Patents
Literature
948 results about "Timeout" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunication and related engineering, the term timeout or time-out has several meanings, including: A network parameter related to an enforced event designed to occur at the conclusion of a predetermined elapsed time. A specified period of time that will be allowed to elapse in a system before a specified event is to take place, unless another specified event occurs first; in either case, the period is terminated when either event takes place. Note: A timeout condition can be canceled by the receipt of an appropriate time-out cancellation signal. An event that occurs at the end of a predetermined period of time that began at the occurrence of another specified event. The timeout can be prevented by an appropriate signal. Timeout allows a more efficient usage of limited resources without requiring additional interaction from the agent interested in the goods that cause the consumption of these resources. The basic idea is that in situations where a system must wait for something to happen, rather than waiting indefinitely, the waiting will be aborted after the timeout period has elapsed.
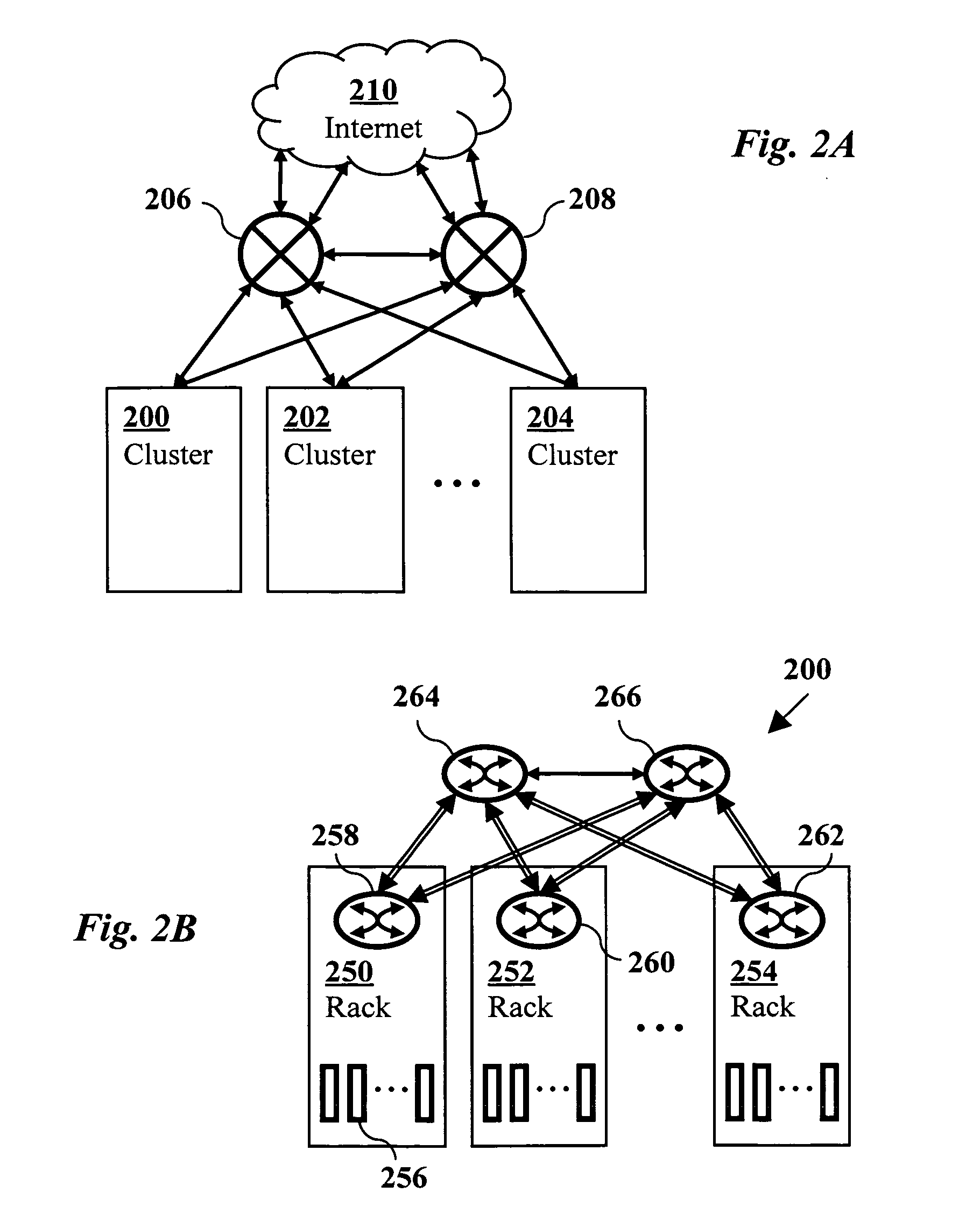
System and method for reforming a distributed data system cluster after temporary node failures or restarts
ActiveUS20040059805A1Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsSelf-healingDistributed computing
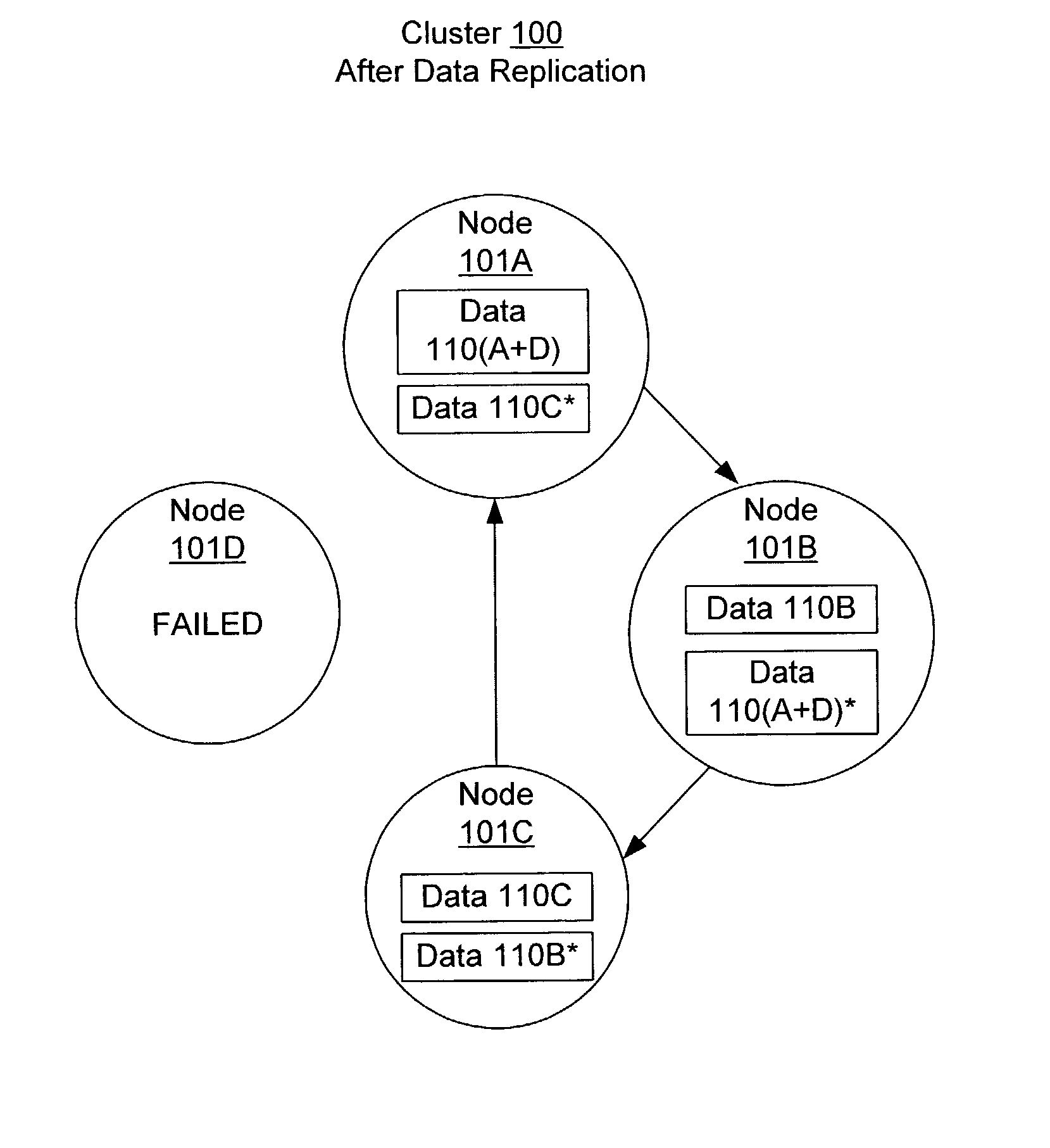
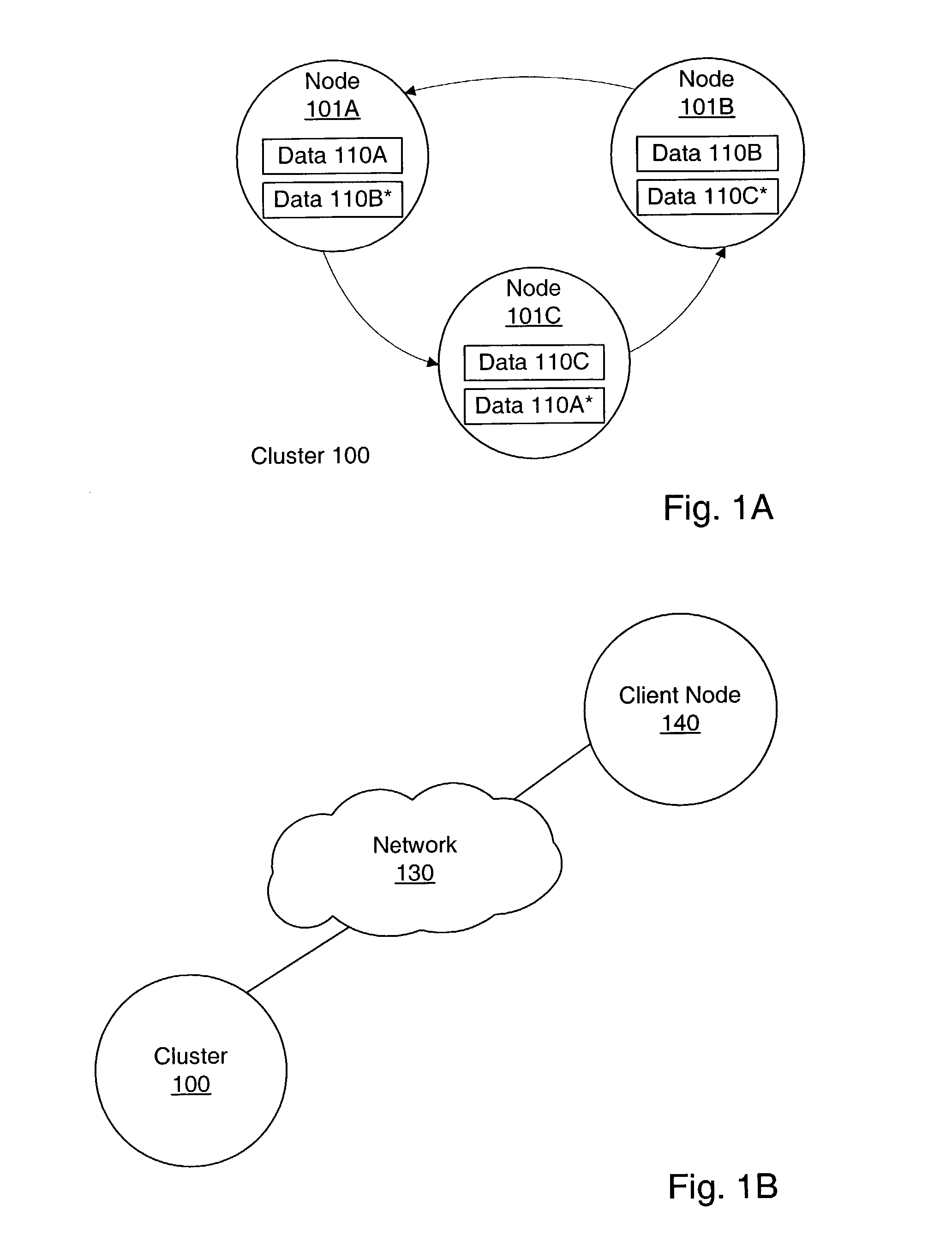
Data stored within a cluster may be distributed among nodes each storing a portion of the data. The data may be replicated wherein different nodes store copies of the same portion of the data. In response to detecting the failure of a node, the cluster may initiate a timeout period. If the node remains failed throughout the timeout period, the cluster may copy the portion of the data stored on the failed node onto one or more other nodes of the cluster. If the node returns to the cluster during the timeout period, the cluster may maintain the copy of the data on the previously failed node without copying the portion of the data stored on the failed node onto any other nodes. By delaying self-healing of the cluster for the timeout period, an unbalanced data distribution may be avoided in cases where a failed node quickly rejoins the cluster.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
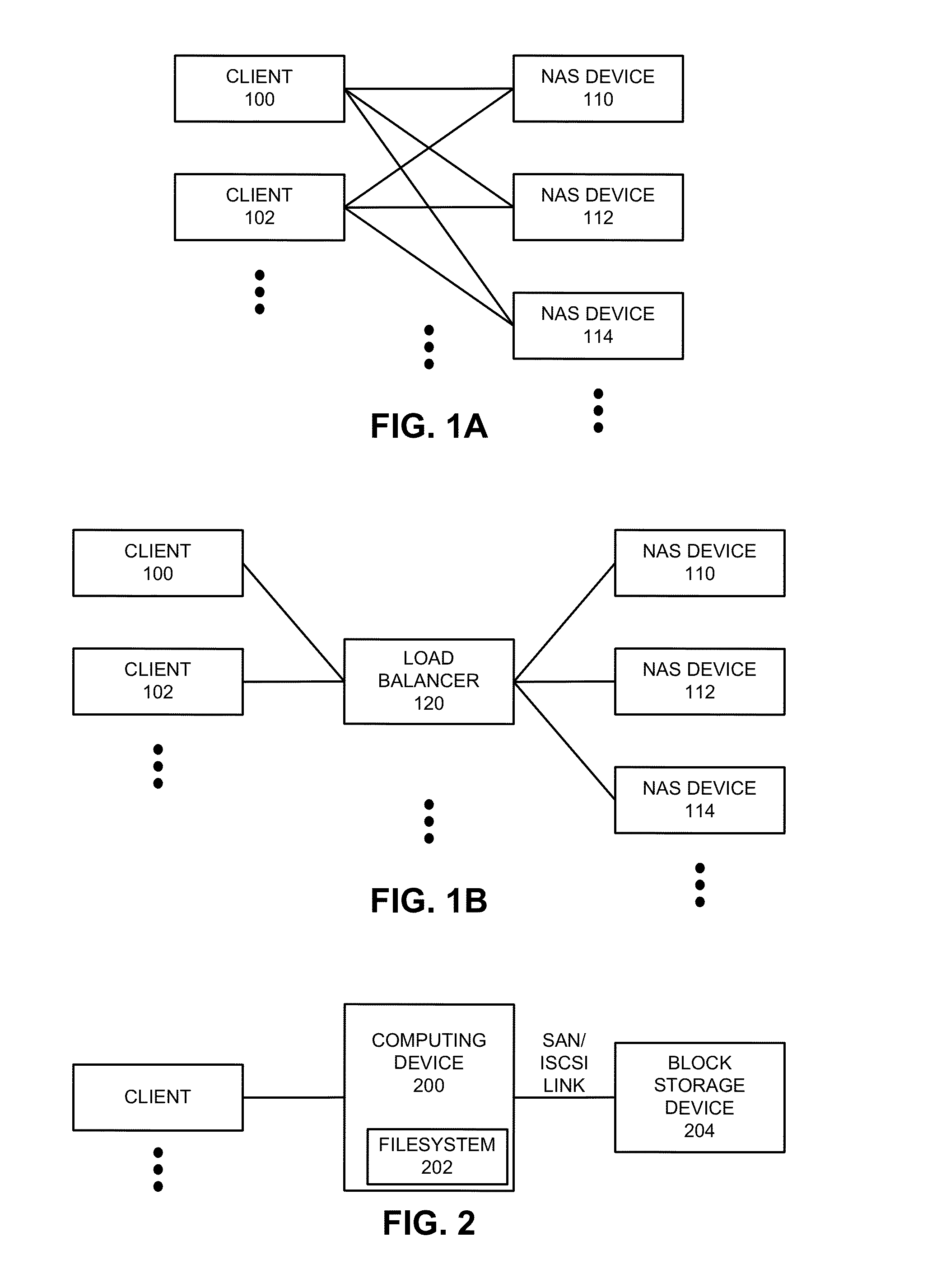
Avoiding client timeouts in a distributed filesystem
ActiveUS20130339407A1Reduce access latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data information retrievalDistributed File SystemFile system
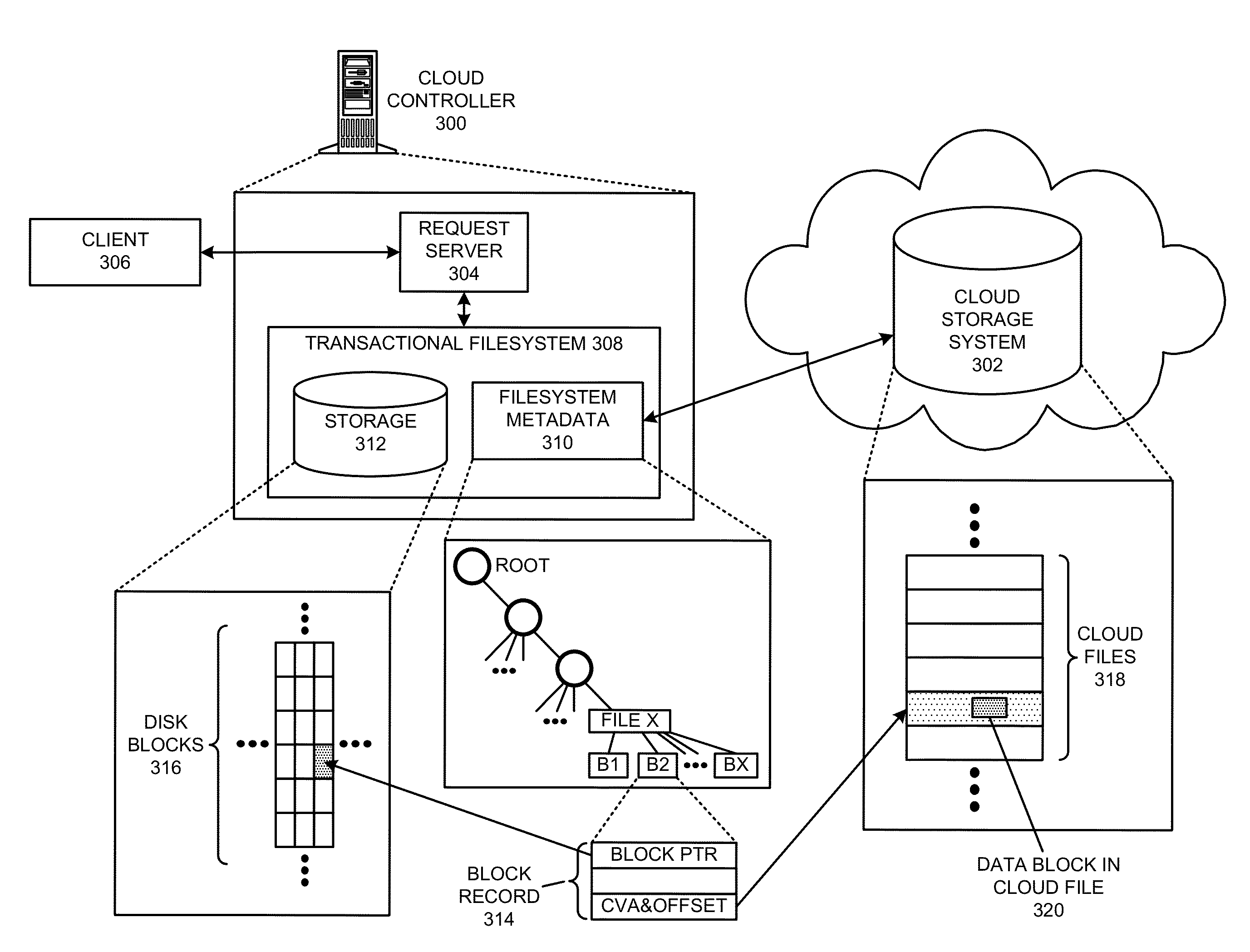
The disclosed embodiments disclose techniques that facilitate of avoiding client timeouts in a distributed filesystem. Multiple cloud controllers collectively manage distributed filesystem data that is stored in one or more cloud storage systems; the cloud controllers ensure data consistency for the stored data, and each cloud controller caches portions of the distributed filesystem in a local storage pool. During operation, a cloud controller receives from a client system a request for a data block in a target file that is stored in the distributed filesystem. Although the cloud controller is already caching the requested data block, the cloud controller delays transmission of the cached data block; this additional delay gives the cloud controller more time to access uncached data blocks for the target file from a cloud storage system, thereby ensuring that subsequent requests of such data blocks do not exceed a timeout interval on the client system.
Owner:PANZURA LLC
System and method for automatically verifying storage of redundant contents into communication equipments, by data comparison
InactiveUS9130918B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationContent IdentifierRedundant code
A method is intended for verifying storage of contents into communication equipments connected to at least one communication network. This method consists, when a first communication equipment stores a content and wants to verify that this content is still stored into a second communication equipment: i) in transmitting a first request, comprising at least an identifier of this content and first data representative of this content and requiring verification of the storage of this content into the second communication equipment, to an auxiliary communication equipment acting as an interface between the communication network and the second communication equipment, ii) in transmitting a second request, comprising at least the content identifier, to the second communication equipment, to require transmission of second data representative of the content to the auxiliary communication equipment, and in triggering a timeout having a chosen duration, and iii) if the auxiliary communication equipment has received the second data before expiration of this timeout, in comparing these received second data, possibly after having processed them, to the received first data, and in transmitting a message representative of the result of this comparison to the first communication equipment.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
