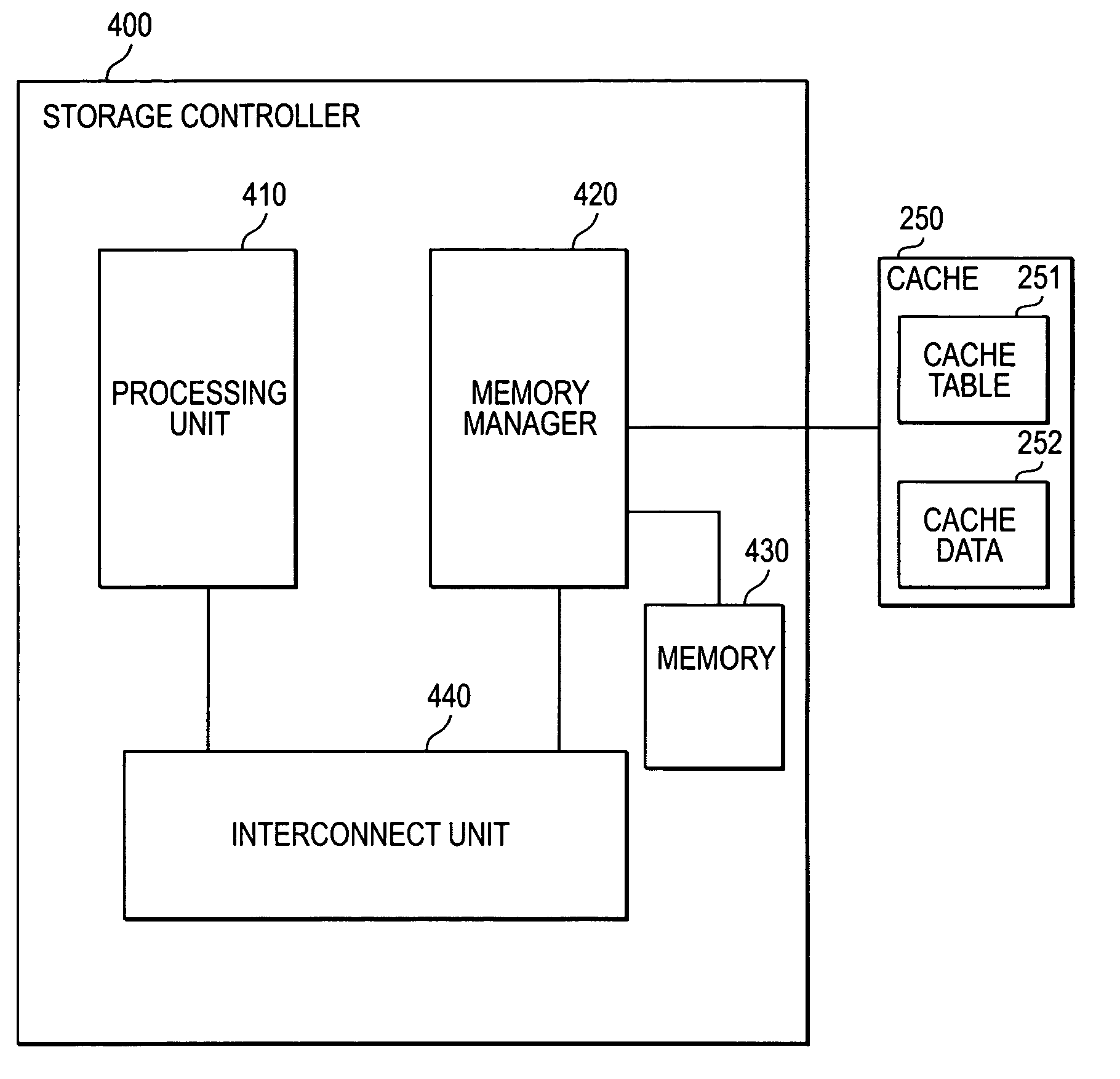
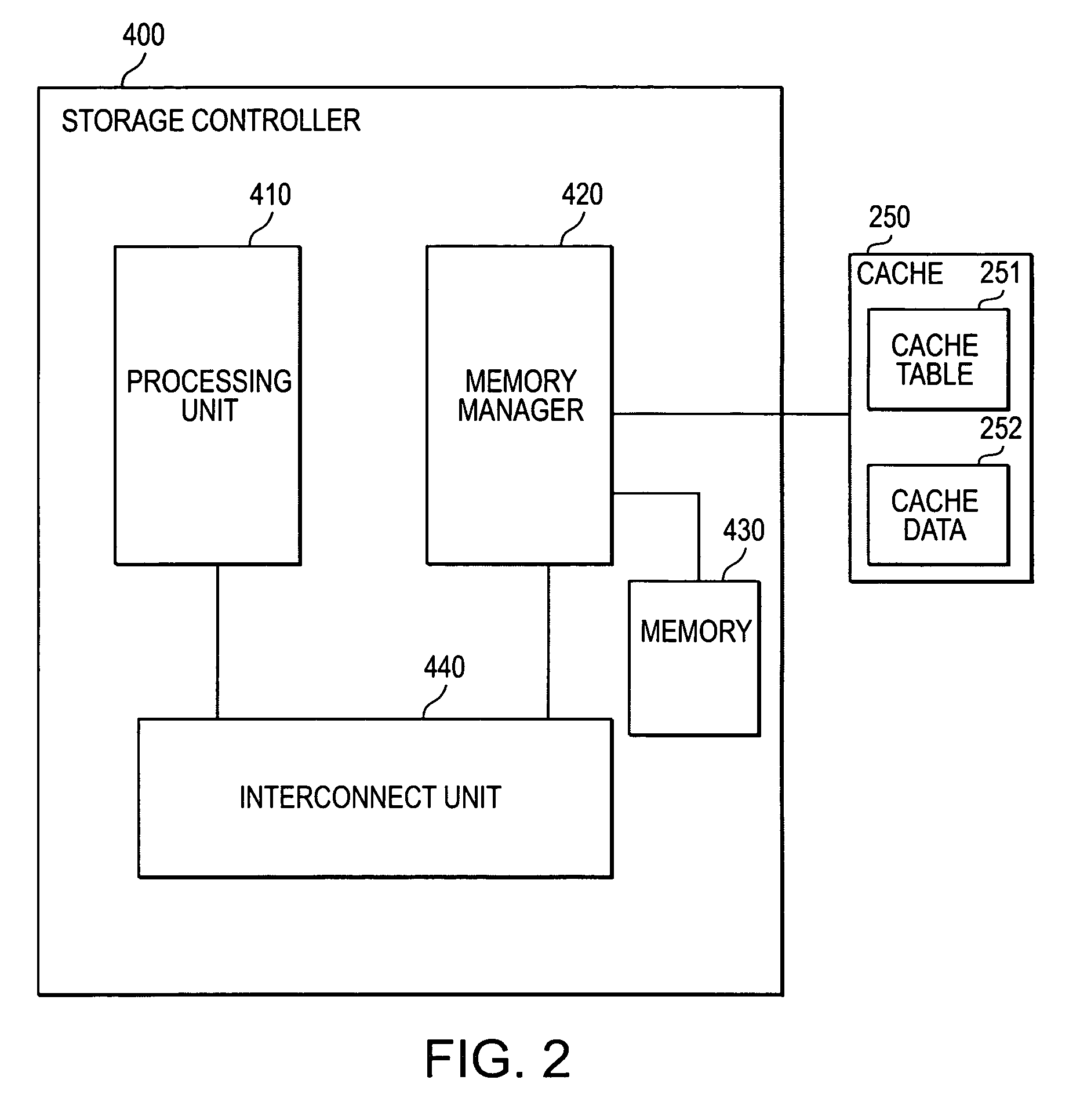
Patents
Literature
2419 results about "Disk array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
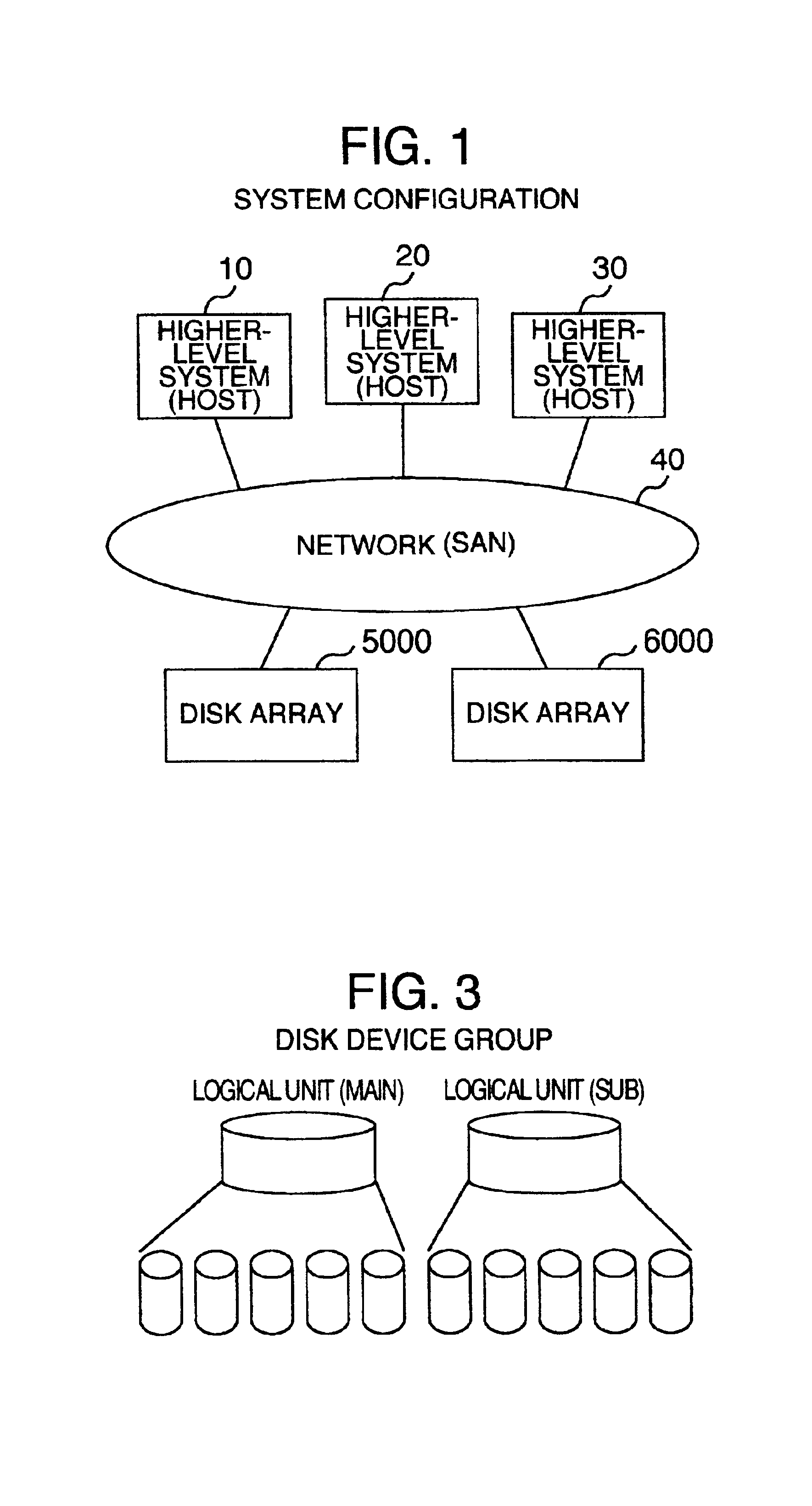
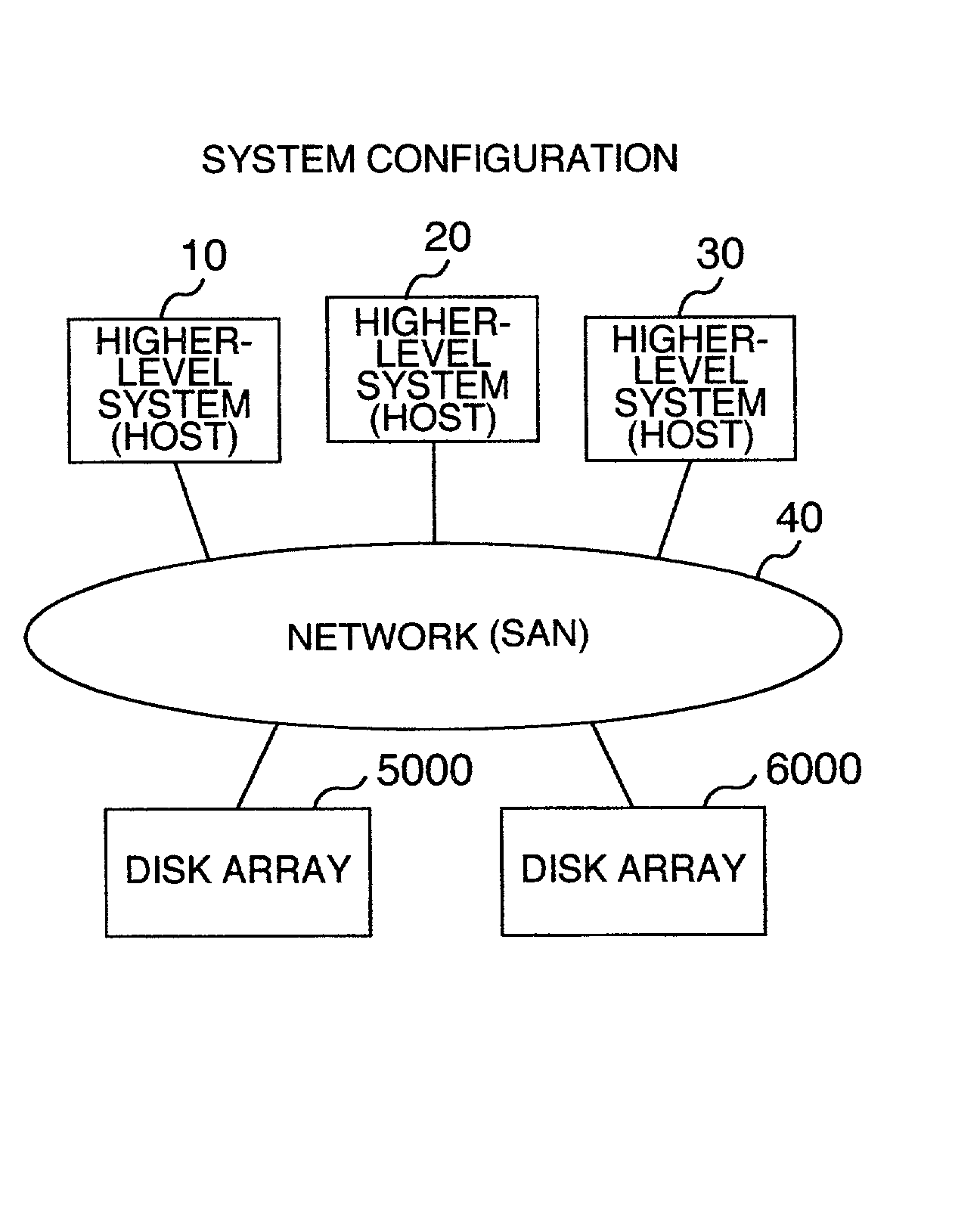
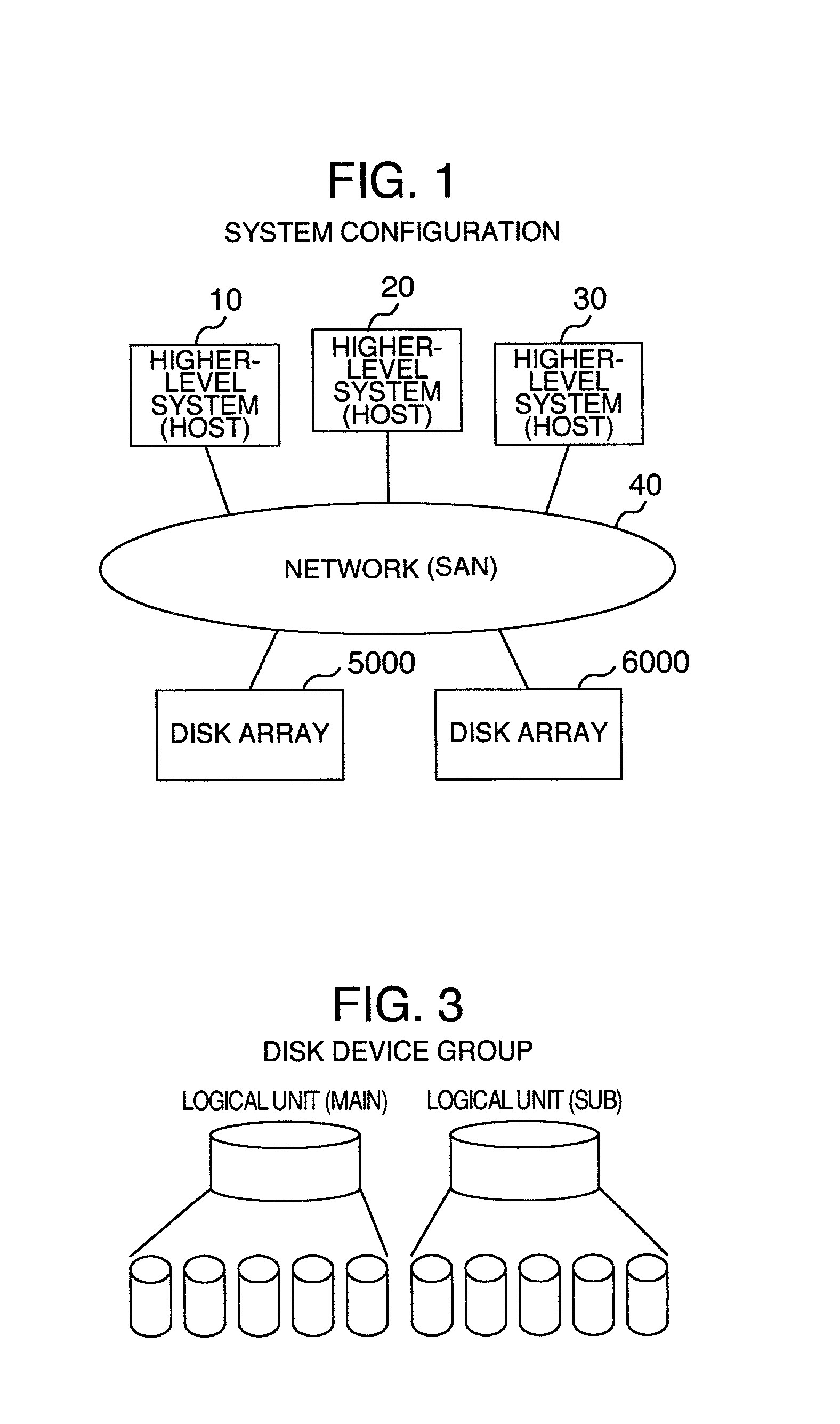
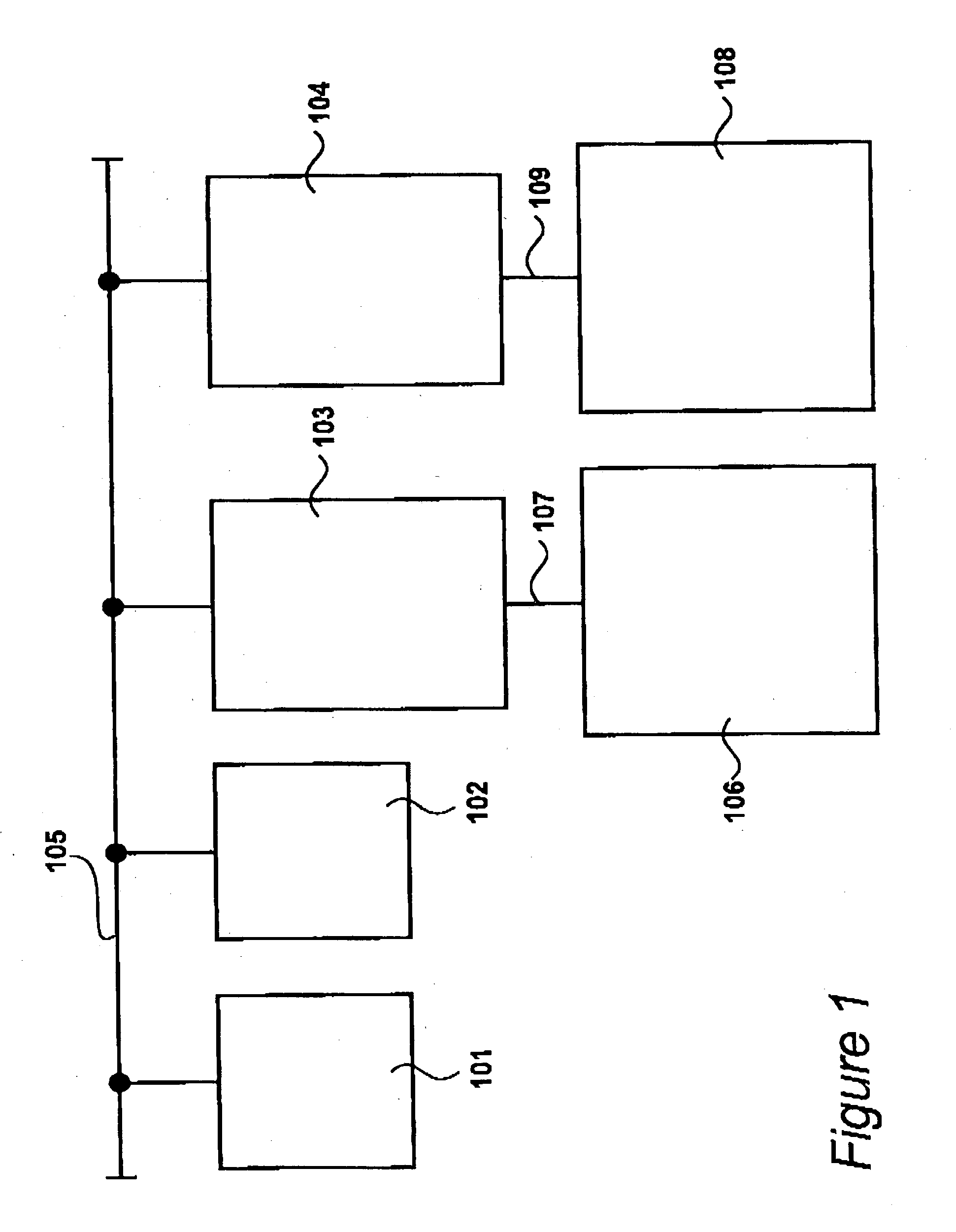
A disk array is a disk storage system which contains multiple disk drives. It is differentiated from a disk enclosure, in that an array has cache memory and advanced functionality, like RAID and virtualization.
Method for allocating files in a file system integrated with a RAID disk sub-system
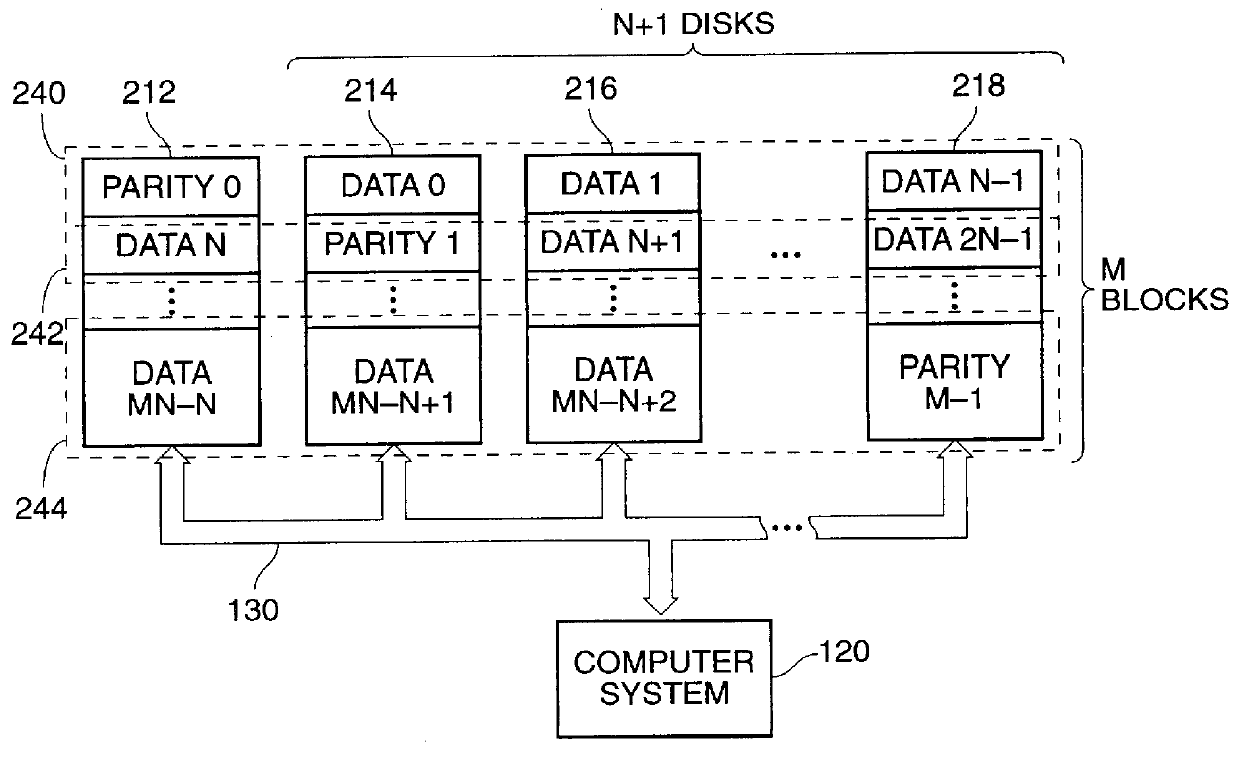
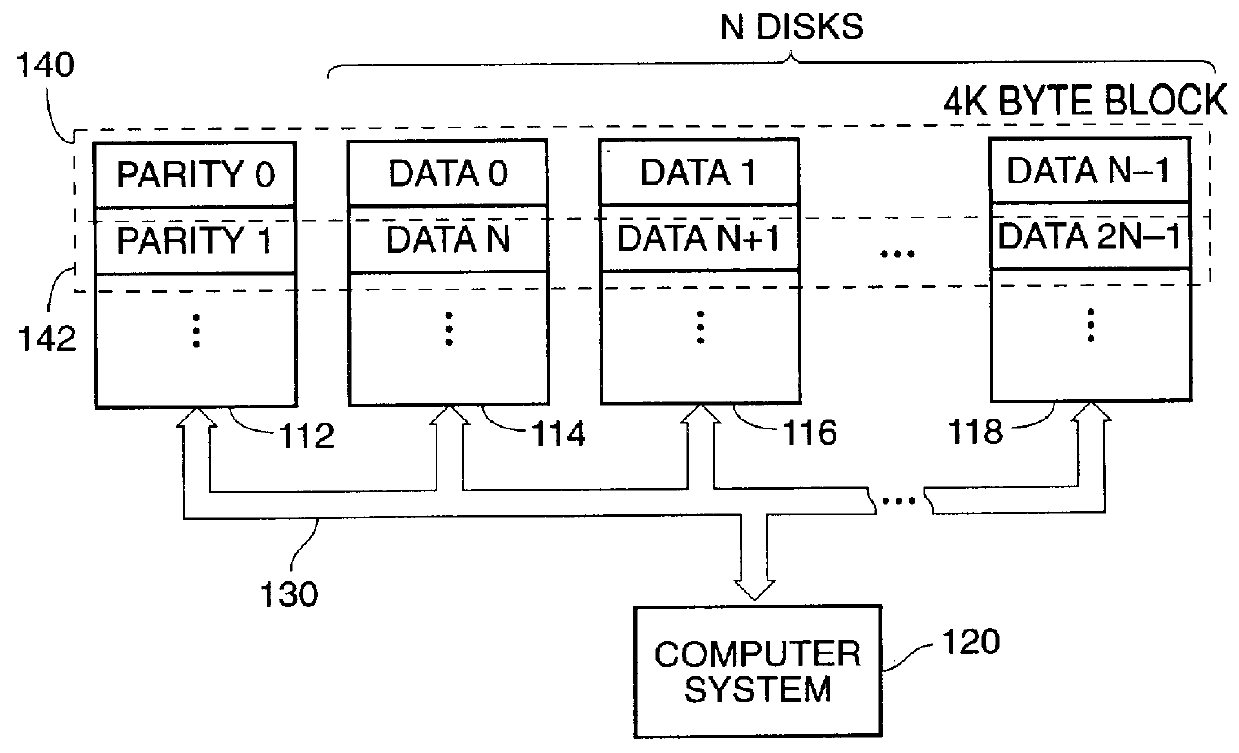
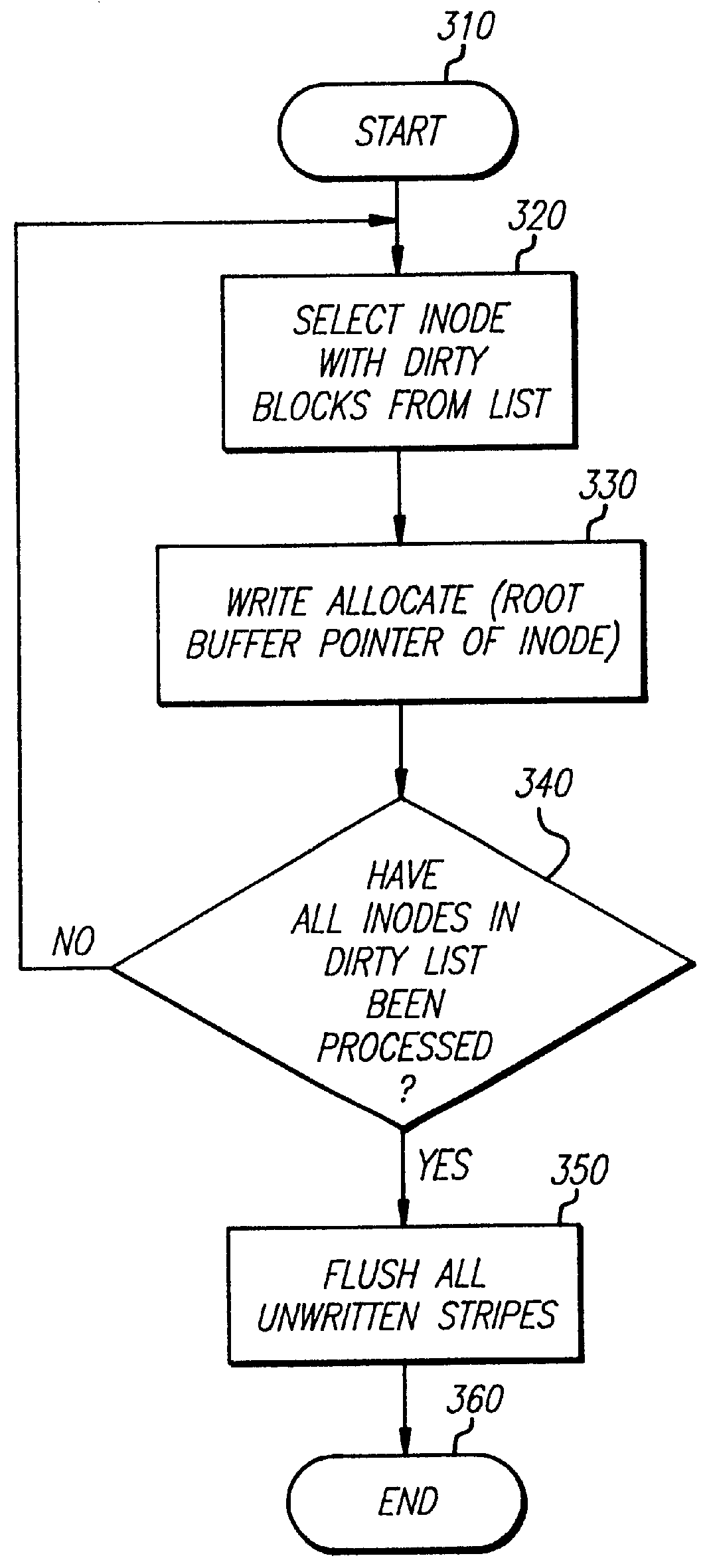
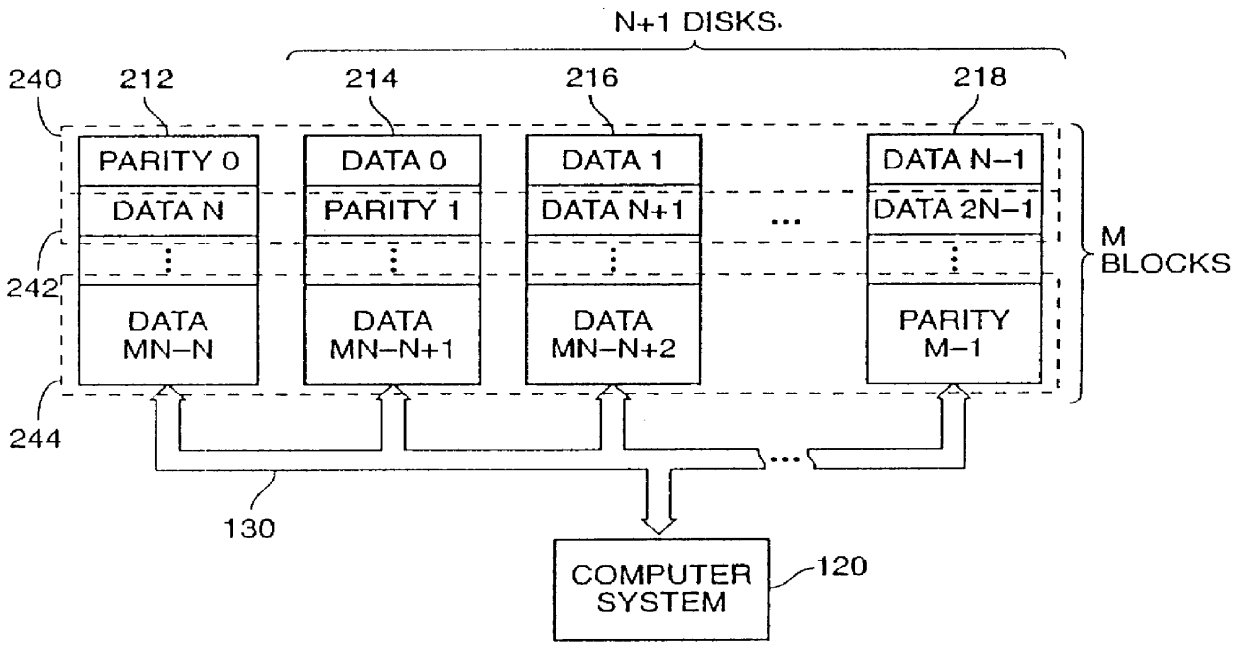
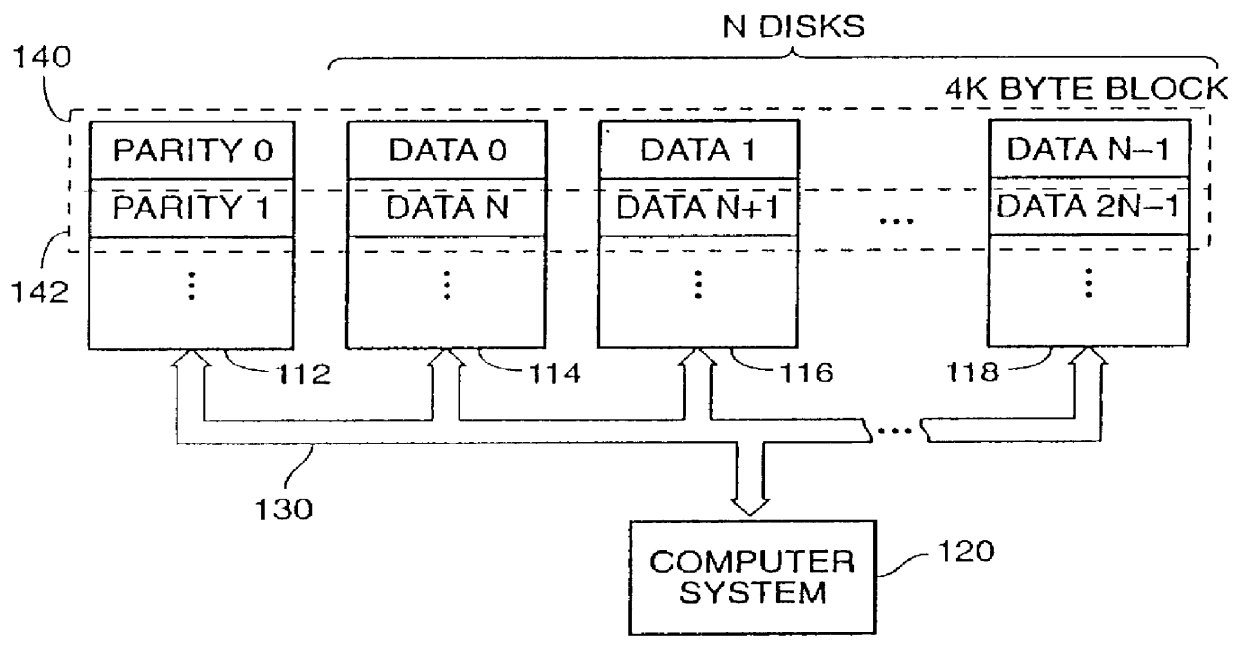
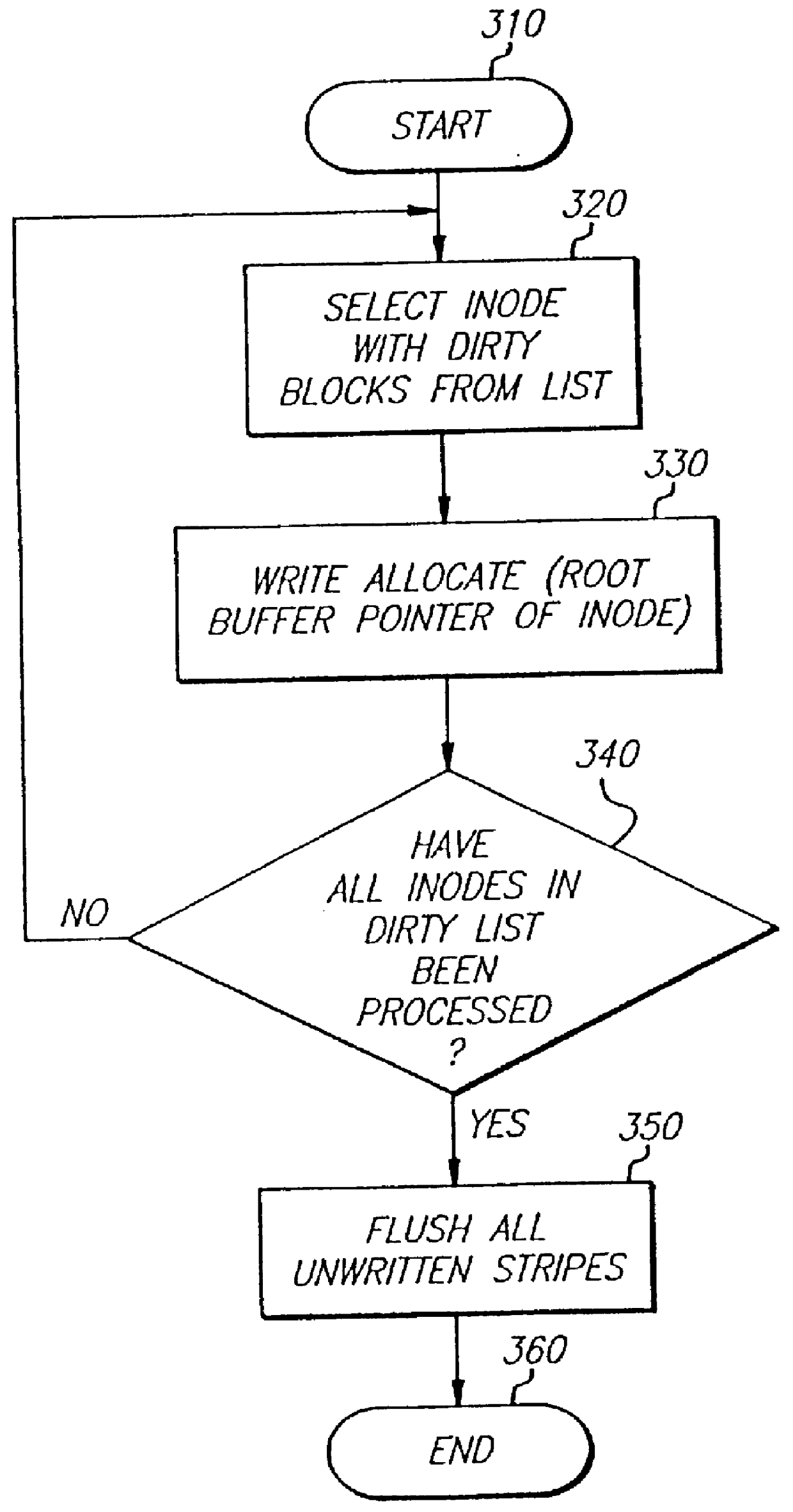
The present invention is a method for integrating a file system with a RAID array that exports precise information about the arrangement of data blocks in the RAID subsystem. The file system examines this information and uses it to optimize the location of blocks as they are written to the RAID system. Thus, the system uses explicit knowledge of the underlying RAID disk layout to schedule disk allocation. The present invention uses separate current-write location (CWL) pointers for each disk in the disk array where the pointers simply advance through the disks as writes occur. The algorithm used has two primary goals. The first goal is to keep the CWL pointers as close together as possible, thereby improving RAID efficiency by writing to multiple blocks in the stripe simultaneously. The second goal is to allocate adjacent blocks in a file on the same disk, thereby improving read back performance. The present invention satisfies the first goal by always writing on the disk with the lowest CWL pointer. For the second goal, a new disk is chosen only when the algorithm starts allocating space for a new file, or when it has allocated N blocks on the same disk for a single file. A sufficient number of blocks is defined as all the buffers in a chunk of N sequential buffers in a file. The result is that CWL pointers are never more than N blocks apart on different disks, and large files have N consecutive blocks on the same disk.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Method for allocating files in a file system integrated with a raid disk sub-system
A method is disclosed for integrating a file system with a RAID array that exports precise information about the arrangement of data blocks in the RAID subsystem. The file system examines this information and uses it to optimize the location of blocks as they are written to the RAID system. Thus, the system uses explicit knowledge of the underlying RAID disk layout to schedule disk allocation. The method uses separate current-write location (CWL) pointers for each disk in the disk array where the pointers simply advance through the disks as writes occur. The algorithm used has two primary goals. The first goal is to keep the CWL pointers as close together as possible, thereby improving RAID efficiency by writing to multiple blocks in the stripe simultaneously. The second goal is to allocate adjacent blocks in a file on the same disk, thereby improving read back performance. The method satisfies the first goal by always writing on the disk with the lowest CWL pointer. For the second goal, a new disks chosen only when the algorithm starts allocating space for a new file, or when it has allocated N blocks on the same disk for a single file. A sufficient number of blocks is defined as all the buffers in a chunk of N sequential buffers in a file. The result is that CWL pointers are never more than N blocks apart on different disks, and large files have N consecutive blocks on the same disk.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Disk array system and a method of avoiding failure of the disk array system
ActiveUS7028216B2Avoid failureReduce the likelihood of occurrenceInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionRAIDDisk array
