Patents
Literature
1765 results about "Packet switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
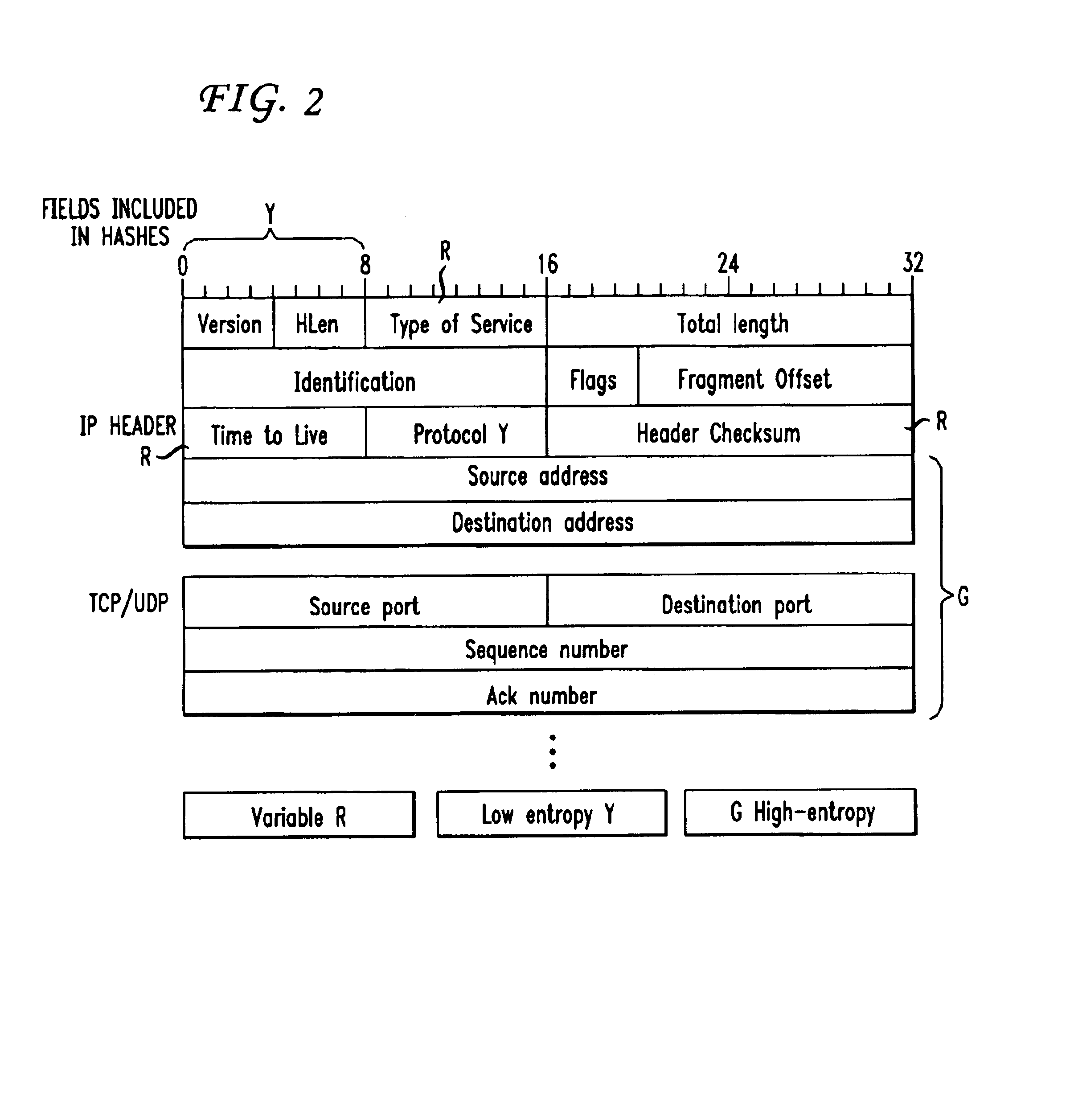
Packet switching is a method of grouping data that is transmitted over a digital network into packets. Packets are made of a header and a payload. Data in the header are used by networking hardware to direct the packet to its destination where the payload is extracted and used by application software. Packet switching is the primary basis for data communications in computer networks worldwide.
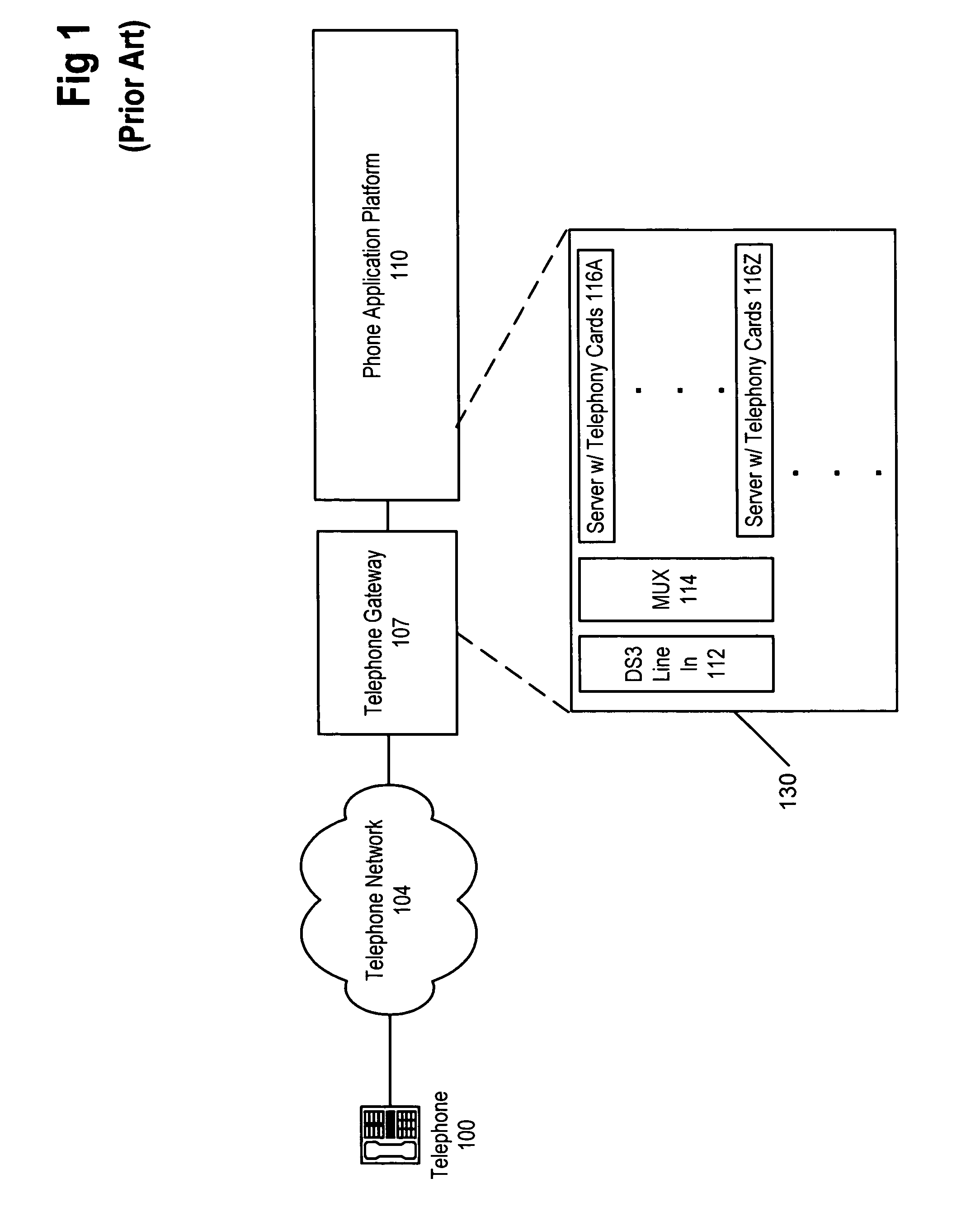
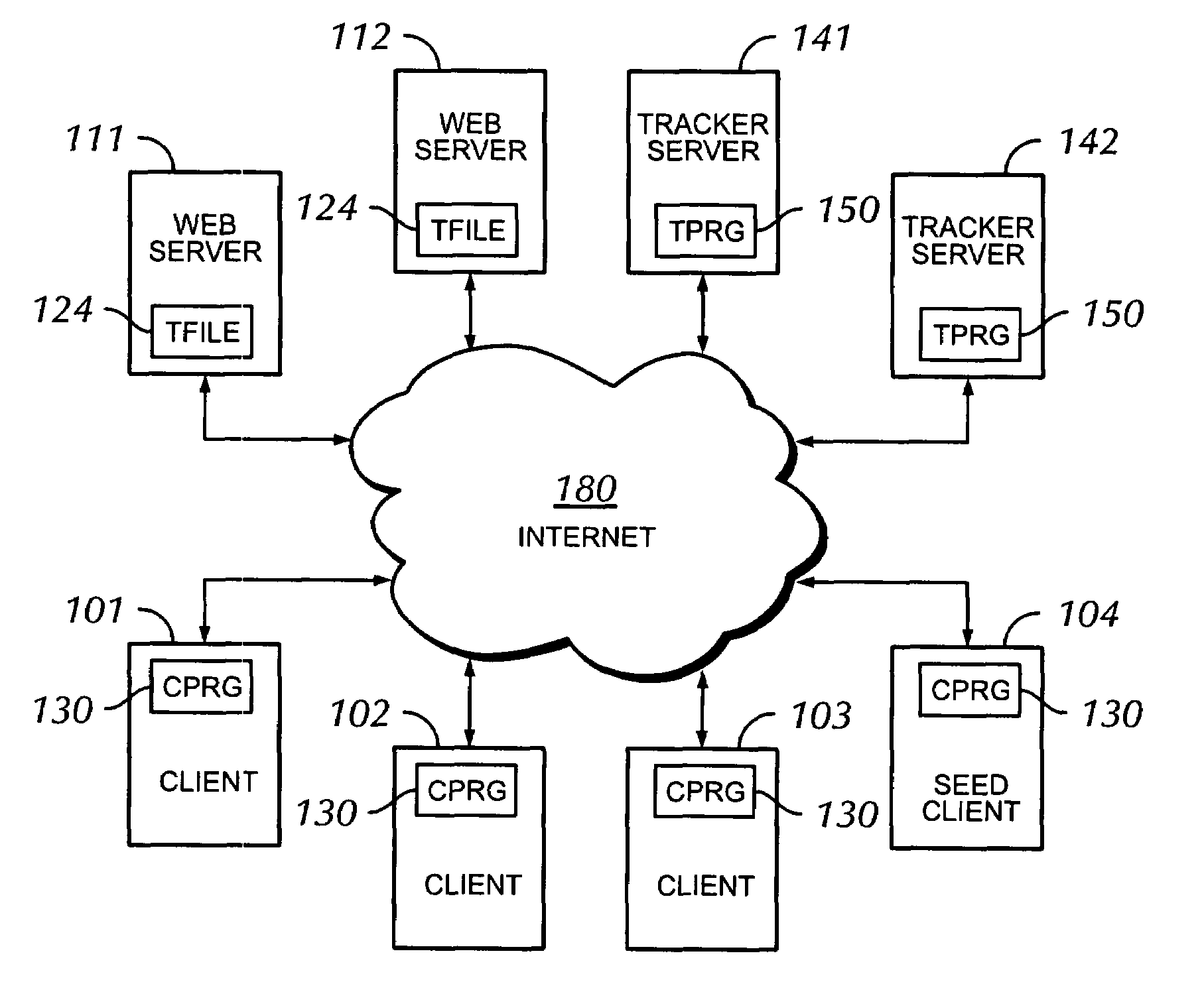
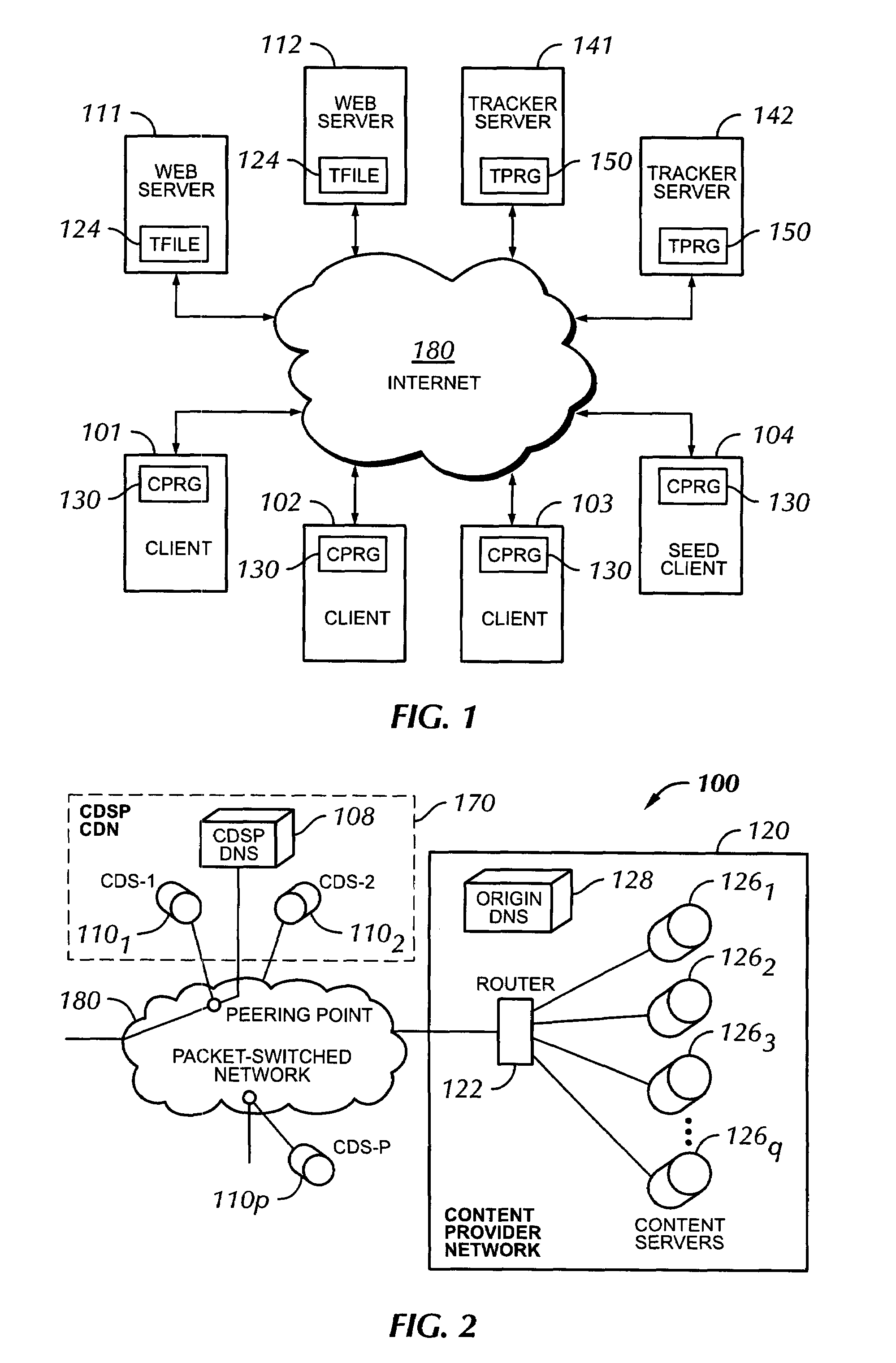
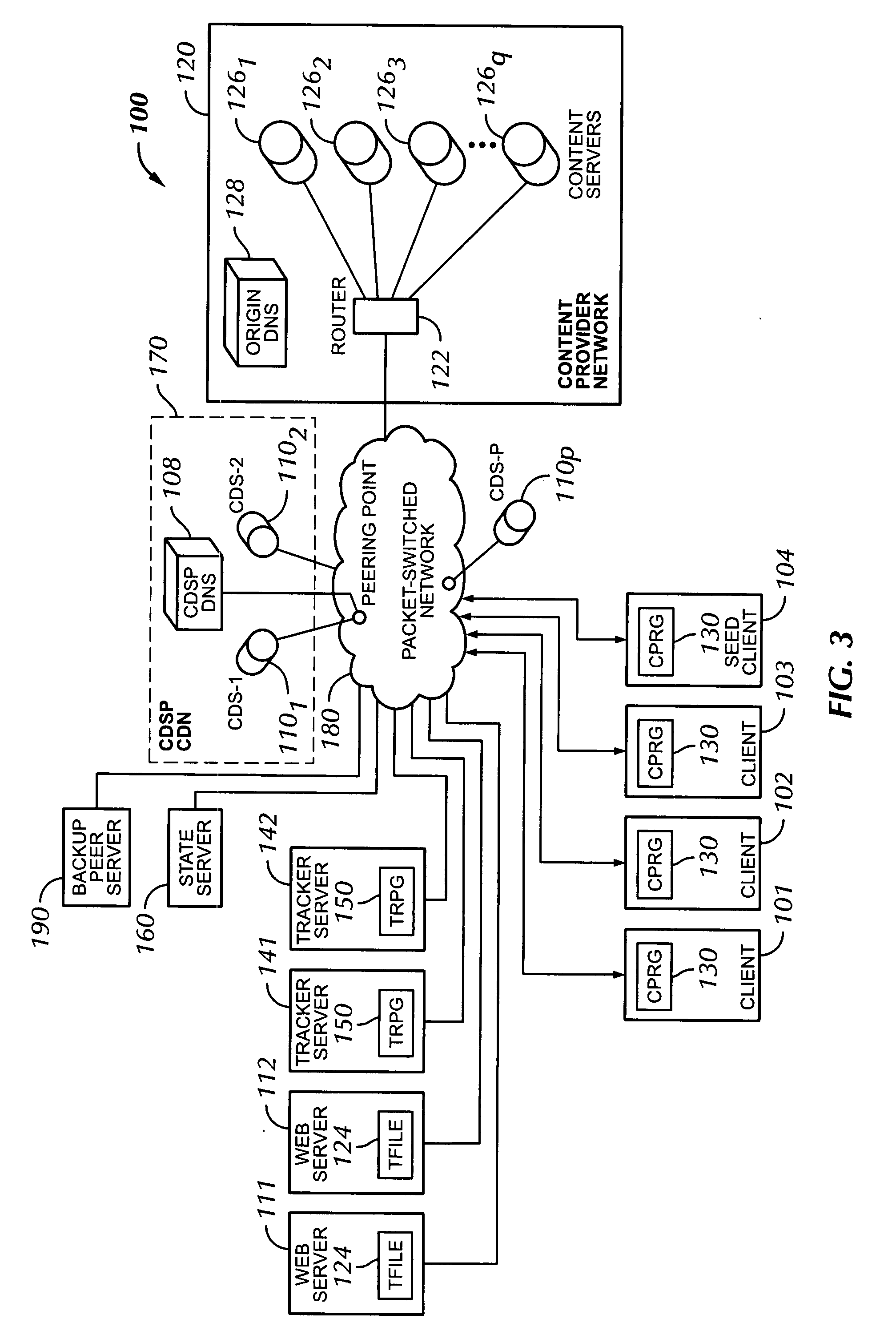
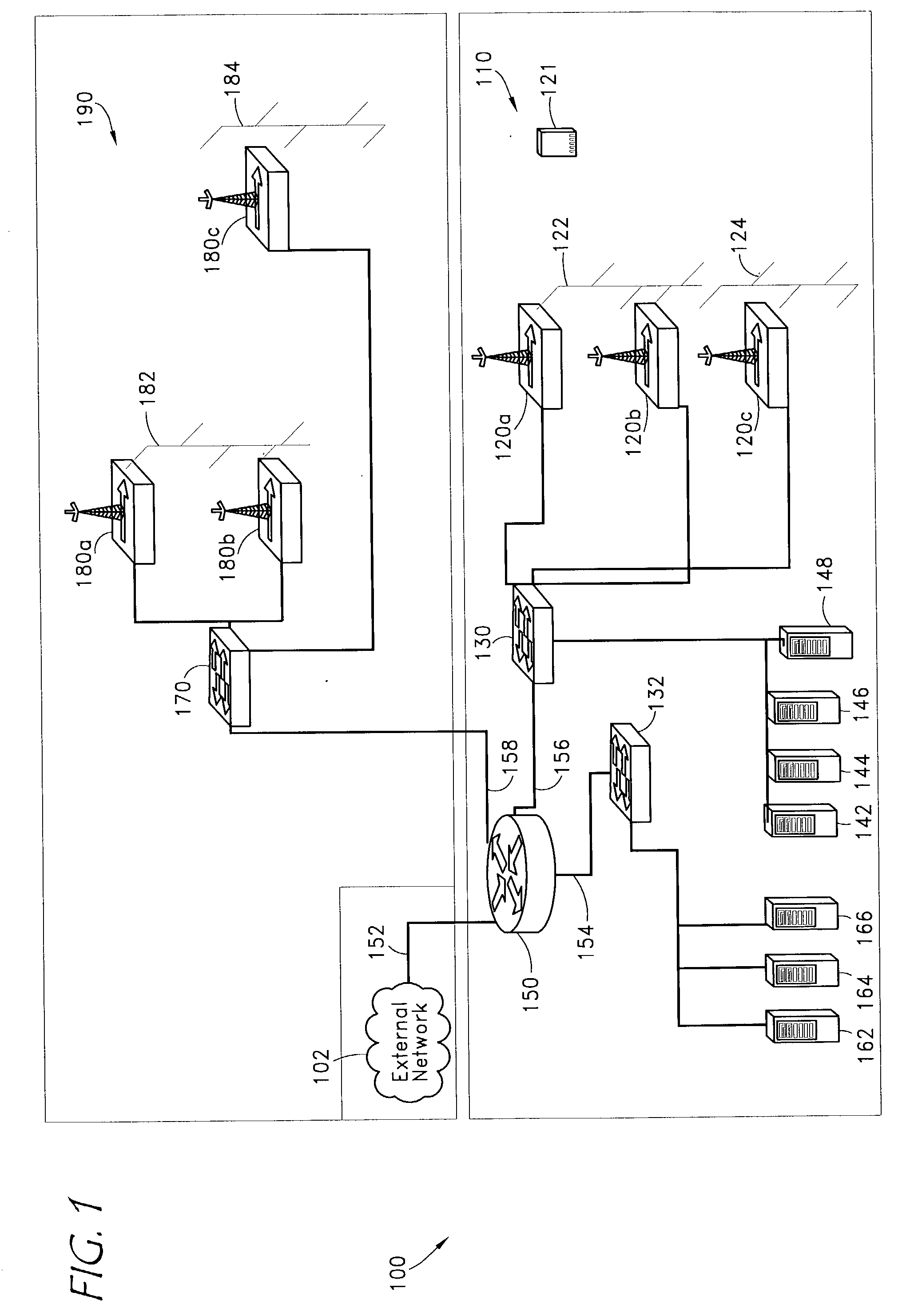
Voice over data telecommunications network architecture
InactiveUS6614781B1Interconnection arrangementsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionNetwork operations centerNetwork architecture
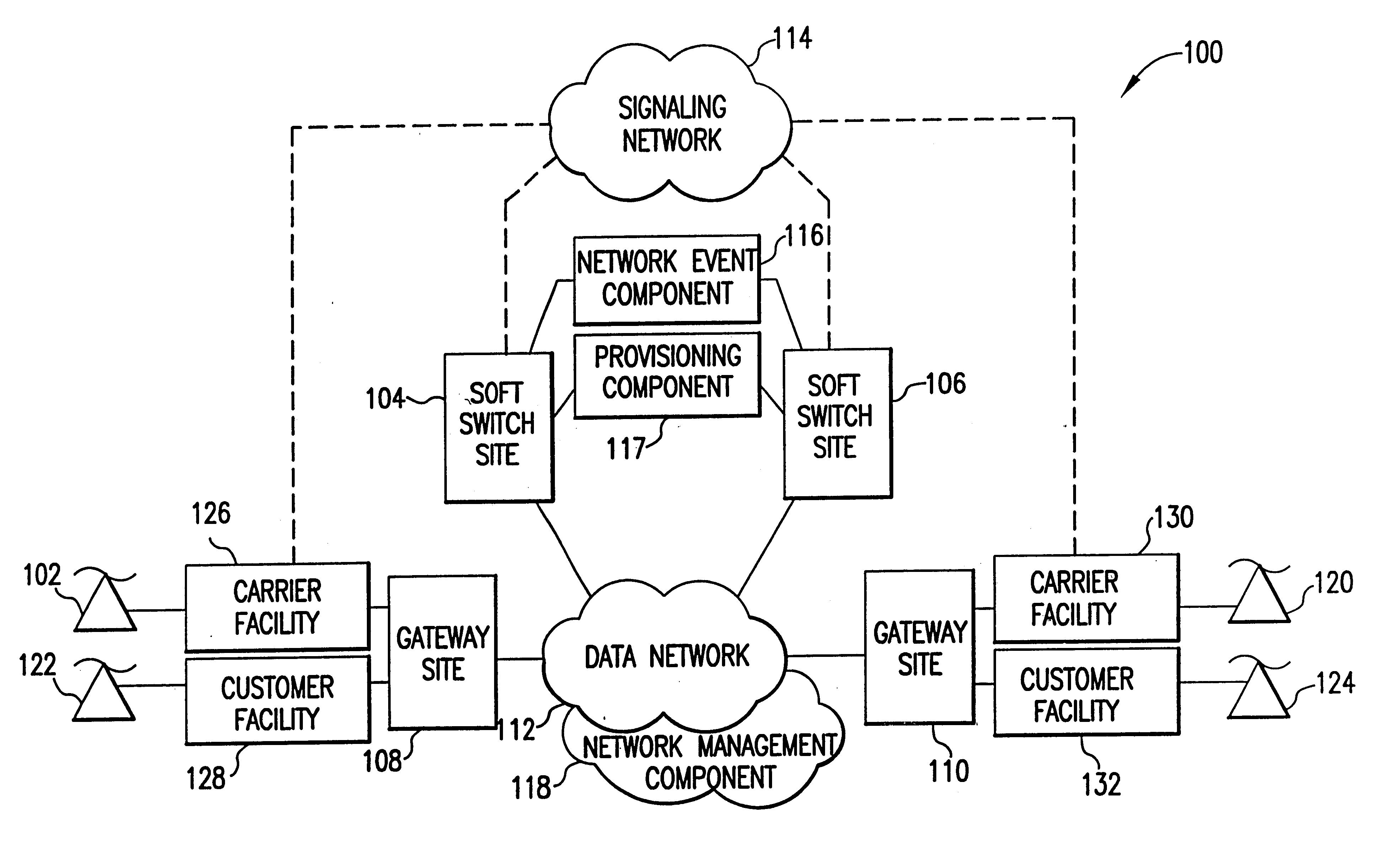
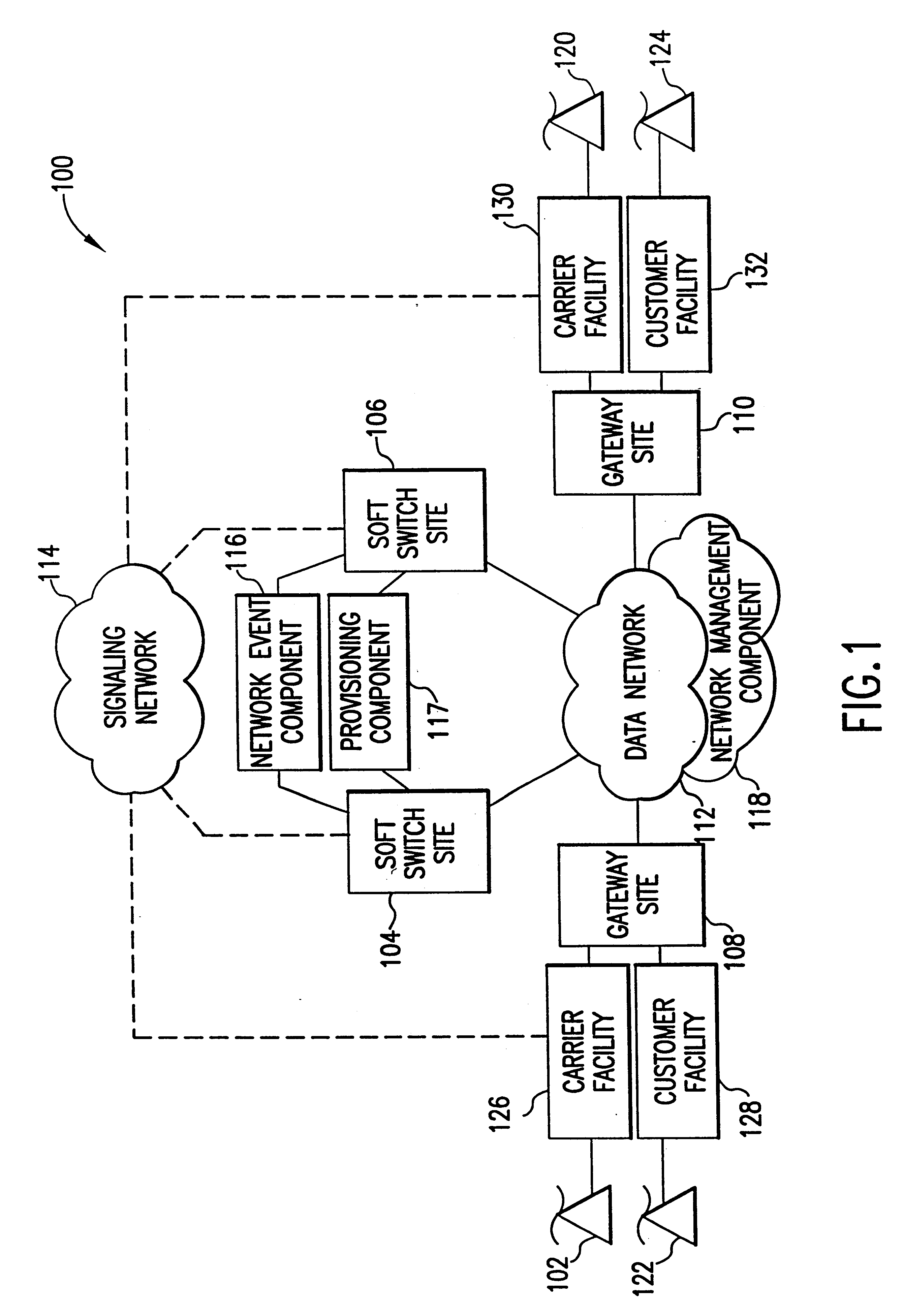
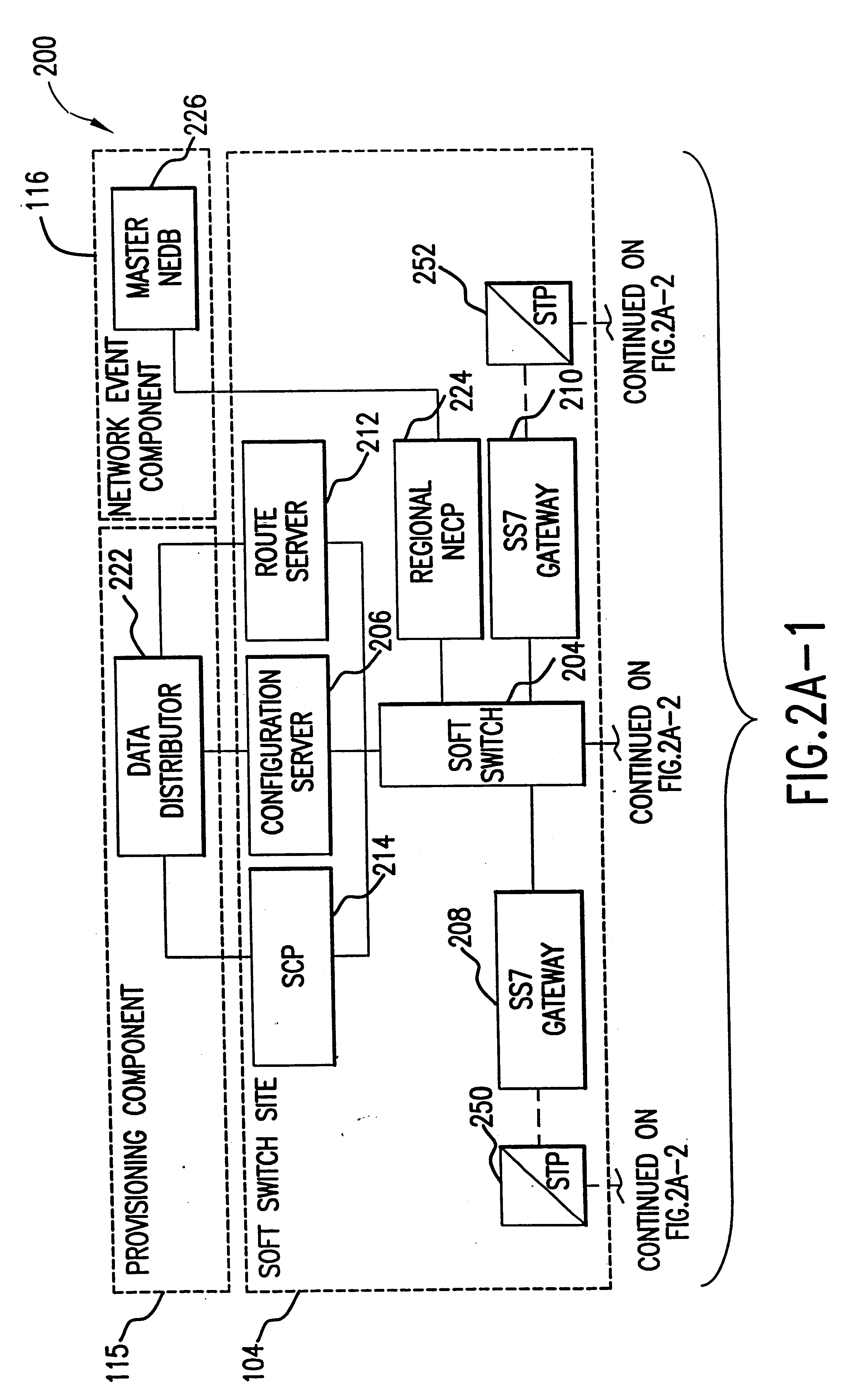
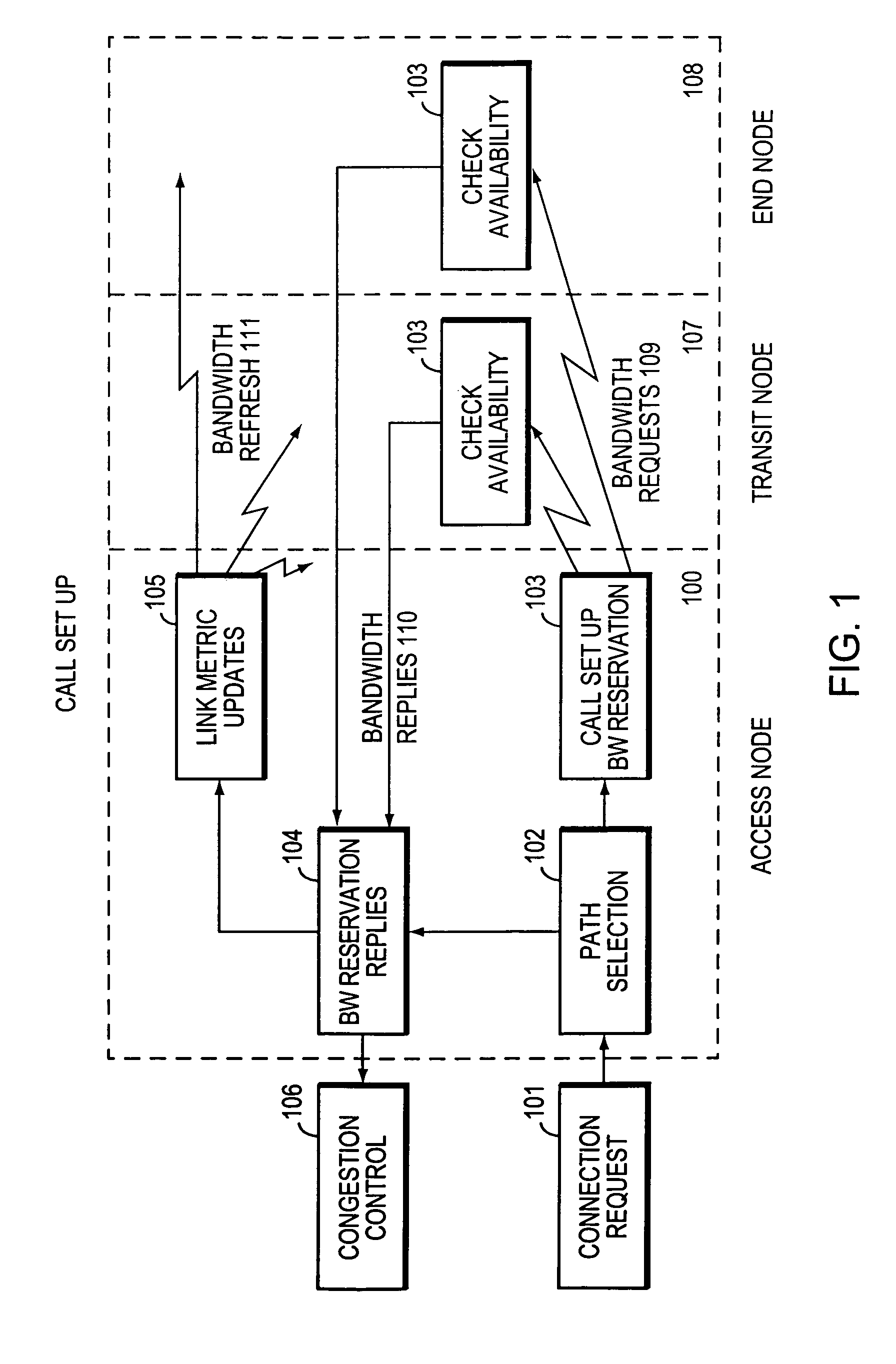
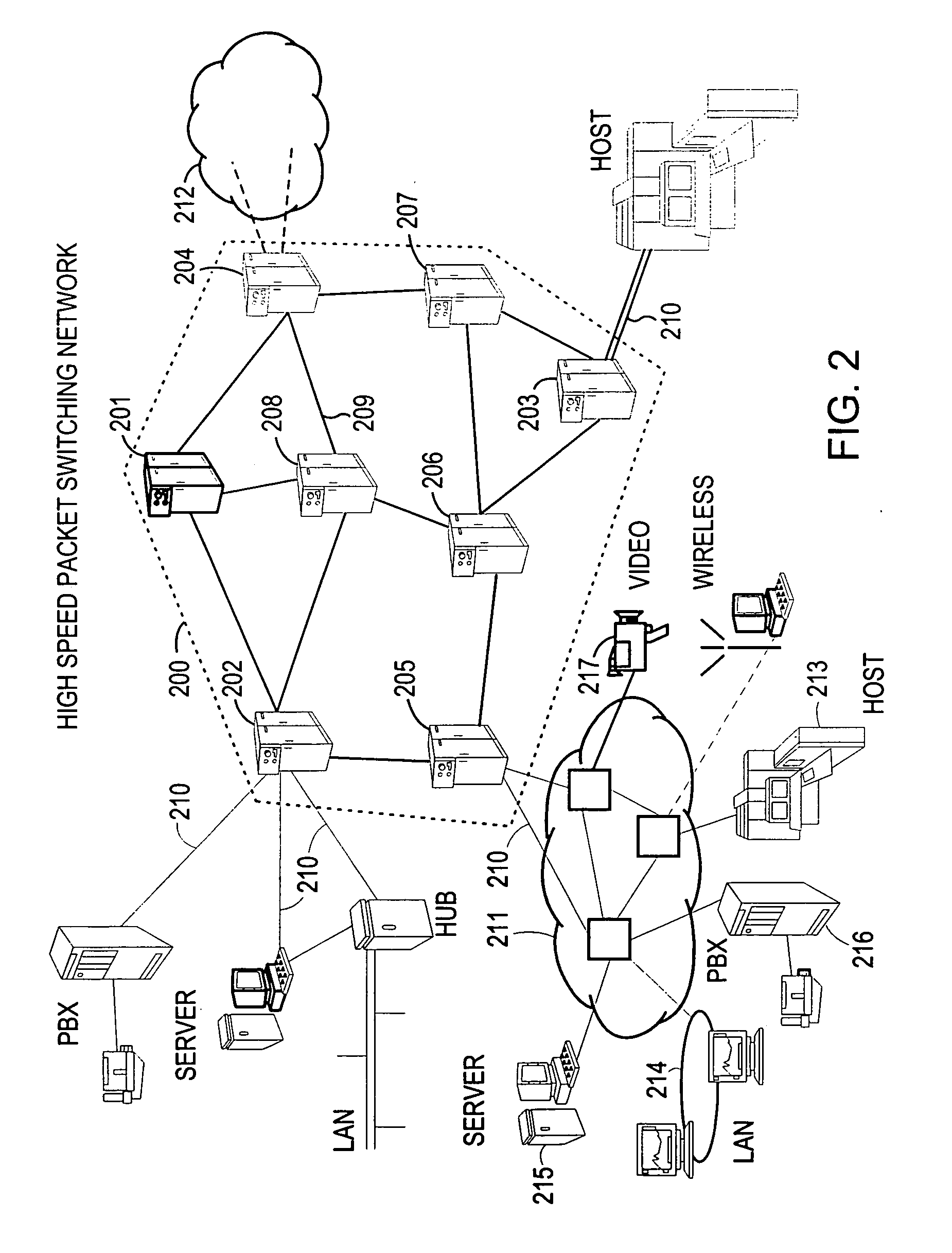
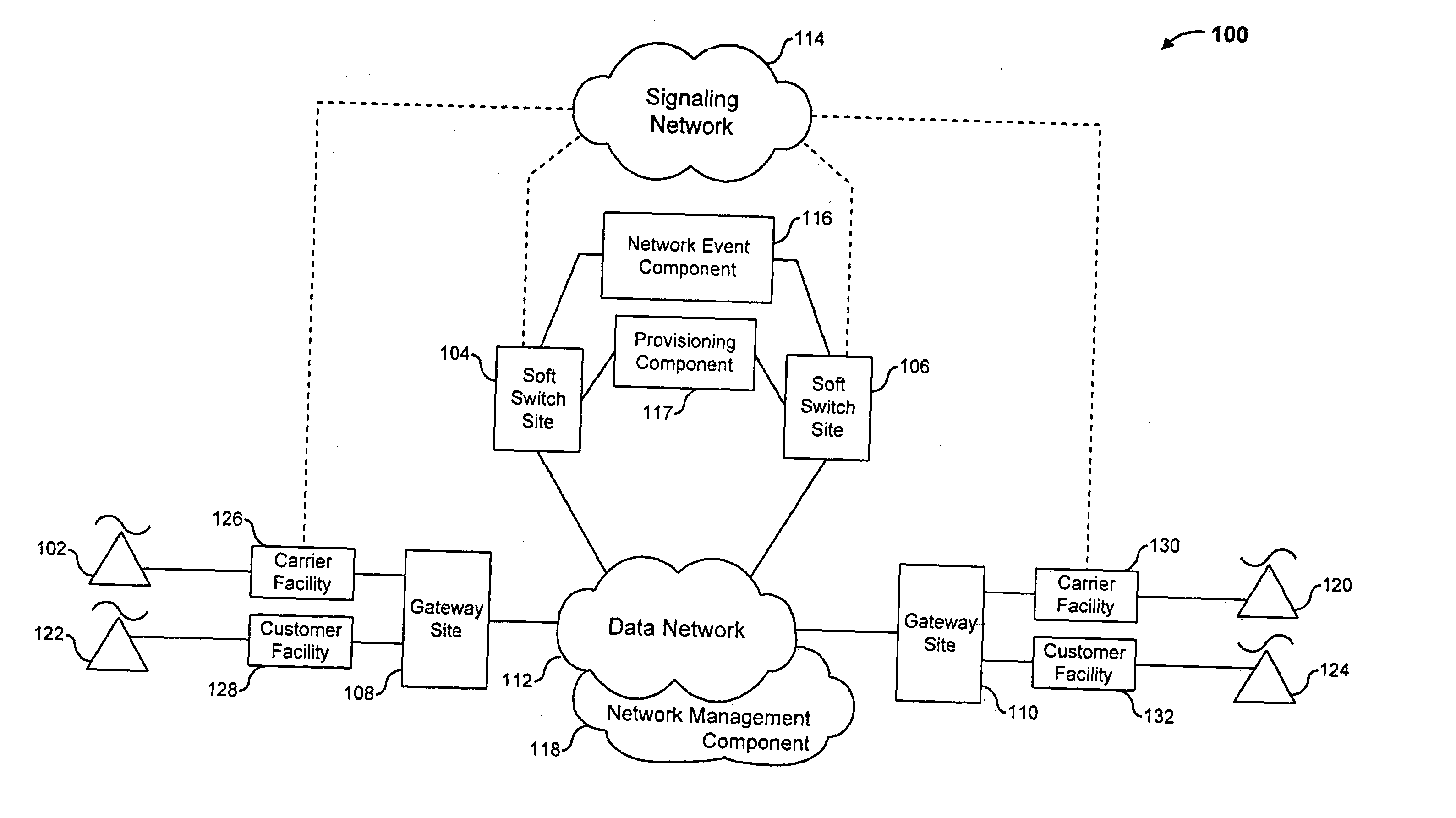
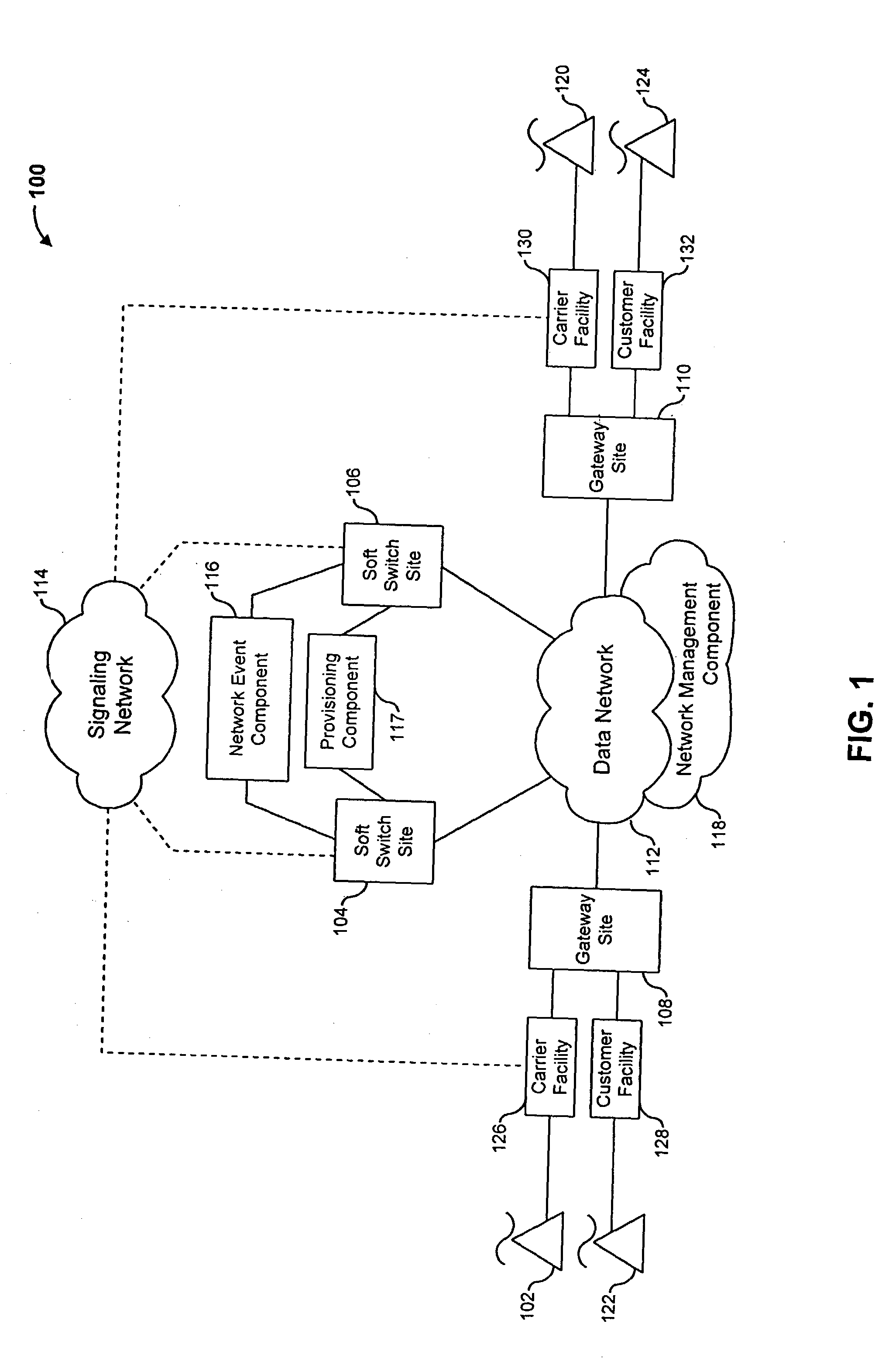
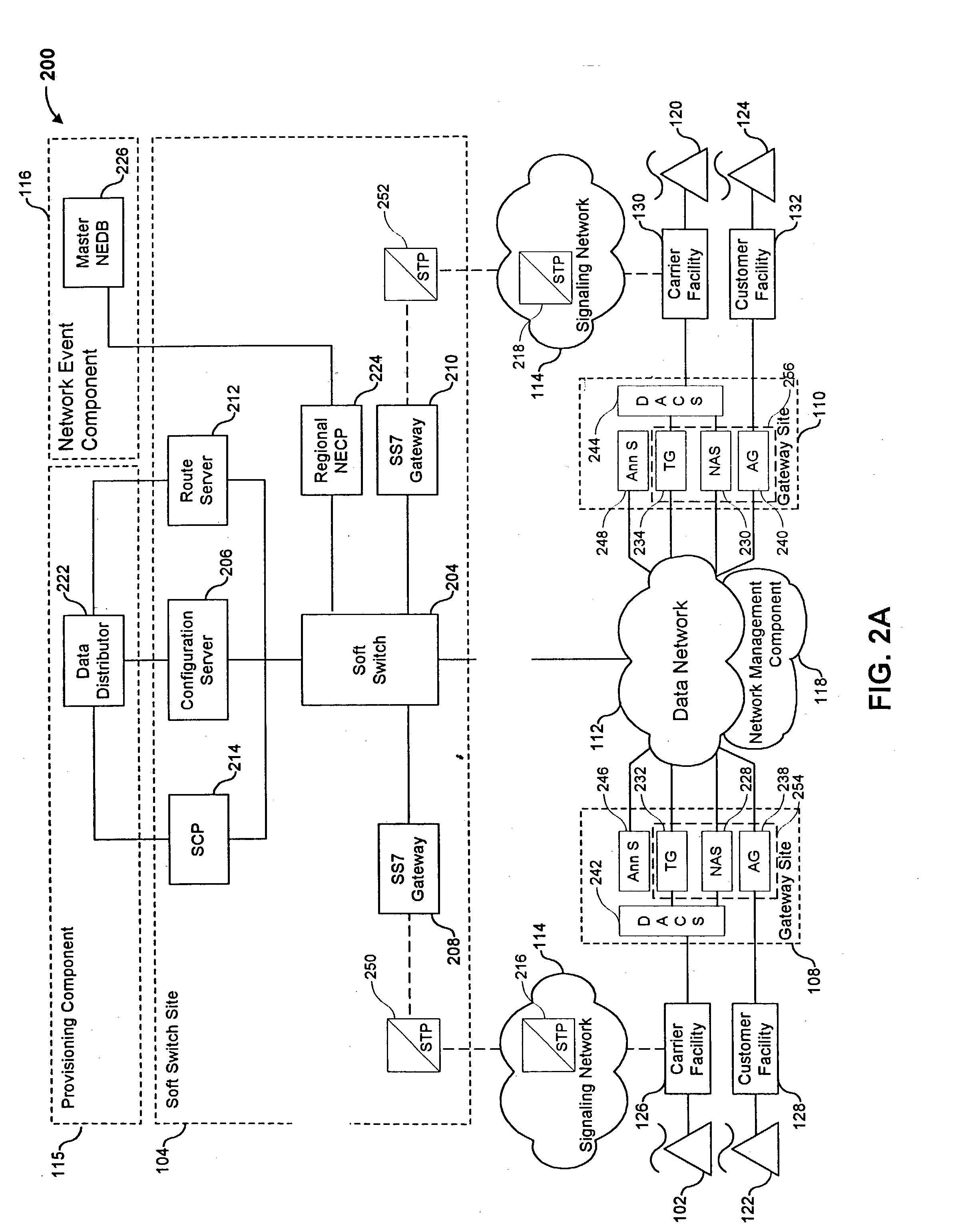
The present invention describes a system and method for communicating voice and data over a packet-switched network that is adapted to coexist and communicate with a legacy PSTN. The system permits packet switching of voice calls and data calls through a data network from and to any of a LEC, a customer facility or a direct IP connection on the data network. The system includes soft switch sites, gateway sites, a data network, a provisioning component, a network event component and a network management component. The system interfaces with customer facilities (e.g., a PBX), carrier facilities (e.g., a LEC) and legacy signaling networks (e.g., SS7) to handle calls between any combination of on-network and off-network callers.The soft switch sites provide the core call processing for the voice network architecture. The soft switch sites manage the gateway sites in a preferred embodiment, using a protocol such as the Internet Protocol Device Control (IPDC) protocol to request the set-up and tear-down of calls. The gateway sites originate and terminate calls between calling parties and called parties through the data network. The gateway sites include network access devices to provide access to network resources. The data network connects one or more of the soft switch sites to one or more of the gateway sites. The provisioning and network event component collects call events recorded at the soft switch sites. The network management component includes a network operations center (NOC) for centralized network management.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
Time-scheduled and time-reservation packet switching
InactiveUS20050058149A1Optimum advantage and efficiencyImprove accuracyMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexData packTime schedule
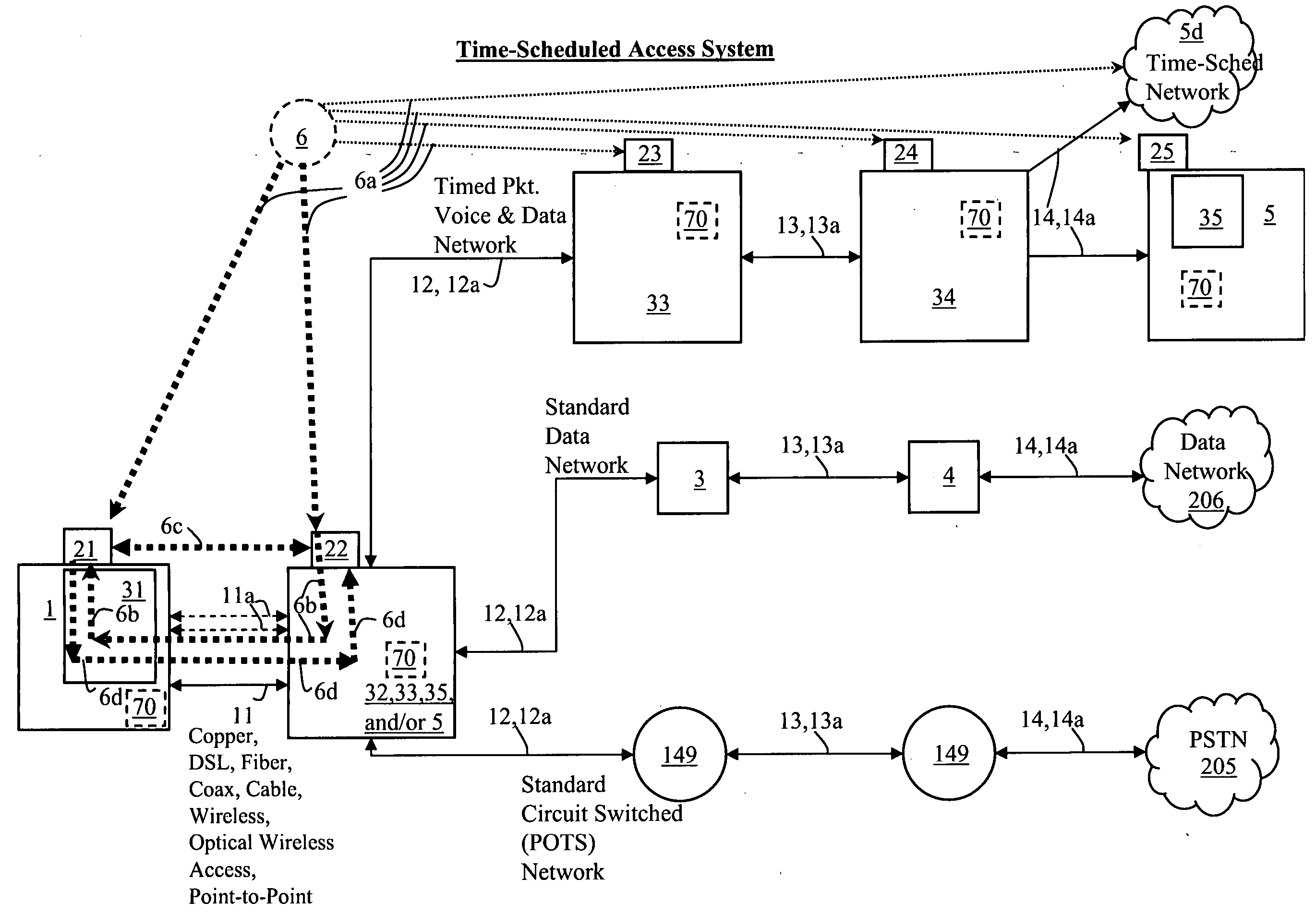
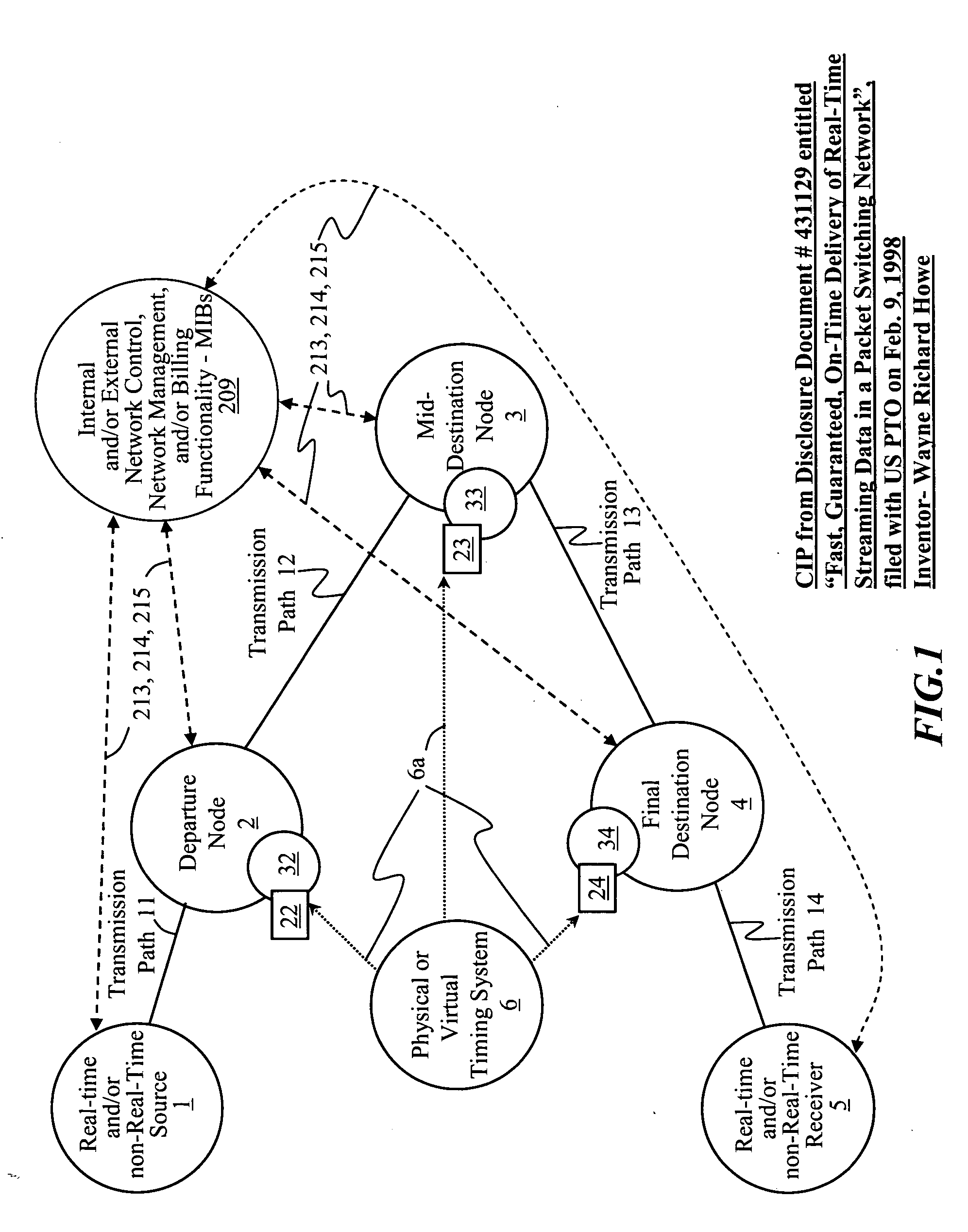
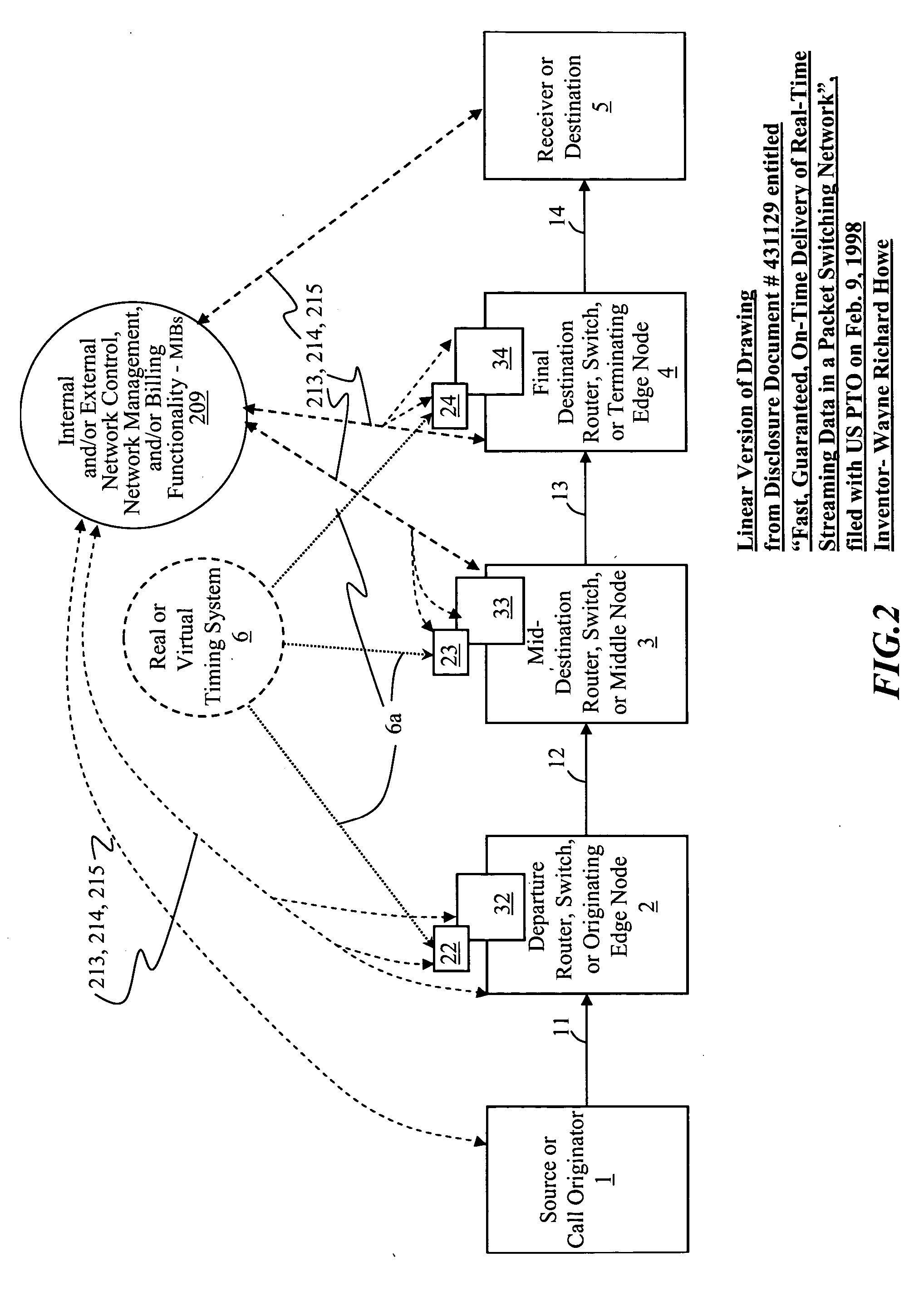
Systems, methods, devices, processes, procedures, algorithms, networks, and network elements are described for time-scheduled and / or time-reserved dat networks. Invention provides capabilities for synchronizing data networks and / or data network links; for establishing time-schedules, time-reservations, time-schedule reservations, and / or reservation time-slots for packets, cells, frames, and / or datagrams; and for transferring, transmitting, switching, routing, and / or receiving time-sensitive, high-reliability, urgent, and / or other time-scheduled, time-reserved, time-allocated, and / or time-scheduled-reservation packets, cells, frames, and / or datagrams, such as real-time and high-priority messages over these networks. The invention(s) enables packet-, cell-, datagram- and / or frame-based networks to thereby efficiently, reliably, and in guaranteed real-time, to switch and / or route data such as voice, video, streaming, and other real-time, high-priority, high-reliability, and / or expedited data with guaranteed delivery and guaranteed quality of service. Networks may be fixed, point-to-point, mobile, ad-hoc, optical, electrical, and / or wireless.