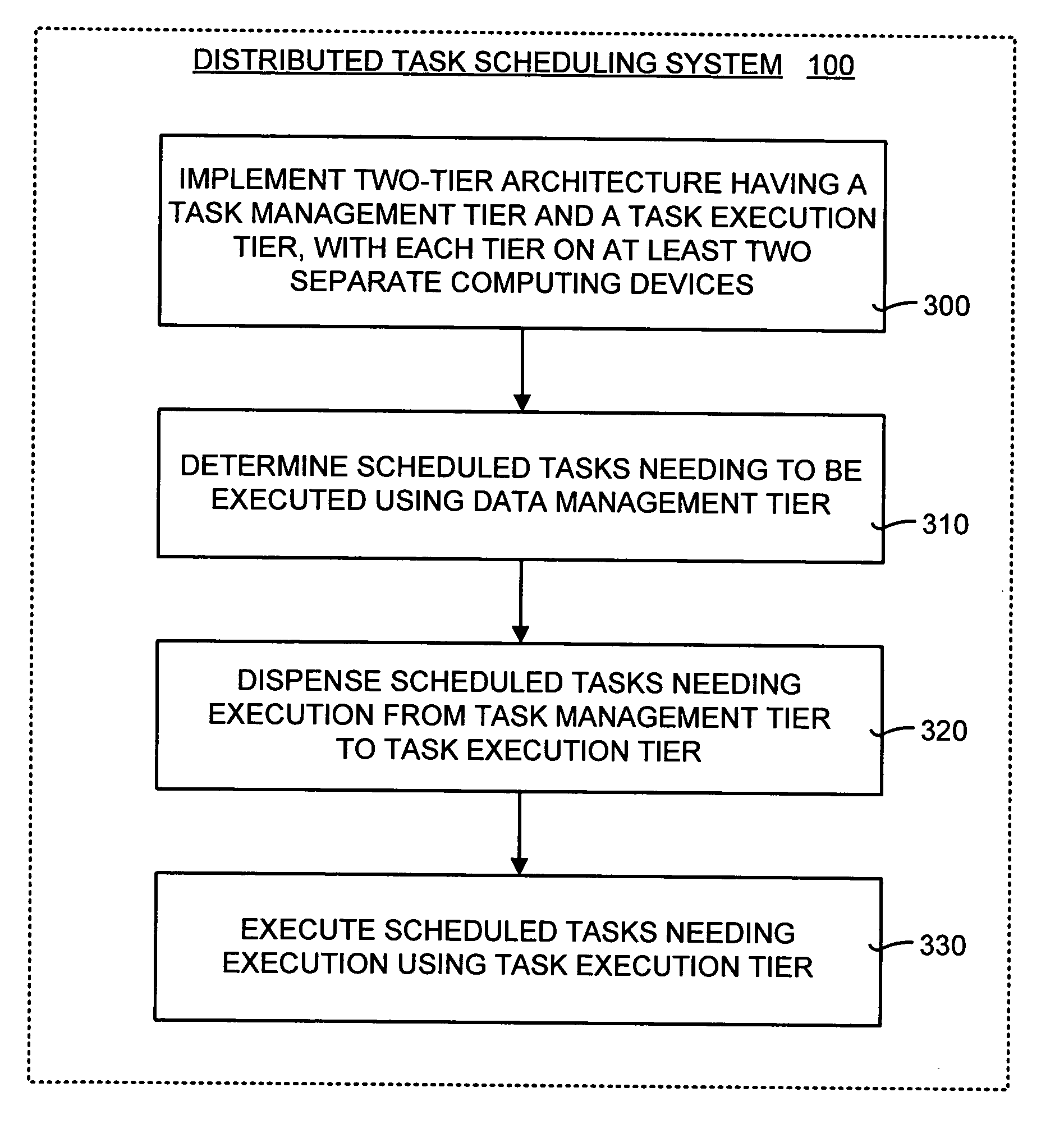
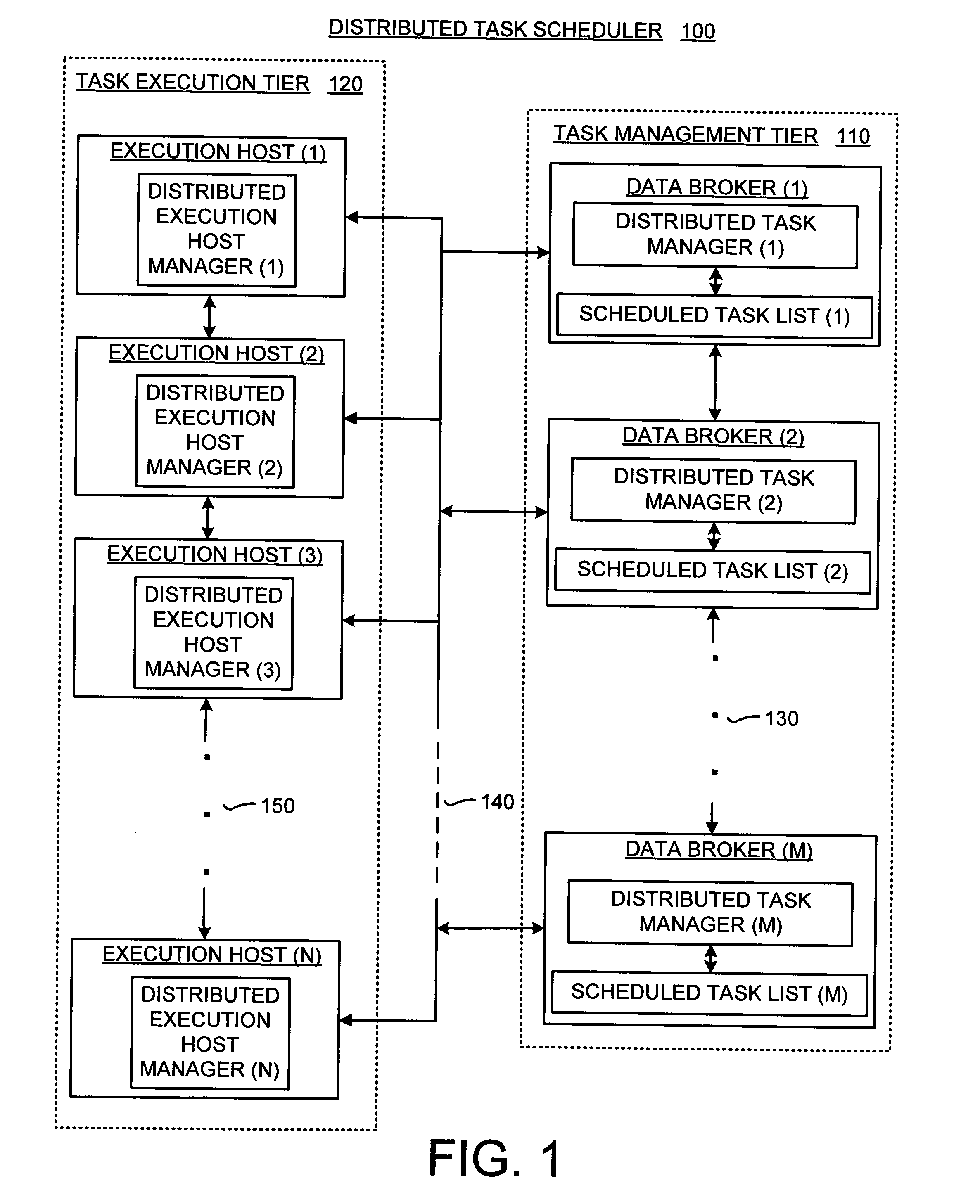
Distributed task scheduler for computing environments
InactiveUS20050268300A1Improve scalabilityResource allocationMemory systemsParallel computingEngineering
A distributed task scheduling method and system that separates and performs task management and task execution on separate computing devices and distributes task execution over multiple computing devices. The distributed task scheduler includes two-tier architecture having at least one execution host and at least one data broker. The execution hosts handle the tasks and the data broker manages the task schedule. The data broker determines any scheduled tasks that need to be executed. Once an available task is found, the data broker dispenses the scheduled task to an execution host. A timeout period is selected for each assigned task. If the assigned execution host does not report back to the data broker within the timeout period the completion of the assigned task, the data broker is free to assign the task to another execution host to ensure reliable execution of the task.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
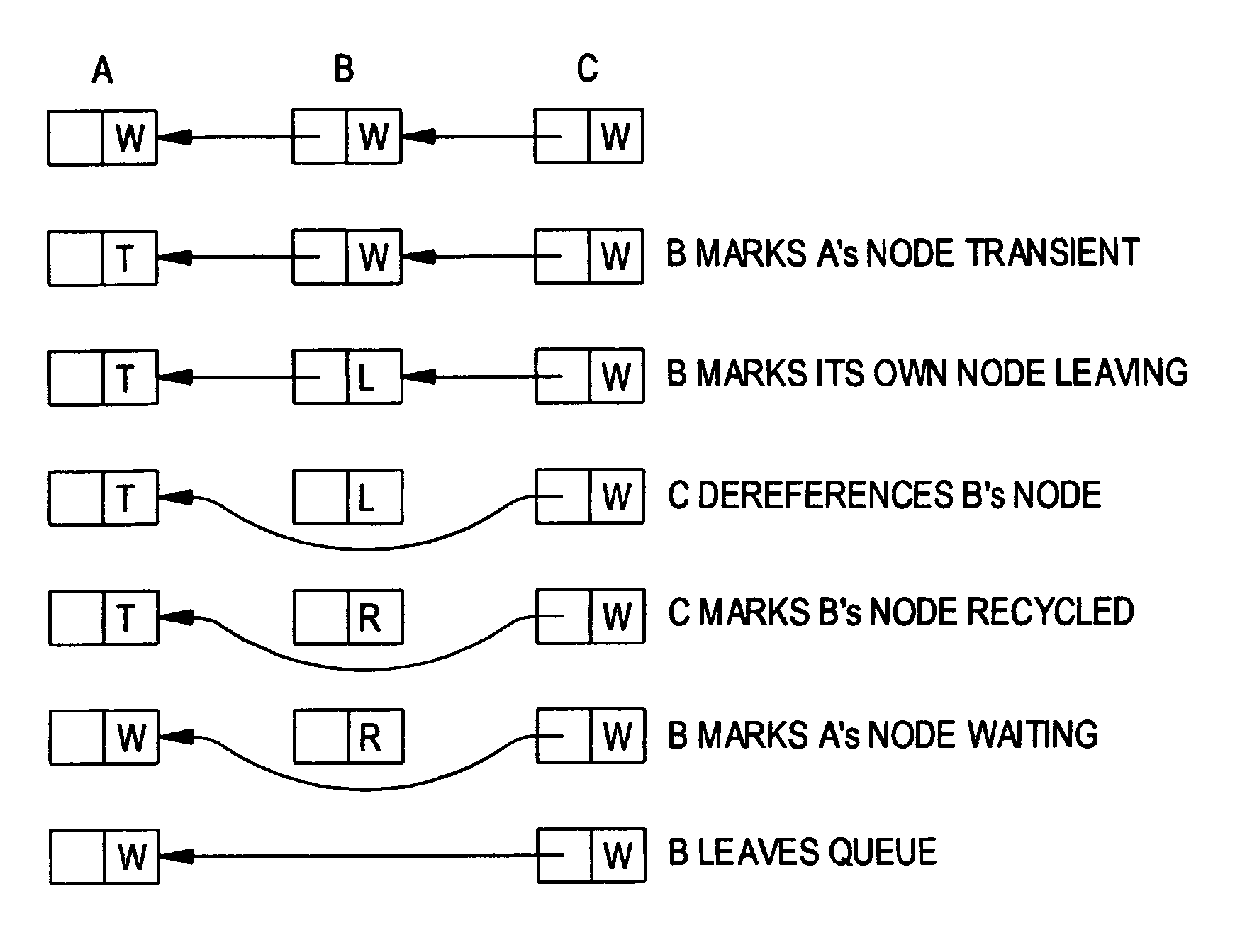
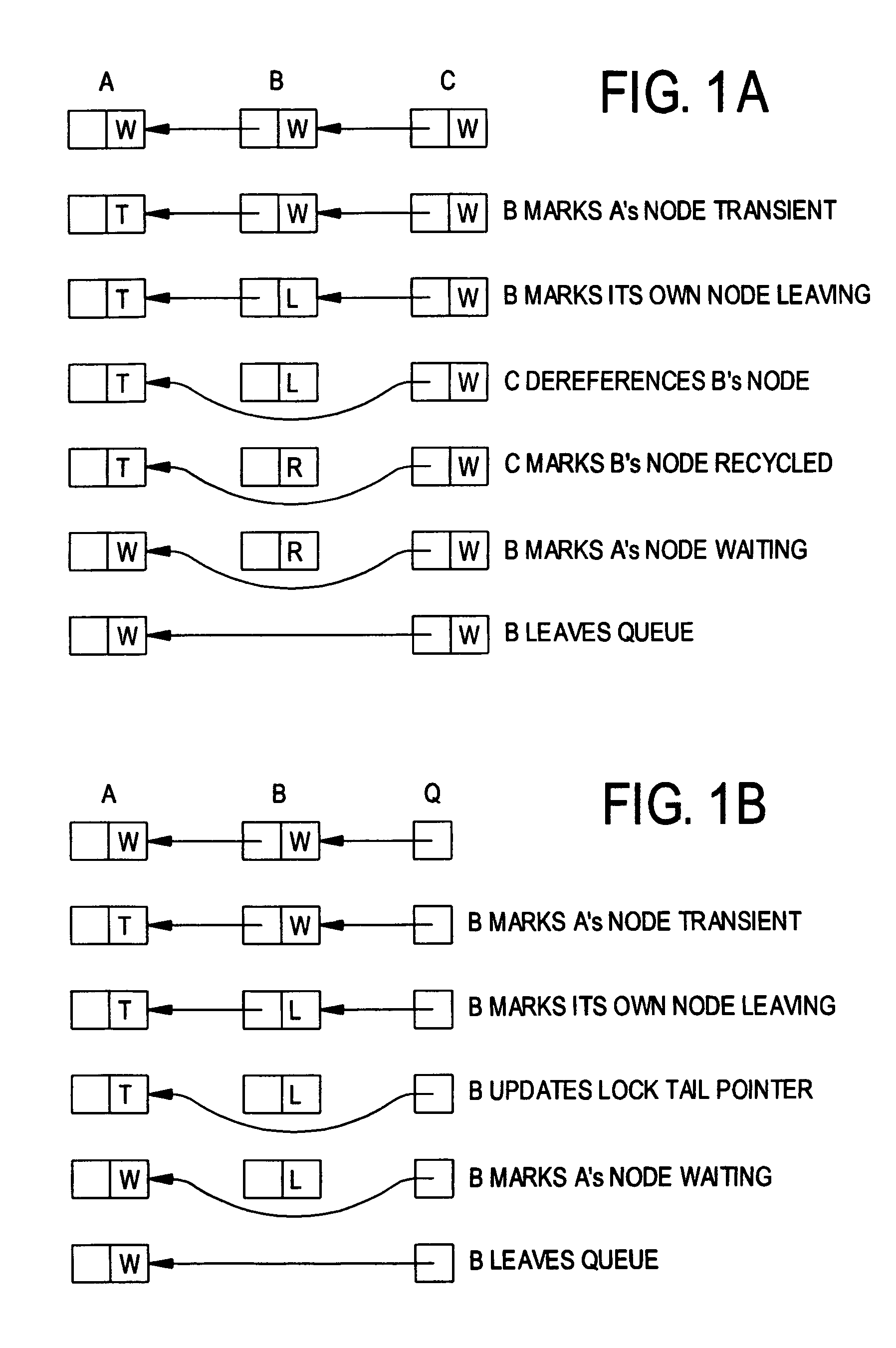
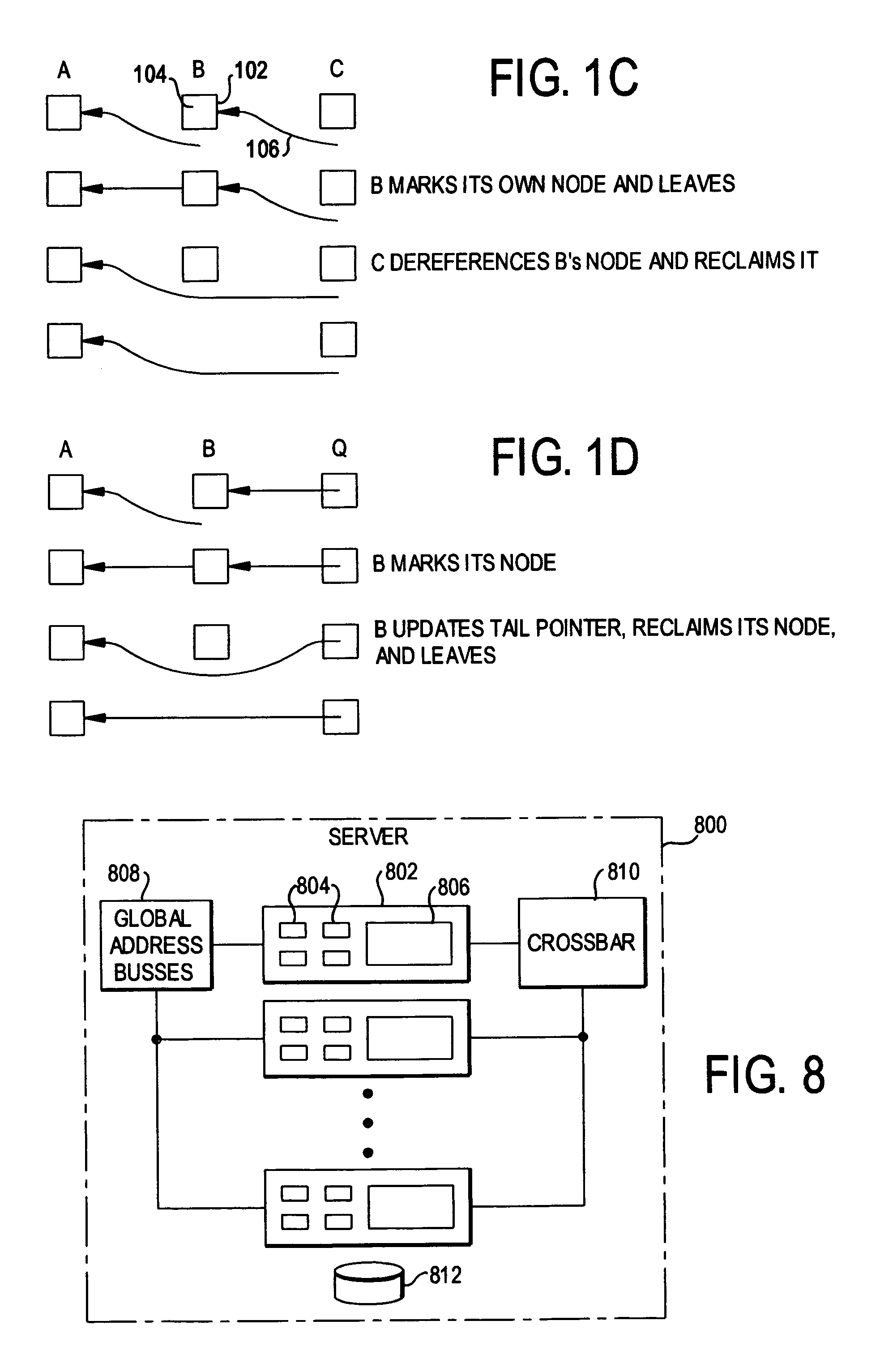
Queue-based spin lock with timeout
InactiveUS6965961B1Easy to scaleProgram synchronisationUnauthorized memory use protectionSpin locksReal-time computing
A queue-based spin lock with timeout allows a thread to obtain contention-free mutual exclusion in fair, FIFO order, or to abandon its attempt and time out. A thread may handshake with other threads to reclaim its queue node immediately (in the absence of preemption), or mark its queue node to allow reclamation by a successor thread.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
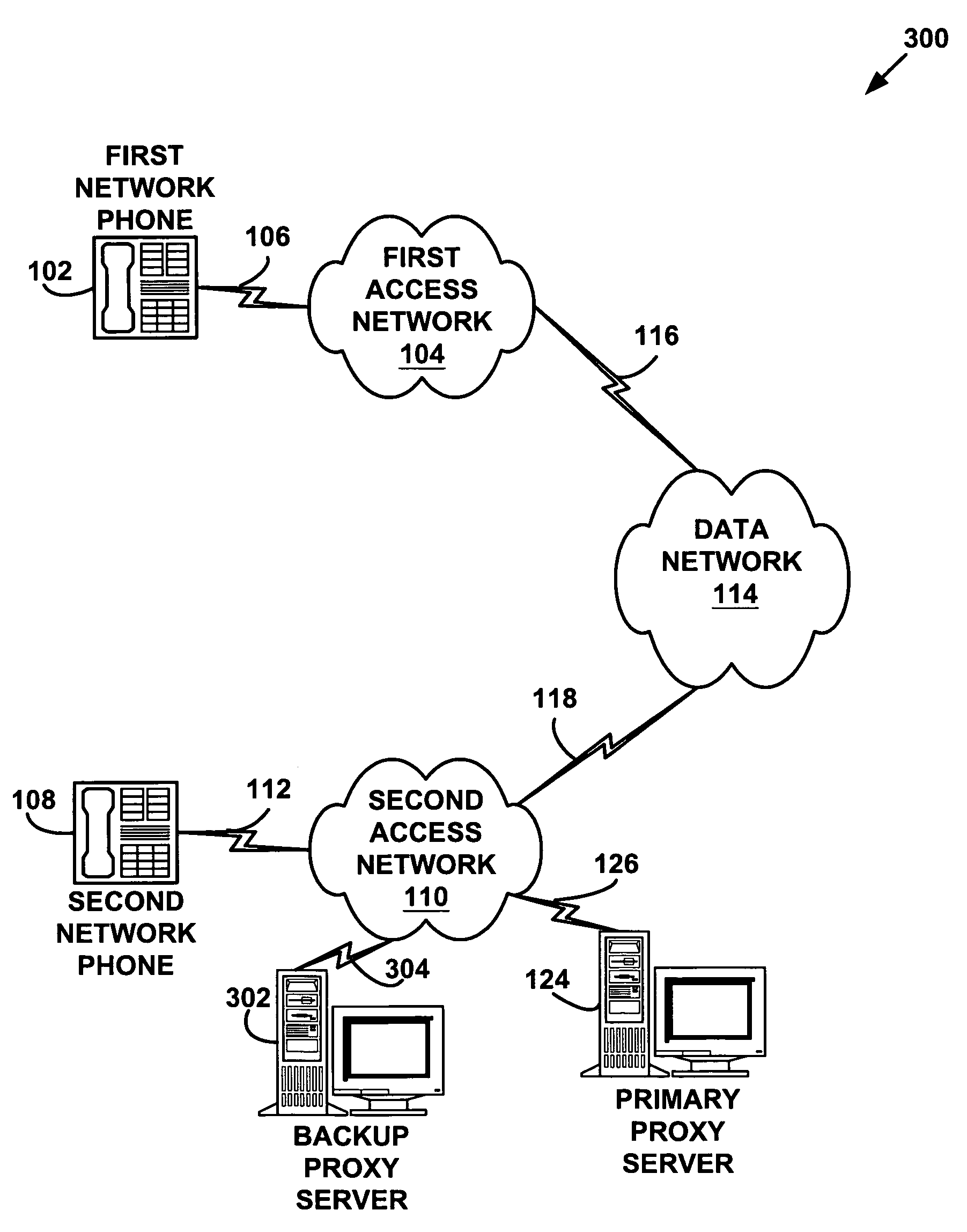
System and method for providing fault tolerance in a network telephony system
A system and method for providing fault tolerance in a network telephony system. Signaling messages according to a signaling protocol, such as the SIP protocol, are modified to include a path attribute with a network address corresponding to a backup proxy server. When a primary proxy server is supported by a backup proxy server, the primary proxy server inserts the Alternate Path tag into one or more signaling messages. When a network entity sends a message, it checks the message to identify the primary proxy server. Upon receiving a failure or timeout when attempting to send to the primary proxy server, the sending network entity should try the backup proxy server specified in the path attribute. When the backup proxy server receives the message, it may modify the message to specify the new routing path. As a result, subsequent messages get routed properly using the backup proxy server.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
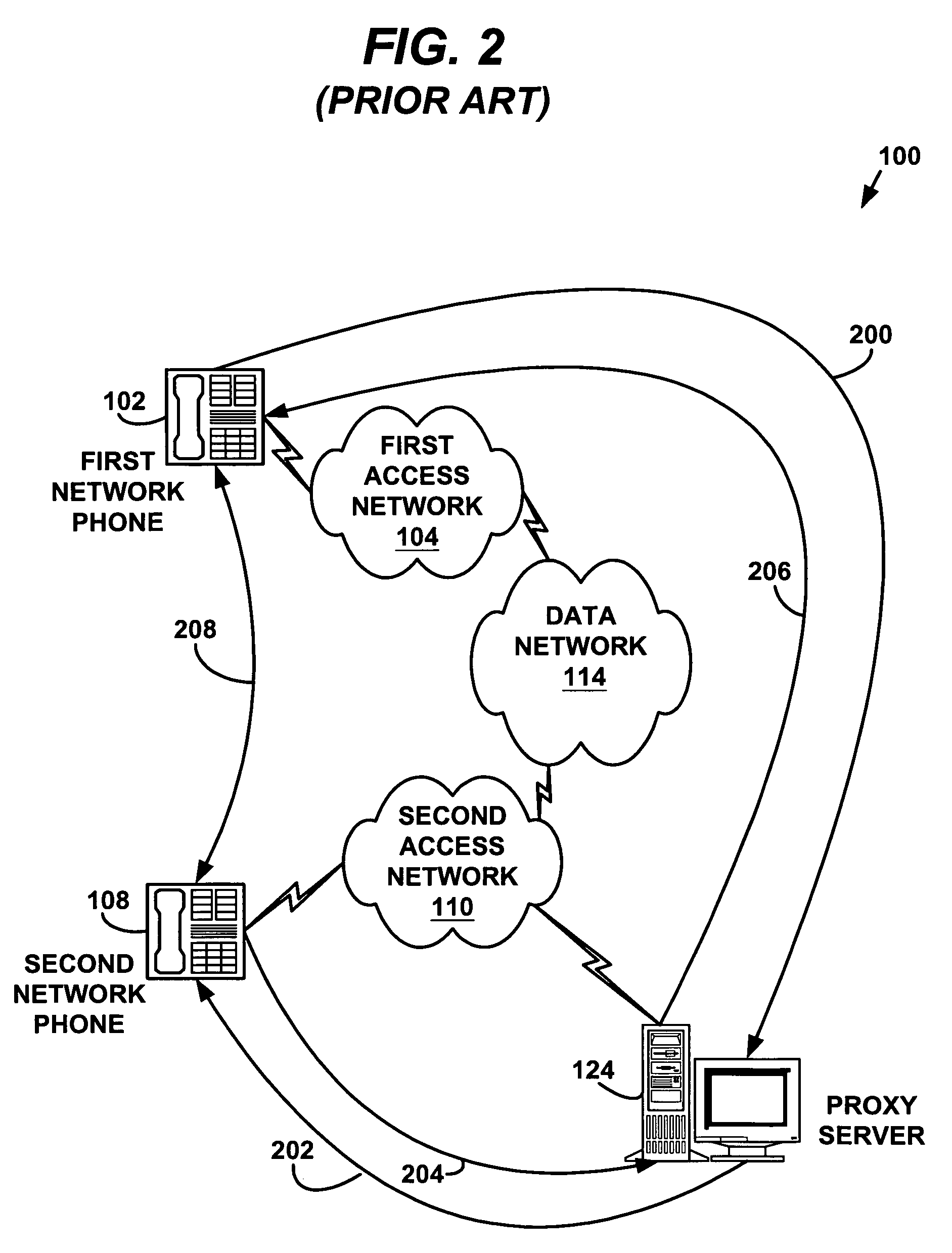
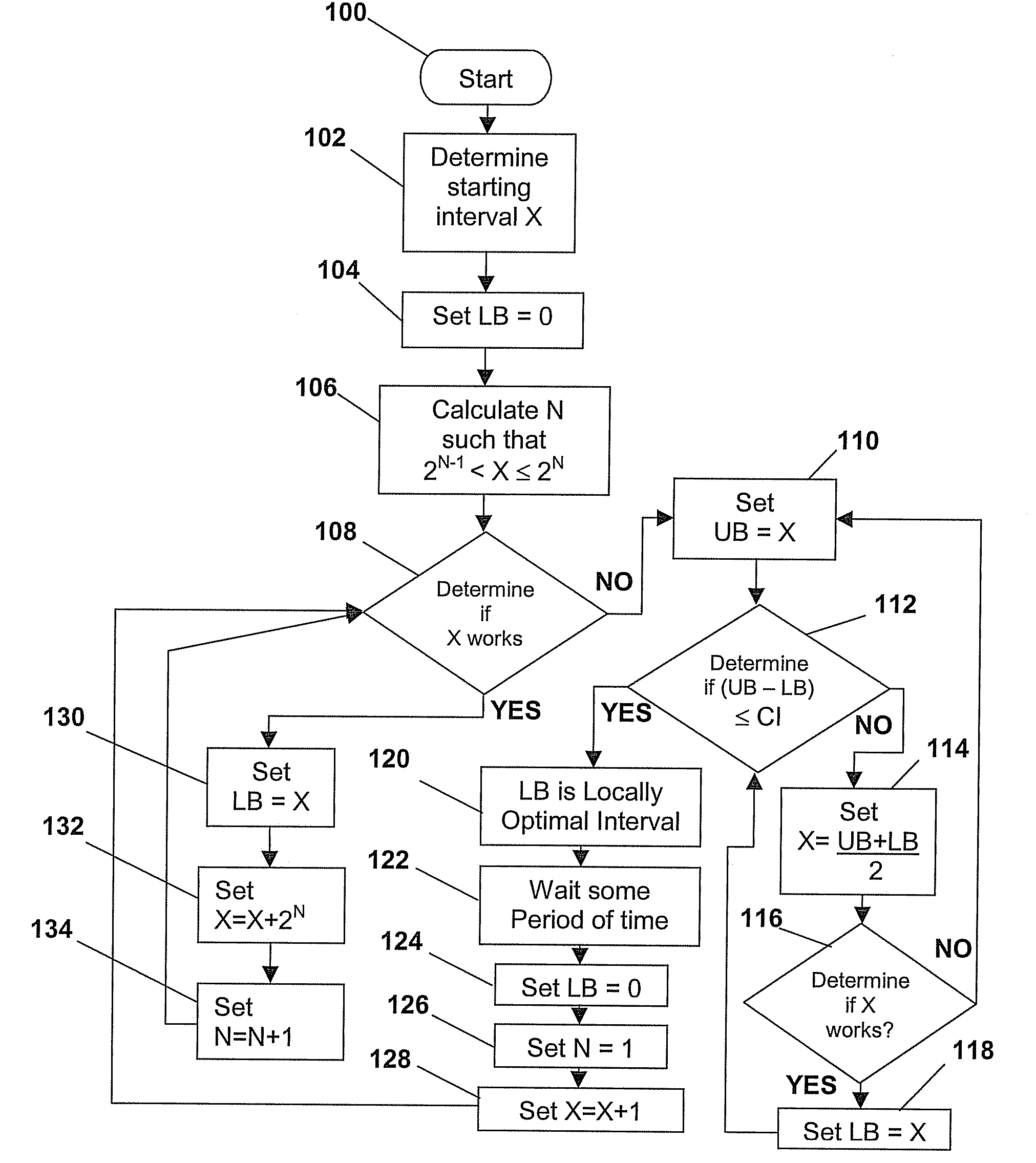
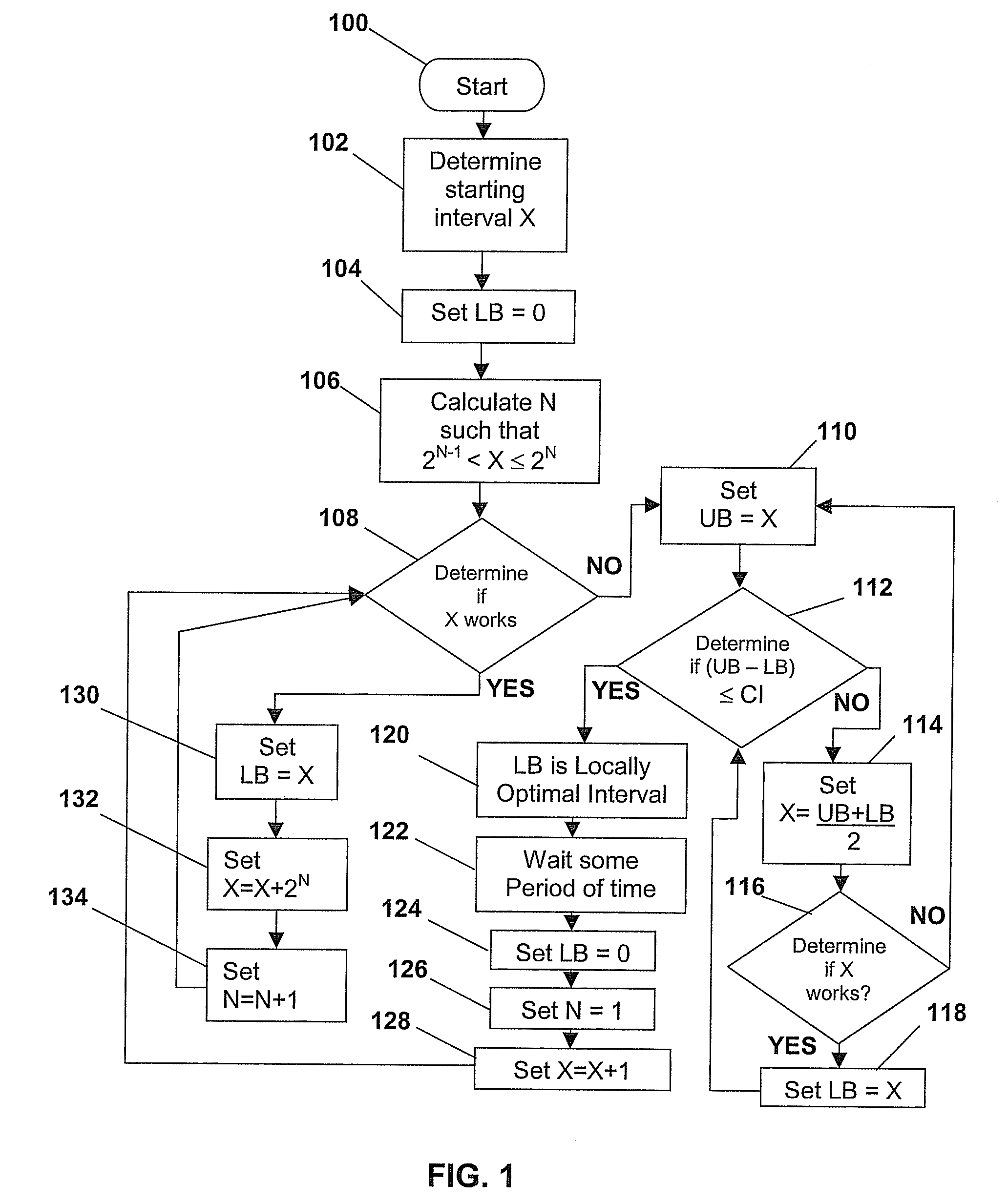
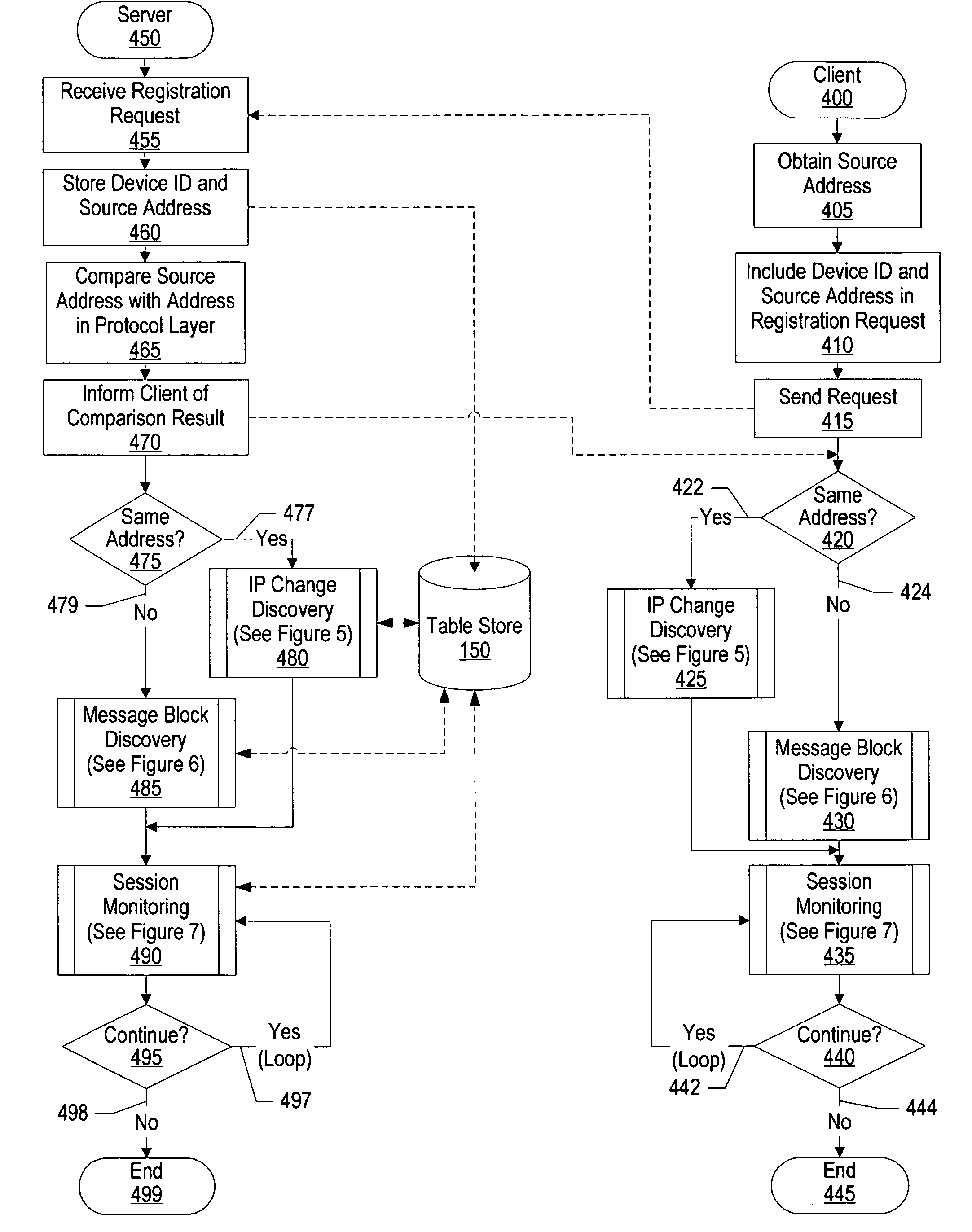
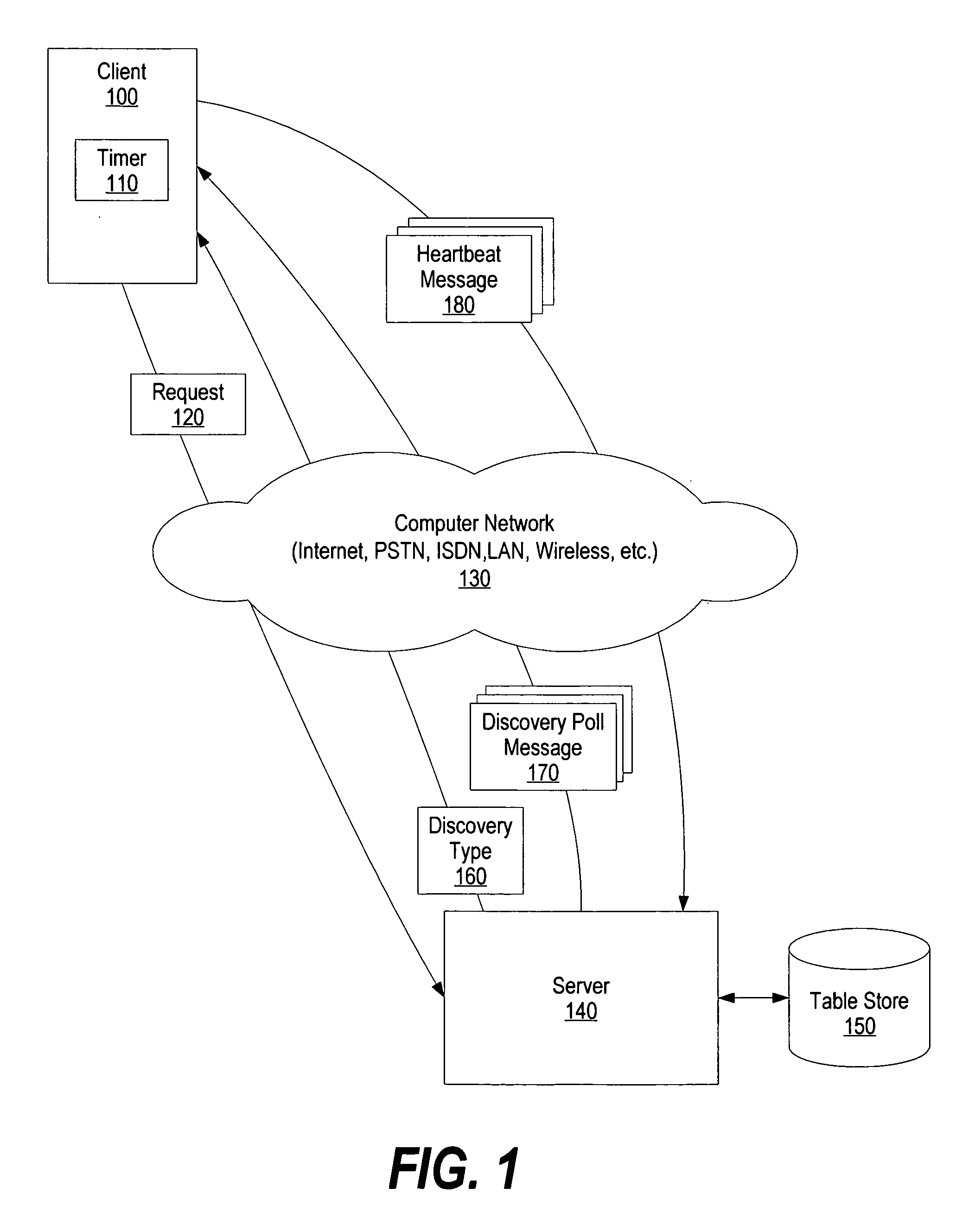
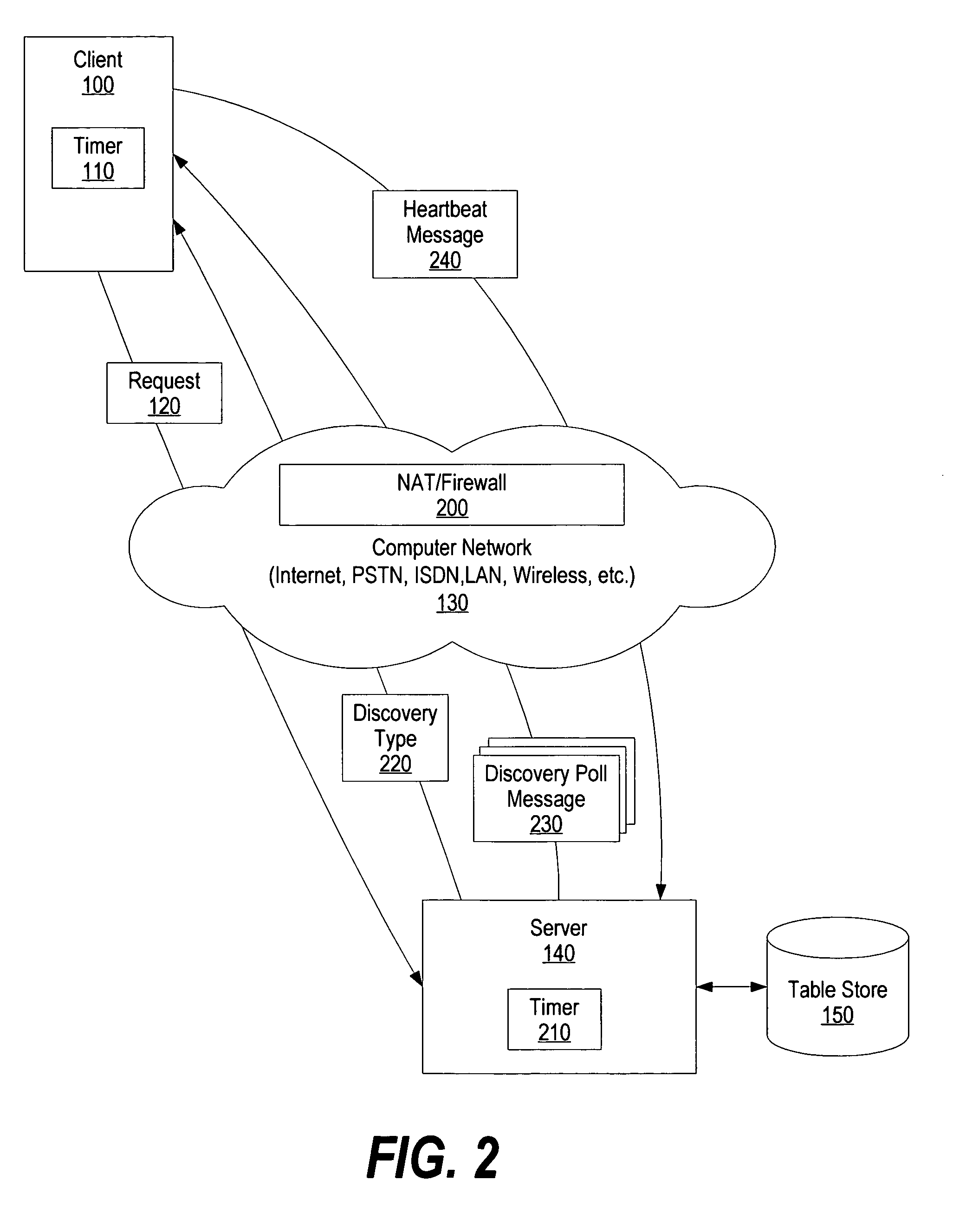
System and method for IP address discovery in rapidly changing network environment
InactiveUS20070214256A1Minimize network trafficTraffic minimizationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInternet trafficIp address
A system and method for Internet protocol (IP) address discovery in a rapidly changing network environment is presented. A server and a client use an adaptive discovery polling process to determine an optimum heartbeat interval that minimizes network traffic and allows the server to monitor the client's source address. The client and server exchange discovery poll messages and heartbeat messages at varying time intervals in order to identify a computer network's timeout period or a network address translator's message block timeout period. Once the timeout period is identified, the client sends heartbeat messages to the server at an “optimum heartbeat interval” that is less than the identified timeout period in order to maintain the network connection. As a result, the server is able to send messages to the client without delay.
