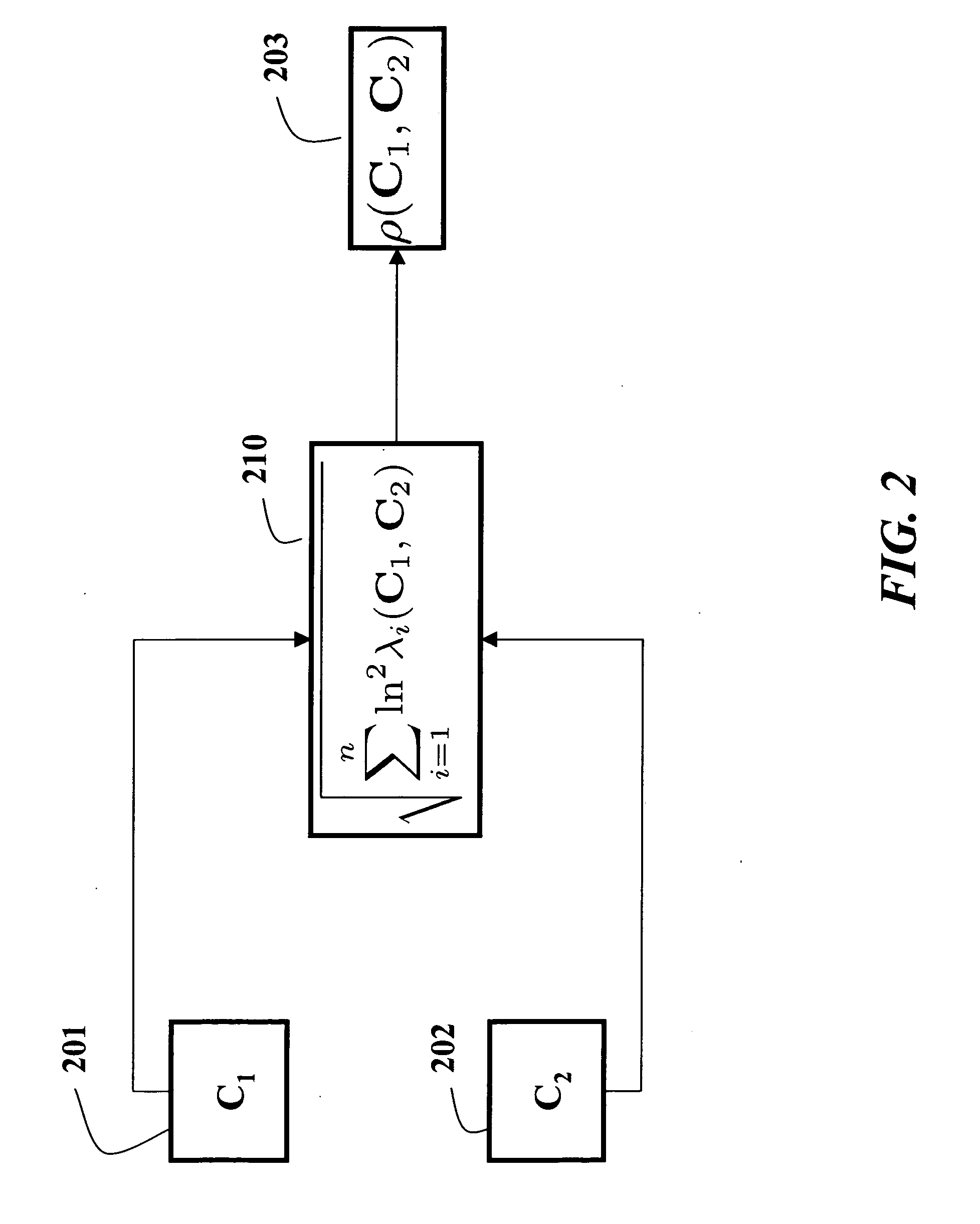
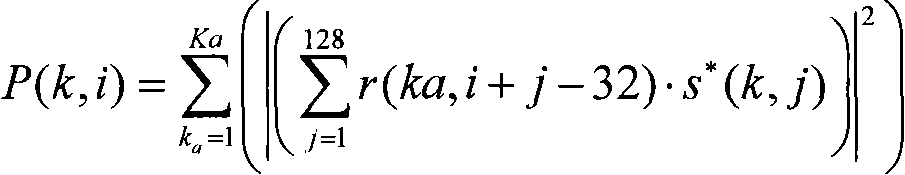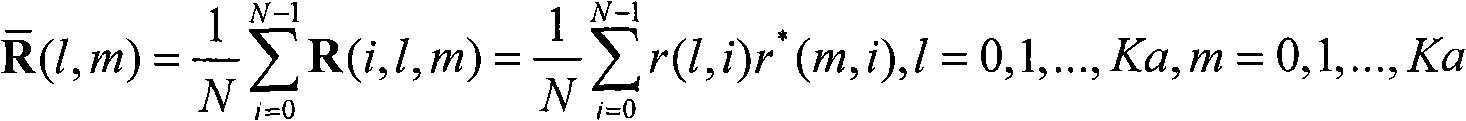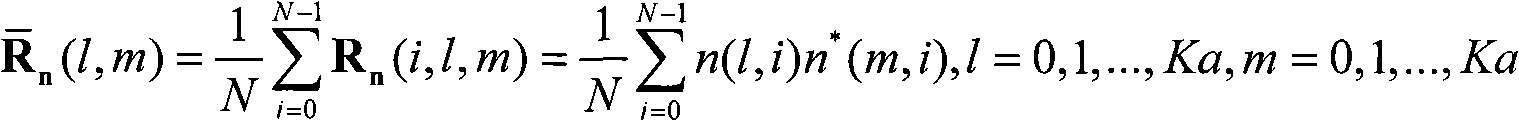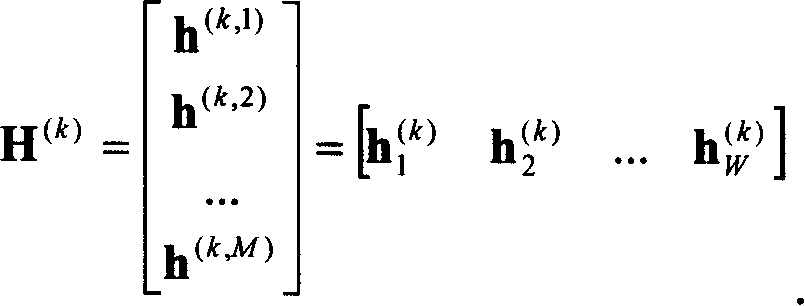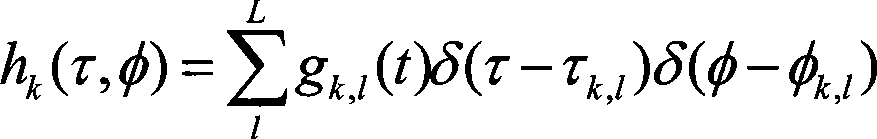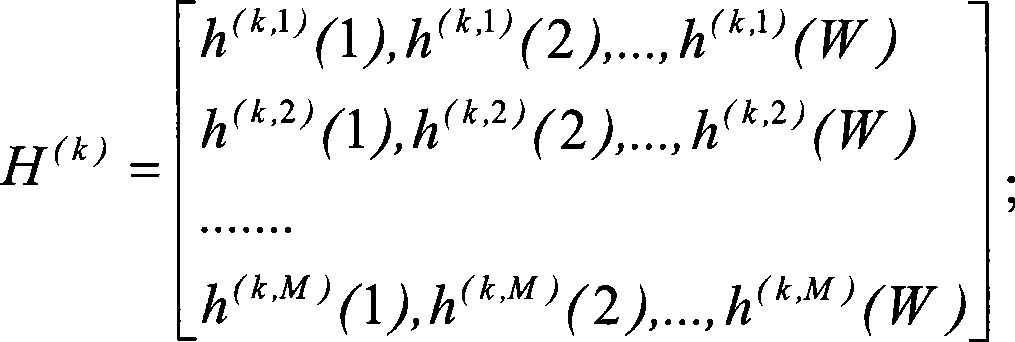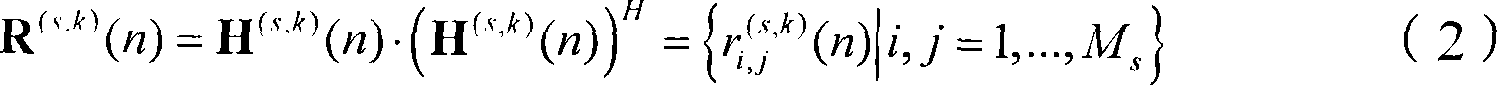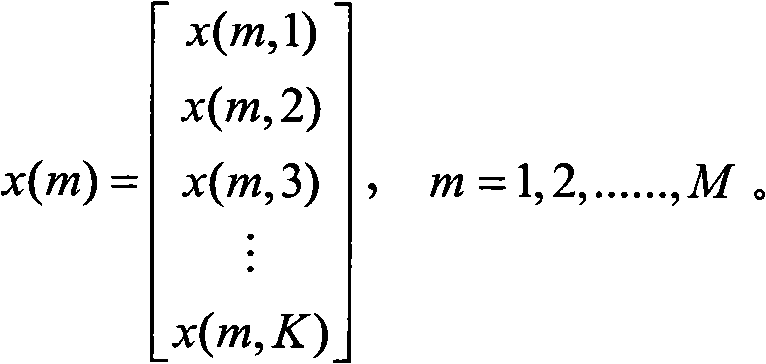Patents
Literature
110 results about "Spatial covariance matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The well-known spatial sign covariance matrix (SSCM) carries out a radial transform which moves all data points to a sphere, followed by computing the classical covariance matrix of the transformed data. Its popularity stems from its robustness to outliers, fast computation, and applications to correlation and principal component analysis.
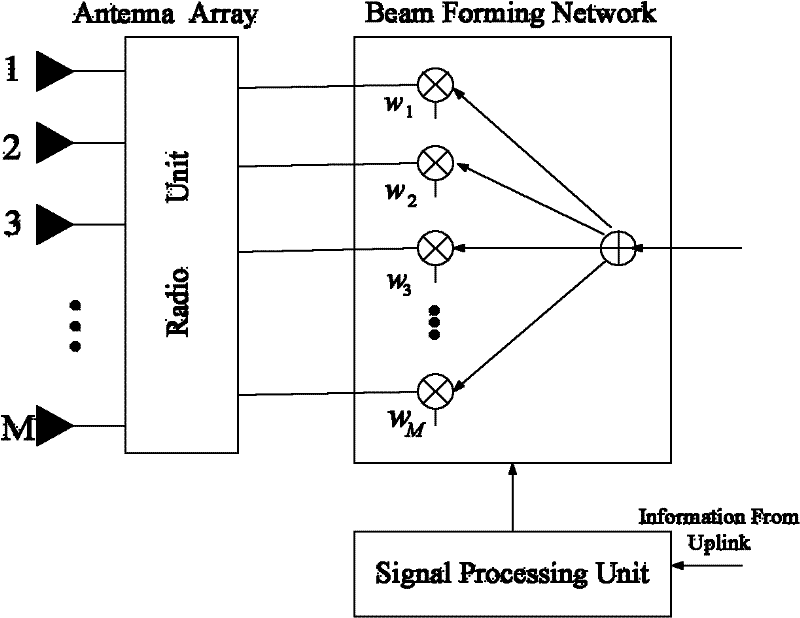
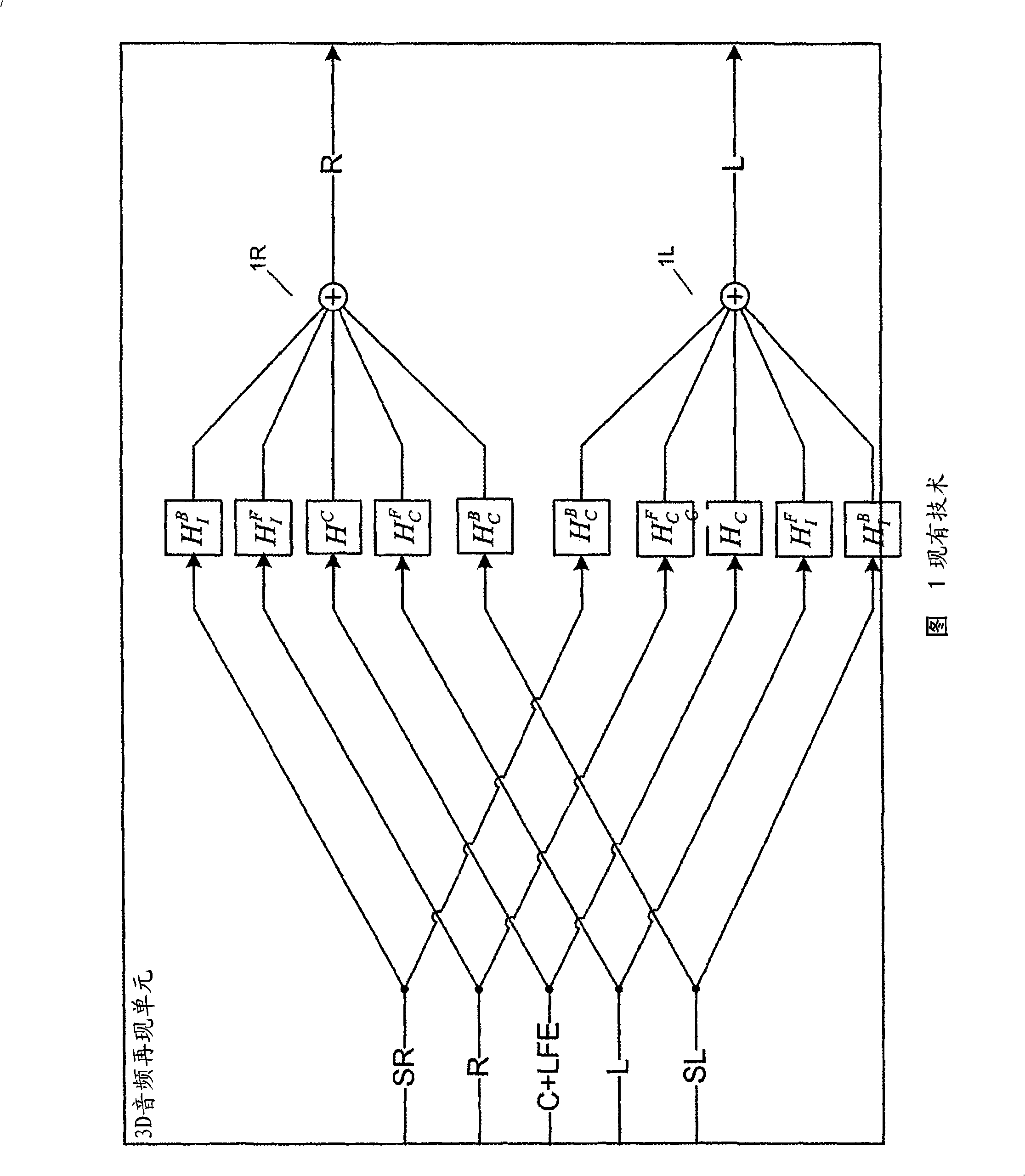
Adaptive antenna array methods and apparatus for use in a multi-access wireless communication system
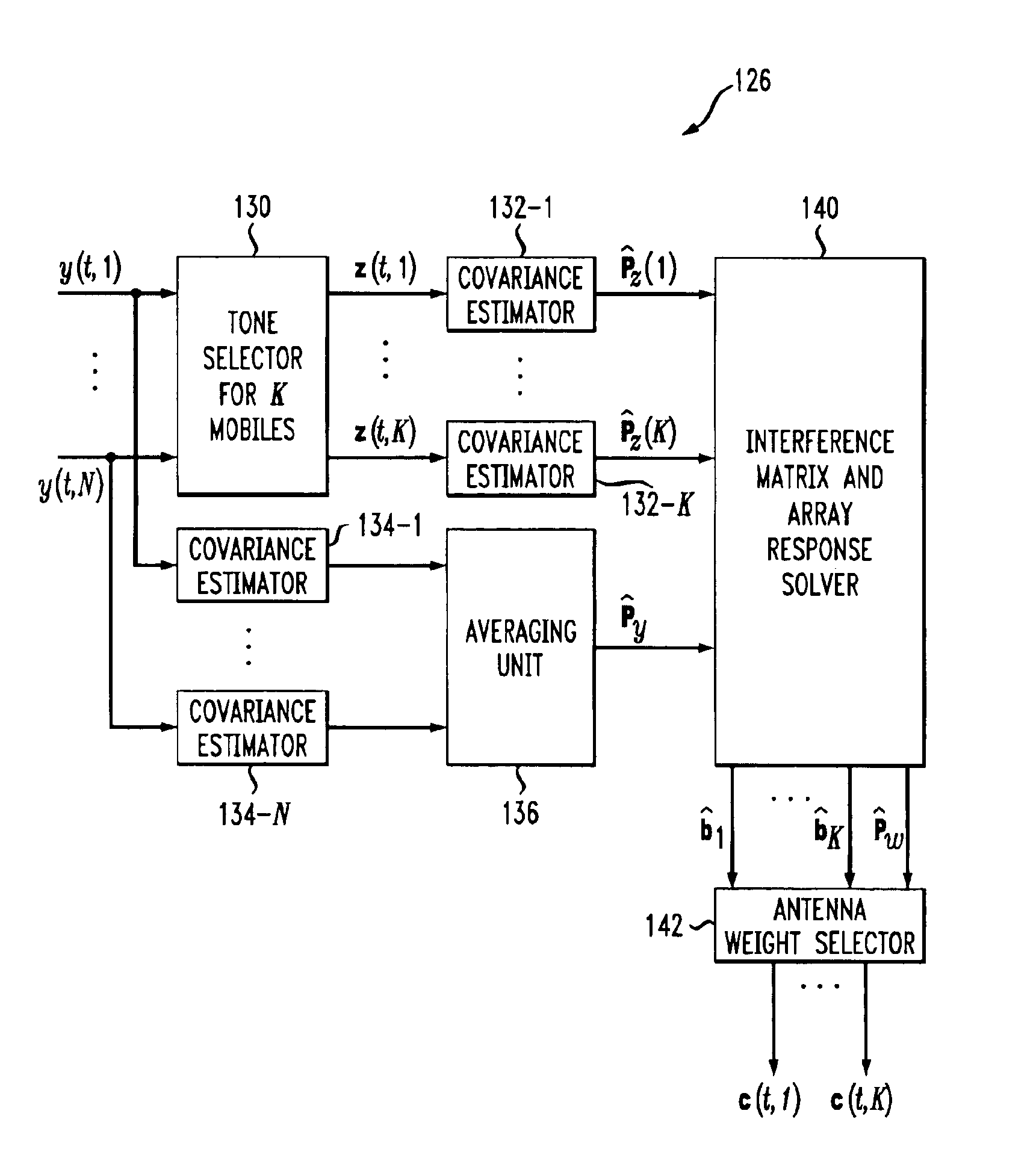
InactiveUS6920192B1Fast convergenceReduce computing costSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityInterference (communication)Communications system
Adaptive antenna array techniques for use in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexed spread-spectrum multi-access (OFDM-SSMA) cellular wireless system or other type of wireless communication system. A base station of the system includes an antenna array and a base station receiver. The base station receiver implements an adaptive antenna gain algorithm which estimates a spatial covariance matrix for each of K mobile stations communicating with the base station. The spatial covariance matrix for a given one of the mobile stations is determined at least in part based on a unique hopping sequence of the mobile station, and provides a correlation between signals received from the mobile station at different antenna elements within the antenna array. An average spatial covariance matrix for a set of received signals is also generated. The individual spatial covariance matrices and the average spatial covariance matrix are processed to generate an estimate of an interference matrix for the K mobile stations, and the estimate of the interference matrix is further processed to generate array responses for each of the mobile stations. The array response for a given mobile station is processed to determine an antenna weighting which is applied to a signal received from the given mobile station in order to facilitate detection of a corresponding transmitted symbol.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
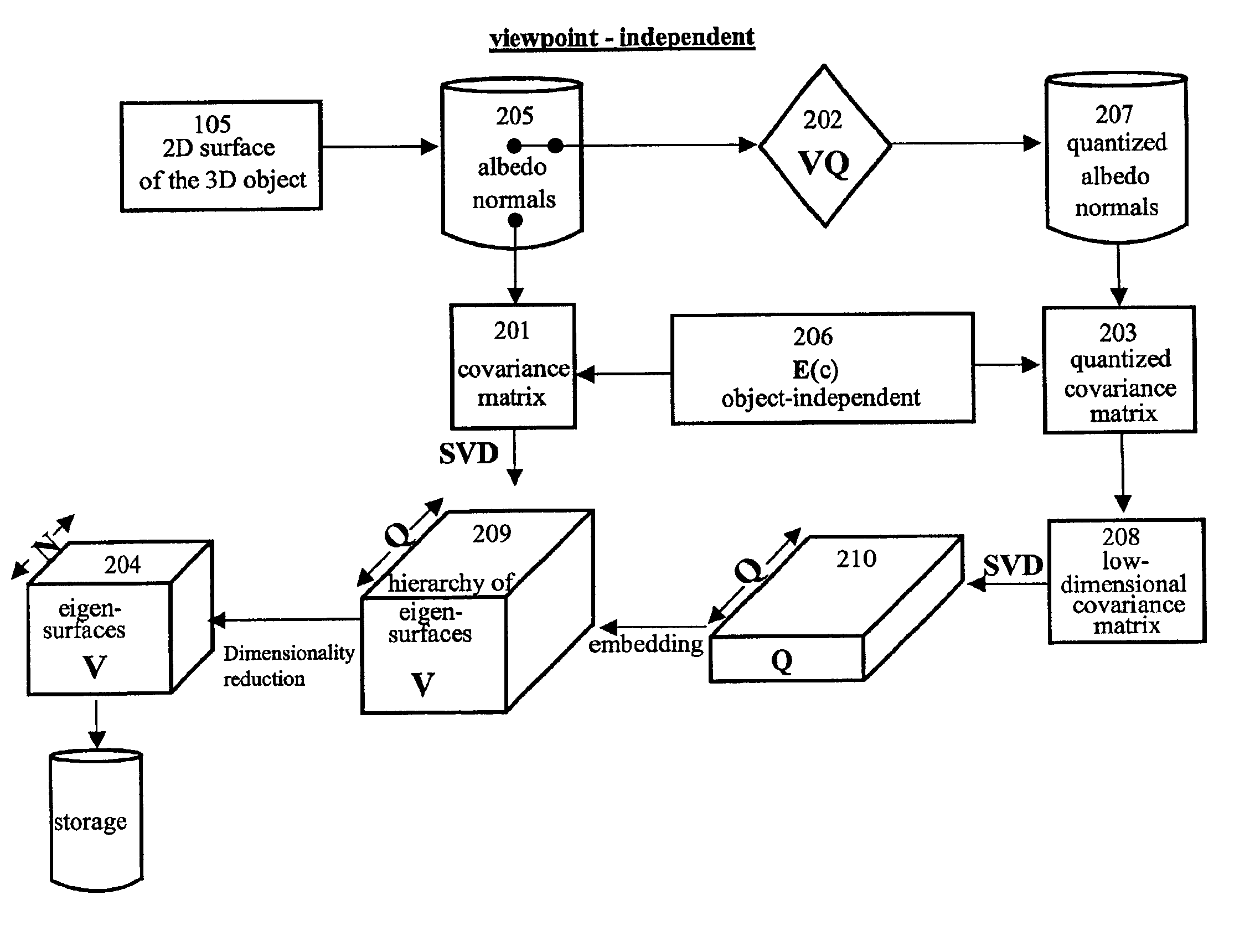
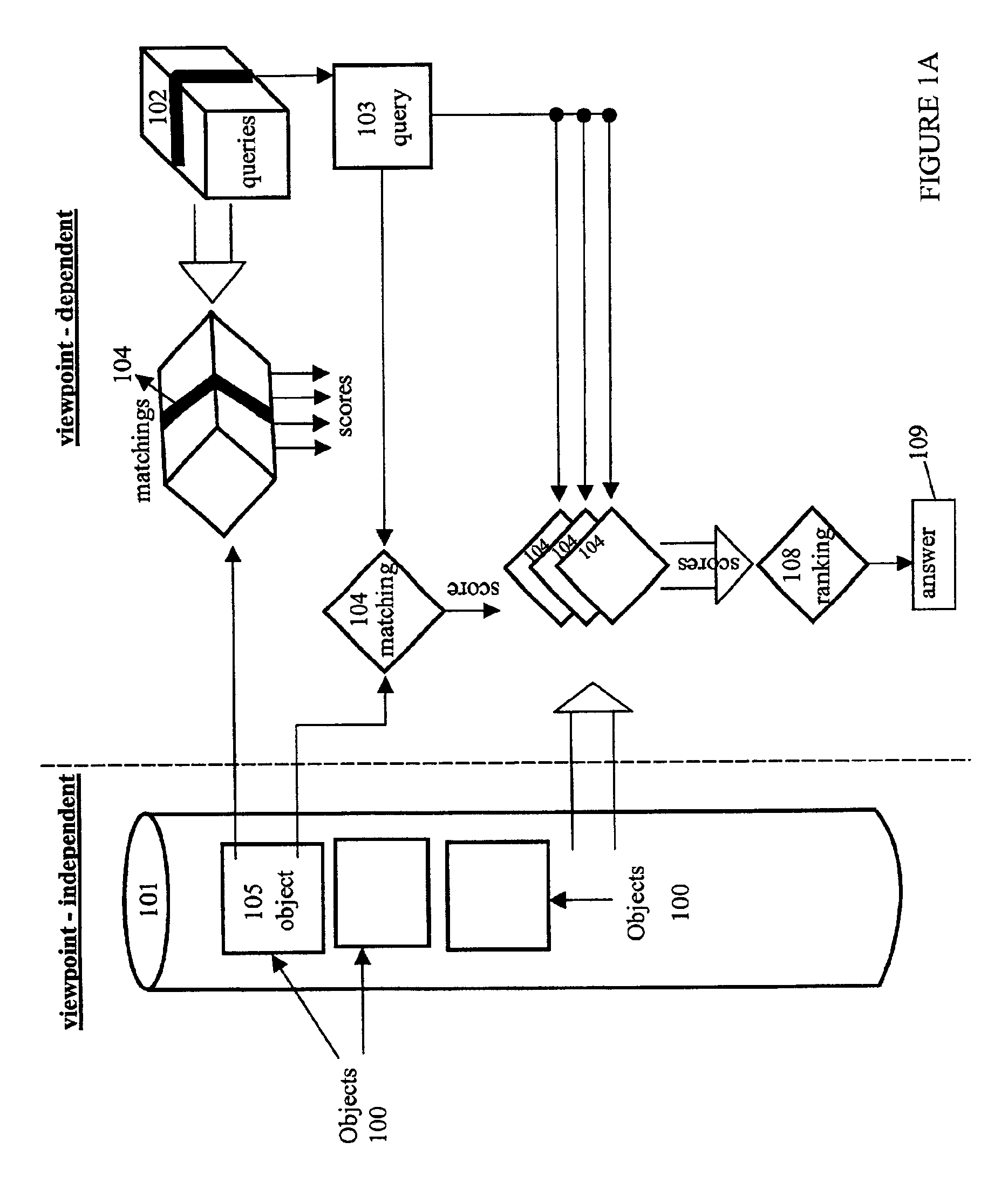
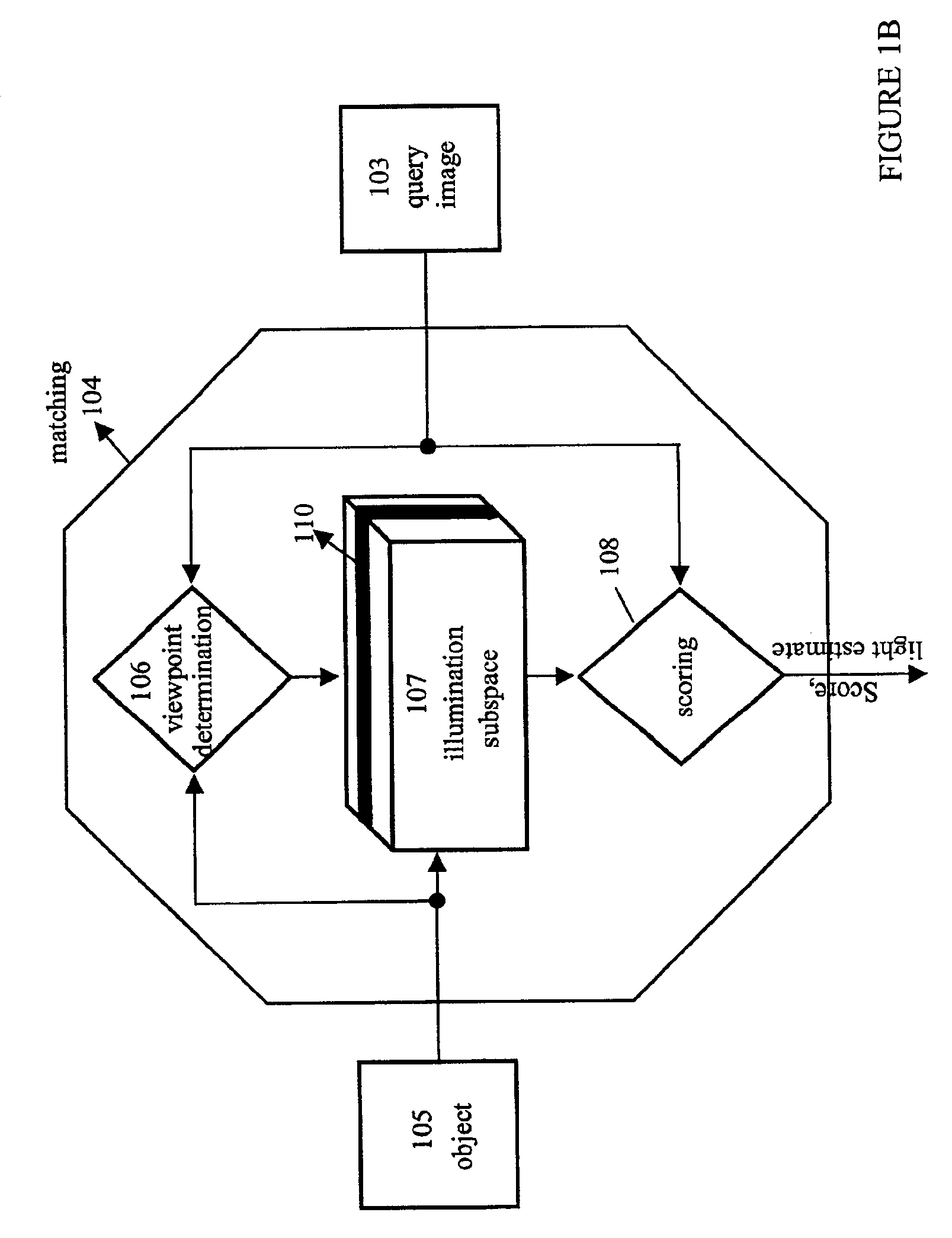
Fast optimal linear approximation of the images of variably illuminated solid objects for recognition
InactiveUS6888960B2Solve the lack of precisionComputationally efficientImage analysisImage codingViewpointsView camera
An efficient computation of low-dimensional linear subspaces that optimally contain the set of images that are generated by varying the illumination impinging on the surface of a three-dimensional object for many different relative positions of that object and the viewing camera. The matrix elements of the spatial covariance matrix for an object are calculated for an arbitrary pre-determined distribution of illumination conditions. The maximum complexity is reduced for the model by approximating any pair of normal-vector and albedo from the set of all such pairs of albedo and normals with the centers of the clusters that are the result of the vector quantization of this set. For an object, a viewpoint-independent covariance matrix whose complexity is large, but practical, is constructed and diagonalized off-line. A viewpoint-dependent covariance matrix is computed from the viewpoint-independent diagonalization results and is diagonalized online in real time.