The invention is intended to reduce disk access during data transfer from a disk in which occurrence of failure is anticipated to a spare disk as much as possible so that occurrence of double-failure is prevented in advance. When occurrence of failure in a disk which configures a RAID group, contents stored in the disk is copied to the spared disk. Simultaneously, another RAID group is paired with the above described RAID group and a secondary volume is provided therein. A write request is directed to the secondary volume. A differential bitmap controls a update data. Data which is not updated is read out from the primary volume, and data which is already updated is read from the secondary volume. When data transfer is completed, contents stored in the secondary volume are copied to the primary volume.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method for erasure coding data across a plurality of data stores in a network
ActiveUS7681104B1Maintain data consistencyEffective applicationError preventionCode conversionData setTheoretical computer science
An efficient method to apply an erasure encoding and decoding scheme across dispersed data stores that receive constant updates. A data store is a persistent memory for storing a data block. Such data stores include, without limitation, a group of disks, a group of disk arrays, or the like. An encoding process applies a sequencing method to assign a sequence number to each data and checksum block as they are modified and updated onto their data stores. The method preferably uses the sequence number to identify data set consistency. The sequencing method allows for self-healing of each individual data store, and it maintains data consistency and correctness within a data block and among a group of data blocks. The inventive technique can be applied on many forms of distributed persistent data stores to provide failure resiliency and to maintain data consistency and correctness.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Disk array apparatus and disk-array control method
InactiveUS20070171562A1Solve problemsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsFilamentary/web record carriersData shippingDisk array
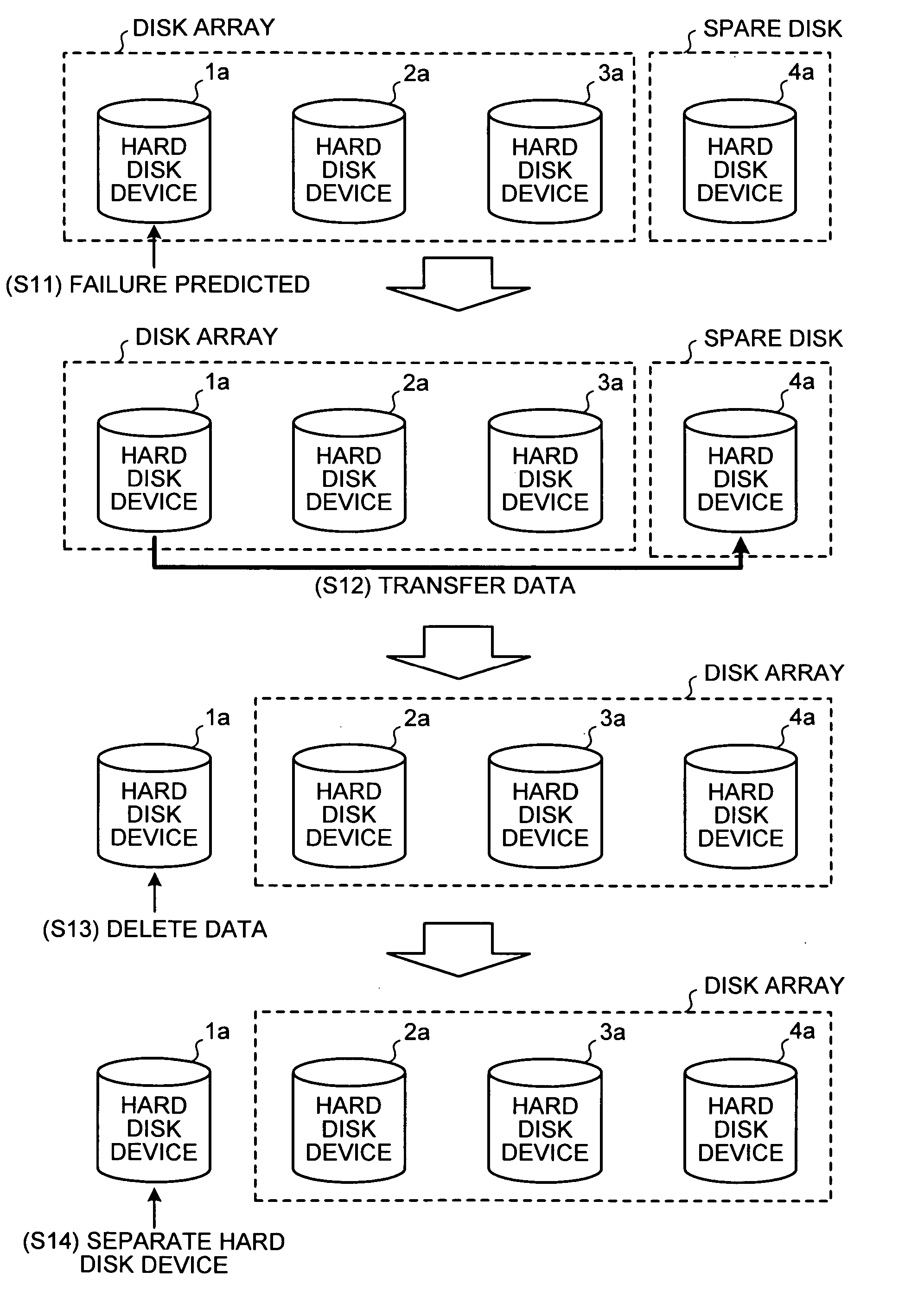
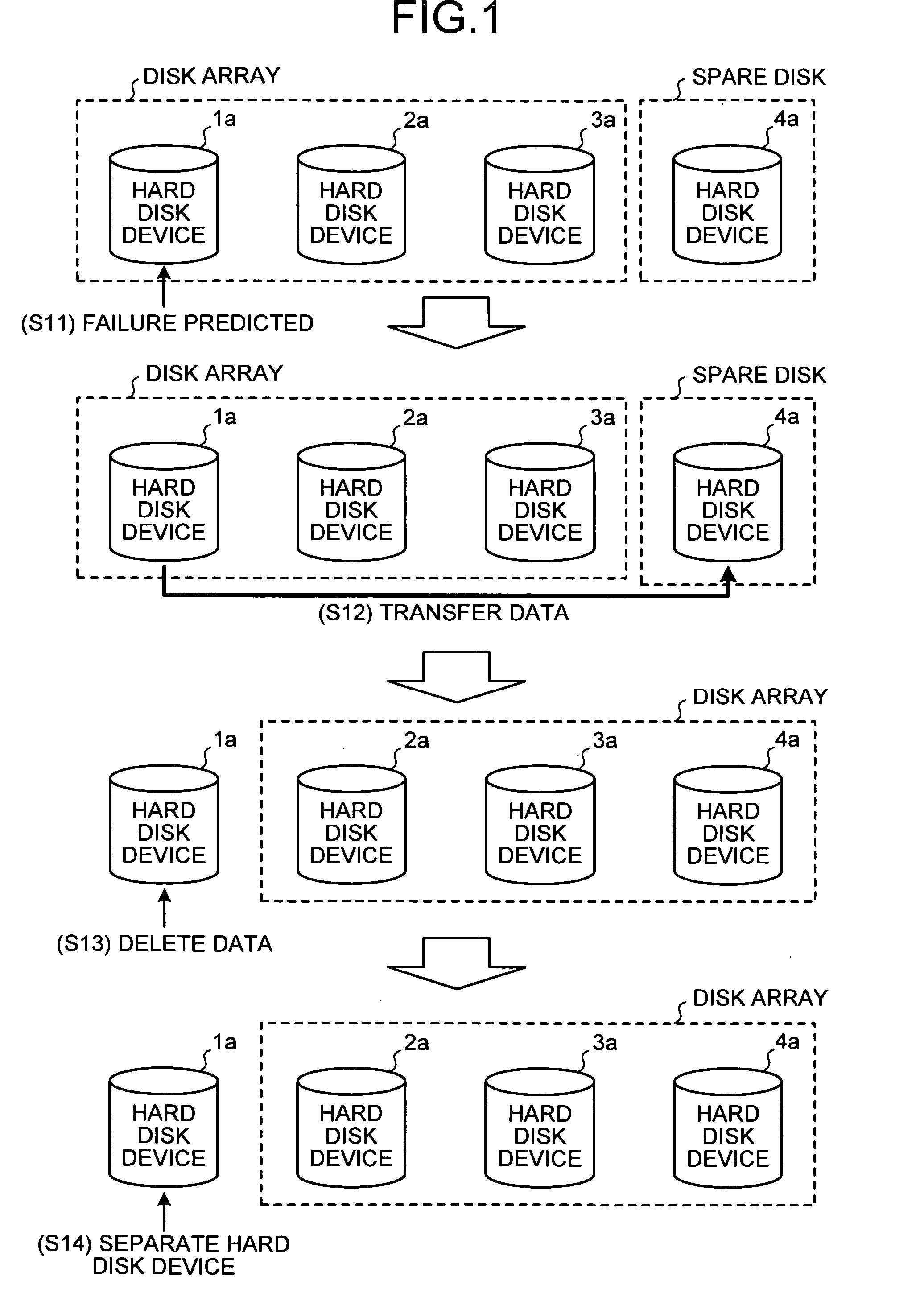
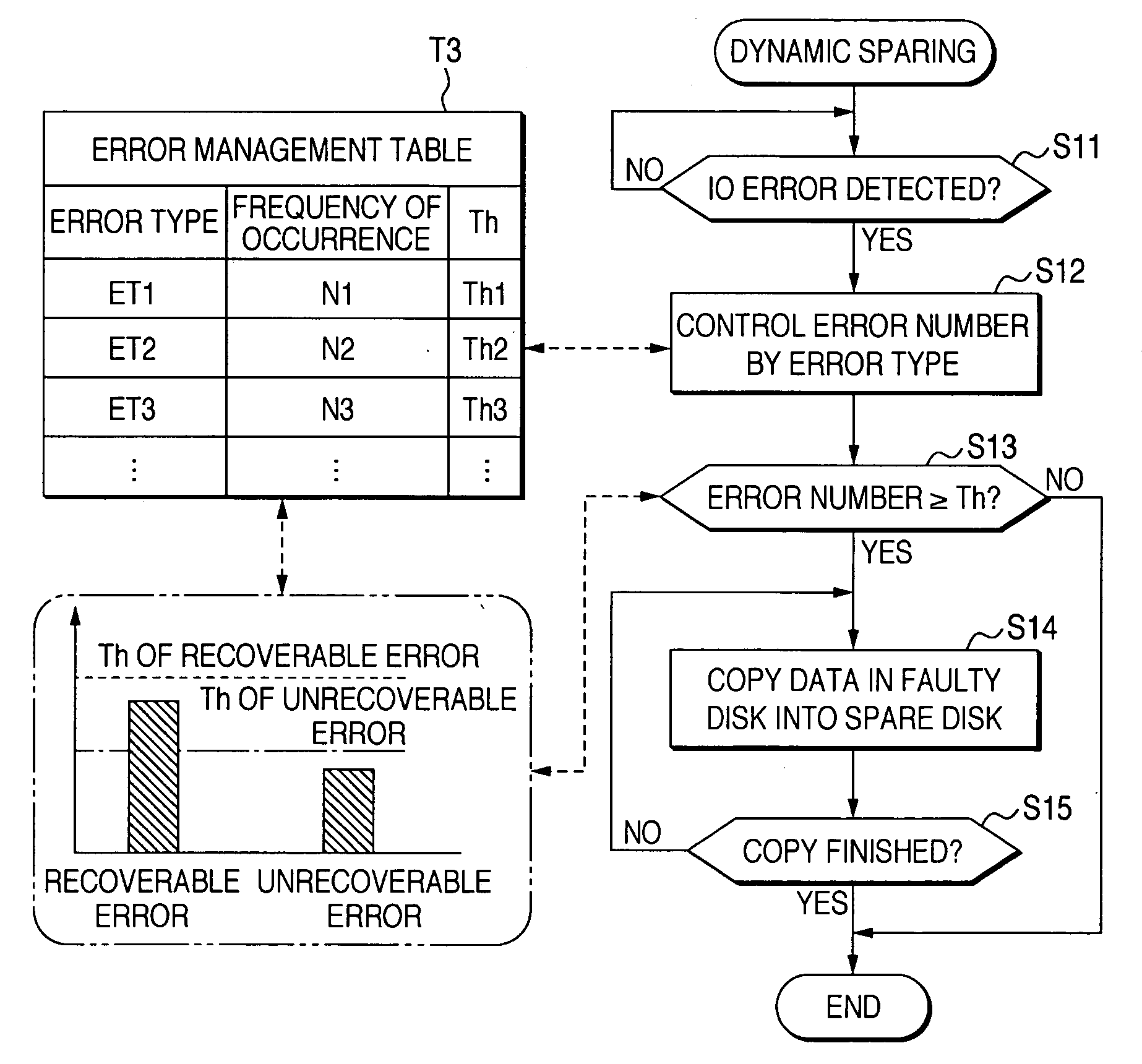
A failure predicting unit predicts a failure in a hard disk device that forms a disk array. A data transferring unit transfers data from a failure-predicted hard disk device for which the failure is predicted by the failure predicting unit to a spare disk. A data deleting unit deletes the data from the failure-predicted hard disk device after the data transferring unit completes transferring the data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Disk failure restoration method and disk array apparatus
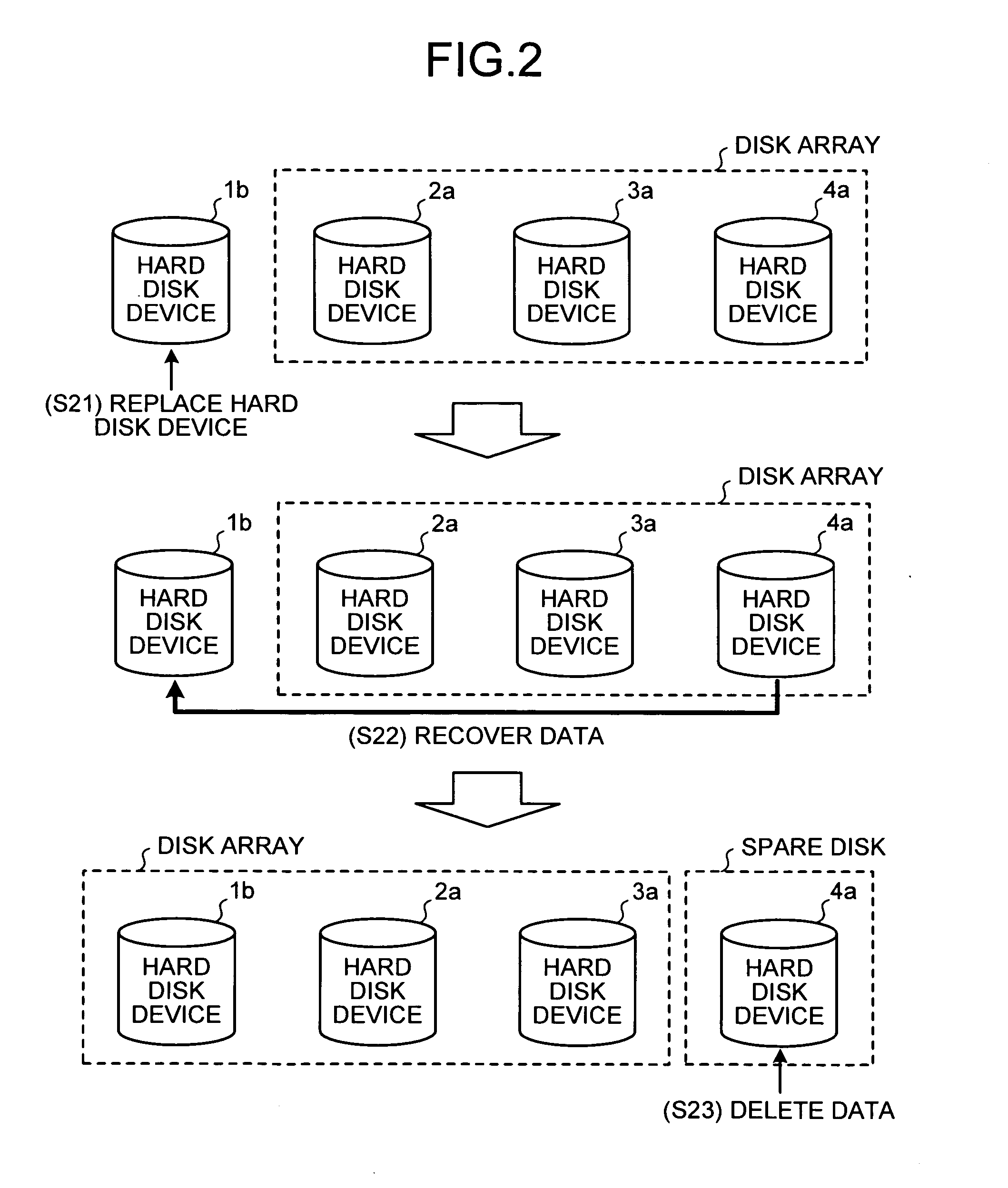
InactiveUS20080178040A1Reduce processing timeRedundant hardware error correctionRestoration methodDisk array
If a disk fails, another disk is used to rebuild the data of the failed disk on a first spare disk. When finishing being rebuilt, the first spare disk is separated from the disk array apparatus. Data to be updated while the first spare disk separated is written in another disk and managed by a bit map. The first spare disk is connected to the disk array apparatus at the position of the failed disk, then only the updated data is rebuilt on the first spare disk using another disk.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
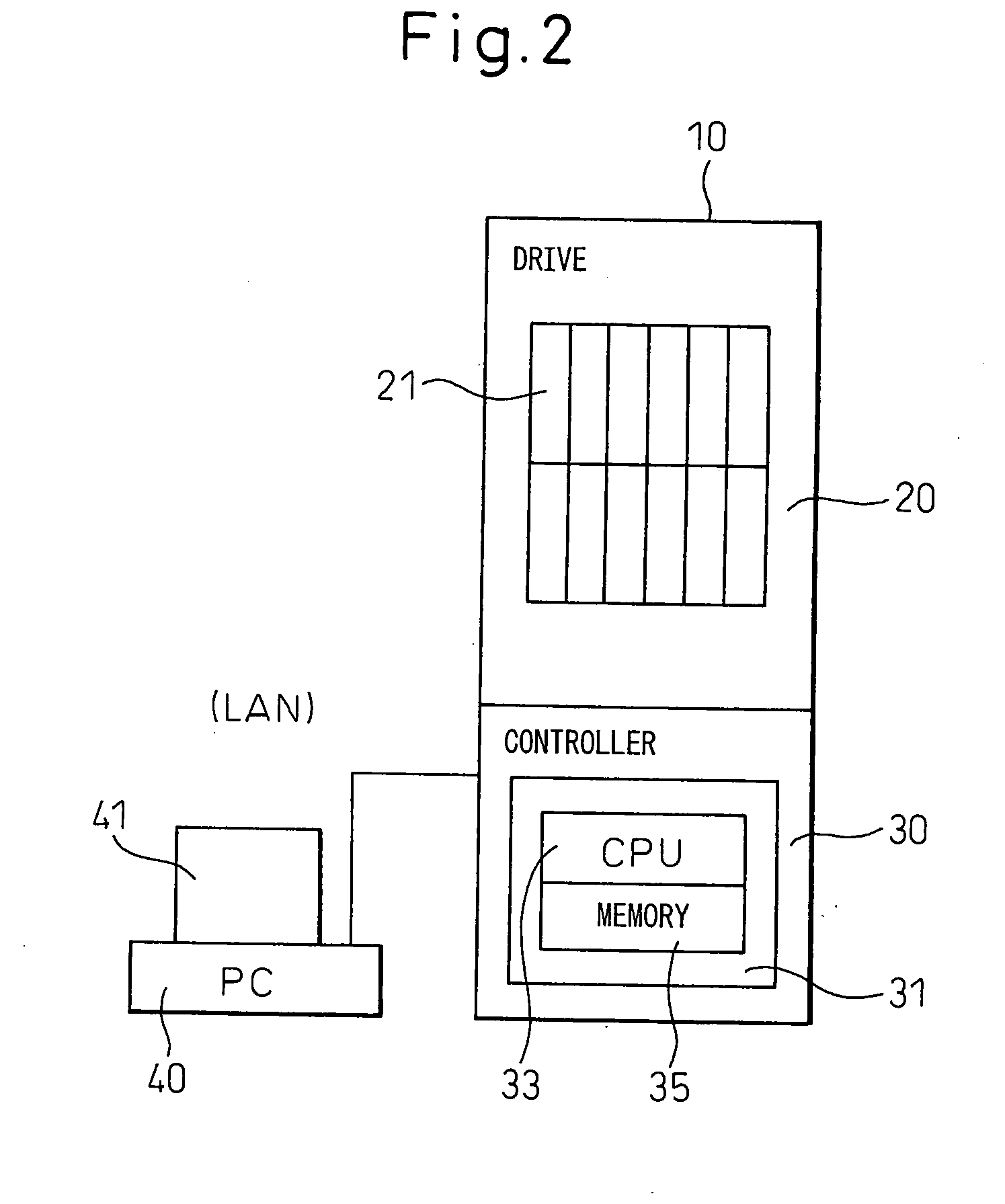
Storage array virtualization using a storage block mapping protocol client and server
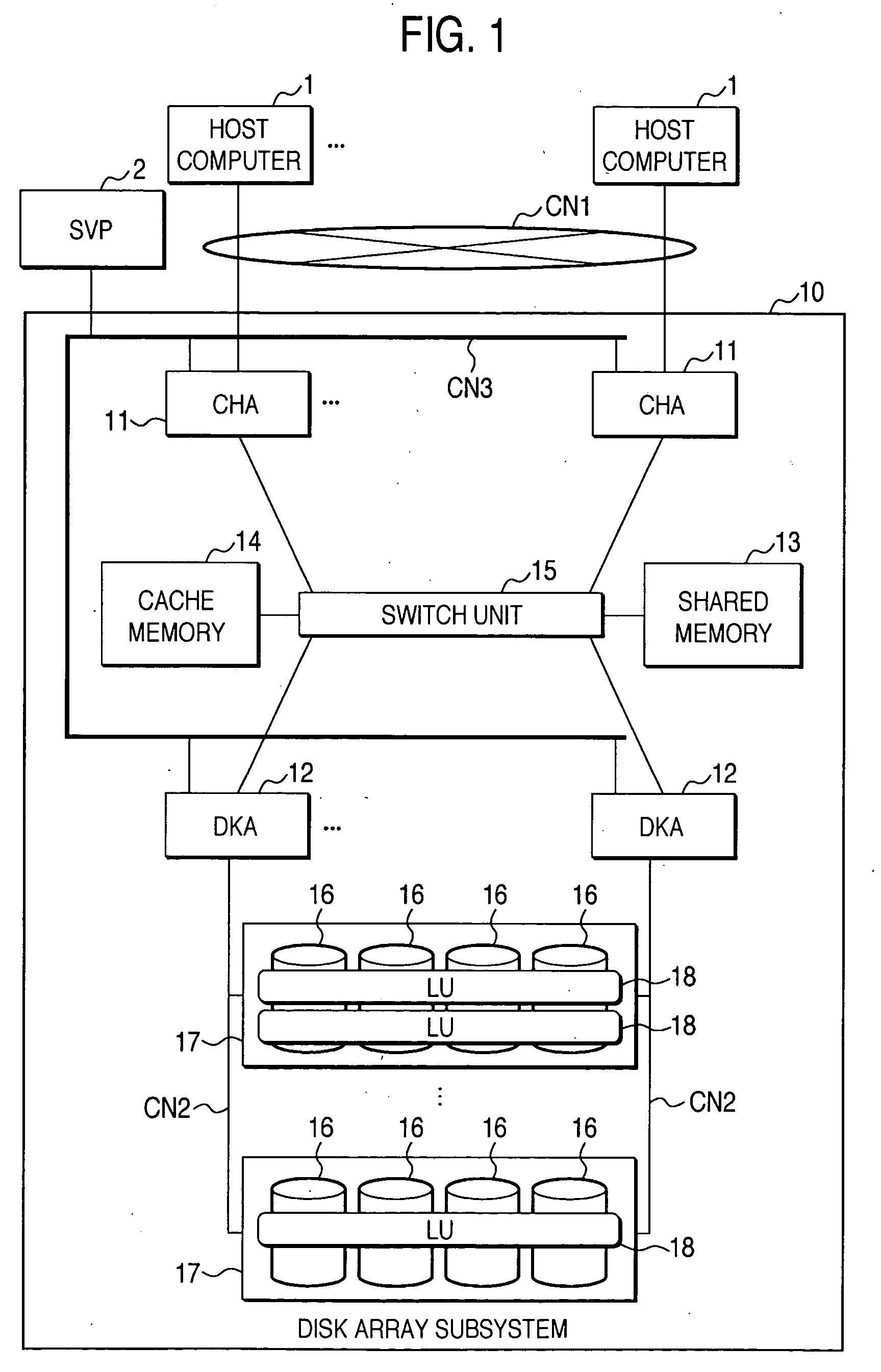