Owner:IBM CORP
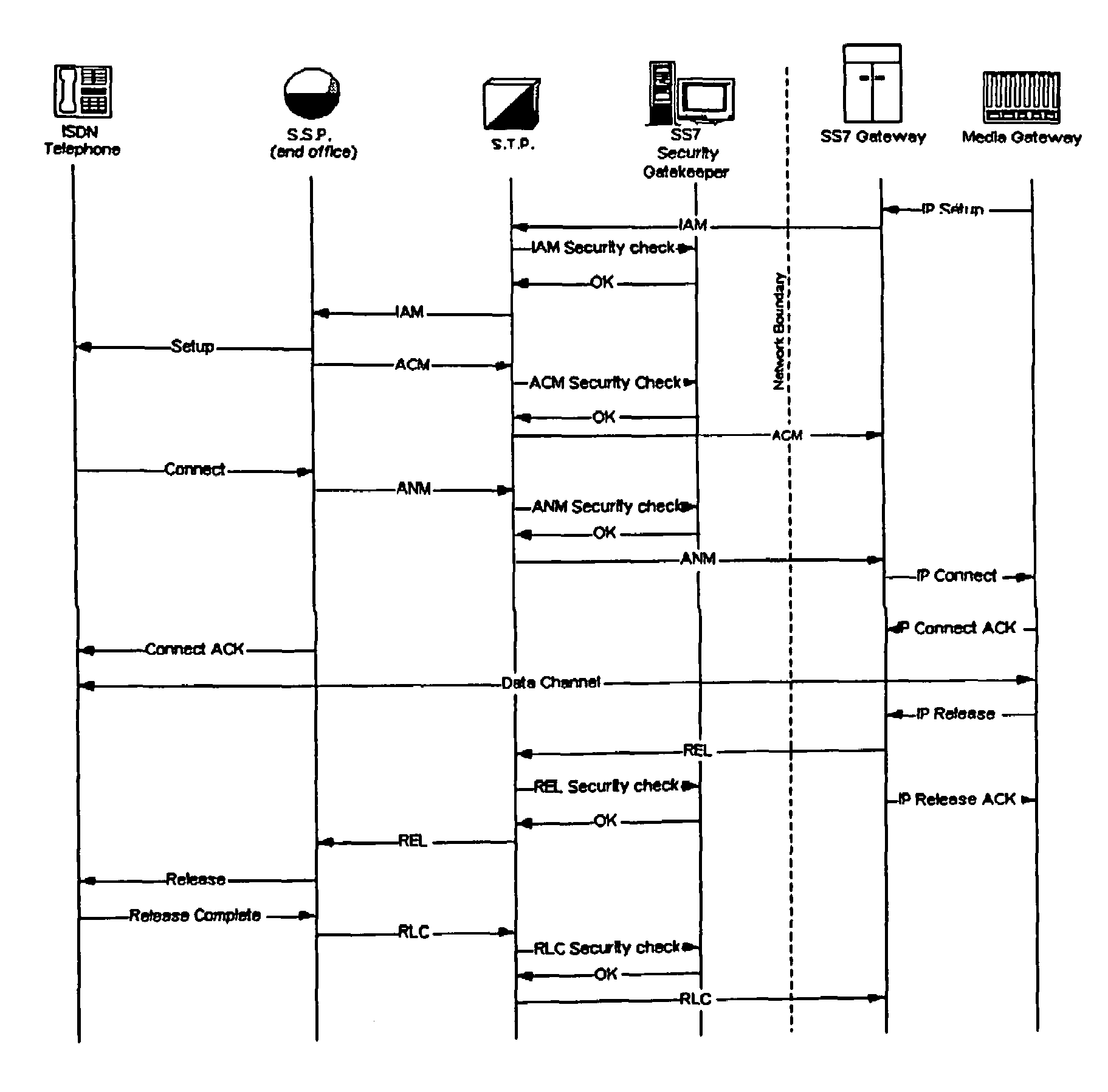
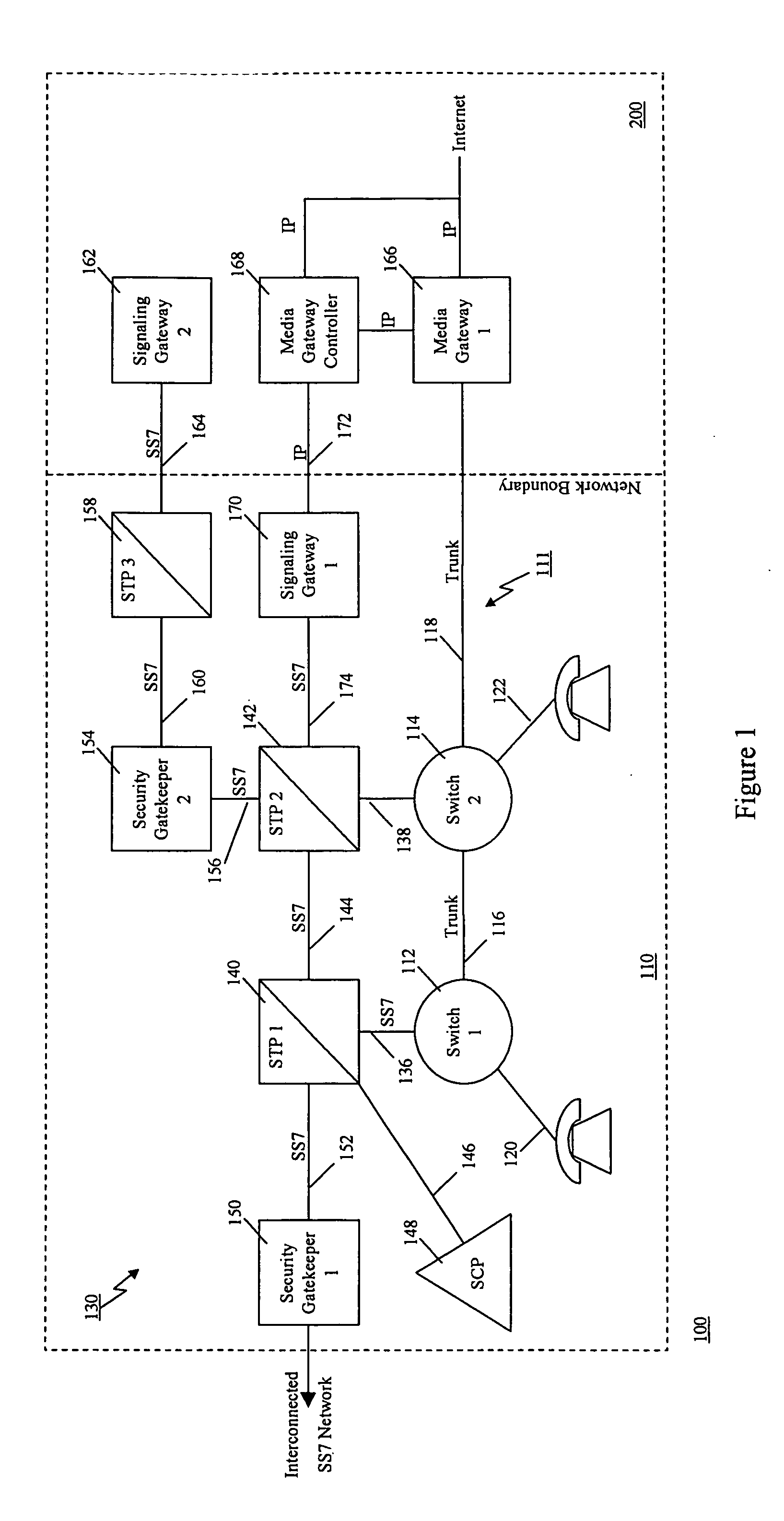
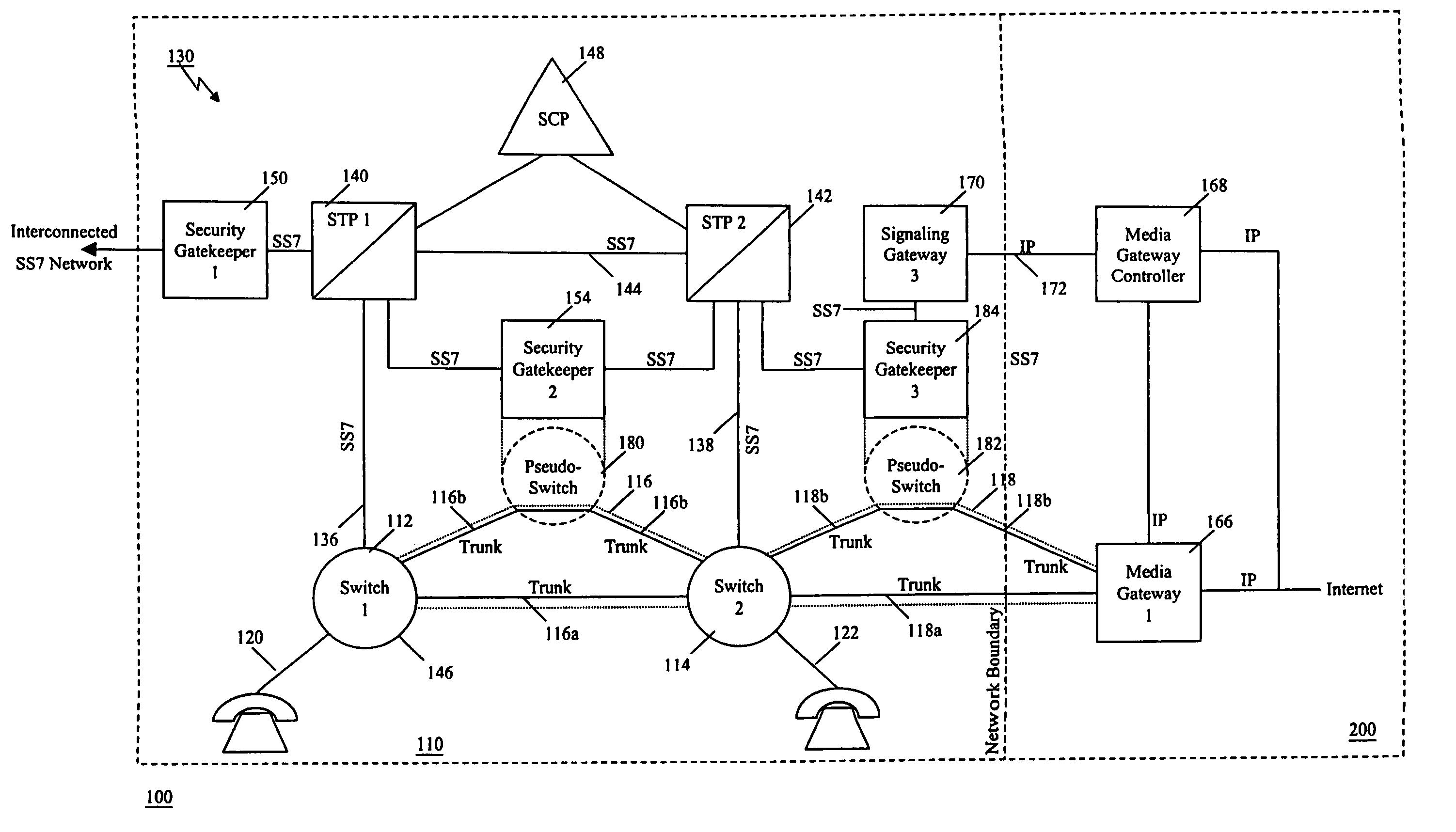
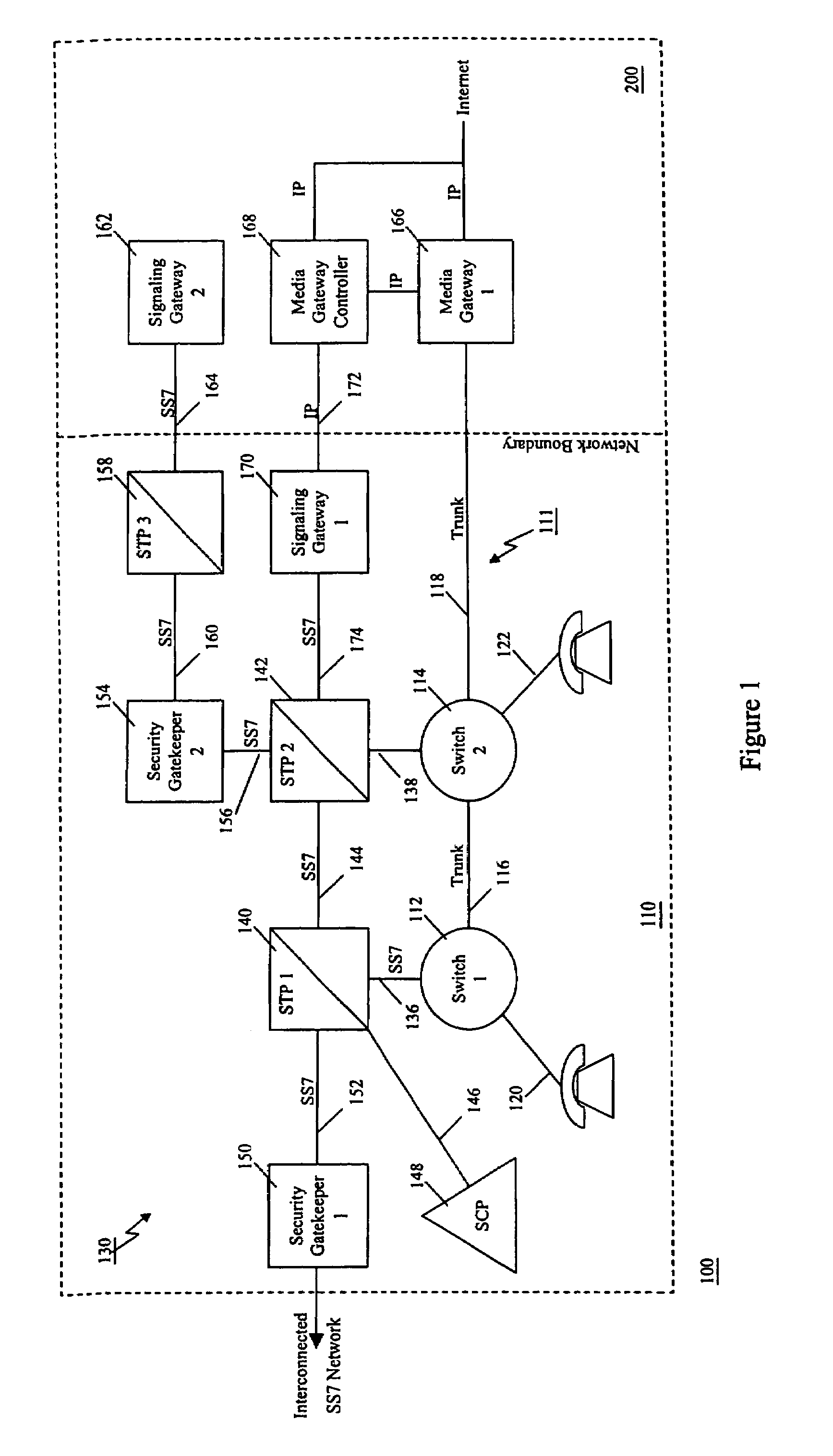
Method of and apparatus for authenticating control messages in a signaling network
InactiveUS7360090B1Fast communicationHeighten needMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTraffic volumeSignaling network
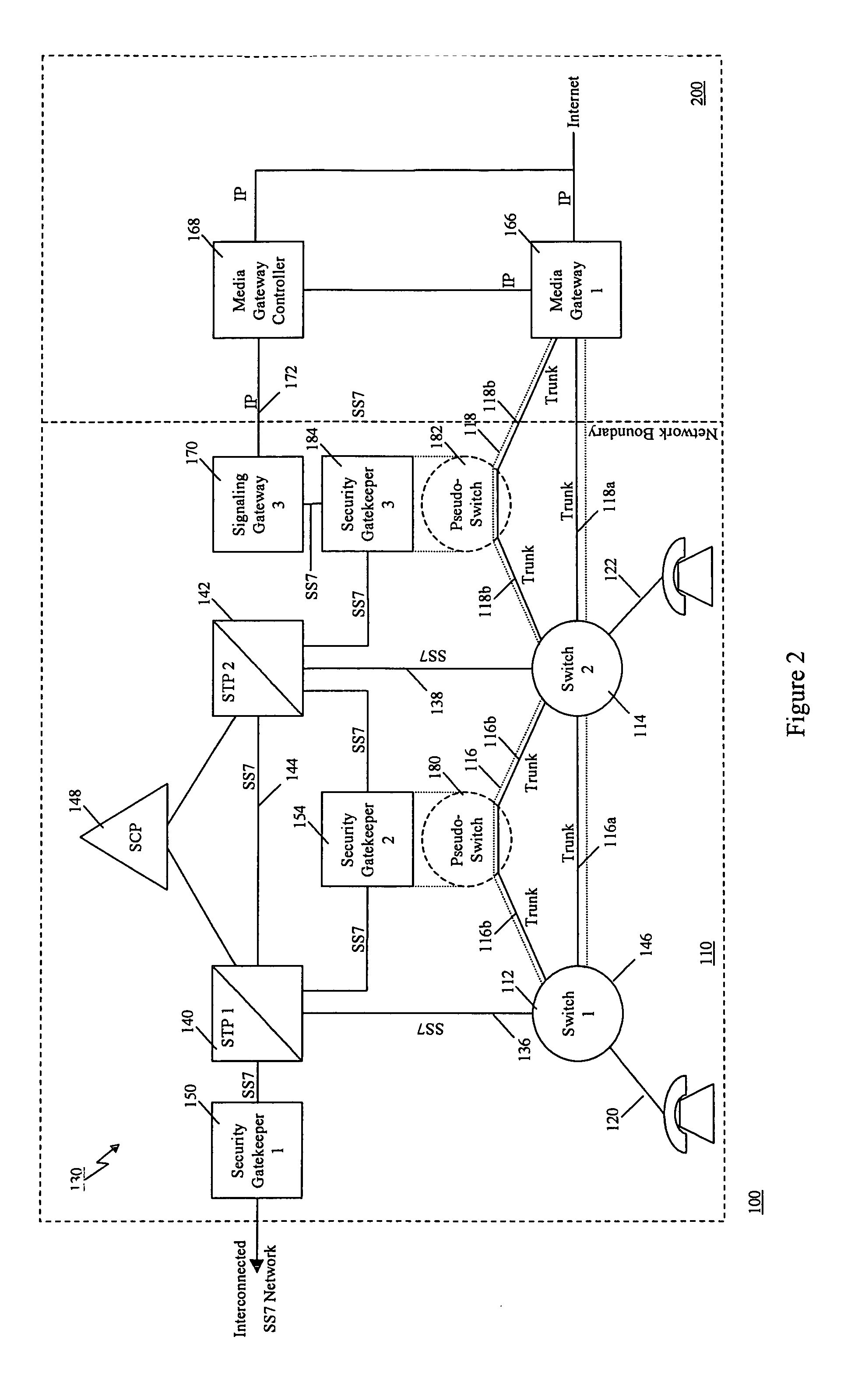
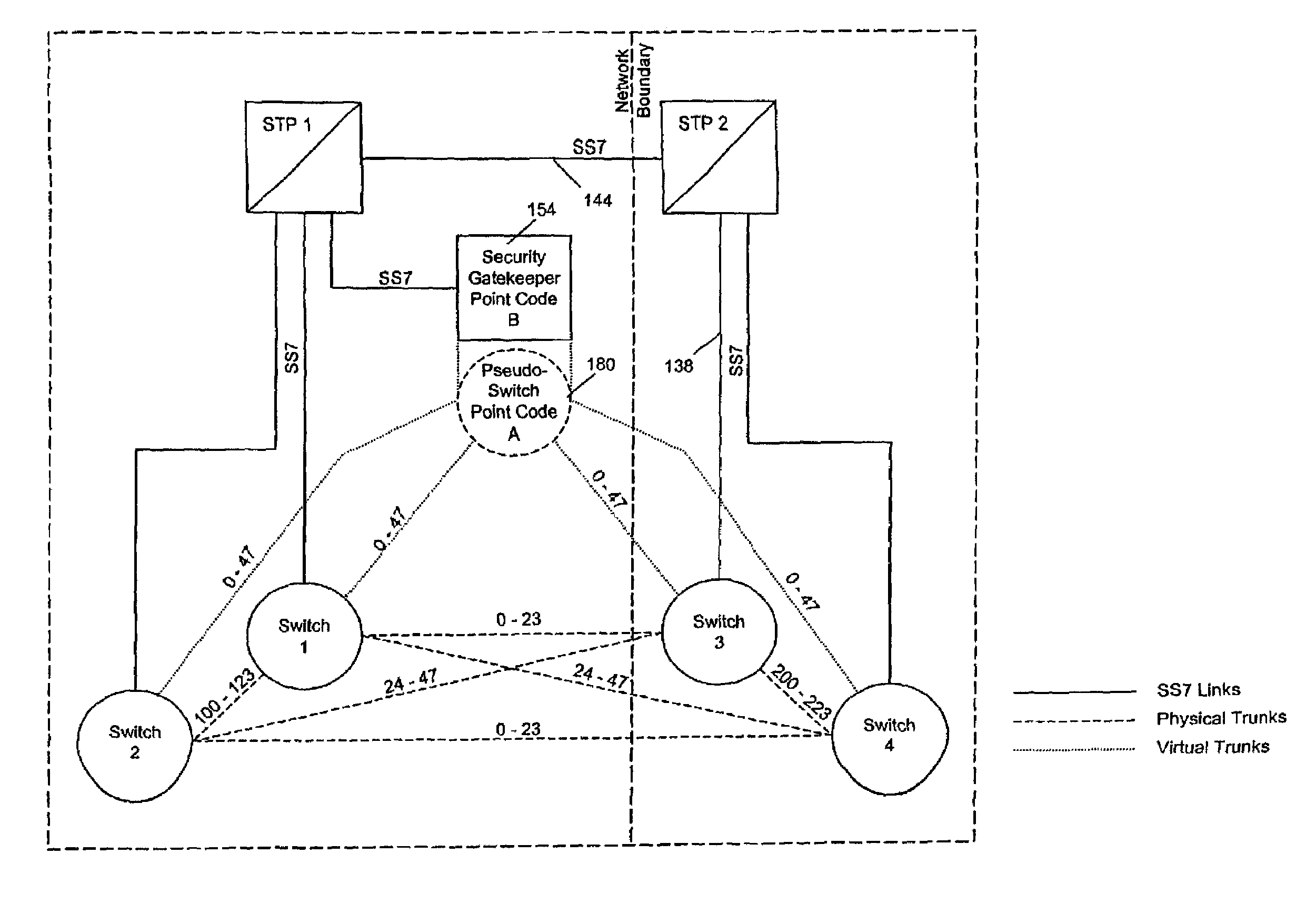
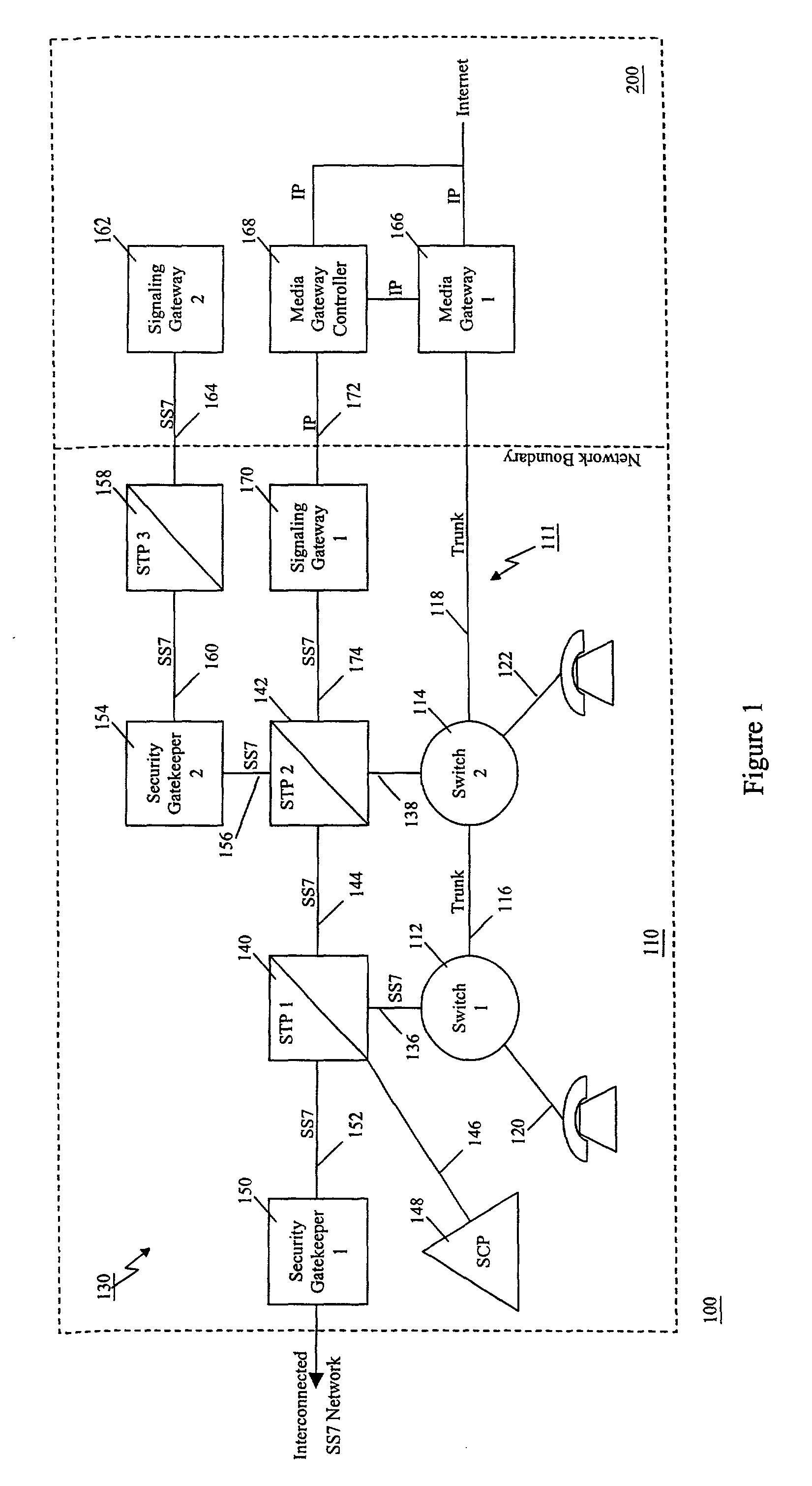
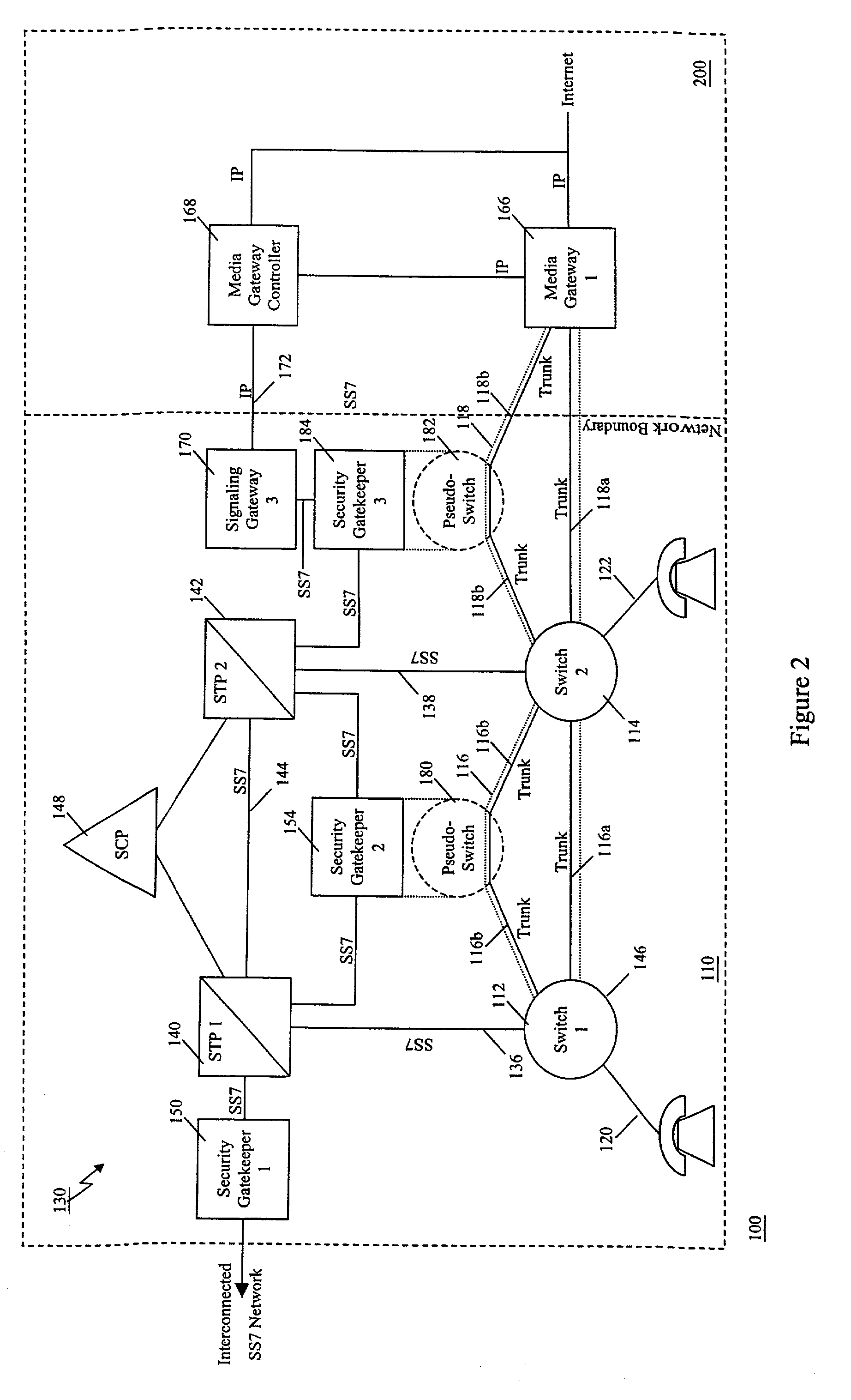
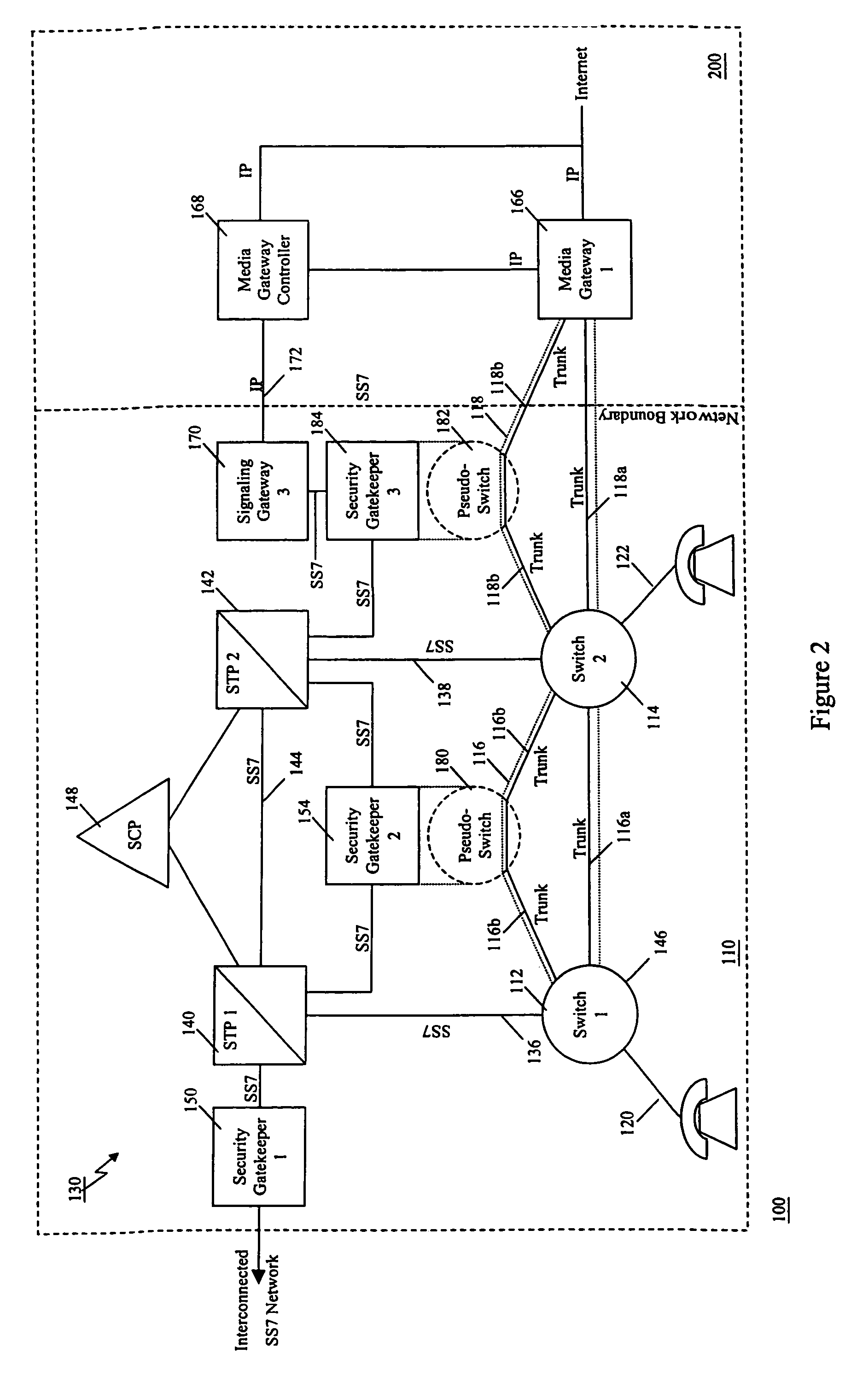
A communication network includes an SS7 Security Gatekeeper that authenticates and validates network control messages within, transiting, entering and leaving an overlying control fabric such as an SS7 network. The SS7 Security Gatekeeper incorporates several levels of checks to ensure that messages are properly authenticated, valid, and consistent with call progress and system status. In addition to message format, message content is checked to ensure that the originating node has the proper authority to send the message and to invoke the related functions. Predefined sets of templates may be used to check the messages, each set of templates being associated with respective originating point codes and / or calling party addresses. The templates may also be associated with various system states such that messages corresponding to a particular template cause a state transition along a particular edge to a next state node at which another set of templates are defined. Thus, system and call state is maintained. The monitor also includes signaling point authentication using digital signatures and timestamps. Timestamps are also used to initiate appropriate timeouts and so that old or improperly sequenced message may be ignored, corrected or otherwise processed appropriately. The SS7 Security Gatekeeper may be located at the edge of a network to be protected so that all messaging to and from the protected network most egress by way of the Gatekeeper. Alternatively, the SS7 Security Gatekeeper may be internal to the protected network and configured as a “pseudo switch” so that ISUP messaging is routed through the Gatekeeper while actual traffic is trunked directly between the associated SSPs, bypassing the Gatekeeper.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
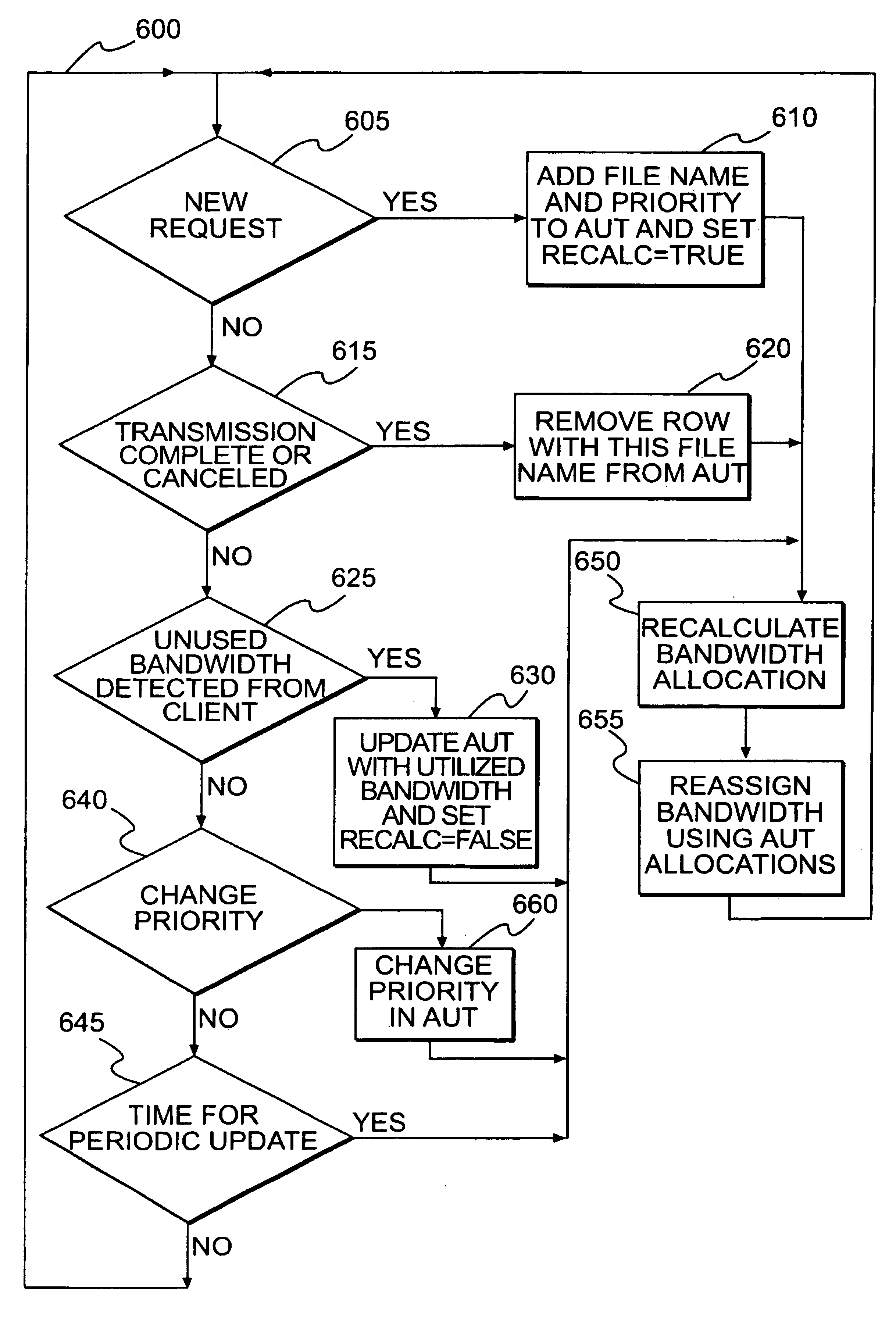
Latency-reducing bandwidth-prioritization for network servers and clients
InactiveUS6968379B2Short response timeLower latencyDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsClient-sideCommunication bandwidth
Communications bandwidth available to network servers and computers running client processes is allocated among connections available to those devices based on sets of priorities. Those priorities include type of information being retrieved, how fast user connections can receive information, which part of a document is being transmitted, user identity, stored indicia indicating importance of the document and the state of application processes running on said computer. Bandwidth is reallocated on an event driven basis upon arrival of a new request for retrieval, finishing sending information in response to a retrieval request, cancellation of a retrieval request, detection of the inability of a user connection to use all of the bandwidth allocated to it, a change of priority and timeout of a timer.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
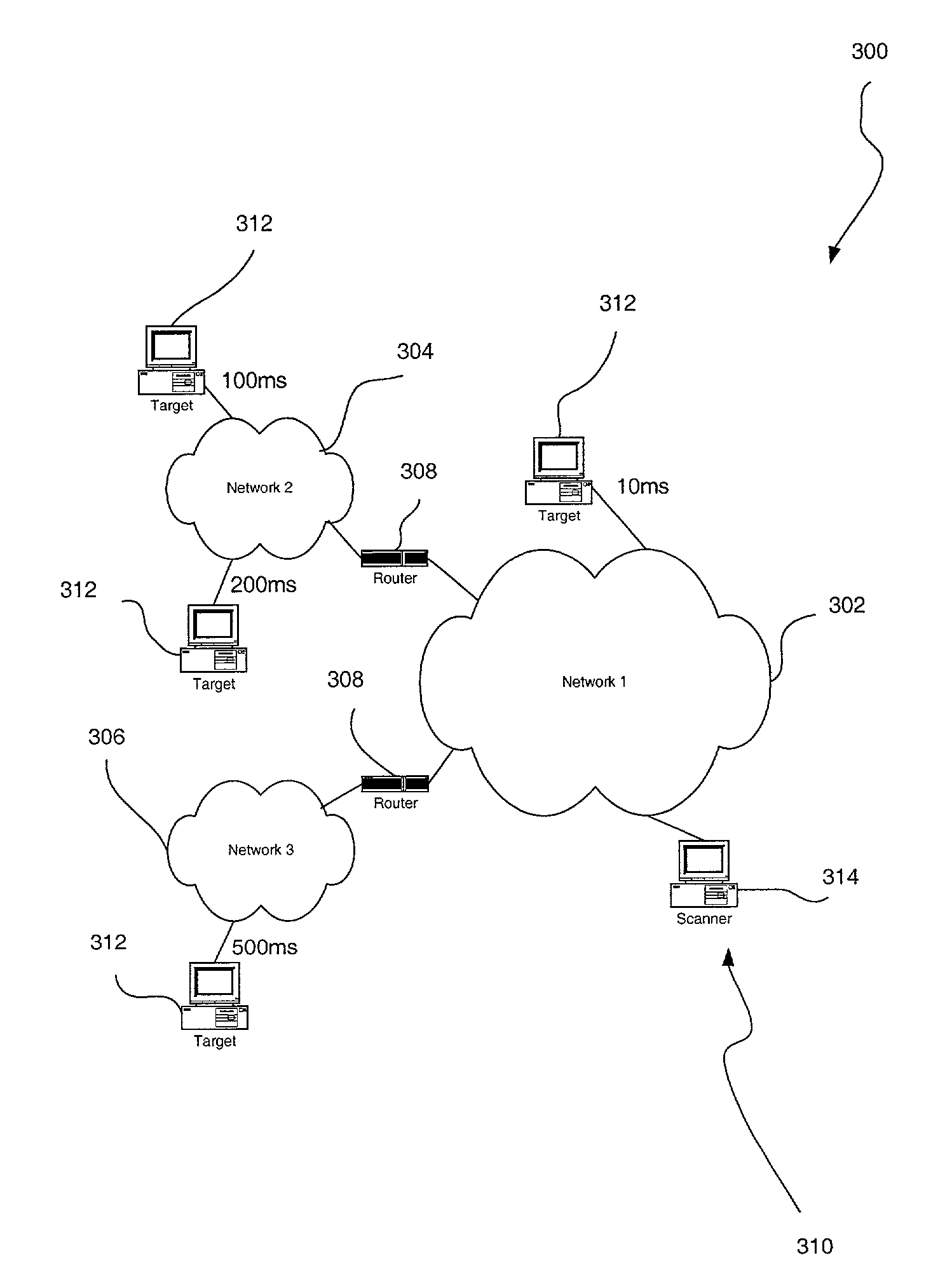
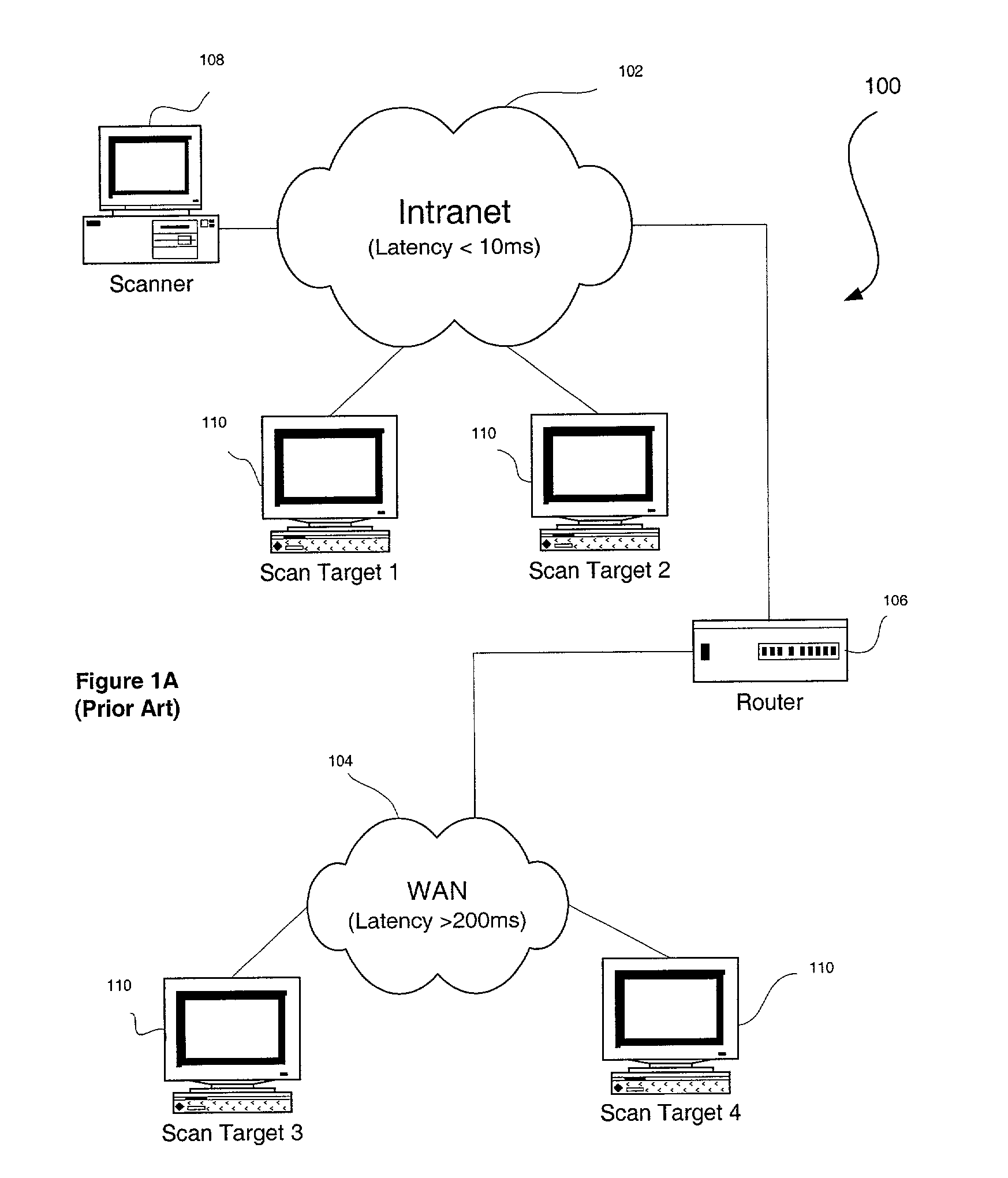
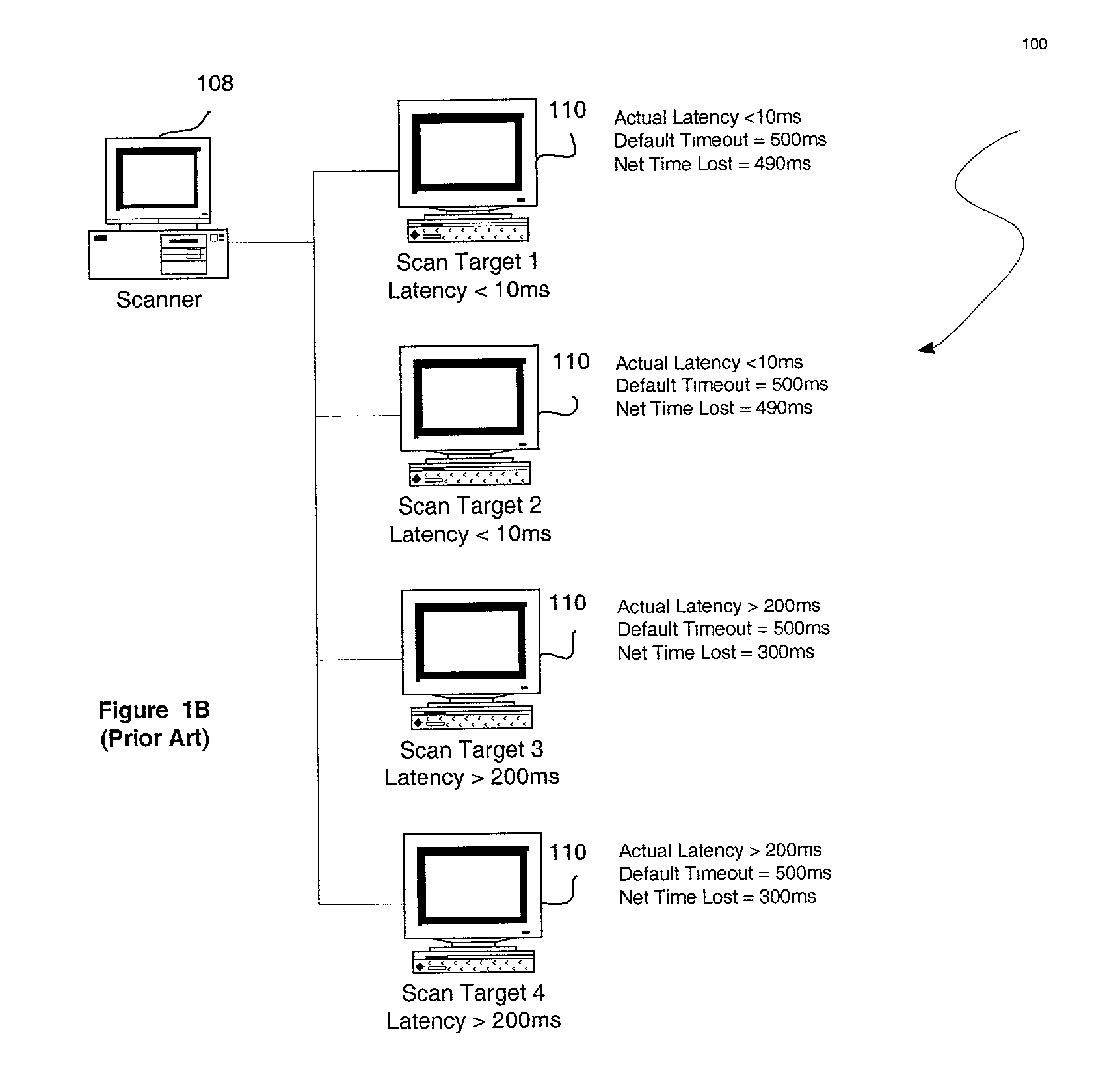
System, method and computer program product for improved efficiency in network assessment utilizing variable timeout values
A system, method and computer program product are provided for executing a risk-assessment scan with a variable timeout duration which is set based on network conditions. Initially, network conditions are measured in a network coupled between a source and a target. Subsequently, a risk-assessment scan is executed on the target from the source. A timeout is performed prior to making a determination that the target is failing to respond to the risk-assessment scan. Such timeout includes a variable duration which is set as a function of the measured network conditions.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
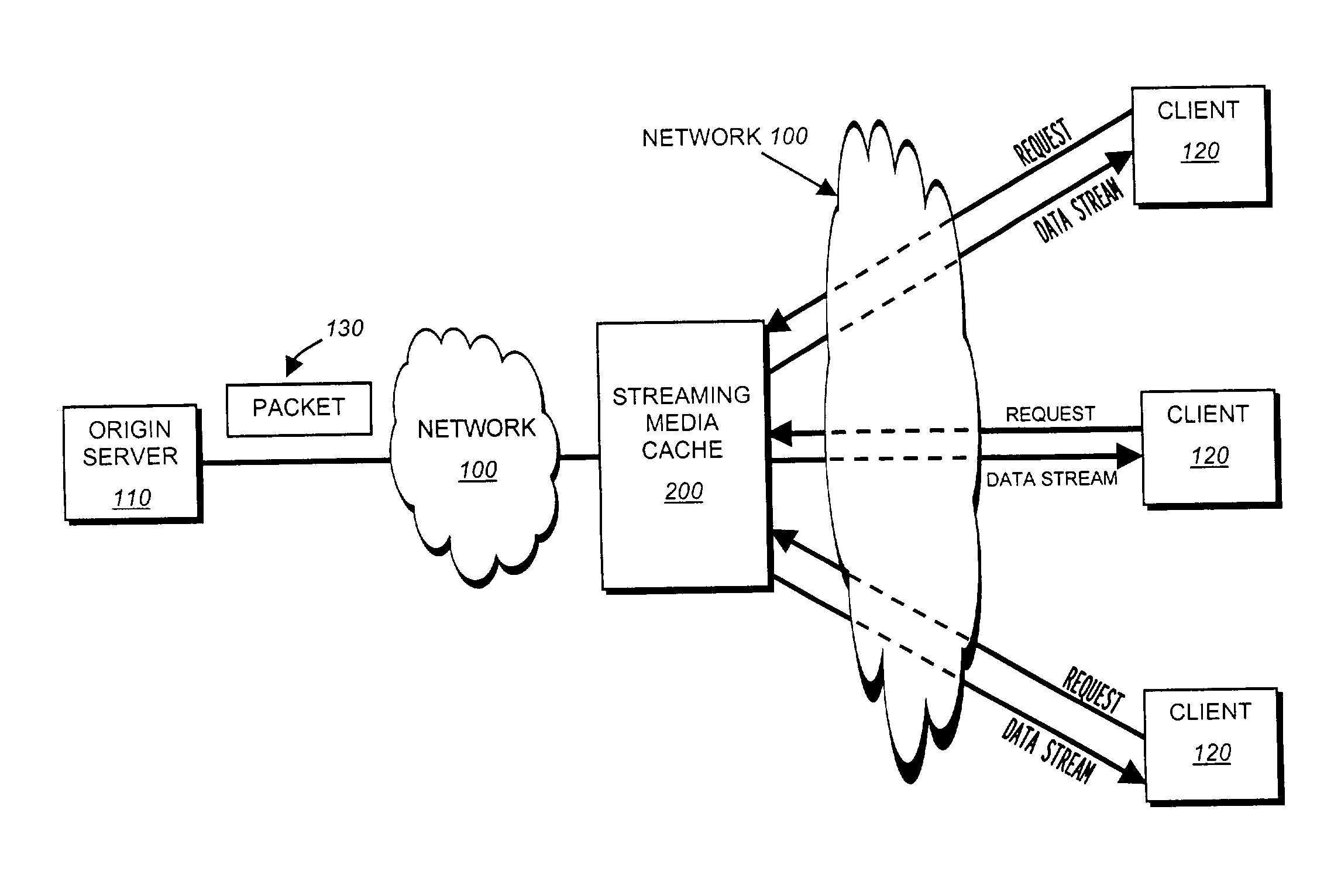
Adaptively selecting timeouts for streaming media
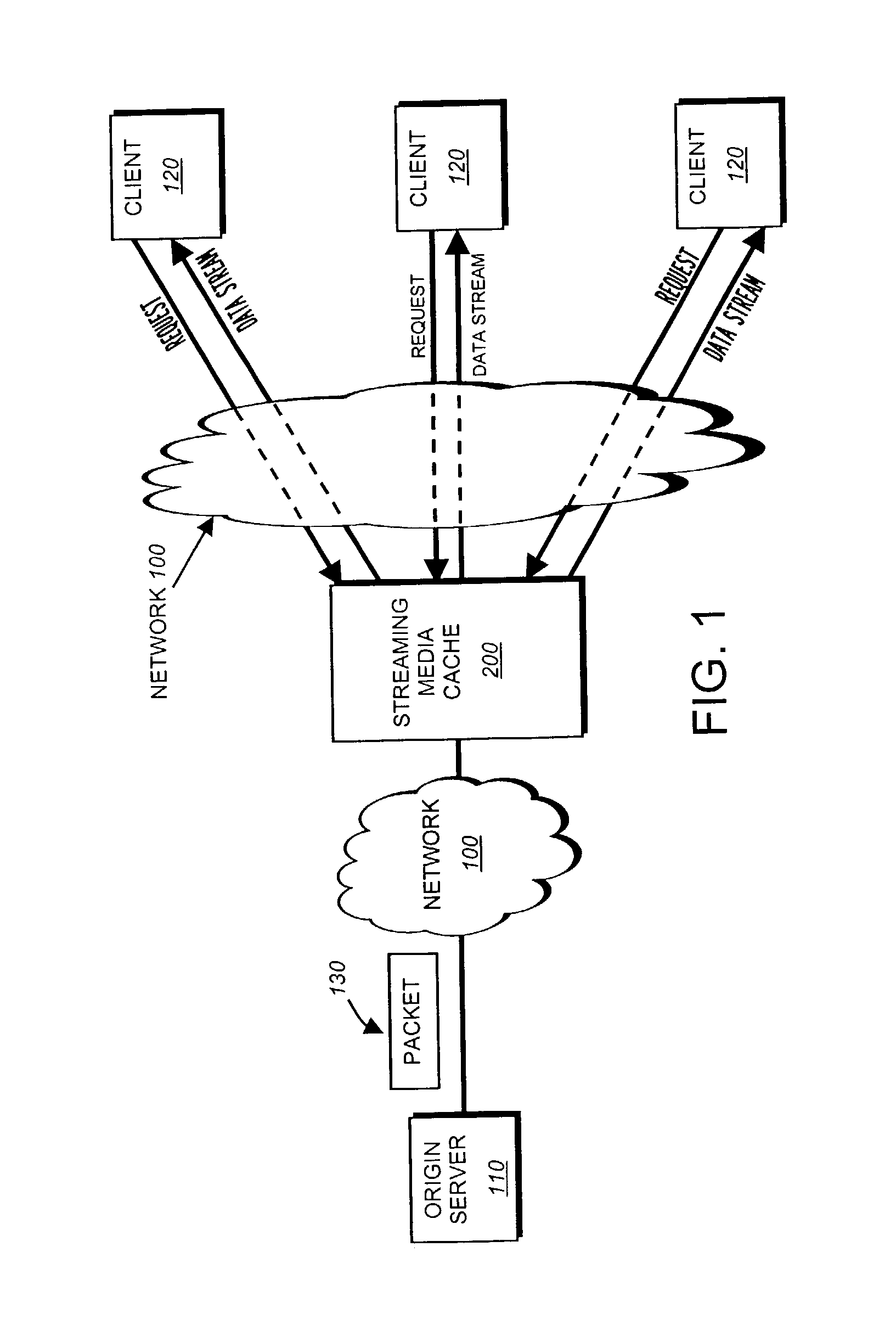
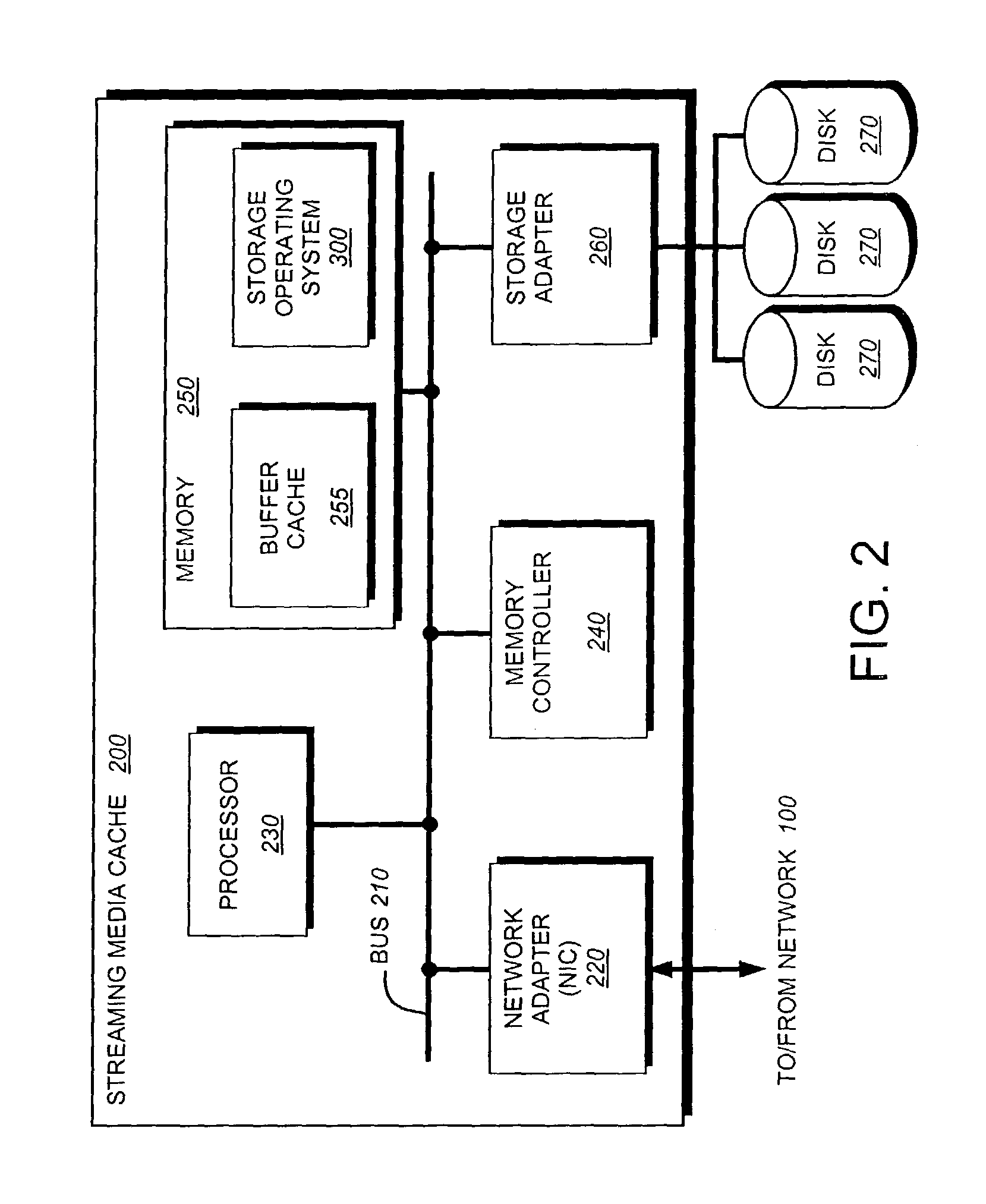
ActiveUS7991905B1Effective bandwidthBandwidth usageMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionHigh bandwidthData stream