Owner:NEC CORP
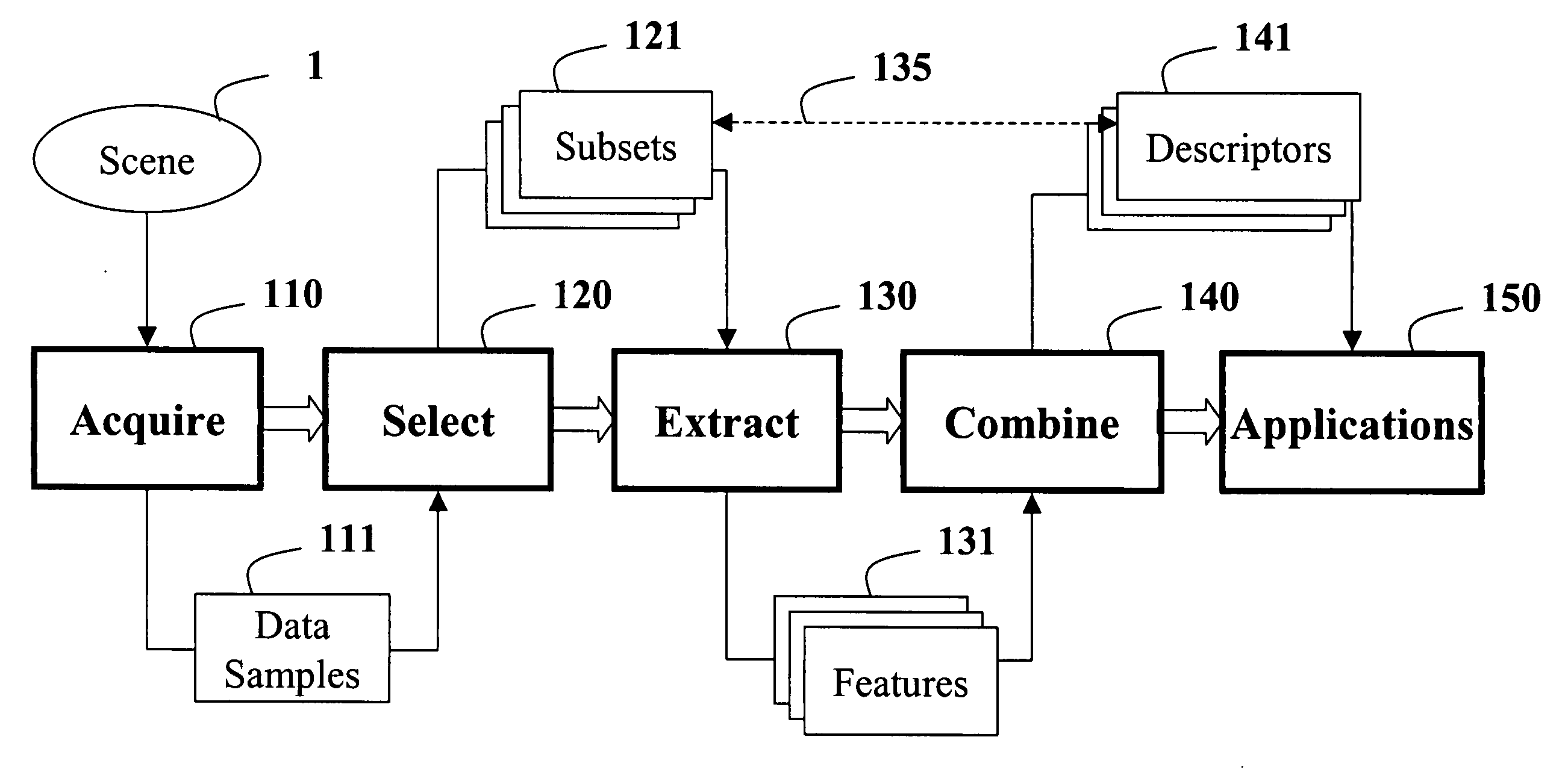
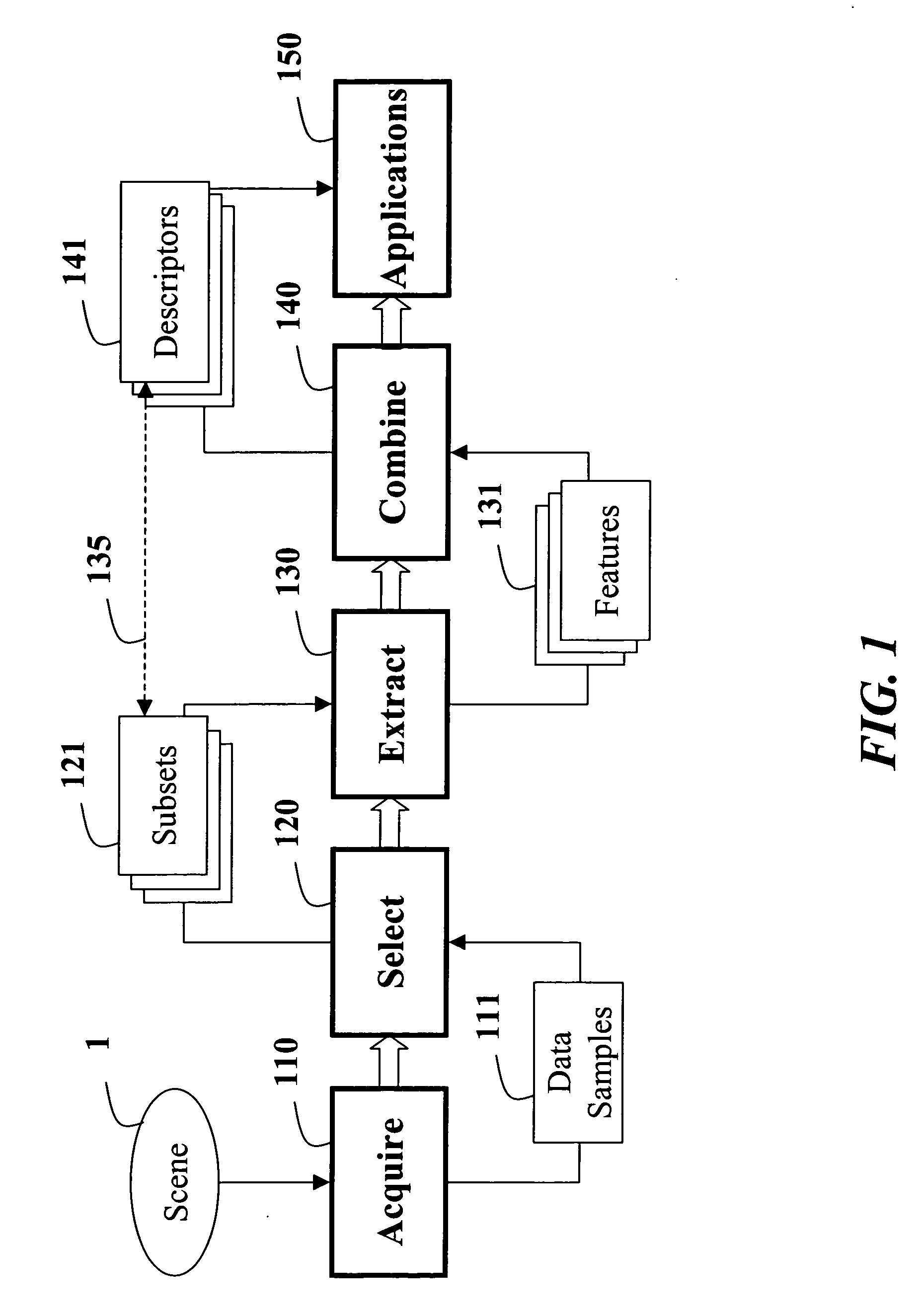
Method for constructing covariance matrices from data features
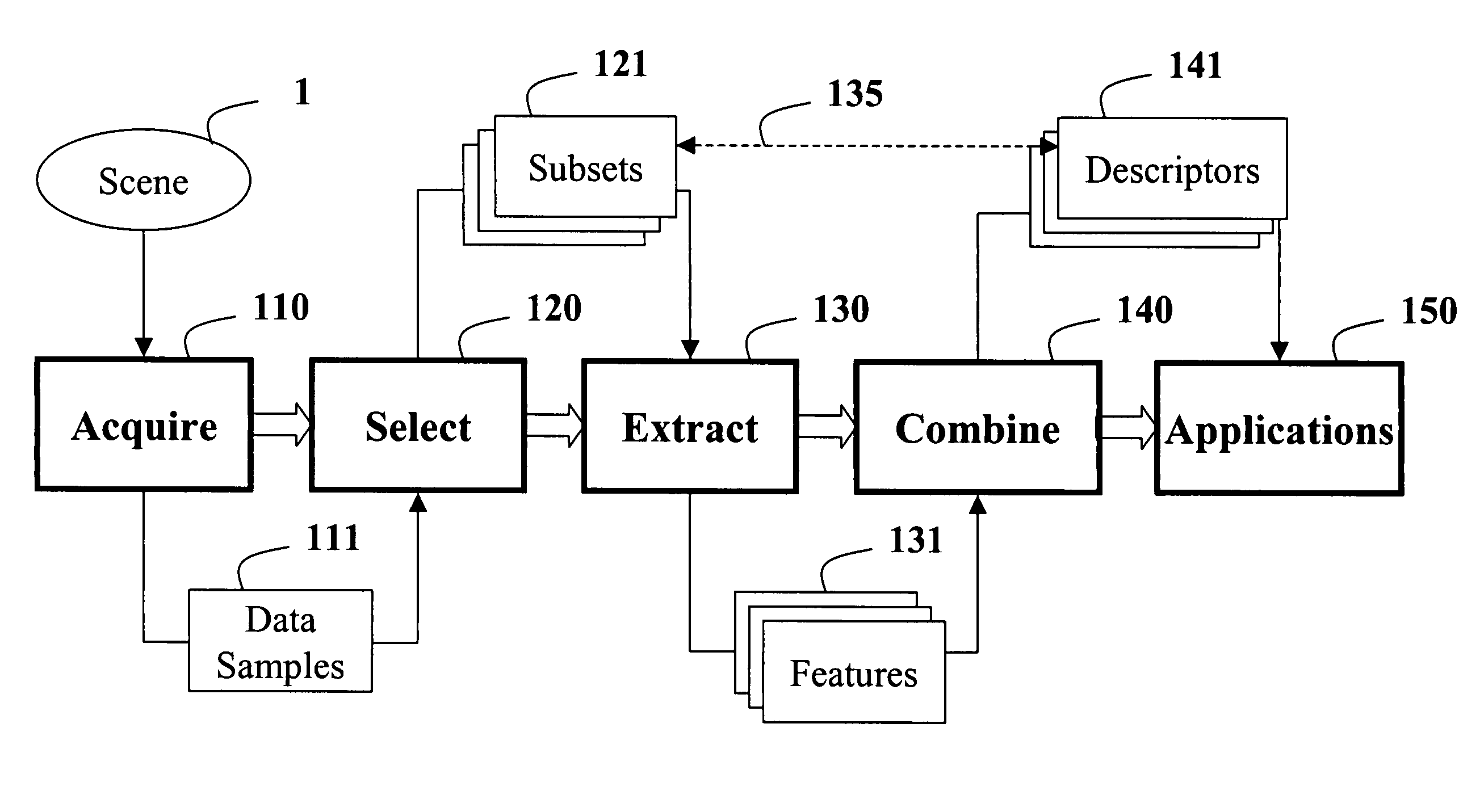
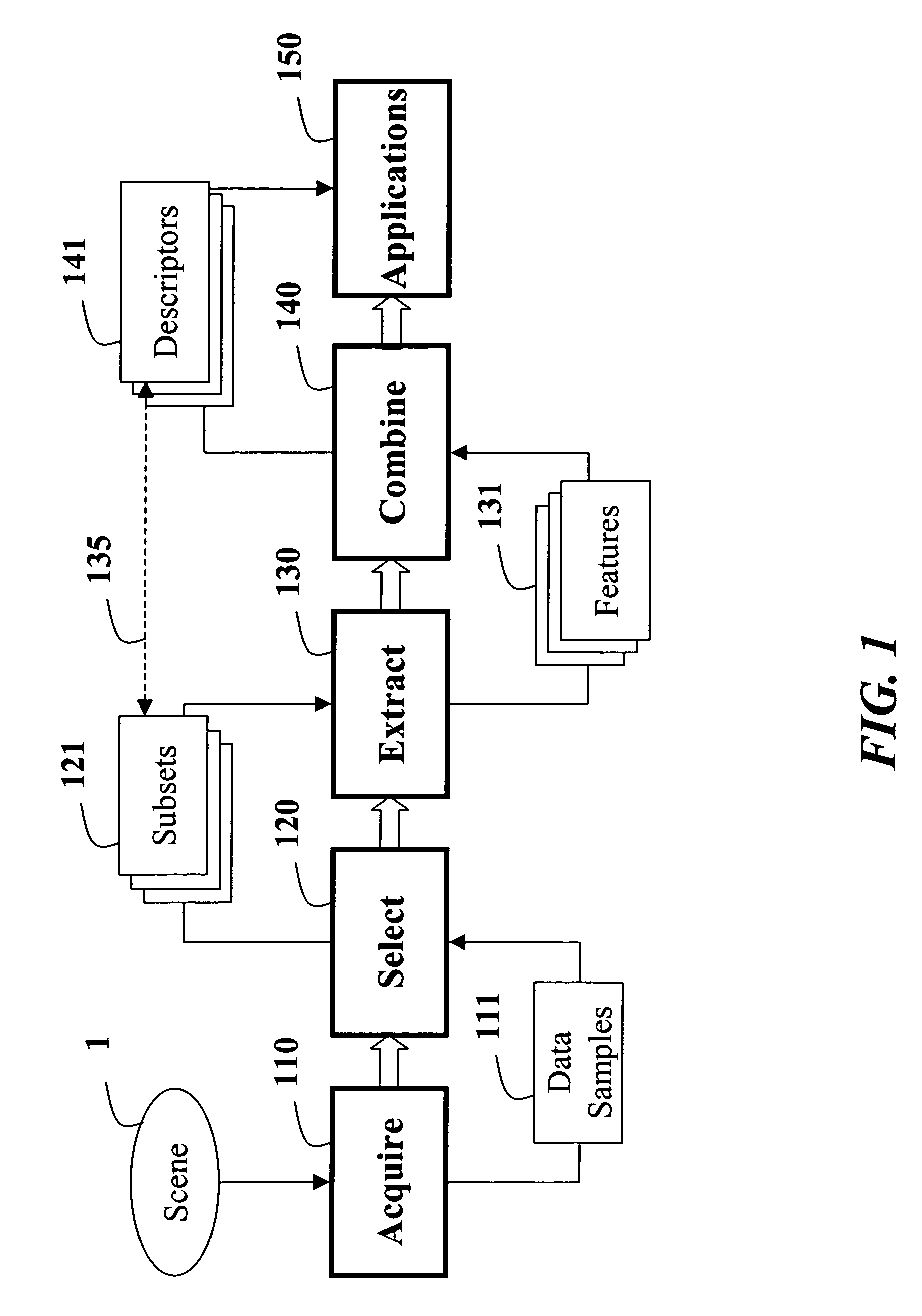
A method constructs descriptors for a set of data samples and determines a distance score between pairs of subsets selected from the set of data samples. A d-dimensional feature vector is extracted for each sample in each subset of samples. The feature vector includes indices to the corresponding sample and properties of the sample. The feature vectors of each subset of samples are combined into a d×d dimensional covariance matrix. The covariance matrix is a descriptor of the corresponding subset of samples. Then, a distance score is determined between the two subsets of samples using the descriptors to measure a similarity between the descriptors.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
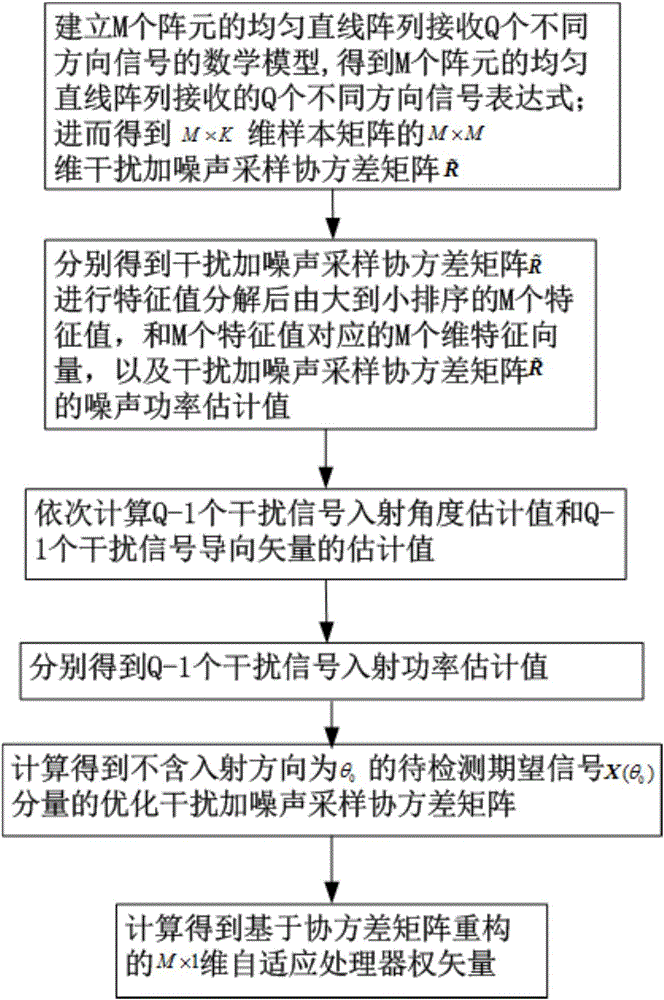
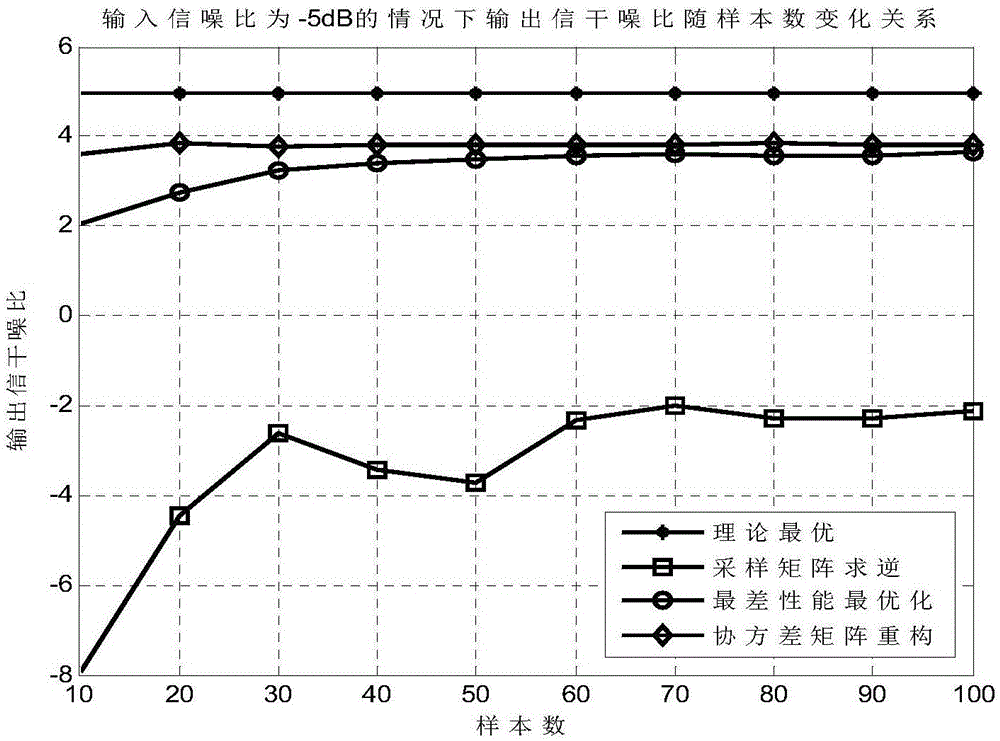
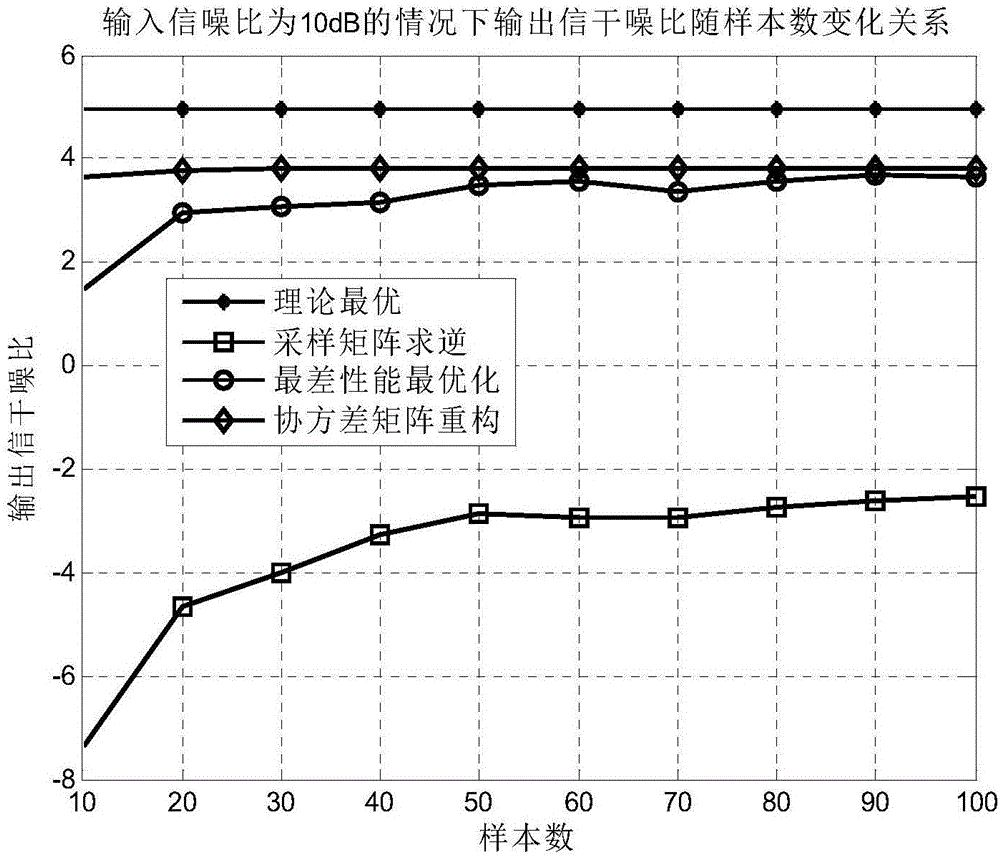
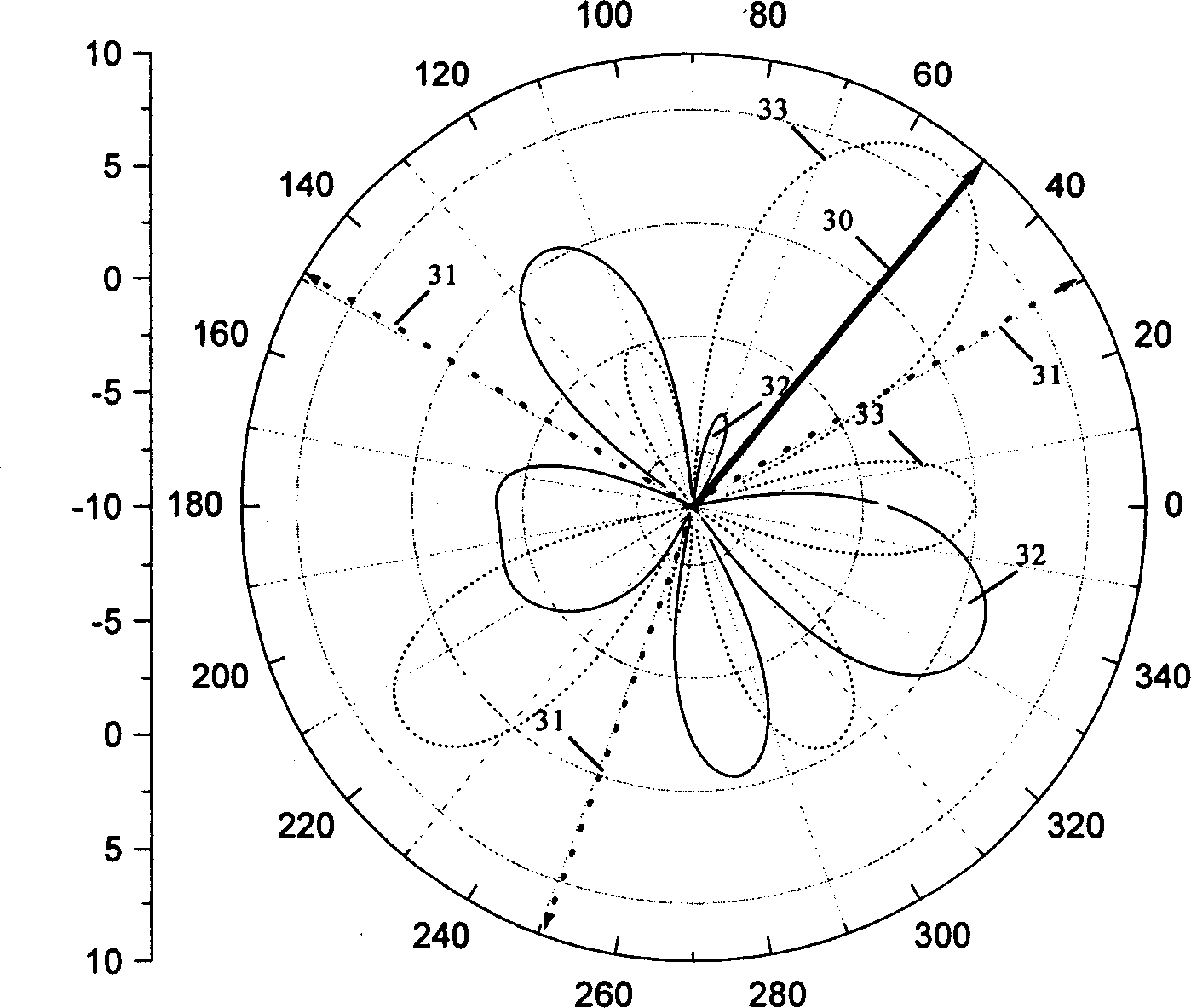
Self-adapting beam forming method based on reconstitution of covariance matrix
ActiveCN106788653AImprove performanceReduction in cancellationSpatial transmit diversityFeature vectorMathematical model
The invention discloses a self-adapting beam forming method based on reconstitution of a covariance matrix. The method comprises the steps of building a mathematical model with M array element and receiving signals in Q different directions by uniform linear arrays, wherein a desired signal to be detected and Q-1 interference signals are included; then acquiring an interference and noise sampling covariance matrix of a sample matrix to perform eigenvalue decomposition, thus respectively acquiring M eigenvalues sorted in a descending order after eigenvalue decomposition, M feature vectors corresponding to the M eigenvalues, and a noise power estimated value; sequentially computing Q-1 interference signal incident angle estimated values and estimated values of Q-1 interference signal steering vectors of the Q-1 interference signal incident angle estimated values; then acquiring an optimized interference and noise sampling covariance matrix of components, not in an incidence direction of [theta]0, of the desired signal to be detected; and at last computing a self-adapting processor weight vector based on the reconstitution of the covariance matrix.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
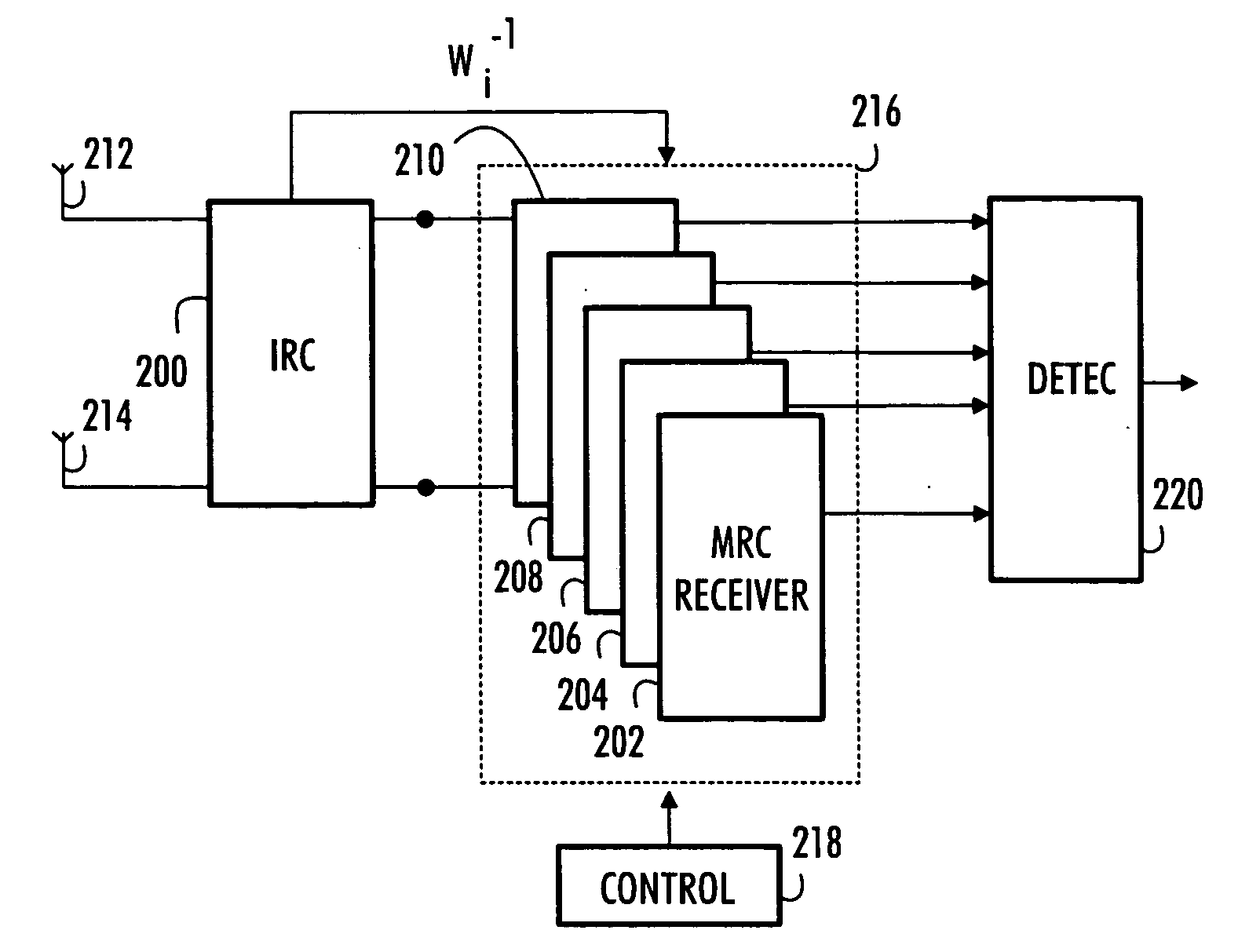
Communication method, receiver and base station
