Patents
Literature
114 results about "Packet-switching node" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
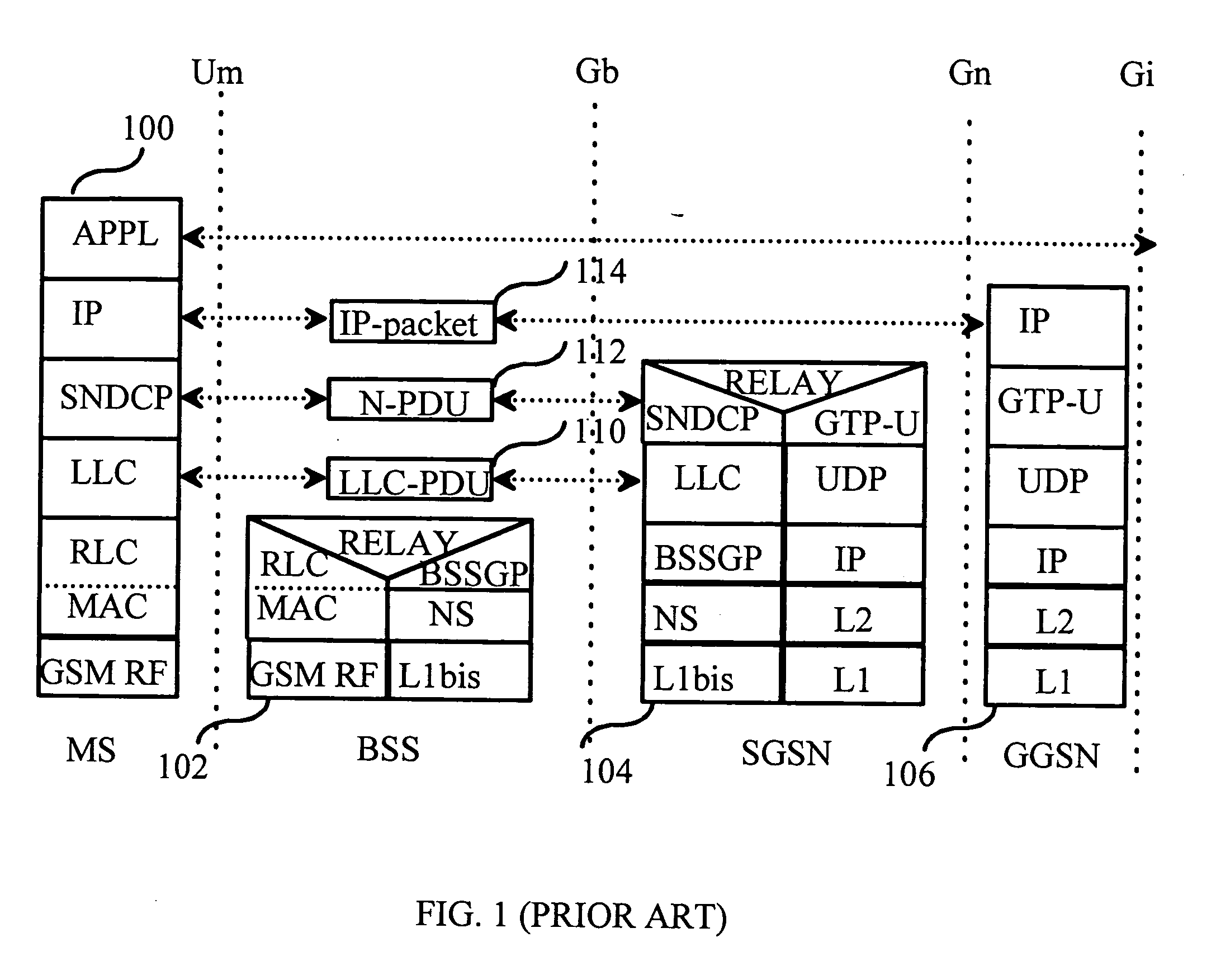
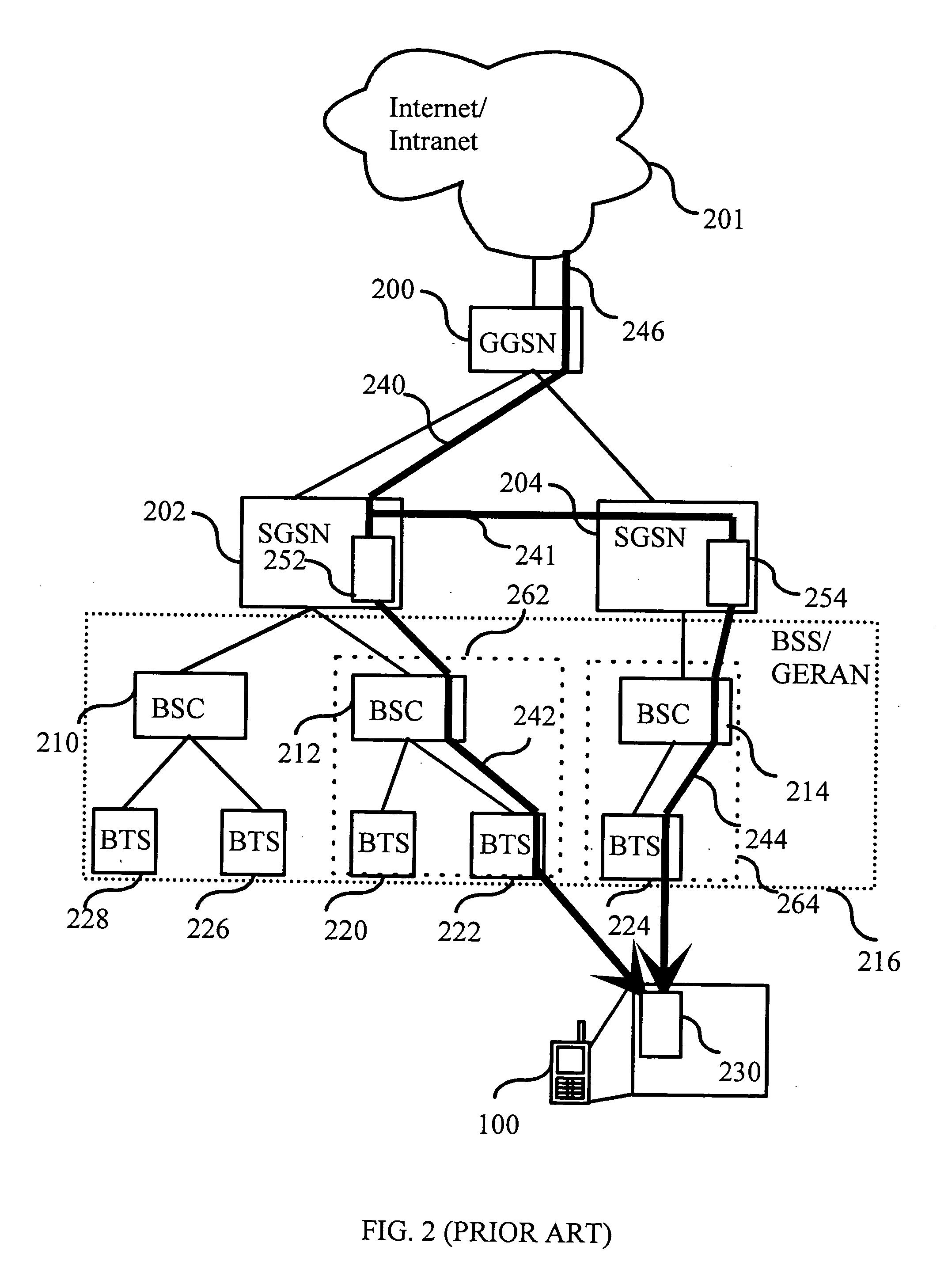
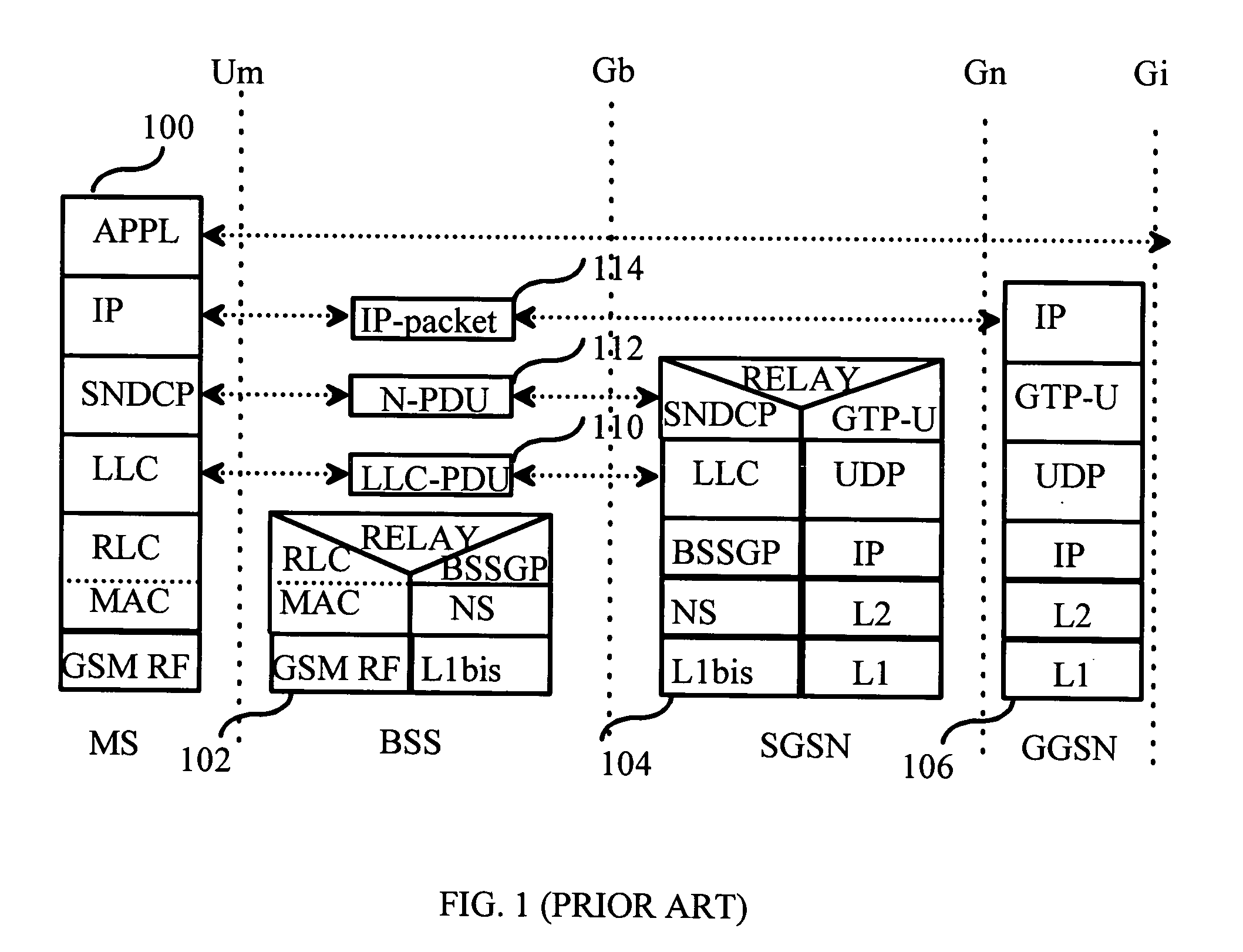
A packet-switching node is a node in a packet-switching network that contains data switches and equipment for controlling, formatting, transmitting, routing, and receiving data packets. This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C" (in support of MIL-STD-188).
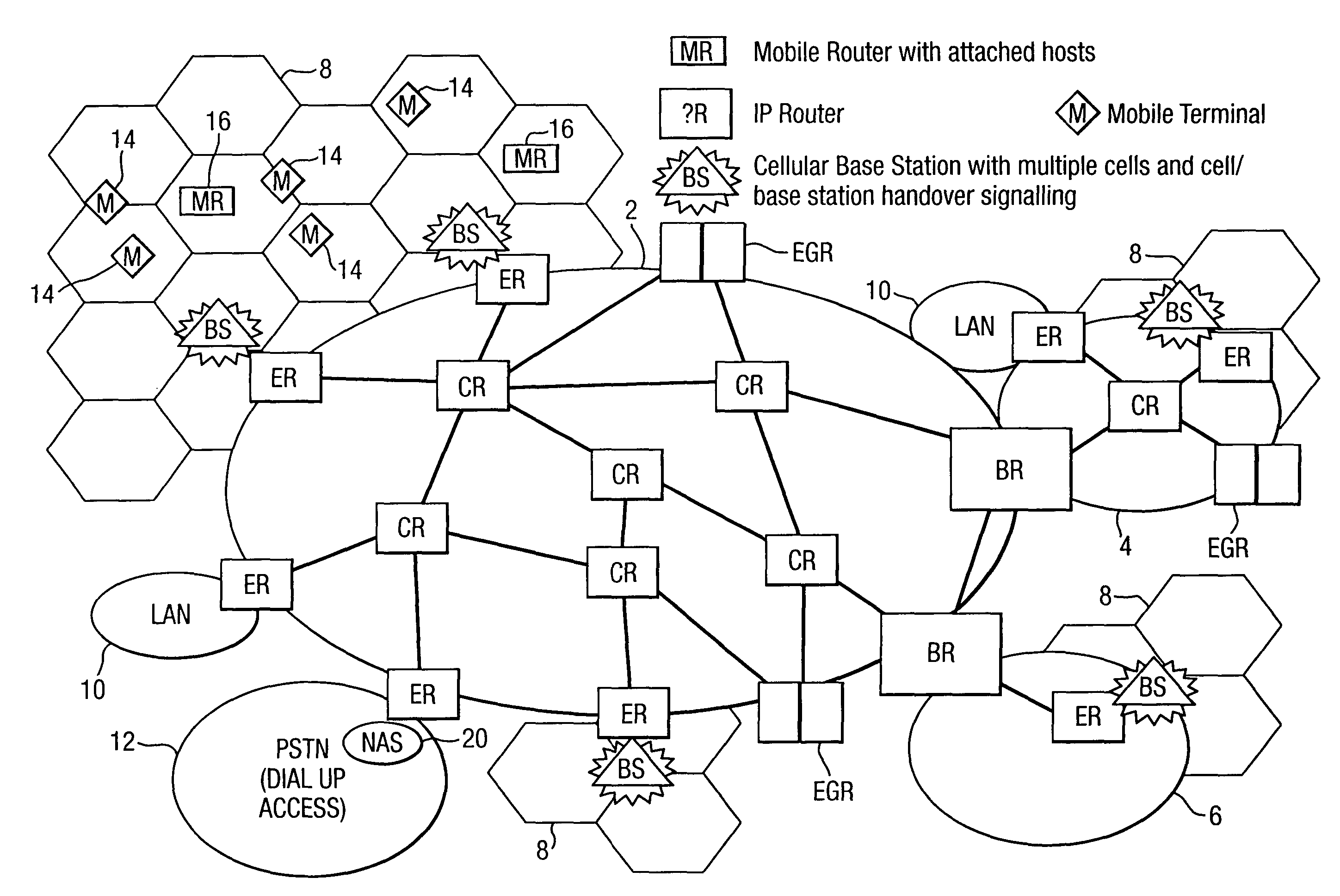
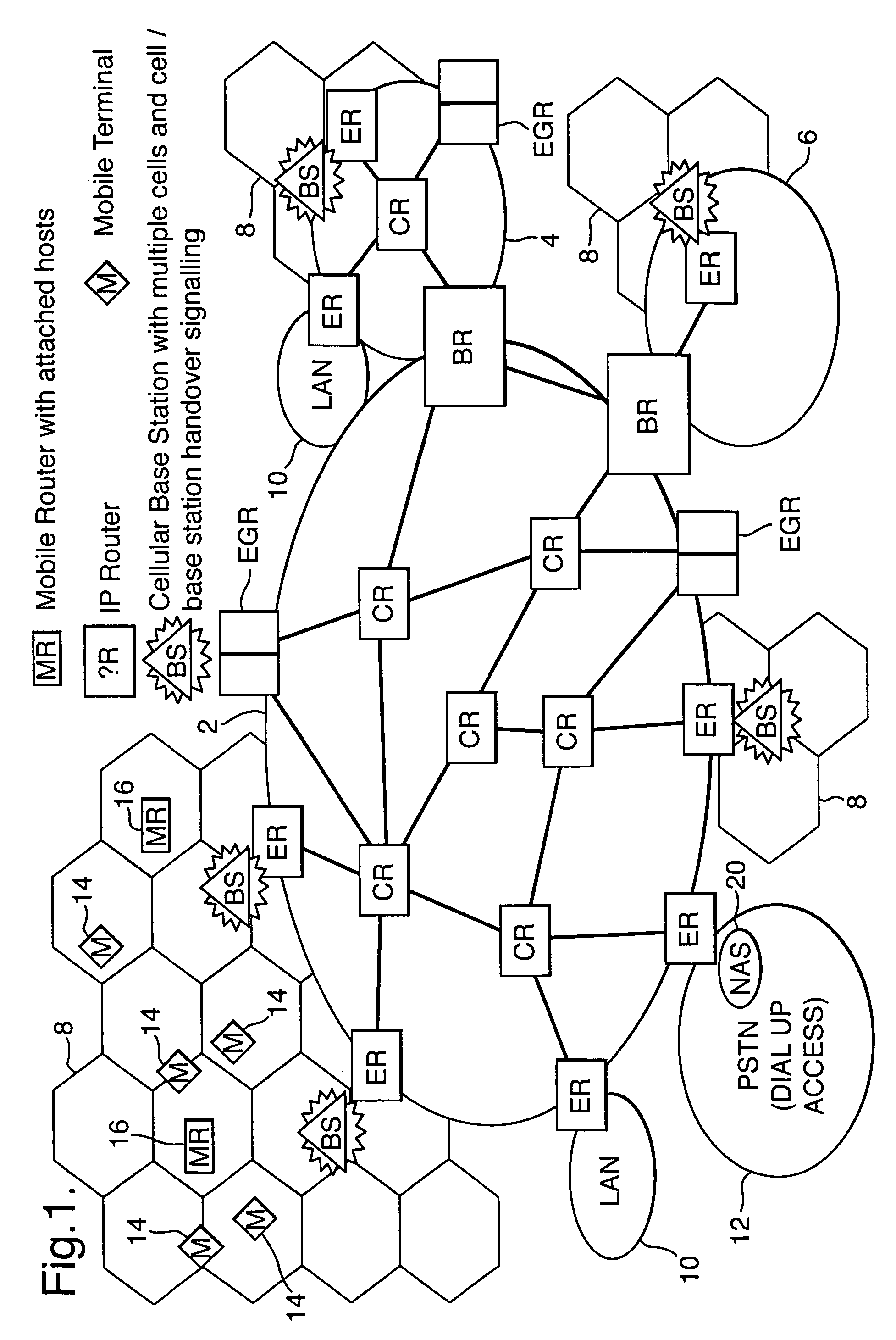
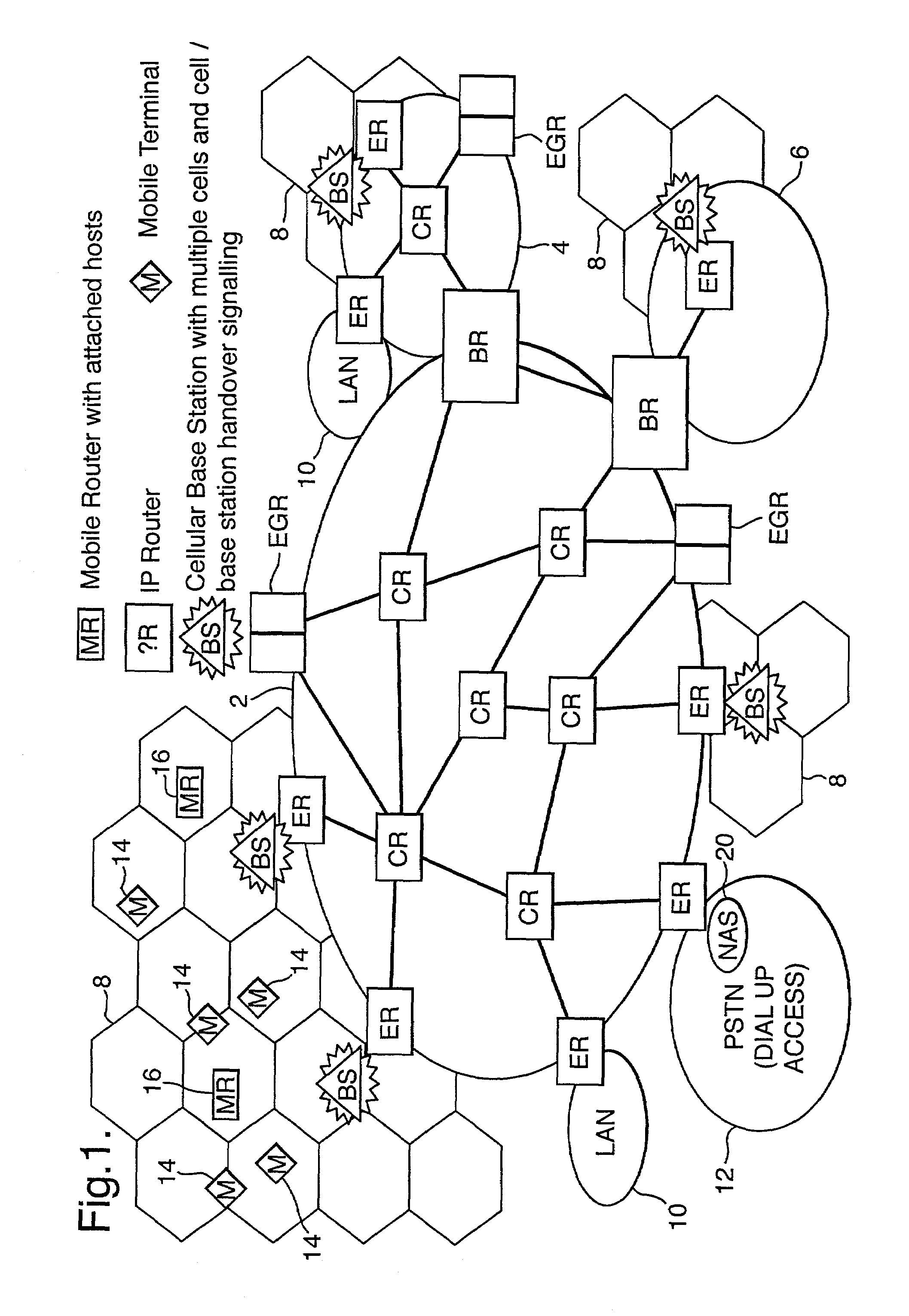
Telecommunication routing using multiple routing protocols in a single domain
InactiveUS7177646B2Improve routing efficiencyAssess restrictionSpecial service for subscribersRouting domainNetwork addressing
Packets are routed in a communications network including an infrastructure of packet switching nodes interconnected by packet transport links, and a plurality of access nodes to which a routing path, defined by data held in packet switching nodes located along the routing path, may be directed in the infrastructure for a given network address. Different types of routing updates are used in a single routing domain.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
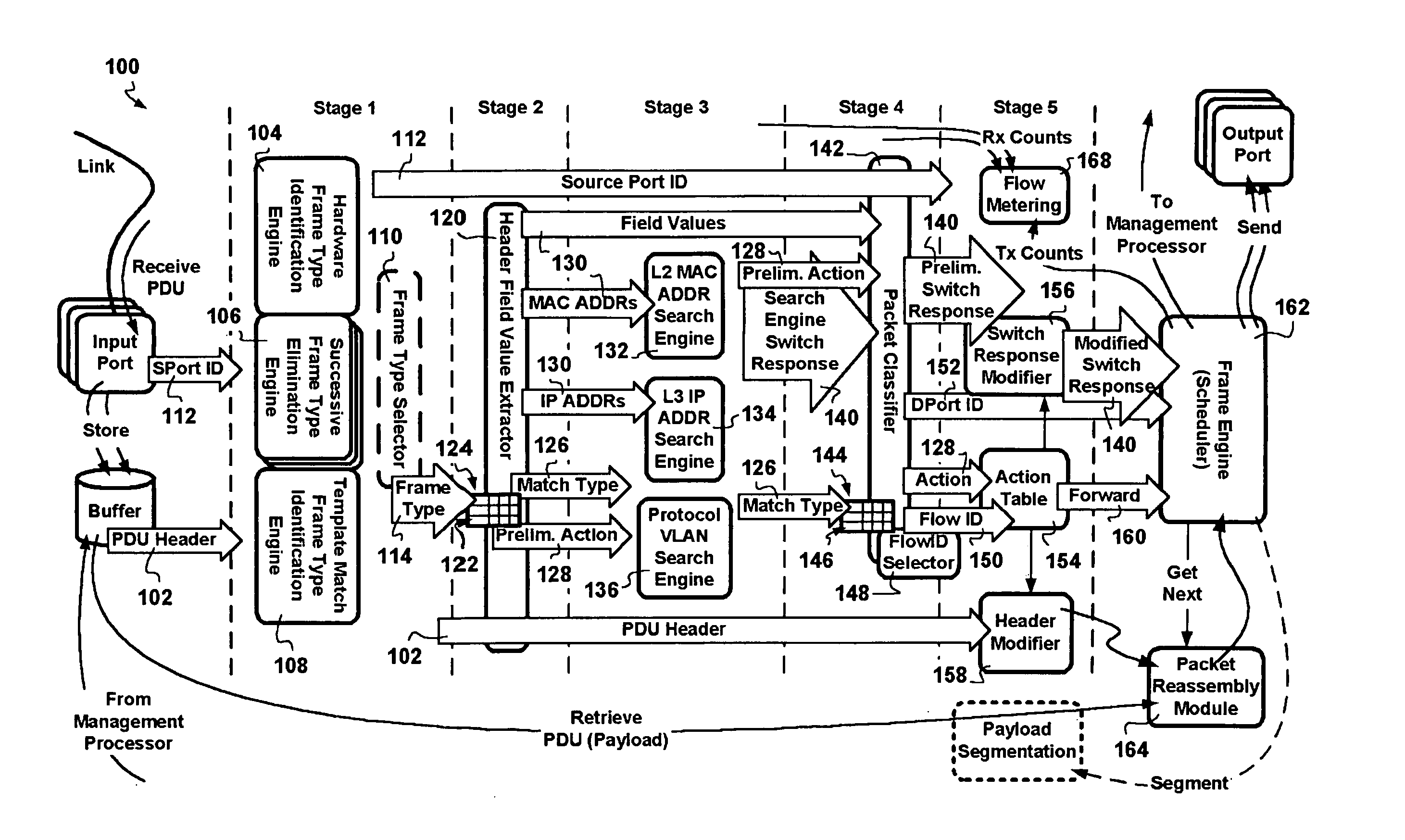
Combined pipelined classification and address search method and apparatus for switching environments
InactiveUS20060002386A1Network degradationReduce data transfer bandwidthTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork addressingObsolescence
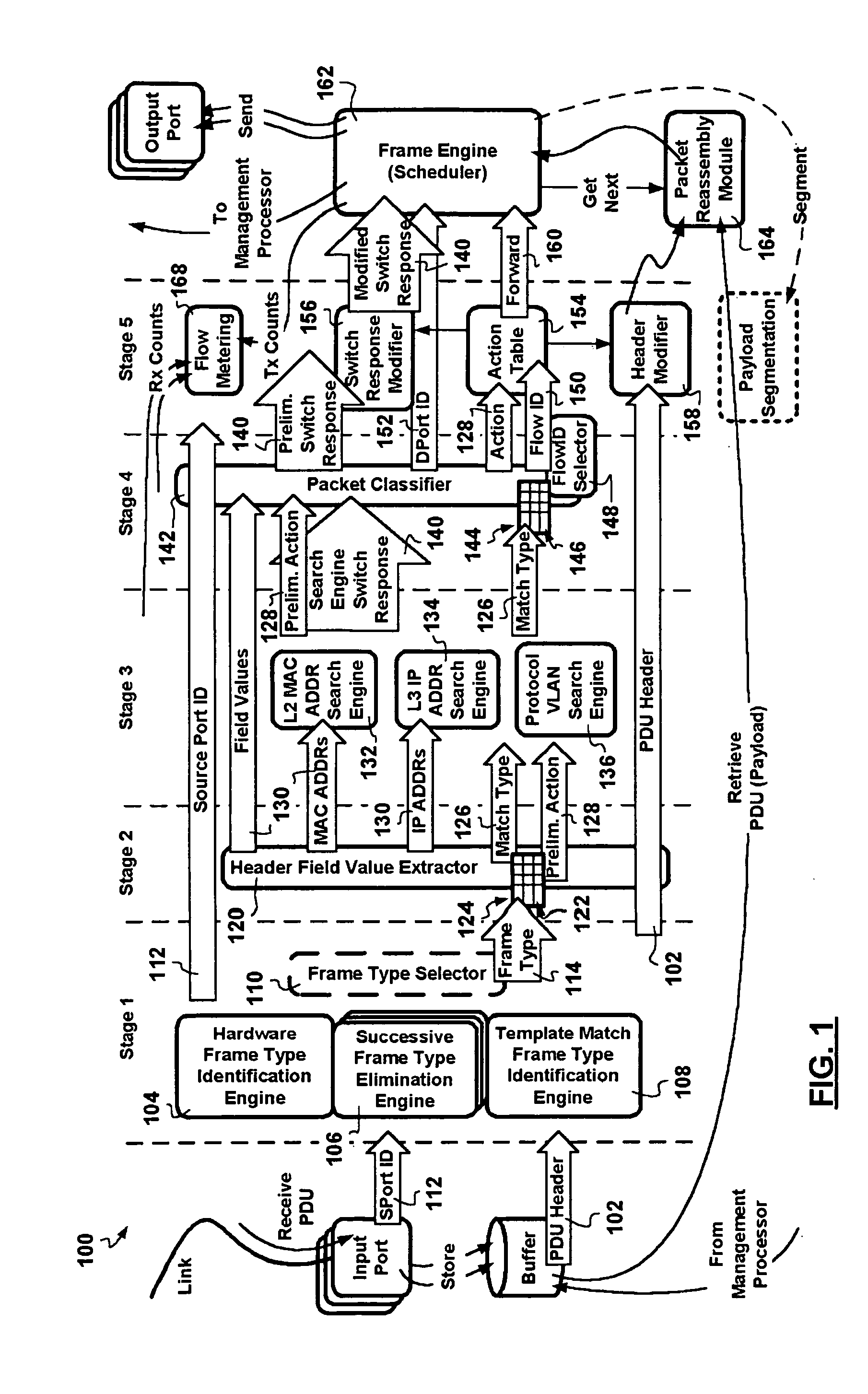
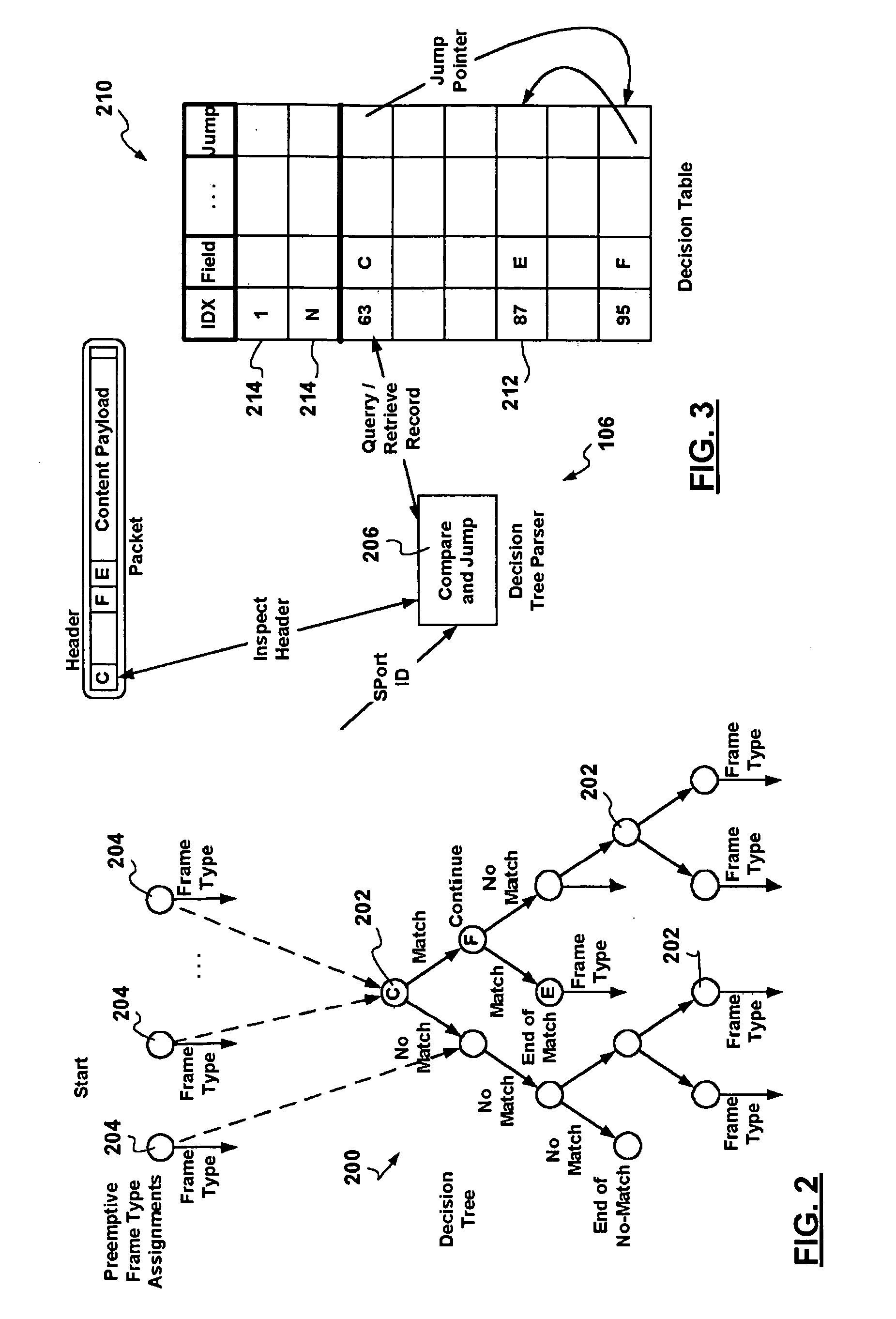
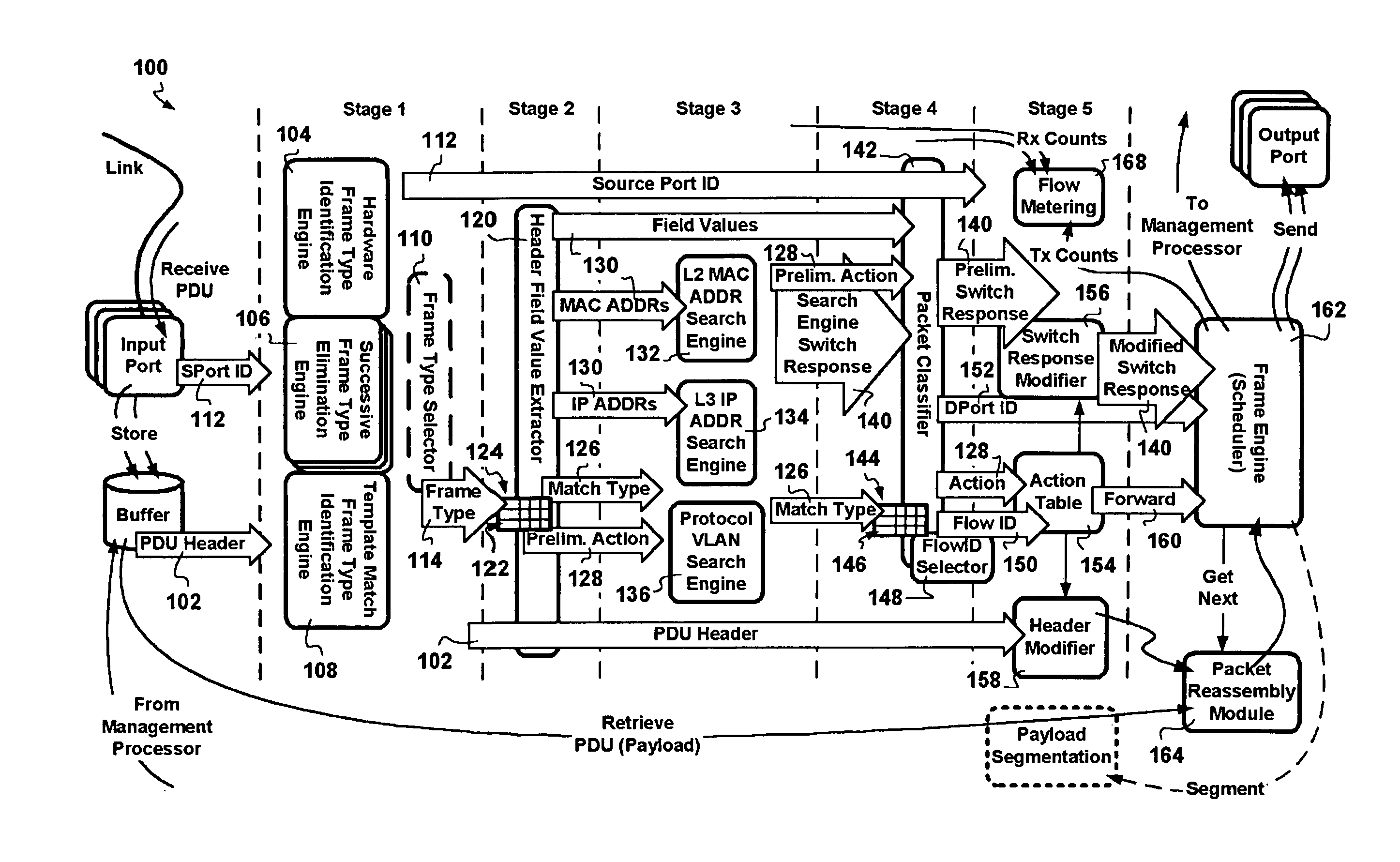
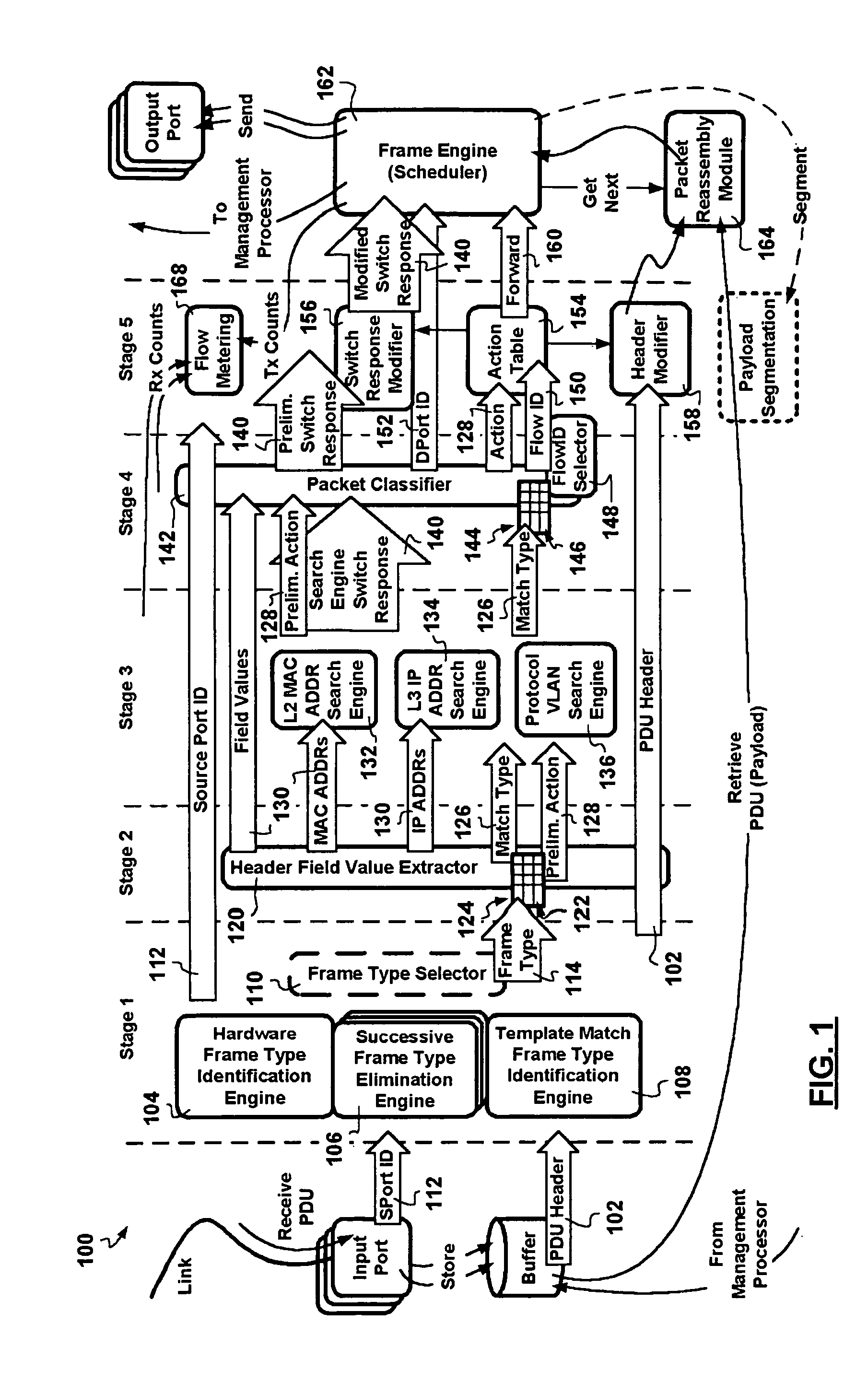
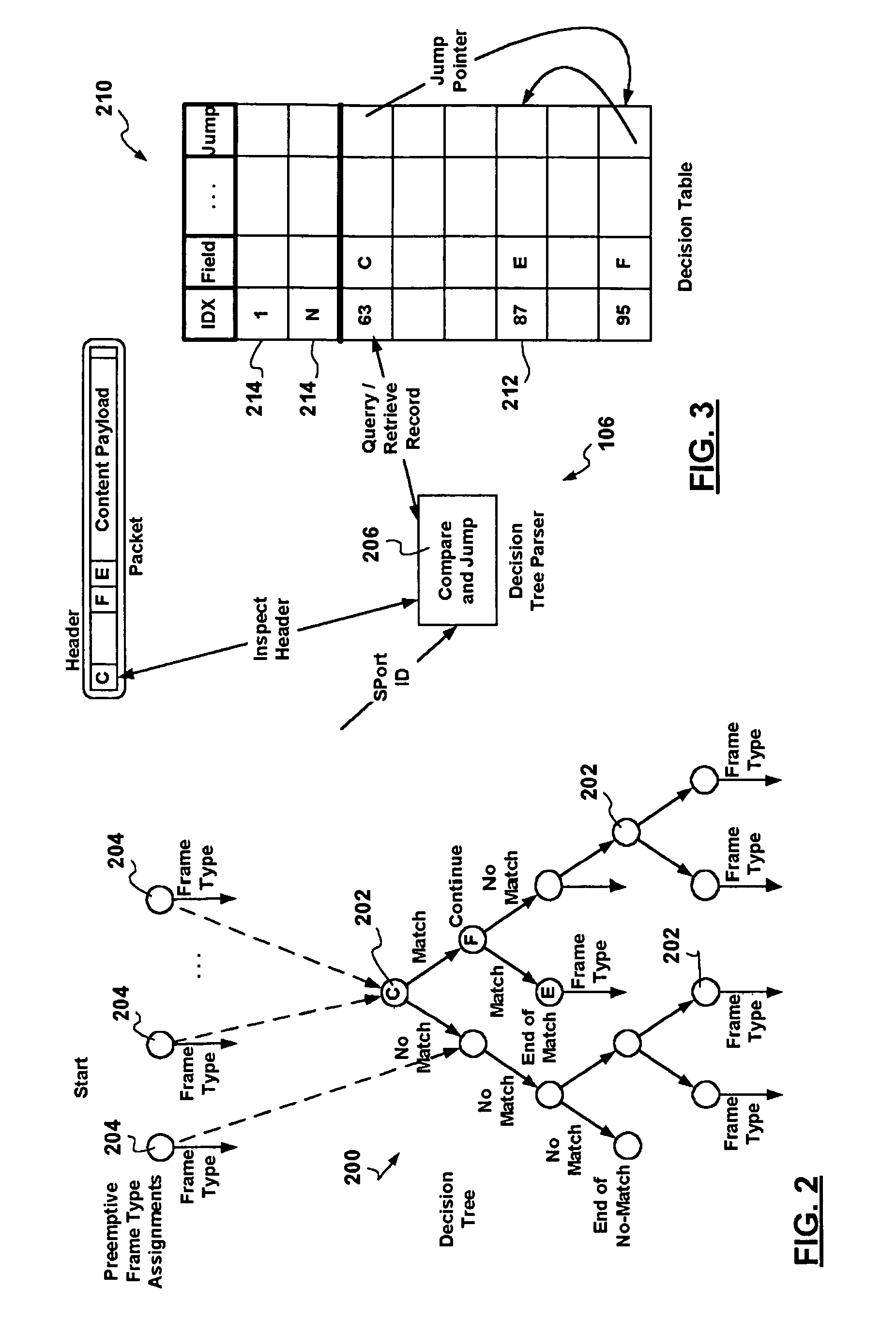
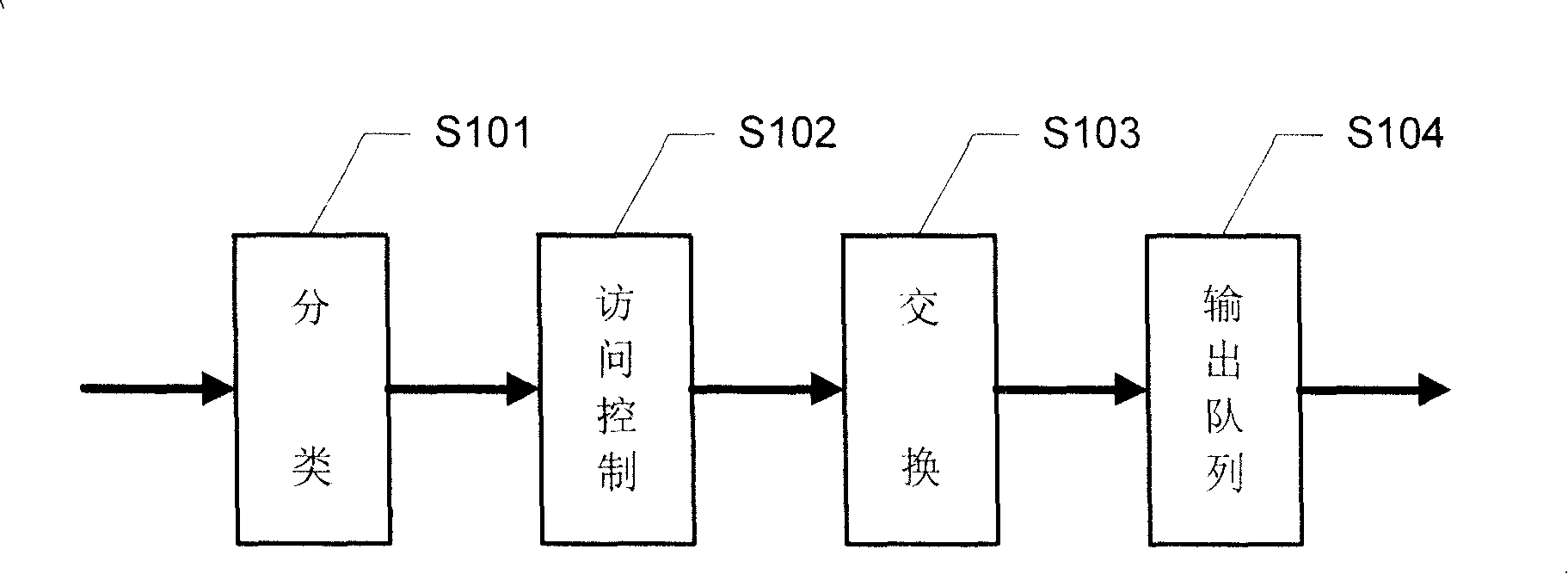
A packet switching node having a pipelined packet processing architecture processing packets received via an input port associated with the packet switching node is presented. The method performed by the apparatus includes: determining a packet frame type of the packet received; selectively extracting packet header field values specific to a packet frame type, the extracted packet header field value including packet addressing information; ascribing to the packet a preliminary action to be performed in respect of the packet; searching packet switching information tracked by the packet switching node based on extracted packet addressing information; formulating a preliminary switch response for the packet; classifying the packet into one of a plurality of packet flows; modifying the preliminary switch response in accordance with one of the preliminary action, the packet flow into which the packet was classified, and a default port action corresponding to the input port; modifying the packet header in accordance with one of the preliminary action, the packet flow, and the default port action; and processing the packet in accordance with the switch response. Advantages are derived from: pipelined processing of packets which enables short-cutting the rest of the processing for improper packets; a flexible frame type determination which is fast for well know frame types yet flexible in support of new frame types delaying obsolescence of a particular implementation; an early determination of a processing action which is successively refined by subsequent stages; a combined Layer-2 and Layer-3 network addressing search engine operating on short bit length indexed Layer-2 and Layer-3 network addresses reducing network address table storage requirements, requiring a reduced data transfer bandwidth for network address table access, a large external hashed primary network address table, and a small internal secondary network address table; an early determination of a switch response; and packet-classification-based switch response and packet header modification.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
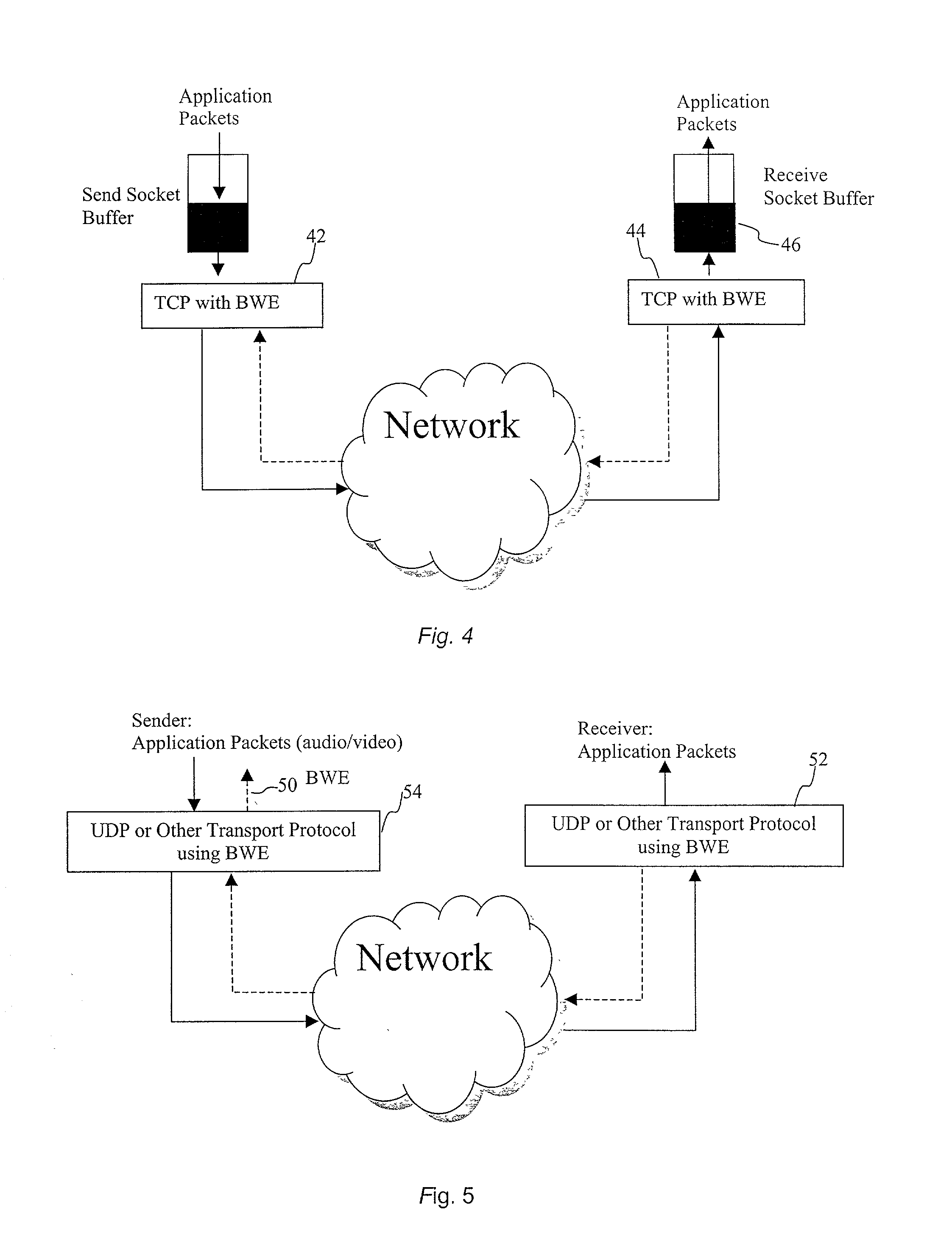
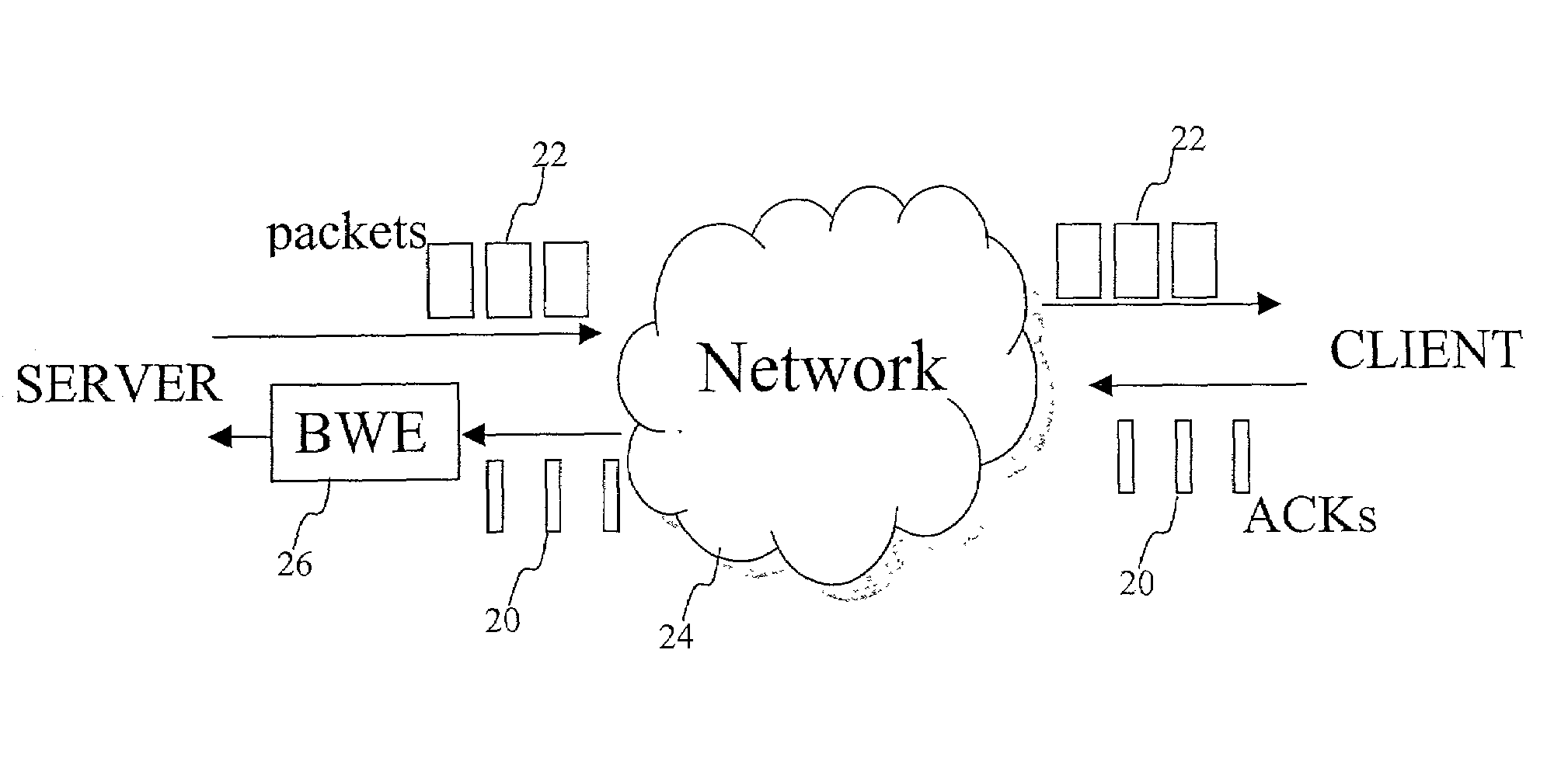
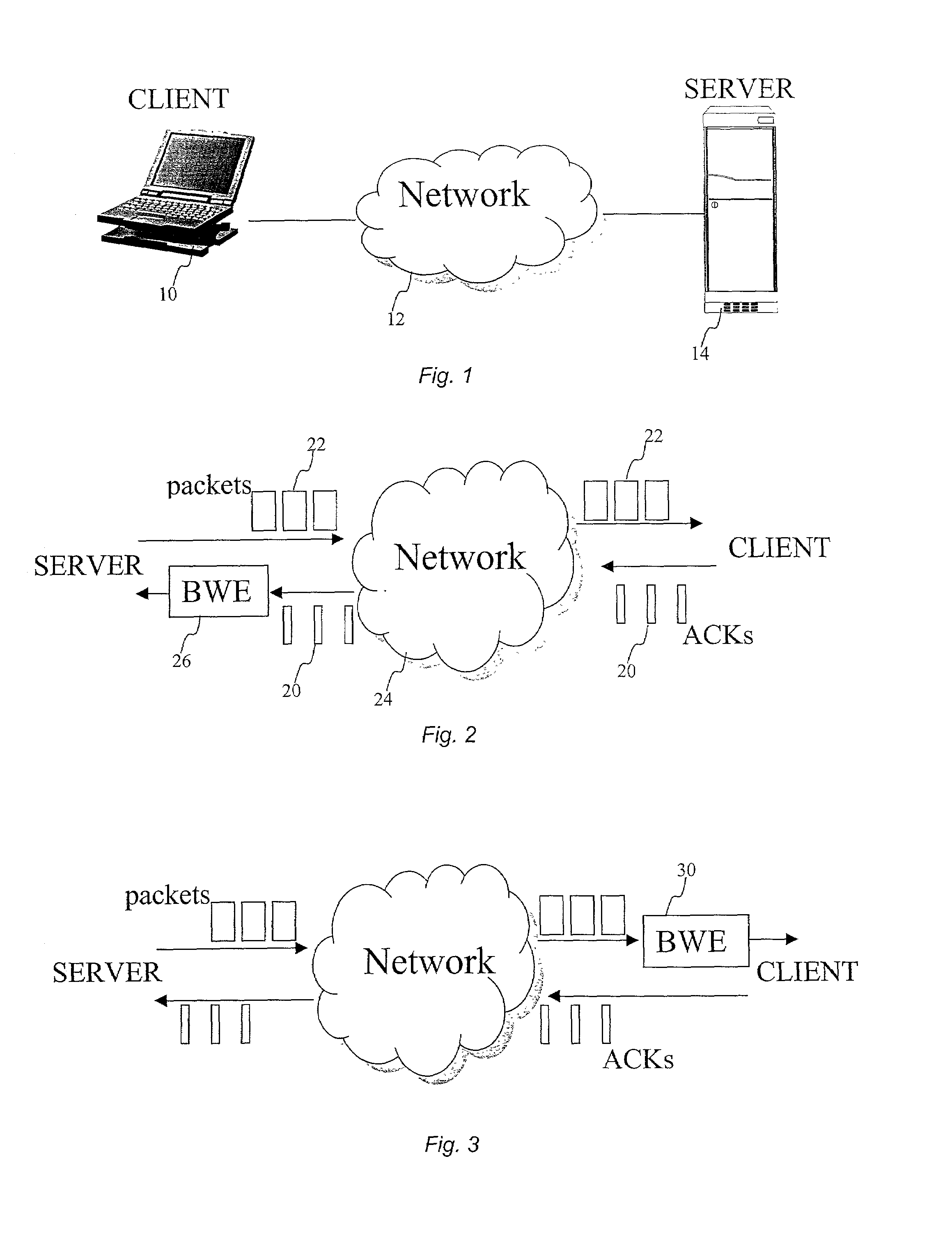
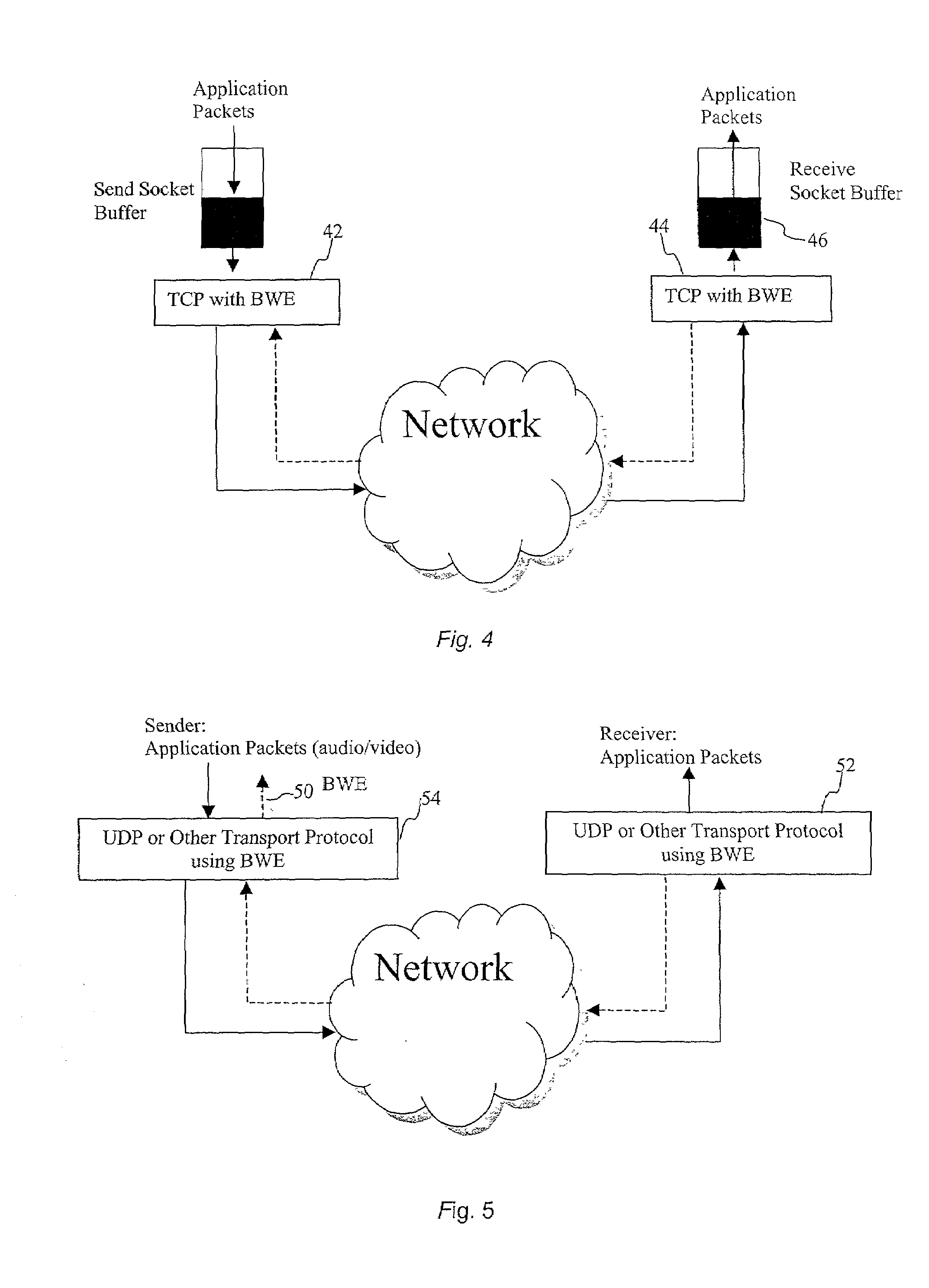
End-to end bandwidth estimation for congestion control in packet switching networks
InactiveUS20020085587A1Improve network bandwidth utilizationImprove fairnessEnergy efficient ICTError preventionTraffic capacityPacket-switching node
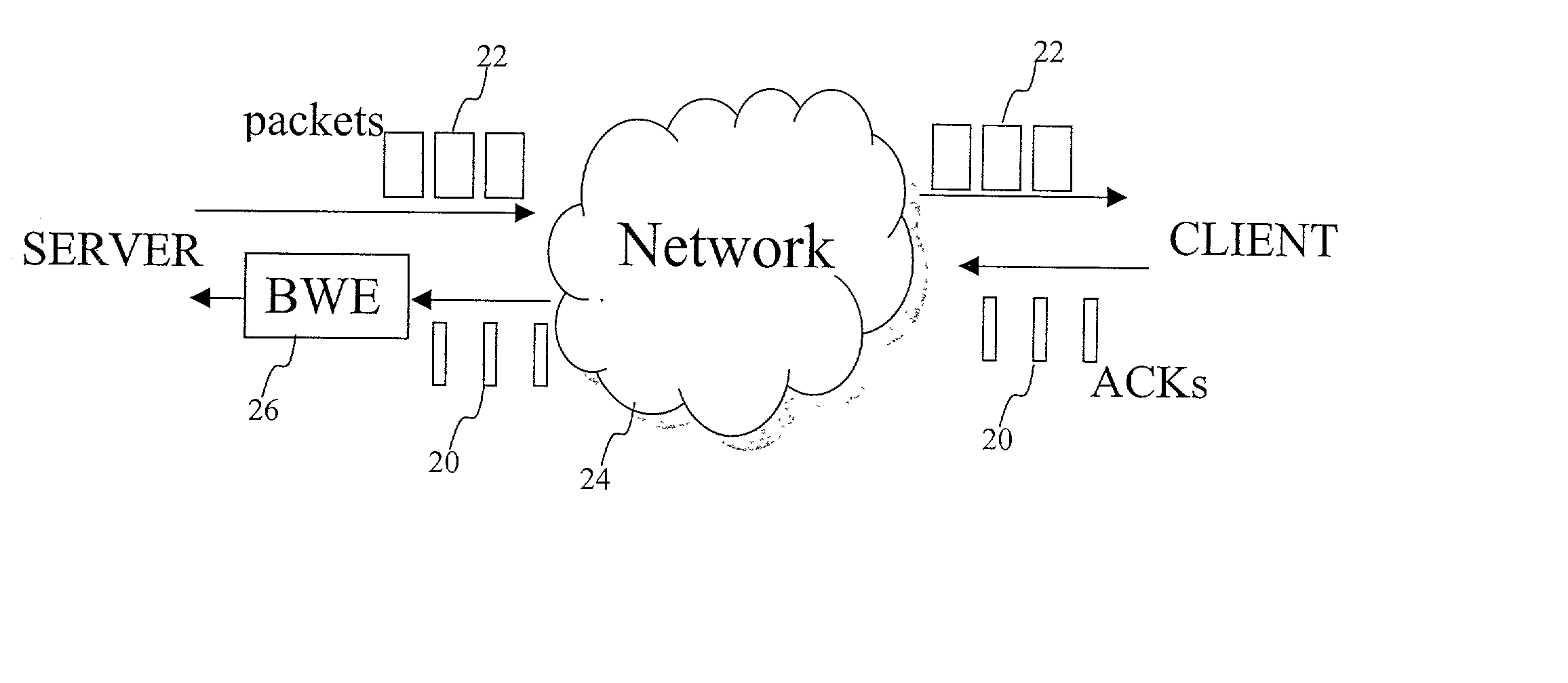
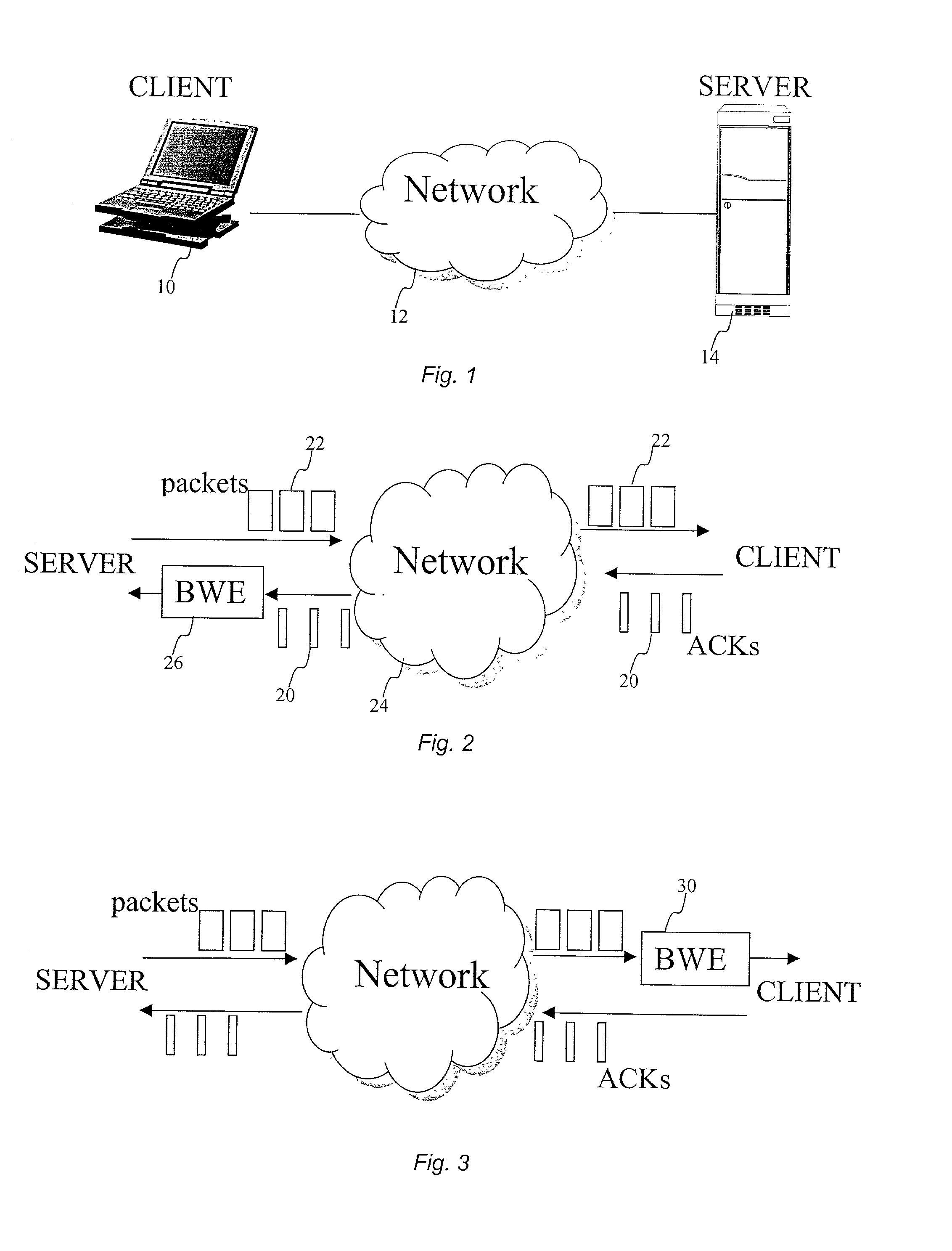