The present invention provides a streaming media cache configured to select a timing interval, chosen from a set of one or more predetermined timing intervals, for each client that requests a data stream from the streaming media cache. Illustratively, clients requesting data streams below a predetermined bit rate (“bandwidth”) are assigned longer timing intervals than clients requesting data streams above the predetermined bit rate. More specifically, because the server can accommodate a larger number of relatively low-bandwidth clients than relatively high-bandwidth clients, the server selects timing intervals of longer duration for the relatively low-bandwidth clients so it may have more time to schedule send times for their requested packets.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
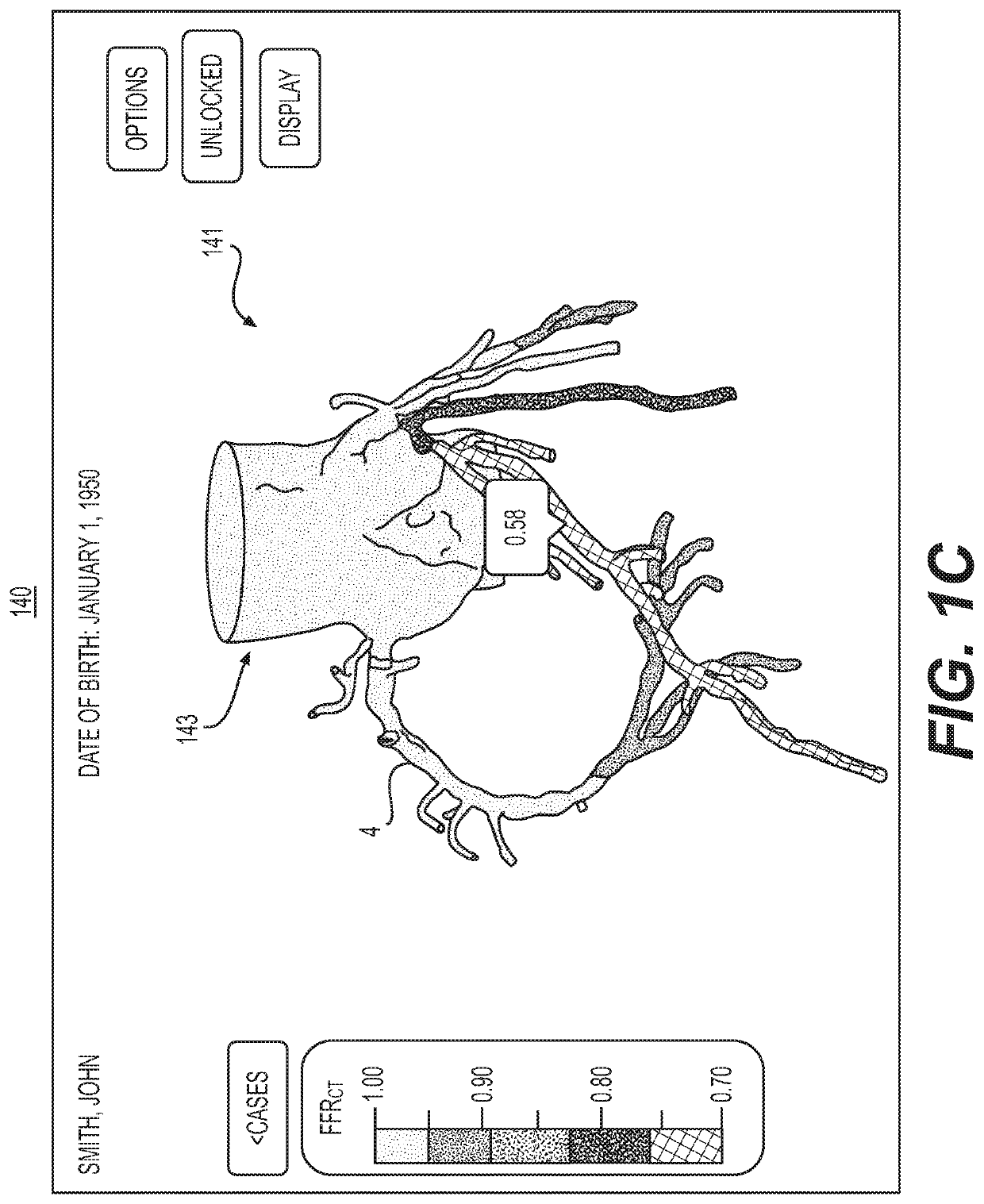
Systems and methods for generating an anonymous interactive display in an extended timeout period
Systems and methods are disclosed for displaying health data during a security timeout. One method includes: displaying an interactive interface; receiving a data type included in the display; detecting a timeout of the interactive interface; hiding or removing the data type from the display in response to the timeout; and initiating an extended timeout including the display with the data type removed.
Owner:HEARTFLOW
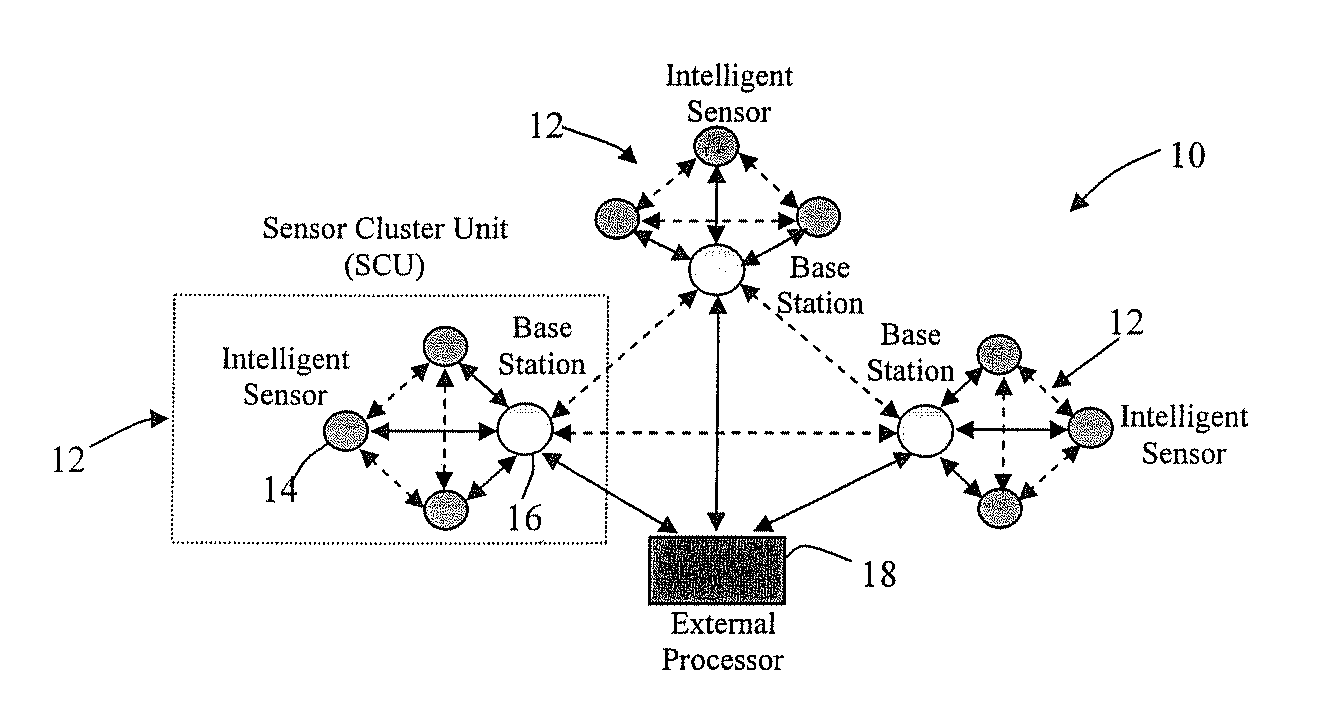
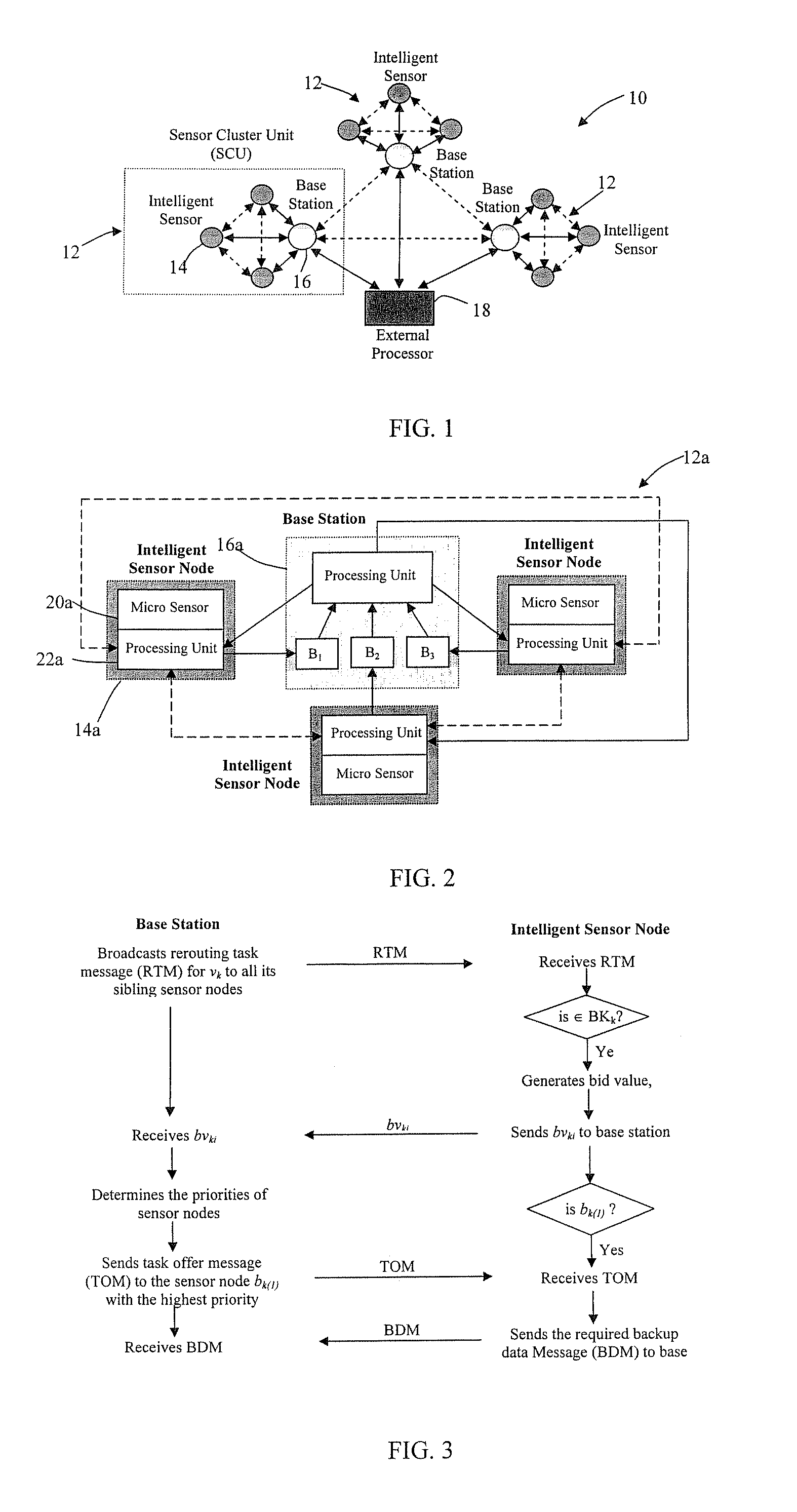
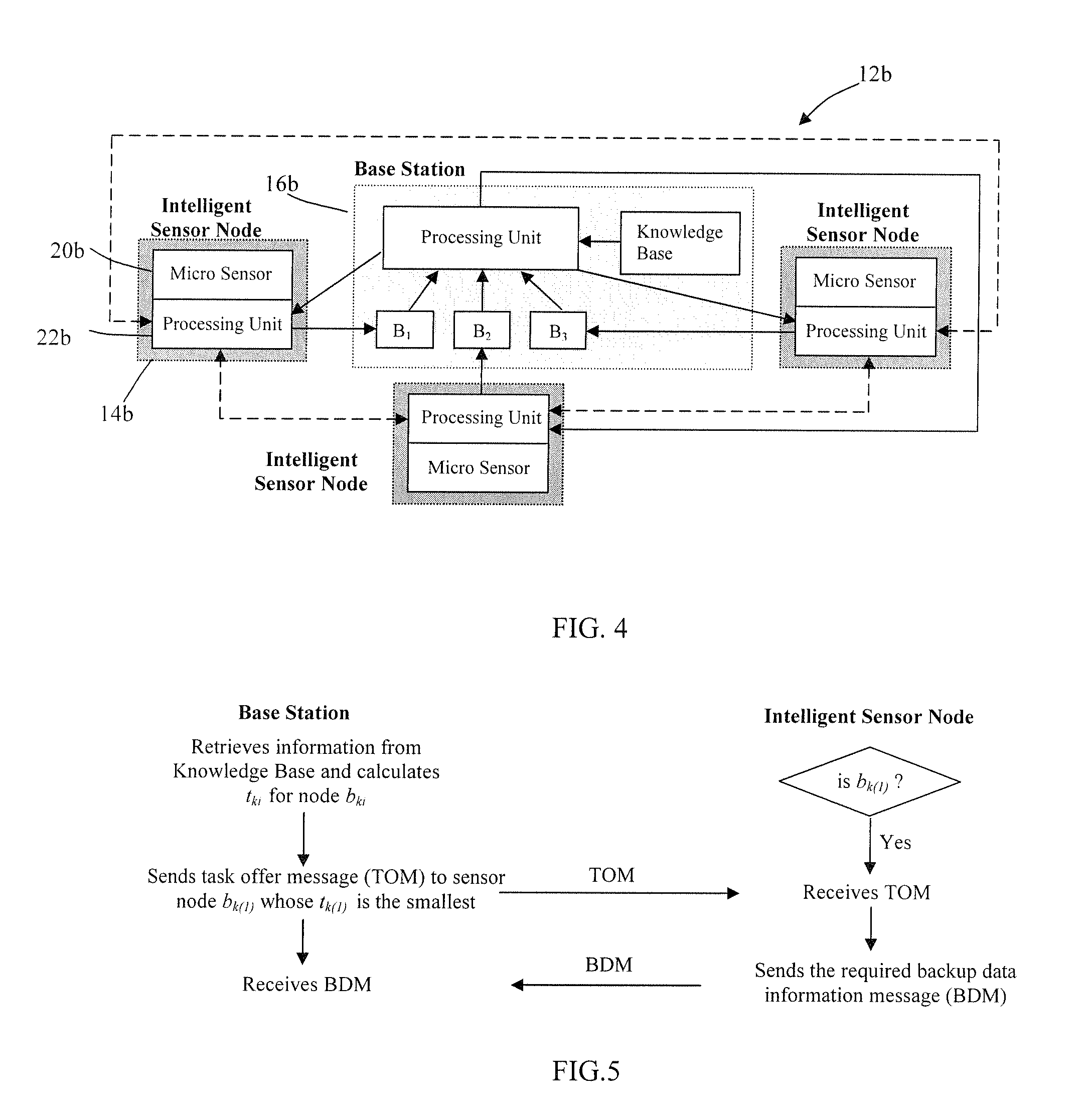
Fault-tolerant timeout communication protocol with sensor integration
A fault-tolerant timeout protocol for distributed sensor arrays and networks in which each sensor has a plurality of backup nodes, each of which is operable to send priority information which includes the product of the time needed for the backup node to transmit sensor information to a base station and the number of tasks offered to the backup node. In another embodiment, the base station stores the two values and calculates their product. In both cases, the lowest resulting value is used by the base station to select the backup node, which then sends backup sensor information. Another aspect of the present invention is a fault-tolerant sensor integration algorithm. The algorithm creates an abstract sensor defined as an interval having values above and below the reading of an associated physical sensor, and finds a range of values common to more than half of the abstract sensors. The algorithm obtains an output value based on the common range of values, and identifies the correct sensors, possibly faulty sensors, and faulty sensors by identifying the abstract sensors that include, respectively, (a) all of the common range, (b) part of the common range, and (c) none of the common range. A further aspect of the invention is a multi-hop information forwarding method for a wireless network. According to this method, a data source node transmits a signal to neighboring nodes among a plurality of distributed nodes, and each neighboring node which receives the signal from the source node transmits a reply signal which includes a weighted sum of factors including an energy factor and a distance factor for the neighboring node, the energy factor being indicative of the neighboring node's energy level and the distance factor being indicative of its distance from the source node. A forwarding node is selected on the basis of the weighted sums, and the source node transmits a data packet to the selected forwarding node, where the data packet is received and retransmitted either to a data sink node, e.g., a base station, or to another forwarding node.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method of and apparatus for mediating common channel signaling messages between networks using a pseudo-switch
InactiveUS7224686B1Fast communicationMeet growth needsInterconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityTimestamp
A communication network includes an SS7 Security Gatekeeper that authenticates and validates network control messages within, transiting, entering and leaving an overlying control fabric such as an SS7 network. The SS7 Security Gatekeeper incorporates several levels of checks to ensure that messages are properly authenticated, valid, and consistent with call progress and system status. In addition to message format, message content is checked to ensure that the originating node has the proper authority to send the message and to invoke the related functions. Predefined sets of templates may be used to check the messages, each set of templates being associated with respective originating point codes and / or calling party addresses. The templates may also be associated with various system states such that messages corresponding to a particular template cause a state transition along a particular edge to a next state node at which another set of templates are defined. Thus, system and call state is maintained. The monitor also includes signaling point authentication using digital signatures and timestamps. Timestamps are also used to initiate appropriate timeouts and so that old or improperly sequenced message may be ignored, corrected or otherwise processed appropriately. The SS7 Security Gatekeeper may be located at the edge of a network to be protected so that all messaging to and from the protected network most egress by way of the Gatekeeper. Alternatively, the SS7 Security Gatekeeper may be internal to the protected network and configured as a “pseudo switch” so that ISUP messaging is routed through the Gatekeeper while actual traffic is trunked directly between the associated SSPs, bypassing the Gatekeeper.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
