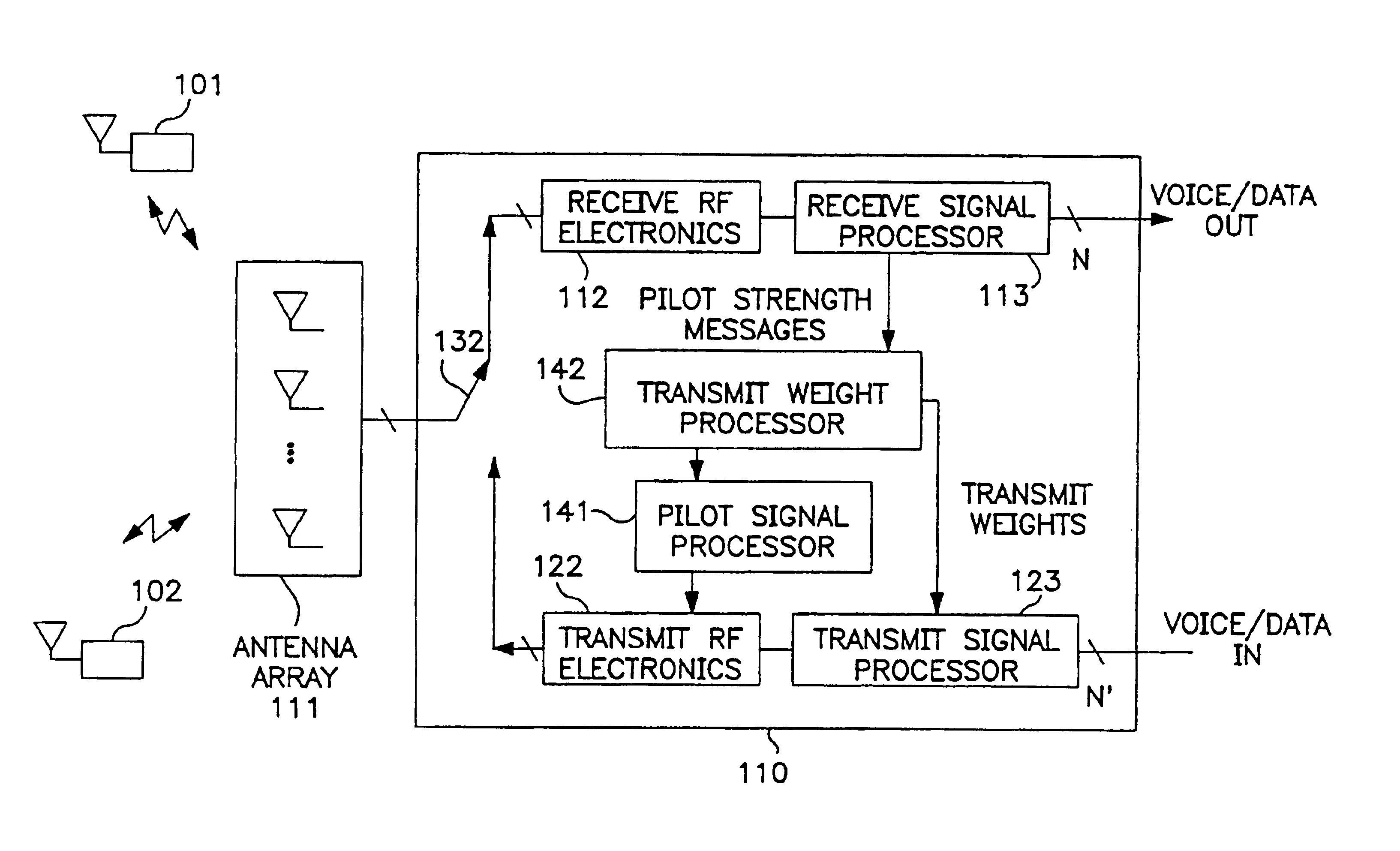
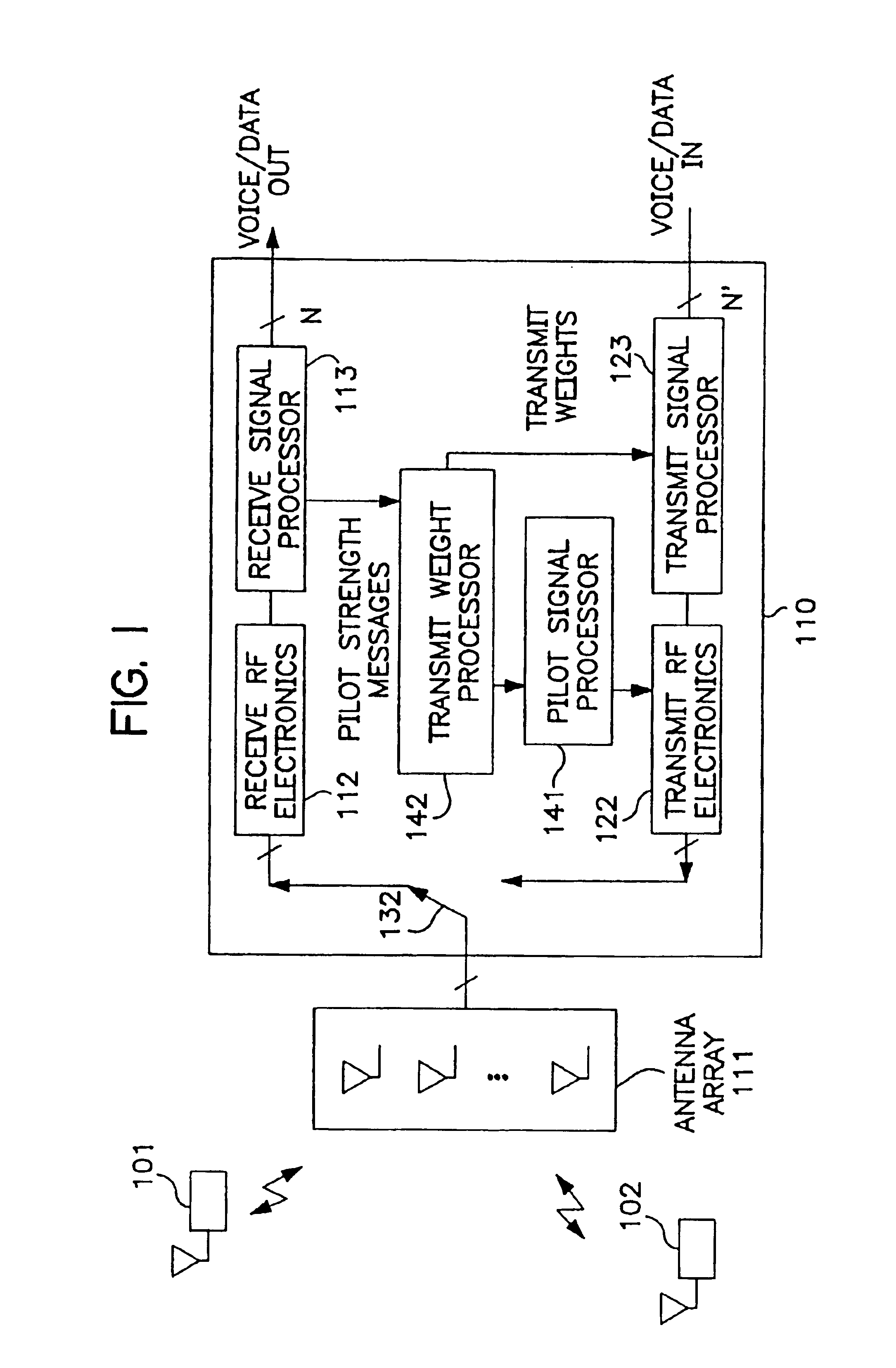
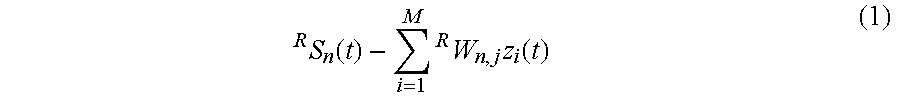Patents
Literature
1457 results about "Cellular communication systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
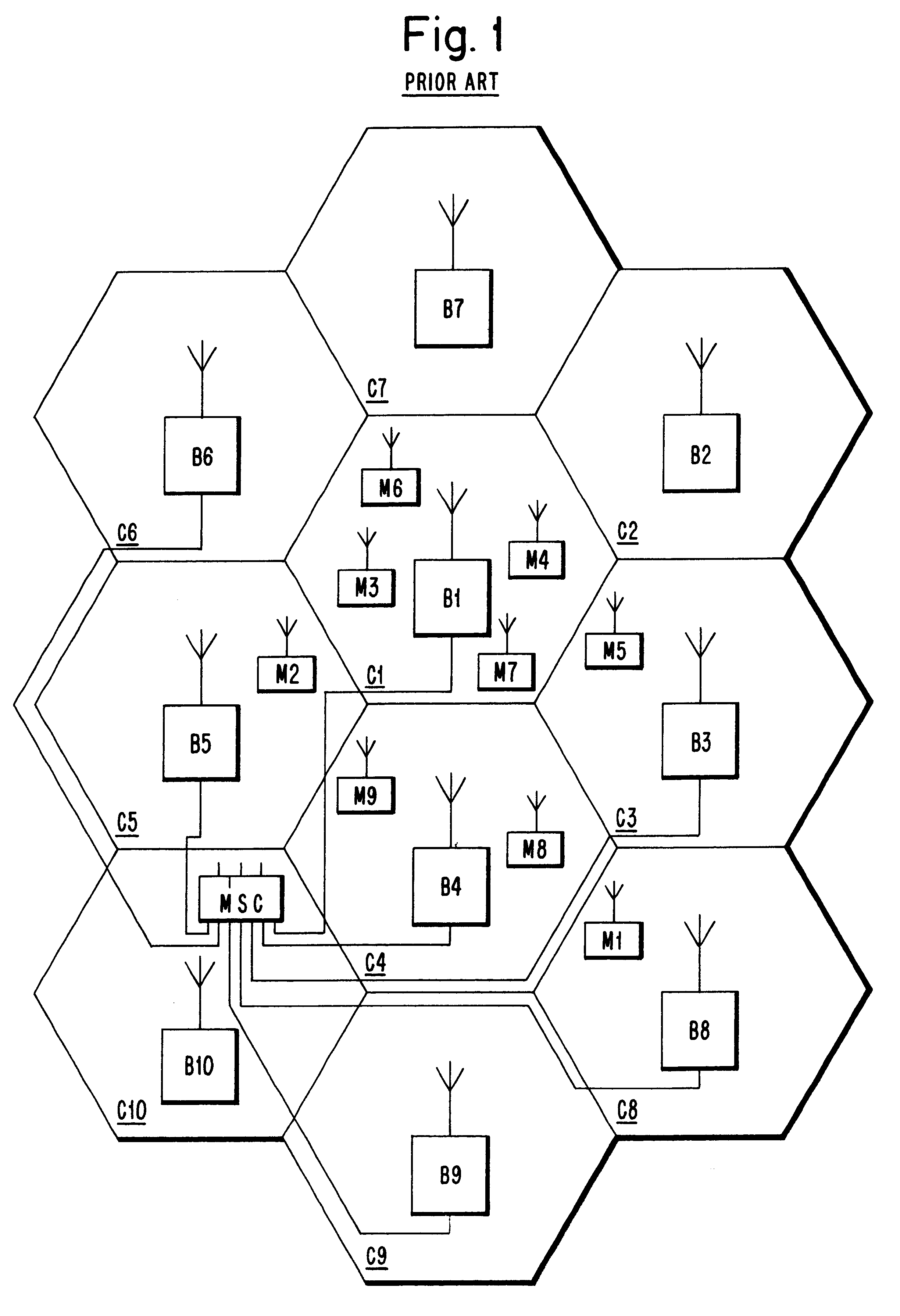
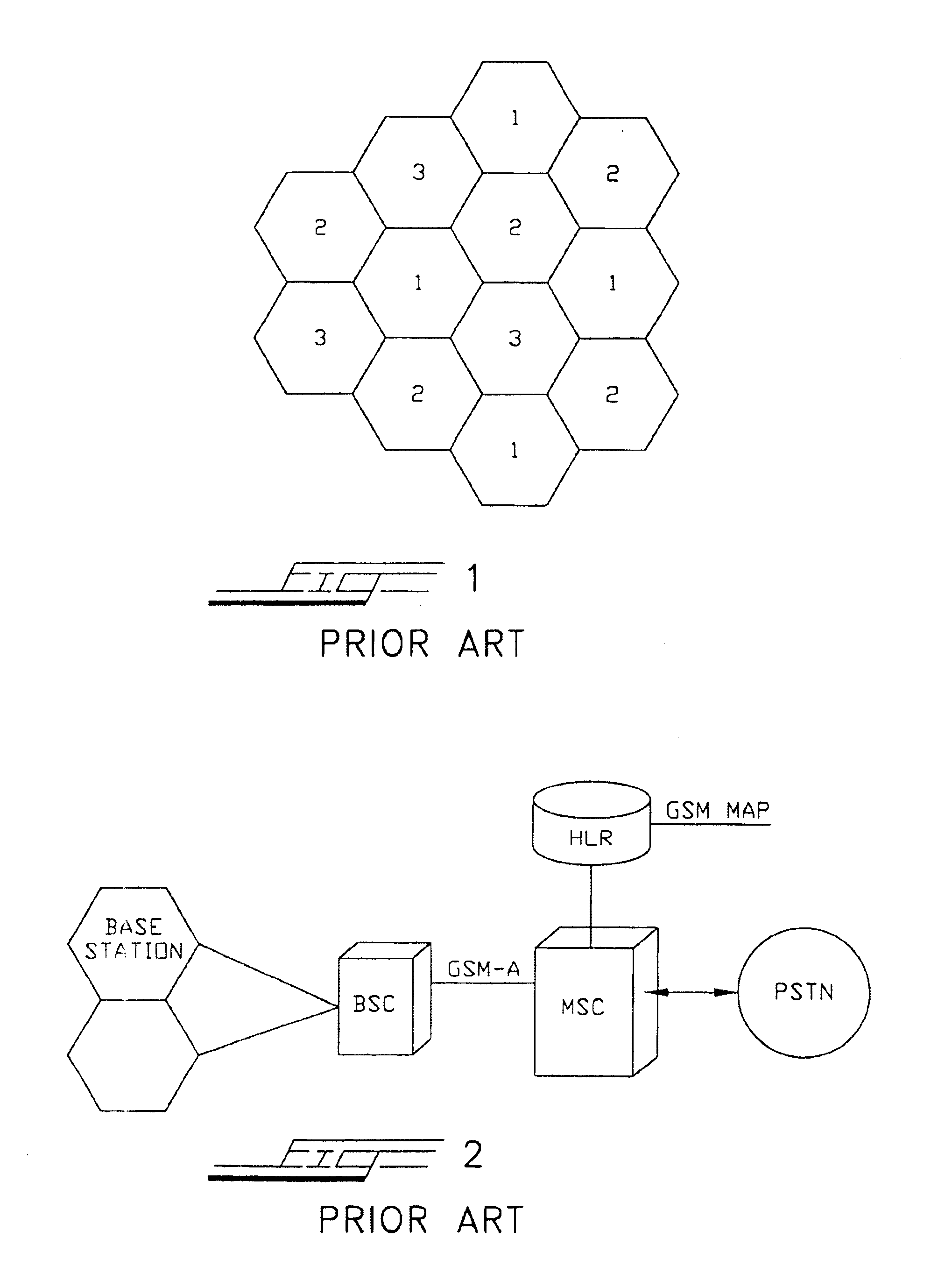
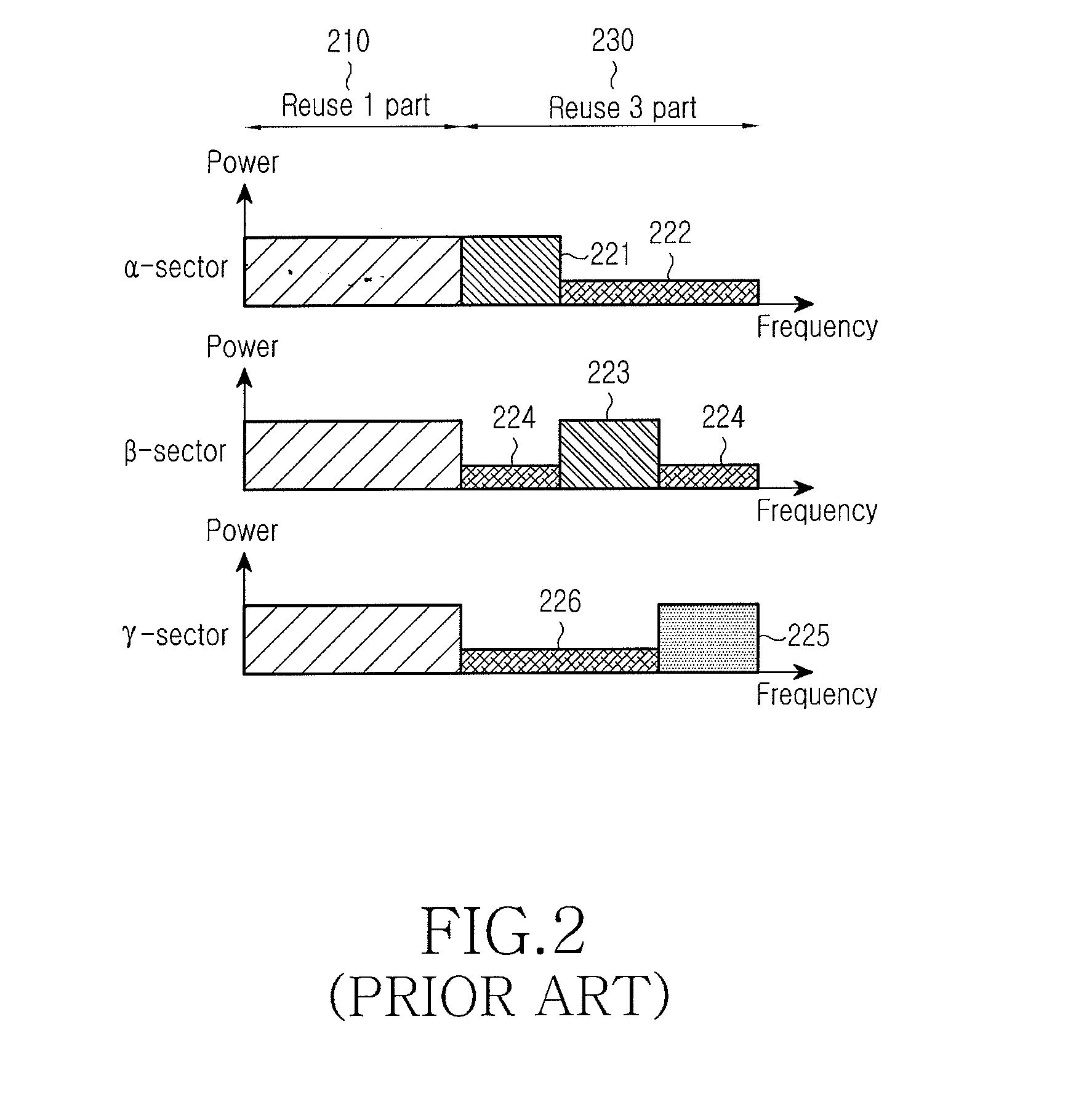
Cellular Communications. Definition. A cellular mobile communications system uses a large number of low-power wireless transmitters to create cells—the basic geographic service area of a wireless communications system. Variable power levels allow cells to be sized according to the subscriber density and demand within a particular region.
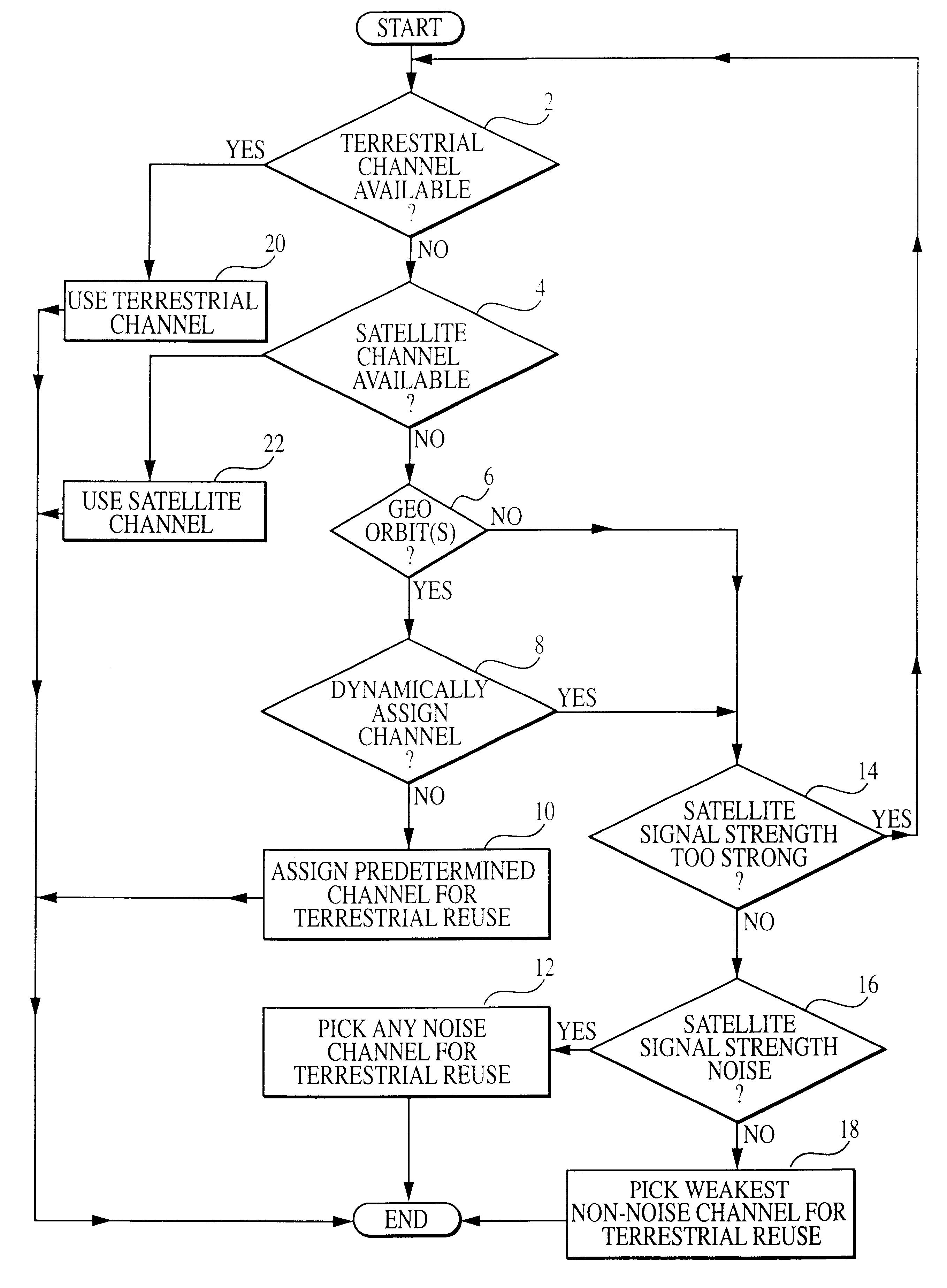
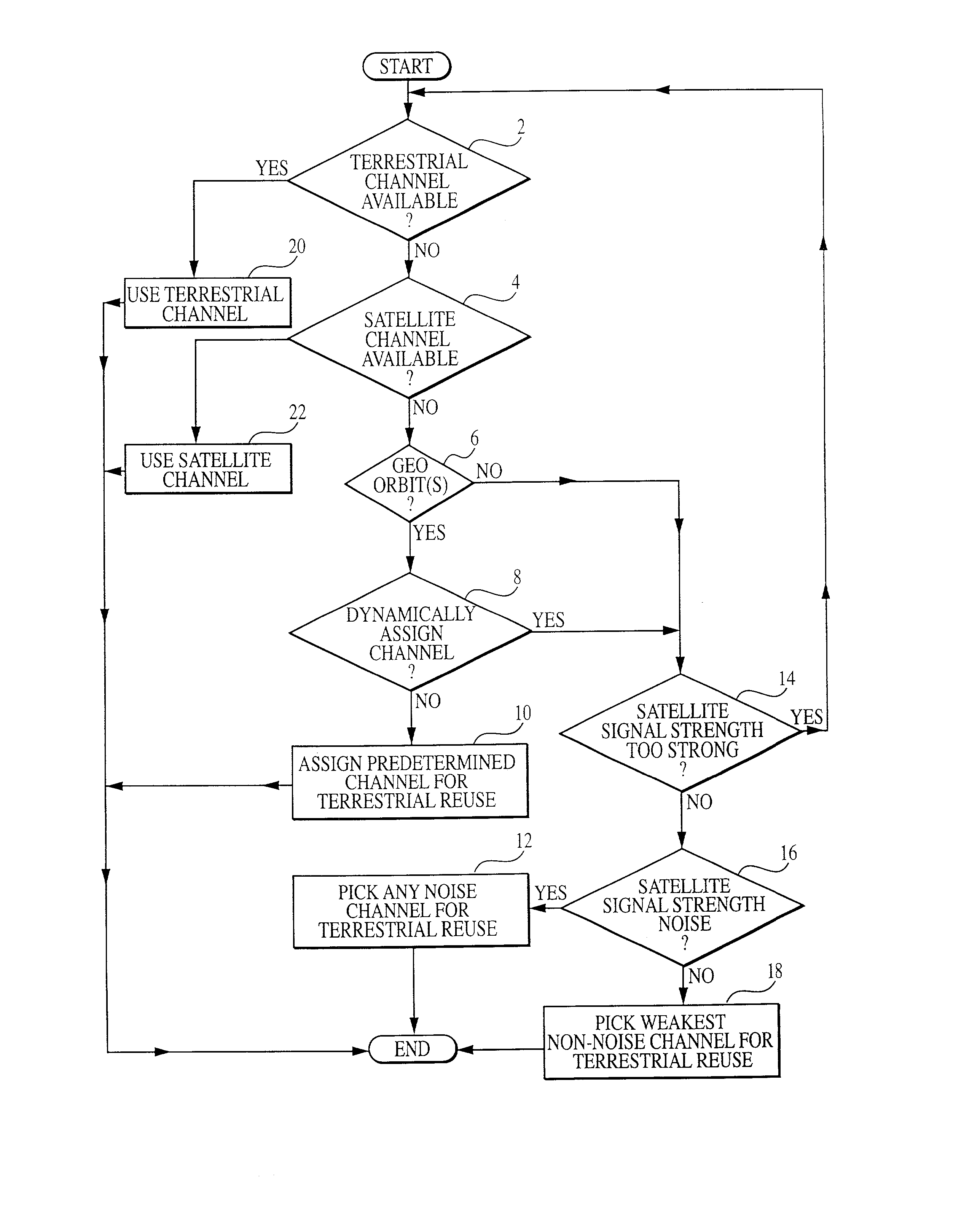
Integrated or autonomous system and method of satellite-terrestrial frequency reuse using signal attenuation and/or blockage, dynamic assignment of frequencies and/or hysteresis
InactiveUS6859652B2Efficient reuseInterference minimizationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentHysteresisUltrasound attenuation
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Routing in a multi-station network
InactiveUS20010036810A1Effective expansionReduce data rateSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemHybrid system
A method of relaying data between mobile stations in a cellular communications system is provided. The system comprises a number of mobile stations and base stations. Each base station makes synchronization transmissions within its area of covers, which define a broadcast control channel for the transmission of broadcast data from the base station to mobile stations within the area of coverage. The synchronization transmissions are received at mobile stations within the area of coverage, which extracts data defining the broadcast control channel, and at least one calling channel on which mobile stations can transmit probe data to one another. The probe data is used by the mobile stations to obtain connectivity information relating to the availability of other mobile stations. The synchronization transmissions also contain data which is used to define at least one traffic channel which is used by the mobile stations to relay message data between themselves. Effectively, the method of the invention provides a hybrid system which combines conventional cellular technology with opportunistic relaying technology.
