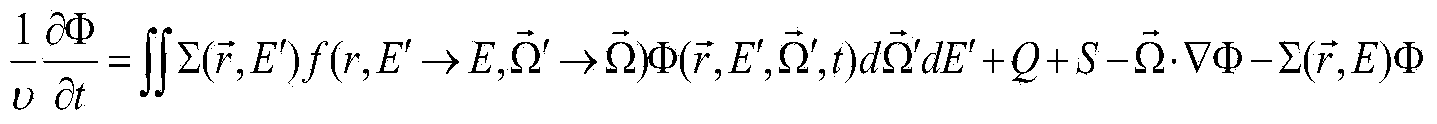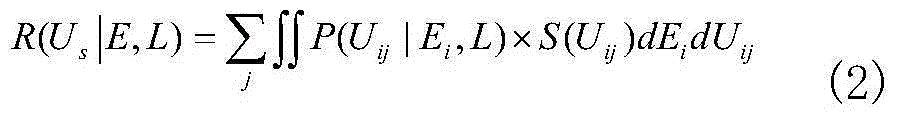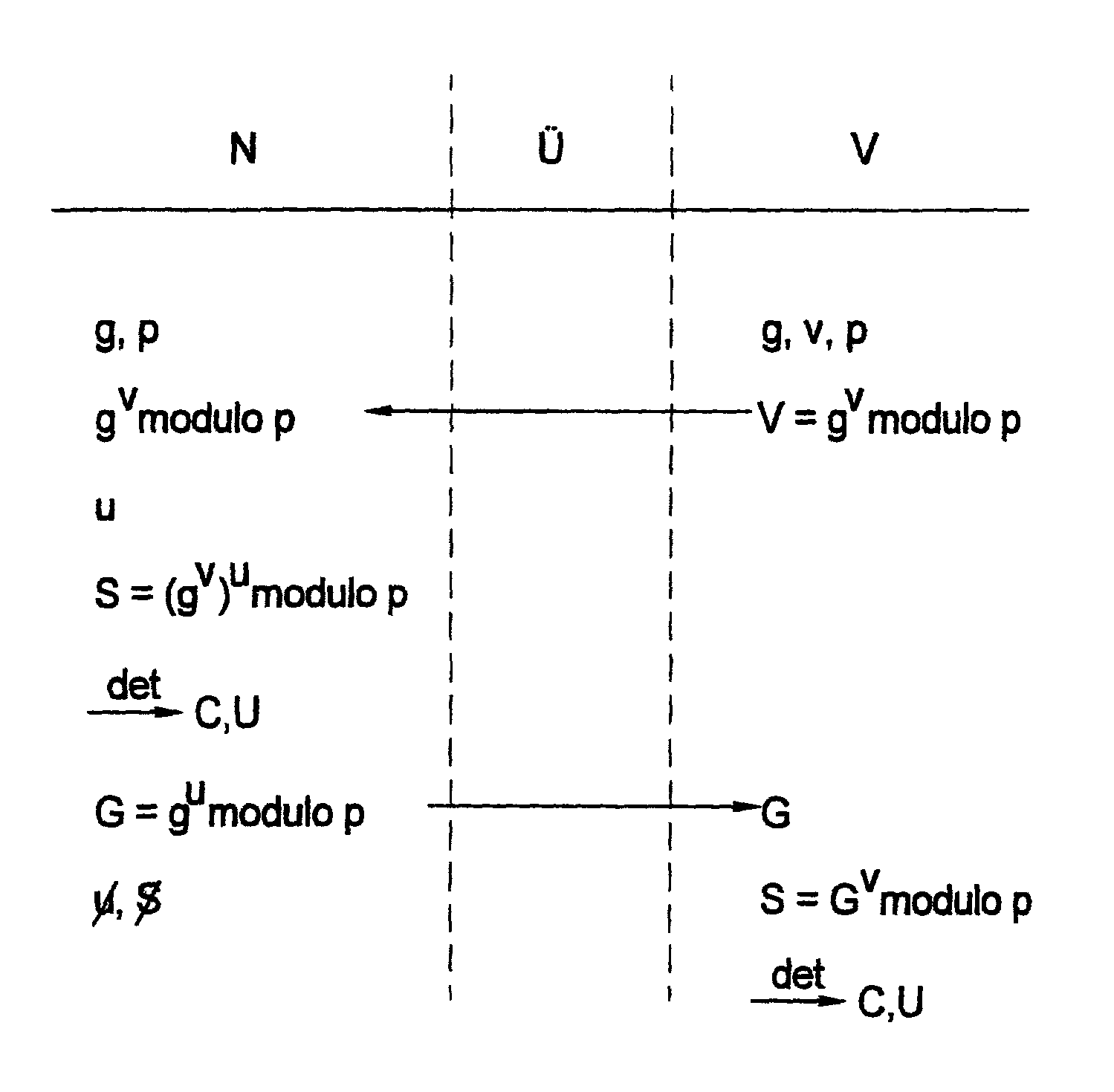Patents
Literature
79 results about "Deterministic method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Deterministic Methods. In practice, the deterministic methods are the simplest and most common methods for establishing the cost contingency reserve fund. The term “deterministic” implies that the cost contingency is determined as a single point estimate, typically as a percentage of the base cost estimate.
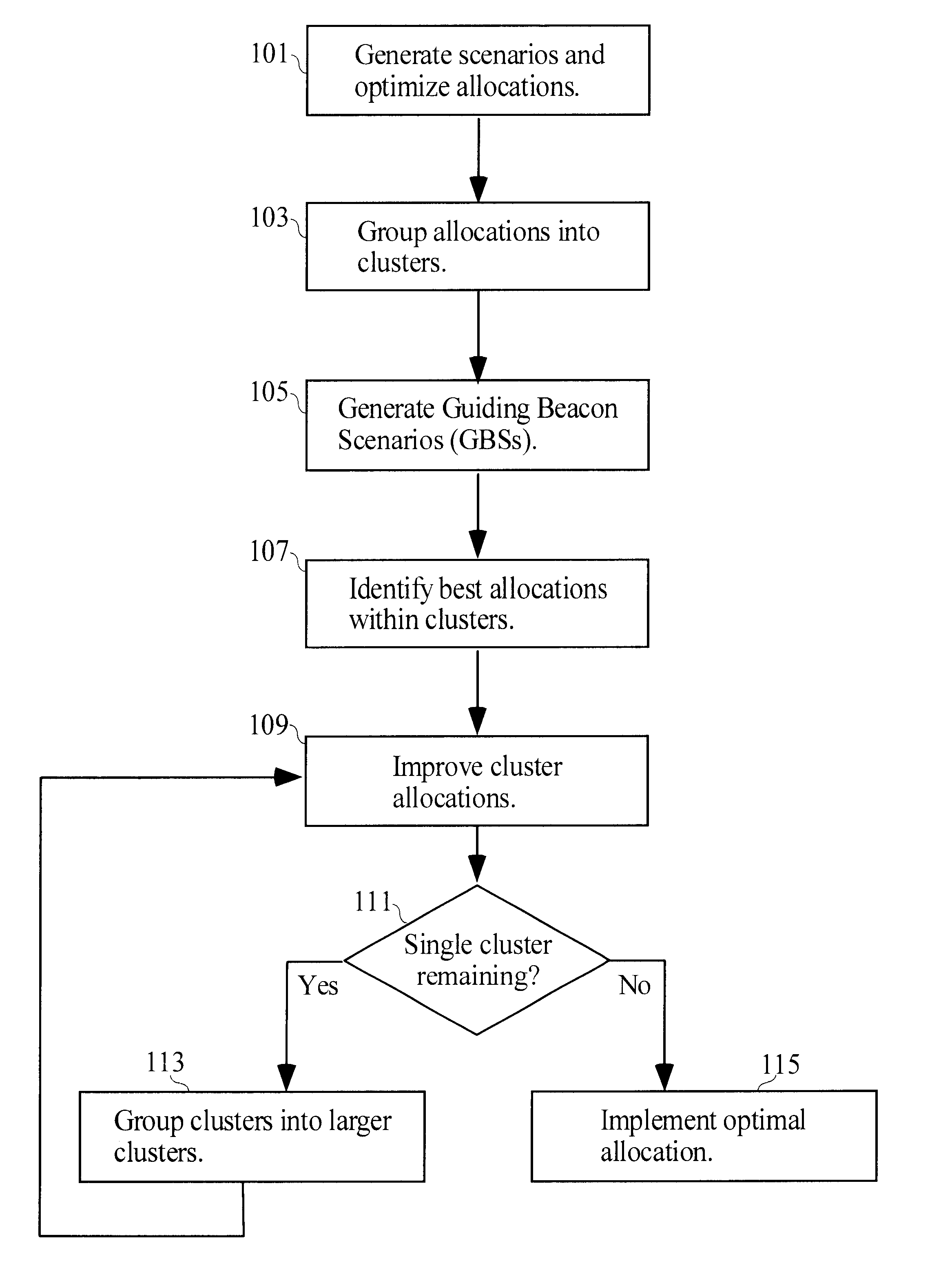
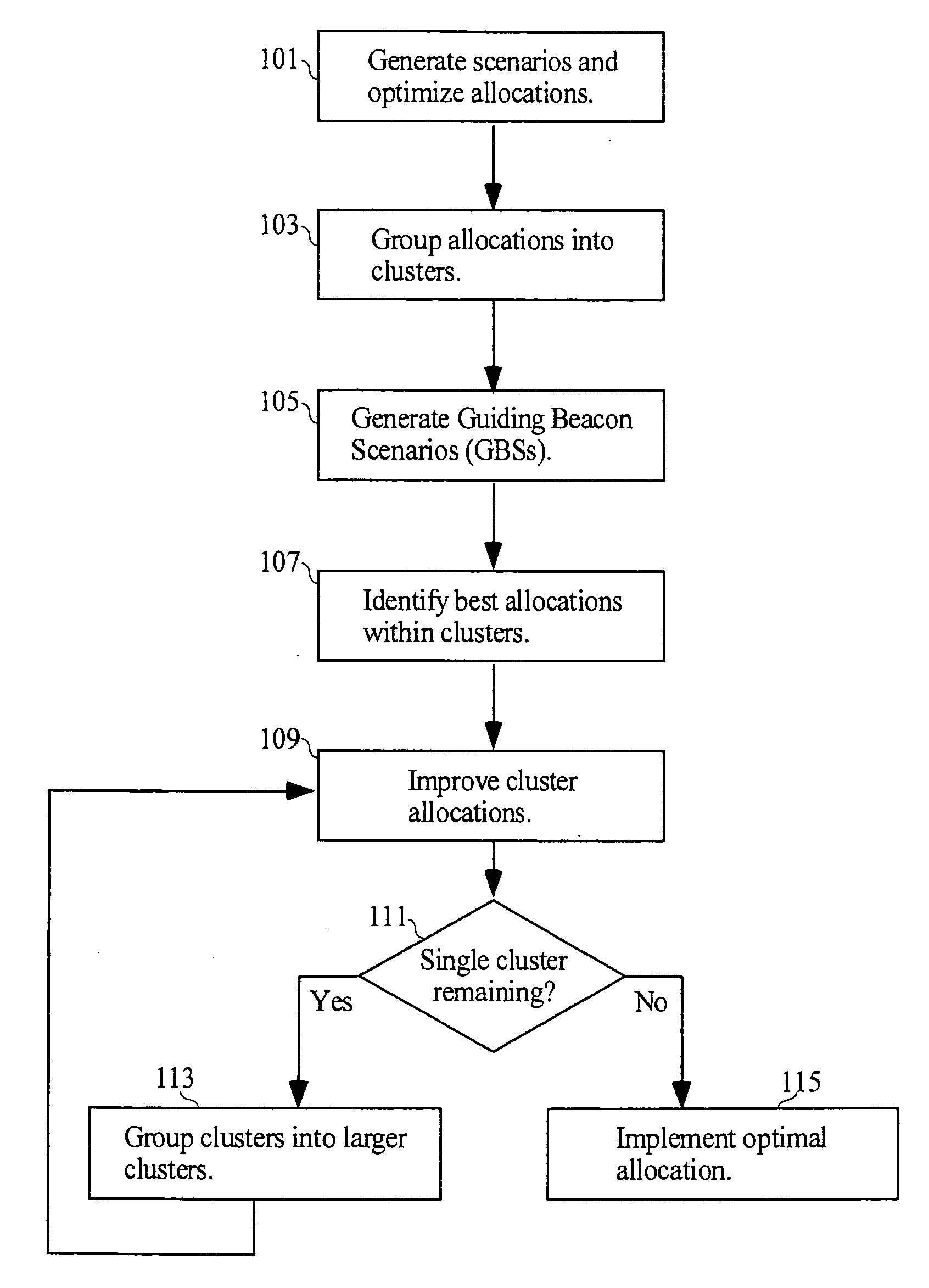
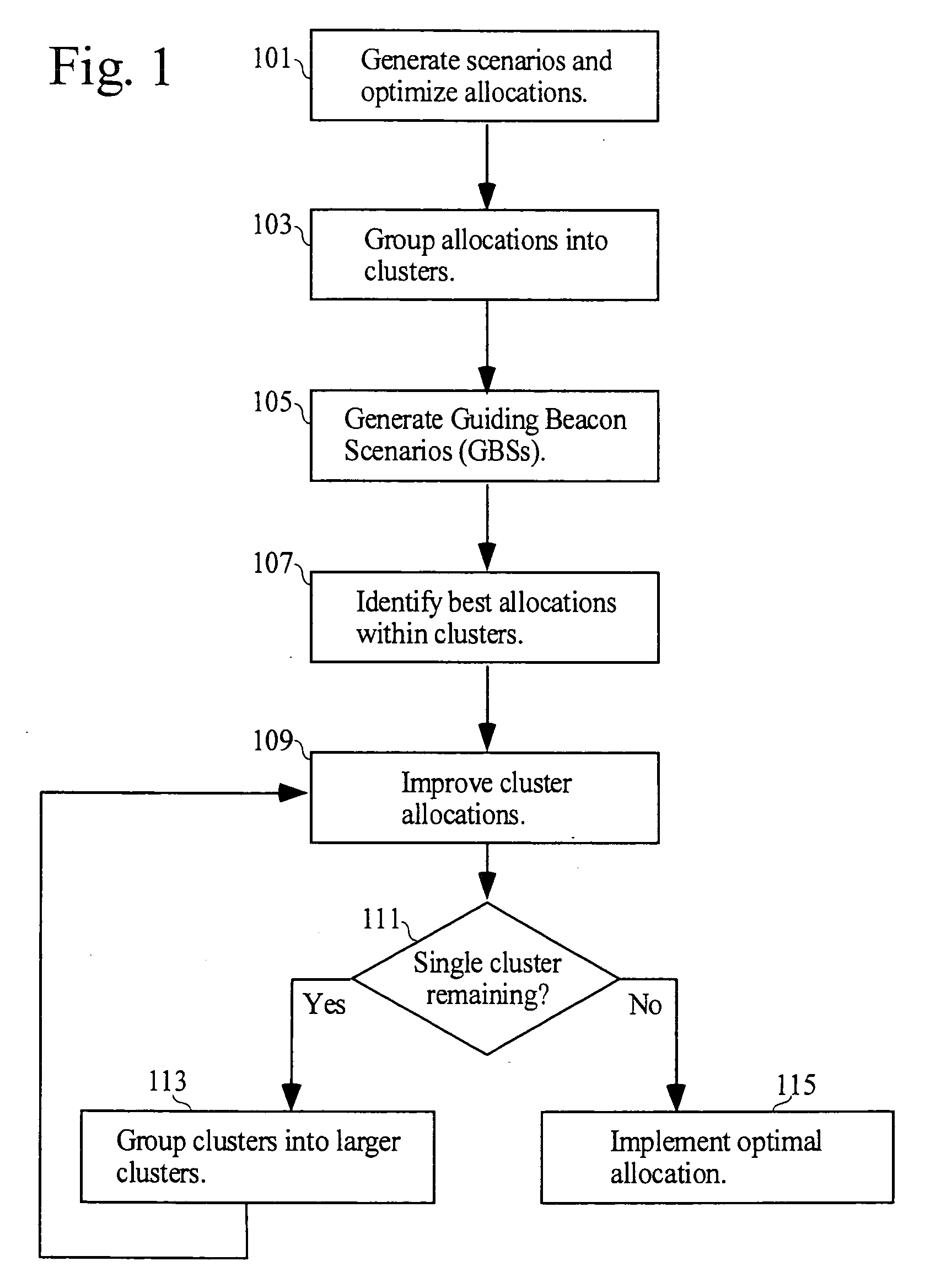
Methods and apparatus for allocating resources in the presence of uncertainty
InactiveUS6219649B1ResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsOrganizational resourceDeterministic method
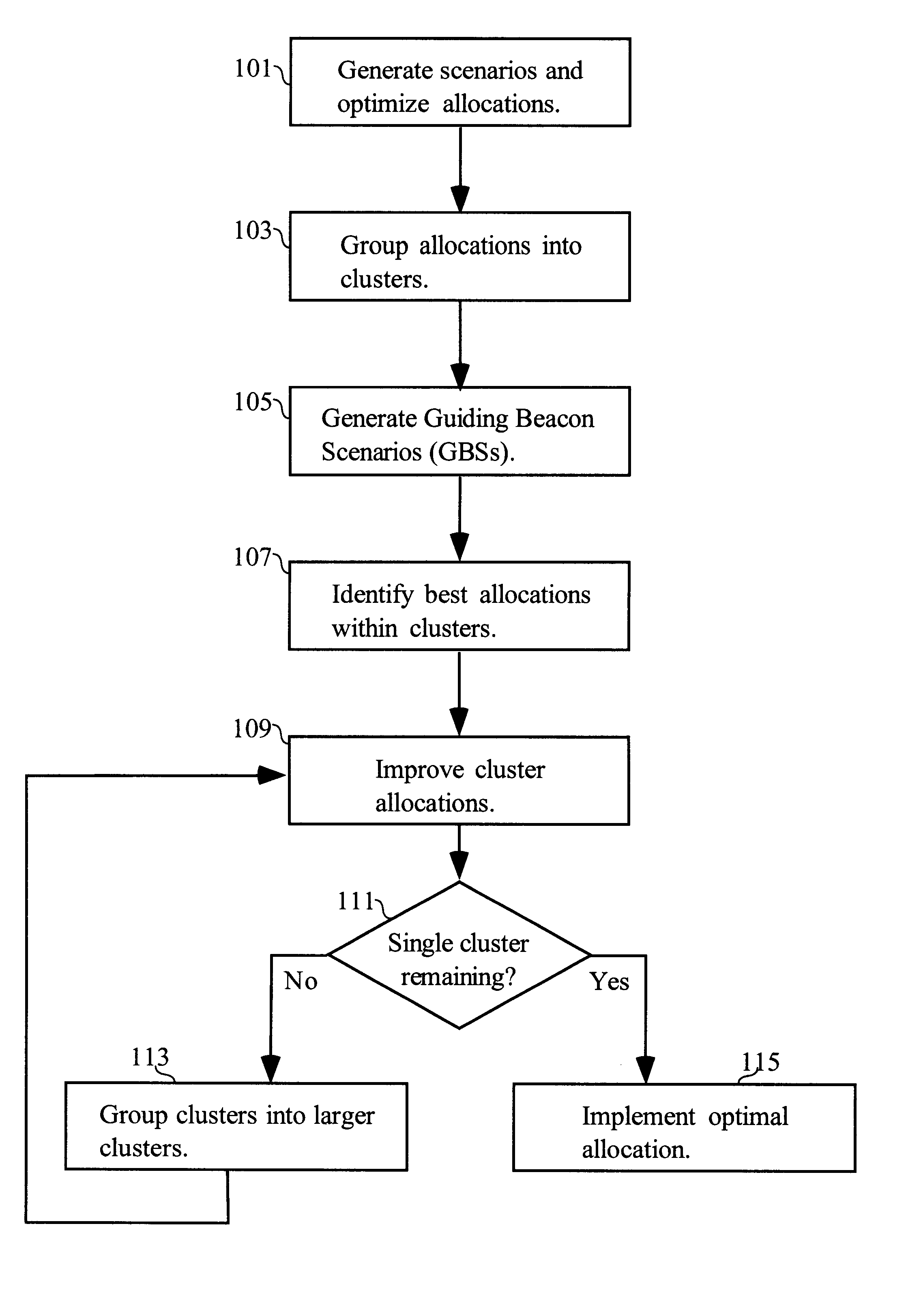
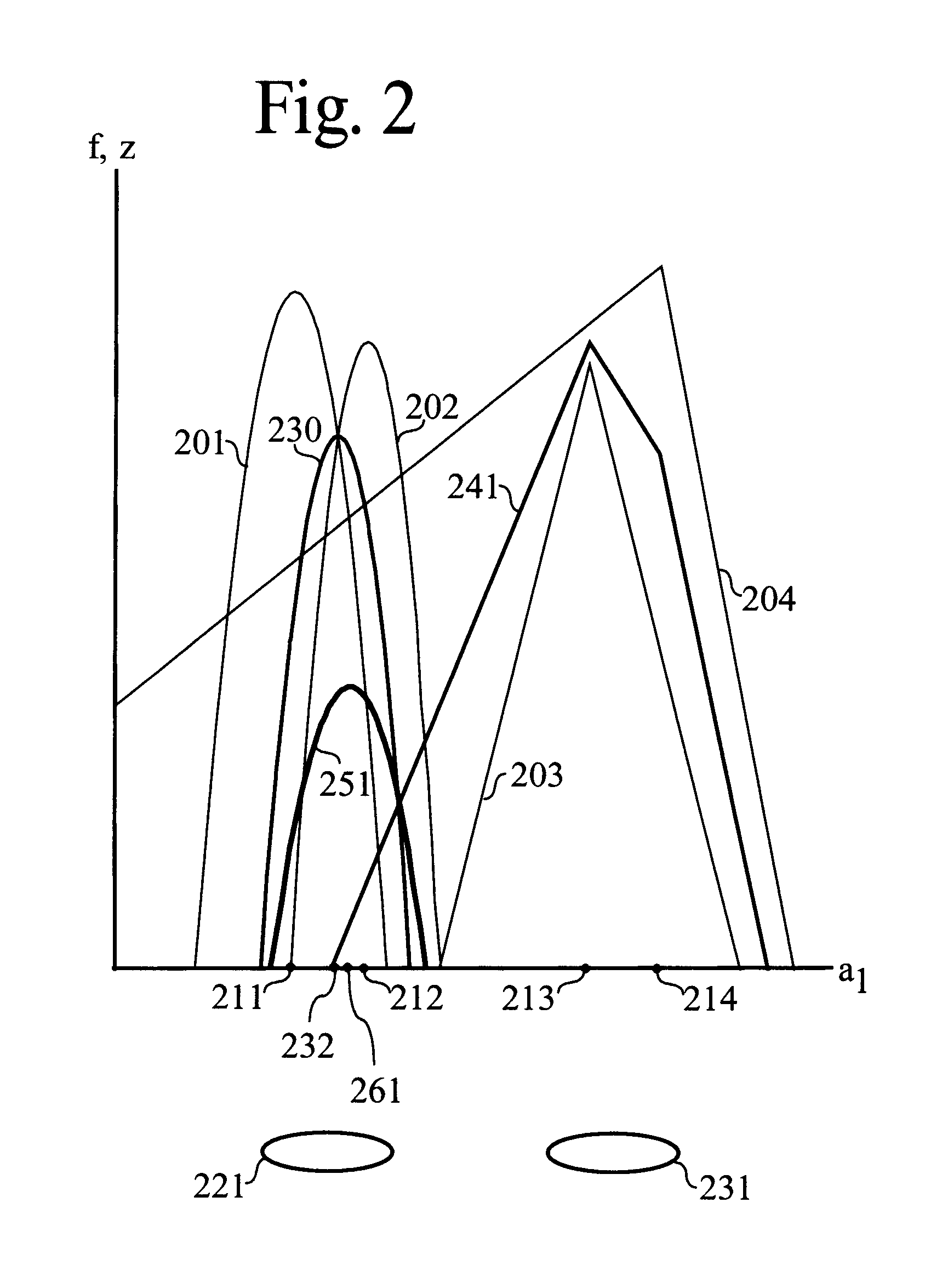
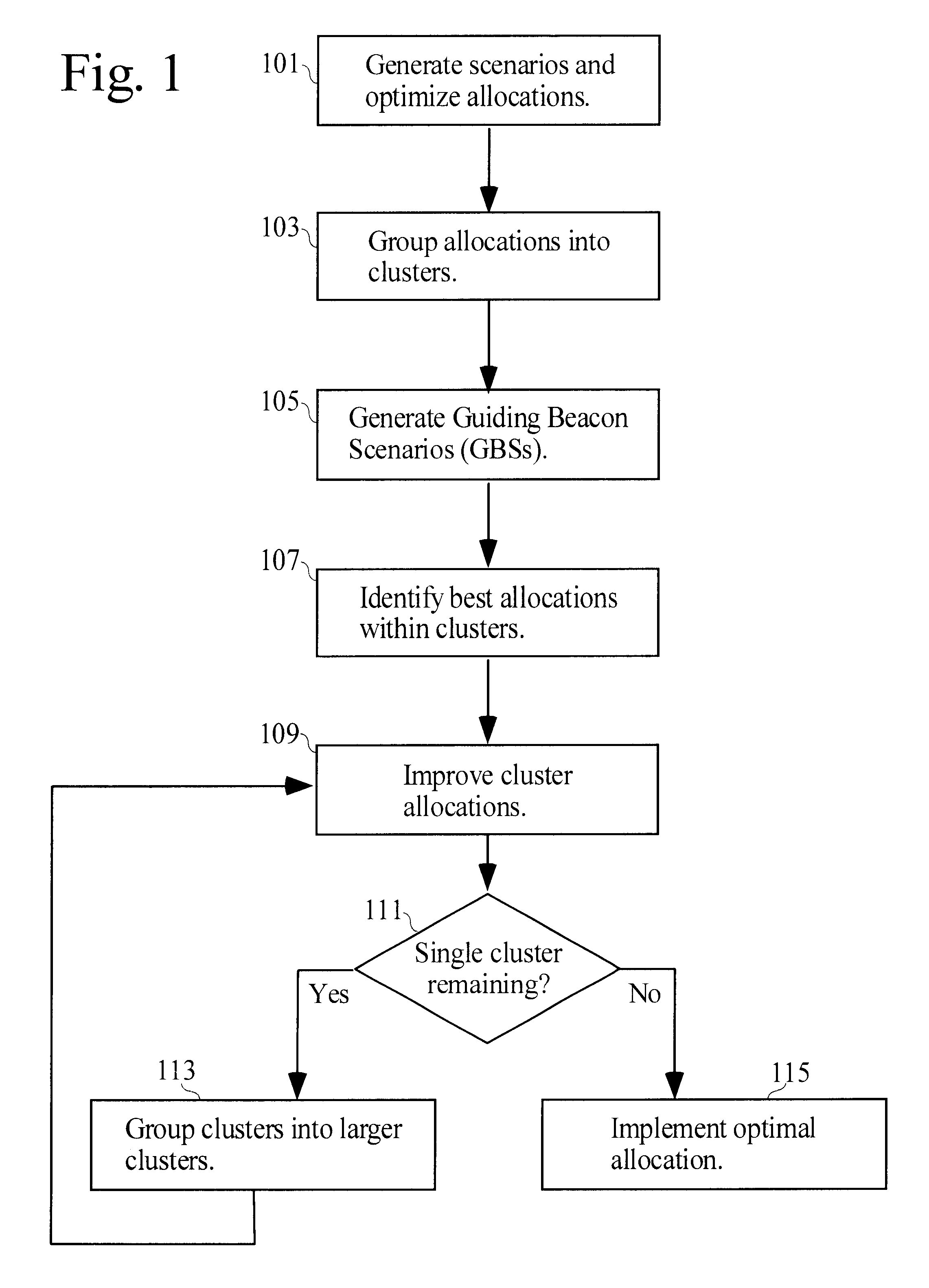
A method of allocating resources in the presence of uncertainty is presented. The method builds upon deterministic methods and initially creates and optimizes scenarios. The invention employs clustering, line-searching, statistical sampling, and unbiased approximation for optimization. Clustering is used to divide the allocation problem into simpler sub-problems, for which determining optimal allocations is simpler and faster. Optimal allocations for sub-problems are used to define spaces for line-searches; line-searches are used for optimizing allocations over ever larger sub-problems. Sampling is used to develop Guiding Beacon Scenarios that are used for generating and evaluating allocations. Optimization is made considering both constraints, and positive and negative ramifications of constraint violations. Applications for capacity planning, organizational resource allocation, and financial optimization are presented.
