Patents
Literature
1398results about "Reliability/availability analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
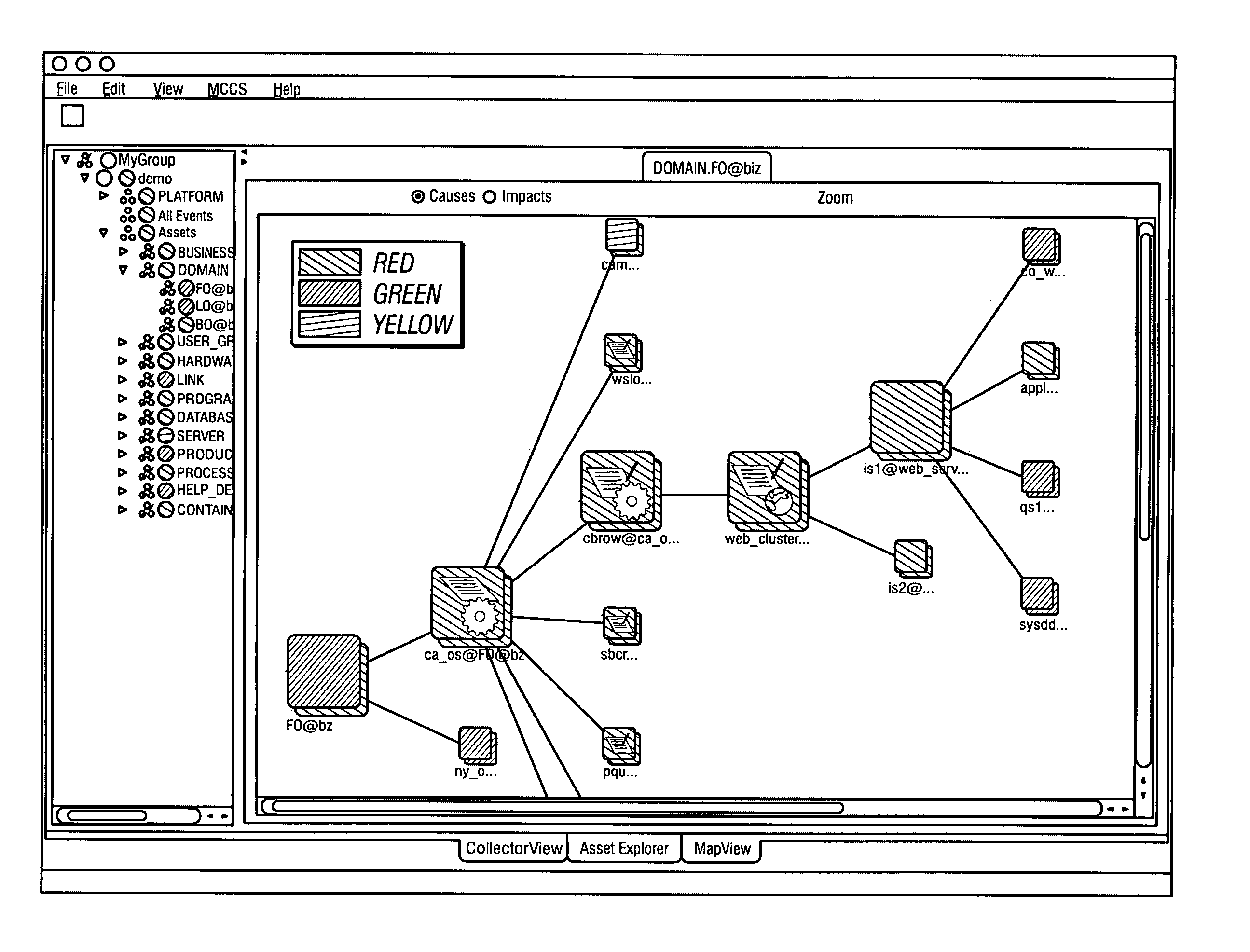
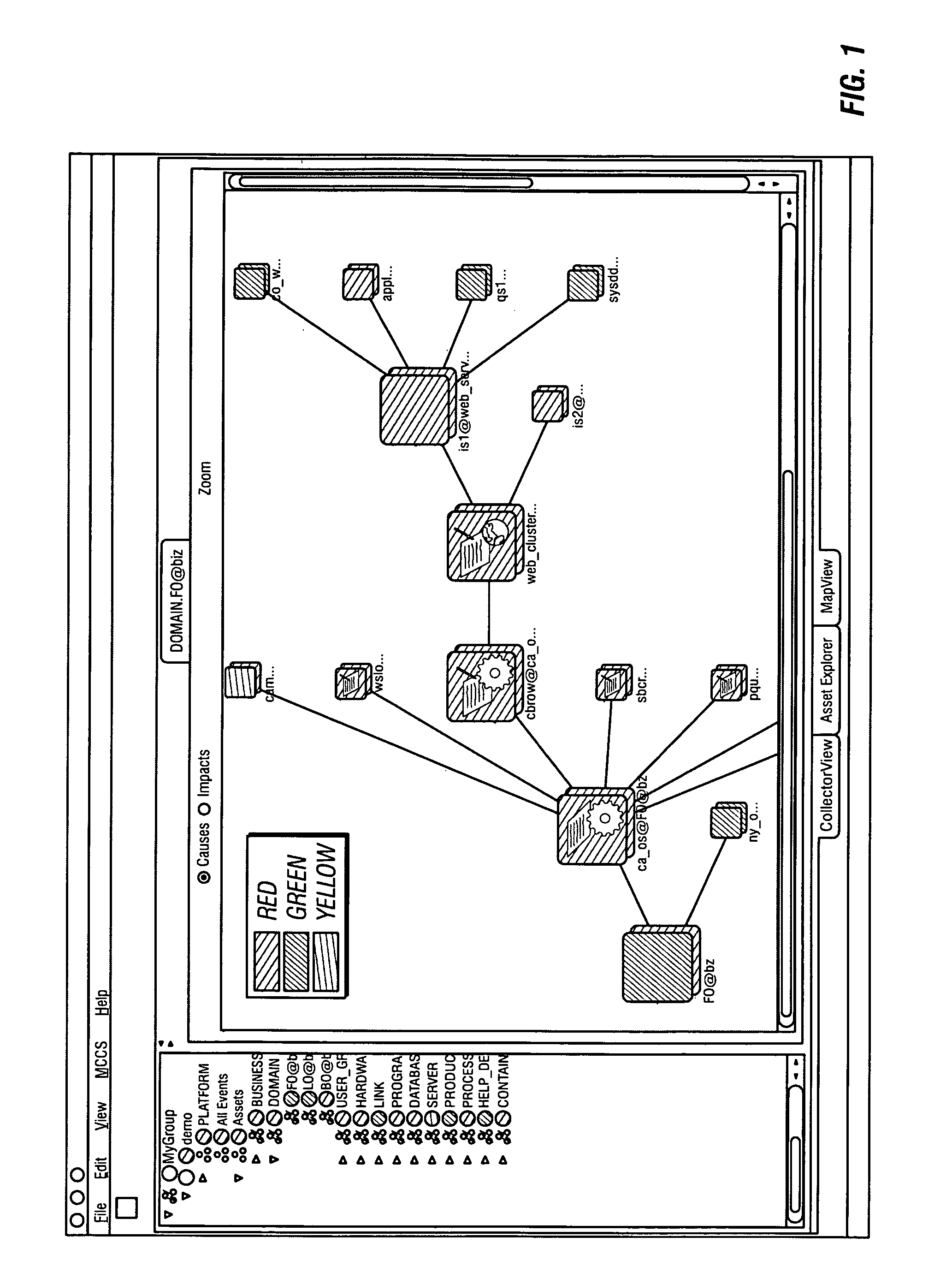
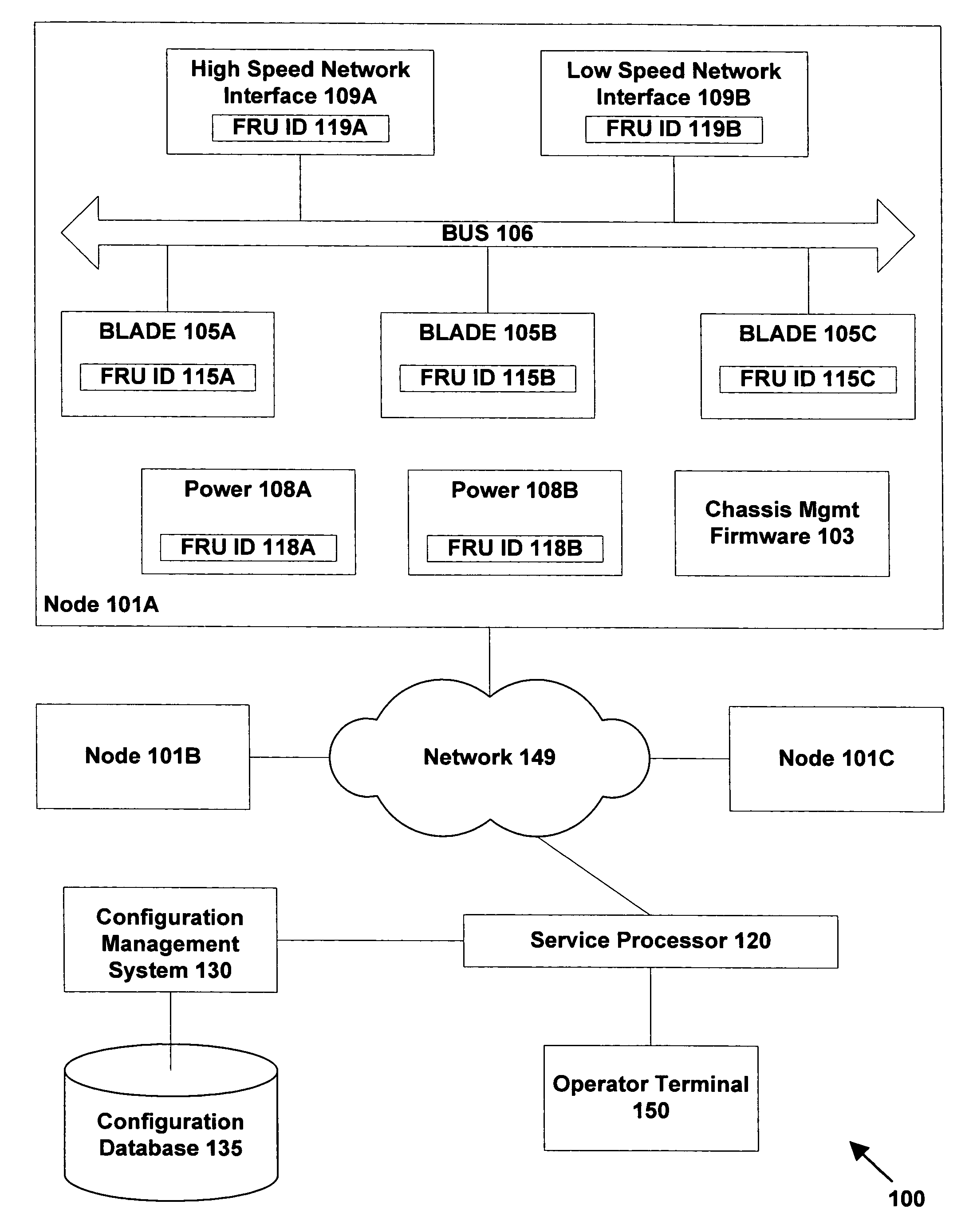
System and method for assessing and indicating the health of components
A system and method for visualization of the components of an enterprise system and the rendering of information about the health or status of the enterprise system, its components, and / or its subcomponents. The invention uses a combination of color codes or other indicators and a combination of algorithms and / or rules-based systems to control the computation of status / severities to associate to components and setup the color codes and indicators.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
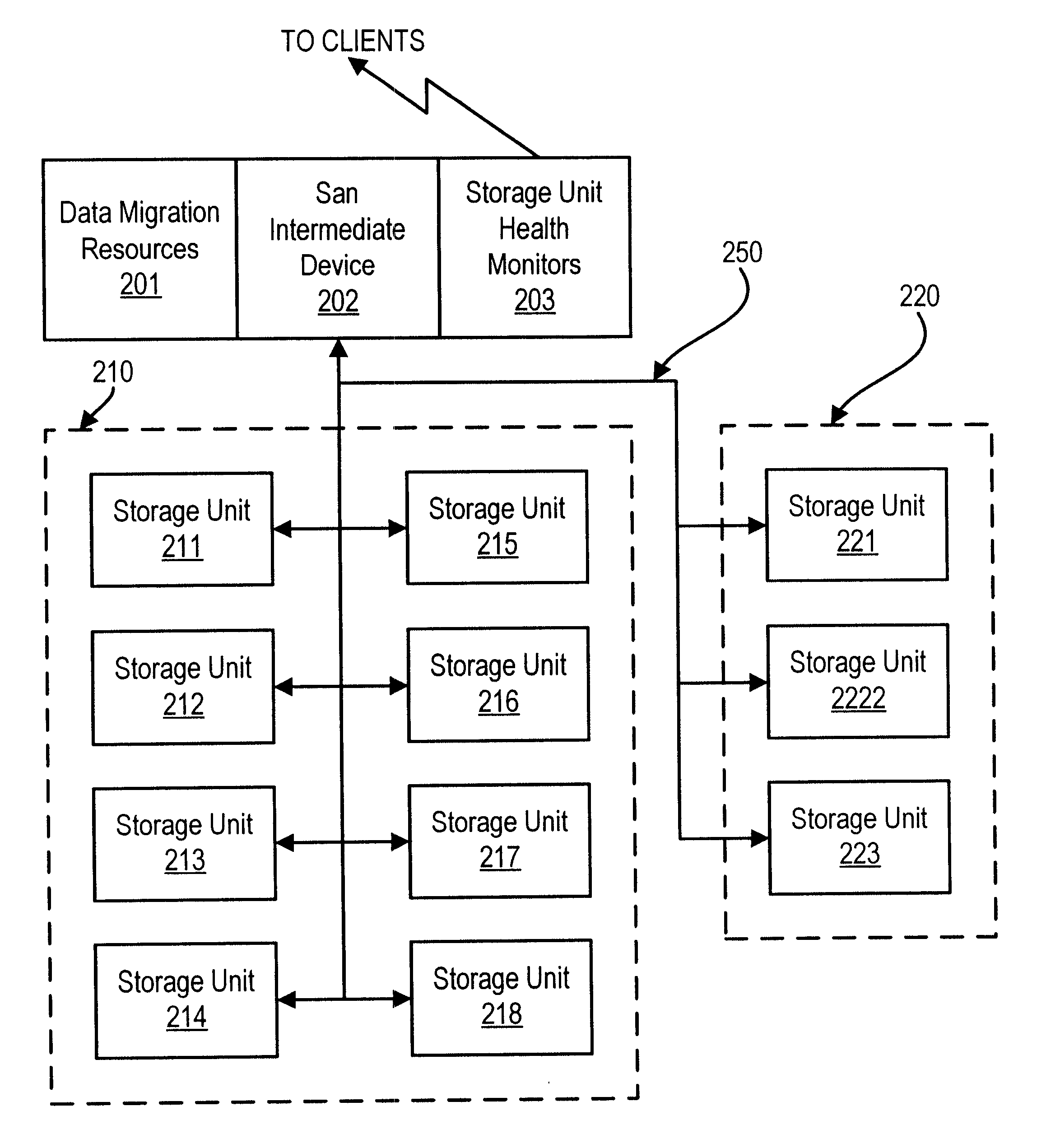
Method and apparatus for storage unit replacement in non-redundant array
InactiveUS6598174B1Lower performance requirementsMaintaining accessMemory loss protectionReliability/availability analysisRAIDData storing
A method and apparatus used in a storage network facilitates the protection of data in, and replacement of, storage devices about to fail before the failure happens. In a network that includes a set of storage devices organized as a non-redundant (for example RAID 0) array, a storage device about to fail in the non-redundant array can be replaced by another storage device, typically from a pool of spares. The method includes detecting a condition of a first particular storage device in the non-redundant array. Conditions which are detected according to various embodiments indicate that the first particular storage device is suffering events indicating that it is likely to fail, or otherwise suffering from reduced performance. The conditions are detected for example, by the receipt of a signal from the storage device itself, or by the monitoring of statistics concerning the performance of the storage device. The method further provides for selecting a particular spare storage device, which can be used in place of the first particular storage device. In response to detecting the condition, data stored in the first particular storage device is migrated to the second particular storage device, and the second particular storage takes the place of the first particular storage device in the non-redundant array. The first particular storage device can then be gracefully removed from the network without loss of service to the clients computers.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
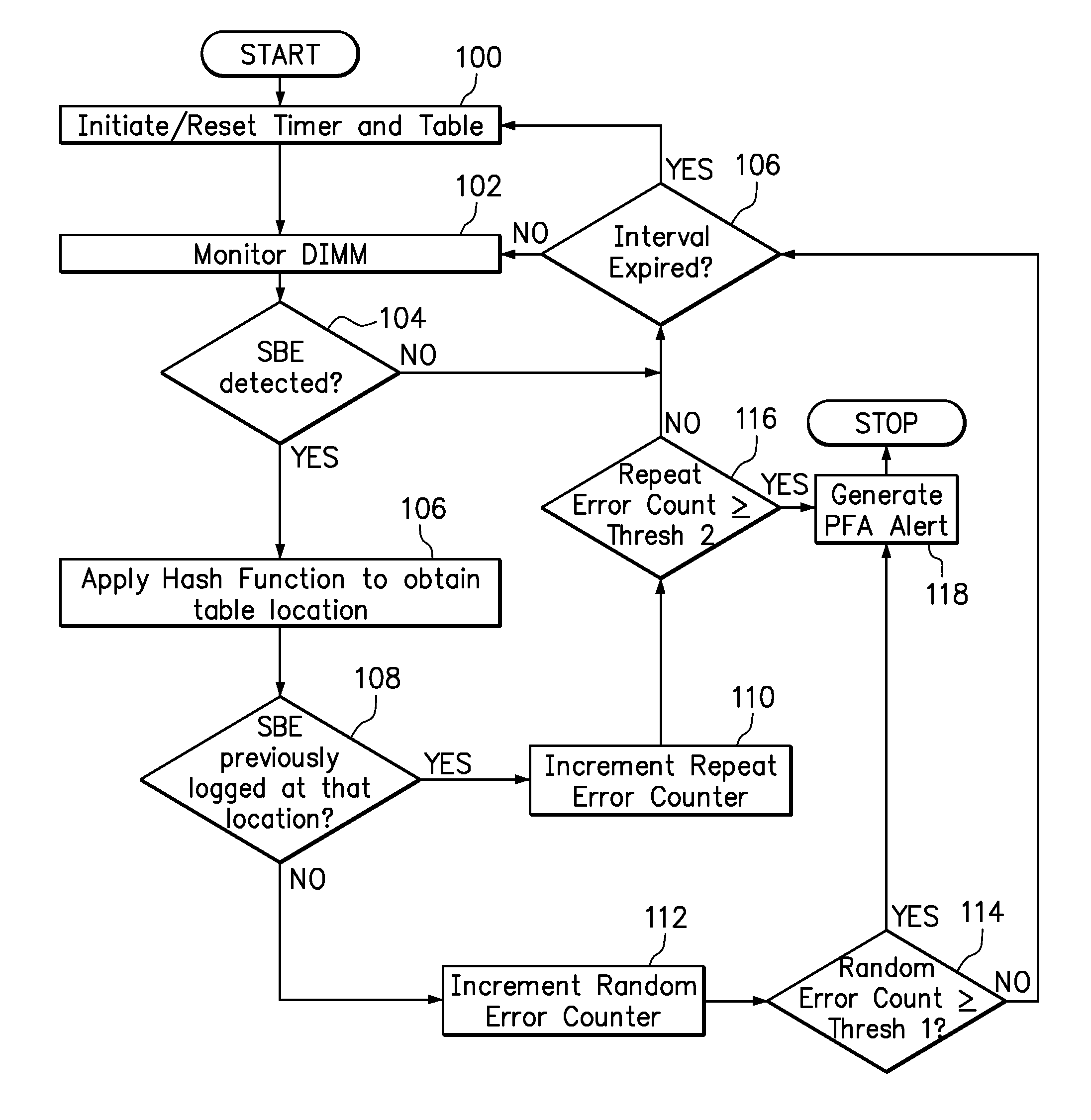
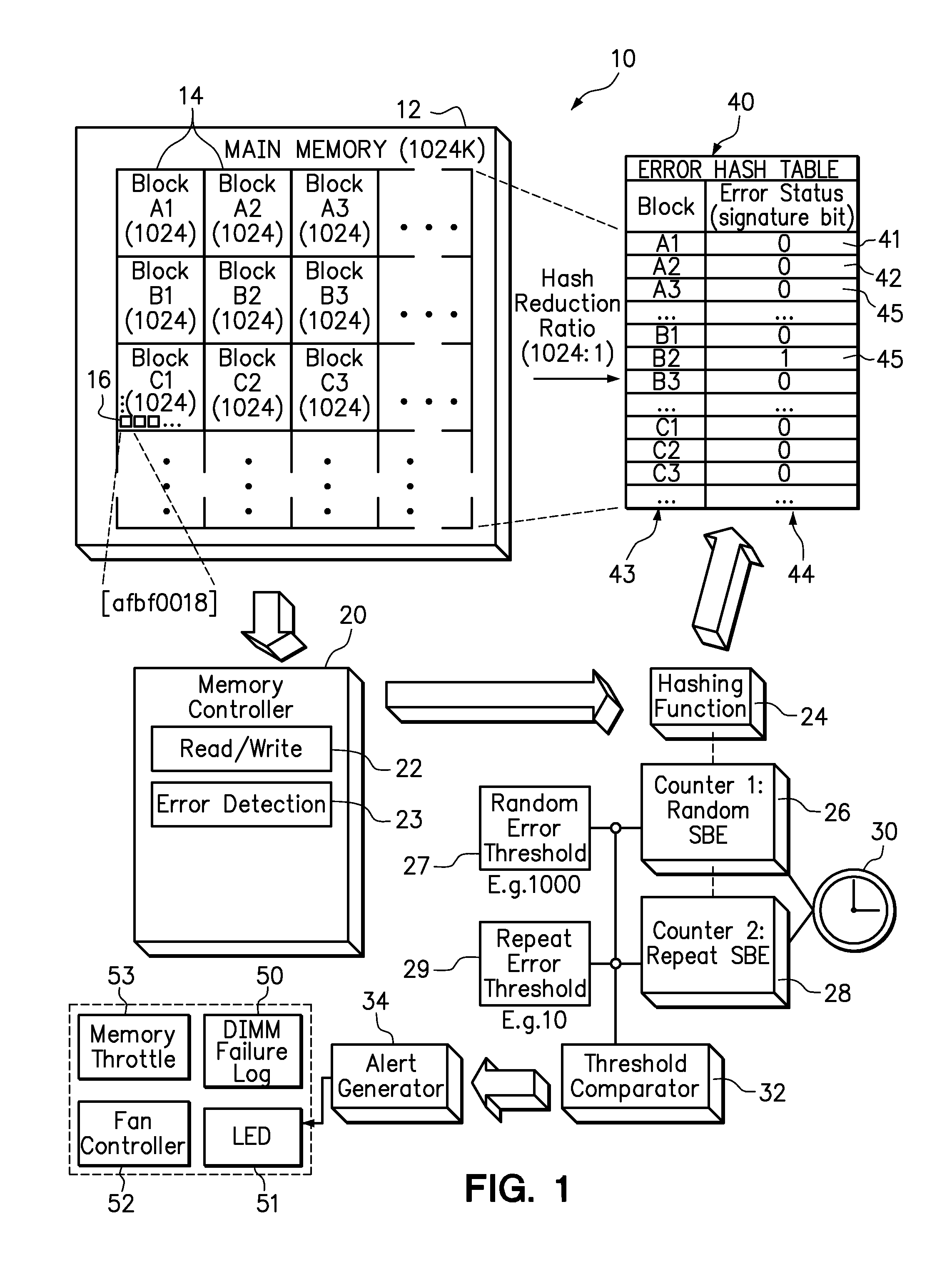
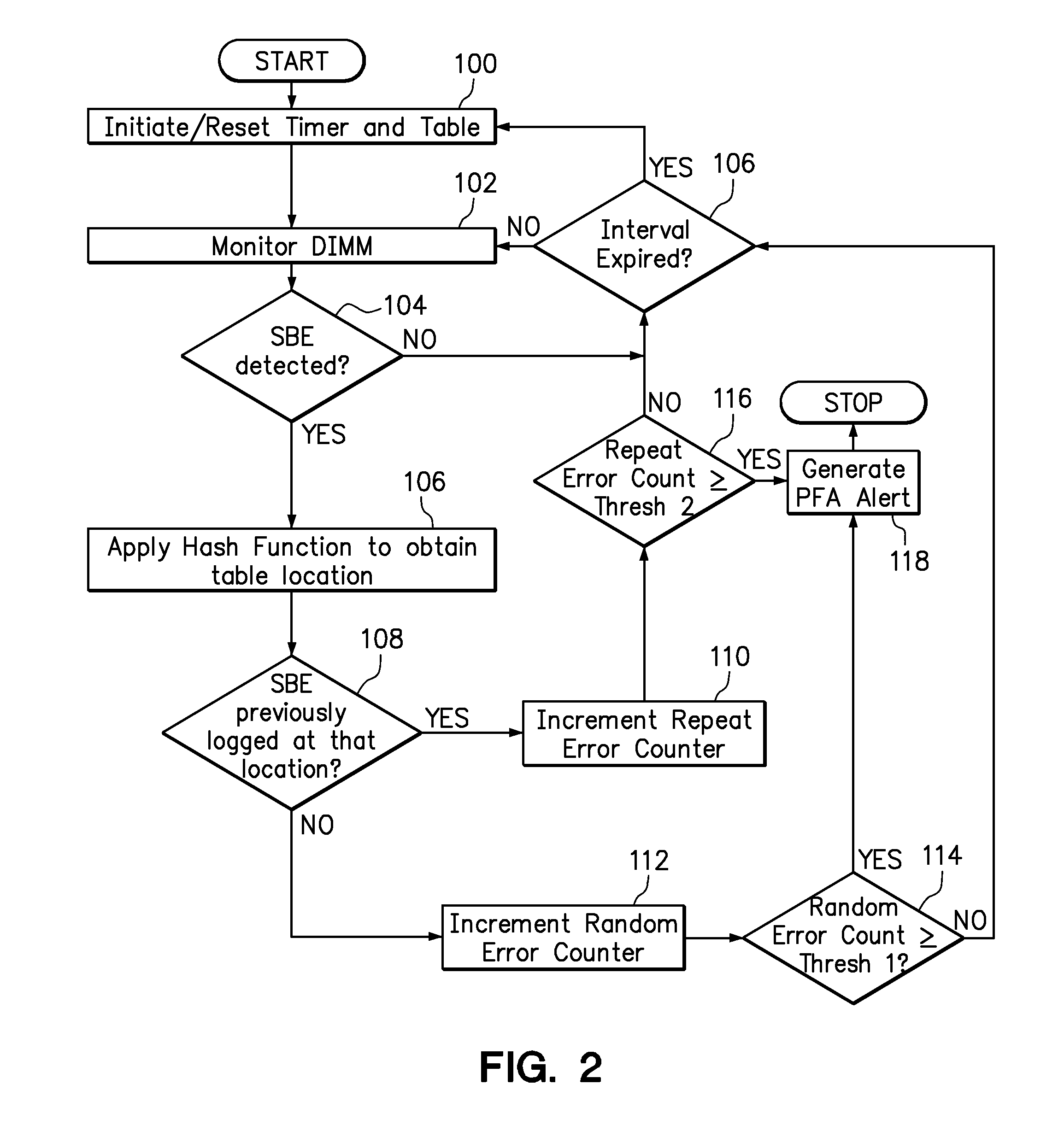
Use of hashing function to distinguish random and repeat errors in a memory system
One embodiment provides an error detection method wherein single-bit errors in a memory module are detected and identified as being a random error or a repeat error. Each identified random error and each identified repeat error occurring in a time interval is counted. An alert is generated in response to a number of identified random errors reaching a random-error threshold or a number of identified repeat errors reaching a repeat-error threshold during the predefined interval. The repeat-error threshold is set lower than the random-error threshold. A hashing process may be applied to the memory address of each detected error to map the location of the error in the memory system to a corresponding location in an electronic table.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
