Patents
Literature
299results about How to "Effective bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
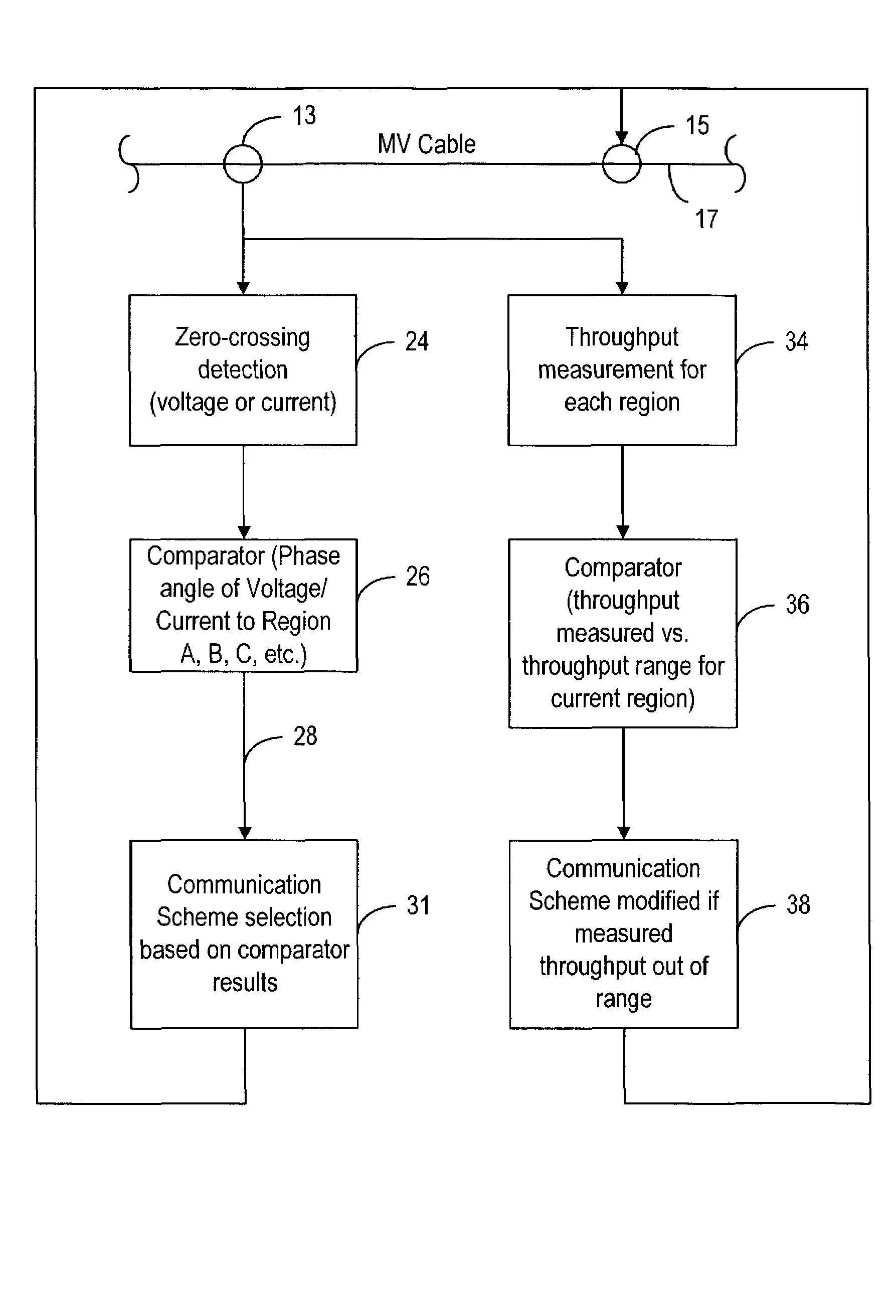
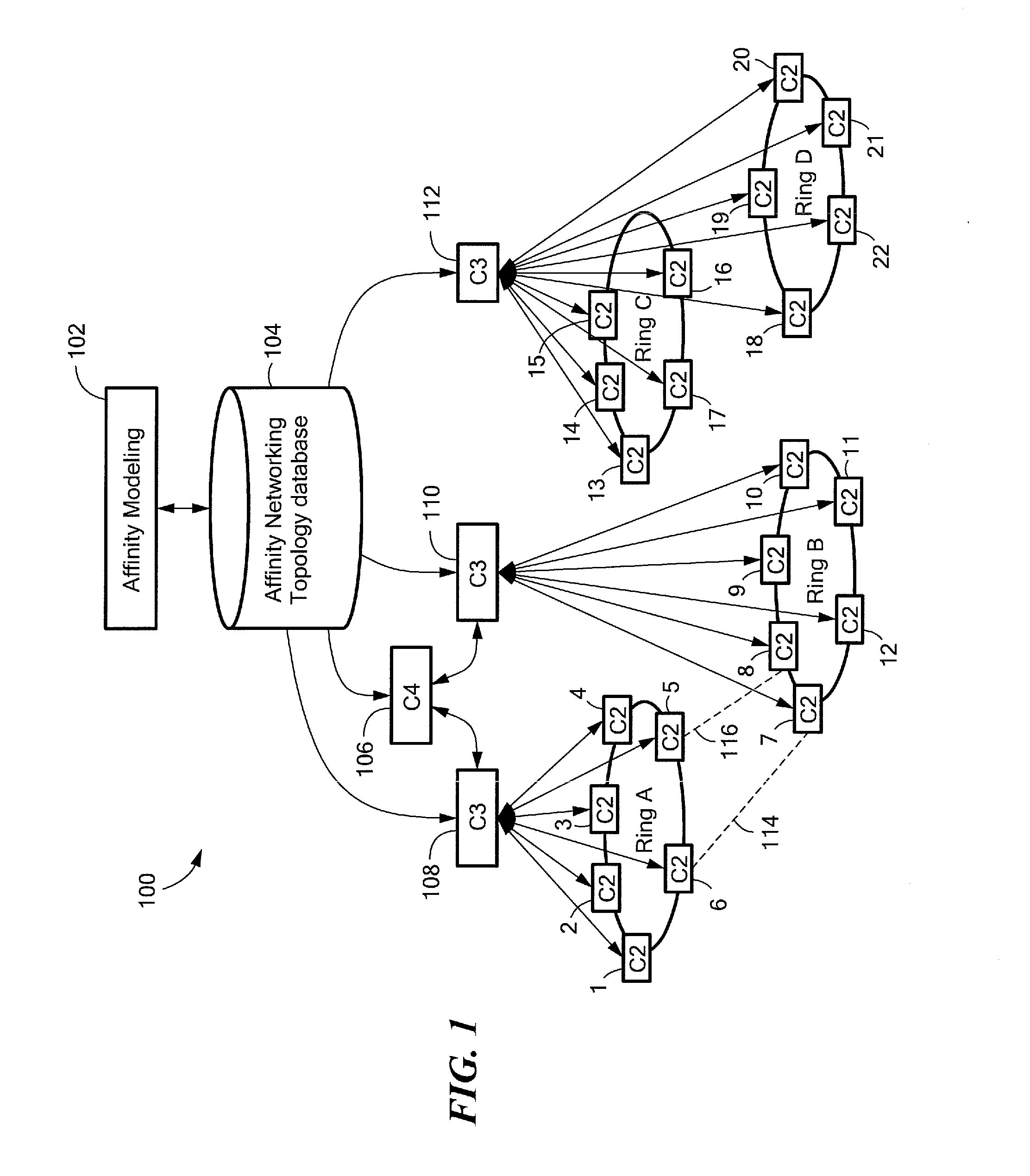
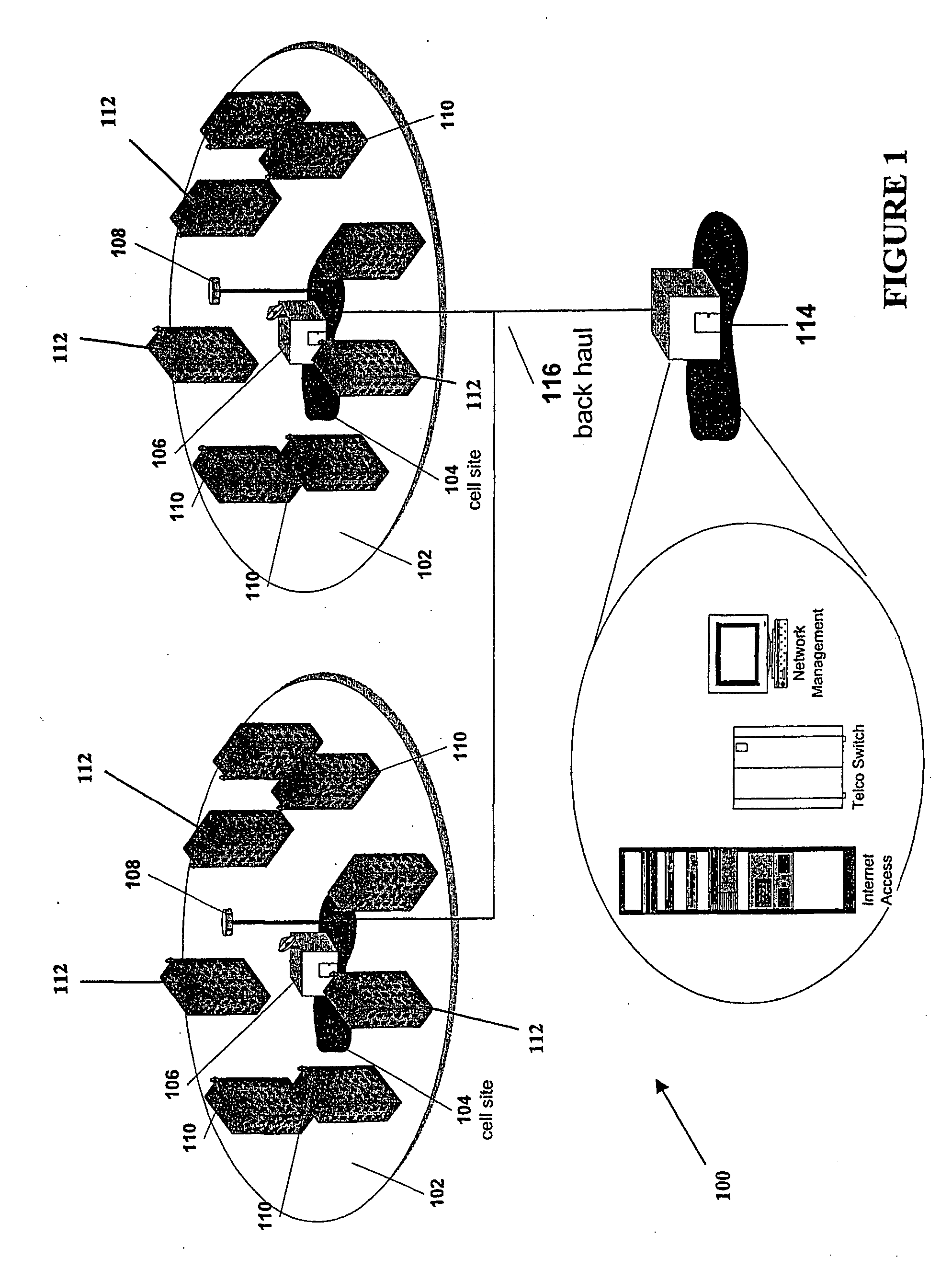
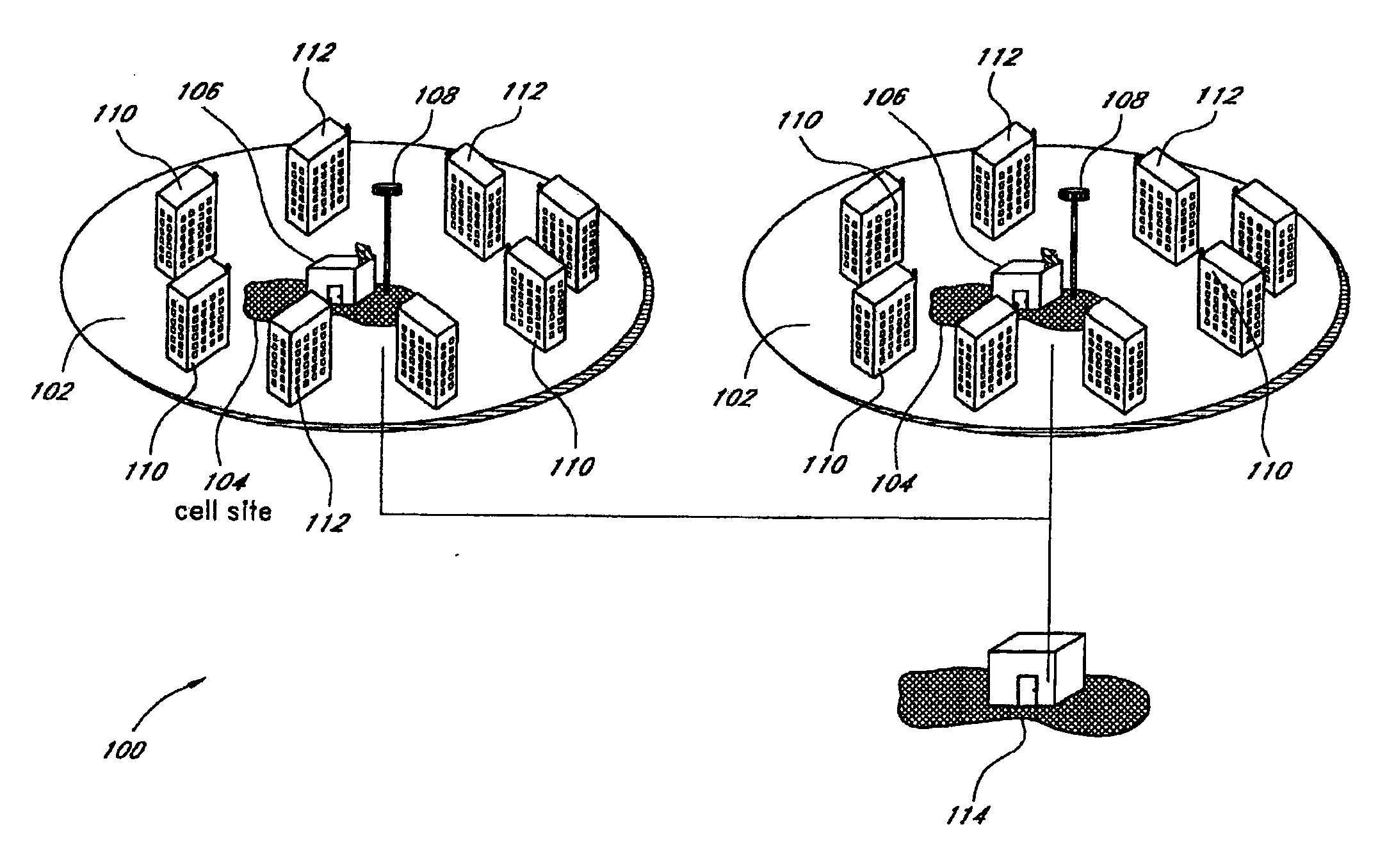
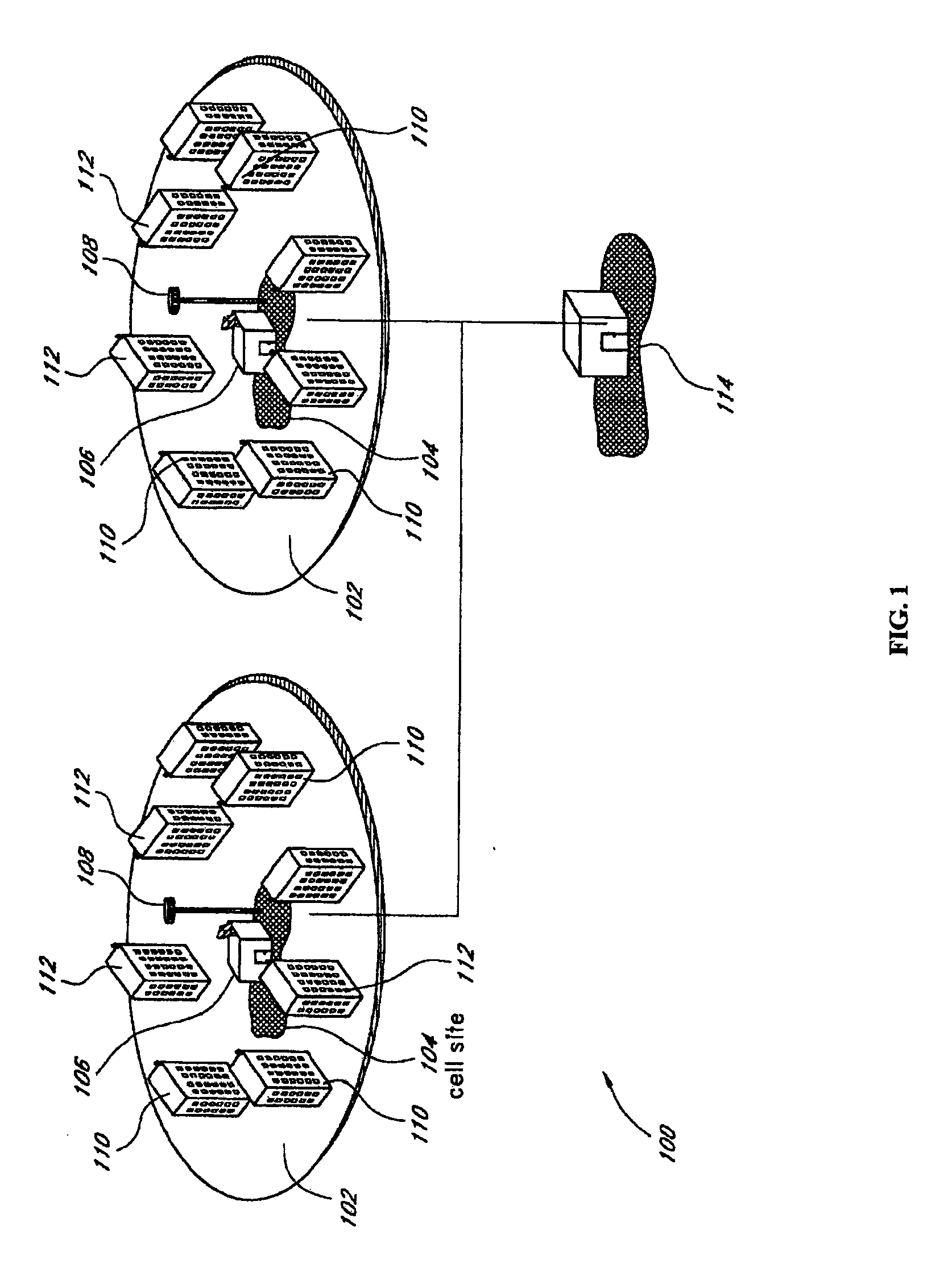
Method and system to increase the throughput of a communications system that uses an electrical power distribution system as a communications pathway
InactiveUS7307357B2High bandwidth efficiencyError correction overheadSystems with measurements/testing channelsPower distribution line transmissionDistribution systemEngineering
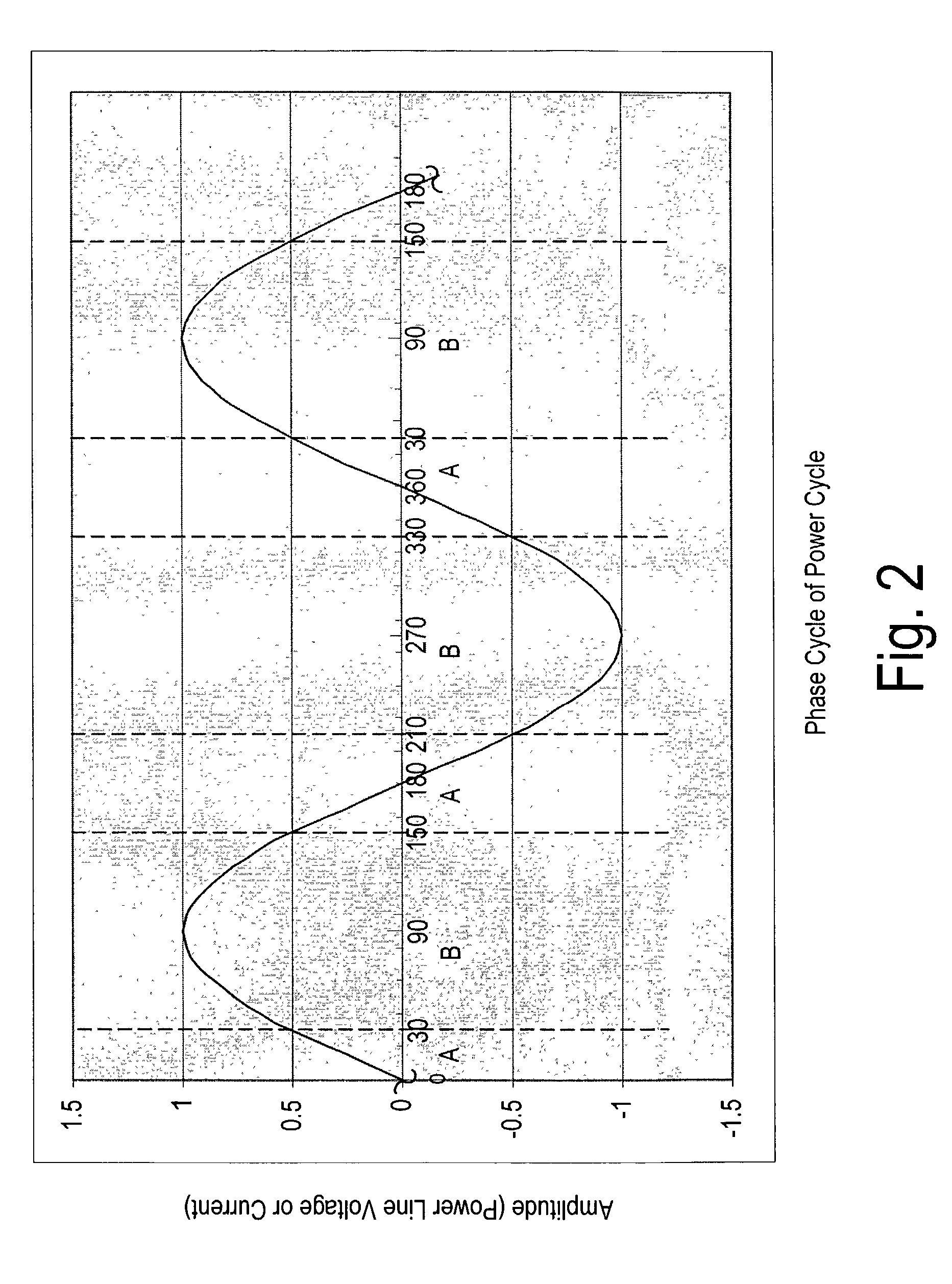
A method and system to increase the throughput of a communications system that uses an electrical power distribution system as a communications pathway, determines the phase of the power distribution power cycle and compares this determined phase to predetermined regions of the power cycle. If the power cycle is within a predetermined region, a particular communication scheme is used for transmitting and receiving information. The power cycle can have two or more predetermined regions. Optionally, the throughput for any or all regions can be determined so as to provide for modification of the associated communication scheme if the throughput is determined to be outside some predetermined range.
Owner:AMPERION
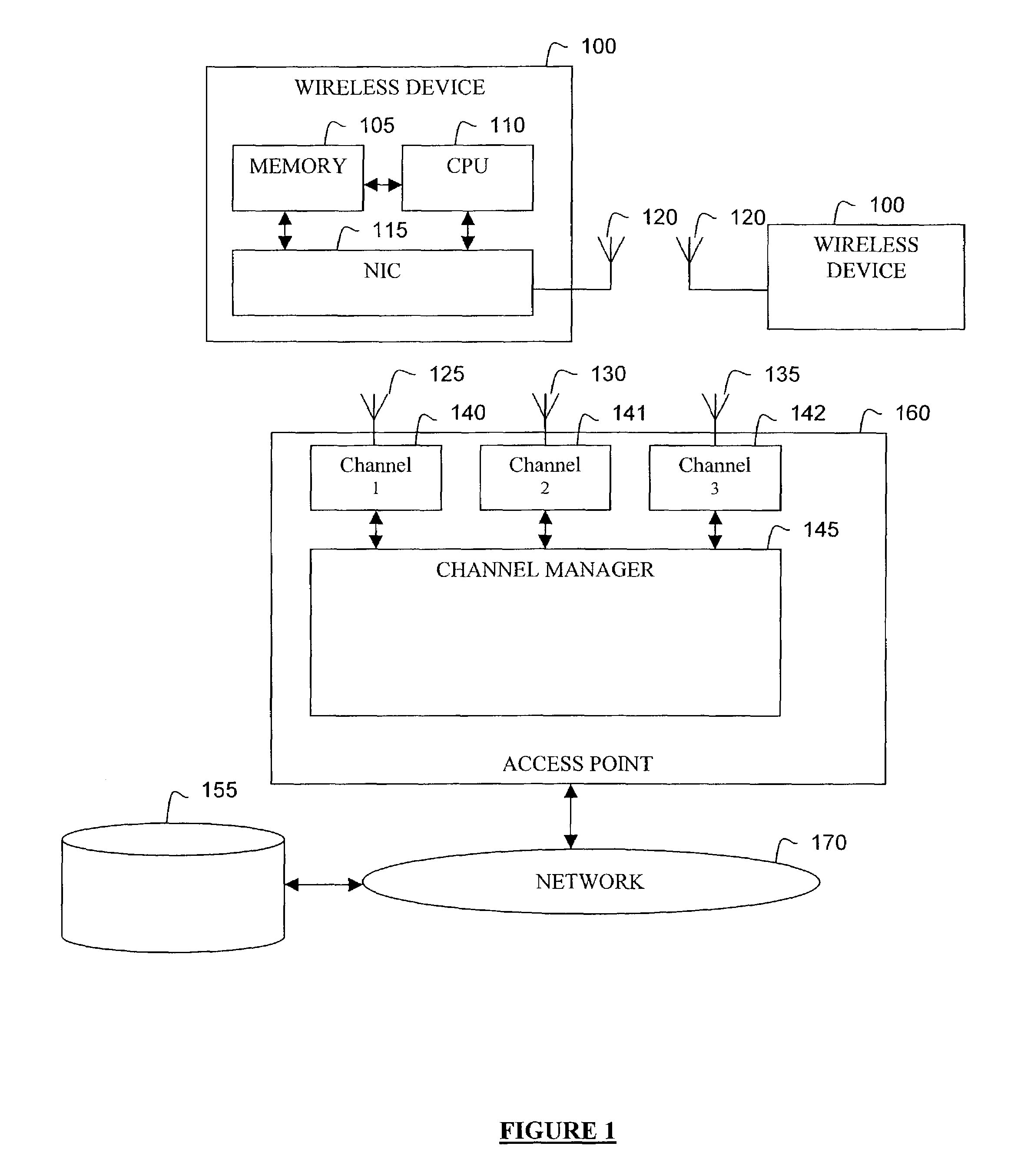
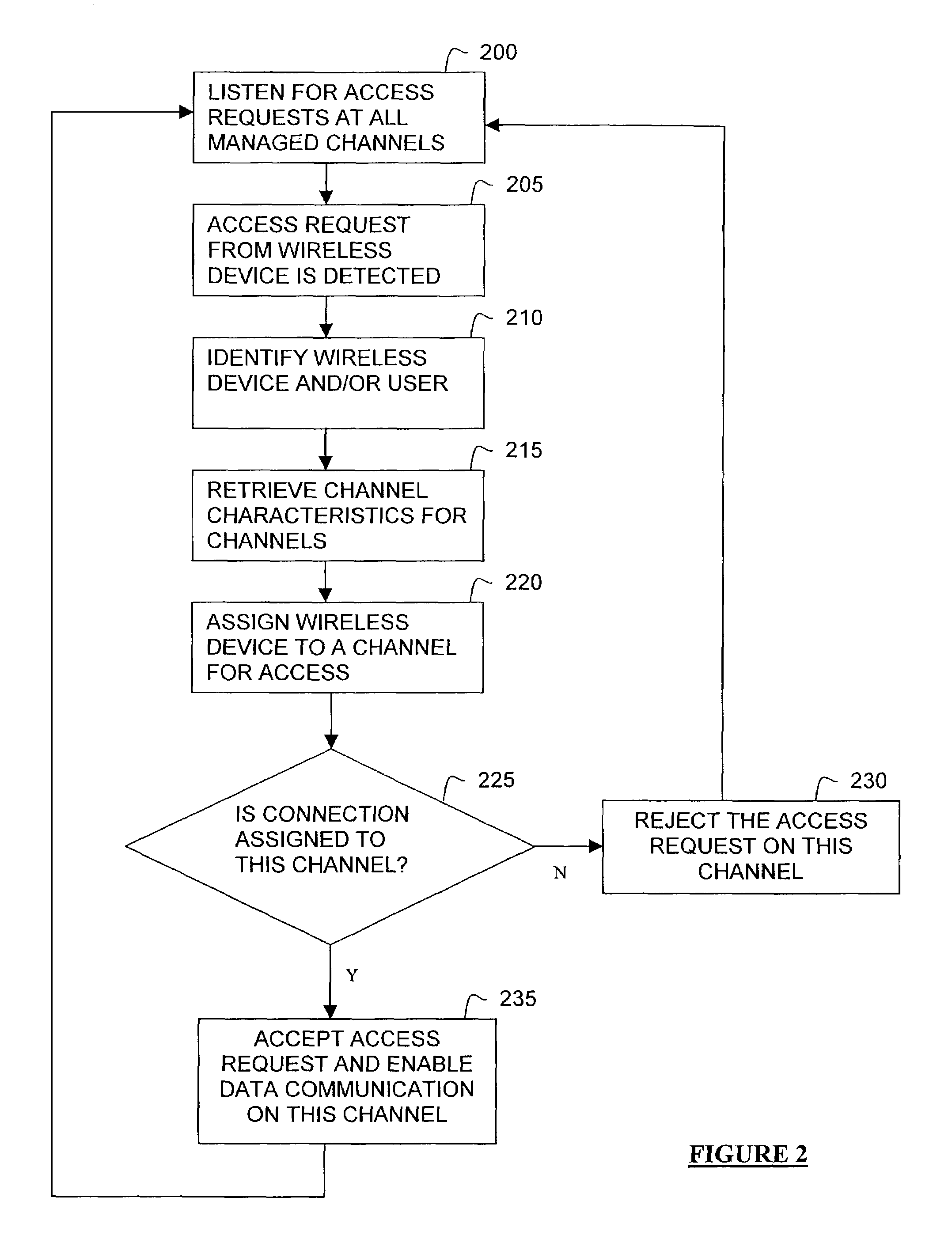
Dynamic allocation of channels in a wireless network
ActiveUS7453844B1Effective bandwidthEfficient deploymentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionQuality of serviceWireless mesh network
Bandwidth is deployed within a wireless network efficiently by making multiple channels available to wireless devices within a coverage area and intelligently controlling access to those channels. For example, channels to which each wireless device is registered with may be based on quality of service factors. According to one embodiment, upon attempted access to a wireless network channel, an access point grants or refuses a wireless device access based on quality of service factors relating to the device, the channel and the other channels that the device could access.
