Patents
Literature
43 results about "Spatial division multiple access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
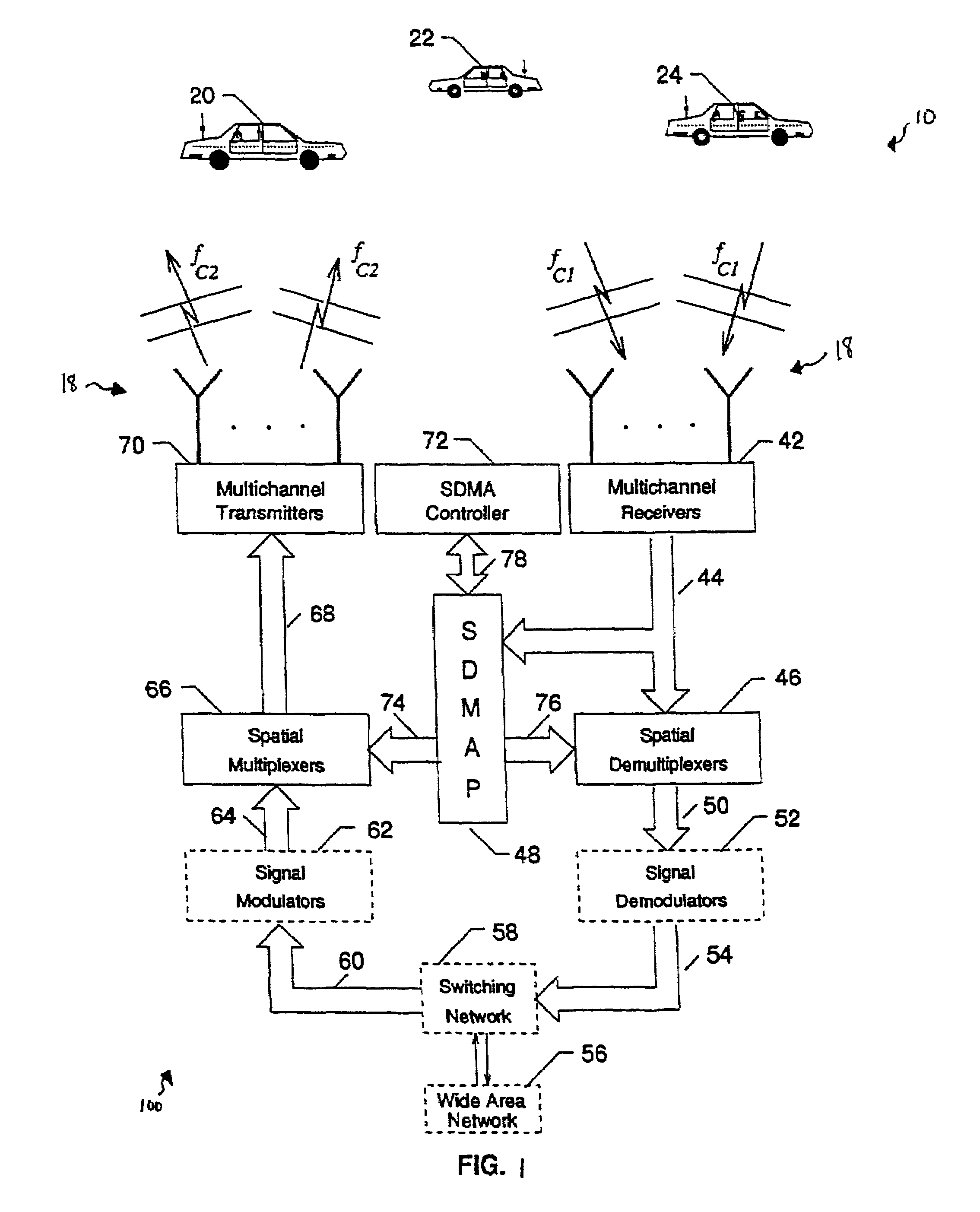
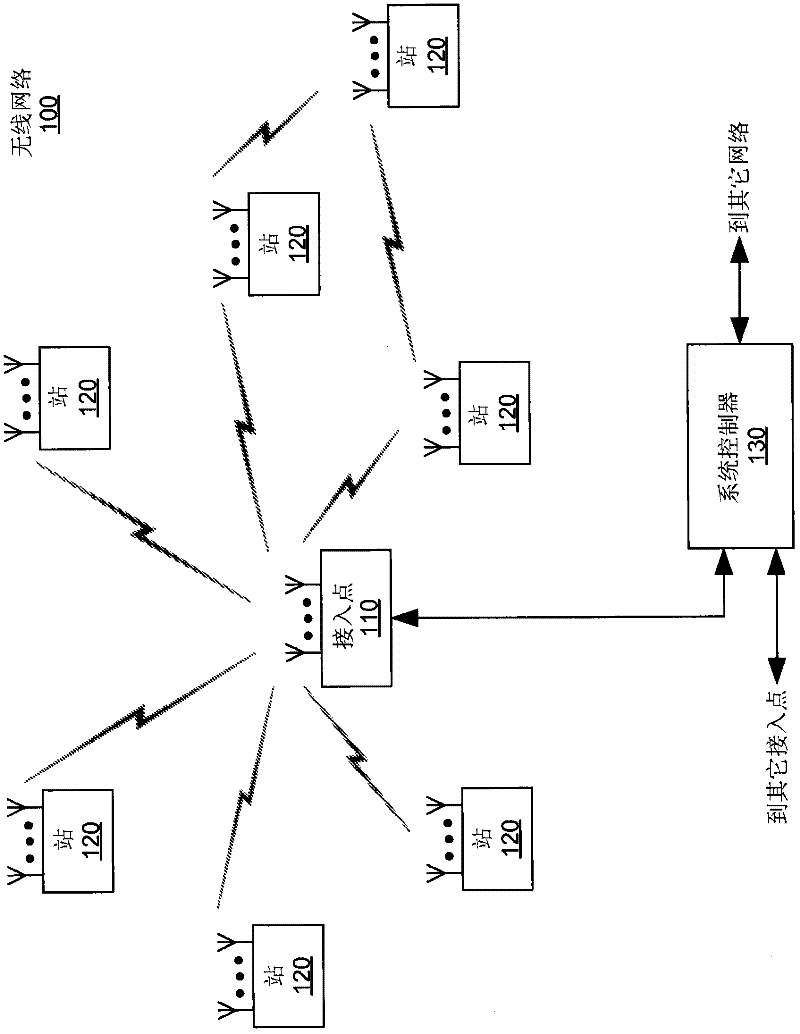
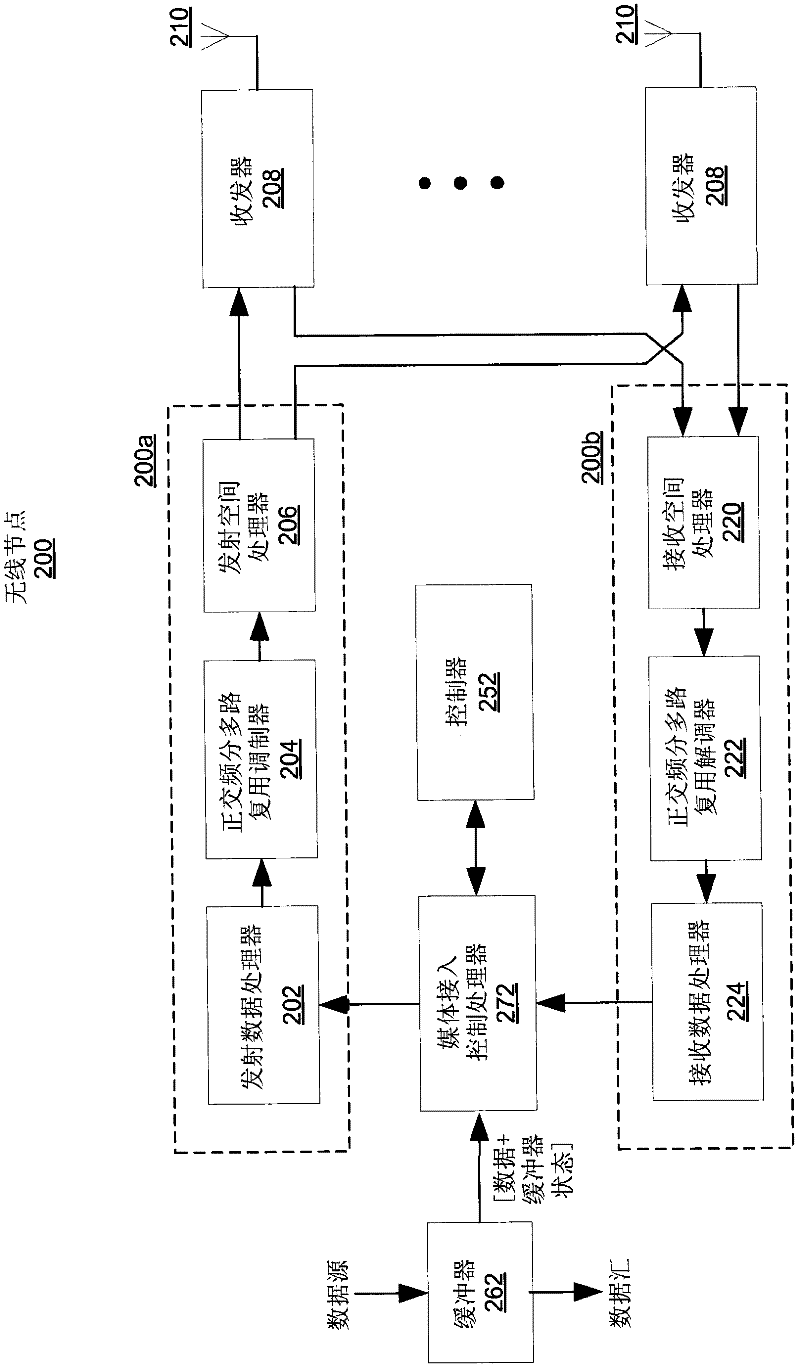
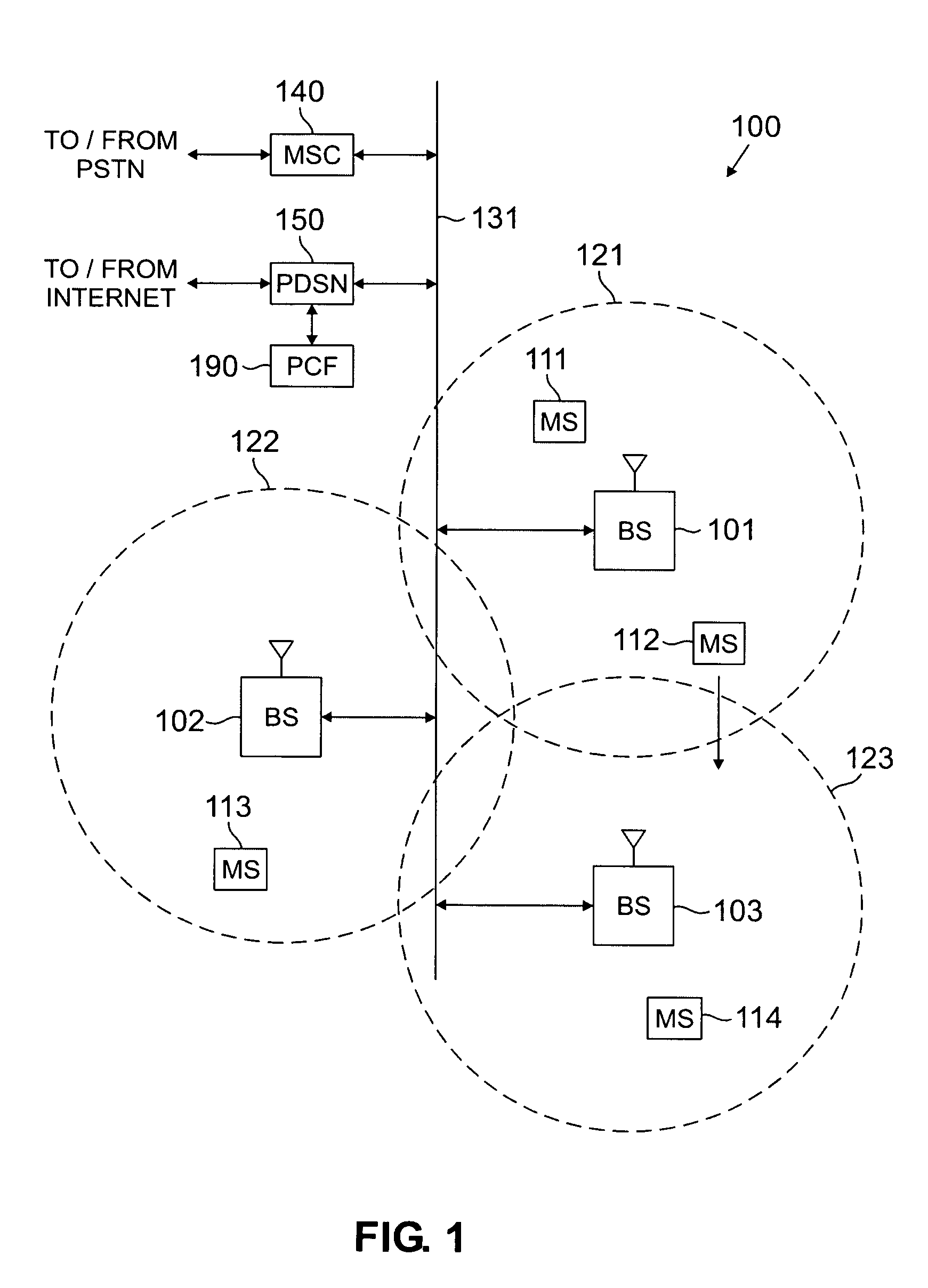
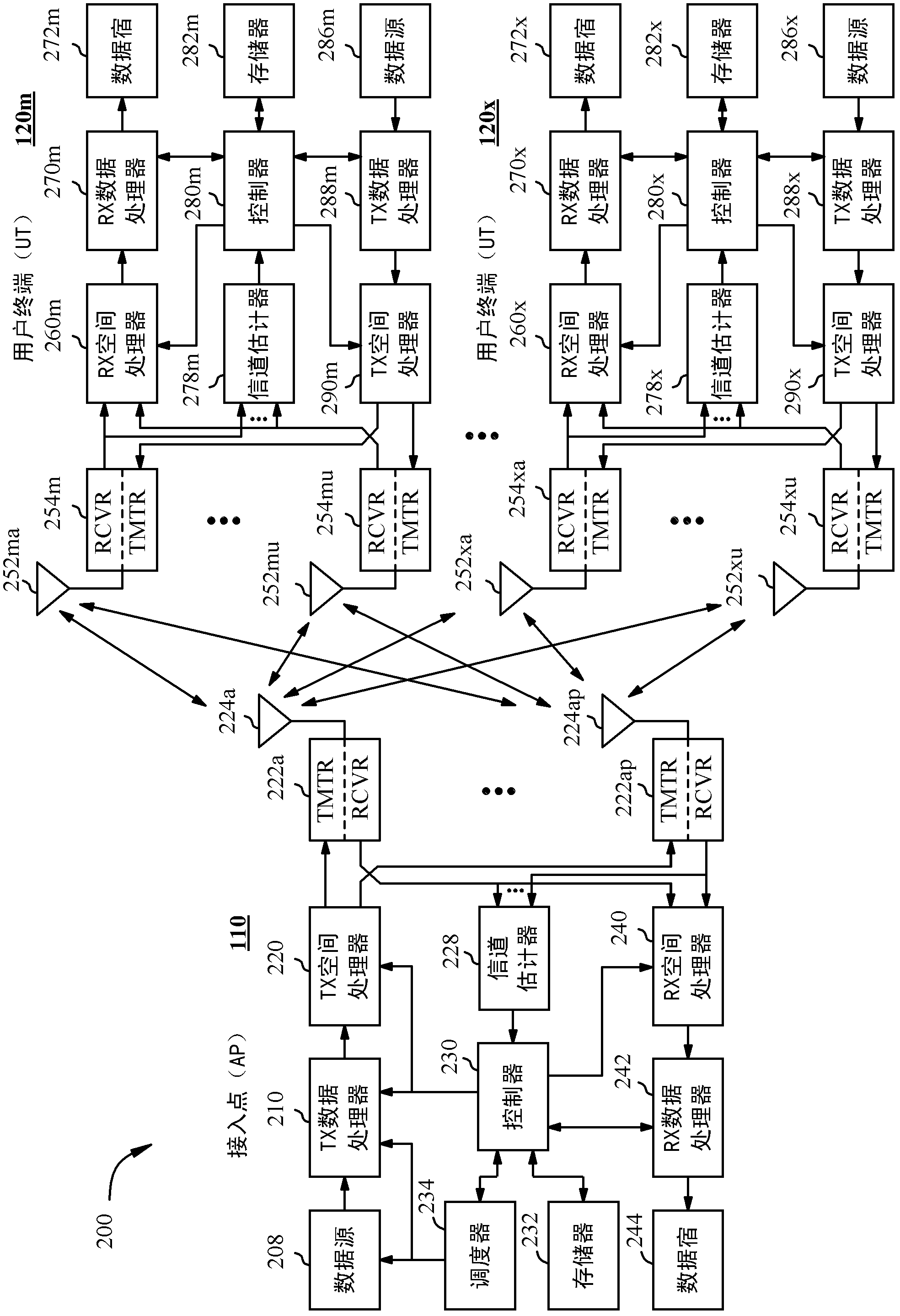
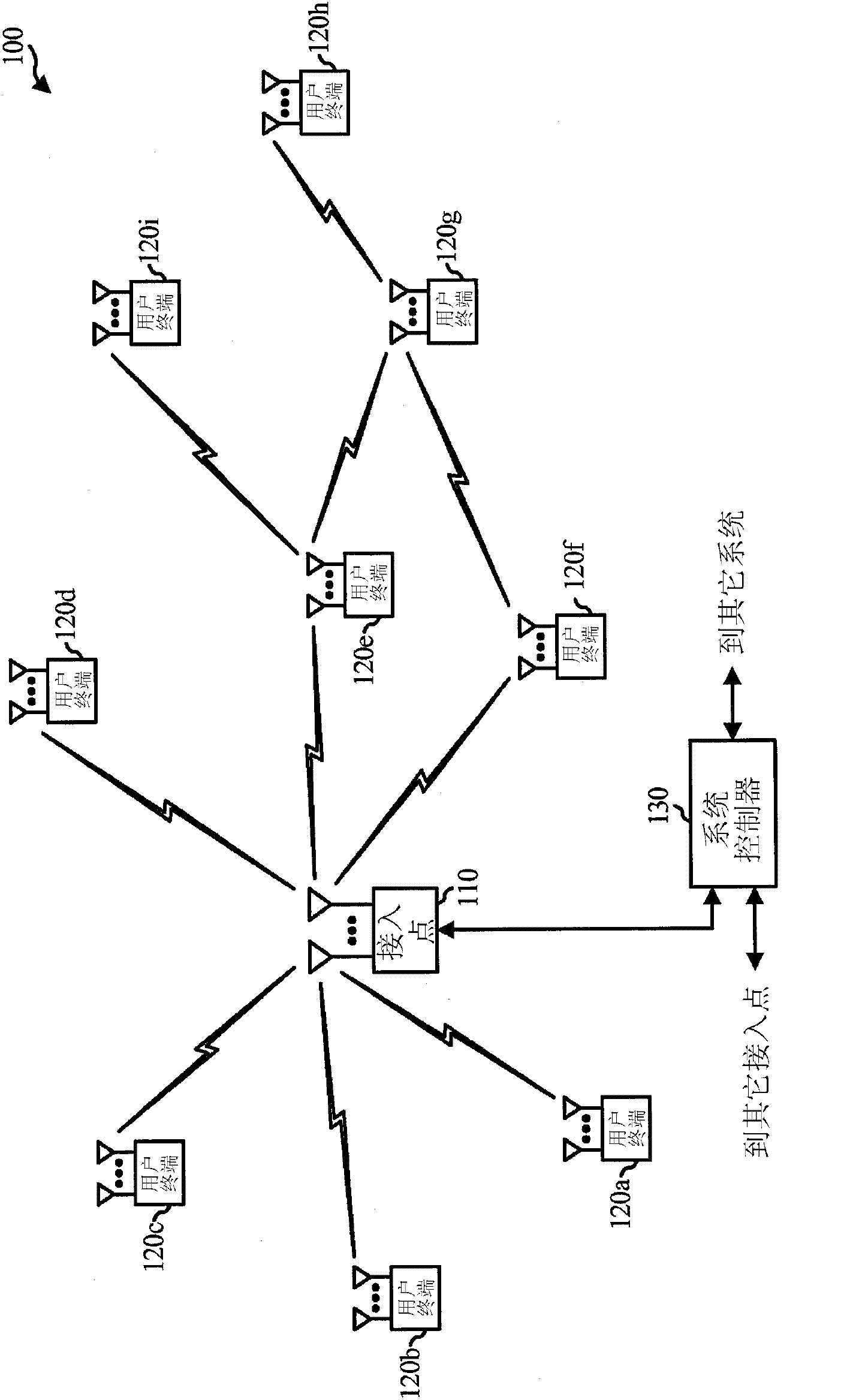
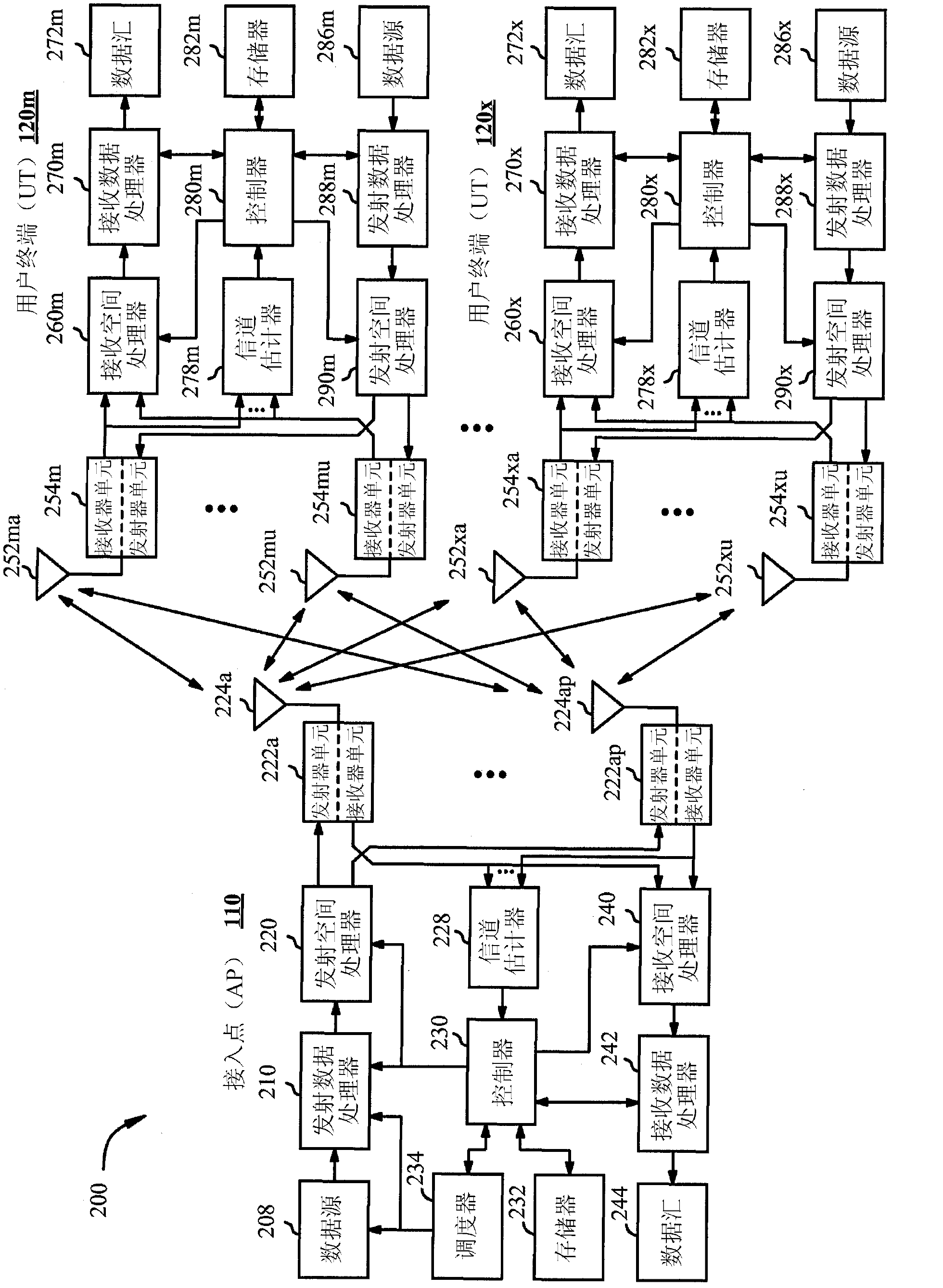
Systems and method for providing in-flight broadband mobile communication services
InactiveUS20110182230A1Efficient use ofImproving average and peak data throughputFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork topologiesTransceiverSpatial division multiple access
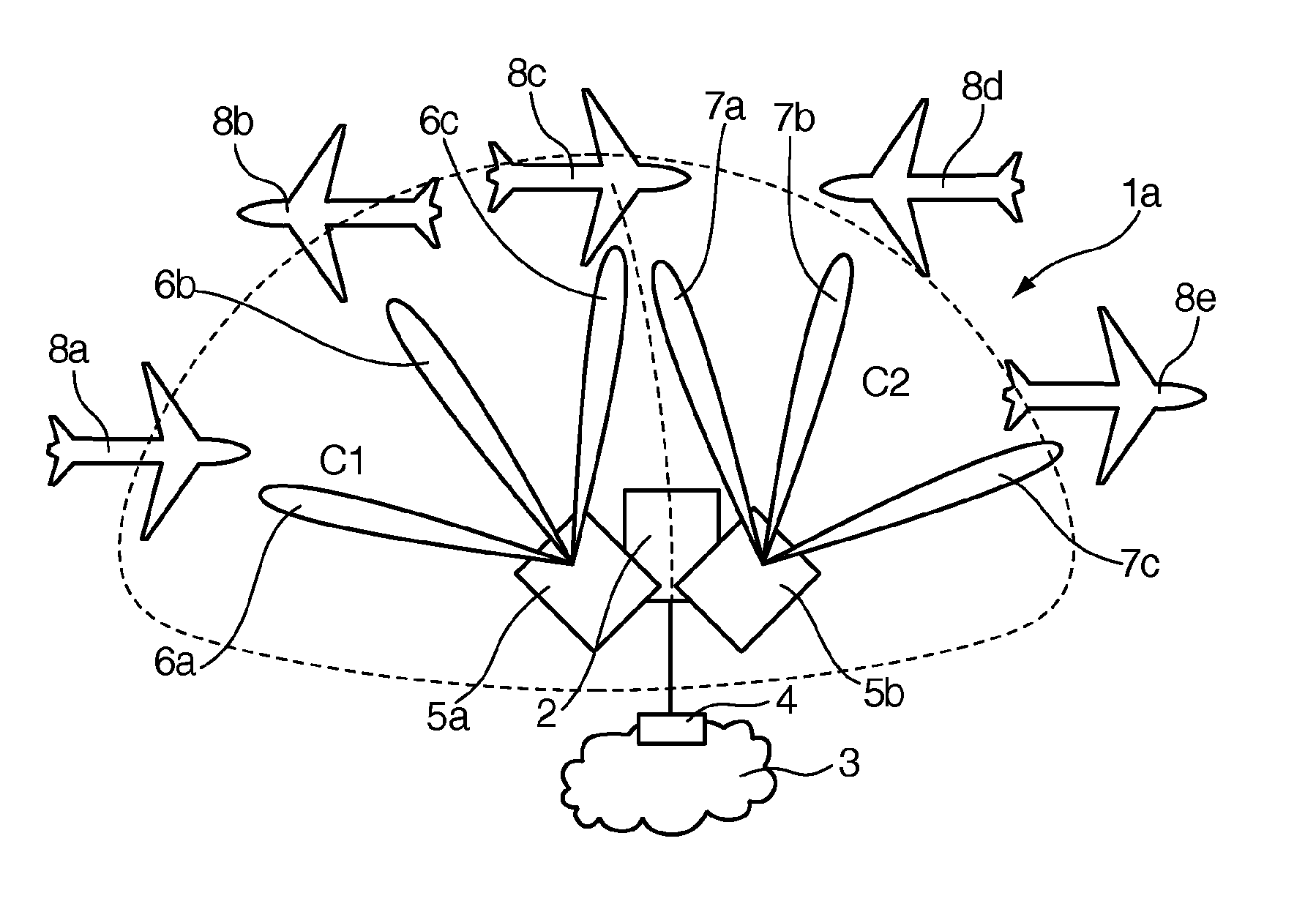
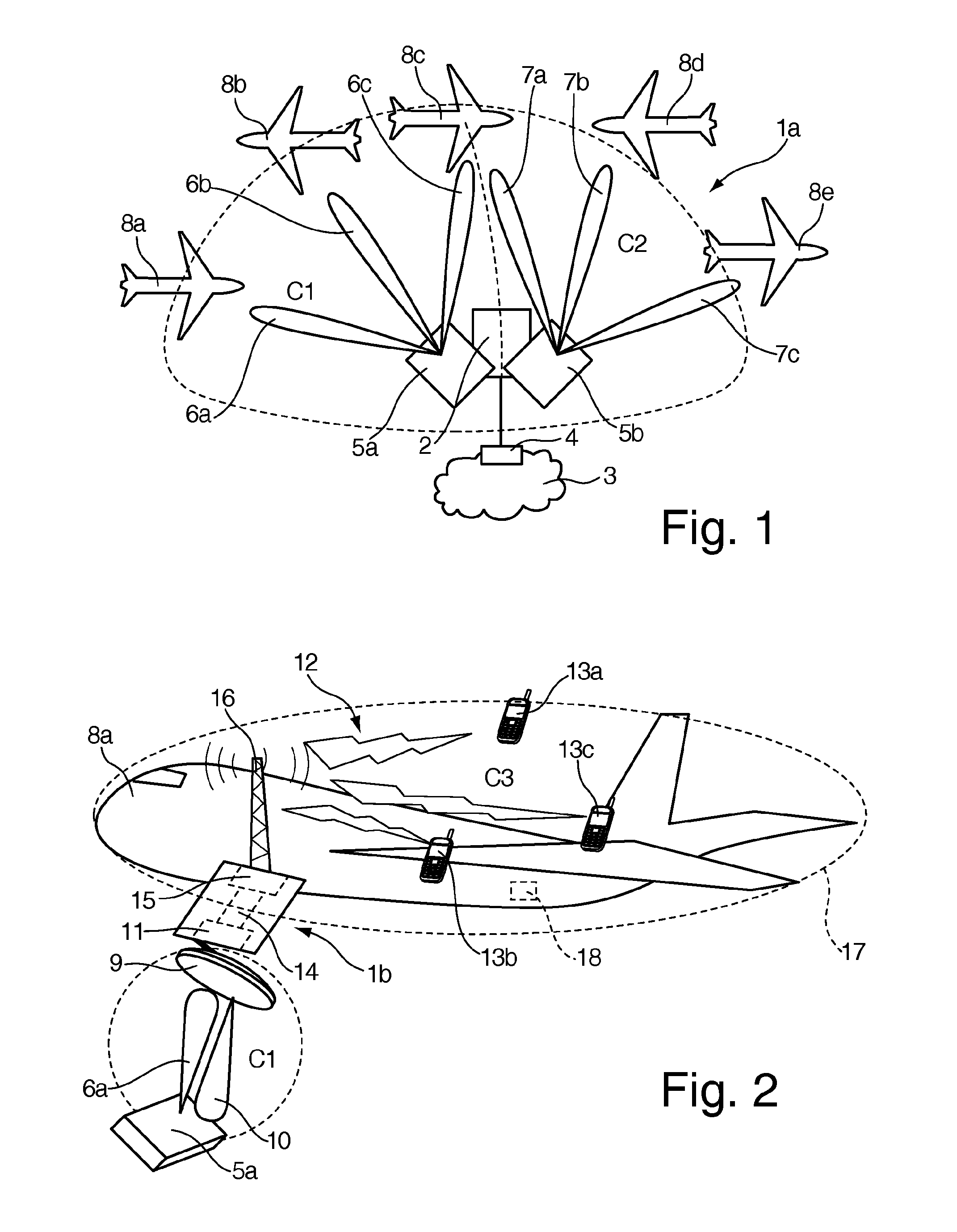
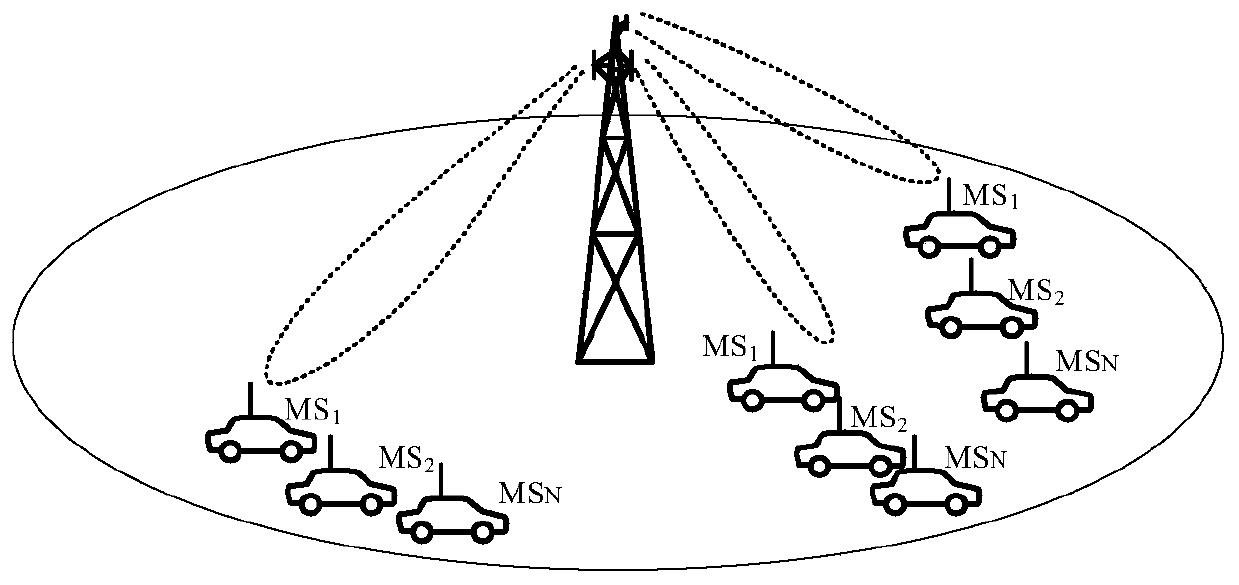
The invention relates to a ground-based wireless cellular communication system (1a) for providing in-flight broadband mobile communication services, comprising: at least one ground-based base station (2) adapted for generating at least one cell (C1, C2) defining a solid angle of the space surrounding the base station (2), the ground- based base station (2) further comprising at least one antenna array (5a, 5a) using two-dimensional-beamforming for generating at least one beam (6a-c, 7a-c) for serving at least one airplane (8a-c, 8c-e) in the space covered by the at least one cell (C1, C2) using spatial-division multiple access, SDMA. The invention also relates to an airplane equipment for providing in-flight broadband mobile communication services, comprising: at least one antenna for exchange of user data with the ground-based wireless cellular communication system (1a), a transceiver unit connected to the at least one antenna for handling the air-to-ground and ground-to-air communication with the ground-based wireless cellular communication system (1a), and an inside-airplane communication system for distributing the user data to and from terminals within the airplane.
