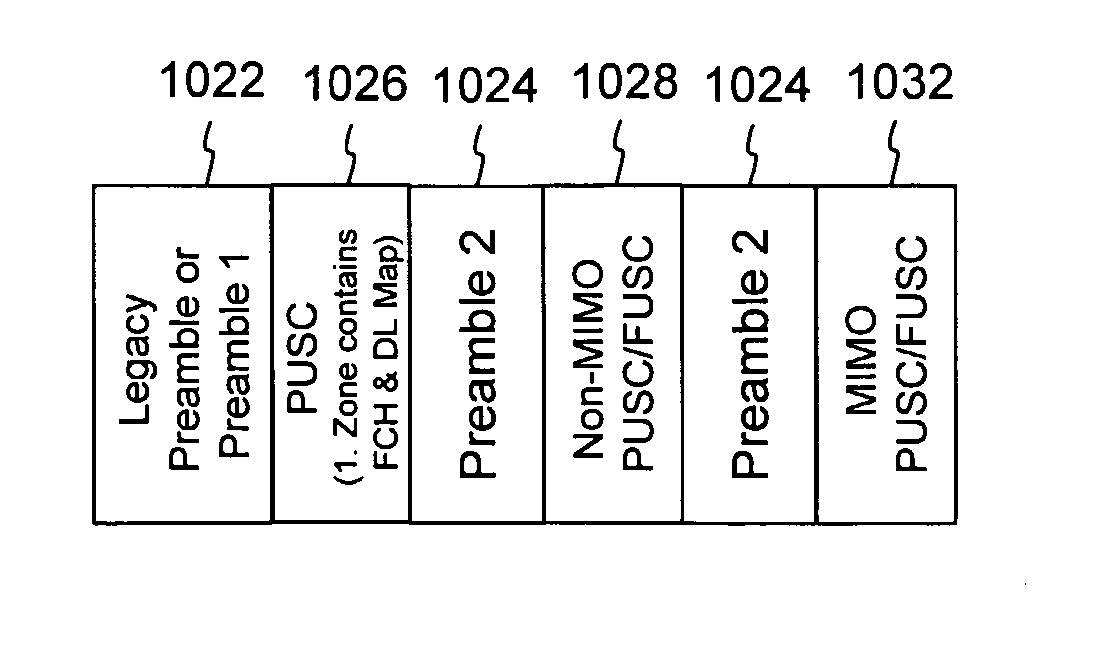
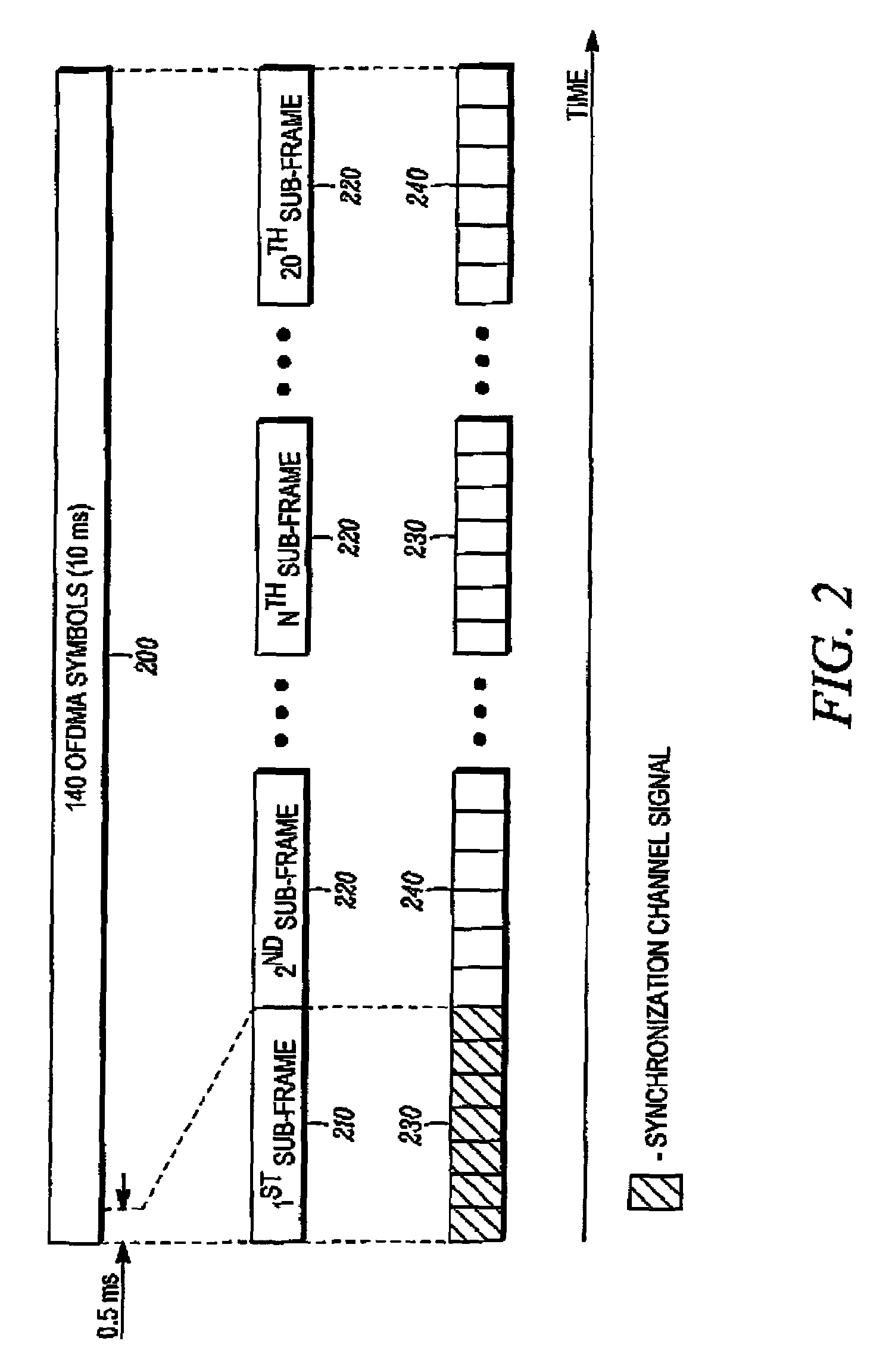
Preambles in Ofdma System
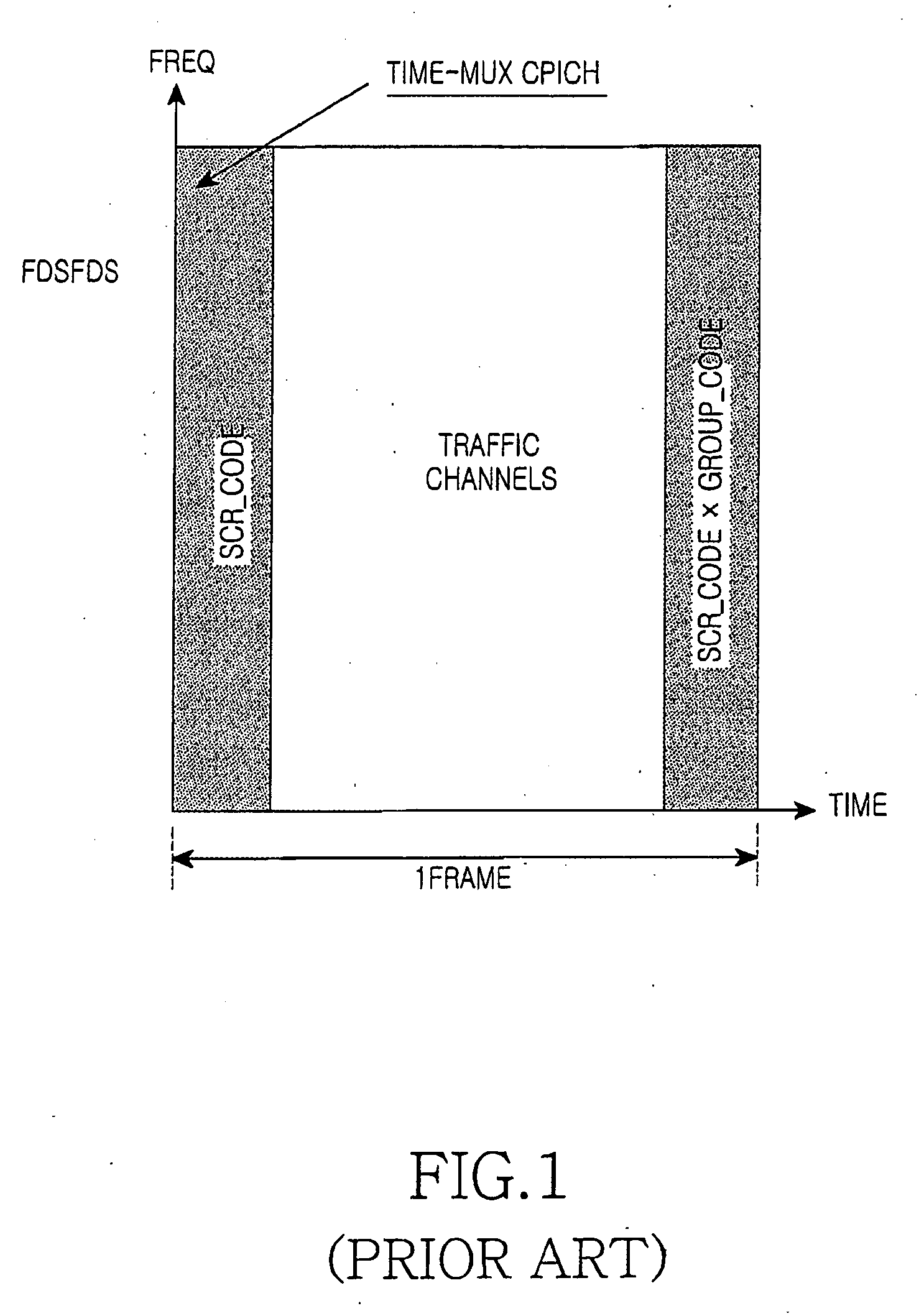
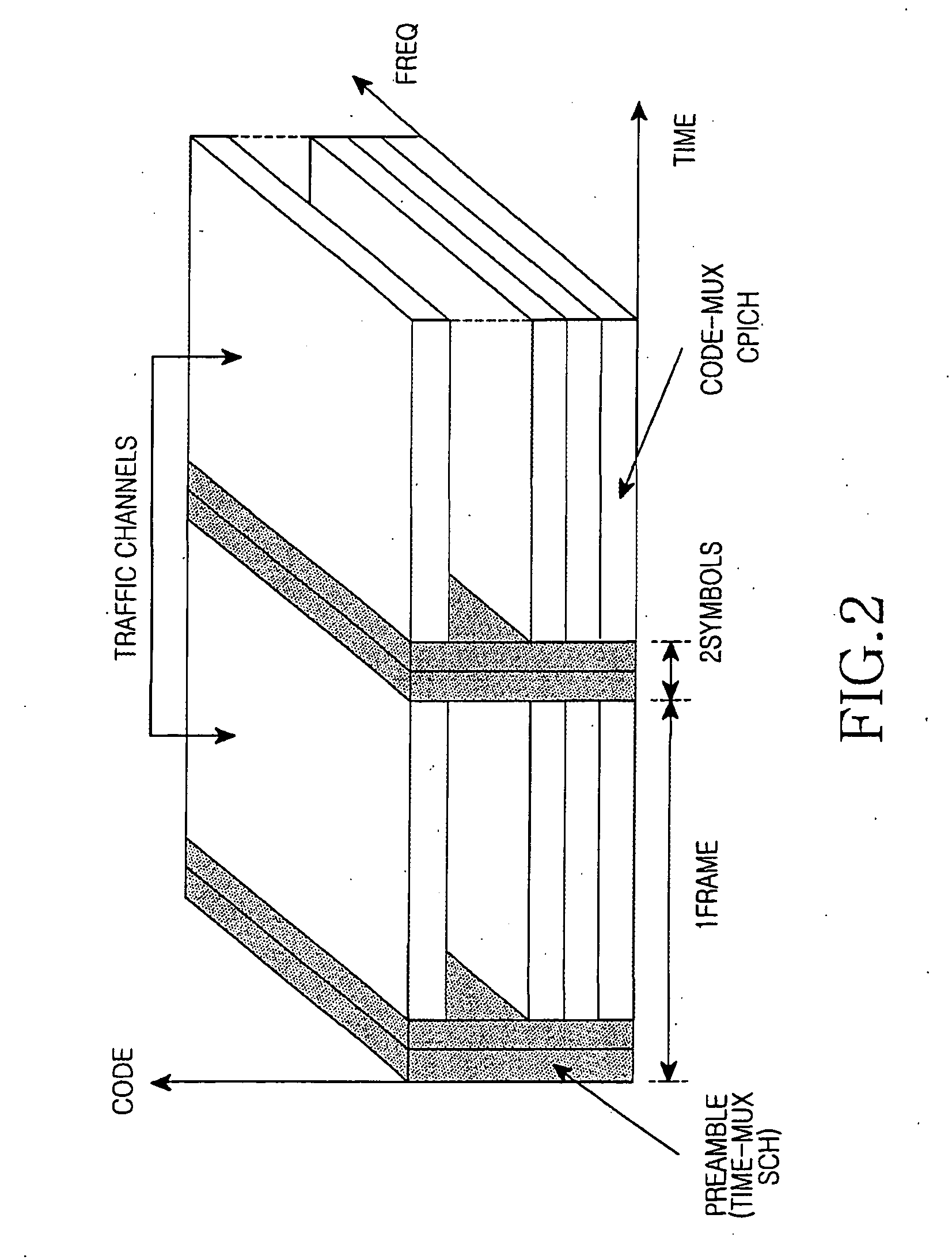
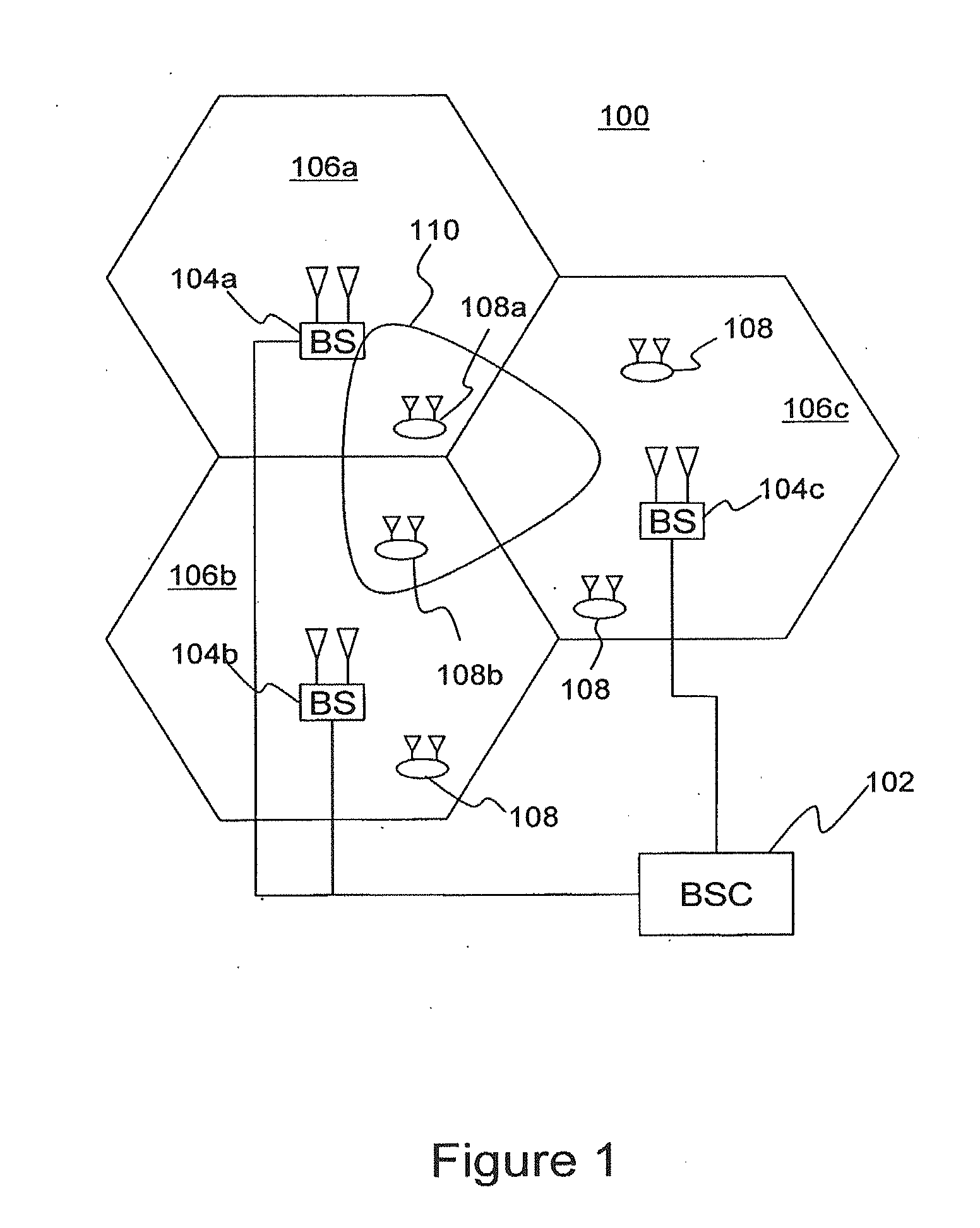
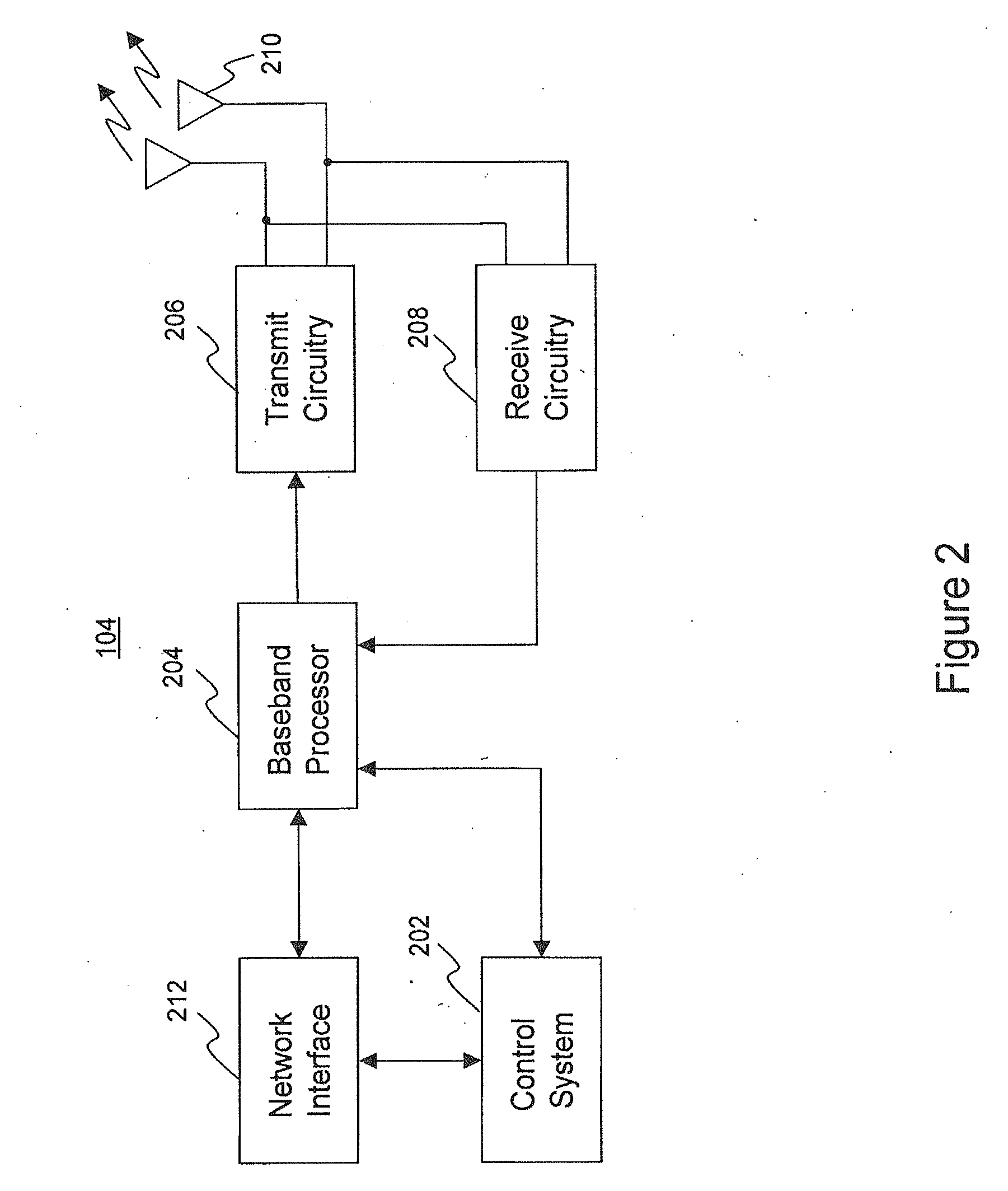
ActiveUS20080039107A1Reducing a search windowModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionMulti inputCell search
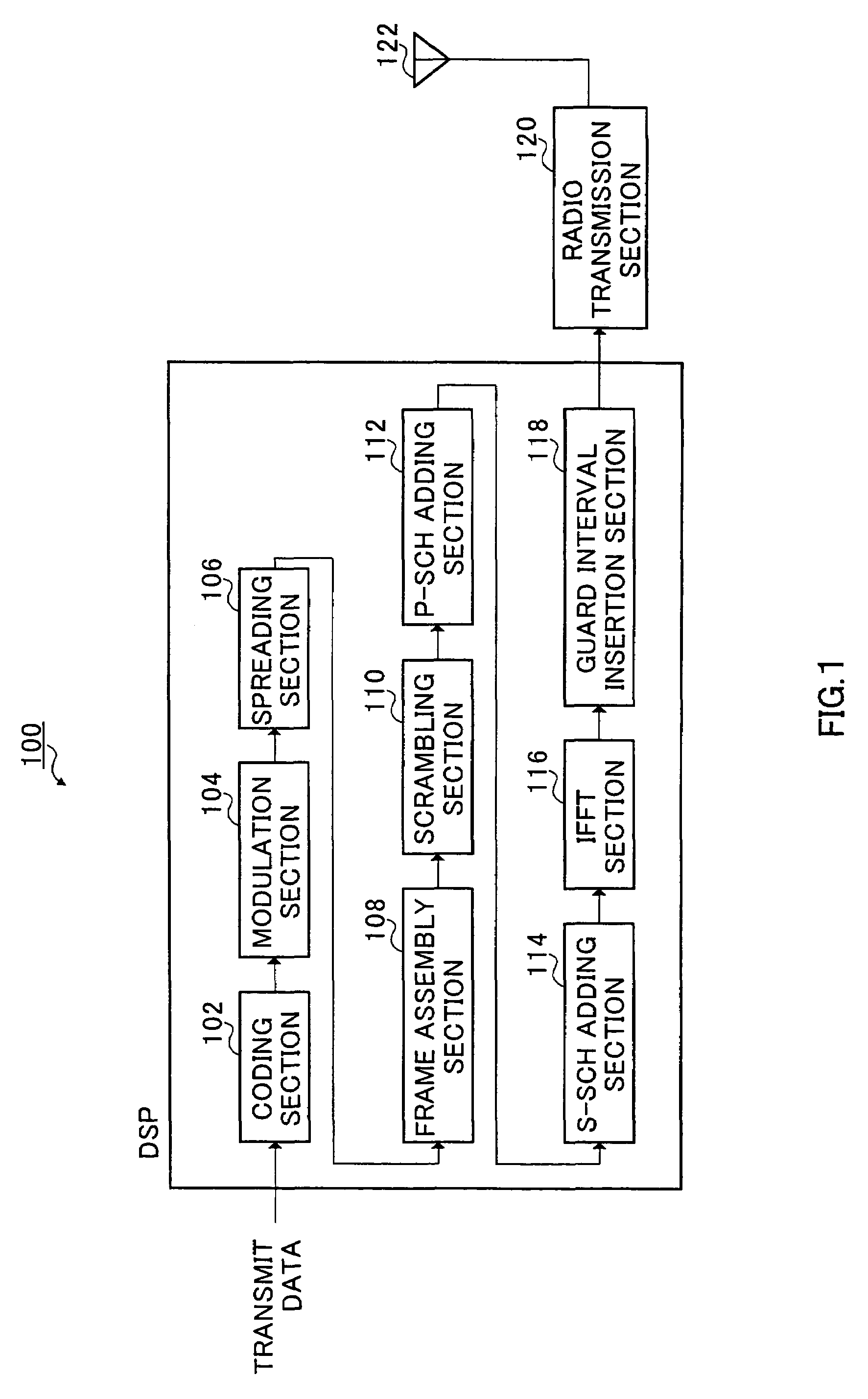
The present invention provides a preamble that is inserted into an OFDMA frame and has a common sequence for all the base stations participating in a transmission. The subscriber station performs fine synchronization using the common sequence on the common preamble, and the resulting peaks will provide the locations of candidate base stations. The base station specific search is then performed in the vicinities of those peaks by using base station specific pseudo-noise sequences. With this two stage cell search, the searching window is drastically reduced. The preamble is matched to known values by a respective receiver to decode the signals and permit multiple signals to be transferred from the transmitter to the receiver. The preamble may comprise two parts, Preamble-1 and Preamble-2, which may be used in different systems, including multioutput, multi-input (MIMO) systems.