Owner:TCL COMM TECH HLDG
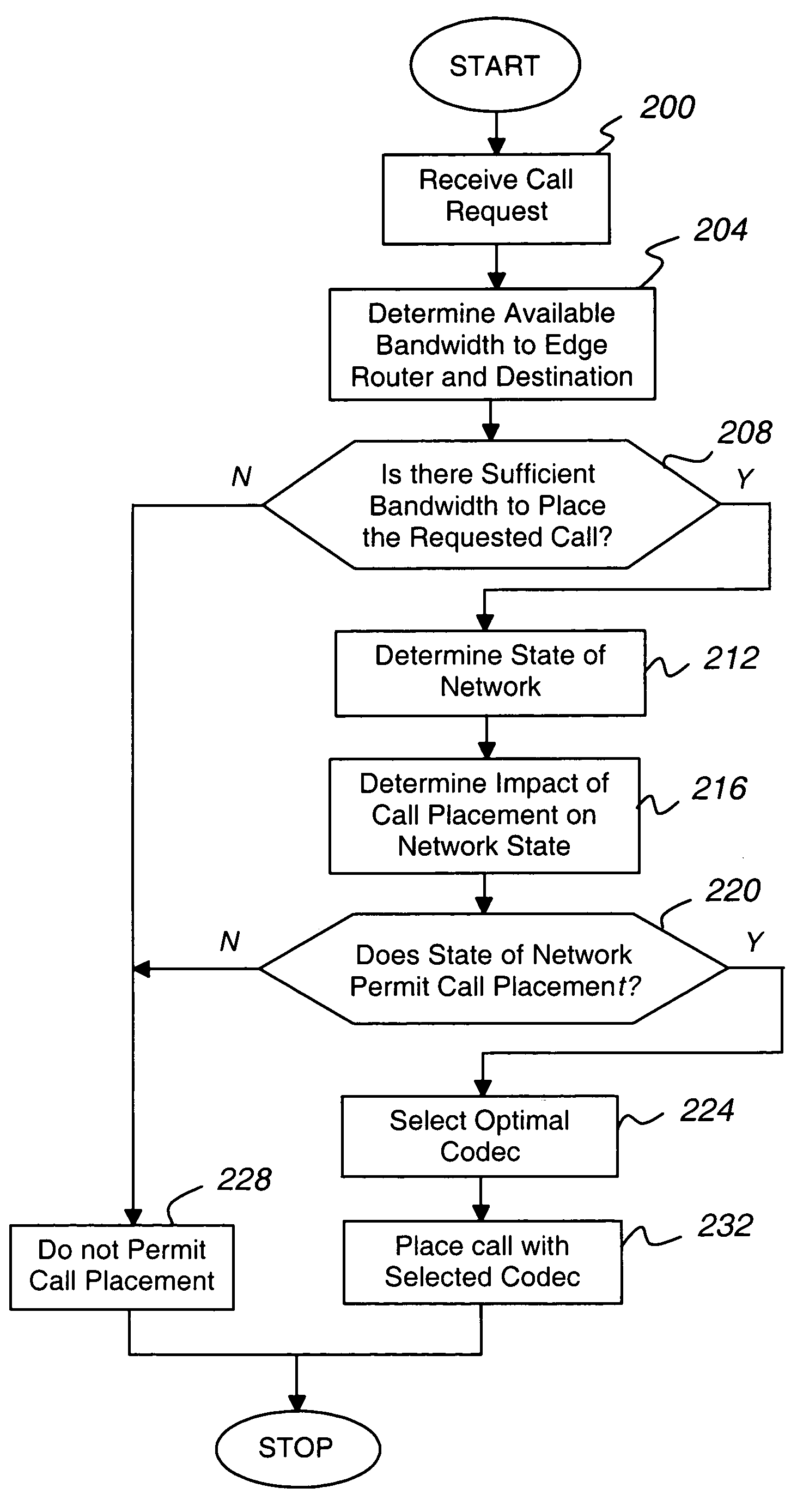
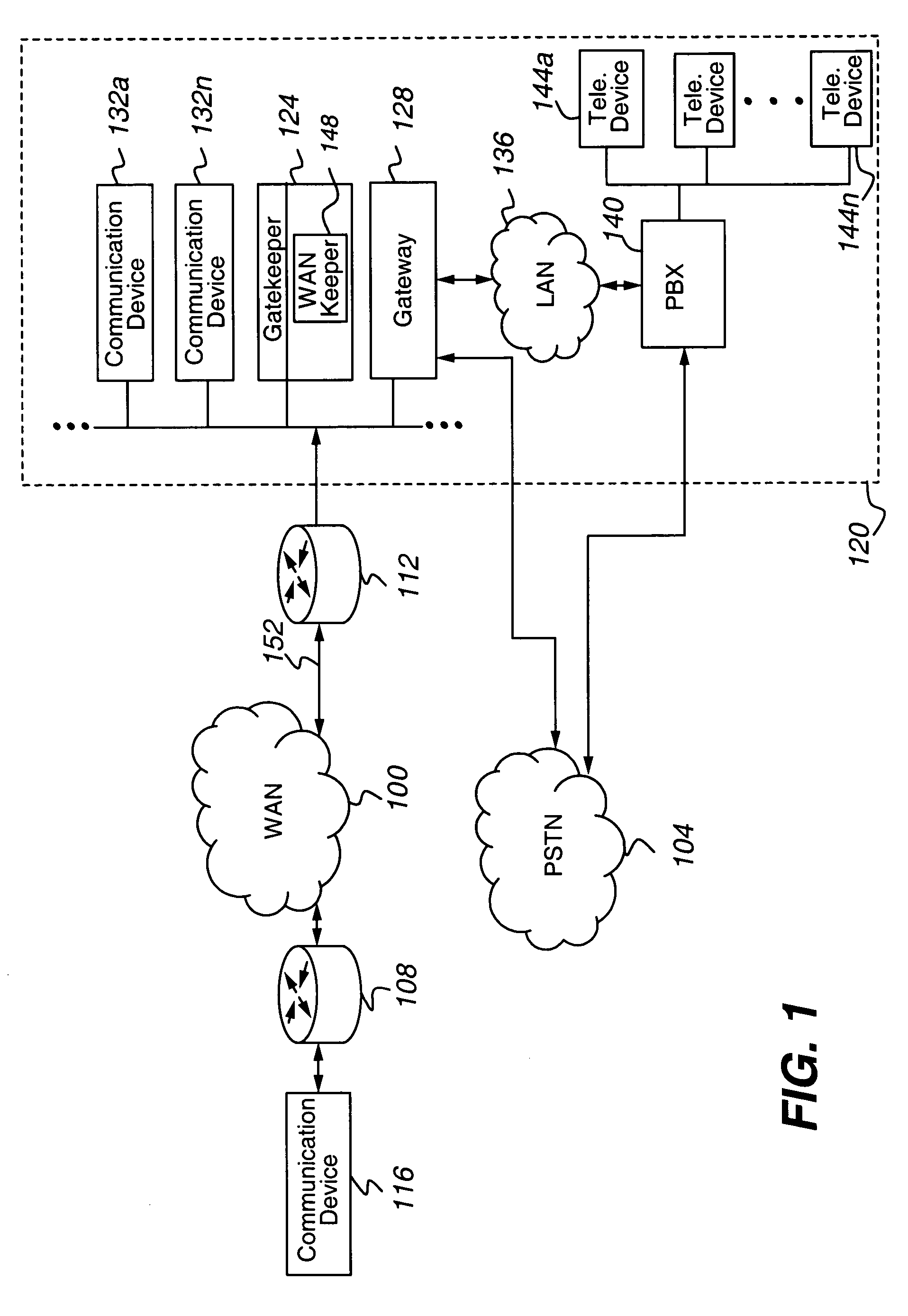
WAN keeper efficient bandwidth management
ActiveUS7643414B1Efficient use ofEnoughInterconnection arrangementsError preventionQuality of serviceLive voice
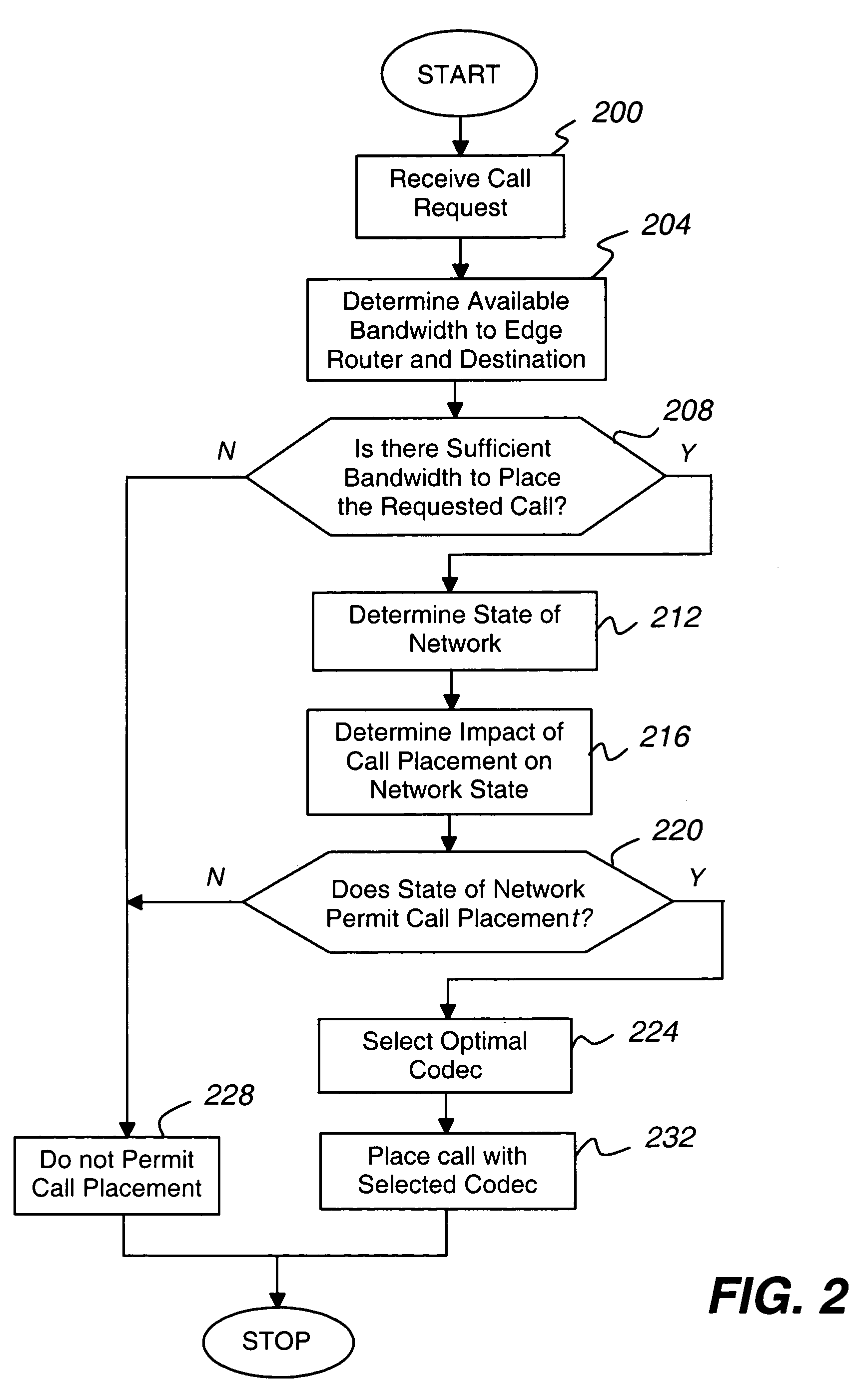
The present invention is directed to a call admission controller that is operable to: (a) determine at least one of (i) a bandwidth utilization level for a first path including a first link; (ii) an available bandwidth level for the first path; and (iii) one or more Quality of Service or QoS metrics for the first path; (b) compare the at least one of (i) a bandwidth utilization level; (ii) an available bandwidth level; and (iii) one or more Quality of Service or QoS metrics to one or more selected thresholds to determine whether a new live voice communication may be set up with a first selected codec; and (iii) when a new live voice communication may not be set up with the first selected codec, perform at least one of the following operations: (i) select a second different codec from among a plurality of possible codecs for the new live voice communication, wherein the second codec has a lower bit rate than the first codec; (ii) change an existing live voice communication from the first codec to the second codec; and (iii) redirect the new live voice communication from the first path to a second different path, wherein the second path does not include the first link.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Dynamic bandwidth allocation and service differentiation for broadband passive optical networks
InactiveUS20060268704A1Effective bandwidthSpace complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionService-level agreementTraffic prediction
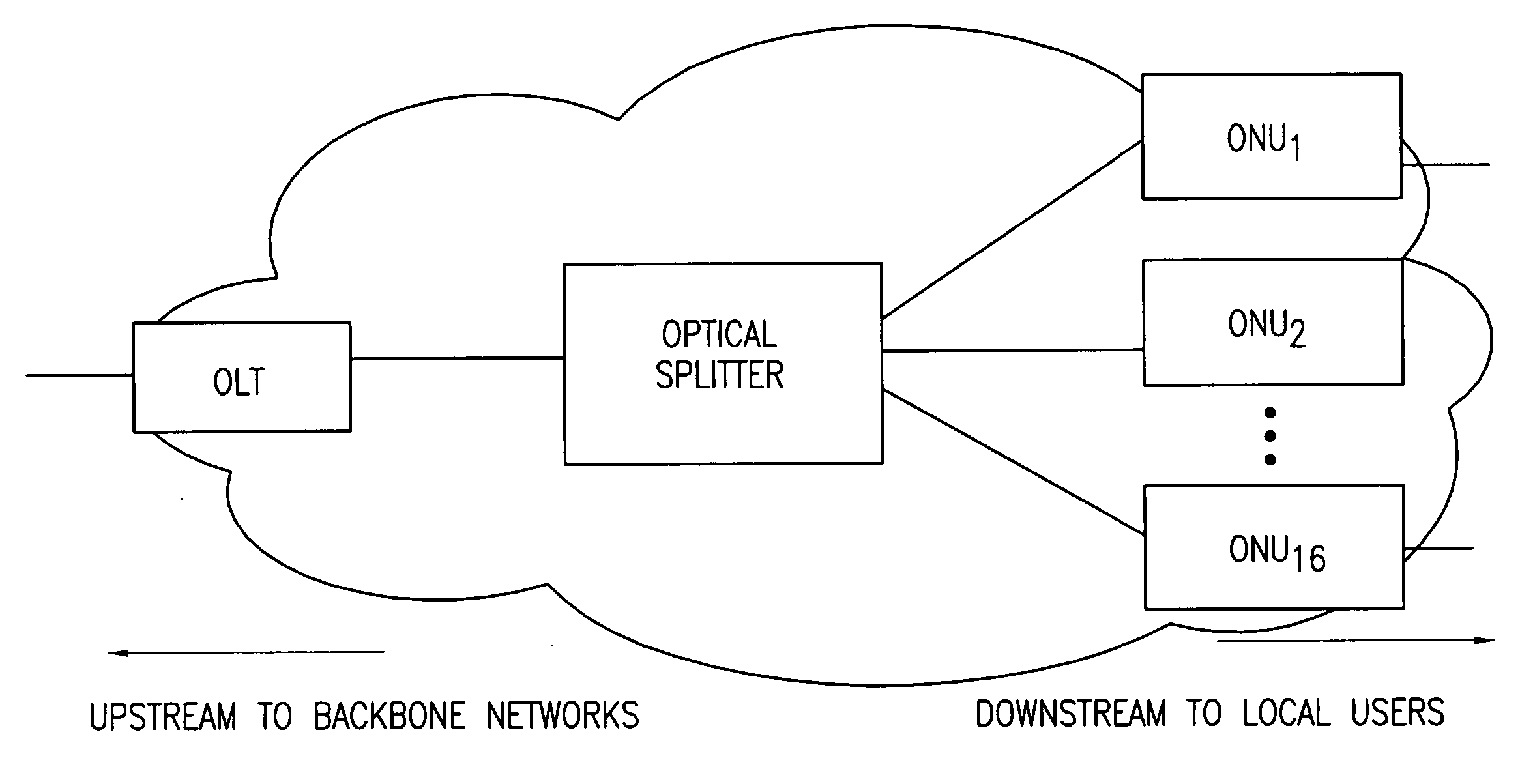
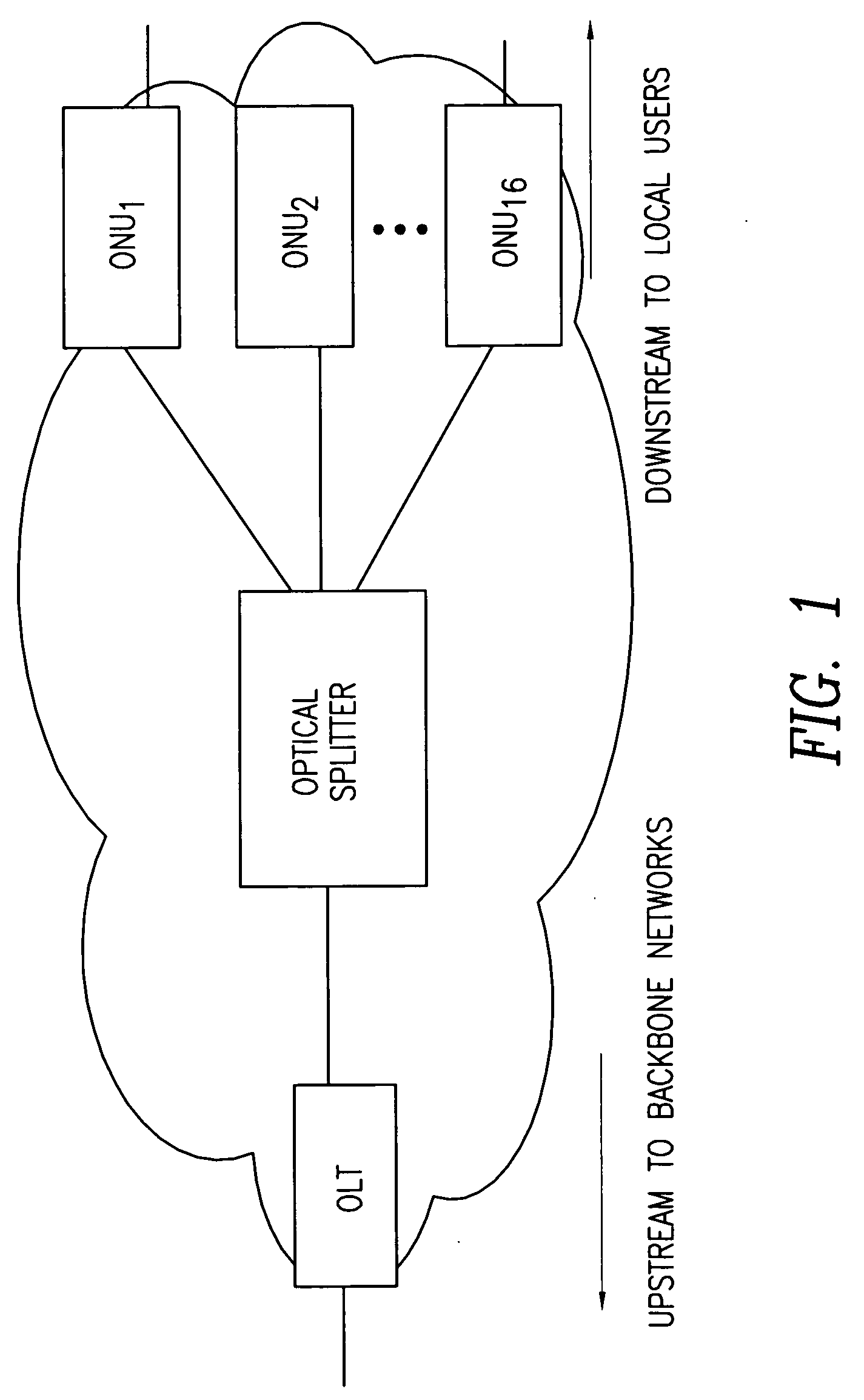
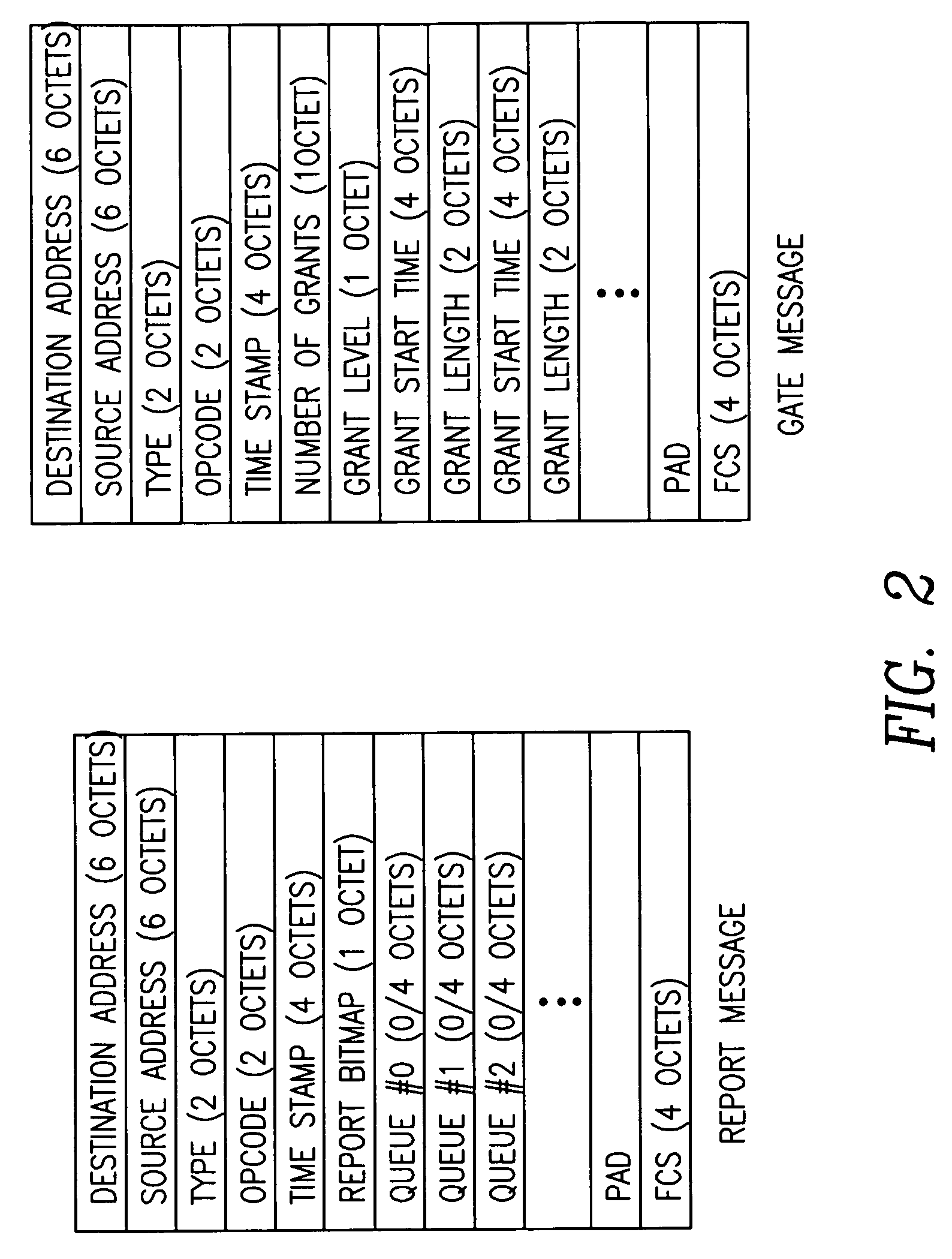
A dynamic upstream bandwidth allocation scheme is disclosed, i.e., limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP), to improve the bandwidth efficiency of upstream transmission over PONs. LSTP adopts the PON MAC control messages, and dynamically allocates bandwidth according to the on-line traffic load. The ONU bandwidth requirement includes the already buffered data and a prediction of the incoming data, thus reducing the frame delay and alleviating the data loss. ONUs are served by the OLT in a fixed order in LSTP to facilitate the traffic prediction. Each optical network unit (ONU) classifies its local traffic into three classes with descending priorities: expedited forwarding (EF), assured forwarding (AF), and best effort (BE). Data with higher priority replace data with lower priority when the buffer is full. In order to alleviate uncontrolled delay and unfair drop of the lower priority data, the priority-based scheduling is employed to deliver the buffered data in a particular transmission timeslot. The bandwidth allocation incorporates the service level agreements (SLAs) and the on-line traffic dynamics. The basic limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP) scheme is extended to serve the classified network traffic.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method and system for providing a secure peer-to-peer file delivery network
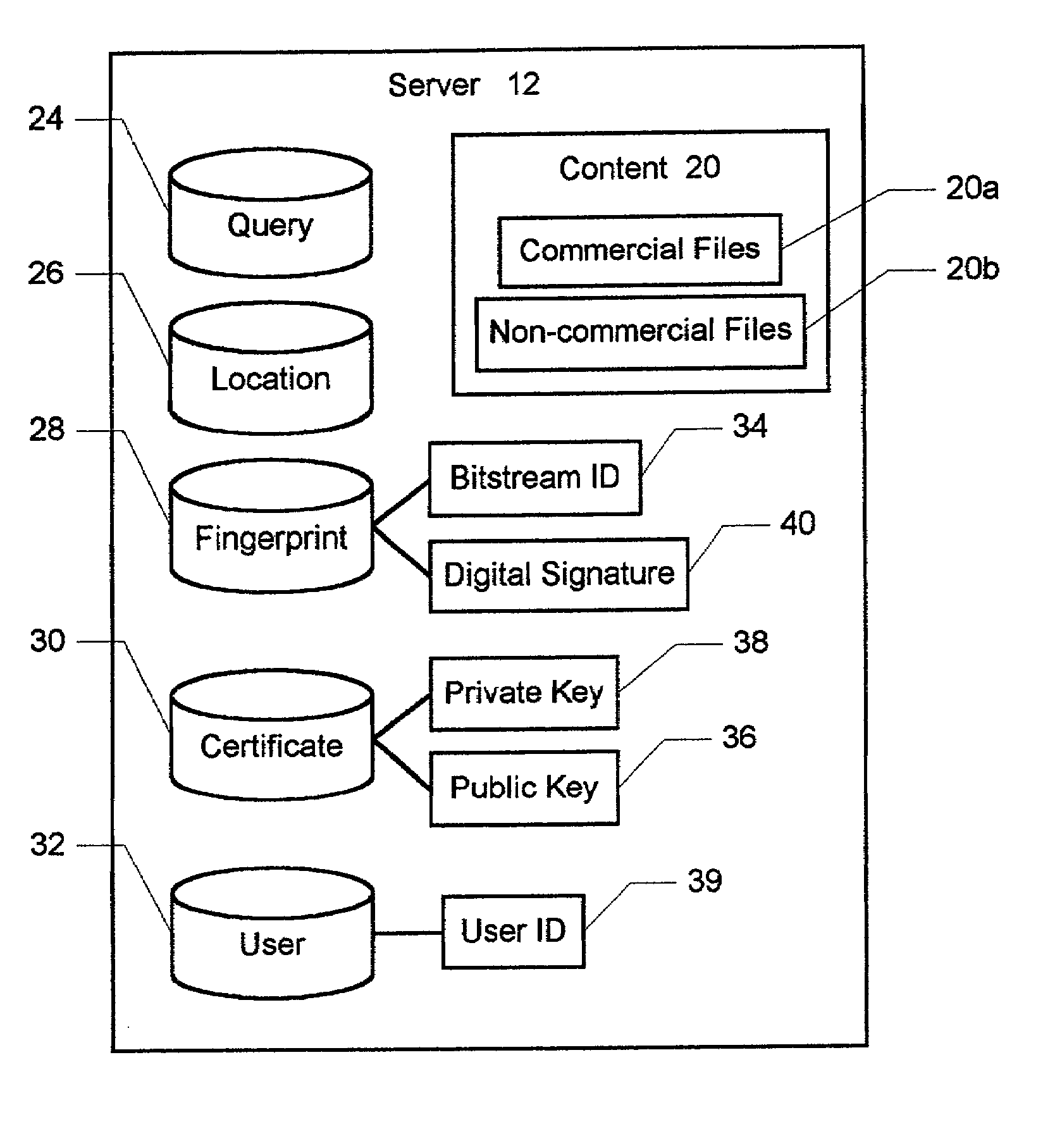
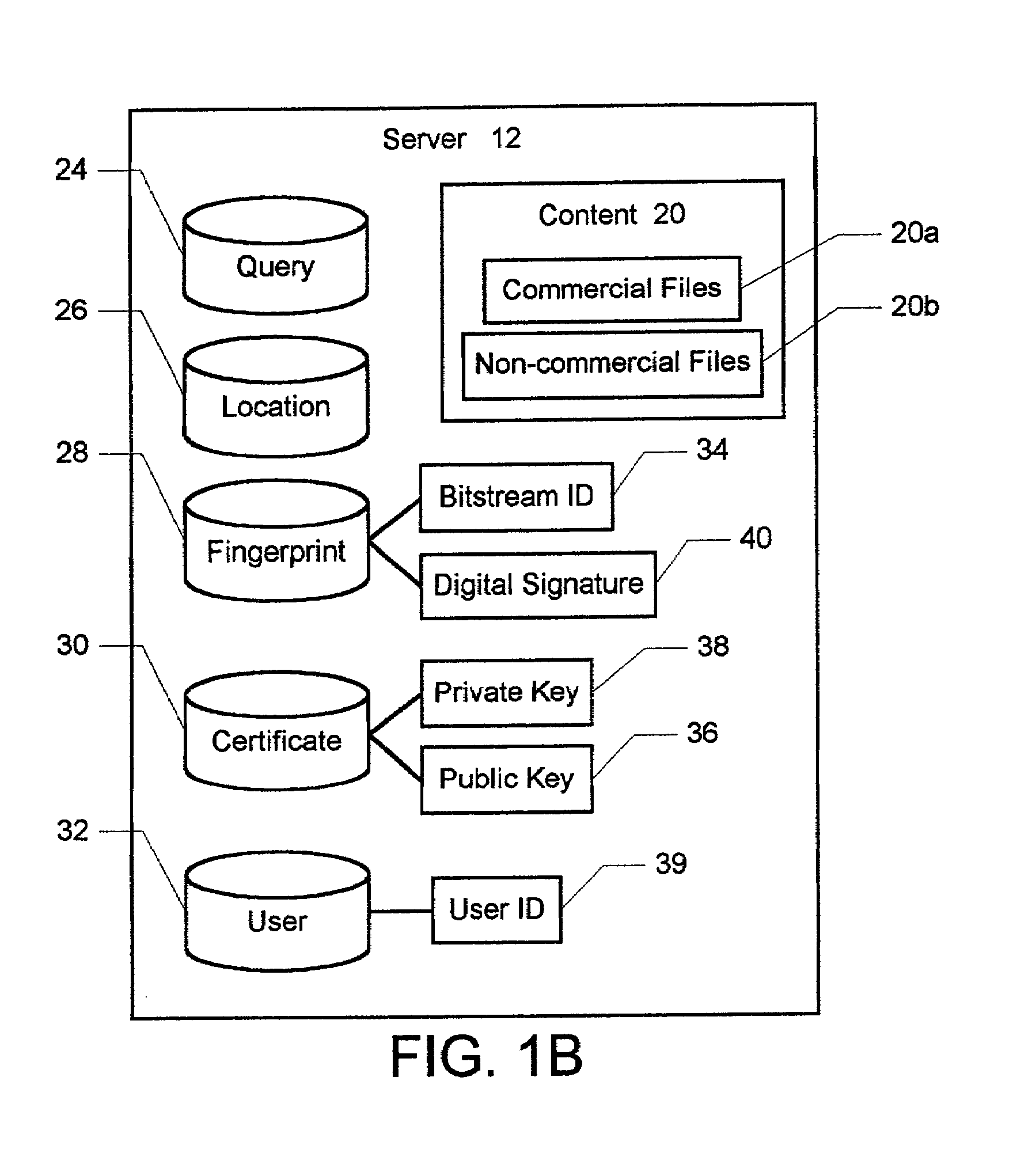
InactiveUS7047406B2Utilizes bandwidth efficientlyEffective bandwidthUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionPublic networkClient-side
A method and system for electronically delivering files over a public network is disclosed. The network includes a plurality of computers including at least one server node and multiple client nodes. In a first aspect of the present invention, the method and system enable secure and reliable peer-to-peer file sharing between two client nodes. First, a digital fingerprint is generated and associated with a file in response to the file being selected for publication on a first client node. An entry for the file is then added to a searchable index of shared files on the server node, and the fingerprint for the file is also stored on the server. In response to a second client selecting the file from the search list on the server node, the file is automatically transferred from the first client node directly to the second client node. The second client node then generates a new fingerprint for the file and compares with the new fingerprint with the fingerprint from the server node, thereby verifying the authenticity of the file and publisher. In a second aspect of the present invention, the method and system also enable subscription-based decentralized file downloads to the client nodes. First, the client nodes are allowed to subscribe with the server node to periodically receive copies of one of the files. To provide a current subscribing client node with the file, the geographically closest client node containing the file is located, and the file is transferred from the closest node directly to the current subscribing node, thereby efficiently utilizing bandwidth.