A cached disk array includes a disk storage array, a global cache memory, disk directors coupling the cache memory to the disk storage array, and front-end directors for linking host computers to the cache memory. The front-end directors service storage access requests from the host computers, and the disk directors stage requested data from the disk storage array to the cache memory and write new data to the disk storage. At least one of the front-end directors or disk directors is programmed for block resolution of virtual logical units of the disk storage, and for obtaining, from a storage allocation server, space allocation and mapping information for pre-allocated blocks of the disk storage, and for returning to the storage allocation server requests to commit the pre-allocated blocks of storage once data is first written to the pre-allocated blocks of storage.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Disk array control device and storage device
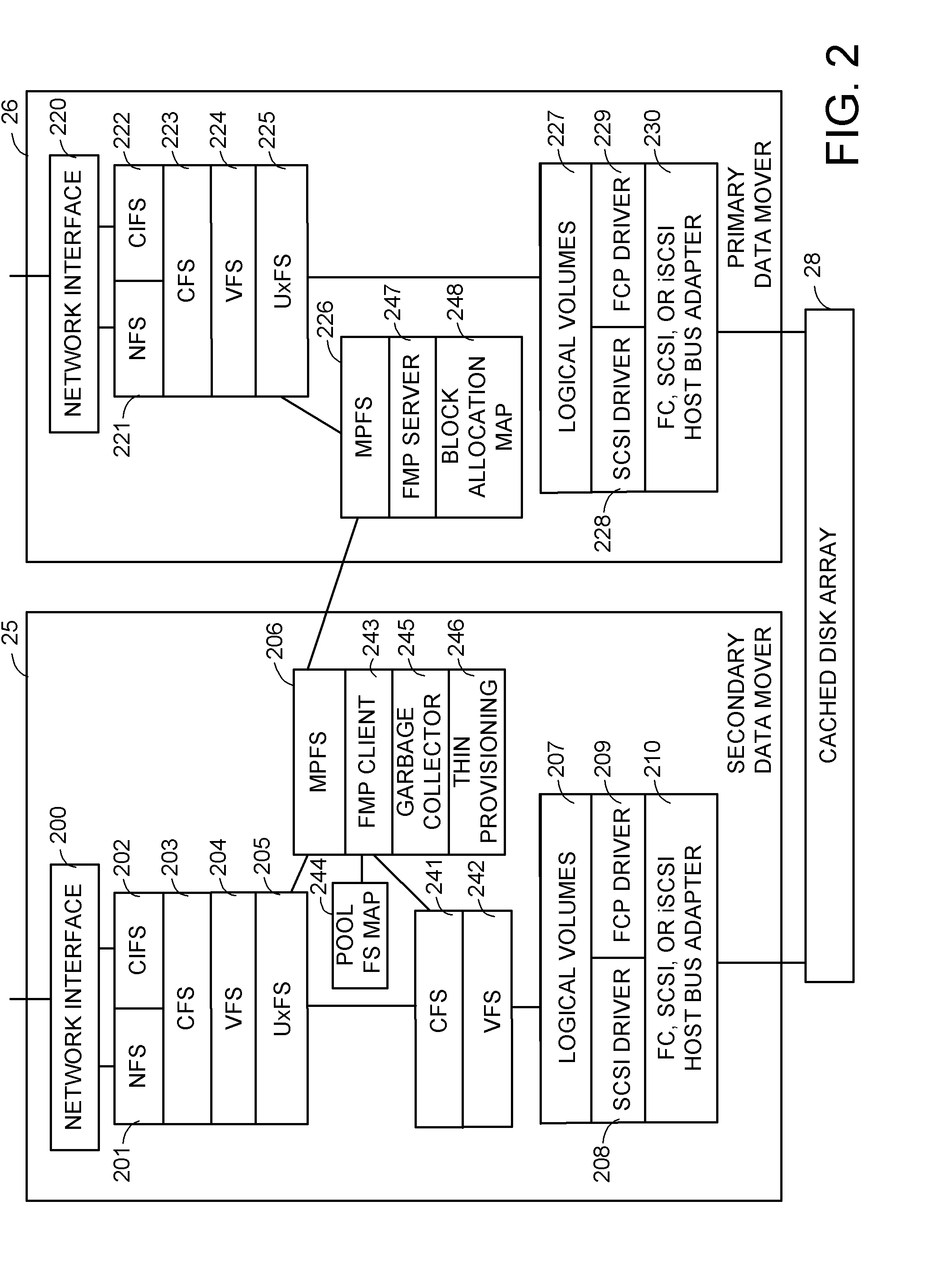
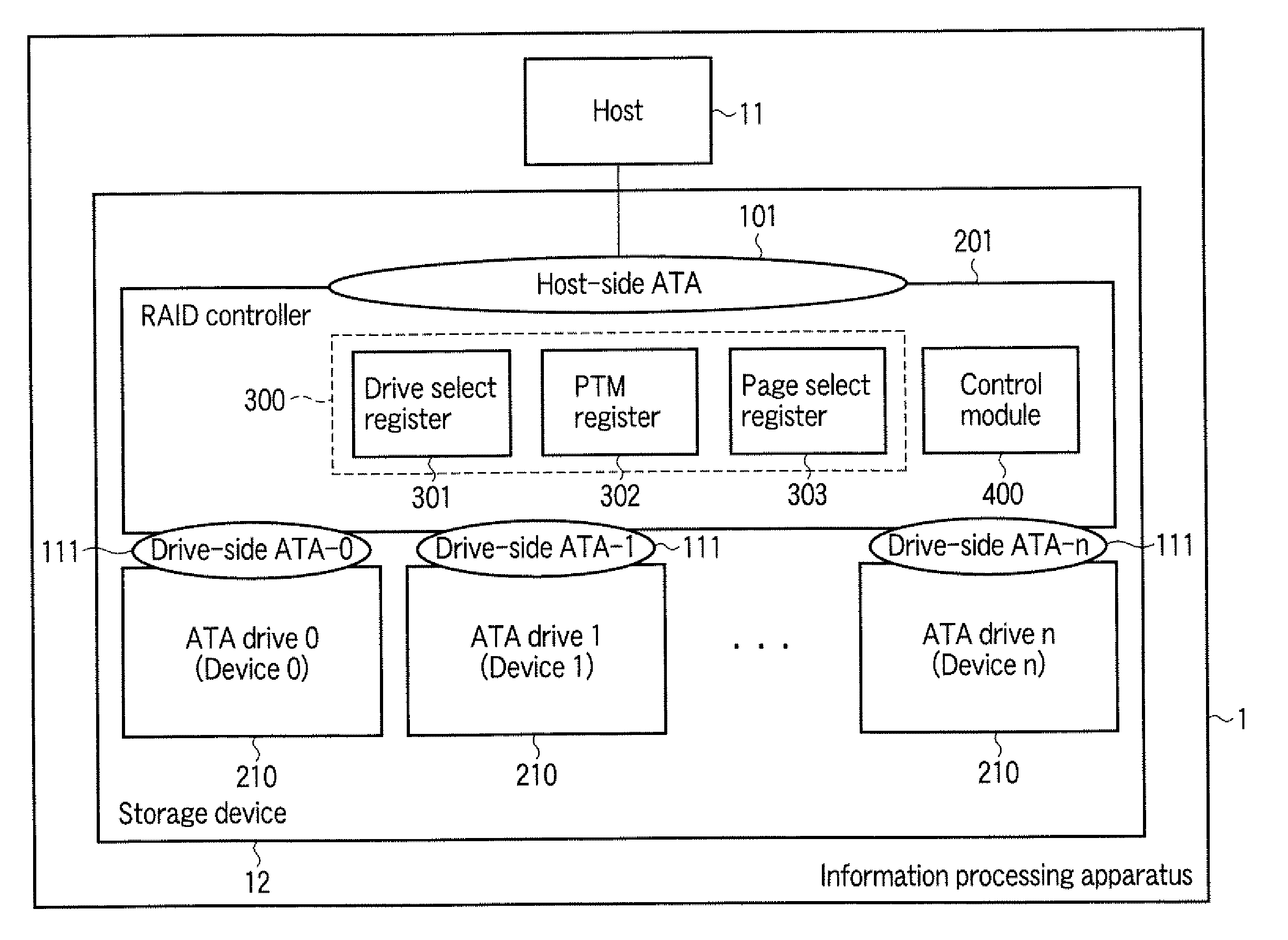
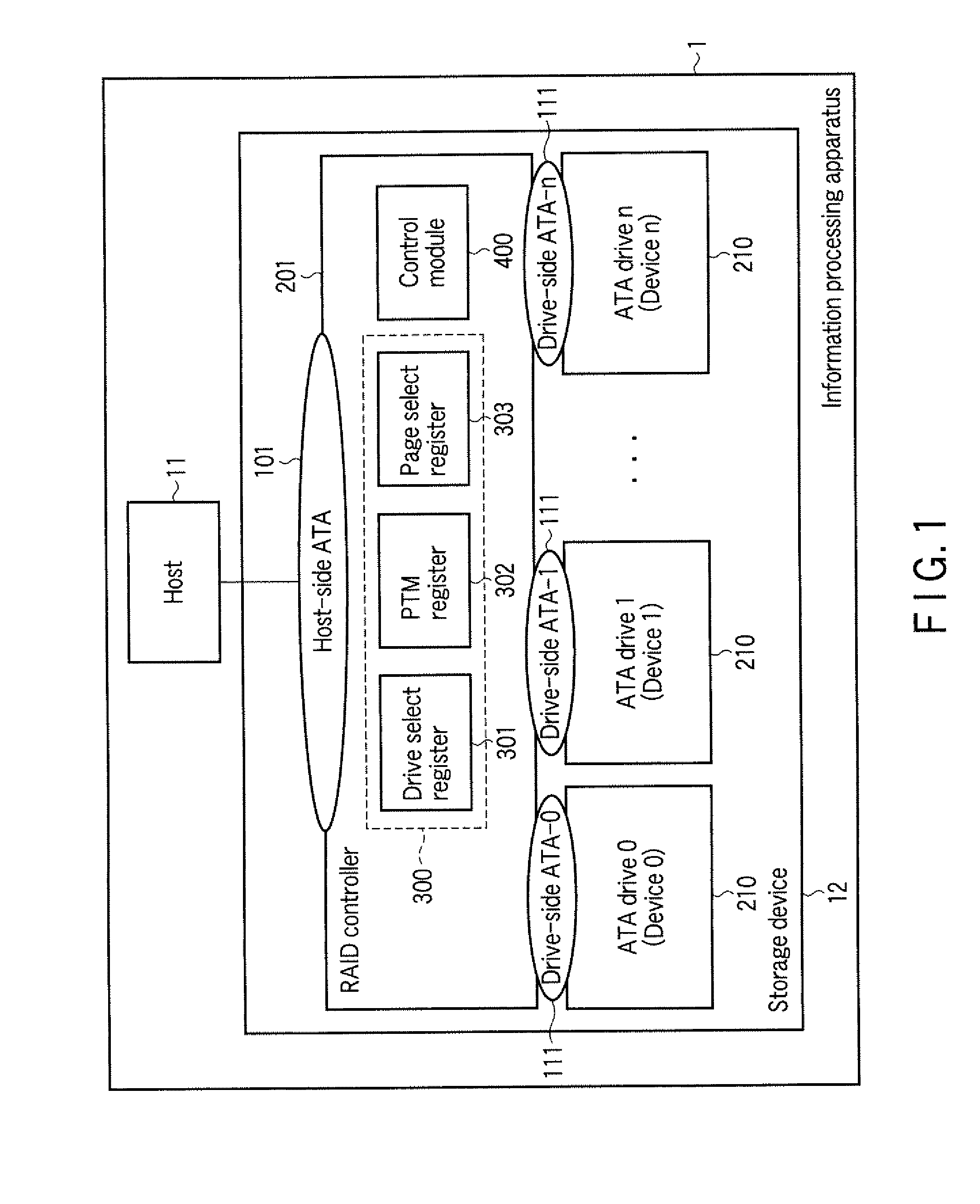
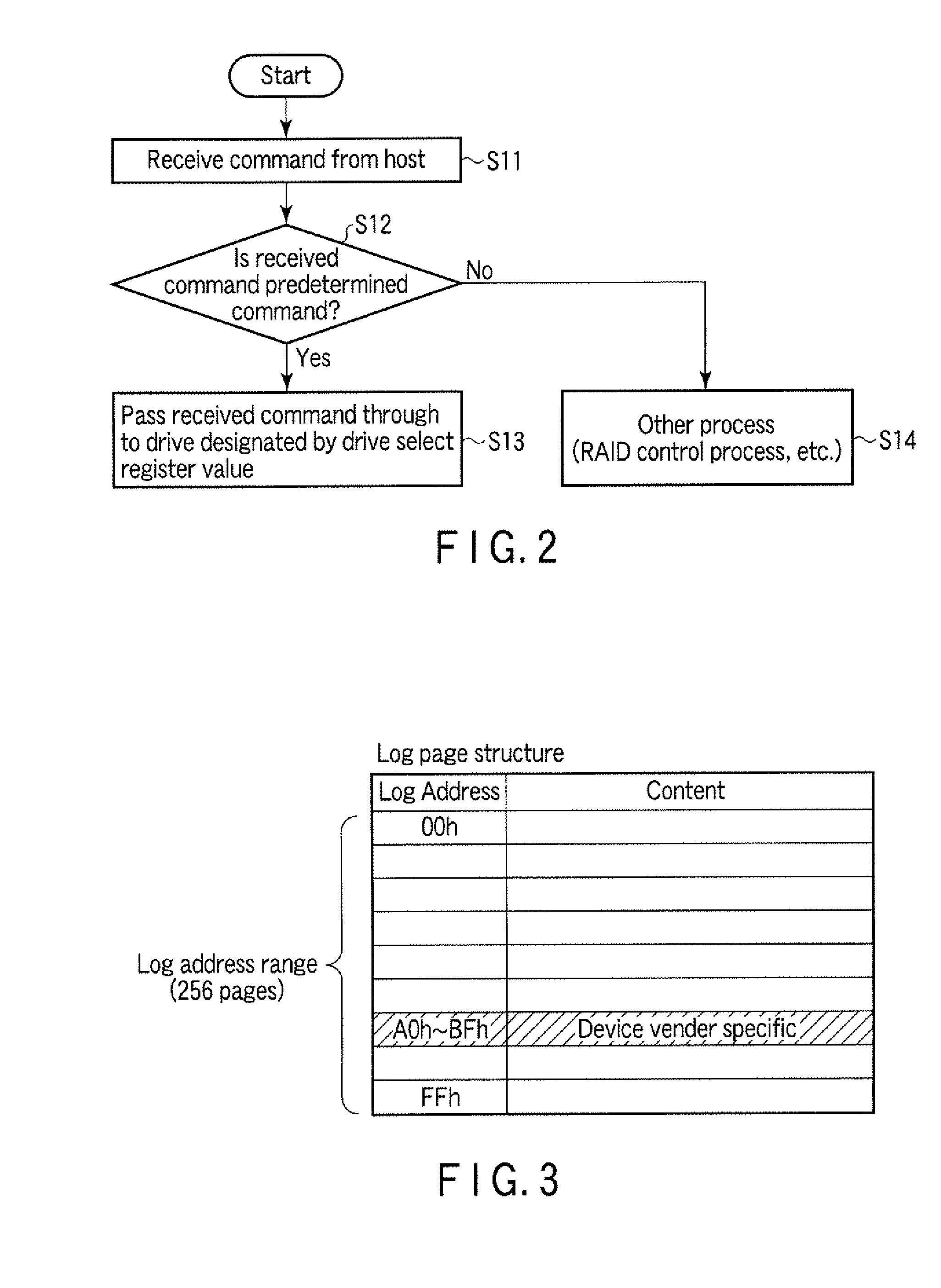
InactiveUS20100106905A1Digital data processing detailsElectrical apparatus contructional detailsProcessor registerDisk array
According to one embodiment, a disk array control device manages a plurality of drives as a single logical drive. The disk array control device includes a first register configured to store a to-he-accessed drive number which is designated by a host, and a control module. The control module is configured to receive a command from the host, determine whether the received command is a predetermined command which is used for maintenance of each of the drives, and execute, in a case where the received command is the predetermined command, a pass-through process of sending the received command to the drive which is designated by the to-be-accessed drive number in the first register.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
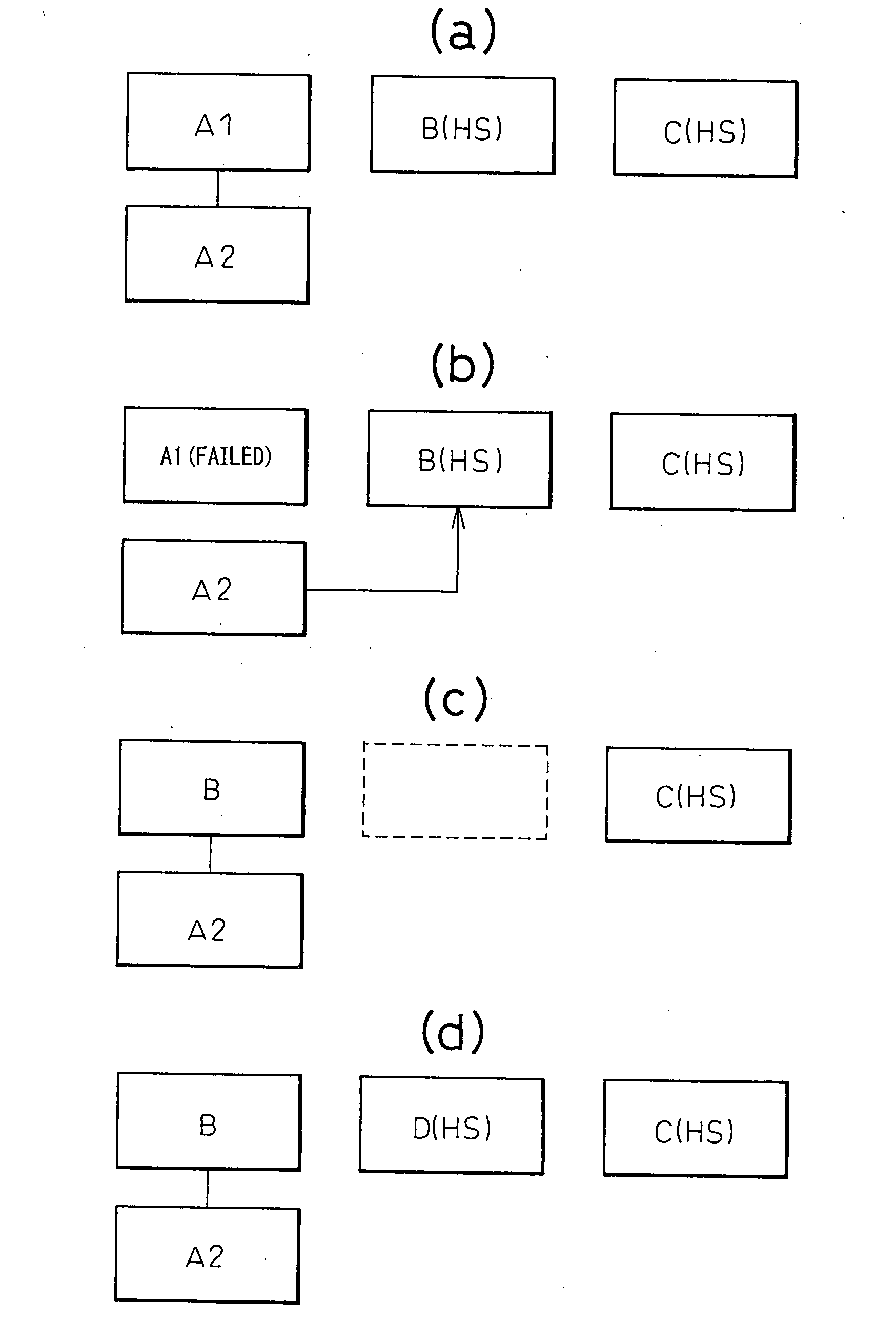
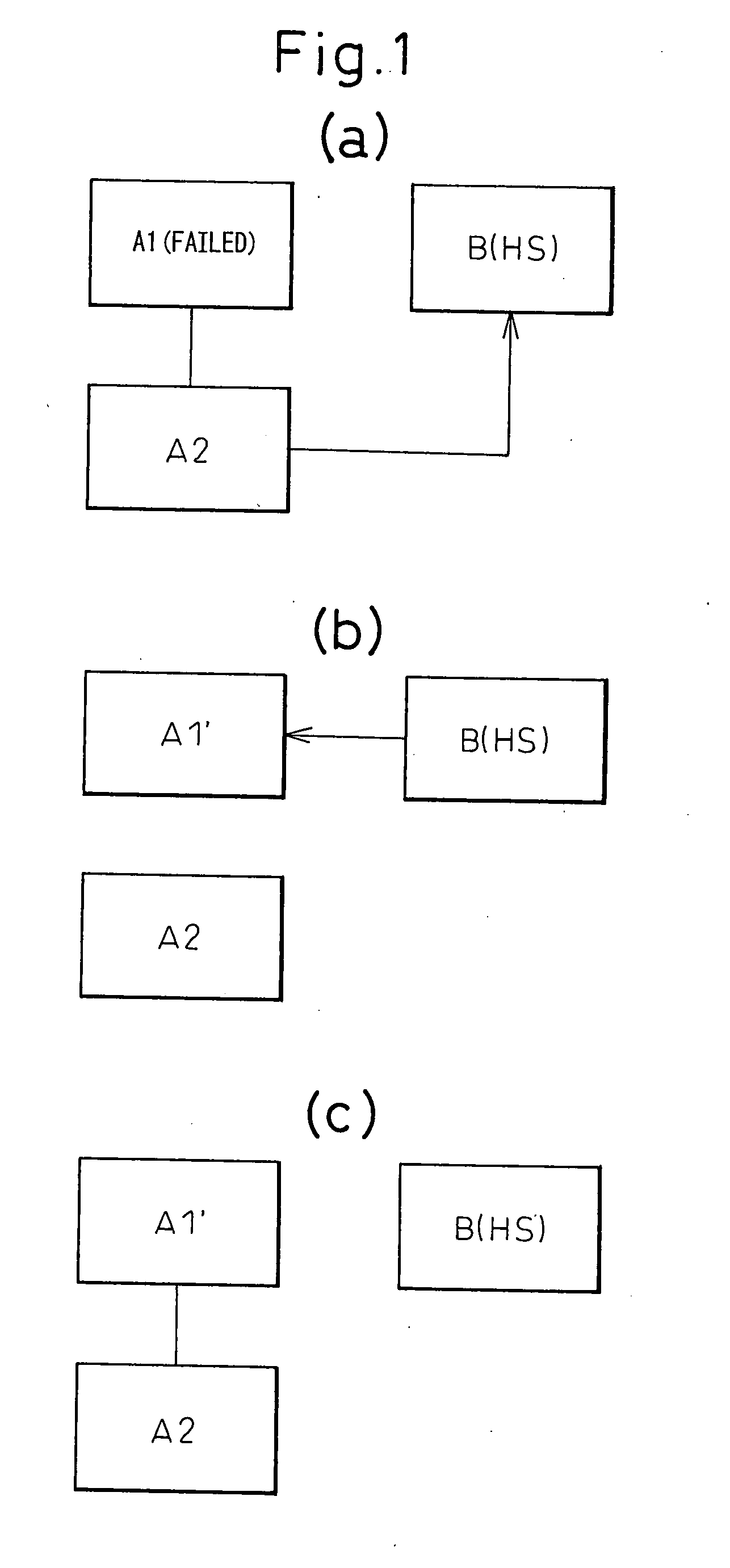
Replacing file system processors by hot swapping
ActiveUS6990547B2Increase capacityImprove reliabilityMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionFile systemNetwork structure
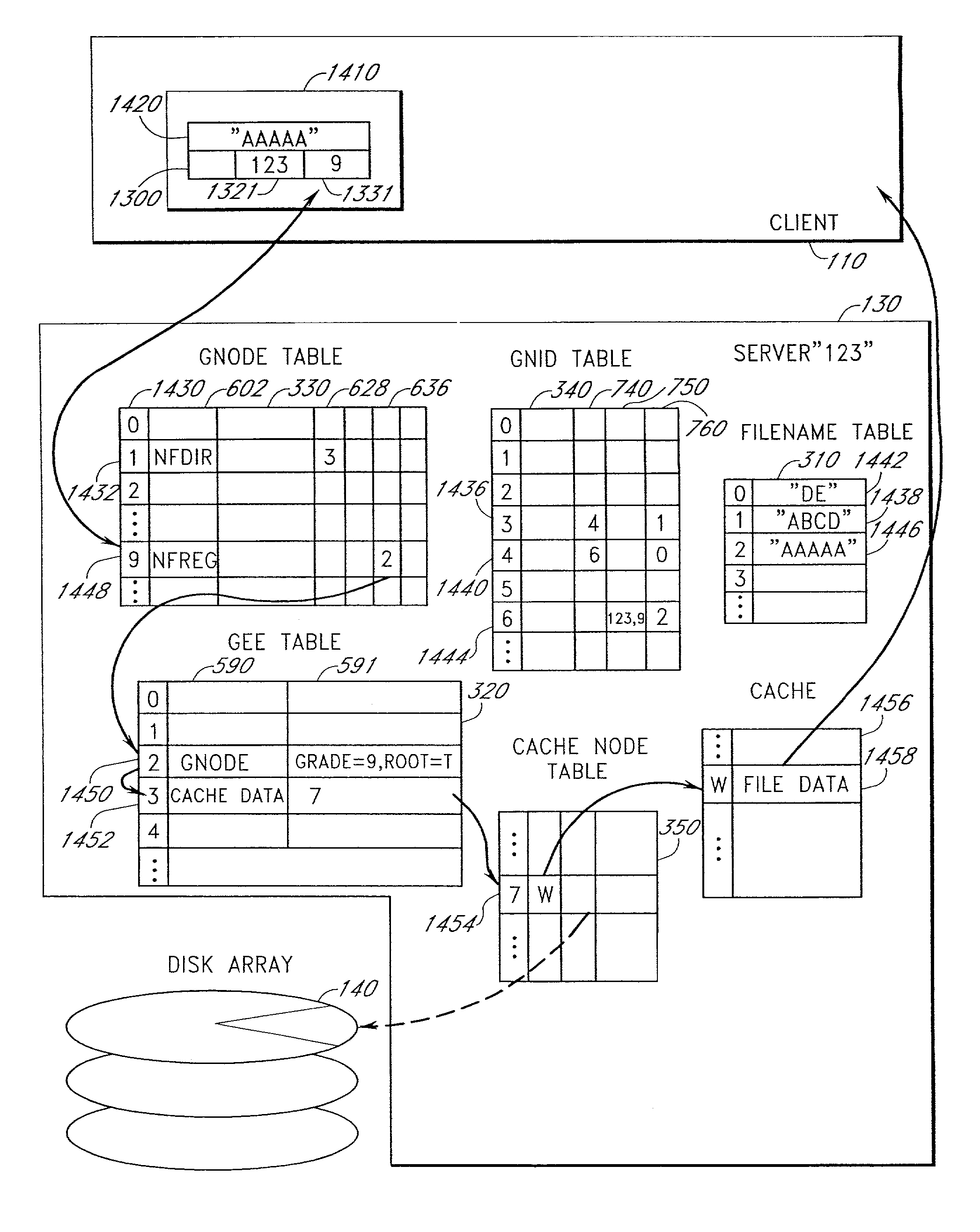
A system and method for replacing file system processors, also known as hot swapping, is described. The system and method operate on a fault-tolerant network file system that includes a first file server that is operably connected to a network fabric and a second file server that is operably connected to the network fabric. The fault-tolerant network file system includes a first disk array that is operably coupled to the first file server and to the second file server and a second disk array that is operably coupled to the first file server and to the second file server. First file system information is loaded on the first file server. The first file system information includes a first intent log of proposed changes to first metadata. Second file system information is loaded on the second file server. The second file system information includes a second intent log of proposed changes to second metadata. The first file server has a copy of the second metadata, and the second file server maintains a copy of the first metadata, thereby allowing the first file server to access files on the second disk array in the event of a failure of the second file server.
Owner:OVERLAND STORAGE INC
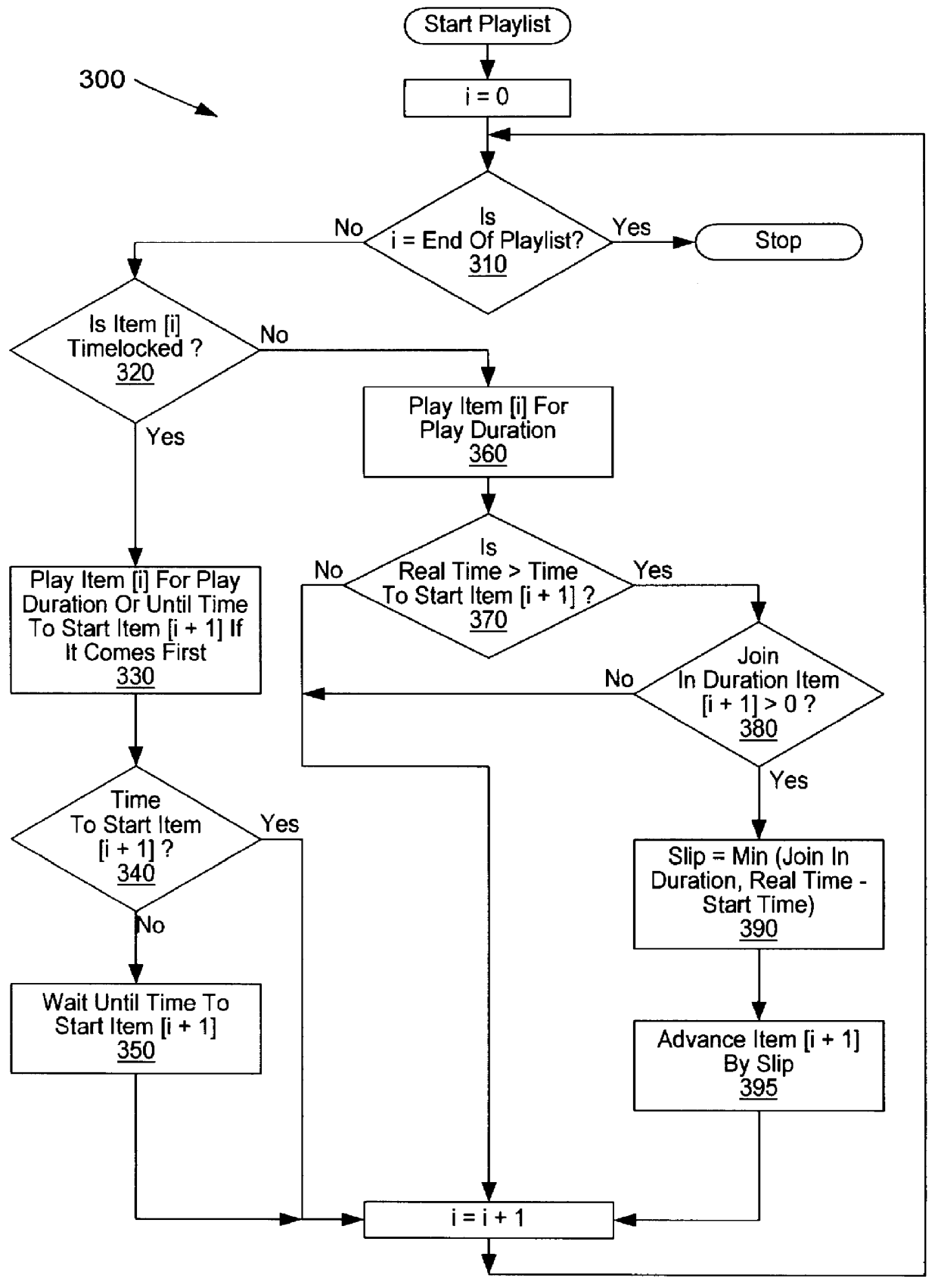
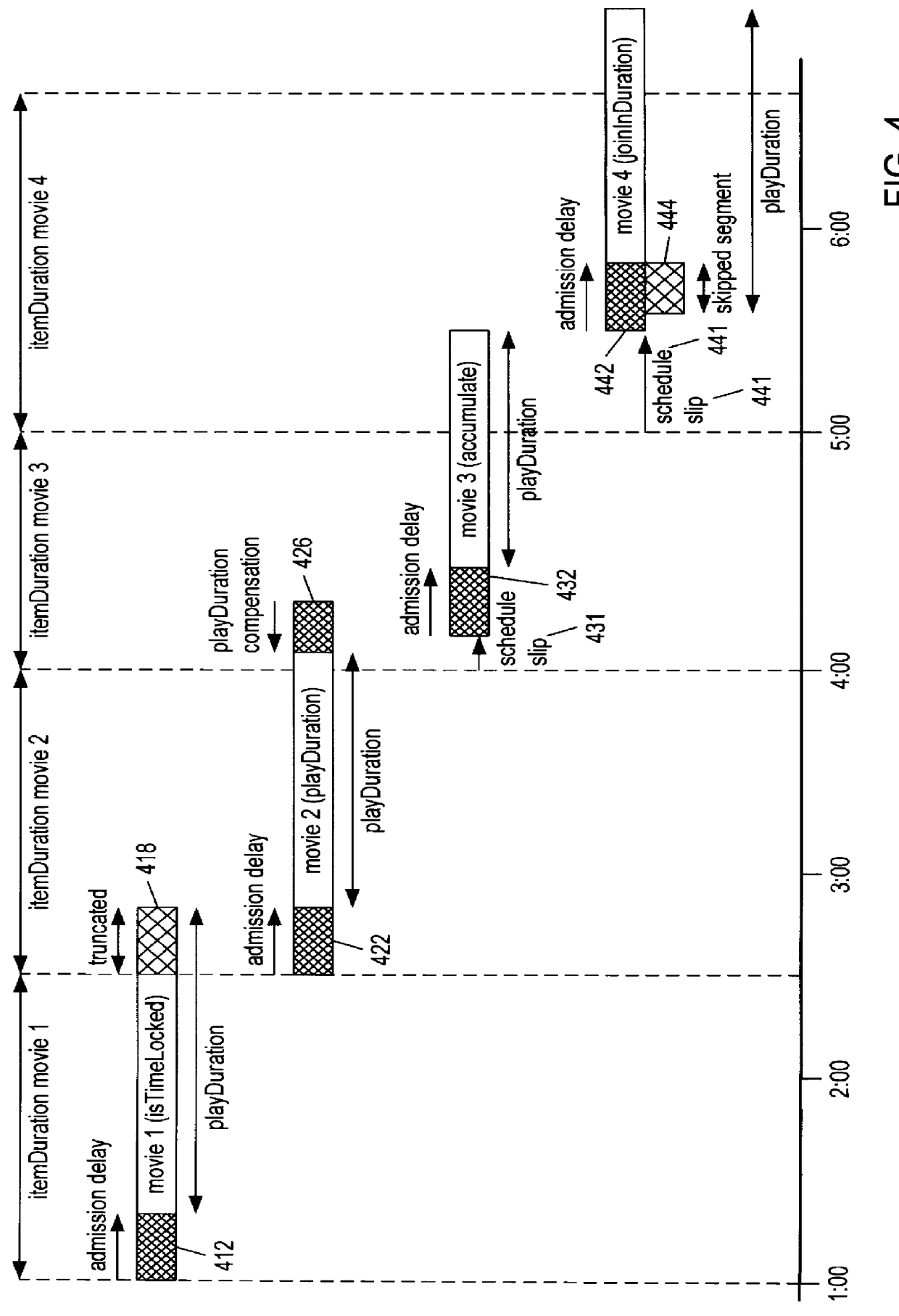
System and method for synchronizing presentation of media stream playlists with real time
InactiveUS6064379AFlat record carrier combinationsRecord information storageFile synchronizationMultimedia servers
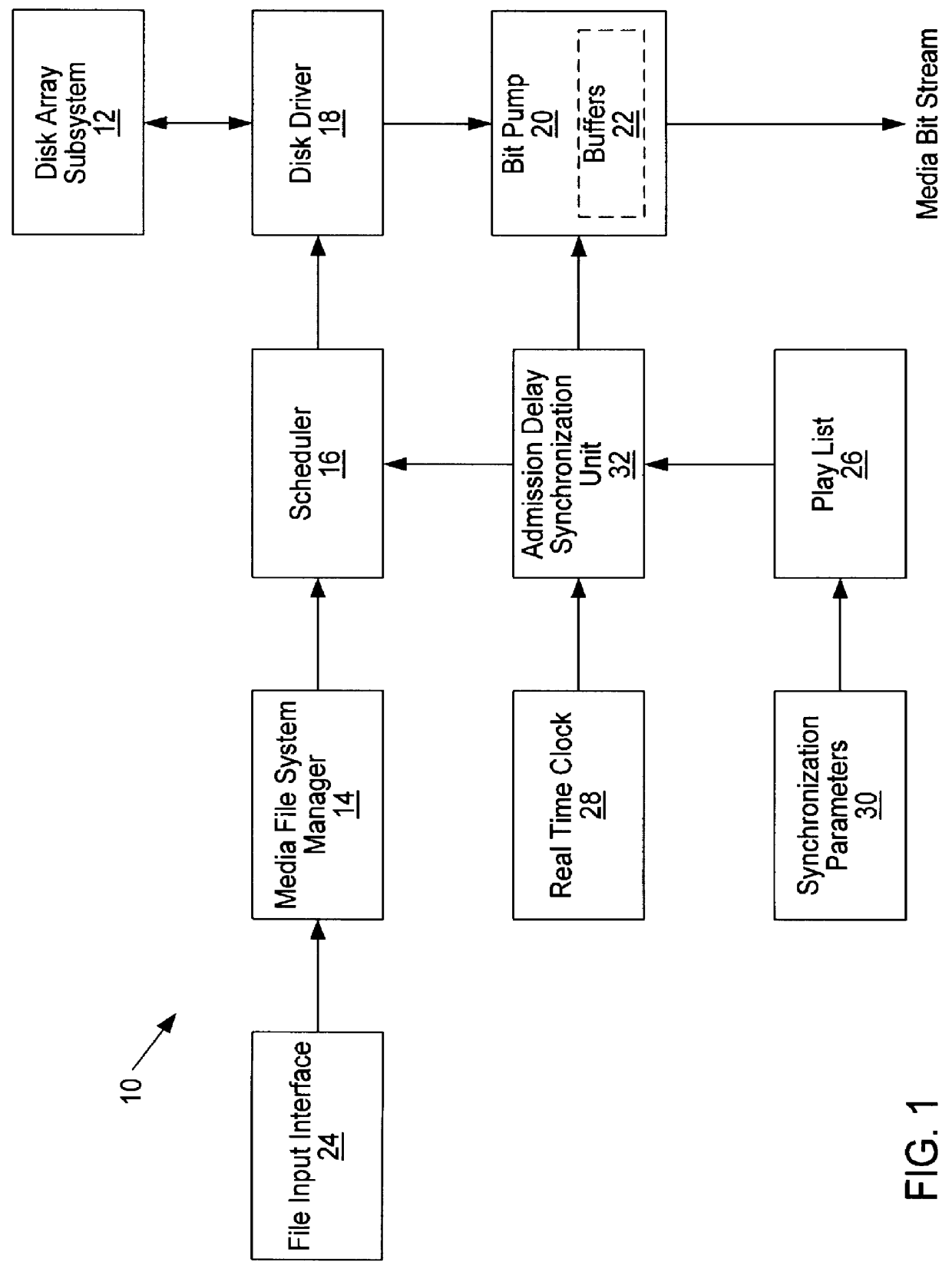
A multimedia server system includes a disk array subsystem including a plurality of multimedia files, e.g., movies, a media file system manager for managing the storage of the plurality of multimedia files within the disk array subsystem, and a playlist which includes a list of titles of specific multimedia files to be played at designated times. The multimedia server system advantageously includes synchronization parameters associated with each of titles specified by the playlist. The synchronization parameters are programmed to specify the manner in which particular files should be truncated in order to compensate for admission delays. An admission delay synchronization unit receives the