Patents
Literature
1234results about "Star-type electromagnetic networks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
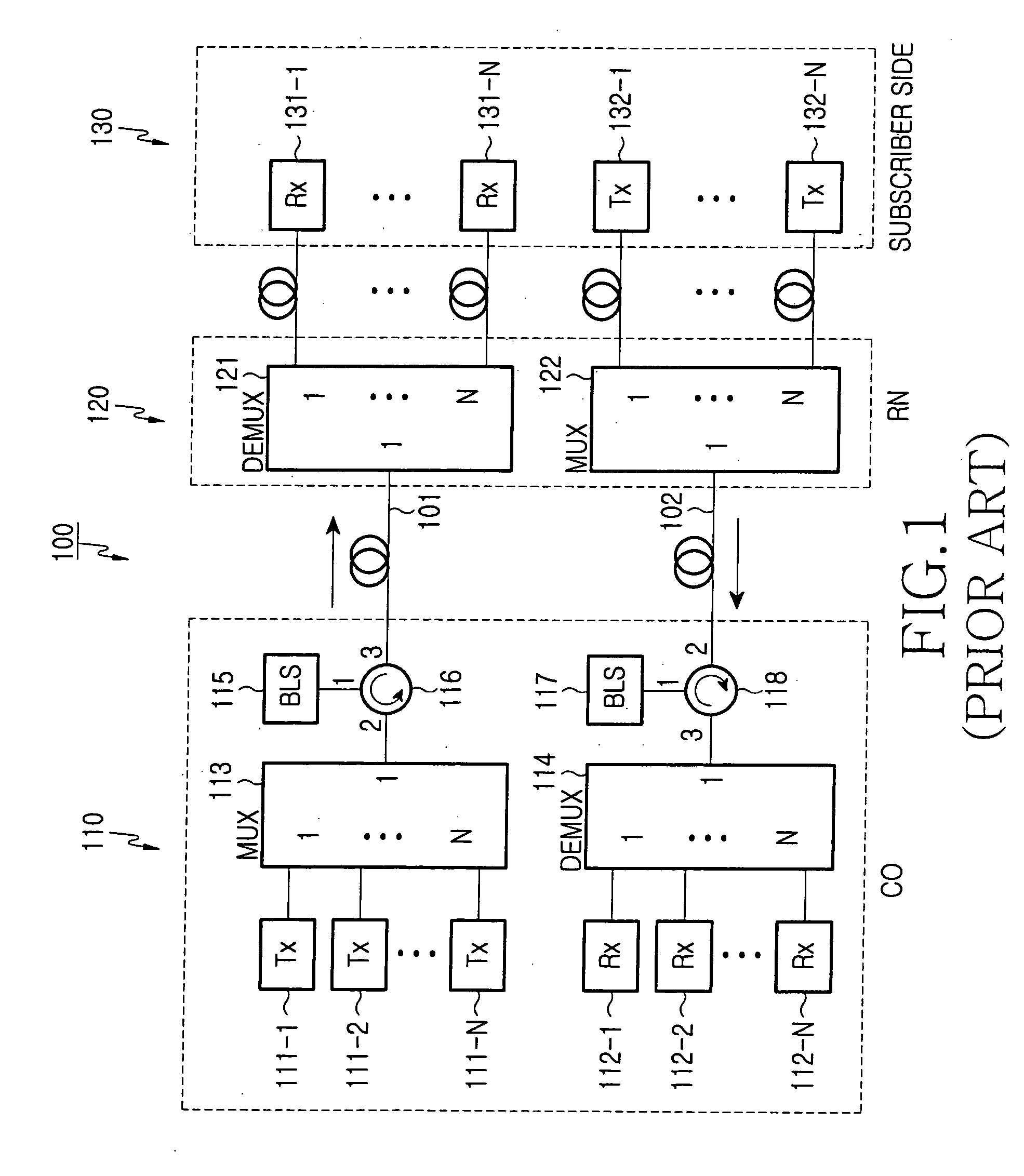
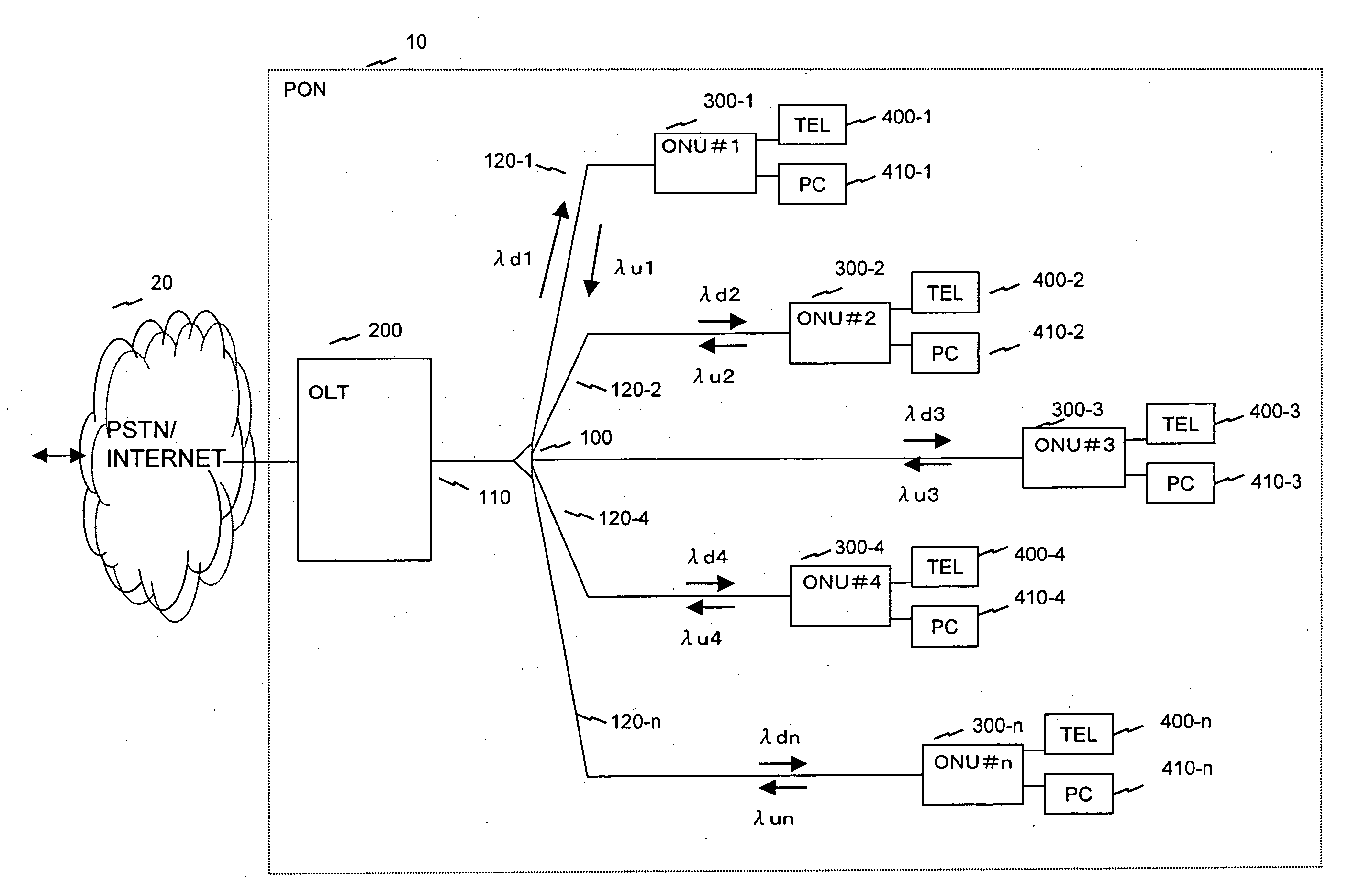
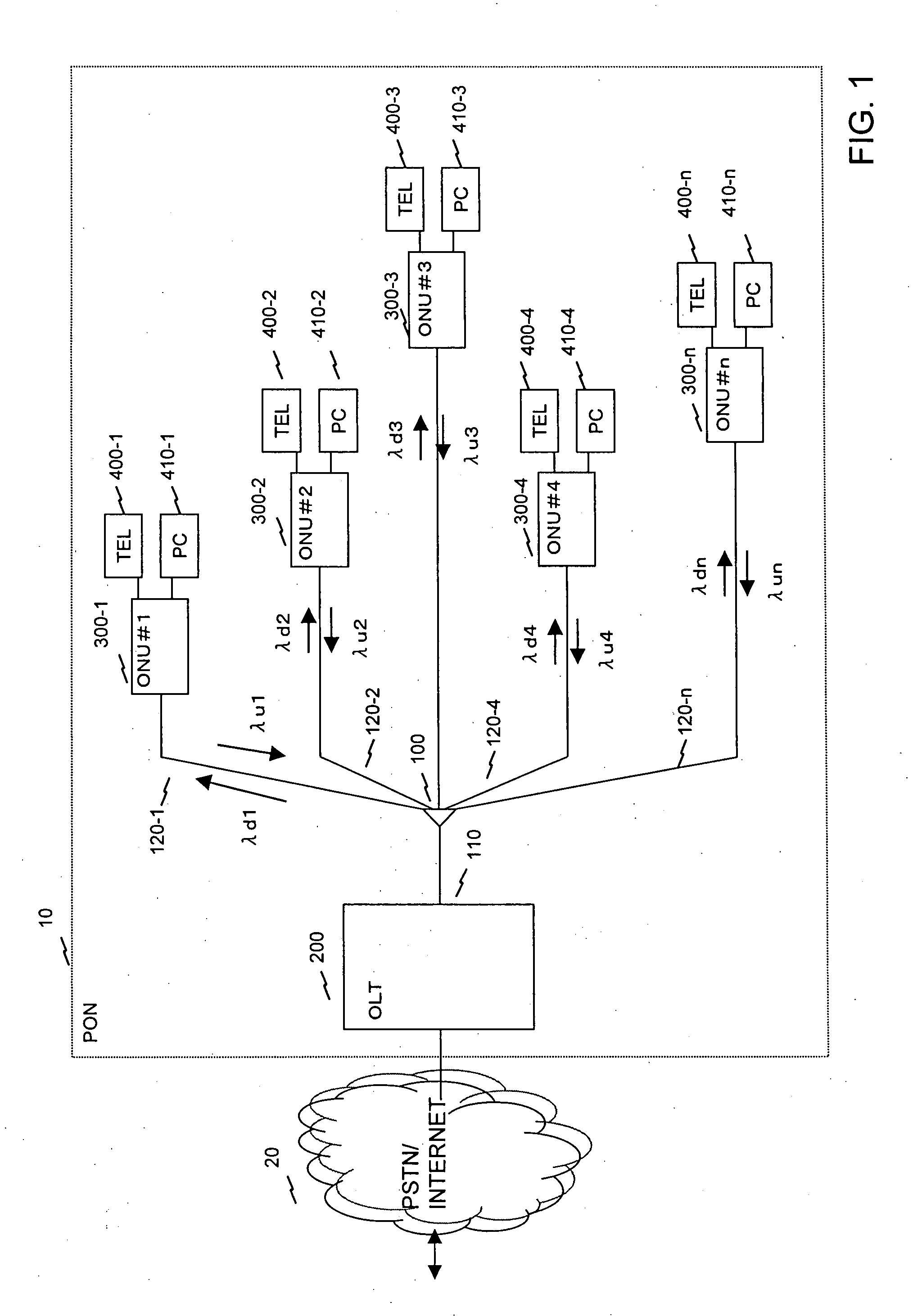
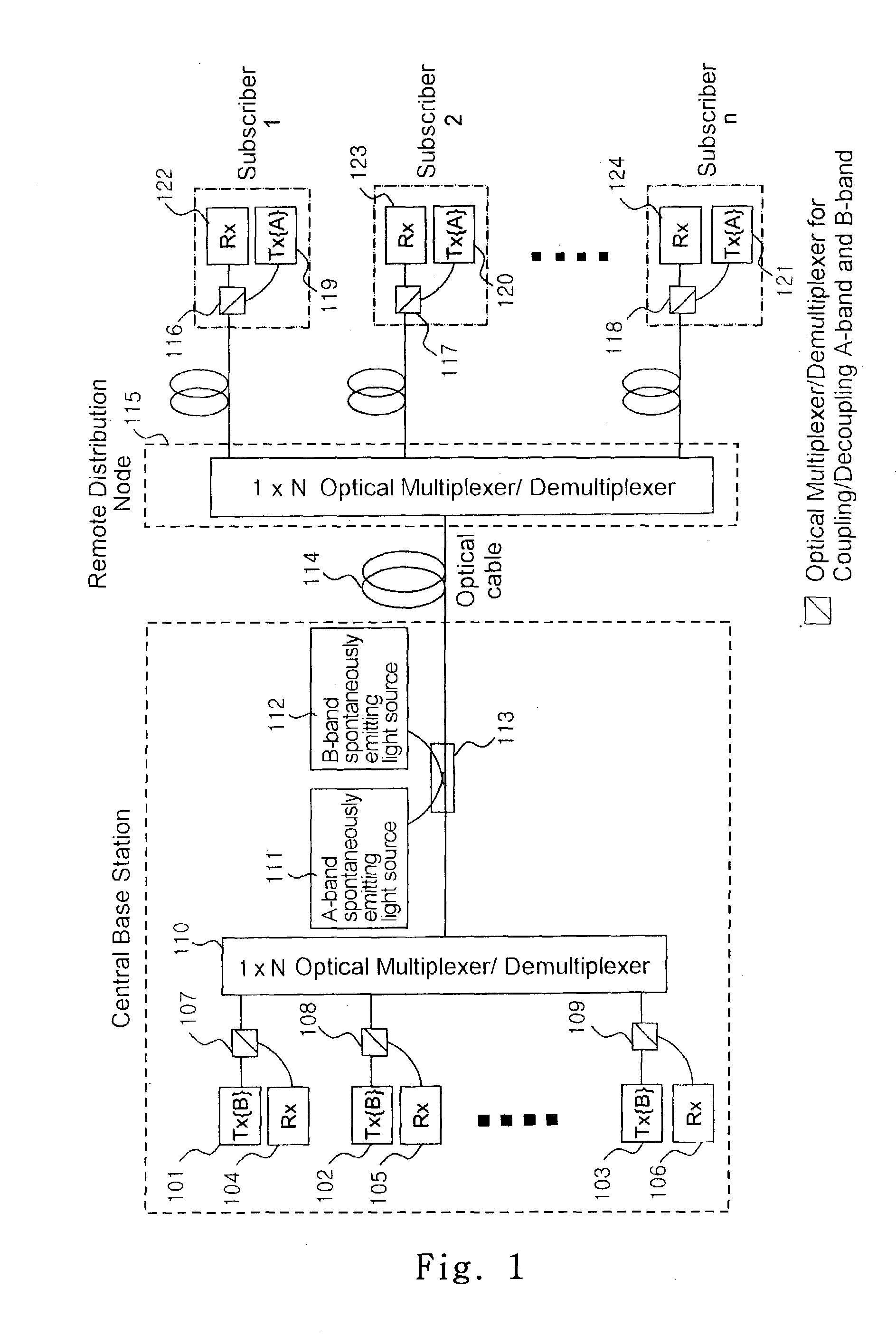
Fiber to the home (FTTH) multimedia access system with reflection PON
InactiveUS20020063924A1Inexpensive, easy-to-serviceEasy to scaleBroadband local area networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingData signal
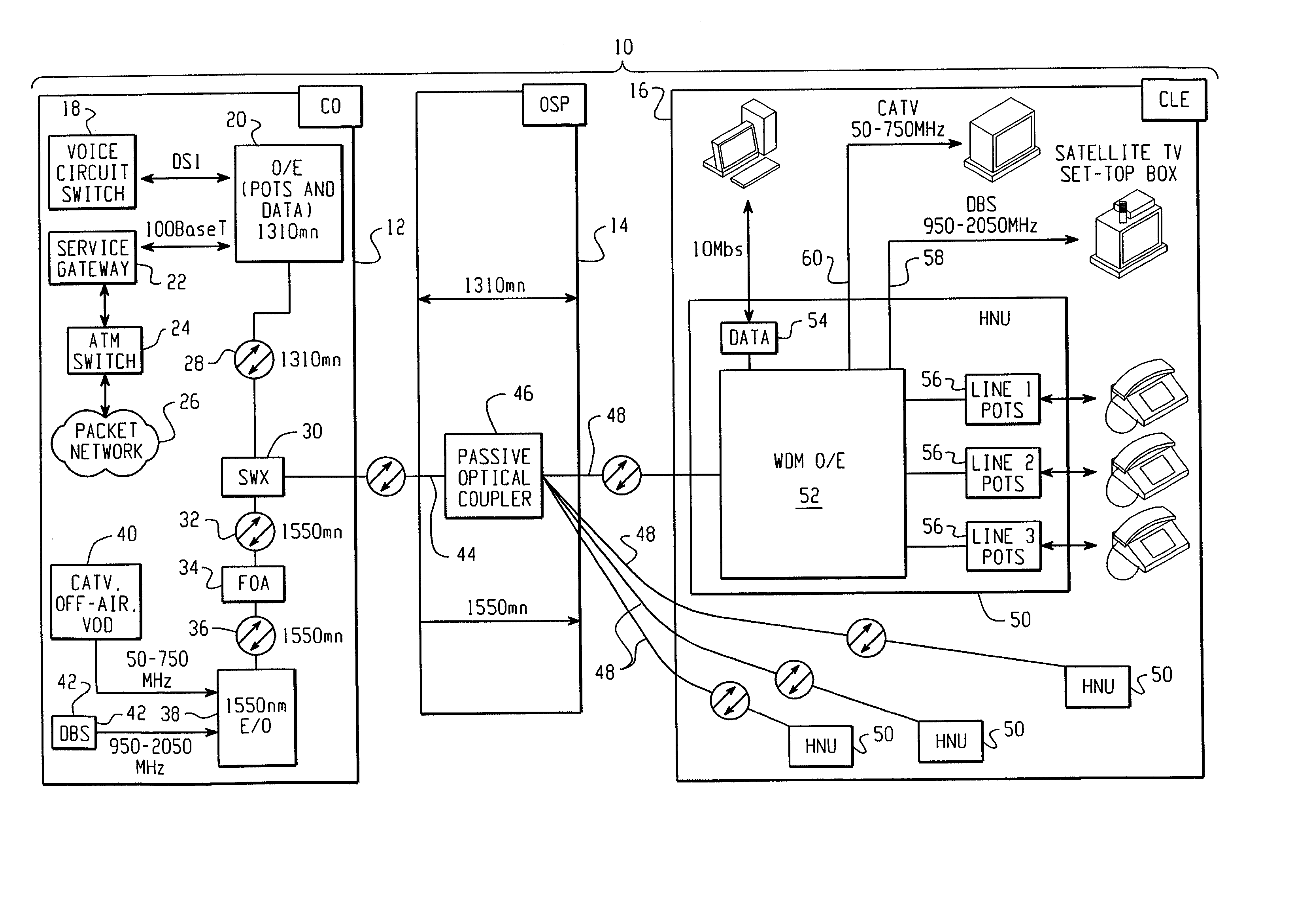
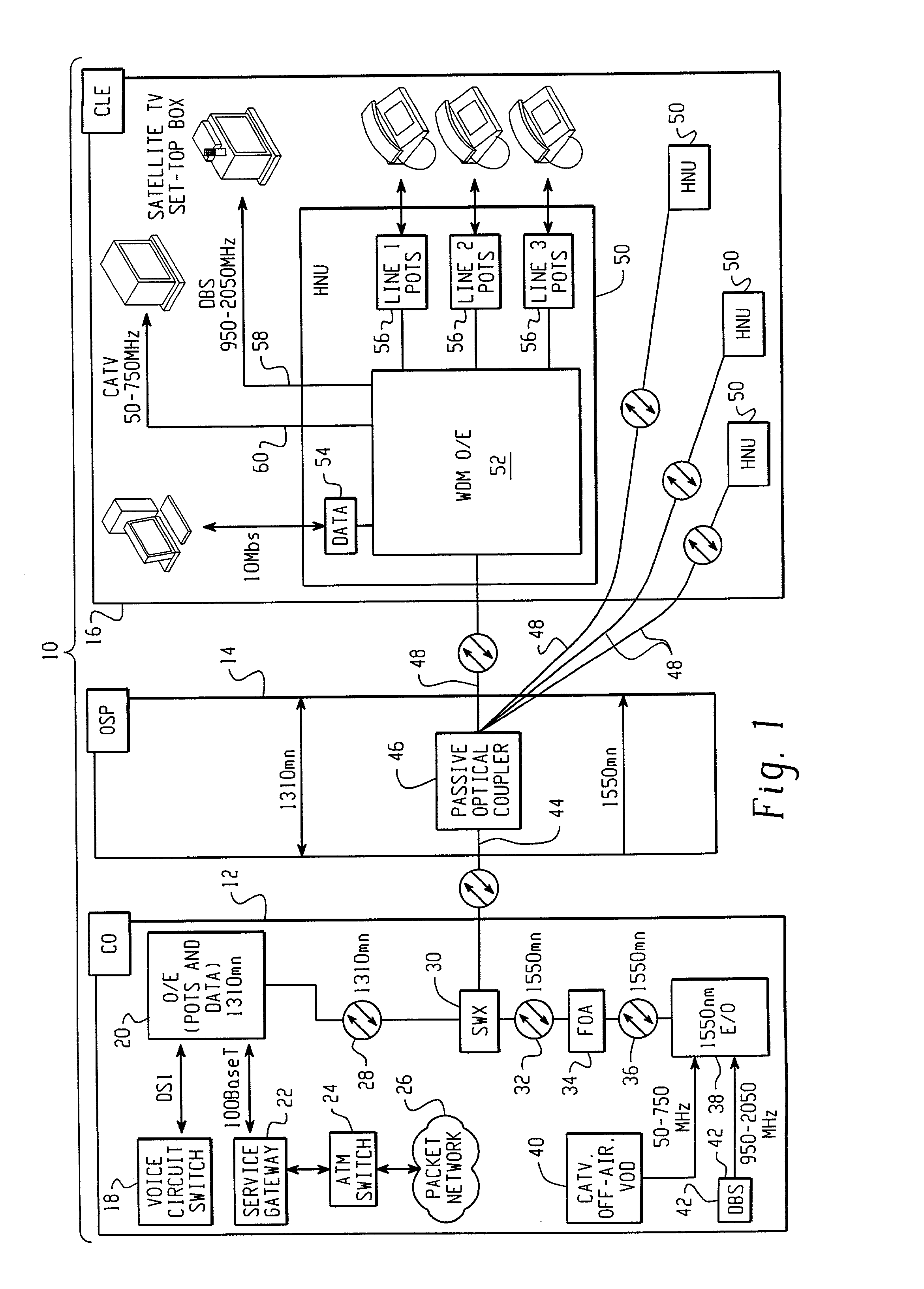
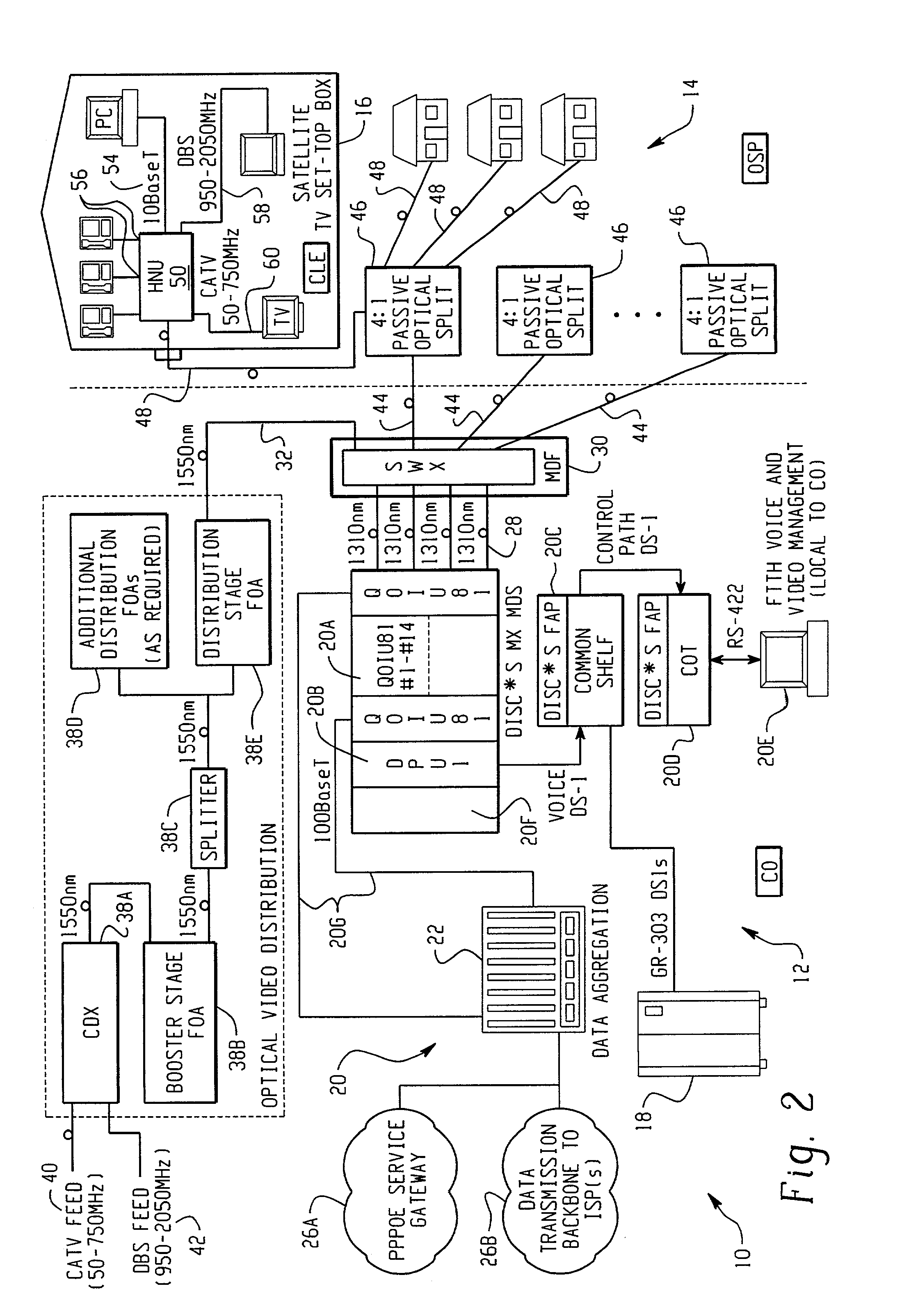
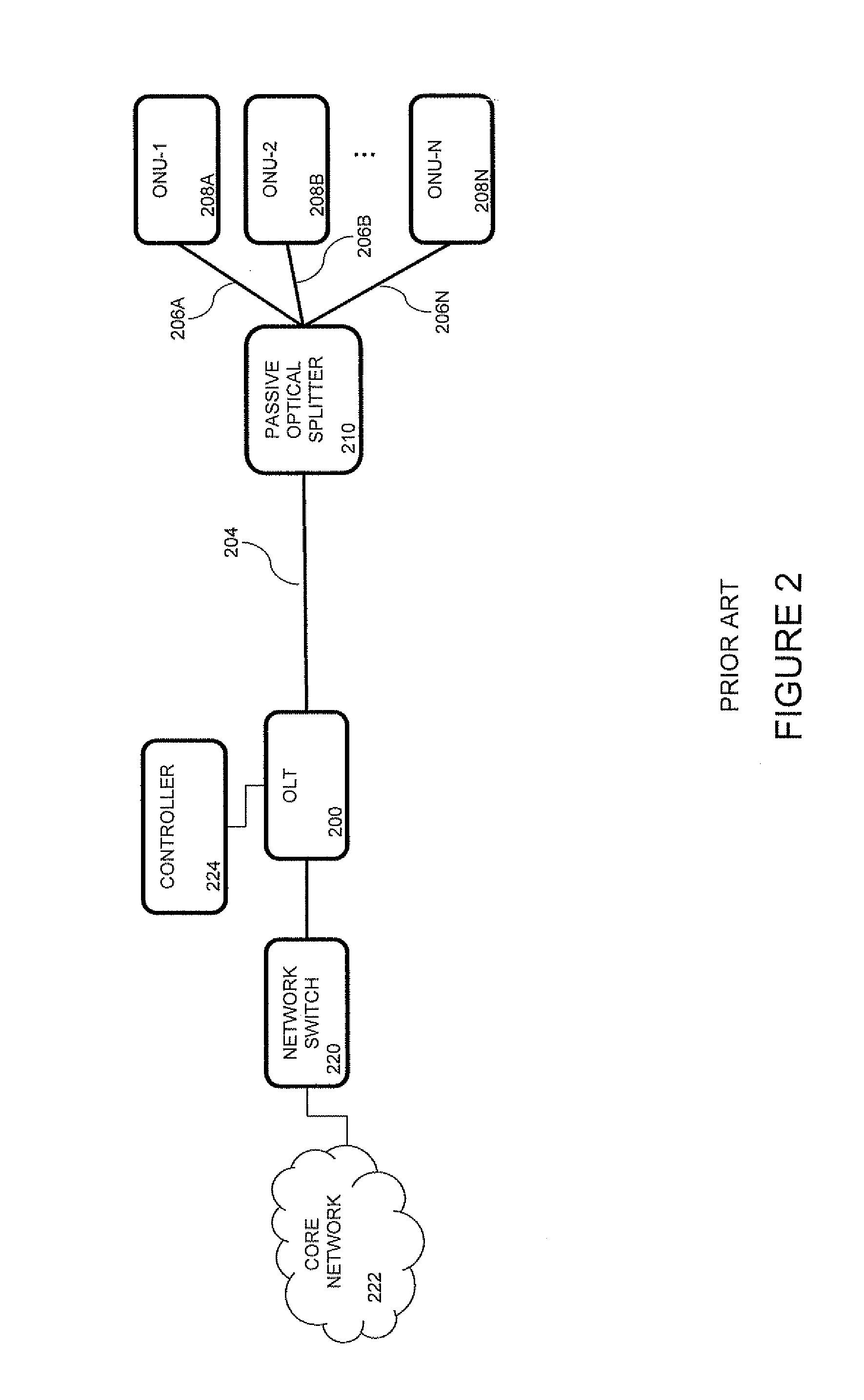
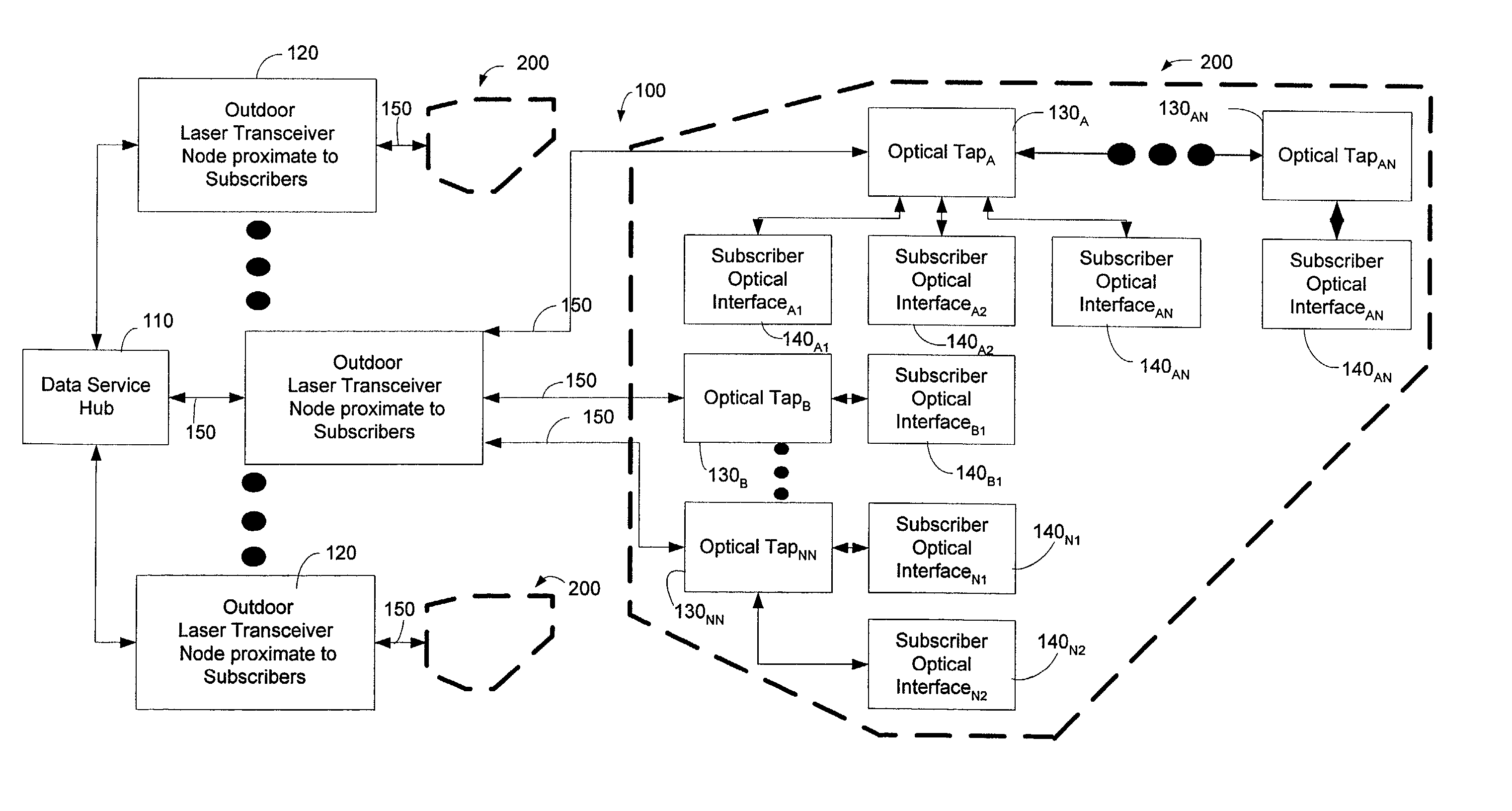
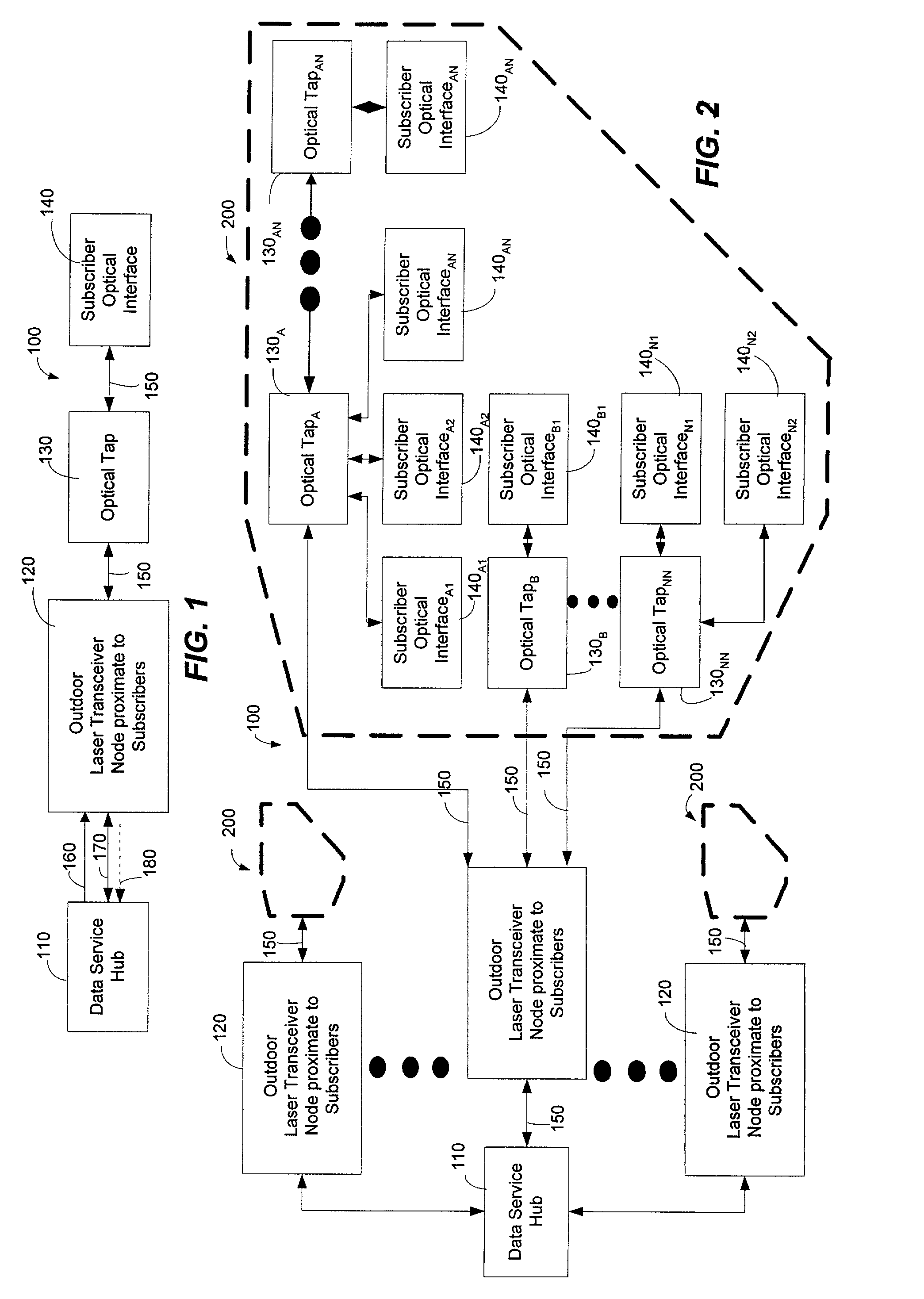
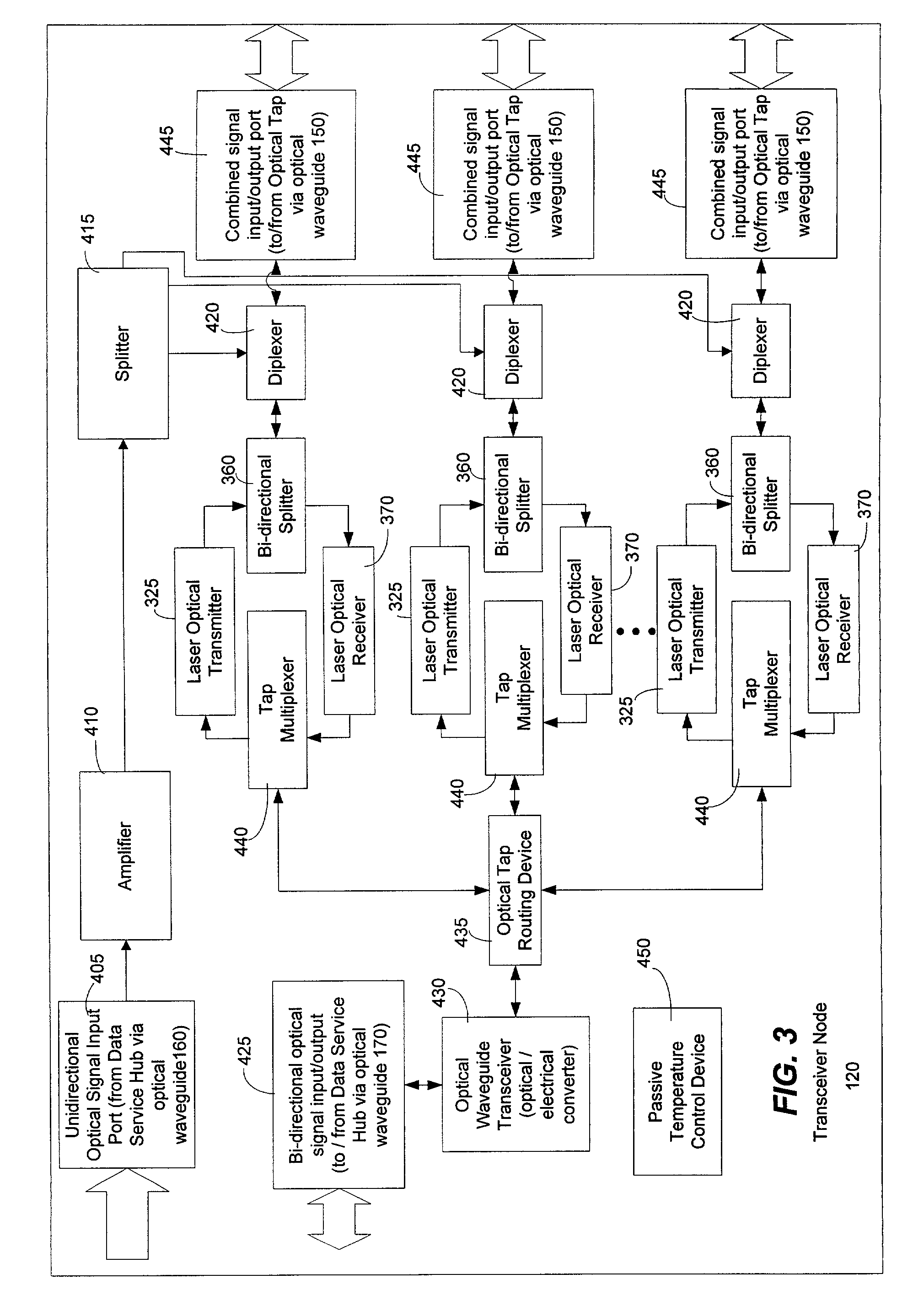
A Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) multi-media access system and method are provided in which voice, video and data signals are transported over a passive optical network (PON) between a central office location and a plurality of subscriber home network units (HNUs). Optical video distribution circuitry and telephony / data distribution circuitry at the central office location are included in the system and operate to send and receive CATV video, PBS video television, telephony and Packet data signals to and from the HNUs via the PON. Optical multiplexing / demultiplexing circuitry operating at the central office combines the video signals, which are operating at one optical wavelength, with the telephony / data signals, which are operating at a second, distinct optical wavelength. These combined optical signals are then transported over the PON to the HNUs. The PON includes a plurality of distribution fibers coupled to a plurality of passive optical splitters, which are each coupled to a plurality of drop fibers that connect to the HNUs. The HNUs receive the combined optical signals, demultiplex and convert the optical signals into corresponding electrical signals, which are in turn coupled through the HNU to the video, data and telephony networks within the home. The HNUs also receive upstream electrical signals from devices within the home, multiplex and convert these electrical signals into upstream optical signals, and transmit these upstream optical signals to the central office.
Owner:ADVANCED FIBER ACCESS CORP
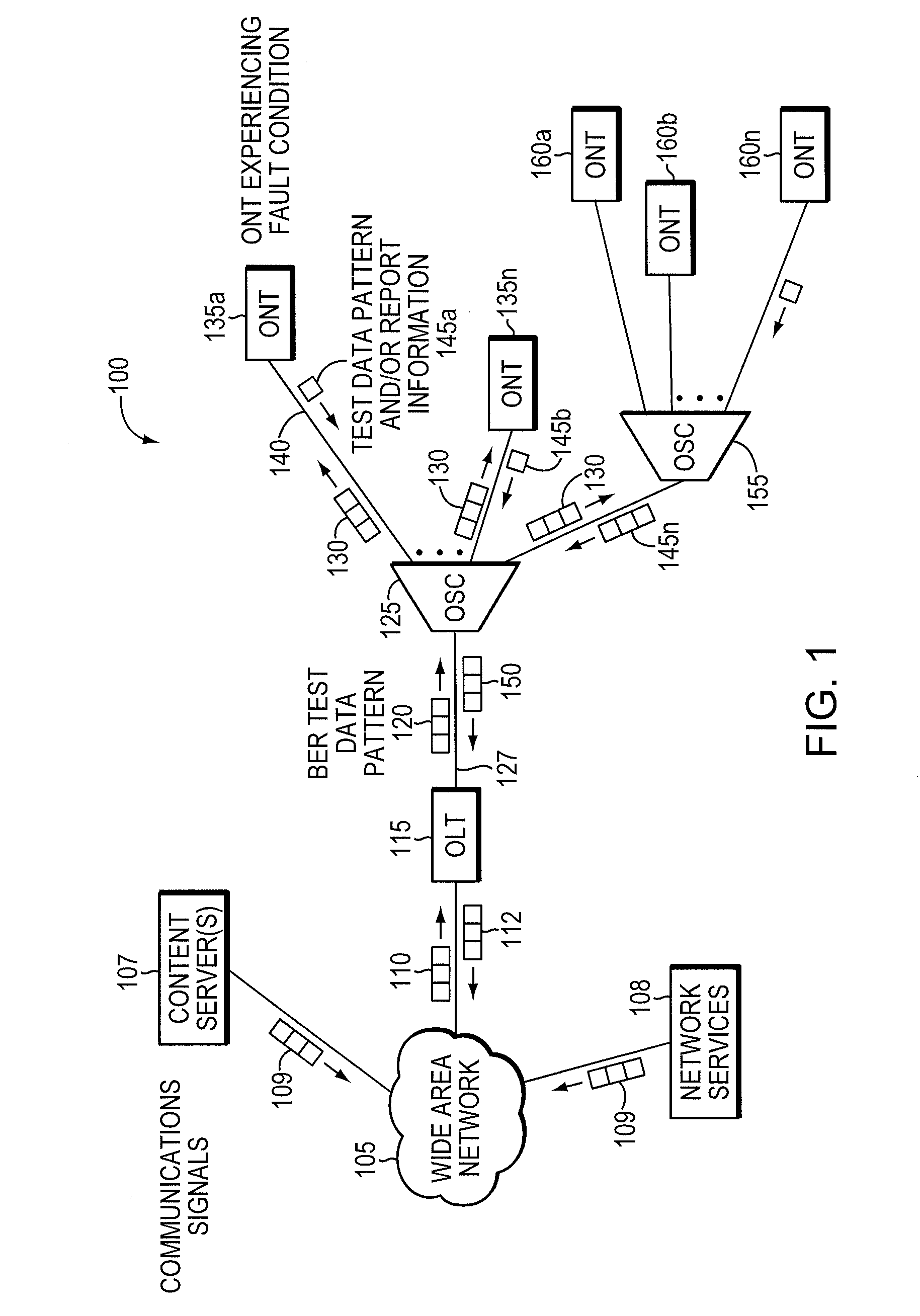
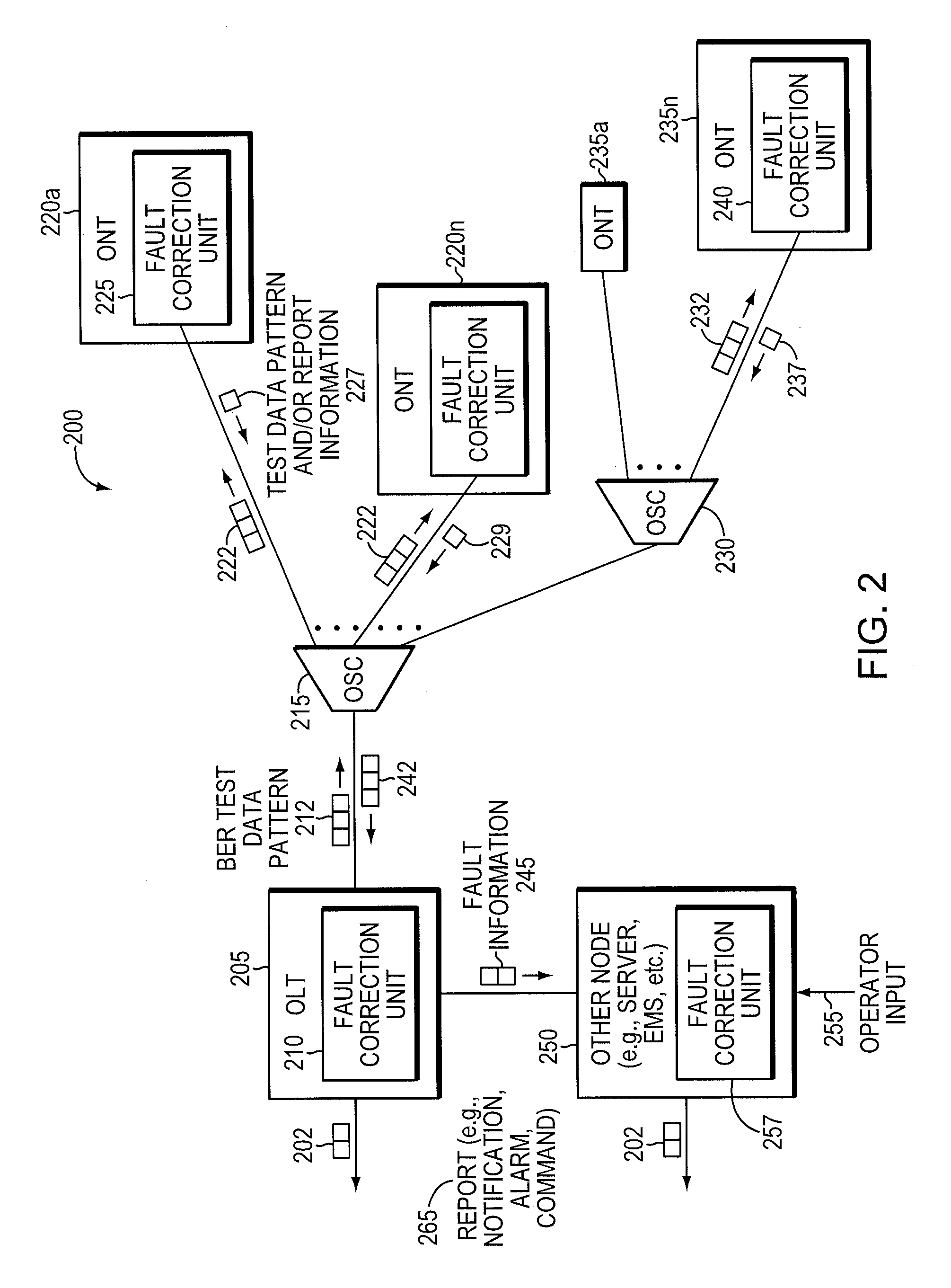
