Patents
Literature
256 results about "Disk array controller" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
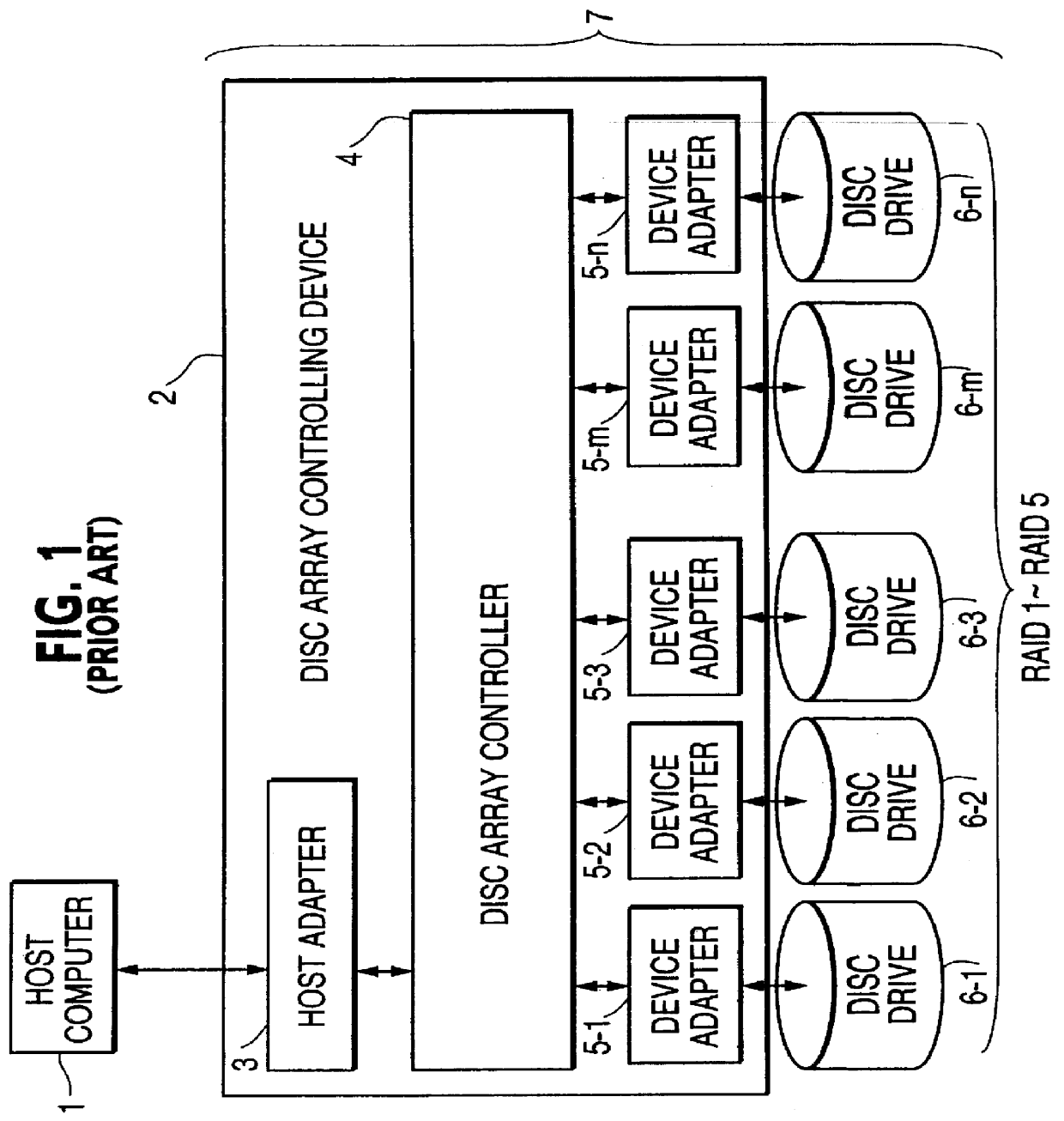
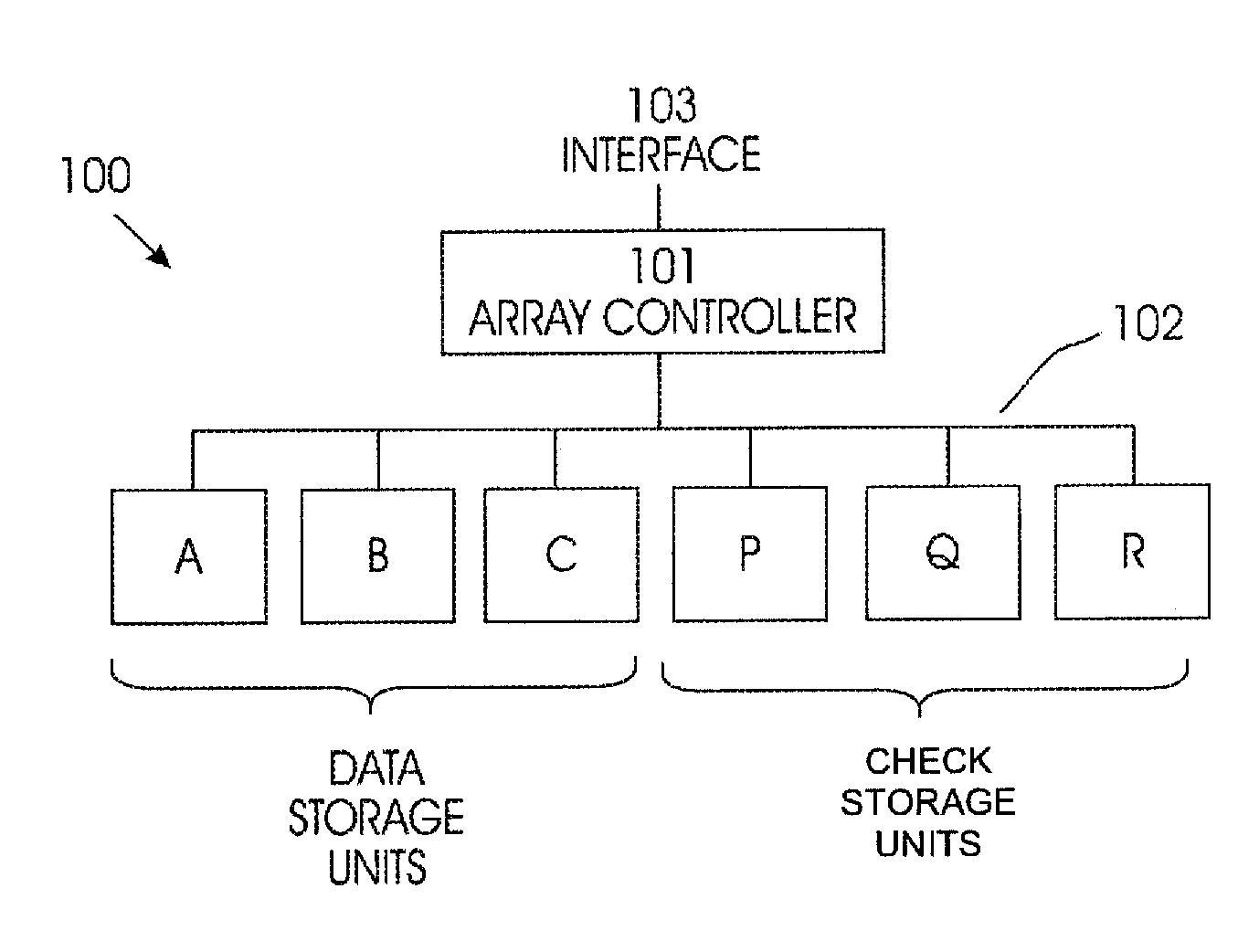
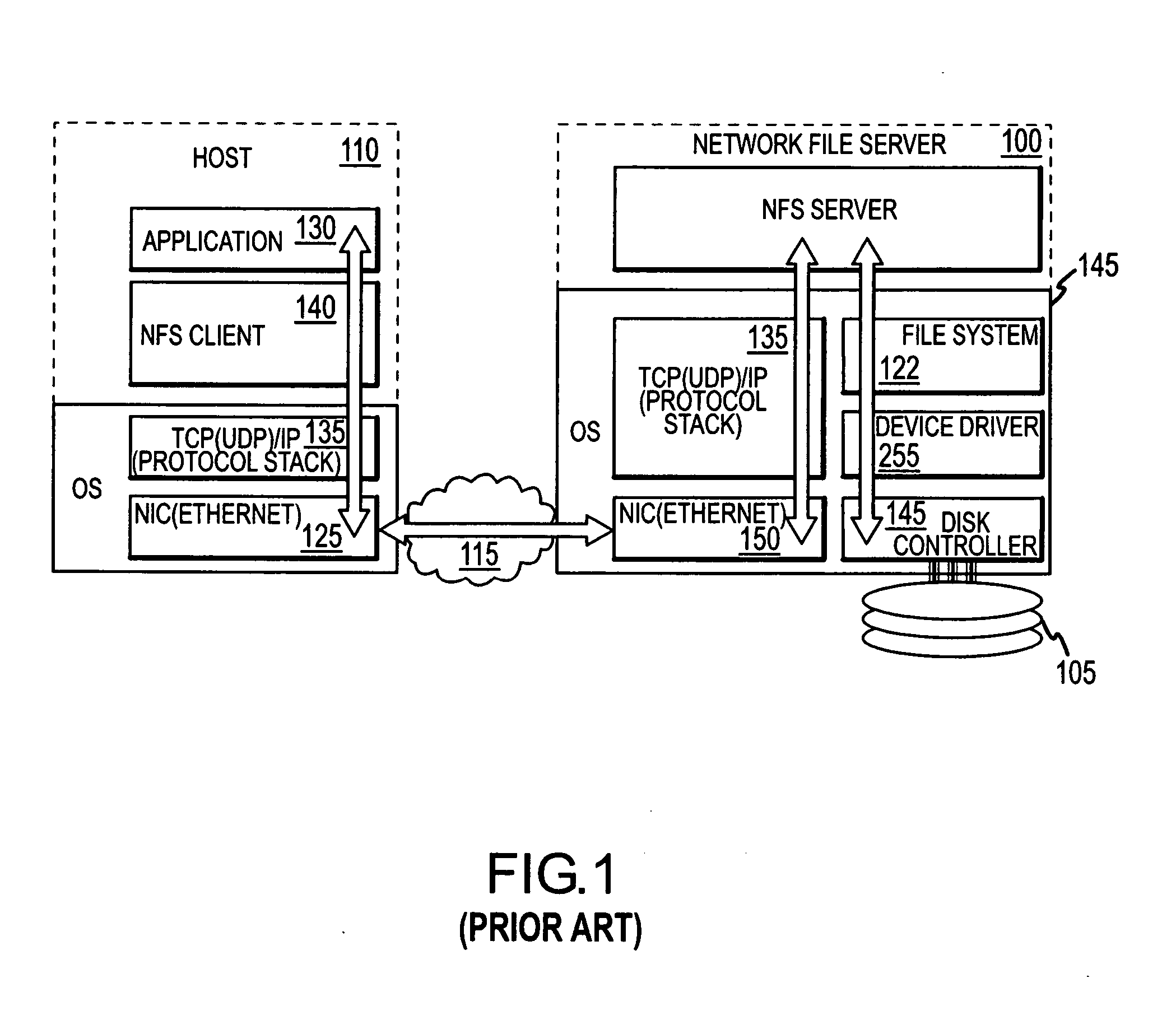
A disk array controller is a device that manages the physical disk drives and presents them to the computer as logical units. It almost always implements hardware RAID, thus it is sometimes referred to as RAID controller. It also often provides additional disk cache.
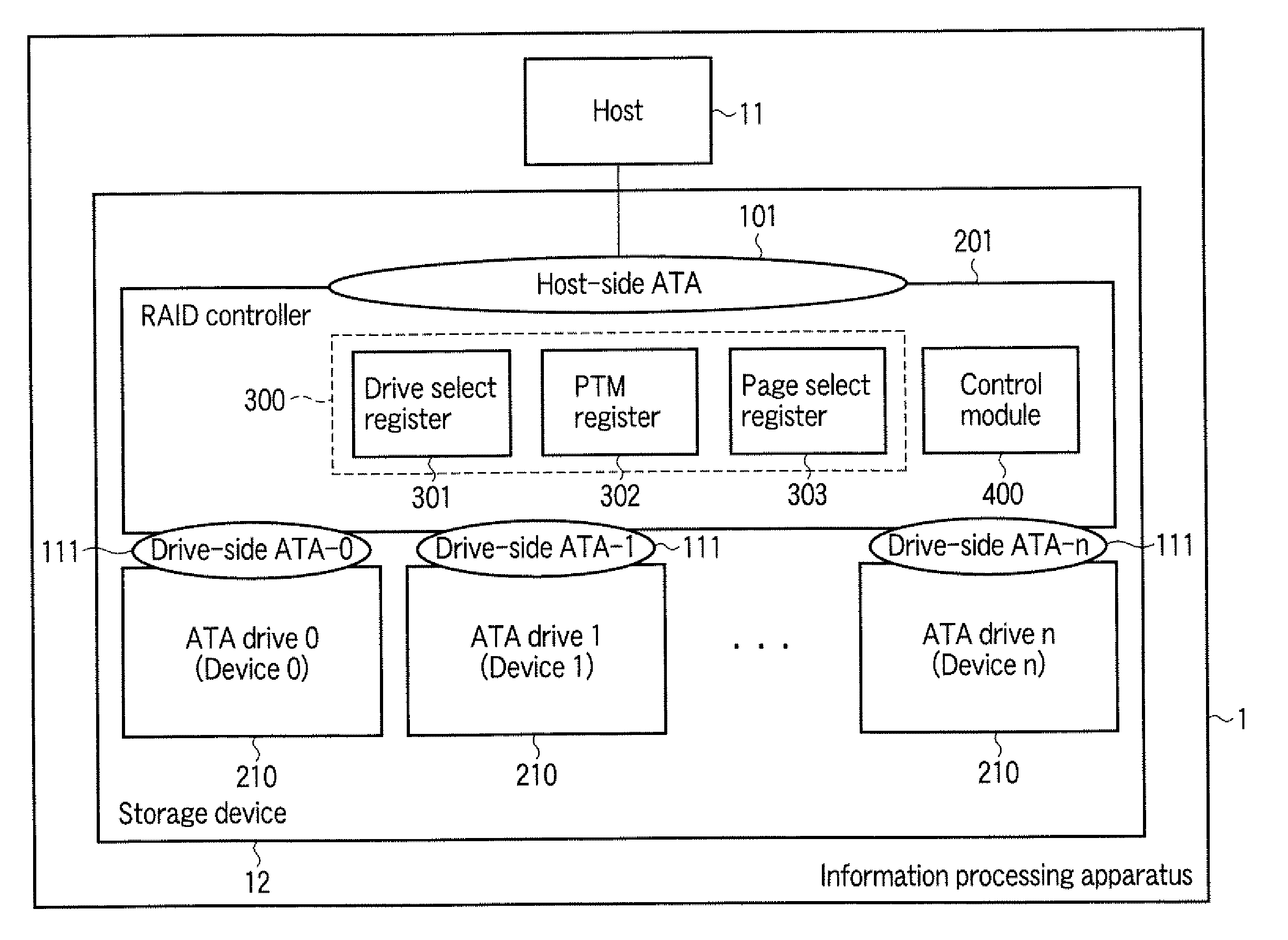
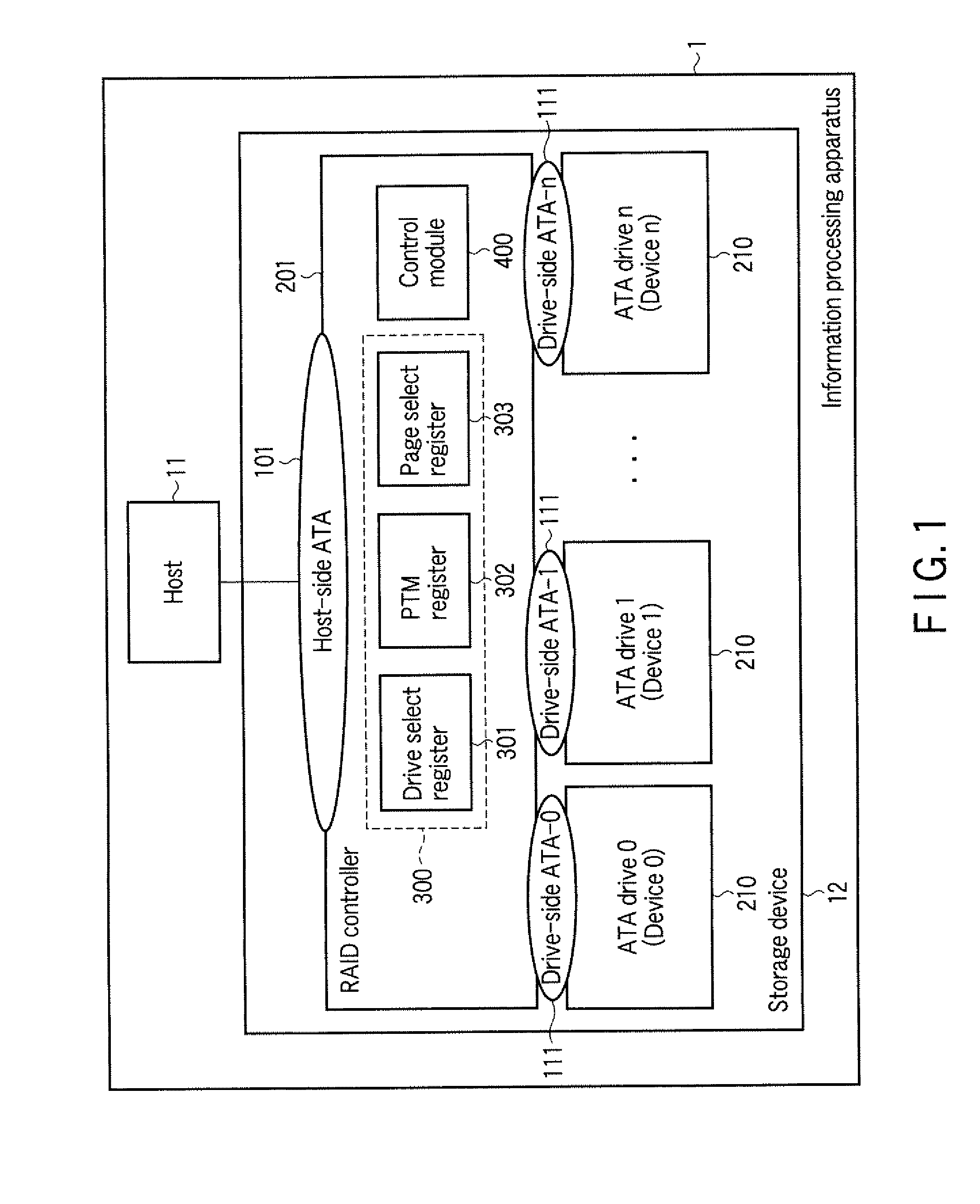
Disk array control device and storage device
InactiveUS20100106905A1Digital data processing detailsElectrical apparatus contructional detailsProcessor registerDisk array
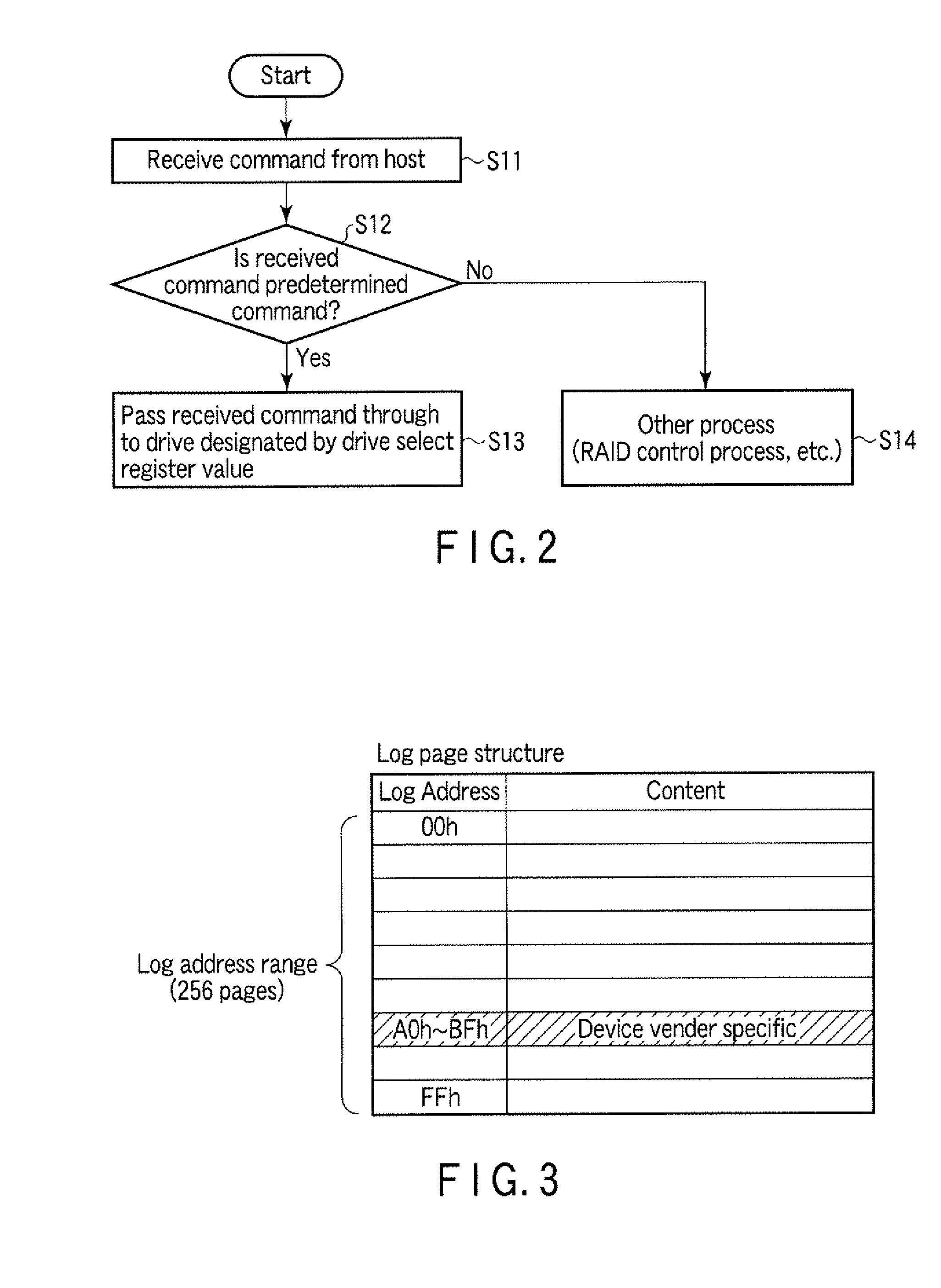
According to one embodiment, a disk array control device manages a plurality of drives as a single logical drive. The disk array control device includes a first register configured to store a to-he-accessed drive number which is designated by a host, and a control module. The control module is configured to receive a command from the host, determine whether the received command is a predetermined command which is used for maintenance of each of the drives, and execute, in a case where the received command is the predetermined command, a pass-through process of sending the received command to the drive which is designated by the to-be-accessed drive number in the first register.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
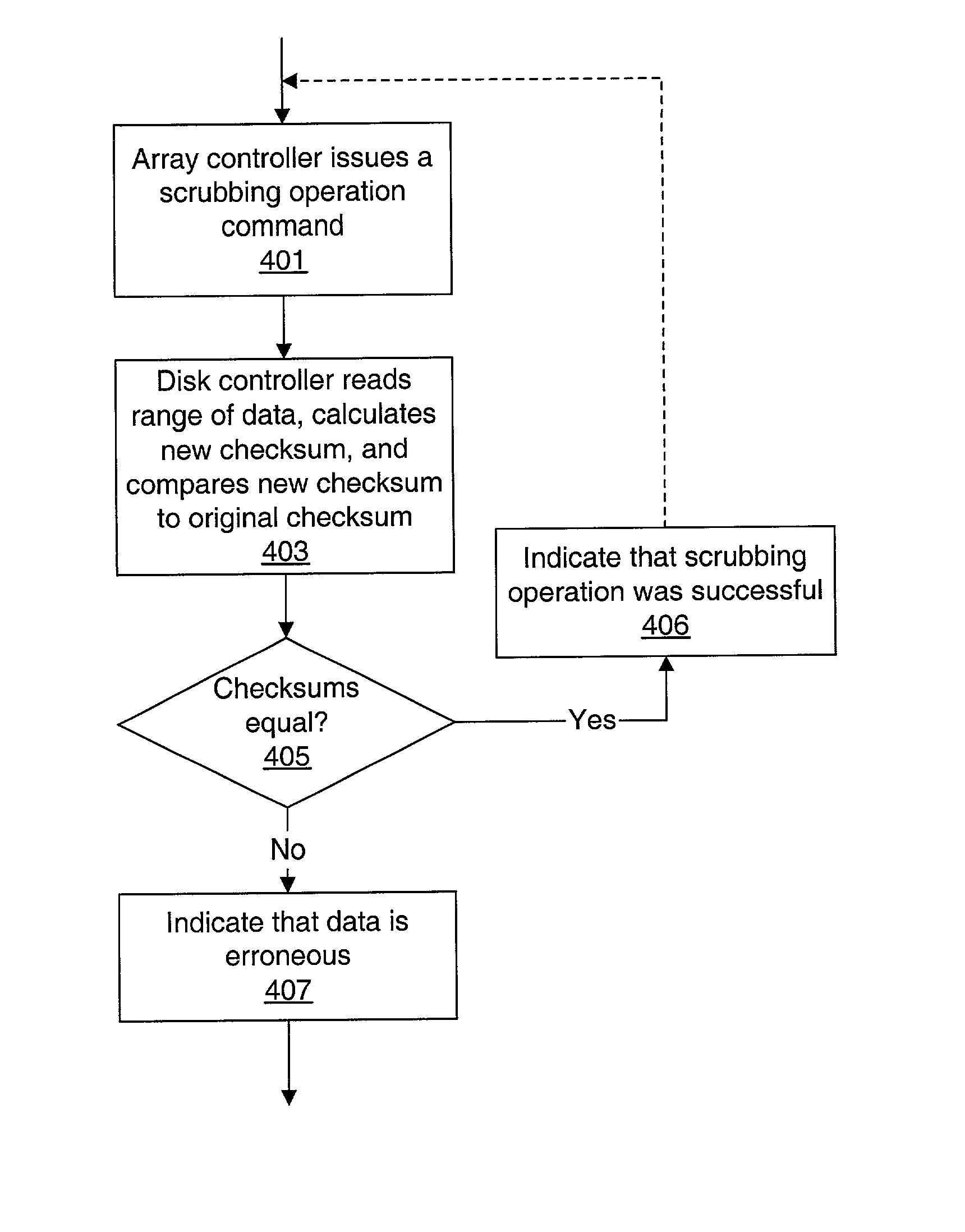
Storage array employing scrubbing operations at the disk-controller level
A storage system comprises a storage array controller and a storage array, which includes multiple disk drives and disk drive controllers. The storage array controller issues scrubbing operation commands to one or more of the disk drive controllers. In response, each disk drive controller that receives a scrubbing operation command reads data from within a data range from at least one of the disk drives, calculates a new checksum for the data, and compares the new checksum to a preexisting checksum for the data. If the new checksum doesn't equal the preexisting checksum, the data within the data range is determined to be erroneous.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
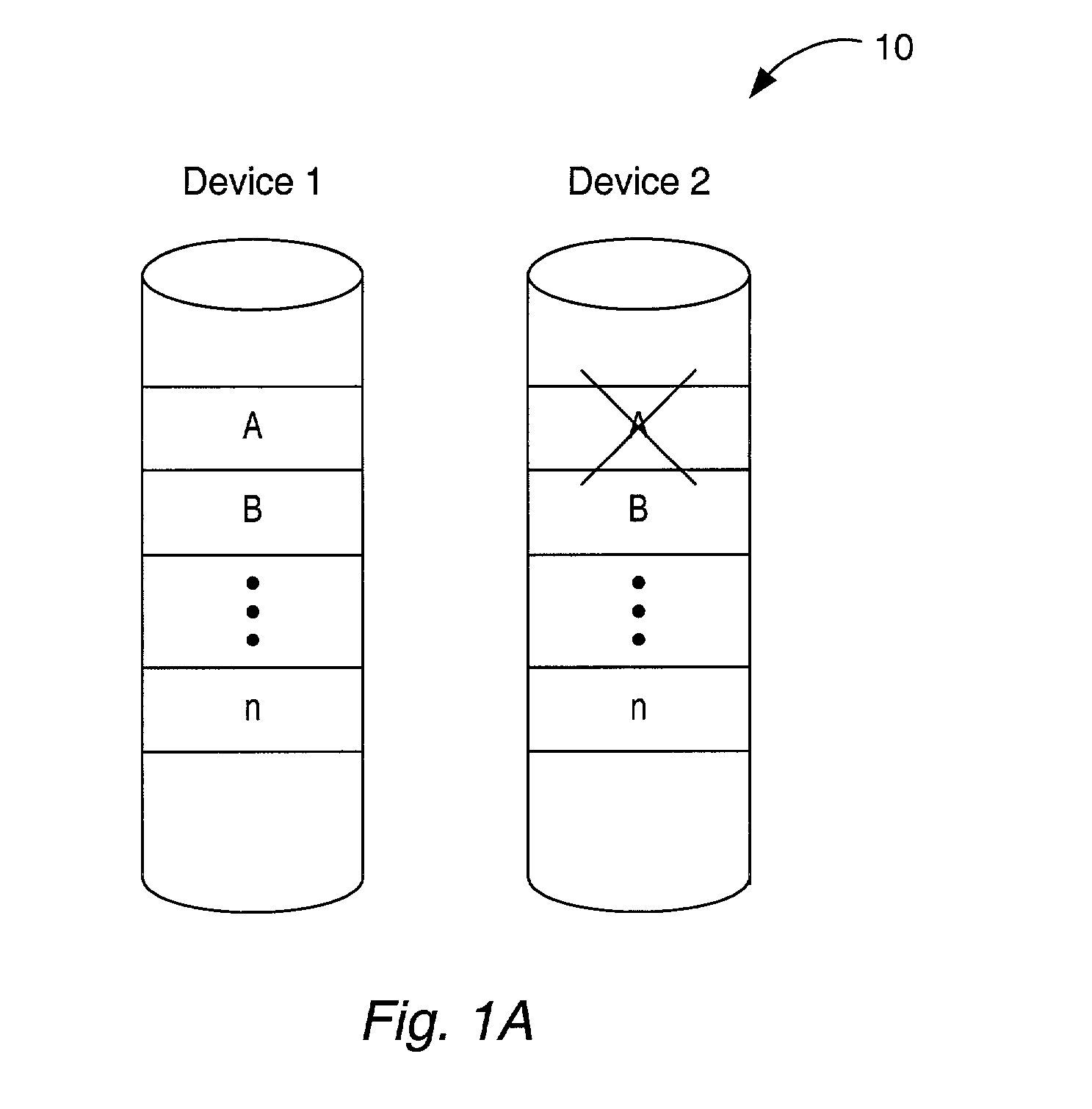
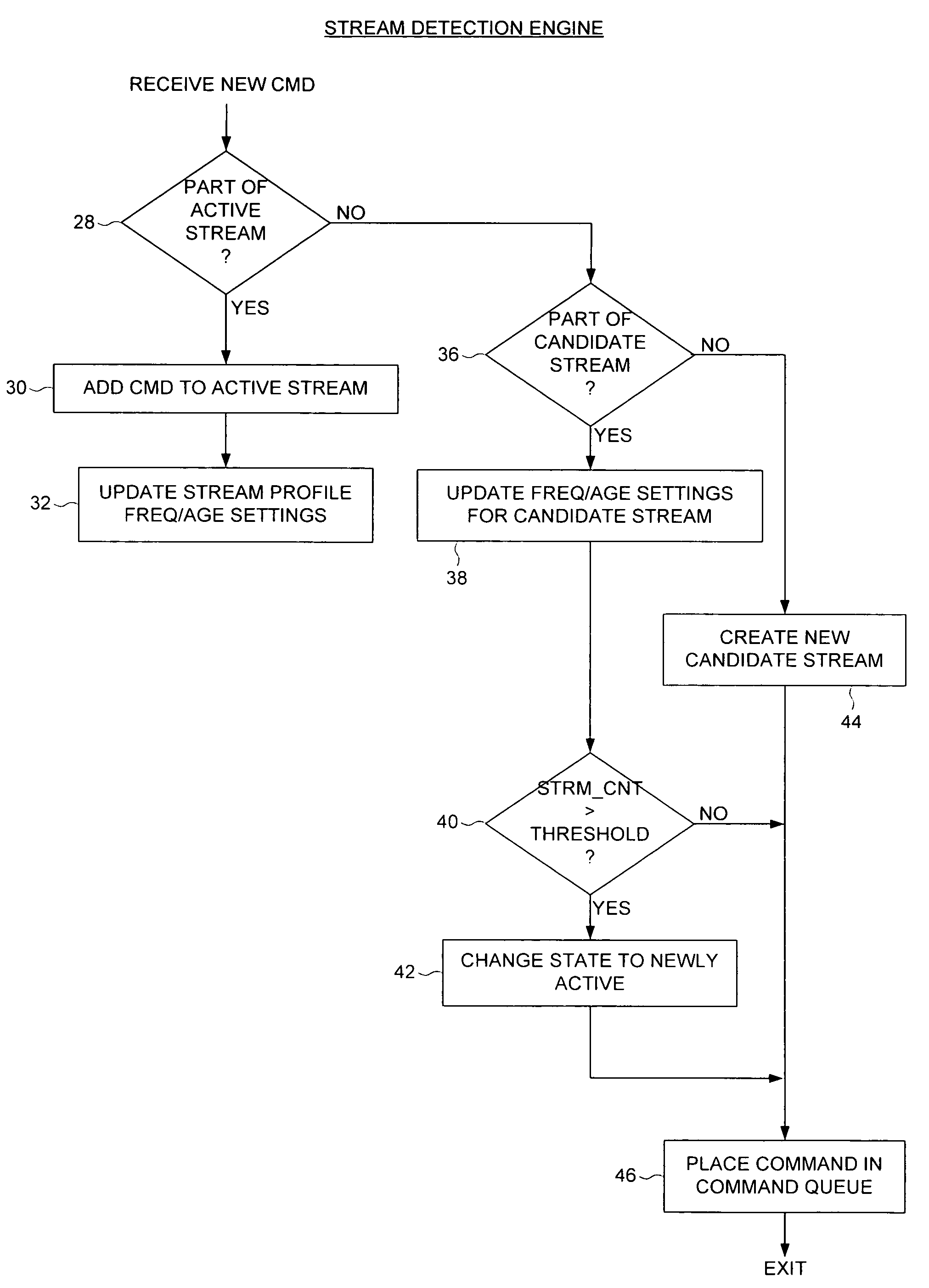
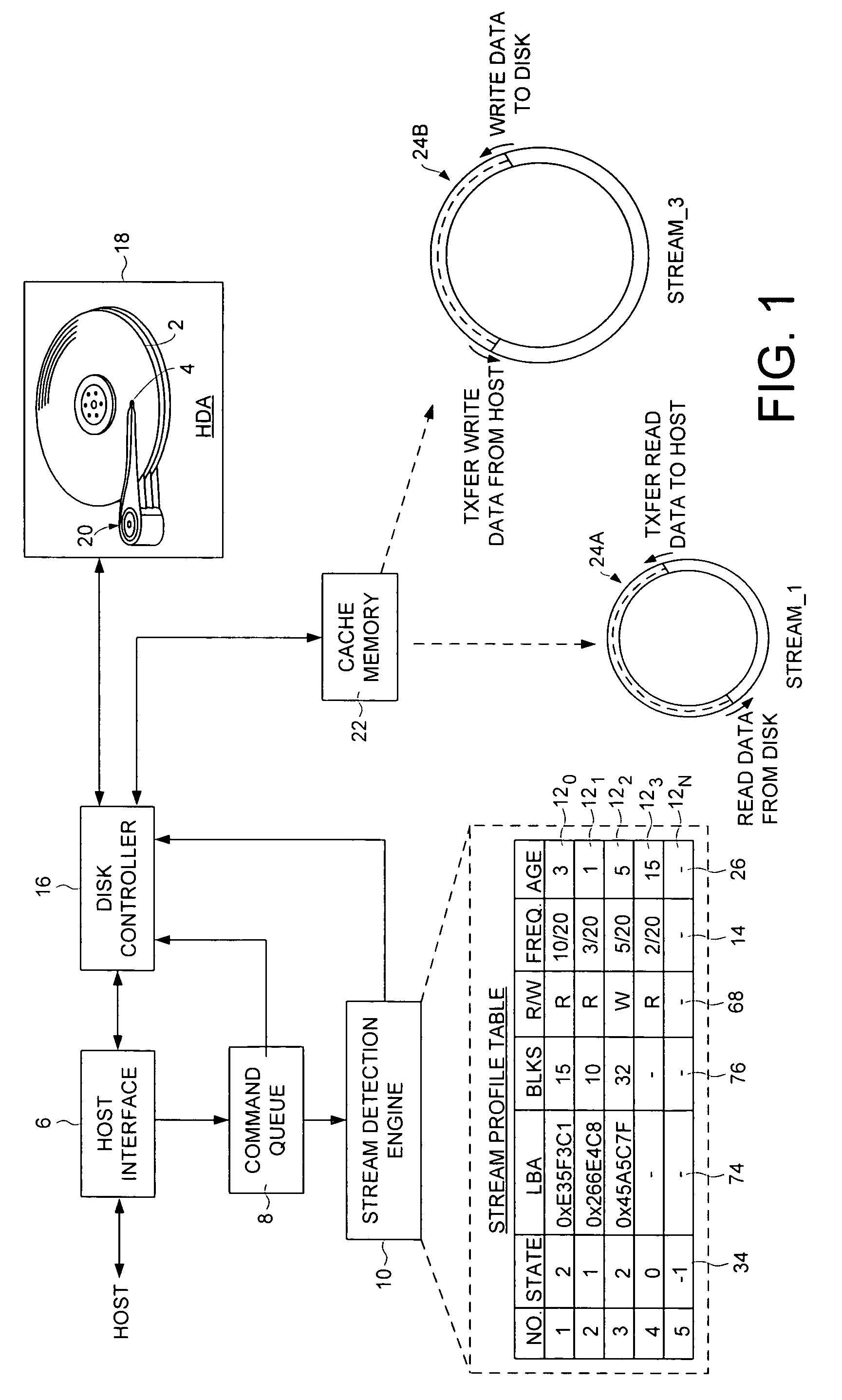
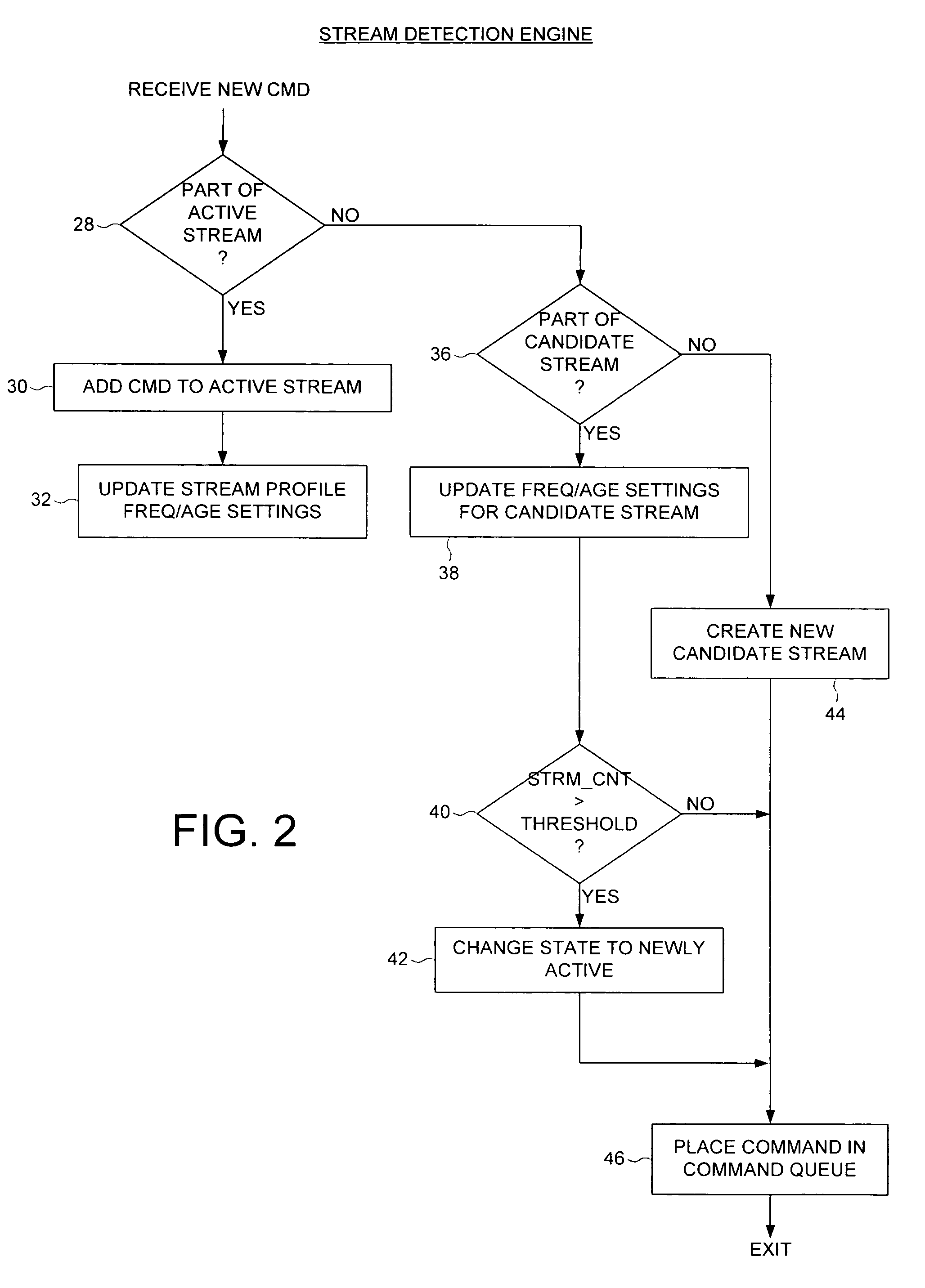
Disk drive employing stream detection engine to enhance cache management policy
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk, a head actuated over the disk, a host interface for receiving disk access commands from a host, a command queue for queuing the disk access commands, and a stream detection engine for evaluating the disk access commands to detect a plurality of streams accessed by the host. The stream detection engine maintains a stream data structure for each detected stream, wherein the stream data structure comprises a frequency counter for tracking a number of disk access commands associated with the stream out of a predetermined number of consecutive disk access commands received from the host. A disk controller selects one of the streams for servicing in response to the frequency counters.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
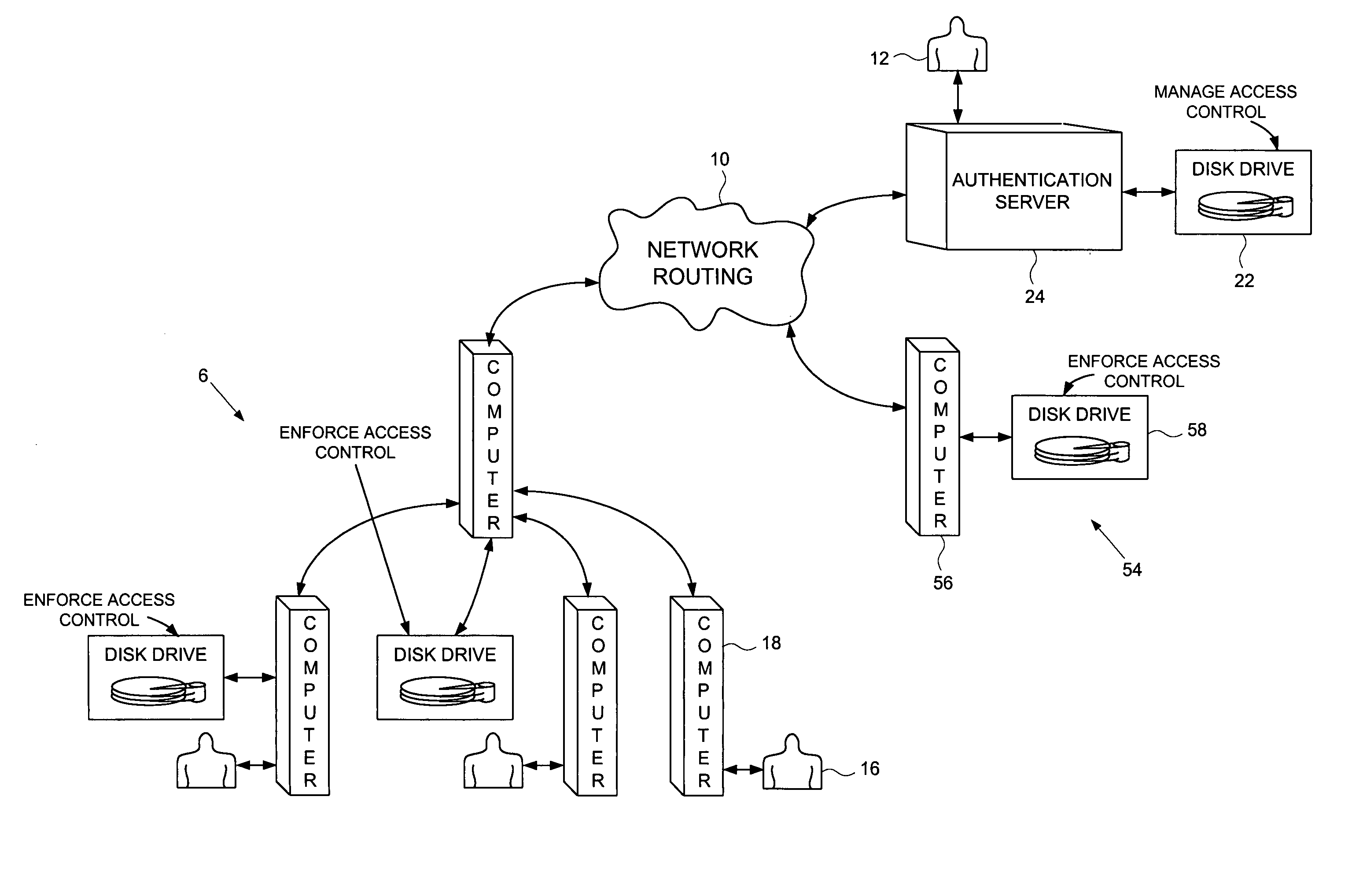
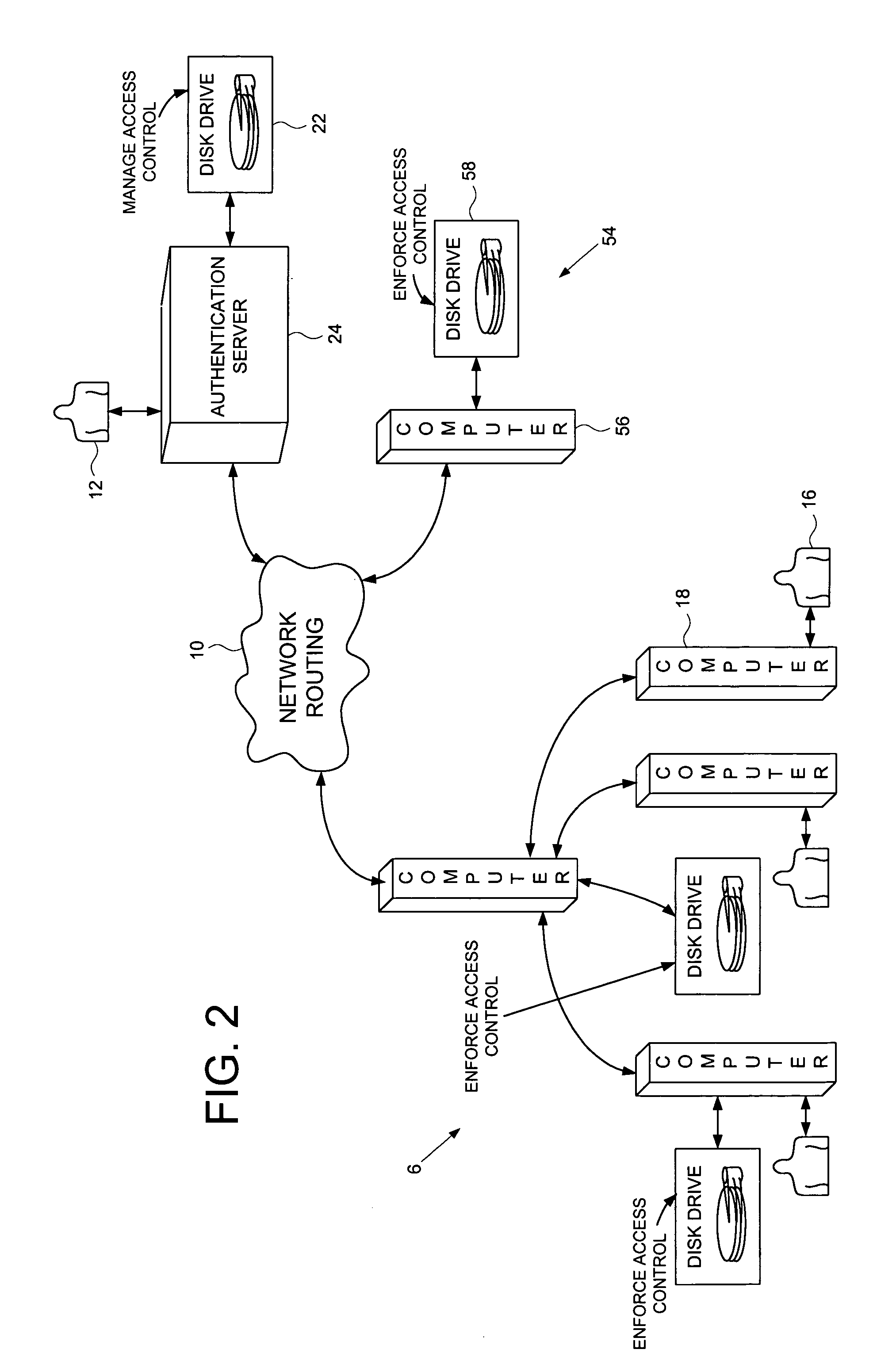
Computer network comprising network authentication facilities implemented in a disk drive