Owner:JAMESON JOEL
Apparatuses and methods for flexible displays
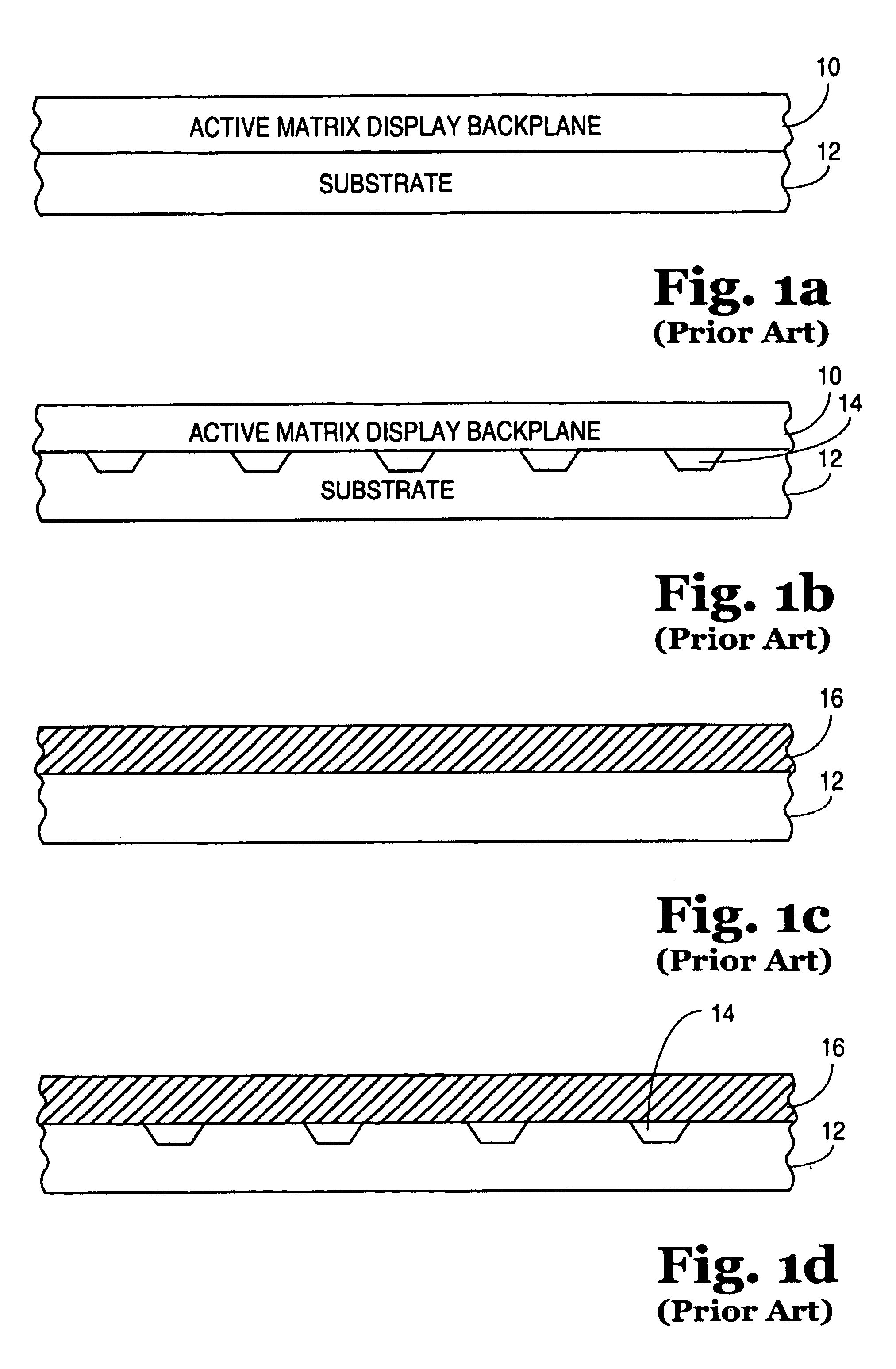
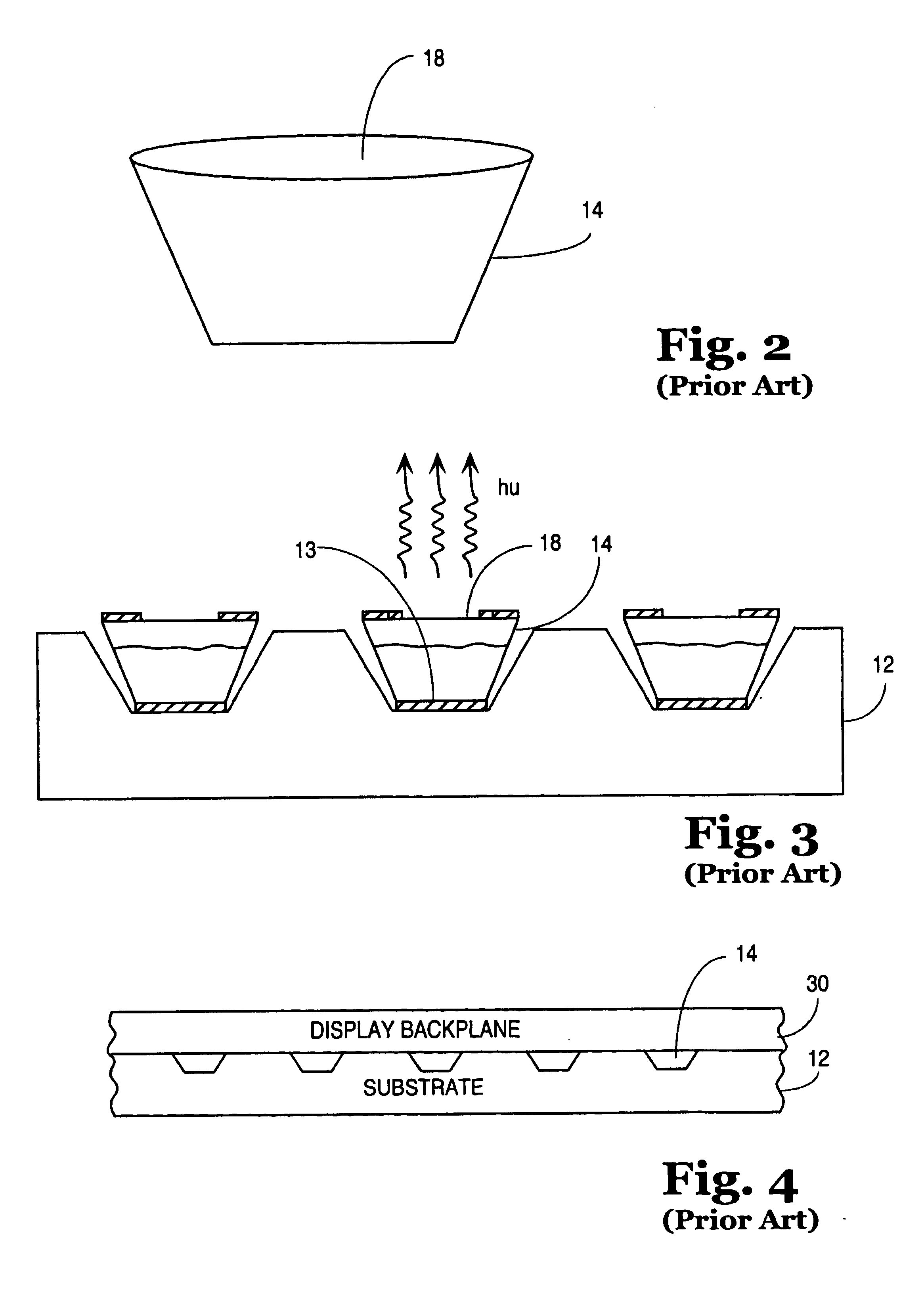
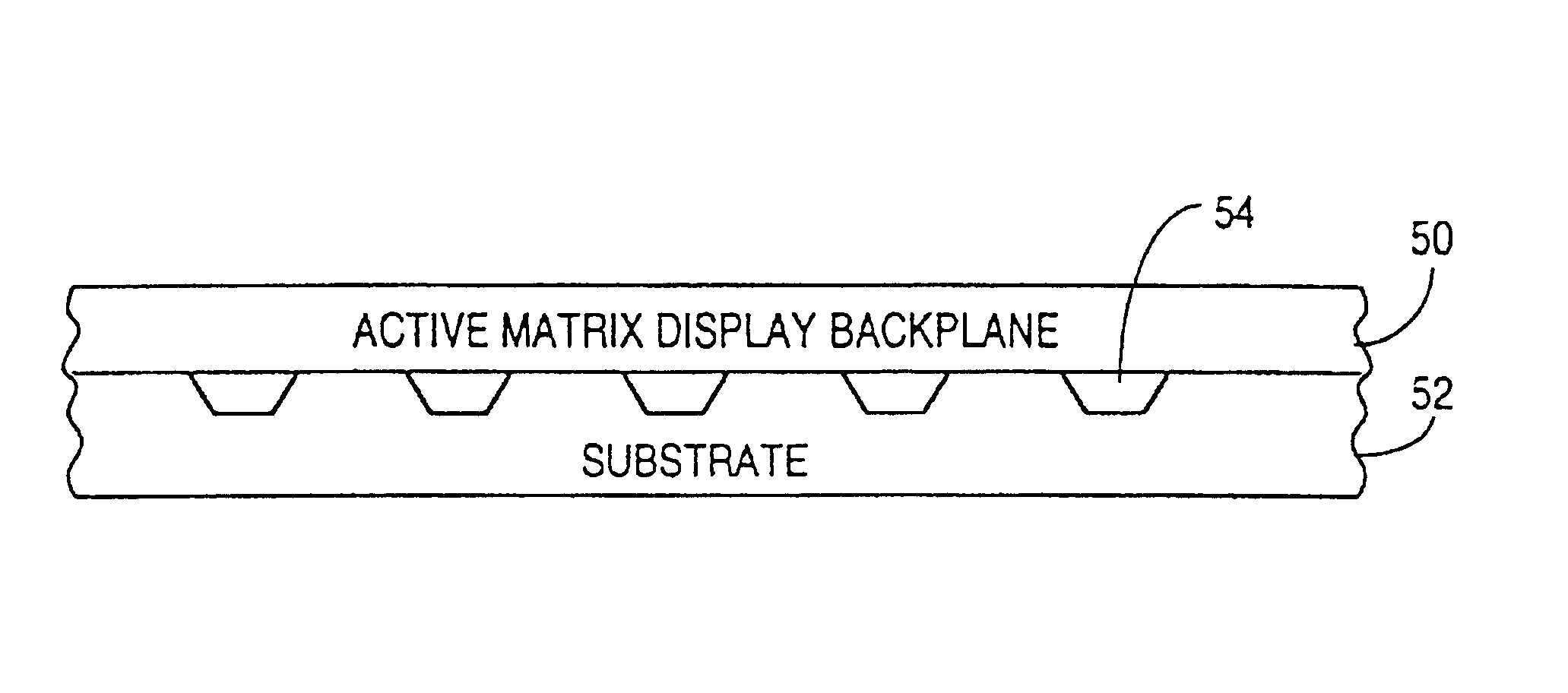
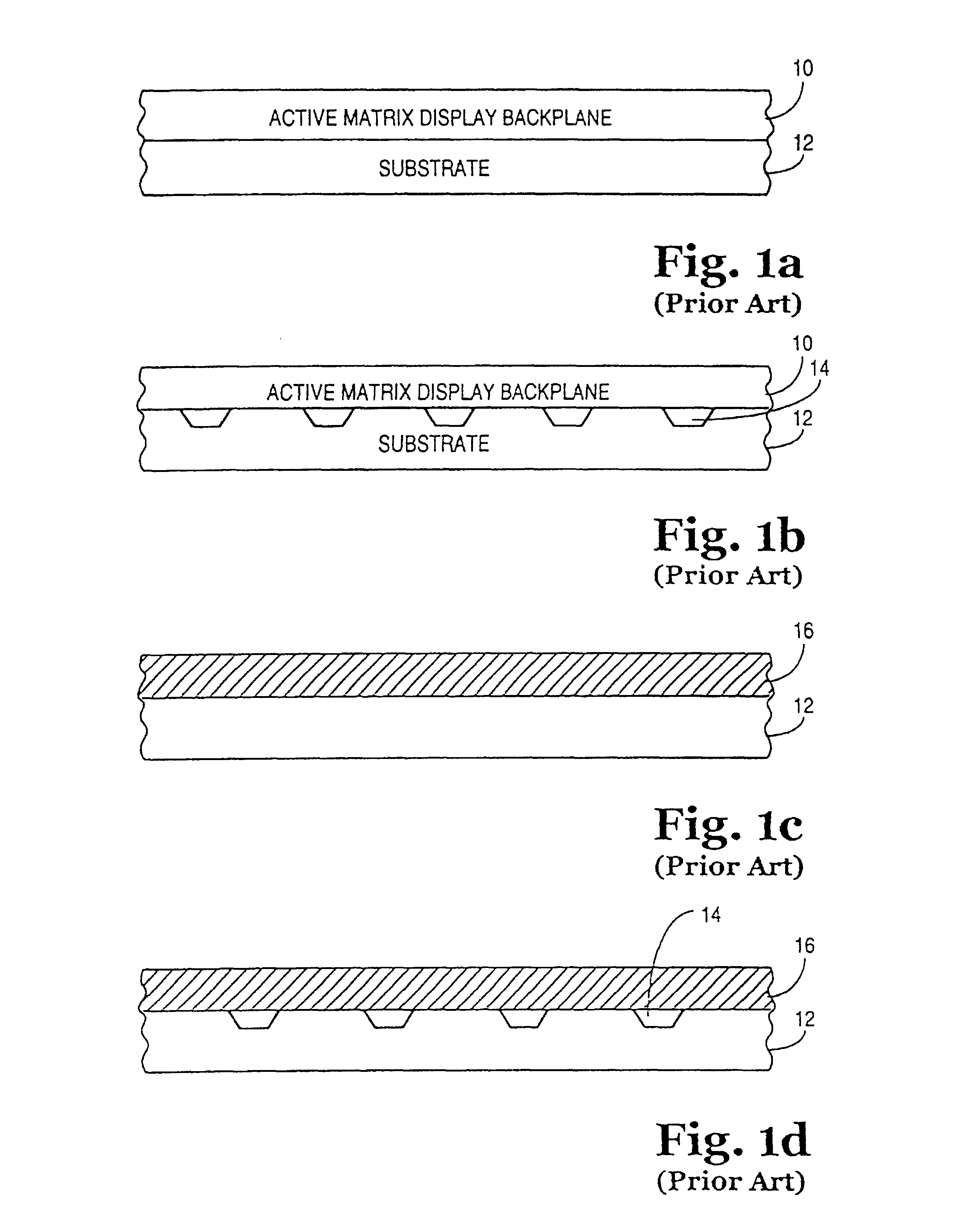
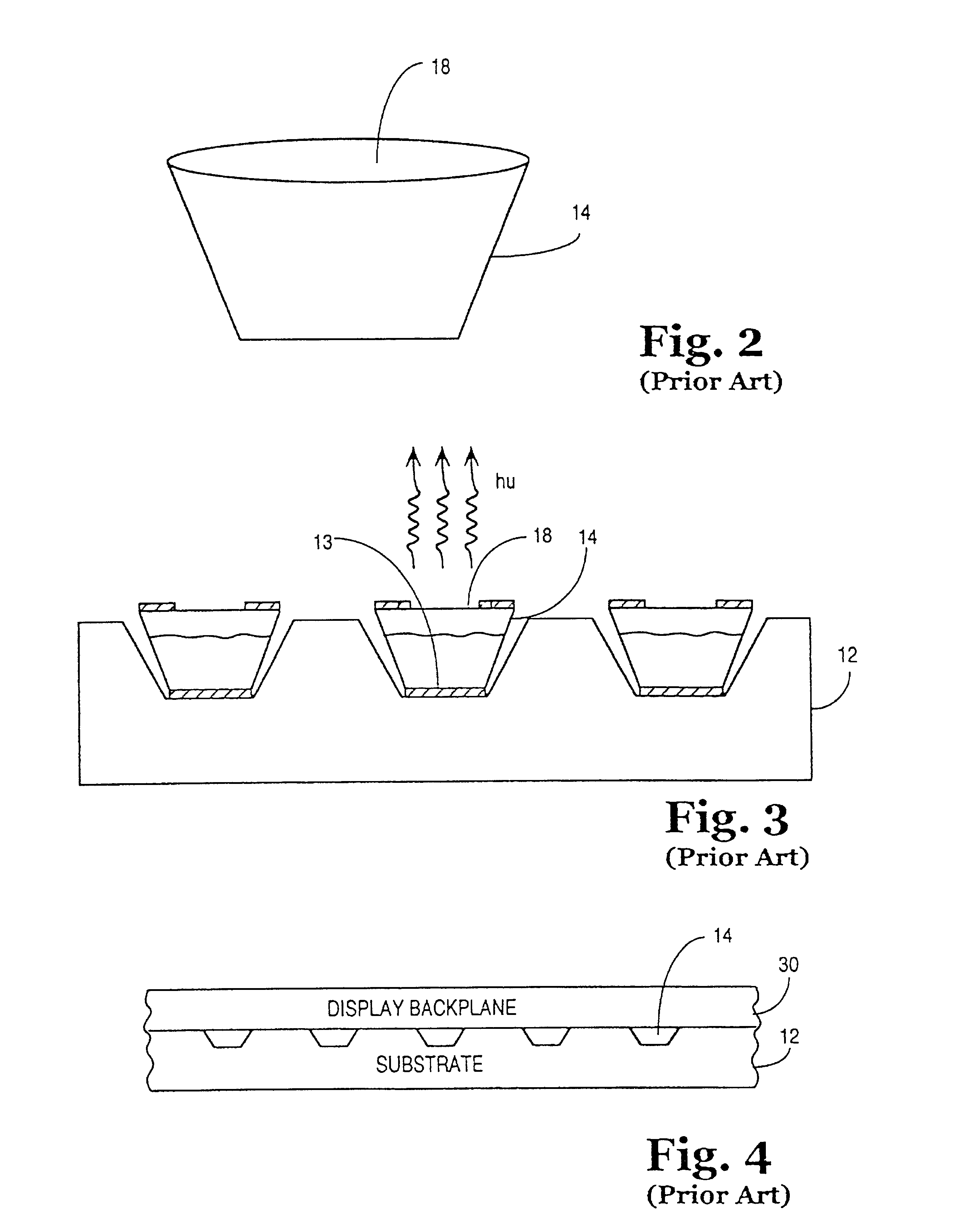
InactiveUS6850312B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeterministic methodActive matrix
Apparatuses and methods for forming displays are claimed. One embodiment of the invention relates to forming a flexible active matrix display along a length of flexible substrate. Another embodiment of the invention relates to forming multiple flexible displays along a continuous flexible substrate. Another embodiment of the invention relates to forming a flexible display along a flexible reflective substrate. Another embodiment of the invention relates to using FSA generally with a flexible web process material. Another embodiment of the invention relates to using FSA and a deterministic method such as “pick and place” to place objects onto a rigid substrate or onto a web process material. Another embodiment of the invention relates to using web processing to deposit and / or pattern display material through an in-line process.
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
Apparatuses and methods for flexible displays
InactiveUS7046328B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeterministic methodActive matrix
Apparatuses and methods for forming displays are claimed. One embodiment of the invention relates to forming a flexible active matrix display along a length of flexible substrate. Another embodiment of the invention relates to forming multiple flexible displays along a continuous flexible substrate. Another embodiment of the invention relates to forming a flexible display along a flexible reflective substrate. Another embodiment of the invention relates to using FSA generally with a flexible web process material. Another embodiment of the invention relates to using FSA and a deterministic method such as “pick and place” to place objects onto a rigid substrate or onto a web process material. Another embodiment of the invention relates to using web processing to deposit and / or pattern display material through an in-line process.