Owner:RPX CORP
Beamforming method and device
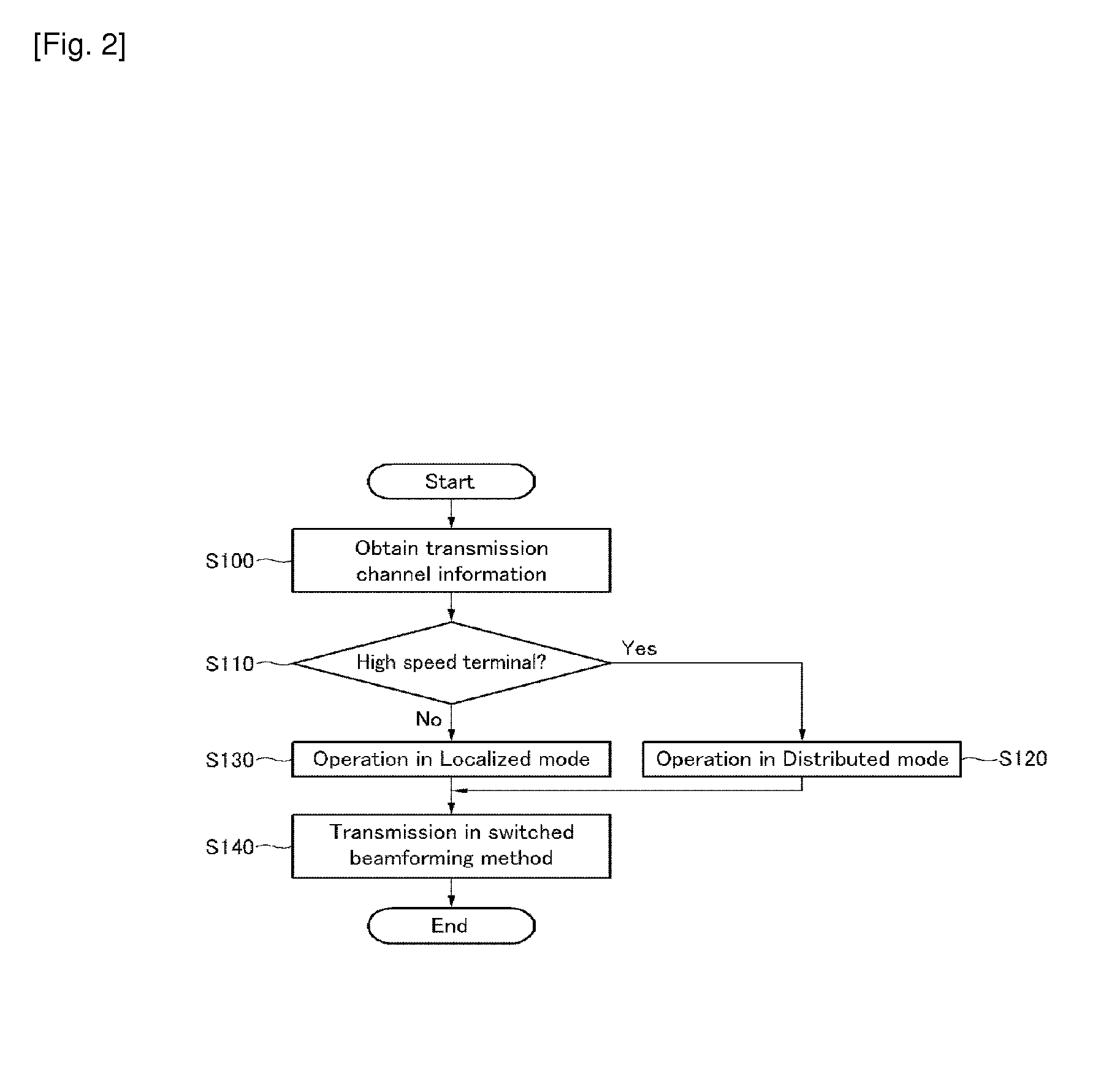
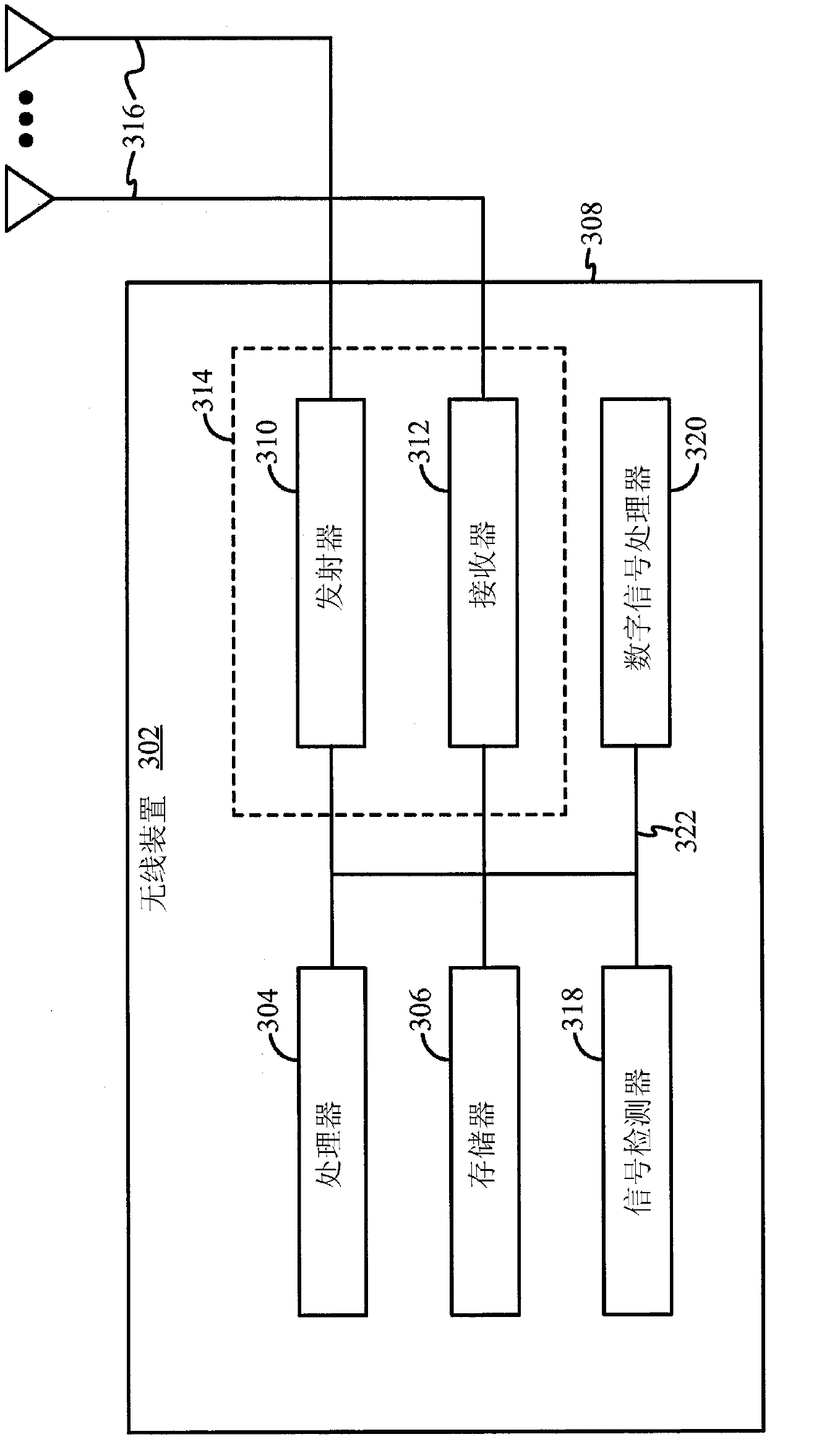
InactiveUS20100103900A1Easy to detectDiversity/multi-antenna systemsWireless commuication servicesSpatial division multiple accessEngineering
The present invention relates to a beamforming device in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing access system, and a method thereof. In the method, a switched beamforming algorithm is applied to perform downlink beamforming, and an adaptive beamforming algorithm is applied to perform uplink receiving beamforming. In addition, a half wavelength array antenna is used to simultaneously allocate the same resource to two terminals separately positioned in two different spaces, so as to support spatial division multiple access (SDMA). In this case, since a base station uses channel status information at transmitter (CSIT) for transmitting beamforming and receiving beamforming, the SDMA may be supported without obtaining additional channel status information at receiver (CSIR) when realizing the uplink receiving beamforming.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
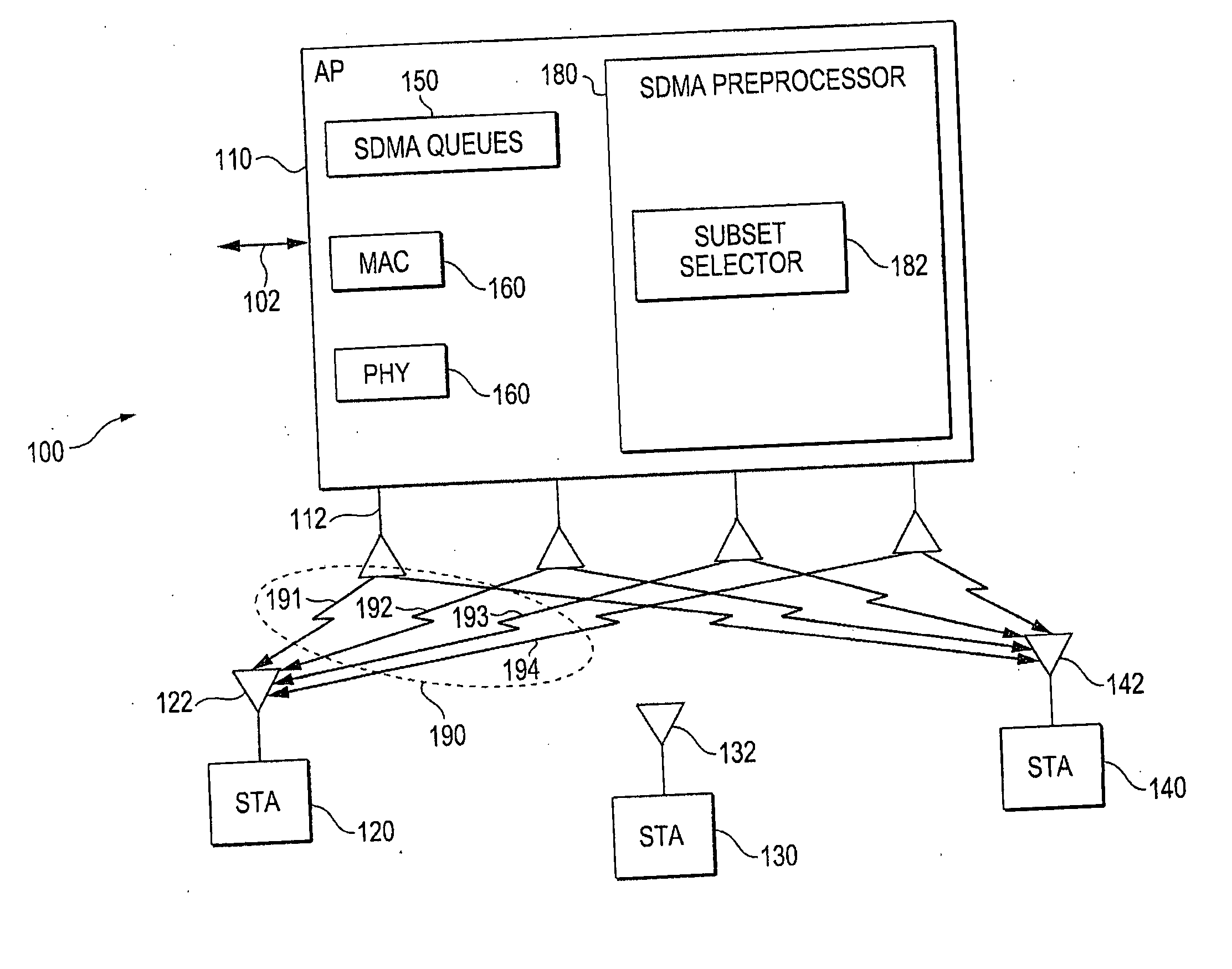
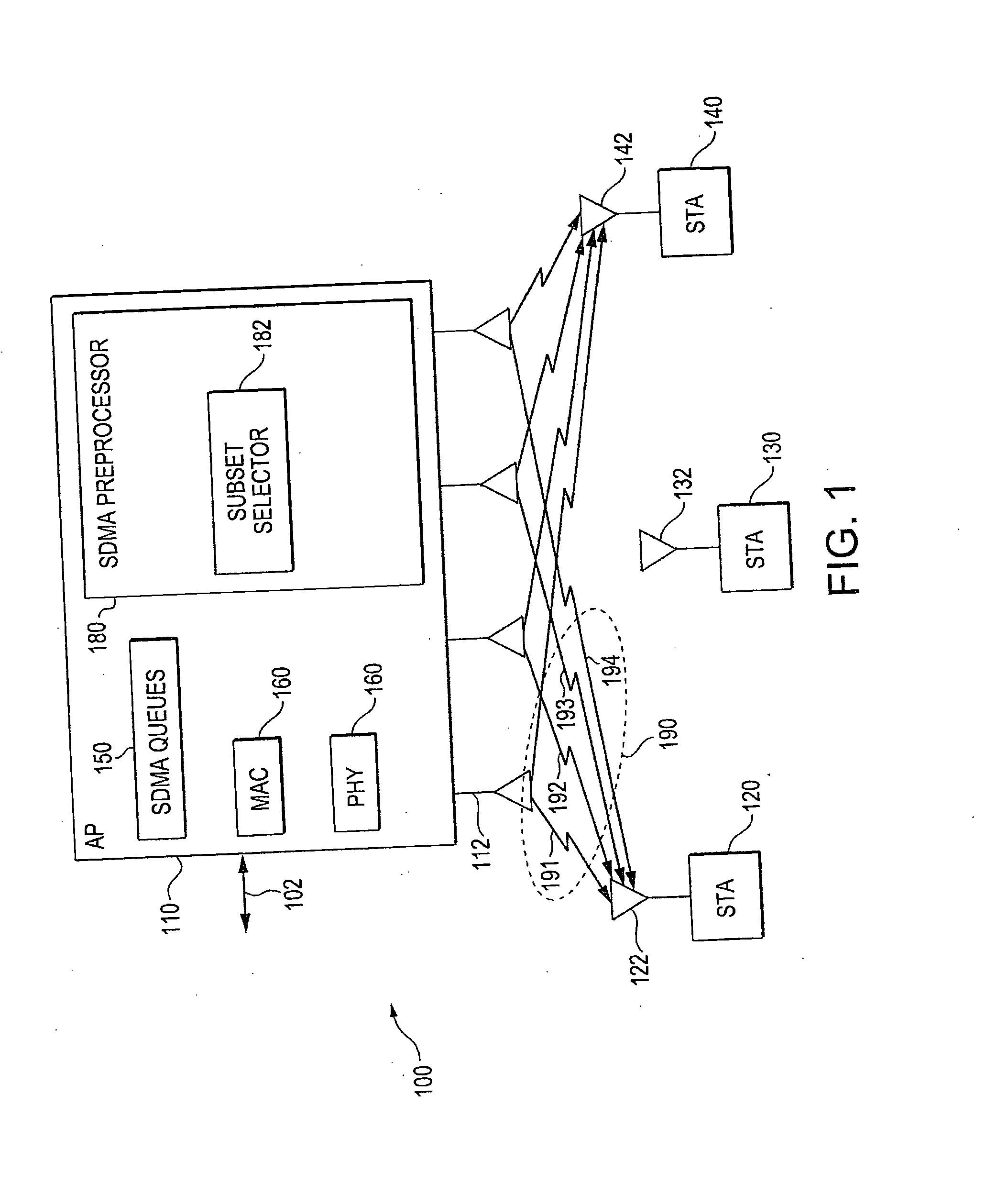
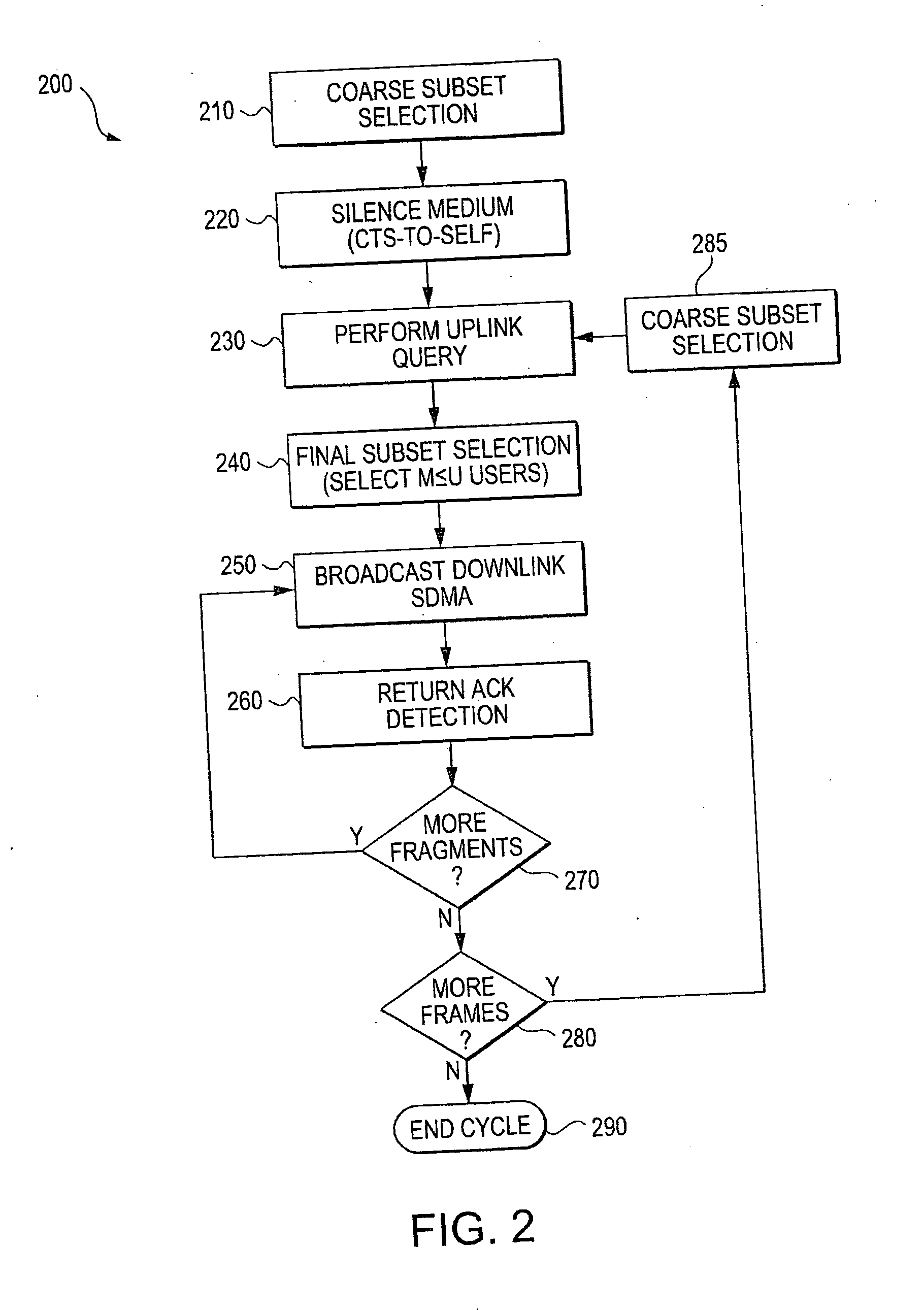
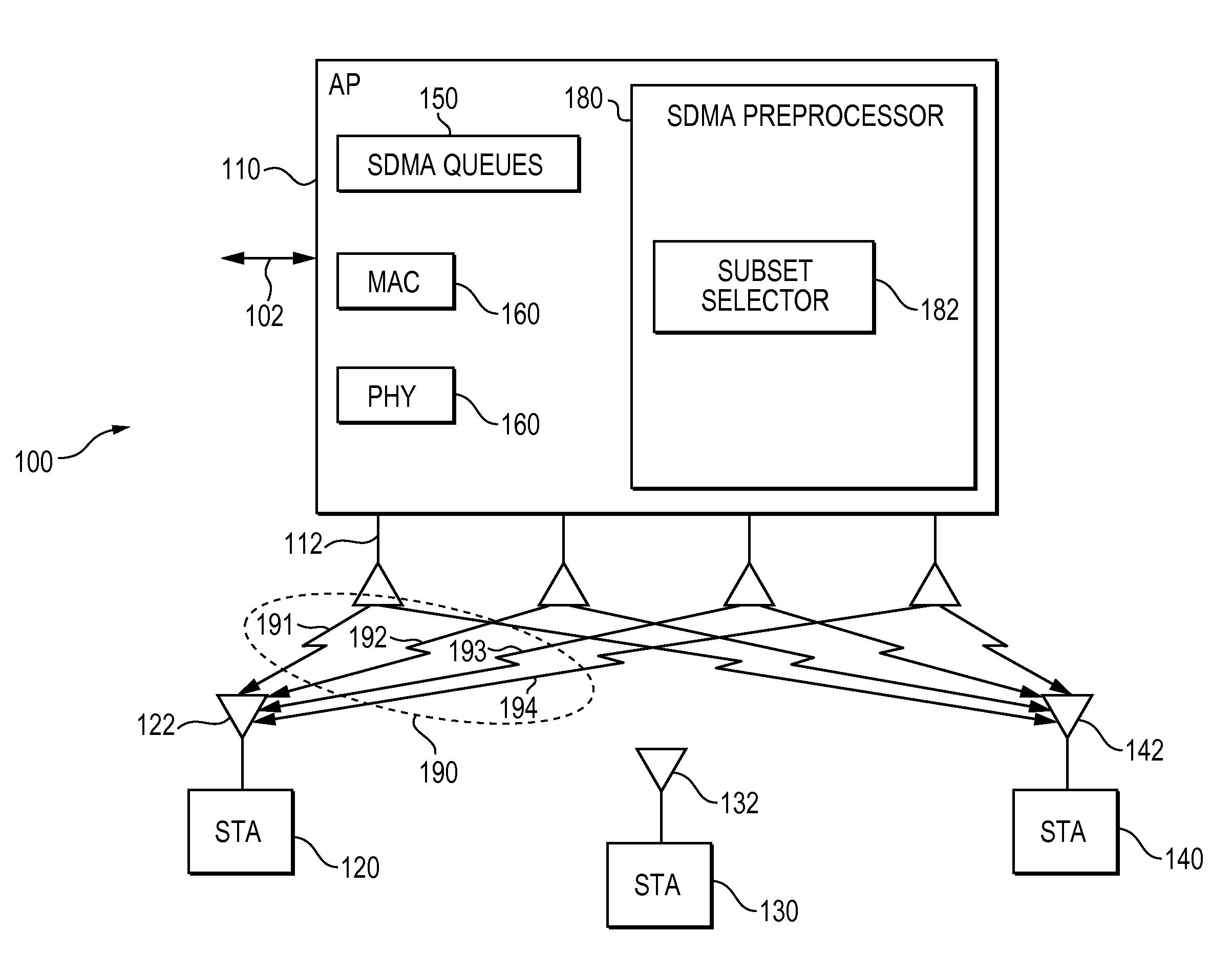
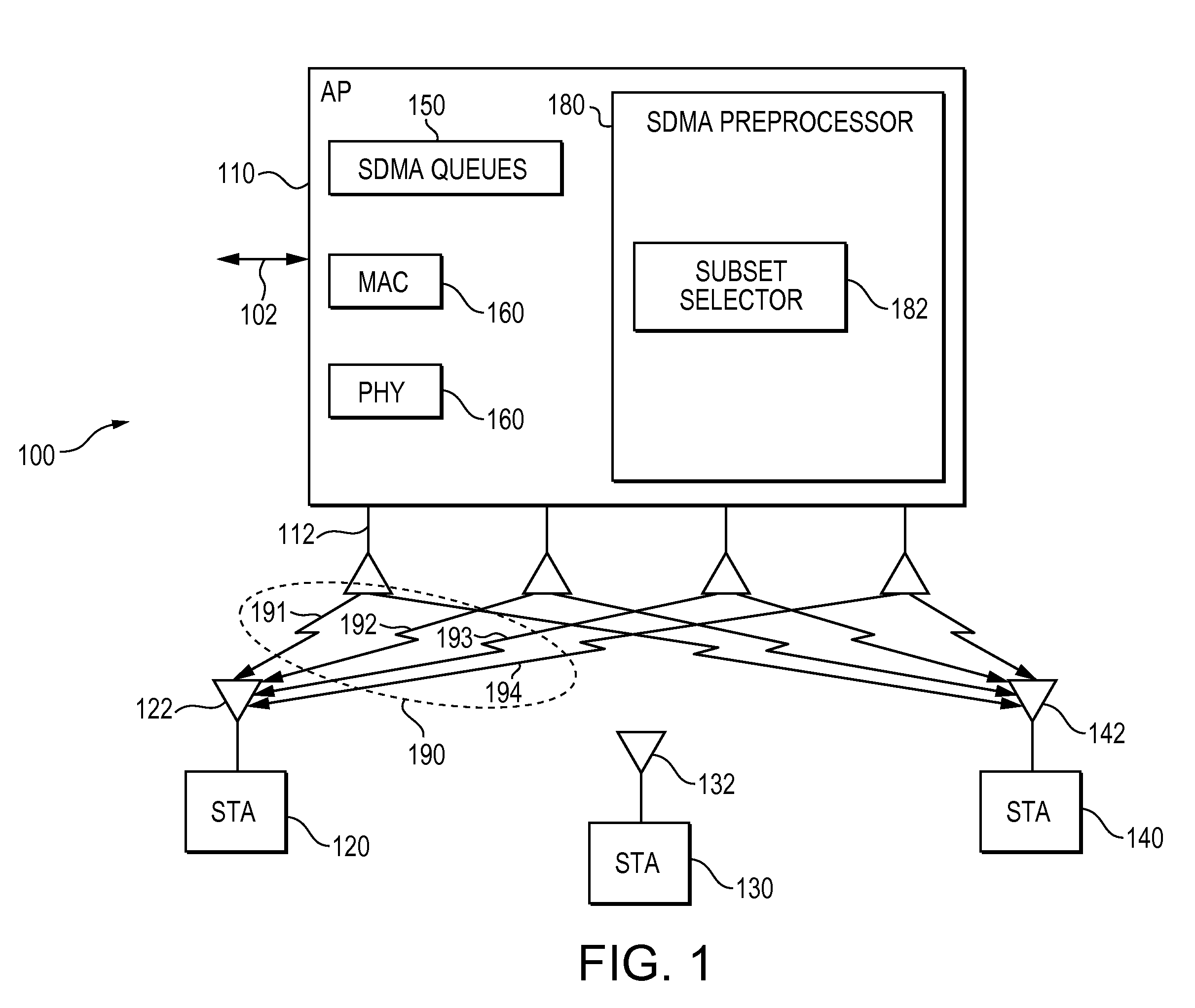
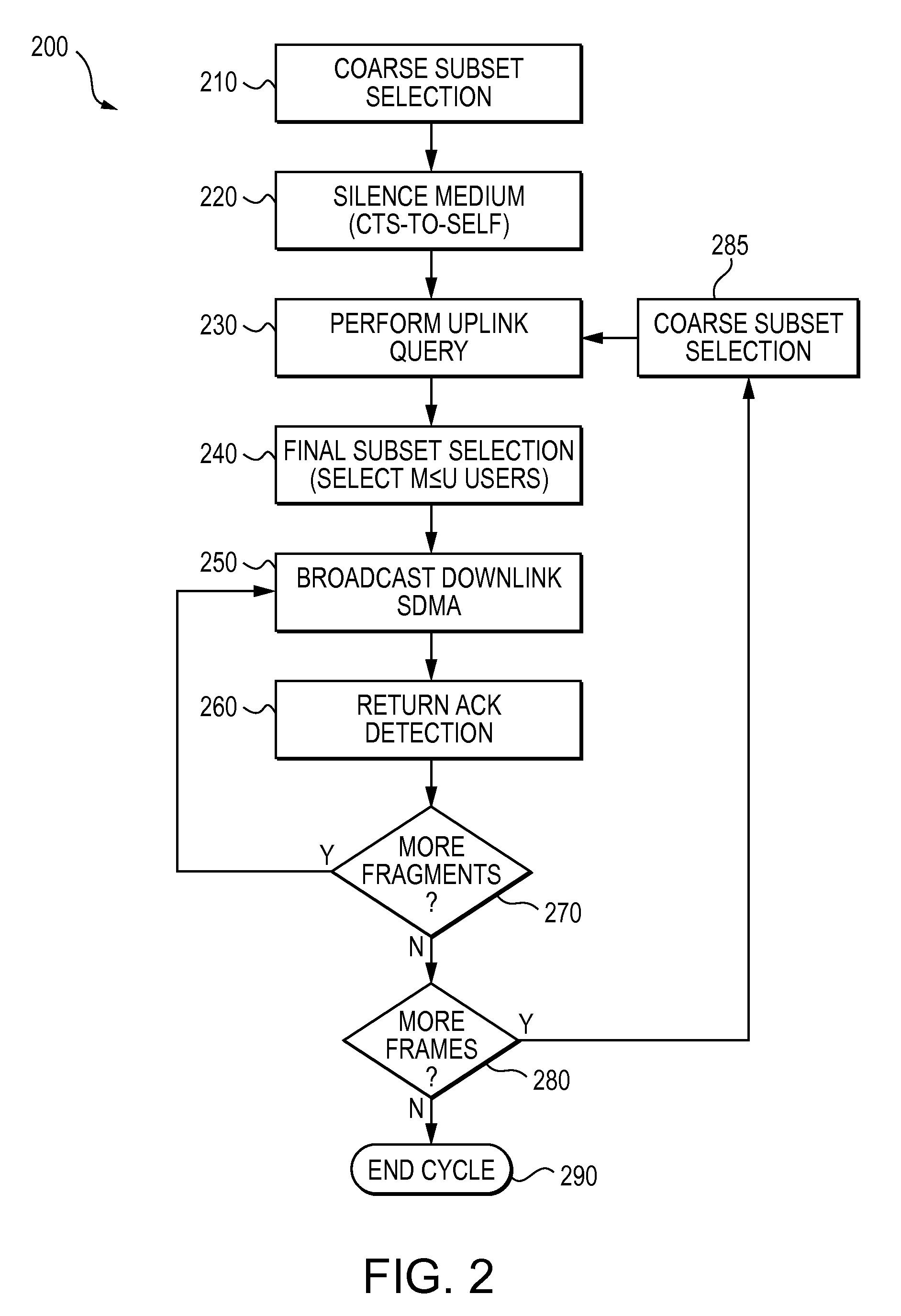
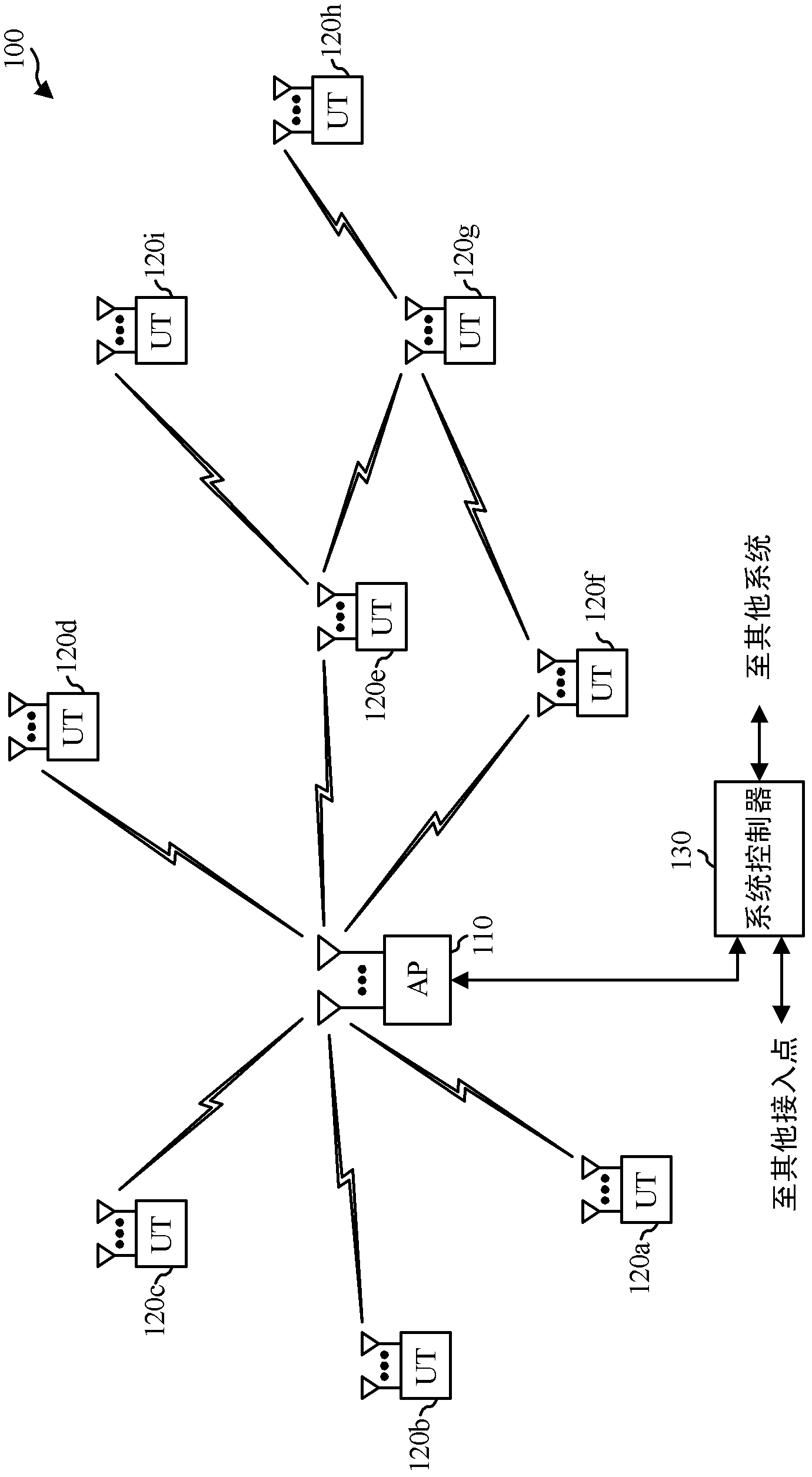
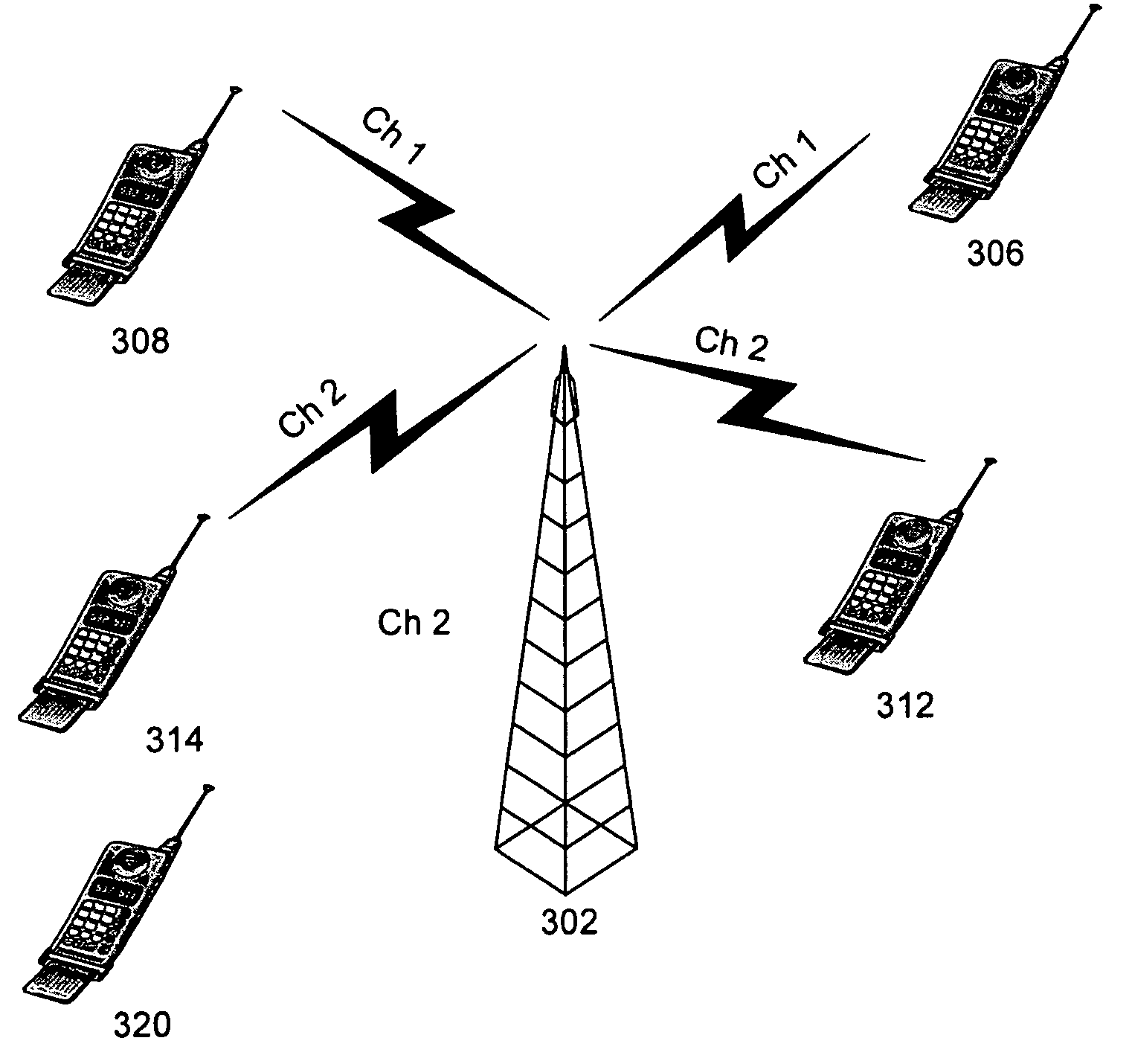
Method, apparatus and system of spatial division multiple access communication in a wireless local area network
InactiveUS20070153754A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesSpatial division multiple accessTelecommunications
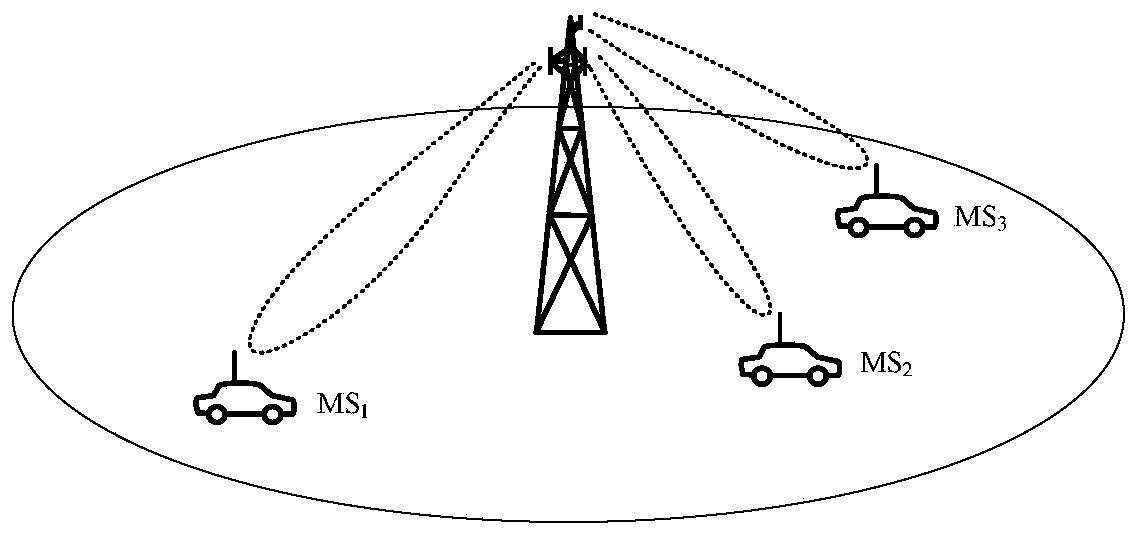
