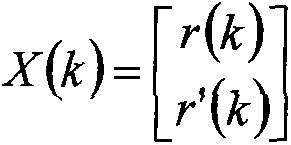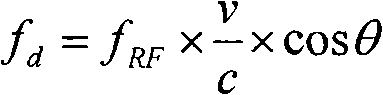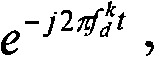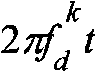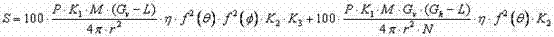Patents
Literature
663 results about "Synchronization code division multiple access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for reinforcing ascending link and implementing fast switch-over
ActiveCN101247647AFast switching speedAvoid timeNetwork traffic/resource managementCode division multiplexResource informationCode division multiple access
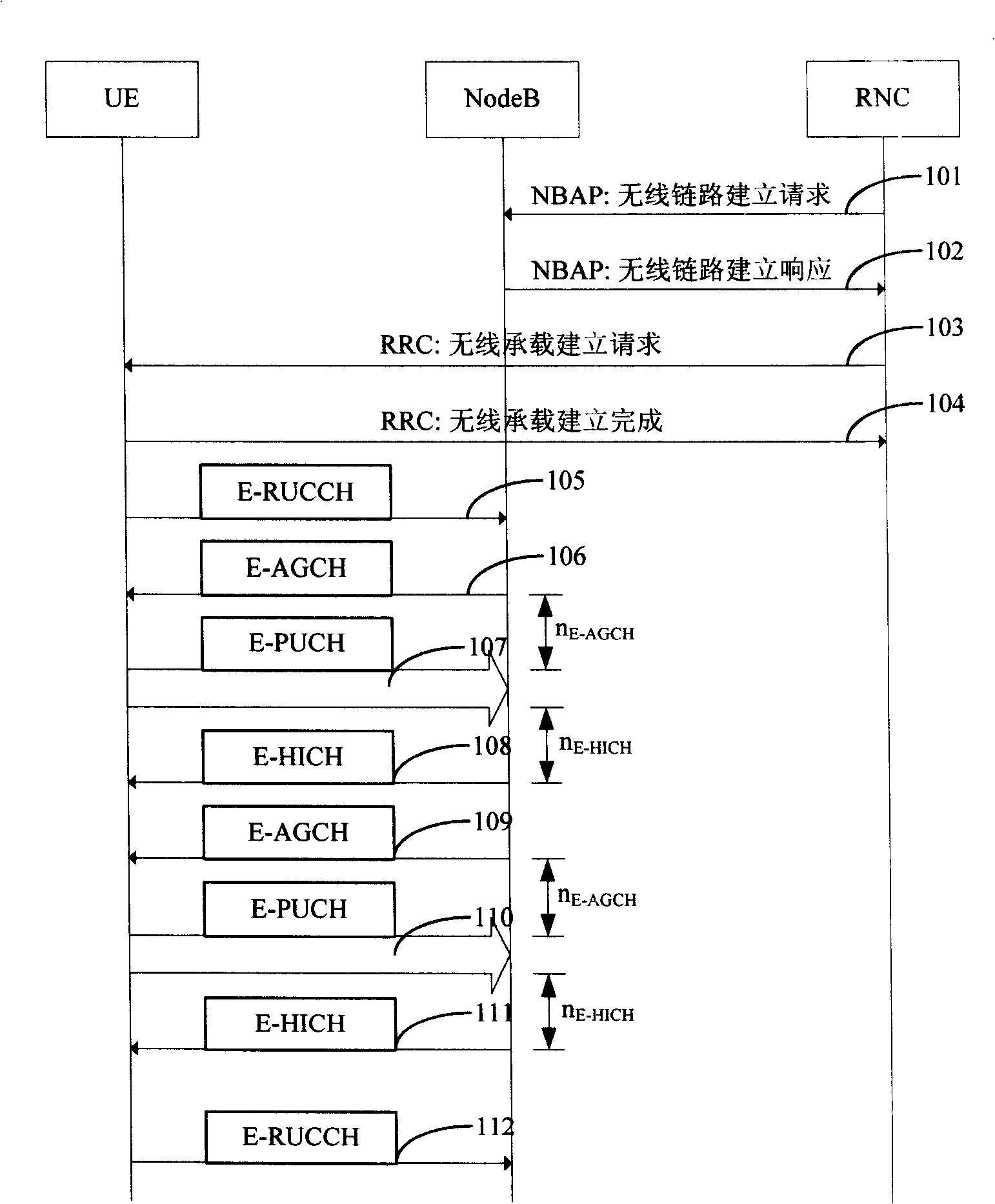
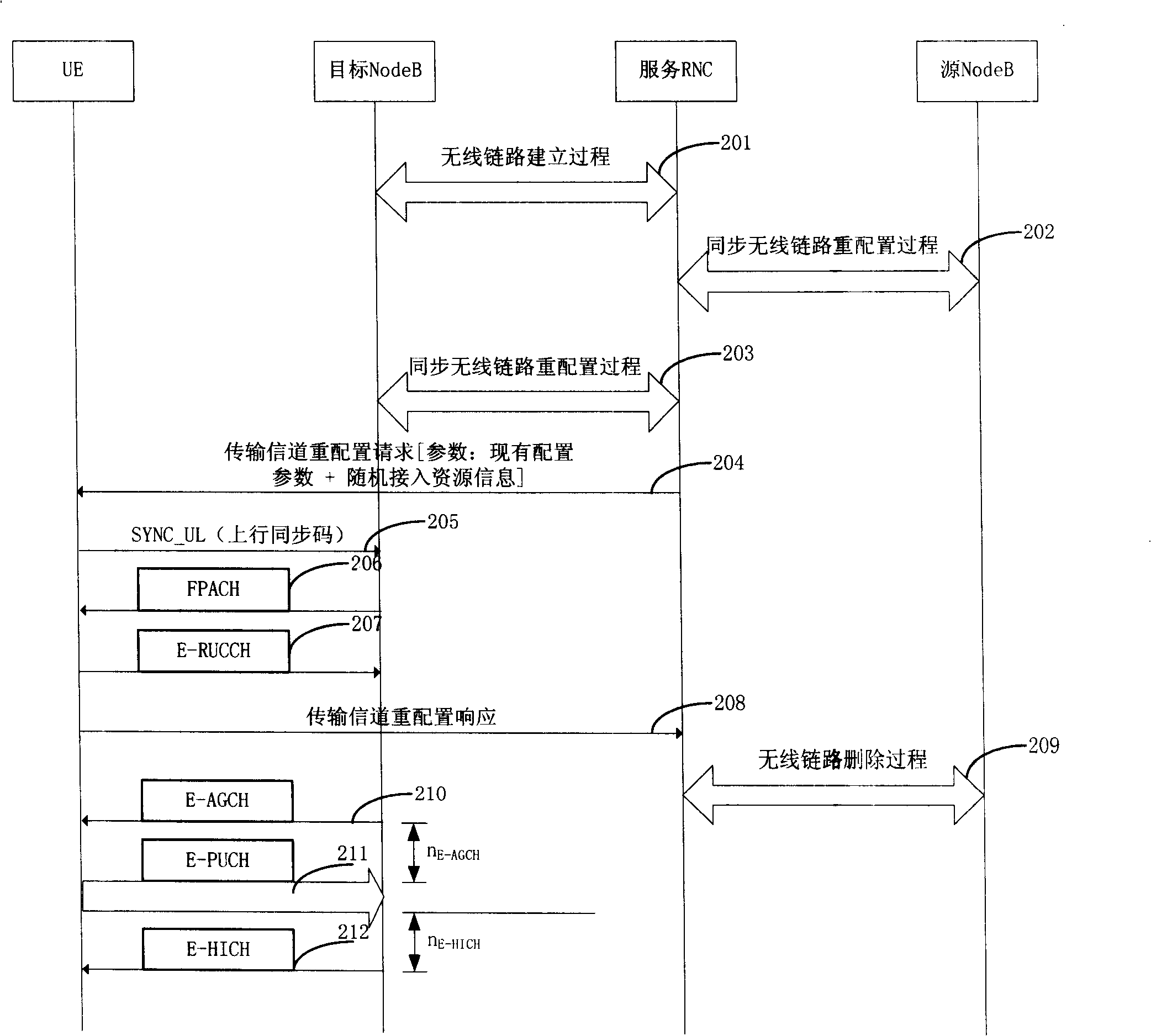
The present invention provides a rapid switch method for enhancing uplink which is used in time division synchronous code division multiple access system and processes district switch in special channel state UE. The method includes steps: (a) when network side determines UE processing enhancing uplink in target district, random access resource information of target district is carried in switch command send to UE; (b) UE rebuilds wireless link in target district, if buffer area corresponding to enhancing uplink wireless carrier has data to send, UE generates enhancing uplink link random access according with random access resource information carried by switch command, and requests scheduling resource to base station Node B. The method makes UE knowing random access resource of target district in advance according with random access resource information of target district carried by switch command, and generates E-RUCCH access rapidly after UE link reconfiguration to new district. The method can avoid UE from reading district broadcast information and obtaining random access resource information, and can improve switch speed.
Owner:ZTE CORP
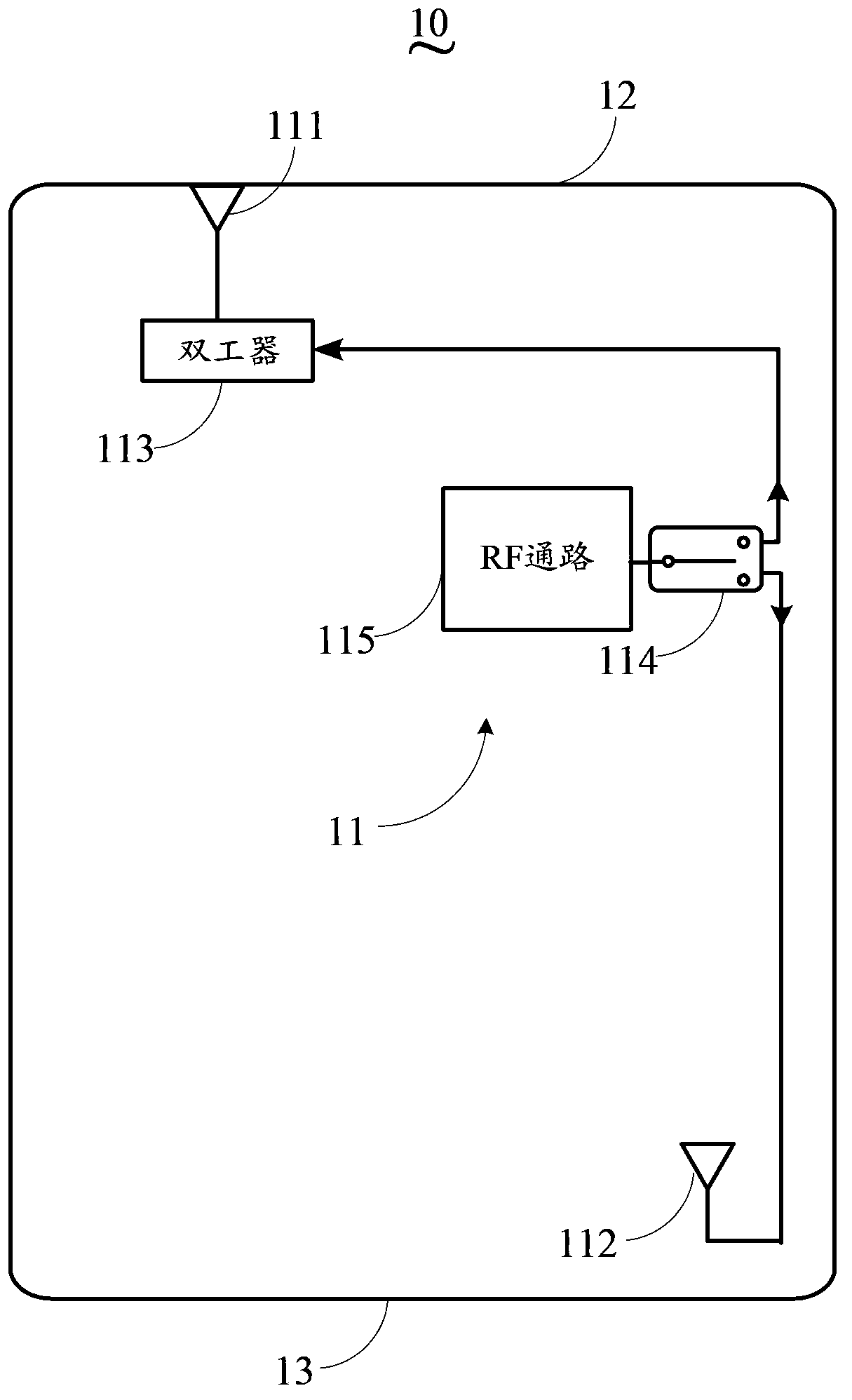
Base station RF index testing system and method, and RF box for TD-SCDMA system
ActiveCN101106787AFully automatedNo human intervention requiredCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsUltrasound attenuationEngineering
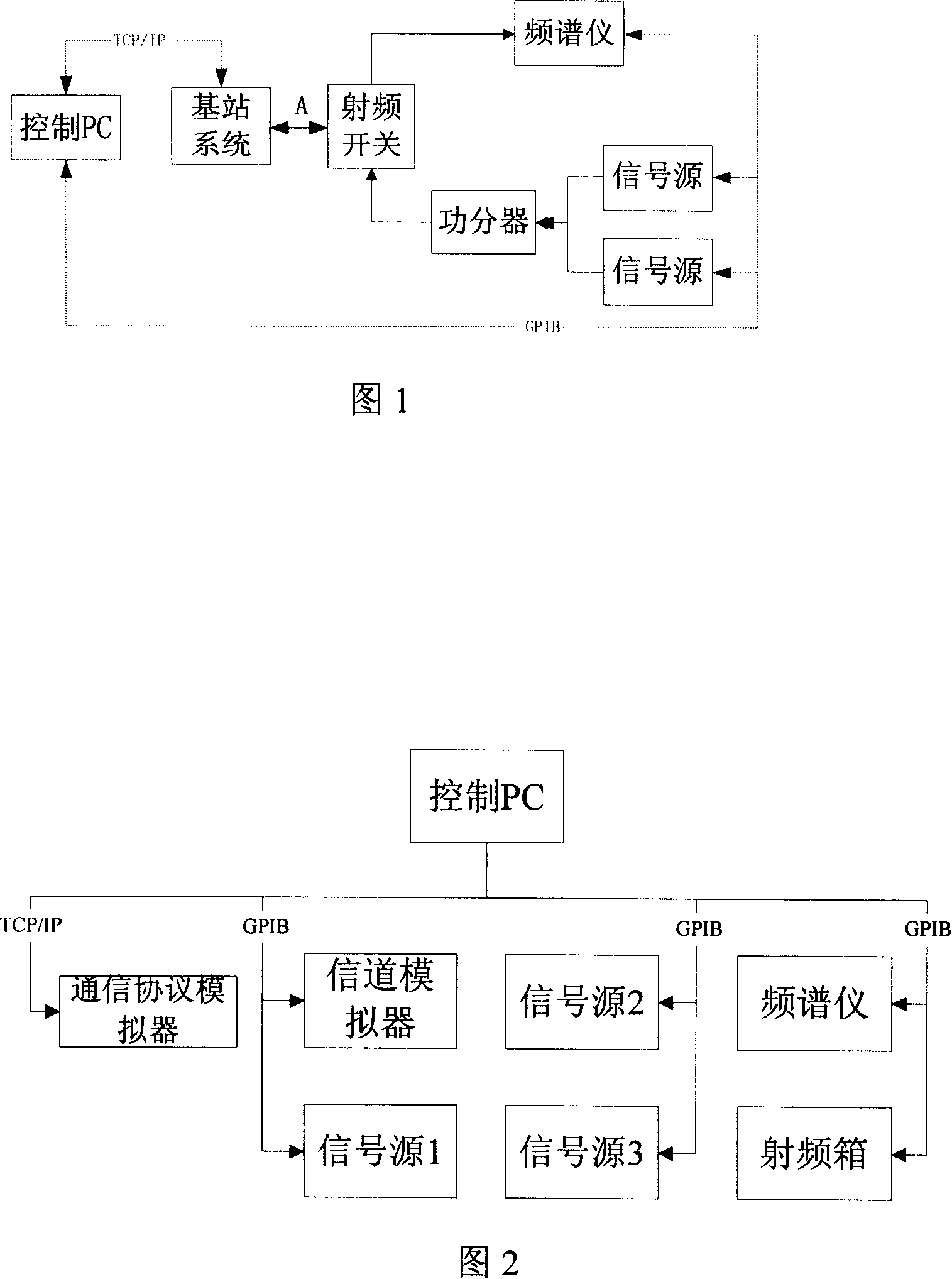
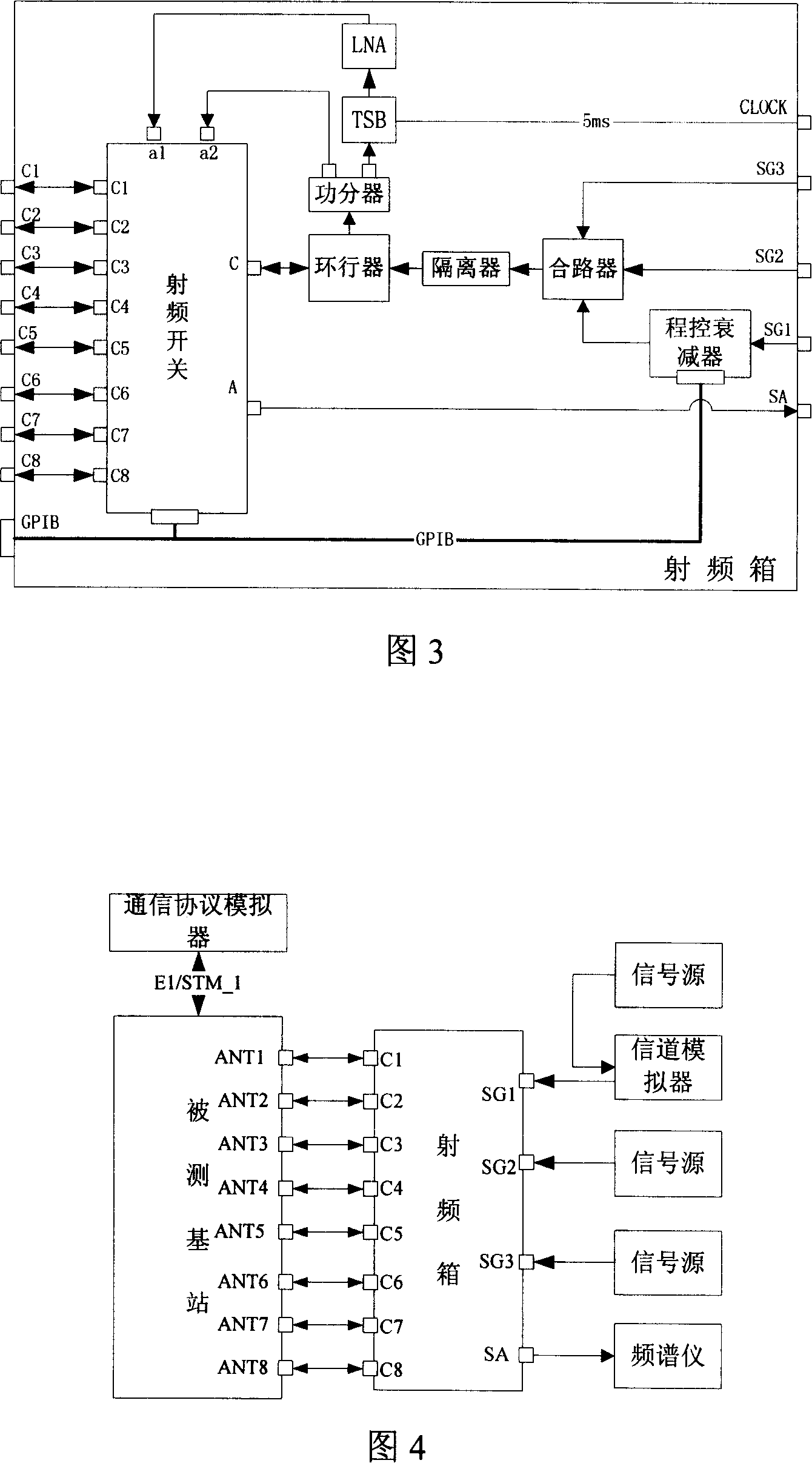
The invention discloses a radiofrequency case suitable for testing base station radiofrequency index of a TD-SCDMA system, and a base station testing system and a method using the radiofrequency case. The radiofrequency case includes a radiofrequency switch, an attenuator, a mixer, an isolator, a circulator and a power divider. Signals from signal sources are inputted into the mixer via a radiofrequency signal inlet on the radiofrequency case and one path of the signal is performed attenuation treatment via the attenuator before it is inputted into the mixer; the radiofrequency signals treated by the mixer is inputted into a common port of the radiofrequency switch via the isolator and the circulator, and then is inputted into the base station via a switch connected with the common port; and meanwhile, the circulator receives downlink signals from the radiofrequency switch and isolates the uplink signals from the downlink signals, then the radiofrequency signals are multiplexed by the power divider and is outputted to a frequency spectrograph for performing radiofrequency index testing. The invention also discloses the base station testing system and the method based on the radiofrequency case. The invention has high automation degree and can achieve correct testing results.
Owner:SHANGHAI DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP +1
Access control method fusing TD-SCDMA cell phone network and self-organizing network
InactiveCN101360339AAchieve conflict-free wireless accessFast decodingConnection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAir interfaceEngineering
A connection controlling method of integrating a time synchronous code division multiple access with a automatic-organizing network belongs to the mobile communication field of the communication technology, based on keeping the unitive air interface of TD-SCDMA honeycomb network physic frame invariable construction, the method is a multi-channel synchronization connecting control method based on the preset pattern and distributing pattern control, the time span resource is divided into the control channel and the data channel by the OVSF (Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor), thus improving the time span reusability through terminal to terminal status to expose the terminal problem, the method maintains the time span status of node within two jumps time span, and realizes the conflict-free wireless connection within two jumps time span; thereby solving the problems of realizing the conflict-free visit time span and performing the reliable alternation communication under integrating network and multi-communication modes.