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
Distributing fault indications and maintaining and using a data structure indicating faults to route traffic in a packet switching system
InactiveUS6990063B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionBroadcast packetDeterministic method
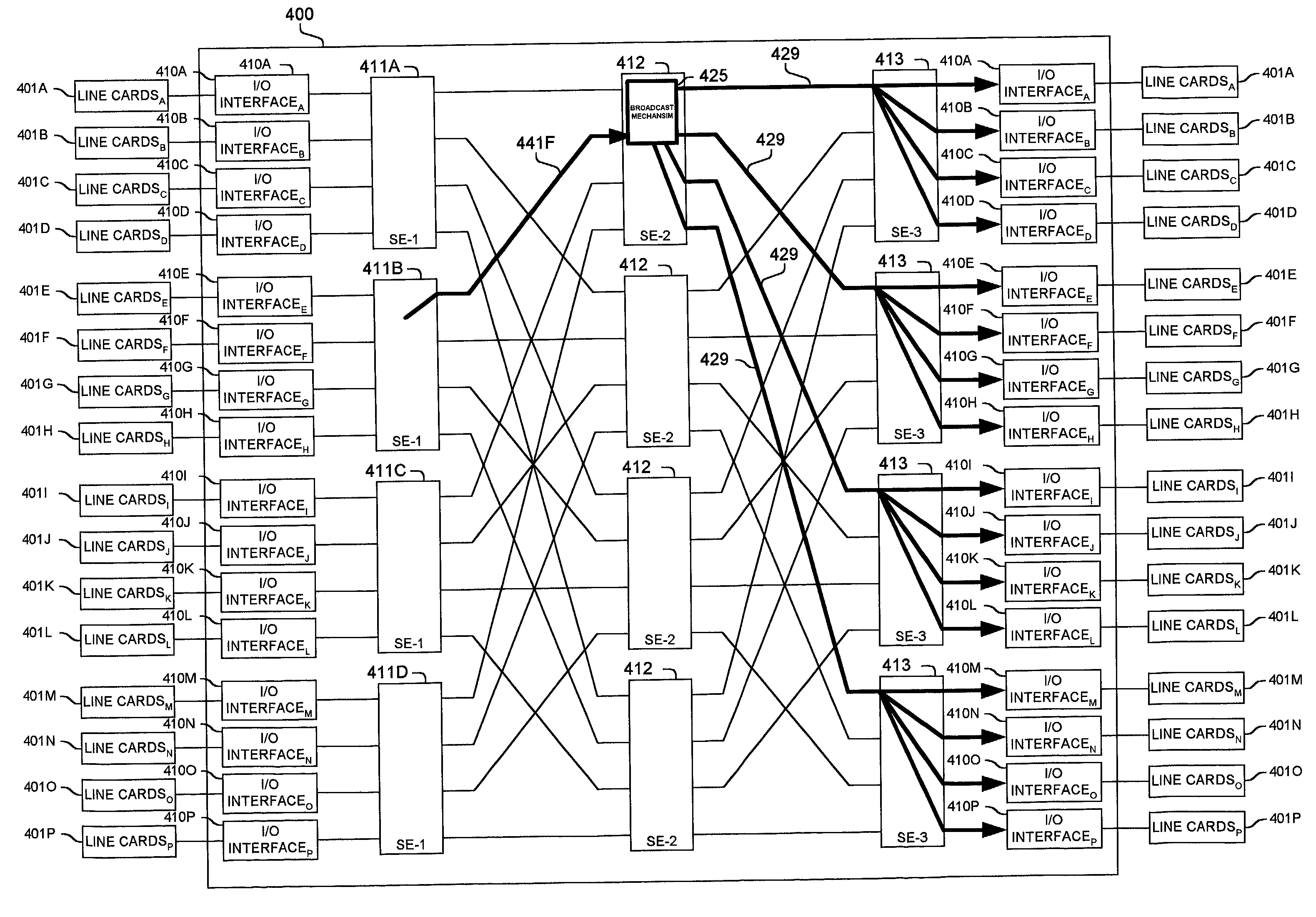
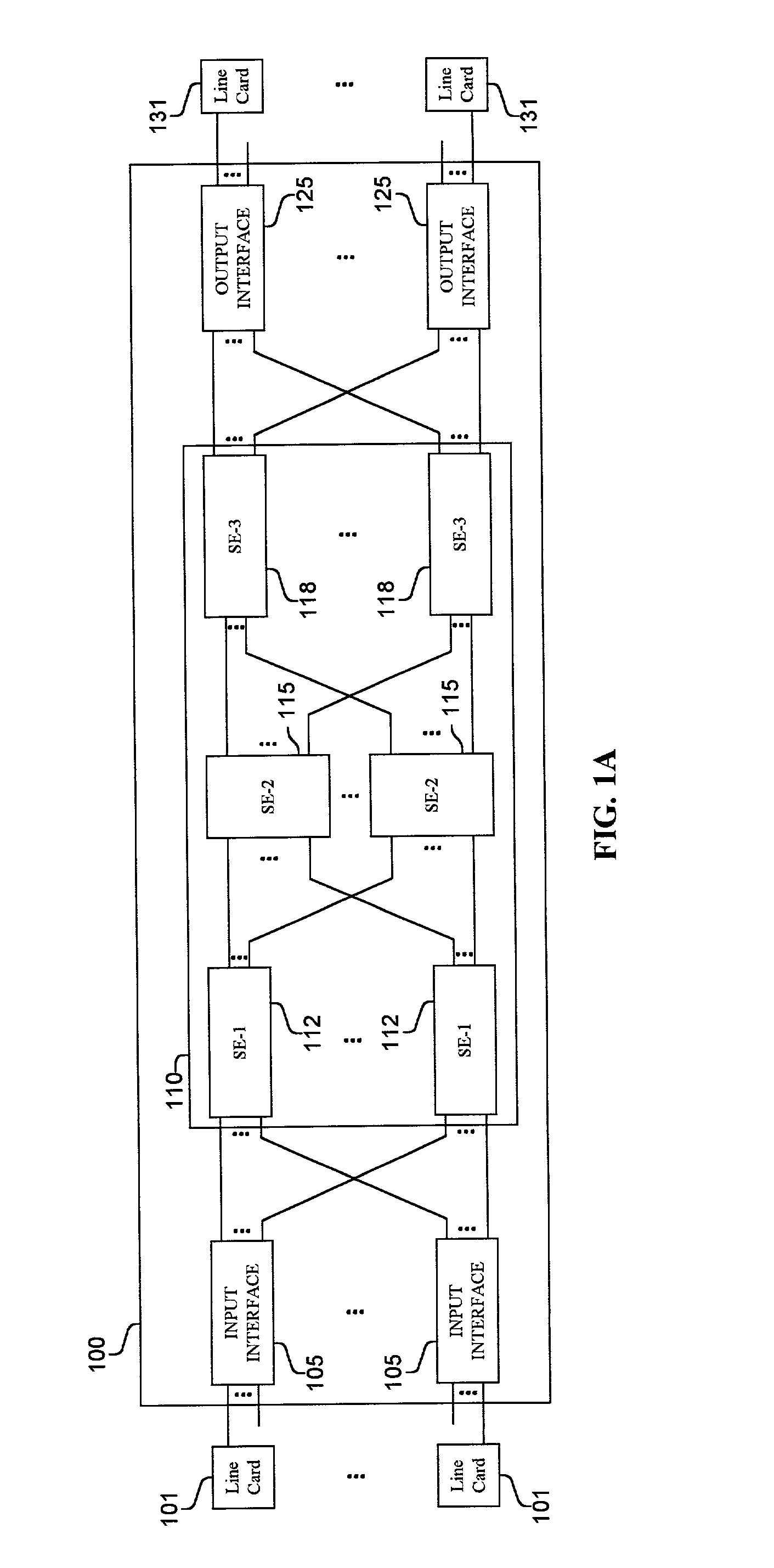
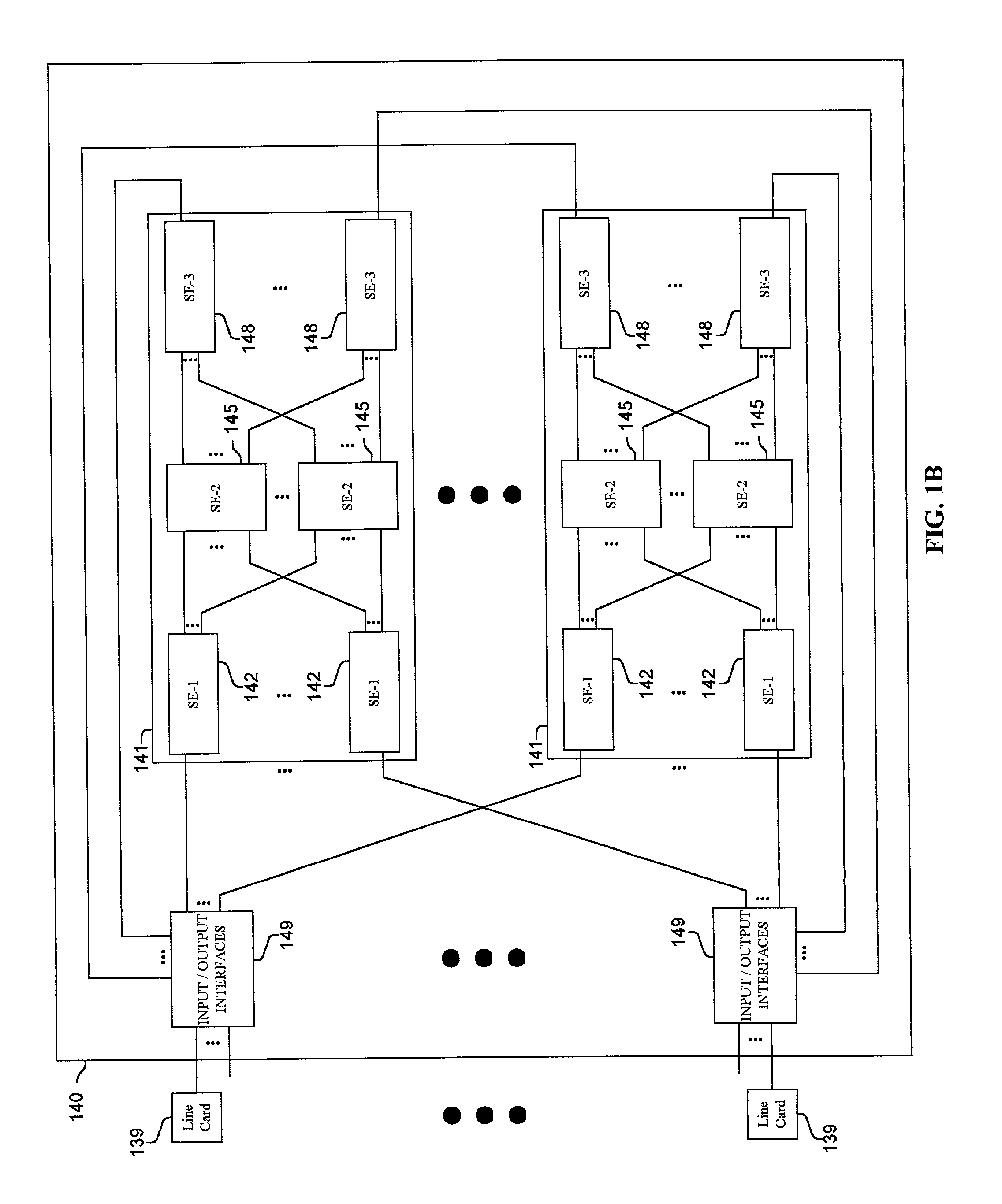
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for distributing fault indications and maintaining and using a data structure indicating faults to route traffic in a packet switching system. In one embodiment, a packet switching system detects faults and propagates indications of these faults to the input interfaces of a packet switch, so the packet switch can adapt the selection of a route over which to send a particular packet. Faults are identified by various components of the packet switching system and relayed to one or more switching components to generate a broadcast packet destined for all input ports (i.e., to each I / O interface in a packet switch having folded input and output interfaces). Other embodiments, generate one or more multicast or unicast packets. The I / O interface maintains one or more data structures indicating the state of various portions of the packet switching system. In one embodiment, an output availability table is maintained indicating over which path a particular destination may be reached, as well as a link availability vector indicating which output likes of the input interface may be currently used. Using these as masks against possible routes in a fully functional system, the packet switching component (e.g., I / O interface) can identify which routes are currently available for reaching the destination of the received packet. These routes can then be selected between using one of numerous deterministic and non-deterministic methods.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
Array of parallel programmable processing engines and deterministic method of operating the same
InactiveUS7401333B2Efficient implementationResource allocationGeneral purpose stored program computerDeterministic methodExchange network
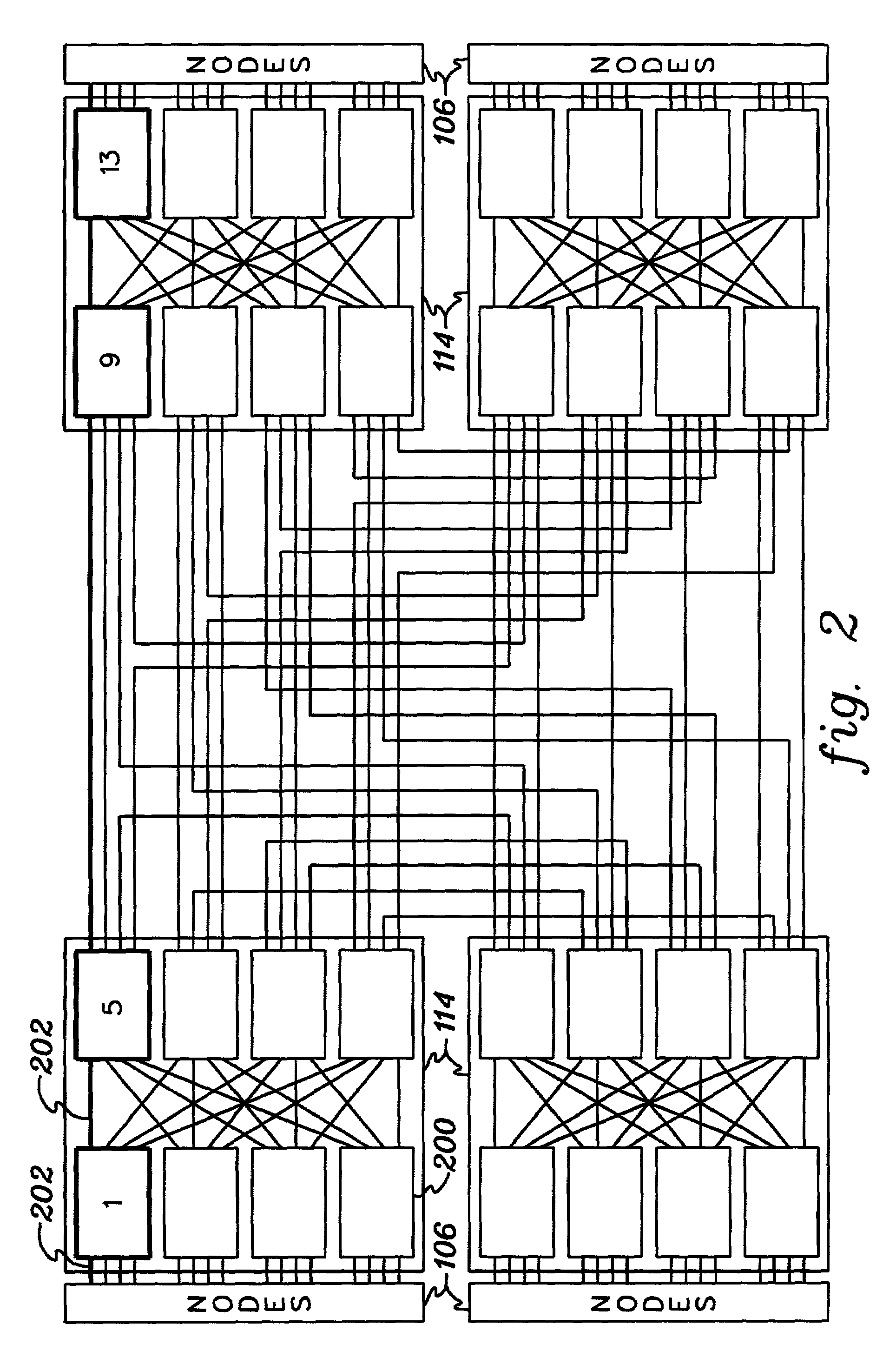
The present invention provides an array of parallel programmable processing engines interconnected by a switching network. At least some of the processing engines execute a thread, and at least some threads communicate with each other through communication objects either internally within one processing engine or through the network. A scheduling step of the parallel programmable processing engines is initiated by one or more events, an event being defined by a change of a state variable of a communication object. The array comprises:means for scheduling a scheduling step of the processing engines, the scheduling means comprising means for executing at least a first set of threads in parallel,means for updating state values of communications objects in response to the parallel executing step, andmeans for repeatedly and sequentially scheduling the executing means and the updating means until no more events occur.The present invention also provides a deterministic method of operating such an array.
Owner:TRANSWITCH
Deterministic computation of radiation doses delivered to tissues and organs of a living organism
InactiveUS20050143965A1Improve computing efficiencyHigh solution accuracyDosimetersComputation using non-denominational number representationInternal radiationIntensity modulation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for deterministic calculation of radiation doses, delivered to specified volumes within human tissues and organs, and specified areas within other organisms, by external and internal radiation sources. Embodiments of the present invention provide for creating and optimizing computational mesh structures for deterministic radiation transport methods. In general these approaches seek to both improve solution accuracy and computational efficiency. Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for planning radiation treatments using deterministic methods. The methods of the present invention may also be applied for dose calculations, dose verification, and dose reconstruction for many different forms of radiotherapy treatments, including: conventional beam therapies, intensity modulated radiation therapy (“IMRT”), proton, electron and other charged particle beam therapies, targeted radionuclide therapies, brachytherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery (“SRS”), Tomotherapy®; and other radiotherapy delivery modes. The methods may also be applied to radiation-dose calculations based on radiation sources that include linear accelerators, various delivery devices, field shaping components, such as jaws, blocks, flattening filters, and multi-leaf collimators, and to many other radiation-related problems, including radiation shielding, detector design and characterization; thermal or infrared radiation, optical tomography, photon migration, and other problems.
Owner:TRANSPIRE
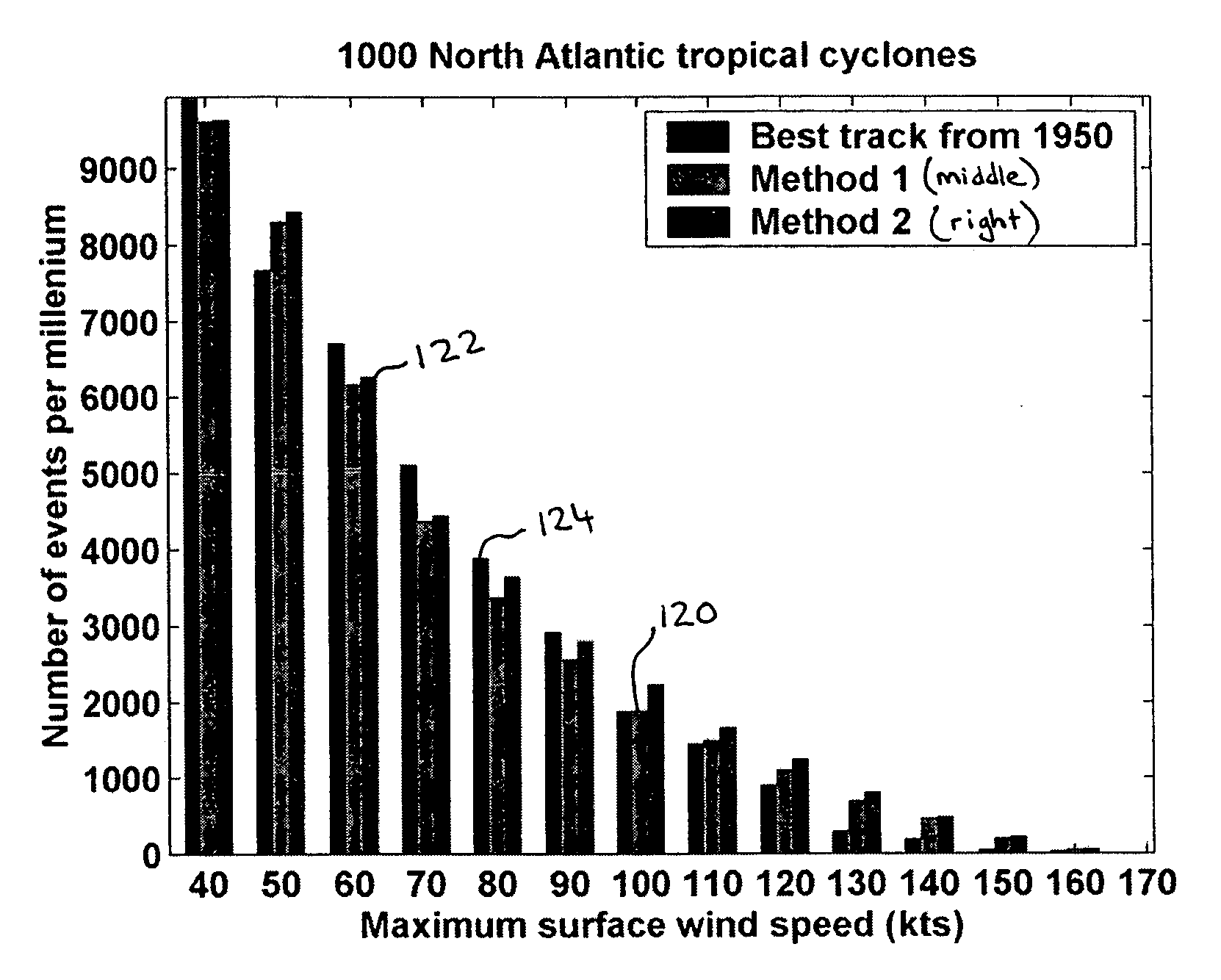
Statistical-deterministic approach to natural disaster prediction
ActiveUS20070168155A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsWeather condition predictionDeterministic methodNatural disaster
A combined statistical-deterministic approach to methods and systems for assessing risk associated with natural disasters, in particular, hurricane wind risk. One example of a method of predicting wind speed distribution within a predetermined distance from a point of interest includes steps of statistically synthesizing a large plurality of wind storm tracks that pass within a predetermined radius of the point of interest, running a deterministic simulation of wind intensity along each one of the large plurality of wind storm tracks to produce an output representative of wind speed distribution along each track, and using the output to estimate an overall wind speed probability distribution from a combination of the wind speed distributions along each track within the predetermined distance from the point of interest.
Owner:RAVELA SAI +1
Methods and apparatus for allocating resources in the presence of uncertainty
InactiveUS6625577B1ResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsOrganizational resourceDeterministic method
A method of allocating resources in the presence of uncertainty is presented. The method builds upon deterministic methods and initially creates and optimizes scenarios. The invention employs clustering, line-searching, statistical sampling, and unbiased approximation for optimization. Clustering is used to divide the allocation problem into simpler sub-problems, for which determining optimal allocations is simpler and faster. Optimal allocations for sub-problems are used to define spaces for line-searches; line-searches are used for optimizing allocations over ever larger sub-problems. Sampling is used to develop Guiding Beacon Scenarios that are used for generating and evaluating allocations. Optimization is made considering both constraints, and positive and negative ramifications of constraint violations. Applications for capacity planning, organizational resource allocation, and financial optimization are presented.
Owner:JAMESON JOEL
Display device with an array of display drivers recessed onto a substrate
InactiveUS6998644B1Gas-filled discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDeterministic methodField emission display
Apparatuses and methods for forming displays are claimed. One embodiment of the invention relates to dispensing display drivers over a substrate. The display drivers, for example, may be a plurality of emitters and gates in order to form a display such as a field emission display (FED). Alternatively, the display drivers may be rods for a plasma display. Another embodiment of the invention relates to forming an electronic device along a length of substrate using template transfer or FSA to deposit display drivers into recessed regions or holes of a substrate. Another embodiment of the invention relates to using FSA and a deterministic method such as “pick and place” to place display drivers onto a substrate. Another embodiment of the invention relates to using donor transfer of display drivers to a substrate.
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
Method for calculation radiation doses from acquired image data
InactiveUS20080091388A1Fast rebuildMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComputation using non-denominational number representationDeterministic methodComputer science
Various embodiments of the present invention provide processes for applying deterministic radiation transport solution methods for calculating doses and predicting scatter in radiotherapy and imaging applications. One method embodiment of the present invention is a process for using deterministic methods to calculate dose distributions resulting from radiotherapy treatments, diagnostic imaging, or industrial sterilization, and for calculating image scatter for the purposes of image reconstruction. In one embodiment of the present invention, a method provides a means for transport of external radiation sources through field-shaping devices. In another embodiment of the present invention, a method includes a process for calculating the dose response at selected points and volumes prior to radiotherapy treatment planning.