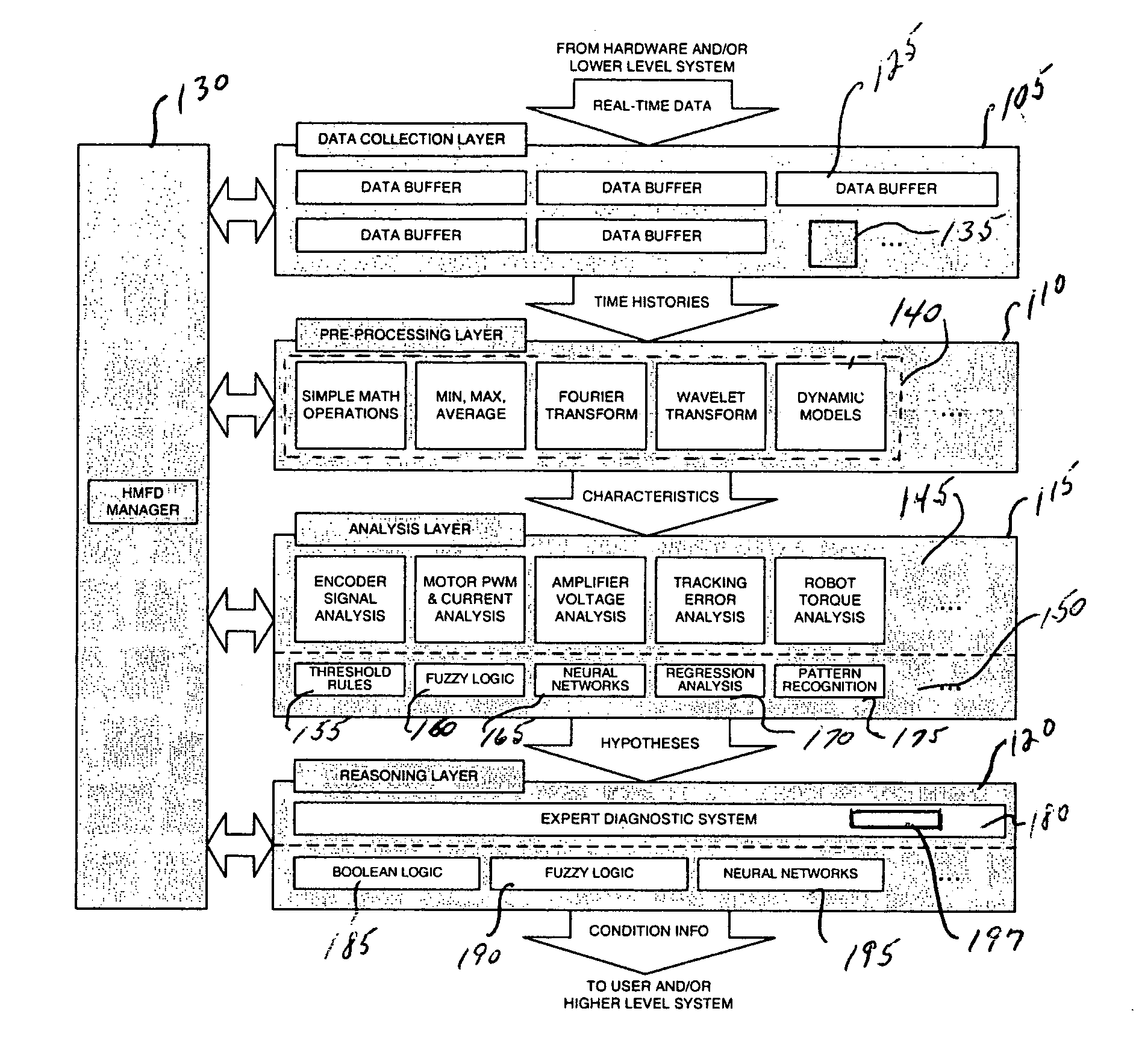
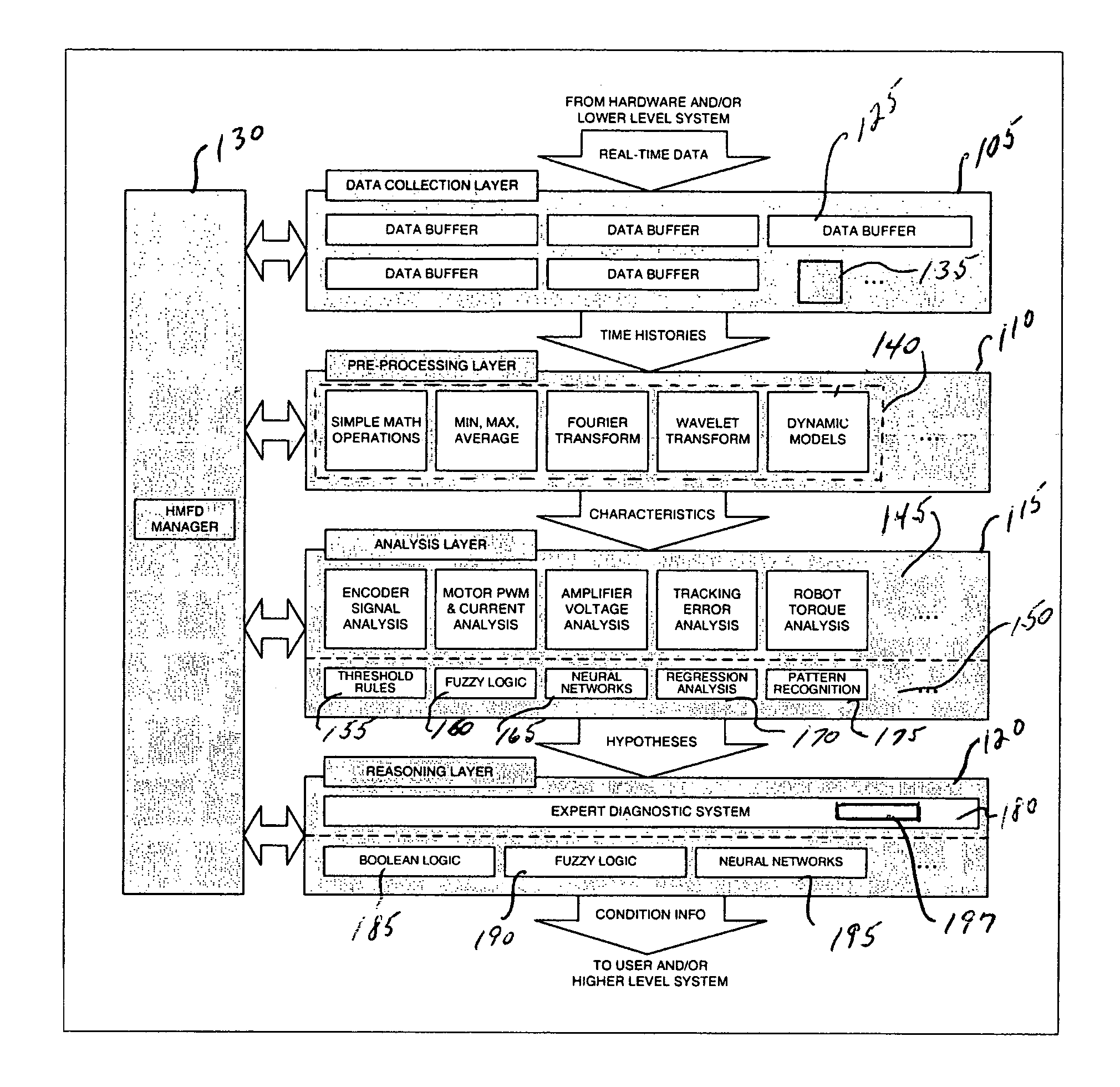
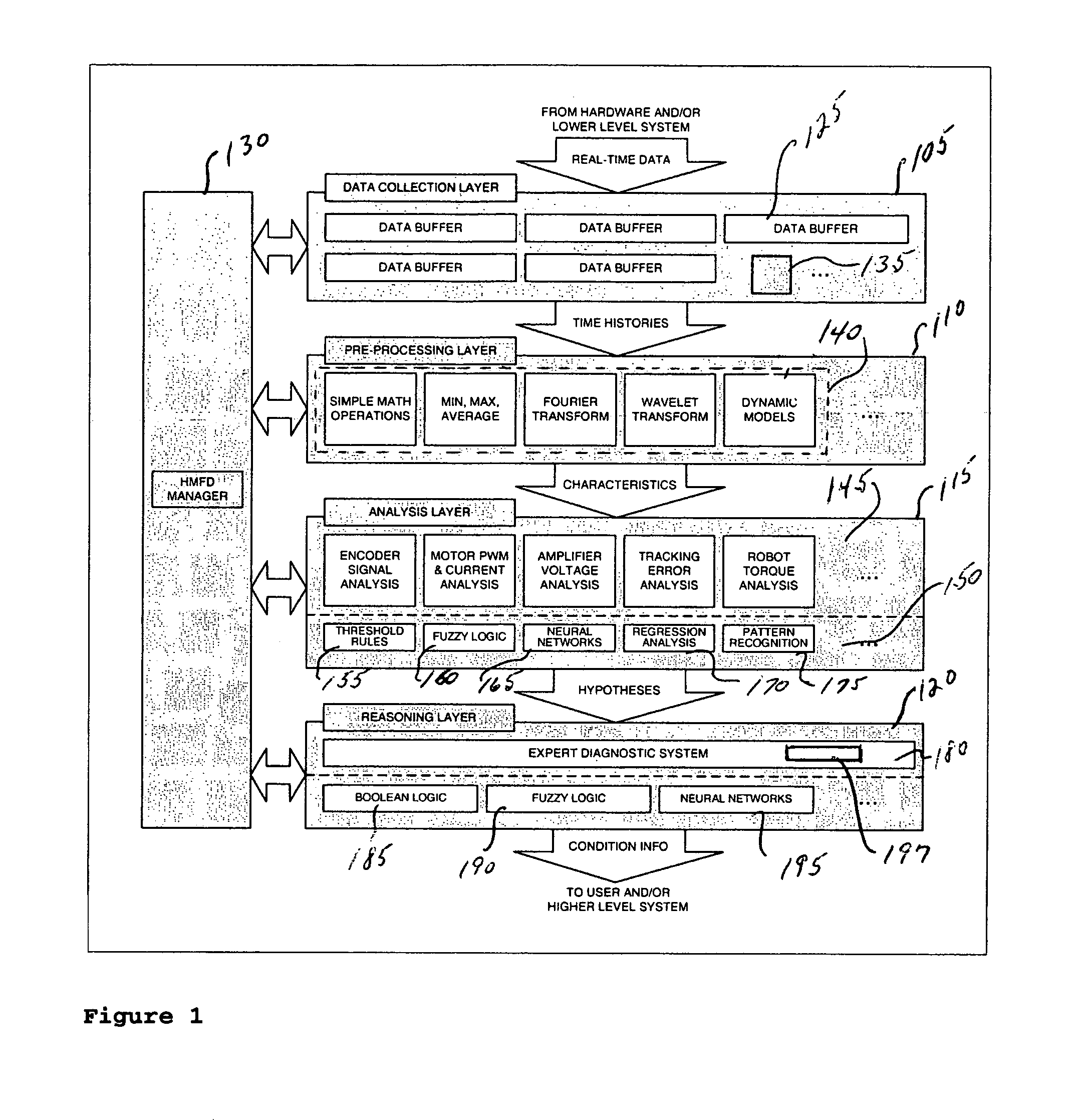
Intelligent condition-monitoring and fault diagnostic system for predictive maintenance
ActiveUS20070067678A1Sufficient weightFacilitates isolation of faultSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementRegistering/indicating working of machinesPredictive maintenanceDiagnostic system
A system for condition monitoring and fault diagnosis includes a data collection function that acquires time histories of selected variables for one or more of the components, a pre-processing function that calculates specified characteristics of the time histories, an analysis function for evaluating the characteristics to produce one or more hypotheses of a condition of the one or more components, and a reasoning function for determining the condition of the one or more components from the one or more hypotheses.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
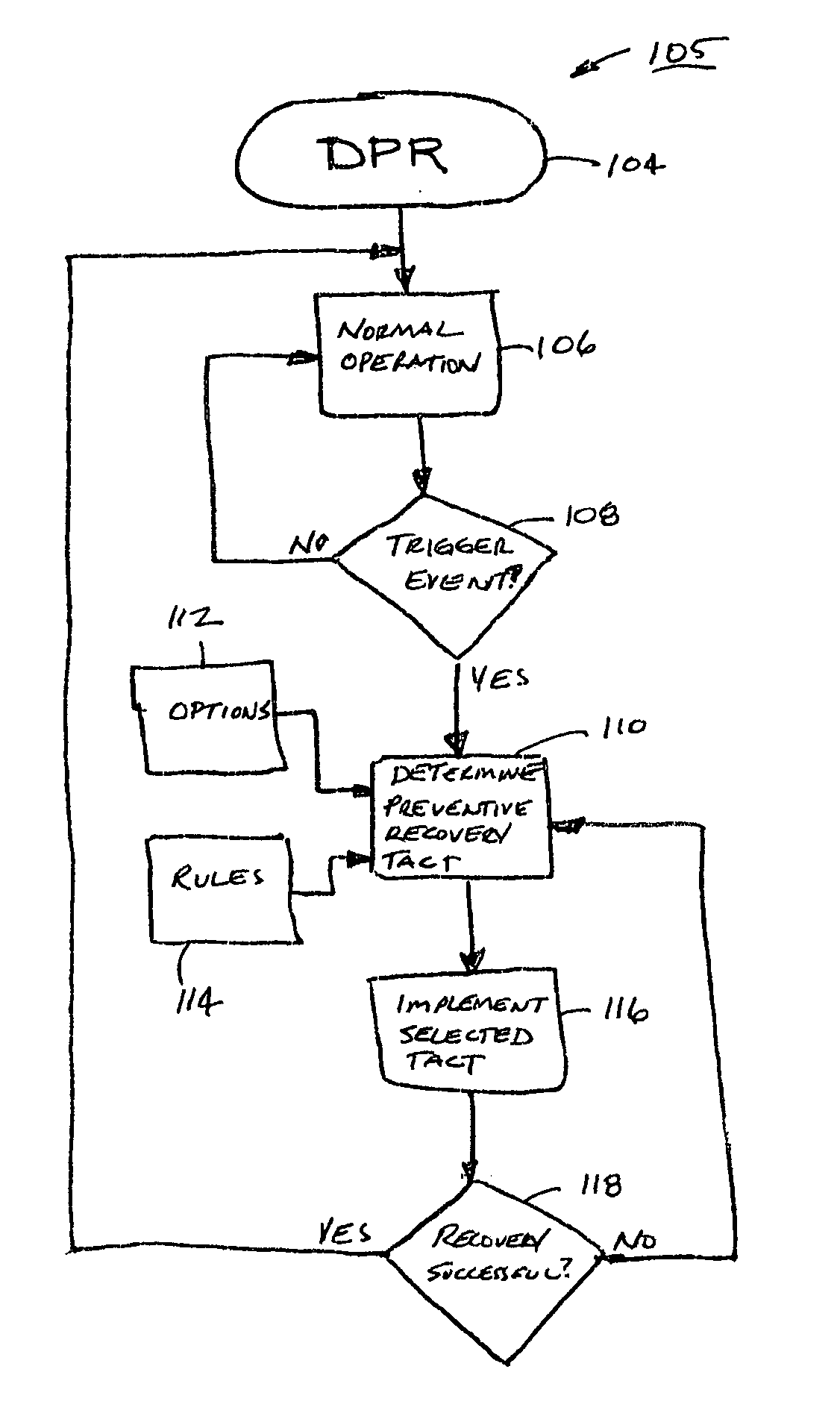
Deterministic preventive recovery from a predicted failure in a distributed storage system
A data storage subsystem in a distributed storage system having a plurality of predictive failure analyzing data storage devices. The subsystem furthermore has a circuit that is responsive to a predicted failure indication by a data storage device in relation to predetermined rules stored in memory for deterministically initiating a preventive recovery either by a data recovery procedure in the data storage device or by a fault tolerance storage arrangement in the subsystem.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
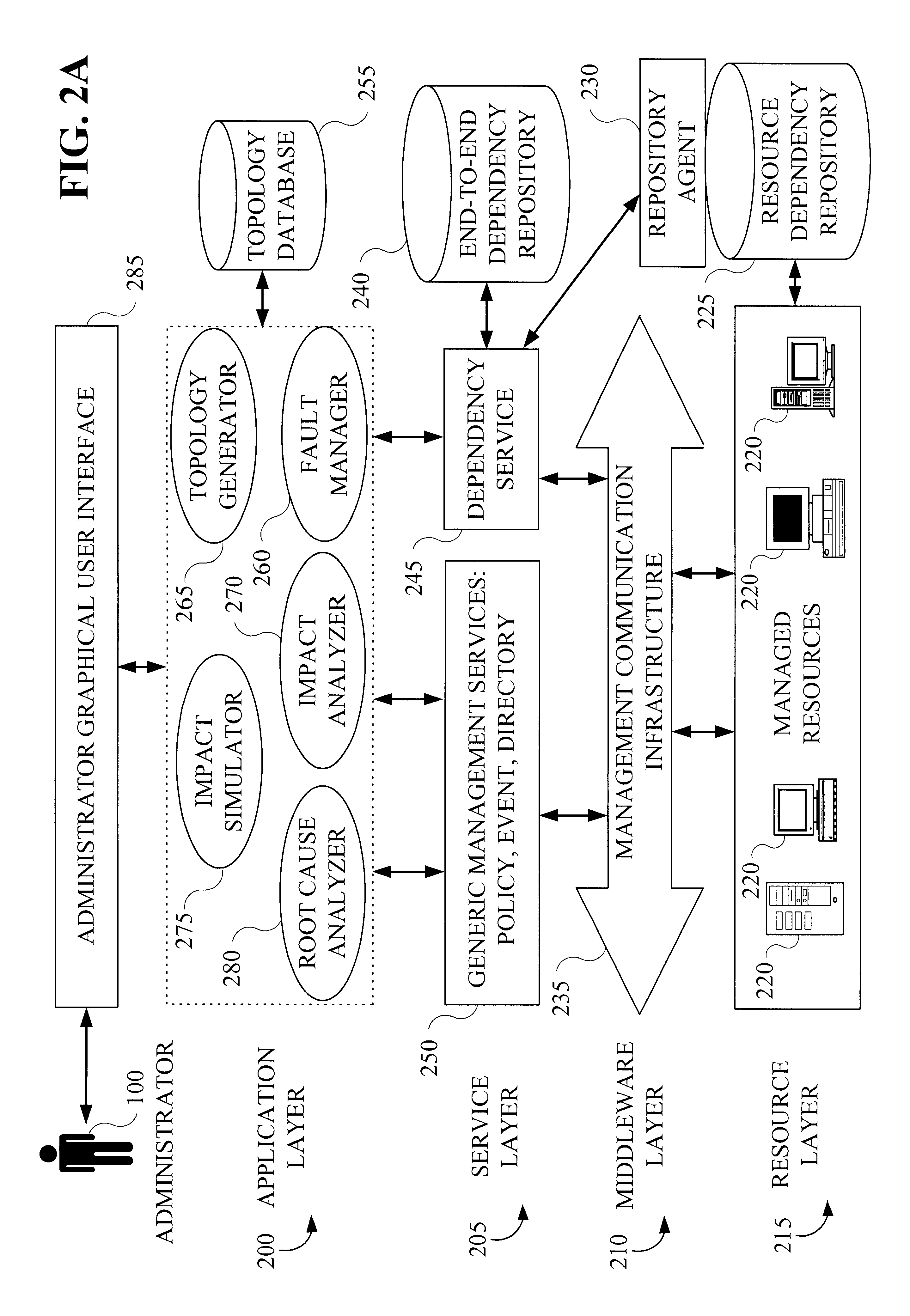
Methods and apparatus for managing dependencies in distributed systems
InactiveUS6847970B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsOperational systemDistributed Computing Environment
Techniques for managing information in a computing environment. Information associated with components of the computing environment is obtained. Then, from at least a portion of the obtained information, a determination is made as to the existence of one or more relationships associated with at least a portion of the components of the computing environment. The determination of the existence of one or more relationships is capable of accounting for a full lifecycle (e.g., including deployment, installation and runtime) associated with at least one component of the computing environment. Thus, techniques for managing runtime dependencies between the various components of computing systems are disclosed which provide a level of abstraction from individual systems and allow the computation of service / component (wherein the component may, for example, be an application, middleware, hardware, a device driver, an operating system and a system associated with the computing environment) dependencies that are related to end-to-end services, as perceived by a customer. By way of example, the inventive techniques may be applied to a distributed computing environment. The computing environment may also be an autonomic computing environment.