InactiveUS20050101253A1Reduce the impact of interferenceReduce impactSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityConjugate transposeEngineering
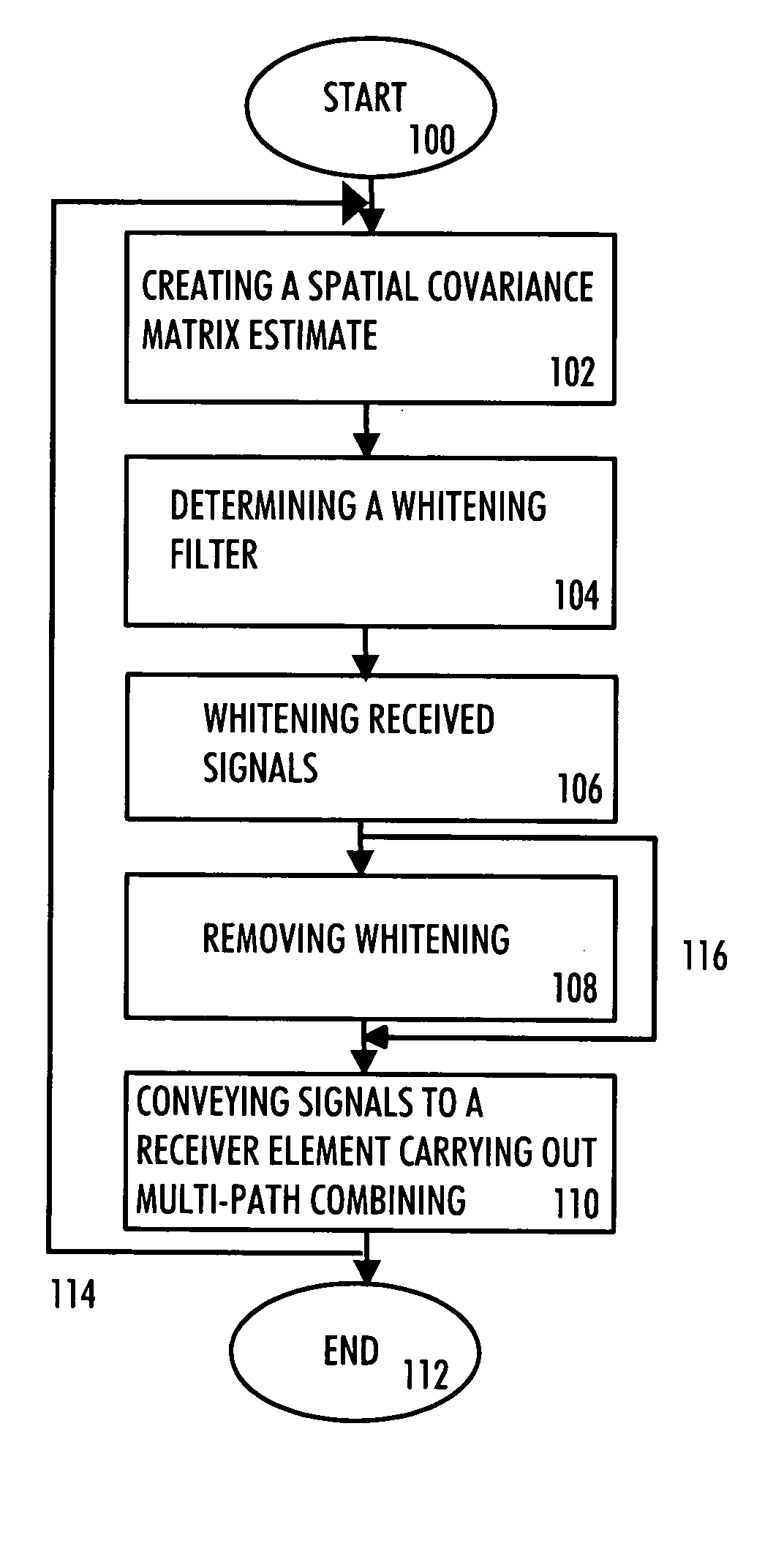
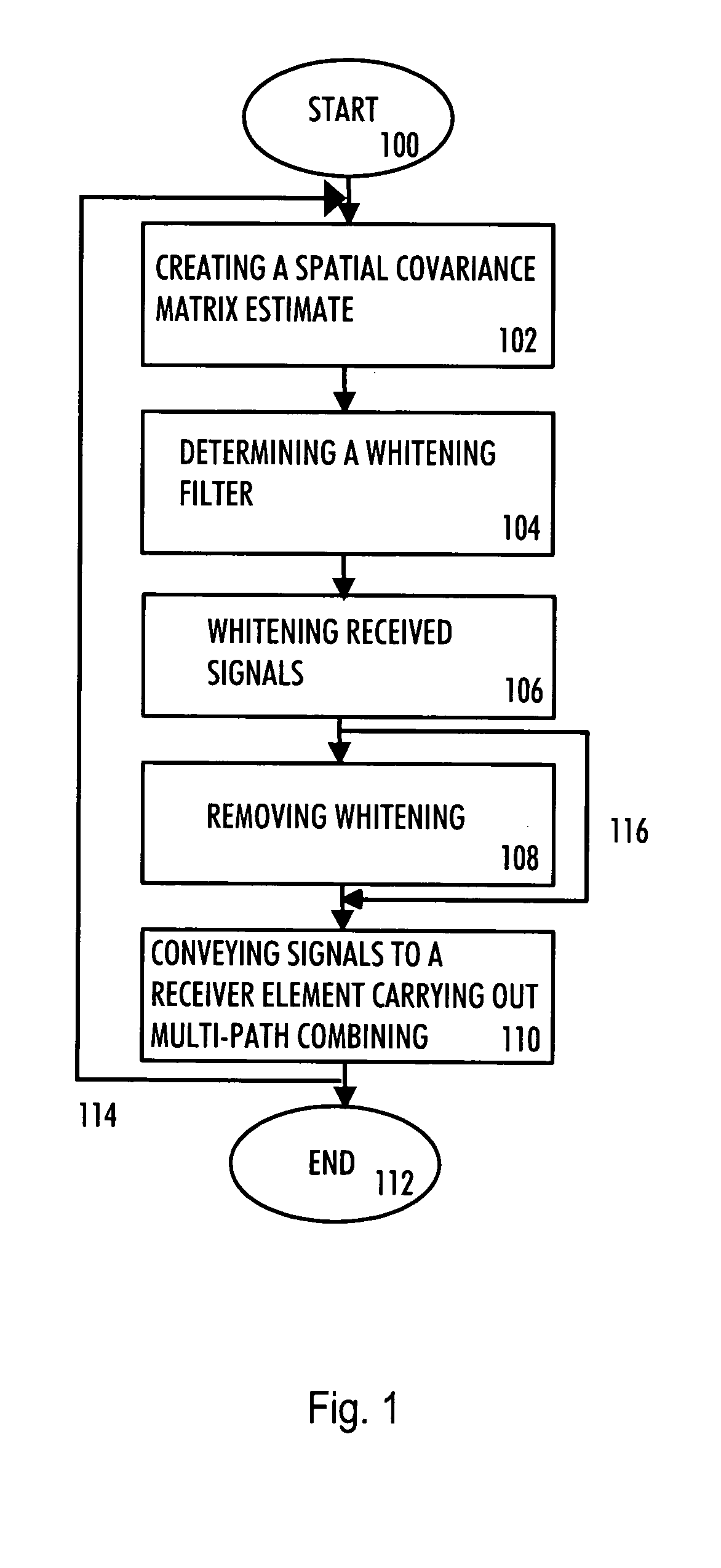
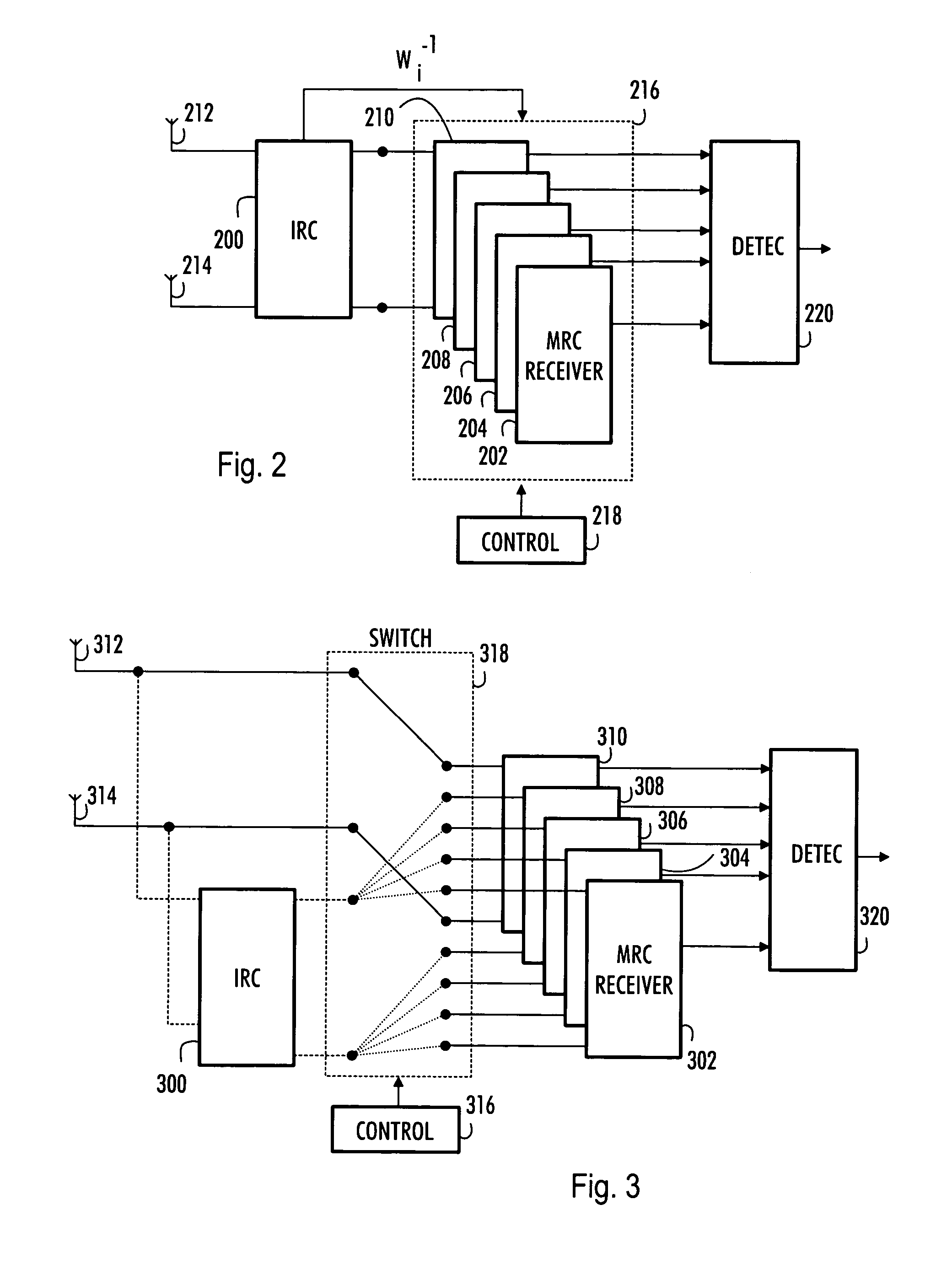
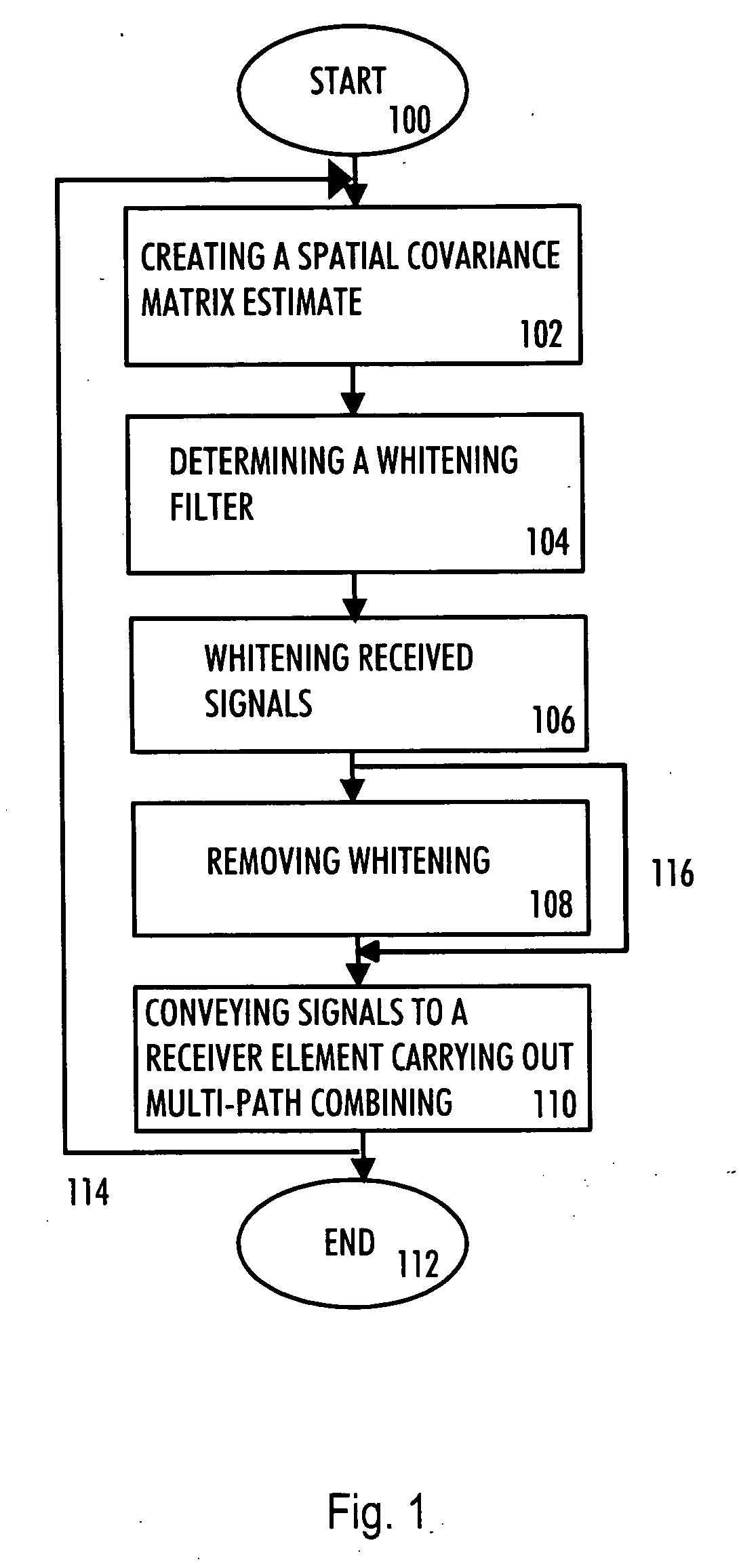
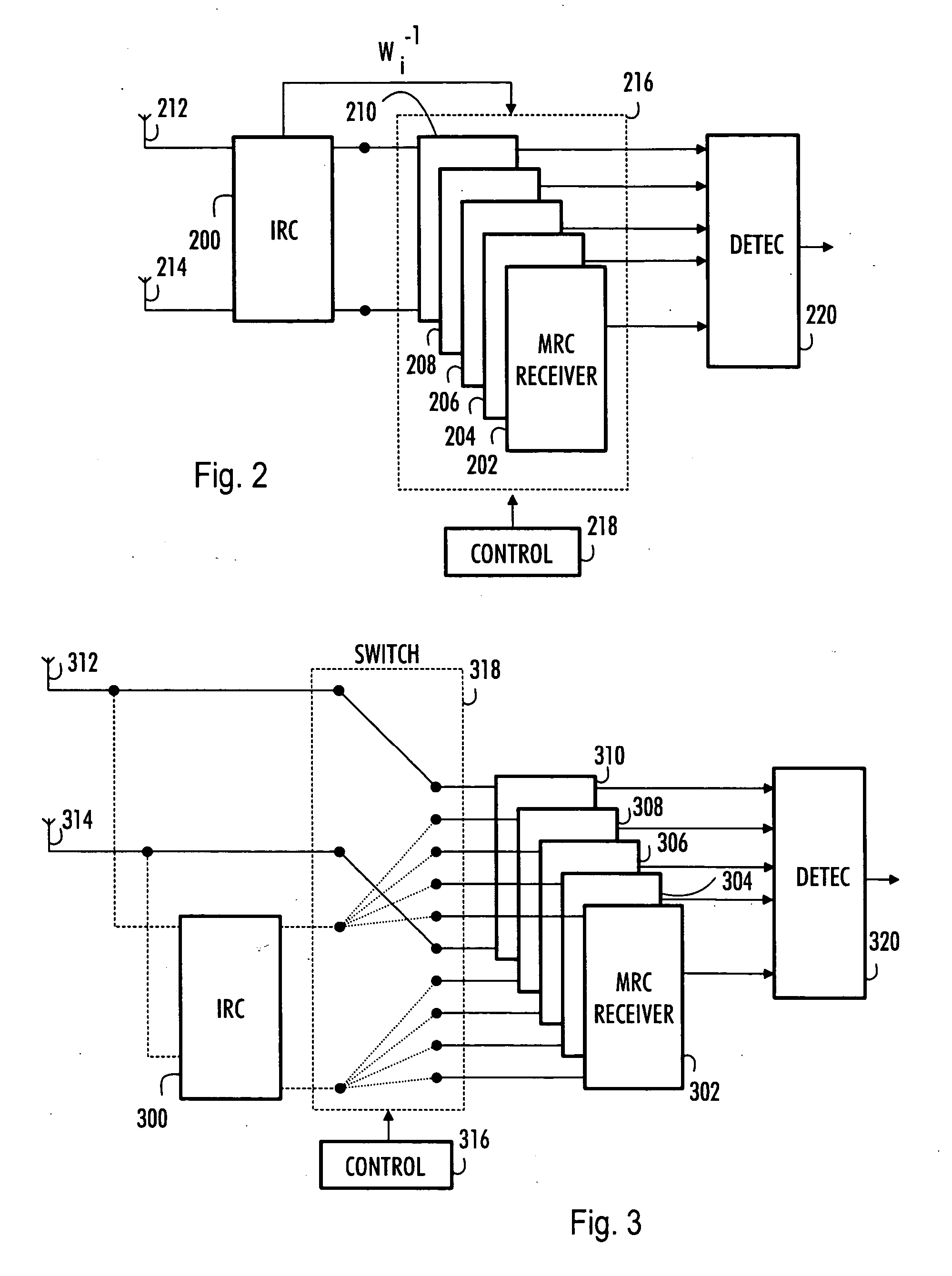
A multi-user receiver which uses at least two antenna elements and in which the influence of interference is reduced, the receiver comprises: means (200) for pre-filtering a wideband antenna signal, the pre-filtering means being determined on the basis of a spatial covariance matrix estimate, which spatial covariance matrix estimate is obtained from wideband antenna signals by sampling, arranging sampled values into a signal vector and by multiplying the signal vector by its conjugate transpose vector, means (210, 218) for removing the whitening from signals of predetermined users by using an inverse matrix of the matrix used in the whitening filter, means (202, 204, 206, 208, 210) for performing multi-path combining and multi-antenna combining.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Beam size enlargement apparatus and method for restraining interference of intelligent antenna
InactiveCN101436893ACorrectly determine the spatial characteristicsSuppress interferenceSpatial transmit diversitySmart antennaEngineering
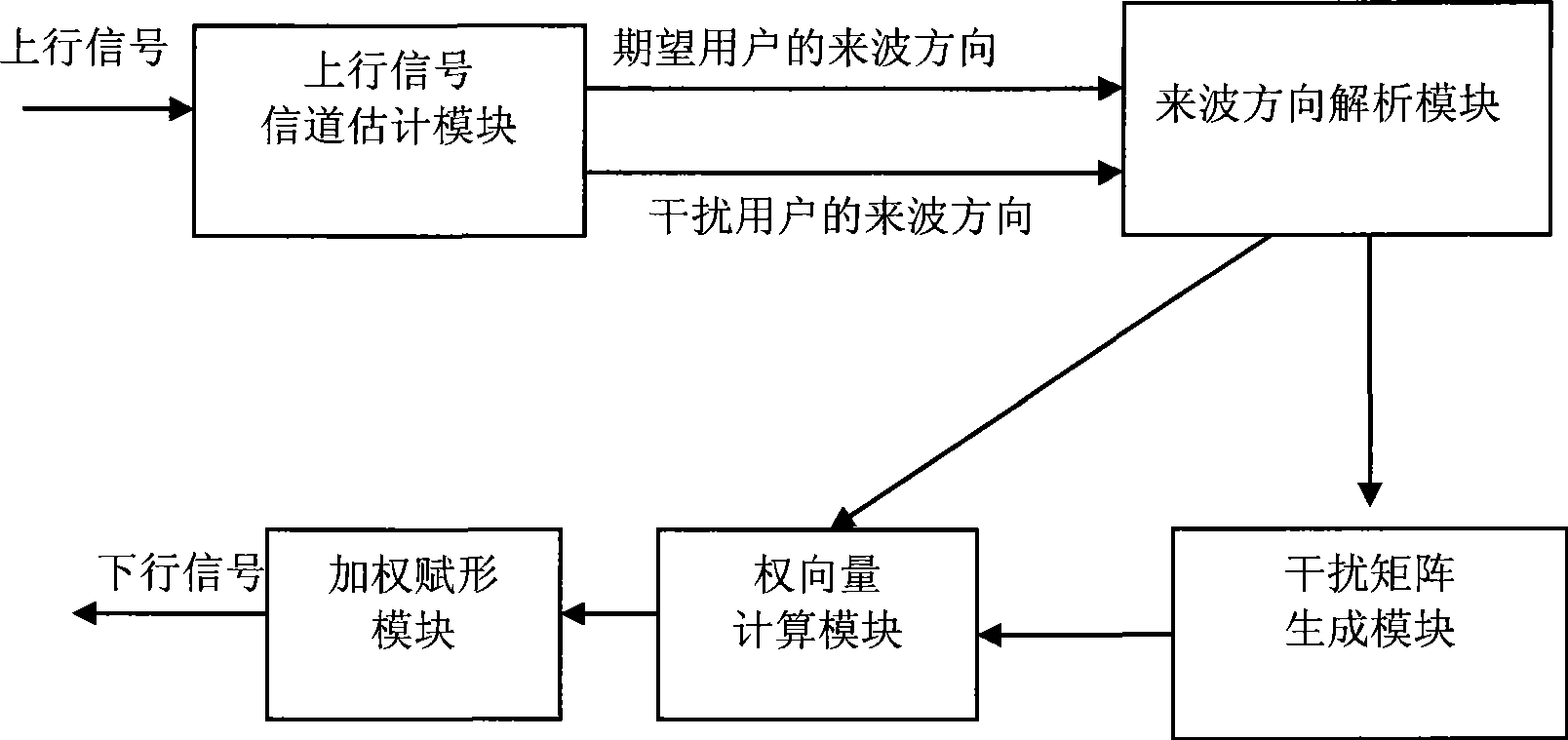
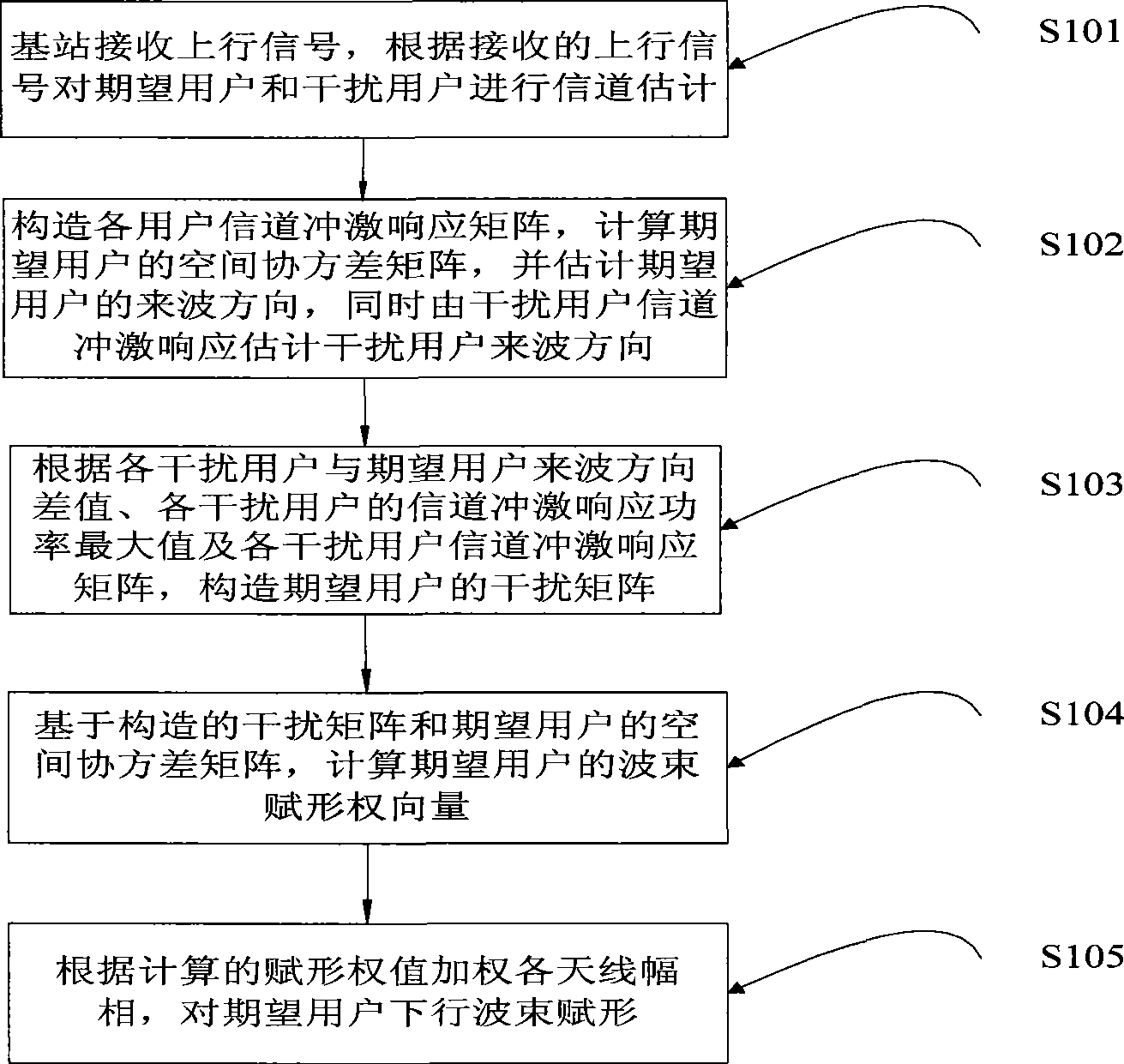
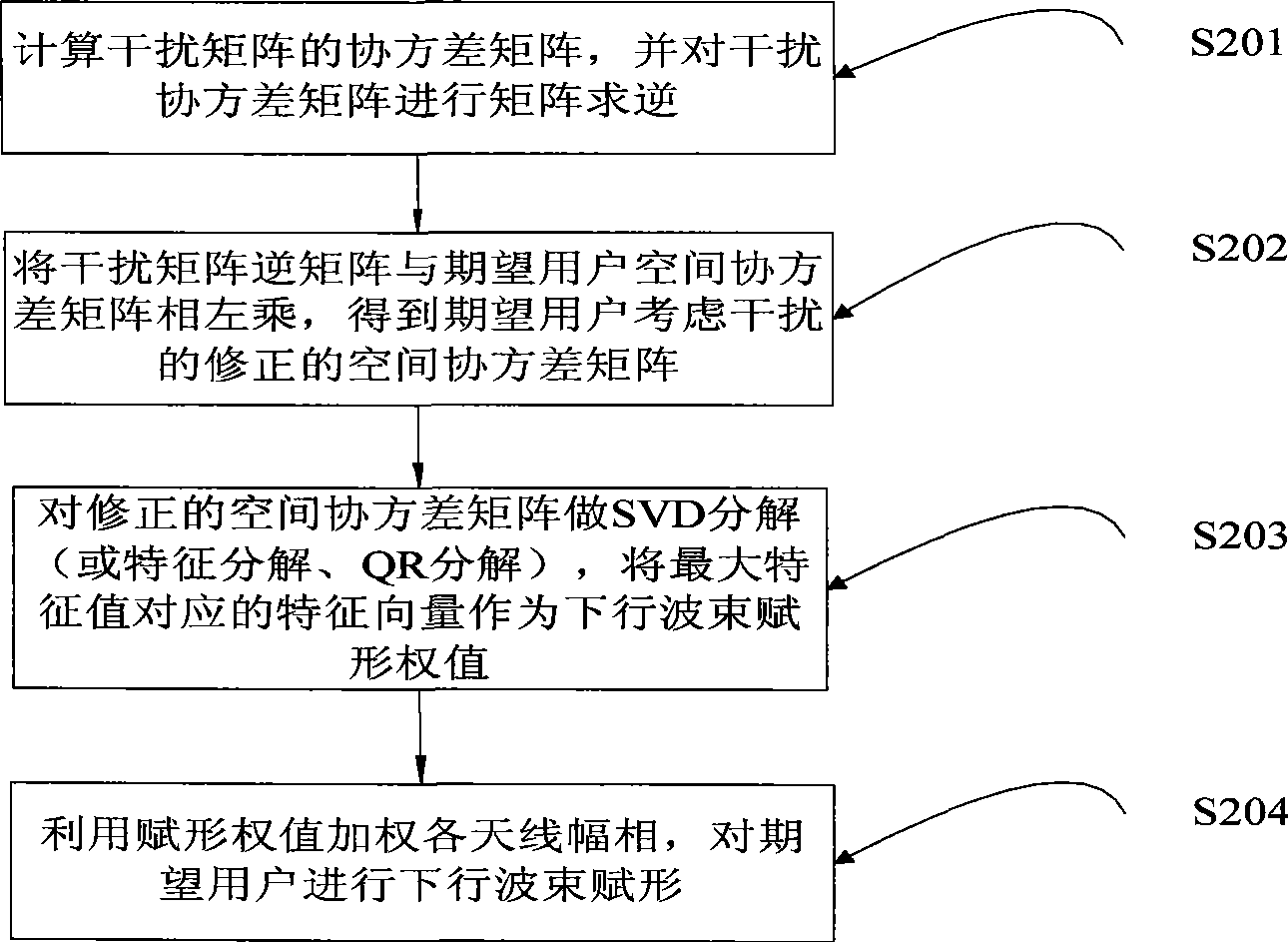
The invention relates to the technical field of communication, and in particular discloses a beam forming method and a device for inhibiting interference in an intelligent antenna. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, according to received uplink signals, carrying out channel estimation on an expected user and an interferential user, and estimating an incoming wave direction of the expected user and an incoming wave direction of the interferential user; secondly, constructing an interference matrix of the expected user; thirdly, calculating a beam forming weight vector of the expected user based on the interference matrix of the expected user and a spatial covariance matrix covariance matrix; and finally, using the beam forming weight vector of the expected user as a formingweight value to weigh each antenna magnitude phase, and forming downlink beams for the expected user. A beam forming device is used for carrying out beam forming treatment according to the beam forming method. The method can inhibit interference, can still accurately determine spatial characteristics of the expected user, and achieve better downlink beam forming.