Owner:PANDA ELECTRONICS GROUP +3
Method for collecting abnormal data of TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) wireless communication network user terminal
InactiveCN102256290ASimplified complaints processImprove satisfactionWireless communicationQuality of serviceData acquisition
Owner:DINGLI COMM
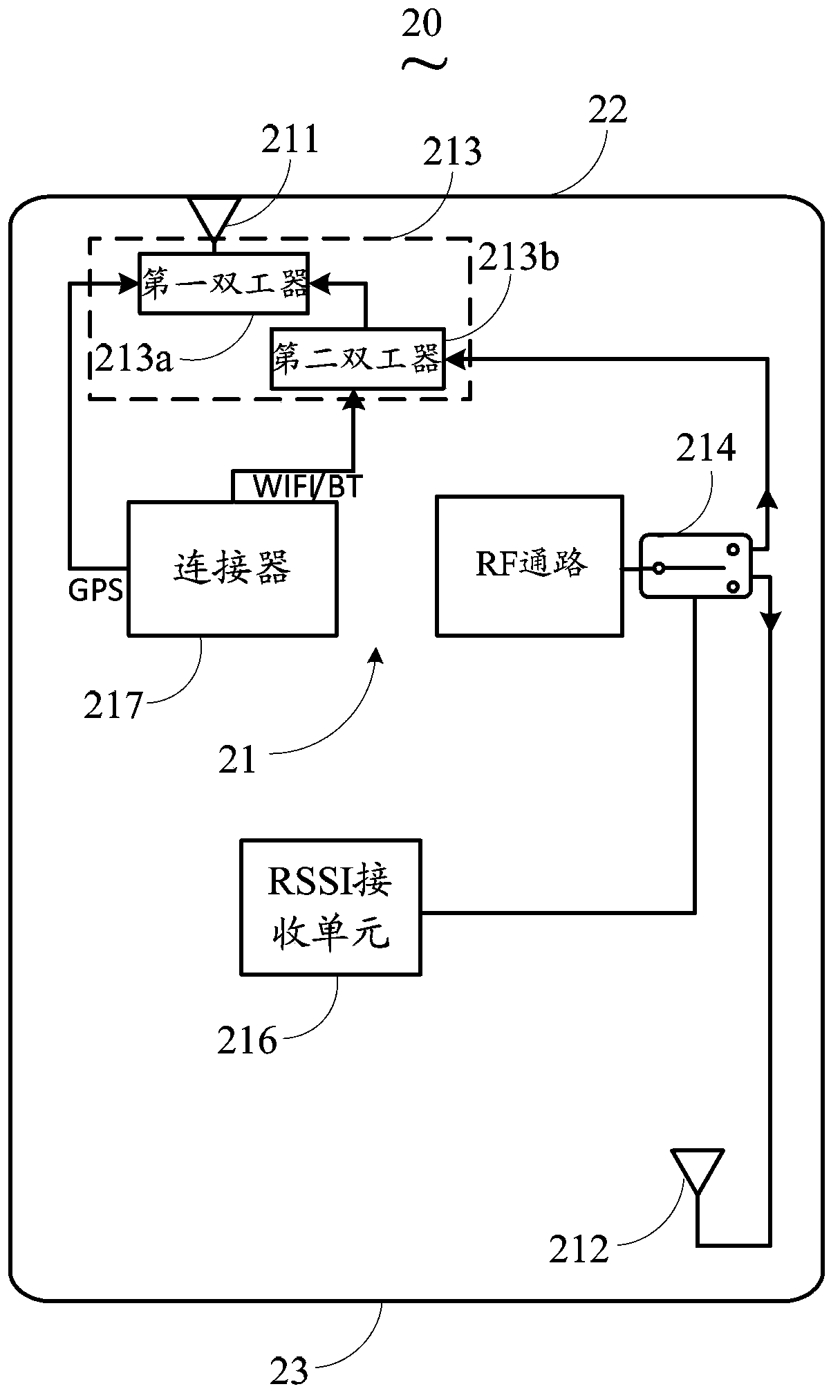
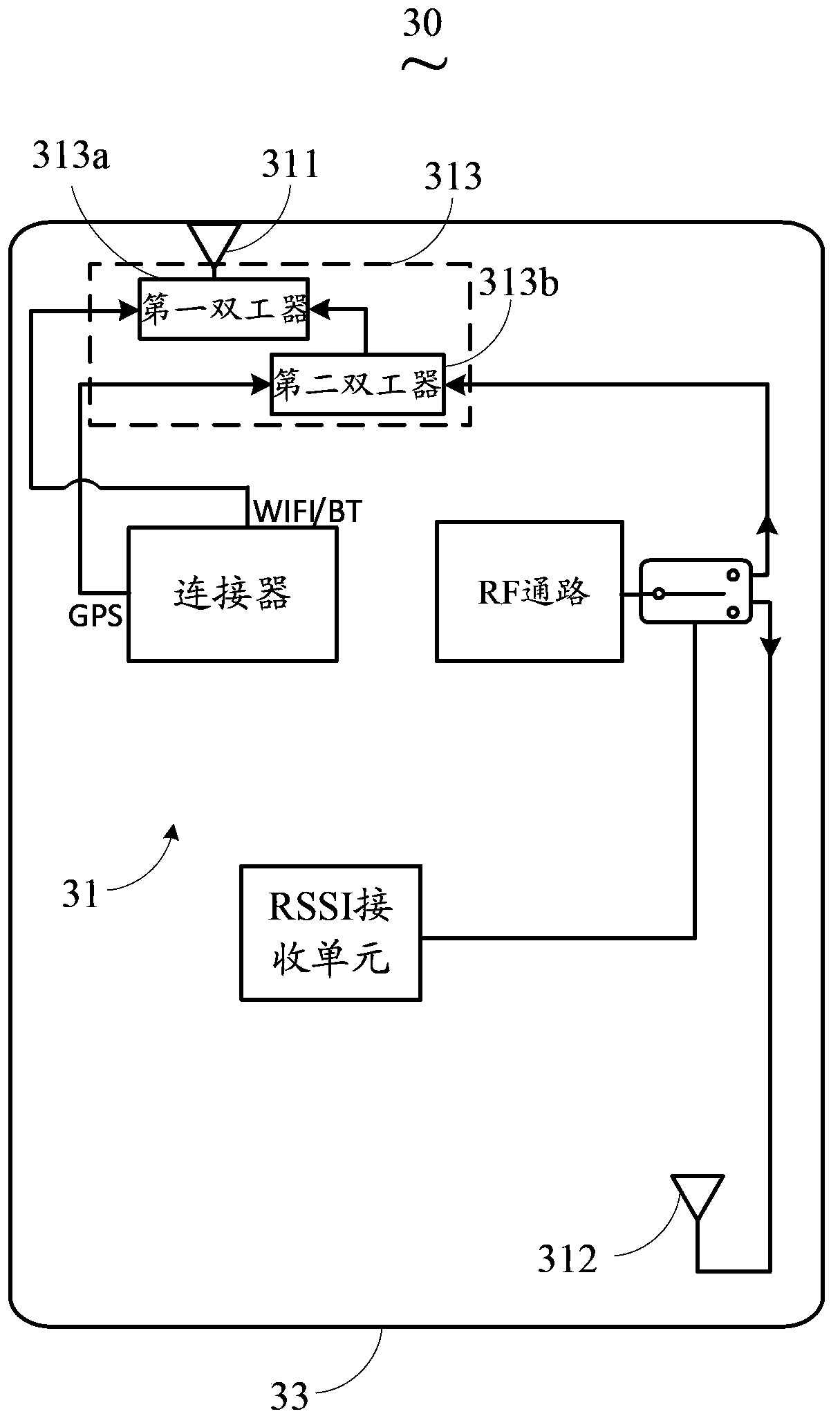
Antenna switching system of mobile terminal
ActiveCN103401577AImprove experienceTransmission monitoringIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsEngineeringComputer terminal
The invention discloses an antenna switching system of a mobile terminal. The antenna switching system comprises a first antenna, a second antenna, at least one duplexer and a switching unit, wherein the first antenna is arranged on the top of the mobile terminal and is used for transmitting and receiving GPS (Global Positioning System), WIFI (Wireless Fidelity) and BT (Bluetooth) signals, and GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications), WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) and TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) signals of at least a first frequency band; the second antenna is arranged on the bottom of the mobile terminal and is used for transmitting and receiving GSM, WCDMA and TD-SCDMA signals of at least a second frequency band; the duplexer is coupled with the first antenna and is used for separating one or more of the GPS, WIFI, BT, GSM, WCDMA and TD-SCDMA signals; the switching unit is used for selecting the first antenna or the second antenna to work. With the adoption of the manner of the antenna switching system, the influences on the performance of the second antenna when a human body is contacted with the bottom of the mobile terminal are avoided, and user experiences are improved.
Owner:HUIZHOU TCL MOBILE COMM CO LTD
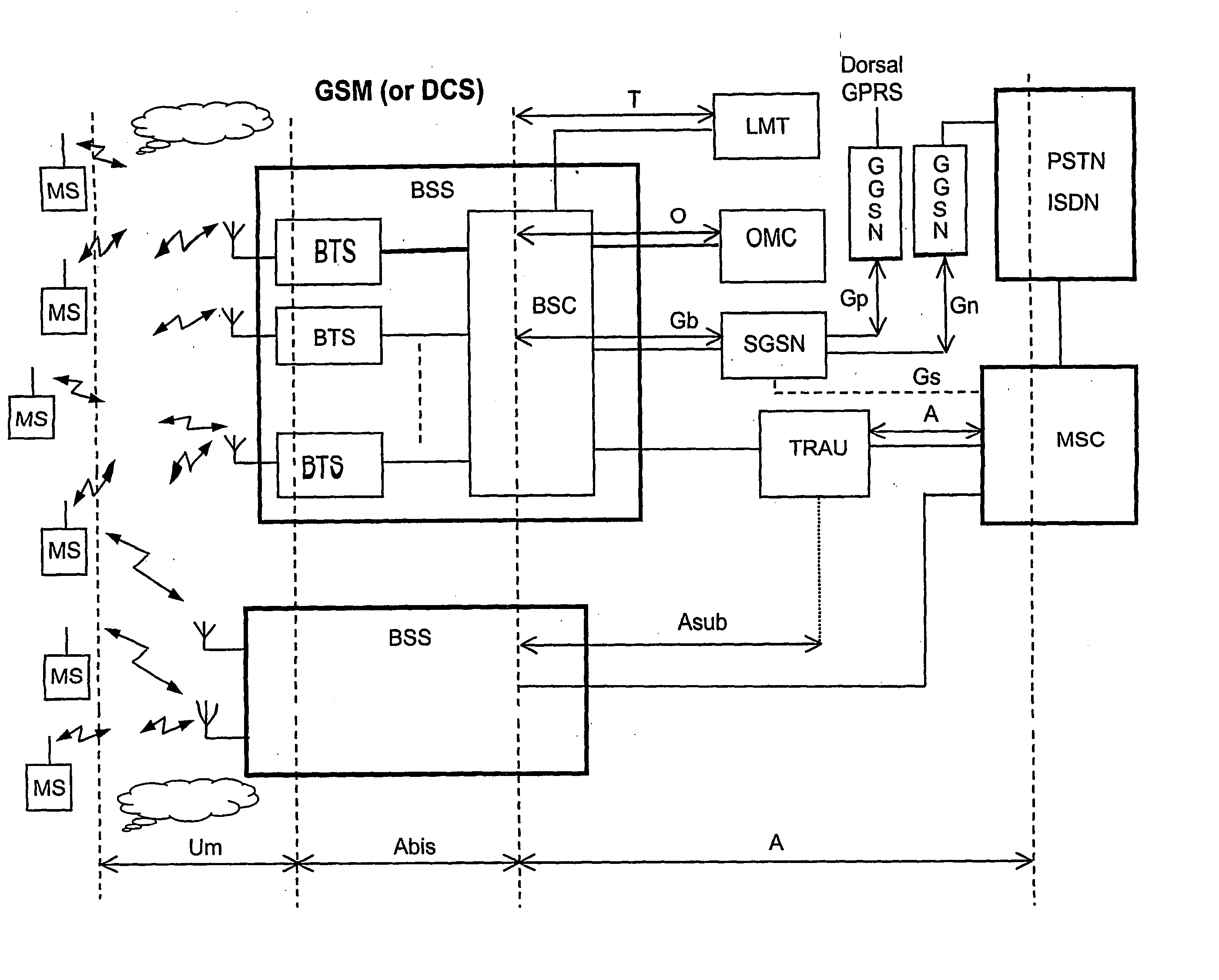
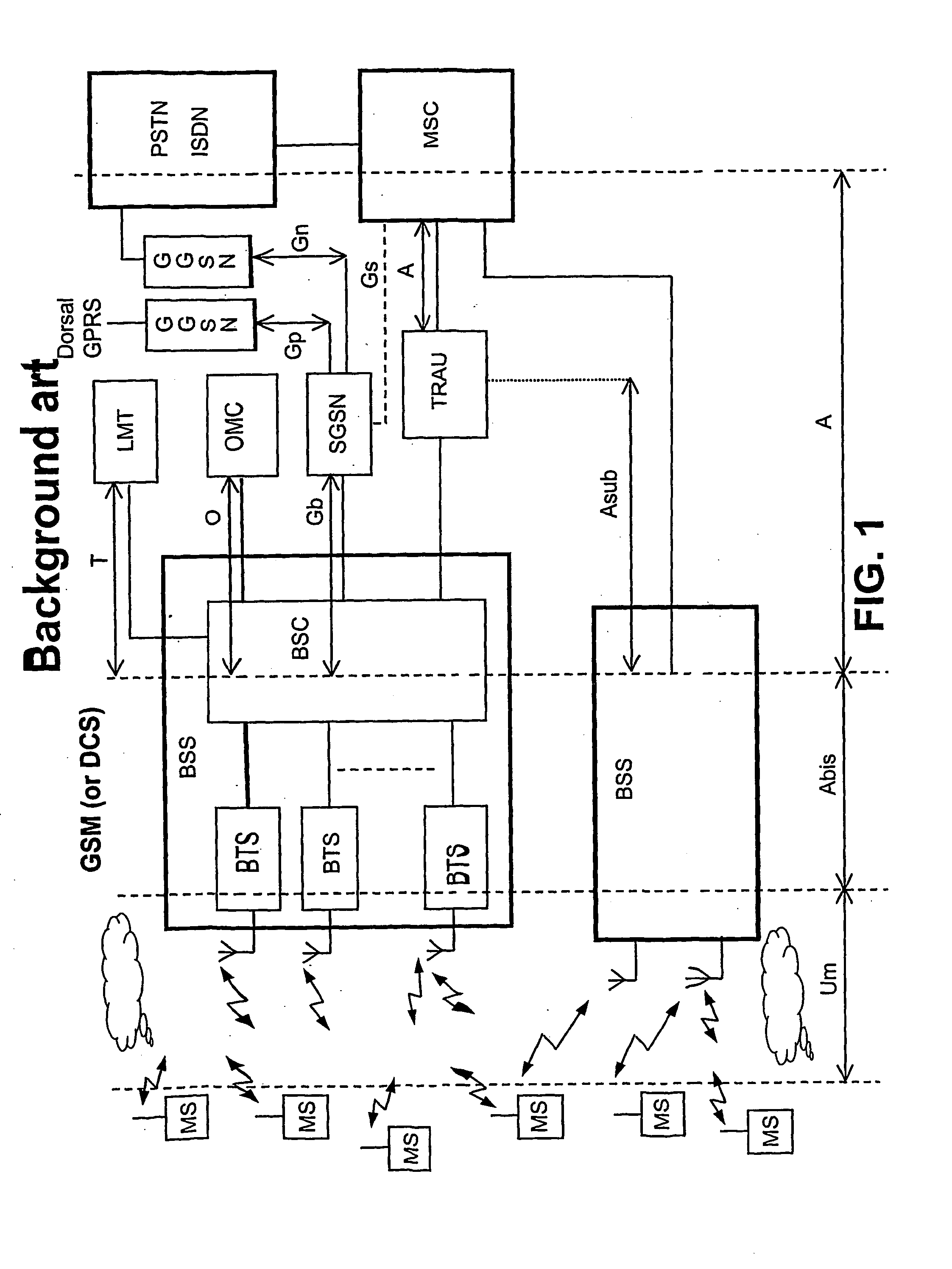
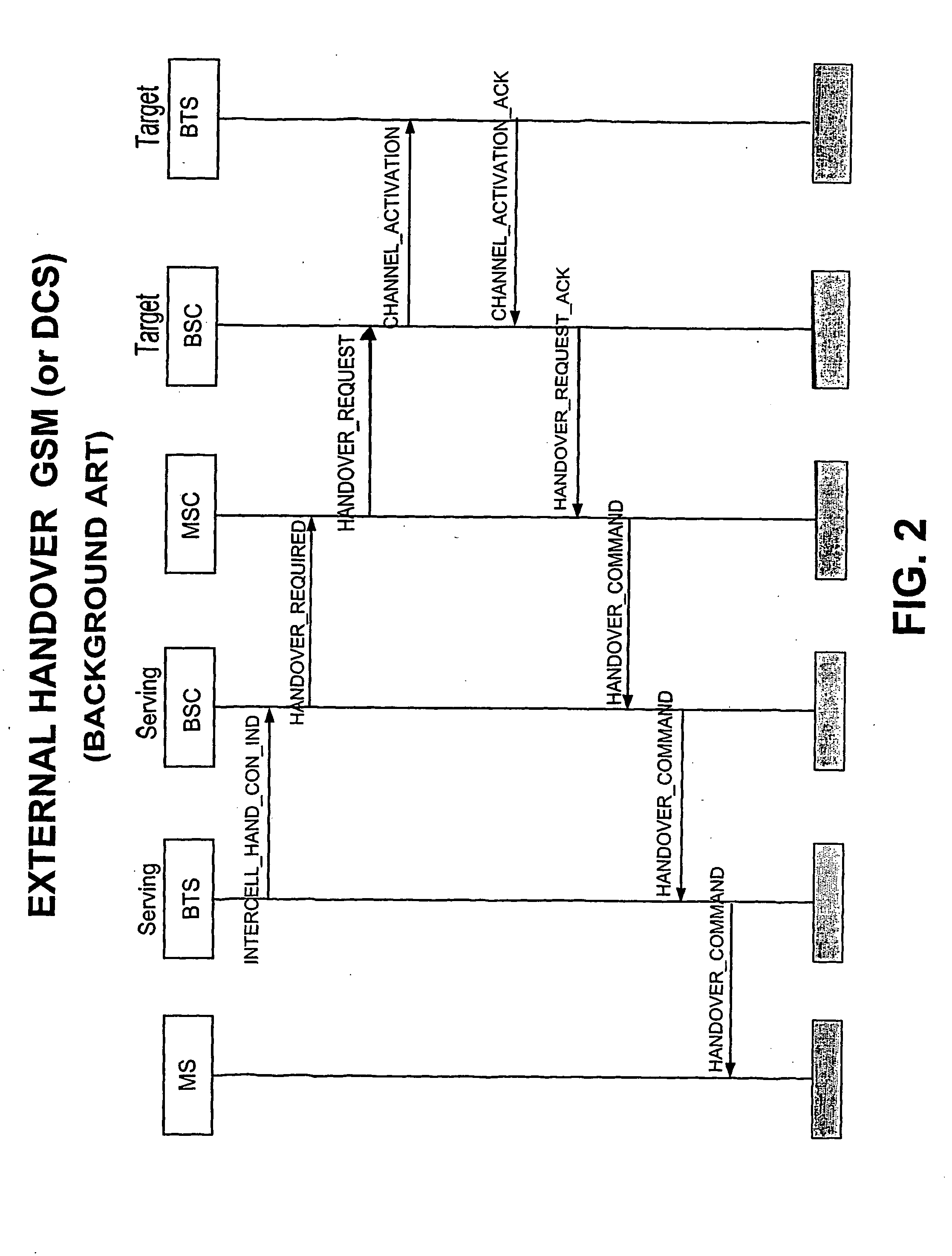
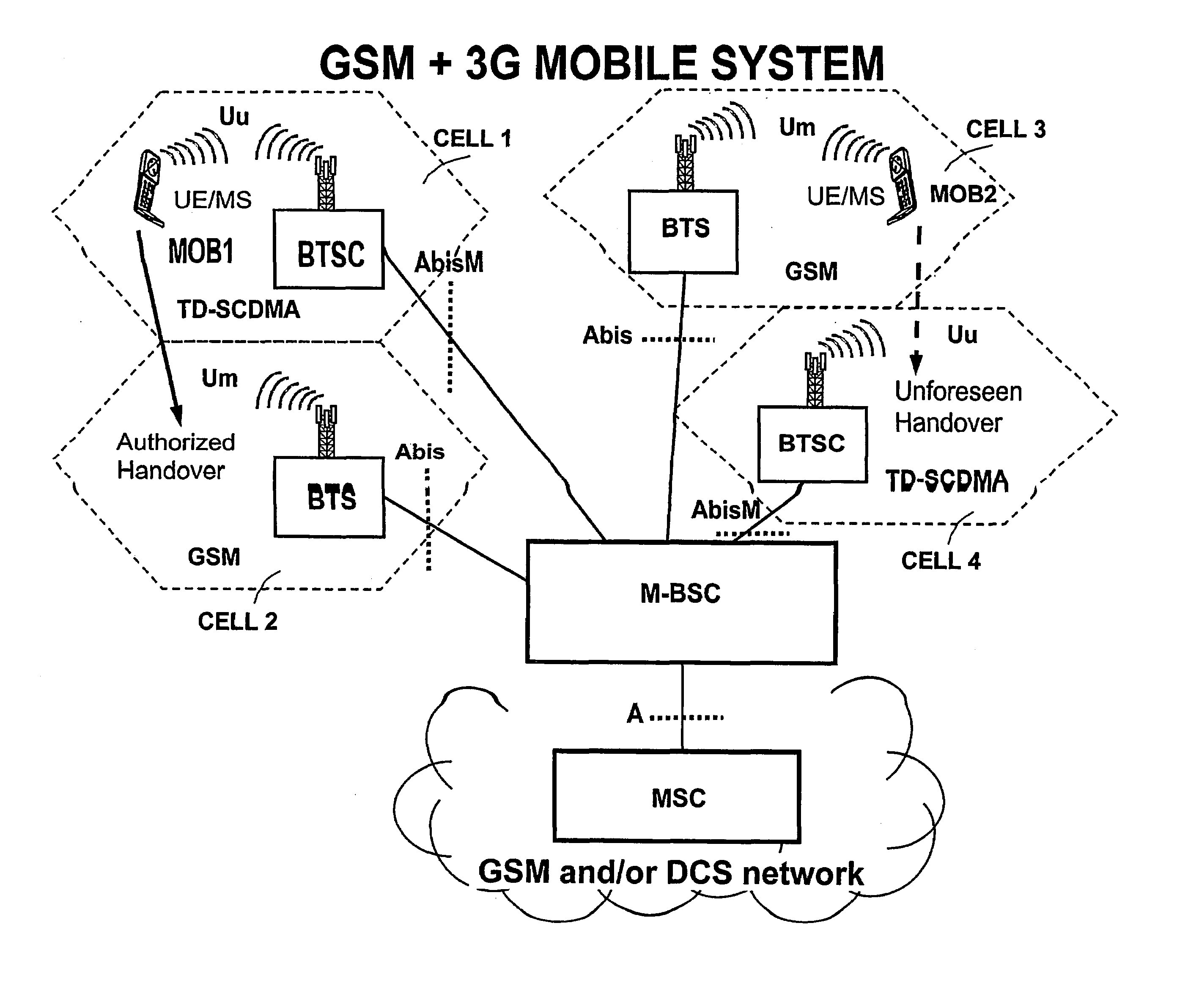
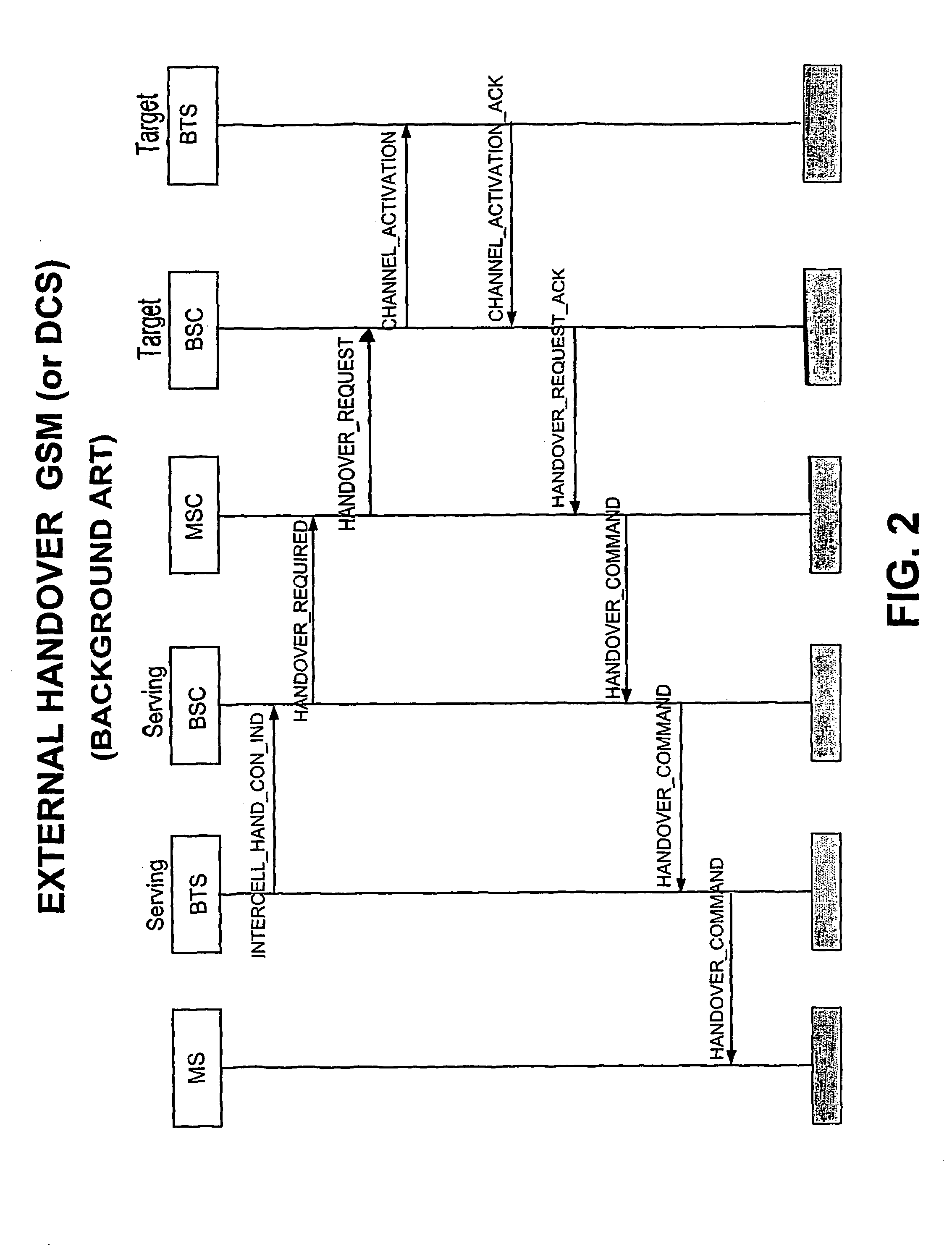
Controller for gsm and 3g base transceiver stations in a gsm core network with external handover possibility from 3g cells to gsm cells trasparent to gsm core network
InactiveUS20050153743A1Failure to successfullySubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsGPRS core networkTransceiver
A station controller (M-BSC) is connected to base transceiver stations BTS of the GSM (Global System for Mobile), or DCS (Digital Cellular System) mobile transceiver system, and to BTSC base transceiver stations of the TD-SCDMA (Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access) system through code division transceiver access technology, typical of 3G systems, and TDD duplexing. The controller is connected to a MSC circuit switch of GSM type. The new 3G technology shares the GSM core network, which on the contrary ignores the existence of the latter. Transparency of the 3G new technology towards the core network is achieved inhibiting any handover from GSM cells to BTSC cells and enabling the external handover (through MSC intervention) from BTSC cells to GSM cells after appropriate treatment of information to be sent to MSC. The ad hoc procedure is carried out by the station controller and consists in reprocessing the mixed list (2G and 3G) of cells candidate for handover furnished with by BTSC, to obtain two lists of cells differing as to radio technology, selecting a list to be forwarded to MSC according to service qualification criteria, comparing in a local memory the (MS / UE) mobile classmarks owned by MSC with those associated to the selected list and, in case of inconsistency, updating MSC classmarks prior to the forwarding of the selected list.