Owner:IWICS INC
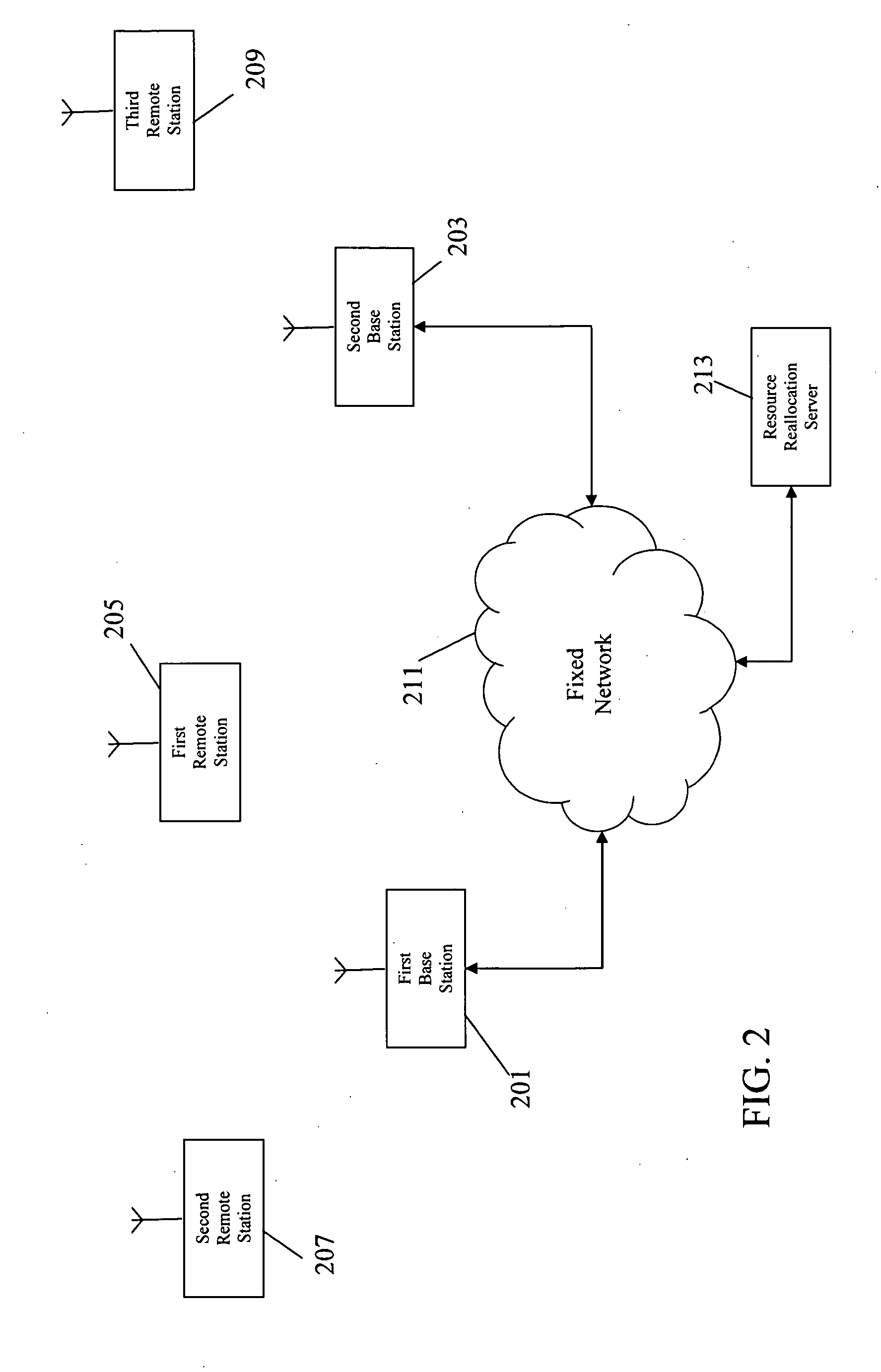
Resource exchange discovery in a cellular communication system
ActiveUS20090161614A1Efficient disseminationEasy to useConnection managementWireless commuication servicesAir interfaceStructure of Management Information
A cellular communication system comprises a set of base stations (201,203) which transmit downlink resource exchange discovery messages to remote terminals in resource allocations of a Media Access Control, MAC, frame structure. The discovery messages may indicate that a base station has resource available for reallocation to another base station or that a base station is seeking resource to be allocated from another base station. A remote terminal (205) comprises a receiver (401, 403) which receives a first message of the downlink resource exchange discovery messages from at least a first base station (201). A discovery message transmit processor (407) generates a second message, which is an uplink resource exchange message comprising resource exchange data determined from the first message, and transmits this to a second base station (203). The second base station (203) then initiates a temporary air interface resource reallocation with the first base station in response to receiving the second message.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Adaptive antenna for use in same frequency networks
InactiveUS6404386B1Spatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringCellular communication systems
An antenna apparatus which can increase capacity in a cellular communication system. The antenna operates in conjunction with a mobile subscriber unit and provides a plurality of antenna elements, each coupled to a respective signal control component such as a switch. The switch position of each antenna element is programmed for optimum reception during, for example, an idle mode which receives a pilot signal. The antenna array creates a beamformer for signals to be transmitted from the mobile subscriber unit, and a directional receiving array to more optimally detect and receive signals transmitted from the base station. By directionally receiving and transmitting signals, multipath fading is greatly reduced as well as intercell interference. Various techniques for determining the proper arrangement of signal control components for each antenna element are accommodated.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
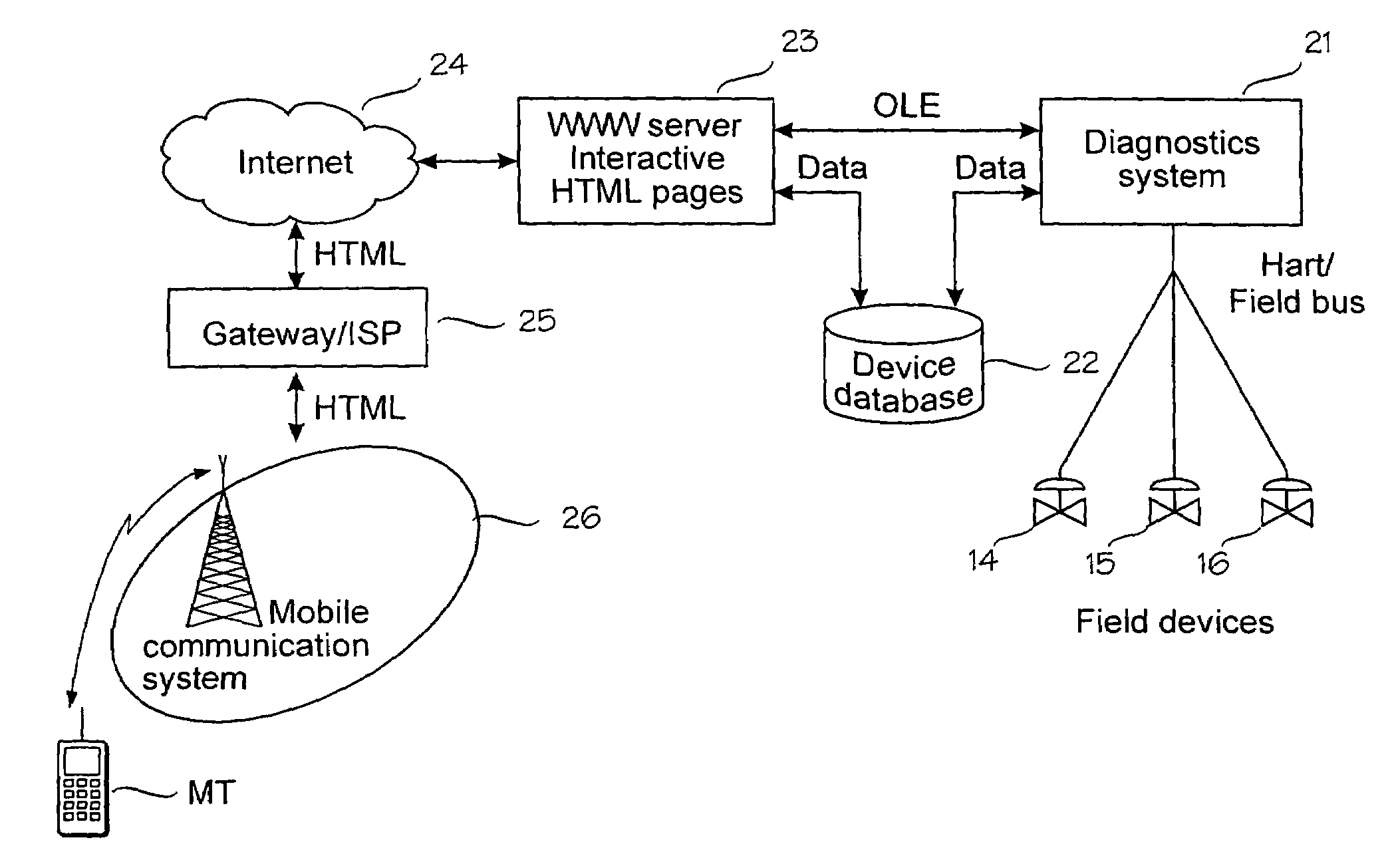
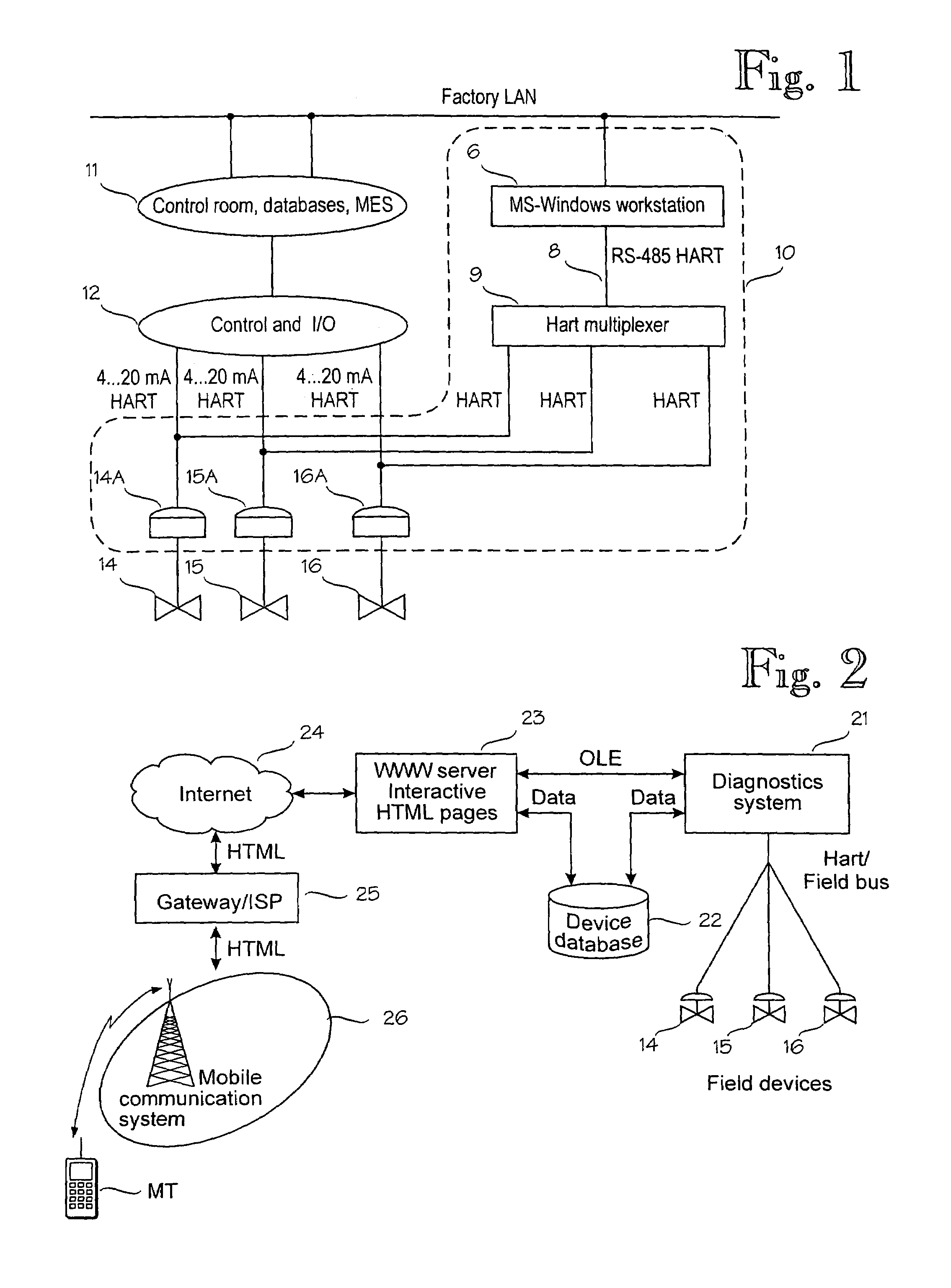
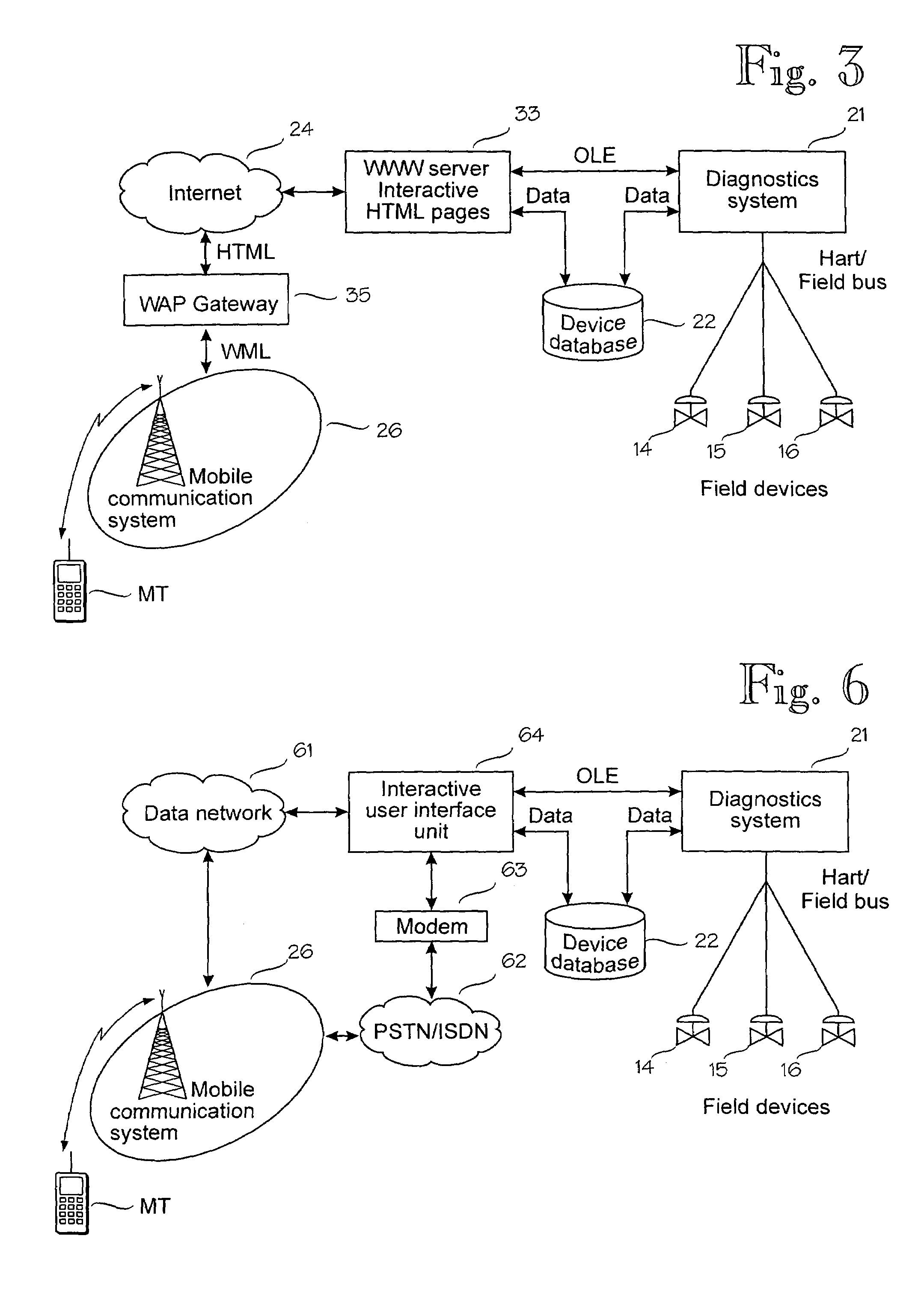
Wireless control of a field device in an industrial process
InactiveUS7010294B1Short response timeQuality improvementElectric testing/monitoringBroadcast transmission systemsData connectionWireless control
A mobile terminal is arranged to communicate over a cellular communication system with a control system connected to a plurality of field devices in an industrial process, in order to remote control, configure or monitor the field devices. The mobile terminal accesses through a dedicated data connection established over the cellular communication system an interactive user interface associated with the control system and arranged to utilize the configuration, control and management data of the control system. In the preferred embodiment, the interactive user interface is provided by a World Wide Web server.
Owner:METSO AUTOMATION OY
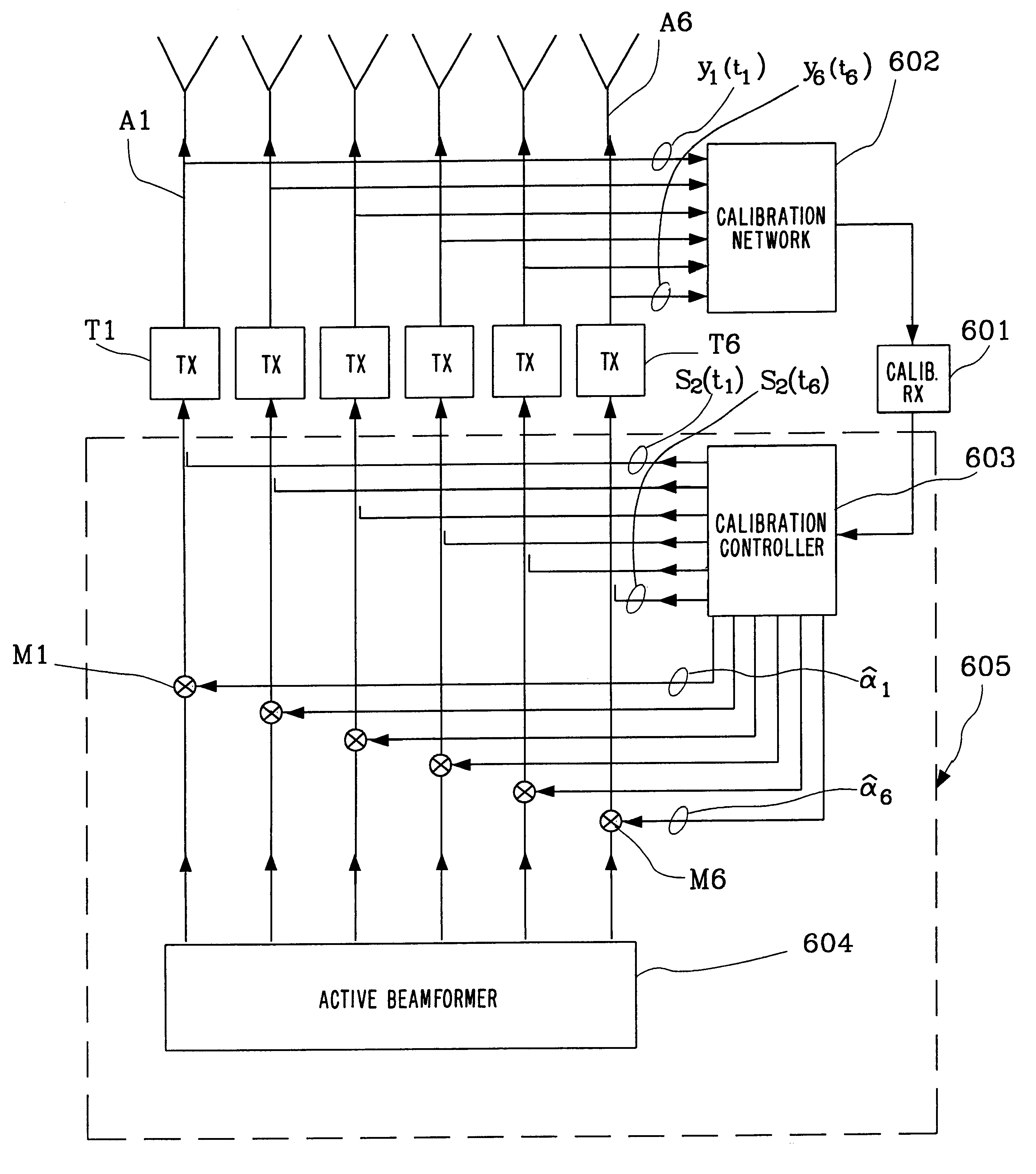
Antenna array calibration
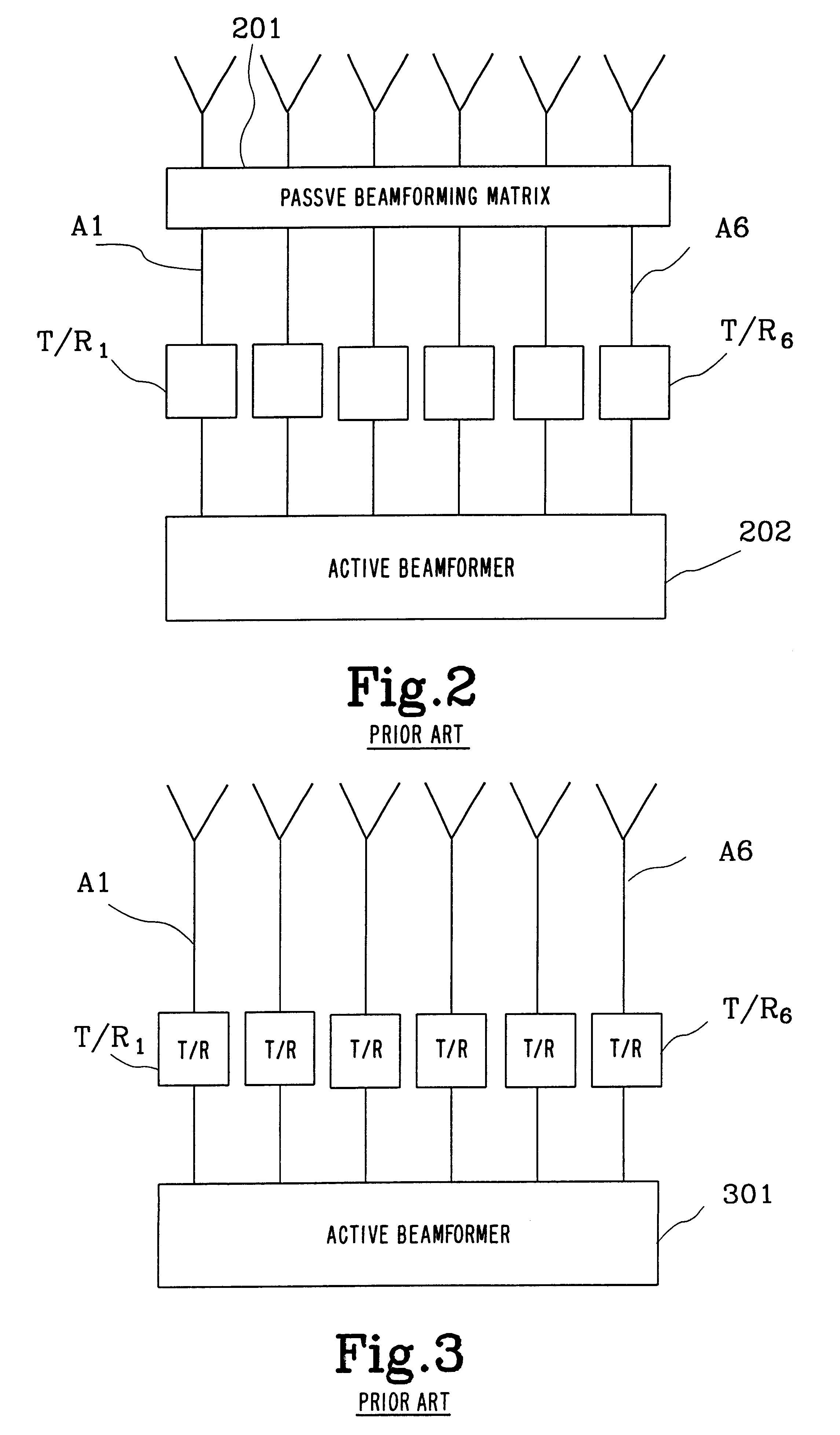
InactiveUS6339399B1Improve performanceImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsAntennasAmplitude distortionCellular communication systems
A method and a system for calibrating the reception and transmission of an antenna array for use in a cellular communication system is disclosed. The calibration of the reception of the antenna array is performed by injecting a single calibration signal into each of a number of receiving antenna sections, in parallel. The signals are collected after having passed receiving components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to received signals. The calibration of the transmission of the antenna array is preformed in a similar way. A single calibration signal is generated and injected into each of a number of transmitting antenna sections, one at a time. The signals are collected, one at a time, after having passed transmitting components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to signals that are to be transmitted.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
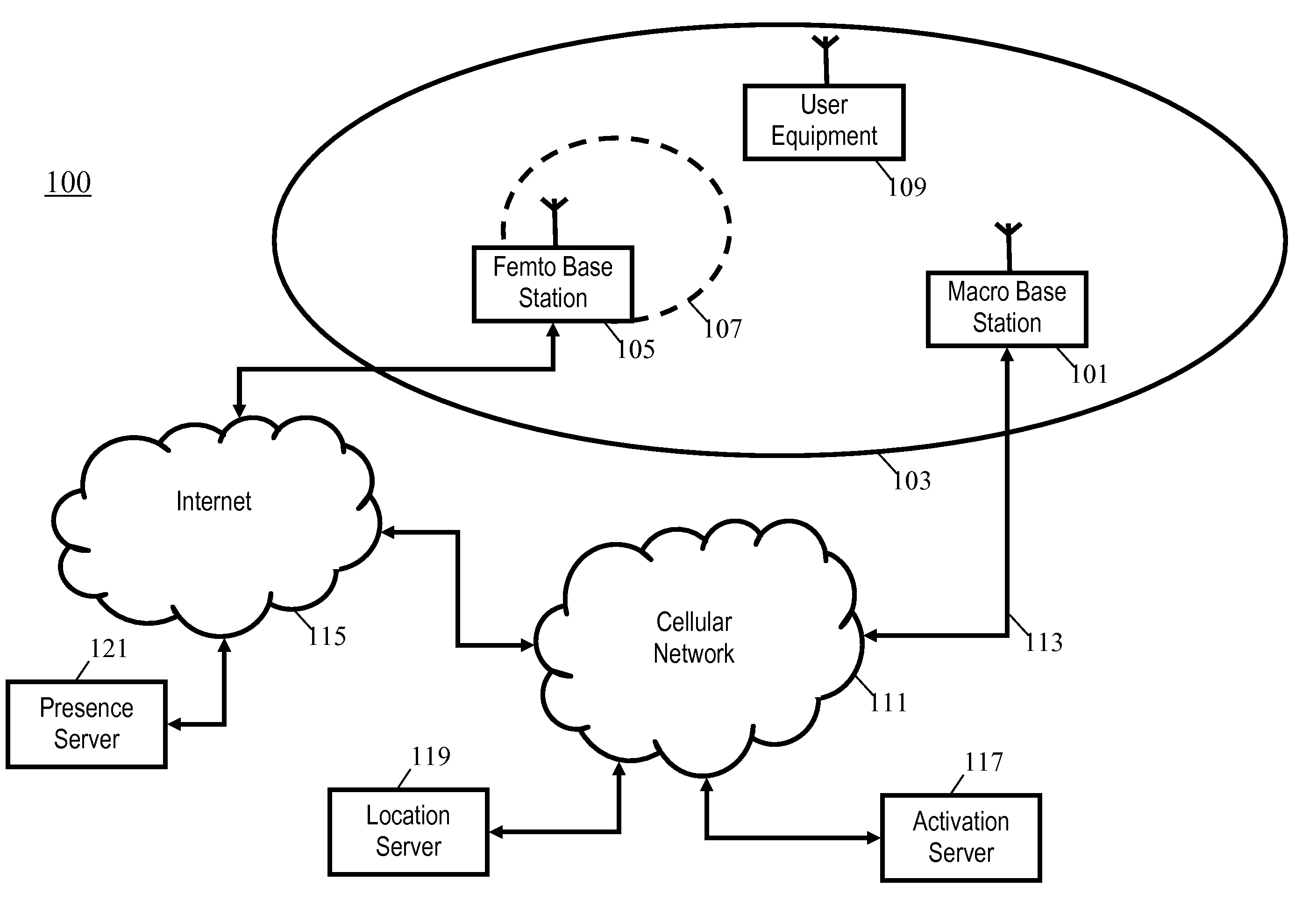
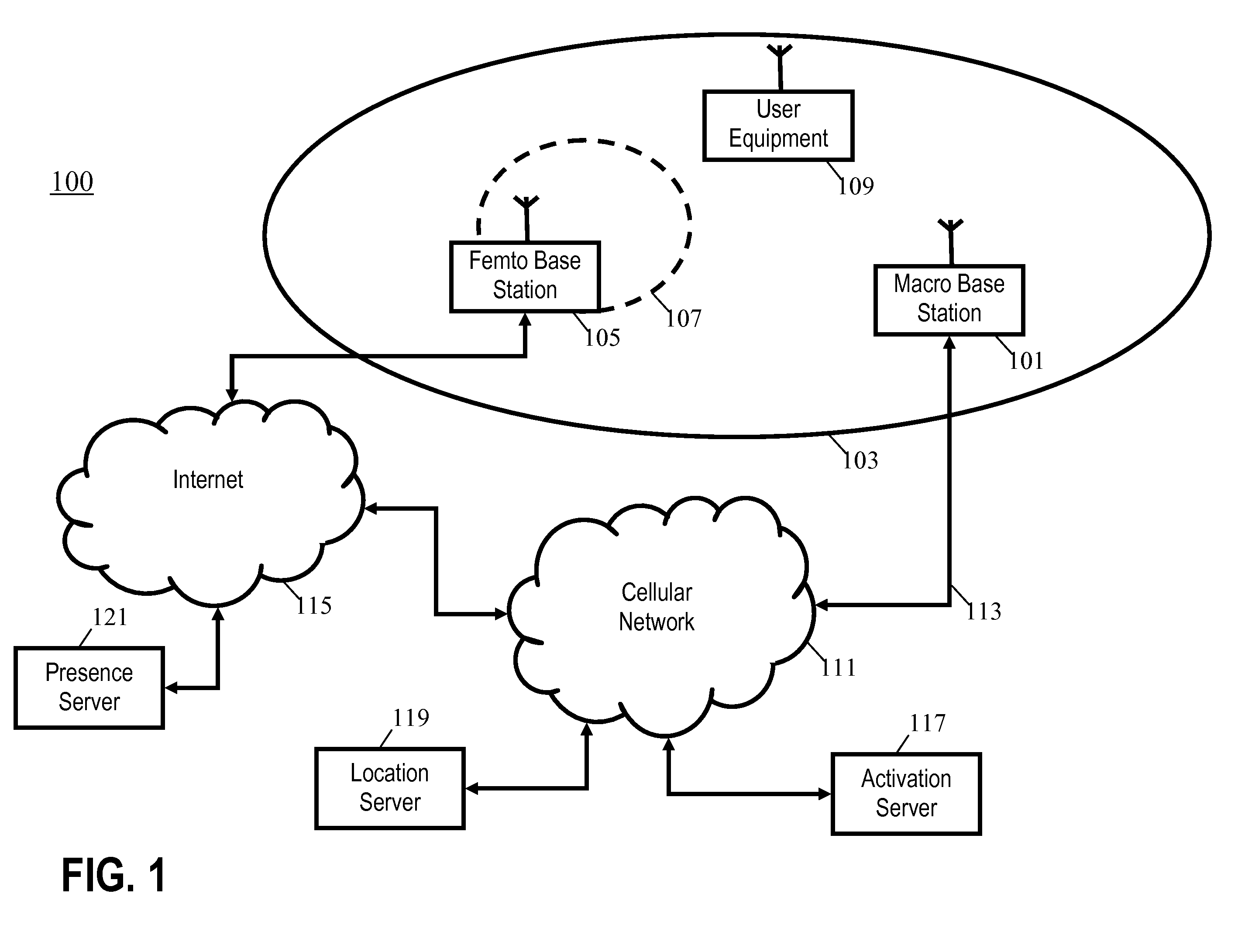
Presence-aware cellular communication system and method
InactiveUS20100056184A1Increase capacityReduce consumptionPower managementAssess restrictionAir interfaceCellular communication systems
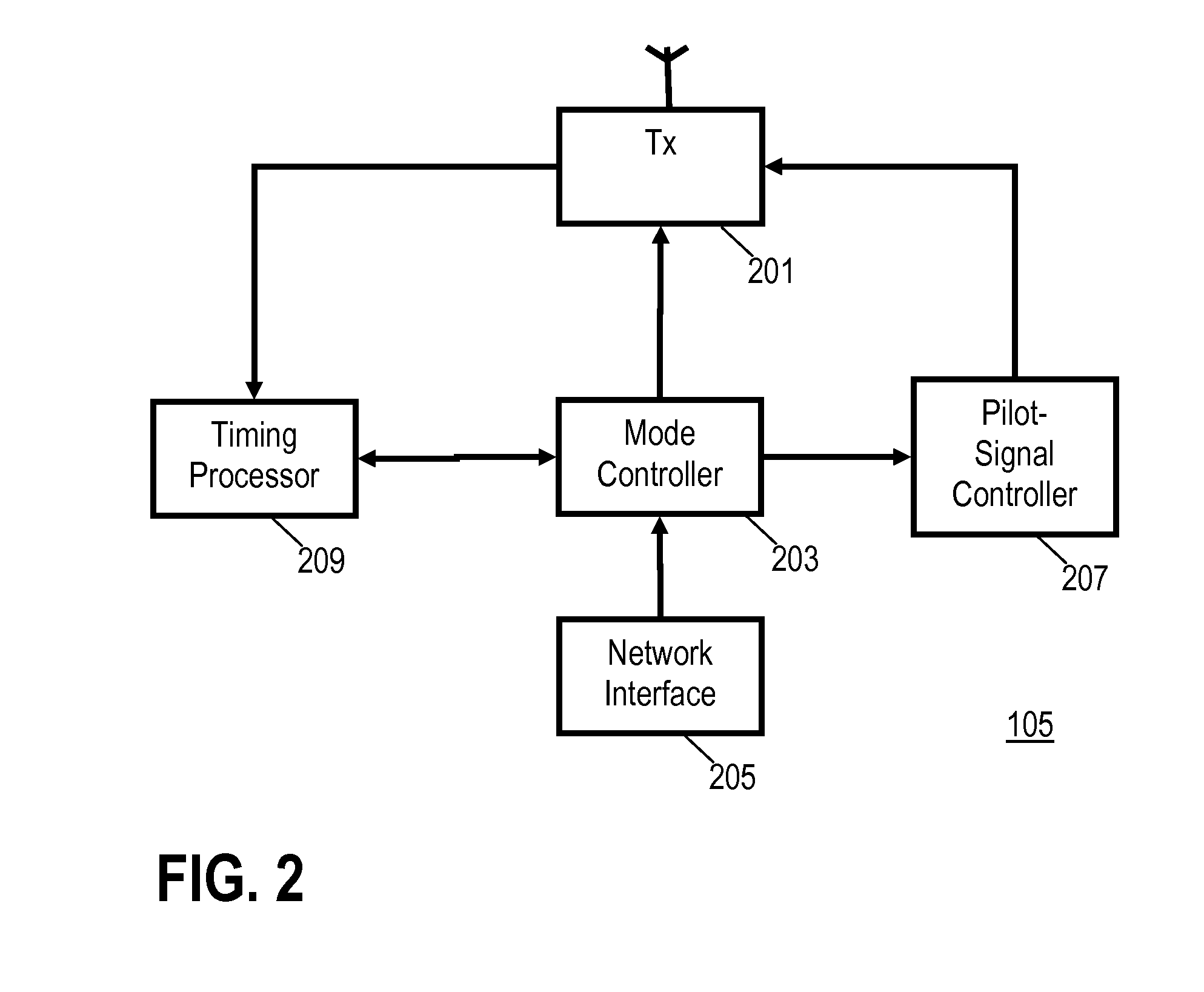