Owner:APPLE INC
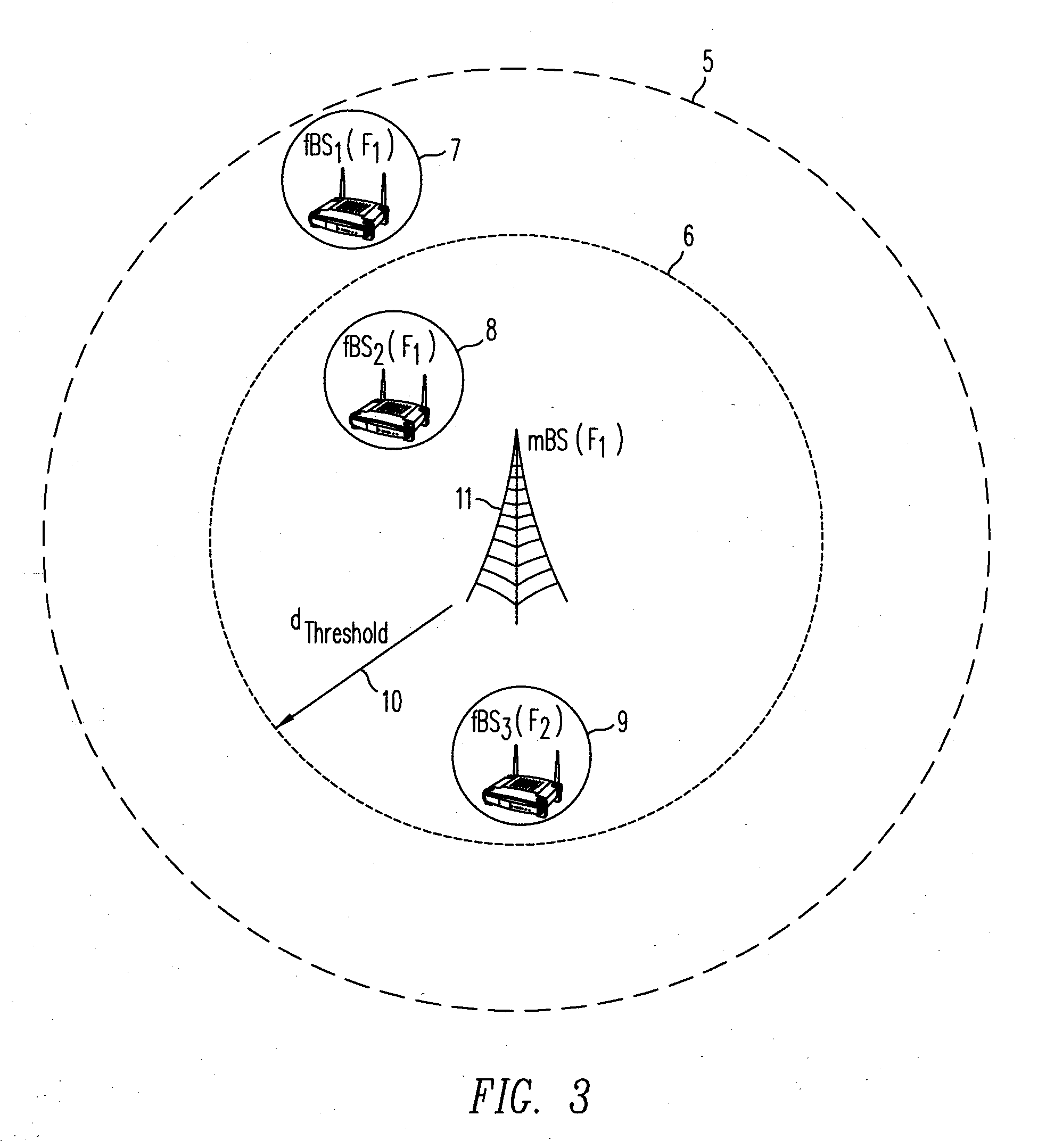
Femtocell Channel Assignment and Power Control for Improved Femtocell Coverage and Efficient Cell Search
ActiveUS20090291690A1Increase efficiency and coverageEfficient managementPower managementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
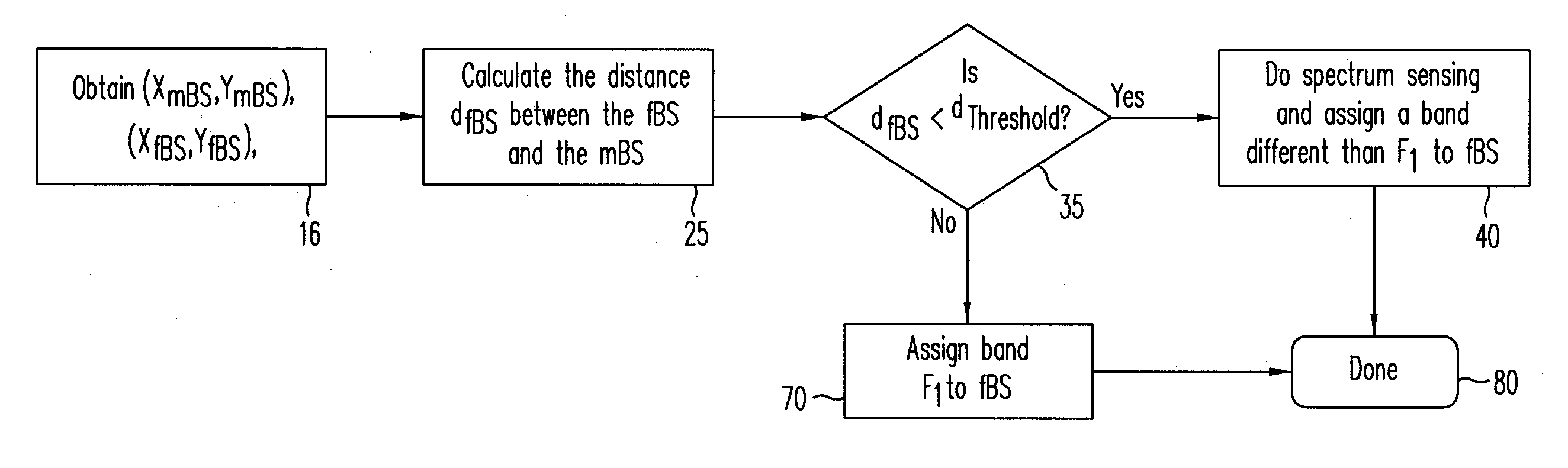
A method and a communication system including femtocells within a macrocell efficiently manage interference between the different femtocells, and between each femtocell and a macrocell. An efficient frequency assignment scheme for the femtocells minimizes interference between a femtocell and a macrocell and among different femtocells using a spectrum-sensing technique carried out by the femtocells. The frequency assignment scheme selects a suitable channel from a set of candidate channels and ensures that the femtocell has an acceptable coverage area even when it is close to the macrocell base station (BS). The frequency assignment scheme favors a co-channel implementation to take advantage of the hand-off and cell search characteristics of the co-channel implementation. In one embodiment, a joint power control and frequency band assignment technique is used, which partitions the coverage area of the macrocell into an inner region, a power control region, and an outer region. Depending on a femtocell's location, it is assigned a certain power level and a frequency band. Power control may be used within the power-control region while, in the other regions, a fixed transmission power may be used.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
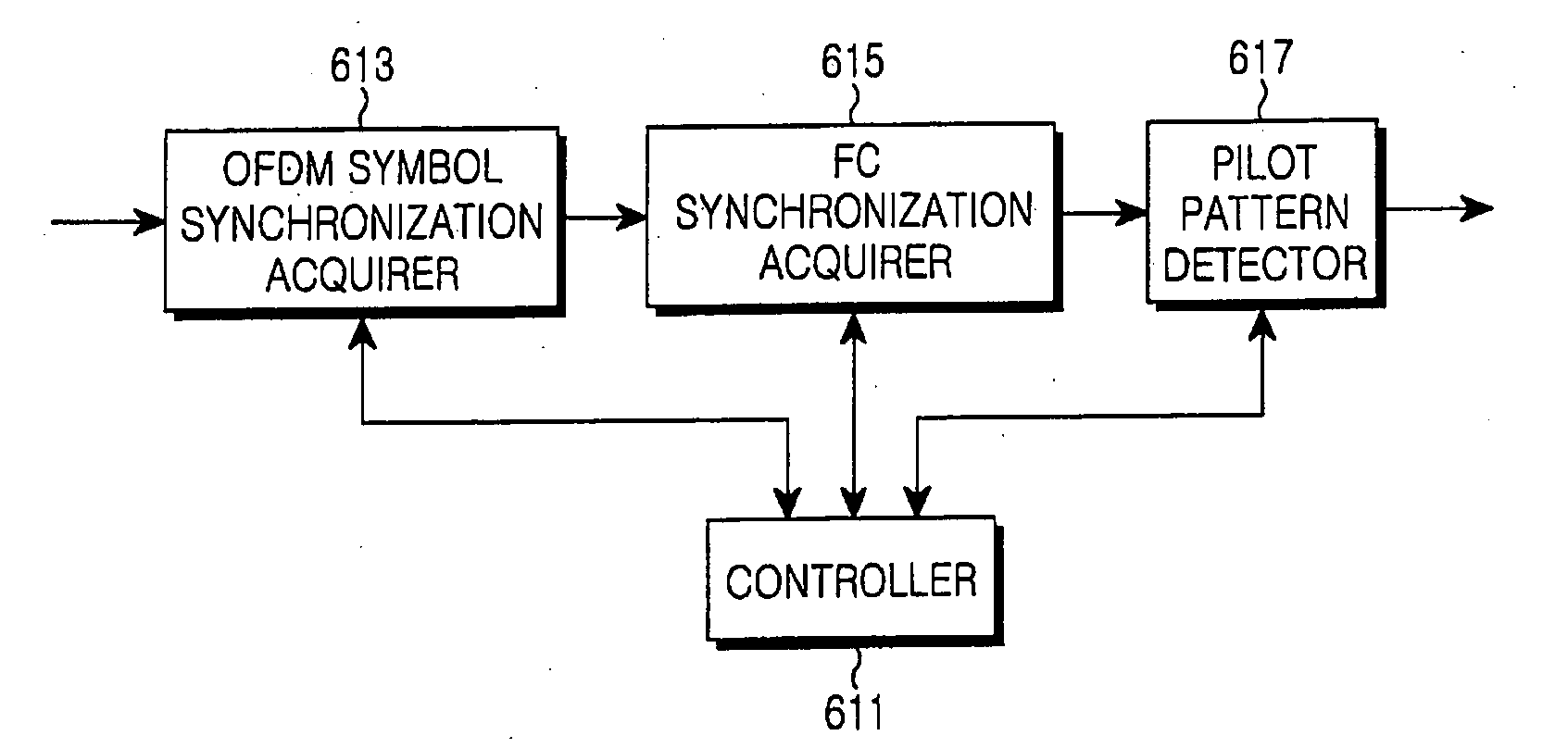
Cell search apparatus and method in a mobile communication system using multiple access scheme
InactiveUS20060126491A1Increasing cell search performanceImprove performanceMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexCell synchronizationCommunications system
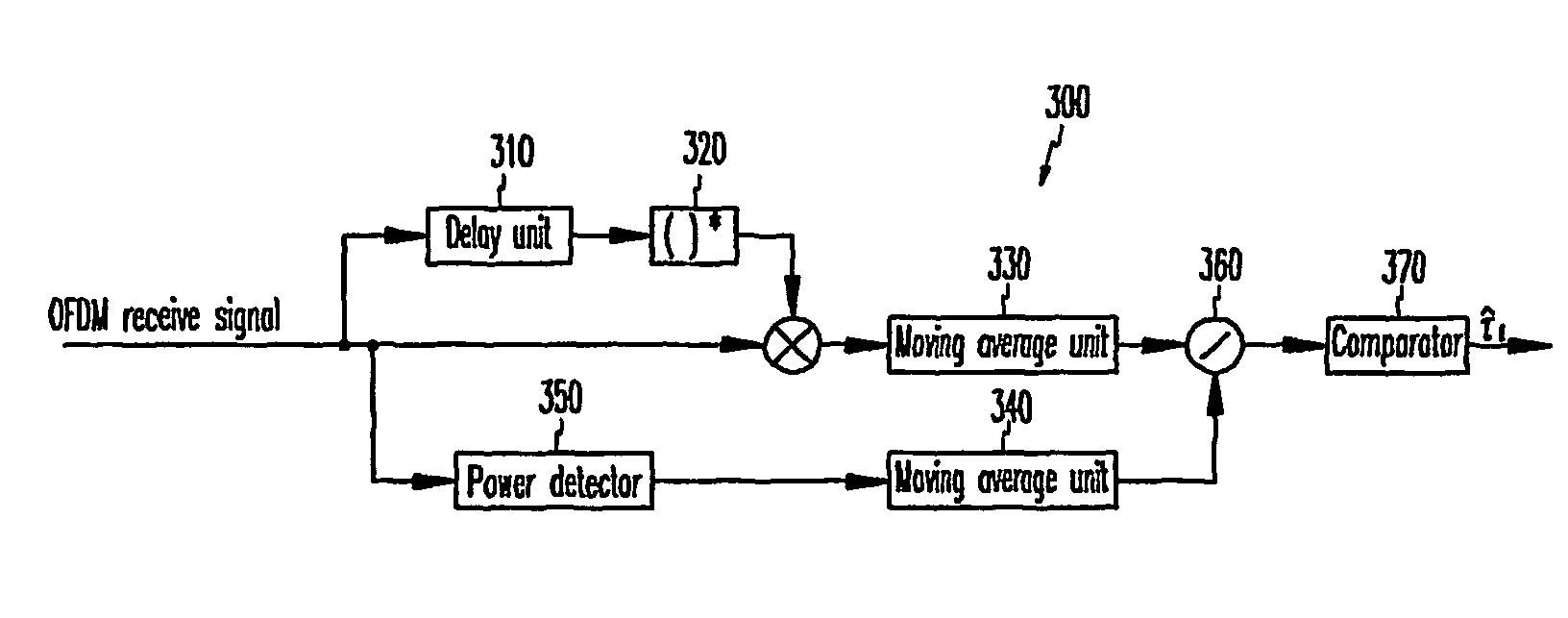
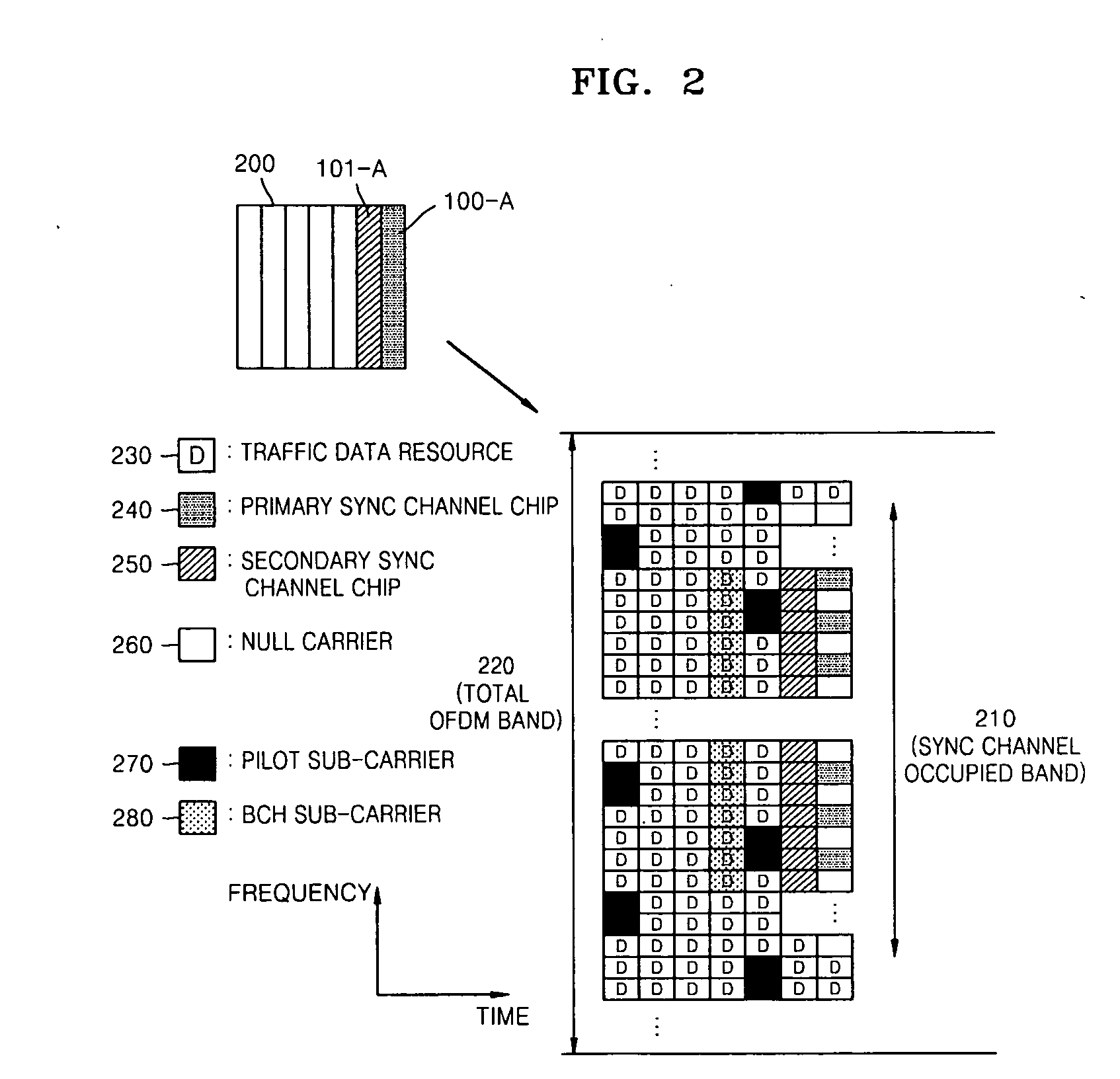
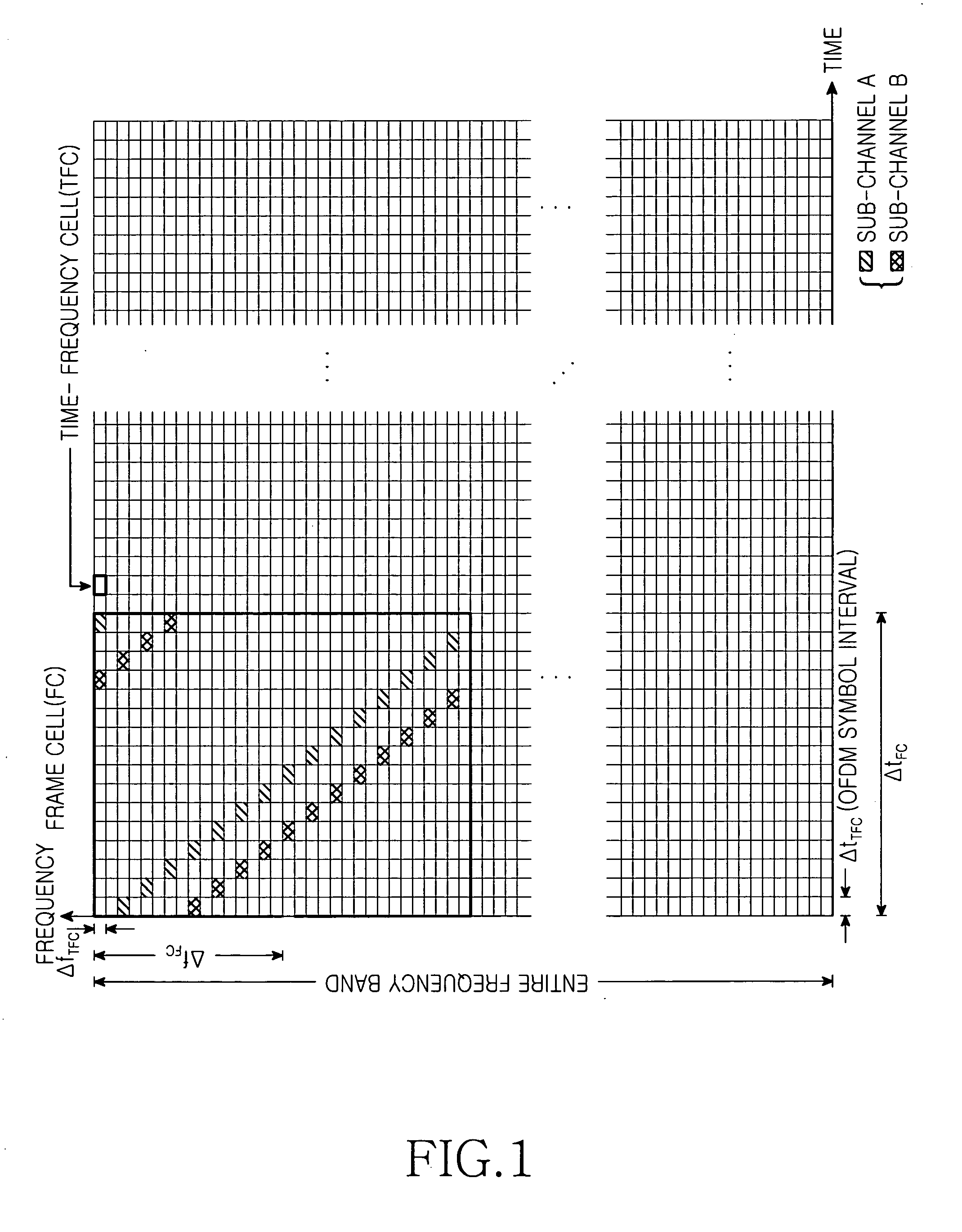
A cell search apparatus and method in an OFDM mobile communication system are provided. In the cell search apparatus, a symbol synchronization acquirer acquires OFDM symbol synchronization by performing CP correlation for a plurality of OFDM symbol intervals. A frame cell synchronization acquirer sorts received OFDM symbols according to the acquired OFDM symbol synchronization, and acquires frame cell synchronization by performing preamble correlation for a plurality of frame cell intervals. A pilot pattern detector sorts received frame cells according to the acquired frame cell synchronization, and detects a pilot pattern for identifying a base station by monitoring a plurality of frame cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for embodying and synchronizing downlink signal in mobile communication system and method for searching cell using the same
InactiveUS20060114812A1Solve the excessive calculationSynchronisation arrangementSignal allocationCell searchCyclic prefix
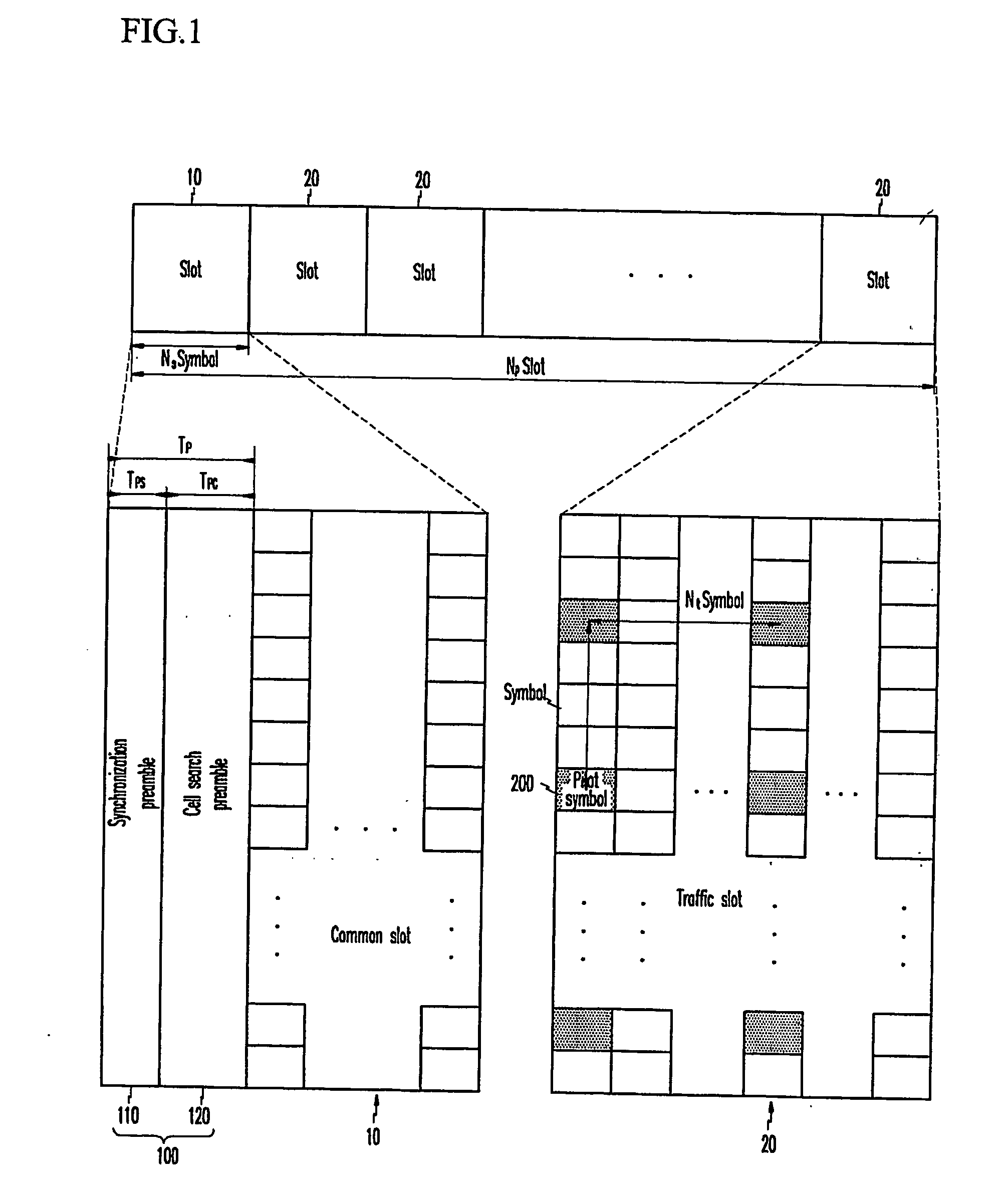
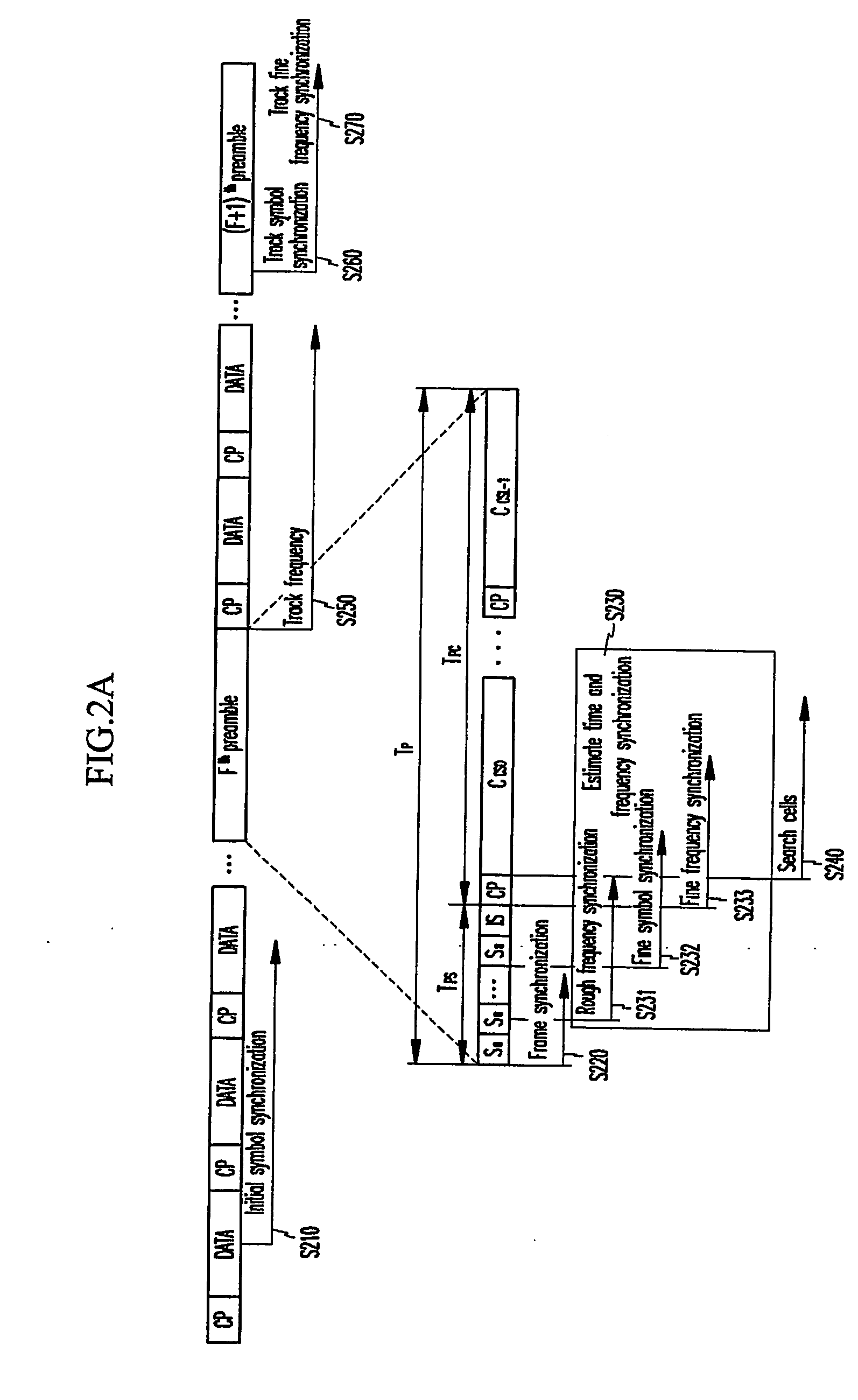
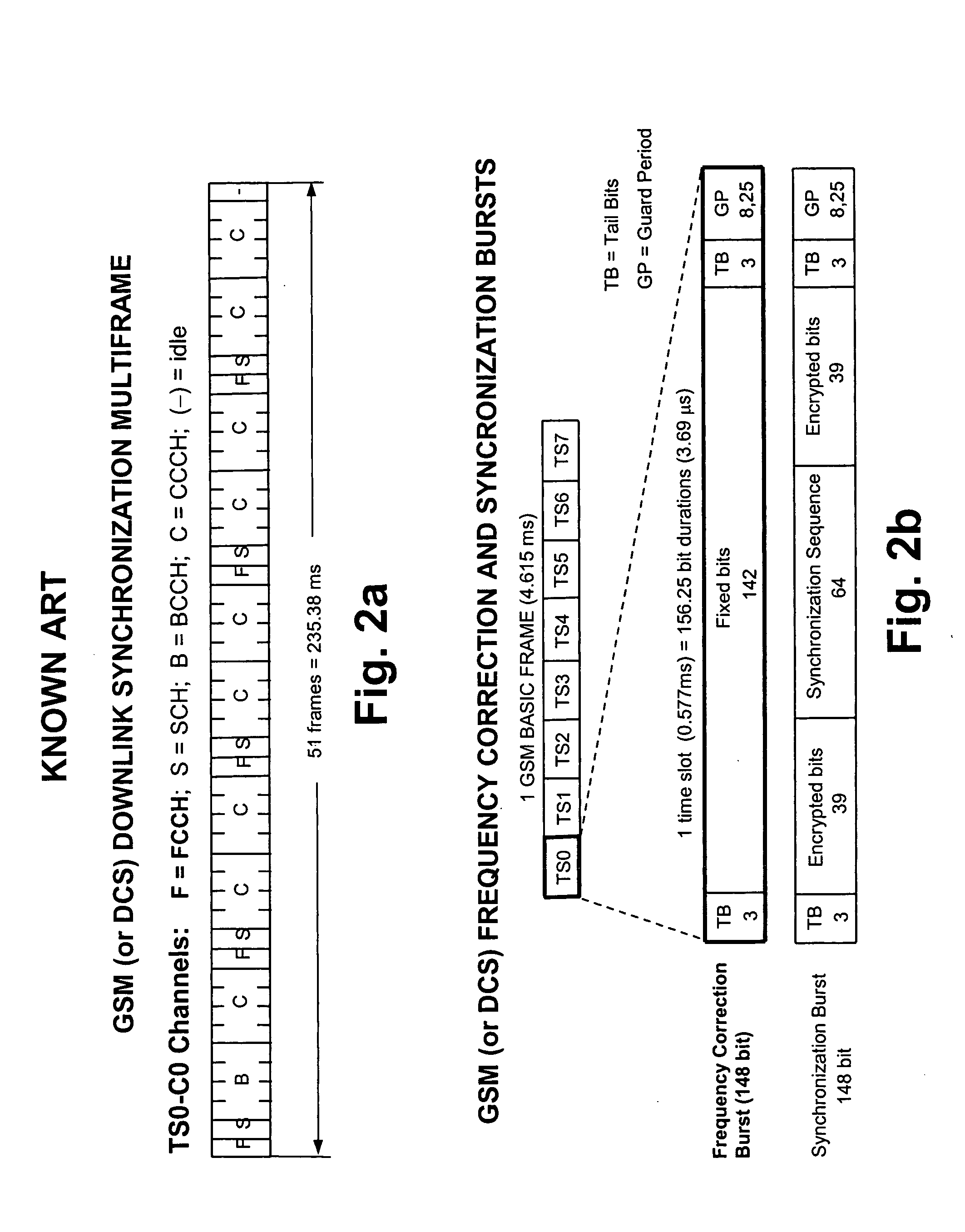
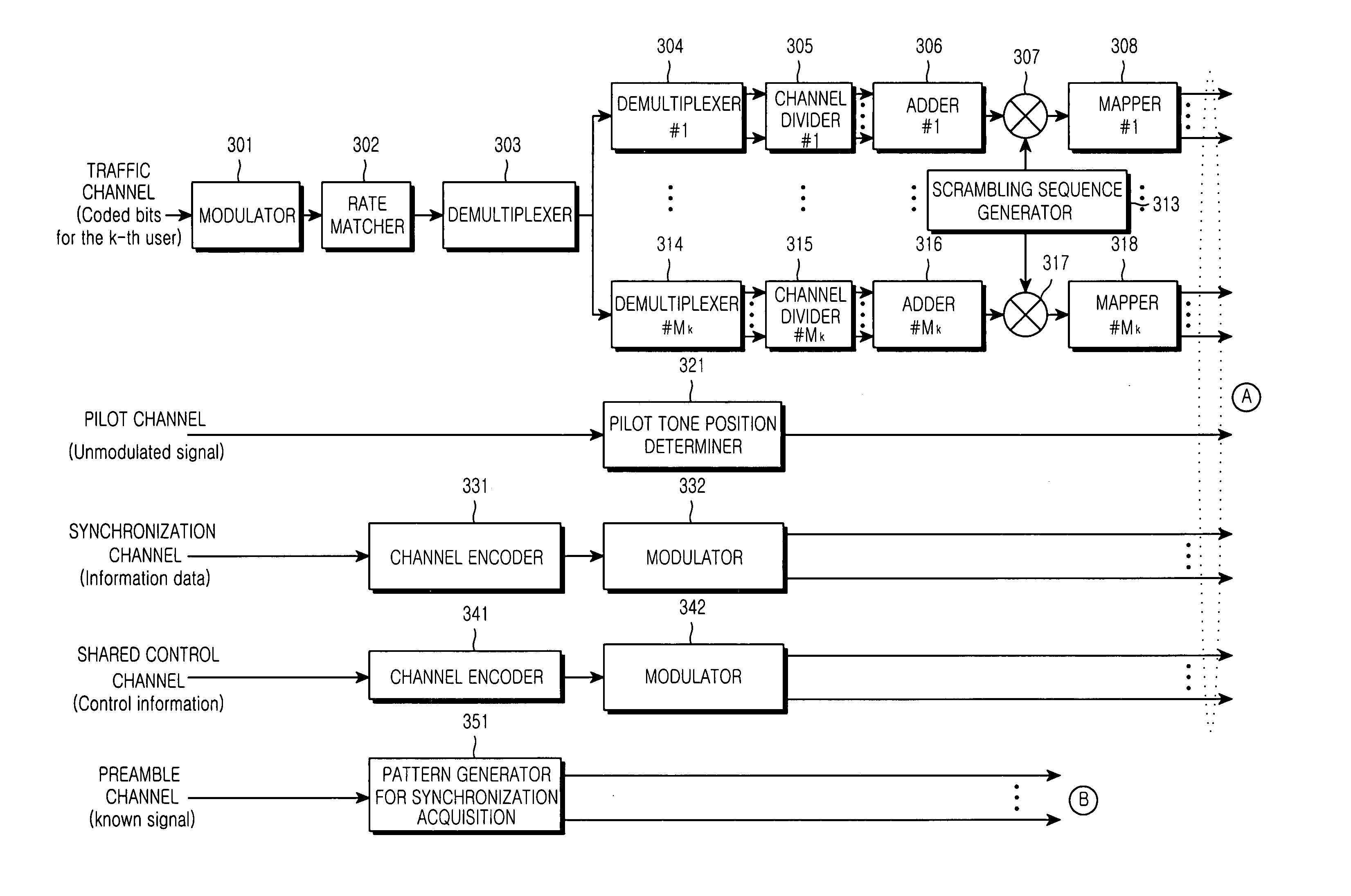
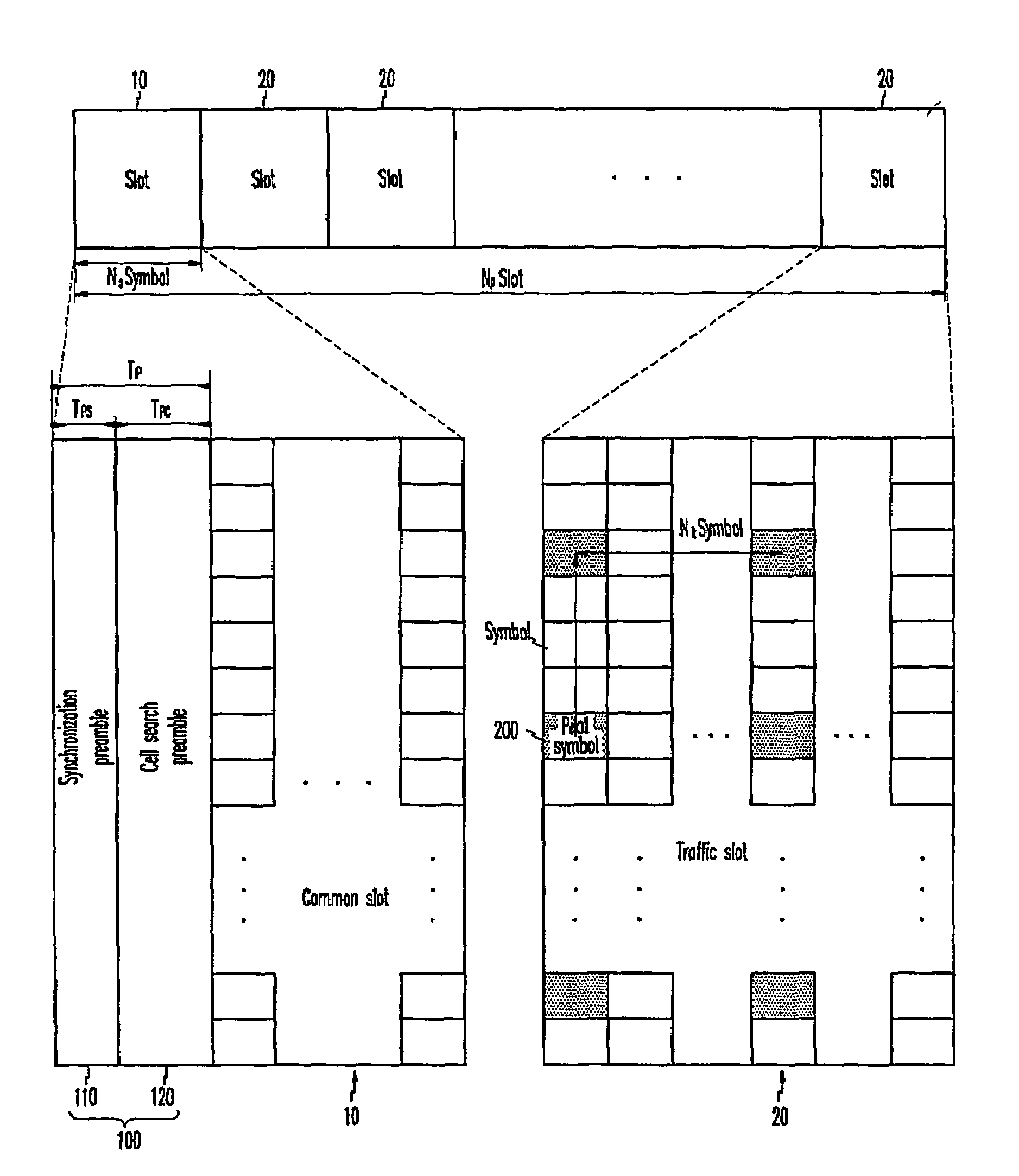
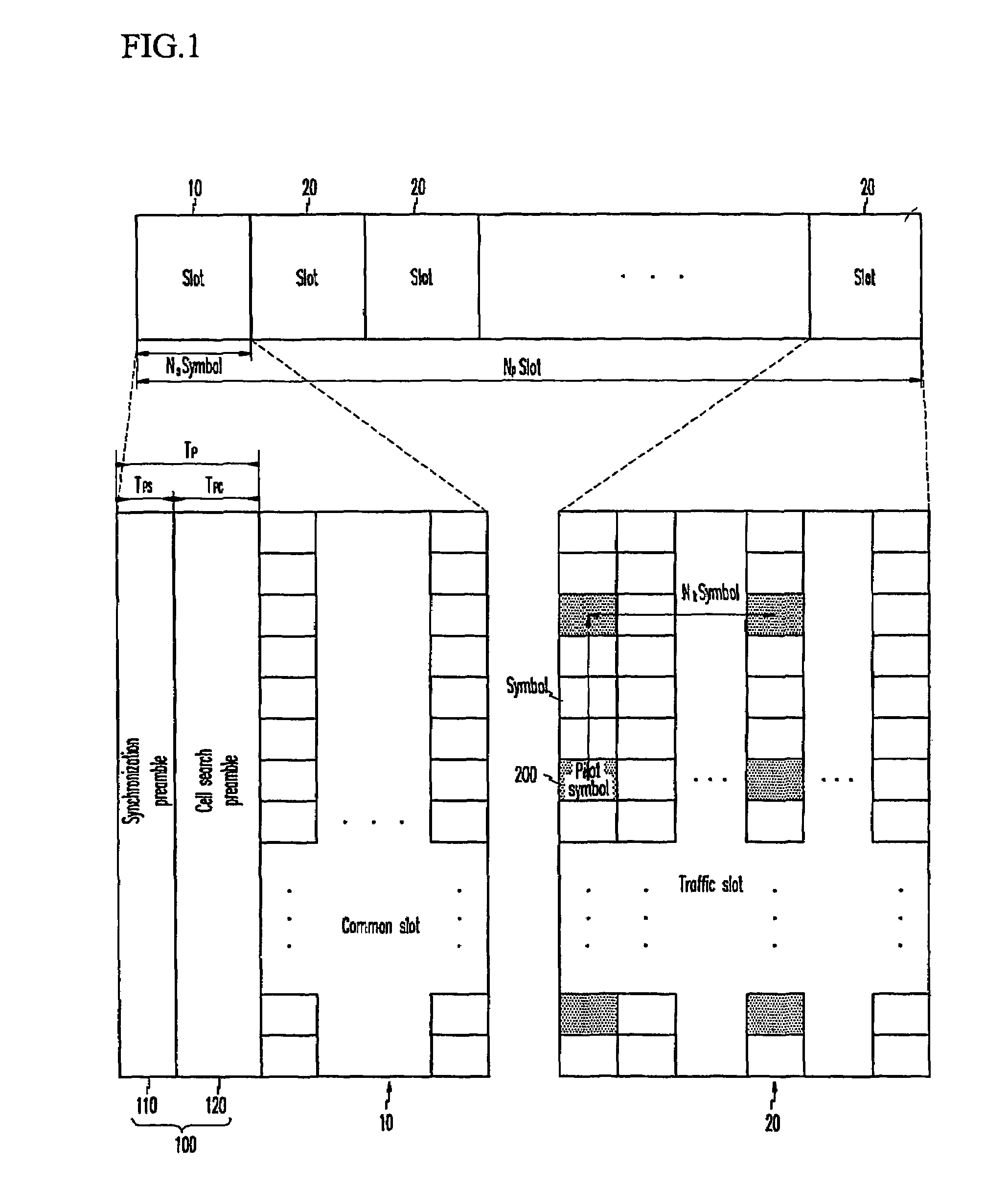
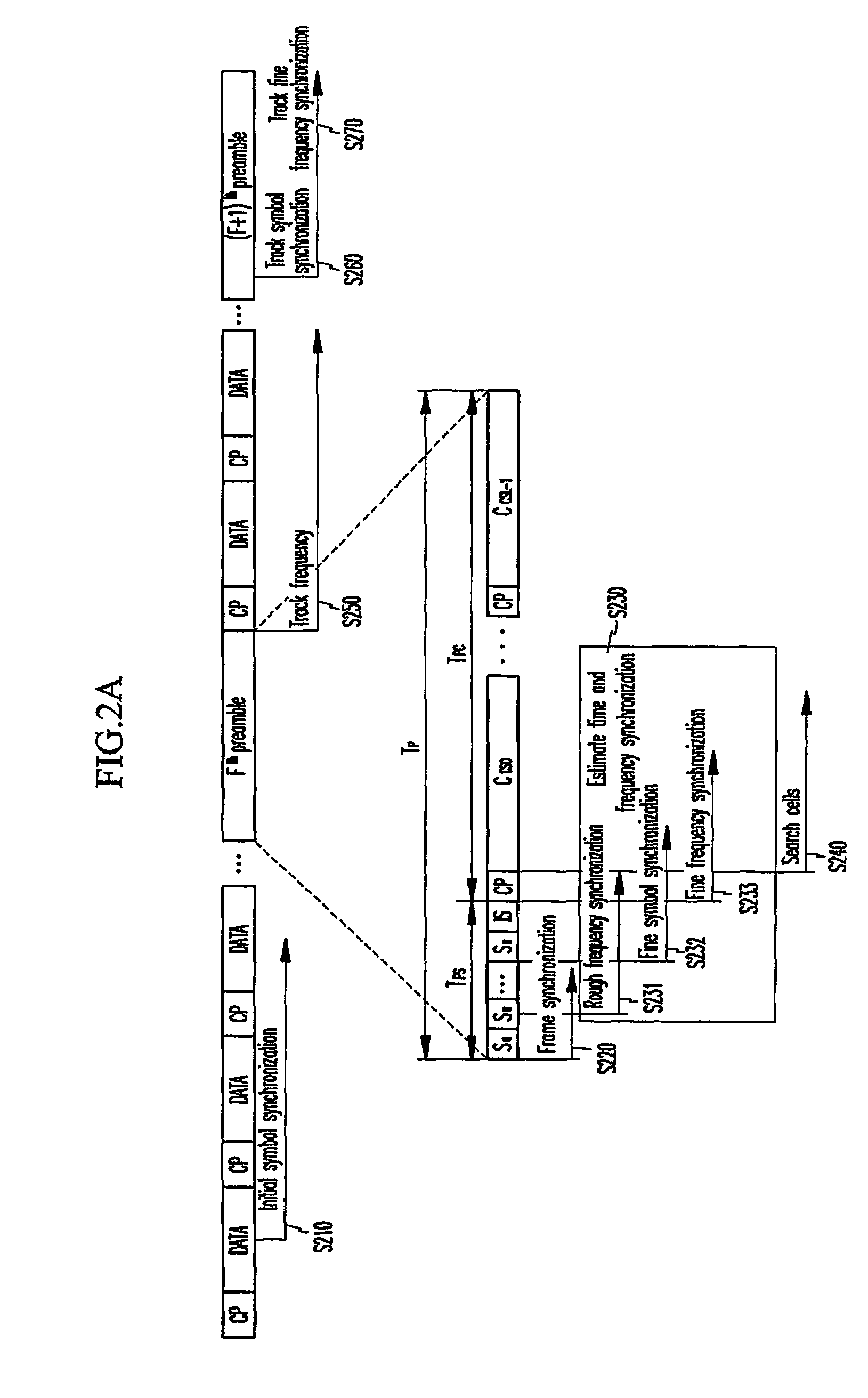
In an OFDMA-based cellular system, a frame of a downlink signal includes a common slot and traffic slots. The common slot includes a synchronization preamble and a cell search preamble. The synchronization preamble has a structure for synchronizing time and frequency, and the cell search preamble has a cell search structure. The traffic slot includes pilot symbols provided on the time and frequency axes. A cyclic prefix is used to estimate initial symbol synchronization, and the initial symbol synchronization and the synchronization preamble are used to synchronize the frame. The synchronization frame and the cell search preamble are used to estimate time and frequency synchronization. The cell search preamble is used to search cells. When the initial synchronization is performed, the cyclic prefix is used to track the frequency, the synchronization preamble is used to track symbol synchronization, and the cell search preamble is used to track fine frequency synchronization.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Method and mobile station to perform the initial cell search in time slotted systems
InactiveUS20050075125A1Speed up scan operationConvenient ArrangementSynchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionLow-pass filterCarrier signal
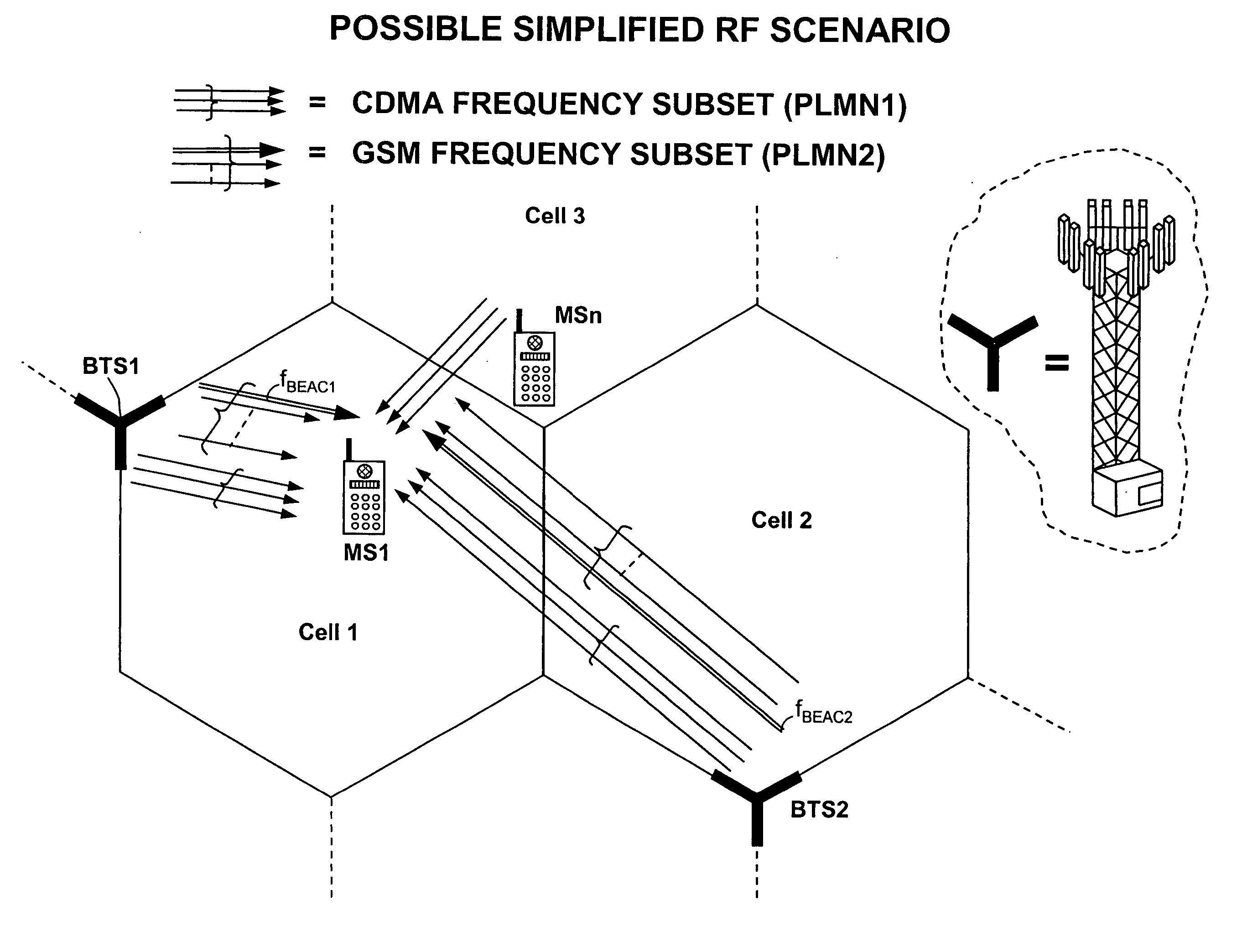
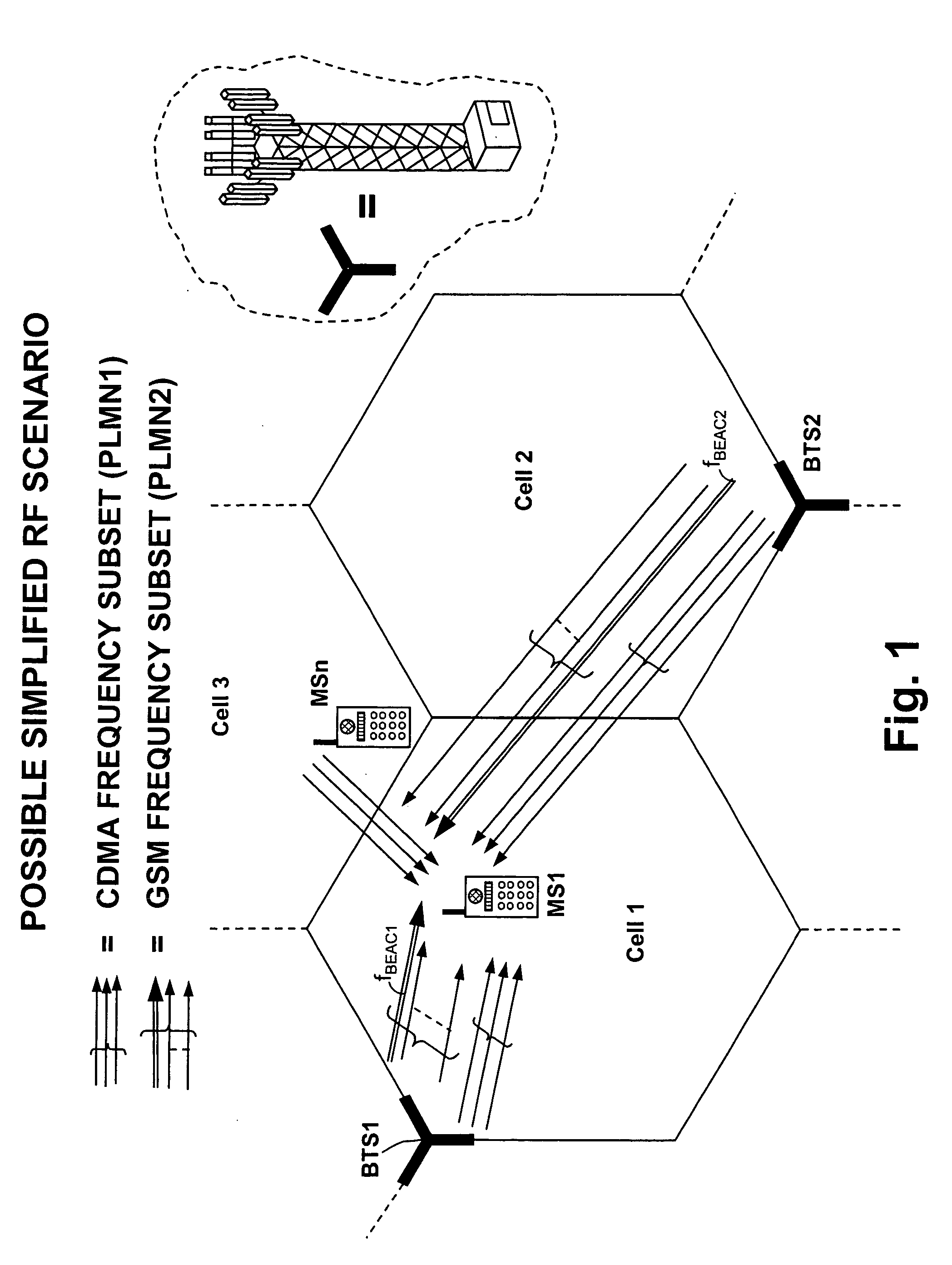