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
TD-SCDMA System and a Method for Controlling HSUPA Random Access Thereof
InactiveUS20100165953A1Avoiding invalid random accessImprove system efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionTime delaysDelayed time
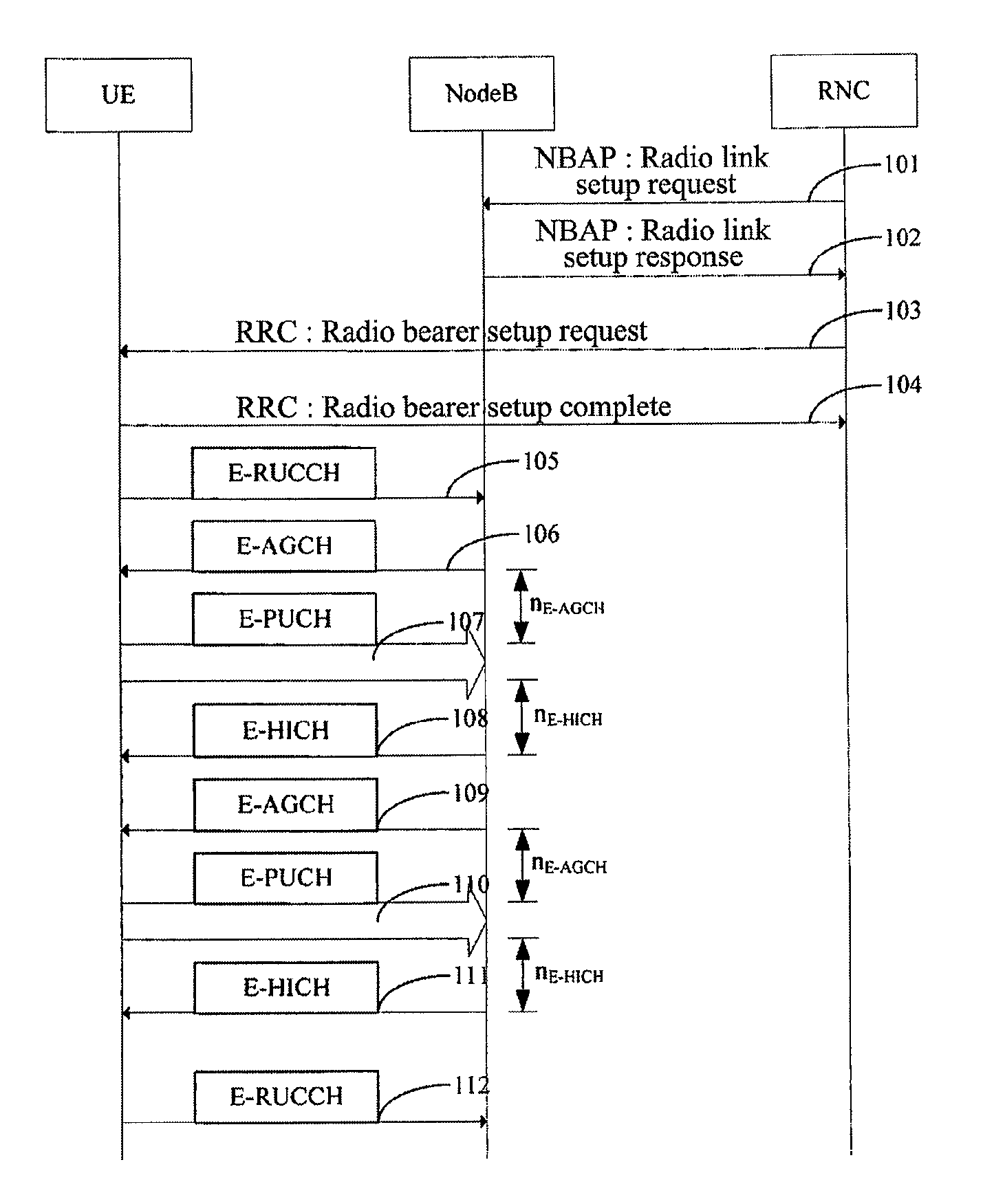
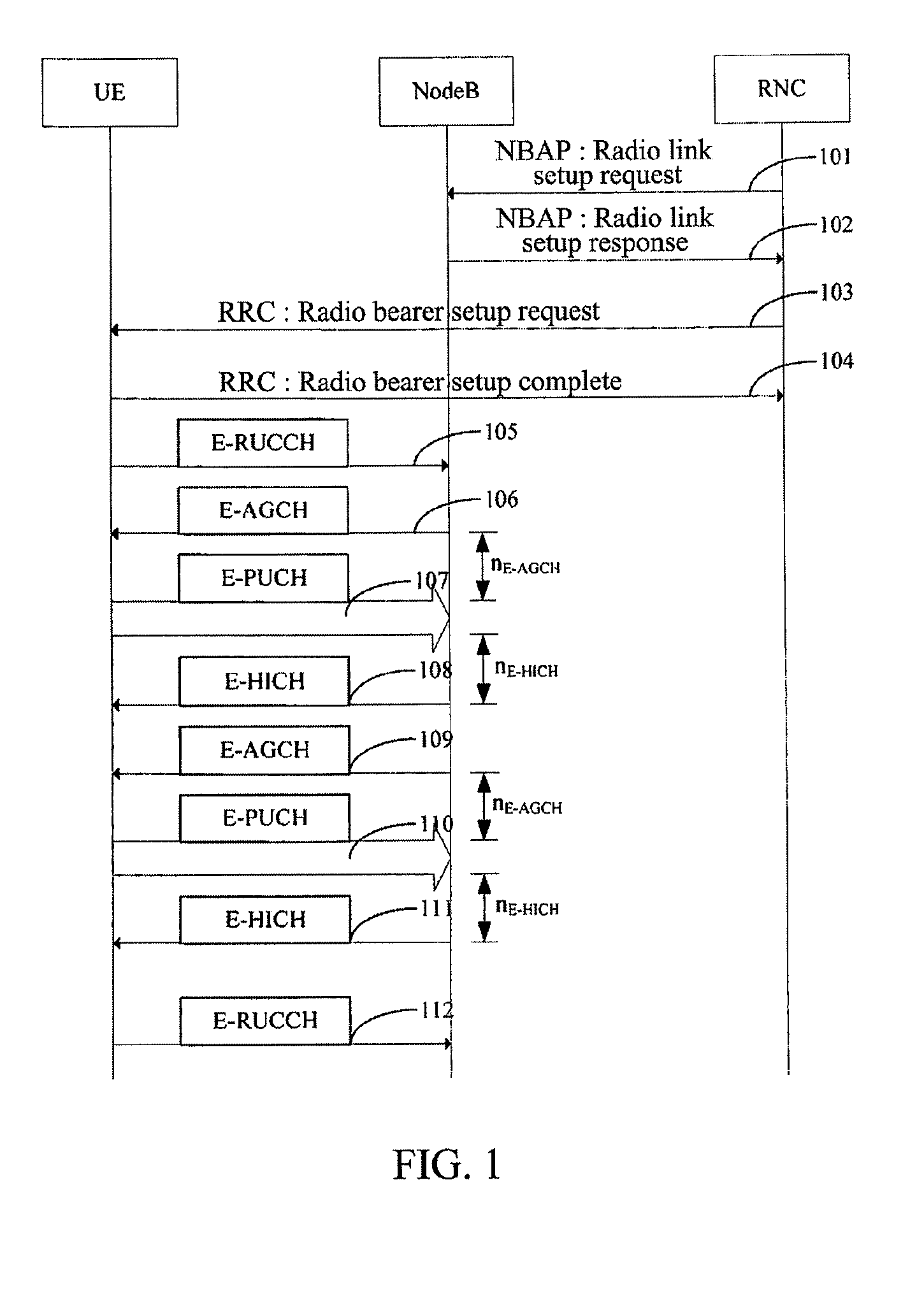
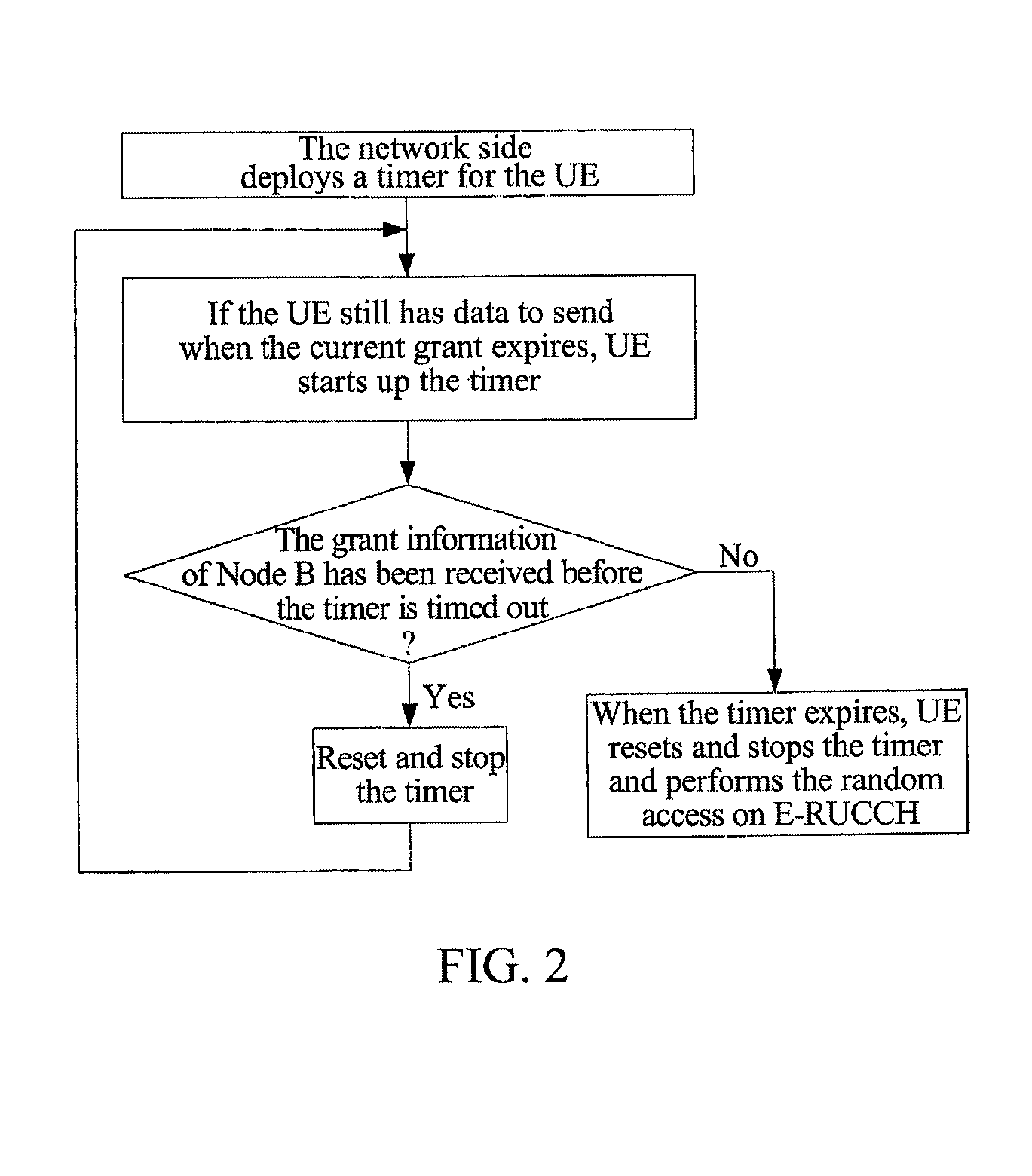
The present invention provides a time division synchronous code division multiple access (TD-SCDMA) system for controlling enhanced uplink random access, including user equipment (UE), node B and serving radio network controller. The present invention also provides a method for controlling the enhanced uplink random access in a time division synchronous code division multiple access system, including: in high speed uplink packet access scheduling service of time division synchronous code division multiple access system, the higher layer of network side deploys a timer at the user equipment side; if the user equipment still needs to transmit data when the current available grant expires, it starts up the timer which is used as the delay time of initiating the enhanced uplink random access. According to the ability of the network side in controlling E-DCH resources, the present invention can be used to control the time delay that UE initiates the enhanced uplink random access after one grant expires, so as to avoid invalid random access; meanwhile the present invention provides a reliable mechanism for the enhanced uplink random access. By using the method of this invention, system resources can be reasonably utilized, thereby greatly improving the system efficiency.
Owner:ZTE CORP
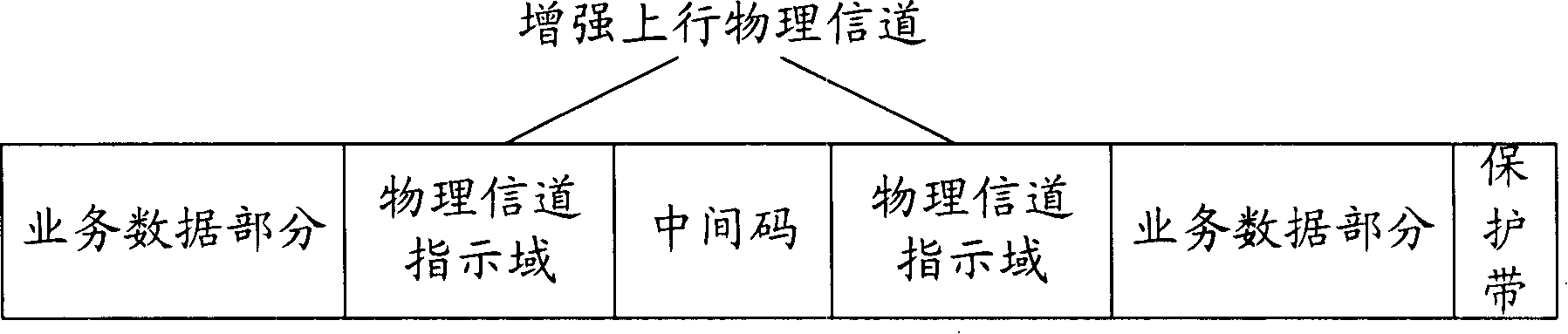
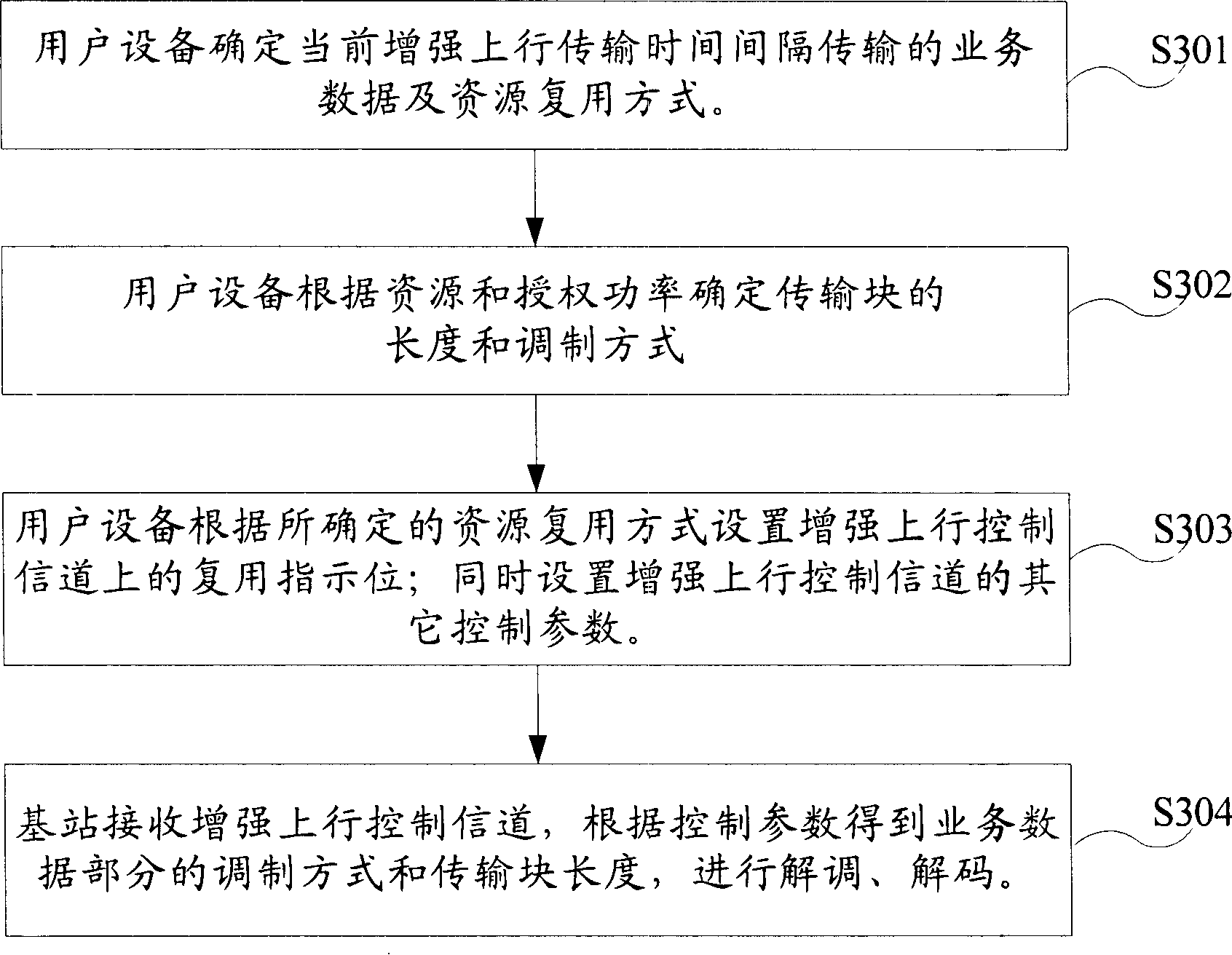
Method of decoding reinforced uplink physical channel of time-division synchronous code division multiple access system
InactiveCN101179836AImprove receiving efficiencyAvoid cachingError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCode division multiple accessUplink transmission
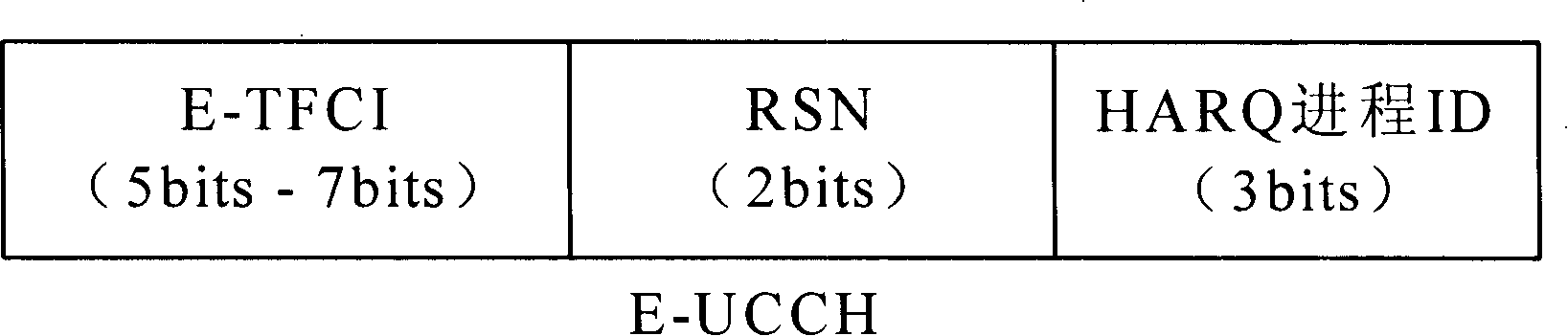
The present invention provides a decoding method for an enhanced uplink physical channel of a time division synchronous code division multiple access system. The method includes the following steps: when an enhanced uplink transmission time interval arrives, the user equipment determines the data type and resources transmitted in the current transmission time interval Multiplexing mode: the user equipment determines the transmission block length and modulation mode of the enhanced uplink service data according to the resource multiplexing situation and authorized power; the user equipment determines the physical layer control channel for this transmission according to the determined service data and resource multiplexing mode parameters; and the base station determines the total number of resources used by the user equipment according to the multiplexing indication in the physical layer control parameters, and combines the enhanced transmission format combination indication to obtain the modulation mode and transmission block length information of the service data part, and then demodulates and decodes . Therefore, without increasing the channel load, the buffering of channel data is avoided, the synchronous demodulation of the channel is realized, and the receiving efficiency of the channel is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
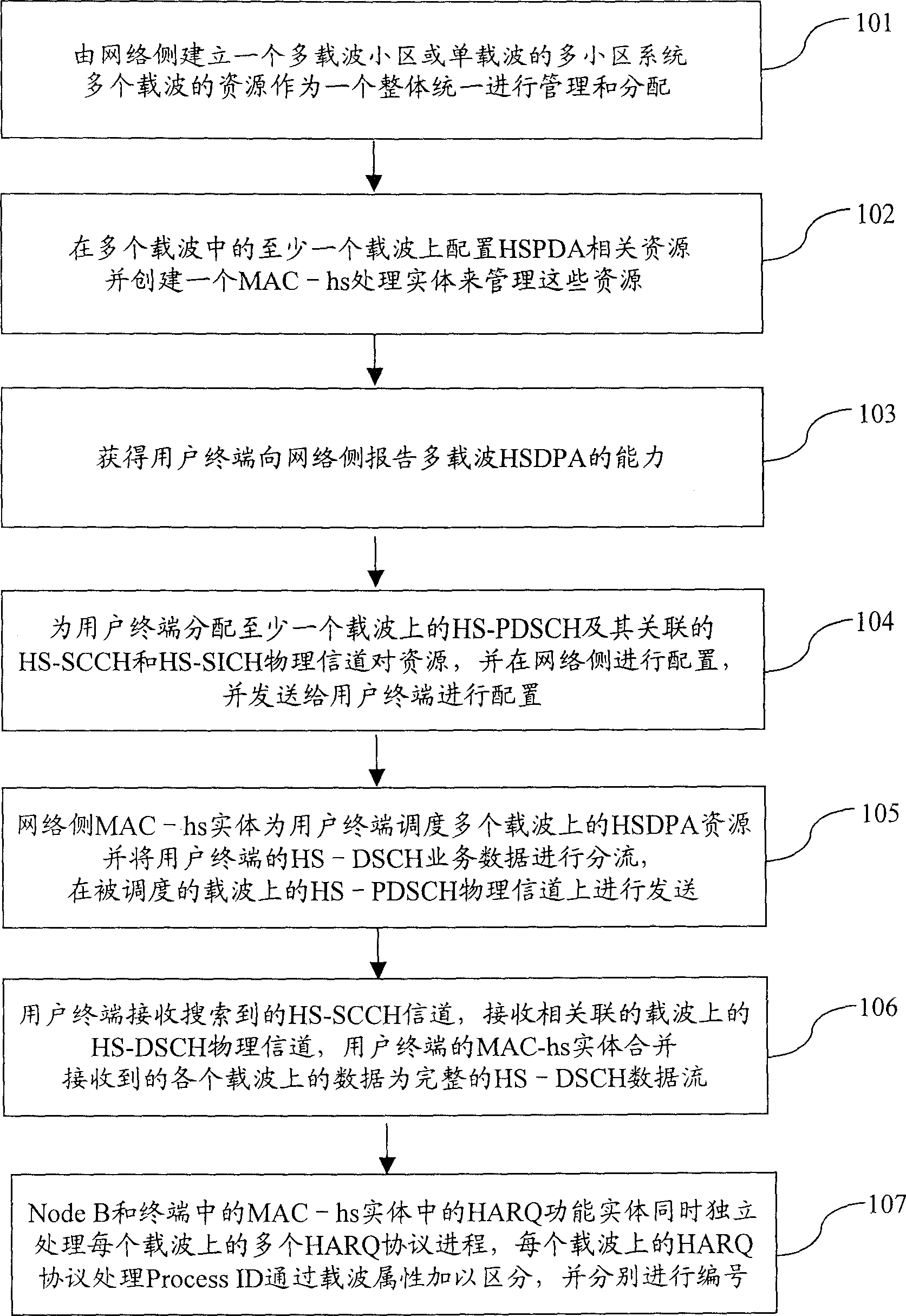
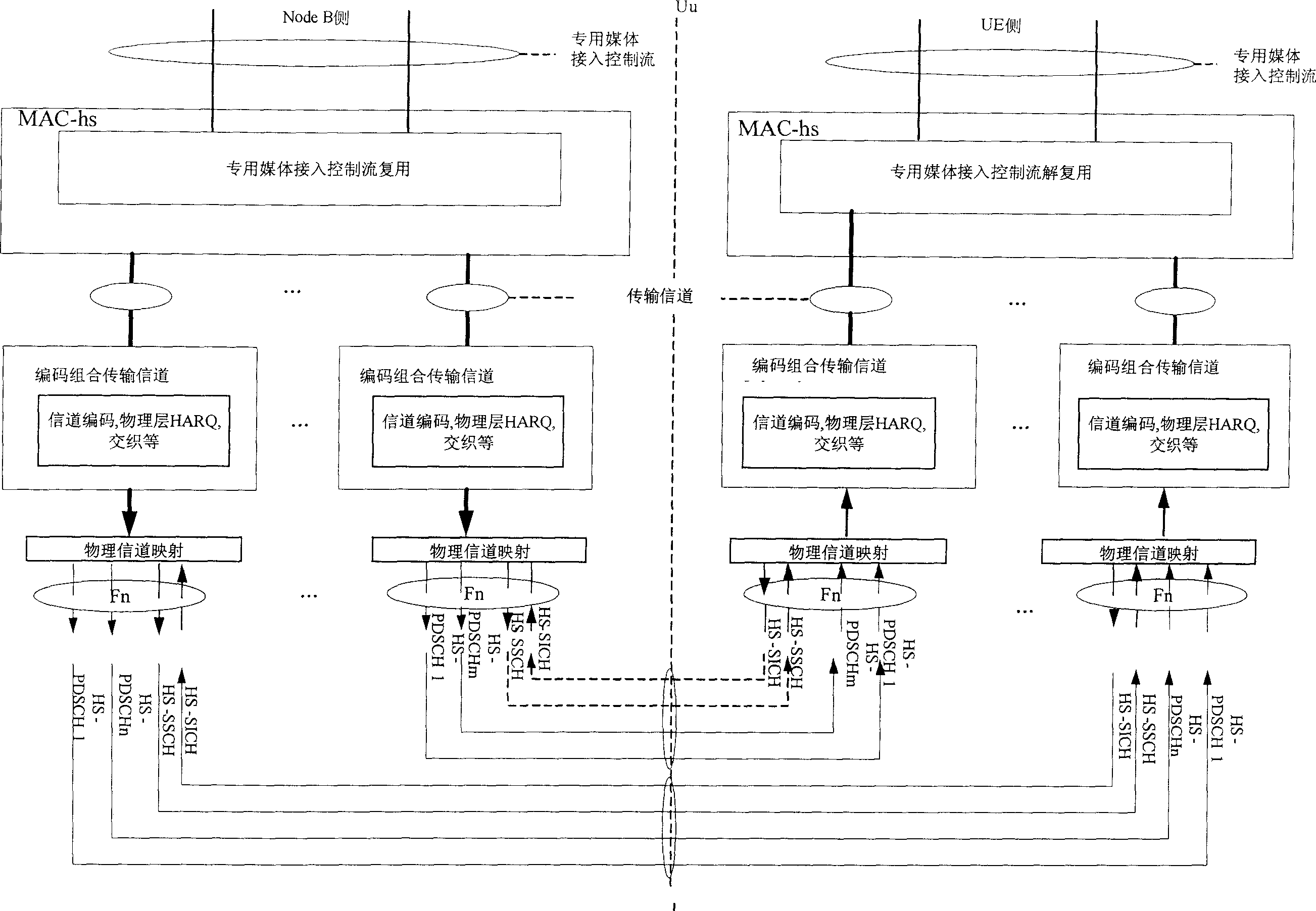
Method for realizing multi-carrier high-speed down group access of time-division synchronus CDMAS system
ActiveCN1758813ASolve the problem of low downlink peak rateDownlink peak rate increasedNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork packetCarrier signal
A method for realizing multicarrier high speed down link packet switching ¿C in of TD ¿C SCDMA system includes setting up a multicarrier cell at network side, configuring HS ¿C PDSCH as well as HS ¿C SCCH and HS ¿C SICH resource on one or multiple carrier, distributing one or multiple carrier with HS ¿C PDSCH resource as well as related one pair or multiple pair of H ¿C SCCH and HS ¿C SICH to user terminal, using HS ¿C PDSCH on one or multiple carrier to bear service data as well as using one related pair of HS ¿C SCCH and HS ¿C SICH to bear control information and feedback information when service data transmission is carrier out.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Adaptive method for switching between single flow mode and double flow mode