Some demonstrative embodiments of the invention include a method, apparatus, and system of performing simultaneous downlink transmission over a wireless medium to a plurality of wireless stations, using Spatial Division Multiple Access (SDMA) in a wireless local area network (WLAN). In one demonstrative embodiment of the invention, the method may include selecting a set of the plurality of wireless stations according to one or more ranking criteria; and reserving the wireless medium for a duration sufficient for completing the simultaneous downlink transmission to the wireless stations of the set. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:CELENO COMMUNICATIONS (ISRAEL) LTD
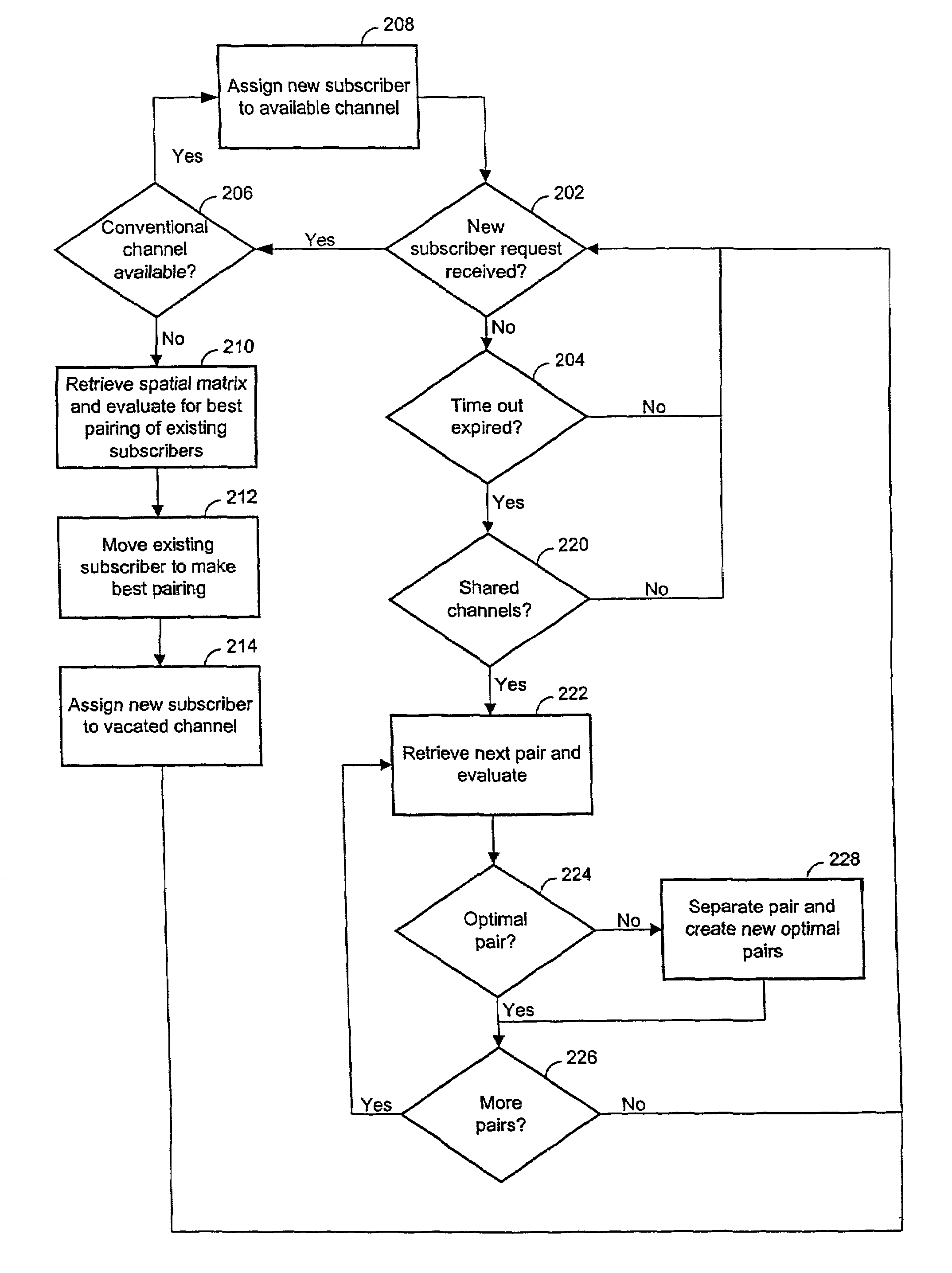
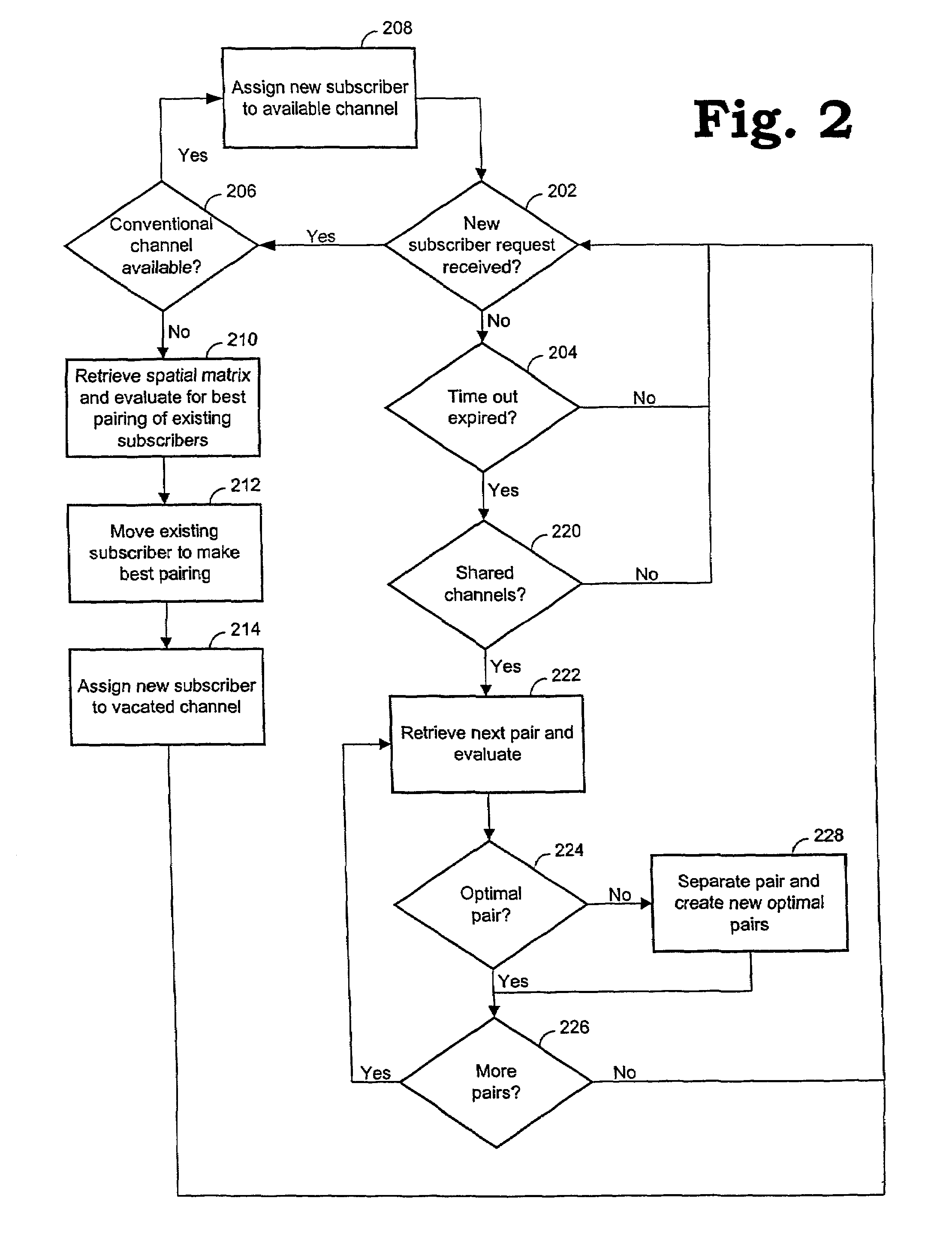
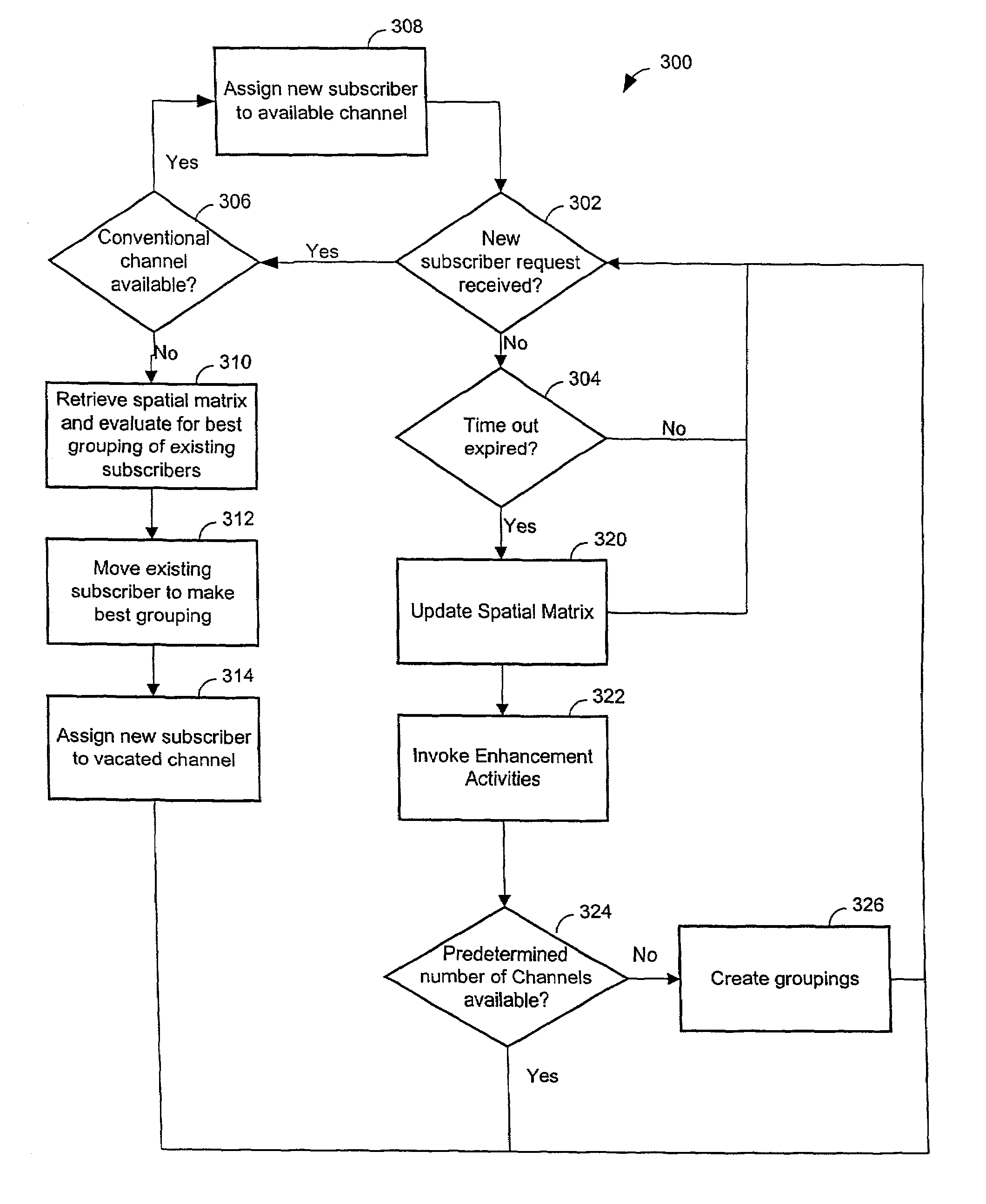
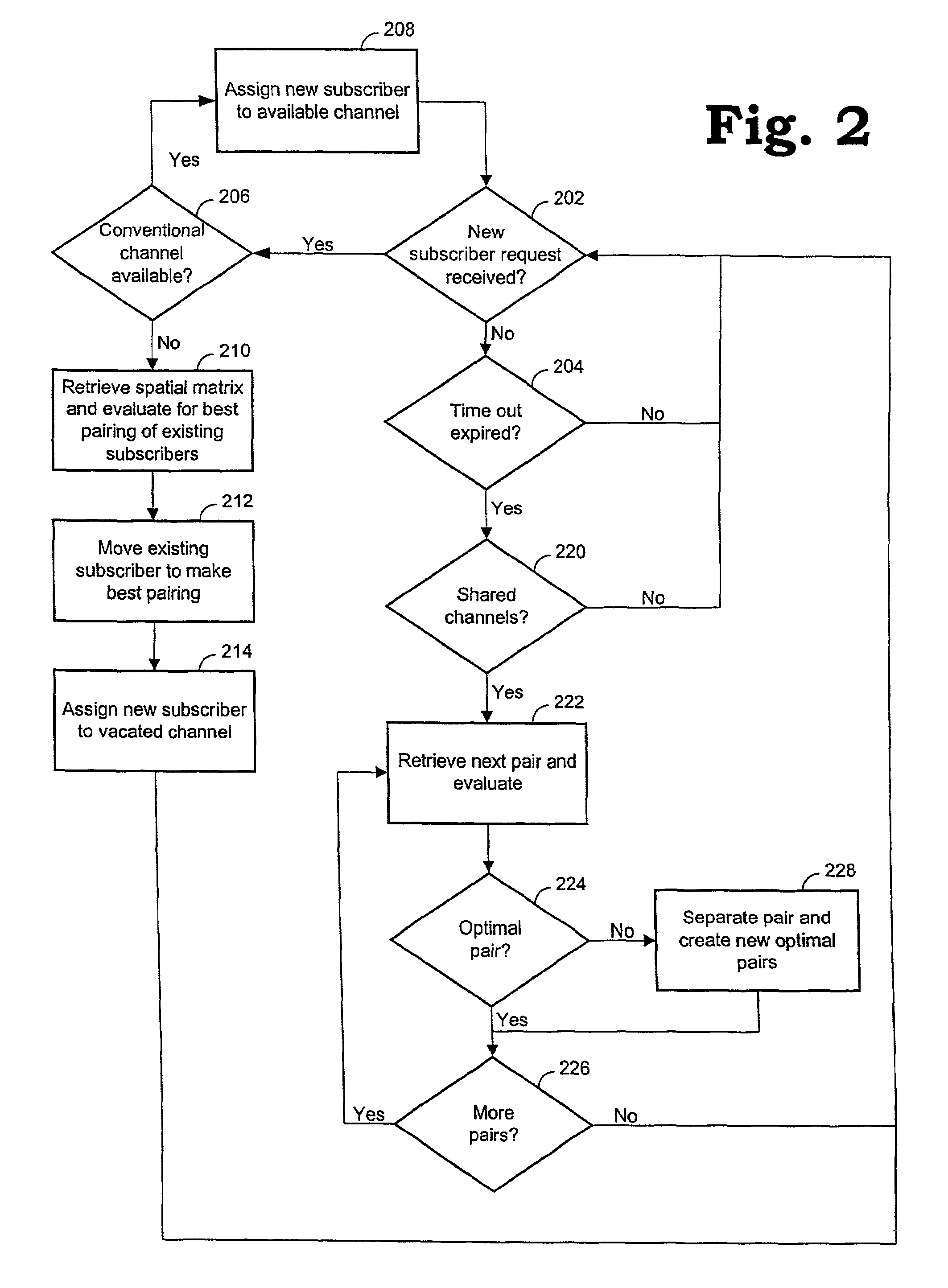
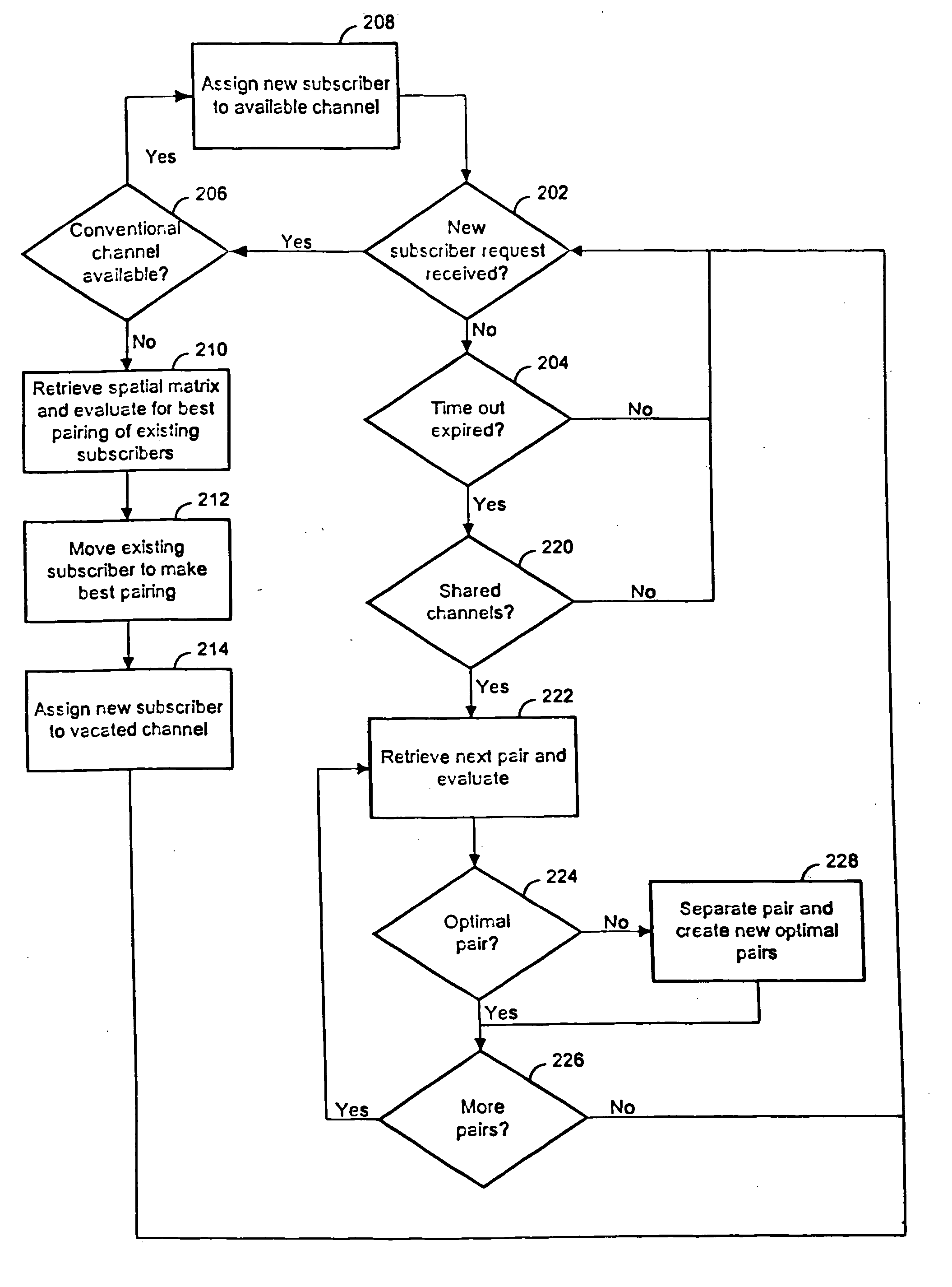
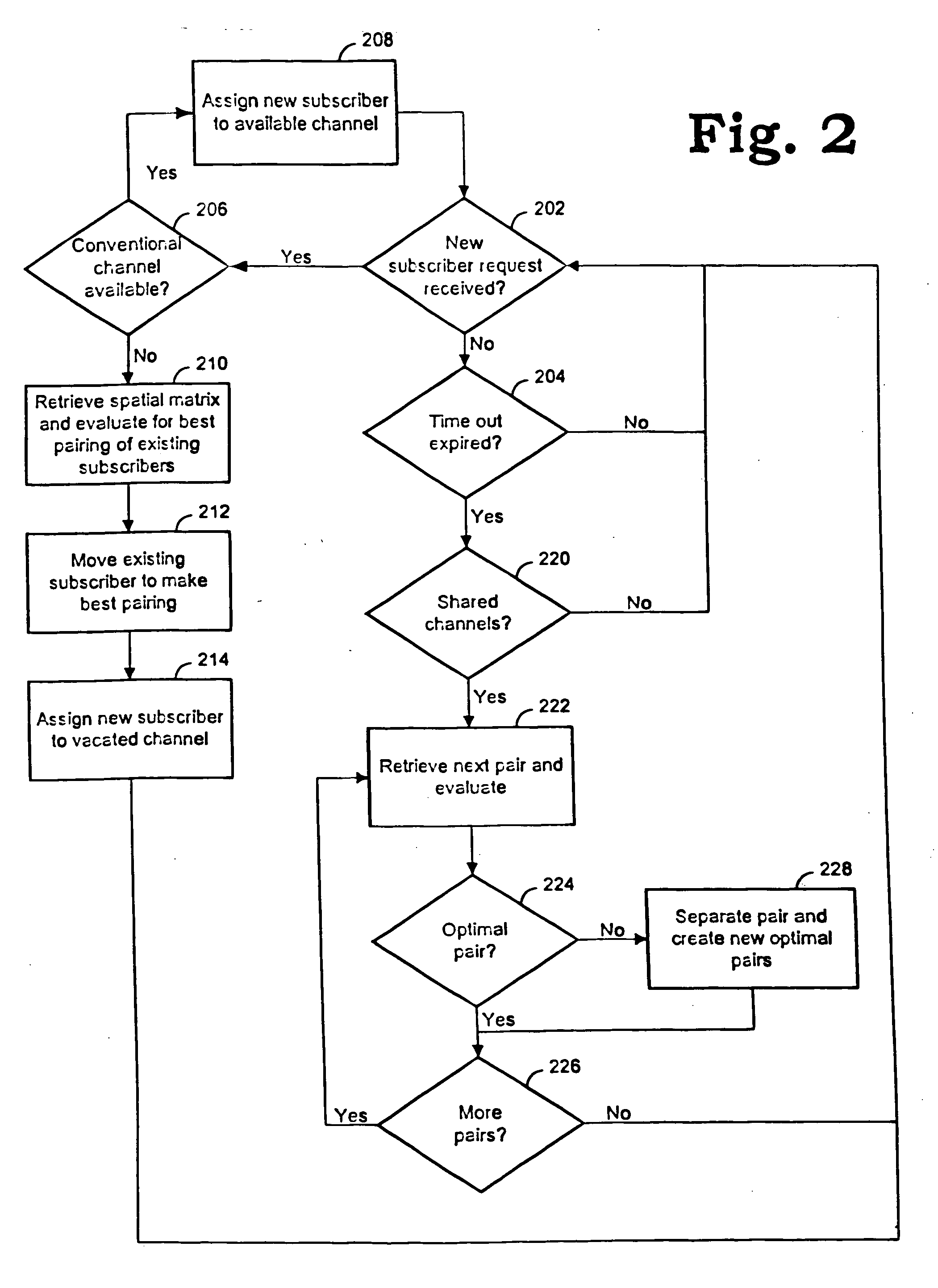
Channel assignments in a wireless communication system having spatial channels including grouping existing subscribers in anticipation of a new subscriber
InactiveUS6999771B1Easy retrievalEvaluate and manage risk in a wireless communication systemMultiplex communicationBroadcast service distributionSpatial division multiple accessCommunications system
Methods and systems are provided for assigning channels in a spatial division multiple access communication network. The network includes a plurality of conventional channels some of which are configurable to be shared concurrently by plural subscribers. The method includes determining combinations of subscribers from the existing subscribers. Existing subscribers are reassigned to share channels thereby freeing resources for new subscribers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method, apparatus and system of spatial division multiple access communication in a wireless local area network
ActiveUS20110182277A1Synchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsSpatial division multiple access
Some demonstrative embodiments of the invention include a method, apparatus for concurrently transmitting data to two or more wireless stations.