Owner:QURIO HLDG
Data center network architecture
ActiveUS20130108263A1Enhance performanceEfficiently allocate bandwidthData switching by path configurationOptical multiplexComputational resourceDistributed computing
Data center network architectures that can reduce the cost and complexity of data center networks. The data center network architectures can employ optical network topologies and optical nodes to efficiently allocate bandwidth within the data center networks, while reducing the physical interconnectivity requirements of the data center networks. The data center network architectures also allow computing resources within data center networks to be controlled and provisioned based at least in part on a combined network topology and application component topology, thereby enhancing overall application program performance.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
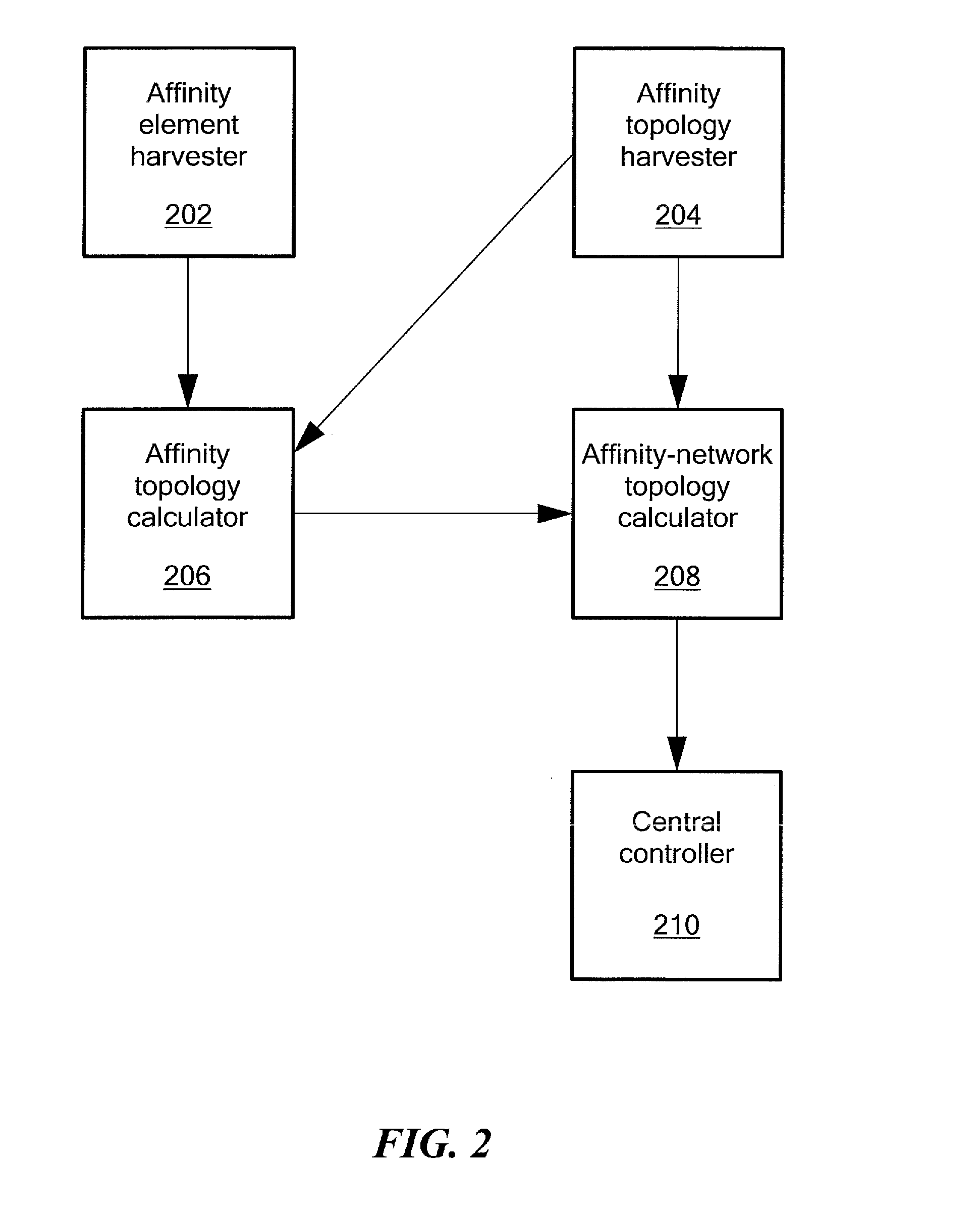
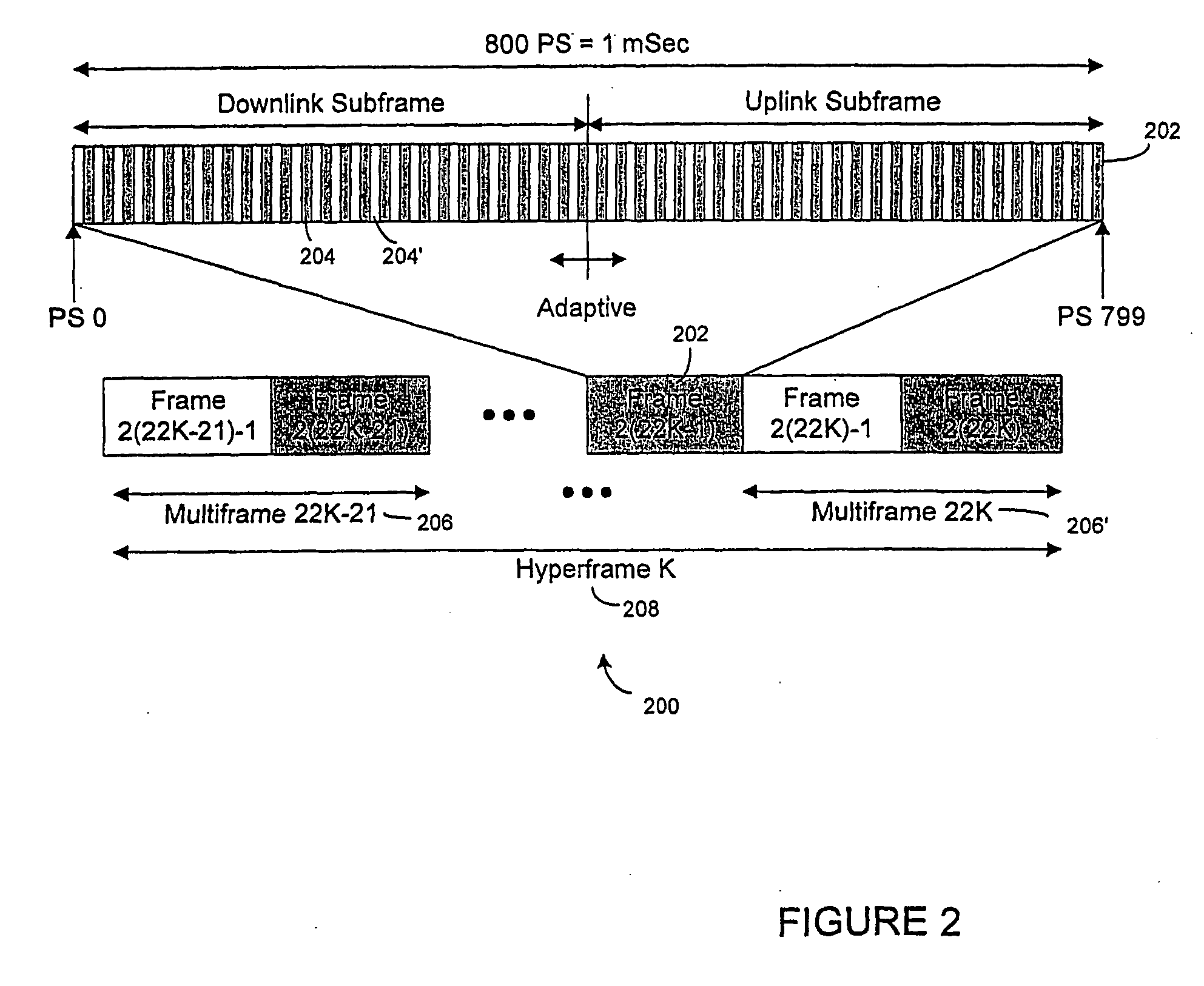
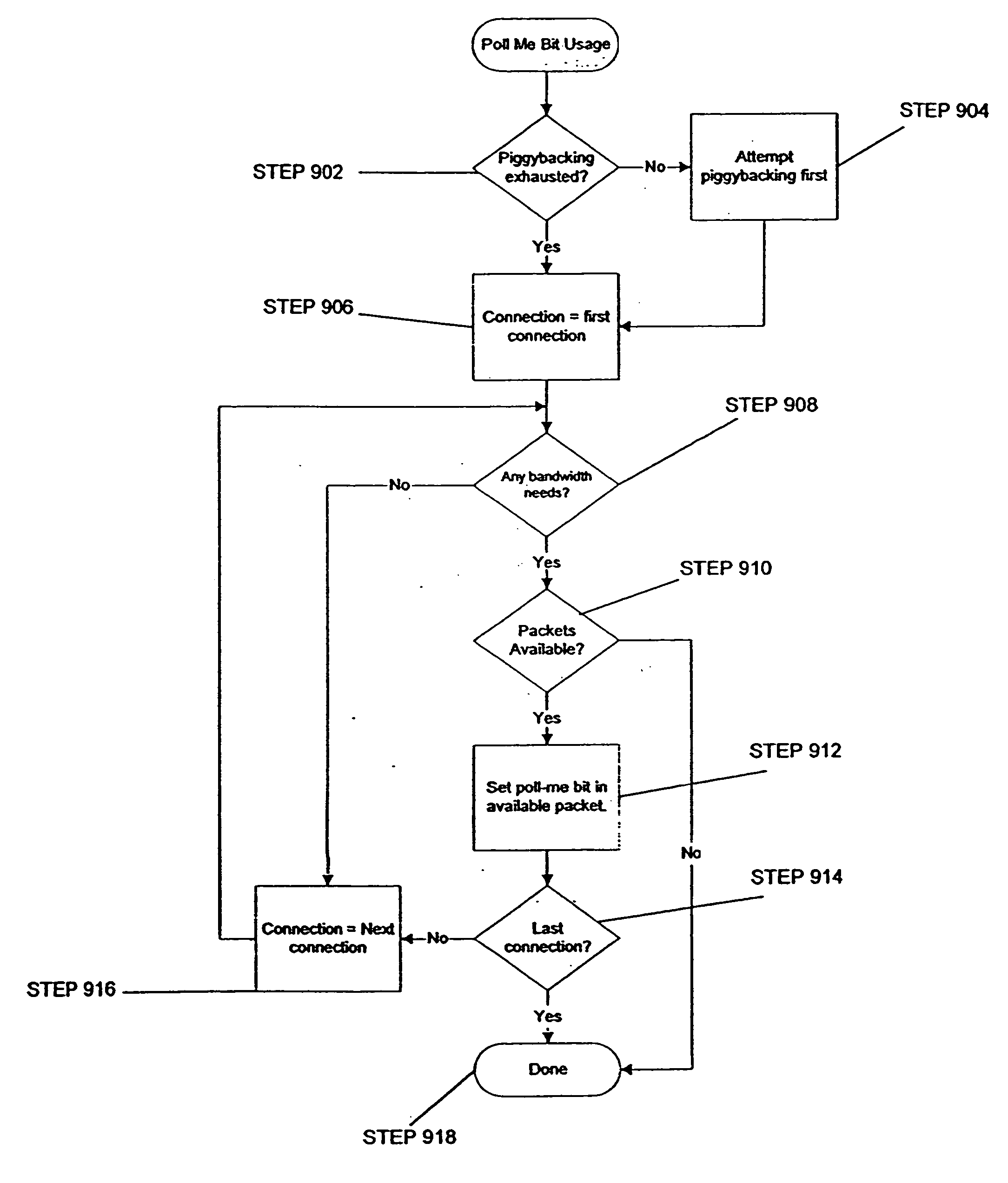
Method and system for adaptively obtaining bandwidth allocation requests
ActiveUS7006530B2Reduce bandwidthReduce amountNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexBroadbandRate adaptation
A method and apparatus for adaptively obtaining bandwidth requests in a broadband wireless communication system. The method and apparatus includes dynamically varying technique combinations enabling a plurality of users to efficiently request bandwidth from a shared base station. A user may “piggyback” a new bandwidth request upon, or set a “poll-me bit” within, presently allocated bandwidth. A base station may poll users, individually or in groups, by allocating unrequested bandwidth for new requests. Polling may respond to a “poll-me bit,” and / or it may be adaptively periodic at a rate based on communication status parameters, such as recent communication activity and connection QoS levels. Group polling permits a possibility of collisions. Polling policies may be established for dynamically varying user groups, or may be determined for each user. Dynamic selection of appropriate polling techniques makes use of efficiency benefits associated with each technique.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Creating frequent application-consistent backups efficiently
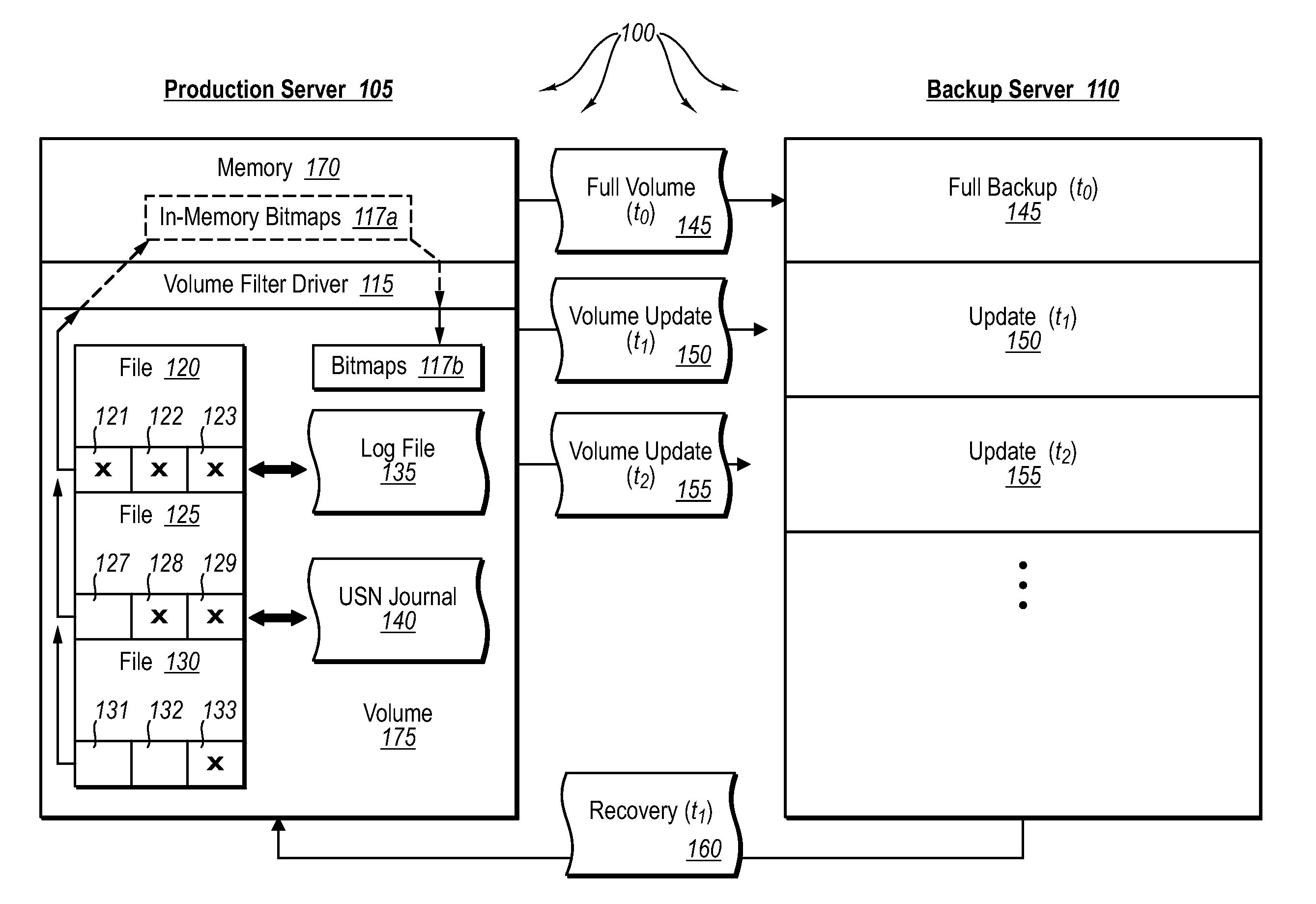
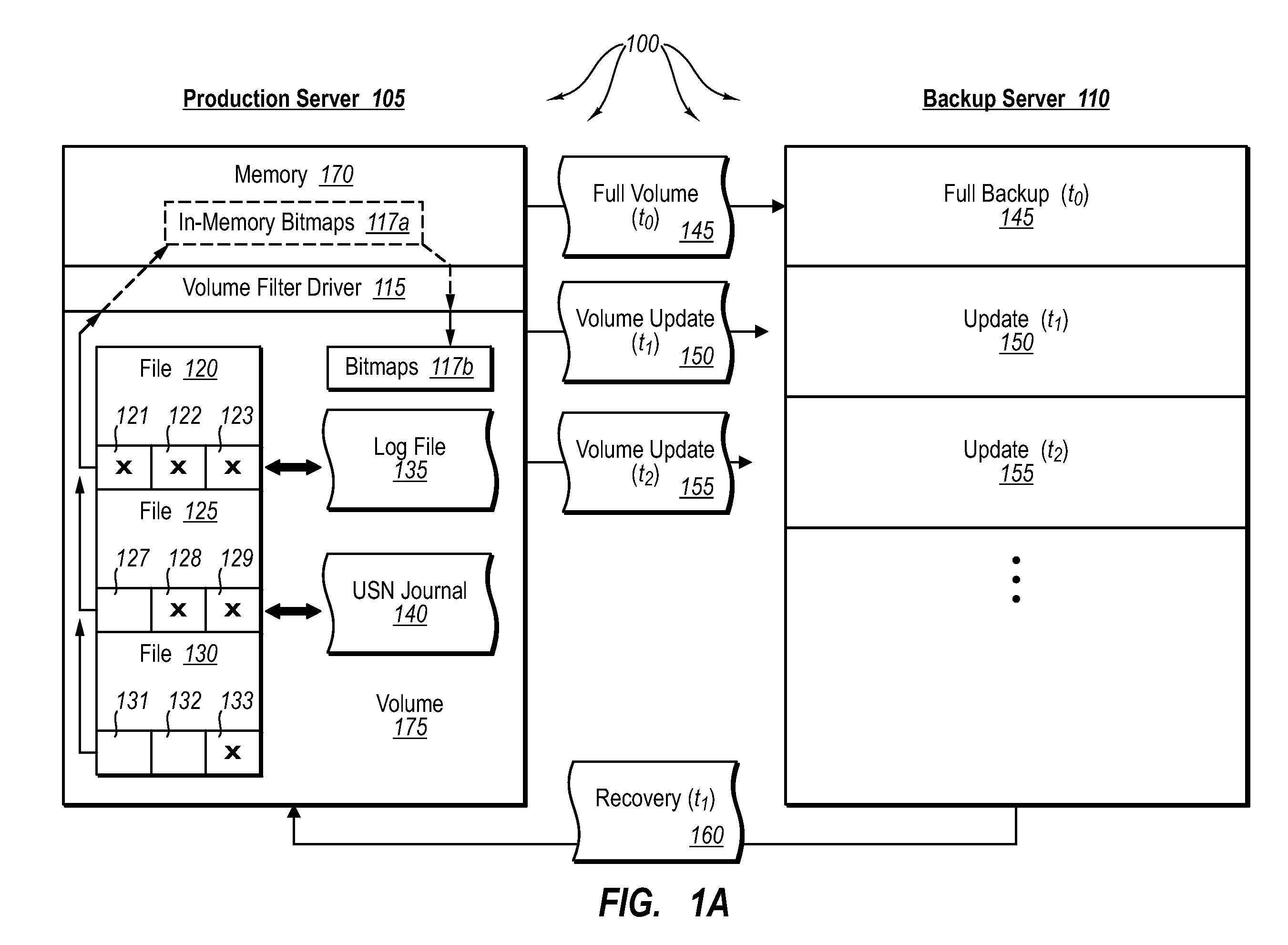
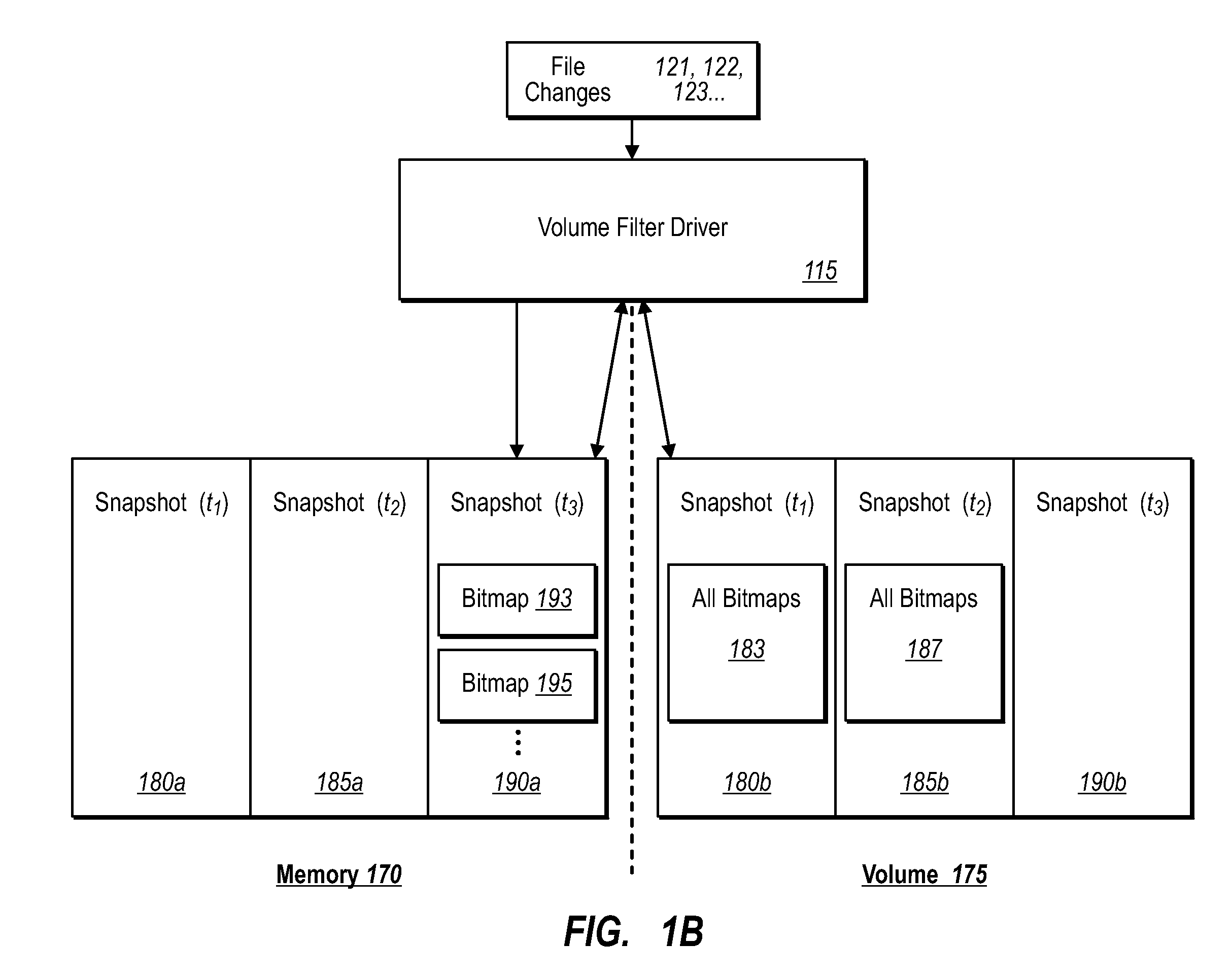
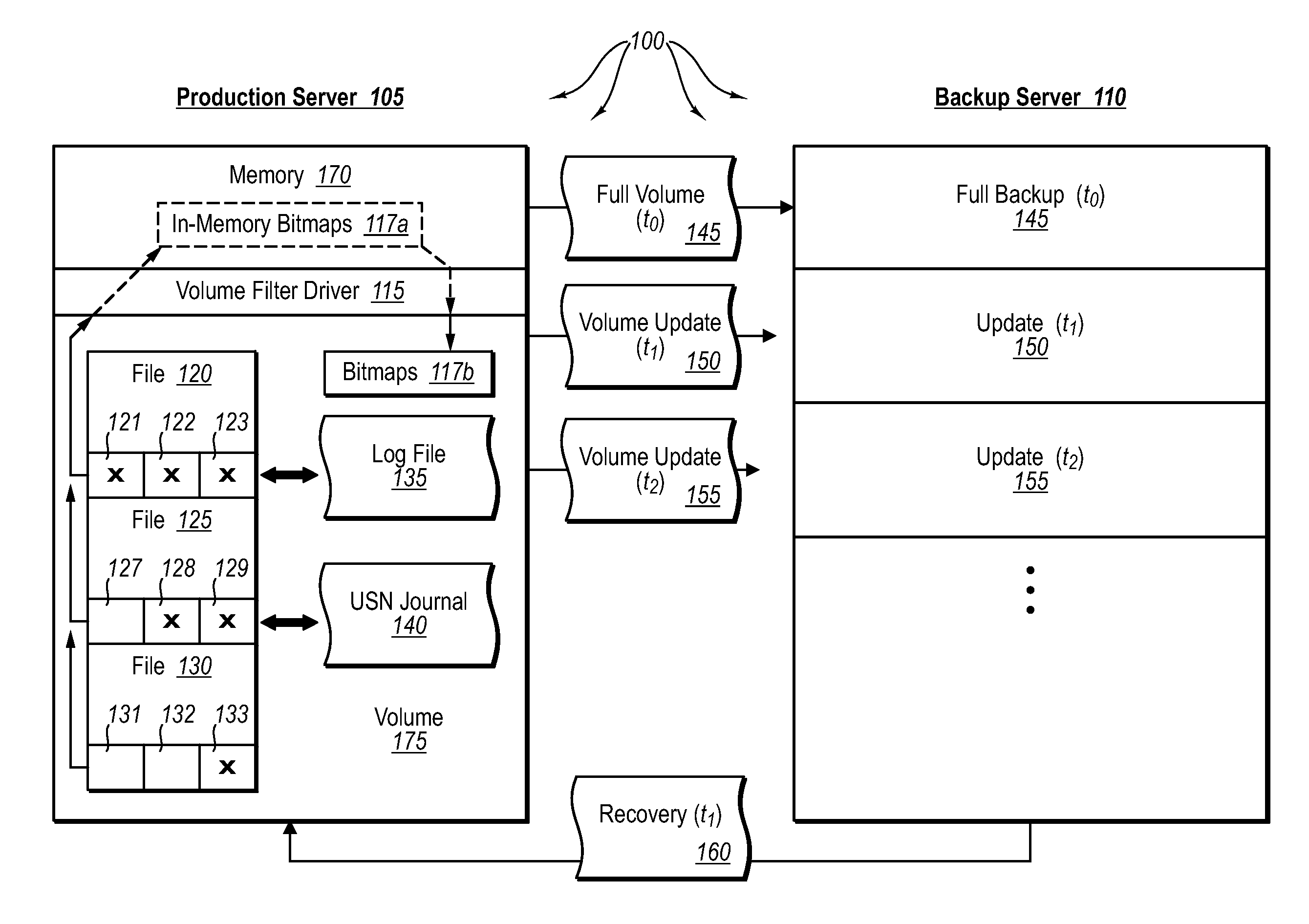
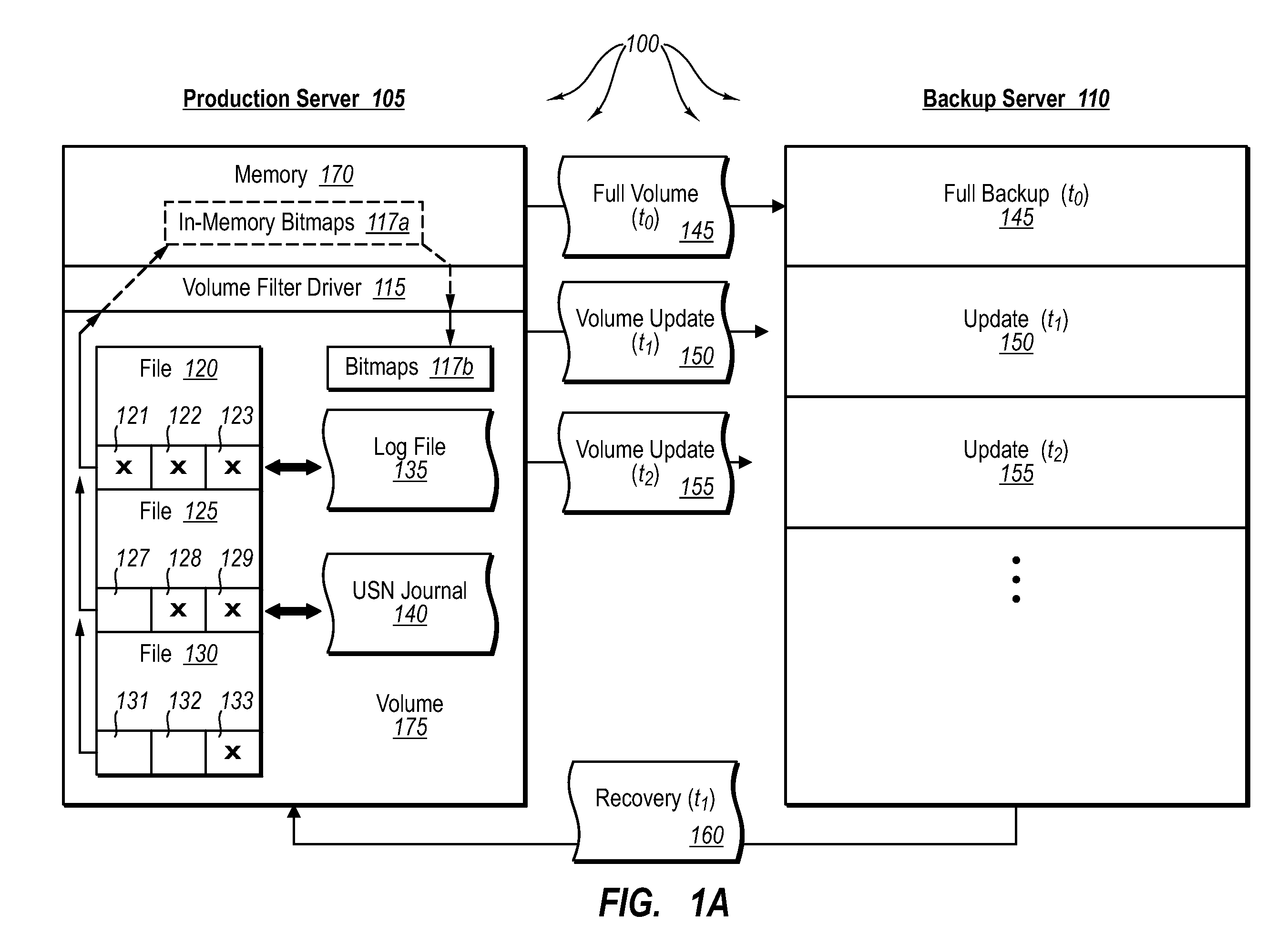
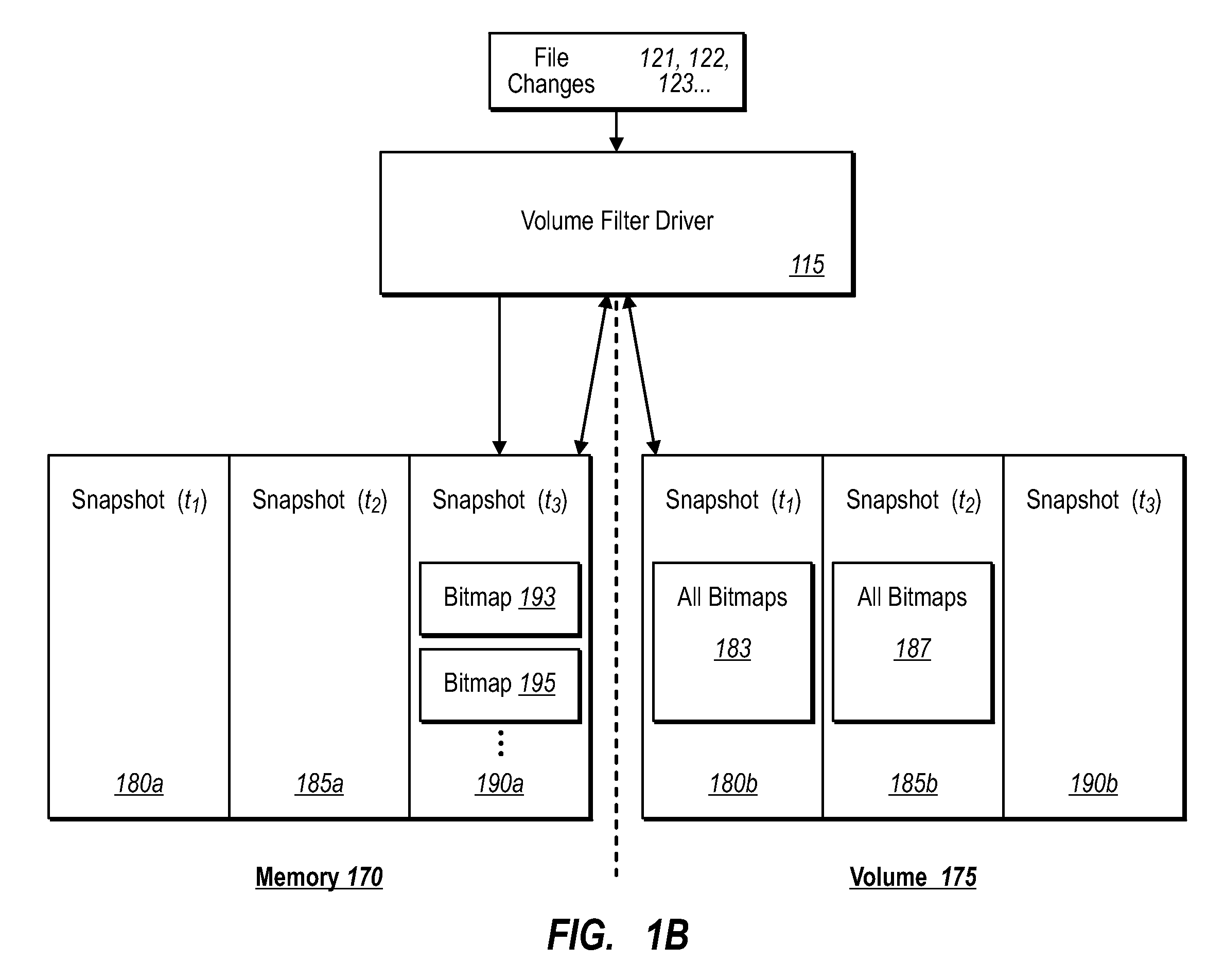
ActiveUS20070276885A1Save resourcesProduction serverData processing applicationsMemory loss protectionApplication softwareBitmap
Data can be protected at a production server in a virtually continuous fashion, without necessarily imposing severe constraints on the source application(s). For example, a production server can create an application-consistent backup of one or more volumes, the backups corresponding to a first instance in time. A volume filter driver can monitor data changes in each volume using an in-memory bitmap, while a log file and / or update sequence number journal can keep track of which files have been added to or updated. The volume updates are also consistent for an instance (later) in time. At the next replication cycle, such as every few minutes (however configured), the volume filter driver passes each in-memory bitmap to the physical disk on the production server. The production server then sends the updates to the backup server, which thus stores application-consistent backups for the volume for multiple instances of time.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
DMA engine for protocol processing
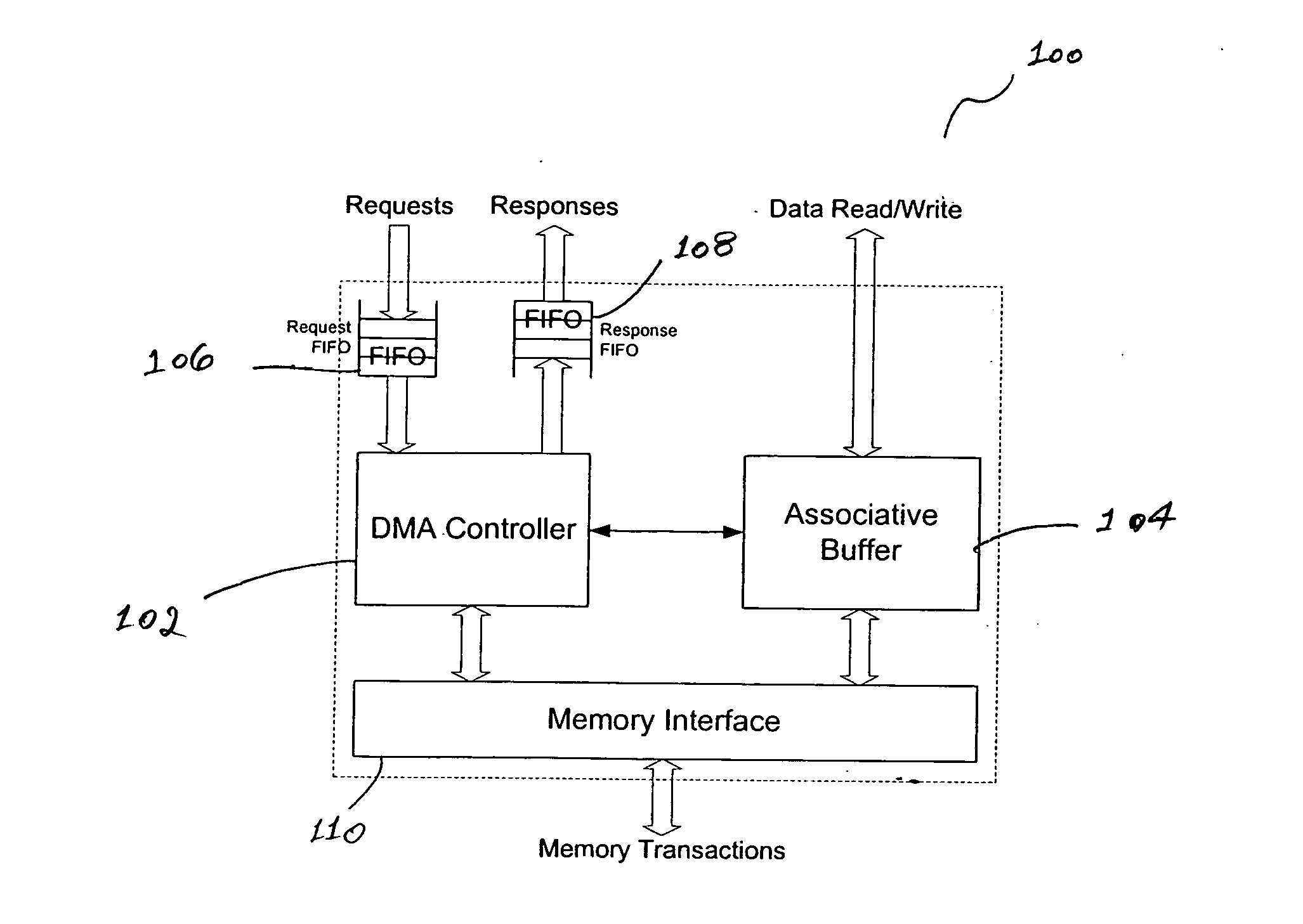
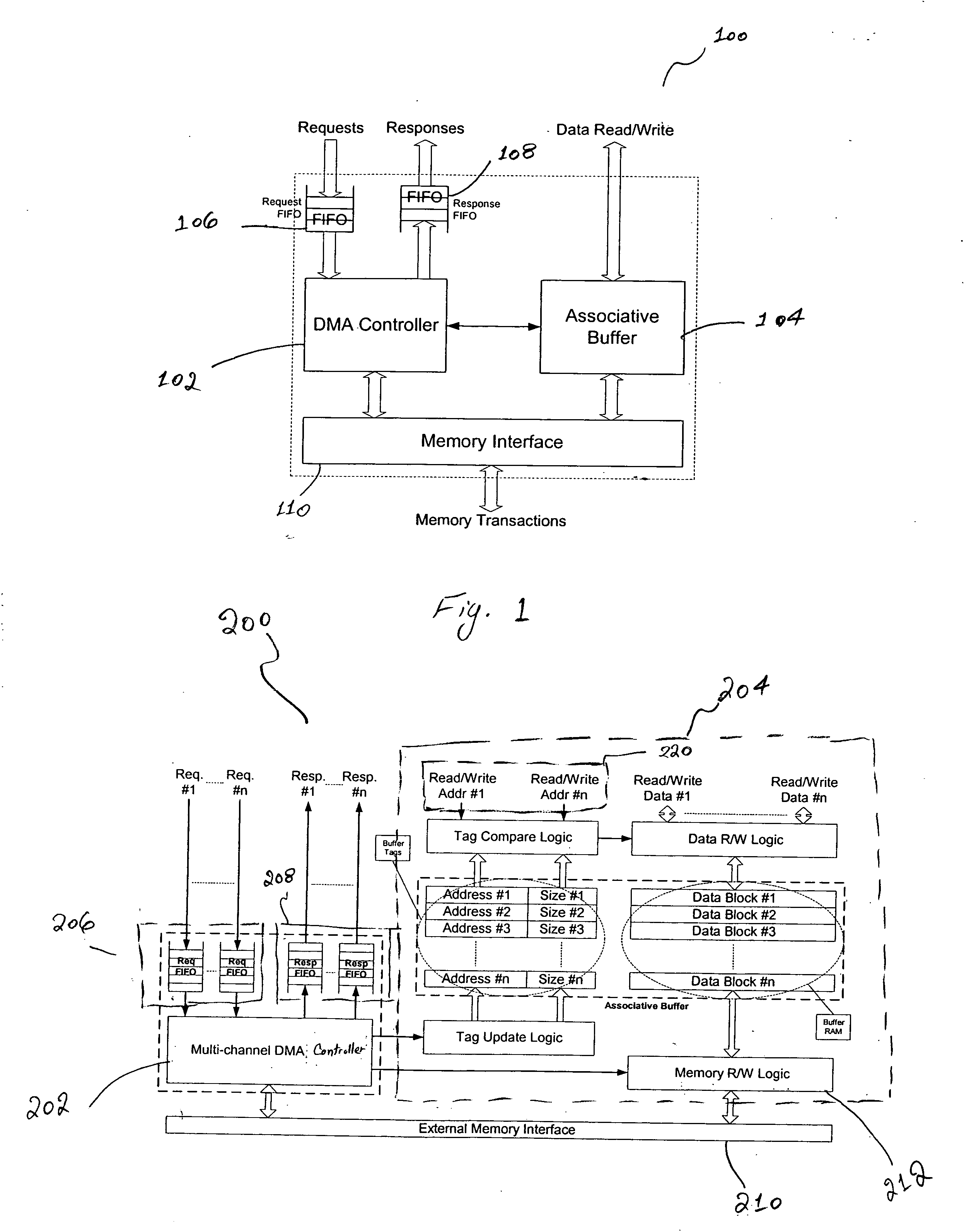
InactiveUS20060206635A1Determinism and uniformity in operationPredictable performance gainElectric digital data processingData transmissionProtocol processing
A DMA engine, includes, in part, a DMA controller, an associative memory buffer, a request FIFO accepting data transfer requests from a programmable engine, such as a CPU, and a response FIFO that returns the completion status of the transfer requests to the CPU. Each request includes, in part, a target external memory address from which data is to be loaded or to which data is to be stored; a block size, specifying the amount of data to be transferred; and context information. The associative buffer holds data fetched from the external memory; and provides the data to the CPUs for processing. Loading into and storing from the associative buffer is done under the control of the DMA controller. When a request to fetch data from the external memory is processed, the DMA controller allocates a block within the associative buffer and loads the data into the allocated block.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
Efficient and robust routing of potentially-variable traffic in IP-over-optical networks with resiliency against router failures
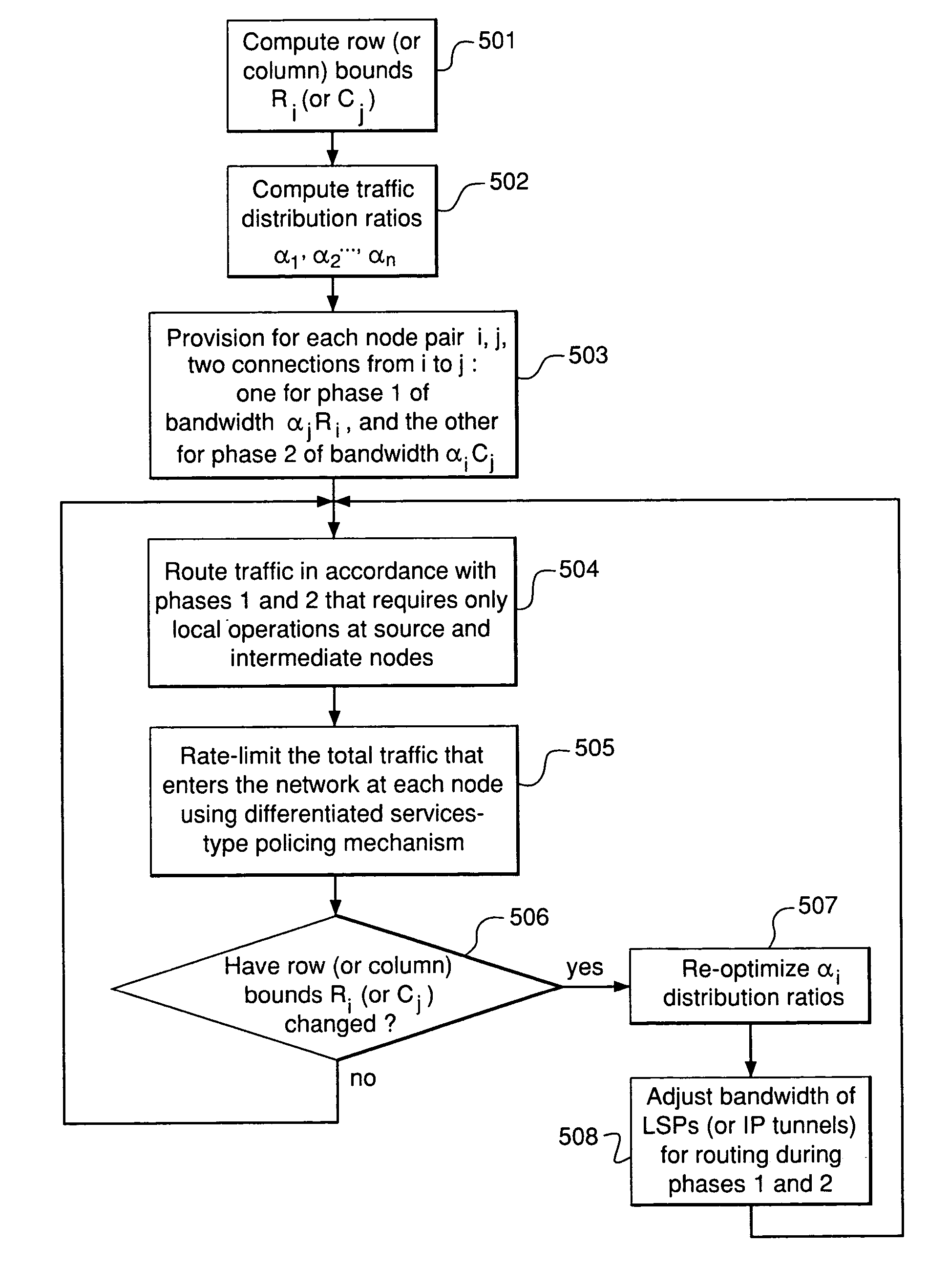
InactiveUS20050265255A1Effective bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsDistributed computingTraffic volume