Owner:FAILLA GREGORY A +3
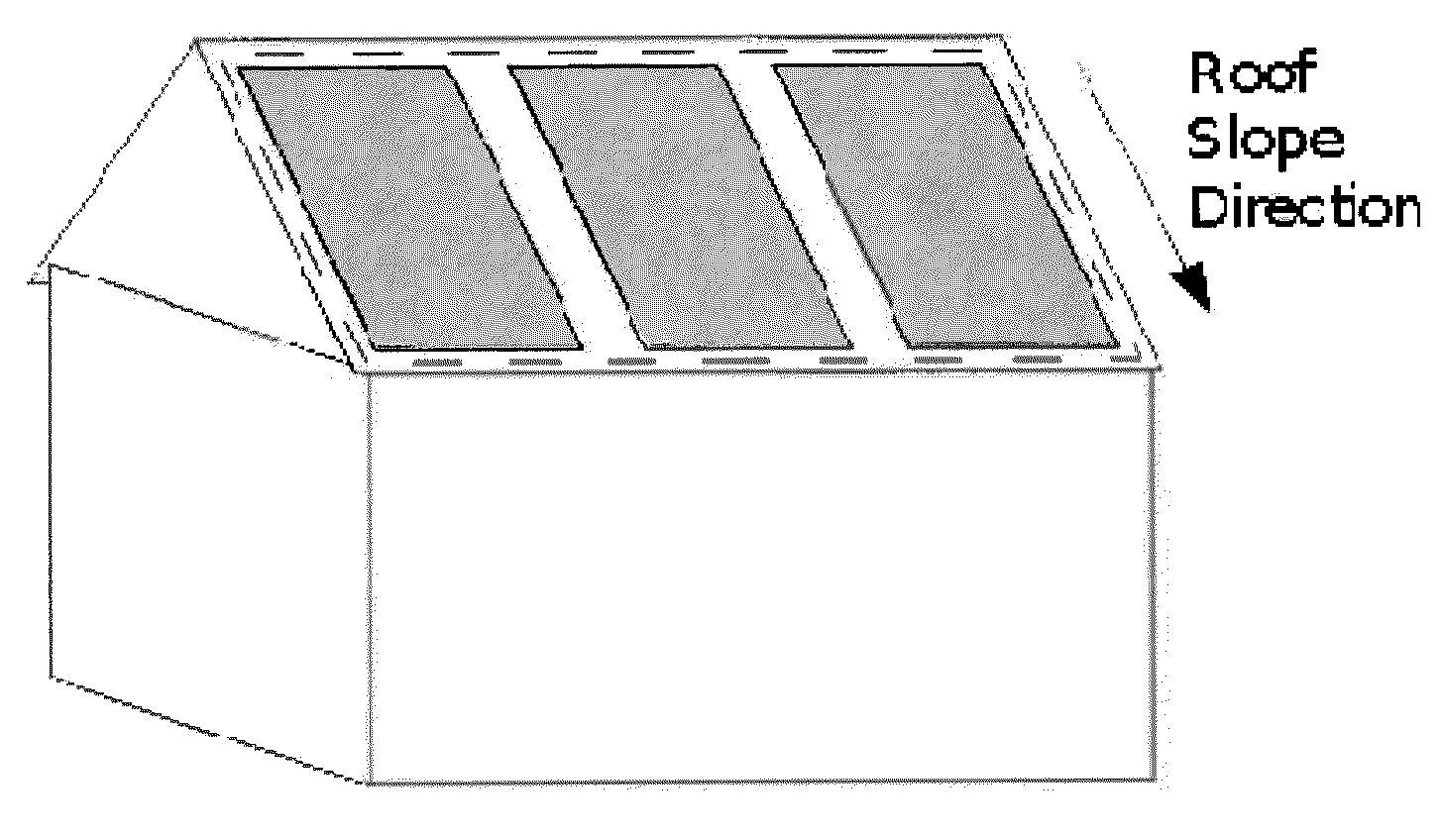
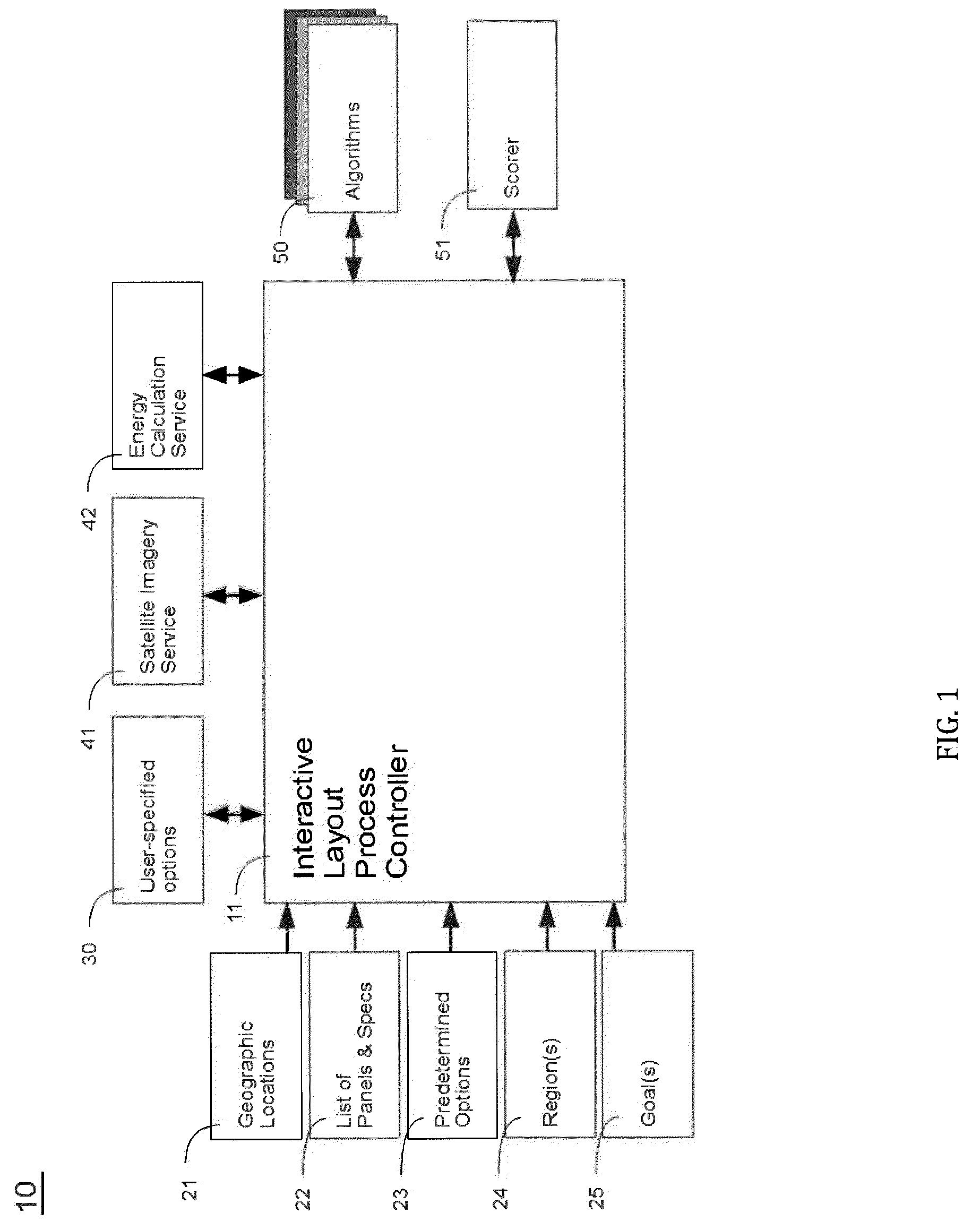
System and Method for Optimized Automated Layout of Solar Panels
InactiveUS20130246010A1Facilitate optimal layoutConvenient rightingPhotovoltaic supportsGeometric CADDeterministic methodGeographic regions
The present invention provides an automated system and method for laying out photovoltaic (PV) solar panels on one or more regions of a roof or ground installation. Automation includes a presentation of optimal comparative layouts, use of different panels (of the same or different manufacturers), and consideration of different energy production characteristics and different layout constraints. Diverse mathematical approaches are used to determine the optimal panel layout for a given geographic region and for particular goals, including, but not limited to, the objective of maximizing the solar production from the designated region(s). The application of two such mathematical algorithms are detailed as parts of an exemplary embodiment: a deterministic edge-aligned approach as well as a nondeterministic approach that employs a genetic evolution simulation.
Owner:MODSOLAR
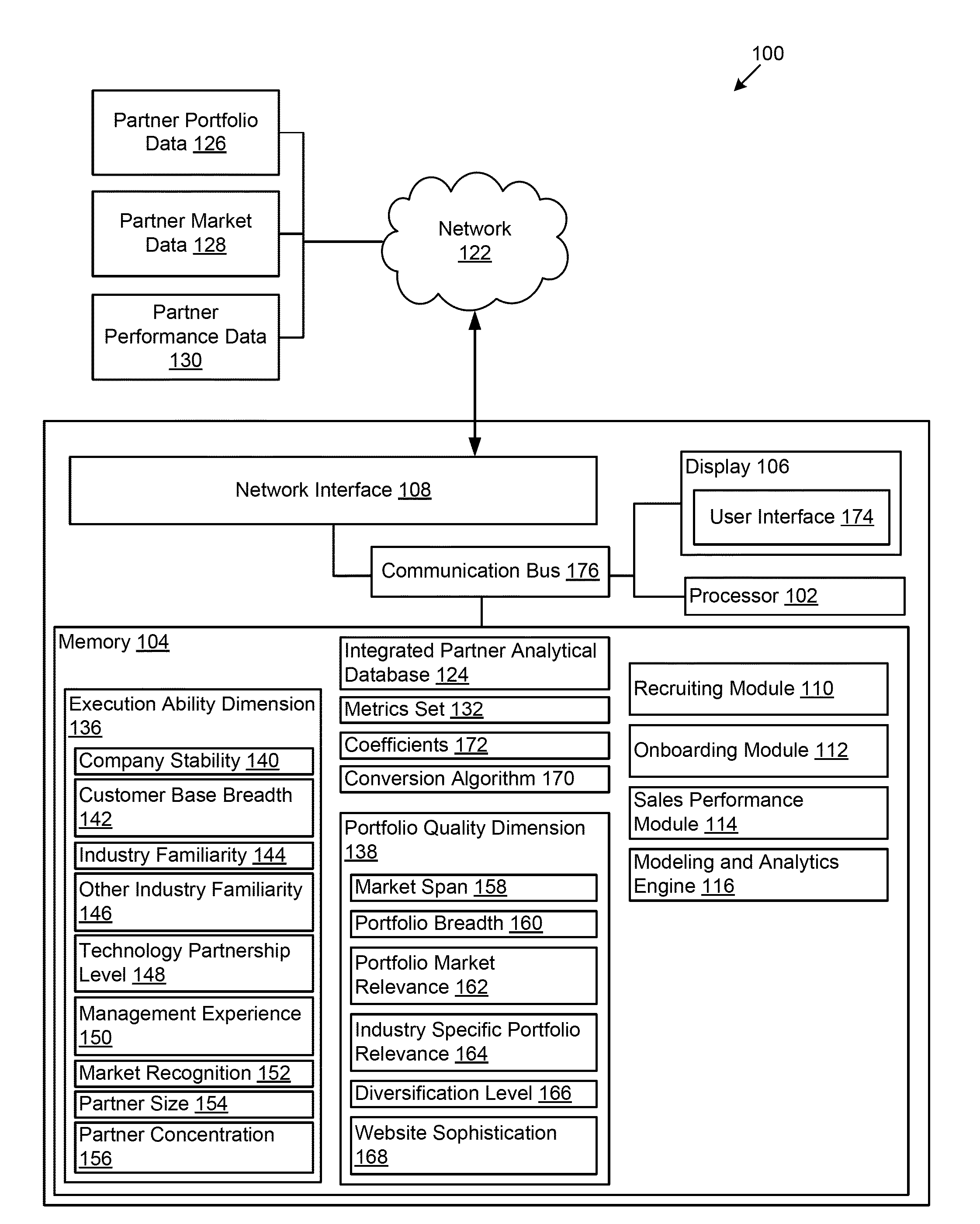
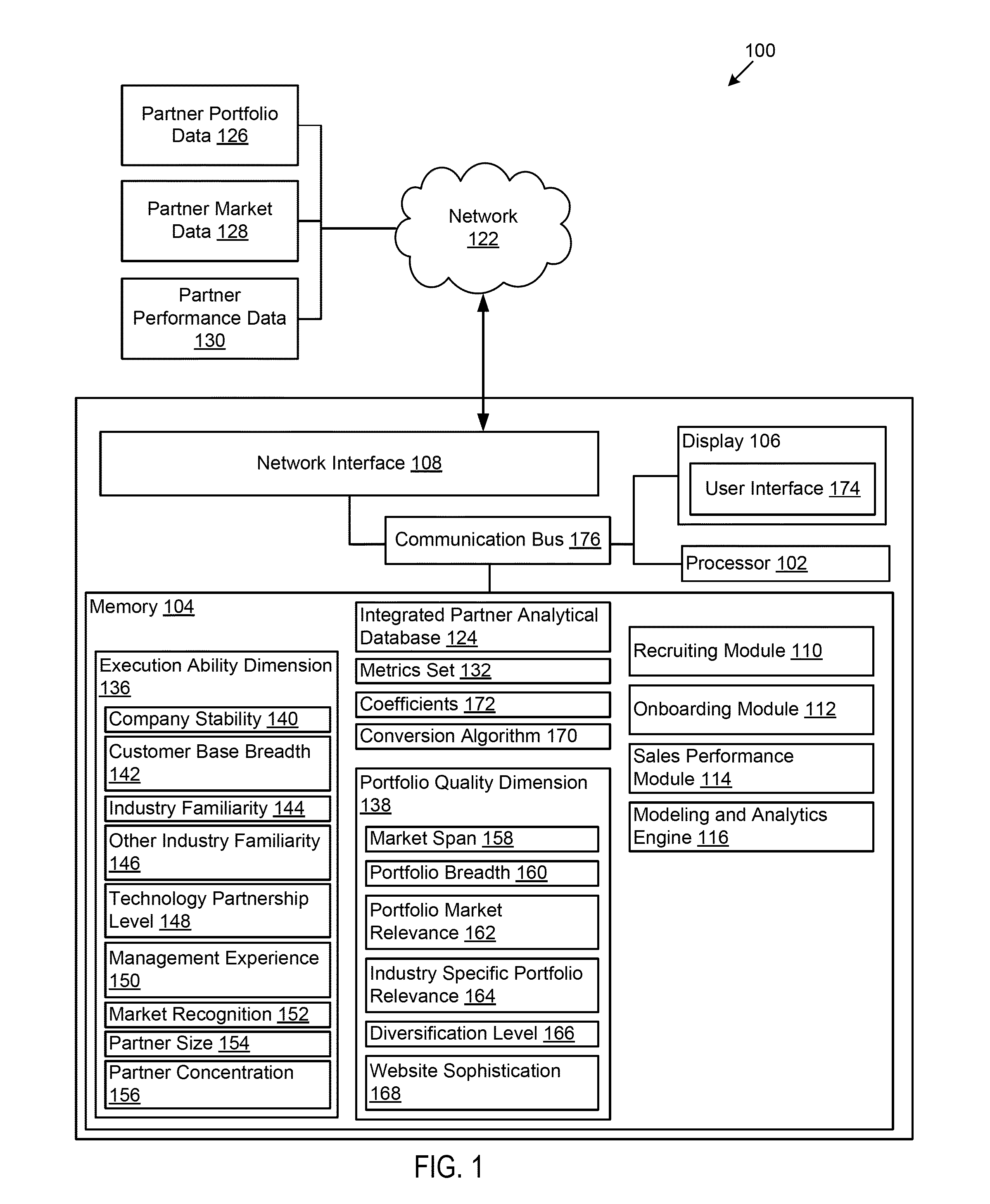
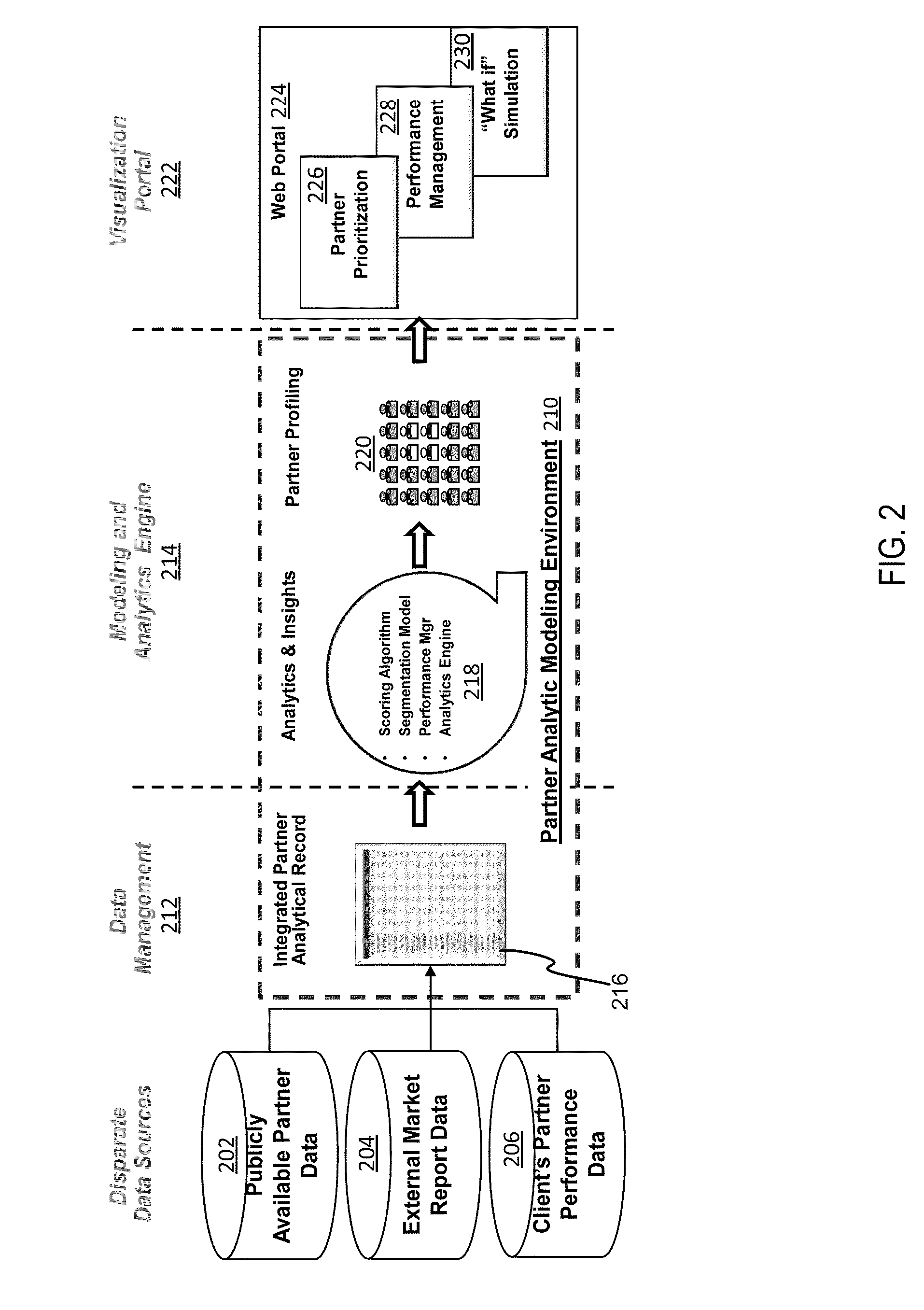
Partner analytics management tool
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Methods apparatus for allocating resources in the presence of uncertainty
InactiveUS20040059621A1ResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsDeterministic methodOrganizational resource
Owner:JAMESON JOEL
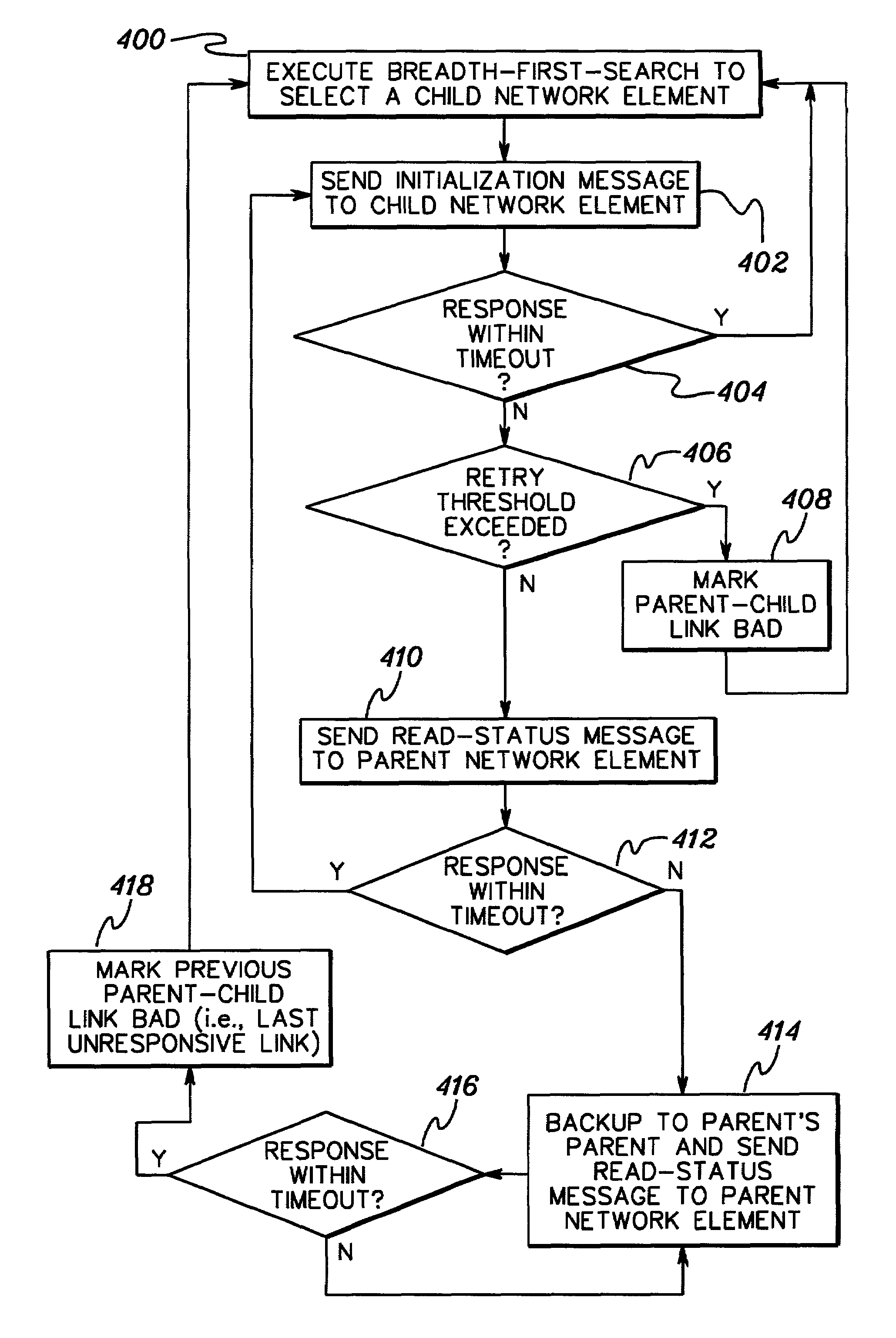
Identifying faulty network components during a network exploration
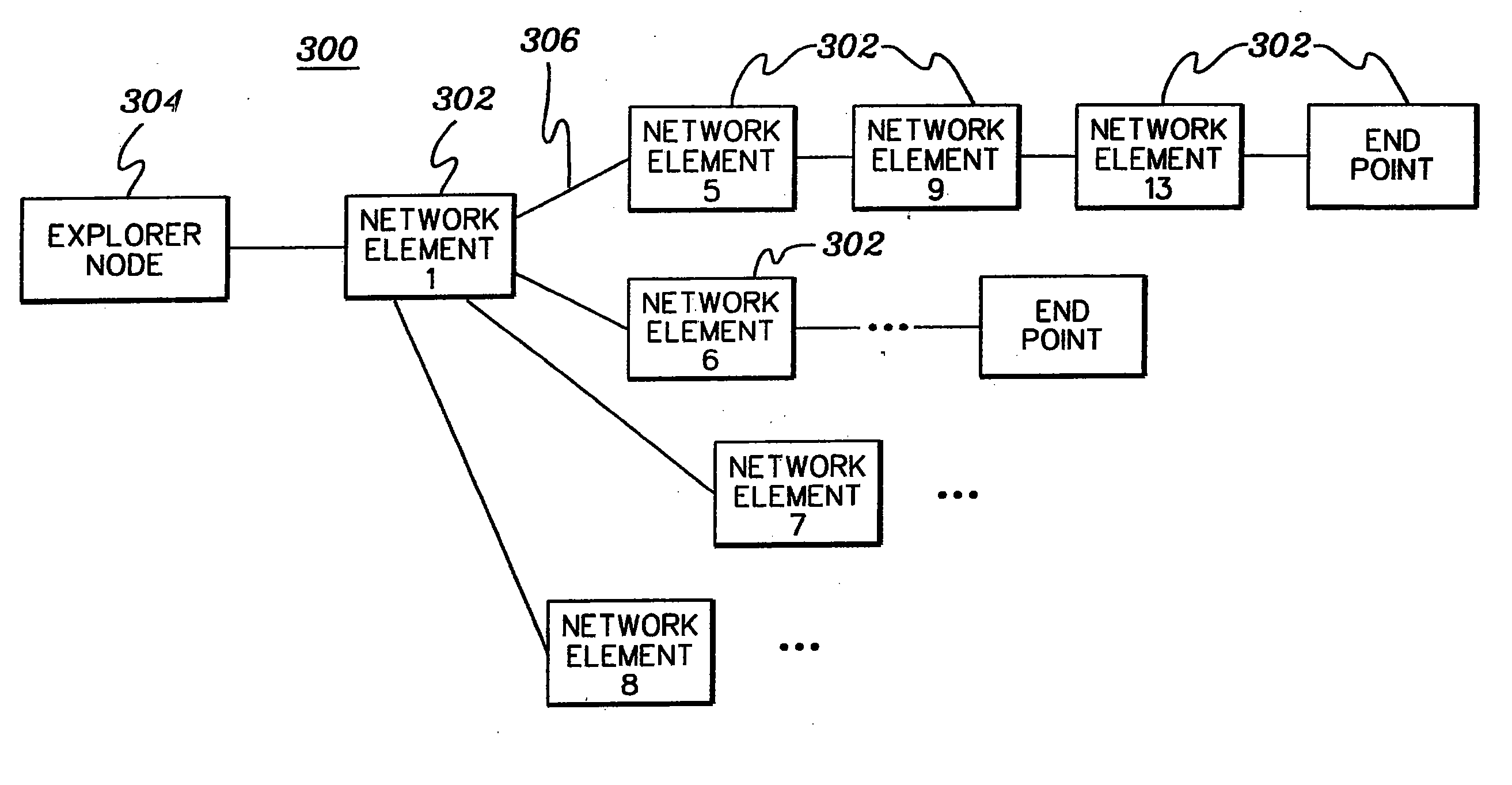
InactiveUS20060268685A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDeterministic methodNetwork exploration
A network exploration is performed to initialize one or more network elements of the network. If during the network exploration a failure is encountered, a systematic and deterministic approach is used to accurately and particularly identify the faulty network component that caused the failure.