A method is disclosed that a Mobile Station MS performs at switch-on to search the most favorable target cell in UMTS systems like the 3GPP CDMA—LCR (Low Chip Rate) option at 1.28 Mcps—TDD (Time Division Duplex) mode and the equivalent TD-SCDMA (Time Division—Synchronous CDMA). Signal at the MS antenna is the sum of different RF downlink frames coming from different carriers in the assigned frequency ranges. A DL synchronization timeslot and a BCCH TS0 are both transmitted with full power in the frames, the first one includes one out of 32 SYNC codes assigned on cell basis. Following a conventional approach the absence of a common downlink pilot and without prior knowledge of the used frequencies would force the MS, for all the frequencies of the channel raster stored in the SIM card, the correlation of the received frame with all the 32 SYNCs stored in the MS, in order to detect the BSIC of a cell to which associate the power measures. Following the two-step method of the invention the power measures are performed in two-step scan of the PLMN band without interleaved correlation steps; once a final frequency is selected the respective frame is the only correlated one. At least one frame duration about 5 ms long of the whole 15 MHz bandwidth is acquired, IF converted, A / D converted and the digital set is stored. A rough scan is performed multiplying the digital set by a digital IF tuned in steps wide as the channel band (1.6 MHz) along the 15 MHz band, and filtering the baseband signal with a Root Raise Cosine low-pass filter. The 5 ms baseband signal is subdivided into 15 blocks of half timeslot (337.5 μs) and the power of each block is measured. The power of the strongest block indicates the priority of the respective frequency. The strongest power values are put in a Spectral Table together with respective frame load indicators. The load indicator is the percentage of timeslots in a frame almost equally loaded as the strongest block. The three strongest frequencies are selected for the successive scan. The second step search is performed like the first one but the IF steps are now 200 kHz wide and cover the only 1.6 MHz spectrum around a selected frequency. A final frequency is selected for the successive correlation step. Then the frequency error of the MS reference oscillator is corrected with data-aided techniques and a calibration value stored for successive connections (FIG. 9).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
Tdm based cell search method for OFDM system
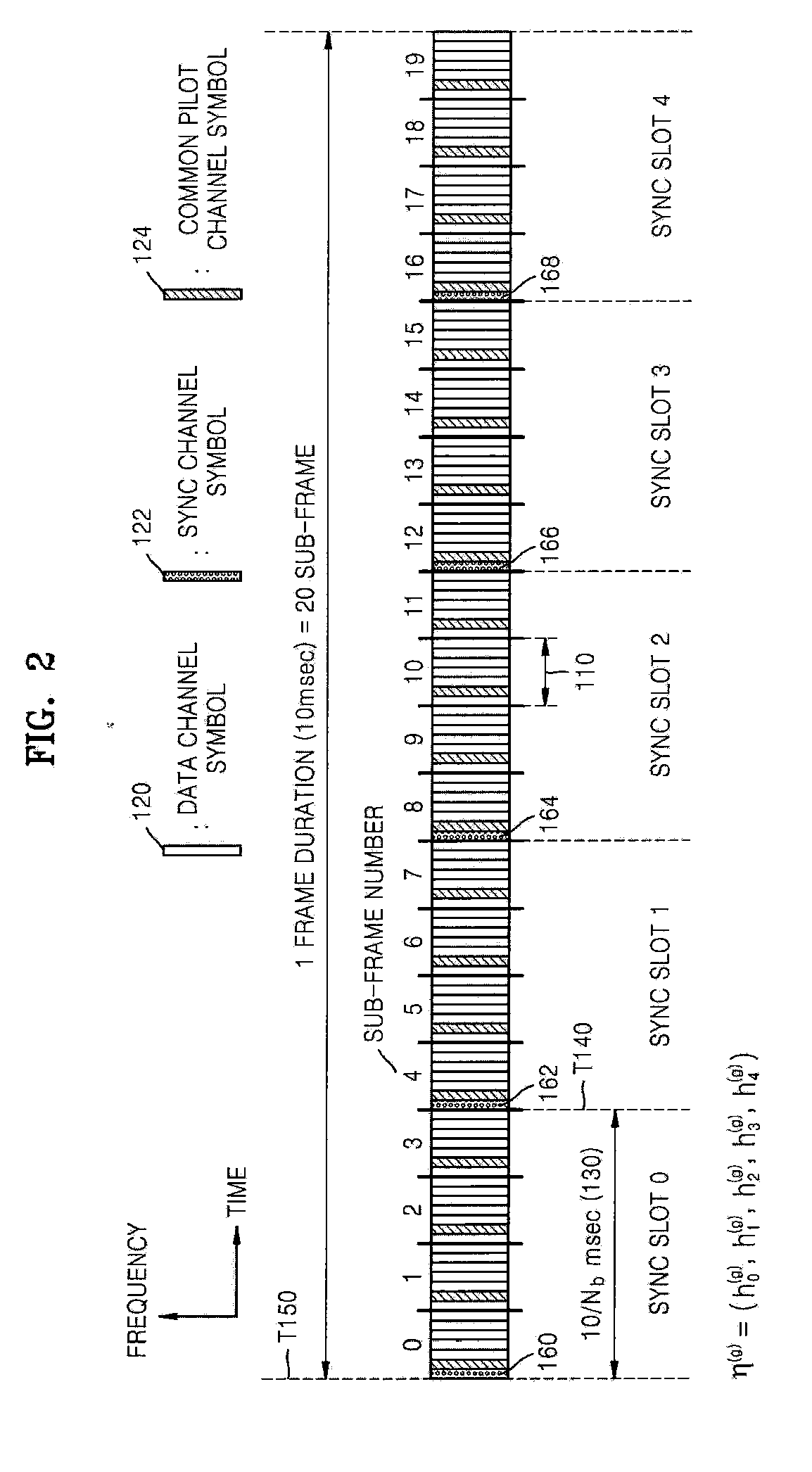
ActiveUS20090196279A1Shorten the timeReduce complexityEnergy efficient ICTSynchronisation arrangementComputer hardwareCell search
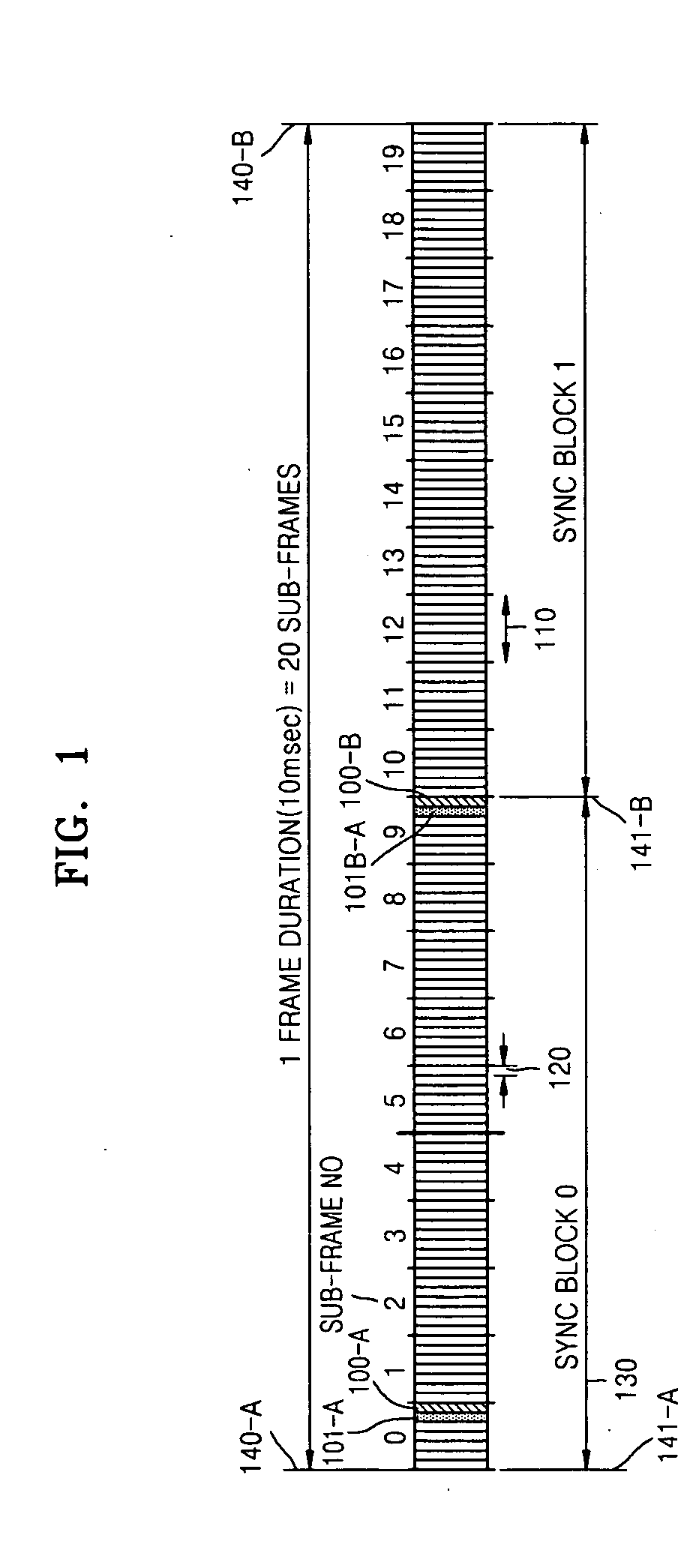
Provided are a sync channel of a forward link, a common pilot channel structure, and an initial cell search method and an adjacent cell search method for handover in a cellular system using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). A cell search method in an OFDM cellular system in which a primary sync channel and a secondary sync channel are configured based on time division multiplexing (TDM) includes acquiring sync block synchronization and a primary sync channel sequence number using a primary sync channel symbol included in a frame received by a terminal, detecting a boundary of the frame and a scrambling code group using the sync block and a secondary sync channel symbol included in the frame received by the terminal, and acquiring a scrambling code using the primary sync channel sequence number and the scrambling code group, thereby reducing cell search time with low complexity.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Apparatus and method for cell search in mobile communication system using a multiple access scheme
InactiveUS20050002369A1Increase speedModulated-carrier systemsTransmission monitoringPattern detectionCell search
An apparatus and a method for cell search in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing-based mobile communication system using a multiple access scheme. The method includes the steps of: detecting a symbol boundary of an input reception signal; detecting a frame cell boundary after synchronizing with the detected symbol boundary; detecting a reference signal for each symbol interval in a preset search interval; and detecting a pattern of the detected reference signals and detecting a base station to which the terminal belongs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
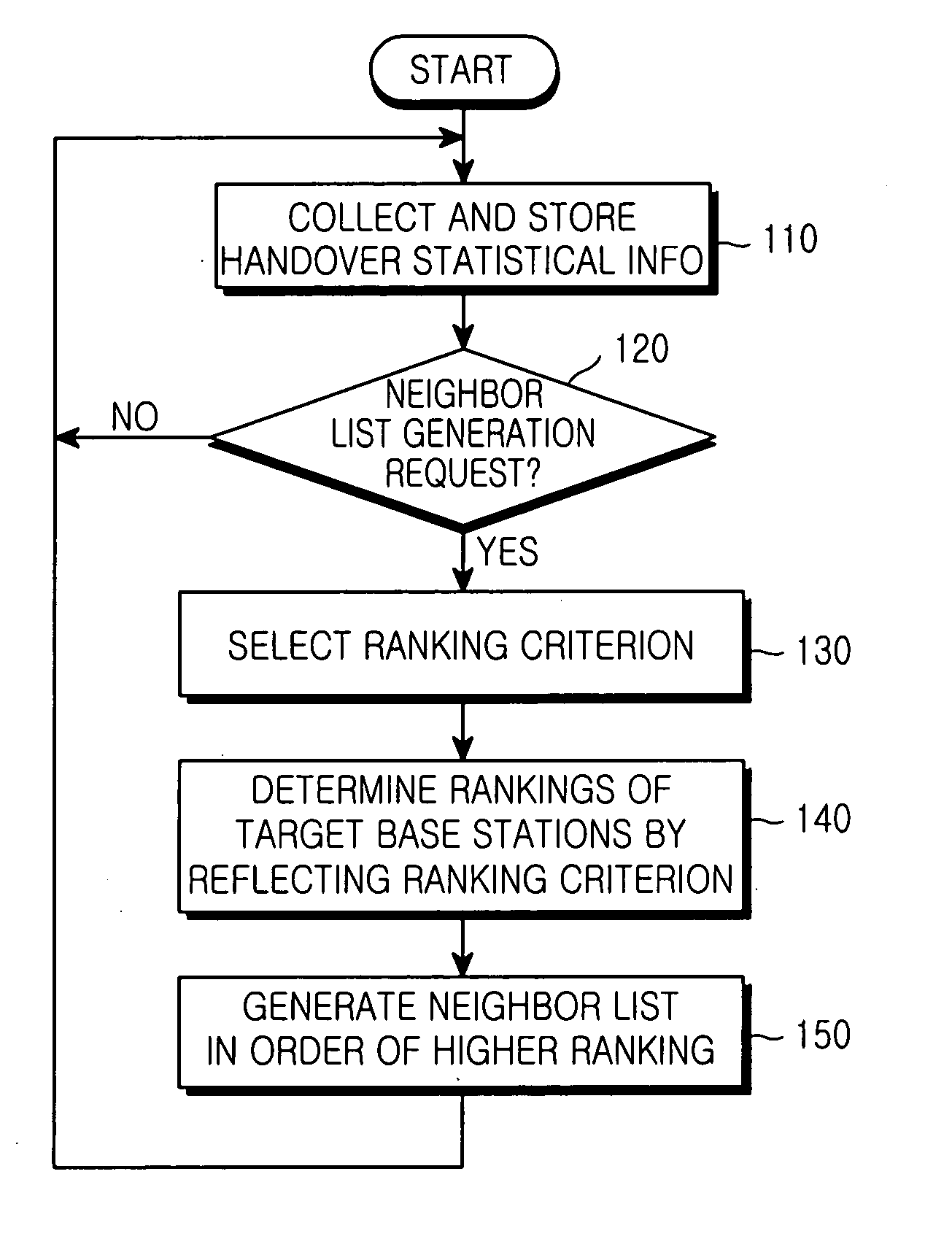
Method and apparatus for generating handover neighbor list in a cellular mobile communication system
ActiveUS20050048974A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationRankingCell search
A method and apparatus for generating a handover neighbor list of base stations capable of communicating with a mobile terminal in a cellular mobile communication system. A UMTS RAN manager (URM) collects handover attempt count and handover ratio data as handover statistical information of a source base station and determines rankings of target base stations in order of handover frequency from the base station according to the handover attempt count or the handover ratio. The URM then generates a neighbor list of the source base station in order of high ranking. The proposed method and apparatus reduces overhead due to cell searching in performing handover.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for cell search in a communication system
InactiveUS20080043702A1Efficient processEfficient methodModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemCell search
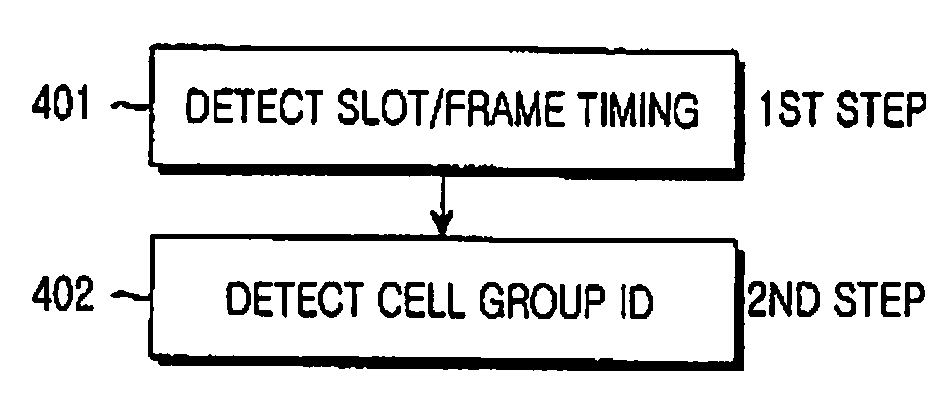
A cell search using a Primary Synchronization Channel (P-SCH) and an Secondary Synchronization Channel (S-SCH) received from a Base Station (BS) are provided, in which a Mobile Station (MS) receives a P-SCH signal including at least two different P-SCH synchronization codes in different slots of a frame and detects slot timing and frame timing using the P-SCH signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and System for Utilizing Transmit Local Oscillator for Improved Cell Search and Multi-Link Communication in Multi-Mode Device