Method and apparatus for correcting faults in a passive optical network
ActiveUS8090258B2Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
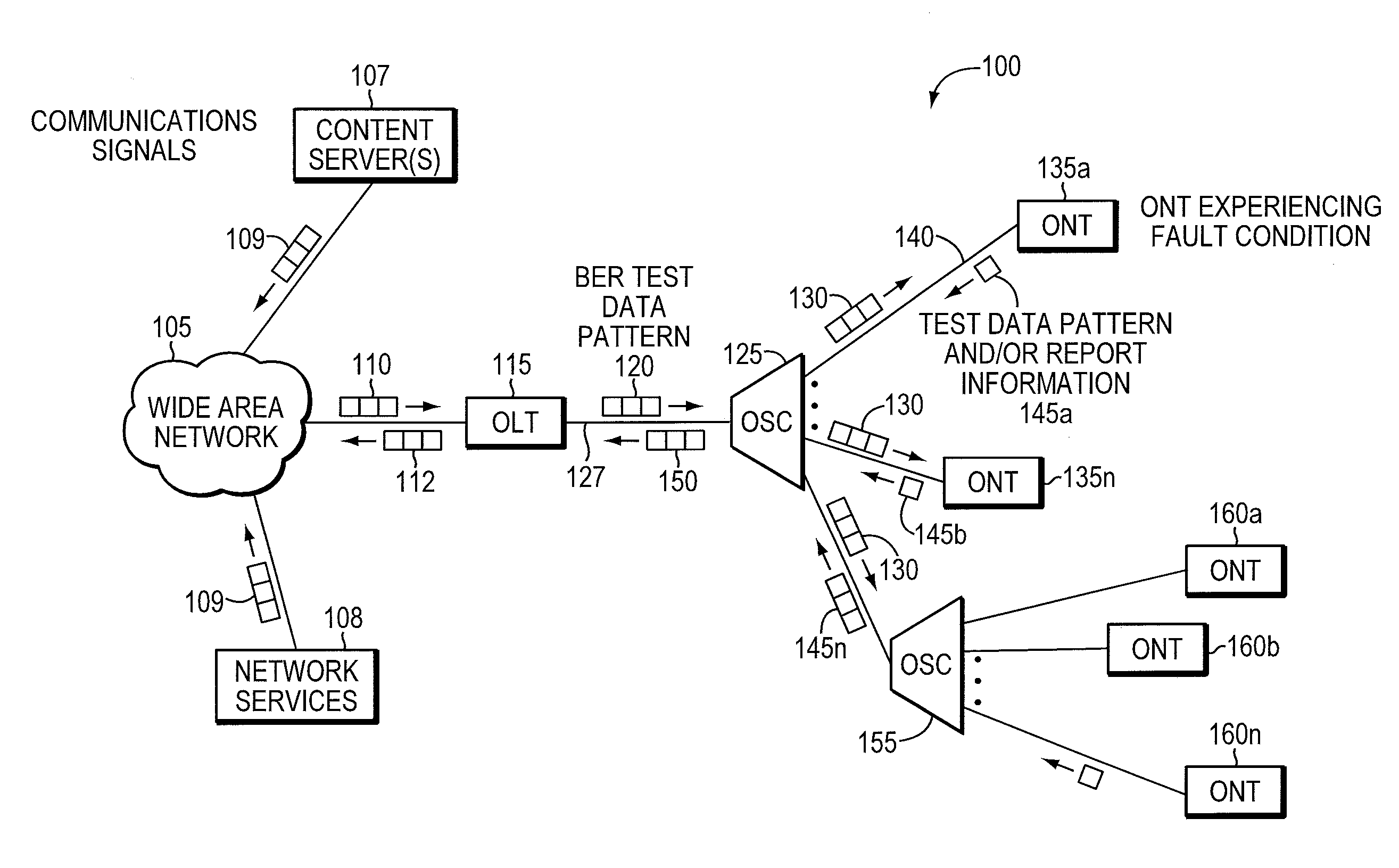
Component malfunctions in passive optical networks (PON) can increase bit error rates and decrease signal-to-noise ratio of communications signals. These faults may cause the receivers of the signals, either the optical line terminal (OLT) or optical network terminals (ONTs), to experience intermittent faults and / or may result in misinterpreted commands that disrupt other ONT's communication, resulting in a rogue ONT condition. Existing PON protocol detection methods may not detect these types of malfunctions. An embodiment of the present invention identifies faults in a PON by transmitting a test series of data patterns via an optical