synchronization parameters and truncates the multimedia files as specified by the synchronization parameters. In one implementation, a first synchronization parameter is used to specify that the current file should be truncated at the time for the play of the next file. A second synchronization parameter specifies that up to a given amount of time should be sacrificed at the beginning of the next file to account for the admission delay of the current file. In this manner, the beginning of the next file is truncated. Still a third synchronization parameter is provided to specify an amount of time up to which the current file will be truncated at it's end to account for it's admission delay. As a result, the truncated file can be played in a shorter amount of time than the scheduled duration, and the "excess time" created is available to absorb any admission delay.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
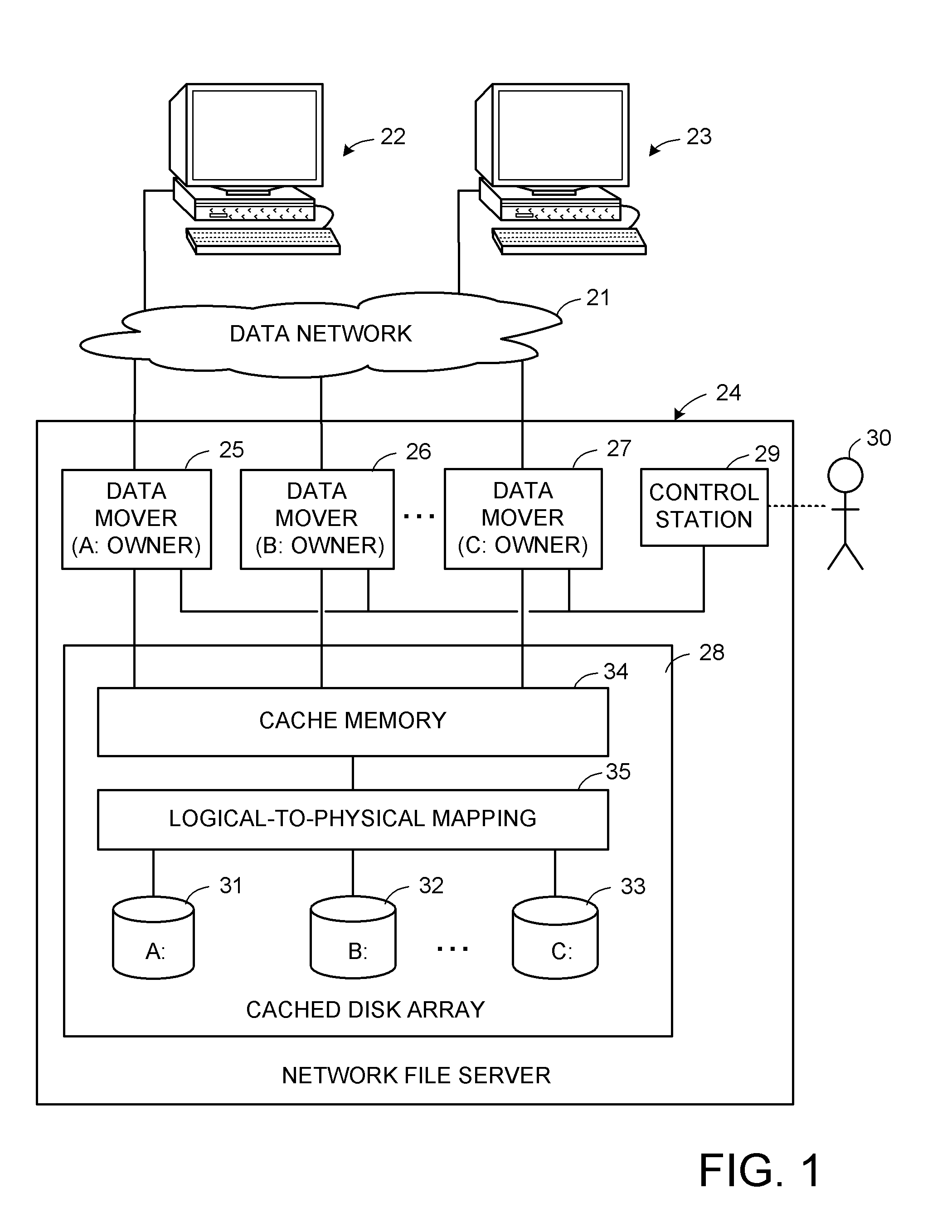
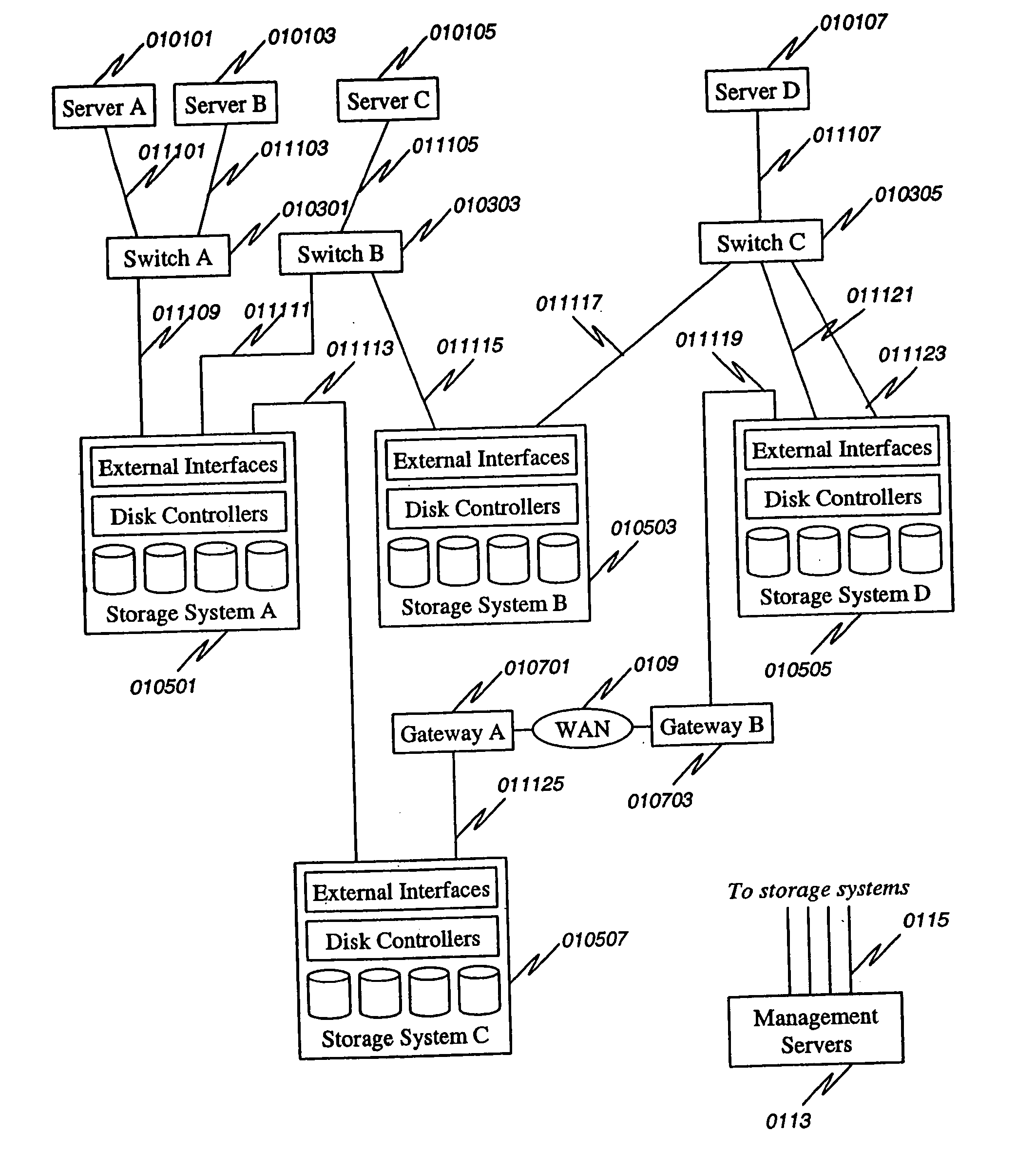
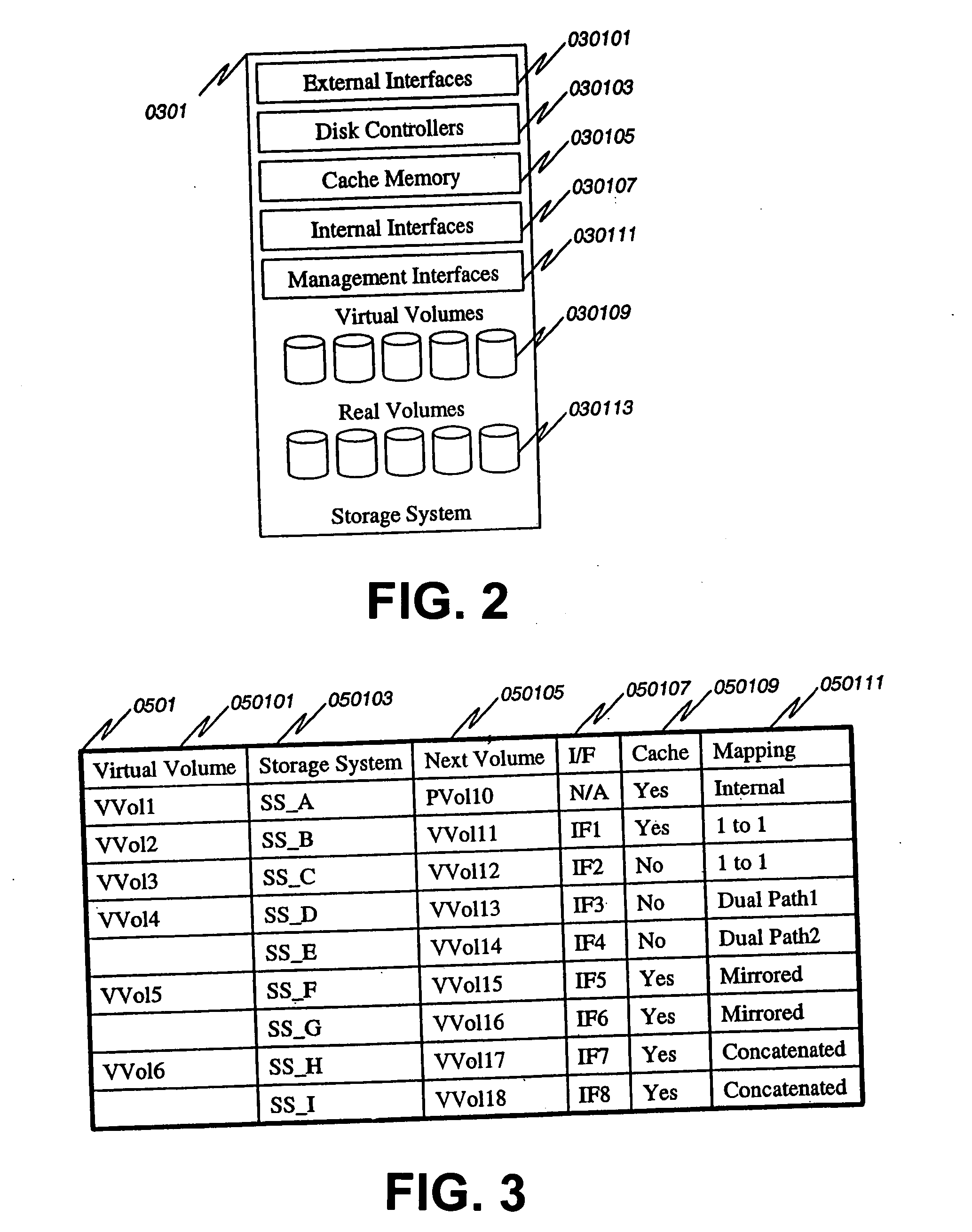
Method and apparatus for disk array based I/O routing and multi-layered external storage linkage
A system and method for linking external storage systems that includes creating a virtual volume mapping at one or more storage systems. Each virtual volume mapping at each storage system associating a virtual storage volume with a physical storage volume and / or one second virtual storage volume at one or more second storage systems. An access request is received at a first storage system specifying a virtual volume. It is determined on which storage system a physical storage volume associated with the specified virtual volume in the access request is located using the virtual volume mapping at the first storage system and / or the virtual volume mapping at one or more second storage systems. Access is provided to the physical storage volume based on which storage system the physical storage volume is located. Useful in Storage Area Networks and many configurations including 1 to 1, dual path, mirrored, and concatenated, etc.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
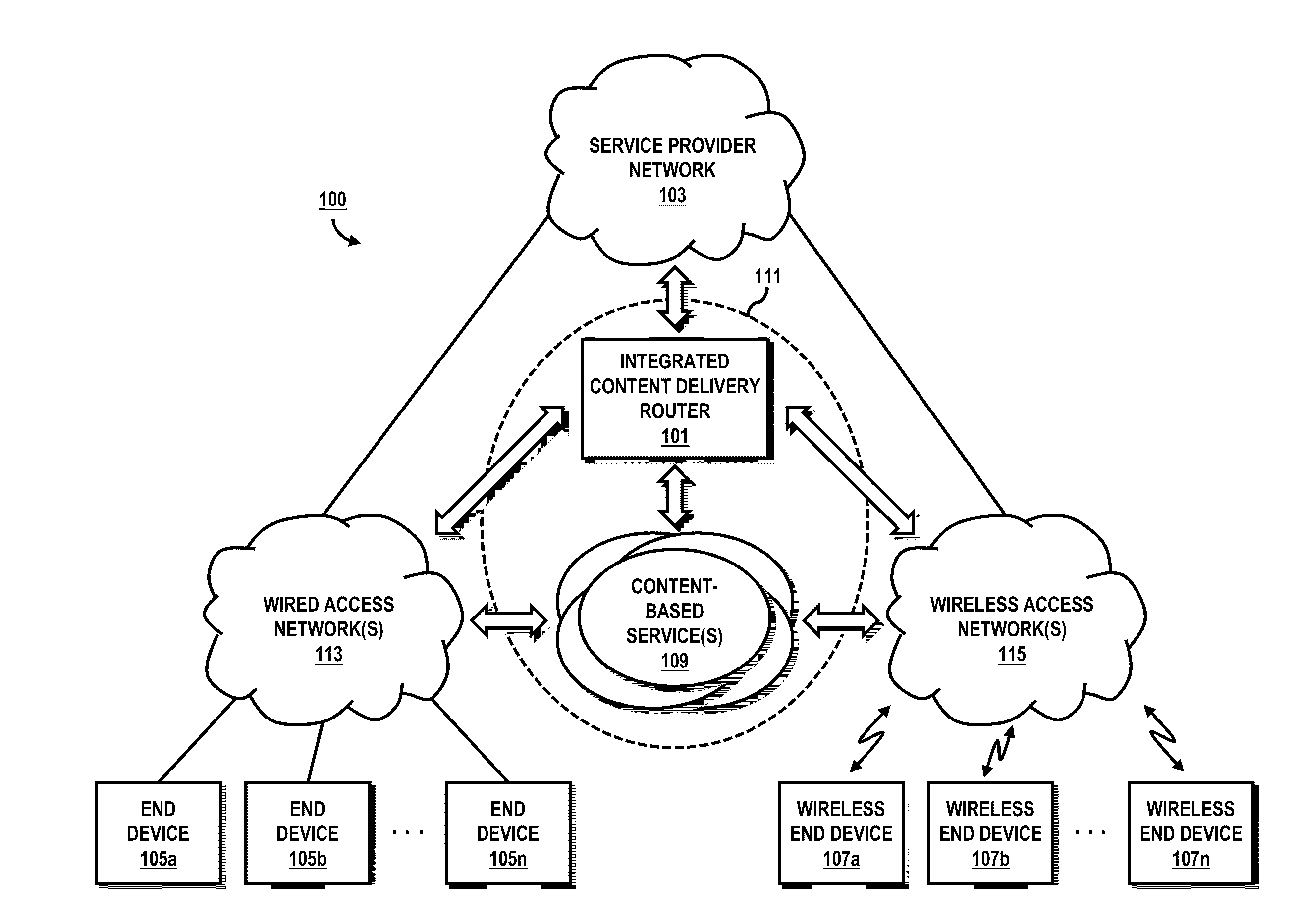
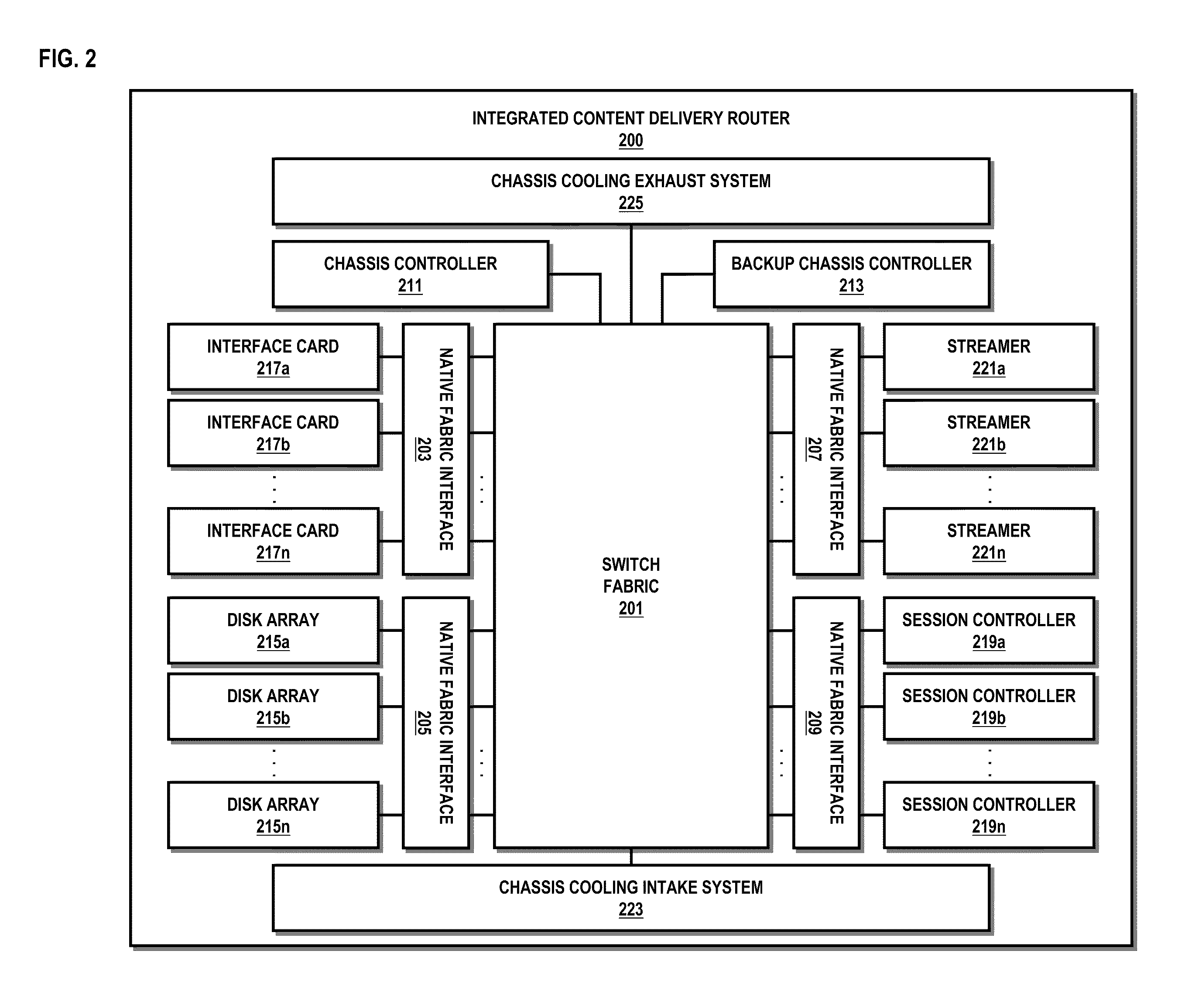
Method and system for providing integrated content delivery
An approach is provided for integrated content delivery. A request for content stored on a disk array of a router is received. In response to the request, one or more disks of the disk array are selected to retrieve the content, wherein the disk array is natively coupled to a switch fabric of the router. A path is determined through the switch fabric for transmission of the content.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
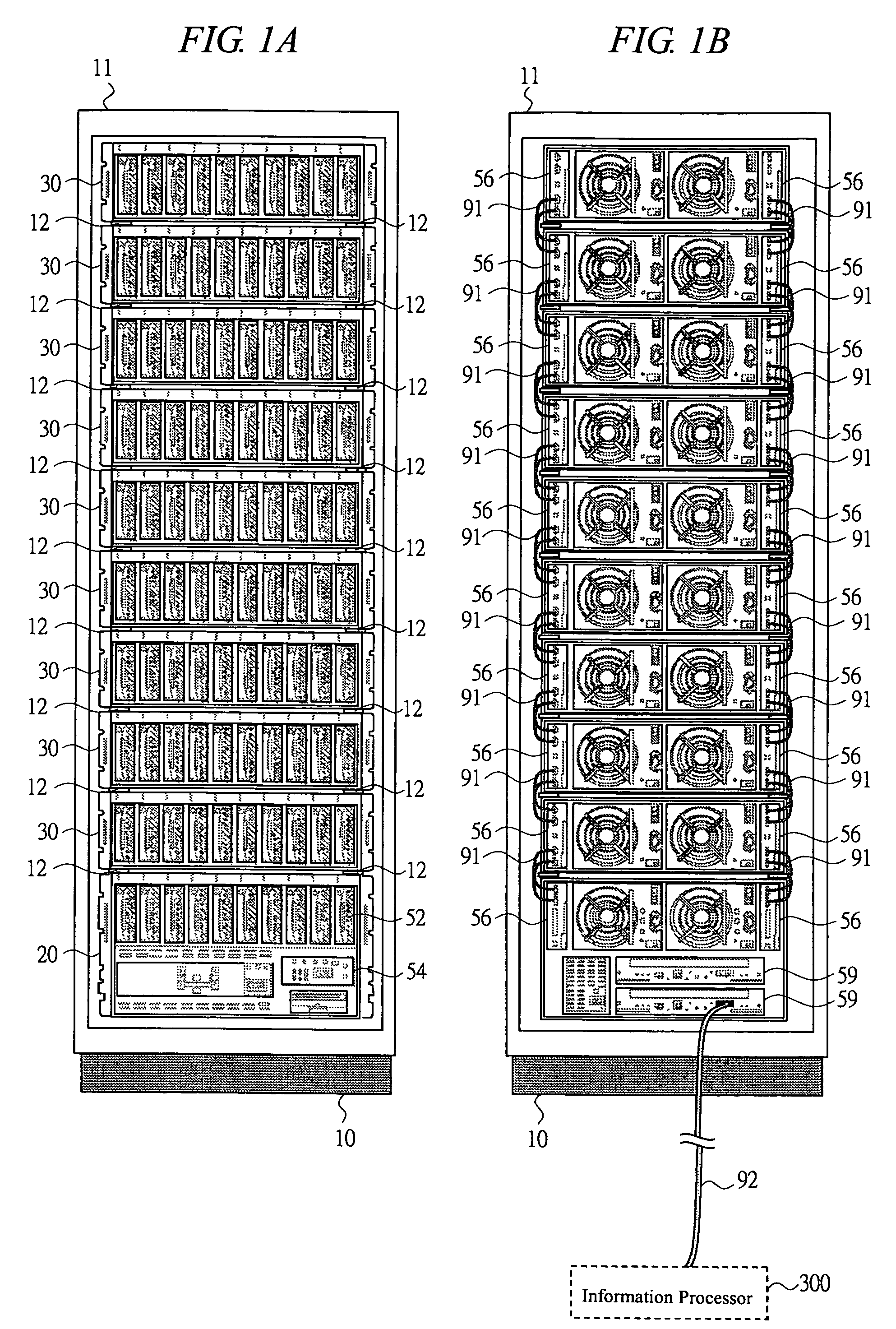
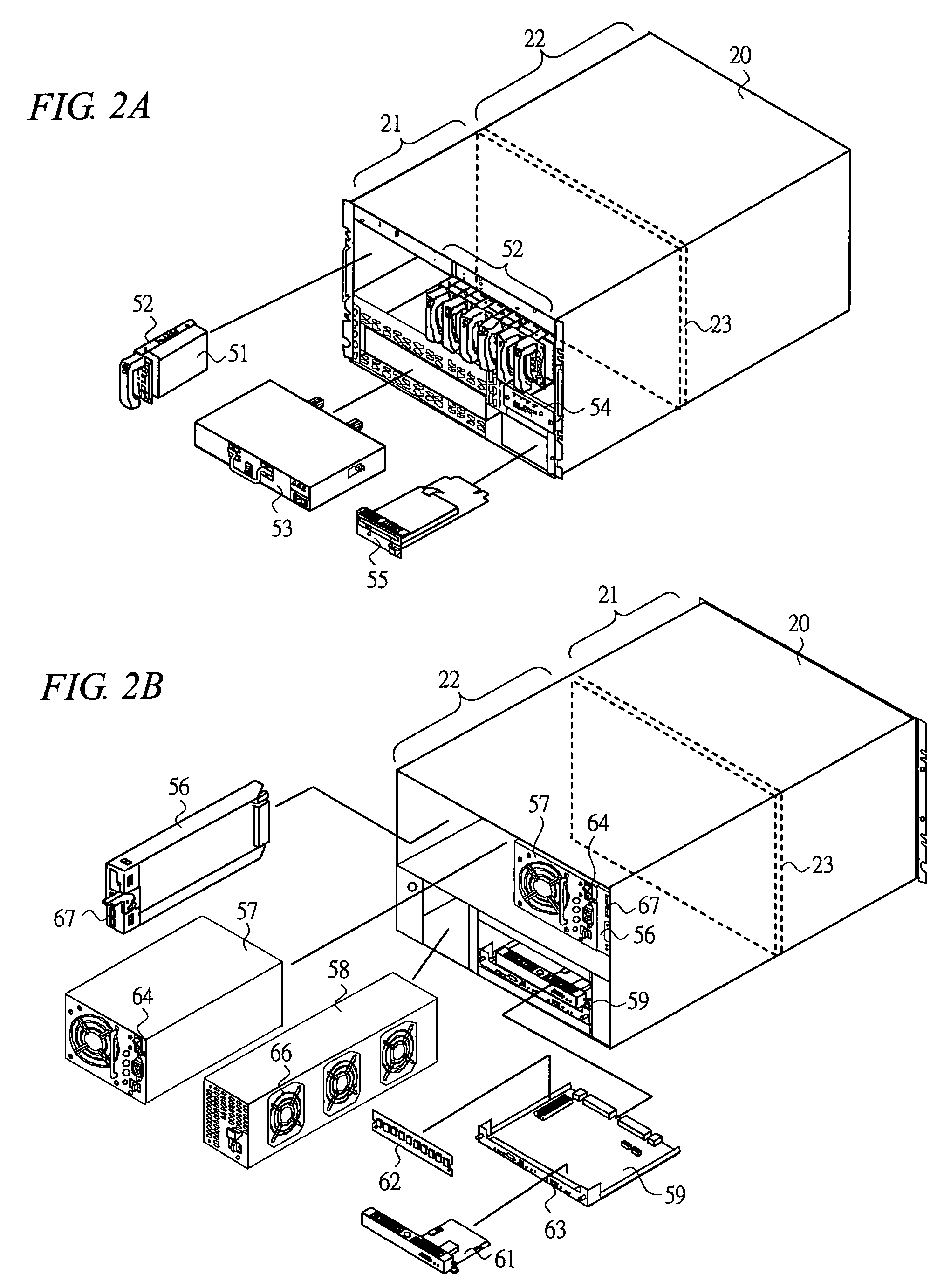
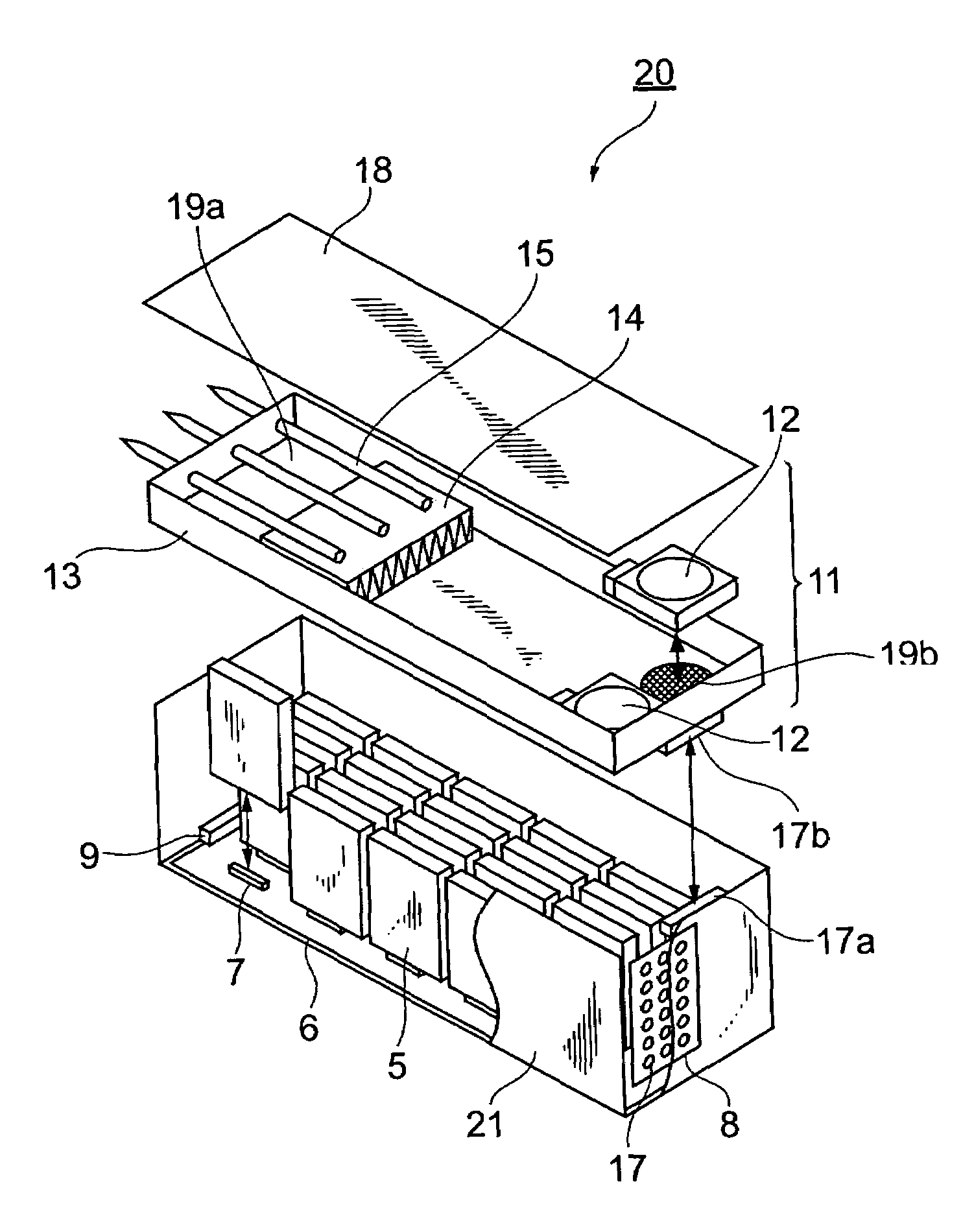
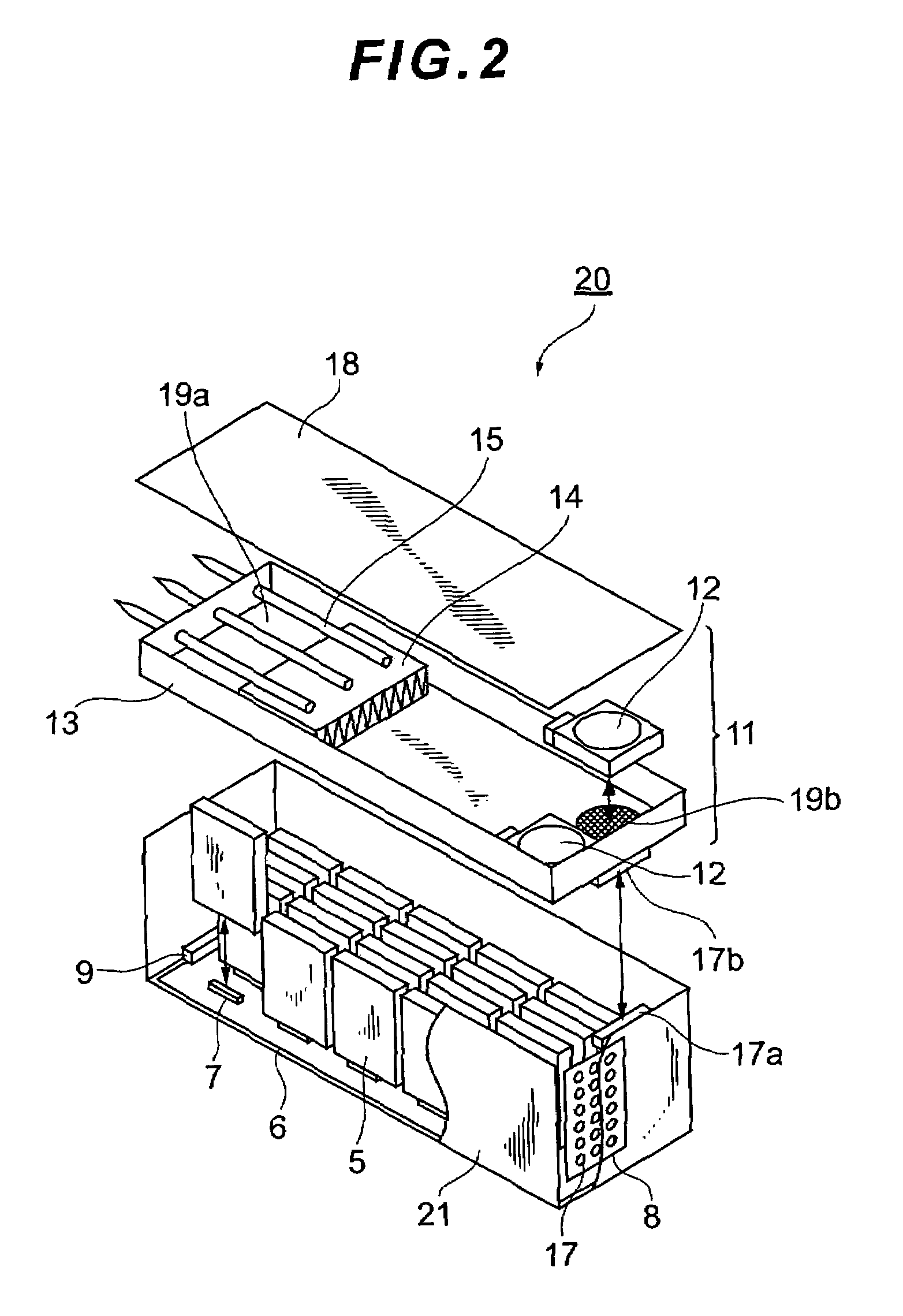
Disk array apparatus
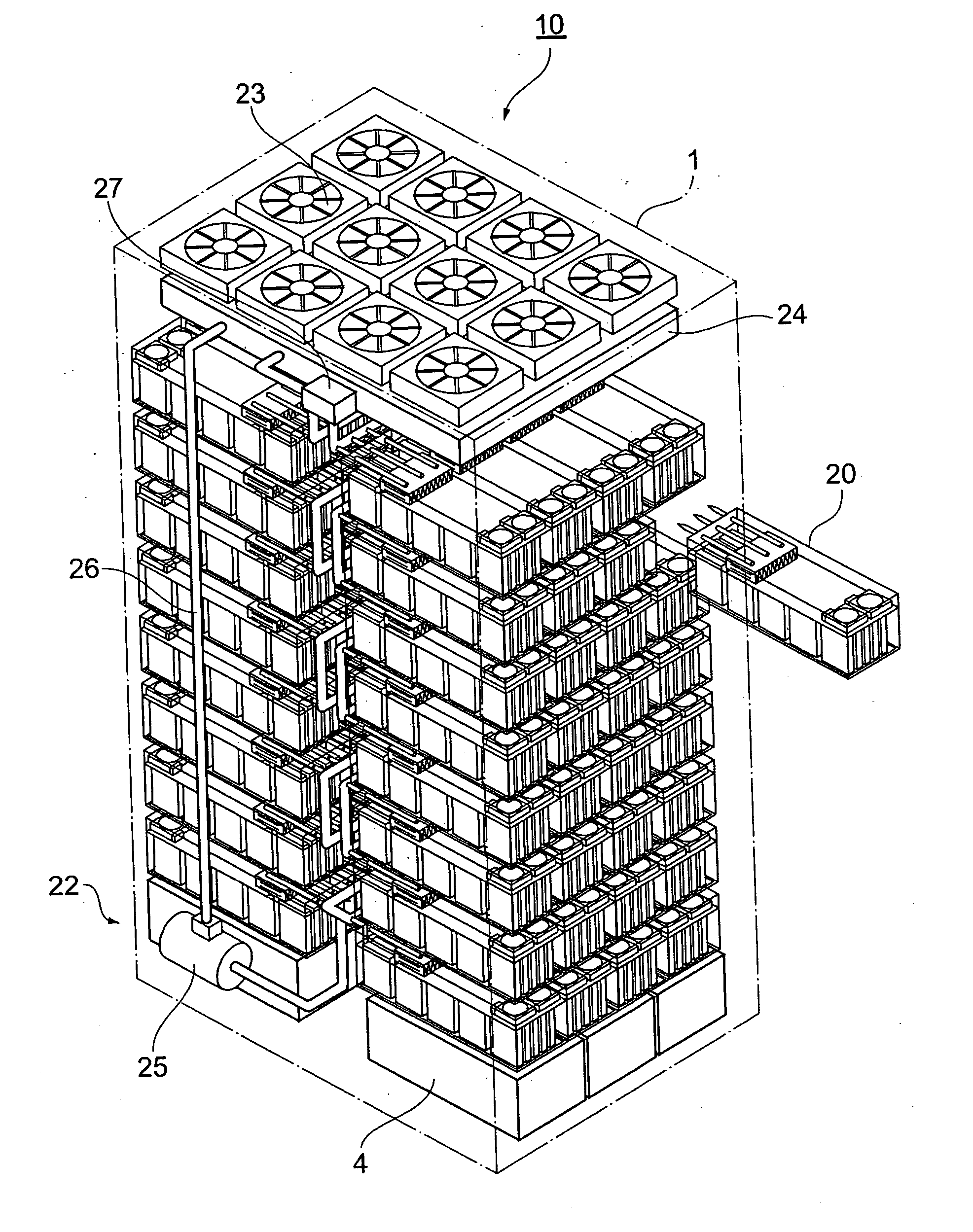
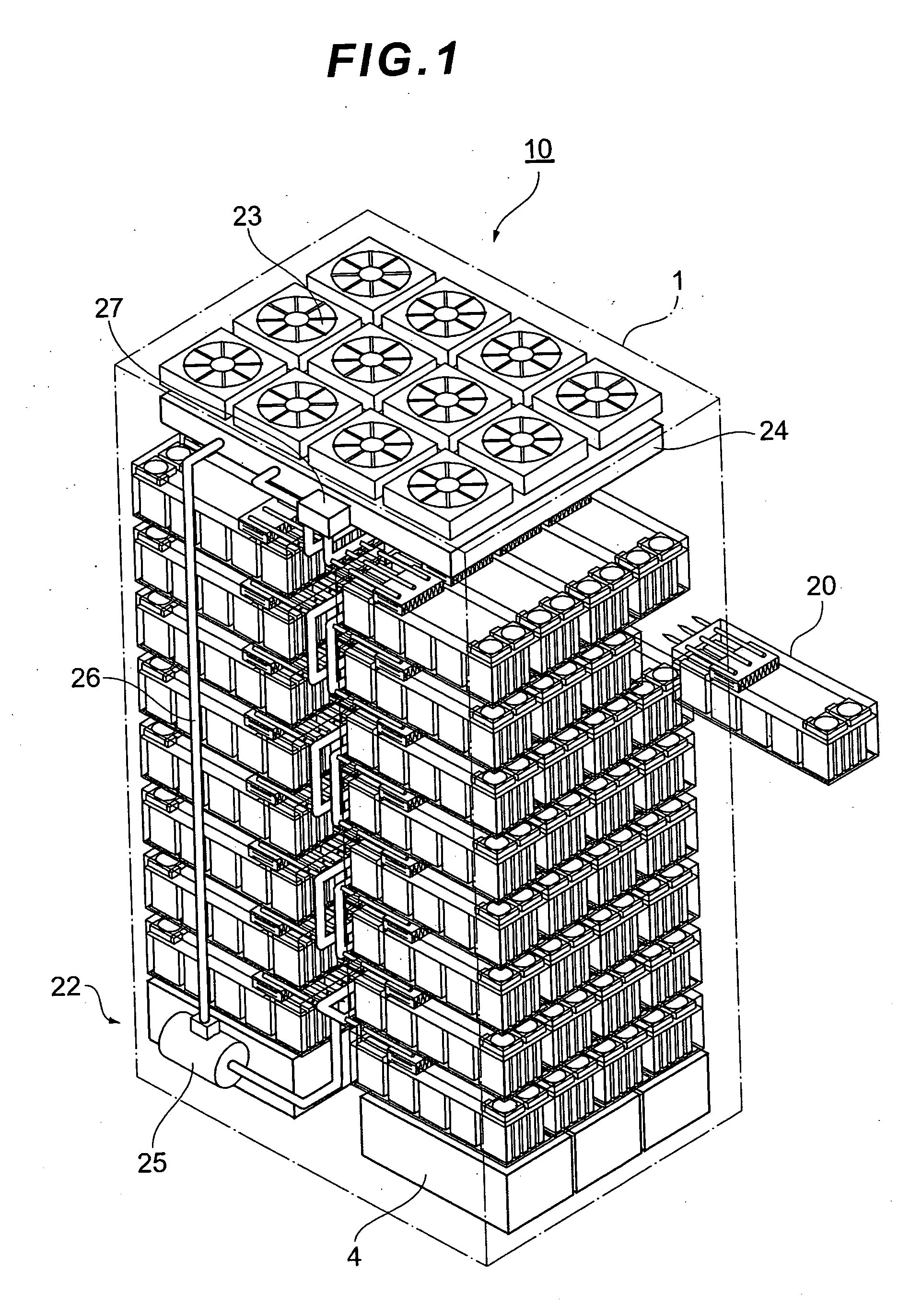
InactiveUS20070053154A1Improve cooling effectEasy to controlReducing temperature influence on carrierCarrier constructional parts dispositionDisk enclosureDisk array
A disk array apparatus including a rack-shaped basic frame, and a plurality of disk boxes that can be inserted into and pulled out of the basic frame depth-wise. Each disk box has: disk drive connectors for connecting a plurality of disk drives arranged in a matrix on a platter substrate, which is the bottom face of the disk box, roughly parallel to the depth direction of the basic frame; and a cooling module for cooling the disk drives. The disk box is a hermetically sealed structure.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Storage subsystem that connects fiber channel and supports online backup
InactiveUS6851020B2Without degrading online processing performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionFiberStorage area network