ActiveUS20090168914A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsTransmission monitoringMulti linkLocal oscillator
A multi-receiver wireless communication device includes a transmitter, a transmit oscillator communicatively coupled to the transmitter, a receive oscillator communicatively coupled to a first receiver and second receiver, and a switching assembly having a first state in which the receive oscillator is coupled to the first and second receivers and a second state in which the receive oscillator is de-coupled from the second receiver and the transmit oscillator is coupled to the second receiver. The first receiver and the second receiver of the wireless communication device are able to operate independent of one another when the switching assembly is in the second state.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
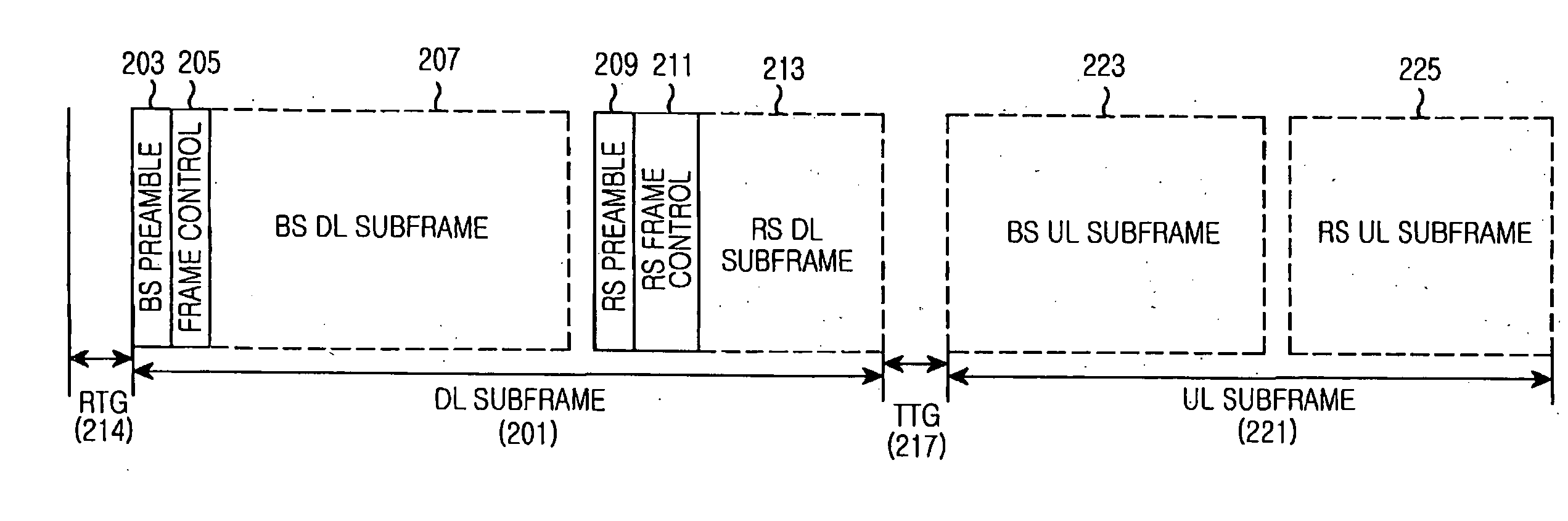
Apparatus and method for supporting multi-link in multi-hop relay cellular network
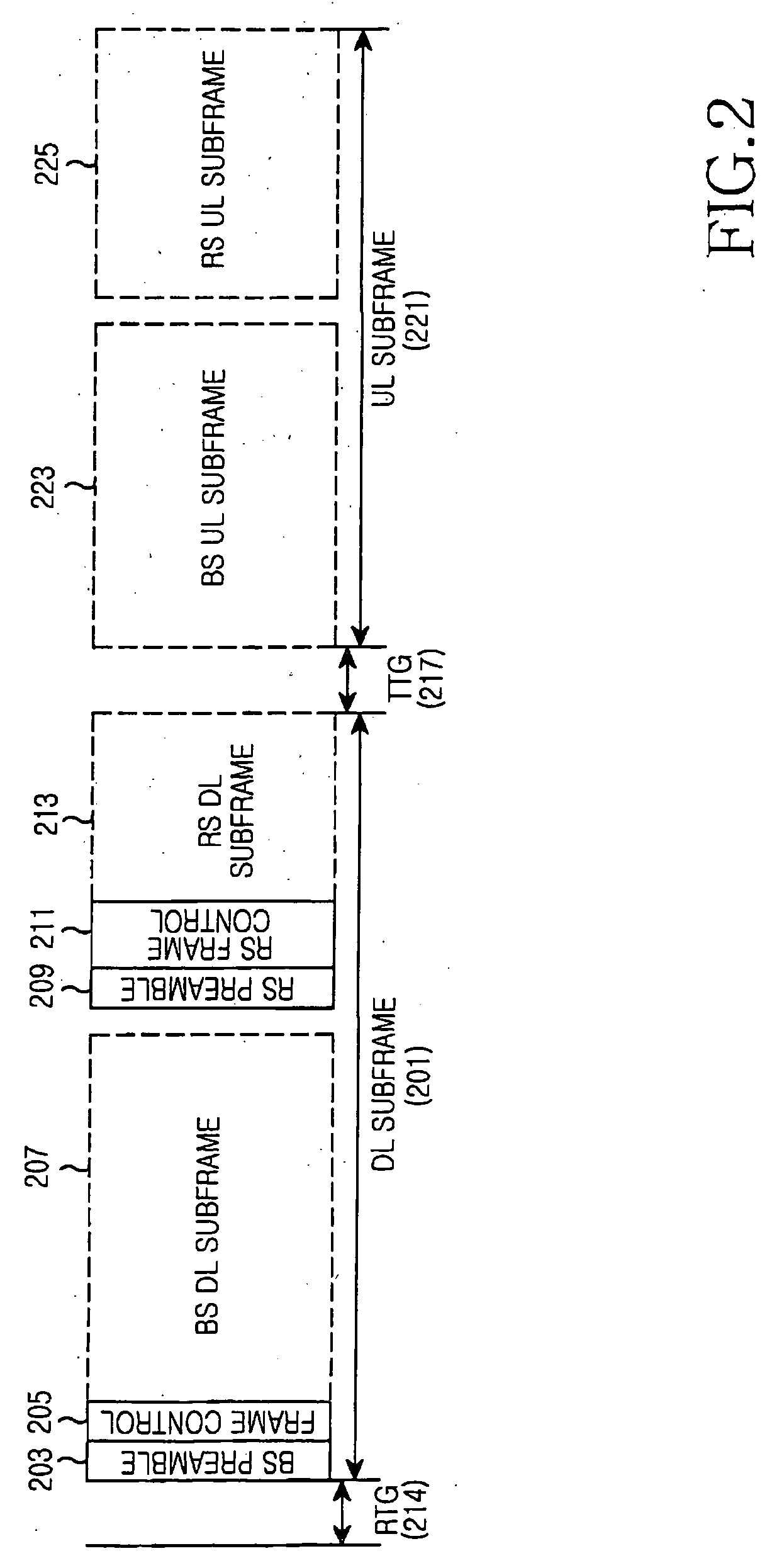
A framing method of fixing a training signal and a control channel for multi-link (direct link and relay link) synchronization in a multi-hop relay cellular network, and a transmitting / receiving apparatus for supporting the framing method. A base station (BS) transmits BS downlink (DL) subframe sequentially including a preamble, control information, and a DL burst to a relay station (RS) or a first mobile station (MS) connected to the BS by direct link. The RS transmits an RS DL subframe sequentially including a DL burst, a postamble, and control information to a second MS connected to the BS by relay link. Therefore, difficulties of initial synchronization, handoff, and cell search can be removed from MSs. Furthermore, multi-link bursts can be located between the preamble and the postamble by Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) or Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for transmitting synchronization signals in an OFDM based cellular communication system
ActiveUS20090219883A1Process stabilityInterference minimizationSynchronisation arrangementTransmission path divisionCell specificFrequency reuse
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for transmitting the synchronization signal in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) based cellular system. The cell search process widely used in the OFDM based cellular system is divided into two steps for obtaining the frame timing synchronization and obtaining the cell-specific scrambling code. When designing the channel for obtaining the frame timing synchronization and the channel for obtaining the cell-specific scrambling code, different frequency reuse factors are applied to the synchronization channels of different steps according to the characteristics of each synchronization obtainment step in order to improve the performance of each step.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET INT LTD
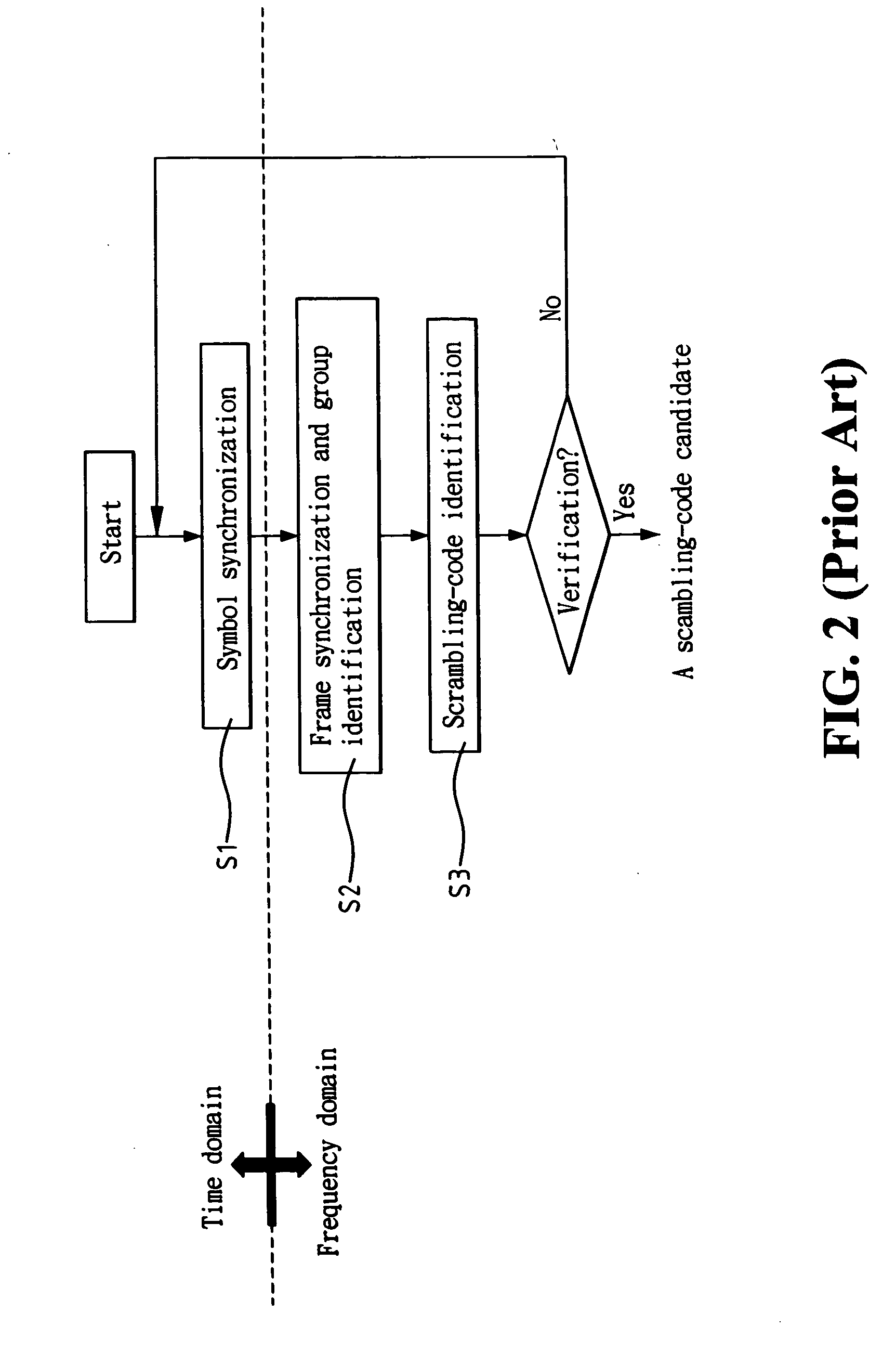
Apparatus for performing initial synchronization and frame synchronization in mobile communications system and method thereof
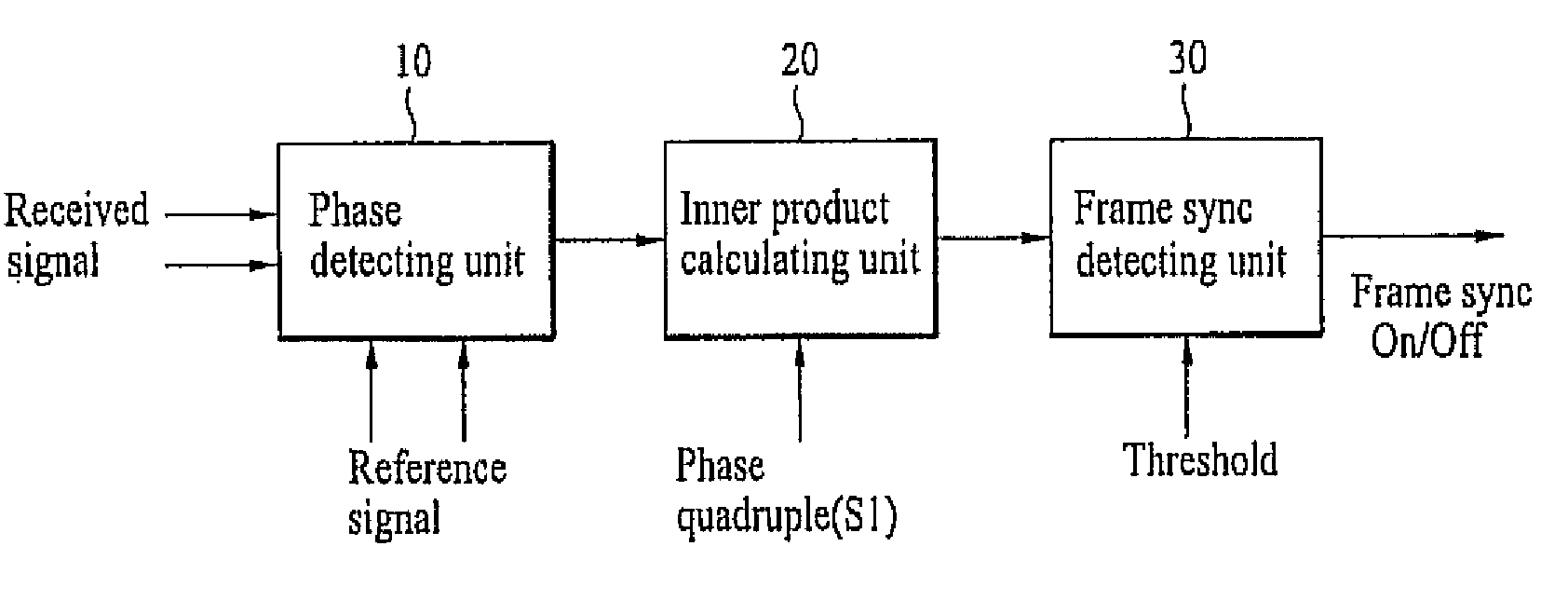
InactiveUS20070098116A1Without increasing excessive memoryDetection errorAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationCommunications systemReference vector
An apparatus for performing initial synchronization and frame synchronization in a mobile communications system and method thereof are disclosed. First of all, a method and apparatus for performing frame synchronization in a mobile communications system using a correlation value between a received signal and a reference vector for a phase according to one embodiment of the present invention are disclosed. Secondly, a method and apparatus for performing frame synchronization by considering all phase modulation possibility and frequency offsets according to another embodiment of the present invention are disclosed. Thirdly, a method and apparatus for performing initial estimation in a manner of dividing at least one subframe received from a base station by a UE in the course of cell search into at least two areas, calculating a correlation for each of the at least two areas and using a maximum value of the calculated correlation value per area are disclosed.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
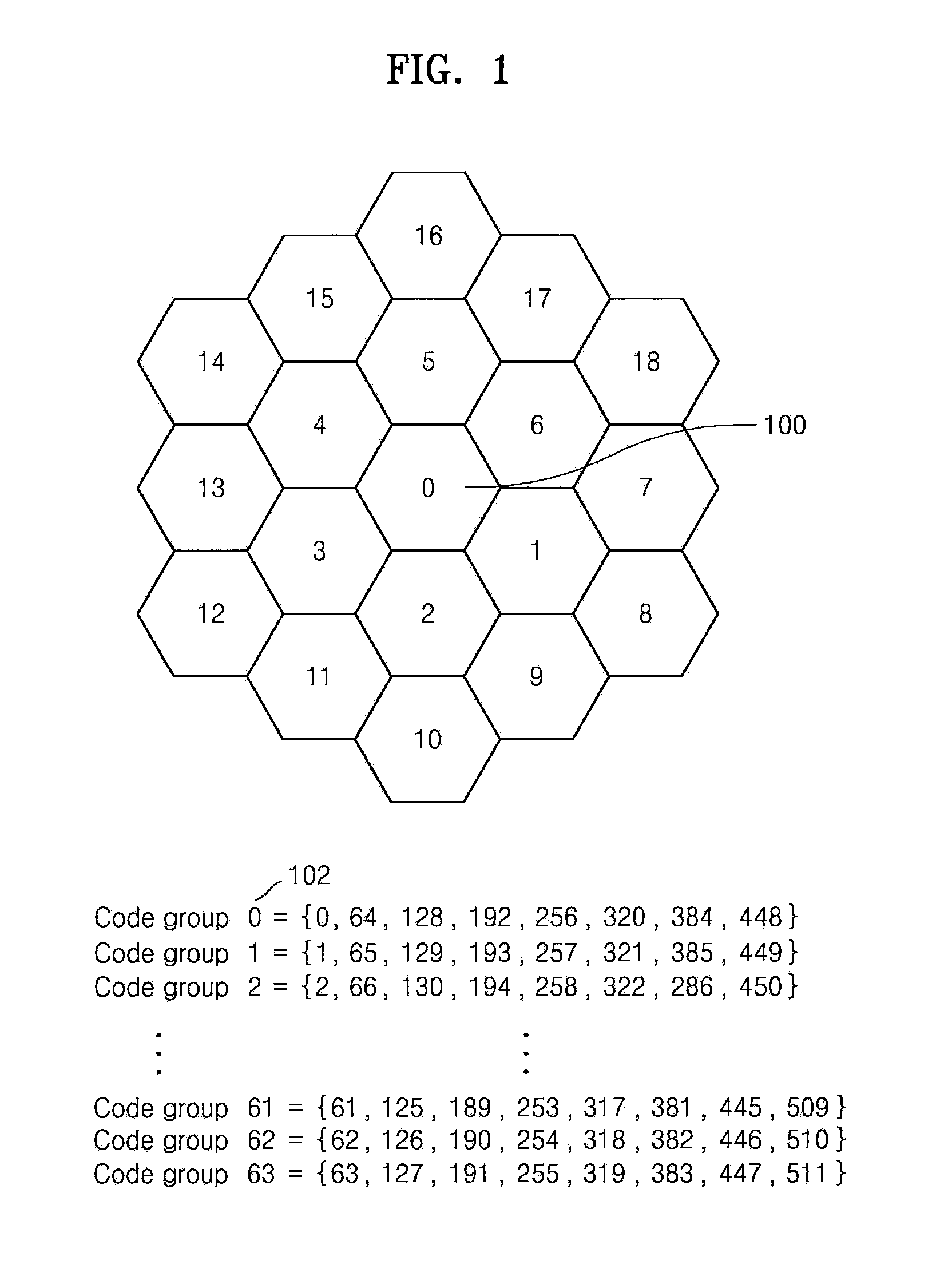
Cell search method in OFDM cellular system, frame transmission method thereof, and forward link frame structure