A cellular communication system comprises a network supporting user equipment over an air interface, the network having a hierarchical cell arrangement with overlay cells and underlay cells. An underlay base station is associated with a subset of registered user equipment. An activation server switches the underlay base station between an inactive mode and an active mode in response to detecting that registered user equipment meets a location criterion. The underlay base station only supports user equipment when in the active mode, e.g., it may only transmit a pilot signal in this mode. Interference and power consumption may be substantially reduced by sending the base station into the inactive mode thereby resulting in increased capacity of the cellular communication system as a whole.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
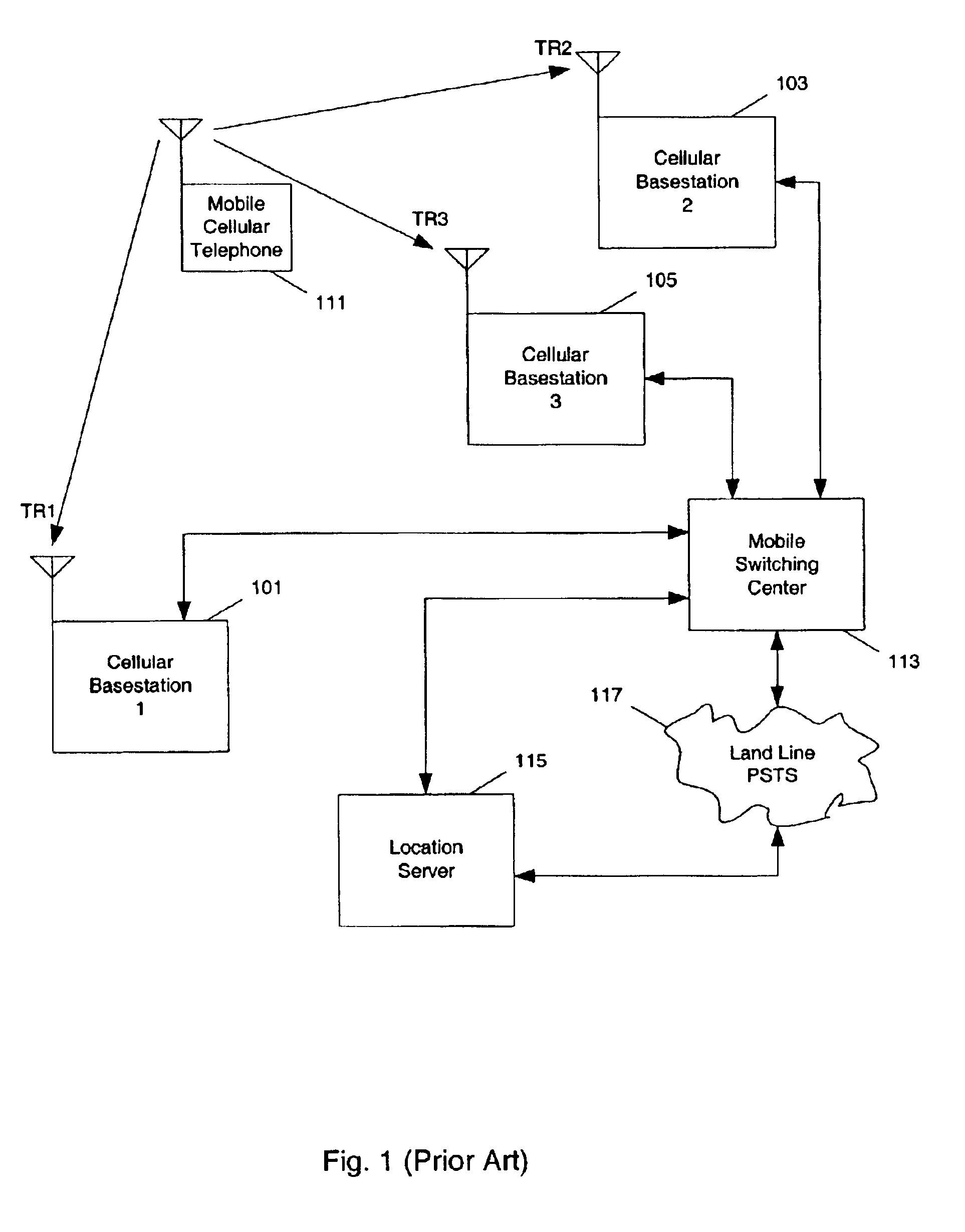
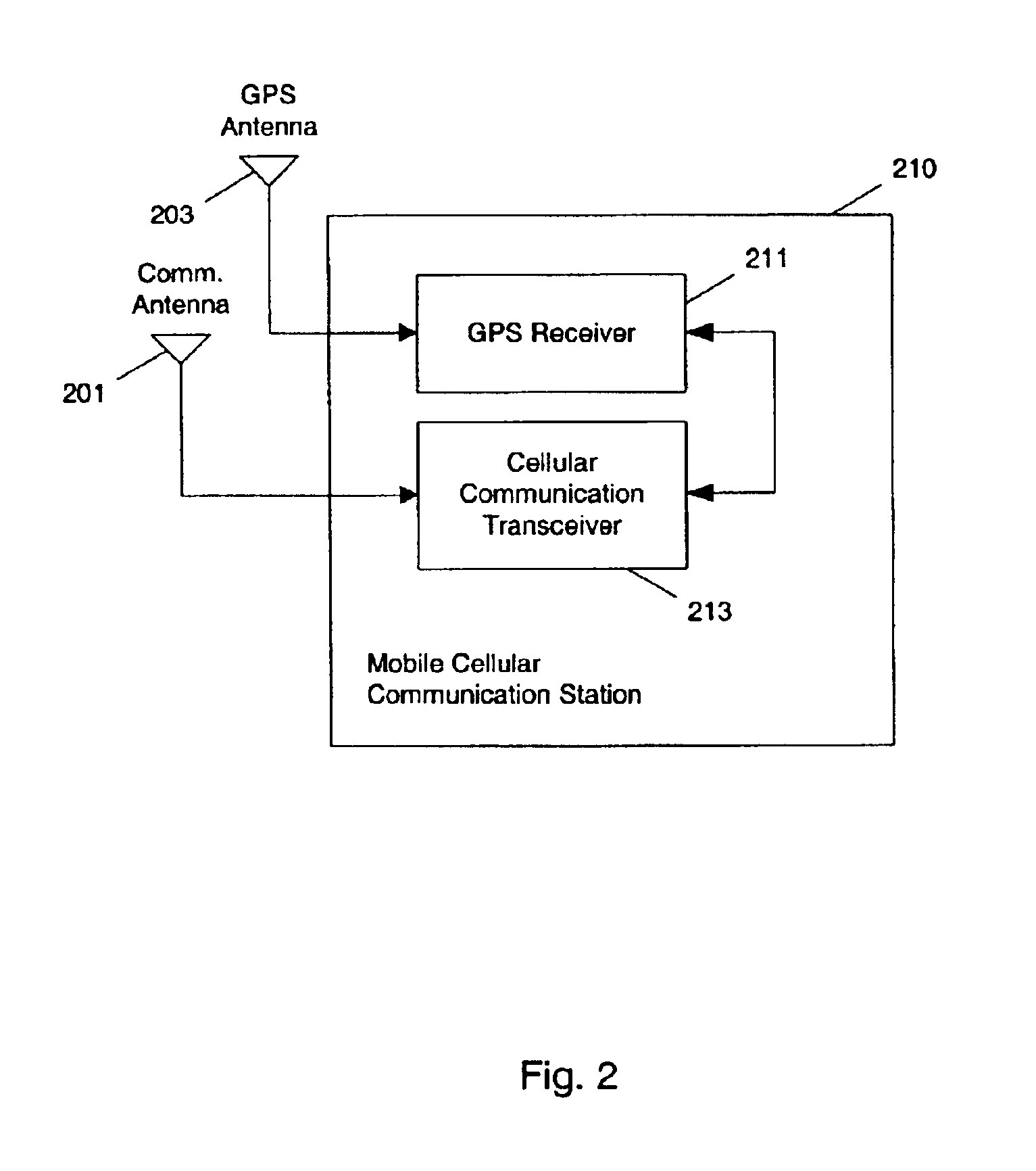
Methods and apparatuses for using mobile GPS receivers to synchronize basestations in cellular networks
InactiveUS6665541B1Low costSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexGeolocationGps receiver
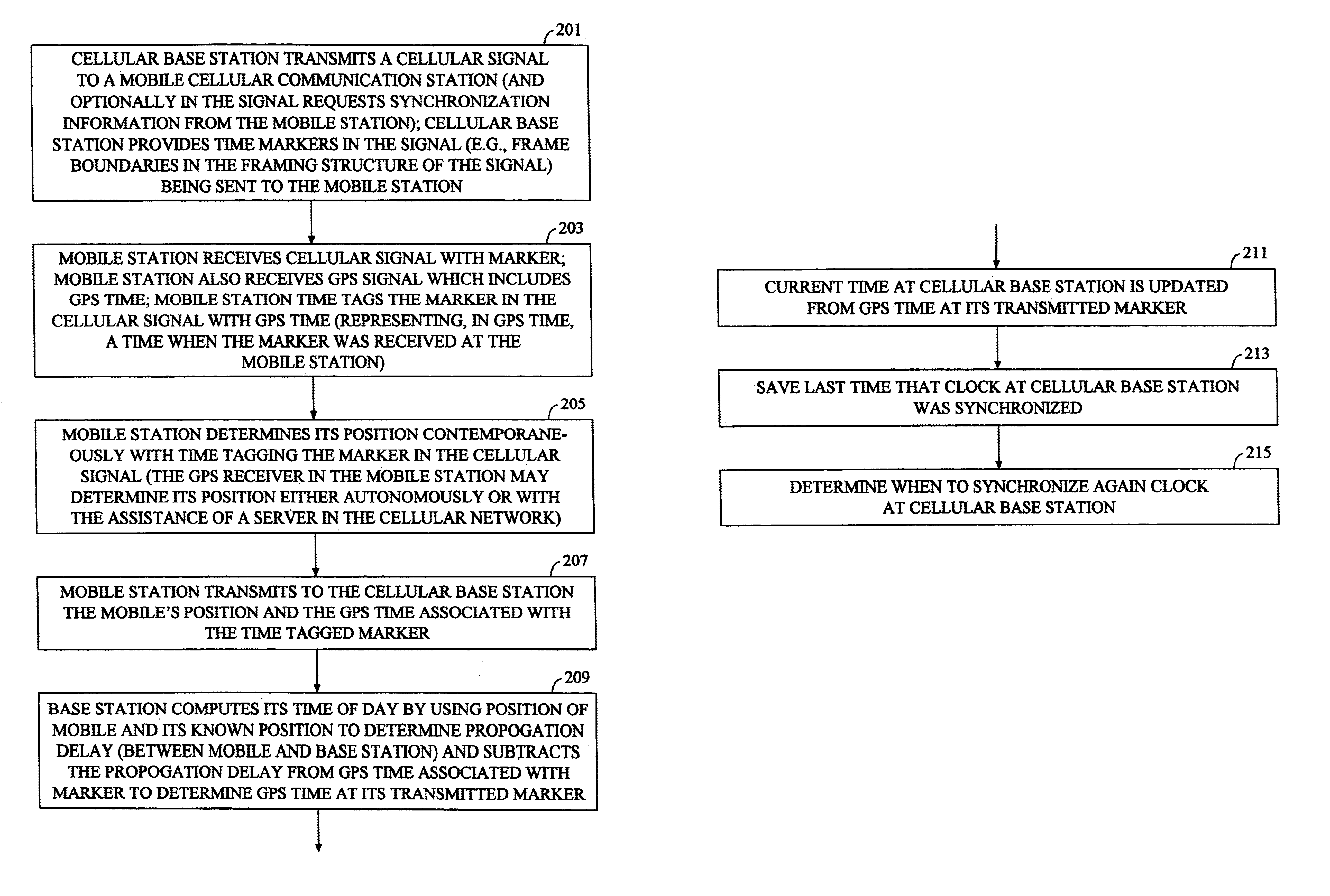
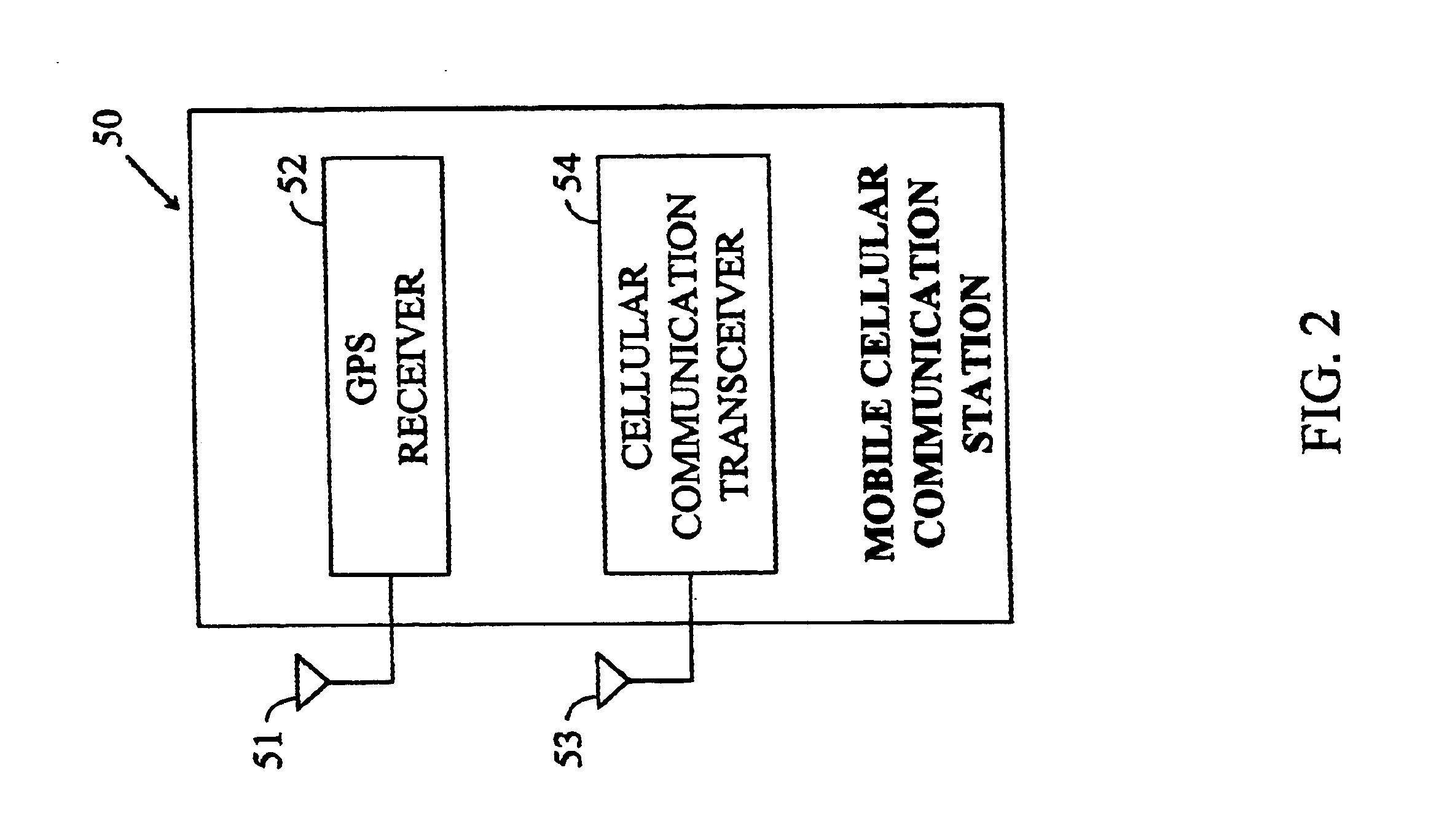
Methods and apparatuses for synchronizing basestations in a cellular network. One exemplary method performs time synchronization between at least two basestations, a first basestation and a second basestation, of a cellular communication system. In this exemplary method, a first time-of-day and a first geographical location of a first mobile cellular receiver station (MS) are determined from a first satellite positioning system (SPS) receiver which is co-located with the first MS, and the first time-of-day and first location are transmitted by the first MS to a first basestation which determines a time-of-day of the first basestation from the first time-of-day and first location and from a known location of the first basestation. Also in this exemplary method, a second time-of-day and a second geographical location of a second MS are determined from a second SPS receiver which is co-located with the second MS, and the second time-of-day and the second location are transmitted to a second basestation which determines a time-of-day of the second basestation from the second time-of-day and the second location and a known location of the second basestation. Other methods and apparatuses are also described for synchronizing basestations in a cellular network.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Systems and method for providing in-flight broadband mobile communication services
InactiveUS20110182230A1Efficient use ofImproving average and peak data throughputFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork topologiesTransceiverSpatial division multiple access
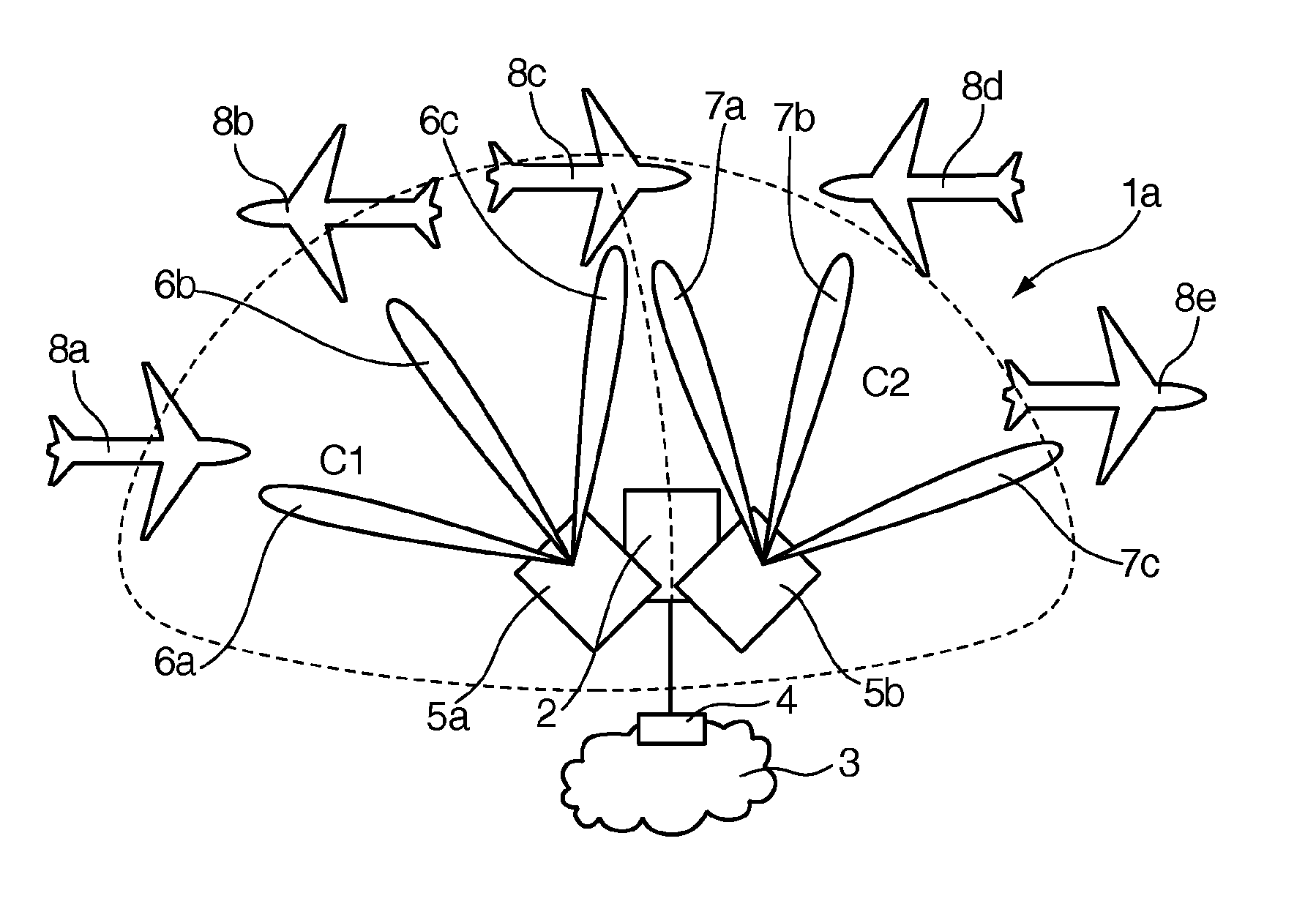
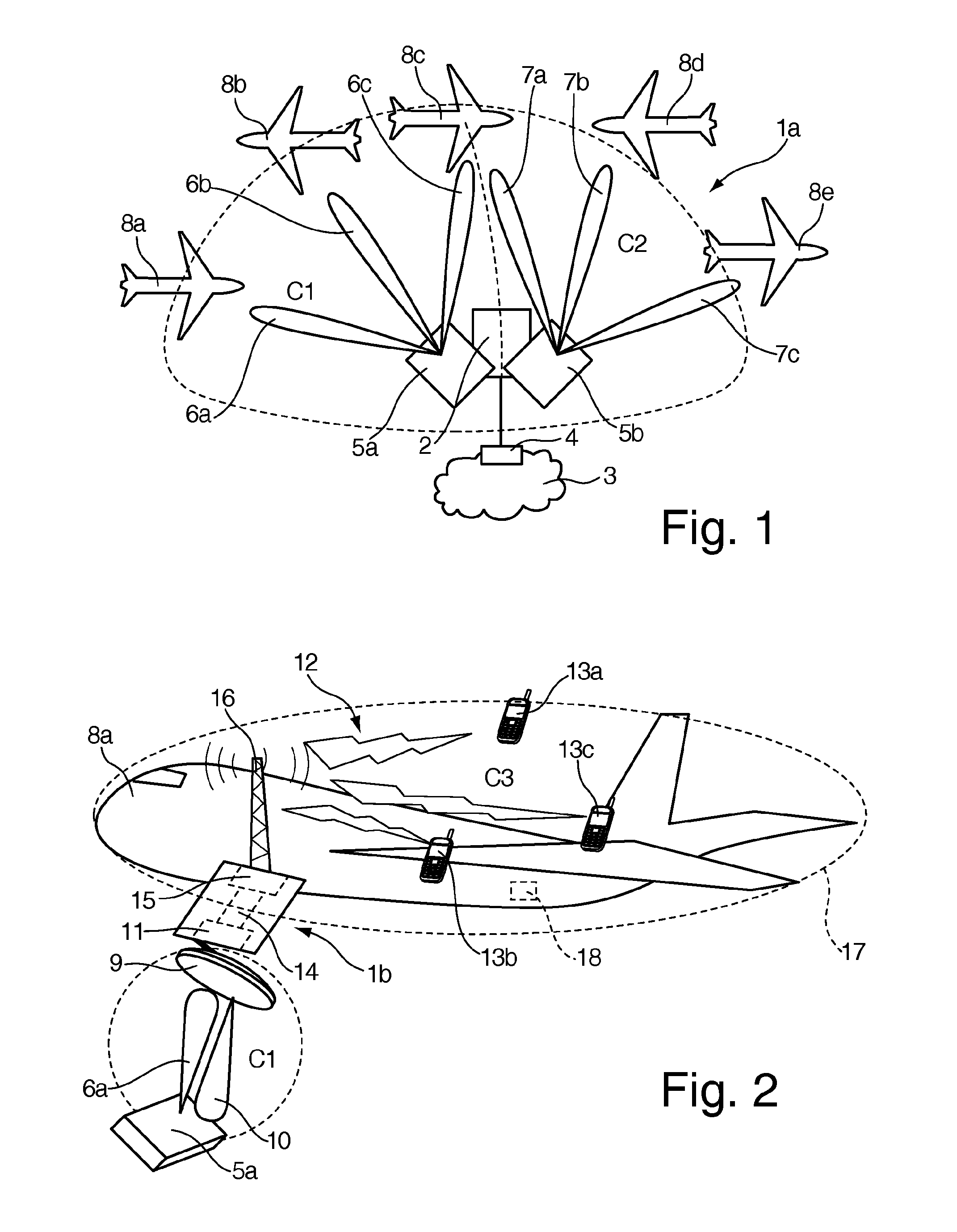
The invention relates to a ground-based wireless cellular communication system (1a) for providing in-flight broadband mobile communication services, comprising: at least one ground-based base station (2) adapted for generating at least one cell (C1, C2) defining a solid angle of the space surrounding the base station (2), the ground- based base station (2) further comprising at least one antenna array (5a, 5a) using two-dimensional-beamforming for generating at least one beam (6a-c, 7a-c) for serving at least one airplane (8a-c, 8c-e) in the space covered by the at least one cell (C1, C2) using spatial-division multiple access, SDMA. The invention also relates to an airplane equipment for providing in-flight broadband mobile communication services, comprising: at least one antenna for exchange of user data with the ground-based wireless cellular communication system (1a), a transceiver unit connected to the at least one antenna for handling the air-to-ground and ground-to-air communication with the ground-based wireless cellular communication system (1a), and an inside-airplane communication system for distributing the user data to and from terminals within the airplane.
Owner:RPX CORP
Routing in a multi-station network
InactiveUS6785510B2Effective expansionReduce data rateSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemHybrid system
A method of relaying data between mobile stations in a cellular communications system is provided. The system comprises a number of mobile stations and base stations. Each base station makes synchronization transmissions within its area of covers, which define a broadcast control channel for the transmission of broadcast data from the base station to mobile stations within the area of coverage. The synchronization transmissions are received at mobile stations within the area of coverage, which extracts data defining the broadcast control channel, and at least one calling channel on which mobile stations can transmit probe data to one another. The probe data is used by the mobile stations to obtain connectivity information relating to the availability of other mobile stations. The synchronization transmissions also contain data which is used to define at least one traffic channel which is used by the mobile stations to relay message data between themselves. Effectively, the method of the invention provides a hybrid system which combines conventional cellular technology with opportunistic relaying technology.