ActiveCN101365229AImprove throughputSpatial transmit diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCode division multiple accessCurrent mode
The invention provides a method for self-adapted switch between a single-current mode and a double-current mode, which is used in a time division SCDMA (Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access) system, wherein, a self-adapted switch method comprises the following steps: S102, a nodal point B estimates an uplink channel, and evaluates the cross correlation of the spatial channel between two transmitting blocks; S104, under the circumstances that the cross correlation of the spatial channel is higher than a first threshold value, the system switches to the single-current mode, and under the circumstances that the cross correlation of the spatial channel is lower than the first threshold value, the subsequent single-current and double-current throughputs are estimated; S106, a nodal point B estimates the throughputs of the single-current mode and the double-current mode according to an instruction of the channel quality of the instruction of the channel quality of the single-current mode and the double-current mode, and under the circumstances that the throughput of the double-current mode is larger than the throughput of the single-current mode by a second threshold, the system switches to the double-current mode, otherwise the system switches to the single-current mode.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for realizing synchronization timing of access point in TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) system
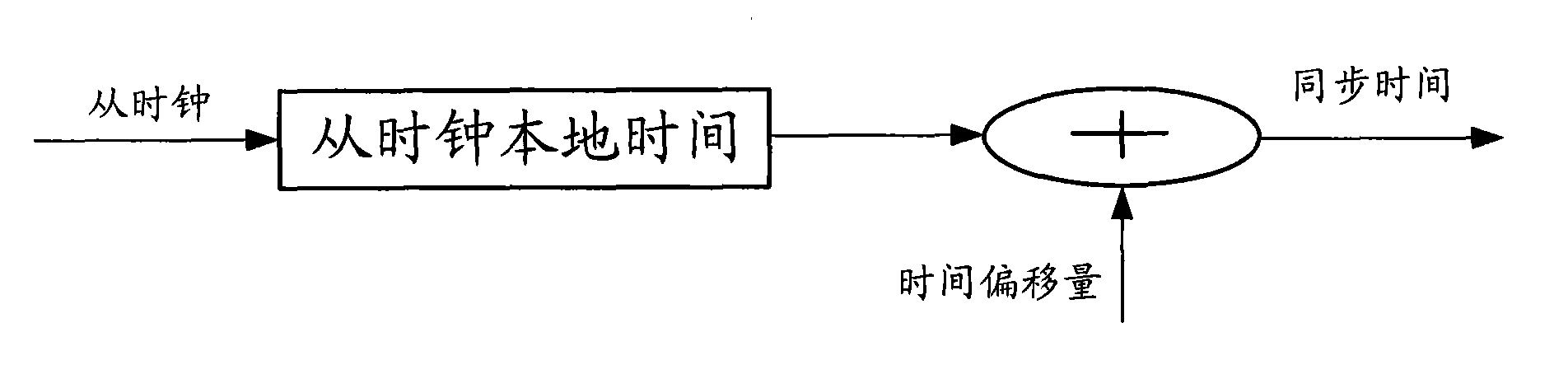
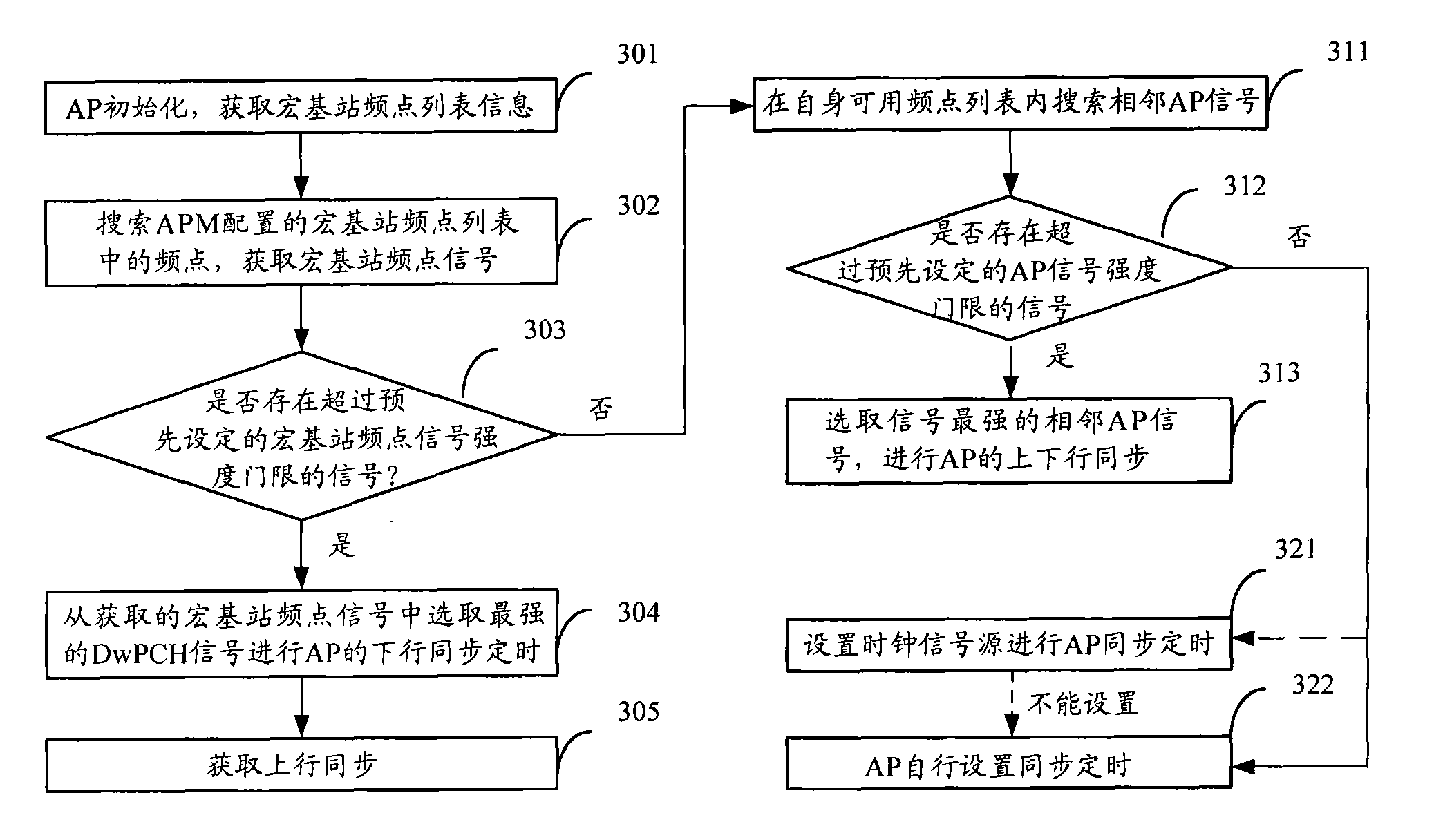
ActiveCN101778467AHigh Synchronous Timing AccuracyIncrease powerSynchronisation arrangementRadio transmission for post communicationMacro base stationsAir interface
The invention discloses a method for realizing synchronization timing of Access Points (AP) in a TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) system. The method comprises the following steps of: searching and acquiring a macro base station frequency point signal in a macro base station frequency point list according to the acquired macro base station frequency point list information; judging whether a signal with signal intensity exceeding a predetermined signal intensity threshold of the macro base station frequency point exists in the acquired macro base station frequency point signal, and selecting the strongest macro base station frequency point signal from the acquired macro base station frequency point signal for the downlink synchronization timing if the signal exists. By adopting the invention, a macro base station corresponding to the strongest signal is selected to execute the air interface synchronization timing of the AP and the macro base station by using the characteristics of higher power, lower penetration loss and high synchronization timing precision of the macro base station at a network side without increasing external synchronous signal sources or new hardware devices, the cost in realizing the AP synchronization timing is low and the operation is simpler, the influence of the factors, such as, delay variation of a transmission network, and the like is avoided and the AP synchronous precision can be ensured.
Owner:TD TECH COMM TECH LTD
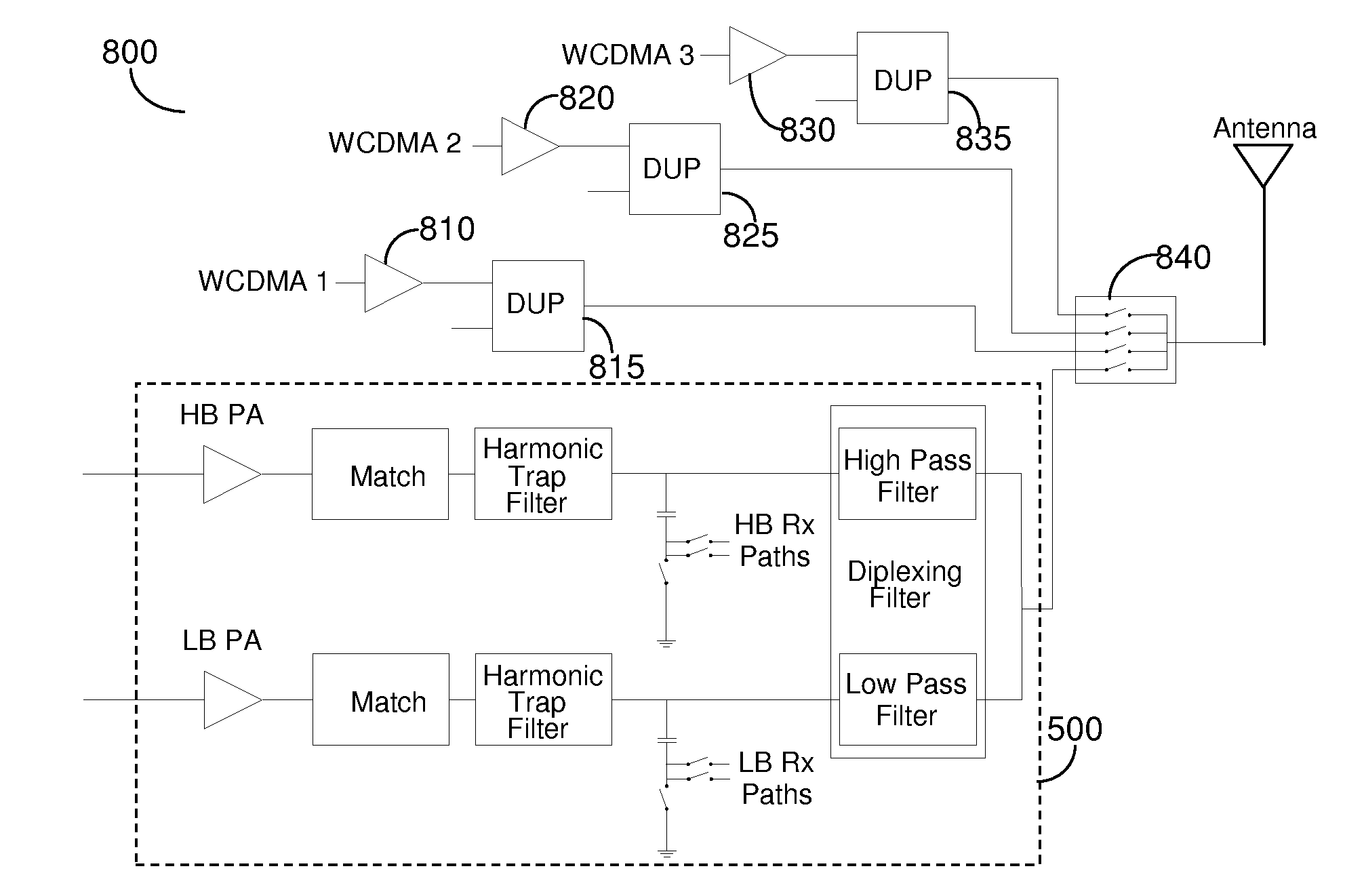
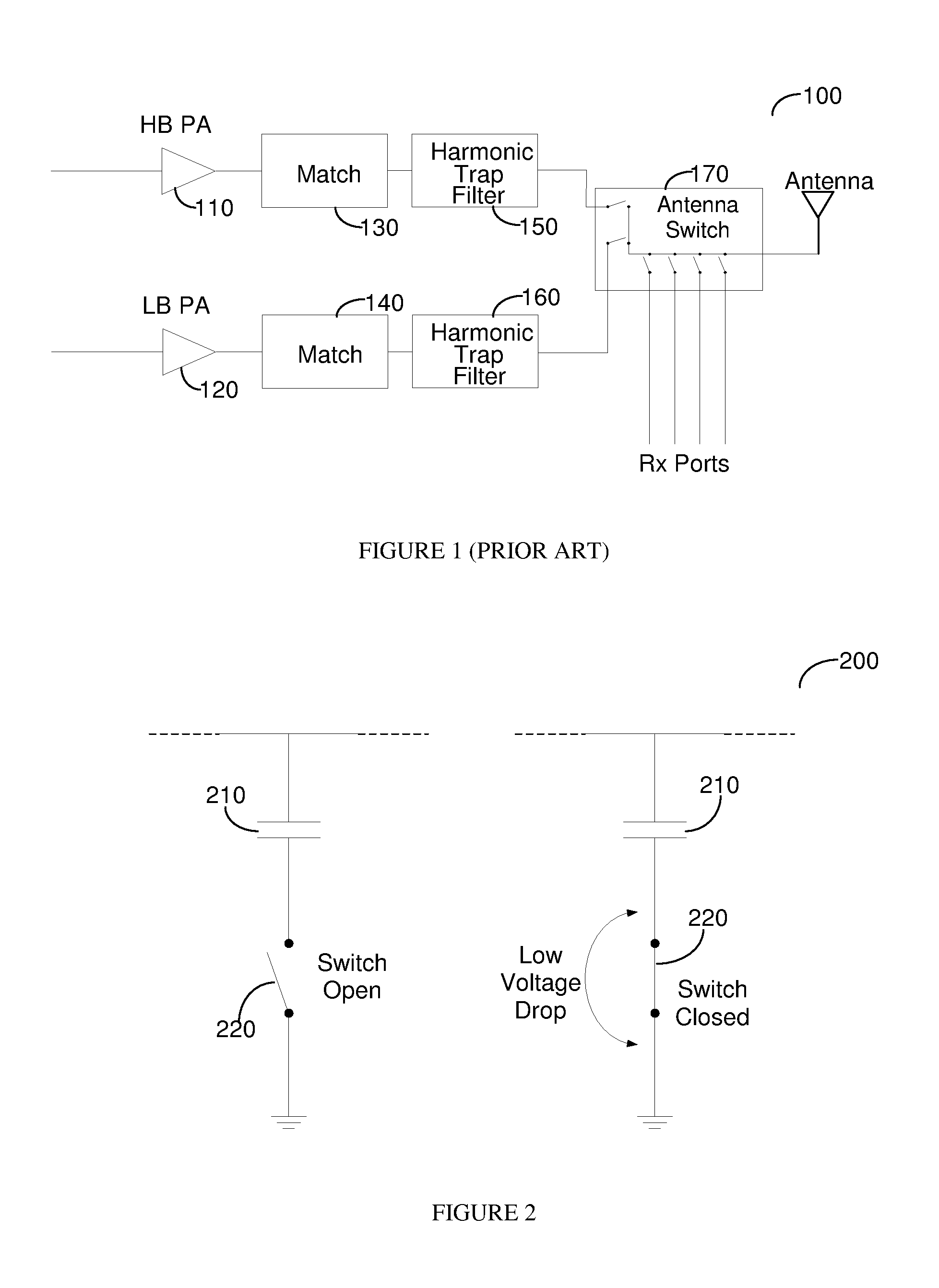
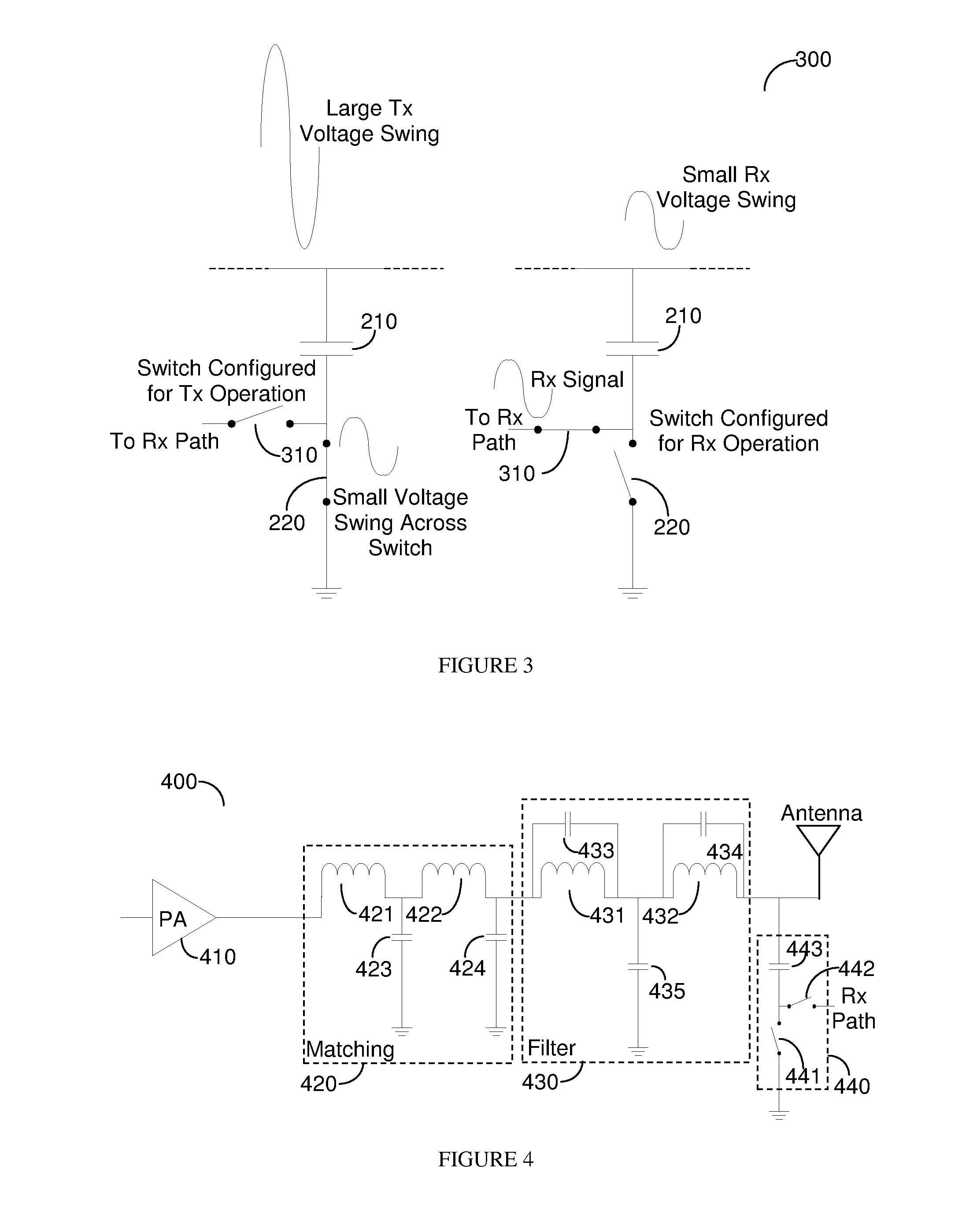
CMOS Switching Circuitry of a Transmitter Module
ActiveUS20140009208A1Gated amplifiersElectronic switchingCode division multiple accessSynchronization code division multiple access
Transmit modules typically constitute passive matching circuitry, harmonic trap filters and an antenna switch to provide isolation between the transmit bands as well as between transmit and receive functions. In complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) processes the switch function is difficult to implement as a large voltage swing may result in breakdown of the MOS oxide, drain diode, source diode as well as substrate diodes. Therefore a switching function is provided at a node that has low impedance during transmit that limits the voltage swing that the MOS switches experience. The approach is particularly useful, but not limited to, half duplex transmissions such as those used in global system for mobile (GSM) communication, enhanced data for GSM Evolution (EDGE), and time division synchronous code division multiple access (TDSCDMA).