A disk array connected to a storage area network via a fiber channel has one or more ports each controlled by a processor. Even the disk array with one port and one processor executes online processing and backup processing at the same time while considering an online processing load. A port controller not only accepts a request from a host computer but issues a request to other storage controllers to allow online processing and backup processing to be executed at the same time. In addition, the disk array, if provided with a plurality of ports, selects ports or schedules processing depending upon the load to prevent backup processing from affecting online processing performance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Disk array system and a method of avoiding failure of the disk array system
ActiveUS20050114728A1Avoid failureReduce the likelihood of occurrenceInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionRAIDDisk array
The invention is intended to reduce disk access during data transfer from a disk in which occurrence of failure is anticipated to a spare disk as much as possible so that occurrence of double-failure is prevented in advance. When occurrence of failure in a disk which configures a RAID group, contents stored in the disk is copied to the spared disk. Simultaneously, another RAID group is paired with the above described RAID group and a secondary volume is provided therein. A write request is directed to the secondary volume. A differential bitmap controls a update data. Data which is not updated is read out from the primary volume, and data which is already updated is read from the secondary volume. When data transfer is completed, contents stored in the secondary volume are copied to the primary volume.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Storage system
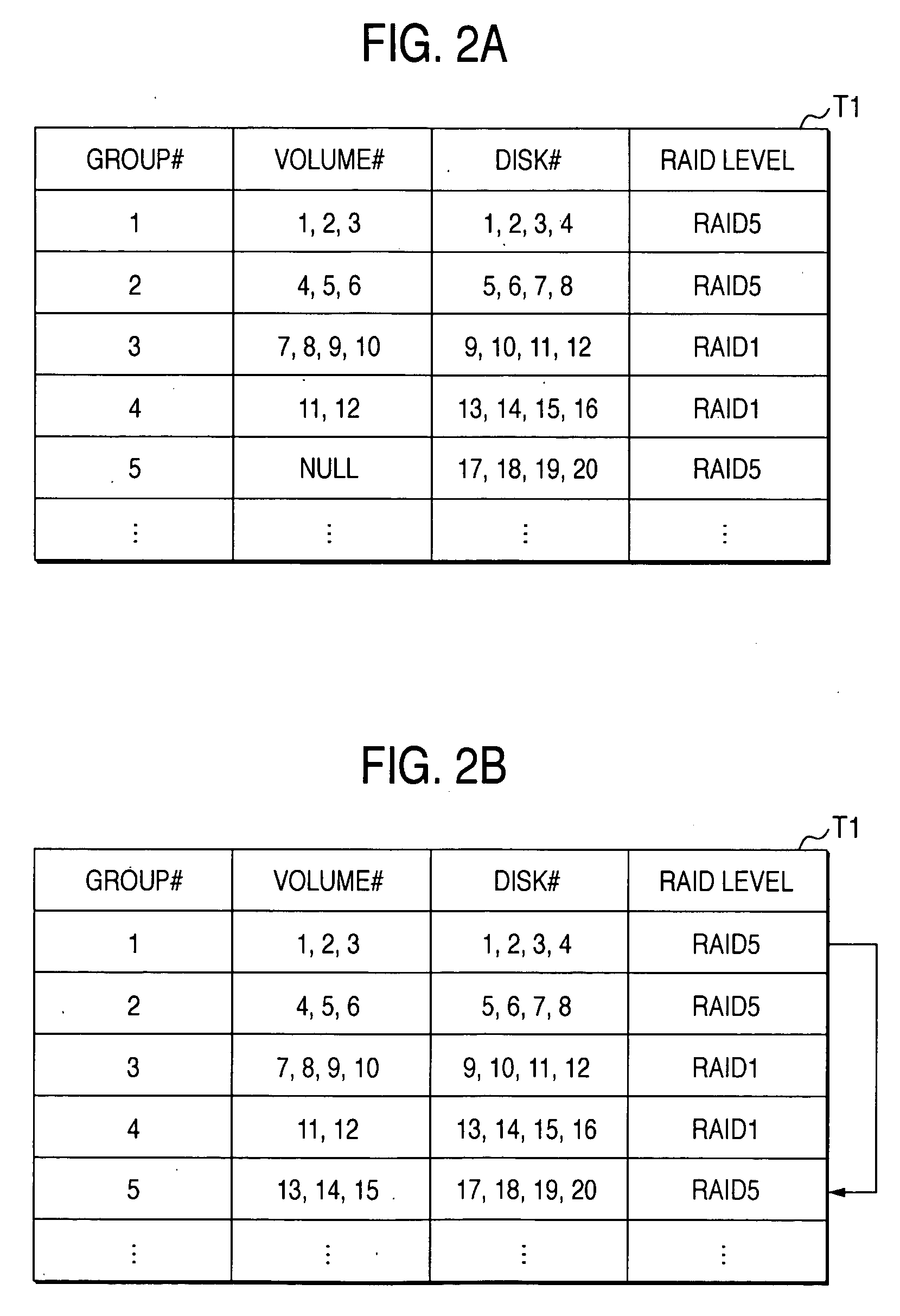
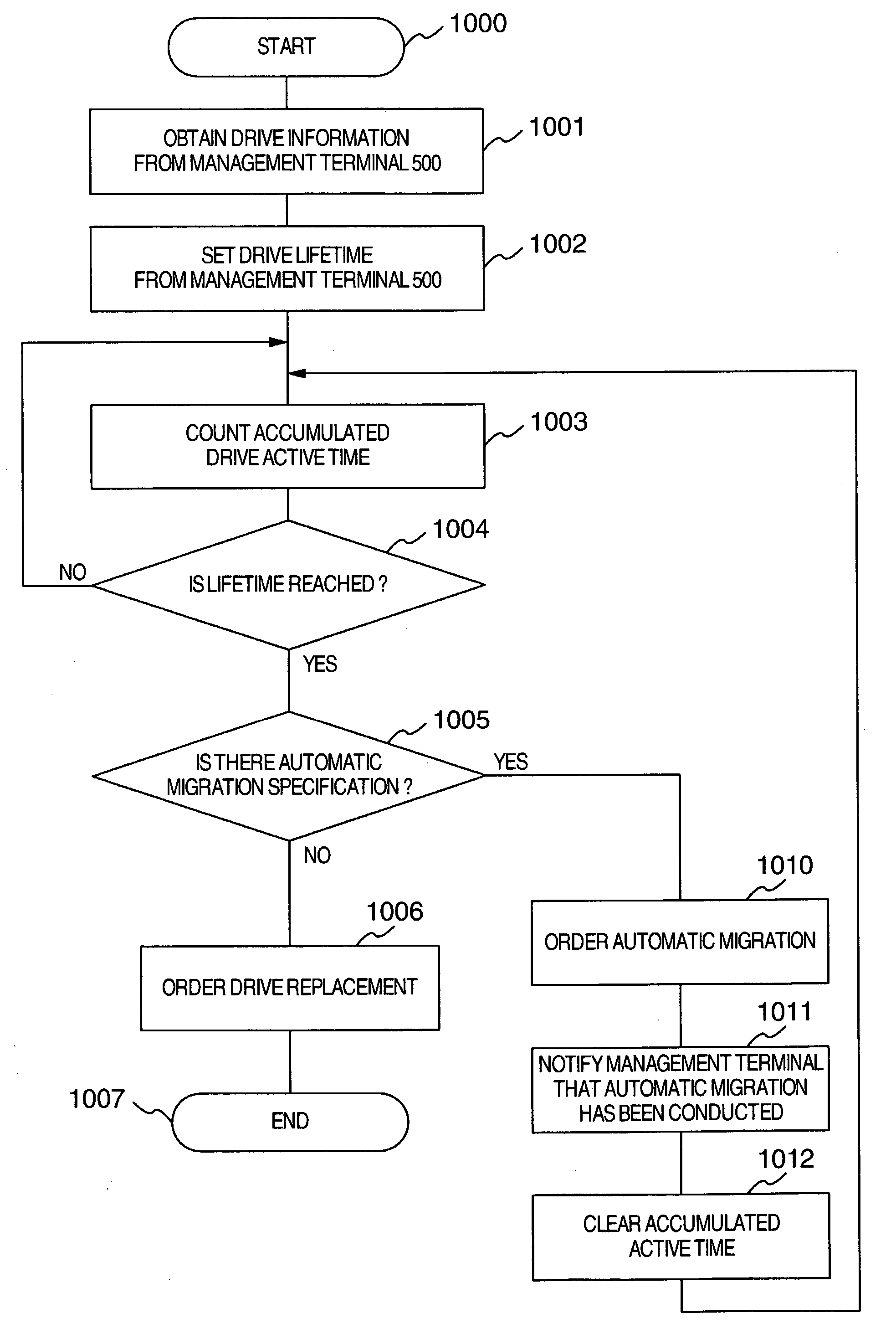
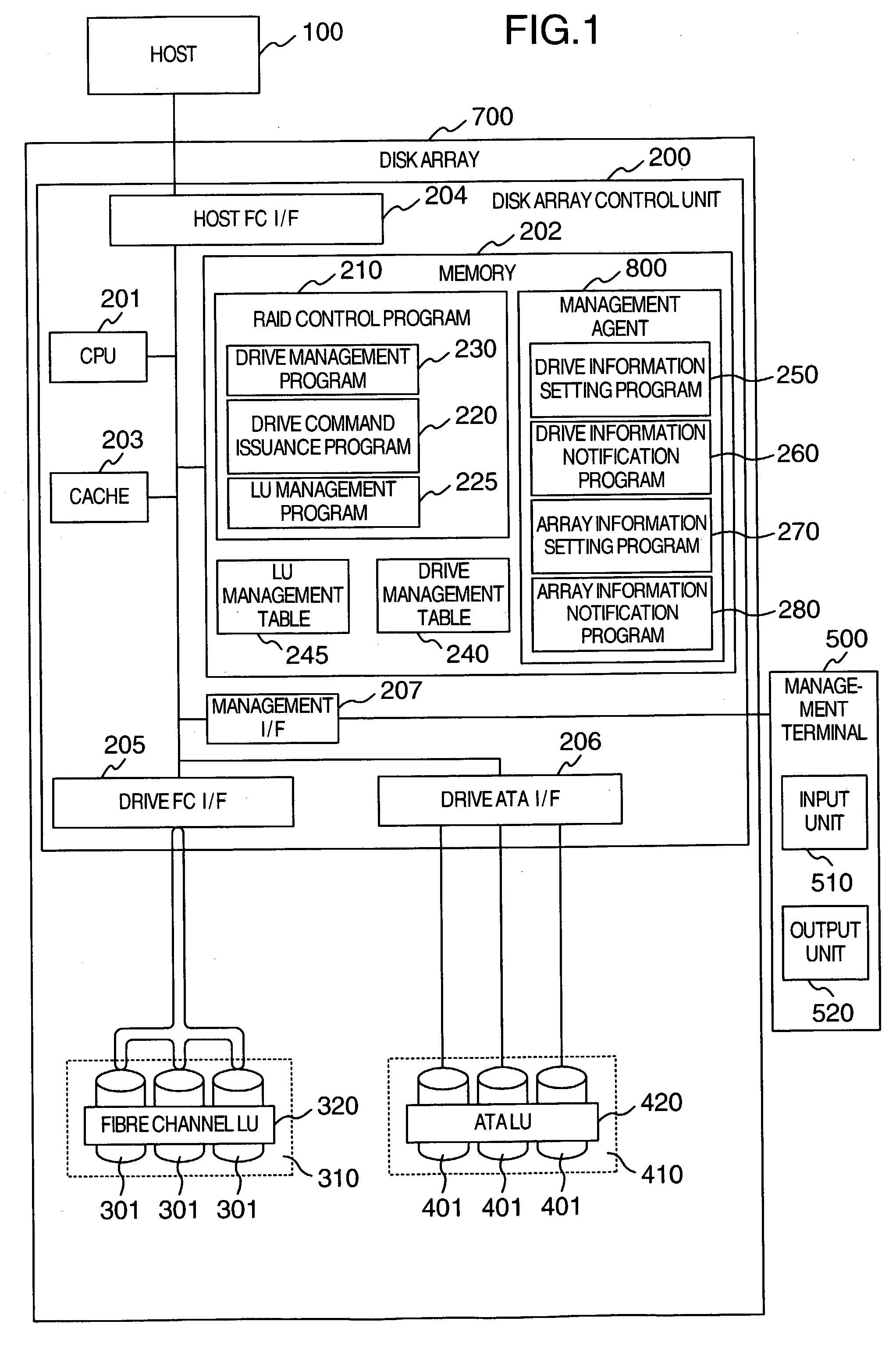
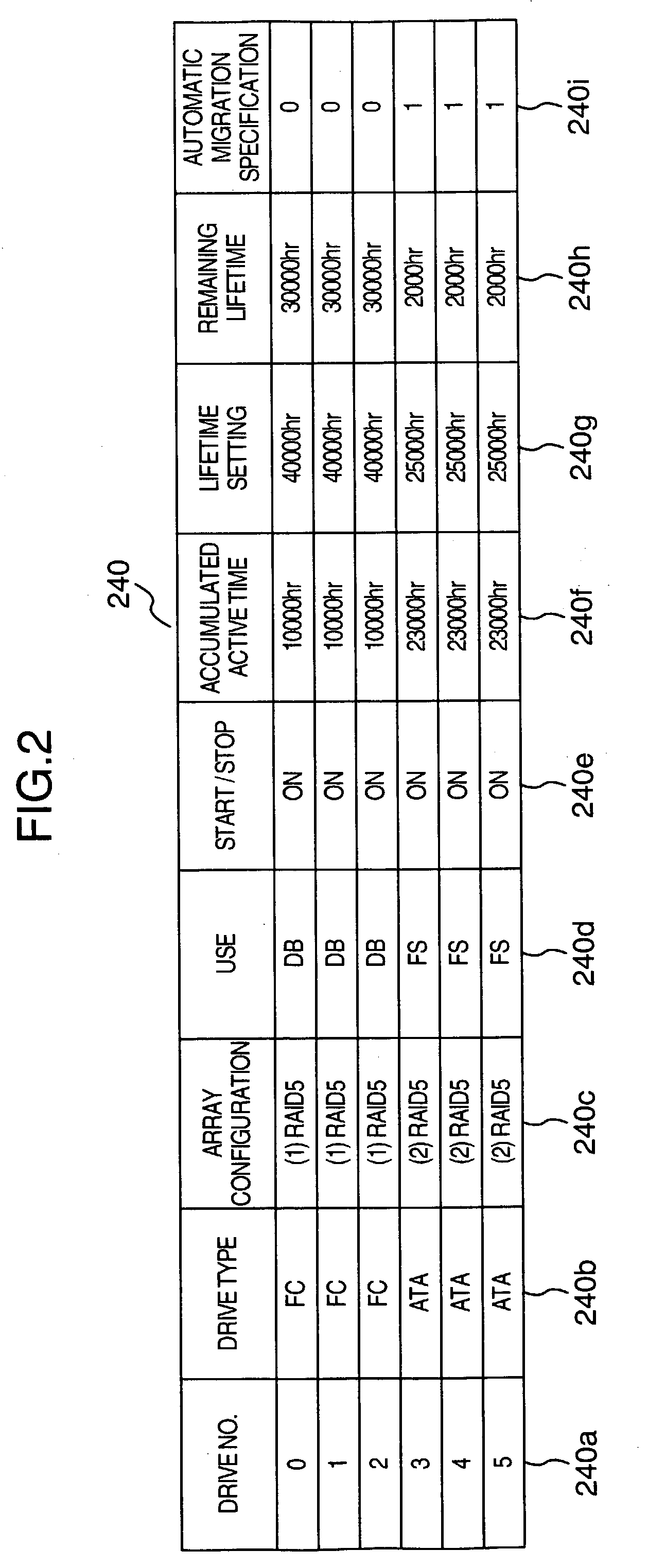
A disk array includes a drive management unit, which is a program for identifying types of disk devices and managing different disk devices separately, and a drive management table for storing information to be utilized by the drive management unit. The disk array further includes a program for managing accumulated time of disk devices. The program includes a drive lifetime setting portion for setting lifetimes of drives, a drive start / stop portion for intentionally starting / stopping ATA disk devices, and an operation time measurement portion for measuring accumulated operation time. Since it is necessary to be conscious of difference in reliability and performance among disk devices when forming a RAID, a drive type notification unit, which is a program for notifying of the type of a disk device when forming the RAID, is provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
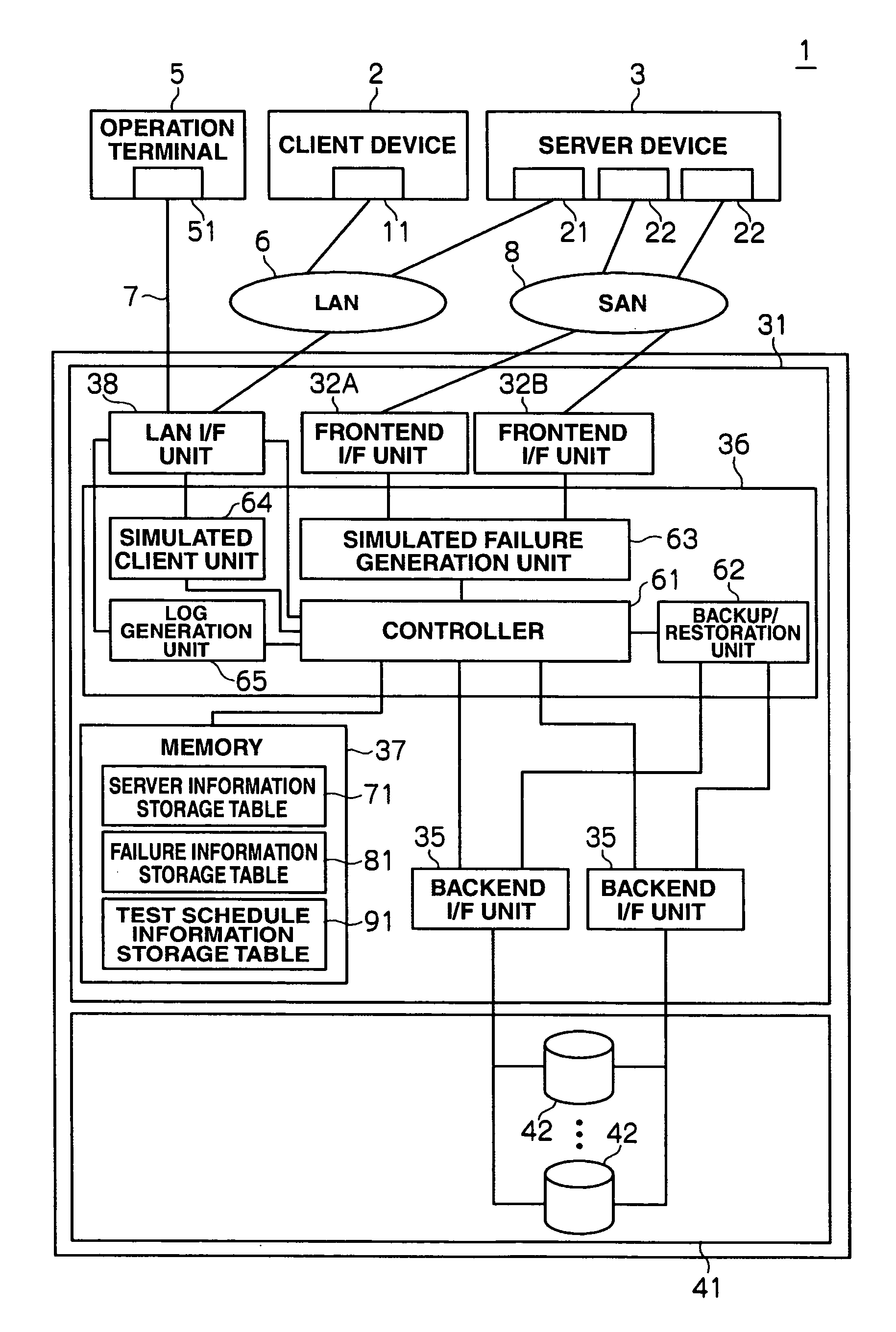
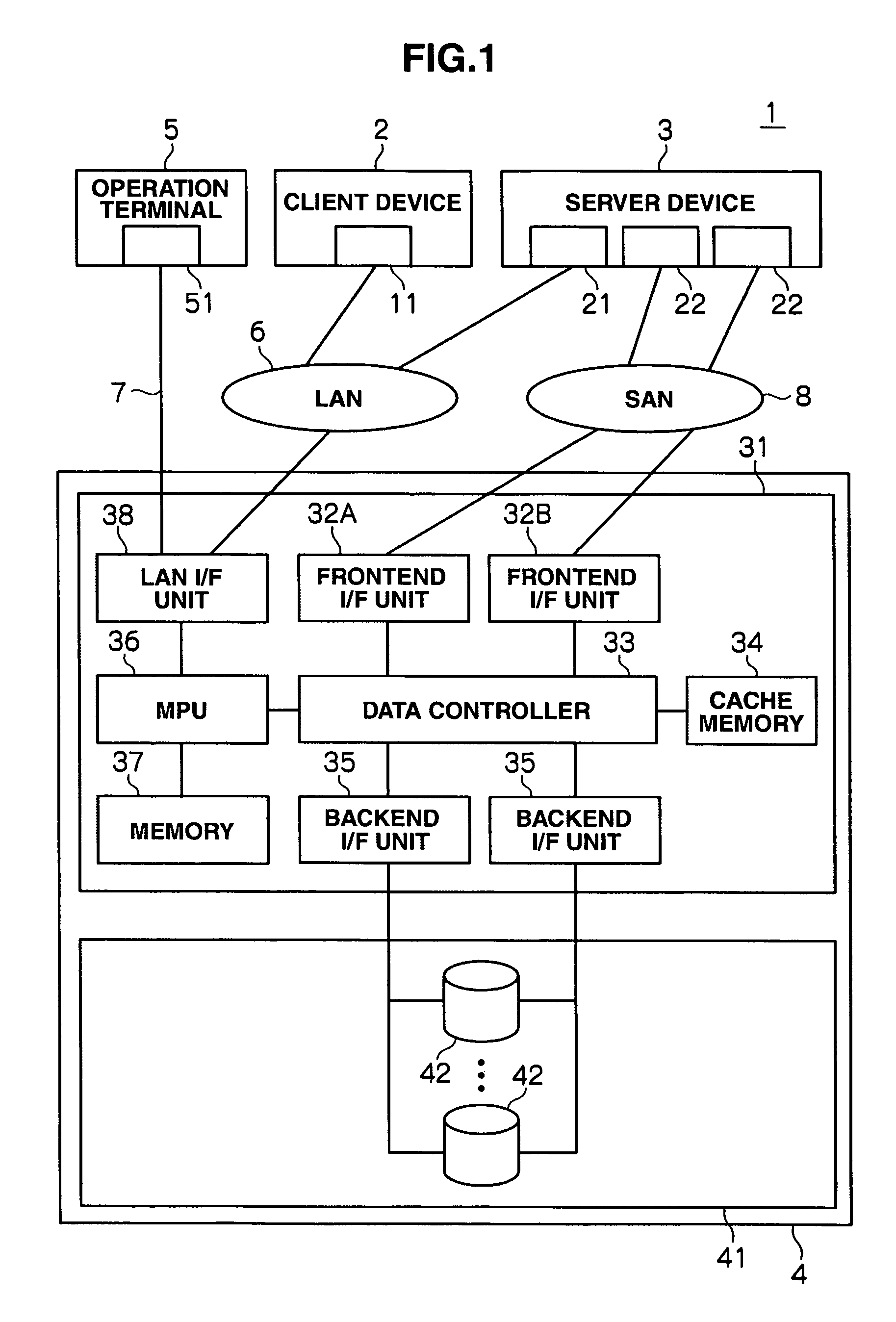
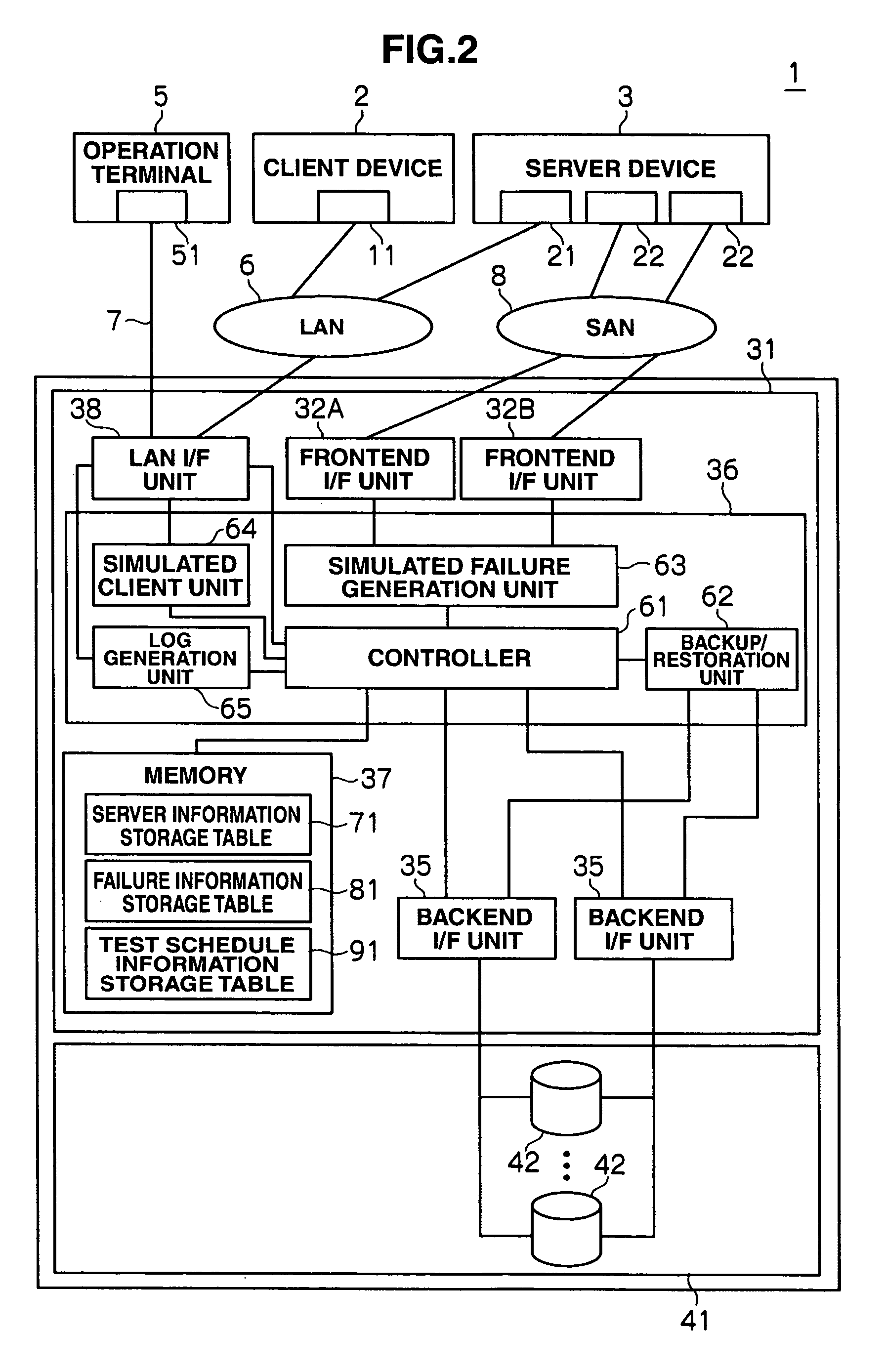
Disk array device and failure response verification method thereof
This disk array device having at least one volume that reads and writes data based on an access request transmitted from a client device via a server device, includes: a failure generation unit for generating a simulated failure in one's own device; an access request transmission unit for transmitting the access request transmitted from the client device to the server device; and a verification unit for verifying the setting of the server device regarding the response to the failure based on the response of the server to the access request transmitted from the access request transmission unit in a state of where the failure is being generated with the failure generation unit.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Disk array apparatus and disk array apparatus control method
InactiveUS7017003B2Reduce storage capacityPromote recoveryInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionRenewal timeDisk array
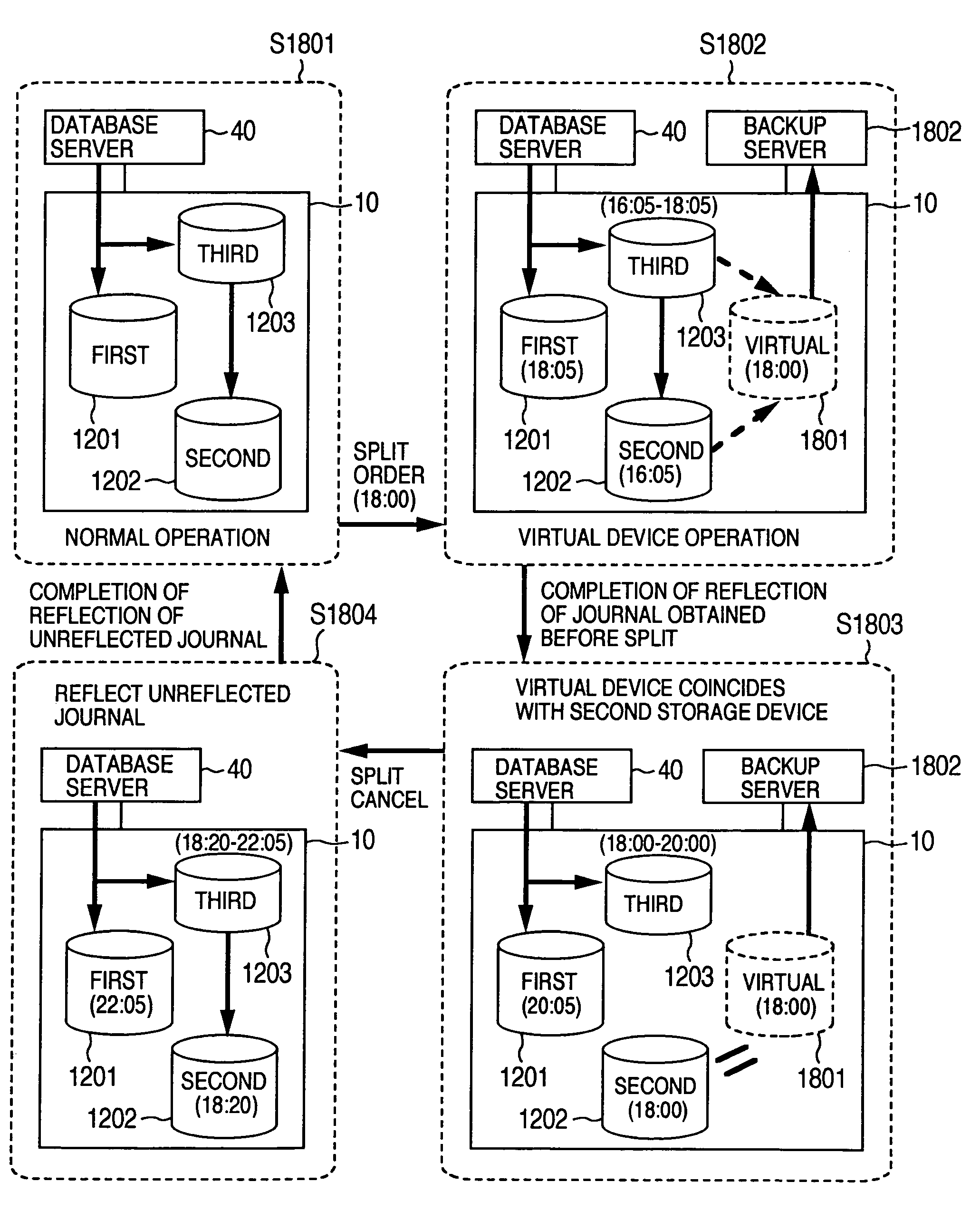