The invention herein described consists of an algorithm, which performs an end-to-end estimation of the bandwidth available in an end-to-end connection established between a server and a client via a packet switching network such as the Internet Protocol Network (IP). This algorithm is used to properly regulate the input rate at the send side. Typical applications are delivering best effort traffic over TCP, or audio and video traffic over RTP / UDP. The invention is particularly effective over wireless Internet and can be used in a content delivery system to dynamically choose the best server between a set of servers to satisfy the request of a client, or to select the best route in a content deliver or global hosting system.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
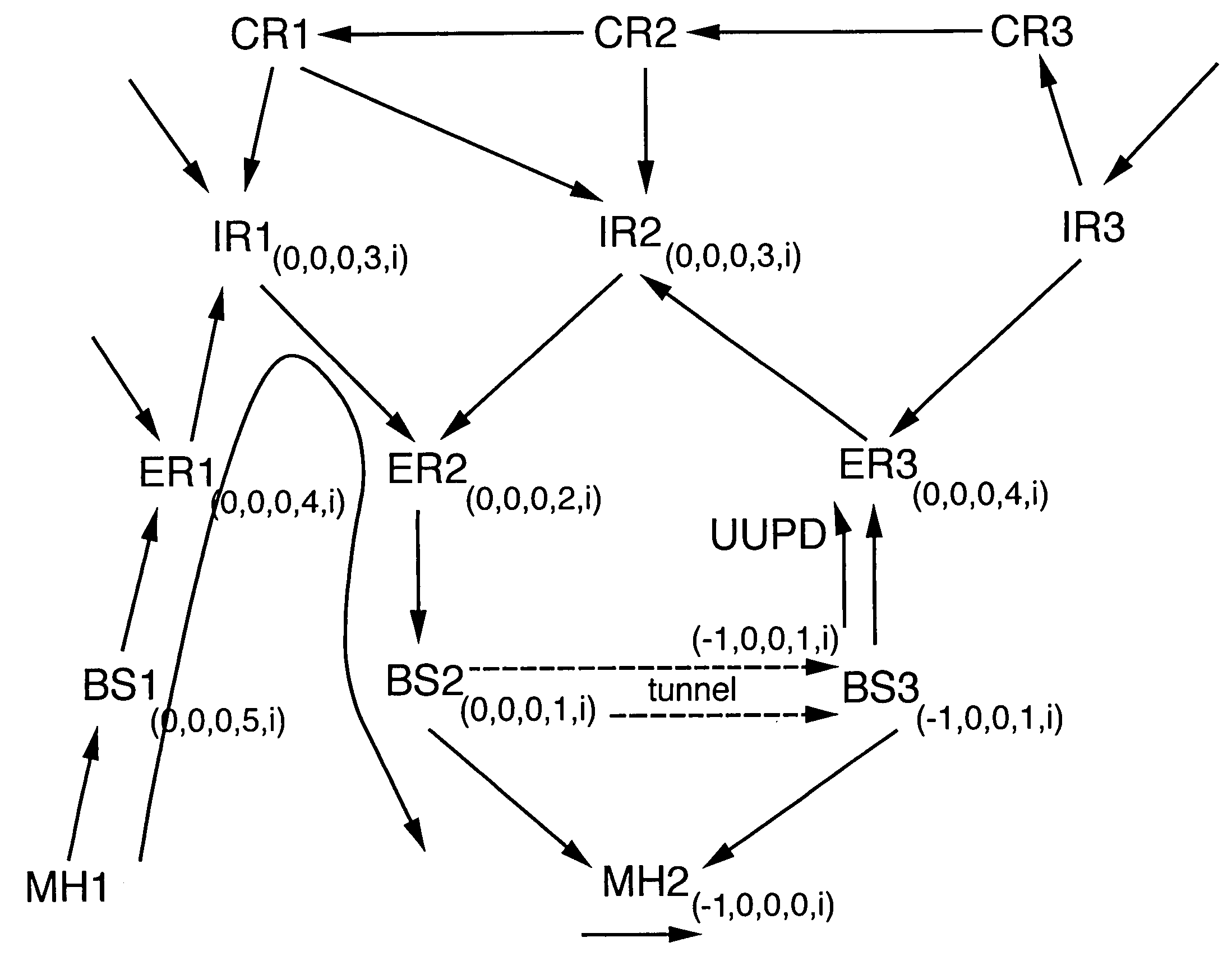
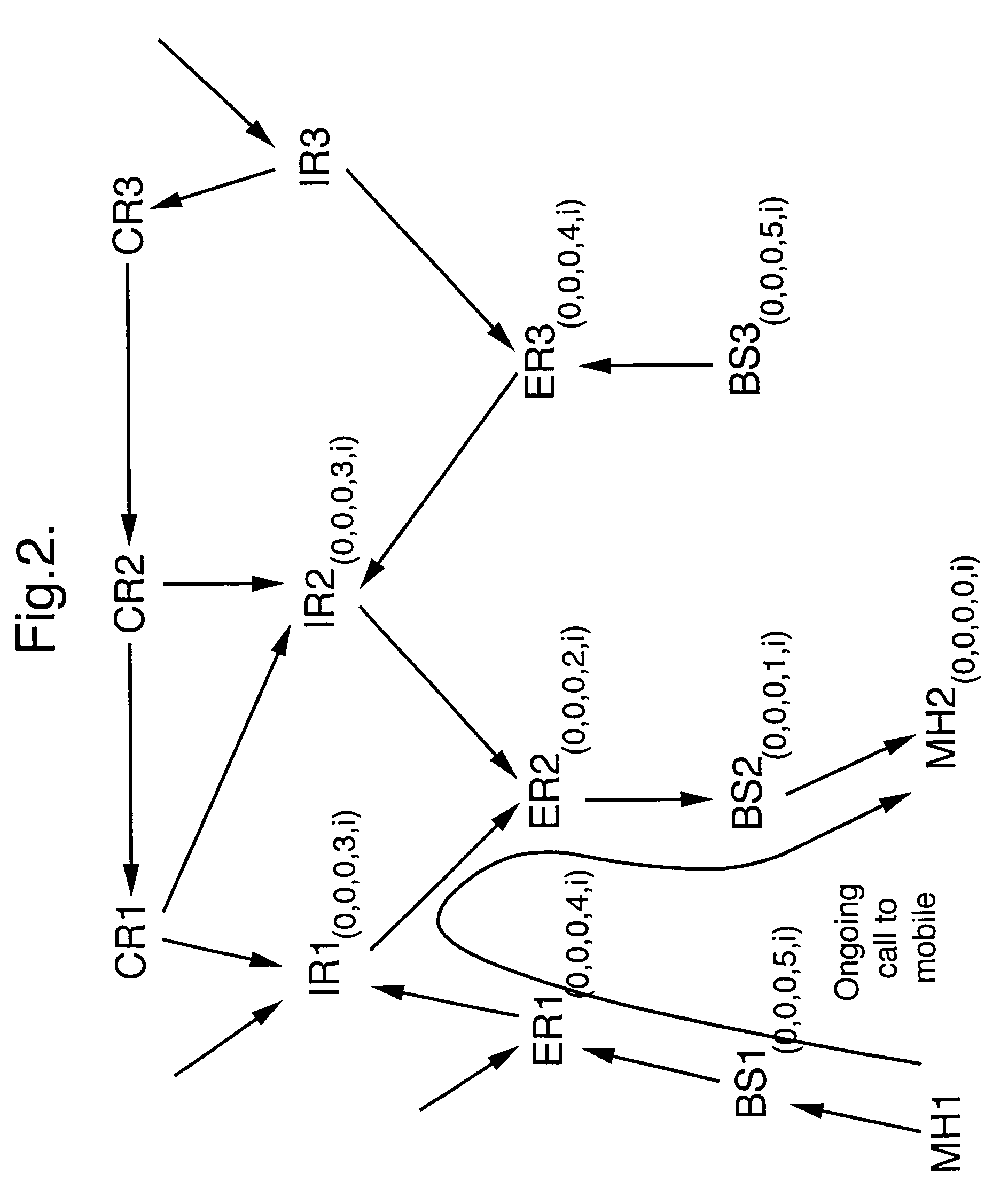
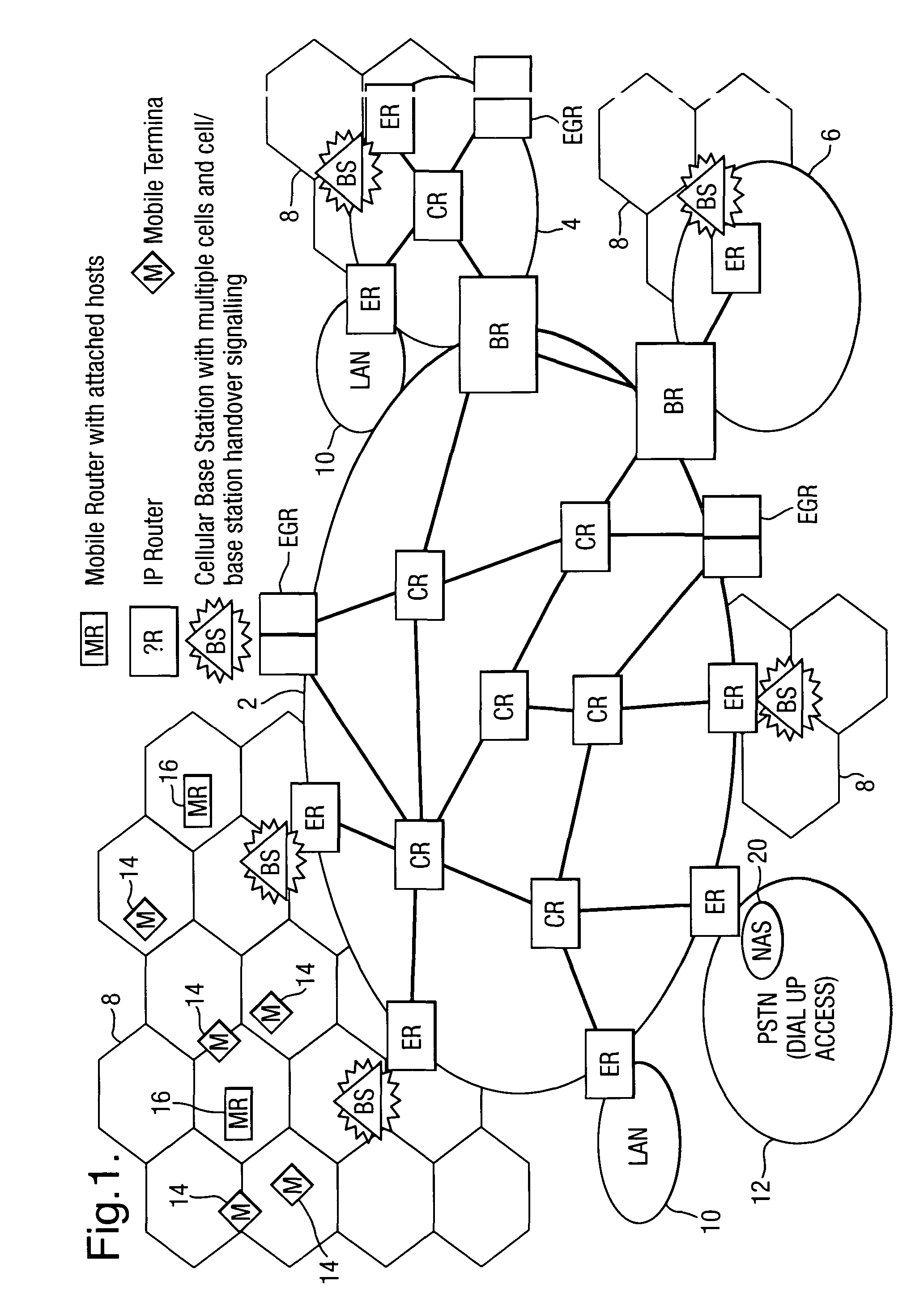
Method of controlling routing of packets to a mobile node in a telecommunications network
InactiveUS7085241B1Reduce signaling loadReduce dataData switching by path configurationWireless communicationTelecommunications networkTelecommunications link
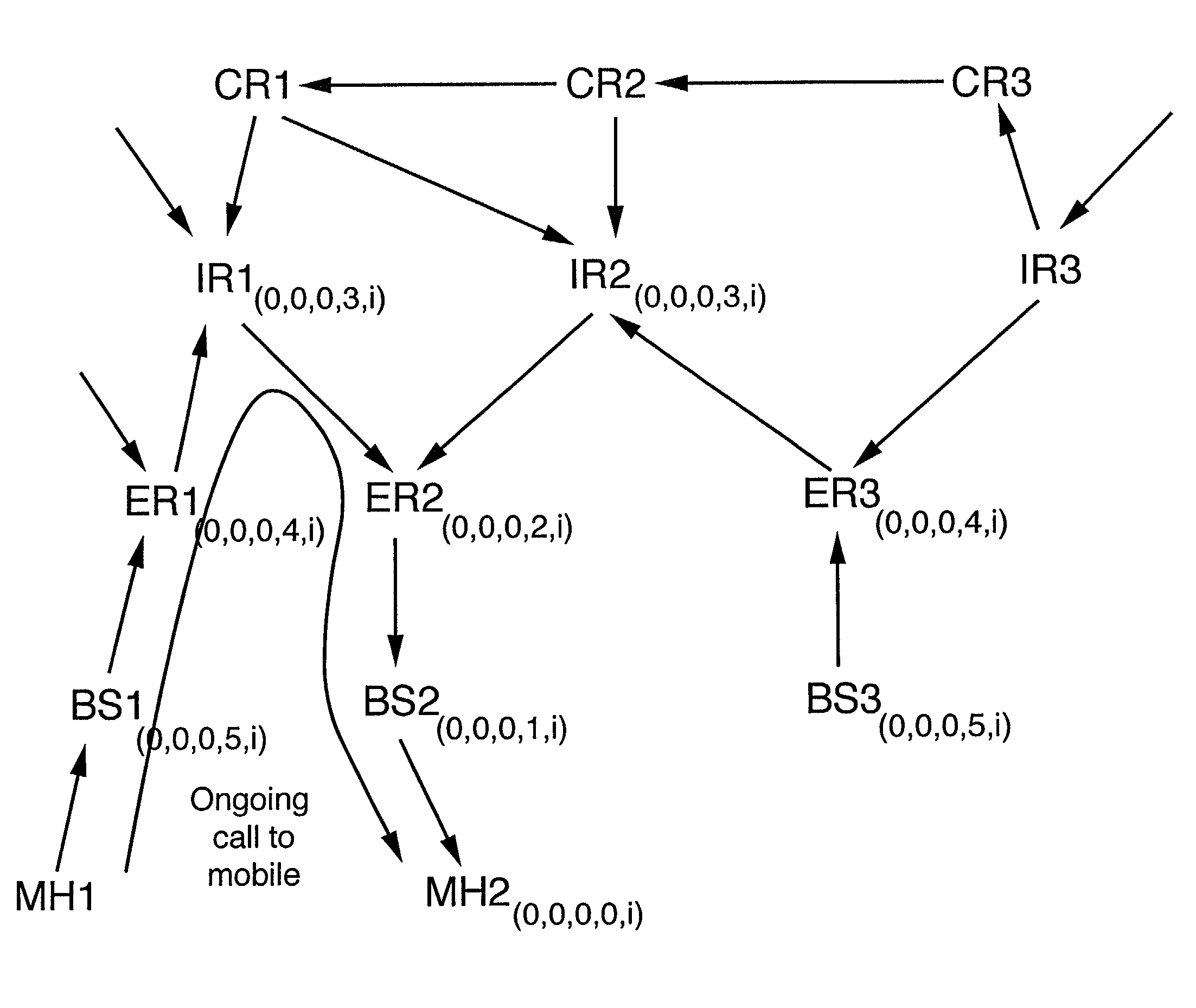
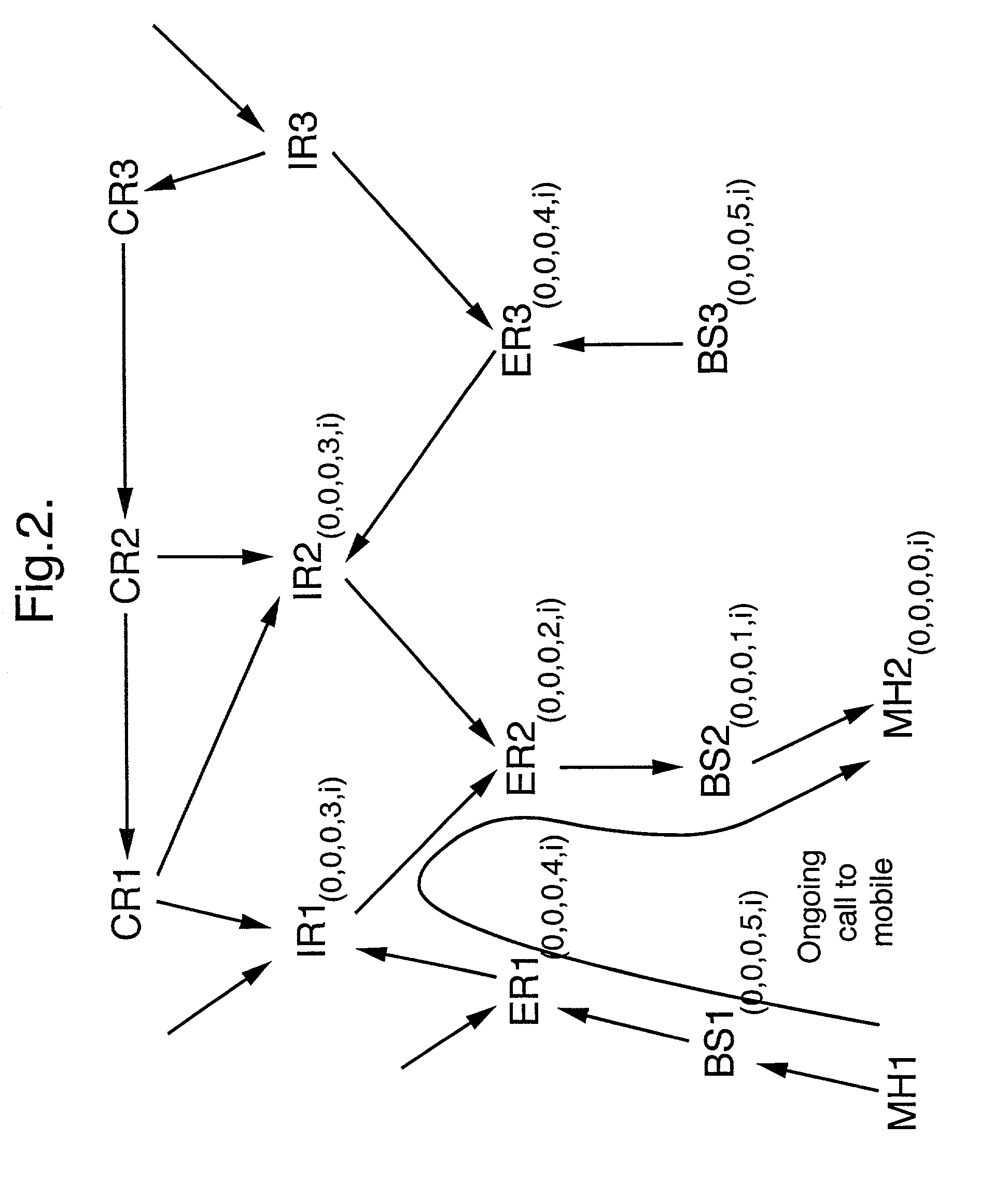
Routing of packets to a mobile node in a packet switching network is controlled. Routing the packets comprises generating first routing protocol data for a network address used by a mobile node of the network, the first routing protocol data specifying a characteristic of a first route passing through a first access node of the network, the first access node serving the mobile node via a communications link, and in response to the mobile node receiving service from a second access node, generating second routing protocol data for the network address, by a routing defining process involving transmitting directed routing update messages to a limited number of the packet switching nodes. The second routing protocol data specifies a characteristic of a second route passing through the second access node such that the first and second routing protocol data are held in different sets of packet switching nodes.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
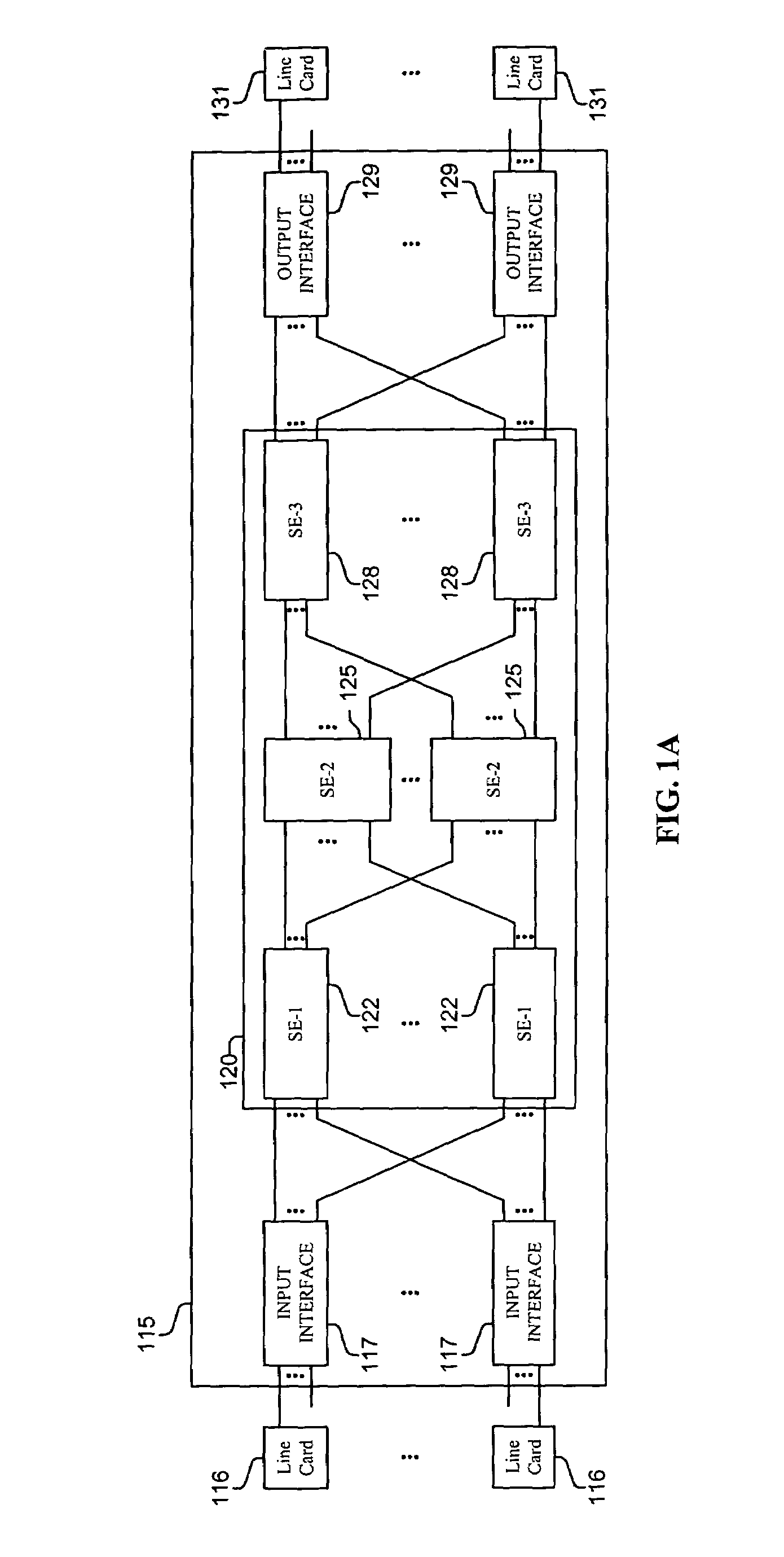
Distributing fault indications and maintaining and using a data structure indicating faults to route traffic in a packet switching system
InactiveUS6990063B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionBroadcast packetDeterministic method
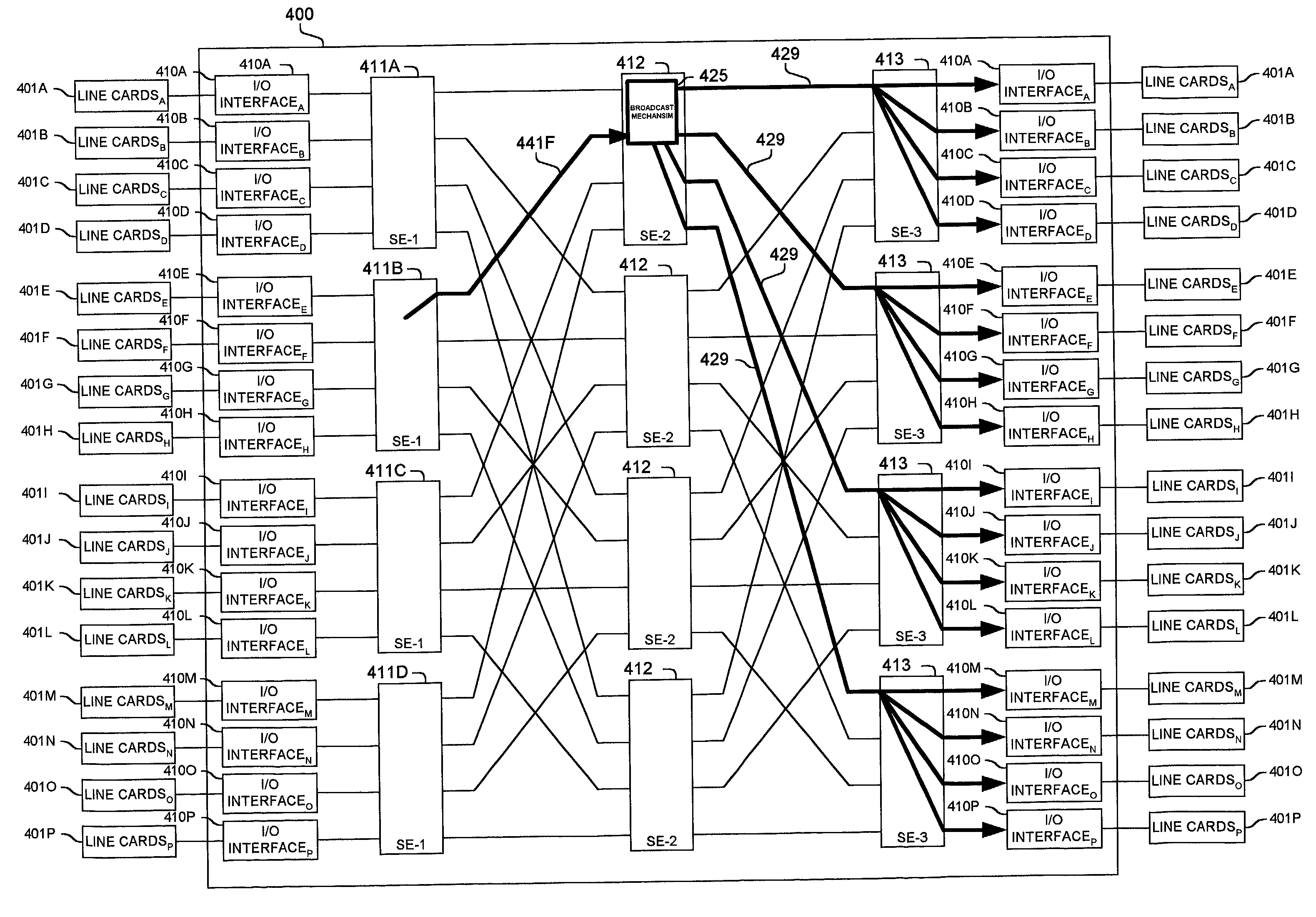
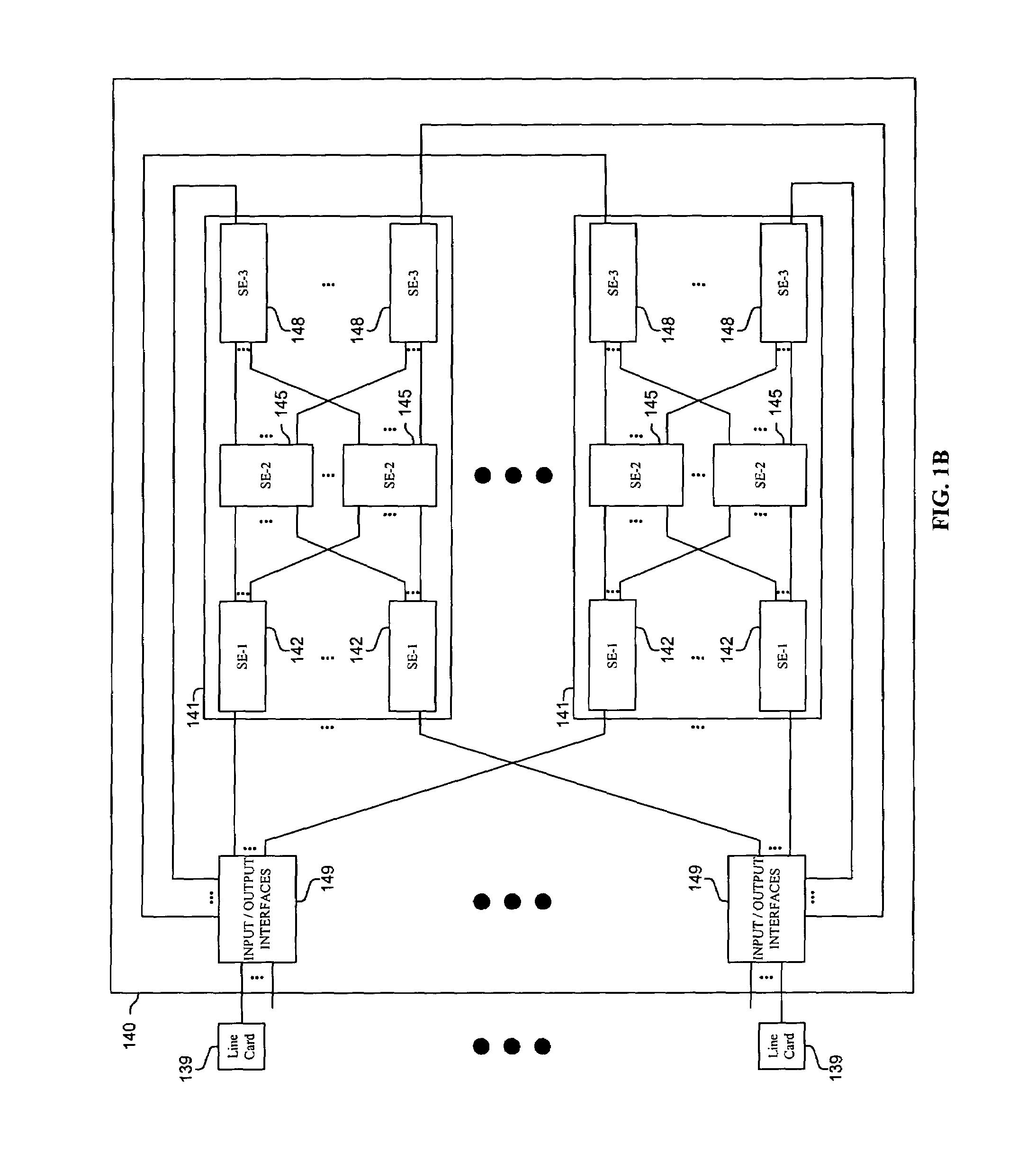
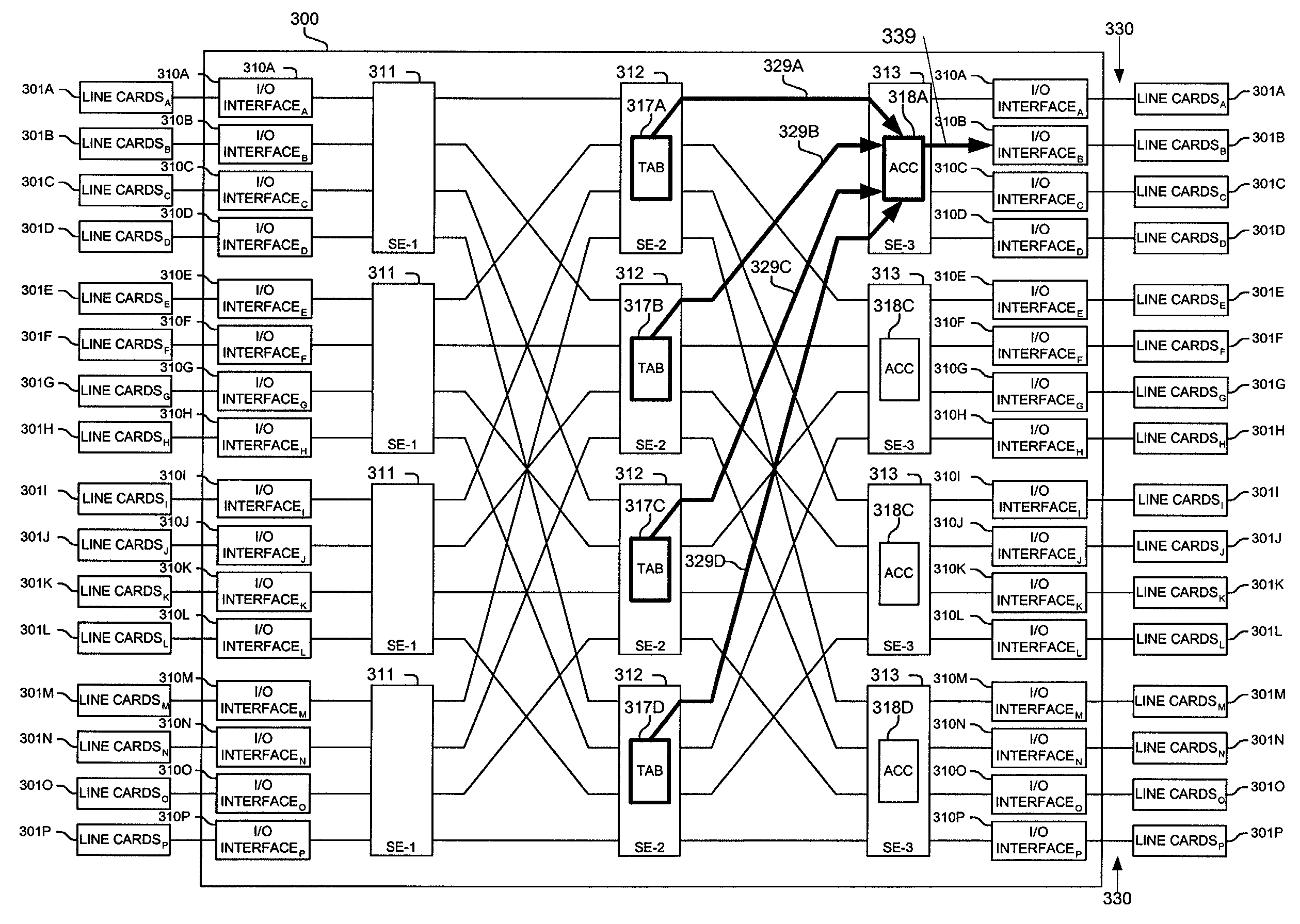
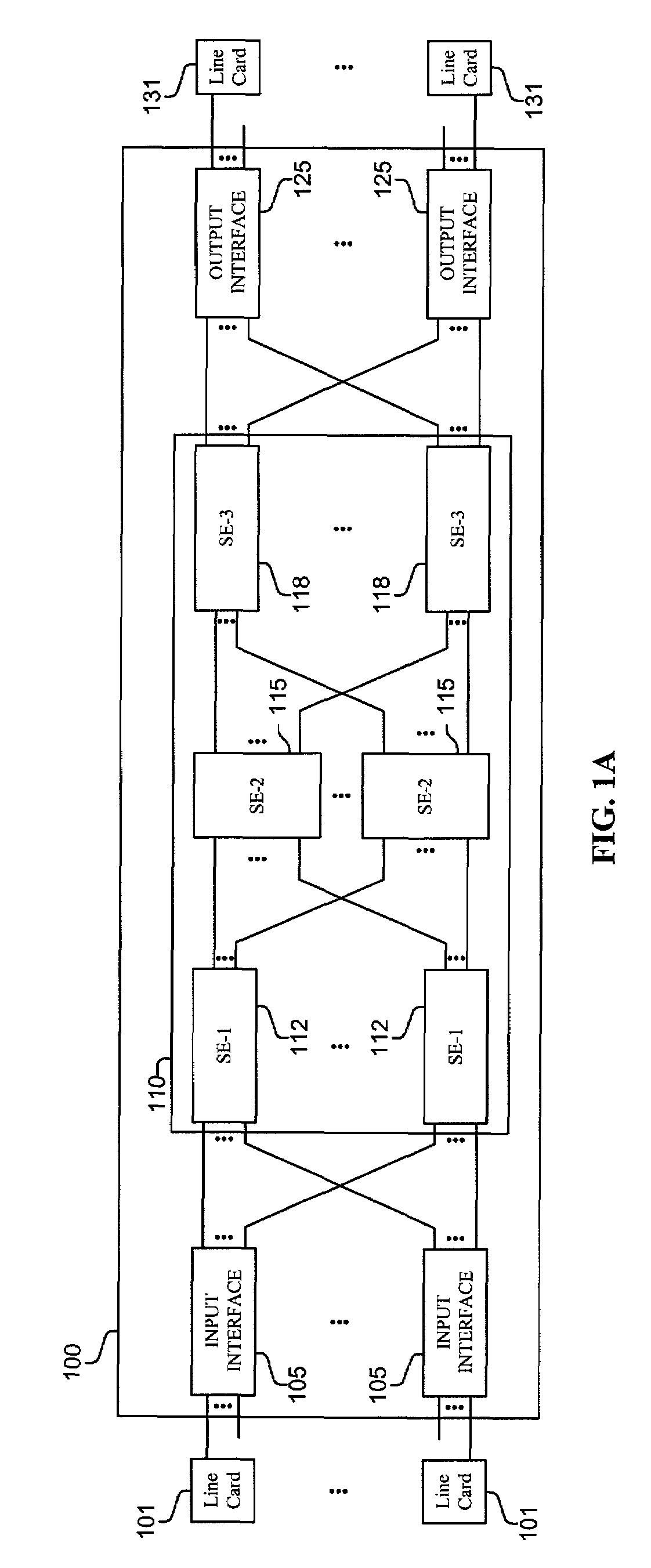
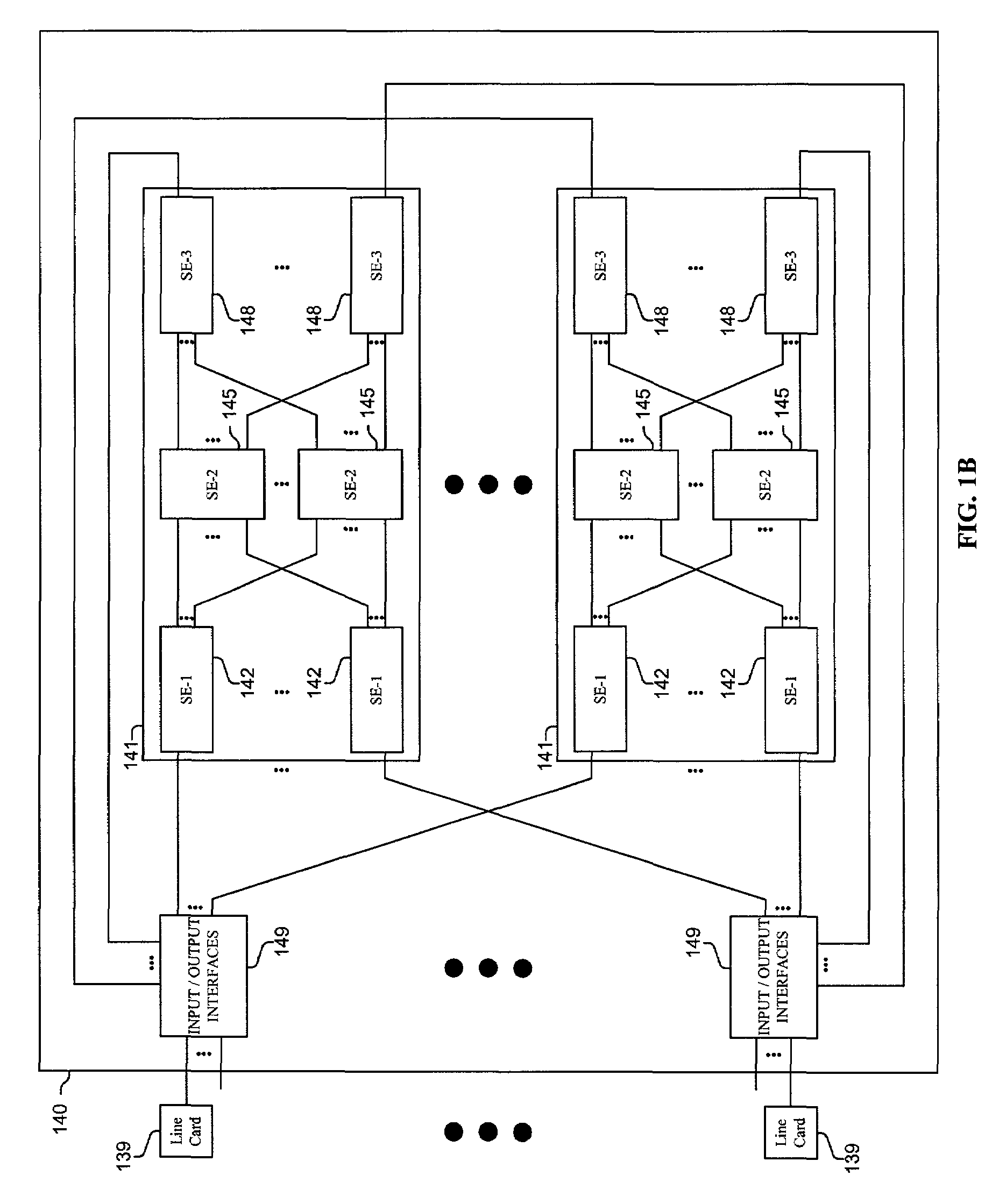
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for distributing fault indications and maintaining and using a data structure indicating faults to route traffic in a packet switching system. In one embodiment, a packet switching system detects faults and propagates indications of these faults to the input interfaces of a packet switch, so the packet switch can adapt the selection of a route over which to send a particular packet. Faults are identified by various components of the packet switching system and relayed to one or more switching components to generate a broadcast packet destined for all input ports (i.e., to each I / O interface in a packet switch having folded input and output interfaces). Other embodiments, generate one or more multicast or unicast packets. The I / O interface maintains one or more data structures indicating the state of various portions of the packet switching system. In one embodiment, an output availability table is maintained indicating over which path a particular destination may be reached, as well as a link availability vector indicating which output likes of the input interface may be currently used. Using these as masks against possible routes in a fully functional system, the packet switching component (e.g., I / O interface) can identify which routes are currently available for reaching the destination of the received packet. These routes can then be selected between using one of numerous deterministic and non-deterministic methods.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
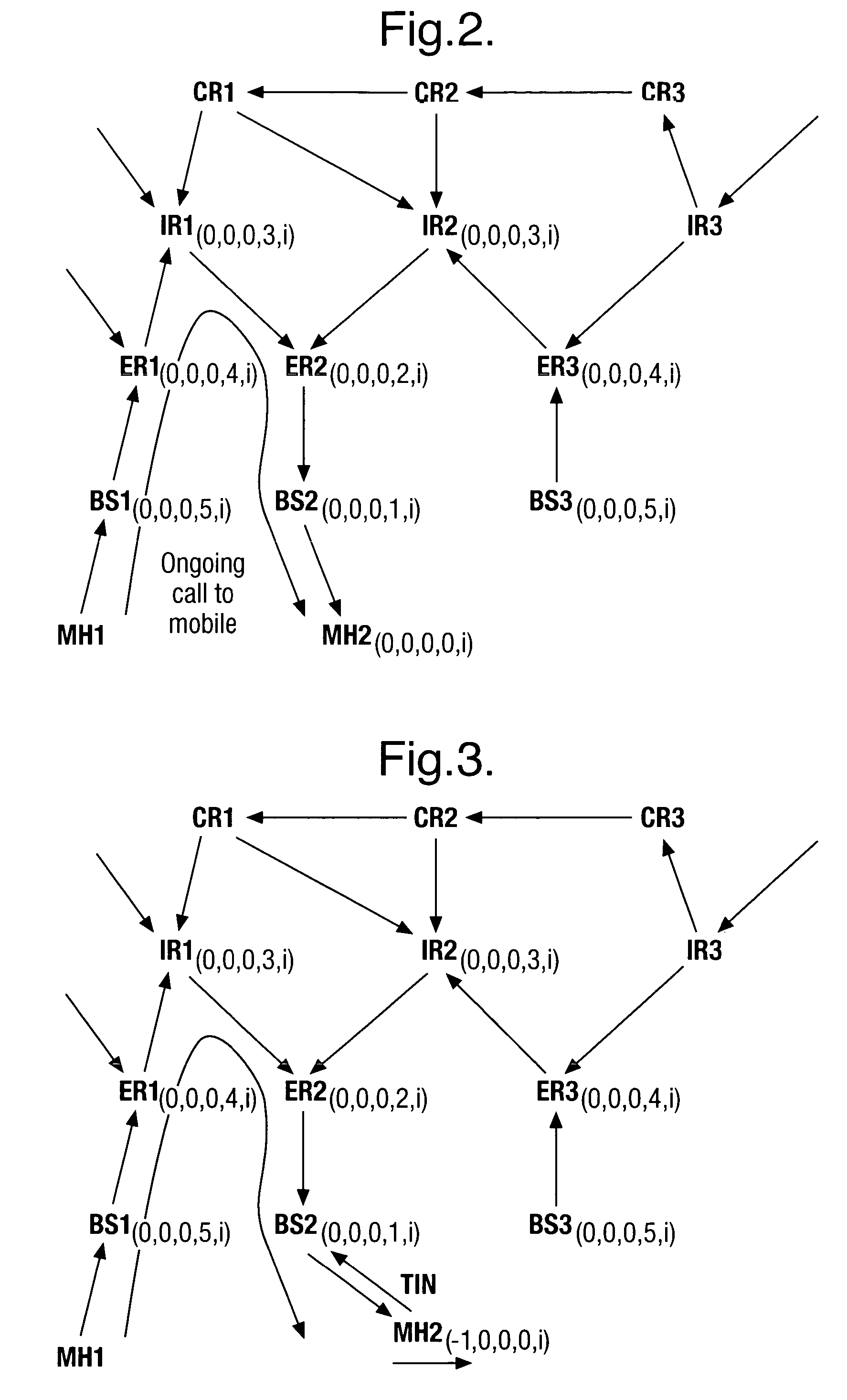
Method for performing packet switched handover in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20050185619A1Improve service qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementQuality of serviceMobile communication systems
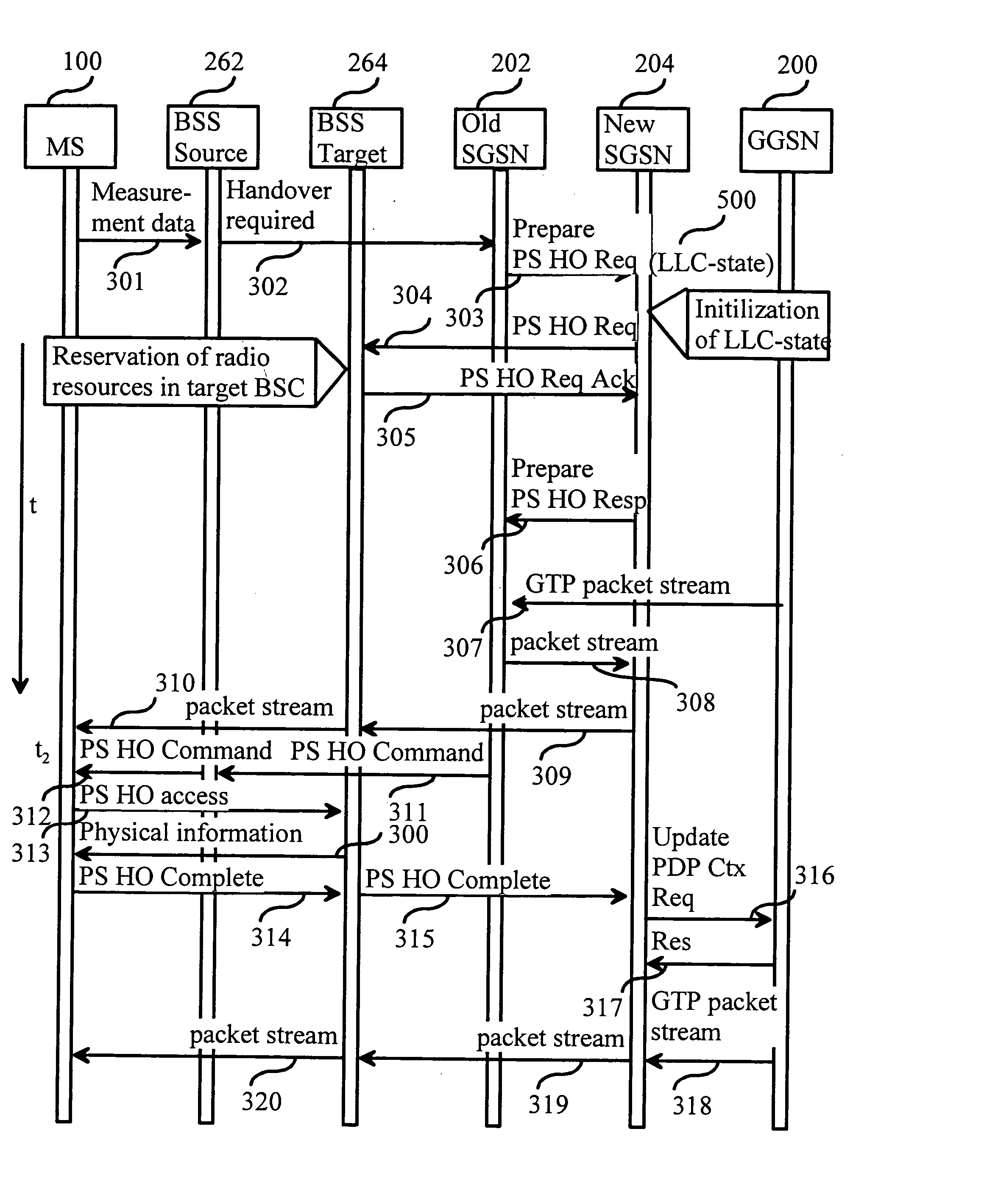
The invention relates to a method and system for performing packet switched handover in a mobile communication network. The system comprises a mobile node, a first and a second packet switching node. The method enables the parallel sending of logical link layer frames from the first and the second packet switching node. This is achieved so that the mobile node does not reject incoming frames received from two logical link layer entities having different states. The benefits of the invention are related to improved quality of service and the avoiding of gaps in received data during handover.