Owner:IBM CORP
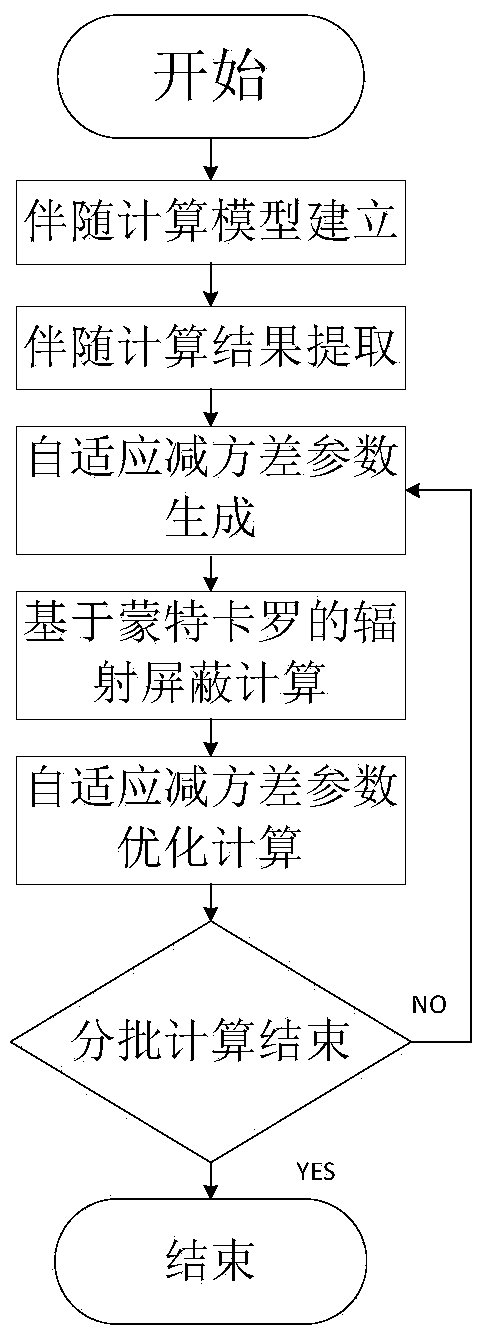
Radiation shielding calculation method based on monte carlo self-adaptive variance reduction
ActiveCN104376217AReduce calculation varianceReduce usageSpecial data processing applicationsDeterministic methodSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a radiation shielding calculation method based on monte carlo self-adaptive variance reduction. Based on a traditional monte carlo method based on weight window variance reduction, according to the specific condition that a deterministic method of the traditional monte carlo method accompanies the flux calculation result, importance parameters are worked out, the parameters are written into an input file of a radiation shielding calculation program based on the monte carlo, and then radiation shielding calculation is conducted. In the process of radiation shielding calculation based on the monte carlo, when the importance parameters obtained in the previous step conduct bias transport on particles while a particle track is stored, that is, lattice cells where all the particles pass are given, a user is helped to automatically interfere with and adjust the set of geometric regional importance parameters in the simulation process, new lattice cell importance parameters are used in the subsequent calculation, and automatic bias is achieved. By means of the radiation shielding calculation method based on monte carlo self-adaptive variance reduction, using of the traditional monte carlo method based on the experimental weight window variance reduction is avoided, and the effects of conducting radiation shielding calculation accurately and rapidly are achieved.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
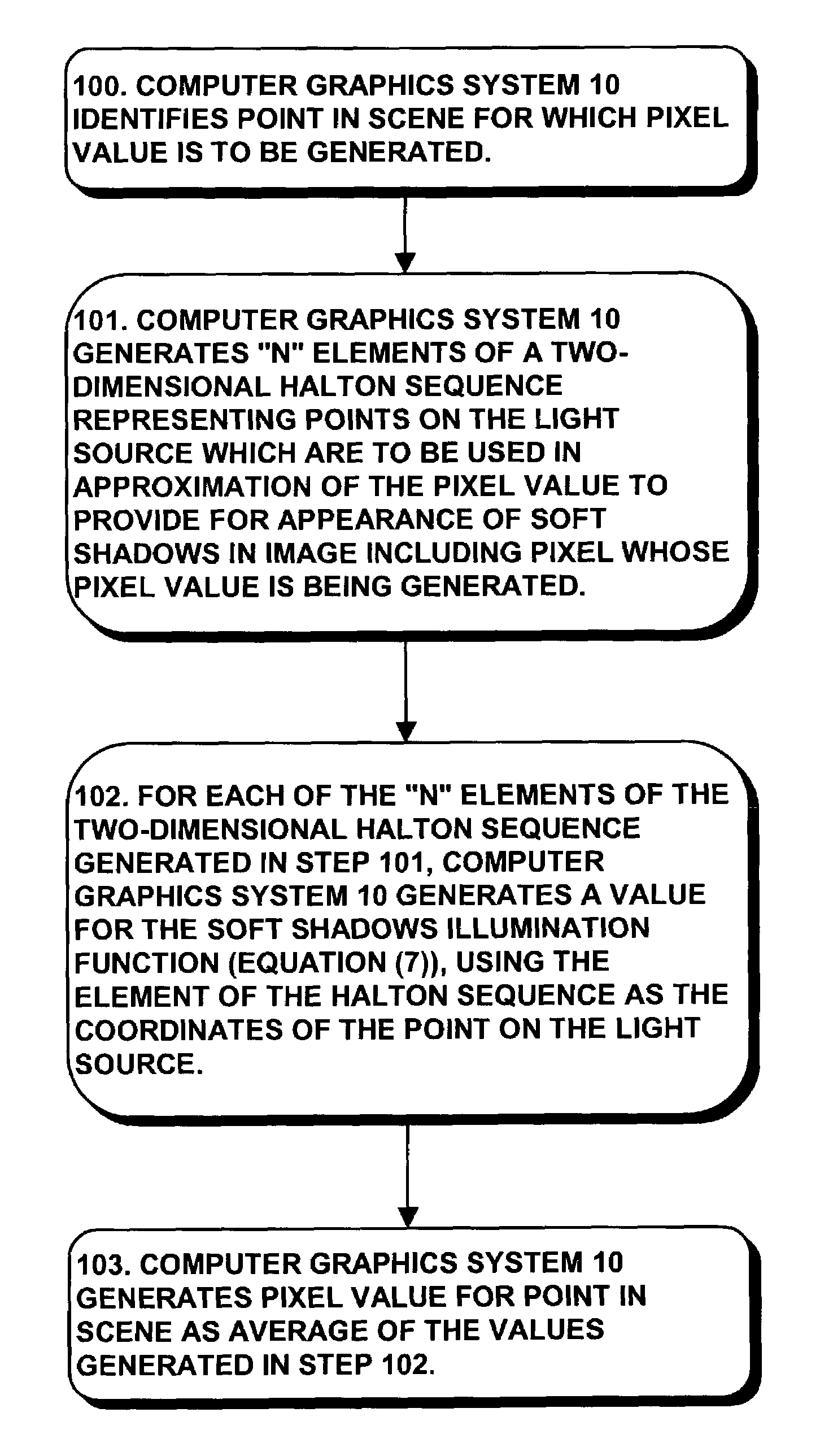
System and method for generating pixel values for pixels in an image using strictly deterministic methodologies for generating sample points
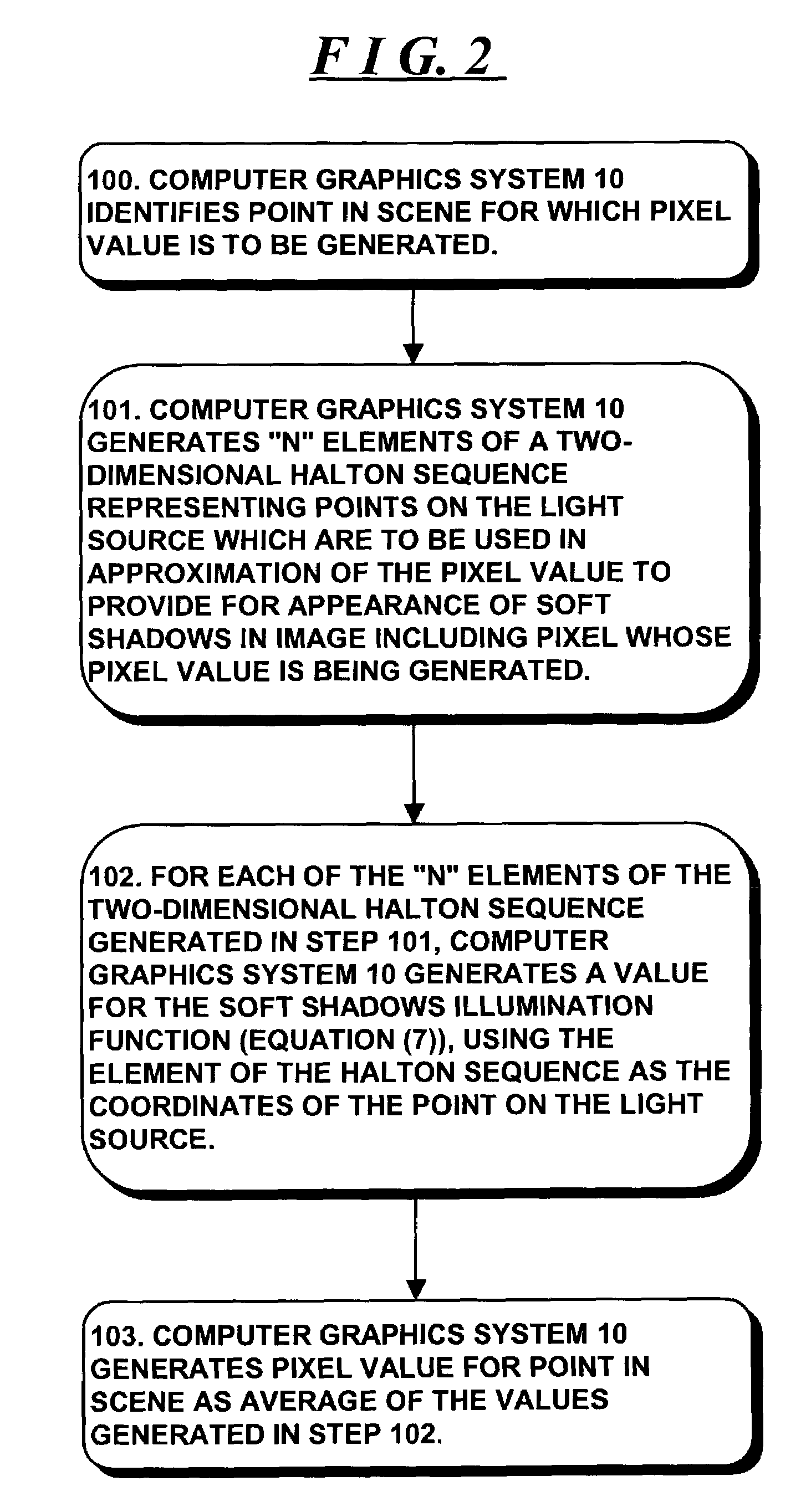
InactiveUS7071938B2Reduce errorsPromote generationCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphicsDeterministic method
A computer graphics system generates pixel values for pixels in an image of objects in a scene, using strictly-deterministic low-discrepancy sequences, as sample points for evaluating integrals which are used to simulate a number of computer graphic techniques, including soft shadows generated for scenes illuminated by a light source having a finite extent, such as a disk, simulation of depth of field; motion blur; and jittering. The computer graphics system uses the low-discrepancy sequence to generate sample points. The low discrepancy sequences ensure that the sample points are evenly distributed over a respective region or time interval, thereby reducing error in the image which can result from clumping of such sample points which can occur in the Monte Carlo technique. The invention facilitates the generation of images of improved quality when using the same number of sample points at the same computational cost as in the Monte Carlo technique.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
Cyclic delay diversity based transmission with delay hopping
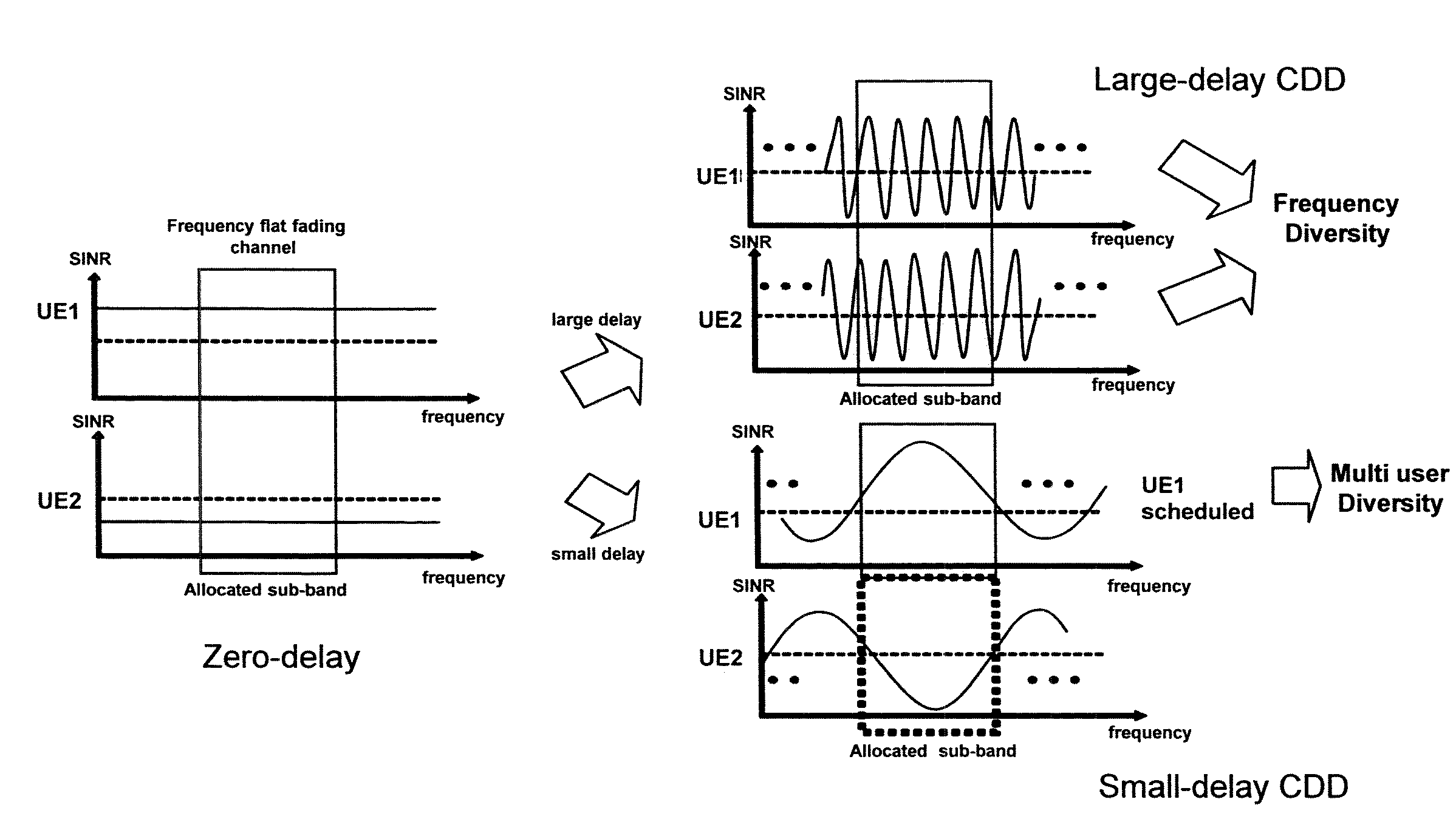
ActiveUS20090275352A1Reduce probabilityIncrease probabilitySimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulated-carrier systemsCyclic delay diversityDeterministic method
A method of providing delay information in a multi-antenna transmission system is provided. A time delay value is selected from a set of time delay values. A mobile station is informed of information related to the selected time delay value. The same data is transmitted from a first antenna and from a second antenna. The data is transmitted from the second antenna after the data is transmitted from the first antenna according to the selected time delay value. The time delay value is selected based on a deterministic method or a random method.
Owner:ROSEDALE DYNAMICS LLC
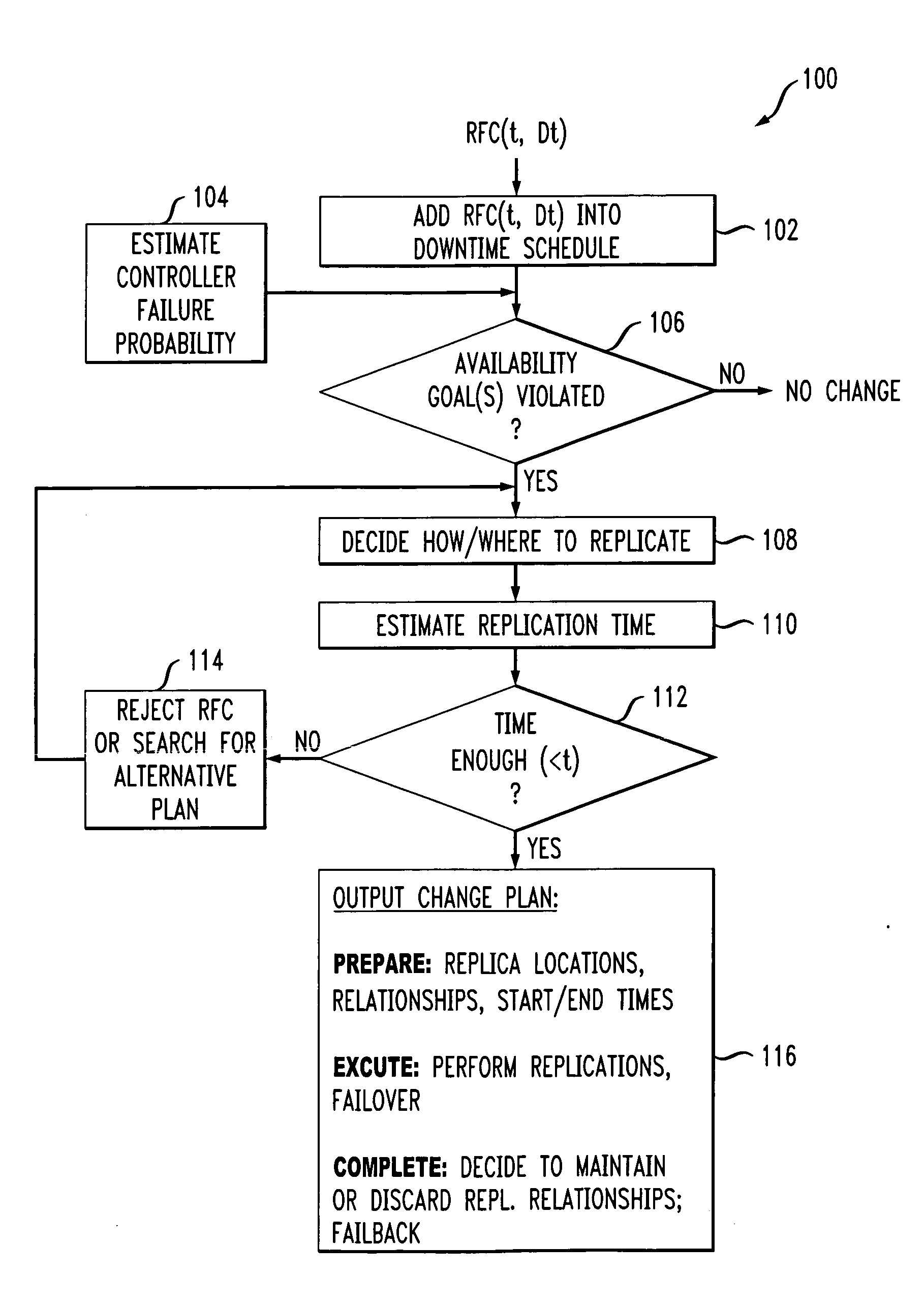
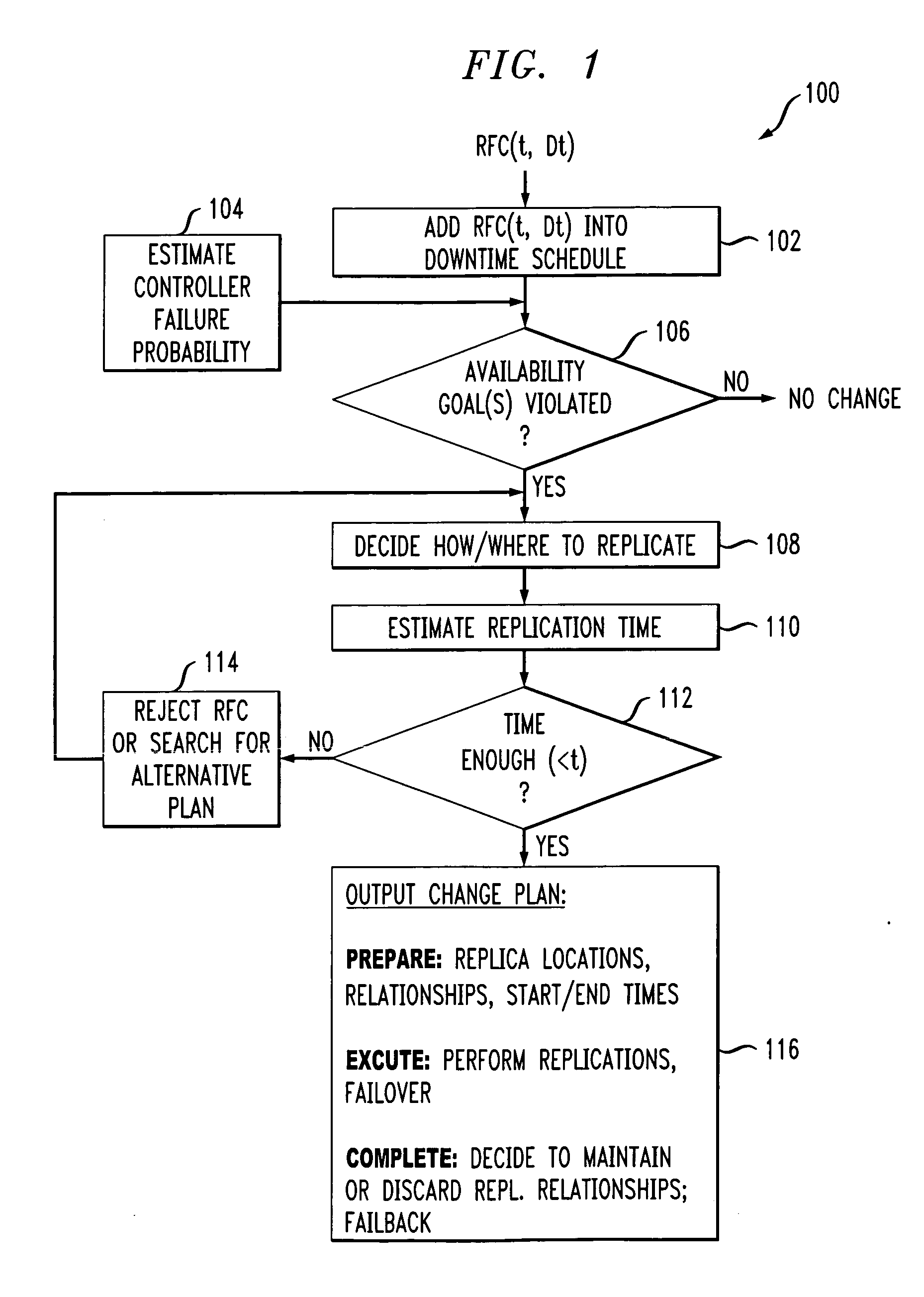
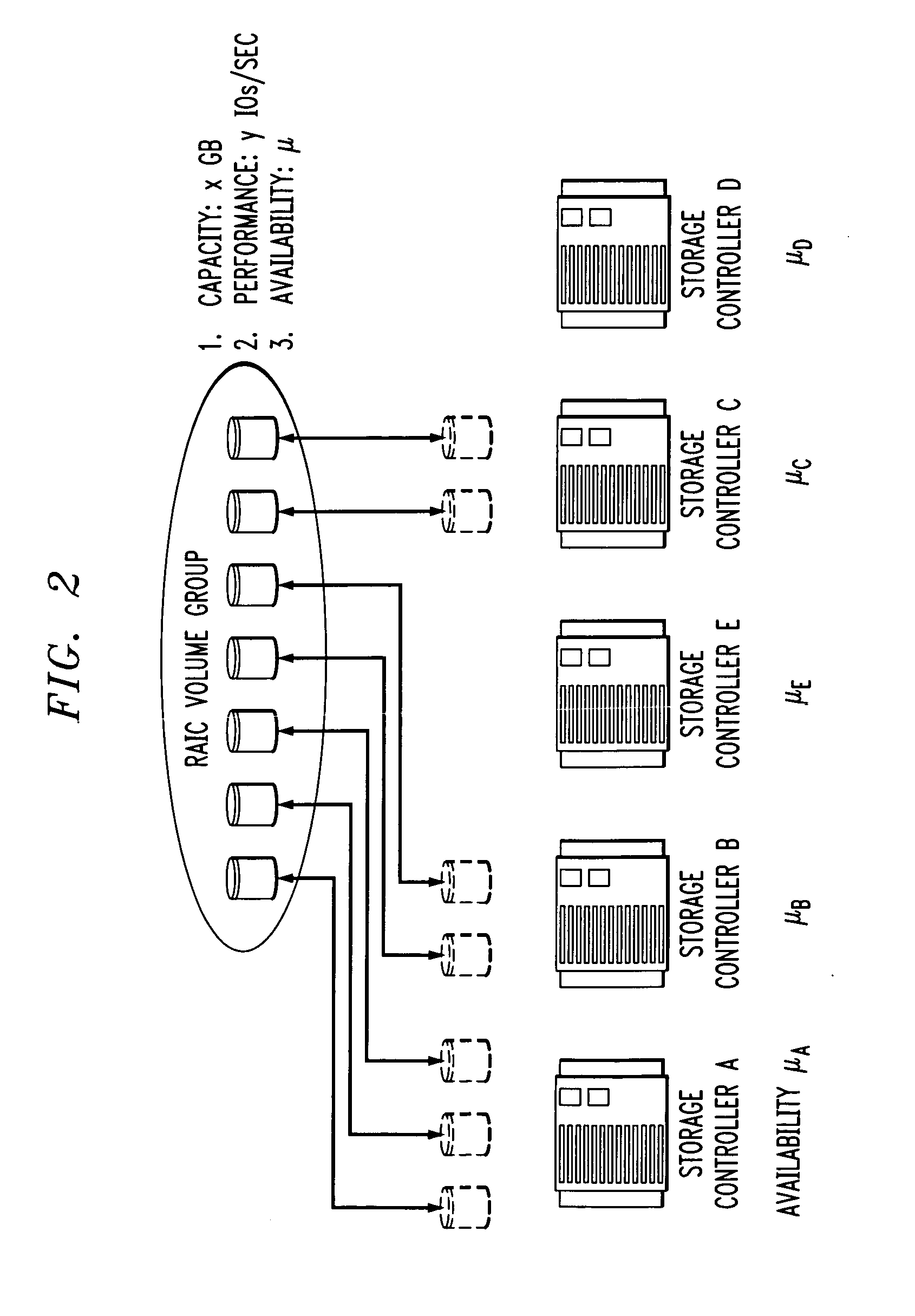
Controlling computer storage systems
Goal-based availability and change management are handled over groups of heterogeneous storage controllers. Probabilistic and deterministic methods are employed to determine the allocation and placement of storage volumes to storage controllers, as well as the degree of data redundancy necessary to achieve data availability goals. The probabilistic methods can take into account past observations of controller availability, and operator beliefs, as well as the state of storage controller configuration, in coming up with a probabilistic estimate of future availability.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Status report missing detection in a communication system
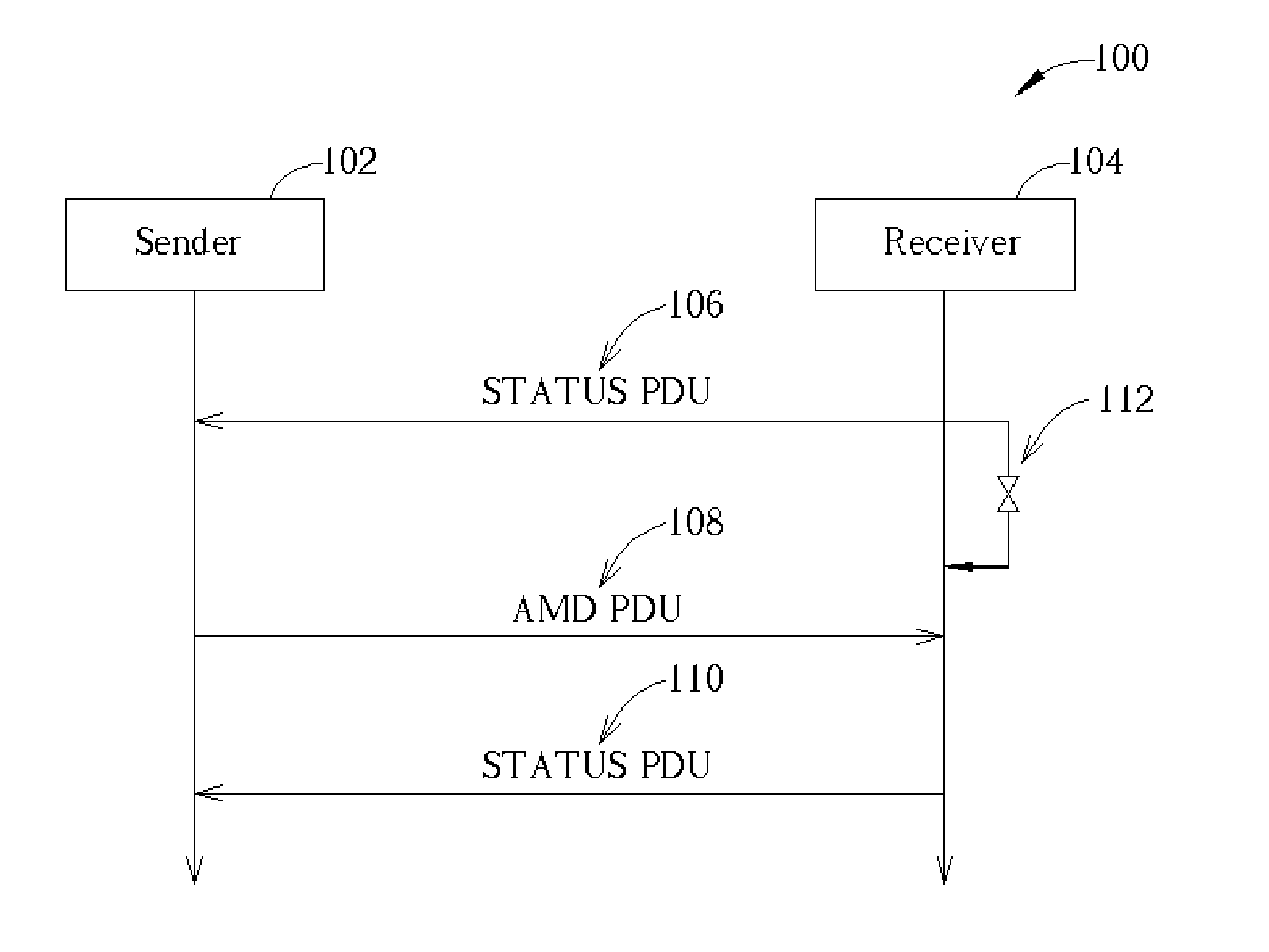
InactiveUS20050066255A1Improve transfer throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching detailsTransmission throughputDeterministic method
A method to detect a lost status report determines that a second status report is required when an AMD PDU not negatively acknowledged in the first status report, an AMD PDU with a polling bit set, or the last negatively acknowledged AMD PDU is received after the expiry of a roundtrip timer and before all the negatively acknowledged AMD PDUs in the first status report are received. The method provides a deterministic way of detecting a lost status report, resulting in improved transmission throughput in a wireless communications system.
