Patents
Literature
77 results about "Downlink beamforming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
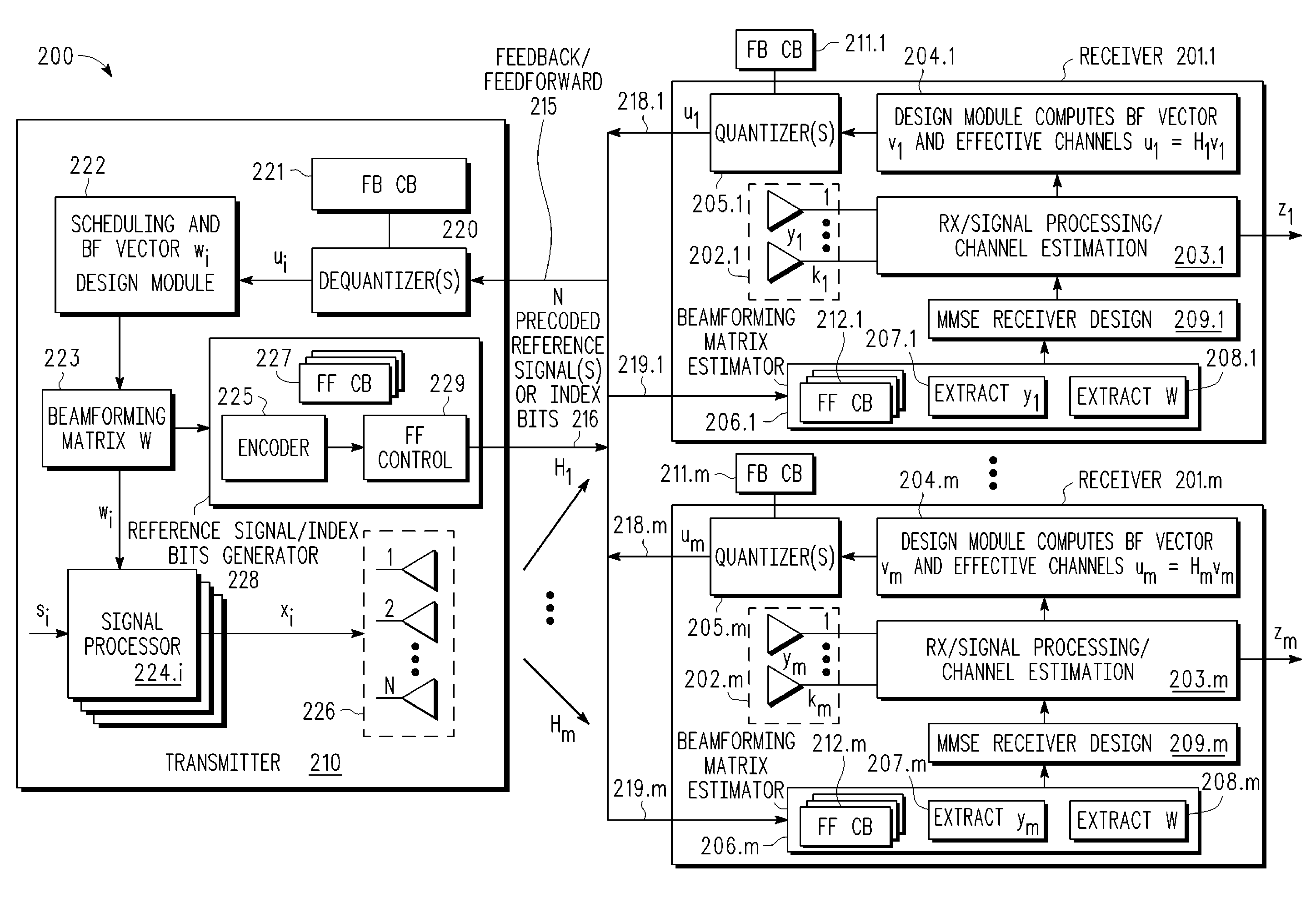
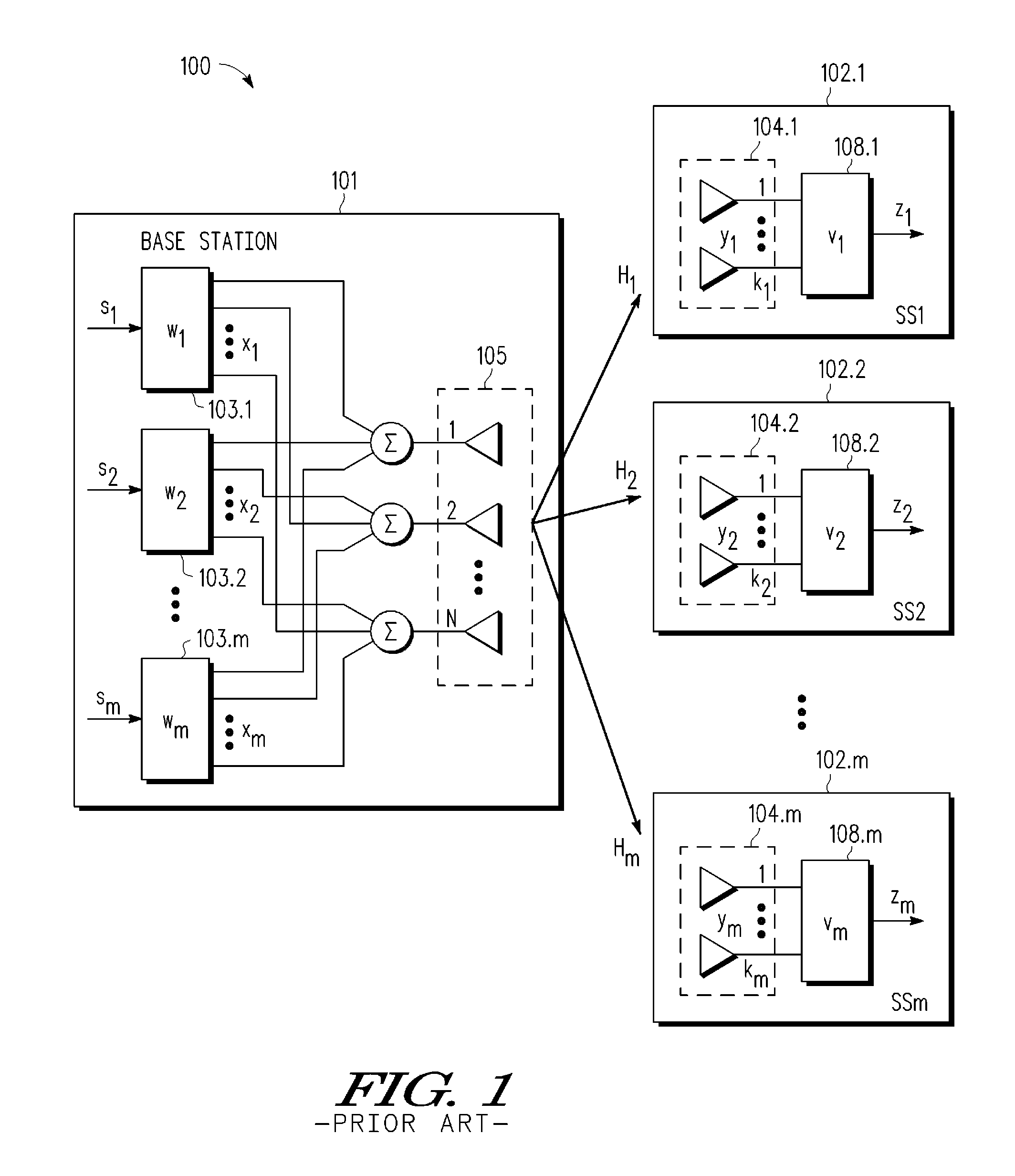
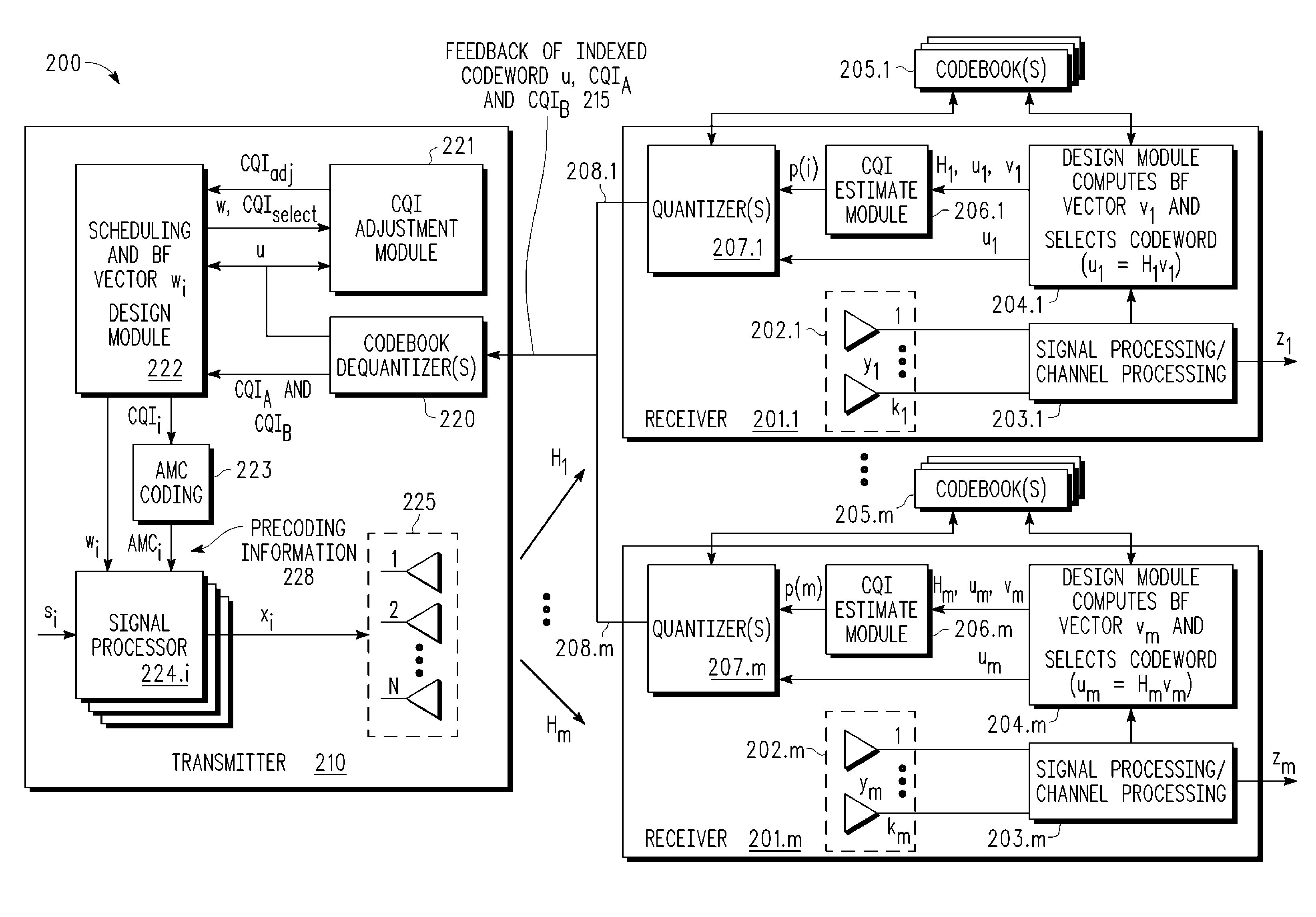
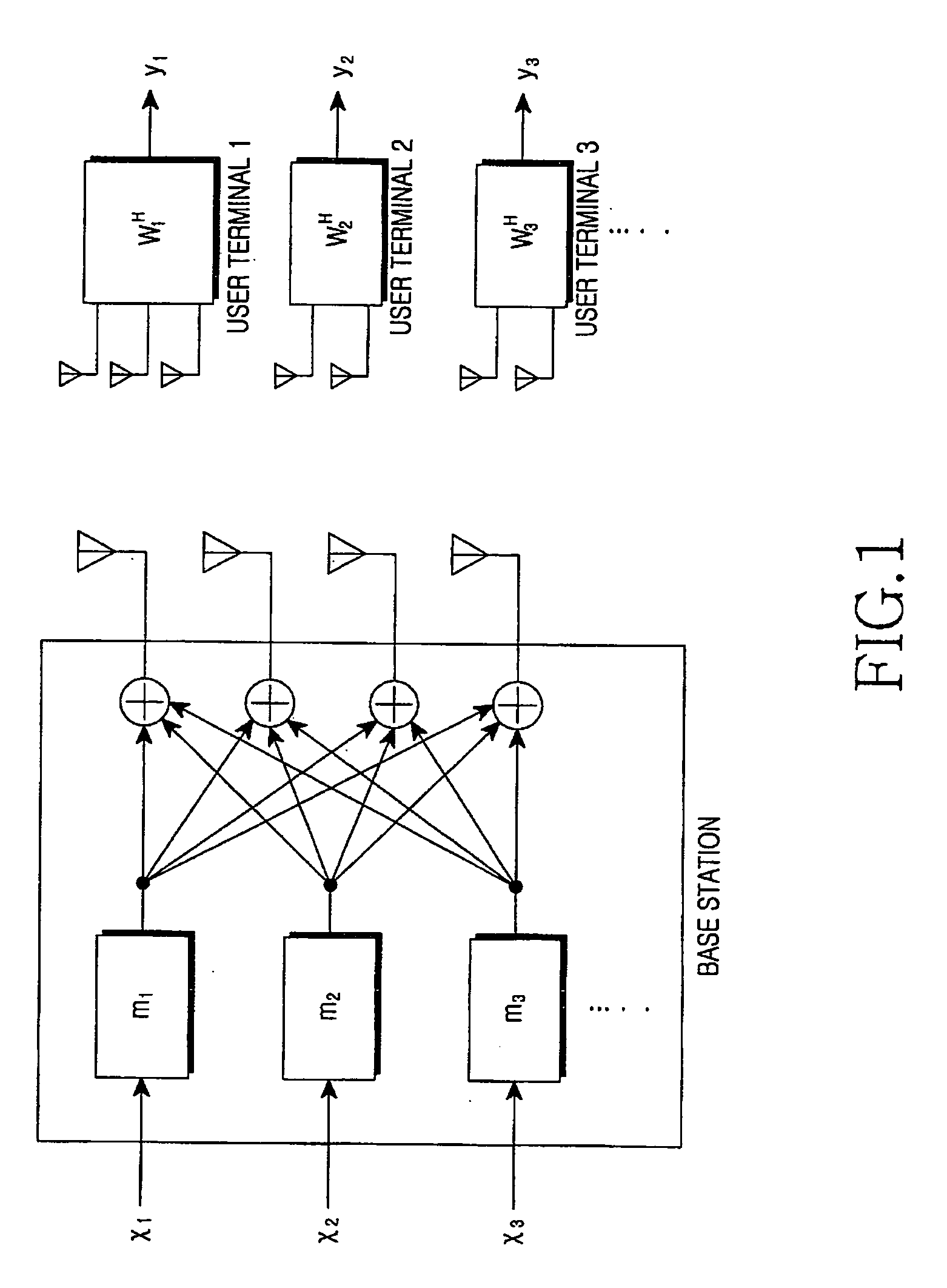
Multi-user MIMO-SDMA for finite rate feedback systems
ActiveUS20080165875A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationDownlink beamformingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
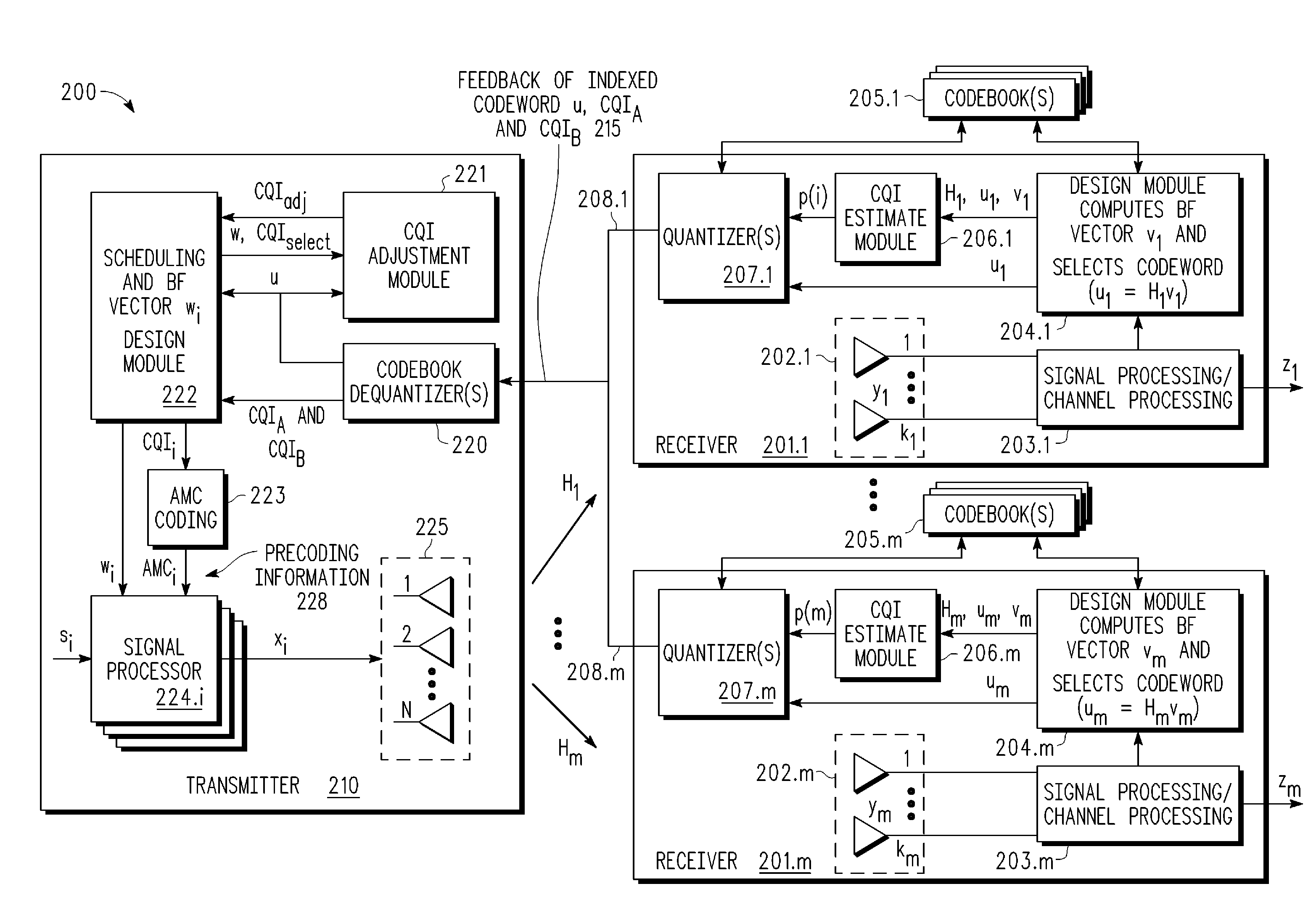
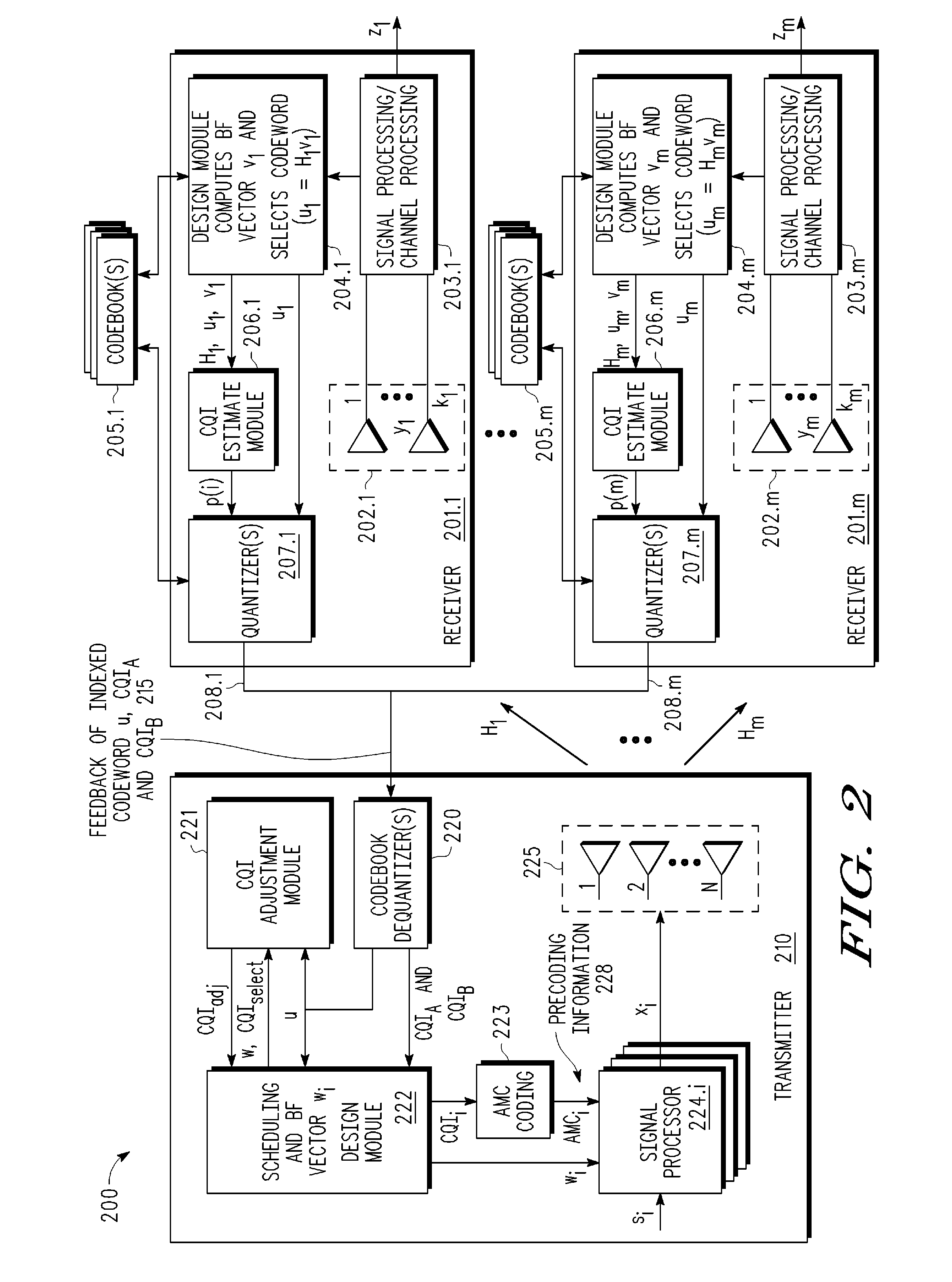
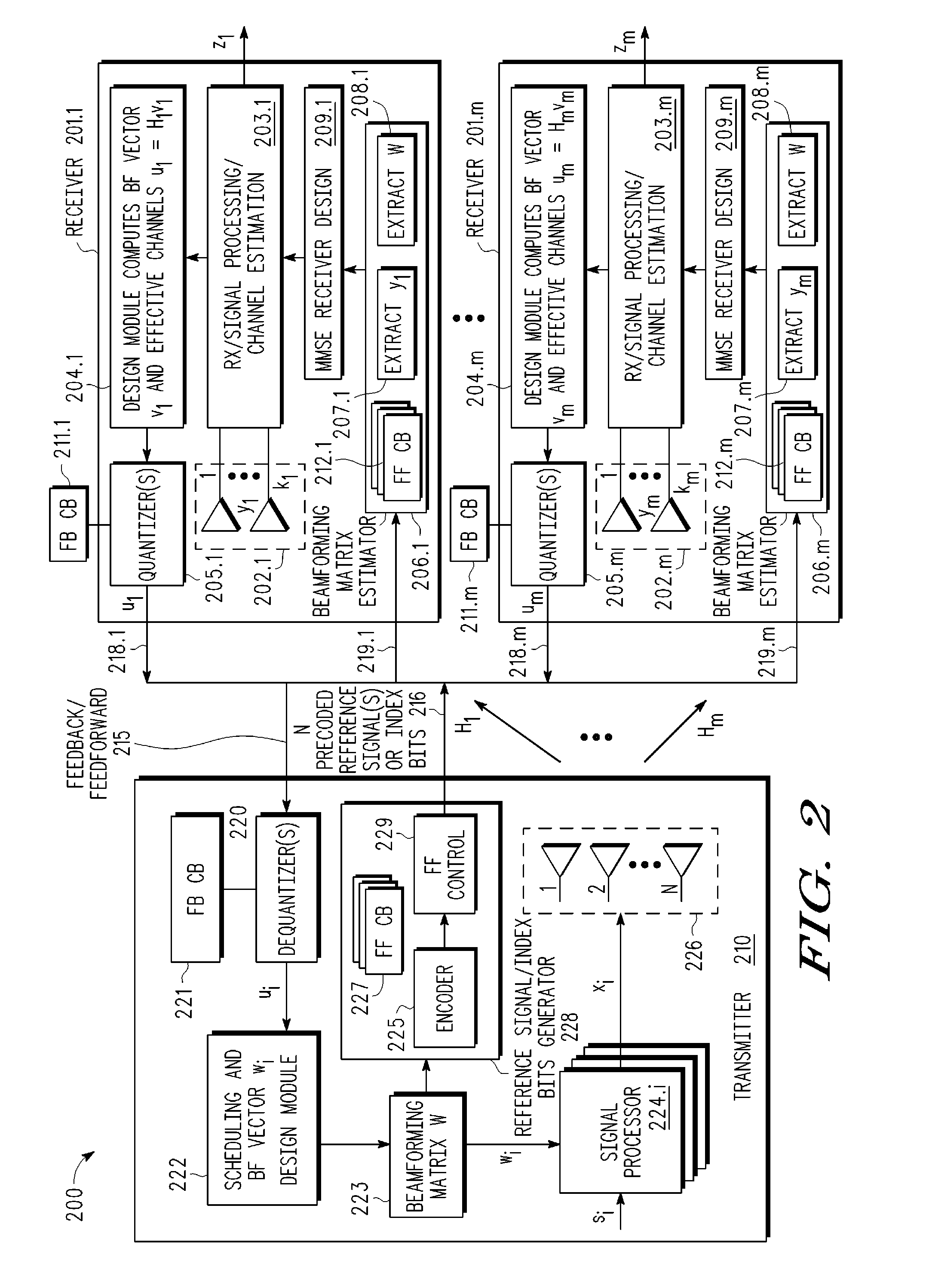
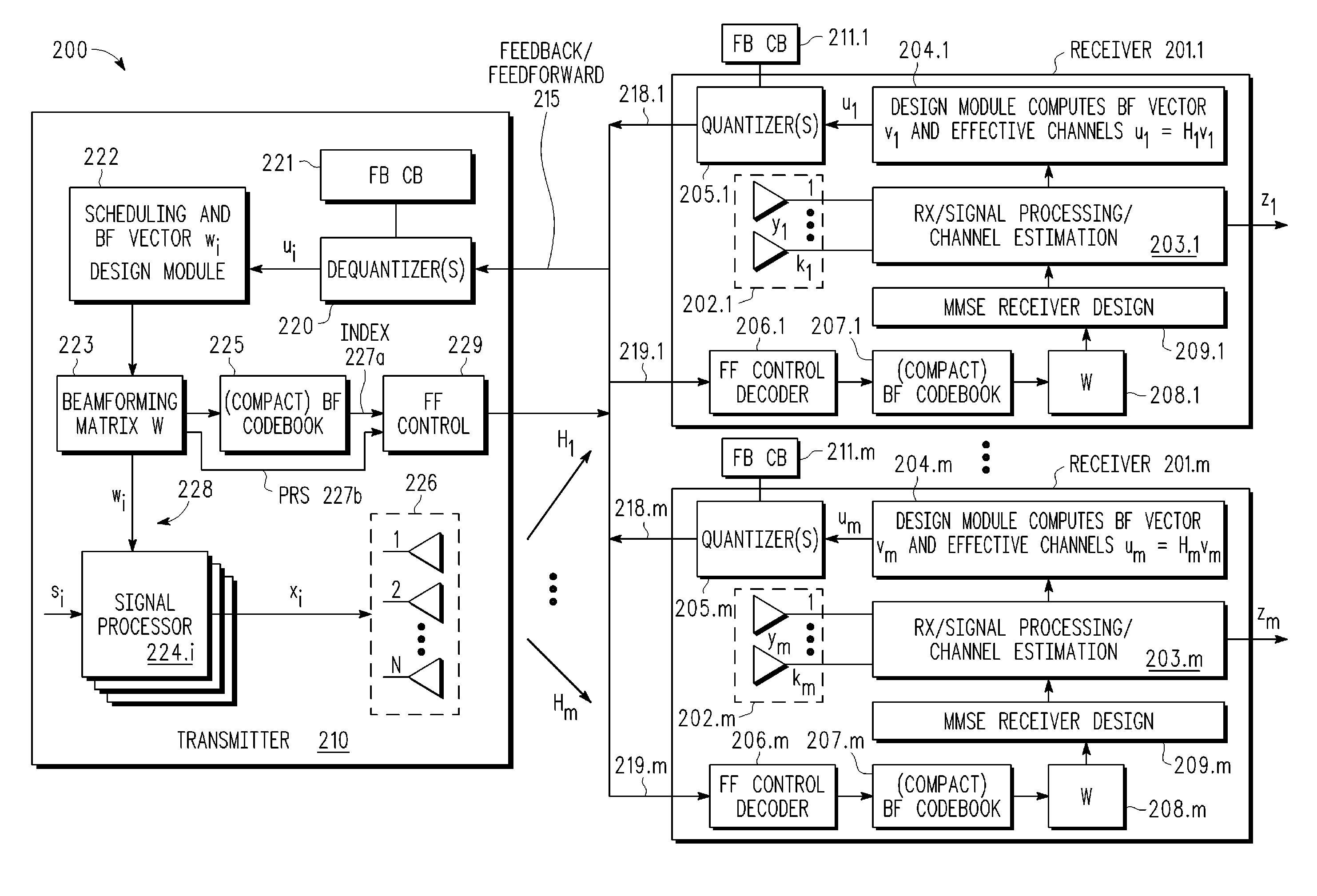
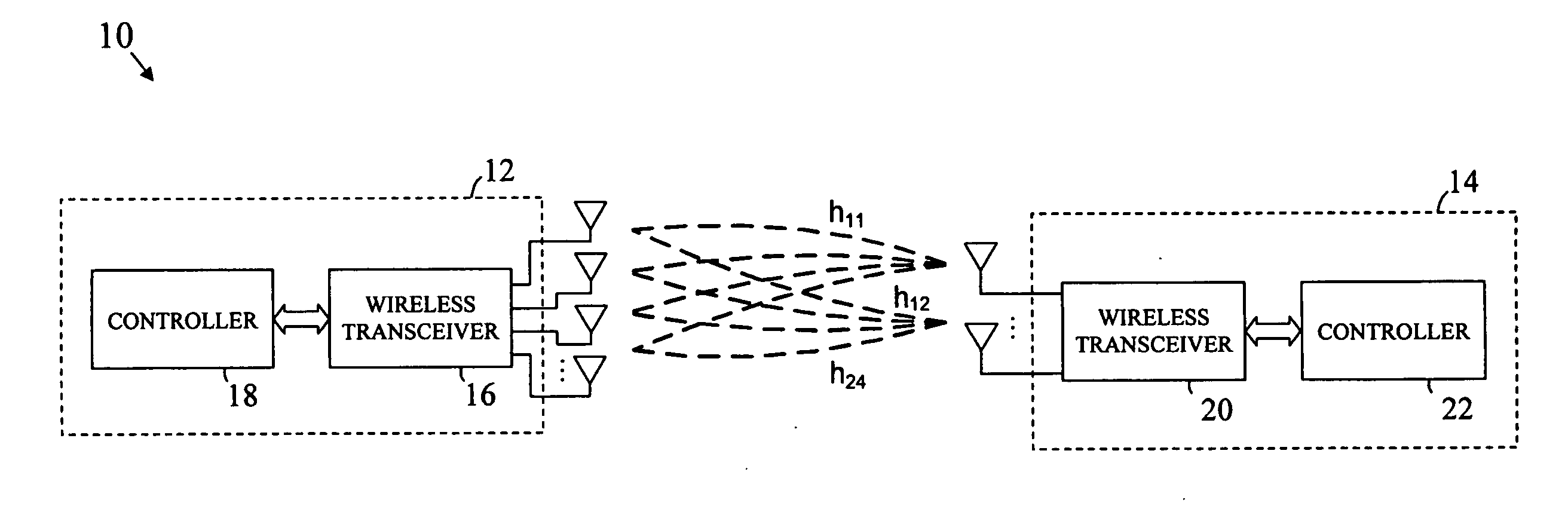
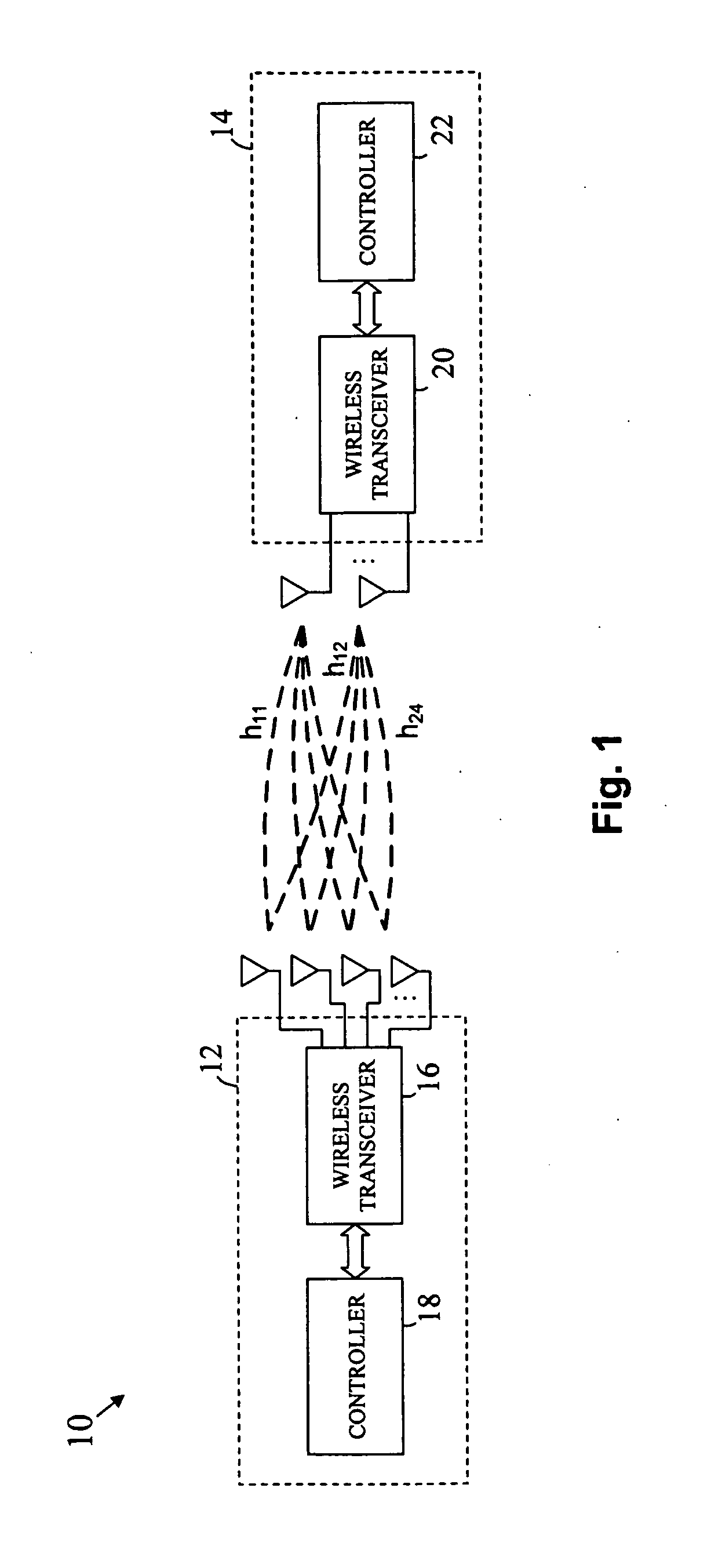
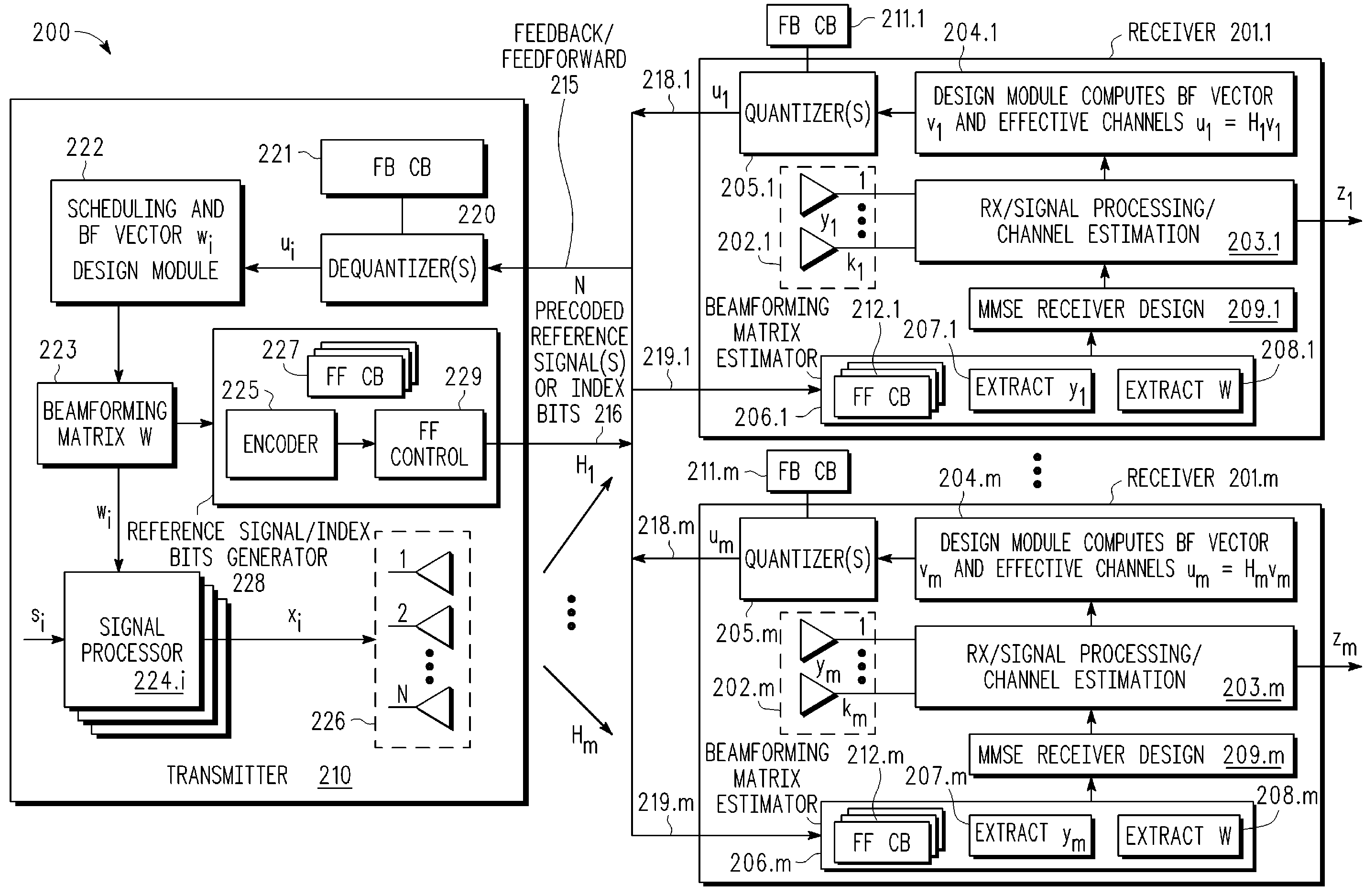
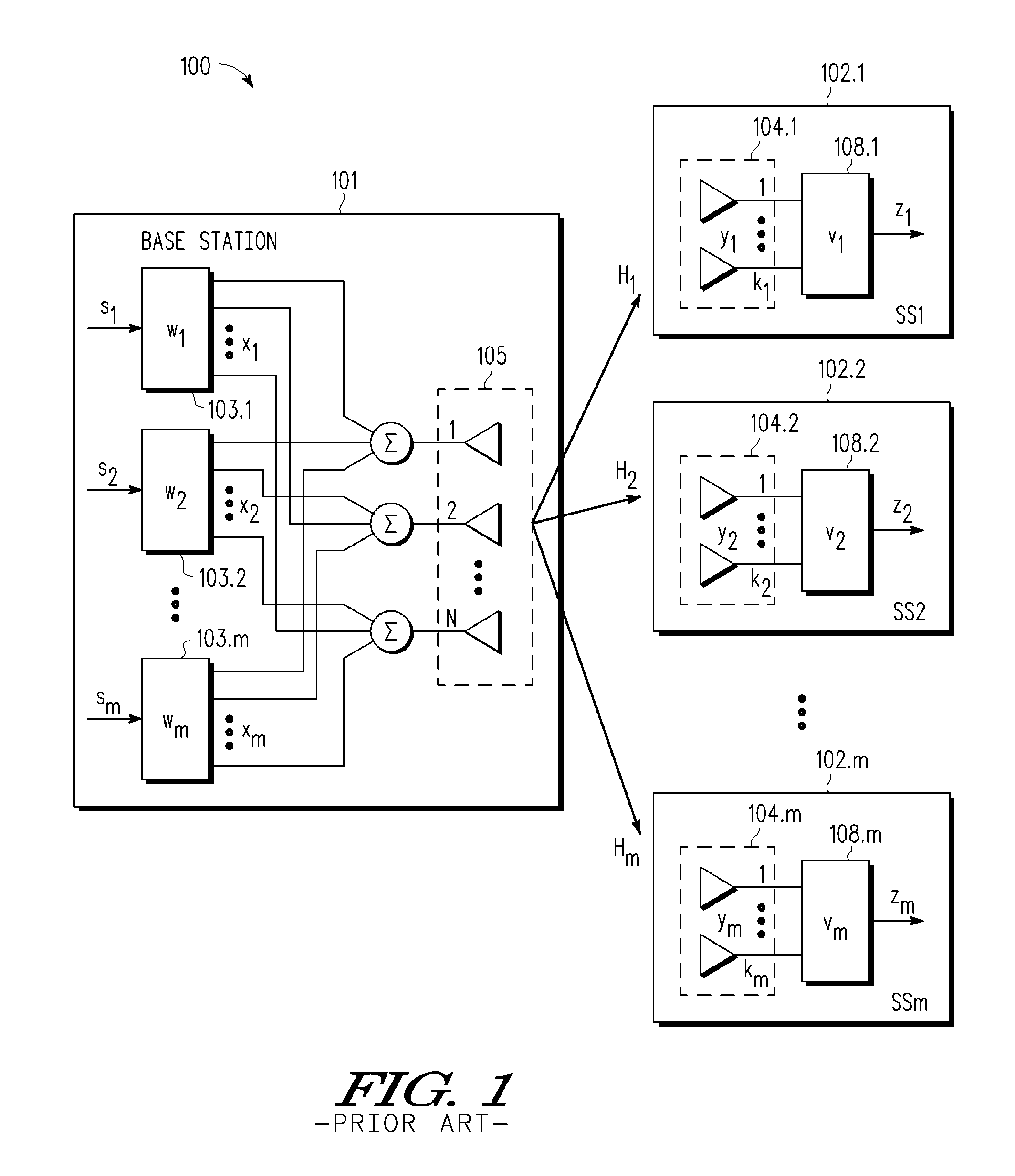
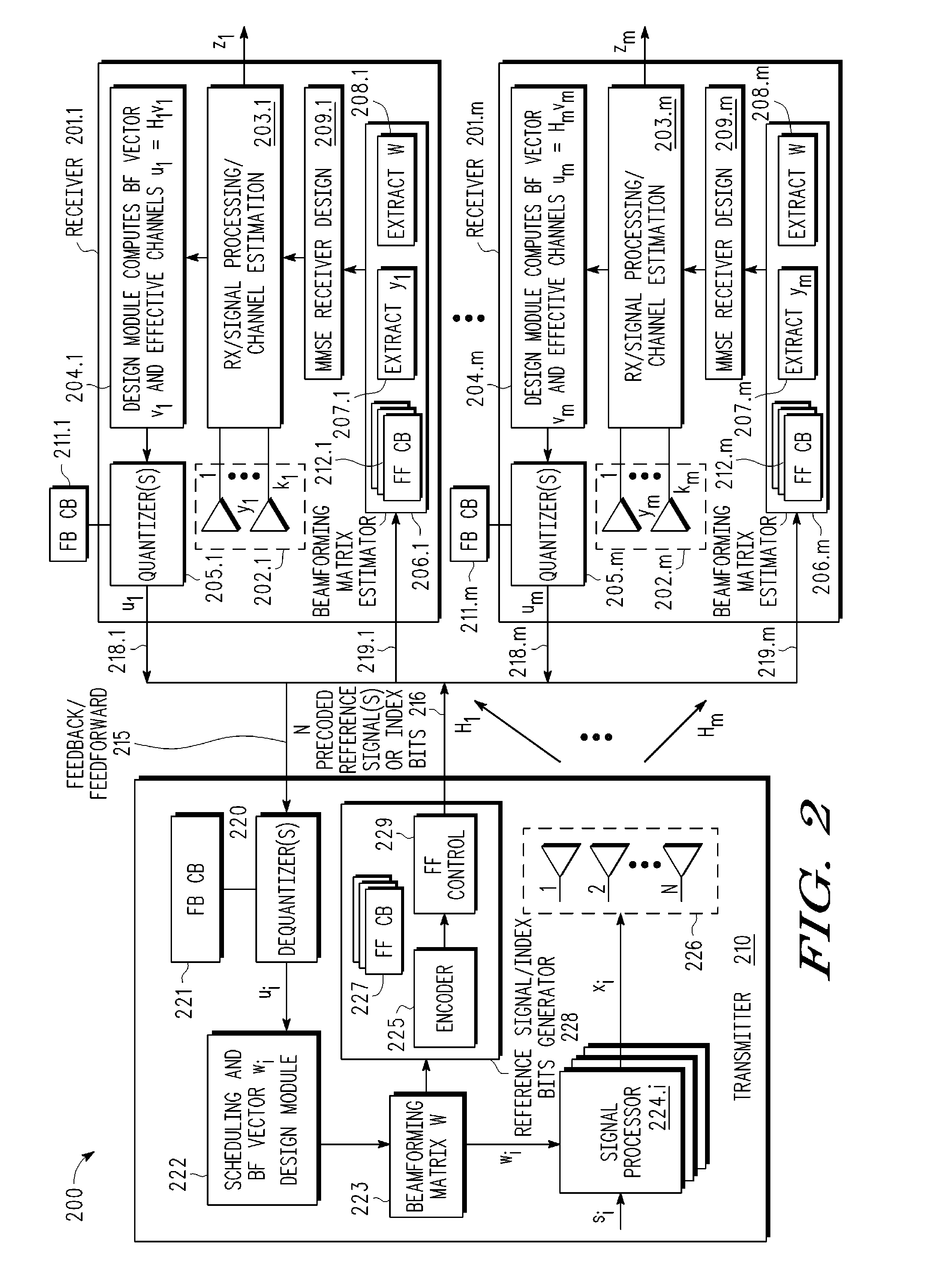
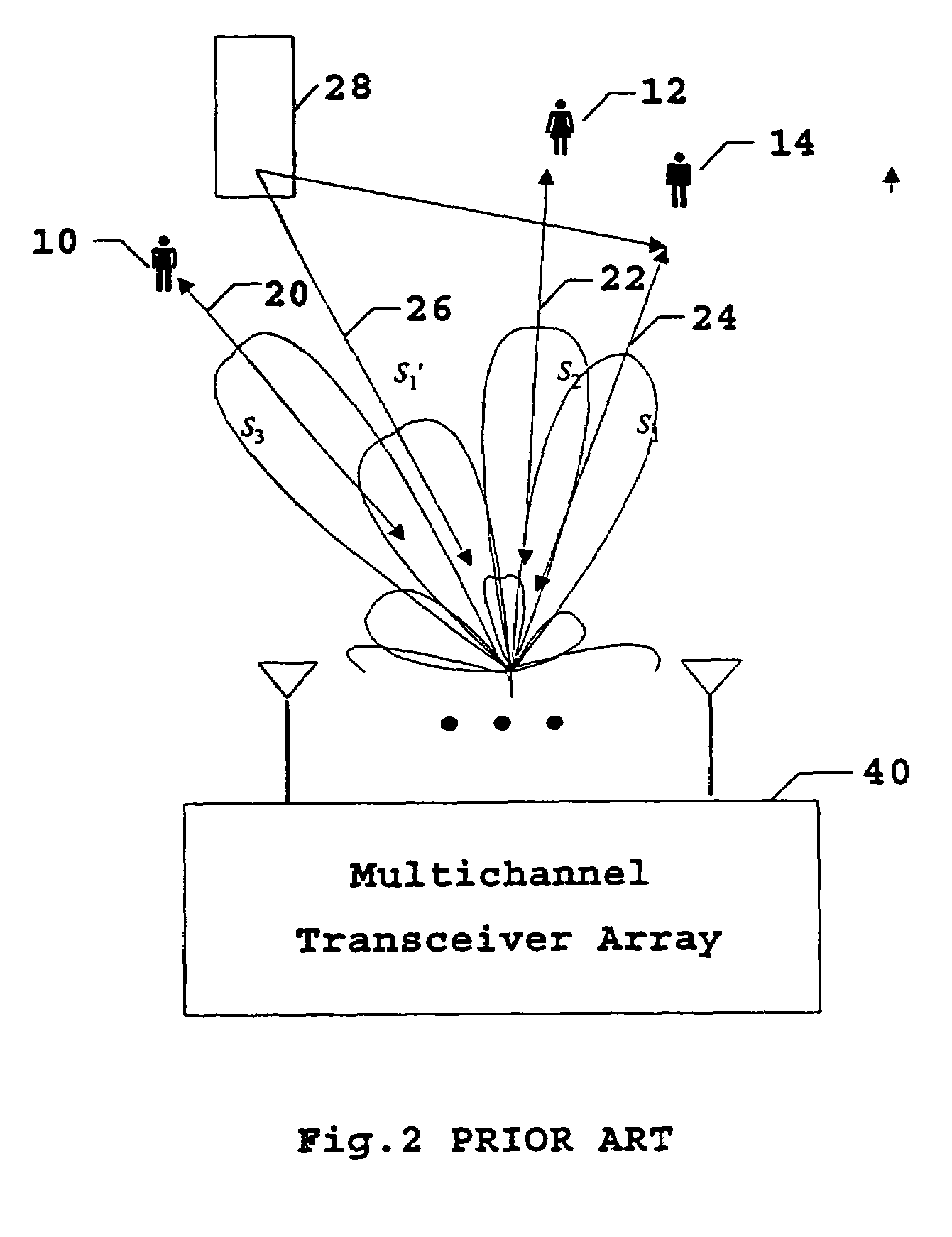
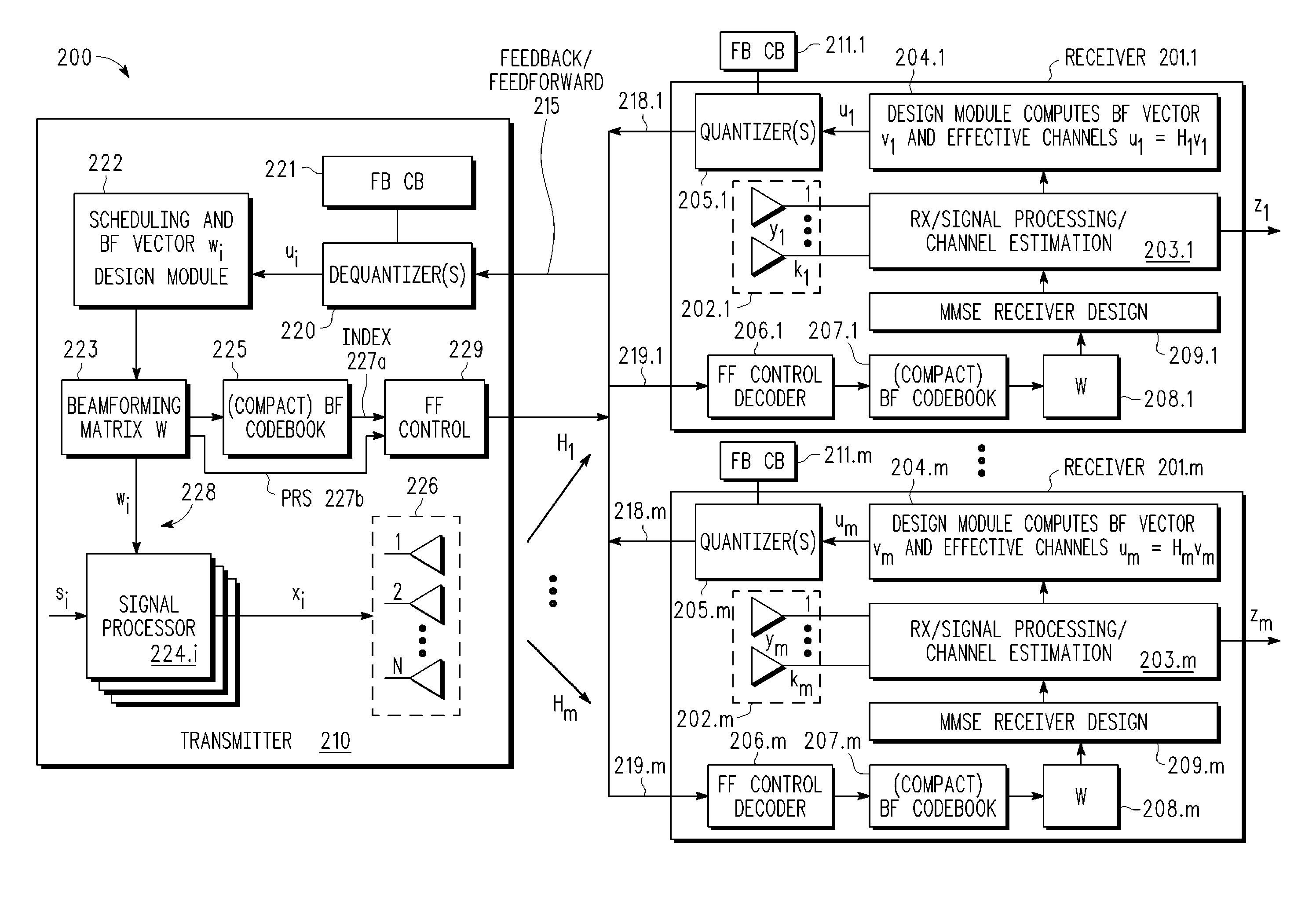
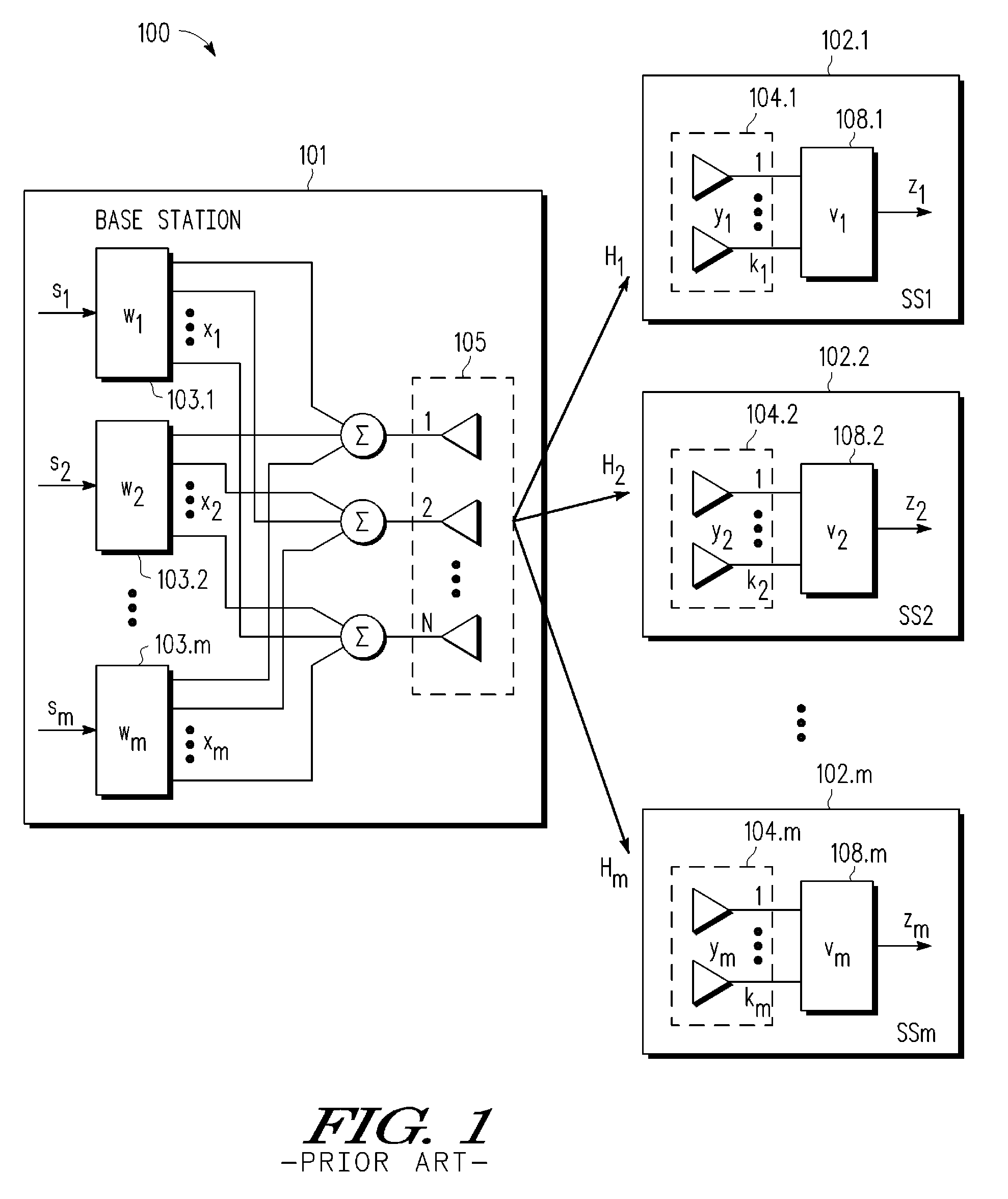
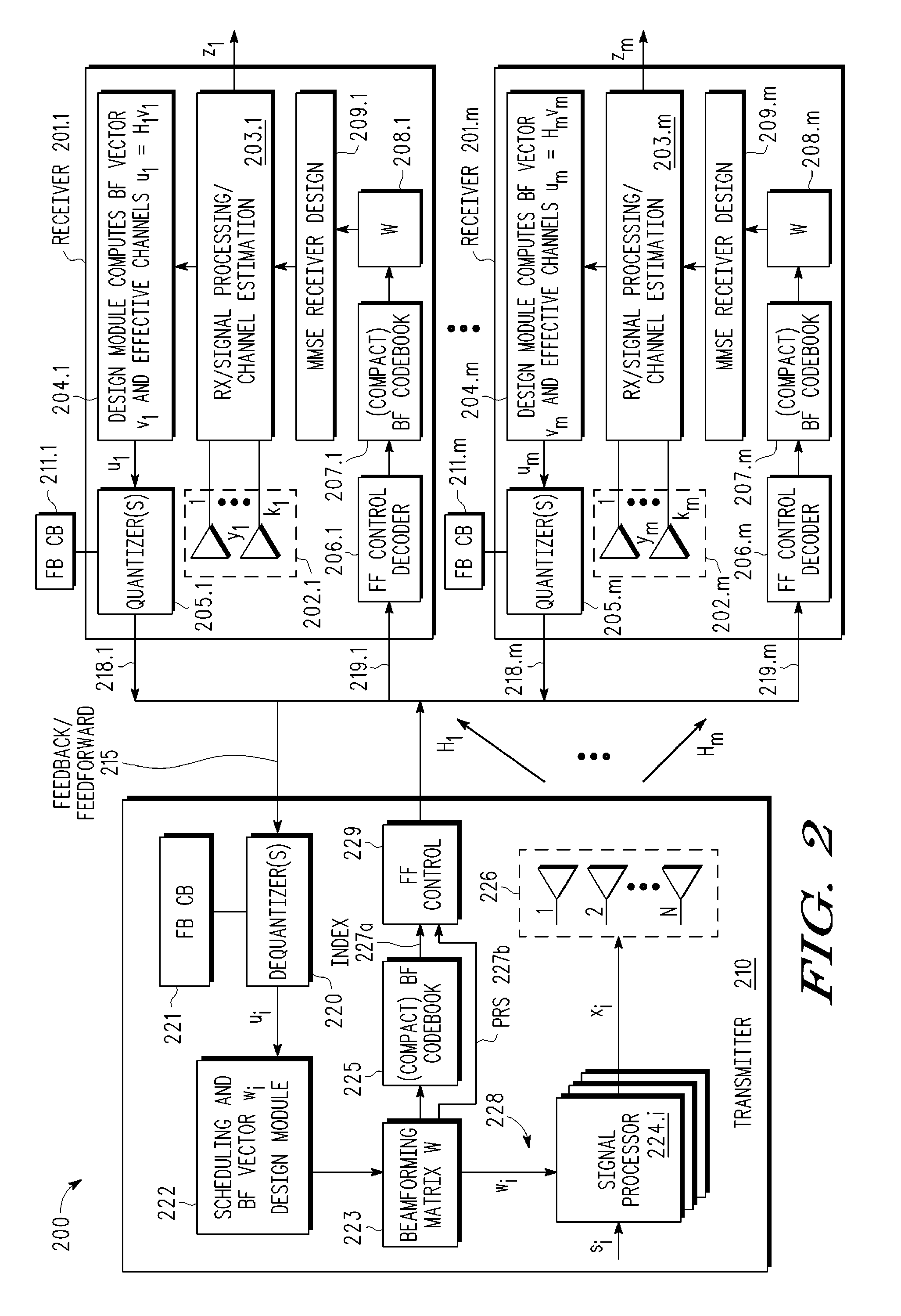
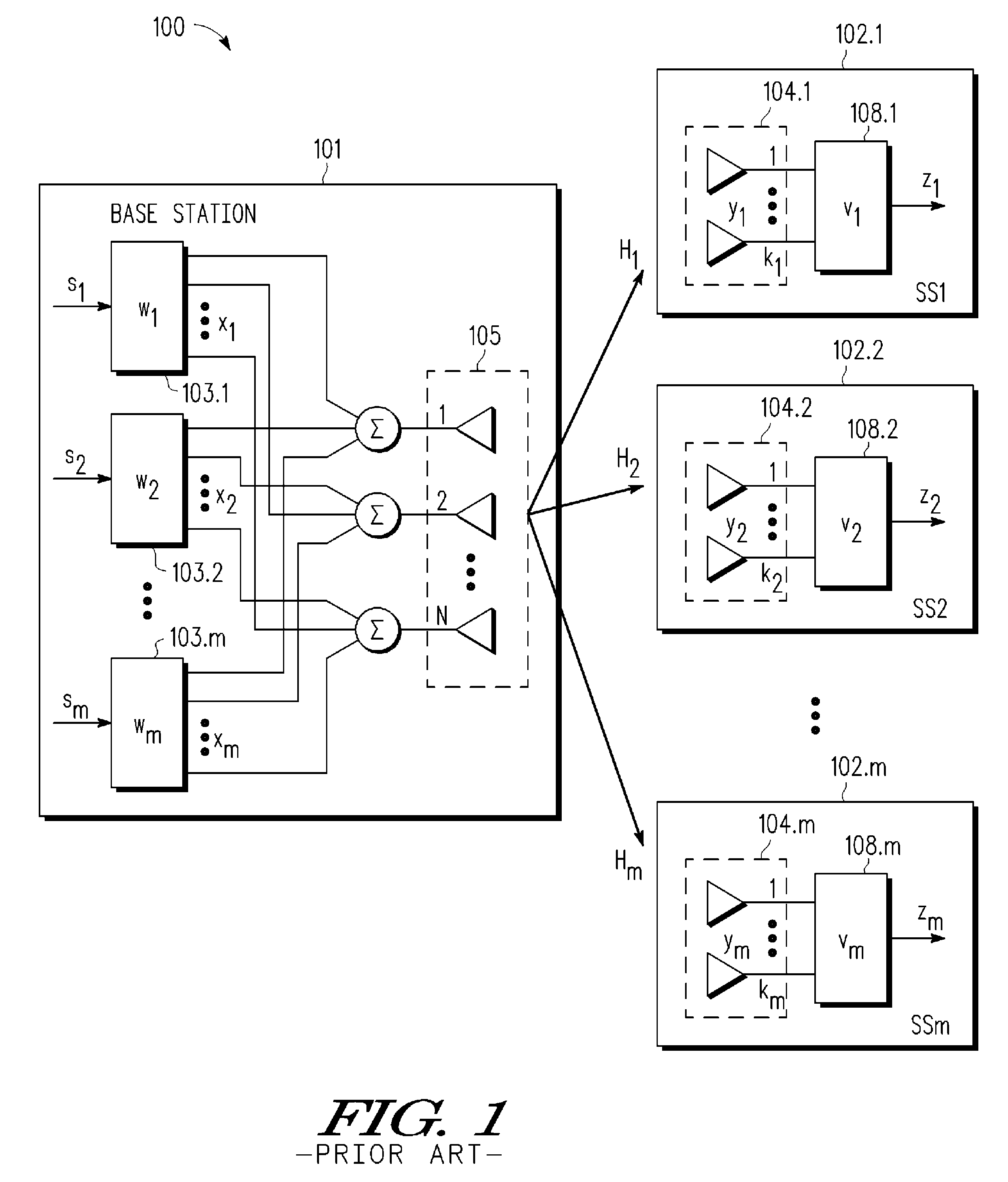
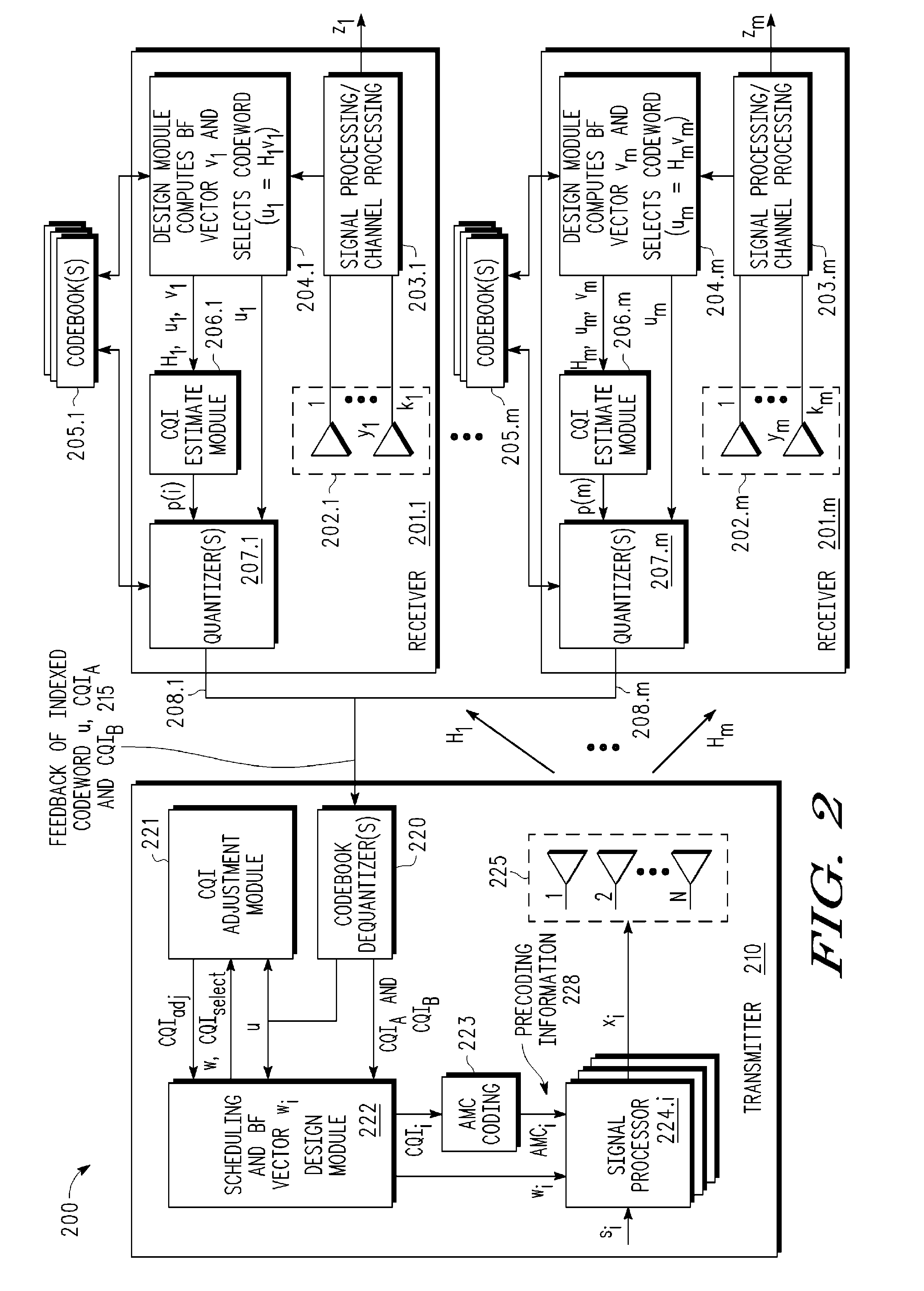
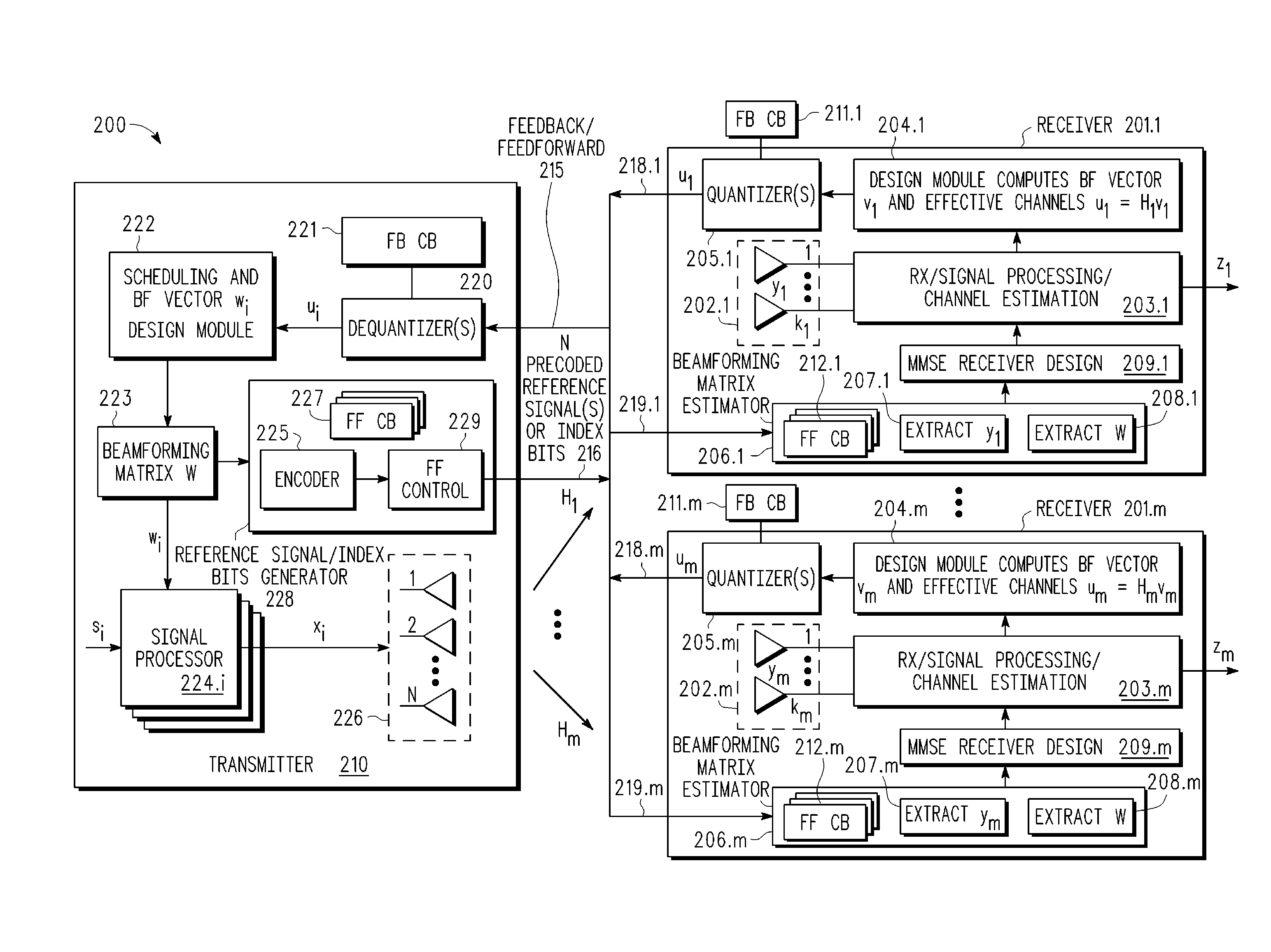
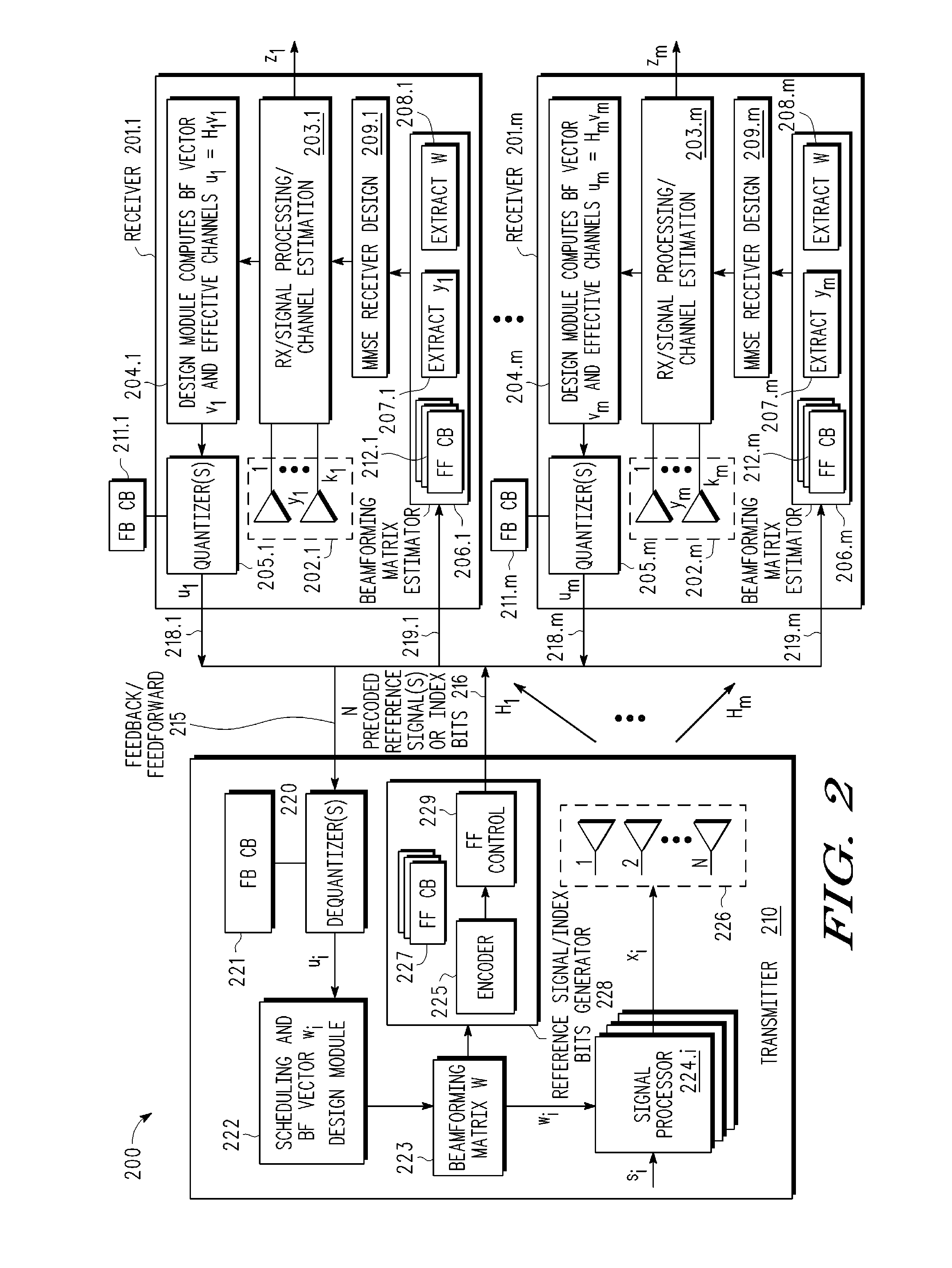
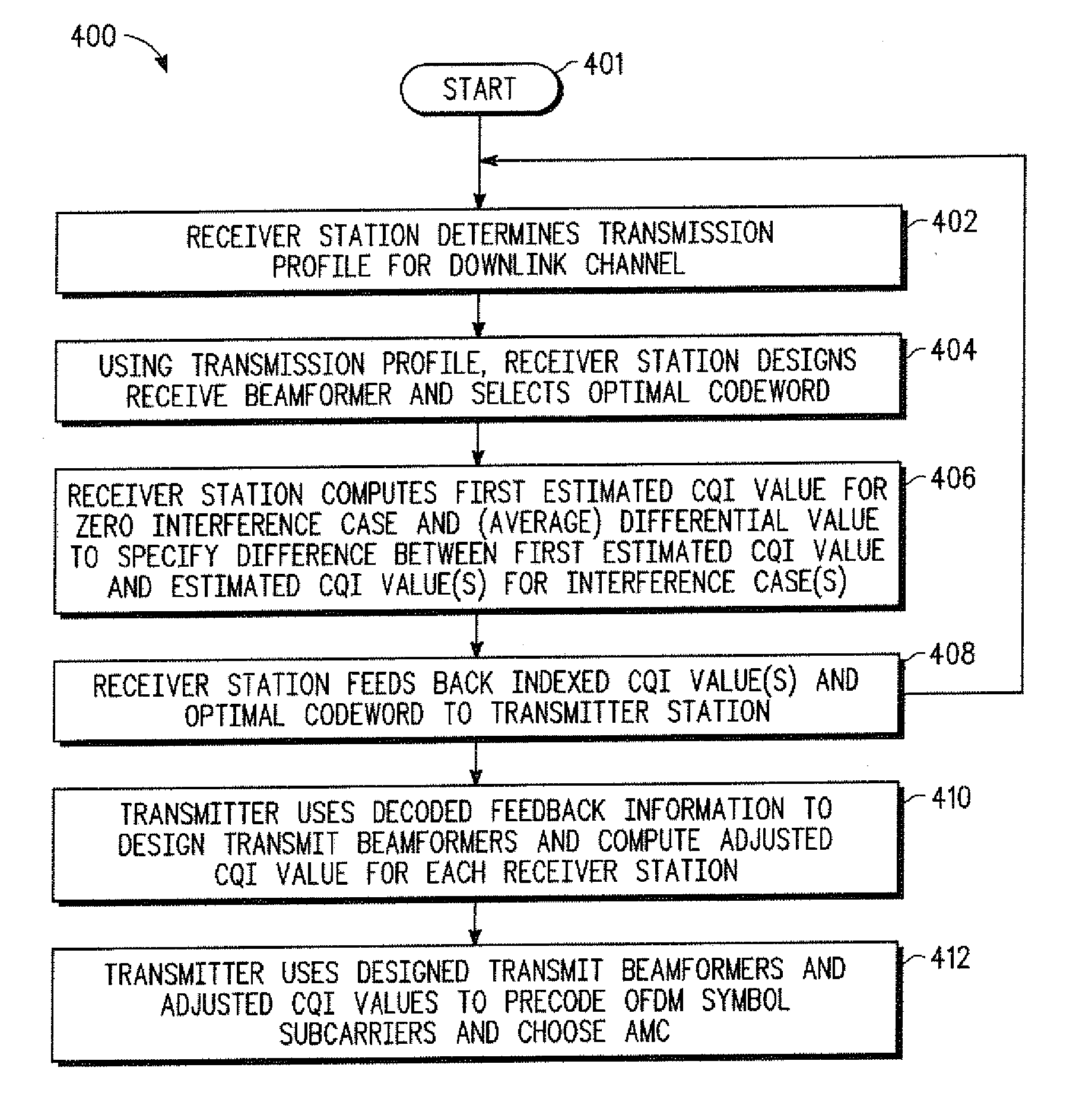
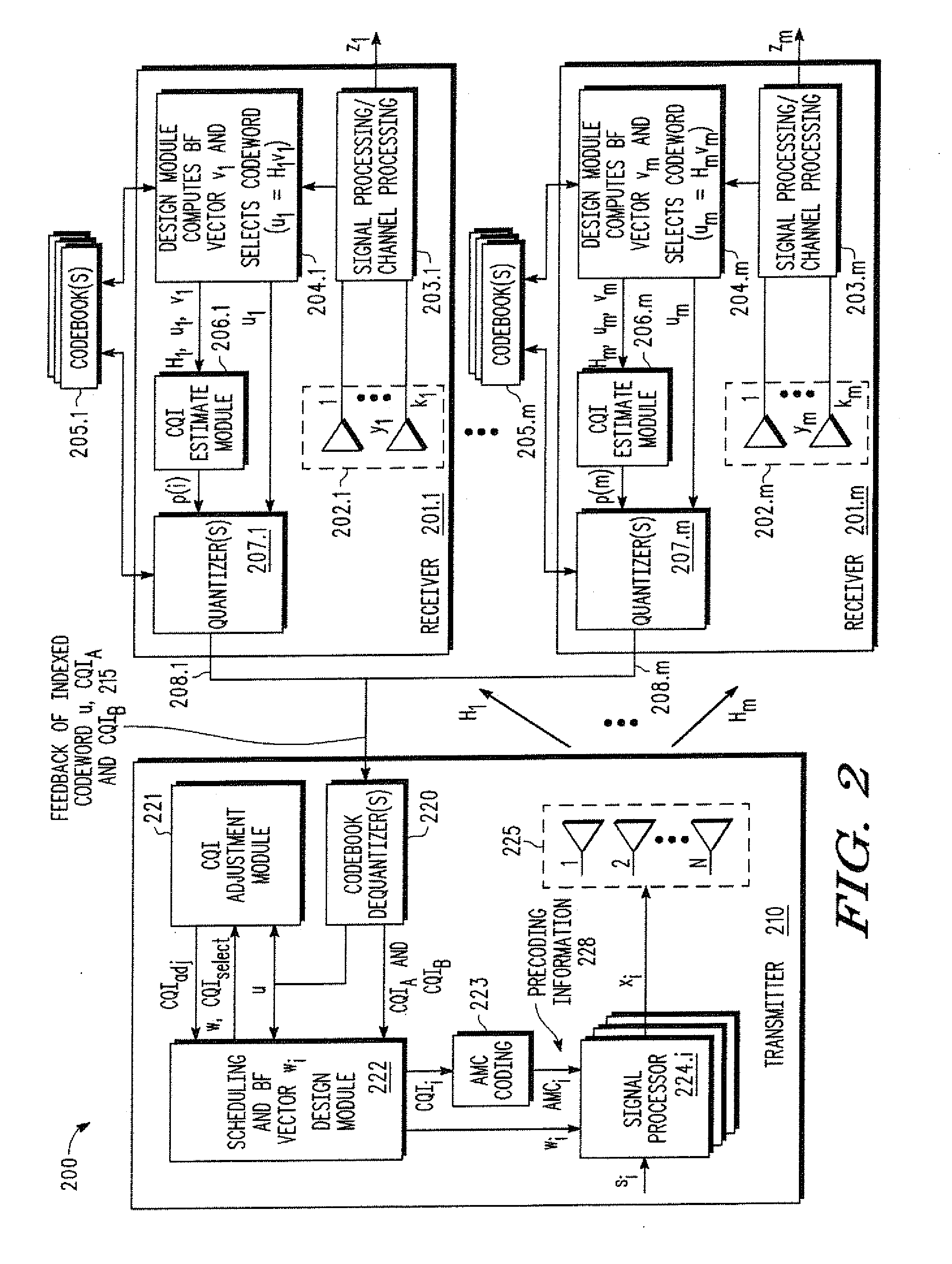
A multi-user MIMO downlink beamforming system with limited feedback (200) is provided to enable preceding for multi-stream transmission, where a channel codeword (ui) and one or more channel quality indicator values (CQIA, CQIB) are computed at the user equipment (201.i) on the basis of maximizing a predetermined SINR performance metric (ρi) which estimates the receive signal-to-noise-ratio (SINR) at the user equipment (201.i). The computed codeword (ui) and CQI values (or differential values related thereto) are quantized and fed back to help the base station (210) which applies a correction to the appropriate CQI value in the course of designing the transmit beamforming vectors w and determining the appropriate modulation and coding level to be used for downlink data transmission.
Owner:APPLE INC
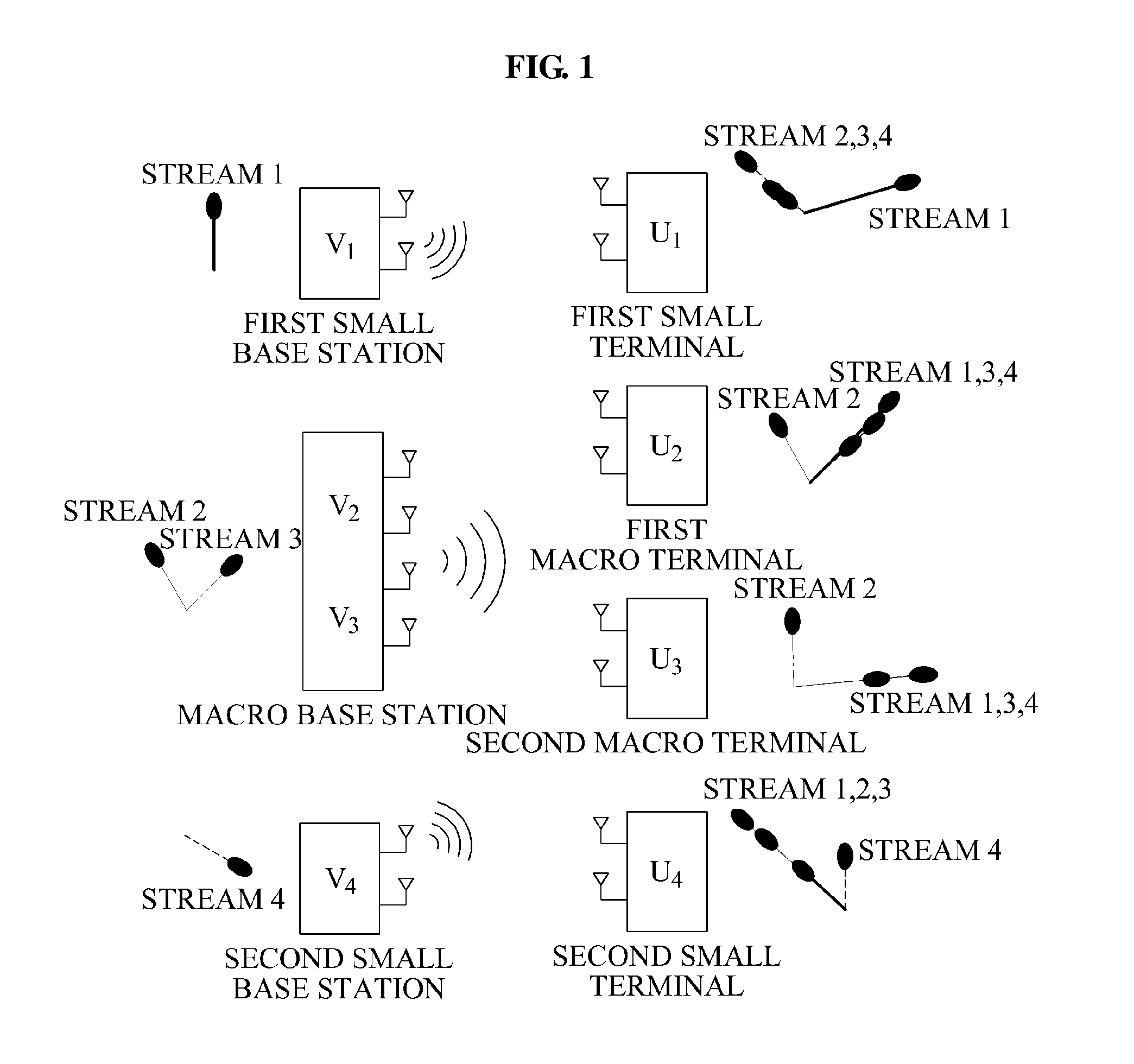
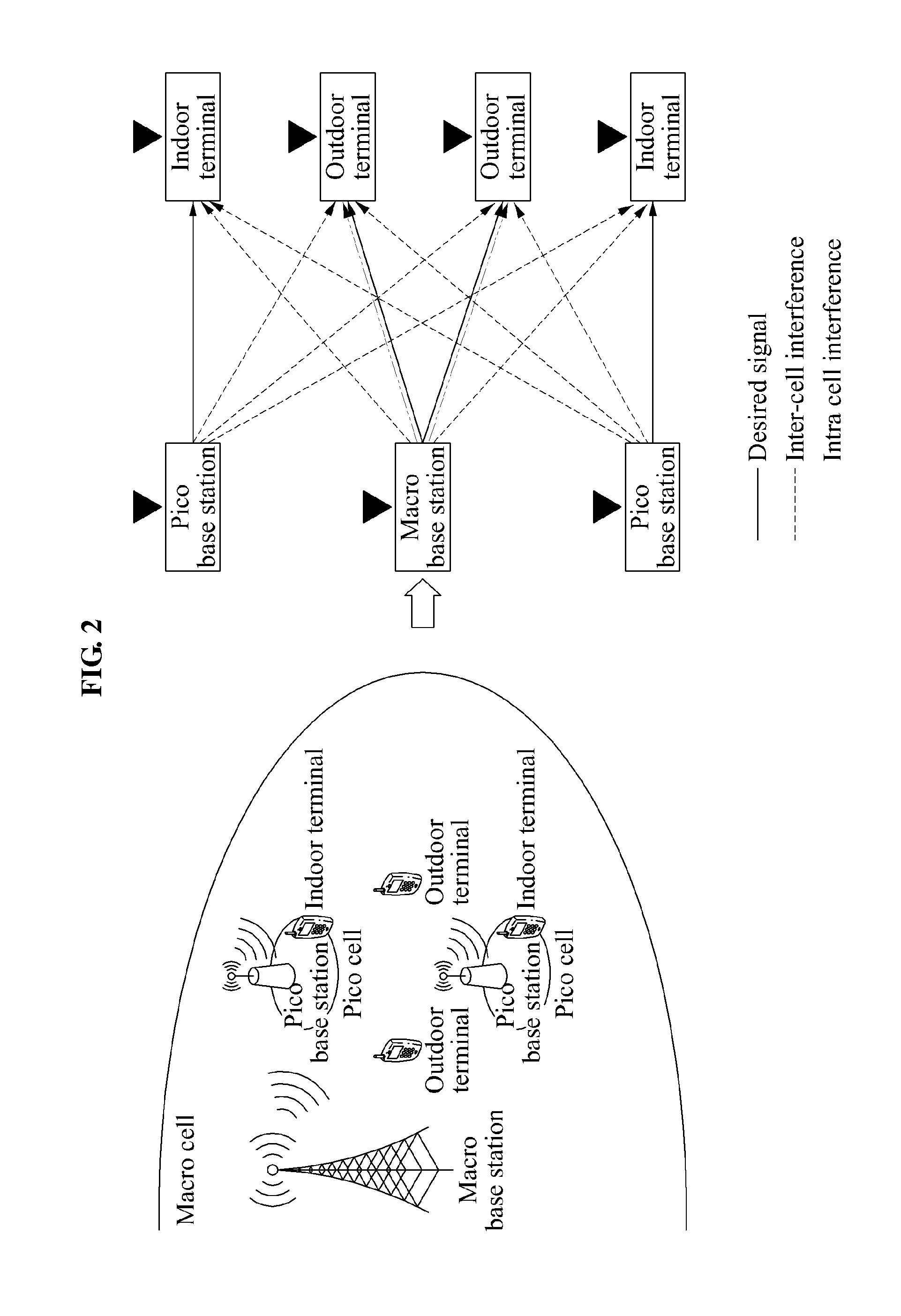
Method and apparatus for determining downlink beamforming vectors in hierarchical cell communication system
InactiveUS20120077485A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionDownlink beamformingCommunications system