Owner:VRINGO INFRASTRUCTURE +1
Method and apparatus for using barrier phases to limit packet disorder in a packet switching system
InactiveUS6967926B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionCommunications systemSource element
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for using barrier phases to limit the disorder of packets which may be used in a computer or communications system. In one packet switching system, source nodes include an indication of their current barrier state in sent packets. For each barrier state, a predetermined range of sequence numbers may be used or a predetermined number of packets may be sent by a source node. The source, destination, and switching nodes are systematically switched between barrier phases, which is typically performed continuously in response to the flow of barrier request and barrier acknowledgement packets or signals. Each source node broadcasts to all forward connected nodes a barrier request to change to a next barrier state. After a switching node has received a barrier request on all incoming links, the switching node propagates the barrier request. Upon receiving barrier requests over all links, each destination stage relays an acknowledgement message to all connected source elements, which then send a barrier acknowledgement in much the same way, and each source element changes its barrier state causing the sequence number or counting space to be reset, and newly sent packets to indicate the new barrier state. Upon receiving all its barrier acknowledgement messages, each destination stage changes its barrier state, and then the destination can manipulate (e.g., resequence, reassemble, send, place in an output queue, etc.) packets marked with the previous barrier state as it knows that every packet from the previous barrier state has been received. This transition of barrier phases and limiting the number of packets sent per barrier phases may be used to limit the range of the sequence number space and the size of outgoing, resequencing, and reassembling buffers, as well providing a packet time-out mechanism which may be especially useful when non-continuous sequence numbers or time-stamps are included in packets for resequencing and / or reassembly purposes.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Routing in a packet switching network with mobile terminals
InactiveUS7161929B1Reliable and goodAvoid the needTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork addressingNetwork address
Packets in a packet switching network are routed along a routing path defined by data held in packet switching nodes. One or more network addresses are assigned to a first access node as home addresses. A first home address is allocated to a first mobile node with at least one routing path being directed to a first access node for that first home address. Routing in the packet switched infrastructure is altered when the first mobile node receives service from a second access node by transmitting routing update messages to a limited subset of localized packet switching nodes such that at least one routing path in the infrastructure is directed to the second access node for the first home address. Routing in the infrastructure is subsequently altered such that at least one routing path is directed to the first access node for the first home address, and the first home address is allocated to a second mobile node served by the first access node.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
End-to-end bandwidth estimation for congestion control in packet switching networks
InactiveUS7130268B2Improve network bandwidth utilizationImprove fairnessEnergy efficient ICTError preventionTraffic capacityPacket-switching node
The invention herein described consists of an algorithm, which performs an end-to-end estimation of the bandwidth available in an end-to-end connection established between a server and a client via a packet switching network such as the Internet Protocol Network (IP). This algorithm is used to properly regulate the input rate at the send side. Typical applications are delivering best effort traffic over TCP, or audio and video traffic over RTP / UDP. The invention is particularly effective over wireless Internet and can be used in a content delivery system to dynamically choose the best server between a set of servers to satisfy the request of a client, or to select the best route in a content deliver or global hosting system.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
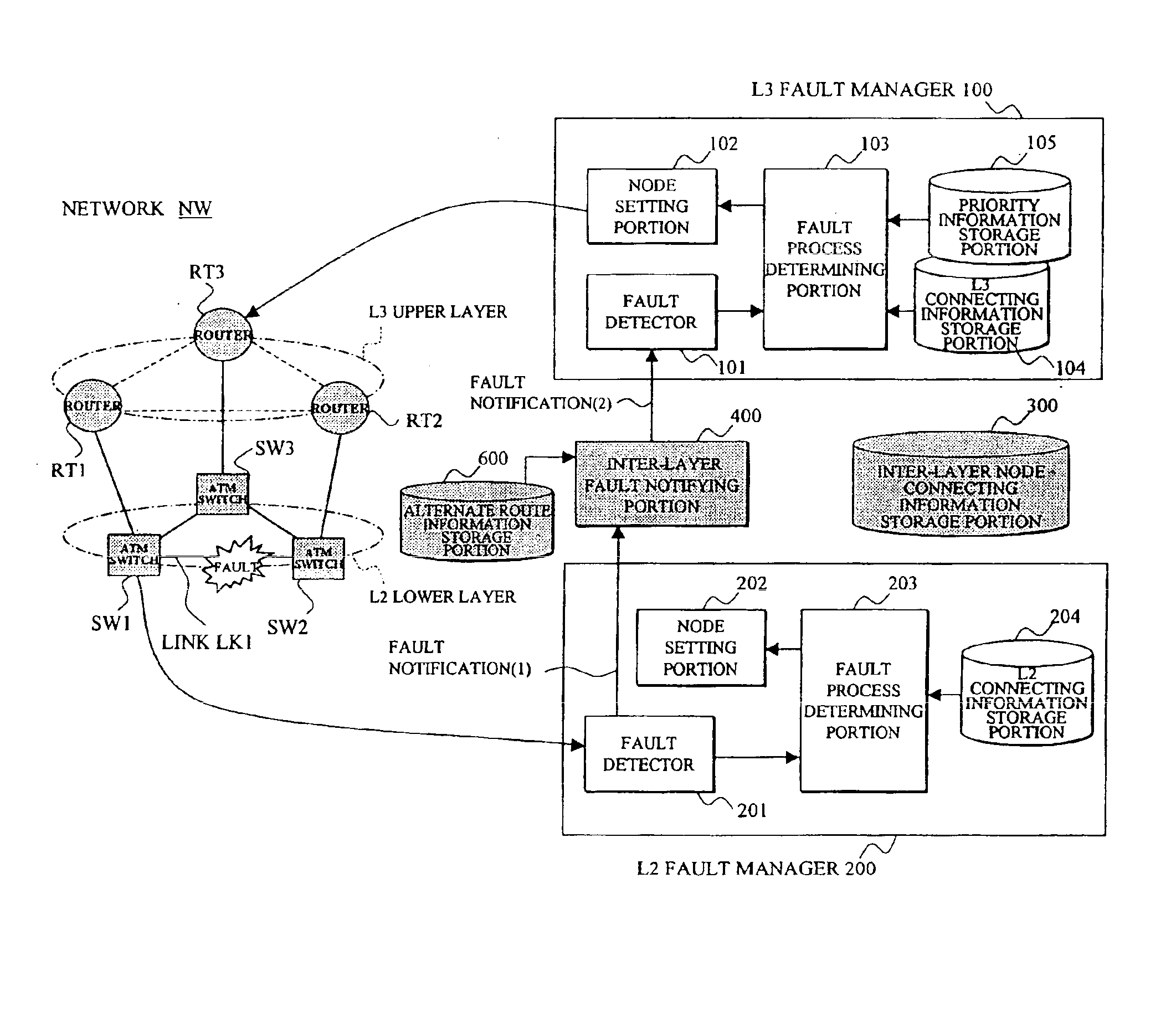
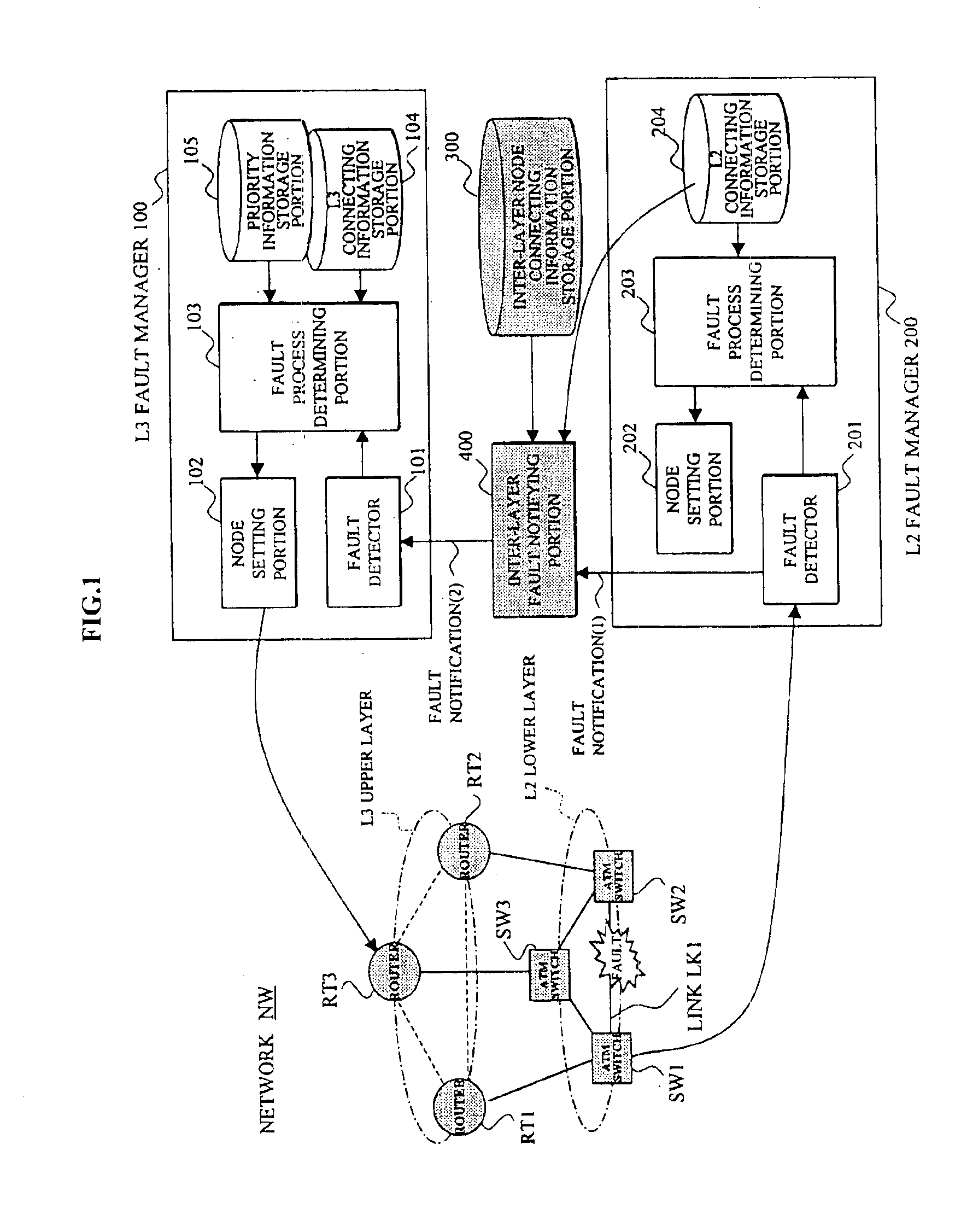