Owner:QORVO INT PTE LTD
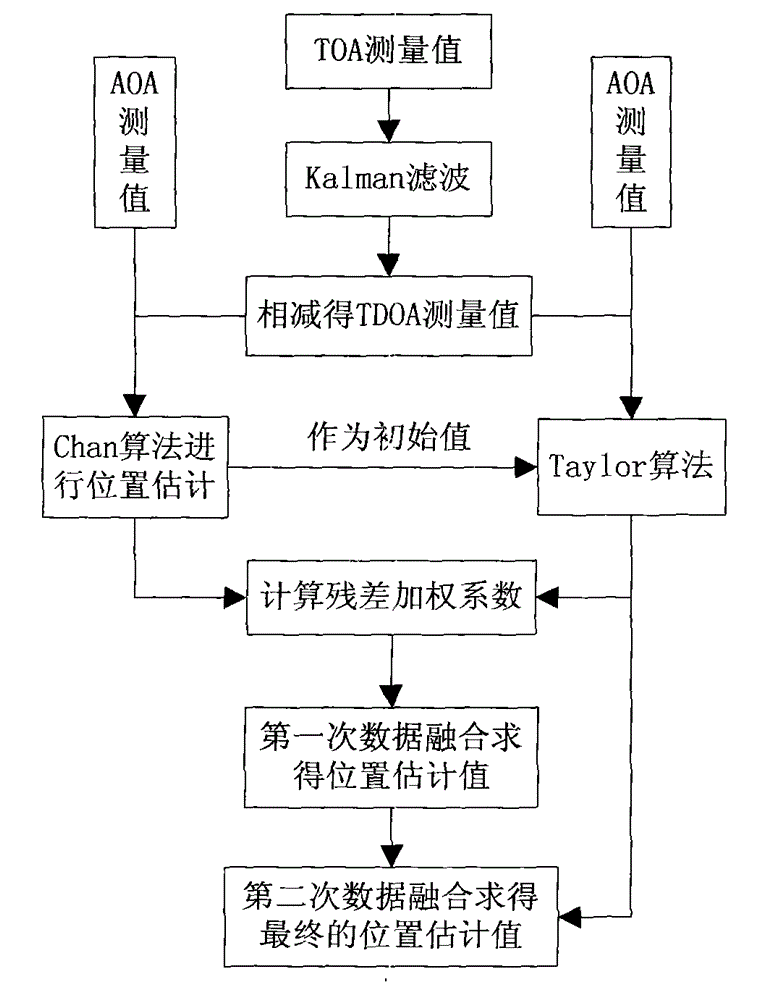
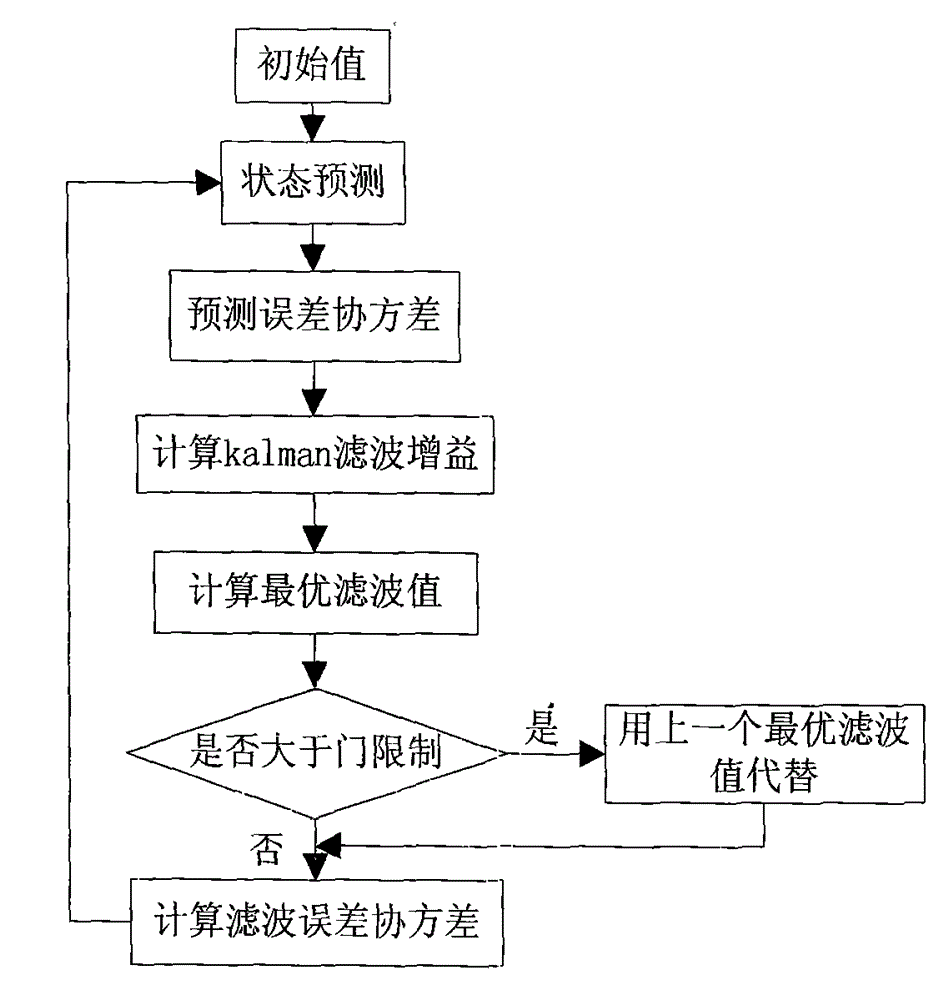
Time division-synchronization code division multiple access (TD-SCDMA) system-based method for accurately positioning underground personnel
ActiveCN103152695ASolve positioning difficultiesHigh positioning accuracyLocation information based serviceResidual methodMobile station
The invention discloses a time division-synchronization code division multiple access (TD-SCDMA) system-based method for accurately positioning underground personnel. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring time of arrival (TOA) and an angle of arrival (AOA) of a signal at a base station; de-noising a TOA value by using an improved kalman filtering algorithm; calculating a time difference of arrival (TDOA) value according to the de-noised TOA value; estimating the position of a mobile station by using a TDOA / AOA mixed Chan algorithm and a TDOA / AOA mixed Taylor algorithm; performing first data fusion on a position estimated value by using a weighted residual method to obtain a new position estimated value; and performing second data fusion on the position estimated value by using Bayesian inference to obtain the final position estimated value. By the method for accurately positioning the underground personnel, the advantages of a TD-SCDMA system and the superiority of the data fusion are utilized, a TDOA / AOA mixed data fusion positioning algorithm is adopted, the positioning accuracy is high, and the problem that the personnel in an underground coal mine are hard to position is solved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Full frequency band frequency point scanning method of time-division-synchronization code multi-address division system
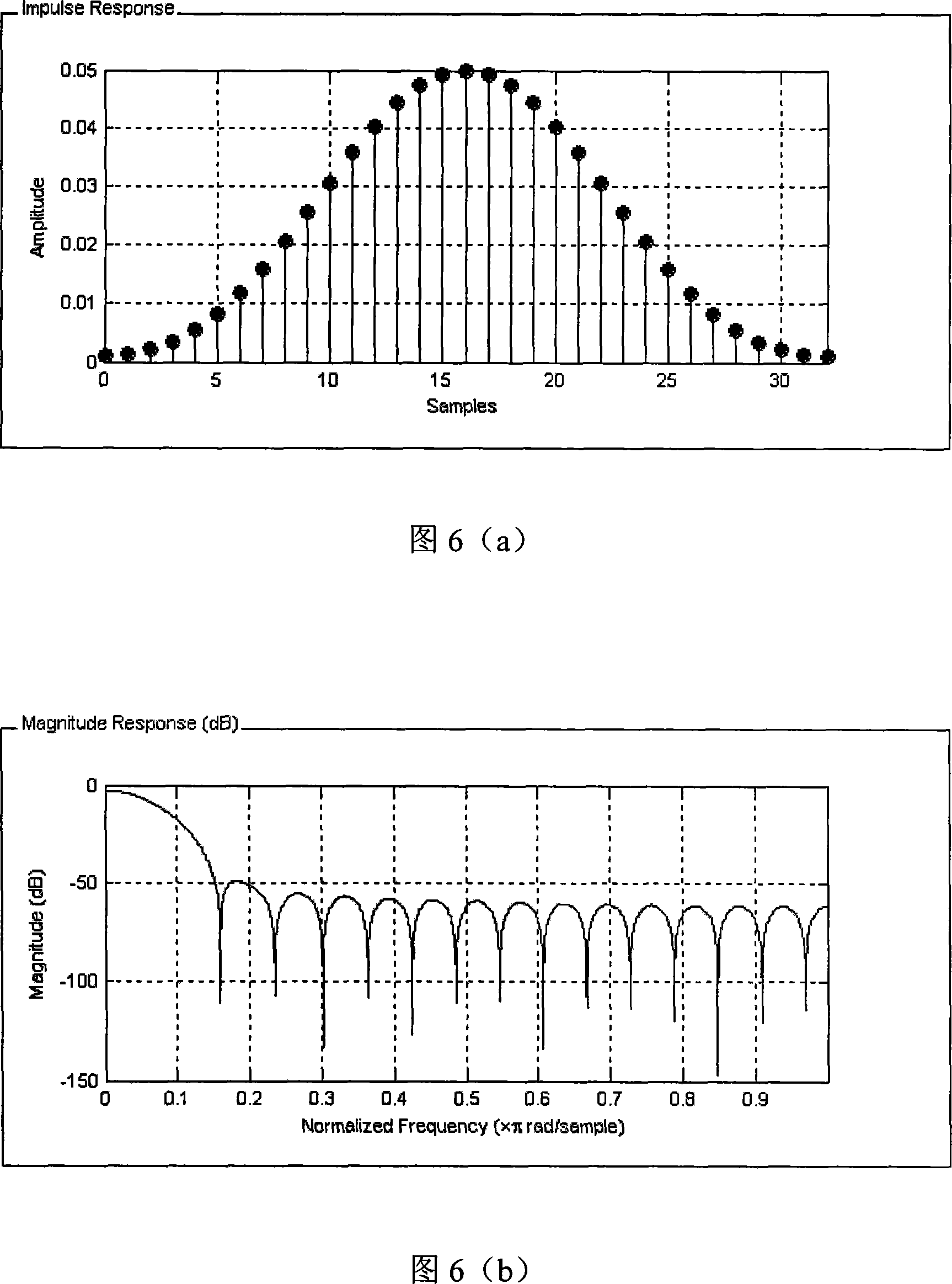
ActiveCN101102121AQuick searchAccurately implement the searchAssess restrictionTransmission control/equalisingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Peak value
The invention is concerned with the point frequency scanning method of mobile terminal frequency segment to perform under interference environment of all sorts. It applies the low connection filtering method to eliminate the disturbance of the signal incept power volume by noise and the channel fading, directs the adjustment of the point frequency AGC and the frequency power measurement with different reference guide line separately, and conducts fitting and smoothing treatment to all the frequency section measuring volume data, and finally, generates the candidate frequency list by applying the method of power section peak value selection.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
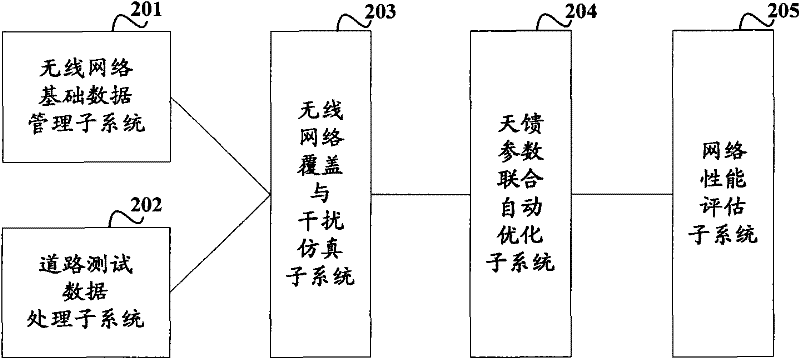
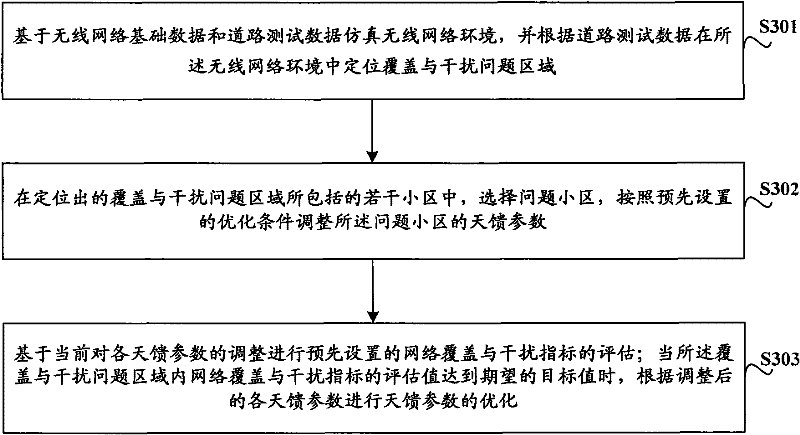
Method and system for optimizing antenna feeder parameters
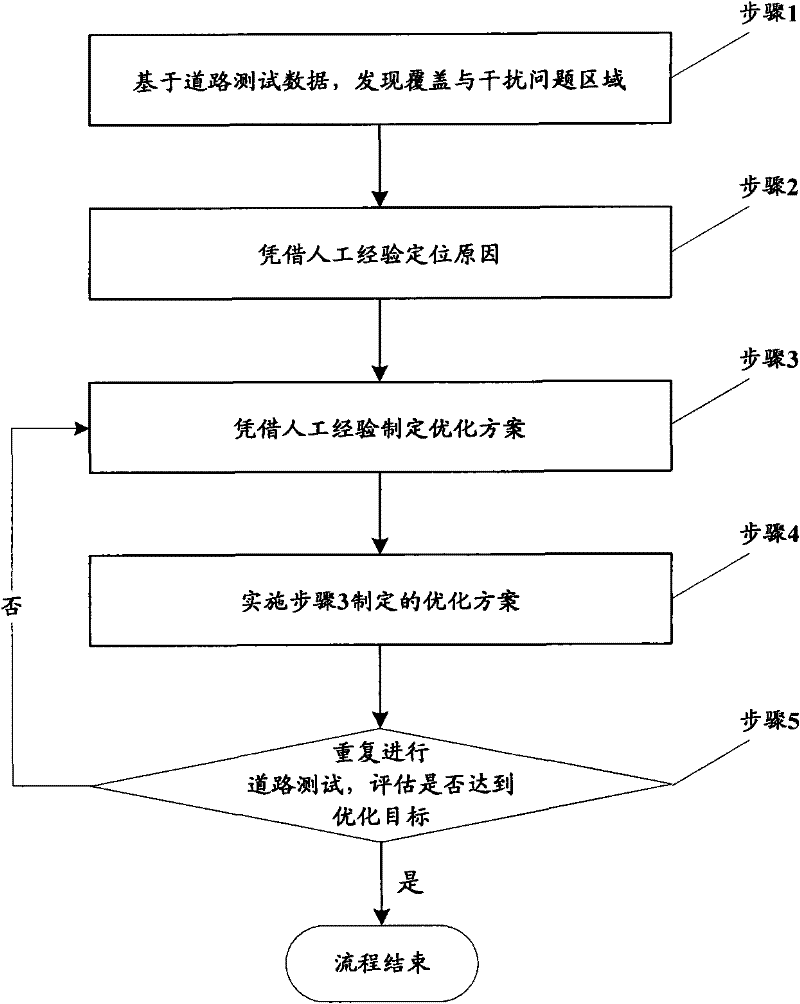
ActiveCN102448087AAchieving joint optimizationTrue reflection of coverageWireless communicationInterference problemAntenna feeder
The invention discloses a method and a system for optimizing antenna feeder parameters, which are used for joint automated optimization of a plurality of antenna feeder parameters in a TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) network, ensuring a whole optimization effect and improving wireless network quality. The optimization method comprises the following steps of: simulating a wireless network environment on the basis of wireless network base data and road test data, and positioning a coverage and interference problem region in the wireless network environment according to the road test data; selecting a problem cell in a plurality of cells included in the positioned coverage and interference problem region, and adjusting each antenna feeder parameter according to the preset optimal condition; and assessing a preset network coverage and interference index on the basis of current adjustment for each antenna feeder parameter, and when an assessed value of the network coverage and interference index in the coverage and interference problem region reaches an expected target value, the optimization of the antenna feeder parameters can be carried out according to the adjusted antenna feeder parameters.
Owner:XINYANG BRANCH HENAN CO LTD OF CHINA MOBILE COMM CORP
PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) network selecting method of multimode terminal
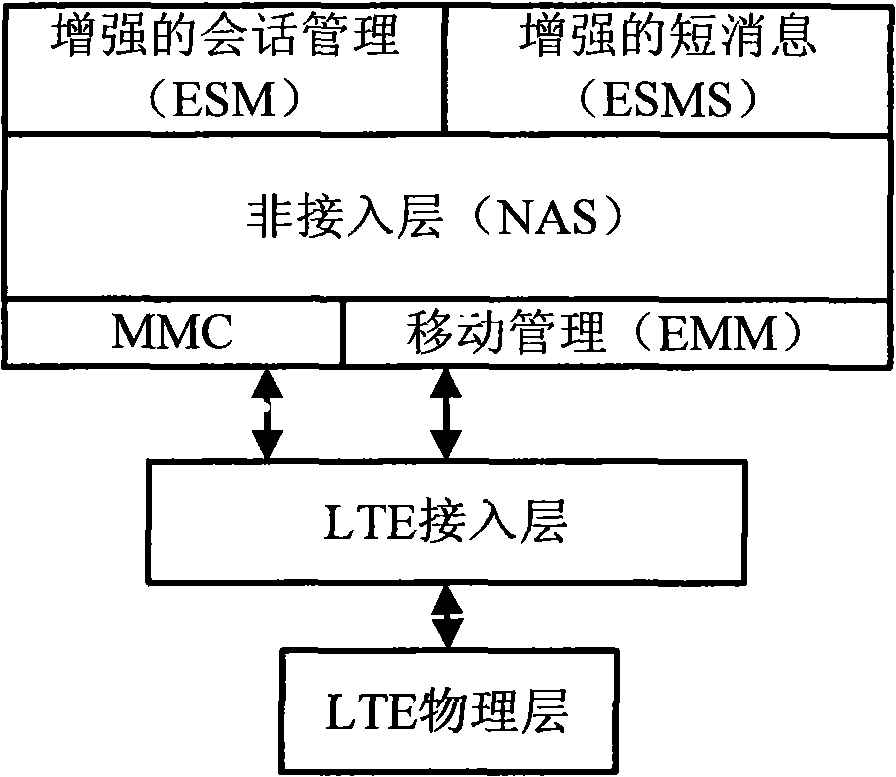
The invention provides a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) network selecting method of a multimode terminal, comprising the steps: when an access mode is LTE (Long Term Evolution) and an access stratum (AS) is in PLMN searching, searched cells with signals are stored in the AS layer; the AS of the terminal leads PLMN_IdentityList of all the cells and signal intensity to form a PossiblePLMN(maxPlmnNum) list; all the lists are reported to a non-access stratum (NAS) together; the PLMN network selecting process of the LTE access technology is fused to the PLMN network selecting method of a GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) and TD-SCDMA (Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) dual-mode terminal. In the PLMN network selecting method provided by the invention, the problems that in the GSM or TD-SCDMA system, one cell only has one PLMN identification and one cell of the LTE can affiliate to different PLMN networks possibly are effectively solved, the characteristics of the existing GSM-TD-SCDMA system are fully utilized, the terminal design is simplified and the hardware cost is reduced.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
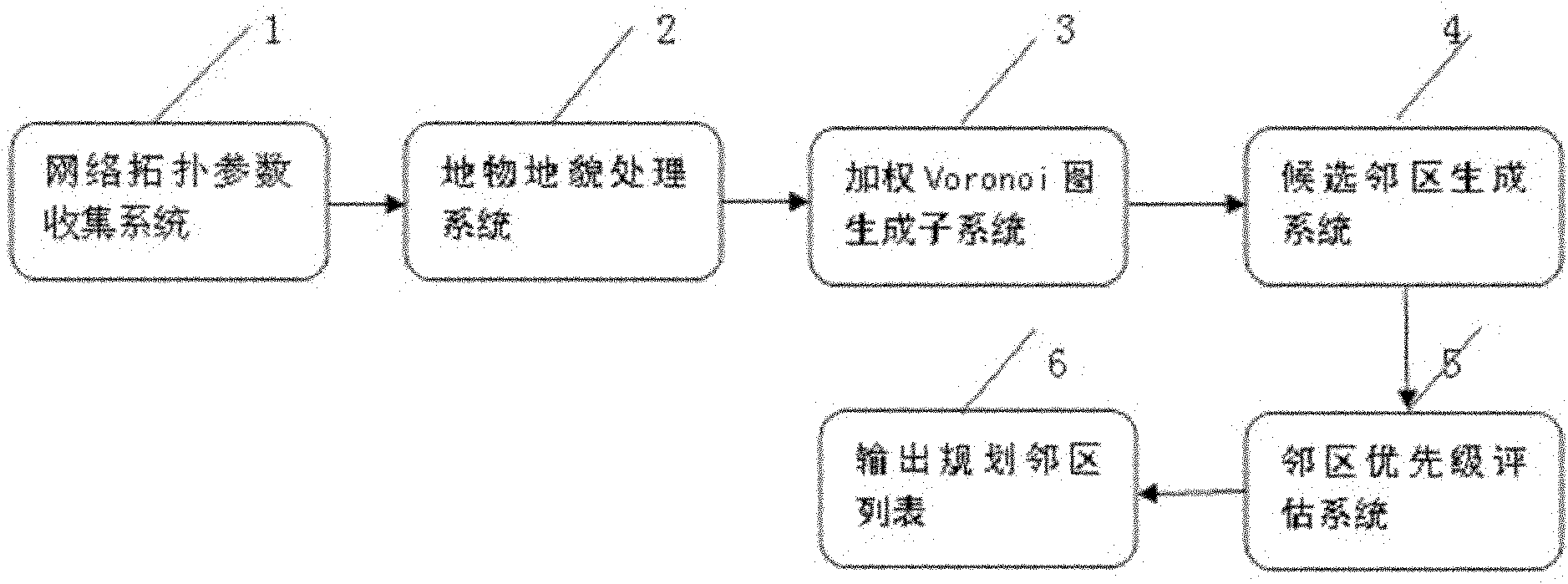
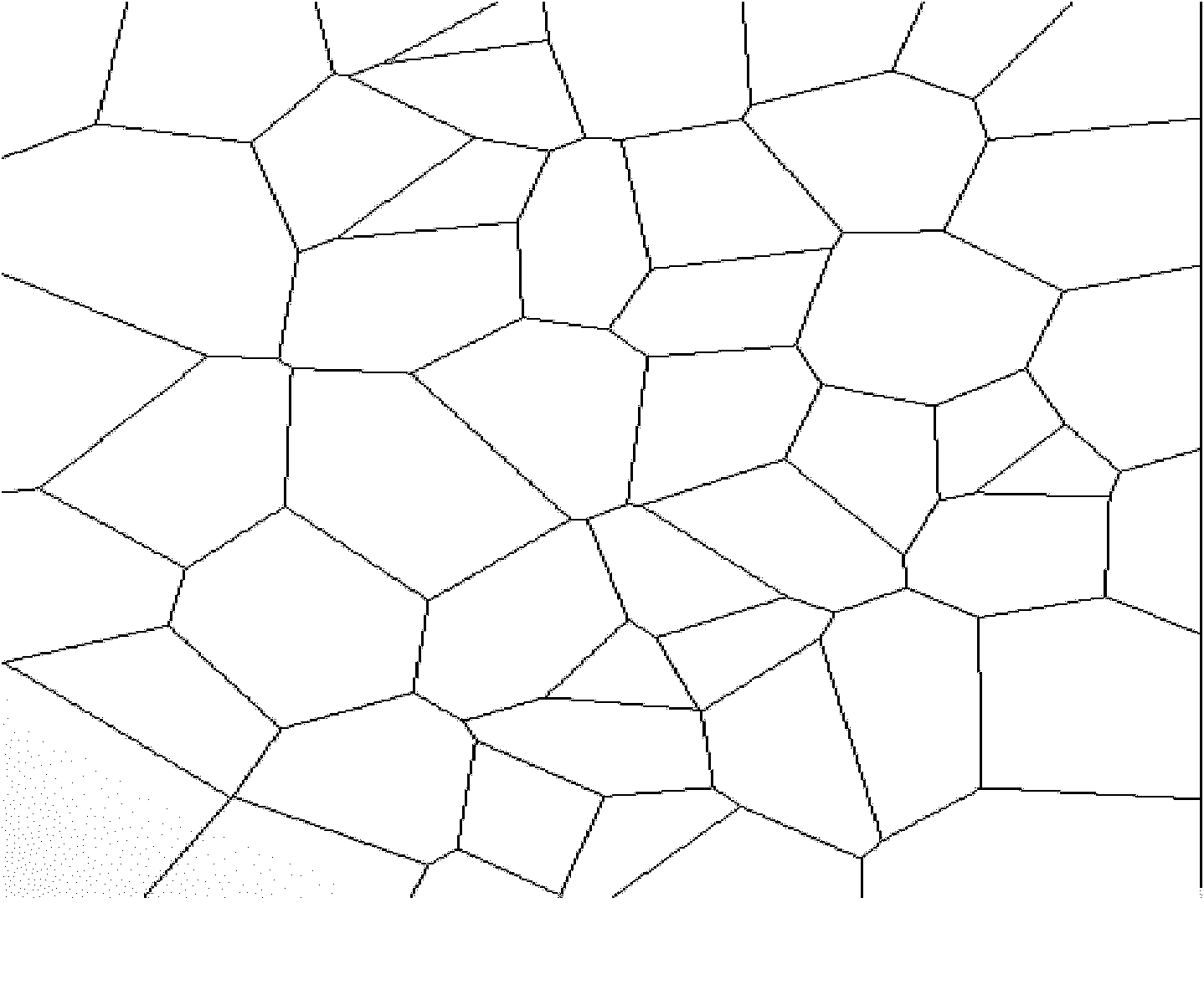
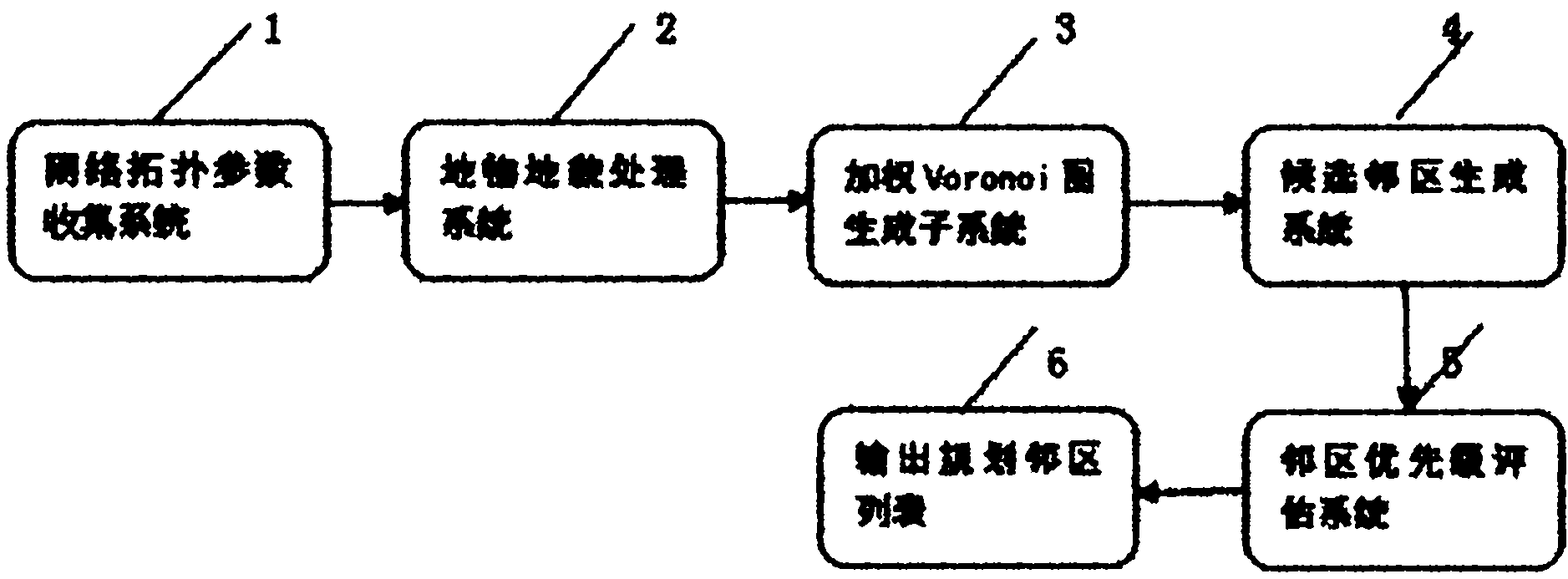
Quick automatic neighbor planning method for related networks
The invention relates to the field of wireless mobile communication, in particular to a quick automatic neighbor planning method for related networks. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: generating a weighted V graph according to network topology parameters by a network topology parameter acquisition system, a weighted Voronoi graph generating subsystem, a geomorphic feature processing system, a candidate neighbor generating system and a neighbor priority evaluation system; and determining polygons covered by each cell according to the generated weighted V graph, determining a first network neighbor list according to the adjacent relationship of a service sector and V graph polygons covered by other cells, generating a candidate neighbor list, and finally outputting a neighbor list according to the weight values of each neighbor. The method is suitable for systems of wideband code division multiple access (WCDMA), code division multiple access 2000 (CDMA 2000), time division-synchronization code division multiple access (TD-SCDMA) and global system for mobile communications (GSM) and 3G-to-2G labeled neighbor planning; and the weighted Voronoi graph data are adopted as a data source, and influences of geomorphic features and buildings on neighbor planning are consulted, so the method has the advantages of high running speed, high planning efficiency and precision and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI BYNEAR TELESOFT
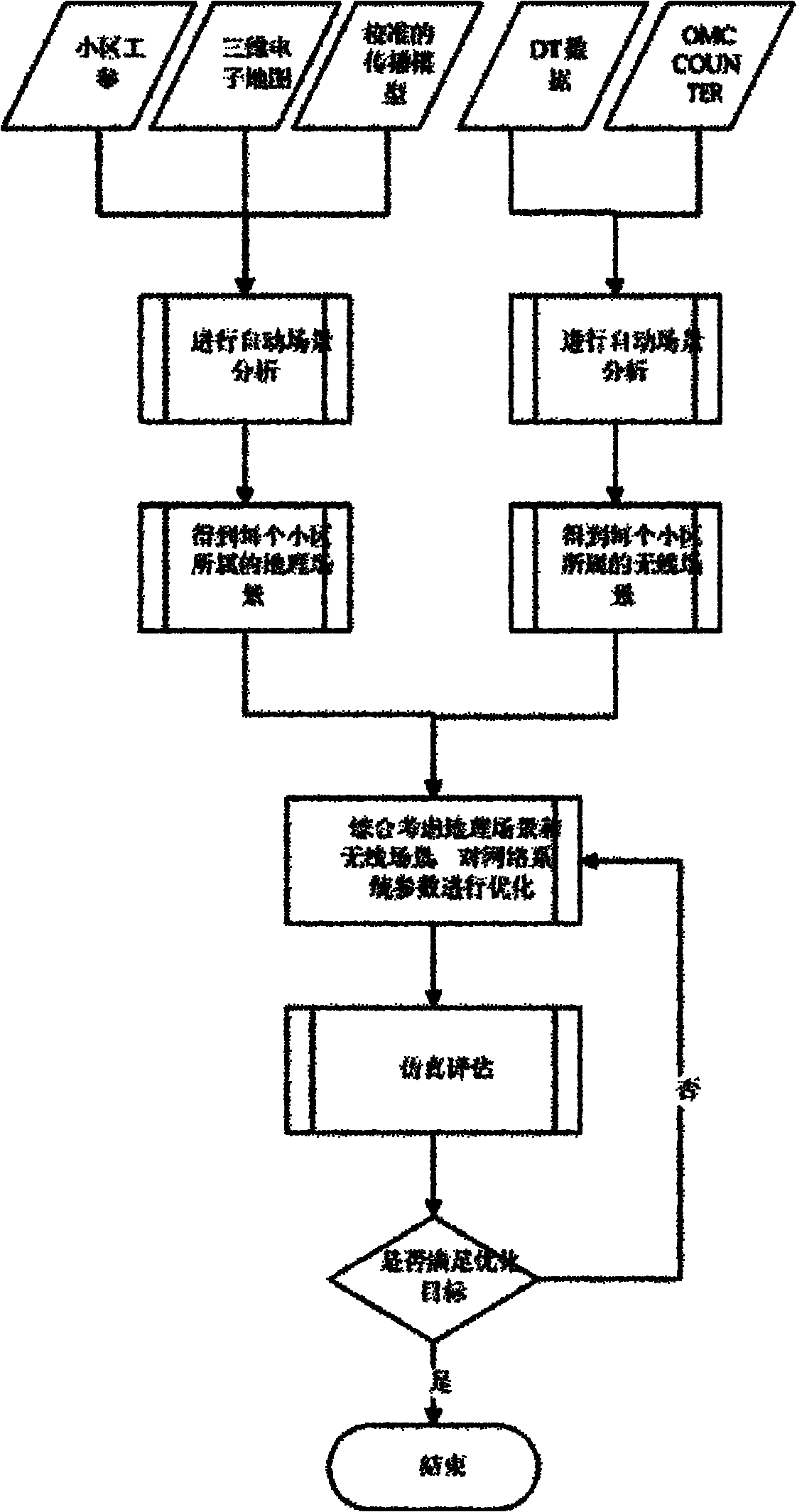
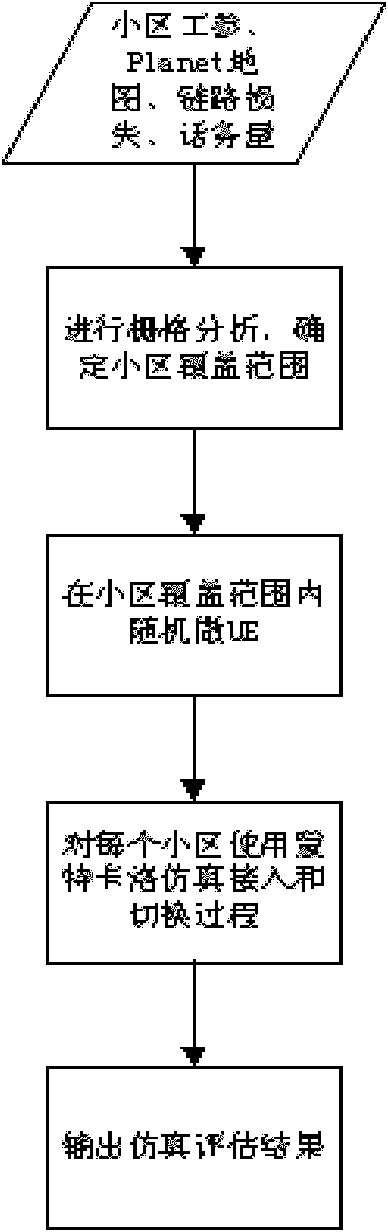
TD-SCDMA (time division-synchronization code division multiple access) system parameter method based on automatic scene analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, in particular to a TD-SCDMA (time division-synchronization code division multiple access) system parameter method based on automatic scene analysis, comprising: a base station tracks movement of a terminal in the whole cell through an intelligent antenna. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: acquiring cell working parameters, a three-dimensional electronic map, a calibrated propagation model, DT (delay time) data and OMC (operation maintenance center) COUNTER data; carrying out automatic scene cluster analysis on a geographical scene and a wireless scene; optimizing network system parameters; carrying out simulation evaluation on optimized parameters; if the parameters reach the optimization object, finishing optimization; and if the parameters do not reach the optimization object, optimizing the network system parameters again. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that data sources adopted for optimization are abundant; the optimization method is simple and convenient; cell scene cluster analysis is adopted, thus cell problems can be accurately positioned; and an expertise library module is adopted, thus network problems can be solved appropriately.