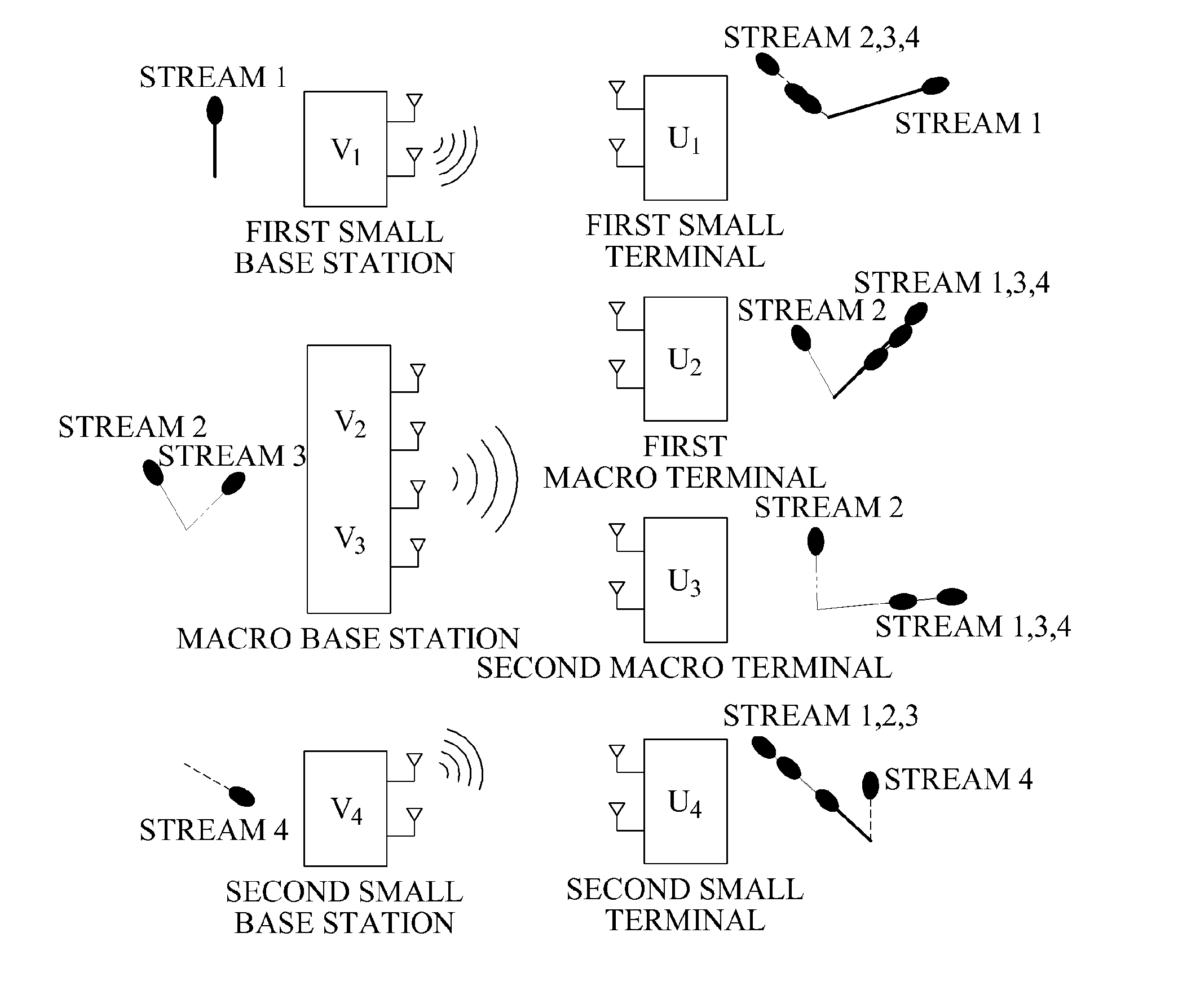
Provided is a method and apparatus for determining a downlink beamforming vector in a hierarchical cell communication system. Small base stations may determine transmit beamforming vectors of the small base stations so that interference from the small base stations may be reduced in a macro terminal. A macro terminal and small terminals may determine receive beamforming vectors based on the transmit beamforming vectors of the small base stations. A macro base station may determine a transmit beamforming vector based on effective channels to terminals using the receive beamforming vectors of the terminals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Generalized reference signaling scheme for MU-MIMO using arbitrarily precoded reference signals
ActiveUS20080225960A1Assess restrictionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsDownlink beamformingHypothesis
A multi-user MIMO downlink beamforming system (200) is provided to enable transmit beamforming vectors to be efficiently provided to a subset of user equipment devices (201.i), where spatial separation or zero-forcing transmit beamformers (wi) are computed at the base station (210) and used to generate precoded reference signals (216). The precoded reference signals (216) are fed forward to the user equipment devices (201.i) which apply one or more hypothesis tests (207.i, 208.i) to the precoded reference signals to extract the precoding matrix (W), including the specific transmit beamforming vector (wUE) designed for the user equipment, and this extracted information is used to generate receive beamformers (vi).
Owner:APPLE INC
Reference signaling scheme using compressed feedforward codebooks for MU-MIMO systems
InactiveUS20080227495A1Spatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsDownlink beamformingTransmission matrix
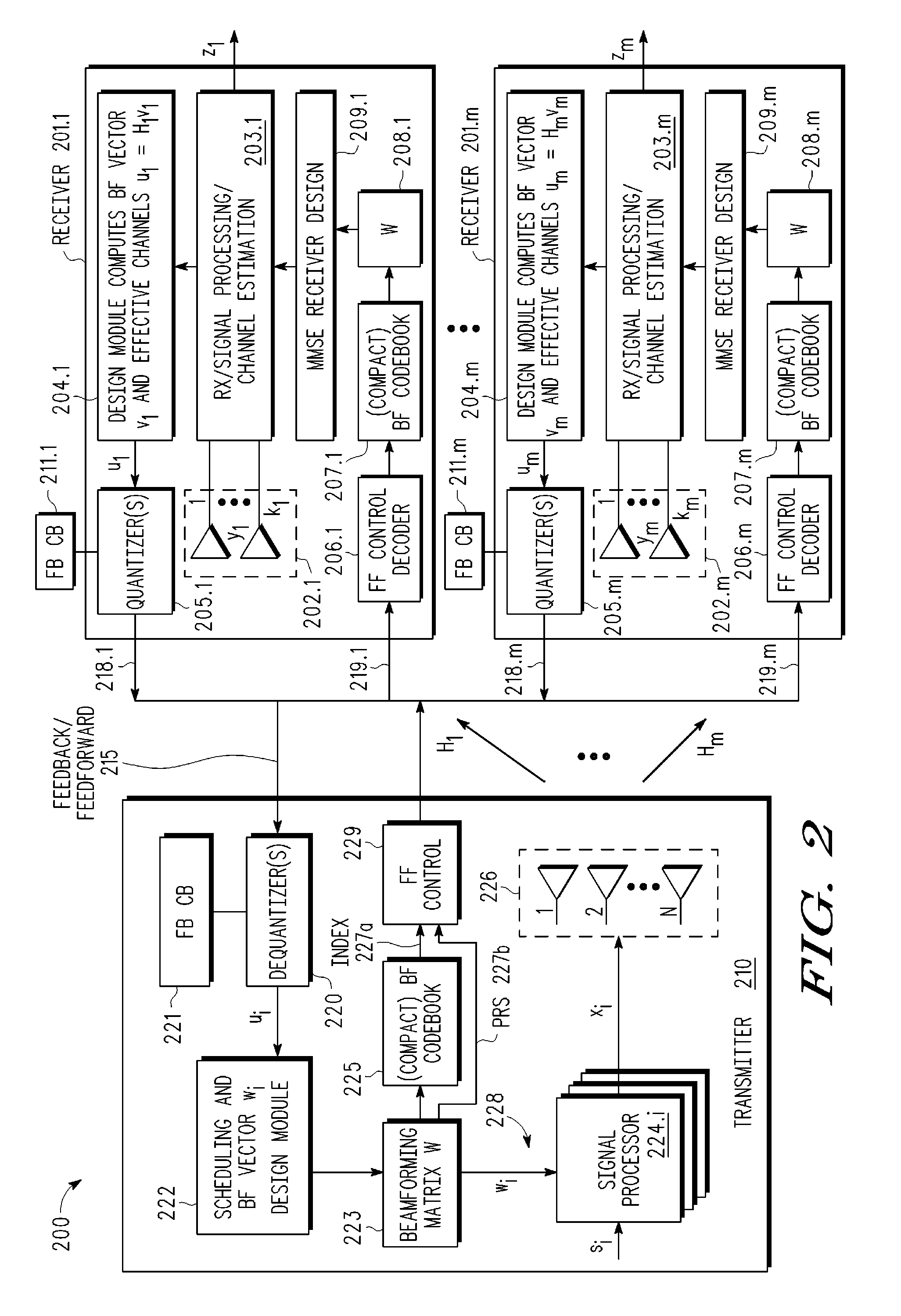
A multi-user MIMO downlink beamforming system with limited feed forward (200) is provided to enable preceding matrix information to be efficiently provided to a subset of user equipment devices (201.i), where zero-forcing transmit beamformers (wi) are computed at the base station (210) and assembled into a precoding matrix (W). The precoding matrix is encoded using a compact reference signal codebook (225, 207.i) for forward link signaling, either by sending bits indicating the index of the