Owner:IBM CORP
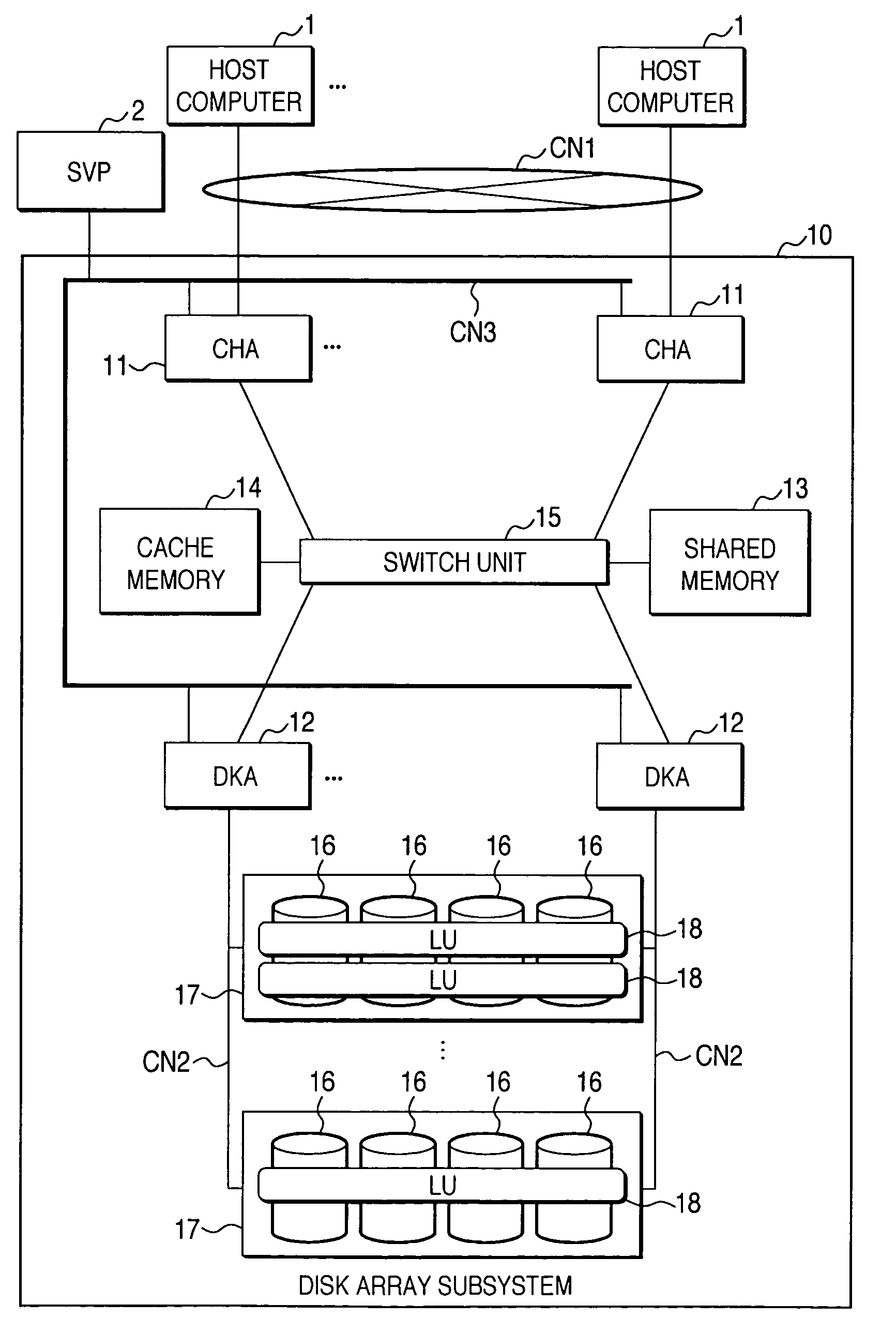
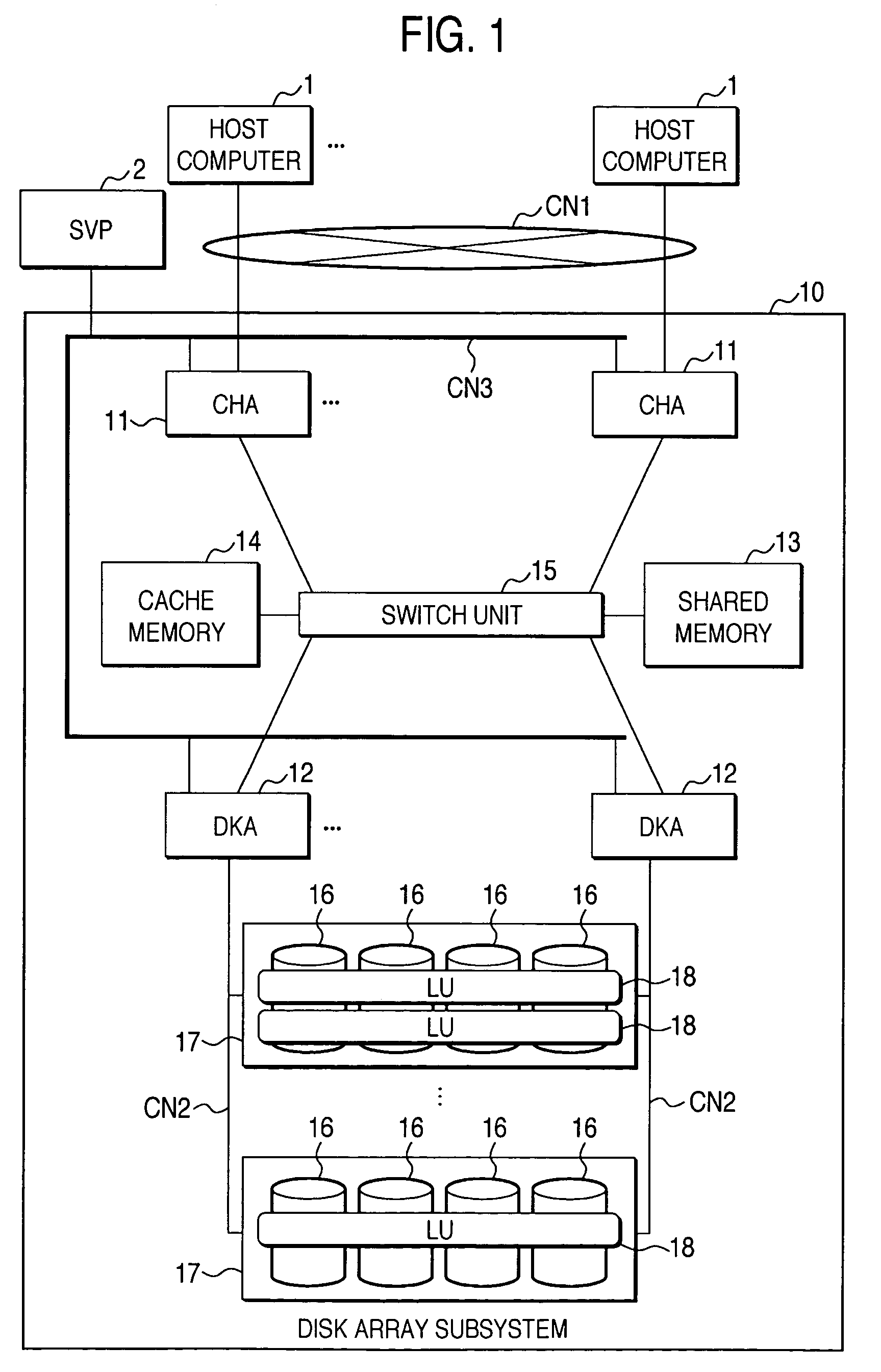
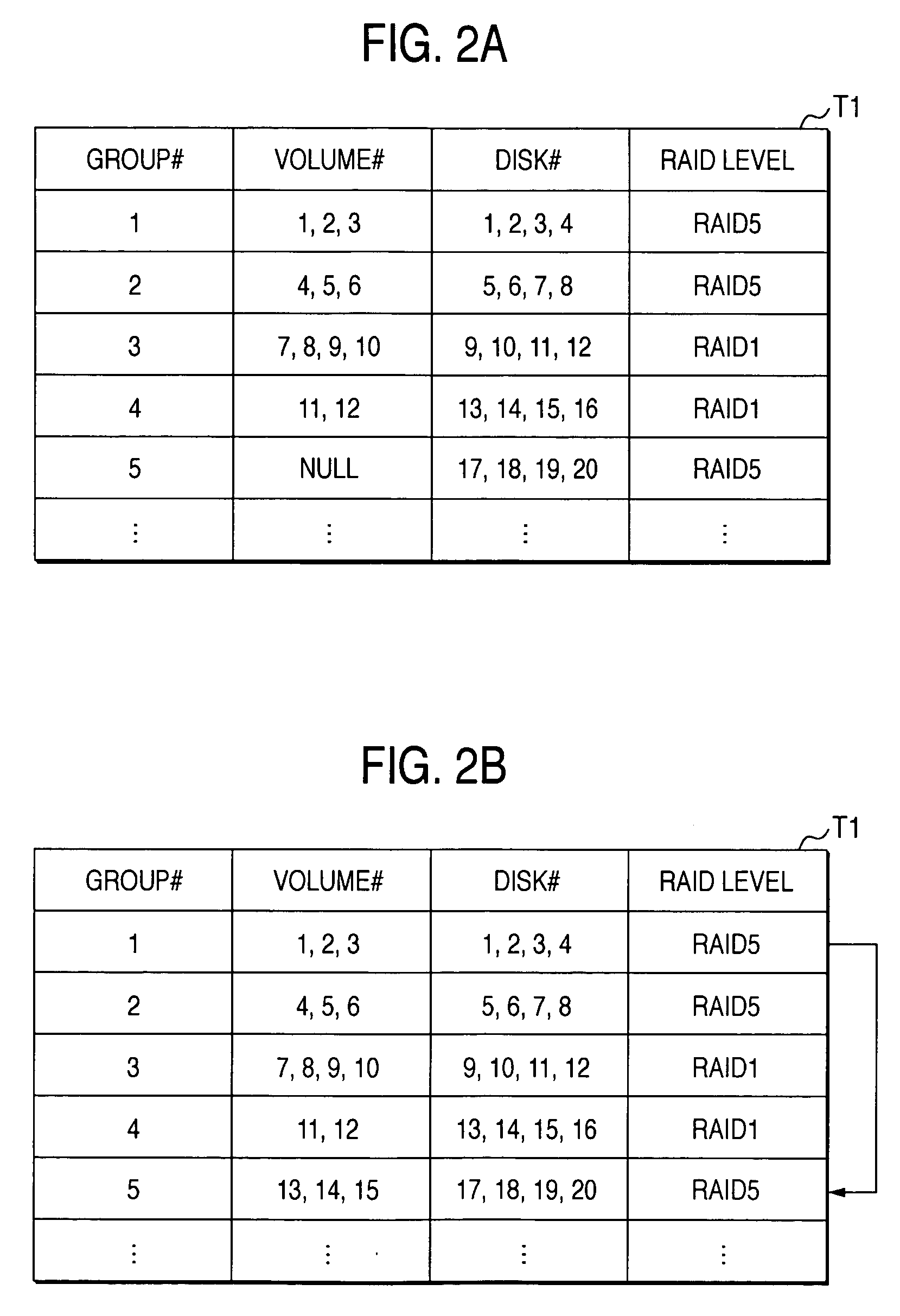
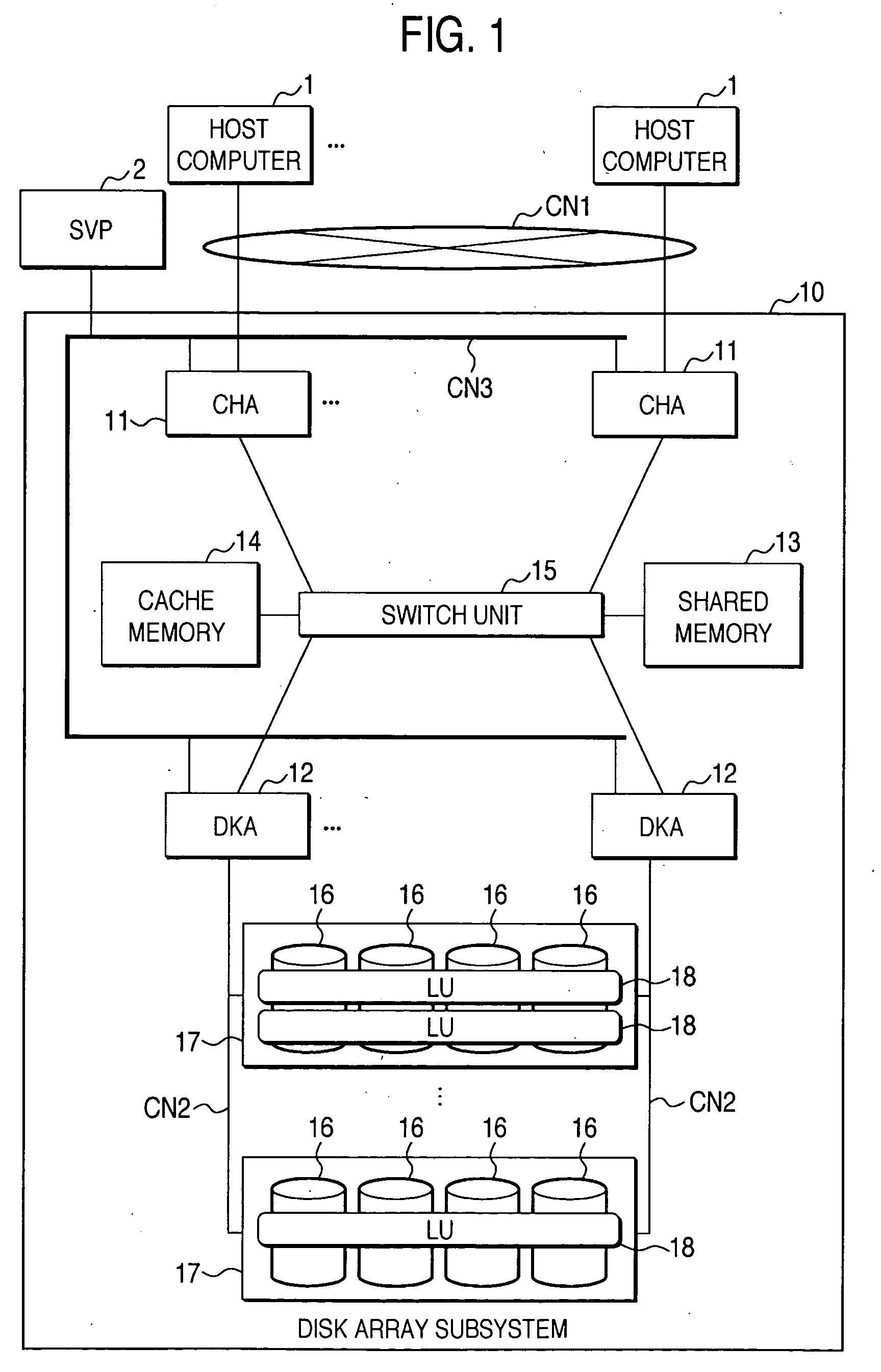
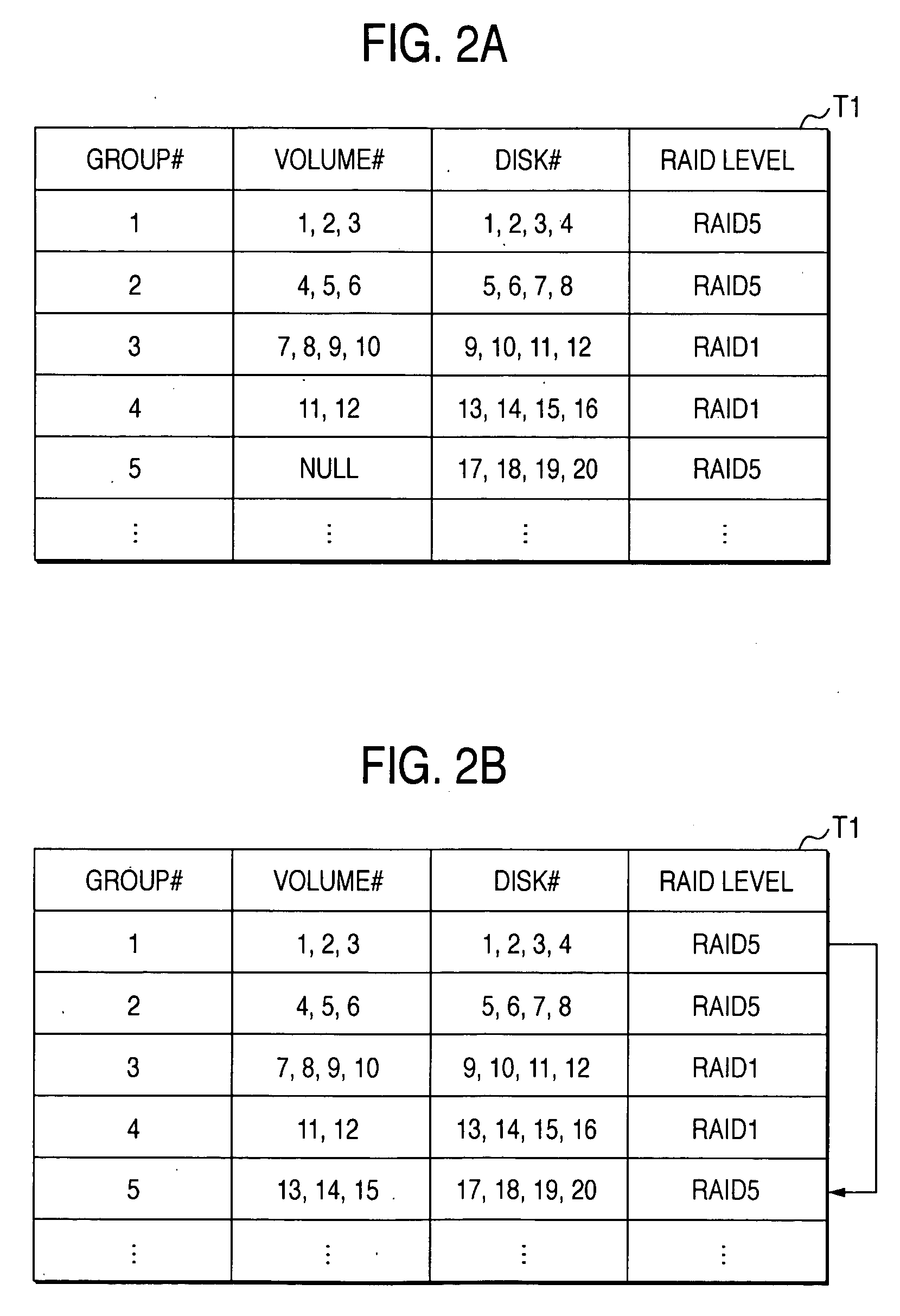
Disk array system and a method of avoiding failure of the disk array system
ActiveUS7028216B2Avoid failureReduce the likelihood of occurrenceInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionRAIDDisk array
The invention is intended to reduce disk access during data transfer from a disk in which occurrence of failure is anticipated to a spare disk as much as possible so that occurrence of double-failure is prevented in advance. When occurrence of failure in a disk which configures a RAID group, contents stored in the disk is copied to the spared disk. Simultaneously, another RAID group is paired with the above described RAID group and a secondary volume is provided therein. A write request is directed to the secondary volume. A differential bitmap controls a update data. Data which is not updated is read out from the primary volume, and data which is already updated is read from the secondary volume. When data transfer is completed, contents stored in the secondary volume are copied to the primary volume.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
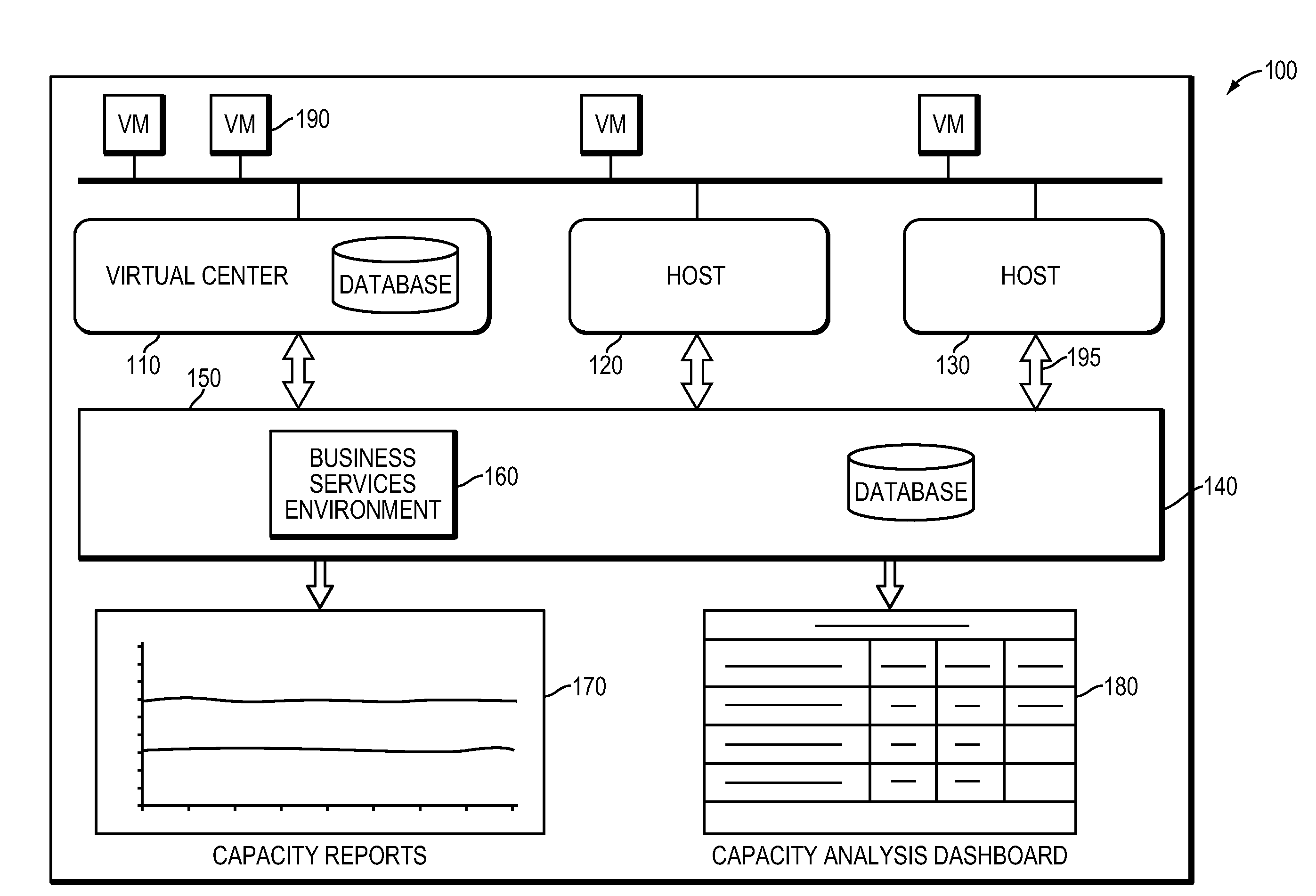
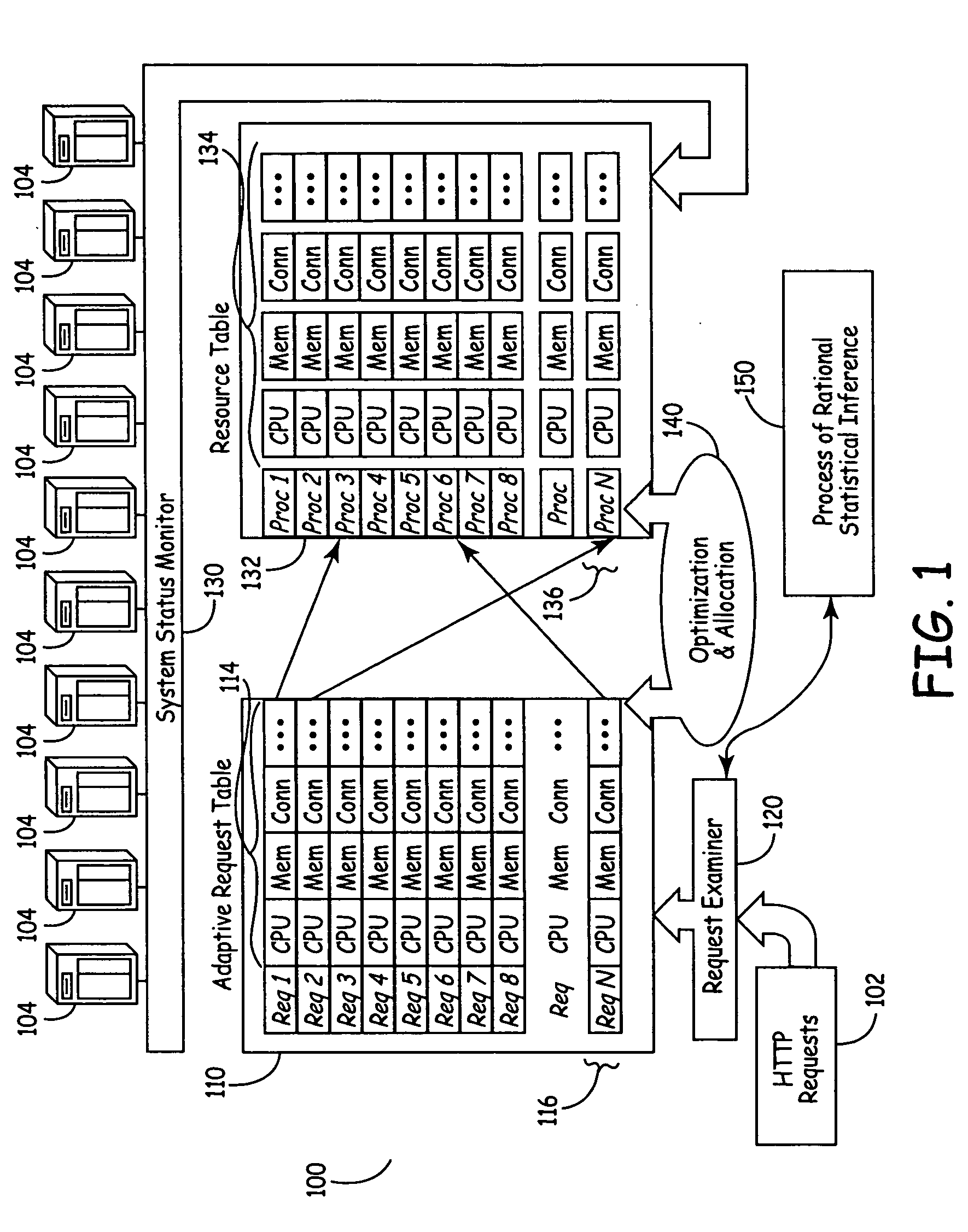
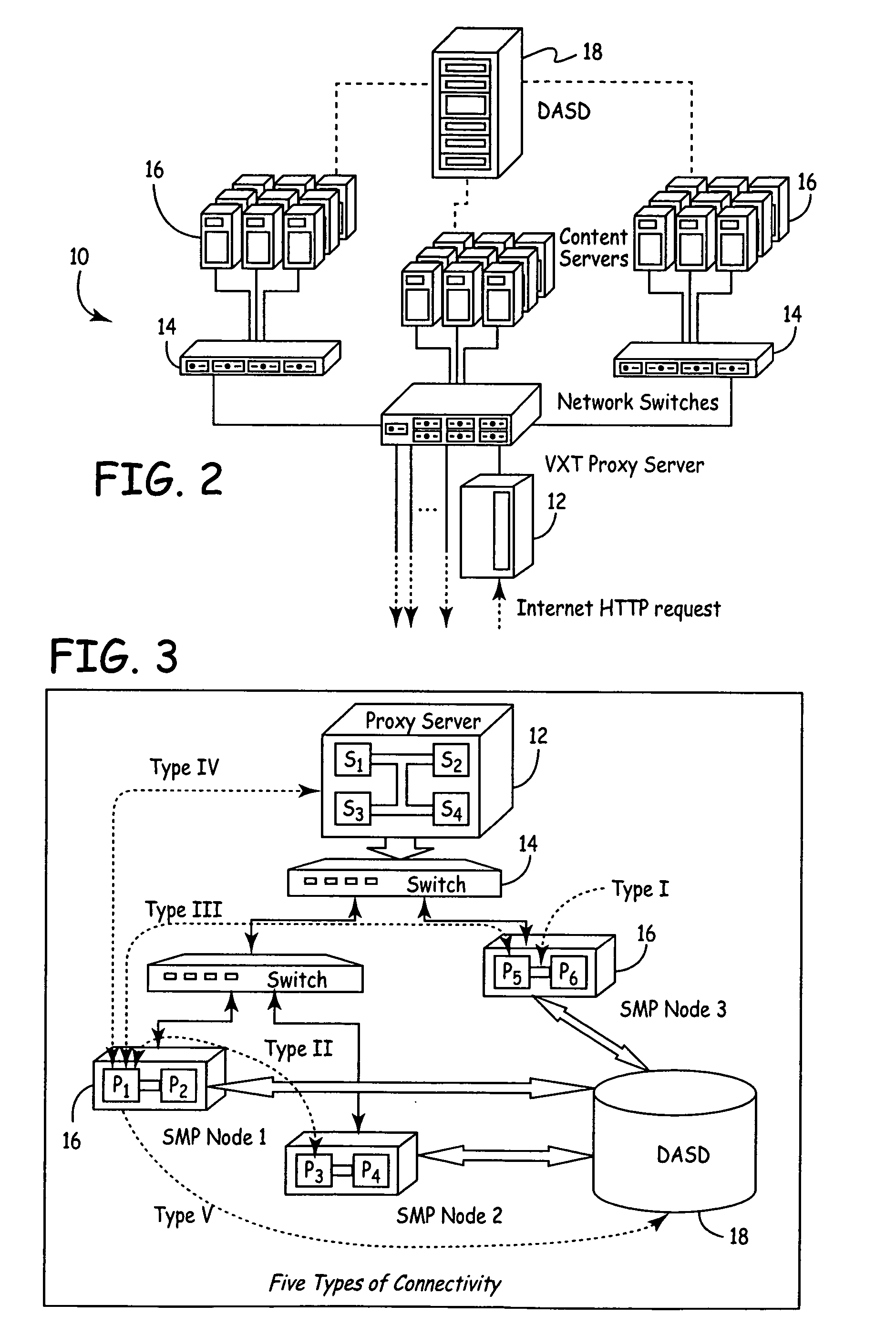
Method, System and Apparatus for Managing, Modeling, Predicting, Allocating and Utilizing Resources and Bottlenecks in a Computer Network
ActiveUS20090300173A1Shorten the timeLow costAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDigital computer detailsVirtualizationResource allocation
A method and apparatus for managing, modeling, predicting, allocating and utilizing resources and bottlenecks in a computer network managing, predicting and displaying of capacity, allocating and utilizing of resources, as well as actual and potential performance-degrading resource shortages in a computer network, is provided. Specifically, exemplary implementations of the present invention provide a method, system and apparatus for calculating, detecting, predicting, and presenting resource allocation, utilization, capacity bottlenecks and availability information, in a computer network, particularly in a virtualized computer environment.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
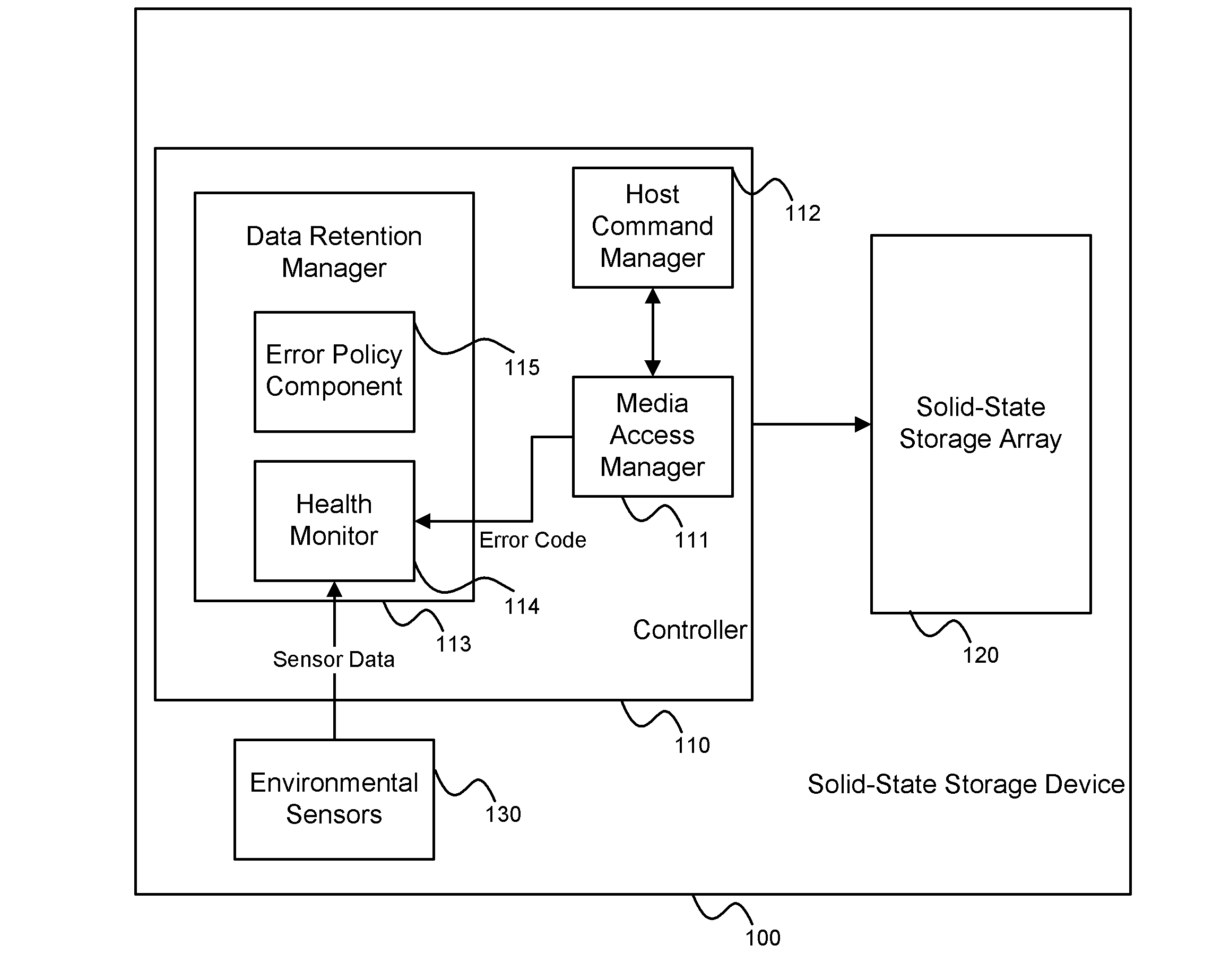
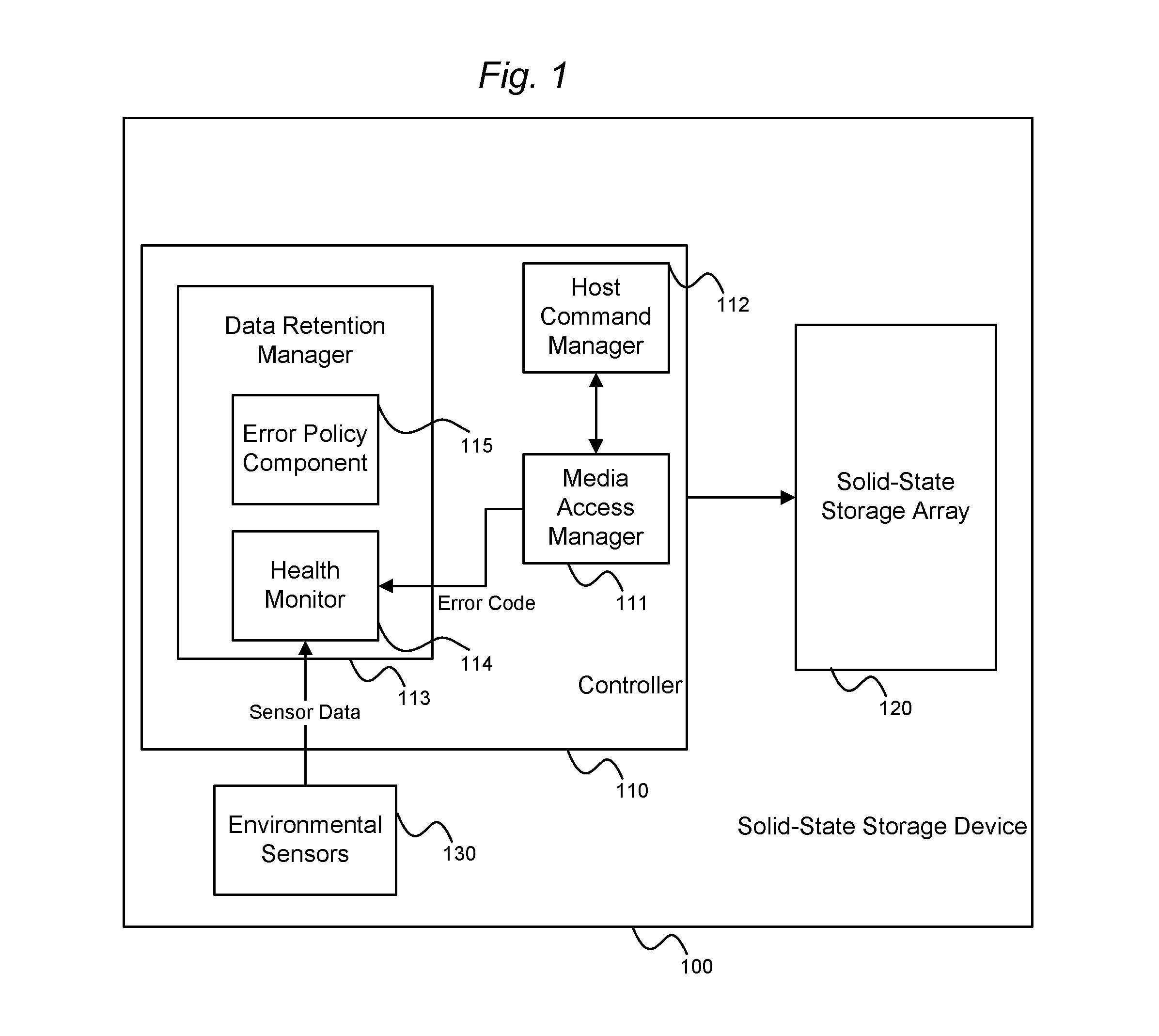
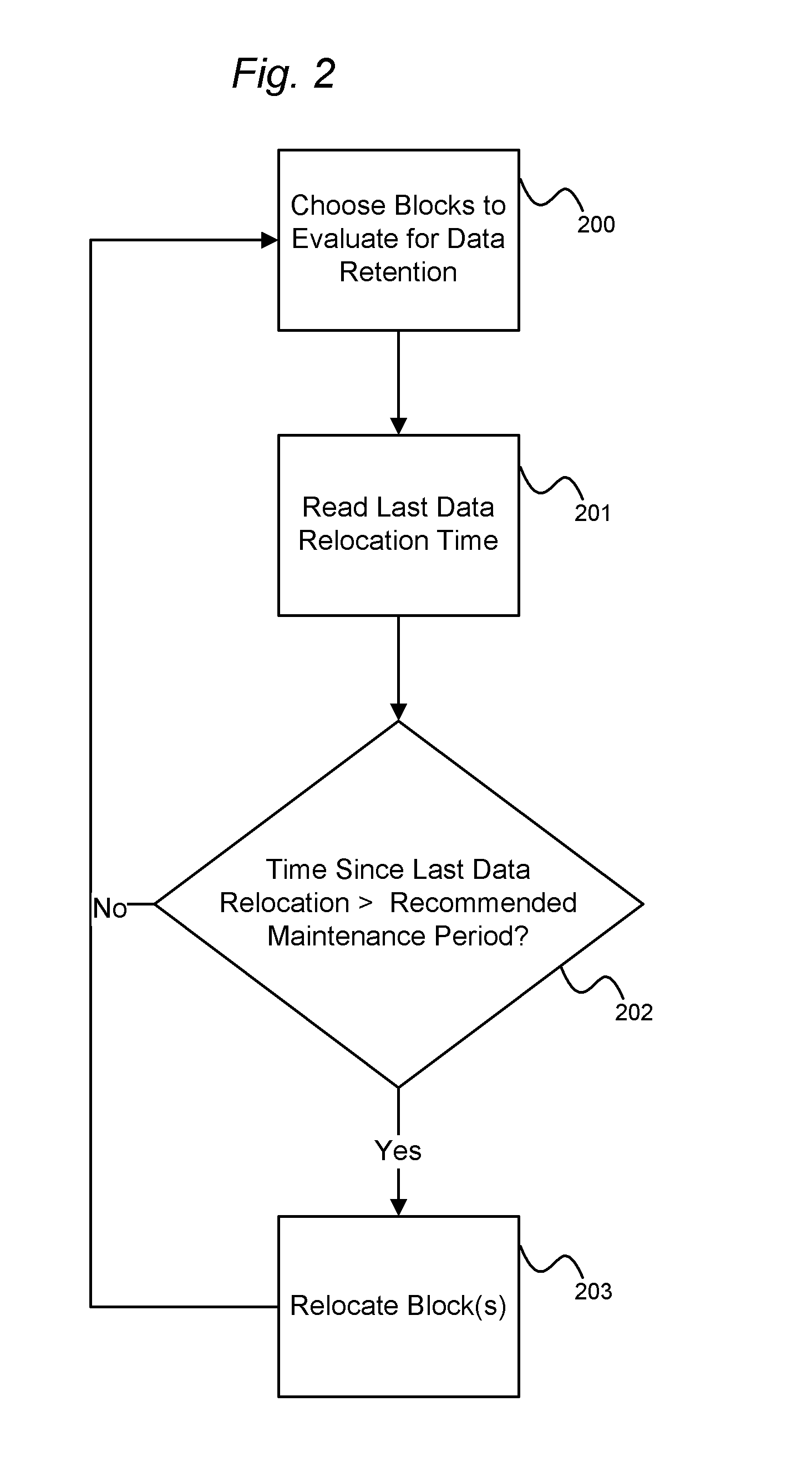
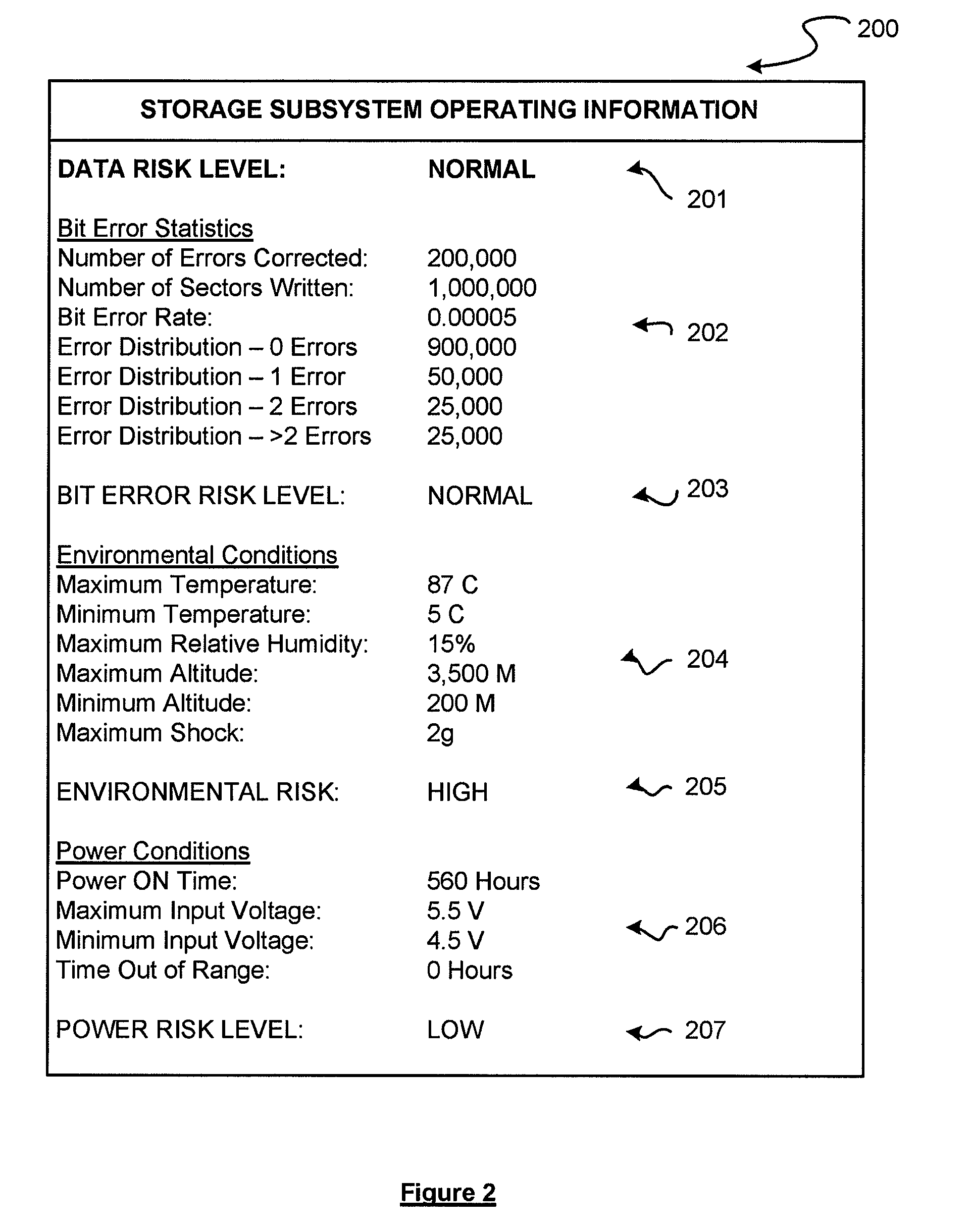
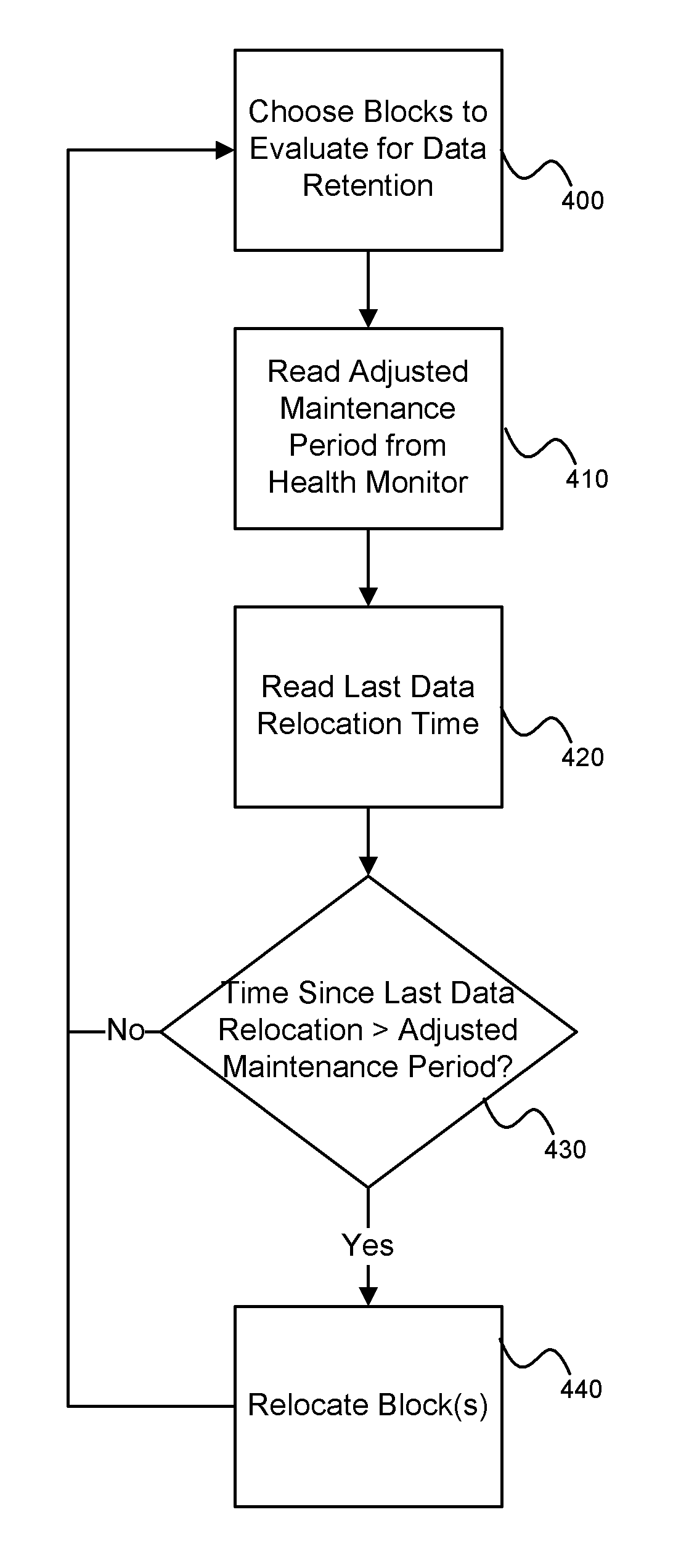
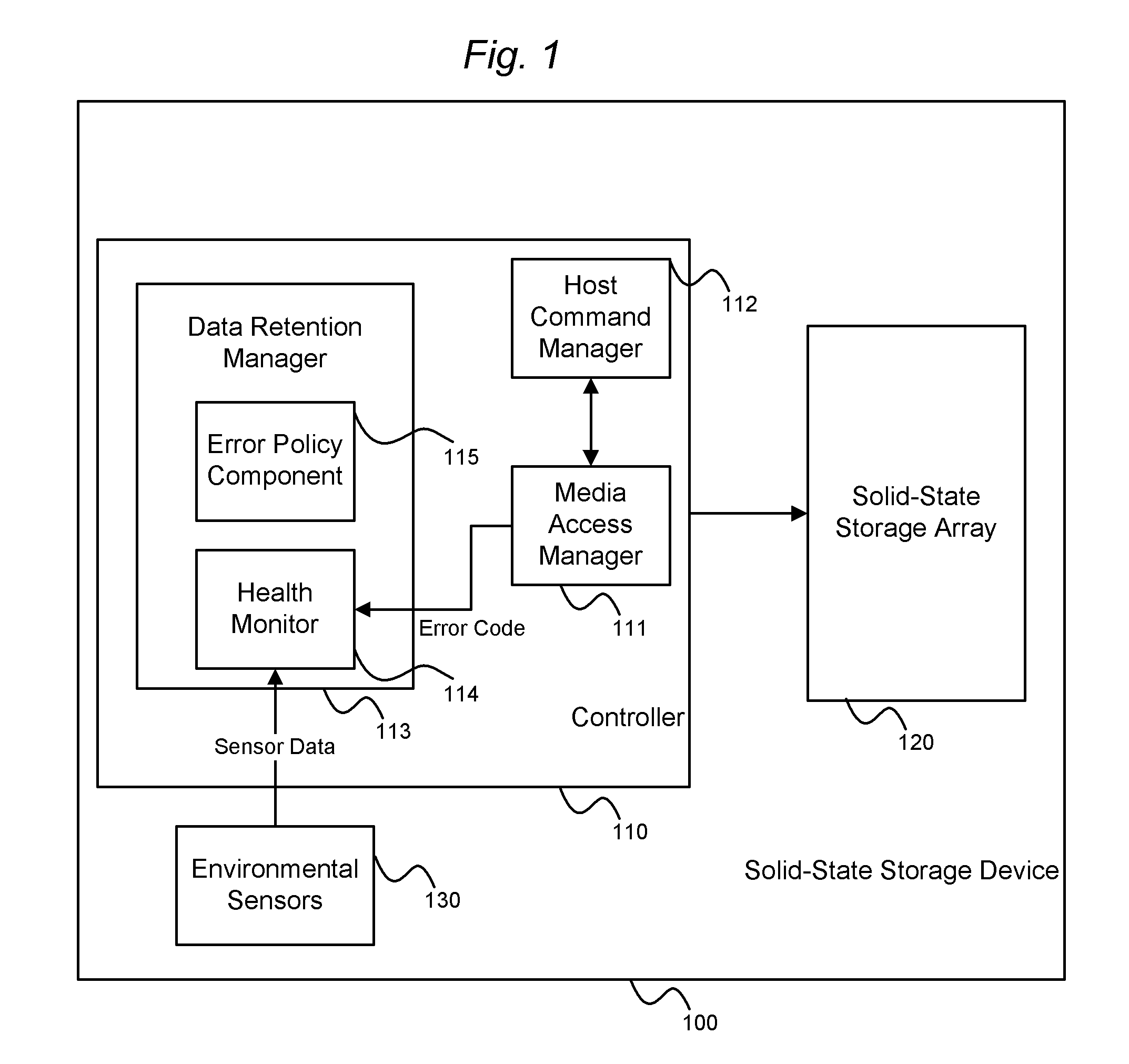
System and method for performing data retention that incorporates environmental conditions
ActiveUS20120324191A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationReliability/availability analysisSolid-state storageIncreased risk