A method for supporting recovery from failure of a node in a network of nodes interconnected by links, wherein the failed node is in a path providing a service level between an ingress point and an egress point of the network, comprises: (a) selecting a set of one or more intermediate nodes between the ingress point and the egress point, the set excluding the failed node; (b) determining, based on available bandwidth of the network, a non-zero fraction of the service level to route from the ingress point to each intermediate node; (c) implementing, during a first routing phase, a first routing method to determine one or more paths from the ingress point to each intermediate node for routing the corresponding fraction of the service level; and (d) implementing, during a second routing phase, a second routing method to determine one or more paths from each intermediate node to the egress point for routing the corresponding fraction of the service level.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
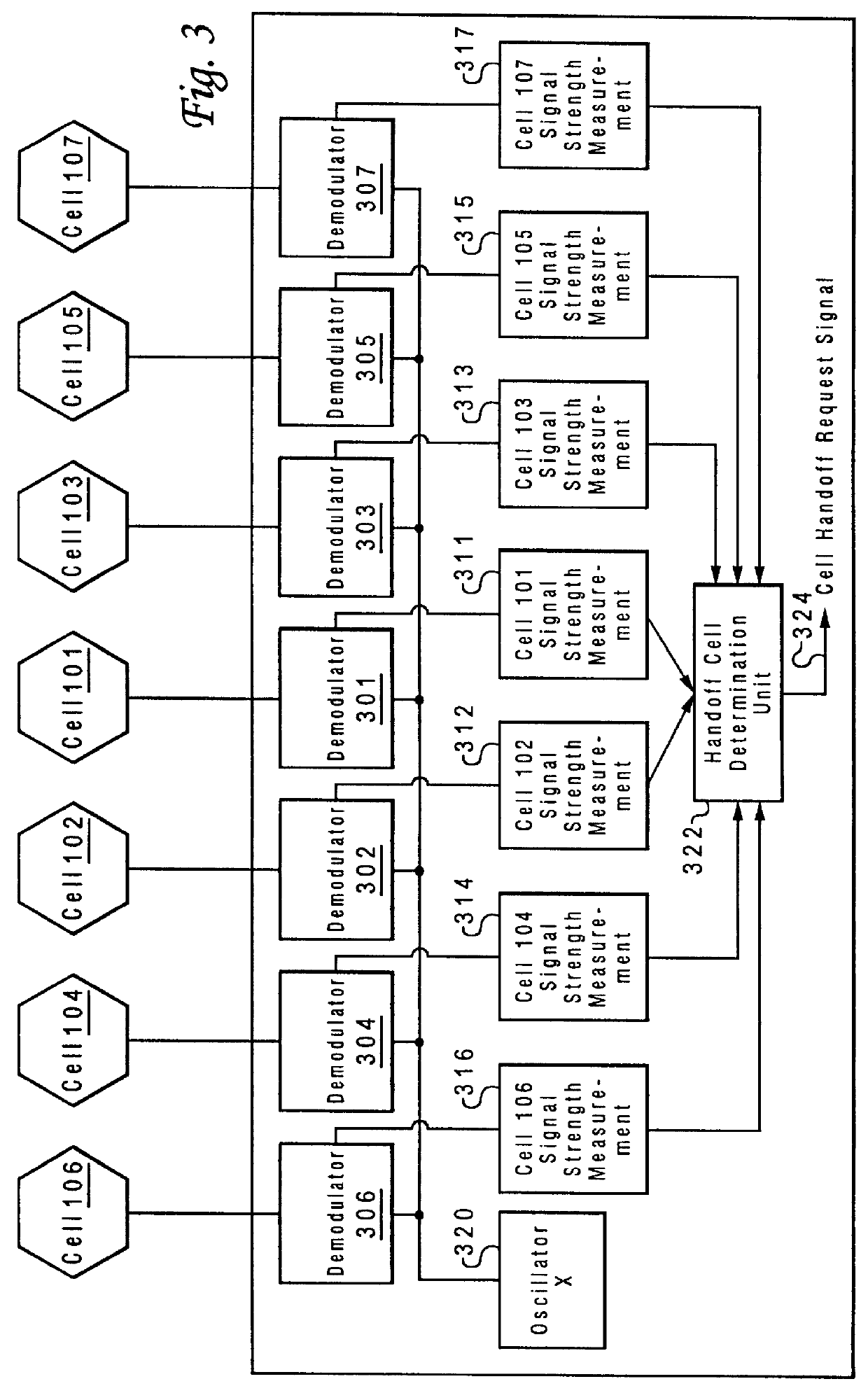
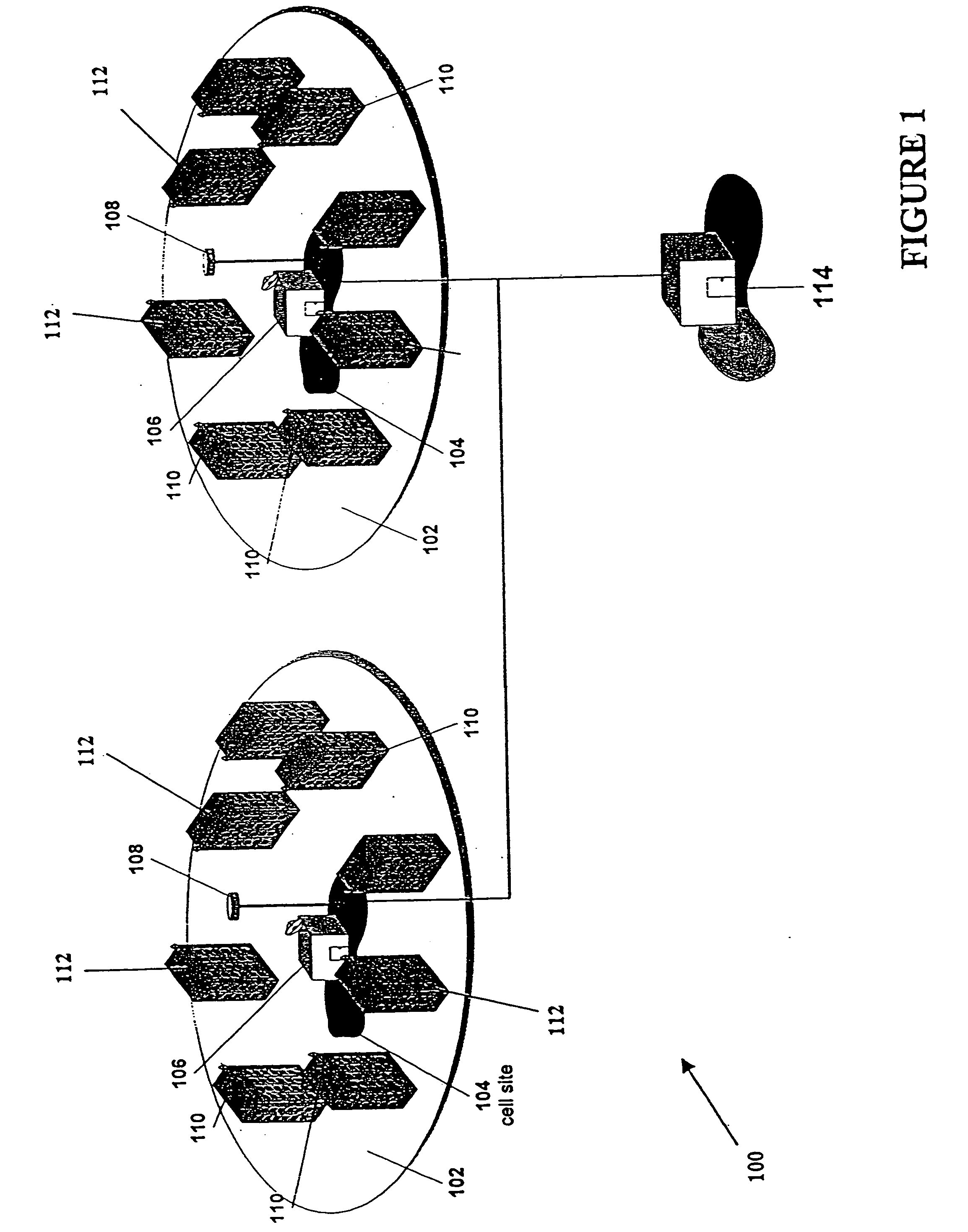
Method and system for assuring near uniform capacity and quality of channels in cells of wireless communications systems having cellular architectures
InactiveUS6011970AMaximized cellular concept of frequency reuseReduce power outputRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringCellular architectureSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method and system for use with wireless communication systems having a cellular architecture with at least a first and a second cell. The method and system provided ensure near uniform capacity and quality of channels within the second cell via the following steps. The noise signal power in unused data channels within the second cell is monitored. When a request for channel access is received, a determination is made whether the request for channel access is either a request for handoff from the first cell into the second cell, or not. In the event that the request is not a request for handoff, a determination is made whether idle channels exist to satisfy the request for channel access. In the event of a determination either that the request for channel access is a request for handoff, or both that the request is not a request for handoff and that idle channels exist to satisfy the request, a measured received signal power of a mobile unit subscriber unit making the request is determined. One of the unused channels in the second cell is then preferentially assigned to the mobile subscriber unit where such preference in assigning is to assign a channel, provided that a signal to noise ratio calculated upon the monitored received signal power and the monitored noise signal power of the preferentially assigned noisy channel meets or exceeds a required signal to noise ratio.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Wavelocker for Improving Laser Wavelength Accuracy in WDM Networks
InactiveUS20110135301A1Easy mappingMaintaining full visibilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLasing wavelengthOptoelectronics
The present invention includes novel techniques, apparatus, and systems for optical WDM communications. Various wavelocker apparatus and methods are disclosed that measure the frequency offsets between signal lasers and reference lasers. The measured offsets are used to adjust the signal laser frequencies to meet their target frequencies. The absolute accuracy of the reference laser frequency is improved by measuring the absorption of the reference laser by a gas cell with known fixed absorption lines versus the reference laser frequency. Apparatus and methods are disclosed to cover scenarios in which the reference laser polarization is aligned with the signal lasers, as well as those in which the reference laser polarization is not aligned with the signal lasers. The wavelocker apparatus may or may not be located at the same network site as the signal lasers.
Owner:VELLO SYST +1
Apparatus and Method for Achieving Accelerator of Sparse Convolutional Neural Network
InactiveUS20180157969A1High concurrency designEfficient processingDigital data processing detailsPhysical realisationAlgorithmConvolution
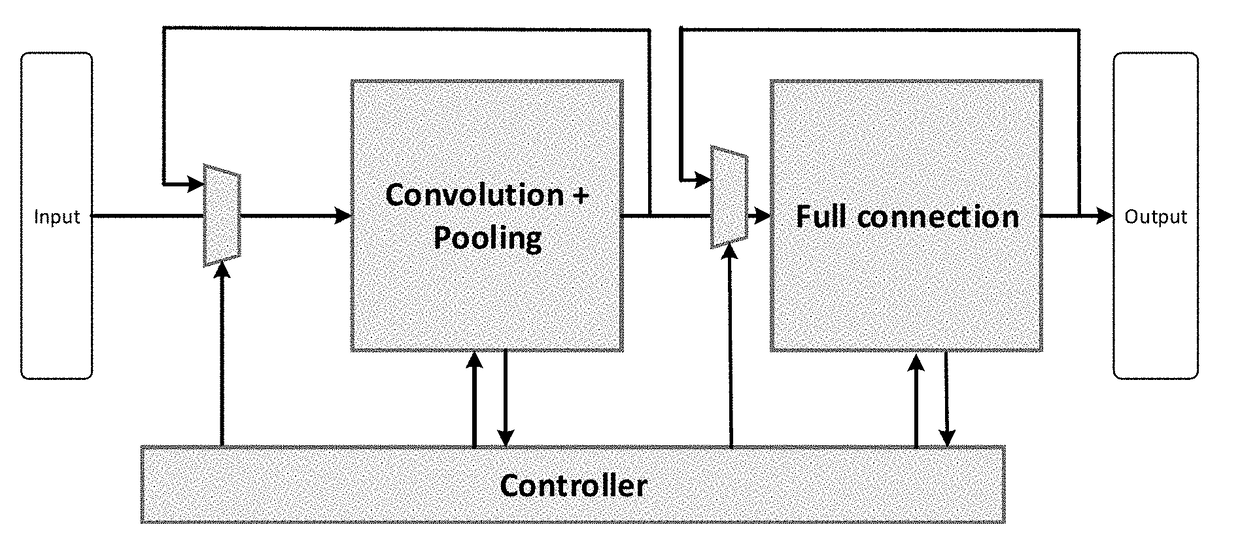
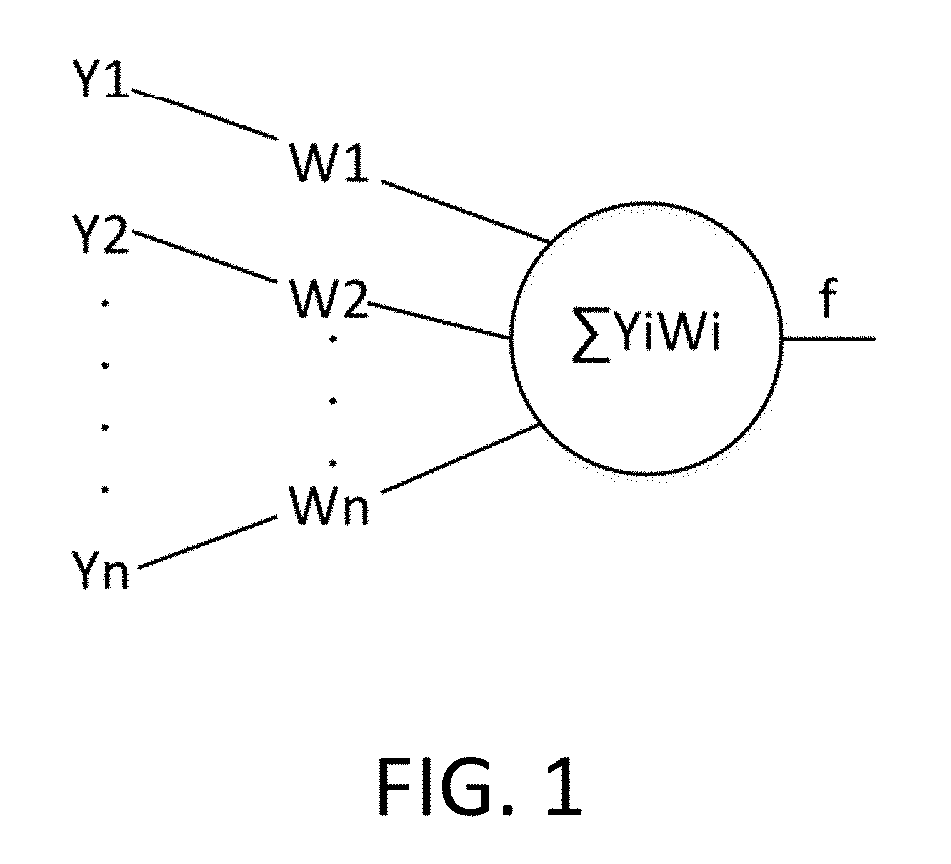
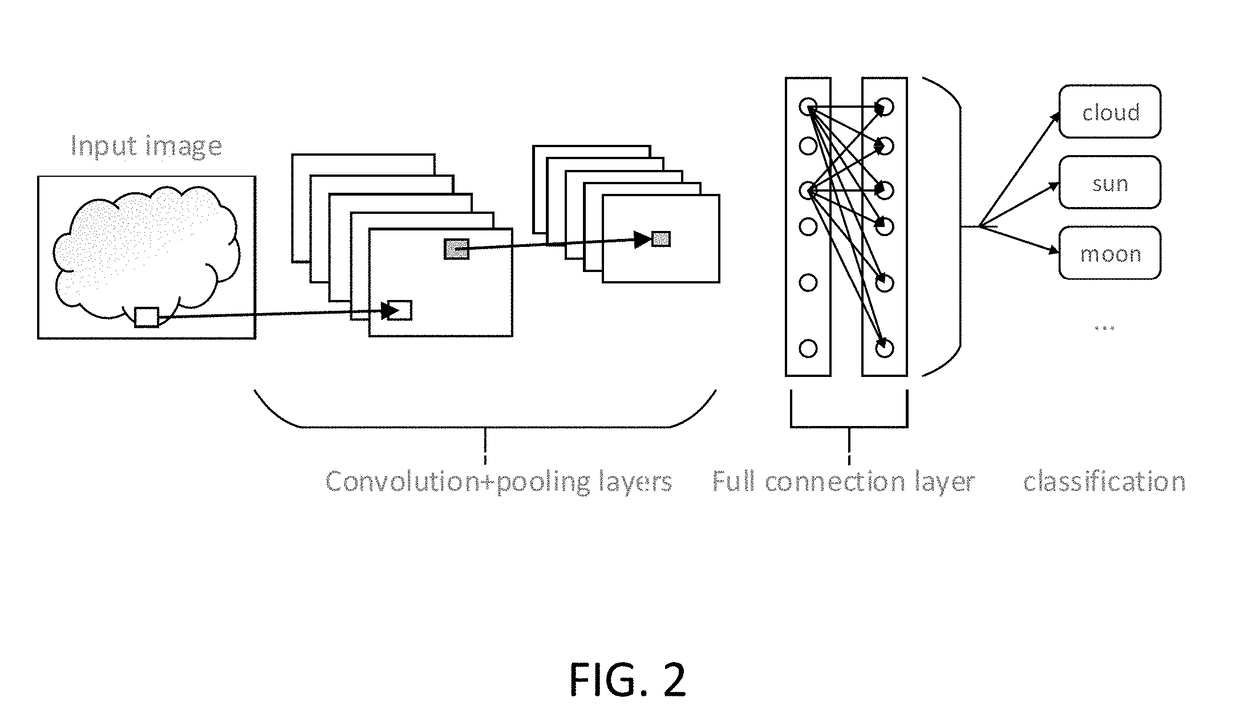
An apparatus for achieving an accelerator of a sparse convolutional neural network is provided. The apparatus comprises a convolution and pooling unit, a full connection unit and a control unit. Convolution parameter information and input data and intermediate calculation data are read based on control information, and weight matrix position information of a full connection layer is also read. Then a convolution and pooling operation for a first iteration number of times is performed on the input data in accordance with the convolution parameter information, and then a full connection calculation for a second iteration number of times is performed in accordance with the weight matrix position information of the full connection layer. Each input data is divided into a plurality of sub-blocks, and the convolution and pooling unit and the full connection unit perform operations on the plurality of sub-blocks in parallel, respectively.