Owner:INNOVATIVE SONIC
Statistical-deterministic approach to natural disaster prediction
ActiveUS7734245B2Cosmonautic condition simulationsWeather condition predictionDeterministic methodNatural disaster
A combined statistical-deterministic approach to methods and systems for assessing risk associated with natural disasters, in particular, hurricane wind risk. One example of a method of predicting wind speed distribution within a predetermined distance from a point of interest includes steps of statistically synthesizing a large plurality of wind storm tracks that pass within a predetermined radius of the point of interest, running a deterministic simulation of wind intensity along each one of the large plurality of wind storm tracks to produce an output representative of wind speed distribution along each track, and using the output to estimate an overall wind speed probability distribution from a combination of the wind speed distributions along each track within the predetermined distance from the point of interest.
Owner:RAVELA SAI +1
System and method for generating pixel values for pixels in an image using strictly deterministic methodologies for generating sample points
ActiveUS20050275660A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsComplex mathematical operationsDeterministic methodGraphics
A computer graphics system generates a pixel value for a pixel in an image, the pixel being representative of a point in a scene as recorded on an image plane of a simulated camera. The computer graphics system comprises a sample point generator and a function evaluator. The sample point generator is configured to generate a set of sample points representing at least one simulated element of the simulated camera, the sample points representing elements of, illustratively, for sample points on the image plane, during time interval during which the shutter is open, and on the lens, a Hammersley sequence, and, for use in global illumination, a scrambled Halton sequence. The function evaluator configured to generate at least one value representing an evaluation of said selected function at one of the sample points generated by said sample point generator, the value generated by the function evaluator corresponding to the pixel value.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
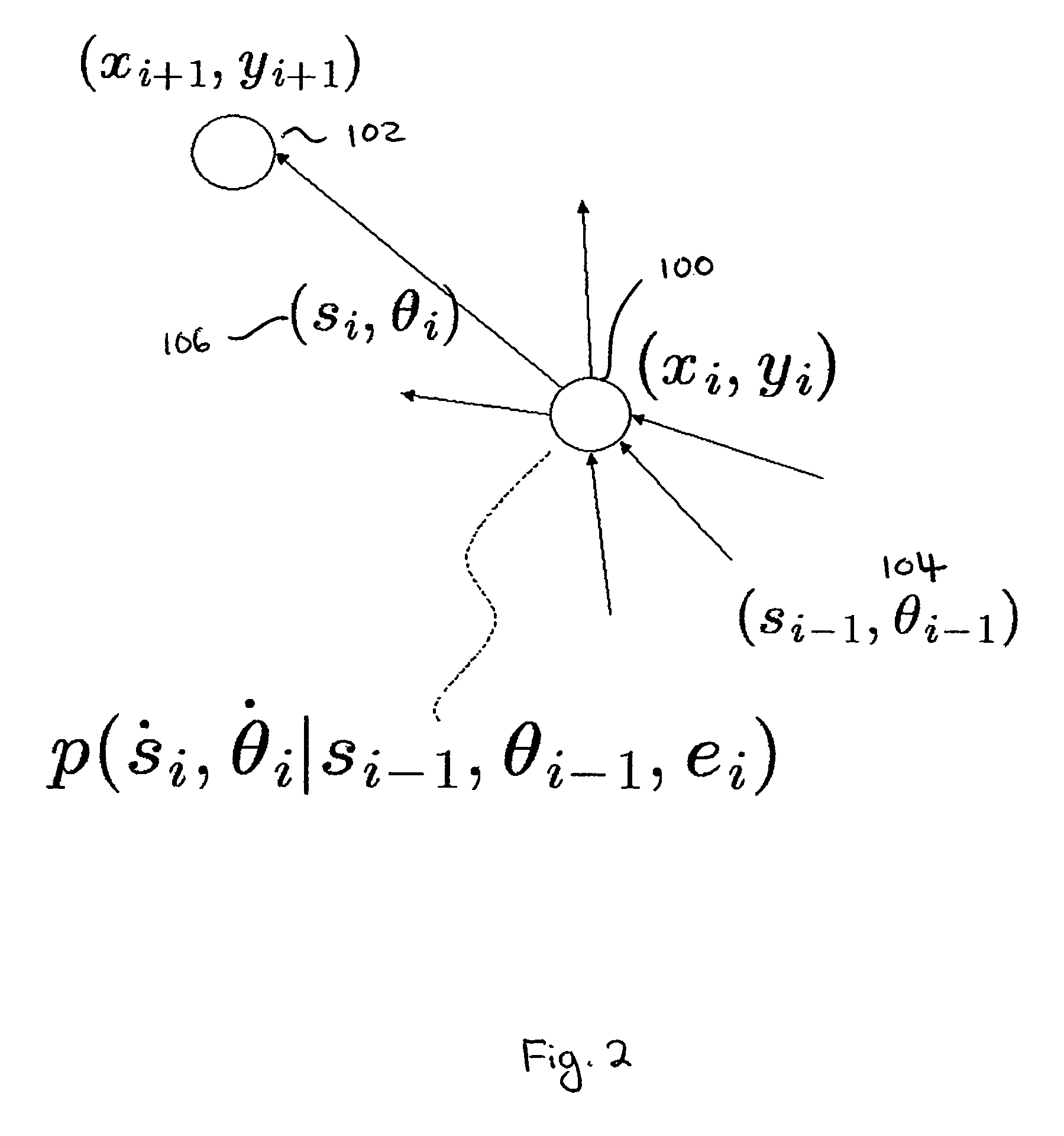
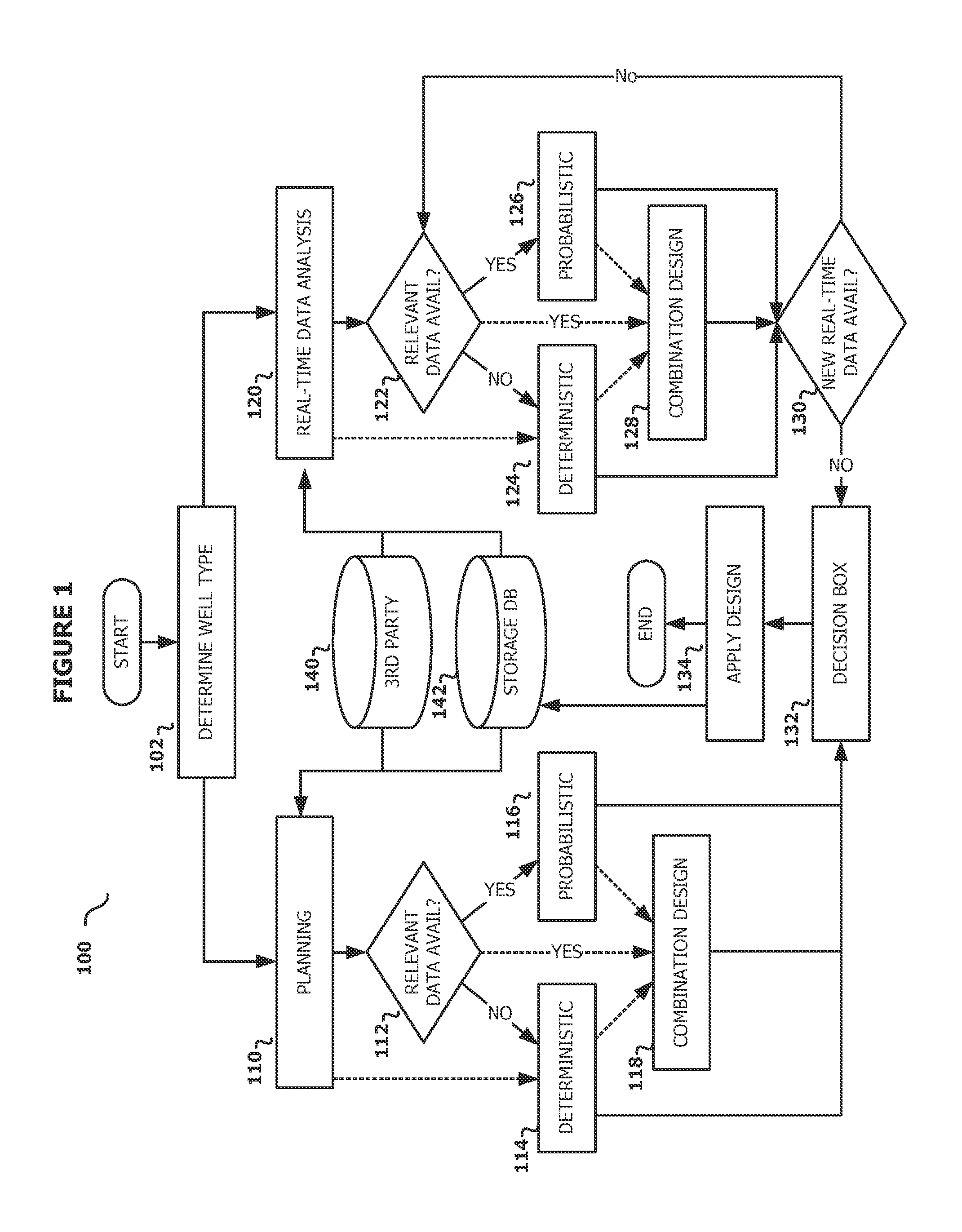
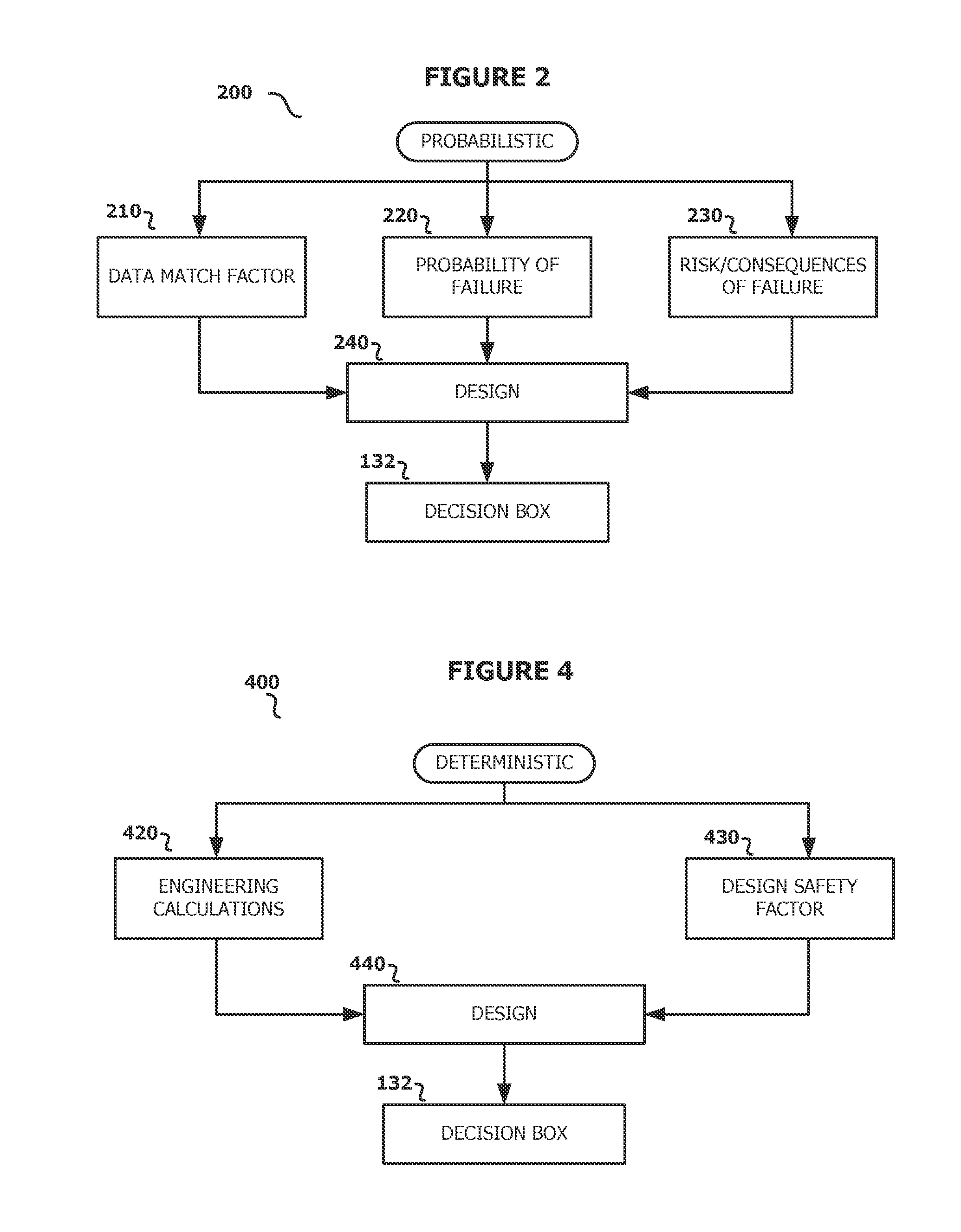
Method and analysis for holistic casing design for planning and real-time
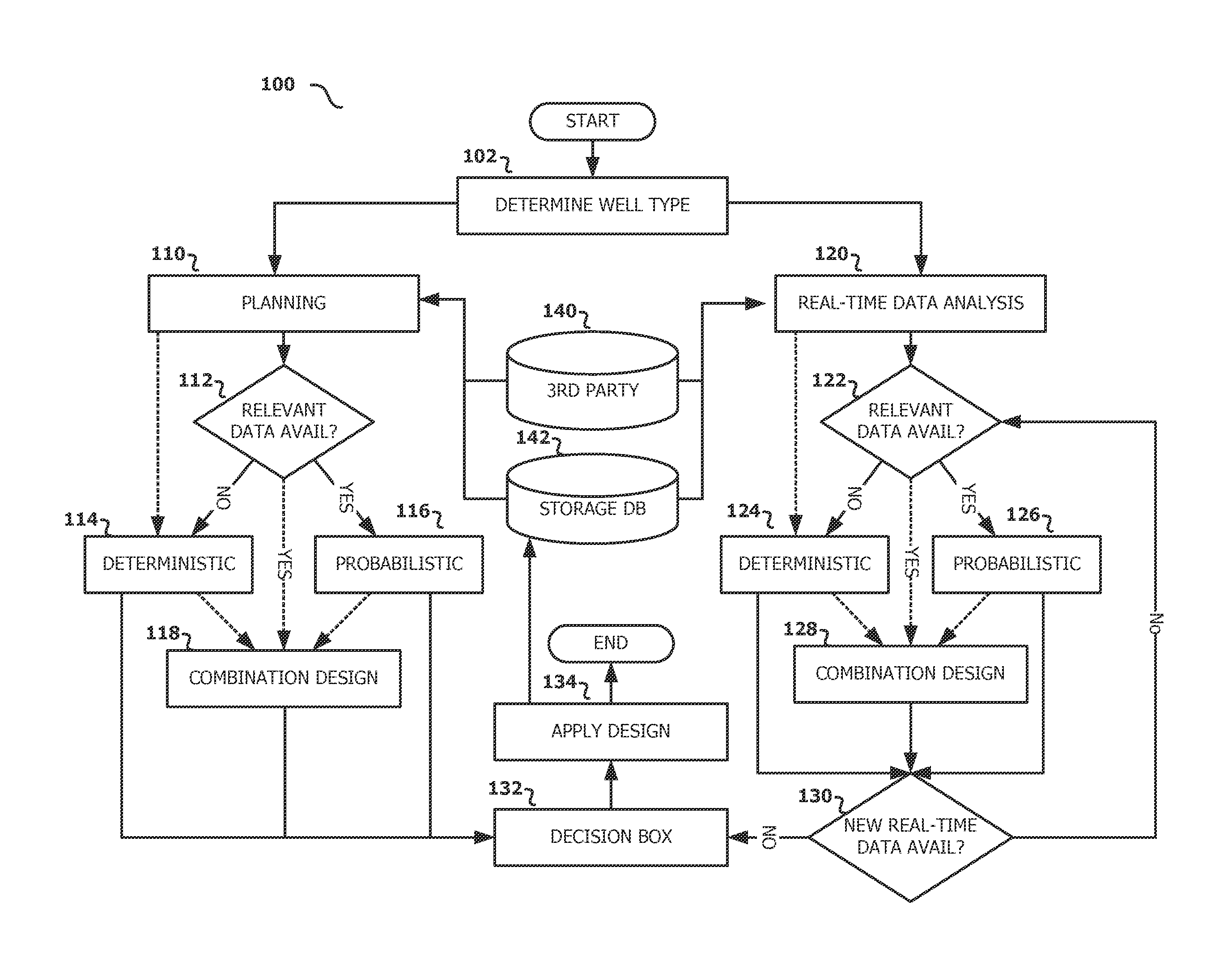