transmission matrix used, or by transmitting one or more precoded pilots or reference signals wherein the pilot signals are precoded using vectors uniquely representative of the transmission matrix used which includes candidate reference signal matrices which meet a predetermined condition number requirement, such as a condition number threshold. The preceding matrix information (227) is extracted at the user equipment devices (201.i) using the compact reference signal codebook (207.i) and used by the MMSE receiver (209.i) to generate receive beamformers (vi).
Owner:APPLE INC
Reference signals for downlink beamforming validation in wireless multicarrier MIMO channel
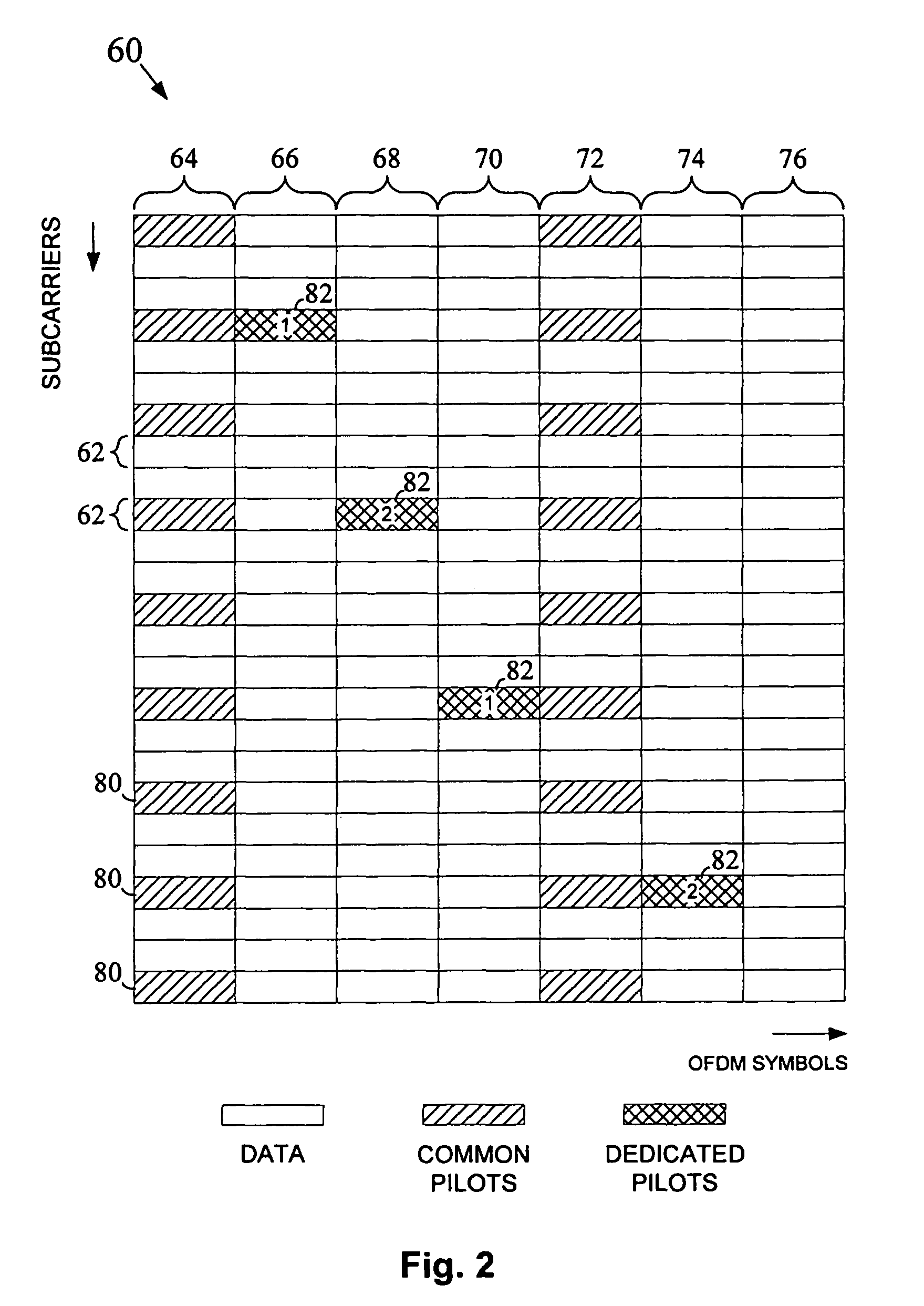
InactiveUS20070293172A1Transmission path divisionRadio transmissionDownlink beamformingTelecommunications
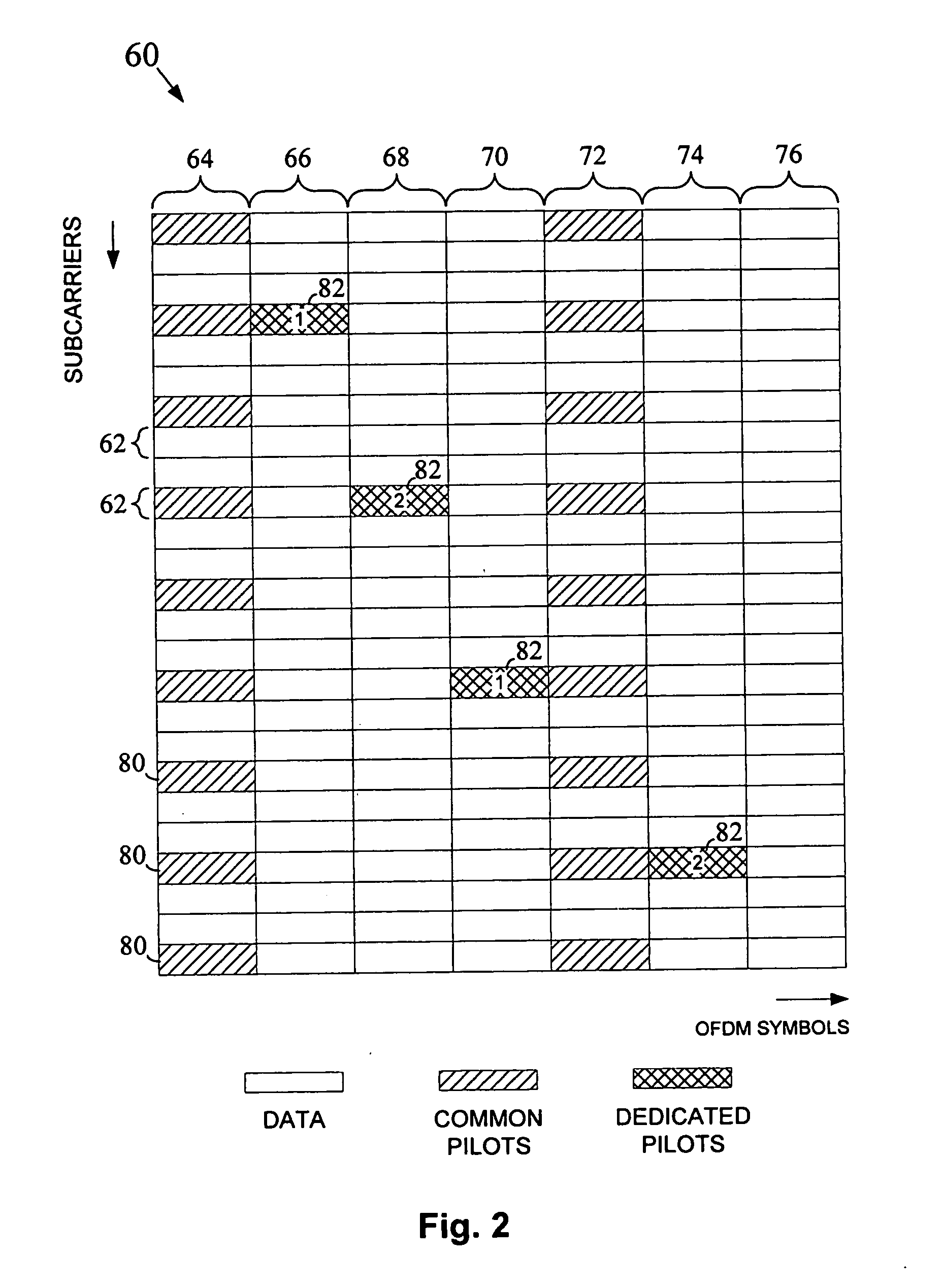
Dedicated pilot signals are transmitted from a transmitting device to a receiving device through a multicarrier MIMO channel in addition to data signals and common pilot signals. The dedicated pilot signals may be used by the receiving device to validate whether a predetermined beamforming matrix (i.e., a beamforming matrix identified by the receiving device) was used by the transmitting device to precode the transmitted data. If a different beamforming matrix was used for the preceding, the receiving device may use this matrix to demodulate the received data.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Generalized reference signaling scheme for multi-user, multiple input, multiple output (MU-MIMO) using arbitrarily precoded reference signals
A multi-user multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) downlink beamforming system (200) is provided to enable transmit beamforming vectors to be efficiently provided to a subset of user equipment devices (201.i), where spatial separation or zero-forcing transmit beamformers (wi) are computed at the base station (210) and used to generate precoded reference signals (216). The precoded reference signals (216) are fed forward to the user equipment devices (201.i) which apply one or more hypothesis tests (207.i, 208.i) to the precoded reference signals to extract the precoding matrix (W), including the specific transmit beamforming vector (wUE) designed for the user equipment, and this extracted information is used to generate receive beamformers (vi).