Owner:XILINX INC
Creating frequent application-consistent backups efficiently
ActiveUS7613750B2Save resourcesProduction serverData processing applicationsMemory loss protectionApplication softwareBitmap
Data can be protected at a production server in a virtually continuous fashion, without necessarily imposing severe constraints on the source application(s). For example, a production server can create an application-consistent backup of one or more volumes, the backups corresponding to a first instance in time. A volume filter driver can monitor data changes in each volume using an in-memory bitmap, while a log file and / or update sequence number journal can keep track of which files have been added to or updated. The volume updates are also consistent for an instance (later) in time. At the next replication cycle, such as every few minutes (however configured), the volume filter driver passes each in-memory bitmap to the physical disk on the production server. The production server then sends the updates to the backup server, which thus stores application-consistent backups for the volume for multiple instances of time.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
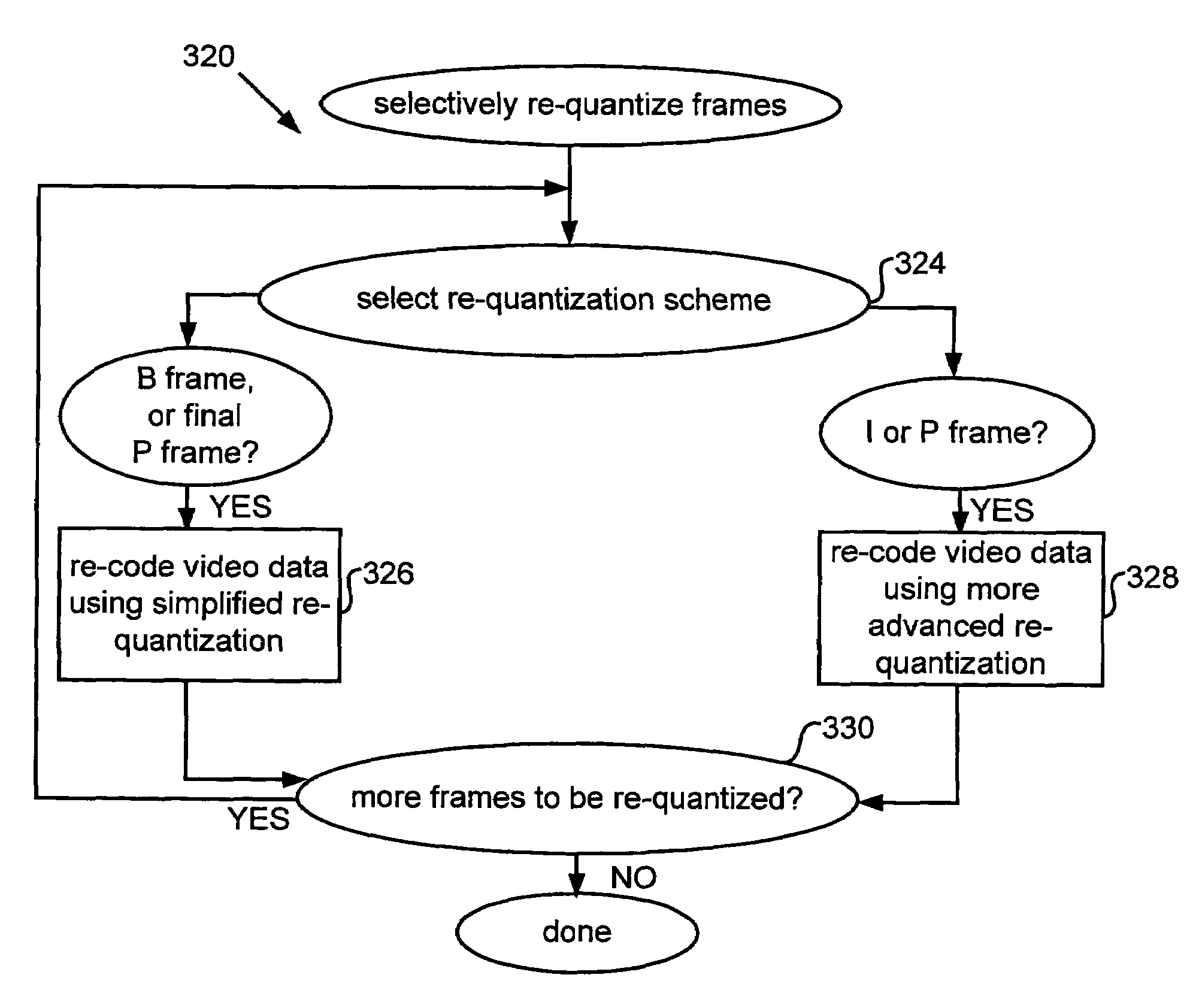
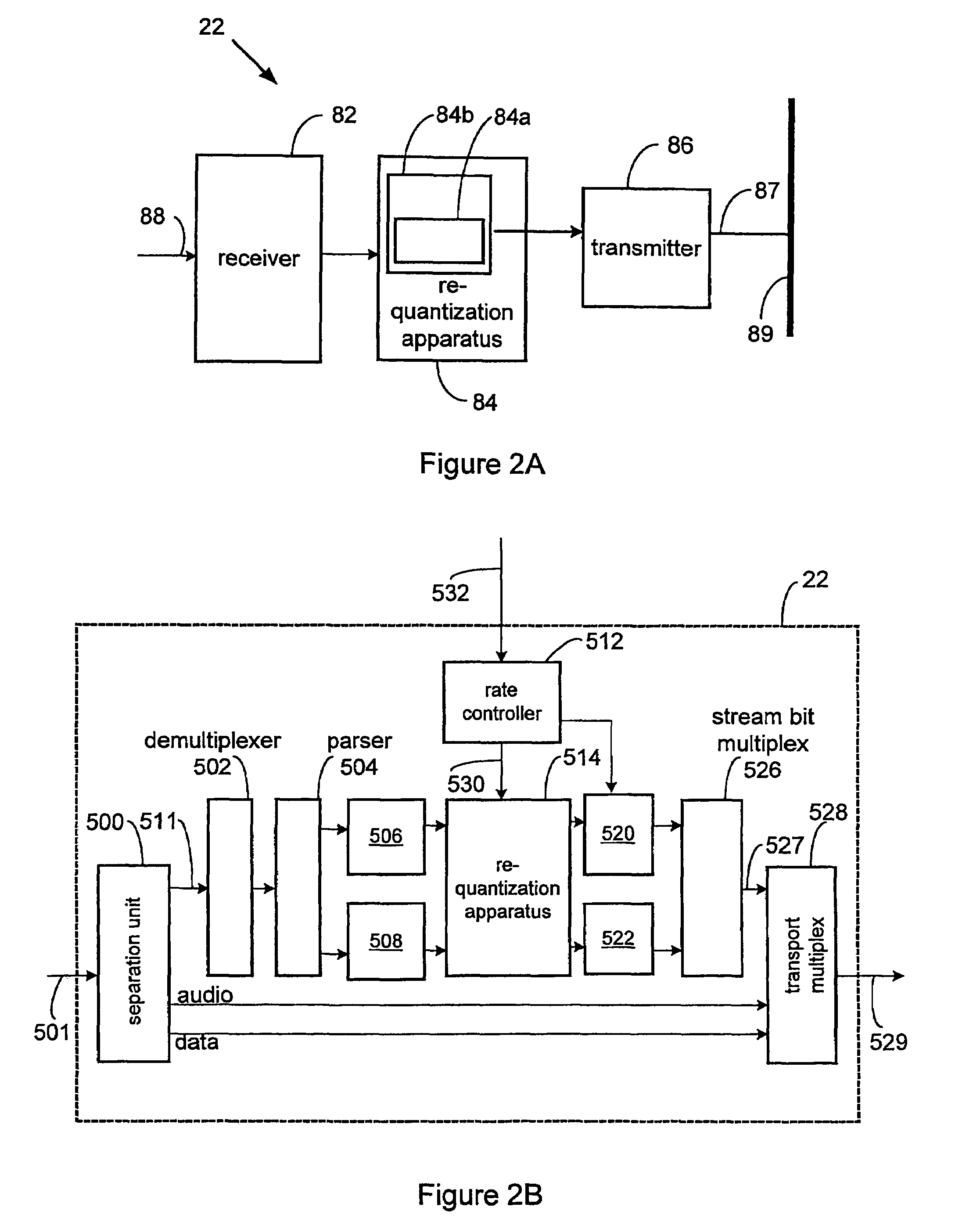
Methods for efficient bandwidth scaling of compressed video data
InactiveUS7477688B1Effective bandwidthGuaranteed data transmission efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData integrityParallel computing
The present invention relates to systems and methods for efficient bit rate alteration of a bitstream to match an available channel capacity. The efficient bit rate alteration includes selective re-quantization of the compressed bitstream. Selective re-quantization according to the present invention applies multiple re-quantization schemes to different portions of a bitstream. In one embodiment, the multiple re-quantization schemes each have a different computational load. By selectively choosing which type of re-quantization is performed on each portion, efficient bandwidth scaling and data transmission may be achieved both when computational capacity is limited and when video data integrity is important.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
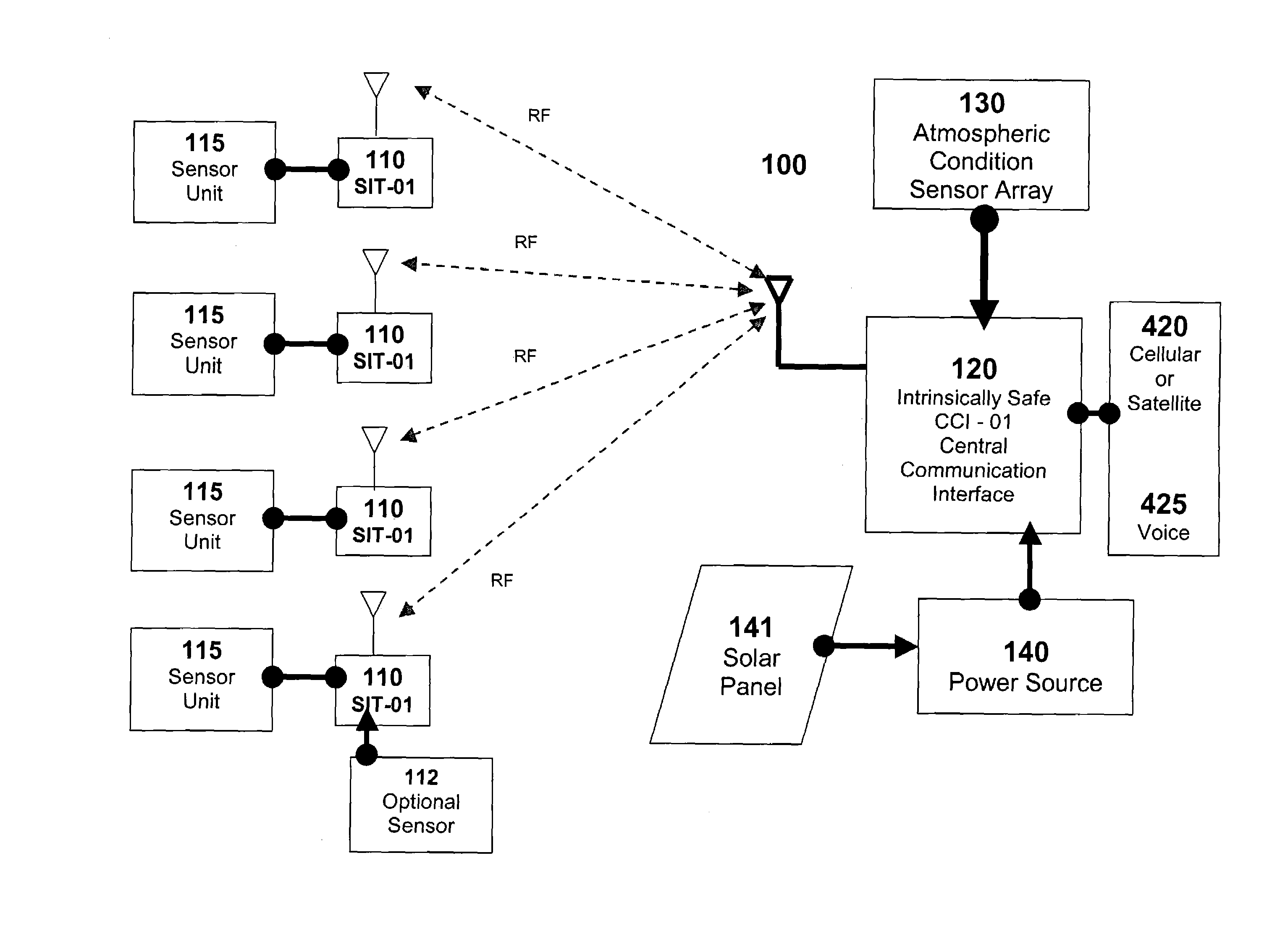
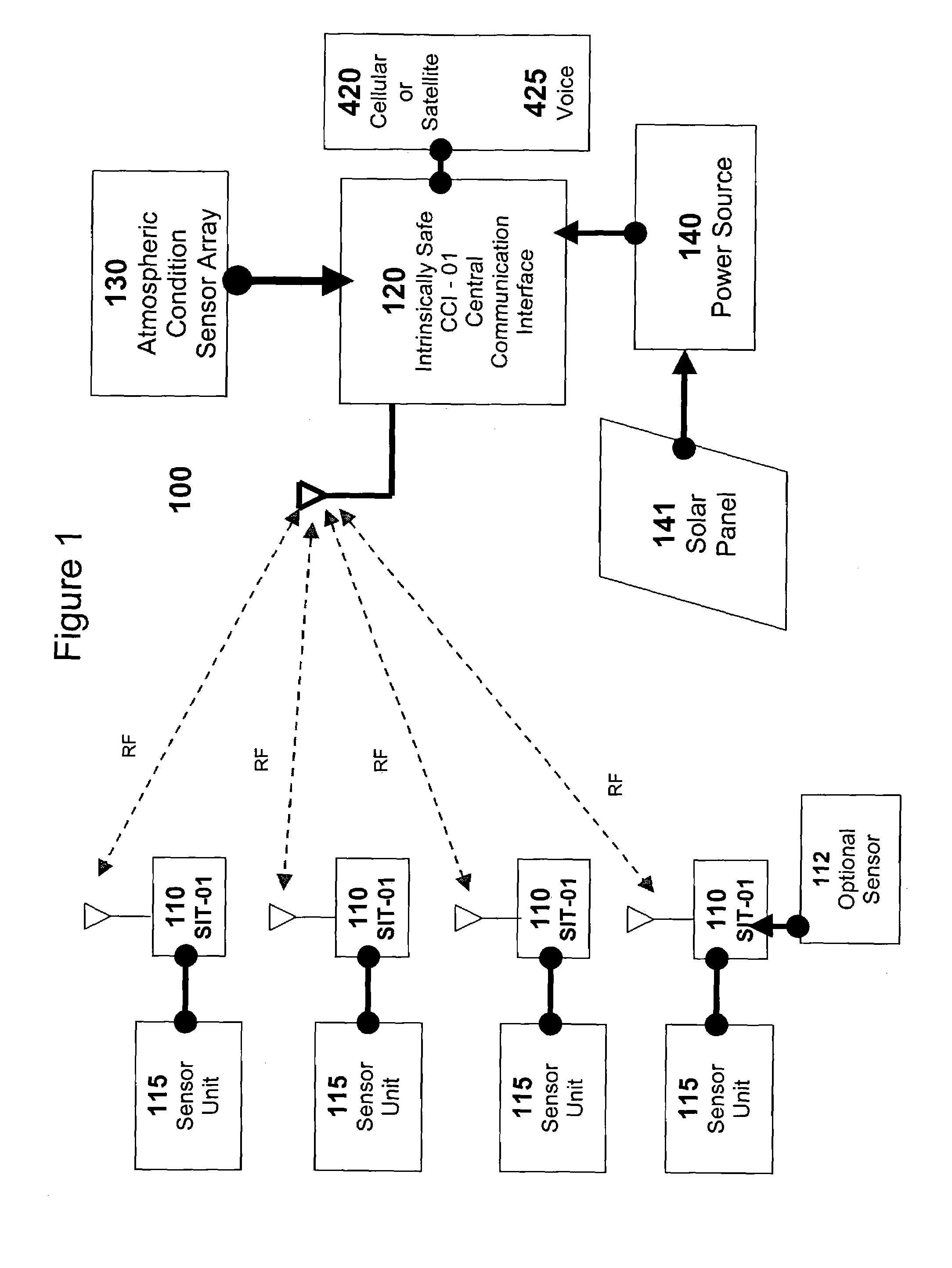
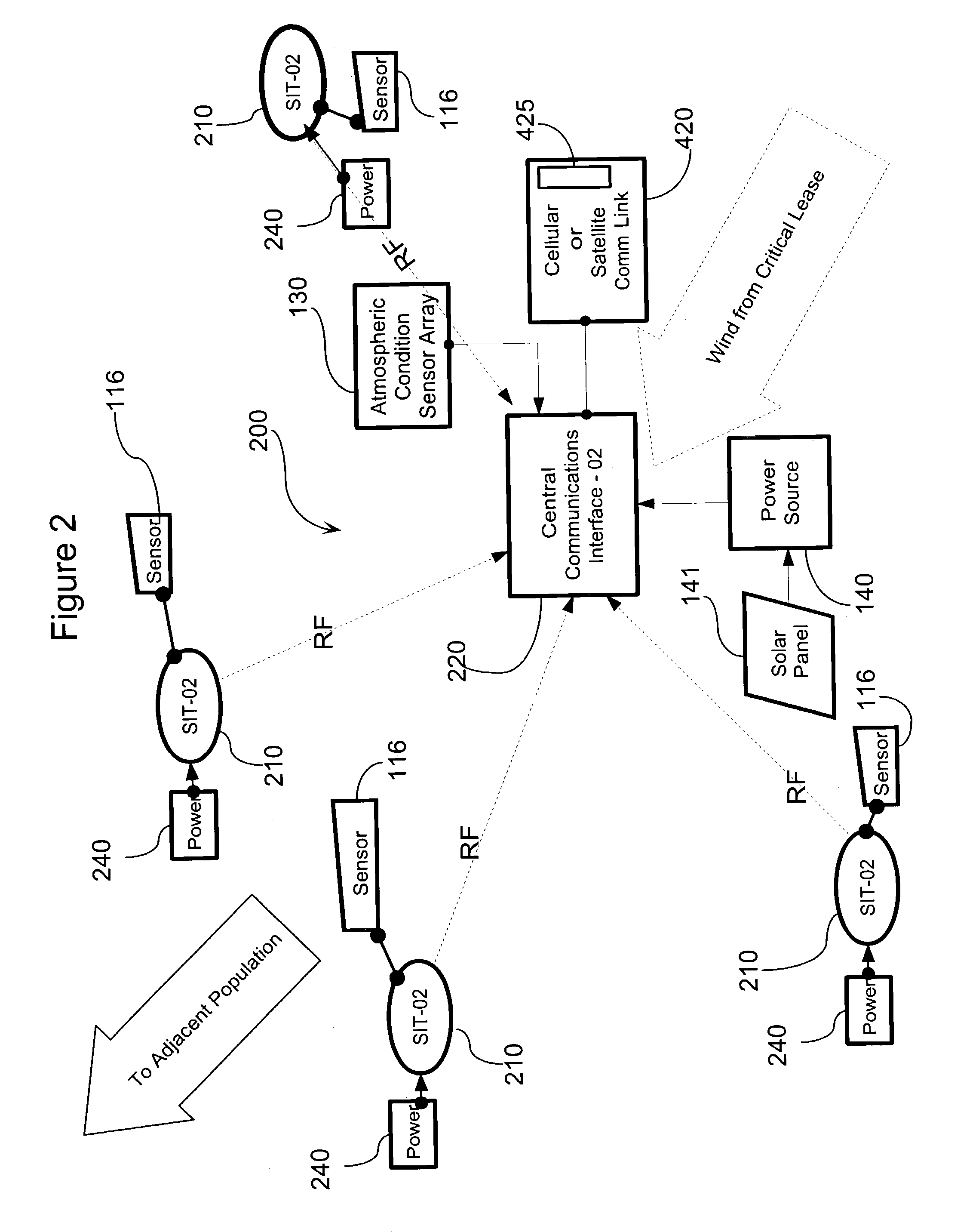
Apparatus system and method for gas well site monitoring
InactiveUS7080544B2Simple and affordable packageImprove convenienceSpecial service provision for substationElectric signal transmission systemsIp addressThe Internet
A System and a Method of initializing and using that system are described in various embodiments all suitable for use remotely monitoring gas escapes on oil or gas well-sites, particularly as early warning technologies for use in preventing injury to workers or populations adjacent those well-sites. The system efficiently uses the Internet to securely transmit pre-processed data off-site for a range of different uses either directly to well-site operators or via a server for value-added handling of and convenient access by operators and others to information based on the data. The system conserves both IP addresses and communications bandwidth without compromising access to detailed data respecting well-site status. The novel system includes means for using multiple modes of long-distance communications technology that can be configured manually or that conveniently auto-senses and auto-selects the appropriate communications mode to use for transmitting data off-site via the Internet according to the location of installation of the system and whether or not it has entered an alarm condition.
Owner:FIREMASTER OILFIELD SERVICES
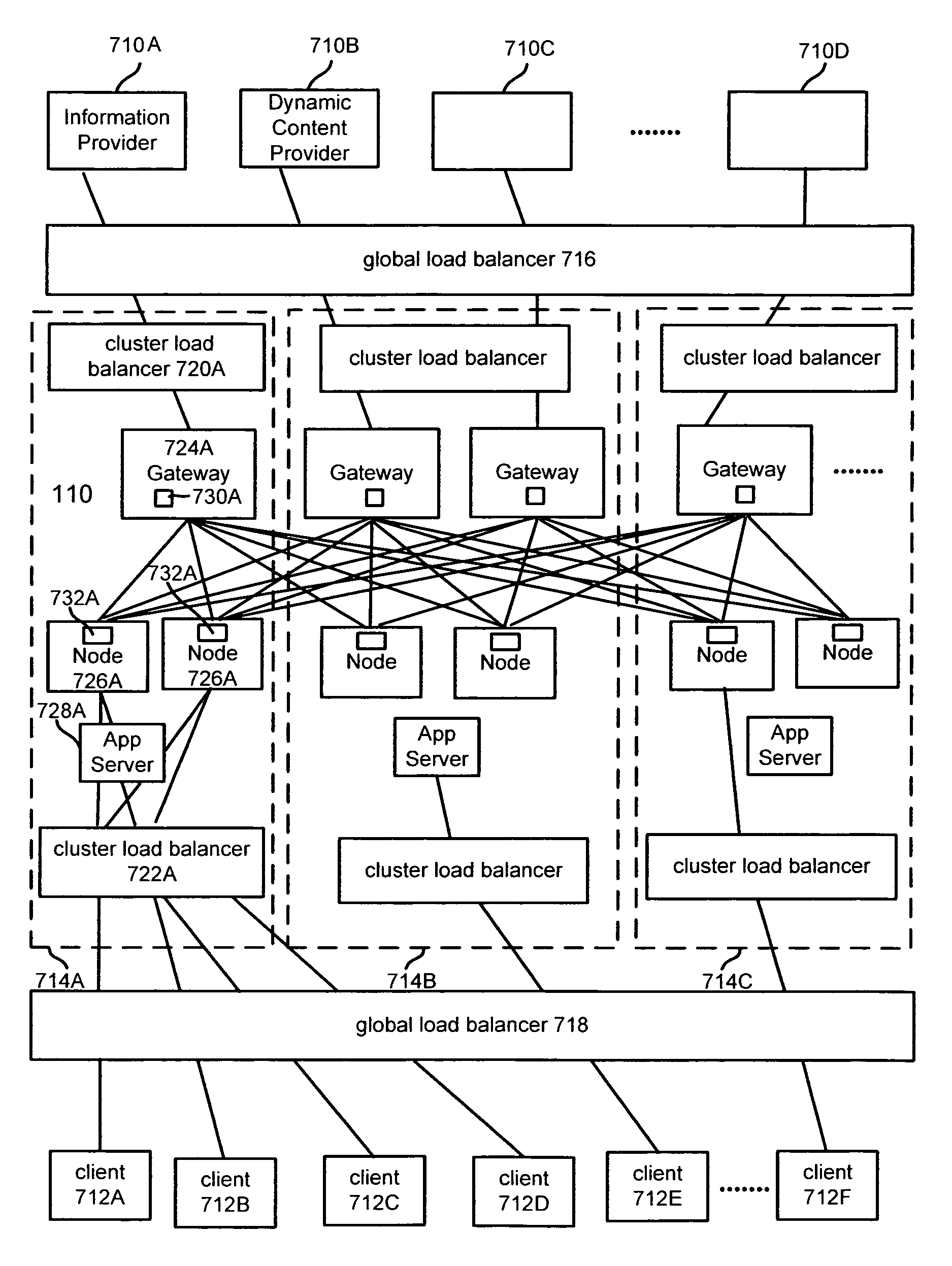
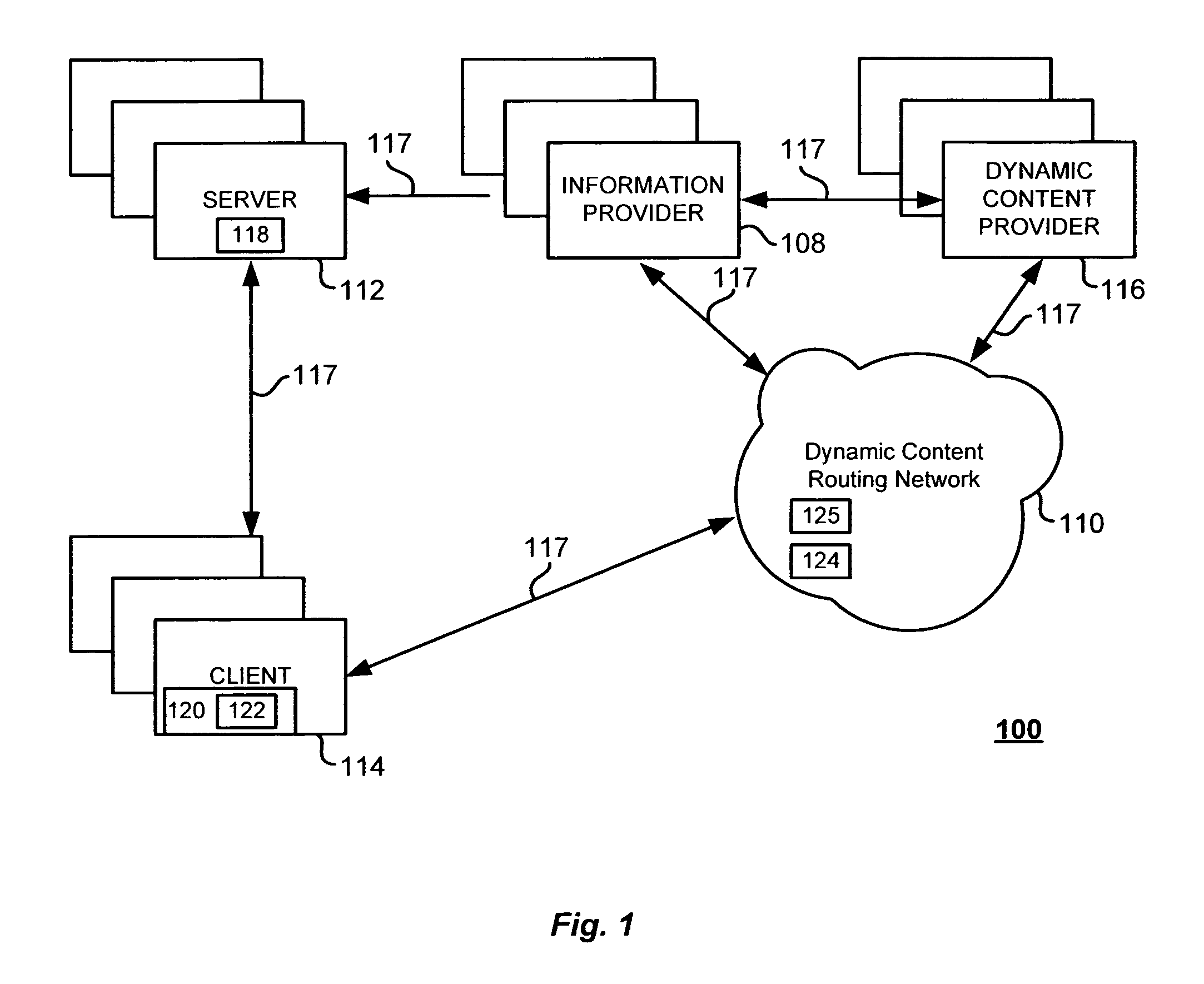
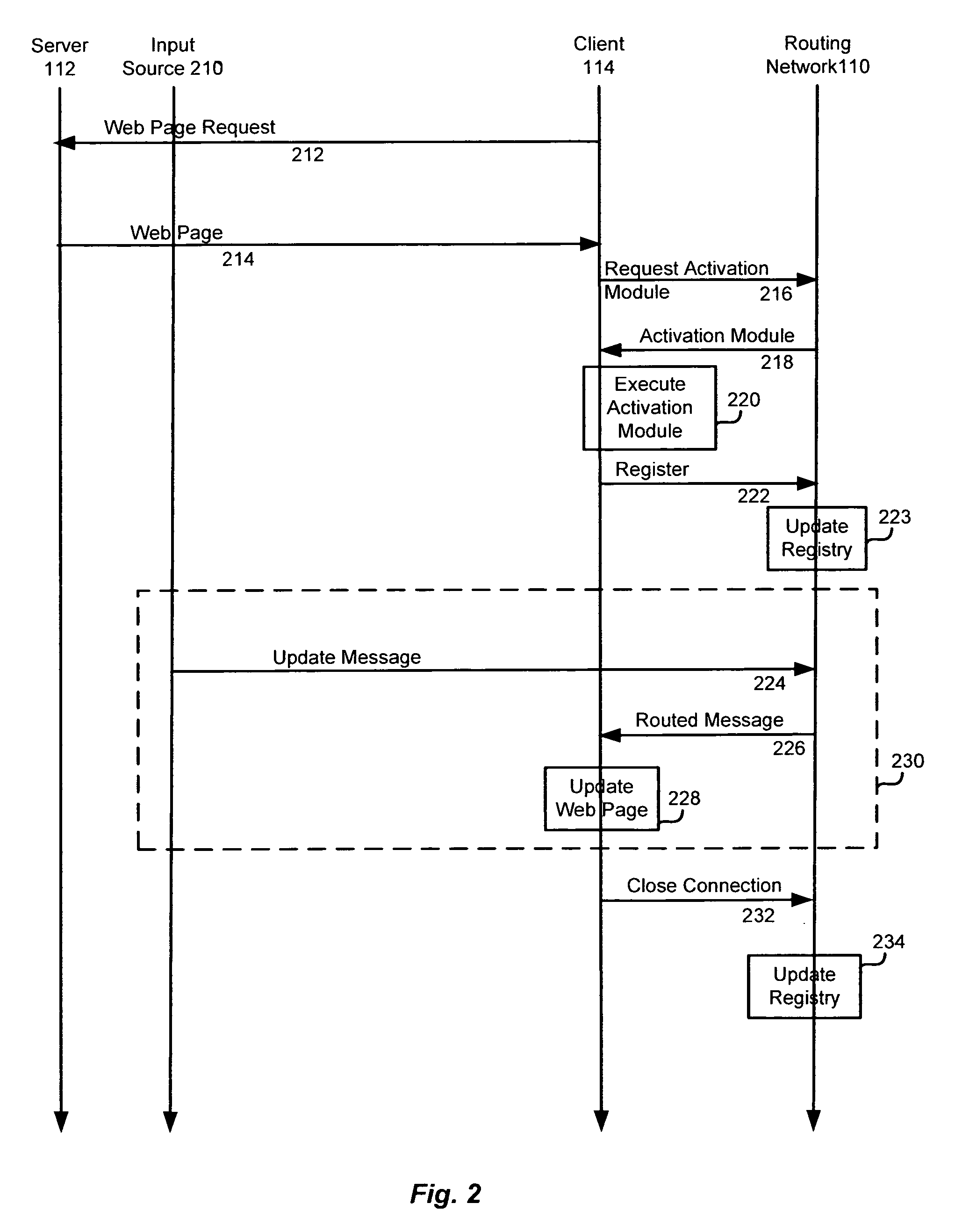
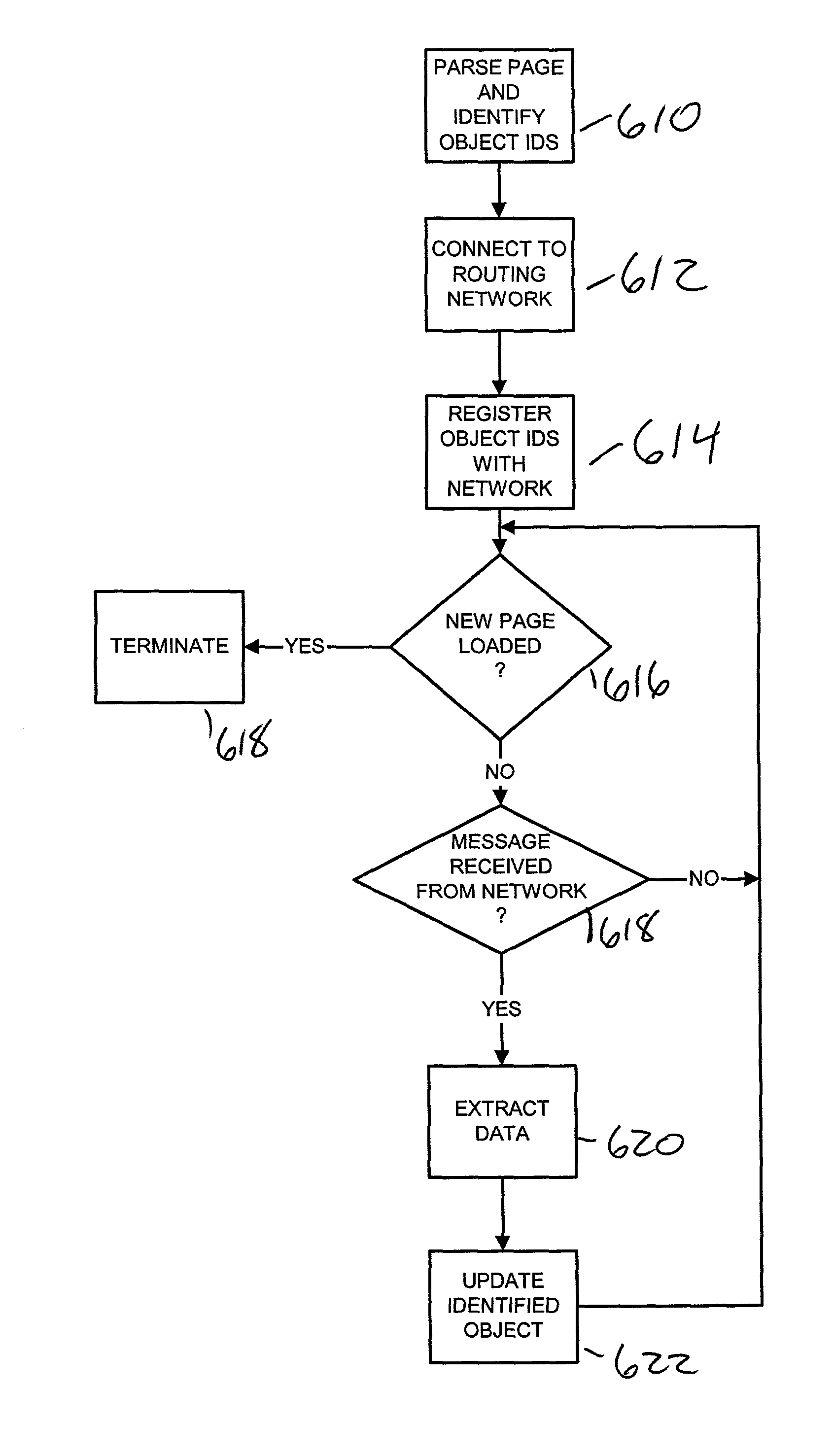
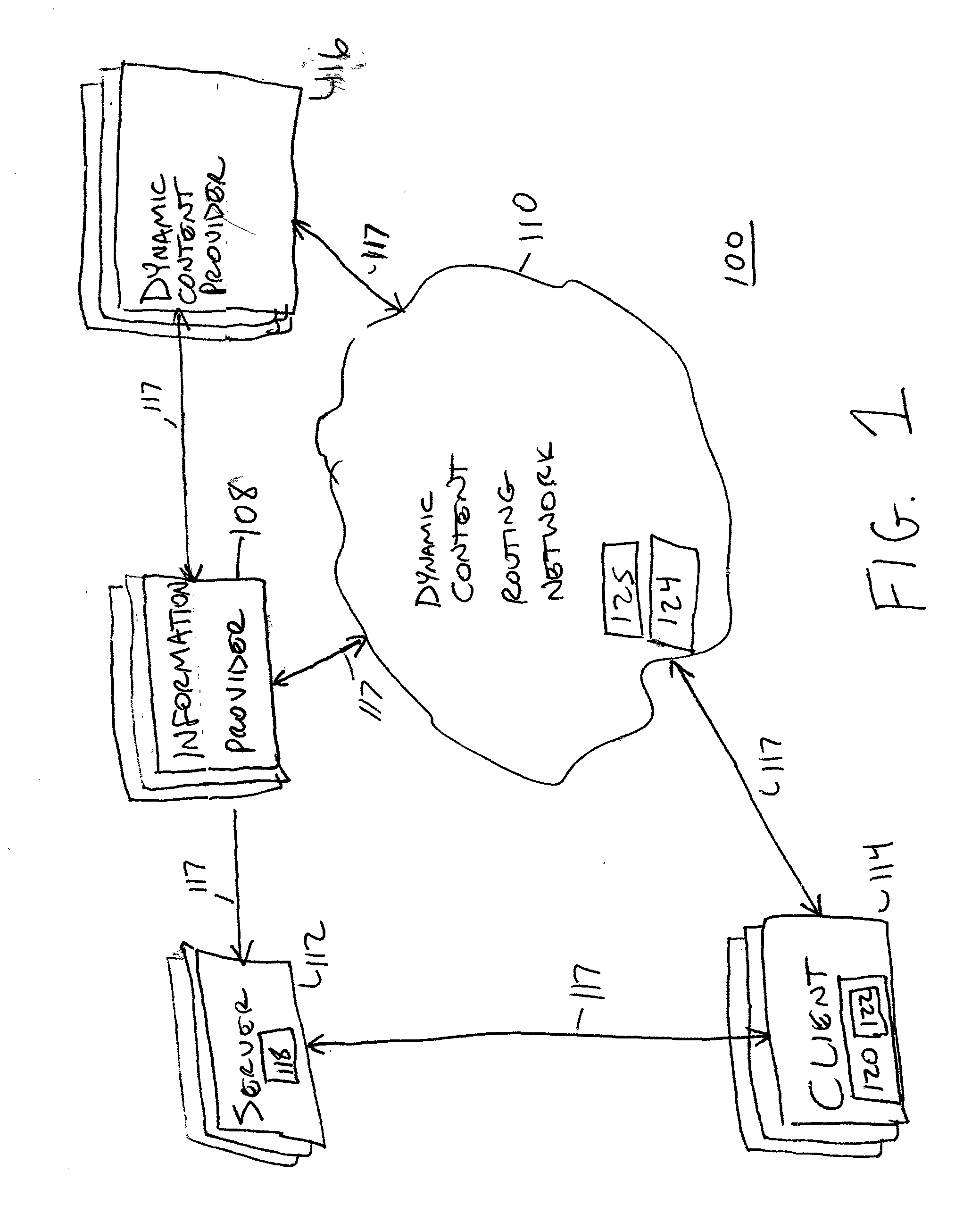
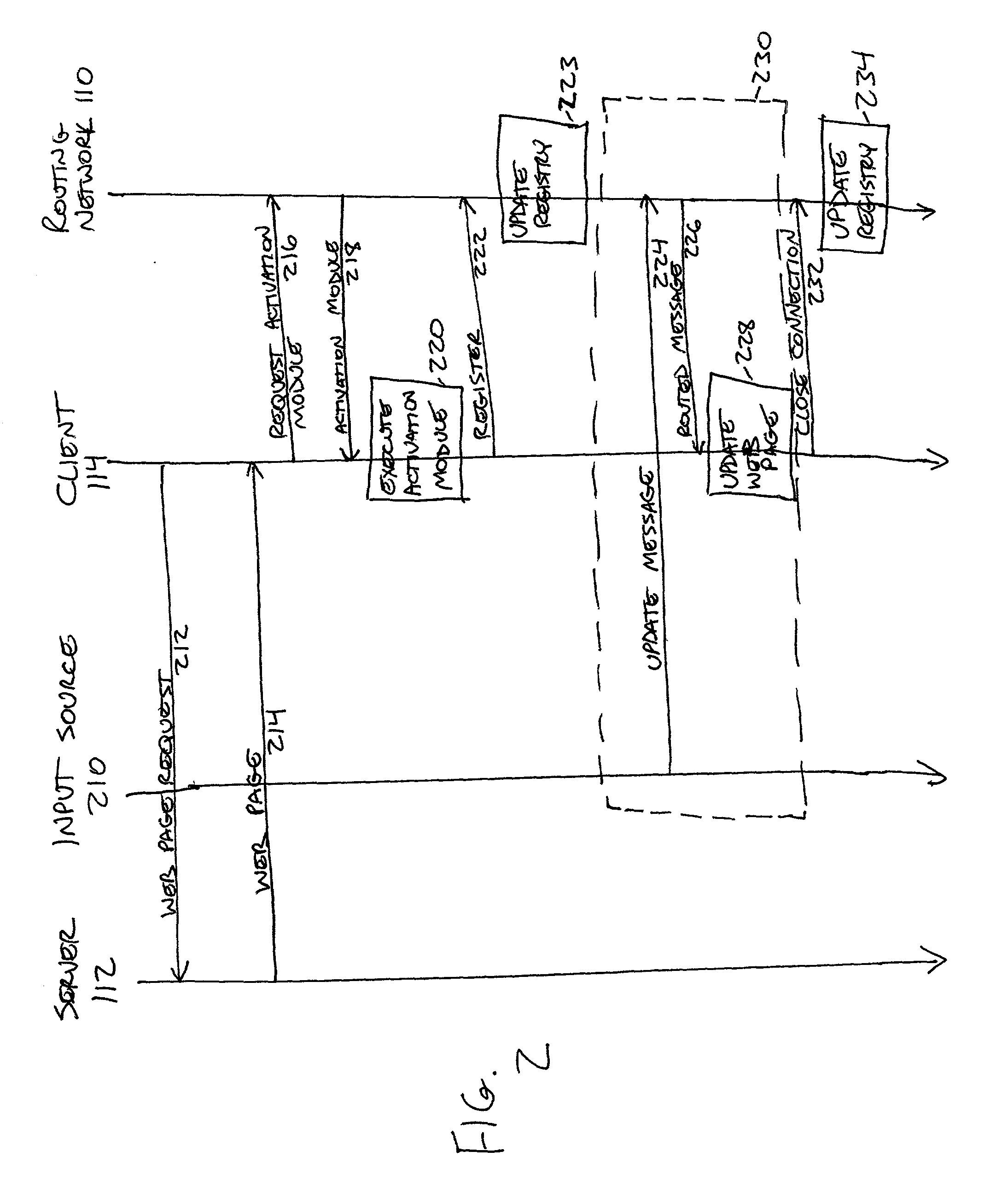
Storing state in a dynamic content routing network
InactiveUS20050278726A1Utilizes bandwidth efficientlyEfficient use ofMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideWeb page
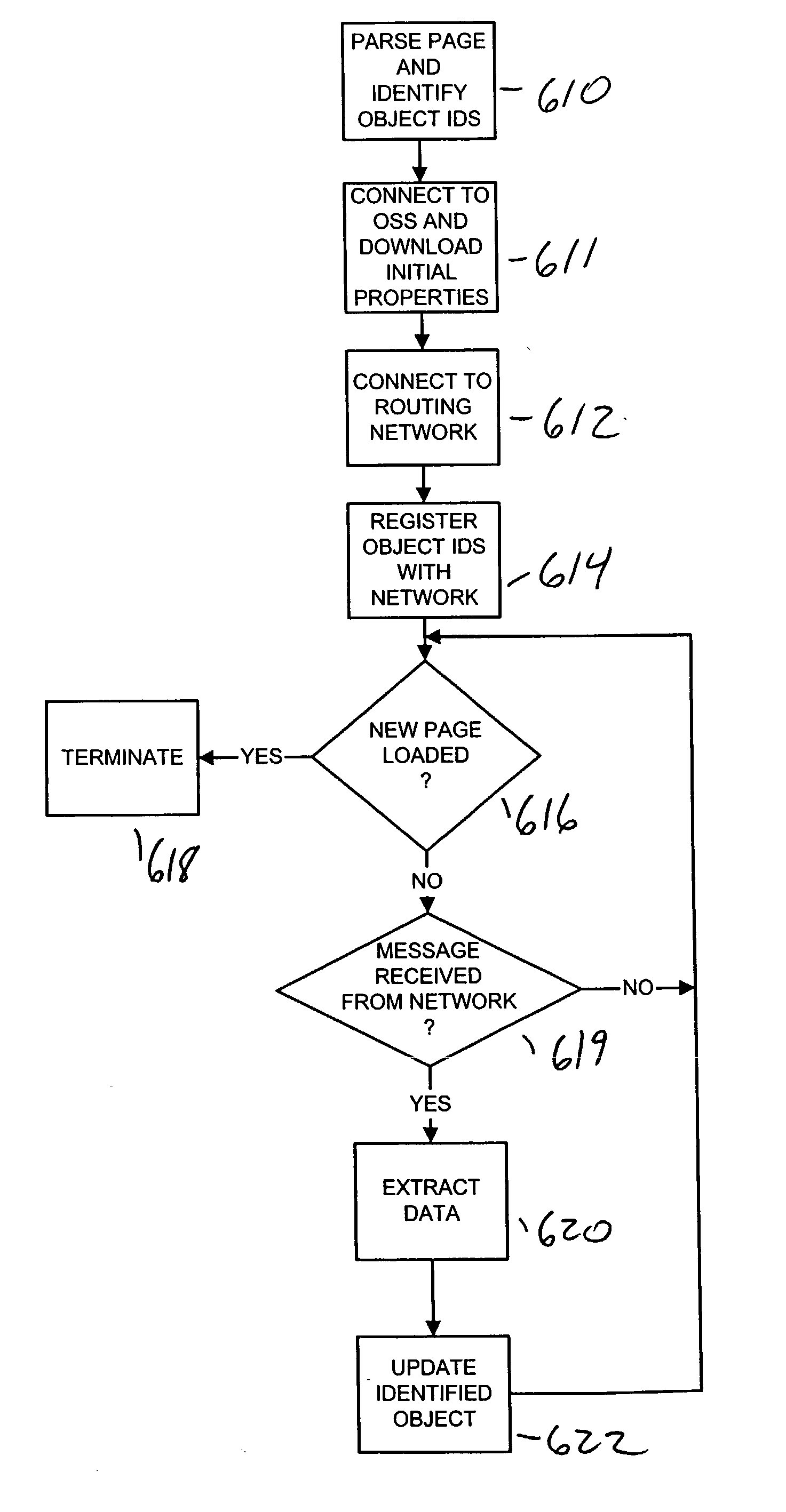
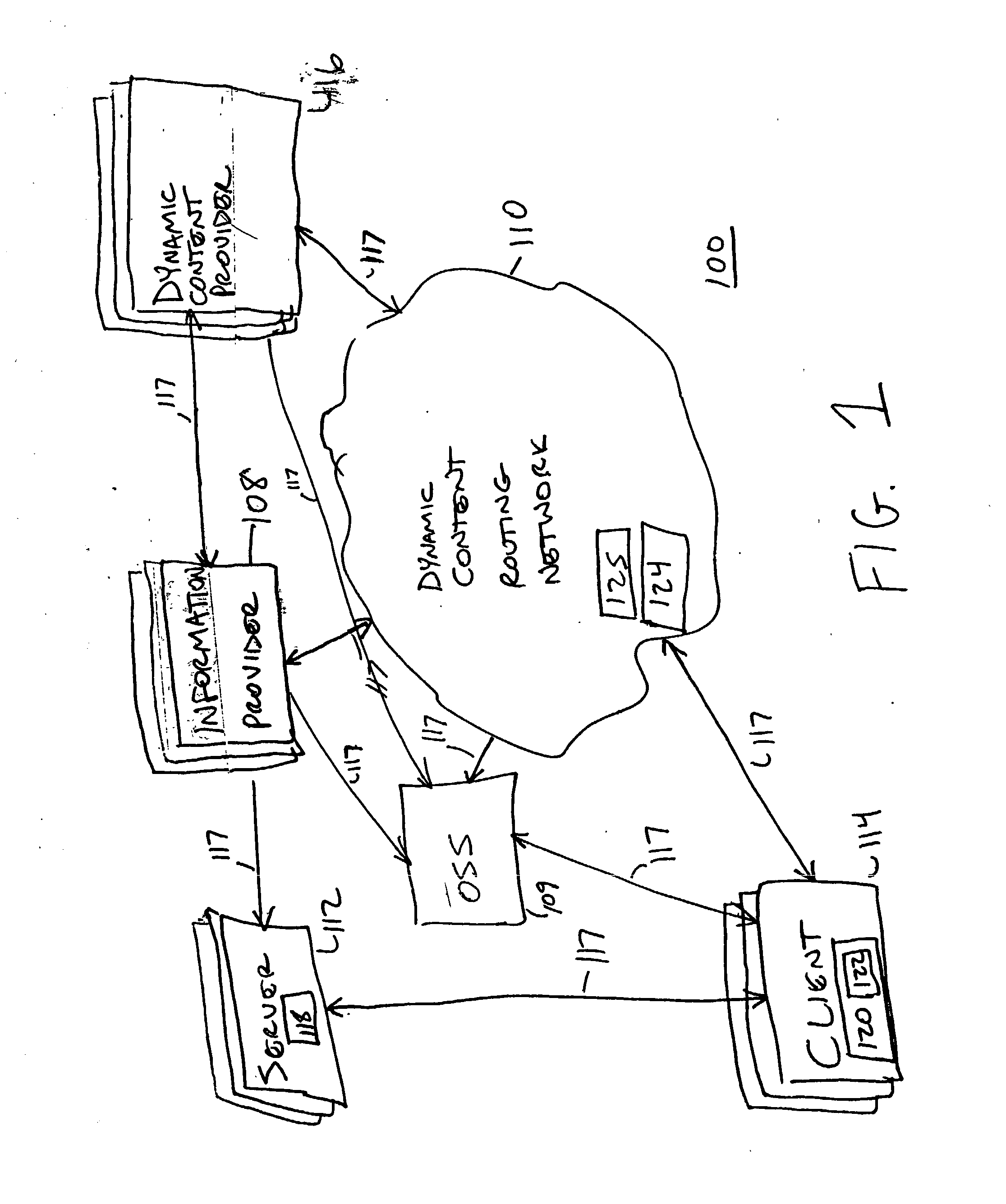
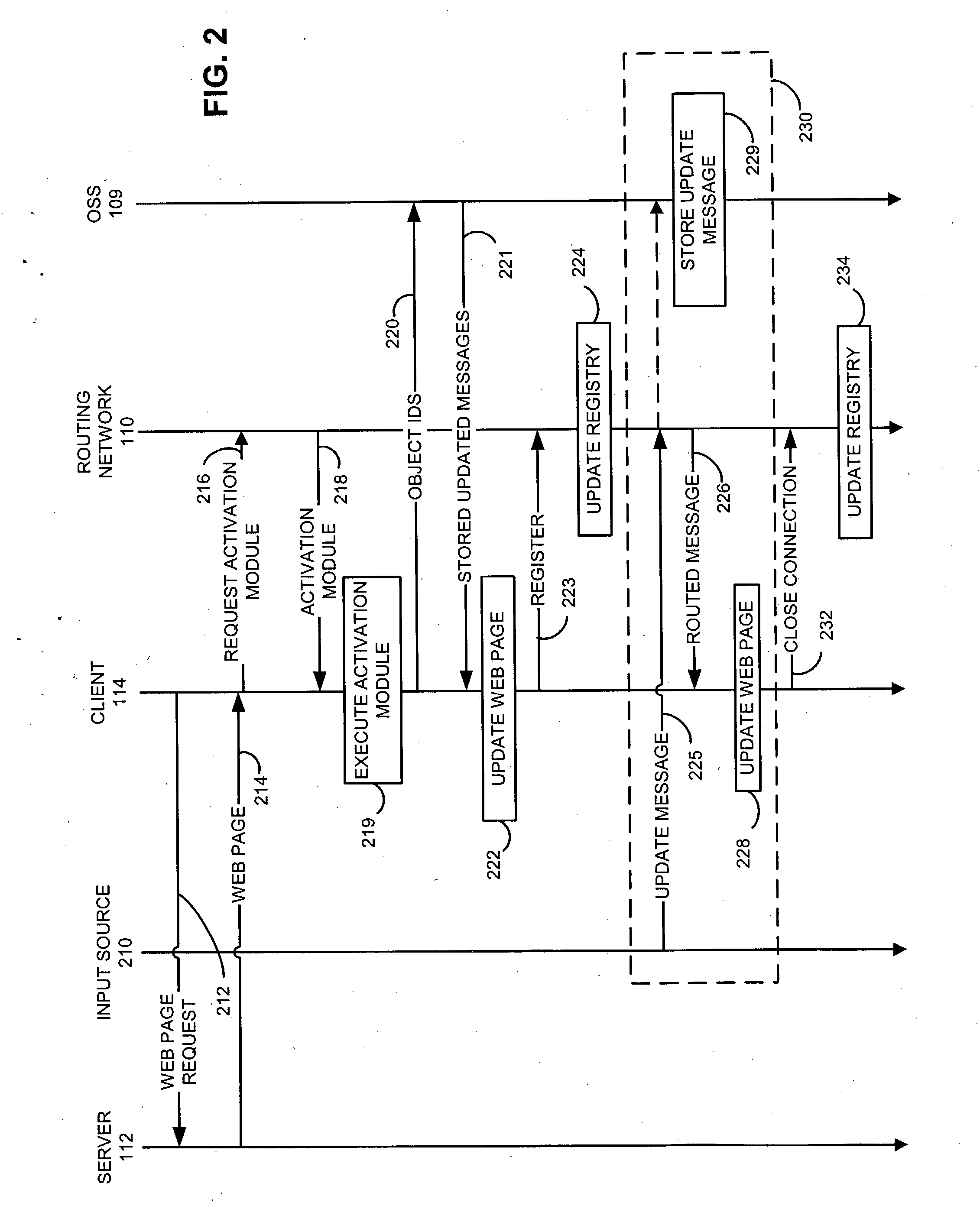
A dynamic content routing network routes update messages containing updates to properties of live objects from input sources to clients. The clients receive a web page having live objects, identify the object IDs associated with the objects, and contact an object state storage to obtain update messages specifying the objects'initial properties. The clients register the object IDs with the routing network. The routing network maintains a registry of object IDs and clients. The input source provides an update message to the routing network containing the object ID and data for updating a property of the object. The routing network routes update messages from the input source to the clients registered for the object ID contained in the message. Upon receipt of the message, a client updates the specified property of the live object. The update messages are also provided to, and stored by, the object state storage.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
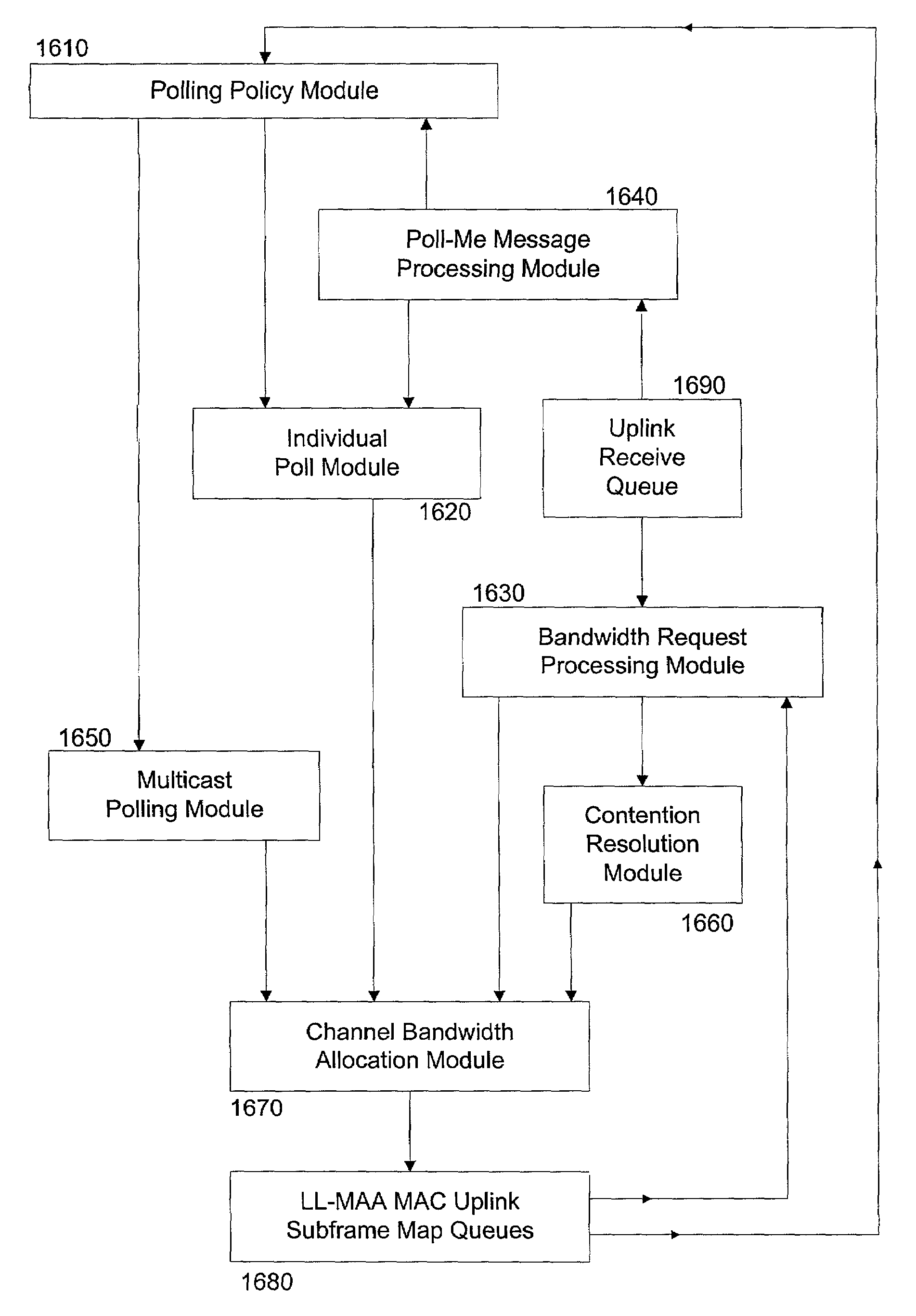
Method and apparatus for bandwidth request/grant protocols in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20050089064A1Efficiently allocate bandwidthReduce the possibilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemModem device