The disclosed embodiments include a method, apparatus, and computer program product for determining a suitable casing design for a well. For example, one disclosed embodiment includes a system that includes at least one processor and at least one memory coupled to the at least one processor and storing instructions that when executed by the at least one processor performs operations for receiving historical data associated with previously drilled wells; in response to a determination that the historical data associated with previously drilled well is relevant to the well, generating a first set of casing designs using a probabilistic approach and generating a second set of casing designs using a combination approach that combines the probabilistic approach with a deterministic approach; and selecting a suitable casing design from a resulting set of casing designs.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
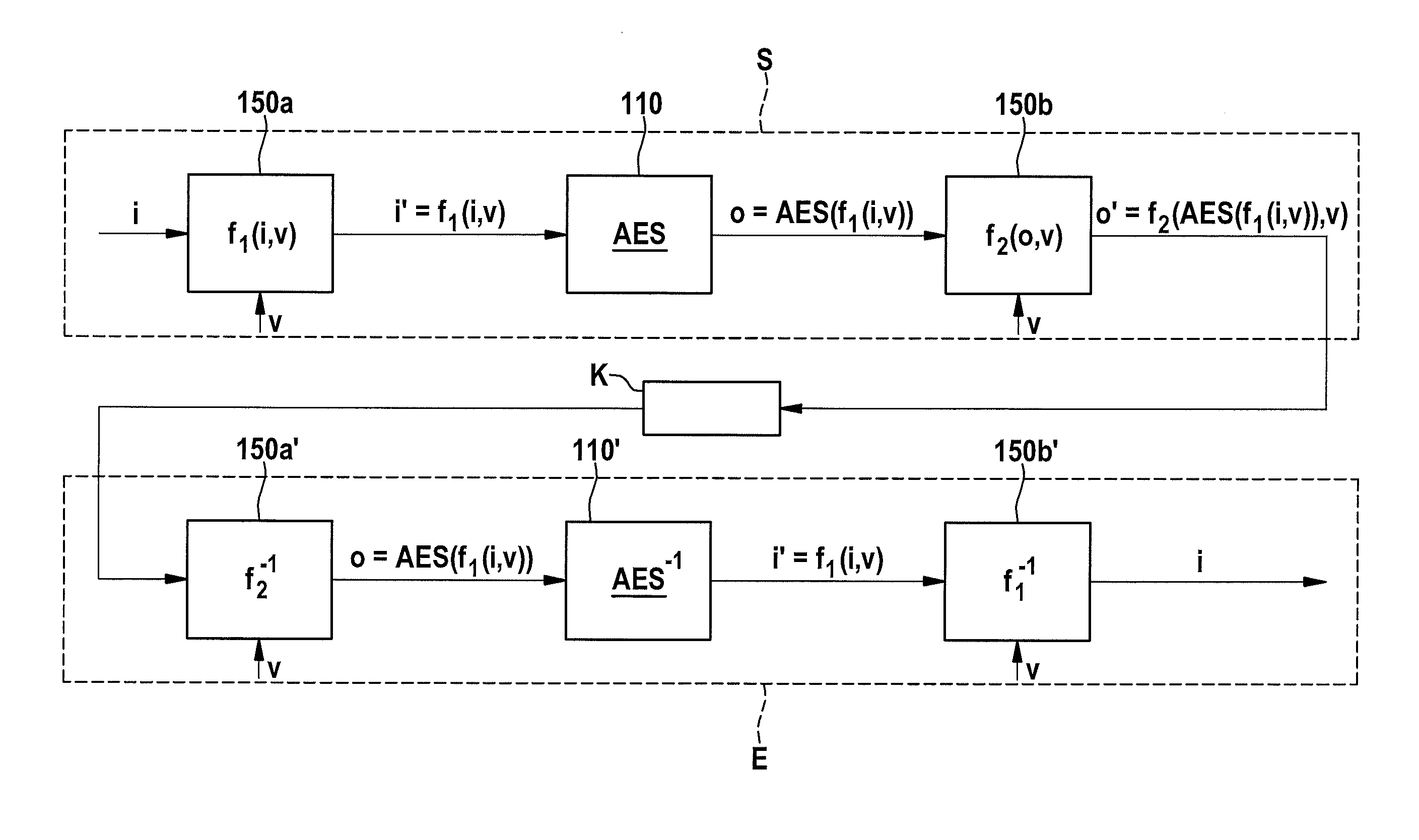
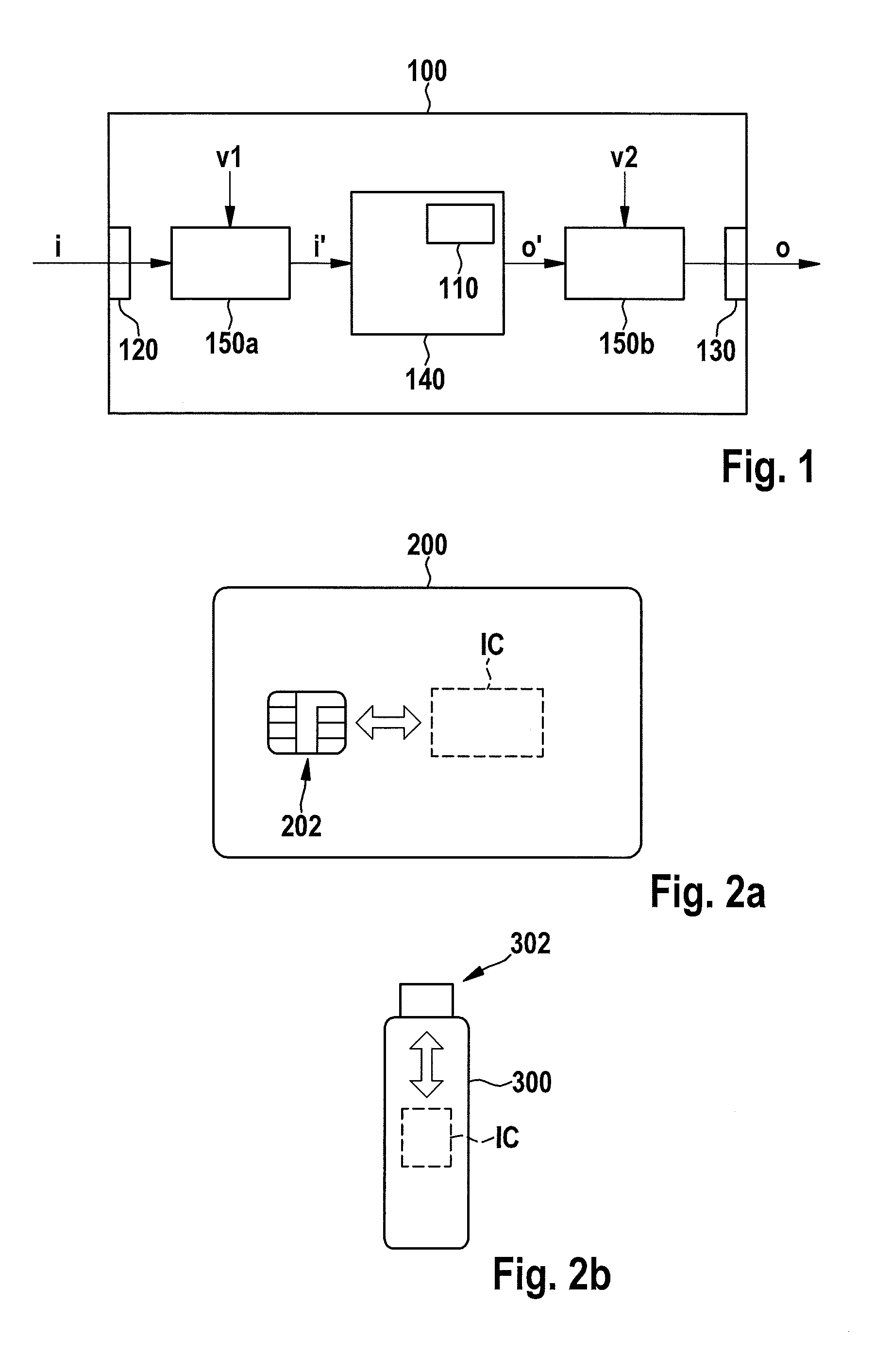
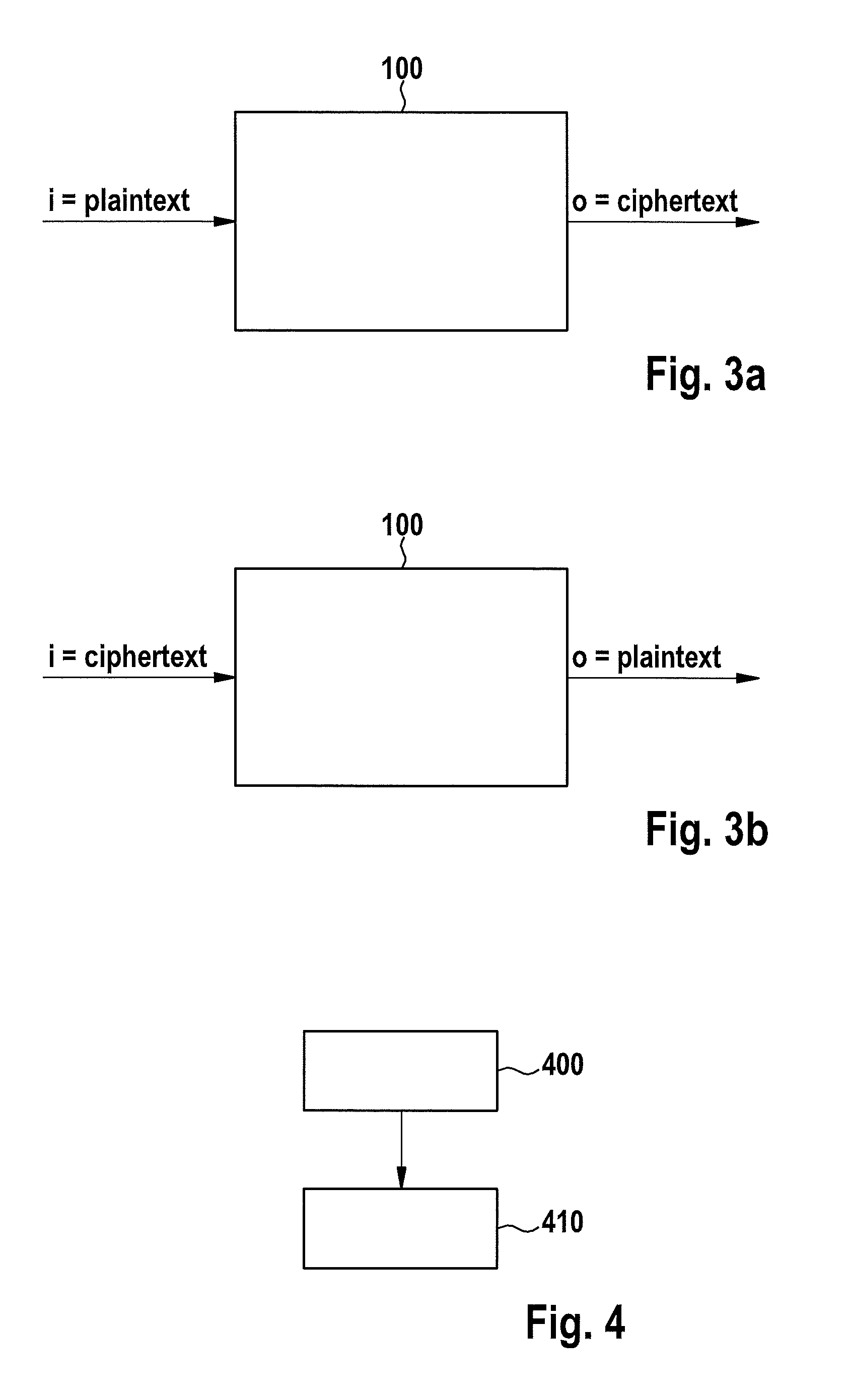
Device for carrying out a cryptographic method, and operating method for same
ActiveUS20130326232A1Improve securityAvoid disadvantagesUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringDeterministic methodData conversion
A device for carrying out a cryptographic method has an input interface for receiving input data, an output interface for outputting output data, and a cryptographic unit for carrying out the cryptographic method. A first functional unit is provided which is designed to convert at least a portion of the input data into transformed input data using a first deterministic method, and to supply the transformed input data to the cryptographic unit, and / or a second functional unit is provided which is designed to convert at least a portion of output data of the cryptographic unit into transformed output data using a second deterministic method, and to supply the transformed output data to the output interface.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
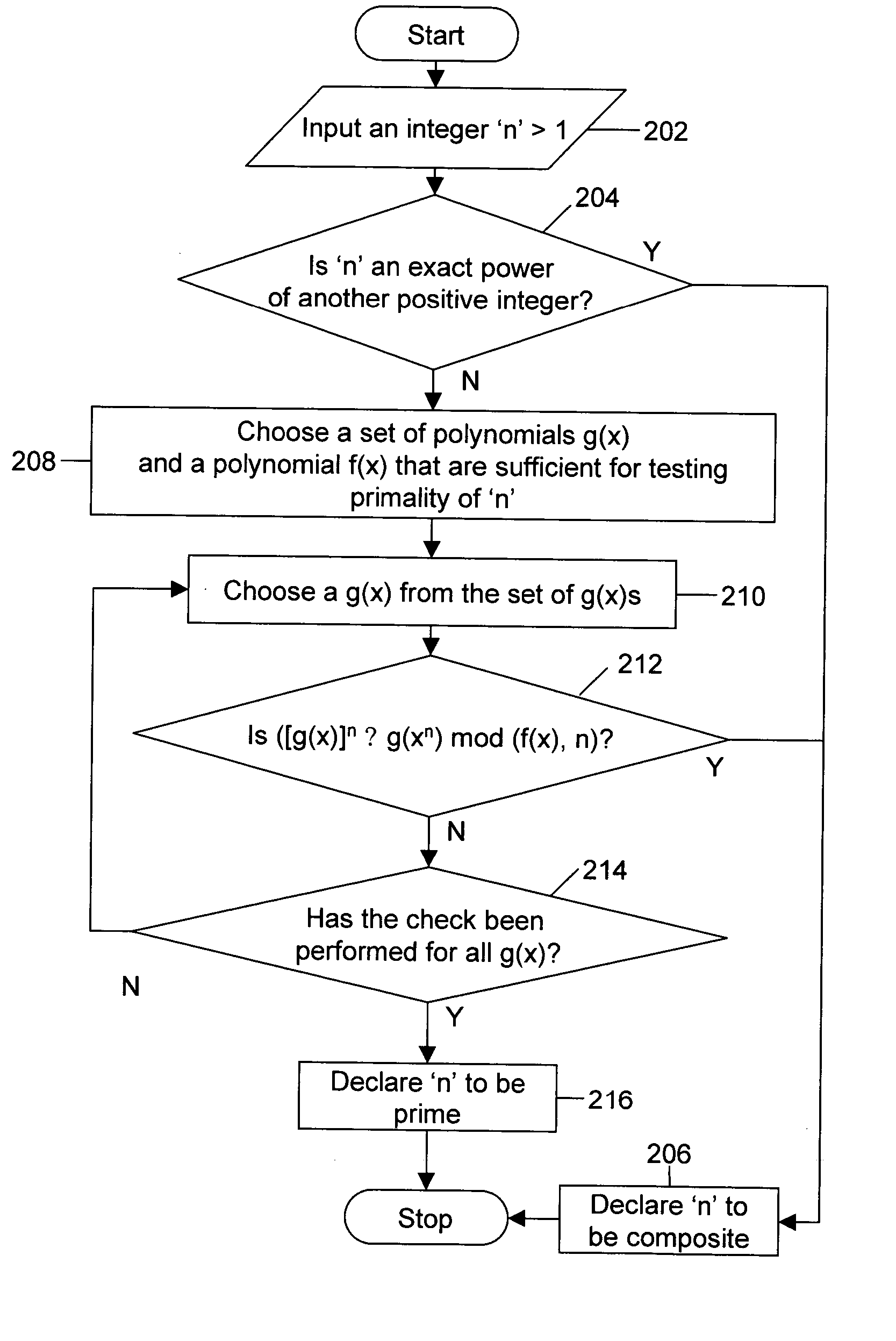
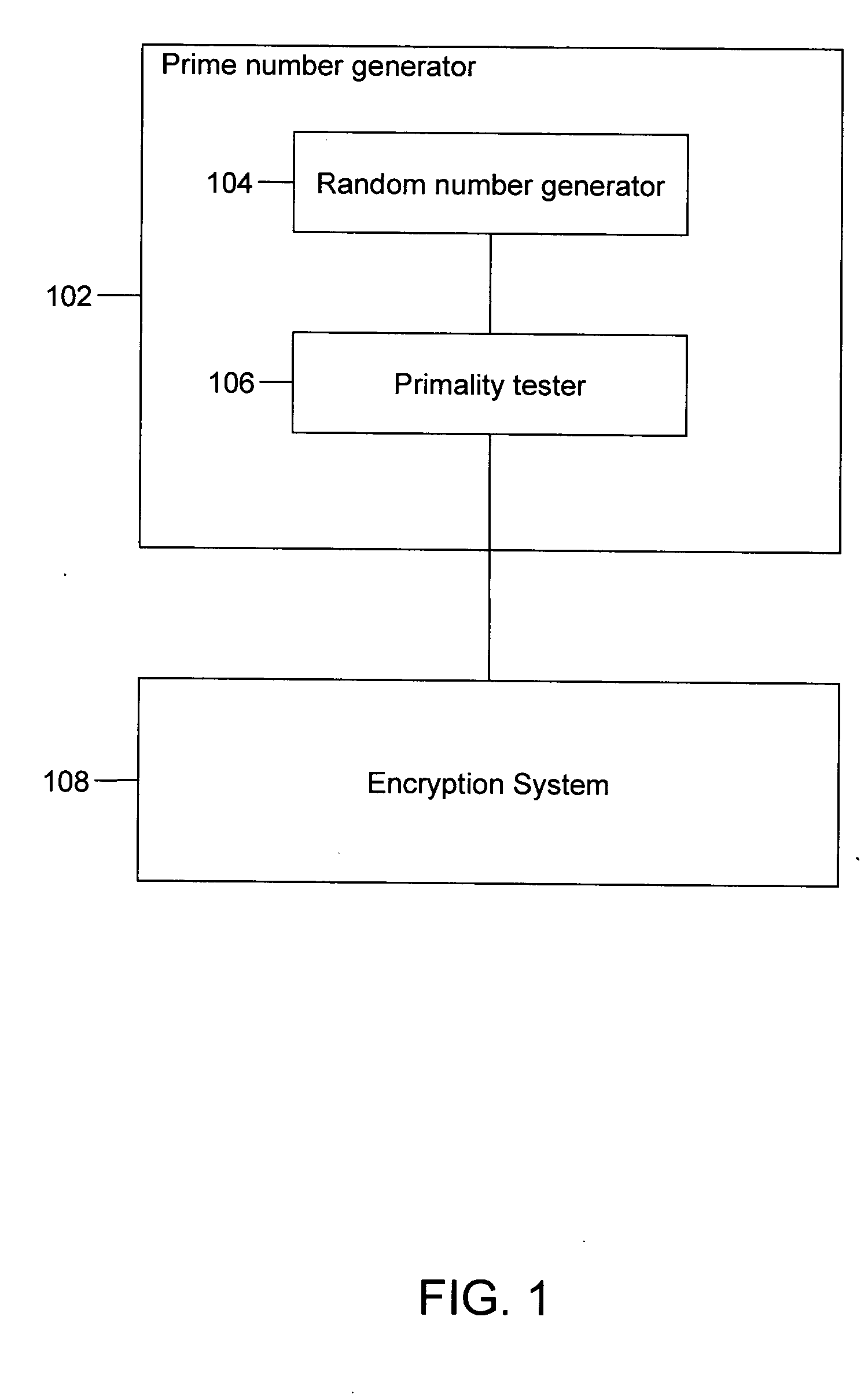
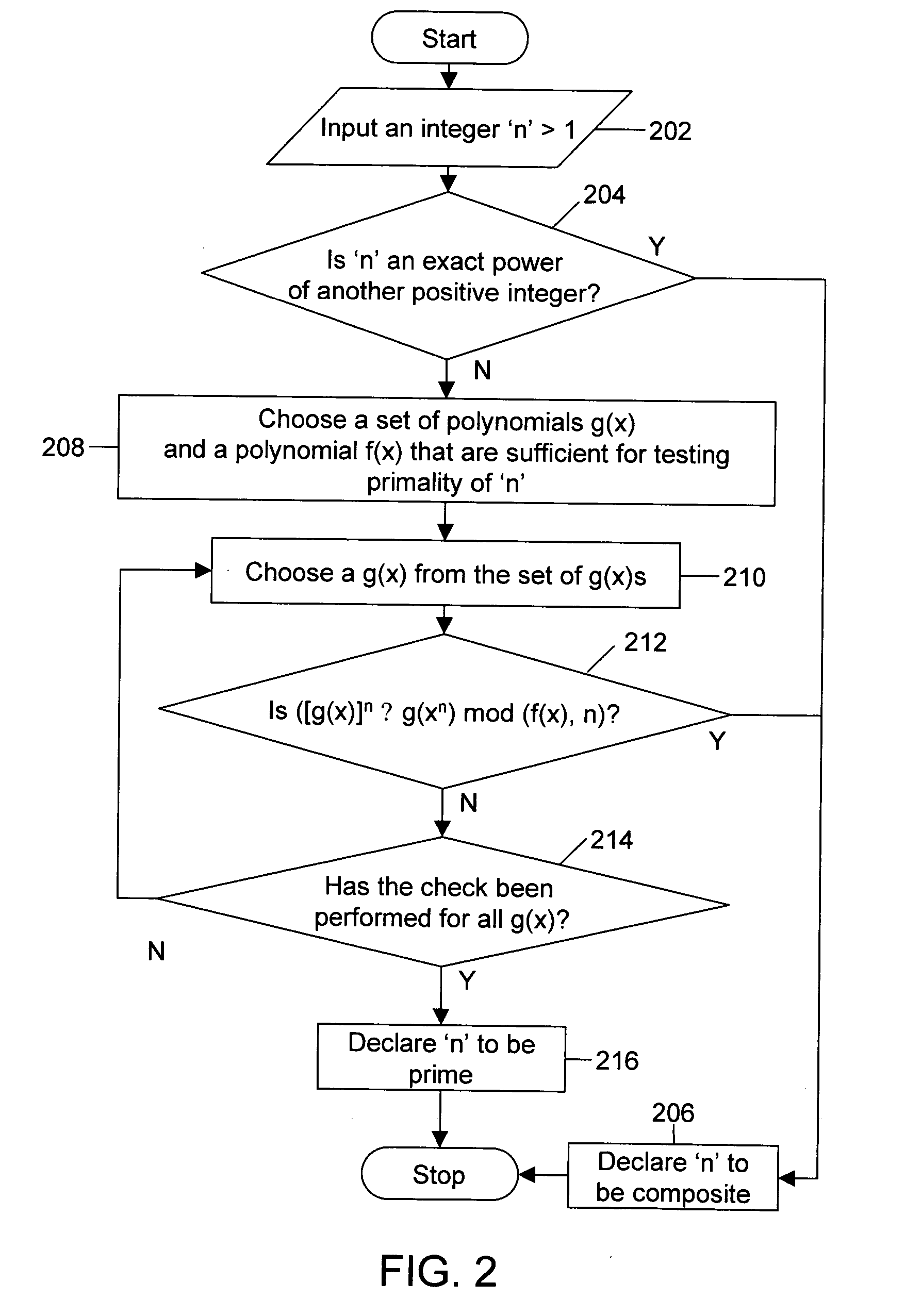
Polynomial time deterministic method for testing primality of numbers
InactiveUS20050027764A1Random number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationDeterministic methodNumber generator
A method and a system for generating prime numbers and testing for primality of an integer. This invention has applicability to “public key” and other encryption techniques that play an important role in the security of information technology and electronic commerce. Generation of prime numbers requires the step of testing the primality. The method includes a deterministic test for testing the primality of a number in polynomial time. The system comprises a random number generator and a primality tester. The random number generator generates a random number and the primality tester tests the primality of this random number. The primality tester can also be used independent of the random number generator. In such a case, the number whose primality is to be tested can be input via a user interface.