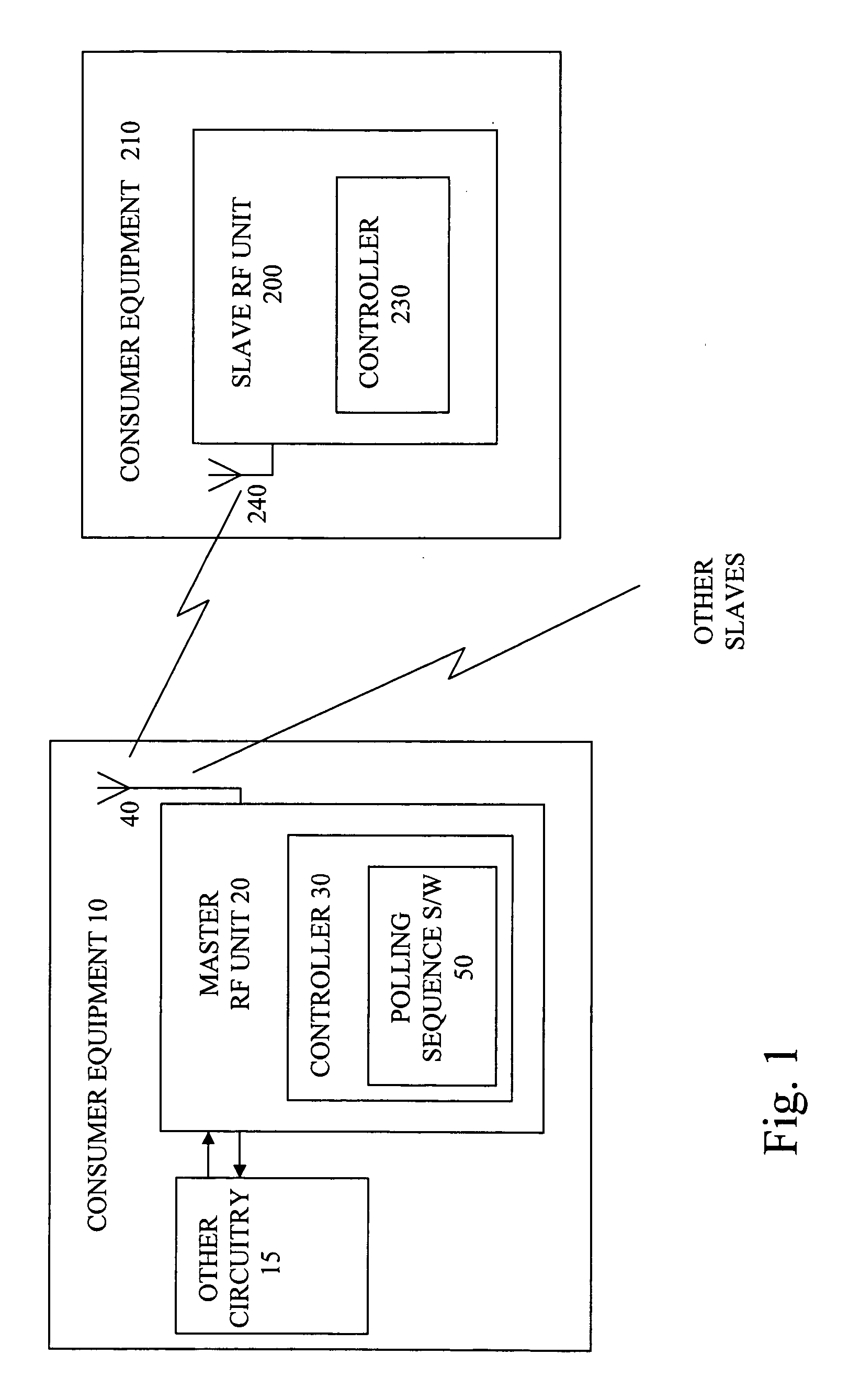
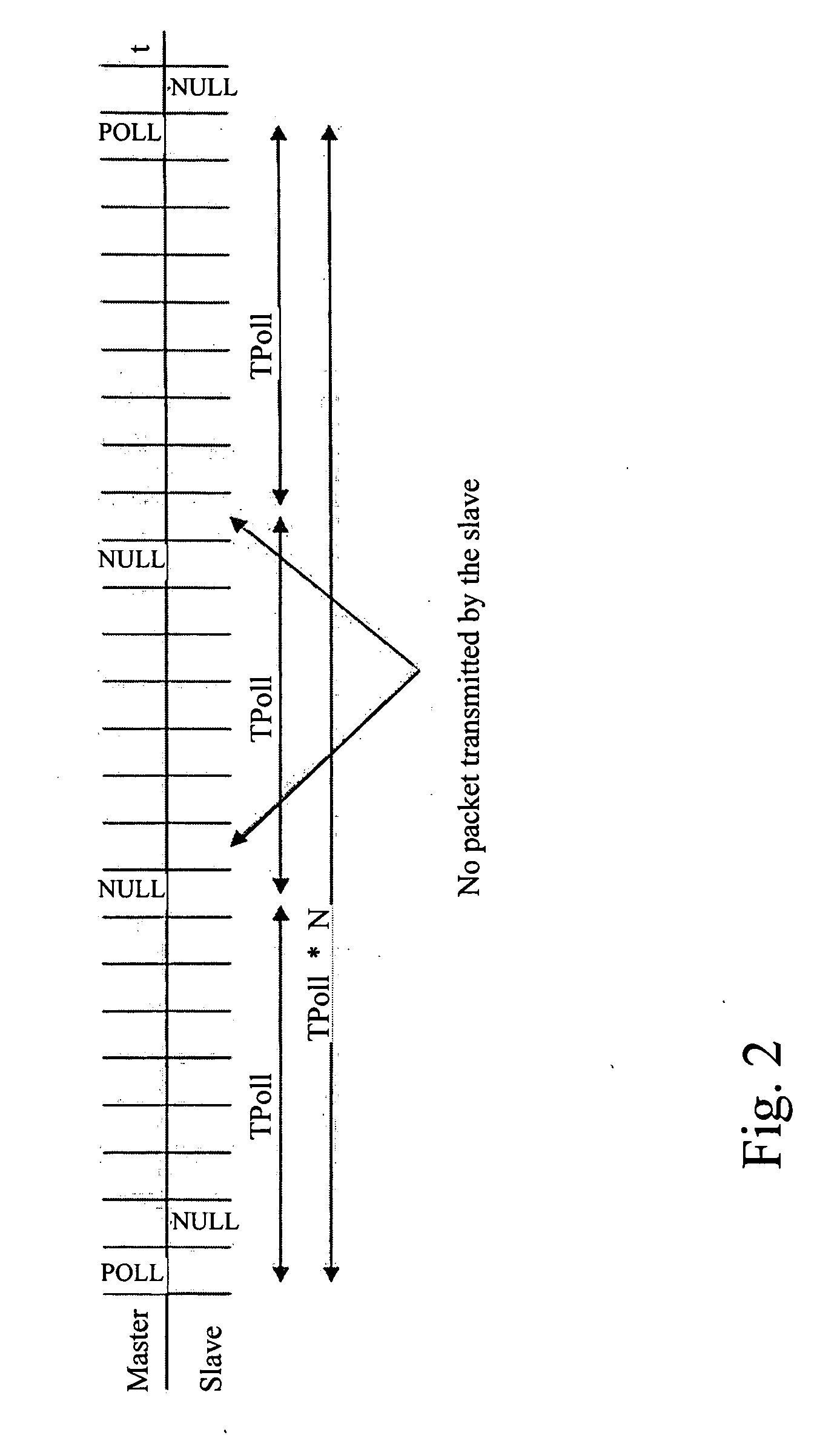
Bluetooth polling with fewer poll packets
ActiveUS20070177567A1Reduce the ratioCritical factor of power consumption can be reducedEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesTimerReal-time computing
A Bluetooth master unit polls a slave unit to enable the slave to resynchronize to the master, by sending POLL packets with sufficient frequency to maintain a connection to the slave, and in the intervals between such packets, sending NULL packets with sufficient frequency to maintain synchronization of the slave. By replacing some POLL packets with NULL packets, since the slave does not have to respond to a NULL packet, it can save some power, and there is reduced interference on other piconets. The frequency of the remaining POLL packets is set according to a Link Supervision Timeout (to avoid having this timer expire and thus keep the Bluetooth Link to the slave alive) and according to the time since the master received the last packet from the slave.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Method and apparatus for in context mediating common channel signaling messages between networks
InactiveUS7218613B1Prevent hangingMaintain network operationMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTraffic capacityTimestamp
A communication network includes a SS7 Security Gatekeeper that authenticates and validates network control messages within, transiting, entering and leaving an overlying control fabric such as an SS7 network. The SS7 Security Gatekeeper incorporates several levels of checks to ensure that messages are properly authenticated, valid, and consistent with call progress and system status. In addition to message format, message content is checked to ensure that the originating node has the proper authority to send the message and to invoke the related functions. predefined sets of templates may be used to check the messages, each set of templates being associated with respective originating point codes and / or calling party addresses. The templates may also be associated with various system states such that messages corresponding to a particular template cause a state transition along a particular edge to a next state node at which another set of templates are defined. Thus, system and call state is maintained. The monitor also includes signaling point authentication using digital signatures and timestamps. Timestamps are also used to initiate appropriate timeouts and so that old or improperly sequenced message may be ignored, corrected or otherwise processed appropriately. The SS7 Security Gatekeeper may be located at the edge of a network to be protected so that all messaging to and from the protected network most egress by way of the Gatekeeper. Alternatively, the SS7 Security Gatekeeper may be internal to the protected network and configured as a “pseudo switch” so that ISUP messaging is routed through the Gatekeeper while actual traffic is trunked directly between the associated SSPs, bypassing the Gatekeeper.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Method and system for pacing, acking, timing, and handicapping (PATH) for simultaneous receipt of documents employing encryption
A method of facilitating substantially simultaneous receipt of electronic content by a plurality of intended recipients is disclosed. The electronic content is encrypted. The encrypted electronic content is transmitted to the plurality of intended recipients. An acknowledgement packet is received from each of the plurality of intended recipients within a predetermined timeout period. A handicap time is calculated for transmitting a decryption key to each of the intended recipient based on a time associated with the acknowledgement packet last received. Decryption keys are transmitted to the plurality of intended recipients using a delay based on the handicap time, where a decryption key having a smaller handicap time is transmitted prior to a decryption key having a larger handicap time.
Owner:ACQUIRE MEDIA U S LLC
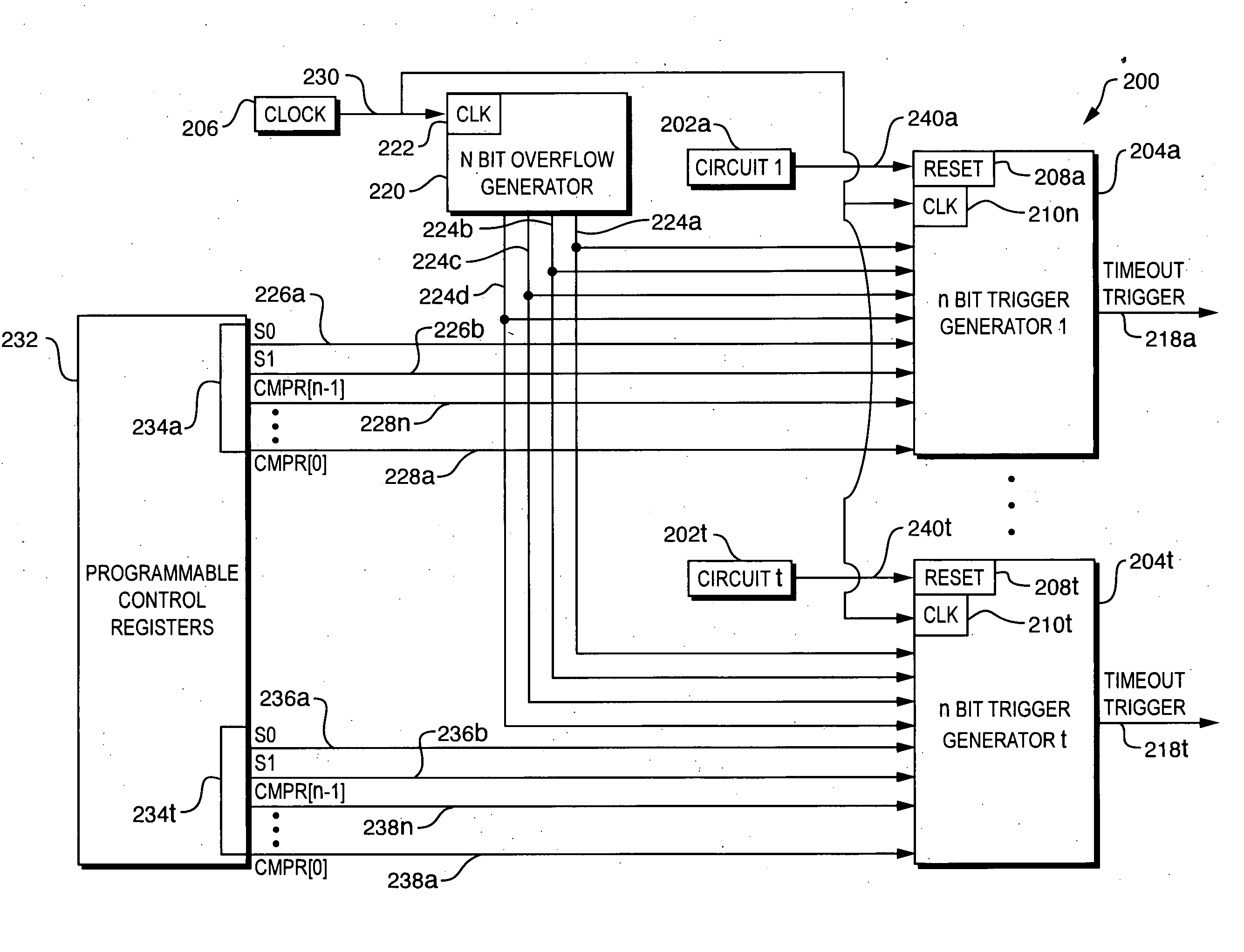
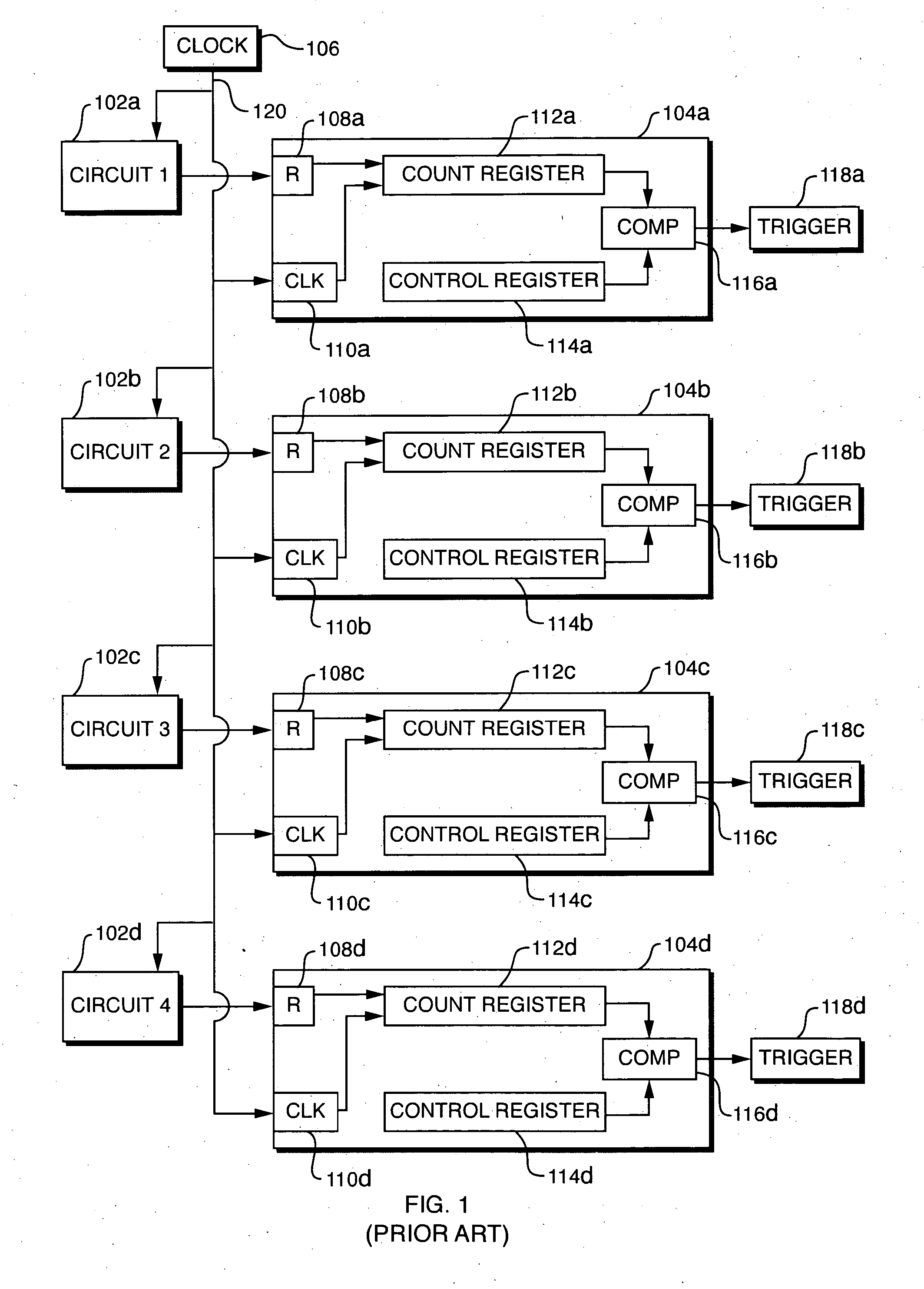
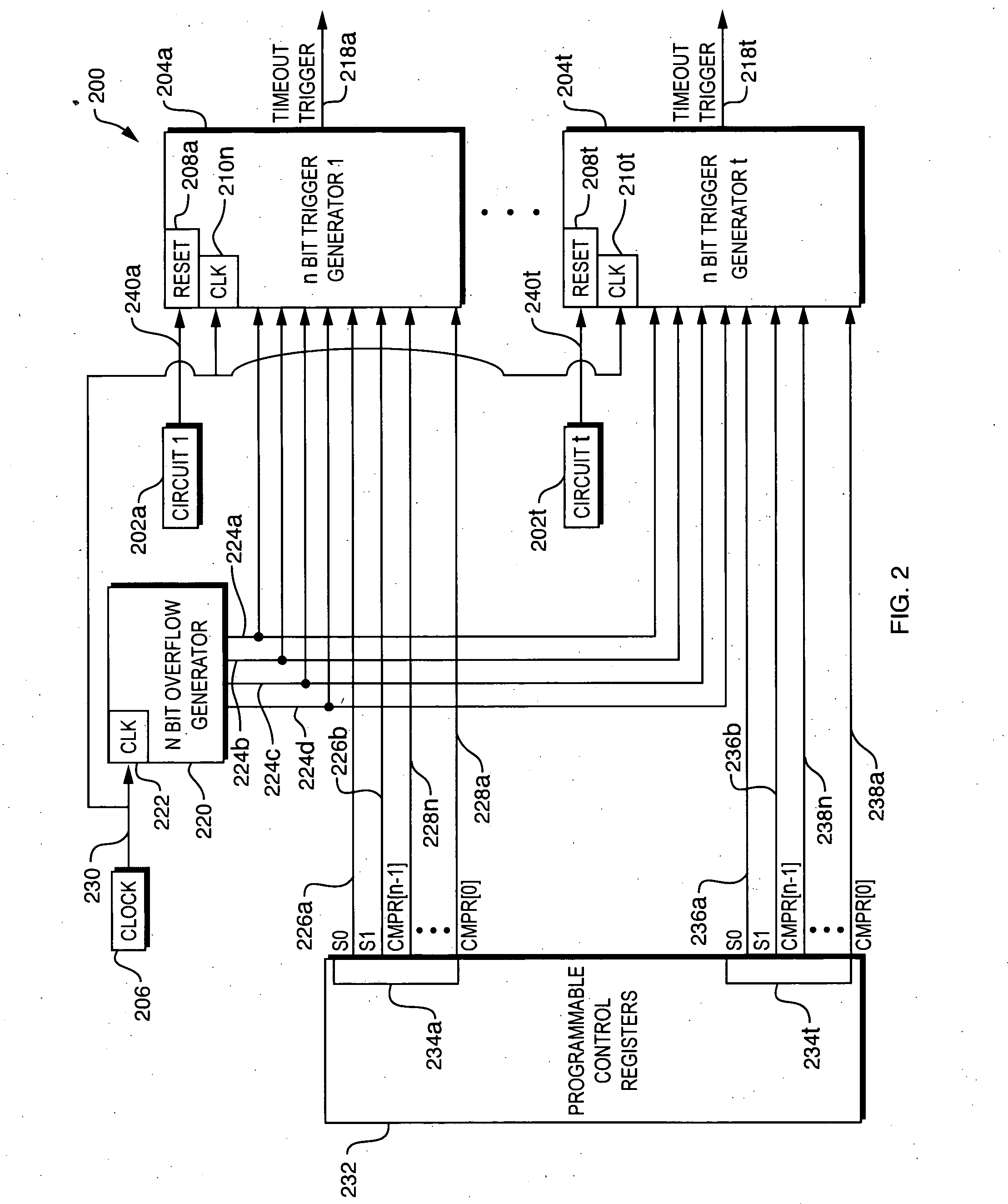
Timeout event trigger generation