Owner:ZTE CORP
An Adaptive High Precision Interferometric SAR Phase Estimation Method
InactiveCN102270341AAccurate estimateAvoid searchingImage analysisRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEstimation methodsMultiple signal classification
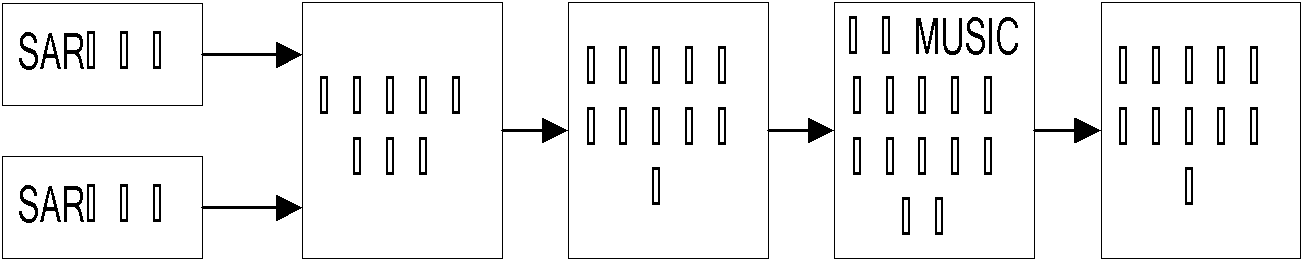
The invention discloses an adaptive high-precision phase estimation method for an interferometric SAR, comprising the following steps of: structuring optimum weight vectors in combination with a Wiener filter theory, performing an eigen decomposition on an optimum covariance matrix composed of the optimum weight vectors to obtain a signal subspace and a noise subspace, adequately utilizing a corresponding pixel pair and the coherent information of the neighboring pixels thereof to structure a space spectrum function according to the orthogonality of the signal subspace and the noise subspace in a MUSIC (multiple signal classification) algorithm, and precisely estimating the interferometric phase between the corresponding pixels via a spectral peak searching. The optimum weight is obtained by only a Wiener filter without the need to determine a registration error and the direction thereof, thereby solving the problem of large computational burden in the traditional InSAR (interferometric synthetic aperture radar) interferometric phase estimation. The adaptive high-precision phase estimation method for the interferometric SAR disclosed by the invention is adaptive to the field of accurate surface parameter inversion of InSAR complex scene and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
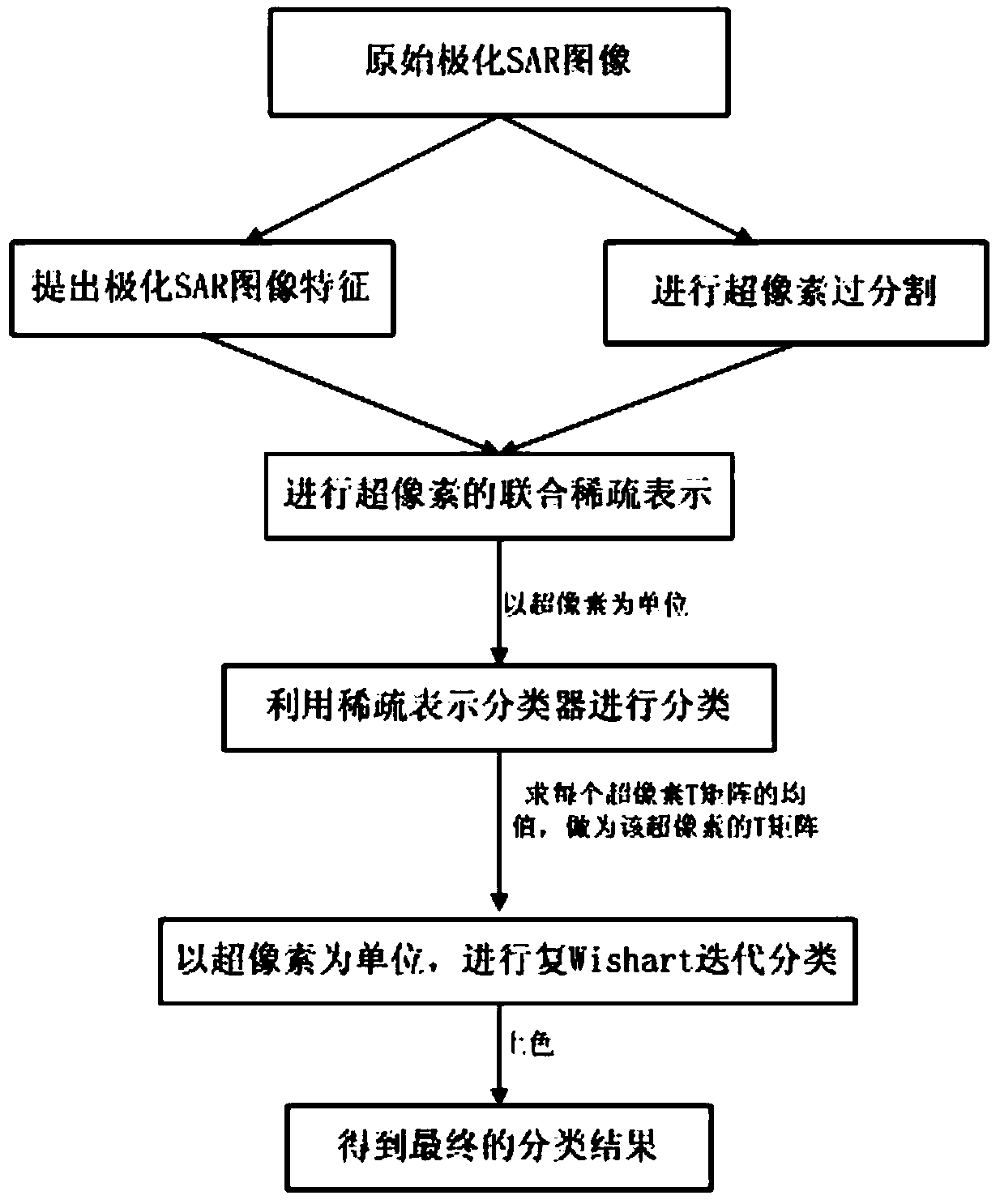
Super-pixel polarimetric SAR land feature classification method based on sparse representation
InactiveCN104123555AMaintain spatial similarityImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSparse representation classifierClassification methods
The invention discloses a super-pixel polarimetric SAR land feature classification method based on sparse representation. The method comprises: inputting polarimetric SAR image data to be classified, processing the image, and thereby obtaining a pseudocolor image corresponding to Pauli decomposition; performing super-pixel image over-segmentation on the pseudocolor image to obtain a plurality of super-pixels; extracting features, which are seven-dimensional, of radiation mechanism of the original polarimetric SAR image as features of every pixel; performing super-pixel united sparse representation to obtain sparse representation of each super-pixel feature; classifying by using a sparse representation classifier; working out the mean value of each super-pixel covariance matrix, then performing super-pixel complex Wishart iteration by using the classifying result in the last step, and at last obtaining a final classifying result. According to the super-pixel polarimetric SAR land feature classification method based on sparse representation, the problem that traditional classifying areas based on the single pixel are poor in consistency is solved, and operating speed of the algorithm is greatly increased on basis of improving accelerate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Communication method, receiver and base station
InactiveUS20070072551A1Reduce the impact of interferenceReduce impactSpatial transmit diversityTransmission noise suppressionConjugate transposeEngineering
A multi-user receiver which uses at least two antenna elements and in which the influence of interference is reduced, the receiver comprises: means (200) for pre-filtering a wideband antenna signal, the pre-filtering means being determined on the basis of a spatial covariance matrix estimate, which spatial covariance matrix estimate is obtained from wideband antenna signals by sampling, arranging sampled values into a signal vector and by multiplying the signal vector by its conjugate transpose vector, means (210, 218) for removing the whitening from signals of predetermined users by using an inverse matrix of the matrix used in the whitening filter, means (202, 204, 206, 208, 210) for performing multi-path combining and multi-antenna combining.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Inter-cell interference mitigation method using spatial covariance matrix estimation method for inter-cell interference mitigation of MIMO antenna OFDM system
ActiveUS20120063529A1Reduce errorsSimple designDiversity/multi-antenna systemsChannel estimationMulti inputMoving average
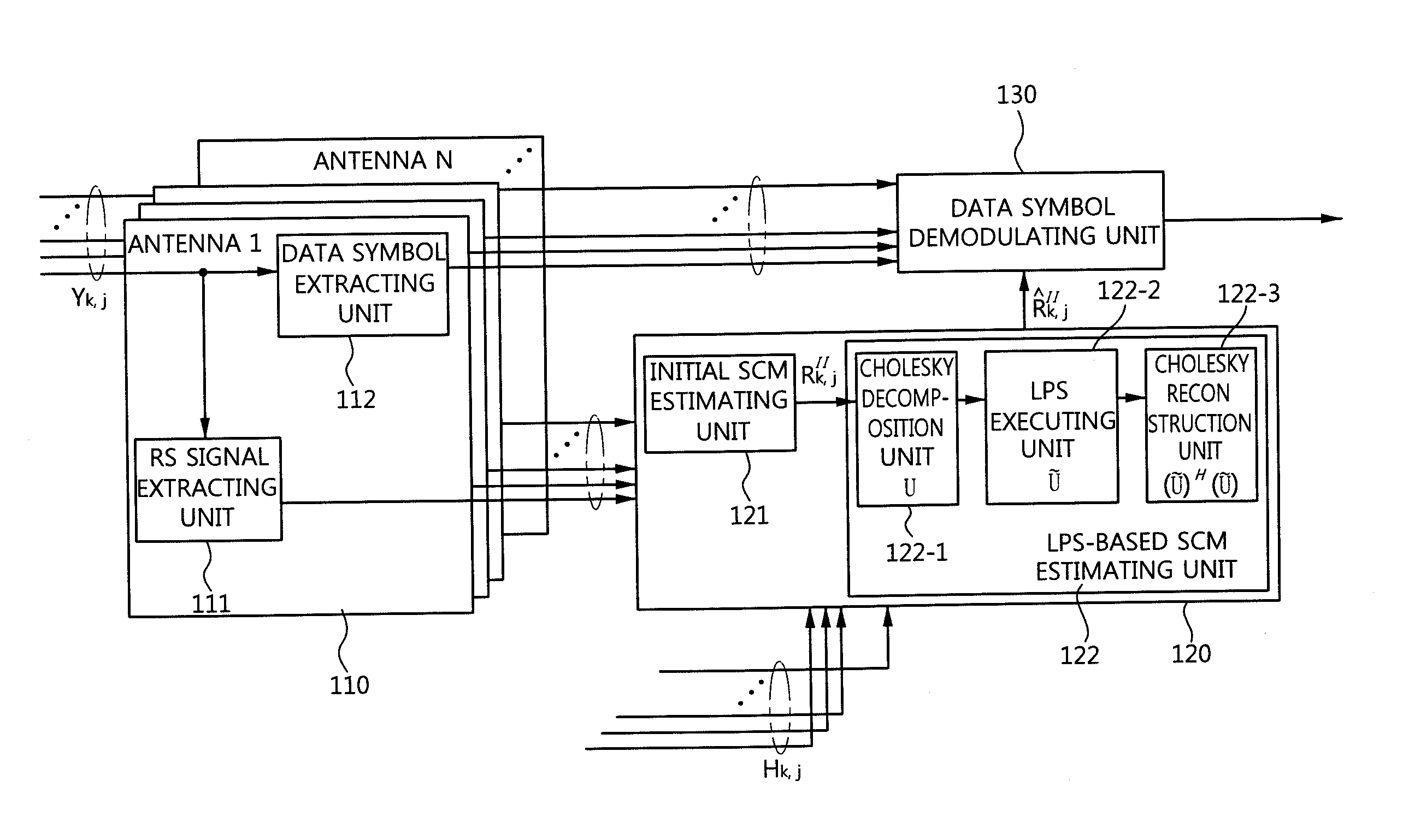
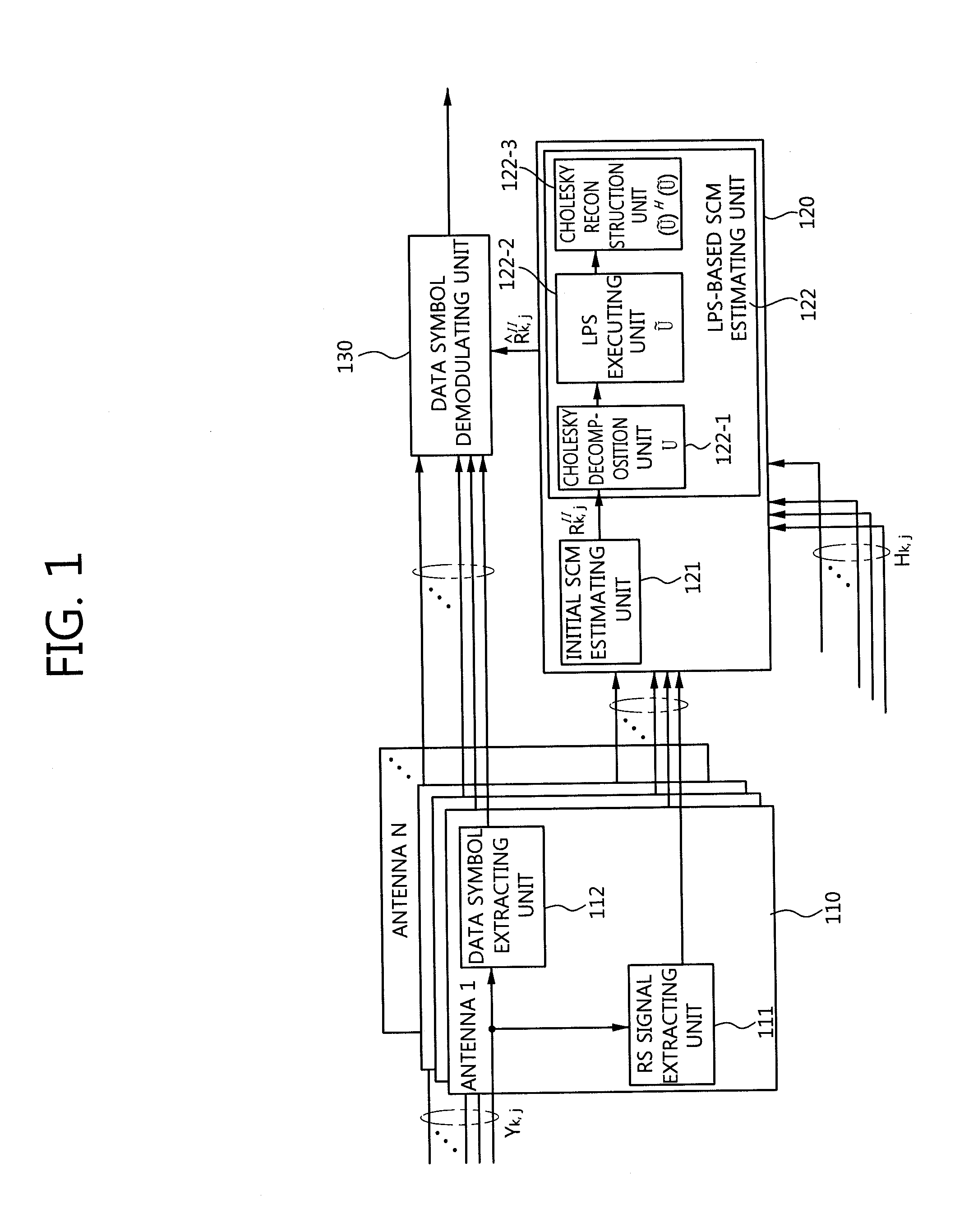
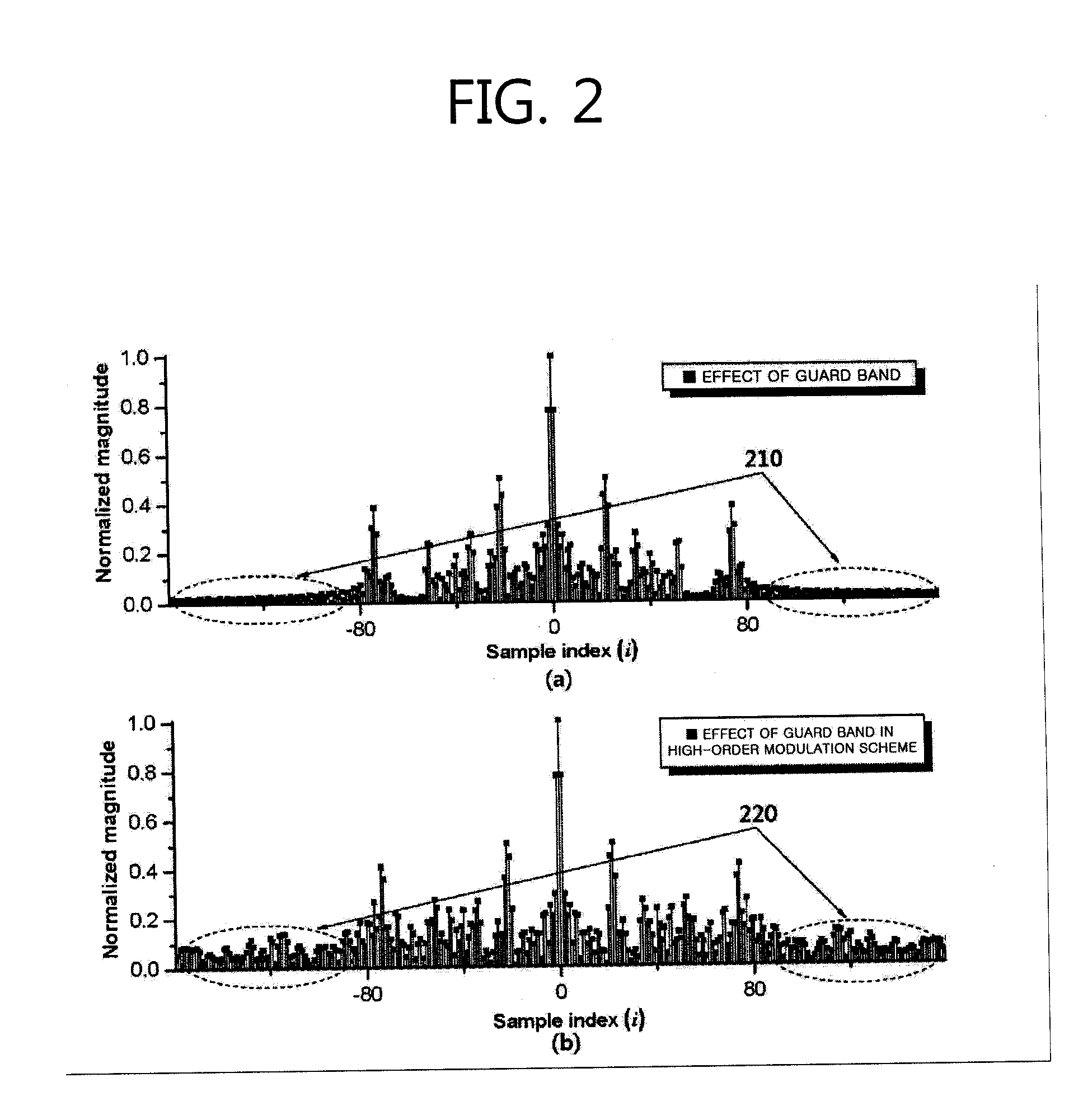
Disclosed is an inter-cell interference mitigation method using a spatial covariance matrix (SCM) estimation method in a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communication system for mitigating interference between asynchronous cells. The inter-cell interference mitigation method includes extracting a reference symbol (RS) of a received OFDM symbol and performing channel estimation, estimating an initial SCM using the RS signal and the channel estimation result, applying time-domain sinc type weighting to the initial SCM and applying an SCM, and demodulating a data symbol with mitigated inter-cell interference using the channel estimation result and the estimated SCM. By applying time-domain sinc type weighting to SCM estimation, it is possible to reduce an SCM estimation error occurring due to a spectral leakage induced by an abrupt change in a signal at a border point between an effective sub carrier zone and a guard band zone, and a simple design of a moving average filter form for a frequency domain signal can be made instead of frequency-time-frequency domain transformation using an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) and fast Fourier transfer (FFT).