Provided are a cell search method, a frame transmission method thereof, and a forward link frame structure thereof. The cell search method used by a terminal to search a target cell using reception signals received from a plurality of base stations, each base station transmitting a frame of its cell, in an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) cellular system comprising a plurality cells to which a cell-specific scrambling code is assigned includes: detecting a hopping pattern of the target cell using reception sync channel symbols, which are signals corresponding to sync channel symbol positions of the reception signals, wherein the frame of each cell comprises M sync channel symbols code-hopped according to a hopping pattern of the cell, where M is a natural number equal to or greater than 2, each hopping pattern containing M sync channel code sequences and respectively corresponding to each code group to which a scrambling code of each cell belongs, and an arbitrary hopping pattern used in the OFDM cellular system differs from a cyclically shifted result of the hopping pattern, other hopping patterns, or cyclically shifted results of the other hopping patterns; and detecting a code group of the target cell based on the detected hopping pattern. Accordingly, a cell search time and the complexity of the cell search can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
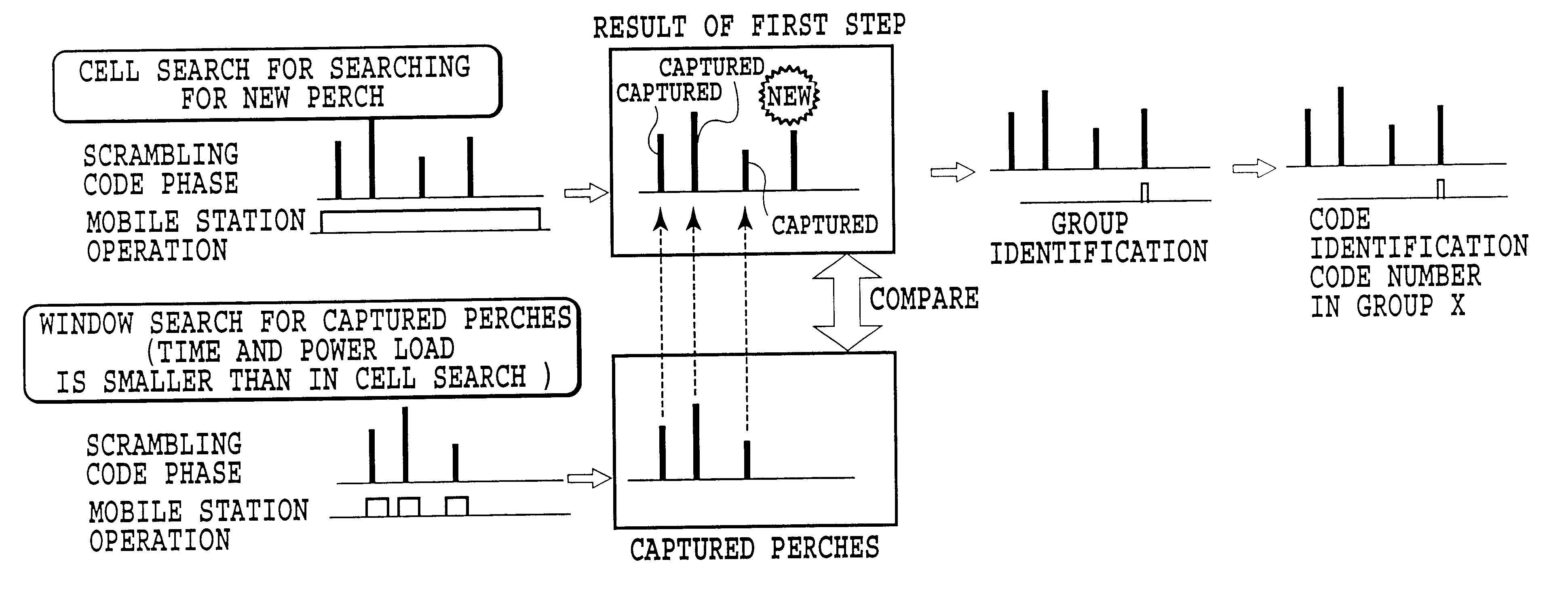
Control method of searching neighboring cells, mobile station, and mobile communication system
InactiveUS6697622B1Improve selection accuracyIncrease frequencyEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemCell search
A control method of searching for a neighboring cell of a mobile station communicating with a base station is provided in a direct sequence CDMA mobile communication system which transmits information by carrying out double modulation using a first spreading code group and a second spreading code. The first spreading code group includes spreading codes that have a same repetition period as an information symbol period and are used in common by the base stations, and the second spreading code has a repetition period longer than the information symbol period. The base stations are assigned different second spreading codes. The control method stores at least one second spreading code and its phase into a first table, which second spreading code corresponds to a perch channel whose second spreading code and phase are known; stores a second spreading code used by a neighboring base station into a second table; searches for a perch channel whose second spreading code and phase are unknown; and searches for a perch channel whose second spreading code and phase are known. The neighboring cell search method can save the power consumption and time required for the mobile station to carry out the cell search with preventing an increase in the total cost of the system.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method and apparatus for transmitting/receiving downlink synchronization channels in a cellular communication system supporting scalable bandwidth
ActiveUS20080080476A1Scalability of systemModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemCell search
Disclosed is a method and an apparatus for transmitting a downlink Synchronization CHannel (SCH) in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)-based cellular wireless communication system supporting a scalable bandwidth. Herein, initial cell search and neighbor cell search are seamlessly performed. The disclosed method and apparatus disclose a synchronization channel structure applicable to both a Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) system and a Time Division Duplex (TDD) system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-carrier transmission/reception apparatus
InactiveUS7386055B2Radio resourceSuppress interferenceAssess restrictionConnection managementCarrier signalCell search
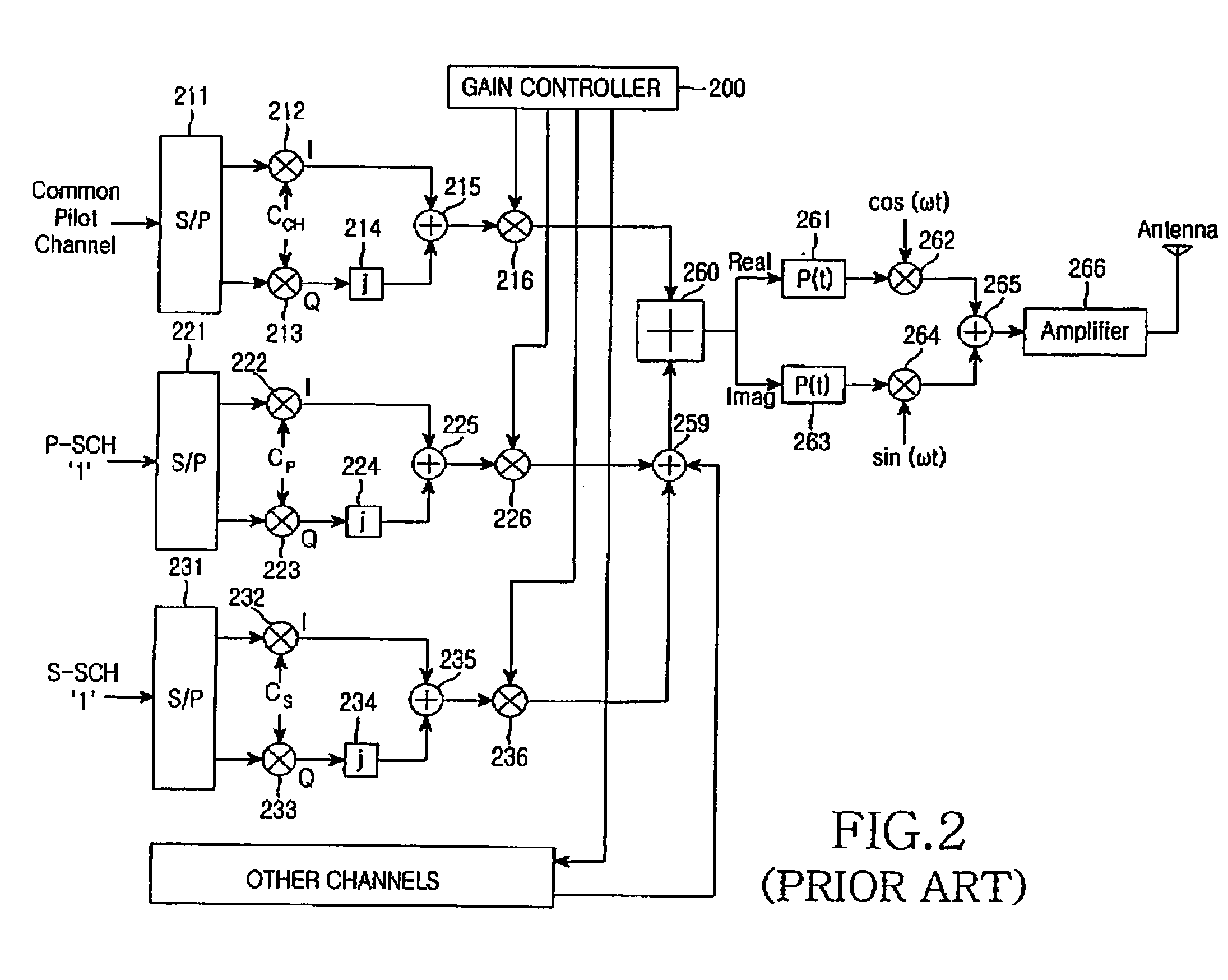
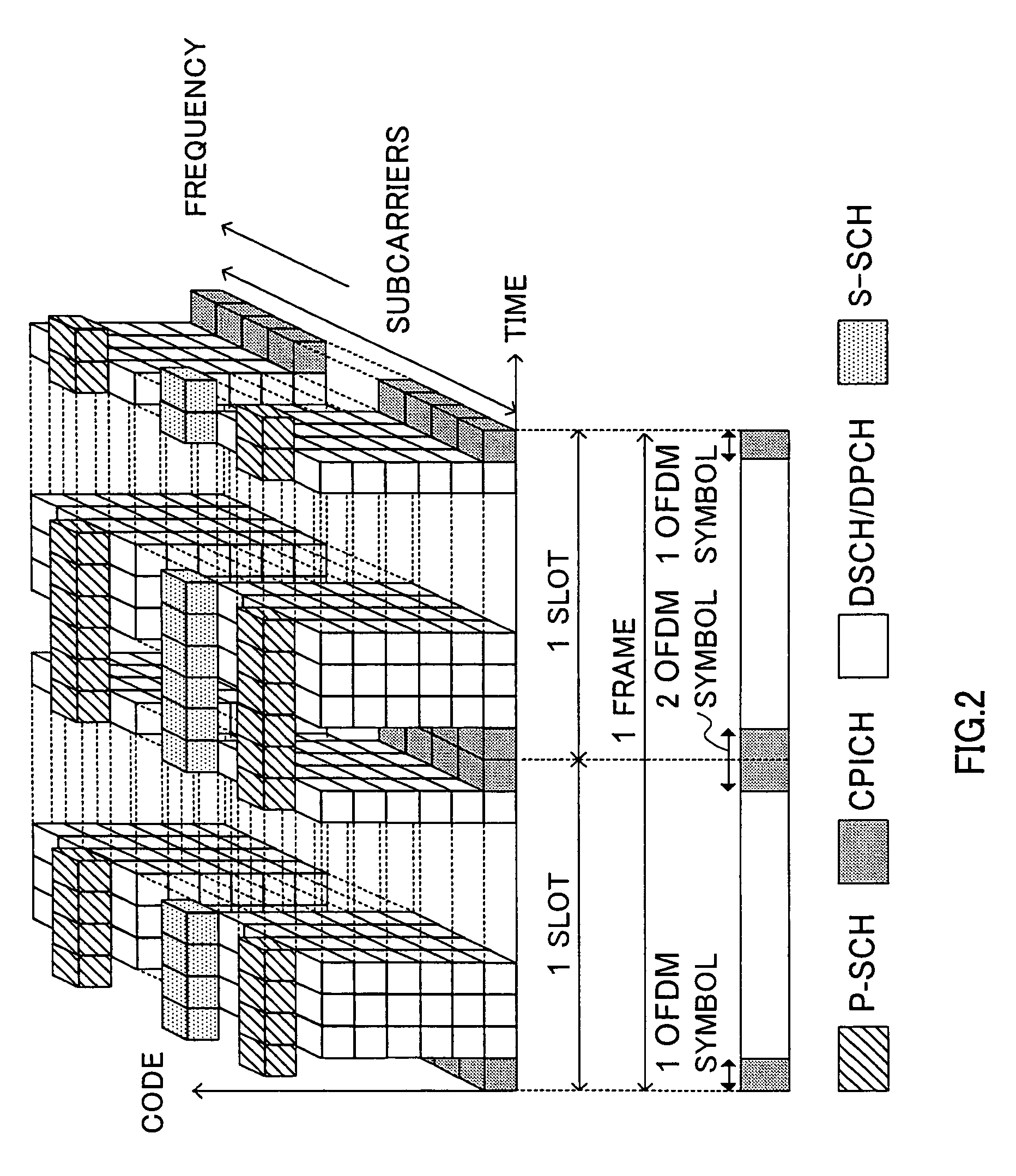
A multicarrier radio communication technology that enables radio resources to be used effectively, interference-to be suppressed, and a cell search to be performed at high speed, in a multicarrier CDMA system. In this technology, a secondary synchronization code (S-SCH signal) for identifying the group of scrambling codes divided into groups beforehand is frequency multiplexed in a plurality of subcarriers. A secondary synchronization code is coded in the time direction. Subcarriers in which a secondary synchronization code is multiplexed are mutually separated and equally spaced. The number of subcarriers in which a secondary synchronization code is multiplexed can be set to a small value with respect to the total number of subcarriers. A secondary synchronization code is an orthogonal code. On the receiving side, a cell search is carried out using such a frequency multiplexed type S-SCH.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method and apparatus for embodying and synchronizing downlink signal in mobile communication system and method for searching cell using the same
In an OFDMA-based cellular system, a frame of a downlink signal includes a common slot and traffic slots. The common slot includes a synchronization preamble and a cell search preamble. The synchronization preamble has a structure for synchronizing time and frequency, and the cell search preamble has a cell search structure. The traffic slot includes pilot symbols provided on the time and frequency axes. A cyclic prefix is used to estimate initial symbol synchronization, and the initial symbol synchronization and the synchronization preamble are used to synchronize the frame. The synchronization frame and the cell search preamble are used to estimate time and frequency synchronization. The cell search preamble is used to search cells. When the initial synchronization is performed, the cyclic prefix is used to track the frequency, the synchronization preamble is used to track symbol synchronization, and the cell search preamble is used to track fine frequency synchronization.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Downlink signal reception method and user equipment, and downlink signal transmission method and base station