A solid-state storage system is described with a method for adjusting the frequency of data retention operations. The data retention operation frequency can be increased or decreased according to a variety of environmental factors such as error code frequency, system temperature, altitude, and other operating conditions. These factors can indicate an increased or decreased risk of failure and accordingly provide increased or decreased rates of data retention operations.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
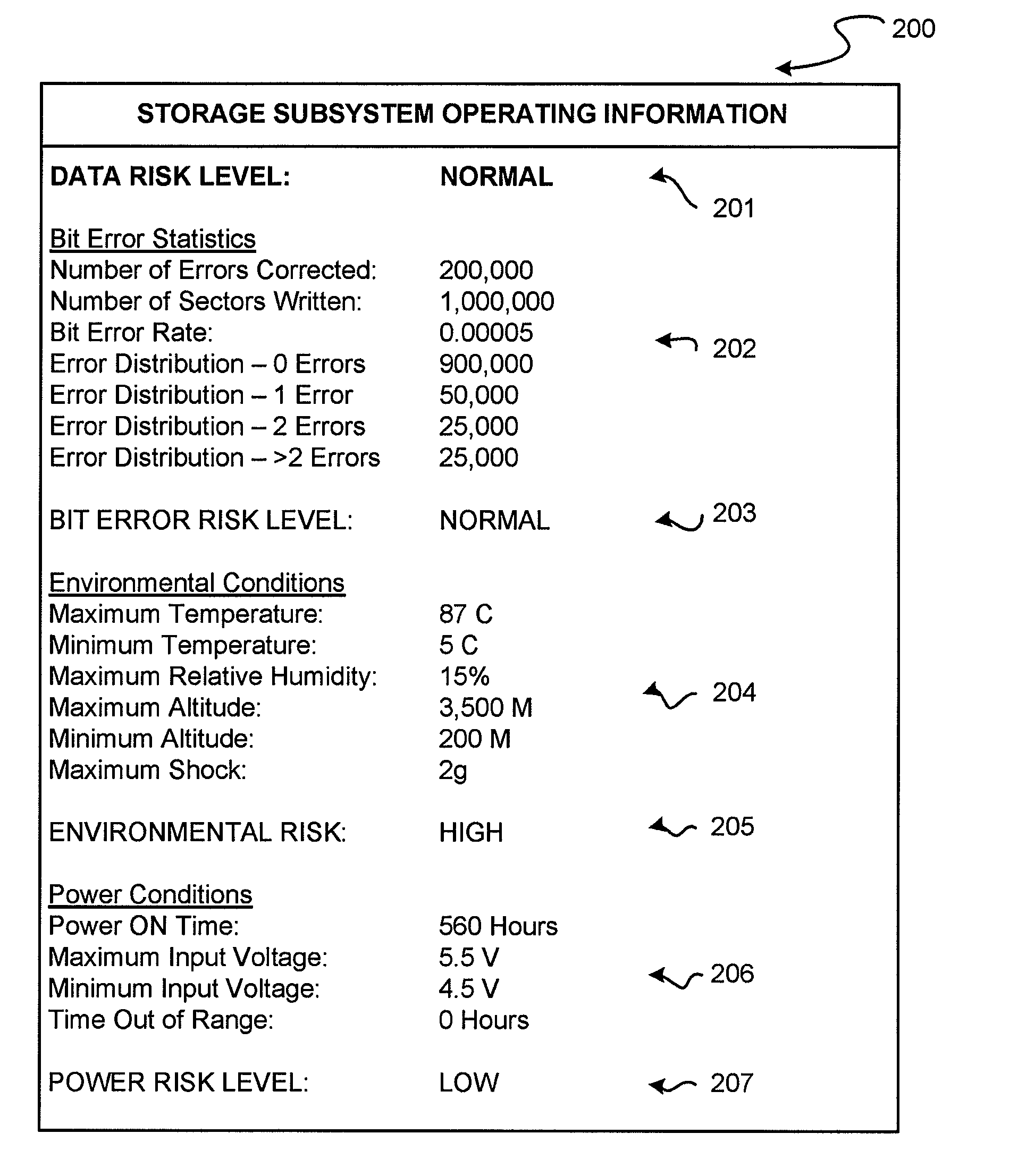
Solid state storage subsystem that maintains and provides access to data reflective of a failure risk
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
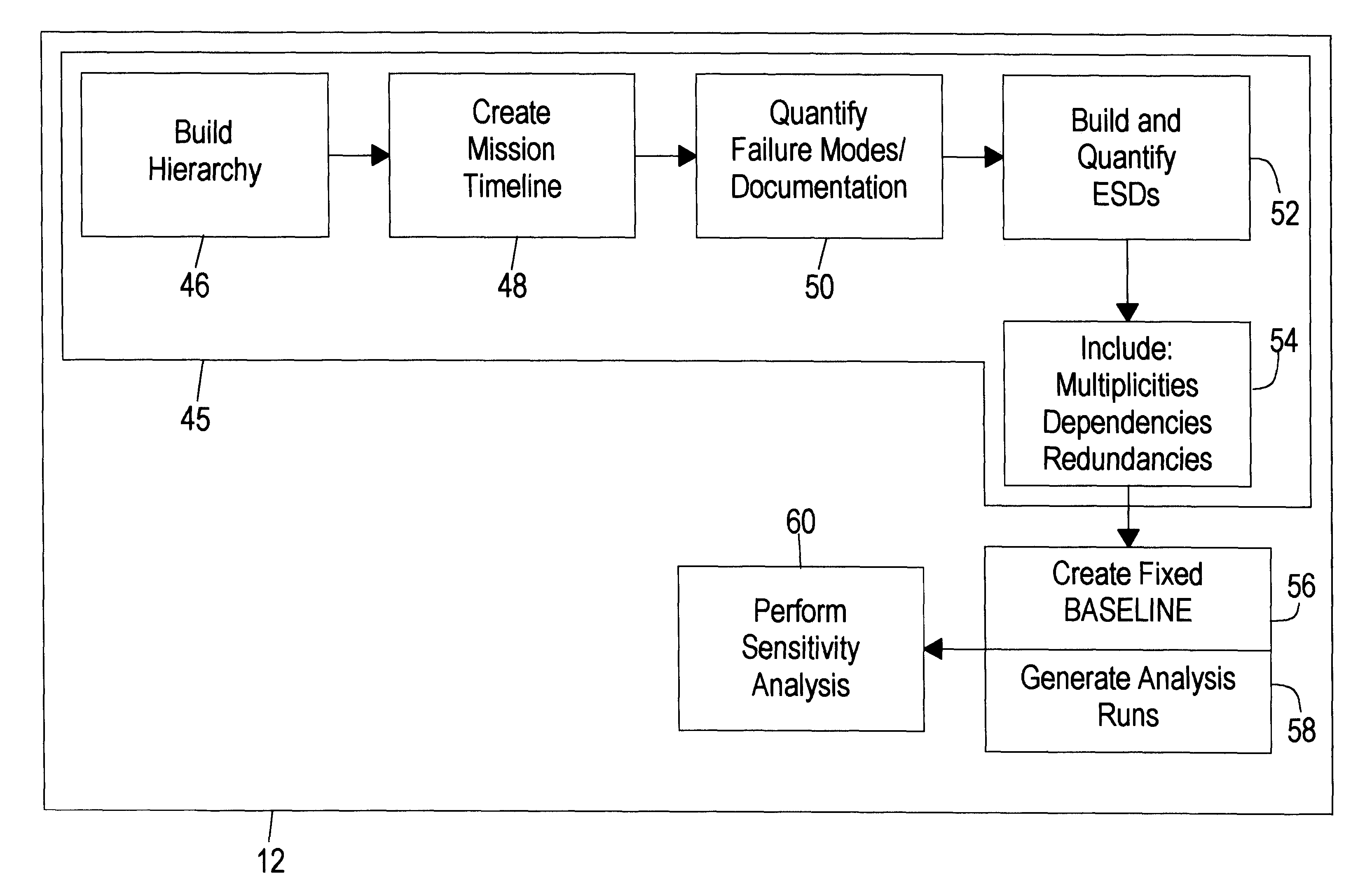
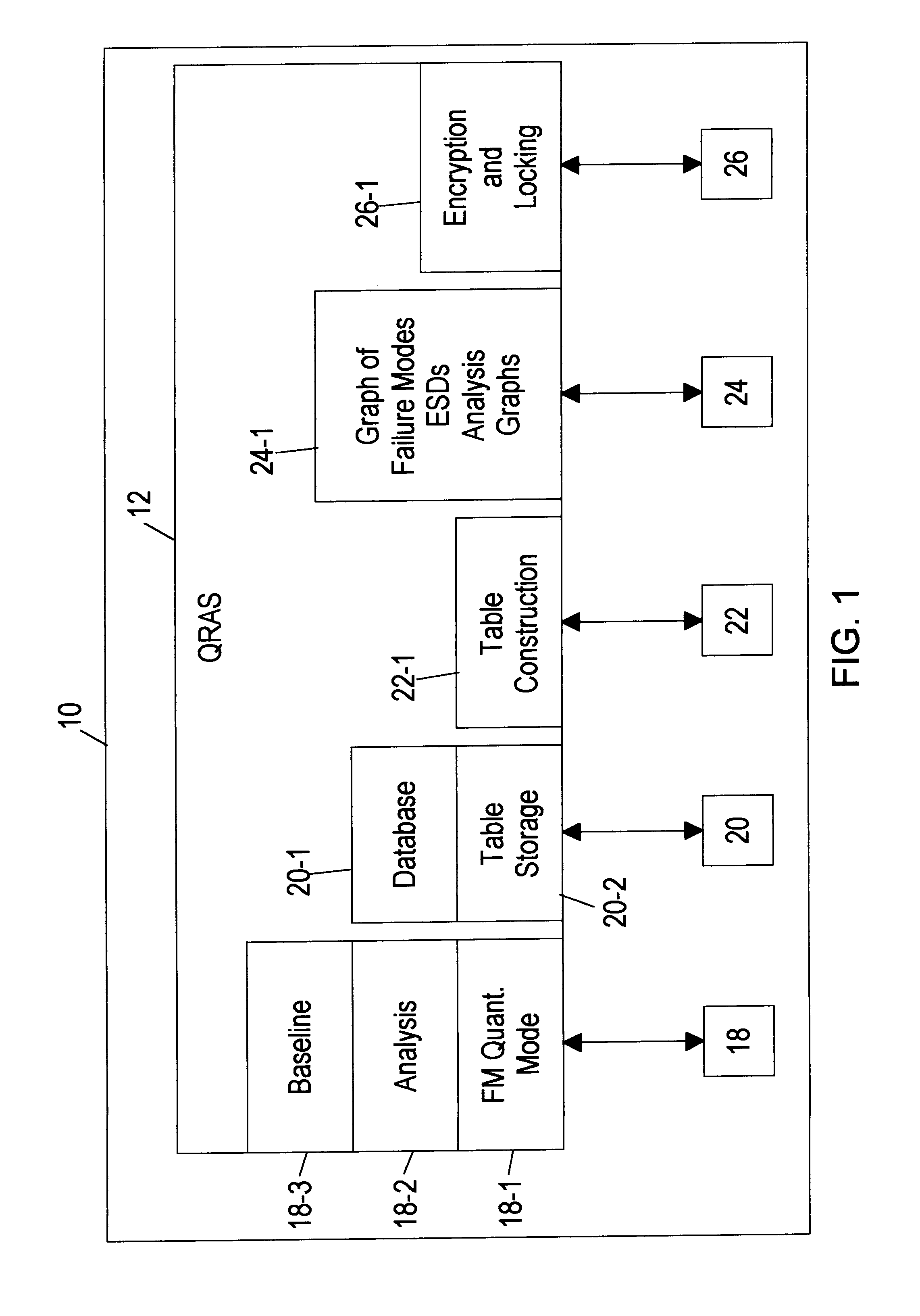
Quantitative risk assessment system (QRAS)
A quantitative risk assessment system (QRAS) builds a risk model of a system for which risk of failure is being assessed, then analyzes the risk of the system corresponding to the risk model. The QRAS performs sensitivity analysis of the risk model by altering fundamental components and quantifications built into the risk model, then re-analyzes the risk of the system using the modifications. More particularly, the risk model is built by building a hierarchy, creating a mission timeline, quantifying failure modes, and building / editing event sequence diagrams. Multiplicities, dependencies, and redundancies of the system are included in the risk model. For analysis runs, a fixed baseline is first constructed and stored. This baseline contains the lowest level scenarios, preserved in event tree structure. The analysis runs, at any level of the hierarchy and below, access this baseline for risk quantitative computation as well as ranking of particular risks. A standalone Tool Box capability exists, allowing the user to store application programs within QRAS.
Owner:NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR +1
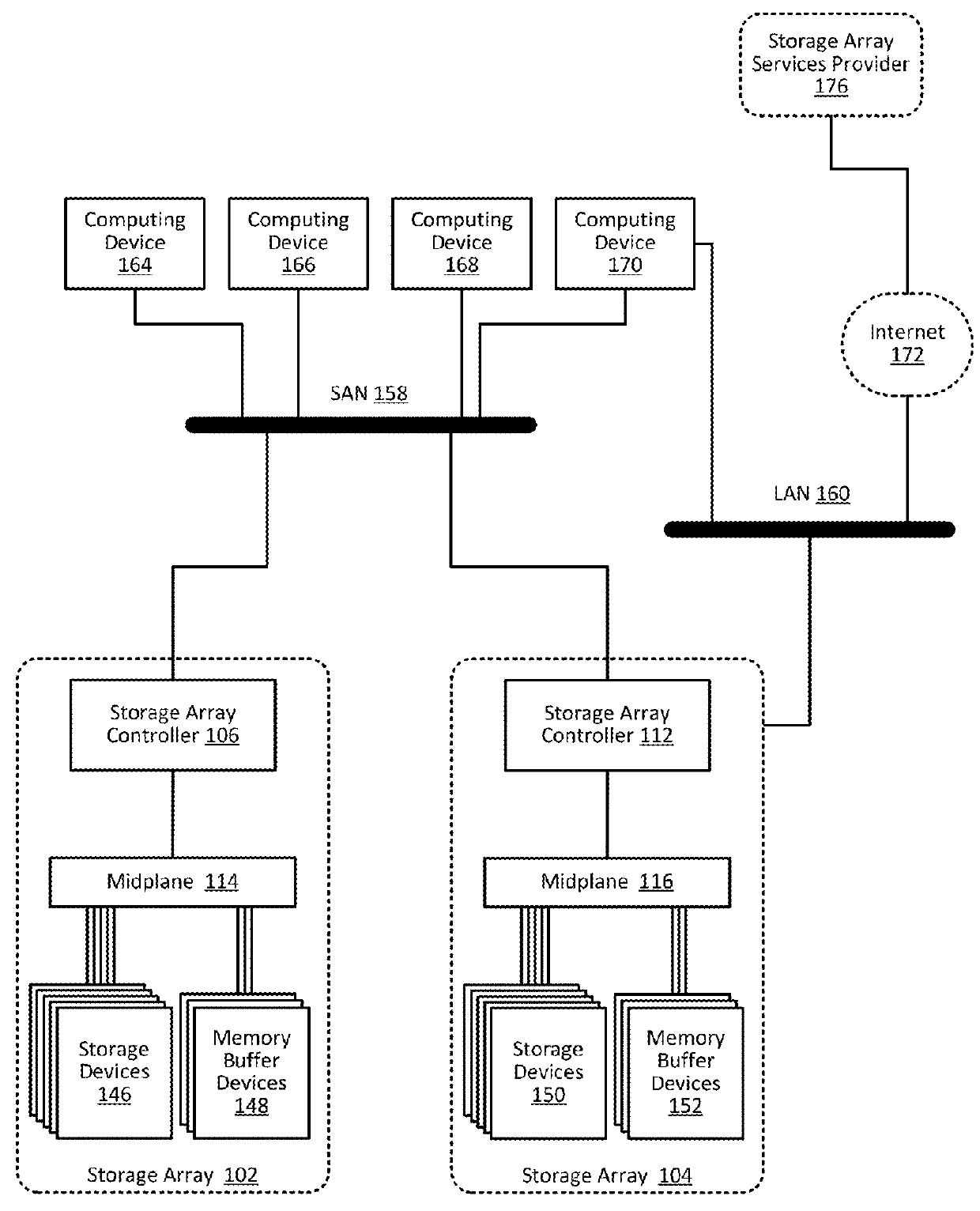
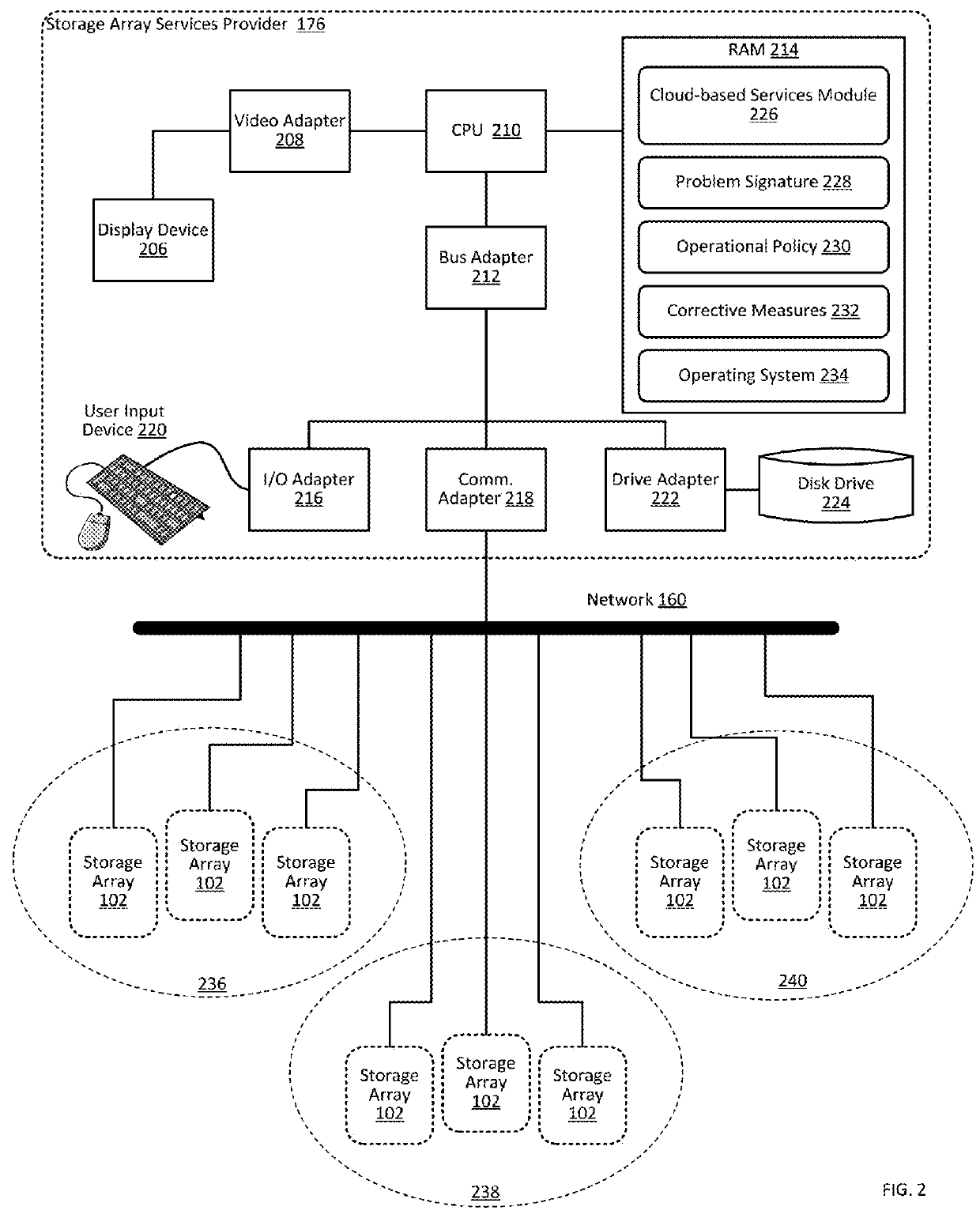
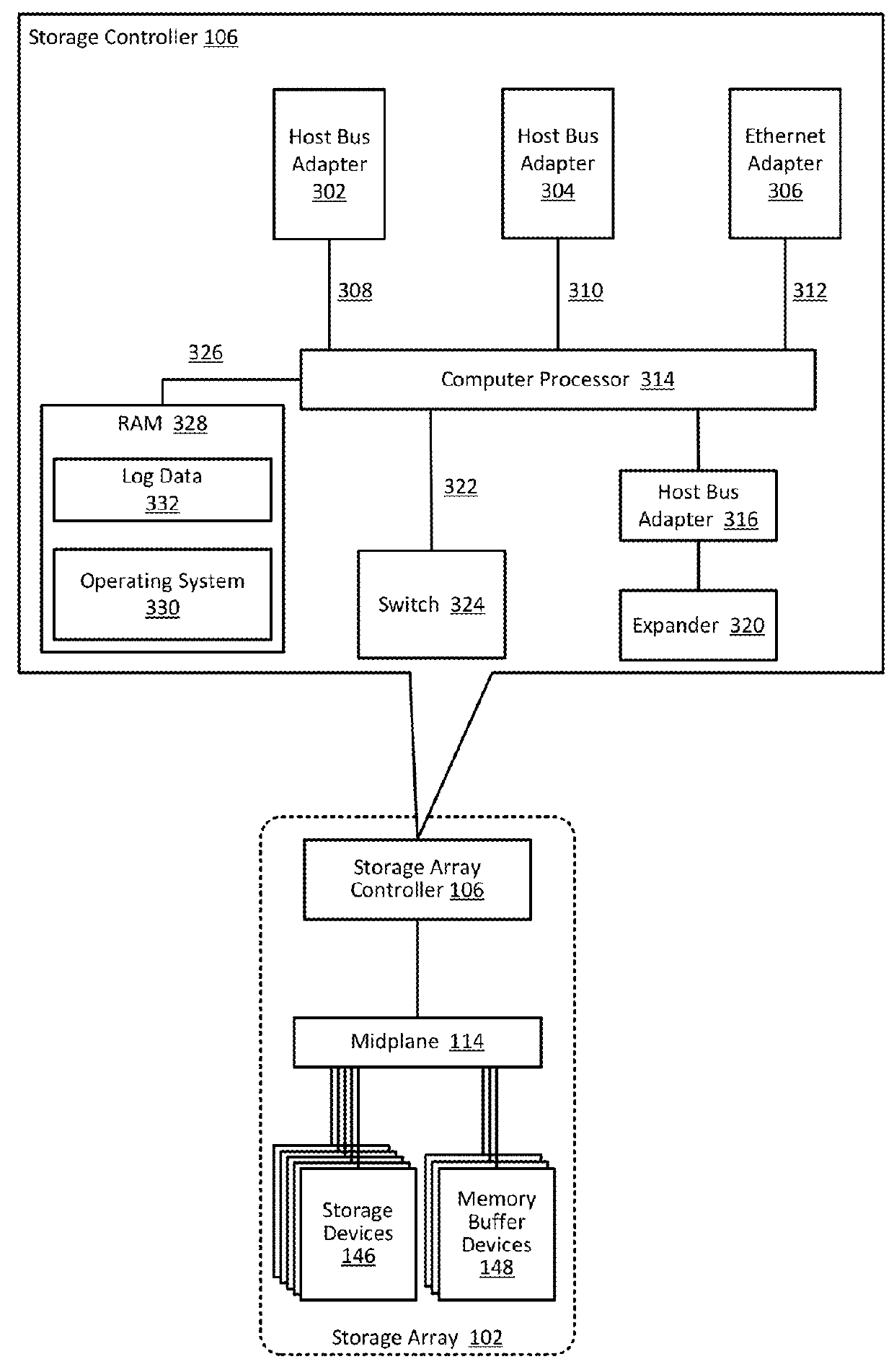
Proactively providing corrective measures for storage arrays
ActiveUS9384082B1Particular problemHardware monitoringReliability/availability analysisReal-time computingOperational policies
Owner:PURE STORAGE
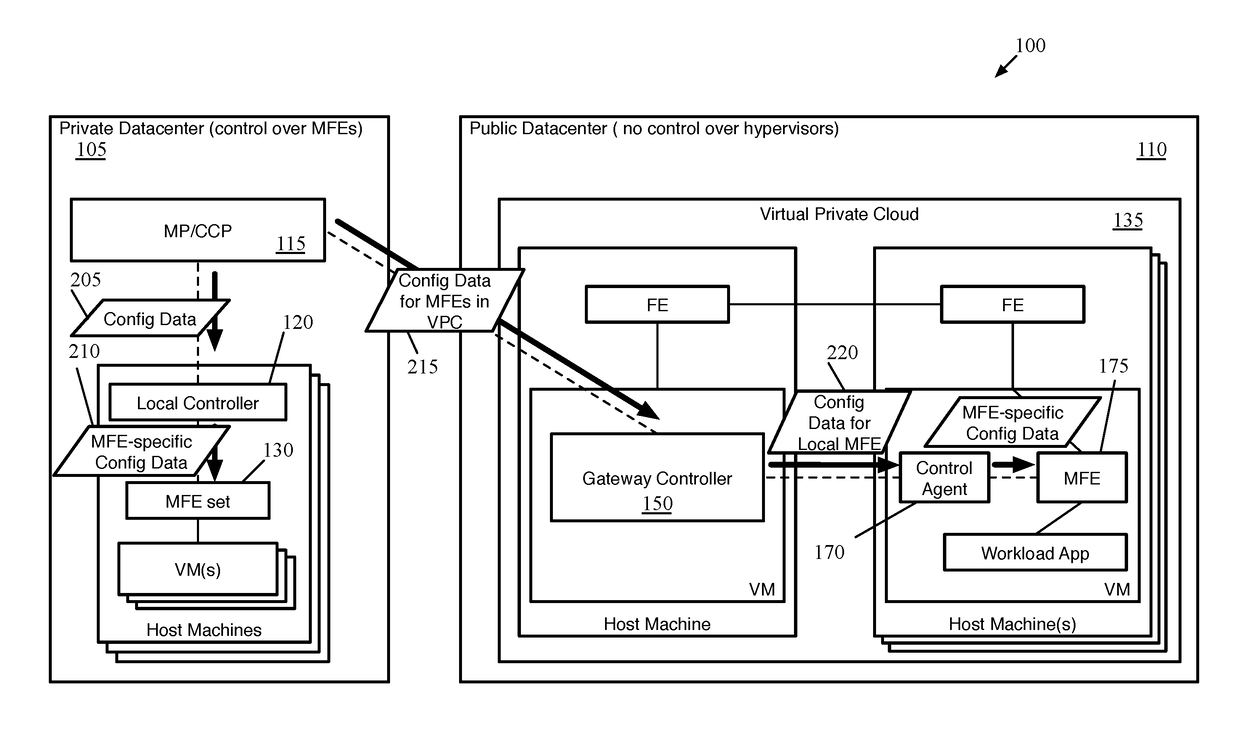
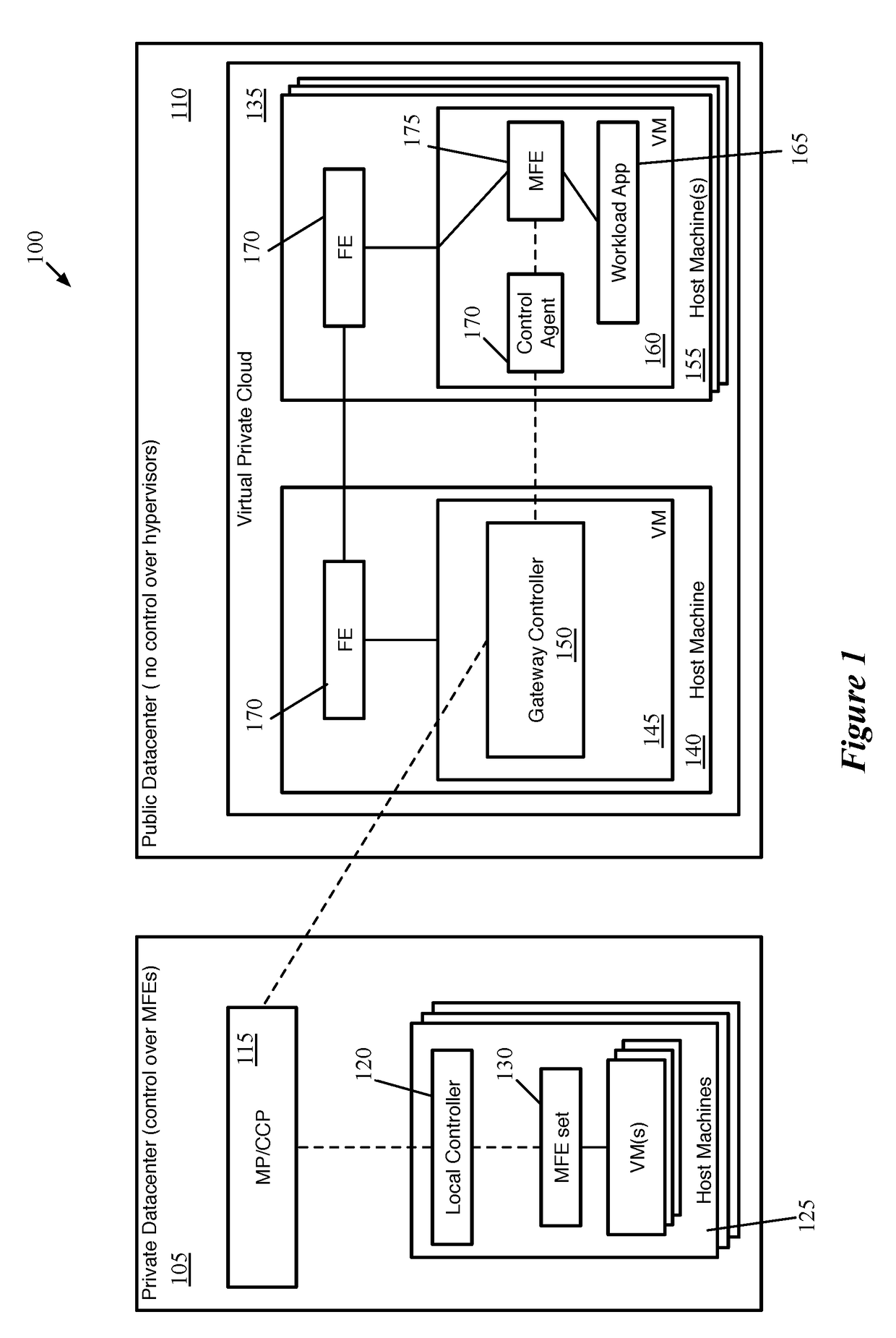
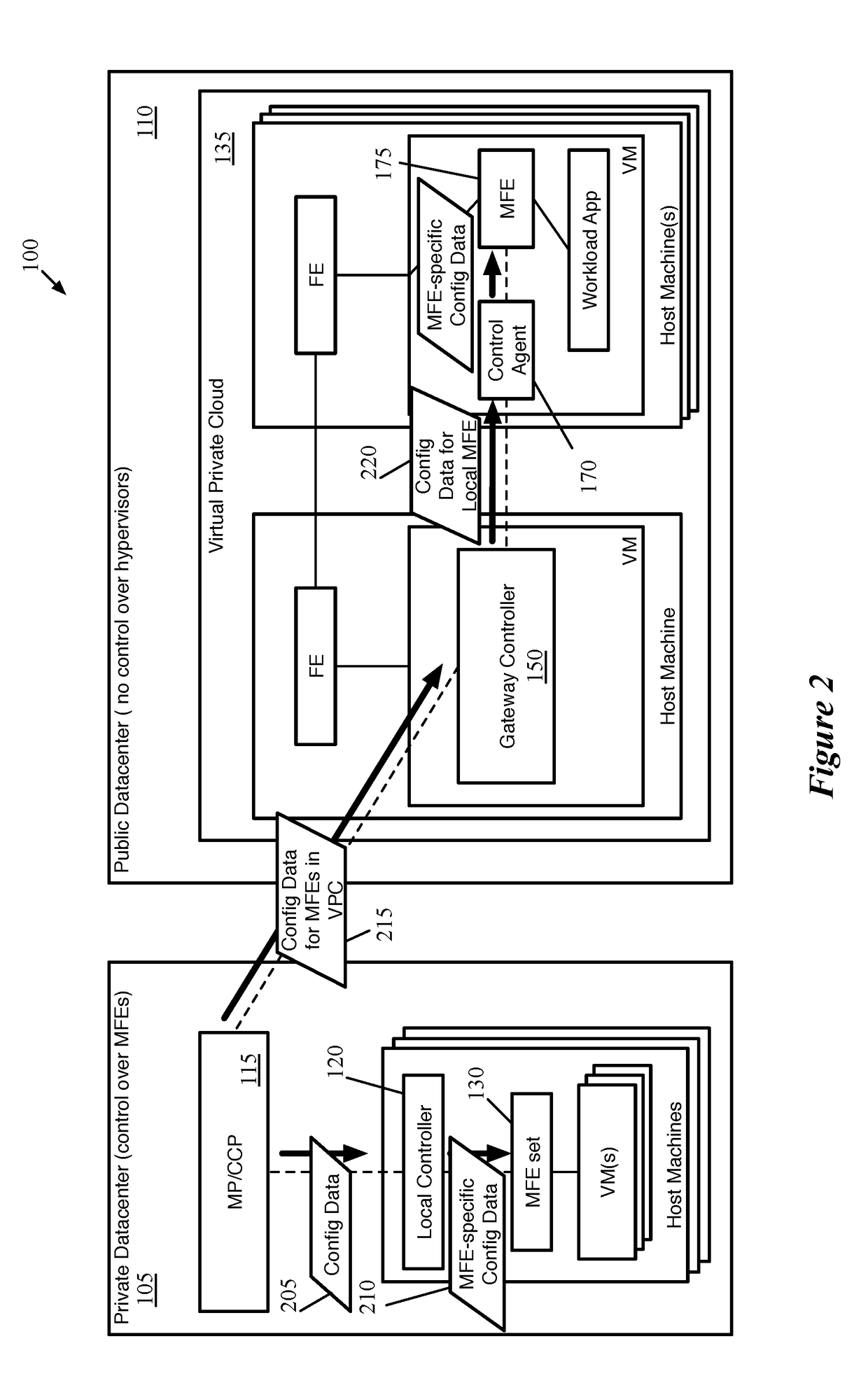
Distributed Network Encryption for Logical Network Implemented in Public Cloud
ActiveUS20180063193A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey distributionKey storage
Some embodiments provide a method for a first data compute node (DCN) operating in a public datacenter. The method receives an encryption rule from a centralized network controller. The method determines that the network encryption rule requires encryption of packets between second and third DCNs operating in the public datacenter. The method requests a first key from a secure key storage. Upon receipt of the first key, the method uses the first key and additional parameters to generate second and third keys. The method distributes the second key to the second DCN and the third key to the third DCN in the public datacenter.
Owner:NICIRA
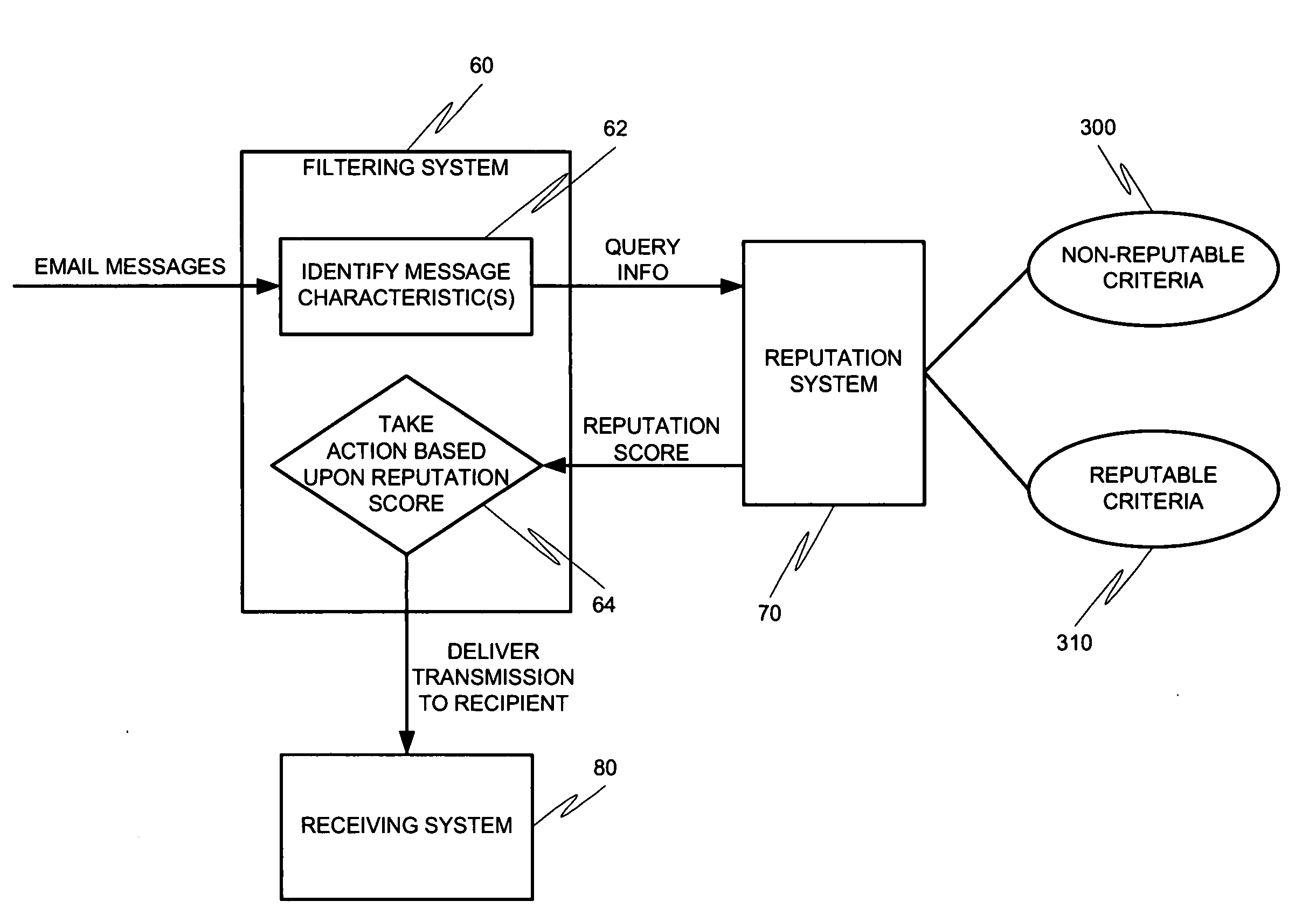
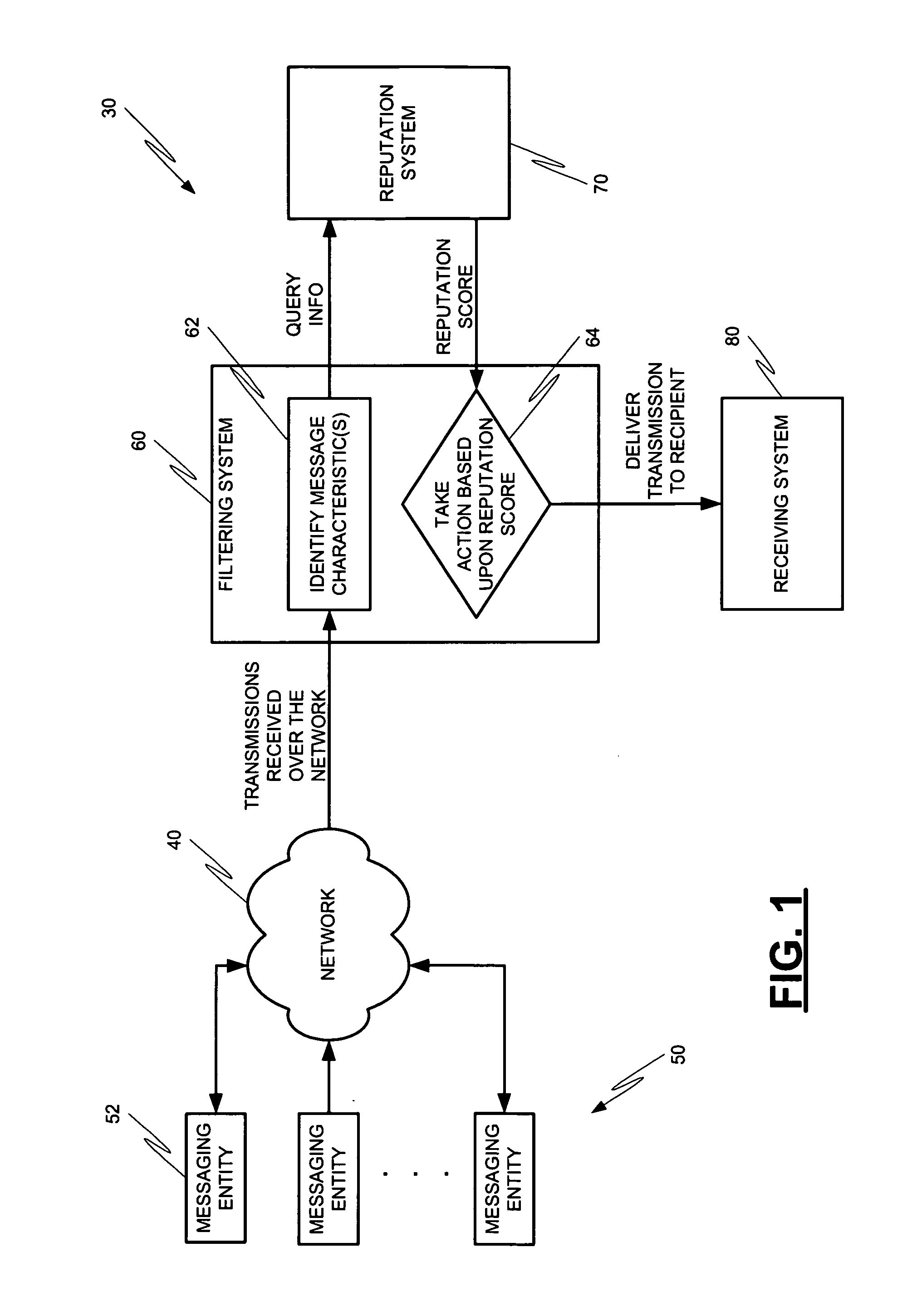