Owner:HOWE WAYNE RICHARD
Method and system for minimizing the connection set up time in high speed packet switching networks
InactiveUS6934249B1Minimize delayMinimize in in to selectError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPacket switched
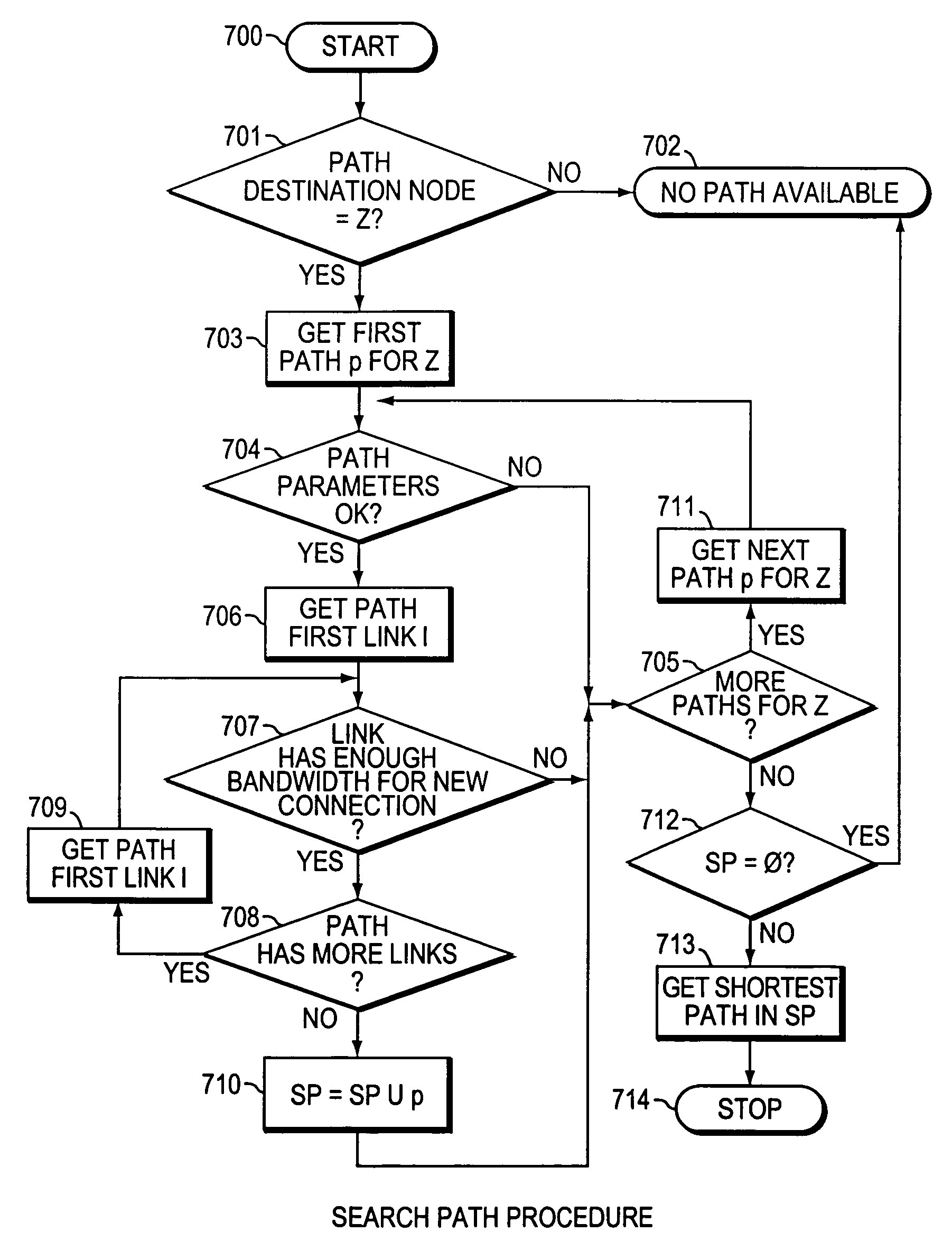
The present invention is directed to a high speed packet switching network and, in particular to a method and system for minimizing the time to establish a connection between an origin and a destination node. Due to high dynamicity of the traffic on transmission links, it is important to select a routing path according to a fully up-to-date information on all network resources. The simpler approach is to calculate a new path for each new connection request. This solution may be very time consuming because there are as many path selection operations as connection set up operations. On another hand, the calculation of paths based on an exhaustive exploration of the network topology, is a complex operation which may also take an inordinate amount of resources in large networks. Many of connections originated from a network node flow to the same destination network node. It is therefore possible to take a serious benefit in reusing the same already calculated paths for several connections towards the same node. The path calculated at the time the connection is requested is recorded in a Routing Database and updated each time a modification occurs in the network. Furthermore, alternate paths for supporting non-disruptive path switch on failure or preemption, and new paths towards potential destination nodes can be calculated and stored when the connection set up process is idle. These last operations are executed in background with a low processing priority and in absence of connection request.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Voice over data telecommunications network architecture
InactiveUS20040022237A1Interconnection arrangementsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionNetwork operations centerNetwork architecture
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
Method and apparatus for performing data flow ingress/egress admission control in a provider network
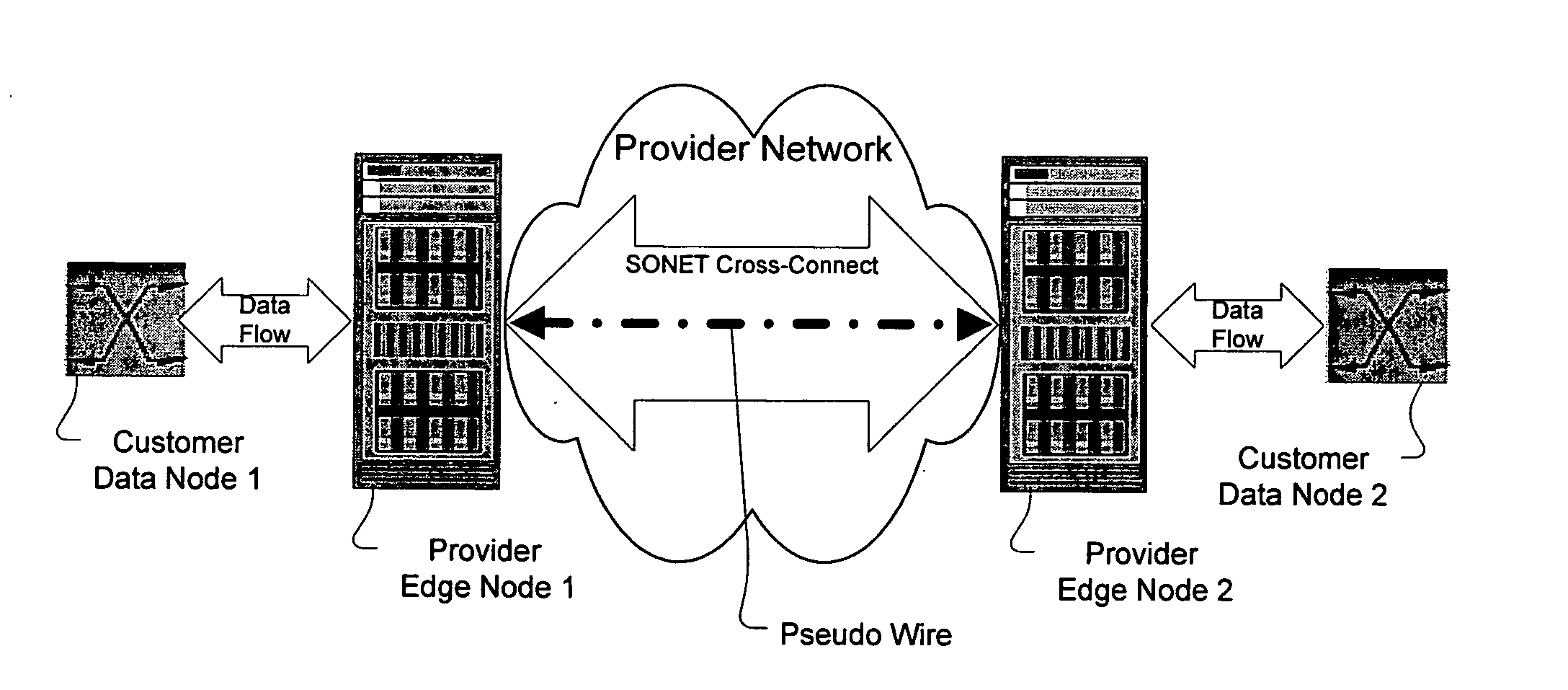
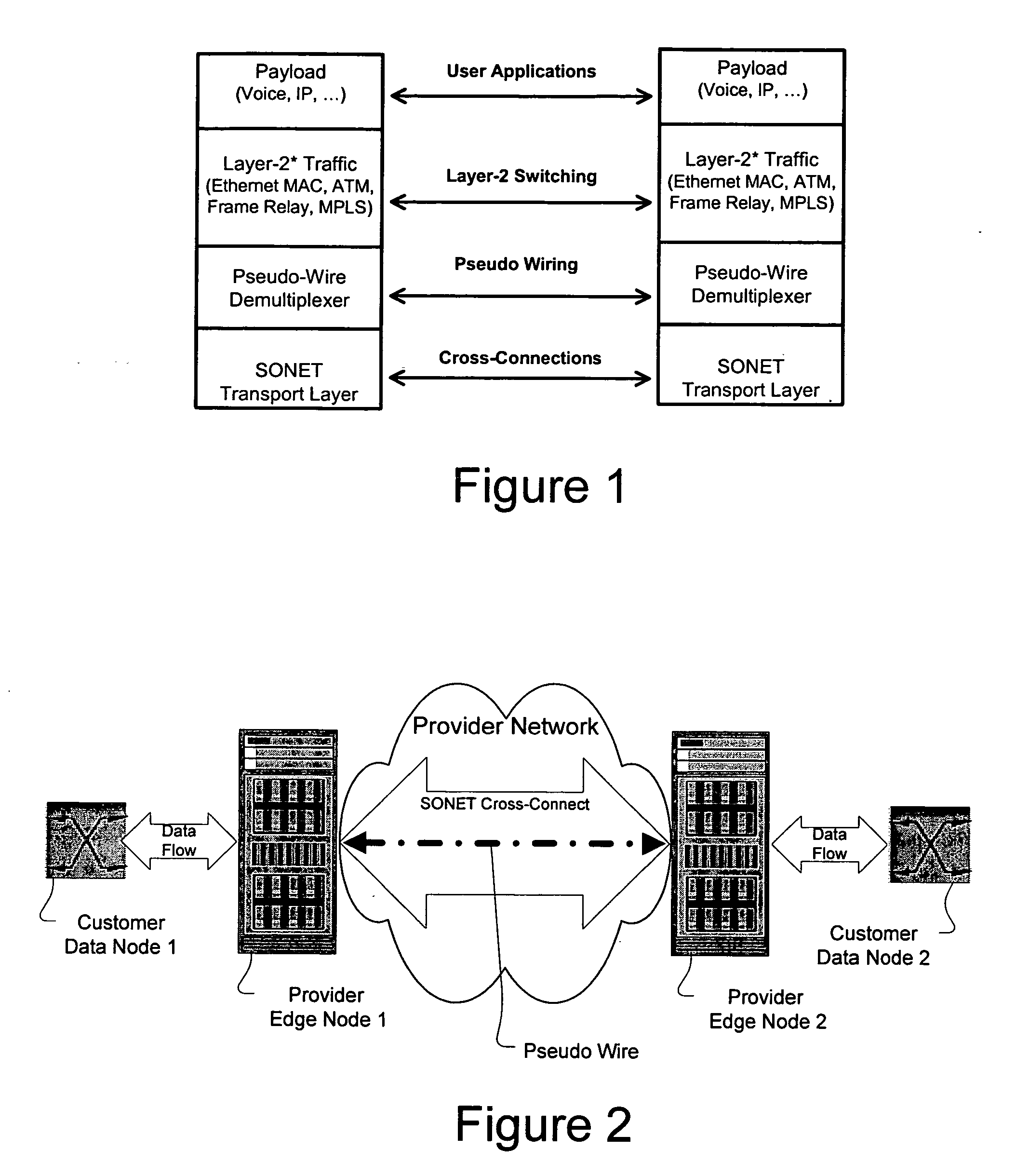
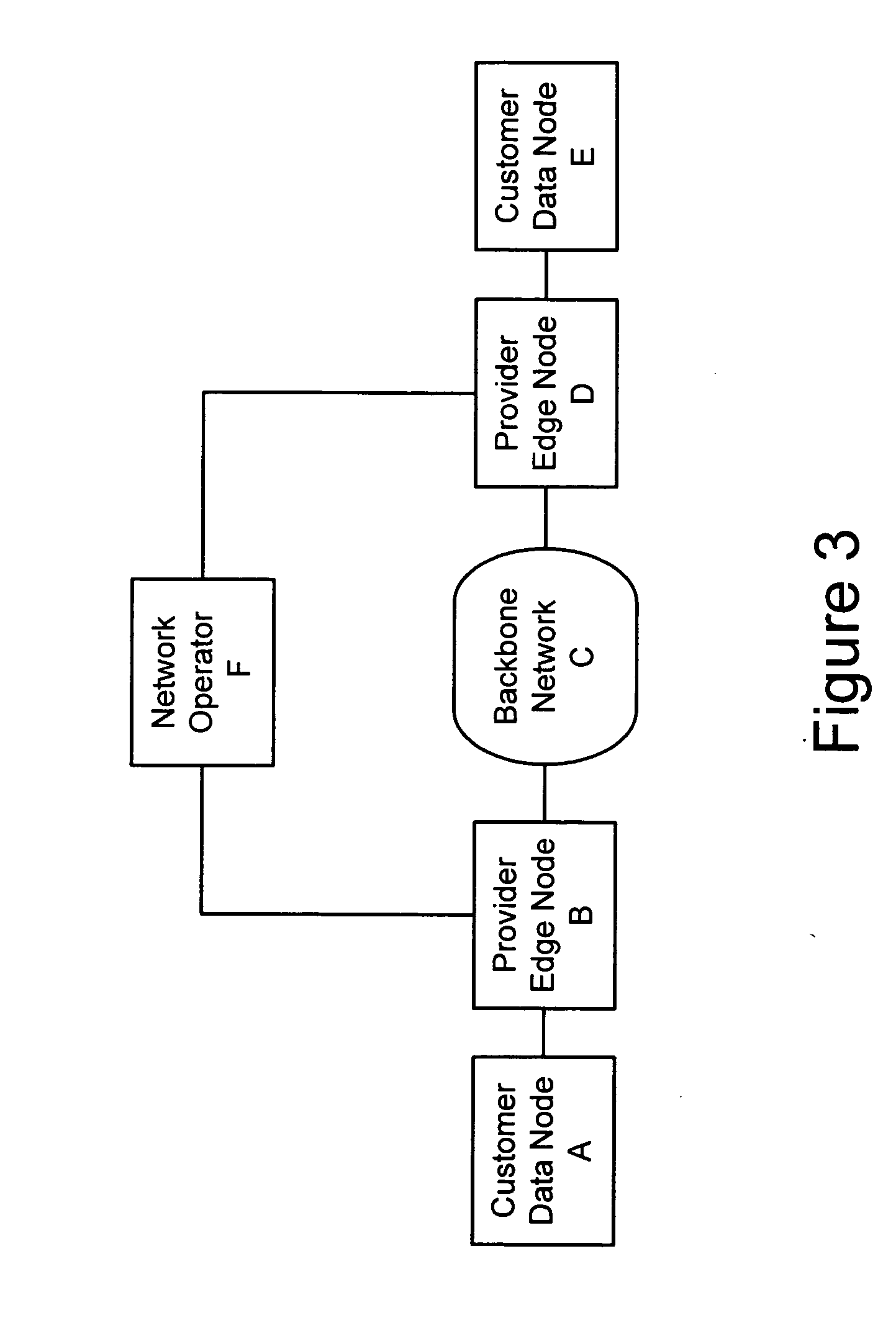
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over MPLS, SONET / SDH, or OTN optical transport networks as well as electrical transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes "pseudo-wires" between, for example, routers, Layer-2 packet switches, or SONET / SDH switches. Inter-related ingress and egress resource tables may be used by provider edge nodes to negotiate consistently managed data tunnels across a provider network on behalf of data flowing from / to a diverse base of customer edge nodes. Detailed network resource information particular to each of the data flows is exchanged between provider edge nodes during the creation of pseudo-wires. Admission control algorithms are applied at the ingress and egress points in order to manage the data flows into a provider network and exiting from a provider network to customer equipment. By applying pseudo-wire shuffling and preemption techniques, the providers can make better use of their network resources by admitting more pseudo-wires.