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
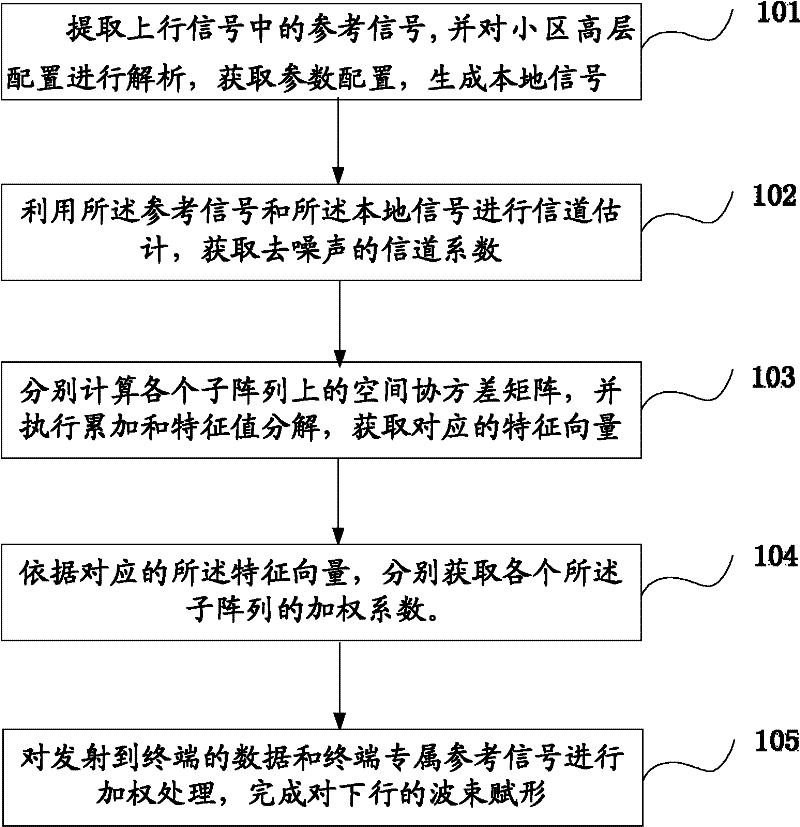
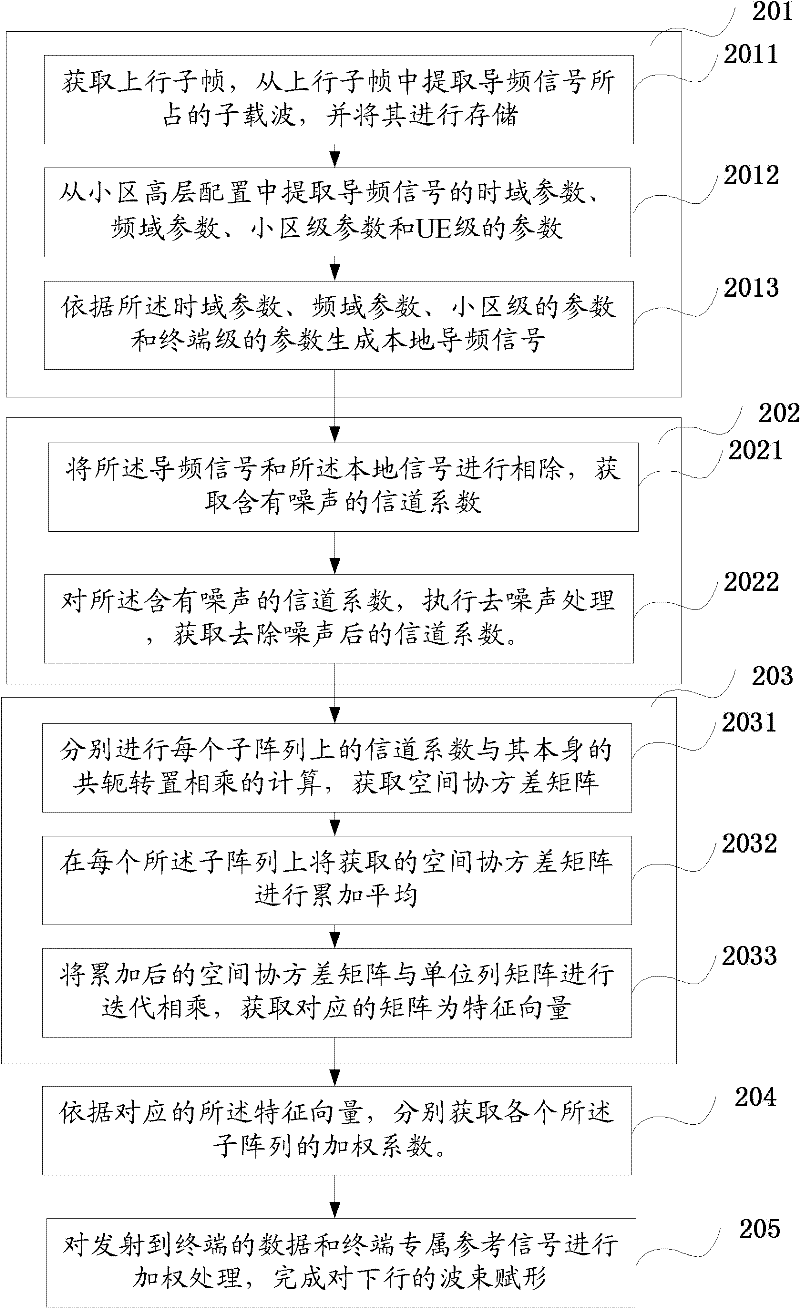
Beam-forming method of and device
ActiveCN102237922AHigh speedImprove implementation speedSpatial transmit diversityFeature vectorDecomposition
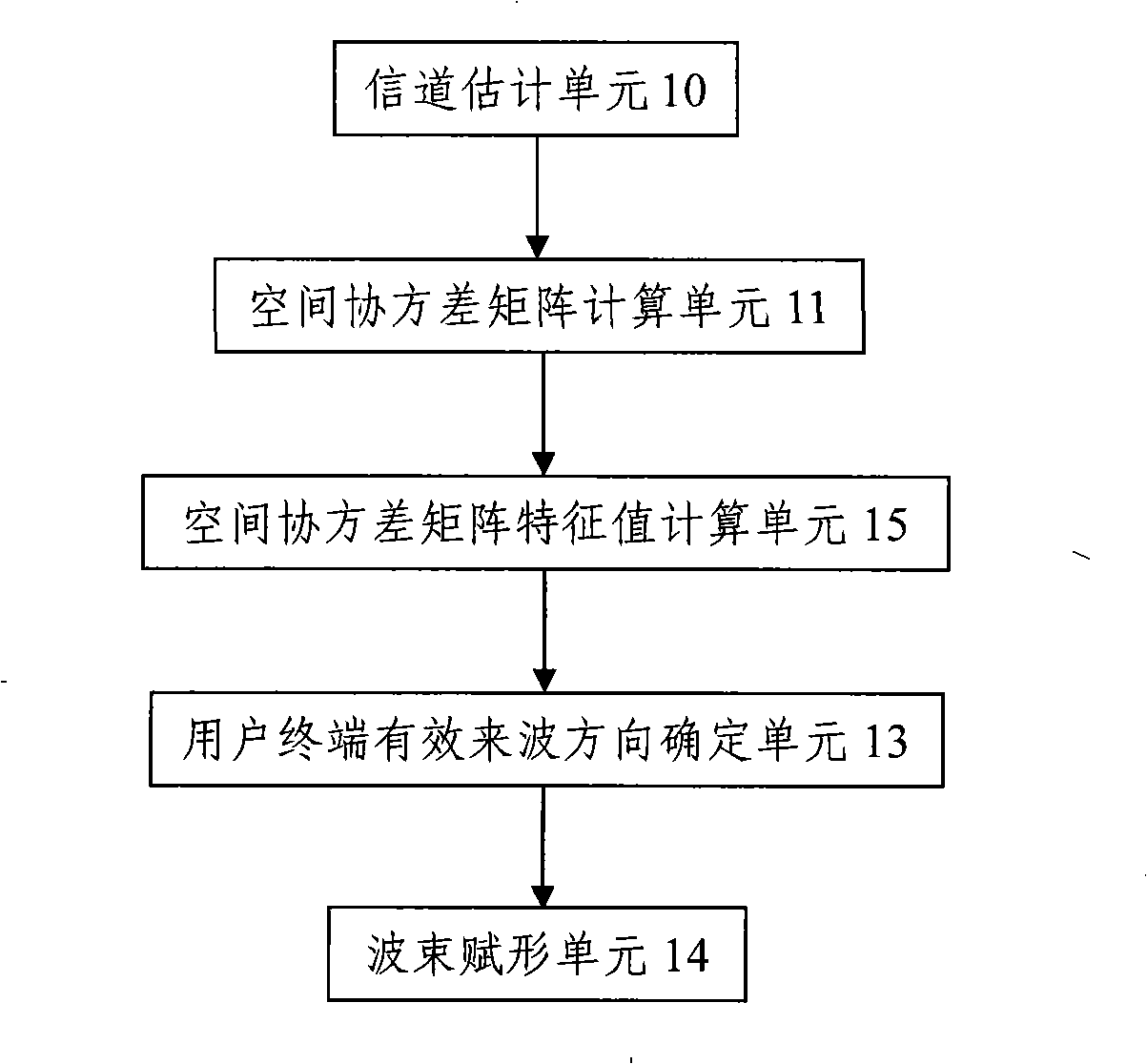
The invention discloses a beam-forming method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting a reference signal from uplink signals and resolving the high-level configuration of a cell to obtain the parameter configuration of the reference signal and generate a local signal; performing channel estimation by using the reference signal and the local signal to obtain a denoised channel coefficient; calculating a space covariance matrix on each subarray by using the channel coefficient; performing characteristic value decomposition on the covariance matrix to obtain a characteristic vector and further obtain a weighting coefficient accordingly; and weighting data transmitted to a terminal and an exclusive reference signal of the terminal by using the weighting coefficient to finish beam forming of a downlink. Due to the adoption of the steps in the method, the calculation process of beam forming is simplified, the beam forming realization speed can be effectively increased under the condition of ensuring a certain beam-forming accuracy, the time delay of a system is reduced, and the aims of pointing at a target terminal, reducing the signal demodulation errors and lowering the interference on other terminals are fulfilled.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
Sequence detecting method and apparatus for multi-antenna system
ActiveCN101291165ASuppress noiseSpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsSequence signalWeight coefficient
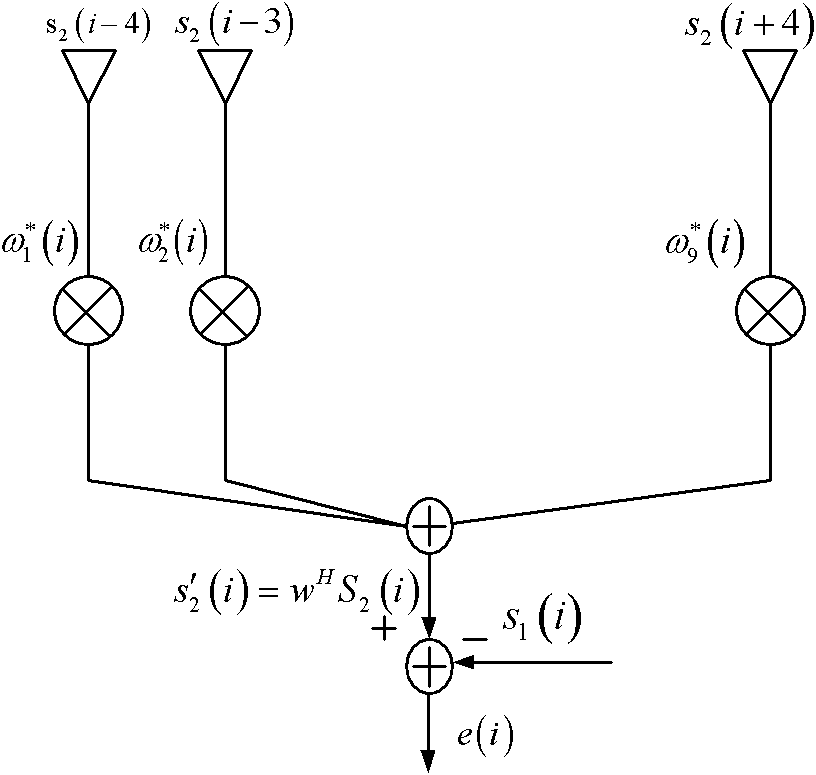
The invention discloses a sequence detection method for a multi-antenna system. The method comprises the steps of: calculating a space covariance matrix according to a sequence signal received by each antenna of the multi-antenna system; estimating a direction of a coming wave according to the space covariance matrix; determining a weight coefficient corresponding to the direction of the coming wave; performing the forming combination to the sequence signals received by the plurality of antennae according to the weight coefficient; and performing the sequence detection to the combined sequence signals. The invention discloses a sequence detection device for the multi-antenna system. The embodiment of the invention estimates the direction of the coming wave through calculating the space covariance matrix to determine the weight coefficient, and utilizes the weight coefficient to perform the forming combination to the received signals, which ensures that a major lobe of a directional diagram aims at the direction of the coming wave of the sequence signals, the directivity is improved, a null steering is formed at the interference direction of the coming wave, effective inhibit to noise and interference is realized, thereby the sequence detection precision is improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
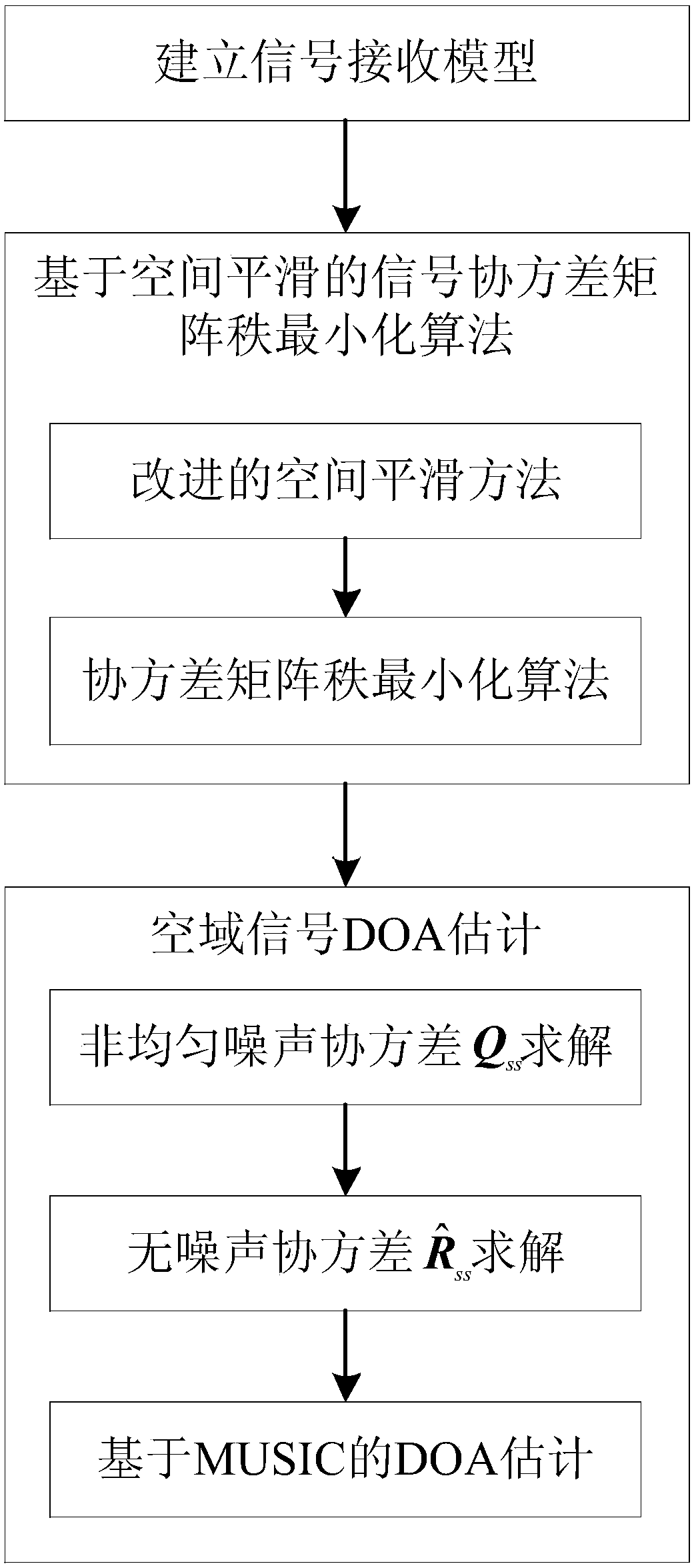
Spatial smoothing-based covariance matrix rank minimization direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation method
ActiveCN107907852AImprove estimation accuracyImprove estimation performanceDirection findersImage resolutionEstimation methods
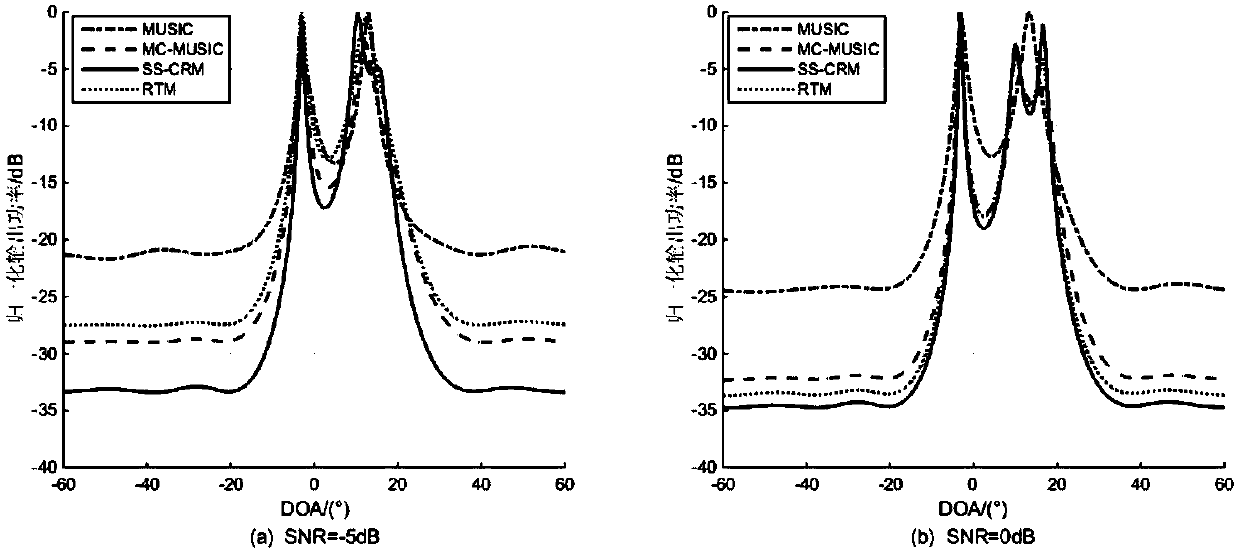
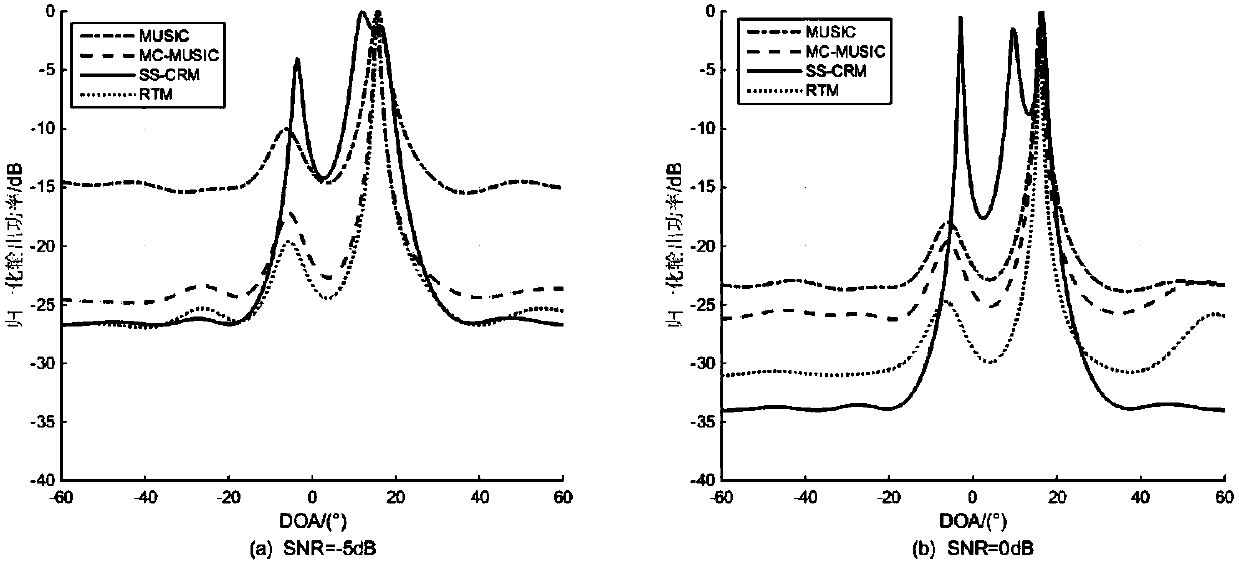
The invention belongs to the signal processing field and relates to a receiving signal covariance matrix rank minimization direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation method based on a spatial smoothing method. The invention aims to solve the problems of low angle estimation poor accuracy and low resolution of a traditional direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation method under a condition of coherent signals and non-uniform noises. According to the receiving spatial covariance matrix rank minimization direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation method based on the spatial smoothing method of the invention, on the basis of the traditional spatial smoothing method, a receiving signal covariance matrix is pre-multiplied and post-multiplied by an exchange matrix separately, so that a spatial backward smoothing covariance matrix can be obtained; the covariance matrix is reconstructed to be a noiseless covariance matrix based on the low-rank feature of the smoothing matrix; and finally a traditional MUSIC(multiple signal classification) algorithm is adopted to achieve DOA estimation. Numerical simulations show that the algorithm provided by the invention can better suppress the influence of non-uniform noises and has high DOA estimation performance under a coherent condition compared with traditional MUSIC, MC-MUSIC and RTM algorithms.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
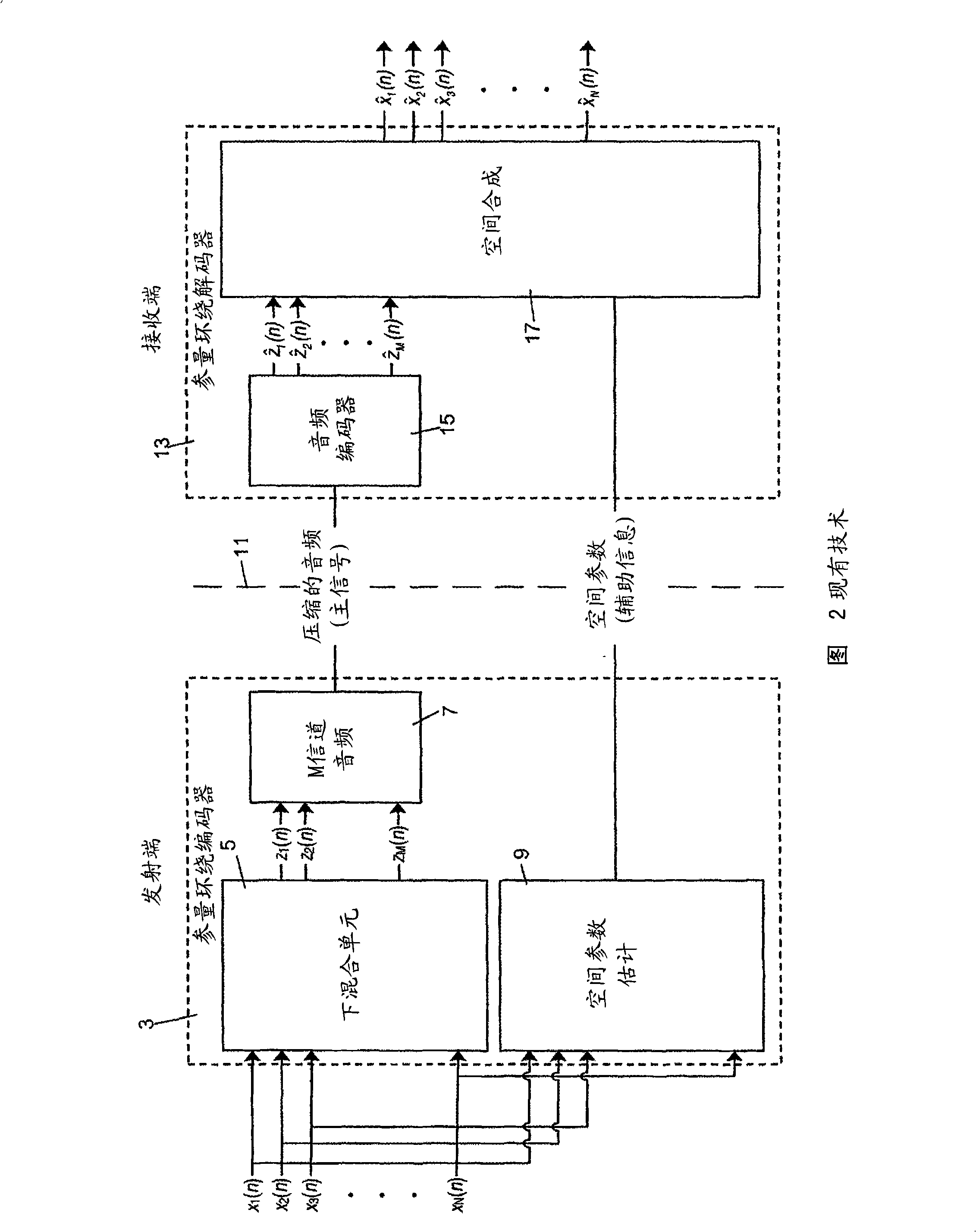
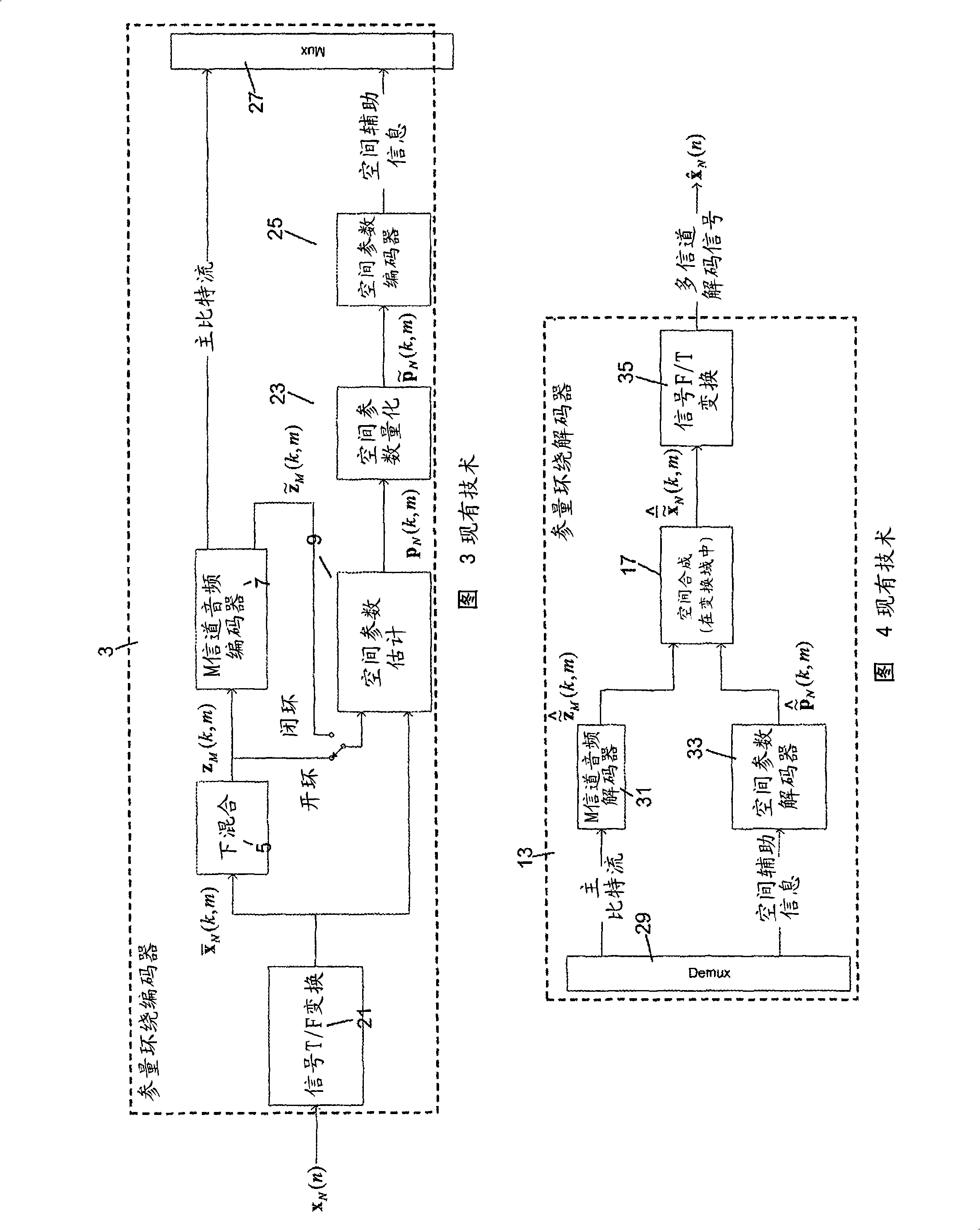
Method and arrangement for a decoder for multi-channel surround sound
ActiveCN101411214AReduce complexityReduce quality problemsSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsSpatial covariance matrixComputer science
The basic concept of the present invention is to extrapolate a partially known spatial covariance matrix of a multi-channel signal in the parameter domain. The extrapolated covariance matrix is used with the downcoded downmix signal in order to efficiently generate an estimate of a linear combination of the multi-channel signals.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
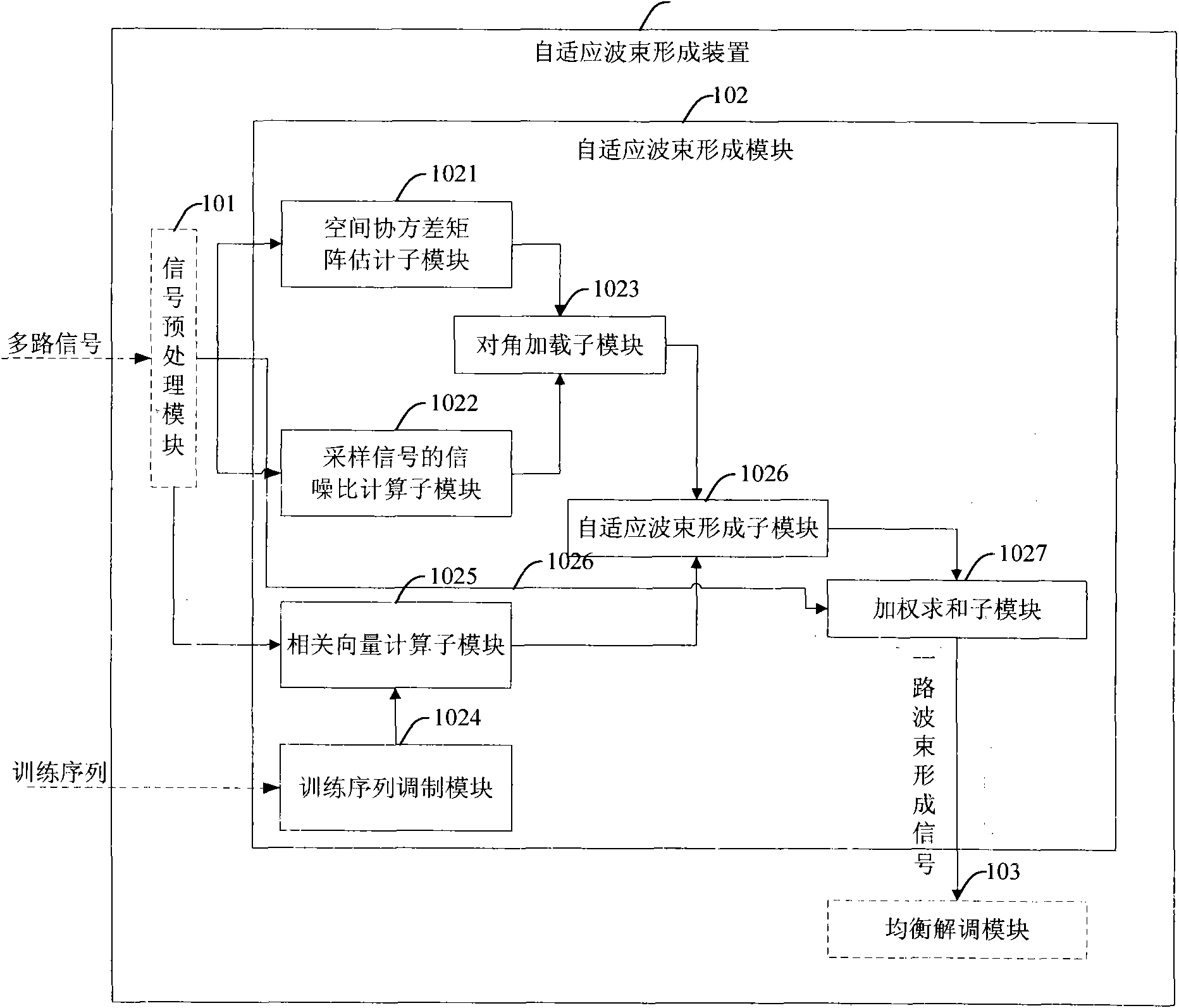
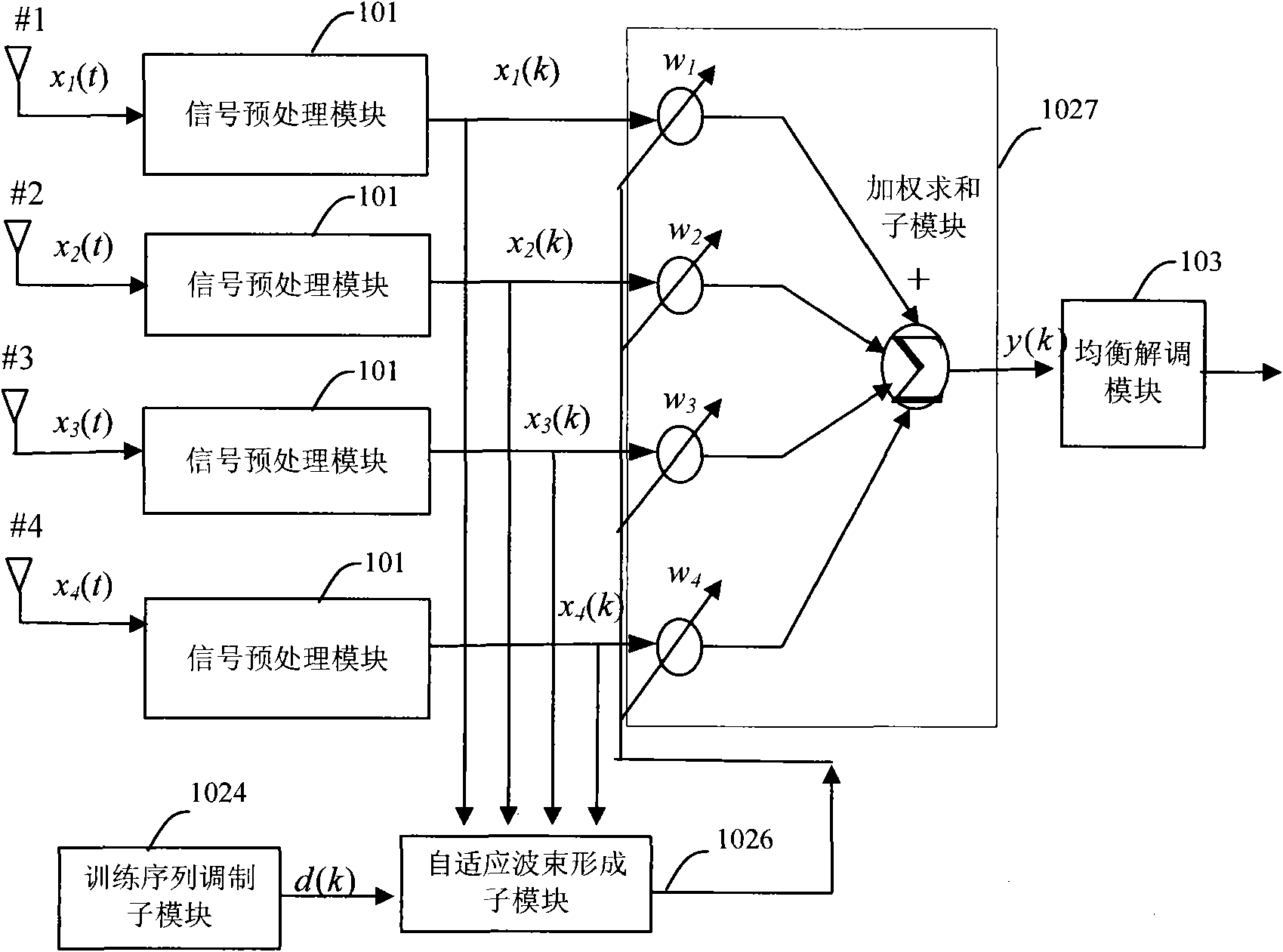
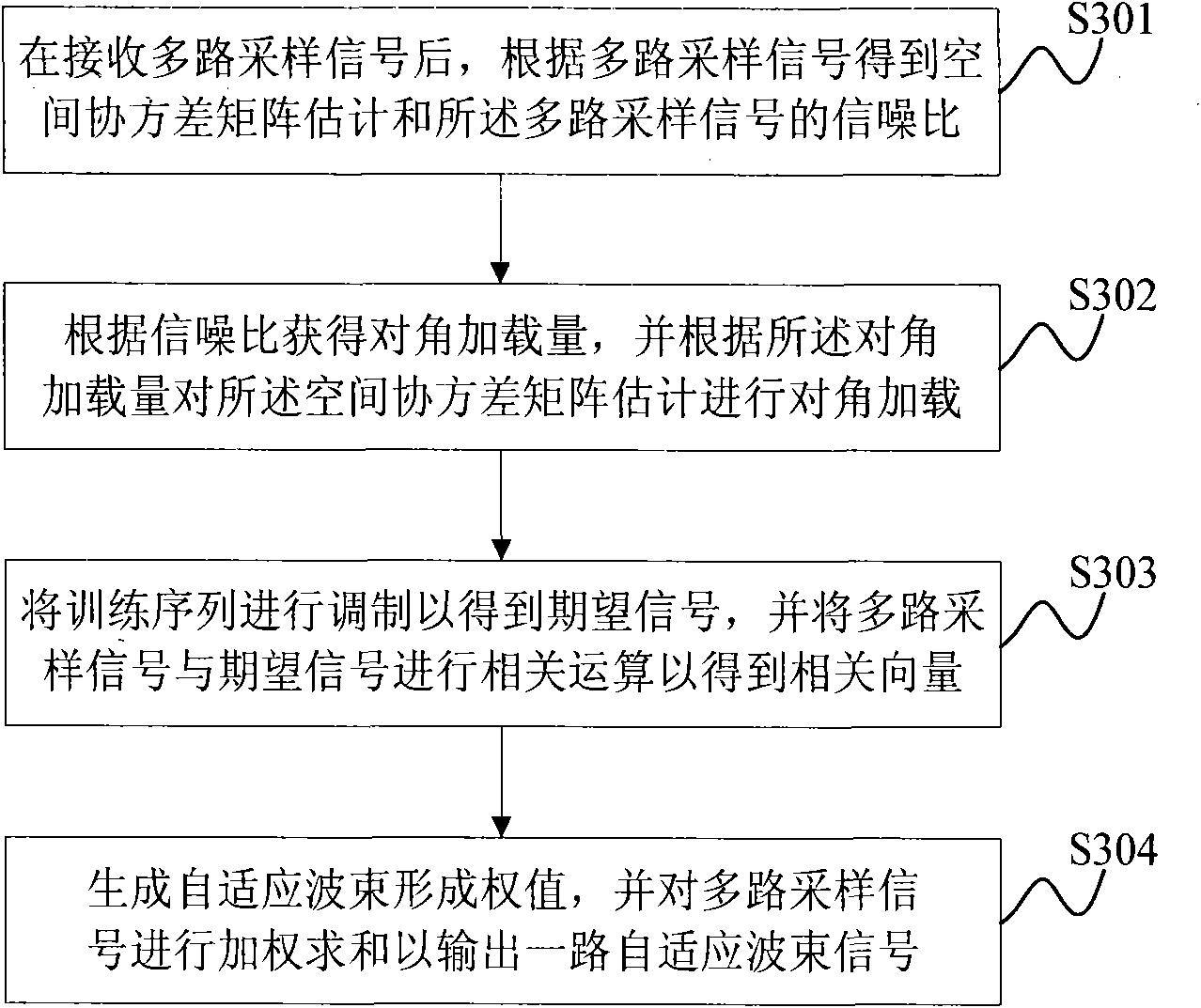
Self-adaptive beam forming method and self-adaptive beam forming device
InactiveCN101527590AImprove robustnessSimplify the beamforming processSpatial transmit diversityNetwork planningSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
The invention discloses a method for a self-adaptive beam forming weight, which comprises the following steps that: after multipath sampling signals are received, the spatial covariance matrix estimation and the signal-to-noise ratio of the multipath sampling signals are acquired according to the multipath sampling signals; the amount of diagonal loading is acquired according to the signal-to-noise ratio, and the diagonal loading is performed on the spatial covariance matrix estimation according to the amount of diagonal loading; a training sequence is modulated to acquire an expected signal, and the multipath sampling signals and the expected signal are subjected to correlation operation to acquire a correlation vector; and the self-adaptive beam forming weight is generated according tothe spatial covariance matrix estimation after the diagonal loading and the correlation vector, and the multipath sampling signals are subjected to weighted sum to output a self-adaptive beam signal according to the self-adaptive beam forming weight. The invention also correspondingly provides a self-adaptive beam forming device. Thus the method and the device can reduce the calculation amount during the formation of self-adaptive beams, improve the robustness of beam formation, and have simple realization.