InactiveUS7155616B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDisk controllerAuthentication server
A computer network is disclosed comprising a plurality of interconnected network devices including a plurality of client computers, an authentication server computer operated by a system administrator, and a disk drive connected to the authentication server computer. The disk drive comprises an interface for receiving the personal authentication data and user access data from the system administrator, a disk for storing data, and a disk controller for controlling access to the disk. An authenticator within the disk drive, responsive to the personal authentication data, enables the disk controller, and cryptographic circuitry encrypts the user access data received from the system administrator into encrypted data stored on the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Time allocation shared memory arbitration for disk drive controller
InactiveUS6178486B1Efficient and effective arbitrationInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsDisk controllerShared memory
A method and apparatus for arbitrating requests for access to a single buffer memory embedded within a disk drive in which a disk data channel is assigned a highest priority for buffer access within a queue. An arbitration cycle progressively services access requests pending within the queue, beginning with providing buffer access to the disk data channel and following with accesses to other channels during an arbitration cycle completion interval in accordance with a round-robin circular priority arrangement providing orderly access to all channels contending for memory access. At the end of completion interval, buffer access returns to the disk data channel, and thereafter, the arbitration cycle is repeated.
Owner:MAXTOR
Multiple disk data storage system for reducing power consumption
InactiveUS7234074B2Digital data processing detailsError detection/correctionDisk controllerSystem maintenance
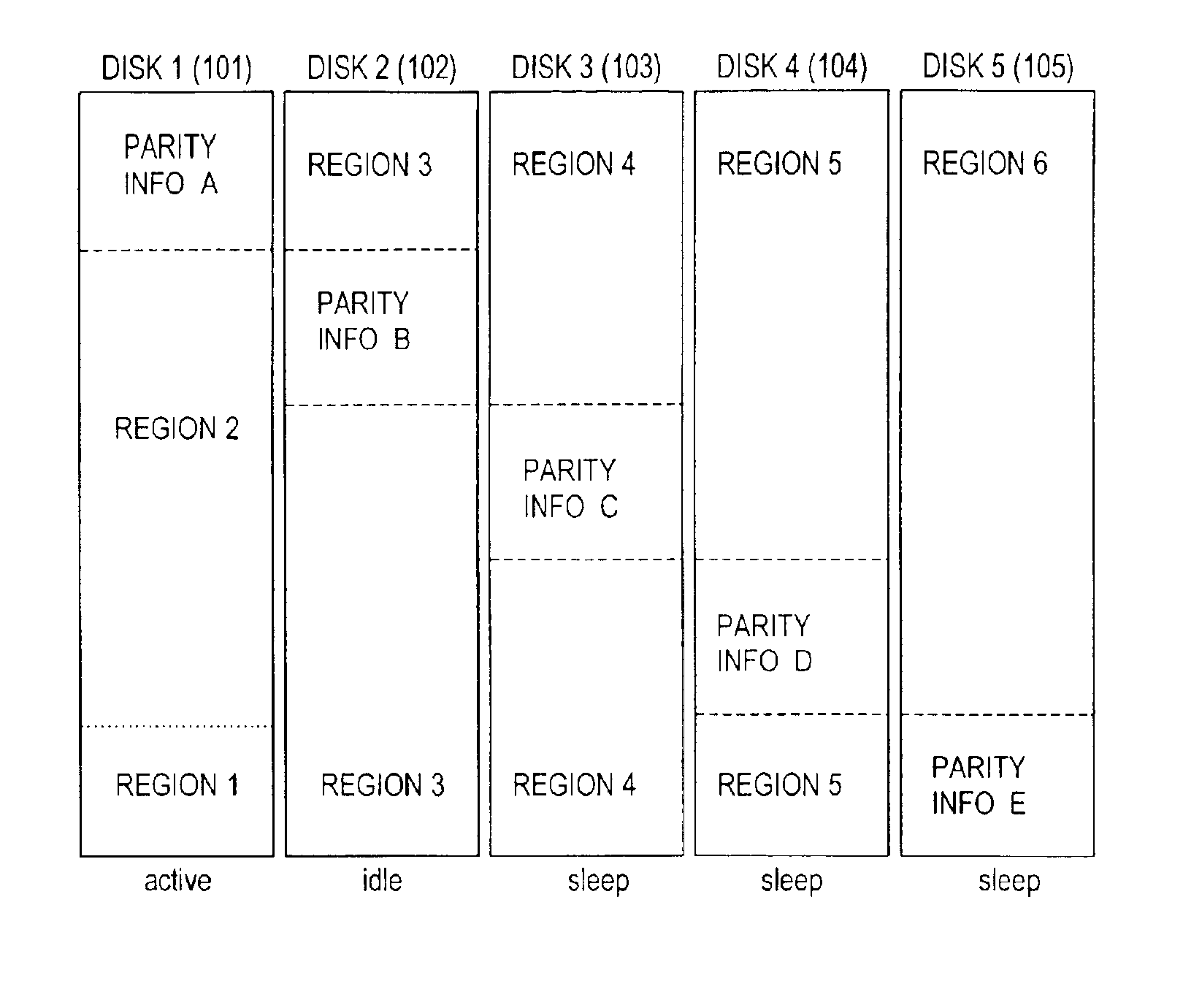
A data storage system in which each of a set of disks has a first portion for either popular data or error correction information (parity or Reed-Solomon code symbols) associated with the popular data, and a second portion used for other data. A disk controller connected to the set of disks maintains a first popular data block in the first portion of a first of the set of disks and a second popular data block in the first portion of a second of the set of disks. The system maintains at least two of the disks in an active state. The active disks are selected to insure that any data in the popular data blocks can be determined from data stored in the active disks. An additional disk is maintained in an active state if write access is permitted or if there is an additional popular data block.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data storewidth accelerator
InactiveUS7376772B2Improve processing speedHigh bandwidthCode conversionBootstrappingData compressionDisk controller
Data storage controllers and data storage devices employing lossless or lossy data compression and decompression to provide accelerated data storage and retrieval bandwidth. In one embodiment of the invention, a composite disk controller provides data storage and retrieval acceleration using multiple caches for data pipelining and increased throughput. In another embodiment of the invention, the disk controller with acceleration is embedded in the storage device and utilized for data storage and retrieval acceleration.