Owner:SHANGHAI BYNEAR TELESOFT
Doppler frequency shift estimation and compensation method in TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) system
InactiveCN101814931AReduce complexityImprove accuracyBaseband system detailsCarrier regulationPhase differenceFrequency shift
The invention relates to a Doppler frequency shift estimation and compensation method in a TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) system. The method comprises the following step of: after a mobile terminal receives a time slot containing the data of the mobile terminal, obtaining a Doppler frequency offset value of a receiving signal of the current time slot through comparing the phase differences of channel estimation sequences of the current time slot and a comparison time slot. The compensation method of the Doppler frequency shift in the TD-SCDMA system comprises the following steps of: after the mobile terminal receives the time slot containing the data of the mobile terminal, obtaining the Doppler frequency offset value of the receiving signal of the current time slot through comparing the phase differences of the channel estimation sequences of the current time slot and the comparison time slot; and correcting the receiving signal in joint detection by combining with the joint combination. The invention improves the accuracy of channel estimation, eliminates the influences of the Doppler frequency shift on correctly receiving demodulation, reduces the error rate and improves the system performance and is particularly suitable for TD-SCDMA terminals under high-speed motion scenes.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and device for concurrent eliminating same frequency interference in TDS-CDMA
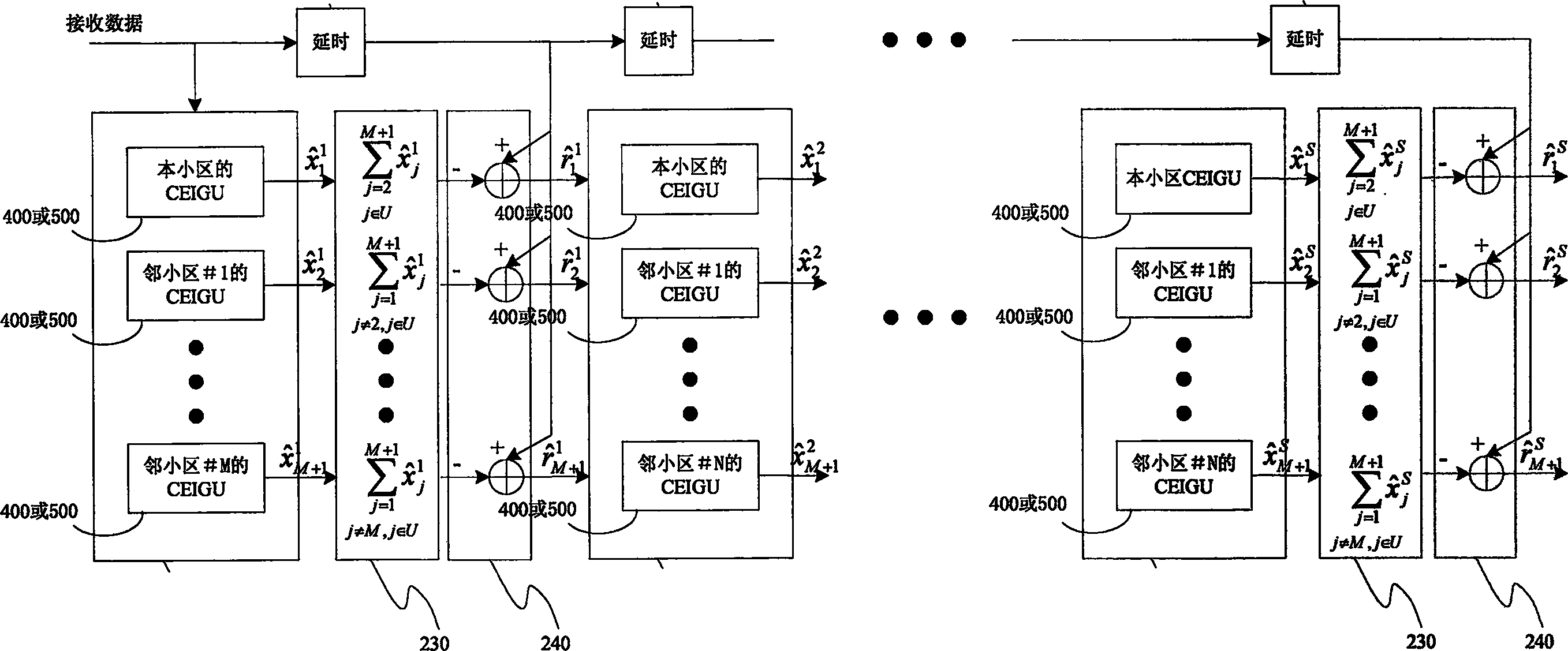
ActiveCN1874189AEliminate the effects ofImprove reception performanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationEngineeringMatched filter
The method and device for eliminating same frequency interference in parallel in TDS-CDMA system includes steps: based on matched filter or based on demodulation symbol generated from united detection to reconstruct interference signal of cell for each cell; superposing signals reconstructed from other interference cells; then removing superposed value of signal reconstructed from other interference cells from the received signal in order to eliminate influence on receiving signal of this cell by interference signals from adjacent cell, executing the steps repeatedly based on number of parallel stage. With lesser complexity of implementation, the method eliminates influence of signals from cells in same frequency to a considerable degree, especially, in malcondition that power of common frequency in adjacent cell is higher than this cell so as to raise performance for receiving signal of this signal.
Owner:XUANPU INDUSTRY CO LTD
Automatic frequency calibration channel selection filter for multi-frequency multi-mode wireless transceiver
The invention discloses an automatic frequency calibration channel selection filter for a multi-frequency multi-mode wireless transceiver, which comprises a fully differential operational amplifier, three switch resistance arrays, a decoder, an automatic frequency calibration circuit, two switch capacitance arrays and a capacitor. The filter can be applied to multi-frequency multi-mode wireless transceivers which support wireless local area network, global mobile communication, radio frequency identification and time division synchronous code division multiple accesses. The filter supports eight different frequency bands, reduces the implementation cost of the system and improves the integrity of the system. The automatic frequency calibration circuit of the filter can realize the accurate adjustment of a cut-off frequency, and the error is within 3 percent.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Ascending reinforced accidental access method, apparatus and equipment
InactiveCN101370245AReduce the probability of collisionImprove access capabilitiesCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAccess methodCarrier signal
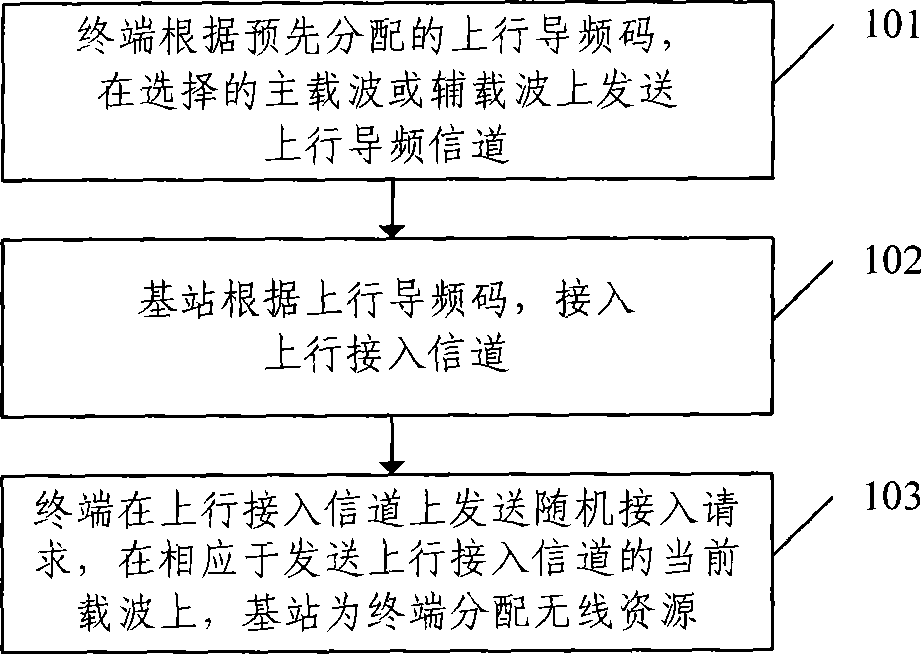
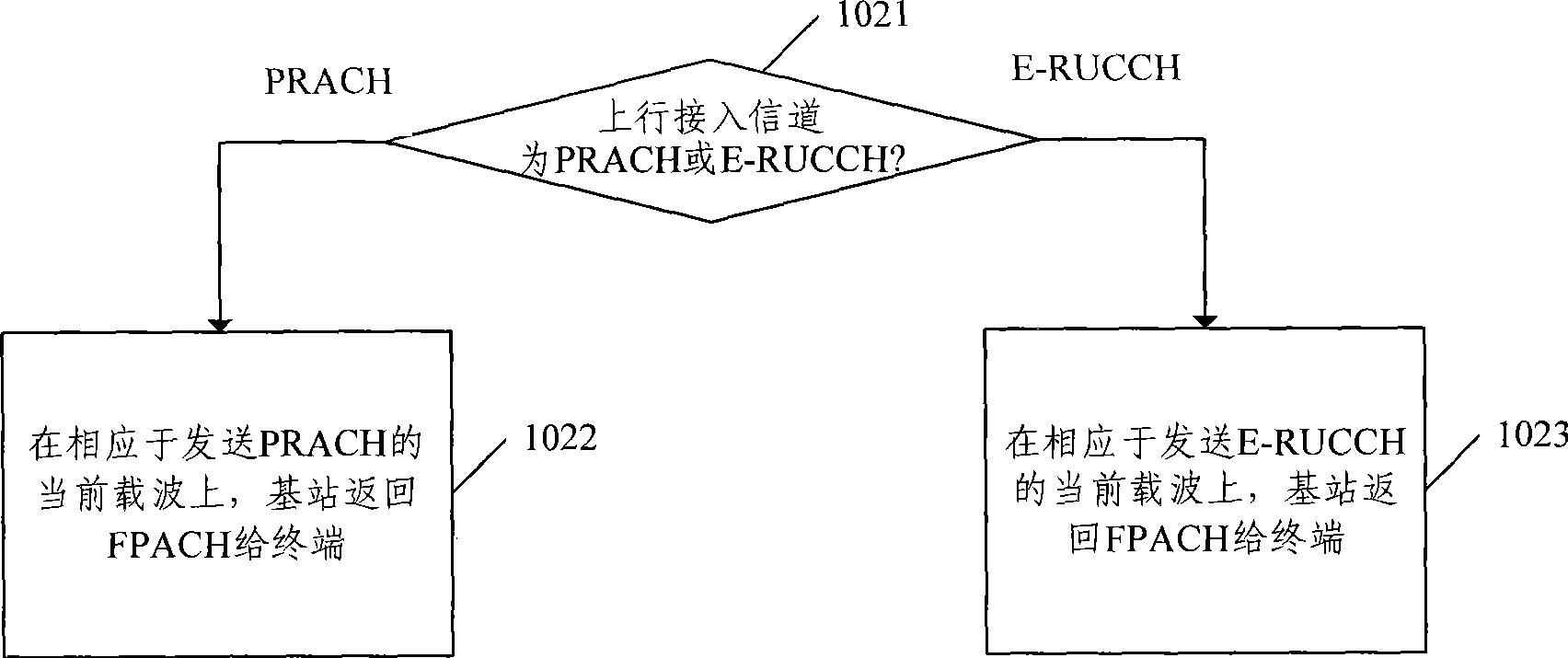
This invention discloses a random access method with enhanced ascending in Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access (TD-SCDMA) system. The method includes following steps: a terminal sends an ascending pilot channel on the selected main carrier or auxiliary carrier based on a pre-distributed ascending pilot code; a base station accesses the ascending pilot channel based on the ascending pilot code; the terminal sends a random access request on the ascending access channel; and the base station distributes the wireless resource for the terminal corresponding to the current carrier sending the ascending access channel. This invention also discloses a random access device with enhanced ascending in Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access (TD-SCDMA) system, a terminal side device and a base station device. All the method, device and apparatus adopting this invention are capable of realizing the random access with enhanced ascending in the N frequency point or multi-carrier TS-SCDMA system.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
Mobile network quality automatic monitoring system and method for GSM and 3G
ActiveCN102333334ASave manpower and material resourcesStrong real-timeWireless communicationGeneral Packet Radio ServiceThird generation
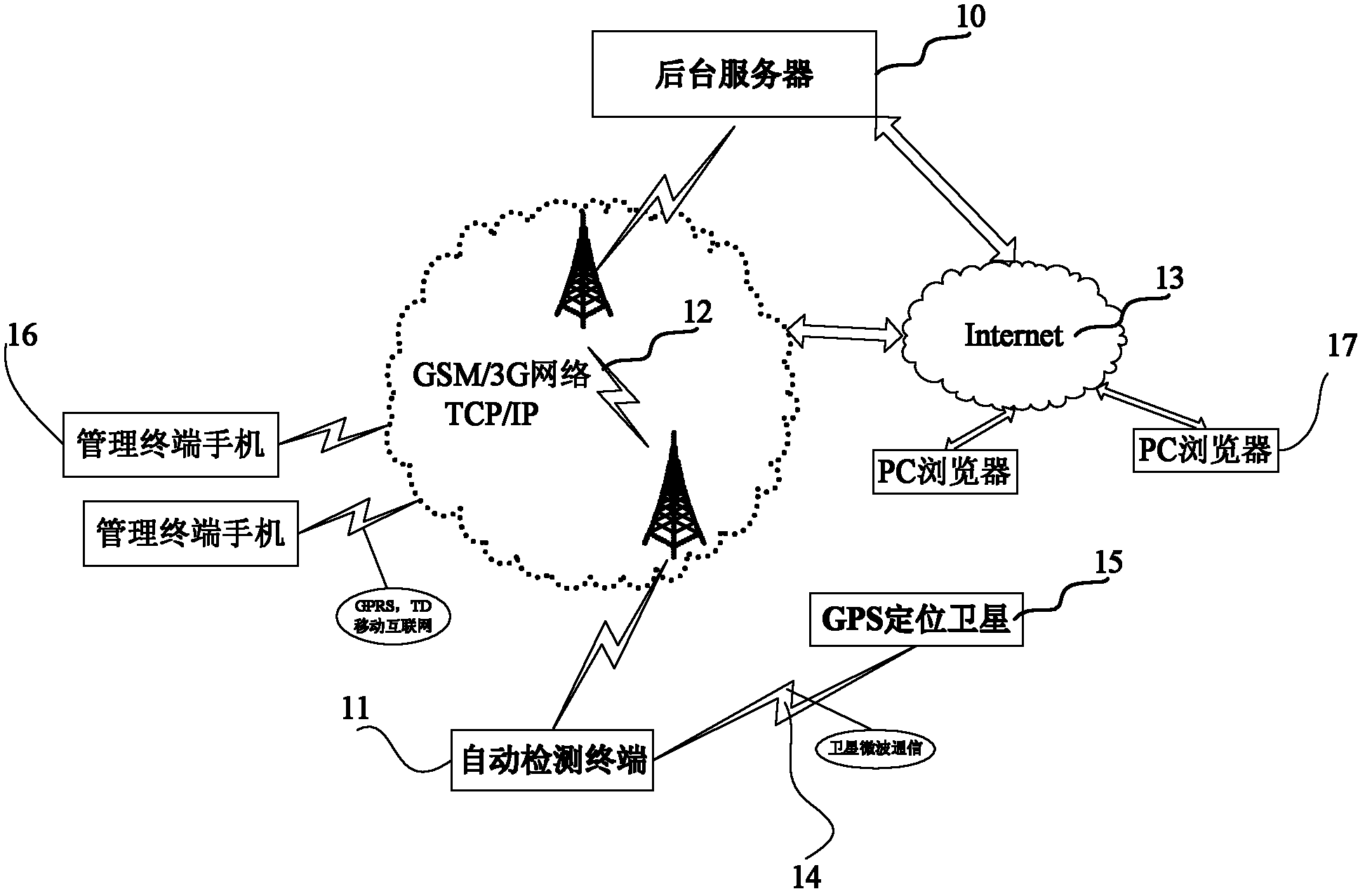
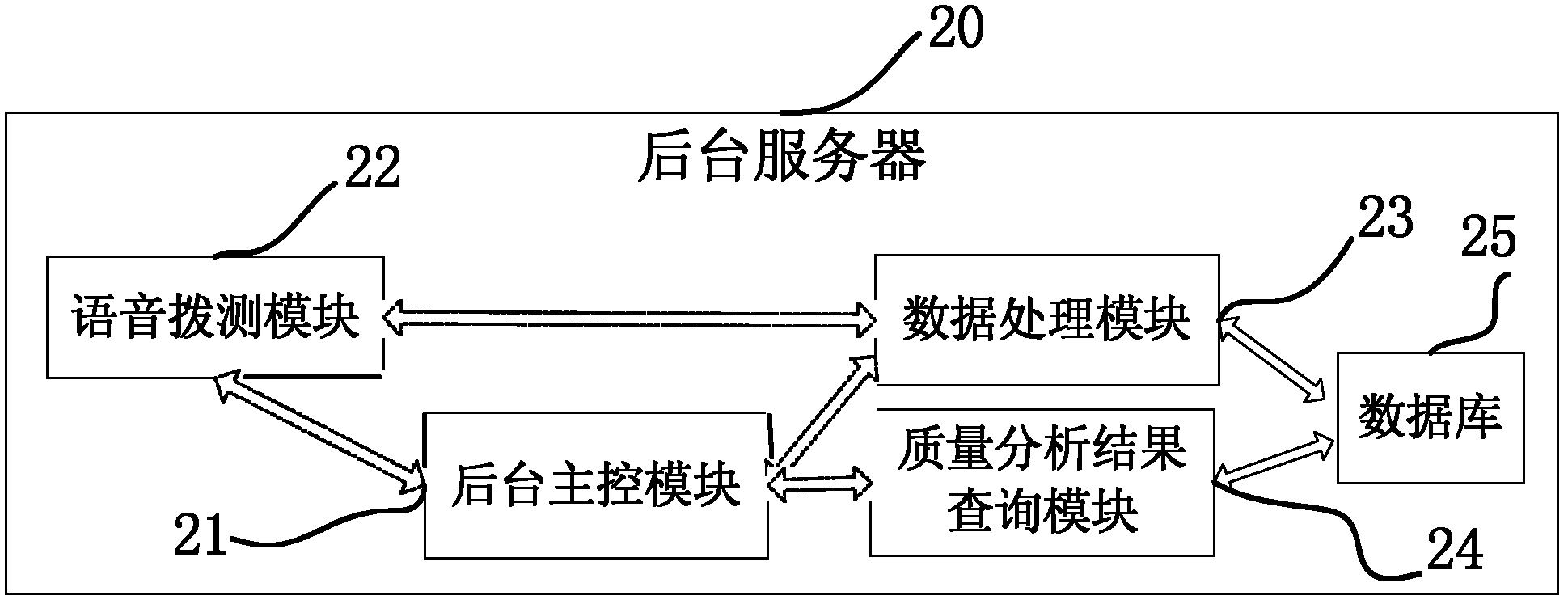
The invention discloses a mobile network quality automatic monitoring system and a method for the GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and the 3G (The 3rd Generation Telecommunication). The system comprises a background server and more than one automatic detecting terminal based on ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) embedded; and the background server is connected with all the automatic detecting terminals based on ARM embedded. The monitoring method comprises the following steps of: automatically obtaining various network quality parameters of a wireless network access module in the GSM / TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) network, executing service test to acquire service quality parameters related to voice telephone traffic, and transmitting the acquired parameters to the background server through a TCP / IP protocol of the GPRS / TD (General Packet Radio Service / Time Division) wireless network when the system is idle so as to analyze and evaluate every parameter of the network quality. The background server processes and stores the network quality parameters returned back by the automatic detecting terminals, which is convenient for managers to access data, and analyze network conditions and solve problems in time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