Owner:CIENA
Dynamic allocation of wireless mobile nodes over an internet protocol (IP) network
InactiveUS6272129B1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsTTEthernetIp address
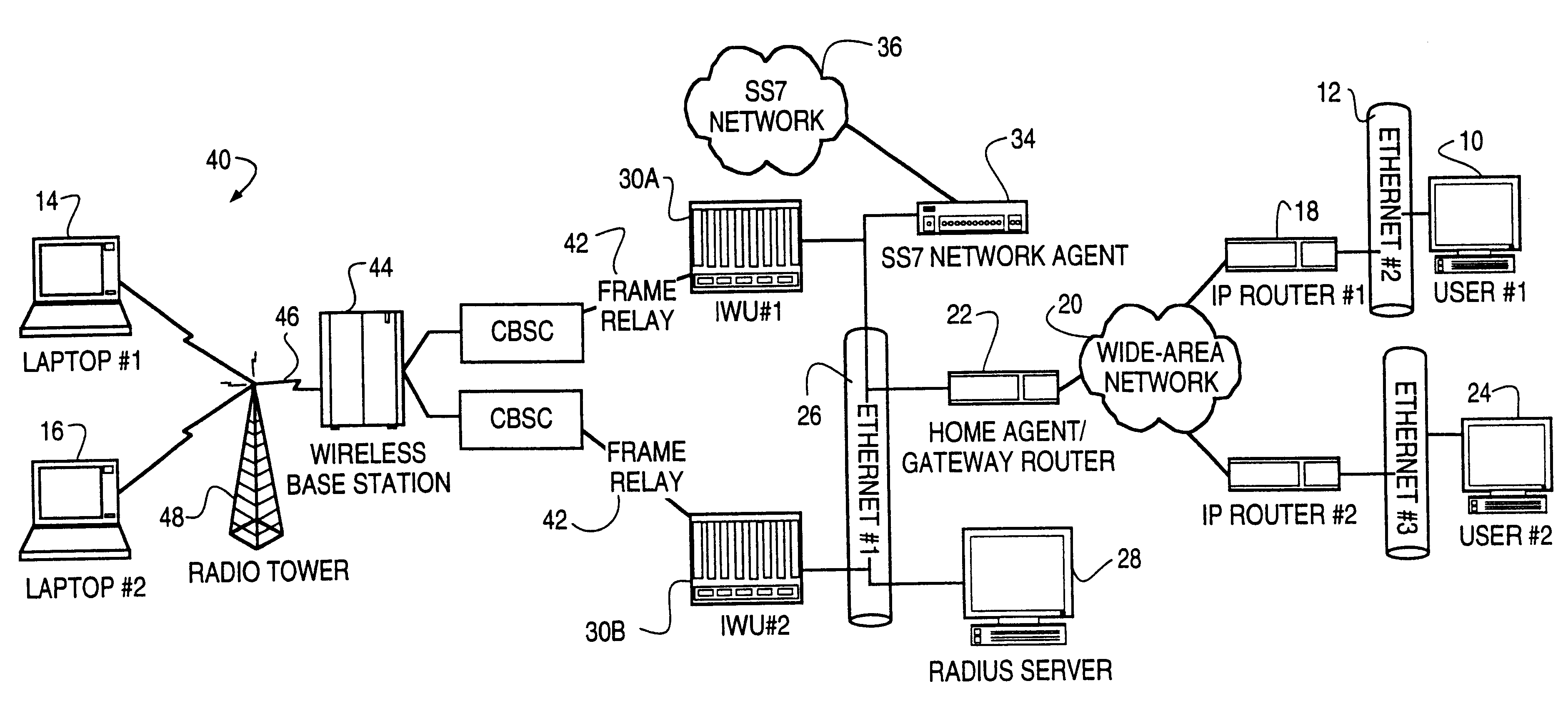
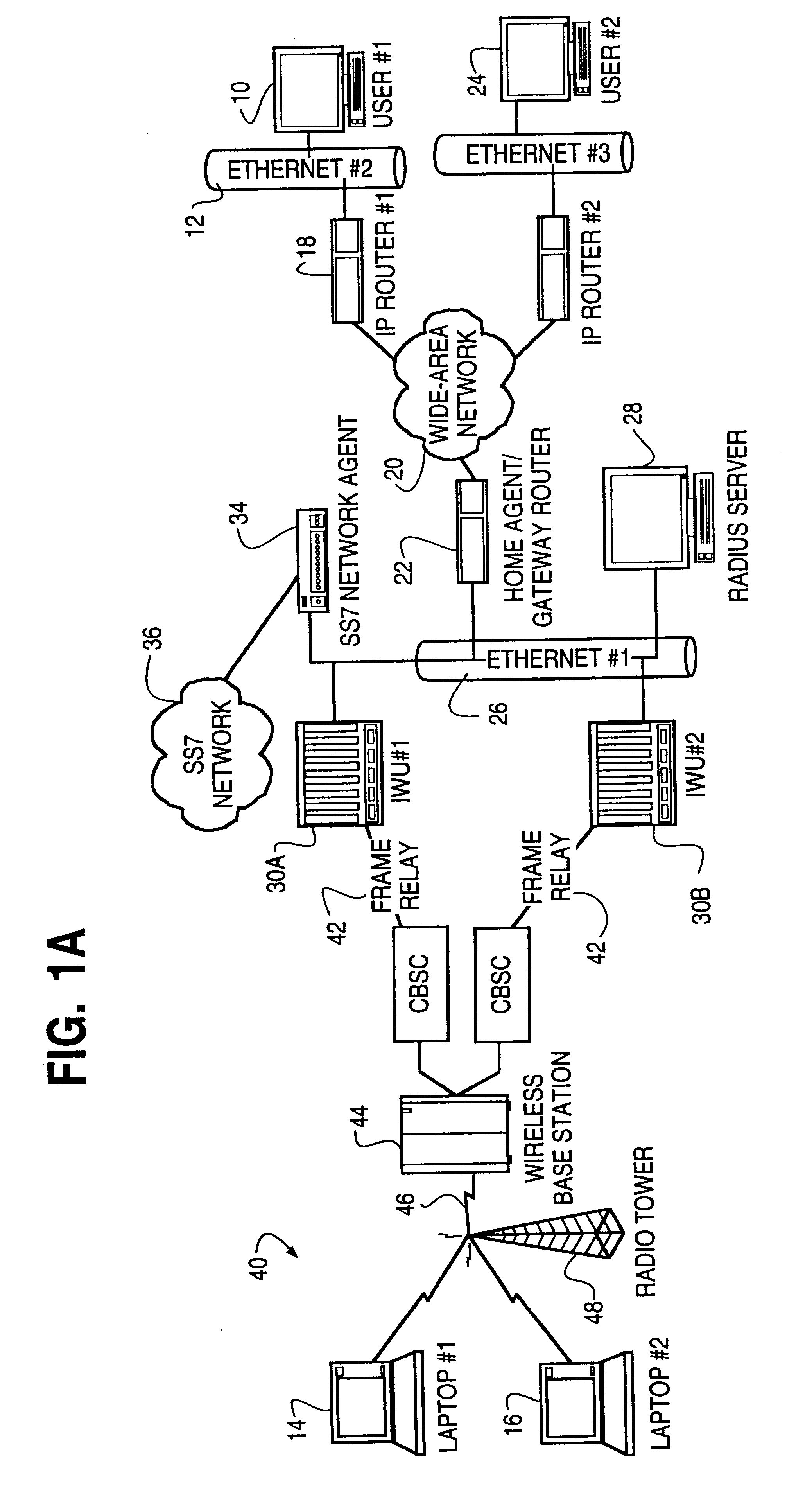
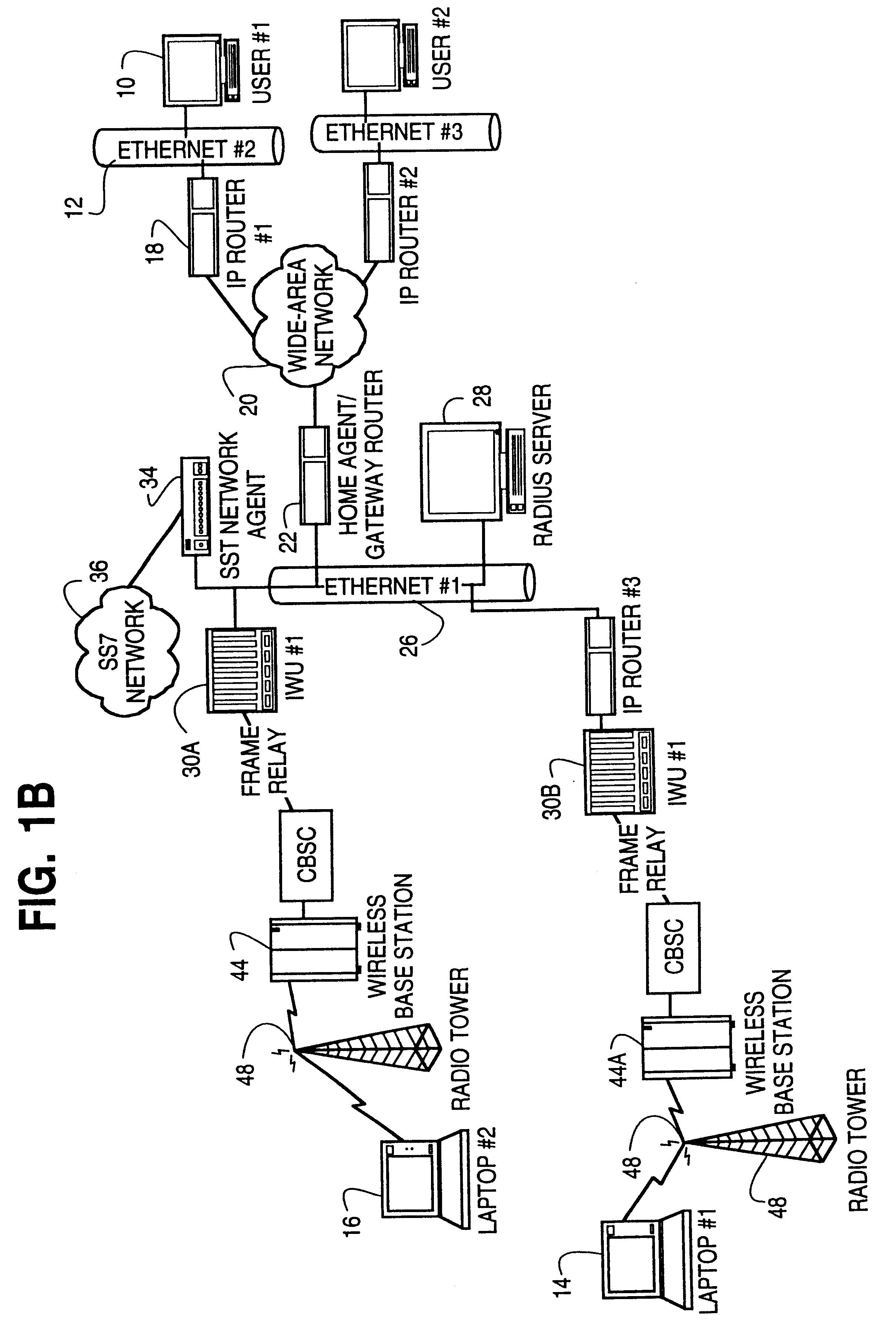
A method is described of automatically locating and connecting a mobile wireless communications device to a packet-switched network such as the Internet. An Internet Protocol (IP) packet from a terminal on the network, destined for receipt by the mobile device, is received at a home agent acting as a gateway or router linking the packet switched network to a second network, such as LAN, coupled to a wireless communications network. The home agent transmits an access-request message to an authentication server. The access-request message includes a destination IP address associated with the mobile device found in the IP packet. The authentication server responsively issues an access-accept message to the home agent if the mobile device is authorized to receive the IP packet. The access-accept message comprises (a) information uniquely identifying said device, such as the IMSI / ESN number for the device, and (b) information identifying a network to use to locate said device. The home agent issues a message containing the information uniquely identifying the device to a mobile node location server. The mobile node location server maintains a table mapping IP addresses for a plurality of mobile communication devices to information uniquely identifying the devices. In the event that the mobile node location server does not find an IP address for the device in the table, the device is paged via the wireless communications network. In response to the page, the mobile device dials into the wireless communications network and second network and initiates a connection to the packet switched network whereby the IP packet is transmitted to the device.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
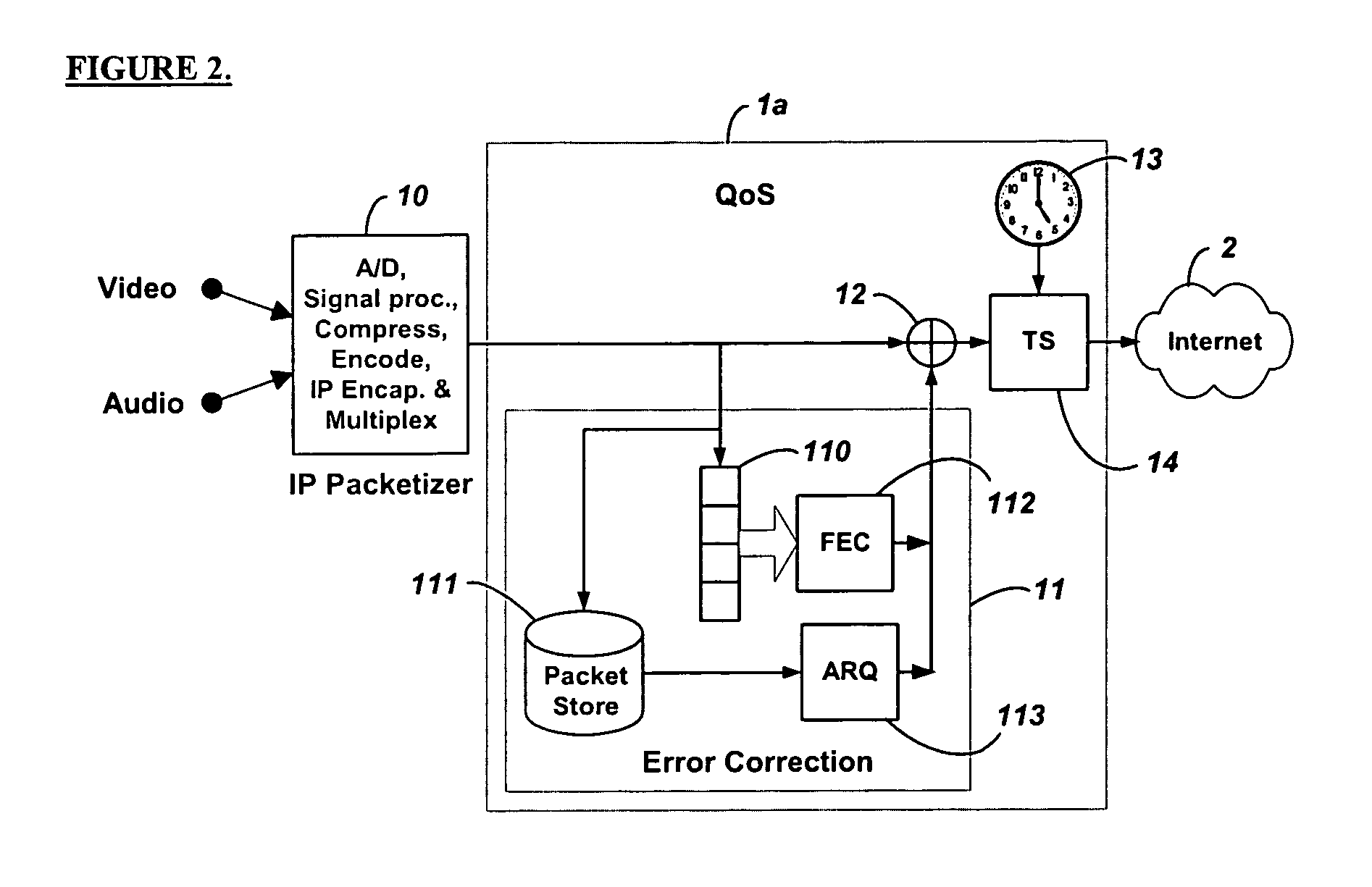
Method and system for providing site independent real-time multimedia transport over packet-switched networks
InactiveUS20060007943A1Minimal latency site-independenceAchieve independenceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData packTimestamp
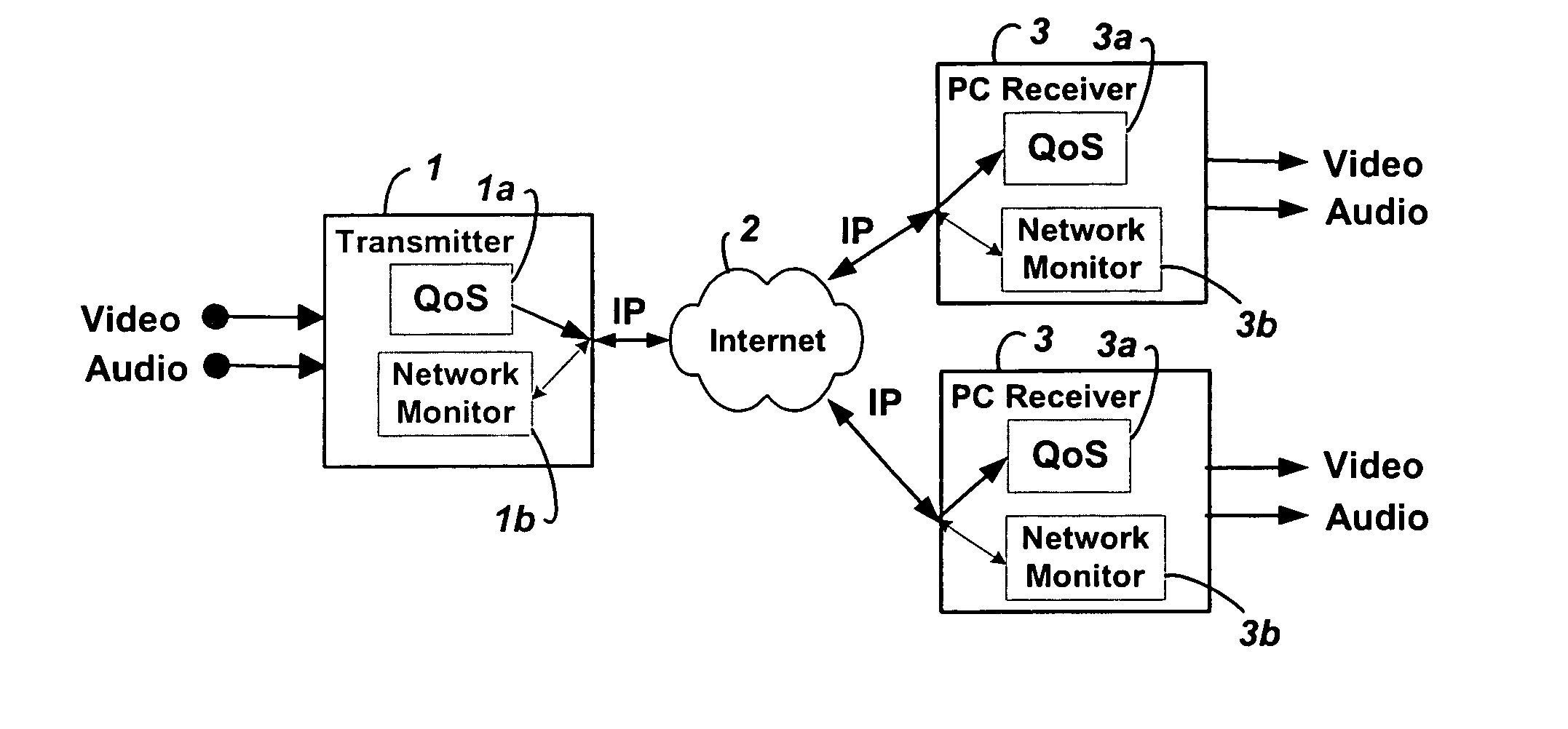
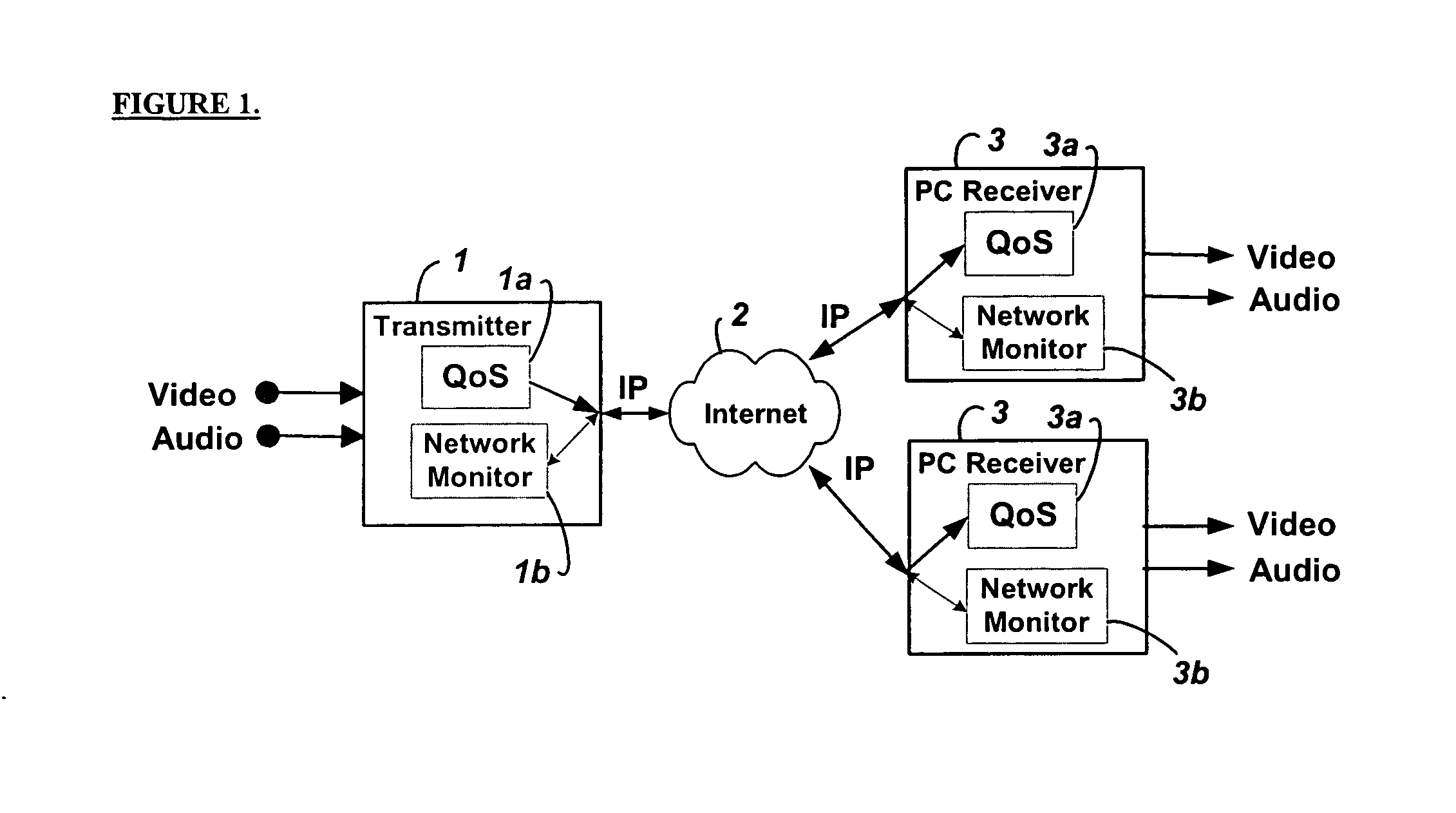
Embodiments of the invention enable minimum latency site independent real-time video transport over packet switched networks. Some examples of real-time video transport are video conferencing and real-time or live video streaming. In one embodiment of the invention, a network node transmits live or real-tine audio and video signals, encapsulated as Internet Protocol (IP) data packets, to one or more nodes on the Internet or other IP network. One embodiment of the invention enables a user to move to different nodes or move nodes to different locations thereby providing site independence. Site independence is achieved by measuring and accounting for the jitter and delay between a transmitter and receiver based on the particular path between the transmitter and receiver independent of site location. The transmitter inserts timestamps and sequence numbers into packets and then transmits them. A receiver uses these timestamps to recover the transmitter's clock. The receiver stores the packets in a buffer that orders them by sequence number. The packets stay in the buffer for a fixed latency to compensate for possible network jitter and / or packet reordering. The combination of timestamp packet-processing, remote clock recovery and synchronization, fixed-latency receiver buffering, and error correction mechanisms help to preserve the quality of the received video, despite the significant network impairments generally encountered throughout the Internet and wireless networks.