Owner:REALTIME DATA
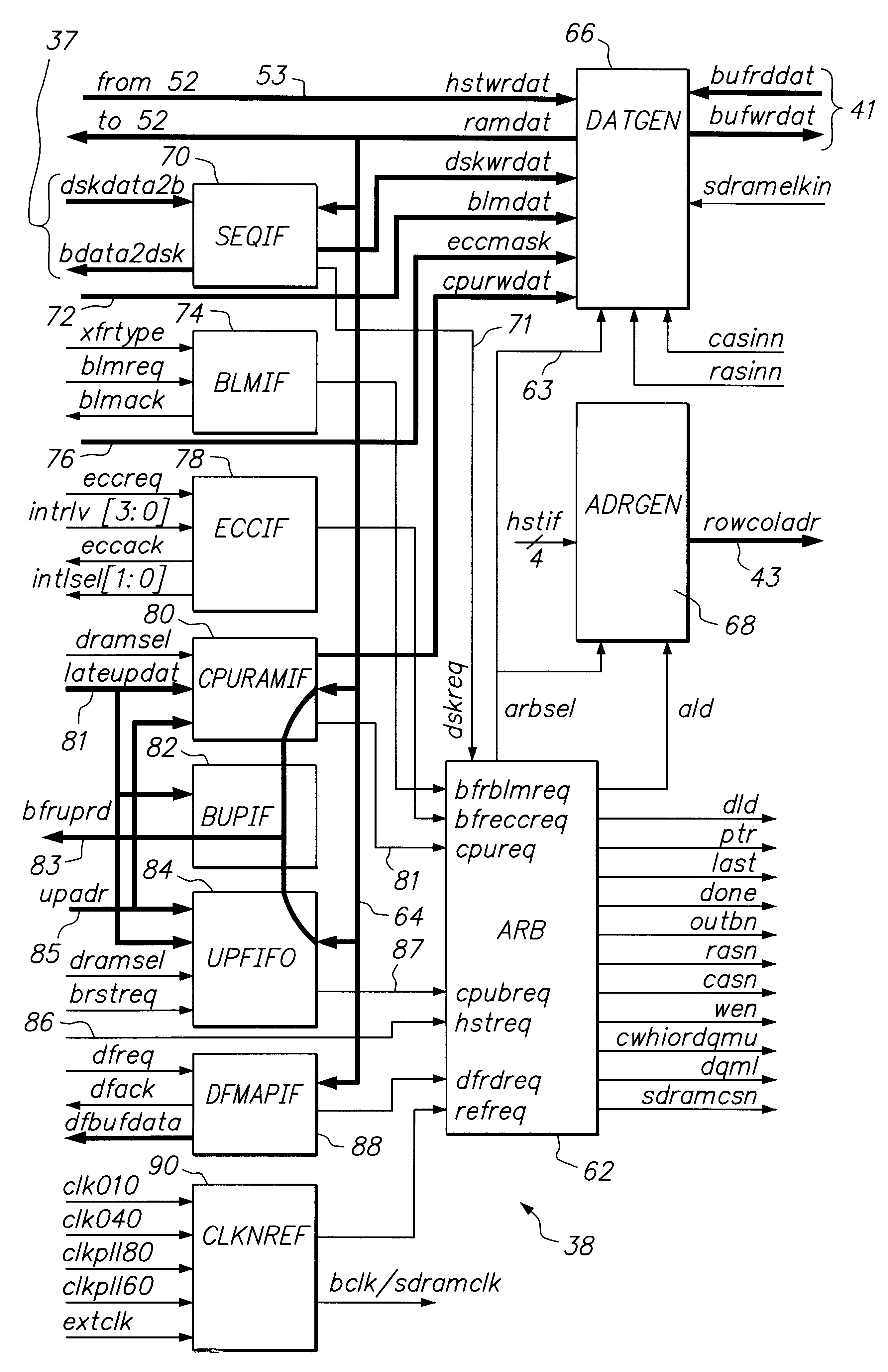
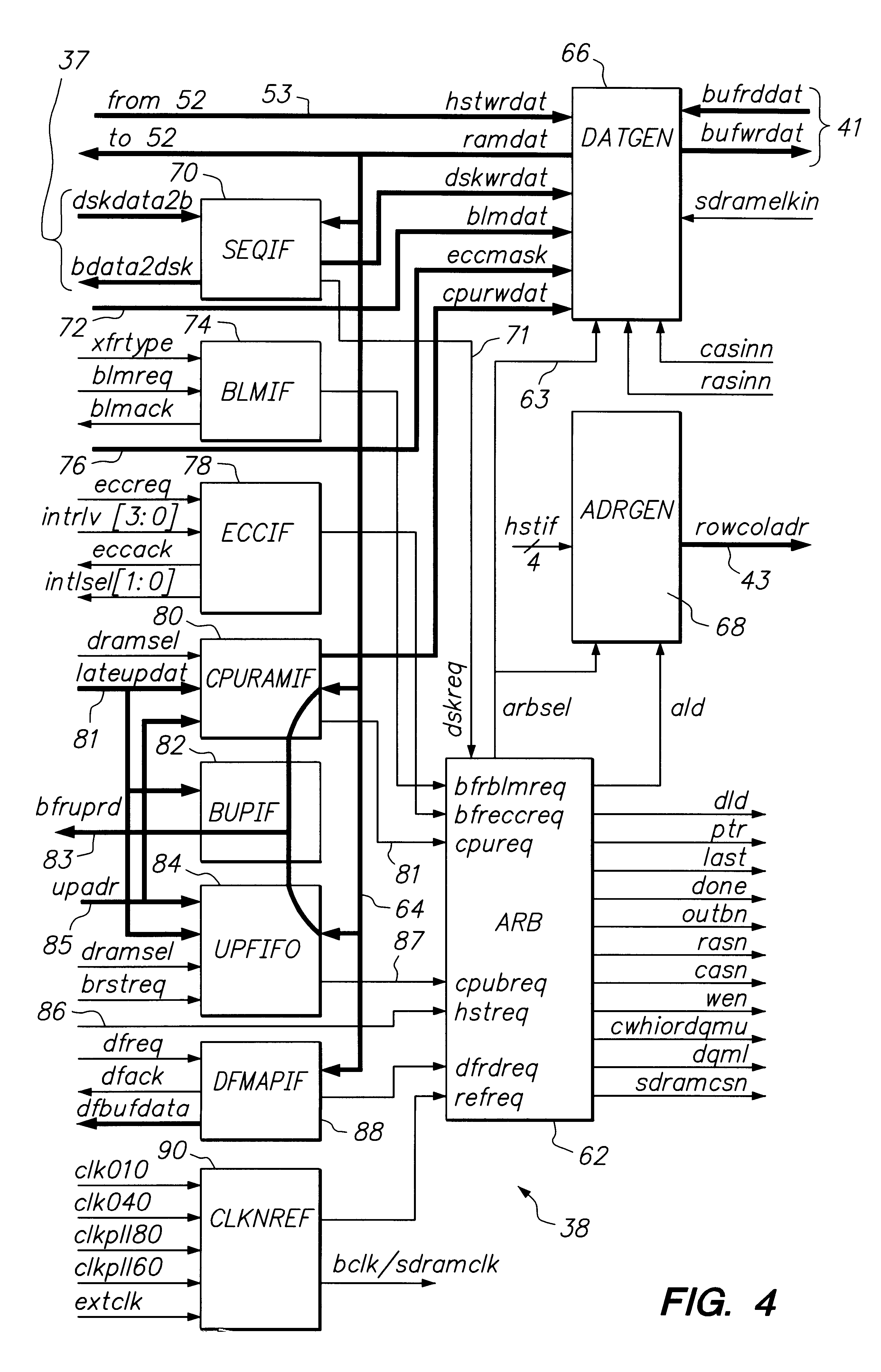
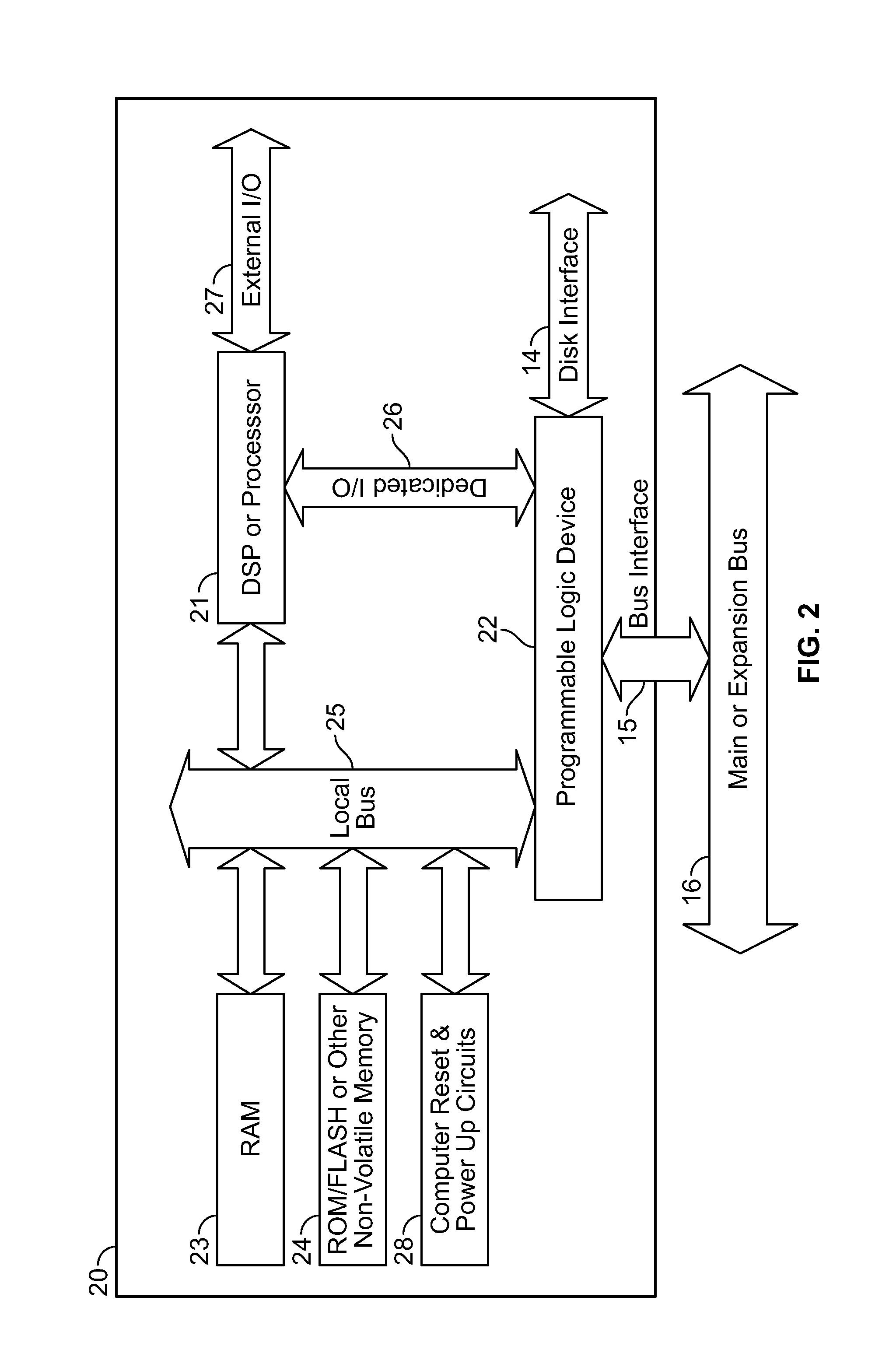
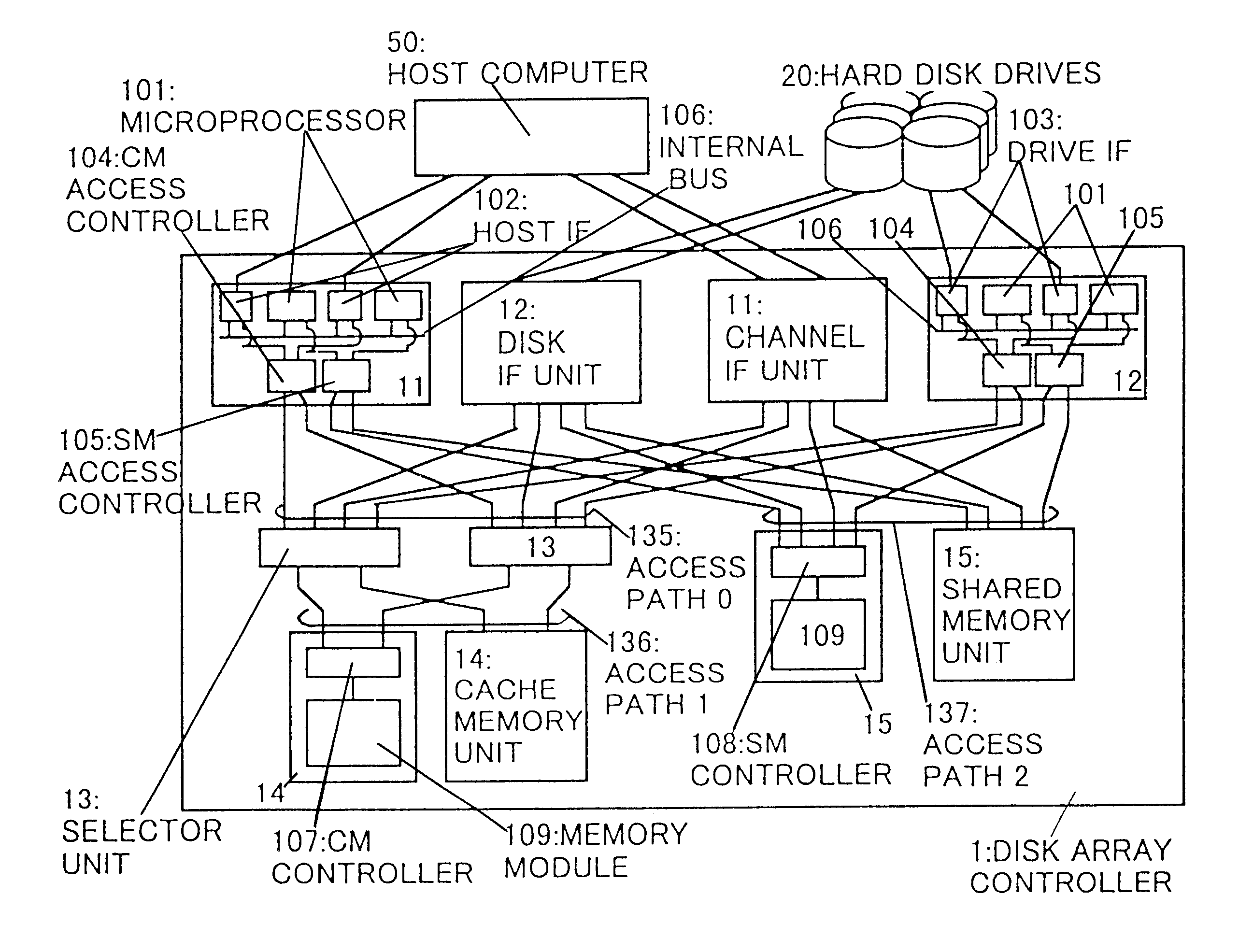
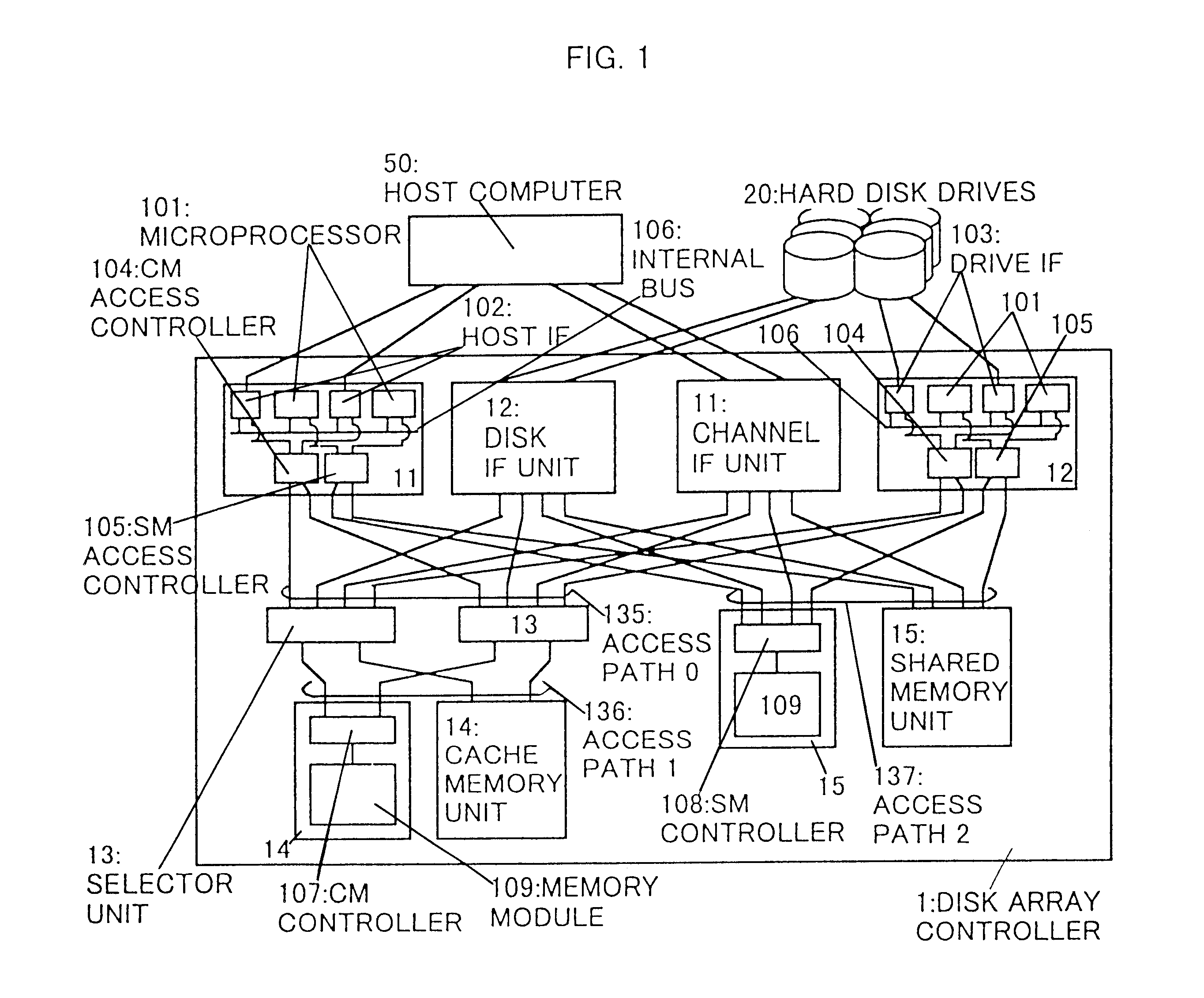
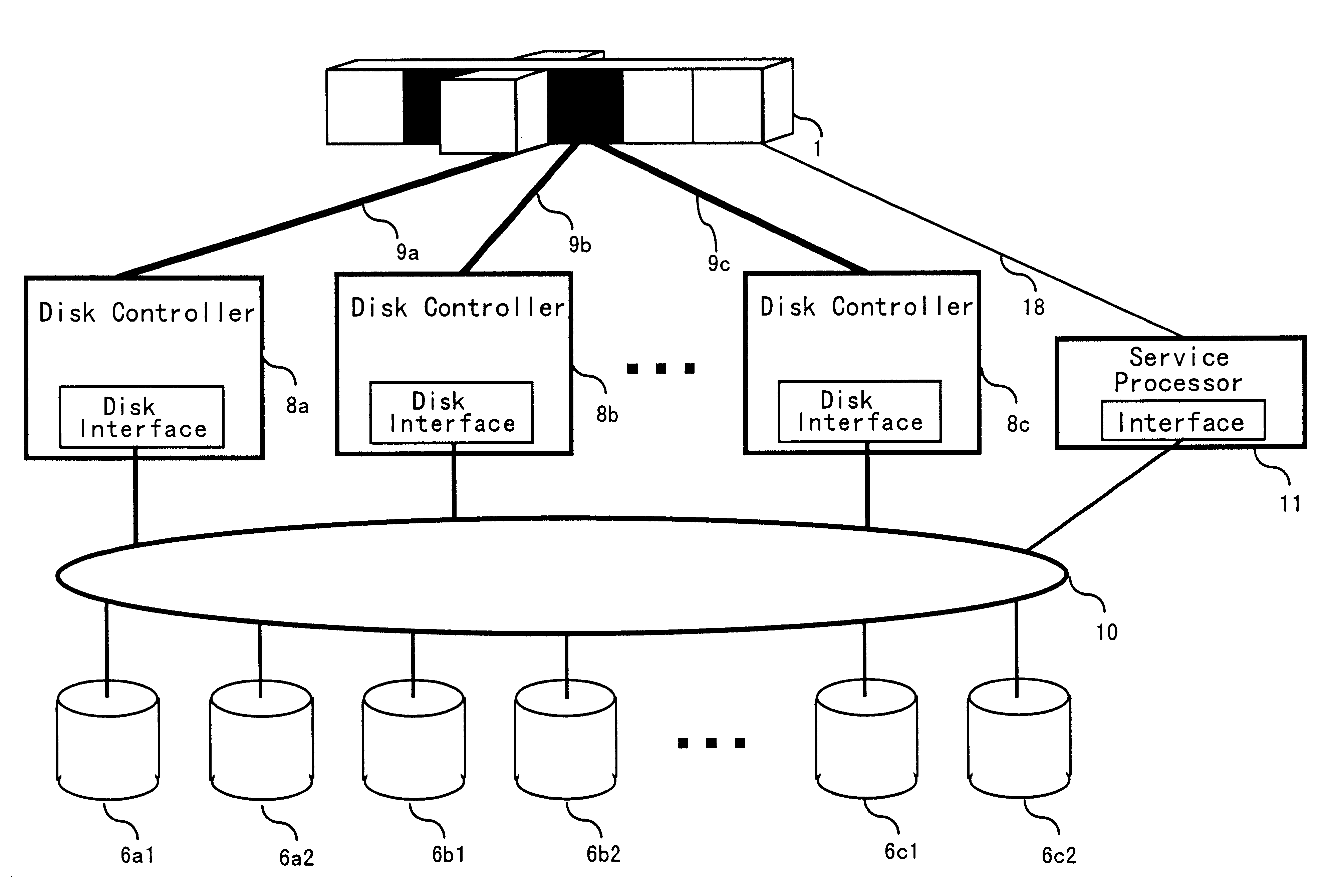
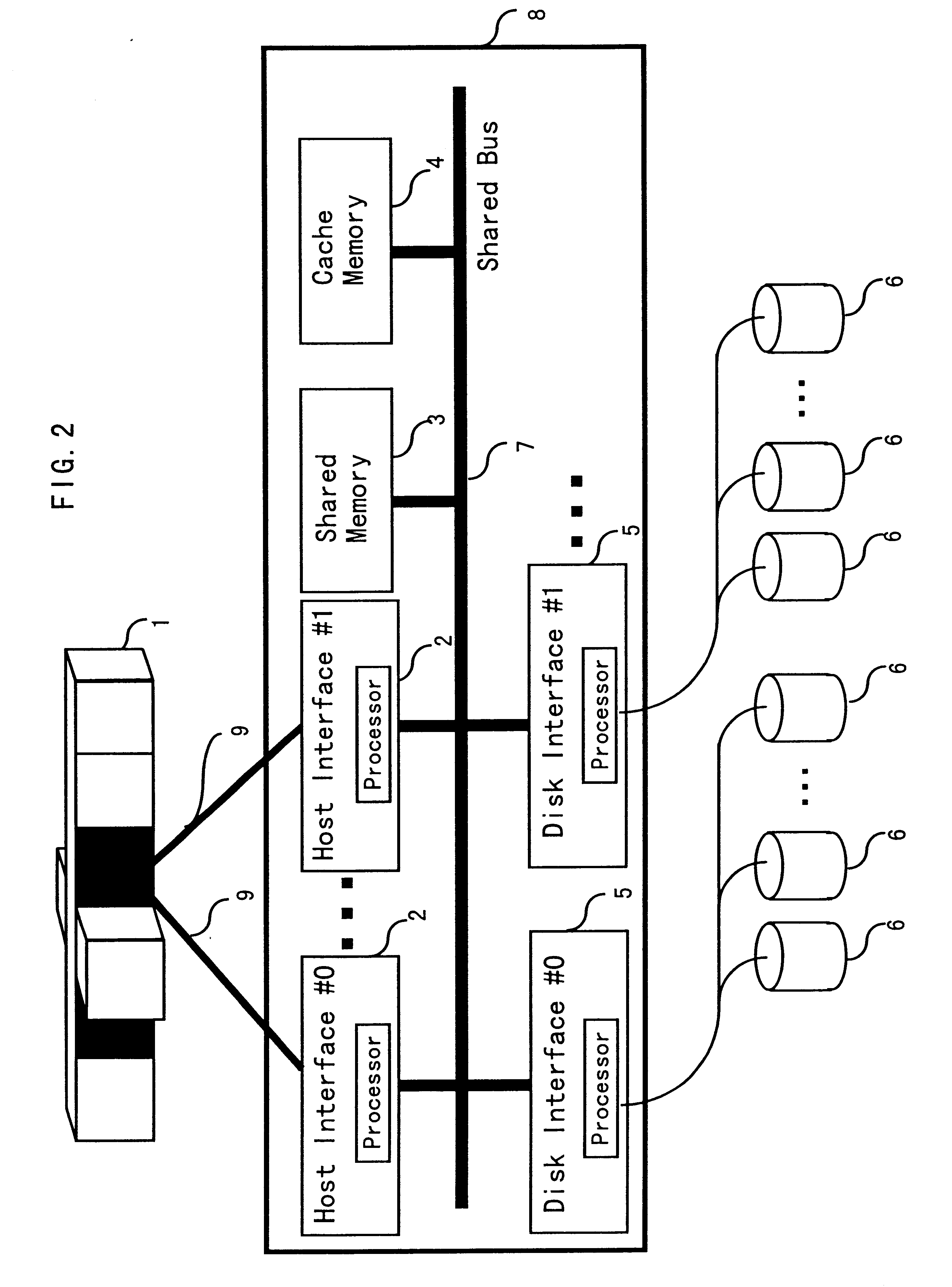
Disk array control device with two different internal connection systems
A disk array control device which includes a plurality of channel interface (IF) units, a plurality of disk IF units, a cache memory unit, and a shared memory unit. The connection system between the plurality of channel IF units and plurality of disk IF units and the cache memory unit is different from the connection system between the plurality of channel IF units and plurality of disk IF units and the shared memory unit. In the invention the plurality of channel IF units and the plurality of disk IF units are connected via a selector to the cache memory unit, whereas the plurality of channel IF units and the plurality of disk IF units are directly connected to the shared memory unit with no selectors.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
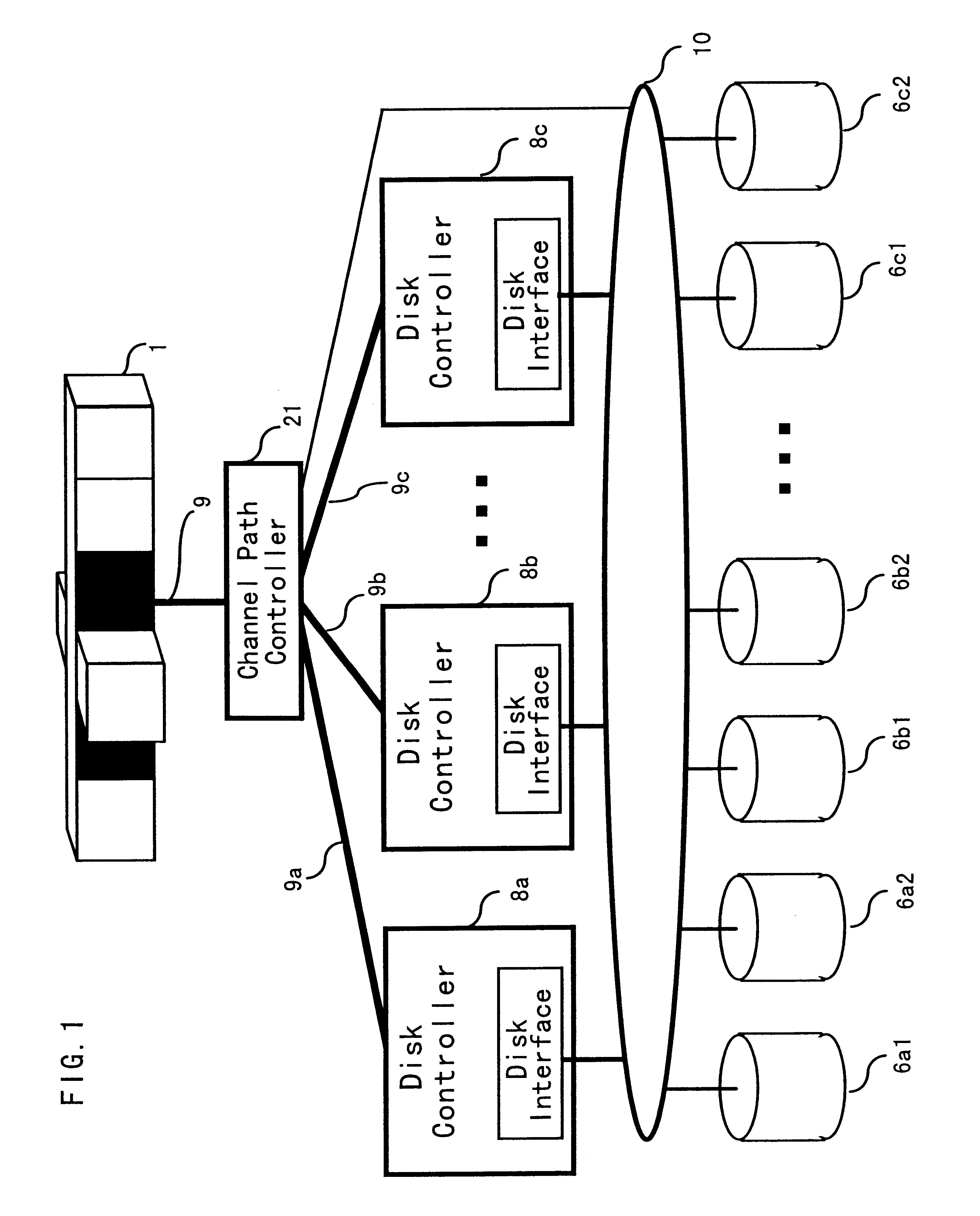
Storage subsystem which balances loads across a plurality of disk controllers
InactiveUS6378039B1Input/output to record carriersMultiprogramming arrangementsMagnetic disksDisk array controller
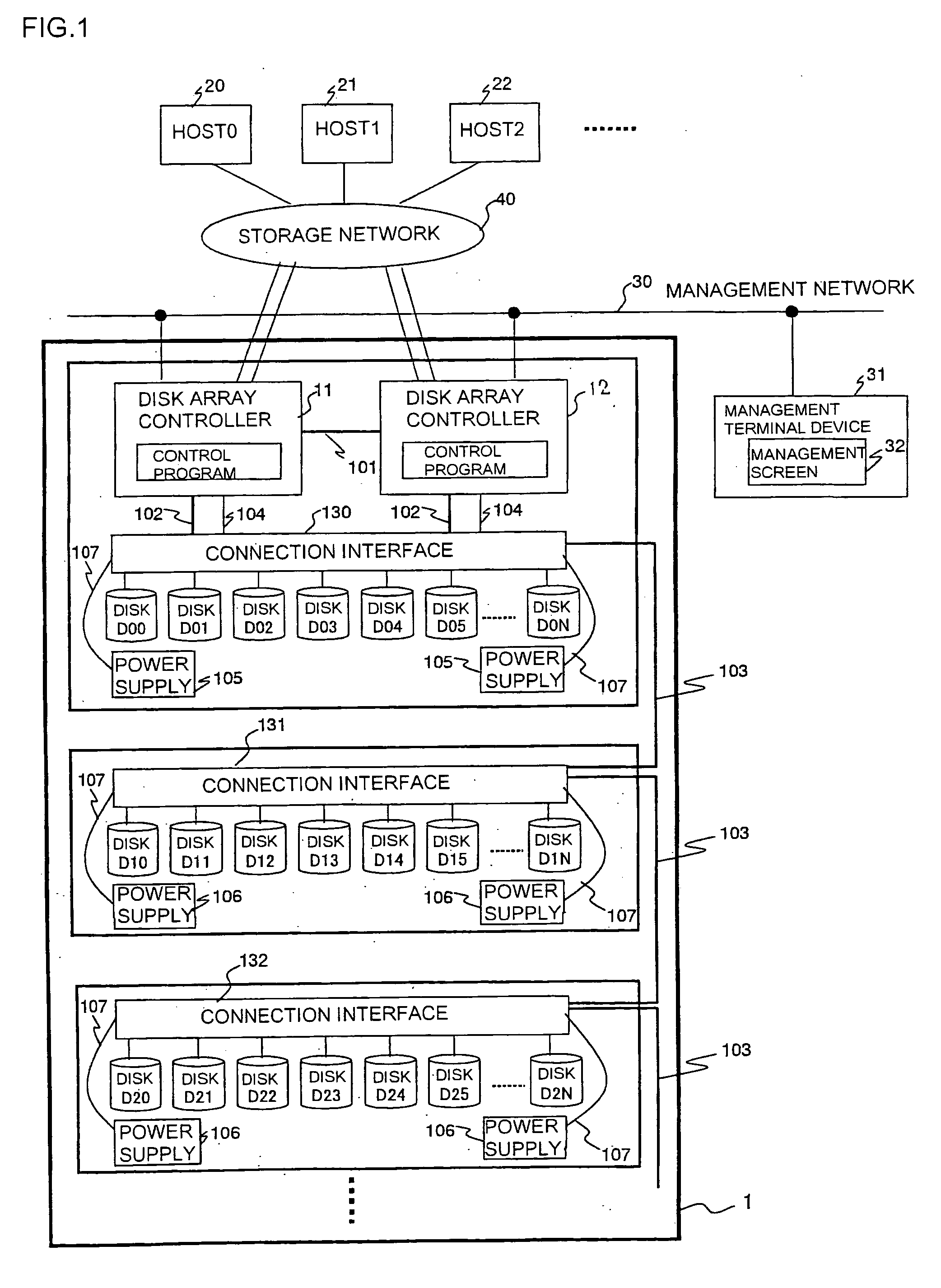
A storage subsystem include: a plurality of disk controllers; a plurality of disk drives connected via a network to the plurality of disk controllers; and a path controller connected to the plurality of disk controllers. The path controller changes a management site, which manages a volume in each of the plurality of disk drives managed by each of the plurality of disk controllers, from one of the plurality of disk controllers to another. The path controller has a correspondence table which stores a correspondence between a volume number of a volume in each of the plurality of disk drives and identification information of the disk controller which manages a volume corresponding to the volume number.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Disc array apparatus checking and restructuring data read from attached disc drives
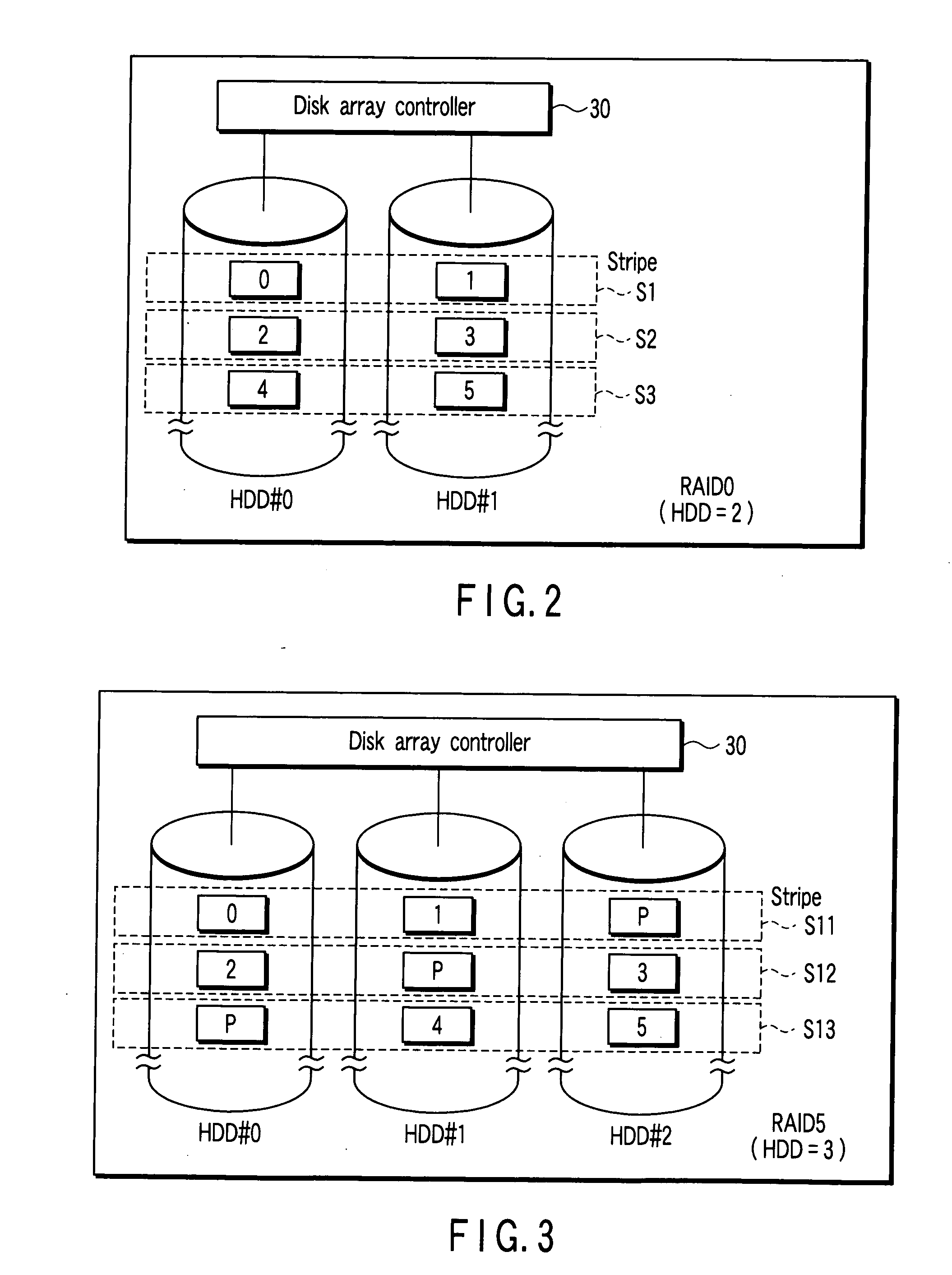
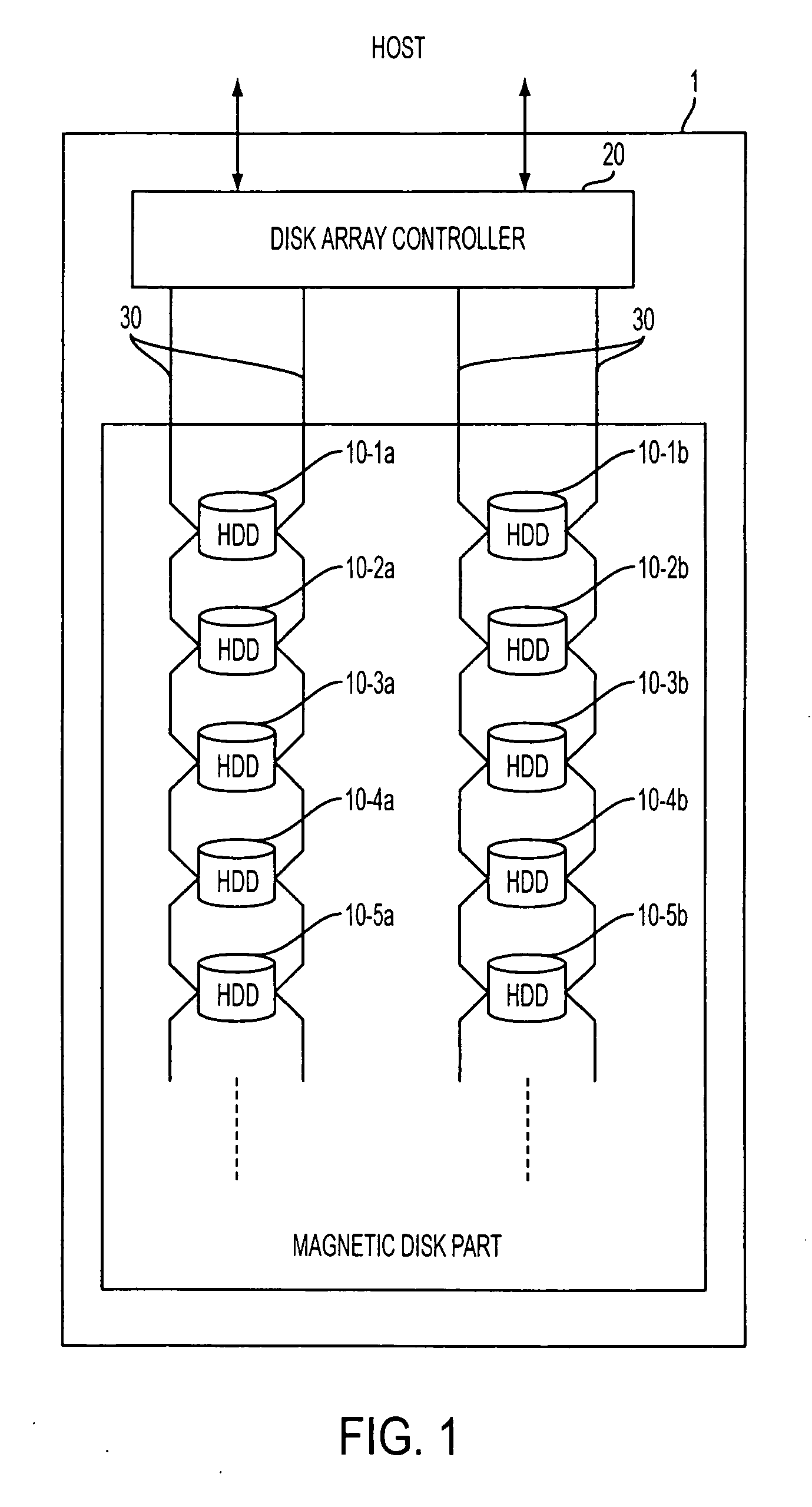
The present invention relates to a disc array apparatus assuring that even if contradiction is detected in matching of parity data during a read parity check, correct host data is Restructured and can always be transferred to the host. The disc array apparatus of the present invention is particularly applicable to disc drives in the RAID configuration. For example, in a disc array apparatus of the present invention implementing RAID level 3, the disc array apparatus adds CRC data to data transferred from a host computer, divides the data, generates parity from the divided data, and stores the data and the parity data into the disc drives. During a read operation, the disc array apparatus of the present invention executes a read parity check. If contradiction is detected between the parity data stored in the disc drives and the parity data generated during the read parity check, the disc array controller sequentially assumes, one disc drive at a time, that one of the disc drives is storing erroneous data, restructures the host data from the divided data and parity