A method and apparatus for allocating bandwidth in a broadband wireless communication system is disclosed. One embodiment uses a self-correcting bandwidth request / grant protocol. The self-correcting bandwidth request / grant protocol utilizes a combination of incremental and aggregate bandwidth requests. CPEs primarily transmit incremental bandwidth requests to their associated base stations, followed by periodic transmissions of aggregate bandwidth requests. The use of periodic aggregate bandwidth requests (that express the current state of their respective connection queues) allows the bandwidth allocation method and apparatus to be “self-correcting”. Another embodiment utilizes an abridged bandwidth request / grant protocol to allocate bandwidth. The abridged bandwidth request / grant protocol system utilizes padding packets to request a reduction in bandwidth allocation to a CPE. A base station modem alerts a base station CPU when the BS modem receives a padding packet from a CPE. After alerting the BS CPU the method can reduce the associated CPE's bandwidth allocation.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Method and system for adaptively obtaining bandwidth allocation requests
InactiveUS20090175235A1Attenuation bandwidthReduce amountNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexRate adaptationBroadband
A method and apparatus for adaptively obtaining bandwidth requests in a broadband wireless communication system. The method and apparatus includes dynamically varying technique combinations enabling a plurality of users to efficiently request bandwidth from a shared base station. A user may “piggyback” a new bandwidth request upon, or set a “poll-me bit” within, presently allocated bandwidth. A base station may poll users, individually or in groups, by allocating unrequested bandwidth for new requests. Polling may respond to a “poll-me bit,” and / or it may be adaptively periodic at a rate based on communication status parameters, such as recent communication activity and connection QoS levels. Group polling permits a possibility of collisions. Polling policies may be established for dynamically varying user groups, or may be determined for each user. Dynamic selection of appropriate polling techniques makes use of efficiency benefits associated with each technique.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Method and system for adaptively obtaining bandwidth allocation requests
InactiveUS20080253394A1Reduced bandwidthReduce amountNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexRate adaptationBroadband
A method and apparatus for adaptively obtaining bandwidth requests in a broadband wireless communication system. The method and apparatus includes dynamically varying technique combinations enabling a plurality of users to efficiently request bandwidth from a shared base station. A user may “piggyback” a new bandwidth request upon, or set a “poll-me bit” within, presently allocated bandwidth. A base station may poll users, individually or in groups, by allocating unrequested bandwidth for new requests. Polling may respond to a “poll-me bit,” and / or it may be adaptively periodic at a rate based on communication status parameters, such as recent communication activity and connection QoS levels Group polling permits a possibility of collisions. Polling policies may be established for dynamically varying user groups, or may be determined for each user. Dynamic selection of appropriate polling techniques makes use of efficiency benefits associated with each technique.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Techniques for updating live objects at clients using a dynamic routing network
InactiveUS7043525B2Effective bandwidthEfficient use ofMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideAdaptive routing
A dynamic content routing network routes update messages containing updates to properties of live objects from input sources to clients having the objects. Certain objects served to clients by a server are indicated as “live.” When the clients receive live objects, the clients identify the object IDs associated with the objects and register the object IDs with the routing network. The routing network maintains a registry of object IDs and clients. An input source provides an update message to the routing network containing the object ID and data specifying an update to a property of the object. The routing network routes the message to each client that has registered for the object ID contained in the message. Upon receipt of the message, a client updates the specified property of the live object.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
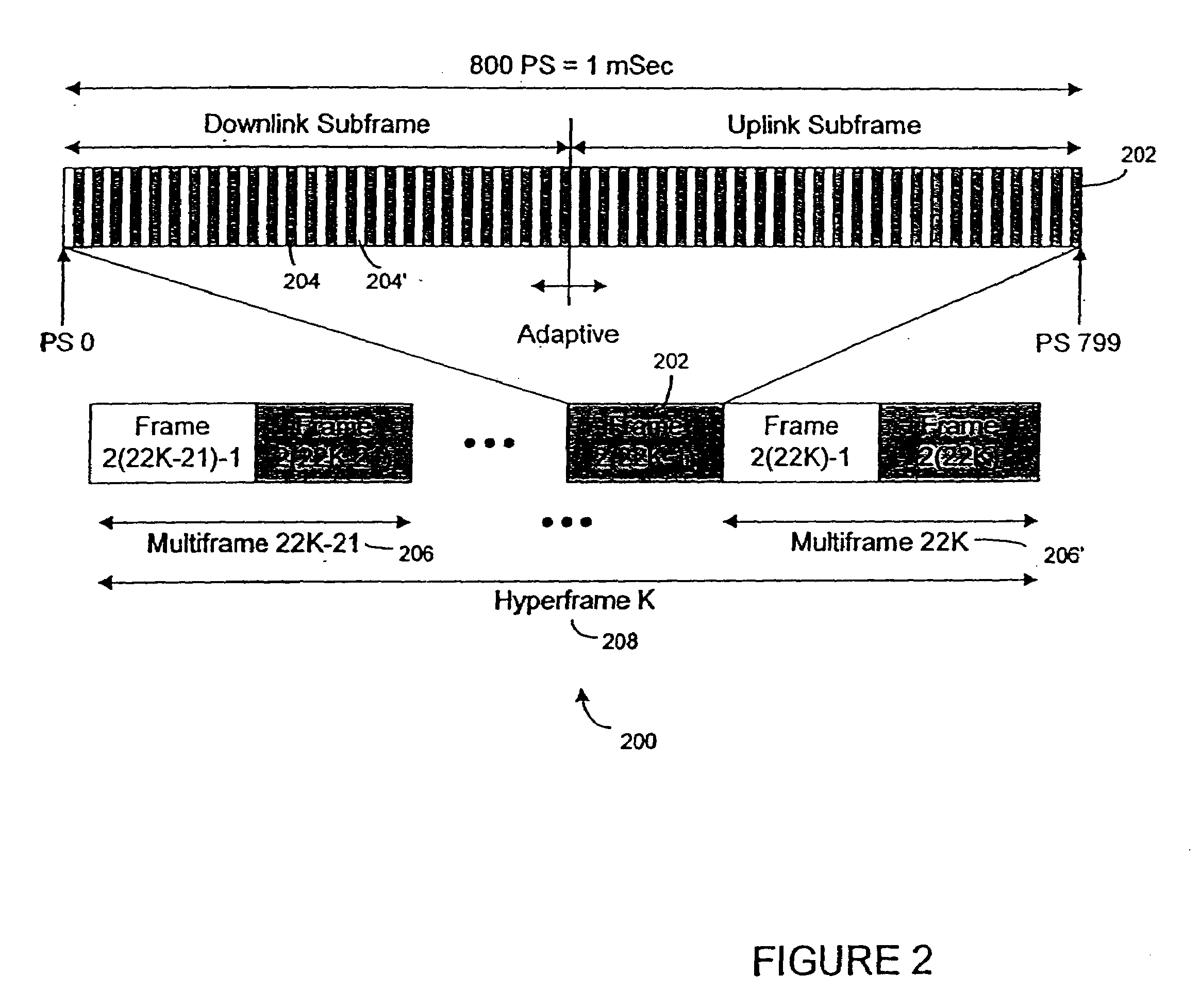
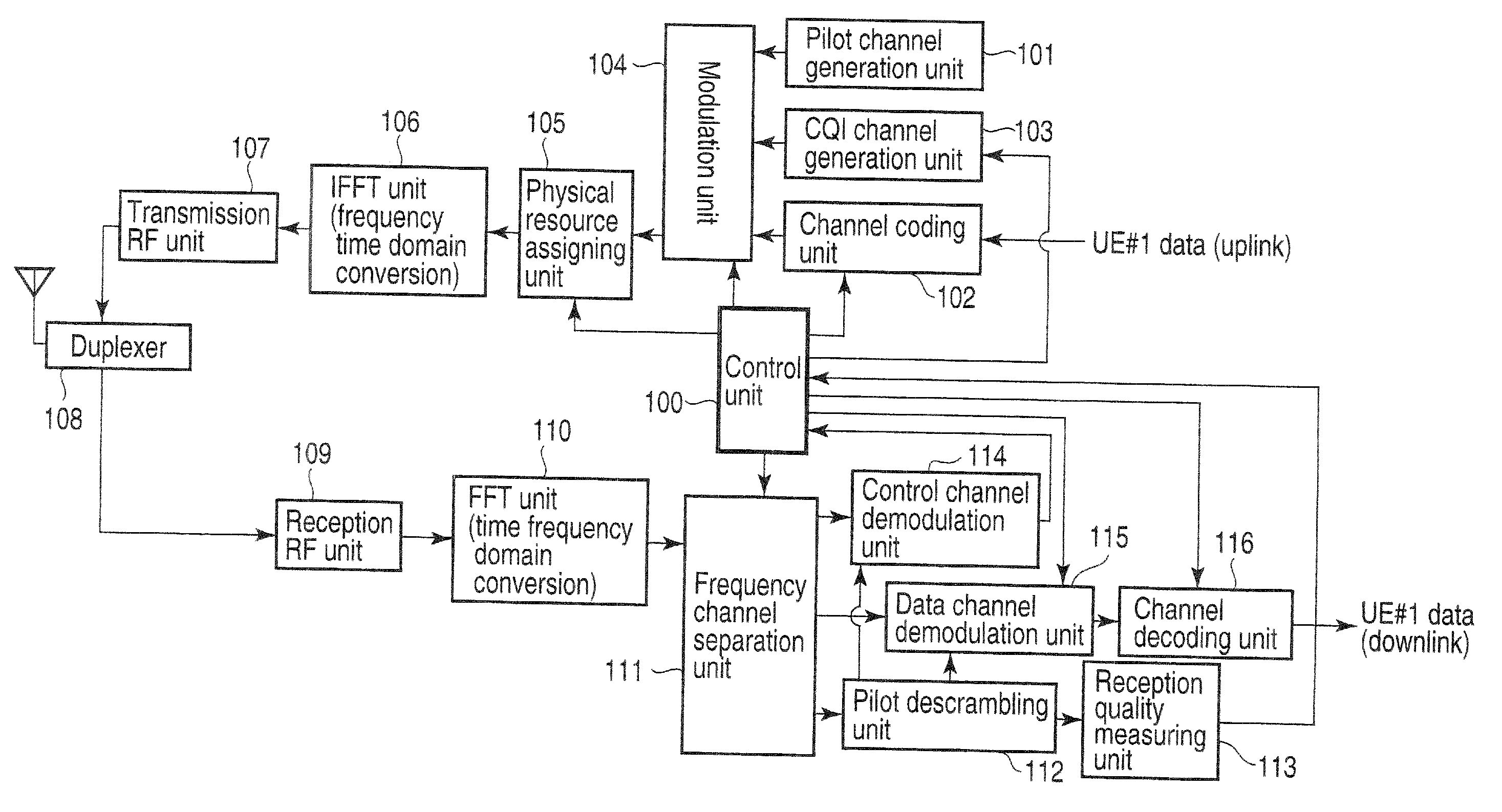
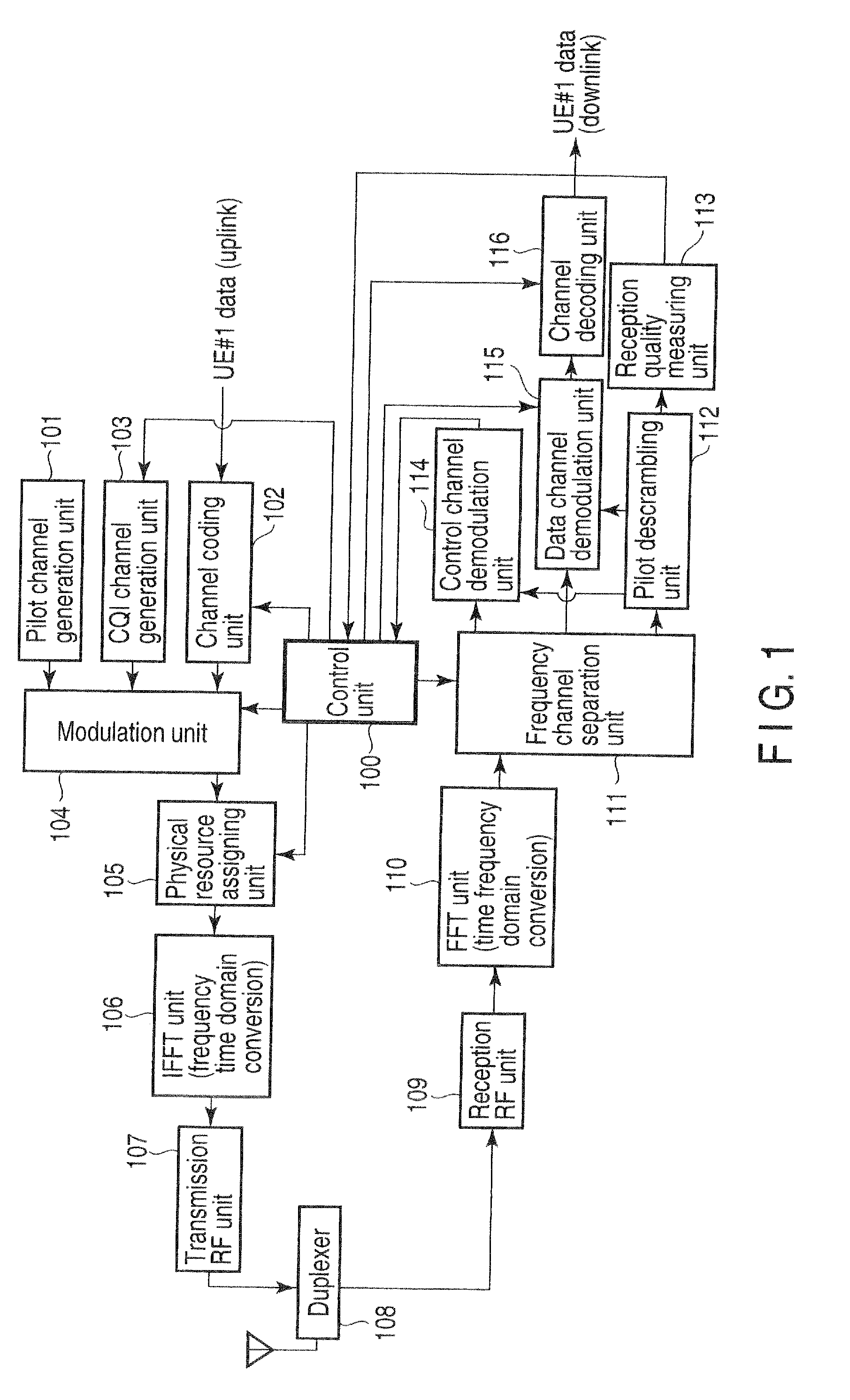
Wireless base station apparatus and mobile wireless terminal apparatus
InactiveUS20100027492A1Prevent degradationEffective bandwidthTransmission path divisionInter user/terminal allocationCarrier signalSubcarrier
In the downlink, the channel band at each end of three 20-MHz channel bands has the DC subcarrier at its center at a position spaced apart from the DC subcarrier of the middle channel band by 18.015 MHz or more and, more specifically, by 18.3 MHz corresponding to a spacing of 300 kHz that is the least common multiple of the 100-kHz channel raster and the 15-kHz subcarrier spacing. The subcarriers at the two ends are rearranged between the channel bands.