Owner:ZTE CORP
A smart antenna downlink wave bundle shaping method and its device
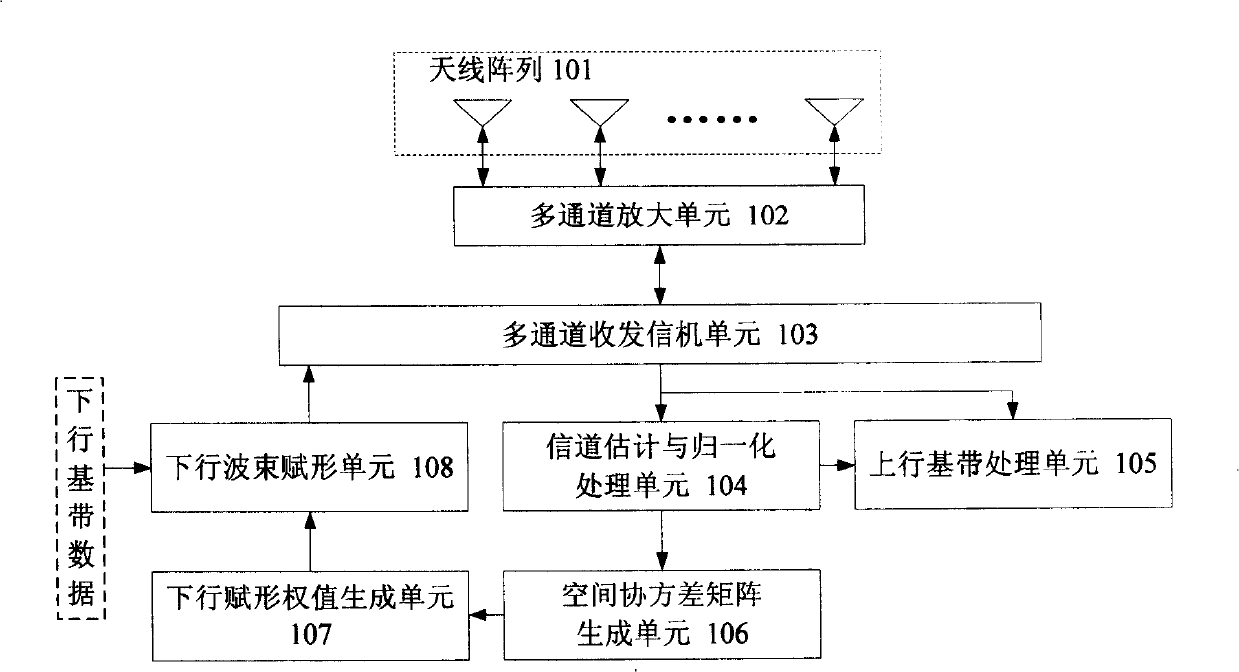
ActiveCN101267236AImprove performanceImprove robustnessSpatial transmit diversityTransceiverSmart antenna
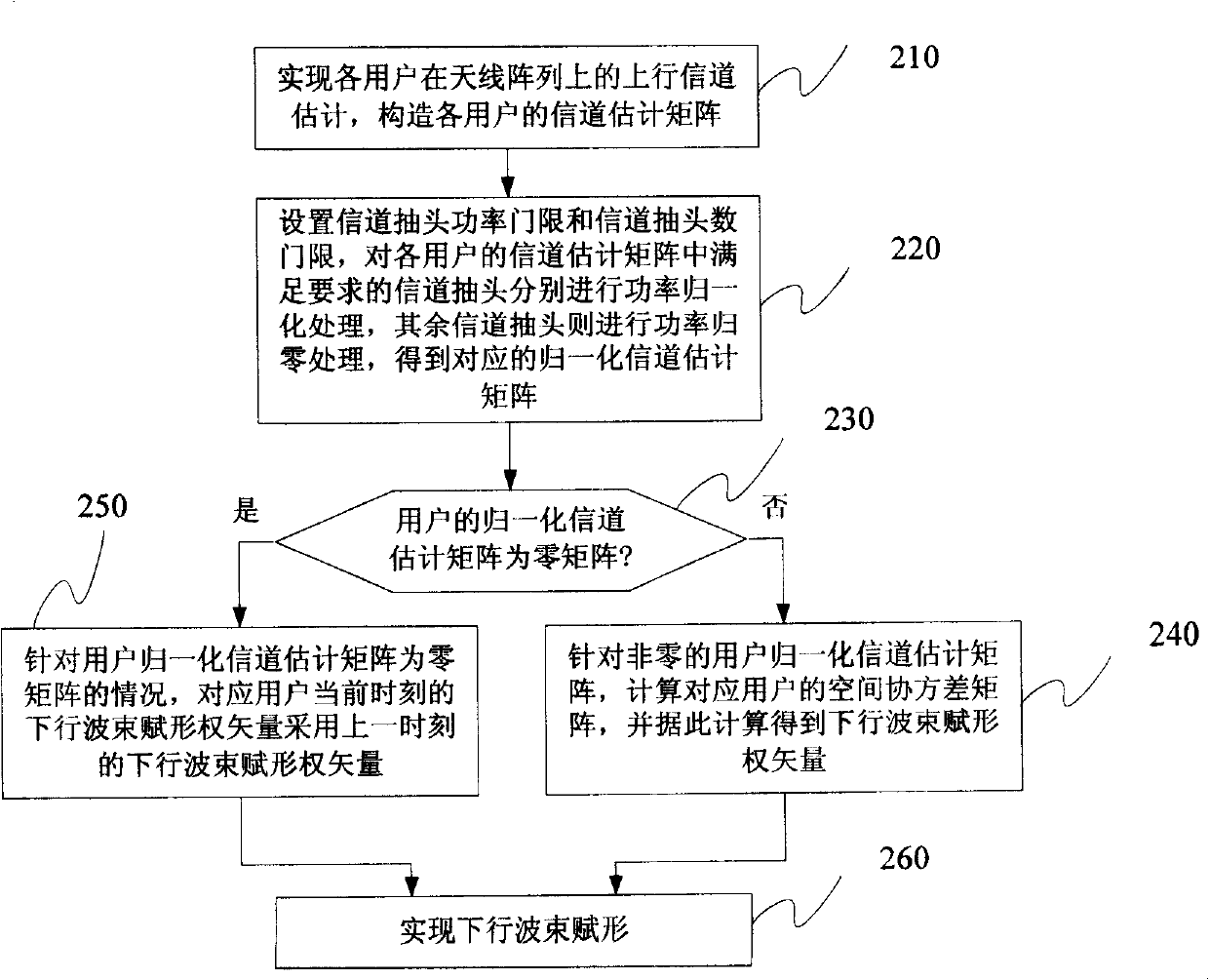
The present invention relates to an intelligent antenna descending wave beam forming method and a device thereof, wherein the device comprises an antenna array (101), a multichannel amplifying unit (102), a multichannel transceiver unit (103), an ascending baseband processing unit (105) and the following components which are connected in sequence: a channel estimating and normalization processing unit (104), a space covariance matrix generating unit (106), a descending wave beam forming authority generating unit (107) and a descending wave beam forming unit (108). The method comprises the following procedures: setting a channel estimation window length W, and constructing each user ascending channel estimation matrix H(k); setting a channel tap power threshold PD and a channel tap number threshold ND, and combining the estimated channel tap power for real-time measuring P1(k) to obtain a power normalization ascending channel estimation matrix H(k) which satisfies the request of the channel tap; and calculating and generating a corresponding space covariance matrix R(k)=H(k)*(H(k))(H) and a descending wave beam forming authority vector w(k) according to that H(k) is not equal to 0 / M*w and forming, or generating a descending wave beam forming authority vector w(k)(t)=w(k)(t-1) according to H(k)=0 / M*w.
Owner:深圳国人无线通信有限公司
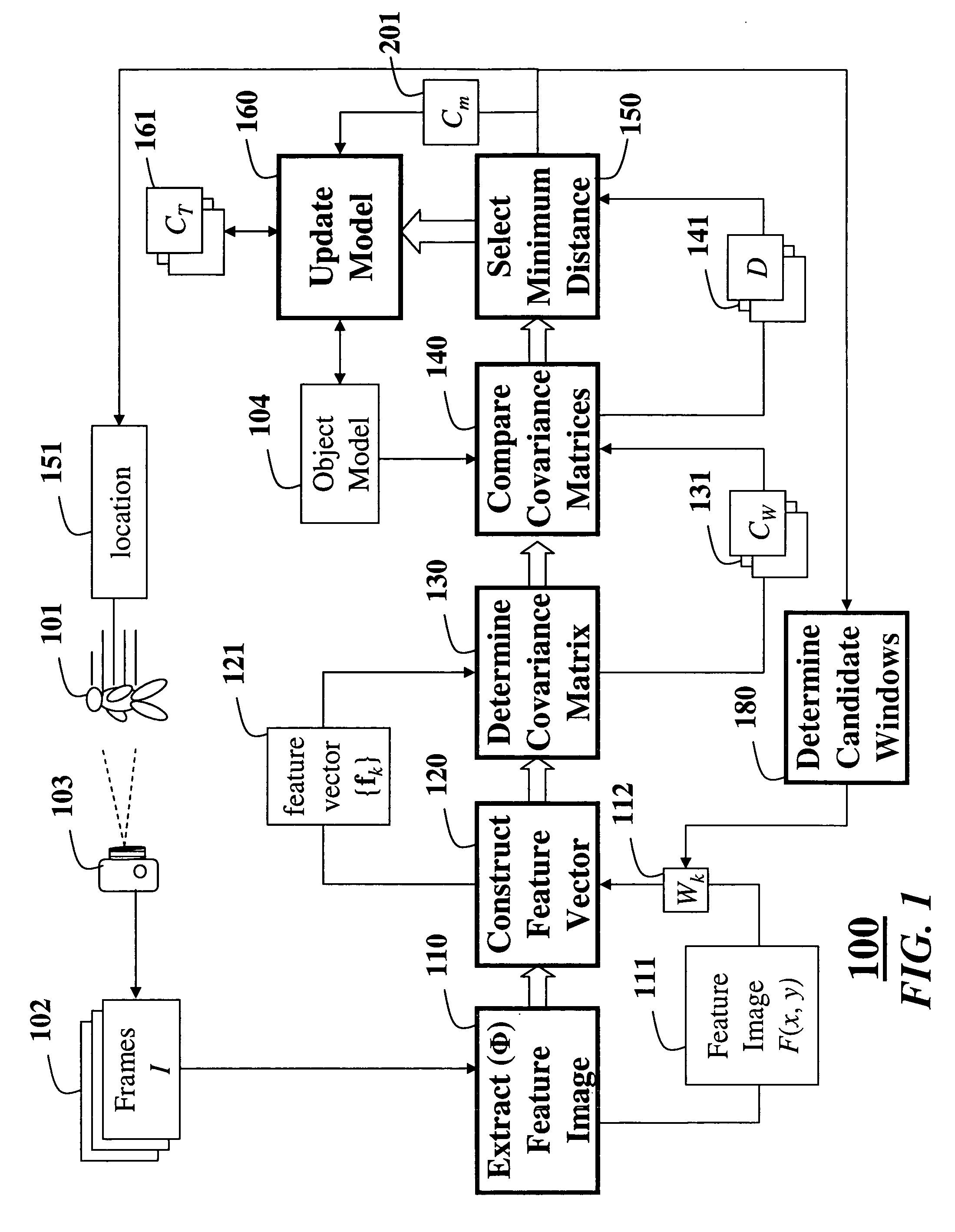
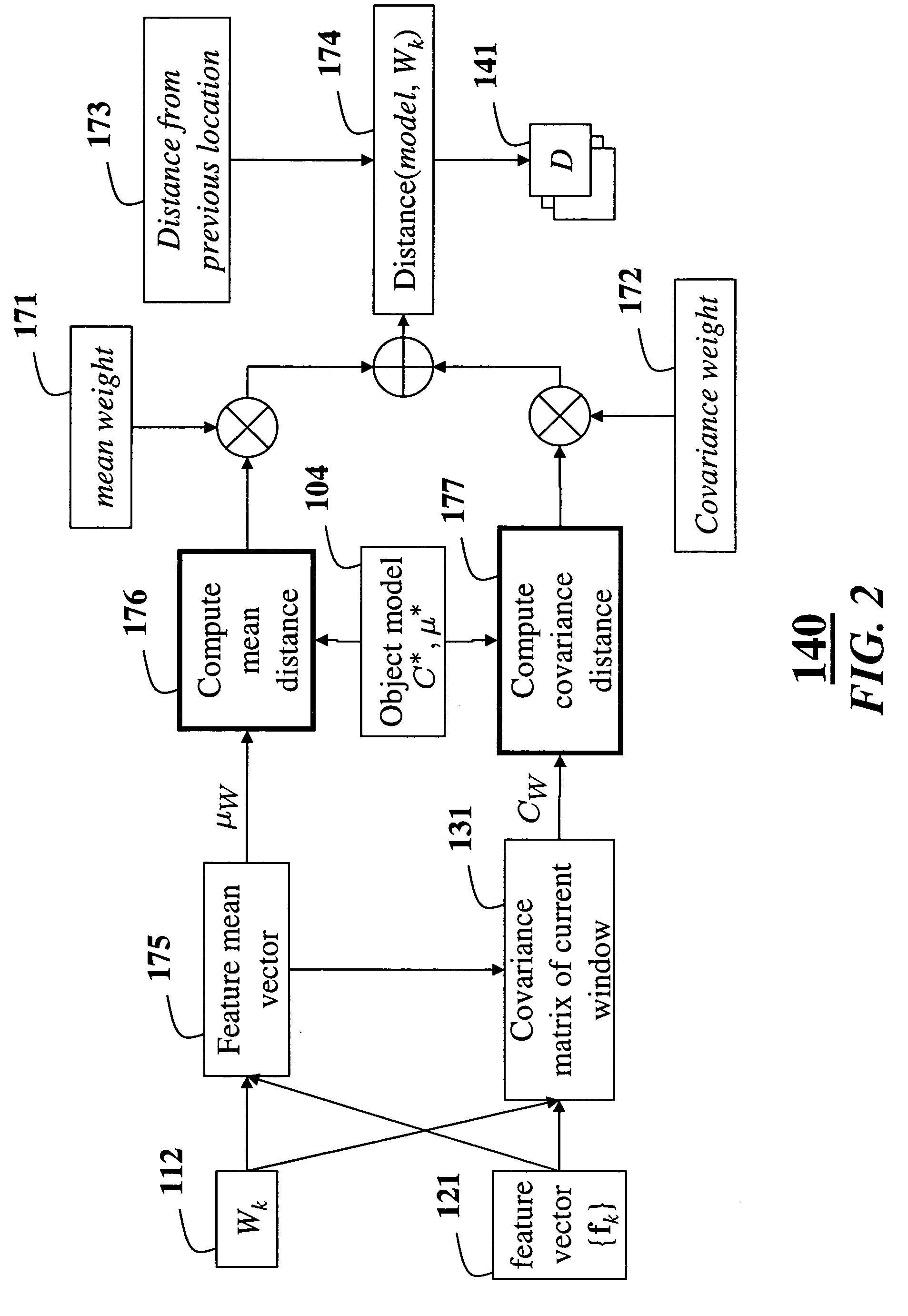
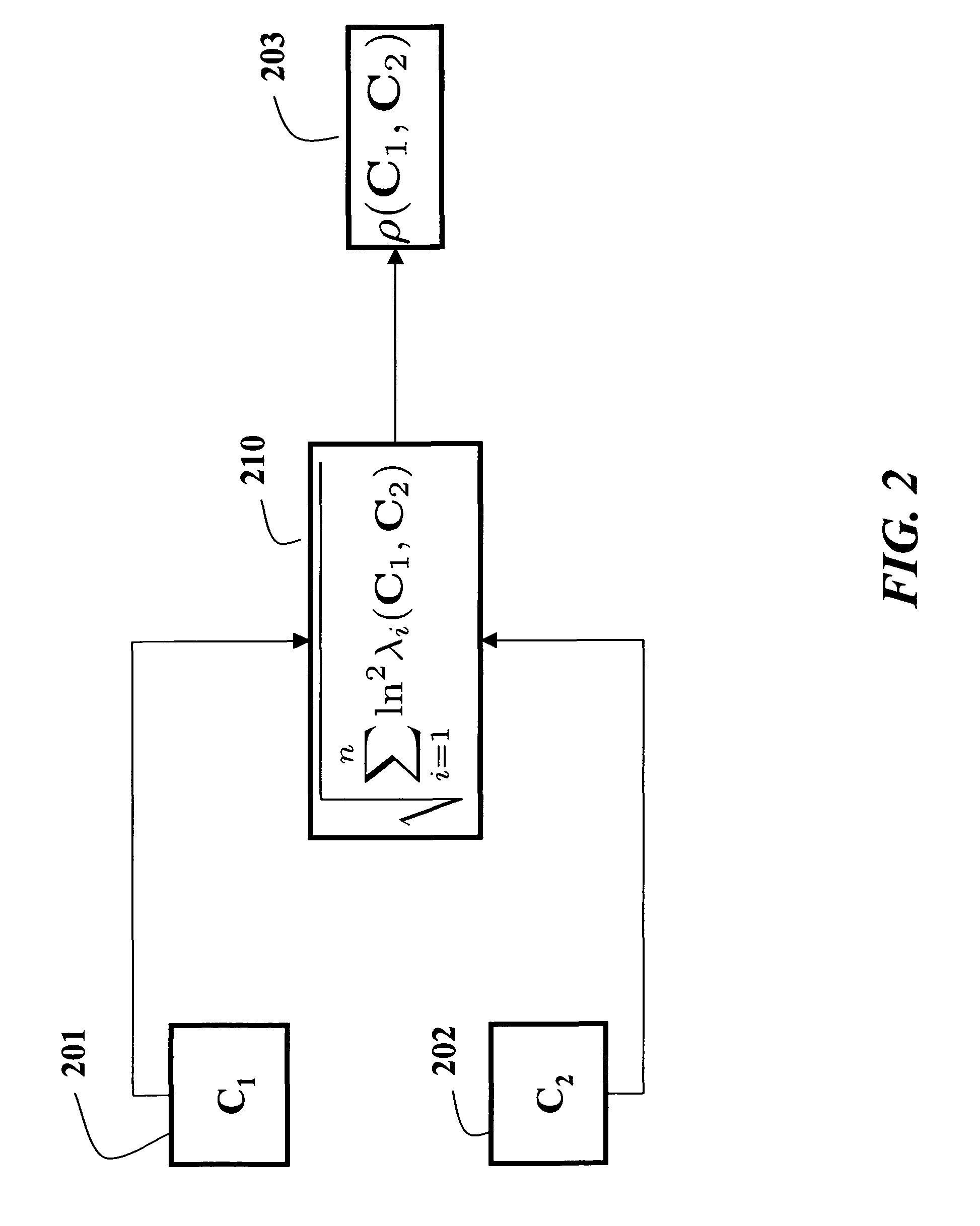
Method for tracking objects in videos using covariance matrices
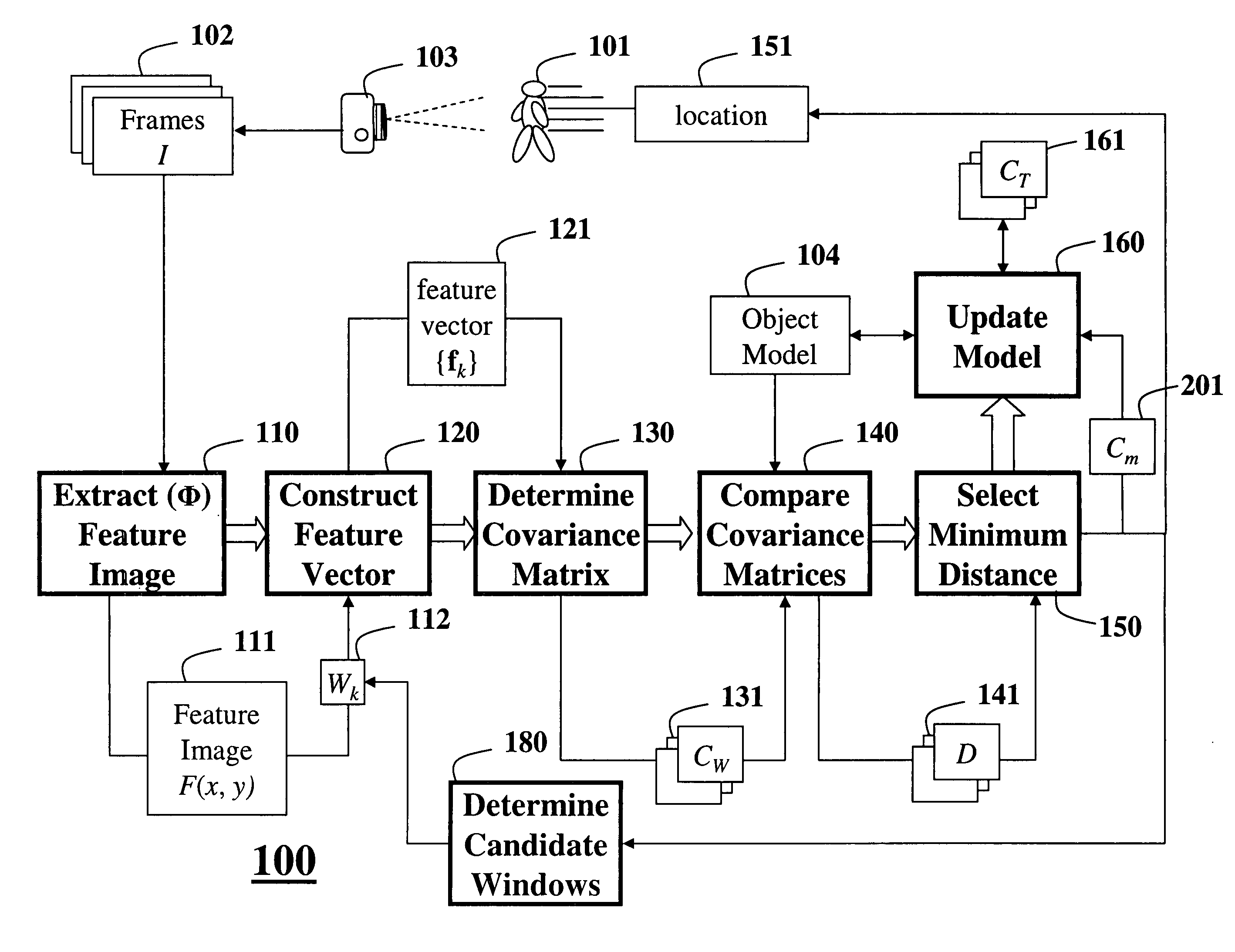
ActiveUS7620204B2Dimensionality is relatively smallEfficient fusionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionManagement object
A method is provided for tracking a non-rigid object in a sequence of frames of a video. Features of an object are extracted from the video. The features include locations of pixels and properties of the pixels. The features are used to construct a covariance matrix. The covariance matrix is used as a descriptor of the object for tracking purposes. Object deformations and appearance changes are managed with an update mechanism that is based on Lie algebra averaging.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
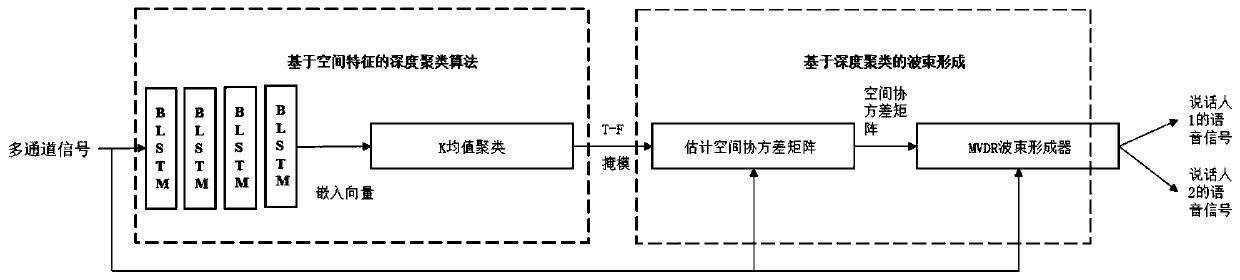
Multi-channel speaker-independent voice separation method based on deep clustering
ActiveCN110970053ATake advantage ofImprove robustnessSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial covariance matrixAcoustics
The invention provides a multi-channel speaker-independent voice separation method based on deep clustering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out short-time Fourier transform on a voice signal to extract amplitude spectrum characteristics of the voice signal, then calculating cosine values of phase differences between different channels to serve as spatial characteristics, and combining the two characteristics to serve as input characteristics for training a deep clustering network; then, training a bidirectional long-short-term memory network, and obtaining estimated masks of different speakers by utilizing the network; and finally, calculating the coefficient of the MVDR beamformer by using the spatial covariance matrix, and multiplying the mixed voice by the obtained beamformer coefficient to obtain separated speaker voice signals. According to the method, the spatial information of the voice signals is better utilized, the high-quality mask is estimated by using the deep clustering network, the separation processing of the mixed voice signals of a plurality of speakers in the reverberation environment can be realized, and the method has better voice separation performance.