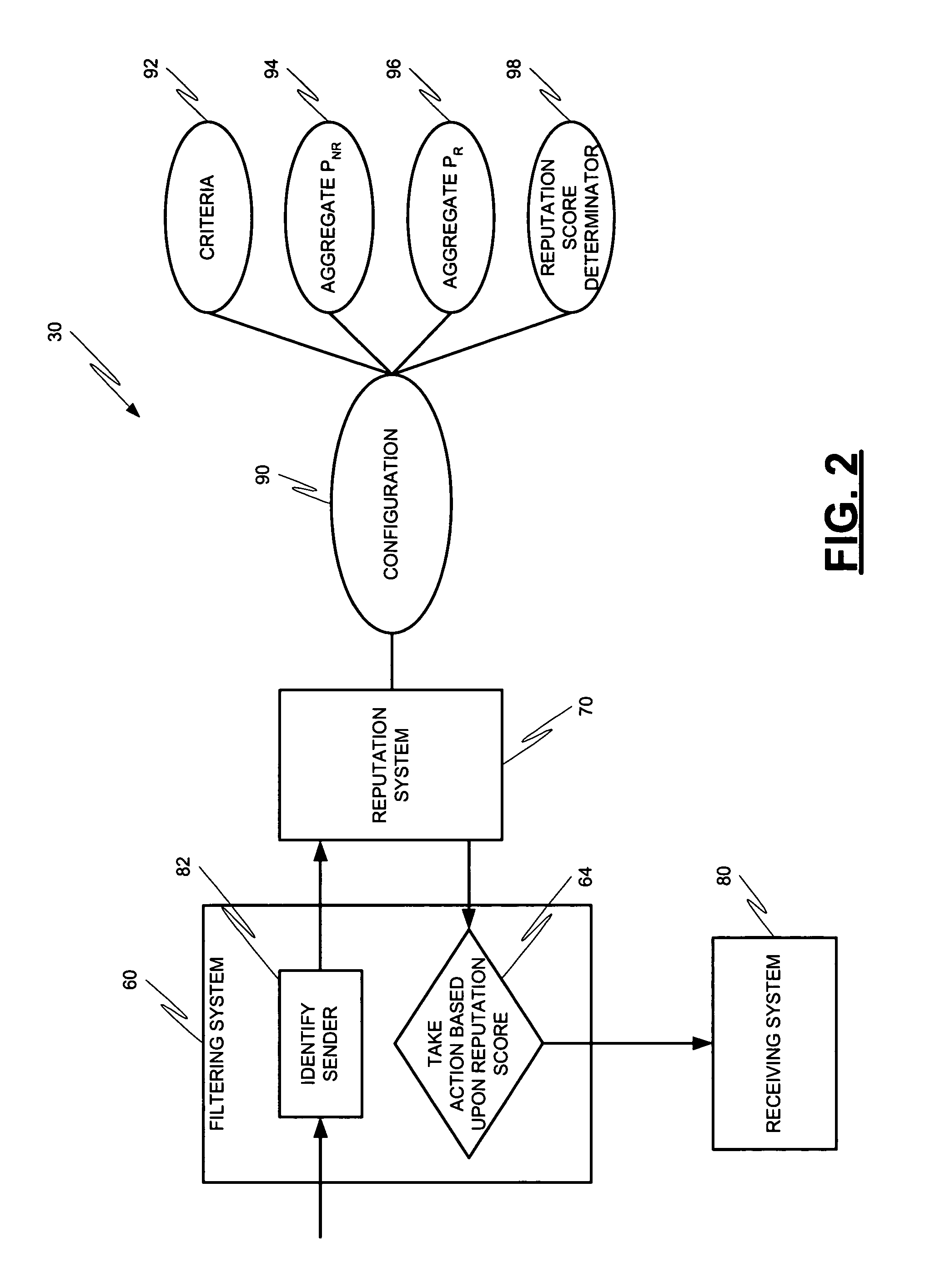
Systems and methods for classification of messaging entities
InactiveUS20060015942A1Memory loss protectionUser identity/authority verificationData treatmentMessage passing
Methods and systems for operation upon one or more data processors for assigning a reputation to a messaging entity. A method can include receiving data that identifies one or more characteristics related to a messaging entity's communication. A reputation score is determined based upon the received identification data. The determined reputation score is indicative of reputation of the messaging entity. The determined reputation score is used in deciding what action is to be taken with respect to a communication associated with the messaging entity.
Owner:MCAFEE INC
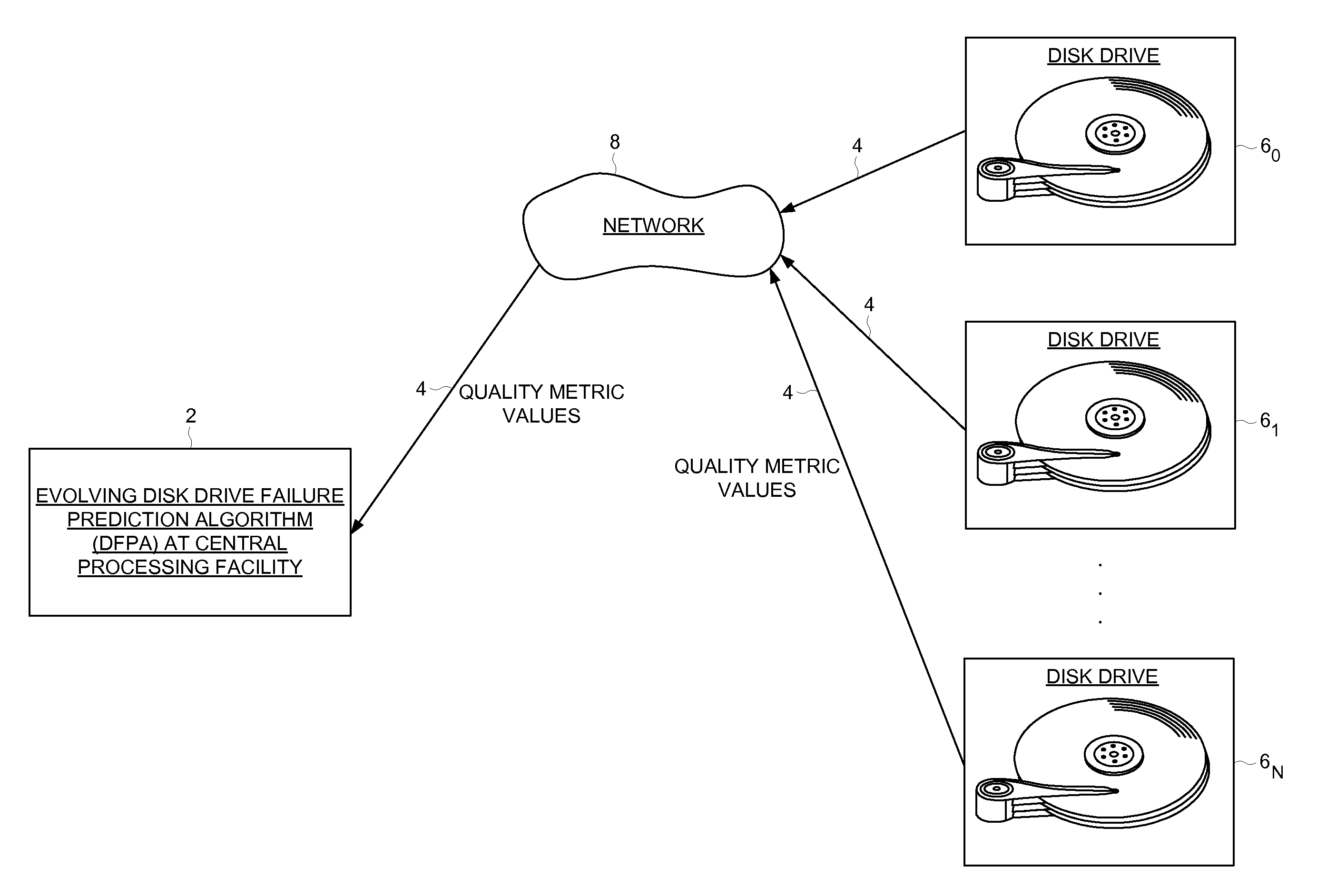
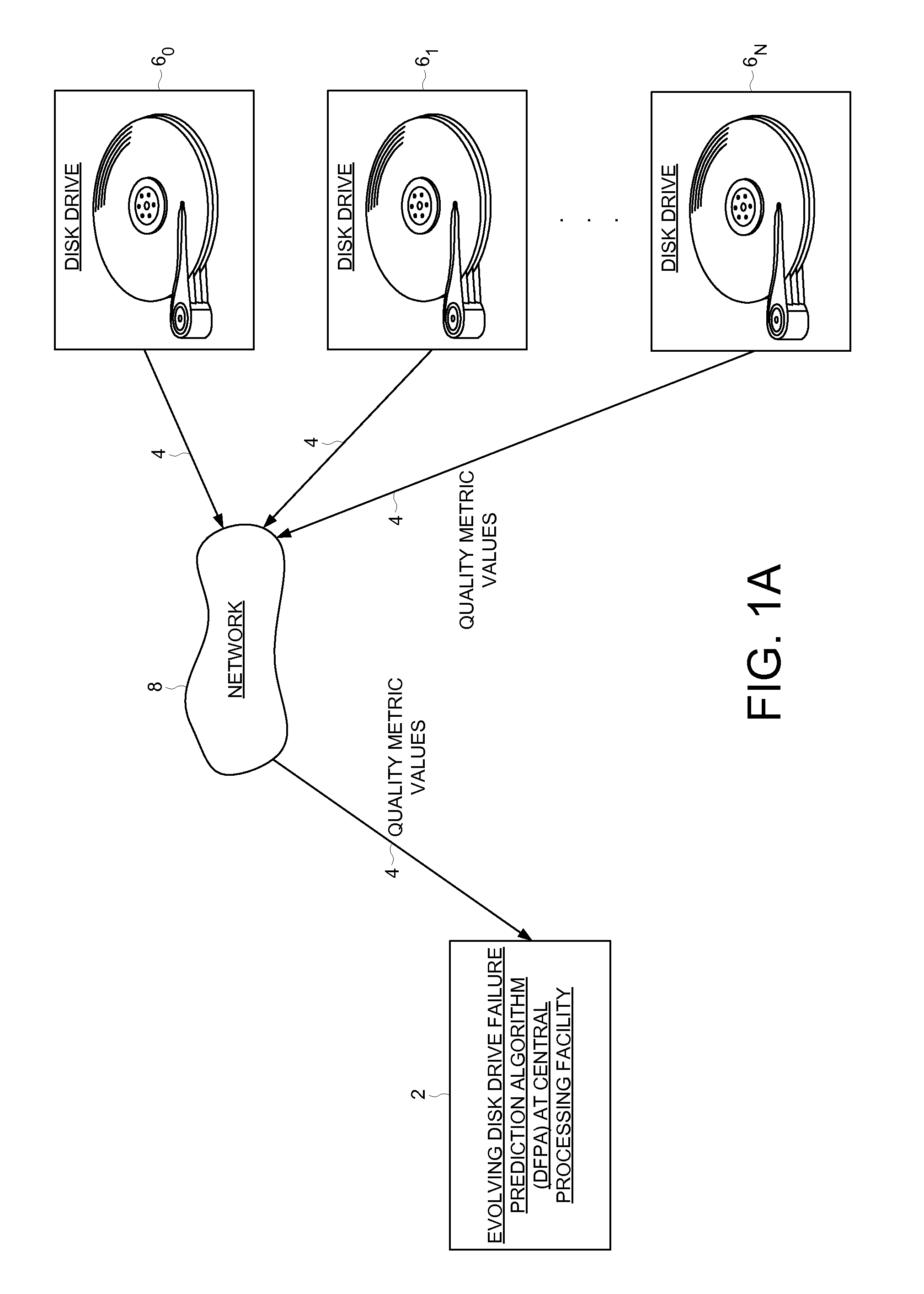
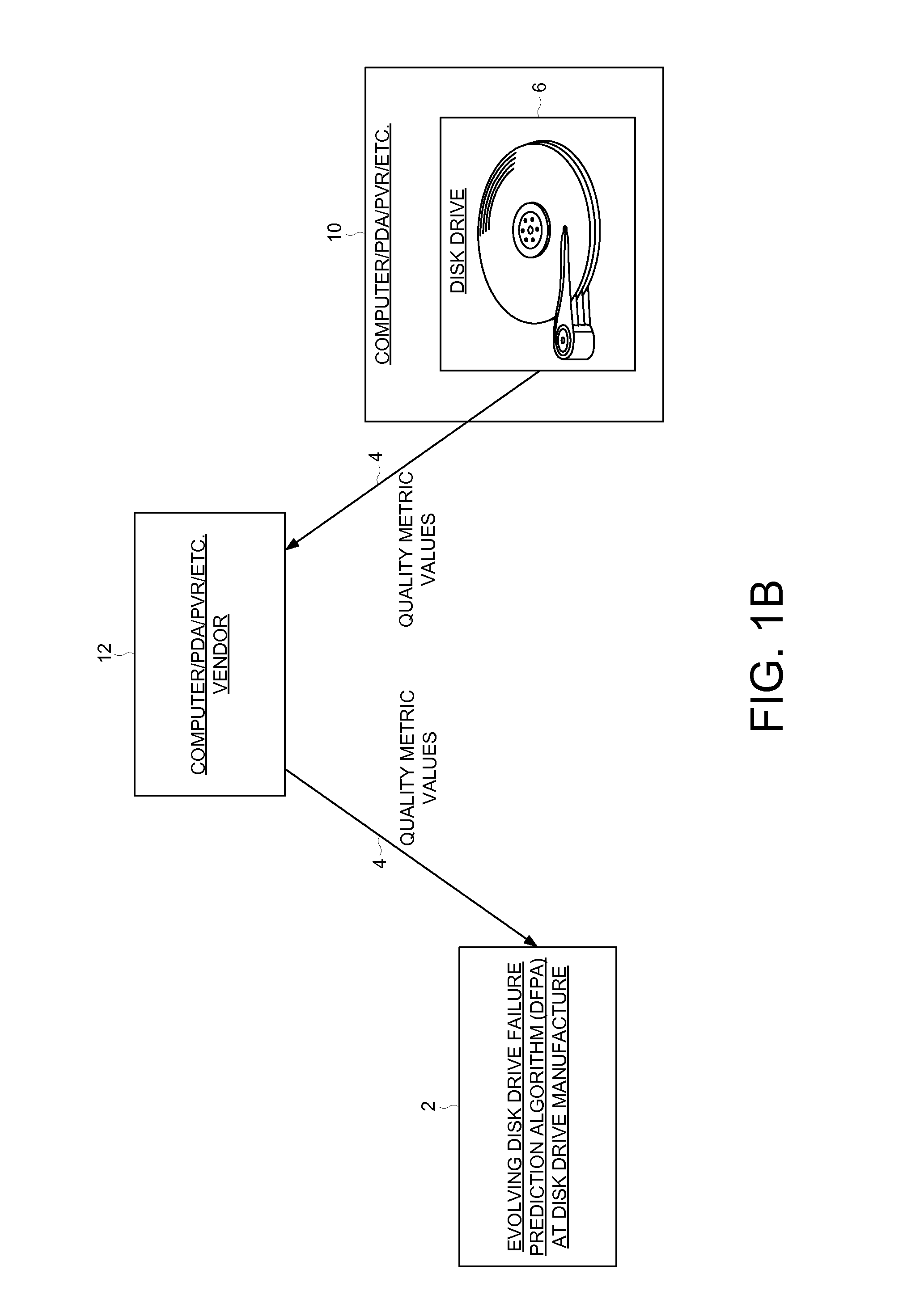
Predicting disk drive failure at a central processing facility using an evolving disk drive failure prediction algorithm
ActiveUS8316263B1Improve the accuracy of the DFPA over timeDigital computer detailsReliability/availability analysisReference databasePrediction algorithms
A method of predicting disk drive failure at a central processing facility using an evolving drive failure prediction algorithm (DFPA) is disclosed. A set of quality metric values are transmitted from each of a plurality of remote disk drives to the central processing facility. The DFPA is executed at the central processing facility in response to the quality metric values to detect an impending failure of at least one of the remote disk drives. The DFPA is evolved at the central processing facility in response to a reference data base of quality metric values and a corresponding failure indicator. The processes is repeated so as to improve the accuracy of the DFPA over time.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
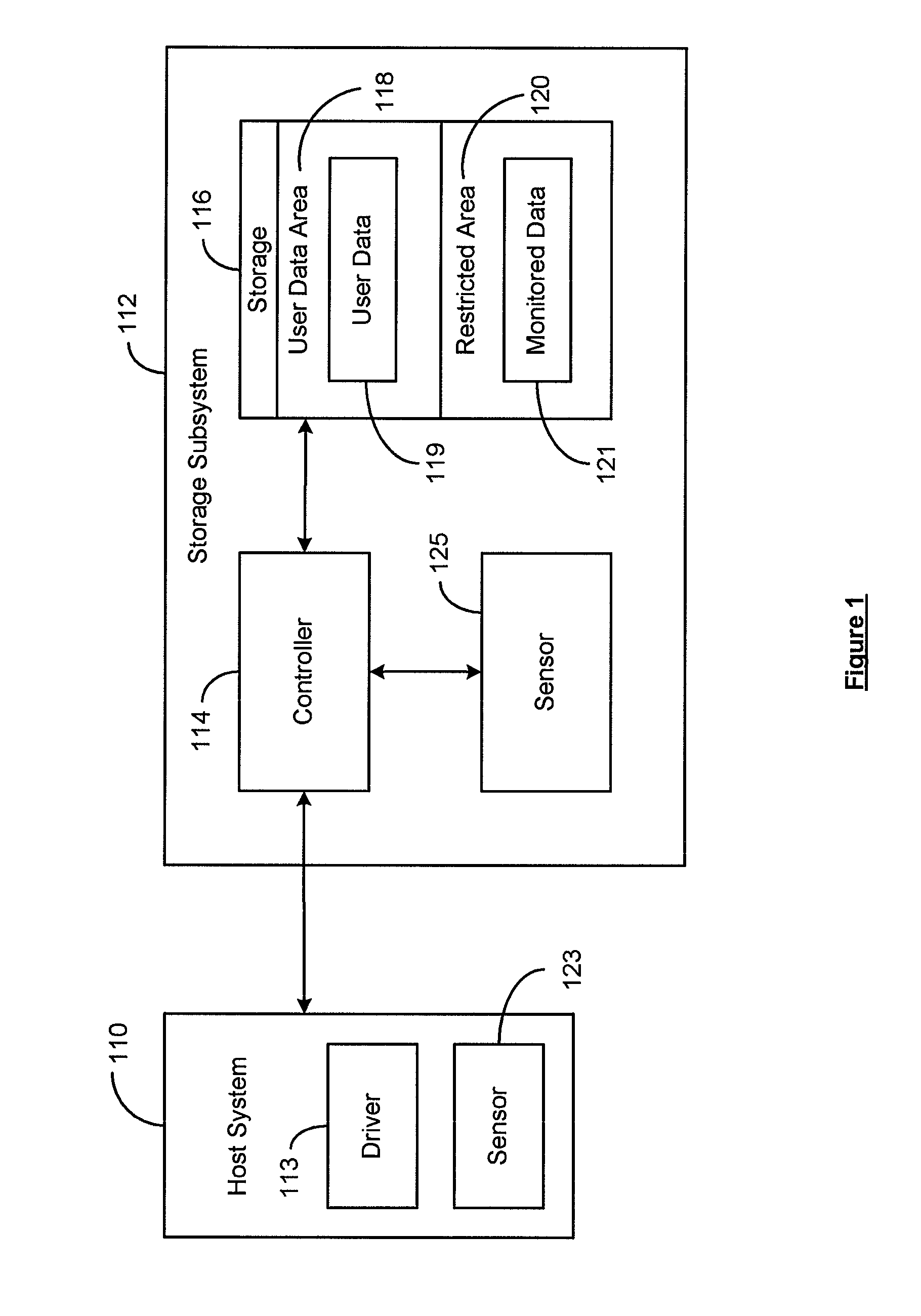
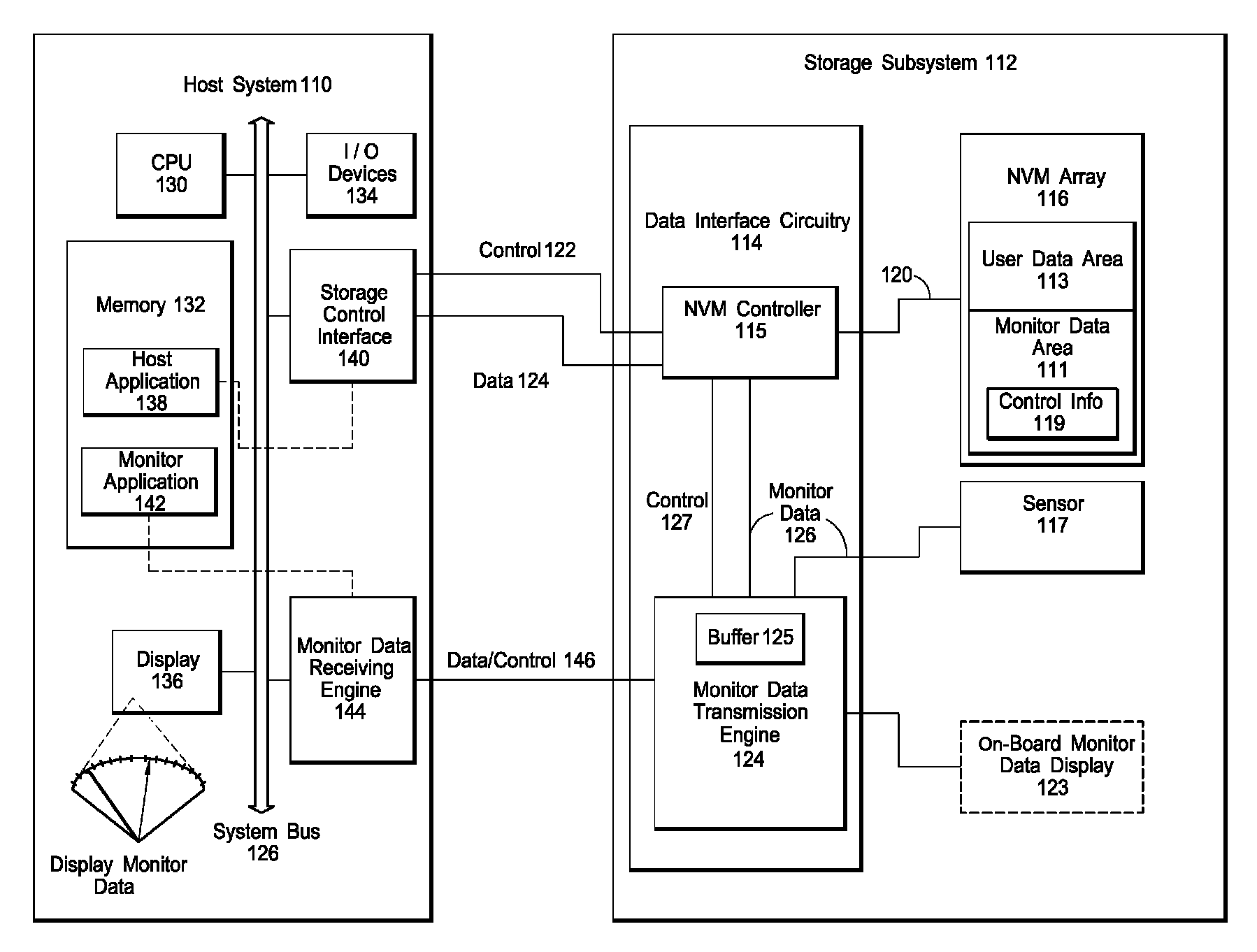
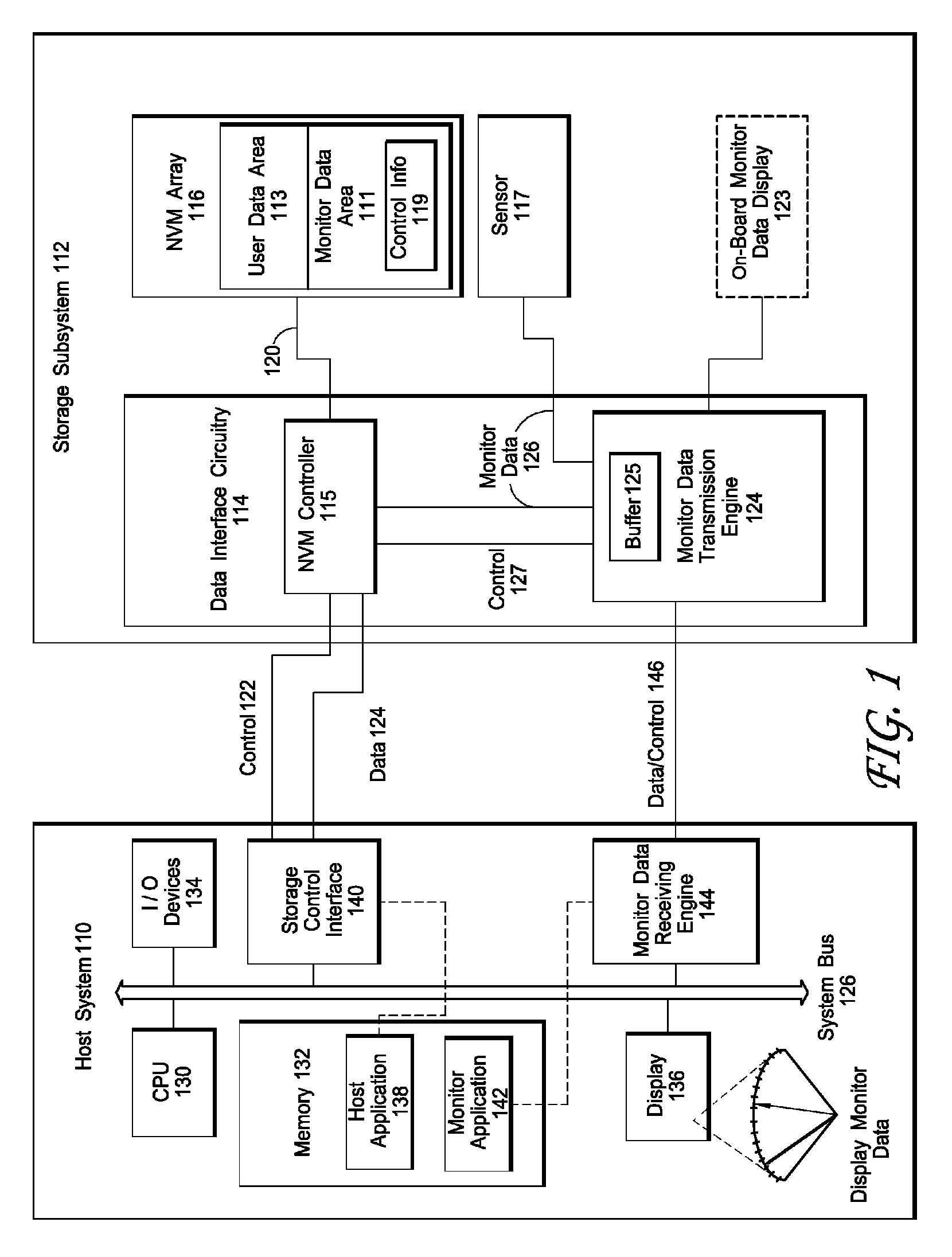
Interface for enabling a host computer to retrieve device monitor data from a solid state storage subsystem
ActiveUS7962792B2Reduce eliminateReduce the possibilityReliability/availability analysisInput/output processes for data processingSolid-state storageDevice Monitor
A non-volatile storage subsystem maintains, and makes available to a host system, monitor data reflective of a likelihood of a data error occurring. The monitor data may, for example, include usage statistics and / or sensor data. The storage subsystem transfers the monitor data to the host system over a signal interface that is separate from the signal interface used for standard storage operations. This interface may be implemented using otherwise unused pins / signal lines of a standard connector, such as a CompactFlash or SATA connector. Special hardware may be provided in the storage subsystem and host system for transferring the monitor data over these signal lines, so that the transfers occur with little or no need for host-software intervention. The disclosed design reduces or eliminates the need for host software that uses non-standard or “vendor-specific” commands to retrieve the monitor data.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