A journal write unit writes journal data into a third storage device. The journal data includes an identifier of a logical volume in a first storage device into which data has been written, information of a location in which the data is stored in the logical volume, update time which is current time acquired from a timing mechanism, and the data. A second write unit refers to update time of the journal data stored in the third storage device, selects journal data for which a difference between current time acquired from the timing mechanism and the update time is longer than a detection time stored in the third storage device, and writes the data into a place indicated by the location information, in a logical volume in the second storage device in the order of update time in the selected journal data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
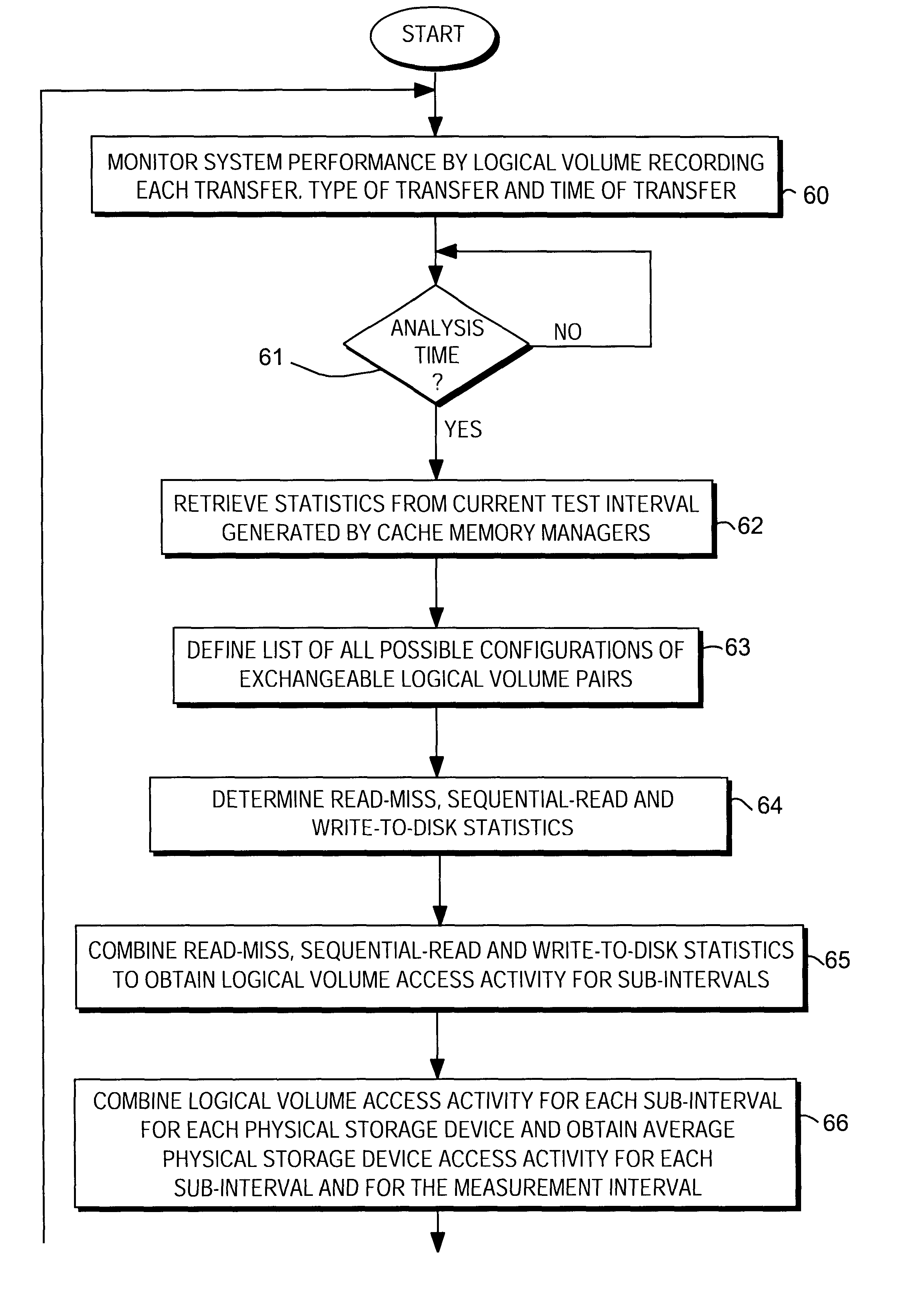
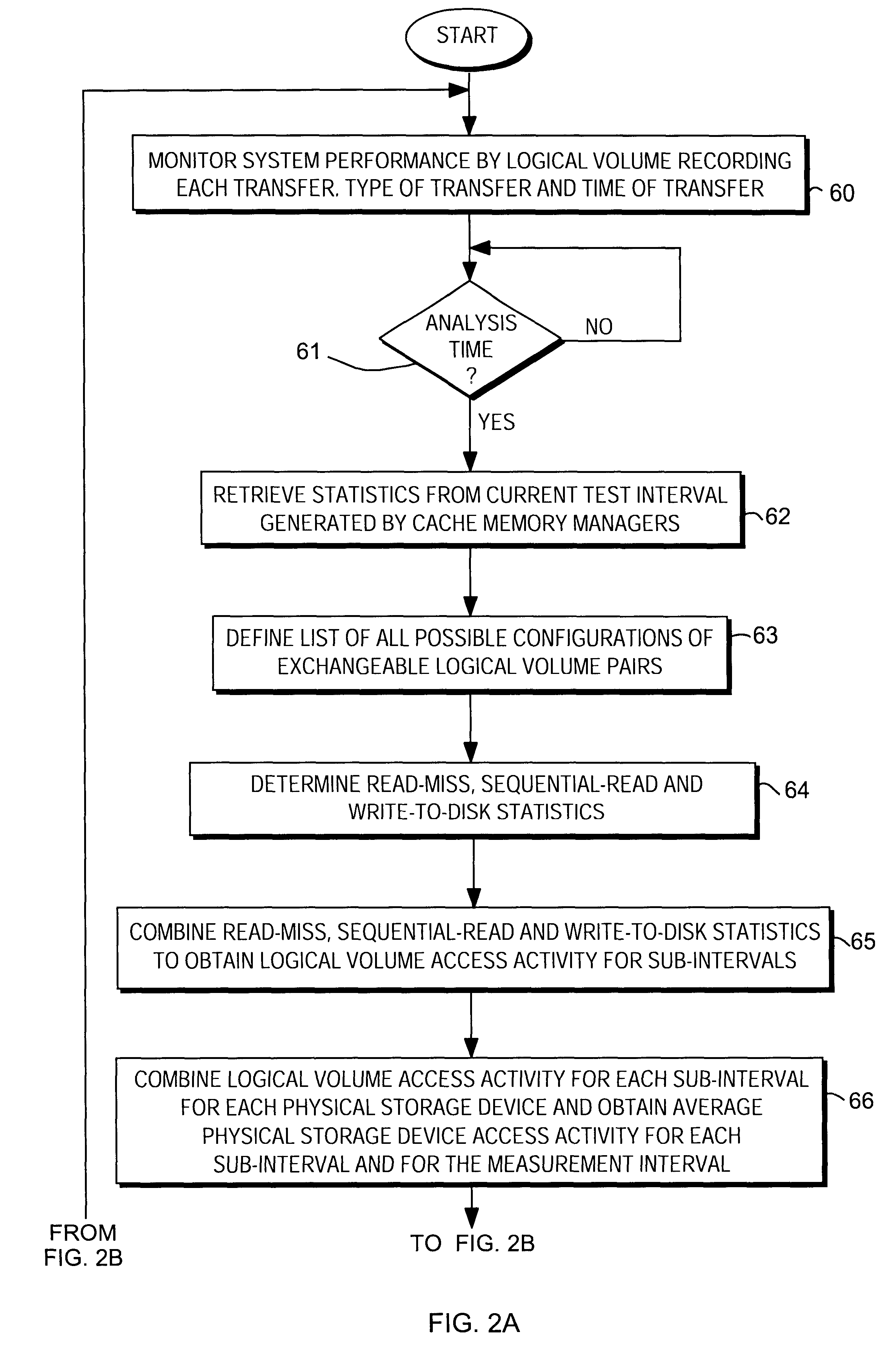
Load balancing on disk array storage device
InactiveUS6711649B1Reduce imbalanceGood for load balancingInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionStatistical analysisDisk array
Load balancing of activities on physical disk storage devices is accomplished by monitoring reading and writing operations to blocks of contiguous storage locations on the physical disk storage devices. A list of exchangeable pairs of blocks is developed based on size and function. Statistics accumulated over an interval are then used to obtain access activity values for each block and each physical disk drive. A statistical analysis leads to a selection of one block pair. After testing to determine any adverse effect of making that change, the exchange is made to more evenly distribute the loading on individual physical disk storage devices.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method for backing up a disk array system
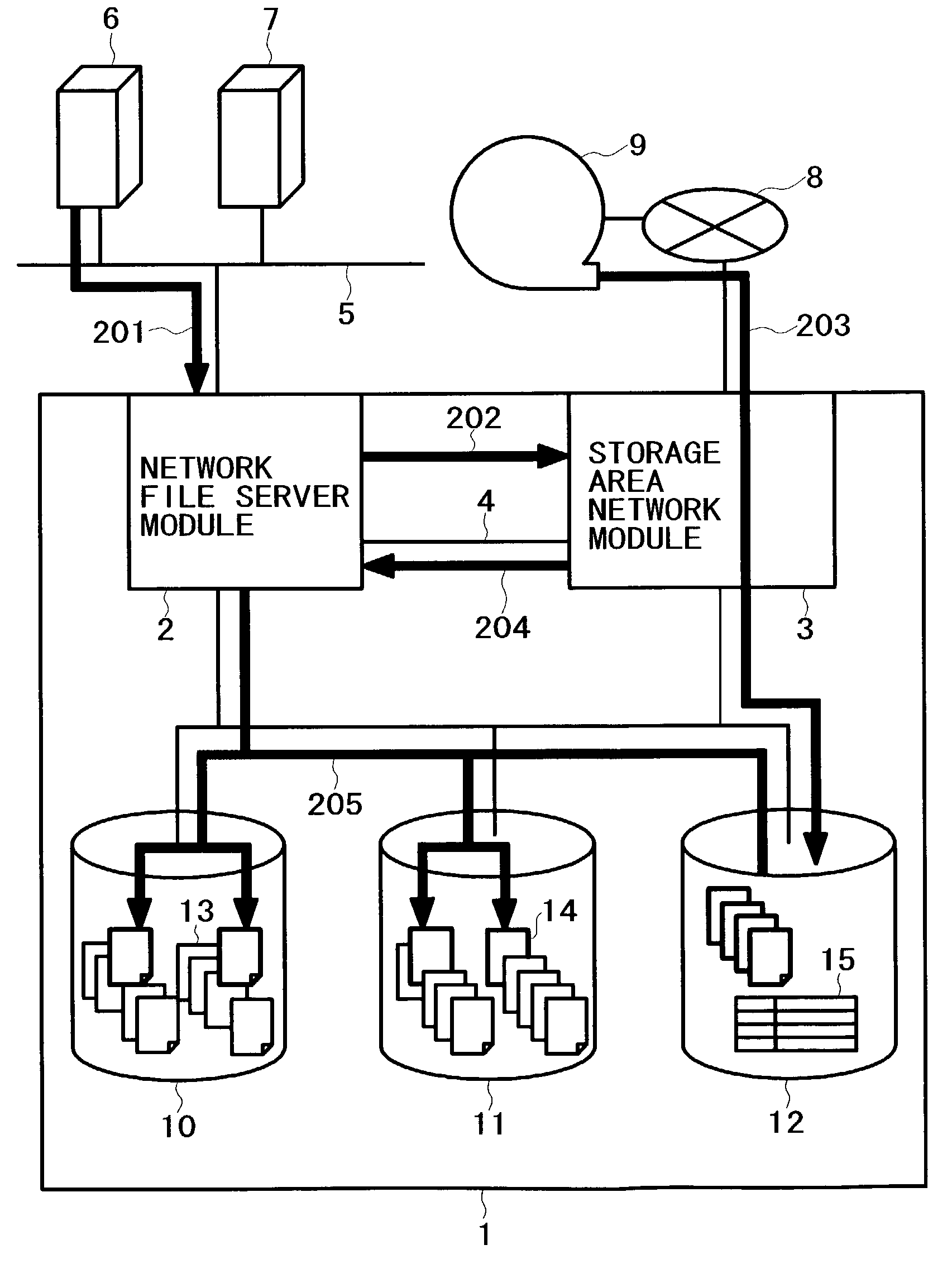
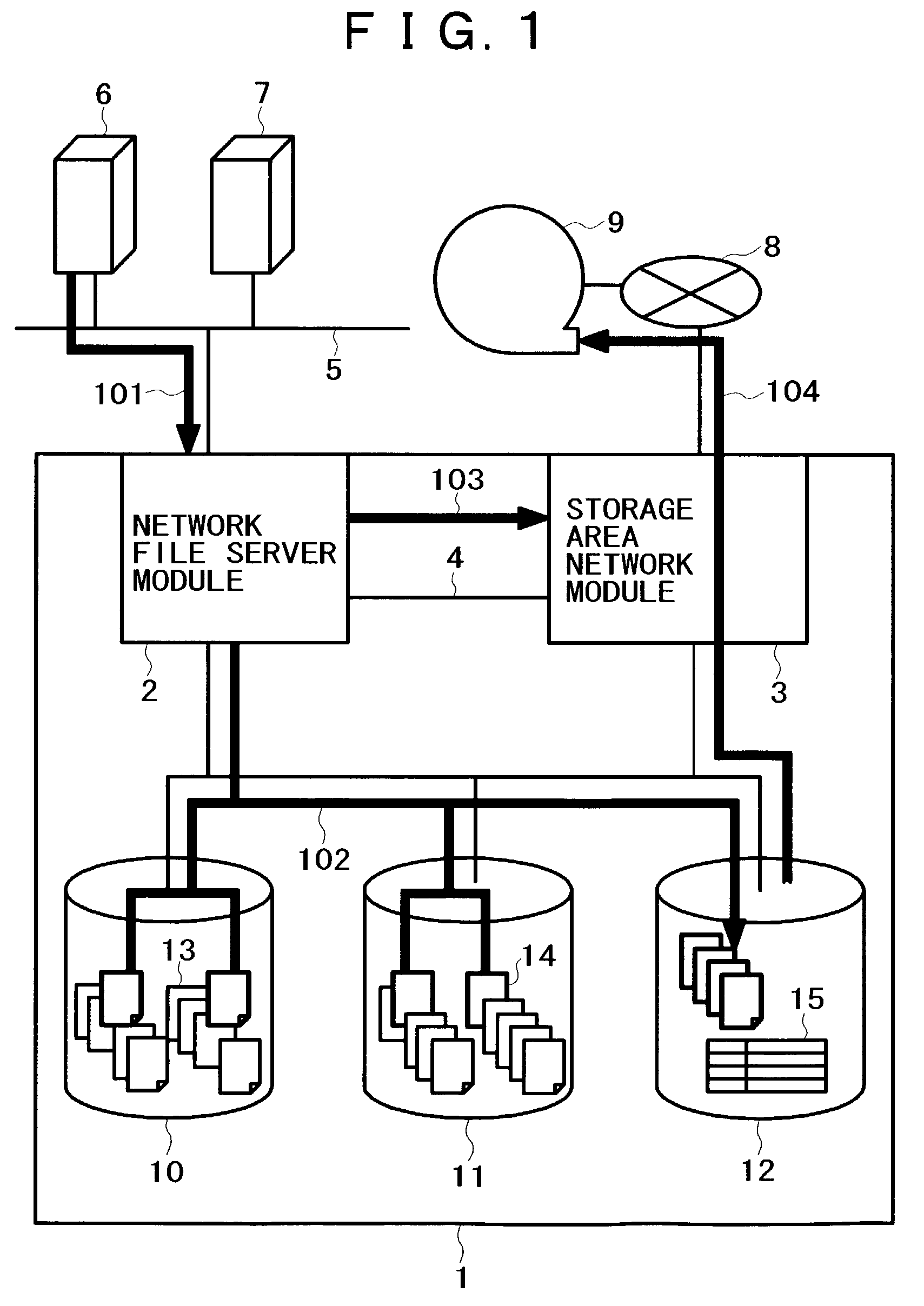
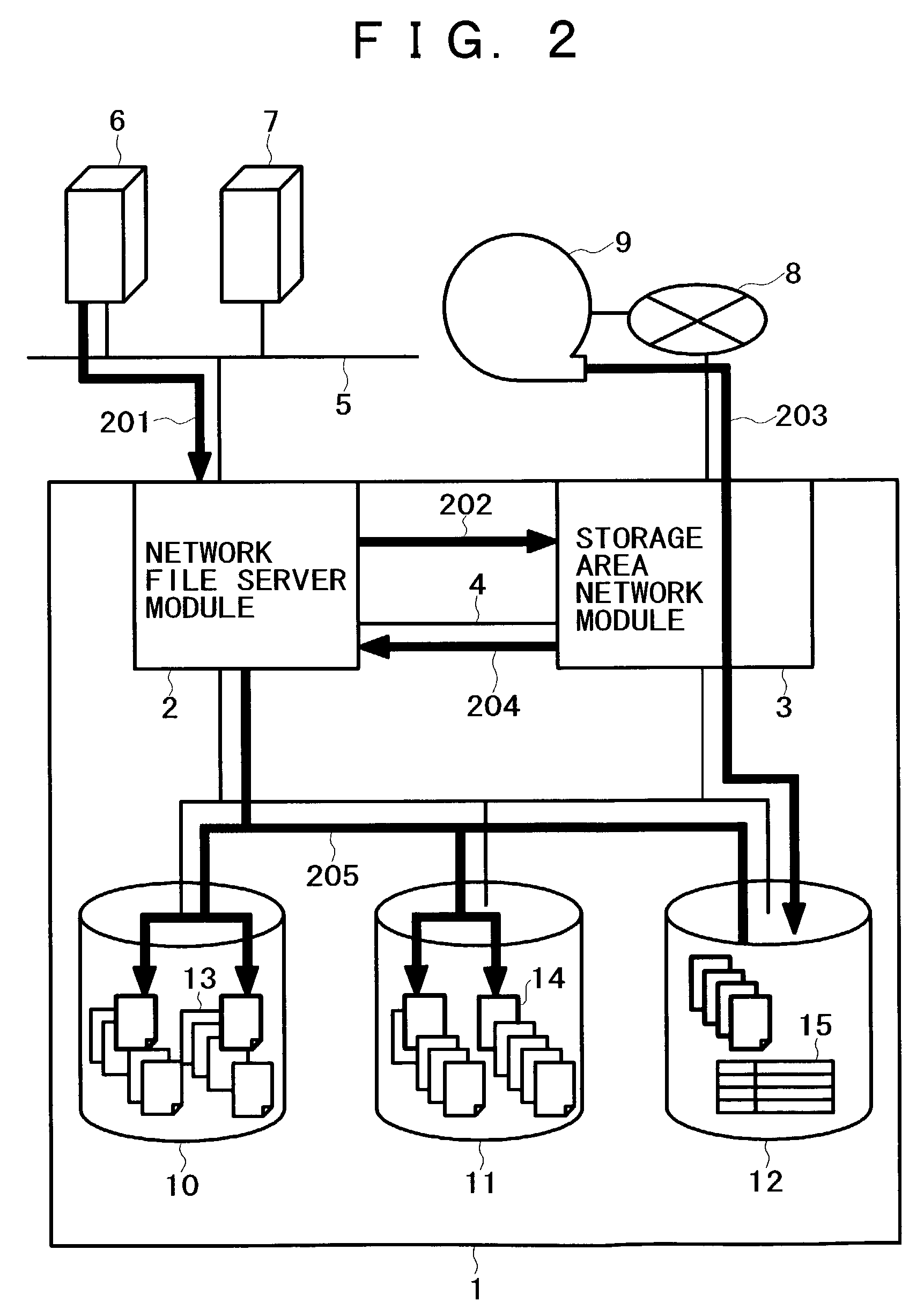
InactiveUS7099901B2Simple processIncrease loadData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersFile replicationExternal storage
A method for backing up the data of a disk array system having network file server and storage area network functions easily and rapidly without using a route for data to be not backed up. Upon receipt of a backup request, a network file server module copies files on the disk array system's regular volumes to a backup volume. The network file server module then requests a storage area network module to copy the files to an external storage device. Finally, the storage area network module copies the current contents of the backup volume to the external storage device. The network file server module can limit the data to be backed up, thereby reducing the backup time requirements. The load on a LAN does not increase because the storage area network module acquires the data to be backed up. The processing speed increases thanks to backup load distribution within the disk array system.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
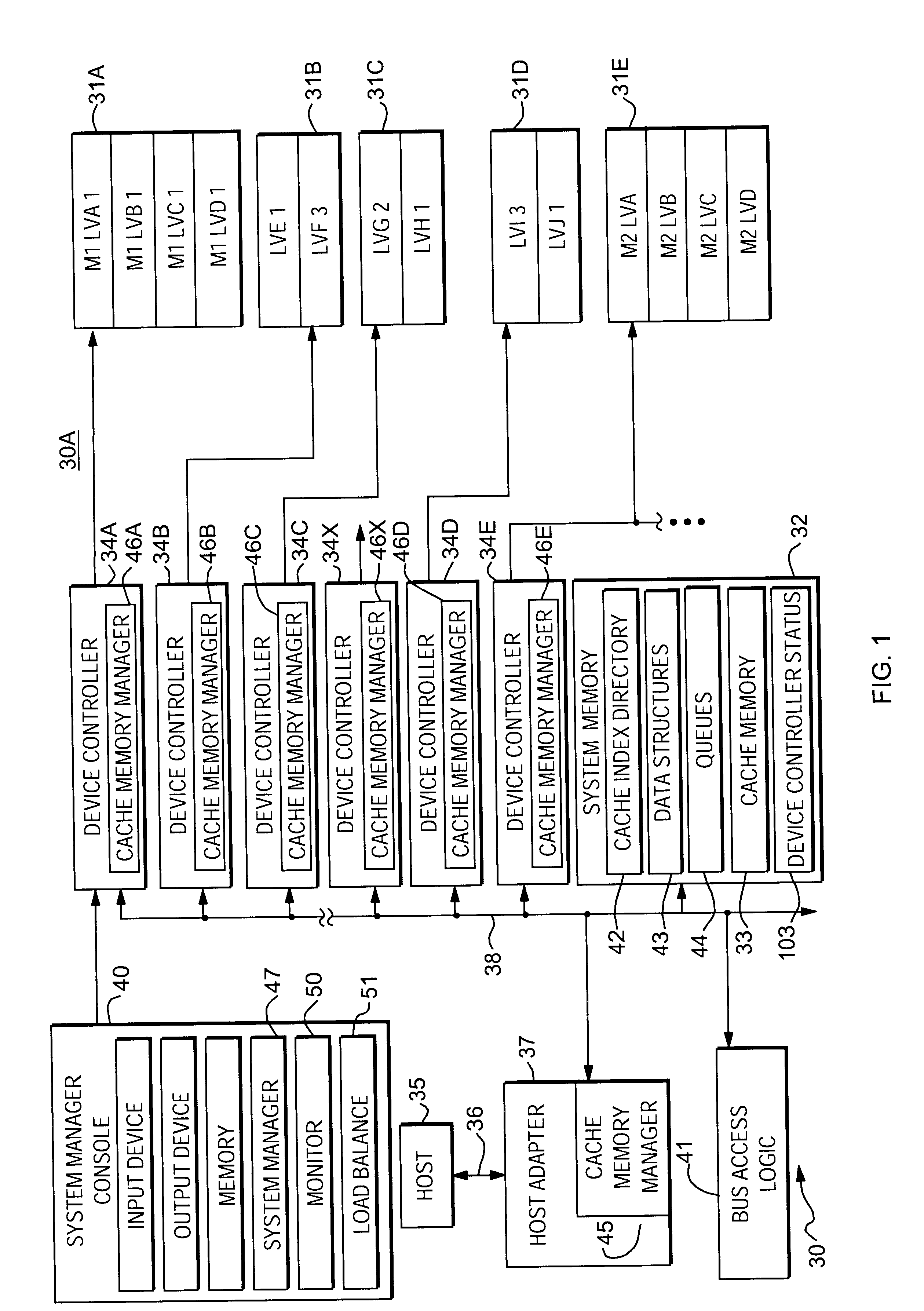
System and method for maintaining cache coherency without external controller intervention
InactiveUS7043610B2Efficiently detectsEfficiently resolveMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSegment descriptorControl store
A disk array includes a system and method for cache management and conflict detection. Incoming host commands are processed by a storage controller, which identifies a set of at least one cache segment descriptor (CSD) associated with the requested address range. Command conflict detection can be quickly performed by examining the state information of each CSD associated with the command. The use of CSDs therefore permits the present invention to rapidly and efficiently perform read and write commands and detect conflicts.
Owner:ADAPTEC
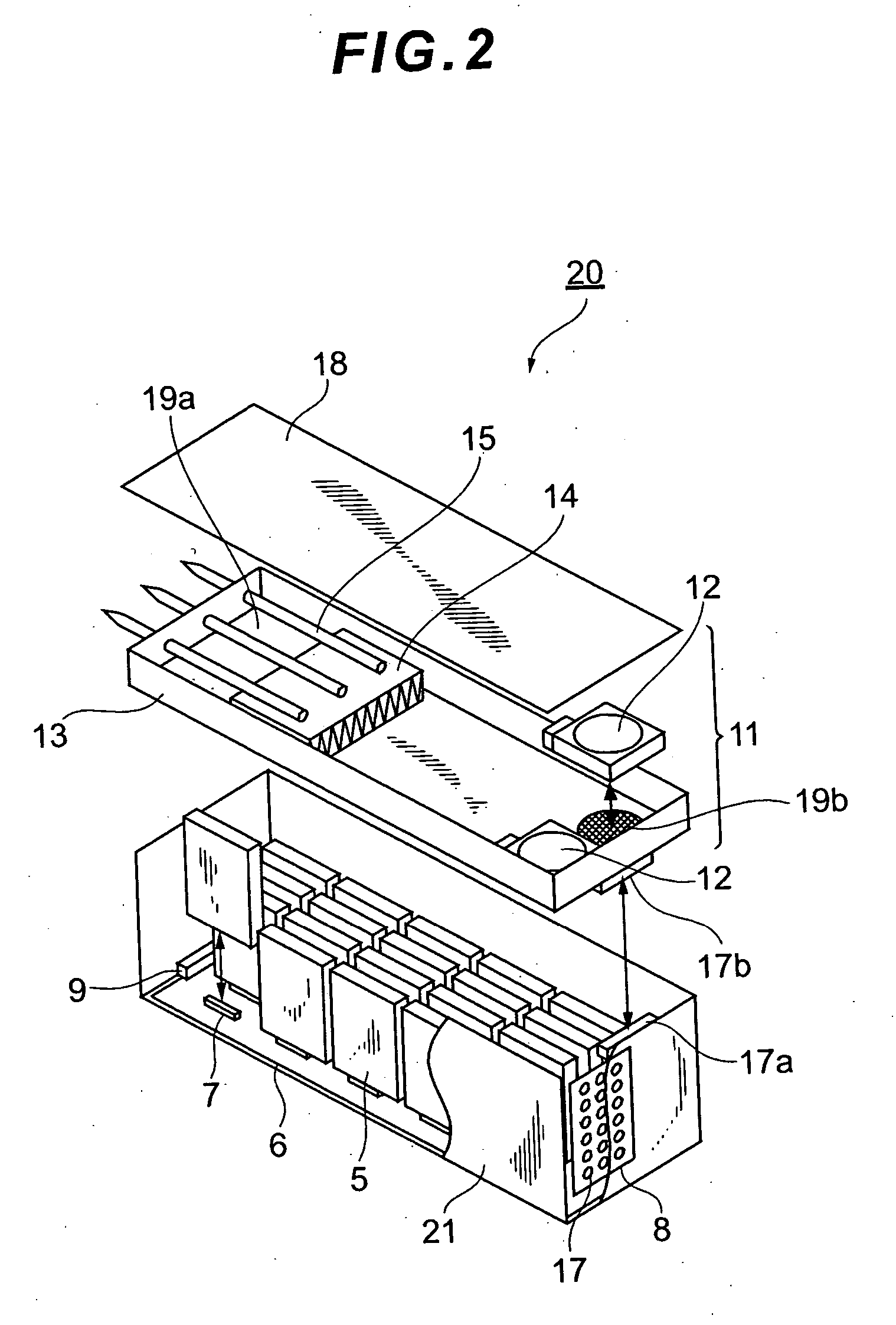
Disk array device
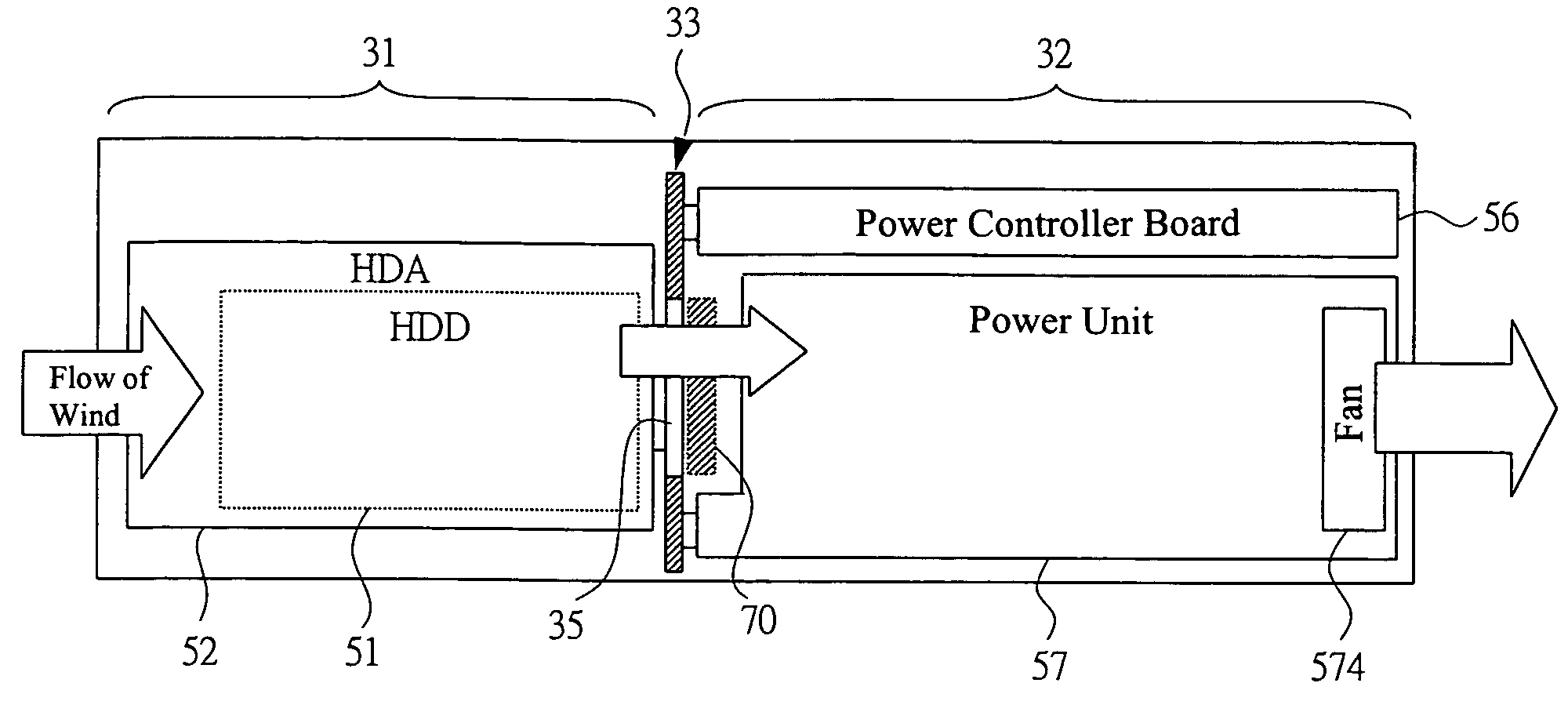
ActiveUS7139170B2Low efficiencyLow flow resistanceDigital data processing detailsAir heatersPower controllerEngineering