Owner:IWICS INC
Method, terminal device and system allowing for handling location services independently from a cellular communication system
ActiveUS20040132465A1Enhanced location serviceGood serviceTelephonic communicationRecord information storageTerminal equipmentEngineering
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Antenna array calibration
InactiveUS6157343AImprove radio communication performanceImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsAntennasAmplitude distortionCellular communication systems
A method and a system for calibrating the reception and transmission of an antenna array for use in a cellular communication system is disclosed. The calibration of the reception of the antenna array is performed by injecting a single calibration signal into each of a number of receiving antenna sections, in parallel. The signals are collected after having passed receiving components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to received signals. The calibration of the transmission of the antenna array is performed in a similar way. A single calibration signal is generated and injected into each of a number of transmitting antenna sections, one at a time. The signals are collected, one at a time, after having passed transmitting components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to signals that are to be transmitted.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
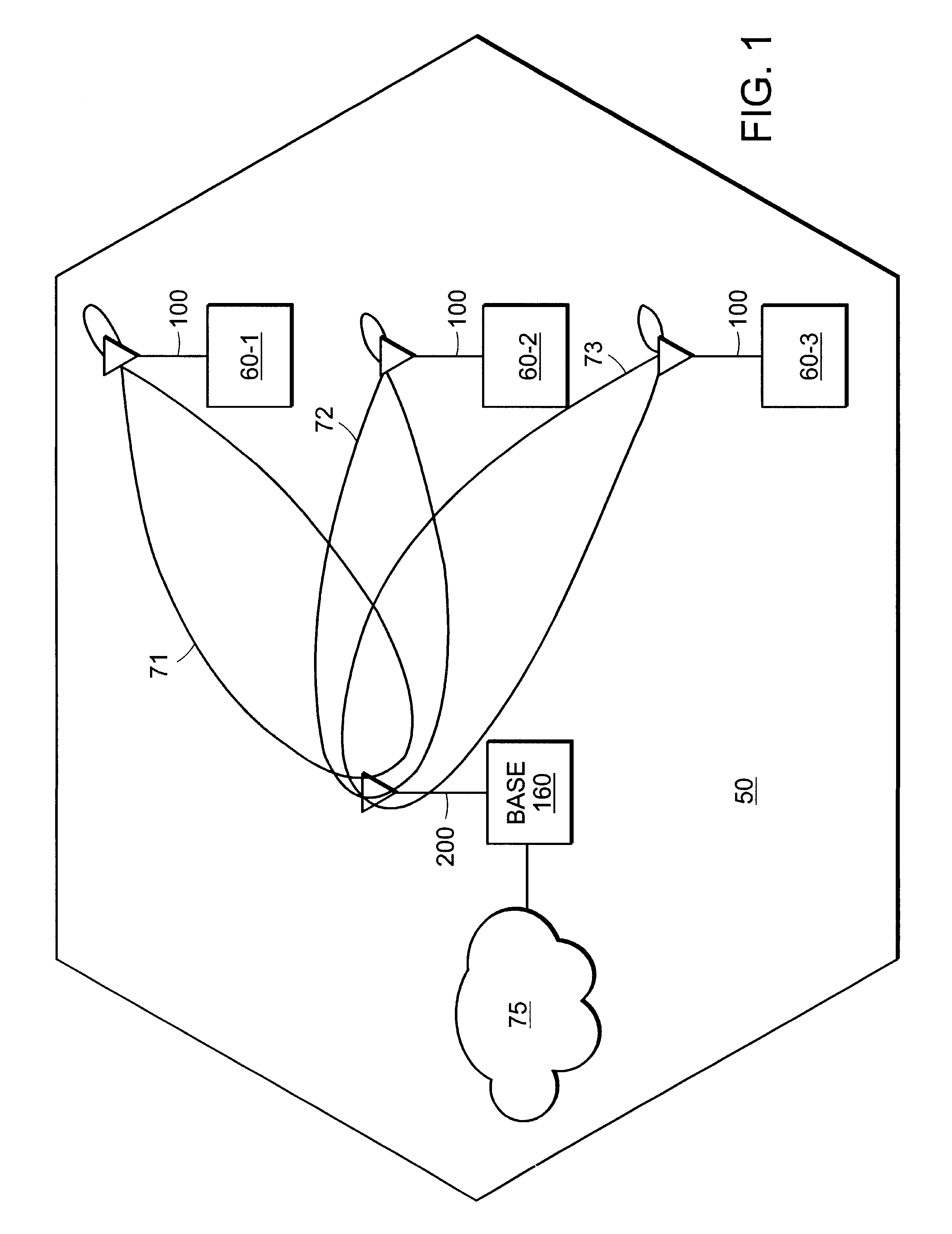
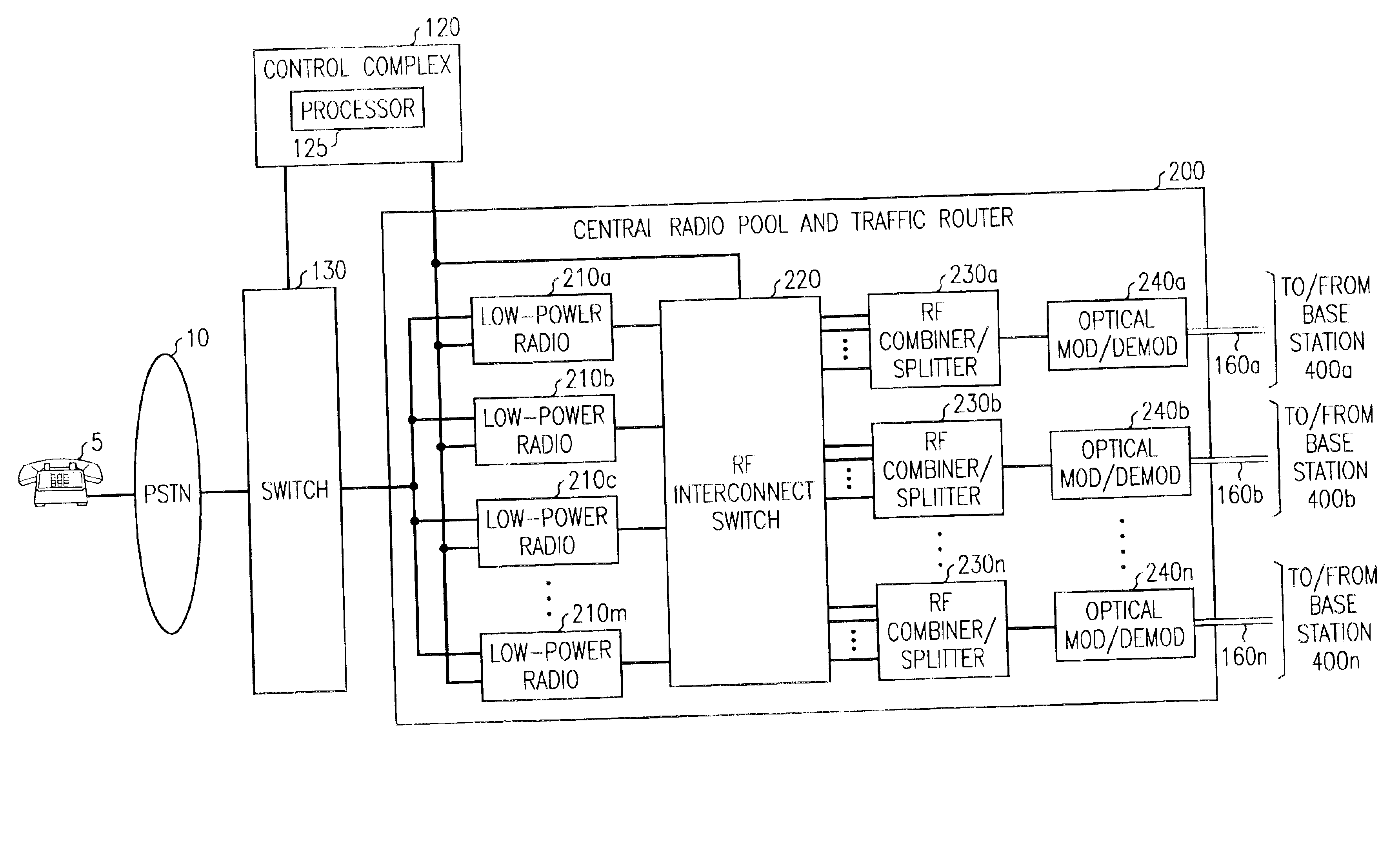
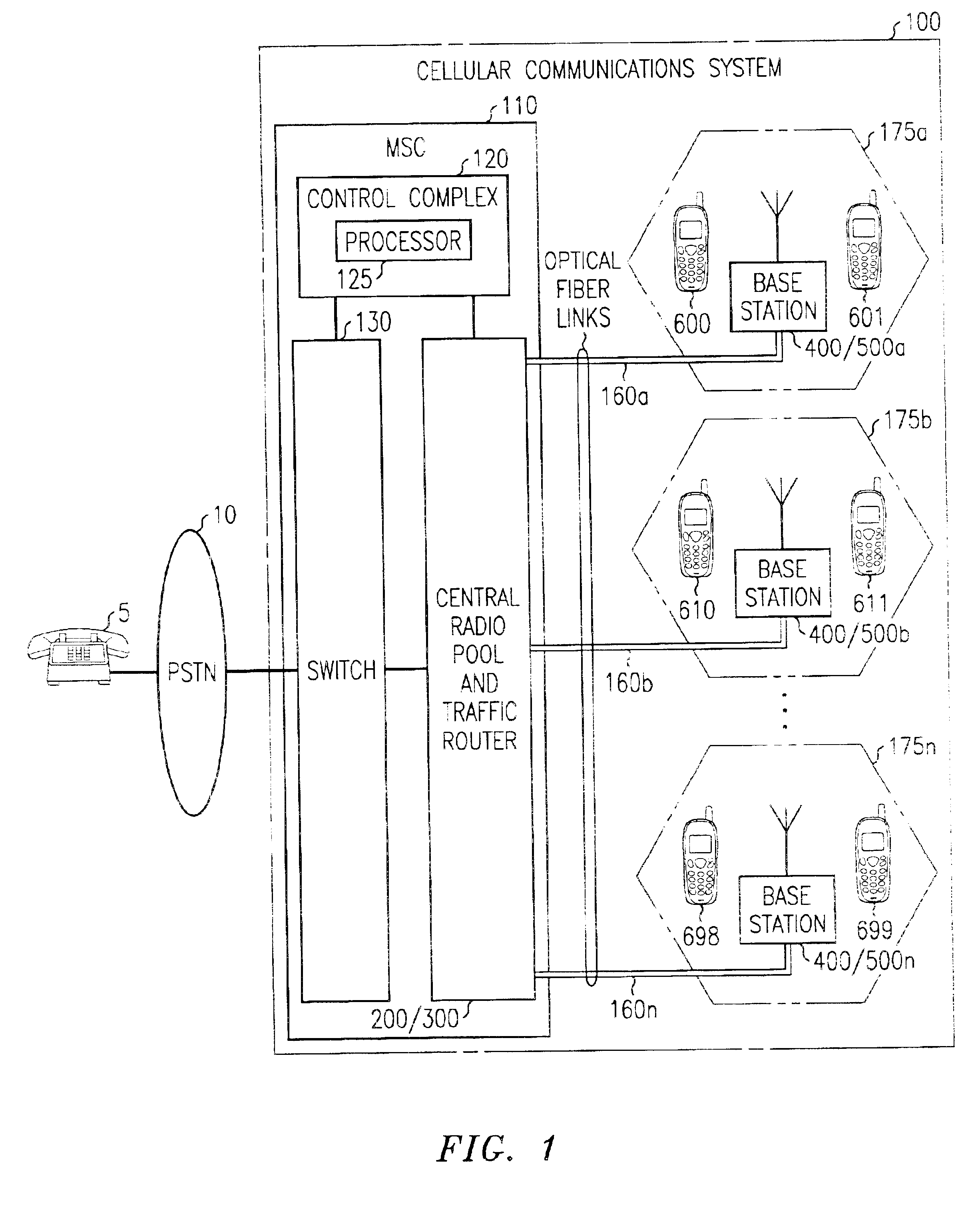
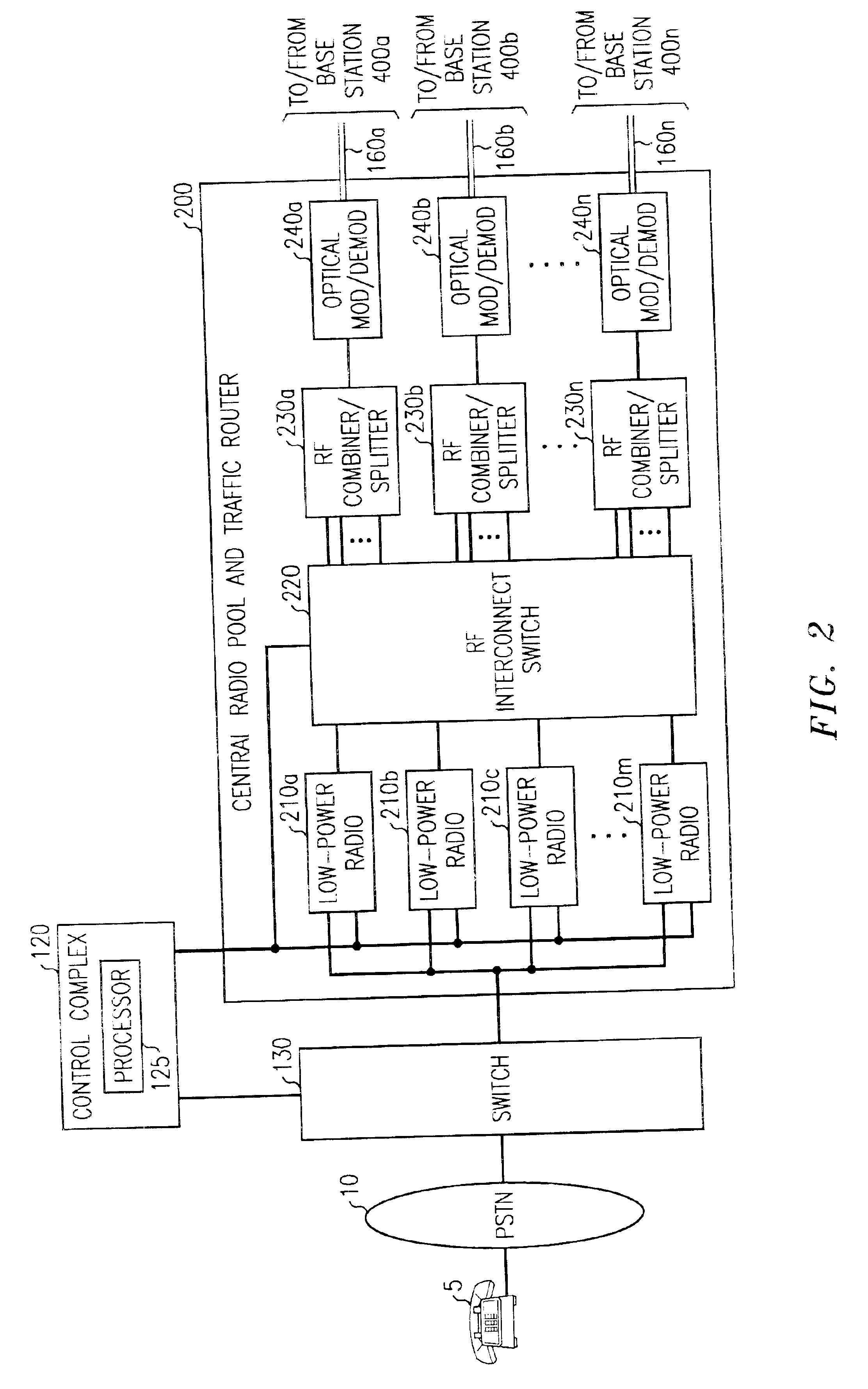
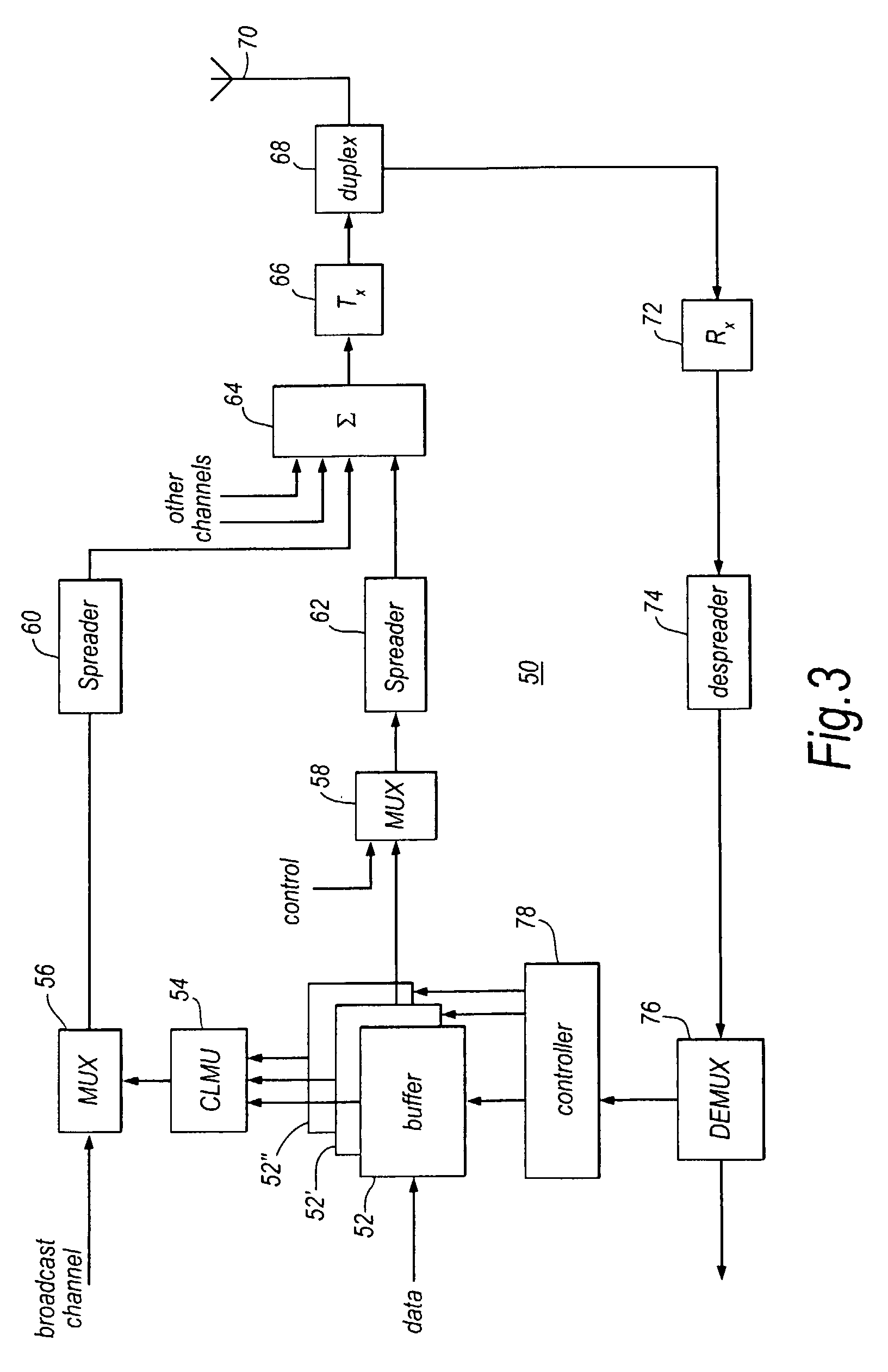
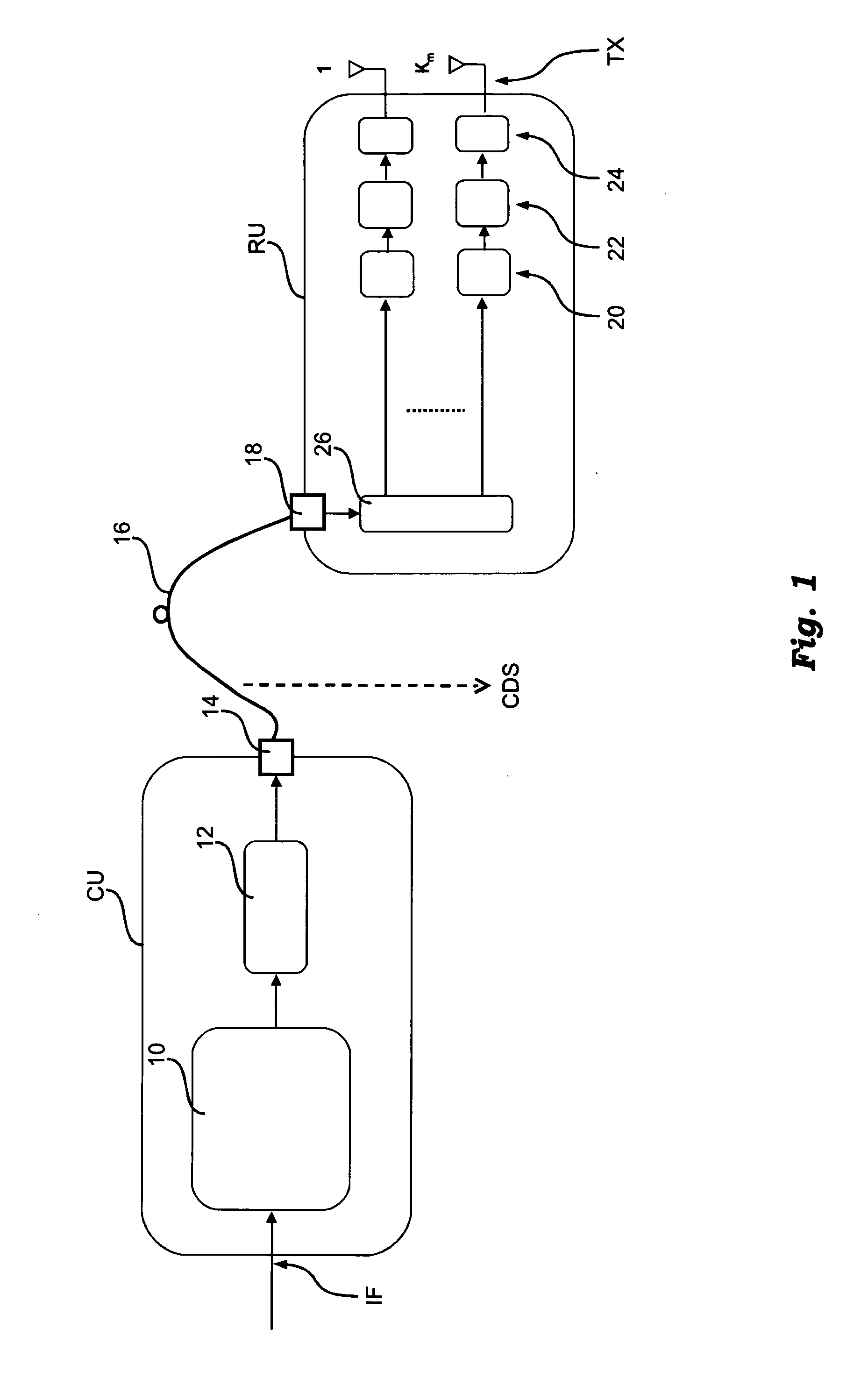
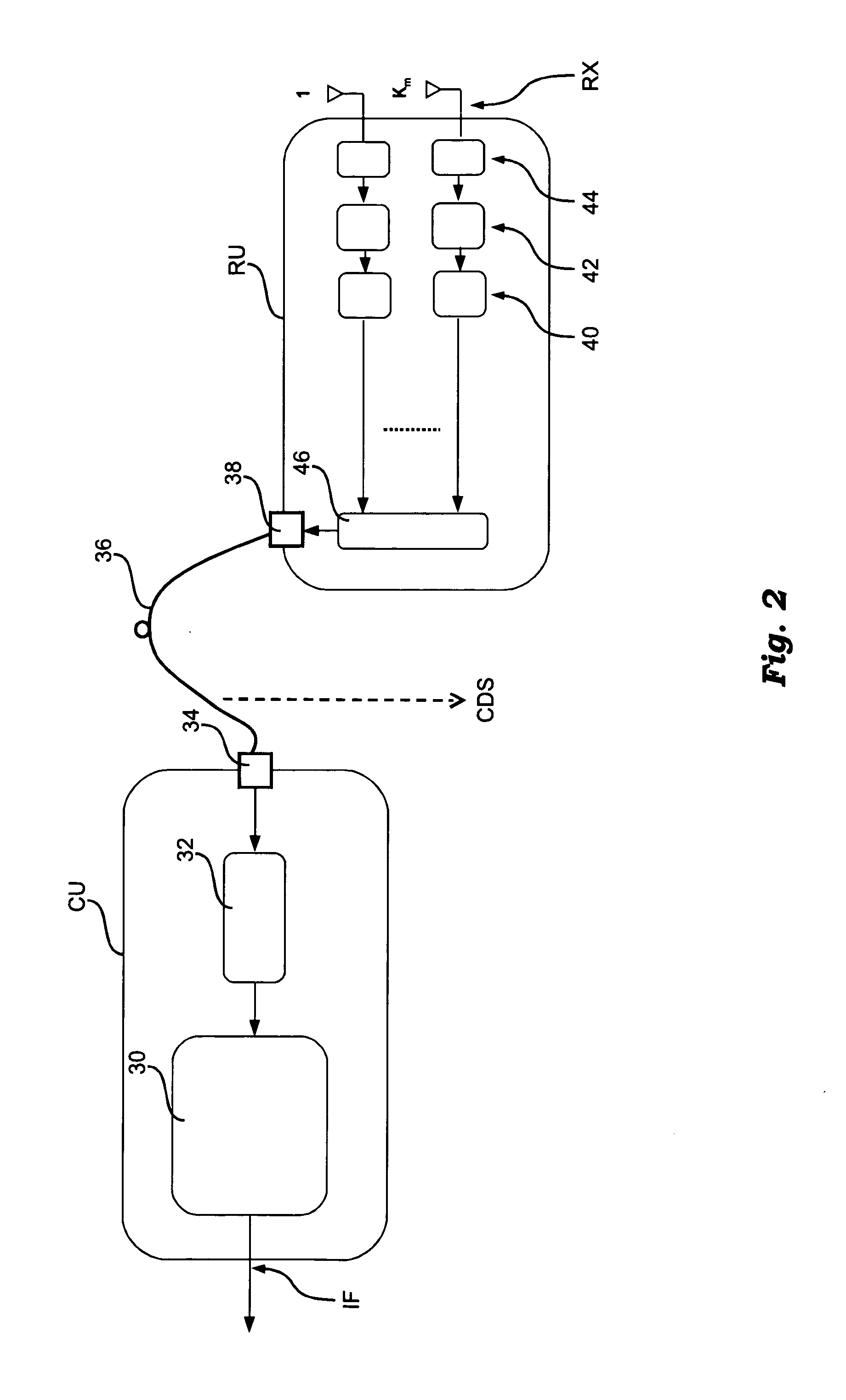
Cellular communications system featuring a central radio pool/traffic router
InactiveUS6865390B2Easy to useEasy maintenanceSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsFiberRadio equipment
The present invention provides a cellular communication system that includes a central radio pool / traffic router (CRP / TR) that sends control and traffic signals over fiber optic transmission links that connect the CRP / TR with base stations of the cellular communication system. The high bandwidth capacity of each fiber link allows a large band of radio frequencies representing many radio channels to pass between the CRP / TR and individual base stations. Radio resources can be shared by all base stations in the cellular communication system, dynamically, when and where needed, to meet access demands throughout the system. The CRP / TR includes low-powered digital and / or analog radios and also switching and modulation means used to convey signals between the radios and various base stations within the system.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Cell selection
InactiveUS7277709B2Avoid the needAccurate measurementError preventionTransmission systemsCell selectionCell site
Cell selection techniques for use in cellular communications systems are disclosed. A decision as to whether to use a cell for data transmission is made in dependence on a measure of a congestion level in the cell. The decision may either be part of a cell selection decision, or used to override a cell selection decision. The techniques may be used in fast cell site selection.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
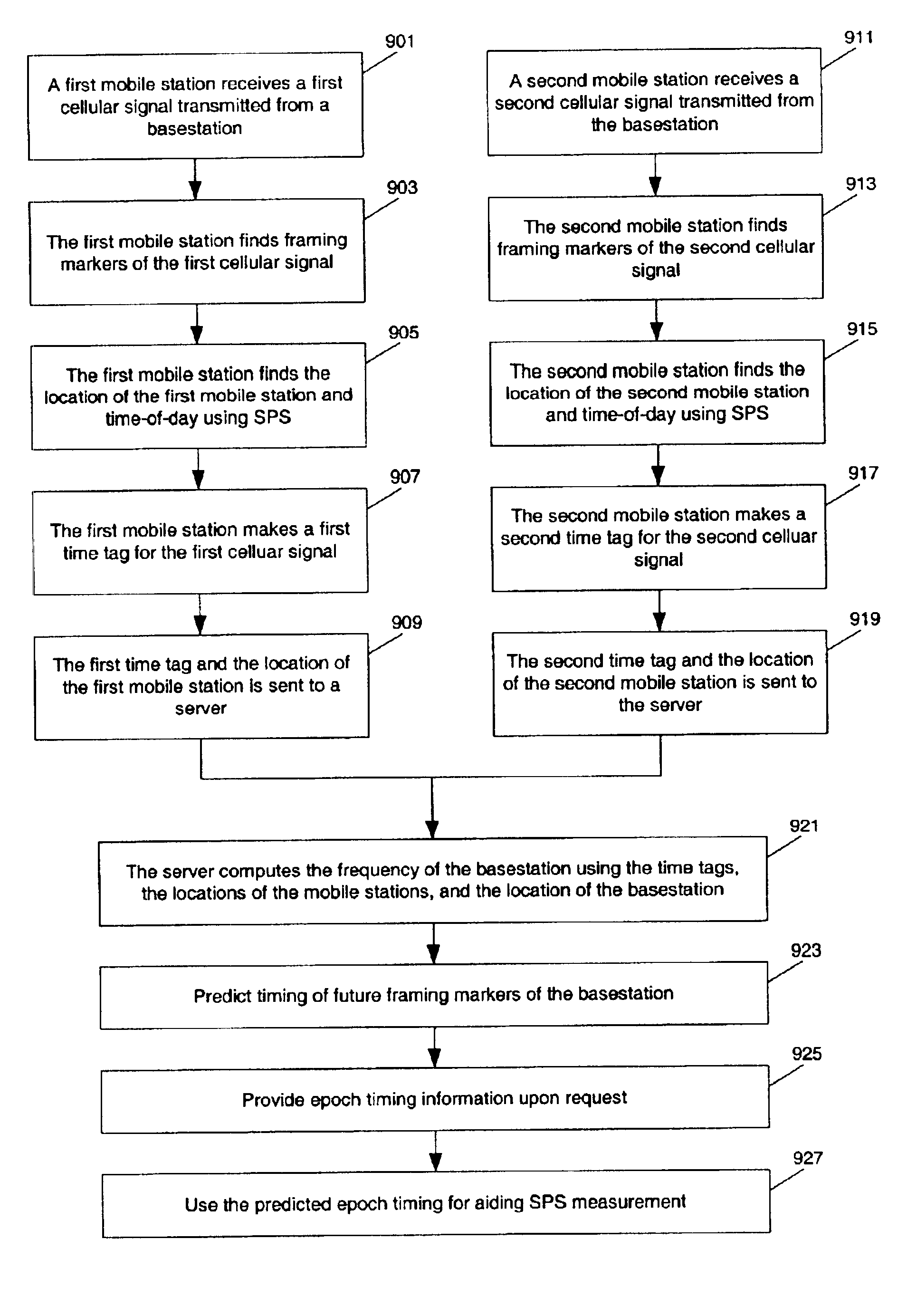
Methods and apparatuses for measuring frequencies of basestations in cellular networks using mobile GPS receivers
InactiveUS6937872B2Synchronisation arrangementSatellite radio beaconingCommunications systemGps receiver
Methods and apparatuses for frequency synchronizing basestations in a cellular communication system. In one aspect of the invention, a method to predict a timing of transmission of a basestation in a cellular communication system includes: receiving a first time tag for a first timing marker in a first cellular signal transmitted from the basestation; receiving a second time tag of a second timing marker in a second cellular signal transmitted from the basestation; and computing a frequency related to the basestation using the first and second time tags. Each of the time tags are determined using at least one satellite positioning system signal received at a mobile station which receives the corresponding time marker.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Integrated or autonomous system and method of satellite-terrestrial frequency reuse using signal attenuation and/or blockage, dynamic assignment of frequencies and/or hysteresis
InactiveUS20020090942A1Efficient reuseInterference minimizationSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionHysteresisUltrasound attenuation
A cellular communications system comprising a space based system comprising a first set of cells, and a ground based system comprising a second set of cells. The space and ground systems can optionally function substantially autonomously, with each using spectrum from at least one predetermined frequency band.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
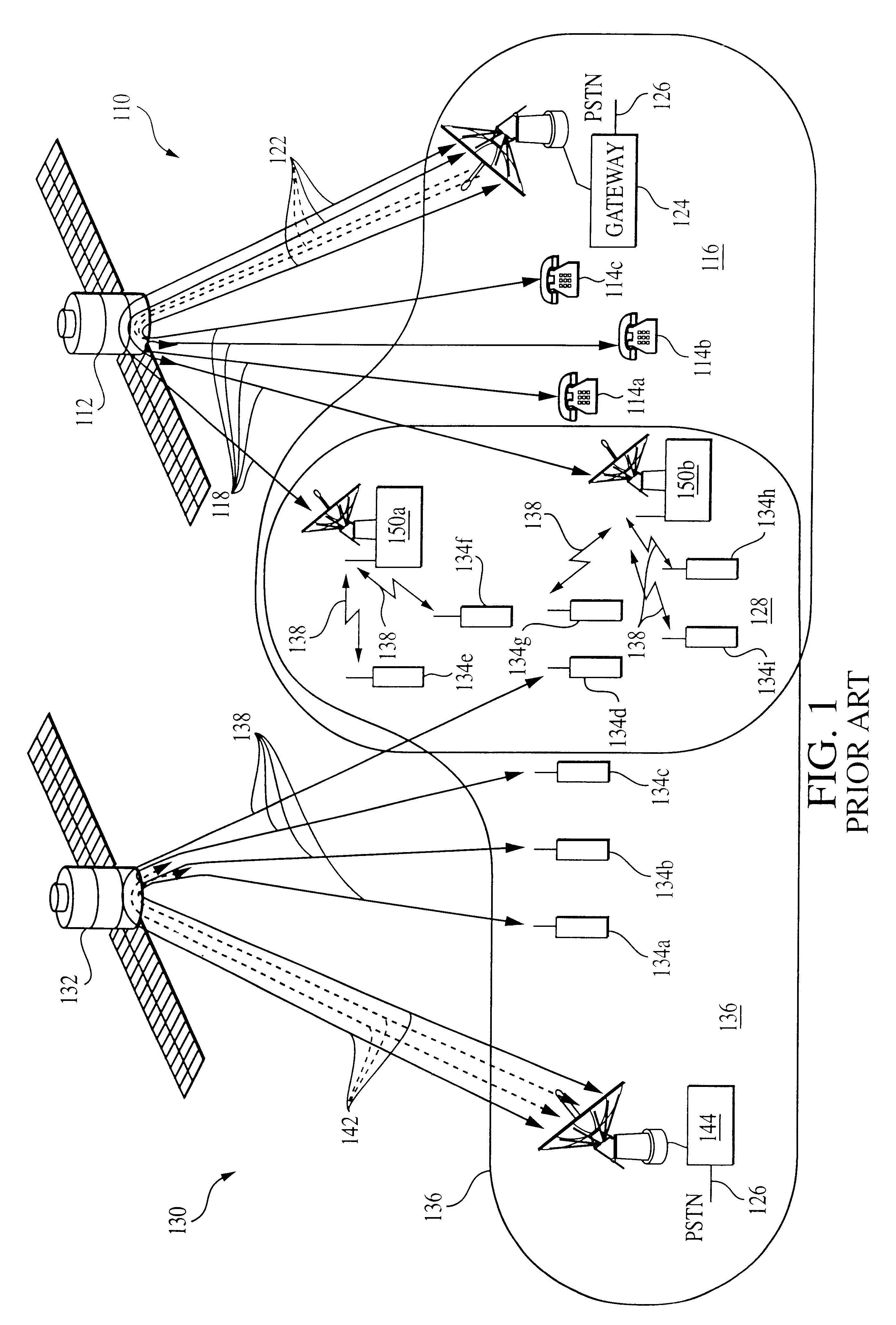
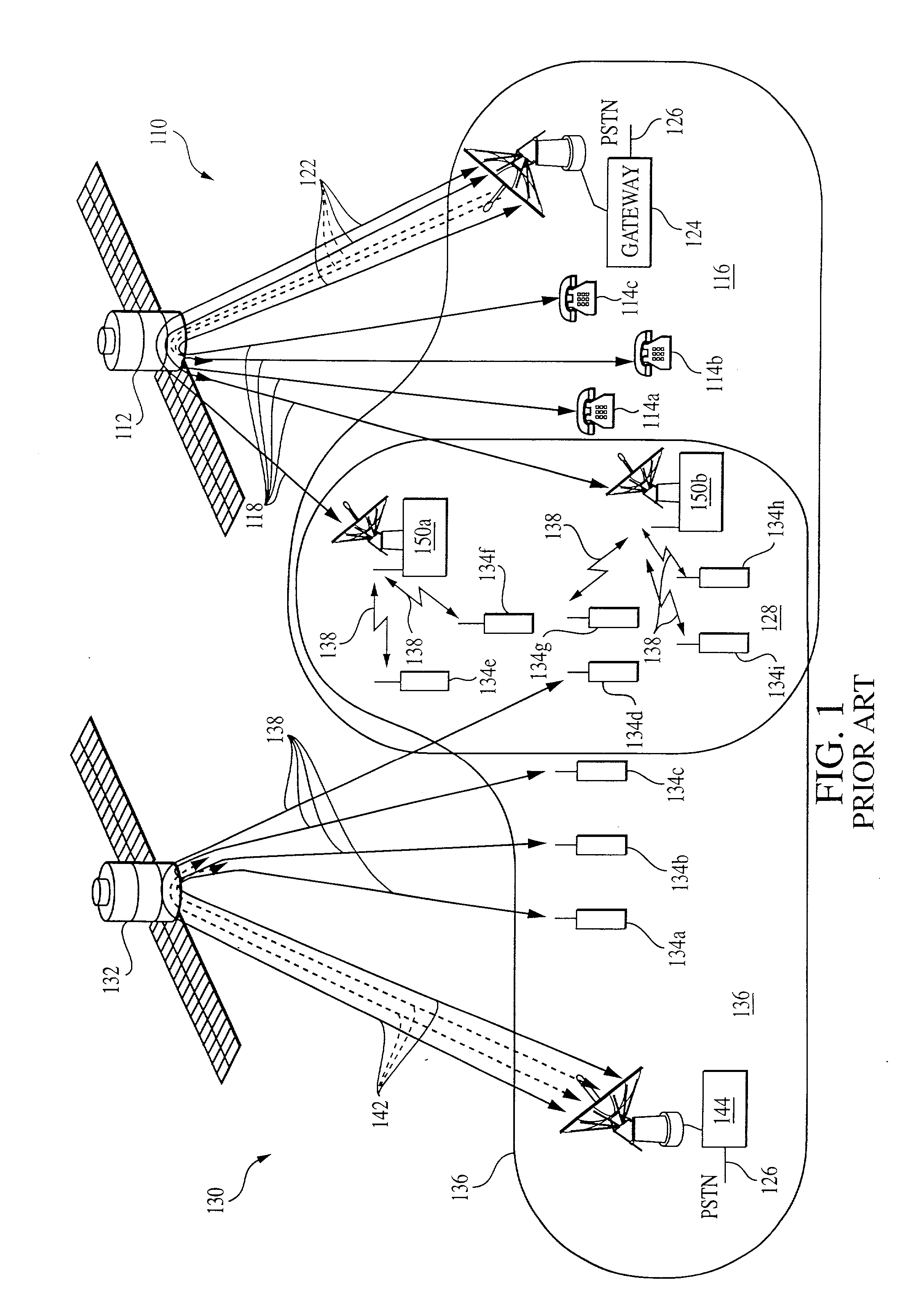
Ad Hoc peer-to-peer mobile radio access system interfaced to the PSTN and cellular networks
InactiveUS6961575B2Complete transparencyHigh transparencyNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationFrequency spectrumOperational costs
An ad-hoc, peer-to-peer radio access system for cellular communications systems using time division duplex as a way of maximizing the bits / hz / km2 for cellular systems. The network architecture of the ad-hoc system allows the radio access to be integrated with the fixed components of a conventional cellular system, PSTN or ISP. The objective is to make the system of the invention transparent to the features and services provided by the external network. The advantages of such a system to a cellular operator are that significantly less infrastructure is required, and that the RF spectrum is more efficiently utilized resulting in much lower building and operating costs. The system architecture is comprised of remote terminals, routers, gateways, and at least one gateway controller that interfaces the ad-hoc system to a cellular network system. The ad-hoc system of the invention allows for both voice and data transmissions and receptions.