Owner:CELENO COMMUNICATIONS (ISRAEL) LTD
Channel assignments in a wireless communication system having spatial channels including enhancements in anticipation of new subscriber requests
InactiveUS6965774B1Easy retrievalFree spaceNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSpatial division multiple accessCommunications system
Methods and systems are provided for assigning channels in a spatial division multiple access communication network. The network includes a plurality of conventional channels some of which are configurable to be shared concurrently by plural subscribers. The method includes determining combinations of subscribers from the existing subscribers. Enhancement activities are invoked to create optimal combinations of existing subscribers. Existing subscribers are reassigned as necessary to share channels thereby freeing resources for new subscribers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
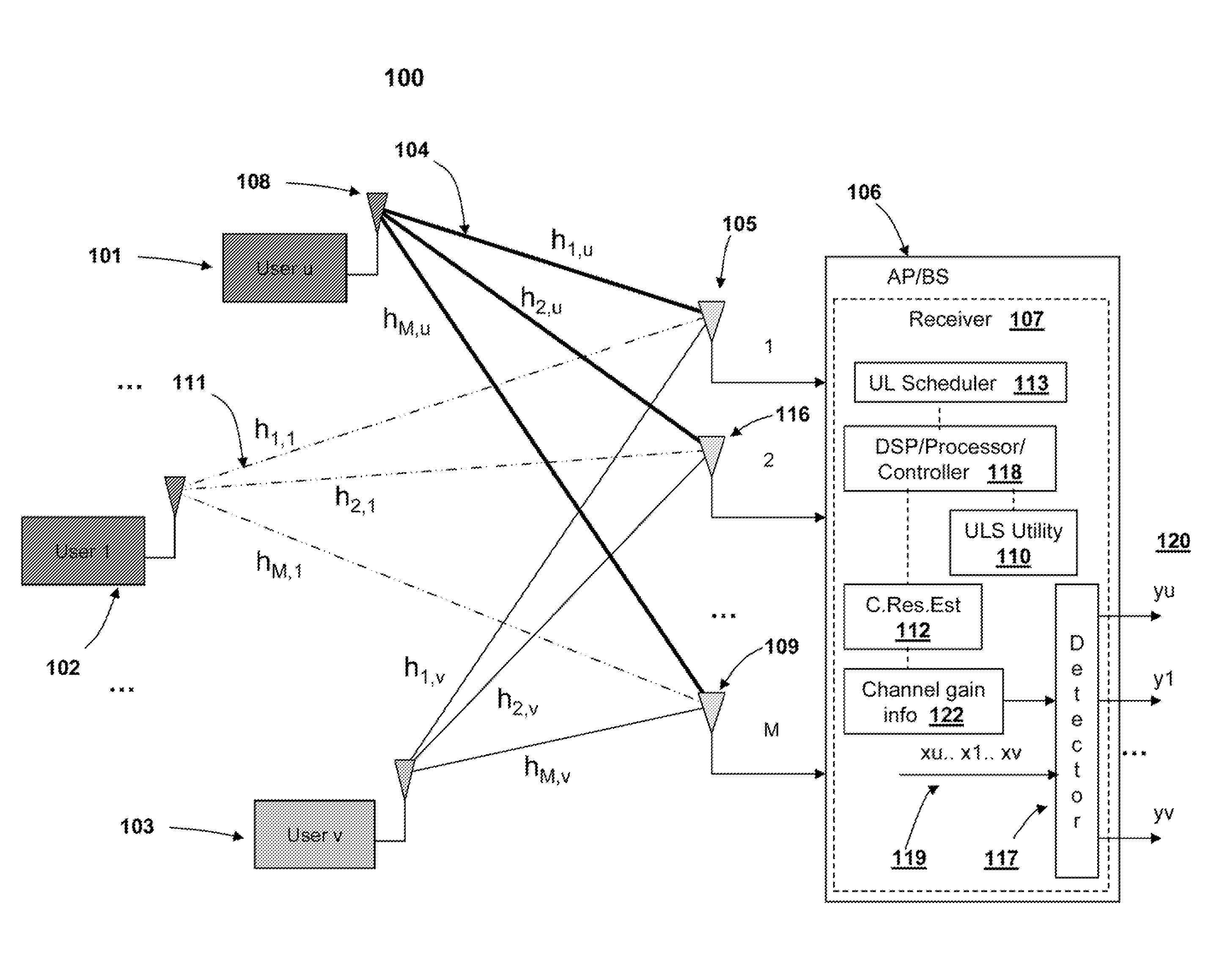
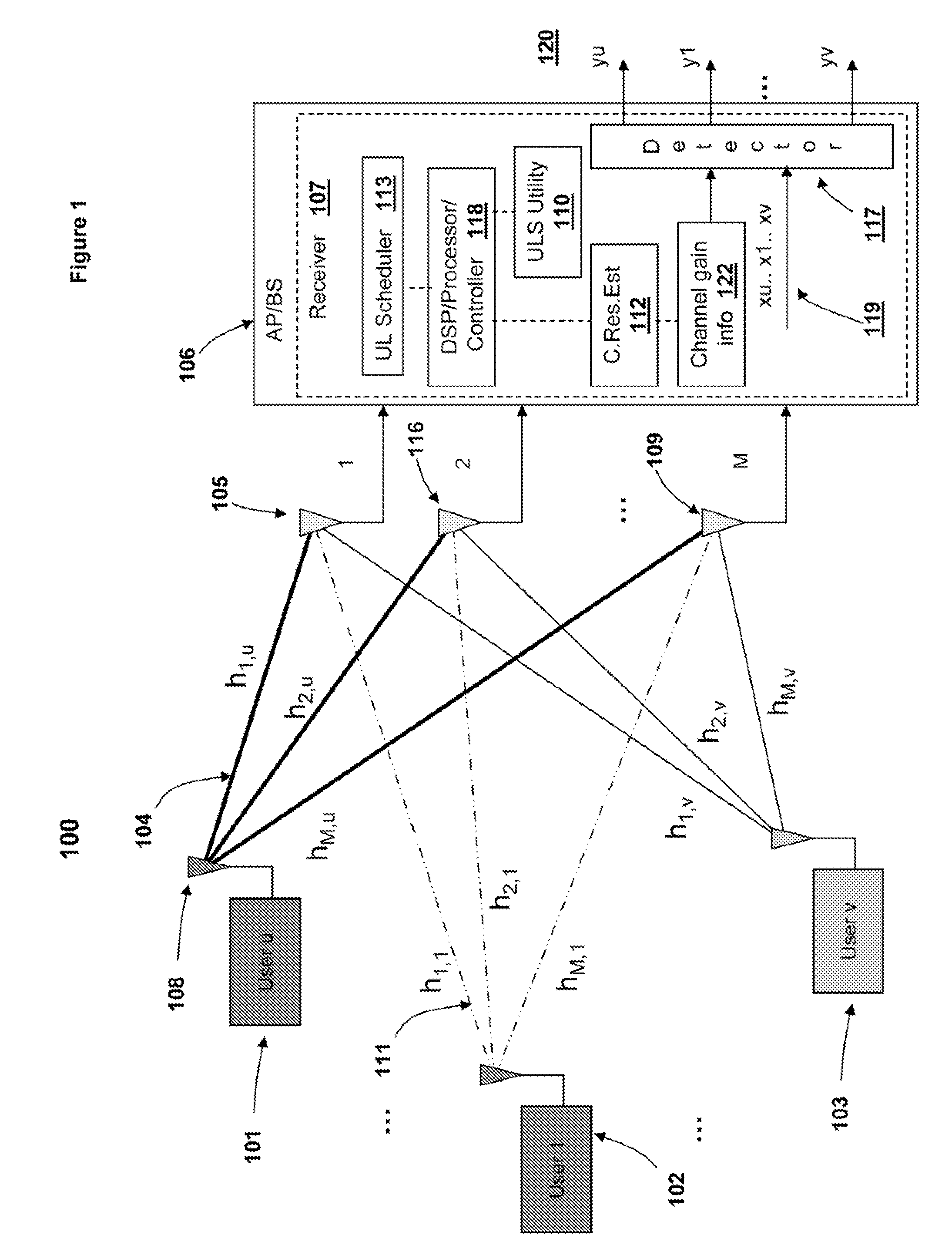
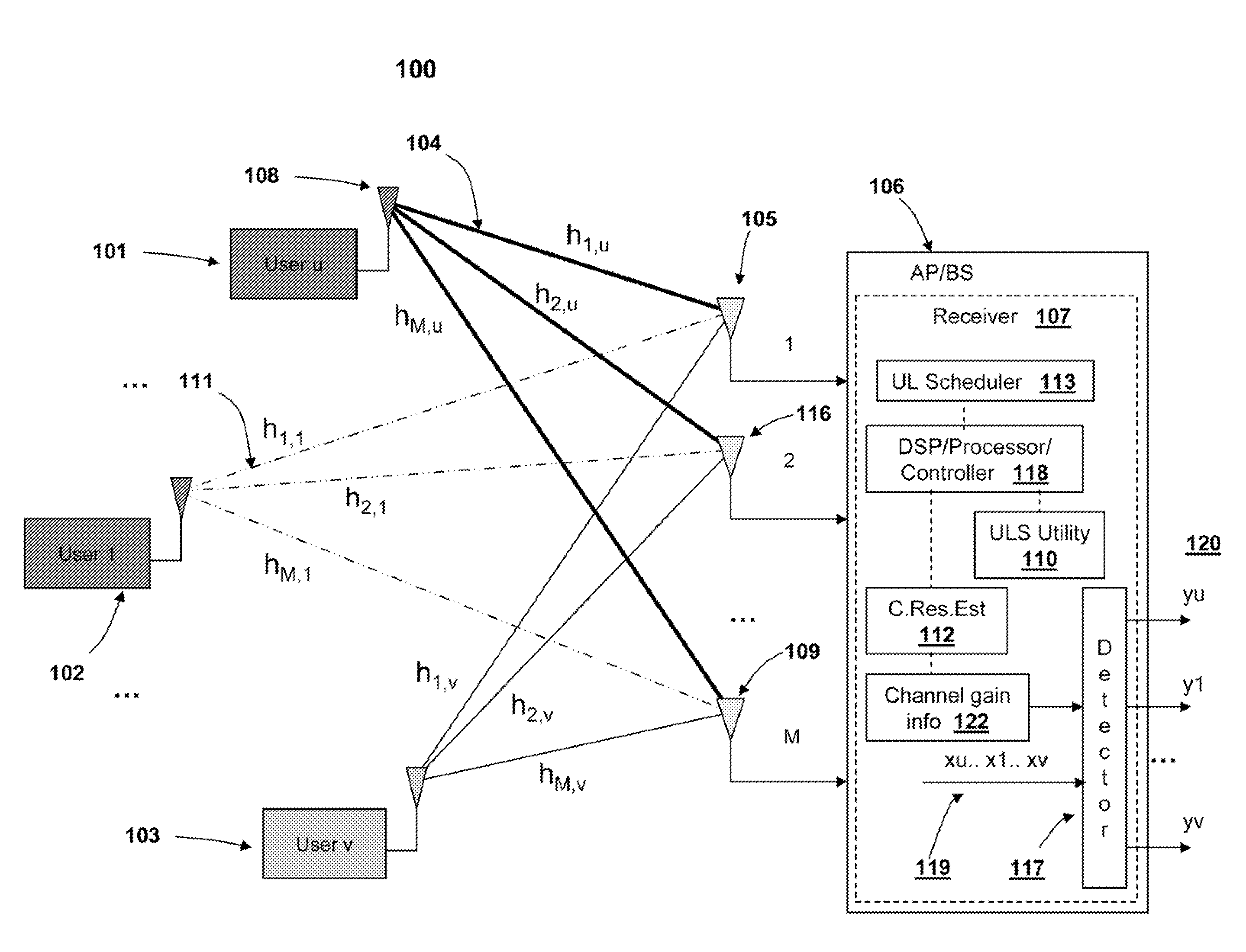
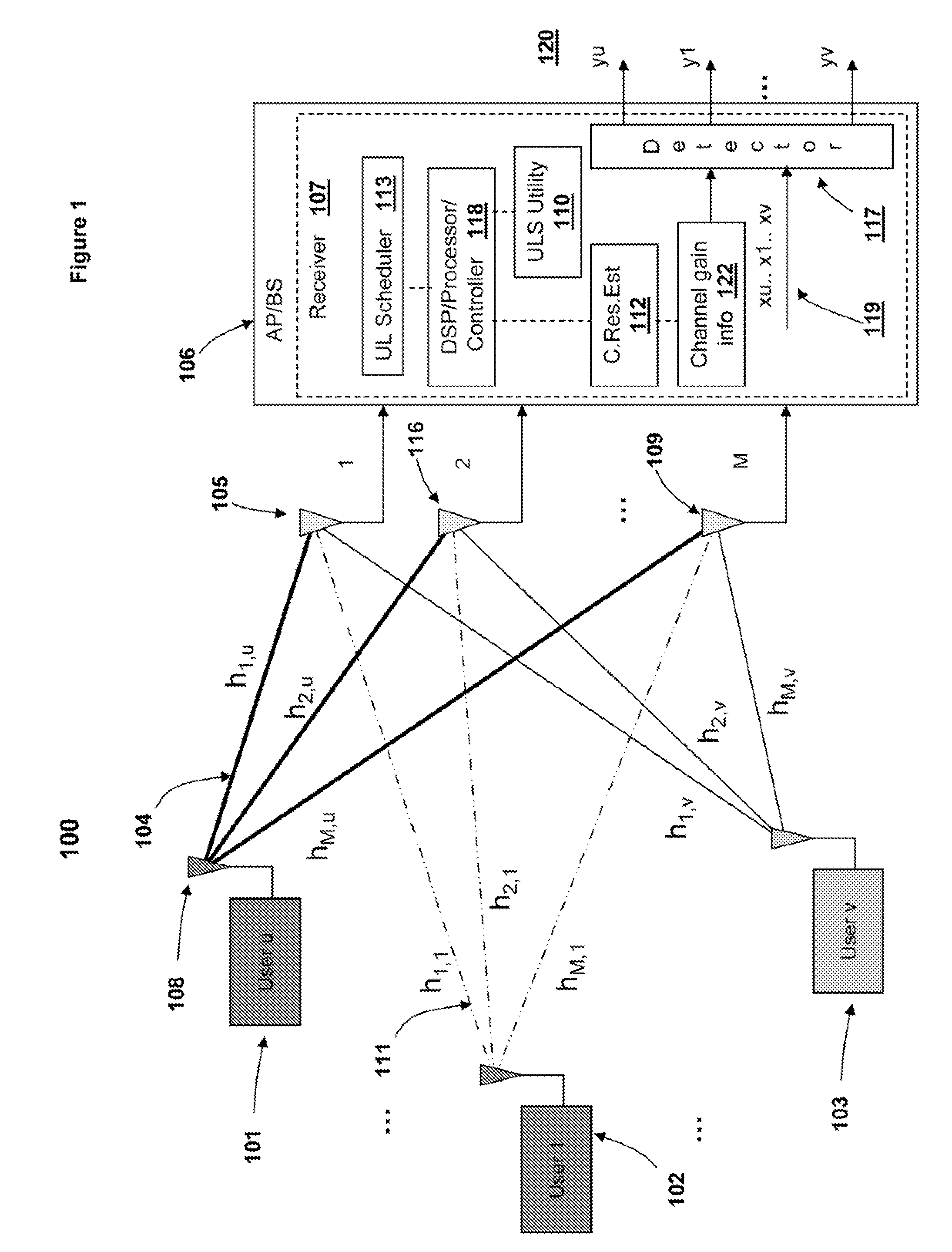
Uplink spatial division multiple access (SDMA) user pairing and scheduling
InactiveUS20100029288A1Substation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDecompositionCovariance
A method, system and communication network for transmitting information signals via uplink (UL) collaborative SDMA, in a wireless communication system. Base station receiver estimates a channel gain associated with the transmission path(s) of each user and keeps a matrix of normalized covariance, between users. Based on the estimated channel gain and the normalized covariance, ULS utility is able to compute channel capacity. Based on capacity estimates of (1) the multiplexed user signals and (2) the individual user signals, signals are either multiplexed for UL SDMA or are transmitted individually. An optimal selection of multiplexed signals may be based upon: (1) a cross user interface measurement; and (2) a selection mechanism based on eigen-decomposition techniques. The ULS utility enables a UL scheduler to pair information signals with clear spatial distinction and minimal correlation, based on capacity evaluations.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
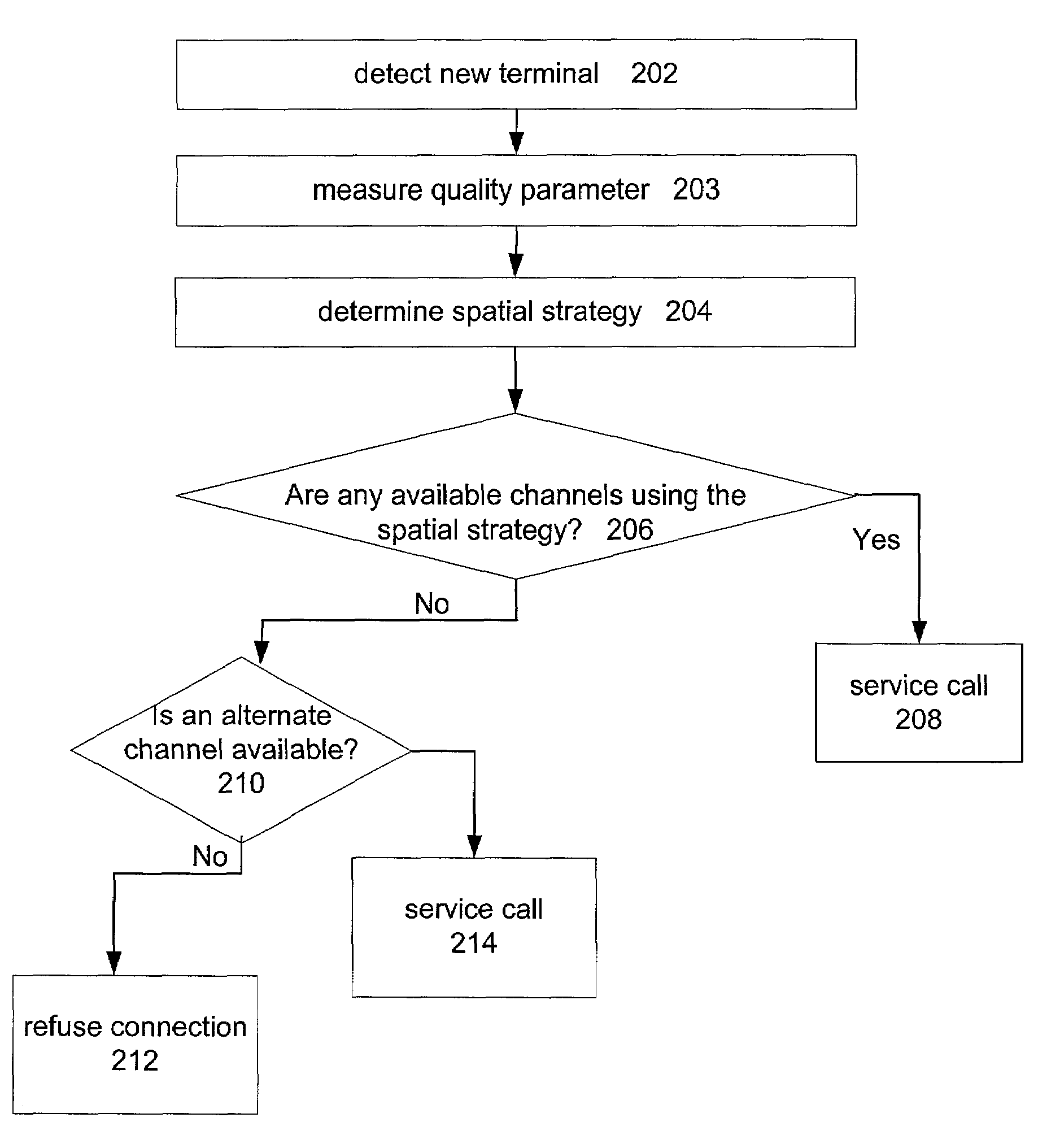
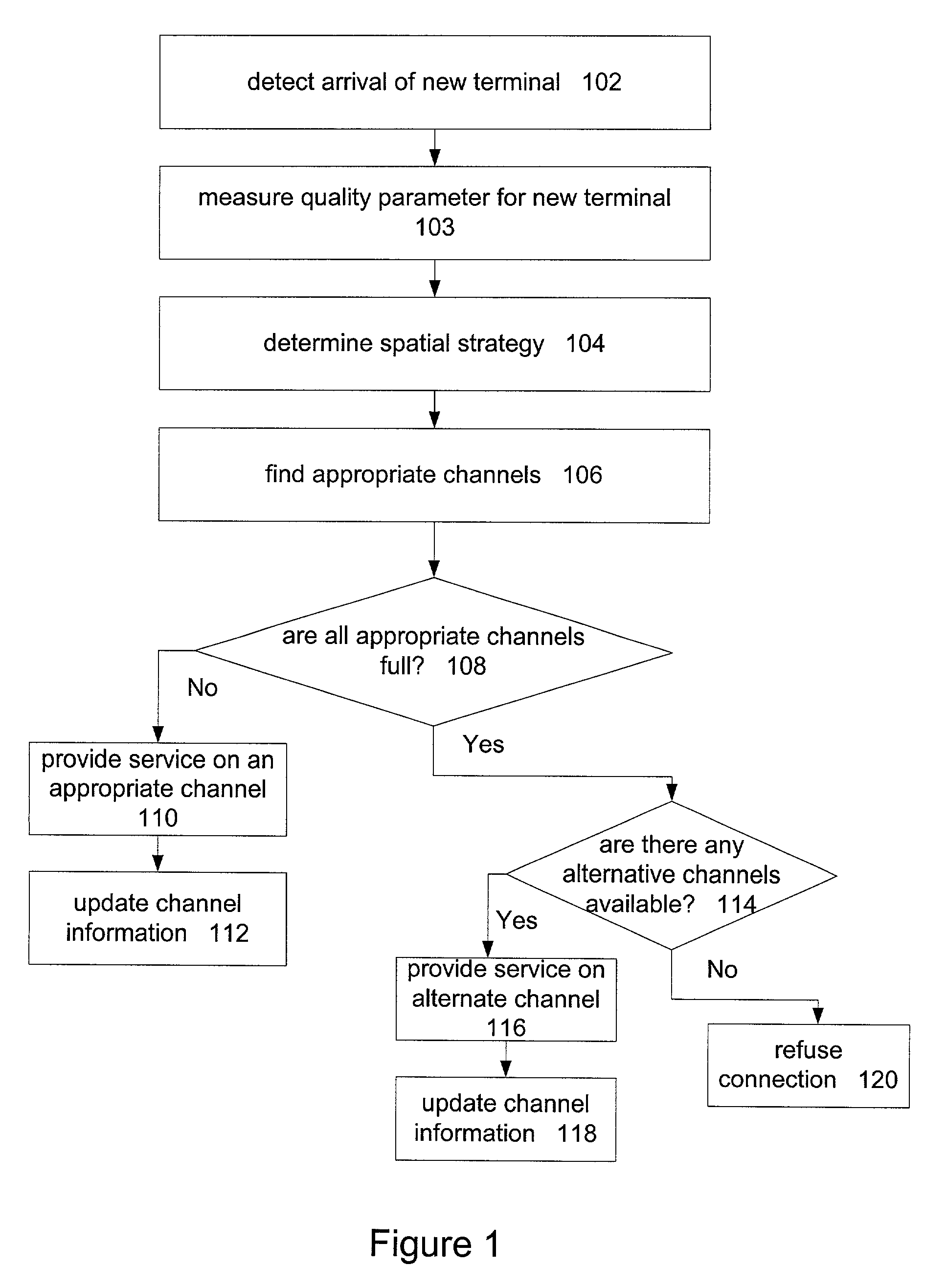
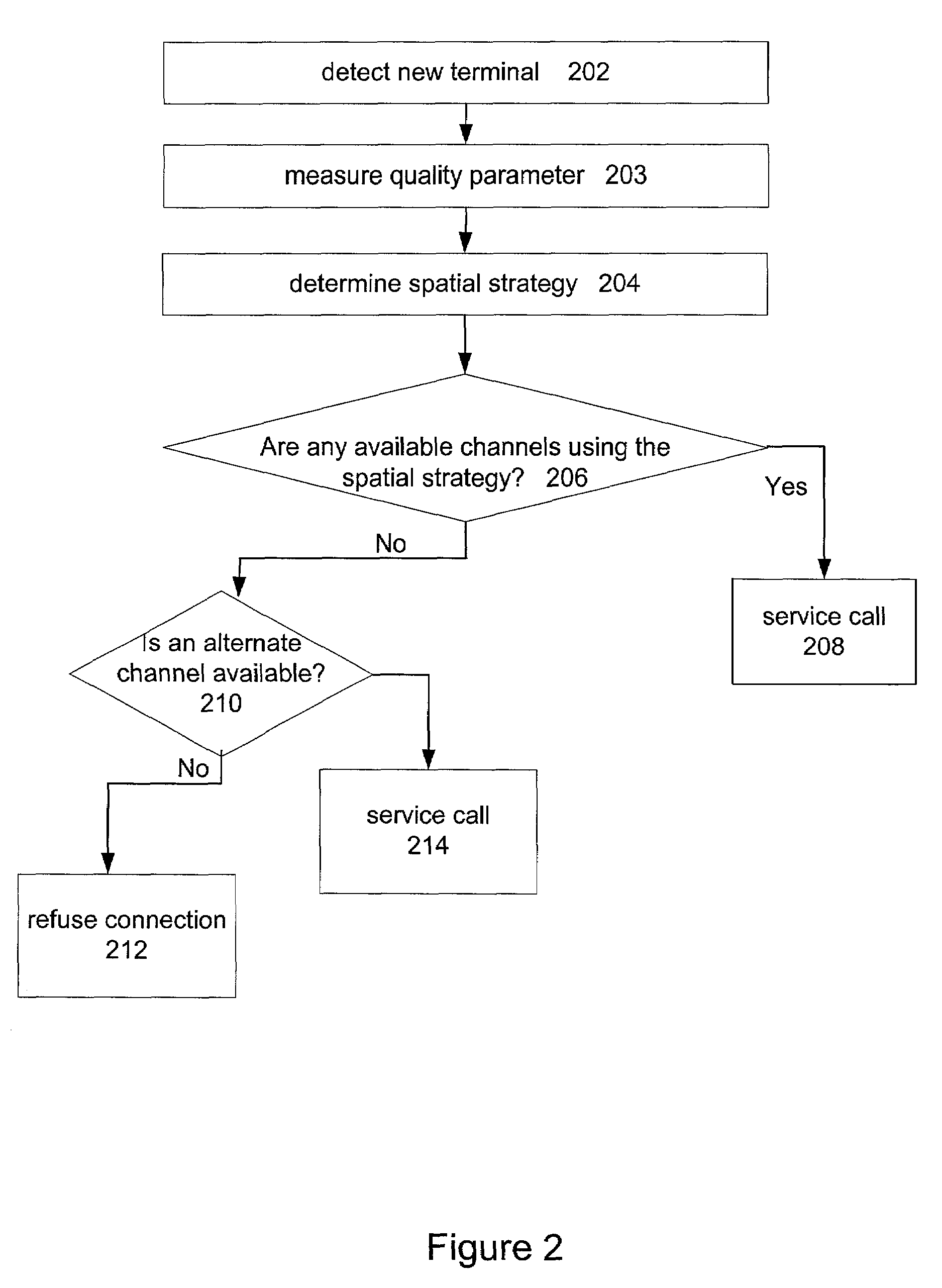
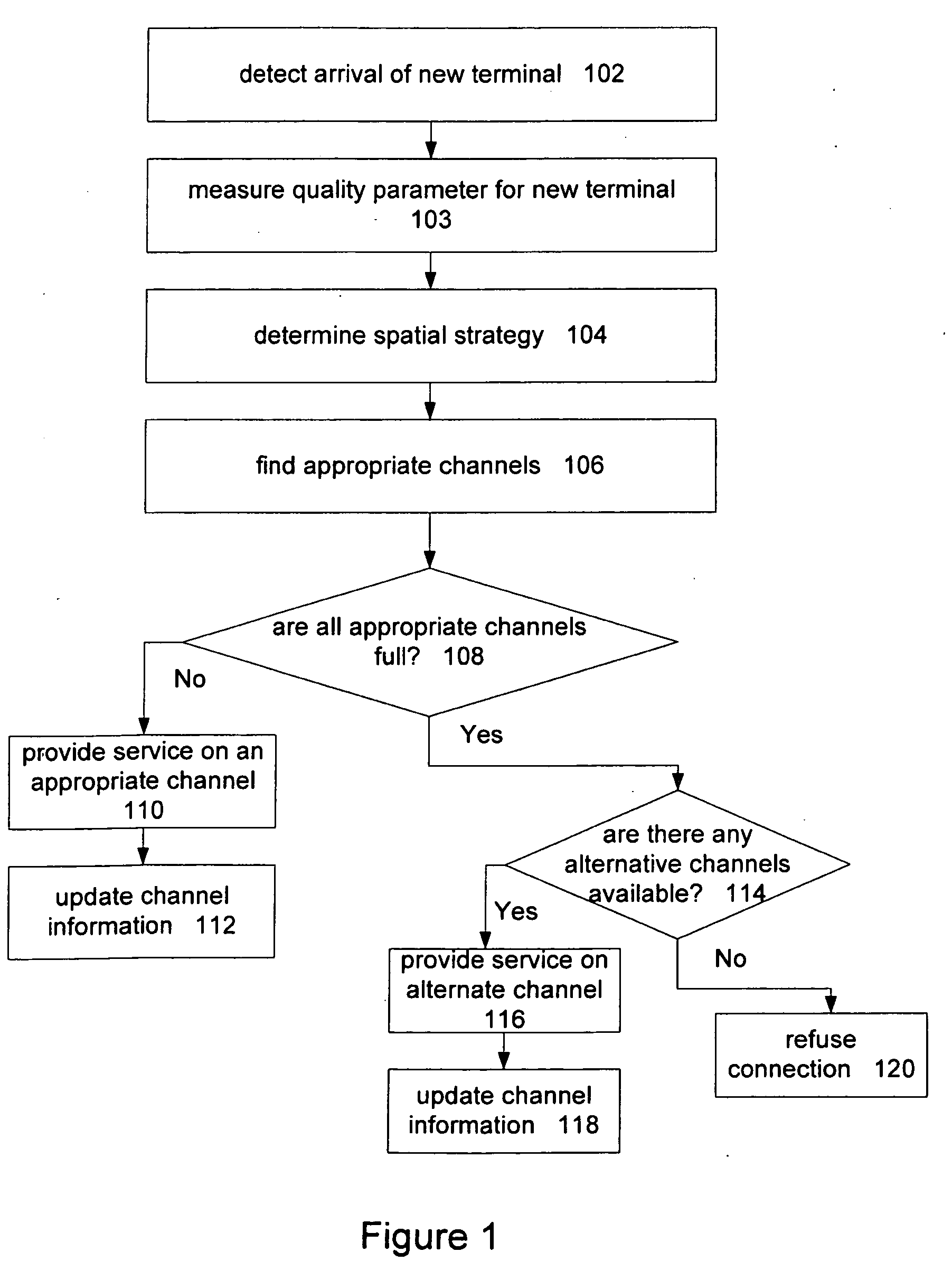
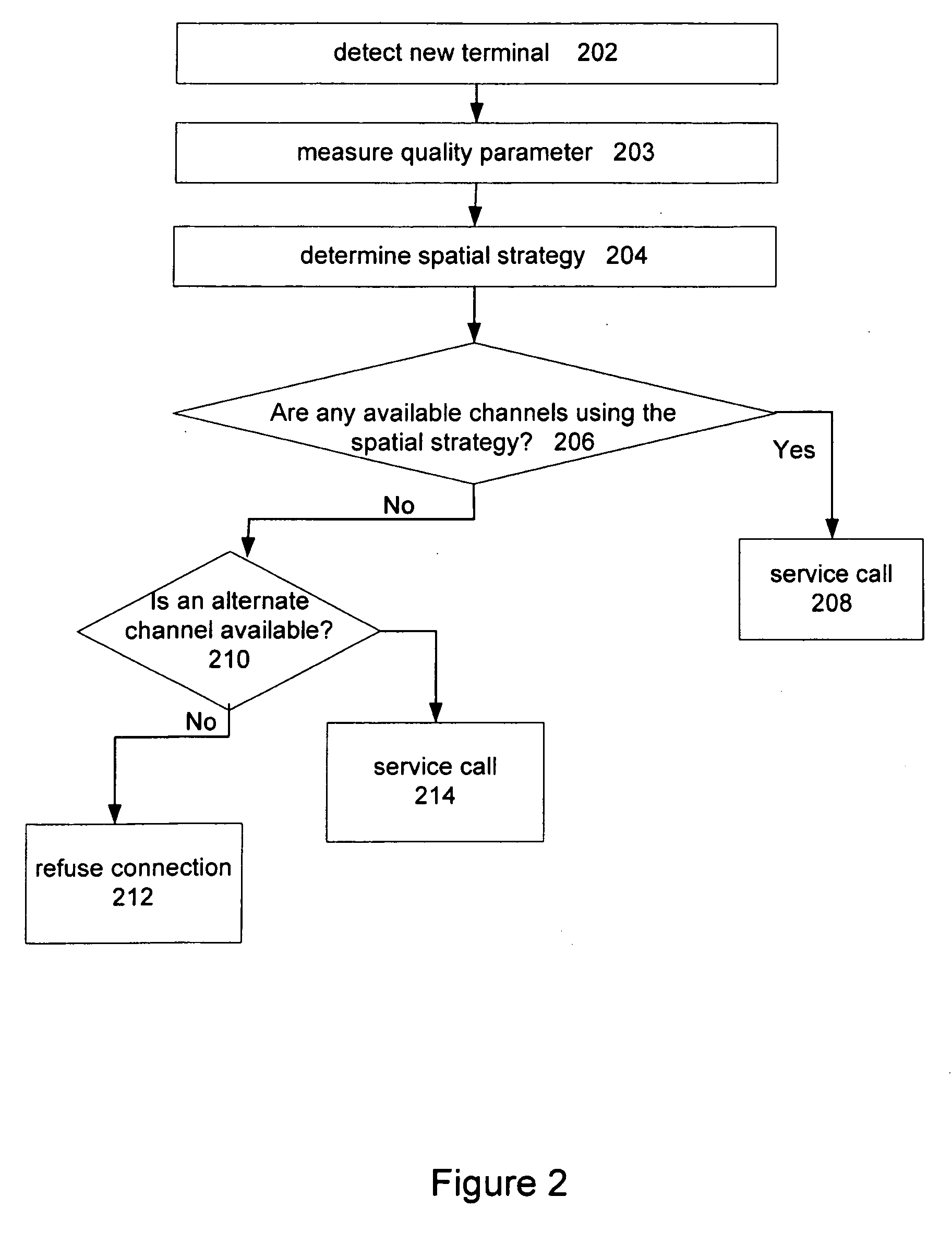
Channel assignment based on spatial strategies in a wireless network using adaptive antenna arrays
InactiveUS7539496B1Improve efficiencyRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringRadio networksWireless mesh network
The present invention can improve efficiency in wireless radio networks using spatial division multiple access (SDMA) strategies. One embodiment of the invention includes determining a quality parameter of a user terminal based on a signal received from the user terminal at a base station. One embodiment further includes determining a co-spatial constraint on the user terminal based on the quality parameter, the co-spatial constraint comprising a limitation on the quantity of additional user terminals with which the user terminal can share a conventional communications channel.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods and apparatuses for scheduling uplink request spatial division multiple access (rsdma) messages in an sdma capable wireless lan
InactiveCN102334374ANetwork topologiesRadio transmissionSpatial division multiple accessTelecommunications
An apparatus for scheduling uplink request spatial division multiple access (RSDMA) messages in an SDMA capable wireless LAN (304), including a processing system configured to receive requests for a spatial division multiplexed transmission from a plurality of nodes over a multiple access medium (312-1, 312-2, 312-3); and initiate the spatial division multiplexed transmission based on a metric related to one or more of the nodes (308), is disclosed. Another apparatus for wireless communications, including a processing system configured to generate data belonging to an access class having contention parameters; and precode at least a portion of the data for transmission over a spatial stream and enter into post backoff following the spatial stream transmission, is also disclosed. Methods for using the apparatuses are also disclosed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
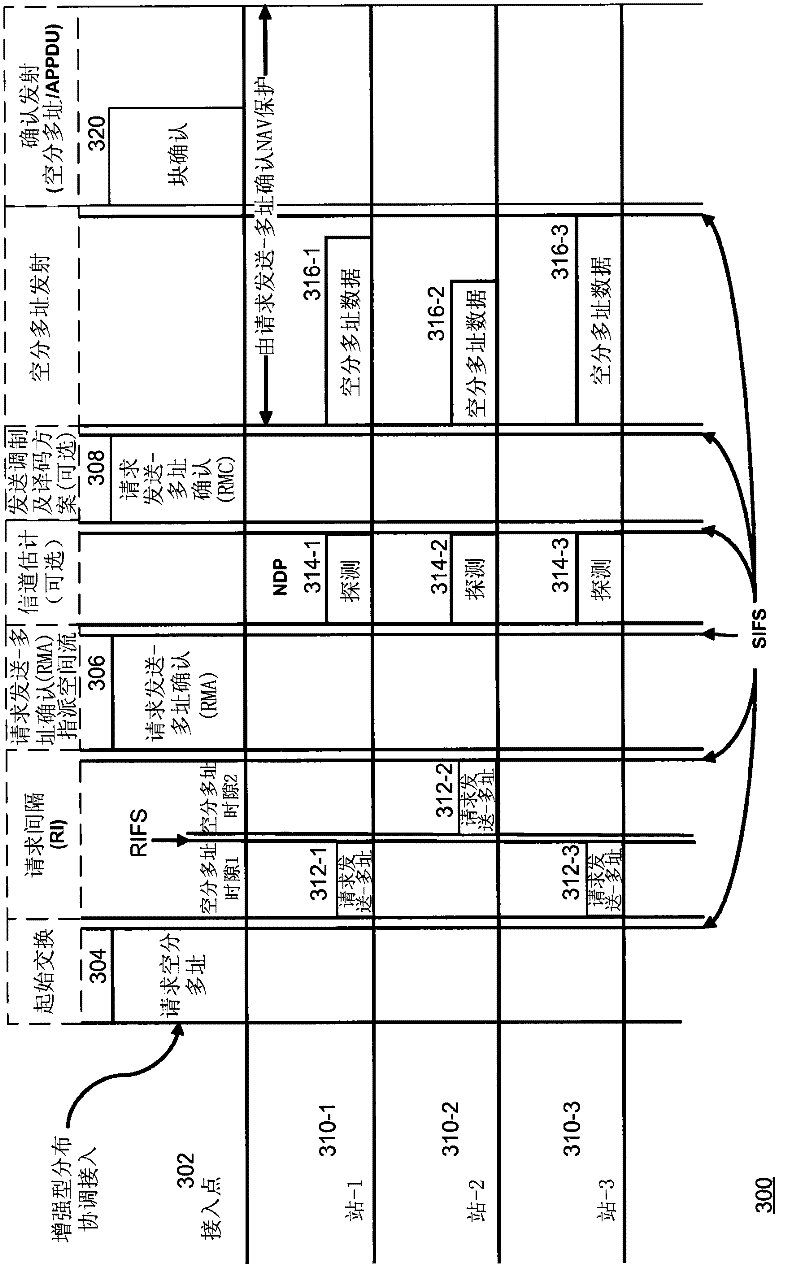
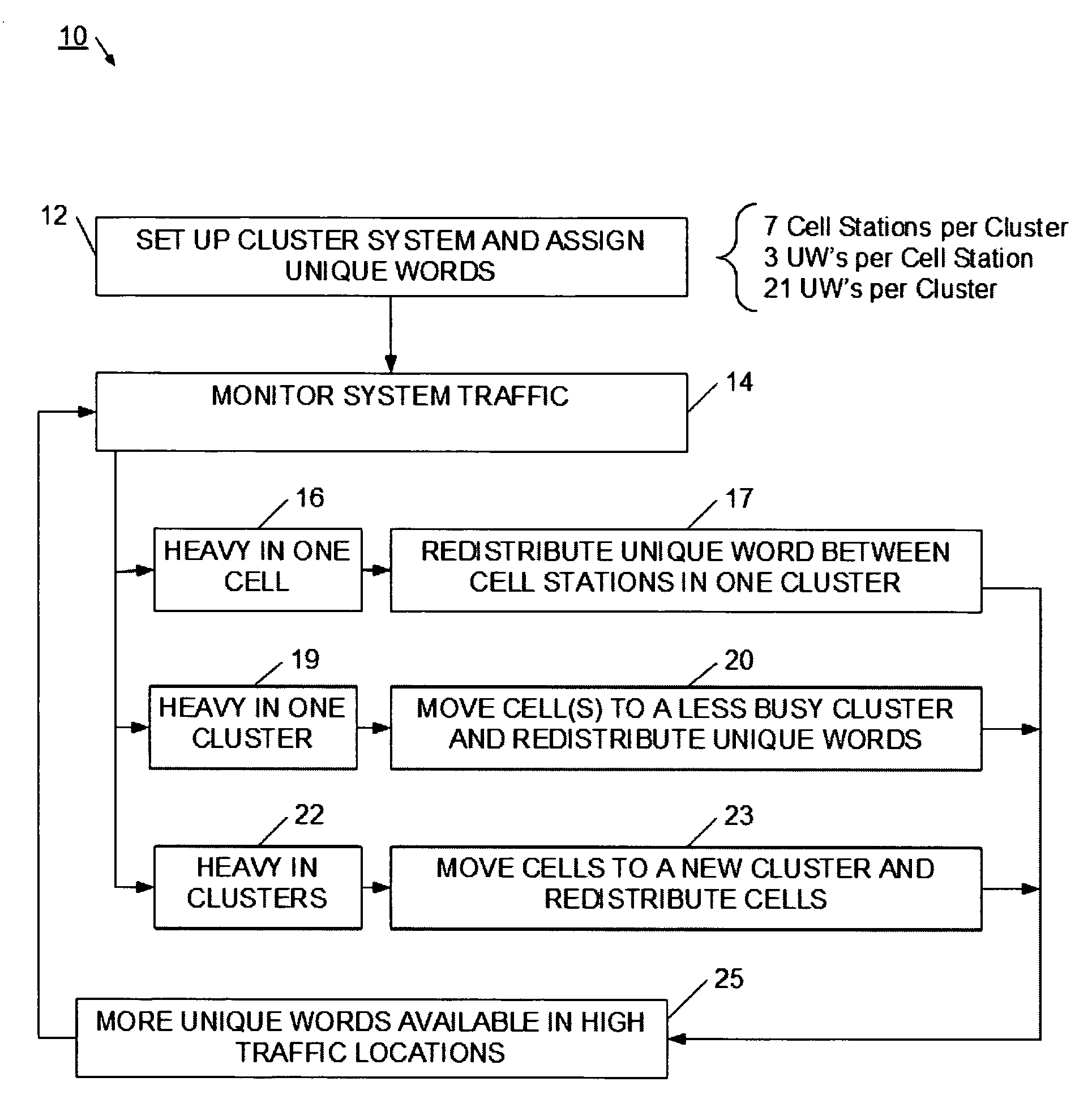
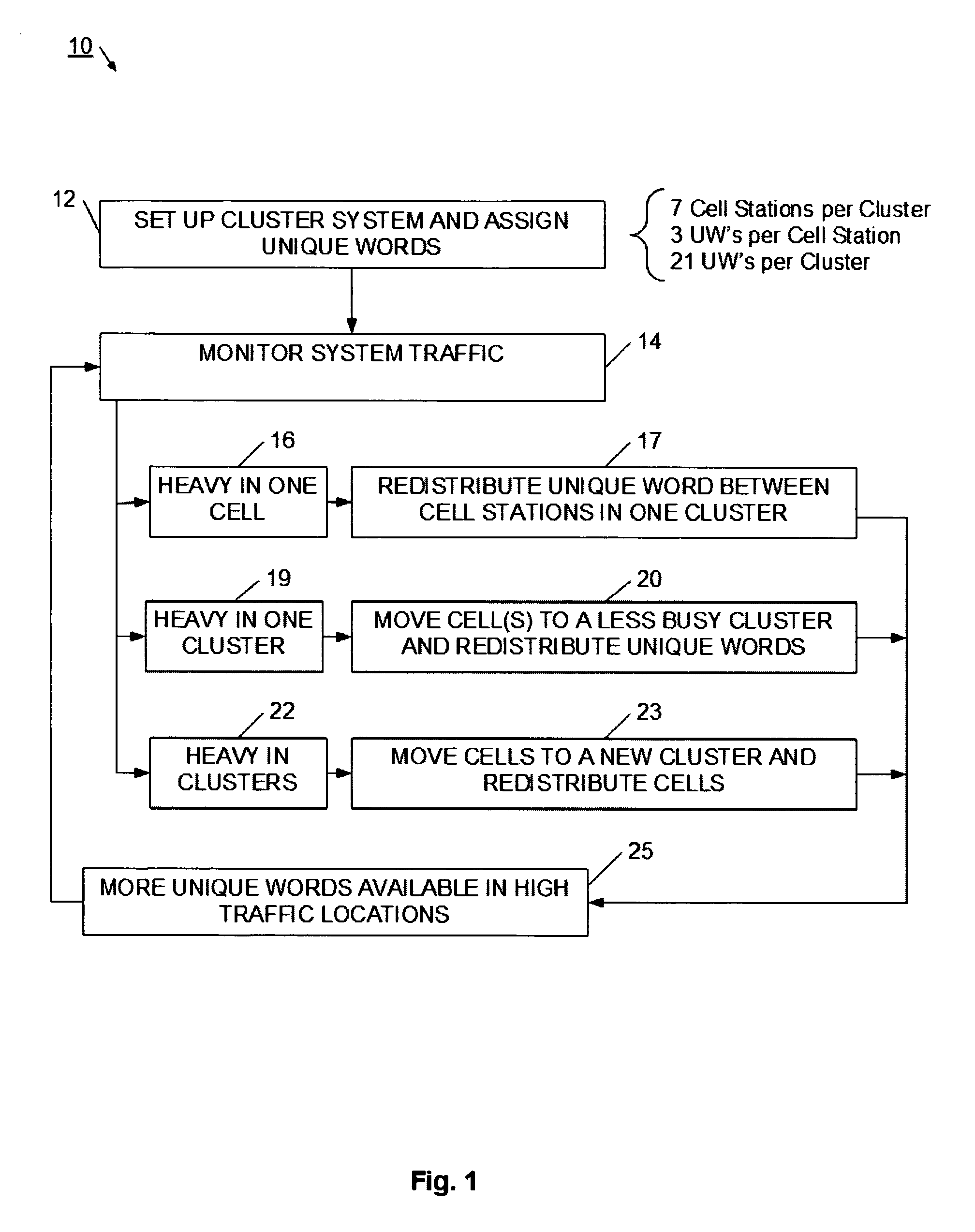
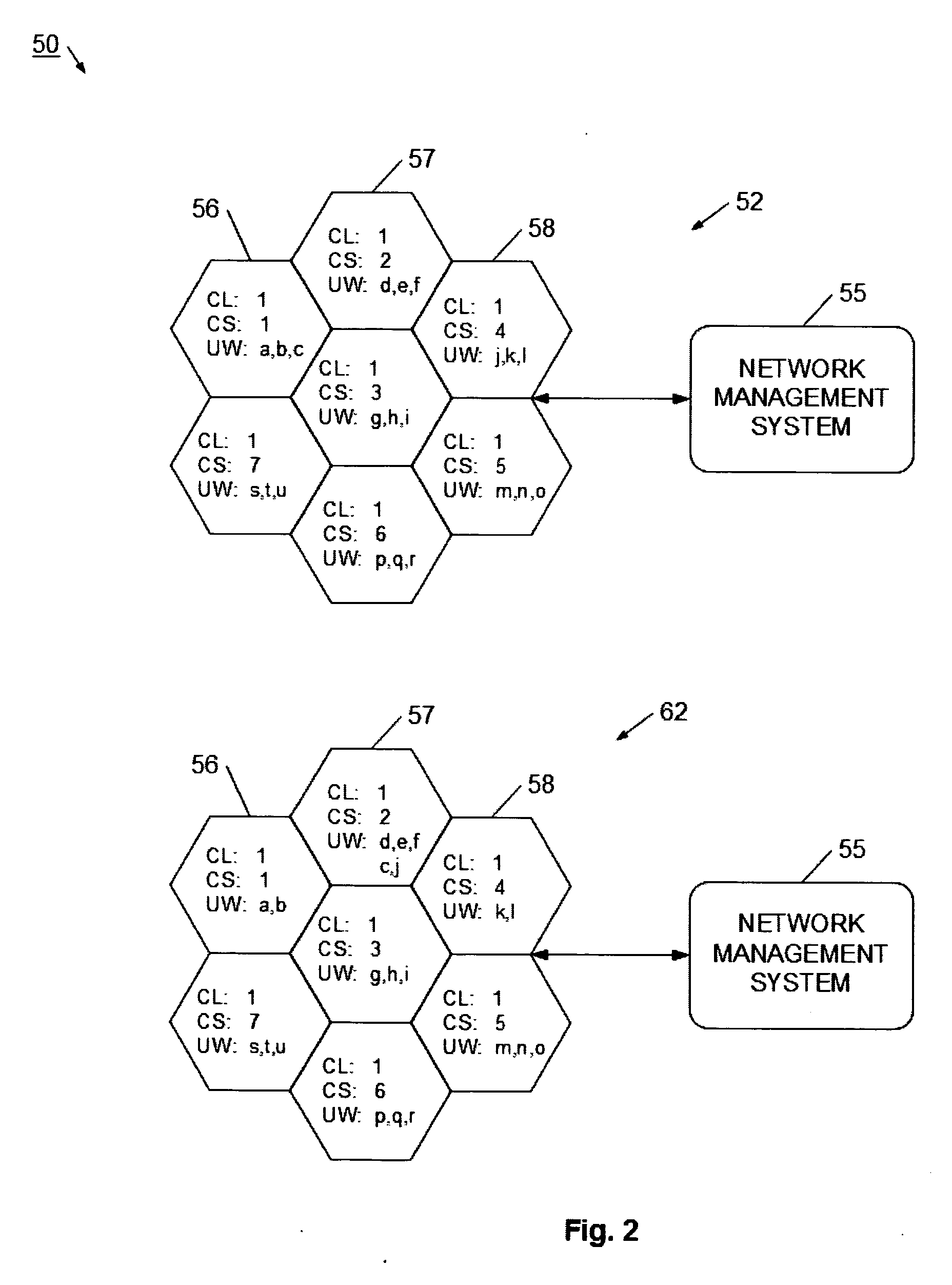
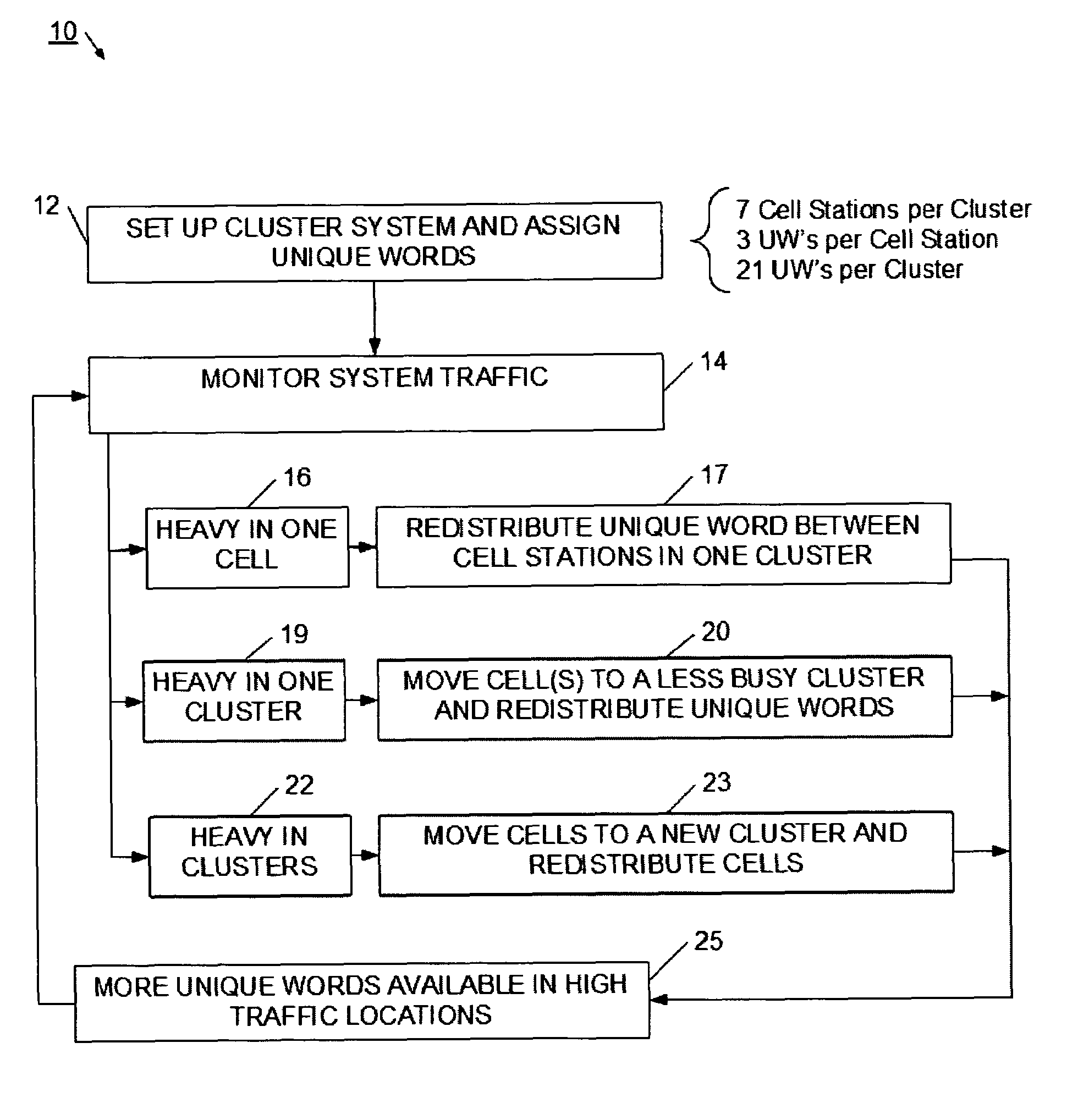
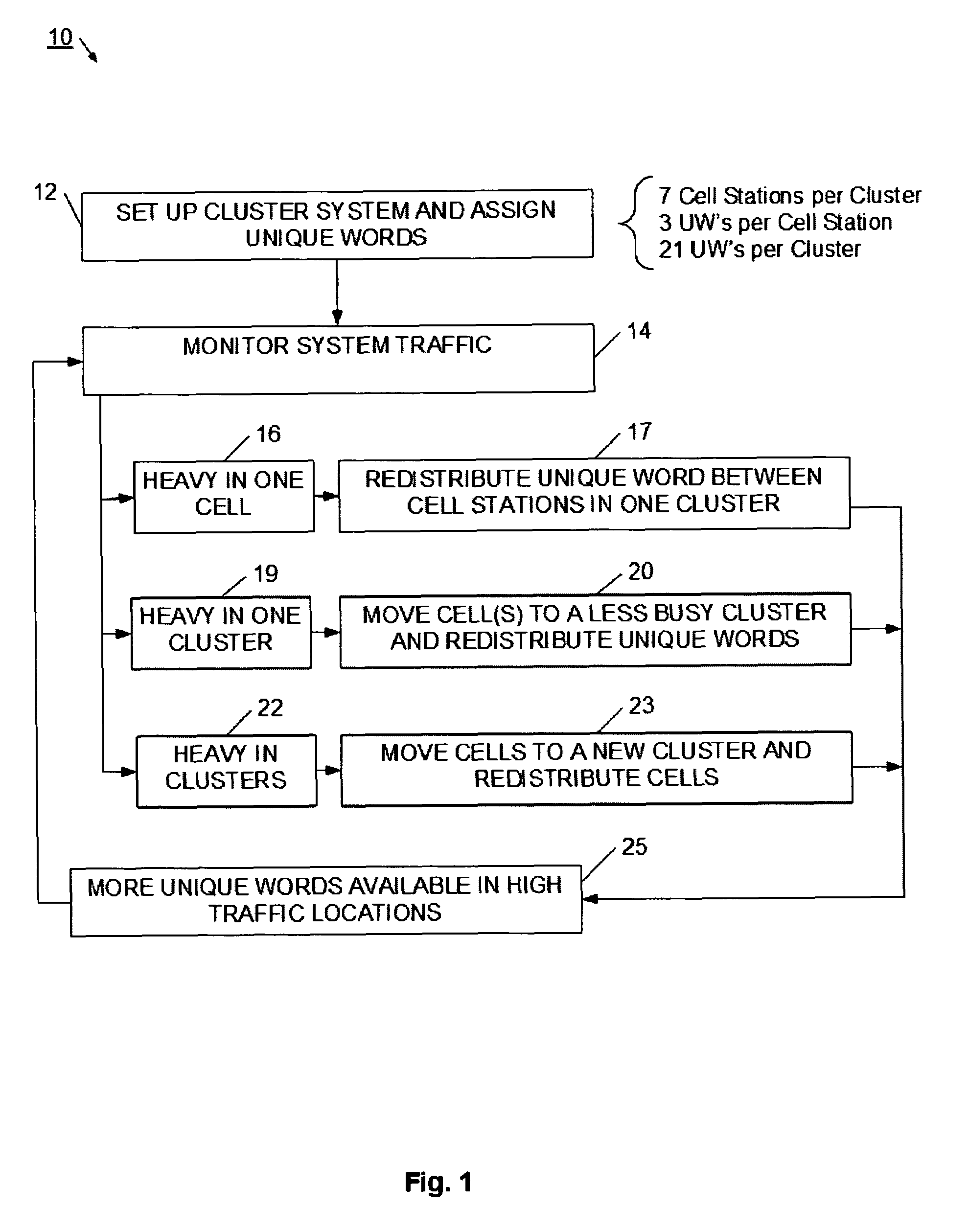
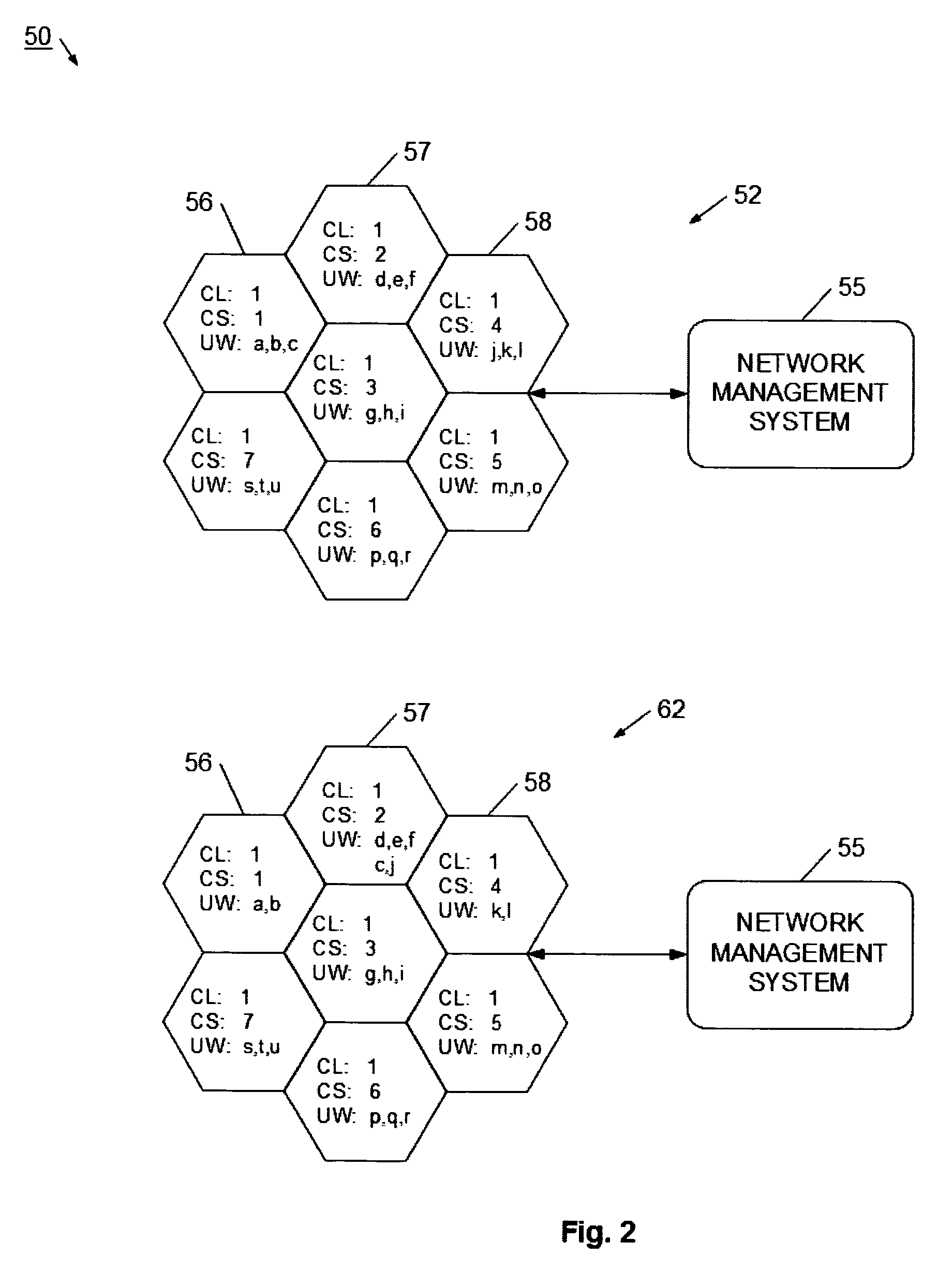
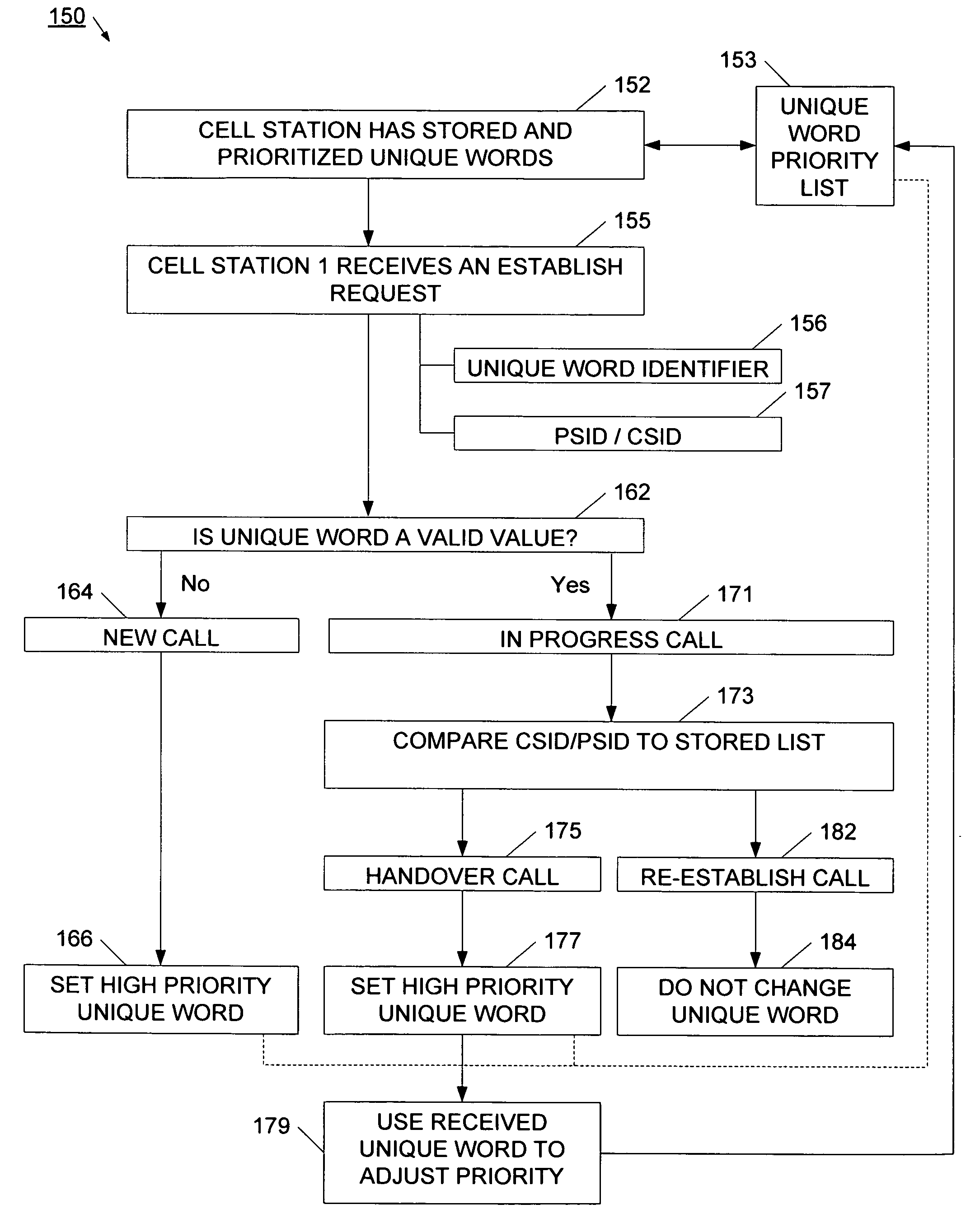
System and method for adaptive assignment of unique words in a communication system
InactiveUS20070173258A1Heavy communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionCommunications systemSpatial division multiple access