data of the disc drives other than the disc drive storing erroneous data for each assumption, and executes a CRC check on the restructured host data for each assumption. Restructured host data is determined to be correct host data when the CRC check detects no error. The principle of the present invention is also implemented in other RAID levels, and using data such as time or counter value, to determine and restructure erroneous data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Data storage system and method of hierarchical control thereof
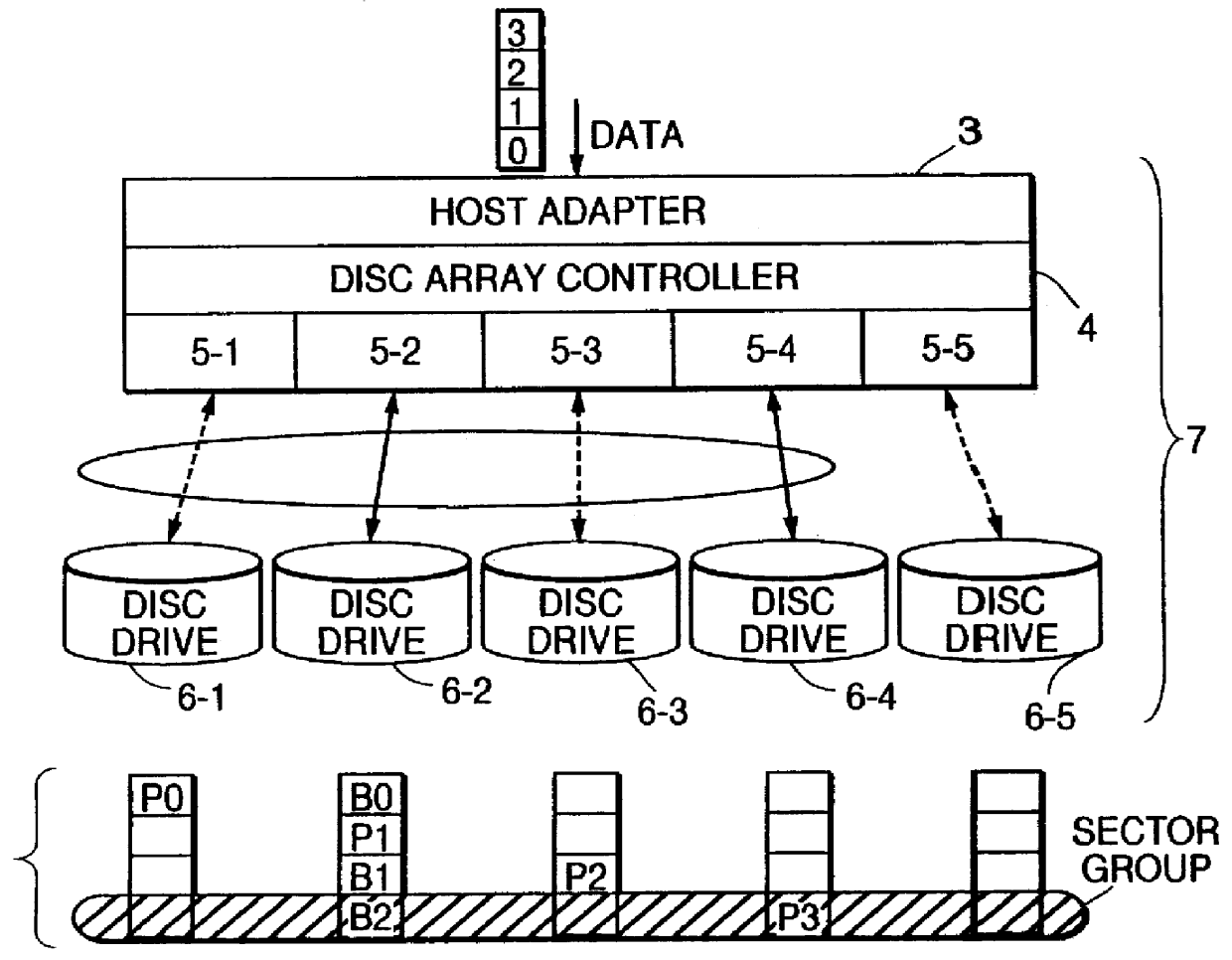
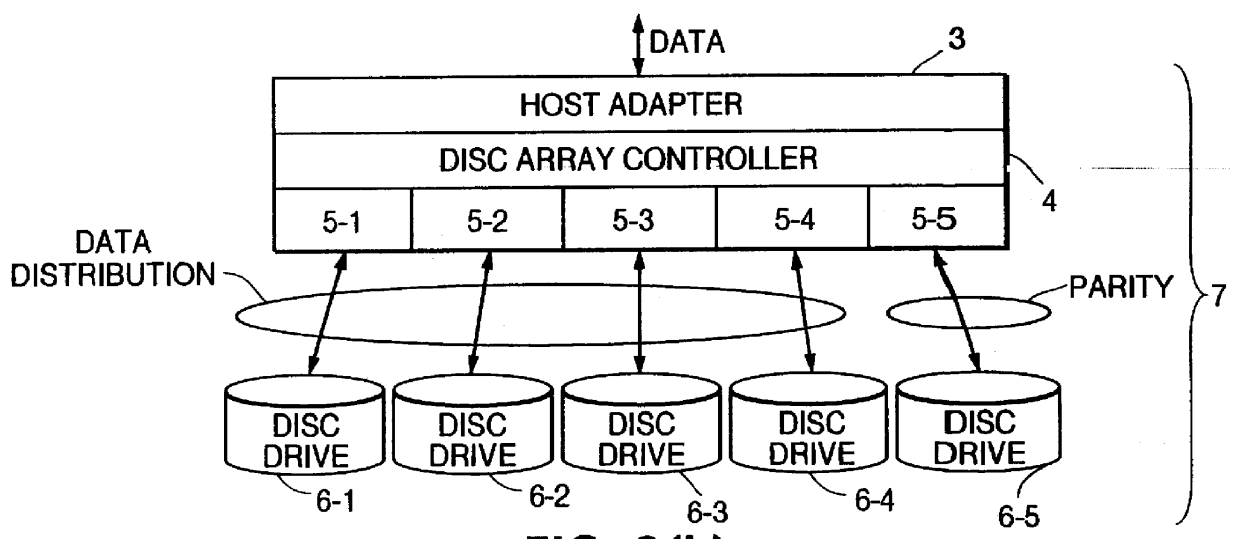
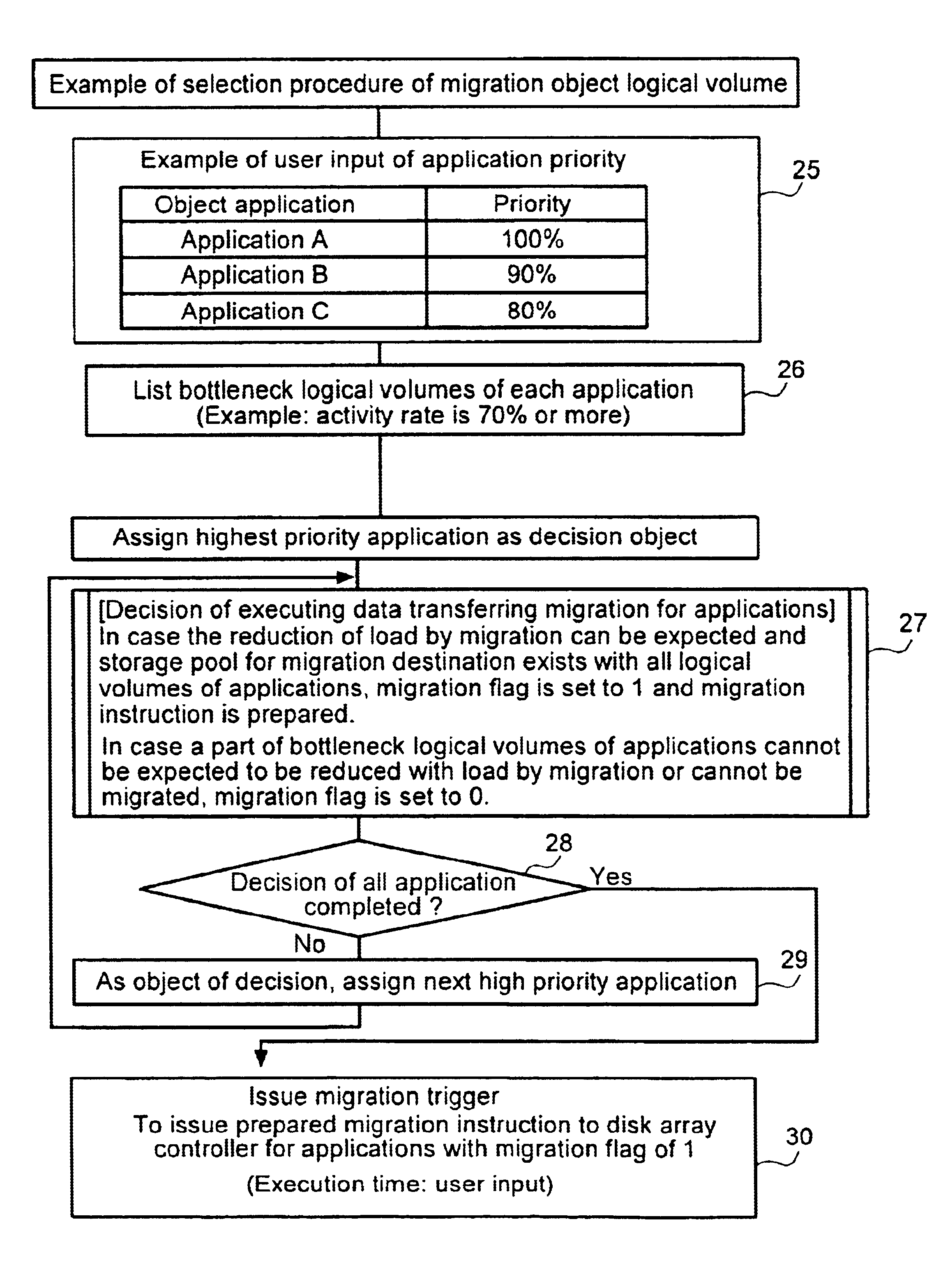
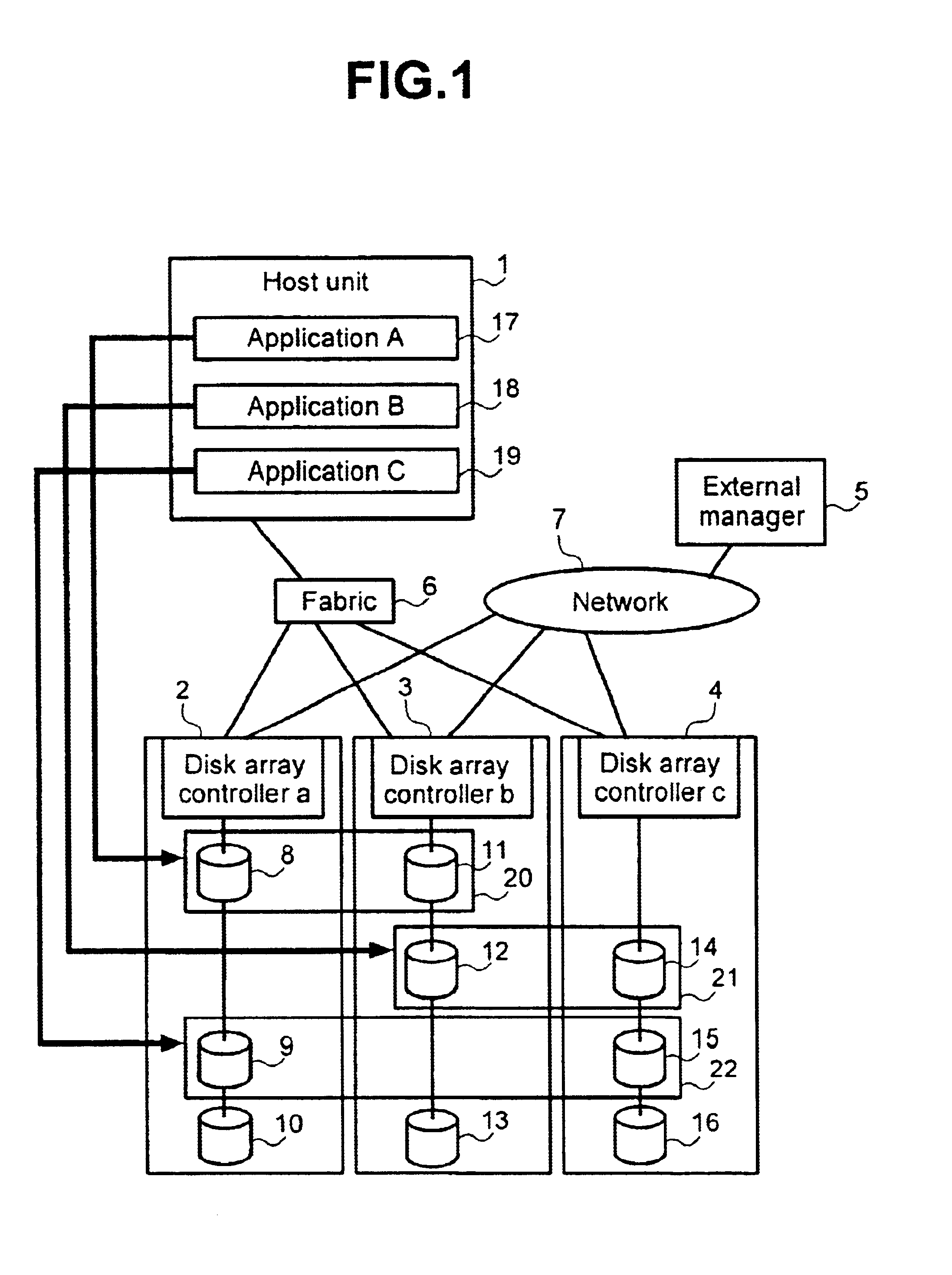
InactiveUS6779078B2Not needlessly consumedImprove efficiencyInput/output to record carriersHardware monitoringParallel computingDisk array
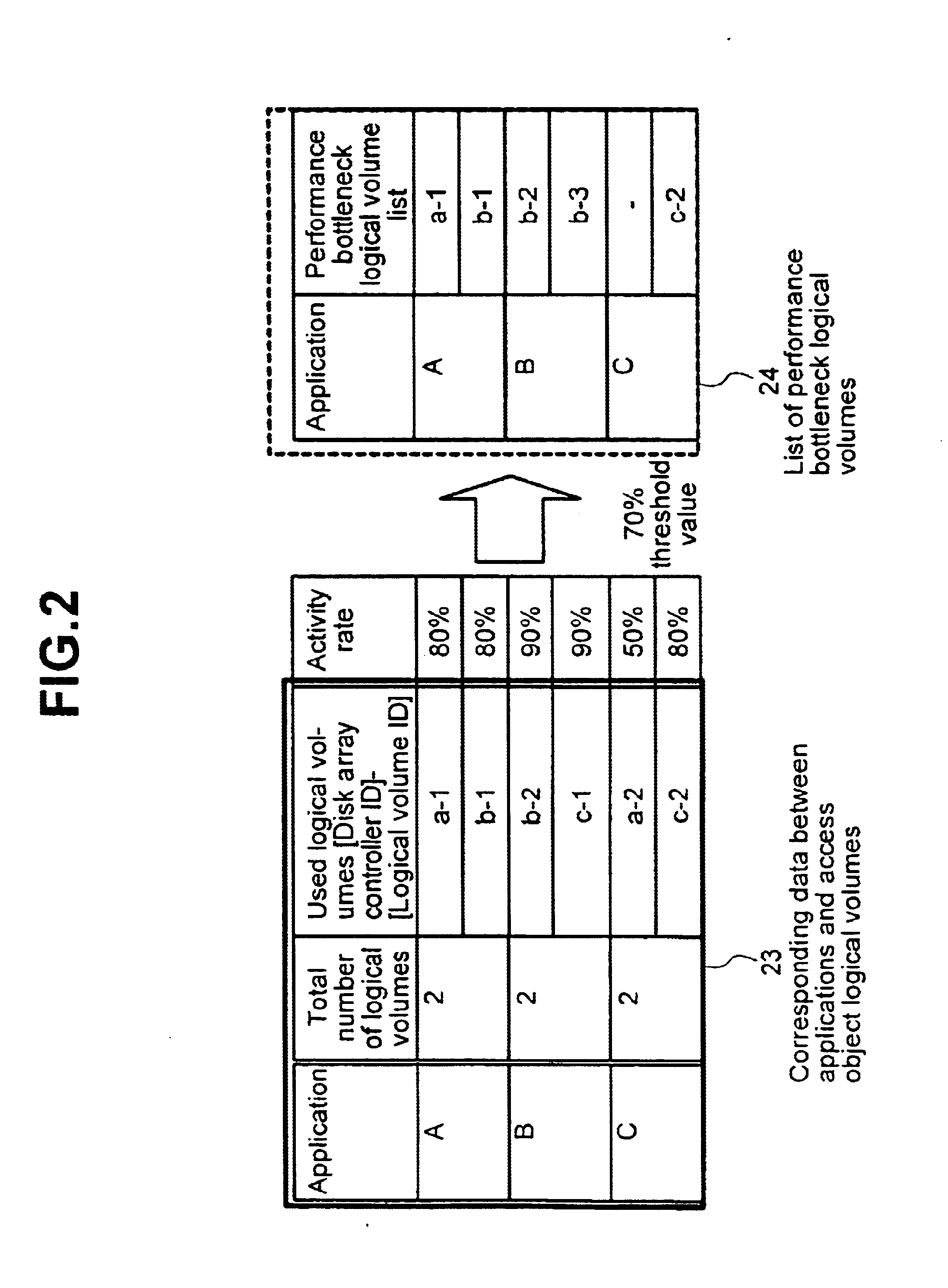
A method of selecting logical volumes that are the targets for data migration to equilibrate the load on a system, based on the accessing data of the physical drives and logical drives under the disk array controllers, without increasing the load of the disk array controller. An external manager communicates with two or more disk array controllers, gathers and manages the access data and the configuration data relating to the physical drives and logical volumes of each disk array controller, and prepares an optimum data migration instruction to equilibrate the access load.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Multiple disk data storage system for reducing power consumption
A disk controller connected to a set of disks in a data storage system is configured to mirror a first class of data on multiple disks while storing a second class of data without mirroring. The controller maintains at least one of the disks containing the first class of data in an operational state while maintaining at least one of the remaining disks in a low power state. The first class of data may contain popular files while the second class of data contains unpopular files. The first data class may be mirrored on each of the disks. The data in the second class may be stored with parity where the parity information is maintained on a single disk. The operational disk may be changed following access to data from the second class of data that is stored on one of the low power state disks.
Owner:IBM CORP
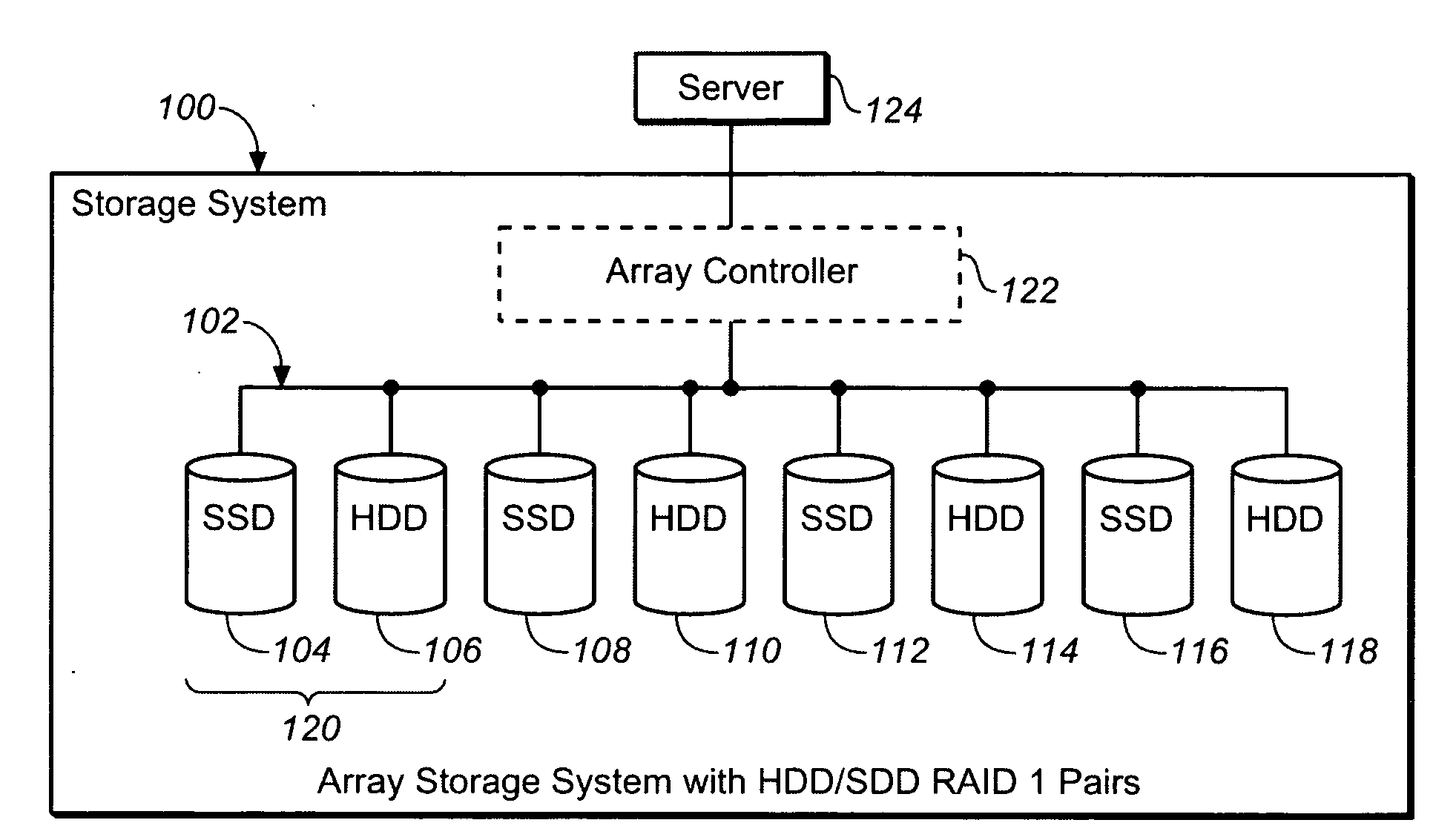
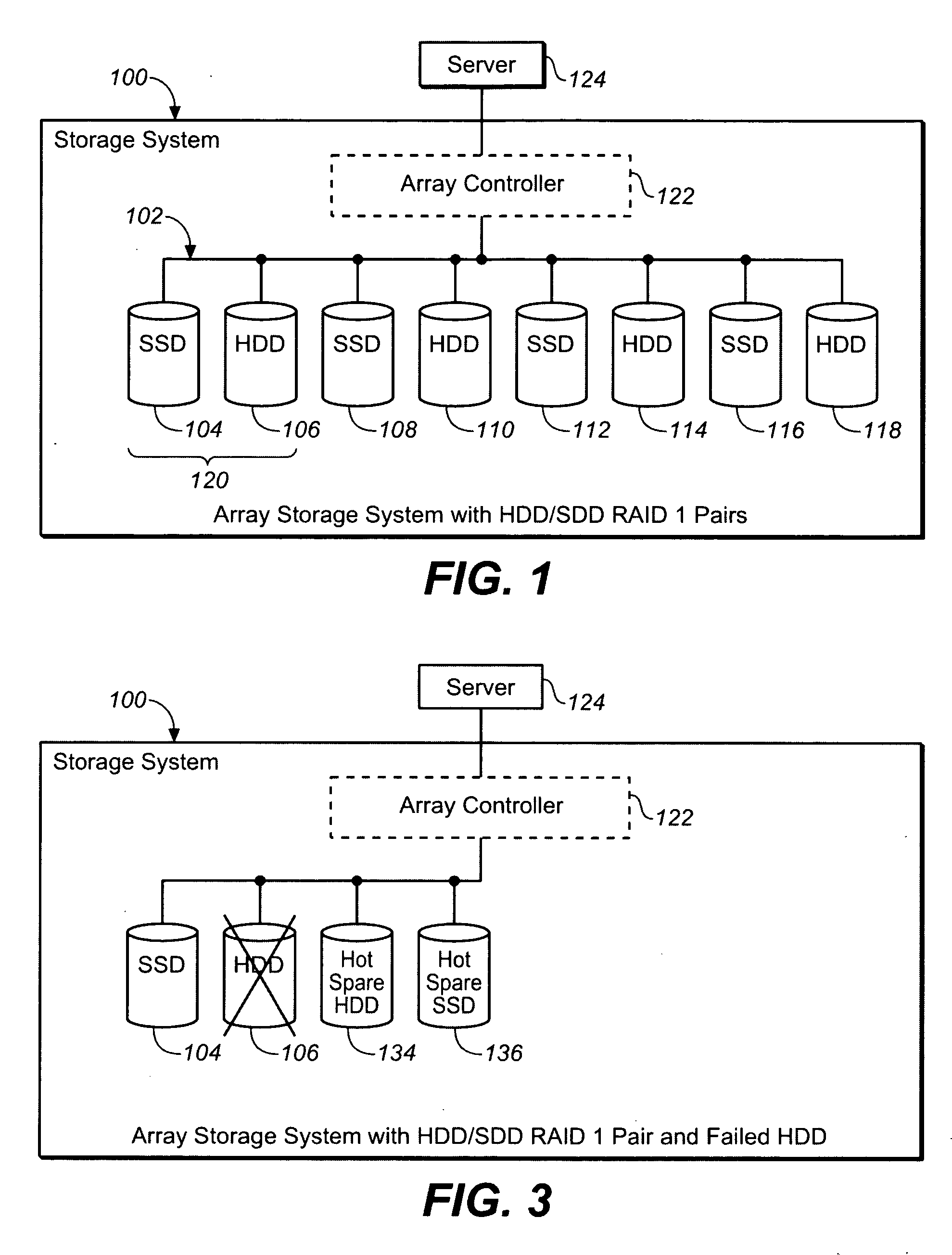
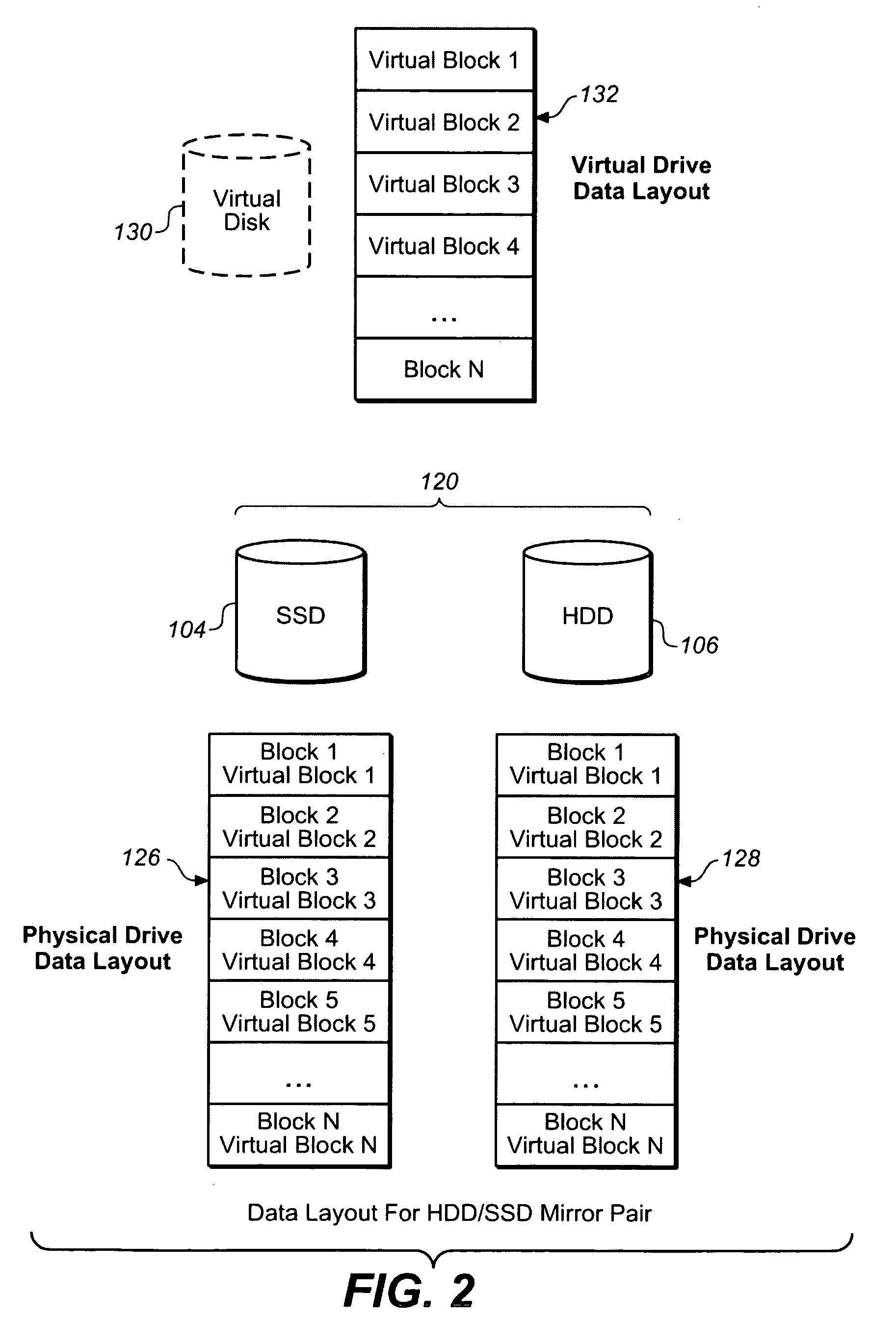
System including solid state drives paired with hard disk drives in a RAID 1 configuration and a method for providing/implementing said system
The present invention is a storage system. The storage system includes a disk array. The disk array includes a disk drive pair which includes a hard disk drive and a solid state disk drive, such as a NAND flash drive. The storage system also includes a disk array controller. The disk array controller may be communicatively coupled with a host server and with the disk array. Further, the disk array controller may be configured for reading from the disk array and writing to the disk array based upon read commands and write commands received from the host server. The disk array may be configured as a Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) configuration, such as a Level 1 RAID configuration (RAID 1). Thus, the disk drive pair may be a RAID disk drive pair, such as a RAID 1 disk drive pair. Further, all the read commands may be directed exclusively to the solid state disk drive and the write commands may be directed to both the solid state disk drive and the hard disk drive.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