Owner:QVIDIUM TECH
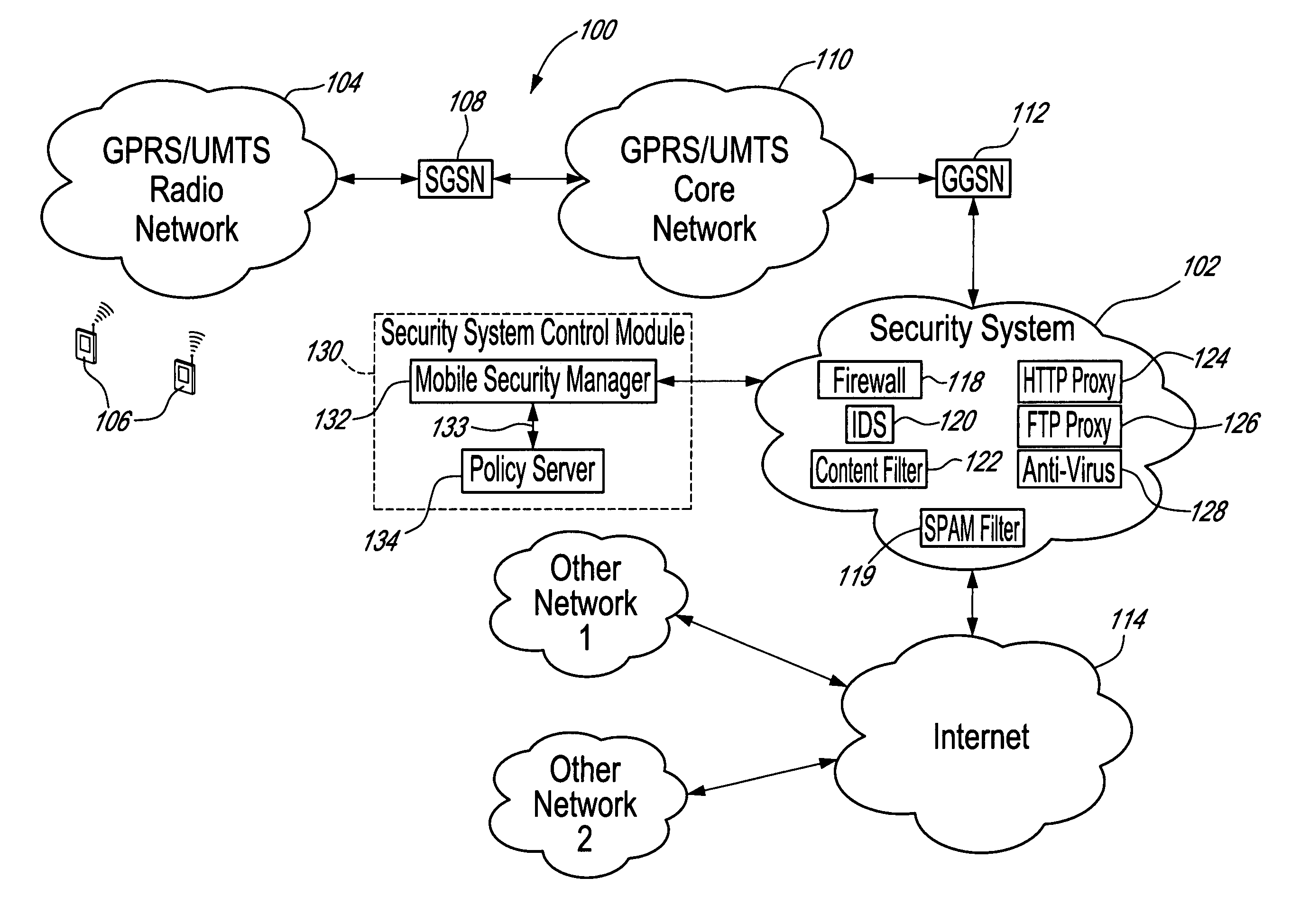
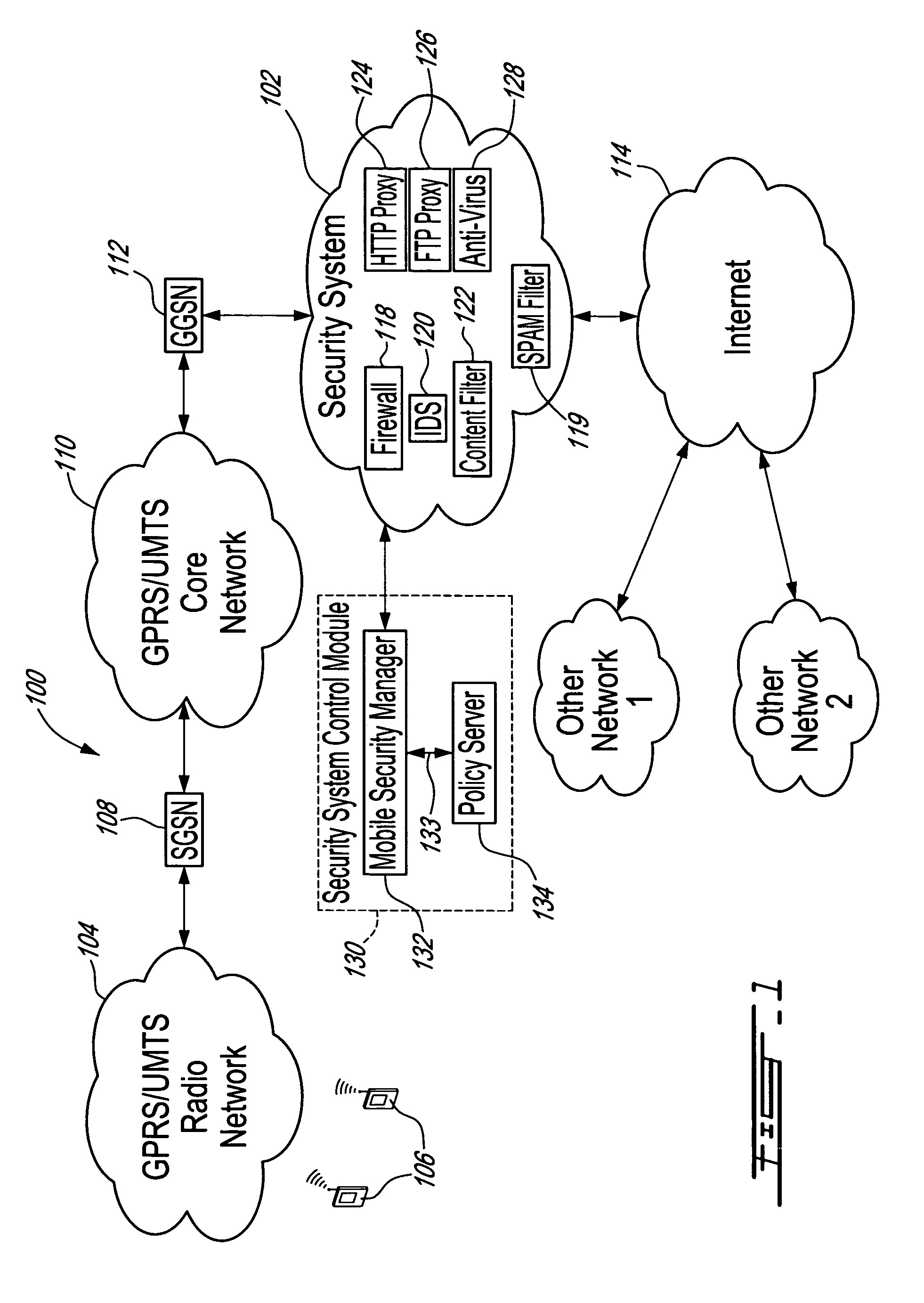
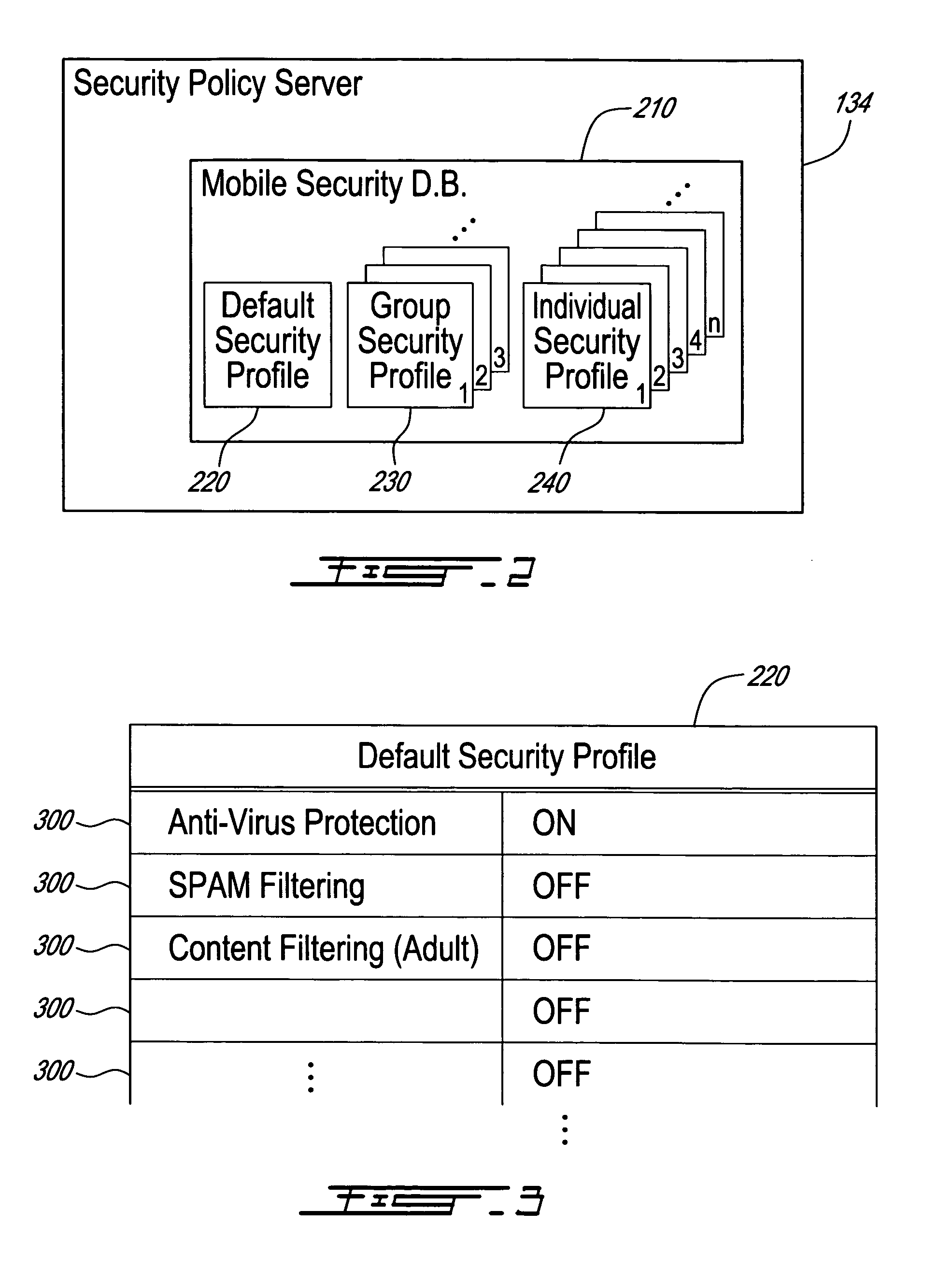
Method, security system control module and policy server for providing security in a packet-switched telecommunications system
ActiveUS7418253B2Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsMobile securityMobile station
A method, security system control module and policy server for providing security for Mobile Stations (MSs) in a Packet-Switched Telecommunications System. When an MS accesses the system, its identity is sent to a security system control module that retrieves a security profile associated with the MS. A policy server of the security system control module stores individual security profiles, default security profiles and group security profiles for registered subscribers. Security settings associated with the MS security profile are returned from the policy server to a mobile security manager of the control module, which then determines if they should be propagated in the system. When no previous network access was made in a given time period by an MS having similar security settings, i.e. belongs to the same group security profile, the settings are propagated in the system in order to be enforced, for providing security protection for the MS.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
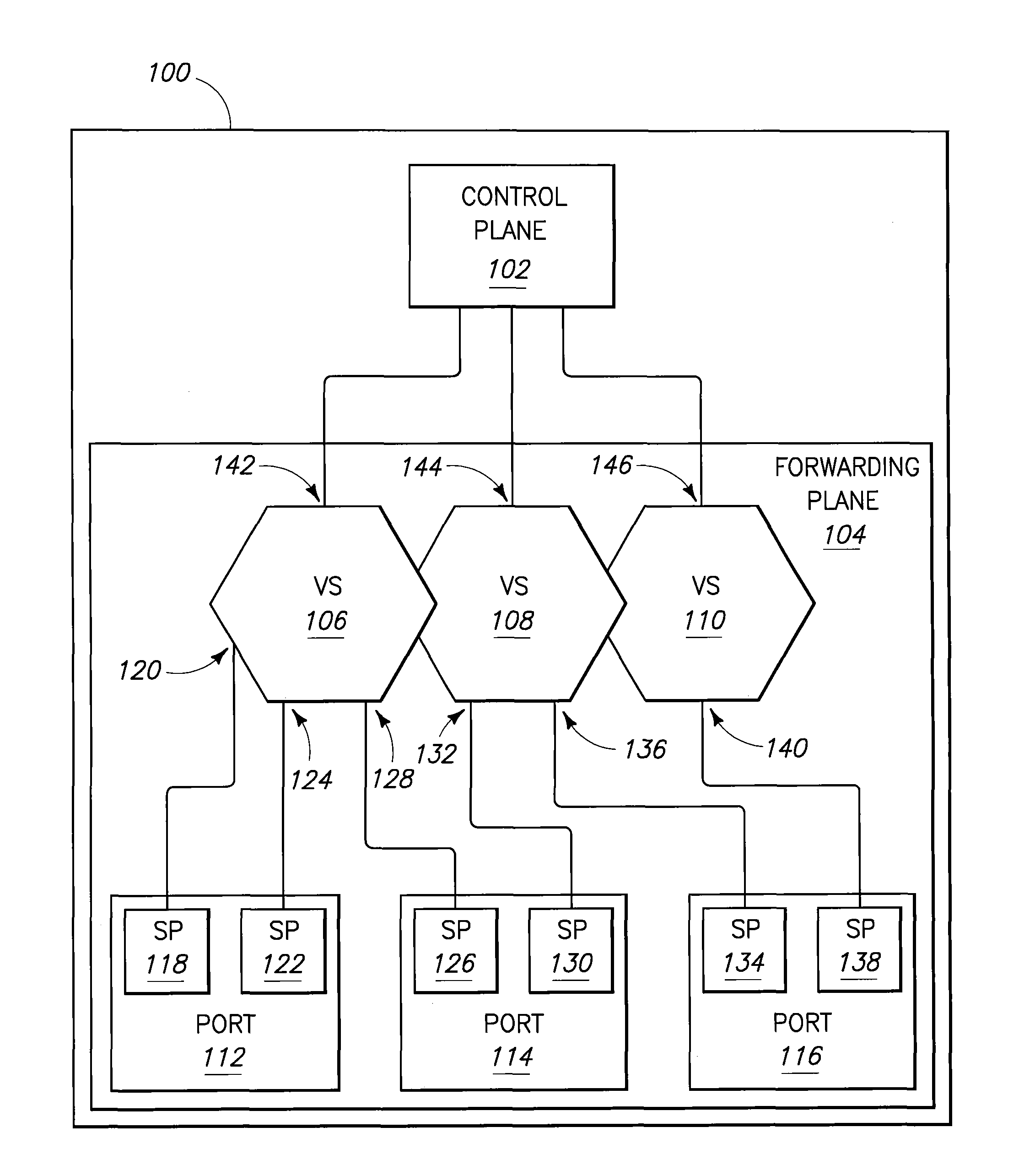
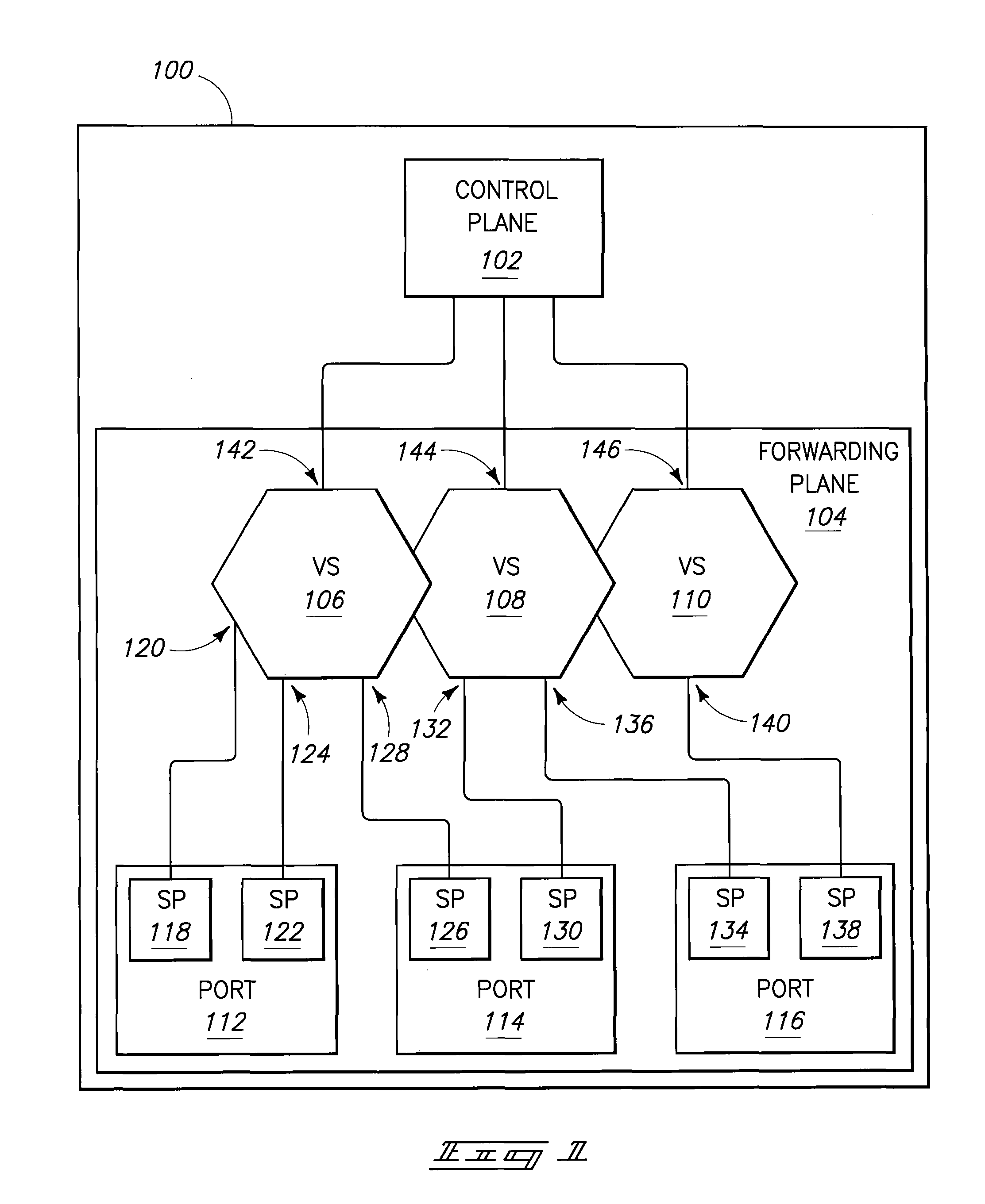
Communicating with a control plane using a forwarding information format and control plane processing of packets devoid of a virtual switch identifier
Packet switch operating methods and packet switches receive a plurality of packets using a forwarding plane of the packet switch. Each packet of the plurality conforms to a different one of a plurality of forwarding information formats. The methods and packet switches modify each packet of the plurality to conform to a common forwarding information format instead of a respective one of the plurality of forwarding information formats and forward the modified packets of the plurality to a control plane of the packet switch.
Owner:WORLD WIDE PACKETS INC
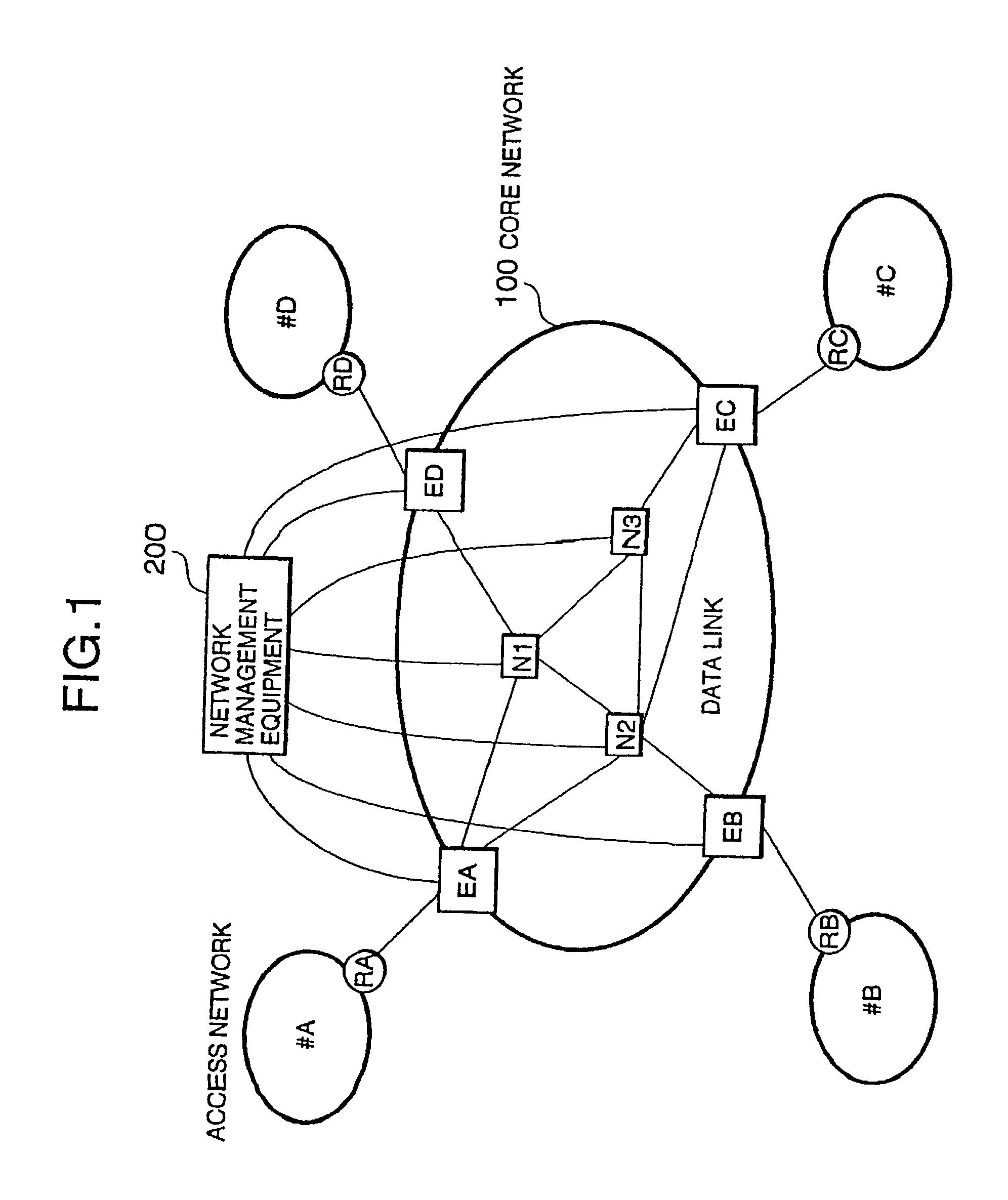
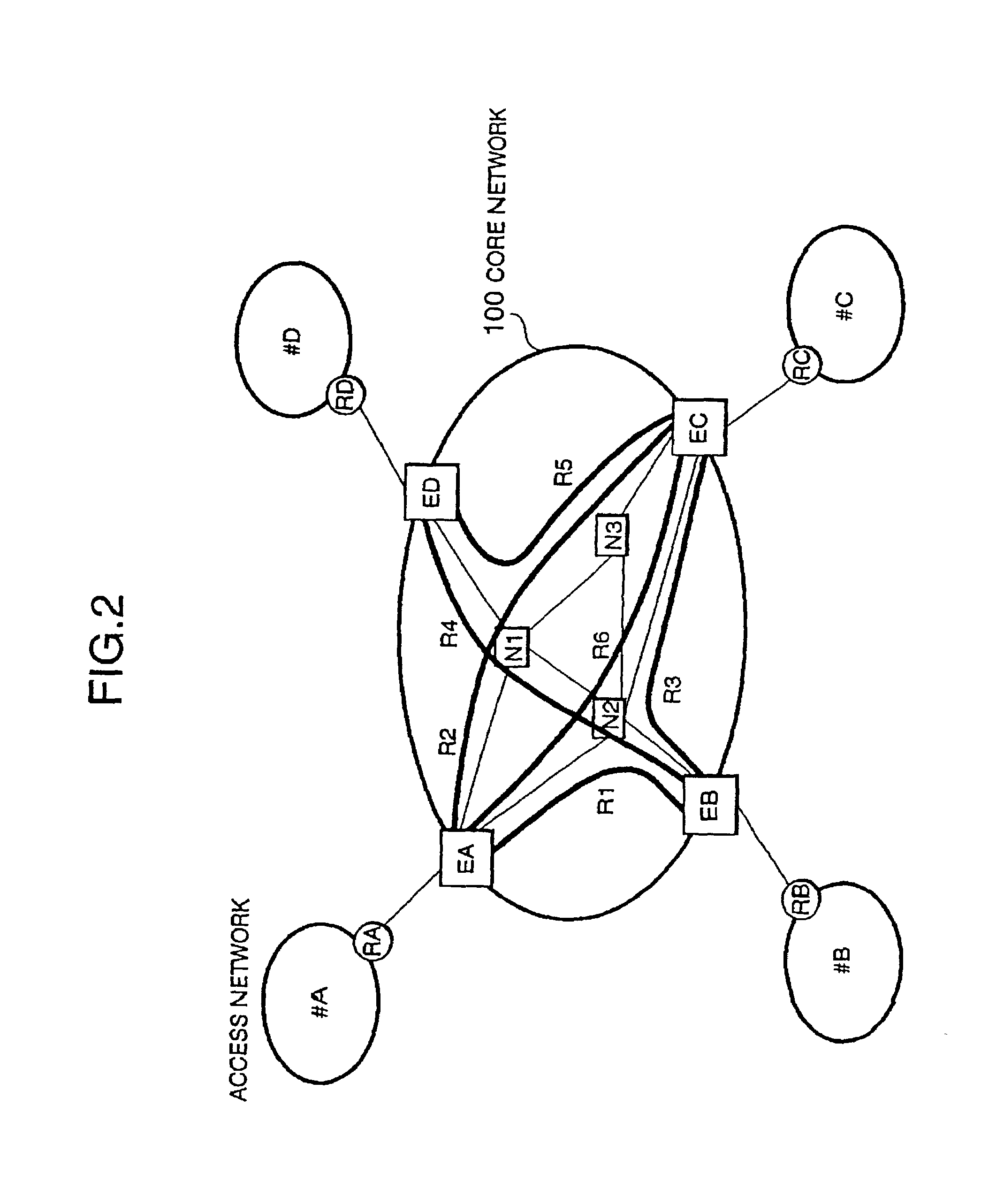
Packet switching network, packet switching equipment and network management equipment
InactiveUS7046630B2Reduces delay variationReduce in quantityError preventionTransmission systemsAccess networkDelayed time
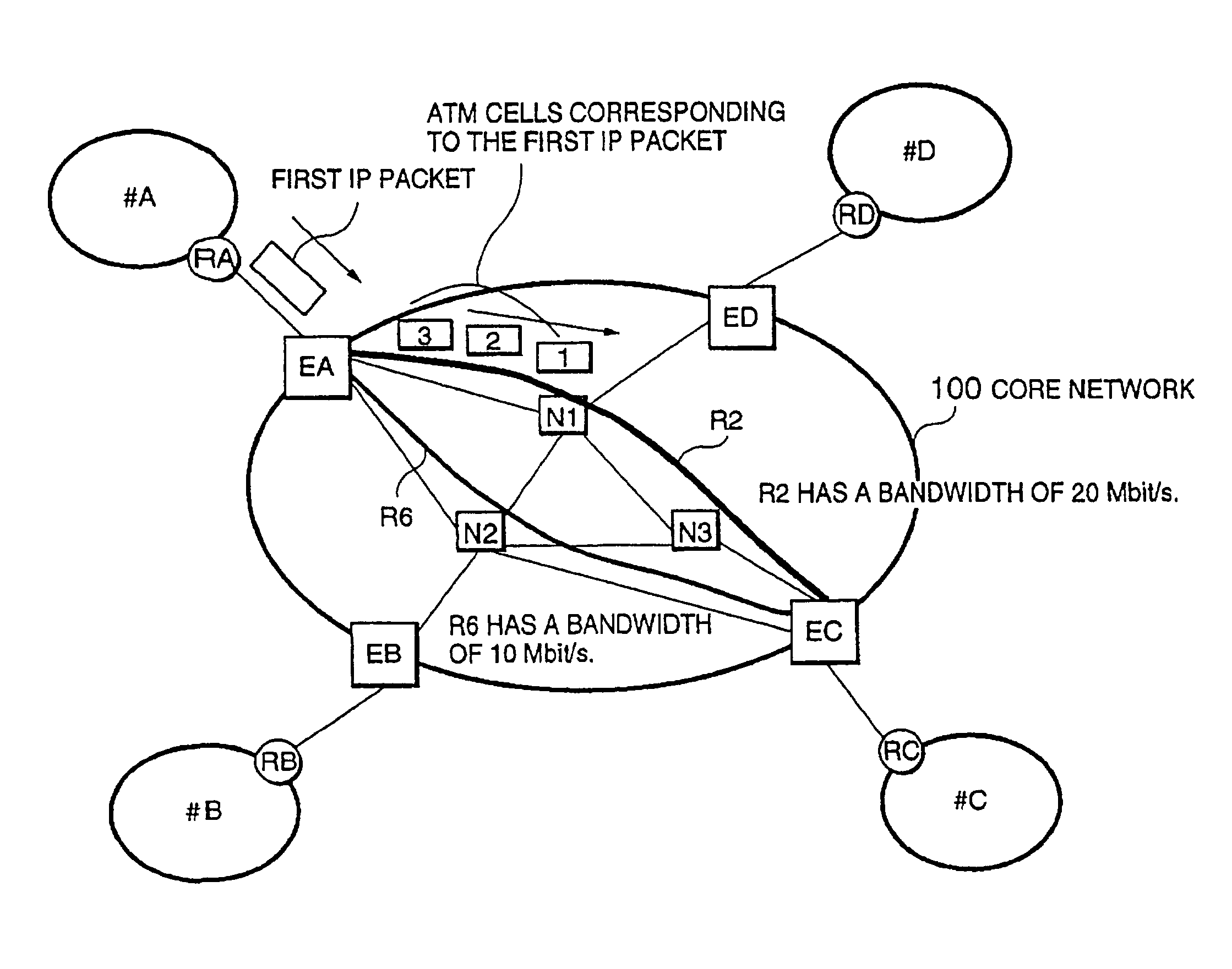
This invention provides a network management equipment and a packet switching equipment which eliminate a connection setup delay time, reduce a delay and a delay variation involved in data transfer, and effectively perform connectionless data flow processing in a large data network. The network is divided into a connection-oriented core network and a plurality of connectionless access networks connected to the core network where a plurality of connections (called permanent virtual route (PVR)) are set up among a plurality of edge nodes. The network management equipment selects one route from a plurality of PVRs for connectionless data flow received from one of the access networks and transfers data along the PVR.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
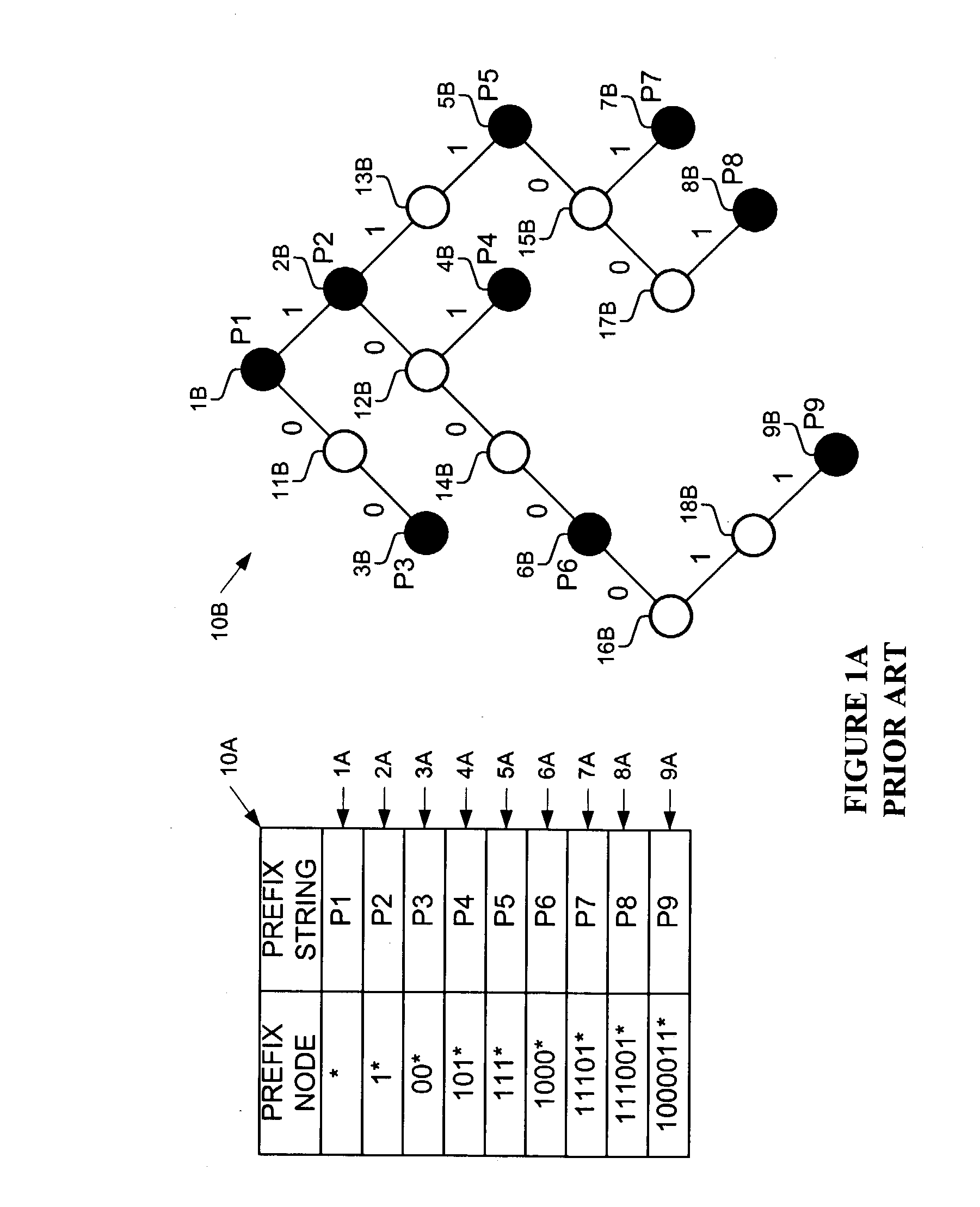
Method and apparatus for generating and using enhanced tree bitmap data structures in determining a longest prefix match
ActiveUS20050157712A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital data information retrievalGeneral purposeArray data structure
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for generating and using an enhanced tree bitmap data structure in determining a longest prefix match, such as in a router, packet switching system. One implementation organizes the tree bitmap to minimize the number of internal nodes that must be accessed during a lookup operation. A pointer is included in each of the trie or search nodes to the best match so far entry in the leaf or results array which allows direct access to this result without having to parse a corresponding internal node. Moreover, one implementation stores the internal node for a particular level as a first element in its child array. Additionally, one implementation uses a general purpose lookup engine that can traverse multiple tree bitmaps or other data structures simultaneously, and perform complete searches, partial searches, and resume partial searches such as after receiving additional data on which to search.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
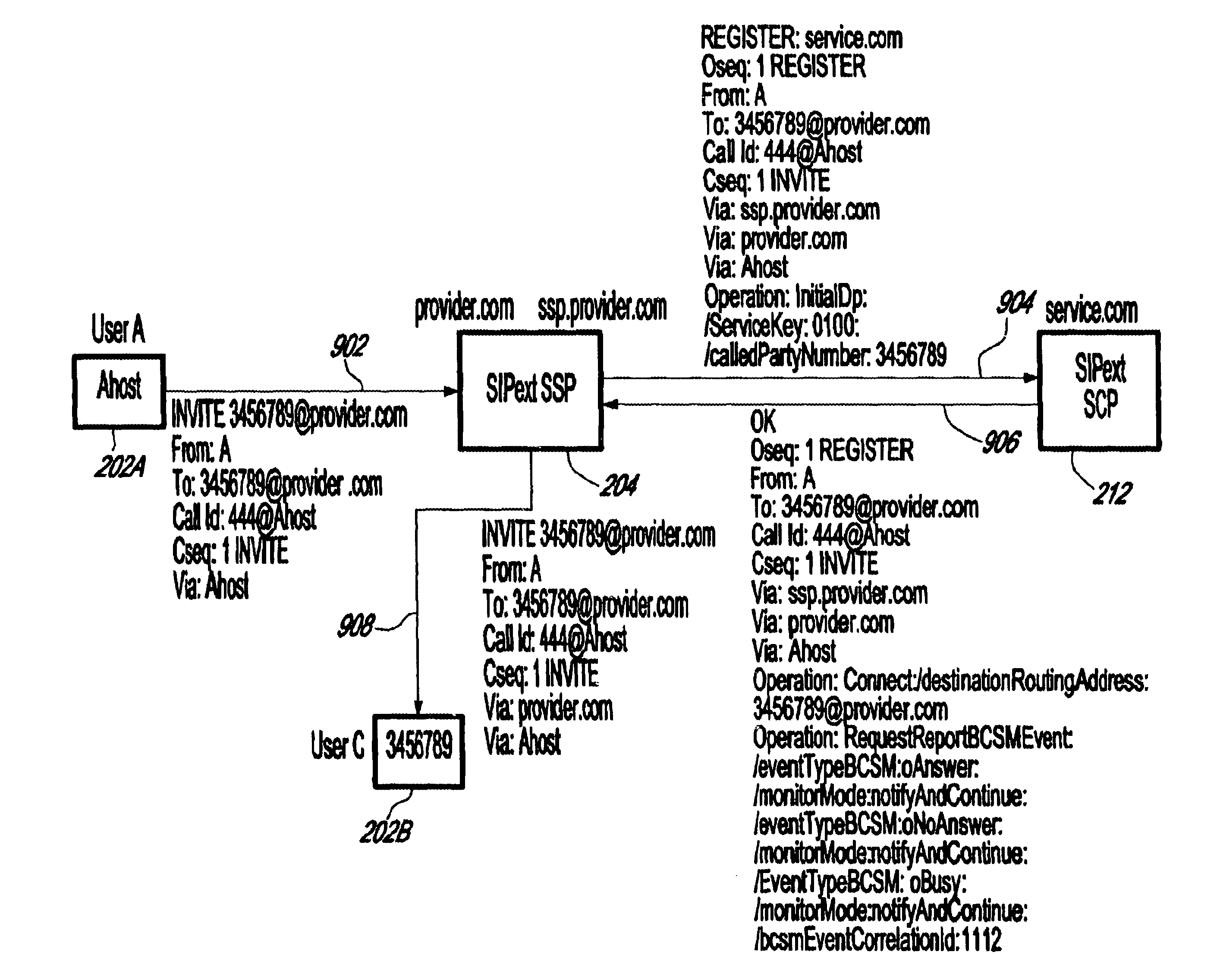
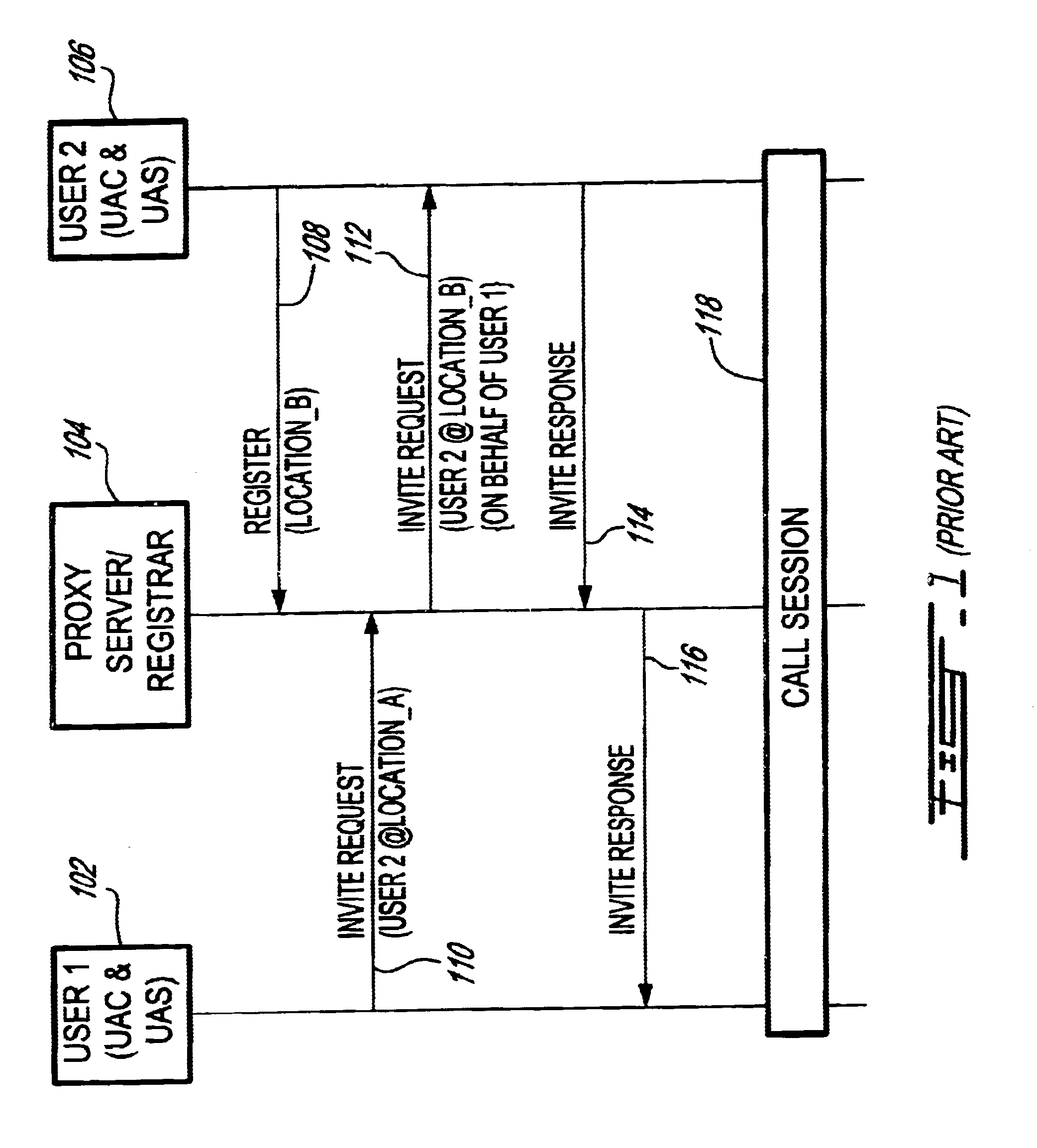
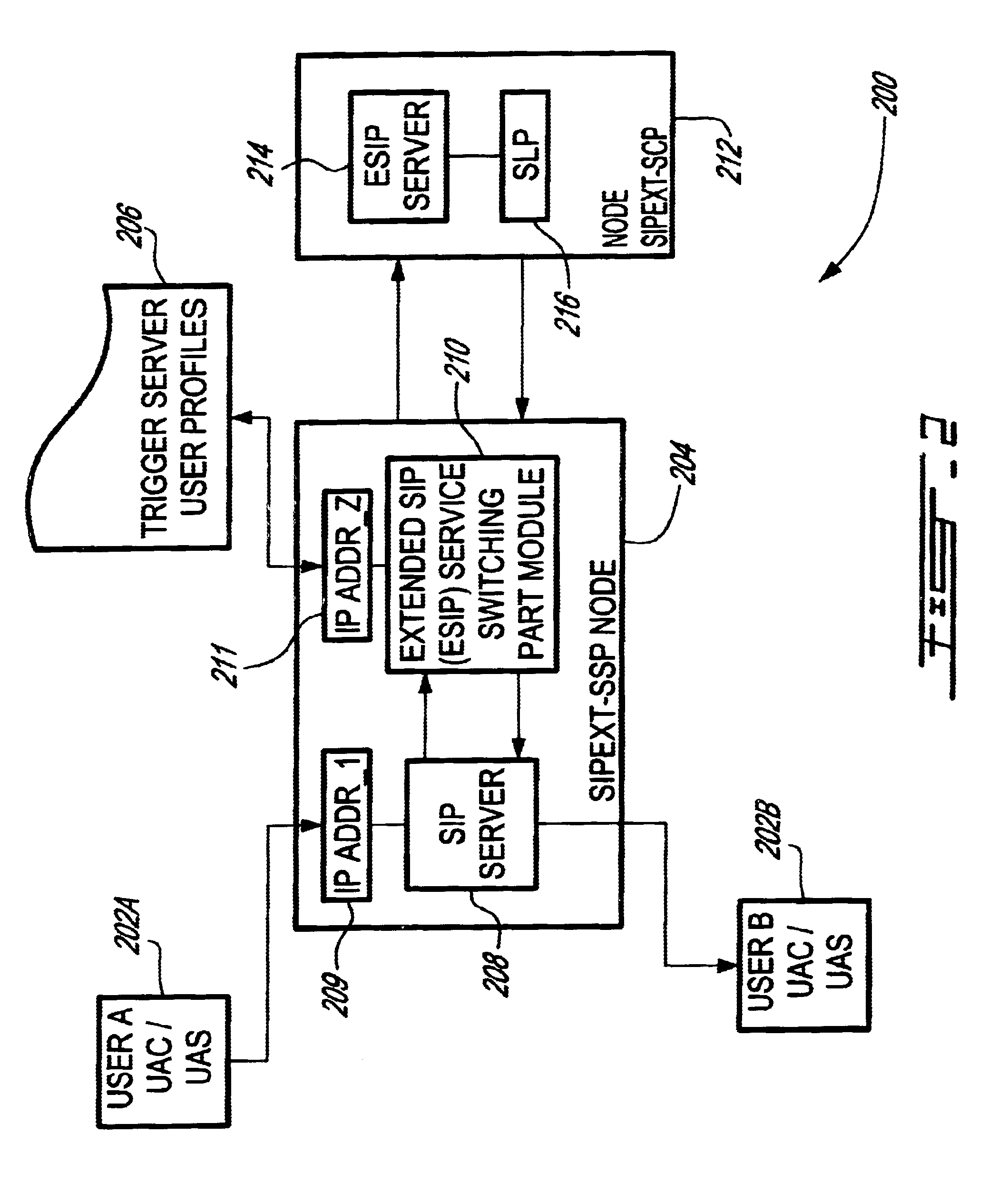
System and method for providing value-added services (VAS) in an integrated telecommunications network using session initiation protocol (SIP)
InactiveUS6625141B1Intelligent networksData processing applicationsSession Initiation ProtocolIntelligent Network
A system and method for providing Value-Added Services (VAS) in an integrated telecommunications network having a packet-switched network portion (PSN) operable with Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). The integrated telecommunications network includes a SIPext SSP server, a trigger server, and a service node having a Service Logic Program (SLP) that is operable with Intelligent Network Application Protocol (INAP). The SIPext SSP and service nodes are provided with the capability to communicate using SIP-compliant messaging. New header fields are provided that specify operations to be performed by the service node with respect to a service. INAP service parametric data is also provided in the header fields in a sequential form. When a call is received in the SIPext SSP server for a user having a subscription for a VAS, it queries the user profile stored in the trigger server. If the user is subscribed for a service, a SIP request message is formulated based on the user profile, wherein appropriate headers are populated with relevant parametric information and call context data. The service node launches the SLP based on the information provided in the request message and sends a SIP response message to the SIPext SSP server with an instruction concerning the provisioning of the VAS. The SIPext SSP server, thereafter, takes an appropriate action based on the response message and any parametric information contained therein.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