A method and system for assigning unique words in an SDMA (spatial division multiple access) communication system is provided. A network management system logically arranges cell stations into clusters of stations, and monitors for a heavy traffic condition. Responsive to determining that a heavy traffic condition exists, the network management system may 1) redistribute unique words within a single cluster; 2) move one or more cell stations from a busy cluster to a less busy cluster; or 3) create a new cluster, and move cells from one or more busy cluster into the new cluster. In this way, the communication system continually adapts so that more unique words are made available at cell stations having heavier communication demands.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
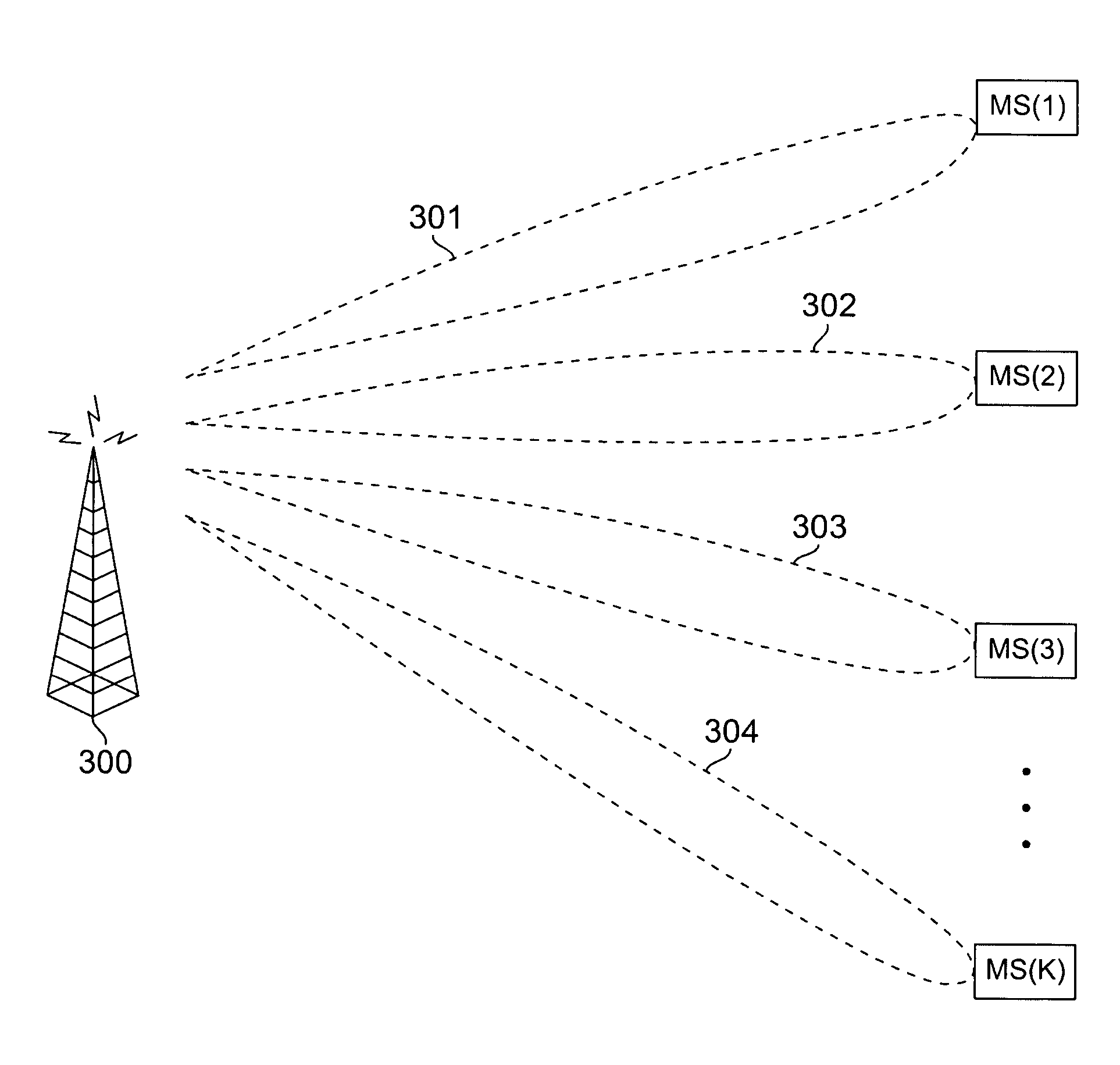
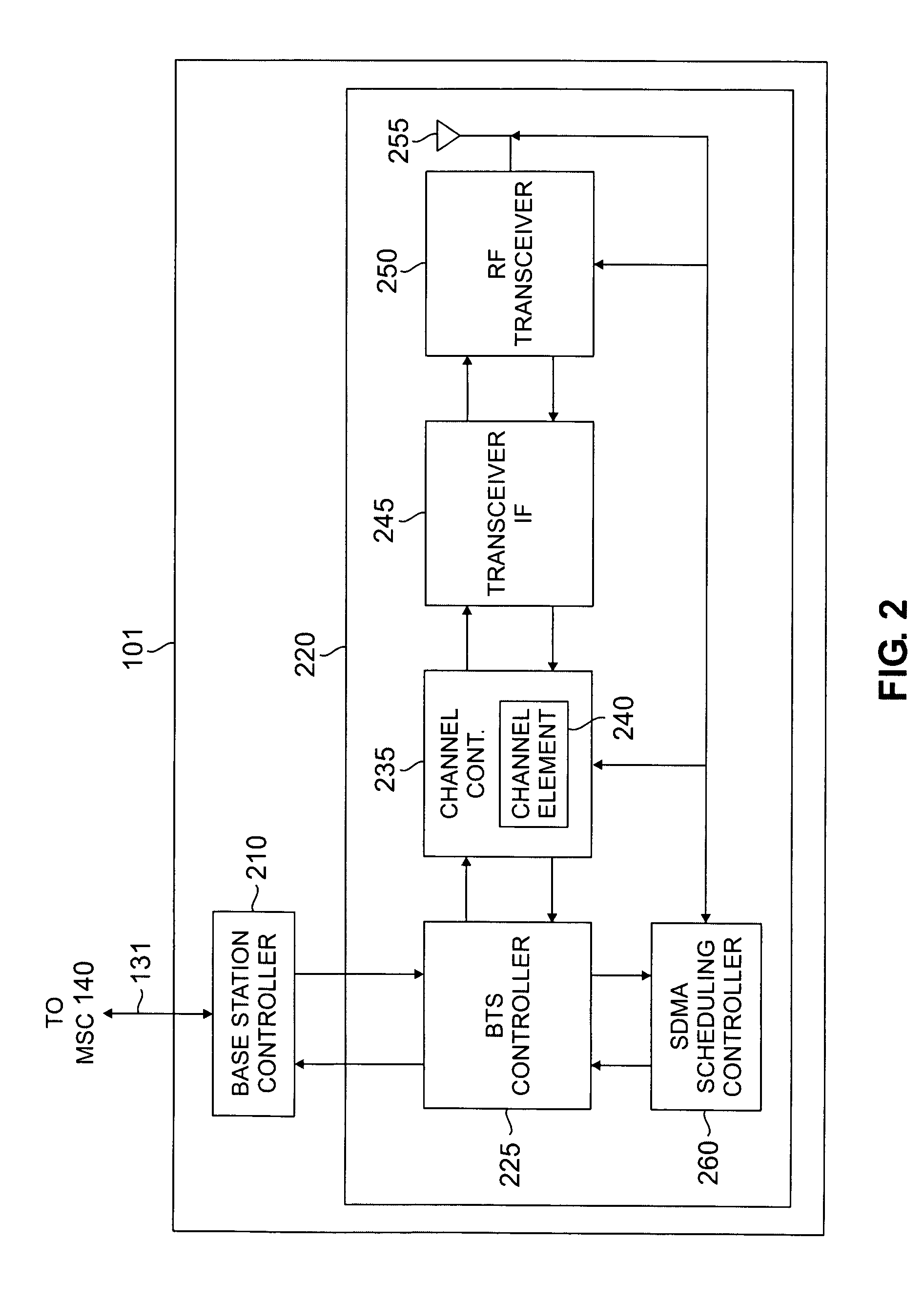
Apparatus and method for downlink spatial division multiple access scheduling in a wireless network
InactiveUS7536205B2Power managementSubstation equipmentComputer networkSpatial division multiple access
A base station for communicating with mobile stations in a coverage area of the wireless network. The base station comprises: 1) a transceiver for transmitting downlink OFDMA signals to each mobile station; 2) an antenna array for transmitting the downlink OFDMA signals to the mobile stations using spatially directed beams; and 3) an SDMA scheduling controller for scheduling downlink transmissions to the mobile stations. The SDMA scheduling controller determines a first mobile station having a highest priority and schedules the first mobile station for downlink transmission in a particular time-frequency slot. The SDMA scheduling controller then determines additional mobile stations that are spatially uncorrelated with the first mobile station, as well as each other, and schedules the additional mobile stations for downlink transmission in that particular time-frequency slot according to priority.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Uplink sdma transmit opportunity scheduling
ActiveCN102550116ARadio transmissionWireless communicationSpatial division multiple accessStart time
Certain aspects of the present disclosure present medium access control (MAC) protocols for uplink Spatial Division Multiple Access (SDMA) transmissions by one or more stations (STAs). An access point (AP) may receive one or more requests for uplink SDMA transmission from a plurality of stations. The access point may schedule the transmissions by sending a signal to the stations to notify them of the parameters of the uplink SDMA transmissions such as start time, duration of the transmission, spatial streams assigned to each station, and so on.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Reassigning channels in a spatial diversity radio communications system
InactiveUS20060099955A1Free spaceReduce in quantityNetwork traffic/resource managementTelephonic communicationSpatial division multiple accessCommunications system
Methods and systems are provided for assigning channels in a spatial division multiple access communication network. The network includes a plurality of conventional channels some of which are configurable to be shared concurrently by plural subscribers. The method includes determining combinations of subscribers from the existing subscribers. Enhancement activities are invoked to create optimal combinations of existing subscribers. Existing subscribers are reassigned as necessary to share channels thereby freeing resources for new subscribers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
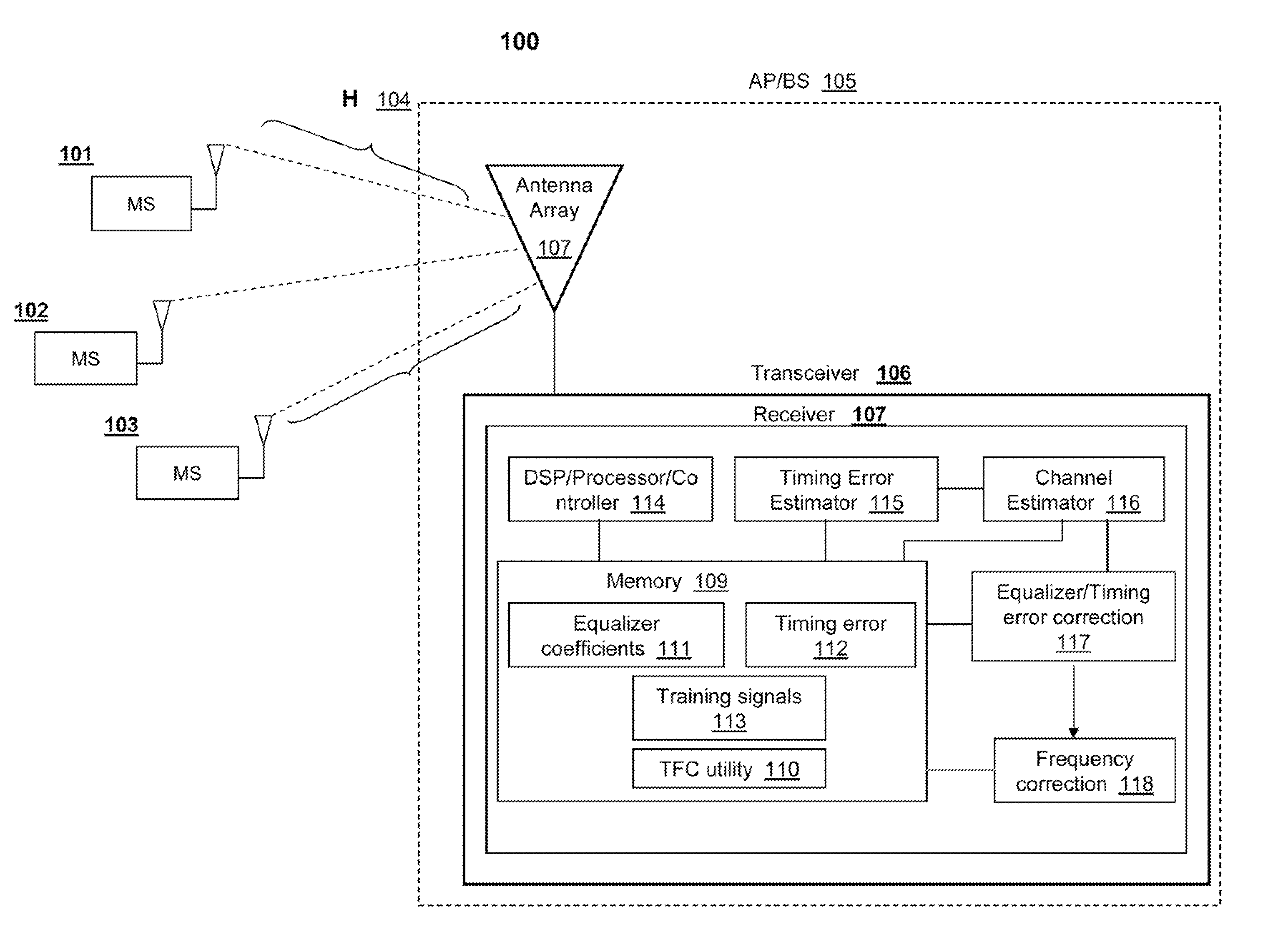
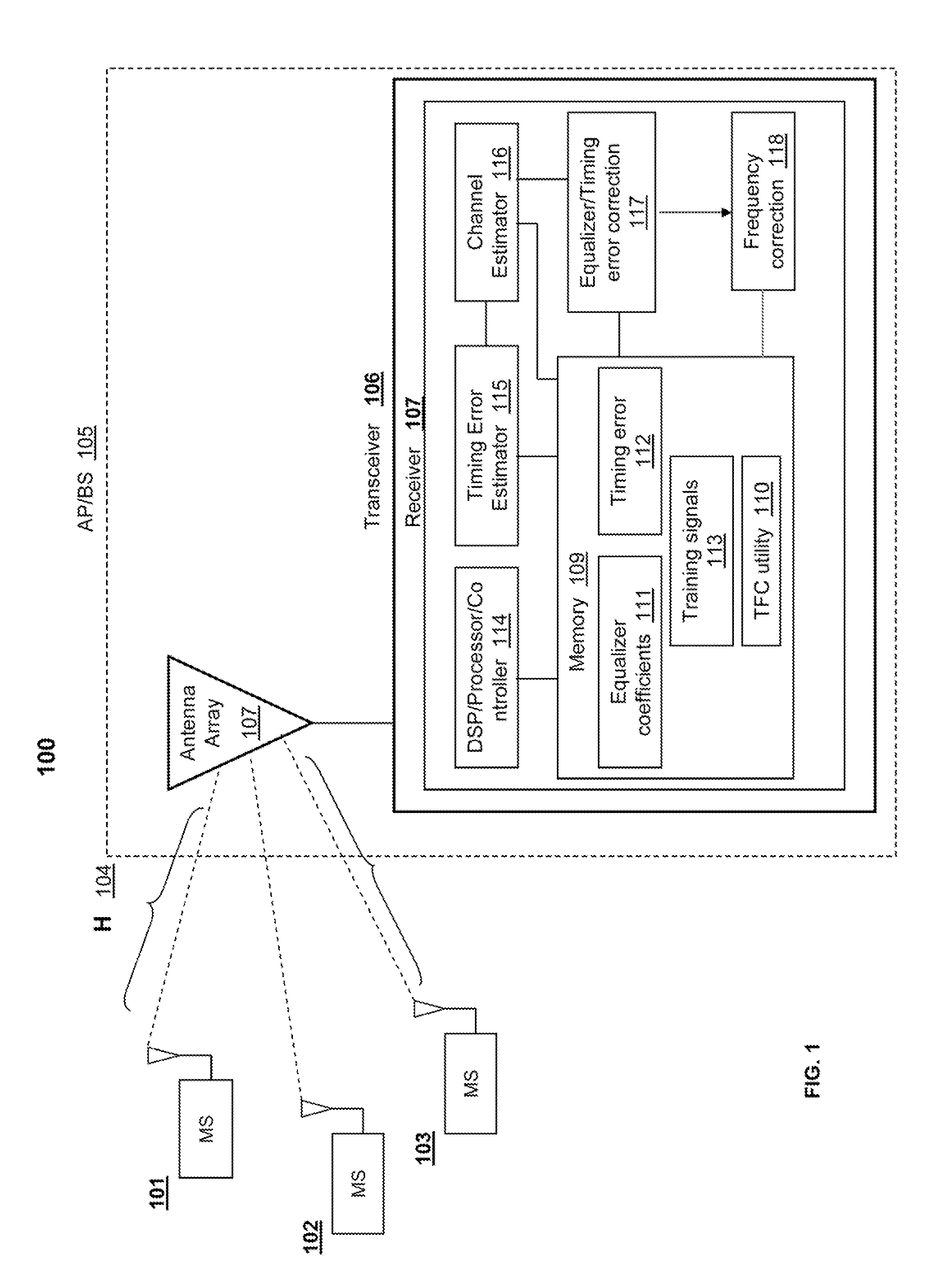
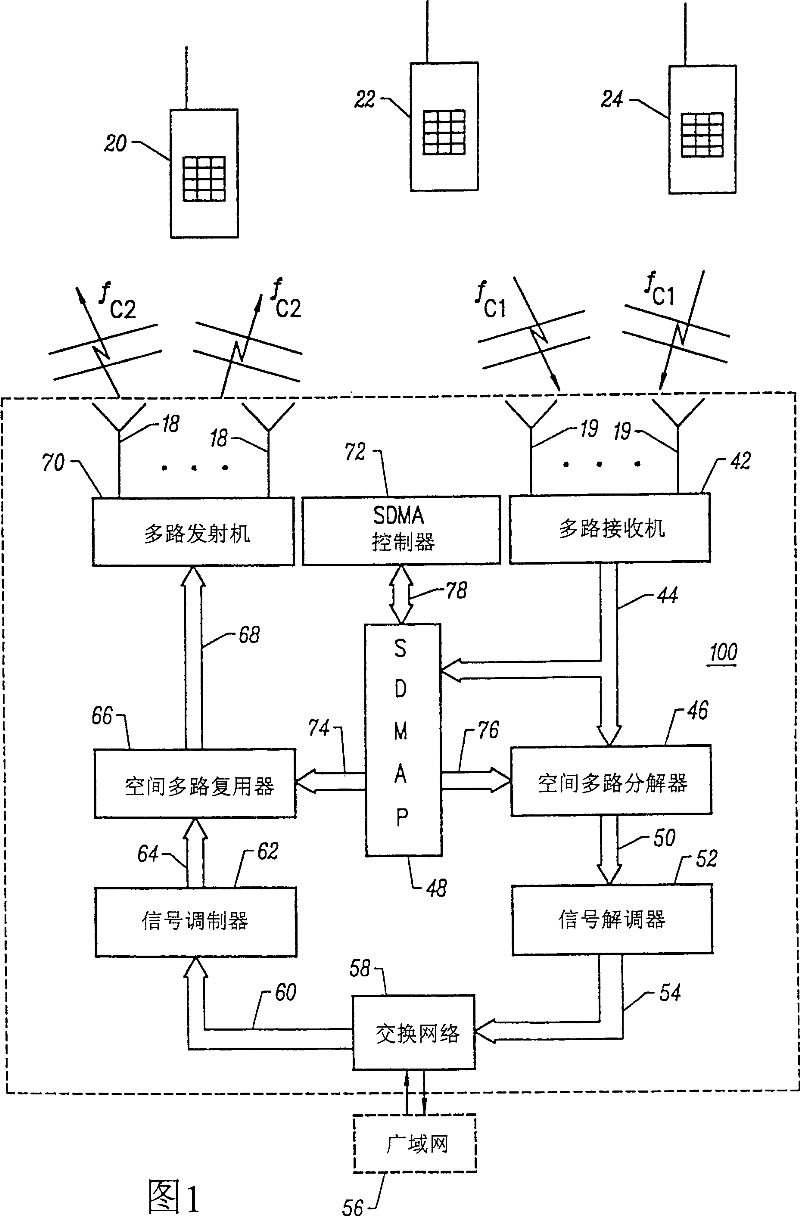
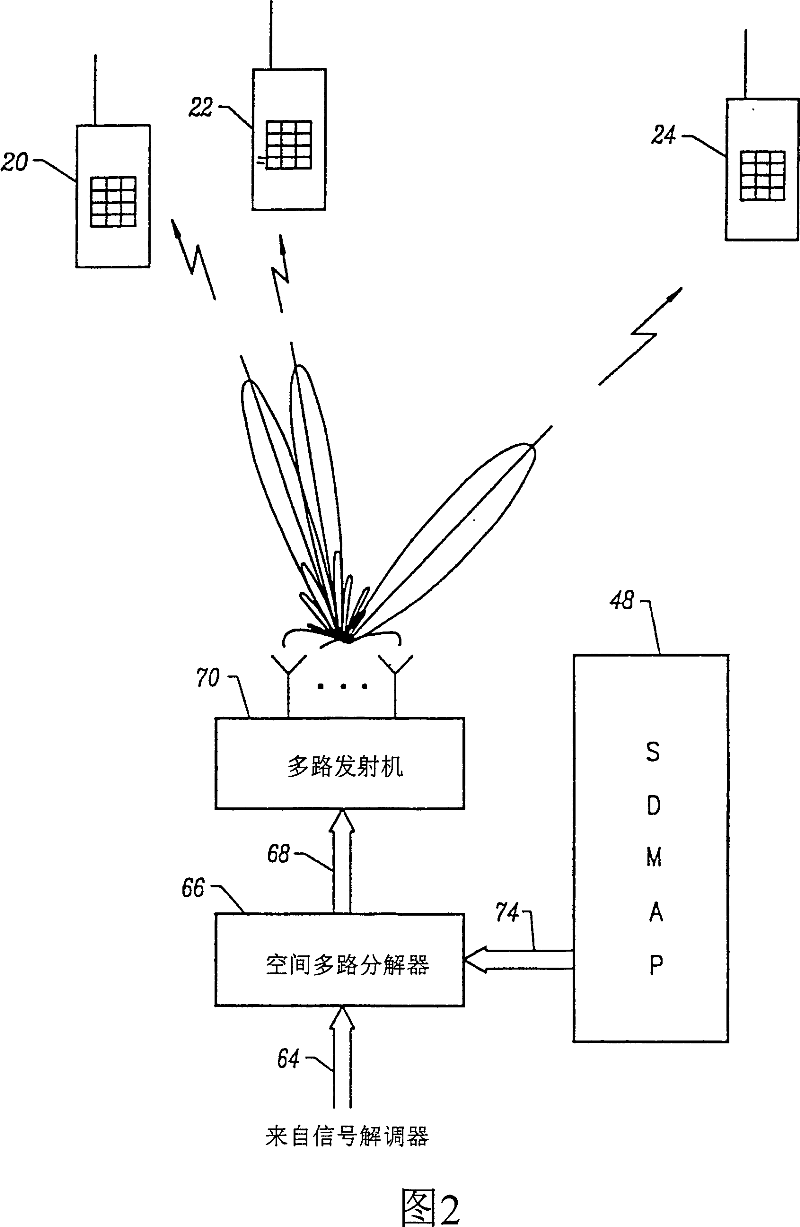
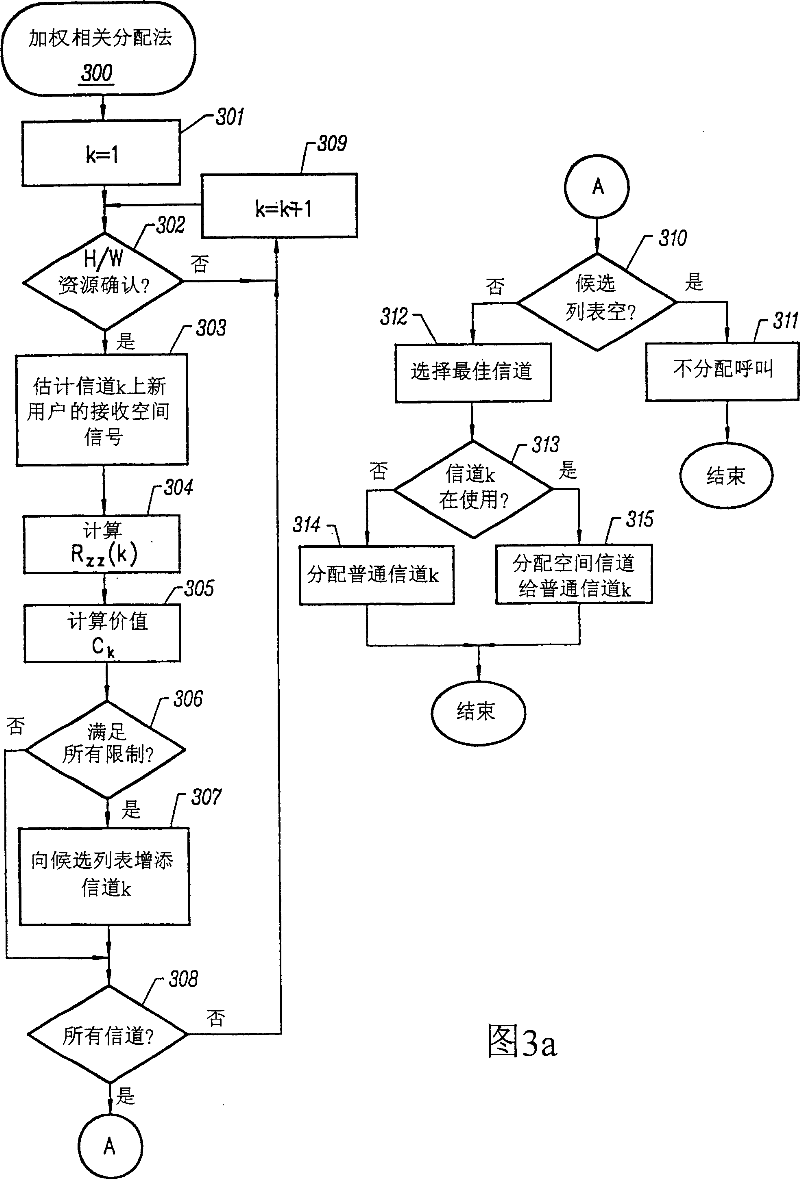
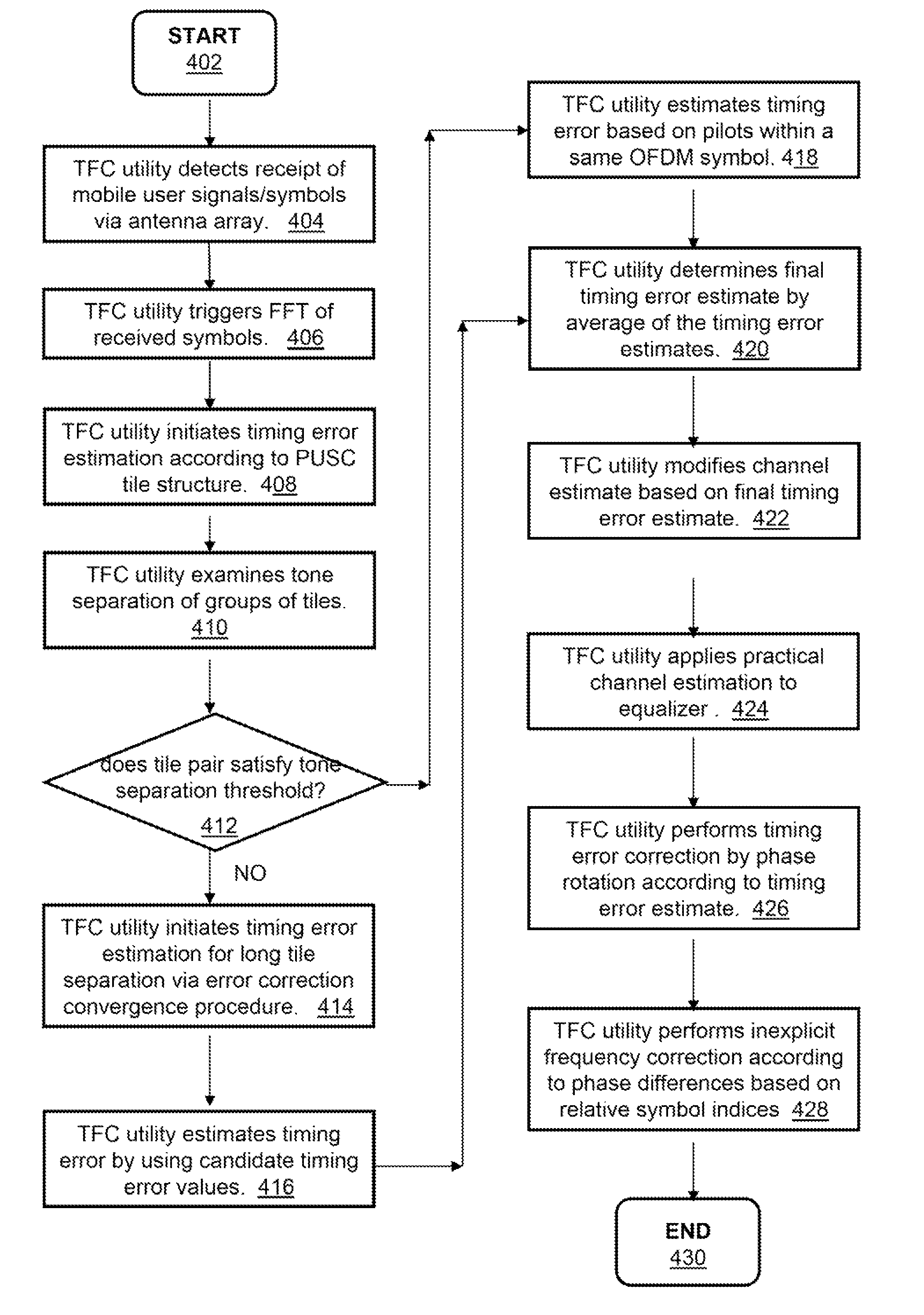
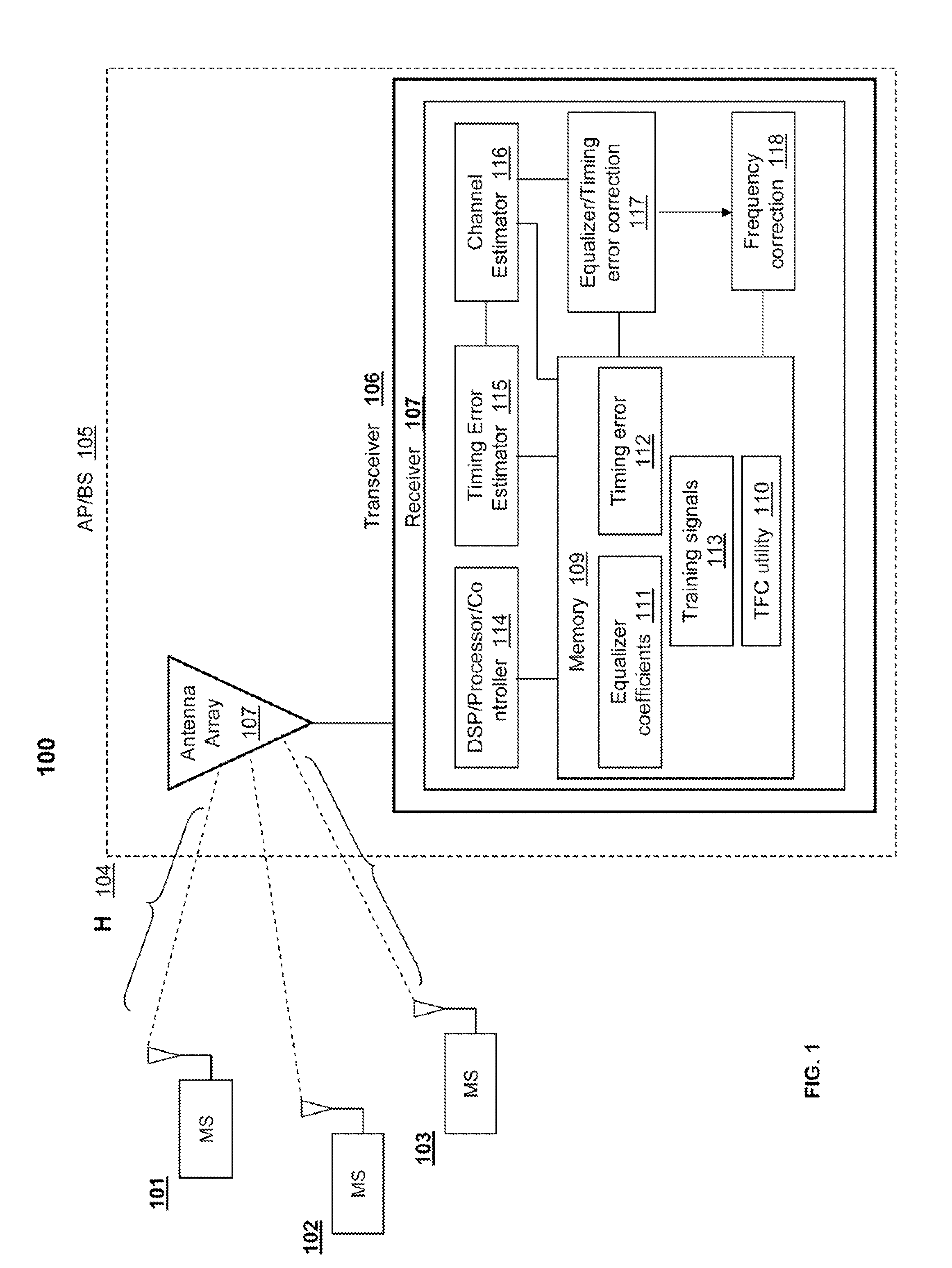
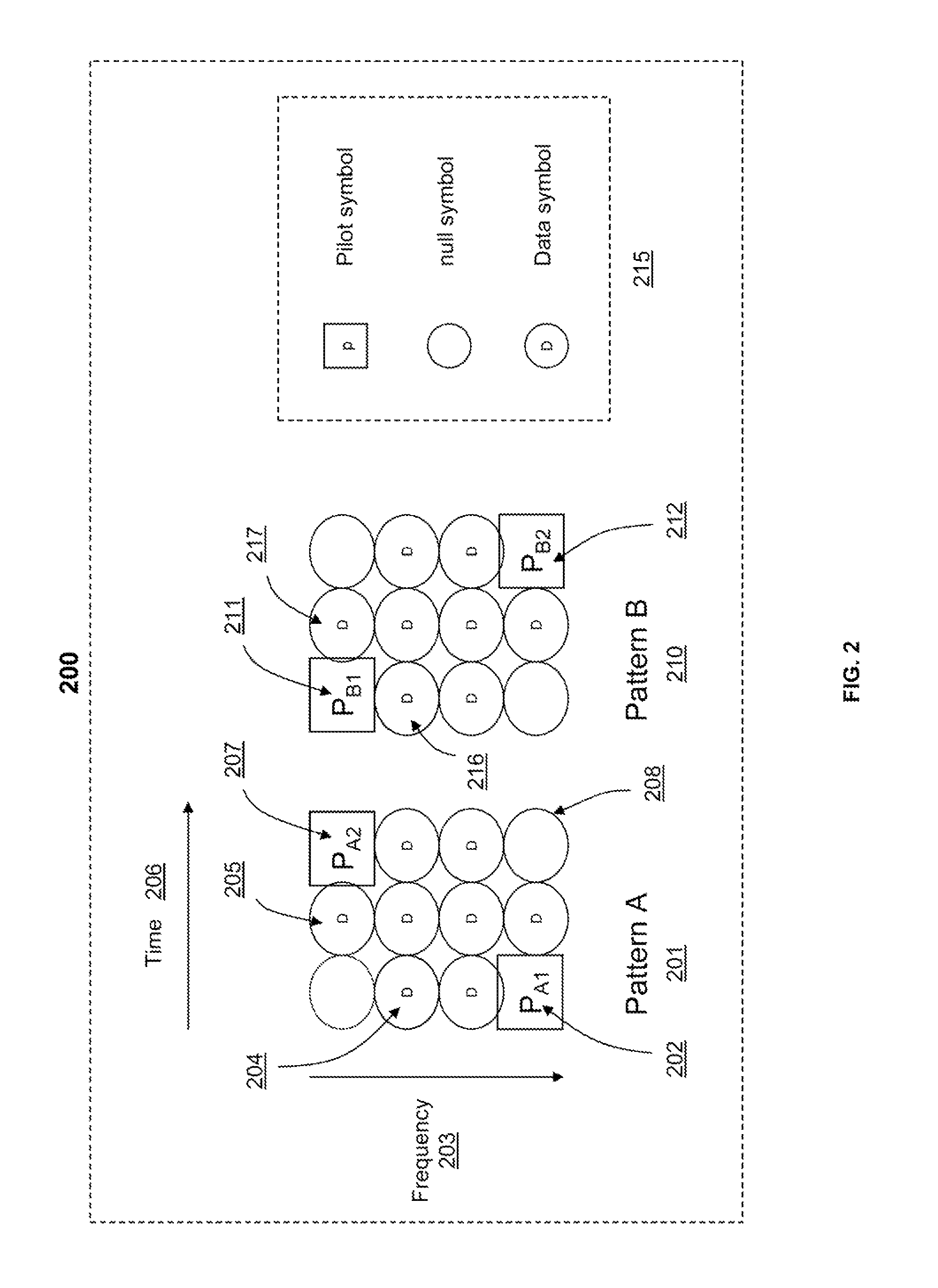
UP-LINK SDMA RECEIVER FOR WiMAX
ActiveUS20100296438A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSpatial division multiple accessPhase difference
A method, a system and a receiver device provide timing and frequency correction in a spatial division multiple access (SDMA) system. A timing and frequency correction (TFC) logic / utility obtains a timing error estimate by using pilot symbols on a slot of six tiles. The TFC logic estimates the timing error based on pilot phase differences between unique pairs of tiles when the frequency separation of the tiles is less than a threshold value. When none of the unique pairs of tiles satisfies the threshold value, the TFC logic estimates timing error based on an exhaustive search for each candidate phase error value. The TFC logic performs timing error correction via a timing error estimate based on pilots from the symbols received on each antenna. The TFC logic performs inexplicit frequency error correction according to phase differences based on relative symbol indices.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
System and method for adaptive assignment of unique words in a communication system
InactiveUS7565151B2Heavy communicationTransmissionNetwork planningSpatial division multiple accessCommunications system