ActiveUS20190230696A1Efficiently transmitted/receivedImprove throughputTransmission path divisionSignal allocationBroadcast channelsCarrier signal
A default subcarrier spacing for use in transmission / reception of a broadcast channel is defined for each frequency range. A base station transmits a broadcast channel in a frequency band, using the default subcarrier spacing defined for a frequency range to which the corresponding frequency band belongs. A user equipment attempts to detect a broadcast channel in the frequency band where a cell search is being attempted, using the default subcarrier spacing defined for a frequency range to which the frequency band belongs.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
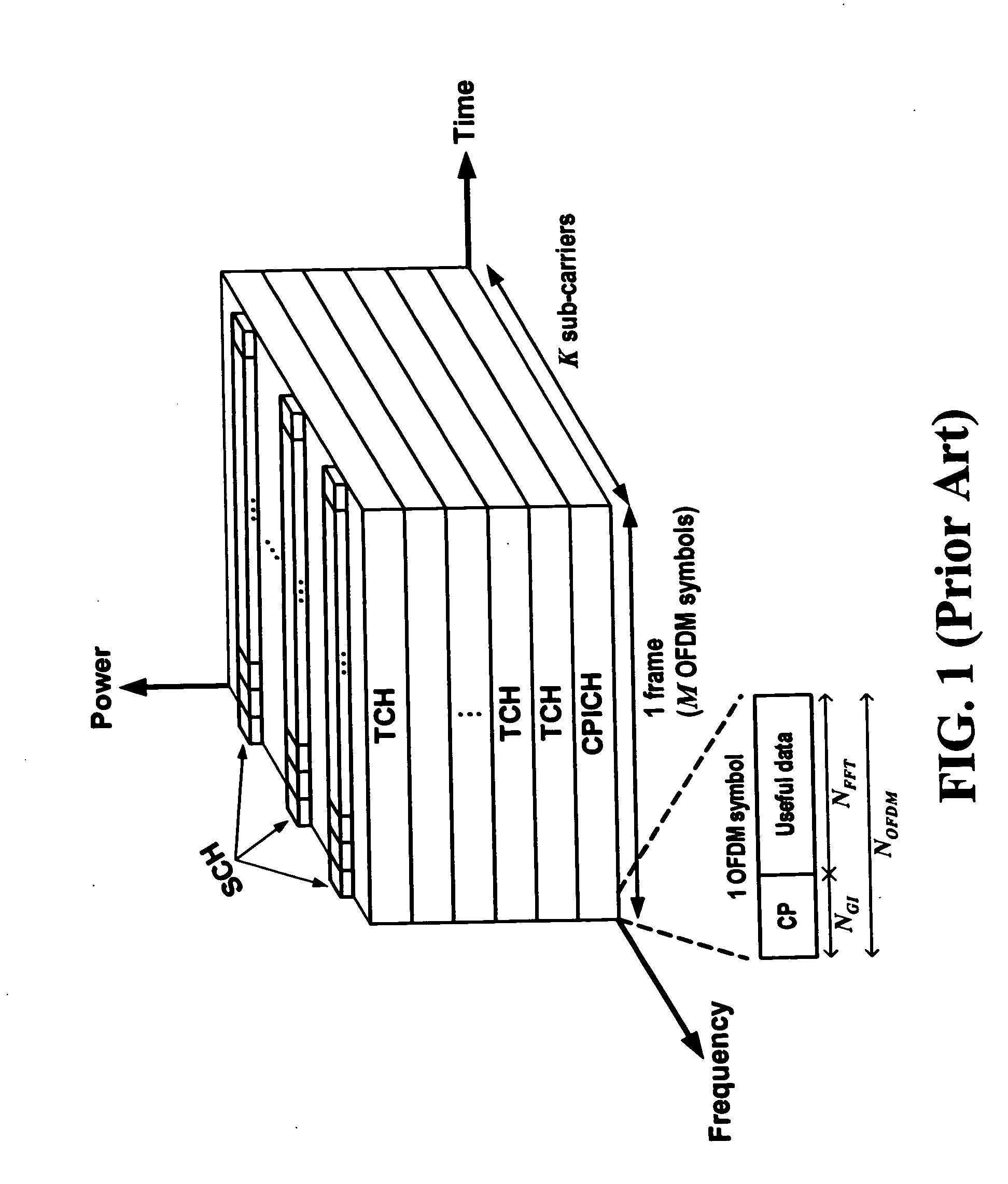
Cell search method for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing based cellular communication system
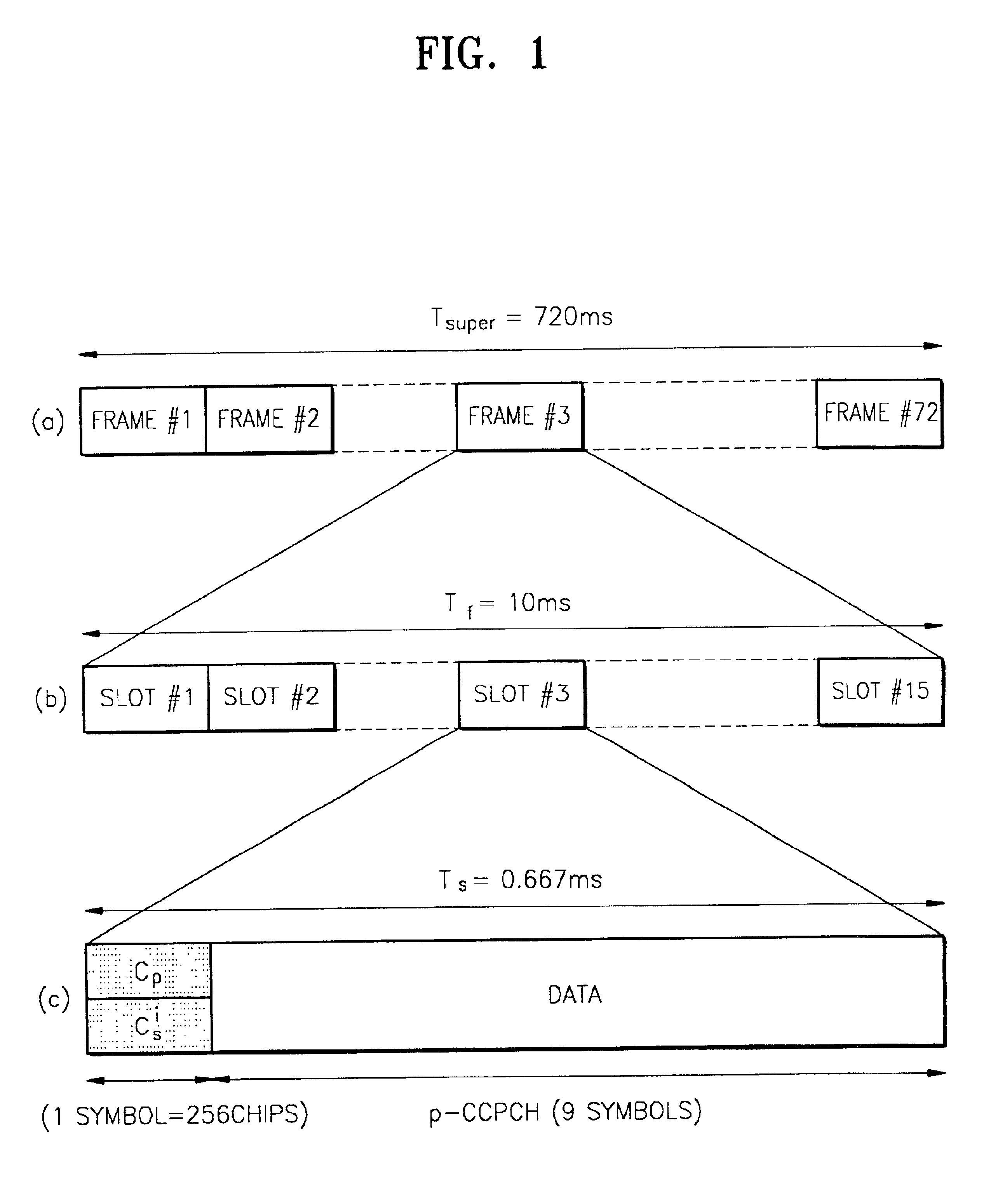
ActiveUS20050157637A1Overcomes shortcomingRobust against channel effectSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementCell searchCellular communication systems
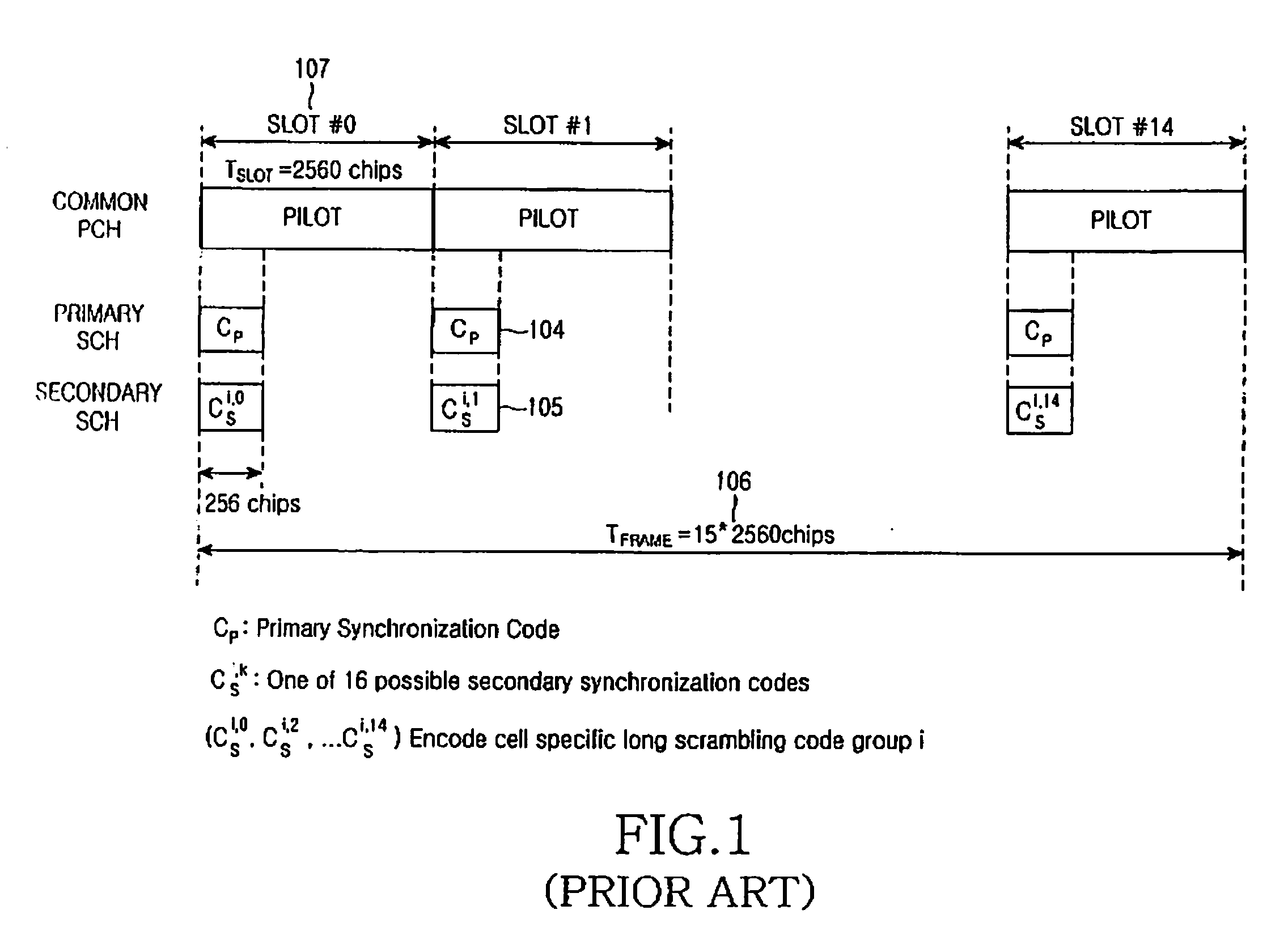
A method for synchronizing and identifying the cell code (scrambling code) of a cell in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) based cellular communication system is provided. In this method, desired cell is found by utilizing a frame structure of OFDM symbols and through a corresponding cell search procedure, where the frame structure has periodic signal pattern and contains the information about the cell code of the desired cell in common pilot channel (CPICH) signal. And, the cell search method utilizes the periodic property of the frame structure to detect frame timing, and the correlation property of CPICH signal to identify the cell code. The cell search method of the present invention offers the advantages of good link quality, fast acquisition, and low power consumption.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
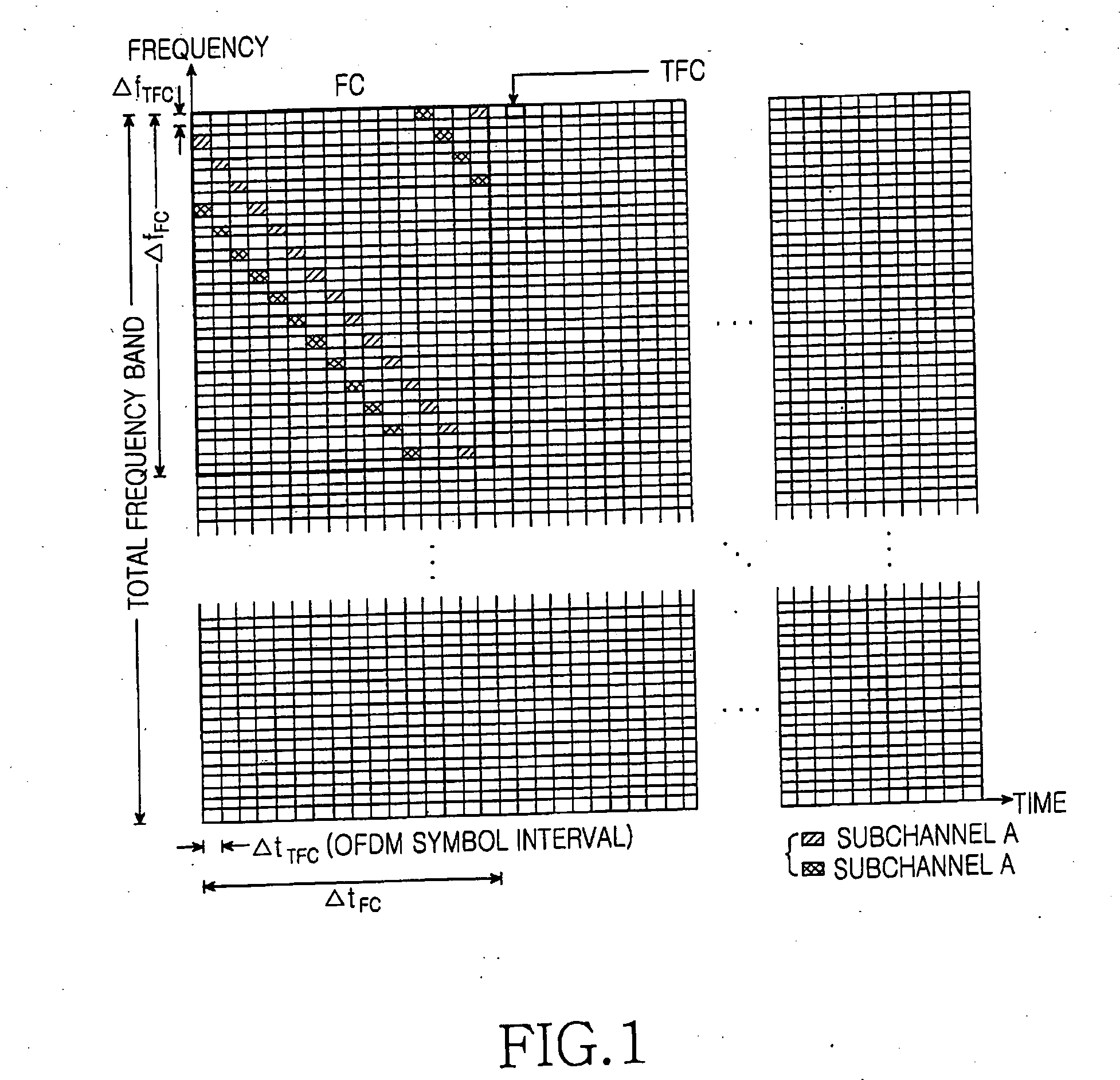
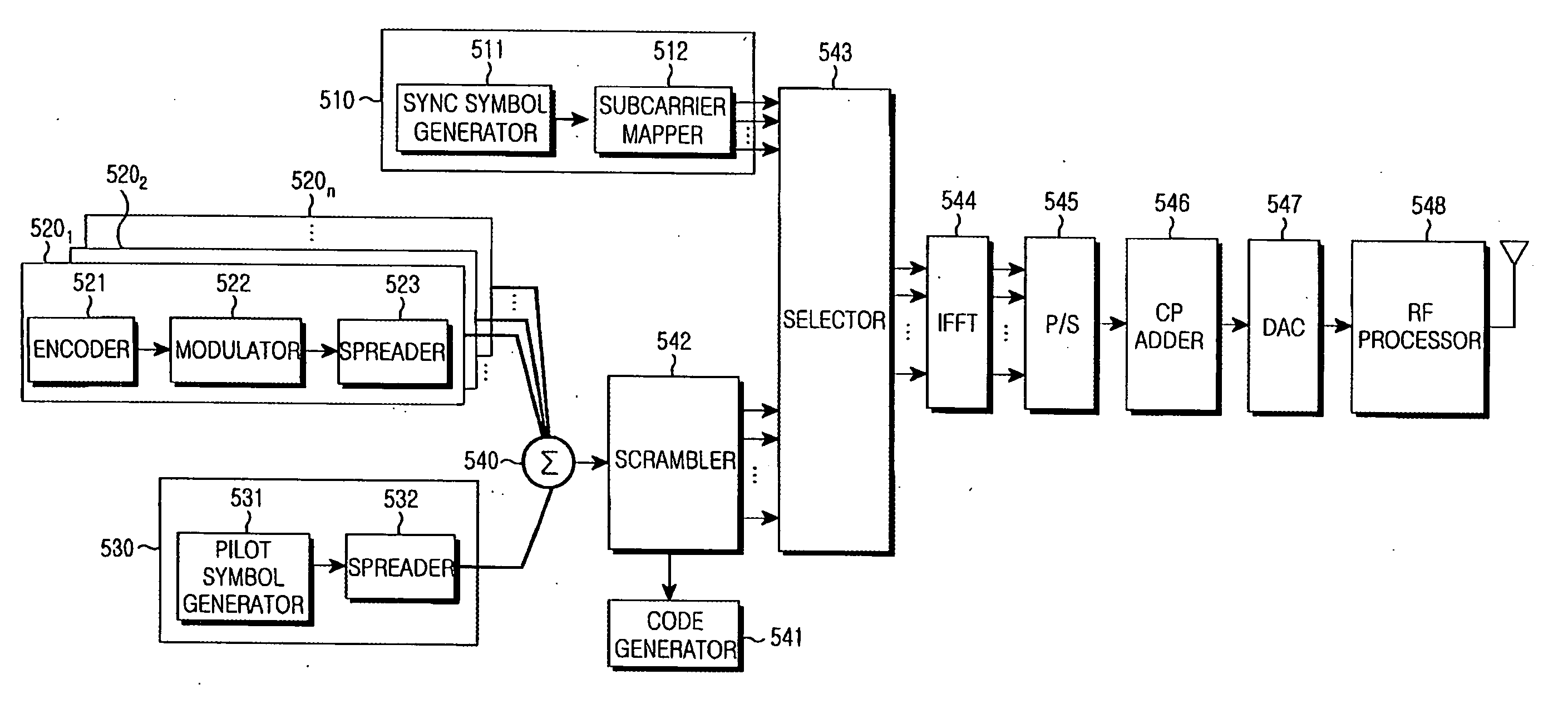
Transmitting/receiving apparatus and method for cell search in a broadband wireless communications system
InactiveUS20070041348A1Efficient searchImprove search capabilitiesRadio transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalCell search
Disclosed is transmitting / receiving apparatus and method for efficient cell search in a broadband wireless communication system using multiple carriers. The apparatus includes a BS generating an SCH signal by mapping predetermined symbols to predetermined subcarriers according to a code group to which the BS belongs, code-multiplexing a TCH signal and a pilot channel signal mapped to a predetermined time-frequency area and scrambling the code-multiplexed signal with a predetermined scrambling code identifying the BS along a time axis first, time-multiplexing the SCH signal with the scrambled signal, OFDM-modulating the time-multiplexed signal, and transmitting the OFDM-modulated signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
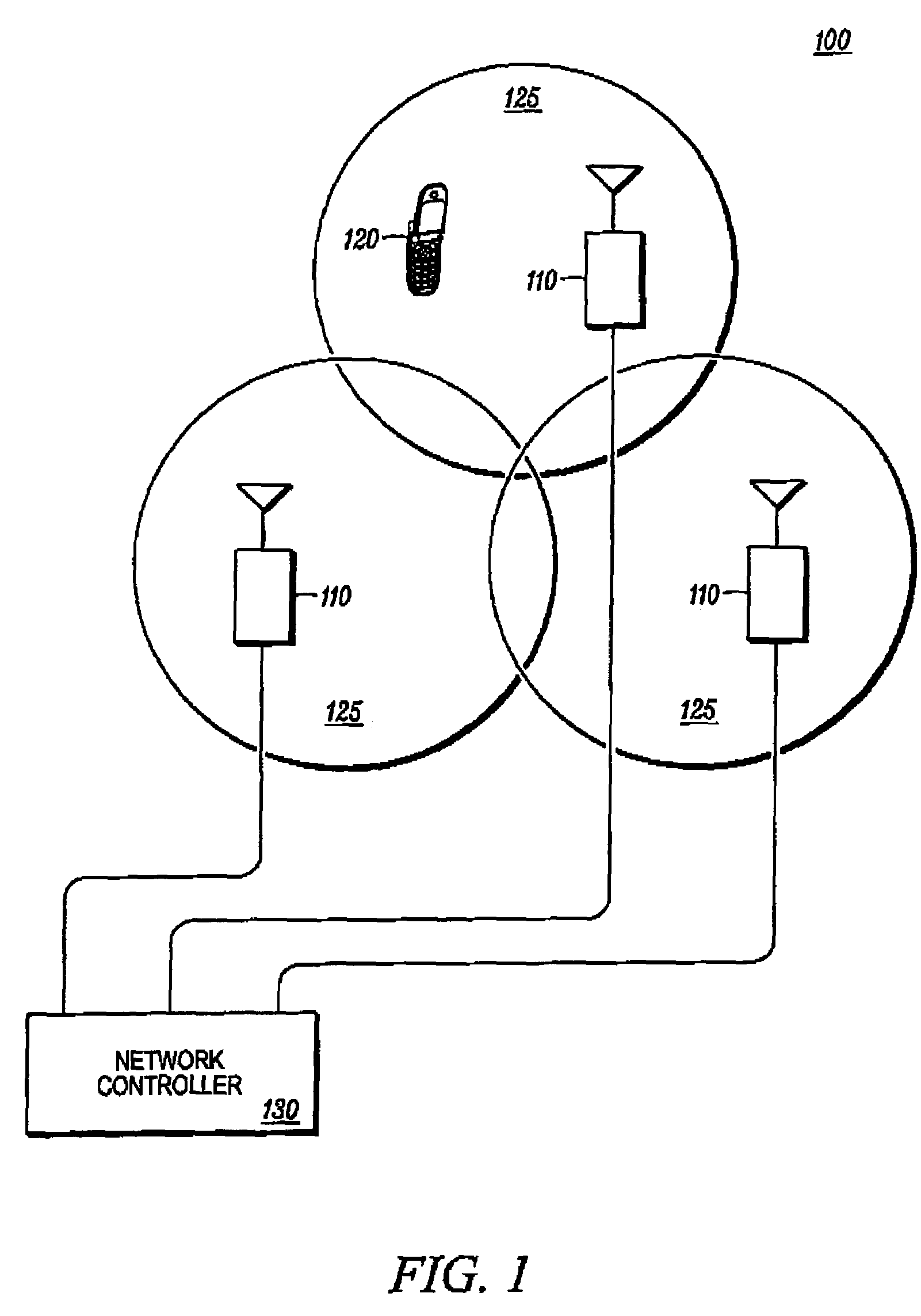
Methods for cell search in synchronous interference limited channels
ActiveUS20120172041A1Synchronisation arrangementSecret communicationTelecommunicationsInterference (communication)
The cell searcher module (CSM) of a wireless communication device detects that the device is in coverage region of an eNB by processing received signal associated with the primary synchronization (PSCH) and secondary synchronization (SSCH) sequences transmitted by the eNB. The wireless device determines whether candidate SCH signals from candidate neighbor cells are synchronous with SCH sequences from the serving cell by implementing one of three methods. In a first method, the CSM generates a joint estimate of the received power of SSCH sequences corresponding to already detected / identified serving cell and a hypothetical neighbor cell. In a second method, the CSM re-constructs SCH sequences corresponding to already detected cells and subtracts the re-constructed SCH sequences from the received signal to obtain a residual signal with reduced serving cell interference. In a third embodiment, the CSM performs a correlation of estimated channel responses to determine whether the neighbor cell is present.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
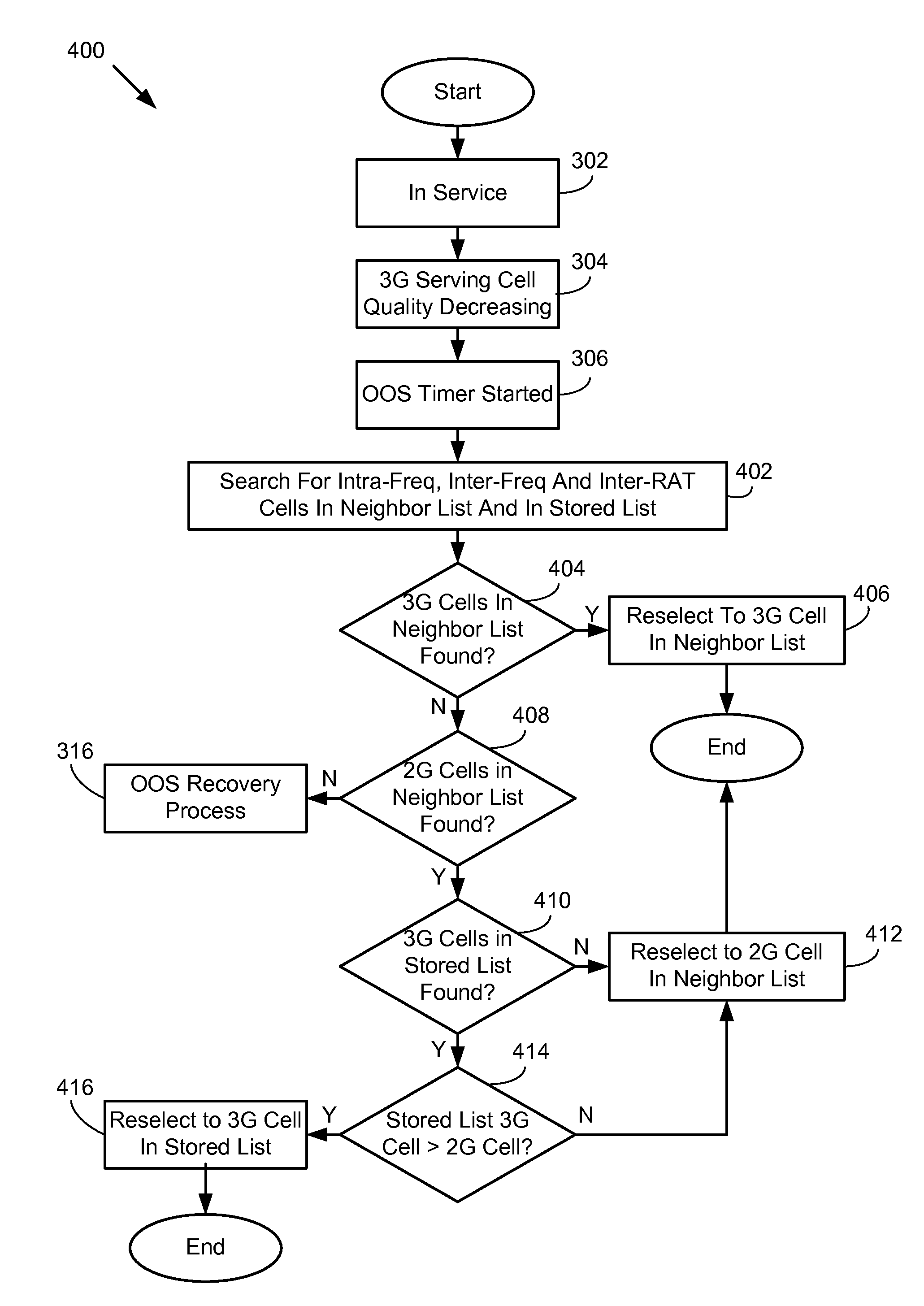
Expanded cell search and selection in a mobile wireless device
ActiveUS20110319076A1Transmission systemsAssess restrictionRadio access technologyTelecommunications
A method and apparatus for expanded cell search and selection in a mobile wireless device. The mobile device locates cells in a first of neighbor cells and in a second list of stored cells and evaluates located cells using suitability criteria. When locating a suitable first cell that uses a first radio access technology (RAT) in the first list, the first cell is selected. When locating a second suitable cell that uses a second RAT in the first list and not locating a suitable cell that uses the first RAT in the second list, the second cell is selected. When locating a third suitable cell that uses the second RAT in the first list and locating a fourth suitable cell that uses the first RAT in the second list, the fourth cell is selected when more suitable than the third cell.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for fast cell search using psync process in a multimode WCDMA terminal