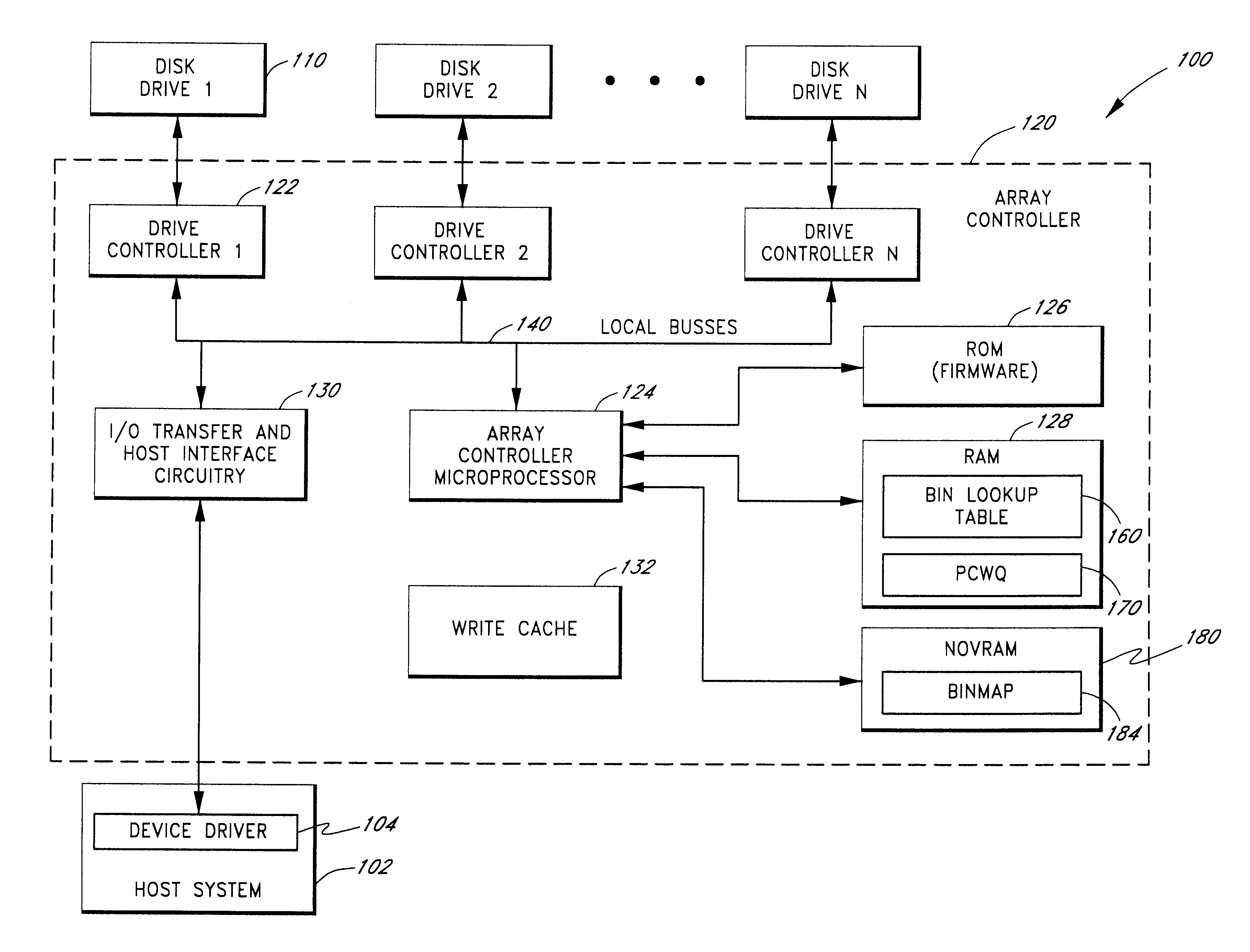
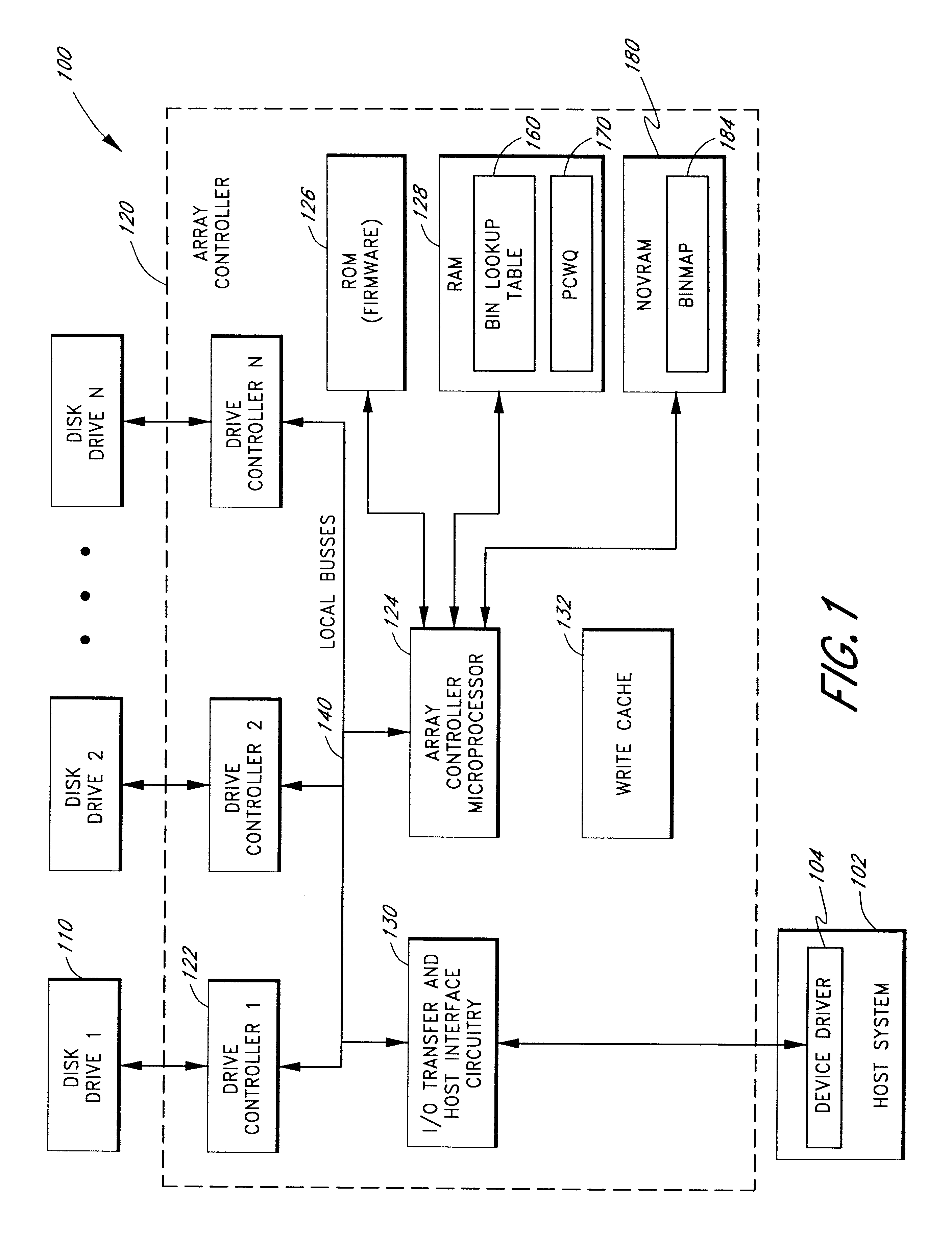
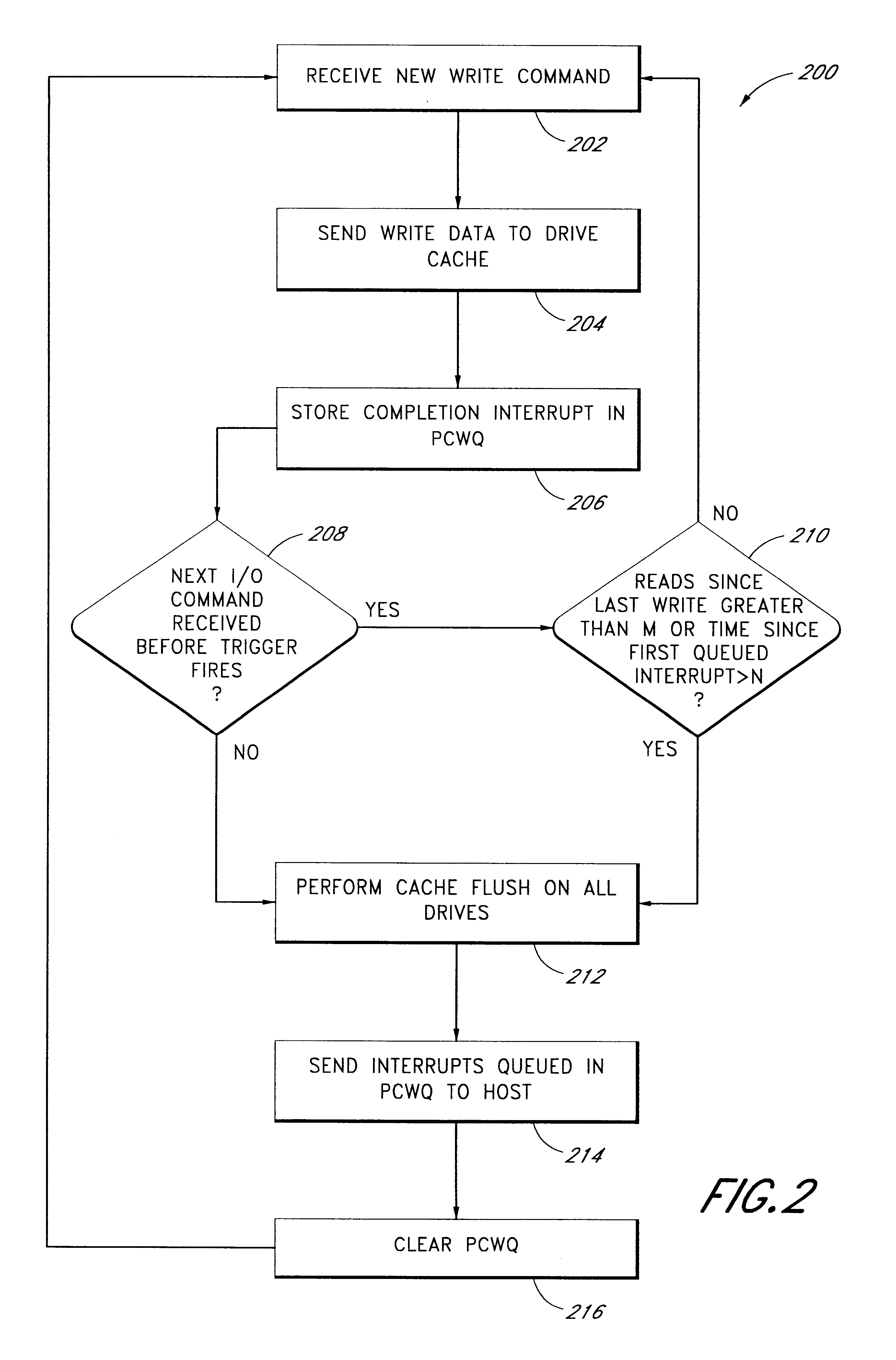
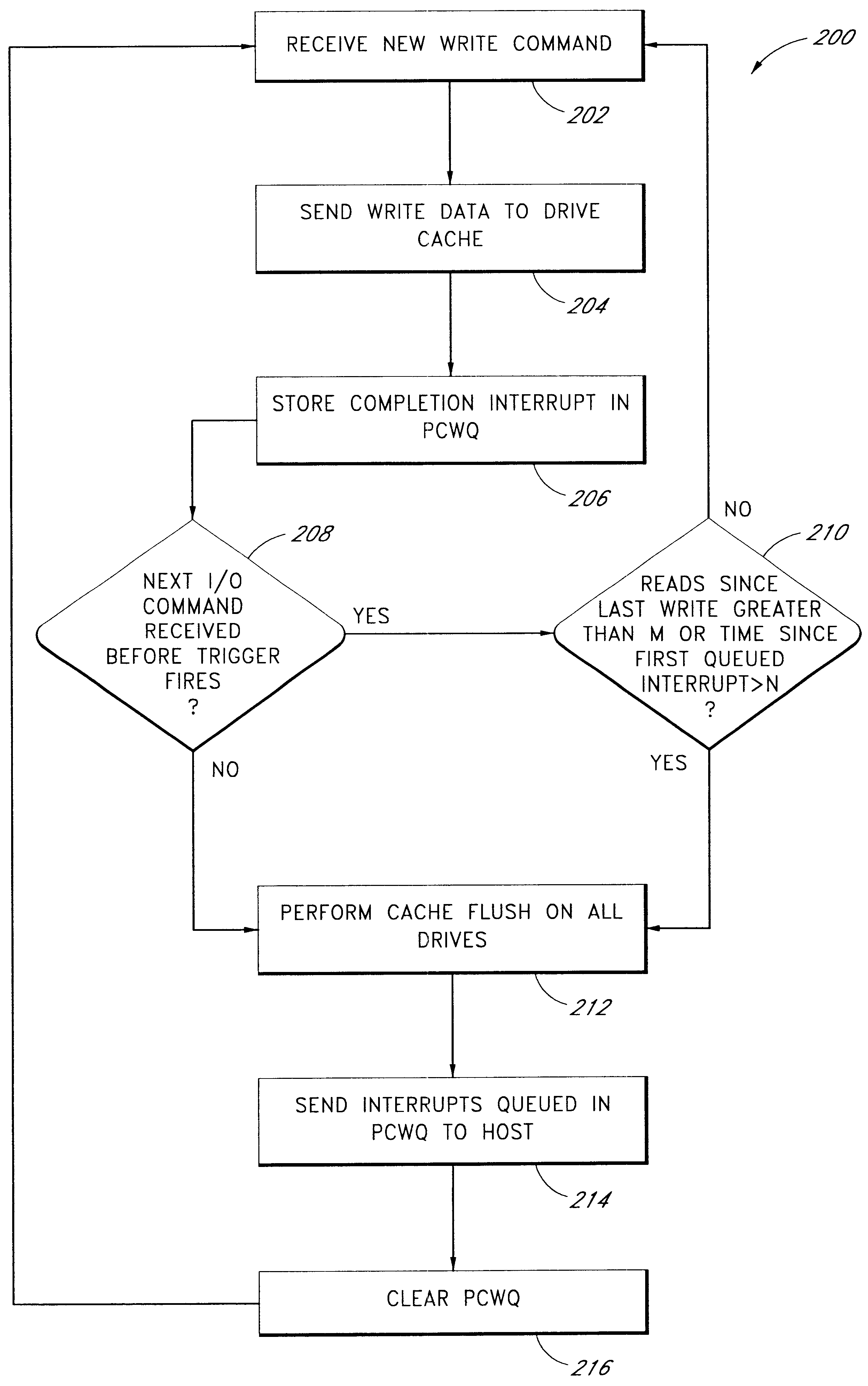
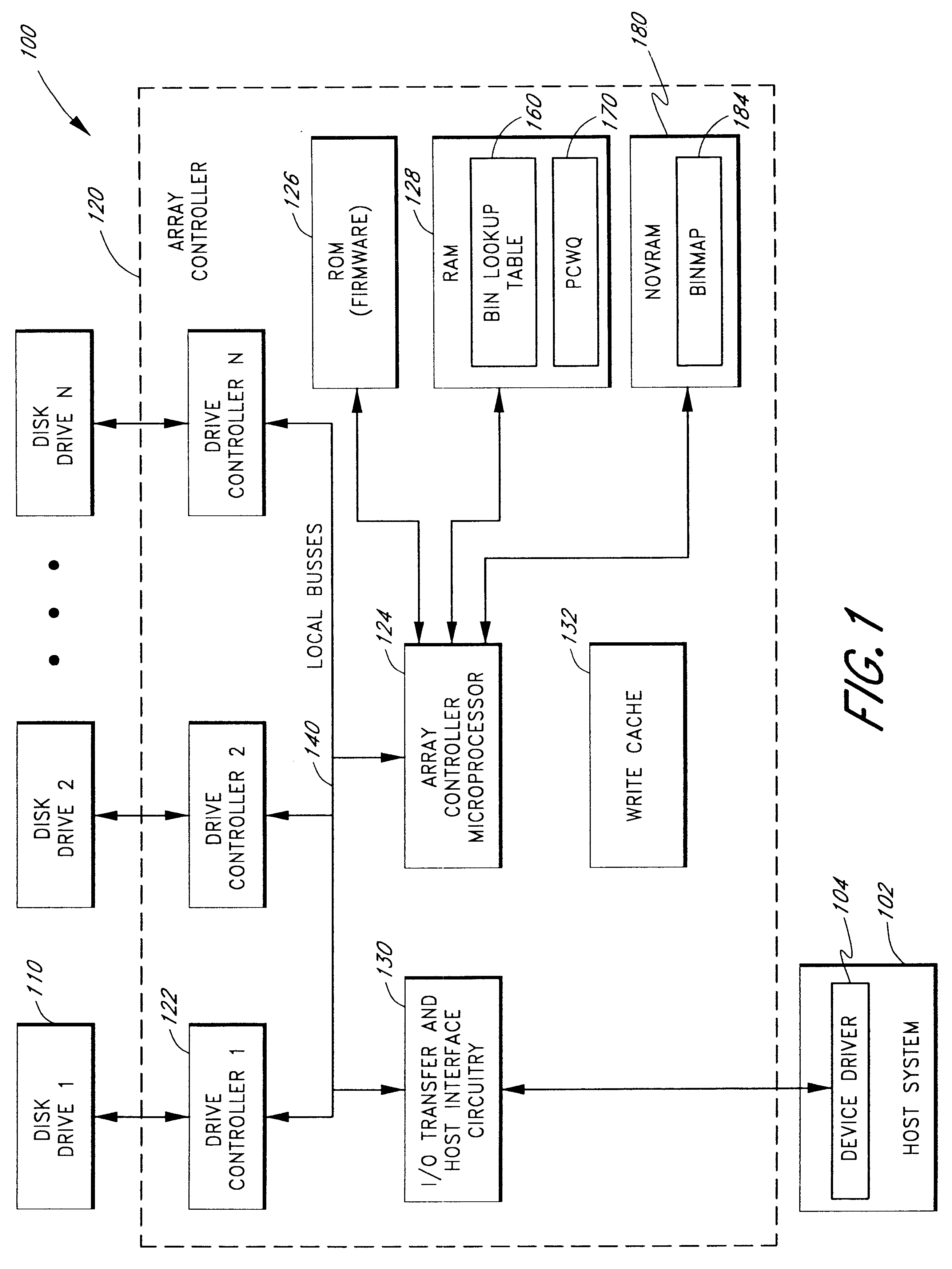
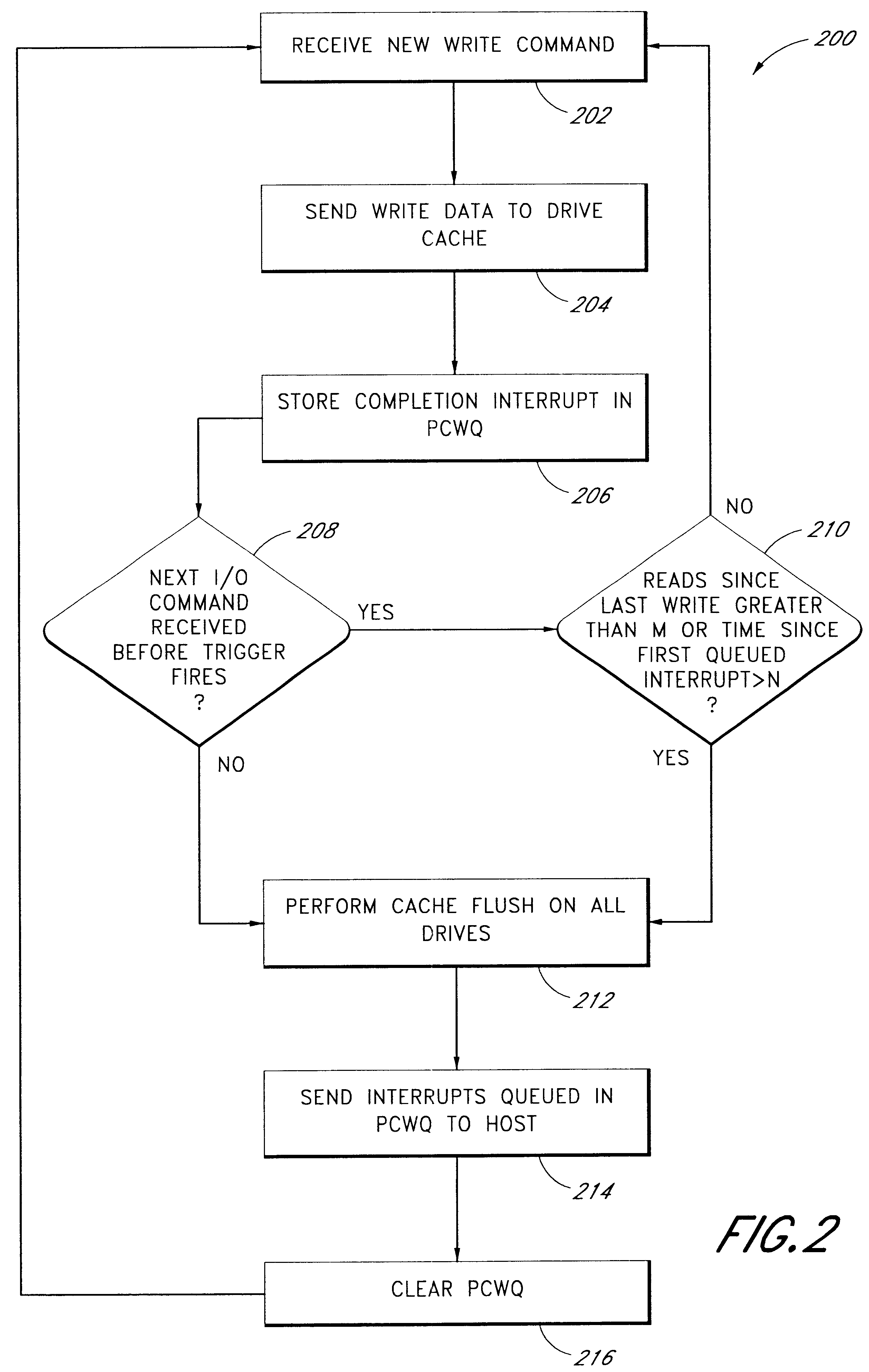
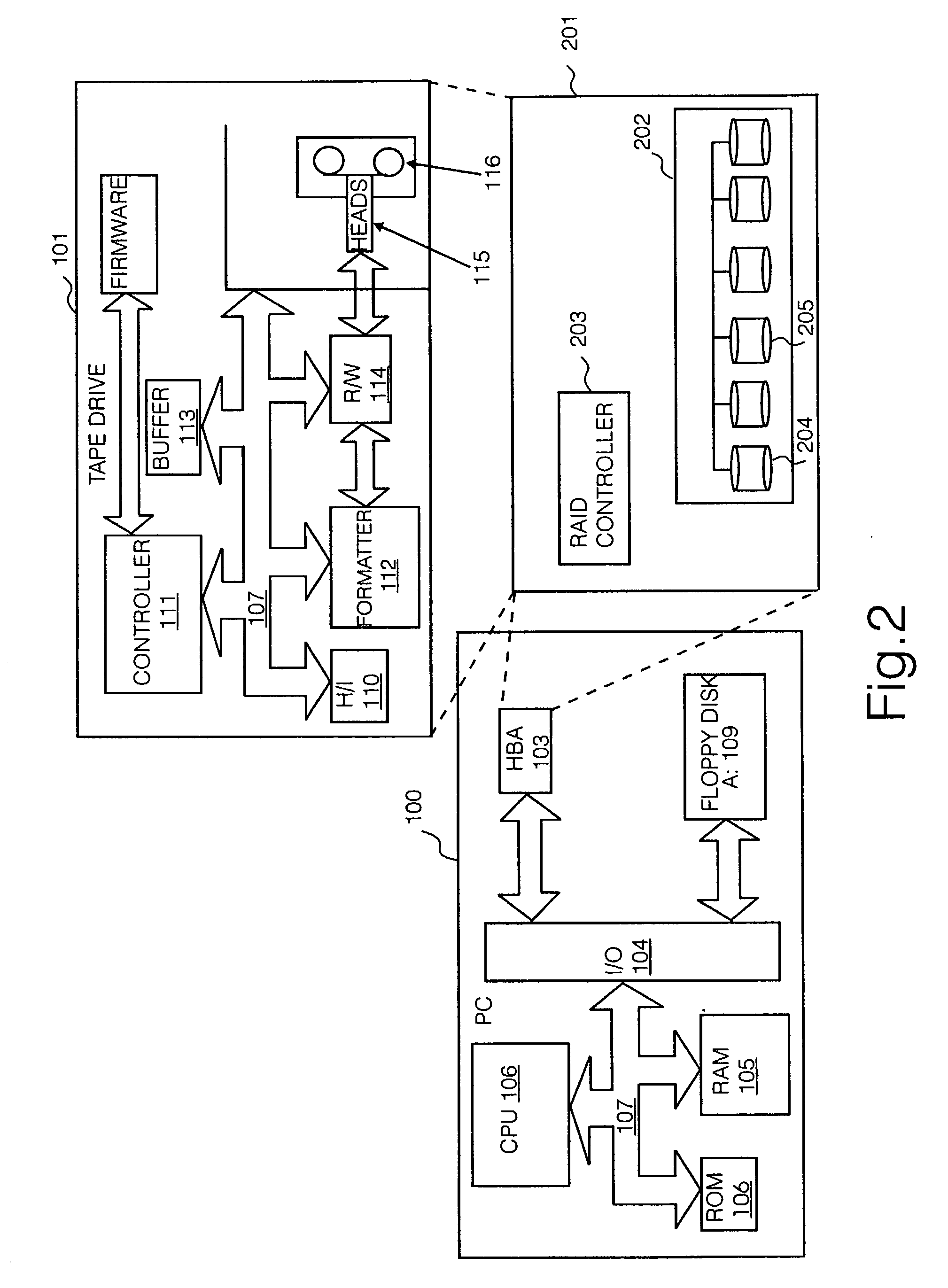
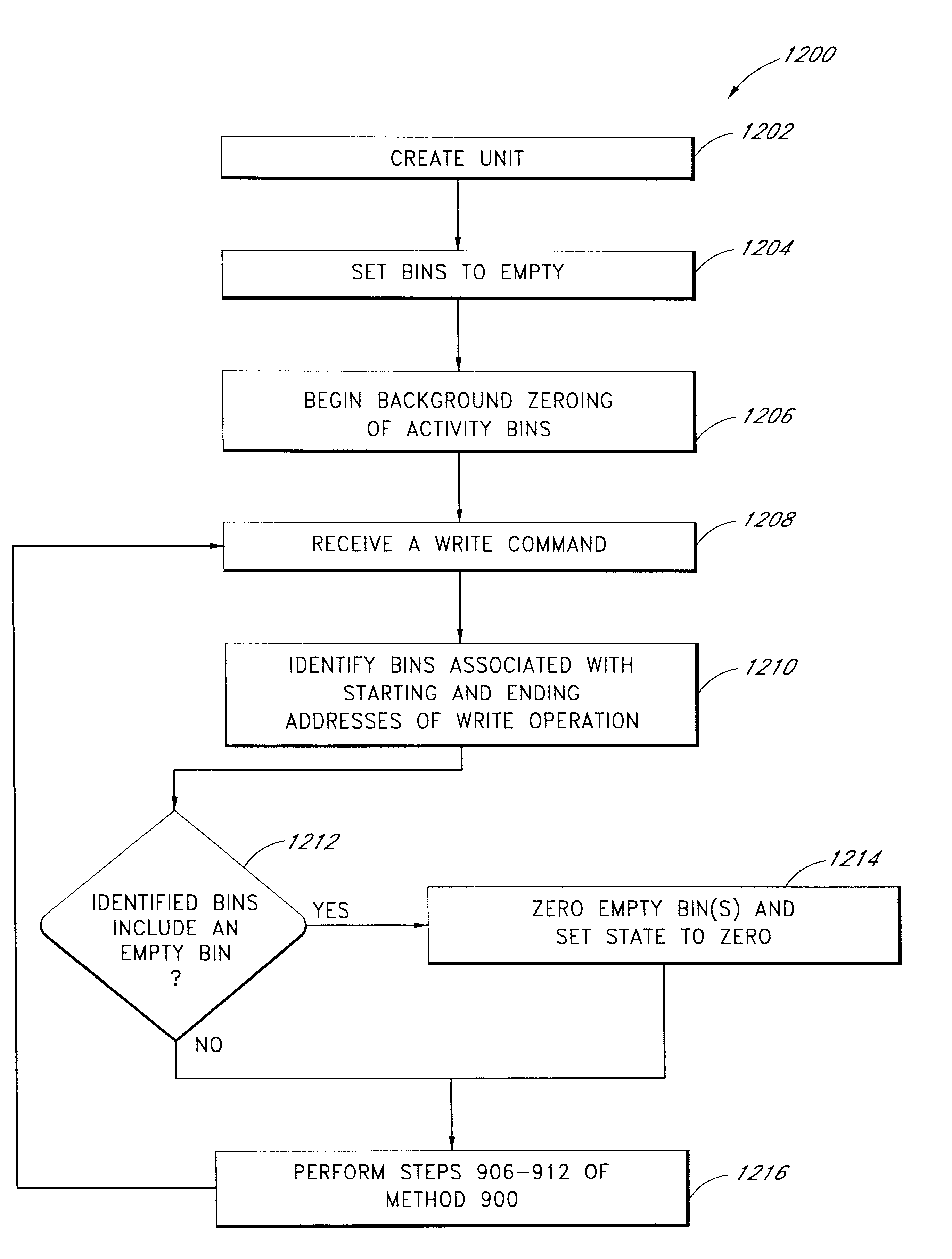
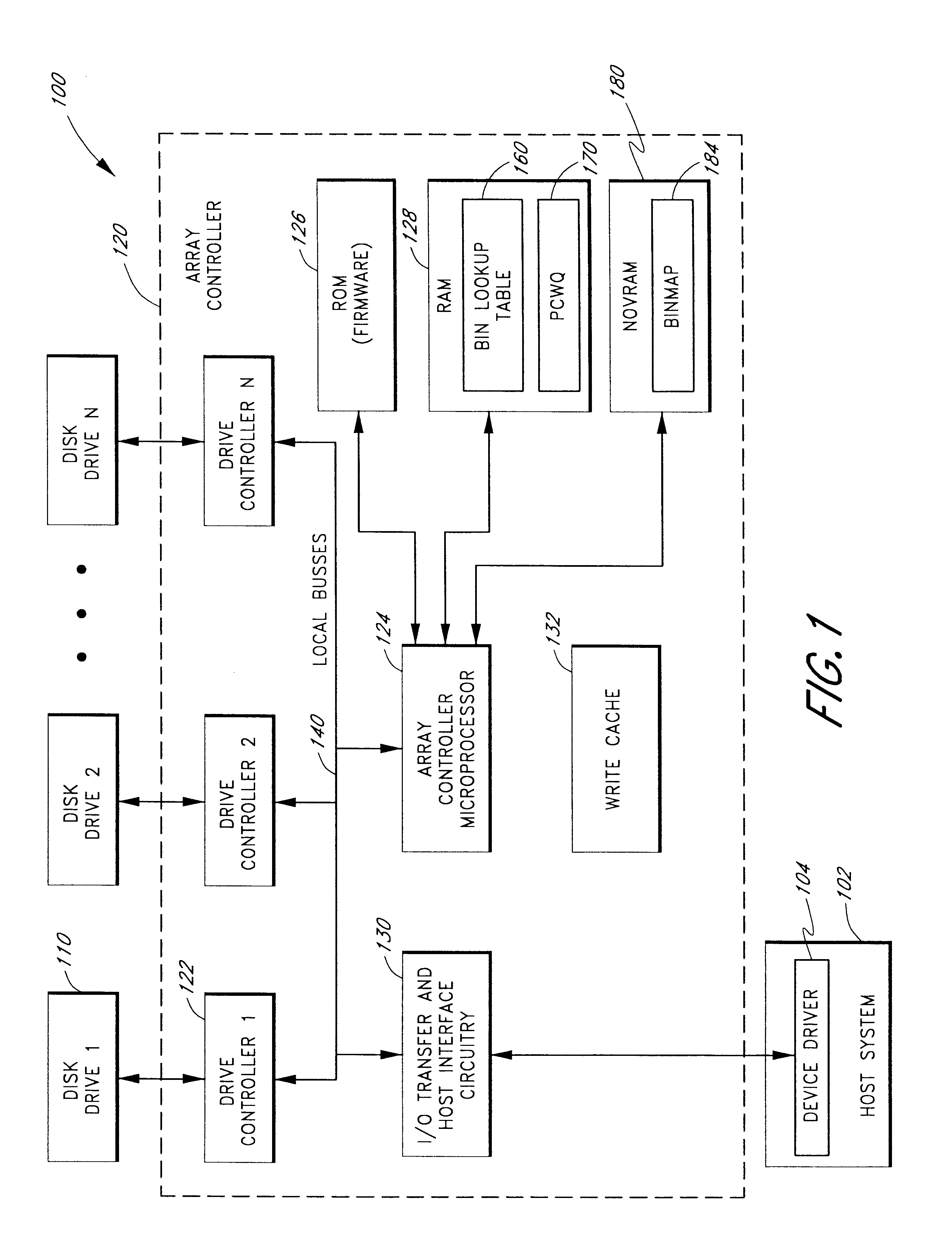
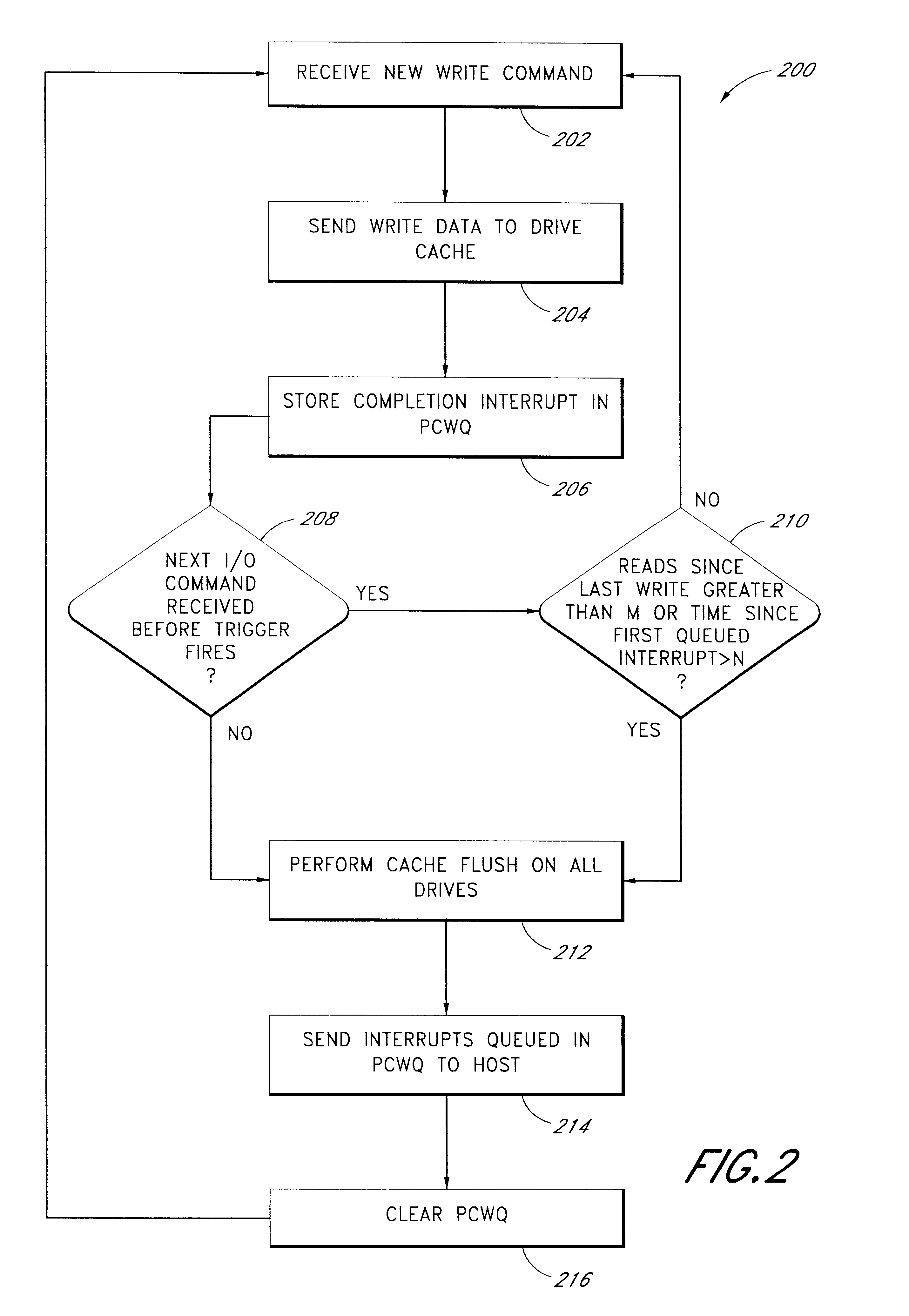
Use of activity bins to increase the performance of disk arrays
A disk array controller reliably improves performance in RAID configurations without the need for a battery backup. Write completion interrupts are queued until a write cache flush has been performed and are then sent to a host system. States of ranges of disk addresses (activity bins) are stored in nonvolatile storage elements associated with the ranges. The states allow rebuild times to be reduced after power failures and drive failures. A range is in a Changing state if at least one of the addresses is the target of a write operation that has been initiated but not completed. The range is in a Stable state if no addresses are the target of an uncompleted write operation. Two additional states are used to identify ranges of disk addresses that have been zeroed or never been written to. The additional states allow substantial reductions in RAID volume creation times.
Owner:SUMMIT DATA SYST
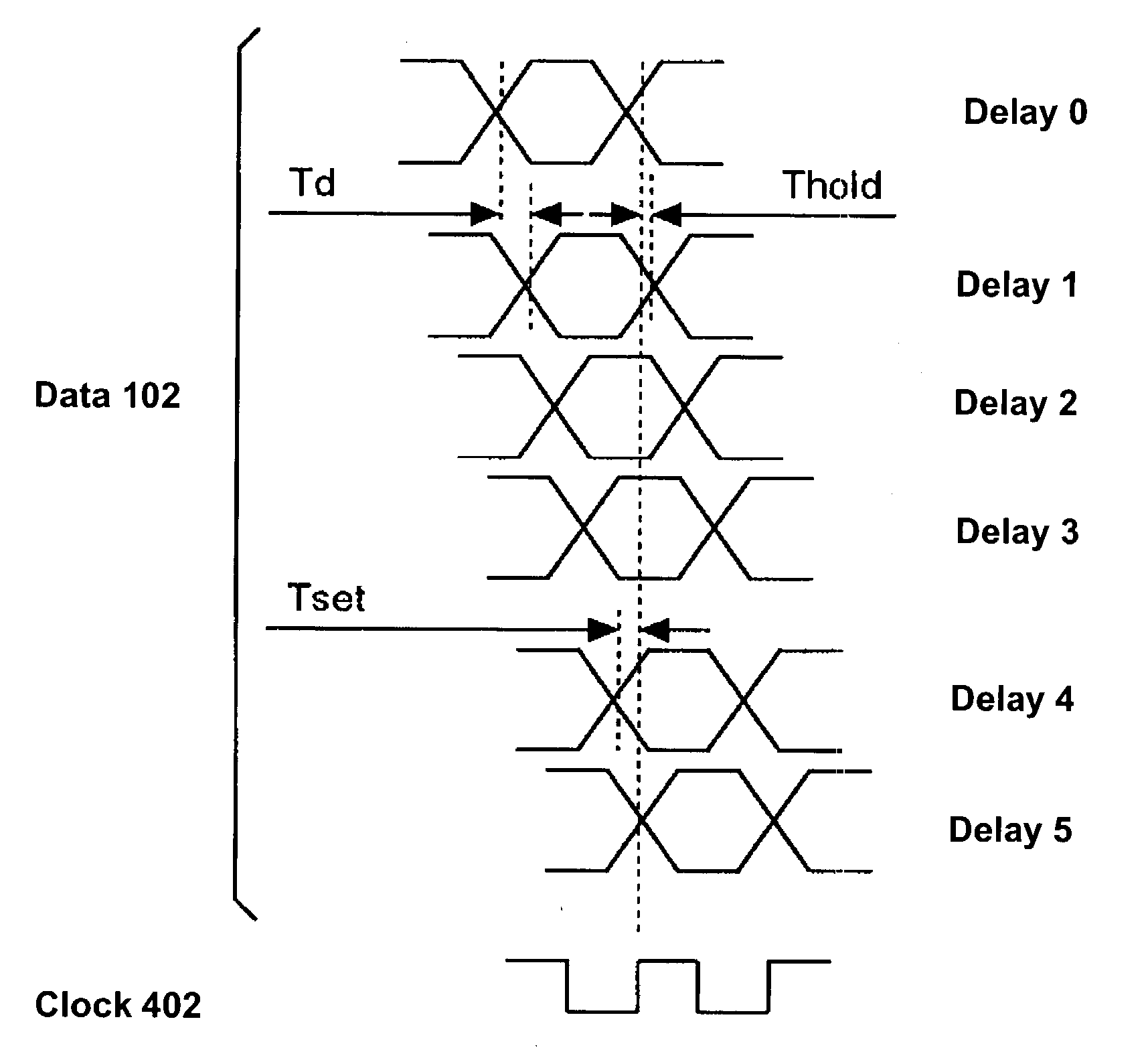
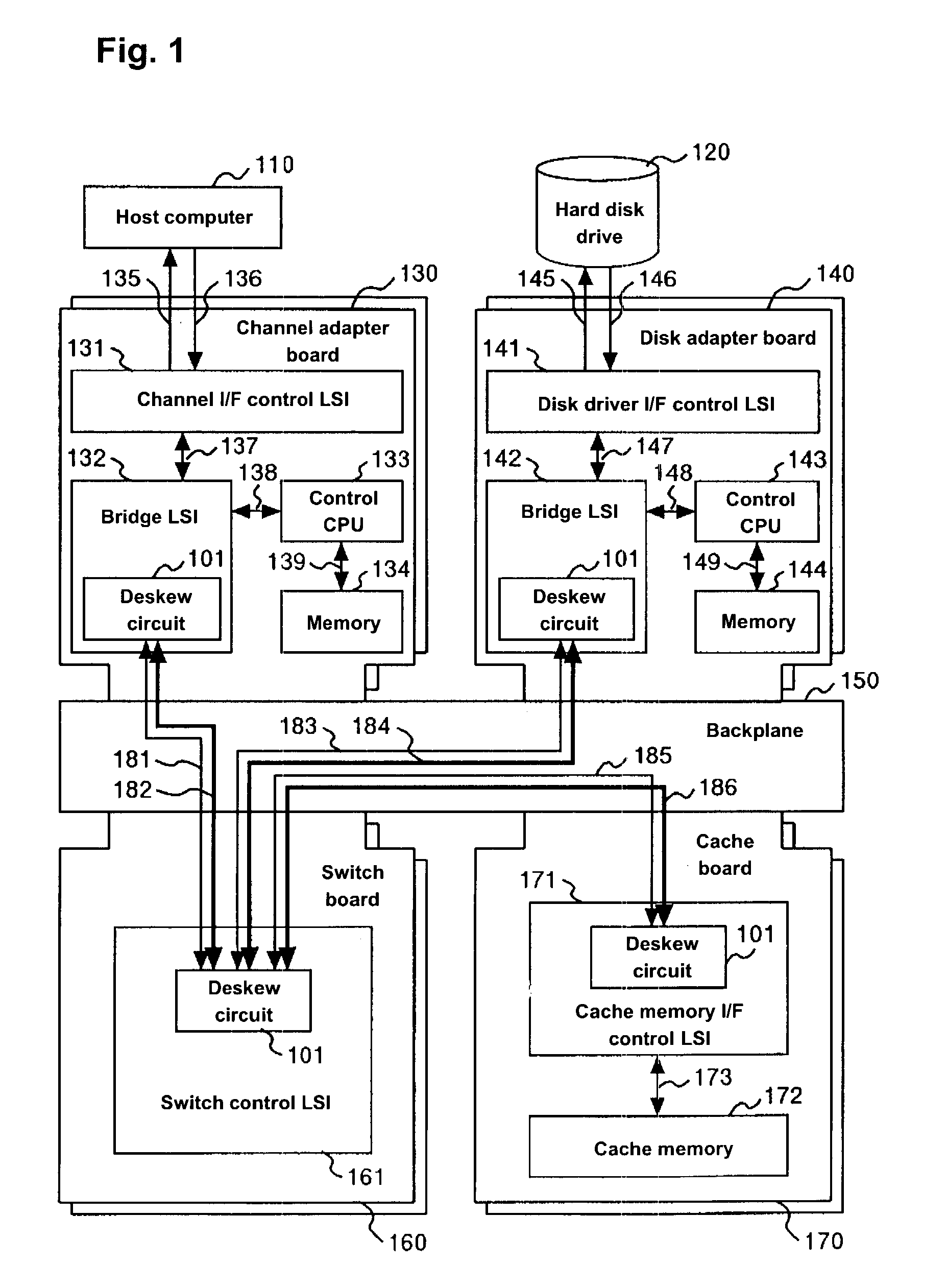
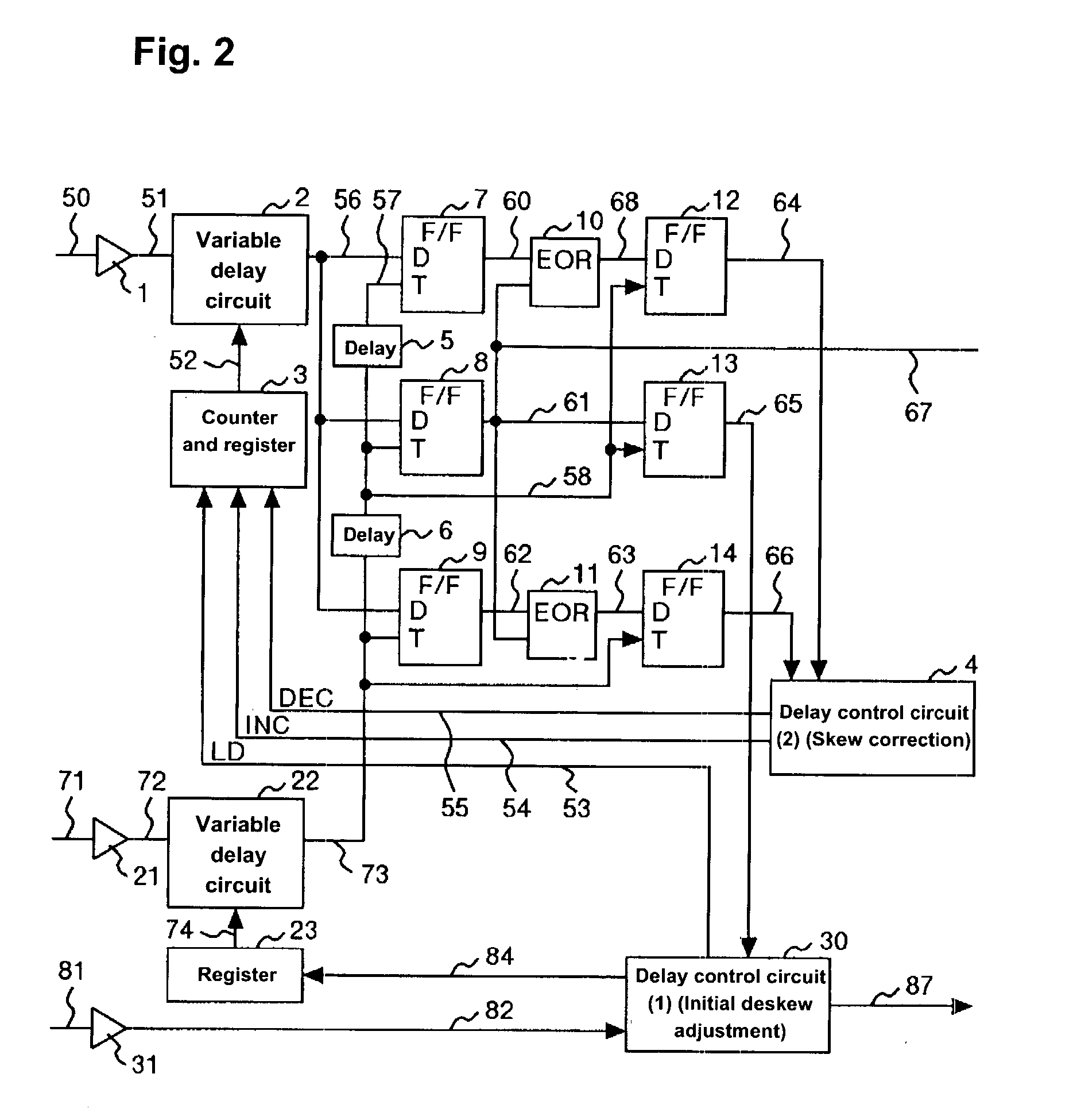
Deskew circuit and disk array control device using the deskew circuit, and deskew method
InactiveUS20040068682A1Input/output to record carriersElectronic circuit testingDisk arrayData transmission
A deskew circuit includes, for clock and every bit of data, a variable delay circuit between a receiver that receives data and a flip-flop that first latches the data, in which a detecting pattern to detect a stable region for receiving data is repeatedly sent before implementing a data transfer, a delay value with which the starting edge and ending edge of the data match the rising edge of the clock is found for the variable delay circuit, and a delay value with which the transfer data can be received in a stable manner is set based on the delay value of the variable delay circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Use of deferred write completion interrupts to increase the performance of disk operations
A disk array controller reliably improves performance in RAID configurations without the need for a battery backup. Write completion interrupts are queued until a write cache flush has been performed and are then sent to a host system. States of ranges of disk addresses (activity bins) are stored in nonvolatile storage elements associated with the ranges. The states allow rebuild times to be reduced after power failures and drive failures. A range is in a Changing state if at least one of the addresses is the target of a write operation that has been initiated but not completed. The range is in a Stable state if no addresses are the target of an uncompleted write operation. Two additional states are used to identify ranges of disk addresses that have been zeroed or never been written to. The additional states allow substantial reductions in RAID volume creation times.