In a disk array device for cooling respective sections including a HDD by a fan, drop of cooling efficiency by the difference of conditions of HDD mounted and unmounted sections is prevented and the use of a dummy HDD is deleted / eliminated. A housing contains a HDA mounted on the HDD, a power controller board for performing control to the HDD, a power unit for supplying power to each section, a fan for cooling the housing therein, and a backboard for connecting all the sections. On one backboard surface, the HDA is mounted, which has a cooling function for making cooling air flowing in the housing and exhausting air from the housing via a region on which the HDA are mounted and via a vent hole on the backboard. For the vent hole, a shutter is mounted, which has a mechanism for adjusting an open area rate of the vent hole by opening when the HDA is mounted and closing when removed.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
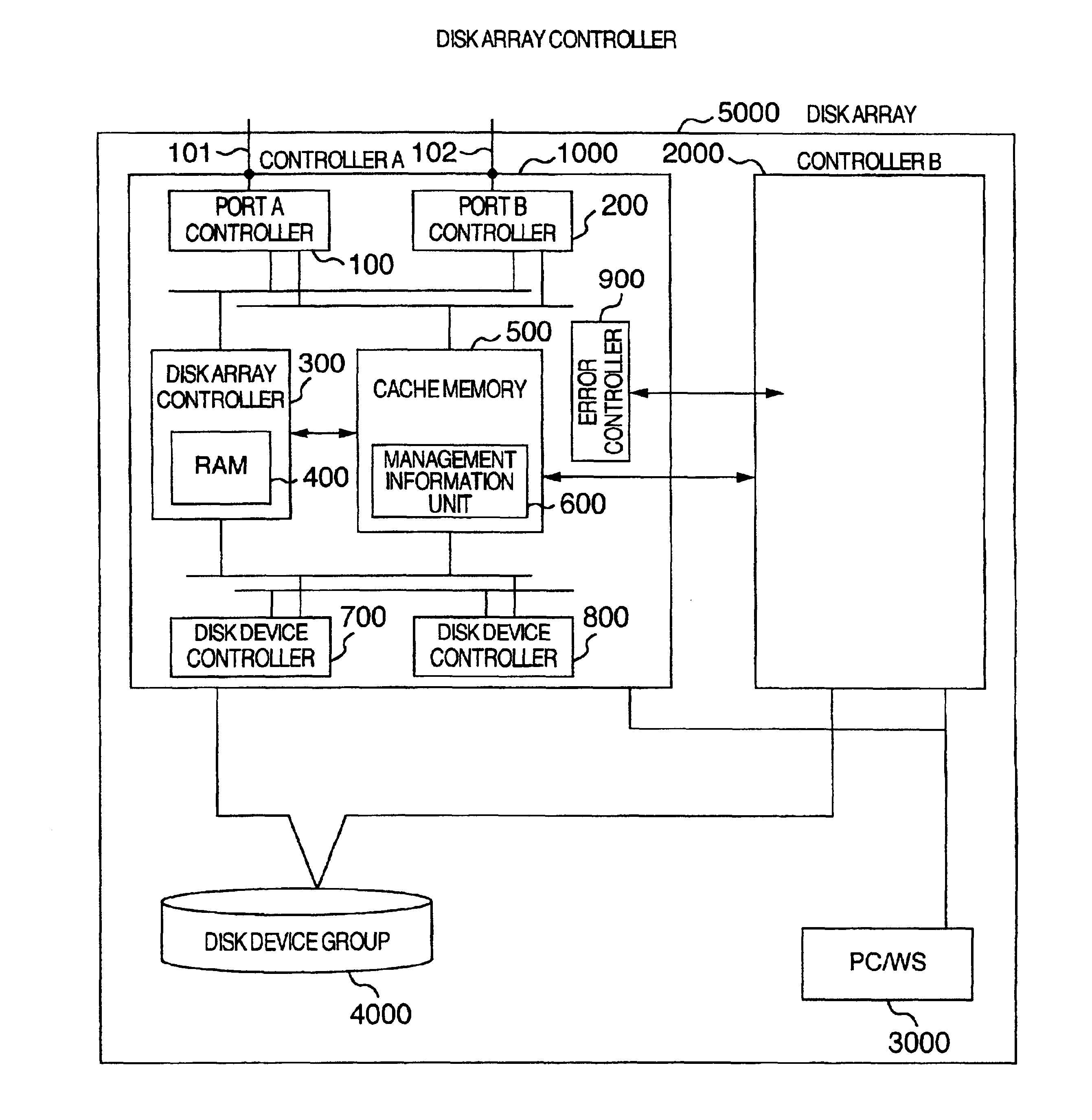
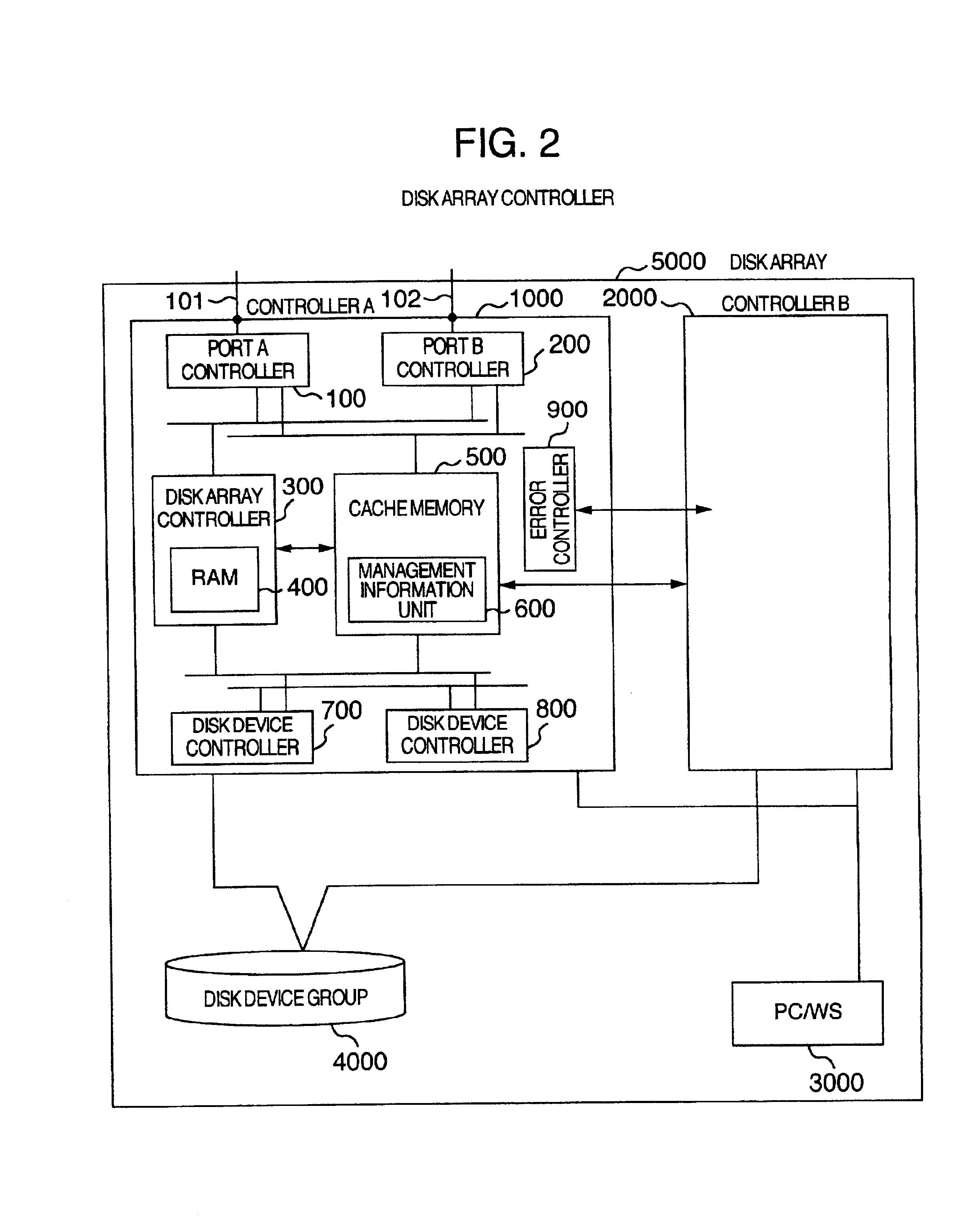
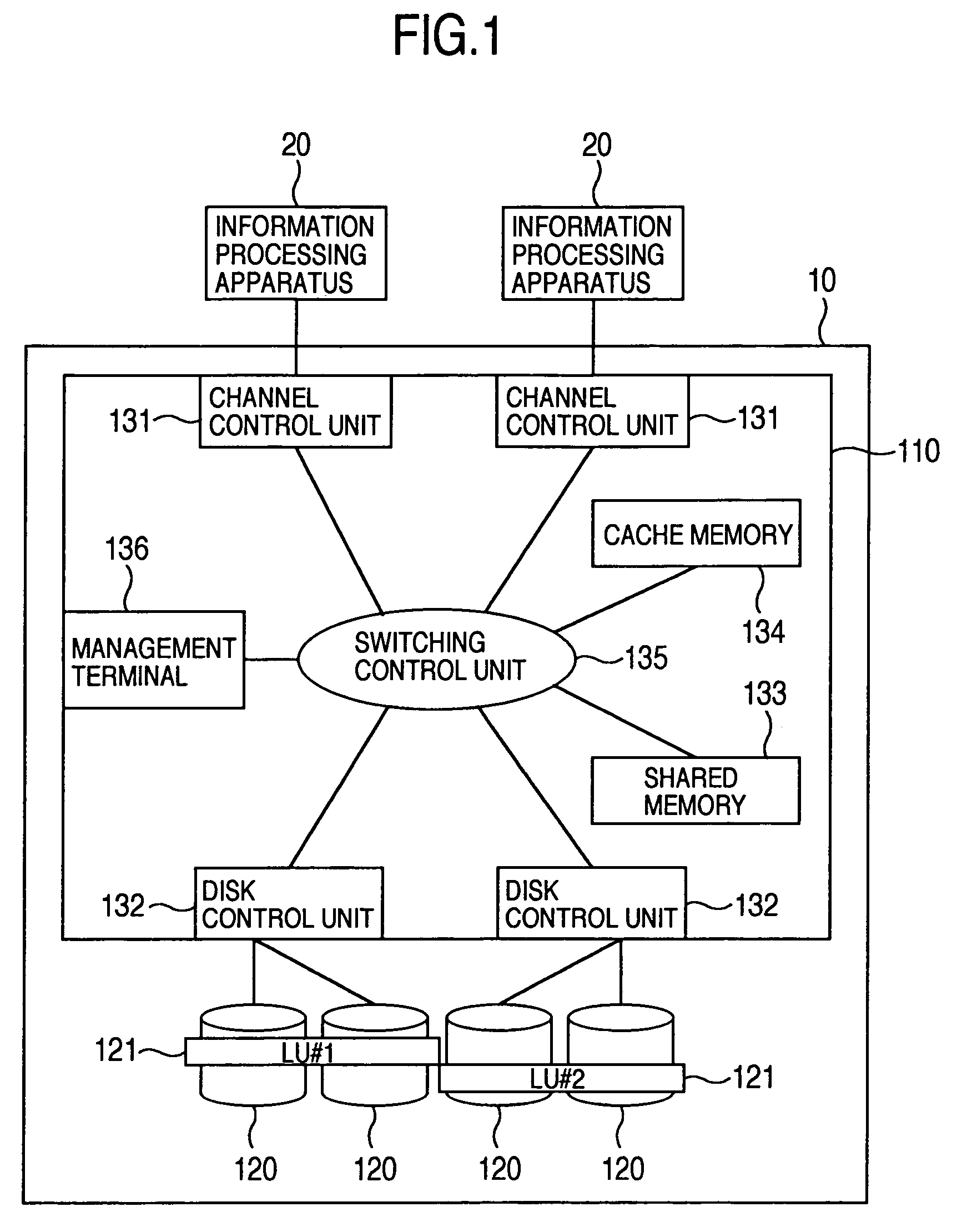
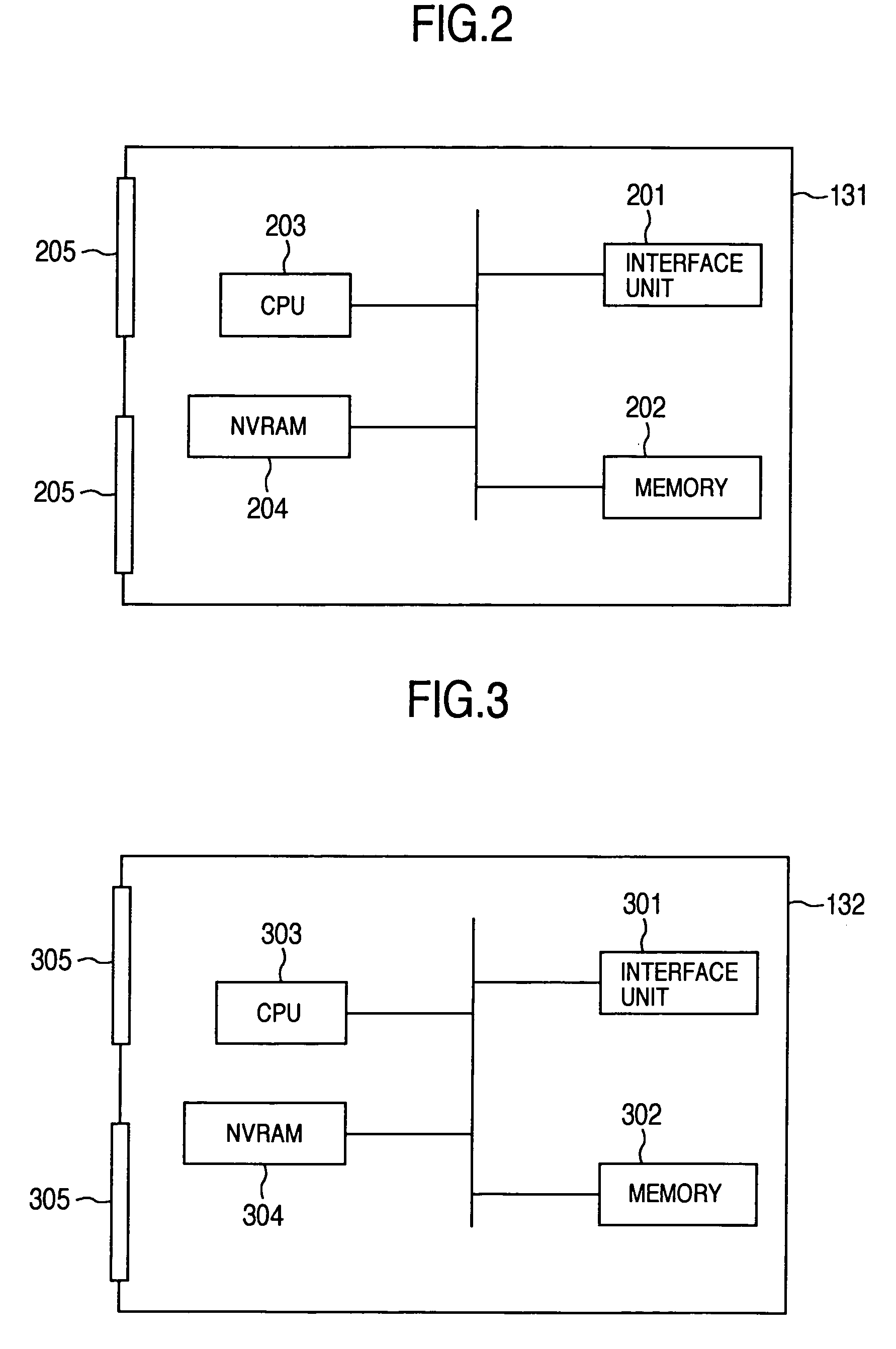
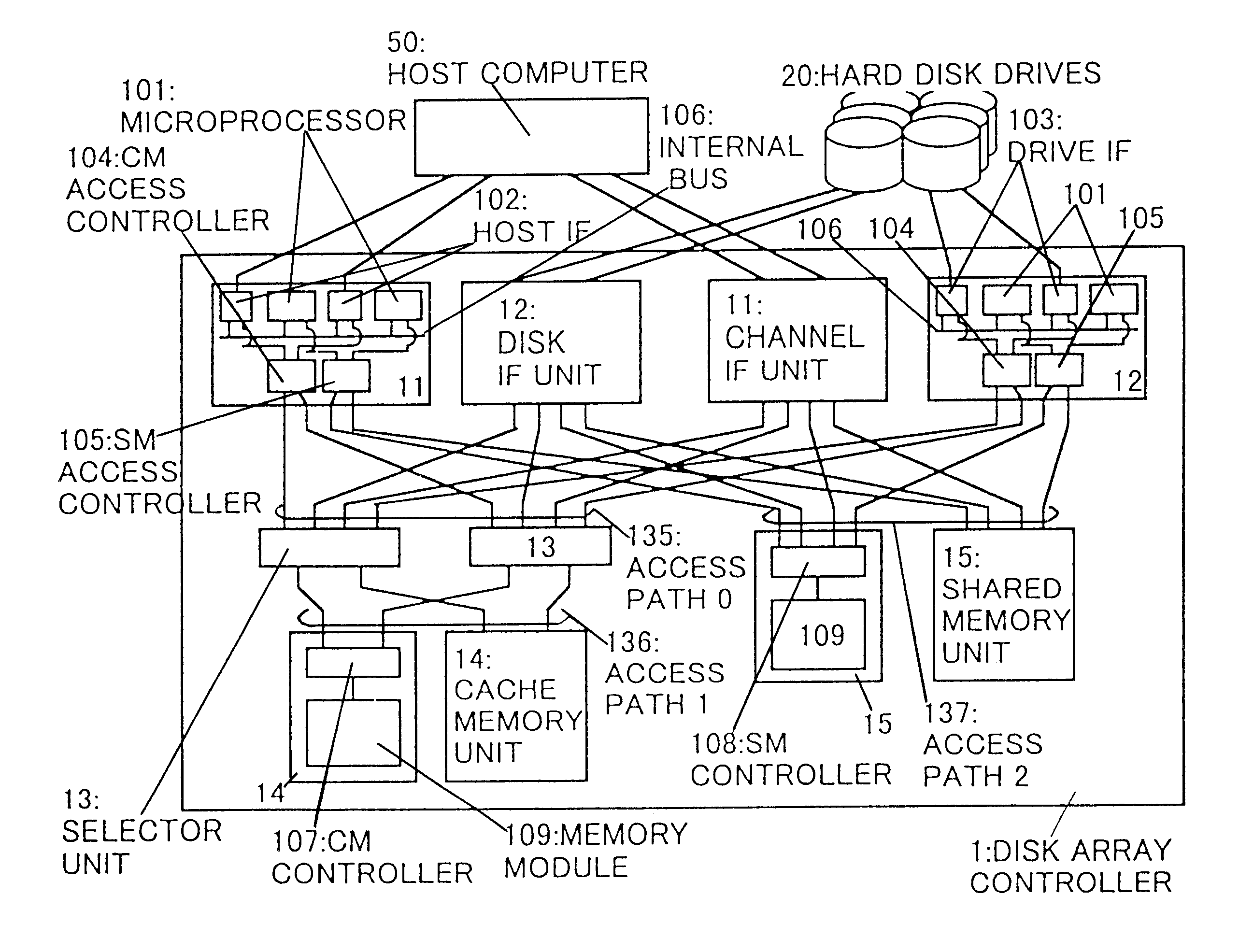
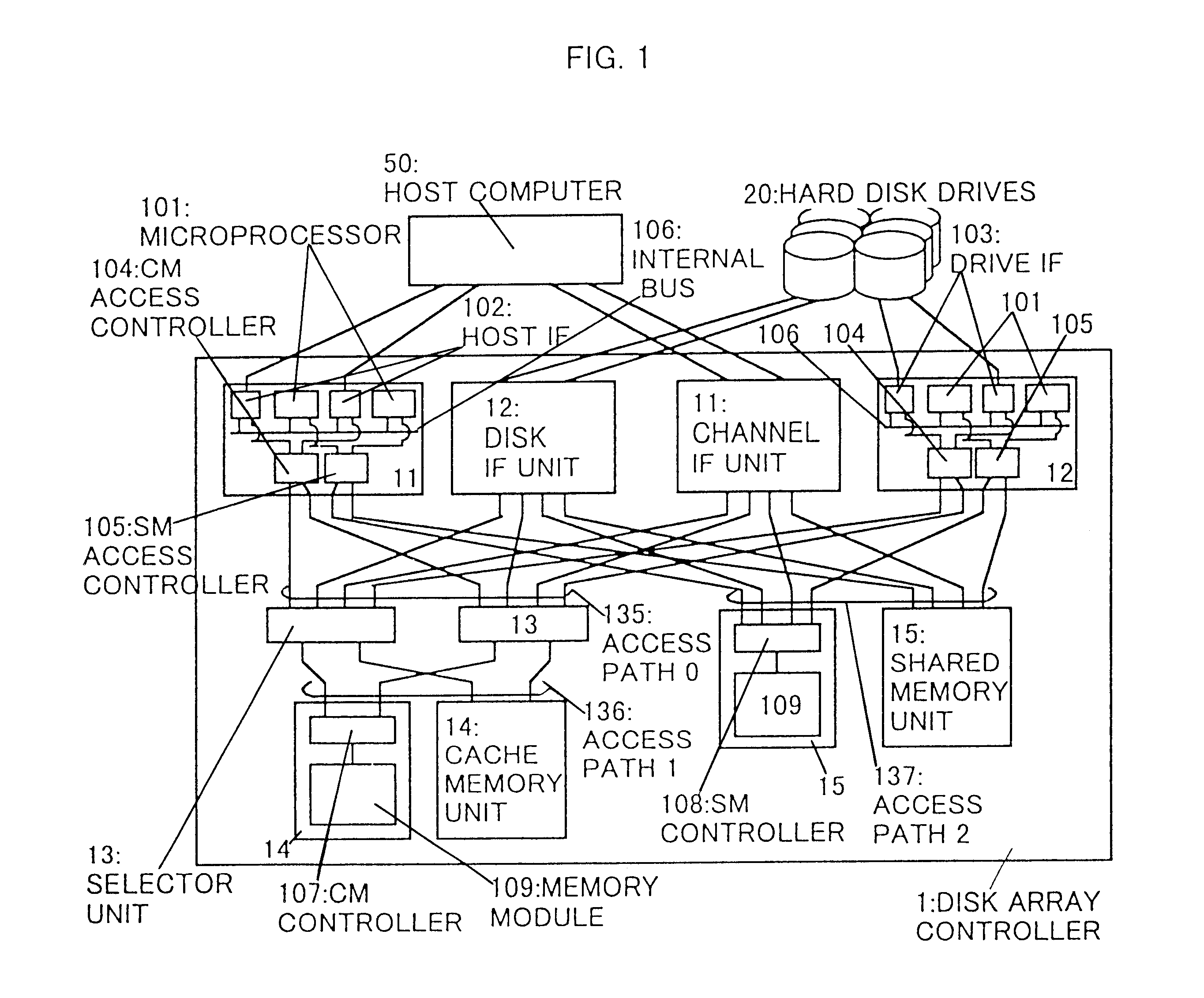
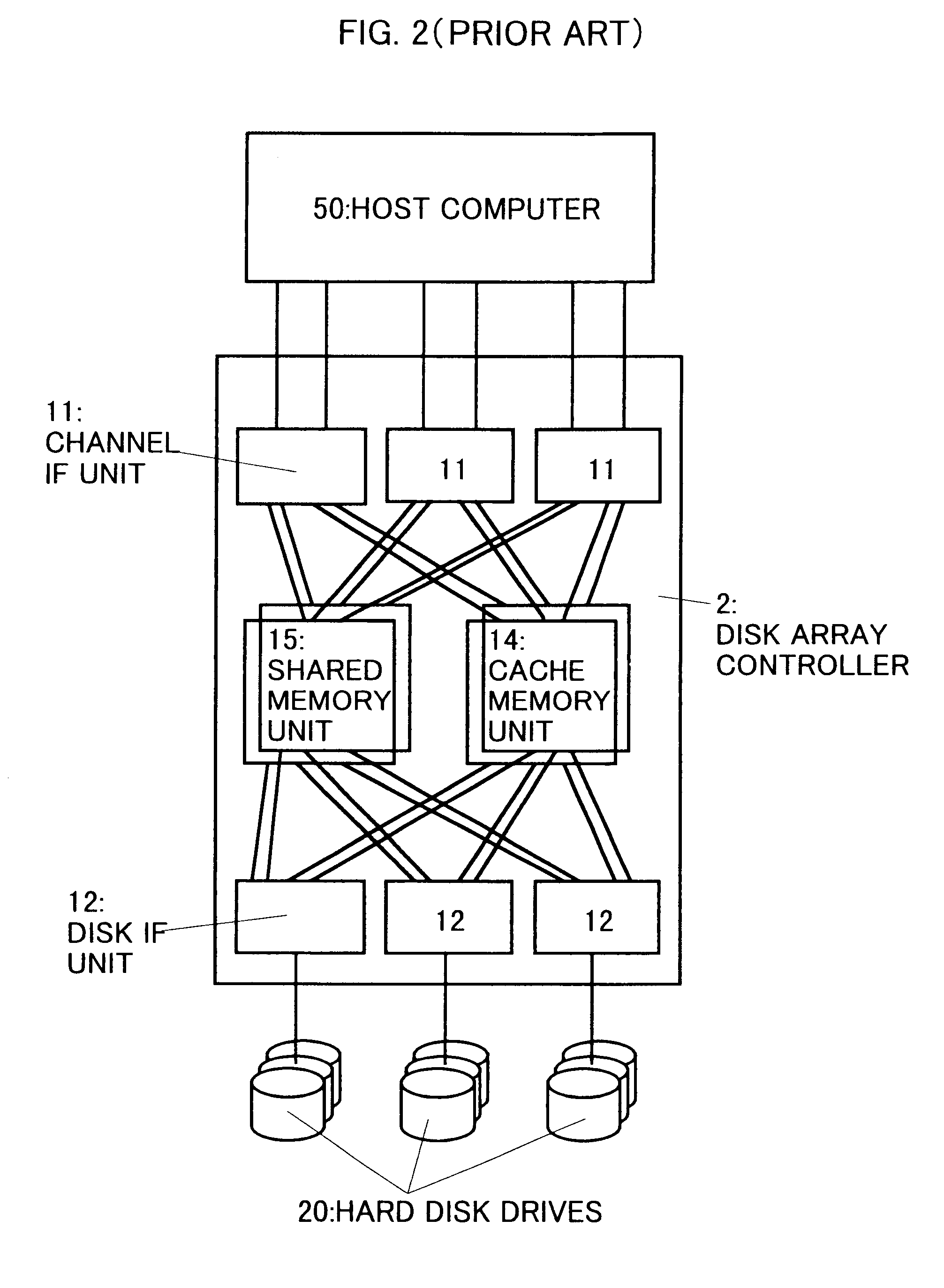
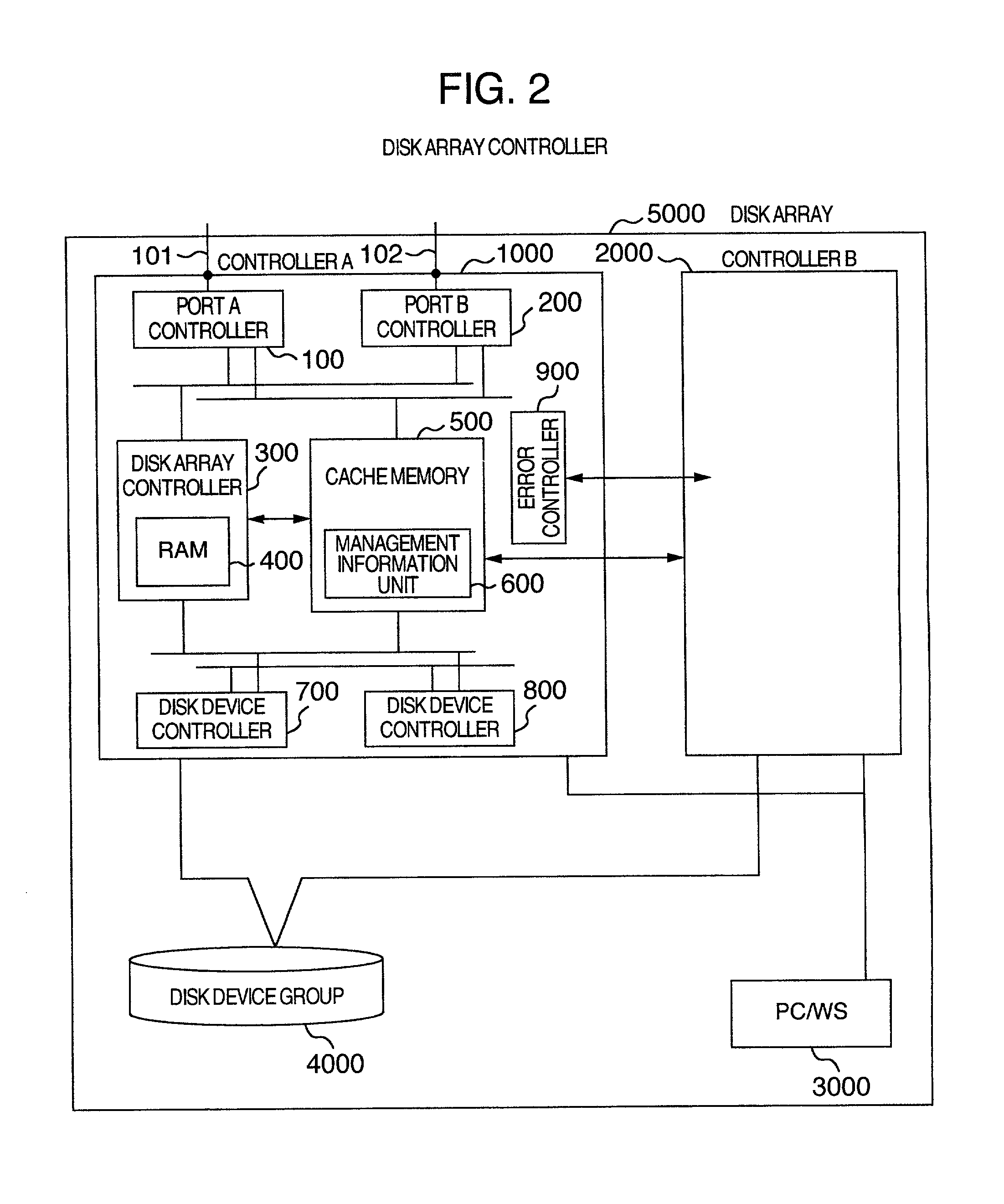
Disk array control device with two different internal connection systems
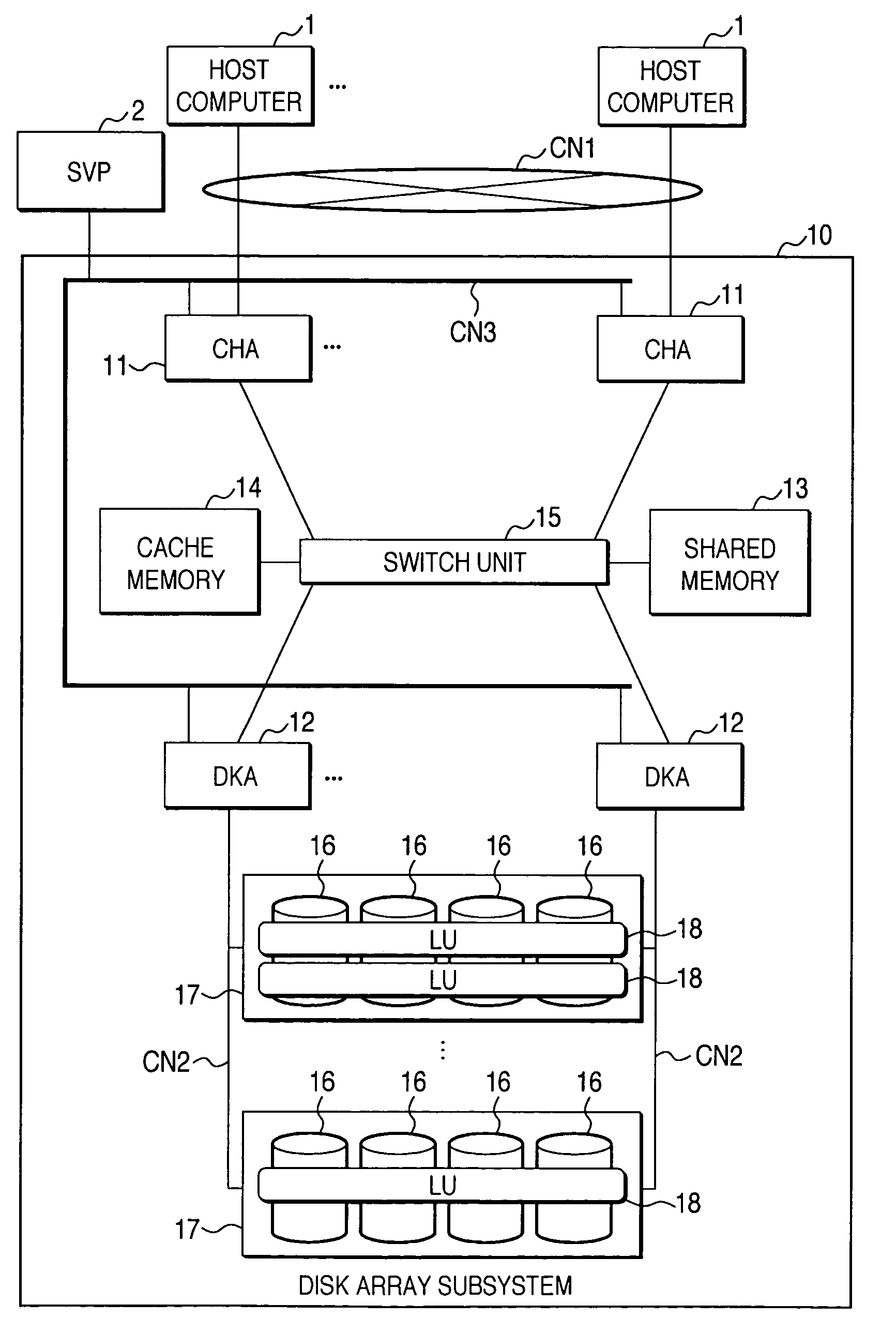
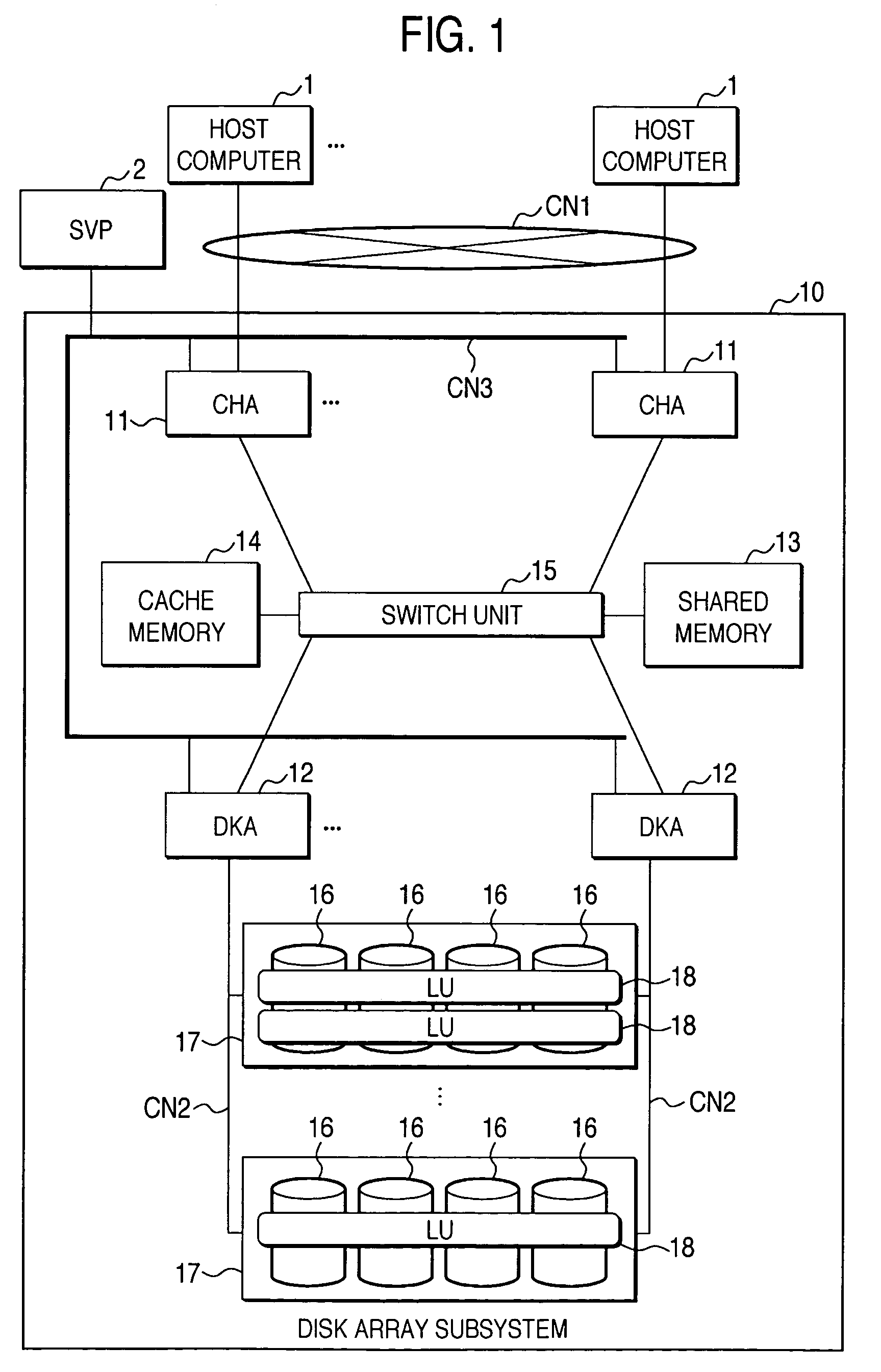
A disk array control device which includes a plurality of channel interface (IF) units, a plurality of disk IF units, a cache memory unit, and a shared memory unit. The connection system between the plurality of channel IF units and plurality of disk IF units and the cache memory unit is different from the connection system between the plurality of channel IF units and plurality of disk IF units and the shared memory unit. In the invention the plurality of channel IF units and the plurality of disk IF units are connected via a selector to the cache memory unit, whereas the plurality of channel IF units and the plurality of disk IF units are directly connected to the shared memory unit with no selectors.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
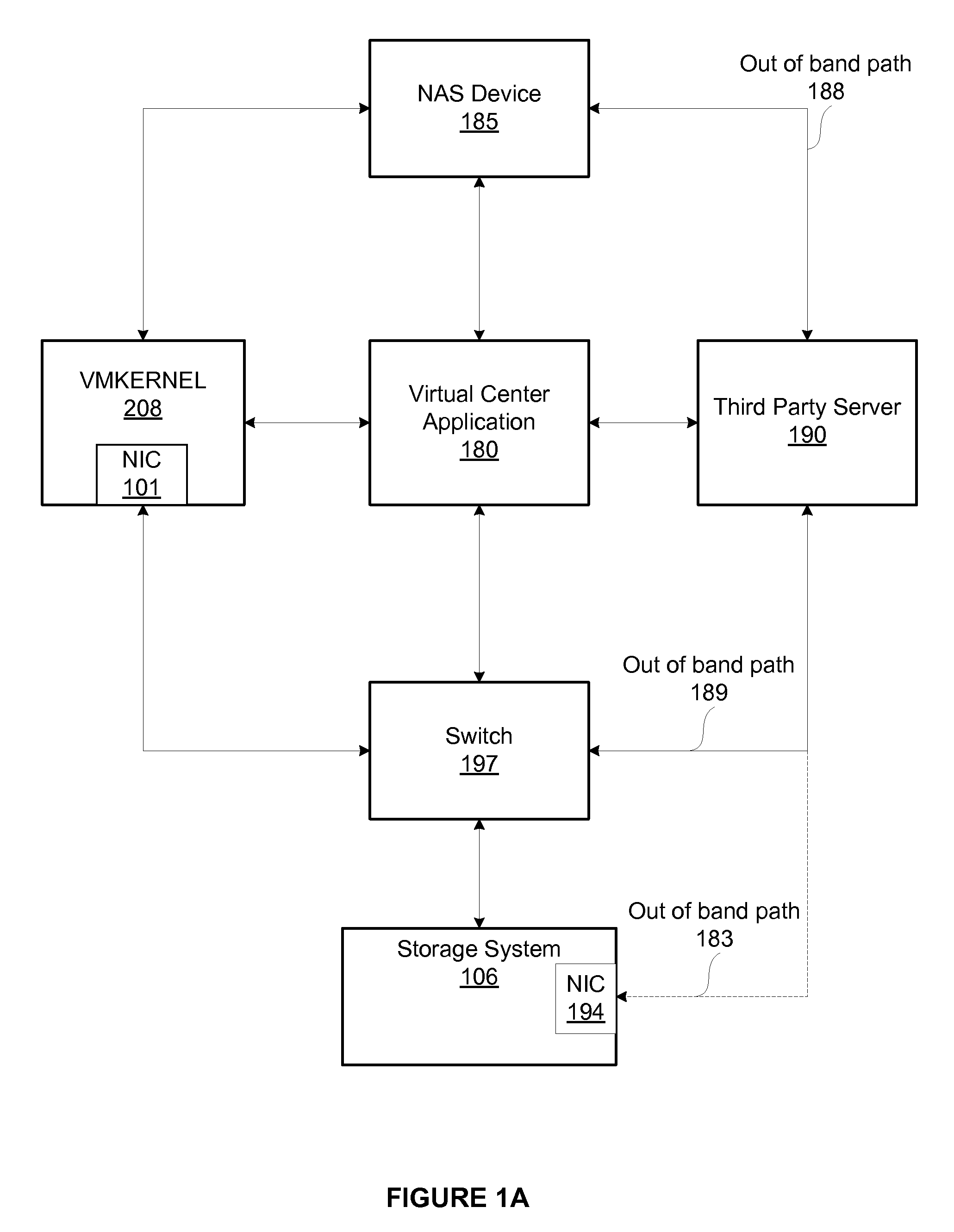
Offloading storage operations to storage hardware using a third party server
In a computer system with a disk array that has physical storage devices arranged as logical storage units and is capable of carrying out hardware storage operations on a per logical storage unit basis, a third party server is provided to offload storage operations from a file system to storage hardware. The third party server transfers configuration information associated with composite storage operations to the physical storage devices through an out-of-band path to enable composite storage operations to be executed without involving the file system.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Disk array apparatus
InactiveUS7457112B2Improve cooling effectEasy to controlReducing temperature influence on carrierCarrier constructional parts dispositionDisk enclosureComputer module
A disk array apparatus including a rack-shaped basic frame, and a plurality of disk boxes that can be inserted into and pulled out of the basic frame depth-wise. Each disk box has: disk drive connectors for connecting a plurality of disk drives arranged in a matrix on a platter substrate, which is the bottom face of the disk box, roughly parallel to the depth direction of the basic frame; and a cooling module for cooling the disk drives. The disk box is a hermetically sealed structure.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
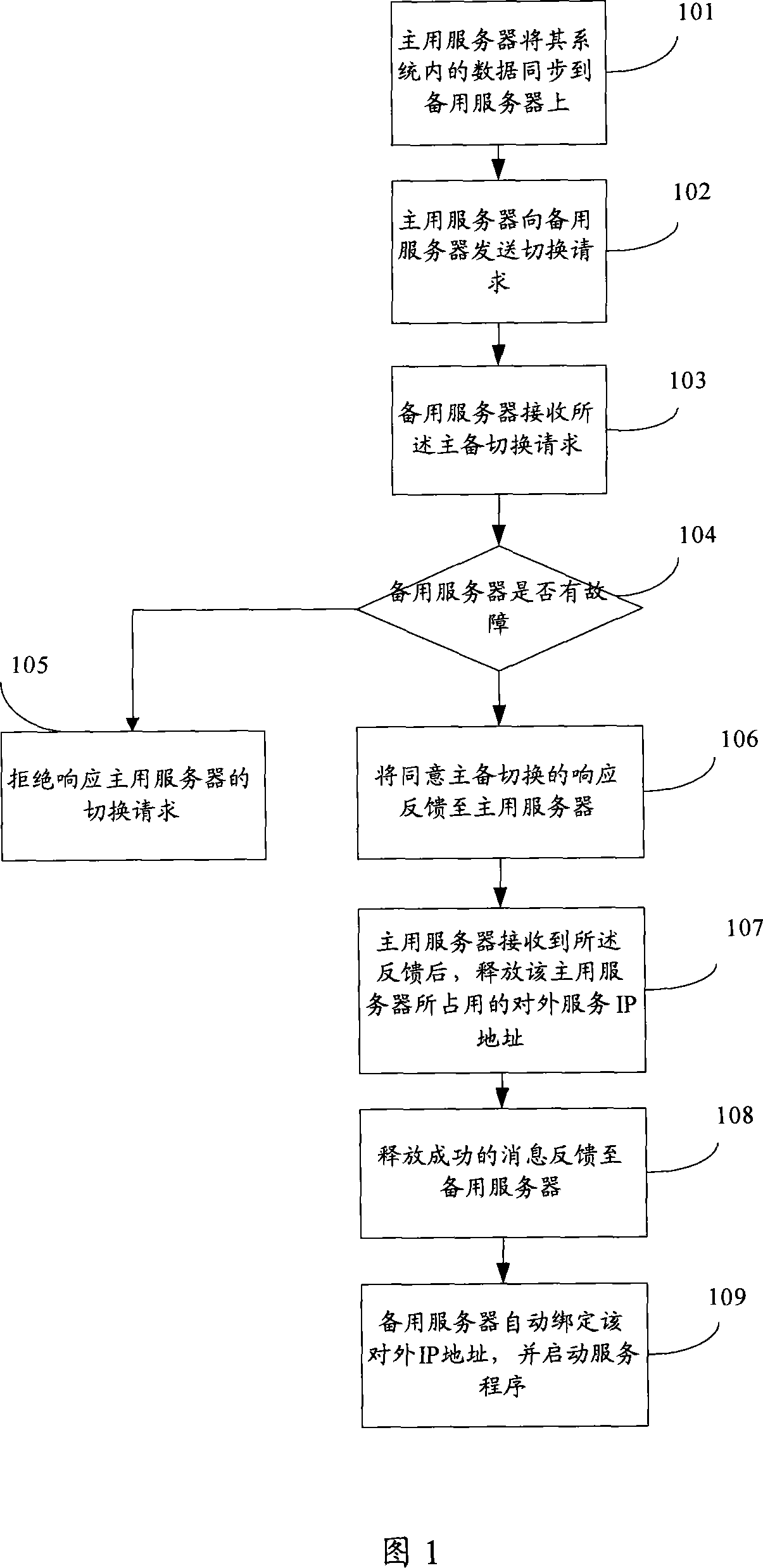
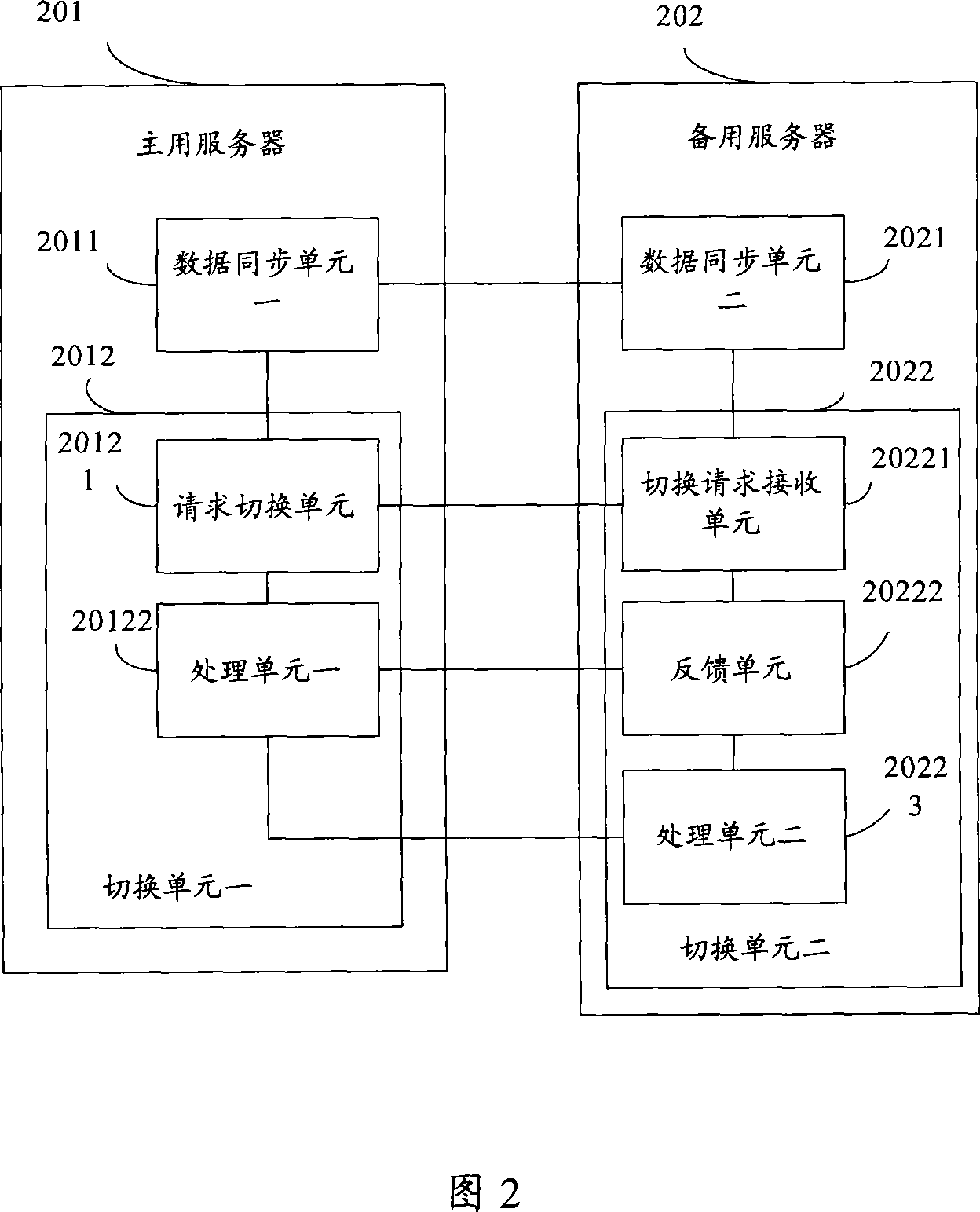
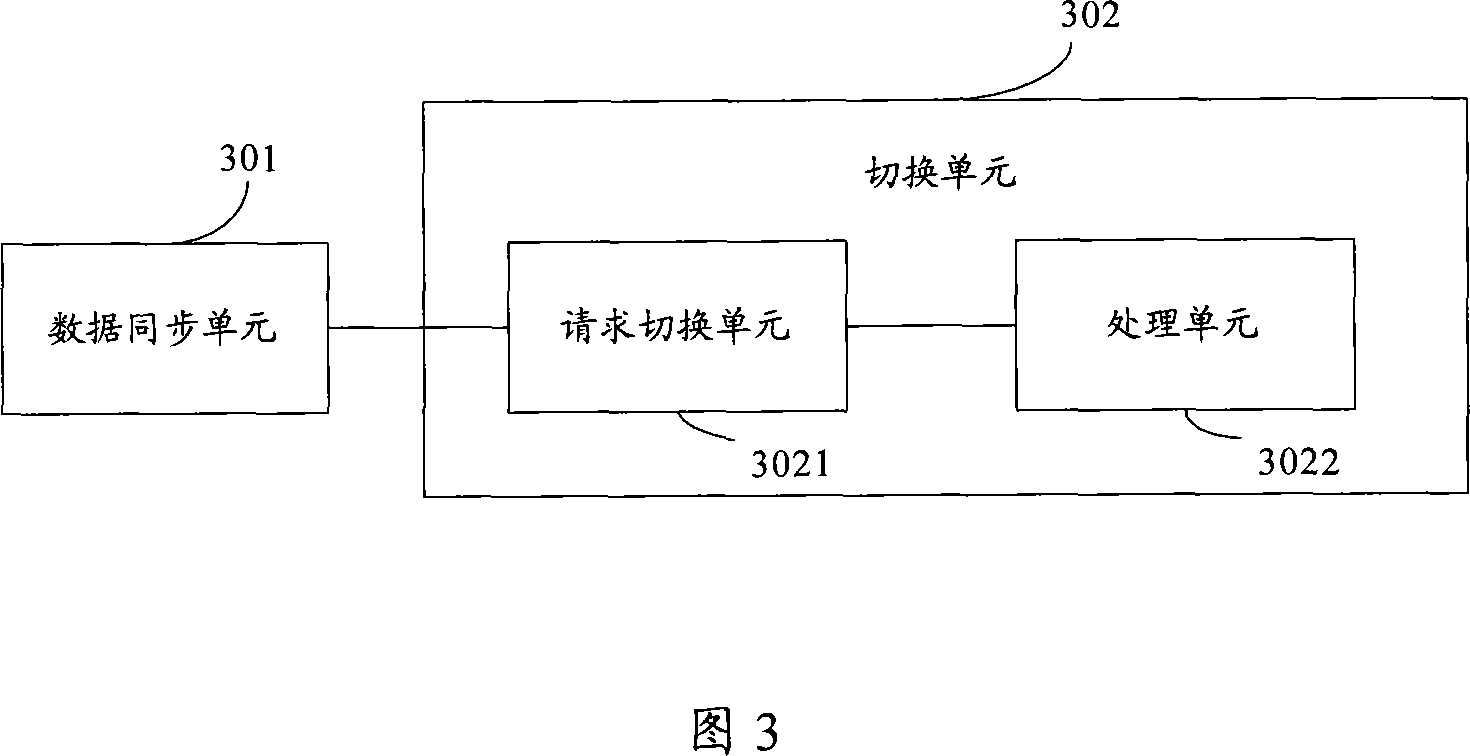
Master and spare server switching method and system and master server and spare server
InactiveCN101060391AReduce switching costsReduce usageError preventionData switching networksData synchronizationDisk array
The invention relates to the server switch method, wherein when the primary host fails, with the server negotiation, deciding whether the standby server takes over the service of the primary server, and switching the servers for primary-standby state. This invention can avoid using disc array, reduces switch cost, and improves system reliability.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