Owner:STRONG FORCE IOT
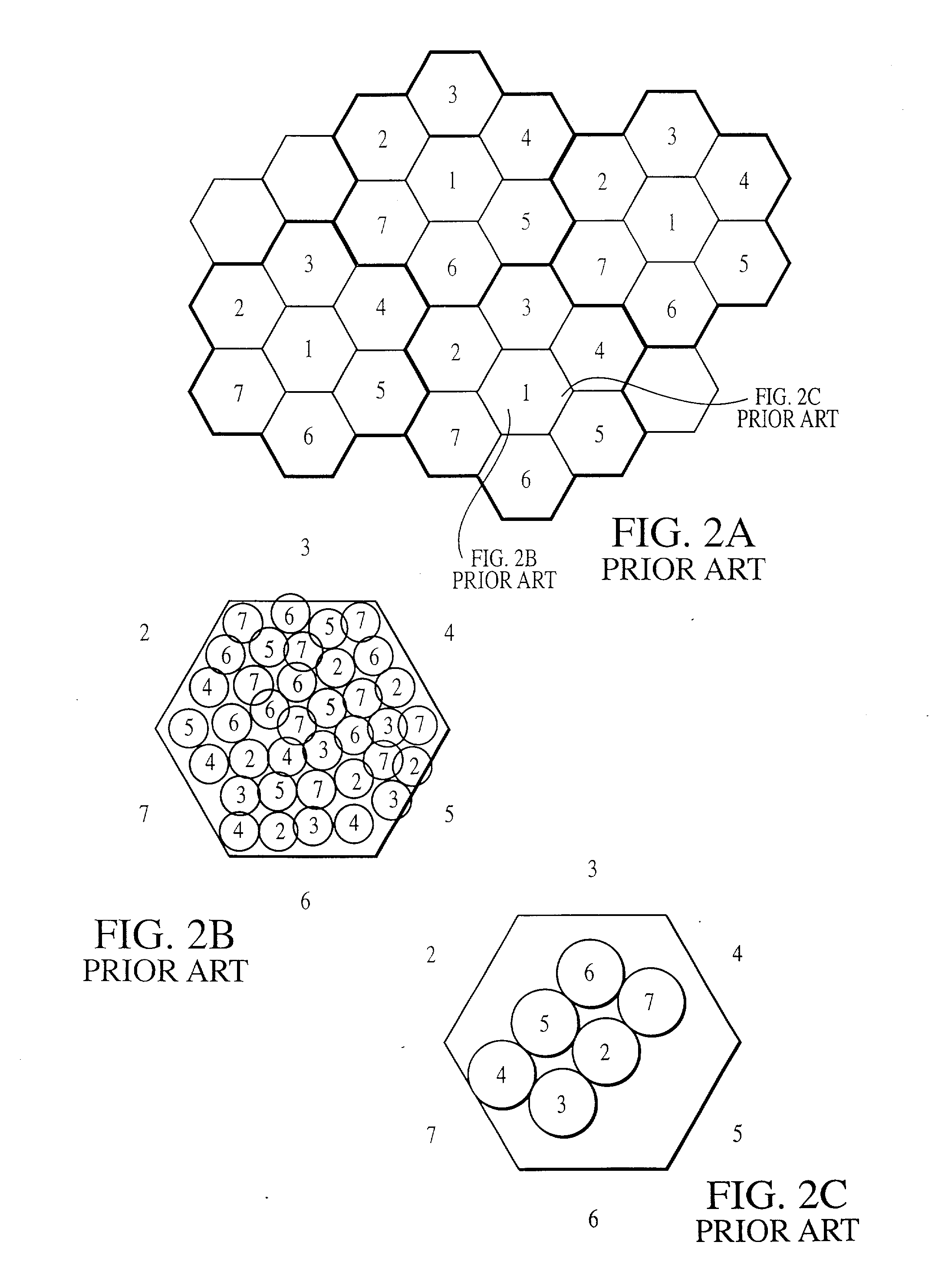
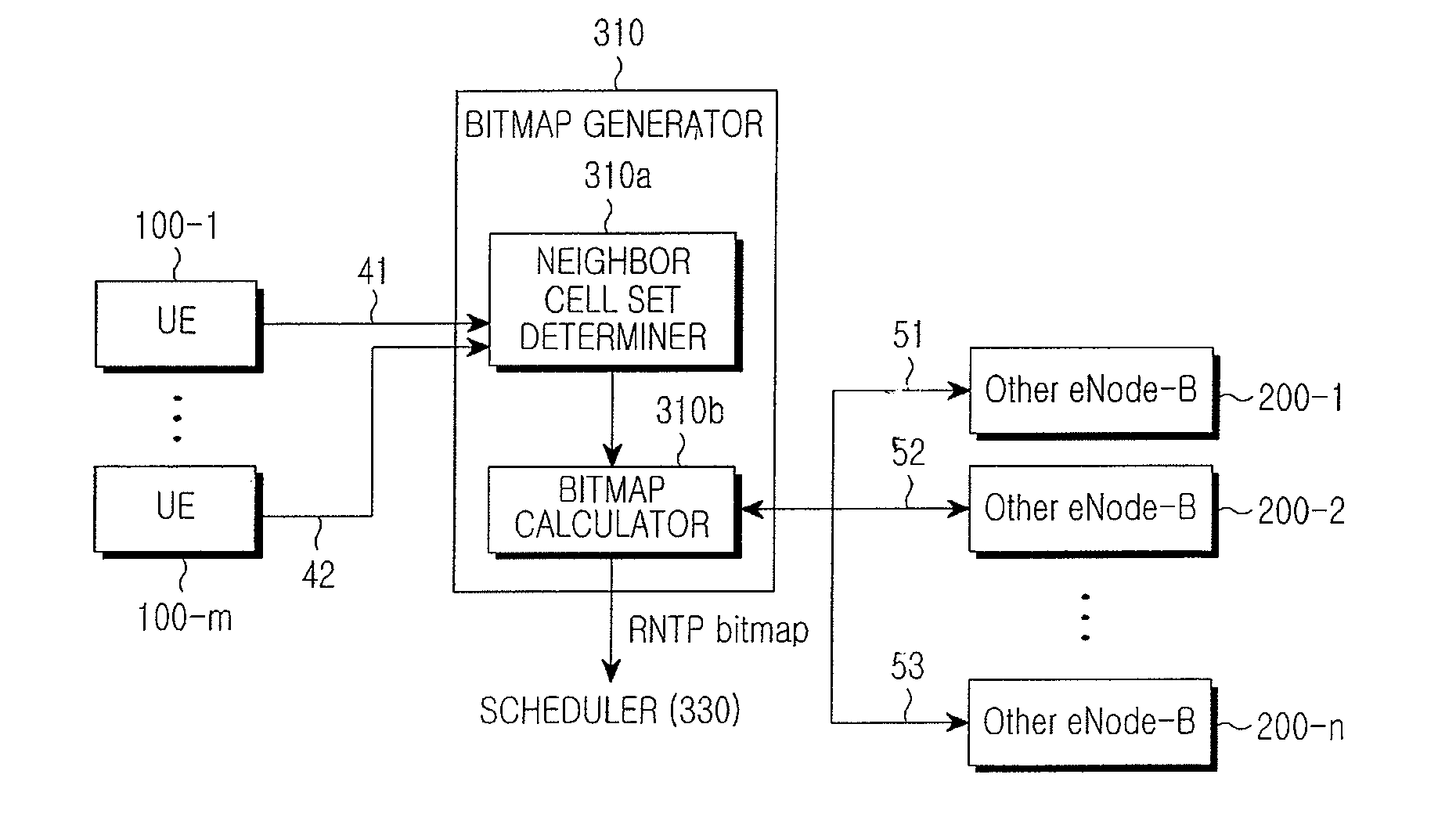
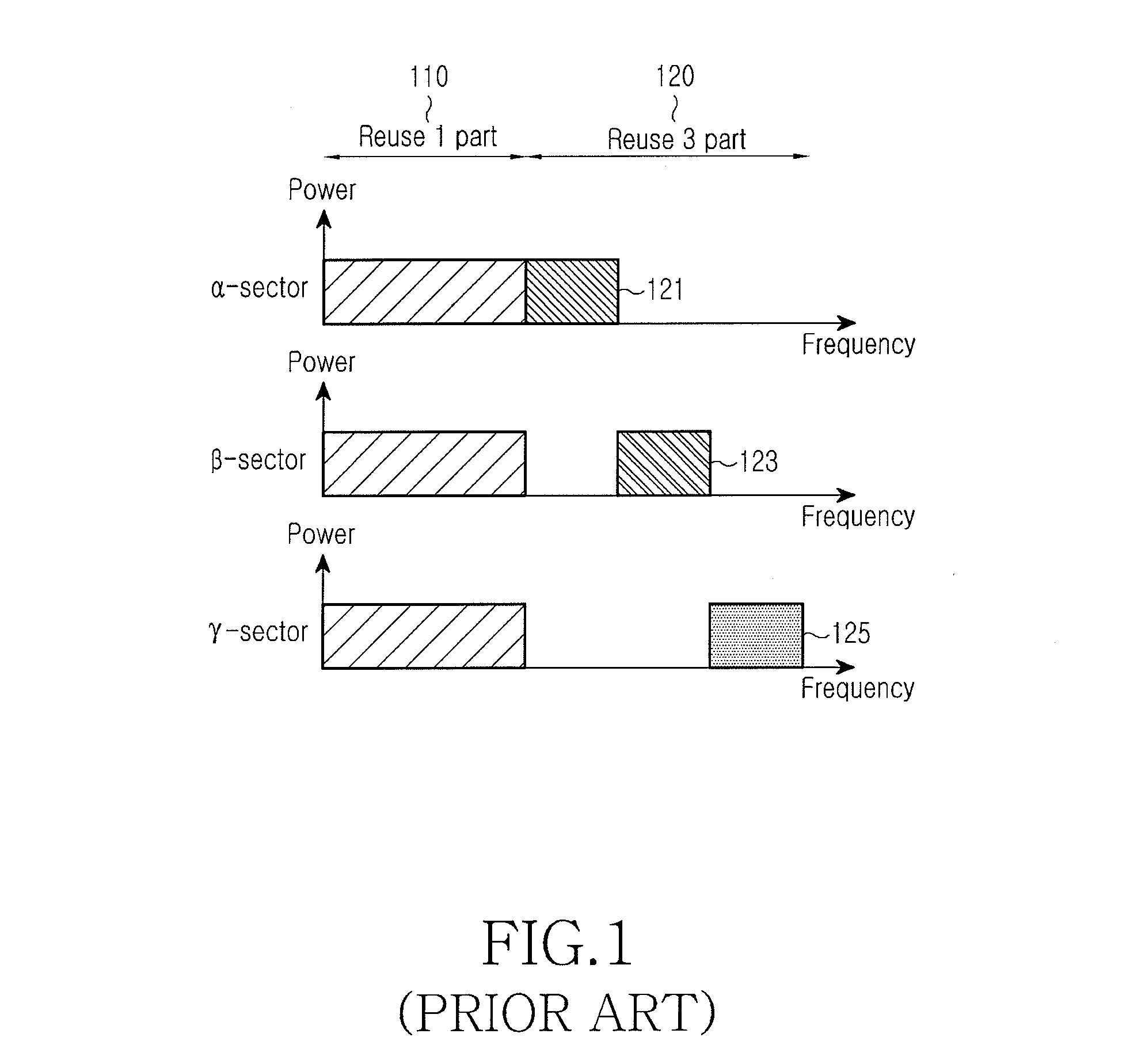
Method and apparatus for scheduling resource allocation to control inter-cell interference in a cellular communication system, and base station thereof
ActiveUS20110183679A1Efficient schedulingNetwork planningFrequency reuseCellular communication systems
A method and apparatus for controlling inter-cell interference in an evolved Node-B for a cellular communication system with a frequency reuse factor of 1 are provided. The apparatus includes a bitmap generator for receiving scheduling information from evolved Node-Bs of a plurality of neighbor cells, and for generating scheduling information including its cell's bitmap information for the resource allocation using the received neighbor cells' scheduling information, and a scheduler for scheduling the resource allocation for UEs in its cell based on the scheduling information provided from the bitmap generator and power allocation information of the UEs in its cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Downlink signal processing in CDMA systems utilizing arrays of antennae
InactiveUS6985466B1Spatial transmit diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCdma systemsCellular communication systems
The present invention is a method for operating a base station (BS) for transmitting information to a subscriber unit (SU) in a cellular communication system. The information is included in a downlink signal sent from a signal processing circuit through an array of antennae. The processing depends on a weight set that is utilized in generating individual signals to be sent on individual antennae in the array to the SU. The weight set is determined by transmitting a plurality of pilot downlink signals from BS to the SU, each pilot downlink signal being processed with a different weight set than that used to process the other pilot downlink signals. Report signals are received for each of the pilot downlink signals and are compared to determine which weight set should be utilized. The present invention may be practiced within existing CDMA cellular standards such as the IS-95 standard.
Owner:INTEL CORP
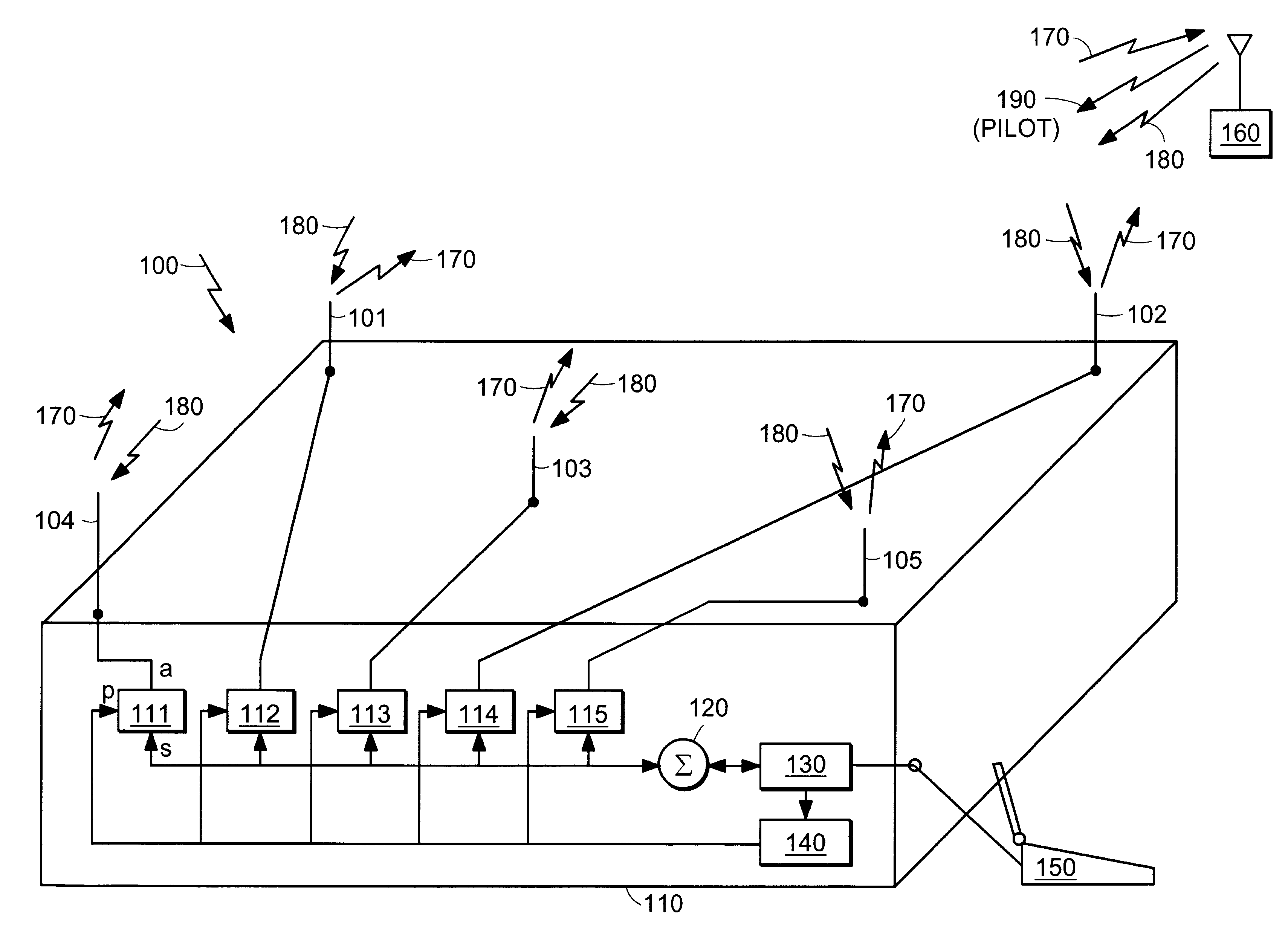
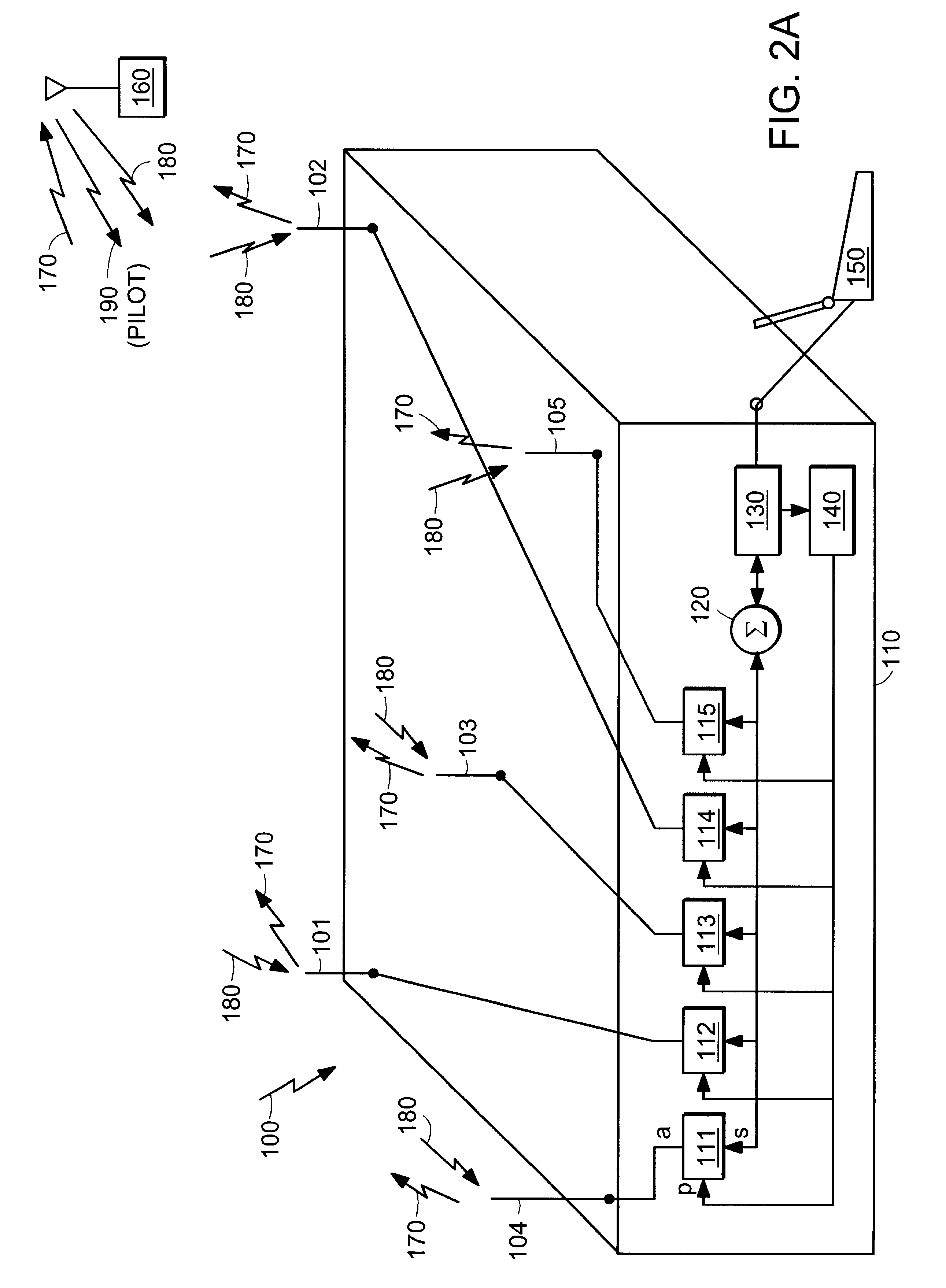
Active antenna array configuration and control for cellular communication systems
InactiveUS20030073463A1Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityBeam patternCellular communication systems
Various antenna arrangements are provided with active transmit and receive antenna elements for transmitting and receiving signals within a cellular communication system. Also presented are specific base station antenna systems and methods, and portions thereof, which improve and control specific characteristics and features of antenna systems including antenna beam patterns. In addition, method for the optimization of a cellular communications network is provided which exploits reverse-link, forward-link, and pilot signal information to optimize network operations.
Owner:CELLETRA
Method for distributed mobile communications, corresponding system and computer program product
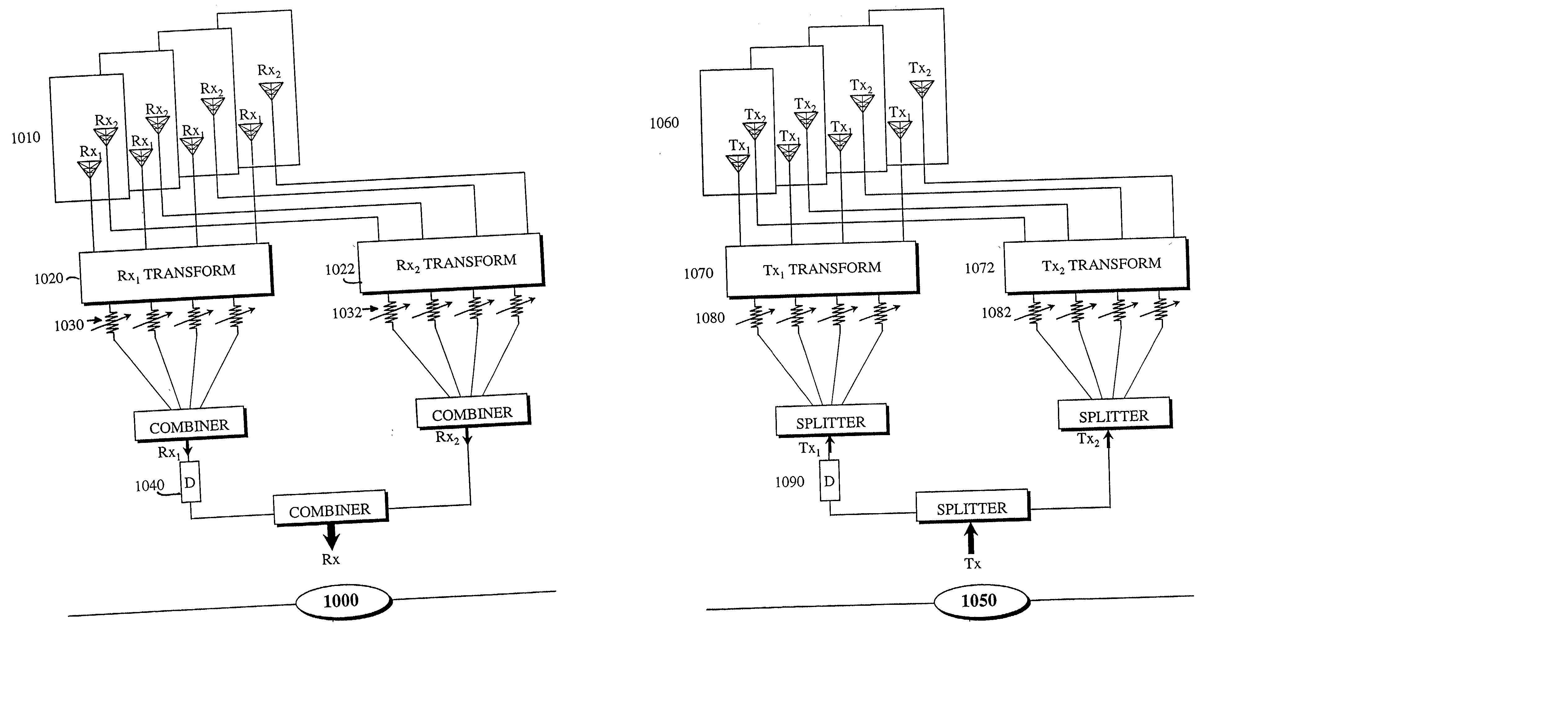
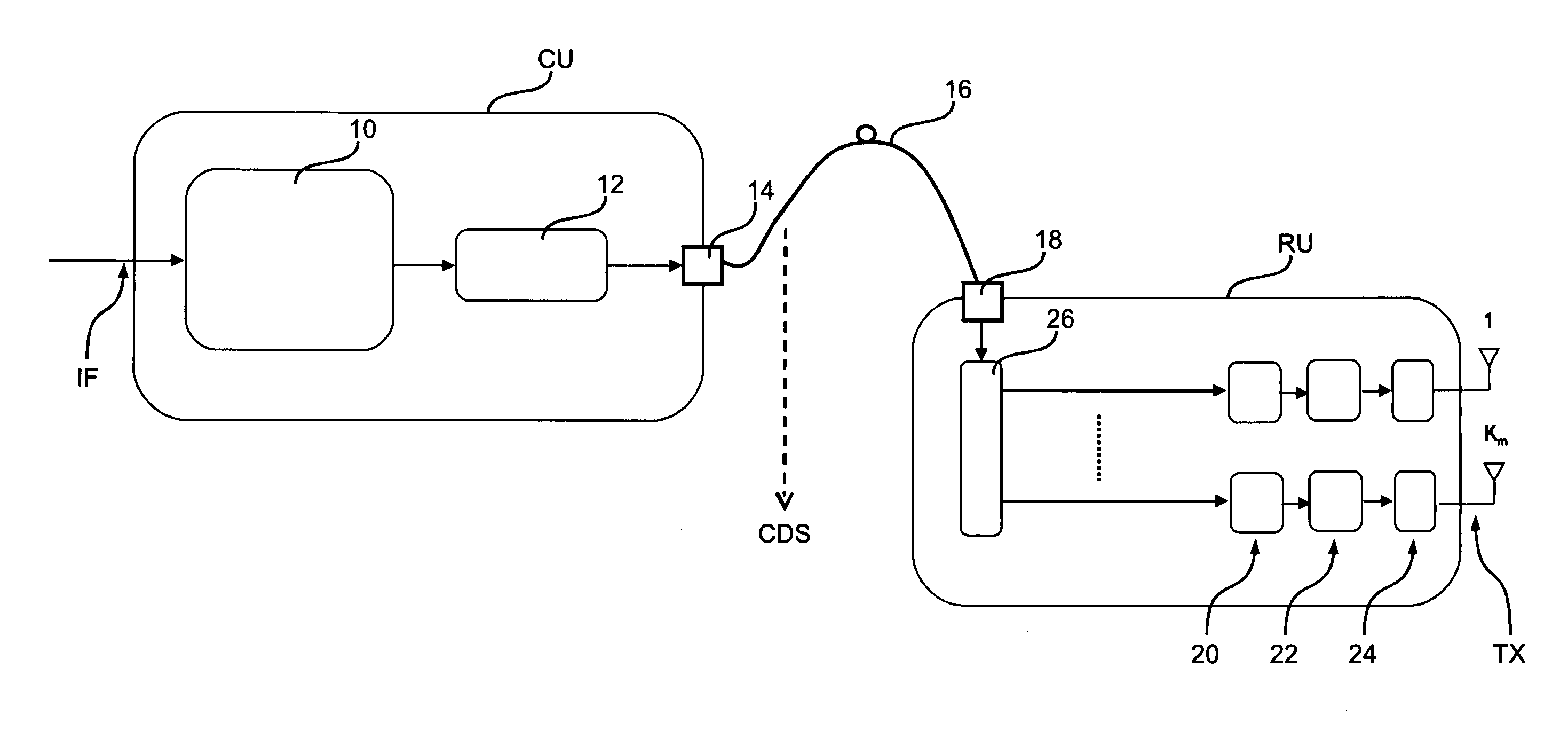
ActiveUS20110268033A1High levelImprove scalabilitySite diversityInformation formatCentral unitEngineering
A method of arranging exchange of signals between user terminals in a cellular communication system and at least one base station. The base station includes a central unit and a plurality of remote units. The signals are exchanged between the central unit and the remote units as aggregated signals for plural user terminals. The signals are processed at the remote units as distinct signals each associated with a respective one of the plural user terminals.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
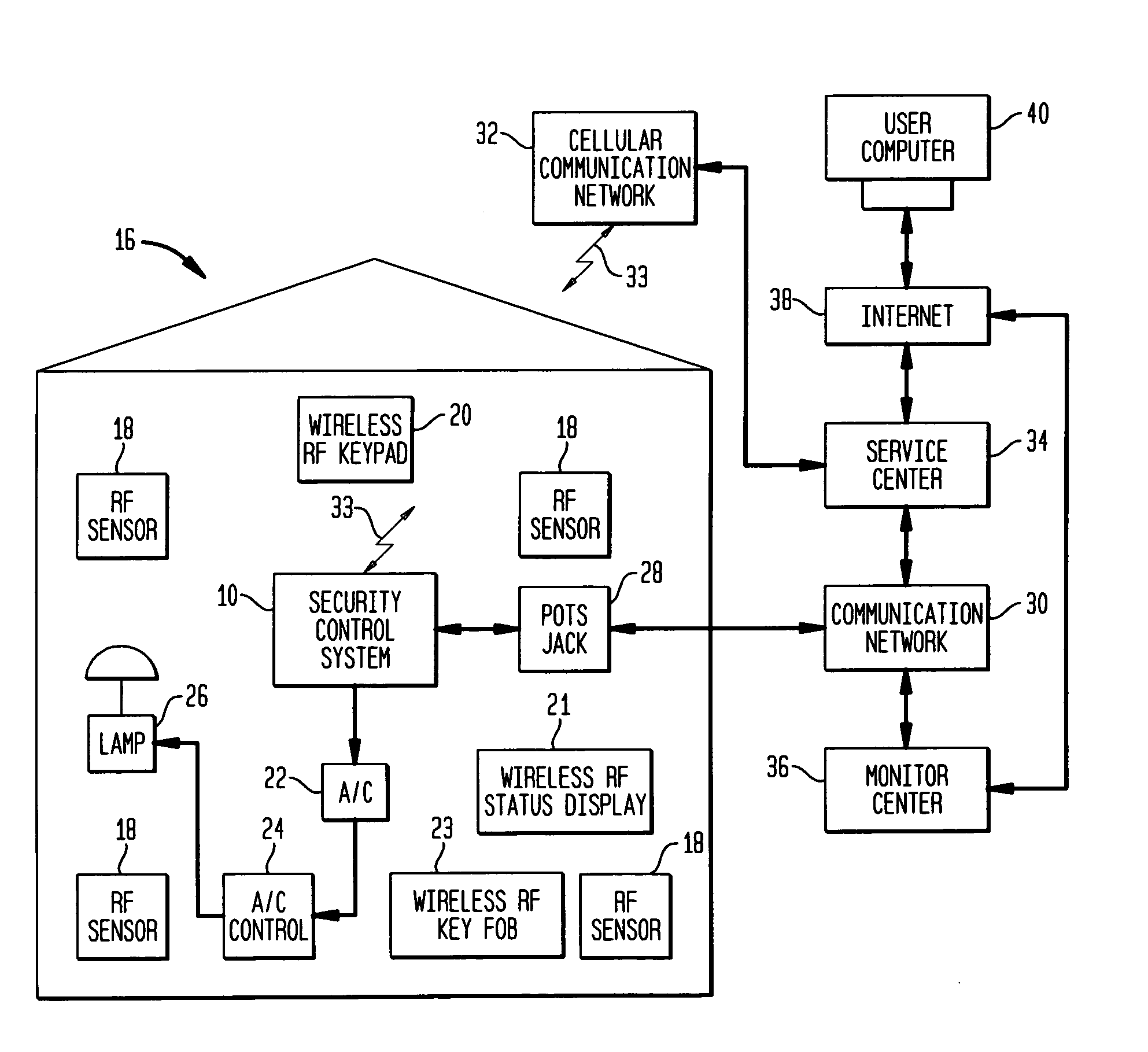
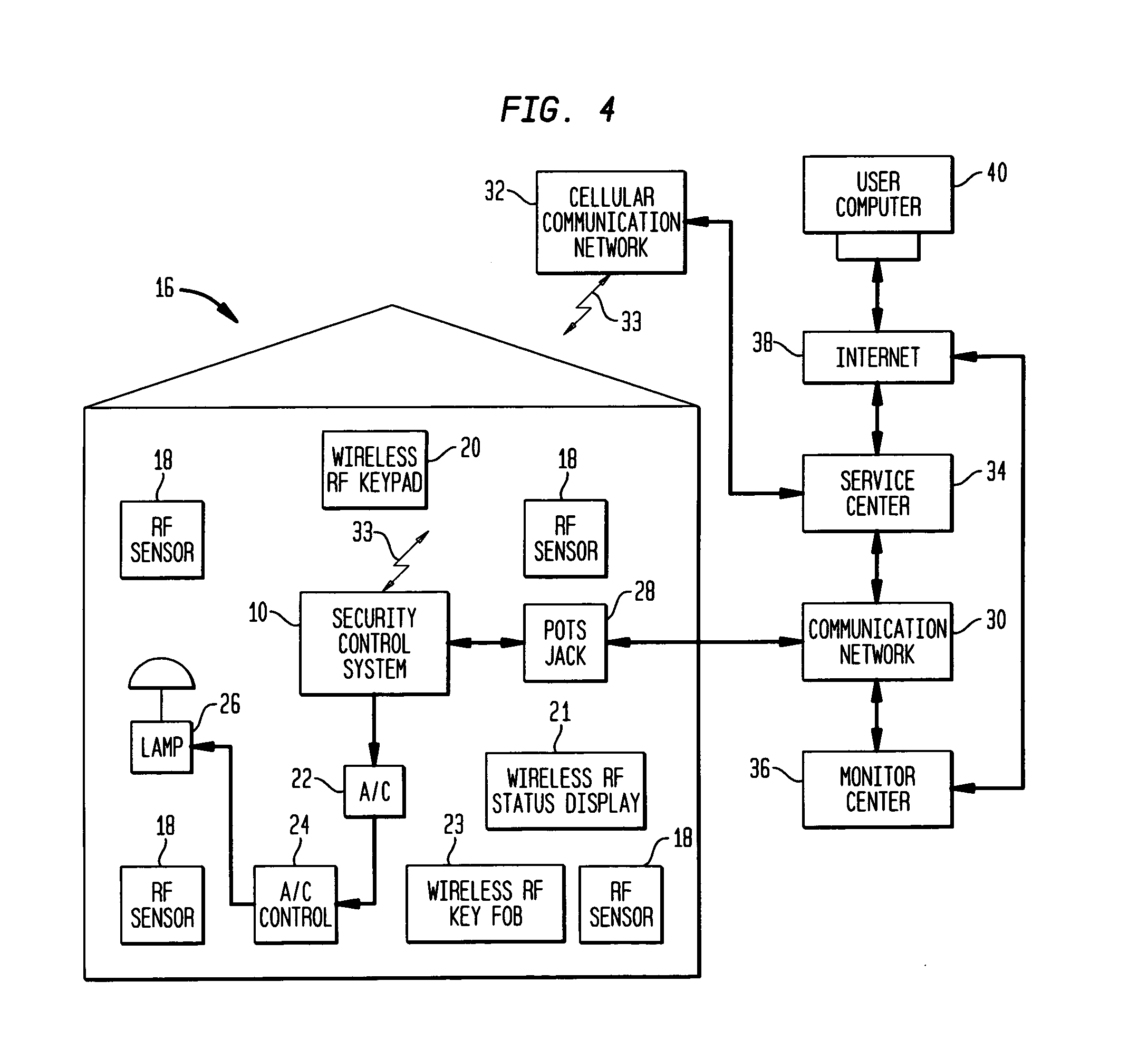
Security control and communication system and method
ActiveUS6999562B2Convenient programmingEasy to installFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelephonic communicationTransceiverDisplay device
An integrated security control system and method which integrate the functions of a wireless security system control panel and a radio transceiver in an integrated security control system unit. The integrated control unit includes a first telephone communication system for communicating security system data by wired telephone communications, and a second radio frequency (RF) cellular communication system for communicating security system data by communications through an RF communication network. The cellular communication system is the primary communication network for reporting a security event, thereby leaving the first telephone communication system open for telephone communications during the reporting of a security event. A separate unit of the security system, such as a wireless RF status display or a wireless RF keypad, is provided with a beeper transducer for sounding entry and exit beeps. The separate unit is positioned at a separate location from the integrated security control system unit, such that the entry beeps do not alert an entering person to the location of the integrated security control system unit. When a security event is triggered, the control unit delays activating a security alarm sounder in the control unit until after the second RF communication system has finished transmitting the alarm message.