Owner:APPLE INC
Smart antenna CDMA wireless communication system
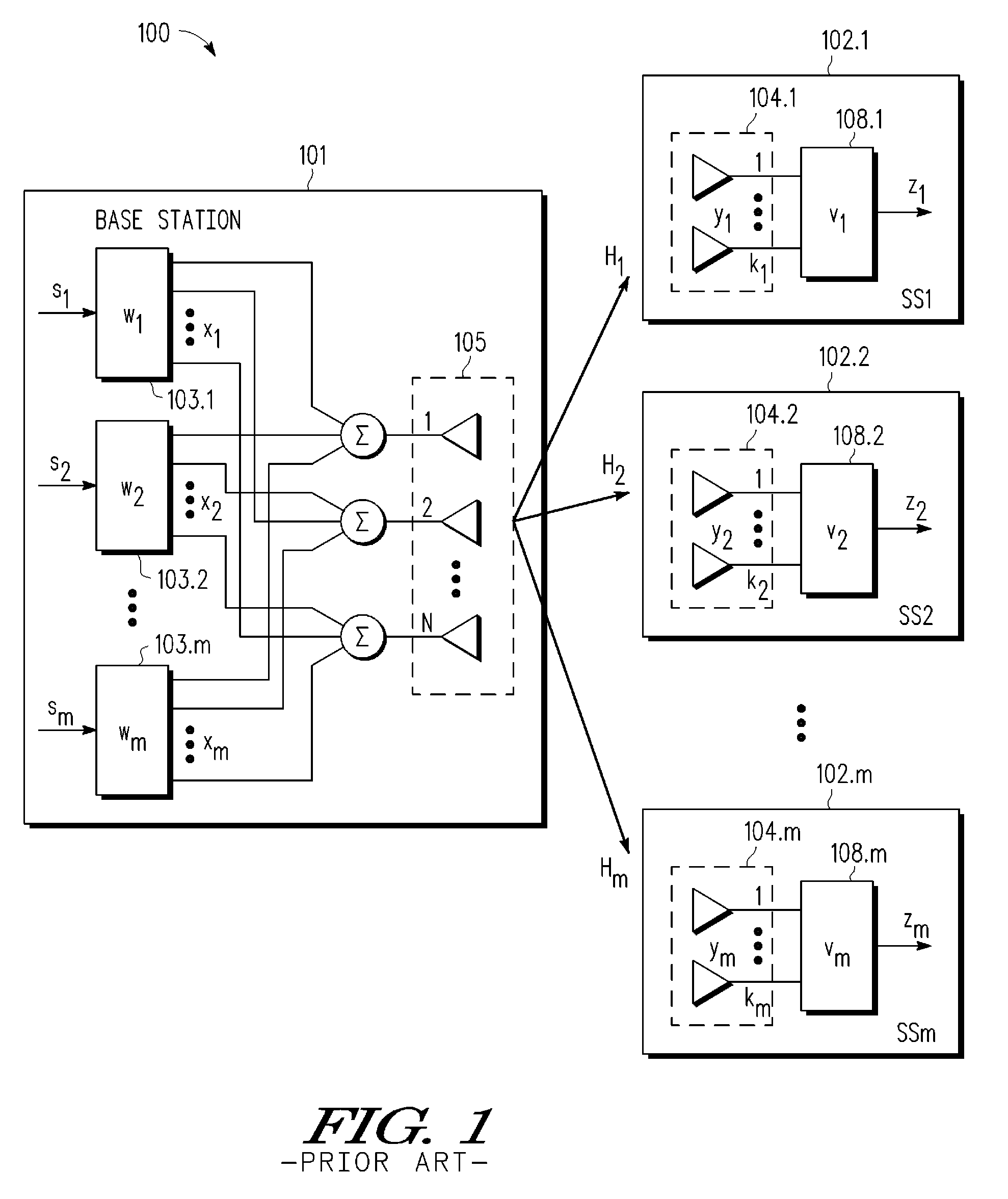
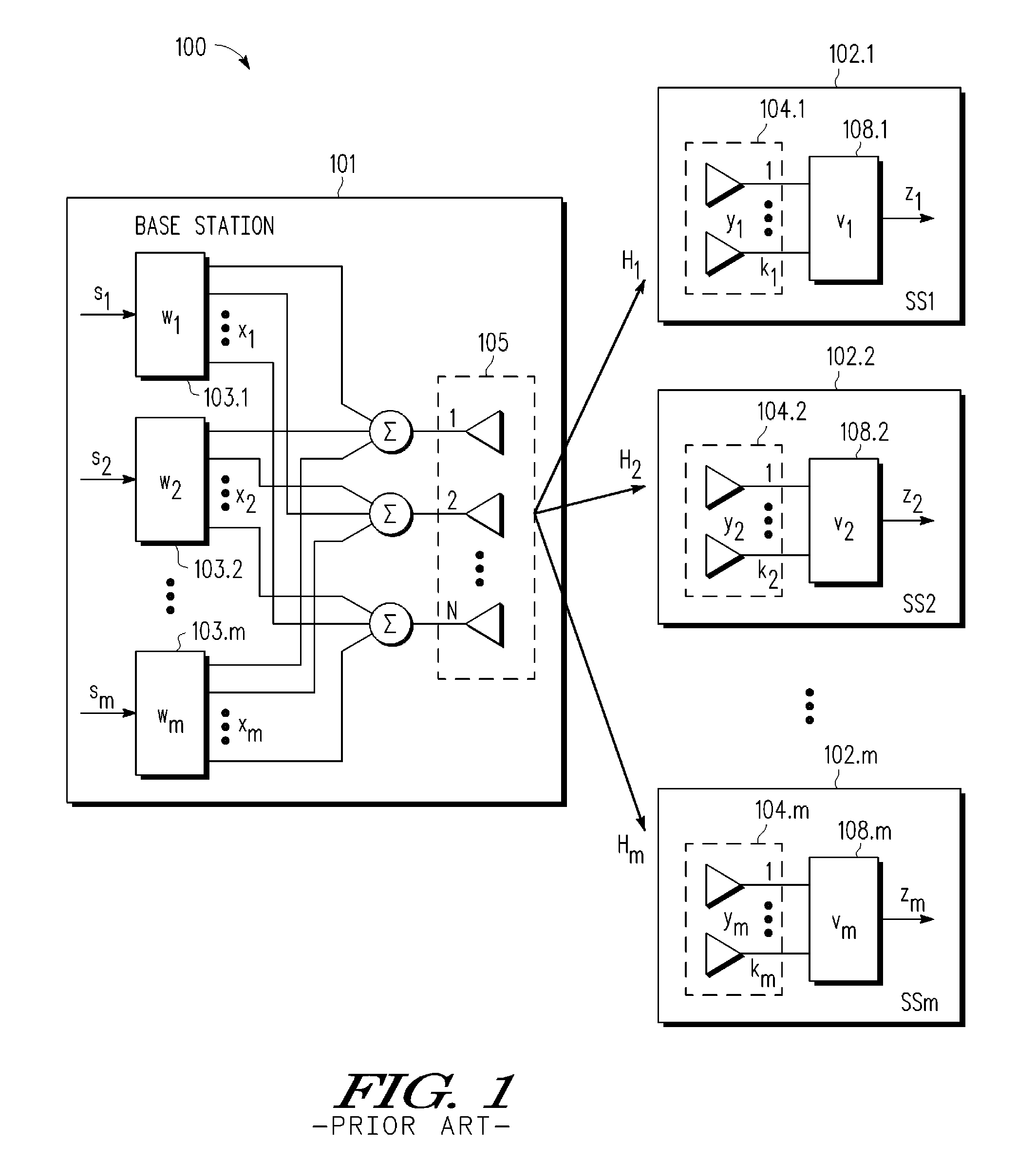
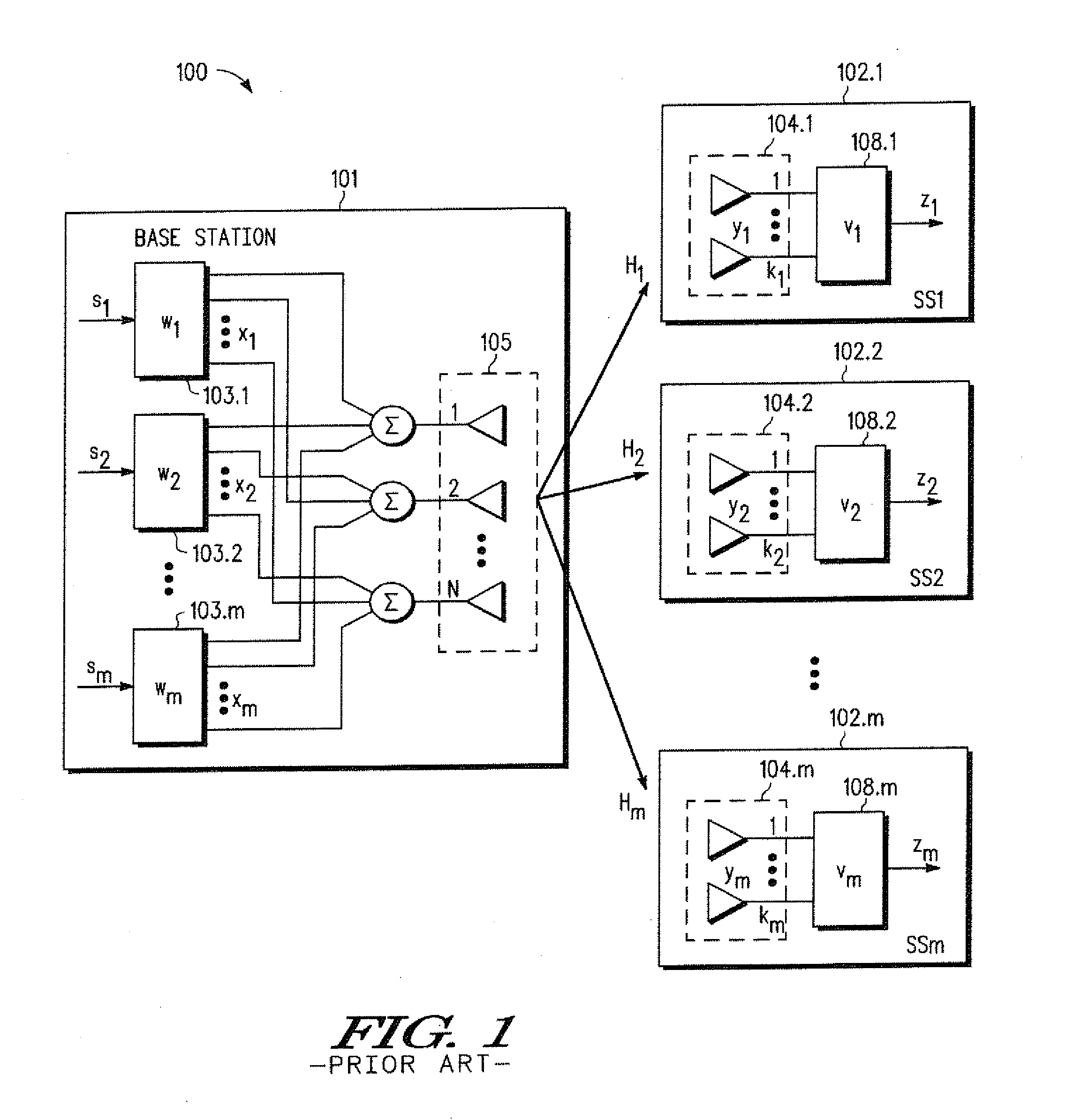
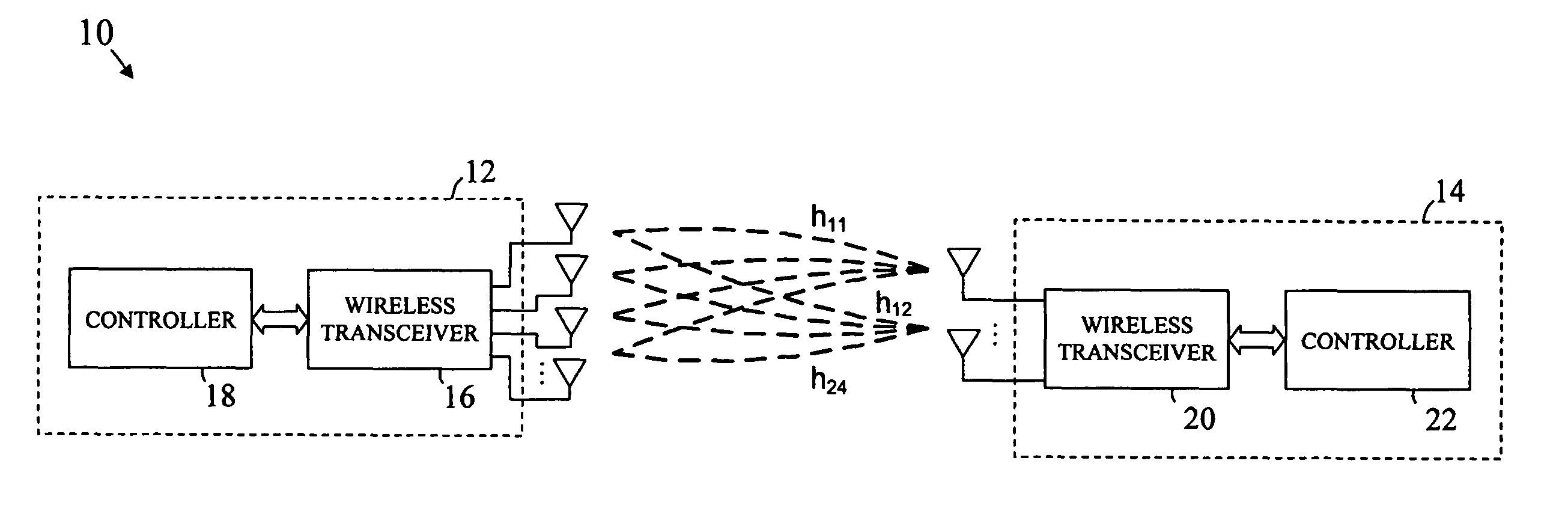
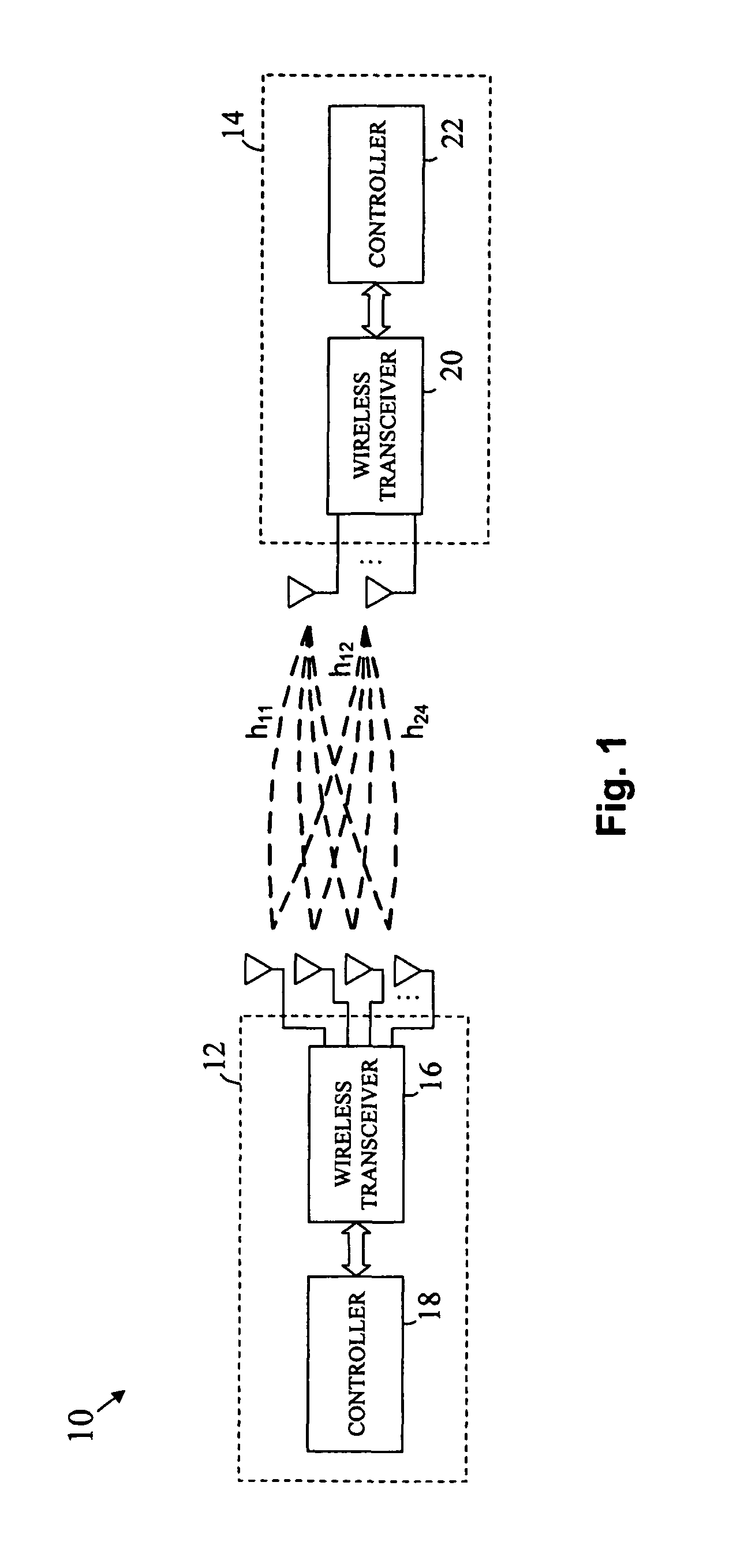
InactiveUS6980527B1Increase capacityImprove performanceSynchronisation arrangementSpatial transmit diversityFir systemDownlink beamforming
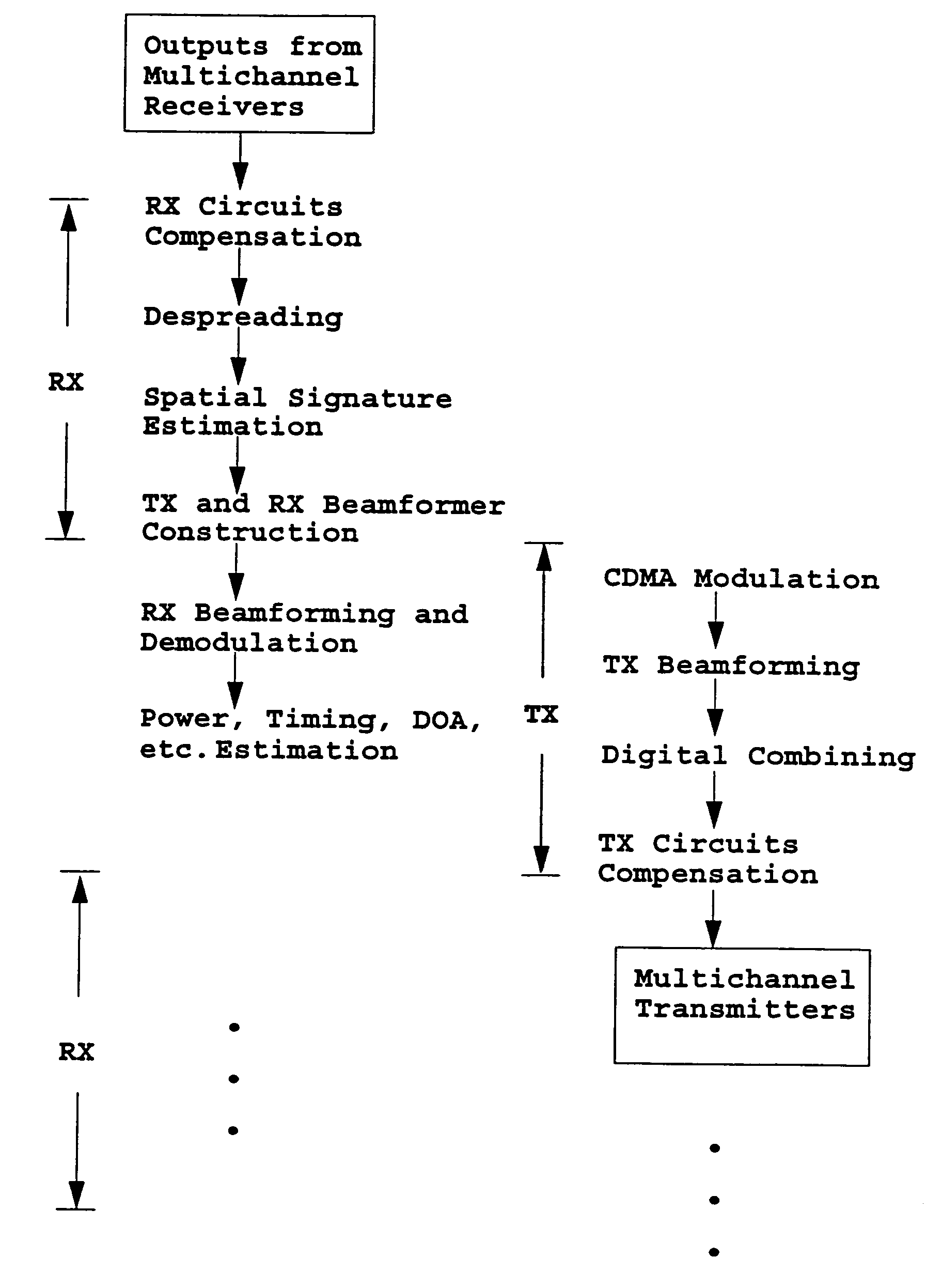
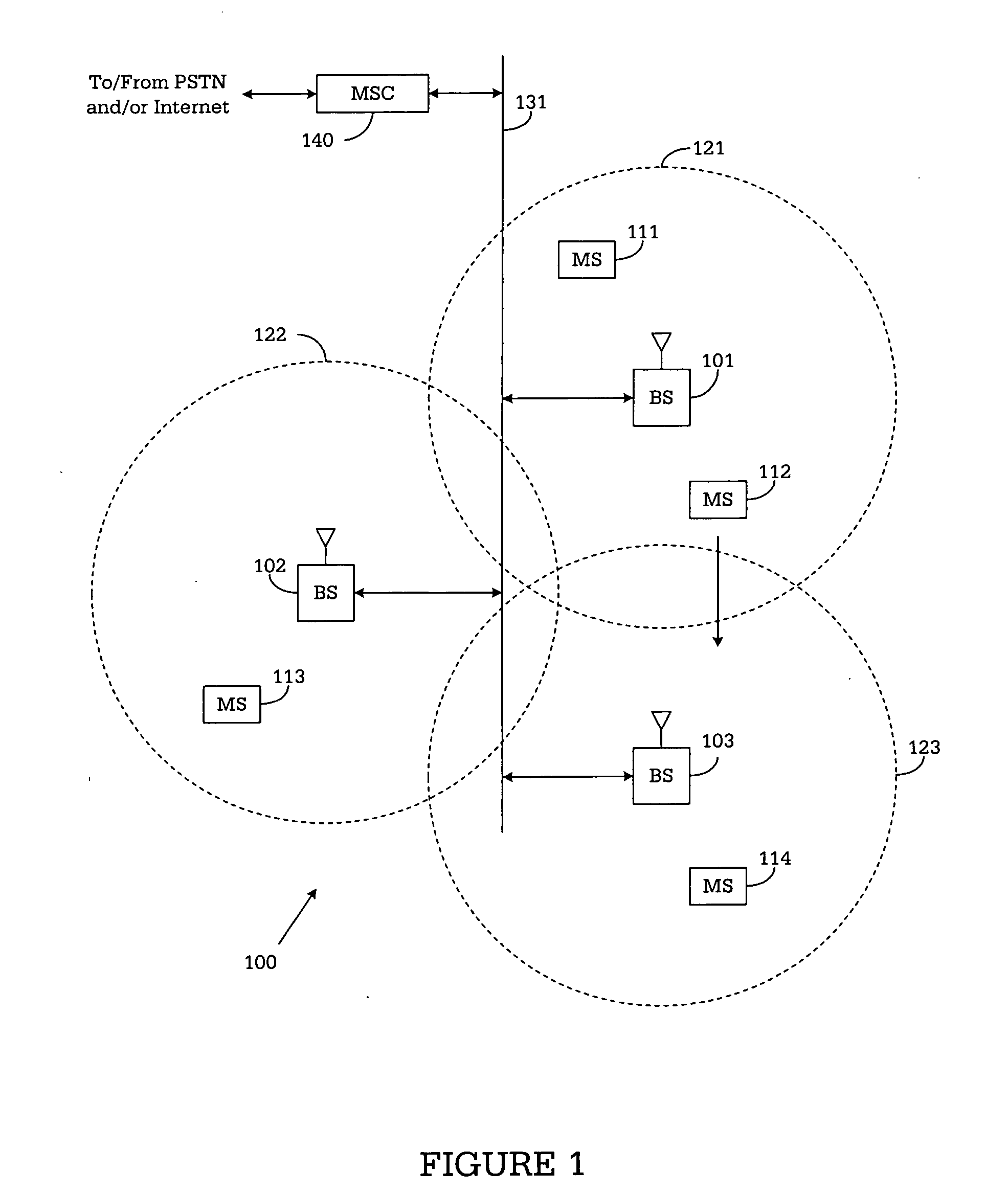
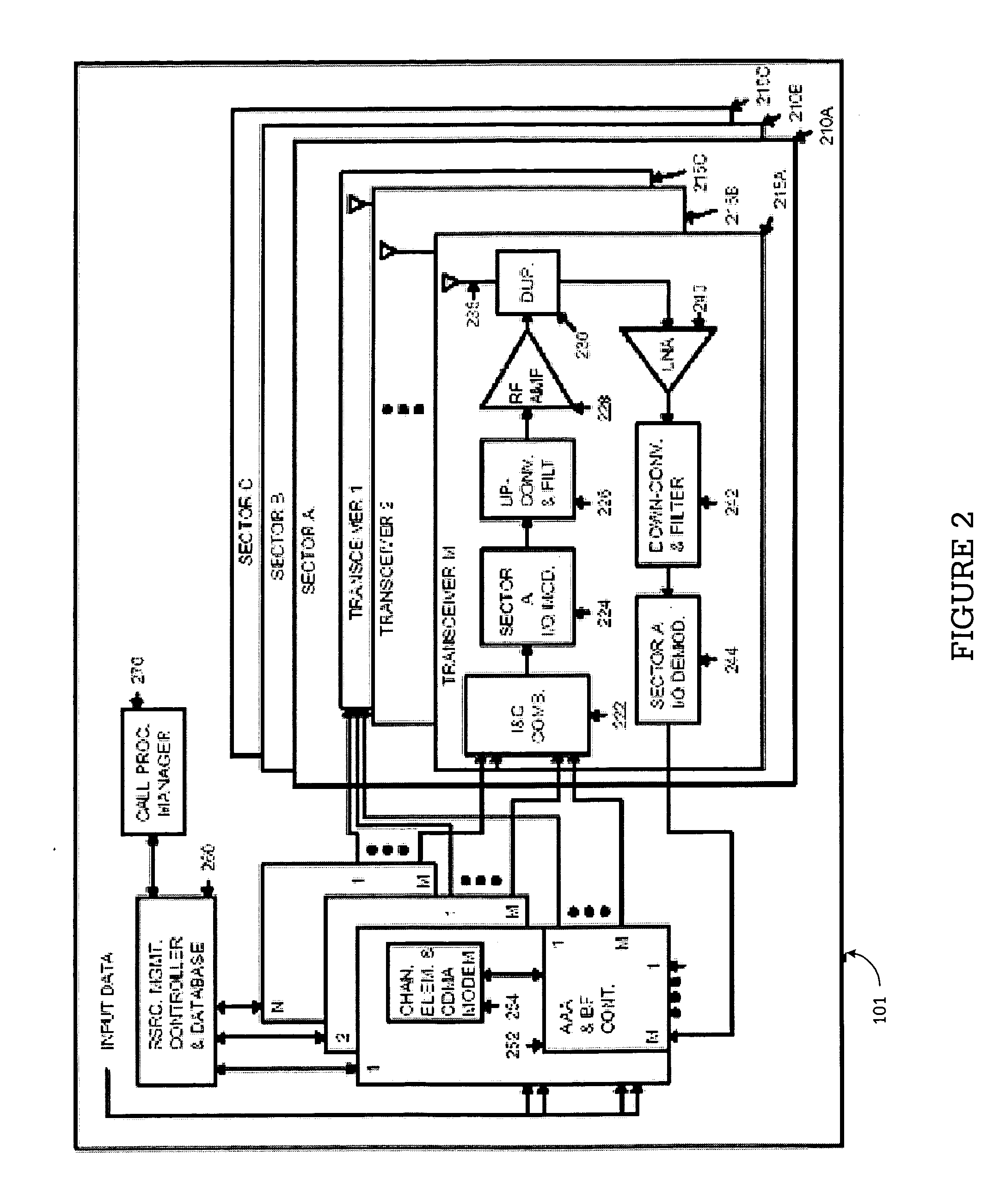
A TDD antenna array S-CDMA system for increasing the capacity and quality of a wireless communications is disclosed. By simultaneous exploiting the spatial and code diversities, high performance communications between a plurality of remote terminals and a base station is achieved without sacrificing system flexibility and robustness. The time-division-duplex mode together with the inherent interference immunity of S-CDMA signals allow the spatial diversity to be exploited using simple and robust beamforming rather than demanding nulling. Measurements from an array of receiving antennas at the base station are utilized to estimate spatial signatures, timing offsets, transmission powers and other propagation parameters associated with a plurality of S-CDMA terminals. Such information is then used for system synchronization, downlink beamforming, as well as handoff management. In an examplary embodiment, the aforementioned processing is accomplished with minimum computations, thereby allowing the disclosed system to be applicable to a rapidly varying environment. Among many other inherent benefits of the present invention are large capacity and power efficiency, strong interference / fading resistance, robustness power control, and easy hand-off.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
Reference signaling scheme using compressed feedforward codebooks for multi-user, multiple input, multiple output (MU-MIMO) systems
InactiveUS7961807B2Spatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsDownlink beamformingTransmission matrix
A multi-user multiple input multiple output (MIMO) downlink beamforming system with limited feed forward (200) is provided to enable precoding matrix information to be efficiently provided to a subset of user equipment devices (201.i), where zero-forcing transmit beamformers (wi) are computed at the base station (210) and assembled into a precoding matrix (W). The precoding matrix is encoded using a compact reference signal codebook (225, 207.i) for forward link signaling, either by sending bits indicating the index of the transmission matrix used, or by transmitting one or more precoded pilots or reference signals wherein the pilot signals are precoded using vectors uniquely representative of the transmission matrix used which includes candidate reference signal matrices which meet a predetermined condition number requirement, such as a condition number threshold.