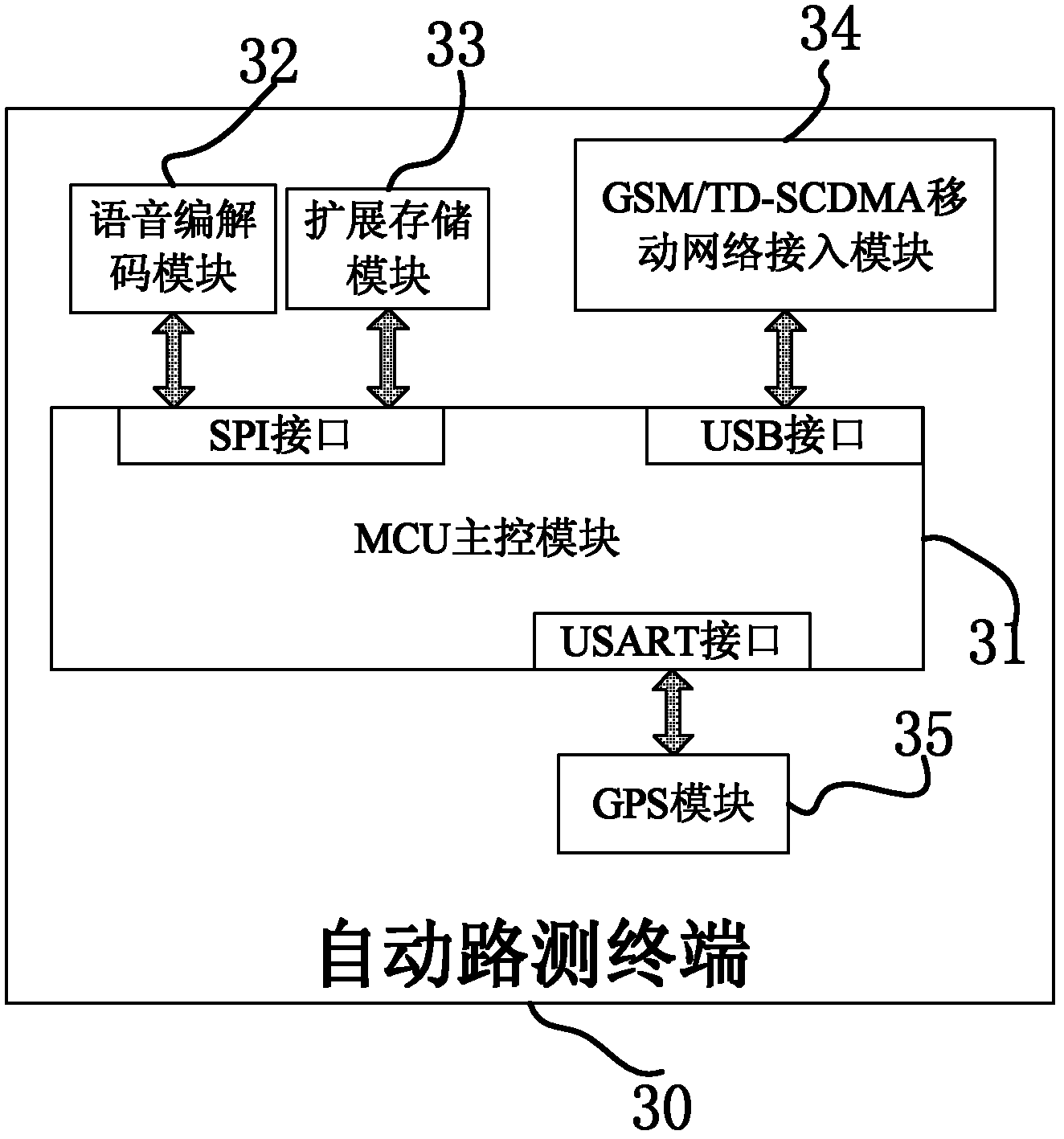
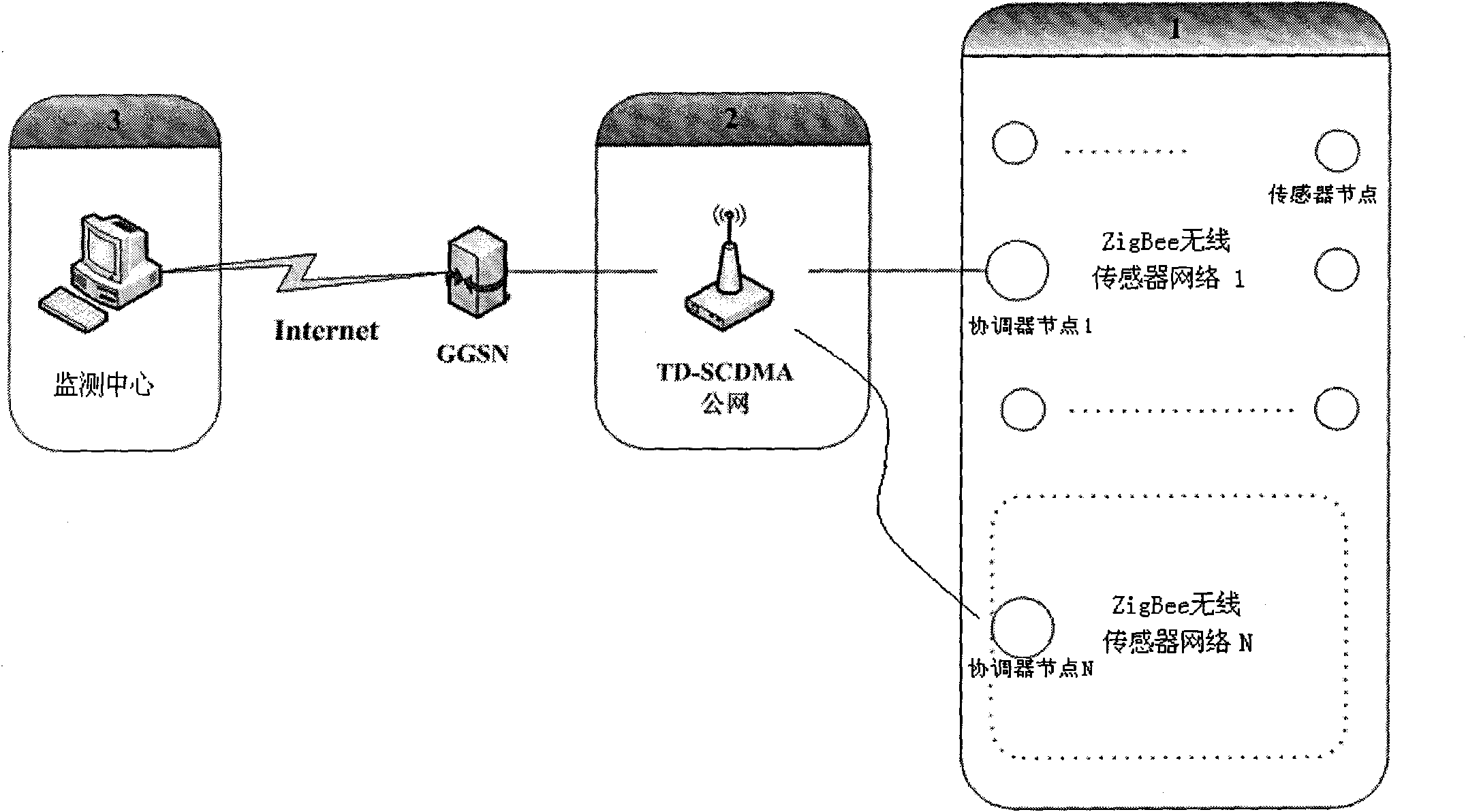
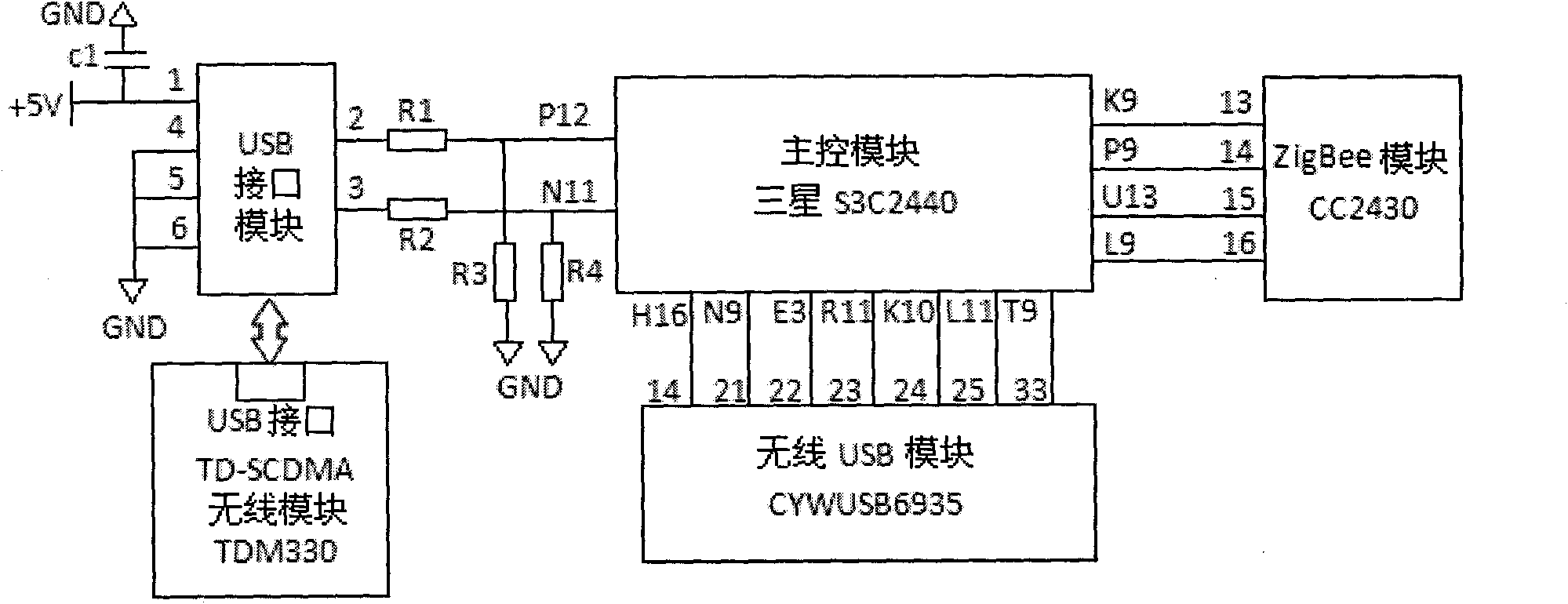
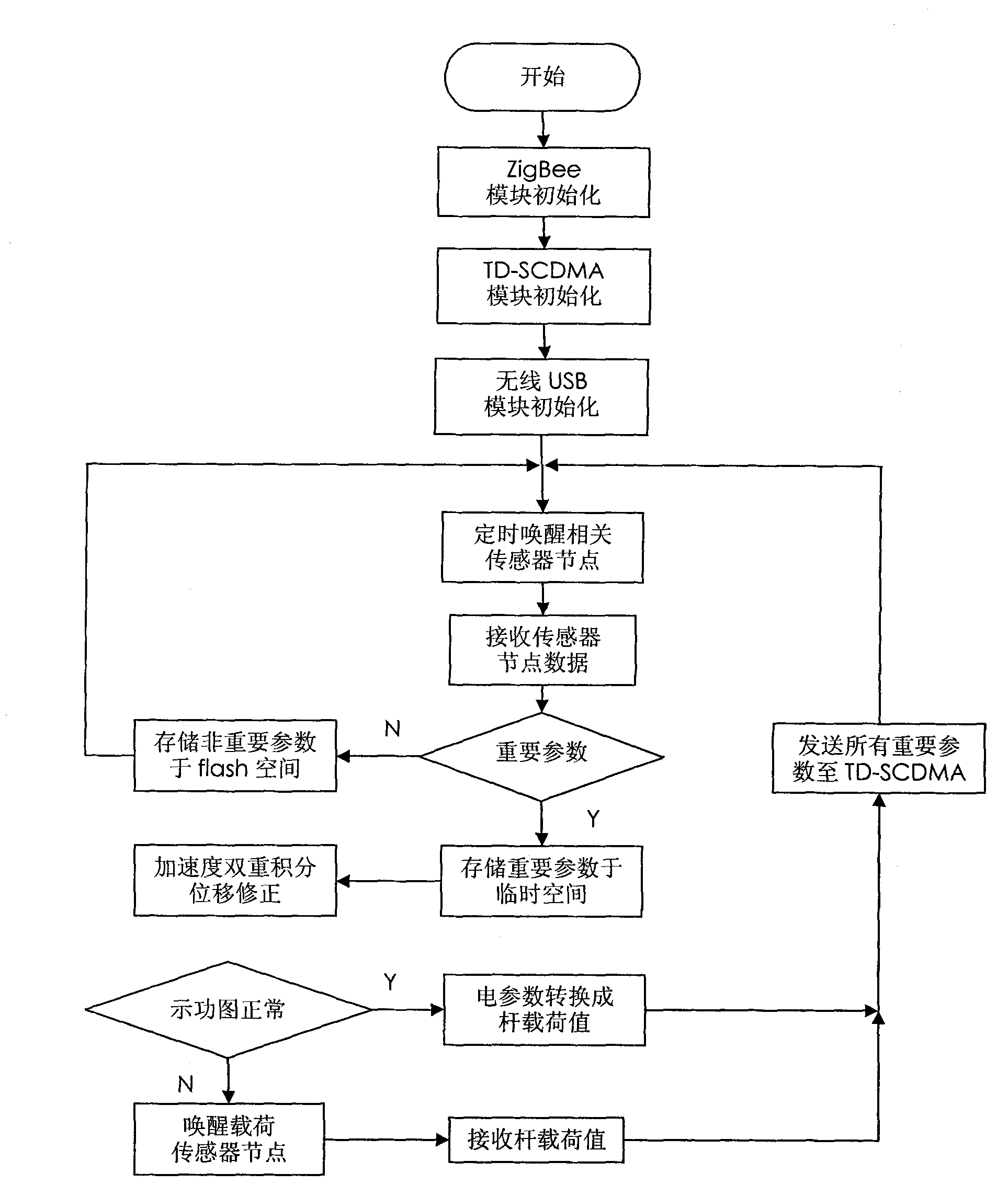
Beam pumping unit remote monitoring method and system based on wireless sensor network and TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access)
InactiveCN101819432AImprove reliabilitySave electricityEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesWireless mesh networkIndicator diagram
The invention discloses beam pumping unit remote monitoring method and system based on a wireless sensor network and a TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access). The system comprises three parts of a wireless sensor network of a local scope, a TD-SCDMA public network and a beam pumping unit remote monitoring center. The wireless sensor network comprises a plurality of sensor nodes and a unique coordinator node which is also used as a ZifBee / TD-SCDMA gateway; important beam pumping unit working condition parameters are uploaded to the beam pumping unit remote monitoring center through the TD-SCDMA gateway on line in real time; general working condition parameters are temporarily stored on the coordinator node, acquired by an inspector with wireless USB acquirer in hand in fixed time and off-line aggregated to the beam pumping unit remote monitoring center; and a beam pumping unit indicator diagram (rod load and displacement relationship diagram) is obtained by adopting a cooperative work mode of indirect and direct measurement, which improves the reliability of the monitoring system. The ZigBee wireless sensor network replaces traditional complicated sensor node wiring communication, which improves the reliability of a field detection system; and moreover, the sensor node adopts an intermittent working mode with timing awakening, which saves the electric energy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Controller for GSM and 3G base transceiver stations in a GSM core network with external handover possibility from 3G cells to GSM cells transparent to GSM core network
A station controller (M-BSC) is connected to base transceiver stations BTS of the GSM (Global System for Mobile), or DCS (Digital Cellular System) mobile transceiver system, and to BTSC base transceiver stations of the TD-SCDMA (Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access) system through code division transceiver access technology, typical of 3G systems, and TDD duplexing. The controller is connected to a MSC circuit switch of GSM type. The new 3G technology shares the GSM core network, which on the contrary ignores the existence of the latter. Transparency of the 3G new technology towards the core network is achieved inhibiting any handover from GSM cells to BTSC cells and enabling the external handover (through MSC intervention) from BTSC cells to GSM cells after appropriate treatment of information to be sent to MSC. The ad hoc procedure is carried out by the station controller and consists in reprocessing the mixed list (2G and 3G) of cells candidate for handover furnished with by BTSC, to obtain two lists of cells differing as to radio technology, selecting a list to be forwarded to MSC according to service qualification criteria, comparing in a local memory the (MS / UE) mobile classmarks owned by MSC with those associated to the selected list and, in case of inconsistency, updating MSC classmarks prior to the forwarding of the selected list.
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
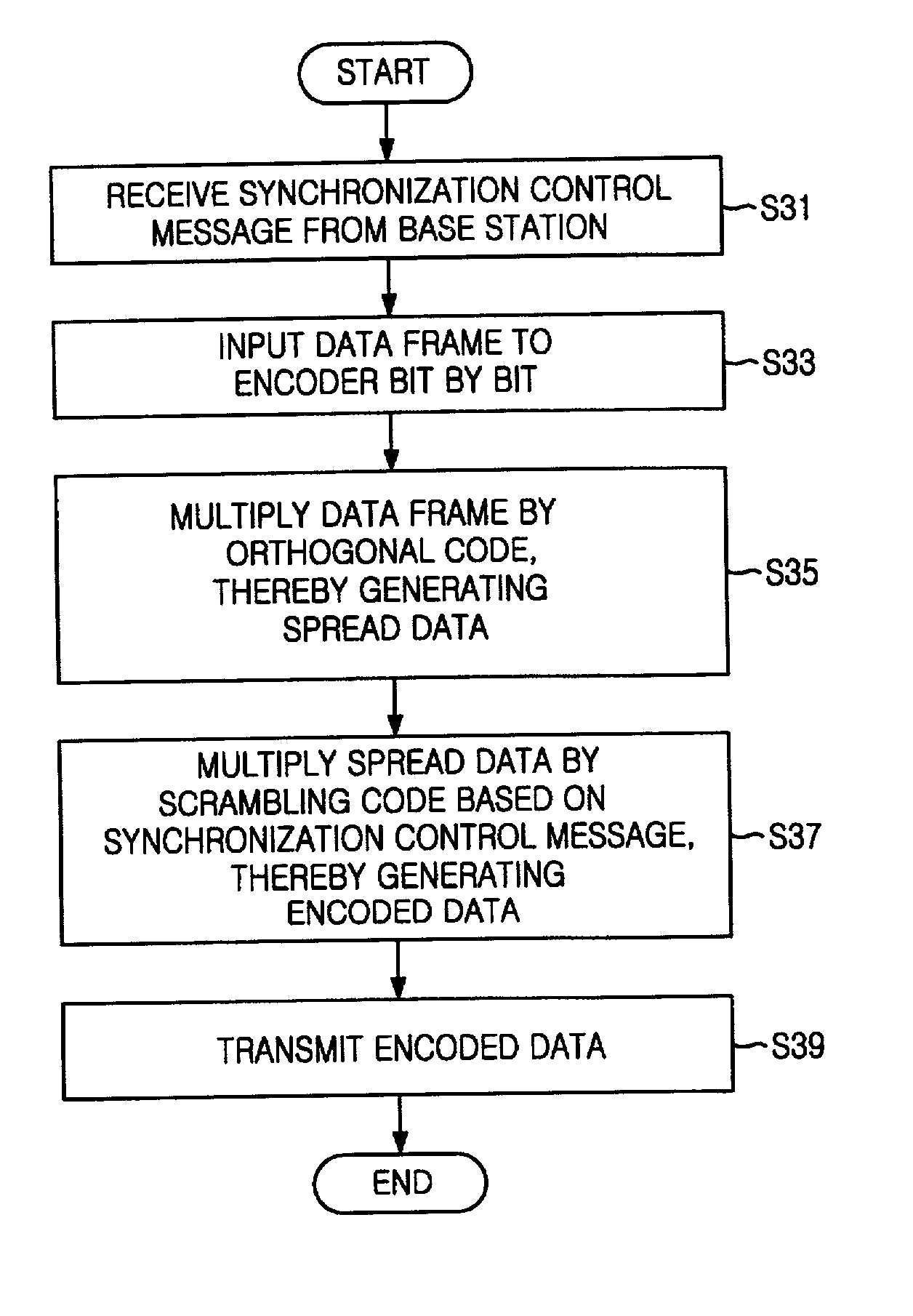
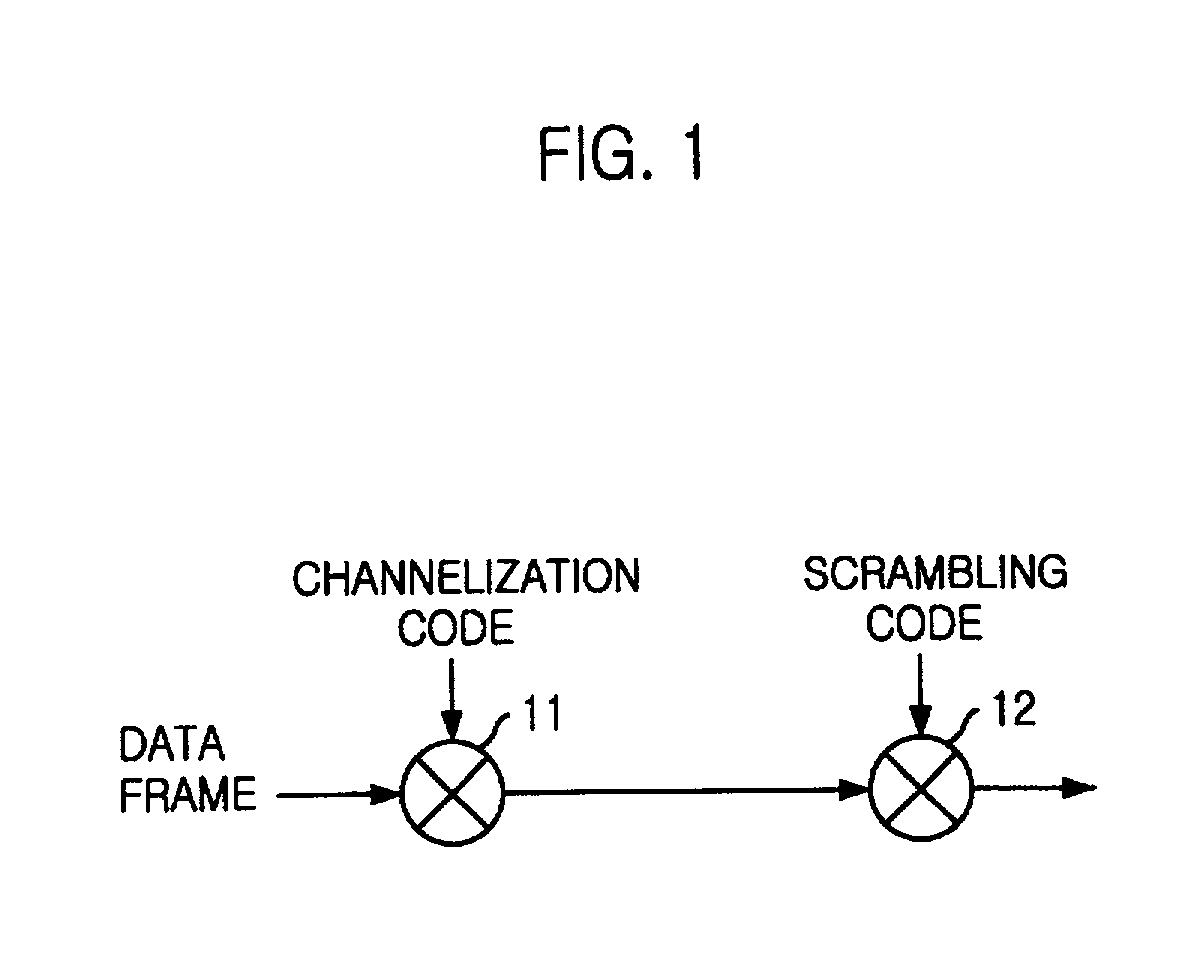
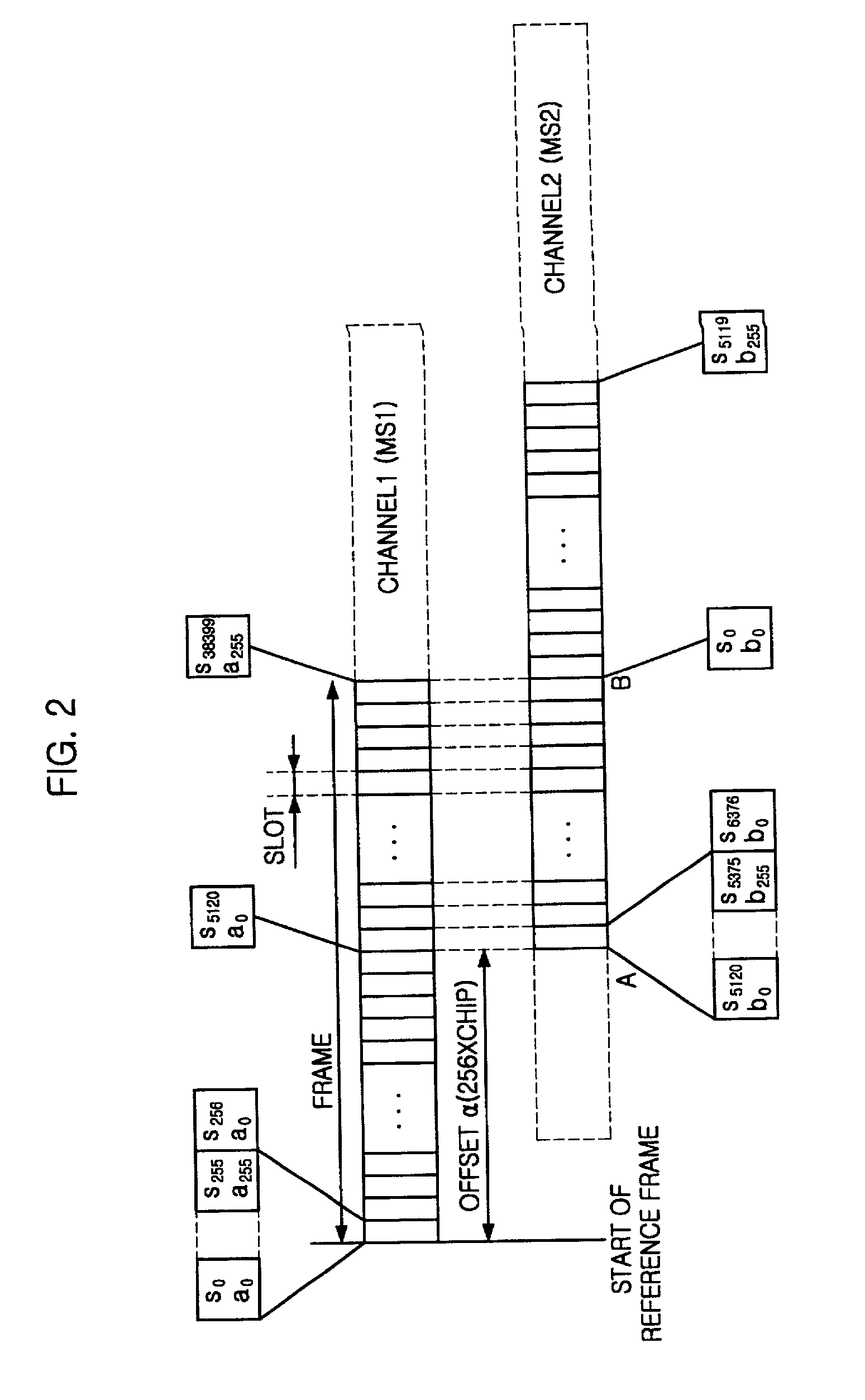
Method for assigning codes in uplink of synchronous wireless telecommunication system
InactiveUS20020003786A1Time-division multiplexConnection managementCode division multiple accessMobile station
A method for assigning codes in an uplink of a synchronous code division multiple access (CDMA) telecommunication system is disclosed. The method for assigning a code in a reverse channel of a synchronous wireless telecommunication system, comprising the steps of: a) at a mobile station, receiving time matching information of a scrambling code from a base station; b) at the mobile station, spreading data frame to be transmitted by an orthogonal code, thereby generating a spread data; and c) at the mobile station, multiplying the spread data by a scrambling code based on the time matching information of the scrambling code, thereby generating an encoded data.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
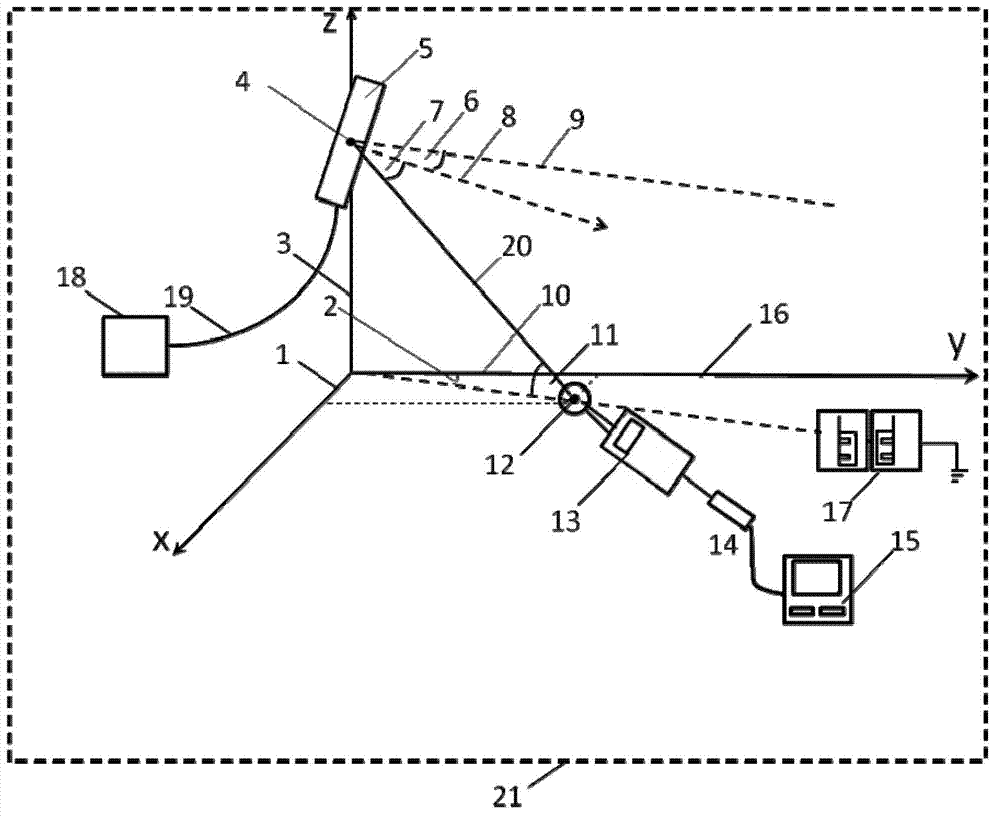
Three-dimensional space prediction method for electromagnetic radiation of TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) mobile communication base station environment
InactiveCN103076505AIncrease coverageReduce site selection costsElectromagentic field characteristicsThree-dimensional spaceEngineering
The invention discloses a three-dimensional space prediction method for electromagnetic radiation of a TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) mobile communication base station environment. The key is to obtain the relationship of the electromagnetic radiation intensity S of a base station and the horizontal distance, the height difference and the azimuth angle of a base station antenna, namely the three-dimensional space distribution result of the electromagnetic radiation level of the base station, through a three-dimensional space prediction mode for the electromagnetic radiation of the TD-SCDMA mobile communication base station environment provided by the invention. According to the characteristic of the environmental influence of the electromagnetic radiation of the TD-SCDMA mobile communication base station, the invention provides a method for obtaining directivity functions f (Theta) and f (Phi) with a smaller error. The correction factor K1 of a base station launch system, the correction factor K2 of the antenna directivity function f (Theta) and the correction factor K3 of the antenna directivity function f (Phi) are added, so that the prediction precision is further increased, the practicality and the operability are increased, the site selection cost of the TD-SCDMA base station of operators is significantly reduced, and the network coverage rate is increased.