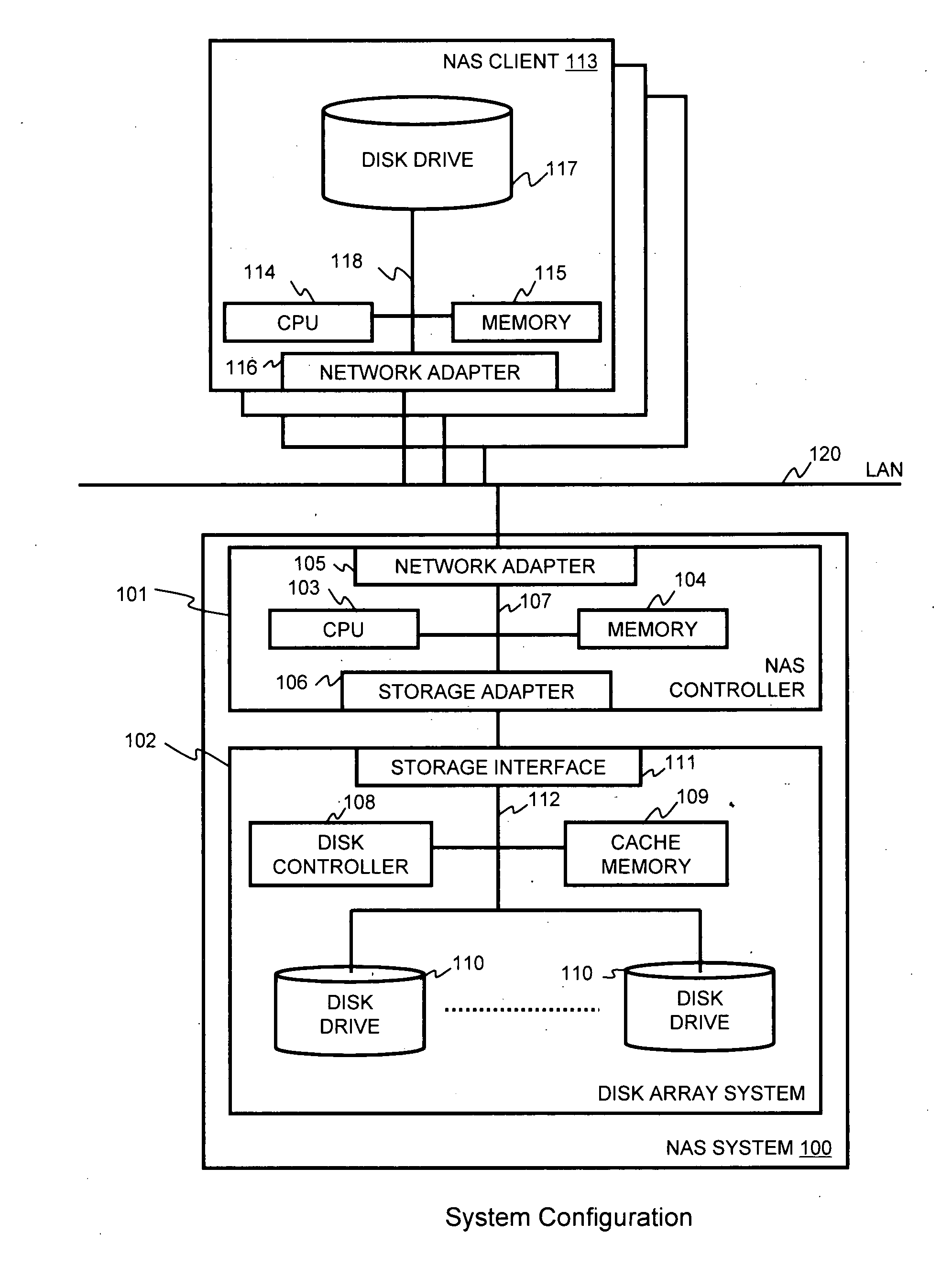
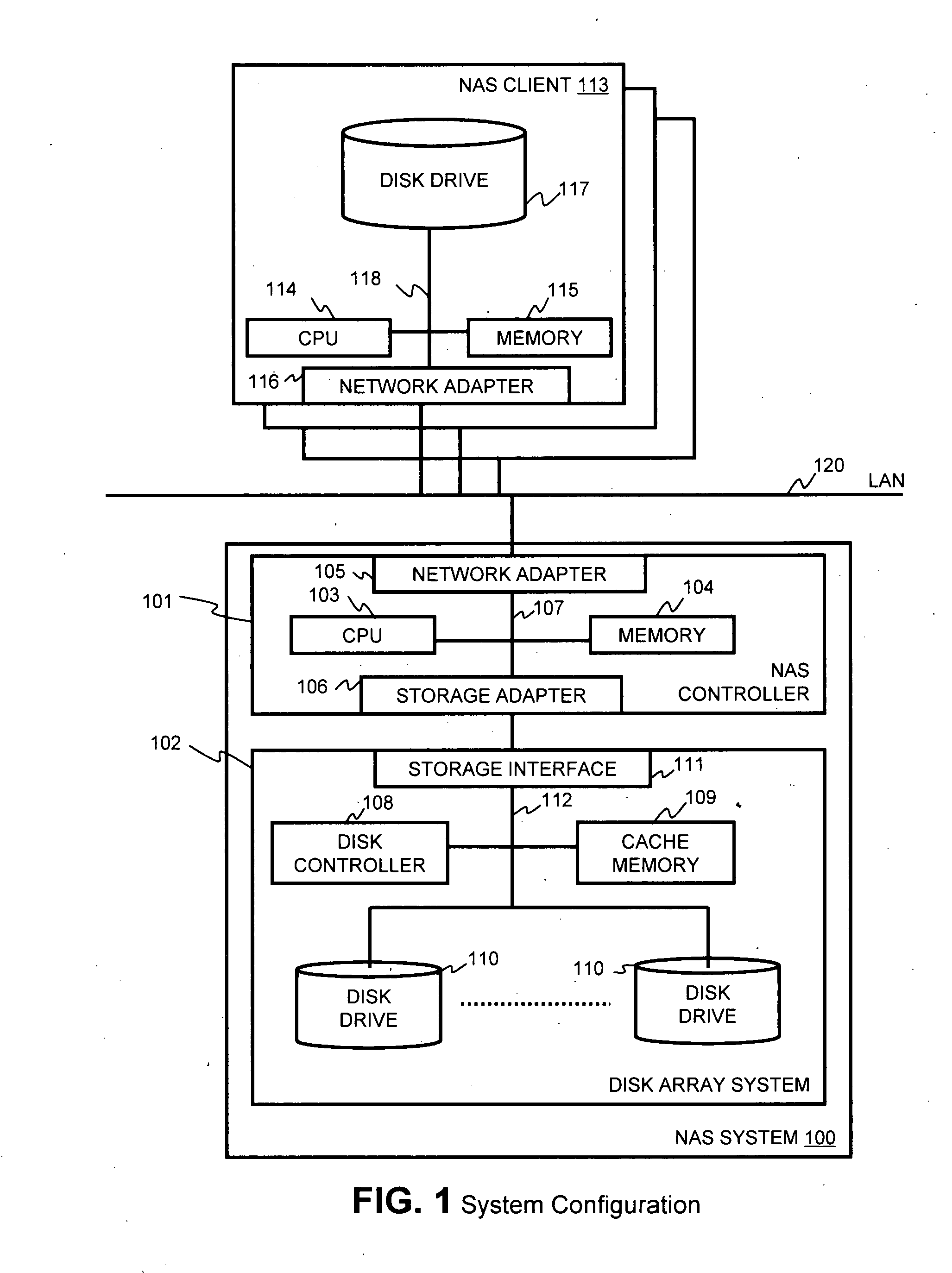
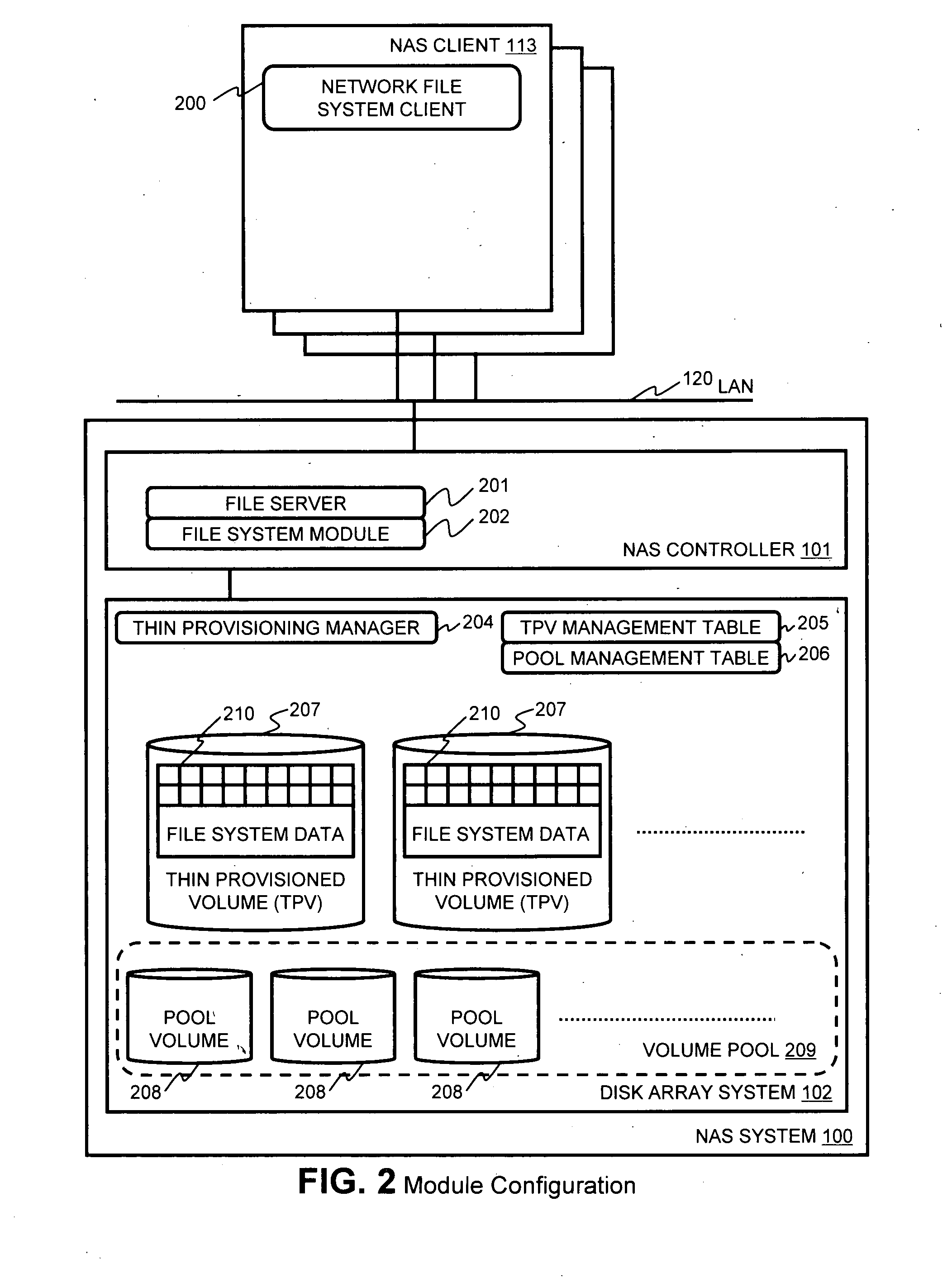
Method and apparatus for enabling a NAS system to utilize thin provisioning
InactiveUS20090077327A1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingFile systemDisk array
A NAS (network attached storage) controller managing file system data is configured for use in a storage system having thin provisioning capability. Physical storage capacity is used efficiently by making it possible for the NAS controller to identify to a disk array system having thin provisioning capability which segments of a thin provisioned volume are no longer in use. File system blocks or block groups no longer in use by the NAS controller are identified by the NAS controller. The NAS controller sends a release request to the disk array system specifying thin provisioning segments that correspond to the identified FS blocks or block groups. The release request instructs the disk array system to release chunks of physical storage capacity assigned to the specified thin provisioning segments so that the physical storage capacity can be made available for reuse in the disk array storage system.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
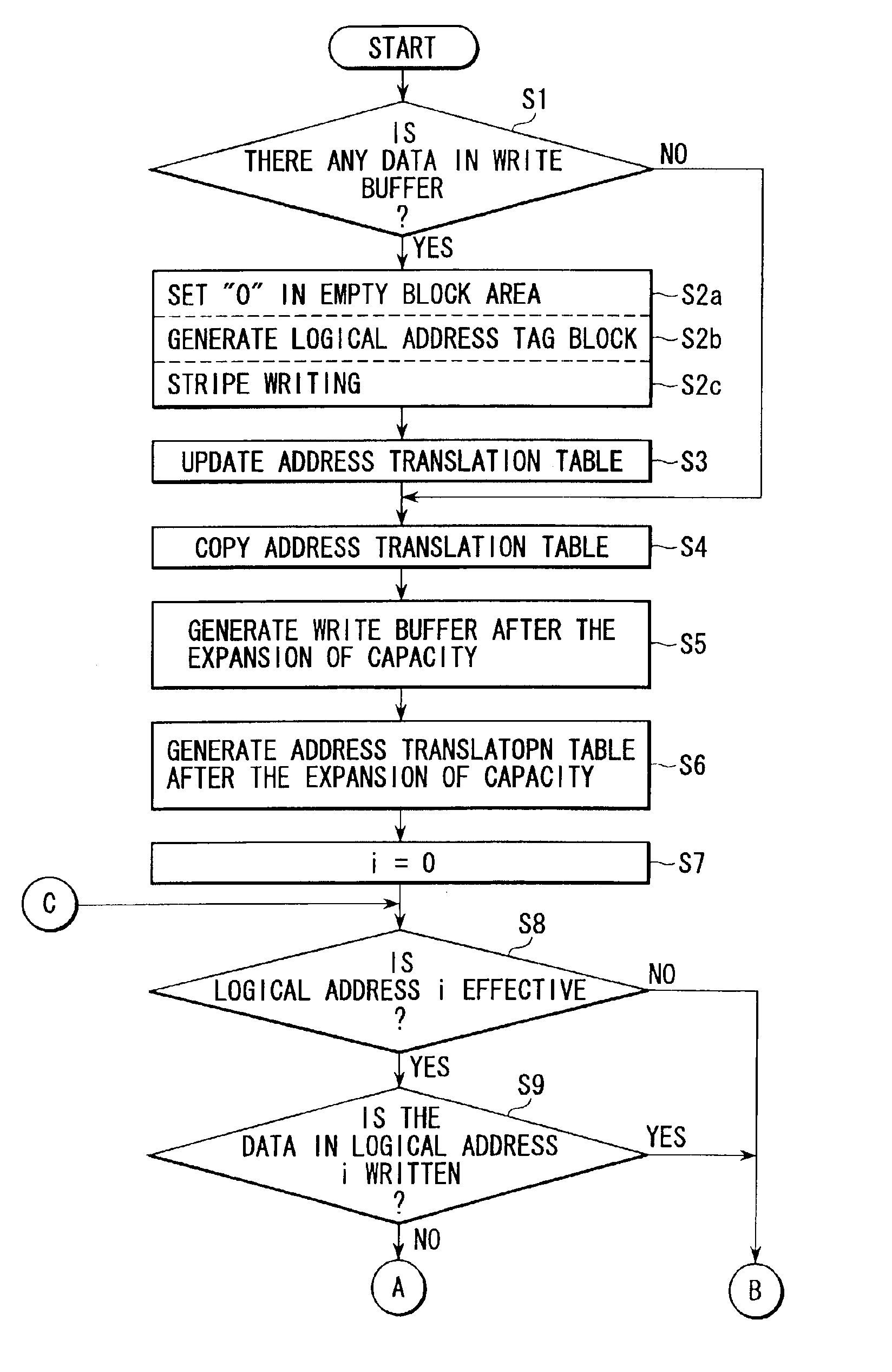
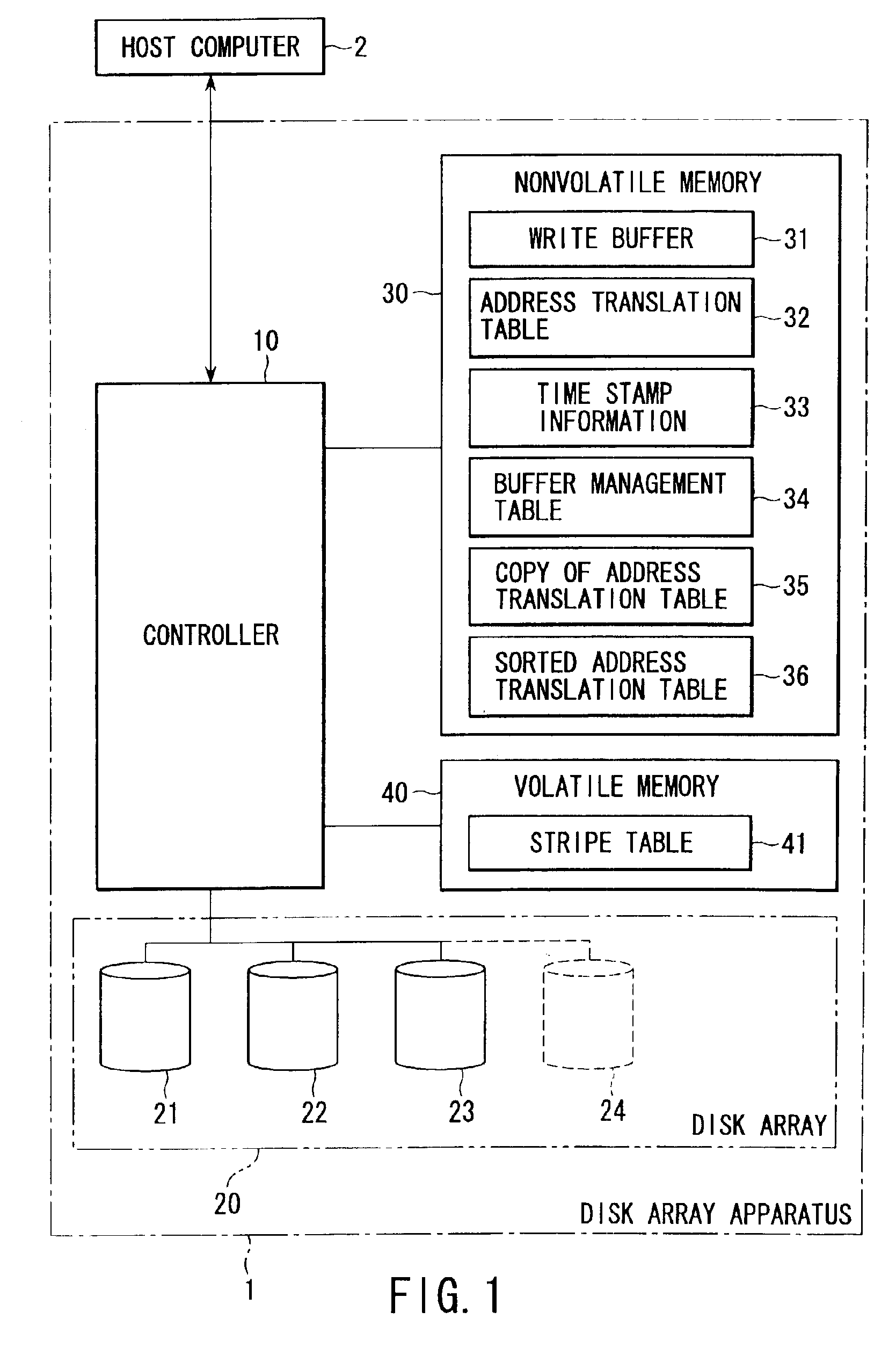
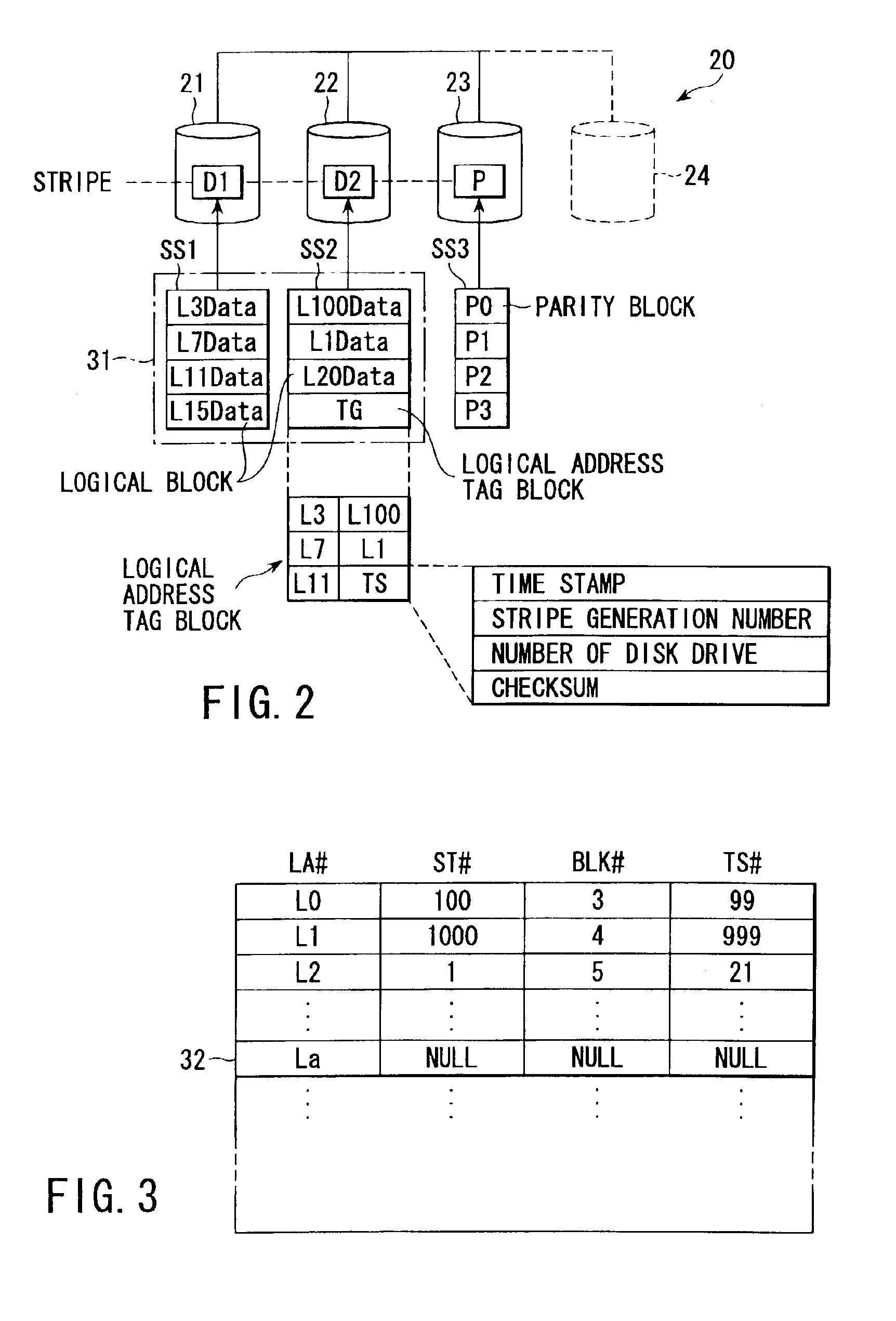
Disk array apparatus for and method of expanding storage capacity dynamically
InactiveUS6901479B2Shorten the timeIncrease storage capacityInput/output to record carriersError detection/correctionWrite bufferDisk array
A controller retrieves effective logical addresses sequentially according to a copy of an address translation table at the time of the start of storage capacity expansion in the process of expanding the storage capacity of a disk array by adding a disk drive to the disk array. The controller stores the data in the logical address into a restructured write buffer each time an effective logical address is retrieved. The controller writes one stripe worth of data blocks including one stripe of logical blocks and a logical address tag block into an empty area different from the area in which the data to be updated has been stored in the data array each time one stripe worth of logical blocks of data is accumulated in the write buffer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Storage subsystem that connects fibre channel and supports online backup
InactiveUS20020124124A1Without degrading online processing performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionFiberStorage area network
A disk array connected to a storage area network via a fiber channel has one or more ports each controlled by a processor. Even the disk array with one port and one processor executes online processing and backup processing at the same time while considering an online processing load. A port controller not only accepts a request from a host computer but issues a request to other storage controllers to allow online processing and backup processing to be executed at the same time. In addition, the disk array, if provided with a plurality of ports, selects ports or schedules processing depending upon the load to prevent backup processing from affecting online processing performance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Image processing
InactiveUS20040091175A1Digital computer detailsStill image data indexingImaging processingRemote system
A method of writing image data files to frame storage means, implemented as an array of disks, on which image data is stored as contiguous clips of frames. A remote system transmits a plurality of data packets over a network in any order, the data packets constituting a plurality of image data files. A local system connected to the frame storage means receives the data packets from the remote system and stores them in a buffer so as to arrange the image data files in a display sequence order. The local system then writes the image data files to the frame storage means as a contiguous clip of frames.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com