Owner:APPLE INC
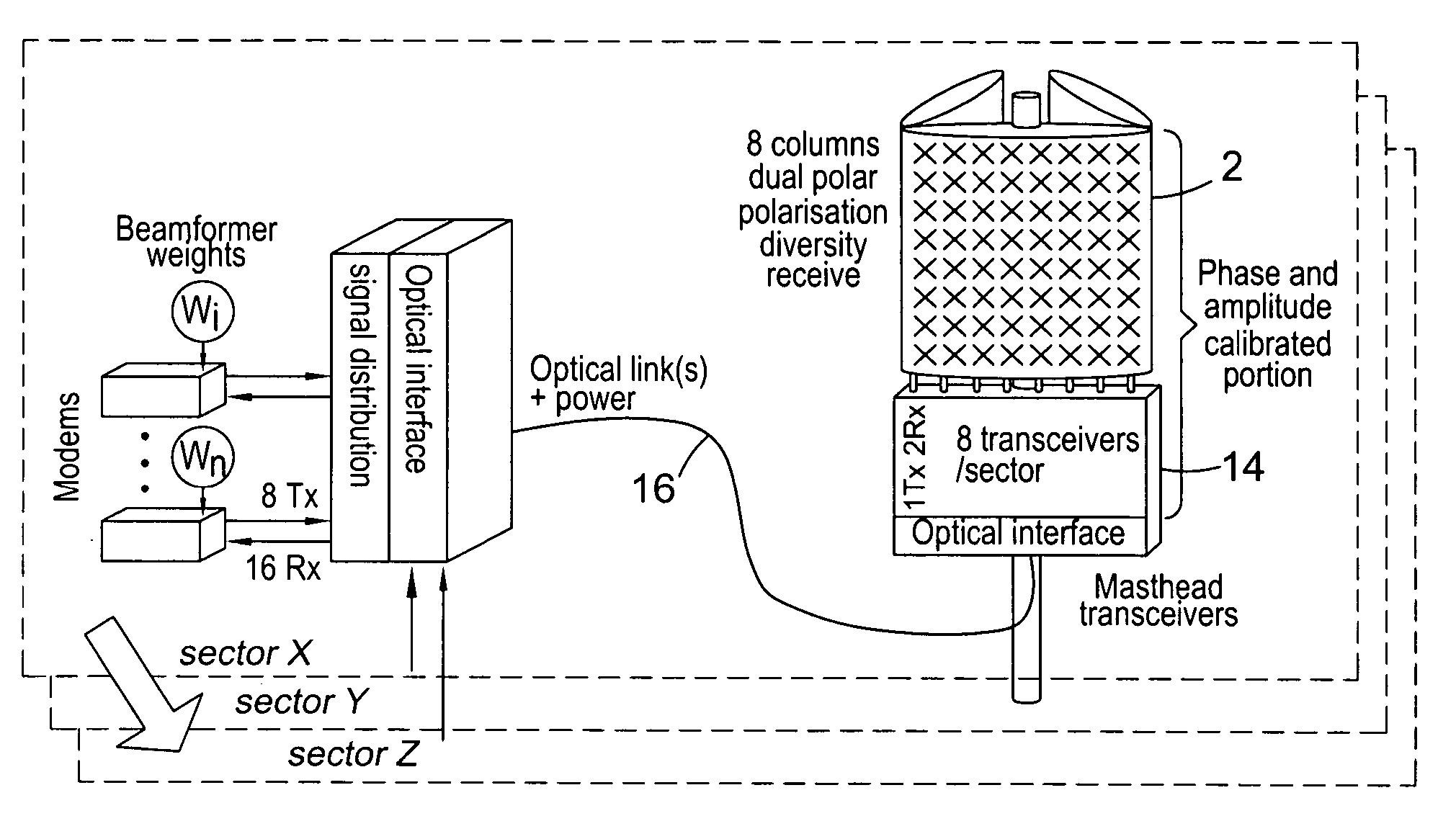
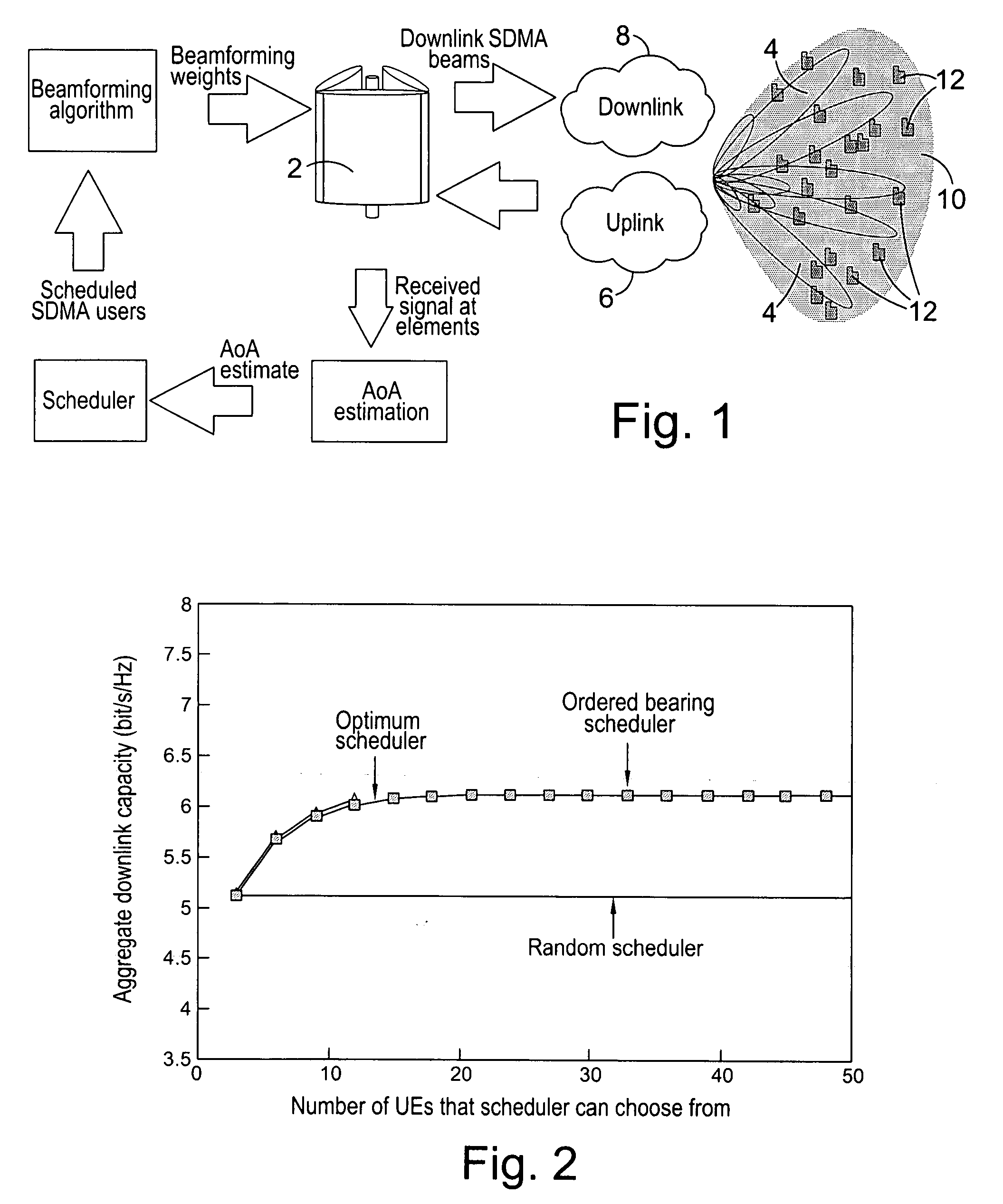
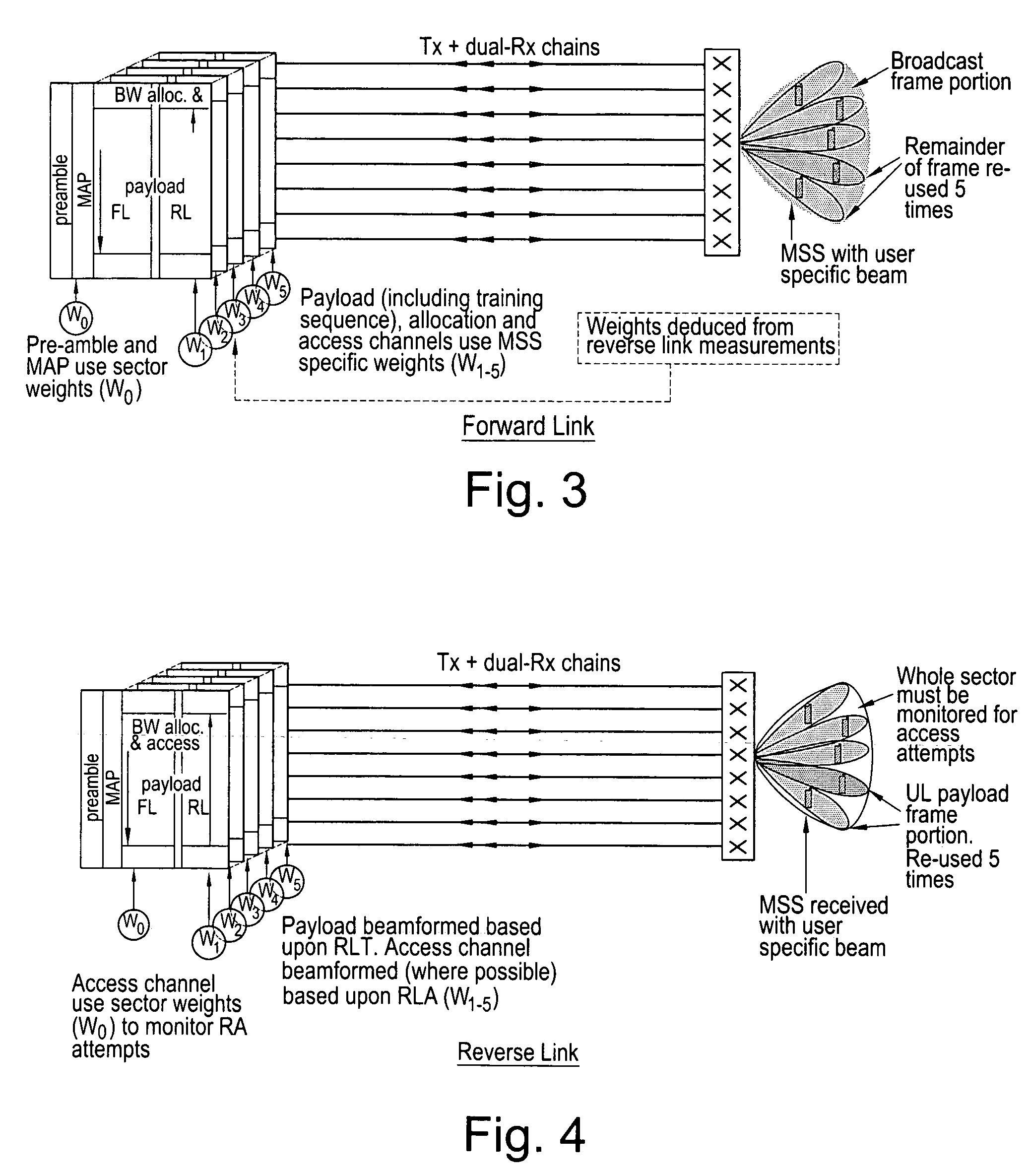
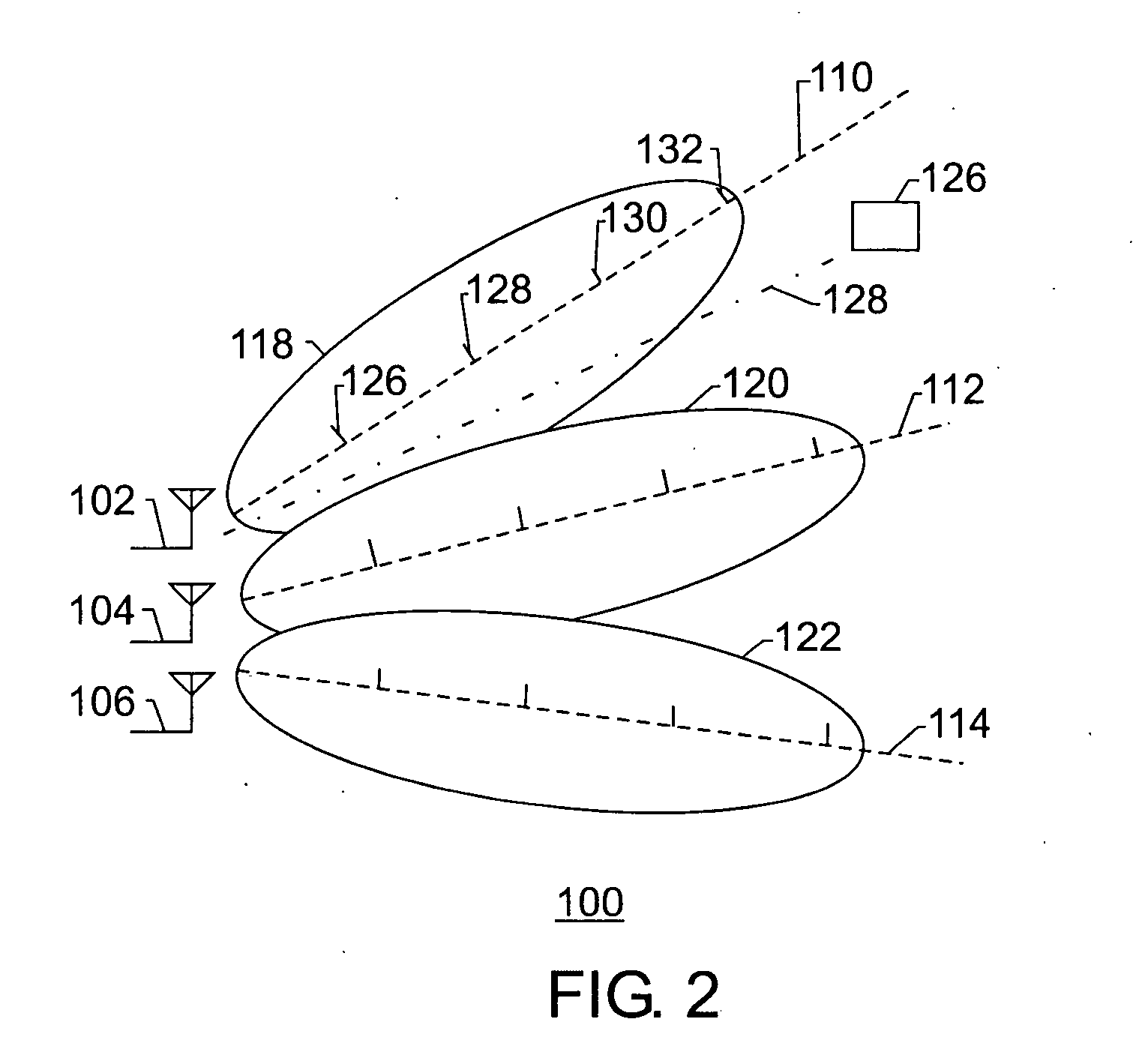
Downlink beamforming for broadband wireless networks
ActiveUS20060281494A1Multiplicative spectral efficiency gainHigh trafficSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionDownlink beamformingFrequency spectrum
Spatial Division Multiple Access (SDMA) offers multiplicative spectral efficiency gains in wireless networks. An adaptive SDMA beamforming technique is capable of increasing the traffic throughput of a sector, as compared to a conventional tri-cellular arrangement, by between 4 and 7 times, depending on the environment. This system uses an averaged covariance matrix of the uplink signals received at the antenna array to deduce the downlink beamforming solution, and is equally applicable to Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) and Time Division Duplex (TDD) systems. A scheduling algorithm enhances the SDMA system performance by advantageously selecting the users to be co-scheduled.
Owner:APPLE INC
Multi-user MIMO-SDMA for finite rate feedback systems
ActiveUS8073069B2Diversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationDownlink beamformingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A multi-user MIMO downlink beamforming system with limited feedback (200) is provided to enable preceding for multi-stream transmission, where a channel codeword (ui) and one or more channel quality indicator values (CQIA, CQIB) are computed at the user equipment (201.i) on the basis of maximizing a predetermined SINR performance metric (ρi) which estimates the receive signal-to-noise-ratio (SINR) at the user equipment (201.i). The computed codeword (ui) and CQI values (or differential values related thereto) are quantized and fed back to help the base station (210) which applies a correction to the appropriate CQI value in the course of designing the transmit beamforming vectors w and determining the appropriate modulation and coding level to be used for downlink data transmission.
Owner:APPLE INC
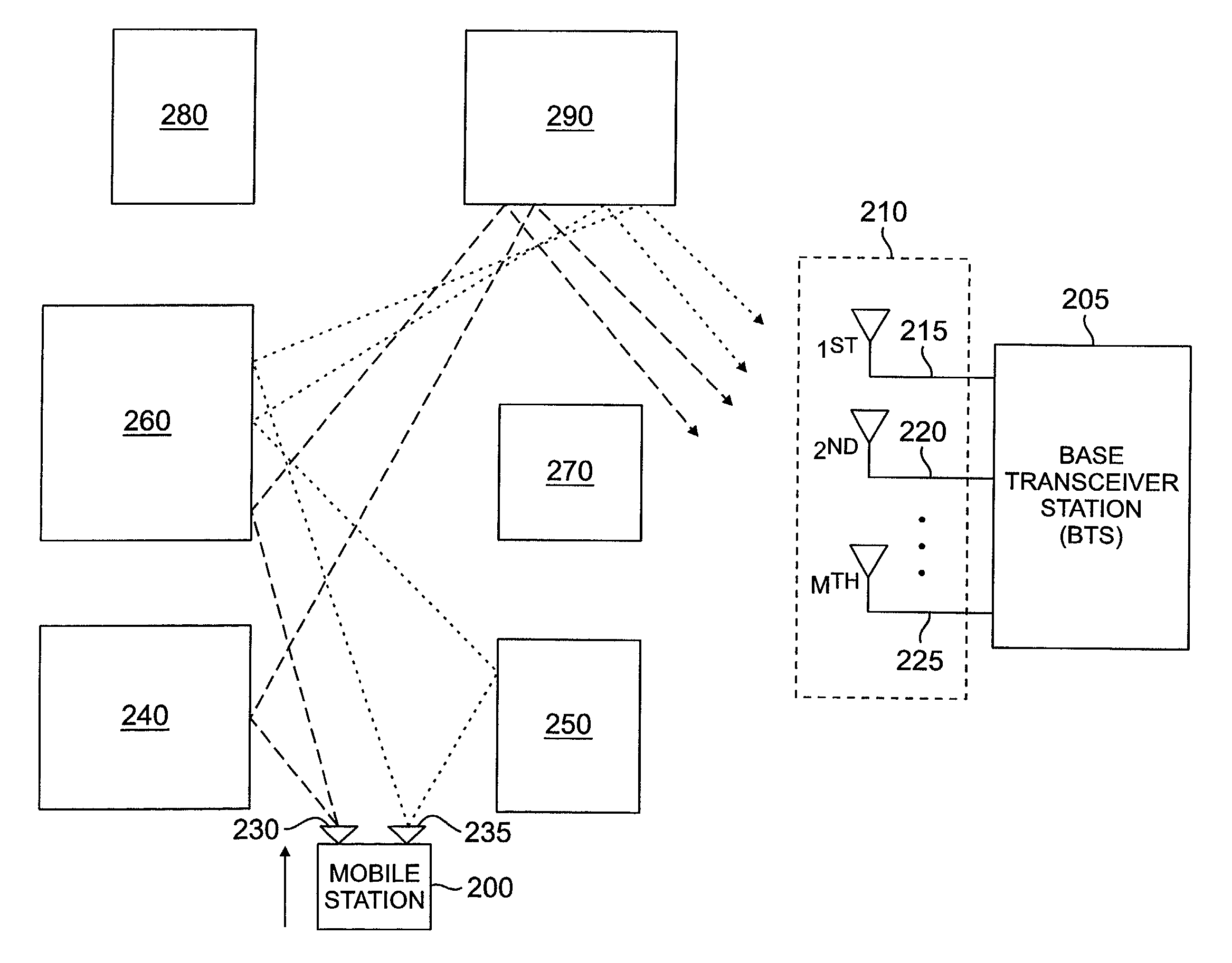
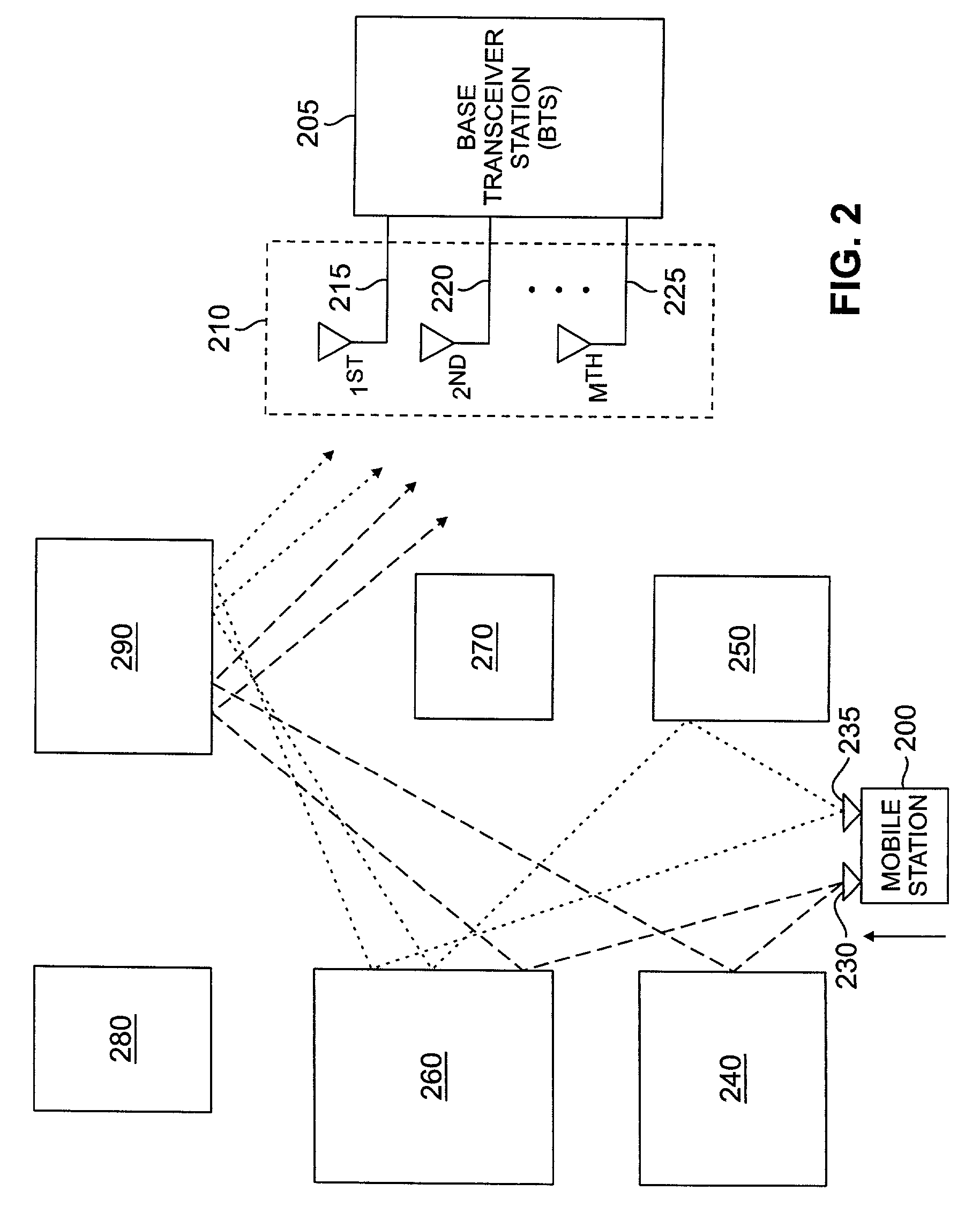
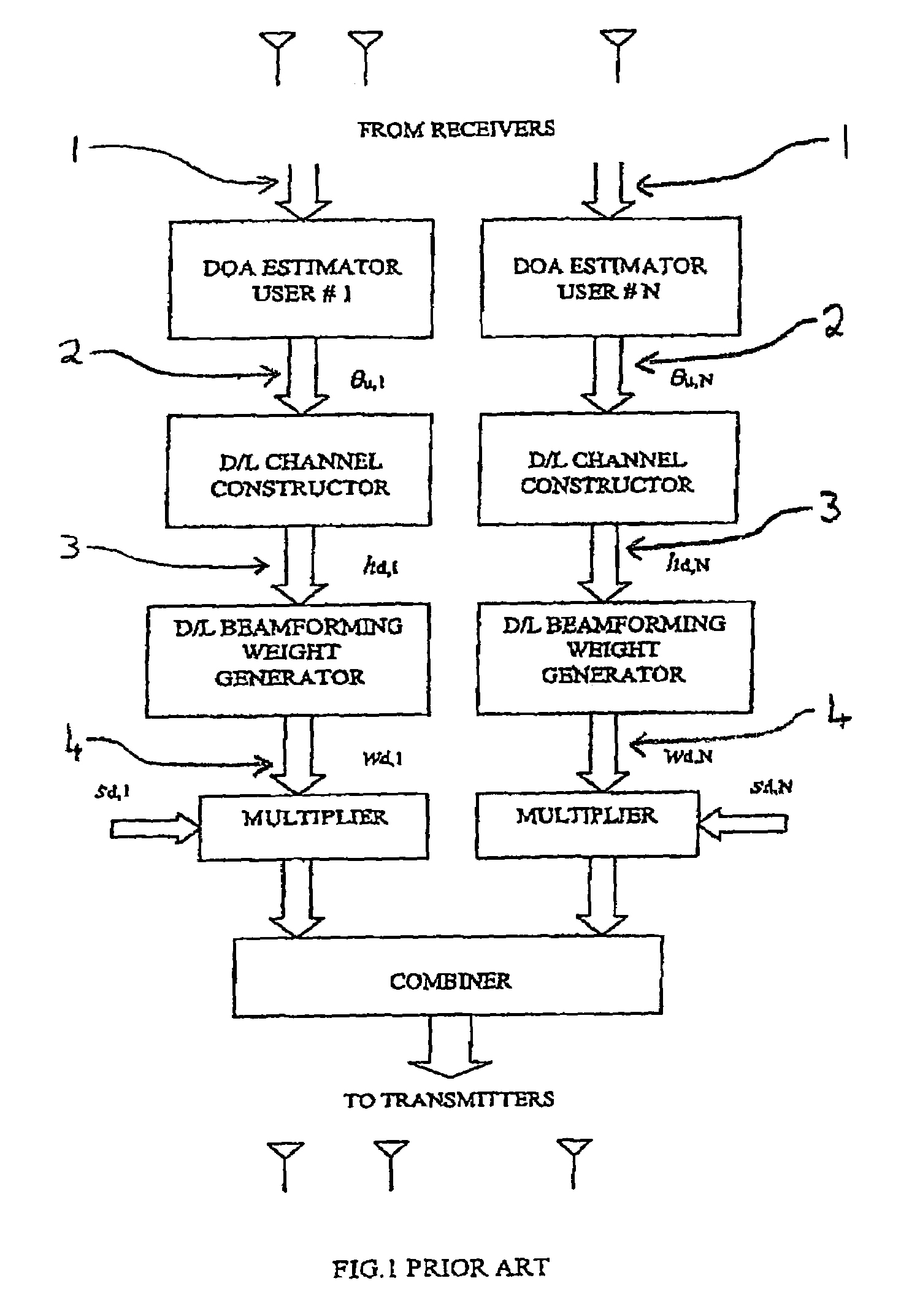
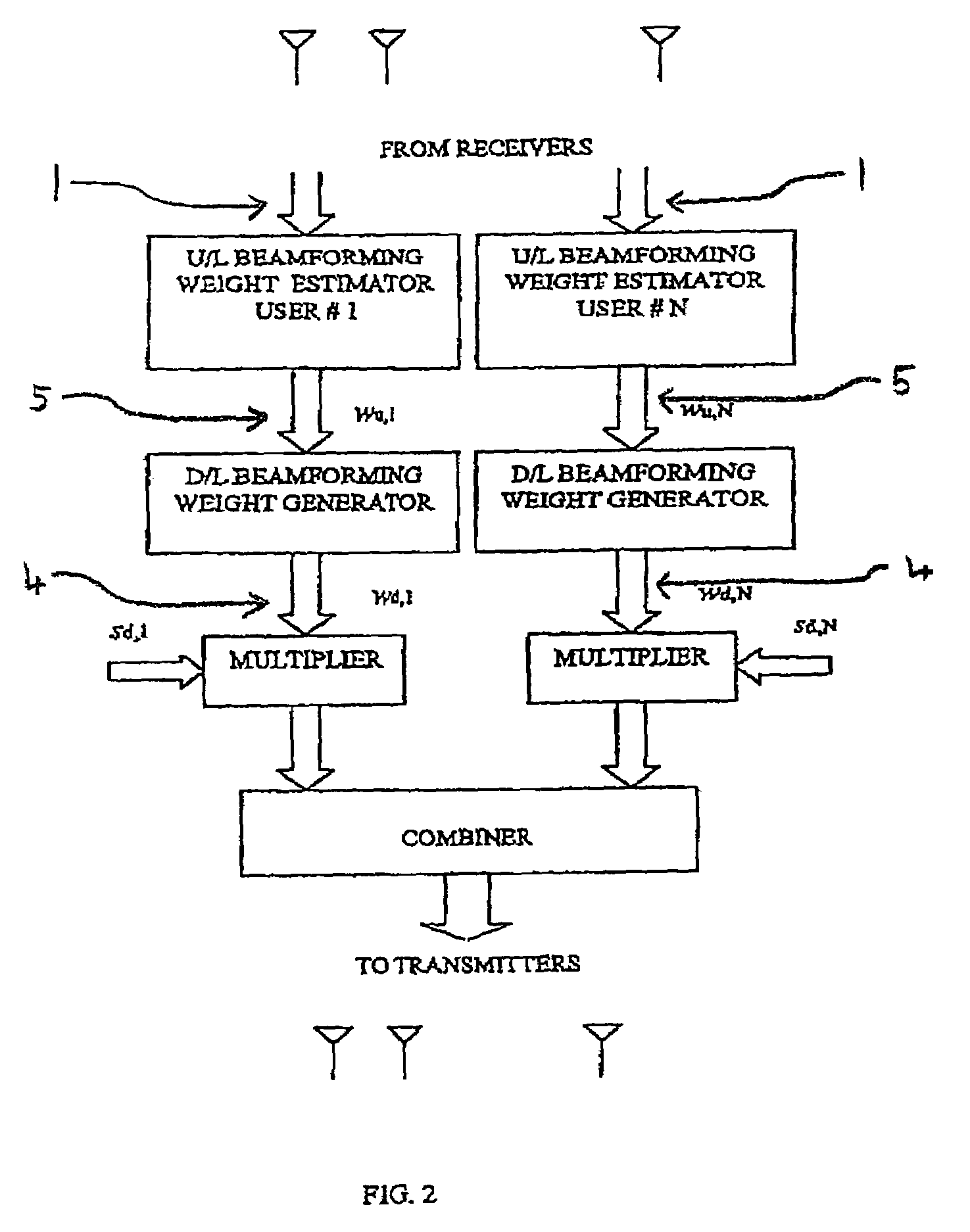
Method and apparatus for estimating downlink beamforming weights in a communications system
InactiveUS6839574B2Spatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentDownlink beamformingCommunications system
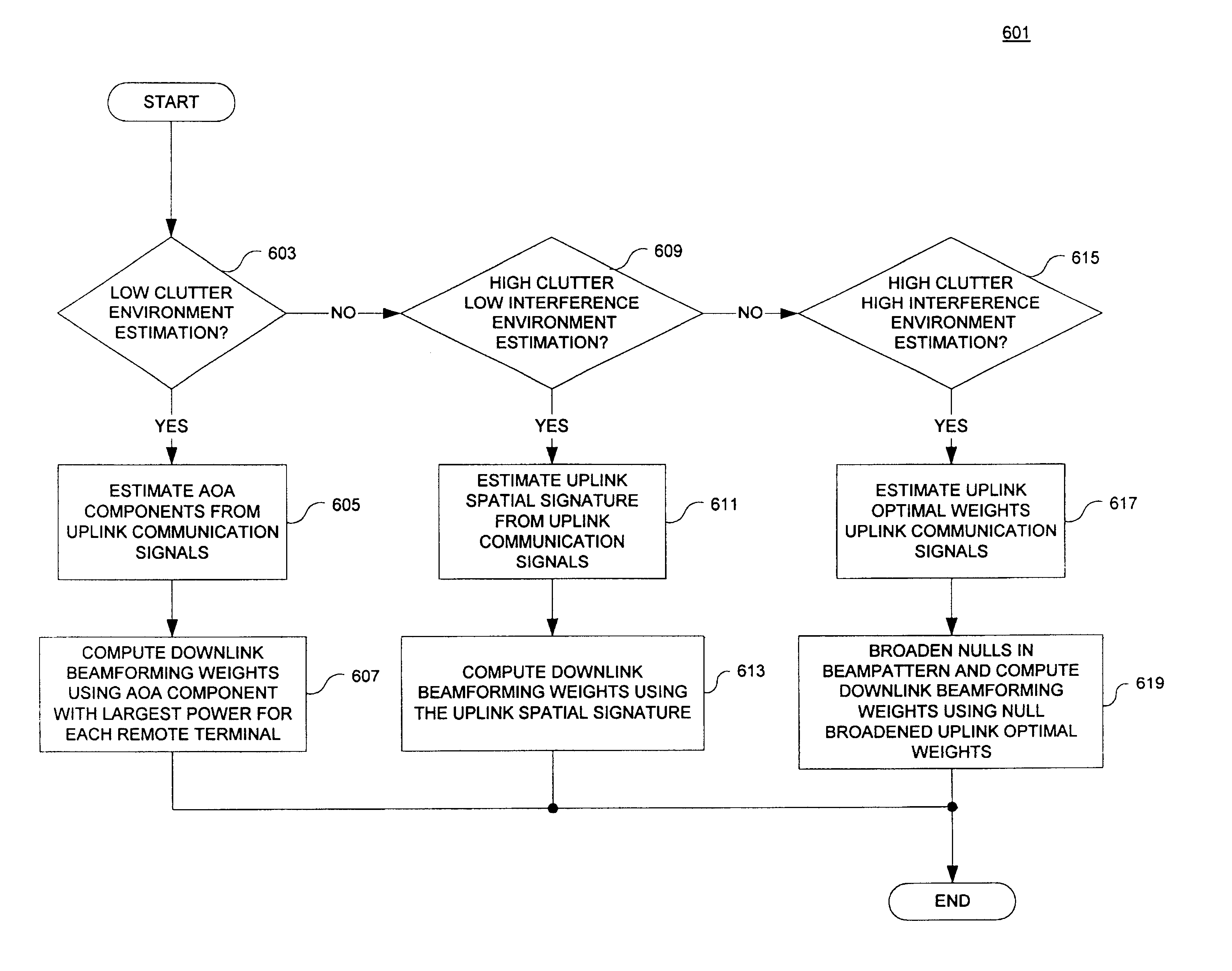
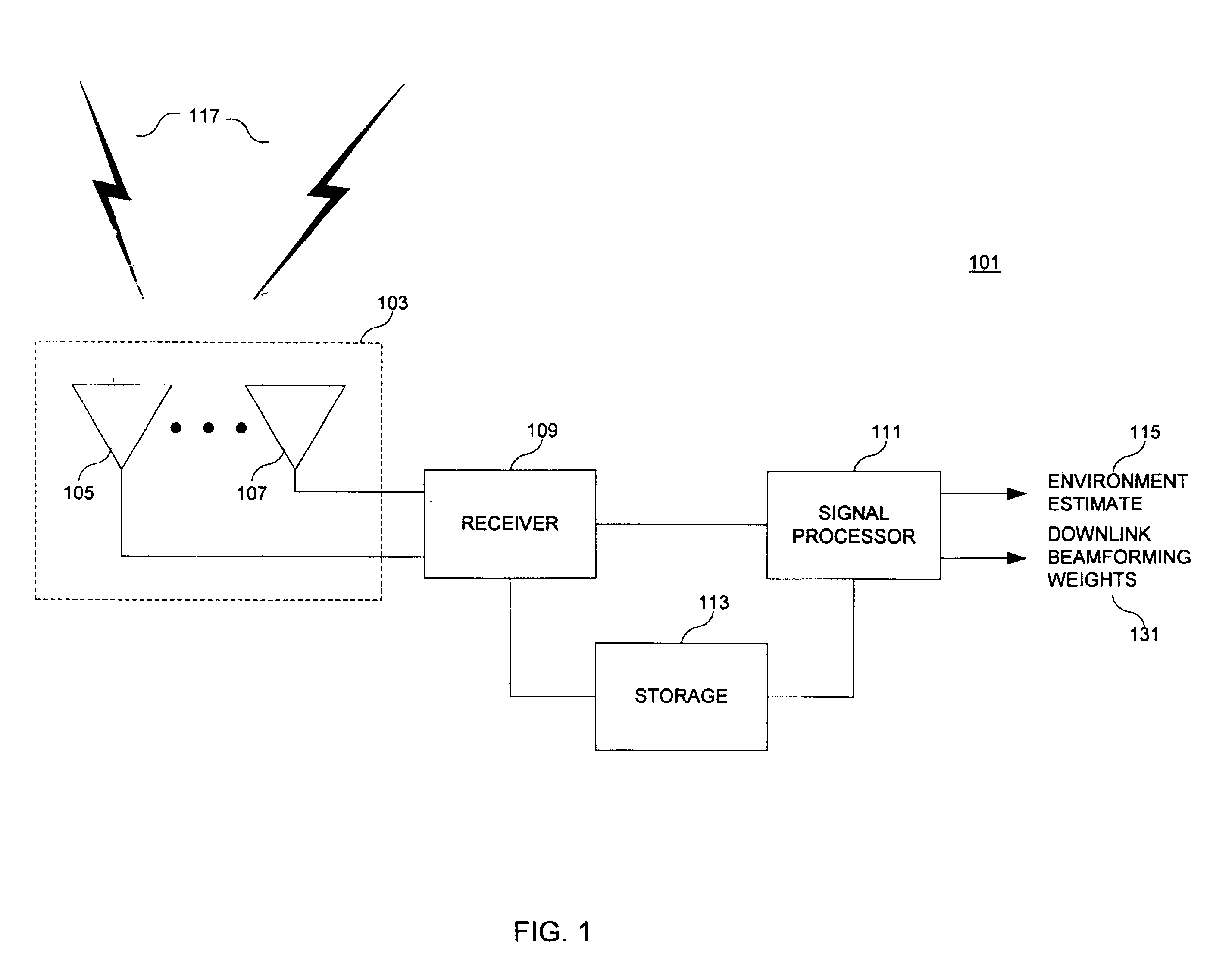
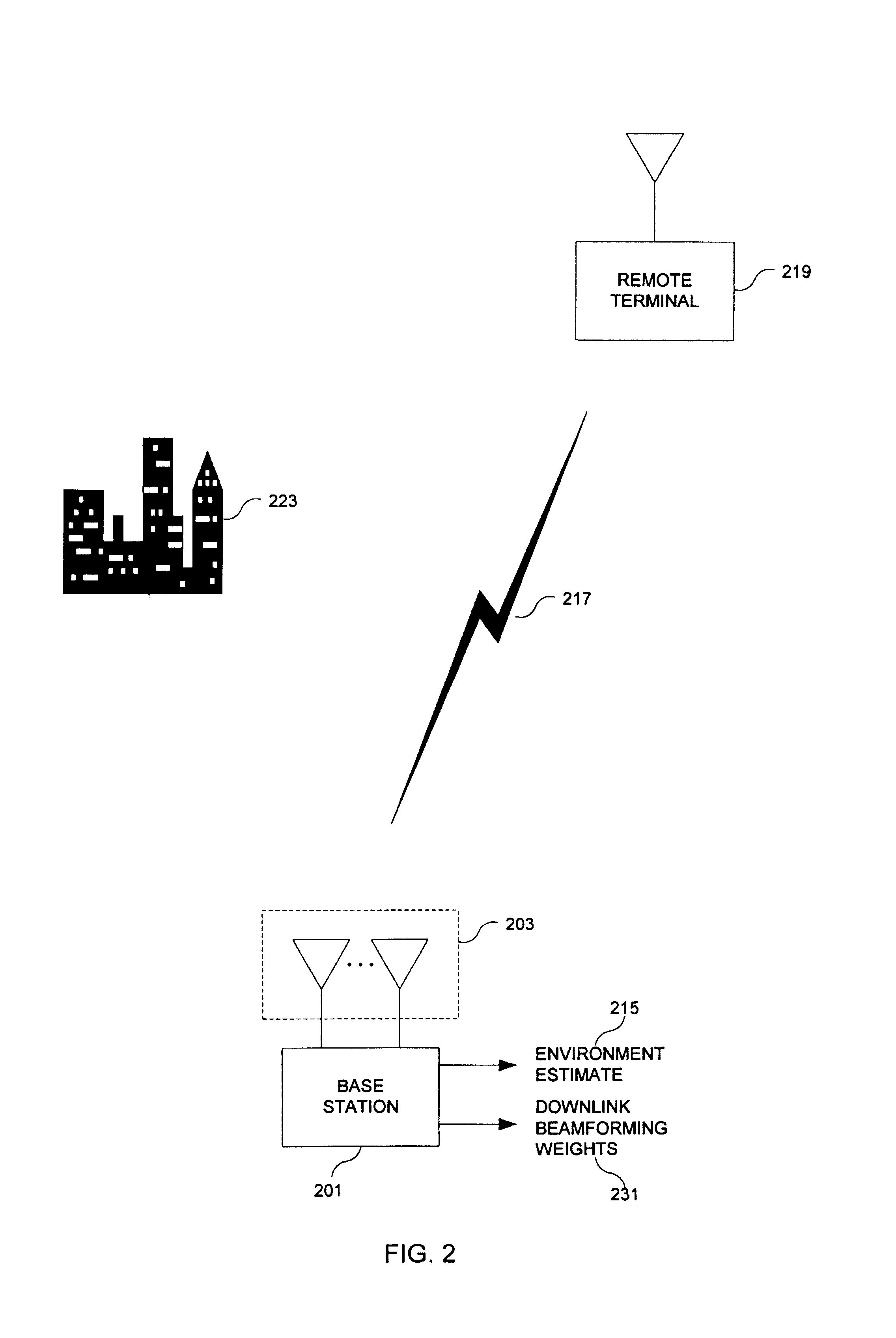
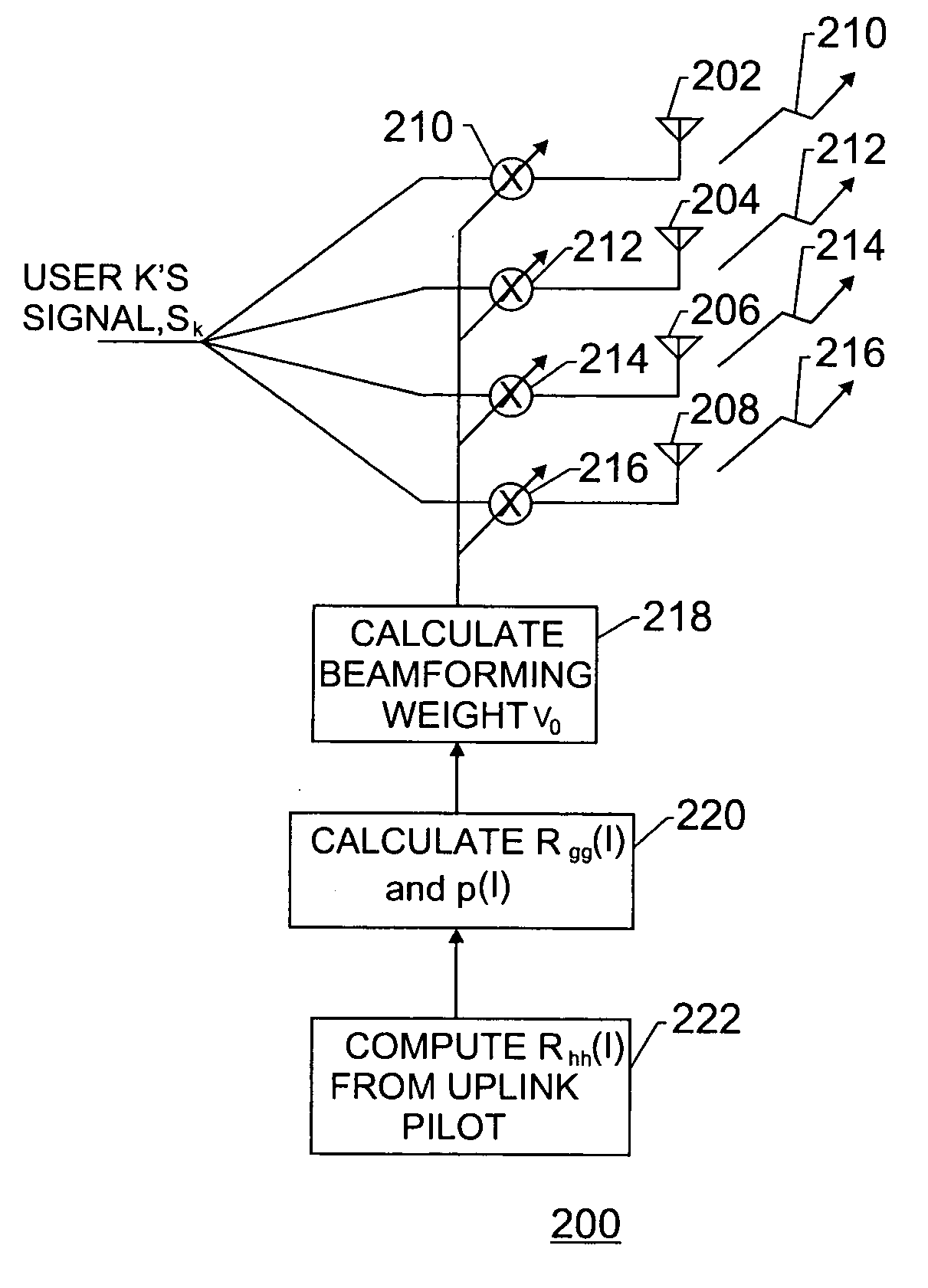
A downlink beamforming apparatus and method. In one embodiment, a method in accordance with the teachings of the present invention includes receiving uplink communication signals from a plurality of antenna array elements, selecting an operating condition of an environment and estimating downlink beamforming weights used in downlink communication signals in response to the selected operation condition of the environment.