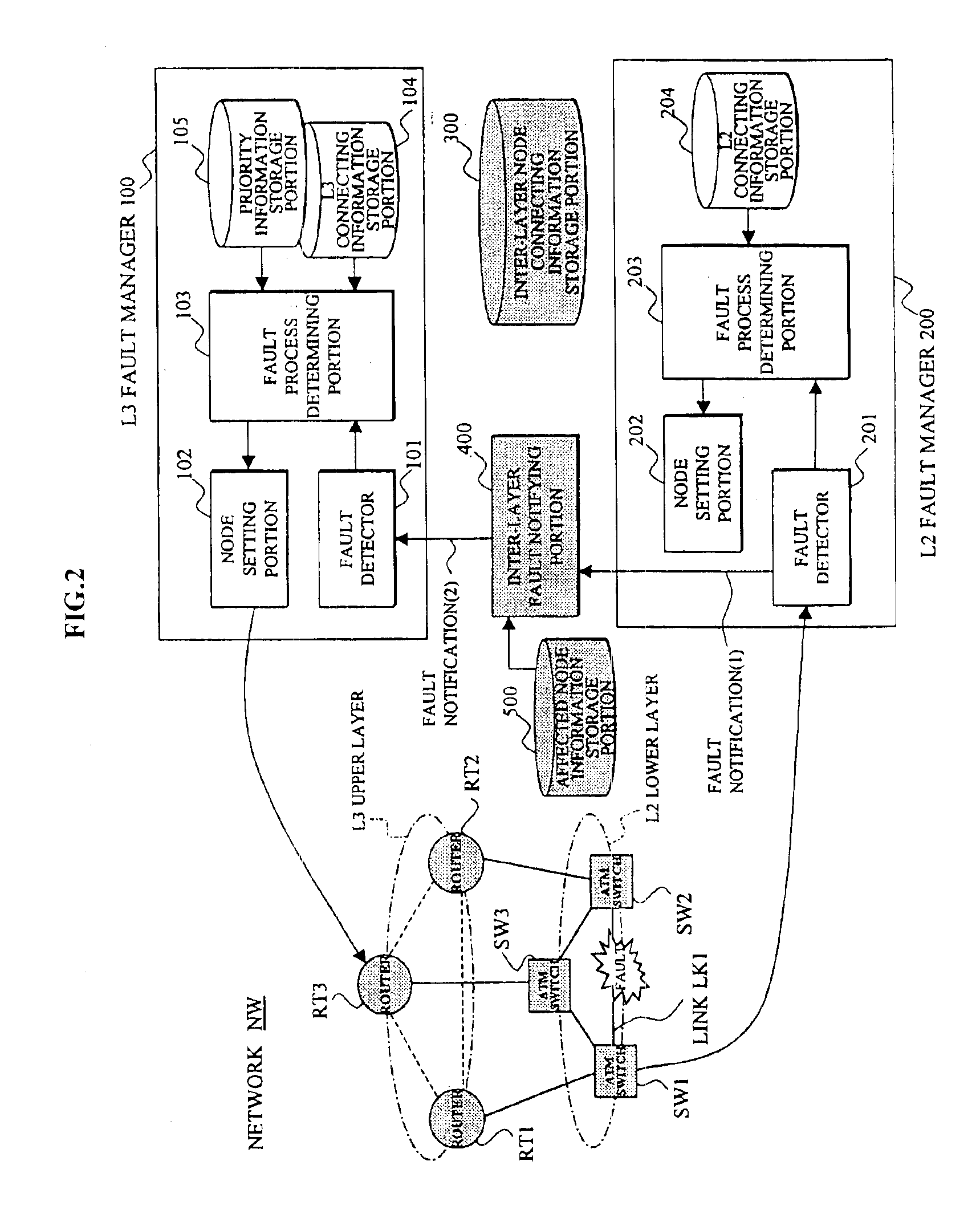
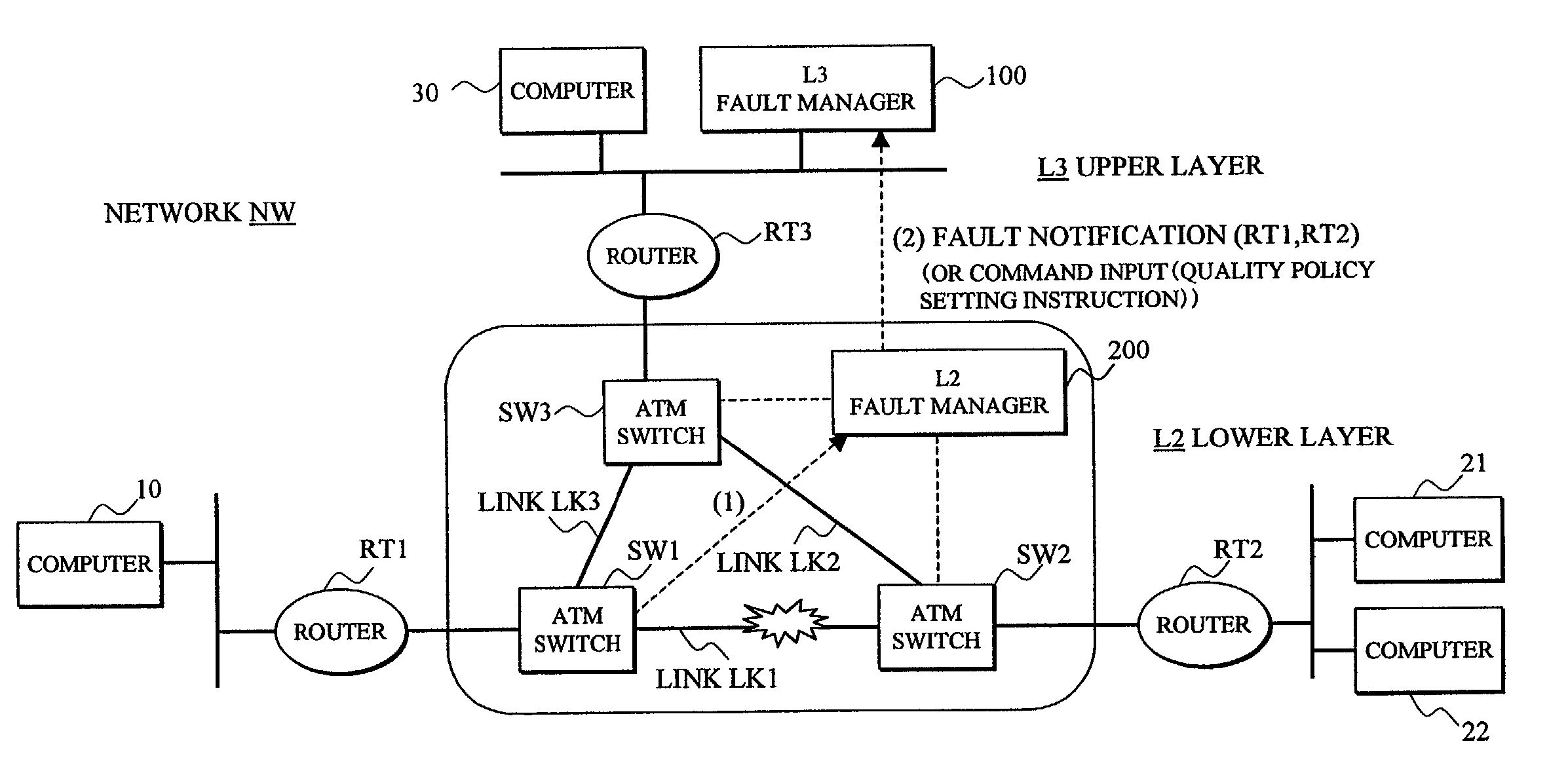
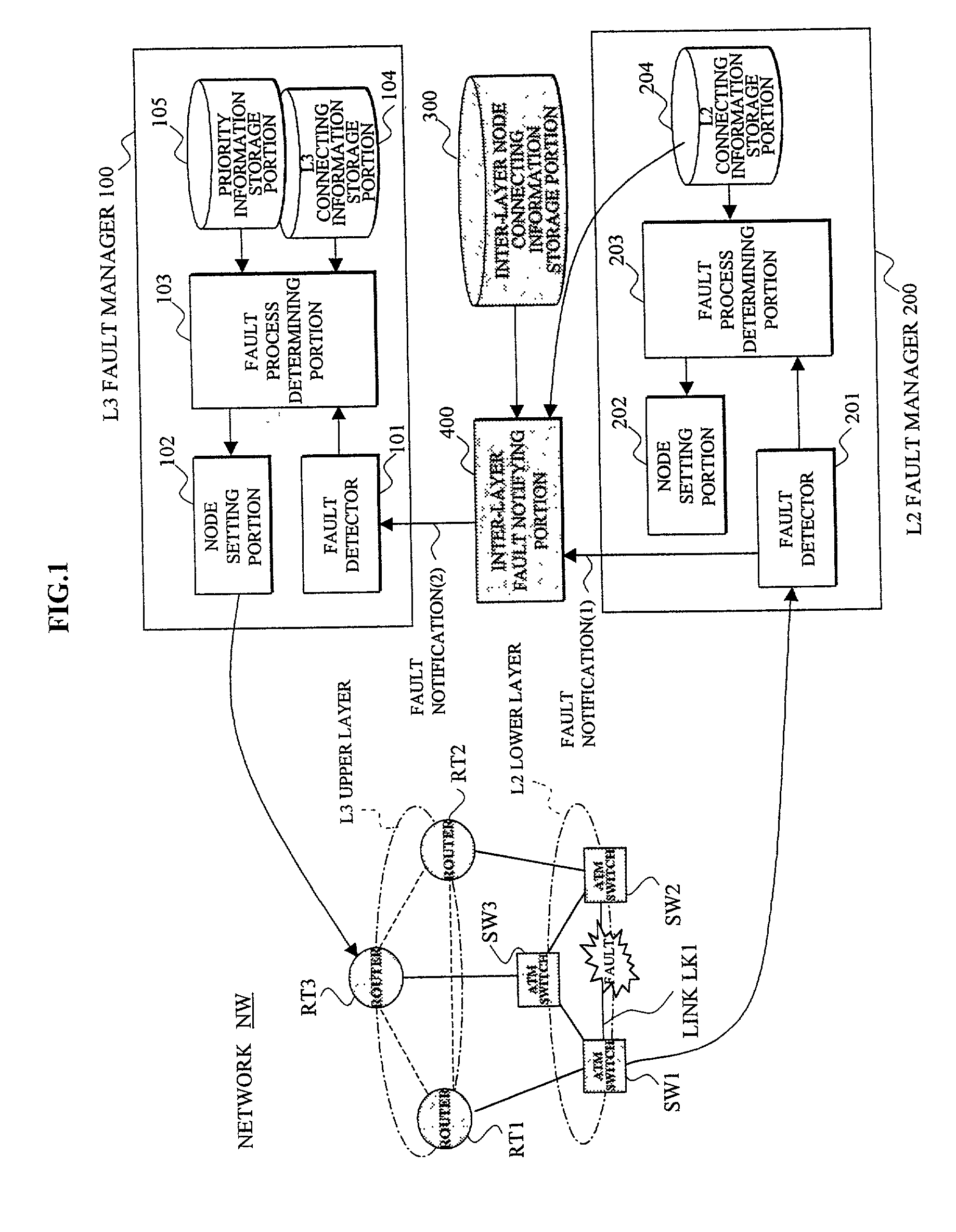
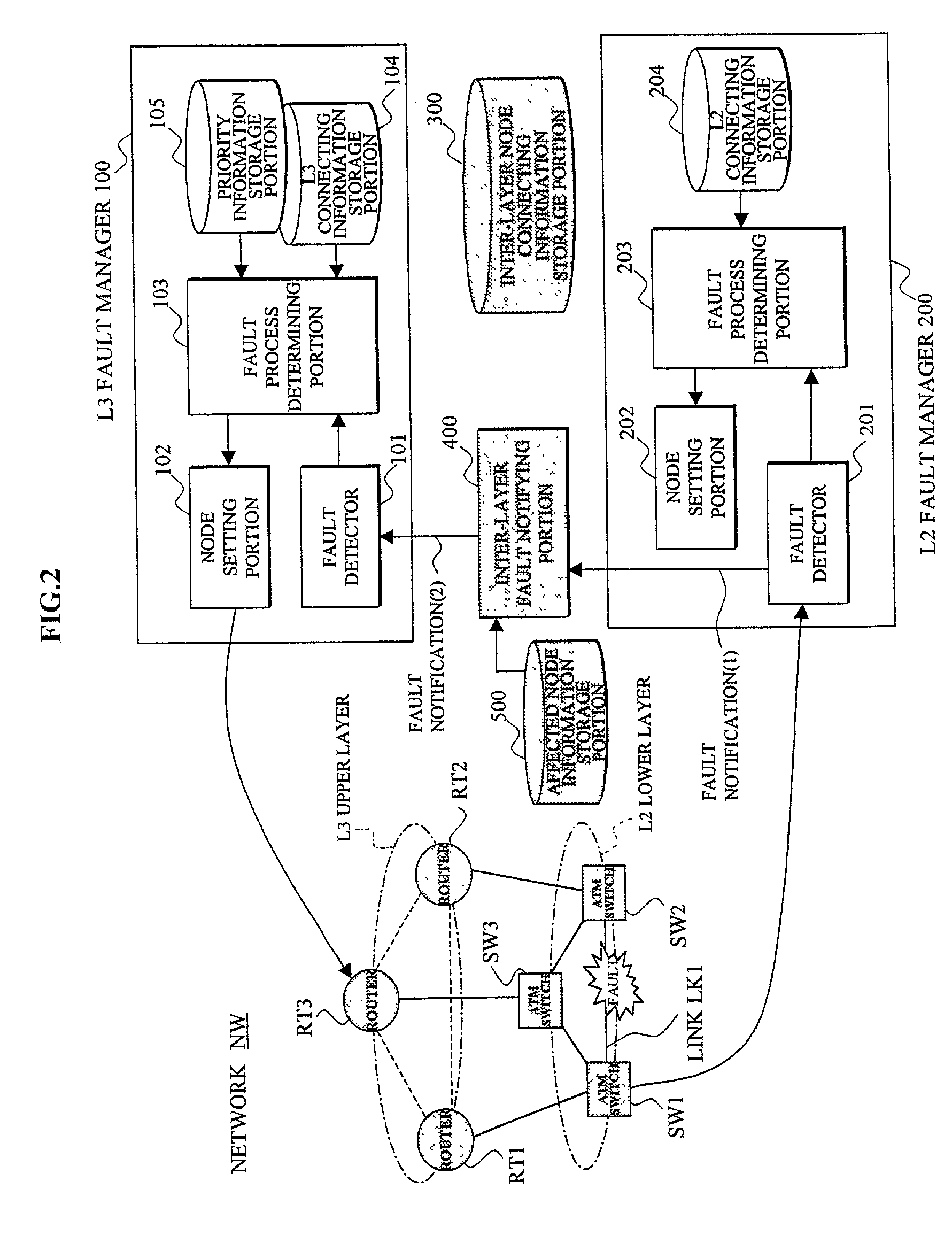
Network management system utilizing notification between fault manager for packet switching nodes of the higher-order network layer and fault manager for link offering nodes of the lower-order network layer
InactiveUS6898630B2Quality improvementShorten the timeMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksInter layerNetwork management
In a network management system performing a fault management process in a hierarchical network, an upper layer fault manager performs a fault management of an upper layer of a hierarchical network, a lower layer fault manager performs a fault management of a lower layer of the network, an inter-layer node connecting information storage portion manages connecting information between packet switching nodes composing the upper layer and link offering nodes composing the lower layer, and an inter-layer fault notifying portion notifies the upper layer fault manager, upon receiving a notification of a link fault which has occurred on a link between the link offering nodes from the lower layer fault manager, that the packet switching nodes affected by the fault are faulted, based on the connecting information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
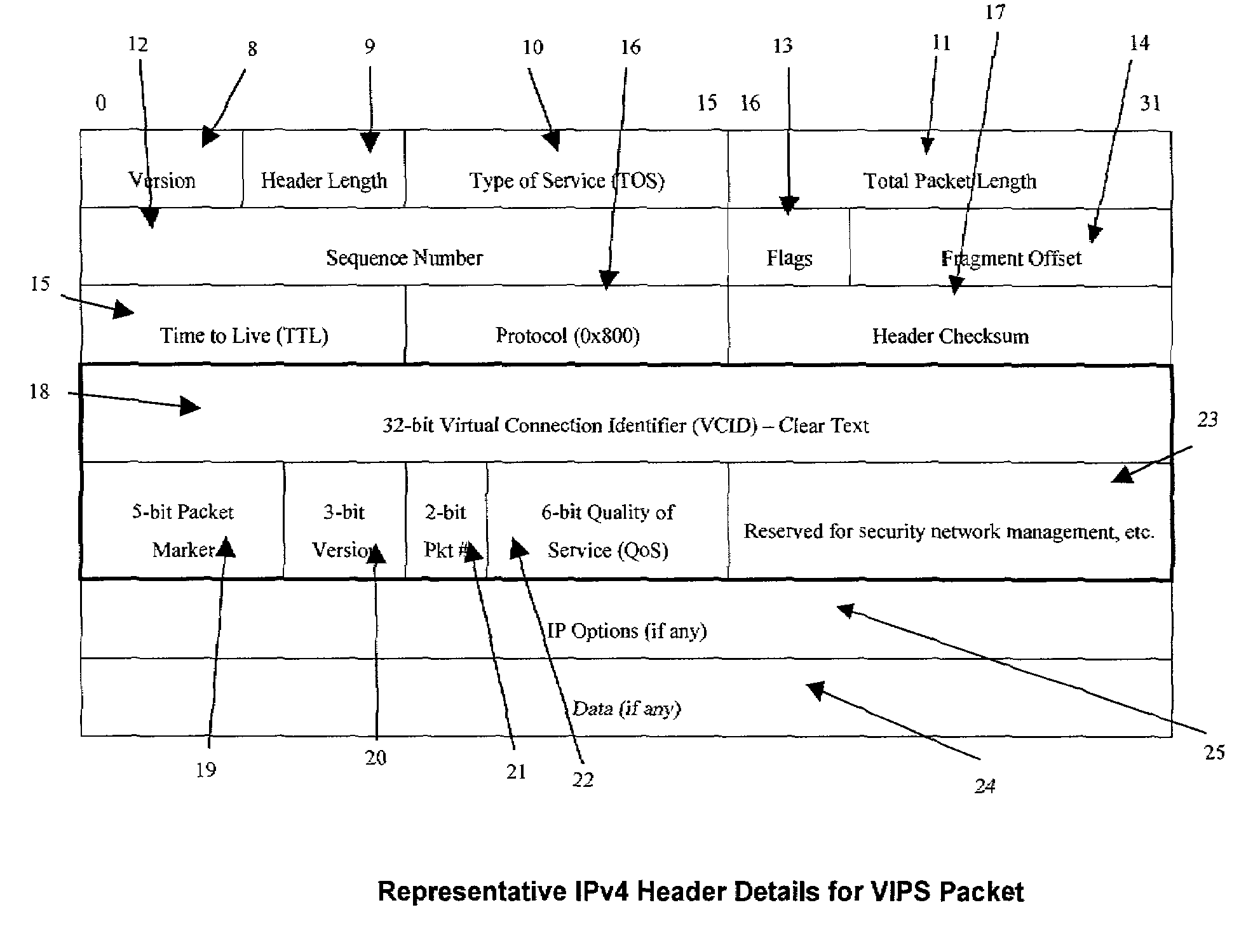
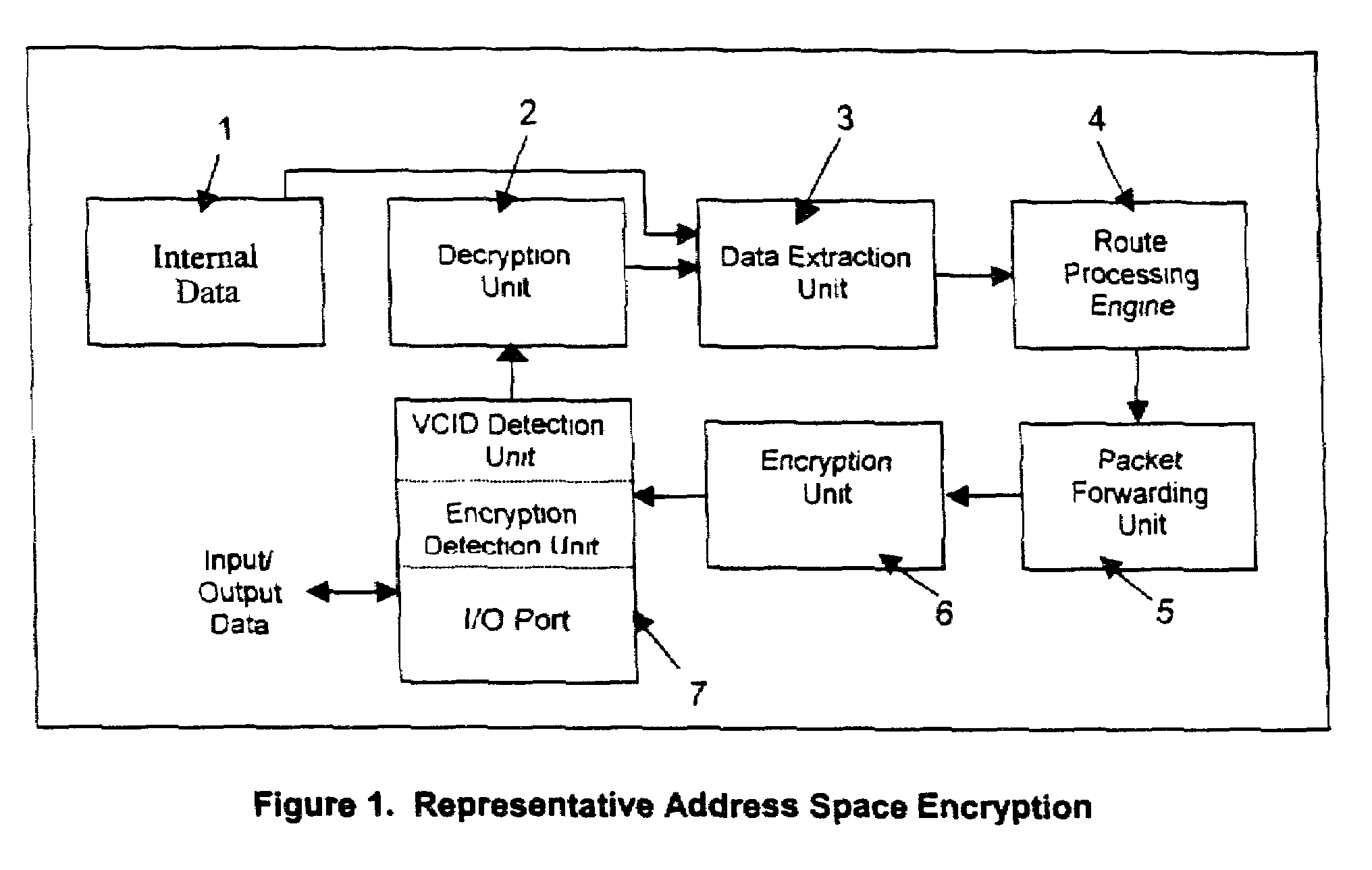
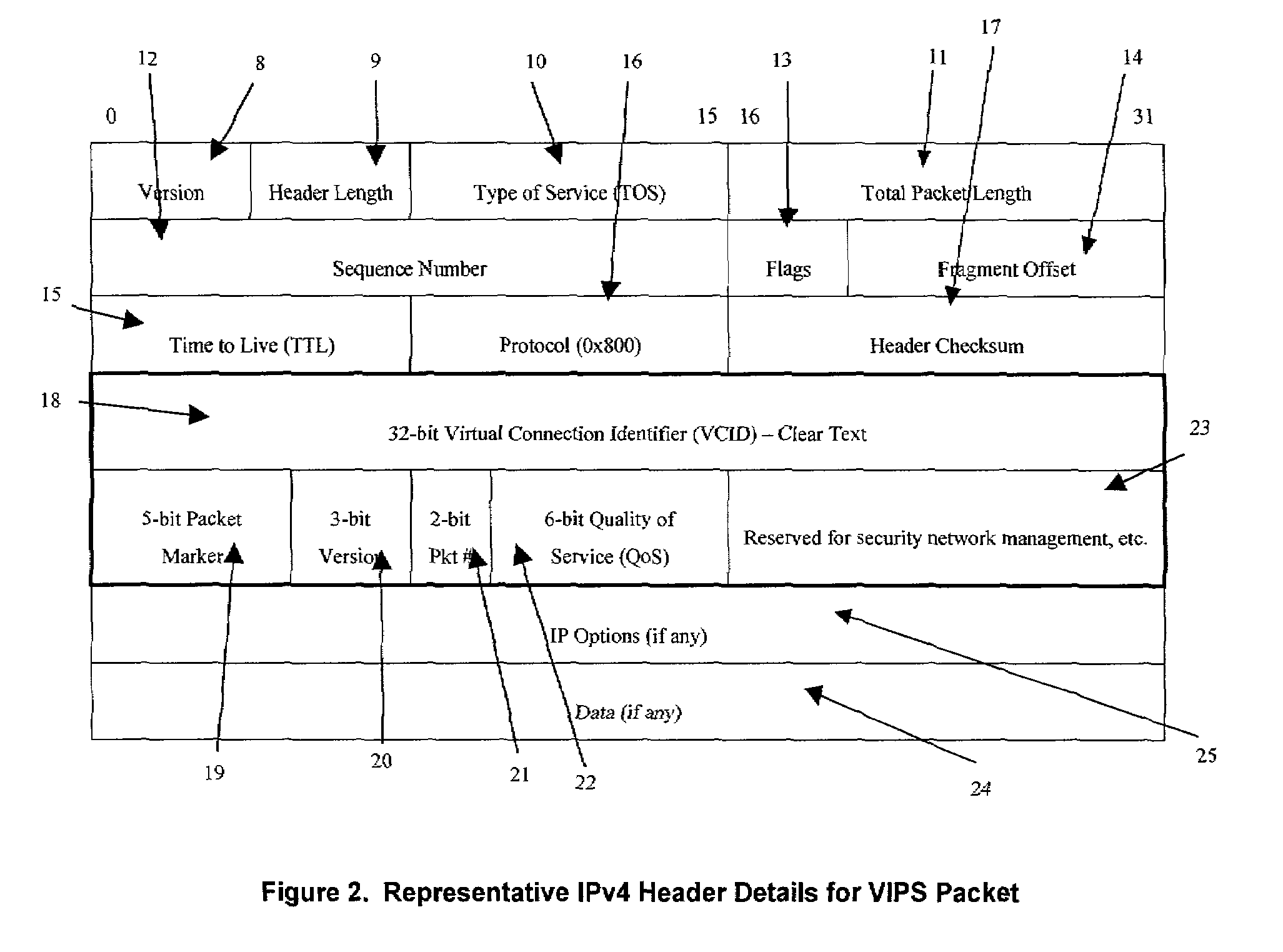
Encryption mechanism in advanced packet switching system
A packet switching system for switching packets over corporate networks and the Internet using Internet Protocol (IP) suite of protocols is provided with an encryption detecting unit that determines whether at least a section of a portion of an incoming packet allocated for Internet Protocol (IP) address fields comprises encrypted data. If the encrypted data is detected, a decrypting unit decrypts the encrypted data. A packet identifying unit detects a virtual connection identifier (VCID) marker indicating that a VCID is provided in the portion of the incoming packet allocated for IP address fields. A data extracting unit extracts the VCID from the decrypted data. For example, the data extracting unit may extracts original source and destination IP addresses, or a Quality of Service (QoS) field for identifying parameters of Quality of Service. A route processing engine determines a route for forwarding the packet, and a packet forwarding unit places the packet into a queue for transmission. An encrypting unit encrypts the VCID of packets transmitted to a network that uses virtual connection identifiers for switching packets.
Owner:SIGNAFOR
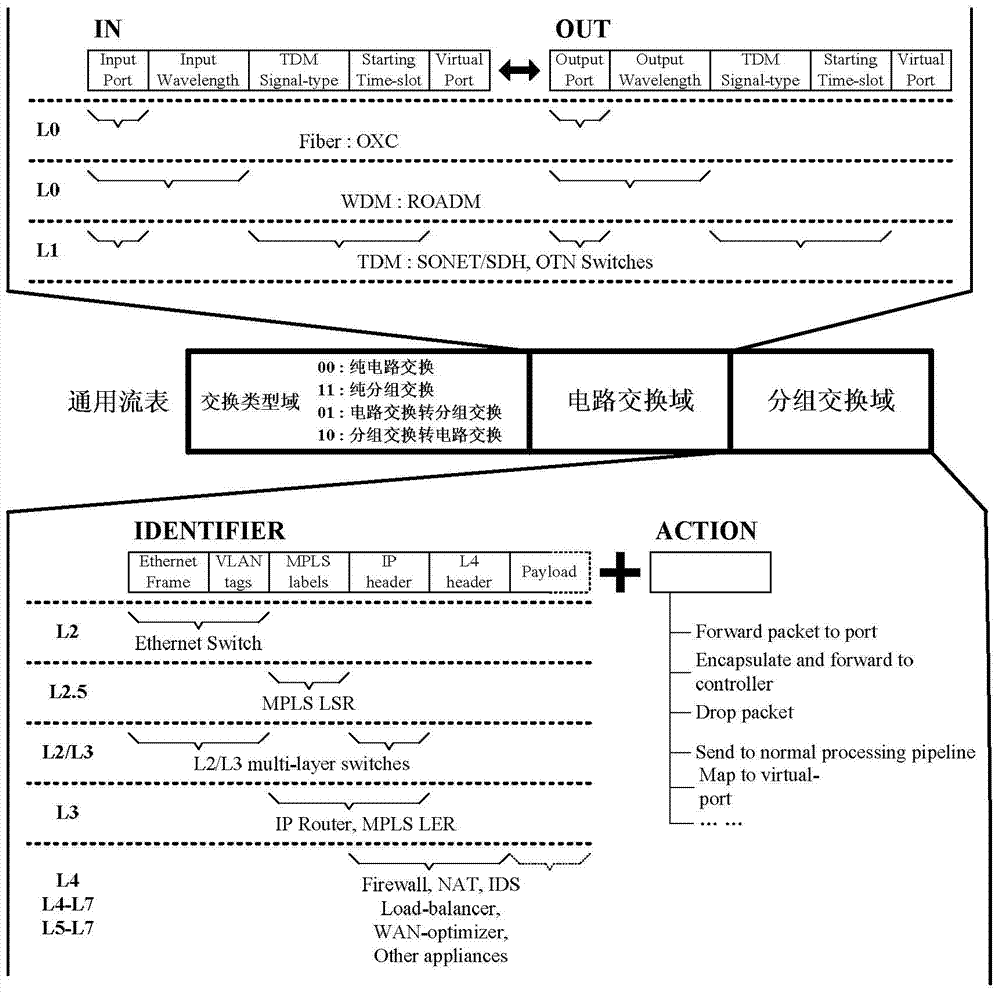
General flow table and method for supporting packet switching and circuit switching in SDN framework
ActiveCN103685033ASimplify the control problemSimplify the management processData switching networksService flowControl layer
The invention provides a general flow table and method for supporting packet switching and circuit switching in an SDN framework, and relates to the SDN framework in the information technology. The general flow table comprises a switching type domain, a circuit switching domain and a packet switching domain. The switching type domain comprises four marks of pure circuit switching, pure packet switching, circuit-packet switching and packet-circuit switching. Service flow is forwarded to a network controller of a control layer through a southbound interface. The network controller is used for judging the type and characteristics of the service flow, computing a forwarding path of the service flow and generating the corresponding general flow table. The network controller issues the general flow table to data forwarding equipment of a data layer through the southbound interface, and establishes corresponding forwarding rules in the data forwarding equipment. The service flow completes packet switching and circuit switching in the data forwarding equipment according to the forwarding rules. The general flow table and method can simultaneously support the packet switching technology and the circuit switching technology, and two existing basis independent networks can be replaced by a data and transmission convergent network efficient in operation.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
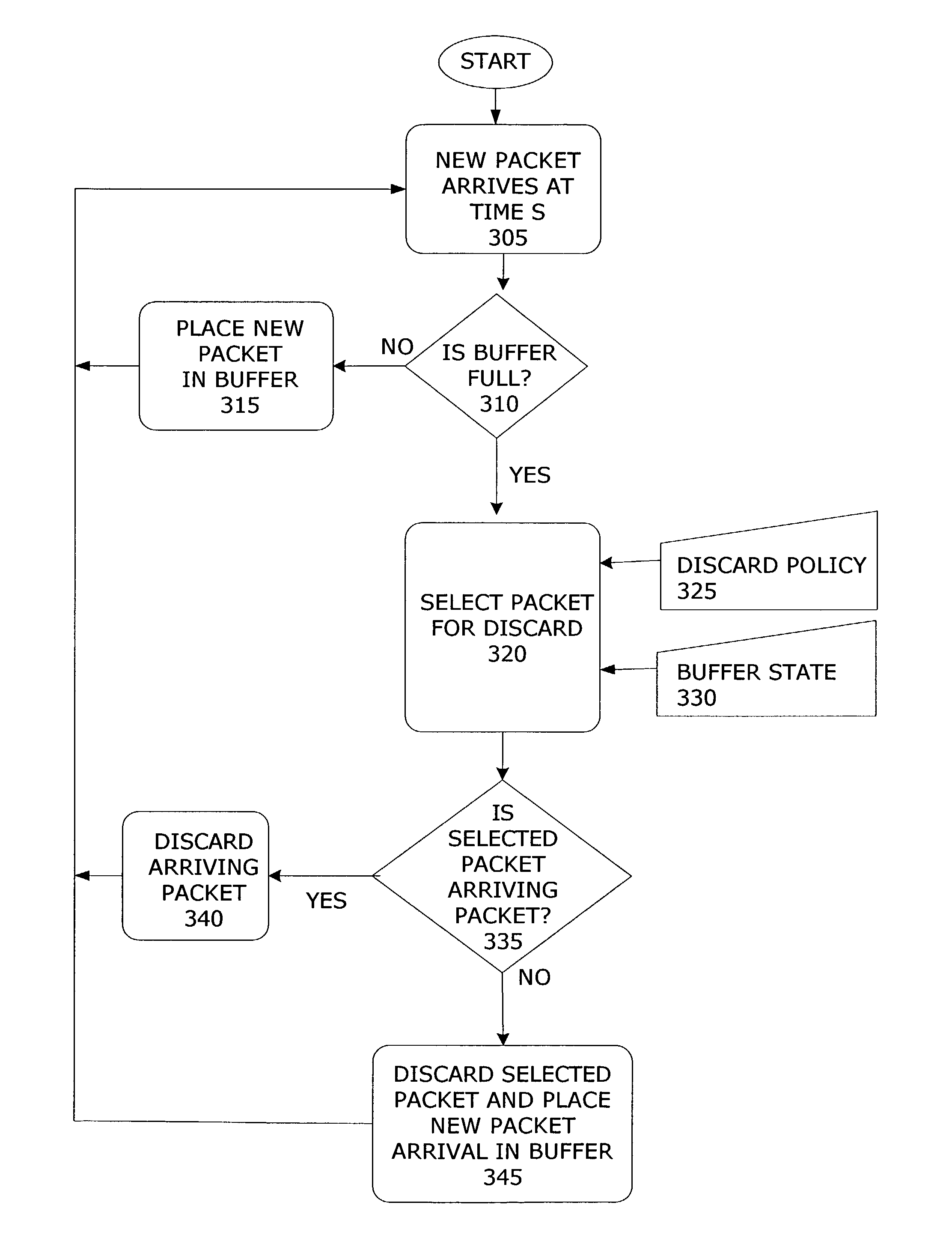
Selective packet discard apparatus and method
InactiveUS7768919B1Improve fairnessAugments conventional measurement-based loss scheduling schemesError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket lossTimestamp