ActiveUS20070189259A1Synchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionRadio access technologyCode division multiple access
Certain aspects of a method and system for a fast cell search using a primary synchronization channel (PSYNC) process in a multimode wideband code division multiple access (WCDMA) terminal are provided. A WCDMA frequency search or a global system for mobile communications (GSM) frequency search is performed based on a current radio access technology (RAT), received signal strength indication (RSSI) scan measurements, and PSYNC detection operations. The RSSI scan measurements may be averaged by making multiple measurements during a measurement period. At least part of the PSYNC detection operations may be performed during a remaining portion of the measurement period. WCDMA carrier frequencies may be marked in accordance with the results of the PSYNC detection operations. For GSM, some of the frequencies may be removed from the search based on the PSYNC marking while the remaining search frequencies may be ranked based on results from the RSSI scan measurements.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
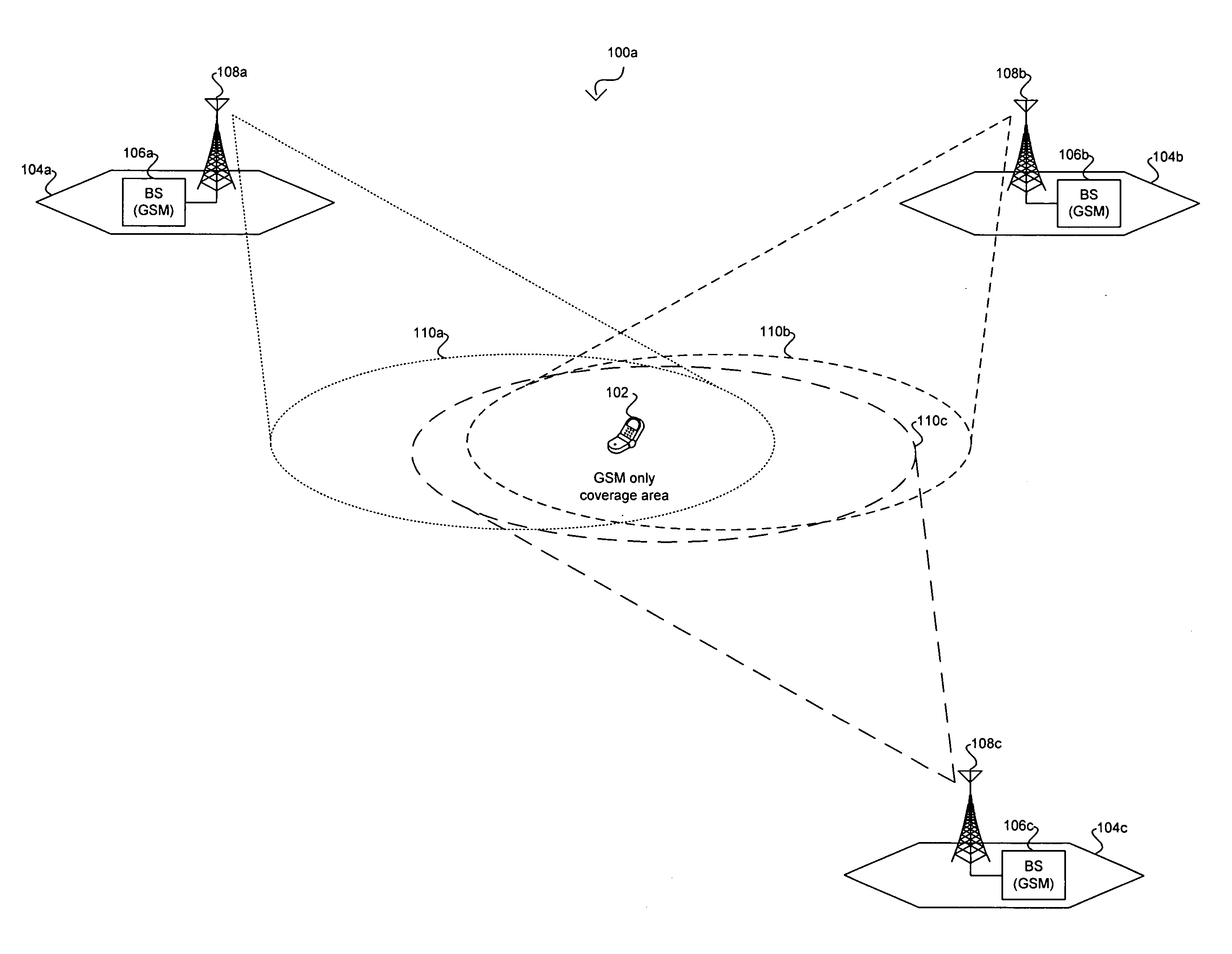
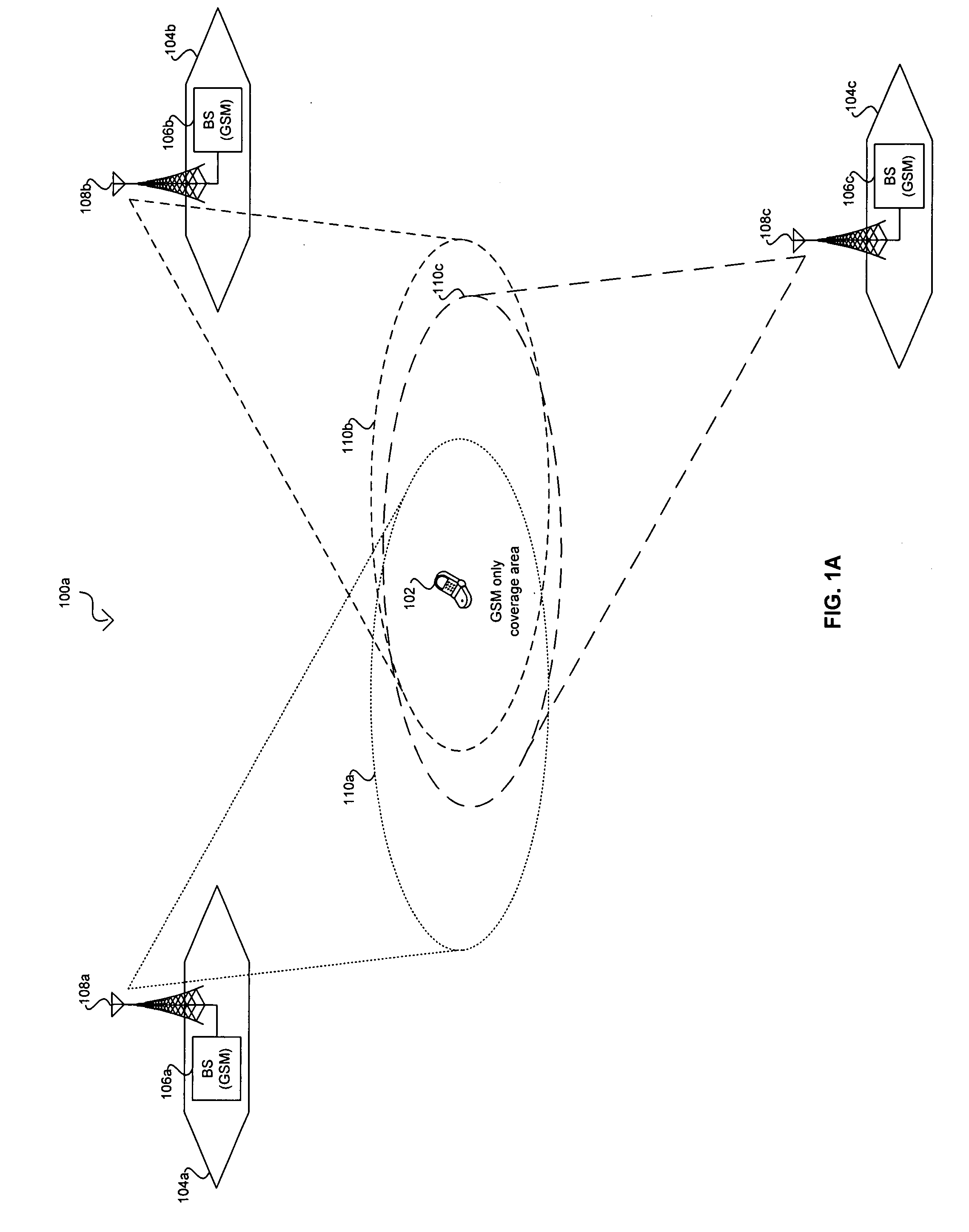
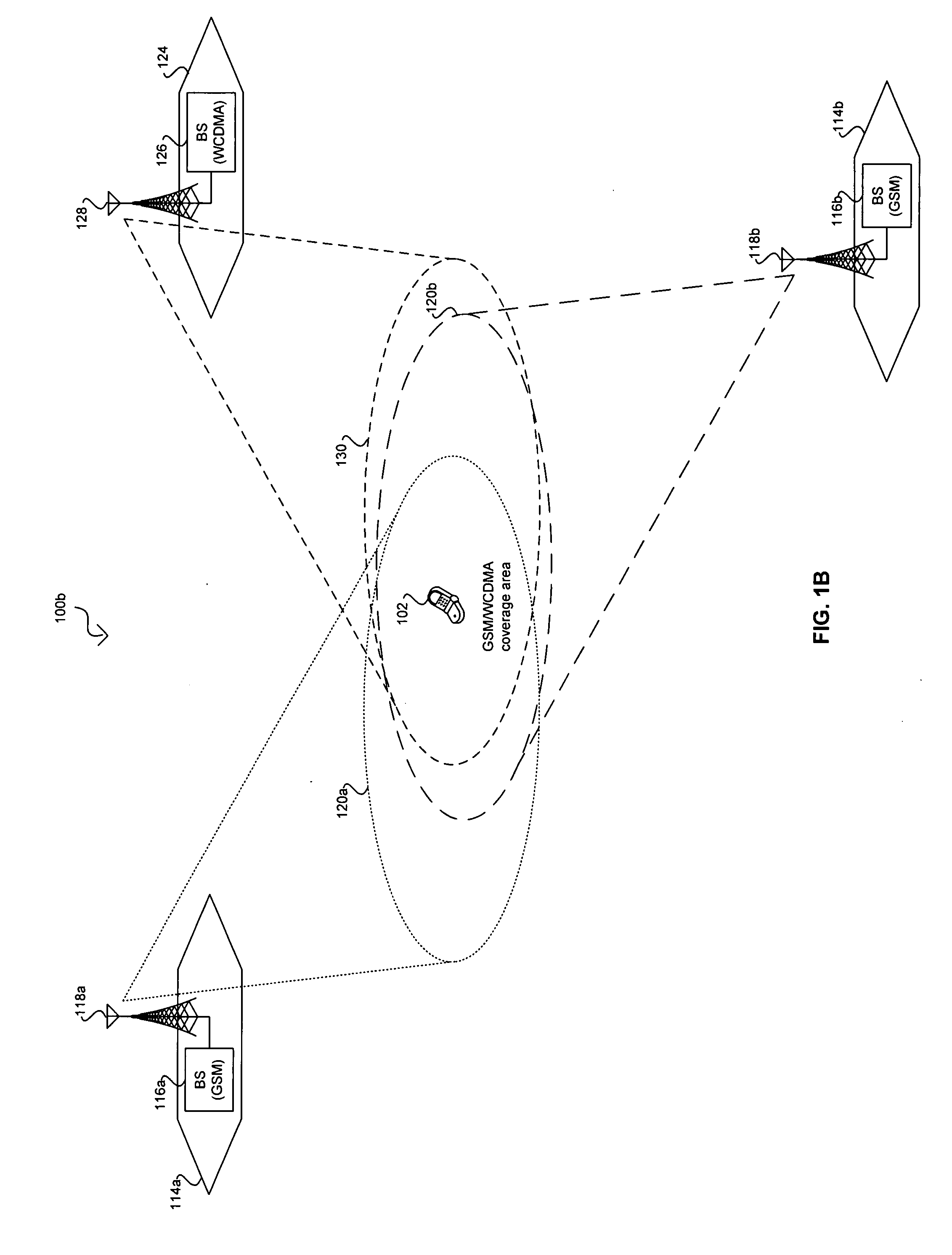
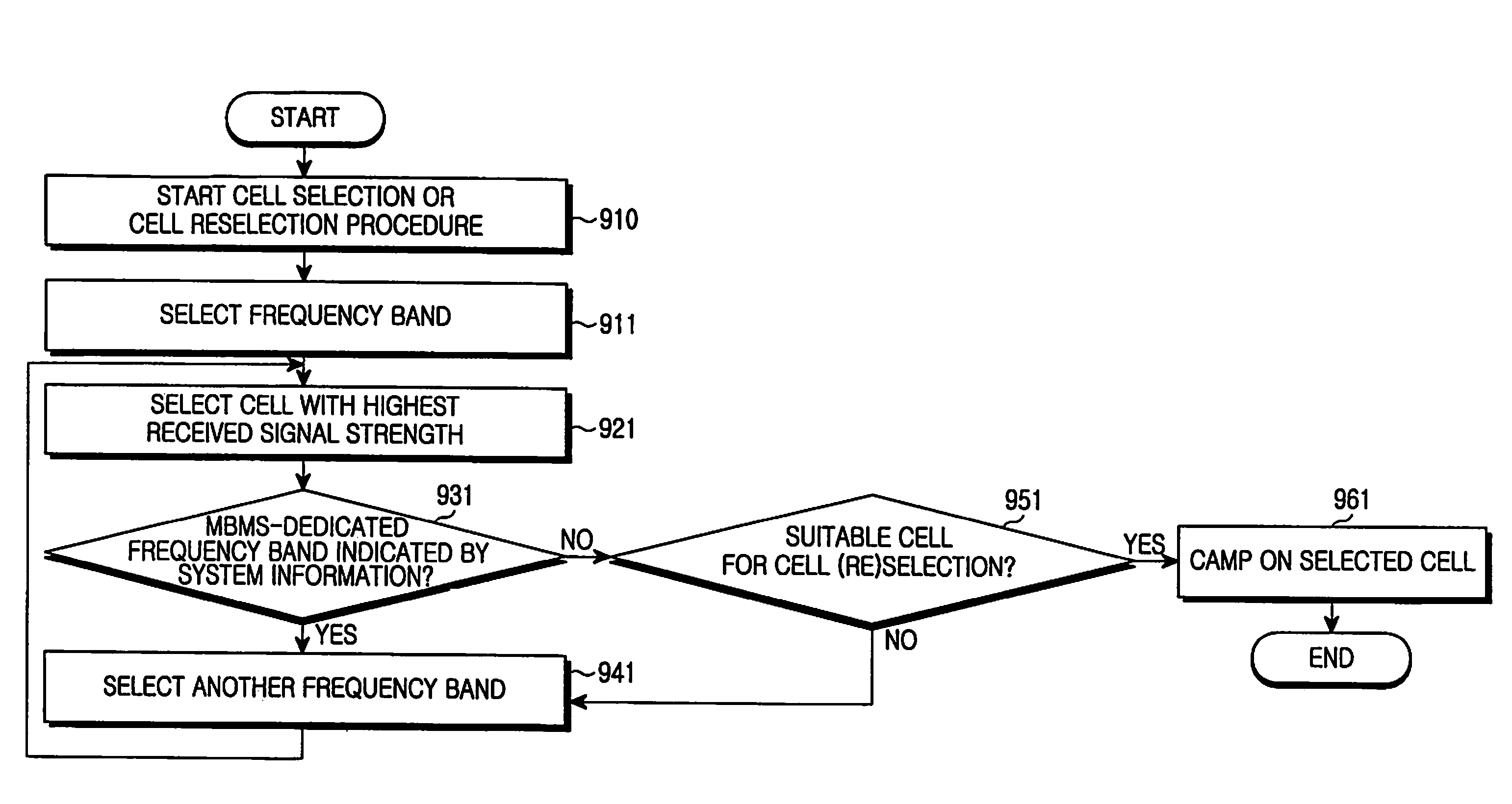
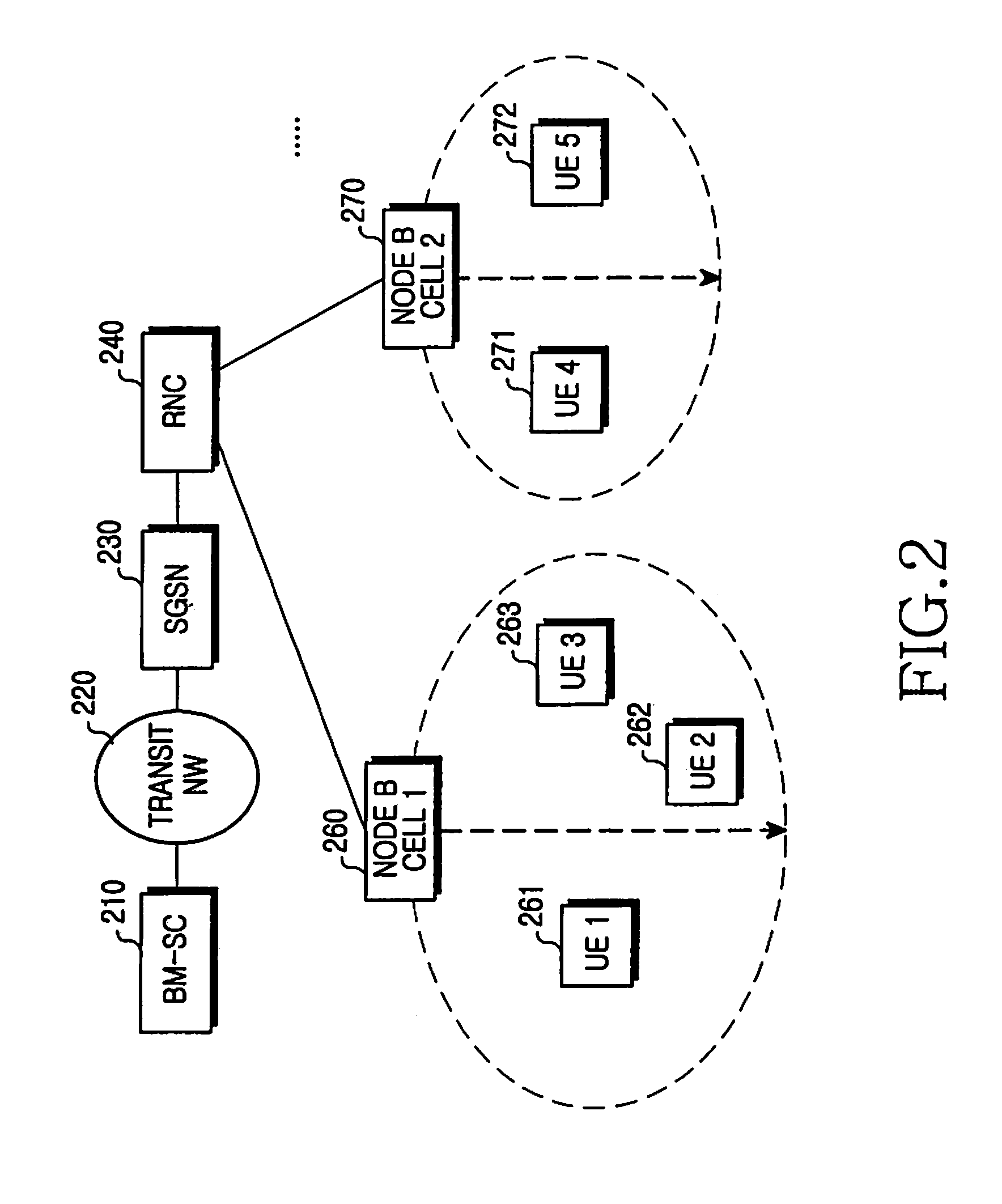
Method for performing cell selection in a mobile communication system and system therefor
A method for performing cell selection in a mobile communication system and a system therefor. Upon receiving a Multimedia Broadcast and Multicast Service (MBMS) service or a unicast service, a User Equipment (UE) performs cell search separately for each frequency band in an overlapping region between an MBMS-dedicated frequency band and a unicast service-available frequency band. In a first example, the UE allocates different cell identification codes for each cell according to types of the corresponding frequency bands to perform cell search. In a second example, the UE uses the system information broadcasted from the network over P-BCH to indicate whether each cell belongs to the MBMS-dedicated frequency band.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Efficient and consistent wireless downlink channel configuration
InactiveUS20100061333A1Fast cell searchOrthogonal multiplexWireless commuication servicesBroadcast channelsCommunications system
A configuration for downlink signals in a wireless communication system, methods of configuring the downlink signals, apparatus for generating the downlink signals, and apparatus for receiving and processing the downlink signals are described herein. Downlink signals in a wireless communication system are reconfigured in series of frames, with each frame carrying a preamble that provides fast cell search and system acquisition. In particular, the preamble includes a primary preamble and a secondary preamble, where the primary preamble is common to all sectors in a base station and all base stations in a system and the secondary preamble is effectively unique to each base station, and may be further distinguished based on a sector basis. In addition, pilot signals are aligned with base stations to occur at the same time within a frame and the PN sequence values of the pilot signals are based on a cell identification an antenna identification, thereby enabling prediction of pilots transmitted by interferers or neighboring base stations from acquisition of secondary preambles. Also, the pilot bits are selectively assigned from a center of an operating band outward. Due to the pilot placement and pilot modulation, the scheme enables interference mitigation and channel estimation without knowing the frequency bandwidth, which is especially advantageous in broadcast channel systems.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Preambles in OFDMA system
ActiveUS7961696B2Reducing a search windowModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionMulti inputCell search
The present invention provides a preamble that is inserted into an OFDMA frame and has a common sequence for all the base stations participating in a transmission. The subscriber station performs fine synchronization using the common sequence on the common preamble, and the resulting peaks will provide the locations of candidate base stations. The base station specific search is then performed in the vicinities of those peaks by using base station specific pseudo-noise sequences. With this two stage cell search, the searching window is drastically reduced. The preamble is matched to known values by a respective receiver to decode the signals and permit multiple signals to be transferred from the transmitter to the receiver. The preamble may comprise two parts, Preamble-1 and Preamble-2, which may be used in different systems, including multioutput, multi-input (MIMO) systems.