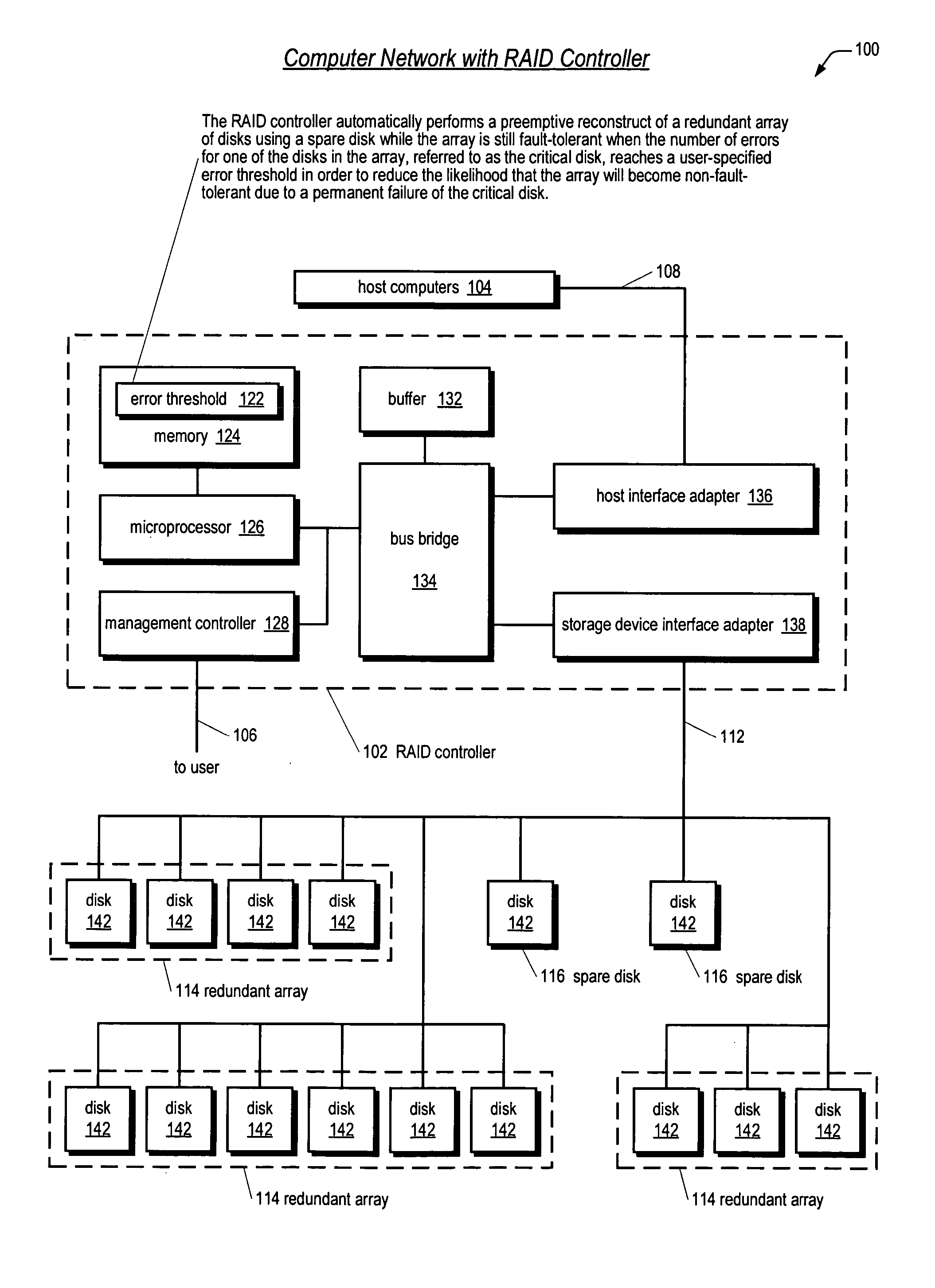
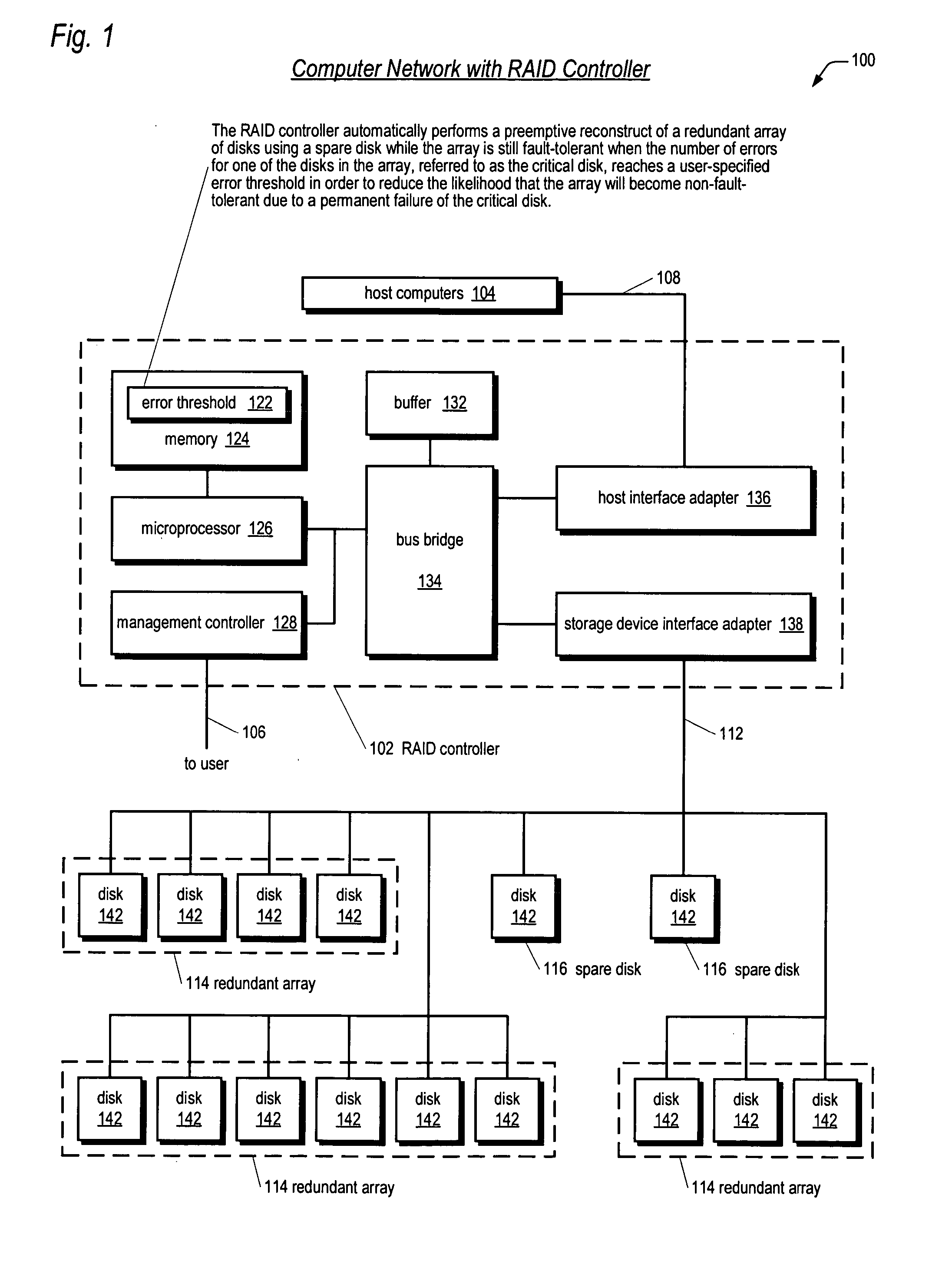
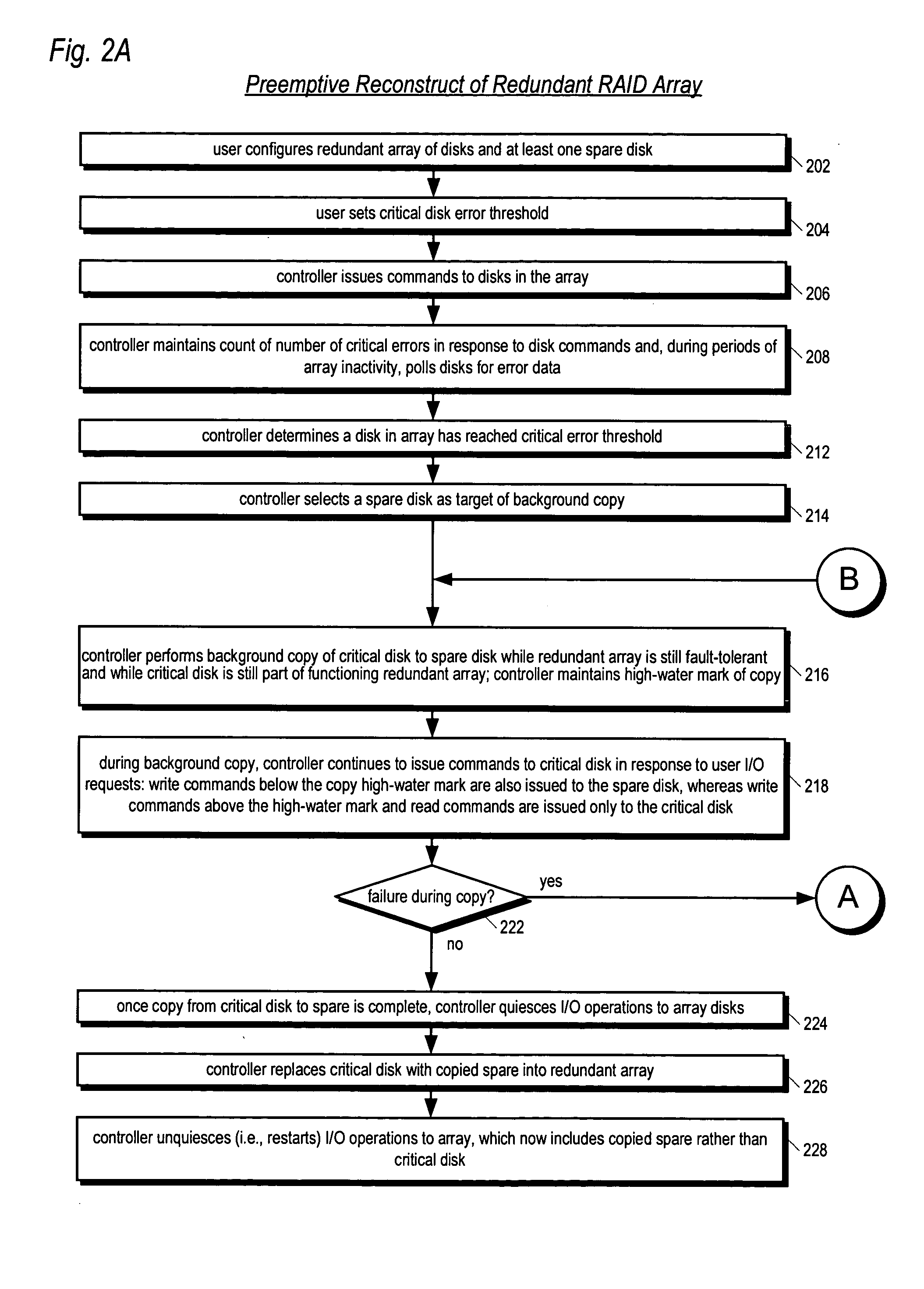
Apparatus and method for performing a preemptive reconstruct of a fault-tolerand raid array
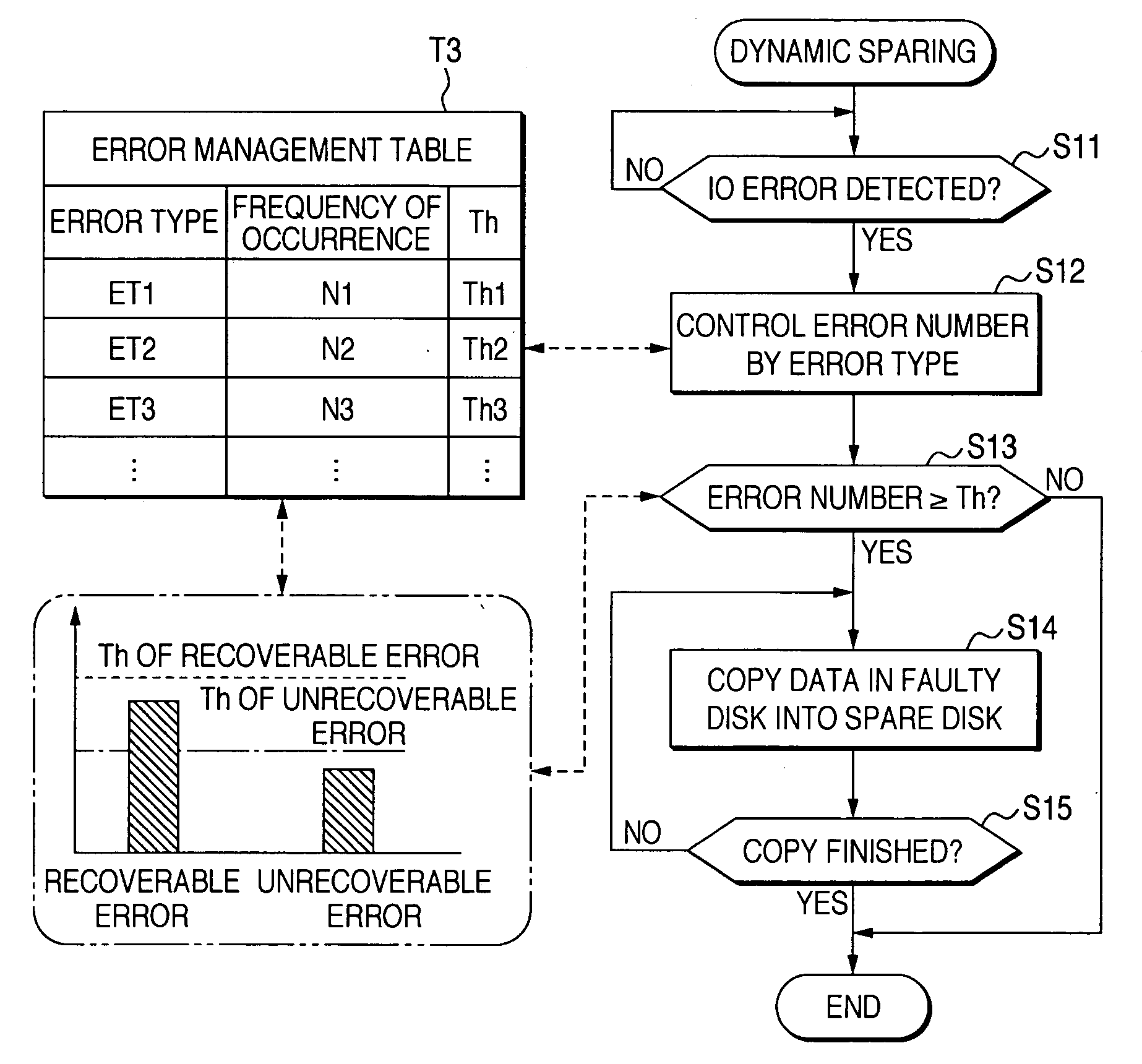
ActiveUS20050283655A1Reduce the possibilityLess timeReliability/availability analysisError avoidanceRAIDUser input
A RAID controller performing a preemptive reconstruct of a redundant array of disks while the array is still fault-tolerant is disclosed. The controller receives user input specifying an error threshold. When a disk in the array (critical disk) exceeds the error threshold, the controller copies the critical disk data to a spare disk. After the copy completes, the controller replaces the critical disk with the spare disk in the array. The controller keeps the critical disk as part of the redundant array during the copy, i.e., continues to read and write the critical disk in response to user I / O requests. Hence, the array remains fault-tolerant during the preemptive reconstruct. In one embodiment, the controller automatically performs the reconstruct without user intervention. If the critical disk fails during the copy, the controller performs a conventional reconstruct to the spare disk starting where the copy left off.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
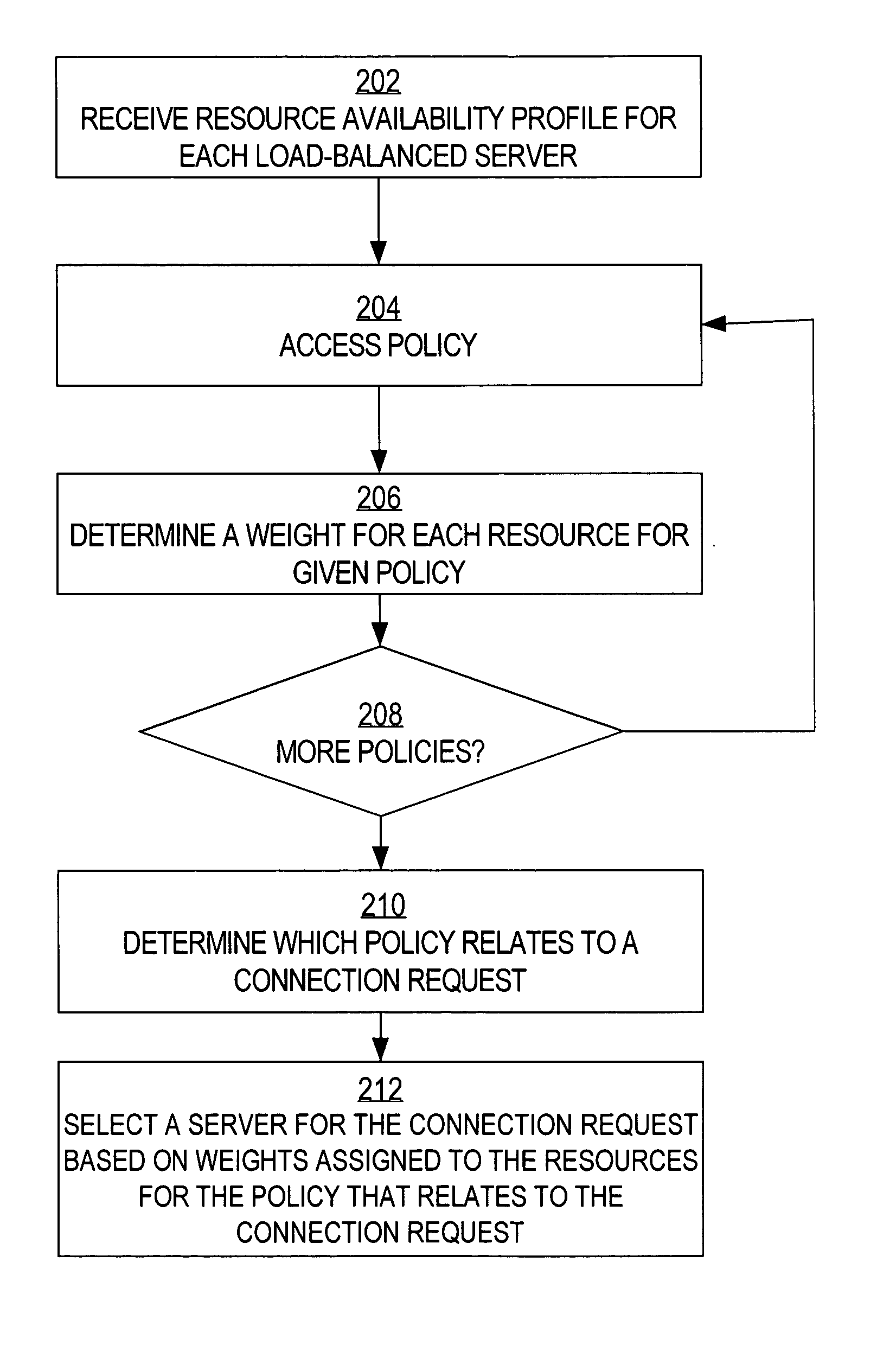
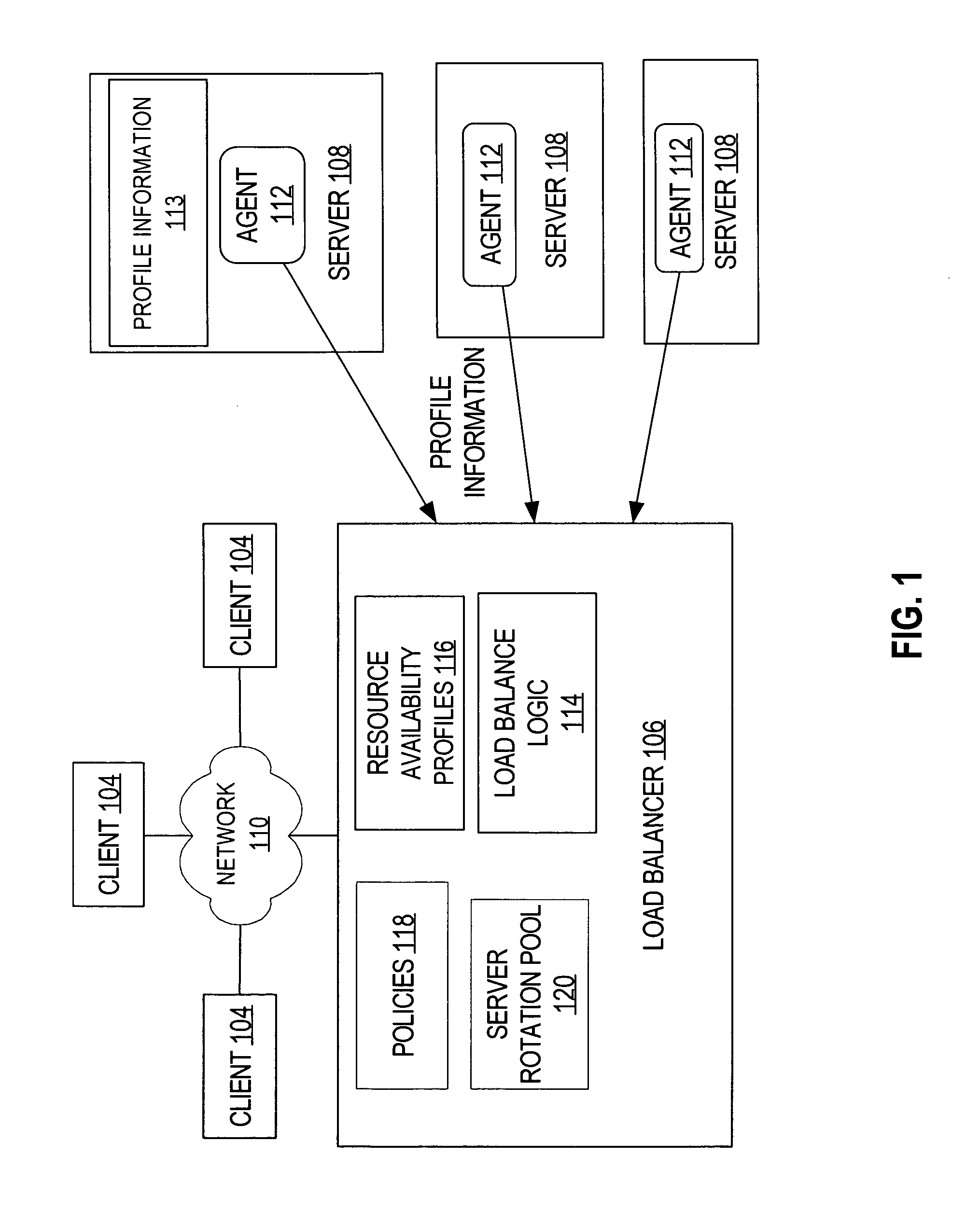
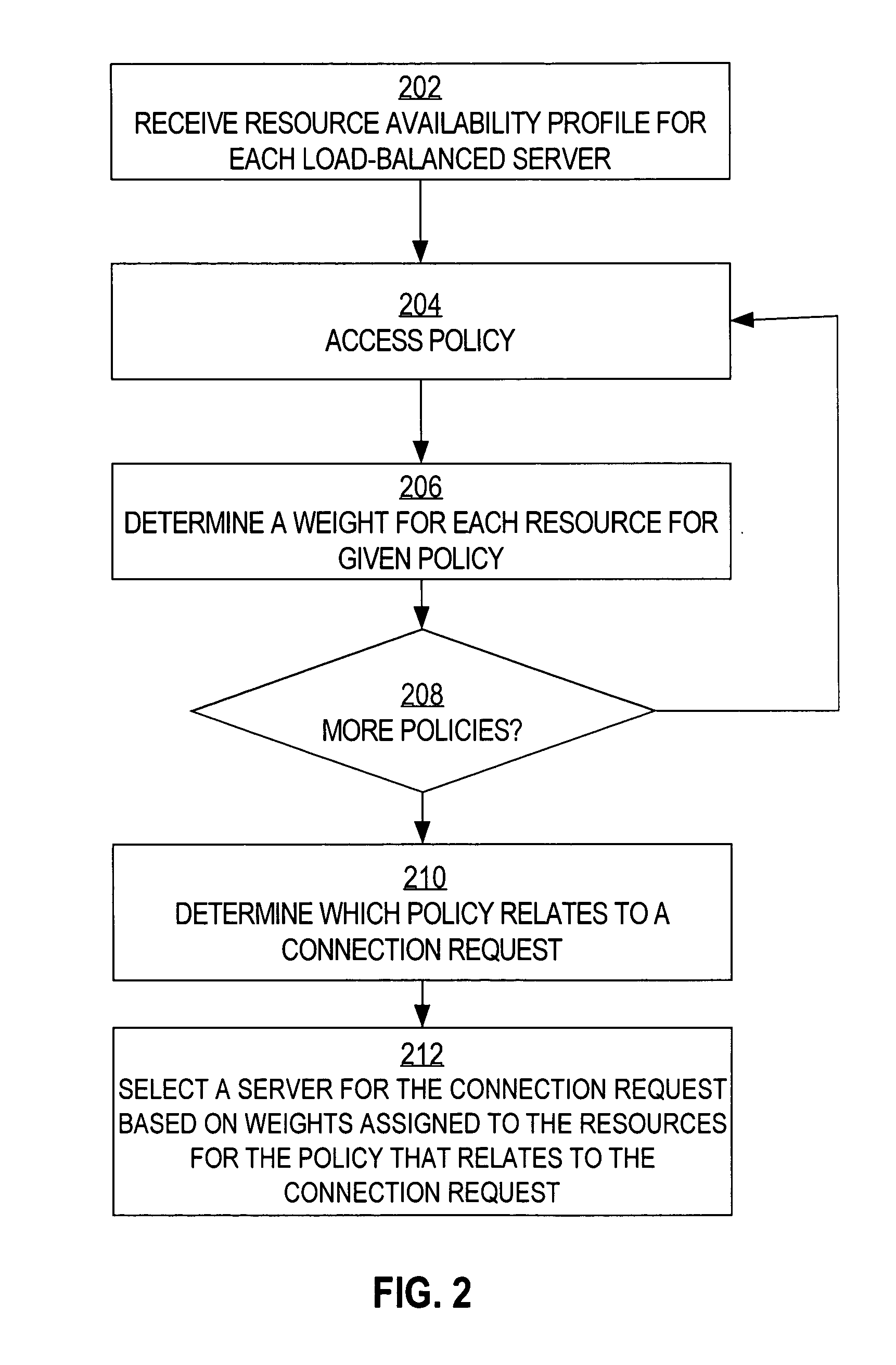
Load balancing mechanism using resource availability profiles
ActiveUS20060106938A1Reliability/availability analysisMultiprogramming arrangementsLoad SheddingConfigfs
Resource availability profiles are received, wherein each resource availability profile describes a resource associated with a server. Each resource is assigned a plurality of weights corresponding to a plurality of policies. The weights are determined by, for each of the plurality of the policies, determining a weight for each resource based a given policy and selected information in the resource availability profiles corresponding to the resources. The method further comprises determining a policy from the plurality of the policies corresponding to a given a context associated with a connection request. A first of the load-balanced servers is selected for the connection request based on the weights assigned to the plurality of resources for the policy for the given context.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
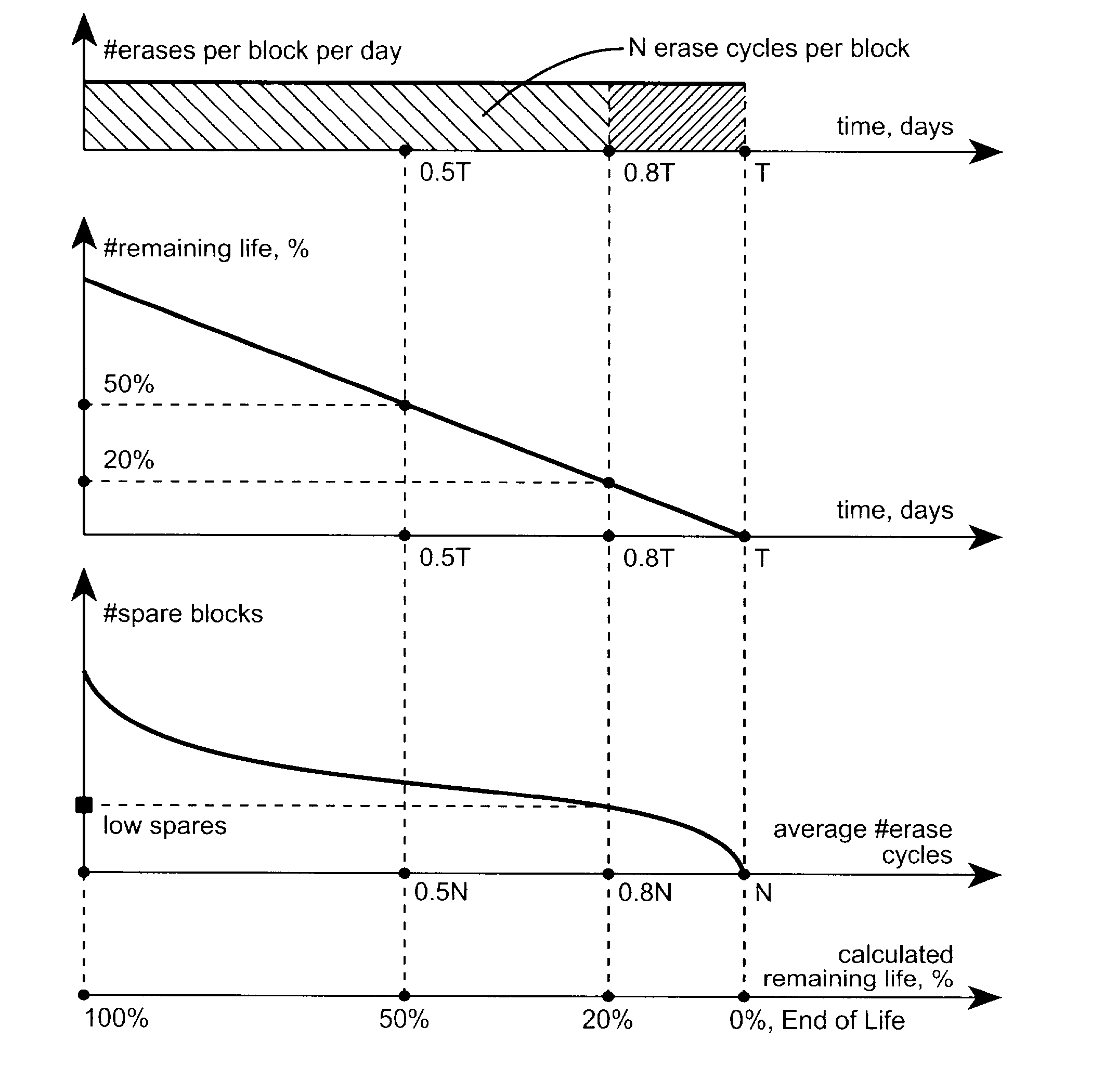
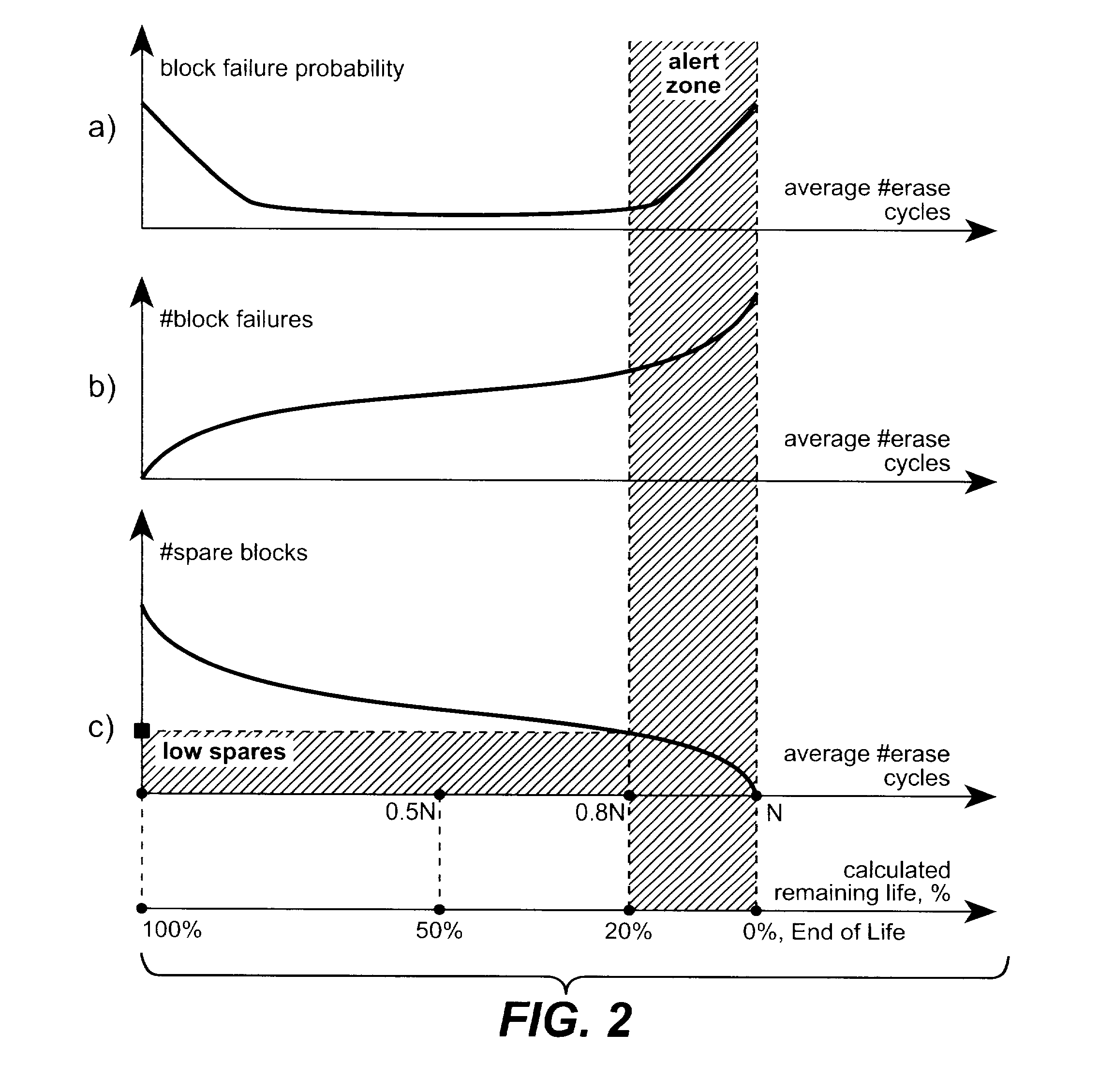
Methods of End of Life Calculation for Non-Volatile Memories
ActiveUS20070266200A1Eliminate dependenciesTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksTerm memoryCalculation methods