A selective packet discard mechanism is disclosed for selectively discarding packets at buffers in packet switches in the event of traffic congestion. The mechanism makes use of ordering information contained in data packets, such as forward sequence numbers or timestamps, to estimate the packet loss that traffic flows may have already incurred at upstream packet-switching nodes. This estimated upstream packet loss information is used to make improved packet discard decisions. The mechanism may be applied independently to a plurality of buffers at a plurality of packet switches to form a distributed data traffic management system.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Transferring compression parameters in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050276247A1High data transmission reliabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementData transmissionPacket-switching node
The invention relates to a method for transmitting compression parameters in a mobile communication system, comprising a mobile node, a first and a second packet switching node. In the method the second packet switching node is informed of the entry of the mobile node to an area controlled by the second packet switching node. At least one compression parameter is received from the first packet switching node to the second packet switching node. The second packet switching node informs at least one of the at least one compression parameter to the mobile node by way of layer-3 parameter renegotiation for a logical link connection. The benefits of the invention are related to improved reliability of packet data transmission to and from a mobile node.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Packet switching system, packet switching network and packet switching method
InactiveUS7463633B2To overcome the large delayConstraint is somewhat limitingData switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionIp addressEdge node
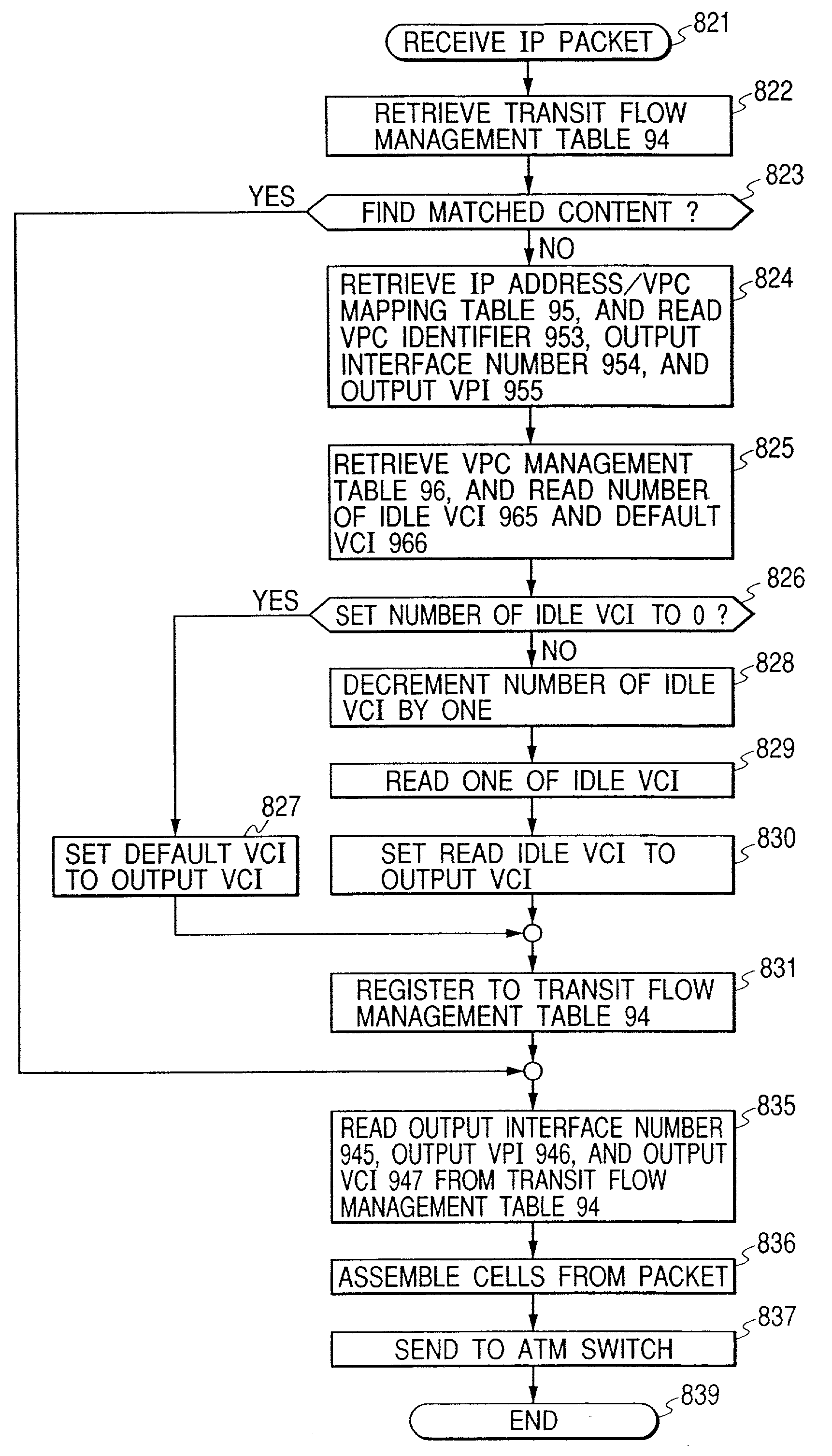
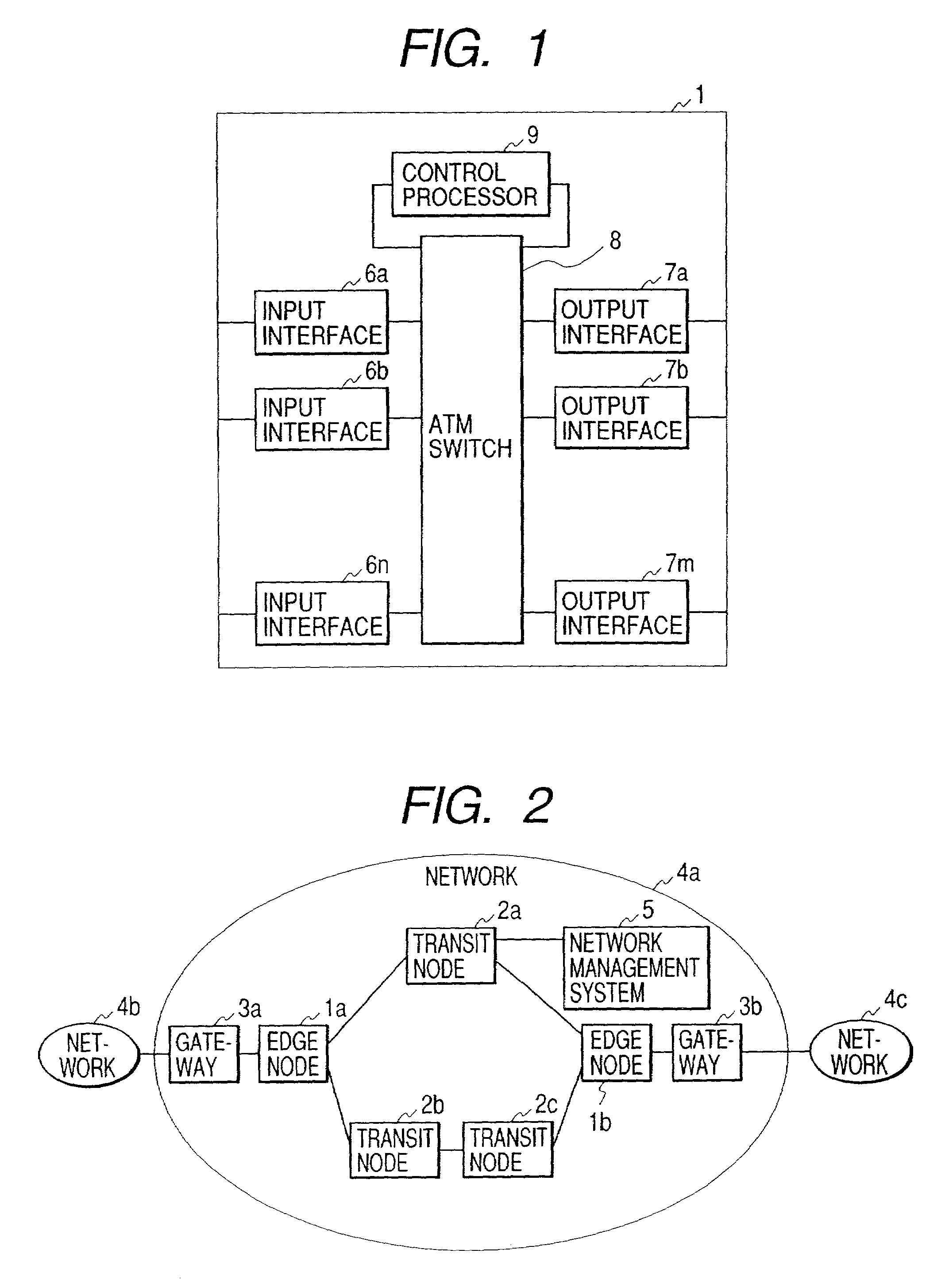
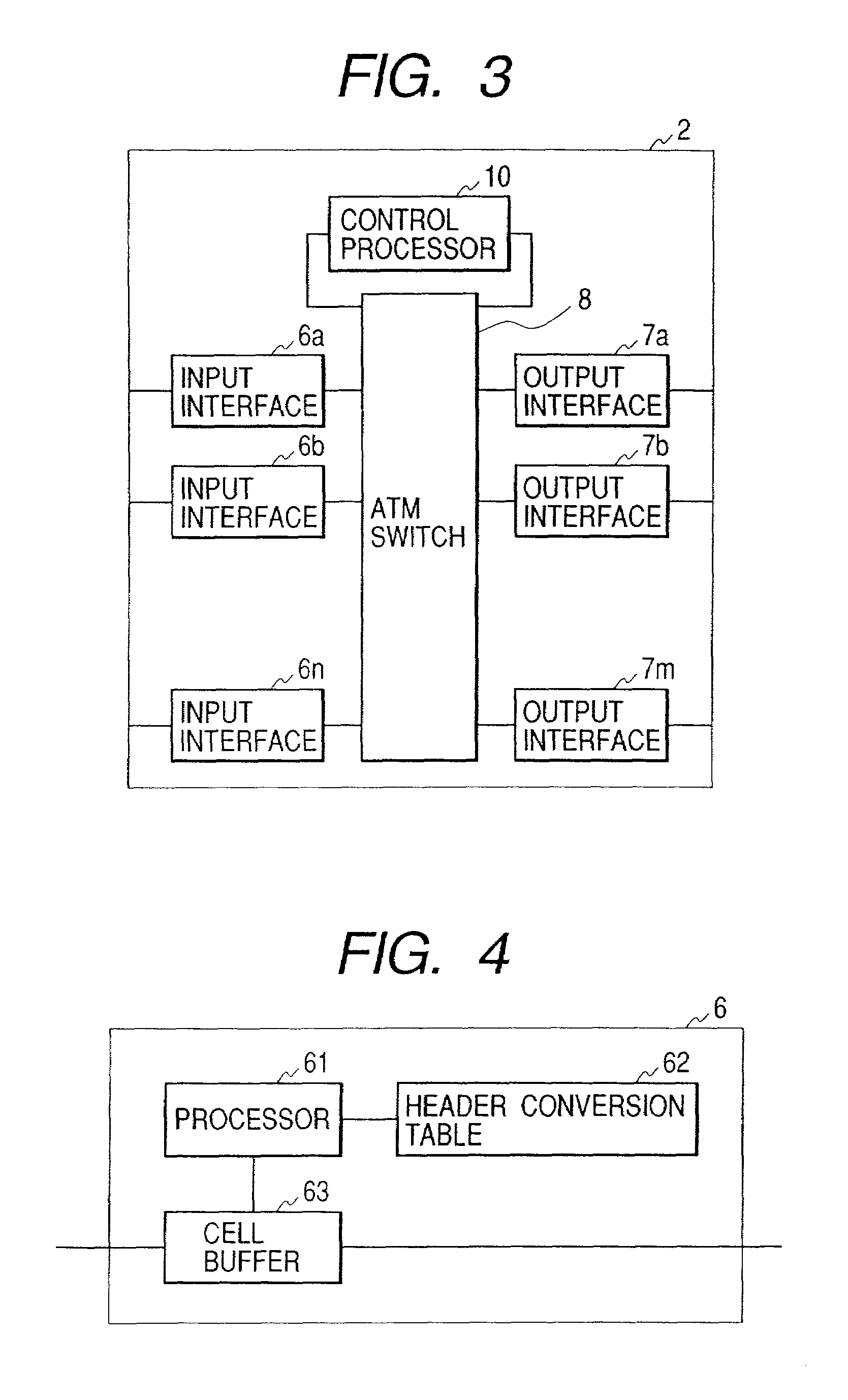
Upon initialization, a VPC is set up between edge nodes. A control processor of each node creates an IP address / VPC mapping table using IP routing information and an address mapping table mapping correspondence between IP addresses and ATM addresses and supplied by a network management system. A gateway assigns a VCC to each packet input to the network. A sending-side edge node inputs the packet to the VPC corresponding to its destination by referring to the IP address / VPC mapping table. A transit node performs packet switching over VP. A receiving-side edge node transfers each packet to the gateway corresponding to its destination. If a series of packets meet a predetermined condition in a given edge node, its control processor sends VCC information to input interfaces of the edge node so that the packets are switched by an ATM switch in the edge node without intervention of the control processor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Combined pipelined classification and address search method and apparatus for switching environments
InactiveUS7760719B2Low implementation costData switching by path configurationPacket-switching nodeReal-time computing
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
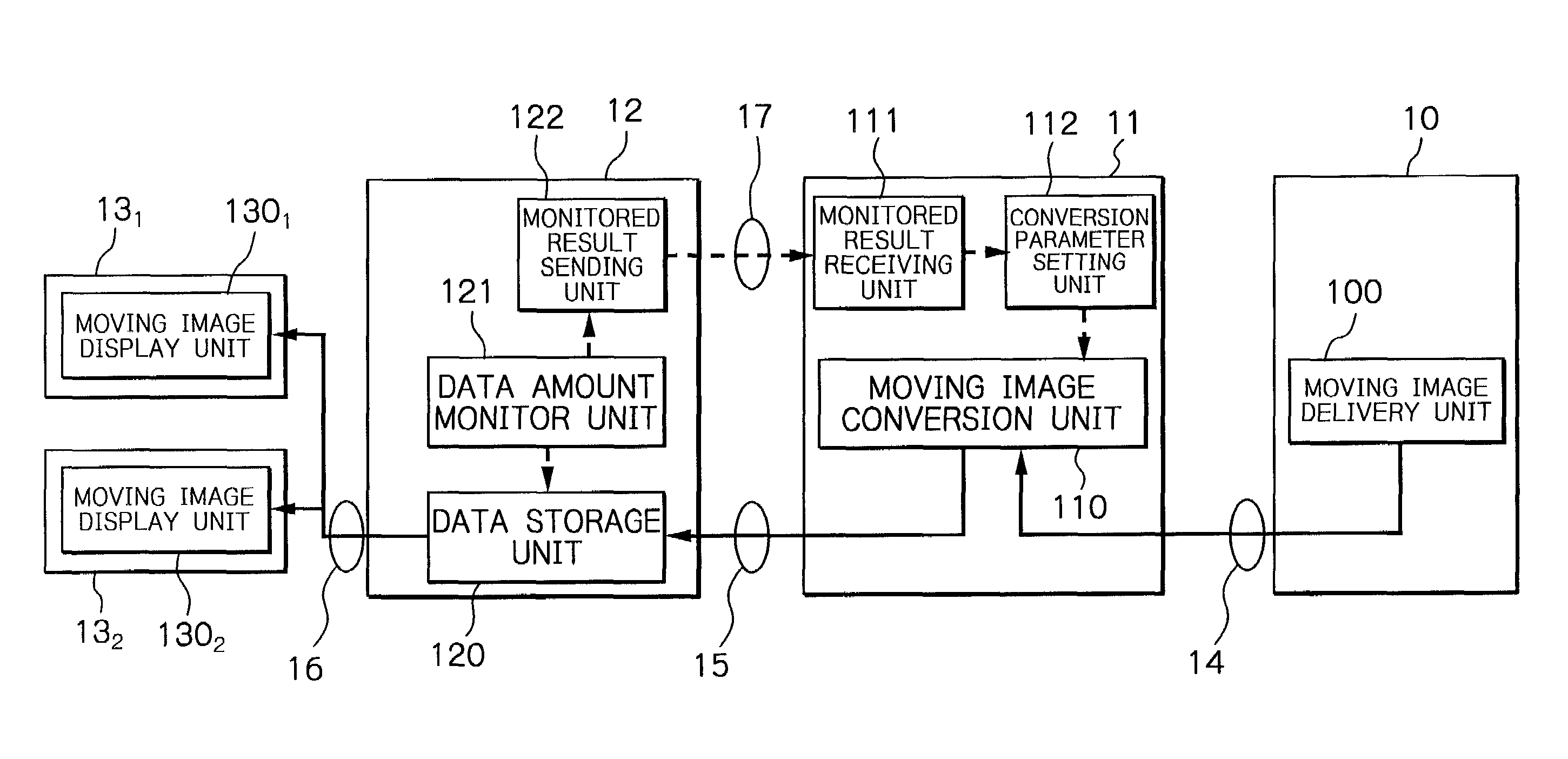
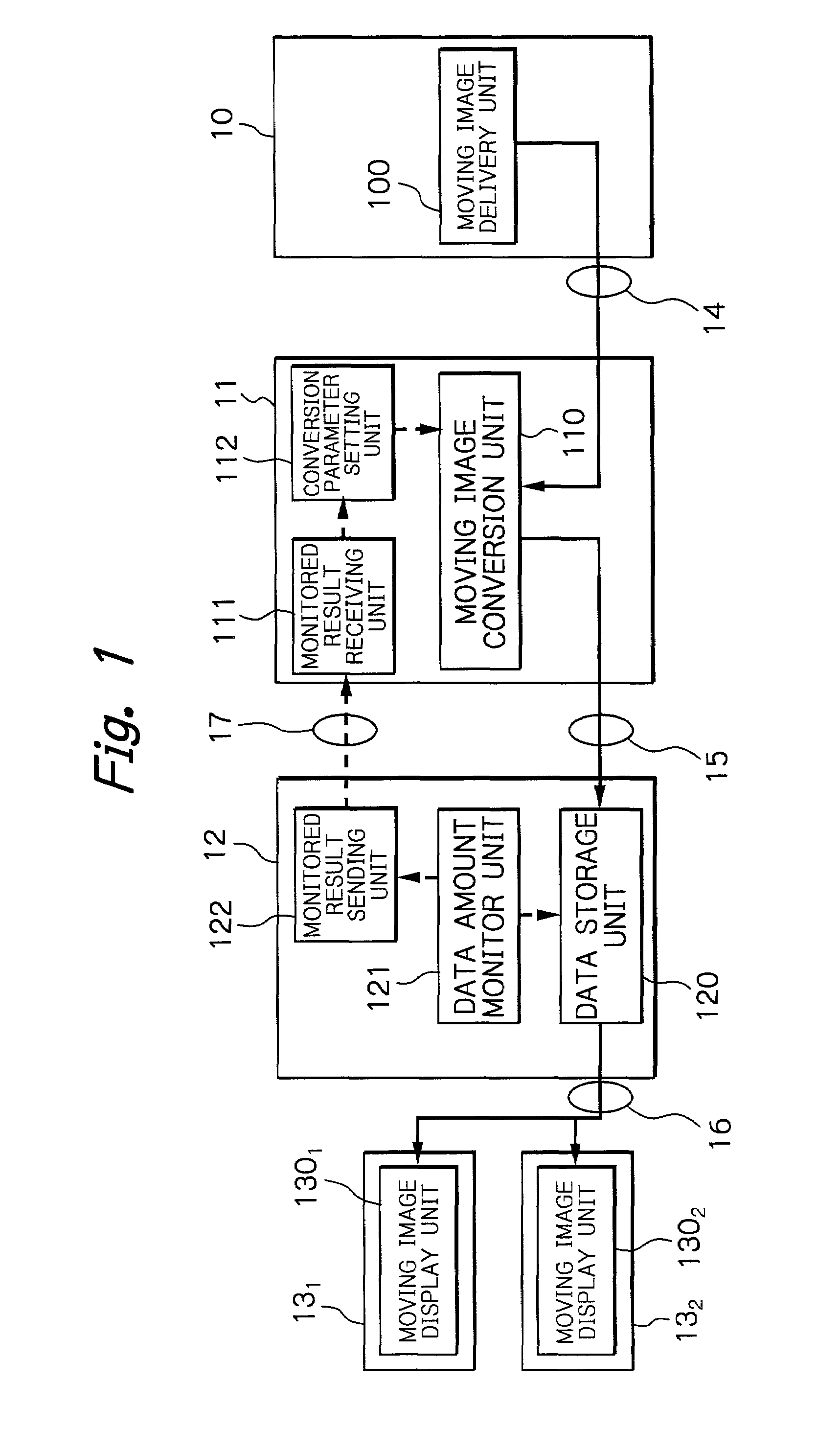
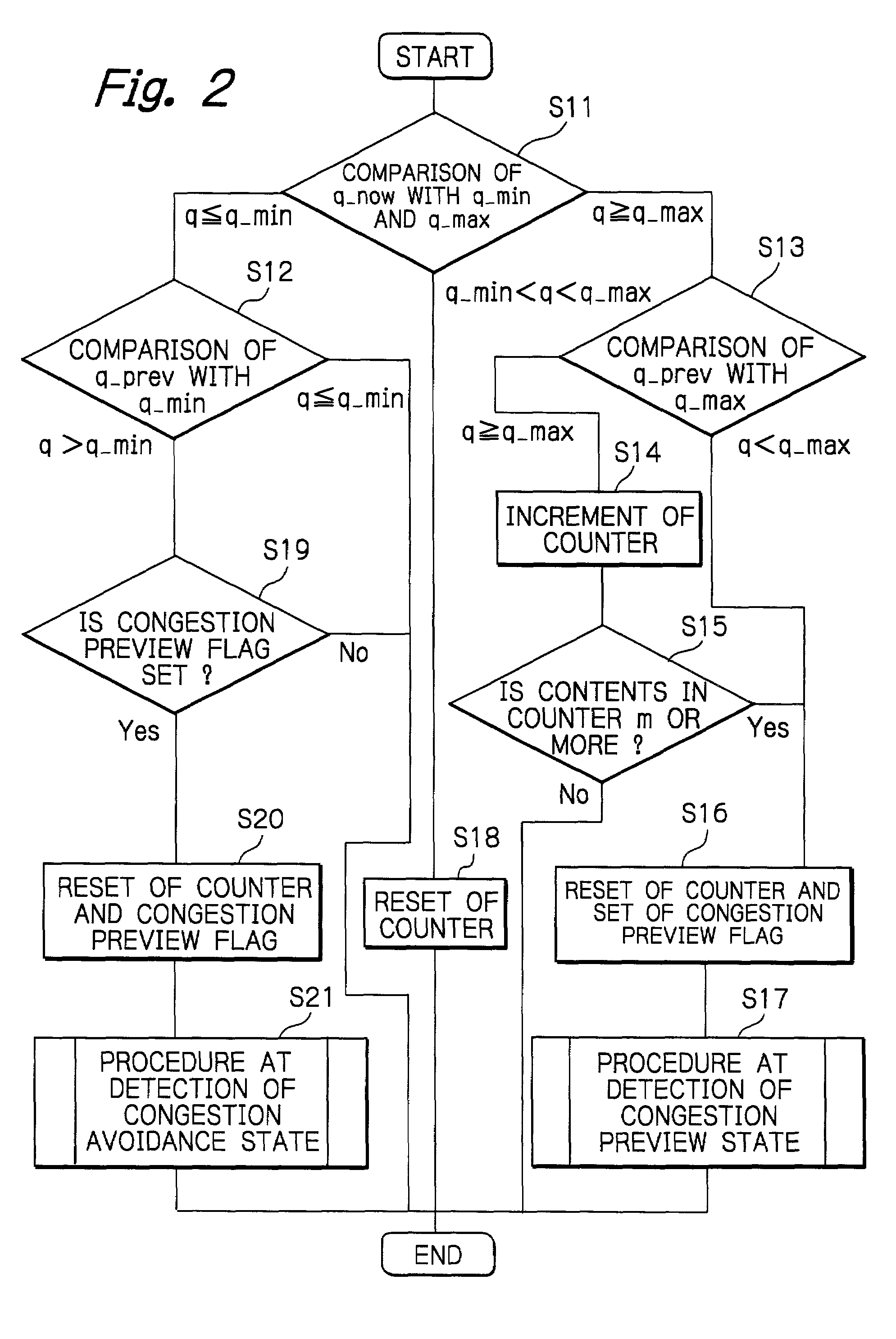
Communication system and method capable of avoiding congestion in moving image data transmission
InactiveUS6992981B2Avoid congestionPulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionCommunications systemImage conversion
A communication system capable of avoiding congestion in transmission of moving image data, includes (1) at least one receiving terminal, (2) a moving image delivery device for delivering moving image data to the at least one receiving terminal, (3) a moving image conversion device which has at least one moving image conversion unit for converting, in accordance with conversion parameters, the moving image data sent from the moving image delivery device, a conversion parameter setting unit for determining the conversion parameters, and a monitored result receiving unit, and (4) at least one packet switching node which has at least one data storage unit for preliminarily storing the moving image data from the moving image conversion device to be sent to the at least one receiving terminal, a data amount monitor unit for monitoring an amount of the moving image data stored in the at least one data storage unit to judge that the monitored data amount reaches a first threshold, and a monitored result sending unit for sending a congestion preview information to the moving image conversion device when the data amount monitor unit judges that the monitored data amount reaches the first threshold. The monitored result receiving unit receives the congestion preview information from the monitored result sending unit, and the conversion parameter setting unit determines the conversion parameters so that the moving image conversion unit converts the moving image data sent from the moving image delivery device into a moving image data with a smaller coding bit rate.