ActiveUS20050188277A1Minimal amountHardware monitoringNon-redundant fault processingEngineeringEvent trigger
A system is disclosed for generating a plurality of timeout event triggers in response to a plurality of kinds of timeout events. The system includes an overflow generator, which generates a plurality of overflow signals having a plurality of periods. The system also includes a plurality of trigger generators corresponding to the plurality of kinds of timeout events. Each of the plurality of trigger generators is associated with a corresponding timeout threshold value representing the minimum amount of time that must elapse for the trigger generator to generate a timeout event trigger. For each of the plurality of timeout triggers, a corresponding selection signal selects one of the plurality of periodic overflow signals. The timeout threshold corresponding to each timeout trigger is equal to the period of the corresponding selected overflow signal multiplied by the value of the corresponding control signal.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Handling packet reordering at a network adapter
A network adapter for handling packet reordering receives a set of packets. The network adapter is configured to aggregate a subset of in-sequence packets from the set of packets into at least one segment before passing the at least one segment from the network adapter to a next layer in a protocol stack. An in-sequence packet from the set of packets is stored into a first segment. Responsive to receiving an out of sequence packet in the set of packets, the out of sequence packet is stored in a second segment. An adaptive timeout timer is activated responsive to receiving the out of sequence packet, and the first segment is held at the network adapter while the adaptive timeout timer runs. Prior to the adaptive timeout timer expiring, a missing packet is received and included in the first segment. The network adapter sends the first segment to the next layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for reliable transport in data networks
InactiveUS20100226384A1Easy to migrateImprovement of flow completion (transfer) timeError preventionData switching by path configurationData streamNetwork data
Rapid and reliable network data delivery uses state sharing to combine multiple flows into one meta-flow at an intermediate network stack meta-layer, or shim layer. Copies of all packets of the meta-flow are buffered using a common wait queue having an associated retransmit timer, or set of timers. The timers may have fixed or dynamic timeout values. The meta-flow may combine multiple distinct data flows to multiple distinct destinations and / or from multiple distinct sources. In some cases, only a subset of all packets of the meta-flow are buffered.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
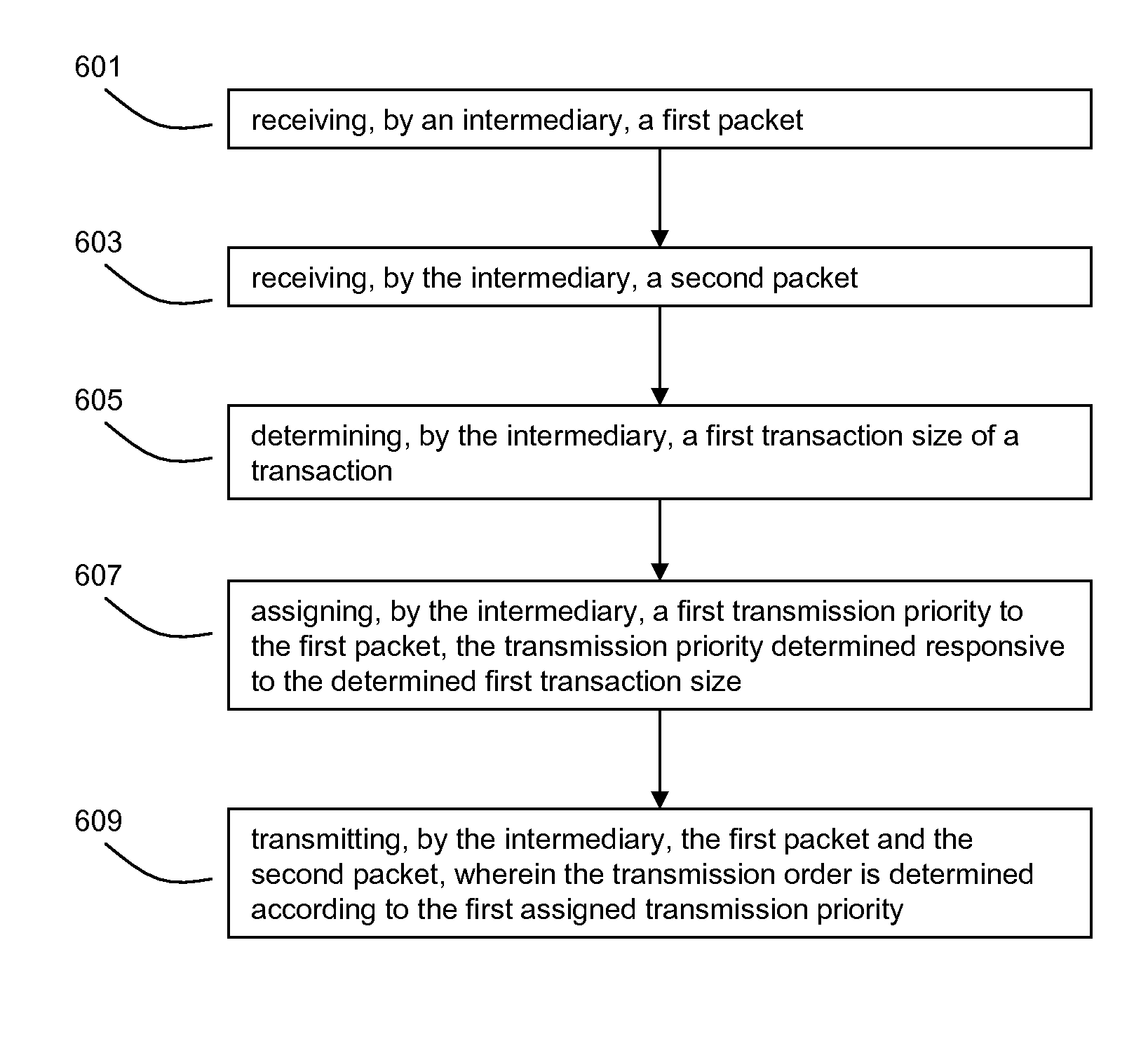
Systems and methods of using packet boundaries for reduction in timeout prevention
ActiveUS8270423B2Improve latencyAvoid delayFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsBoundary detectionClient-side
Systems and methods for utilizing transaction boundary detection methods in queuing and retransmission decisions relating to network traffic are described. By detecting transaction boundaries and sizes, a client, server, or intermediary device may prioritize based on transaction sizes in queuing decisions, giving precedence to smaller transactions which may represent interactive and / or latency-sensitive traffic. Further, after detecting a transaction boundary, a device may retransmit one or more additional packets prompting acknowledgements, in order to ensure timely notification if the last packet of the transaction has been dropped. Systems and methods for potentially improving network latency, including retransmitting a dropped packet twice or more in order to avoid incurring additional delays due to a retransmitted packet being lost are also described.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Method for faster detection and retransmission of lost TCP segments
InactiveUS20070133414A1Quick supportError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsClock timeTransmitter
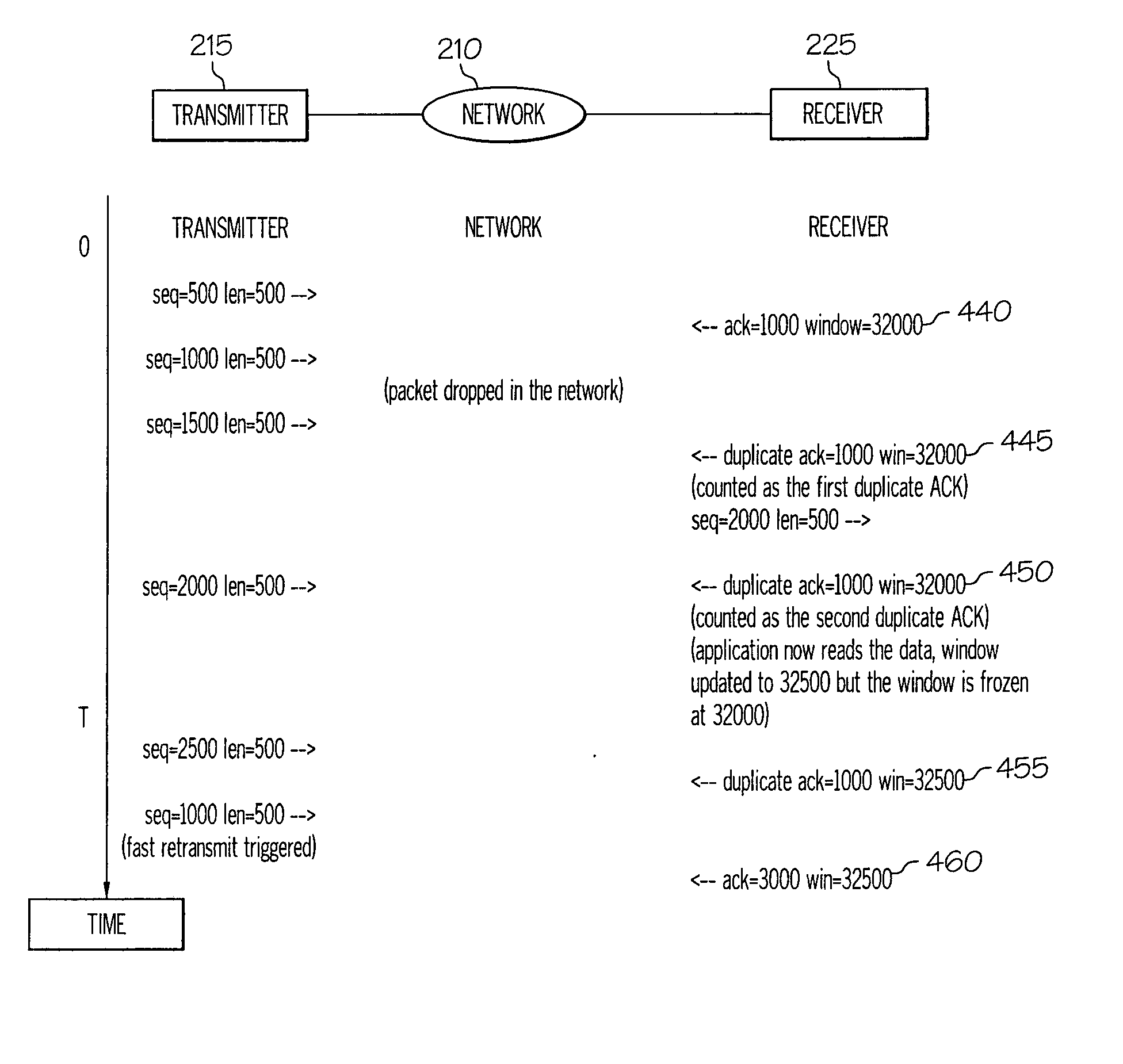
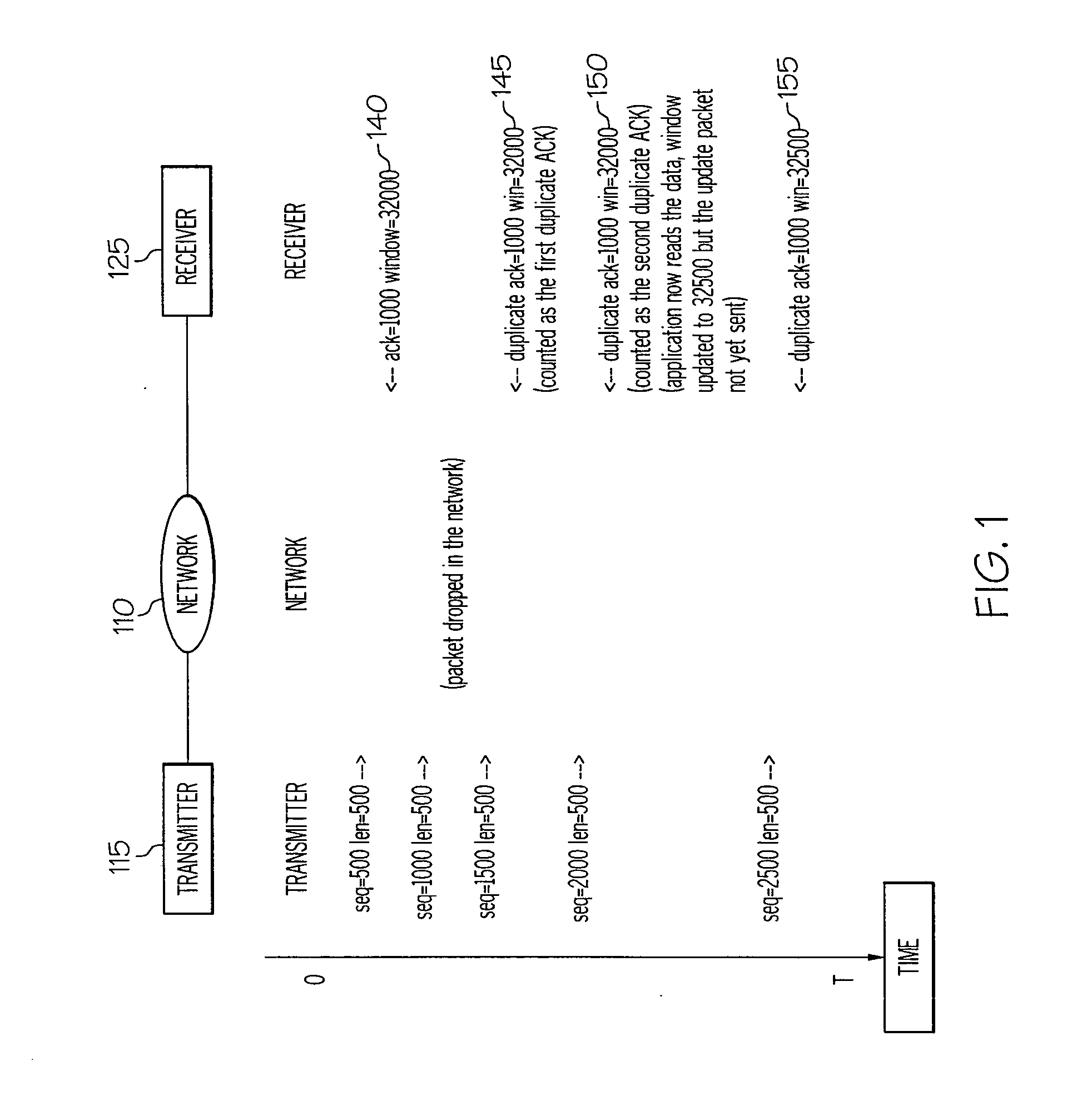
A method, network receiver and TCP network that enables a receiver-side triggering of the fast retransmit mechanism when a TCP packet / segment is lost or received out-of sequencing order. The receiver is enhanced with a Fast Retransmit Support (FRS) utility that monitors when a next received packet is out-of-order and responds by transmitting a duplicate acknowledgment (ACK) response that includes therein the same window value as the previous ACK. By including the previous clock time, even when the current window value has advanced, the fast retransmit algorithm at the transmitter is triggering before the timeout period.