A system and methods are given for providing information on the amount of life remaining for a memory having a limited lifespan, such as a flash memory card. For example, it can provide a user with the amount of the memory's expected remaining lifetime in real time units (i.e., hours or days) or as a percentage of estimated initial life. An end of life warning can also be provided. In a particular embodiment, the amount of remaining life (either as a percentage or in real time units) can be based on the average number of erases per block, but augmented by the number of spare blocks or other parameters, so that an end of life warning is given if either the expected amount of remaining life falls below a certain level or the number of spare blocks falls below a safe level.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Intelligent condition-monitoring and fault diagnostic system for predictive maintenance
ActiveUS7882394B2Sufficient weightFacilitates isolation of faultSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementTesting/monitoring control systemsPredictive maintenanceDiagnostic system
A system for condition monitoring and fault diagnosis includes a data collection function that acquires time histories of selected variables for one or more of the components, a pre-processing function that calculates specified characteristics of the time histories, an analysis function for evaluating the characteristics to produce one or more hypotheses of a condition of the one or more components, and a reasoning function for determining the condition of the one or more components from the one or more hypotheses.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
System for balance distribution of requests across multiple servers using dynamic metrics
InactiveUS20060036743A1Improve performanceMaximizing numberResource allocationHardware monitoringDynamic metricsClient-side
Owner:ASPENGINES +1
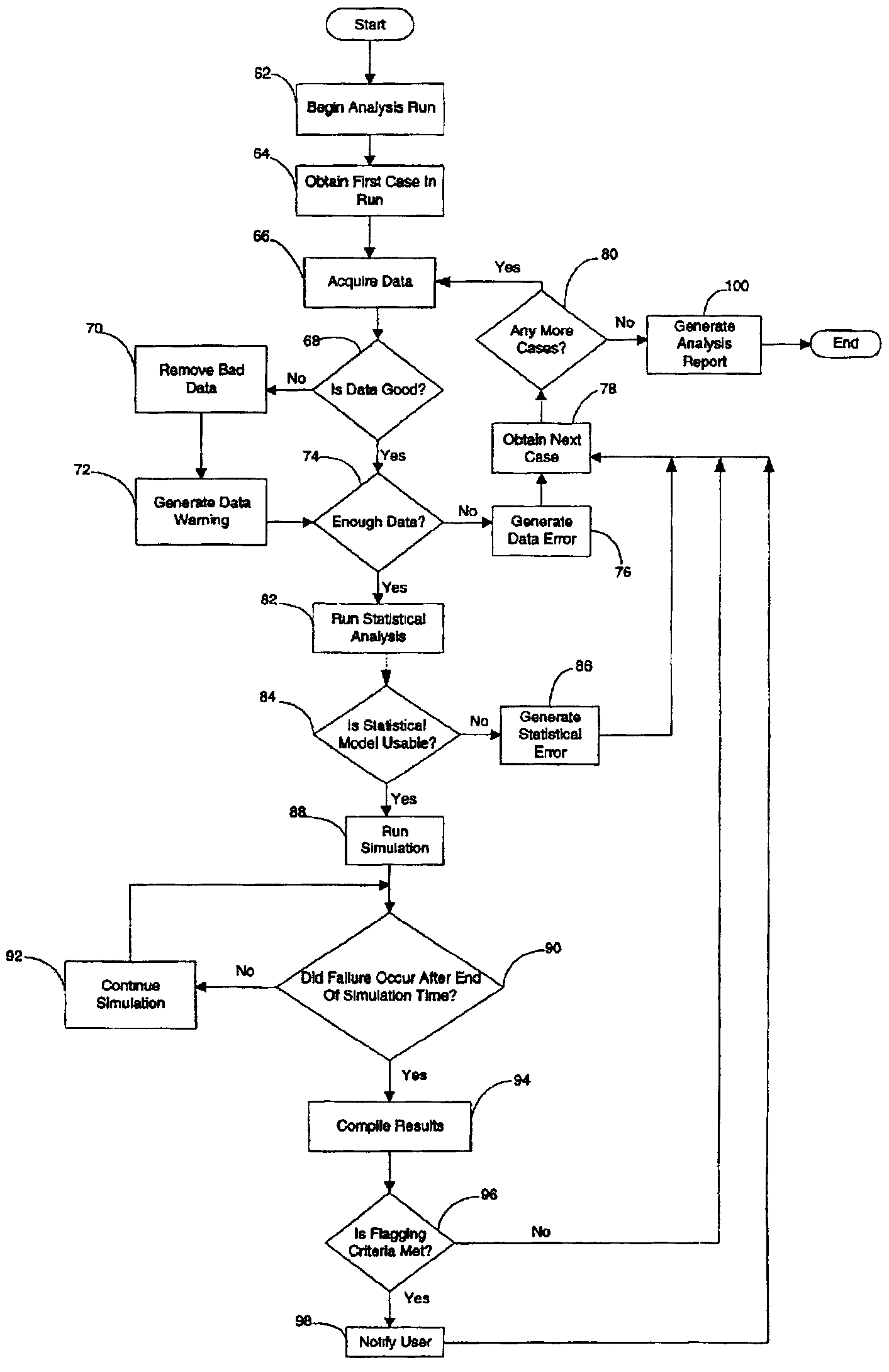
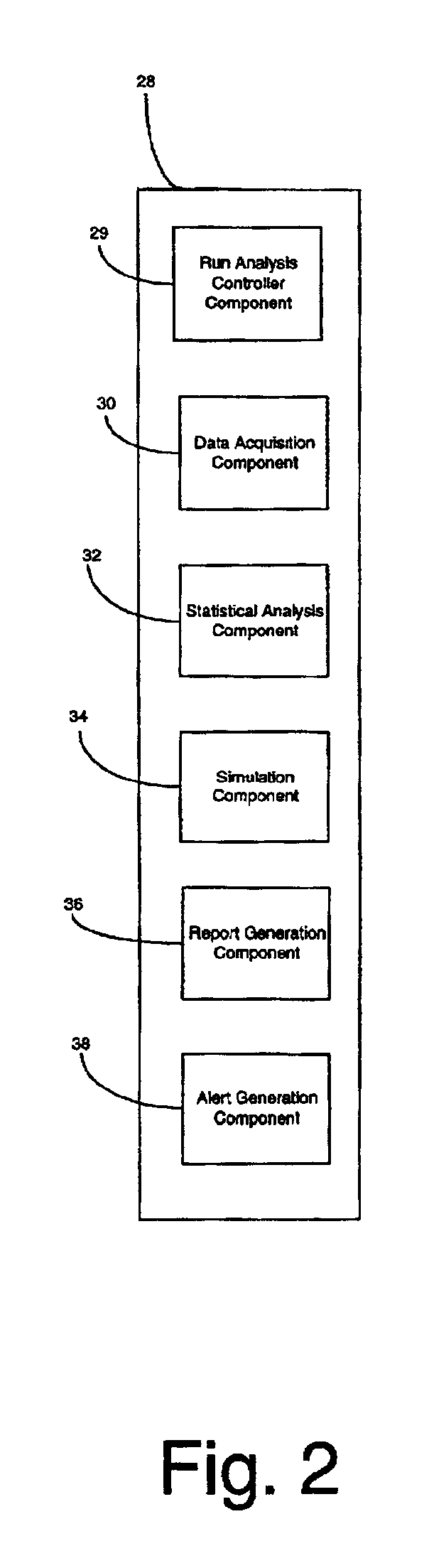
System, method and computer product for performing automated predictive reliability
System, method and computer product for performing automated predictive reliability. A data acquisition component acquires service data for a complex system from a data repository. A statistical analysis component generates a statistical model for the service data. A simulation component predicts the reliability of the complex system according to the statistical model. An alert generation component generates alerts when predicted failures determined by the simulation component exceed predetermined alert criteria. A report generation component generates a summary of the analysis performed in the data acquisition, statistical analysis and alert generation components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for predictive failure management
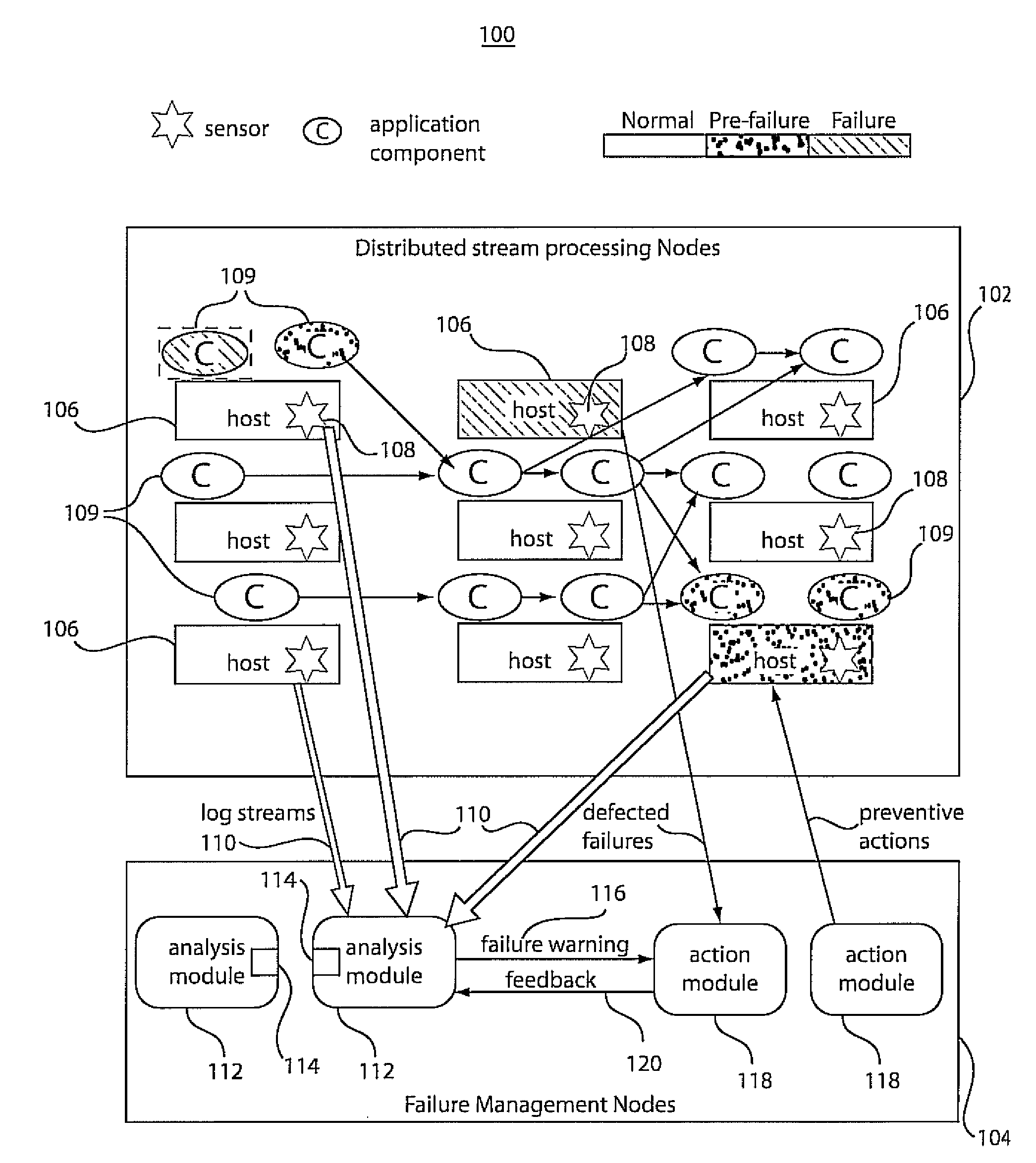
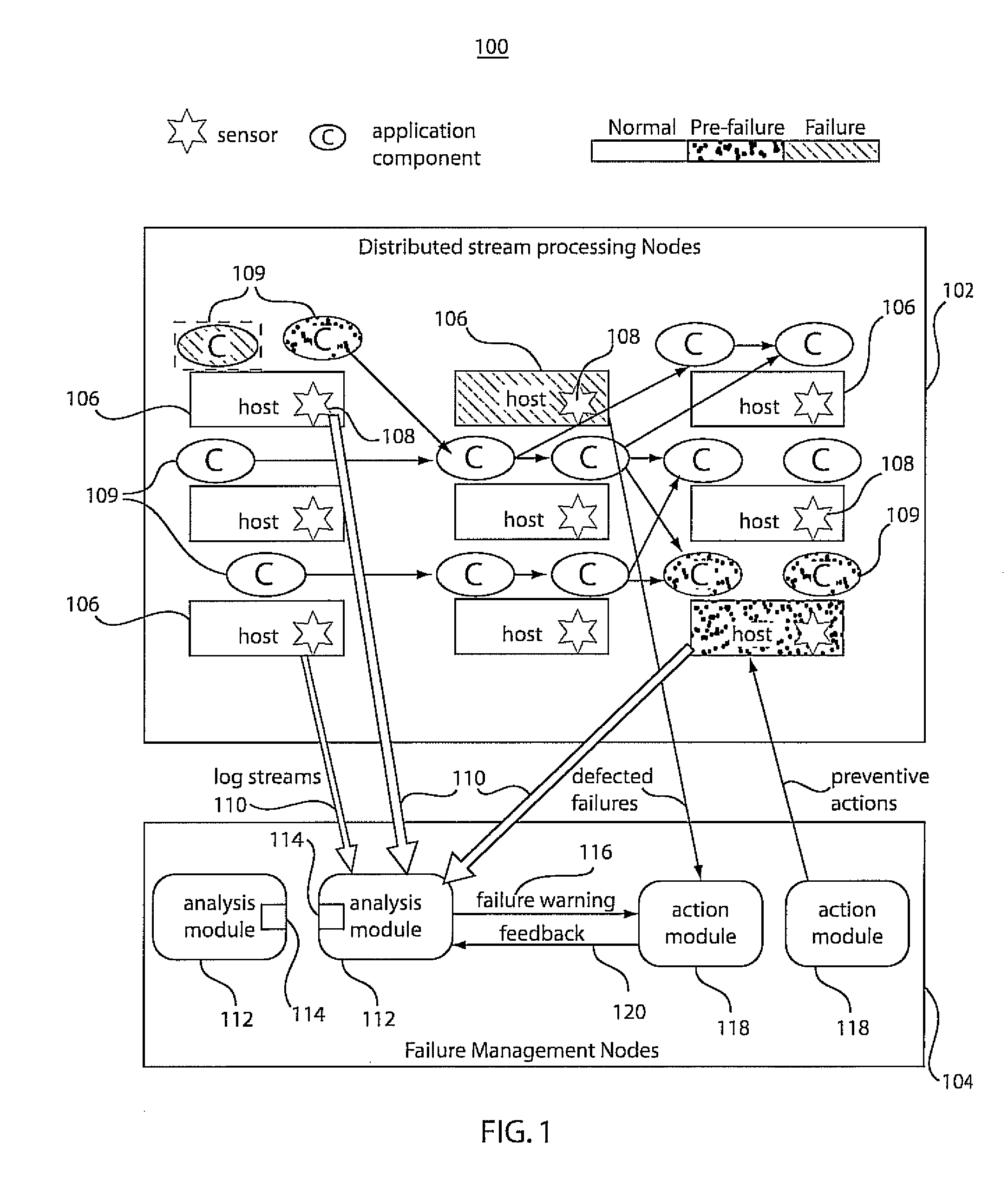
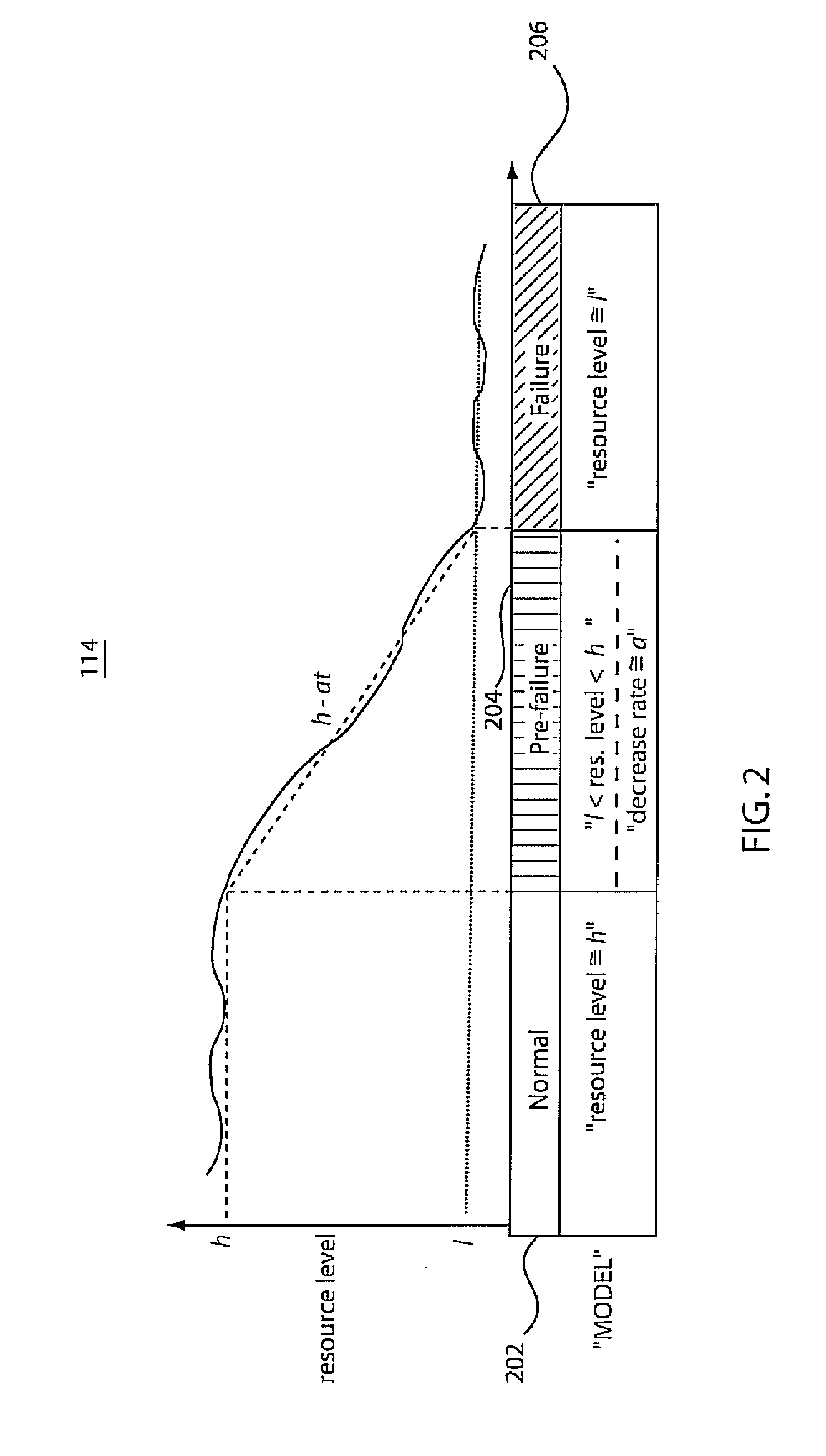
ActiveUS20080250265A1Efficient fault-tolerant CQ processingMinimize impactReliability/availability analysisNon-redundant fault processingFailure preventionCluster systems
A system and method for using continuous failure predictions for proactive failure management in distributed cluster systems includes a sampling subsystem configured to continuously monitor and collect operation states of different system components. An analysis subsystem is configured to build classification models to perform on-line failure predictions. A failure prevention subsystem is configured to take preventive actions on failing components based on failure warnings generated by the analysis subsystem.