Owner:INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KANPUR
Automatic tuning of motion controllers using search techniques
ActiveUS7035694B2Improve performanceGradient is effectivelyComputer controlSimulator controlDeterministic methodControl system
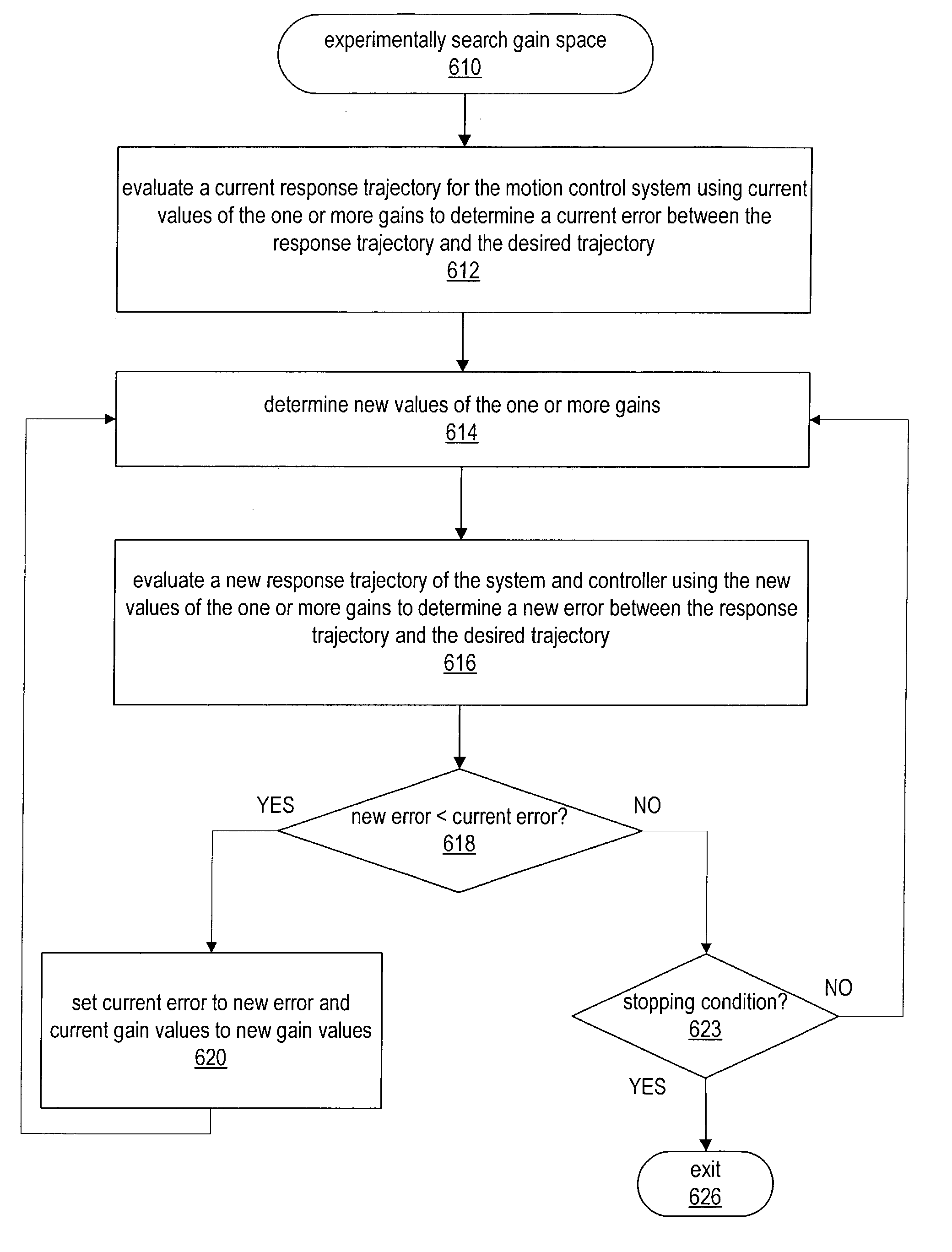
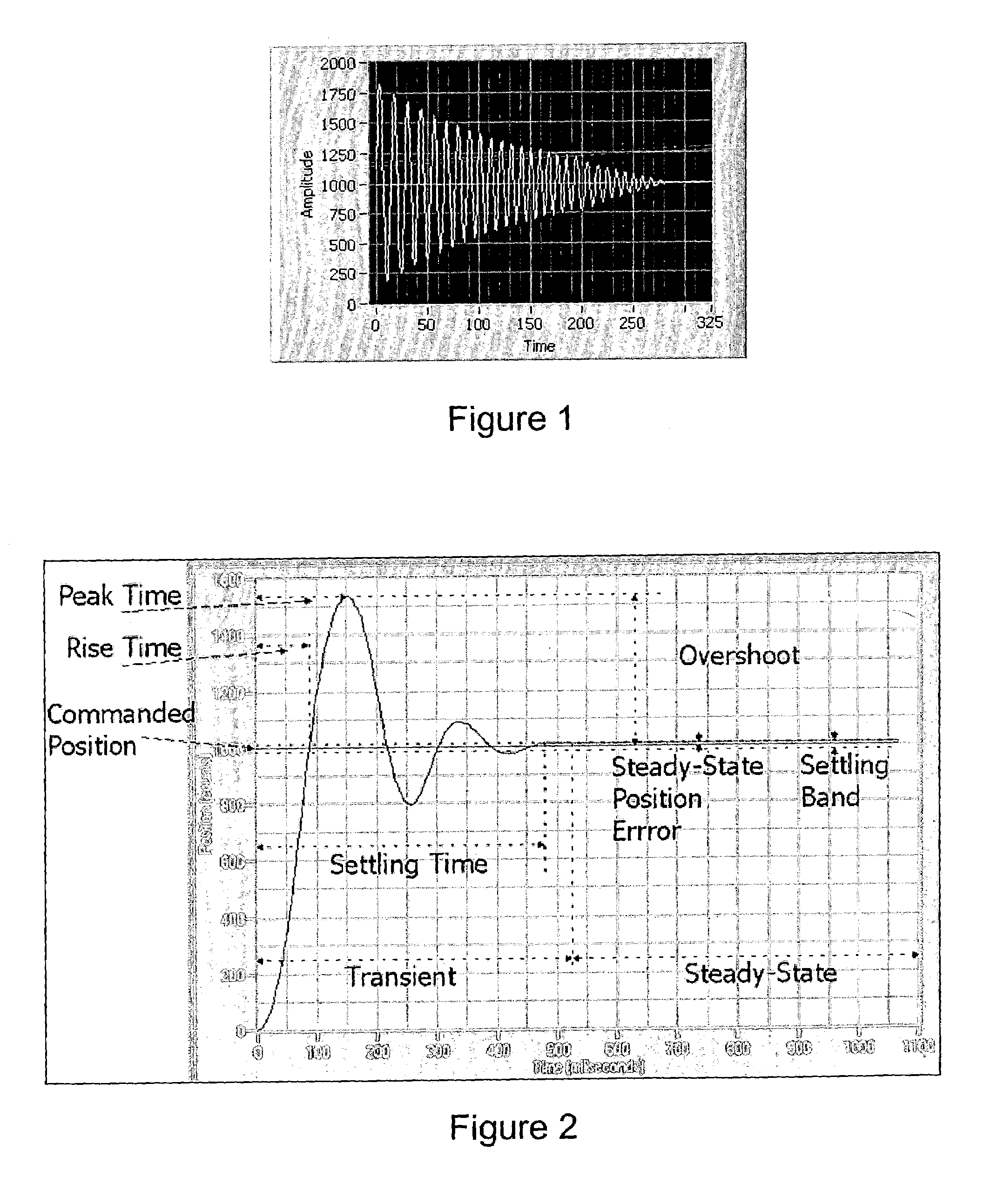
System and method for user configuration of an autotuning algorithm for a controller in a motion control system. A desired trajectory in one or more dimensions for the motion control system is received. Values of one or more gains for a controller are initialized. A response trajectory of the controller and motion control system in response to the desired trajectory is received, and an error determined between the response trajectory and the desired trajectory. A gain space is then experimentally searched to determine final values of the one or more gains for the controller that minimize the error (e.g., Euclidean norm) between the response trajectory and the desired trajectory, e.g., via simulated annealing, or other stochastic, quasi-random, and / or deterministic approaches. After experimentally searching, the controller is operable to control the motion control system substantially in accordance with the desired trajectory using the determined values of the one or more gains.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
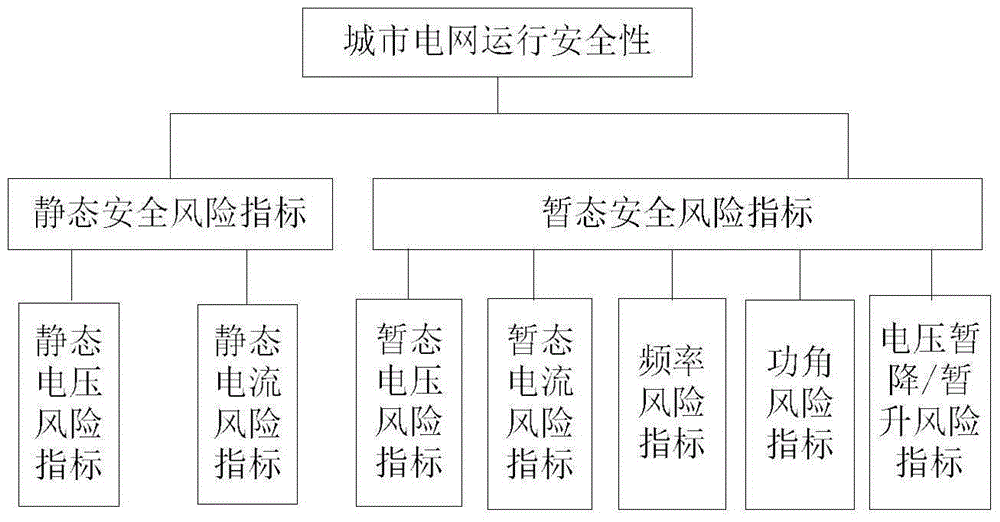
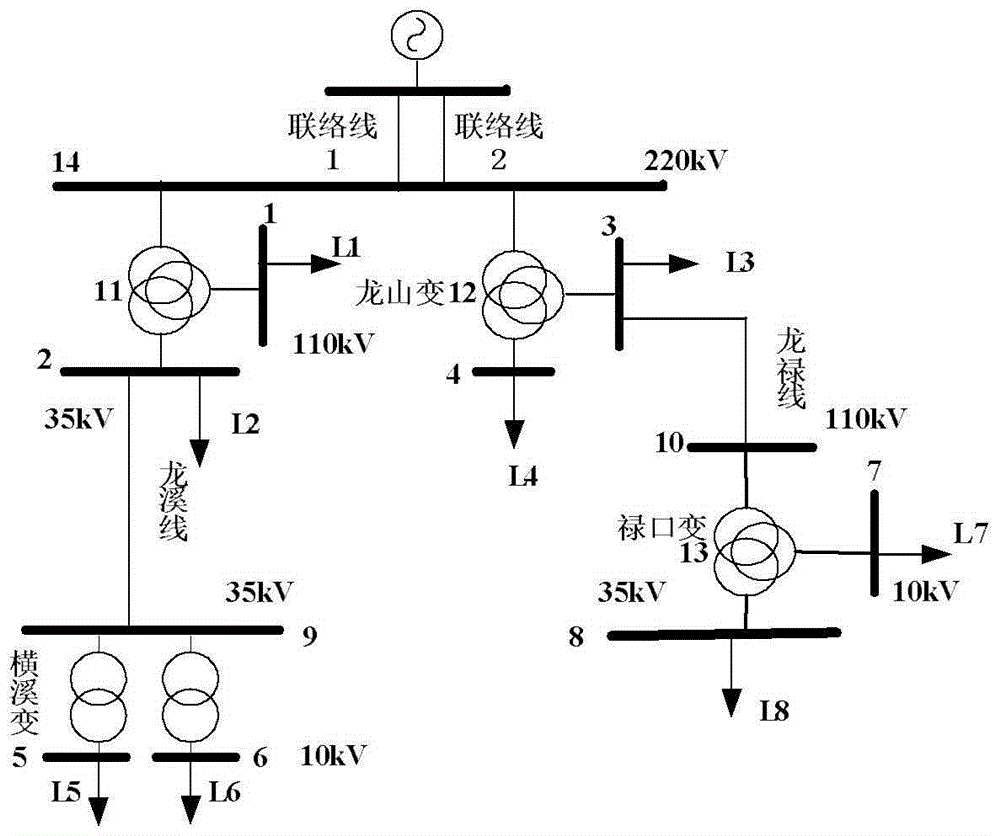
Risk-considered urban power network operation security assessment method
InactiveCN105205571AIncrease uncertaintyComprehensively evaluate the level of operational safetyForecastingRisk indicatorLoad following power plant
The invention discloses a risk-considered urban power network operation security assessment method. The risk-considered urban power network operation security assessment method comprises the following steps: analyzing an urban power network operating risk source which is divided into two types, namely a small disturbance risk source including both load fluctuation and distributed power supply output fluctuation, and a fault risk source including both internal network faults and external network faults; as for the two risk sources, respectively building static security risk index models and transient security risk index models to assess the urban power network operating safety level. A traditional deterministic security assessment method only attaches importance to the most serious and credible accidents, so that the result is conservative. A probabilistic assessment method overcomes the defect of the deterministic assessment method, and additionally considers the uncertain factor (probability of occurrence). The risk-considered urban power network operation security assessment method is a modification and improvement of the original probabilistic assessment method and can quantify the accident results.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Identifying faulty network components during a network exploration
InactiveUS7200118B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDeterministic methodNetwork exploration
A network exploration is performed to initialize one or more network elements of the network. If during the network exploration a failure is encountered, a systematic and deterministic approach is used to accurately and particularly identify the faulty network component that caused the failure.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for the secure, distributed generation of an encryption key
ActiveUS7970135B1Eliminate needAvoid misuseKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationDeterministic methodEncryption
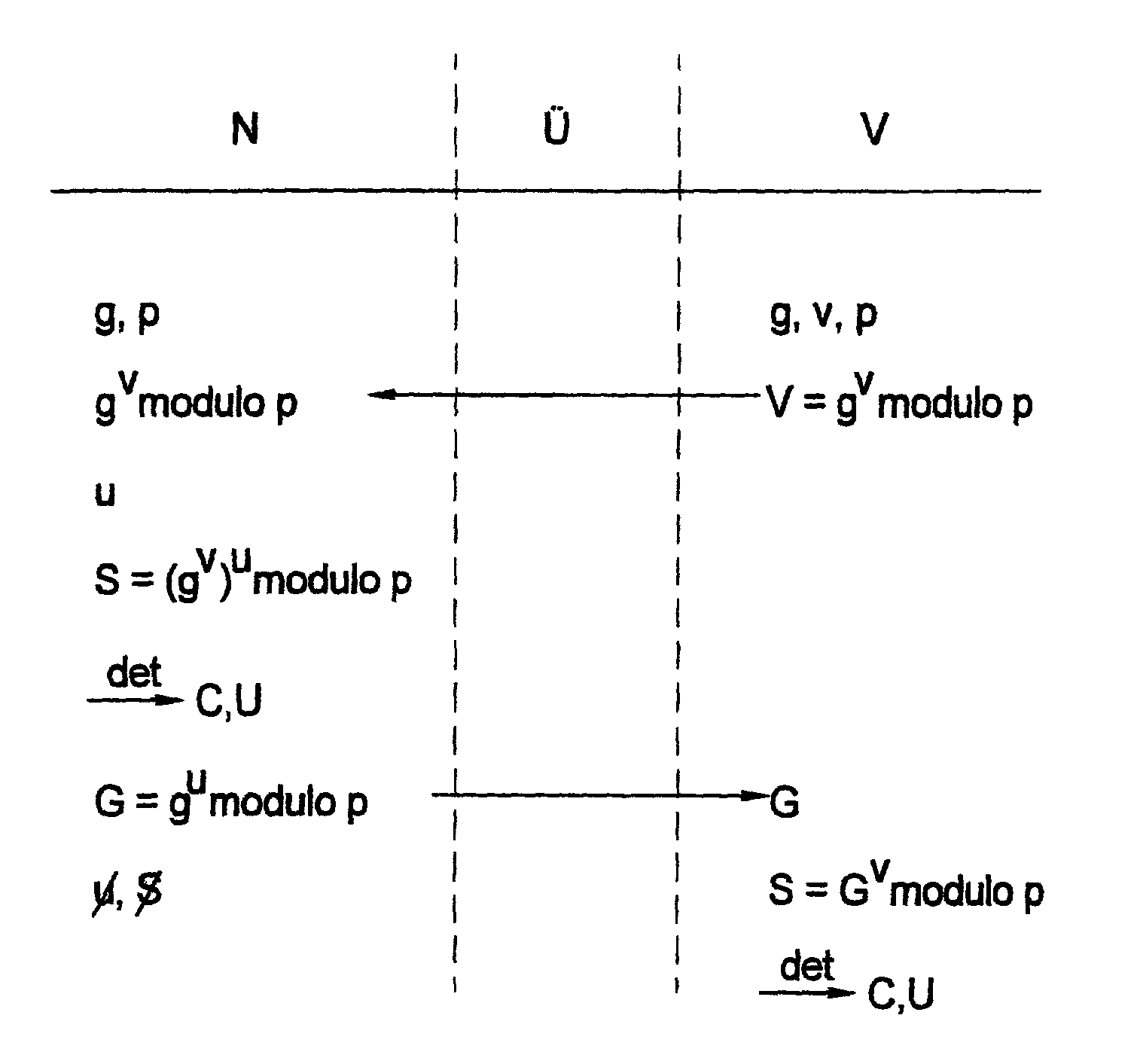
In a method for the secure, distributed generation of an encryption key for a cryptographic method, where the encryption key, as well as a public key are generated using deterministic methods from a large random number (seed), the seed (S) is generated on the user side by consulting variables known only to the user, and a public key (V) that is transmitted in advance from the trust center. Generation information suitable for generating the seed and, on the basis of which, the seed is able to be derived deterministically from the trust center, by consulting information known only to the center, is produced on the user side, and transmitted to the trust center to create the seed in parallel.
Owner:DEUTSCHE TELEKOM AG
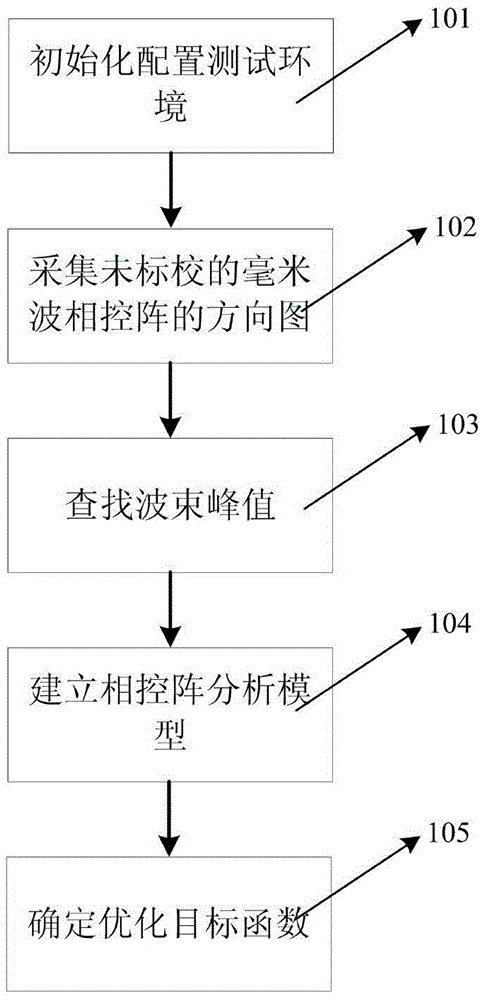
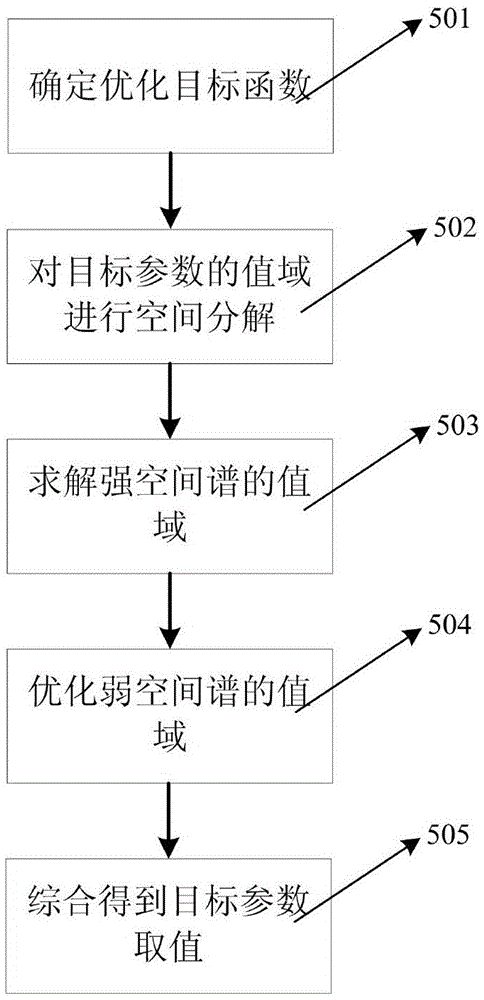
Millimeter wave phased array test and calibration method
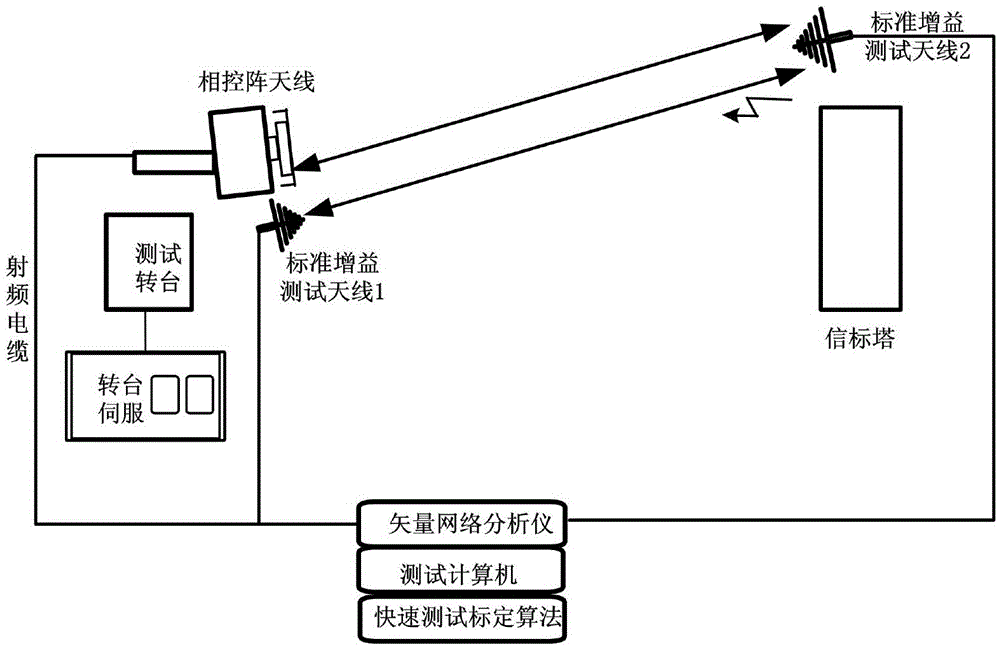
ActiveCN105606906AReduce testing workloadSave human effortSatellite radio beaconingAntenna radiation diagramsDeterministic methodGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses a millimeter wave phased array test and calibration method, relates to a millimeter wave phased array calibrated error characteristic analysis and especially relates to the channel inconsistency of a phased-array antenna and a method for calculating element antenna phase center offset. The method comprises: step1, correlation functions including phased-array antenna channel inconsistency and element antenna phase center offset are established according to a phased-array antenna pattern obtained in the test; step2, range space decomposition is performed on an optimized target parameter; and step3, the range corresponding to the strong spatial spectrum component is calculated by adopting a deterministic method, and the range corresponding to the weak spatial spectrum component is optimized by adopting a genetic algorithm. According to the invention, the calibration of the phased array pointing accuracy can be realized under a condition of less test work, the test workload is greatly reduced, the labor, material resources and working time are saved, a complex and precise flat scanning frame is not needed to use, and the complexity and input cost of the system are reduced.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
System and method for rendering images using a strictly-deterministic methodology for generating a coarse sequence of sample points
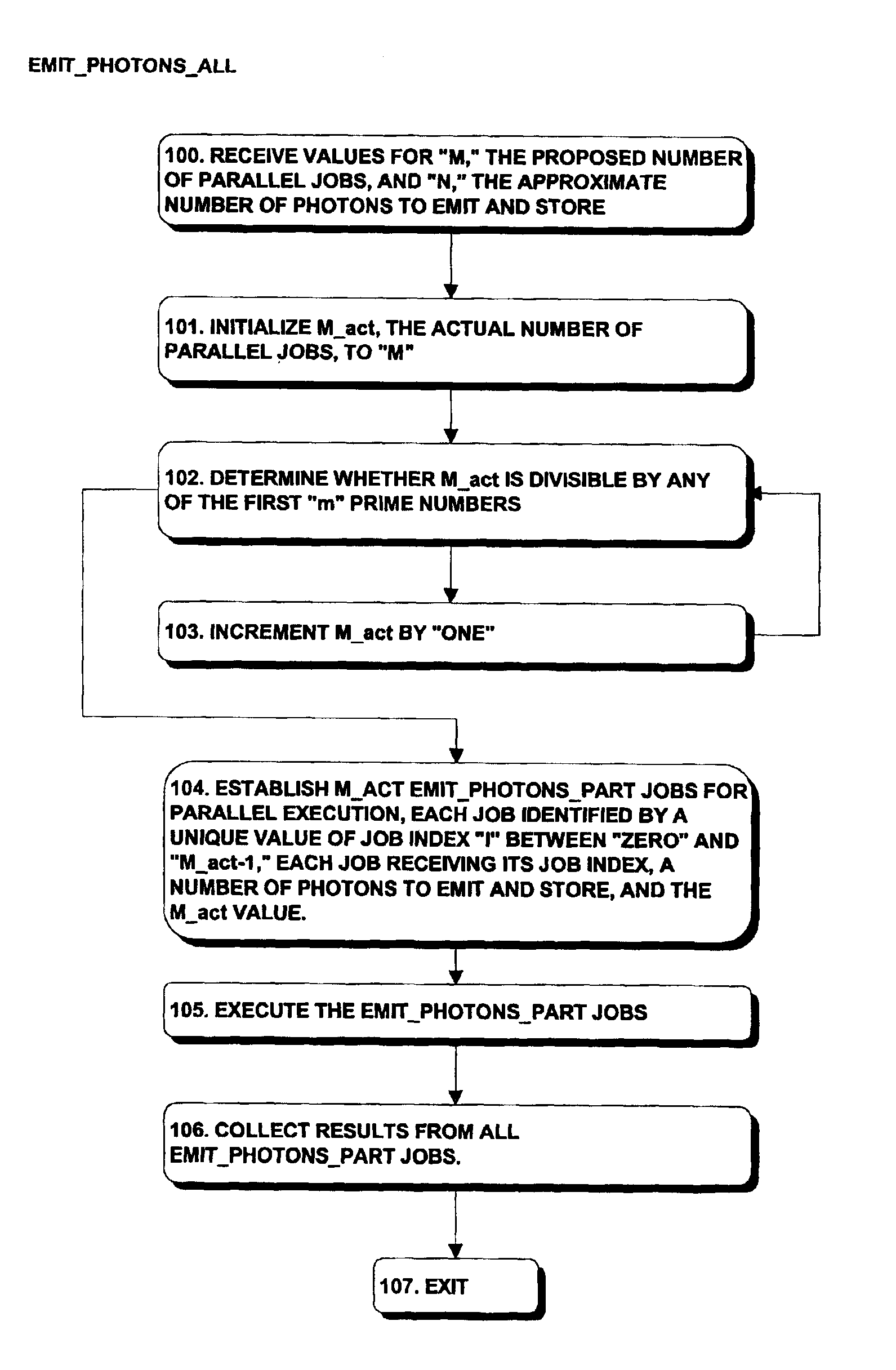
InactiveUS6911976B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationDeterministic methodAlgorithm
A system and method for generating sample points that can generate the sample points in parallel. The sample points can be used in processing in parallel, with the results subsequently collected and used as necessary in subsequent rendering operations. Sample points are generated using a coarse Halton sequence, which makes use of coarse radical inverse values Φbi,M(j) as follows:Φbi,M(j)=Φb(jM+i)where base “b” is preferably a prime number, but not a divisor of “M,” and “i” is an integer. Using this definition, the s-dimensional coarse Halton sequence USCHal,i,M, which may be used to define sample points for use in evaluating integrals, is defined asUsCHal,i,M=(Φb1i,M(j), . . . , Φb<sub2>s< / sub2>i,M(j))where b1, . . . , bs are the first “s” prime numbers that are not divisors of “M.” Each value of “i” defines a subsequence that is a low-discrepancy sequence, and so can be used in connection with processing. Similarly, the union of all subsequences for all values of “i” between “zero” and “M−1” is also a low-discrepancy sequence, so results of processing using the coarse Halton sequences for all such values of “i” can be collected together and used in the same manner as if the results had been generated using a Halton sequence to define the sample points.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com