A method and system for assigning unique words in an SDMA (spatial division multiple access) communication system is provided. A network management system logically arranges cell stations into clusters of stations, and monitors for a heavy traffic condition. Responsive to determining that a heavy traffic condition exists, the network management system may 1) redistribute unique words within a single cluster; 2) move one or more cell stations from a busy cluster to a less busy cluster; or 3) create a new cluster, and move cells from one or more busy cluster into the new cluster. In this way, the communication system continually adapts so that more unique words are made available at cell stations having heavier communication demands.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Channel Assignment Based on Spatial Strategies in a Wireless Network Using Adaptive Antenna Arrays
InactiveUS20090233614A1Secret communicationTransmission monitoringSpatial division multiple accessTime division multiple access
Channels are assigned based on co-spatial constraints in wireless network using spatial division multiple access. In one example, the invention includes assigning a co-spatial constraint to each of a plurality of conventional traffic communications channels of a base station, and receiving a request from a user terminal to communicate using a traffic communication channel of the base station. The invention further includes measuring a quality parameter of the request deriving a co-spatial constraint for the user terminal, assigning the user terminal co-spatial constraint to the user terminal, and assigning the user terminal to a traffic communication channels having a channel co-spatial constraint that is no less than the user terminal co-spatial constraint and that has no more assigned radios than permitted by the channel co-spatial constraint.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Protocol to support adaptive station-dependent channel state information feedback rate in multi-user communication systems
InactiveCN102549992AError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversitySpatial division multiple accessCommunications system
Methods and apparatuses are proposed for supporting one or more user-dependent channel state information (CSI) feedback rates in a downlink spatial division multiple access (SDMA) system. For certain aspects, an access point (AP) may receive a channel evolution feedback from one or more stations and send a request for CSI to the stations whose CSI values need to be updated. For certain aspects, the AP may poll the stations for updated CSI values. For certain aspects, deterministic back-off timers may be assigned to the stations indicating when to send their CSI feedback. The proposed methods may improve system performance.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Uplink spatial division multiple access (SDMA) user pairing and scheduling
A method, system and communication network for transmitting information signals via uplink (UL) collaborative SDMA, in a wireless communication system. Base station receiver estimates a channel gain associated with the transmission path(s) of each user and keeps a matrix of normalized covariance, between users. Based on the estimated channel gain and the normalized covariance, ULS utility is able to compute channel capacity. Based on capacity estimates of (1) the multiplexed user signals and (2) the individual user signals, signals are either multiplexed for UL SDMA or are transmitted individually. An optimal selection of multiplexed signals may be based upon: (1) a cross user interface measurement; and (2) a selection mechanism based on eigen-decomposition techniques. The ULS utility enables a UL scheduler to pair information signals with clear spatial distinction and minimal correlation, based on capacity evaluations.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Method and apparatus for spatial division multiple access of downlink control channel of super cell, and base station
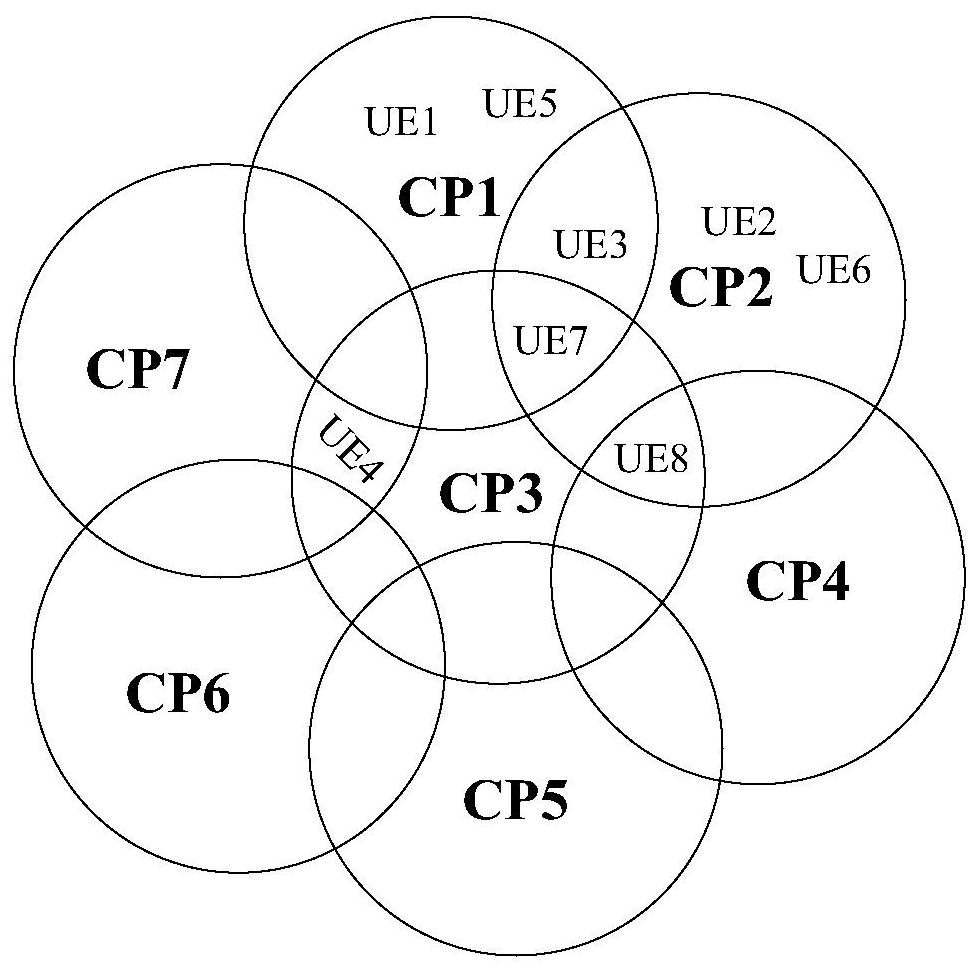
ActiveCN107404763AIncrease profitIncrease capacityHigh level techniquesWireless communicationSystem capacitySpatial division multiple access
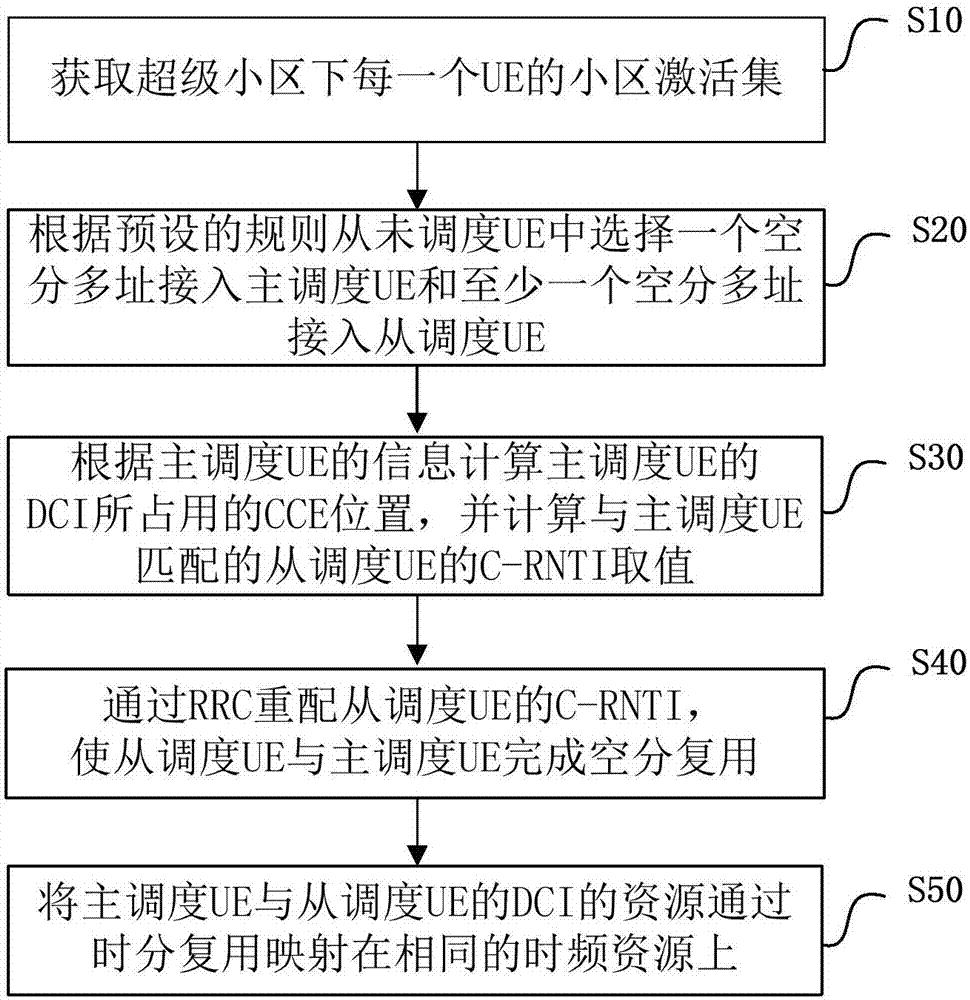
The invention discloses a method and apparatus for spatial division multiple access of a downlink control channel of a super cell, and a base station. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a cell activation set of each UE in the super cell; according to a preset rule, selecting one spatial division multiple access for access to master scheduling UE and at least one piece of slave scheduling UE from unscheduled UE; according to information of the master scheduling UE, calculating a starting position of a control channel element (CCE) occupied by downlink control information (DCI) of the master scheduling UE, and calculating a value of a cell radio network temporary identifier (C-RNTI) of the slave scheduling UE matching the maser scheduling UE; redistributing the C-RNTI of the slave scheduling UE through a radio resource control (RRC) protocol so as to enable the slave scheduling UE and the master scheduling UE to complete spatial division multiplexing; and mapping DCI resource of the master scheduling UE and the slave scheduling UE to the same time-frequency resource through time division multiplexing. According to the invention, the utilization rate of the time-frequency resource can be improved, the capacity of the downlink control channel is enhanced, and the system capacity is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