communications path from a first optical network node to a second optical network node. The test series is compared to an expected series of data patterns. An error rate may be calculated as a function of the differences between the test series and expected series. The error rate may be reported to identify faults in the PON. Through use of the embodiment, network faults can be identified and optionally automatically corrected, saving a network service provider from expending technician time and maintaining an operating state of the network.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
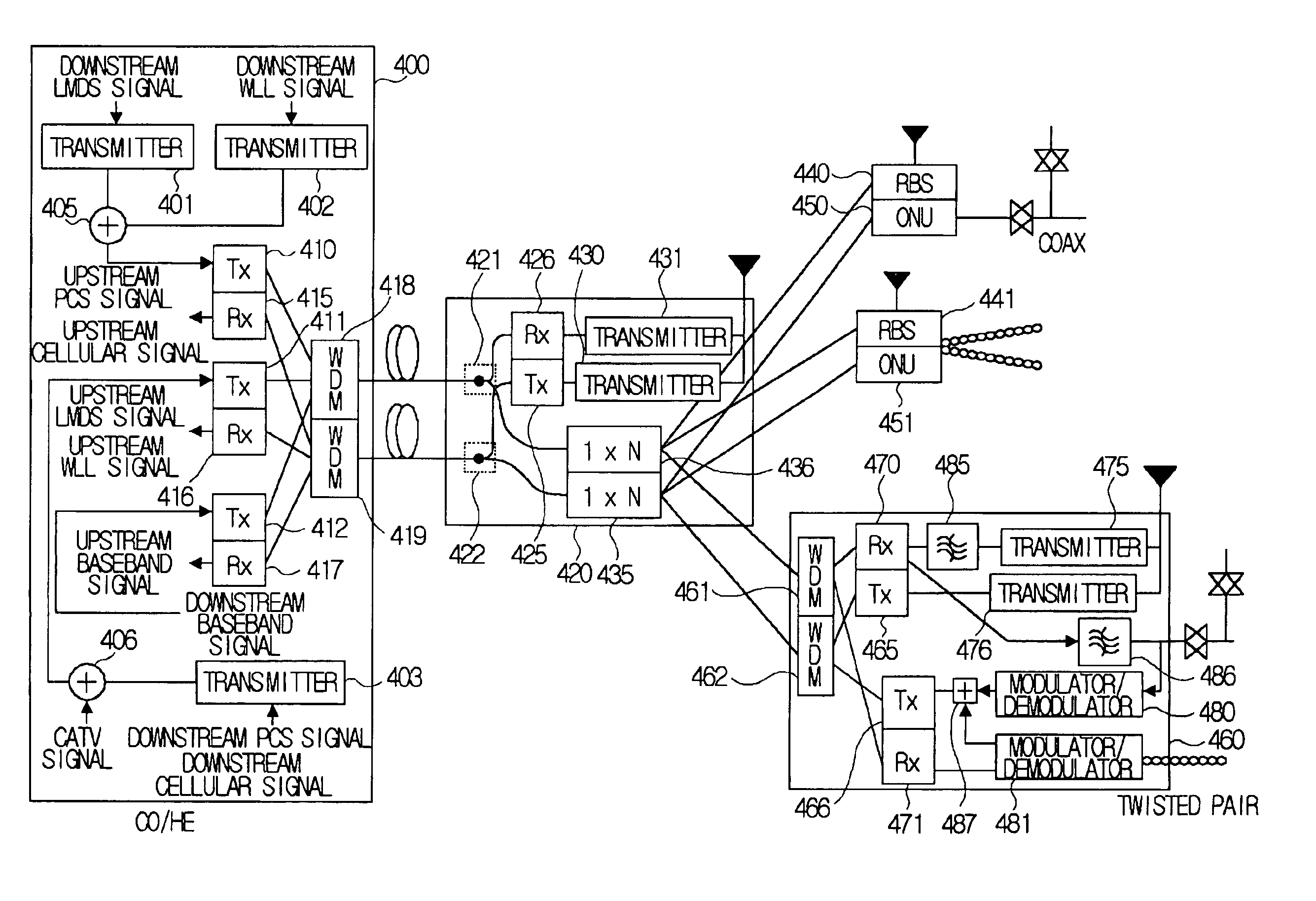
Multi-purpose optical fiber access network
InactiveUS6895185B1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsWireless communicationAccess networkCoaxial cable