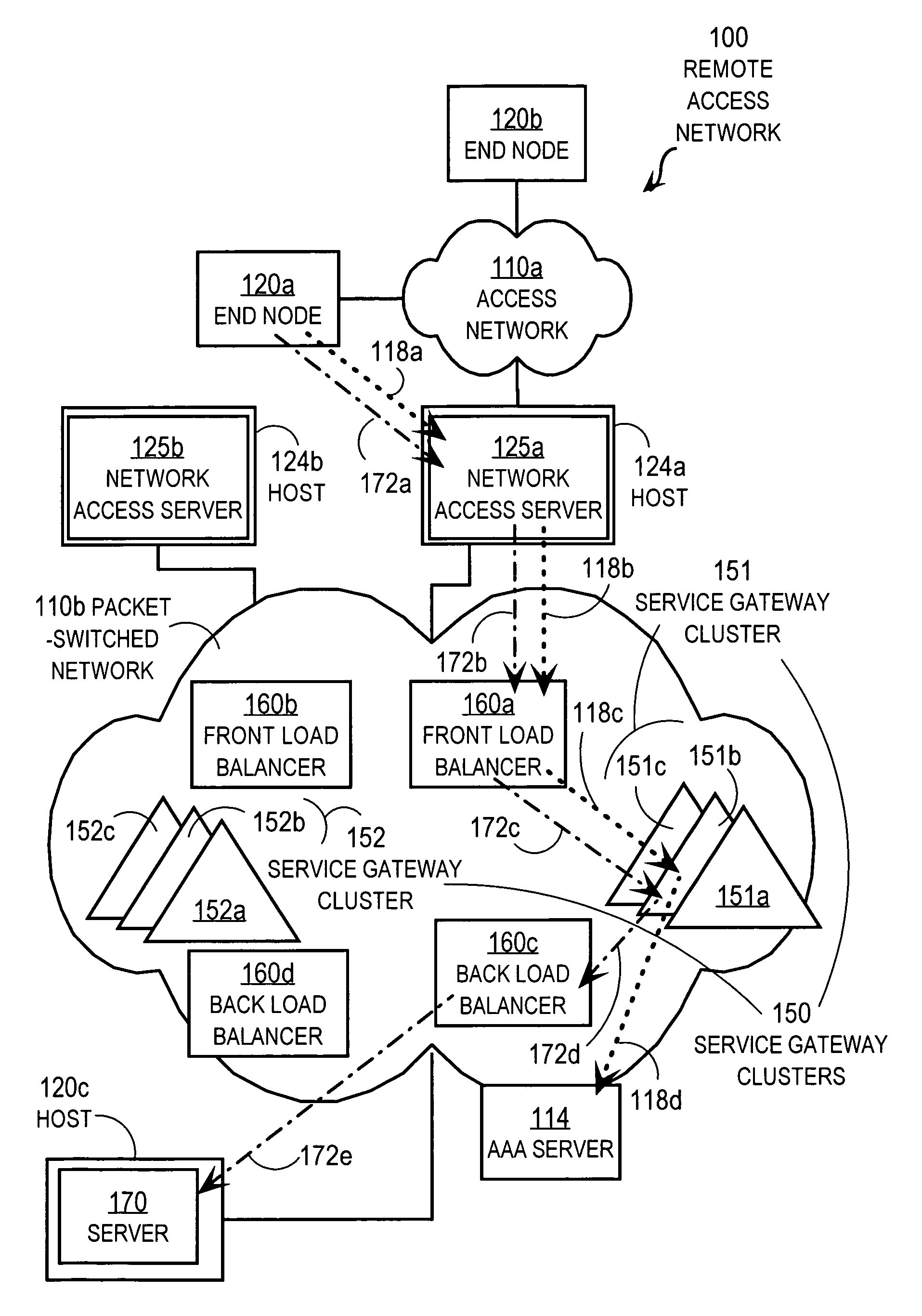
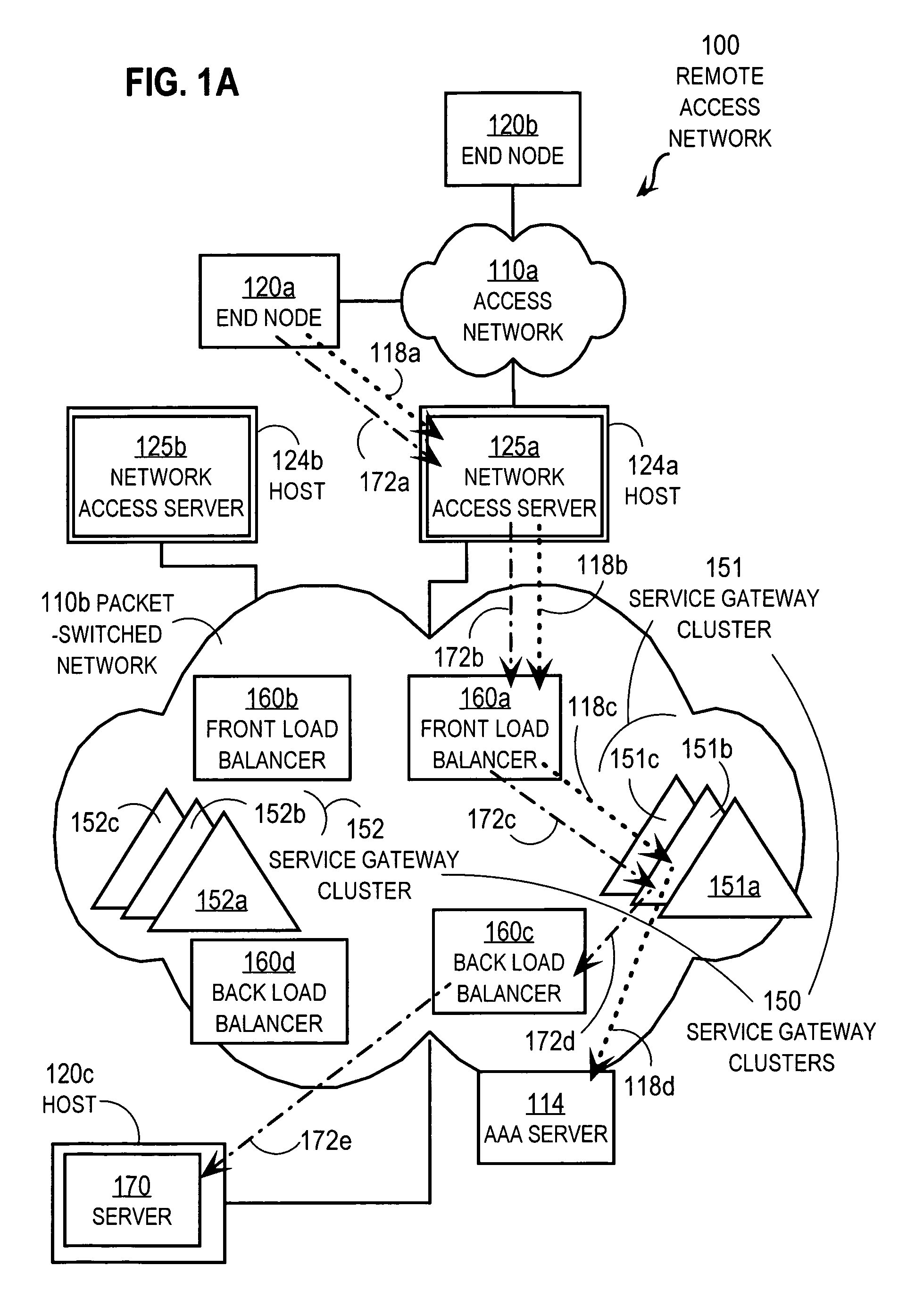
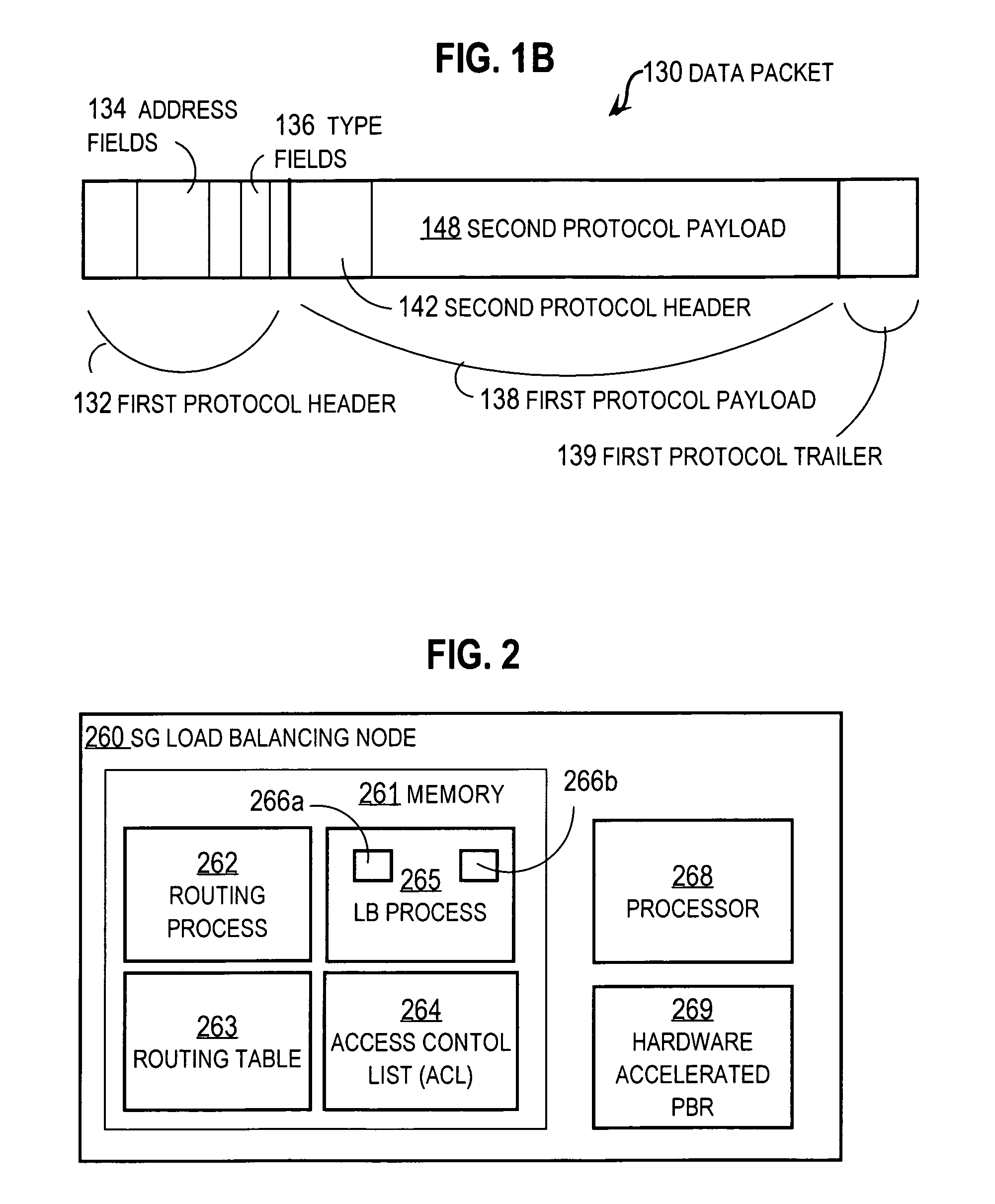
Techniques for load balancing over a cluster of subscriber-aware application servers
InactiveUS20070165622A1Digital computer detailsNetwork connectionsApplication serverDistributed computing
Techniques for distributing control plane traffic, from an end node in a packet switched network to a cluster of service gateway nodes that host subscriber-aware application servers, include receiving a control plane message for supporting data plane traffic from a particular subscriber. A particular service gateway node is determined among the cluster of service gateway nodes based on policy-based routing (PBR) for the data plane traffic from the particular subscriber. A message based on the control plane message is sent to a control plane process on the particular service gateway node. Thereby, data plane traffic and control plane traffic from the same subscriber are directed to the same gateway node, or otherwise related gateway nodes, of the cluster of service gateway nodes. This approach allows currently-available, hardware-accelerated PBR to be used with clusters of subscriber-aware service gateways that must also monitor control plane traffic from the same subscriber.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Localized voice over internet protocol communication
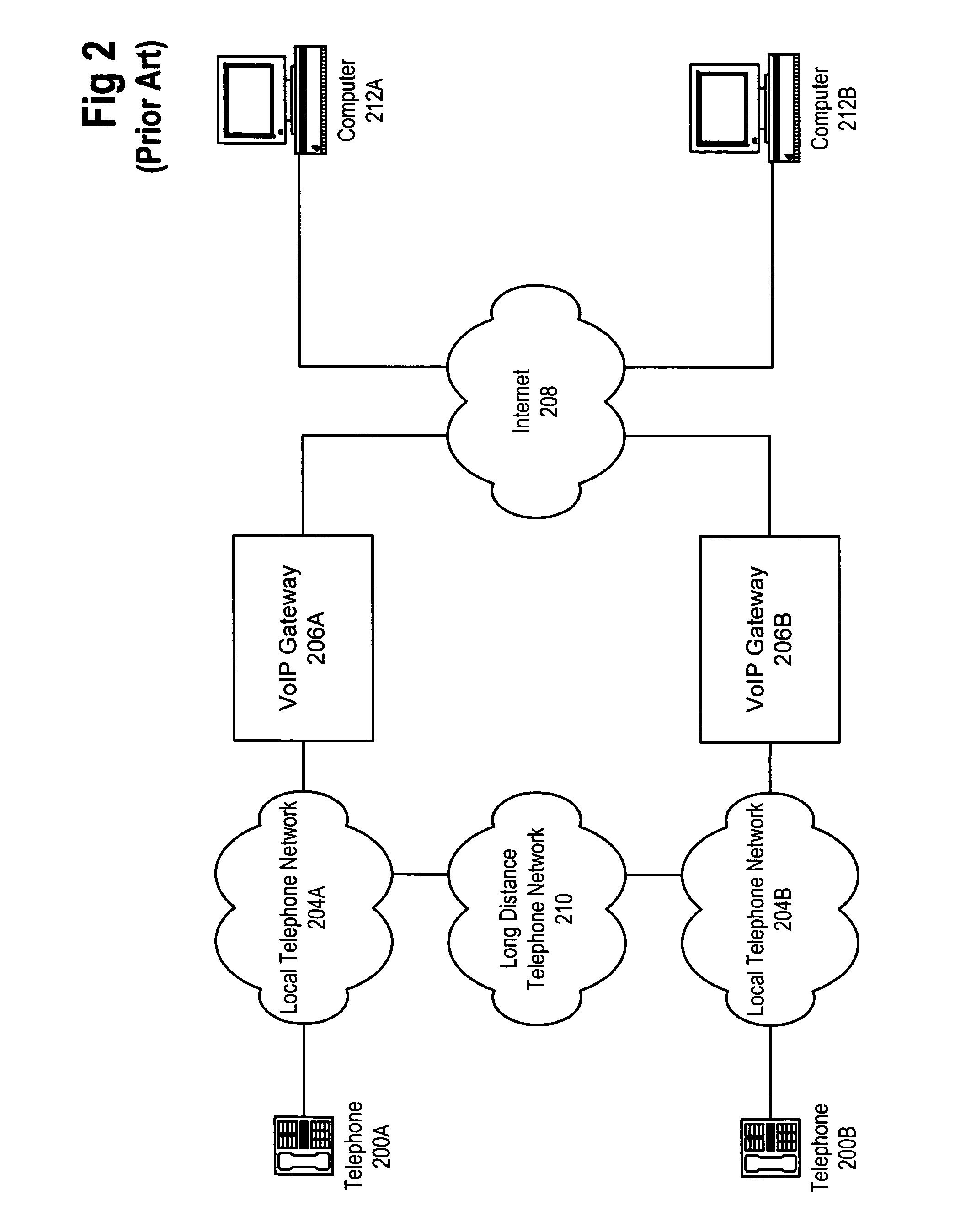
InactiveUS7286521B1Add supportHandled more elegantlyInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersShortest distanceSound file
An approach to abstracting the circuit switched nature of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) by using VoIP to provide voice actuated services is disclosed. By carrying a telephone call using VoIP technology for a short distance (frequently within a server room) significant benefits to call handling and capacity management can be obtained. Specifically, a PSTN-to-IP gateway is used to receive (and place) calls over the PSTN and route those calls internally to servers over an IP network in a packet switched format. A number of computer systems can receive and handle the calls in the IP format, including: translating the packets into an audio format suitable for speech recognition and creating suitable packets from computer sound files for transmission back over the PSTN.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
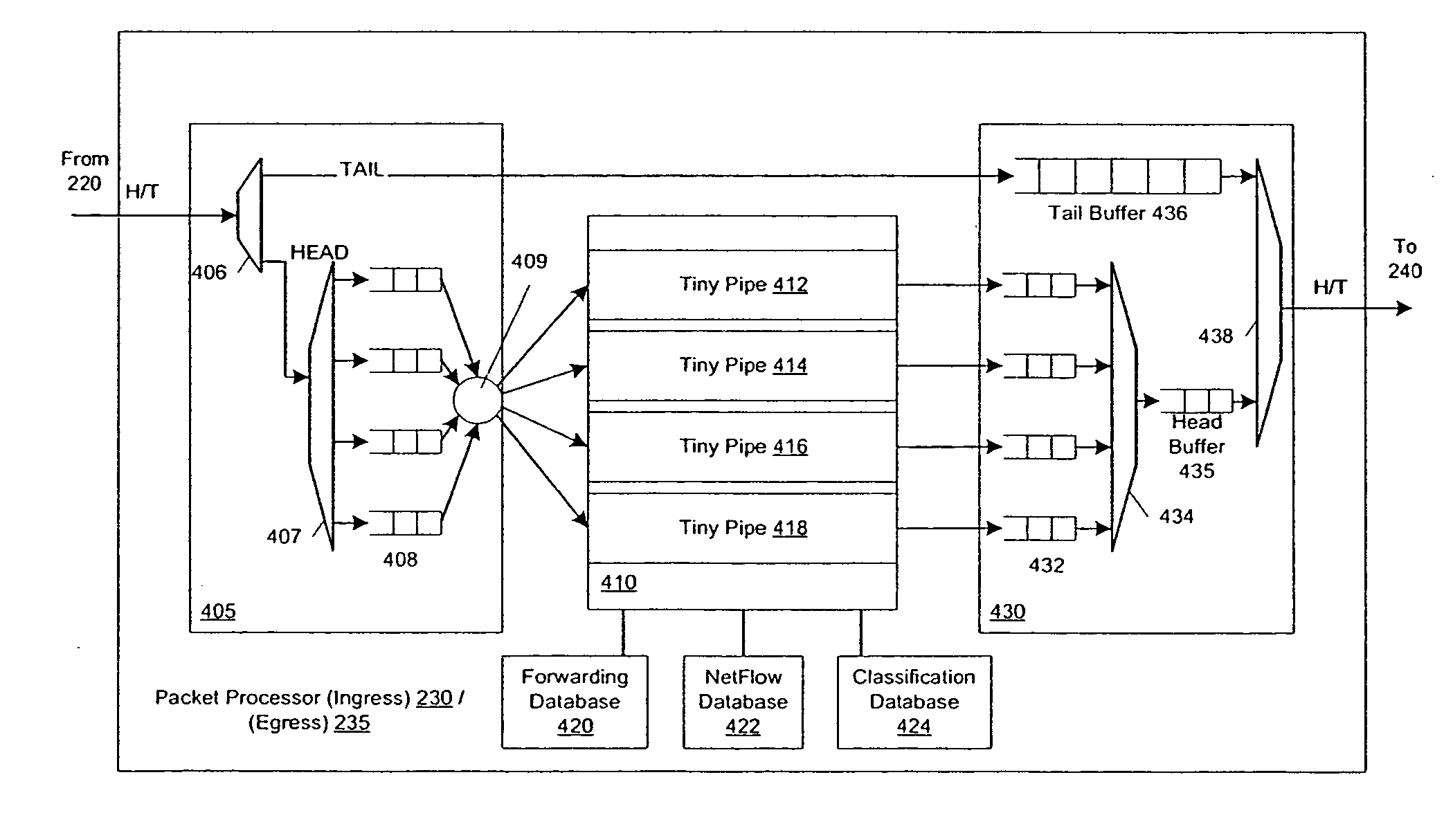
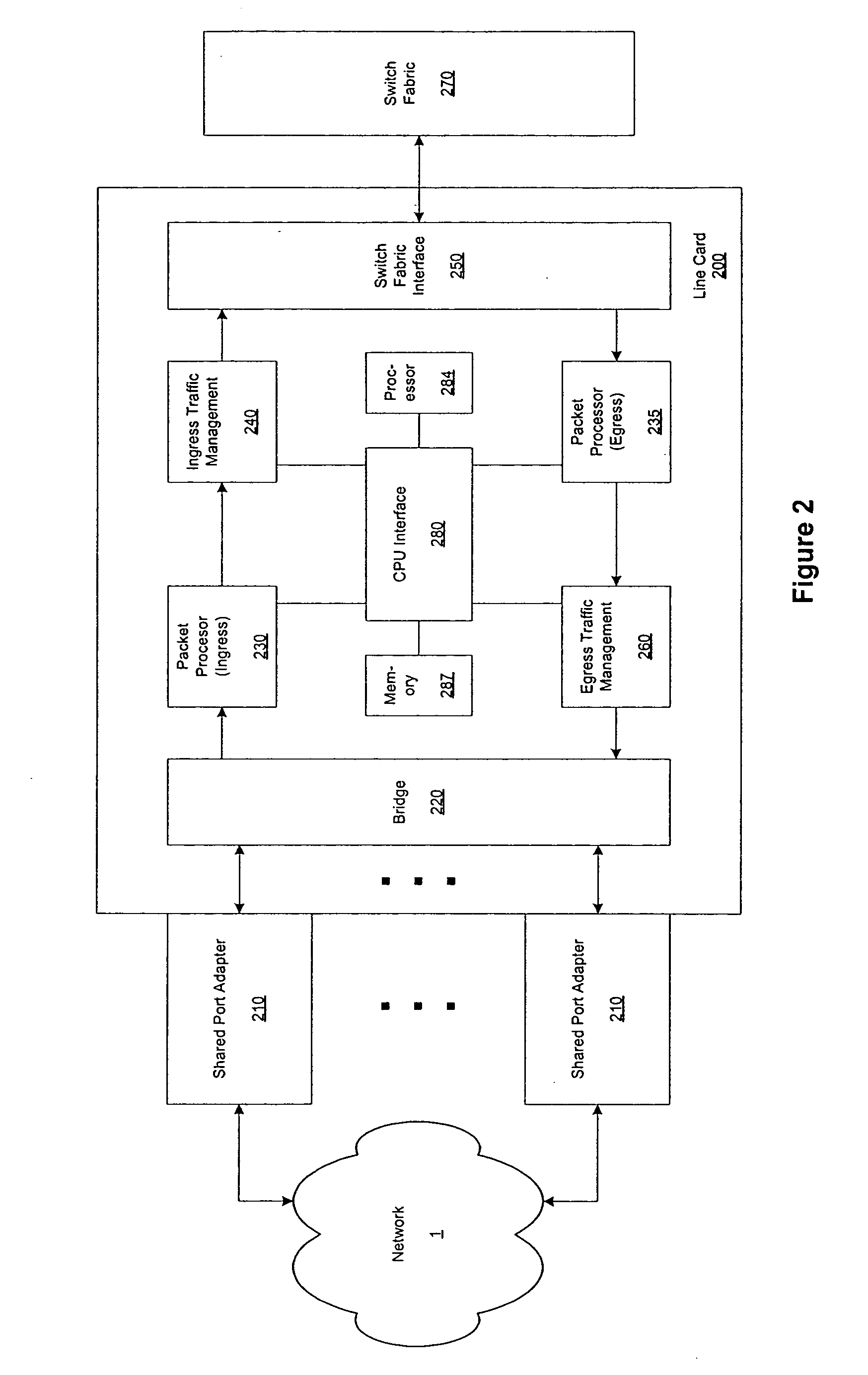
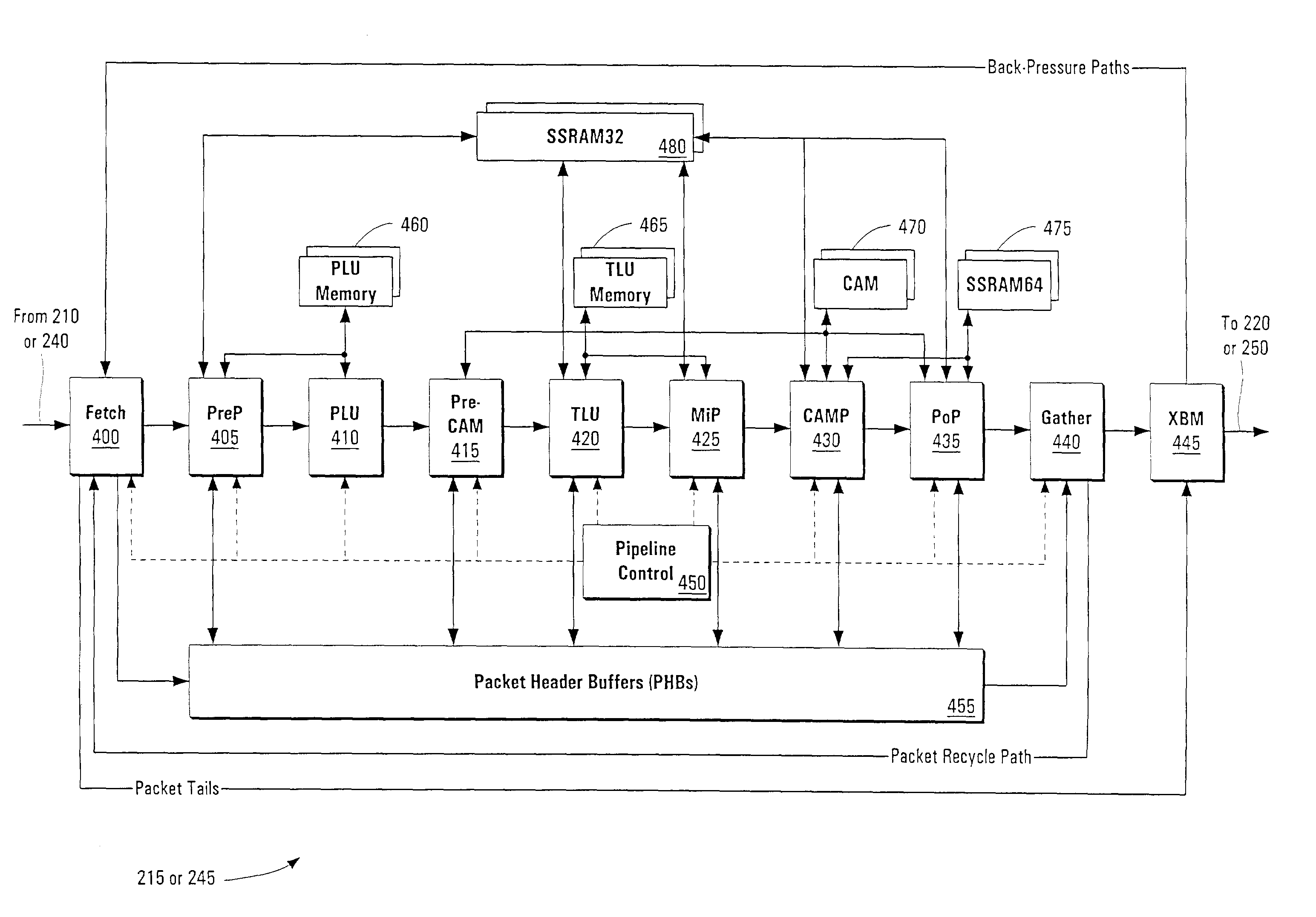
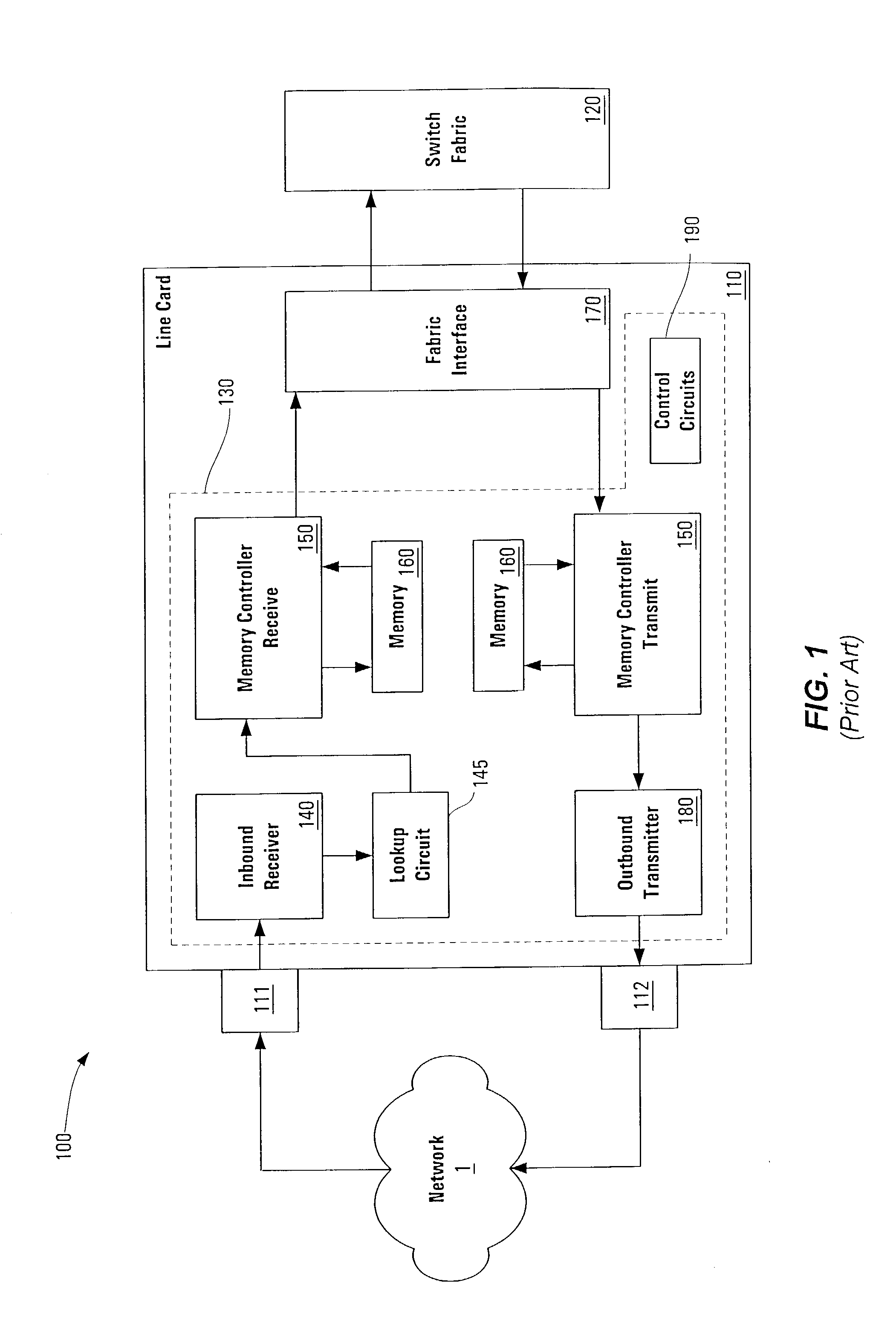
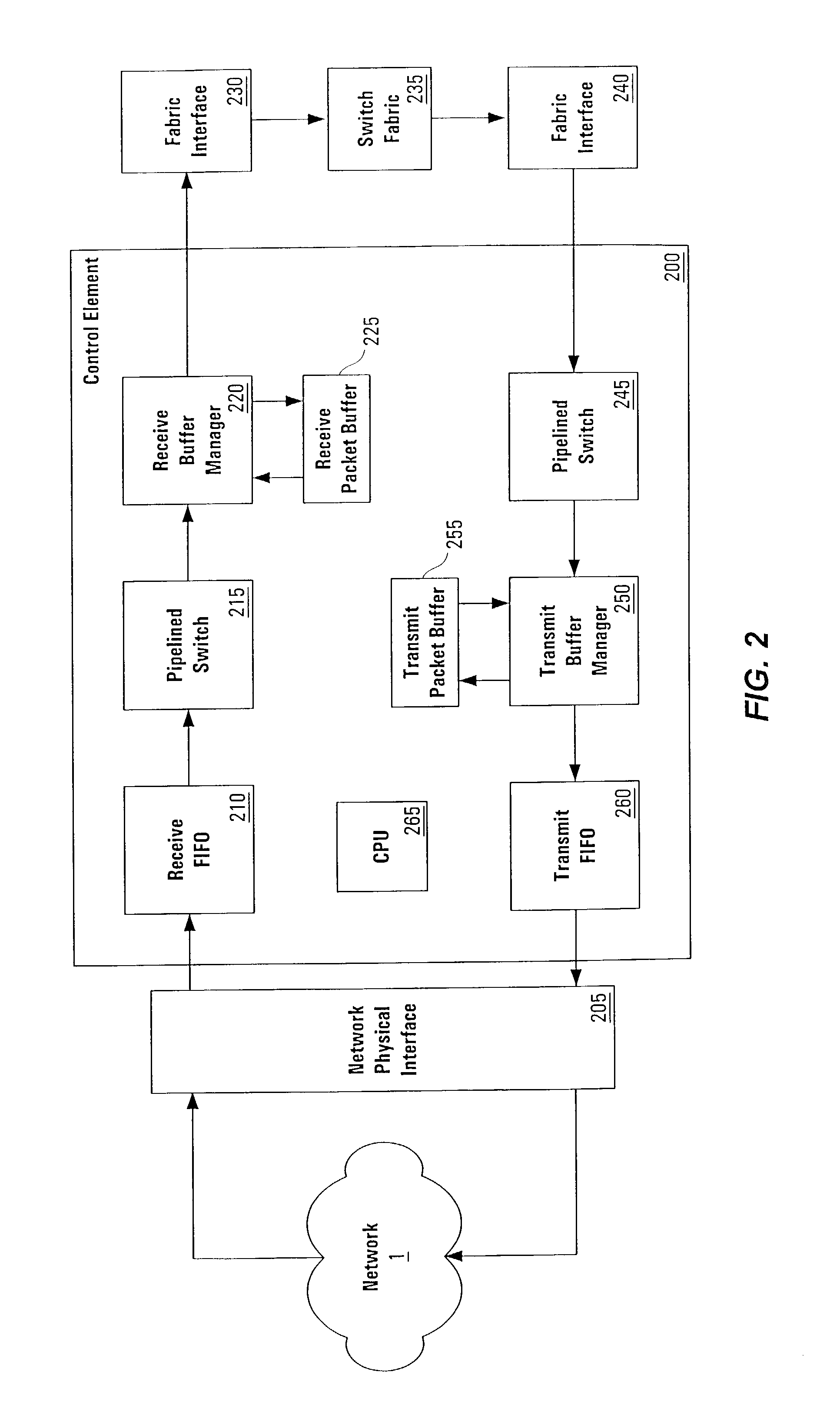
Pipelined packet switching and queuing architecture
An architecture for a line card in a network routing device is provided. The line card architecture provides a bi-directional interface between the routing device and a network, both receiving packets from the network and transmitting the packets to the network through one or more connecting ports. In both the receive and transmit path, packets processing and routing in a multi-stage, parallel pipeline that can operate on several packets at the same time to determine each packet's routing destination is provided. Once a routing destination determination is made, the line card architecture provides for each received packet to be modified to contain new routing information and additional header data to facilitate packet transmission through the switching fabric. The line card architecture further provides for the use of bandwidth management techniques in order to buffer and enqueue each packet for transmission through the switching fabric to a corresponding destination port. The transmit path of the line card architecture further incorporates additional features for treatment and replication of multicast packets.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Telecommunication routing using multiple routing protocols in a single domain
InactiveUS7177646B2Improve routing efficiencyAssess restrictionSpecial service for subscribersRouting domainNetwork addressing
Packets are routed in a communications network including an infrastructure of packet switching nodes interconnected by packet transport links, and a plurality of access nodes to which a routing path, defined by data held in packet switching nodes located along the routing path, may be directed in the infrastructure for a given network address. Different types of routing updates are used in a single routing domain.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Method and apparatus providing prepaid billing for network services using explicit service authorization in an access server
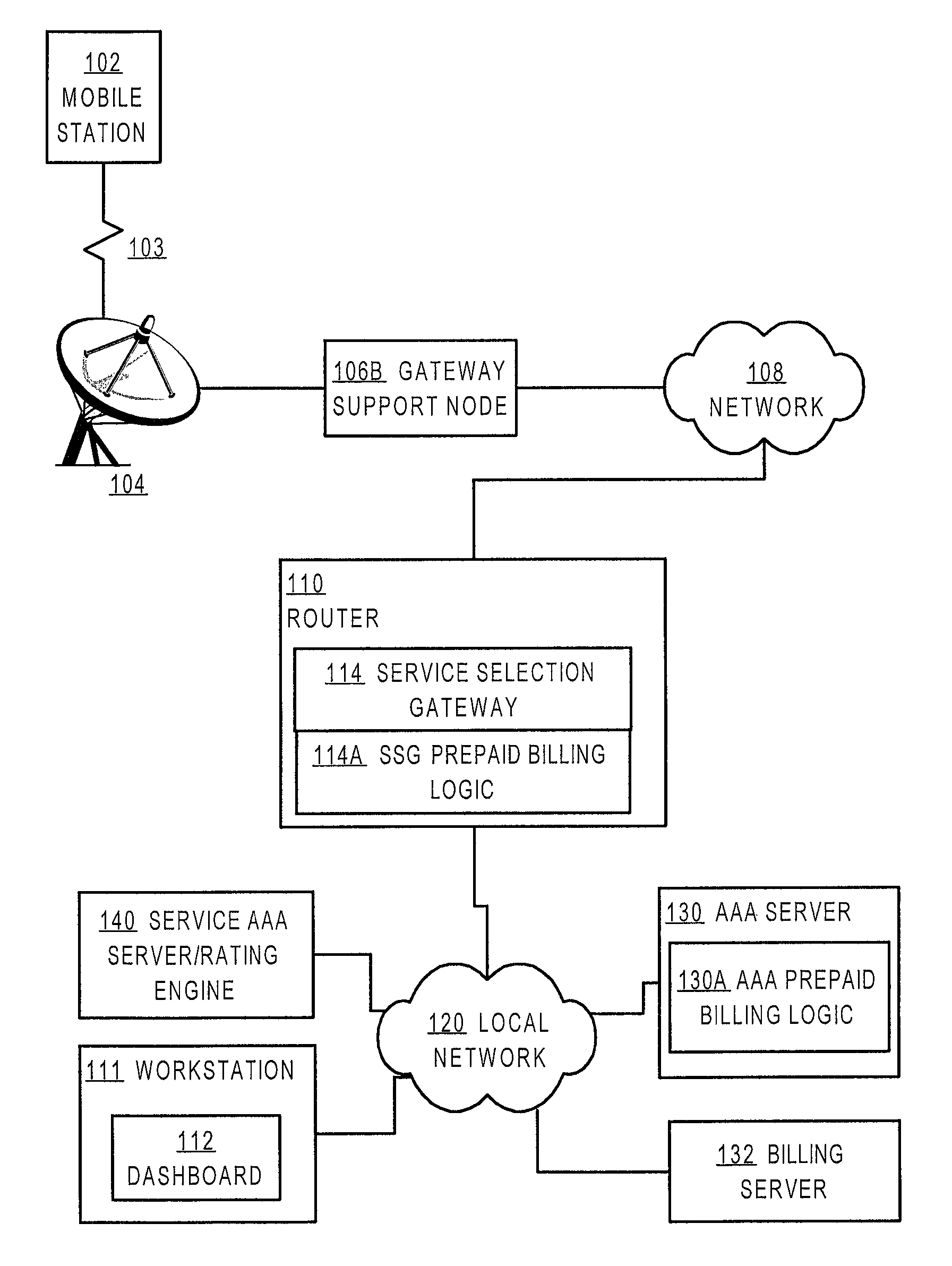
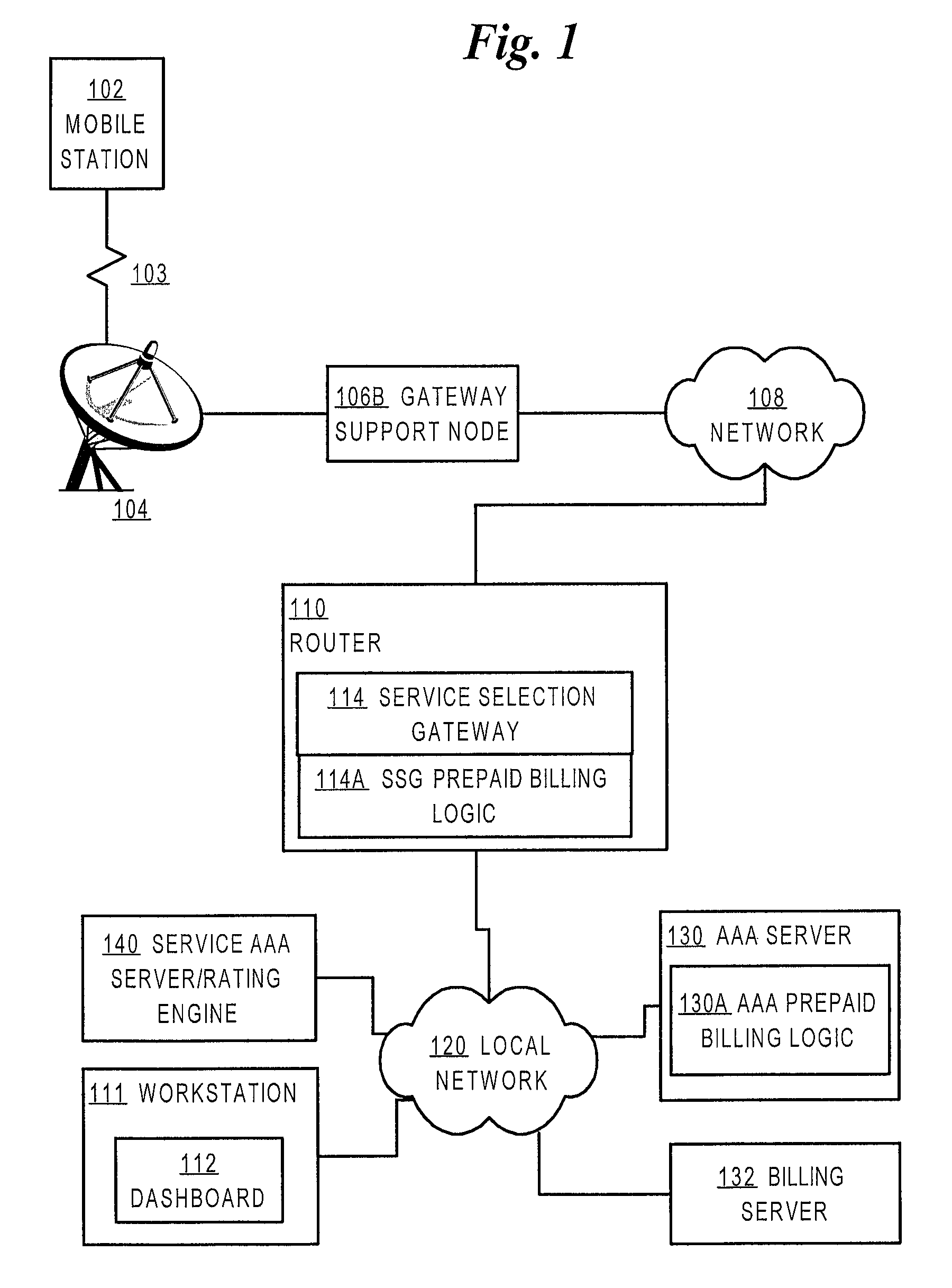
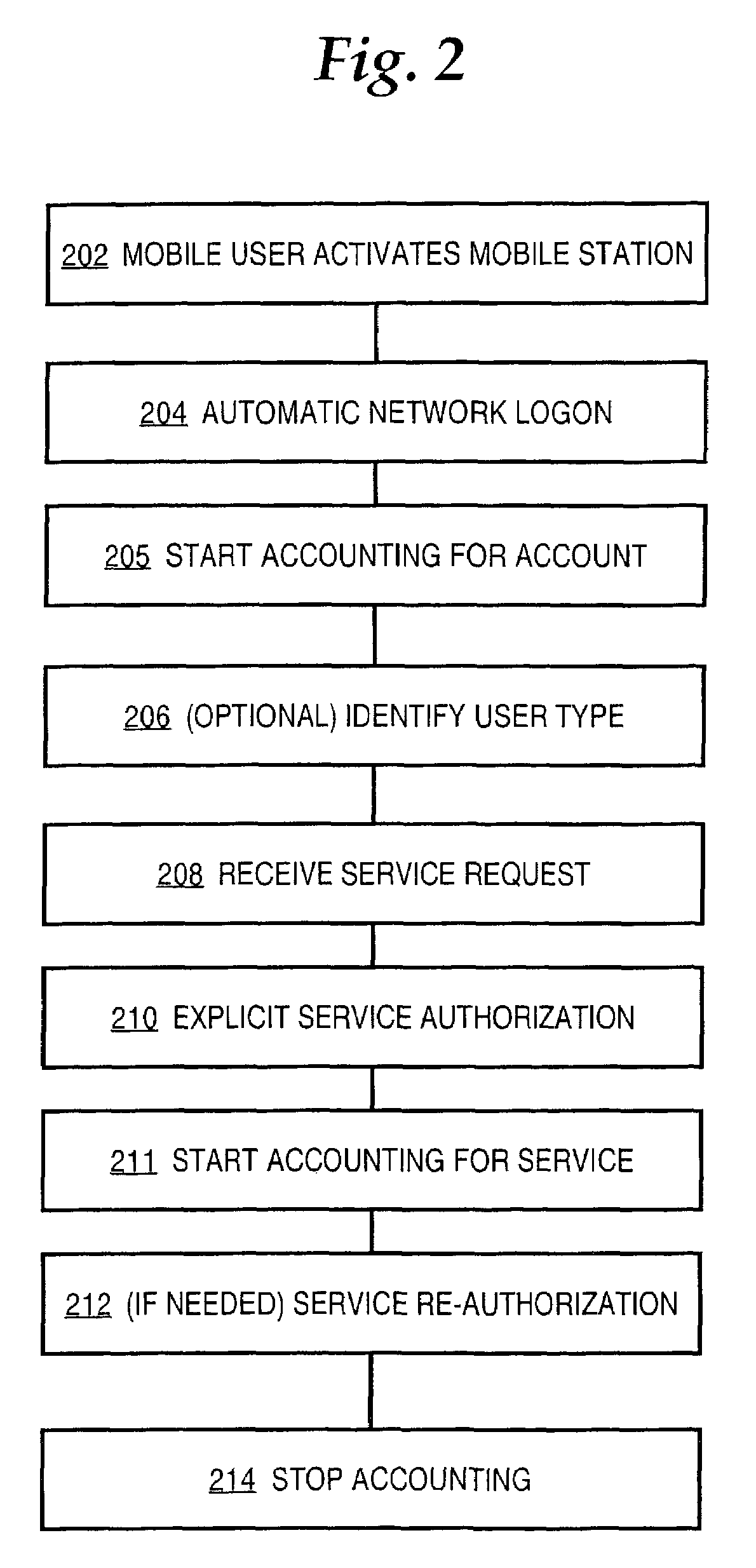
ActiveUS7720960B2Complete banking machinesAccounting/billing servicesNetwork terminationTraffic capacity