Owner:RES & DEV INST OF NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV IN SHENZHEN +1
Direction of arrival estimation method
InactiveCN101431354AHigh precisionReduce correlationSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemChannel impulse response
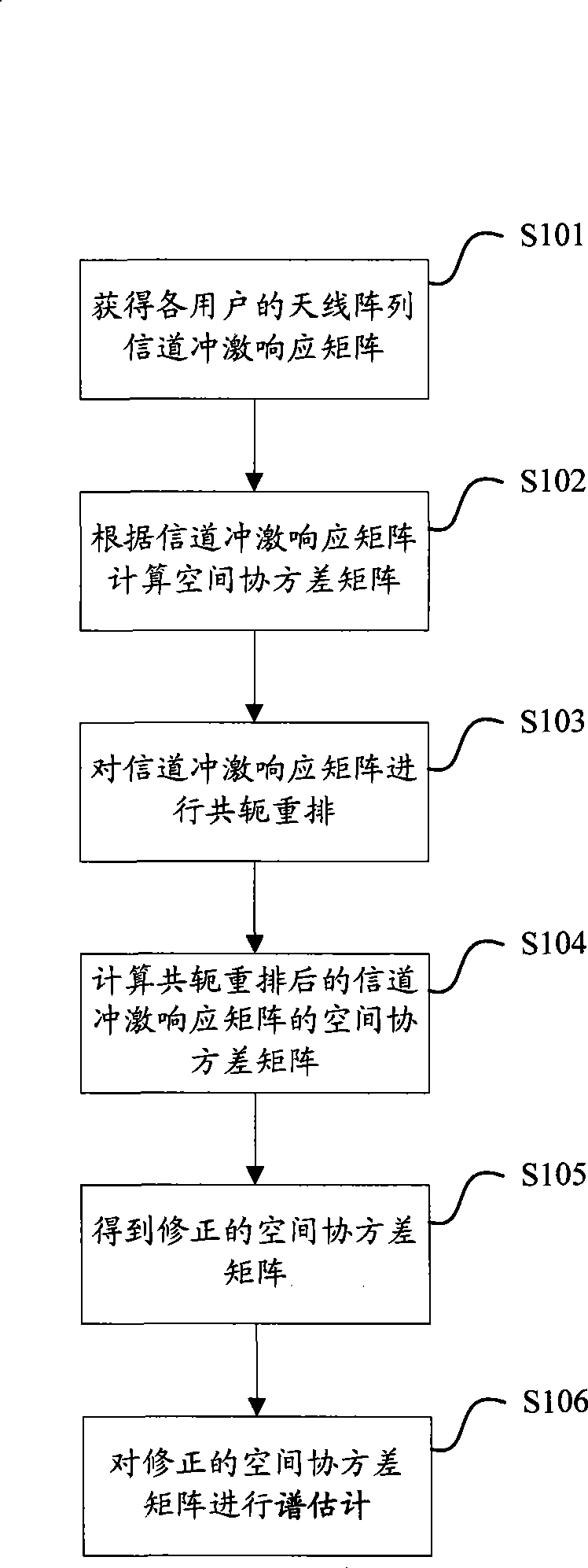
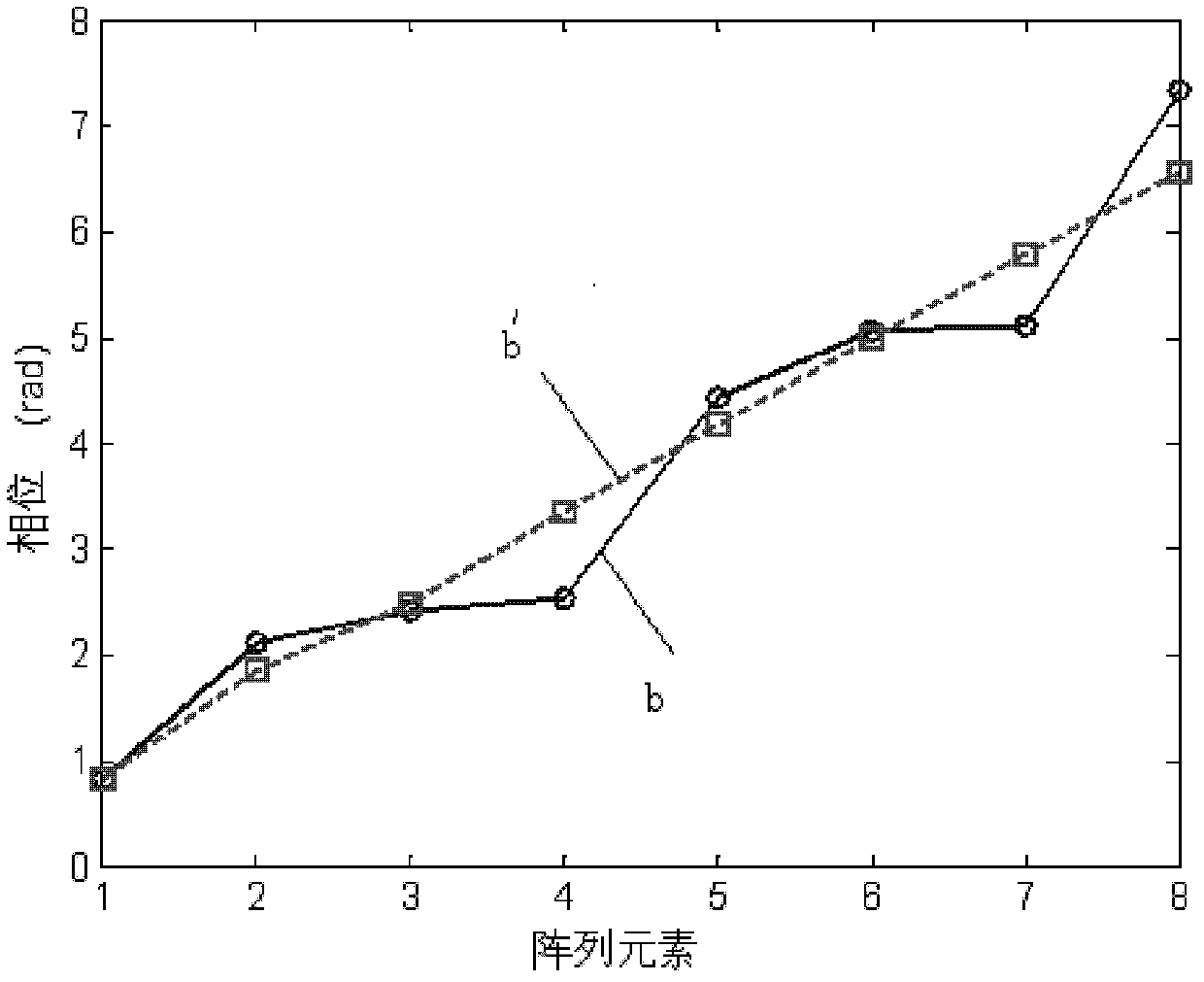
The invention discloses a method for direction of arrival estimation which is applied to a wireless communication system using a smart antenna, and is characterized in that after a channel impulse response matrix H of a user is obtained, conjugation rearrangement is carried out on the H or a complex conjugation matrix R* of a space covariance matrix R corresponding to the H to obtain a space covariance matrix R' which is in the conjugation rearrangement, and spectrum estimation is carried out on Rm equal to alpha mulitplies R' plus beta mulitplies R to obtain a direction of arrival angle estimated value. Compared with the existing DOA estimation method based on the space covariance matrix to estimate the spectrum, the DOA estimation method based on the space covariance matrix after the conjugation rearrangement to estimate the spectrum can efficiently enhance the accuracy of the DOA estimation, lowers the correlation among multipath signals of the user, and can improve the performance of carrying out the DOA estimation on the multipath signals of the desired user by utilizing high resolution algorithm in a system. Under the condition that the method does not reduce related multipath number which can be estimated, the calculation amount has no obvious increase.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Target signal robust space-time adaptive processing method based on amplitude and phase constraints
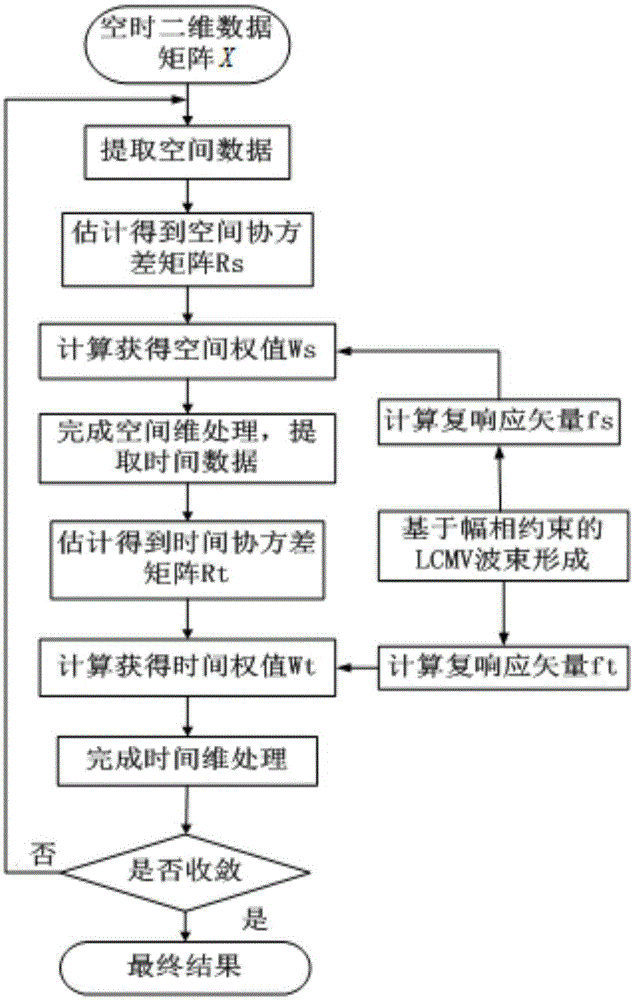
ActiveCN105137409AImprove robustnessImprove performanceWave based measurement systemsComplex responseRadar
The invention discloses a radar target signal robust space-time adaptive processing method based on amplitude and phase constraints. The method comprises steps: target signals are set to be a radar space-time data matrix, a first space-time adaptive weight matrix for the radar space-time data matrix is obtained, and an optimality condition equation is further obtained; then, according to the optimality condition equation, a second space-time adaptive weight matrix for the radar space-time data matrix is calculated, and an amplitude and phase constraint-based linear constrained minimum variance beam former complex response vector is built; and after an amplitude and phase constraint-based beam former space-time adaptive weight matrix is obtained through calculation, an amplitude and phase constraint-based beam former unconstrained cost function is obtained through calculation, a robust time covariance matrix and a robust space covariance matrix are calculated respectively, a robust correction space steering vector and a robust correction time steering vector are calculated respectively, a robust correction space-time steering vector is further obtained, and a final target signal through space-time processing is obtained through calculation finally.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
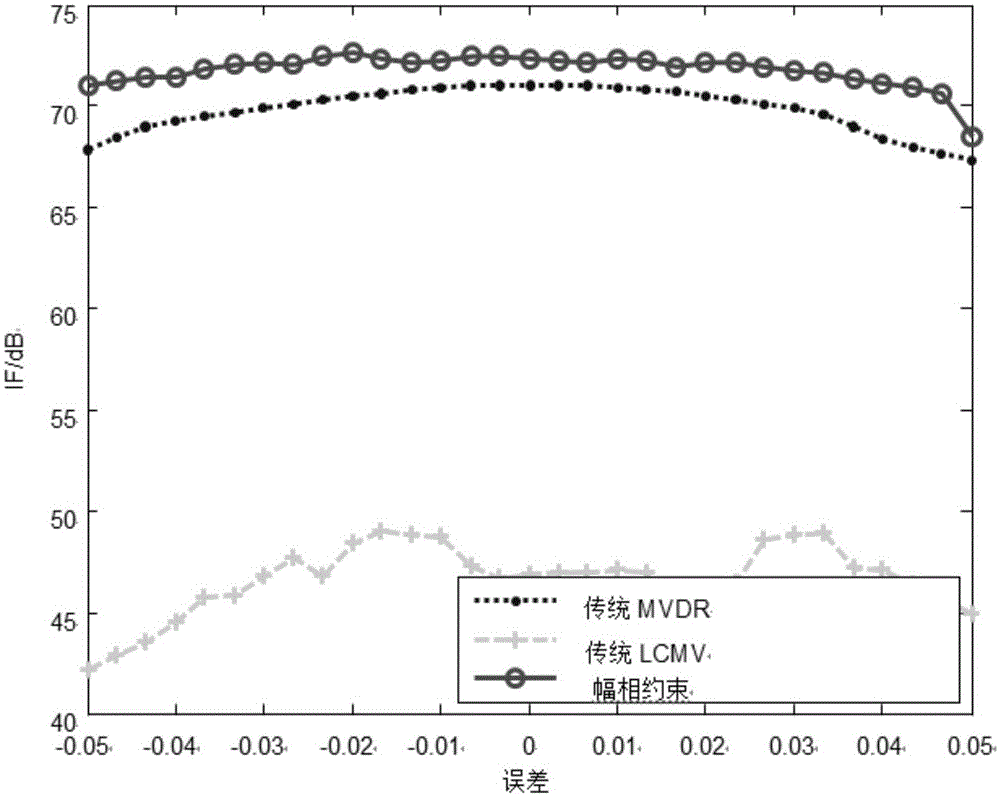
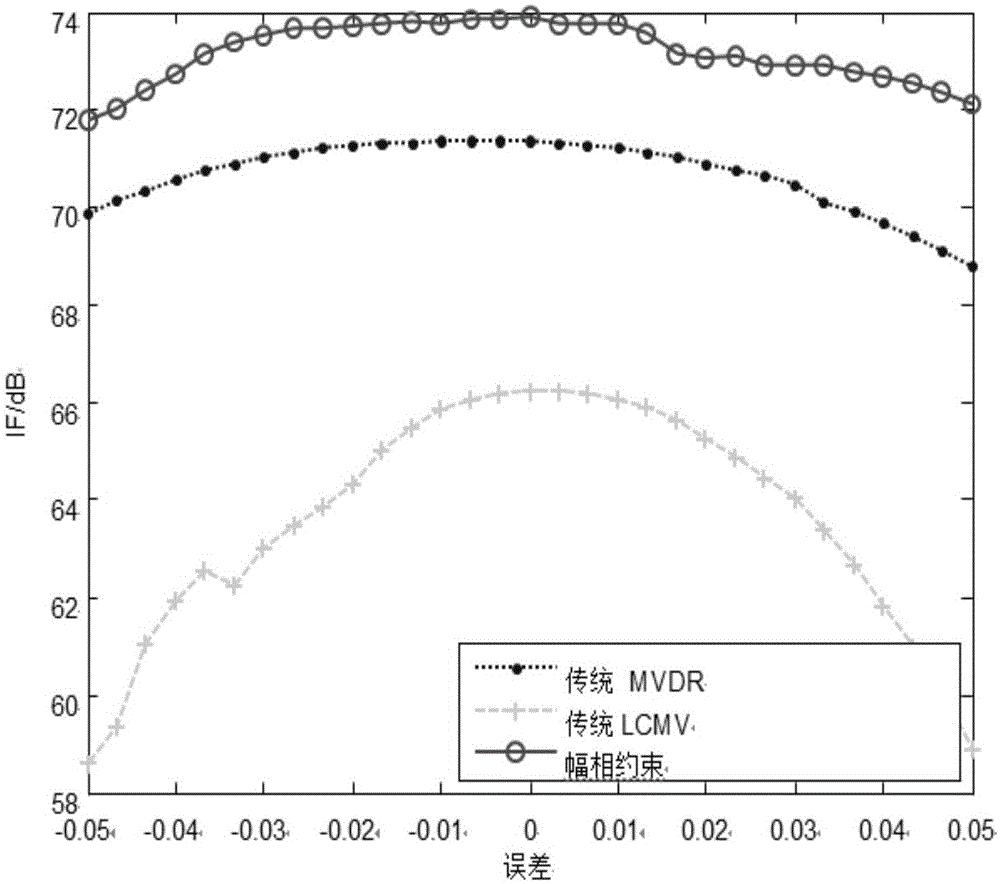
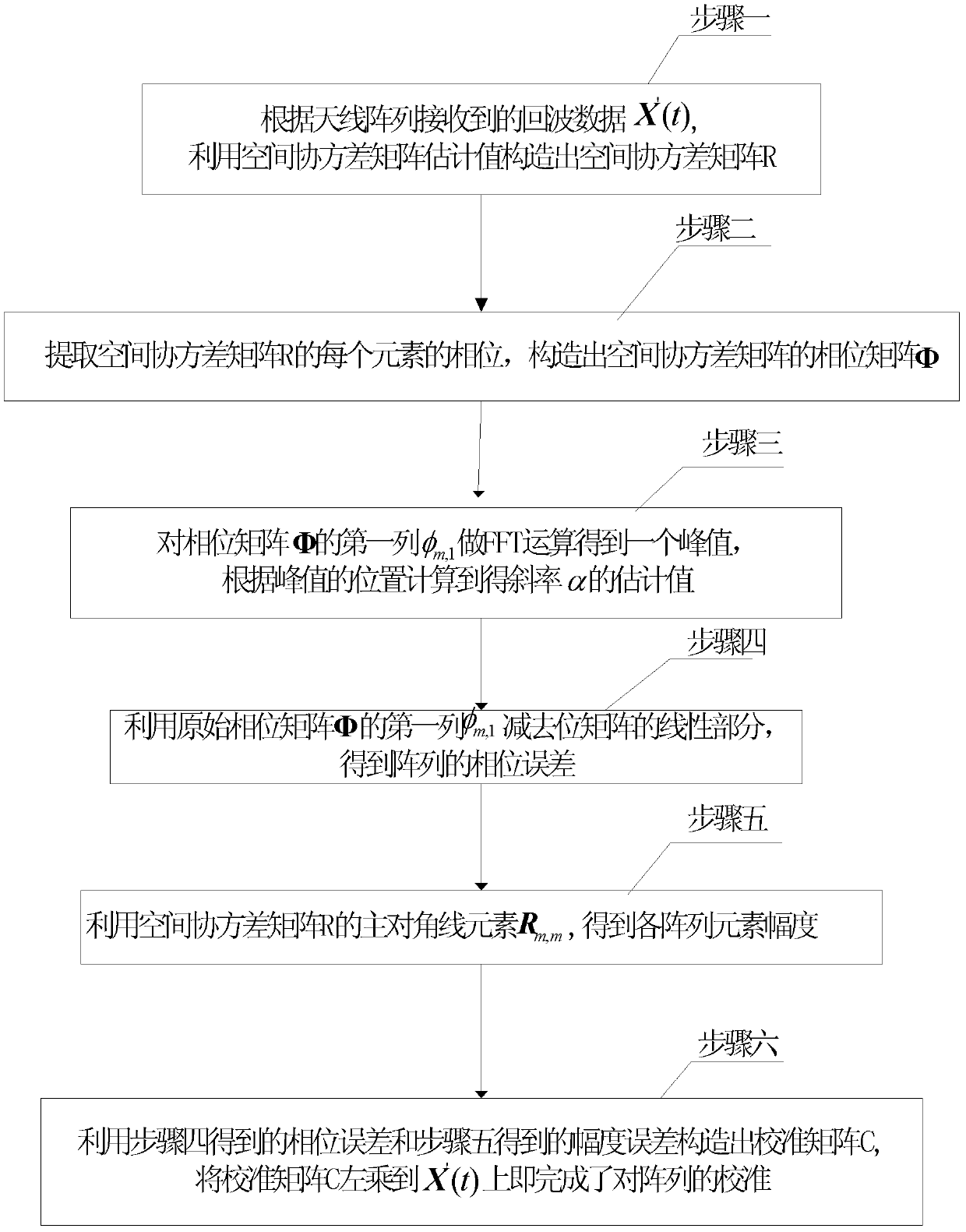
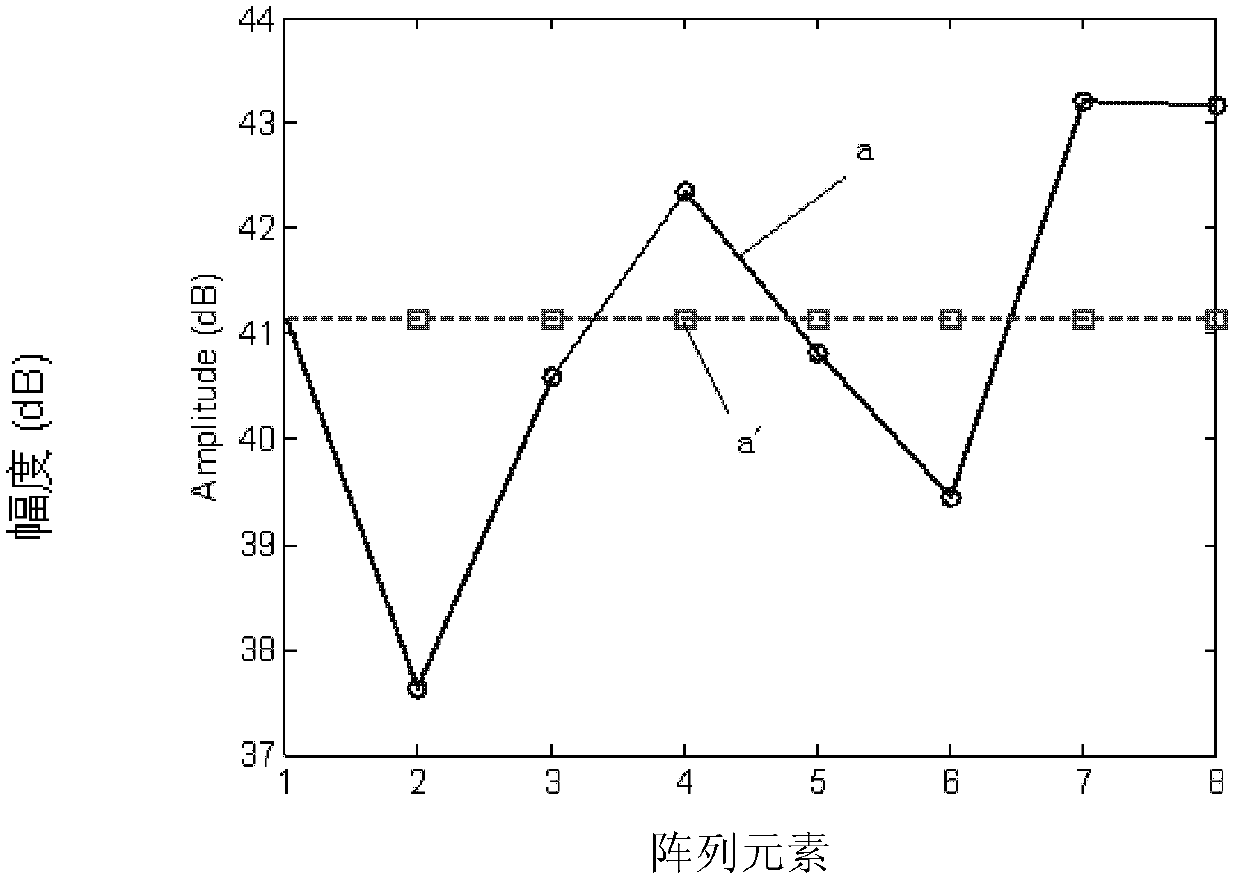
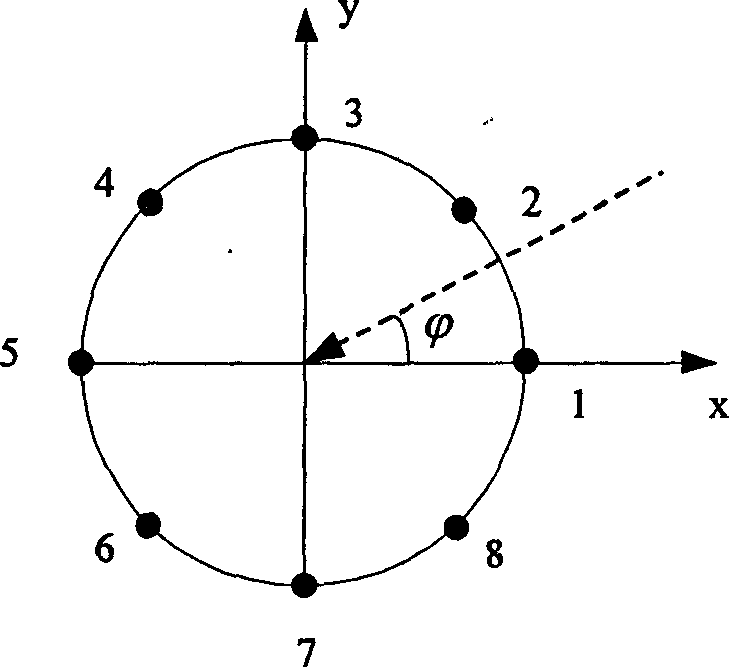
Uniform linear array calibration method based on strong scattering points
The invention relates to a uniform linear array calibration method based on strong scattering points, and aims to solve the problem that a conventional array calibration method is not accurate enough. The uniform linear array calibration method comprises the following steps: a spatial covariance matrix R is constructed by utilizing a spatial covariance matrix estimated value according to echo data received by an antenna array; phase positions of all elements of the spatial covariance matrix R are extracted to construct a phase matrix Phi of the spatial covariance matrix; the first row Phi m,1 of the phase matrix Phi is subject to FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) operation to obtain a peak value, the estimated value of slope Alpha is obtained according to the position of the peak value, and the linear part of the phase matrix is subtracted from the first row Phi m,1 of the original phase matrix Phi according to the estimated value of the slope Alpha to obtain the phase error of the array; a calibrated matrix C is constructed by utilizing the obtained phase error and amplitude error according to all the obtained array element amplitudes; and array calibration is completed through pre-multiplying the calibrated matrix C to the received echo data. The uniform linear array calibration method is used for calibrating uniform arrays and is more accurate in calibration.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for wave beam shaping
InactiveCN101359946AImprove reception qualityImplement multi-beam beamformingSpatial transmit diversityRadio transmission for post communicationShaped beamEngineering
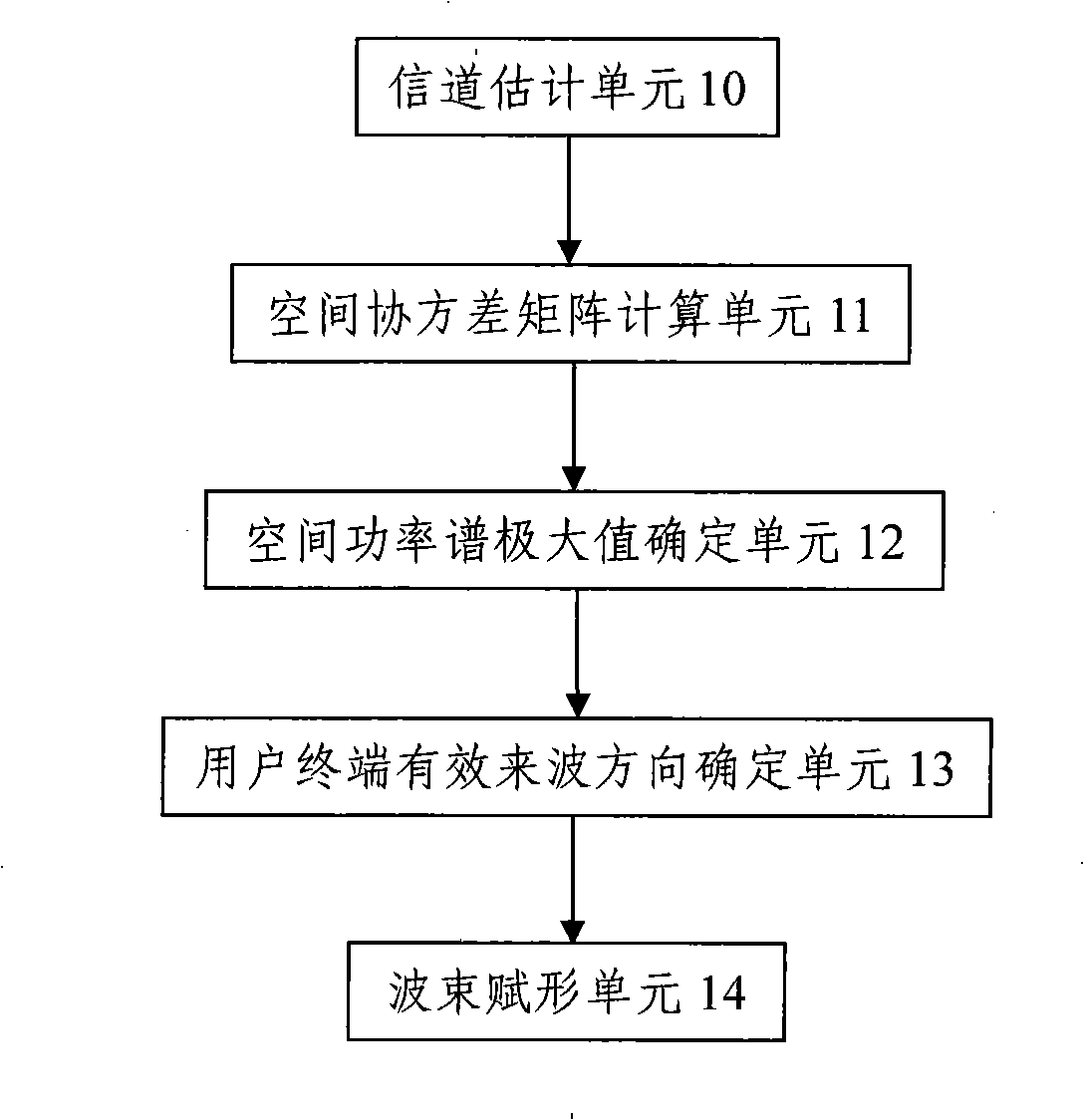
The invention discloses a method of shaped-beam, relating to the shaped-beam technique, aiming at developing the poor performance of the current shaped-beam in a multi-path environment. The method adopts the technical proposal of: A. processing channel estimation to the user signals received by an antenna array and calculating space covariance matrix and all the characteristic values of the received signals, or determining all the maximums of a spatial power spectrum of the received signals according to the space covariance matrix; B. determining all the directions of arrival of the user signals according to the spatial power spectrum or the characteristic values of the space covariance matrix; and C. using one or a plurality of the directions of arrival as the direction of shaped-beam and processing shaped-beam to the signals sent to a user terminal. A device for realizing the method is also disclosed. The invention processing shaped-beam to each effective multi-path direction develops the receiving quality of signals of the user terminal and better copes with the multi-path environment change.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
Method for constructing covariance matrices from data features
A method constructs descriptors for a set of data samples and determines a distance score between pairs of subsets selected from the set of data samples. A d-dimensional feature vector is extracted for each sample in each subset of samples. The feature vector includes indices to the corresponding sample and properties of the sample. The feature vectors of each subset of samples are combined into a d×d dimensional covariance matrix. The covariance matrix is a descriptor of the corresponding subset of samples. Then, a distance score is determined between the two subsets of samples using the descriptors to measure a similarity between the descriptors.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for tracing covariance matrix based on grayscale restraint
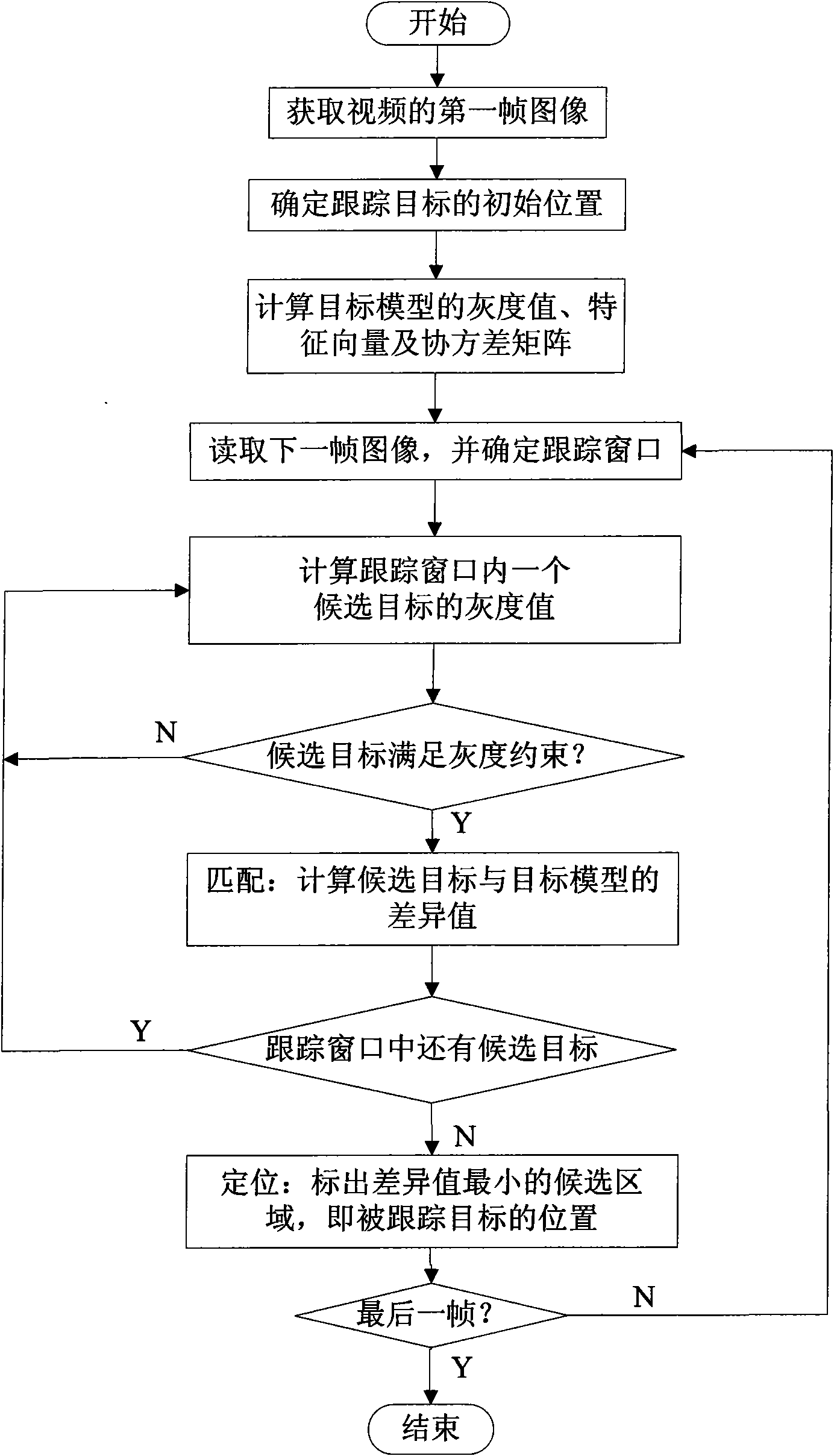
InactiveCN101650829AAccurate targetingReduce matching calculationsImage analysisFeature vectorImage detection
The invention belongs to the technical field of image detection and relates to a method for tracing a covariance matrix based on grayscale restraint, which comprises the following steps: selecting a rectangular area of a image as a target model to trace; calculating a grayscale value of each point of the target model; extracting the characteristic vector of each point of the target model; calculating the covariance matrix of the target model; after the length and the width of a subsequent frame are respectively amplified by taking the target model as a center, obtaining a tracing window, selecting a candidate target and checking whether the candidate target meets the grayscale restraint or not; and calculating a difference value of the covariance matrix of the candidate target which meetsthe grayscale restraint and the target model, wherein the candidate target area with the minimal difference value is the position of a traced target. The invention has the advantages of more accuratetarget positioning, higher tracing speed and higher instantaneity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Beam shaping method for inhibiting interferes