Owner:INTEL CORP
A method for reducing bandwidth of ir interface and distributed base station
InactiveCN102291855AReduce bandwidth requirementsIncrease occupancy ratioBaseband system detailsActive radio relay systemsDownlink beamformingControl signal
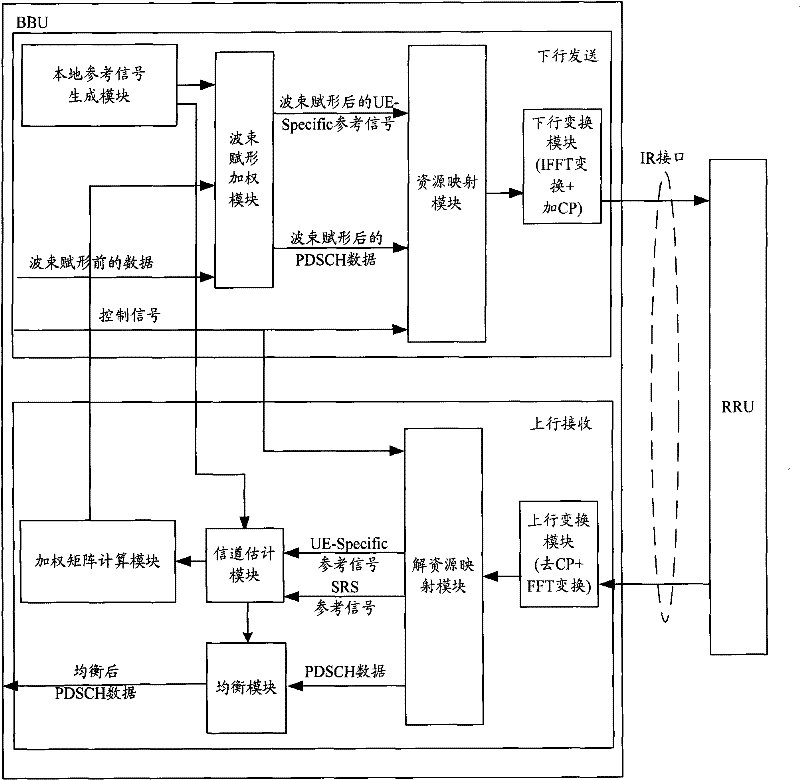
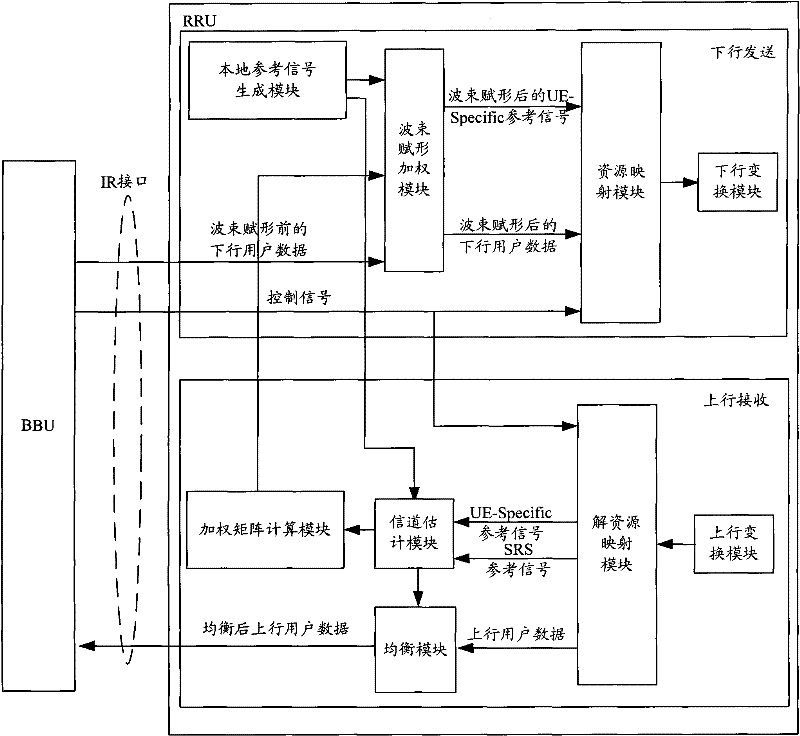
The present invention provides a method for reducing the bandwidth of an Ir interface, which is applied to a remote baseband system that introduces a beamforming function. The method includes: when sending downlink, the indoor baseband processing unit BBU transmits The downlink user data and downlink control signals are sent to the remote radio unit RRU, and the RRU performs downlink beamforming processing according to the downlink user data and downlink control signals; when receiving uplink, the BBU sends the uplink control signals to the RRU through the Ir interface , the RRU performs uplink equalization processing on the received uplink user data according to the uplink control signal, and sends the equalized uplink user data obtained after the uplink equalization processing to the BBU through the Ir interface. The present invention also provides a distributed base station corresponding to the above method. The application of the present invention can greatly reduce the bandwidth requirement of the Ir interface, and increase the effective data occupancy ratio of the Ir interface.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH
Generalized Reference Signaling Scheme for MU-MIMO Using Arbitrarily Precoded Reference Signals
ActiveUS20110019631A1Assess restrictionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsDownlink beamformingHypothesis
A multi-user MIMO downlink beamforming system (200) is provided to enable transmit beamforming vectors to be efficiently provided to a subset of user equipment devices (201.i), where spatial separation or zero-forcing transmit beamformers (wi) are computed at the base station (210) and used to generate precoded reference signals (216). The precoded reference signals (216) are fed forward to the user equipment devices (201.i) which apply one or more hypothesis tests (207.i, 208.i) to the precoded reference signals to extract the precoding matrix (W), including the specific transmit beamforming vector (wUE) designed for the user equipment, and this extracted information is used to generate receive beamformers (vi).
Owner:APPLE INC
Apparatus and method for allocating walsh codes to mobile stations in an adaptive antenna array wireless network
ActiveUS20050105485A1Spatial transmit diversityCode division multiplexDownlink beamformingMobile station
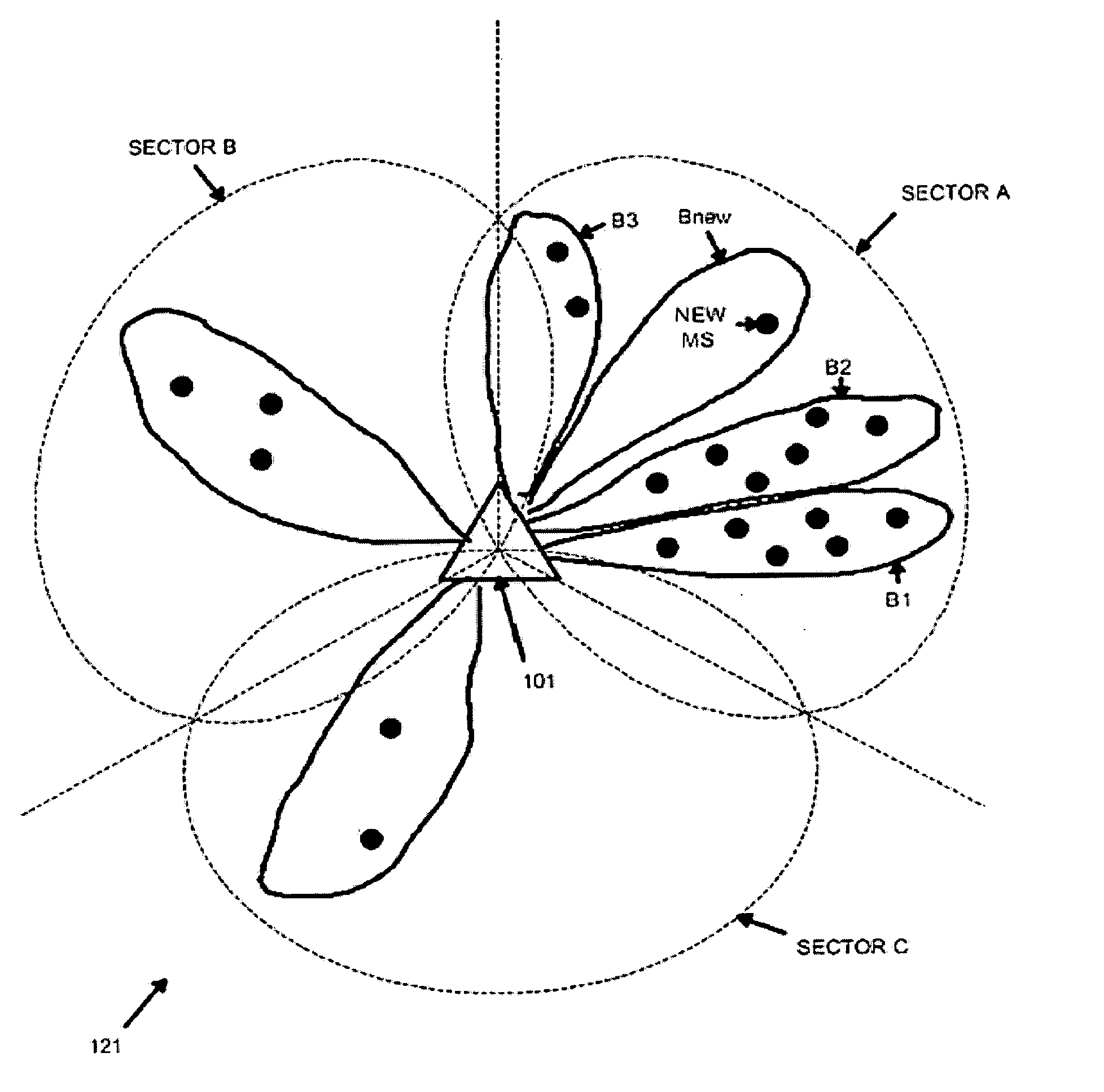
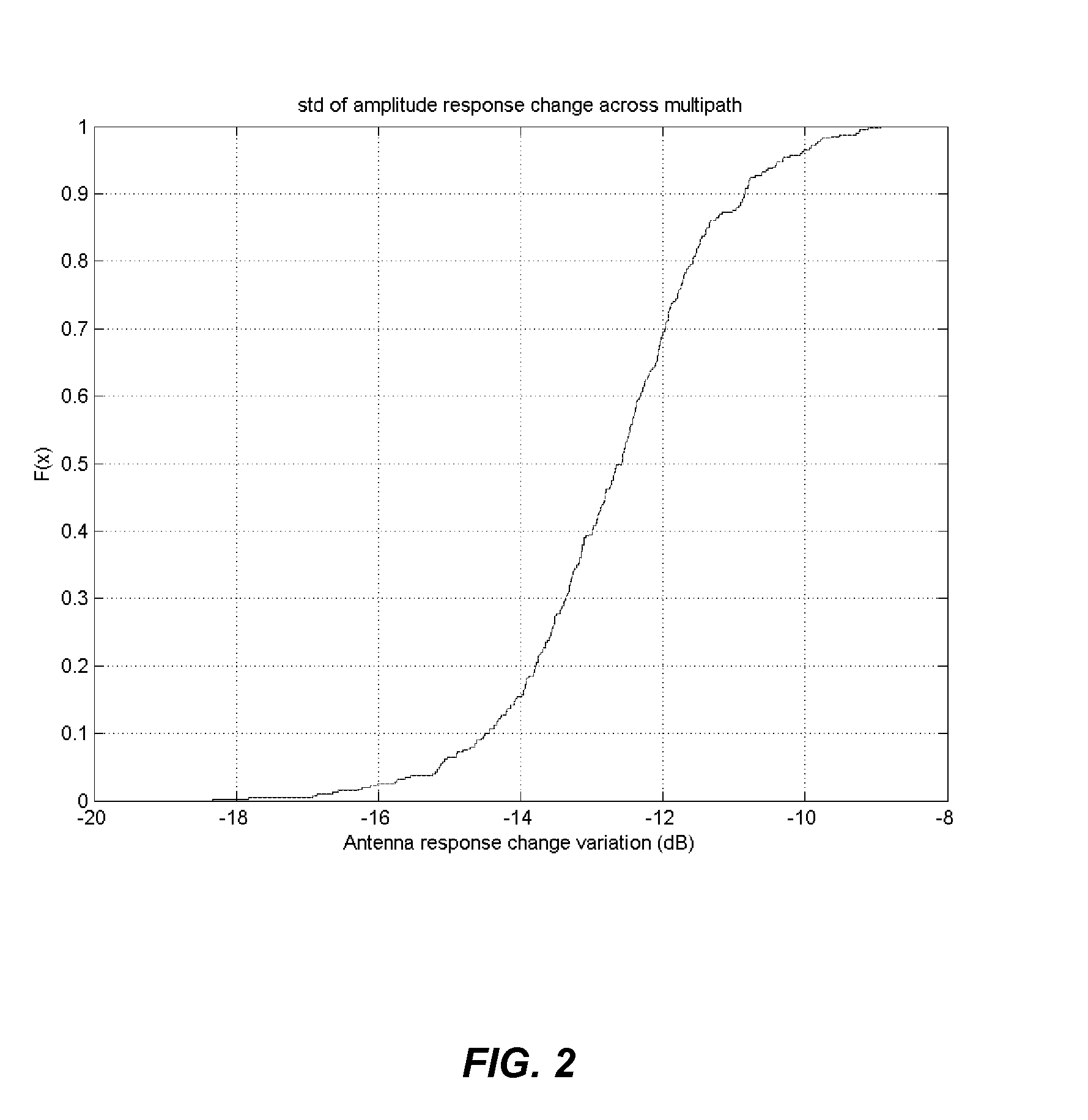
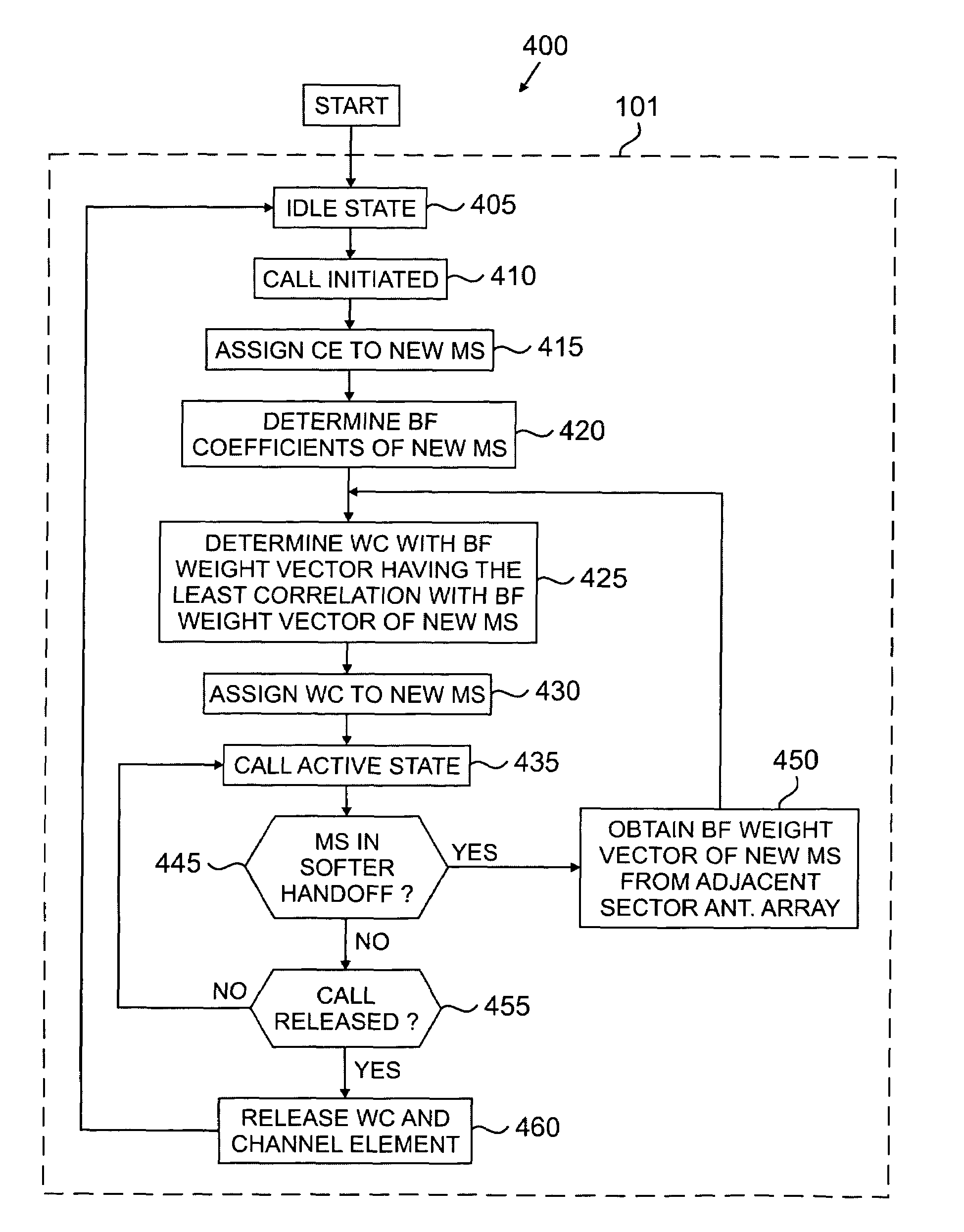
An apparatus for allocating orthogonal codes to mobile stations for use in a CDMA base station that transmits using an adaptive antenna array. The apparatus comprises a database for storing R records. Each record is associated with an active mobile station and comprises an active orthogonal code associated with the active mobile station, corresponding downlink beamforming coefficients associated with the active mobile station, and mobility information associated with the active mobile station. The apparatus further comprises a controller for comparing estimated downlink beamforming coefficients associated with a new mobile station to the R records. The controller selects a first active orthogonal code associated with a first active mobile station to communicate with the new mobile station. The selection is based on the degree of correlation between the estimated downlink beamforming coefficients and first corresponding downlink beamforming coefficients, and 2) first mobility information associated with the first active mobile station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for beamforming with limited feedforward channel in multiple input multiple output wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090016460A1Reduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsDownlink beamformingCommunications system
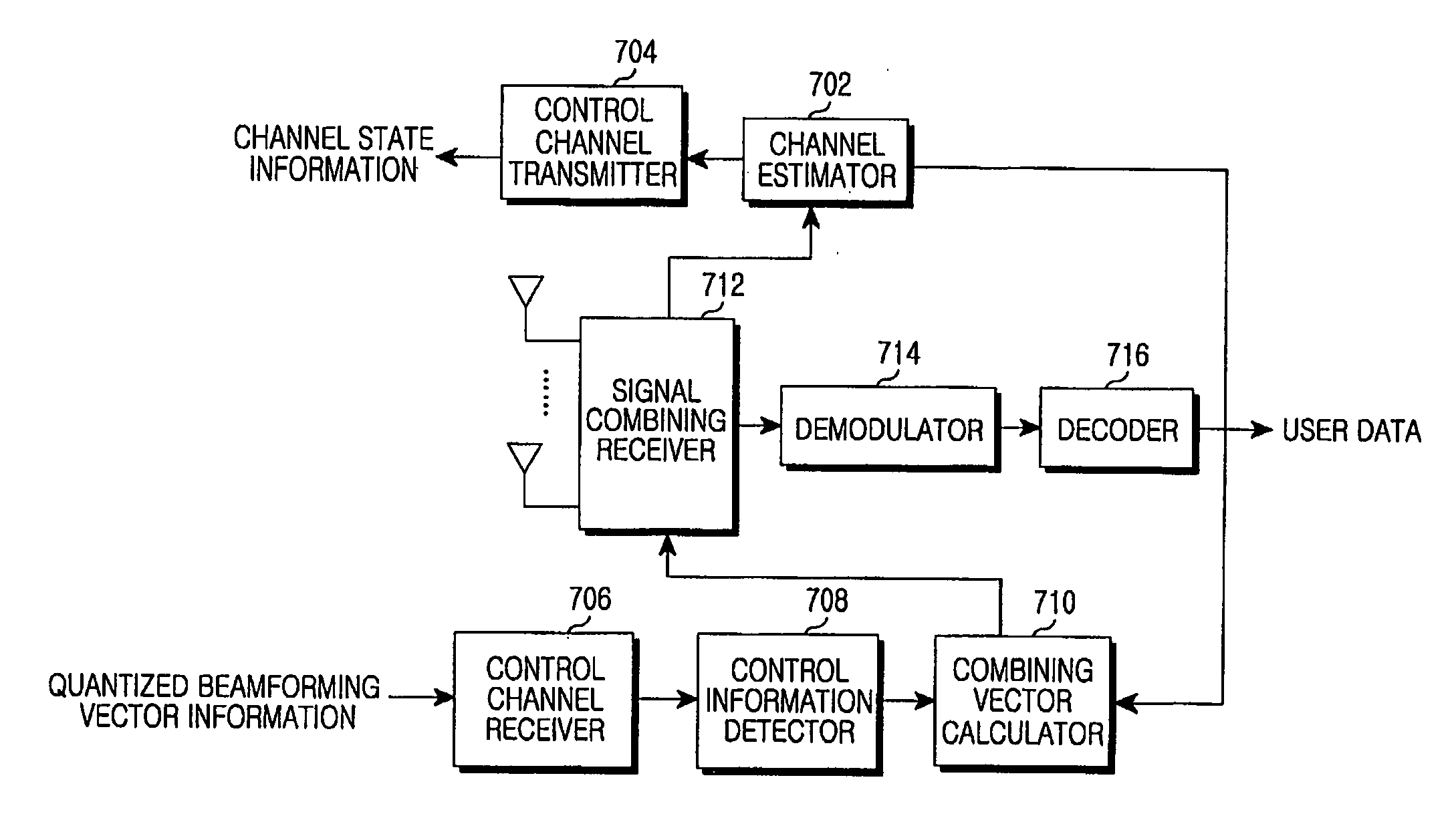
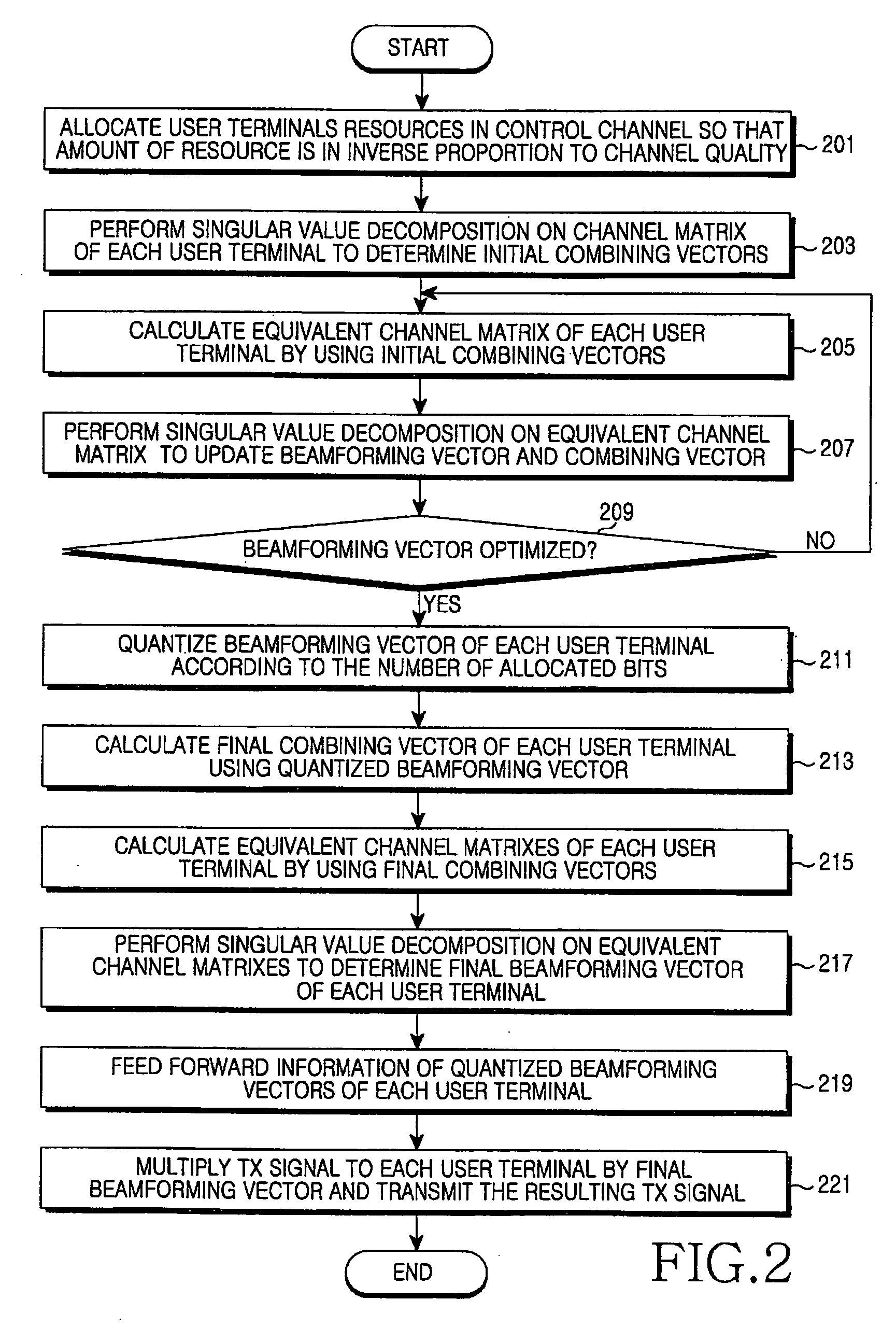
An apparatus and method are provided for beamforming in a MIMO wireless communication system. A base station includes a first calculator that repeatedly calculates downlink beamforming vectors of the user terminals to calculate the optimal beamforming vectors for the user terminals, a quantizer that quantizes the downlink beamforming vectors in order to transmit information of the downlink beamforming vectors, a control channel transmitter that feeds forward information of the quantized downlink beamforming vectors to the user terminals, a second calculator that calculates the final downlink beamforming vectors of the user terminals, and a beamforming transmitter that sums the beamformed TX signals of the user terminals and transmits the summed TX signals through a plurality of TX antennas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Downlink beamforming method in mobile communication intelligent antenna system
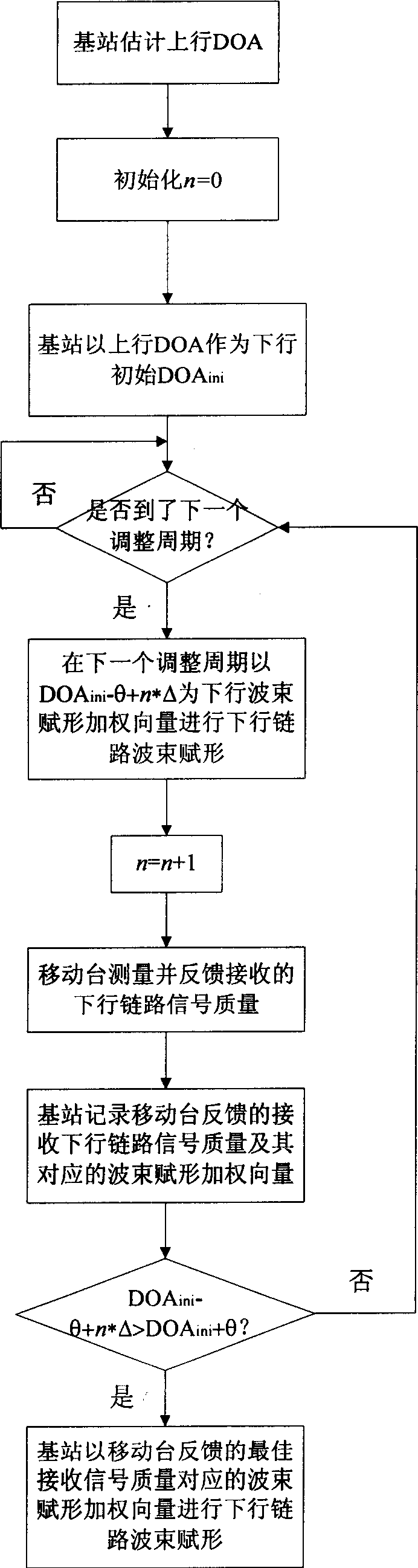
ActiveCN1700801AStrong wireless environmentSimple structureAntenna arraysRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDownlink beamformingEmission channeling
This invention relates to one mobile communication intelligent antenna down linkage wave beam endows method, which is characterized by the following: the basic station measures and feeds back the linkage signals to adjust the down linkage-weighted vector. The advantages of this invention lie in the following: a, of not strict requirement of aptitude and phase of receiving and emission channels; b, suitable for upper and down linkage and easy for wireless environment and suitable for wireless environment; c, without strict correction of receiving and emission channels.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Multi-user mimo-sdma for finite rate feedback systems
ActiveUS20120076032A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsDownlink beamformingPrecoding
A multi-user v downlink beamforming system with limited feedback (200) is provided to enable precoding for multi-stream transmission, where a channel codeword (ui) and one or more channel quality indicator values (CQIA, CQIB) are computed at the user equipment (201.i) on the basis of maximizing a predetermined SINR performance metric (ρi) which estimates the receive signal-to-noise-ratio (SINR) at the user equipment (201.i). The computed codeword (ui) and CQI values (or differential values related thereto) are quantized and fed back to help the base station (210) which applies a correction to the appropriate CQI value in the course of designing the transmit beamforming vectors w and determining the appropriate modulation and coding level to be used for downlink data transmission.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for providing user specific downlink beamforming in a fixed beam network
ActiveUS7054664B2Resonant long antennasAntenna supports/mountingsCorrelation coefficientDownlink beamforming
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system and method for providing user specific beams in a fixed beam network, the fixed beam network comprising a plurality of fixed beams, each of the plurality of fixed beams being defined by a plurality of fixed beam correlation coefficients. The system may comprise a device that computes reception correlation data for a received signal, and a beamformer that is adapted to determine transmission weighting coefficients to be applied to a return signal based on the difference between the reception correlation data and the fixed beam weighting coefficients associated with at least one of the plurality of fixed beams.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
System and method for improving performance of an adaptive antenna array in a vehicular environment
InactiveUS7139593B2Improve adaptabilitySpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentMobile antennasDownlink beamforming
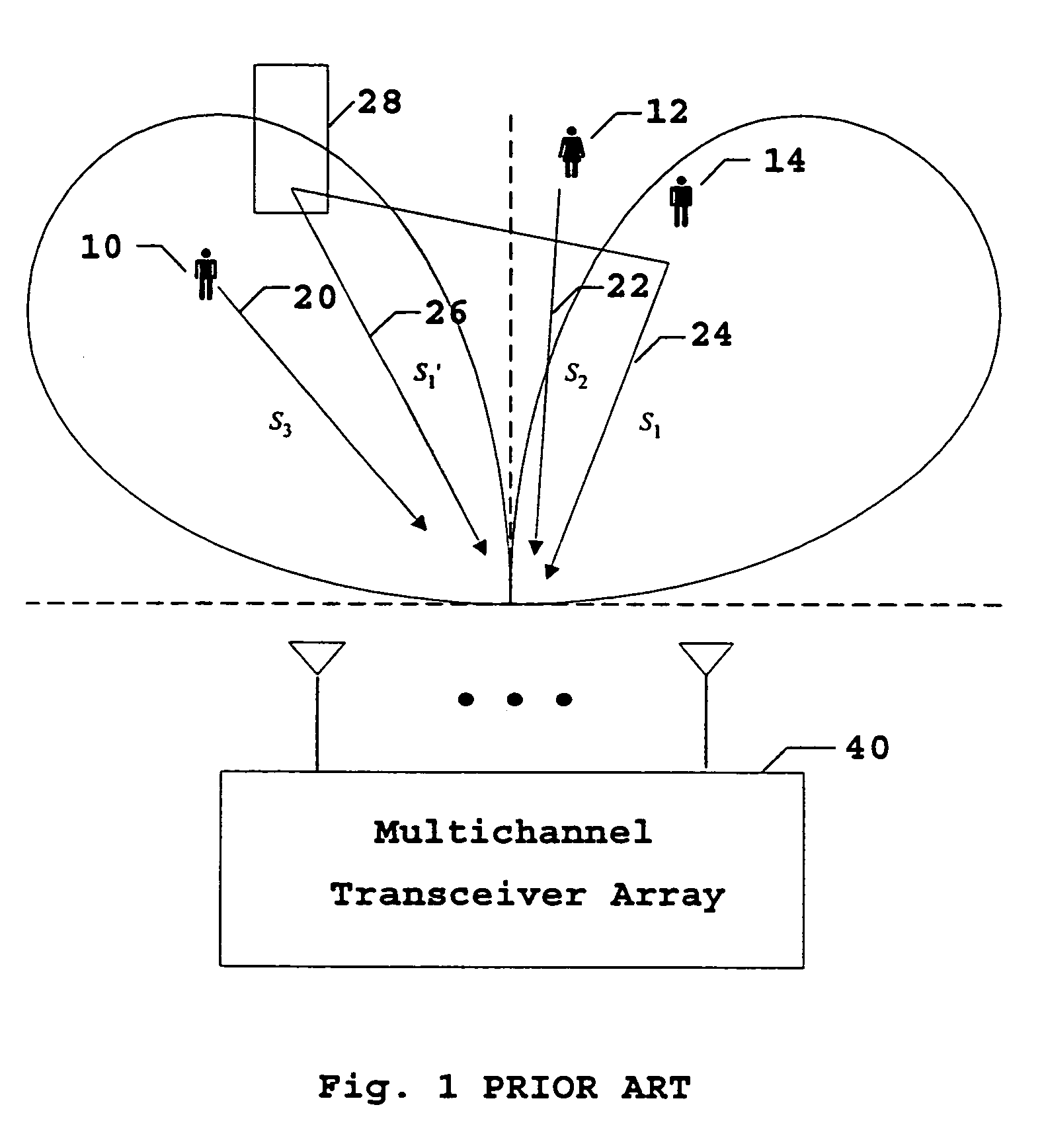