A method is disclosed for authorizing a prepaid network service in a data network. A network end station issues a request for a prepaid network service. At a network node, such as a router serving as a gateway for selecting services, a determination is made about whether a user associated with the end station is authorized to access the prepaid network service. Network traffic from the end station is forwarded to a service provider only when the user is authorized to use the prepaid network service. Specific embodiments provide message flows among a mobile station, gateway support node, router, and authentication server that support providing prepaid services in a packet-switched network for mobile communication. In certain embodiments, a connection is held open for an end station while a prepaid quota value is refreshed at a portal, thereby reducing overhead and precluding the need to repeat user logon steps. Further, unused quota amounts can be returned to the authentication server for use in association with multiple concurrent connections of the same device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Combined pipelined classification and address search method and apparatus for switching environments
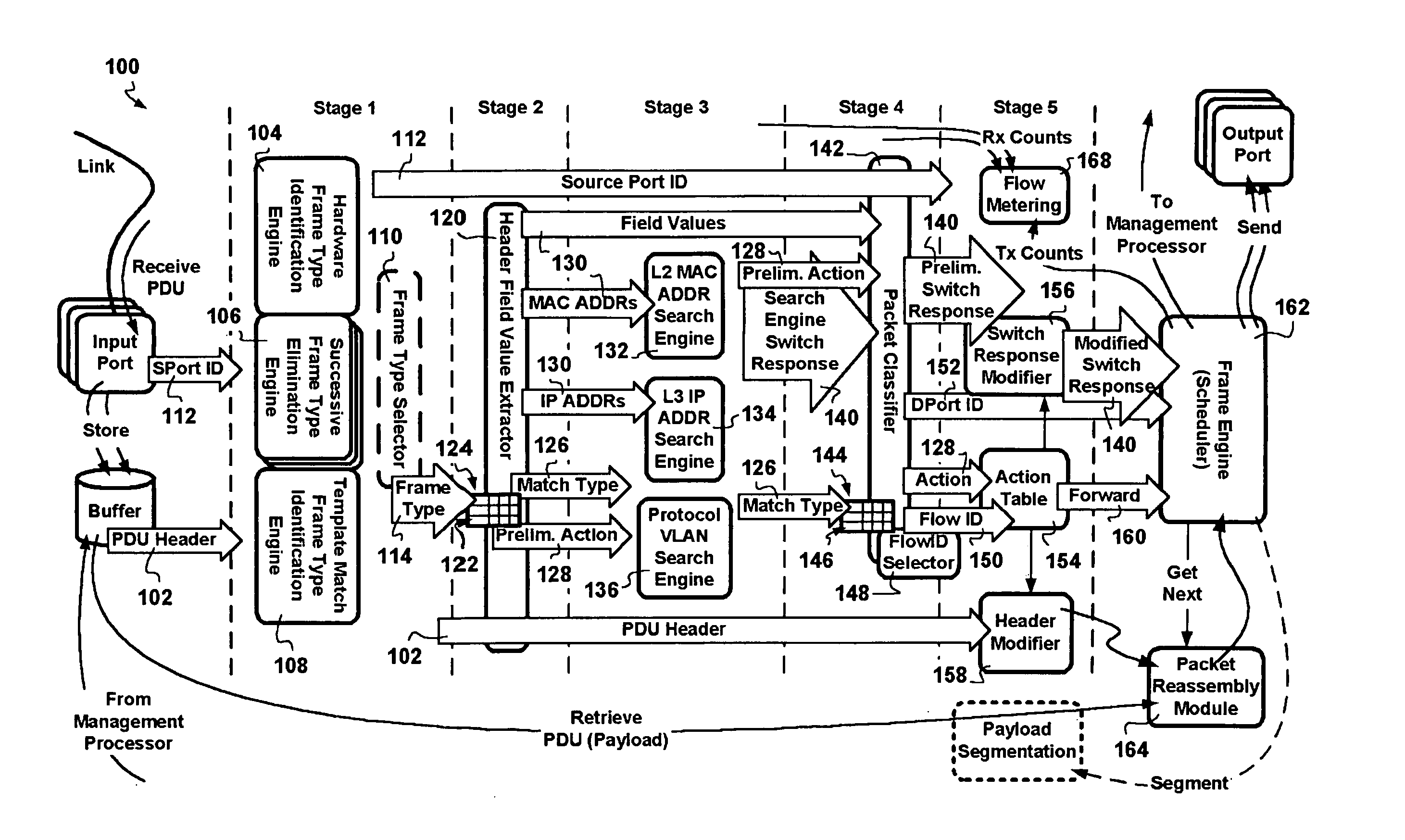
InactiveUS20060002386A1Network degradationReduce data transfer bandwidthTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork addressingObsolescence
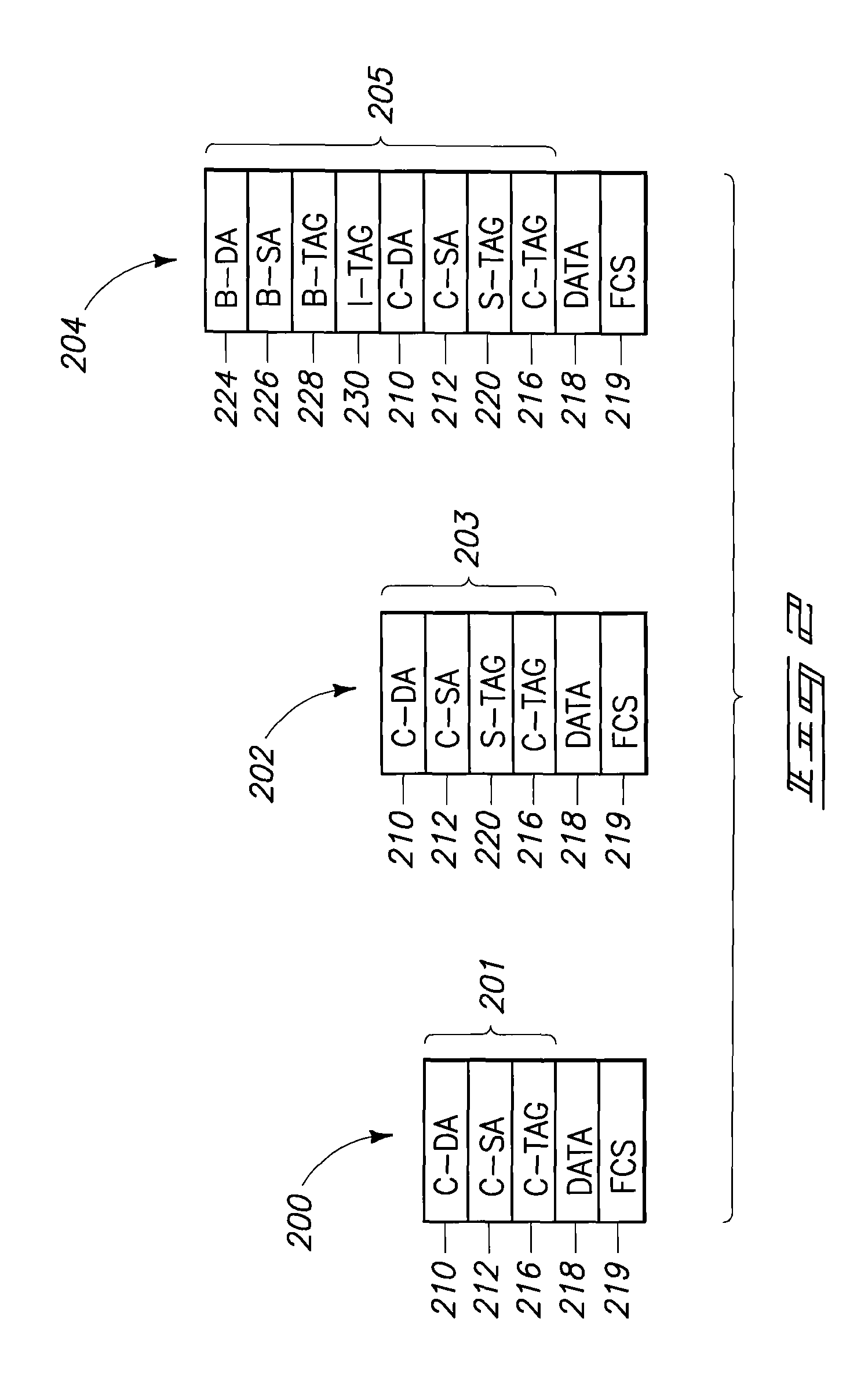
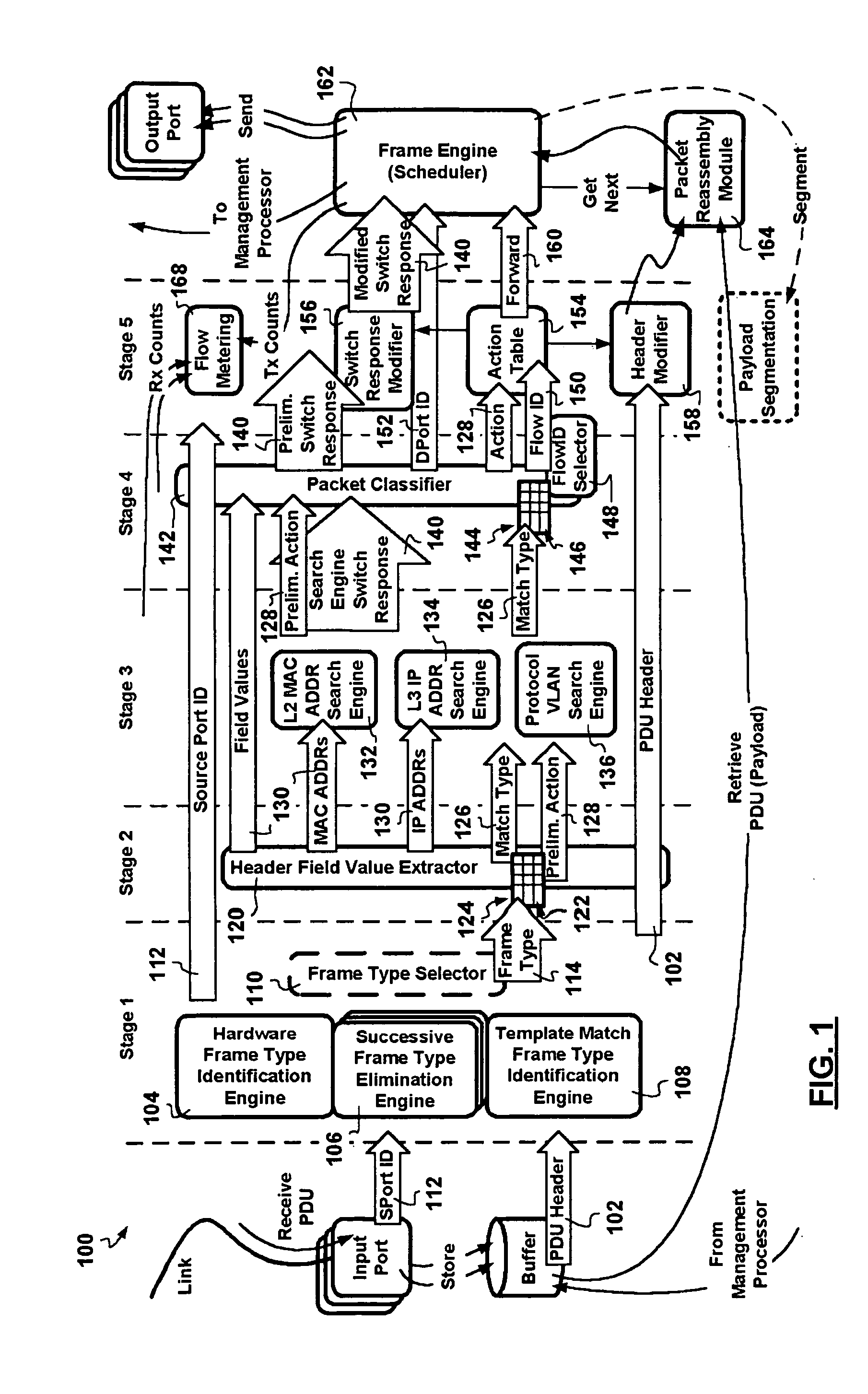
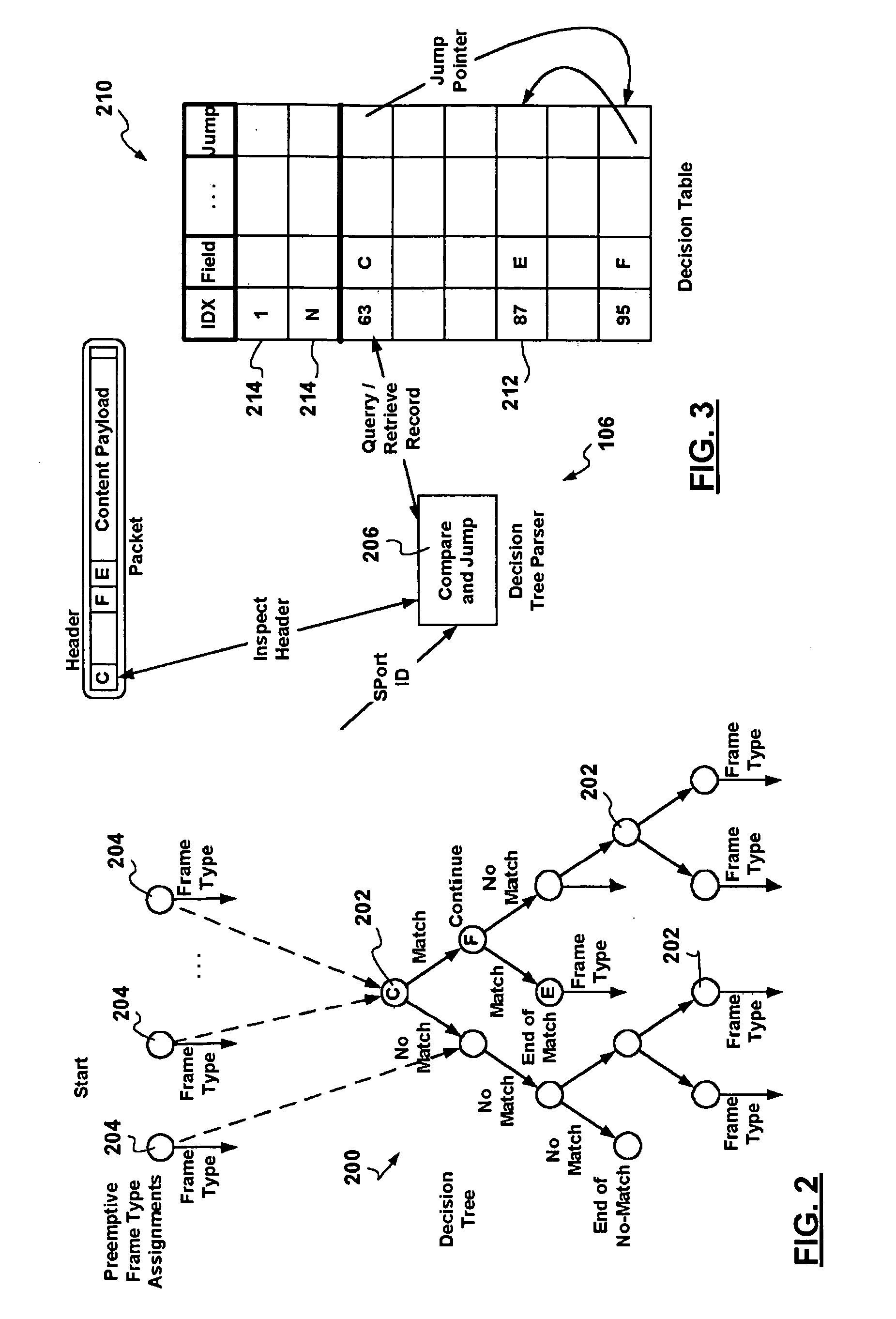
A packet switching node having a pipelined packet processing architecture processing packets received via an input port associated with the packet switching node is presented. The method performed by the apparatus includes: determining a packet frame type of the packet received; selectively extracting packet header field values specific to a packet frame type, the extracted packet header field value including packet addressing information; ascribing to the packet a preliminary action to be performed in respect of the packet; searching packet switching information tracked by the packet switching node based on extracted packet addressing information; formulating a preliminary switch response for the packet; classifying the packet into one of a plurality of packet flows; modifying the preliminary switch response in accordance with one of the preliminary action, the packet flow into which the packet was classified, and a default port action corresponding to the input port; modifying the packet header in accordance with one of the preliminary action, the packet flow, and the default port action; and processing the packet in accordance with the switch response. Advantages are derived from: pipelined processing of packets which enables short-cutting the rest of the processing for improper packets; a flexible frame type determination which is fast for well know frame types yet flexible in support of new frame types delaying obsolescence of a particular implementation; an early determination of a processing action which is successively refined by subsequent stages; a combined Layer-2 and Layer-3 network addressing search engine operating on short bit length indexed Layer-2 and Layer-3 network addresses reducing network address table storage requirements, requiring a reduced data transfer bandwidth for network address table access, a large external hashed primary network address table, and a small internal secondary network address table; an early determination of a switch response; and packet-classification-based switch response and packet header modification.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Consistent sampling for network traffic measurement
InactiveUS6873600B1Reduce ambiguityIncrease choiceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsHash functionNetwork measurement
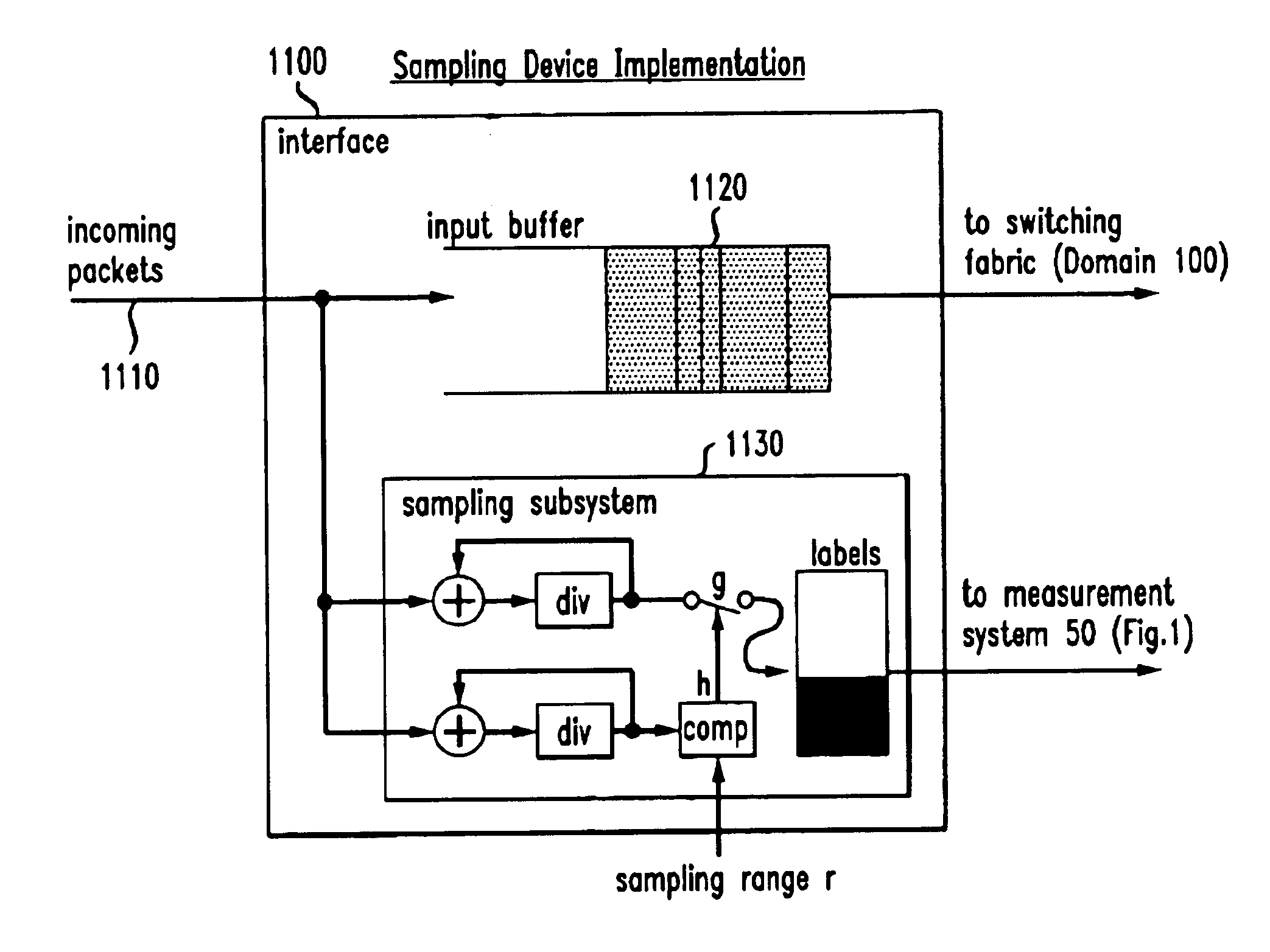
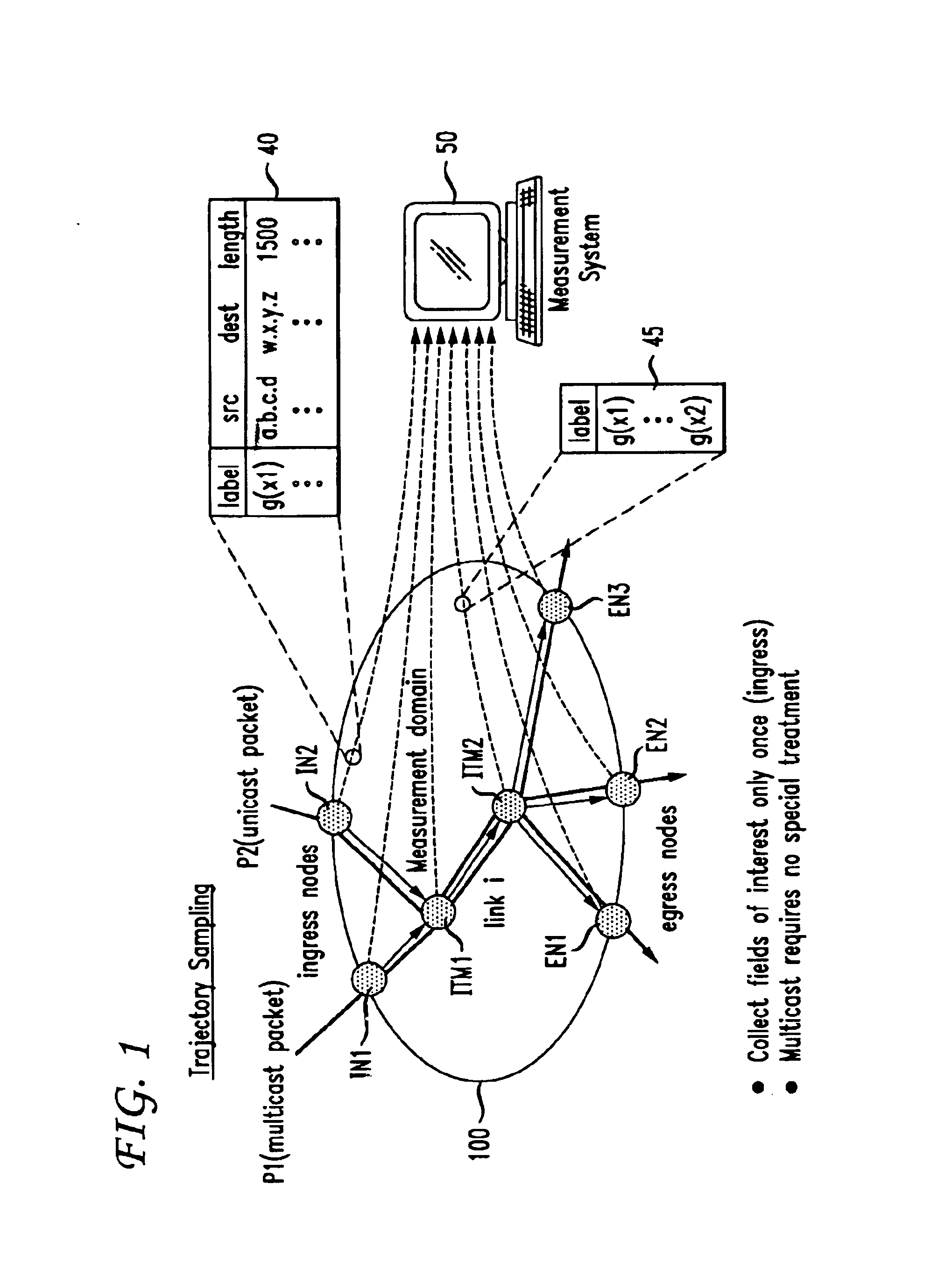
Traffic measurement should make it possible to obtain the spatial flow of traffic through the domain, i.e., the paths or trajectories followed by packets between any ingress and egress point of the domain. A method of sampling packet trajectories in a packet switching network allows the direct inference of traffic flows through a measurement domain by observing the trajectories of a subset of all packets traversing the network. A method which assumes that the measurement domain does not change comprises the steps of selecting packets for sampling in accordance with a sampling function of the packet content and generating a practically unique label for each sampled packet. The method does not rely on routing state, its implementation cost is small, and the measurement reporting traffic is modest and can be controlled precisely. Using the same hash function will yield the same sample set of packets in the entire domain, and enables us to reconstruct packet trajectories. An alternate embodiment which assumes no constraints and that the measurement domain may change comprises the steps of applying a sampling function and altering an invariant bit position as a signaling flag in each packet selected for sampling.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
On-line interactive system and method for transacting business
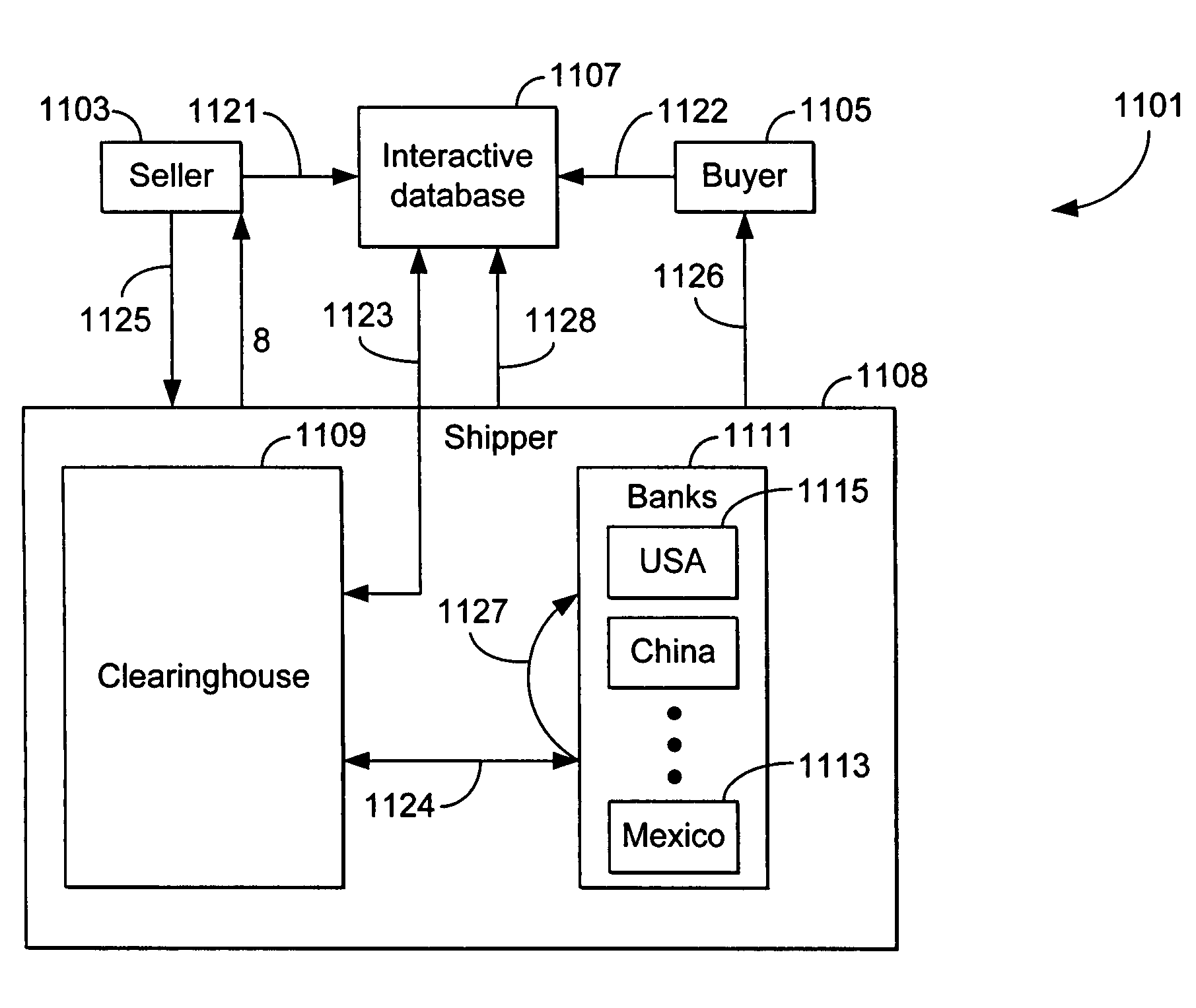
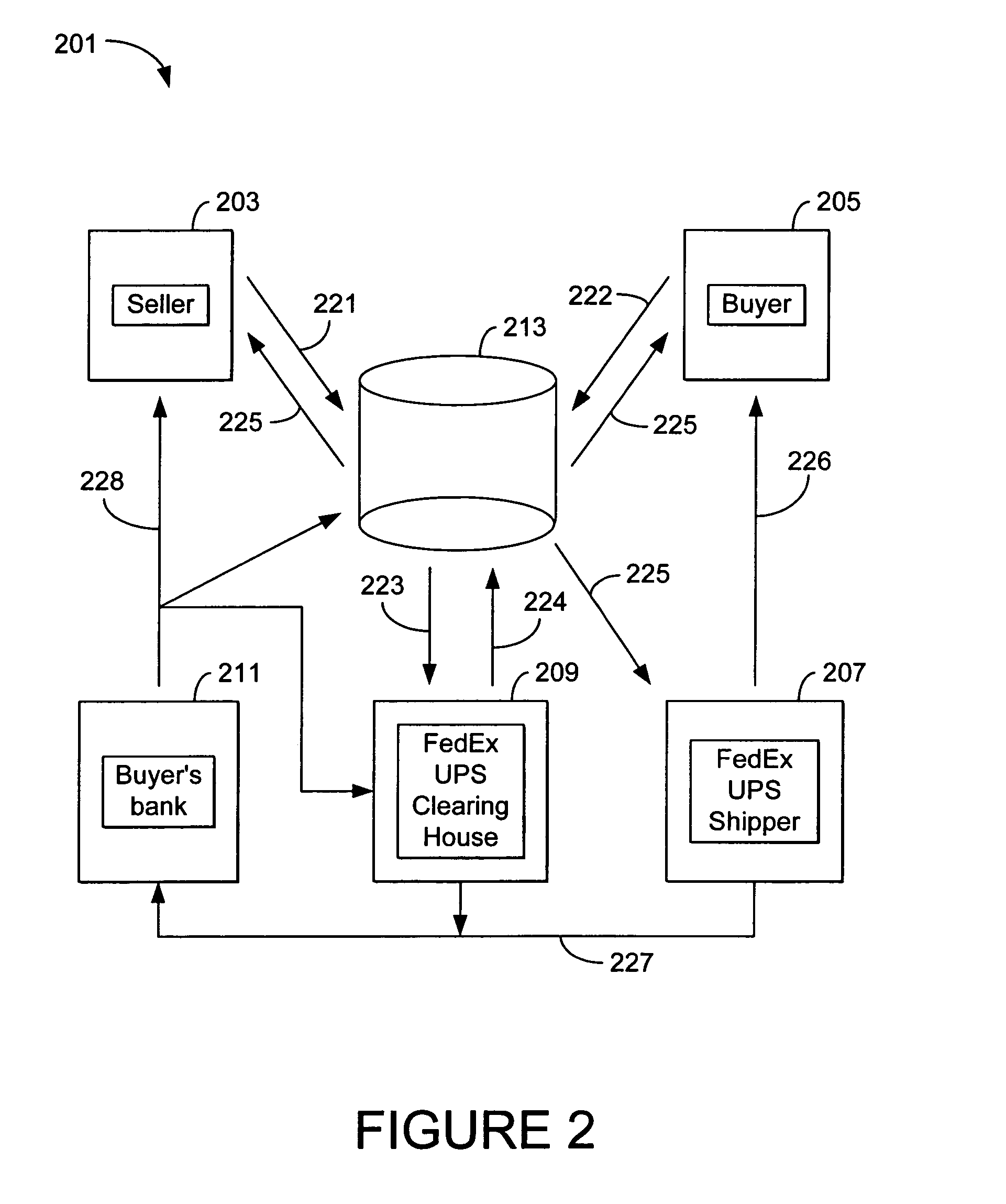
The present invention includes a method for transacting business over a network between multiple buyers and sellers. In an exemplary embodiment, the invention operates within an improved extranet system which is a secure, limited access network which operates within the larger public packet switched network (Internet) and allows only registered buyers and sellers to access the website while the system communicates with, and takes advantage of, existing credit, billing, collection, clearinghouse, insurance, transportation, tracking and banking systems. The interactive database includes real-time information in connection with a transaction, where the buyer submits a request for product and the request for the product locks out the requested product from selection by any other buyers.