Owner:广东省辐射防护协会 +1
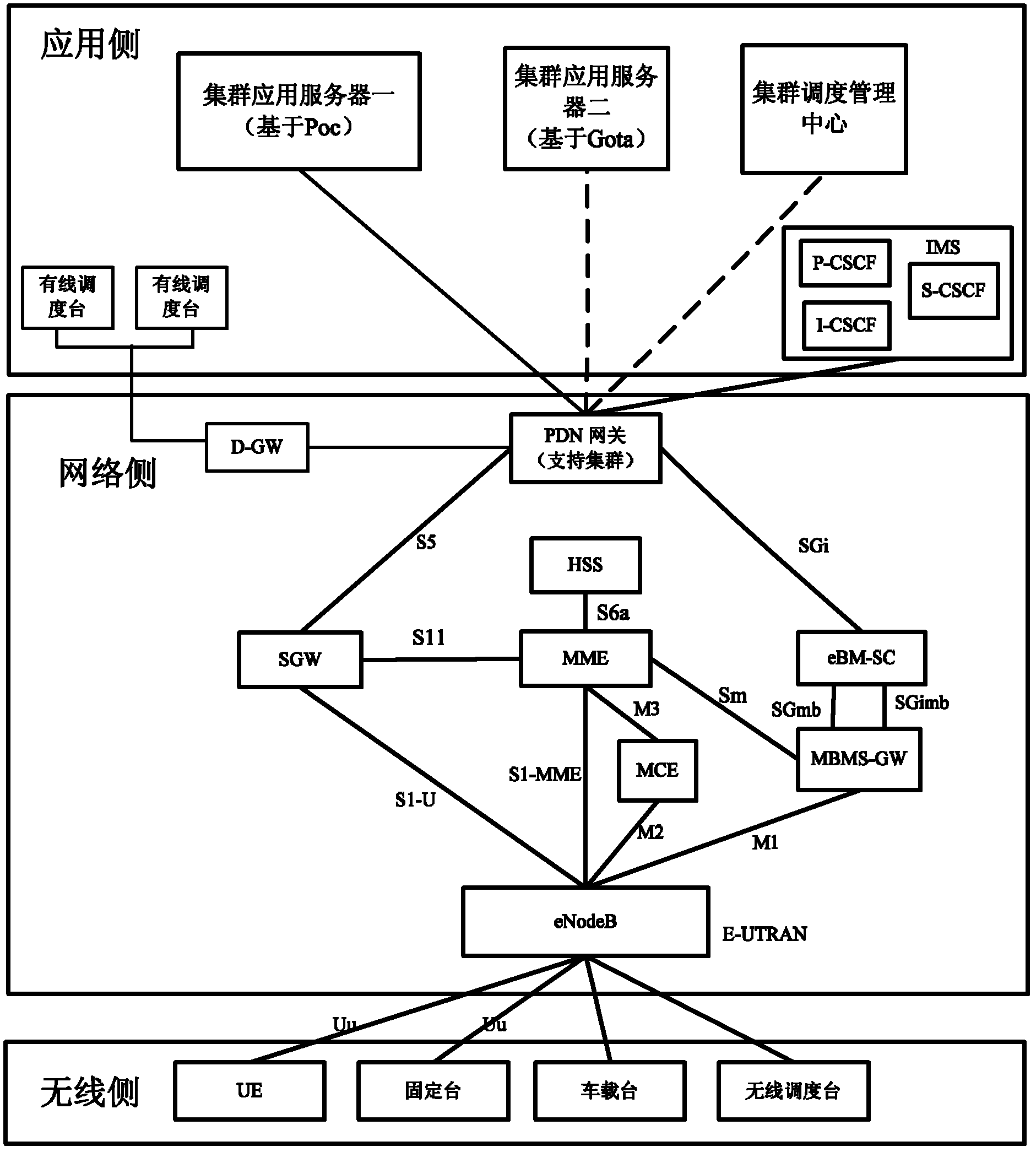
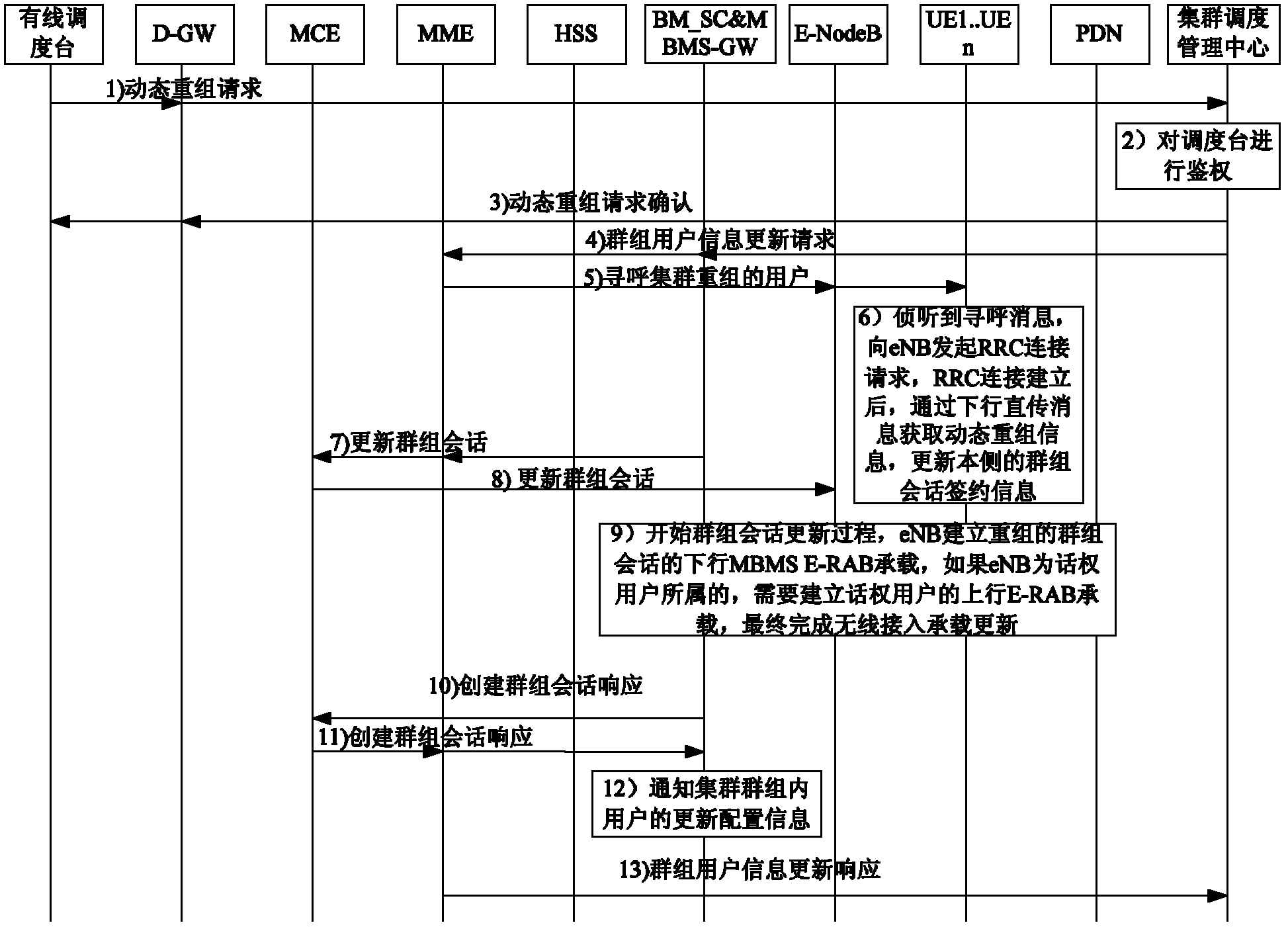
Achieving method of dynamic regrouping serve and broadband digital cluster system
InactiveCN103167421ARealize dynamic reorganization functionNetwork topologiesBroadcast service distributionTime-Division Long-Term EvolutionCluster systems
The invention provides an achieving method of dynamic regrouping serve and a broadband digital cluster system. The method is applied to the broadband digital cluster system based on time division long term evolution (TD-LTE). The method includes that after a cluster scheduling management center receives dynamic regrouping requests, authentication is conducted to objects sending the requests and users in operation objects carried in the requests; the dynamic regrouping requests further carry operation indication information; after the authentication is passed, the cluster scheduling management center sends group user information updating requests to a mobile management entity (MME), and the group user information updating requests carry label information of all users inside groups related by the operation; and after MME receives the group user information updating requests, corresponding users conduct updating of user group information through a group paging method. The achieving method achieves a dynamic regrouping function through minimal standard agreement modification, and is an important constituting part of the broadband digital cluster system based on TD-LTE.
Owner:ZTE CORP
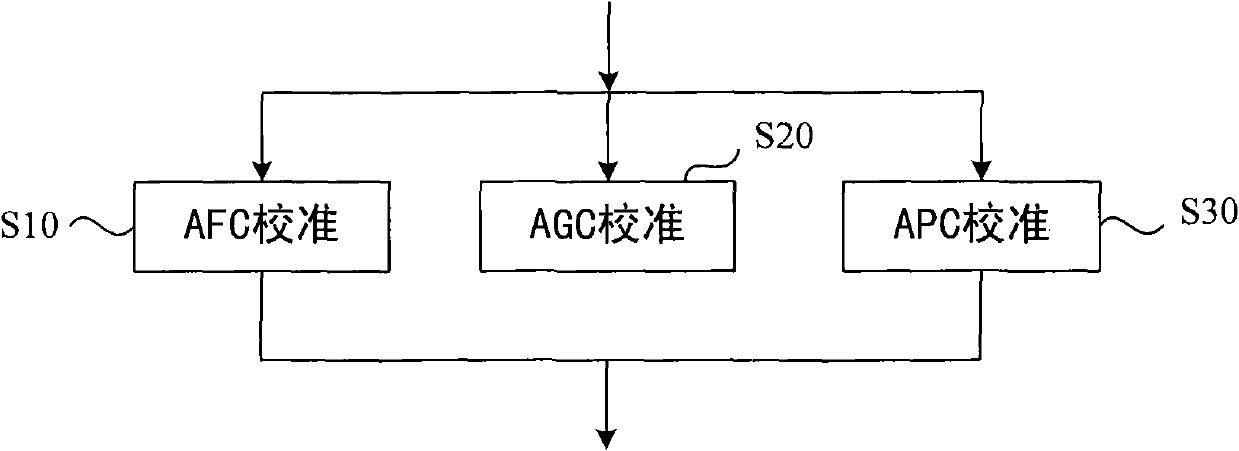
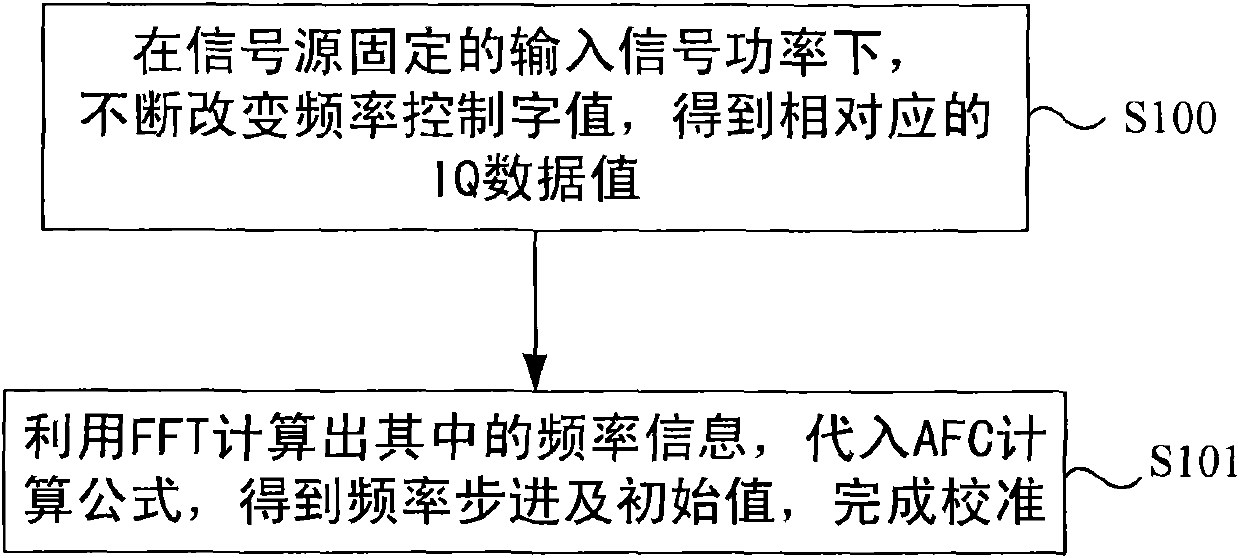
Calibration method of time division-synchronization code division multiple access (TD-SCDMA) terminal
InactiveCN102088321AImprove utilization efficiencyReduce the number of output changesSubstation equipmentTransmission monitoringSpectrographAutomatic frequency control
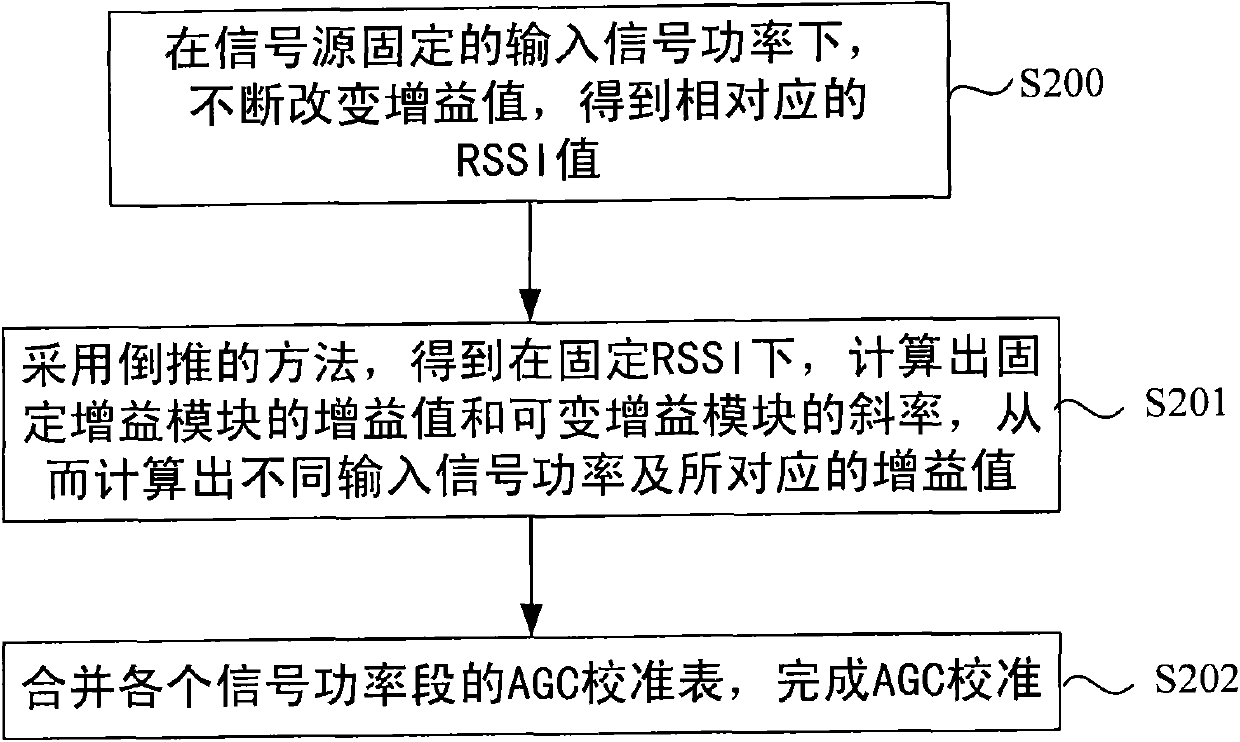
The invention discloses a calibration method of a time division-synchronization code division multiple access (TD-SCDMA) terminal, which increases terminal calibration speed and enhances terminal calibration accuracy. The technical scheme comprises three aspects, namely automatic frequency control calibration, automatic gain control calibration and automatic power control calibration, wherein the automatic frequency control calibration comprises the following steps of: under the fixed input signal power of a signal source, changing a control word; demodulating to acquire data of a plurality of frames; calculating frequency information; and performing linear variation to acquire a step change value and an automatic frequency control initial value; the automatic gain control calibration comprise the following steps of: under the fixed input signal power of the signal source, changing the control word to acquire a plurality of groups of receiving signal intensity values, a gain value of a fixed gain module and a gain slope of a variable gain module; calculating input signal power and a gain value and combining automatic gain calibration tables; and the automatic power control calibration comprises the following steps of: transmitting a power list by gradually increasing or decreasing control words at a fixed periodic interval by using the terminal; acquiring data by using a frequency spectrograph; and selecting a power value and a control word.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
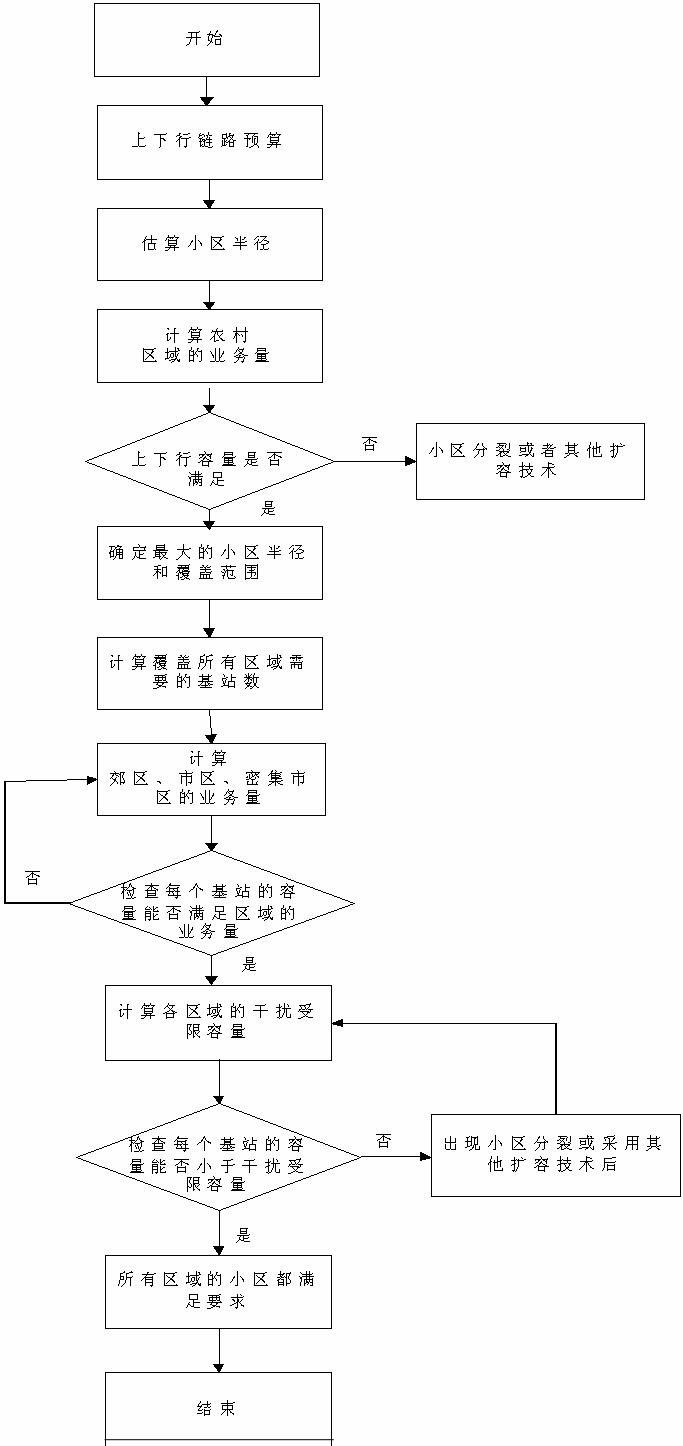
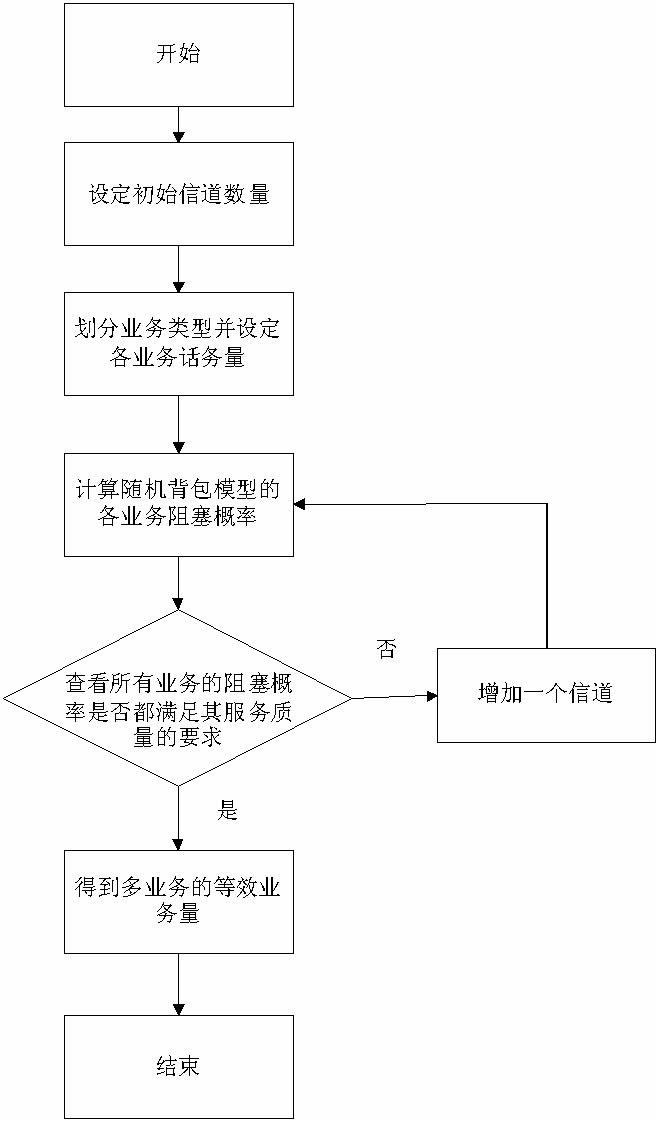
Capacity and coverage combined design method for TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) cluster system
InactiveCN102231884APrecise Interference SituationAchieve balanceNetwork planningSystem capacityComputer architecture
The invention discloses a capacity and coverage combined design method for a TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) cluster system and relates to cluster communication. The technical scheme of the method comprises the following steps of: establishing a corresponding propagation model according to the maximum link loss of links; respectively calculating traffic volume of each cell according to the user density of different service cell types, the average traffic volume of each user and the coverage area of the current base station; estimating service cell radiusaccording to traffic volume and a communication satisfaction degree threshold and calculating the interference limited capacity of each service cell; checking whether or not the interference limited capacity of base stations in the cells meets the capacity requirement of coverage areas of the base stations in the cells one by one; and if not, performing a capacity expansion technology till the capacity requirement of the coverage areas can be met, and then determining the number of channels. The method can be applied to the plan and optimization of a TD-SCDMA cluster network.
Owner:SHENZHEN TINNO WIRELESS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com