Owner:IBM CORP
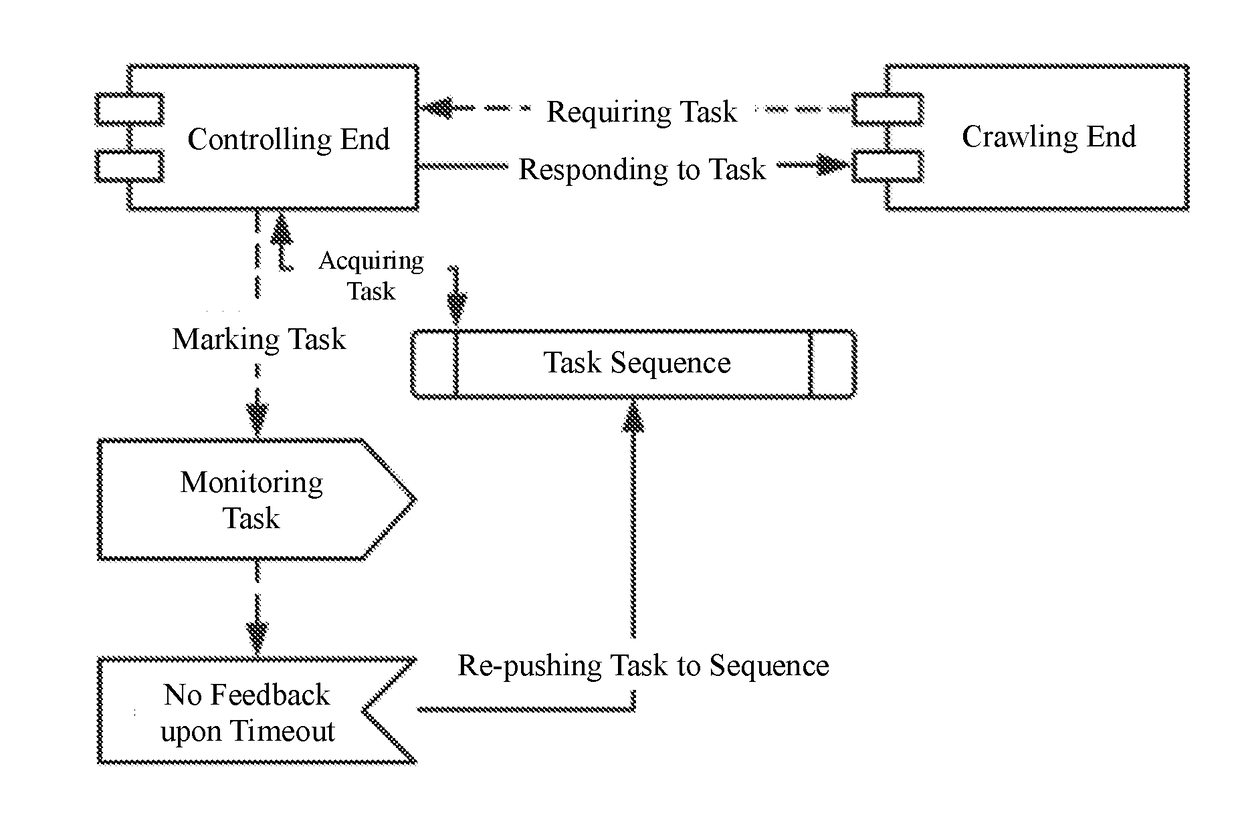
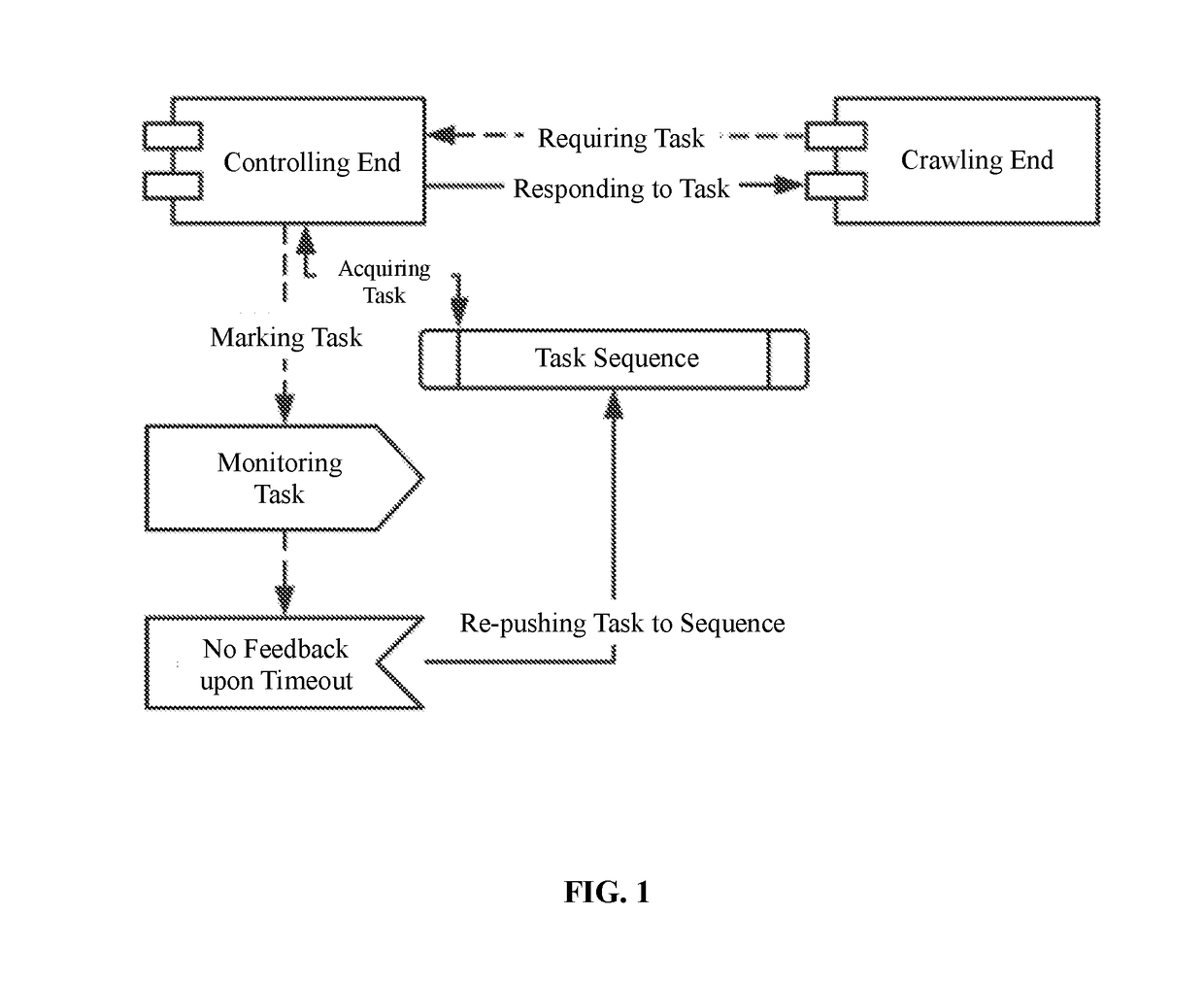
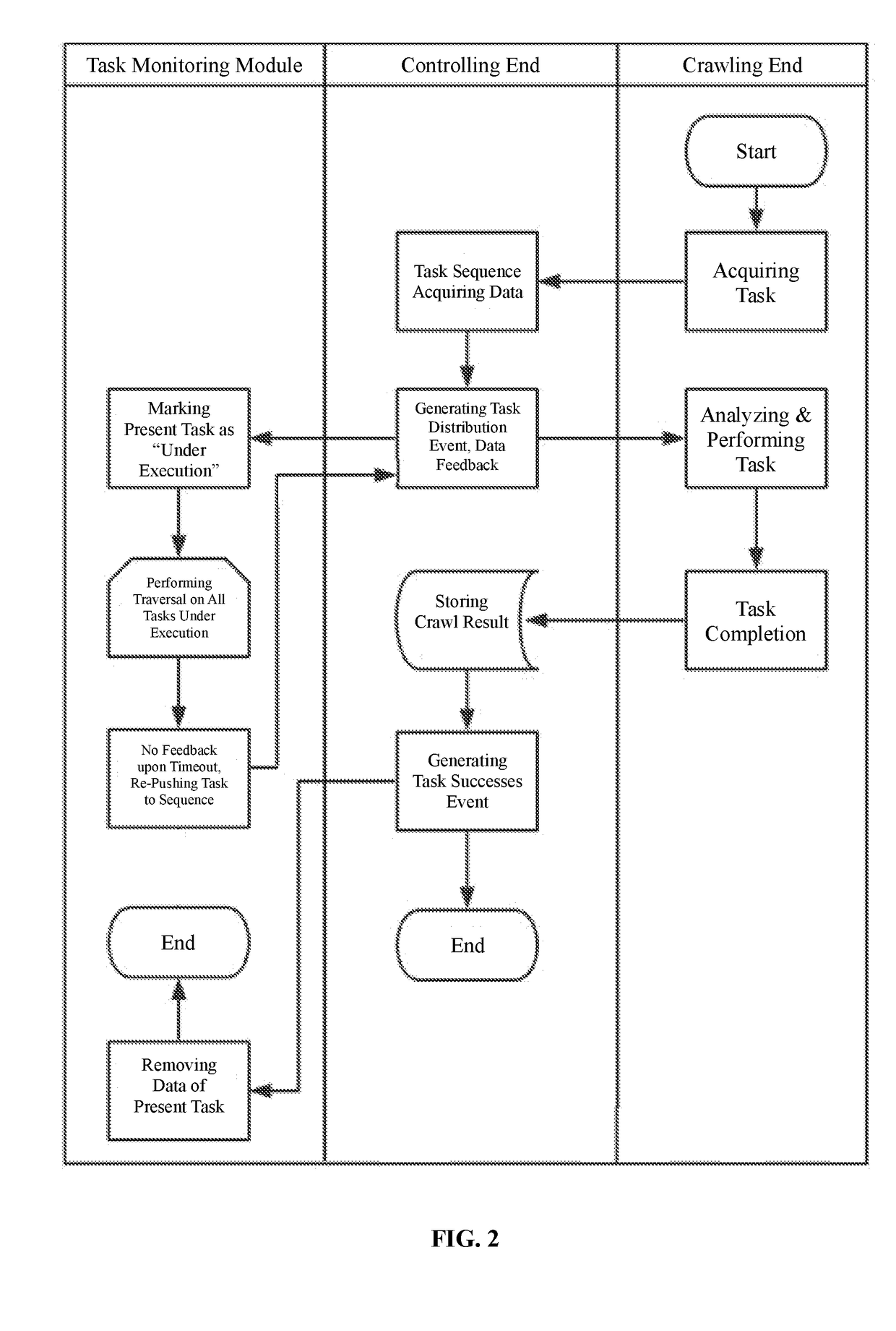
Task-crawling system and task-crawling method for distributed crawler system
InactiveUS20170068735A1Avoiding failure of taskWeb data indexingTransmissionTimestampEmbedded system
A task-crawling system for a distributed crawler system includes a controlling end, a crawling end, and a task monitoring module. The crawling end acquires a corresponding task, and sends data of the task to the controlling end. The controlling end works for assigning a number to the task, defining a timeout period for the task, generating a task-distribution event, and storing timestamp data of distribution of the task. The controlling end distributes the task distribution to the task monitoring module and the crawling end. The crawling end performs corresponding crawling logic to the crawl task, and sends information about completion of the task to the controlling end. In case of abnormality that prevents the crawl task from being performed properly, the task monitoring module re-pushes the task to the controlling end, thereby avoiding failure of the task otherwise caused by web-related problems.
Owner:MOLBASE SHANGHAI BIOTECH CO LTD
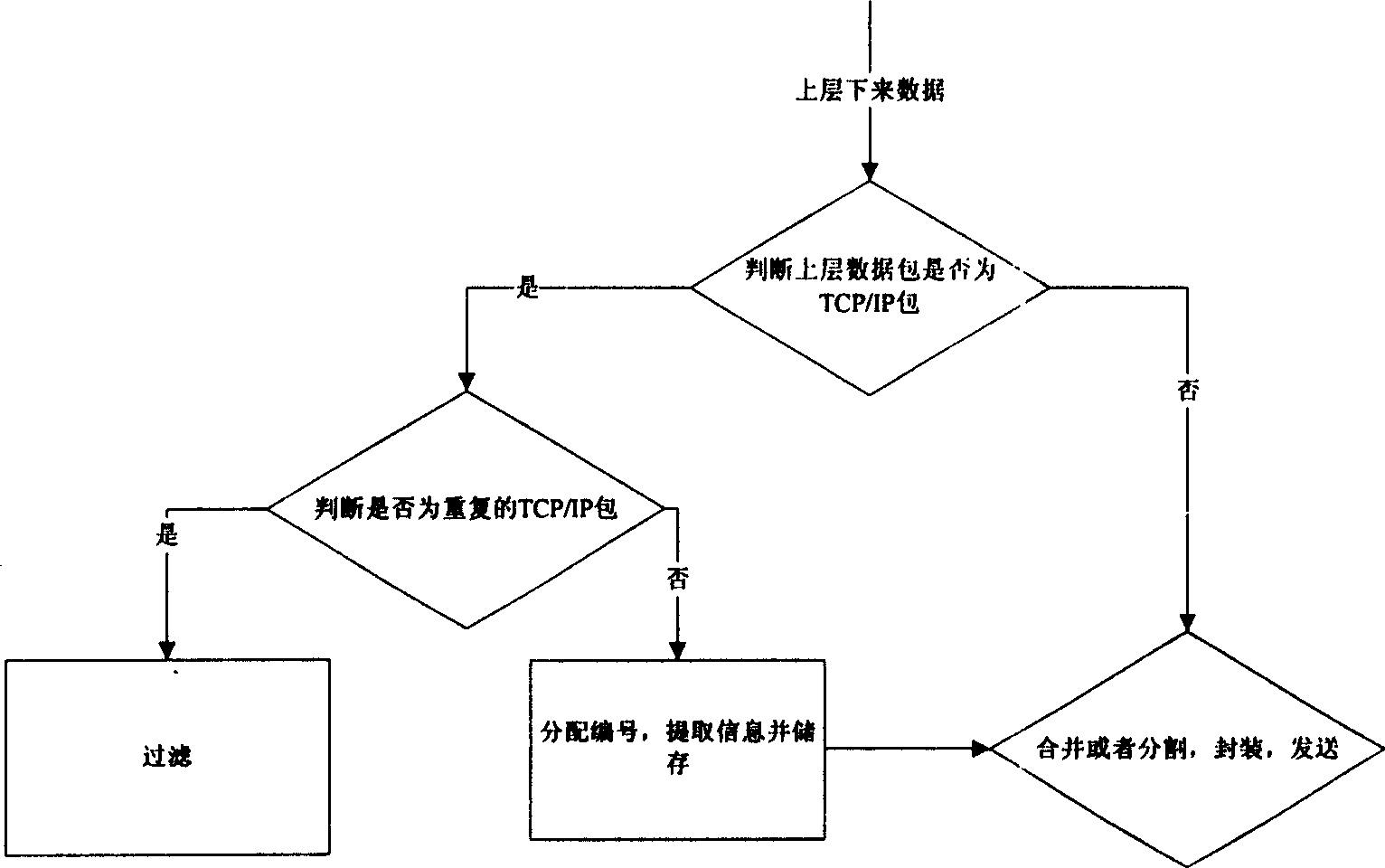
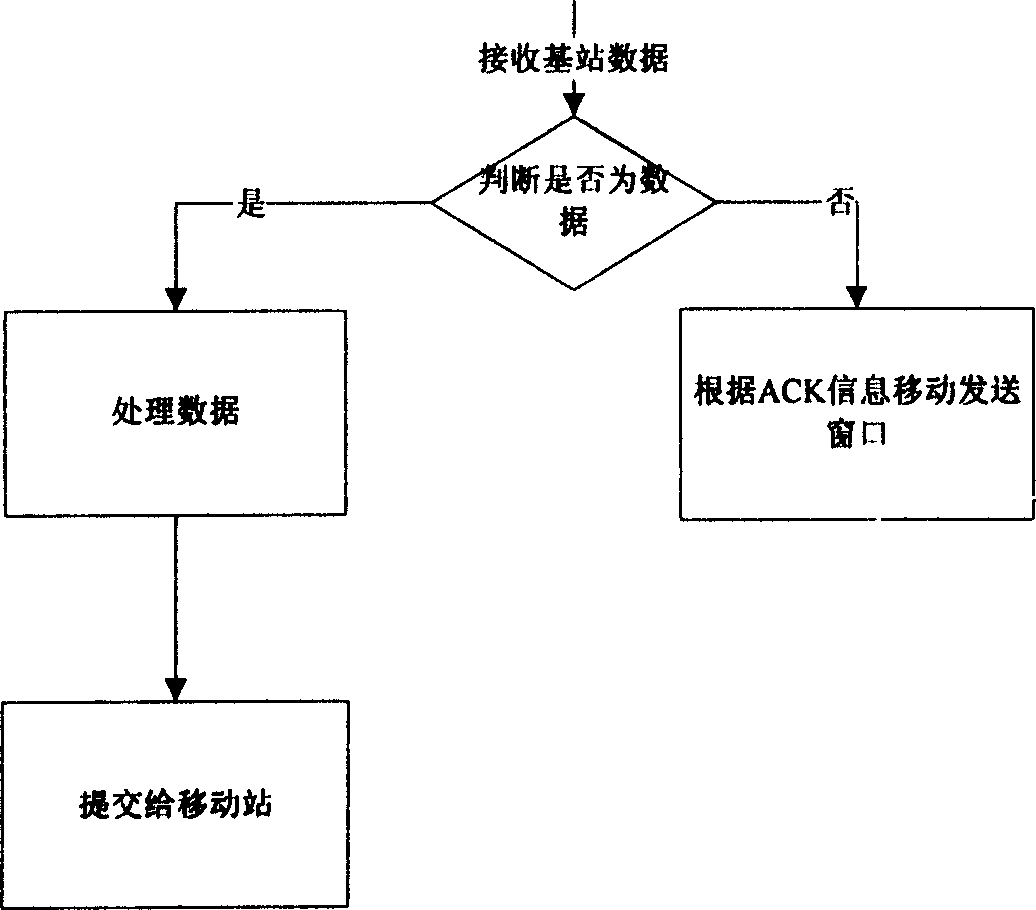
Base station TCP agency confirmation method based on ARQ information and its system
InactiveCN1753354AOvercoming the problem of reduced throughputShorten the timeError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksTransmission time delayMobile station
This invention discloses a base station TCP proxy confirmation method based on ARQ information and its system. The method includes sending / receiving and processing the up and down data. The system includes a base station and a mobile station connected by radio links, in which, the base station includes a base station start up and control module, a sending and analyzing module, a base station segment and reassembling module, a proxy confirmation module and a receiving and analyzing module, the mobile station includes a start and control module, a segment reassembling module and a filter module, which increases the mobile rate of the TCP sending window and reduces the probability of timeout of TCP resulted in increasing transmission time delay by the data link layer ARQ.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
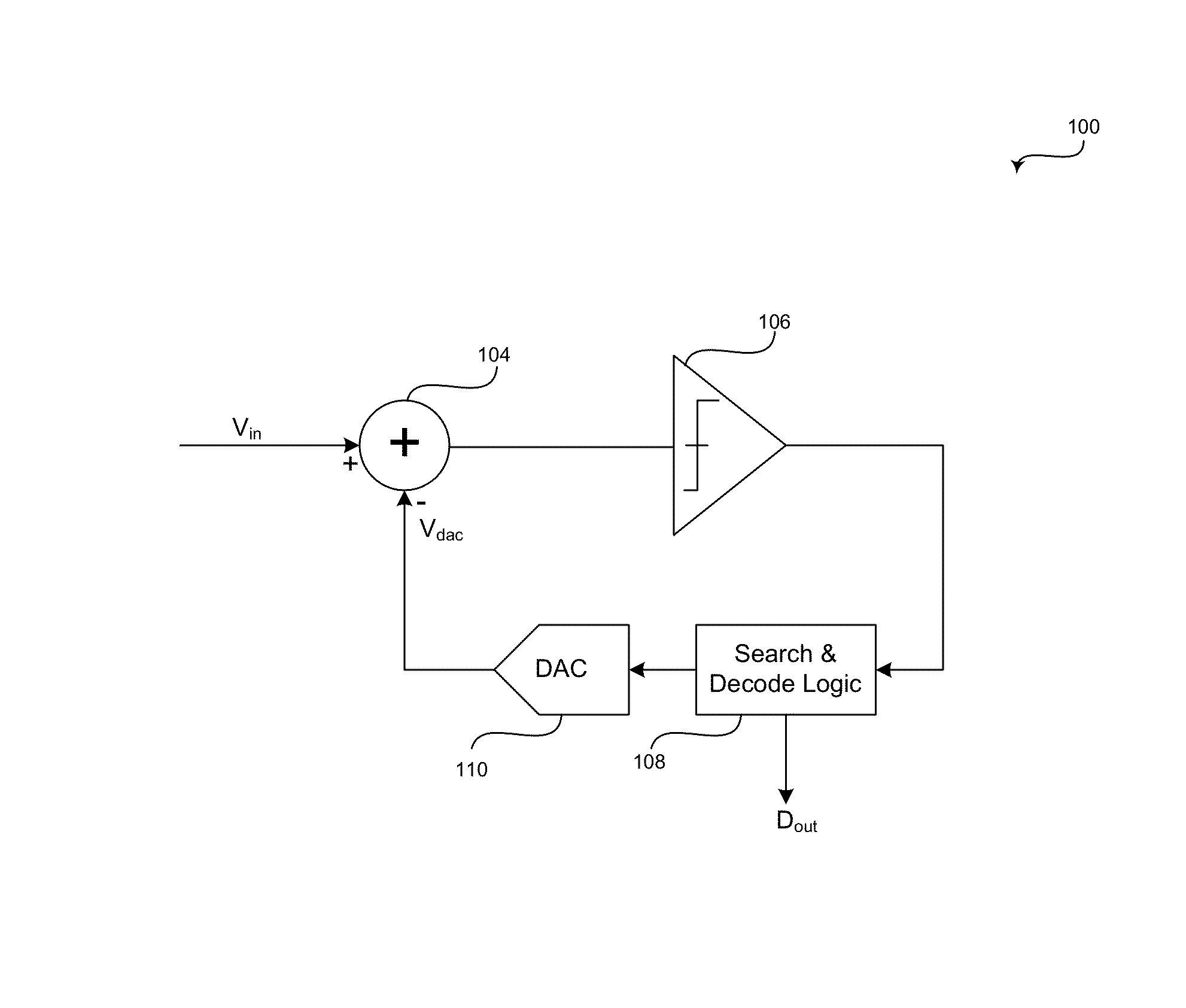
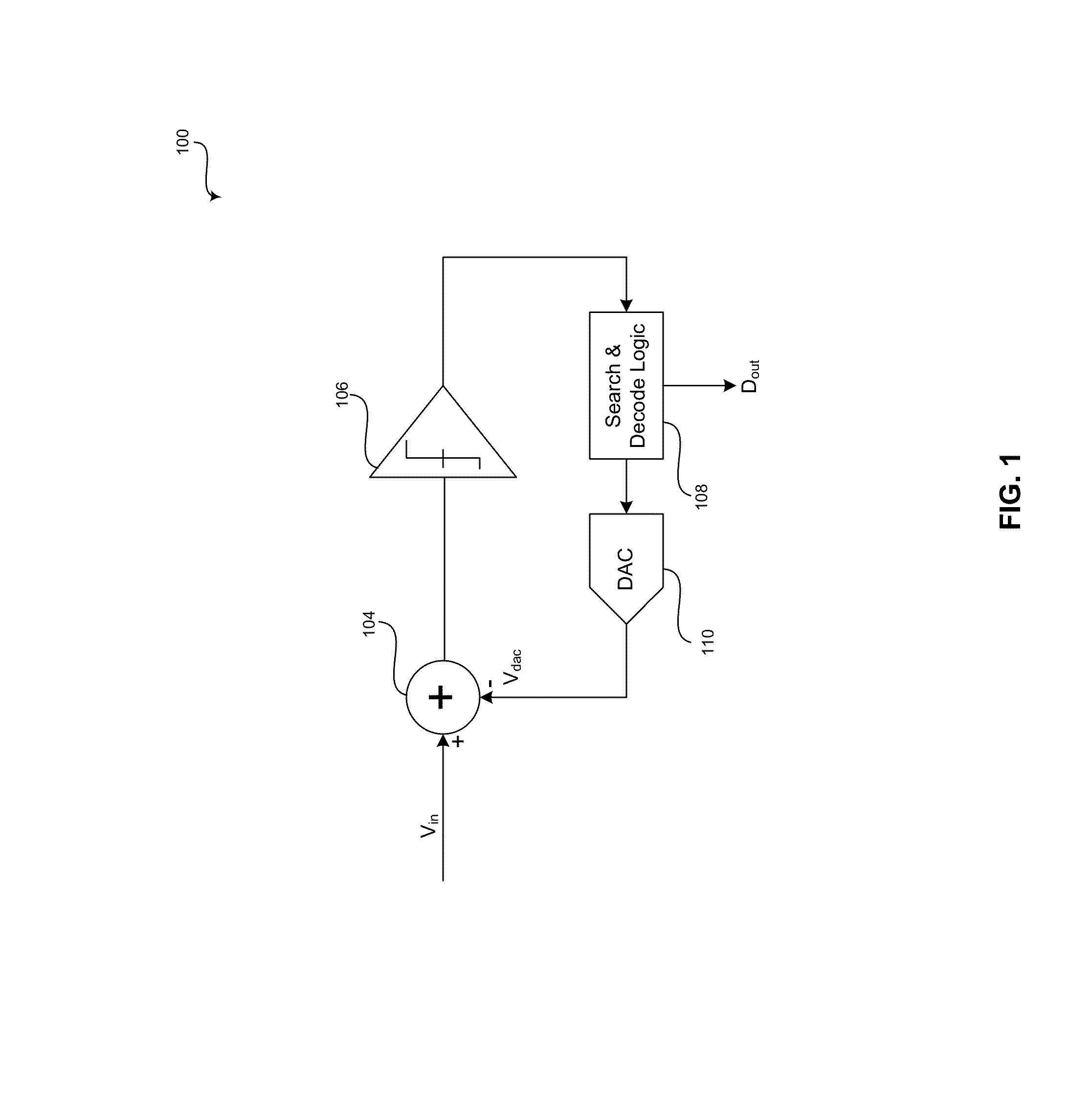
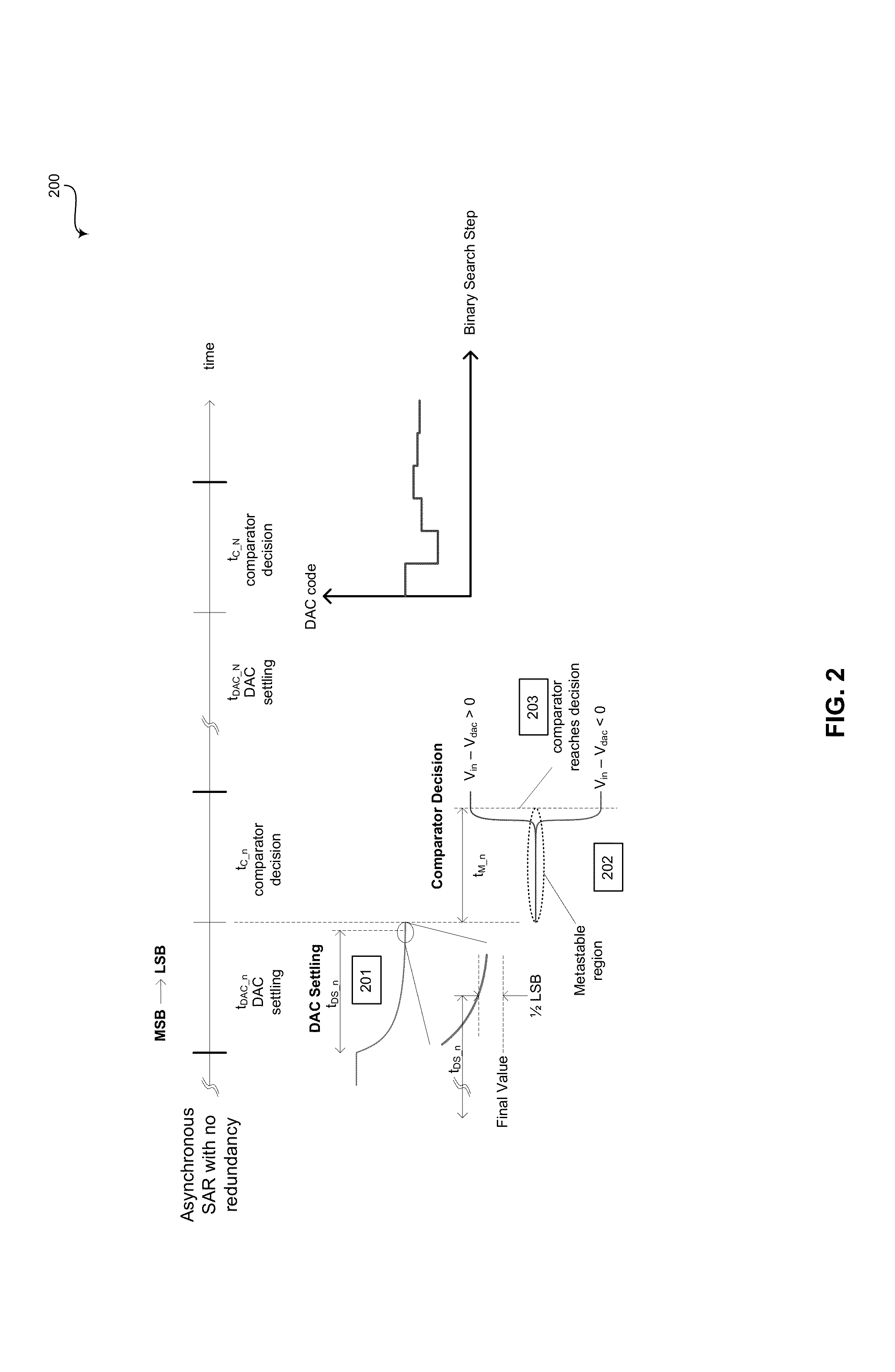
Method and system for asynchronous successive approximation register (SAR) analog-to-digital converters (ADCS)
ActiveUS20140043175A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital/analogue conversionA d converterAnalog-to-digital converter
An asynchronous successive approximation register analog-to-digital converter (SAR ADC), which utilizes one or more overlapping redundant bits in each digital-to-analog converter (DAC) code word, is operable to generate an indication signal that indicates completion of each comparison step and indicates that an output decision for each comparison step is valid. A timer may be initiated based on the generated indication signal. A timeout signal may be generated that preempts the indication signal and forces a preemptive decision, where the preemptive decision sets one or more remaining bits up to, but not including, the one or more overlapping redundant bits in a corresponding digital-to-analog converter code word for a current comparison step to a particular value. For example, the one or more remaining bits may be set to a value that is derived from a value of a bit that was determined in an immediately preceding decision.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
Model framework to facilitate robust programming of distributed workflows
ActiveUS20140304380A1Digital computer detailsNon-redundant fault processingLeader electionParallel computing
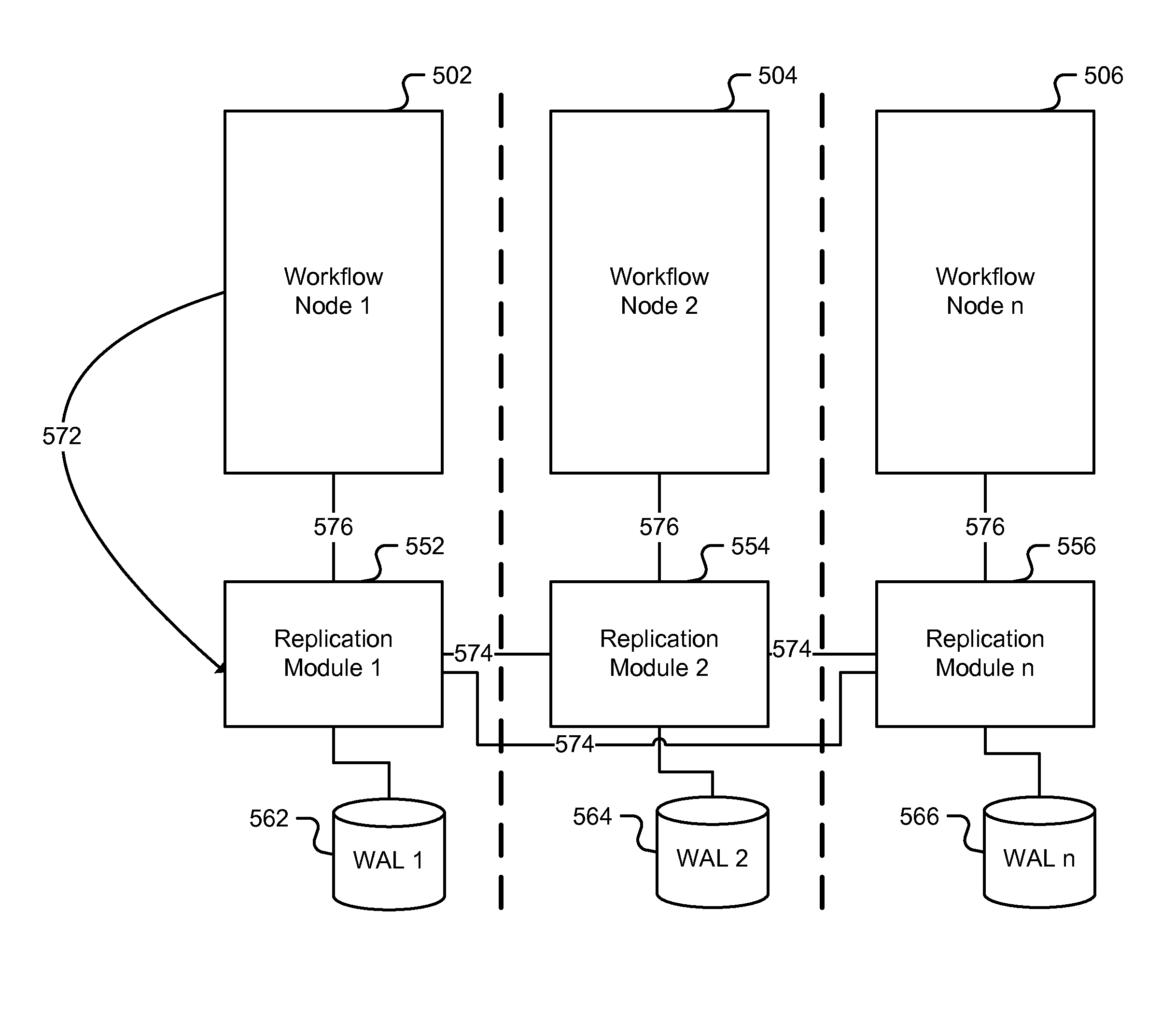