Owner:KDDI R&D LAB INC
Telecommunications routing
InactiveUS7242678B2Prevent unwanted routing loopsTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork addressingNetwork address
Routing of packets is controlled in a communications network including an infrastructure of packet switching nodes interconnected by packet transport links, and a plurality of access nodes to which a routing path, defined by data held in packet switching nodes located along the routing path, may be directed in the infrastructure for a given network address.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Ethernet switching method and device incorporating circuit switching and packet switching
ActiveCN101212424AImprove reuse rateIncrease profitHybrid switching systemsData switching by path configurationPacket-switching nodeTime division switching
The invention relates to a method for switching an Ethernet integrating circuit switching and packet switching, wherein an output slot of an output-port part of the Ethernet is divided according to unit transmission time of a fixed-length Ethernet frame and each output slot is flexibly appointed to participate the packet switching or a time division switching; after the input-port part of the Ethernet receives the fixed-length Ethernet frame, corresponding list items forwarded according to L2 / L3 of a switching unit is to switch the participate time division switching fixed-length Ethernet frame to the appointed slot of the appointed Ethernet port or to switch the participate packet switch ,the output-port part of the Ethernet port sends the fixed-length Ethernet frame according to serial number of the output slot under coordination of synchronization information. And a corresponding Ethernet switching device (500) consists of a switching unit (510), a forwarding table (520), at least two Ethernet ports (530) which are time-division multiplexed according to the unit transmission time of the fixed-length Entherent and a synchronization unit (540) used for keeping network synchronization.
Owner:北京紫光通信科技集团有限公司
Quick retransmission technique based on packet switching network
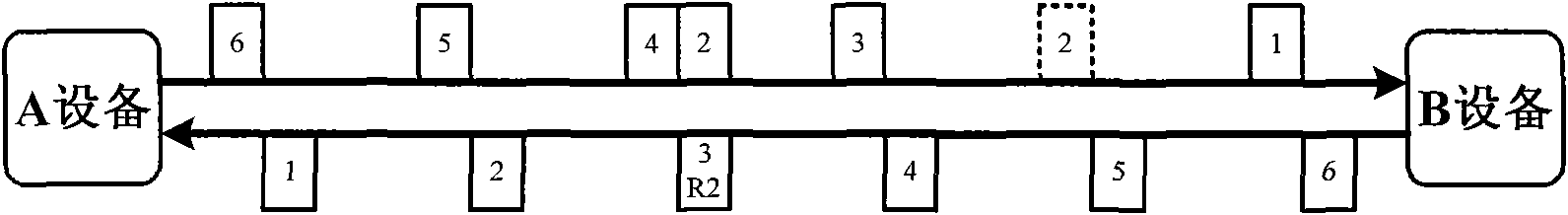
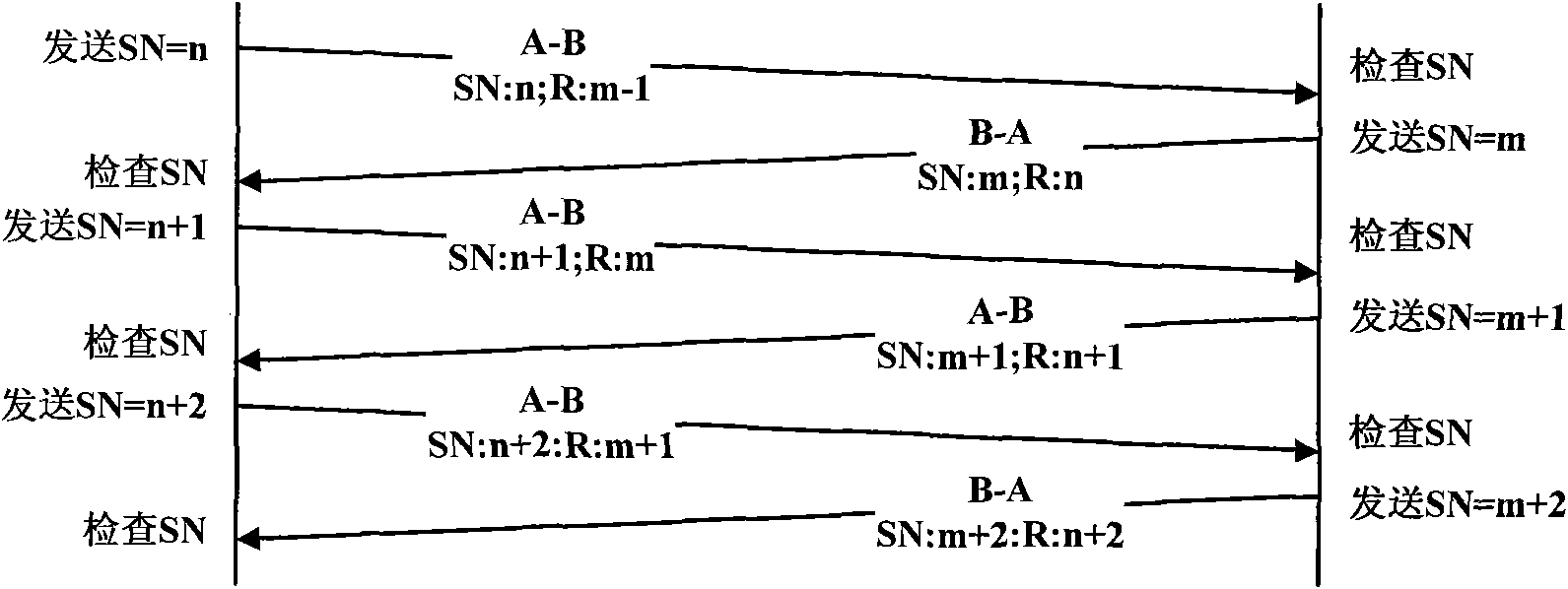
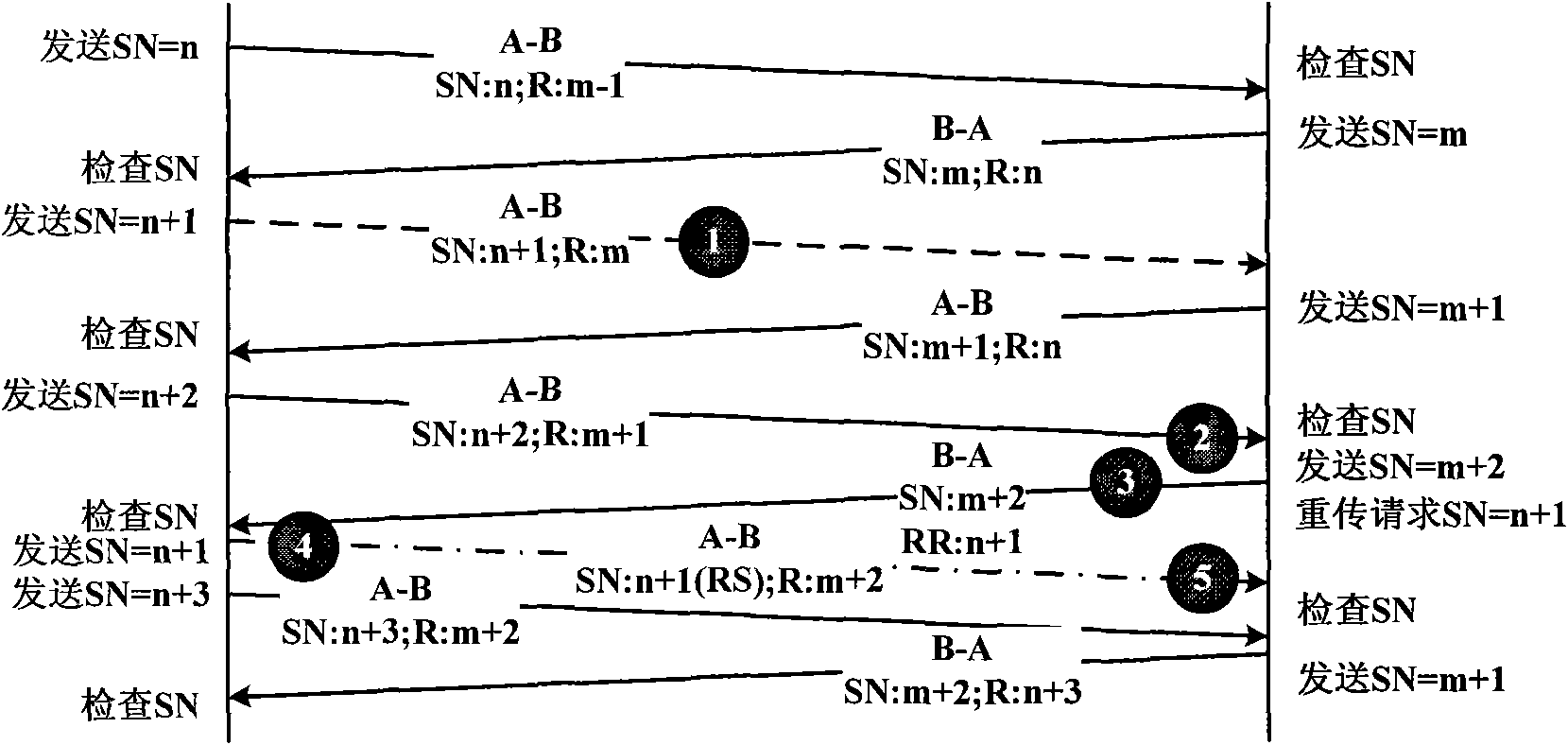
ActiveCN101588225AIntegrity guaranteedFast transmissionError prevention/detection by using return channelData transmissionPacket-switching node
This invention belongs to the technical field of network communication, in particular to a quick retransmission technique based on packet switching network, mainly comprising steps as follows: 1) sticking a serial number on each data packet during data packet transmission, and ensuring that serial numbers of data packets transmitted to the same user are continuous; 2) requiring for continuous serial numbers and field for confirming reception serial numbers while transmitting data packets; 3) checking continuous serial numbers in the transmitted data packets and checking continuity of serial numbers on reception side, thereby judging whether there is lost data packet, if so, transmitting a data packet retransmission request using the field for confirming reception serial numbers; 3) adopting original serial number and mark of retransmitted data by the retransmitted data packet. Accordingly, this invention saves bandwidth and achieves high data transmission speed, through which it quickly initiates retransmission to lost data packets in unreliable packet switching network, thereby achieving reliable transmission of data packets.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NEW ZAILING TECH CO LTD
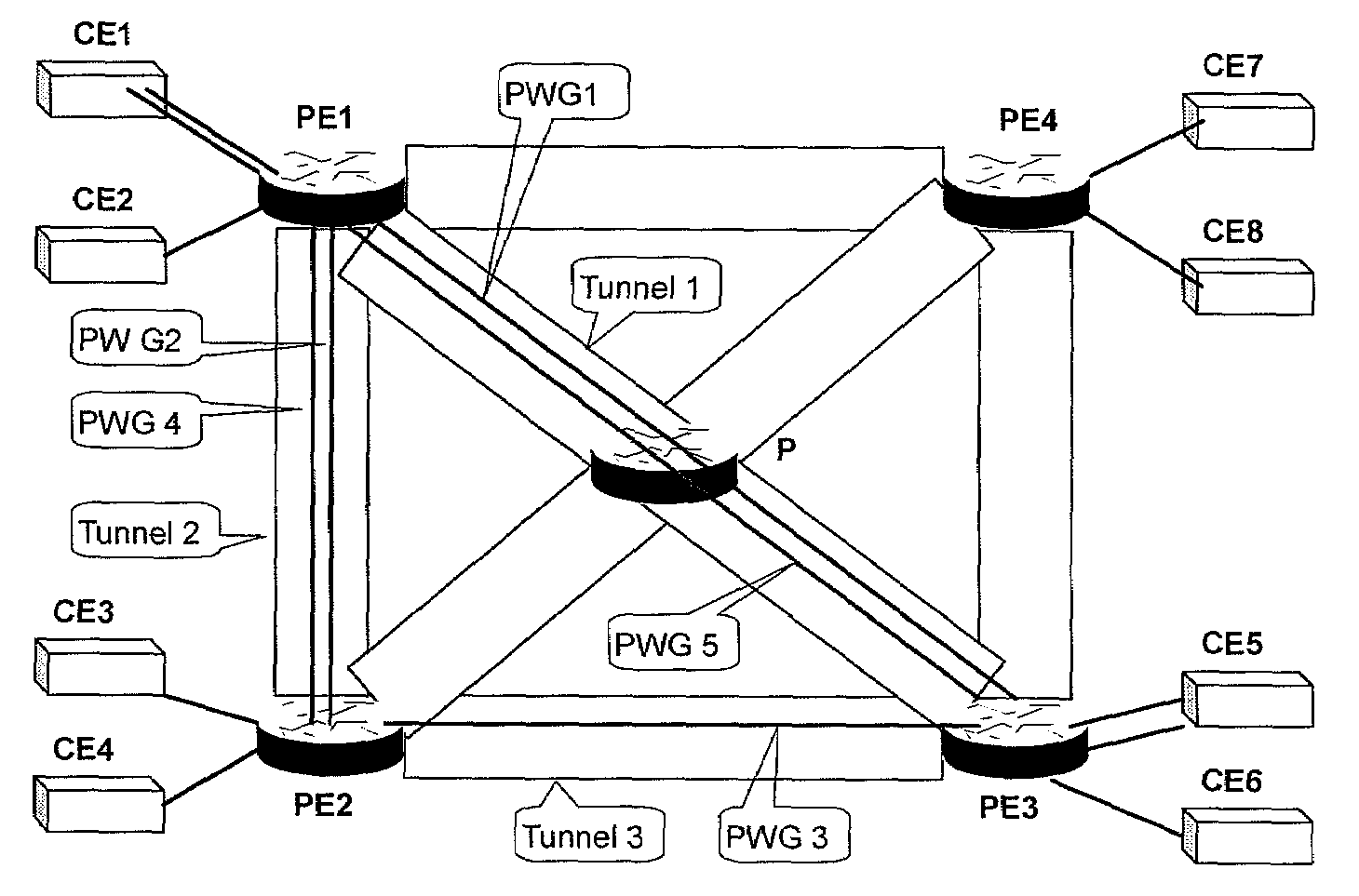
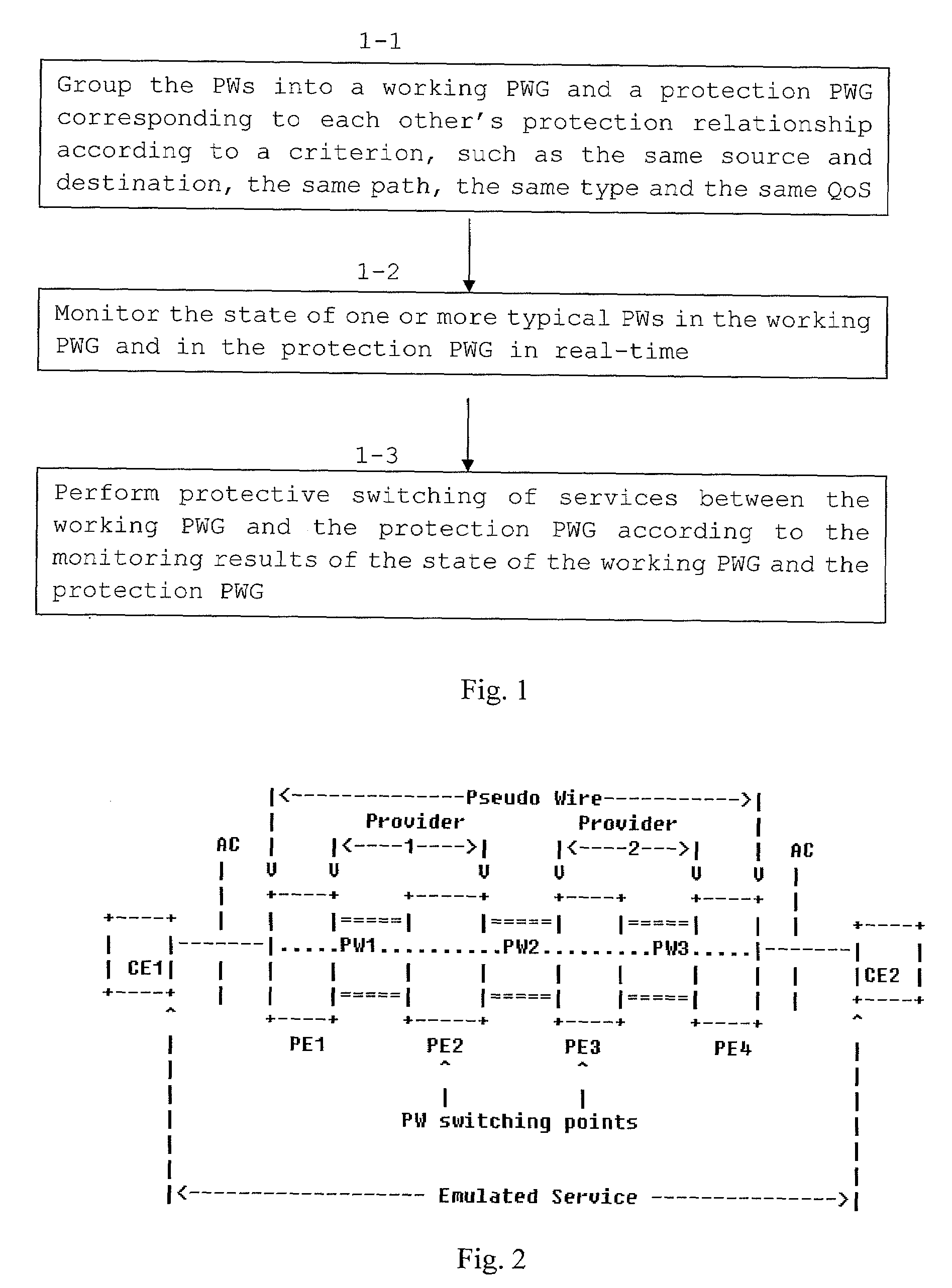
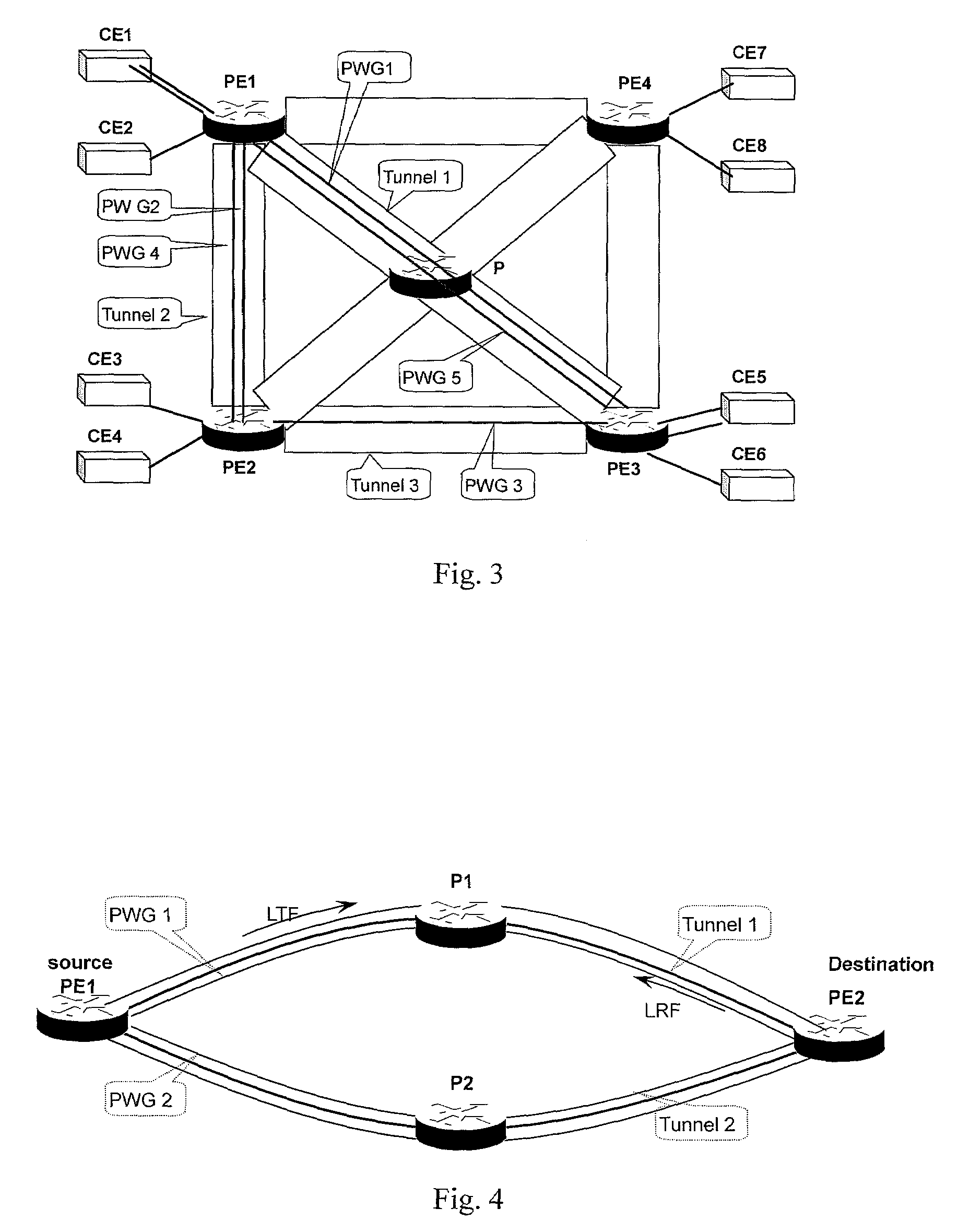
Method and device for protective switching of pseudo-wires on packet switching network
InactiveUS20080175234A1Solve the real problemImprove switching efficiencyData switching by path configurationPacket-switching nodePseudo-wire
The present invention provides a method and device for protective switching of pseudo-wires on a Packet Switching Network. The method includes grouping the pseudo-wires on the Packet Switching Network into a working pseudo-wire group and a protective pseudo-Wire group corresponding to each other's relationship of protection; performing on services the protective switching between the working pseudo-wire group and the protective pseudo-wire group according to the state of the working pseudo-wire group and protective pseudo-wire group. The method of the present invention can be used to perform edge-to-edge grouped protective switching of the pseudo-wires on the Packet Switching Network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