Owner:FUJITSU TOSHIBA MOBILE COMM LTD
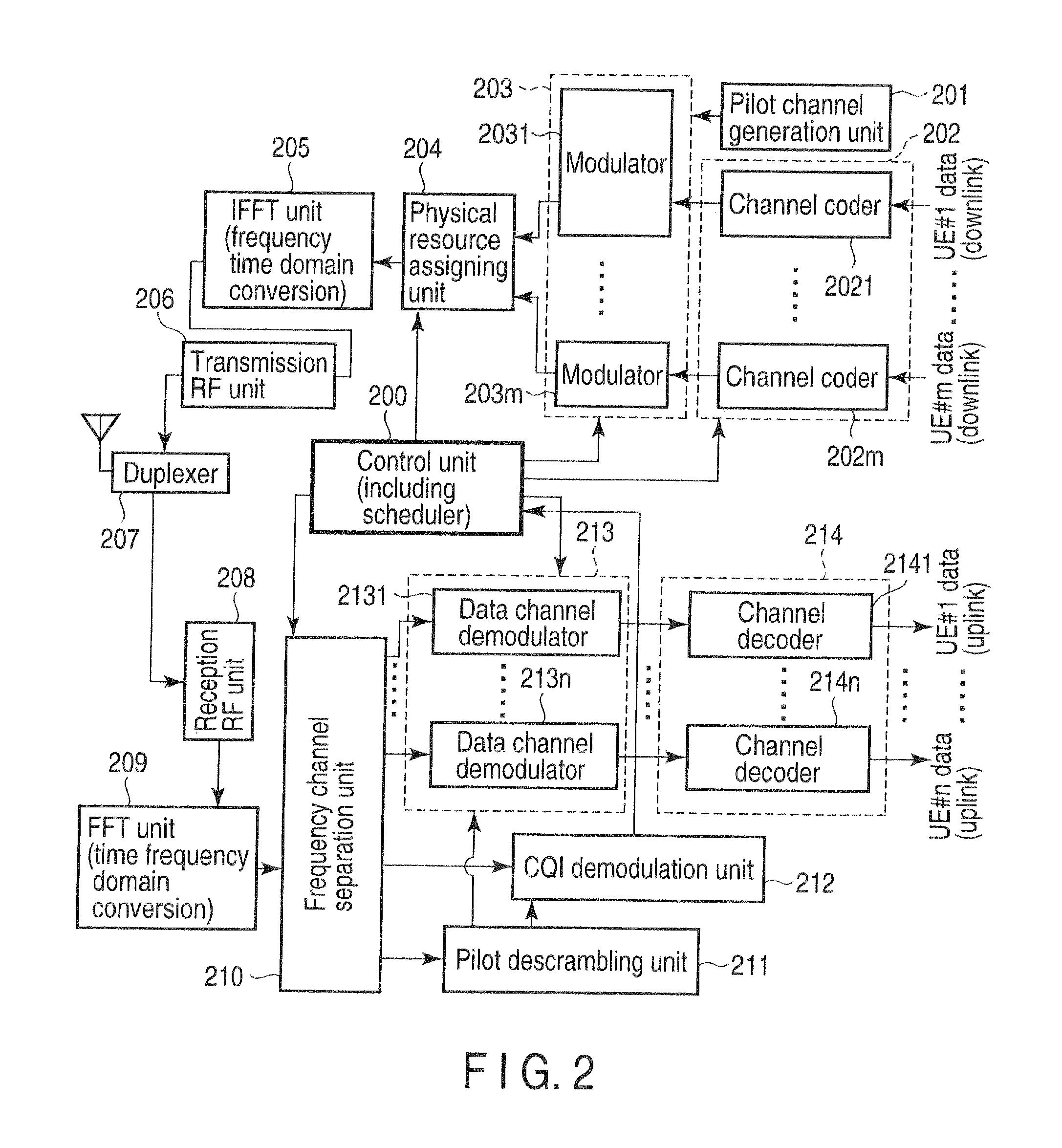
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access Based Virtual Passive Optical Network (VPON)
InactiveUS20090092394A1Effective bandwidthWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar-type electromagnetic networksEngineeringLength wave
Various types of passive optical networks operate simultaneously in one passive optical network system comprising an optical line terminal, a passive remote node, and multiple optical network units. Downstream data is orthogonal frequency division multiplexed onto a single wavelength optical carrier transmitted on a primary downstream optical beam from the optical line terminal to a splitter in the passive remote node. The primary downstream optical beam is split into multiple secondary downstream optical beams; each is transmitted to a specific optical network unit. Upstream data is orthogonal frequency division multiplexed onto a single wavelength optical carrier transmitted on a secondary upstream optical beam from each optical network unit to a coupler in the passive remote node. The upstream wavelength for each optical network unit is different. The wavelength division multiplexed optical beam is transmitted from the passive remote node to a parallel signal detector in the optical line terminal.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
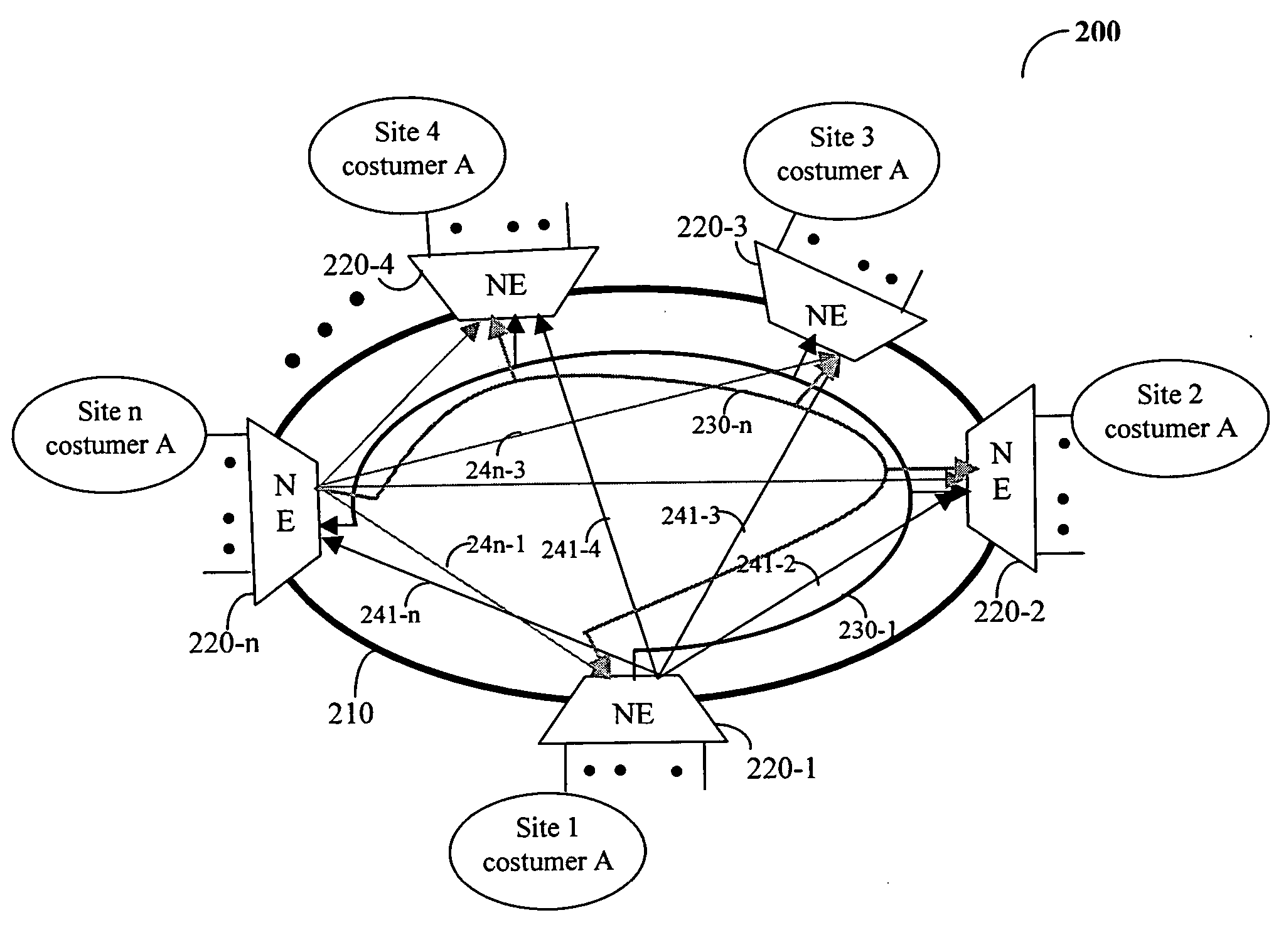
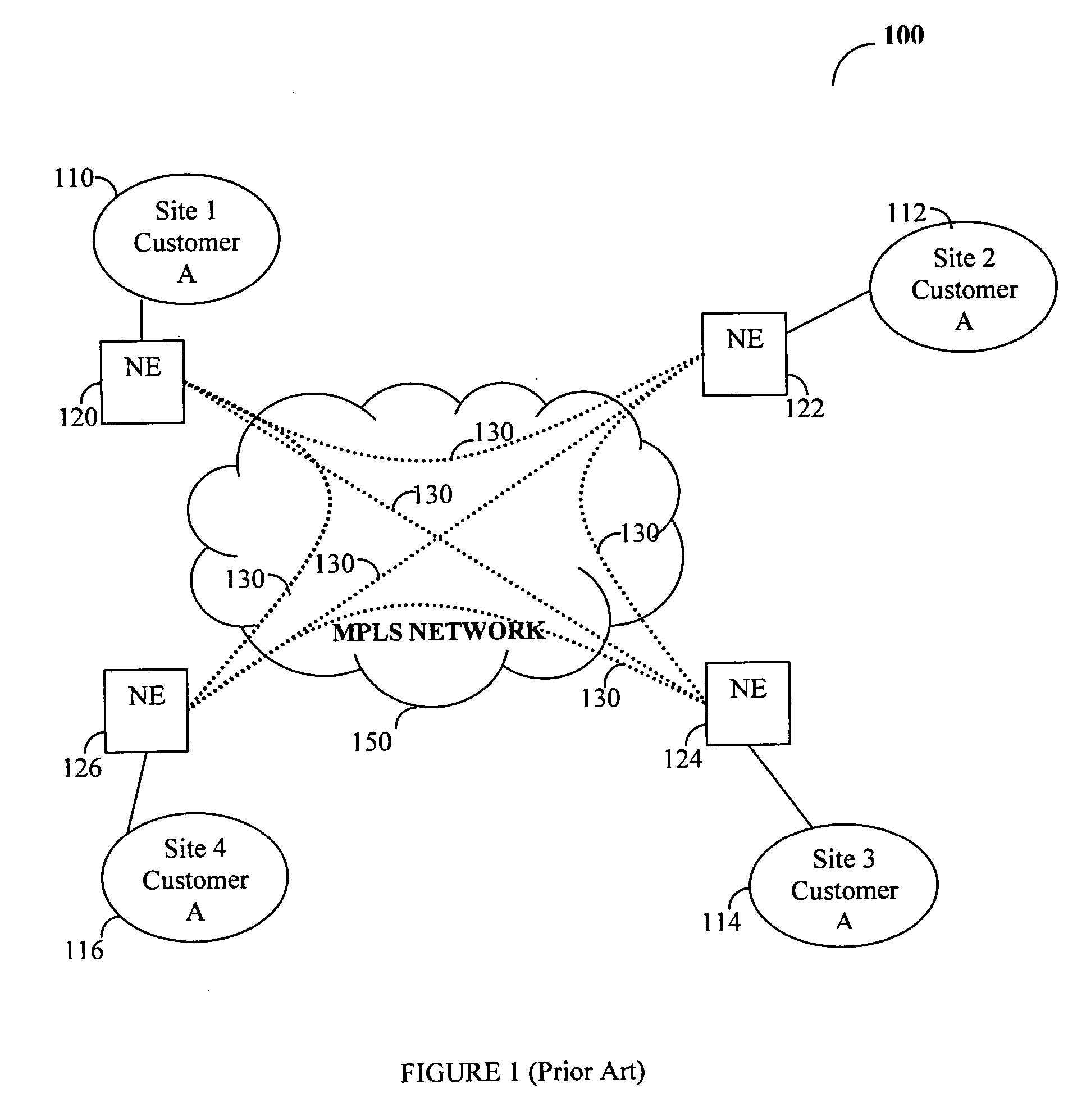
Method for providing efficient multipoint network services
InactiveUS20050271036A1Efficient bandwidth utilizationEasy maintenanceSpecial service provision for substationNetworks interconnectionNetwork serviceDistributed computing
A method, system and device for enabling efficient bandwidth utilization of a multipoint network service over an arbitrary topology network that includes a plurality of network elements (NEs). In a preferred embodiment, the method comprises the steps of setting up a full connectivity between the NEs and providing the multipoint network service using the full connectivity, whereby data packets of the multipoint network services are transmitted from a source NE to at least one edge NE through at least one intermediate NE, and whereby data packets that need to be flooded are not replicated or at the source NE. The full connectivity includes an arbitrary combination of a first plurality of point-to-multipoint connections between each source NE and each edge NE and a second plurality of point-to-point connections between each source NE and every edge NE.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
System and method for connecting multicast or broadcast control information to mobile stations
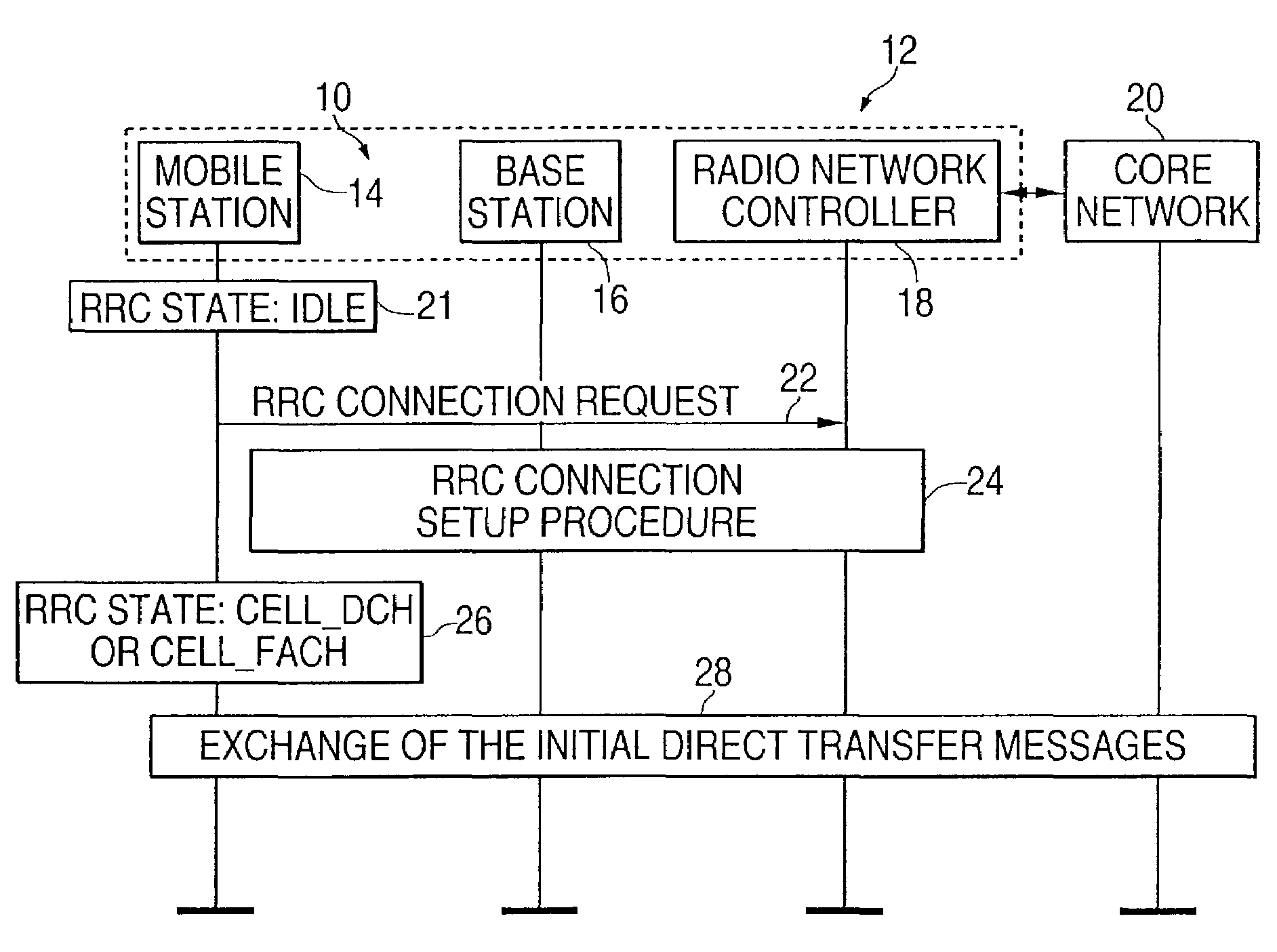
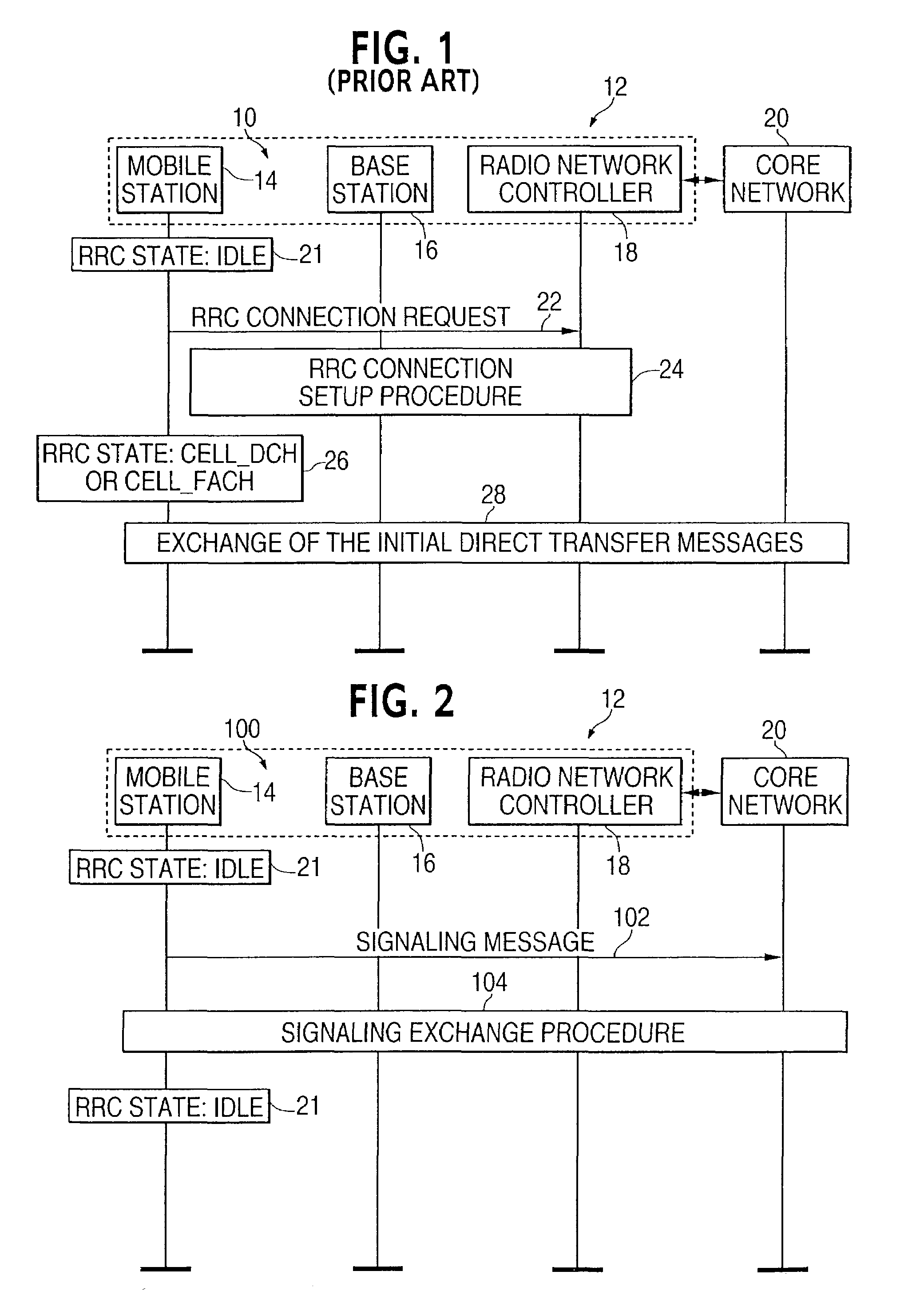
InactiveUS7031708B2Effective bandwidthLiquid carbonaceous fuelsBroadcast service distributionMobile stationBroadcasting
This invention is a system and a method of connecting at least one mobile station (14) in a wireless network (12) including mobile stations and a controller (18) to another network (20). The method includes transmitting a communication from at least one mobile station, while the at least one mobile station is activated in the wireless network, but is not terminated to the controller, to the another network to establish a connection between the at least one mobile station and the another network; and the another network transmits a transmission of control information using the connection to the at least one mobile station while the at least one mobile station is activated but is not terminated to the controller.