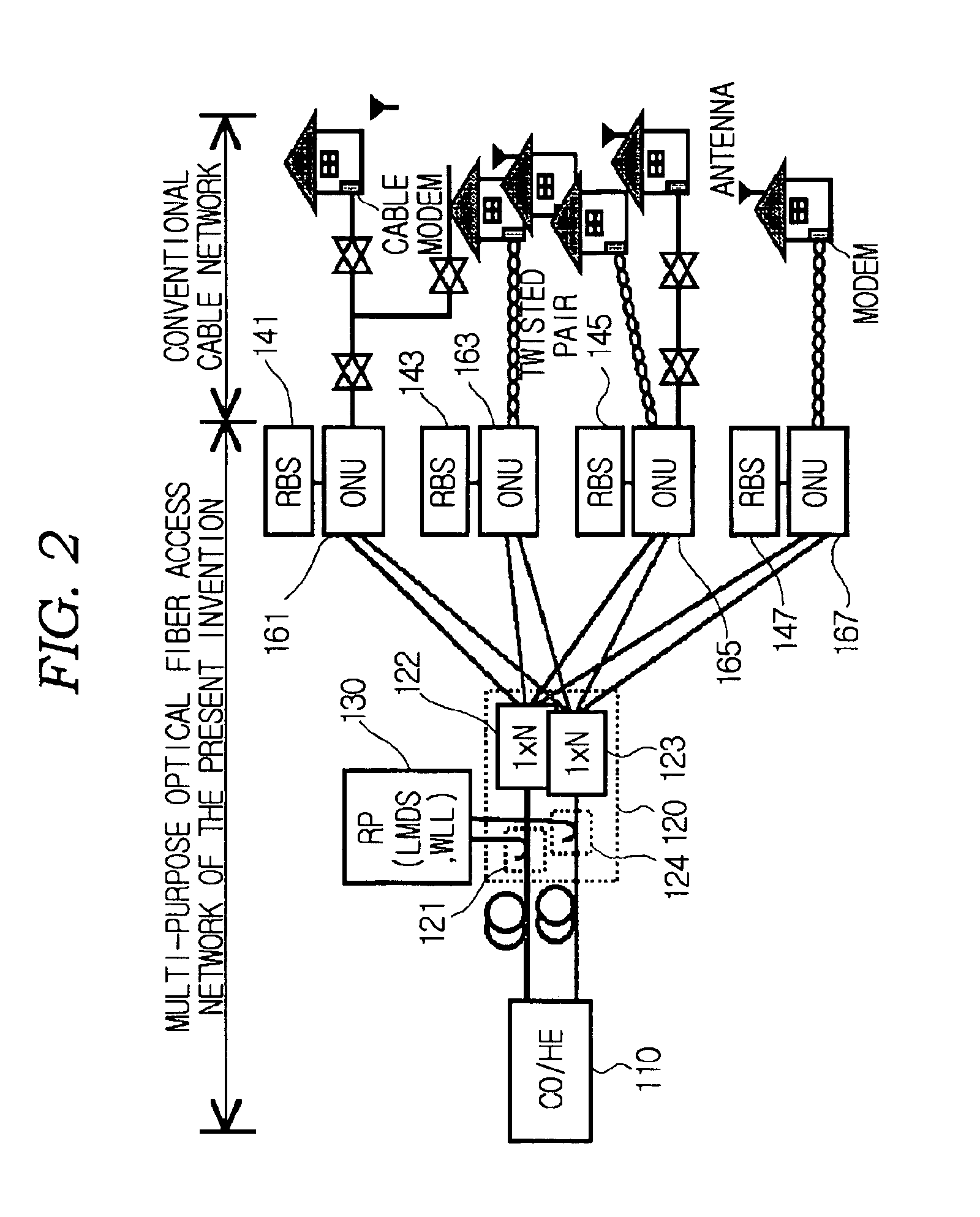
The present invention relates to an optical fiber access network, and more particularly, to a multi-purpose optical fiber access network capable of accepting all services provided by hybrid wireline / wireless access network.According to the present invention, in an optical fiber access network of double star structure where a central office / headend and several optical network units are connected through a splitting / combining device, a multi-purpose optical fiber access network capable of accepting not only wired telephone service, wired CATV and wired data service but also various kinds of wireless services including LMDS, WLL, PCS and so forth, in which LMDS local wireless base station is located in a place adjacent to the splitting / combining device, WLL local wireless