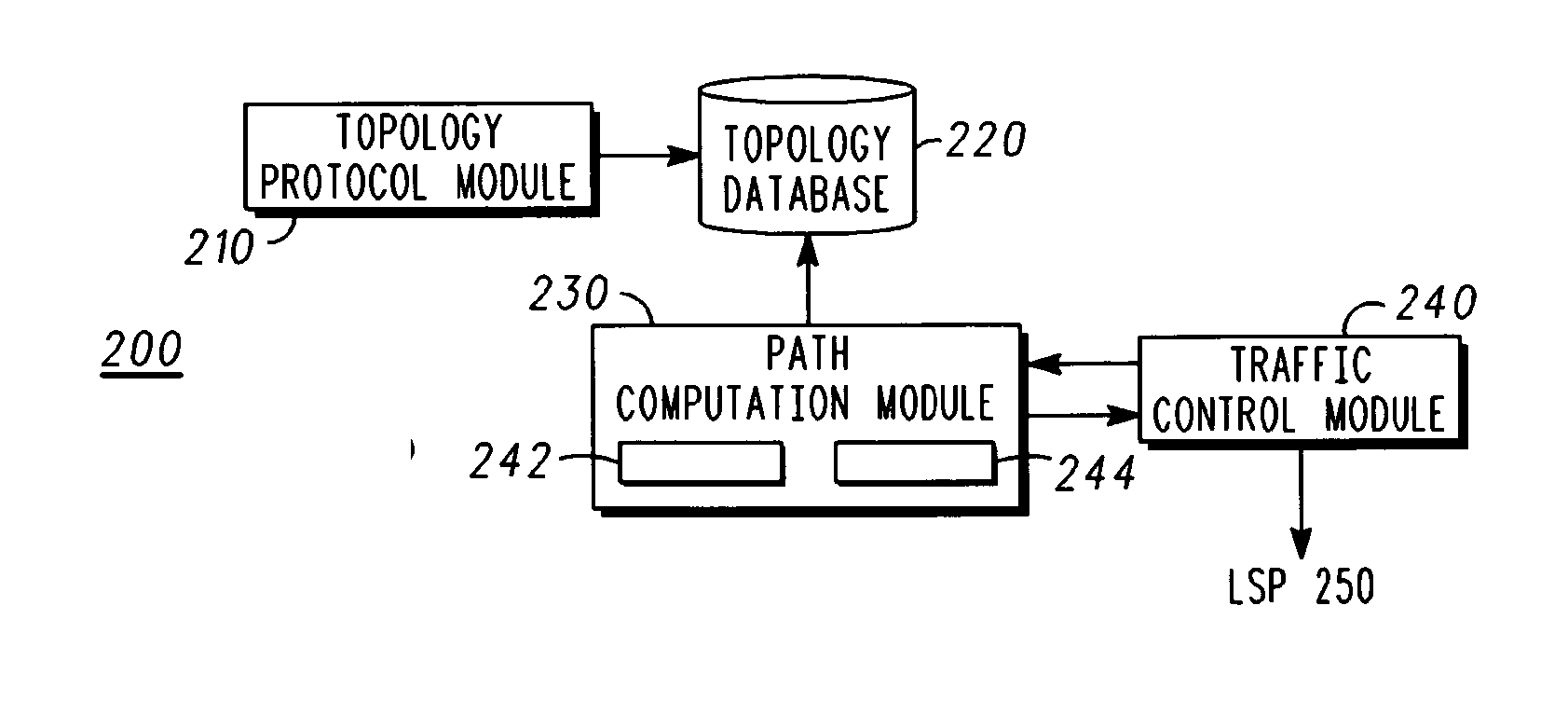
Method and apparatus for generating a degree-constrained minimum spanning tree
A method and apparatus for generating a degree-constrained minimum spanning tree (MST) may include a plurality of point-to-point (P2P) packet switching nodes for receiving and sending data packets; a plurality of point-to-multi-point (P2MP) packet switching nodes for sending and receiving the data packets; and a plurality of transmission links coupling pairs of the plurality of packet switching nodes, where each of the plurality of transmission links has a distance. A path computation module may determine a degree-constrained MST such that each of the plurality of P2P packet switching nodes has a degree of two. An extended Bellman-Ford algorithm successively analyzes each of the plurality of packet switching nodes as a present node and calculates the degree-constrained MST as a function of the distance of each of the plurality of transmission links and whether a previous node from the present node is a P2P packet switching node or a P2MP packet switching node.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Time based packet scheduling and sorting system
Methods and systems for controlling scheduling in a packet switching node in a network are provided which enable the scheduling of packets from different sources in an earliest deadline first order. The packets are assigned timestamp deadlines and placed in input queues. The timestamps are determined according to maximum delay or minimum throughput quality of service requirements specified for the packets. The packets are scheduled in the earliest deadline first order in an output packet store. The packet closest to its timestamp deadline is selected from the output packet store by using an index.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Controlling Traffic in a Packet Switched Communications Network
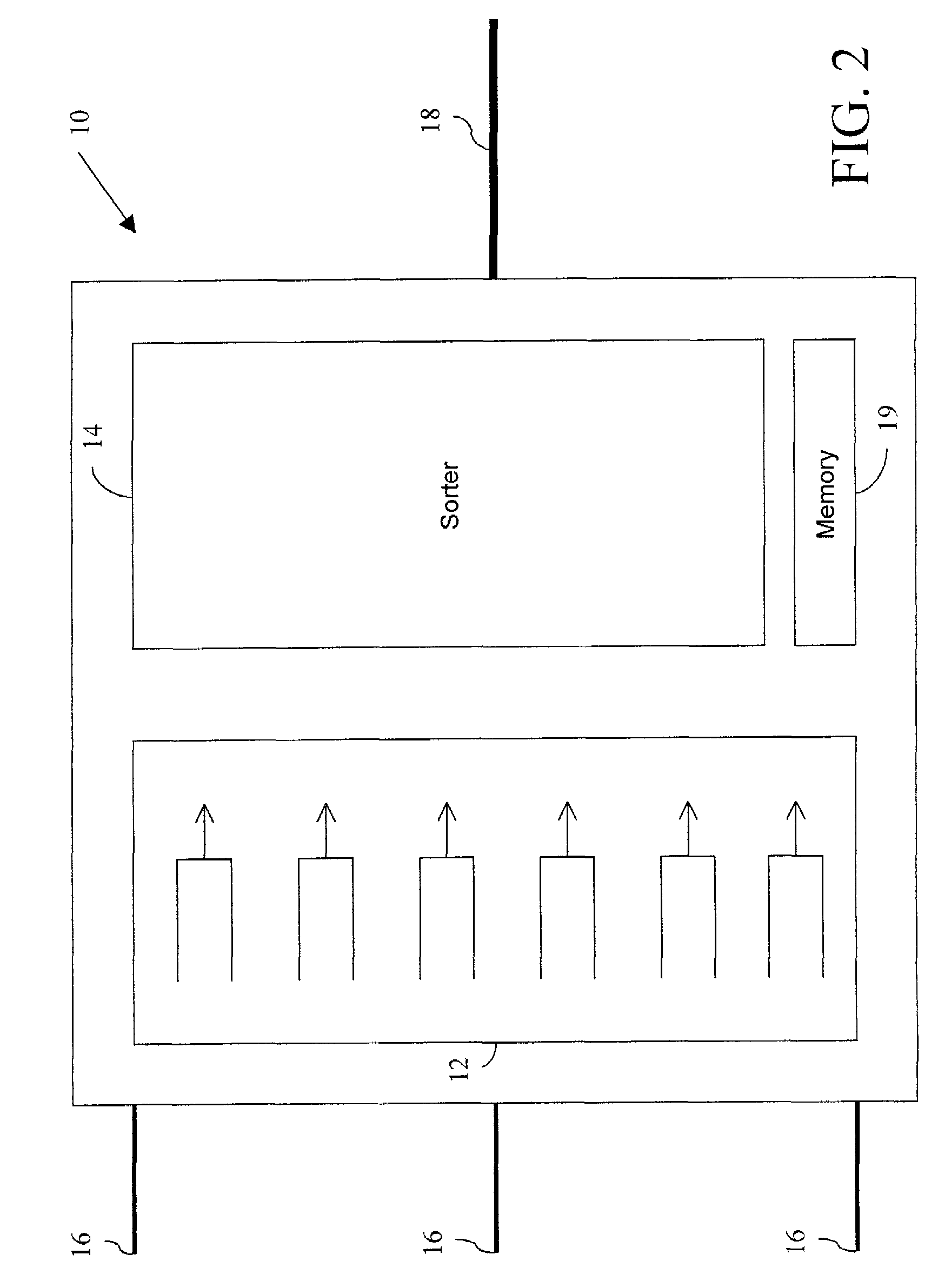
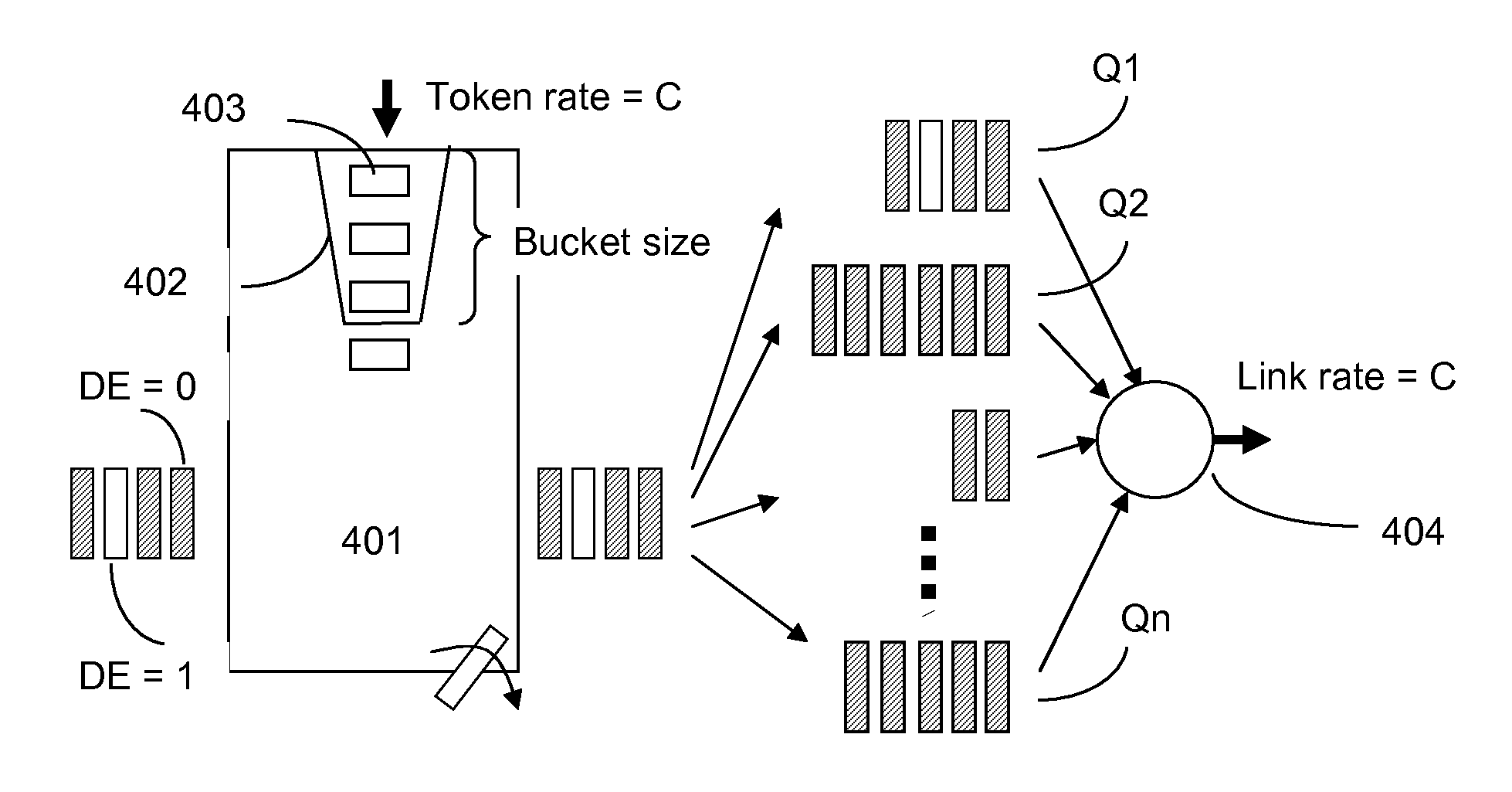
InactiveUS20100195492A1Improve overall utilizationError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityPacket switched
The present invention relates to a packet switched communications network especially to an Ethernet network in which User Network Interfaces (UNI) are standardized between client network (202) and core network (203) with a number of UNI service attributes. In one aspect of the invention a method is used in current packet switched nodes implementing a policer function. The task of the function is to decide whether packets with high drop preference need to be dropped or not due to resource shortage on the given interface. All outgoing packets at a given port will undergo this policer (401) irrespective of the source, destination, identification codes or traffic class. Policer (401) drops packets with high drop preference in one traffic class before a packet of low drop preference is dropped in any other traffic class, and drops packets with high drop preference before a packet of low drop preference is dropped in the same queue. In the course of dropping packets, policer (401) prevents the reordering of packets with low drop preference and packets with high drop preference within the same flow.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
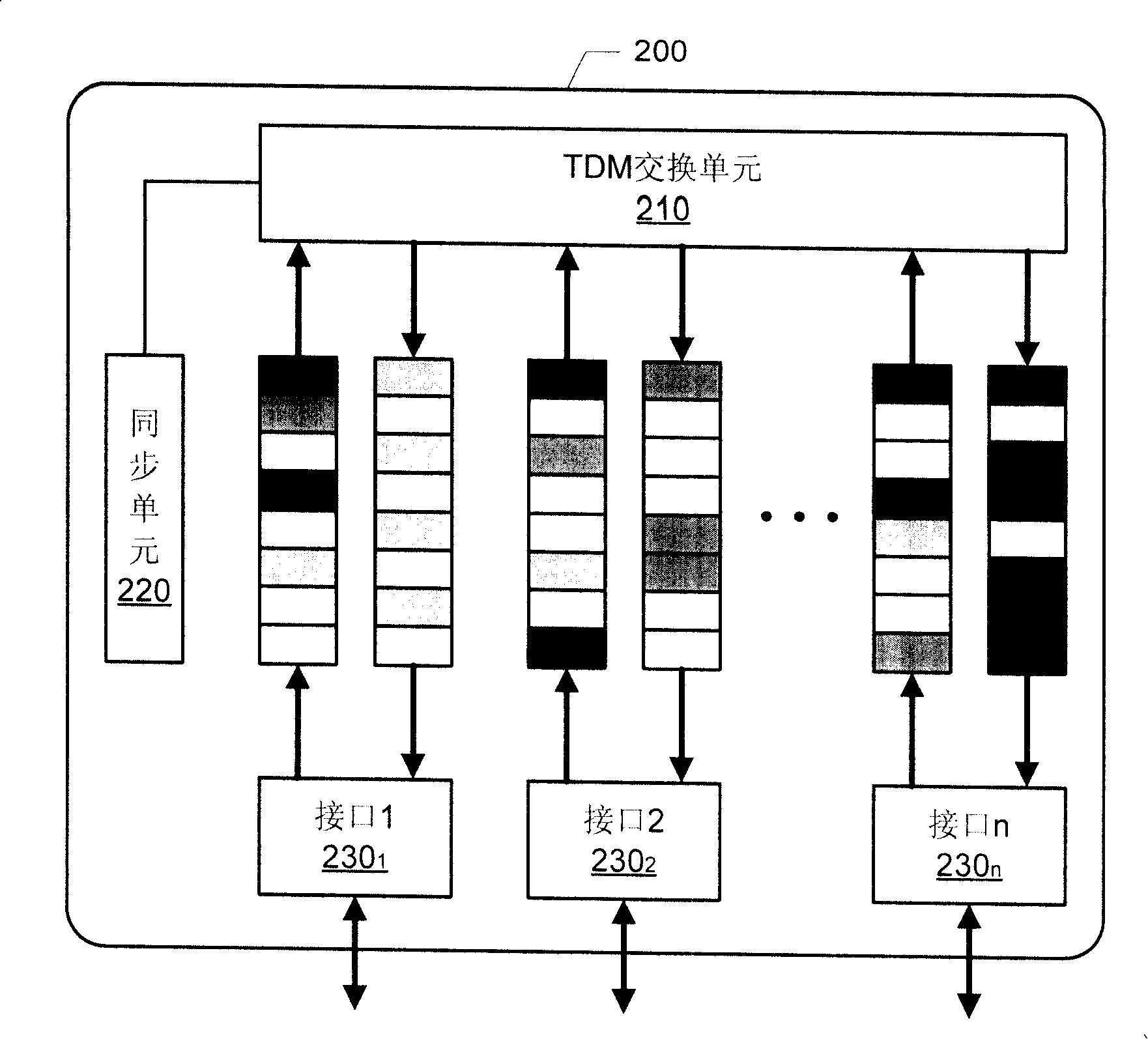
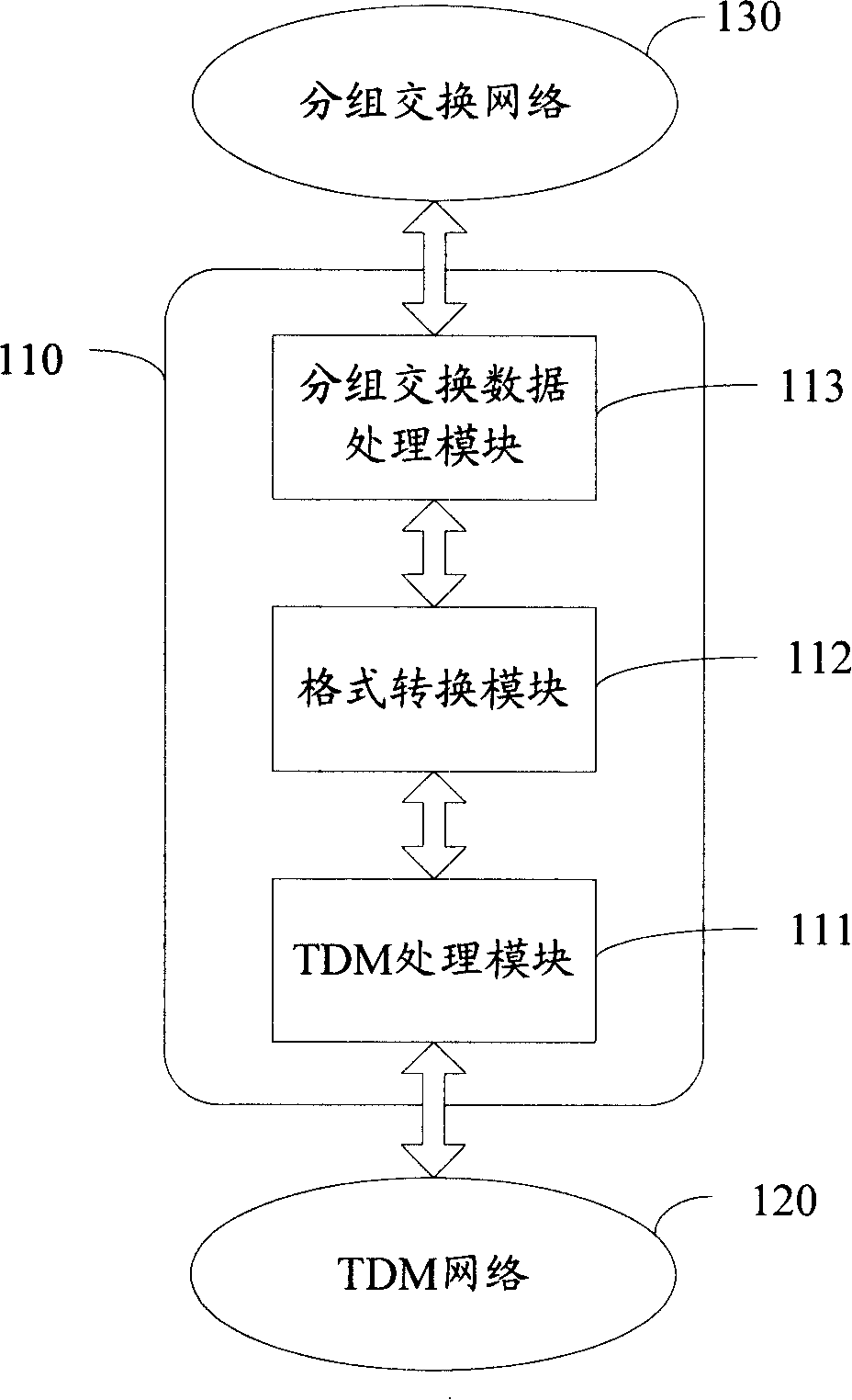
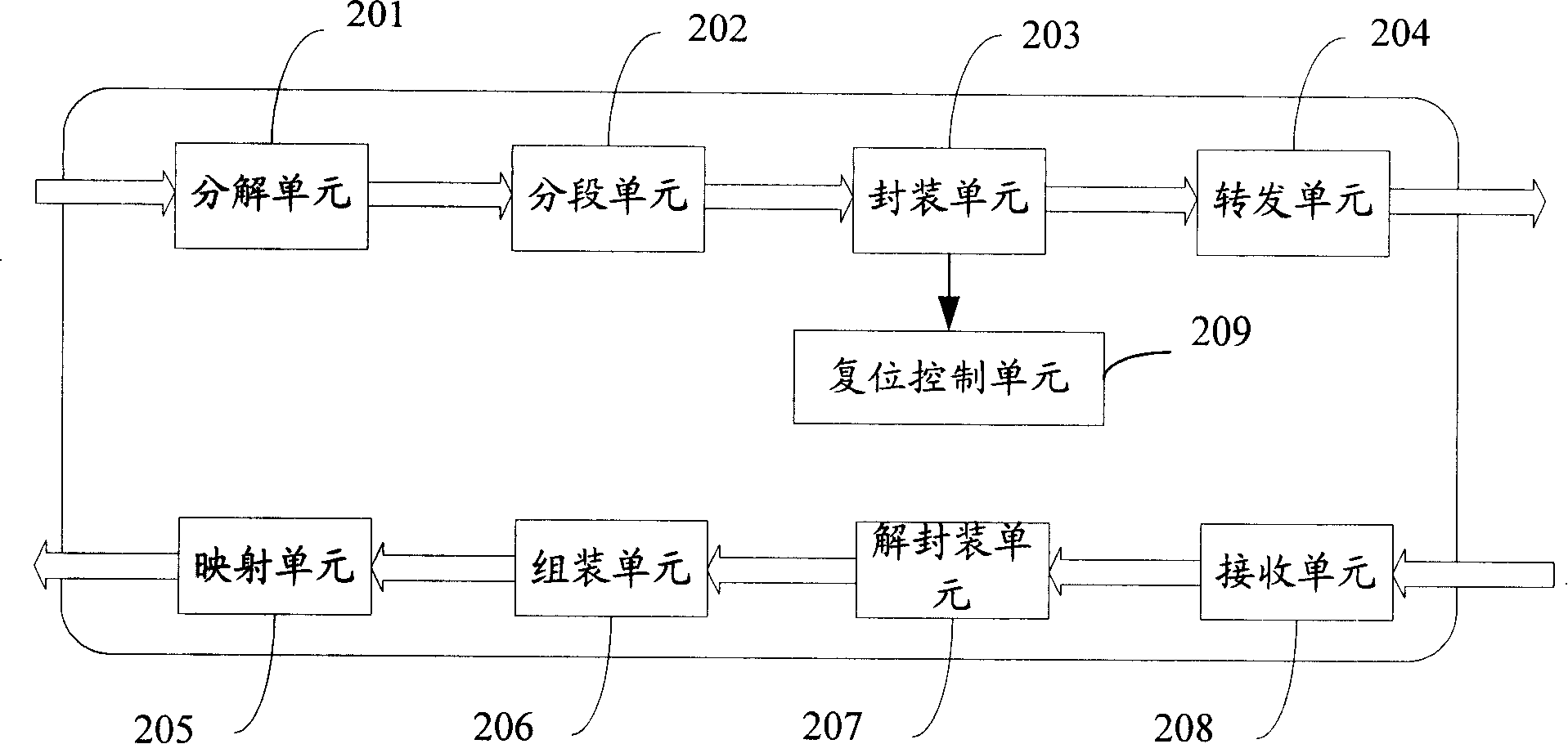
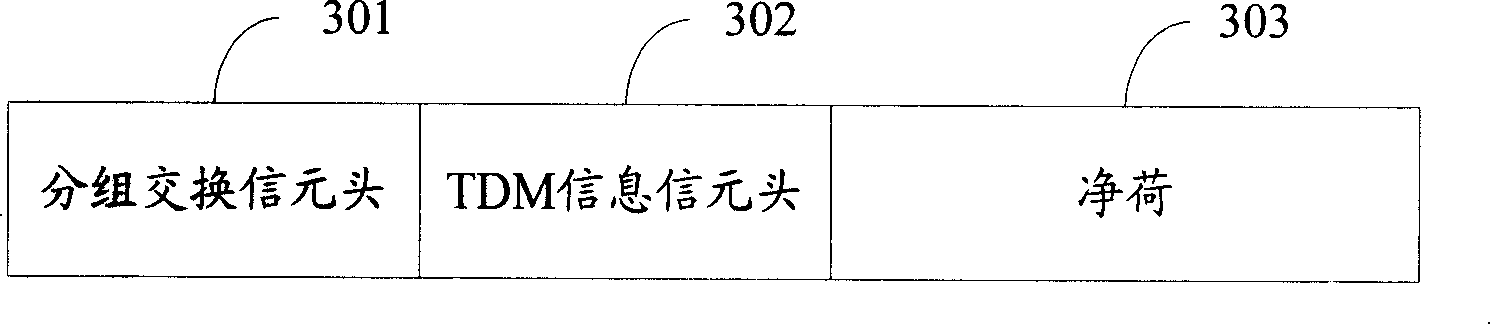
A TDM operation transmission method, device and system by packet switching network
ActiveCN101217452ATo achieve the effect of transmissionRealize dual-network integrationNetworks interconnectionTime-division multiplexing usagePacket-switching nodeReal-time computing
The invention discloses a method for TDM business of packet switching network transmission, comprising the following steps: A. analyzing TDM data frame and extracting the payload and TDM assembling information; B. sealing the payload and the TDM assembling information in the packet switching data packet and sending the information to the packet switching network to be transmitted. The invention also discloses a device and a system which are used for realizing TDM business of packet switching network transmission. The invention can combine the TDM network and the packet switching network together so as to transmit the TDM business through the packet switching network.