A system and method is disclosed for improving downlink performance of an adaptive antenna array in a vehicular environment. The system comprises a mobile station that has a first mobile antenna and a second mobile antenna. A spatial signature estimator associated with a base transceiver station obtains spatial signatures from signals from the first mobile antenna and from the second mobile antenna within an uplink interval. Correlation circuitry uses the spatial signatures to identify a least changing spatial signature to obtain an optimal downlink beamforming weight vector to be used in the transmission of a signal to the mobile station in the next downlink interval.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Beam synthesis method for downlink beamforming in FDD wireless communication system
InactiveUS7359733B2Practical and inexpensive and efficientMaximize capacitySpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentDownlink beamformingCommunications system
A method for downlink beamforming in a frequency-division-duplex wireless communications system comprising a base station with an antenna array and terminals that are physically remote from said base station, the method comprising the steps of: receiving at said base station antenna array combinations of arriving uplink signals from said plurality of remote terminals, estimating an uplink beamforming weight vector for each of said terminals from said combinations of arriving uplink signal; identifying uplink nulls and an uplink main beam position from said uplink beamforming weight vector; transforming each of said uplink nulls to form a corresponding downlink null; generating a downlink beamforming weight vector from all downlink nulls; and transmitting a set of information signals from said base station antenna array according to said downlink. beamforming weights.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Method and apparatus for providing user specific downlink beamforming in a fixed beam network
ActiveUS20050096090A1Resonant long antennasAntenna supports/mountingsCorrelation coefficientDownlink beamforming
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system and method for providing user specific beams in a fixed beam network, the fixed beam network comprising a plurality of fixed beams, each of the plurality of fixed beams being defined by a plurality of fixed beam correlation coefficients. The system may comprise a device that computes reception correlation data for a received signal, and a beamformer that is adapted to determine transmission weighting coefficients to be applied to a return signal based on the difference between the reception correlation data and the fixed beam weighting coefficients associated with at least one of the plurality of fixed beams.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
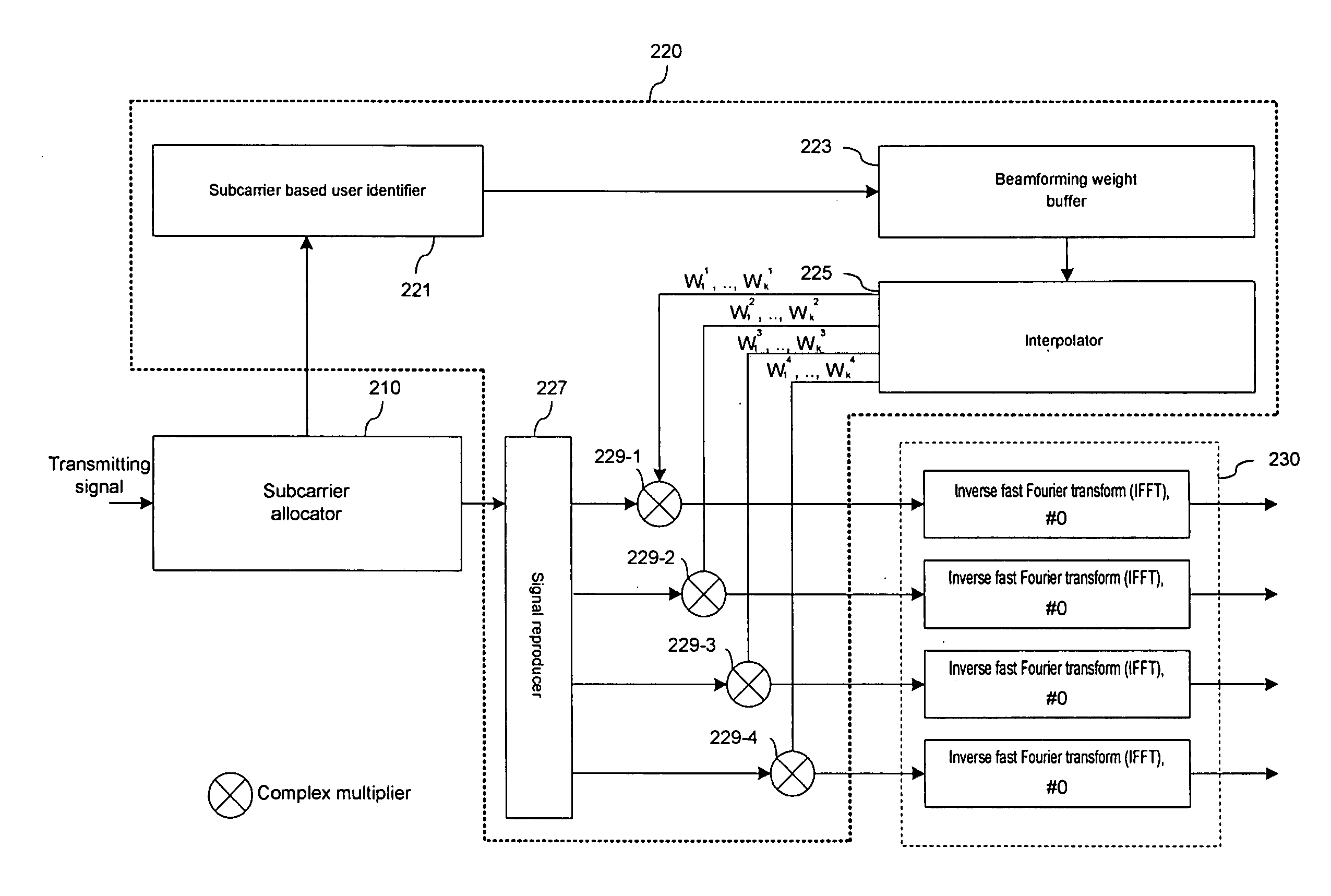
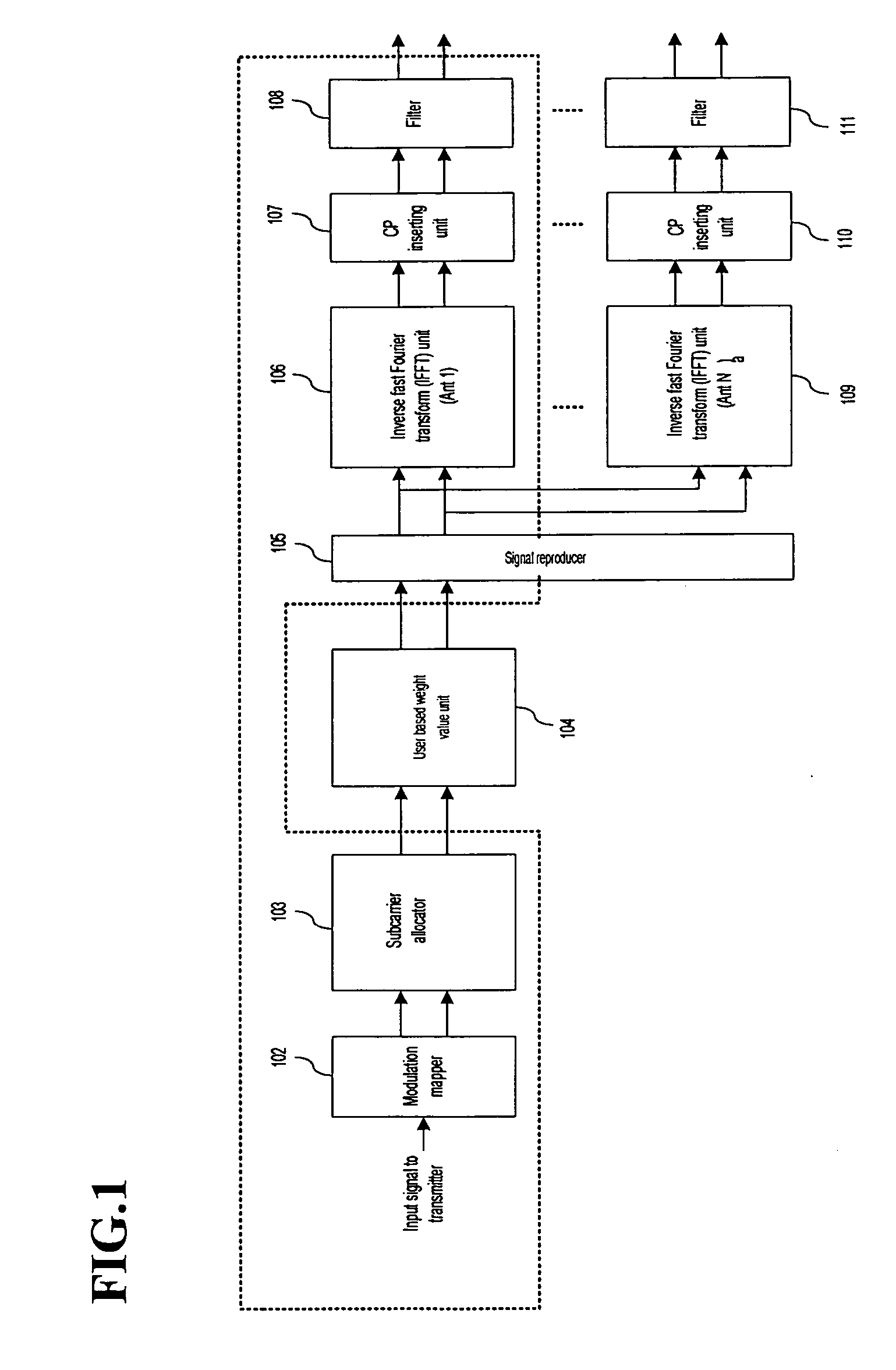
Downlink beamforming apparatus in OFDMA system and transmission apparatus including the same
InactiveUS20070135052A1Reduce power consumptionEffective structureModulated-carrier systemsLine-faulsts/interference reductionDownlink beamformingCarrier signal
A downlink beamforming apparatus and a transmission apparatus including the same includes a subcarrier based user identifier for dividing subcarriers according to users, a beamforming weight buffer for storing first beamforming weights for the subcarriers by each of transmitting antennas, an interpolator for outputting second beamforming weights for each transmitting antenna by interpolating the first beamforming weights, and a signal reproducer for reproducing the signal for each transmitting antenna. Subcarriers are allocated to the signal by each user; and a complex multiplier multiplies the signal for each transmitting antenna by the second beamforming weights.
Owner:KT CORP +4
Reference signals for downlink beamforming validation in wireless multicarrier MIMO channel
InactiveUS7720470B2Transmission path divisionRadio transmissionDownlink beamformingTelecommunications
Owner:INTEL CORP
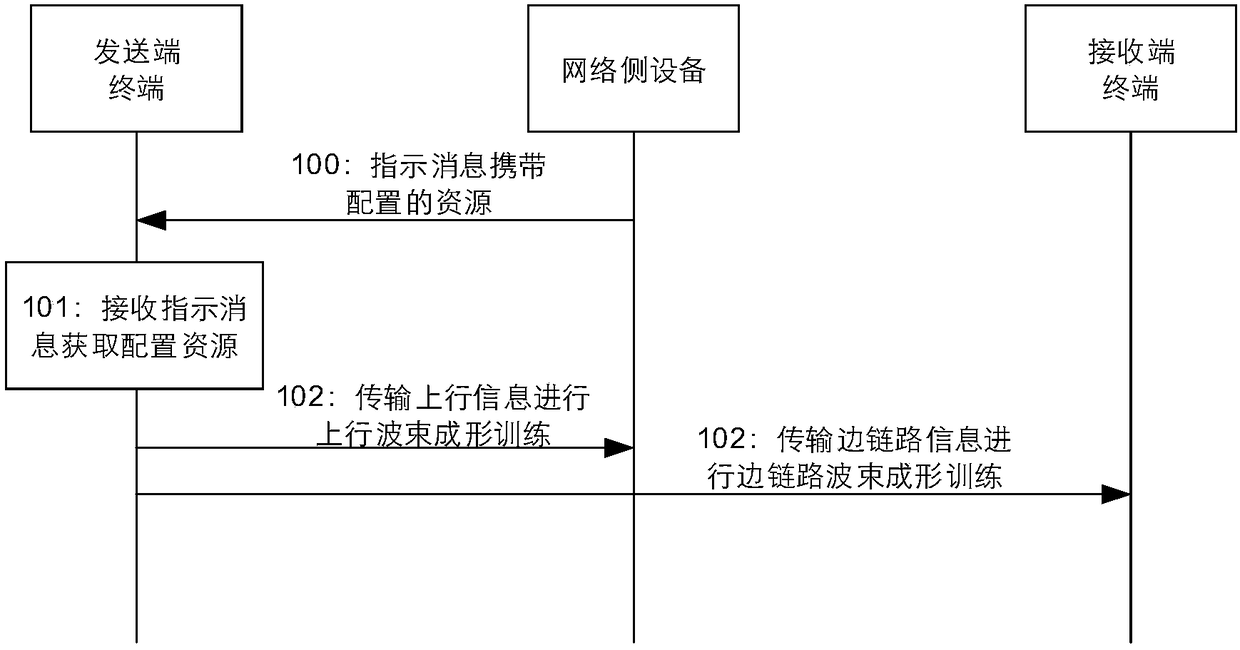
Communication method between terminal and terminal, network side equipment and terminal
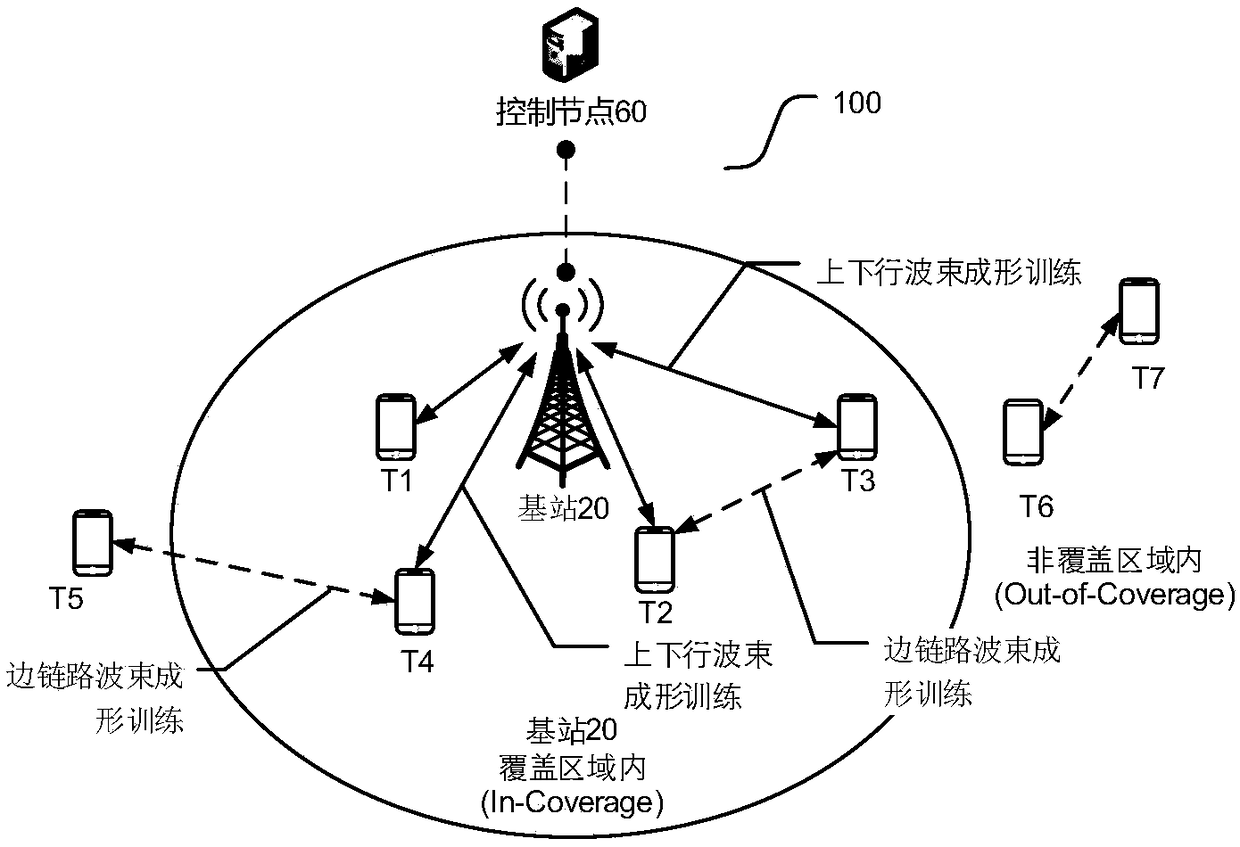
ActiveCN108419295AImprove communication efficiencySave time and frequency resourcesSignal allocationConnection managementDownlink beamformingTime domain
The application relates to the technical field of wireless communication, and provides a communication method between a terminal and the terminal, network side equipment and the terminal. The method comprises the following steps: the network side equipment distributes time frequency resource for transmitting uplink information and sidechain information for the terminal; the terminal transmits theuplink information for performing uplink beam training to the network side equipment at the same moment in the time frequency resource range on the time frequency resource, and transmits the sidechaininformation for performing sidechain beam training to another terminal. Through the scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the terminal can perform the beamforming training of the sidechain without additionally using the new time frequency resource based on the traditional uplink and downlink beamforming training procedure.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Frequency transformation based transmit beamforming in a communication system
InactiveUS20100008268A1Little processingRobust responseTransmission path divisionSubstation equipmentPhase correctionDownlink beamforming
The present invention provides a system and method for transmit beamforming in a Frequency Division Duplex communication system. A first step (600) includes correcting for differences between transceiver receive and transmit responses within a base station. A next step (604) obtaining a beamforming weight of a phase antenna array on an uplink. A next step (606) transforming the uplink beamforming weight a downlink beamforming weight by applying a phase correction that is a function of wavelength at the uplink and downlink frequencies and distance between antenna elements.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Apparatus and method for allocating walsh codes to access terminals in an adaptive antenna array CDMA wireless network
InactiveUS7411899B2Maximizing re-useSpatial transmit diversityRadio transmission for post communicationDownlink beamformingWireless network
An apparatus having: 1) a database for storing R active wireless terminal records, each of the R active wireless terminal records containing: a) an active orthogonal code and b) corresponding downlink beamforming coefficients used to communicate with one of the wireless access terminals; and 2) a controller associated with the database that receives a notification that a new wireless access terminal is accessing the base station and, in response to the notification, compares each of the R active wireless terminal records to new downlink beamforming coefficients associated with the new wireless access terminal. The controller determines at least one active wireless terminal record containing corresponding downlink beamforming coefficients that have the least correlation with the new downlink beamforming coefficients.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
HSDPA system power, synchronization control, beam shaping method and base station
InactiveCN101316126AImprove accuracyEffective control of signal powerSpatial transmit diversityTransmission control/equalisingDownlink beamformingSynchronous control
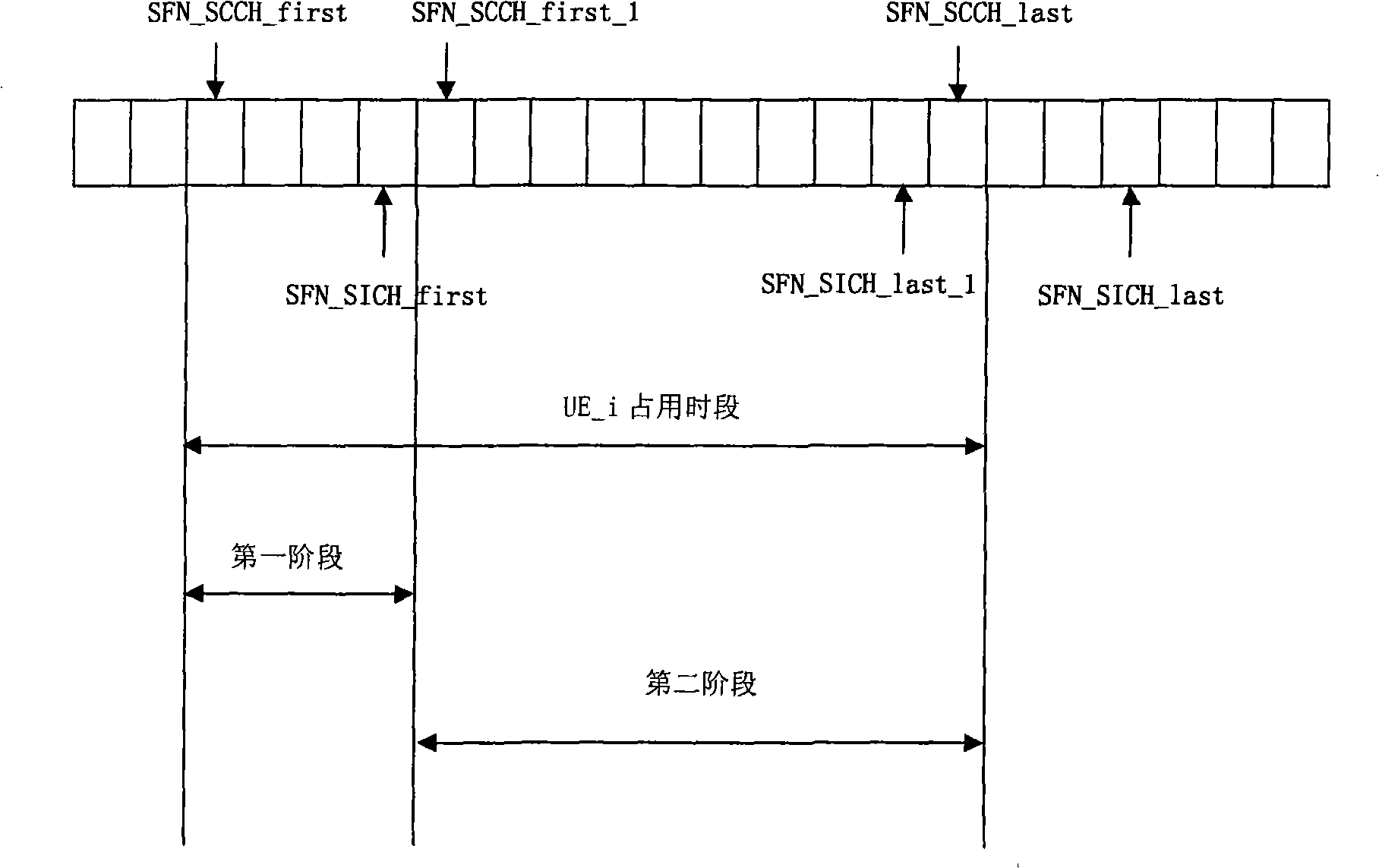
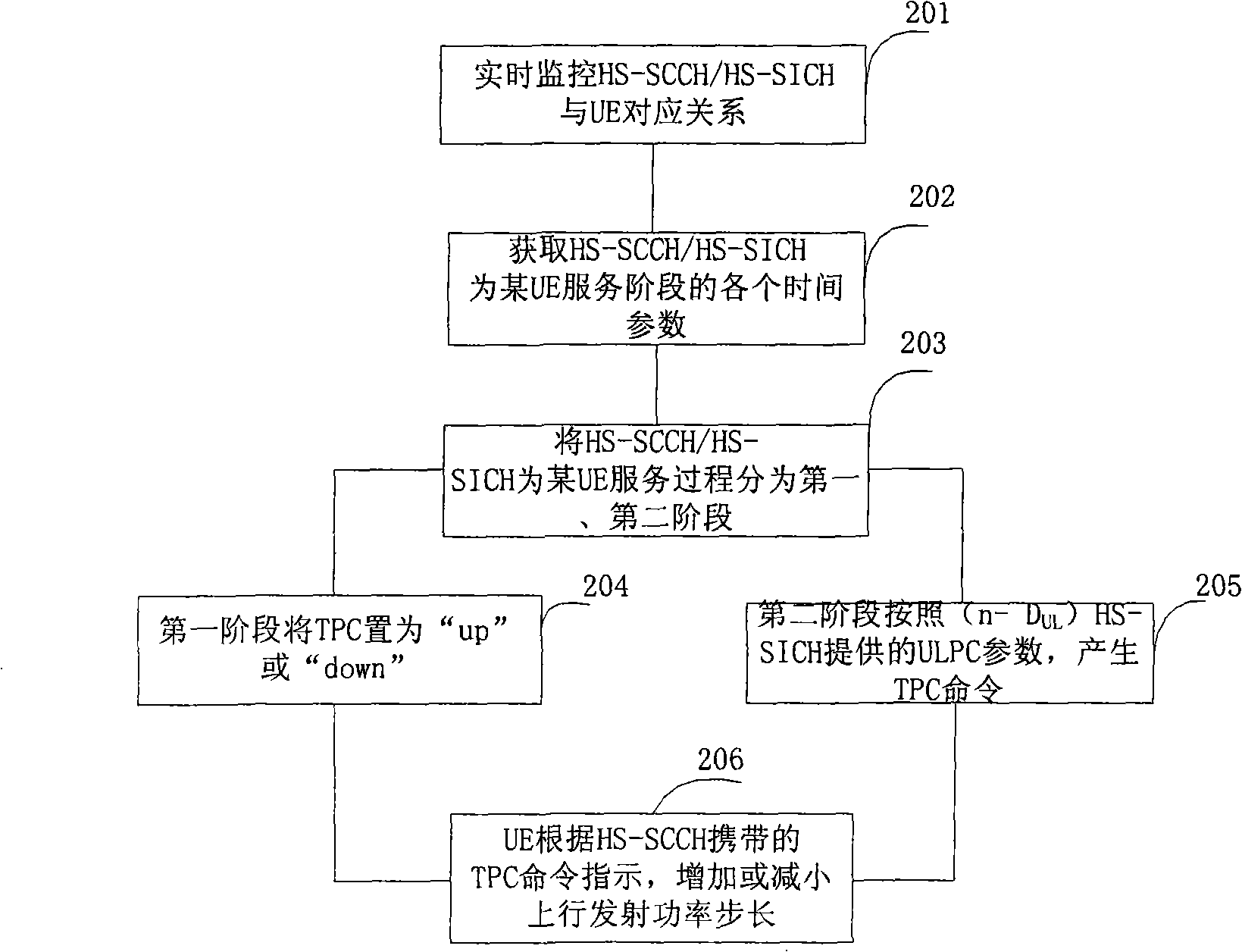
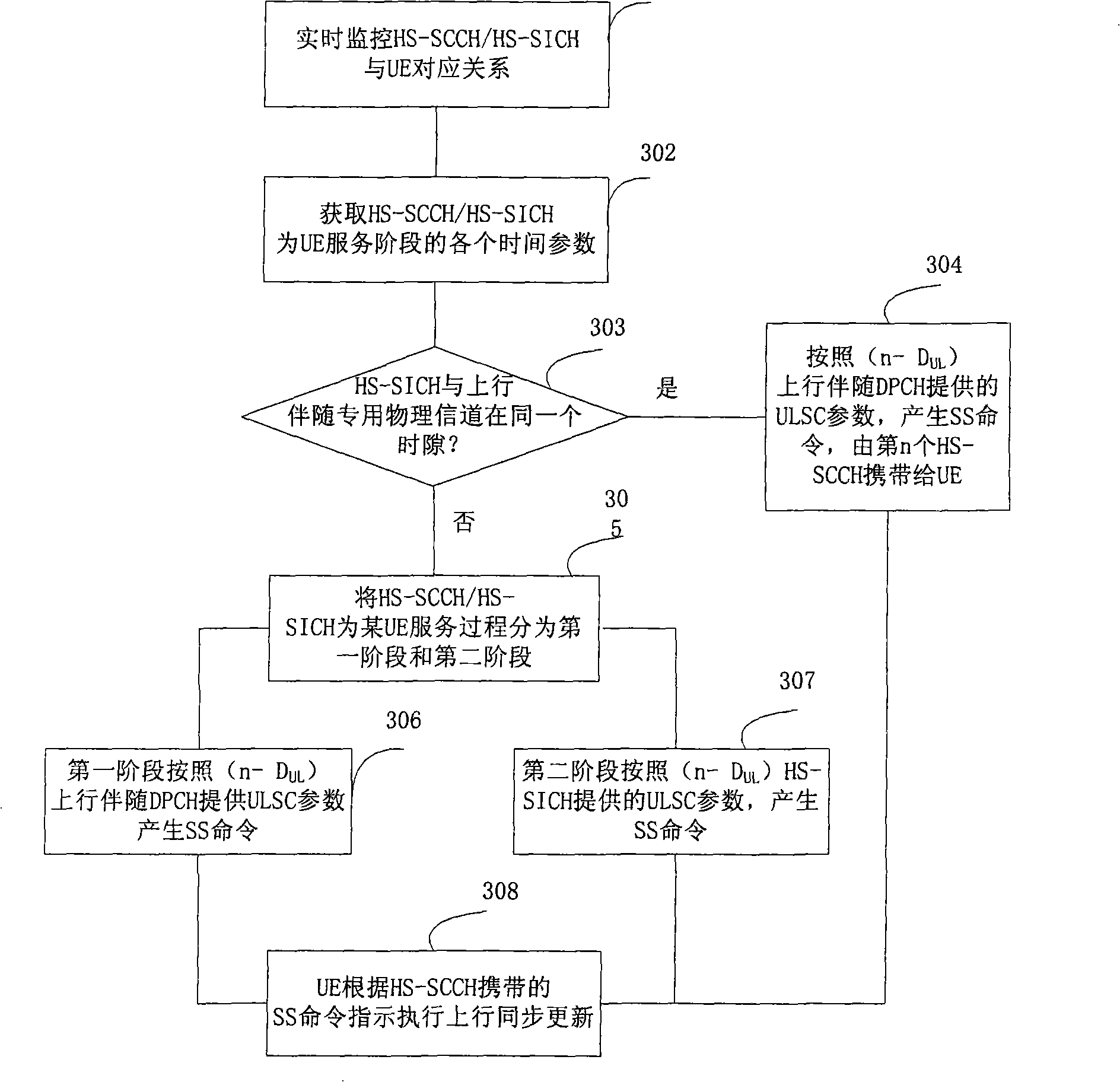
The invention discloses a method for controlling the power of the HSDPA system, which aims at the HS-SICH and includes the steps of: real-time monitoring the corresponding relationship between the HS-SCCH as well as the HS-SICH and UE, and obtaining a time parameter of the corresponding relationship between the channel and the UE; a first stage, which is the stage from the first HS-SCCH subframe transmitted from the base station to the generation of the power control instruction by utilizing the first HS-SICH subframe fed back by the UE, wherein, the power control instruction can be set to be up or down randomly or alternately; a second stage, which is the stage from the generation of the power control instruction by utilizing the first HS-SICH subframe fed back by the UE to the last HS-SCCH subframe transmitted for the UE, wherein, the power control instruction can be set by utilizing the power control parameters obtained from the calculation of the HS-SICH subframe; the base station transmits the HS-SCCH subframe carrying the power control instruction to the UE. The invention also discloses a power control method aiming at the HS-SCCH, a base station and a down beam shaping proposal.