A method is disclosed. A finite state machine model for a single system workflow is replicated across a plurality of distributed nodes associated with a leader election protocol. A leader is determined amongst the plurality of distributed nodes to perform a next action of the finite state machine model based at least in part on the leader election protocol. One or more nodes amongst the plurality of distributed nodes are configured to submit a timeout ticket if the next action of the finite state machine model does not appear to have been performed by the leader within a prescribed time.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method and Apparatus for Dynamically Adjusting the Number of Packets in a Packet Train to Avoid Timeouts
InactiveUS20080095193A1Reduce trainingEasy to adjustTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationReal-time computingNetwork packet
A sending device dynamically adjusts a target number of data packets in a packet train by projecting a train property in advance of timeout, and adjusts the target accordingly. Preferably, the target size of the packet train is adjusted downward by checking the number of accumulated packets in the train at some predetermined time in the timeout interval, and halving the target packet train size if the accumulated packets number less than some intermediate target. This process can be repeated more than once in the same timeout interval. The target size is preferably adjusted upwards more slowly.
Owner:IBM CORP
Aircraft systems and methods for detecting non-compliant pilot action
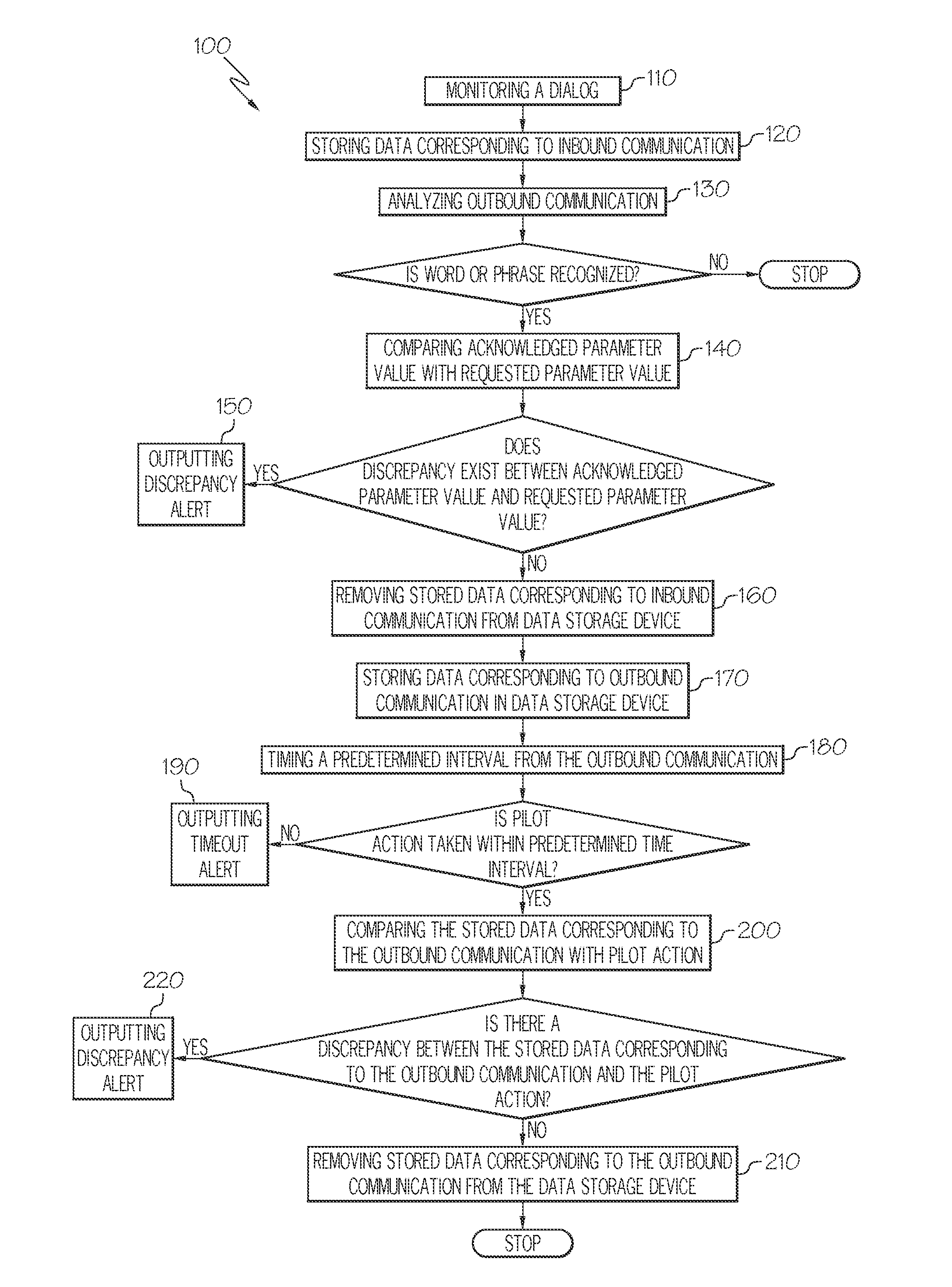
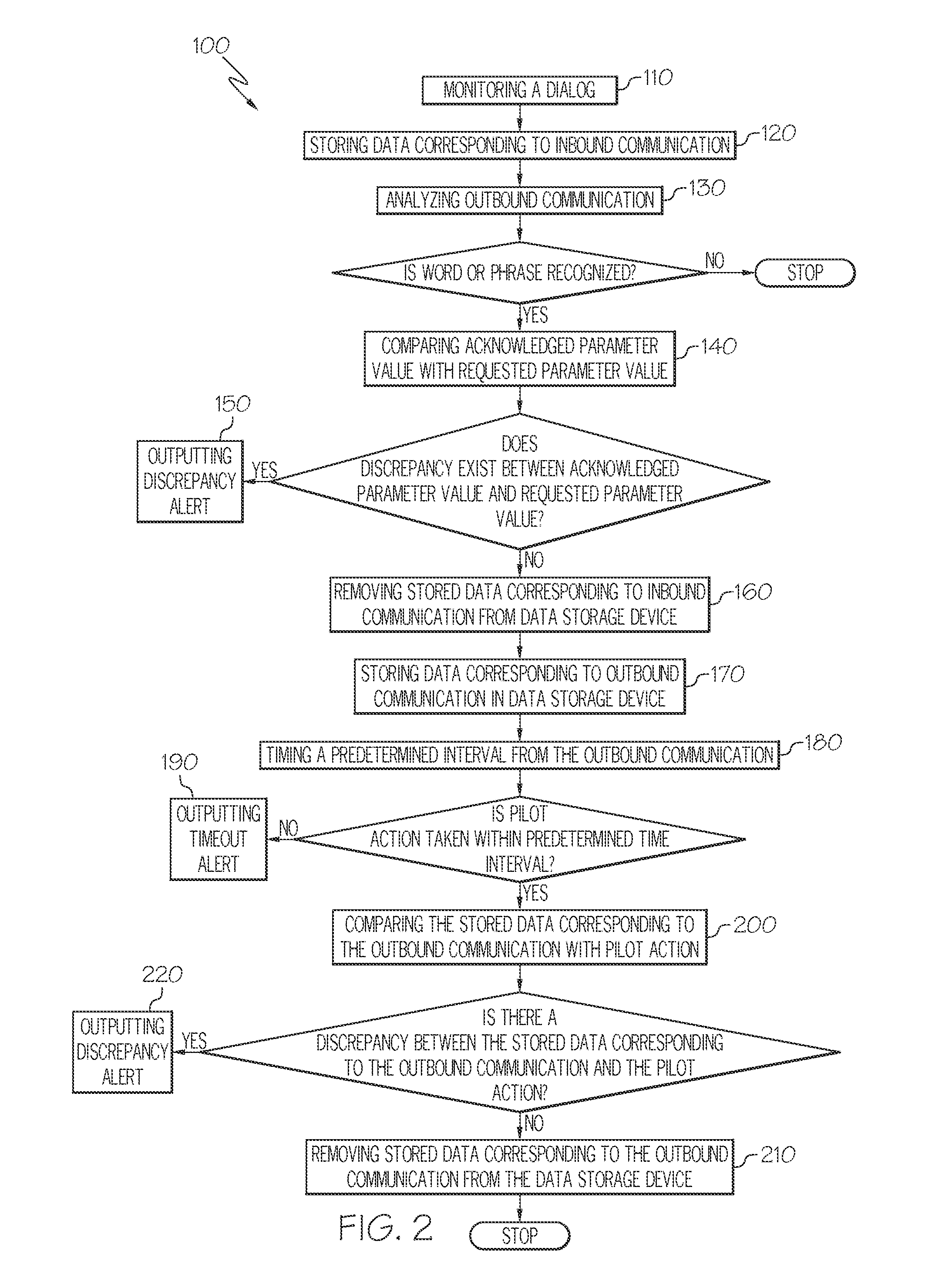
ActiveUS20150081138A1Improve communication efficiencyImprove flight safetyDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsOutbound communicationFlight vehicle
Aircraft systems and methods for detecting non-compliant pilot action are provided. The method comprises analyzing an outbound communication from an aircraft to recognize a word or phrase corresponding to a parameter associated with a prior request for pilot action. If the word or phrase is recognized, the method further comprises storing data corresponding to the outbound communication in a data storage device. The stored data and pilot action taken are compared to determine if there is a discrepancy between the pilot action and the stored data. A discrepancy alert is outputted if the discrepancy is determined to exist. A predetermined time interval is timed from the outbound communication. A timeout alert is outputted at a timeout of the predetermined time interval unless the requested pilot action is taken within the predetermined time interval.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
HPLC communication networking method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment
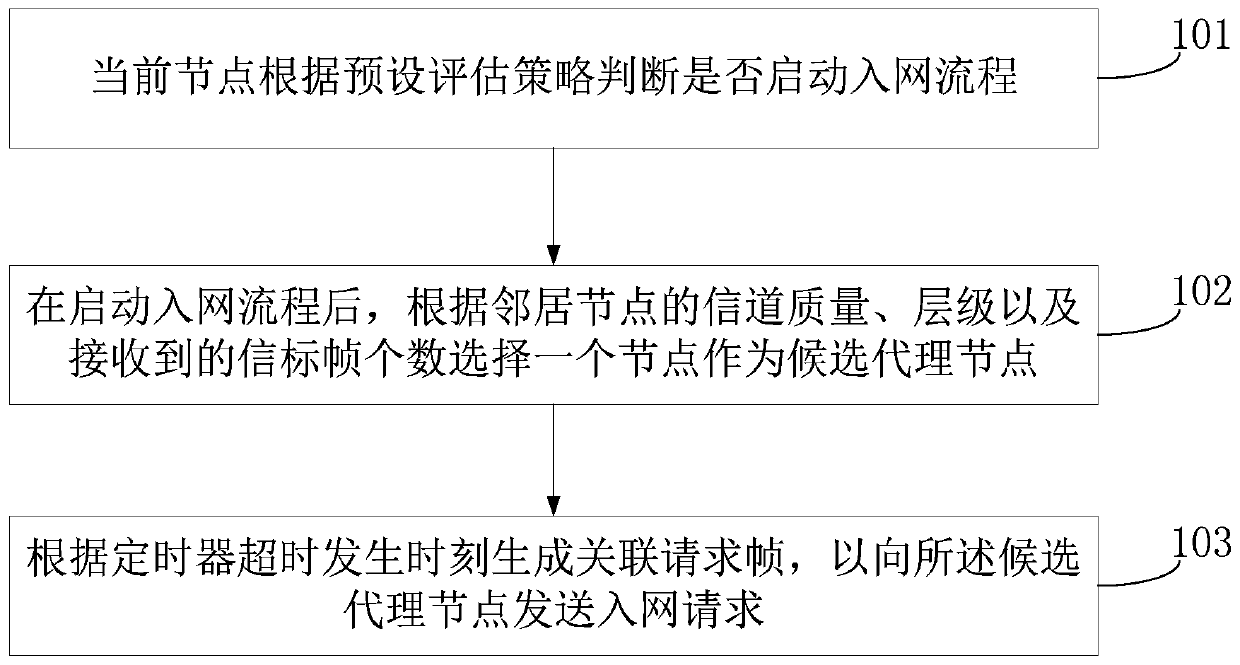
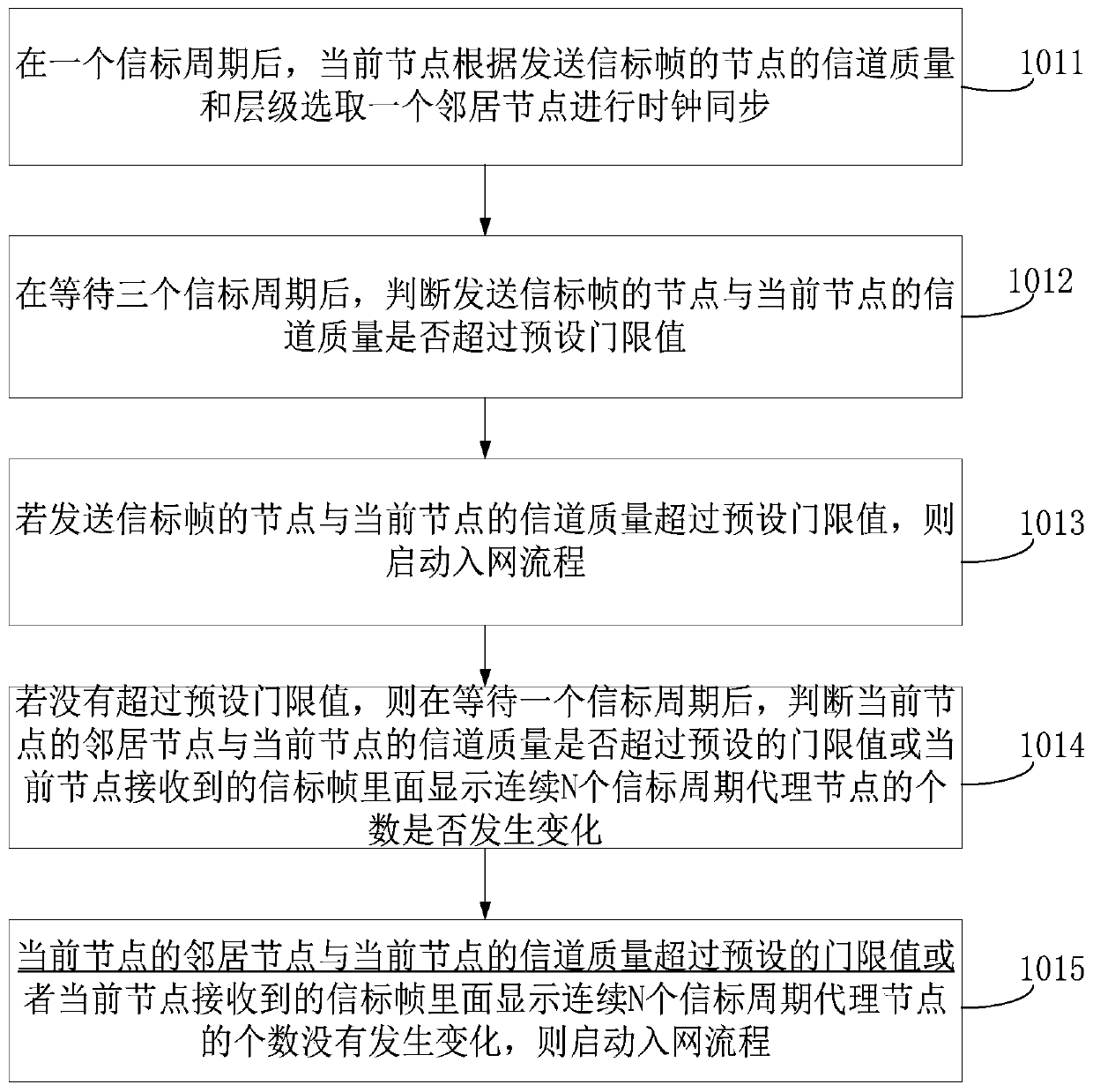
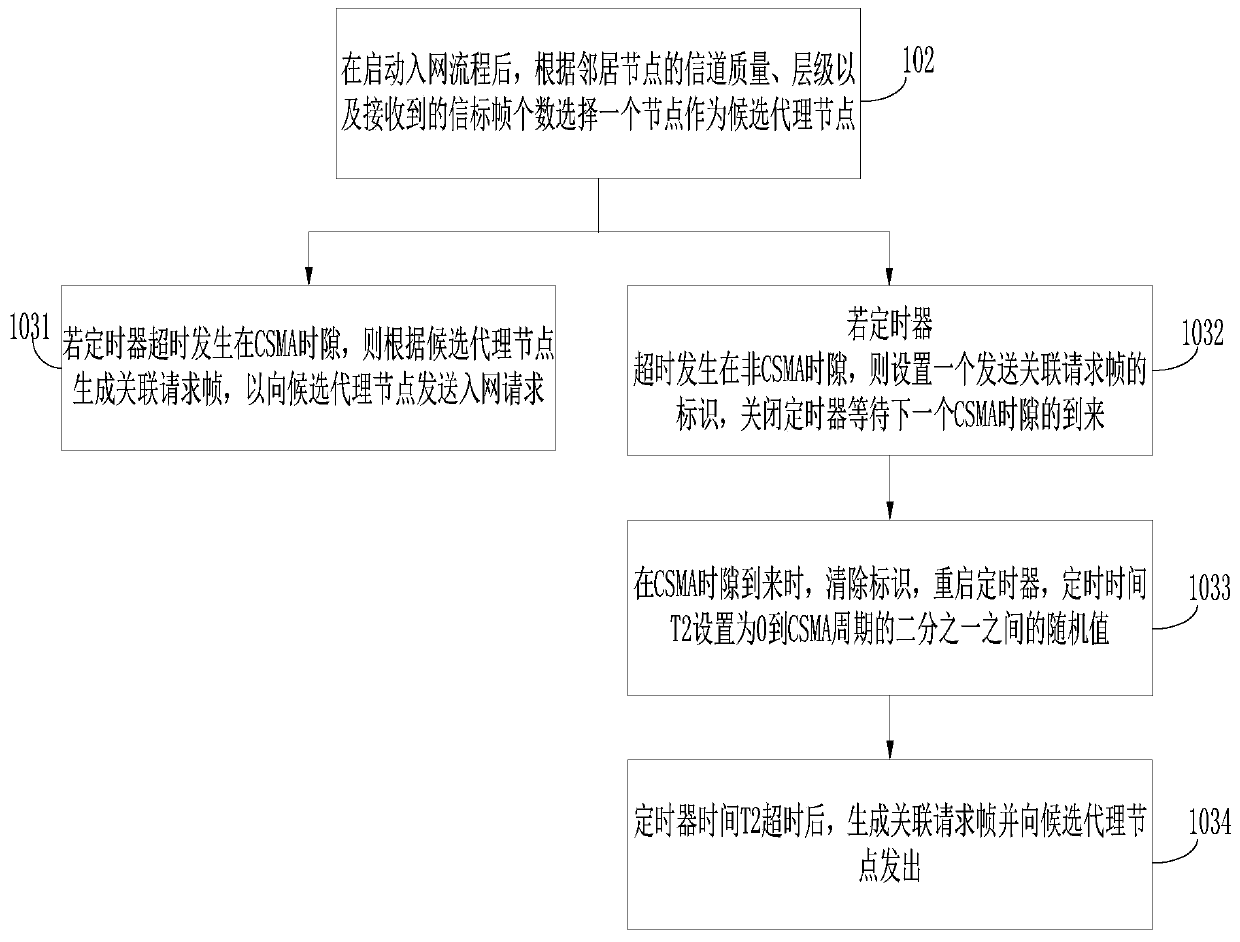
ActiveCN110661870AReduce the numberImprove communication efficiencyPower distribution line transmissionData switching networksBeacon frameCarrier signal
The invention relates to an HPLC communication networking method, and relates to power line carrier communication, and the method comprises the steps of enabling a current node to judge whether to start a network access flow or not according to a preset evaluation strategy; after the network access process is started, selecting one node as a candidate proxy node according to the channel quality and hierarchy of the neighbor nodes and the number of received beacon frames; and generating an association request frame according to the timeout occurrence time of the timer so as to send a network access request to the candidate proxy node. According to the invention, the probability of agent change during network access is reduced, the number of SOF frames in a network optimization stage is reduced, and the overall communication efficiency of a carrier channel is improved.
Owner:青岛联众芯云科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com