Owner:泰州市海通资产管理有限公司
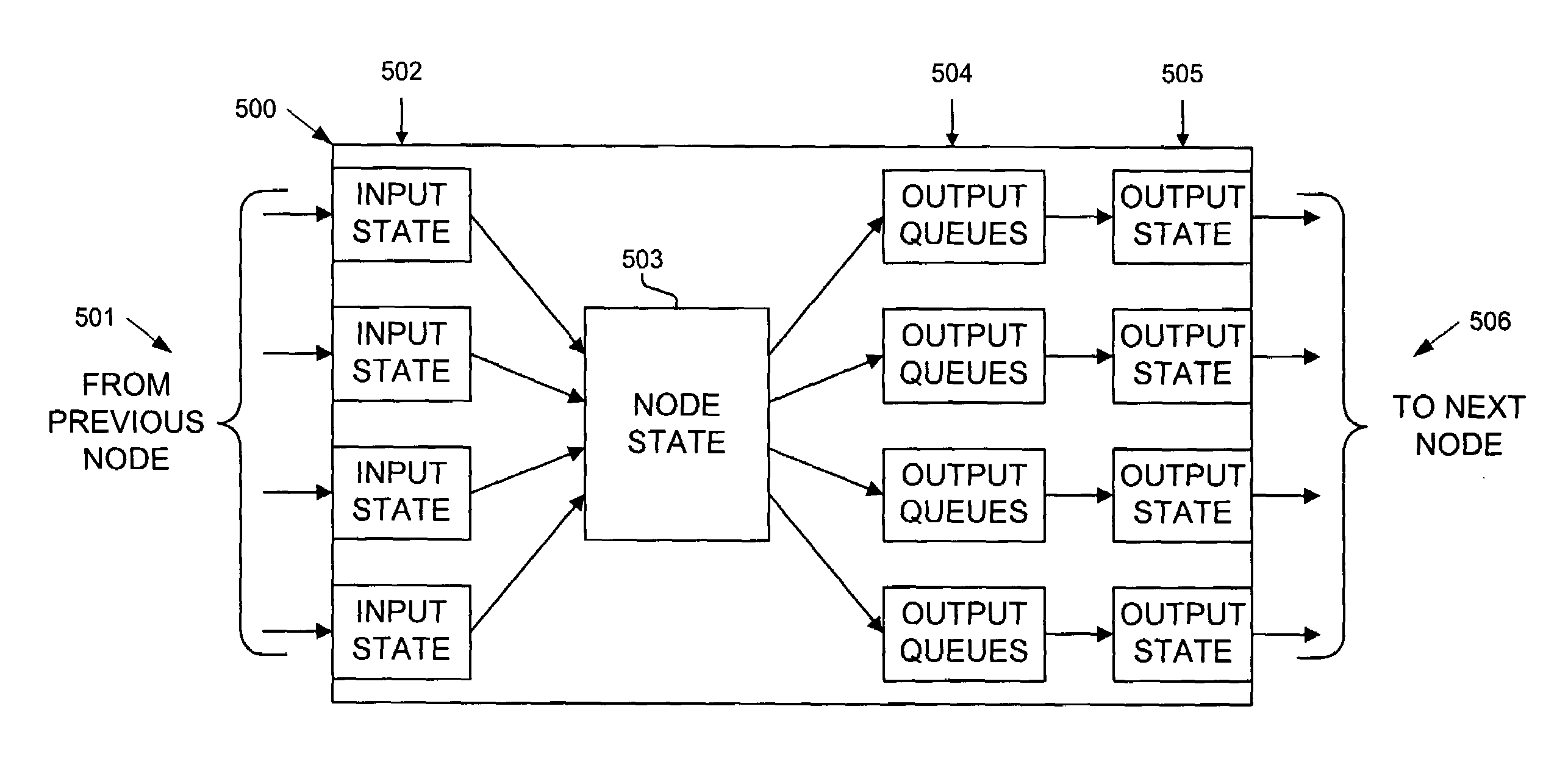
Method and apparatus for accumulating and distributing traffic and flow control information in a packet switching system
Traffic information is accumulated and flow control information distributed in a packet switching system. Traffic information is collected in multiple elements, which forward in a coordinated fashion to collecting elements indications of congestion and other types of information. The collecting elements manipulate the received indications and generate flow control messages which are sent to individual sending components of the packet switching system. In one implementation, a switching element maintains for each destination a count of packets within itself which are addressed to the particular destination. An indication of a portion of this collected information is included in a packet header forwarded from each of the elements each packet time. Each of the elements are assigned a different offset, such that they send an indication of a different portion of their collected information, so a view of the traffic conditions and / or buffer occupancies within a packet switching system is efficiently produced.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Precise compensation of video propagation duration
InactiveUS20110164178A1Television system detailsTime-division multiplexTimestampPacket-switching node
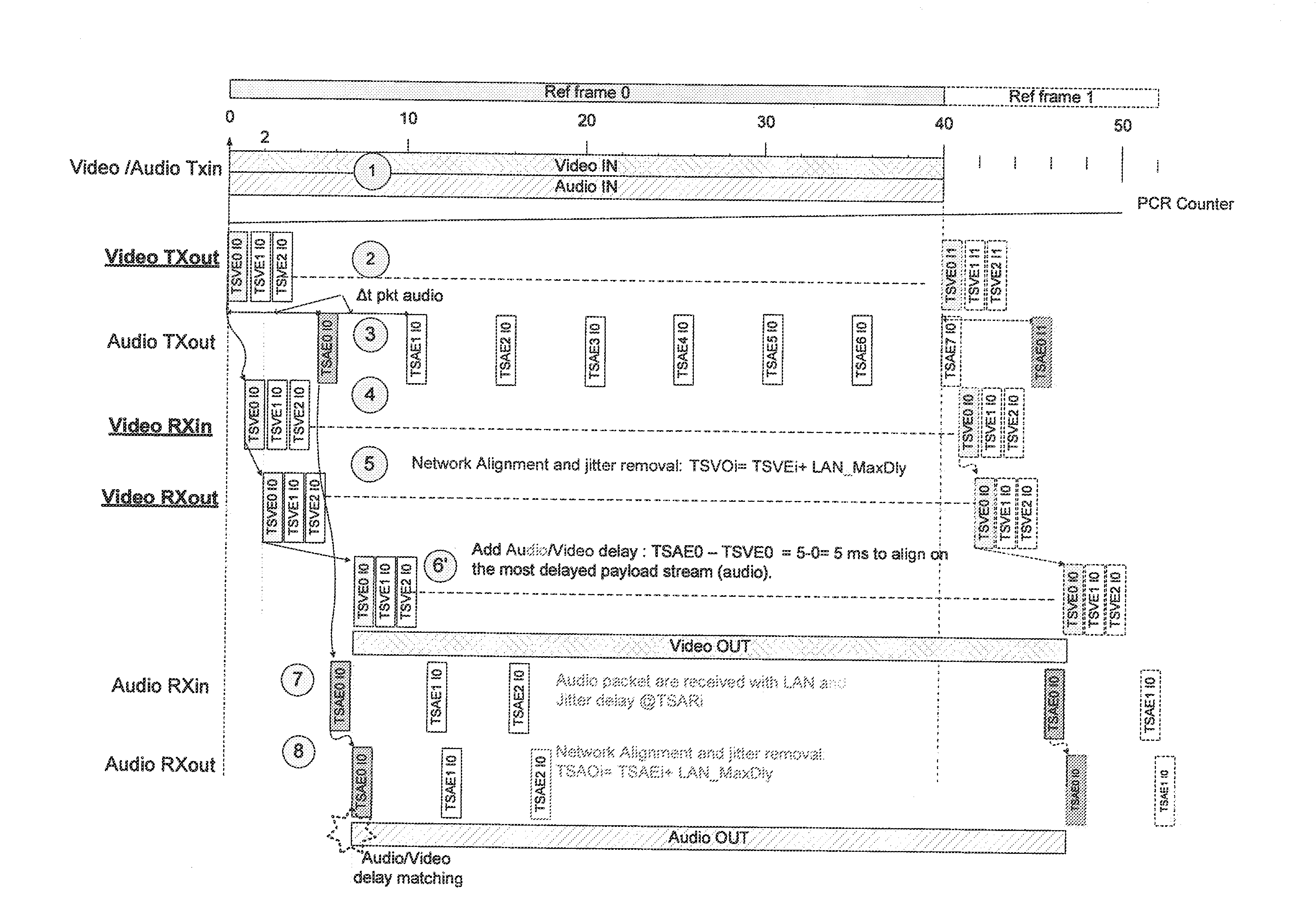
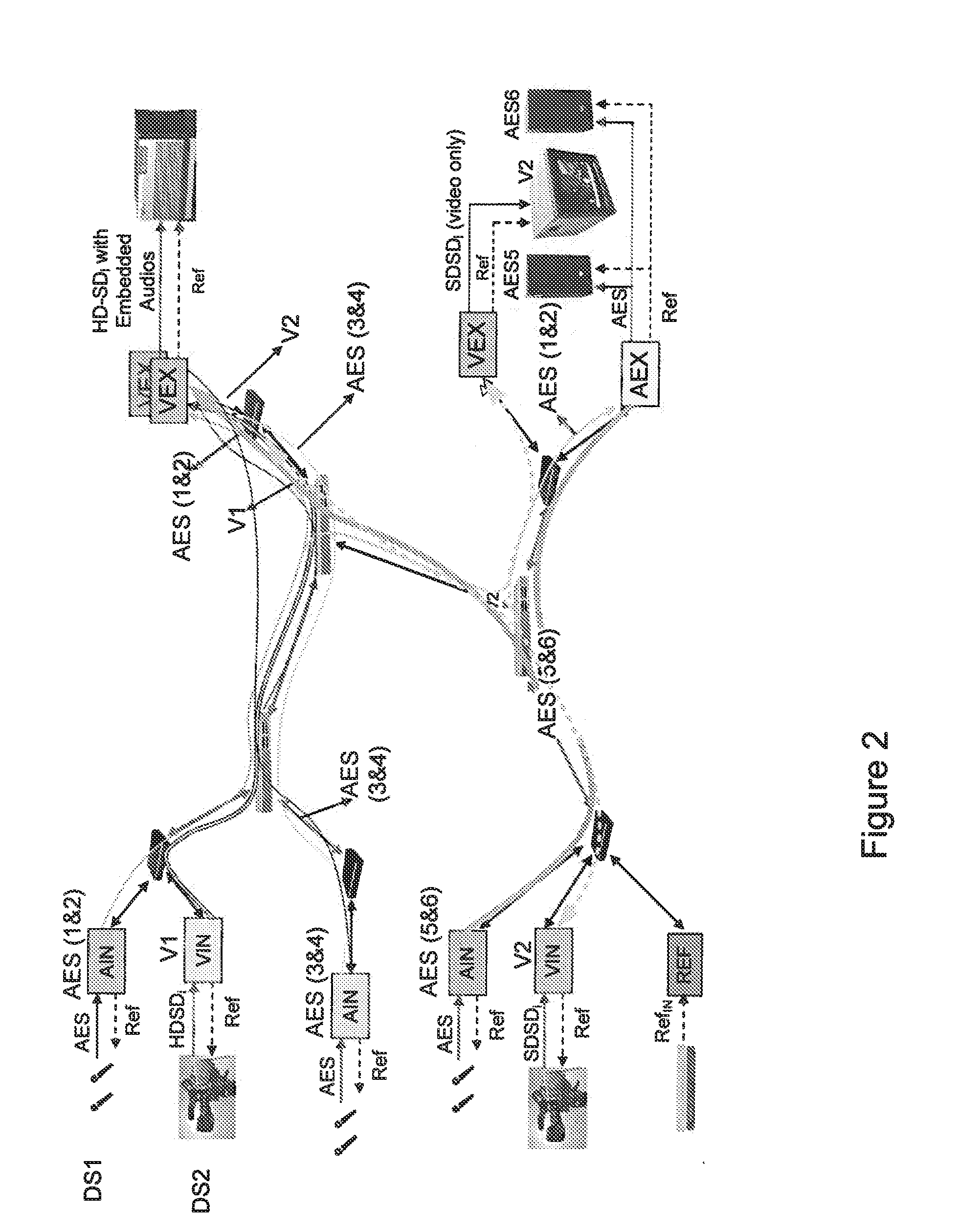
The invention relates to the field of the synchronization of data delivery onto equipments connected over a packet switching network, in particular when the equipments are devoted to video and audio data or Auxiliary data linked to processing and are connected over a local area network for forming a video / audio production studio.More precisely the invention concerns a data inserter device for inserting a timestamp in packets, and a delay compensating device for extracting said timestamp and compensating the delivery delay and in particular the jitter, the network delay and the packet generation duration or any additional user delay.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
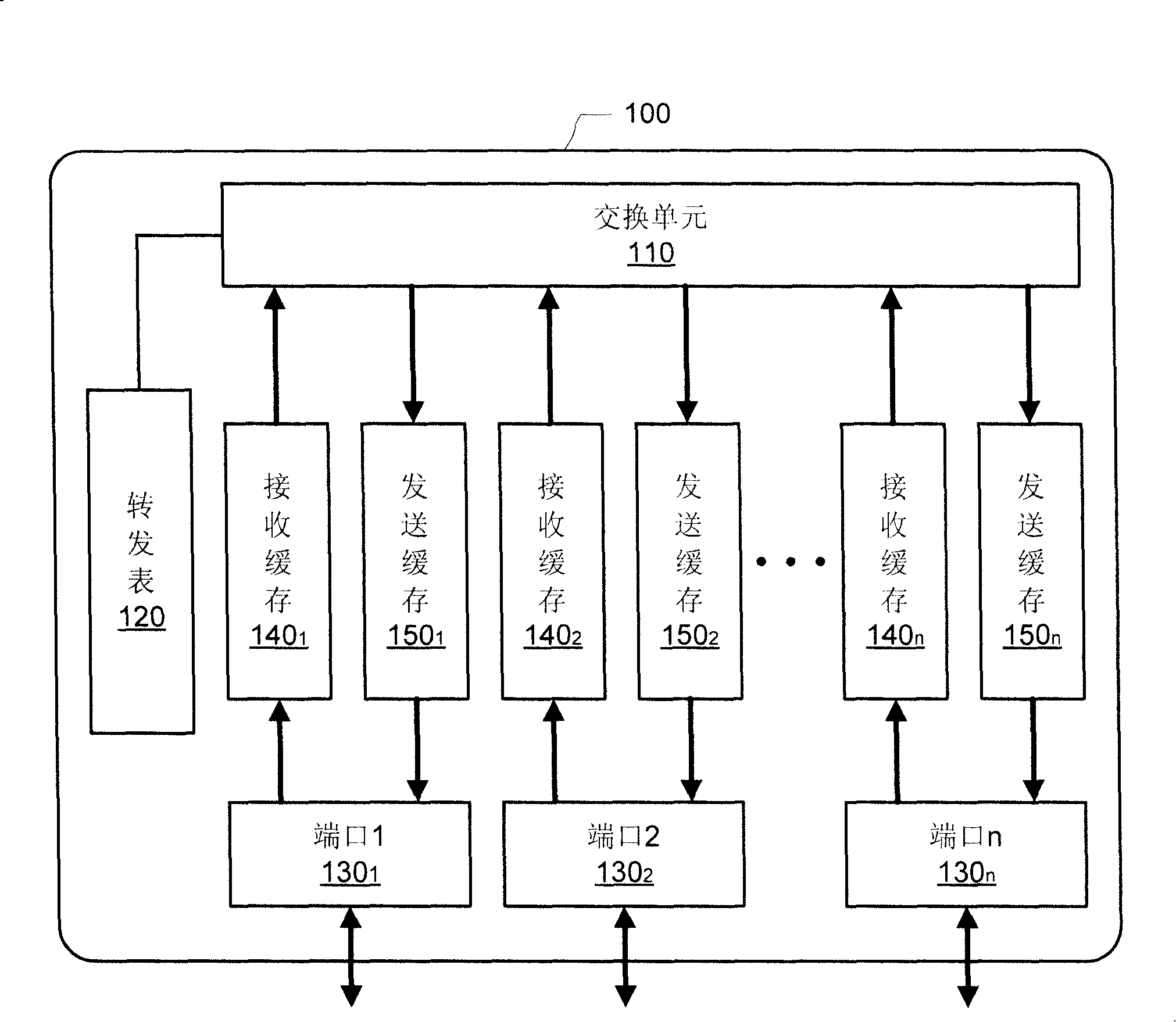
Compact packet switching node storage architecture employing double data rate synchronous dynamic RAM
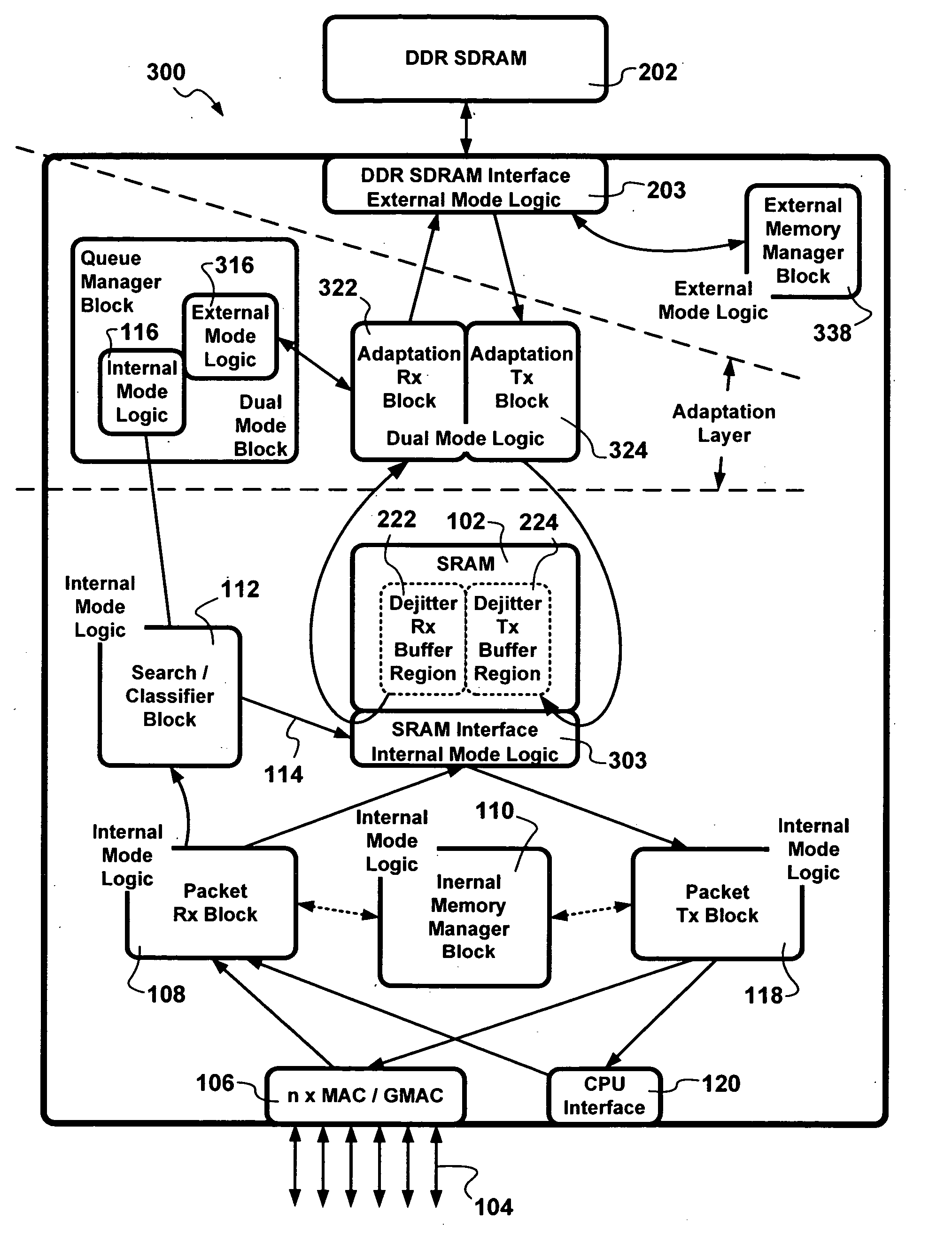
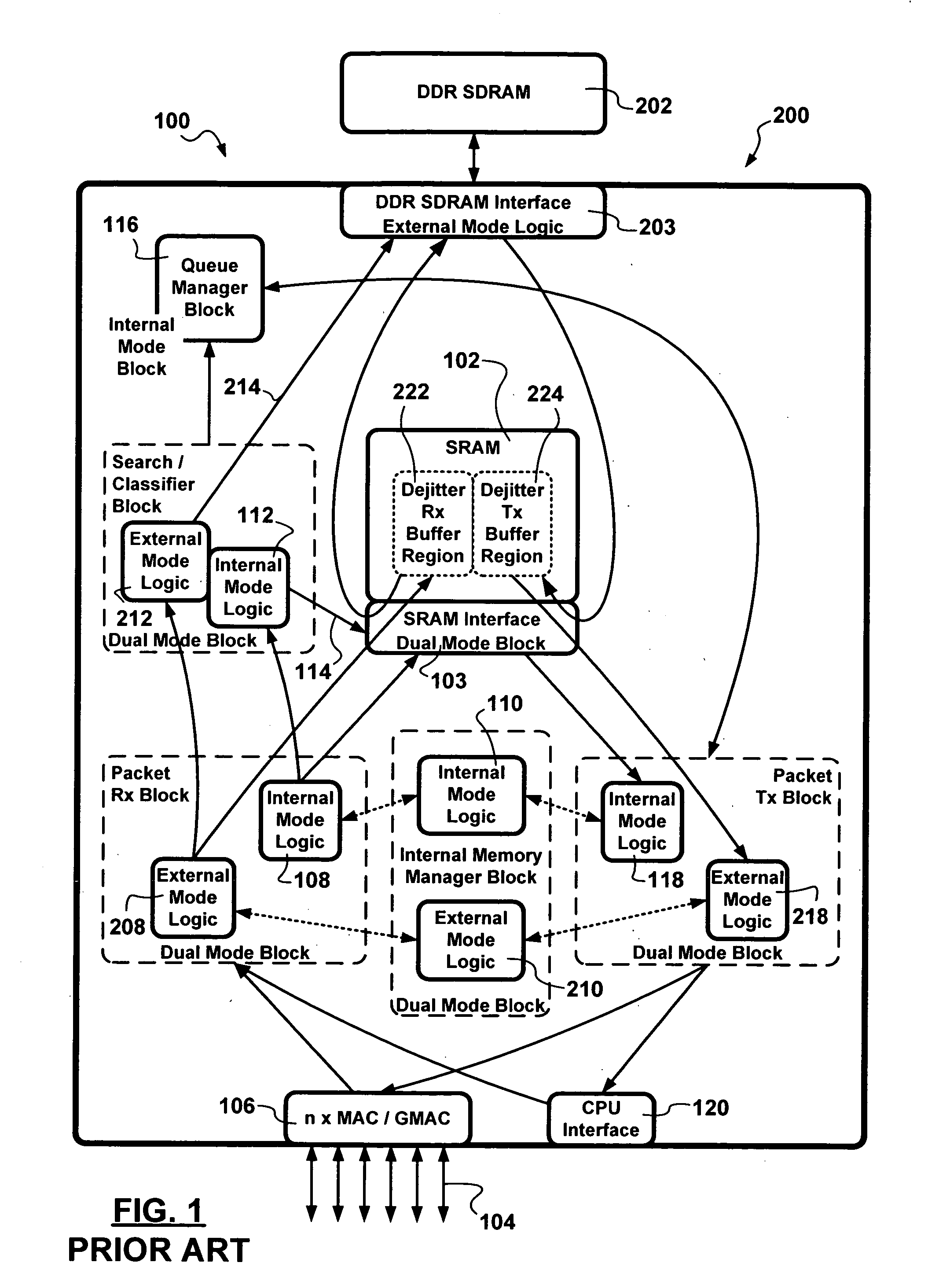
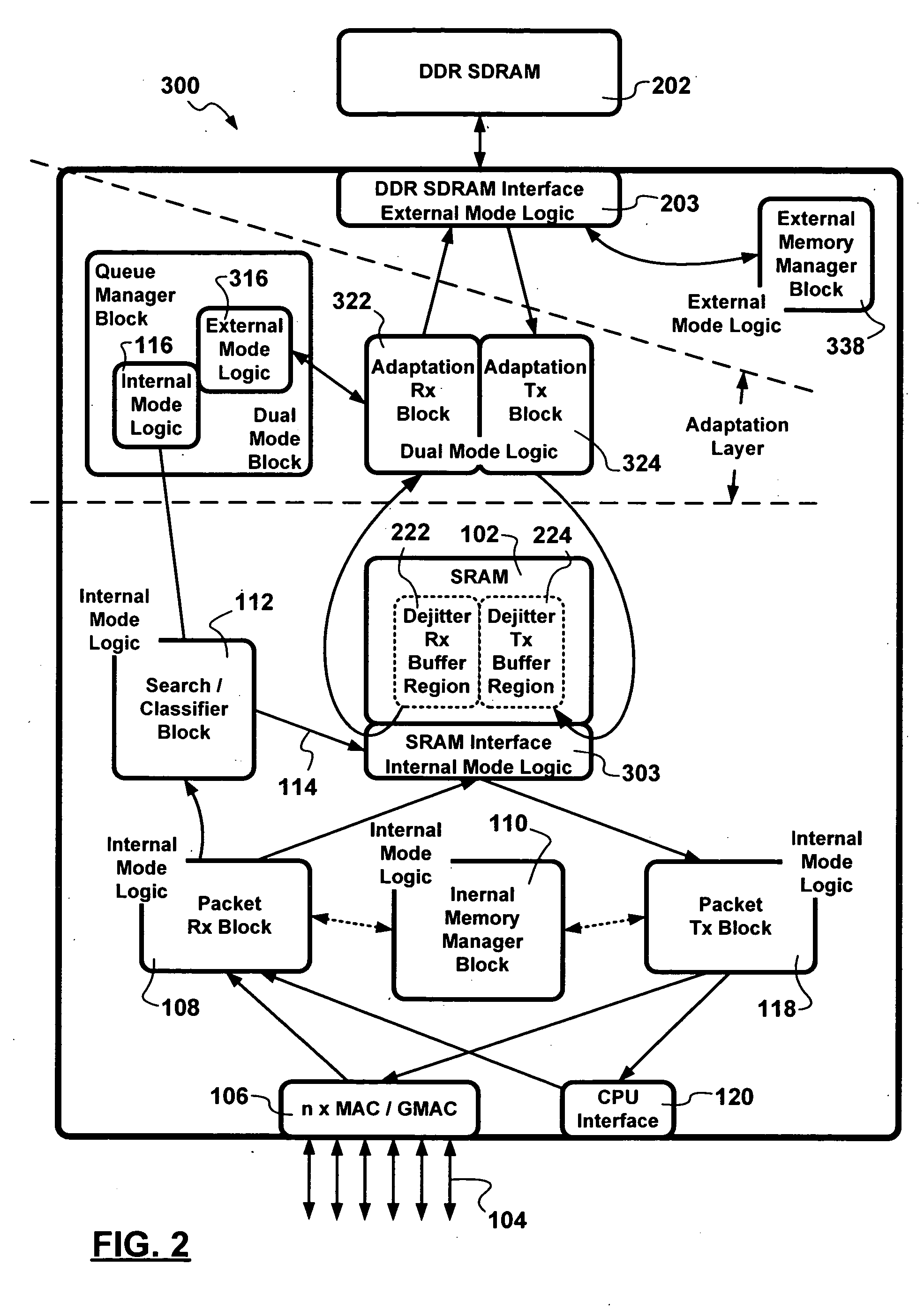
A two-chip / single-die switch architecture and a method for accessing a DDR SDRAM memory store in a switching environment are presented. The two-chip / single-die architecture includes an internal memory storage block on the single-die, an external memory storage interface to a Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (DDR SDRAM), an external memory manager, and a packet data transfer engine effecting packet data transfers between an internal memory store and the external DDR SDRAM memory. The packet data transfer engine operates as an adaptation layer addressing issues related to employing appropriate: addressing schemes, granule sizes, memory transfer burst sizes, access timing, etc. The packet data transfer engine includes a minimal number of dual mode operational blocks such as: a queue manager, and adaptation receive and transmit blocks. The method relates to a packet data transfer discipline addressing random memory access latencies incurred in employing DDR SDRAM, using predictive bank switching to hide random access latencies, packet length dependent variable memory write burst lengths to minimize bank switching, and performing memory read and write operations during corresponding read and write windows. Advantages are derived from the a space-efficient two-chip / single-die switching node architecture implemented with a reduced amount of dual mode logic, and also from DDR SDRAM bandwidth utilization efficiencies.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
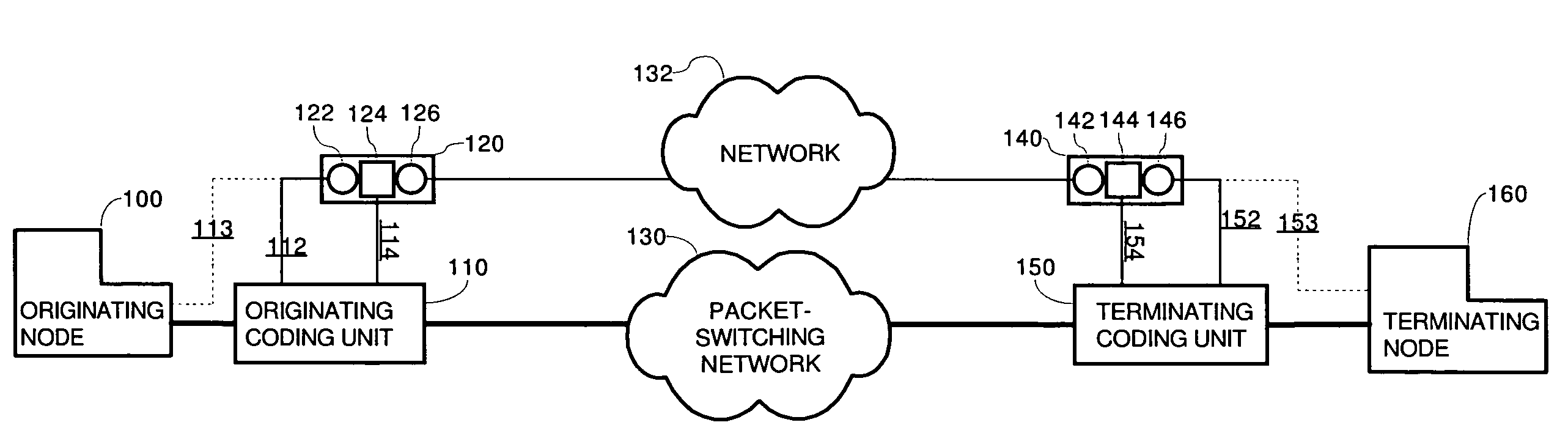
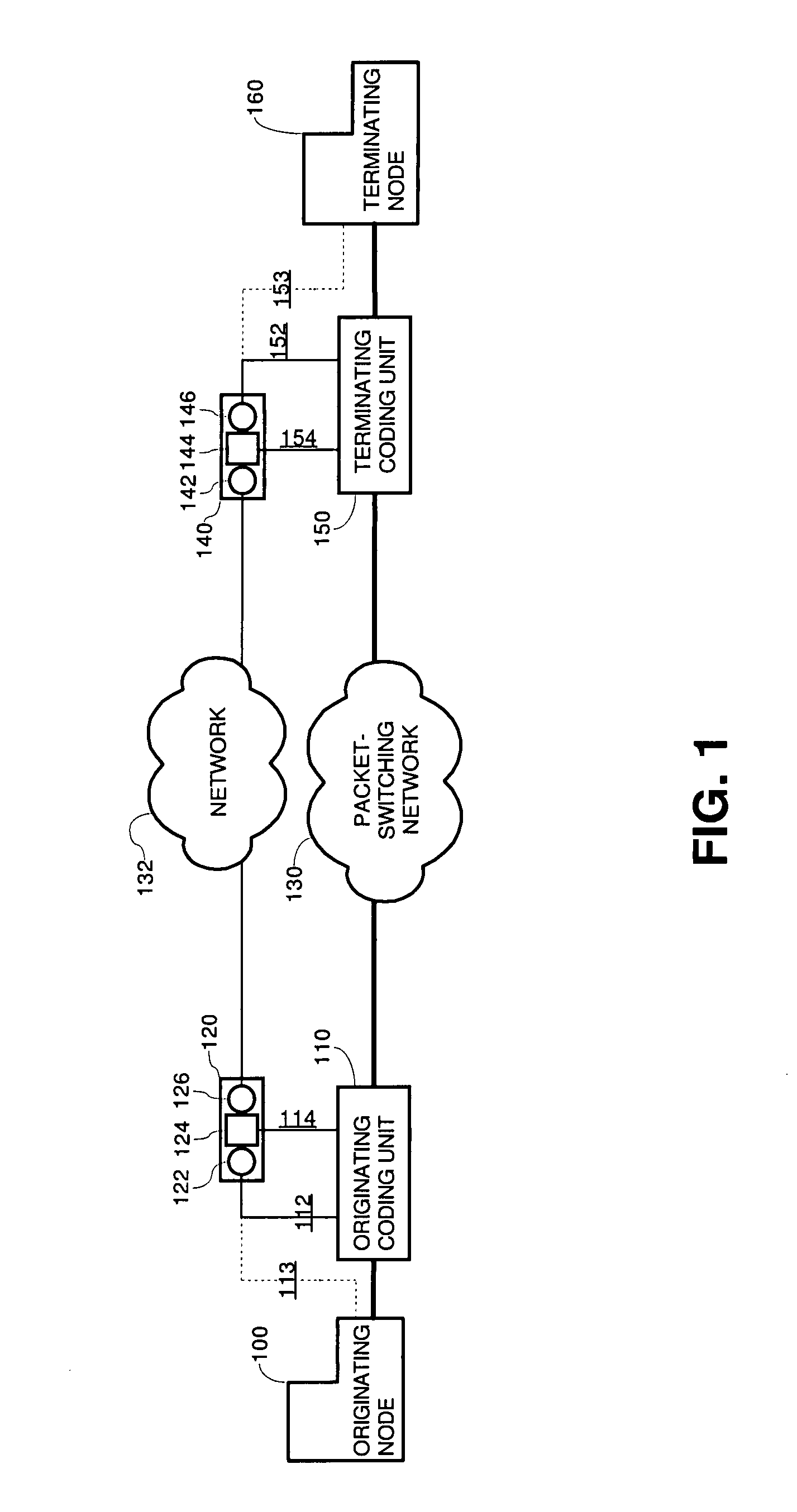
System using a signaling protocol for controlling voice calls originating in a circuit switching telephone network and routed over a packet switching network
InactiveUS7369545B1Time-division multiplexHybrid transportTelecommunications networkNetwork addressing
Communicating voice over a packet-switching network is implemented on a telecommunications network that includes the packet-switching network, two coding units coupled to the packet-switching network and two signaling apparatuses. Signaling data for establishing the voice call is received by an originating signaling apparatus, which generates a message that encapsulates the signaling data in accordance with a common signaling protocol, and transmits the message to a destination signaling apparatus. The message, in accordance with the common signaling protocol, includes a call identifier that uniquely identifies the voice within the packet-switching network, the network address of a signaling apparatus, and / or a connection descriptor for a coding unit.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Network management system
InactiveUS20020010770A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksInter layerNetwork management
In a network management system performing a fault management process in a hierarchical network, an upper layer fault manager performs a fault management of an upper layer of a hierarchical network, a lower layer fault manager performs a fault management of a lower layer of the network, an inter-layer node connecting information storage portion manages connecting information between packet switching nodes composing the upper layer and link offering nodes composing the lower layer, and an inter-layer fault notifying portion notifies the upper layer fault manager, upon receiving a notification of a link fault which has occurred on a link between the link offering nodes from the lower layer fault manager, that the packet switching nodes affected by the fault are faulted, based on the connecting information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com