ActiveCN1855770ASuppress interferenceSuppress noiseAntenna arraysRadio transmission for post communicationChannel impulse responseWeight coefficient
Owner:SHANGHAI ULTIMATE POWER COMM TECH
Channel covariance feedback for enhanced fd-mimo
ActiveCN109314559ASpatial transmit diversityRadio transmission for post communicationMulti inputChannel state information
Channel covariance feedback is disclosed for enhanced full-dimension multiple input, multiple output (eFD-MIMO) systems. Channel state information (CSI) reference signal (CSI-RS) feedback operations are implemented using spatial covariance feedback of a covariance estimate. After obtaining a set of orthogonal basis vectors, a user equipment (UE) measures the CSI-RS from a base station and determines the spatial covariance matrix from the signal. The UE may then compress the spatial covariance matrix into a lower-dimension covariance estimate matrix using the orthogonal basis vectors. The lower-dimension matrix along with element-wise quantization allows for feedback of spatial covariance for eFD-MIMO systems without excessive feedback overhead.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for estimating elevation angle of intelligent antenna multi-subarray system
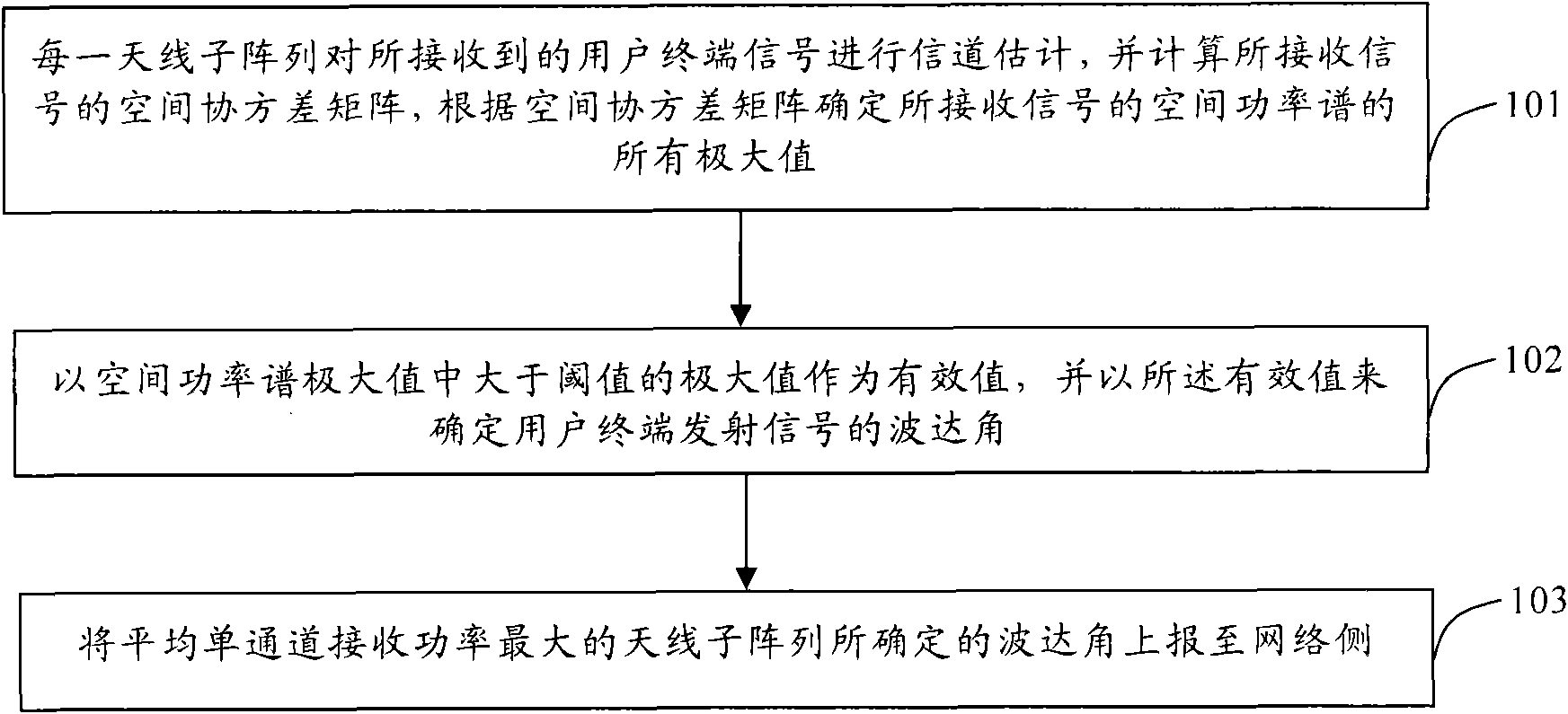
ActiveCN101615943AEstimates are accurateEasy to implementSpatial transmit diversityMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesElevation angleSpace power
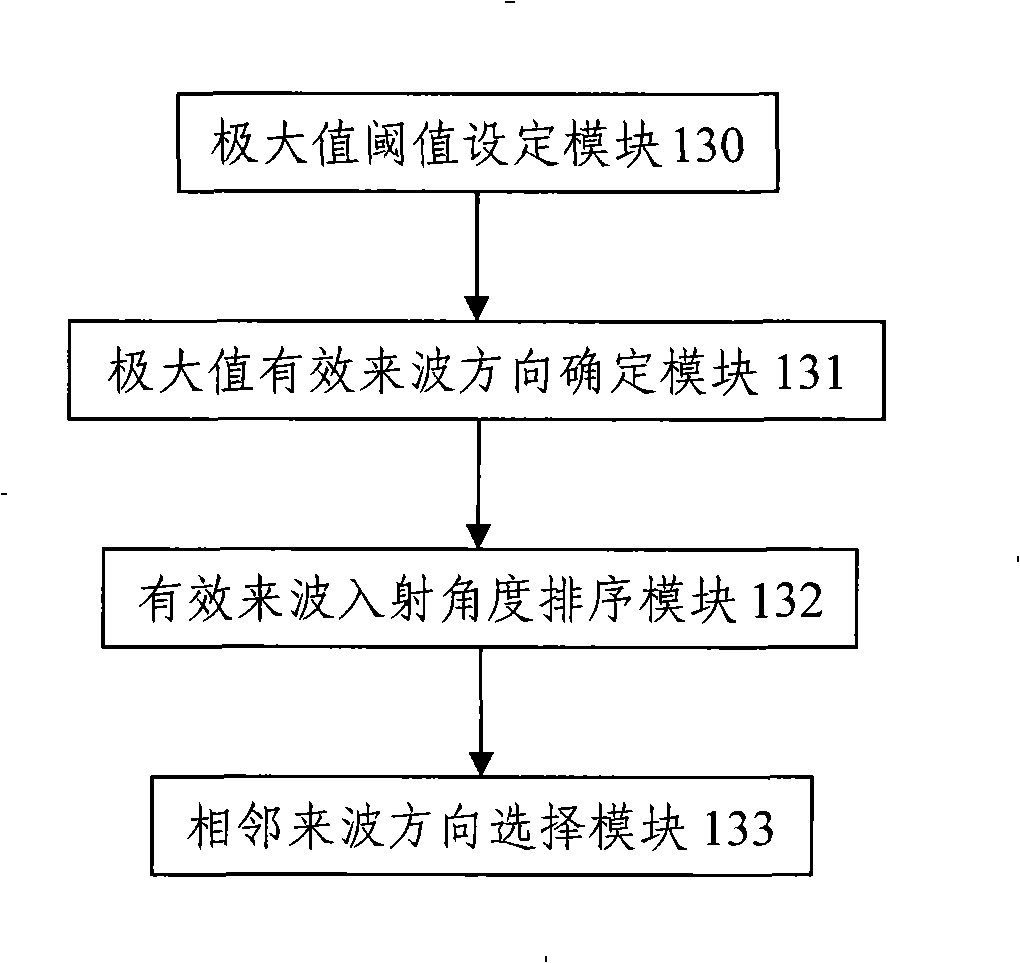
The invention discloses a method for estimating an elevation angle of an intelligent antenna multi-subarray system, comprising the following steps: each antenna subarray estimates a channel of a received user terminal signal, computes a space covariance matrix of the received user terminal signal and then determines all maximal values of a space power spectrum of the received user terminal signal according to the space covariance matrix; taking one maximal value of the maximal values of the space power spectrum, which is greater than a threshold value, as an effective value, and determining the elevation angle of the signal sent by a user terminal by the effective value; and reporting the elevation angle determined by the antenna subarray with maximal average single-channel receiving power to a network side. The invention is easy to realize, and an elevation value of the reported elevation angle is more accurate.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Dense trajectory covariance descriptor-based behavior recognition method
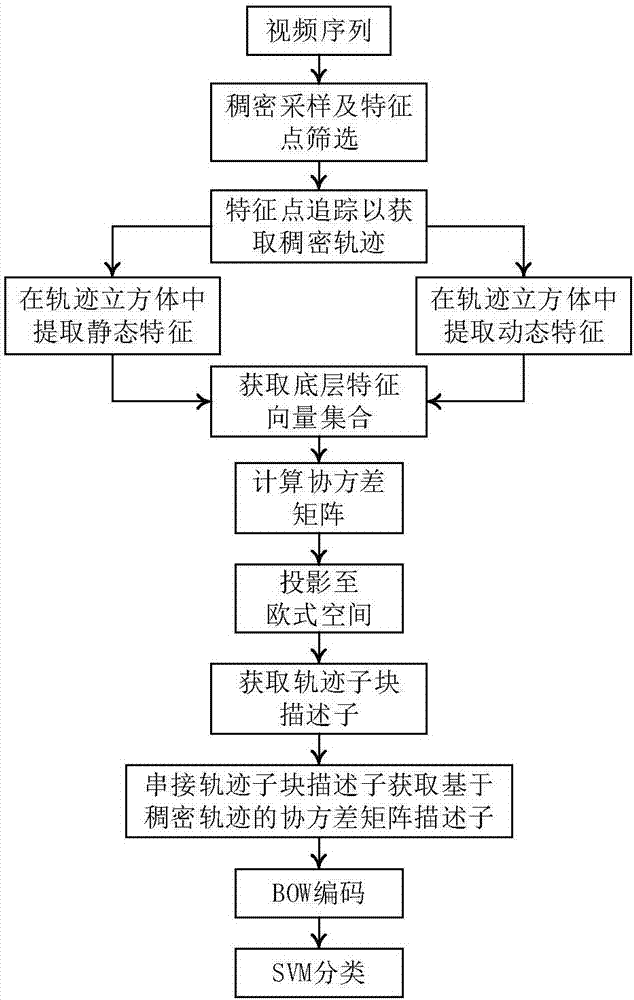
ActiveCN107194366AAccurately reflect speed informationBehavior recognition results improvedImage enhancementImage analysisVideo monitoringFeature set
The invention discloses a dense trajectory covariance descriptor-based behavior recognition method, and mainly aims at solving the problem that the behavior recognition correctness is low as the prior art does not consider the correlation between different features and cannot correctly describe the movements of behavioral agents. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) extracting dense trajectories of a video, and for each pixel point in a trajectory cube, obtaining a gradient, a spatial position and time derivatives of the gradient, a light stream and a movement boundary, and taking the features as bottom-layer features; 2) obtaining a bottom-layer feature set, solving a covariance matrix of the bottom-layer feature set and projecting the bottom-layer feature set to an Euclidean space to obtain descriptors of trajectory sub-blocks; 3) connecting the descriptors of the trajectory sub-blocks in series so as to obtain a dense trajectory-based covariance matrix descriptor; and 4) carrying out BOW coding on the covariance matrix descriptor and then carrying out behavior recognition on the covariance matrix descriptor by utilizing a linear SVM classification model. The method has the effect improving the behavior description ability and the recognition correctness, and can be used for the complicated environment of video monitoring.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
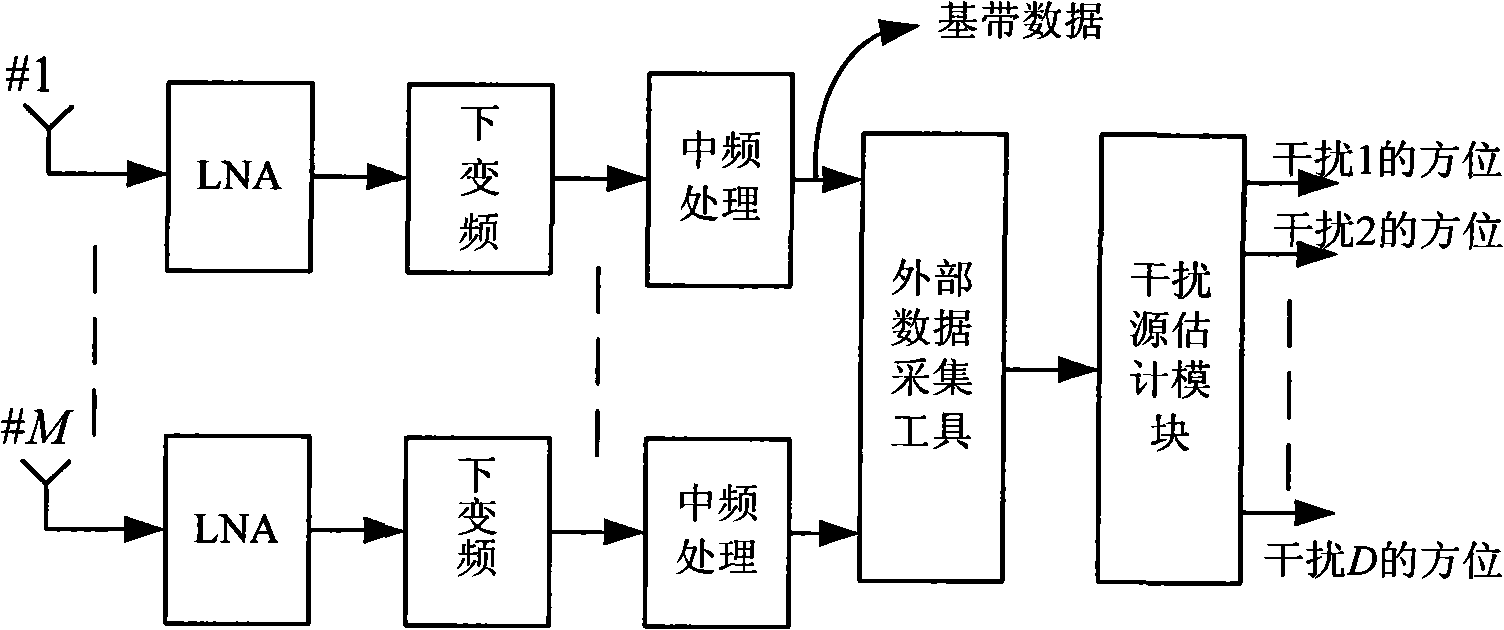
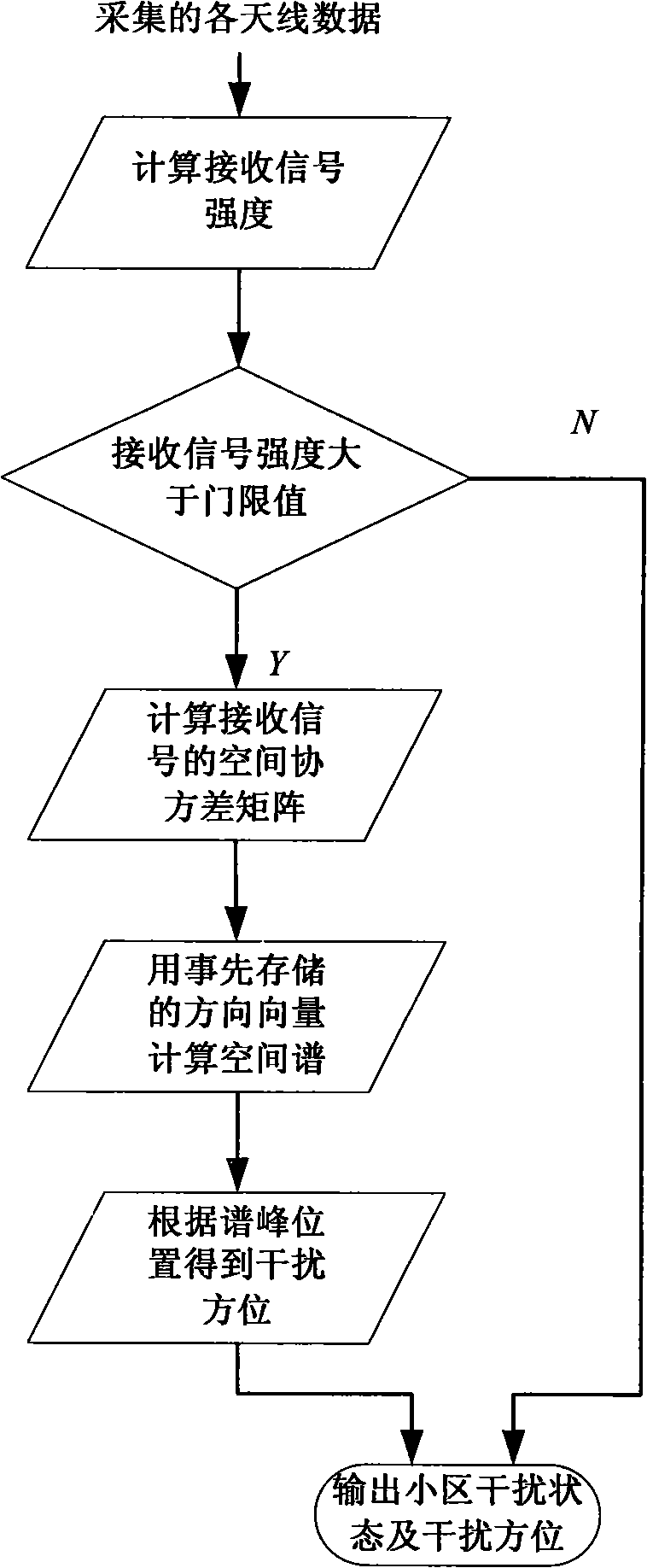
Method for detecting interference source outside cell in TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) system
InactiveCN101990216AAchieve positioningTransmission monitoringWireless communicationSpace powerPeak value
The invention discloses a method for detecting an interference source of a TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) system, comprising the following steps of: when no user exist in a target cell, receiving the receiving signals of all chips outside the target cell on preset upstream time slots in preset subframes in a detection carrier frequency by utilizing each receiving antenna of a base station for the target cell, and calculating the average power of the received receiving signals of all chips; determining whether the interference source exists or not according to the average power, if so, determining a covariance matrix in an interference signal space of each preset subframe and a covariance matrix in interference signal average space of all preset subframes; determining the space power spectrum of the interference signals by utilizing the covariance matrix of the average space and the preset direction vector, wherein a direction corresponding to a peak value in the space power spectrum is the direction of the interference source, and the peak value is an interference power. The method can be applied to positioning the interference source on account of the interference outside the cell of the TD-SCDMA system.
Owner:TD TECH COMM TECH LTD
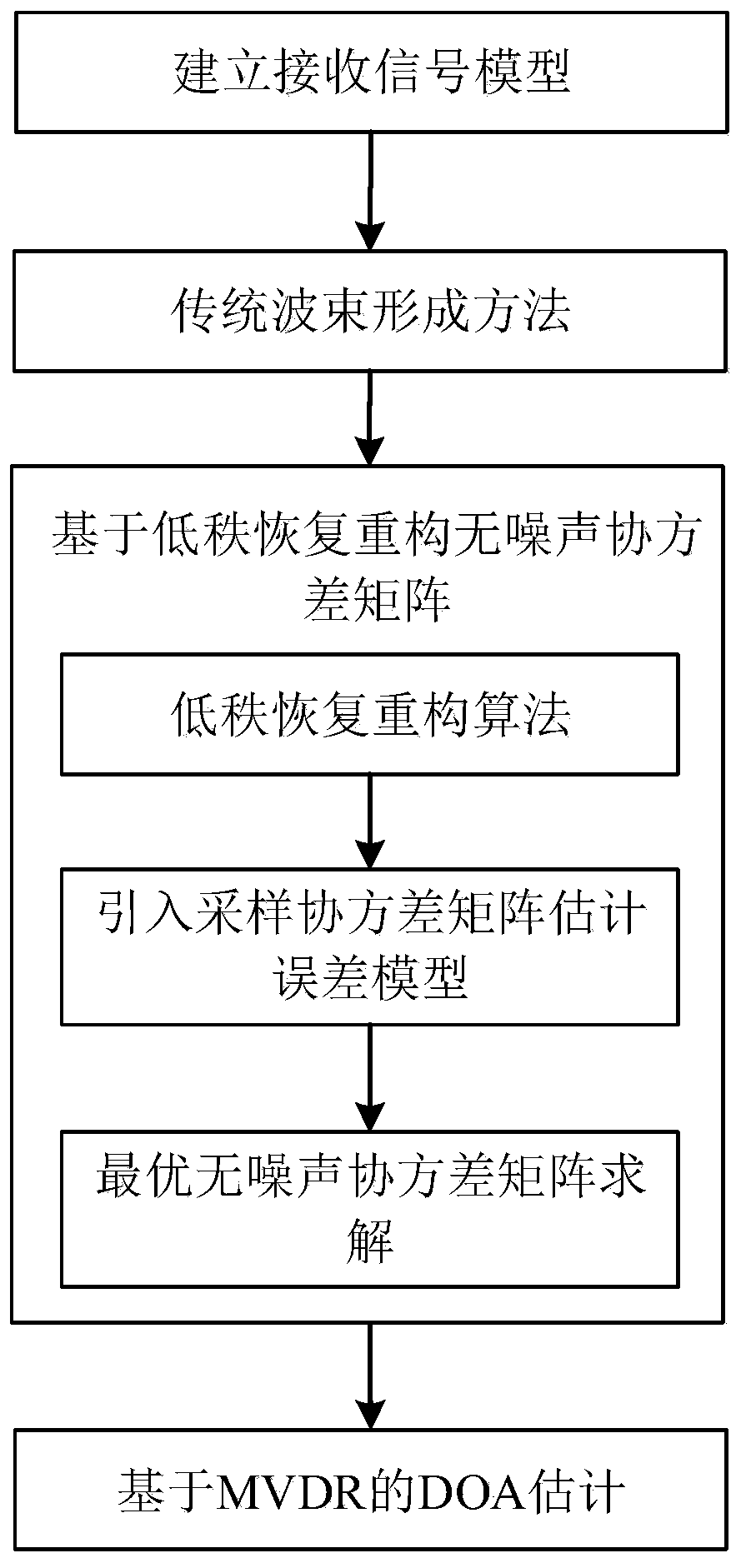
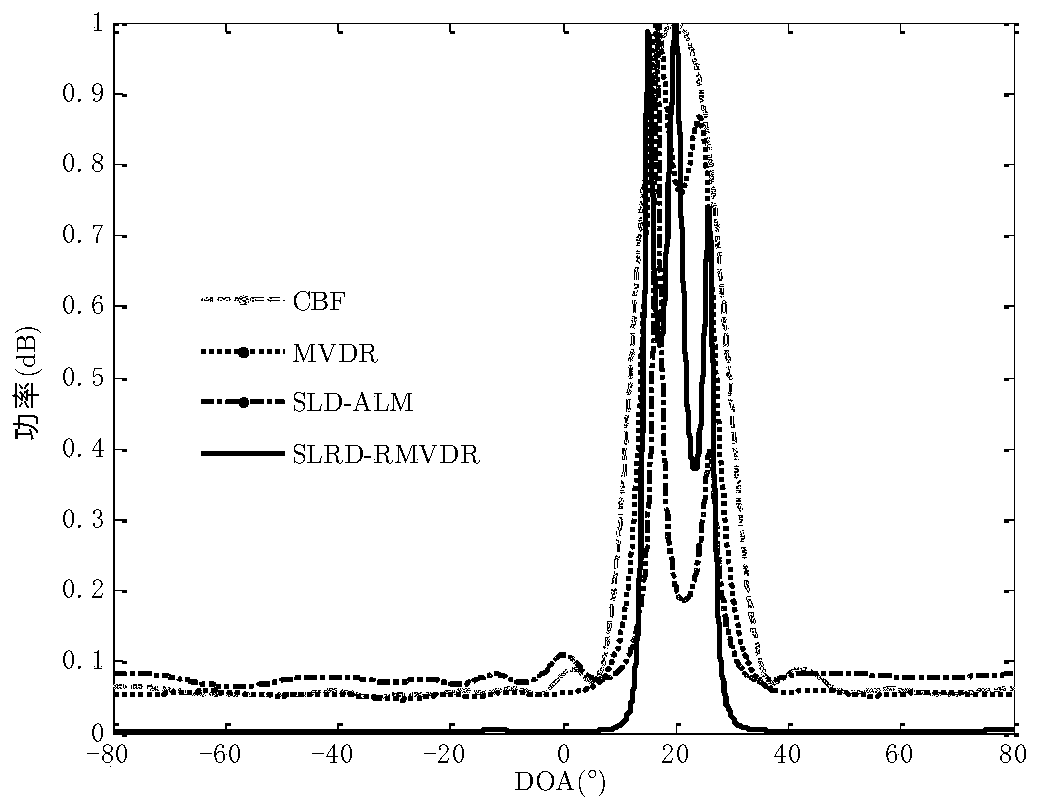
Robust direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method based on sparse and low-rank recovery
ActiveCN110045321AError parameter ηImprove estimation performanceDirection findersHigh level techniquesEstimation methodsFactor selection
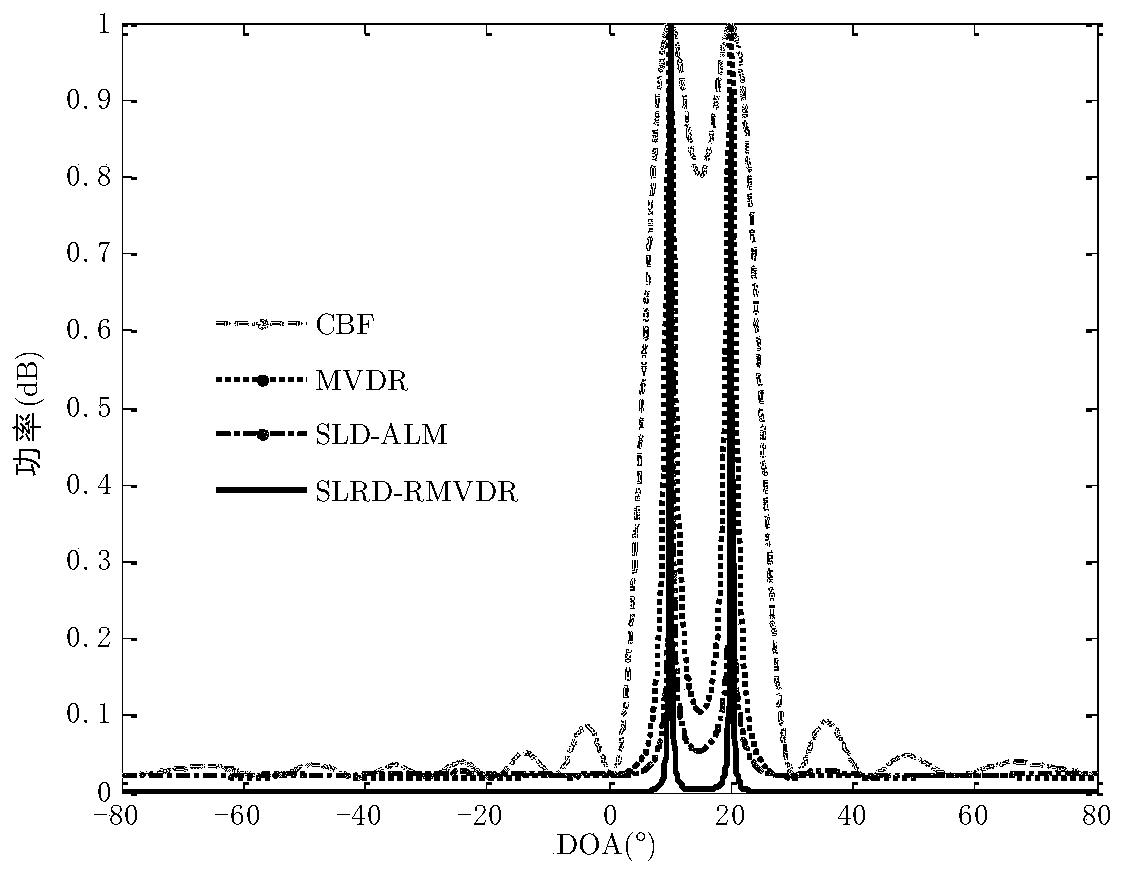
The invention belongs to the field of signal processing, and particularly relates to a robust direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method based on sparse and low-rank recovery. According to the technical scheme, firstly, based on a low-rank matrix decomposition method, a received signal covariance matrix is modeled as the sum of a low-rank noise-free covariance matrix and a sparse noise covariance matrix; then the convex optimization problem about a signal and noise covariance matrix is constructed based on a low-rank recovery theory; then a convex model about the sampling covariance matrix estimation error is constructed, and a convex set explicitly includes the convex optimization problem; and finally, based on the obtained covariance matrixes, DOA estimation is achieved through a MVDRmethod. In addition, based on the statistical characteristic that the sampling covariance matrix estimation error submits to progressive normal distribution, an error parameter factor selection criterion is derived to reconstruct the covariance matrixes. Numerical simulation shows that under the limited sampling conditions, compared with traditional CBF and MVDR algorithms, a proposed algorithm ishigh in DOA estimation accuracy and robust in performance.
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com