Owner:DUNCAN VENTURES INC
Method and apparatus for delivery of adapted media
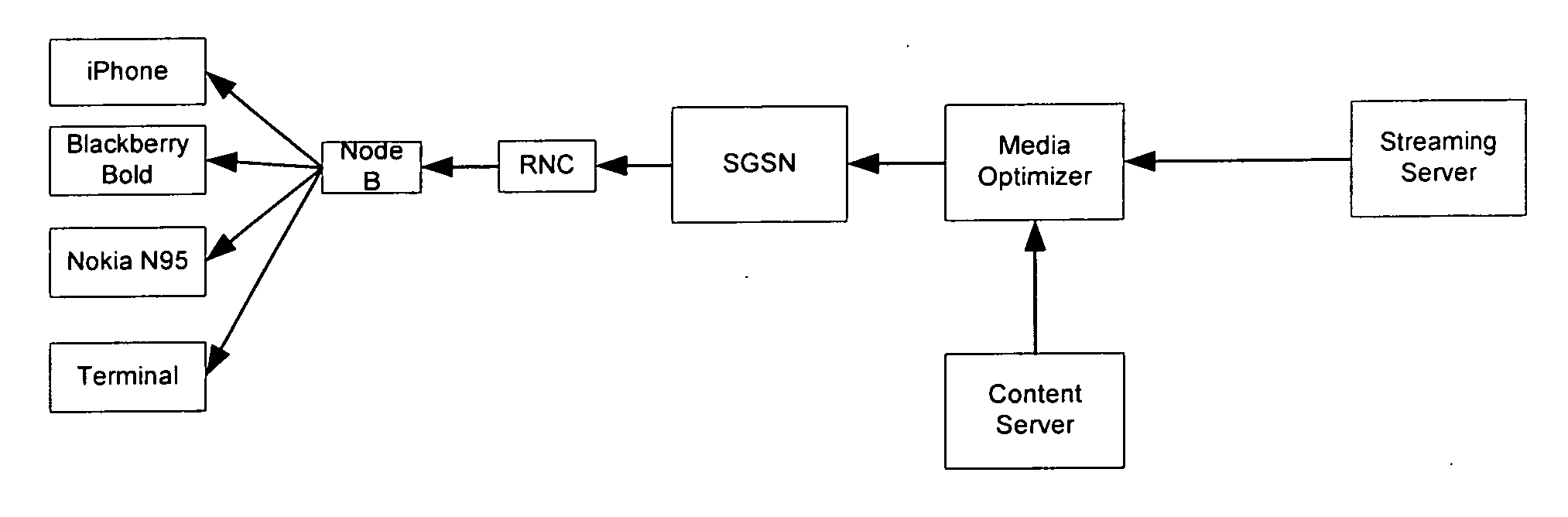
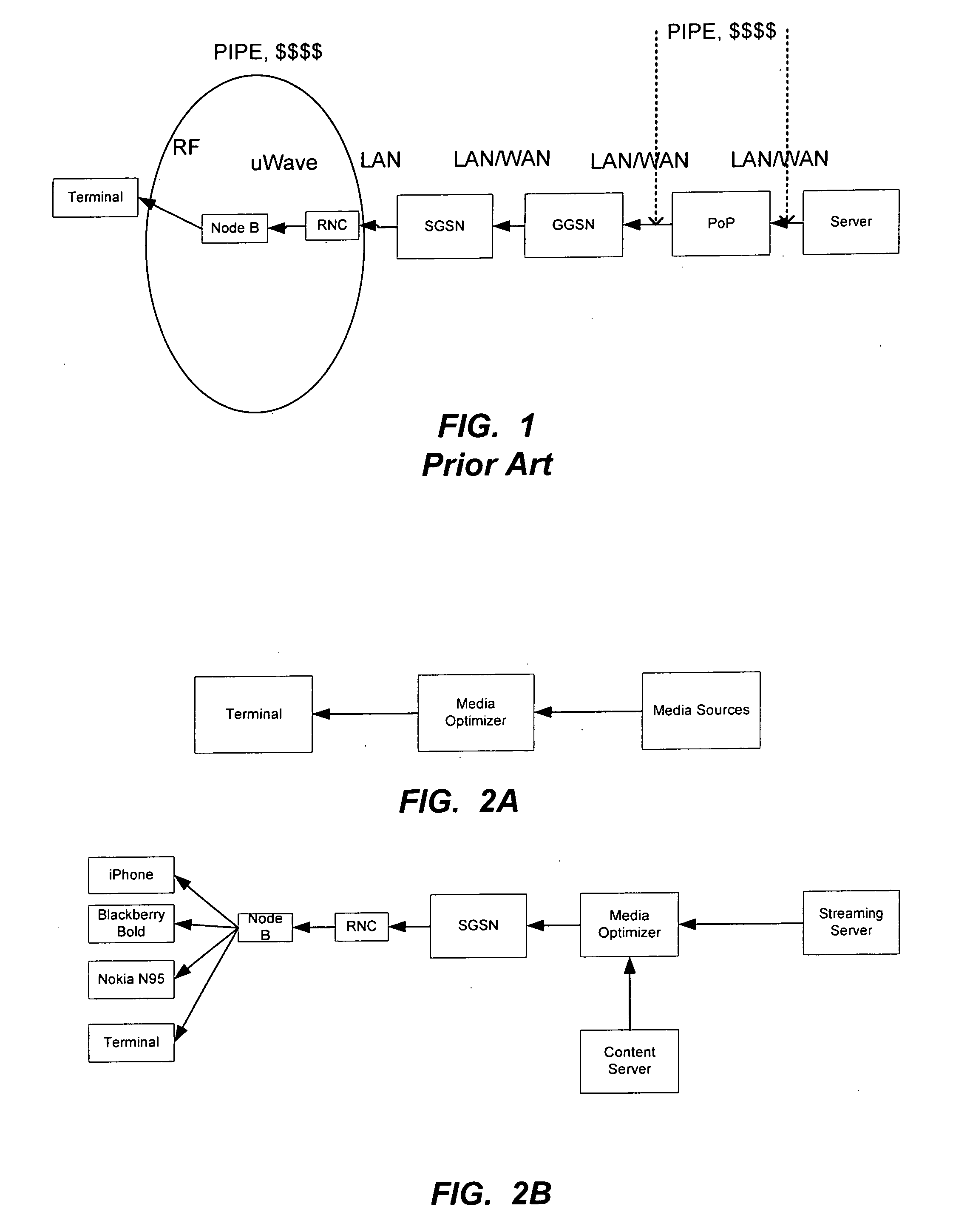
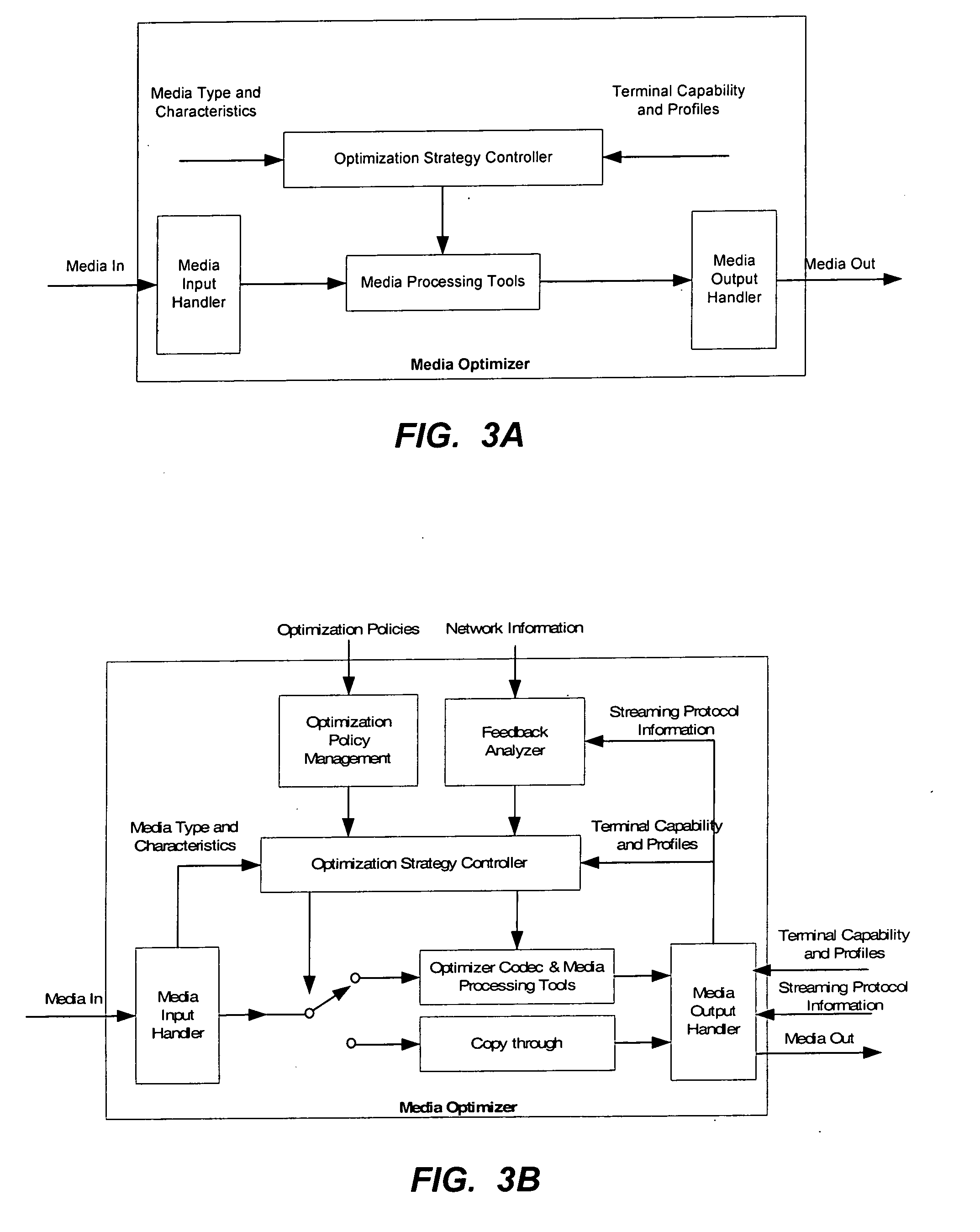
InactiveUS20100268836A1Network traffic/resource managementMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideDistributed computing
A method of transmitting media to a client by an infrastructure device in a packet-switched network includes receiving a media stream at the infrastructure device. The method also includes determining an adaptation strategy according to at least one of one or more pieces of network information associated with the packet-switched network, one or more pieces of client information associated with the client, or one or more policies. The method further includes adapting the media stream according to the adaptation strategy to produce an output media stream.
Owner:ONMOBILE GLOBAL LTD
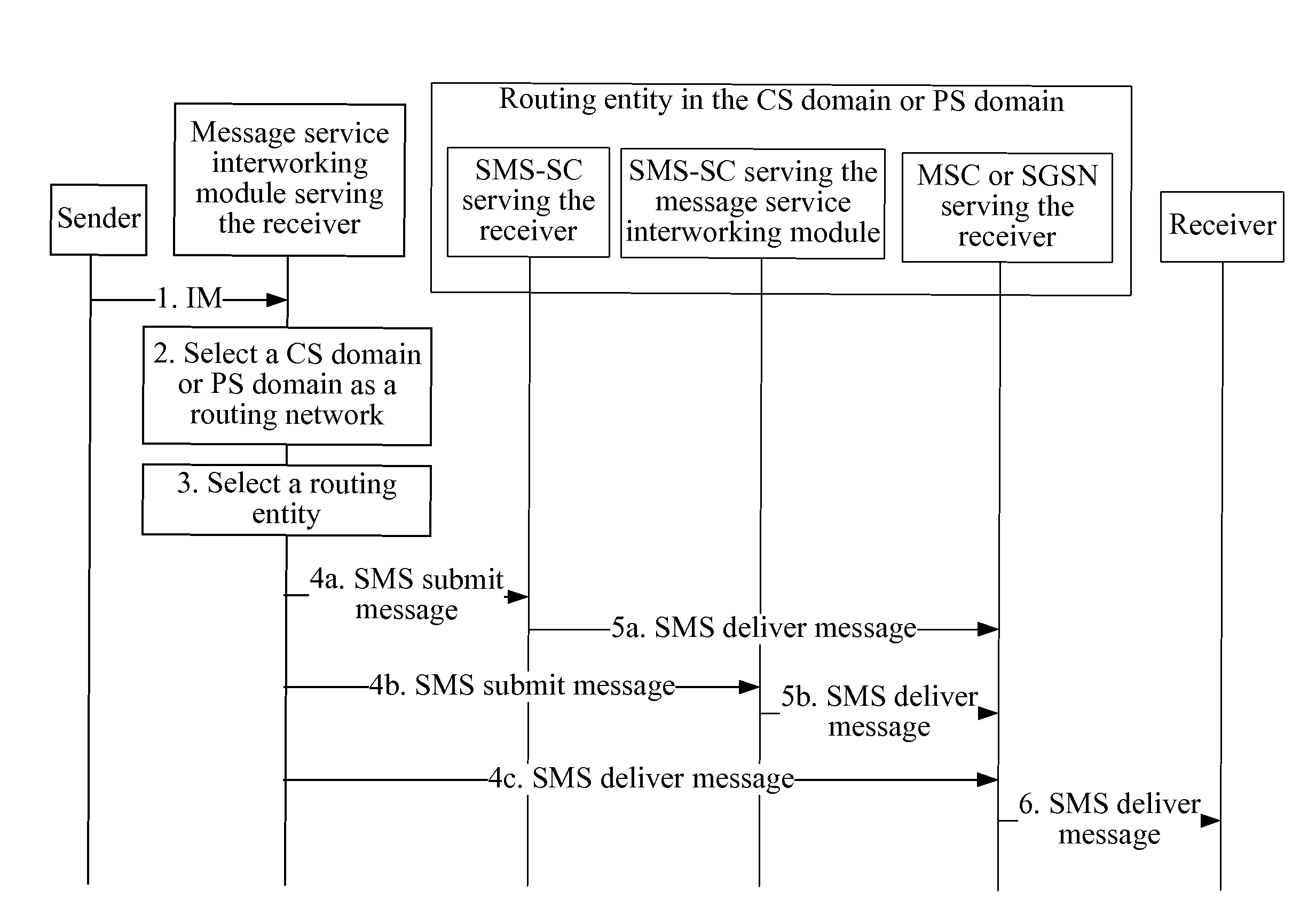
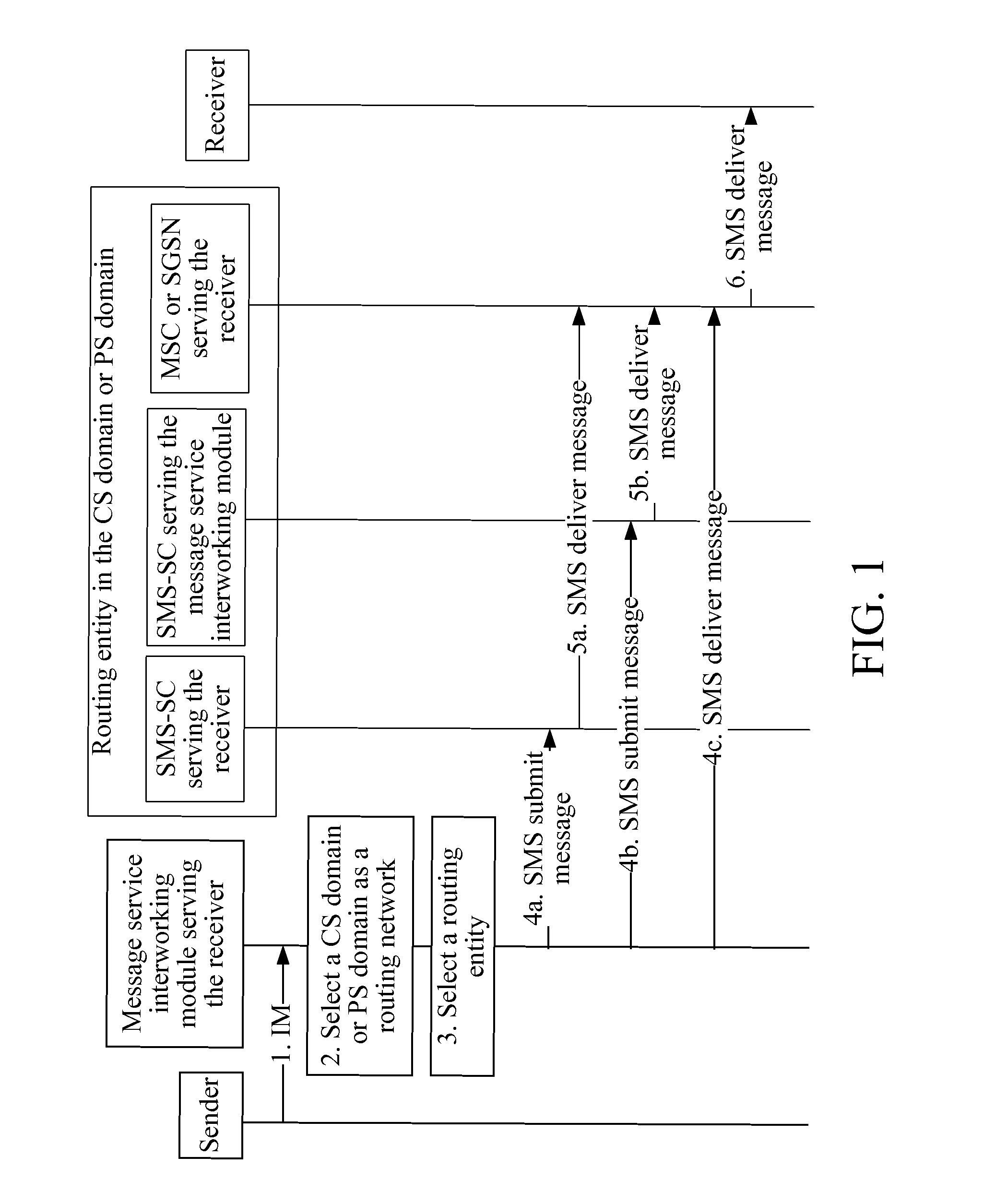
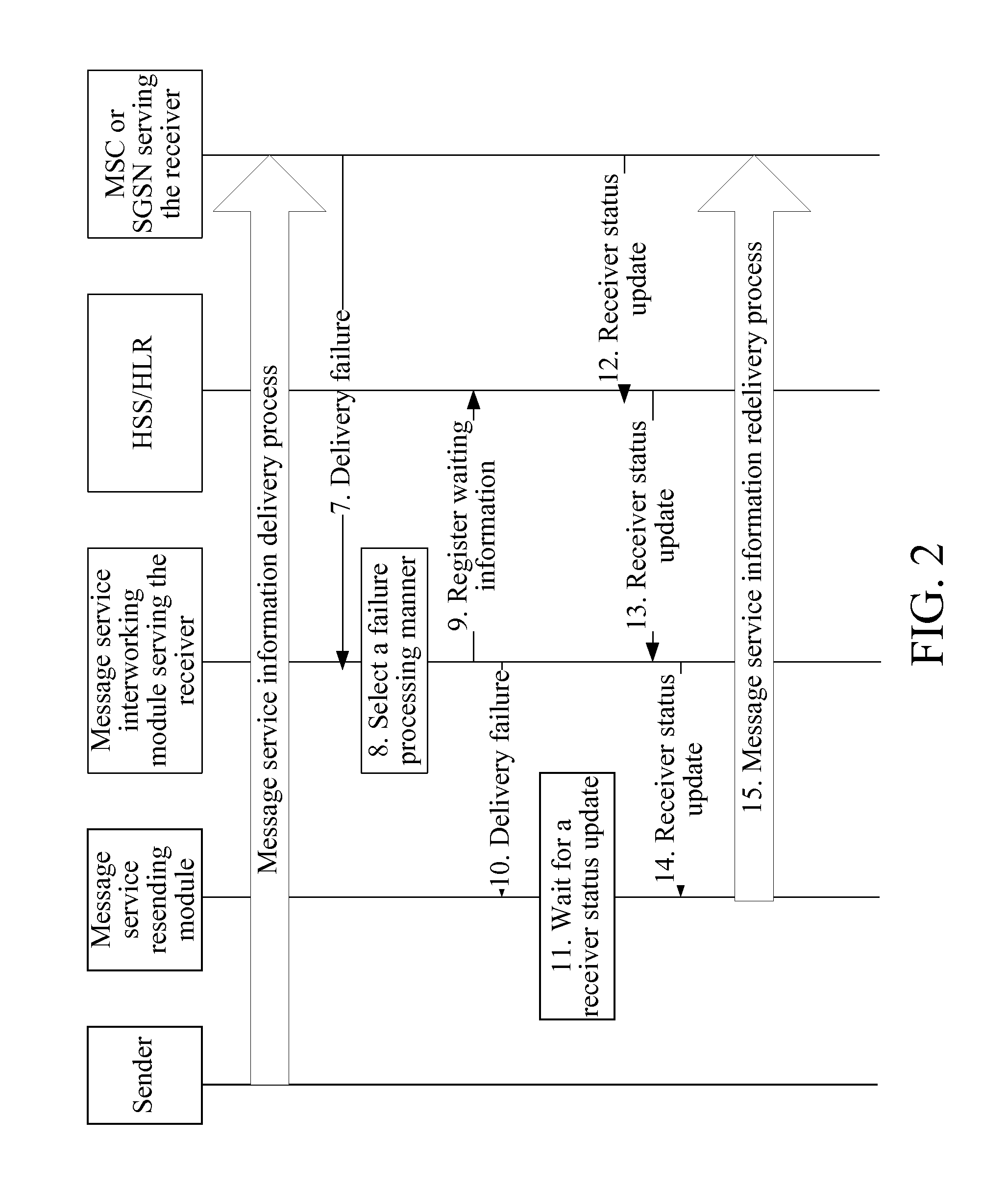
Method, system, and message service interworking module for implementing message service interworking
A method for implementing message service interworking is provided. The method includes: receiving, by a message service interworking module serving a receiver, an instant message sent by a sender; selecting, by the message service interworking module, a circuit switched domain (CS domain) or packet switched domain (PS domain) as a routing network; selecting, by the message service interworking module, a routing entity in the conventional CS domain or PS domain; and converting, by the message service interworking module, the instant message into a short message, and sending the short message to the receiver through the selected routing entity. A system and a message service interworking module for implementing message service interworking are also provided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Detecting network denial of service attacks
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
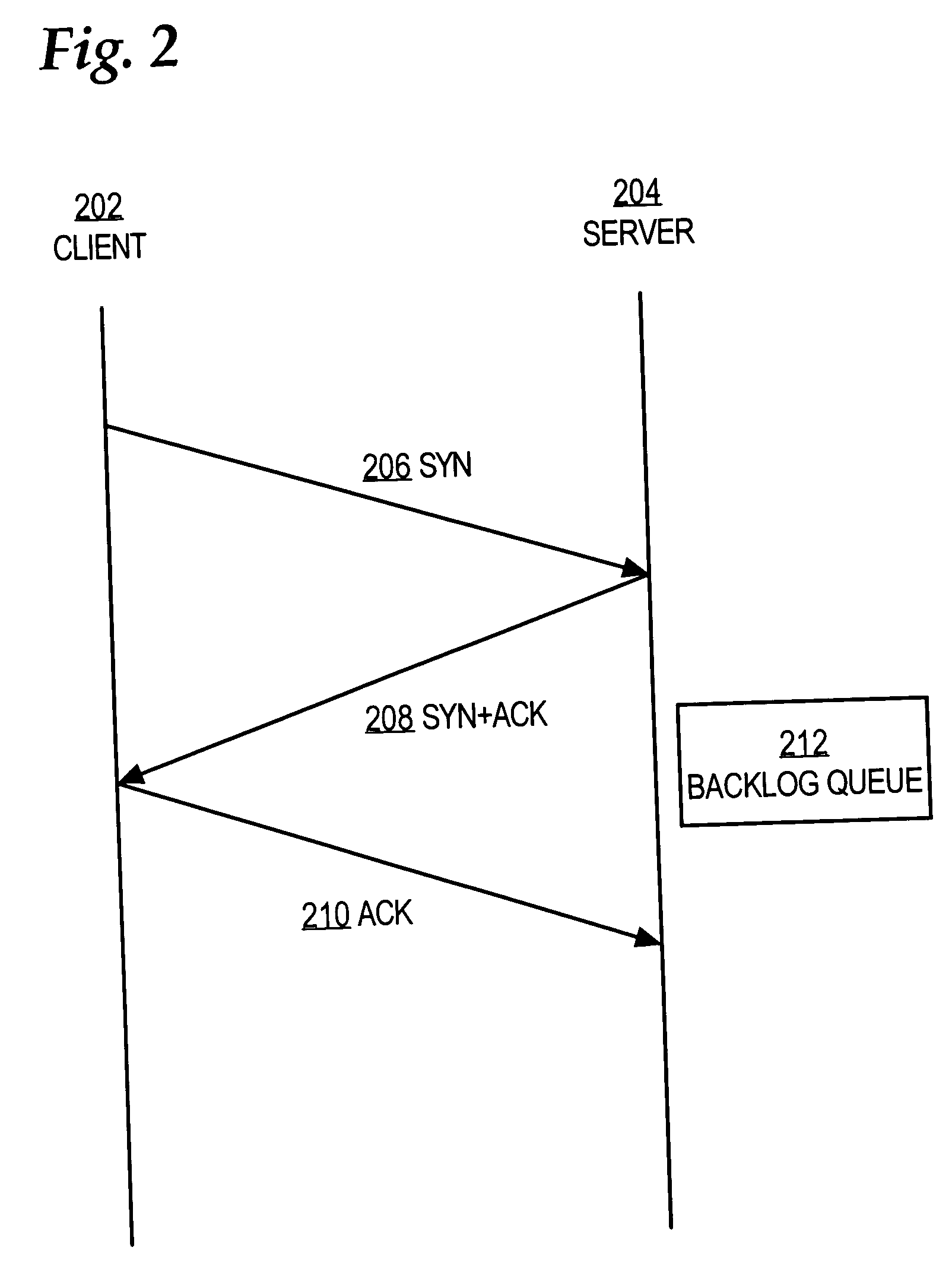
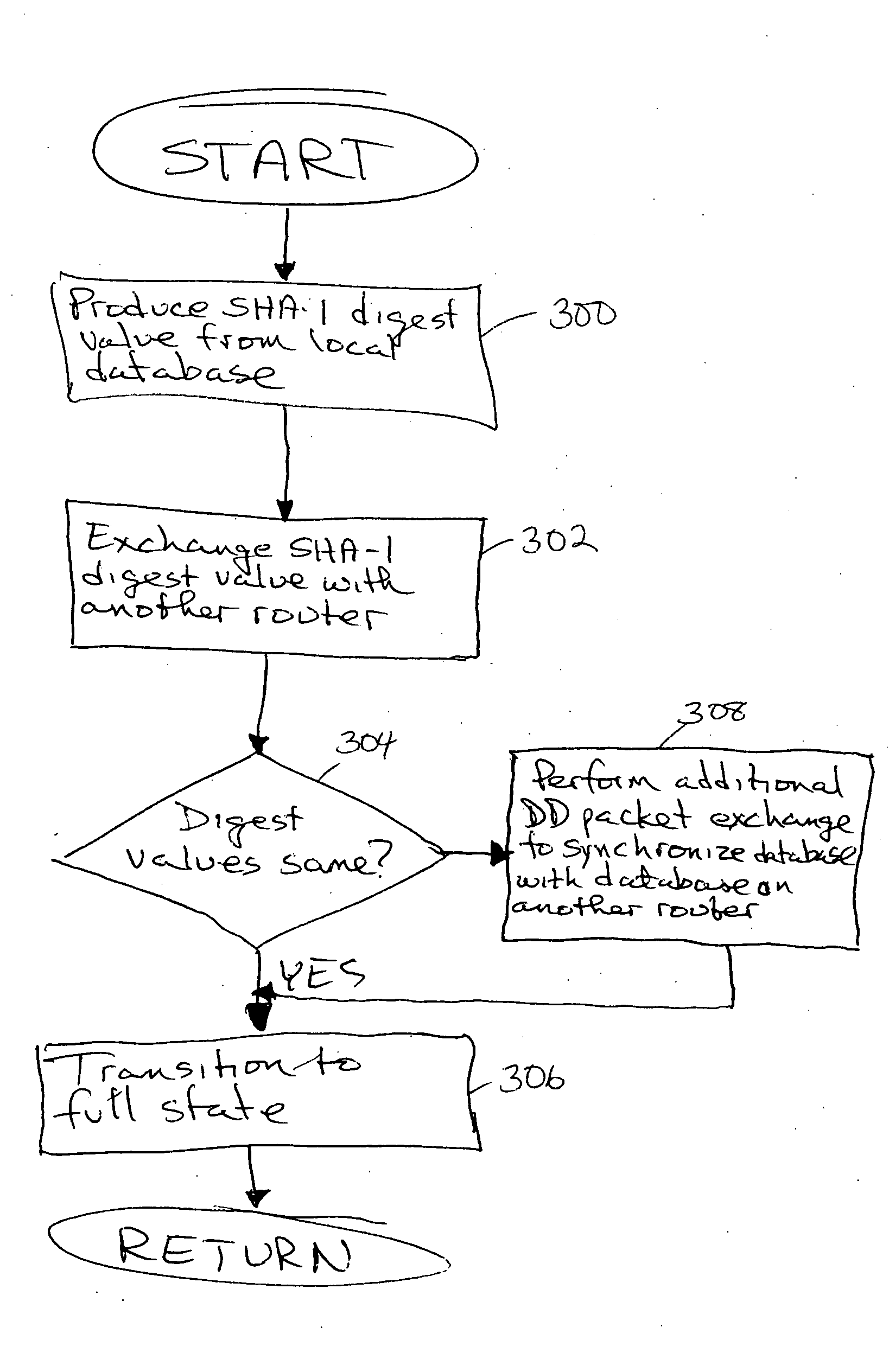
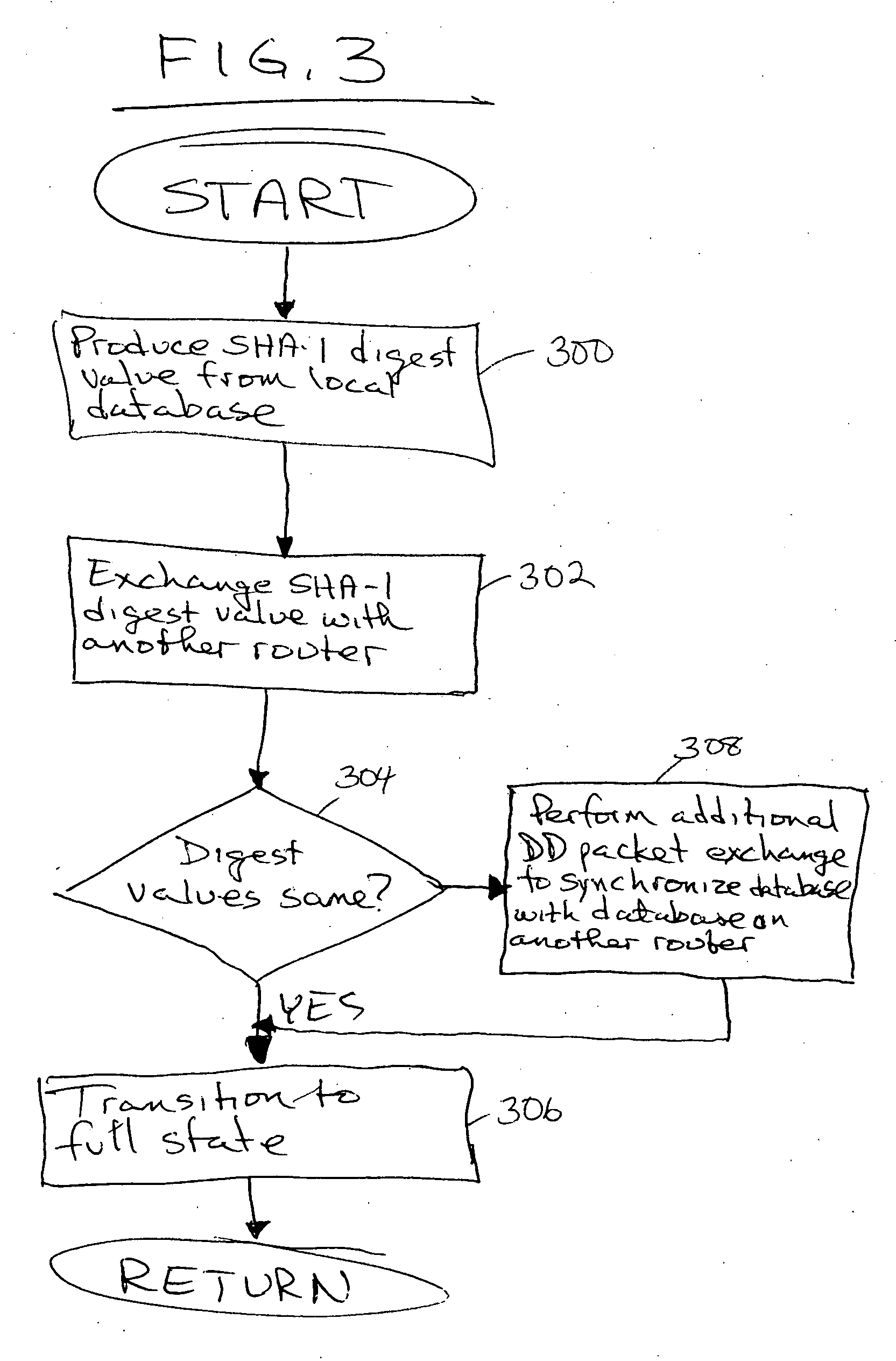
Method and apparatus to minimize database exchange in OSPF by using a SHA-1 digest value
The present invention provides a method of determining whether database located on a first router is synchronized with the database located on a second router by performing a hash function on the values contained in a link state database to derive a SHA-1 digest value. In an embodiment, the digest value is based on LSA type. The digest value is exchanged initially during a database description packet swap between the first router and second router. If the digest values are the same, the databases are already synchronized. The routers thus skip the database description packet exchange of LSAs in the database and go directly to FULL state, indicating full synchronization between databases on the first and second router and announcing adjacency to each other. If the digest differs, normal database description packet exchange is performed as specified in OSPF.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method to control transactions on communication channels based on universal identifiers
InactiveUS20070073888A1Minimizing effect of changeMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionOutbound communicationAutomatic routing
The present invention is a method to control communication channels using universal and persistent identifiers in circuit / packet switched or converged networks. The method involves linking domain specific addresses or concrete identifiers of communication end points within or across channels, domains and networks with an abstract, persistent and universal identifier that represents the single point of contact or principal identity of the user. The principal identity can specify parameters of inbound / outbound communication relationships with other specified / unspecified users / entities inter-alia through default / specific levels of control in communication relationships on / across / through normal or alternate channels, domains, applications, networks, etc., based on universal / persistent identifiers such as XRI. All transactions originating from, or terminating on, the principal identity are authenticated, asserted securely and routed automatically to an appropriate channel based on the principal identity's current context (state, location, presence, etc.) and privileges (or contracts) defined in rules created by the principal identity for access, usage, privacy, synchronization, compliance, expiry, etc. The principal identity is also empowered with multi-level control over attributes and metadata including rules for what data to expose / share and what data to eclipse / hide for which user. Control / user data, or traffic, and program / client / sequence logic, may be resident / executed / exchanged / carried on, or across, diverse networks / channels / media / devices / domains etc.