Owner:APPLE INC
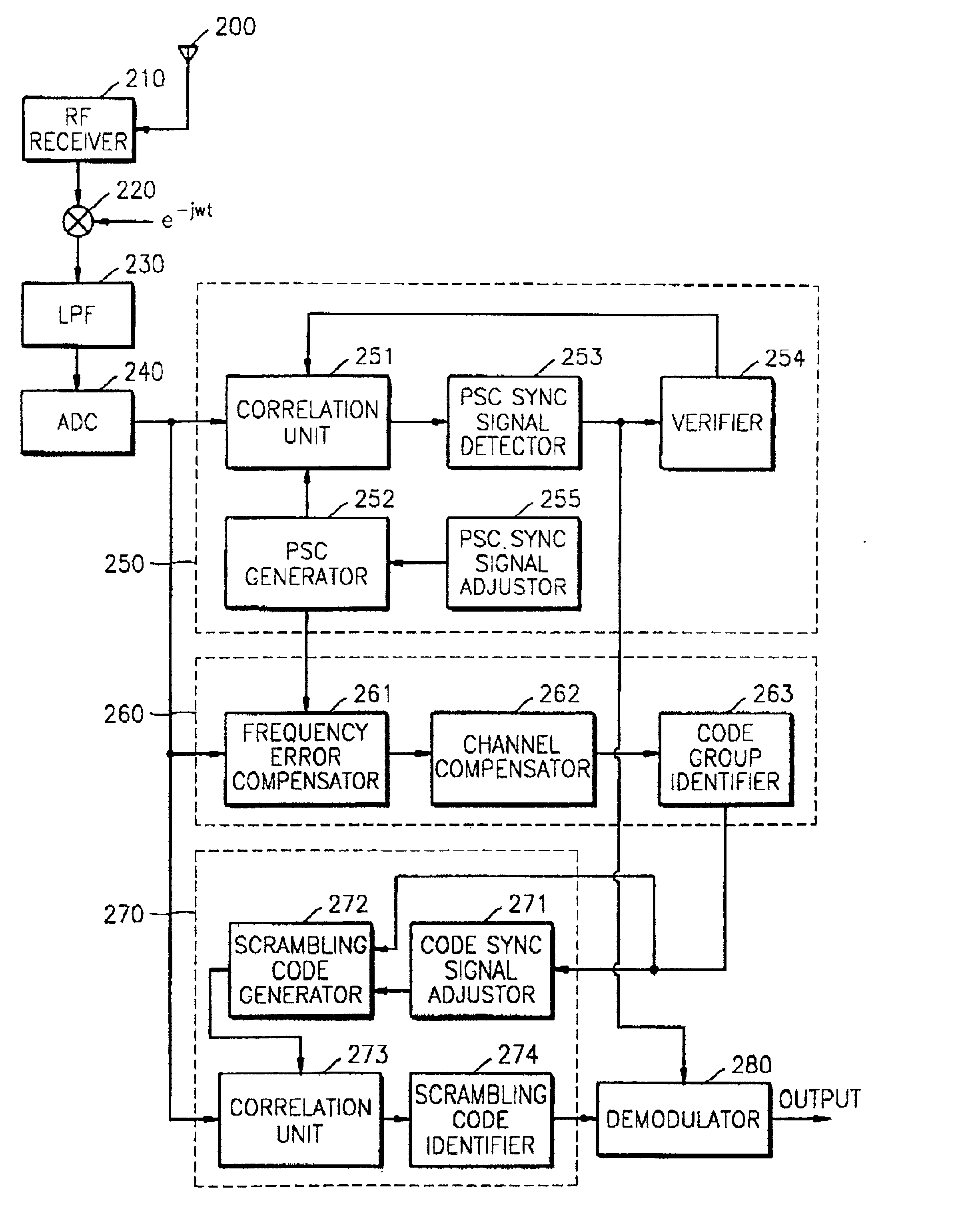
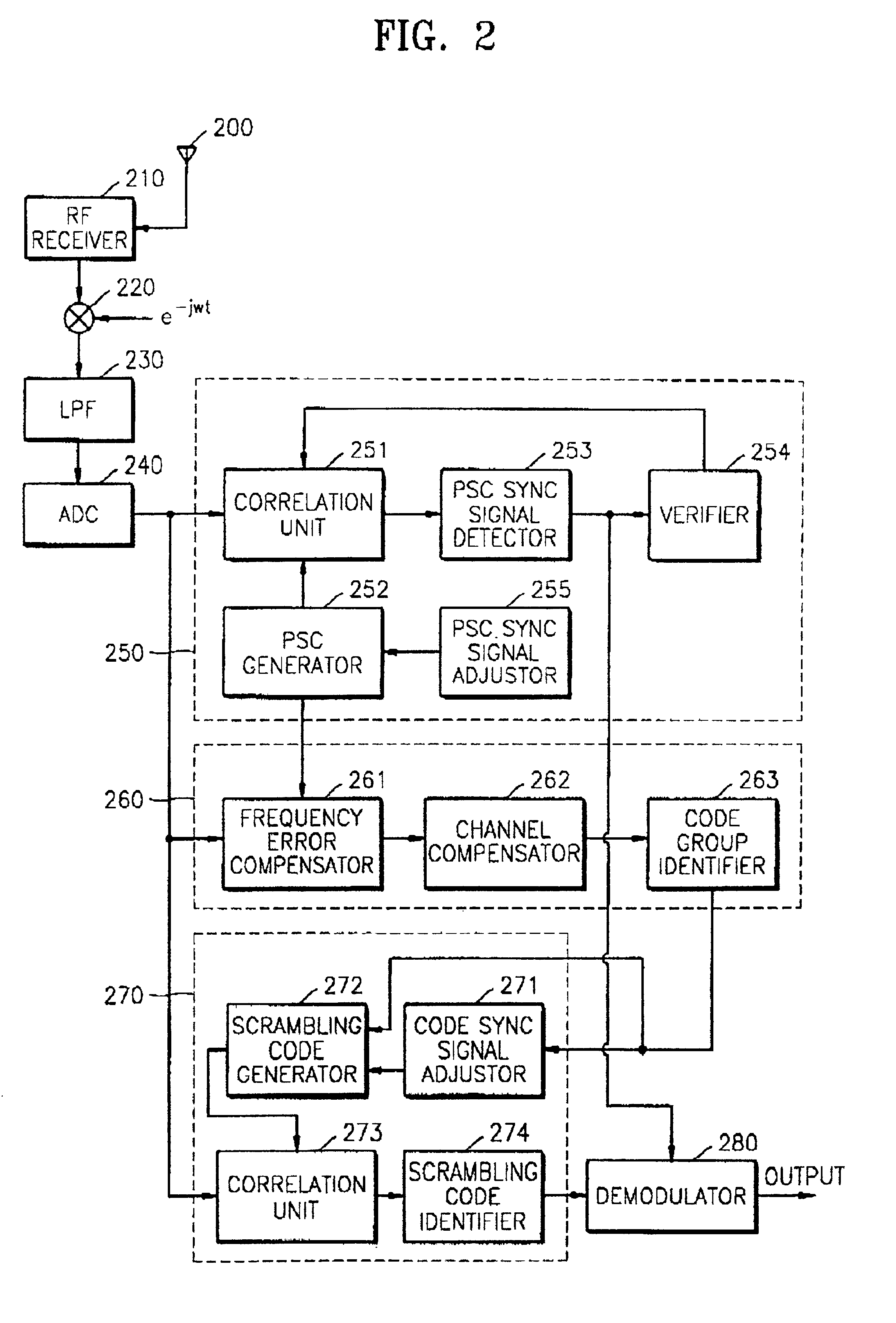
Apparatus for searching for a cell and method of acquiring code unique to each cell in an asynchronous wideband DS/CDMA receiver
InactiveUS6888880B2Assess restrictionRadio transmission for post communicationCdma signalParallel computing
An apparatus for searching for a cell and a method of acquiring a code unique to each cell in an asynchronous wideband Direct-Sequence Code Division Multiple Access (DS / CDMA) receiver, wherein the cell searching apparatus searches for a cell based on a received asynchronous wideband DS / CDMA signal in a receiver, the apparatus including a code group identifying unit for estimating and compensating for a frequency error between the synchronous channel and an internally generated primary synchronization code, estimating and compensating for channel degradation which the synchronous channel has experienced, and performing correlation on the compensated synchronous channel and available secondary synchronization codes, thereby identifying the code group; and a scrambling code identifying unit for performing correlation on a plurality of scrambling codes belonging to the code group, thereby obtaining a scrambling code unique to each cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Preambles in ofdma system
ActiveUS20110222504A1Reducing a search windowModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionMulti inputCell search
Owner:APPLE INC
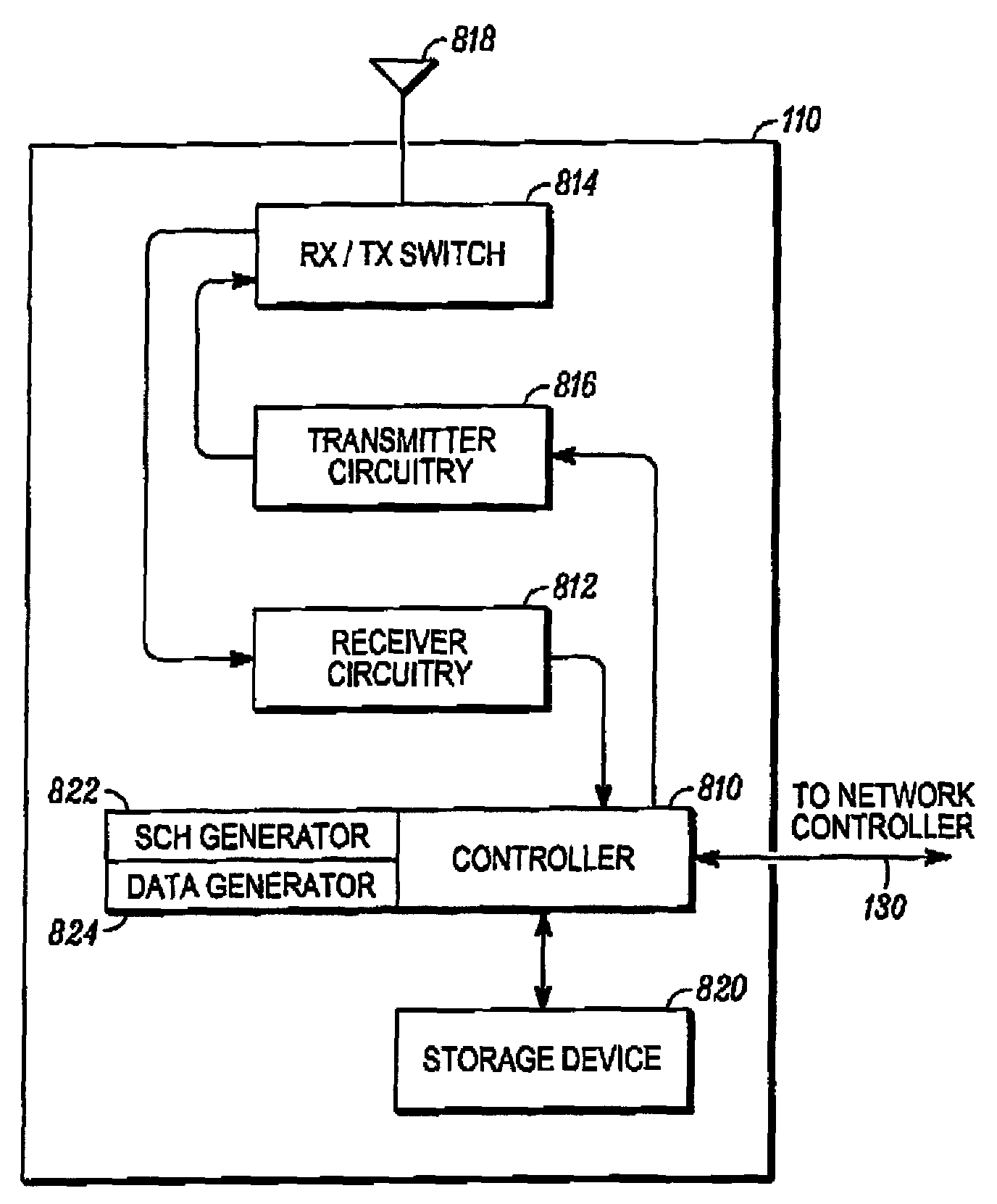
Method and apparatus for a synchronization channel in an OFDMA system
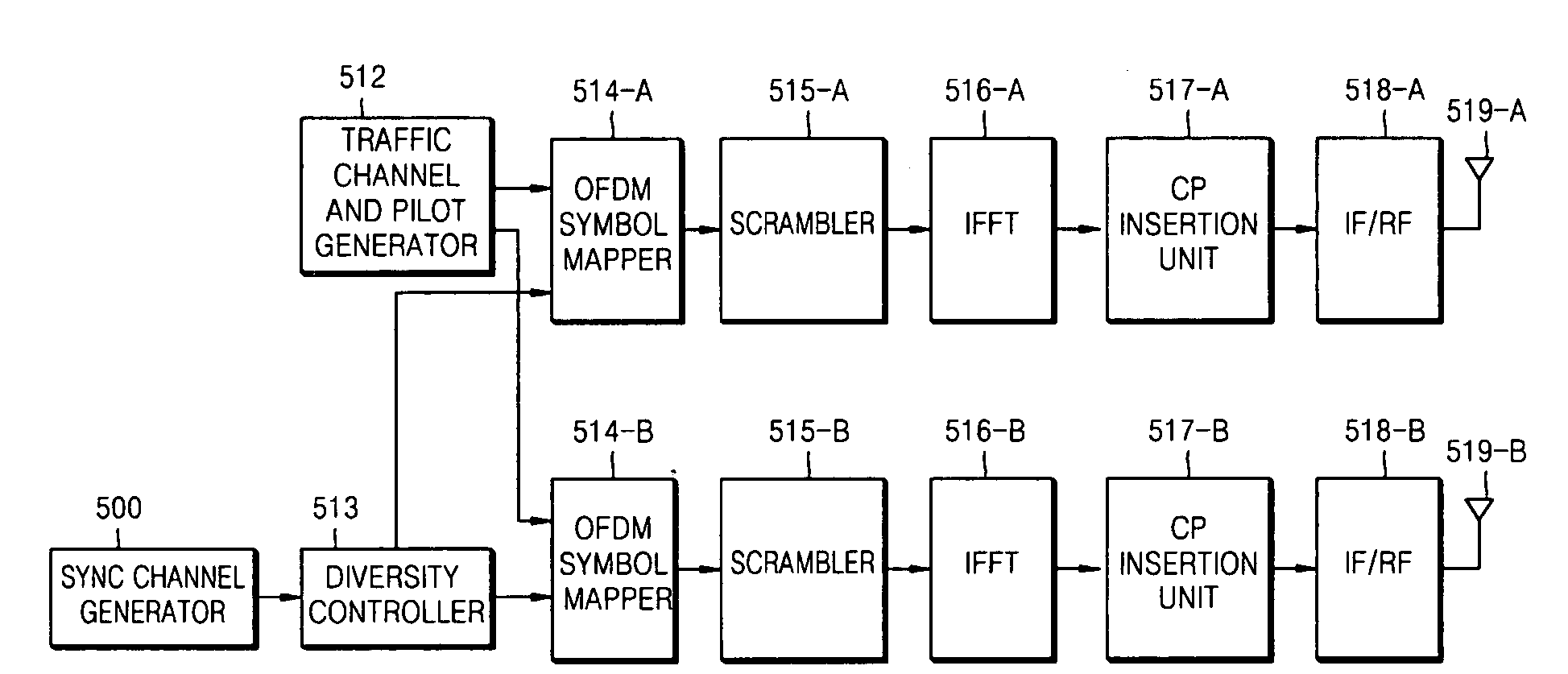
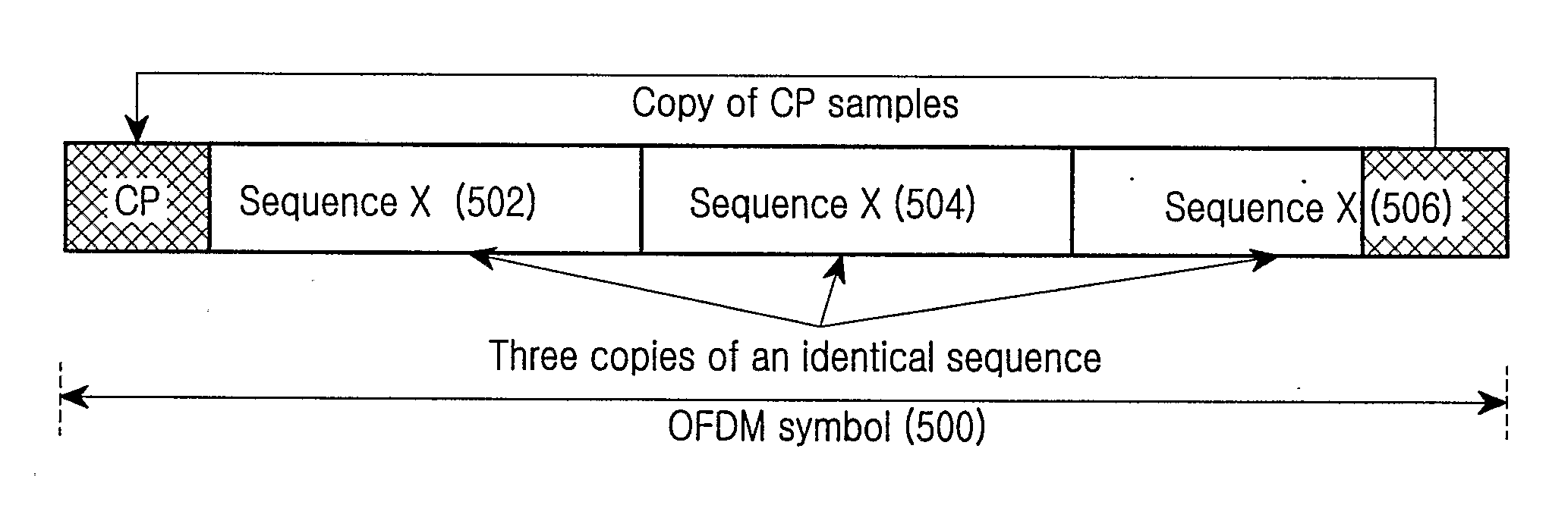
A method and apparatus is provided for transmitting an orthogonal frequency domain multiple access (OFDMA) signal including a synchronization channel signal transmitted within a localized portion of a bandwidth of the OFDMA signal (818), the synchronization channel signal having predetermined time domain symmetry within the localized portion of the bandwidth (816). The synchronization channel signal enables an initial acquisition and cell search method with low computational load which provides OFDMA symbol timing detection and frequency error detection by differential processing of sequence elements of the synchronization channel signal (1112) and frame boundary detection and cell specific information detection (1114) in an OFDMA system supporting multiple system bandwidths, both synchronized and un-synchronized systems, a large cell index and an OFDMA symbol structure with both short and long cyclic prefix length.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com