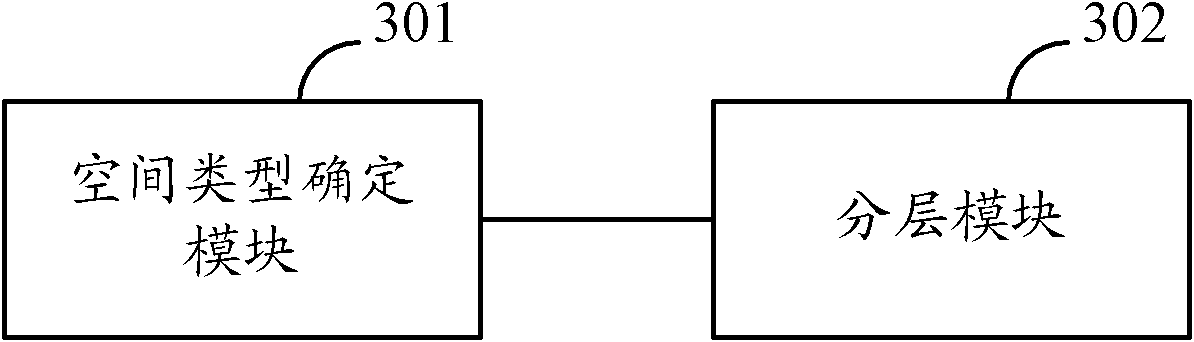
Resource layering method and device of spatial division multiple access system
ActiveCN102026383AReduce layeringReduce the numberSpatial transmit diversityWireless communicationSpatial division multiple accessCode division multiple access
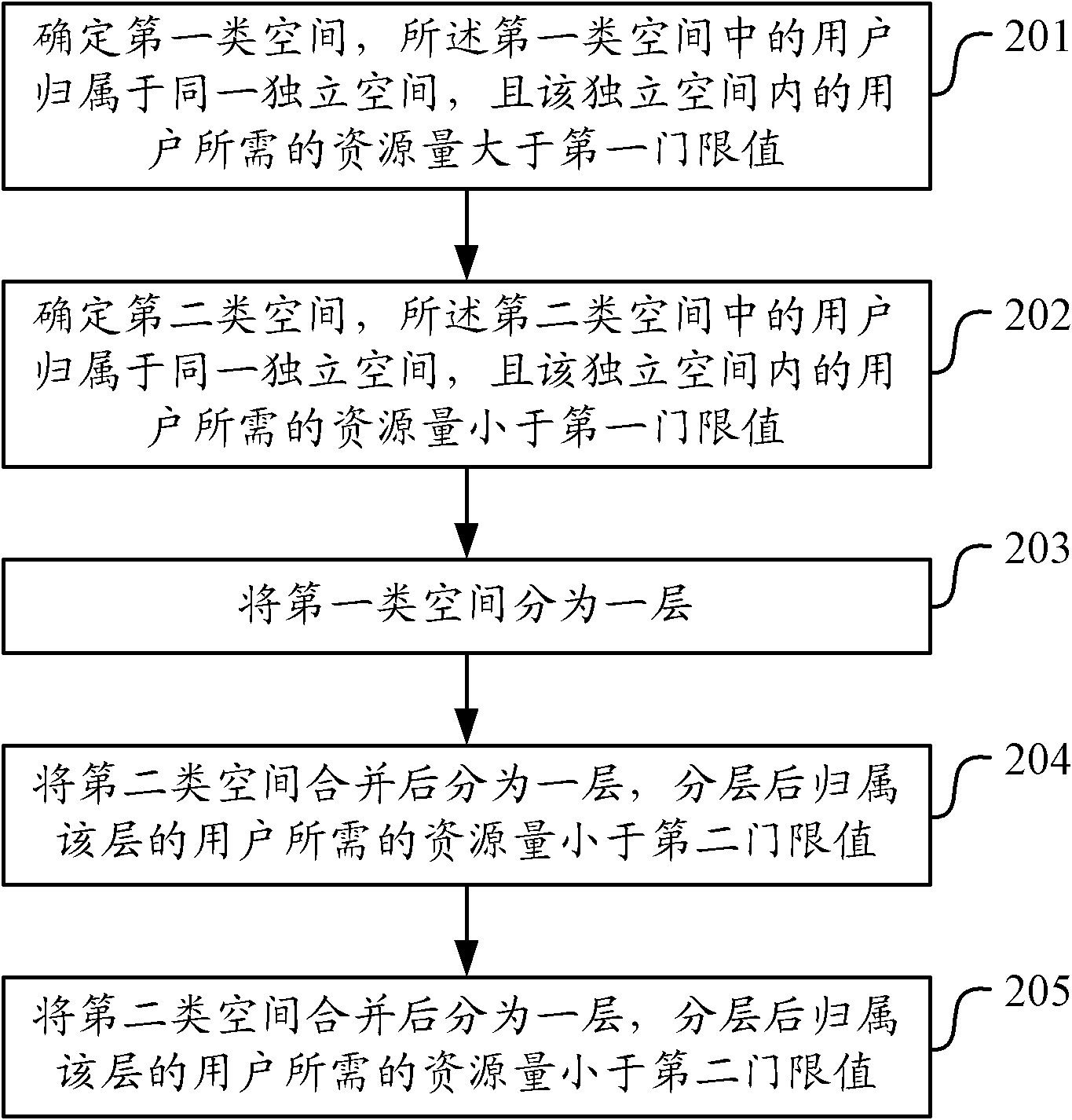
The invention discloses a resource layering method and device of a spatial division multiple access system. The method comprises the following steps of determining first class spaces, wherein users in the first class spaces are assigned to a same independent space, and the resource quantity needed by the users in the independent space is larger than a first threshold; determining second class spaces, wherein users in the second class spaces are assigned to a same independent space, and the resource quantity needed by the users in the independent space is smaller than the first threshold; distributing the first class spaces into a layer; combining the second class spaces to be a layer, wherein the resource quantity needed by the users assigned to the layer subjected to layering is smaller than a second threshold; and respectively layering the second class spaces which are not combined, wherein the first threshold is less than or equal to the second threshold. By utilizing the invention, the resource layering can be reduced and the times of resource reassortment by the users can be reduced when an assigning space is switched, therefore, the signalling overhead used for resource scheduling is reduced.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
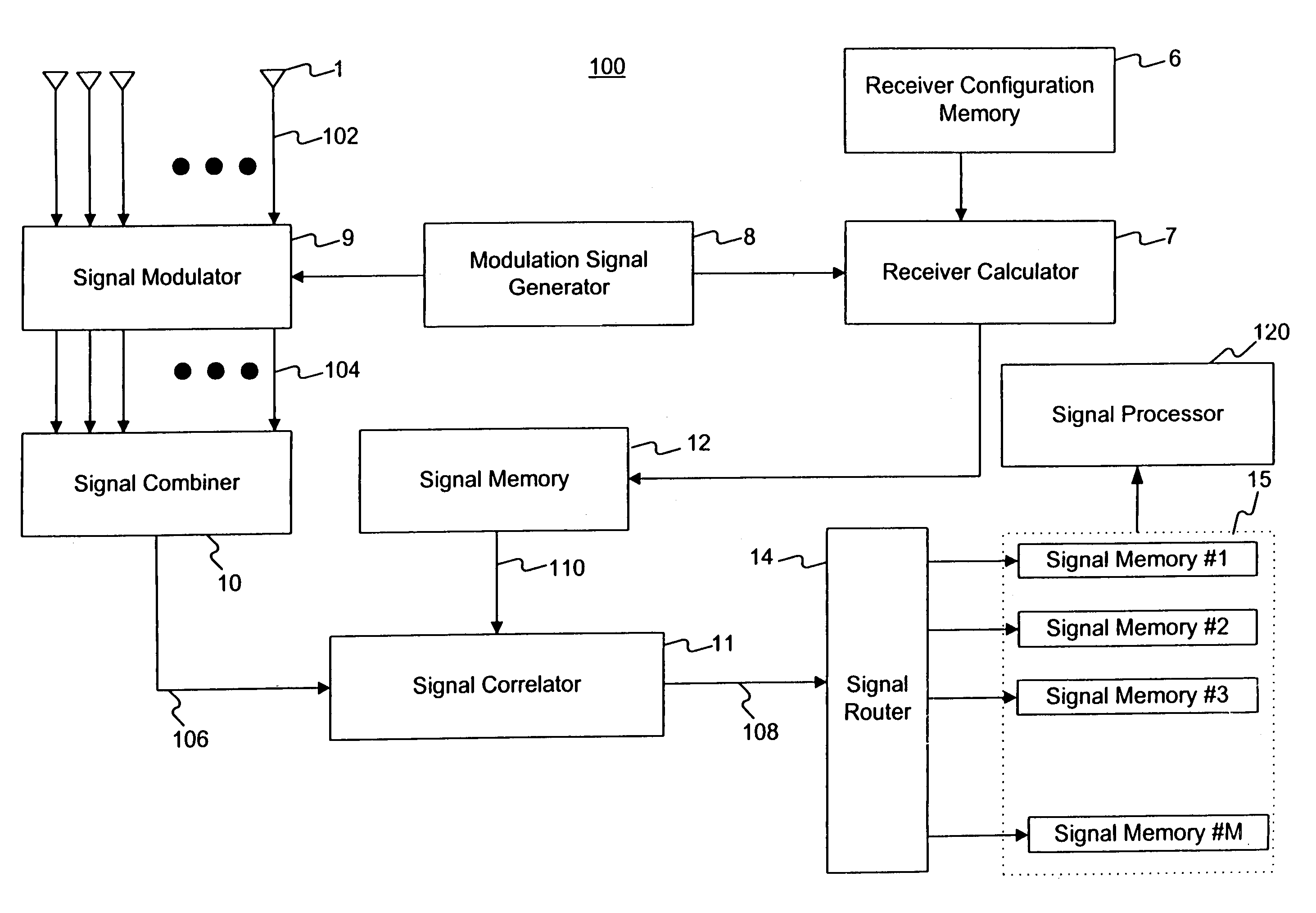
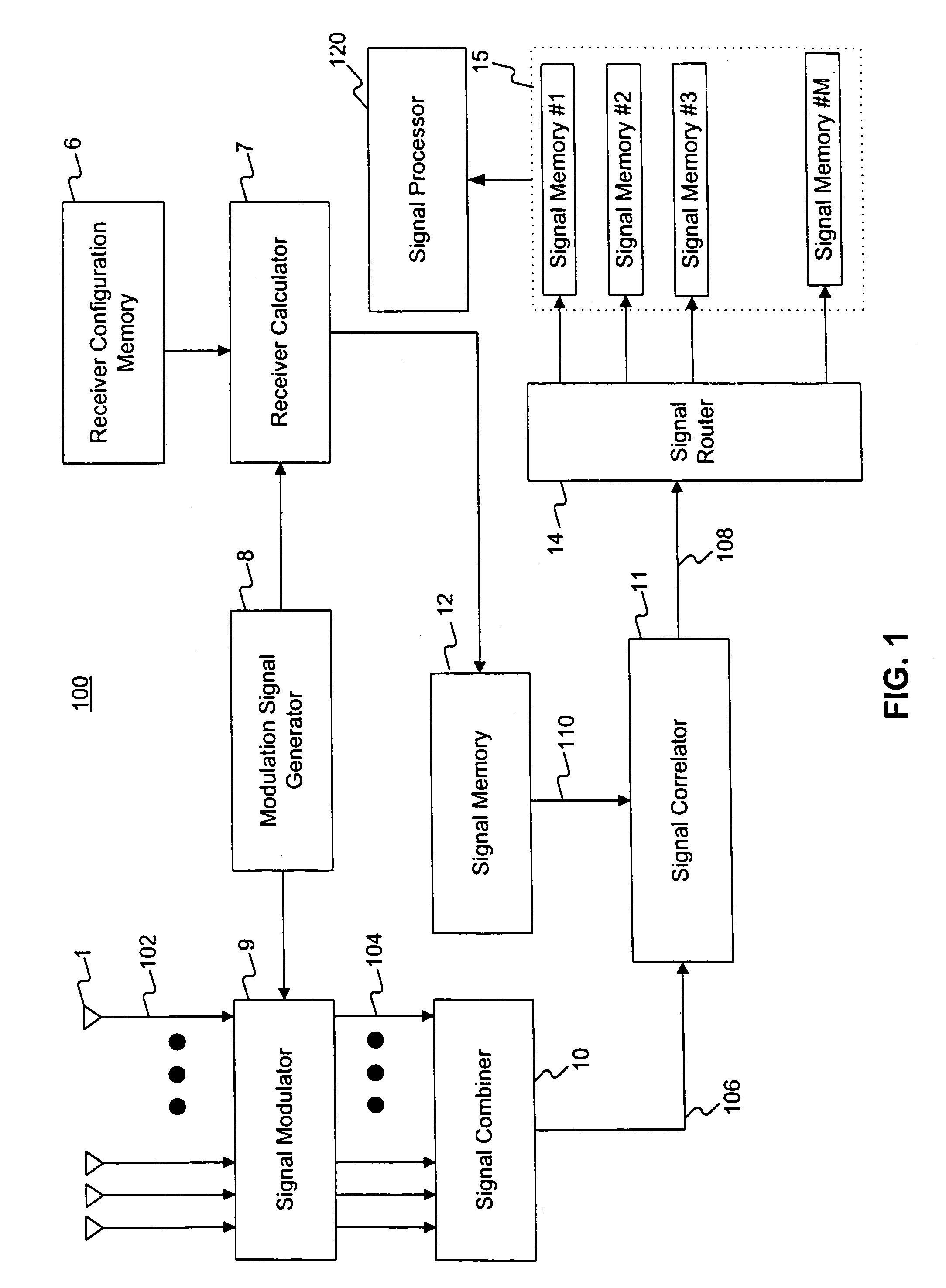
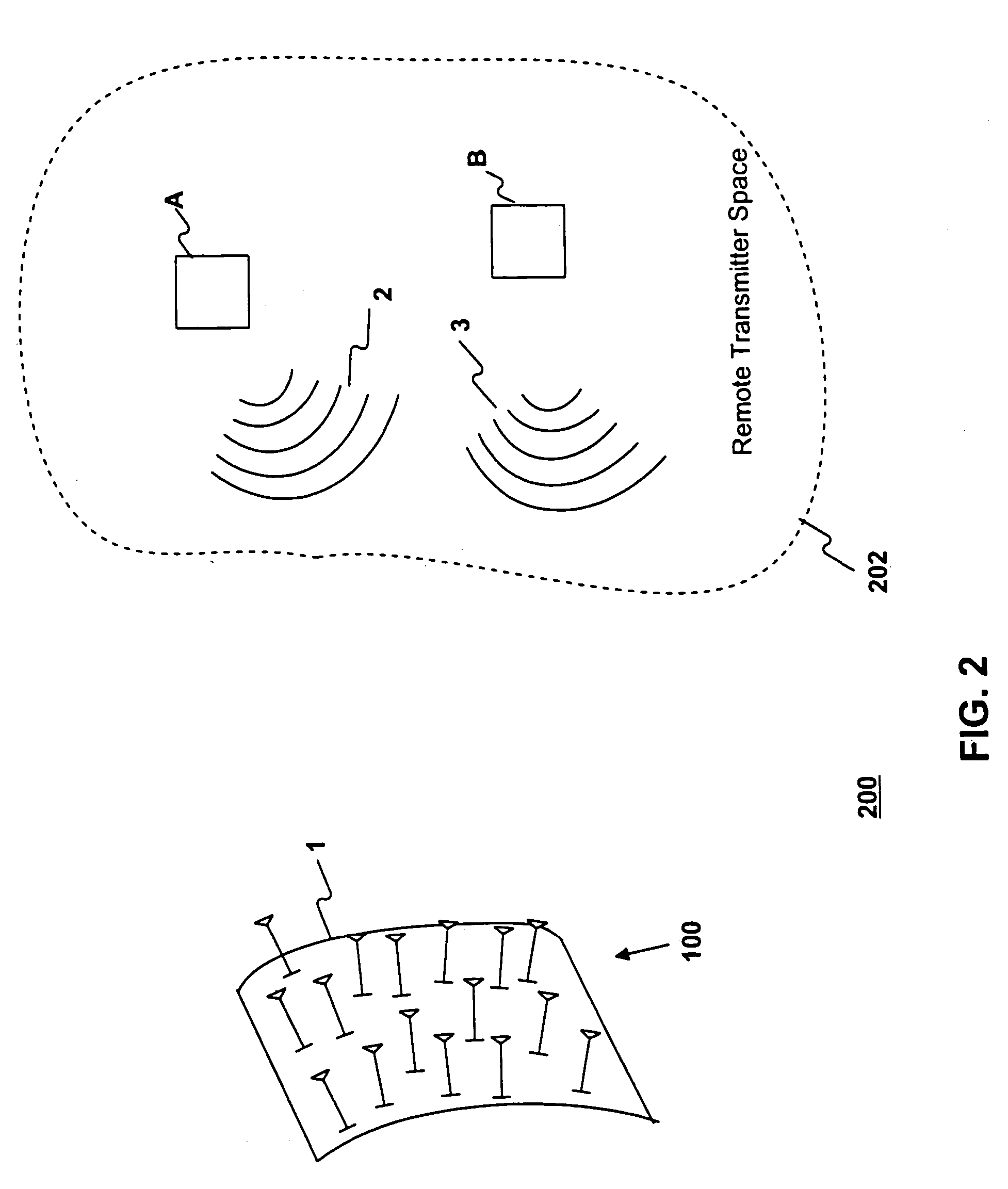
Method and apparatus for space division multiple access receiver
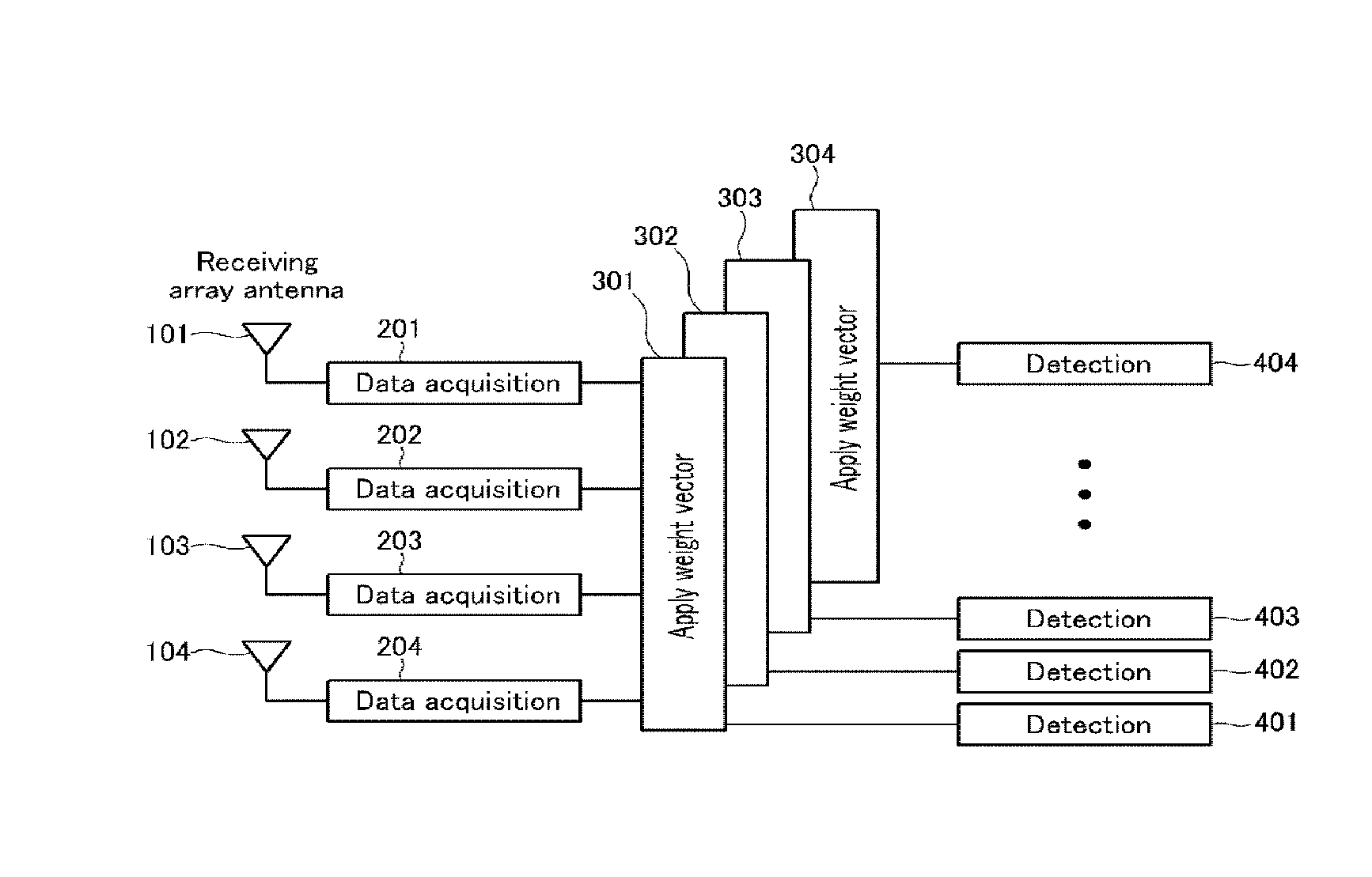
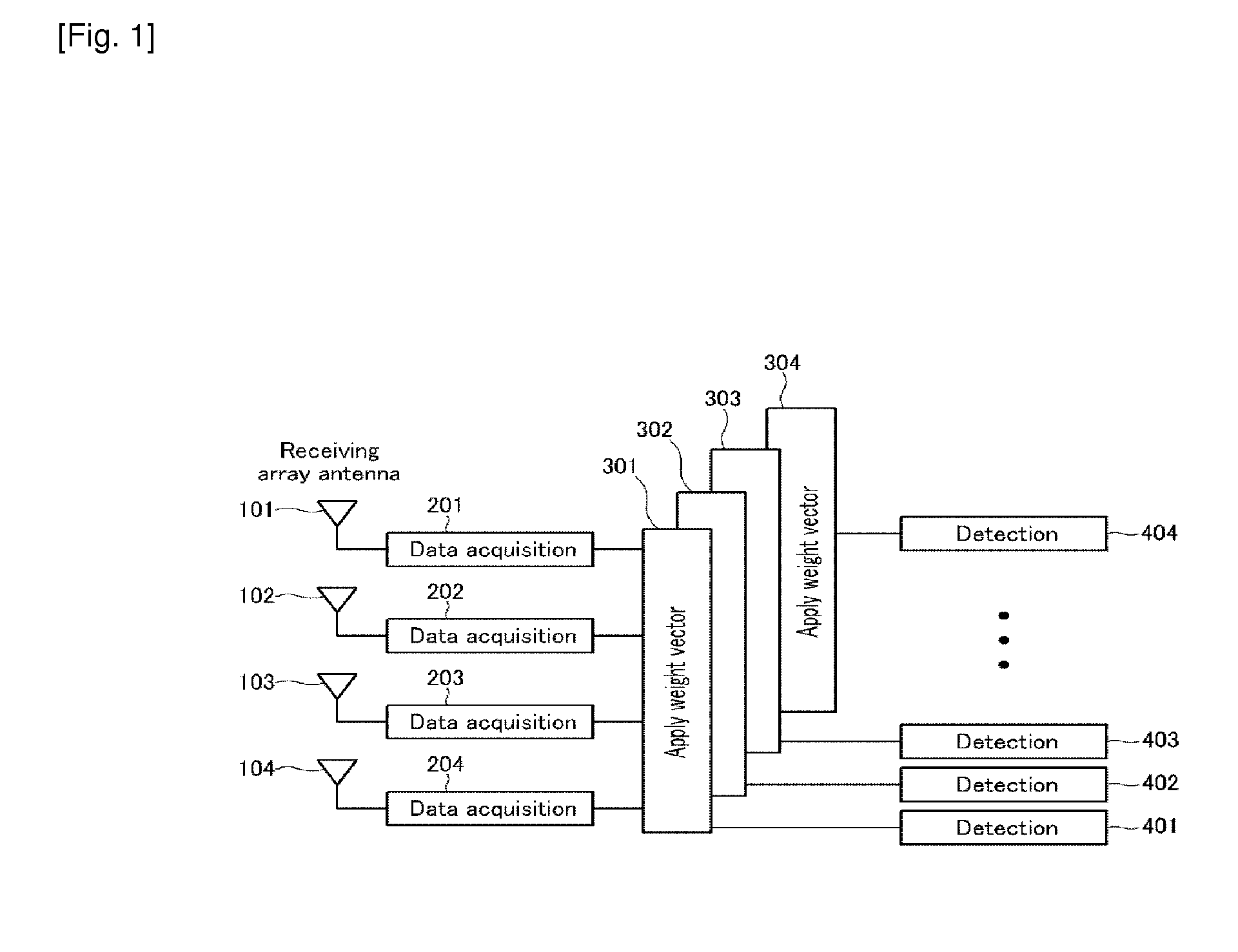
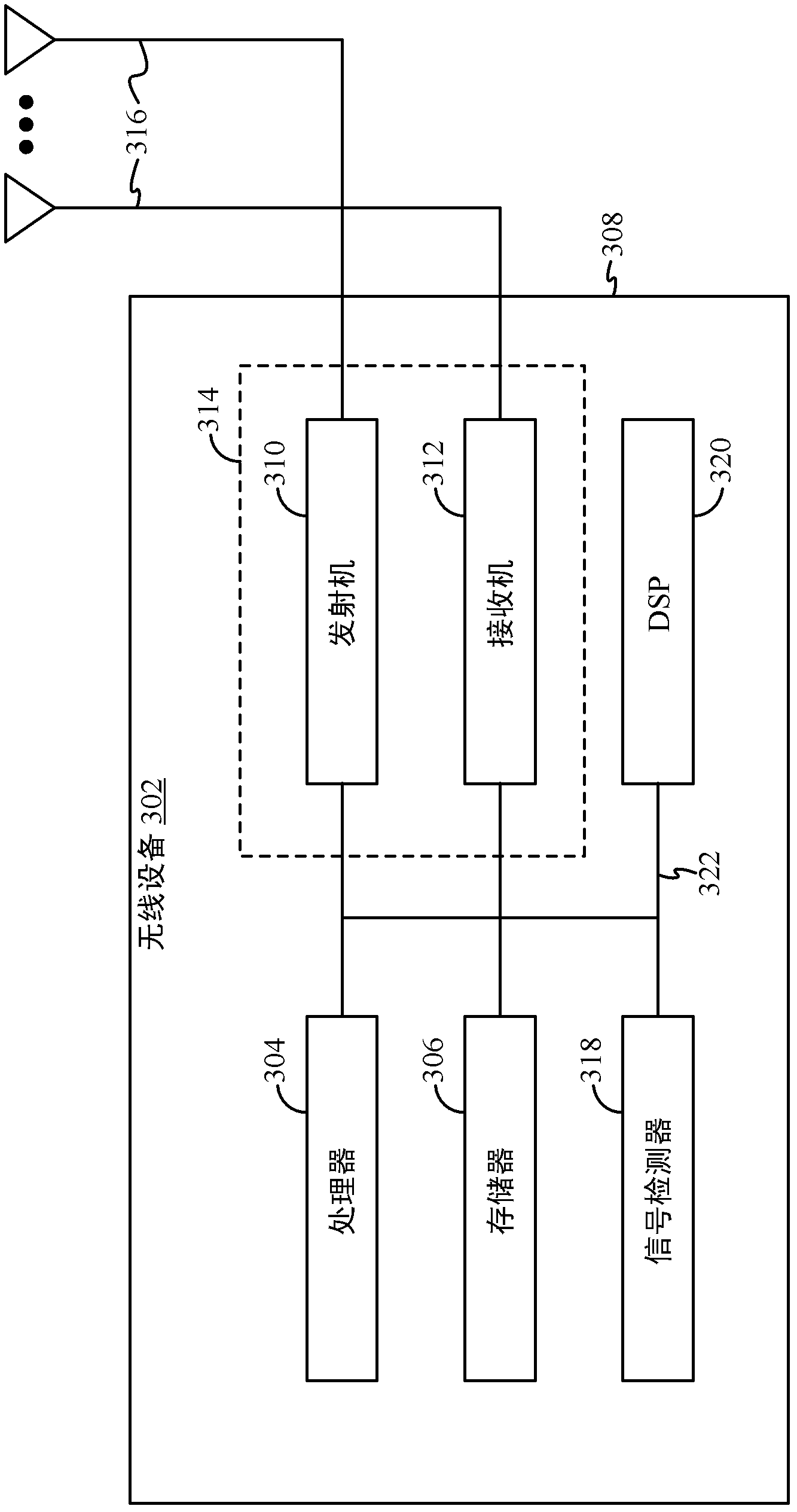
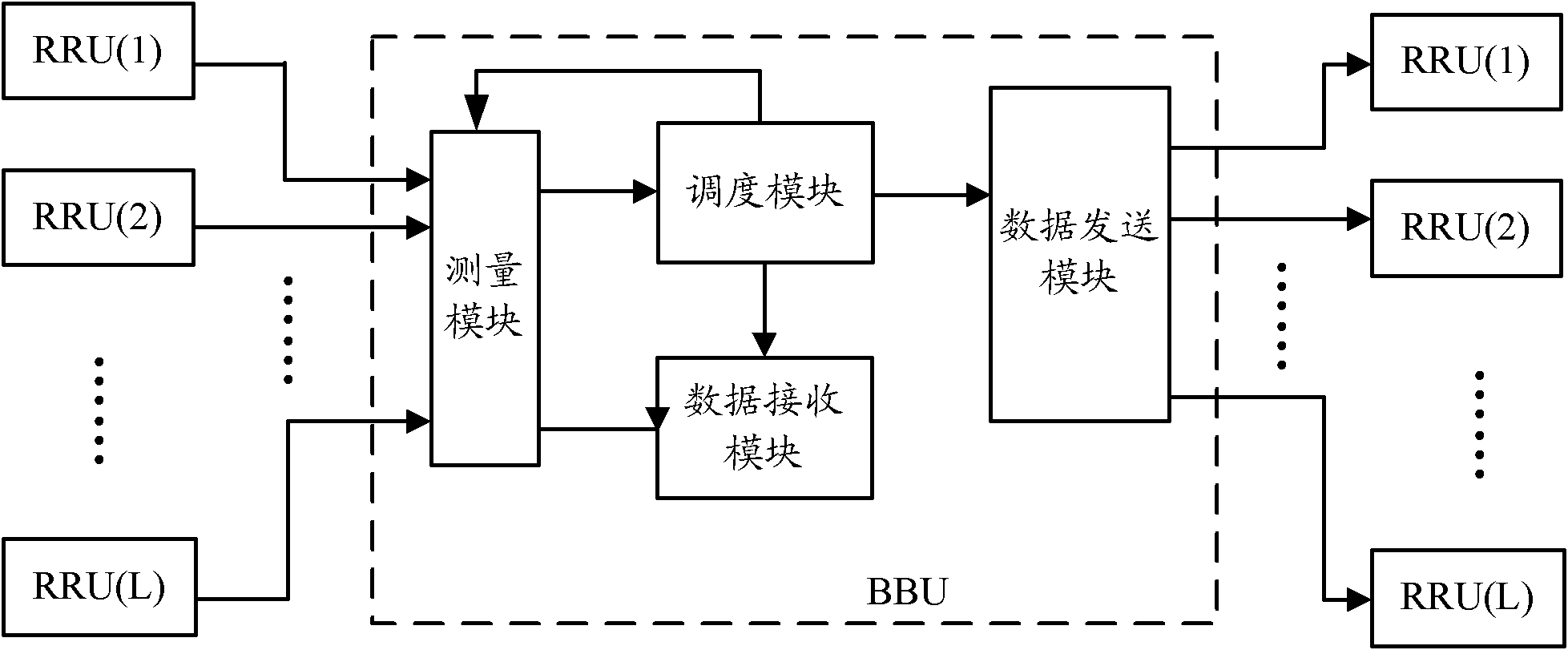
InactiveUS7251286B2Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringSpace-division multiple access
Methods and systems consistent with this invention receive a plurality of transmitted signals in a receiver having a plurality of receive elements, wherein each transmitted signal has a different spatial location. Such methods and systems receive the plurality of transmitted signals at the plurality of receive elements to form a plurality of receive element signals, form a combined signal derived from the plurality of receive element signals, and detect each of the plurality of transmitted signals from the combined signal by its different spatial location. To achieve this, methods and systems consistent with this invention generate a plurality of arbitrary phase modulation signals, and phase modulate each of the plurality of receive element signals with a different one of the phase modulation signals to form a plurality of phase modulated signals. Such methods and systems then combine the plurality of phase modulated signals into a combined signal, generate expected signals, and cross- correlate the combined signal with the expected signals to form correlation signals. Such methods and systems then store the correlation signals in a correlation signal memory and analyze the correlation signals to extract information from the transmitted signals.
Owner:GREENWICH TECH ASSOCS
Channel assignment and call admission control for spatial division multiple access communication systems
InactiveCN101039501APower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemSpatial division multiple access
The invention discloses a method for allocating channels in a wireless communication station and a call access control method. In the invention, for each of a plurality of common channels, interference levels achieved by common channel assignment can be computed, which are functions of space feature of a user station which is communicated with a base station; and the interference levels responding the computation, which select the common channels from a plurality of common channels for assignment.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Up-link SDMA receiver for WiMAX
ActiveUS8199845B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTelecommunicationsSpatial division multiple access
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
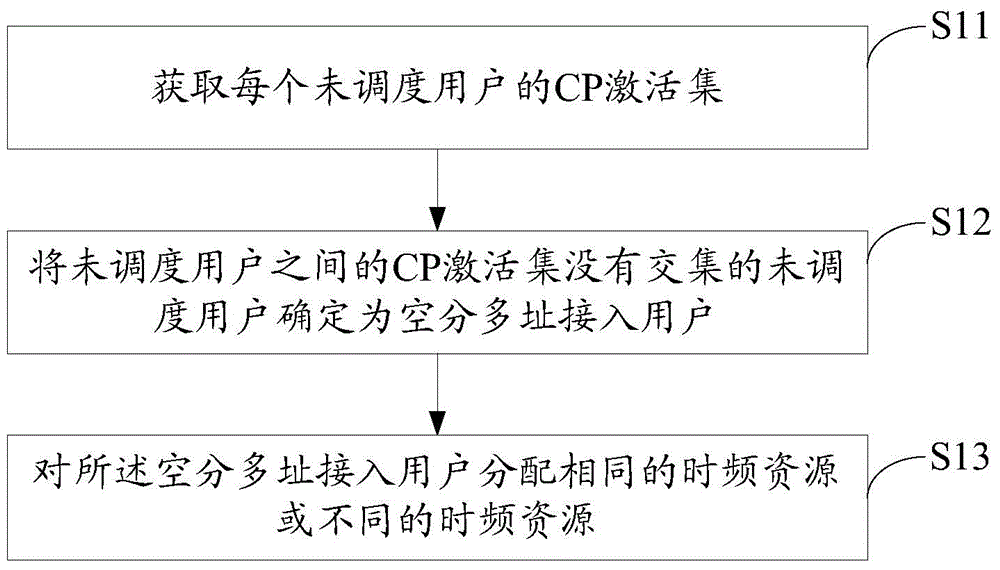
Super-cell SDMA (Spatial Division Multiple Access) method and base station
InactiveCN105744623AIncrease flexibilityWireless communicationSpatial division multiple accessResource allocation
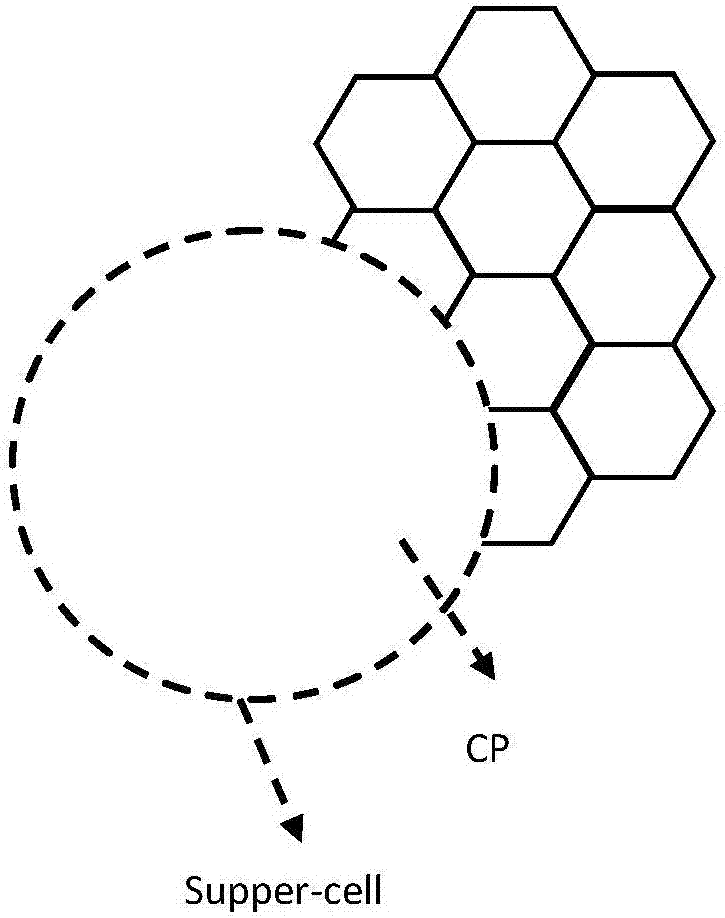
The invention discloses a super-cell SDMA (Spatial Division Multiple Access) method, and the method comprises the steps: firstly obtaining a CP excitation set of each user which is not dispatched; secondly determining the users with no intersection between the CP excitation sets of the users which are not dispatched as the SDMA users; and finally distributing the same time frequency resource or different time frequency resources to the SDMA users. The invention also discloses a super-cell SDMA base station. The method provided by the invention improves the SDMA probability and resource distribution flexibility.