Owner:IBM CORP
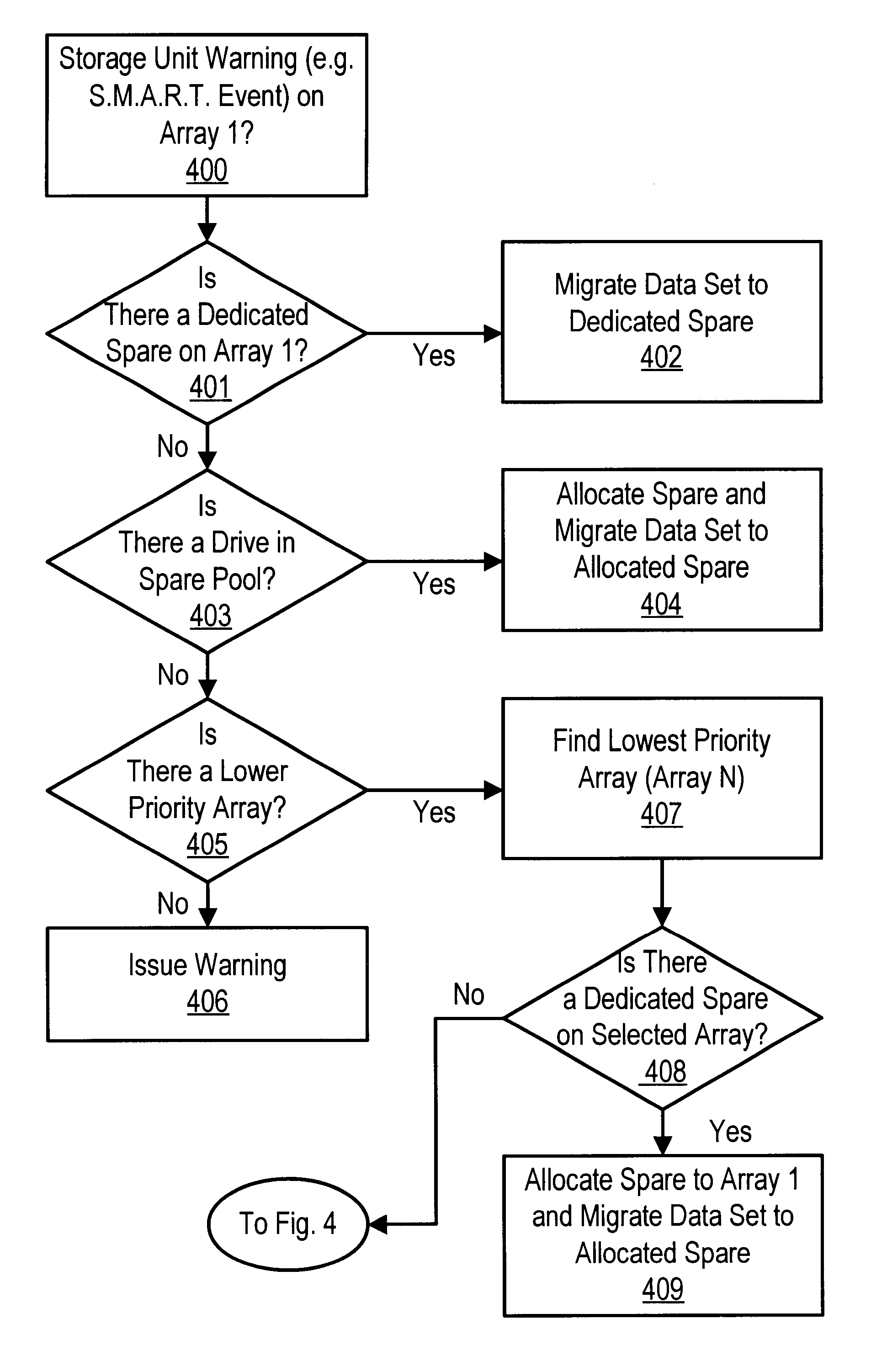
Method and apparatus for storage unit replacement according to array priority
InactiveUS6571354B1Lower performance requirementsAffect performanceReliability/availability analysisComputer hardwareData set
A method and apparatus used in a storage network facilitates the protection of data in, and replacement of, storage devices about to fail before the failure happens. In a network that includes a plurality of sets of storage devices which store respective data sets, a storage device about to fail in one set can be replaced by another storage device from another set of storage devices which is being used to store data having a lower priority. The method comprises assigning priorities to sets of storage devices in the network which store respective data sets. In addition, the method includes detecting a condition of a first particular storage device in a particular set of storage devices that has a first priority. Conditions which are detected according to various embodiments indicate that the first particular storage device is suffering events indicating that it is likely to fail, or otherwise suffering from reduced performance. The conditions are detected for example, by the receipt of a signal from the storage device itself, or by the monitoring of statistics concerning the performance of the storage device. The method further provides for selecting a second particular storage device in a second particular set of storage devices having a second priority, which can be used in place of the first particular storage device. In response to detecting the condition, the data set stored in the first particular storage device is migrated to the second particular storage device, and the second particular storage devices identified as a member of the first particular set. The first particular storage device can be gracefully removed from the network, while only affecting the performance of the data access in the lower priority second particular set of storage devices.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
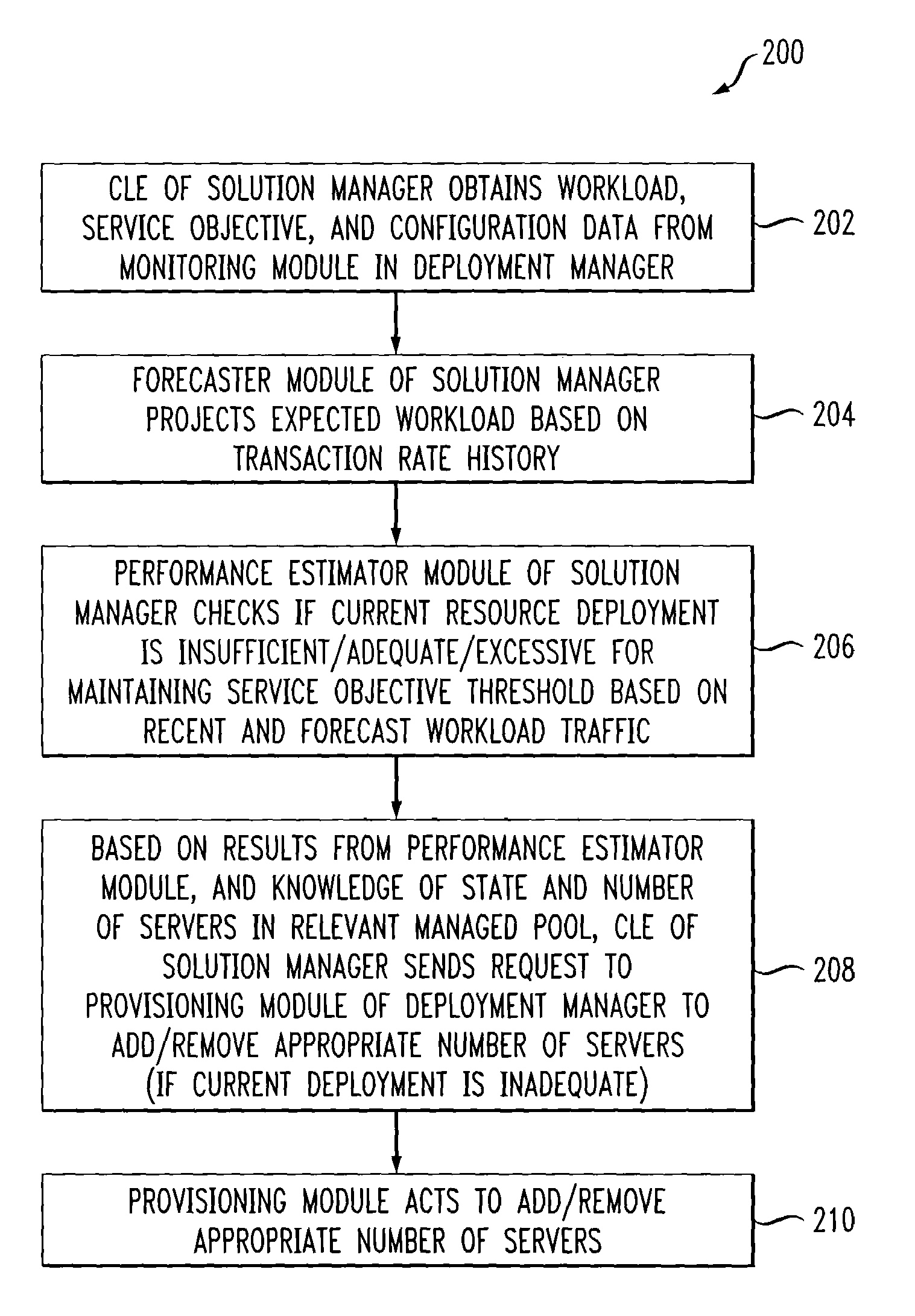
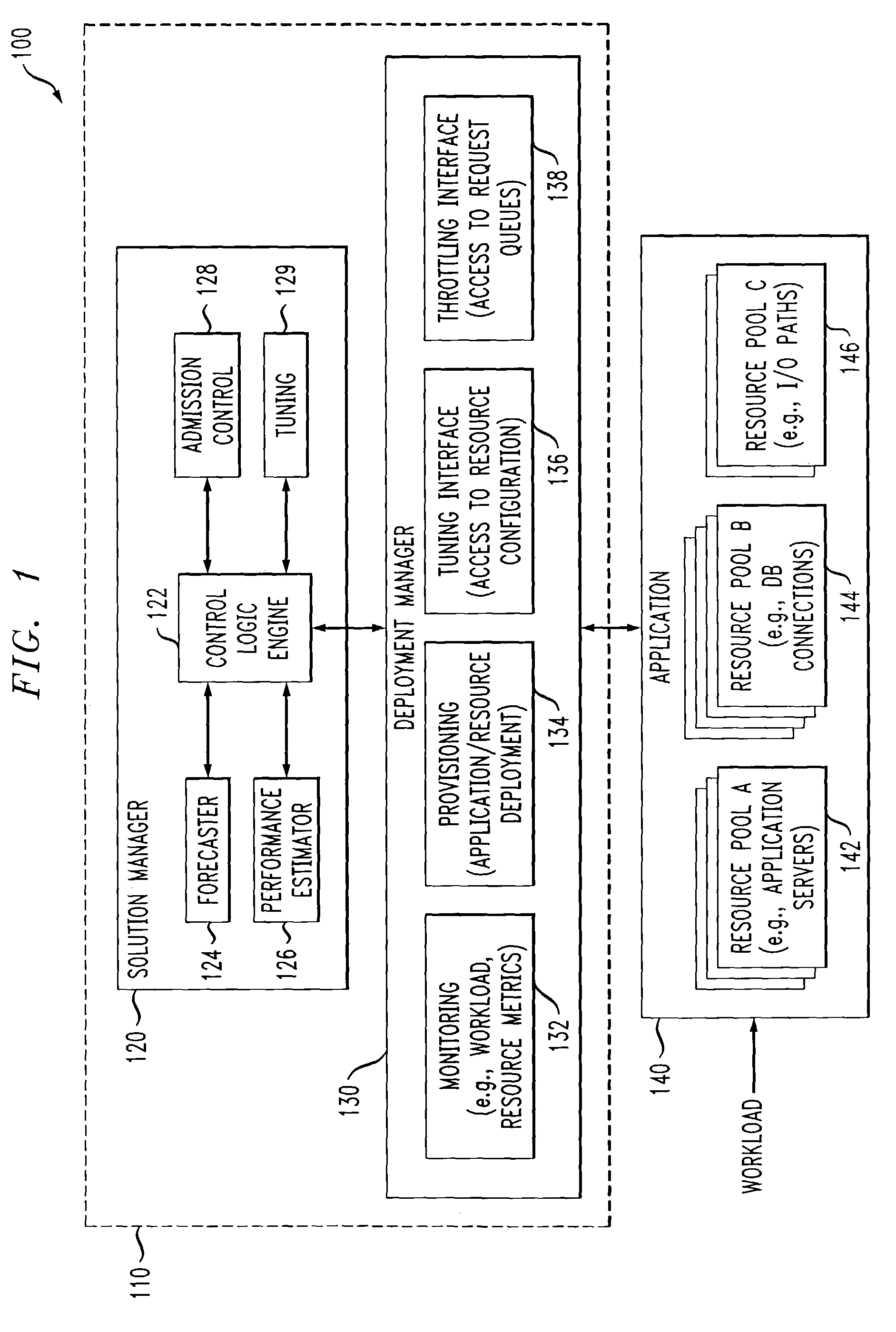
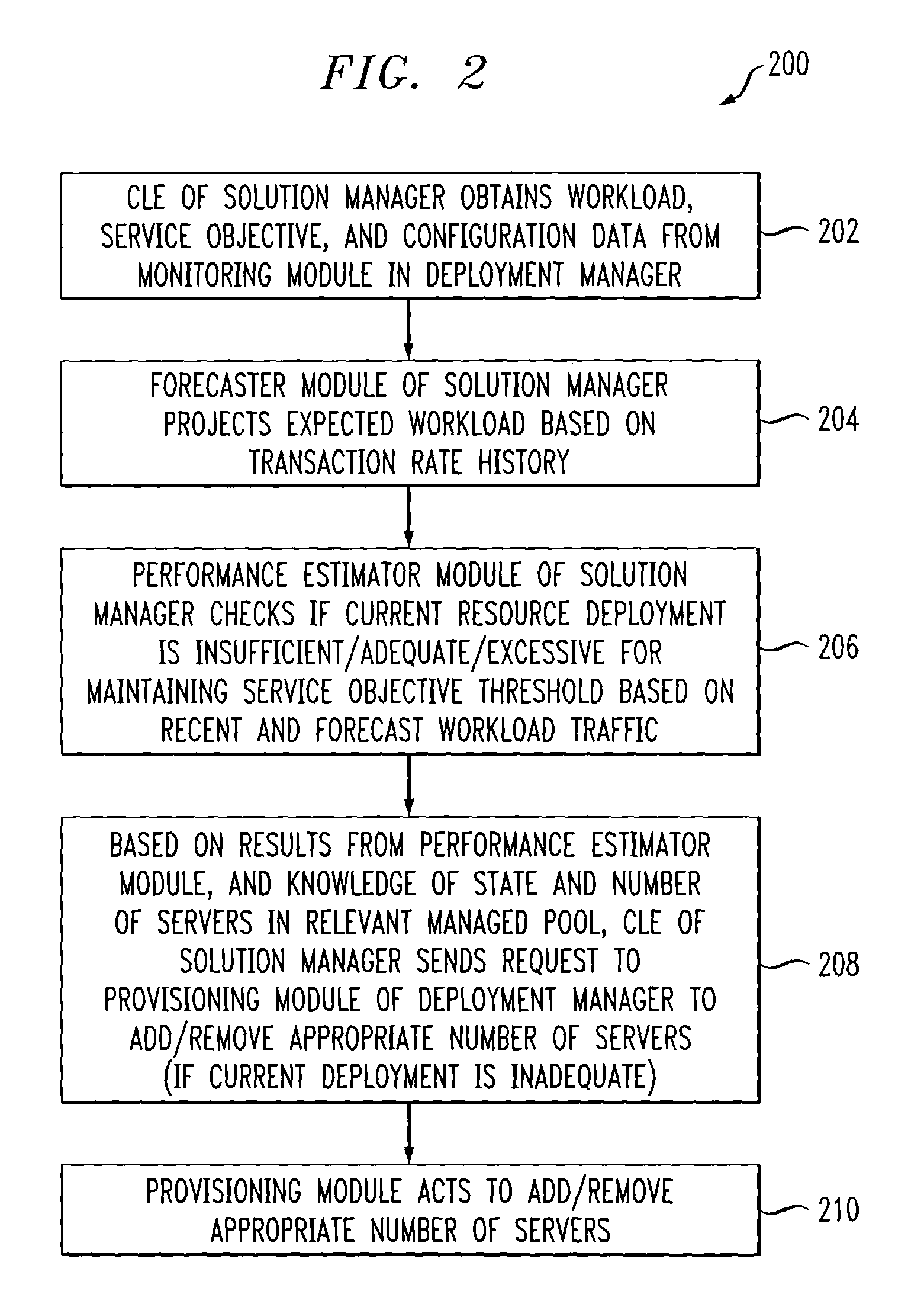
Methods and apparatus for managing computing deployment in presence of variable workload
ActiveUS7350186B2Efficient and effectiveAccommodating unanticipated workloadResource allocationReliability/availability analysisWorkloadDistributed computing
Automated or autonomic techniques for managing deployment of one or more resources in a computing environment based on varying workload levels. The automated techniques may comprise predicting a future workload level based on data associated with the computing environment. Then, an estimation is performed to determine whether a current resource deployment is insufficient, sufficient, or overly sufficient to satisfy the future workload level. Then, one or more actions are caused to be taken when the current resource deployment is estimated to be insufficient or overly sufficient to satisfy the future workload level. Actions may comprise resource provisioning, resource tuning and / or admission control.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
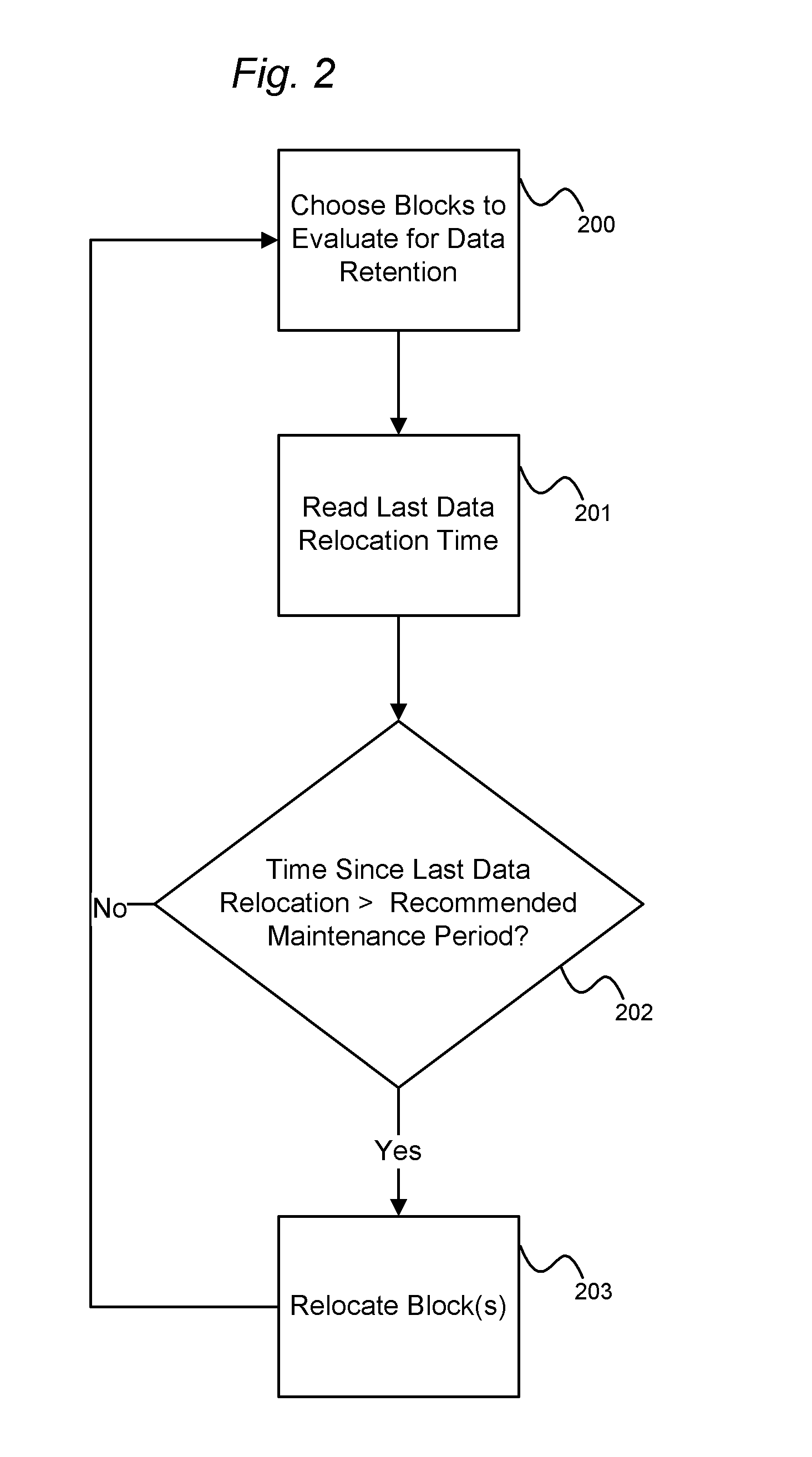
System and method for performing data retention that incorporates environmental conditions
A solid-state storage system is described with a method for adjusting the frequency of data retention operations. The data retention operation frequency can be increased or decreased according to a variety of environmental factors such as error code frequency, system temperature, altitude, and other operating conditions. These factors can indicate an increased or decreased risk of failure and accordingly provide increased or decreased rates of data retention operations.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
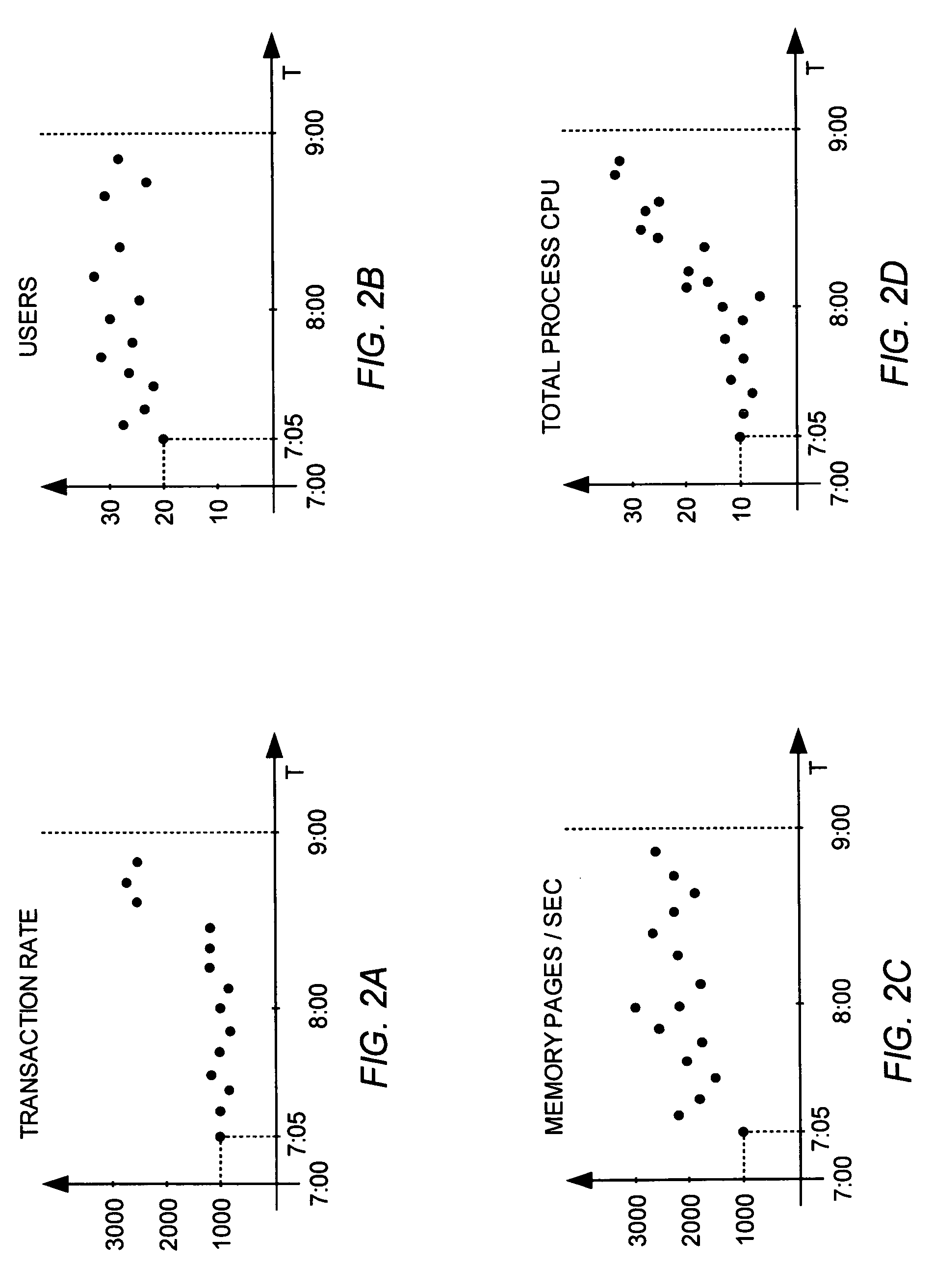
Clustering process for software server failure prediction
InactiveUS20070101202A1Reliability/availability analysisNon-redundant fault processingComputer scienceSoftware
Embodiments of the present invention allow the prevention and / or mitigation of damage caused by server failure by predicting future failures based on historic failures. Statistical data for server parameters may be collected for a period of time immediately preceding a historic server failure. The data may be clustered to identify cluster profiles indicating strong pre-fault clustering patterns. Real time statistics collected during normal operation of the server may be applied to the cluster profiles to determine whether real time statistics show pre-fault clustering. If such a pattern is detected, measures to prevent or mitigate server failure may be initiated.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Method and apparatus for determining a predicted failure rate
ActiveUS7539907B1Alter the predicted failure rate(s)Less reliableReliability/availability analysisFailure rateComputer science
A method and apparatus for determining predicted failure rates for computational resources provided by a system comprising multiple components. The method comprises storing failure rate information about individual components and determining a current configuration of components within the system. The method further comprises identifying from the current configuration dependencies between components within the system. The stored failure rate information and the identified current configuration dependencies can then be used to generate predicted failure rates for the computational resources in the current configuration of the system.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Disk array system and a method of avoiding failure of the disk array system
ActiveUS20050114728A1Avoid failureReduce the likelihood of occurrenceInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionRAIDDisk array
The invention is intended to reduce disk access during data transfer from a disk in which occurrence of failure is anticipated to a spare disk as much as possible so that occurrence of double-failure is prevented in advance. When occurrence of failure in a disk which configures a RAID group, contents stored in the disk is copied to the spared disk. Simultaneously, another RAID group is paired with the above described RAID group and a secondary volume is provided therein. A write request is directed to the secondary volume. A differential bitmap controls a update data. Data which is not updated is read out from the primary volume, and data which is already updated is read from the secondary volume. When data transfer is completed, contents stored in the secondary volume are copied to the primary volume.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Systems and methods for performing risk analysis
A method for analyzing a network element may include assigning values to each of a plurality of vulnerabilities. The method may also include identifying a vulnerability associated with the network element and generating a risk indicator for the network element based on the assigned value associated with the identified vulnerability.
Owner:EBATES PERFORMANCE MARKETING
Popular searches
Software testing/debugging Specific program execution arrangements Special data processing applications Knowledge based models Redundant hardware error correction Digital storage Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Medical equipment Multiple digital computer combinations Data switching networks
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com