Owner:TD TECH COMM TECH LTD
Method, device and system for beamforming smart antenna
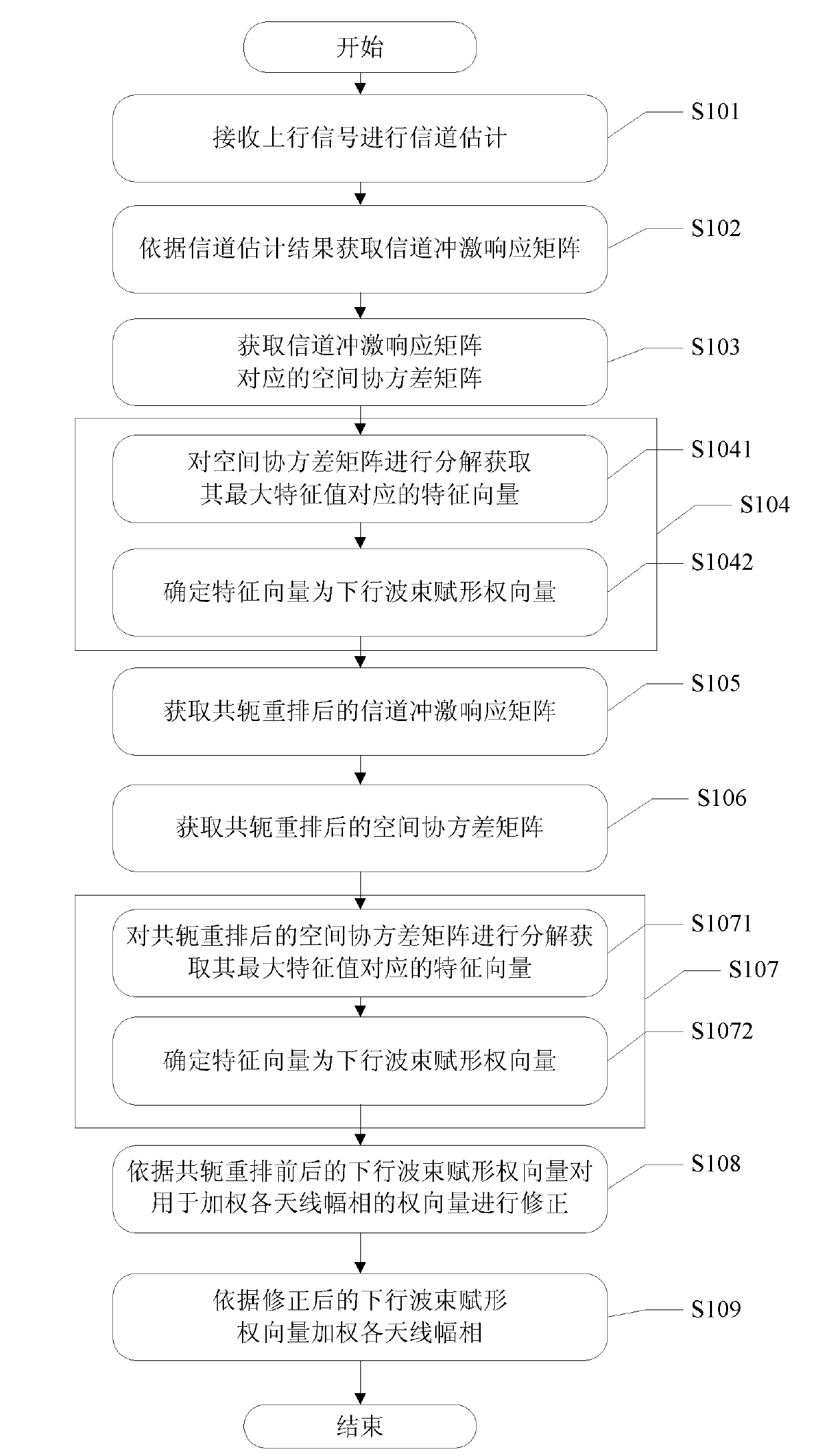
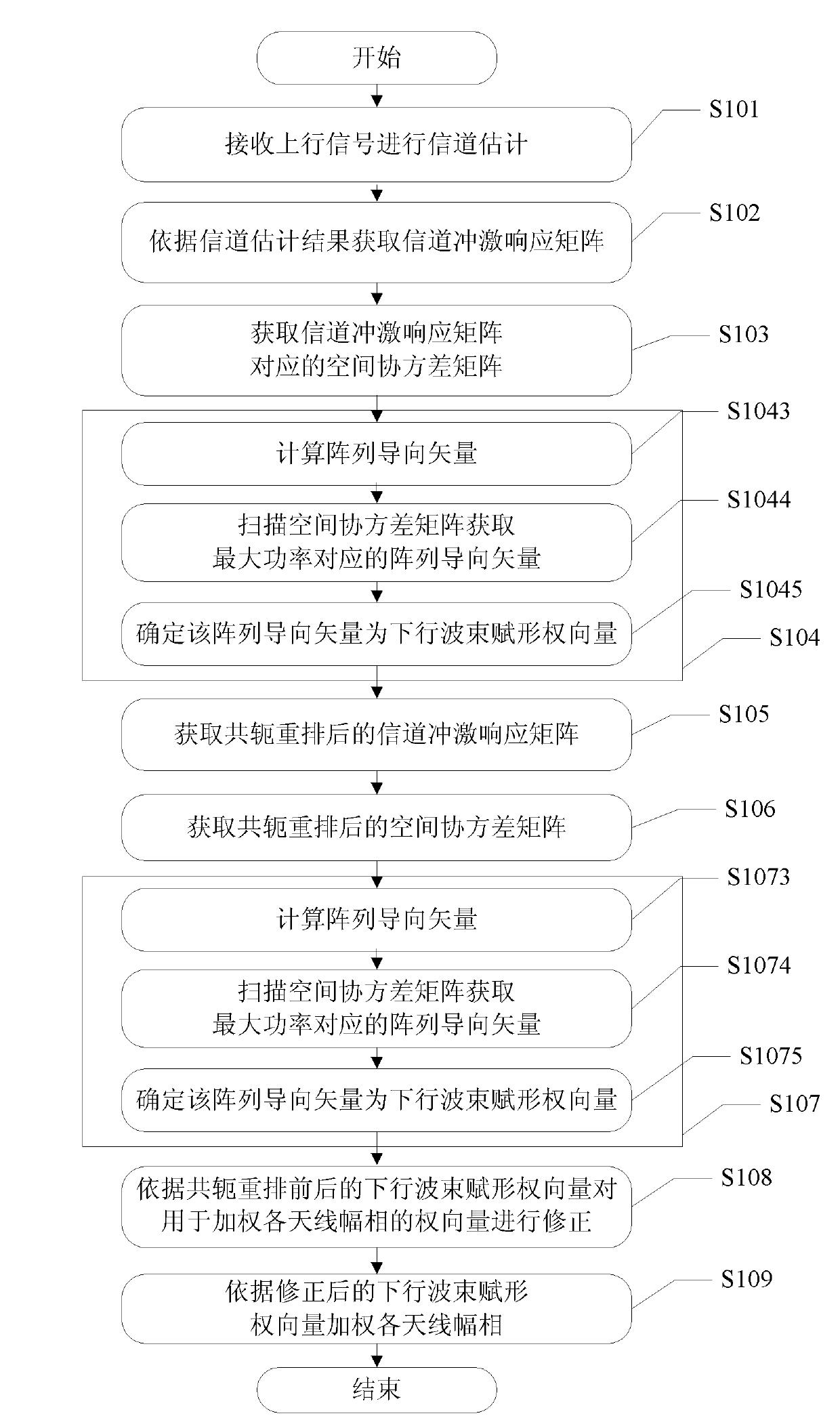
ActiveCN102170303AReduced apertureReduce multipath signal correlationSpatial transmit diversityDownlink beamformingChannel impulse response
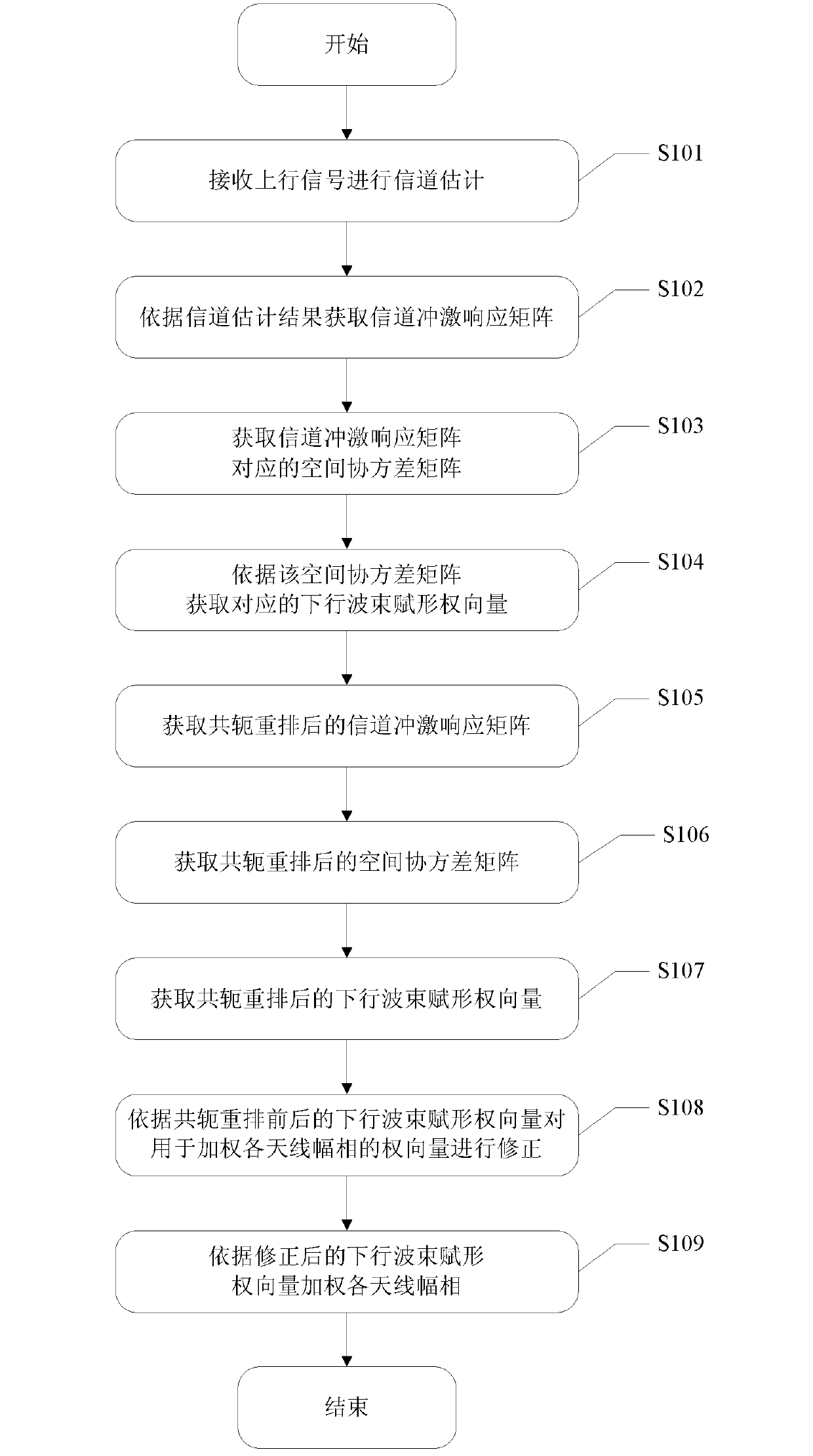
The invention discloses a method, a device and a system for beamforming a smart antenna. The method comprises the following steps: calculating a downlink beamforming weight vector UR according to a spatial covariance matrix R corresponding to a channel impulse response matrix H acquired in advance; calculating a downlink beamforming weight vector URm according to a spatial covariance matrix Rm corresponding to a channel impulse response matrix Hm determined after the channel impulse response matrix H is rearranged in a conjugated way; determining a corrected downlink beamforming weight vectorby taking the downlink beamforming weight vector UR and downlink beamforming weight vector URm as correct parameters; utilizing a downlink beamforming weight vector U to weight each antenna amplitudephase so as to realize downlink beamforming of a user. The method can reduce multipath signal correlation under the condition of not increasing calculation quantity and not reducing array antenna aperture and can still realize better downlink beamforming even if strong correlative signal exists.
Owner:HENAN INFORMATION CONSULTATION DESIGN & RES
Network node and method of taking a mobility decision by considering the beamforming capabilities of the neighbouring nodes
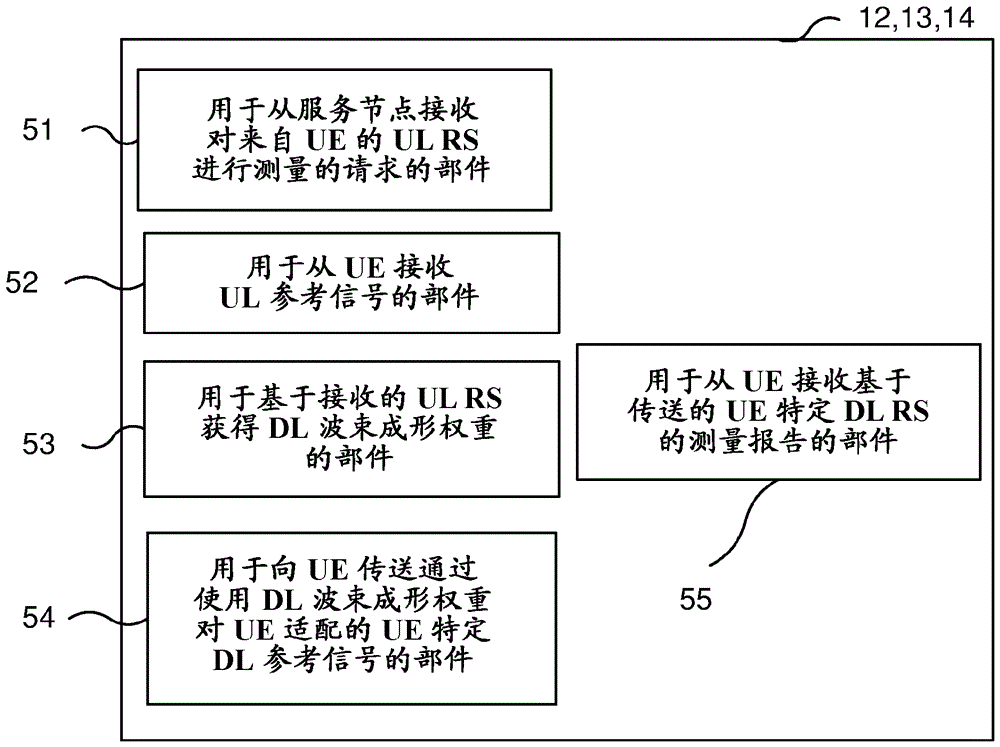
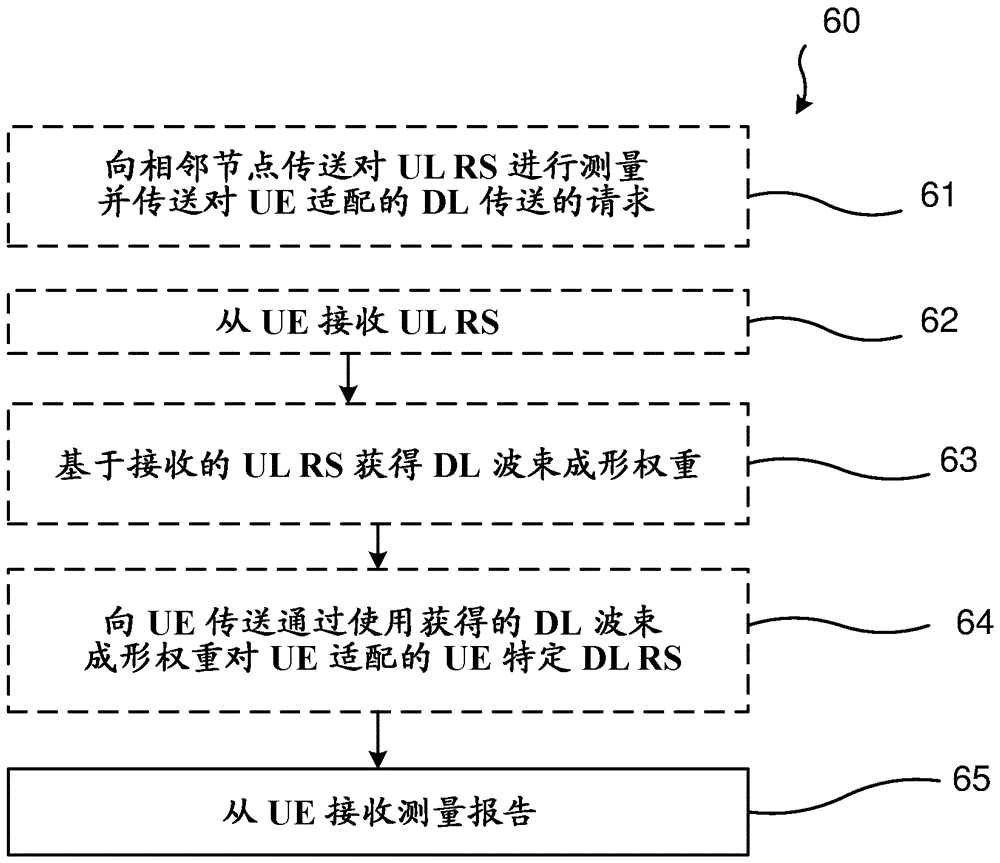
The disclosure relates to a method (13) for enabling accurate measurement results for a communication device (16). The method comprises sending (102), by a serving node (12) serving the communication device and to a neighbour network node (13), a request for measuring on the uplink reference signals from the communication device; the serving and neighbour nodes receiving (103), from the communication device, uplink reference signals; the serving and the neighbour nodes obtaining (104) downlink beamforming weights based on the received uplink reference signals; the serving and the neighbour nodes transmitting (105), to the communication device, specific downlink reference signals adapted for the communication device by using the downlink beamforming weights; the UE transmitting (107) a downlink measurement report to the serving node; the serving node taking a mobility decision based on the UE report (108). The disclosure also relates to the corresponding network nodes, computer programs and computer program products.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
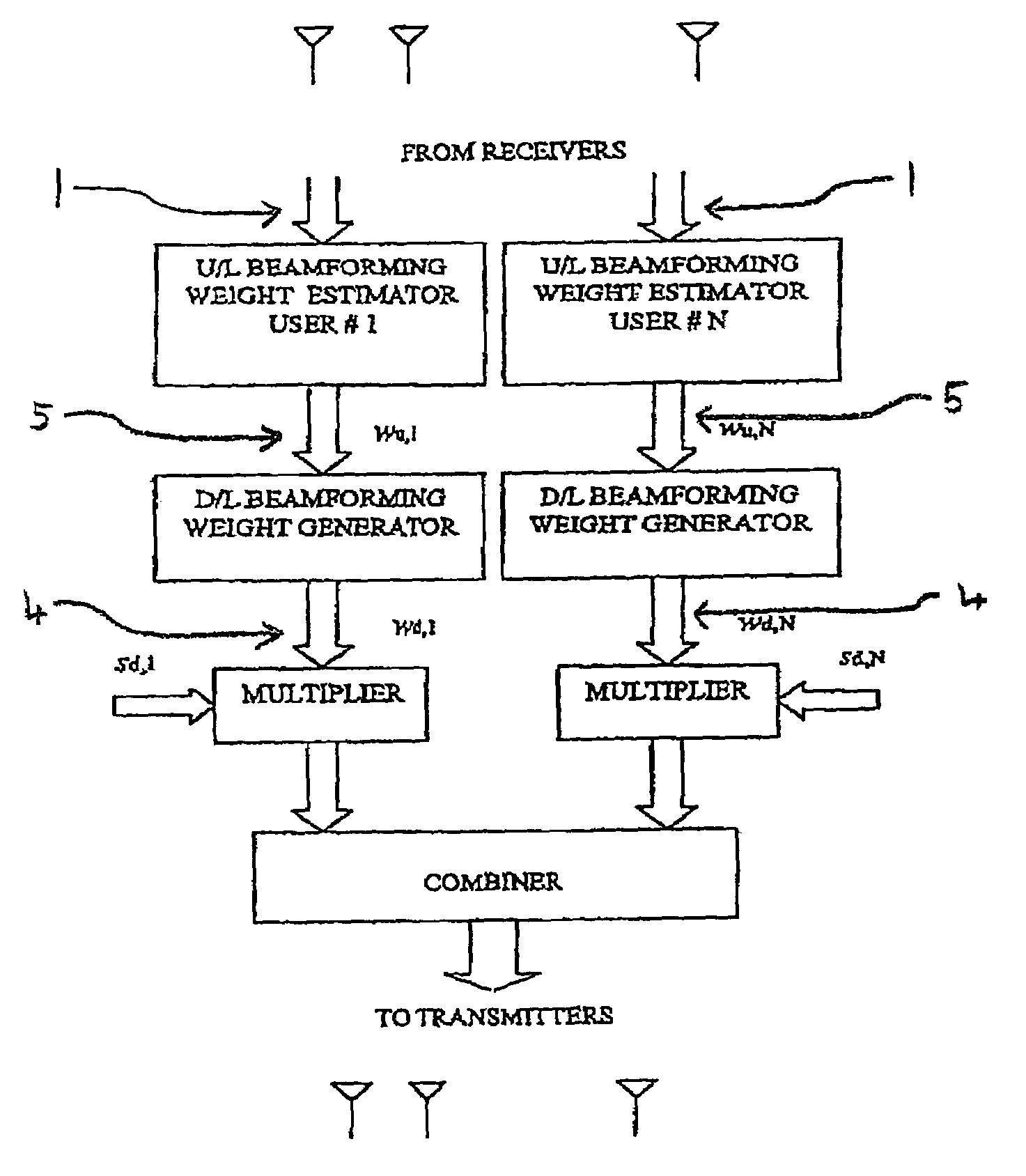
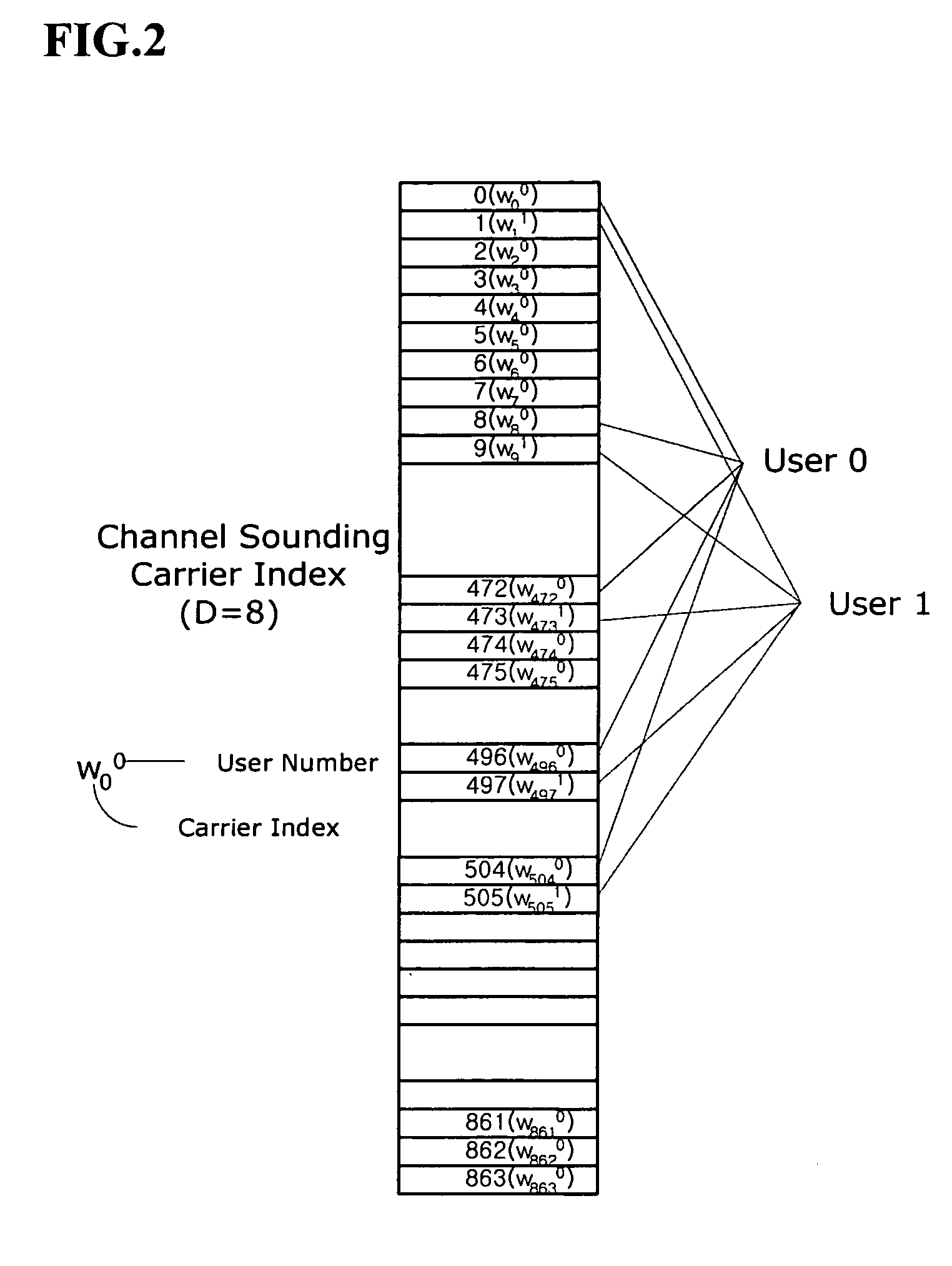
Beamforming Weight Generation Using Adaptive Trigonometric Waveform Interpolation Techniques
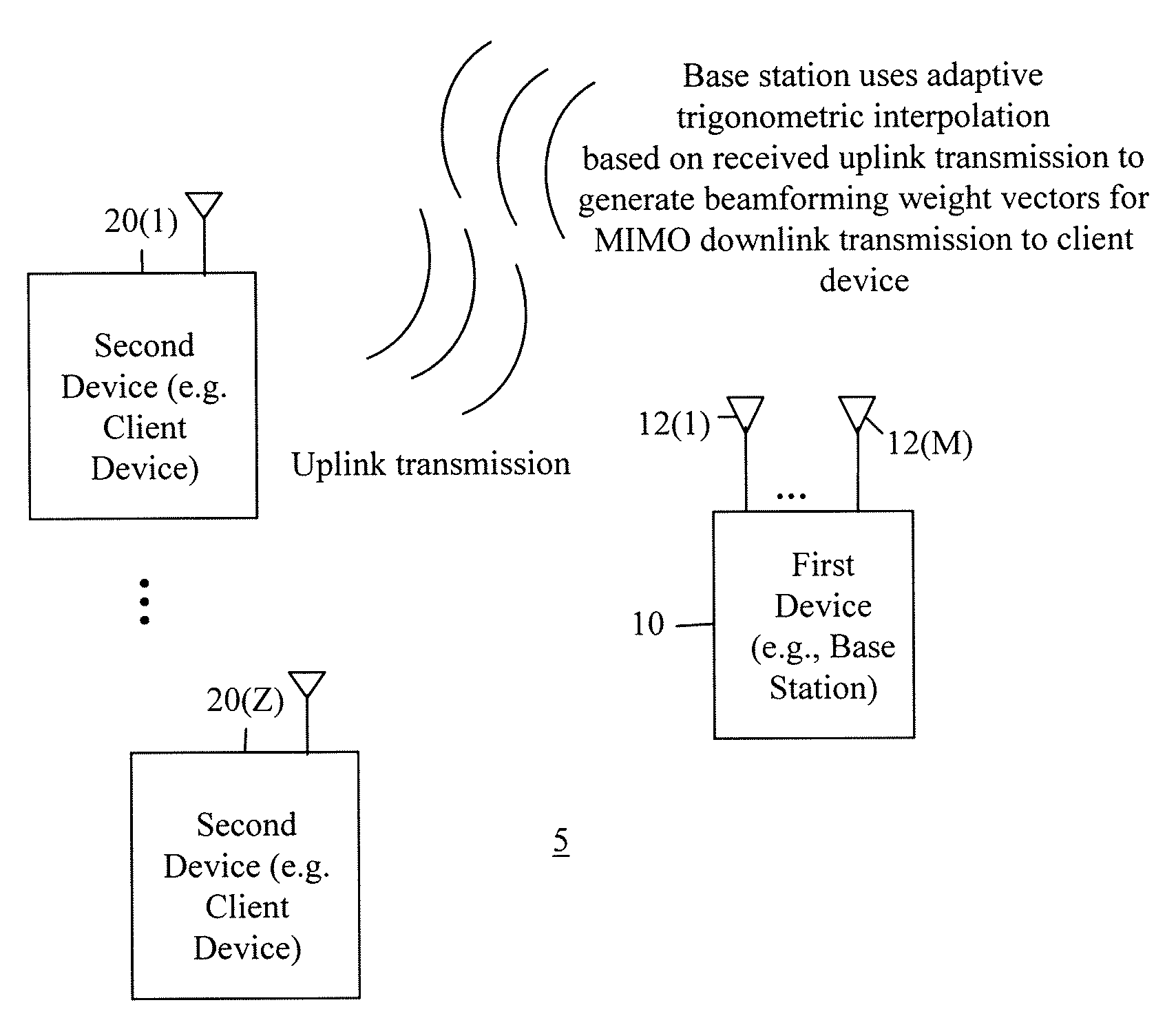
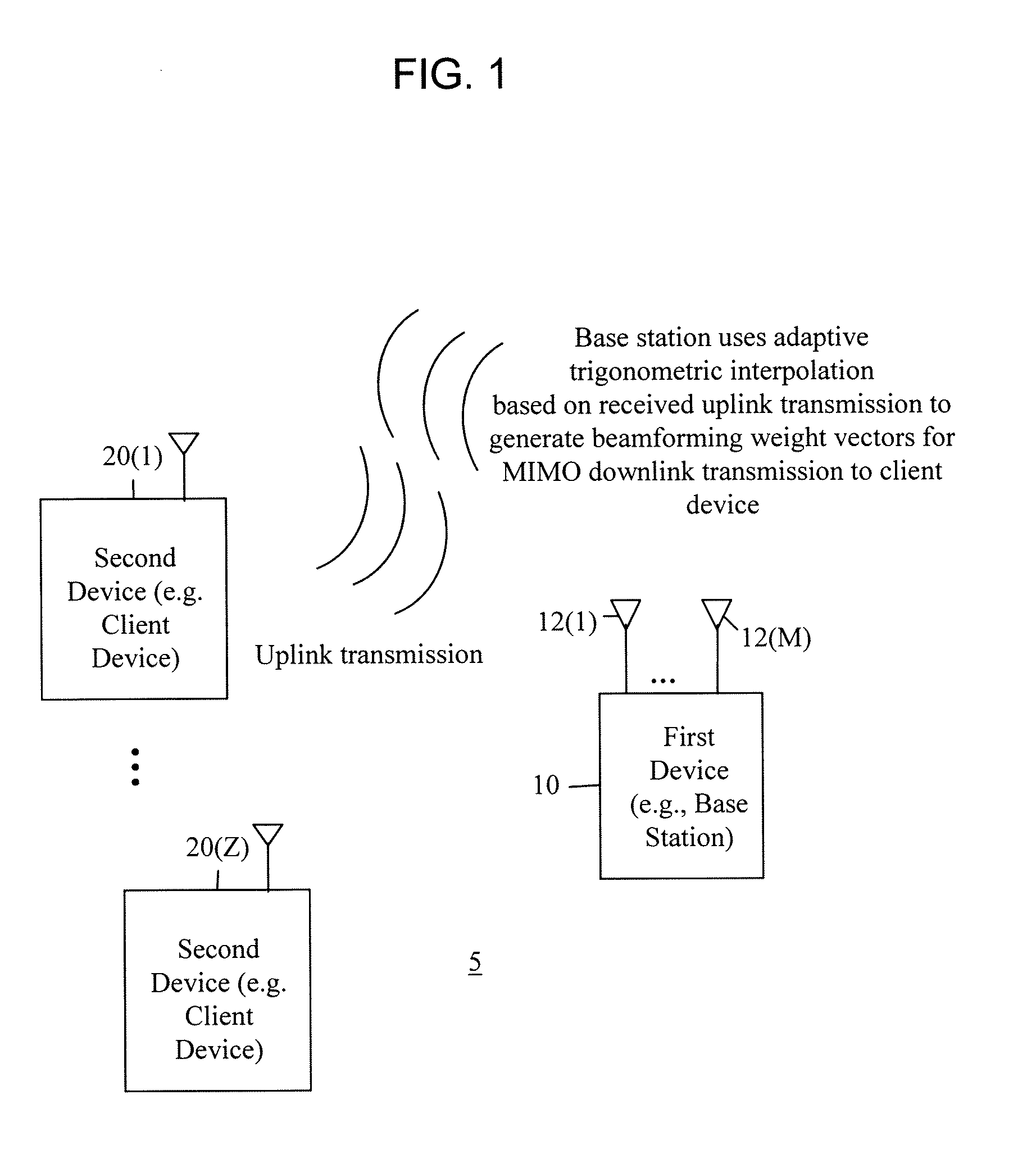
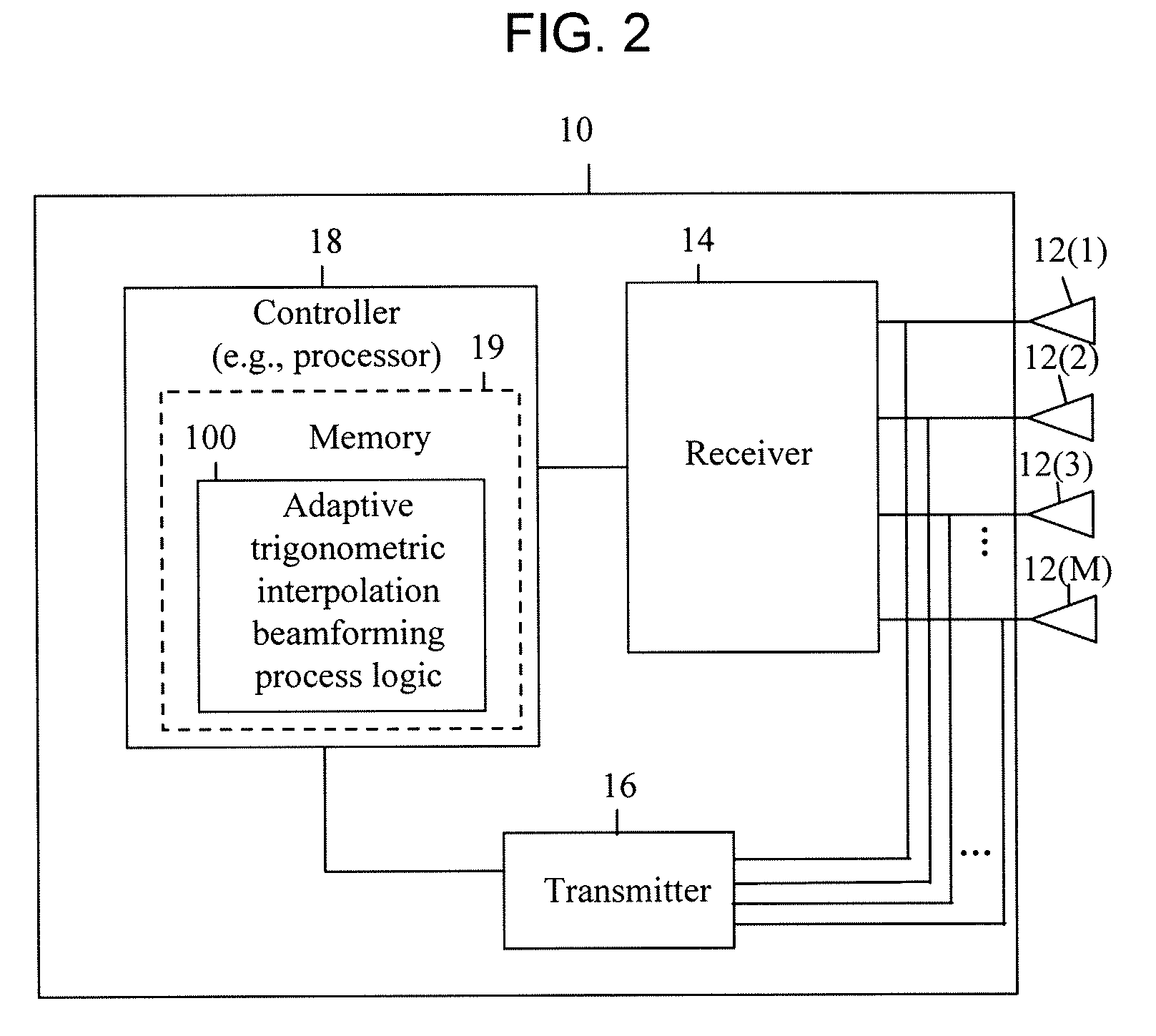
Techniques are provided herein to generate beamforming weight vectors for transmissions to be made from a first wireless communication device, e.g., a base station, to a second wireless communication device, e.g., a client device. The first device has a plurality of antennas and receives uplink transmissions from the second device, each uplink transmission comprising a group of frequency subcarriers. The first device computes channel information from the received uplink transmission and computes one or more trigonometric waveforms determined to approximate the channel information. One or more downlink beamforming weight vectors are computed at any given frequency subcarrier (thus in any frequency subband) by interpolation using the one or more trigonometric waveforms.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com