Owner:ZTE CORP
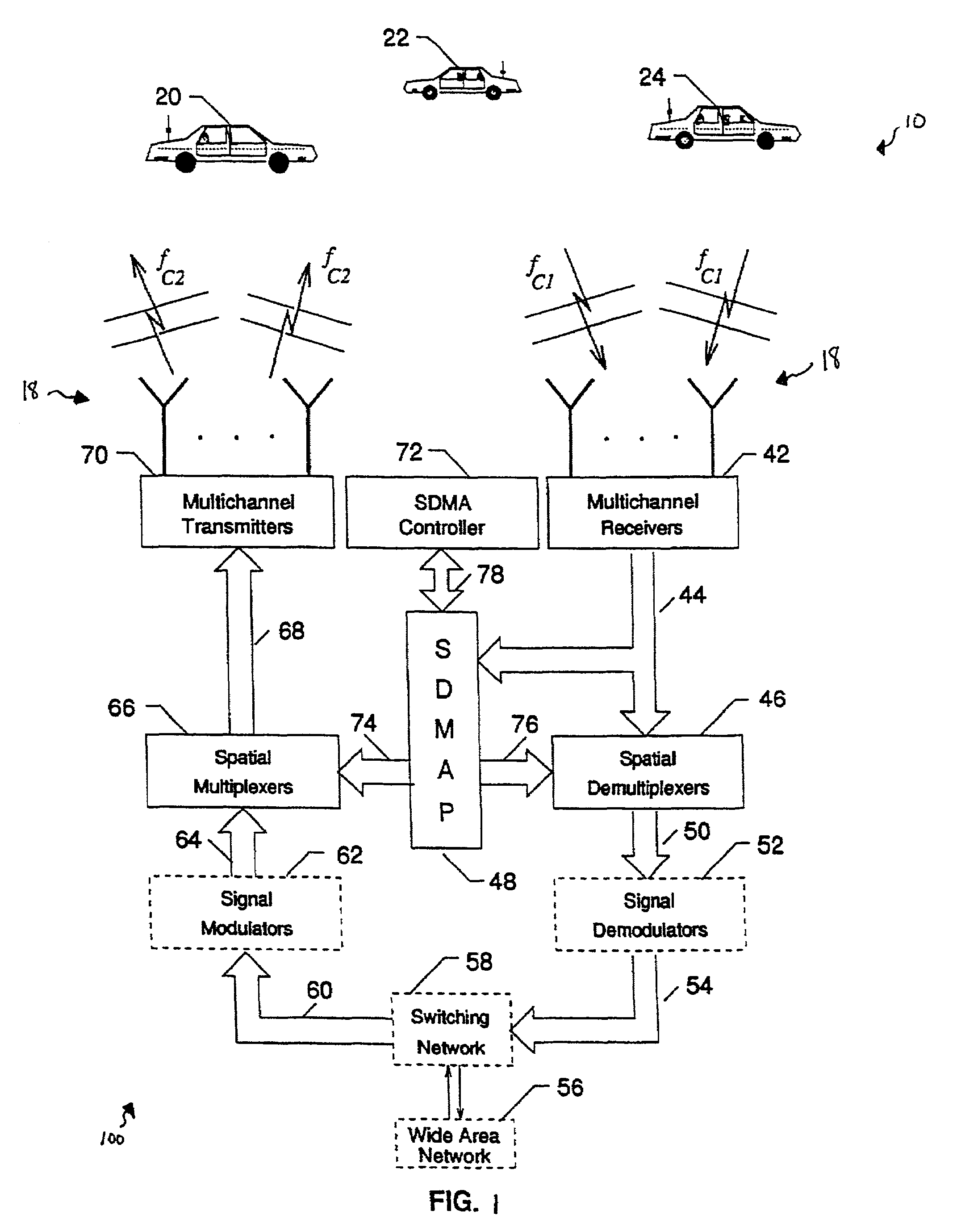
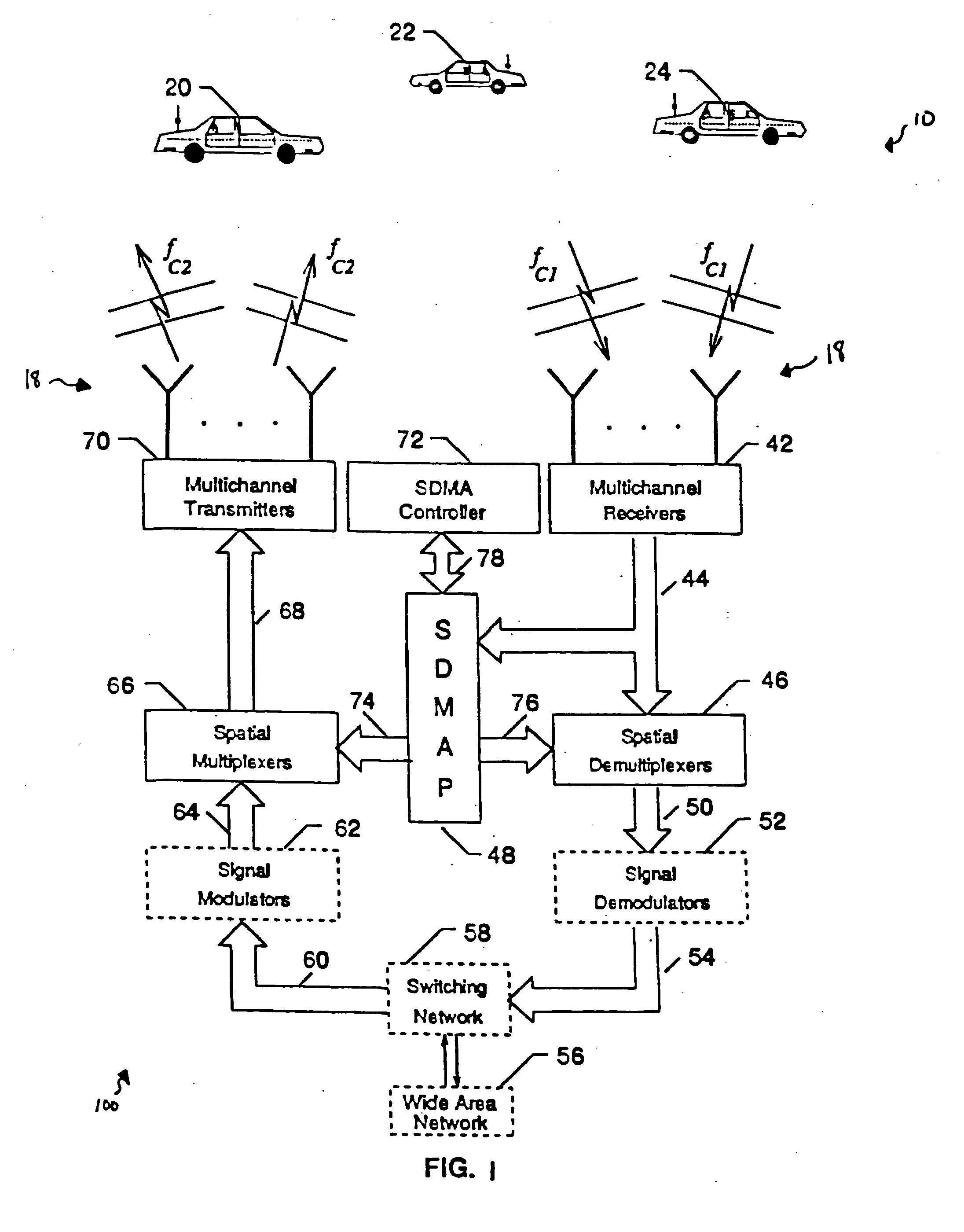
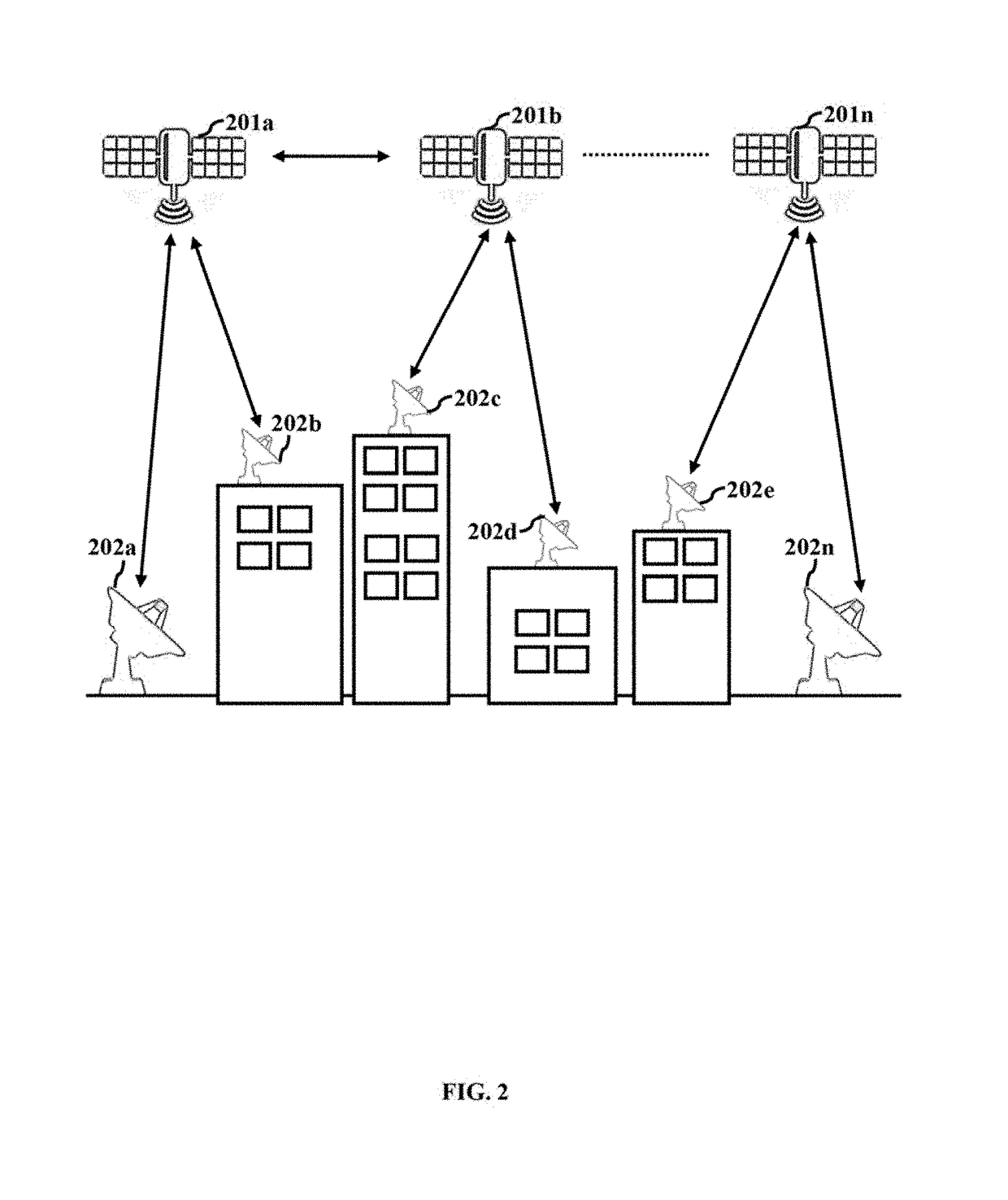
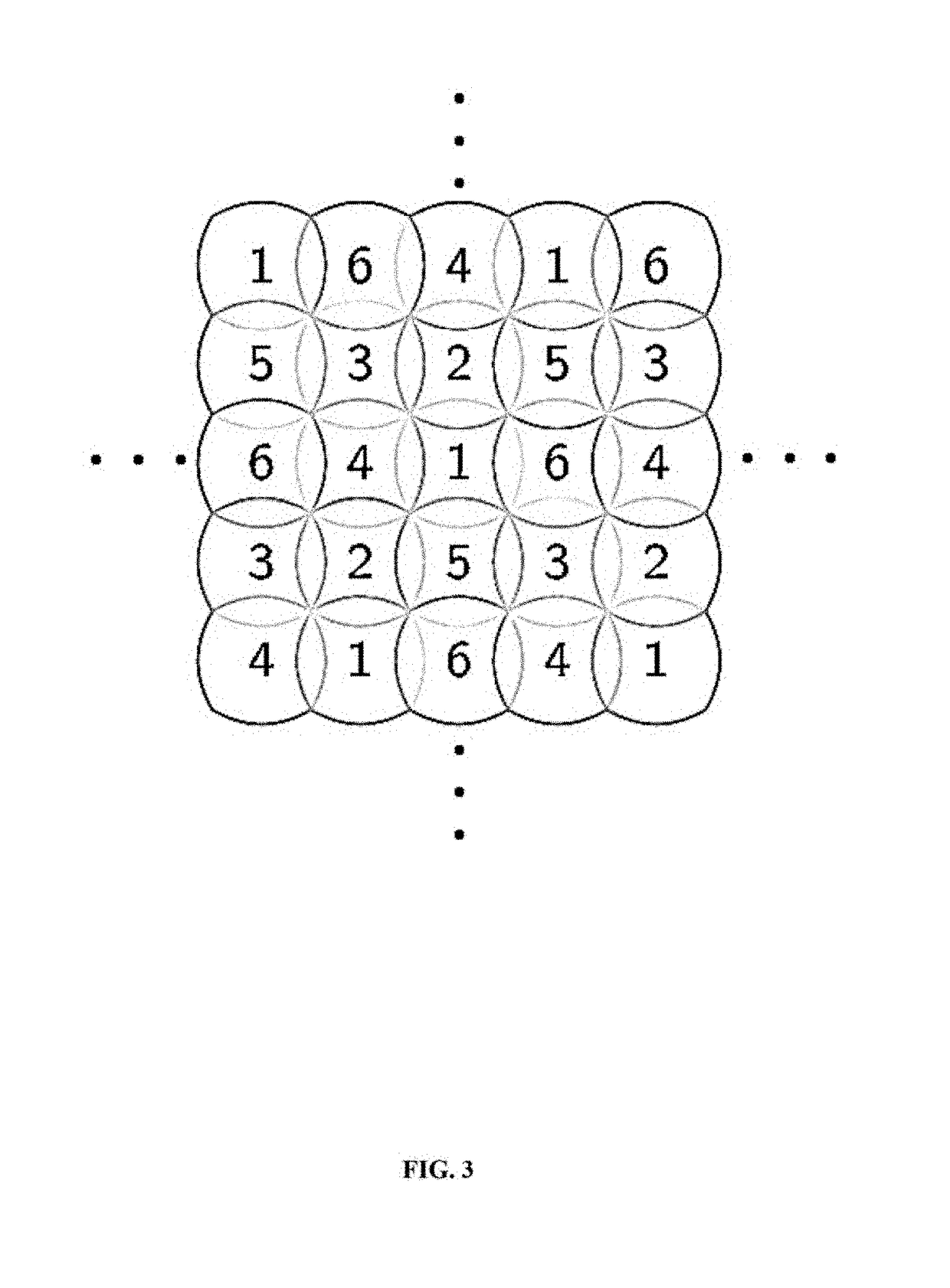
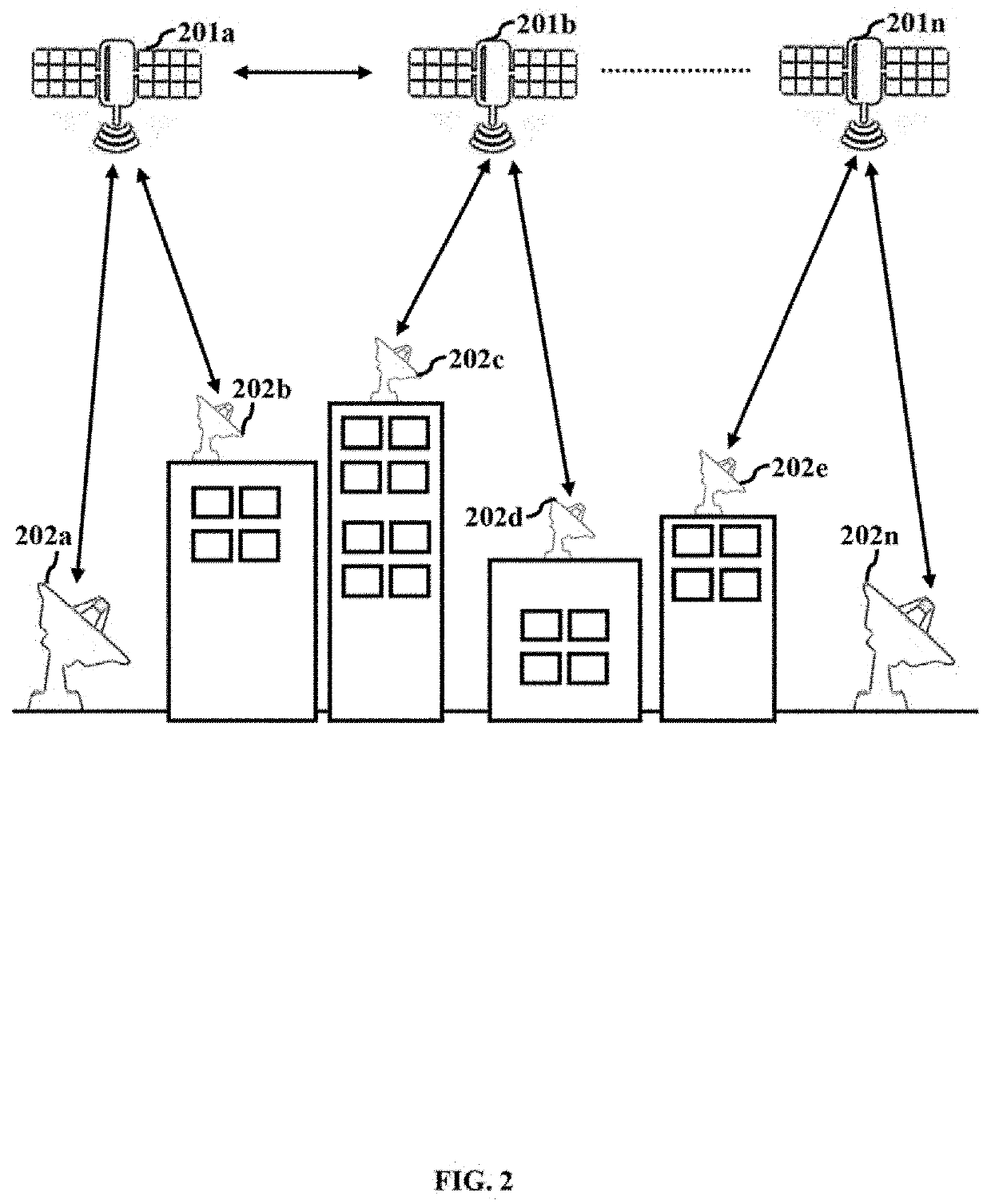
System and method for two-way ground and satellite based communication using millimeter waves
ActiveUS20190020119A1Effective utilization of availableReliable communicationPower managementSpatial transmit diversityFrequency spectrumSpatial division multiple access
The embodiments herein provide a system and method for terrestrial to terrestrial or terrestrial and space or space to space communication systems, with millimeter waves. The system enables narrow angle beam and wide angle beam communication between receivers and transmitters that are in relative motion with other receivers and transmitters in the system. The system provides uninterrupted service and good spectrum utilization by combining Spatial Division Multiple Access (SDMA) and Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) technologies. The system minimizes overall power required by a communication system by dynamically enabling and disabling specific channels based on user-availability and need. The system also increases or decreases power based on channel quality in order to maintain desired bit-rate of communication. The system also covers a large service area through a plurality of narrow angle signal beams.
Owner:ASTROME TECH PTE LTD
System and method for two-way ground and satellite based communication using millimeter waves
ActiveUS10658759B2Effective utilization of availableReliable communicationPower managementSpatial transmit diversityFrequency spectrumSpatial division multiple access
The embodiments herein provide a system and method for terrestrial to terrestrial or terrestrial and space or space to space communication systems, with millimeter waves. The system enables narrow angle beam and wide angle beam communication between receivers and transmitters that are in relative motion with other receivers and transmitters in the system. The system provides uninterrupted service and good spectrum utilization by combining Spatial Division Multiple Access (SDMA) and Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) technologies. The system minimizes overall power required by a communication system by dynamically enabling and disabling specific channels based on user-availability and need. The system also increases or decreases power based on channel quality in order to maintain desired bit-rate of communication. The system also covers a large service area through a plurality of narrow angle signal beams.
Owner:ASTROME TECH PTE LTD
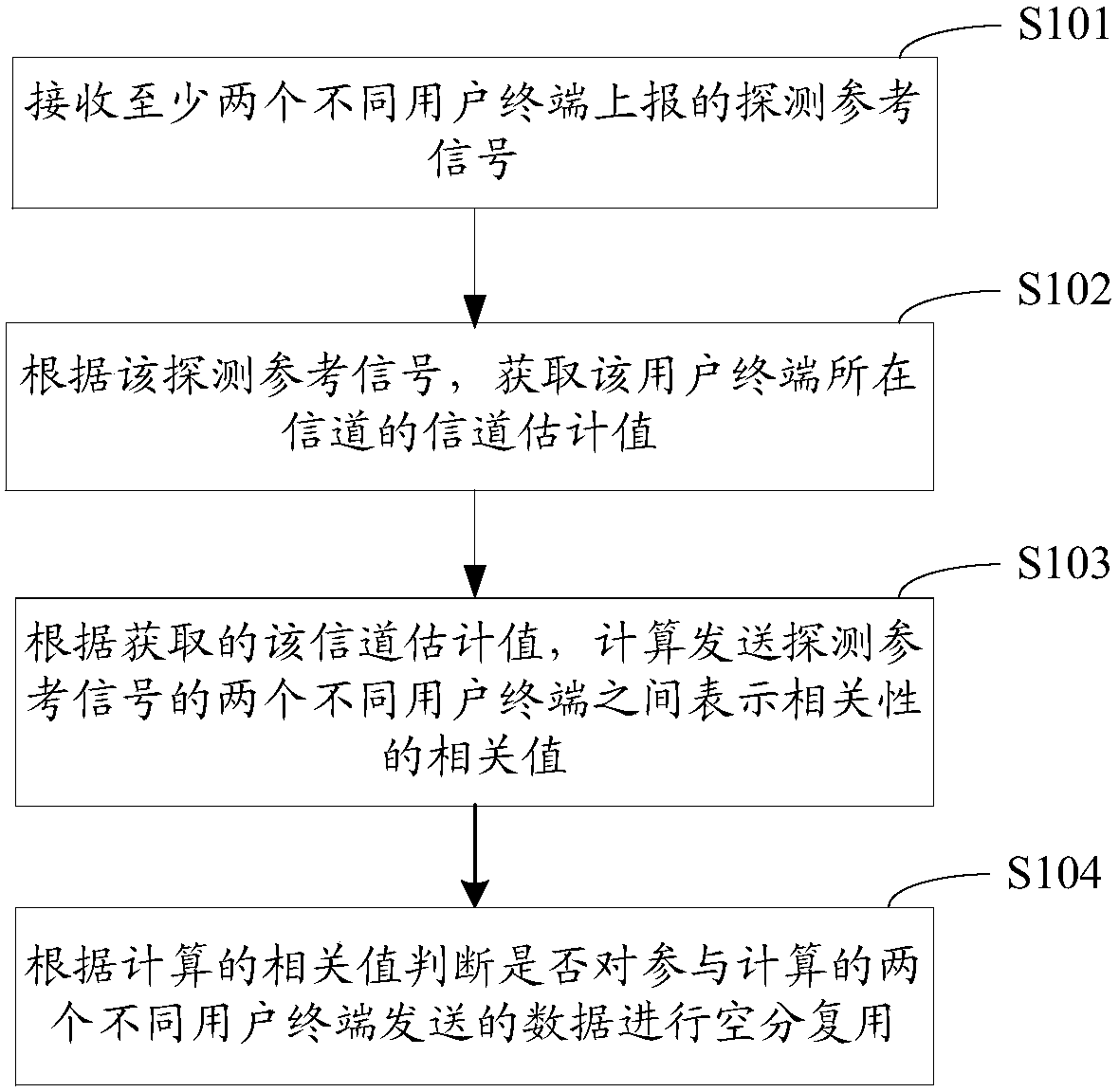
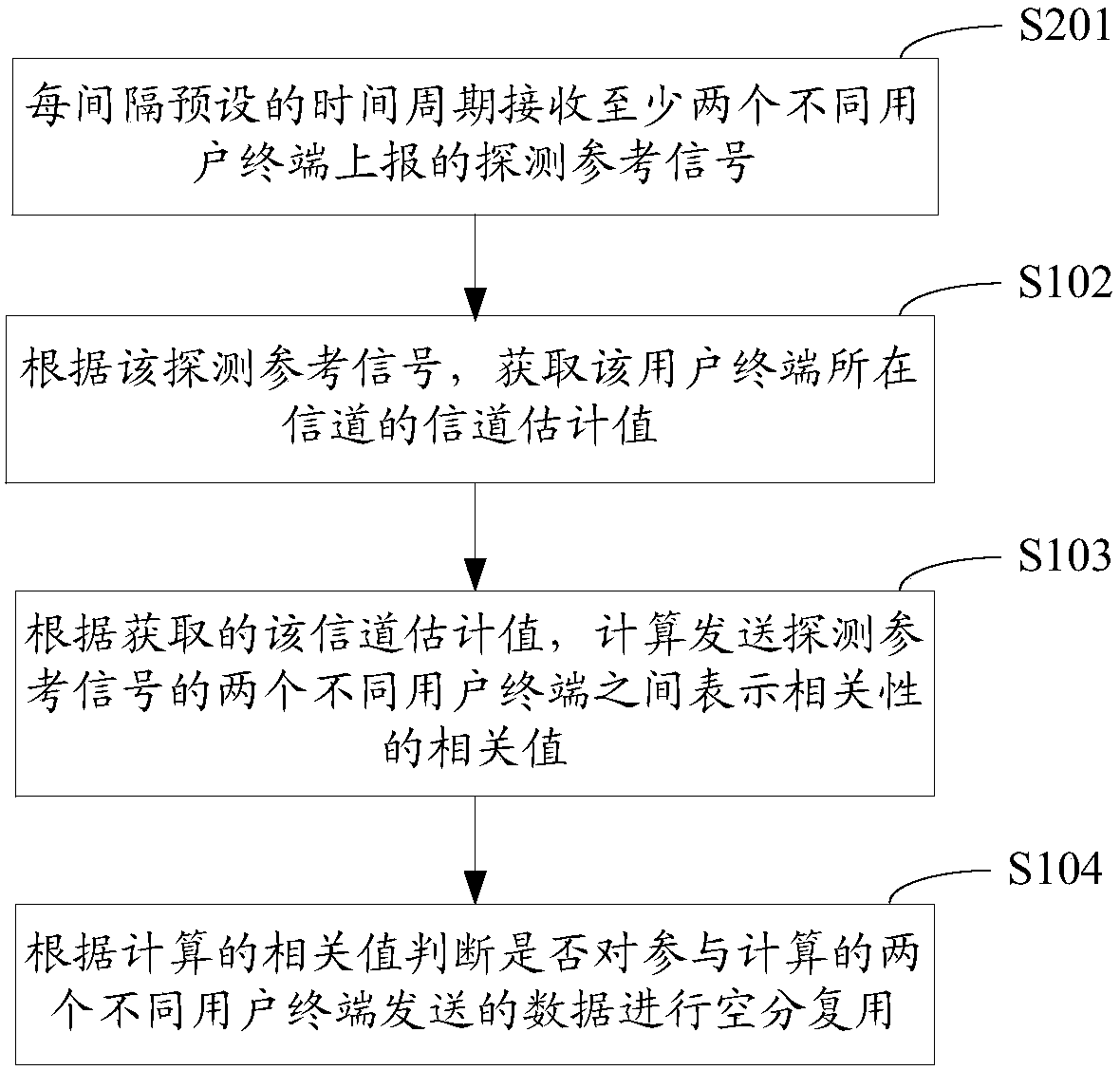
Spatial division multiple access user grouping method, apparatus, base station, and storage medium
InactiveCN108989006AIncrease upstream trafficTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationTraffic capacitySpatial division multiple access
The invention relates to a user grouping method, a device, a base station and a storage medium of space division multiple access. The user grouping method of SDMA comprises the following steps: receiving detection reference signals reported by at least two different user terminals; obtaining a channel estimation value of a channel in which the user terminal is located according to the detection reference signal; Calculating a correlation value representing a correlation between two different user terminals transmitting the detection reference signal according to the obtained channel estimationvalue; it is judged whether the data sent by the two different user terminals participating in the calculation is spatially multiplexed according to the calculated correlation value. The invention carries out space division multiplexing according to the correlation between different user terminals, and carries out space division multiplexing on the data sent by the user terminals with little correlation, so the the base station does not cause decoding error after space division multiplexing because the user terminals select orthogonal codes the interfere with each other, and the effective uplink flow in determining the bandwidth resources is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Space division multiple access method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable medium
PendingCN112702150AInter user/terminal allocationWireless communicationComputer hardwareComputer network
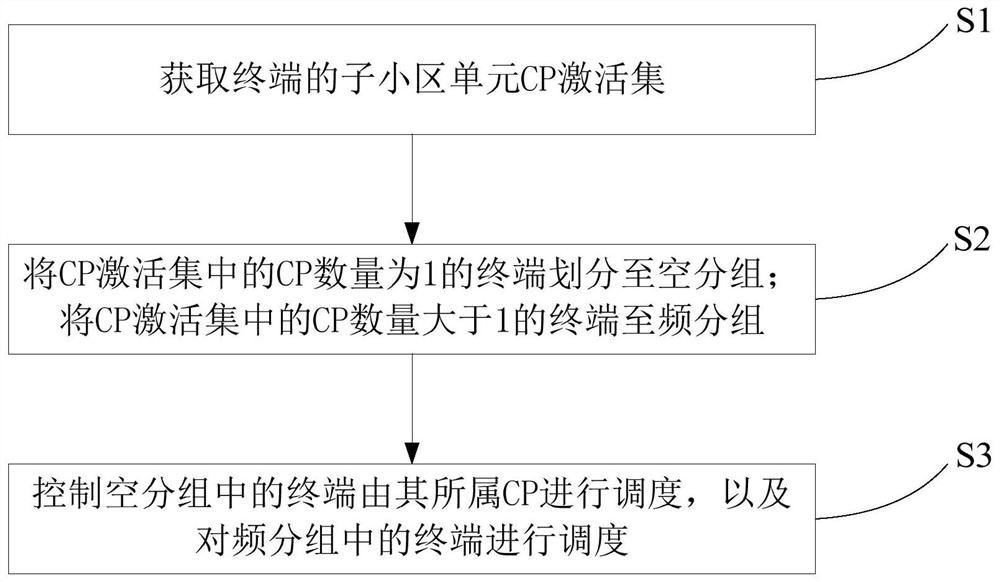
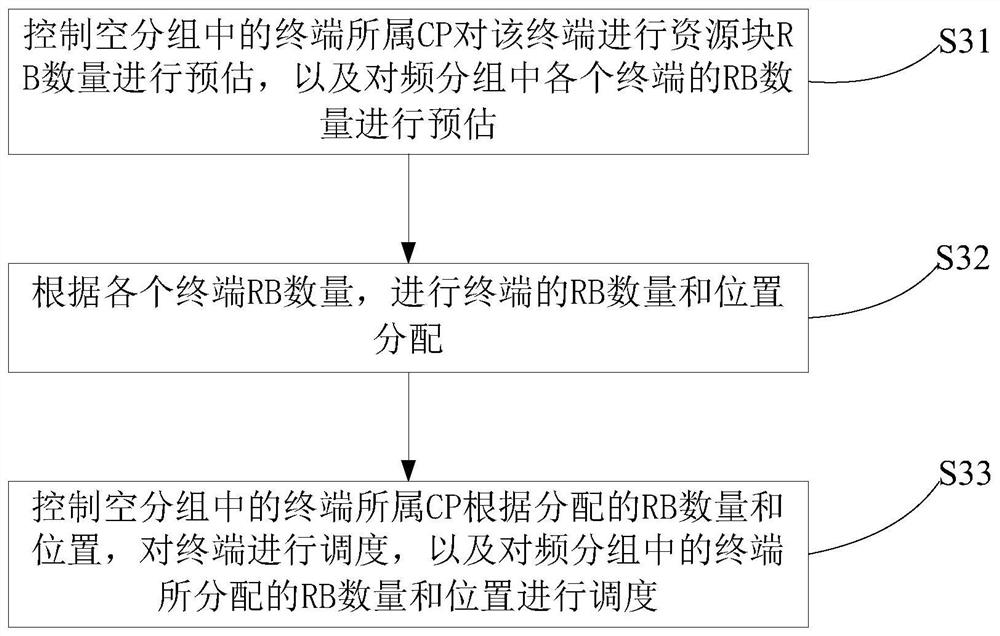
The invention provides a space division multiple access method under a super cell. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a sub-cell unit CP activation set of a terminal; dividing terminals with the CP number of 1 in the CP activation set into empty groups; grouping the terminals of which the CP number in the CP activation set is greater than 1 into frequency groups; controlling the terminals in the empty packets to be scheduled by the CPs to which the terminals belong, and scheduling the terminals in the frequency packets. The invention further provides a space division multiple access device under the super cell, electronic equipment and a computer readable medium.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Space division multiple access communication method based on harmonic modulation technology
PendingCN111132334AIncrease profitTap and inspire potentialRadio transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsInformation transmissionSpatial division multiple access
The invention discloses a space division multiple access communication method based on a harmonic modulation technology. According to the method, an adaptive array antenna is adopted to realize spacedivision and form different wave beams in different user directions, and different antenna wave beams are used to provide information access for users in different areas. The same carrier frequency ordifferent carrier frequencies used for serving different areas covered by the antenna beams adopt fundamental frequency and harmonic wave for information transmission. The information transmission process comprises the following steps: firstly, modulating different information, then respectively loading the modulated information on different harmonic components or component combinations, and finally demodulating fundamental frequency and harmonic information received by a receiving end. According to the method, the capability of harmonic information transmission is fully utilized, the utilization rate of the frequency spectrum is greatly improved, potential of the existing frequency spectrum resource is greatly mined and excited, and therefore the existing space division multiple access communication method can be greatly splendid in the upcoming 5G era.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
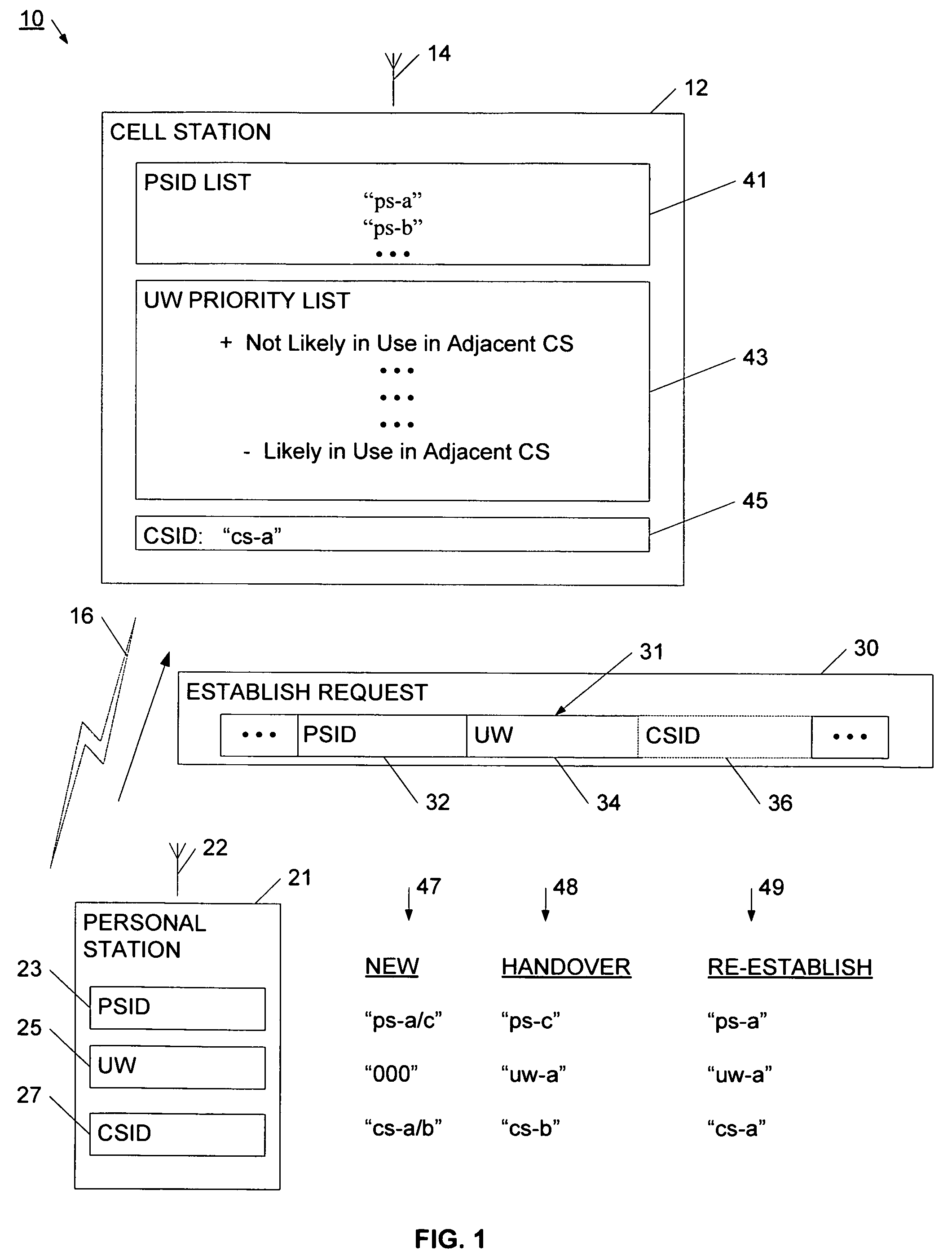
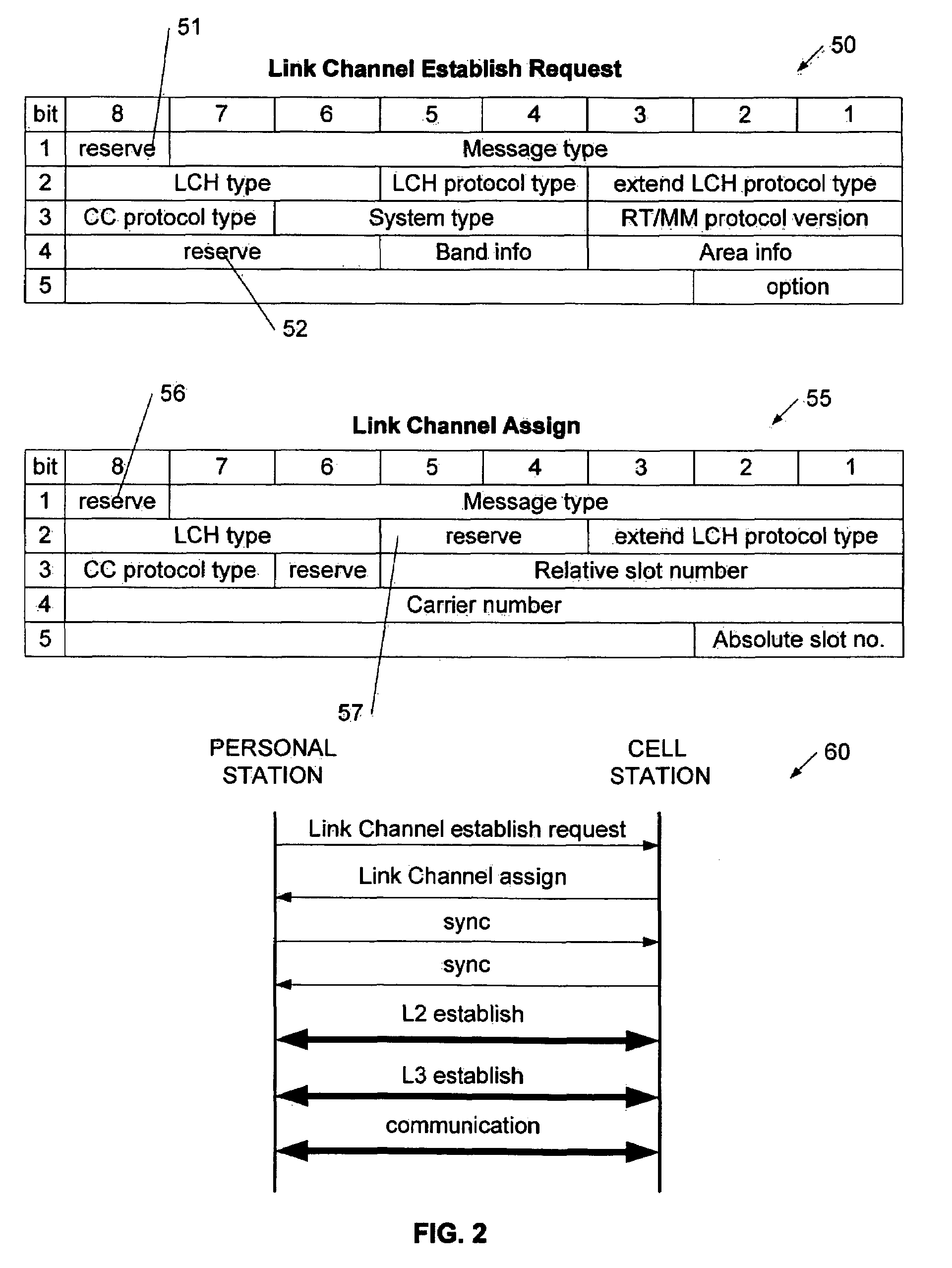
Method for assigning a unique word in a communication system
InactiveUS7697494B2Promote differentiationHigh sensitivityData switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesSpatial division multiple accessCommunications system
A method and system for assigning unique words in an SDMA (spatial division multiple access) communication system is disclosed. A base station has a set of available unique words from which to select and assign unique words. The base station prioritizes the set of unique words by determining which unique words are likely to interfere with adjacent base stations, and setting those words to a low priority. In this way, over time, the base station assigns unique words that have a lower level of correlation to allow for better signal differentiation and improved communication sensitivity. When a mobile device enters a base station's geographic area, it generates an establish request message that indicates what unique word it is using in the adjacent cell. The base station extracts this unique word, and sets it to a low priority in its set of unique words. The base station is therefore able to assign unique words that facilitate improved communications.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com