Owner:ADEMCO INC
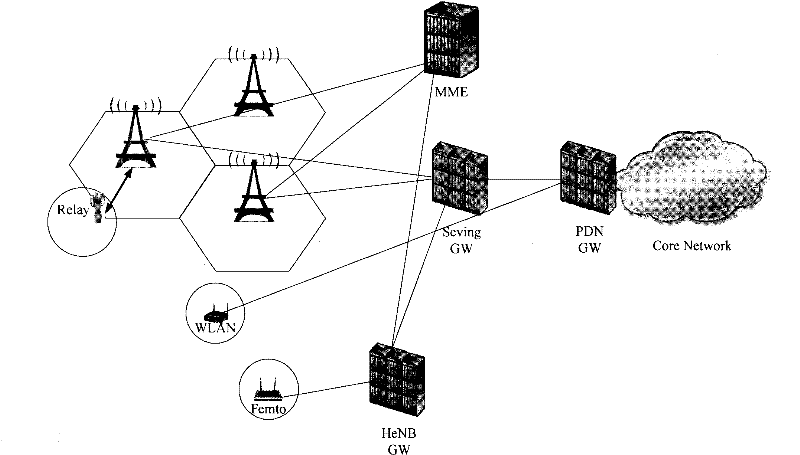
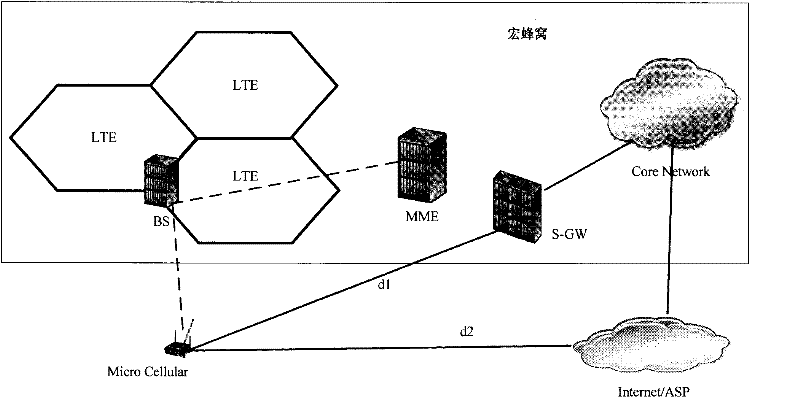
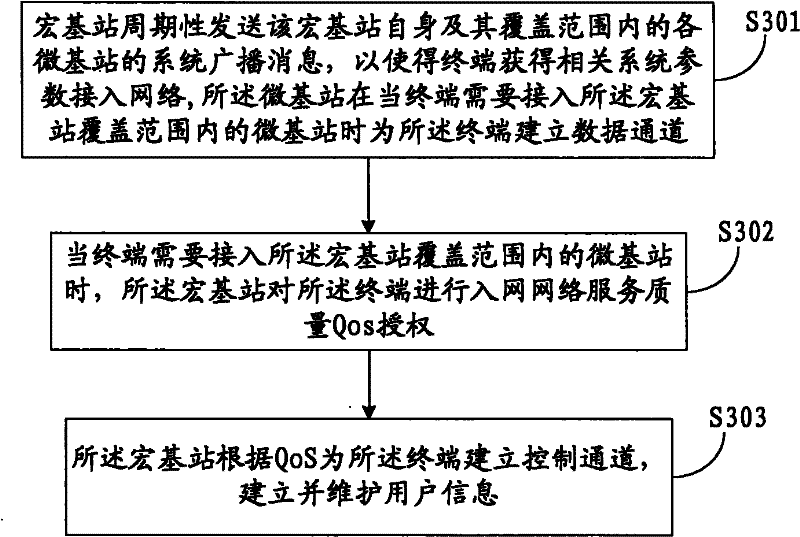
Cellular communication system, method for inter-cell handover of terminal and macro base station
InactiveCN102348244AReduce negative impactAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesMacro base stationsMicro cell
The invention discloses a cellular communication system, a method for the inter-cell handover of a terminal and a macro base station. The cellular communication system comprises the macro base station and at least one micro base station within the coverage of the macro base station. The macro base station is used for establishing a control channel for the terminal of the micro base station, performing accessing management operations on the micro base stations within the coverage, receiving a handover request of the terminal and realizing the handover of the terminal to another micro base station within the coverage. The micro base station is used for establishing a data channel for an accessing terminal to perform data transmission with the terminal. By the system, the method and the macro base station, a user control plane and a data plane under a micro cell can be separated, so that the resources of the micro base station can be better used for data communication. Therefore, negative impact on the system can be reduced in a macro cell-micro cell coexisting networking way.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Multi-hop wireless communications system having relay equipments which select signals to forward
InactiveUS7184703B1Minimizes noise amplificationGreat amplificationRepeater/relay circuitsActive radio relay systemsCommunications systemCellular communication systems
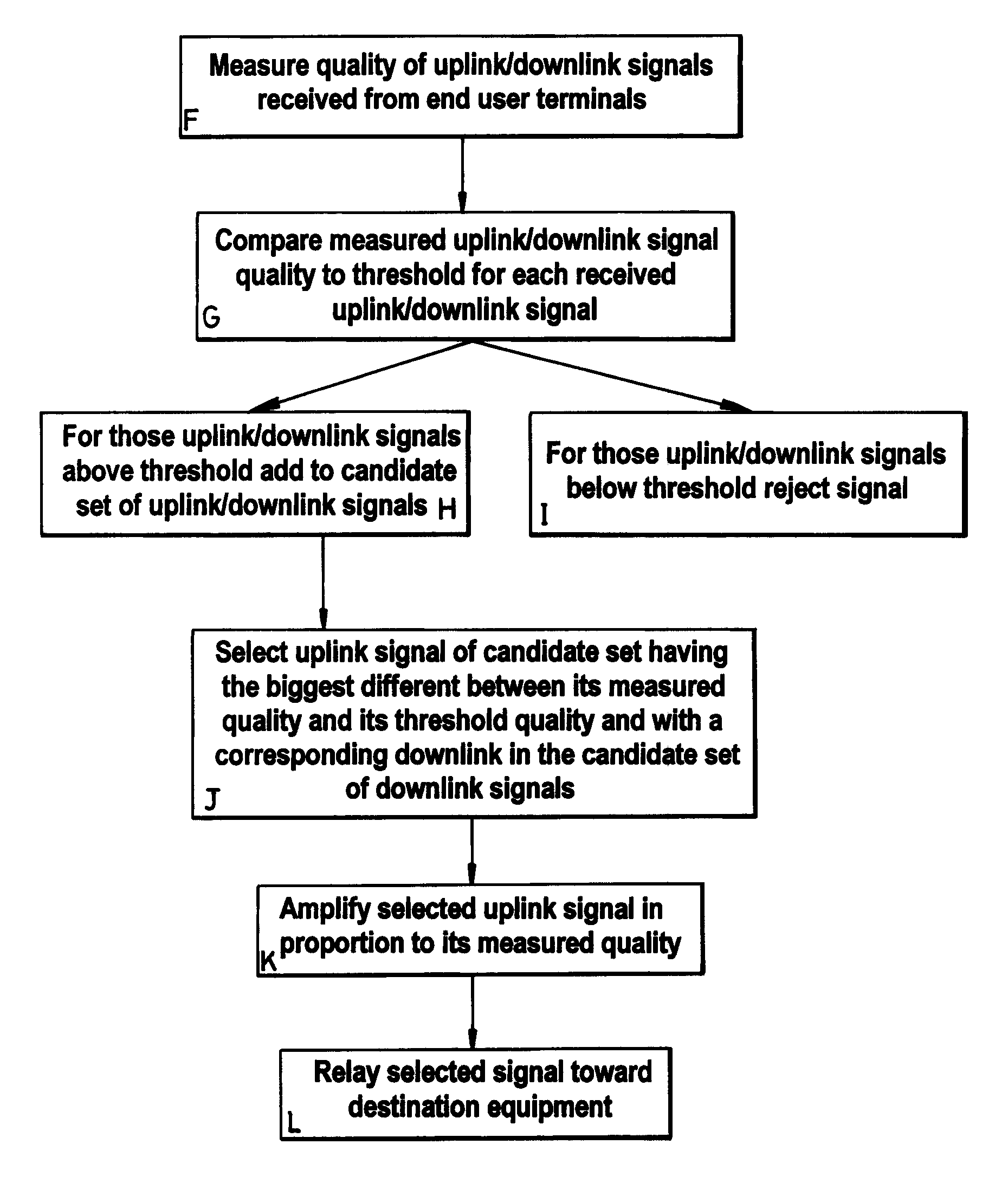
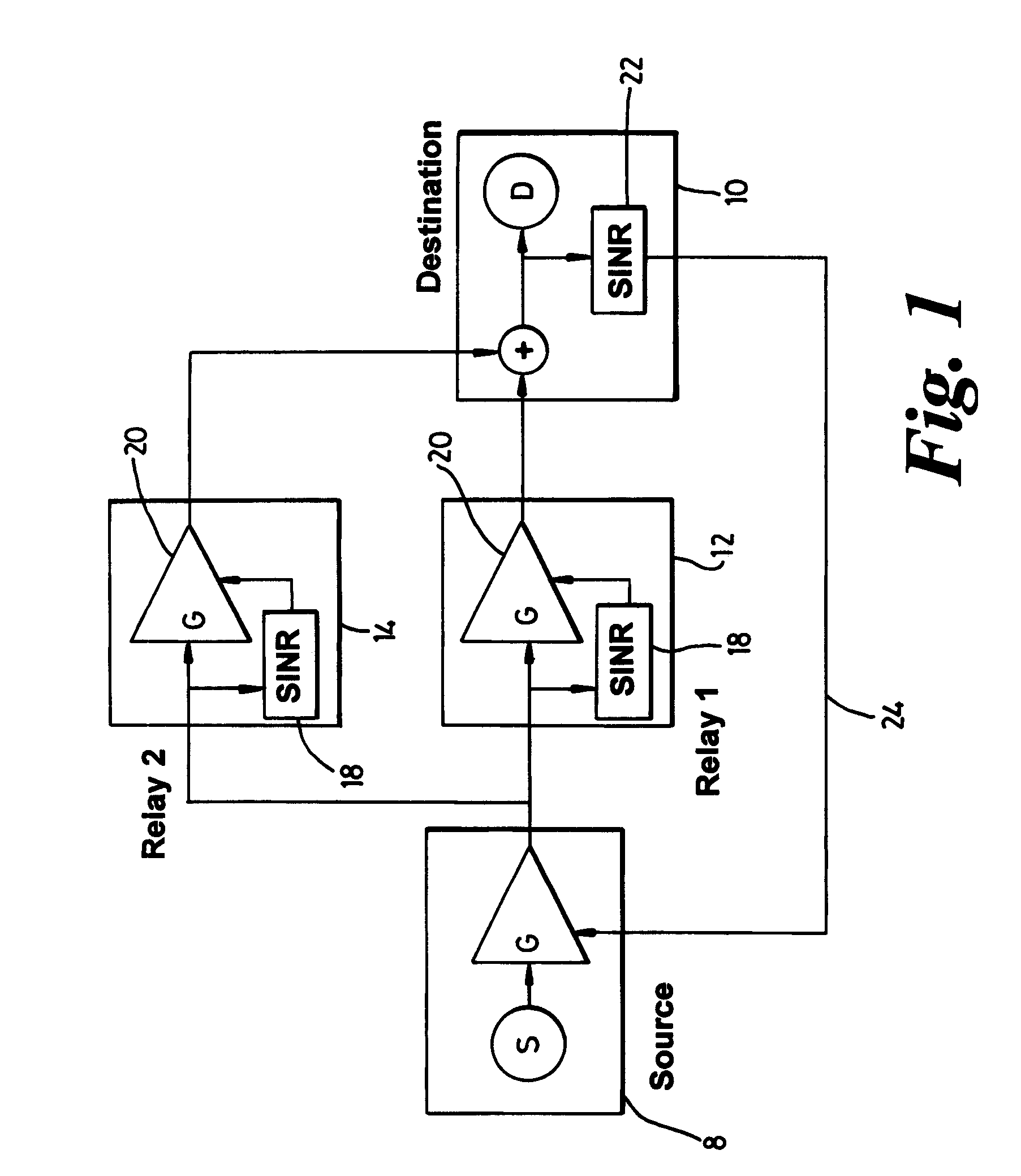
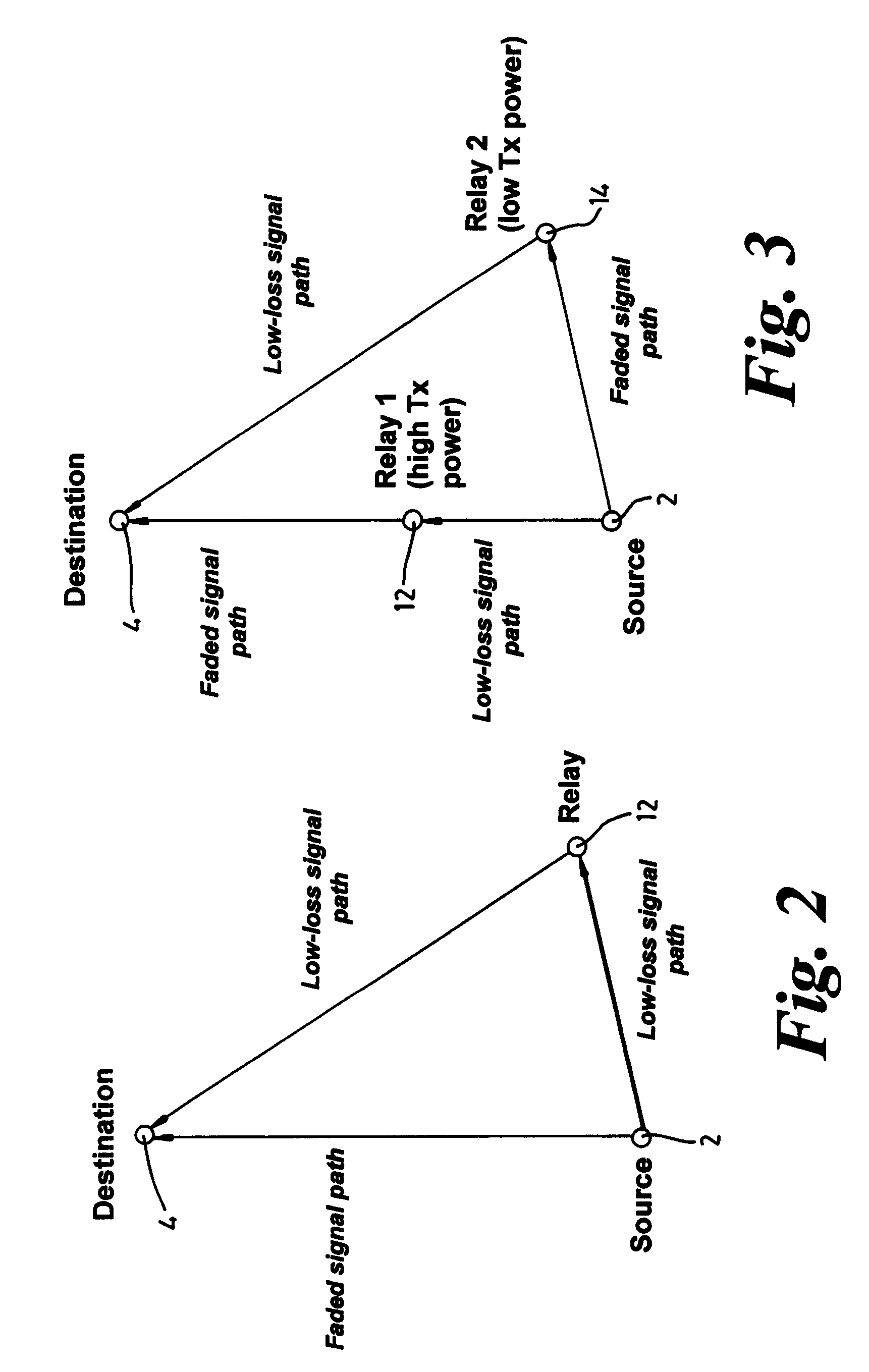
A multi-hop wireless, for example cellular, communications system is provided comprising a source equipment which may be one of a base station or an end user terminal for transmitting signals towards a destination equipment which may be the other of a base station or an end user terminal via at least one relay equipment. The relay equipment receives a plurality of signals transmitted from one or more source equipments of the system and from this plurality of signals selects a signal to relay. In this way the decision about which relays are included in which communication paths in the system is distributed to the relay equipments of the system, thus reducing the signalling overhead as compared with link state protocols which are typically used for routing in such multi-hop systems.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH +1
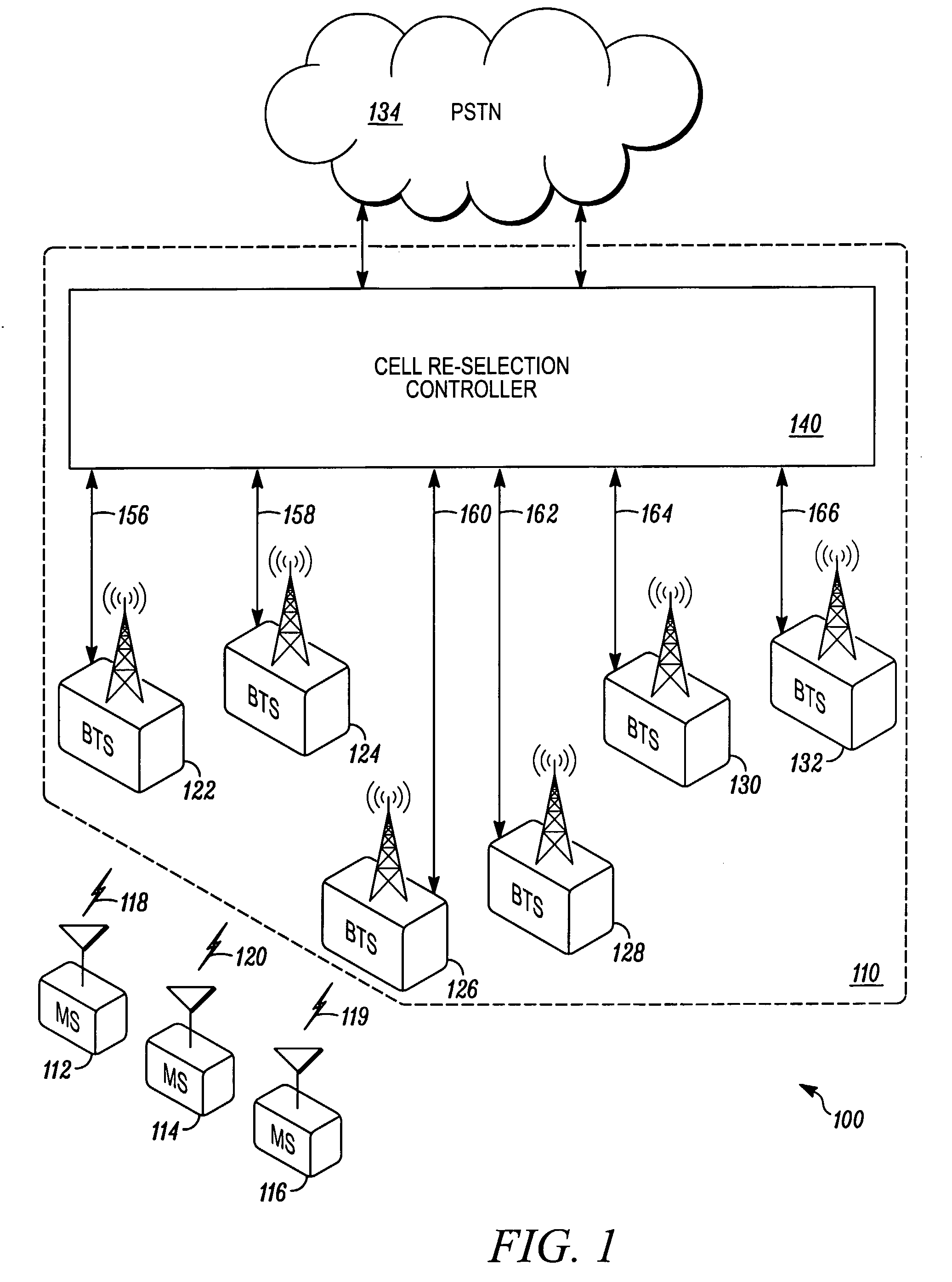
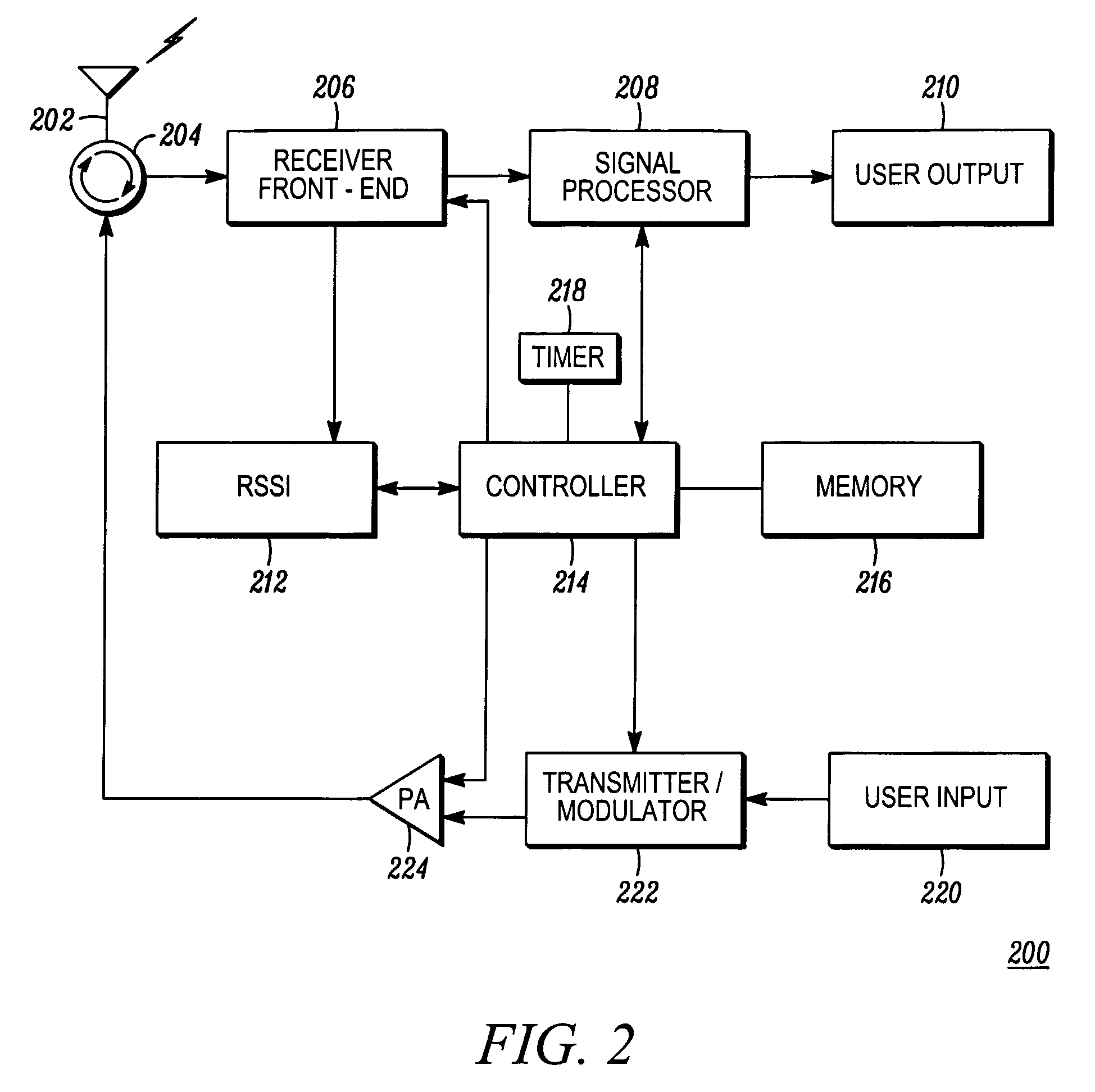
Mobile station, infrastructure processor, system and method for use in cellular communications
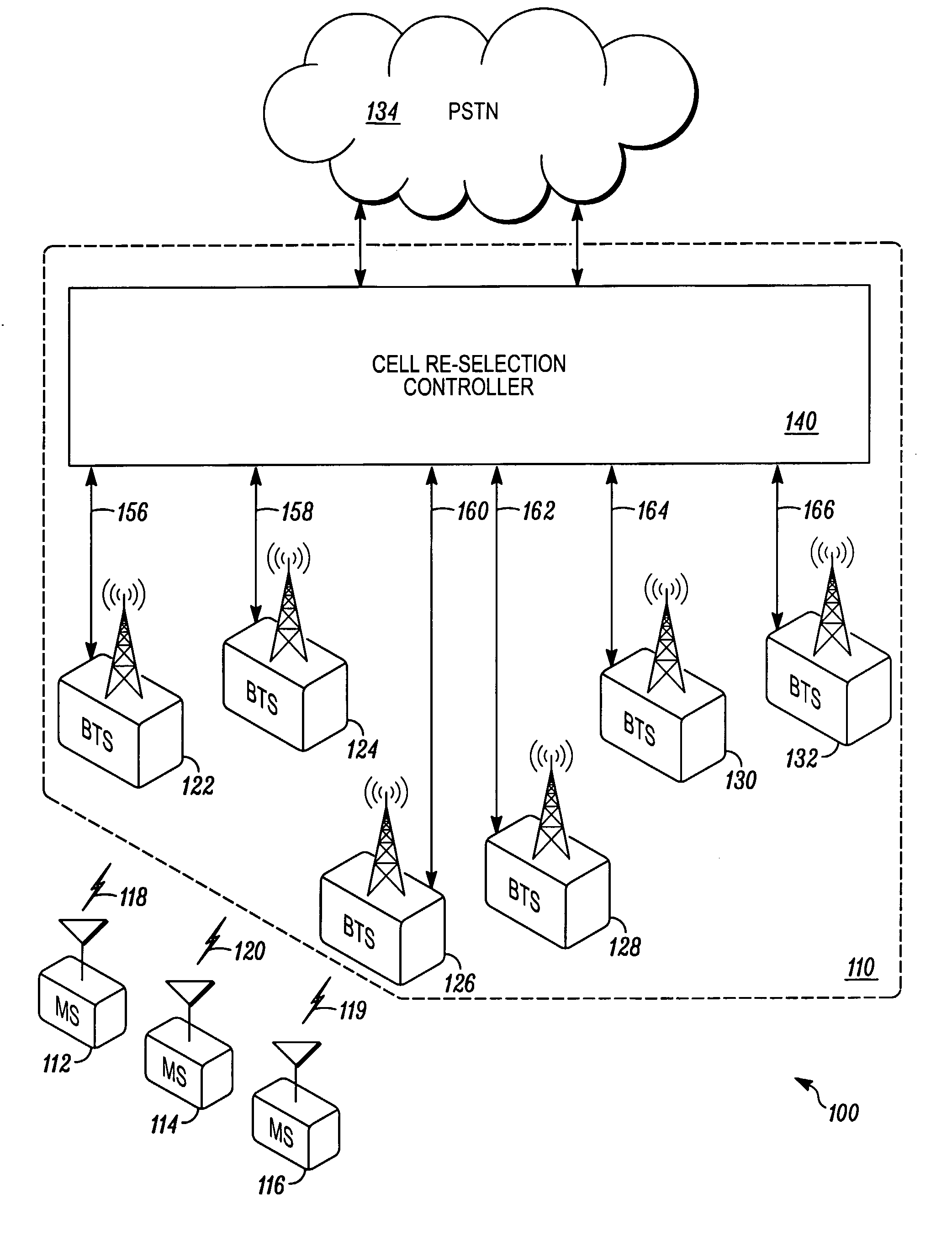
A mobile station for use in a cellular communication system includes a transceiver and a processor operable to apply a cell re-selection procedure which includes determining whether the mobile station should change its serving base station, wherein the transceiver is operable to receive via its serving base station a signal from an infrastructure processor advising or instructing the mobile station to select a particular base station in its cell re-selection procedure, and the processor of the mobile station is operable to apply a cell re-selection procedure to determine whether the mobile station should change its serving base station to the particular selected base station, wherein the particular selected base station has been selected and specified by the infrastructure processor based upon the location of members of a group of mobile stations with which the mobile station is to communicate.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