Owner:SUMMIT DATA SYST
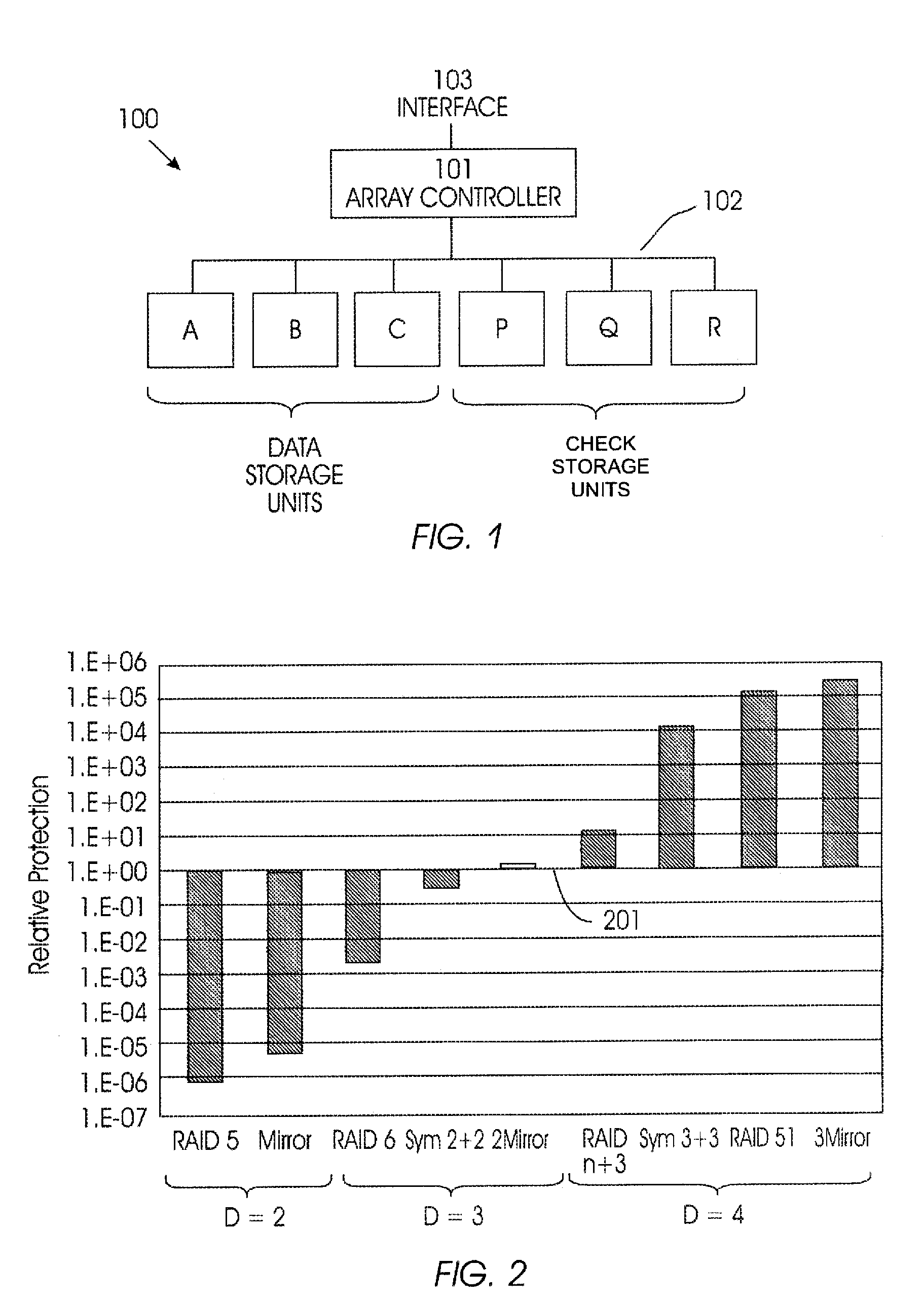
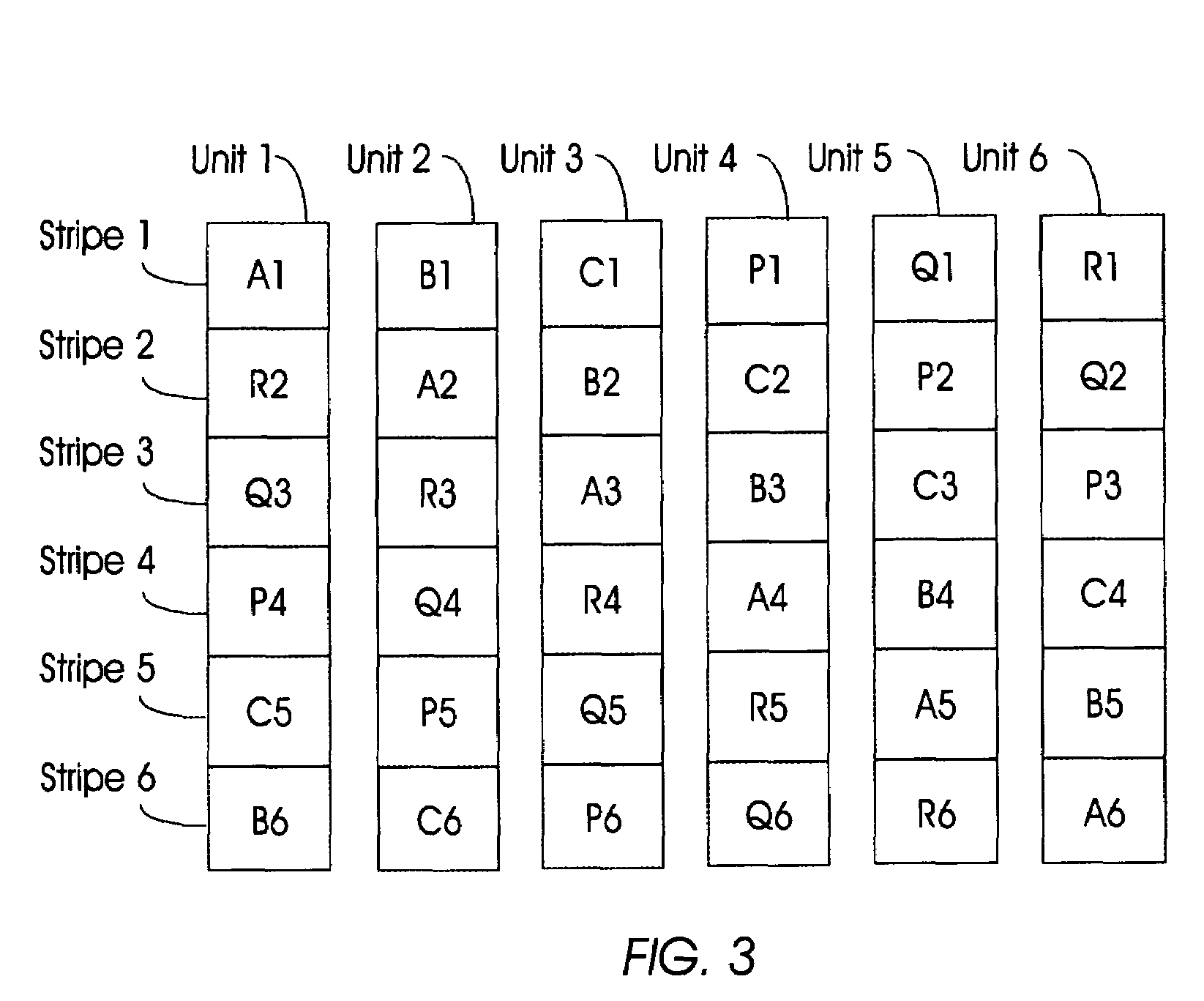
Raid 3+3
ActiveUS7254754B2Improve efficiencyImprove performanceInput/output to record carriersCode conversionParallel computingData storing
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
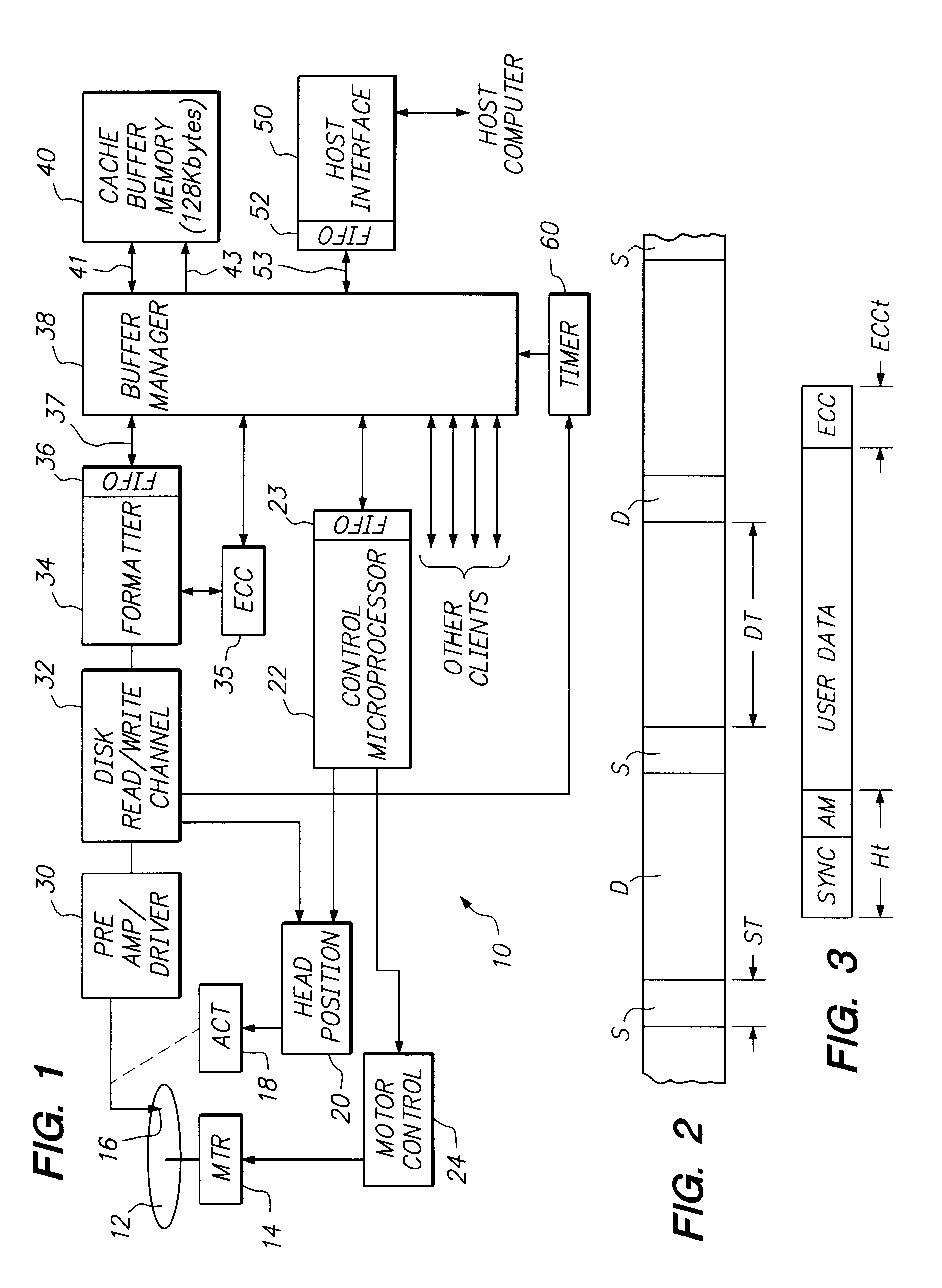
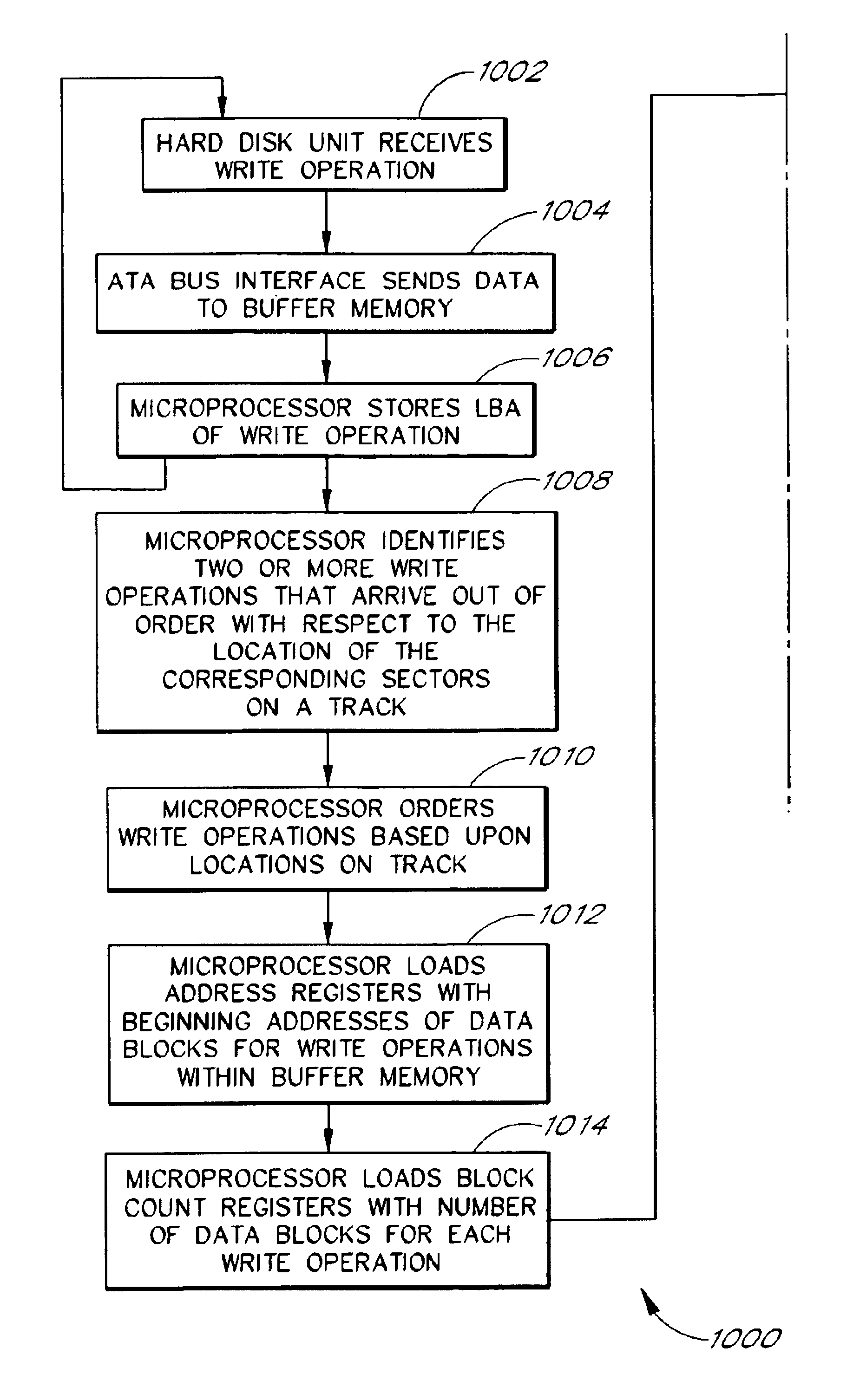
Disk controller configured to perform out of order execution of write operations
InactiveUS6826650B1Input/output to record carriersRecord information storageMemory addressDisk controller
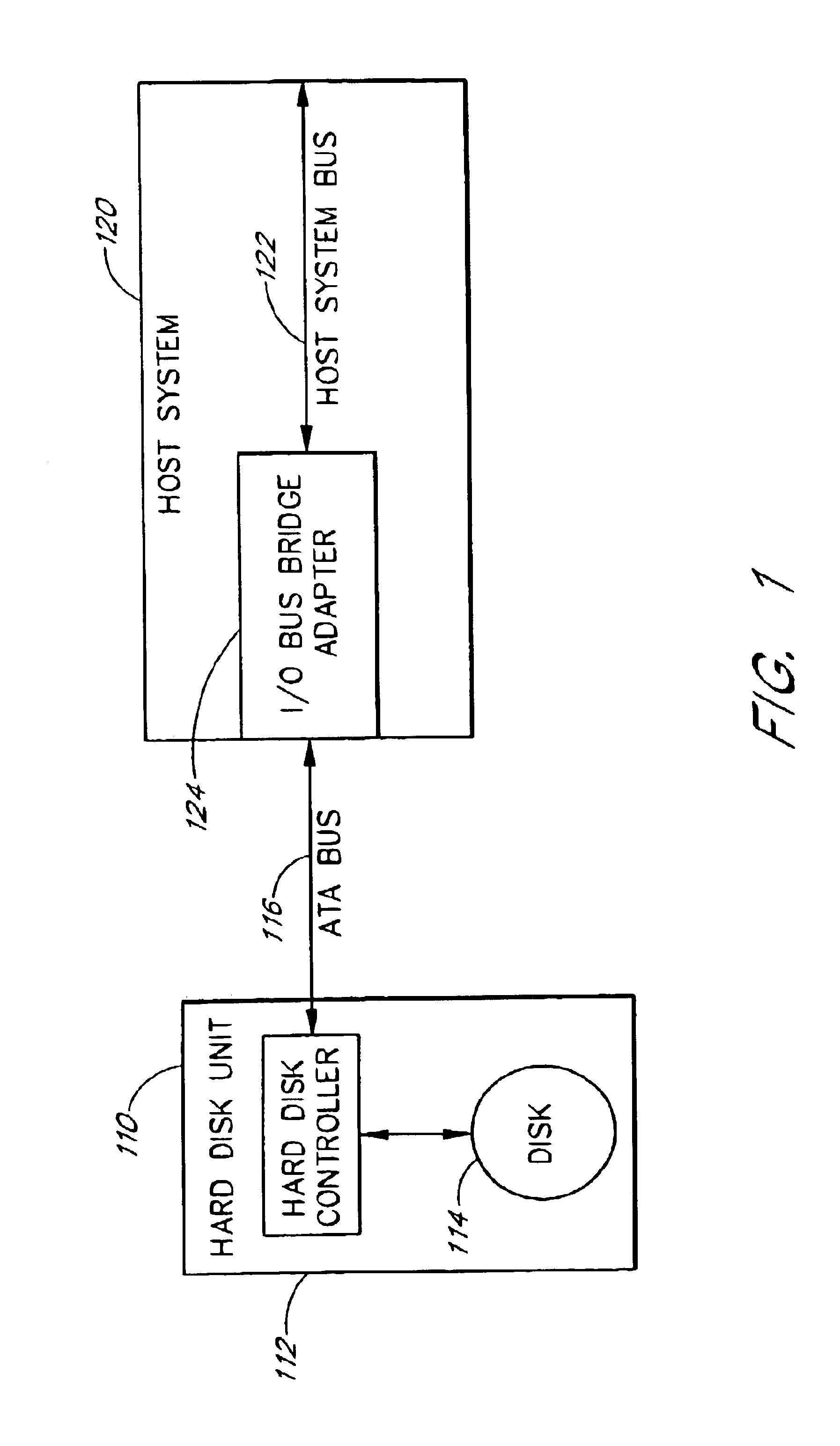
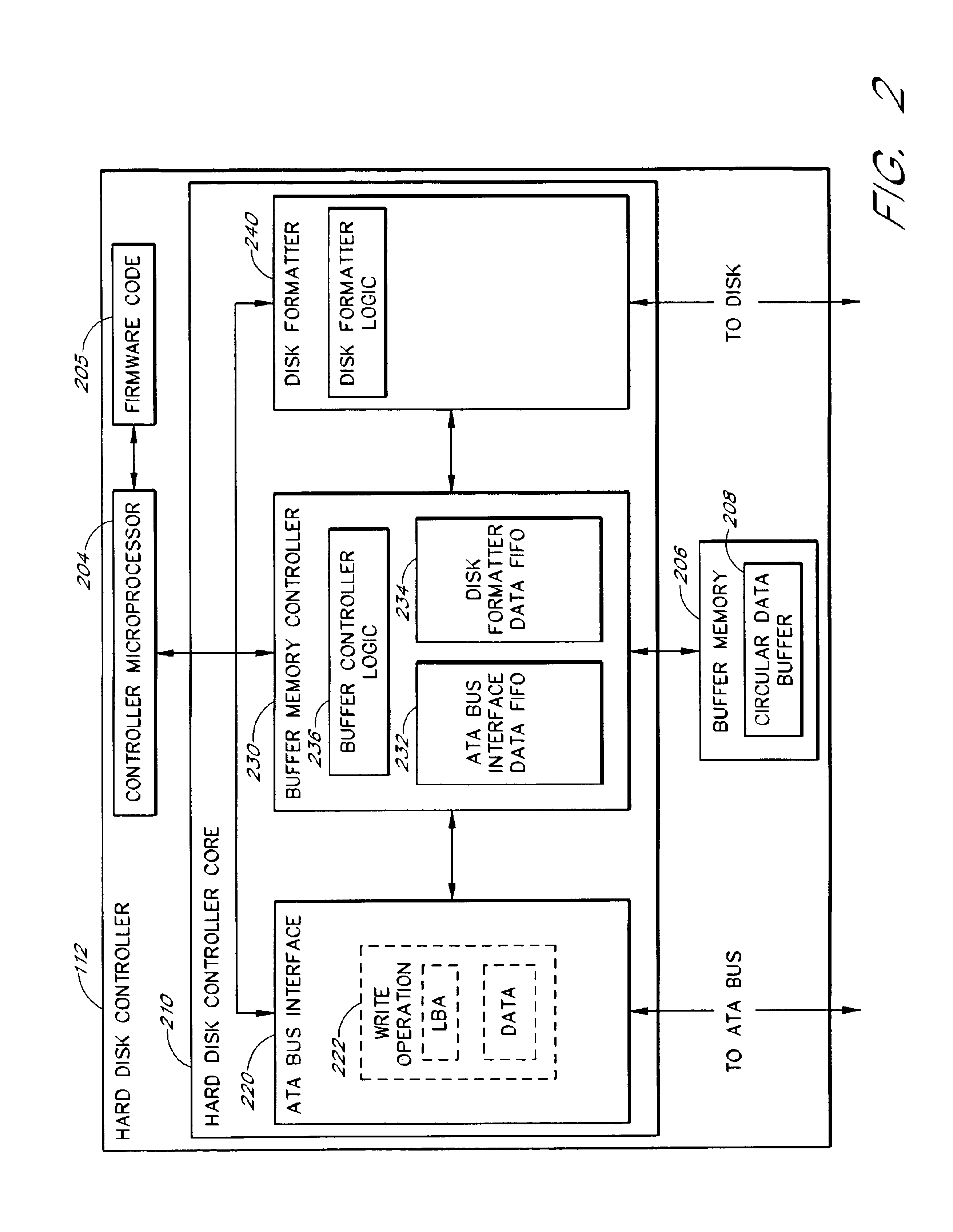
A hard disk unit includes a disk, controller microprocessor, host bus interface, buffer memory, buffer memory controller and disk formatter. The bus interface receives write operations, and the corresponding write operation data is stored in the buffer memory. The buffer memory controller also includes a set of address registers and a set of block count registers. The microprocessor loads the address registers with the buffer memory addresses of data of multiple write operations and loads the block count registers with the size of the corresponding data. The microprocessor then issues a single command to the buffer memory controller to transfer the data from the buffer memory to the disk formatter. The address registers and block count registers enable the data of multiple write operations to be transferred and written to a disk in an order other than the order in which the write operations were received at the bus interface.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method, disaster recovery record, back-up apparatus and RAID array controller for use in restoring a configuration of a RAID device
InactiveUS20020194528A1Wide rangeRedundant data error correctionRedundant operation error correctionOperational systemRecovery record
A computer system has (1) an array of data storage devices, (2) an operating system stored on a RAID device and (3) a RAID controller. In response to detection of a computer system failure, the RAID device configuration is automatically restored. A system back-up memory stores a recovery record of physical drive to logical drive mapping for the RAID device. The RAID controller enables the recovery record to be processed in response to detection of a system failure. In response to computer system failure detection, the recovery record information restores the RAID array configuration. Following system failure, a computer system manager instigates the procedure by pressing a button.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Use of activity bins to increase the performance of disk arrays
A disk array controller reliably improves performance in RAID configurations without the need for a battery backup. Write completion interrupts are queued until a write cache flush has been performed and are then sent to a host system. States of ranges of disk addresses (activity bins) are stored in nonvolatile storage elements associated with the ranges. The states allow rebuild times to be reduced after power failures and drive failures. A range is in a Changing state if at least one of the addresses is the target of a write operation that has been initiated but not completed. The range is in a Stable state if no addresses are the target of an uncompleted write operation. Two additional states are used to identify ranges of disk addresses that have been zeroed or never been written to. The additional states allow substantial reductions in RAID volume creation times.
Owner:SUMMIT DATA SYST
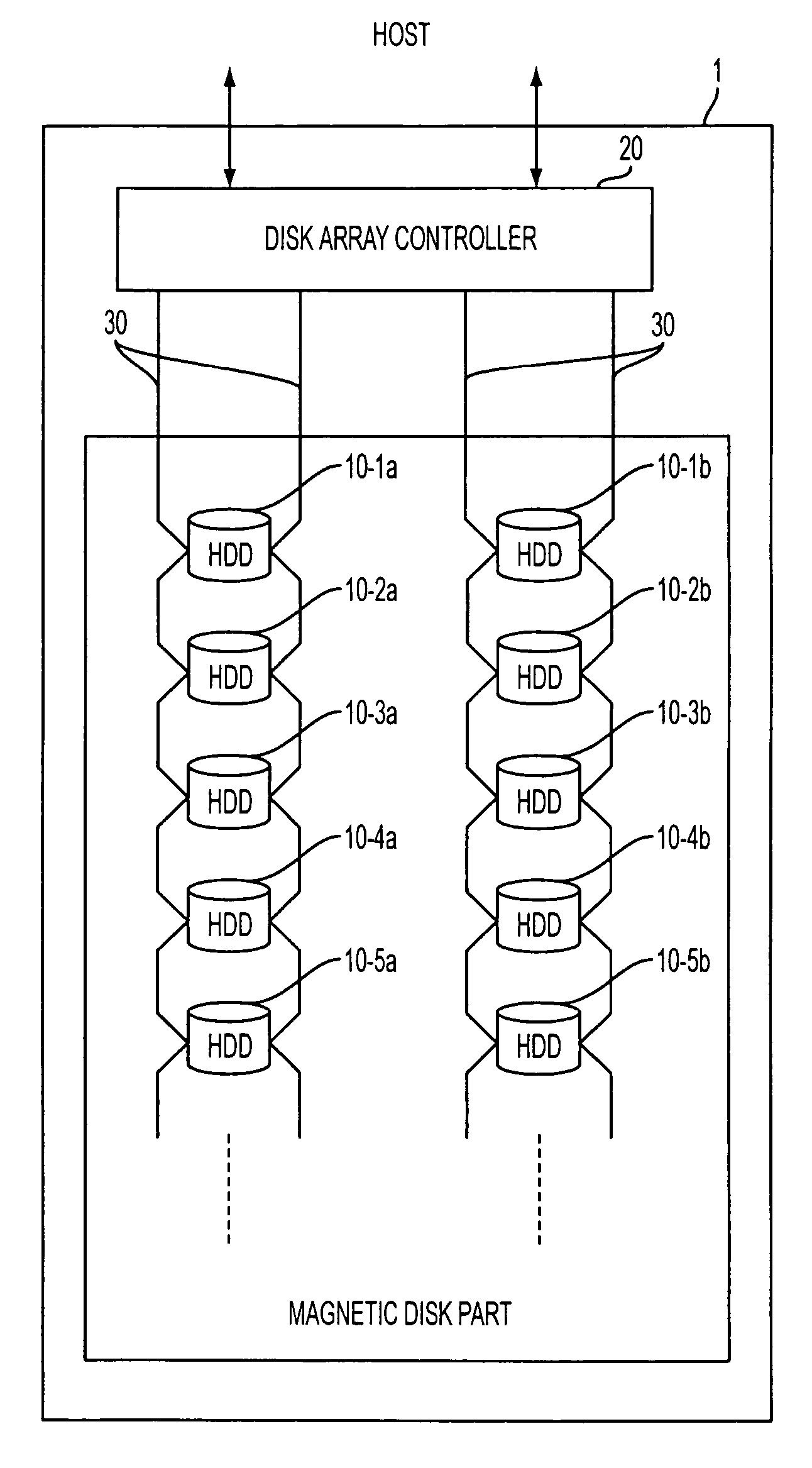
Disk array device
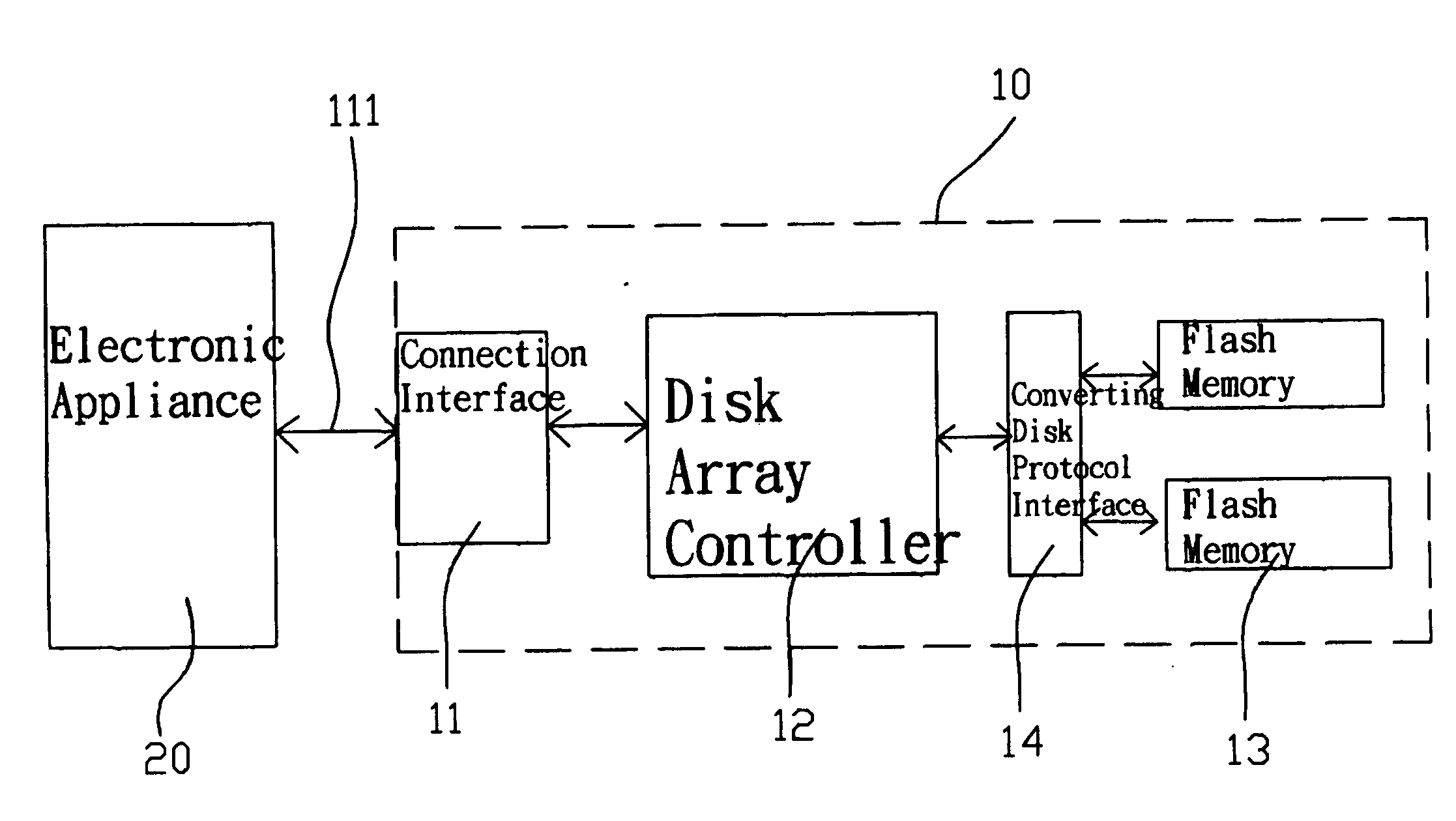
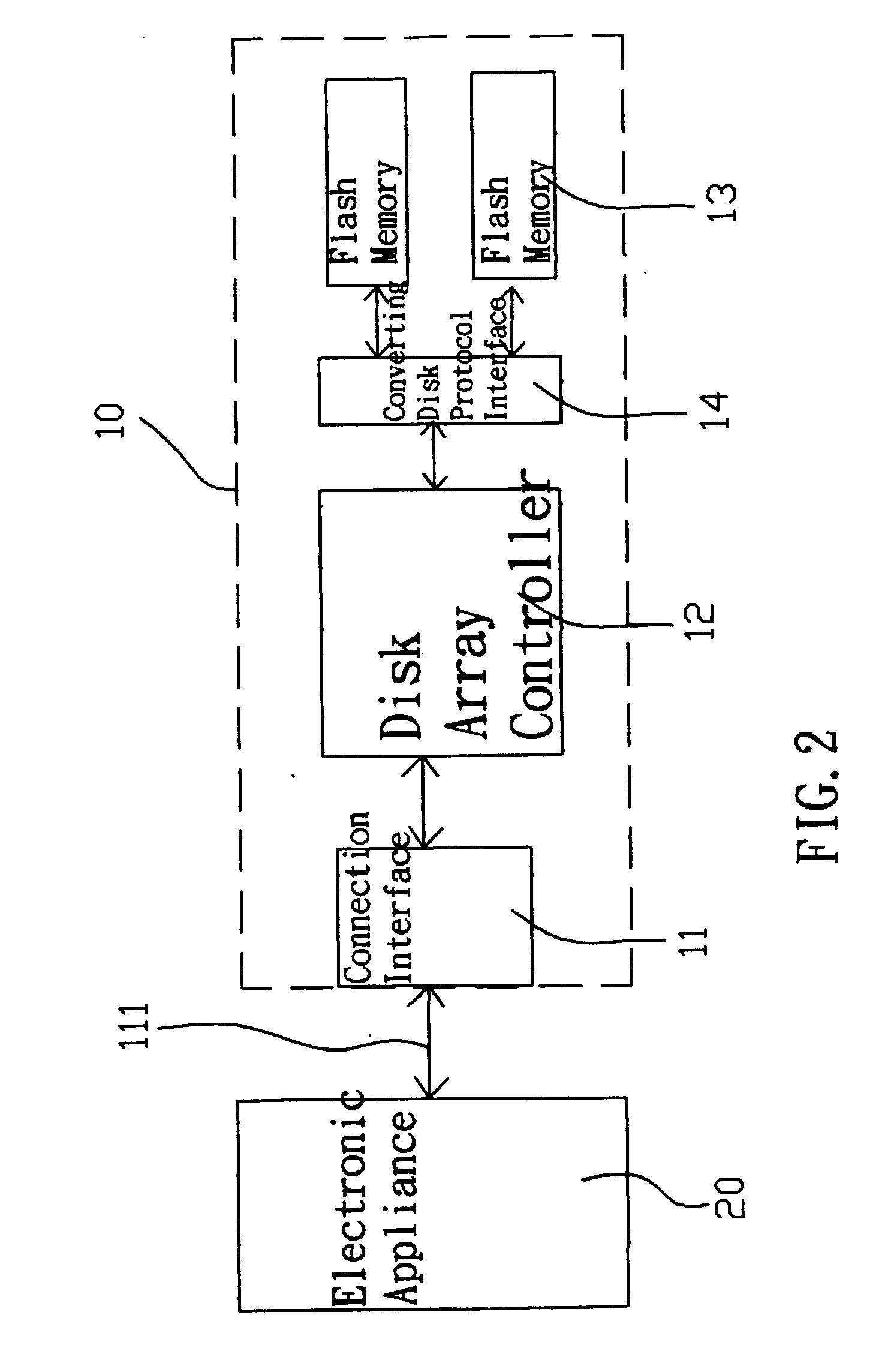
InactiveUS20080147963A1Easy to carryOptimize dataMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingElectricityDisk controller
The present invention discloses a disk array device including a connection interface, a disk array controller and at least one set of flash memories. The connection interface is electrically connected to an electronic appliance, such that the electronic appliance can be connected to the disk array device through the connection interface for an application, and the disk array controller controls the storage and reading of data in the disk array device. The flash memories are provided for storing and backing up data, so that data can be transmitted between the disk array device and the electronic appliance. The disk array device developed from the flash memories has the features of a quiet and fast storage, a light, thin, short and compact design, and a convenient carry, so as to provide better data storage and backup.