Owner:AMSOFT SYST PTE LTD
Time division multiplexing over broadband modulation method and apparatus
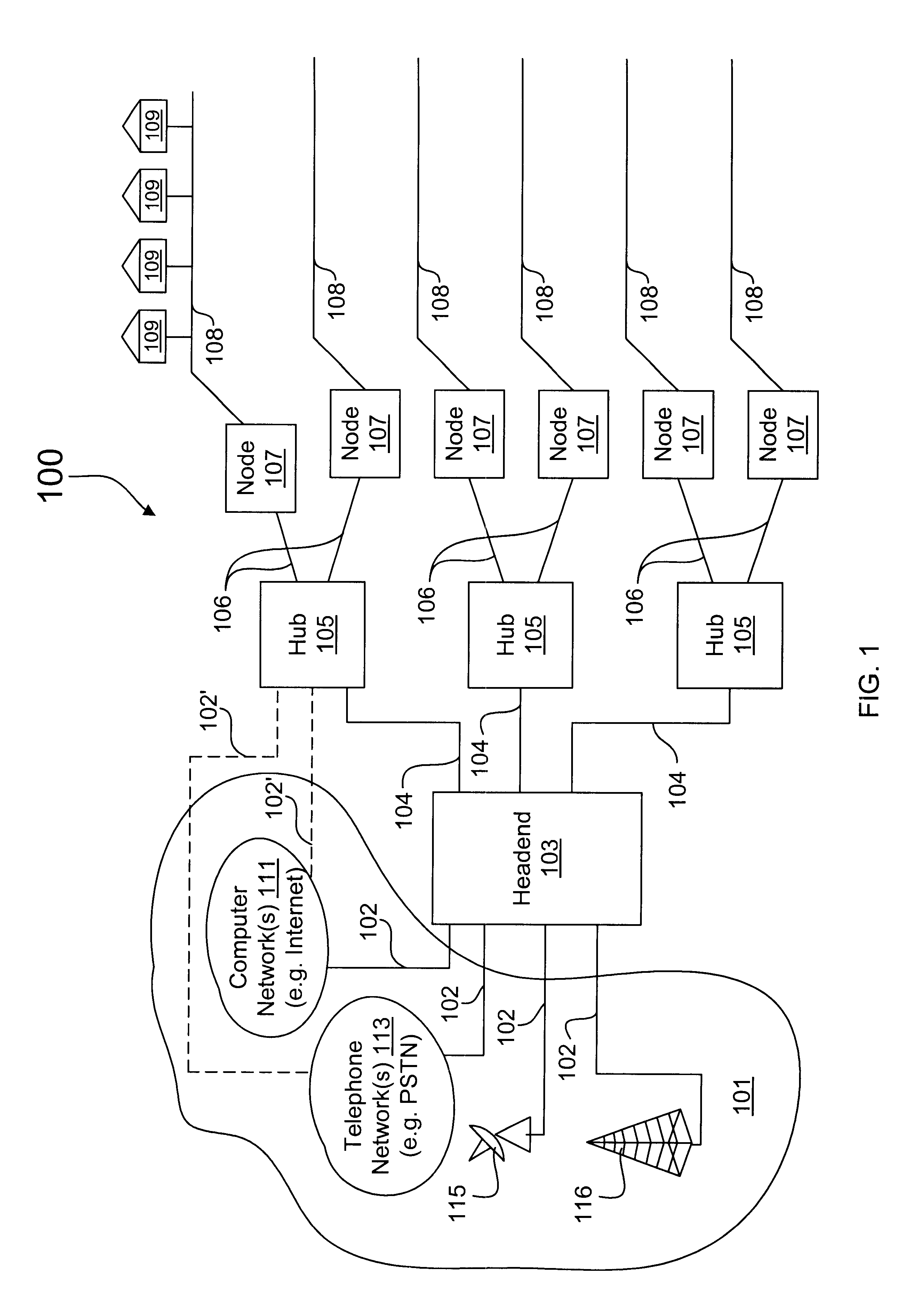
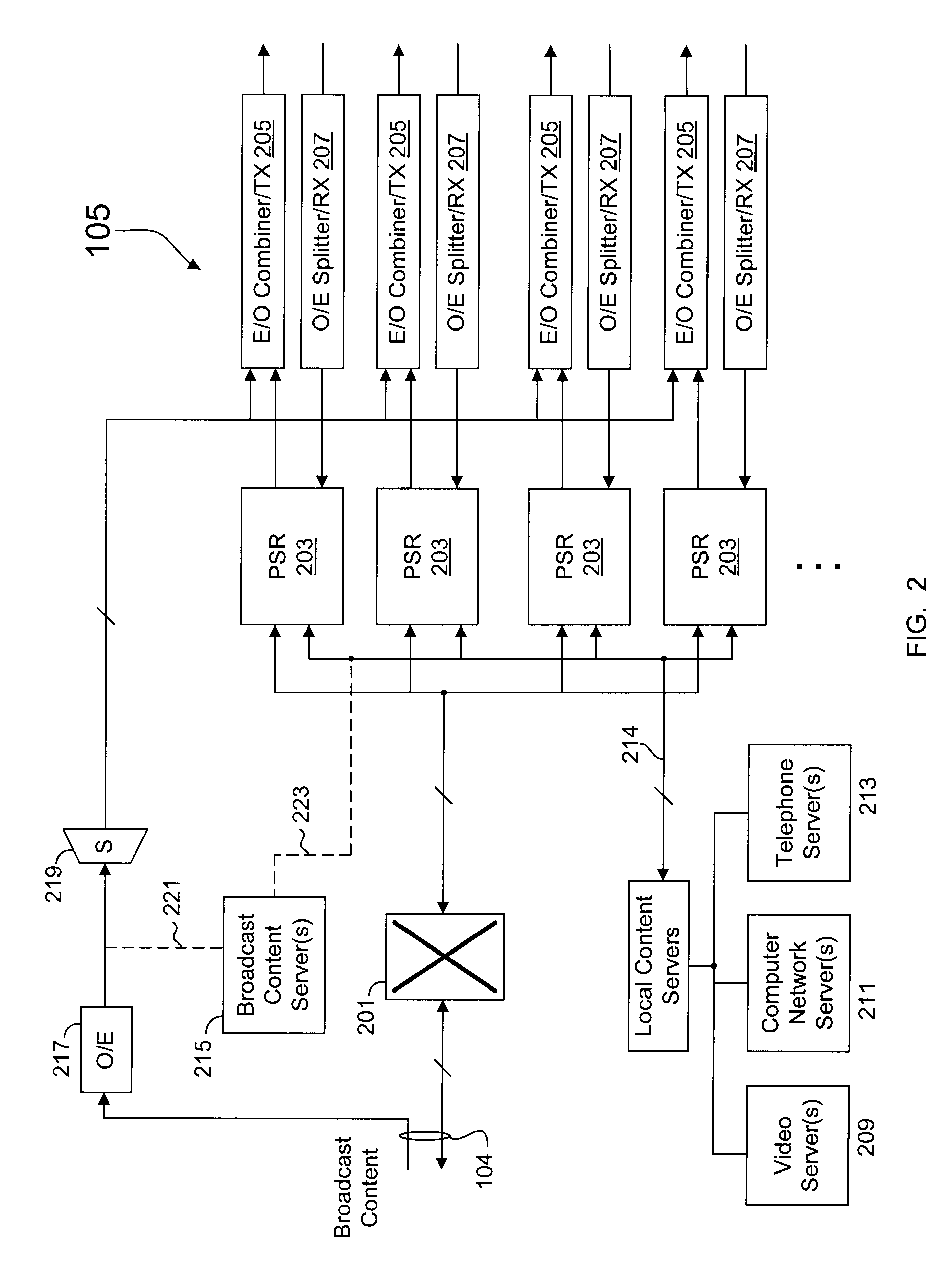
InactiveUS6763025B2Low costReduce developmentBroadcast with distributionTime-division optical multiplex systemsFiberData stream
A packet switch router that processes downstream digital information to provide dedicated bandwidth to each subscriber destination in a hybrid fiber coax (HFC) network. The router includes a network module that terminates a network connection, a switch that forwards data from the network module, and a channel module. The channel module includes a switch interface, a cell processing engine, one or more modulators, and a radio frequency (RF) transmitter network. The switch interface forwards packetized data from the switch to the cell processing engine. The cell processing engine organizes the packetized data into multiple data streams, encapsulates data in each data stream into data cells, and multiplexes the data cells into a multiplexed cell stream. Each modulator is configured to modulate a multiplexed cell stream into an analog signal. The RF transmitter network up converts and combines a plurality of analog signals into a combined electrical signal for transmission.
Owner:ADVENT NETWORKS +1
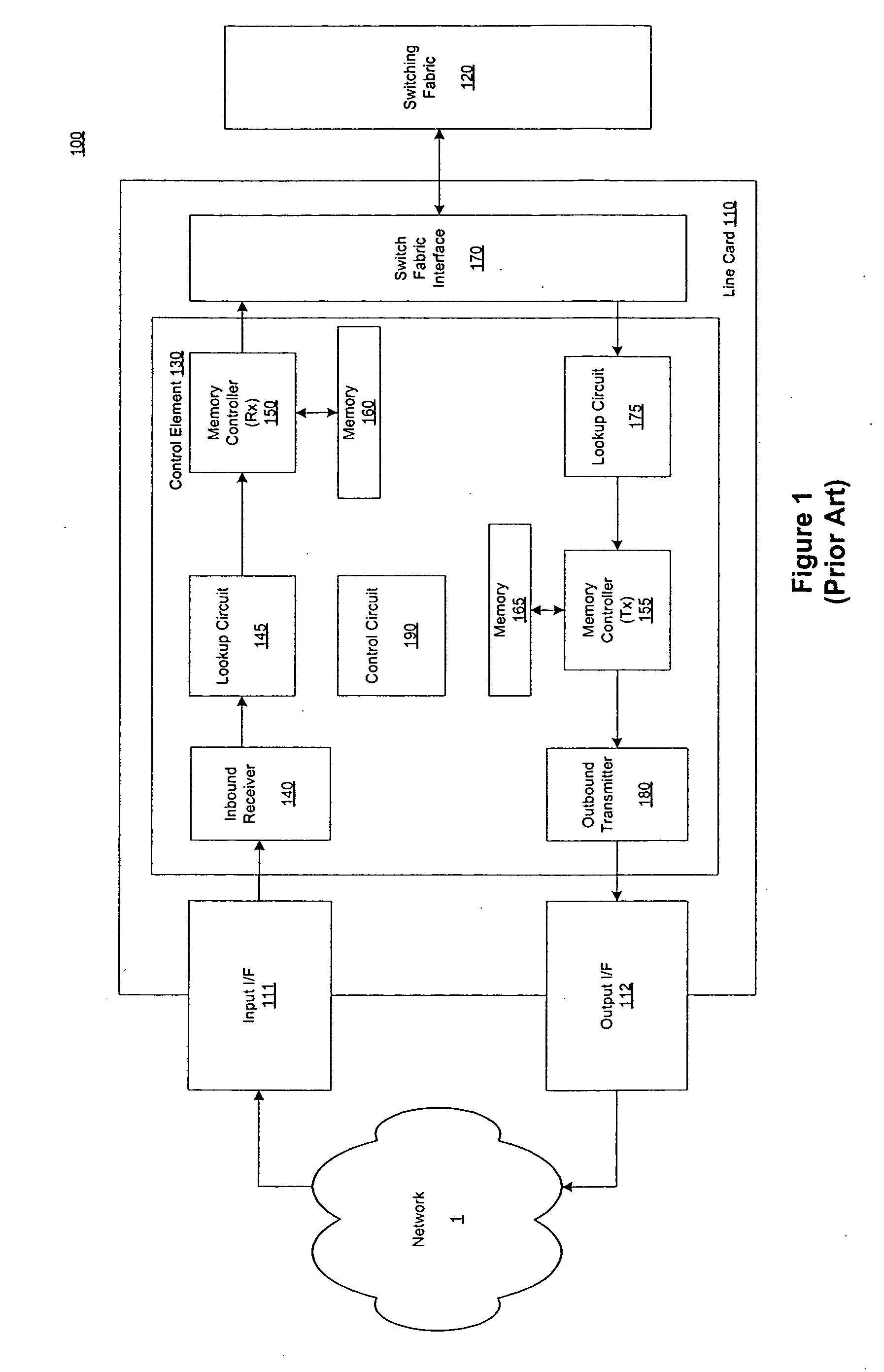
Pipelined packet switching and queuing architecture
InactiveUS6980552B1Quick implementationImprove throughputData switching by path configurationParallel processingBandwidth management
A pipelined linecard architecture for receiving, modifying, switching, buffering, queuing and dequeuing packets for transmission in a communications network. The linecard has two paths: the receive path, which carries packets into the switch device from the network, and the transmit path, which carries packets from the switch to the network. In the receive path, received packets are processed and switched in a multi-stage pipeline utilizing programmable data structures for fast table lookup and linked list traversal. The pipelined switch operates on several packets in parallel while determining each packet's routing destination. Once that determination is made, each packet is modified to contain new routing information as well as additional header data to help speed it through the switch. Using bandwidth management techniques, each packet is then buffered and enqueued for transmission over the switching fabric to the linecard attached to the proper destination port. The destination linecard may be the same physical linecard as that receiving the inbound packet or a different physical linecard. The transmit path includes a buffer / queuing circuit similar to that used in the receive path and can include another pipelined switch. Both enqueuing and dequeuing of packets is accomplished using CoS-based decision making apparatus, congestion avoidance, and bandwidth management hardware.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Pseudo-ethernet switch without ethernet media-access-controllers (MAC's) that copies ethernet context registers between PCI-express ports
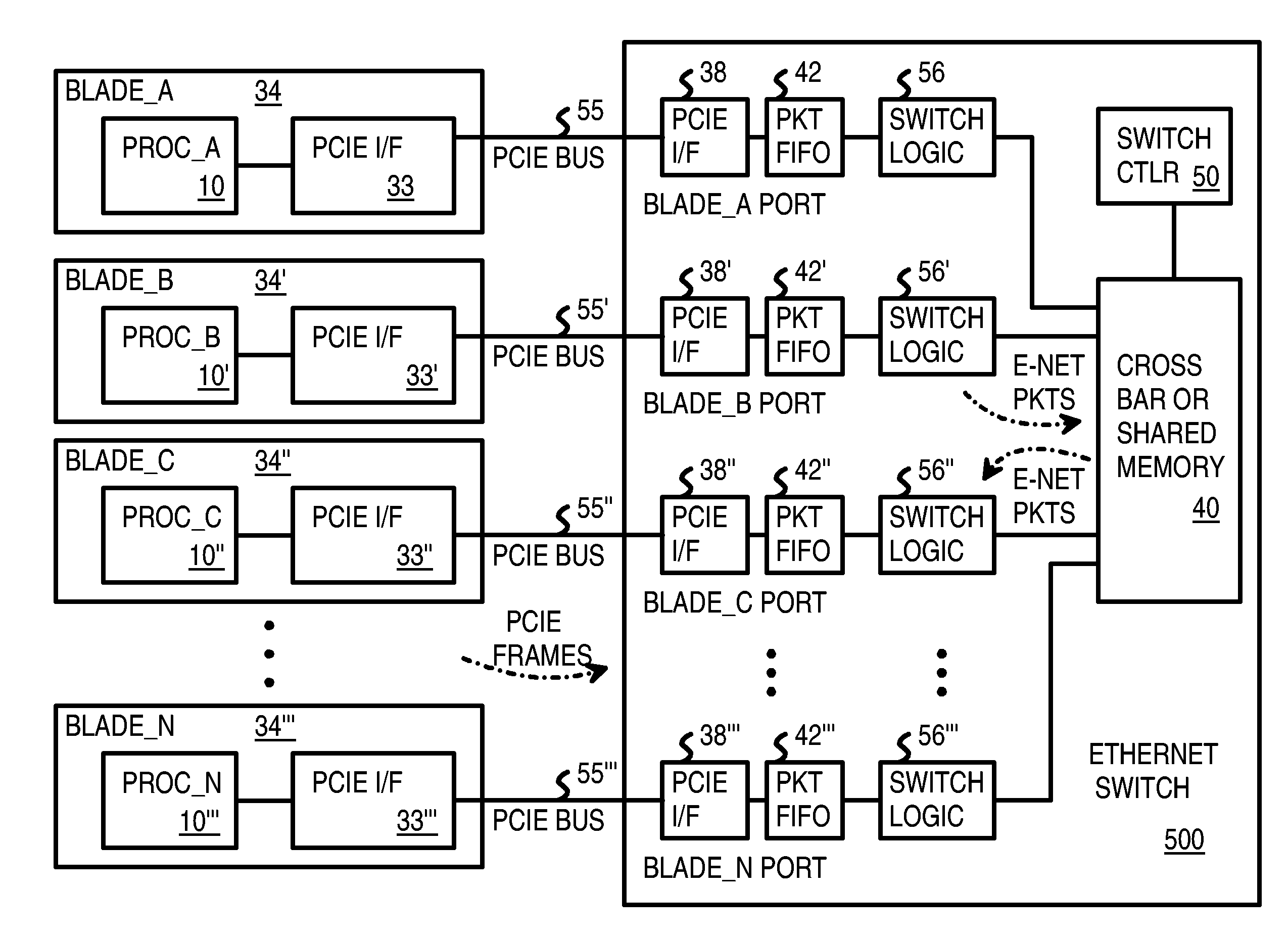
A Pseudo-Ethernet switch has a routing table that uses Ethernet media-access controller (MAC) addresses to route Ethernet packets through a switch fabric between an input port and an output port. However, the input port and output port have Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIE) interfaces that read and write PCI-Express packets to and from host-processor memories. When used in a blade system, host processor boards have PCIE physical links that connect to the PCIE ports on the Pseudo-Ethernet switch. The Pseudo-Ethernet switch does not have Ethernet MAC and Ethernet physical layers, saving considerable hardware. The switch fabric can be a cross-bar switch or can be a shared memory that stores Ethernet packet data embedded in the PCIE packets. Write and read pointers for a buffer storing an Ethernet packet in the shared memory can be passed from input to output port to perform packet switching.
Owner:DIODES INC
Method and apparatus for transferring files to clients using a peer-to-peer file transfer model and a client-server transfer model
InactiveUS20080235391A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTelevision systemsTransfer modelClient-side
A method and apparatus is provided for delivering a content file to a client over a packet-switched network. The method begins by determining a suitable throughput required to deliver the content file to the client. Next, the throughput available in a peer-to-peer network for delivering the content file to the client is determined. The required throughput is compared to the available throughput. If the available throughput is less than the required throughput, the available throughput is supplemented with additional throughput. The content is then delivered to the client over the packet-switched network using the available throughput of the peer-to-peer network and the additional throughput.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
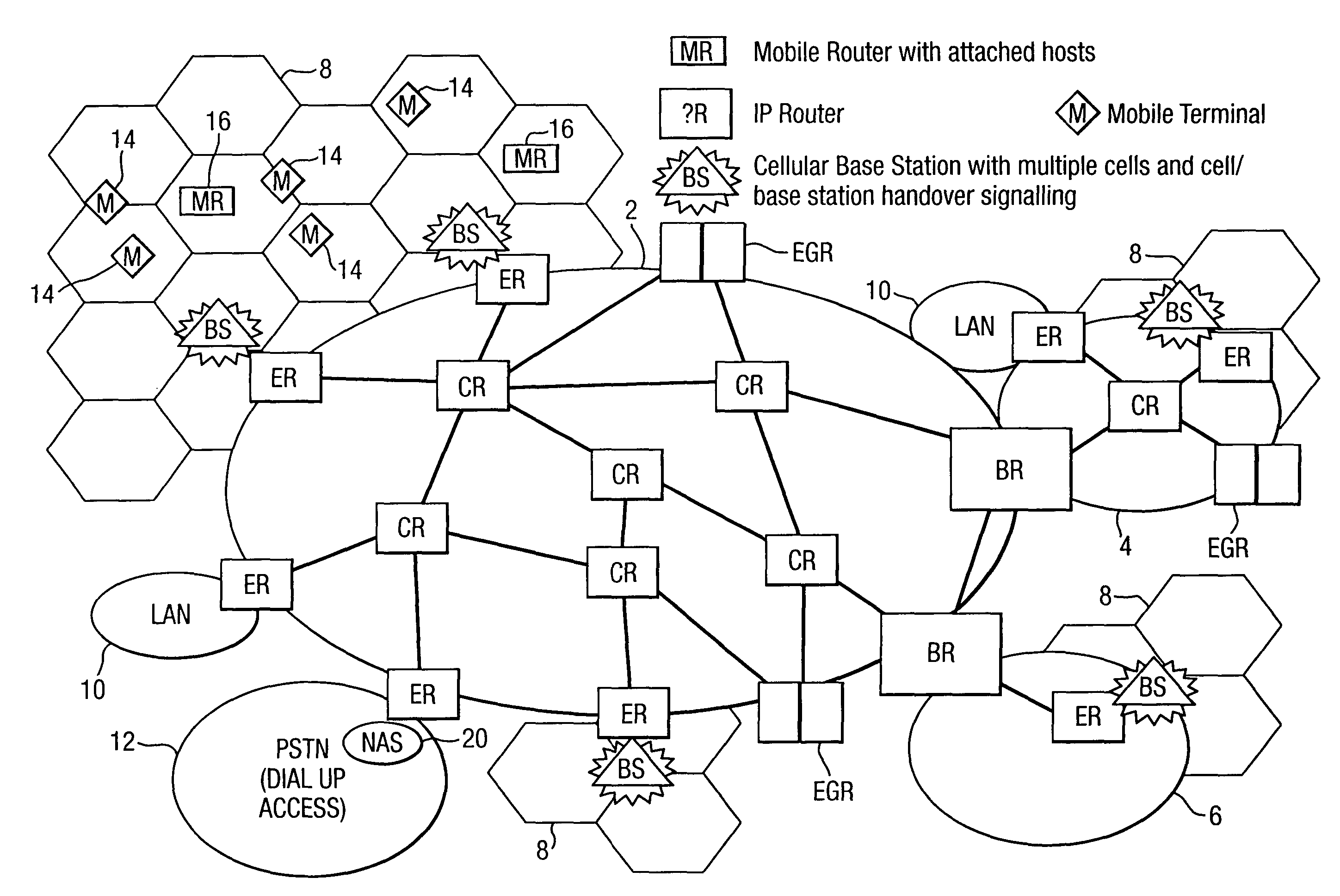
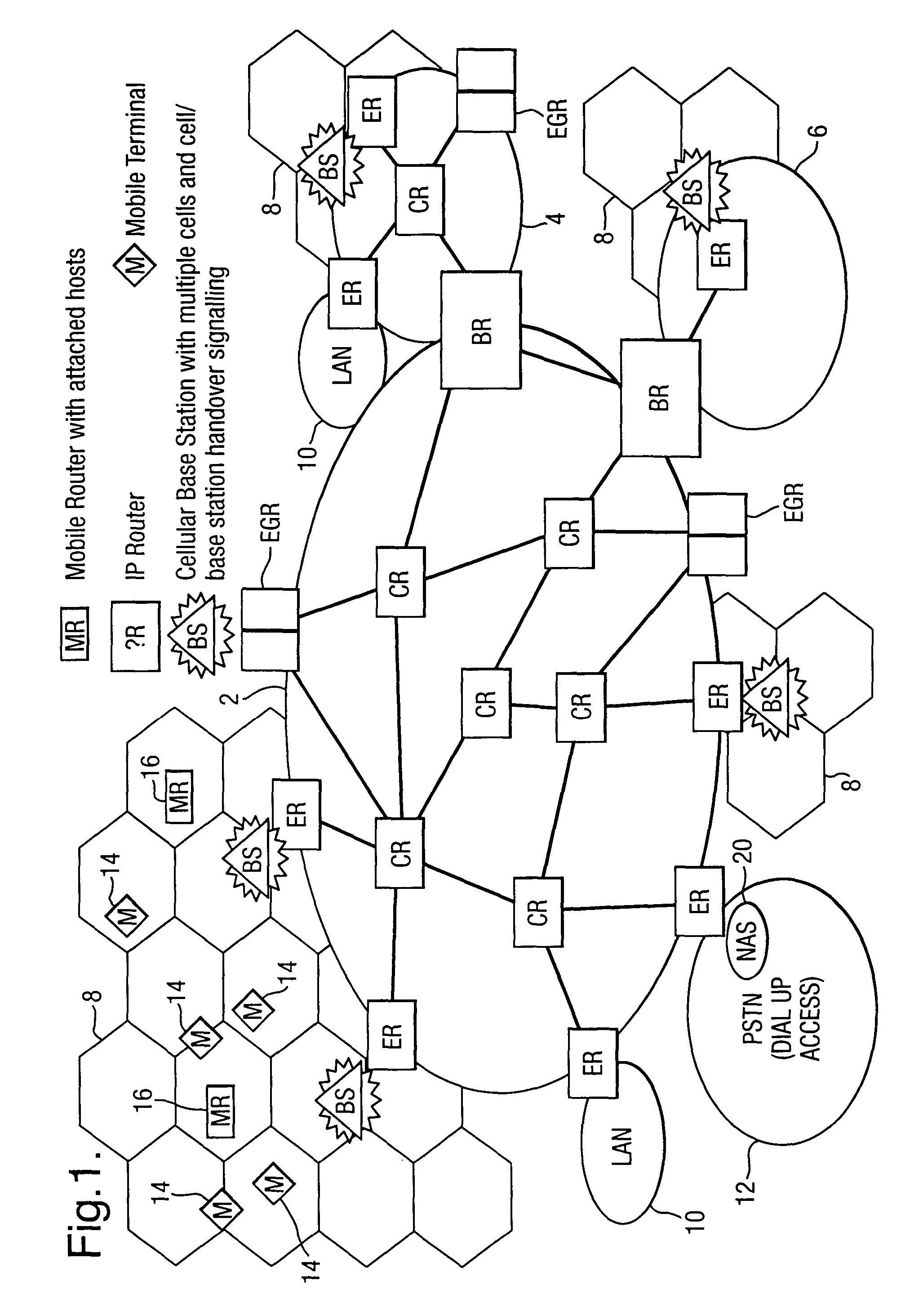
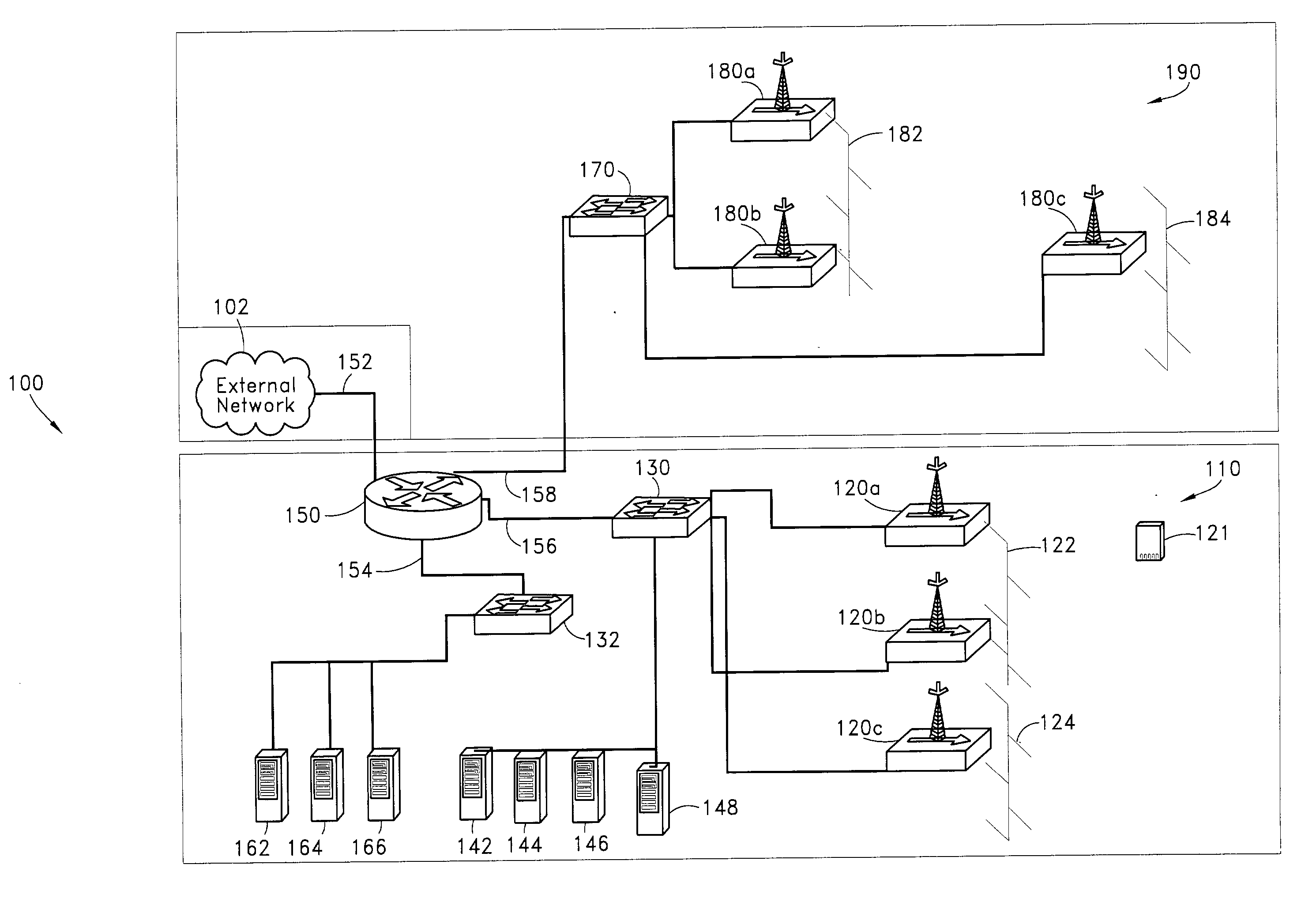
Wireless metropolitan area network system and method
InactiveUS20040022222A1Network topologiesTime-division multiplexAccess networkWireless metropolitan area network
A system and method are disclosed for providing a high speed wireless network. In one embodiment, a network is configured in a star configuration having a single router at the center. A Metropolitan Access Network (MAN) is configured with a plurality of access points that provide a wireless interface using defined physical layer and Media Access Control (MAC) layer. Packet data delivered to and from the access points are connected to the single router using a plurality of layer two links, which may include point to point links and packet switches. All links within the network operate at layer two or below and do not modify the packet data. The single router at the center of the MAN star network uses layer three information to direct packets between Local Area Networks (LANs) or sub-networks connected to different ports on the router.
Owner:VUIT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com