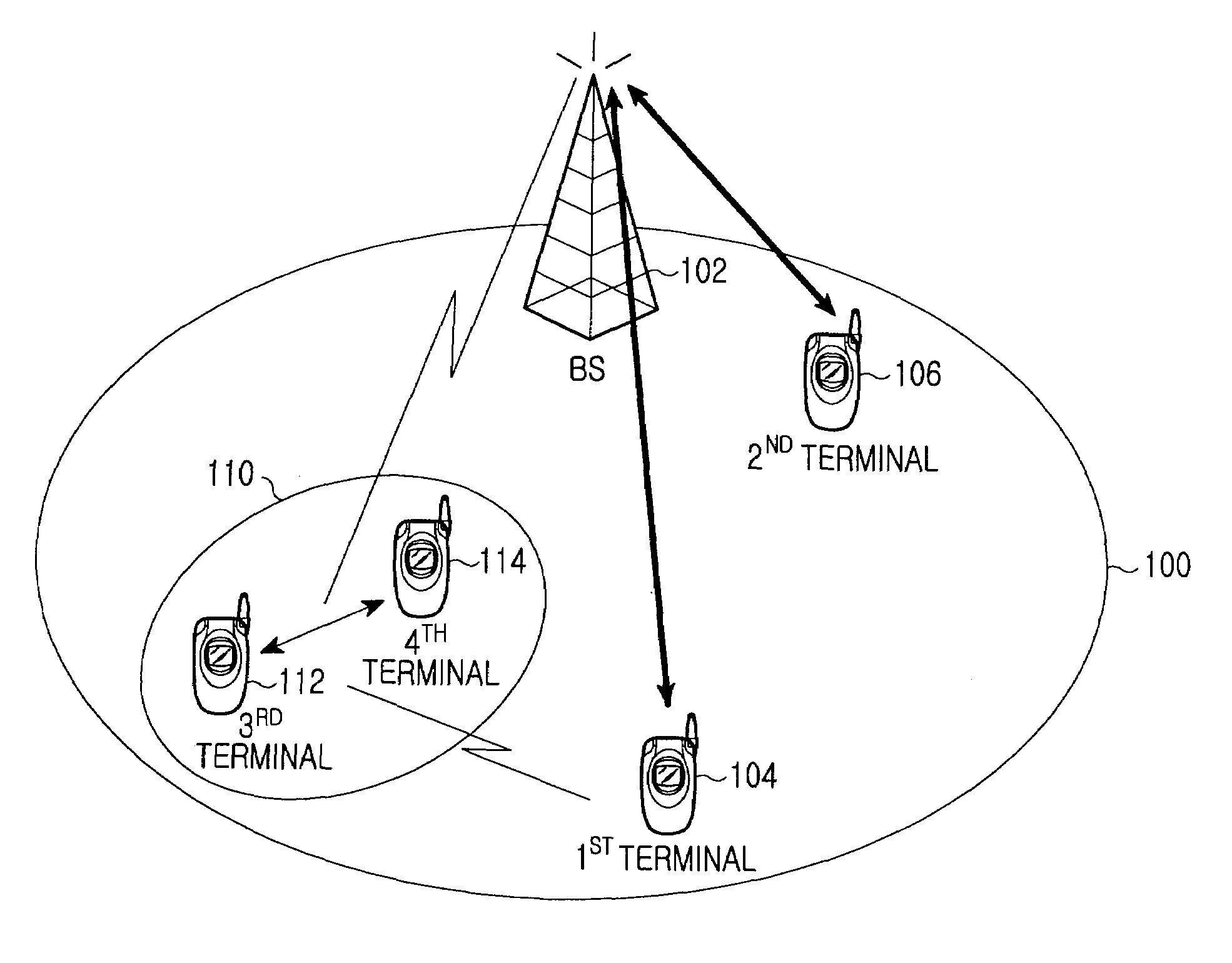
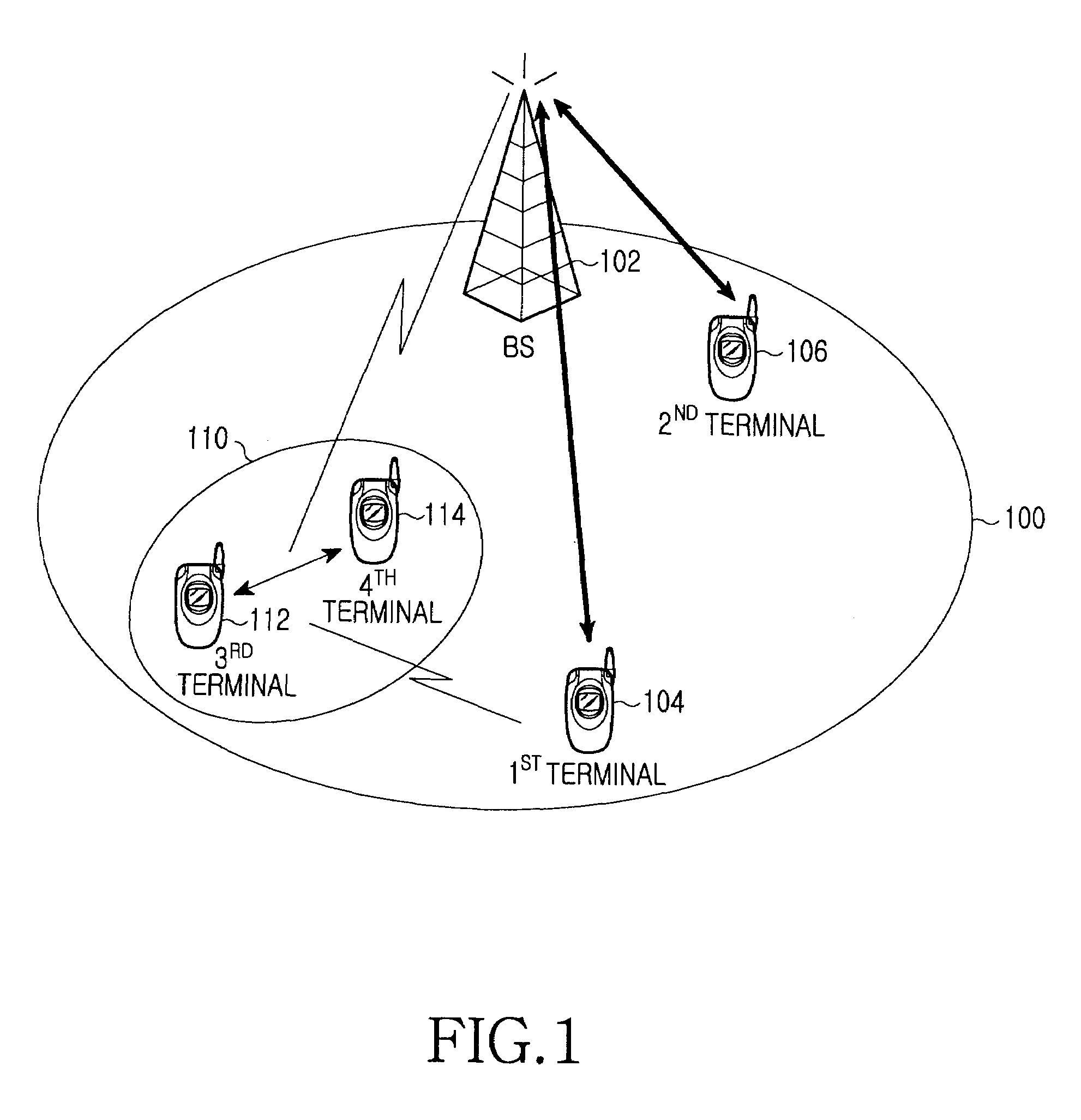
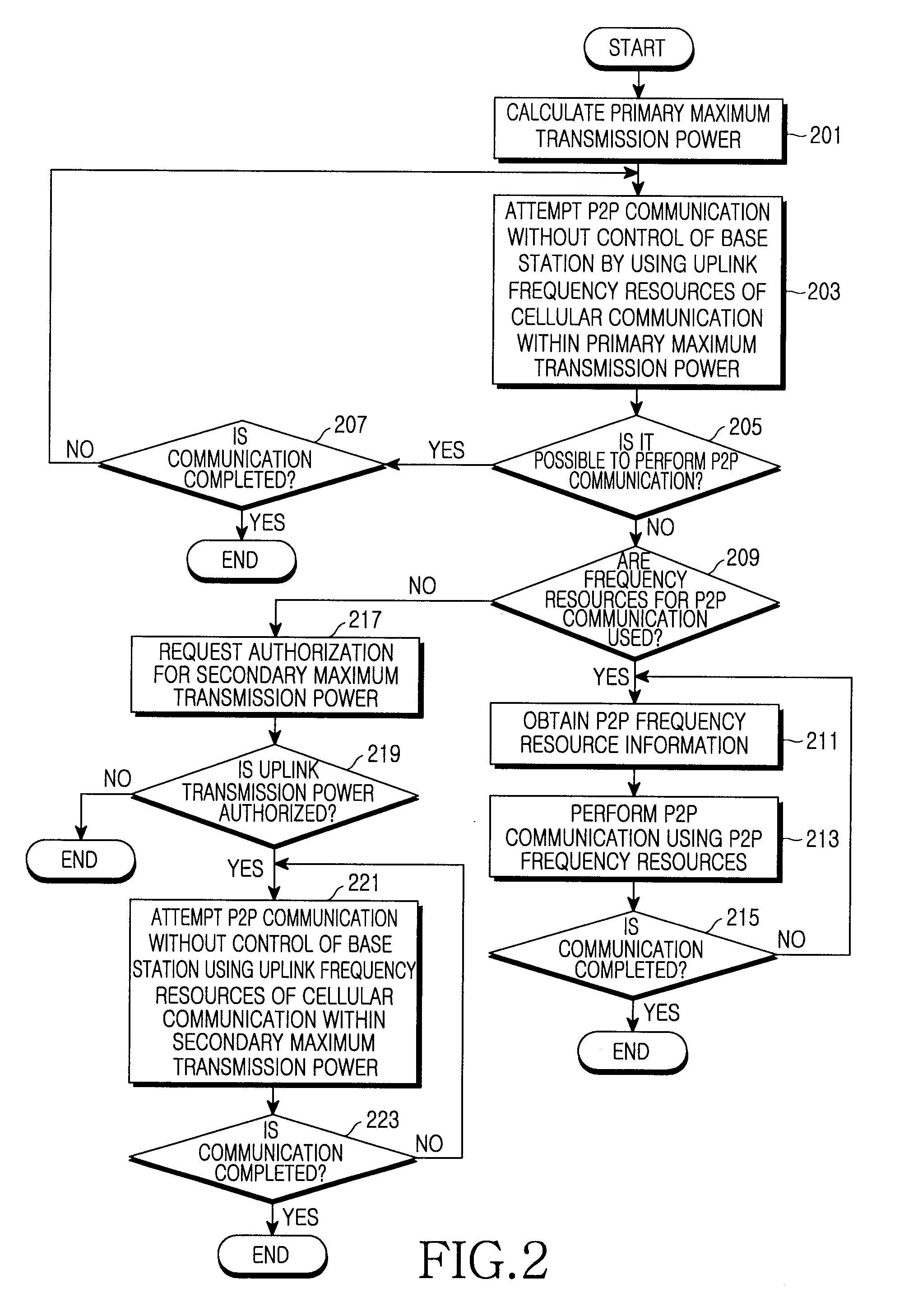
Apparatus and method for determining resources for peer to peer communication in communication system
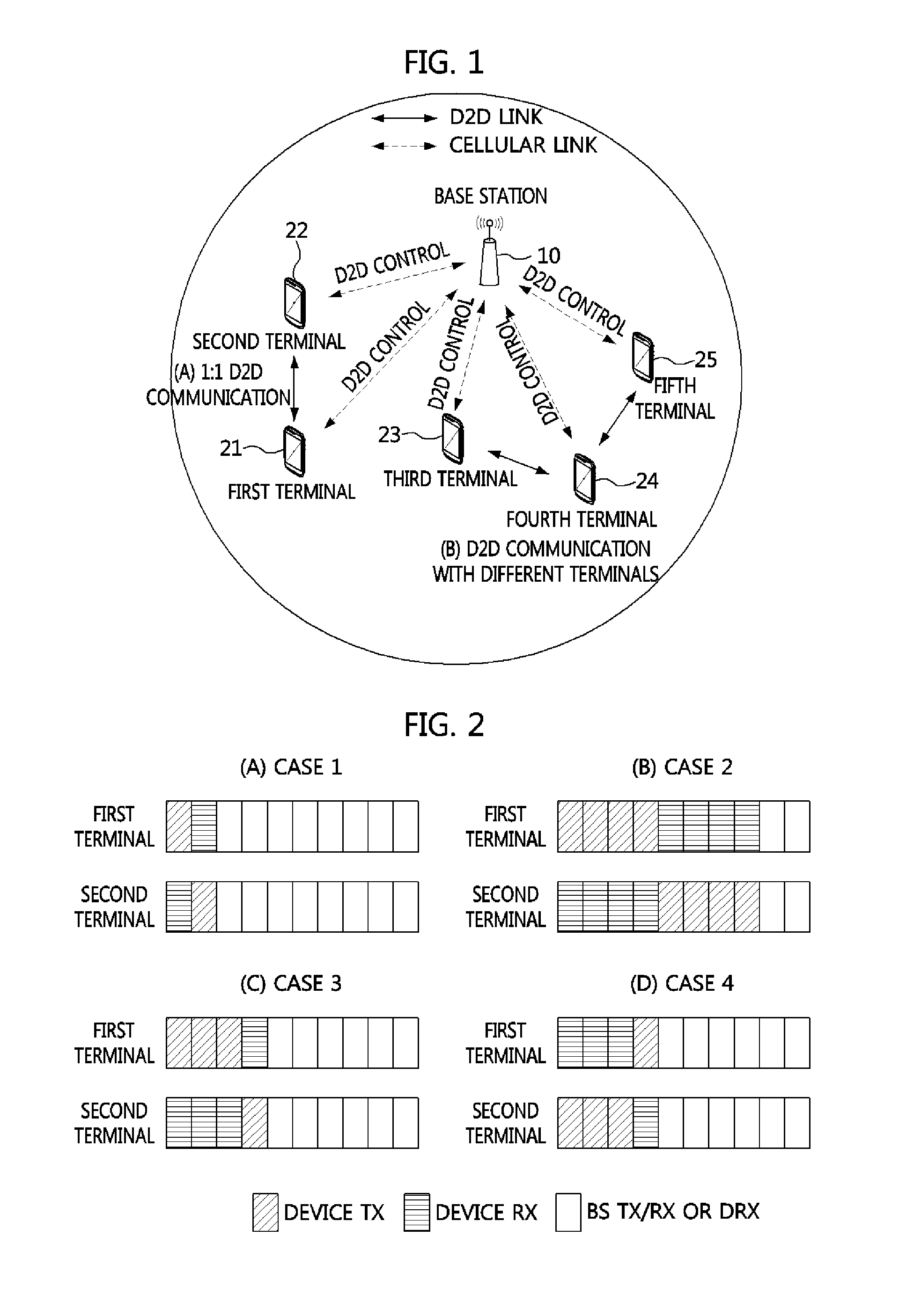
ActiveUS20090011770A1Reduce resource consumptionWithout reducing capacityEnergy efficient ICTTransmission path divisionCommunications systemCellular communication systems
A method and apparatus for allocating frequency resources for peer to peer (P2P) communication between terminals without a base station are provided. The method determines resources used for a direct communication between two terminals in a communication system. The method includes determining uplink frequency resources of a cellular communication system for use in the direct communication between the two terminals, determining a primary maximum transmission power to minimize interference caused by the direct communication on the cellular communication system and performing the direct communication between the two terminals by using the uplink frequency resources and a transmission power less than the determined primary maximum transmission power.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
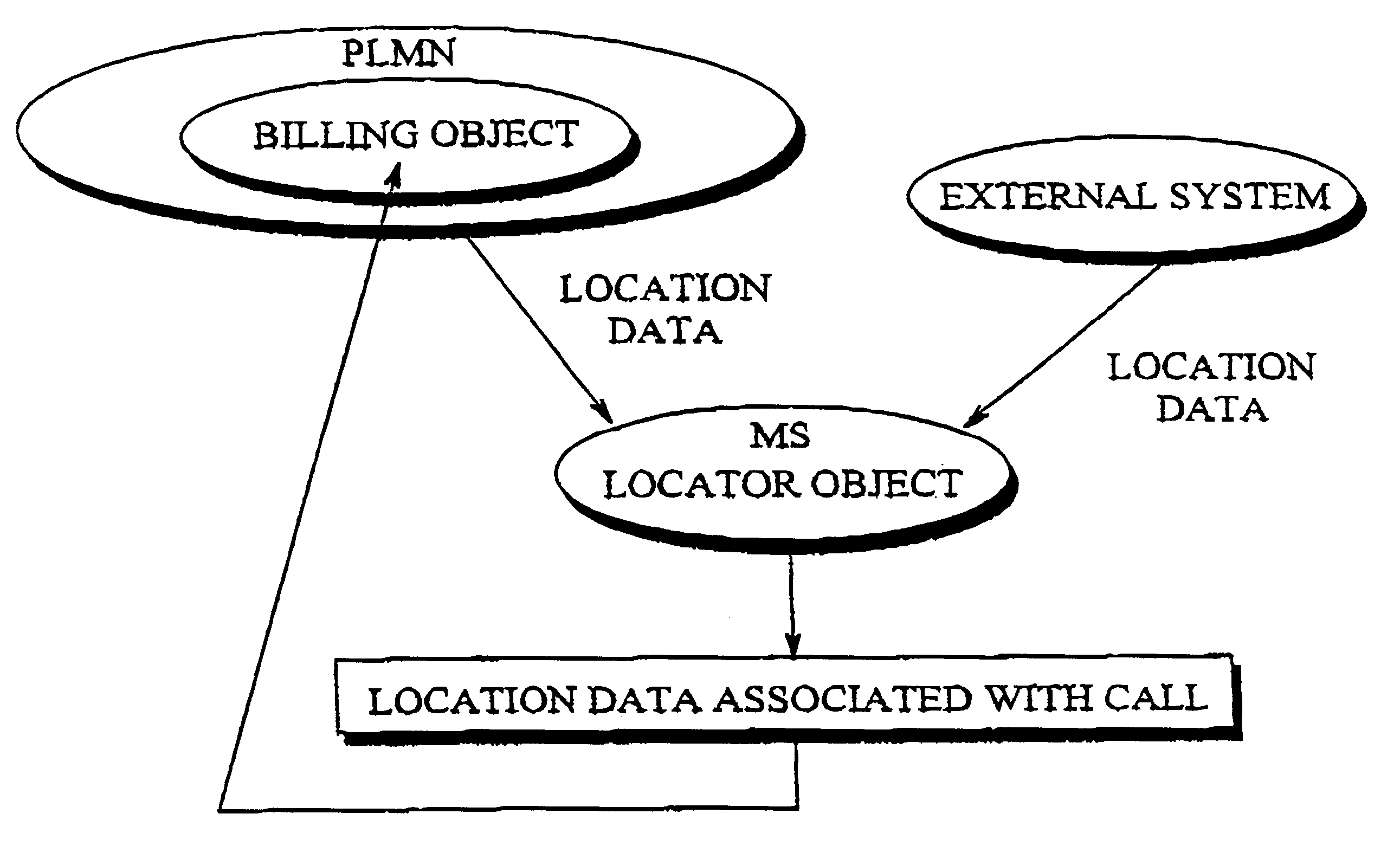
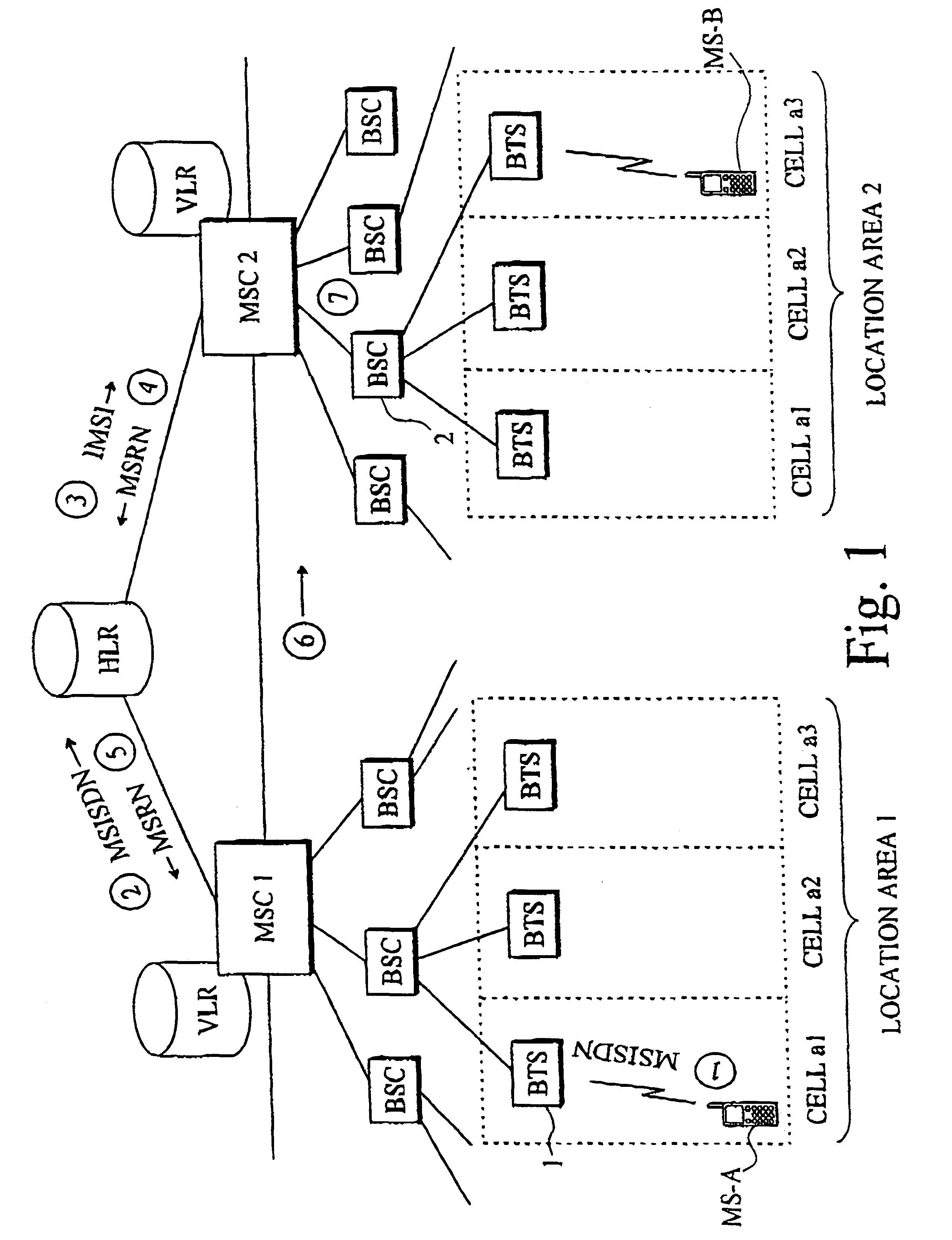
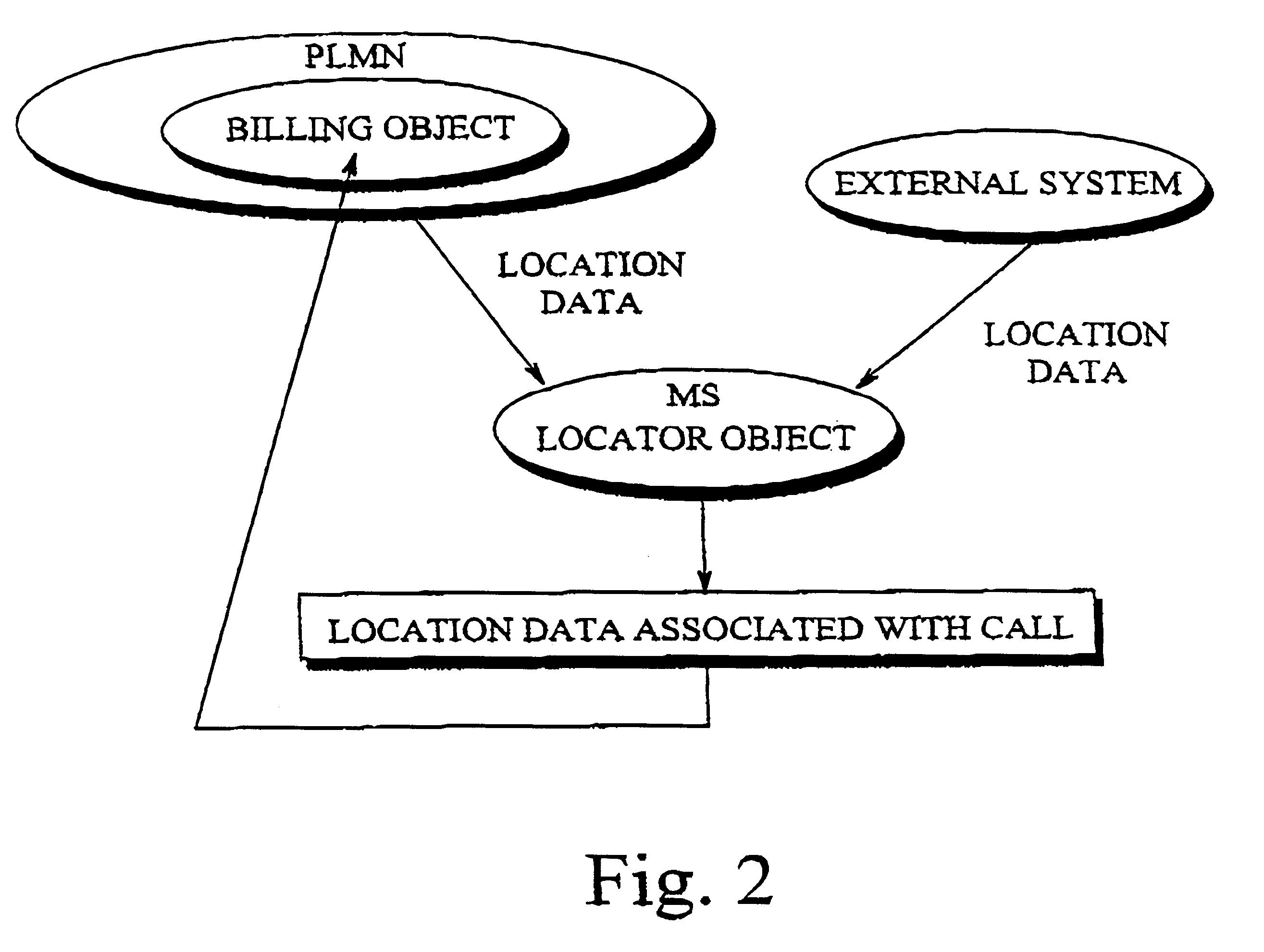
Method and apparatus for calculating call charge rates in a mobile telecommunication system
Rate charging rules and principles concerning mobile calls in a cellular communication system can be improved by providing the mobile station with a locator object which, at certain intervals, determines the cell in which the mobile station is currently located. Stored in the mobile station is a list of cells or areas in which a special rate is to be applied in charging for calls originating from the mobile station. The locator object monitors calls made from the mobile station and, when it detects that a call is being made, it determines whether the mobile station was in a denoted special rate area at the time that its location was most recently determined. If so, then the object informs the network that the call is entitled to the special rate. Since the last location function was executed just before call setup commenced, a special rate call is possible even if the mobile station has thereafter moved some distance into a cell applying a normal rate. Disposed in a billing center is a billing object, to which the locator object sends data indicating whether the call was initiated from a cell or area in which a special rate is applicable, as well as data identifying the particular call. The second object receives the billing records generated by the mobile switching center, which also contain call identifying data, and compares the call-specific data in those records with the data sent by the first object. In this way, the second object can identify from the billing records those calls that are entitled to a special rate, regardless of whether the mobile station has moved during call setup from the original cell into a cell where another rate, e.g. a higher rate, is applicable.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
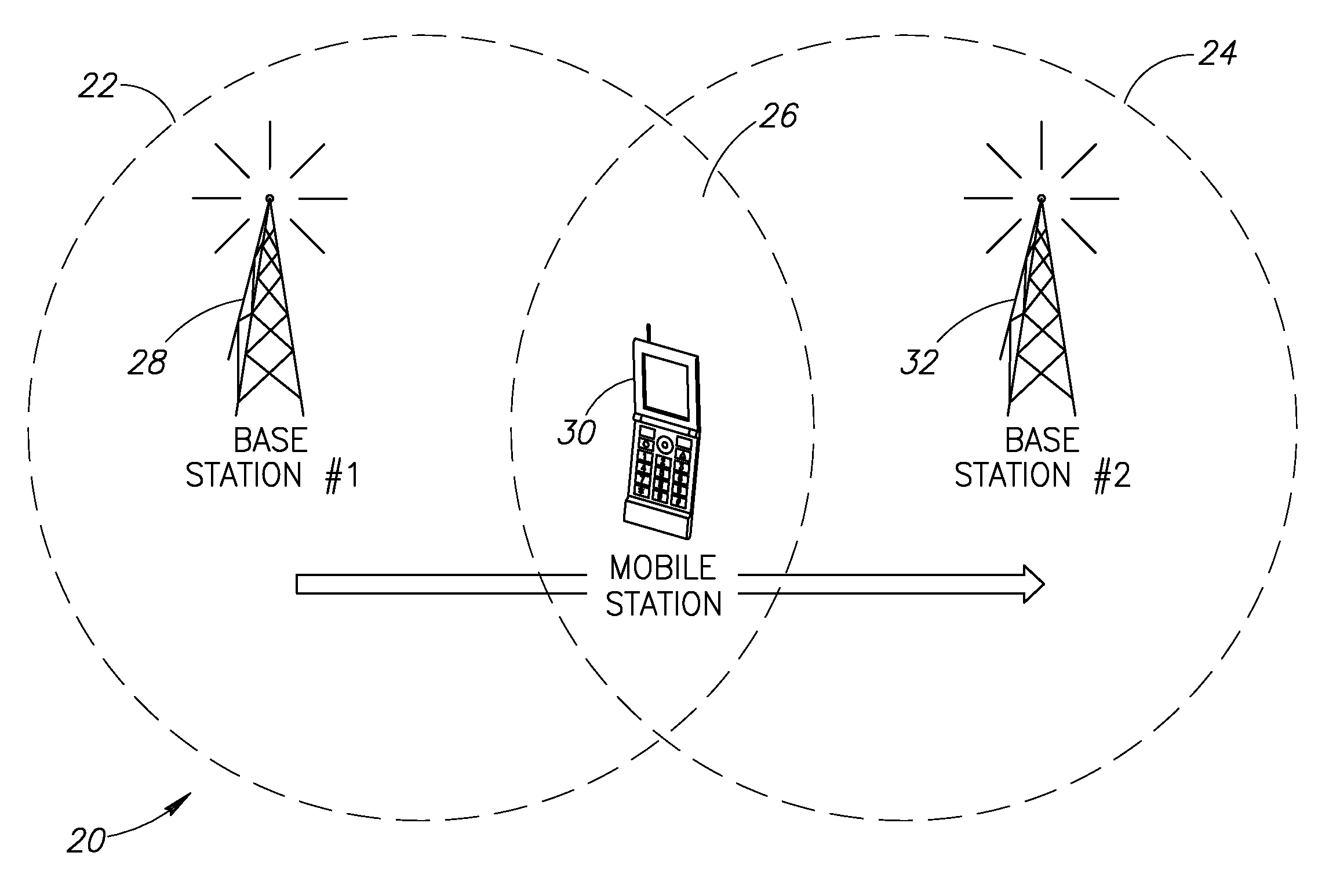
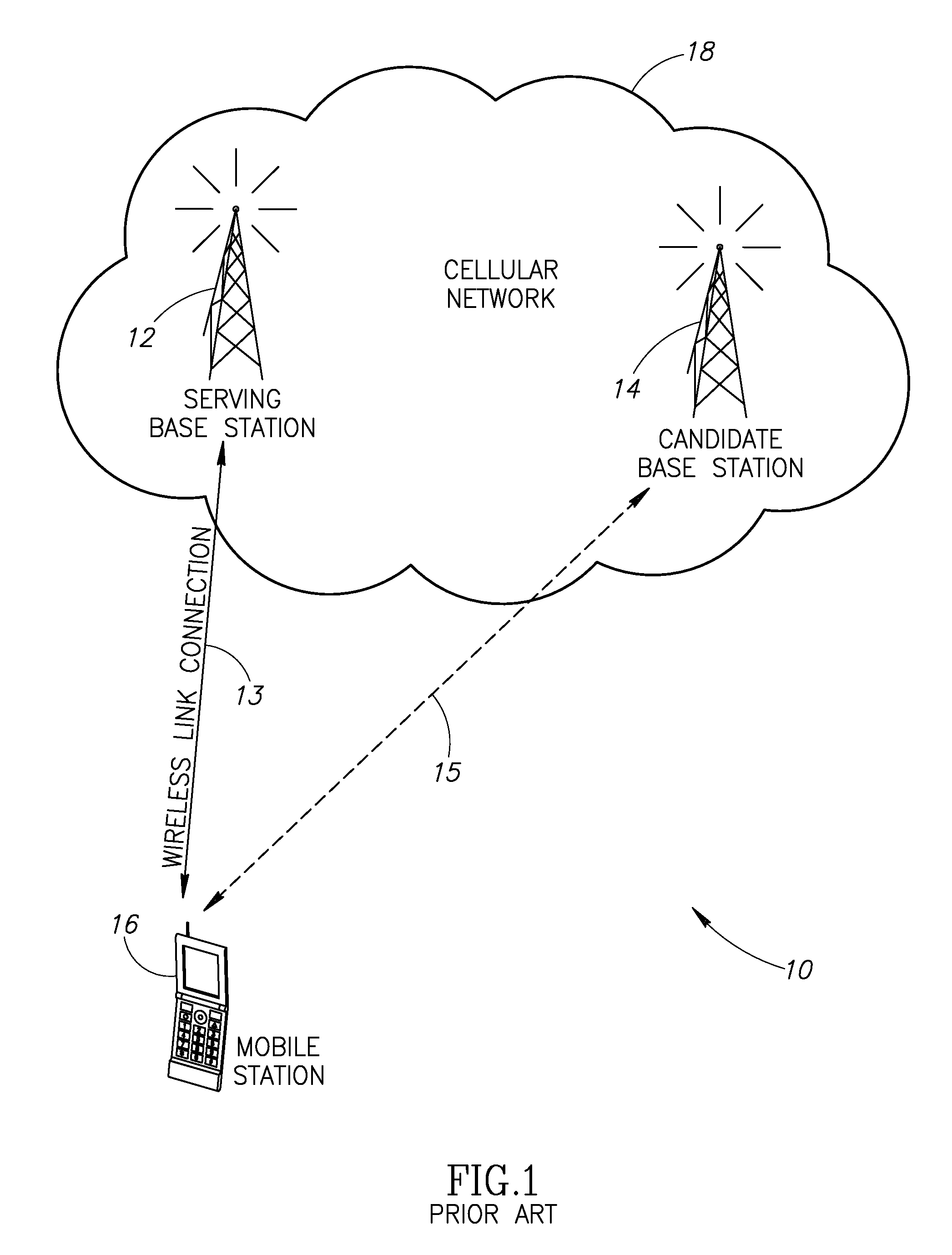
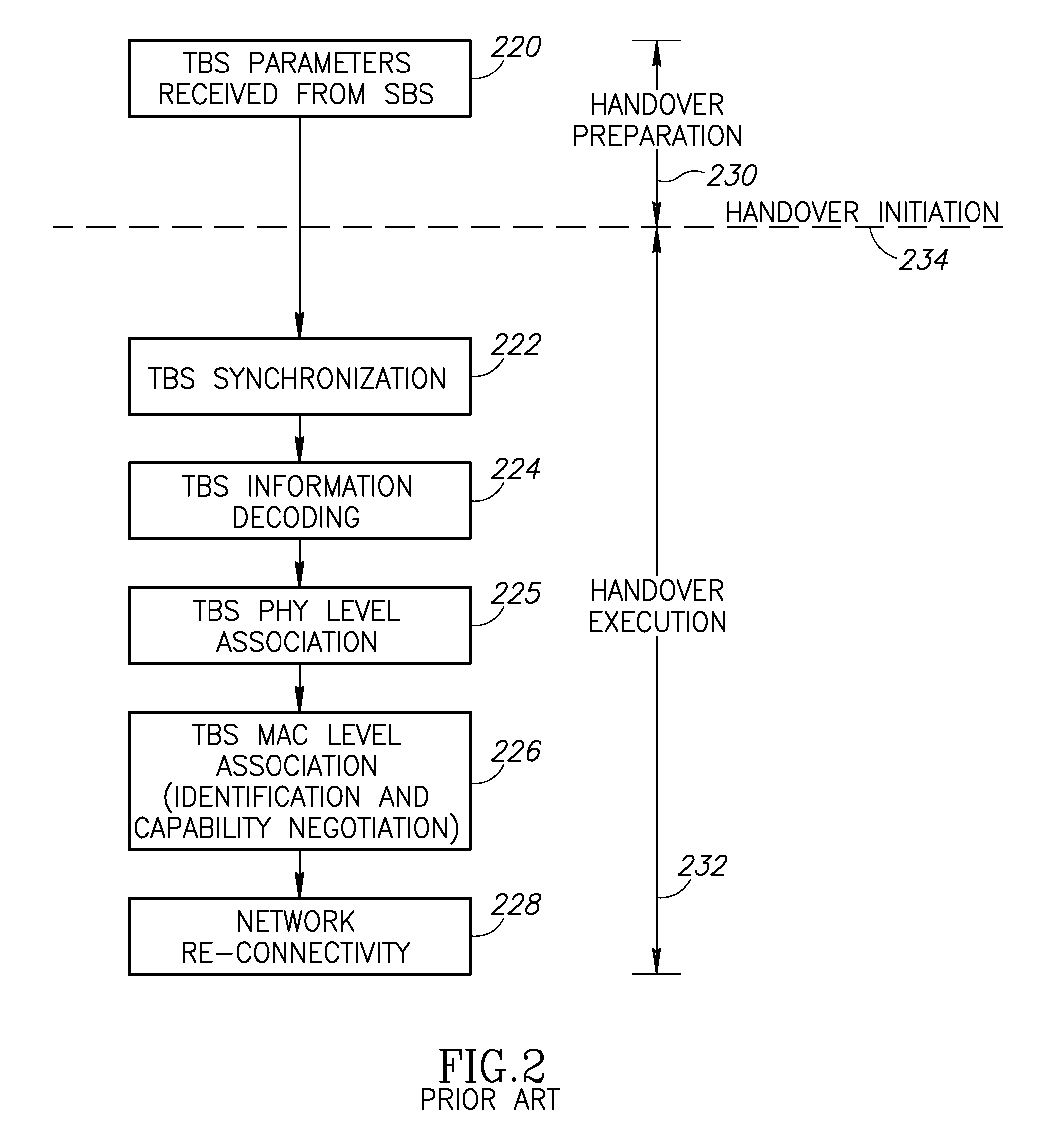
Autonomous anonymous association between a mobile station and multiple network elements in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20090290555A1Improve service qualityImprove acquisitionServices signallingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemCellular communication systems