Owner:ACCUSYS
Disk array controller and information processing apparatus
InactiveUS20050229033A1Input/output to record carriersDigital signal formattingInformation processingDisk array
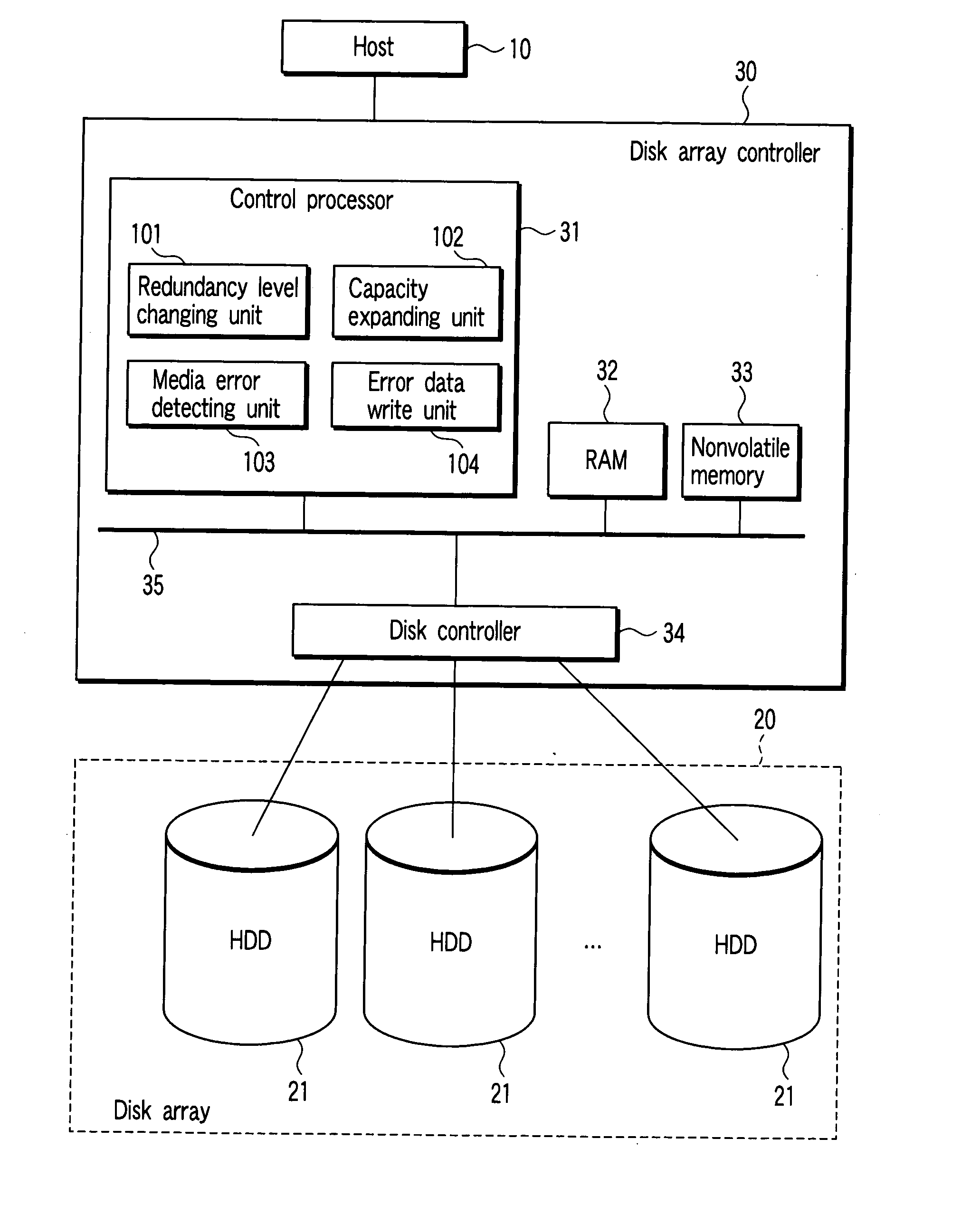
A disk array controller has a function of relocating a plurality of data blocks stored in a disk array. The controller includes a read unit which reads data blocks to be relocated from the disk array, a determining unit which determines whether an error has occurred in the to-be-relocated data block read by the read unit, a write unit which writes the to-be-relocated data block read by the read unit in a relocating destination position on the disk array which corresponds to the to-be-relocated data block if the determining unit determines that the error has not occurred in the to-be-relocated data block, and a unit which sets error information with respect to the relocating destination position if the determining unit determines that the error has occurred in the to-be-relocated data block, the error information causing occurrence of an error in response to read access of the relocating destination position.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Disk array apparatus and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS20060224826A1Low costEasy to assembleMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionManagement unitParallel computing
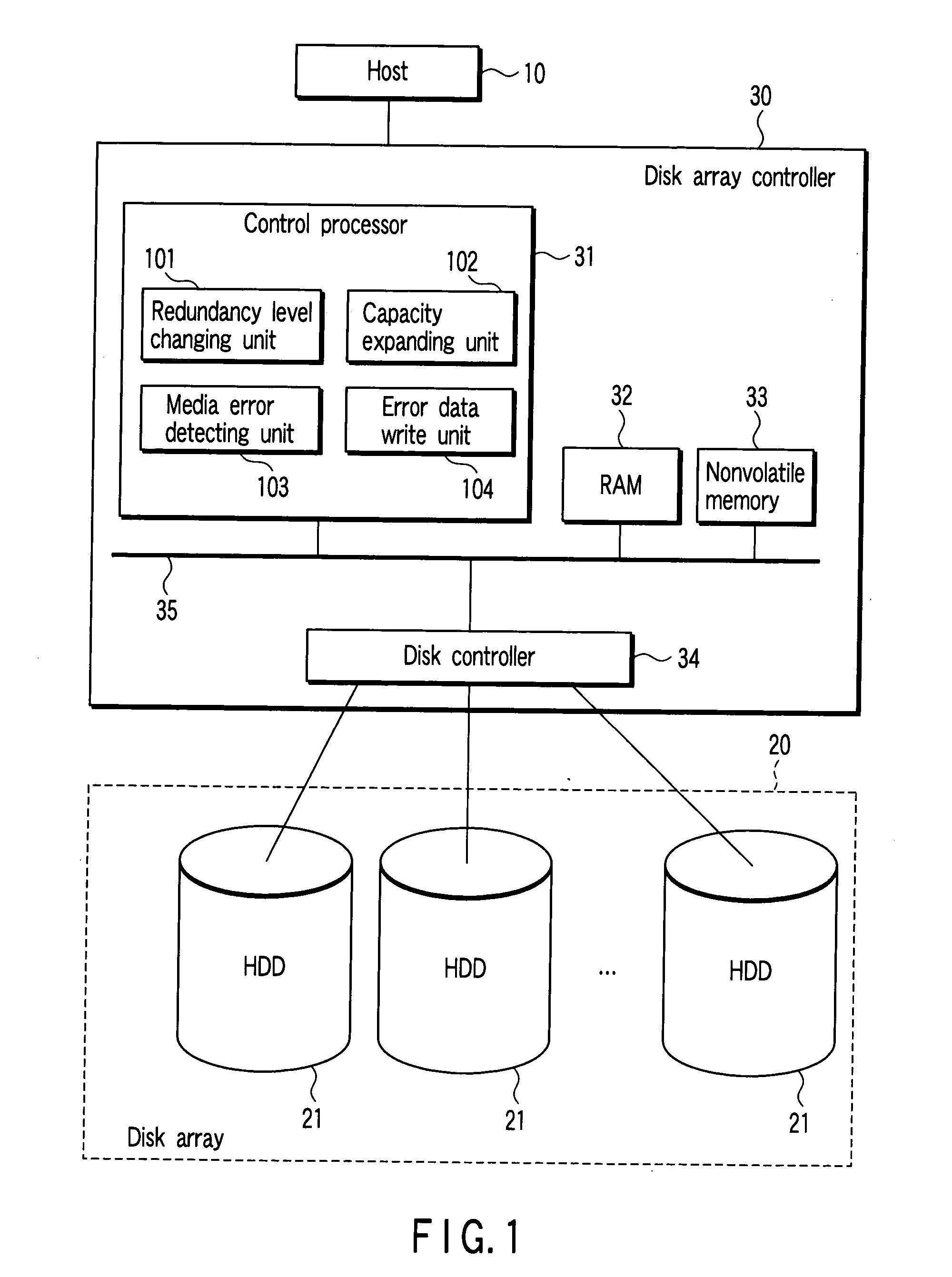
To efficiently manage performance resources while preventing a failure of a control processing from affecting another control processing in a disk array apparatus. A disk array apparatus 1 has a disk array controller 11, the disk array controller 11 has a CPU incorporating a plurality of processor cores 1110 that cannot be physically separated from each other, each processor core serves as an unit processor, one unit processor manages the unit processors separately, allocates a self-contained control program to each unit processor in such a manner that the operation of the unit processor can be terminated appropriately or in such a manner that the unit processor can operate until the operation of the whole CPU is terminated, and manages the processing load or processing status of the allocated control program on a unit-processor basis.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
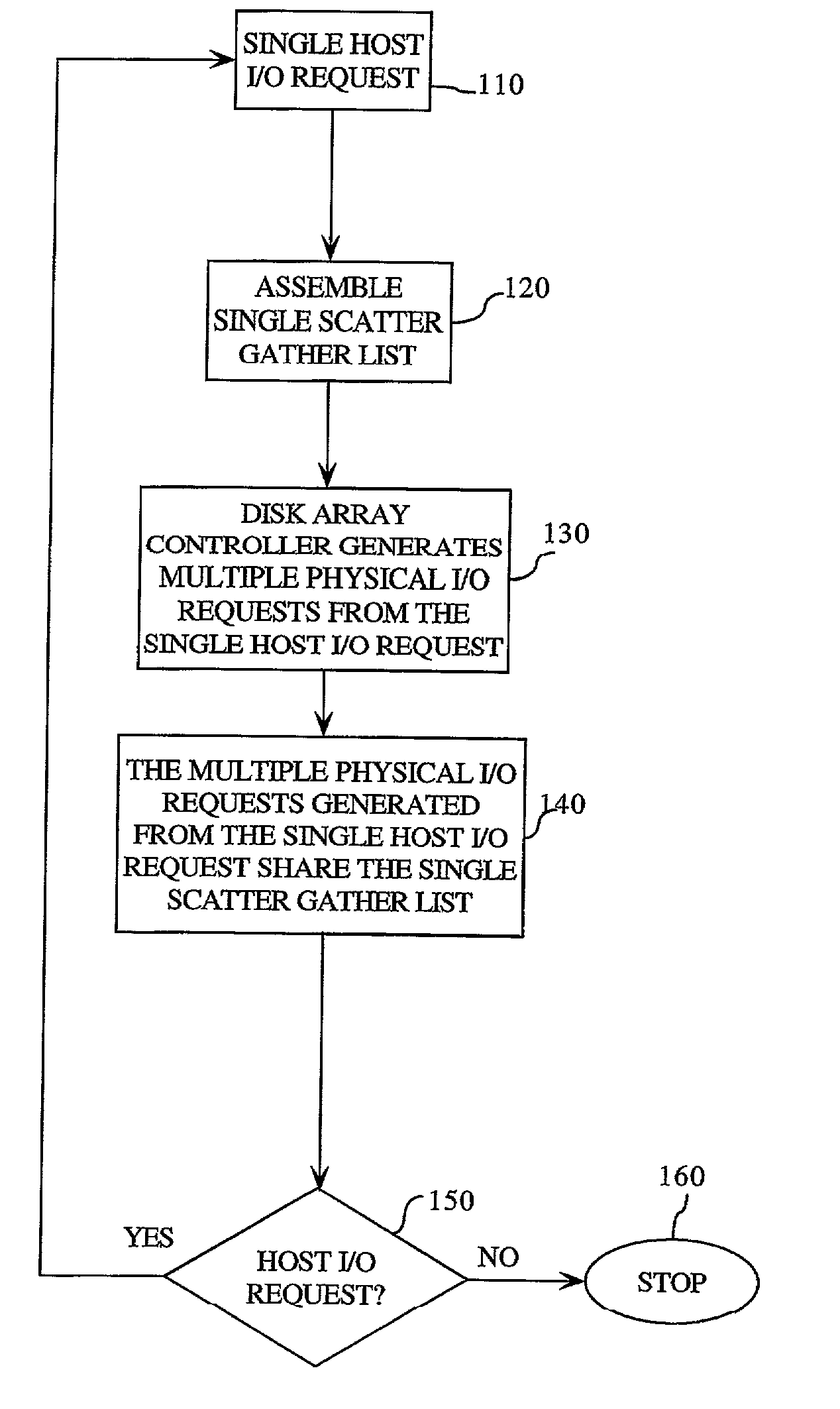
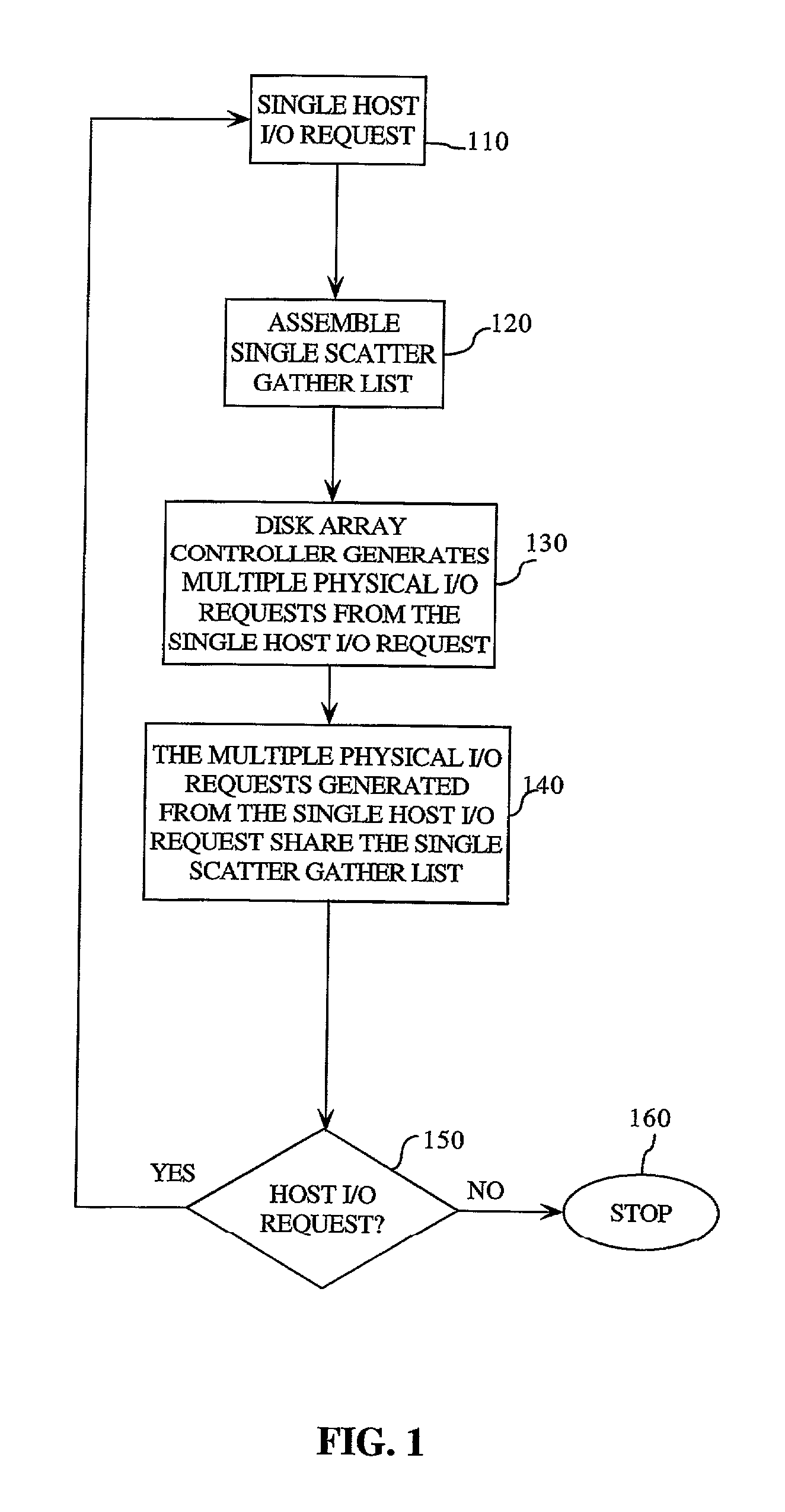
Method for raid striped I/O request generation using a shared scatter gather list
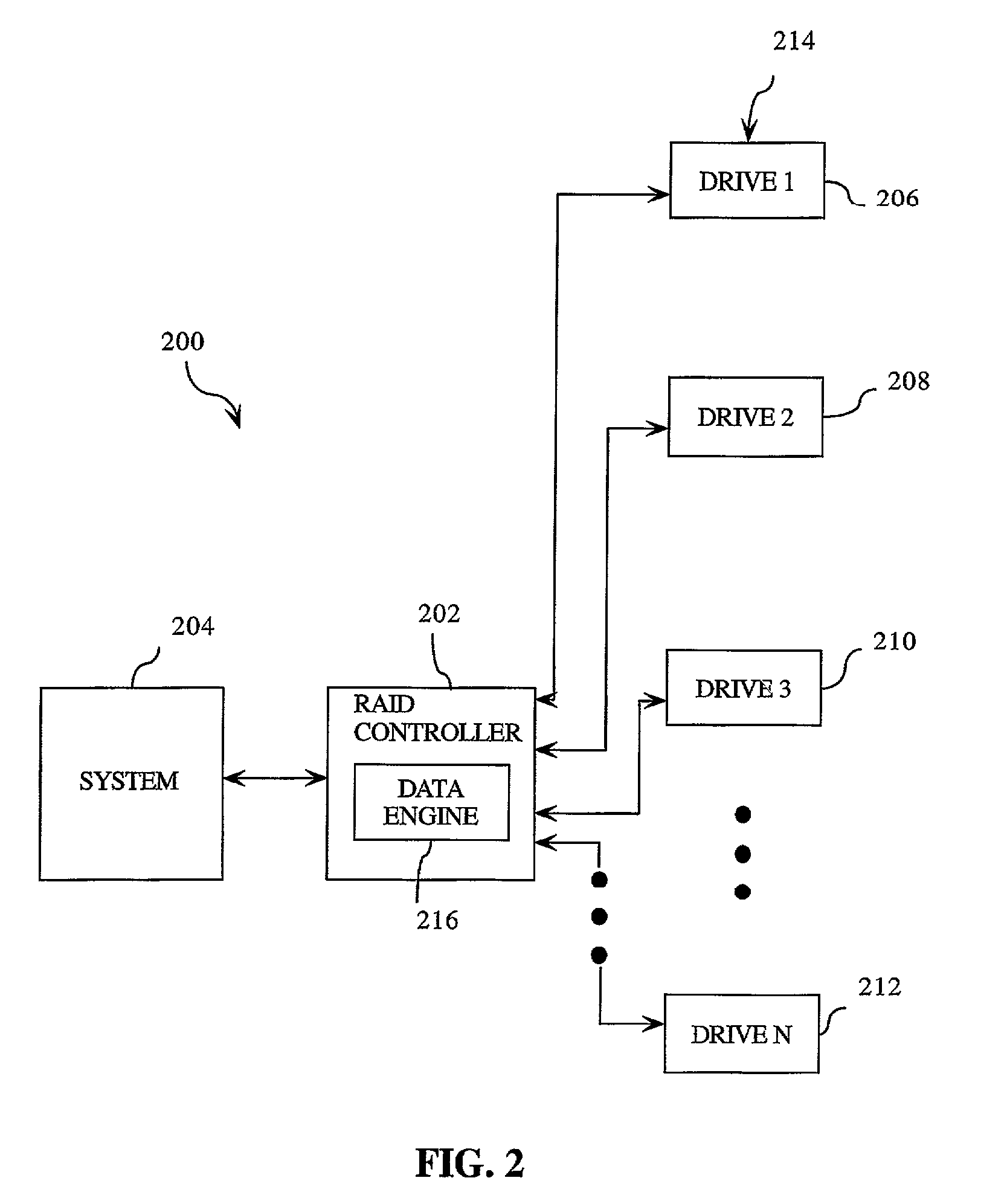
InactiveUS7155569B2Low costReduce actionInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsData transmissionTransfer operation
A code efficient transfer method in response to a single host I / O request generates a single scatter gather list. The disk array controller transforms the single host I / O request into multiple physical I / O requests. Each of these multiple physical I / O requests uses the single scatter gather list to perform the data transfer operation. Each physical I / O request corresponds to the data transfer of one data stripe. The data stripe is an initial or header stripe of about 0.5K or a stripe of at least 64K.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
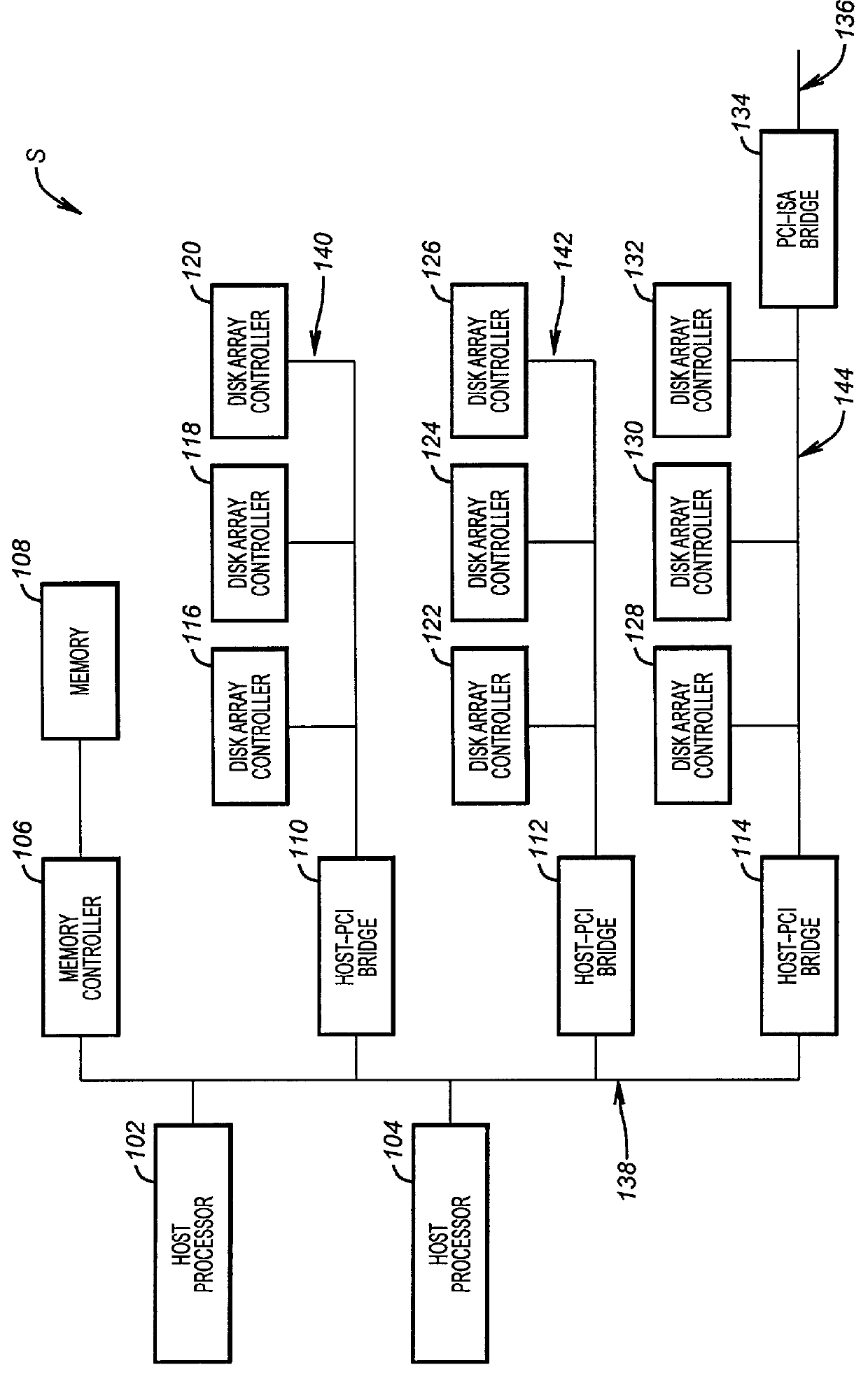
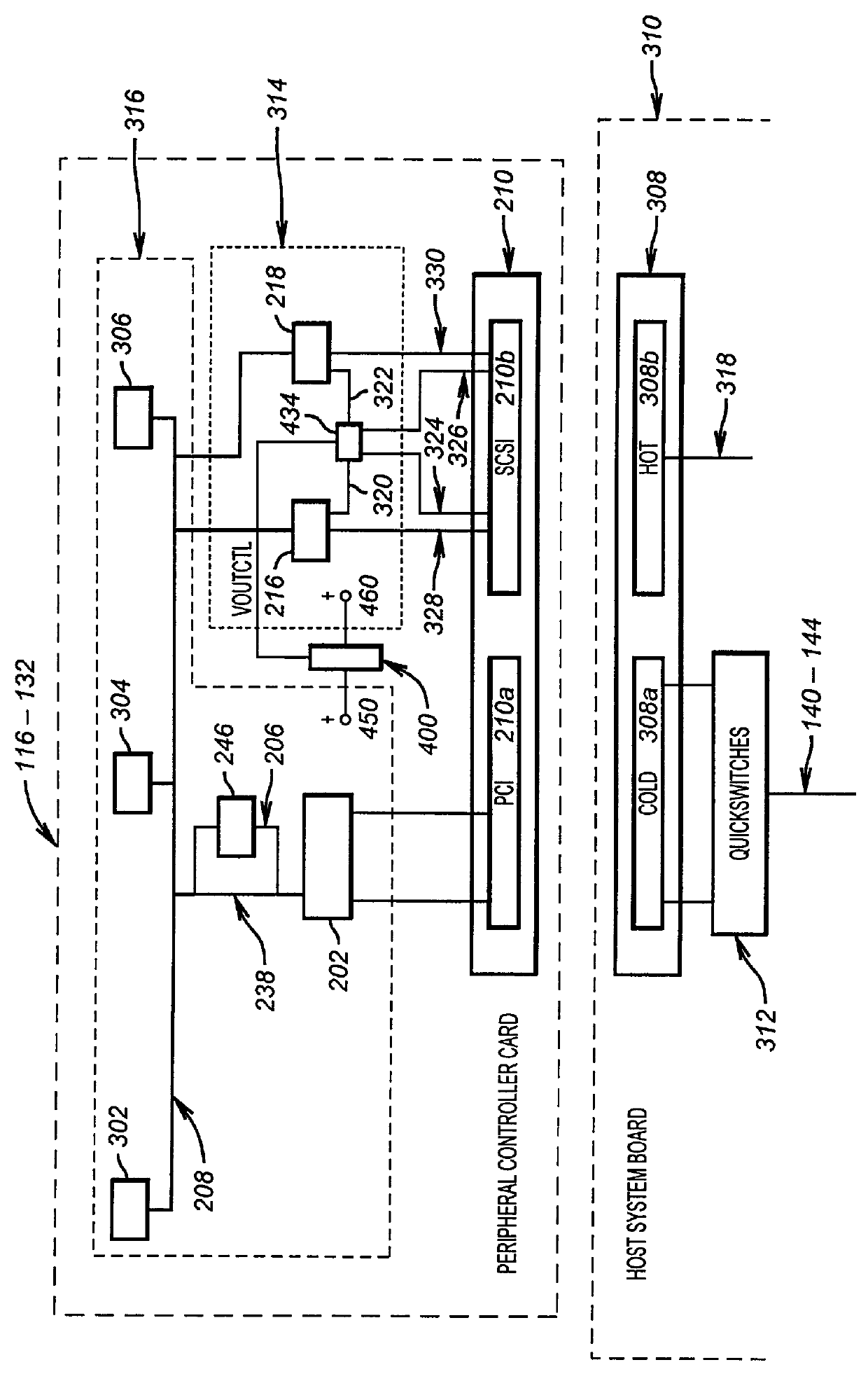
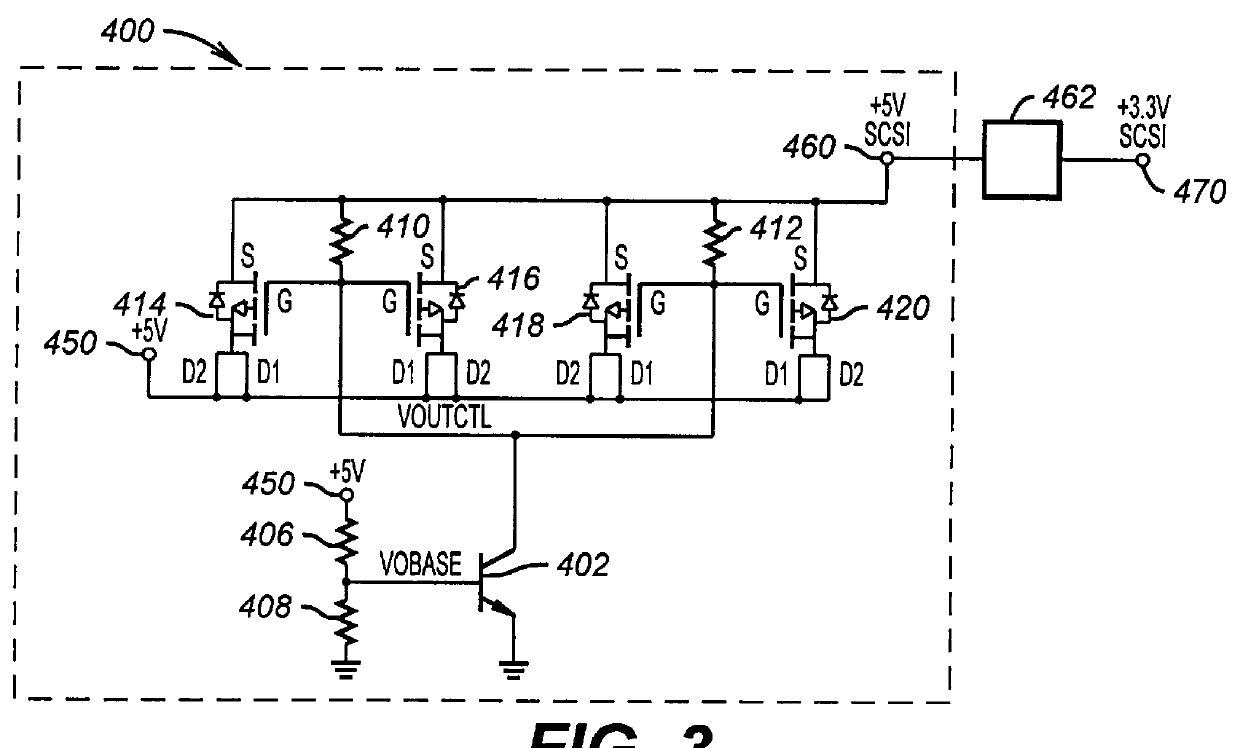
Technique for hot plugging a peripheral controller card containing PCI and SCSI buses on a single connector into a host system board
InactiveUS6061752AComponent plug-in assemblagesDigital processing power distributionMass storageOperational system
An embodiment of the present invention discloses a technique that allows hot plugging a peripheral controller card, containing both a local bus and a peripheral bus on a single connector, into a host system board containing a host system bus and a host I / O bus. When mating the peripheral controller card to the host system board a local device power supply (LDPS) is inactive, a peripheral device power bus (PDPB) is powered, and signal lines of a peripheral device are maintained in a high impedance state. Following a delay after the mating, the LDPS is activated by the host operating system (OS). Following the activation of the LDPS, the host system bus is coupled to the single connector through switches that are under OS control. In response to the activation of the LDPS, the signal lines of the peripheral device are enabled. In a disclosed embodiment the peripheral controller card is a disk array controller card, the local bus is a PCI bus, and the peripheral bus is a SCSI bus. In one embodiment the disk array controller card is coupled to a mass storage peripheral and in another embodiment is programmed for RAID. An advantage of an embodiment of the present invention is that a PCI bus and a SCSI bus are carried on a single peripheral connector which provides cable management and readily allows hot plugging a redundant peripheral controller card into the host system board.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Storage apparatus, control method therefor and program