Owner:RPX CORP
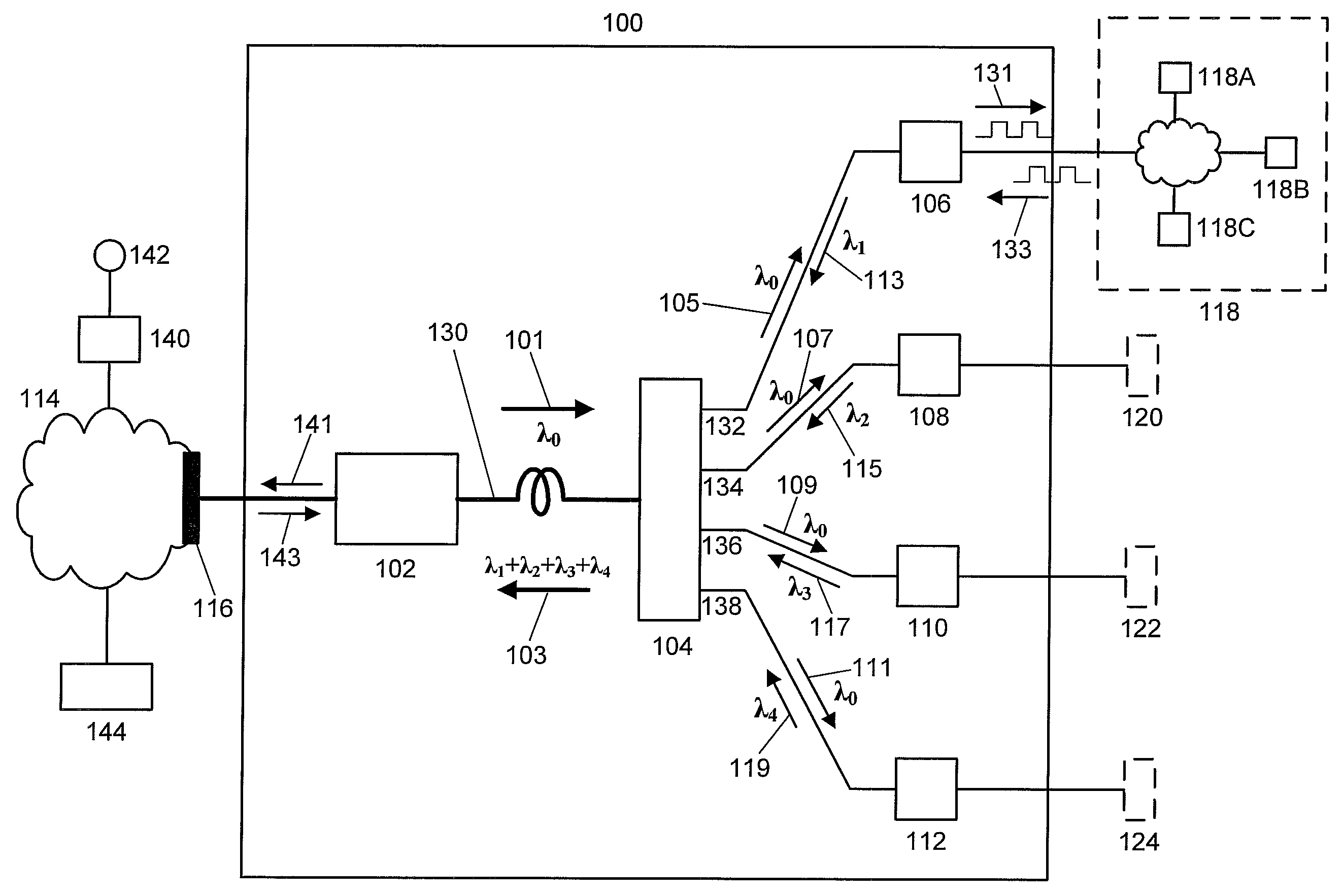
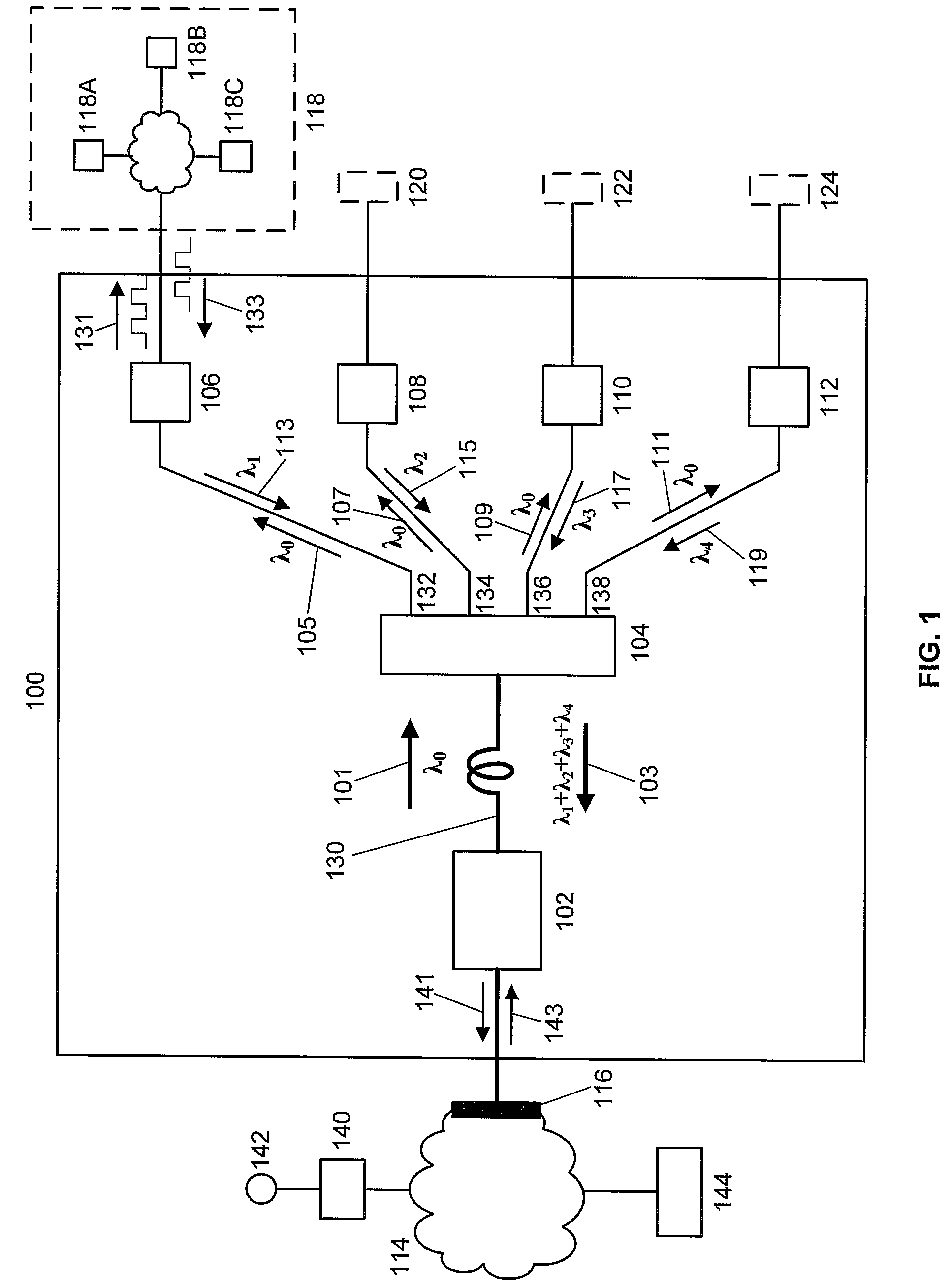
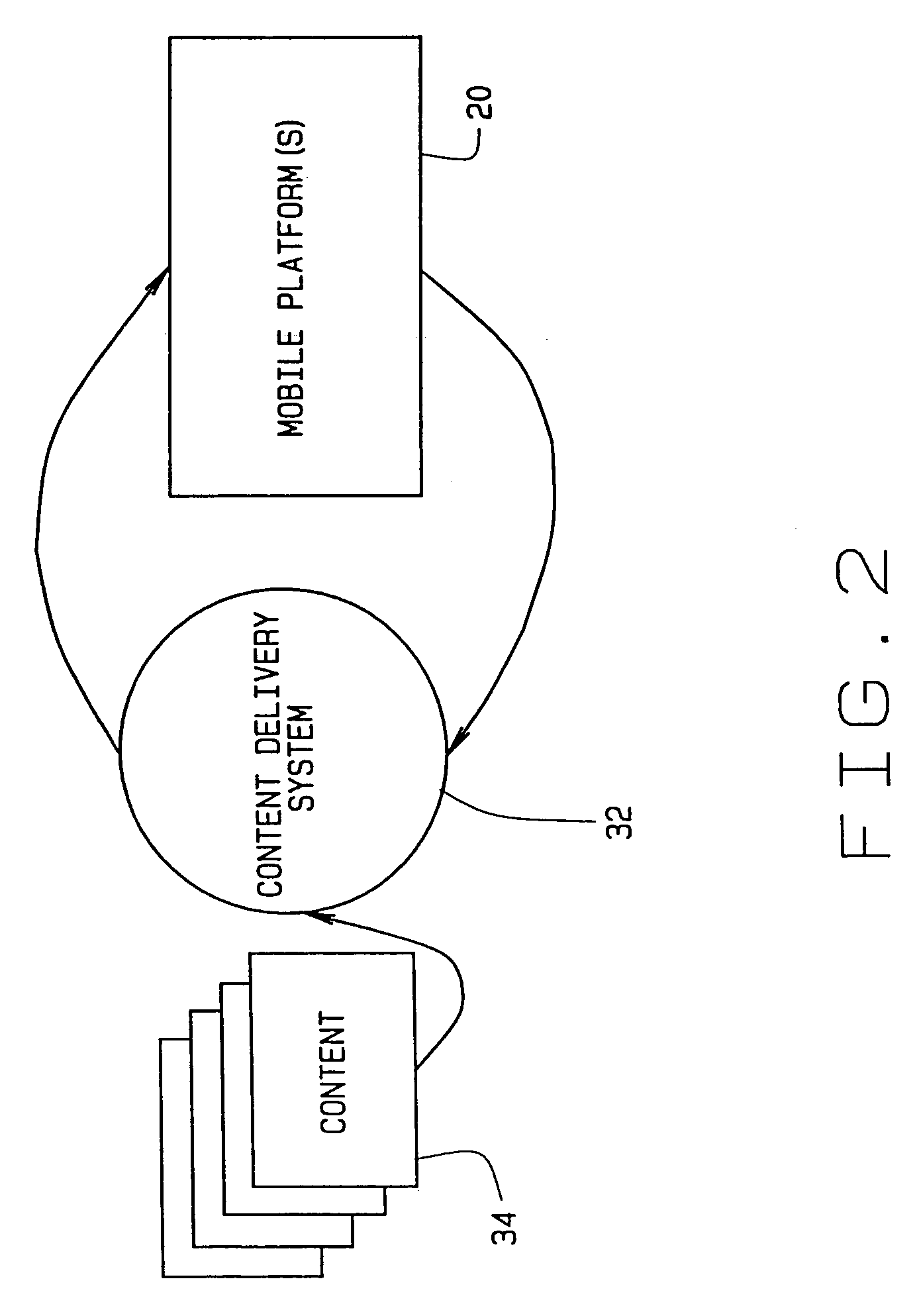
Method of maximizing use of bandwidth for communicating with mobile platforms
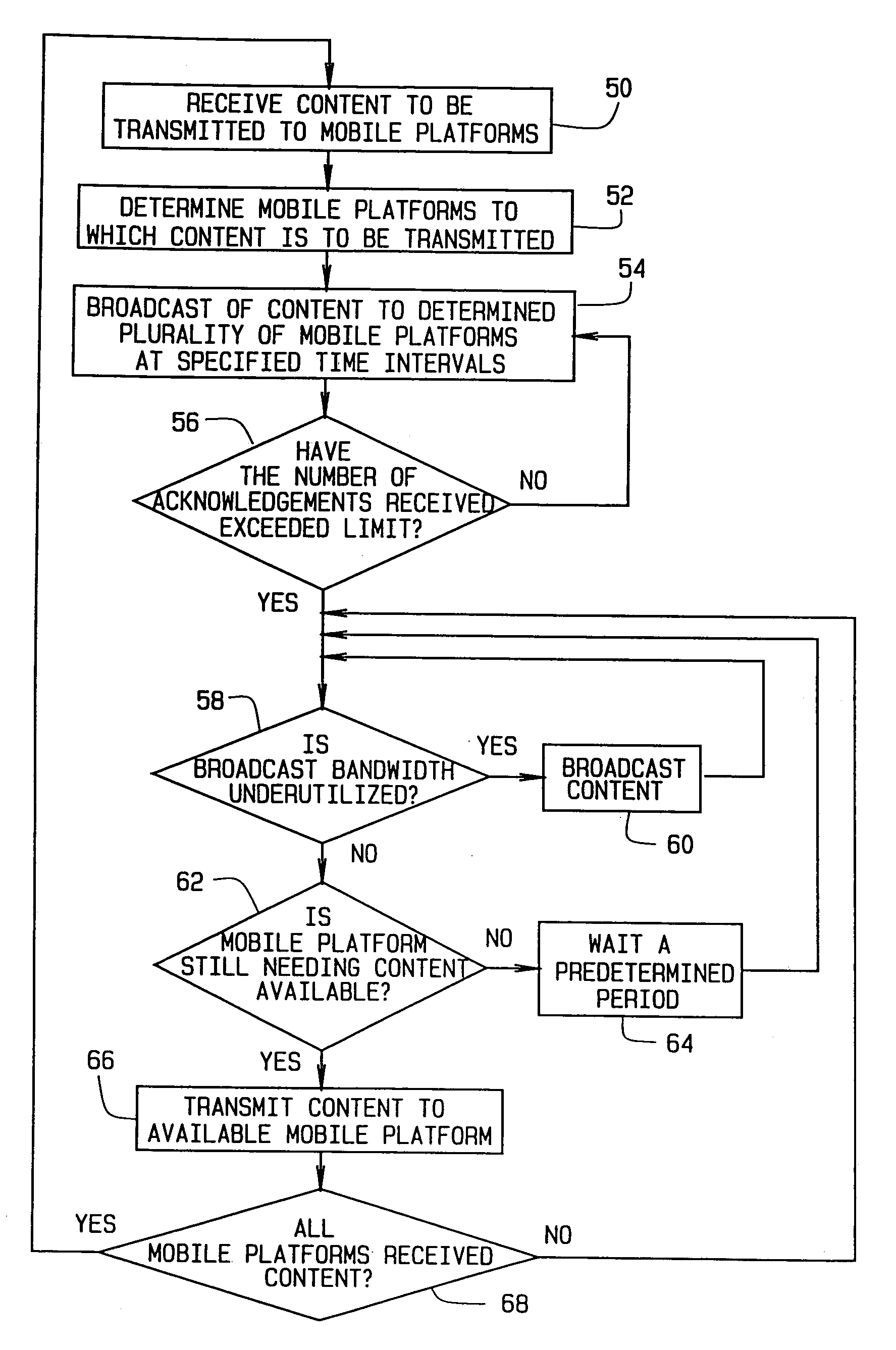
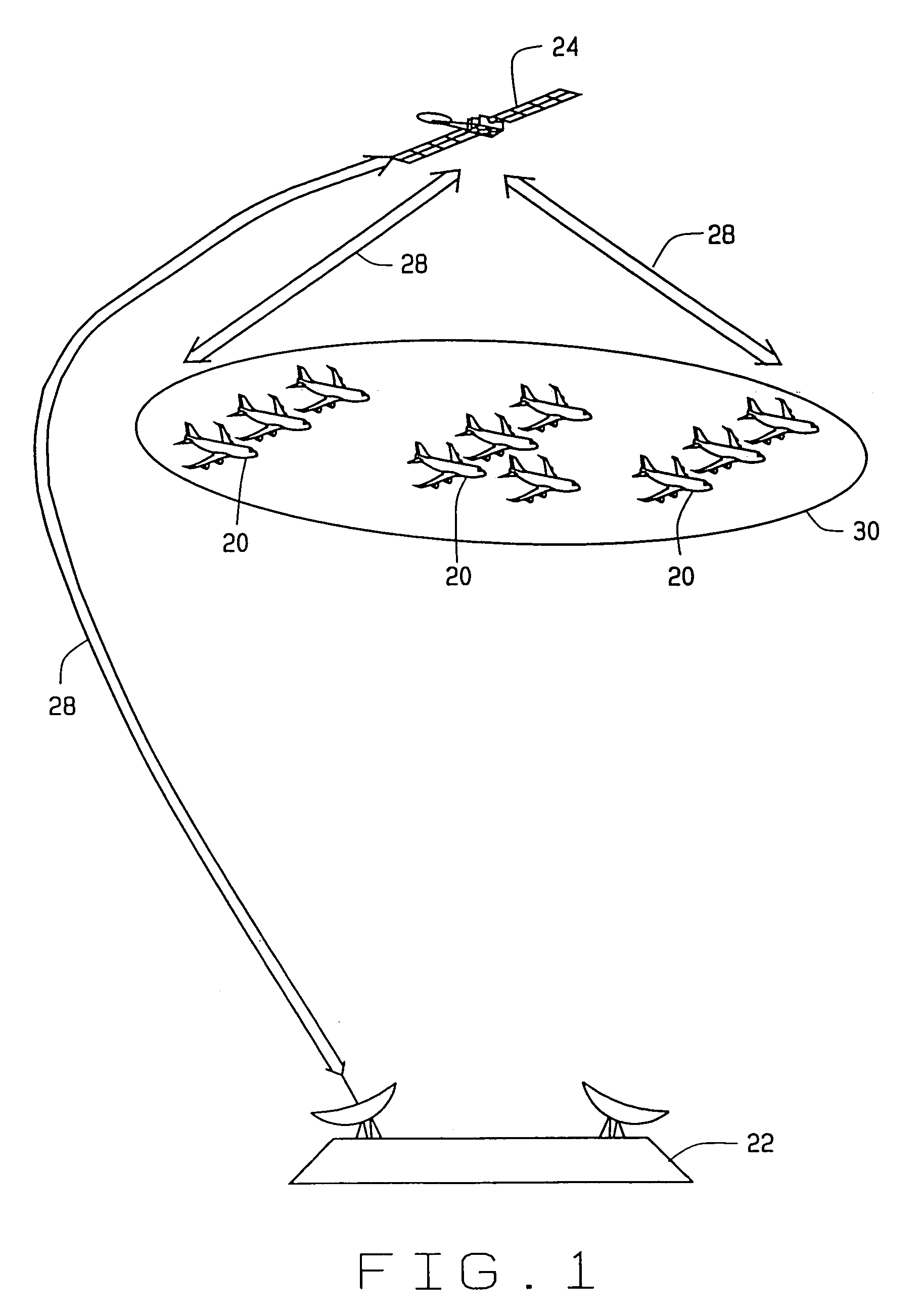
ActiveUS7187690B2Maximize bandwidth usageMaximize bandwidth for communicatingTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionData contentTransfer mode
A system and method for switching between transmission modes provides more efficient use of available bandwidth. A content delivery system determines, based upon a predetermined limit, whether to broadcast content to a plurality of mobile platforms or unicast the data content via a point-to-point communication link. Acknowledgment signals from the mobile platforms are used to determine if the predetermined limit has been exceeded. A specific number or percentage defines the predetermined limit within a specified time period. The number of acknowledgment signals received is compared to the limit to determine if an exceedance condition has occurred.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method and system for adapatively obtaining bandwidth allocation requests
InactiveUS20060146863A1Reduce amountEffective bandwidthNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexRate adaptationState parameter
A method and apparatus for adaptively obtaining bandwidth requests in a broadband wireless communication system, The method and apparatus includes dynamically varying technique combinations enabling a plurality of users to efficiently request bandwidth from a shared base station. A user may “piggyback” a new bandwidth request upon, or set a “poll-me bit” within, presently allocated bandwidth. A base station may poll users, individually or in groups, by allocating unrequested bandwidth for new requests. Polling may respond to a “poll-me bit,” and / or it may be adaptively periodic at a rate based on communication status parameters, such as recent communication activity and connection QoS levels Group polling permits a possibility of collisions. Polling policies may be established for dynamically varying user groups, or may be determined for each user. Dynamic selection of appropriate polling techniques makes use of efficiency benefits associated with each technique.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Techniques for updating live objects at clients using a dynamic routing network
ActiveUS20060031282A1Utilizes bandwidth efficientlyEfficient use ofMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideAdaptive routing
A dynamic content routing network routes update messages containing updates to properties of live objects from input sources to clients having the objects. Certain objects served to clients by a server are indicated as “live.” When the clients receive live objects, the clients identify the object IDs associated with the objects and register the object IDs with the routing network. The routing network maintains a registry of object IDs and clients. An input source provides an update message to the routing network containing the object ID and data specifying an update to a property of the object. The routing network routes the message to each client that has registered for the object ID contained in the message. Upon receipt of the message, a client updates the specified property of the live object.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
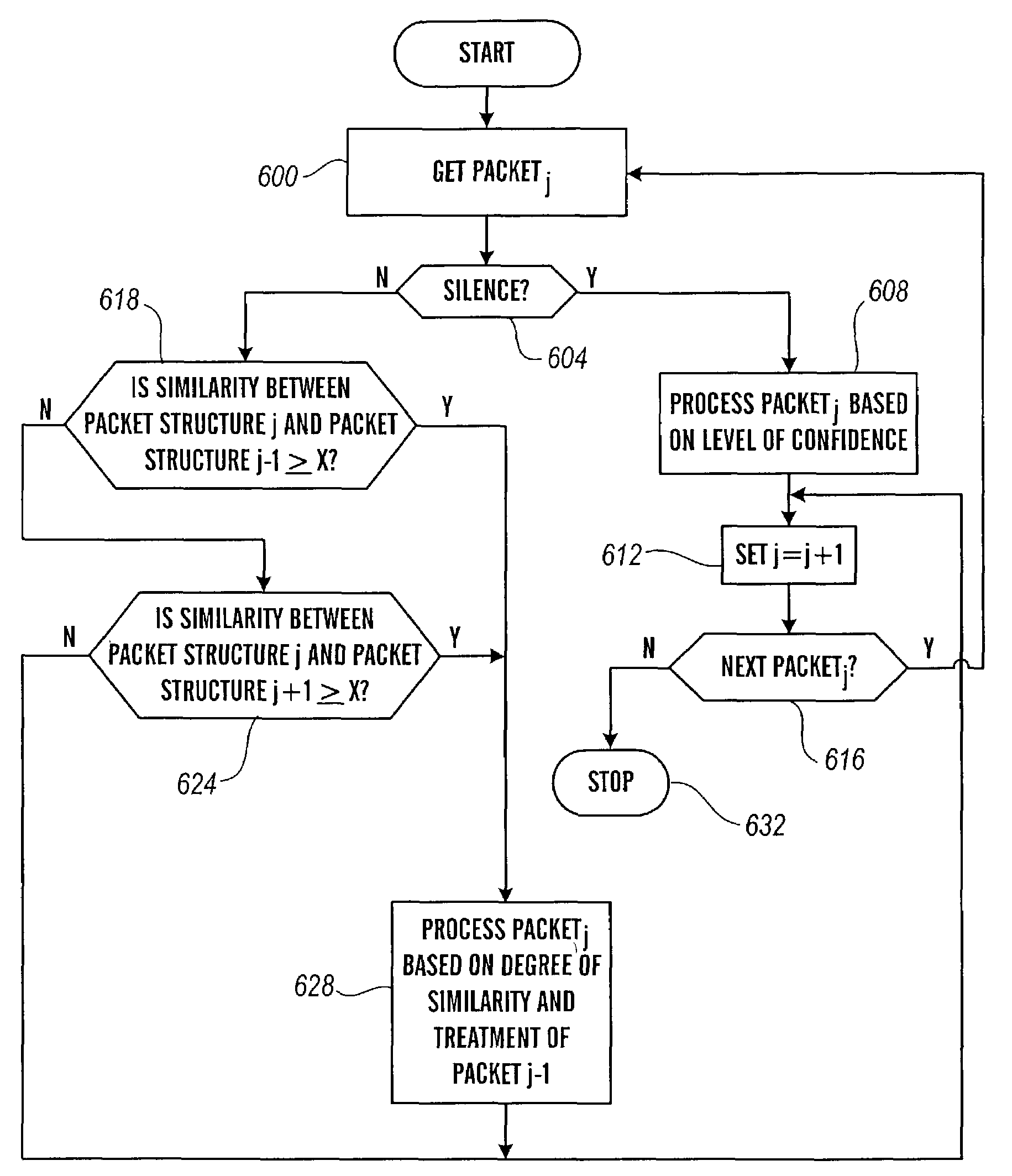
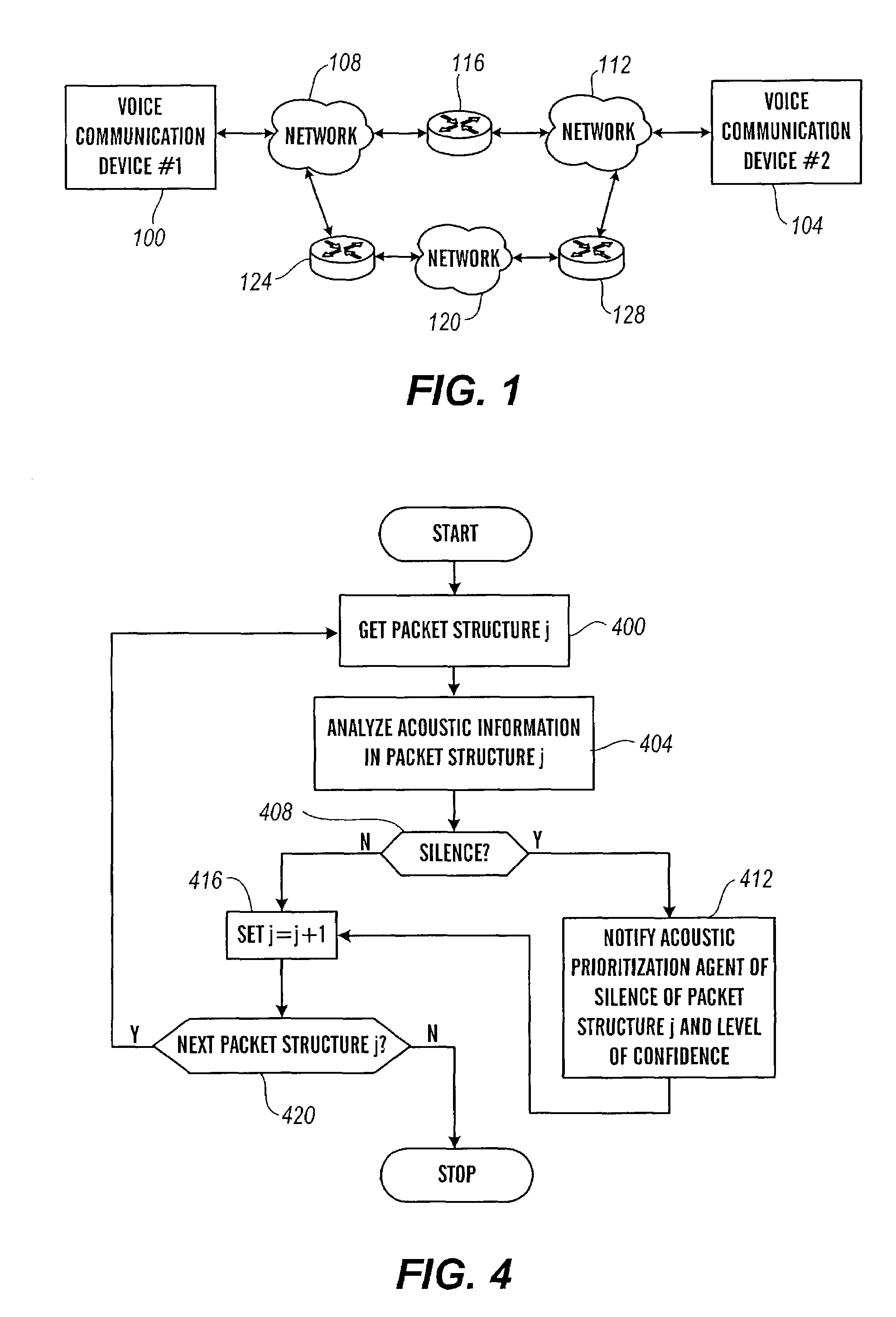
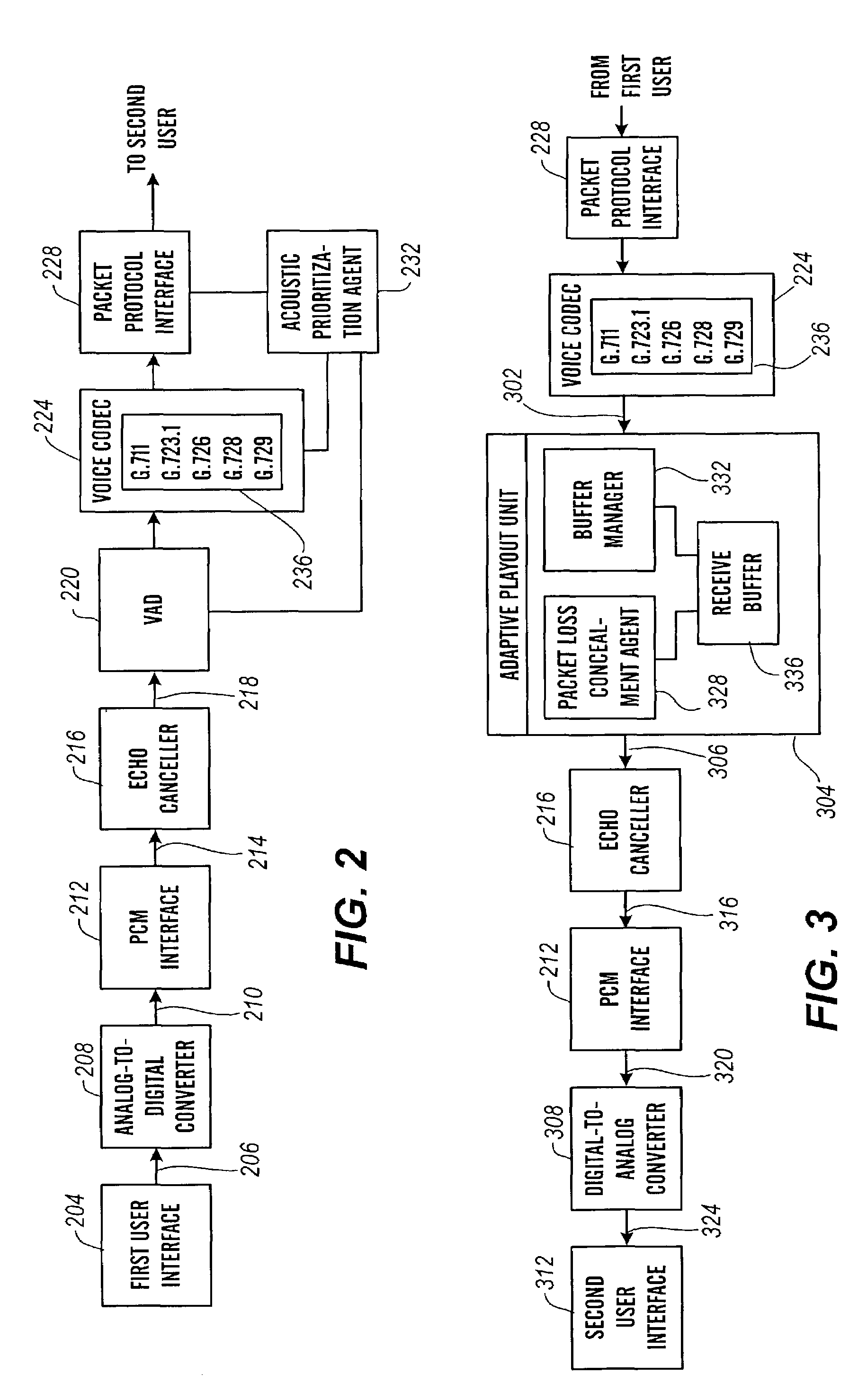
Packet prioritization and associated bandwidth and buffer management techniques for audio over IP
ActiveUS7359979B2Raise priorityReduce the possibilityMultiple digital computer combinationsSpeech recognitionVoice communicationVoice activity
The present invention is directed to voice communication devices in which an audio stream is divided into a sequence of individual packets, each of which is routed via pathways that can vary depending on the availability of network resources. All embodiments of the invention rely on an acoustic prioritization agent that assigns a priority value to the packets. The priority value is based on factors such as whether the packet contains voice activity and the degree of acoustic similarity between this packet and adjacent packets in the sequence. A confidence level, associated with the priority value, may also be assigned. In one embodiment, network congestion is reduced by deliberately failing to transmit packets that are judged to be acoustically similar to adjacent packets; the expectation is that, under these circumstances, traditional packet loss concealment algorithms in the receiving device will construct an acceptably accurate replica of the missing packet. In another embodiment, the receiving device can reduce the number of packets stored in its jitter buffer, and therefore the latency of the speech signal, by selectively deleting one or more packets within sustained silences or non-varying speech events. In both embodiments, the ability of the system to drop appropriate packets may be enhanced by taking into account the confidence levels associated with the priority assessments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Method for enabling multipoint network services over a ring topology network
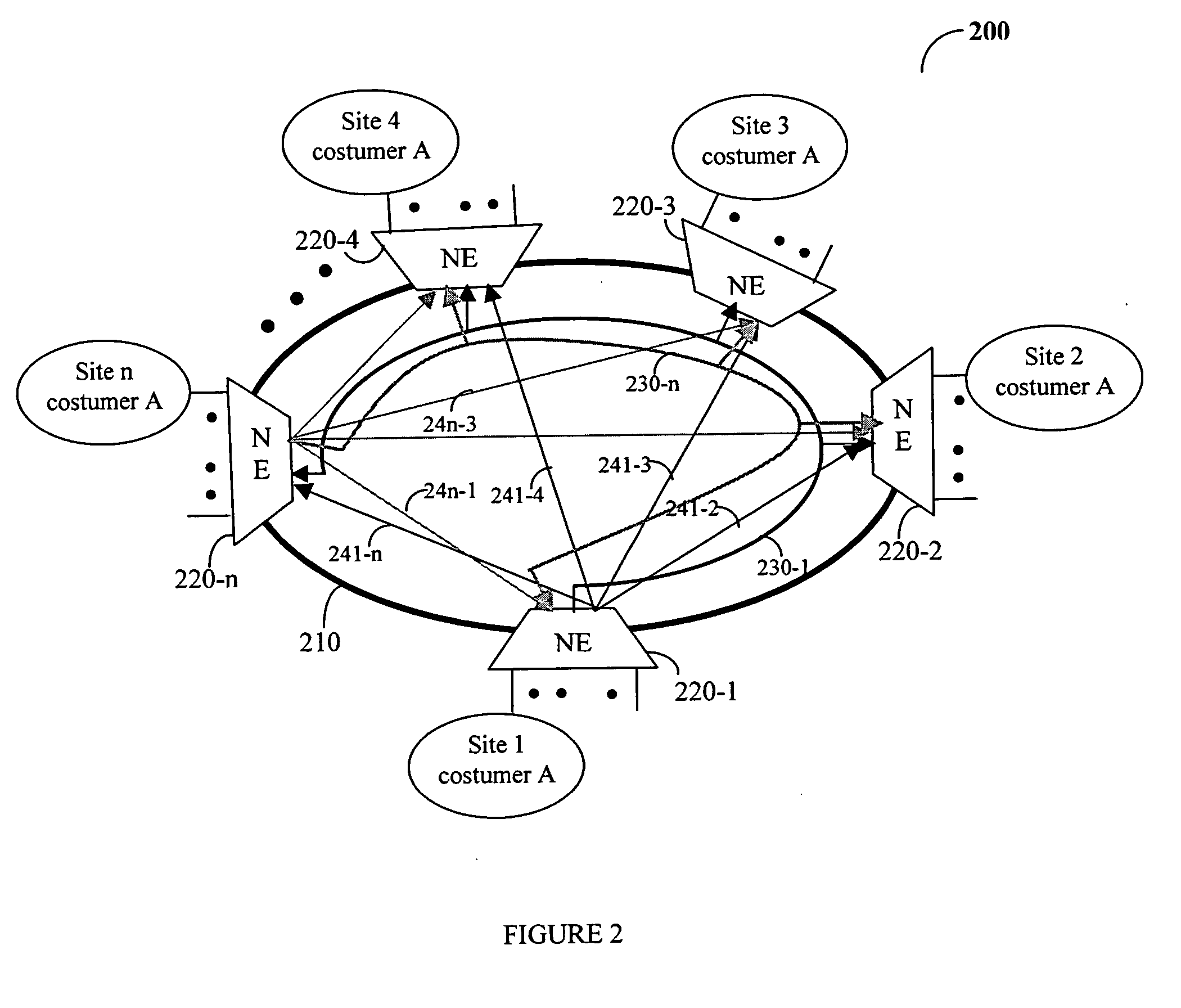
InactiveUS20050271035A1Efficient bandwidth utilizationEasy maintenanceSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork serviceDistributed computing
A method, device, and system for providing multipoint network services over a ring topology network. According to the disclosed method point-to-point connections and point-to-multipoint connections are established between network elements (NEs) providing the same network services. These connections eliminate the need for replicating packets at a source NE and, as a result, the bandwidth utilization is significantly improved. In one embodiment of this invention the multipoint network services provided by the present invention is a virtual private LAN service (VPLS).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com