A novel and useful autonomous association mechanism for use in user equipment (UE) network connections in one or more cellular communications systems. The handover process is optimized by improving the selection of target base stations and optimizing the discontinuity period from the time of disconnection from a serving base station and connection to a target base station and by establishing anonymous bidirectional communications with base stations. The mechanism facilitates multiple cell association in a network unaware manner while preserving single endpoint connectivity. The UE does not need to negotiate for or receive pre-allocated opportunities from the network for making associations with neighboring base stations. Association opportunities are created by the UE autonomously in accordance with UE activity patterns. Association opportunities are used to exchange preliminary information needed for handover between the UE and candidate base stations over the same or a plurality of access technologies. The information includes any parameter that can affect the handover process, e.g., link quality, etc.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
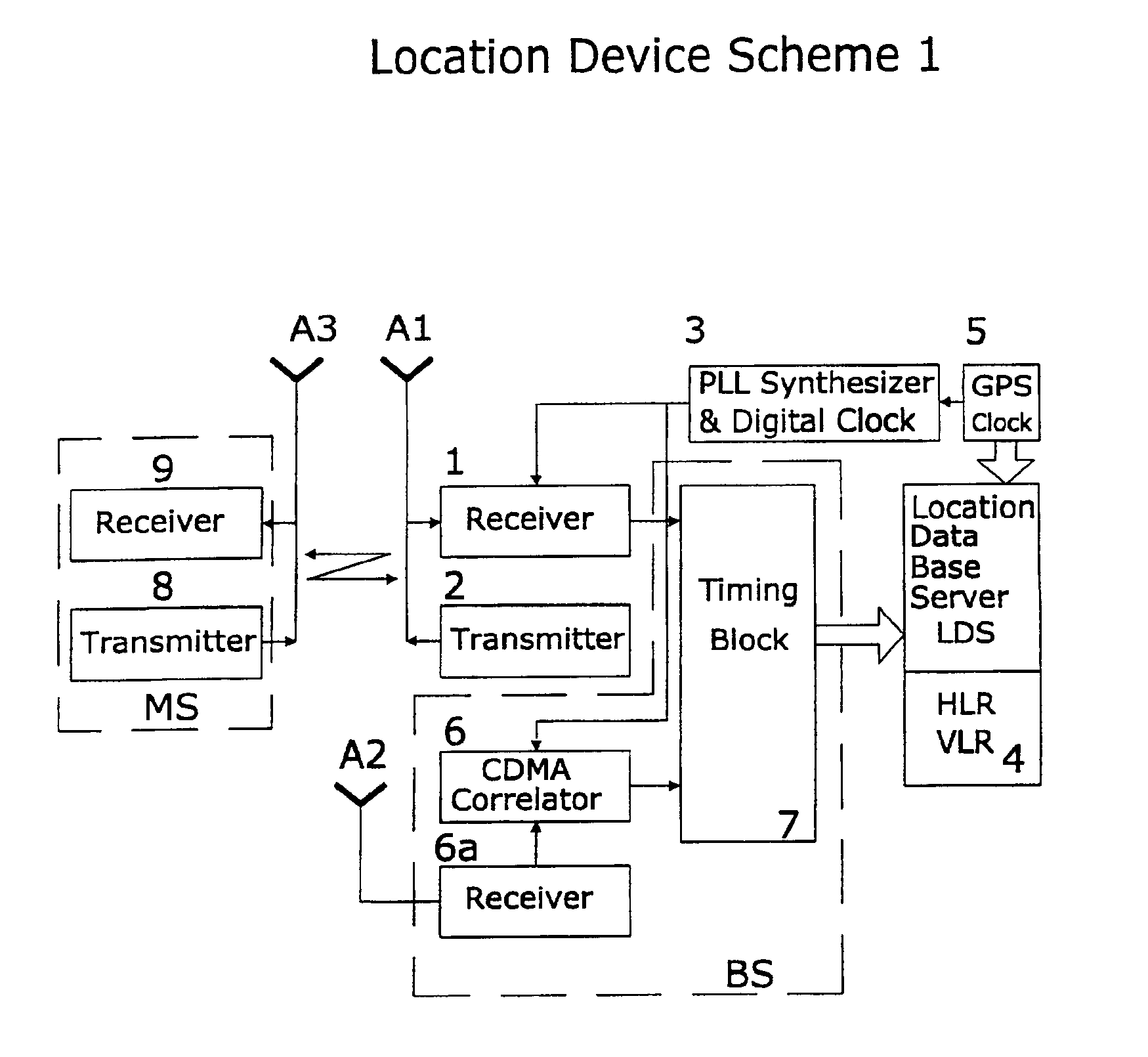
Method and system for mobile station positioning in cellular communication networks
InactiveUS6901264B2Improve accuracy of manyExpand coverageDirection finders using radio wavesNavigation instrumentsMultilaterationMobile station
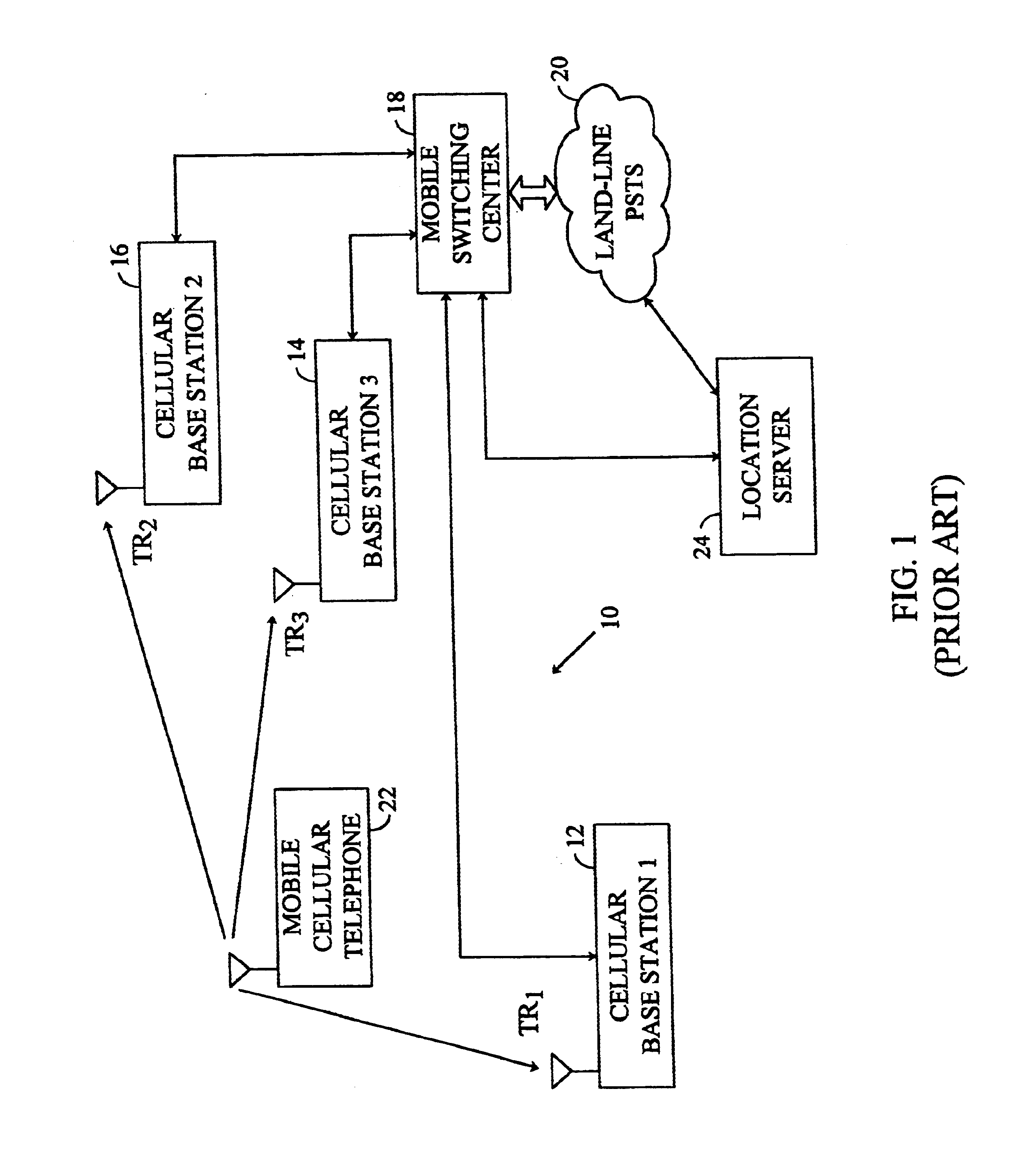
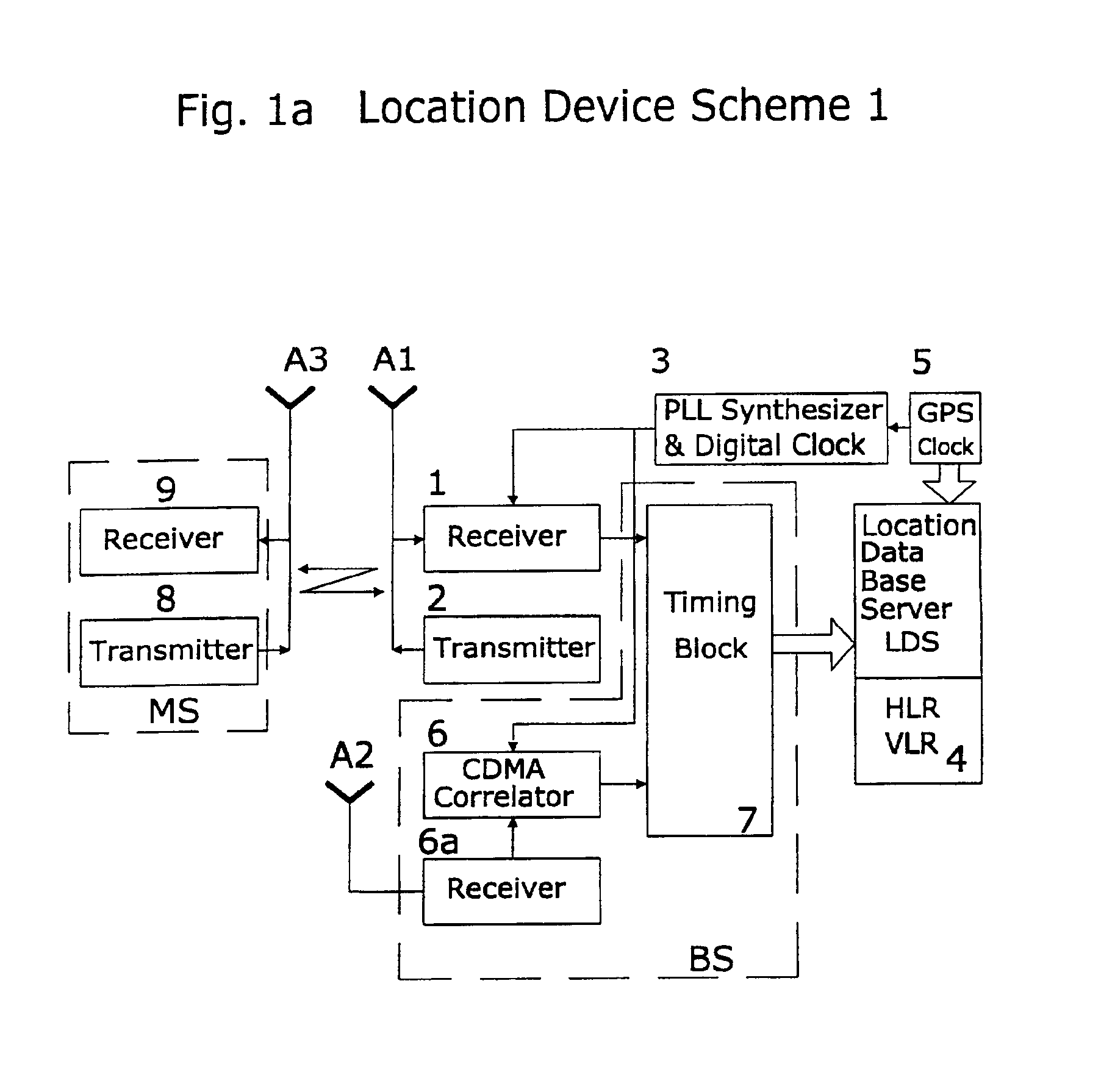
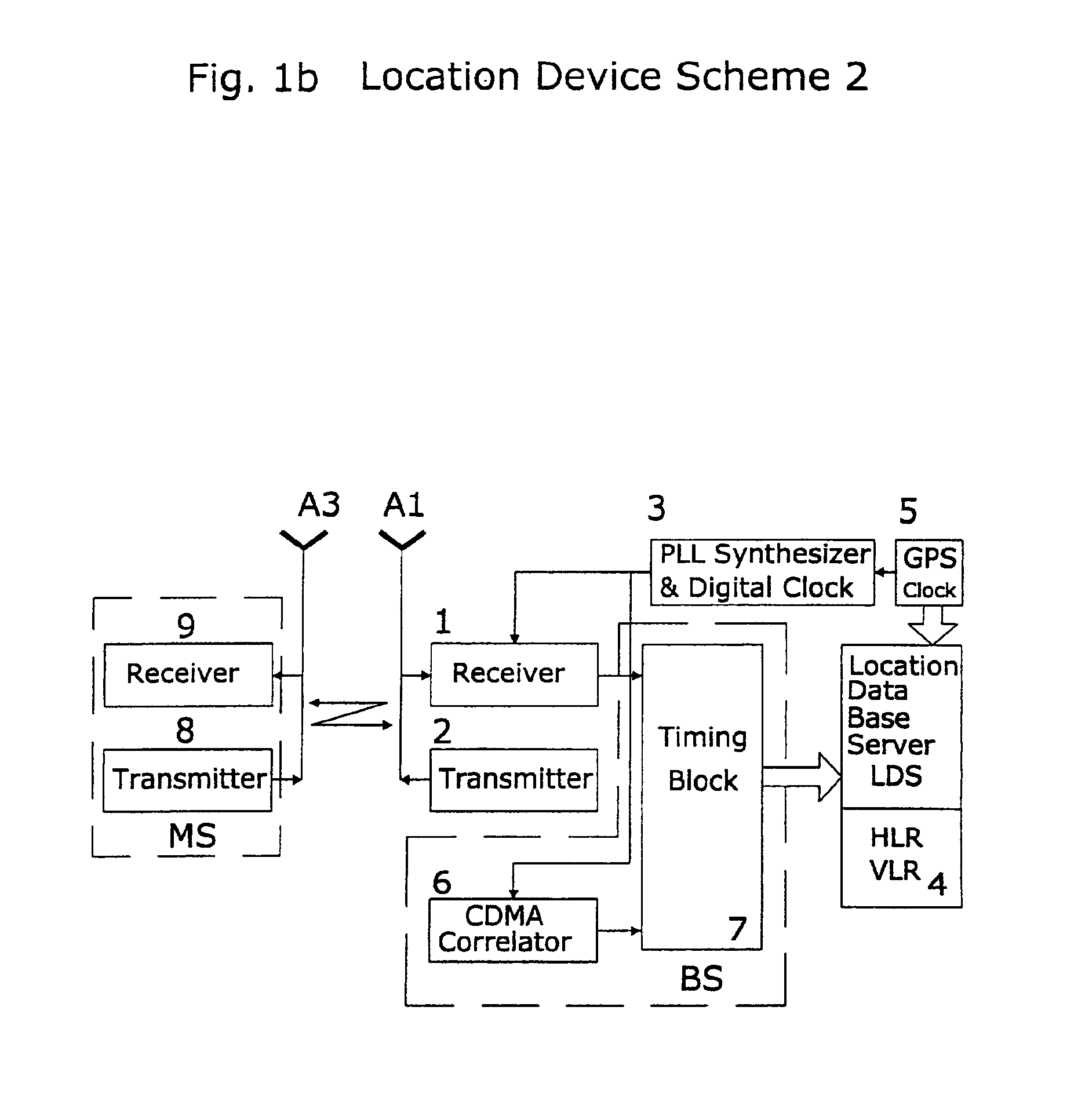
A system of cell phone positioning in real time is provided with specialized location device installations on multiplicity of base stations BSs in CDMA and TDMA cellular communication networks. The purpose of the positioning system is to enable tracking and locating large quantities of anonymous mobile cell phones MS in any number of network cells to be used for real time traffic-forecasting systems, emergency services E911, and other client-initiated position requests. Location data thus obtained can be continuously updated from vehicular-based cellular phones, collected, processed and used as a basis for input to intelligent transportation systems, such as real time urban traffic guidance for vehicular congestion and intelligent traffic control systems. The system is capable of covering large urban geographical areas and number of independent cell structures serving thousands of mobile cell phone clients. It is an independent plug-in solution with specialized synchronized location device installations in each cell BS. Centrally located specialized location software based on Time of Arrival (TOA) and Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) methods for high speed location processing in central Location Database Server (LDS). The inventive system consists of number of component functions: Operator-initiated functions, location device functions and software enabled positioning functions.
Owner:MAKOR ISSUES & RIGHTS
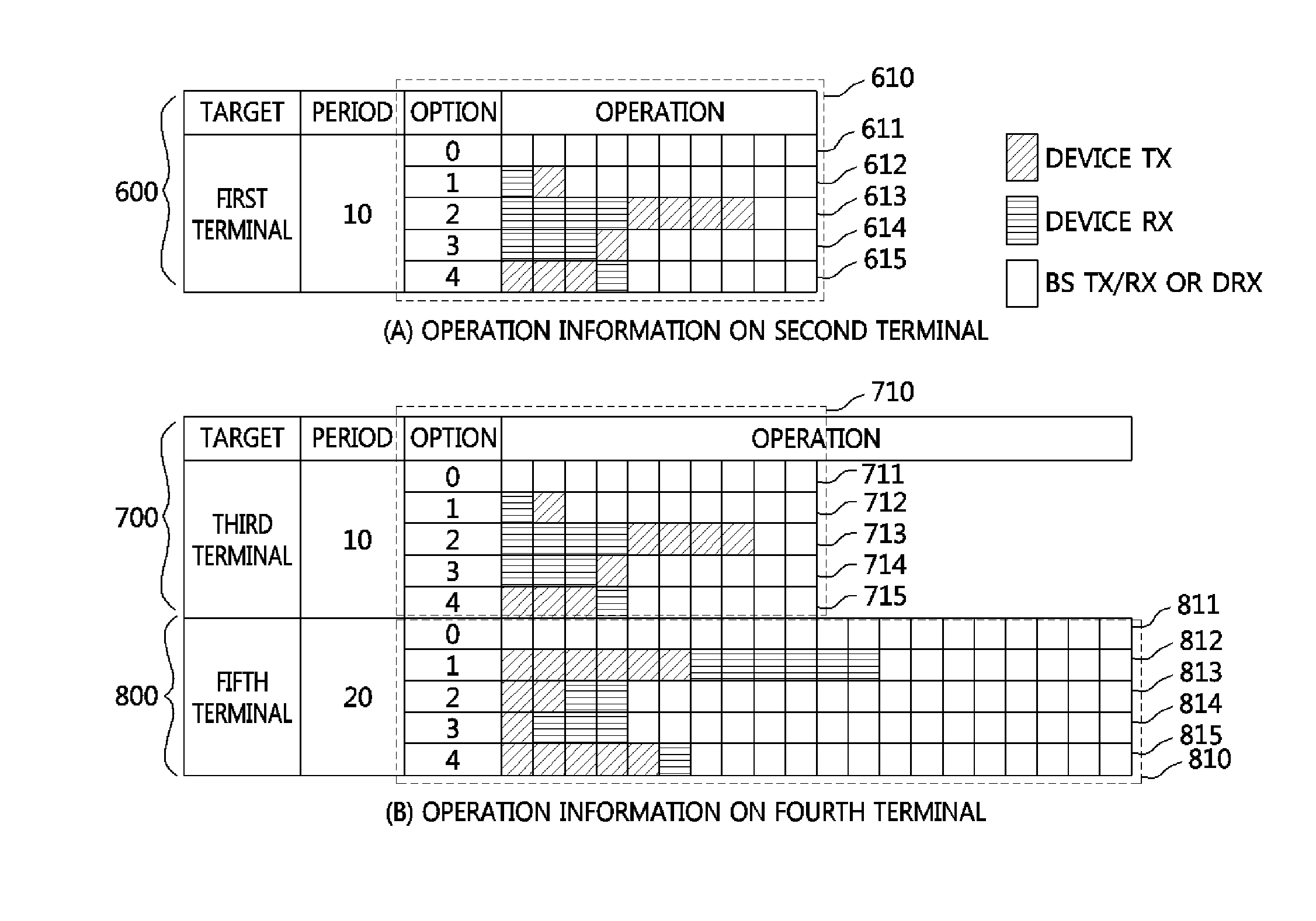
Method of allocating radio resources for device-to-device communication in cellular communication system
InactiveUS20130258996A1Reduce capacityFlexible and efficient resource allocationWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsComputer terminal
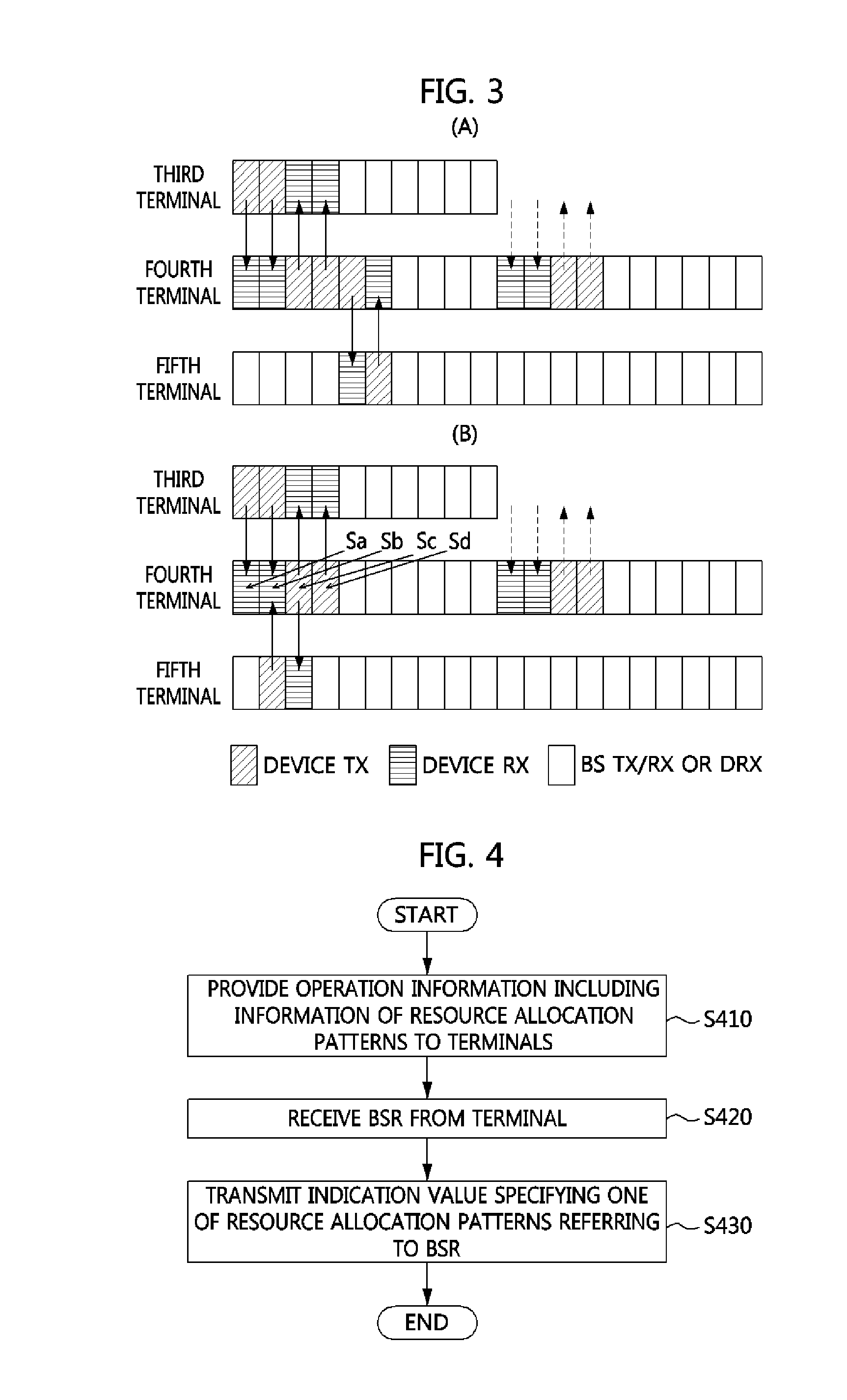
A resource allocation method of a base station for a device-to-device (D2D) communication link based on a cellular communication system includes providing operation information which includes information about one or more resource allocation patterns available for the D2D communication link to terminals which perform D2D communication according to each terminal and each D2D communication link, receiving a buffer status report (BSR) from the terminals which perform the D2D communication, and transmitting an indication value which indicates at least one of the resource allocation patterns based on the BSR. Accordingly, in the resource allocation method, low capacity of downlink control channels is required by the base station, yet flexible and efficient allocation of resources is enabled.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com