InactiveUS20060215297A1Without degrading performanceEliminating and substantially reducing intervalError detection/correctionRecord information storageComputer architectureDisk array
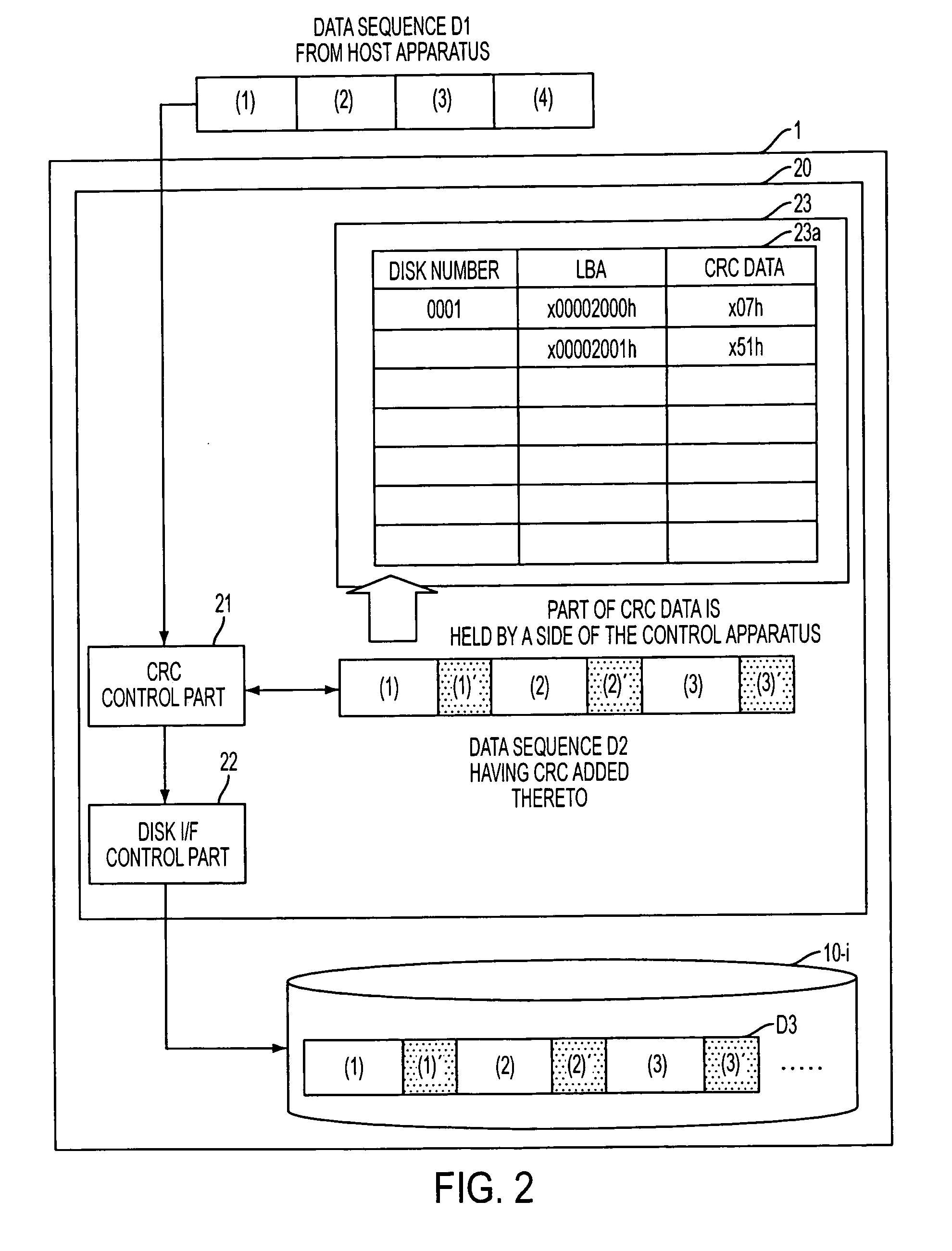
A magnetic disk array apparatus has a function of positively verifying read data with a configuration by which overhead can be reduced as much as possible. Upon writing data to each magnetic disk 10-I, verification, such as CRC data, is additionally written for each writing block, and also, in a disk array controller 20, the same CRC data is held (see FIG. 2).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
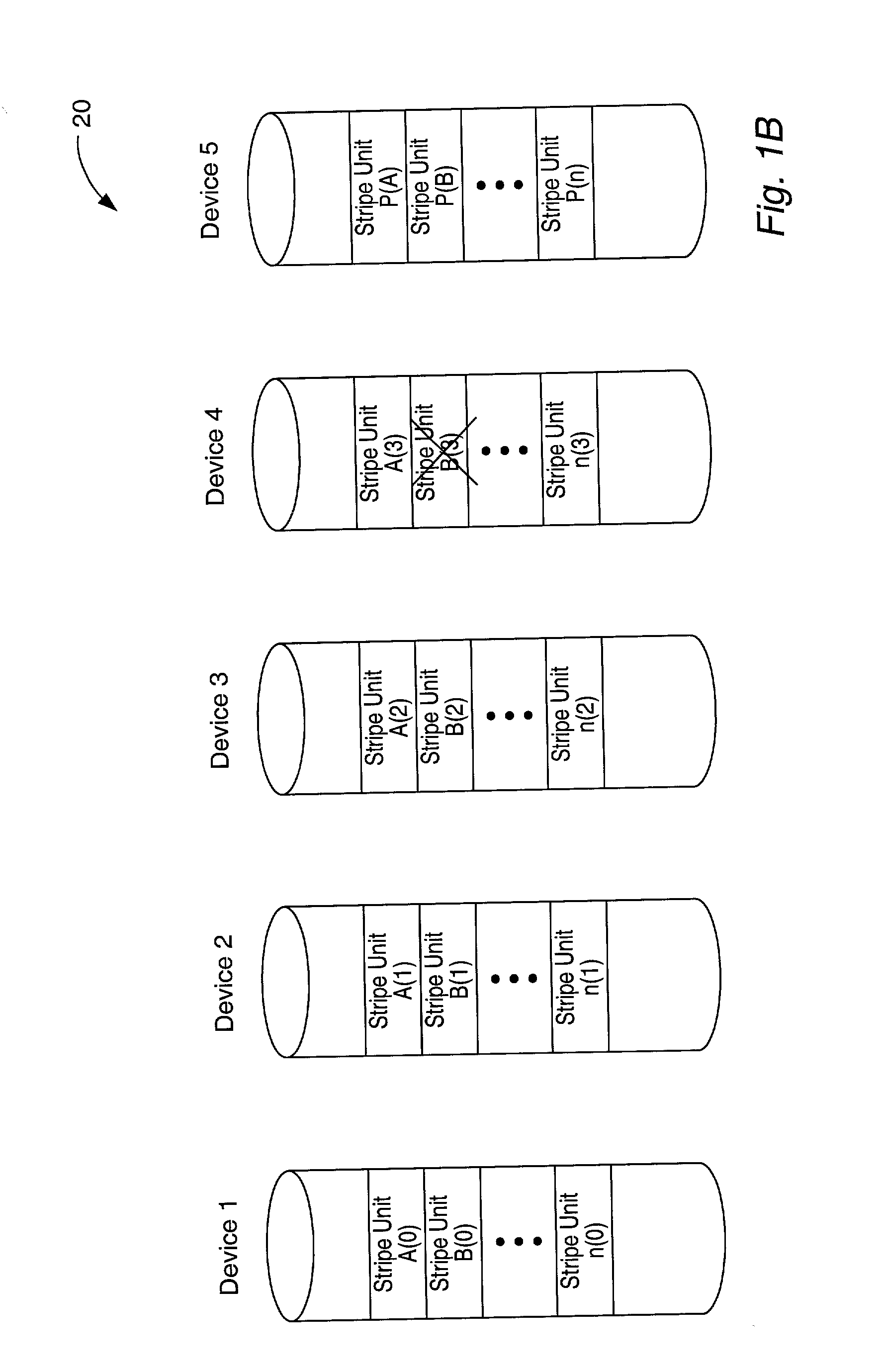
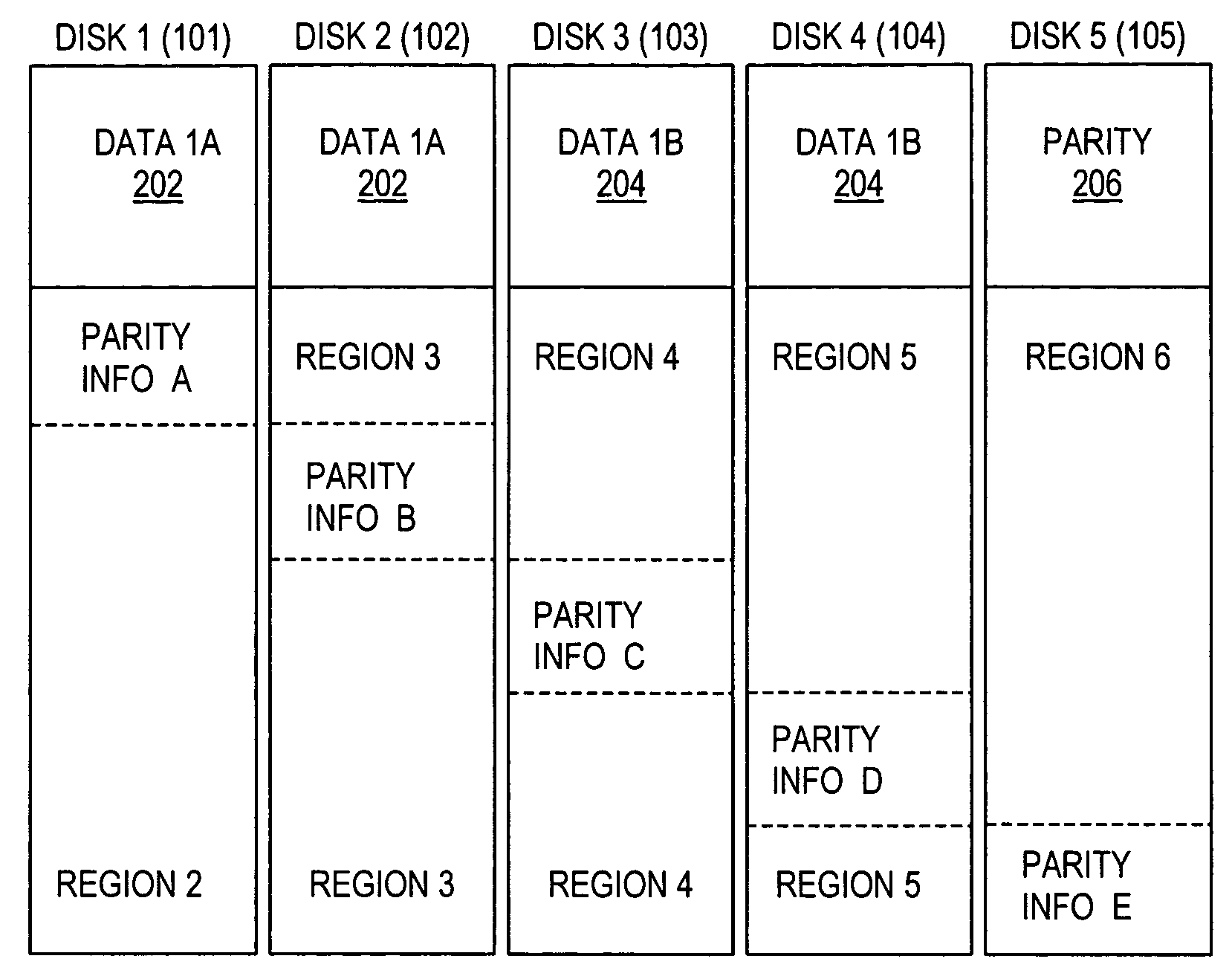
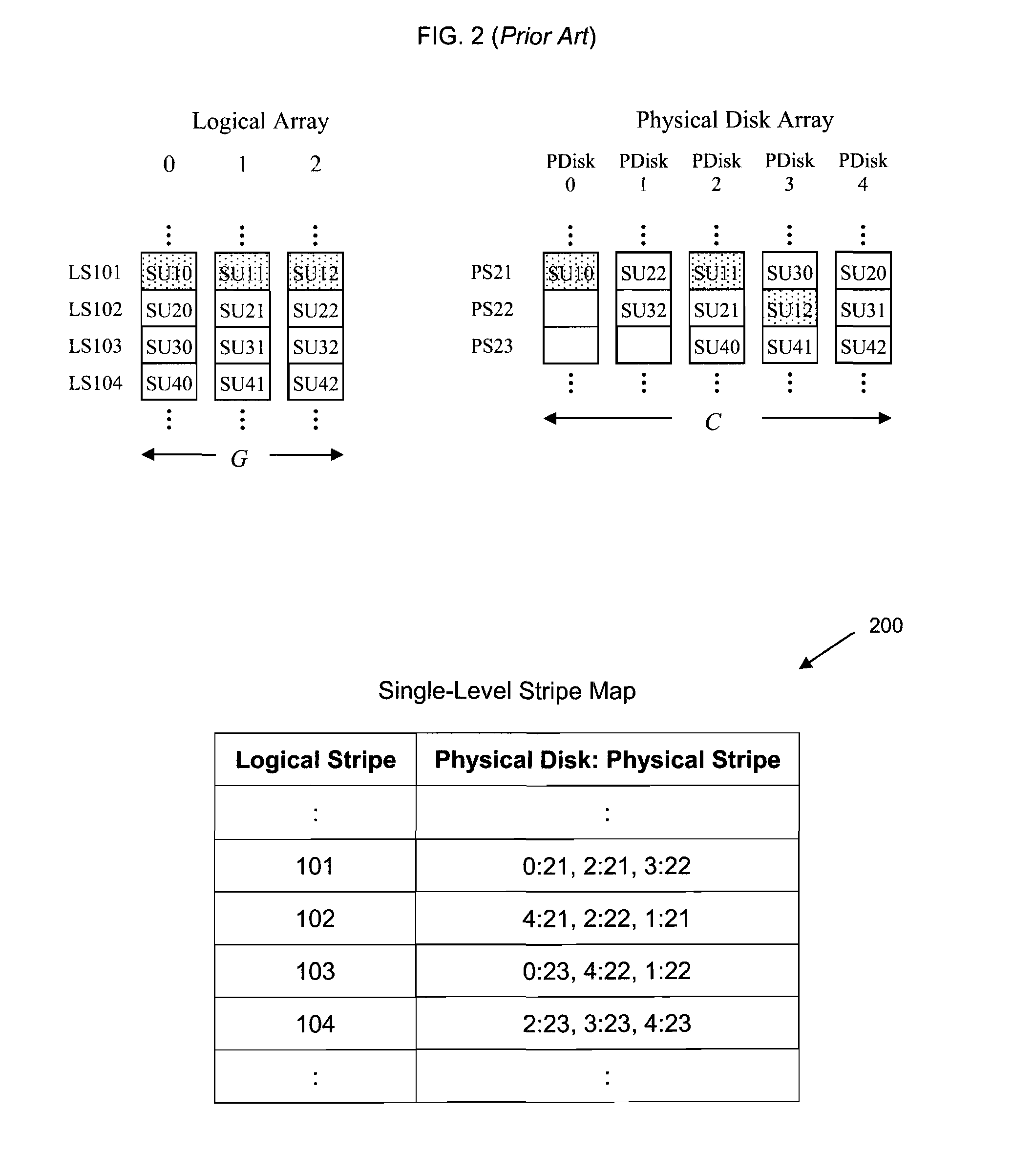
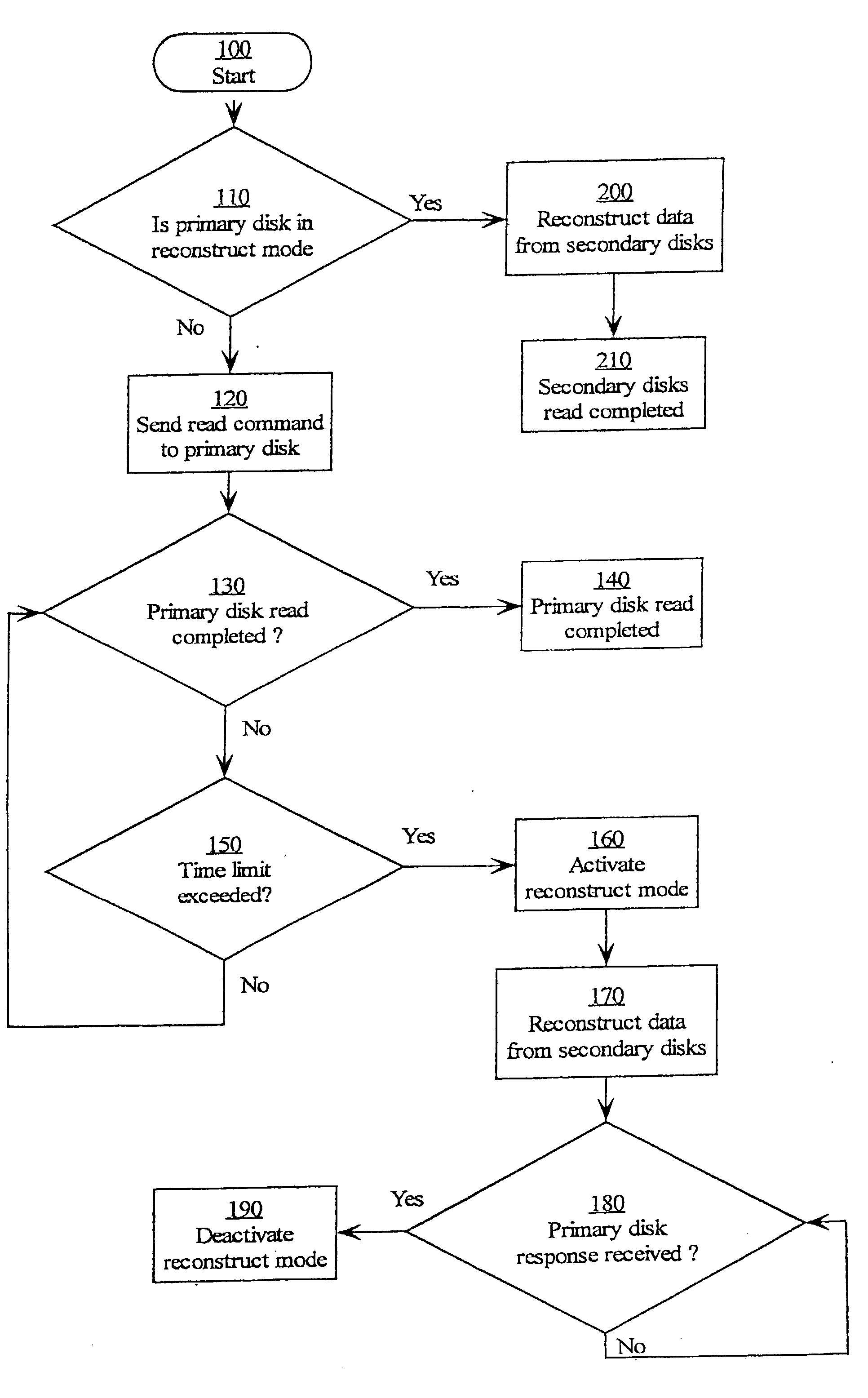
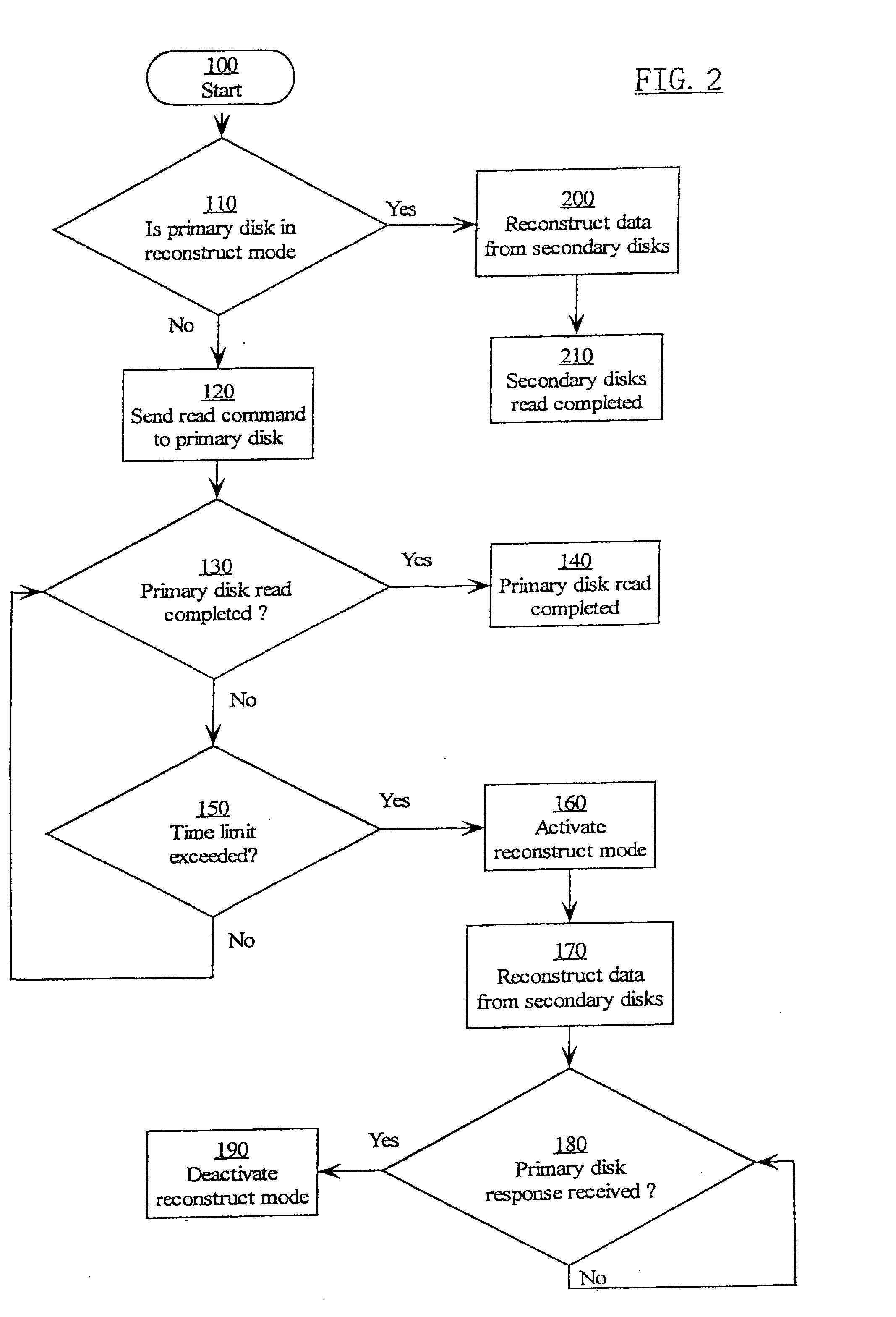
Parity declustered storage device array with partition groups
This disclosure relates to parity declustered storage device arrays having partition groups. In an exemplary embodiment, the storage system includes a storage device array, such as disk array. Each storage device is divided into partitions. Each partition includes stripe units, such as hundreds or thousands of stripe units in exemplary embodiments. The storage system also includes a physical array controller coupled to the storage device array. In an exemplary embodiment, the array controller includes a partition group lookup table and stores and retrieves data and parity in the storage devices based on the partition group lookup table. In this exemplary embodiment, the array controller also includes a stripe lookup table and / or a log. In an exemplary embodiment, the partition group lookup table and the stripe lookup table take up less memory (e.g., by an order of magnitude) than a single-level stripe map conveying the same information.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fan array control system
A fan array fan section in an air-handling system includes a plurality of fan units arranged in a fan array and positioned within an air-handling compartment One preferred embodiment may include an array controller programmed to operate the plurality of fan units at peak efficiency by computing the power consumed in various configurations and selecting the configuration requiring minimum power to operate.
Owner:NORTEK AIR SOLUTIONS
Data storage array method and system
InactiveUS20030212858A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionOriginal dataComputer data storage
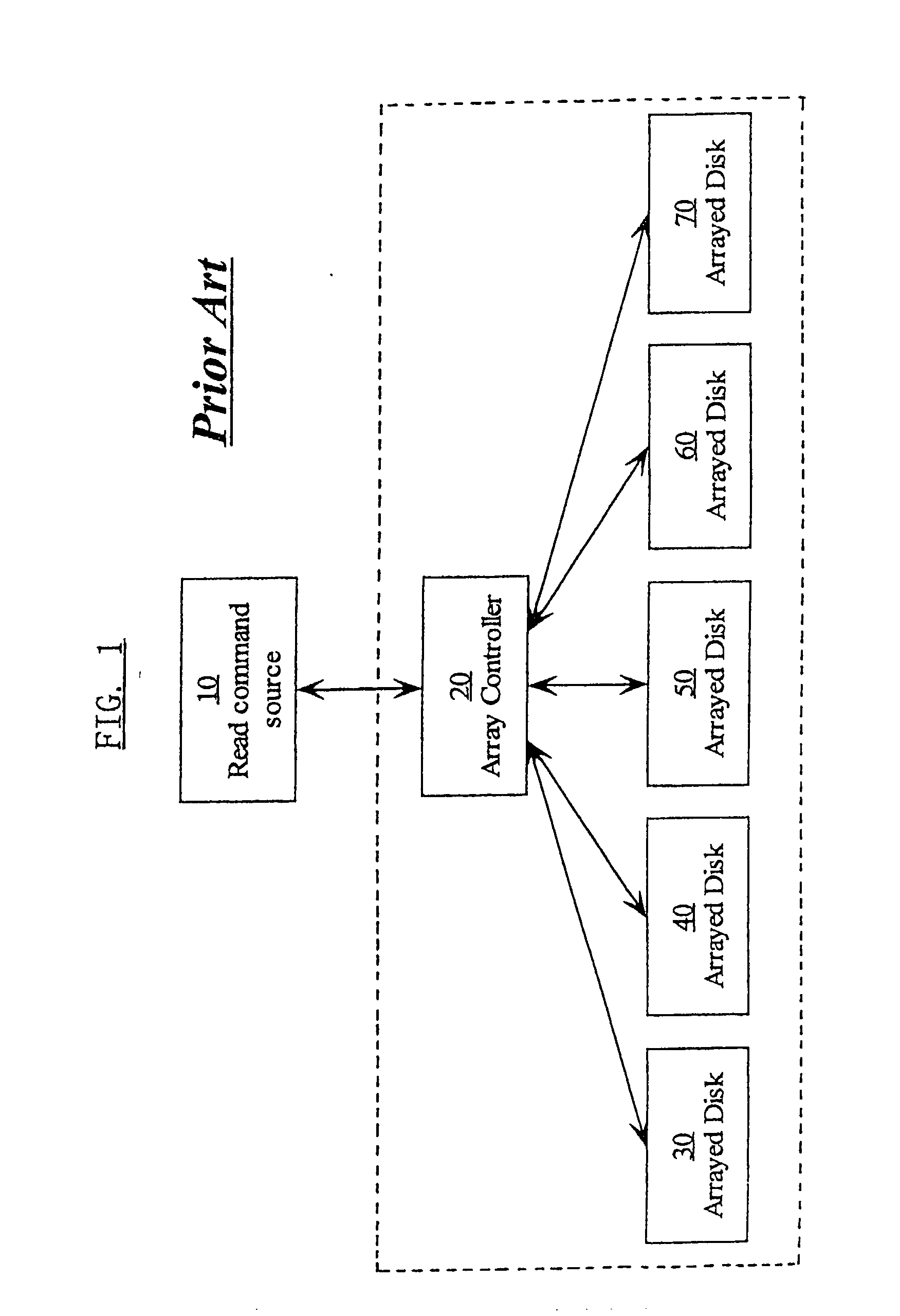
A method and system for reading data from a redundant array of computer data storage media elements without having to wait for a timeout in a drive in the redundant array. If the requested data is from a drive that is temporarily in a timeout, the requested data is reconstructed using other drives in the redundant array, and the reconstructed data is sent to the requester via an array controller. When the drive holding the originally requested data comes back from the timeout and responds to the original request by transmitting the original data, the array controller ignores the original data since the request has already been fulfilled by the reconstructed data.
Owner:IBM CORP
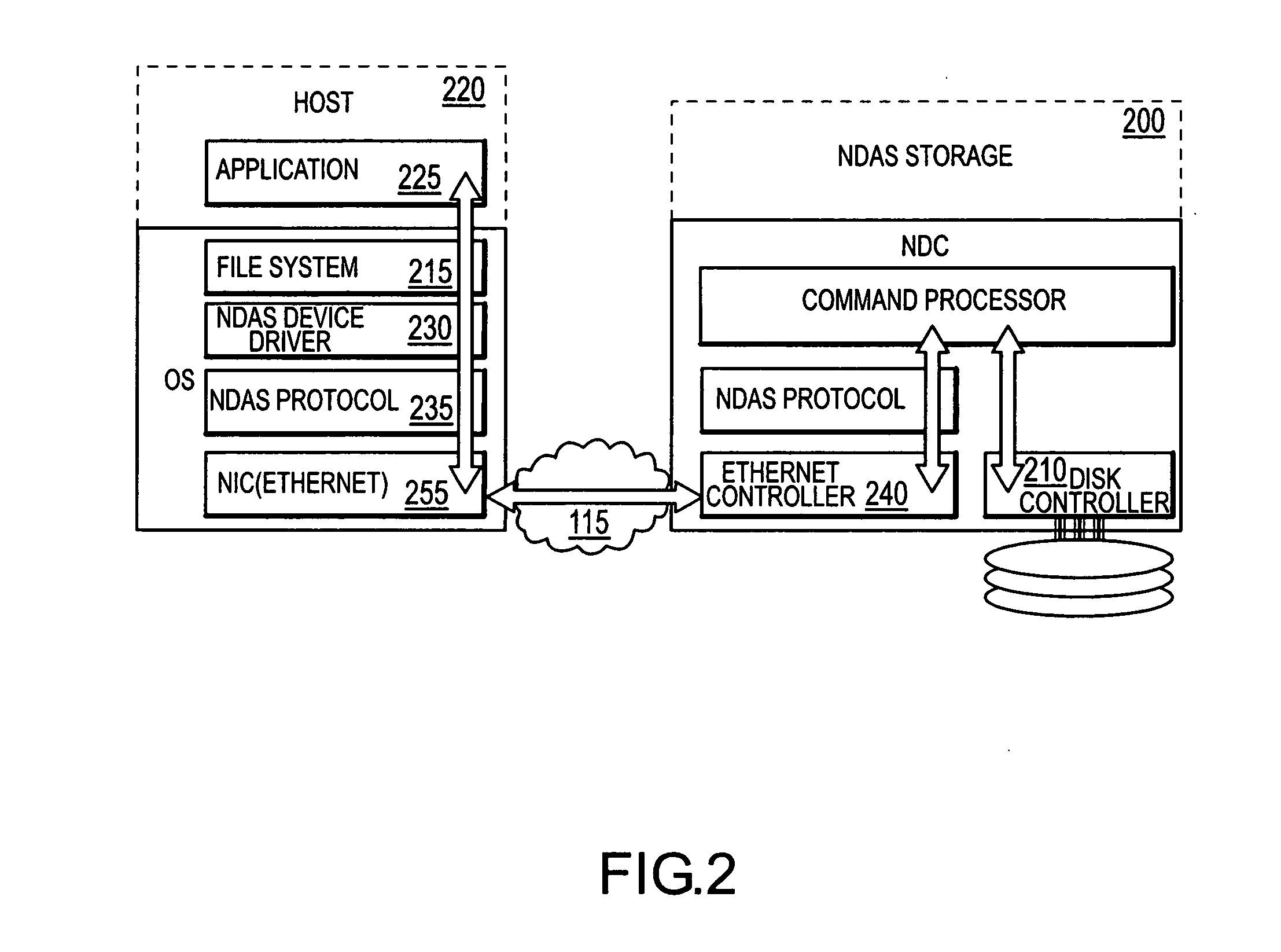
Enhanced network direct attached storage controller
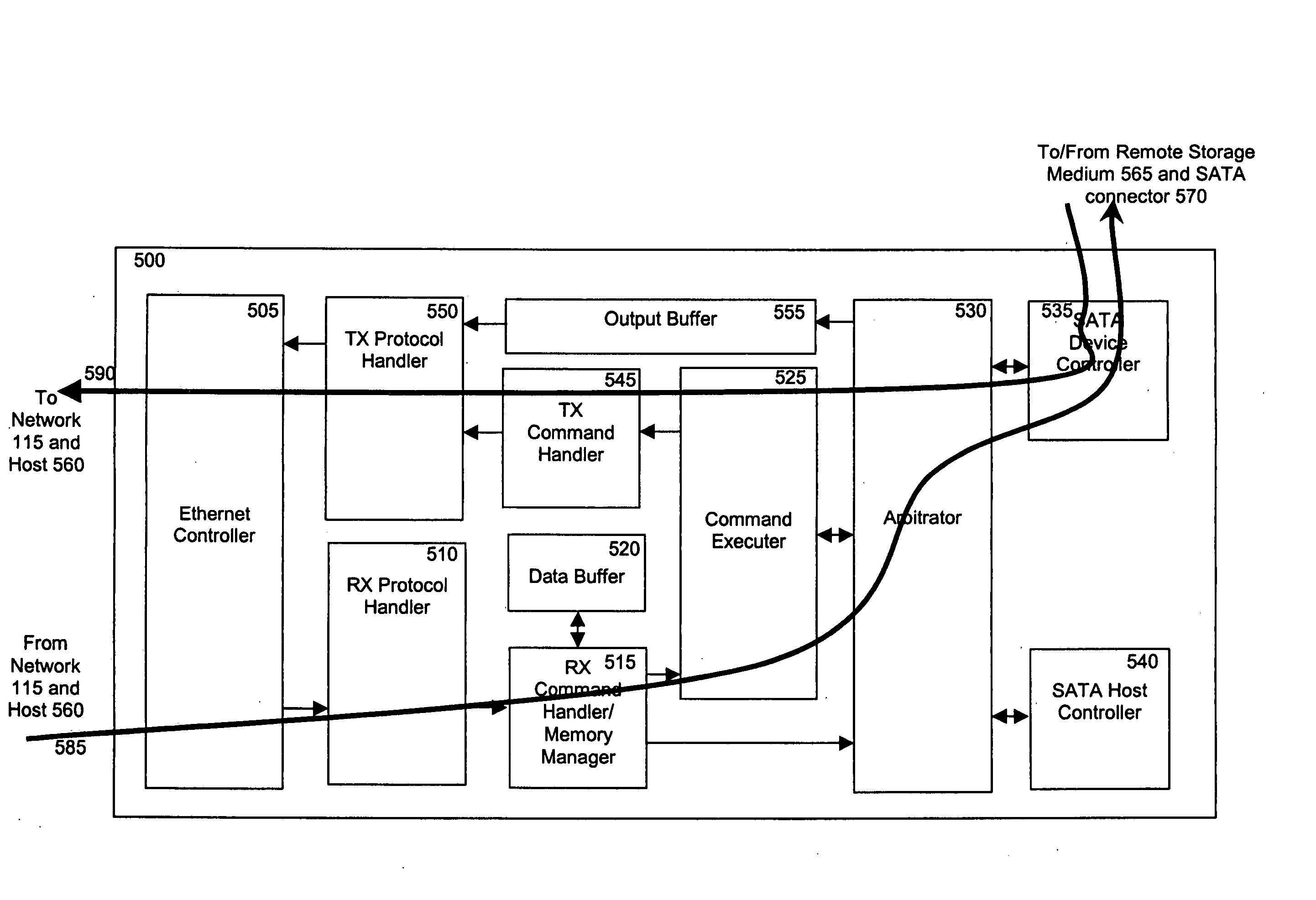
ActiveUS20070008988A1Time-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsFile systemDisk controller
An apparatus and method for providing a storage medium accessible across a network to a host. The storage medium's operation is generally controlled by a network disk controller. The network disk controller may receive a packet from a remote host, decapsulate the packet, and act on the packet to either transmit data from a storage medium or write data to a storage medium. Generally, the network disk controller does not execute any file system. Rather, the file system for communication between the host and controller is executed by the host. The performance of the network disk controller generally matches that of a local (i.e., non-network) disk controller in terms of data access and writing.
Owner:SYNKLOUD TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com