base station is located in a place adjacent to the splitting / combining device, optical network unit connects the conventional wired network composed of said optical fiber access network, twisted pair and coaxial cable, telephone service, data service and CATV service are provided through the optical network unit and PCS local wireless base station is located in a place adjacent to the optical network unit, is provided.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
WDM type passive optical network
InactiveUS20070092256A1Increasing ONUs easierImprove communication bandwidthWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar/tree networksLength waveOptical transmitter
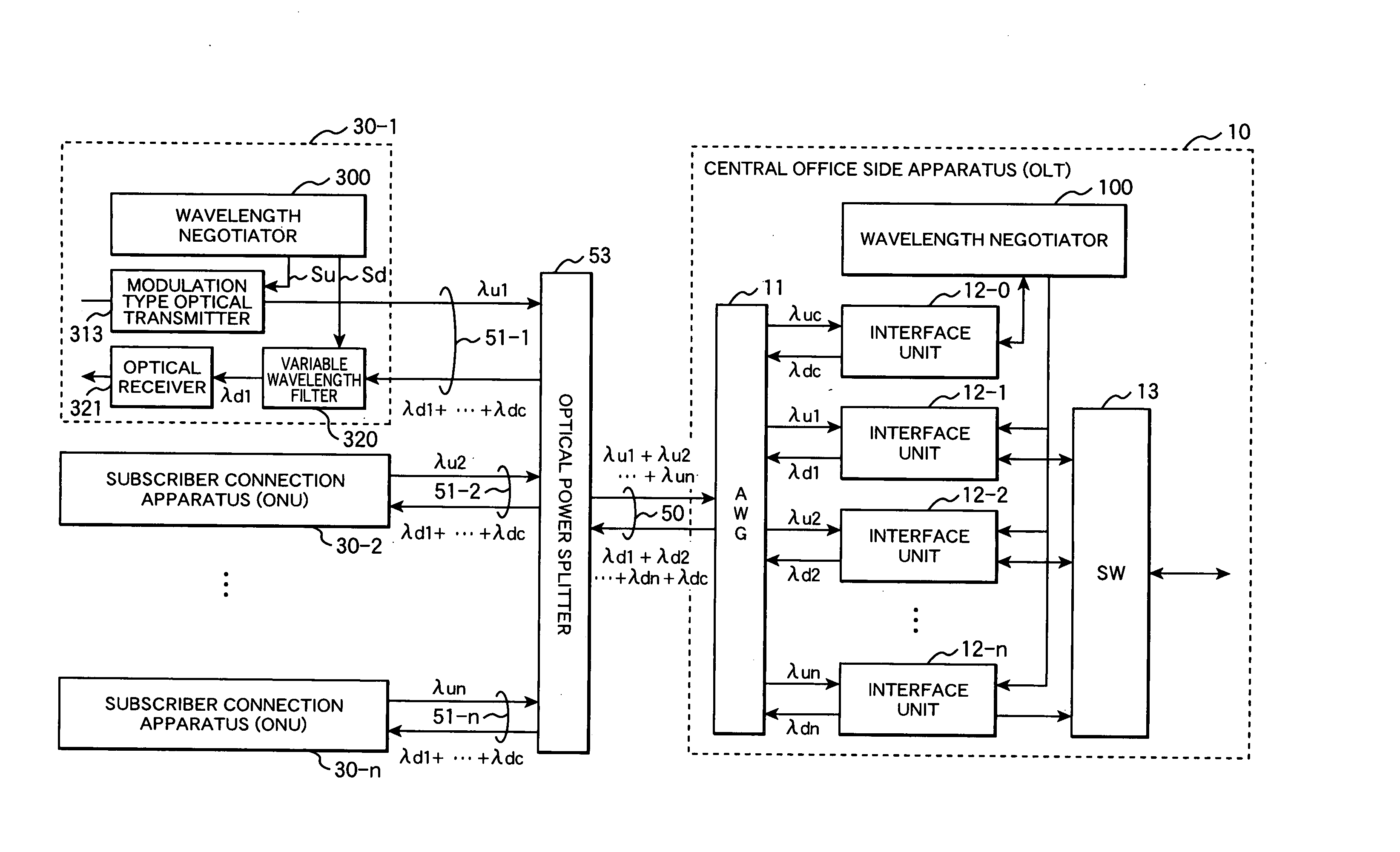
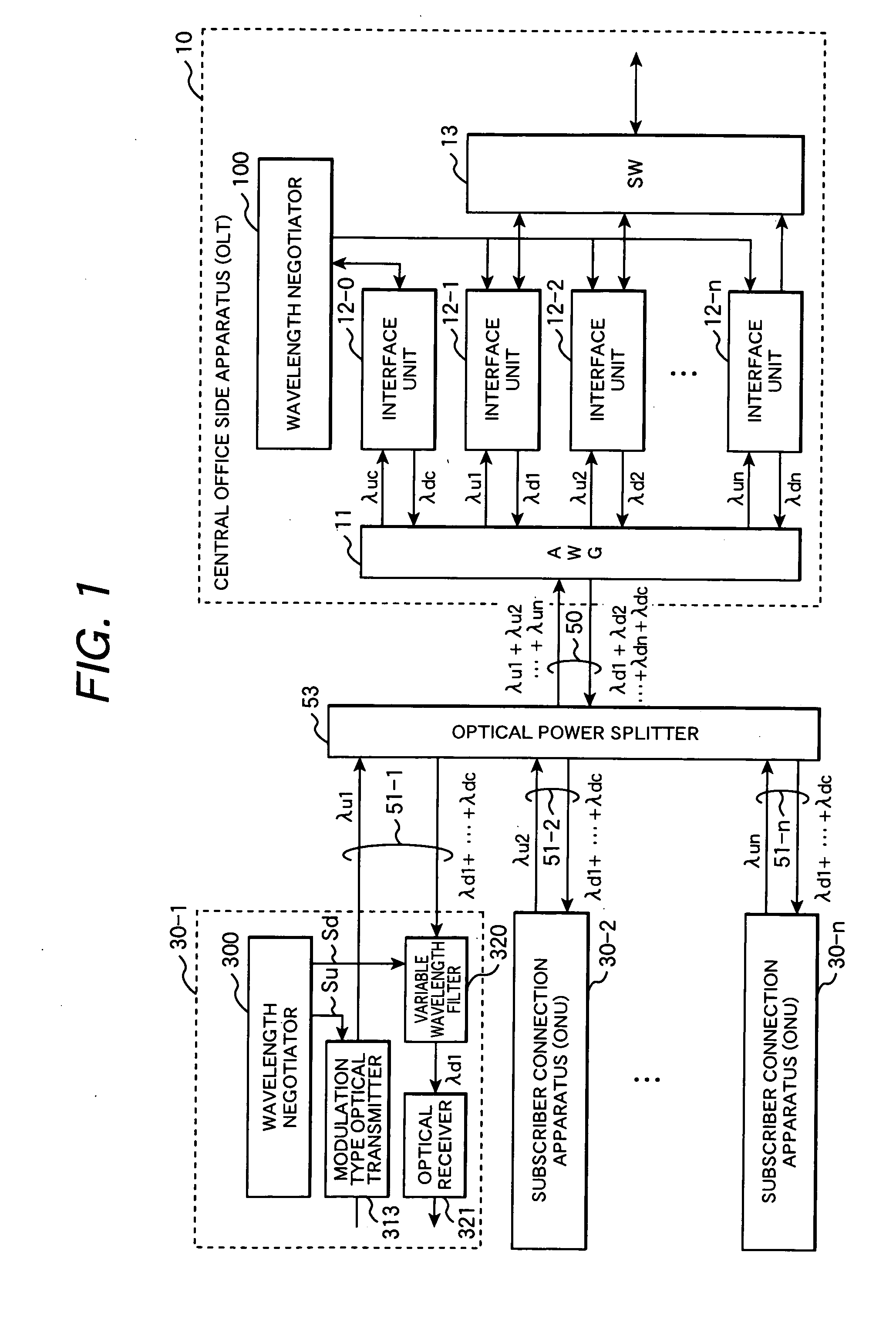
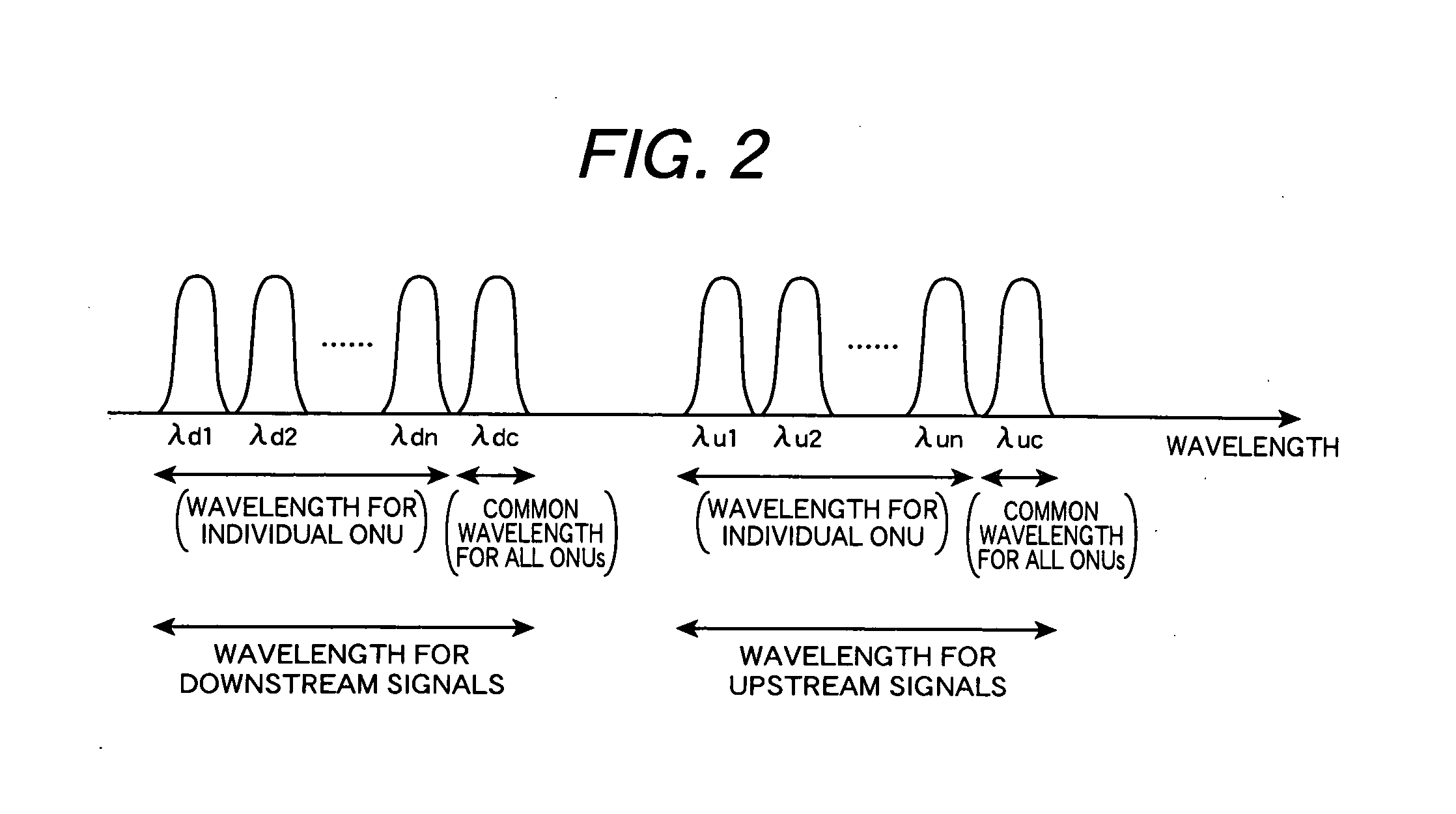
In a WDM type PON system, each ONU comprises an optical transmitter capable to transmit optical signals with variable wavelengths, an optical signal receiving filter variable its receiving wavelength, and a control unit. An OLT selects in response to a wavelength allocation request from each ONU, a transmitting wavelength and a receiving wavelength out of currently free wavelengths and allocates these wavelengths to the requester ONT. The control unit of the ONU switches the transmitting wavelength of the optical transmitter and the receiving wavelength of the optical signal receiving filter to the wavelengths specified in a response message from the OLT and starts data communication.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Buried fiber optic system including a sub-distribution system and related methods
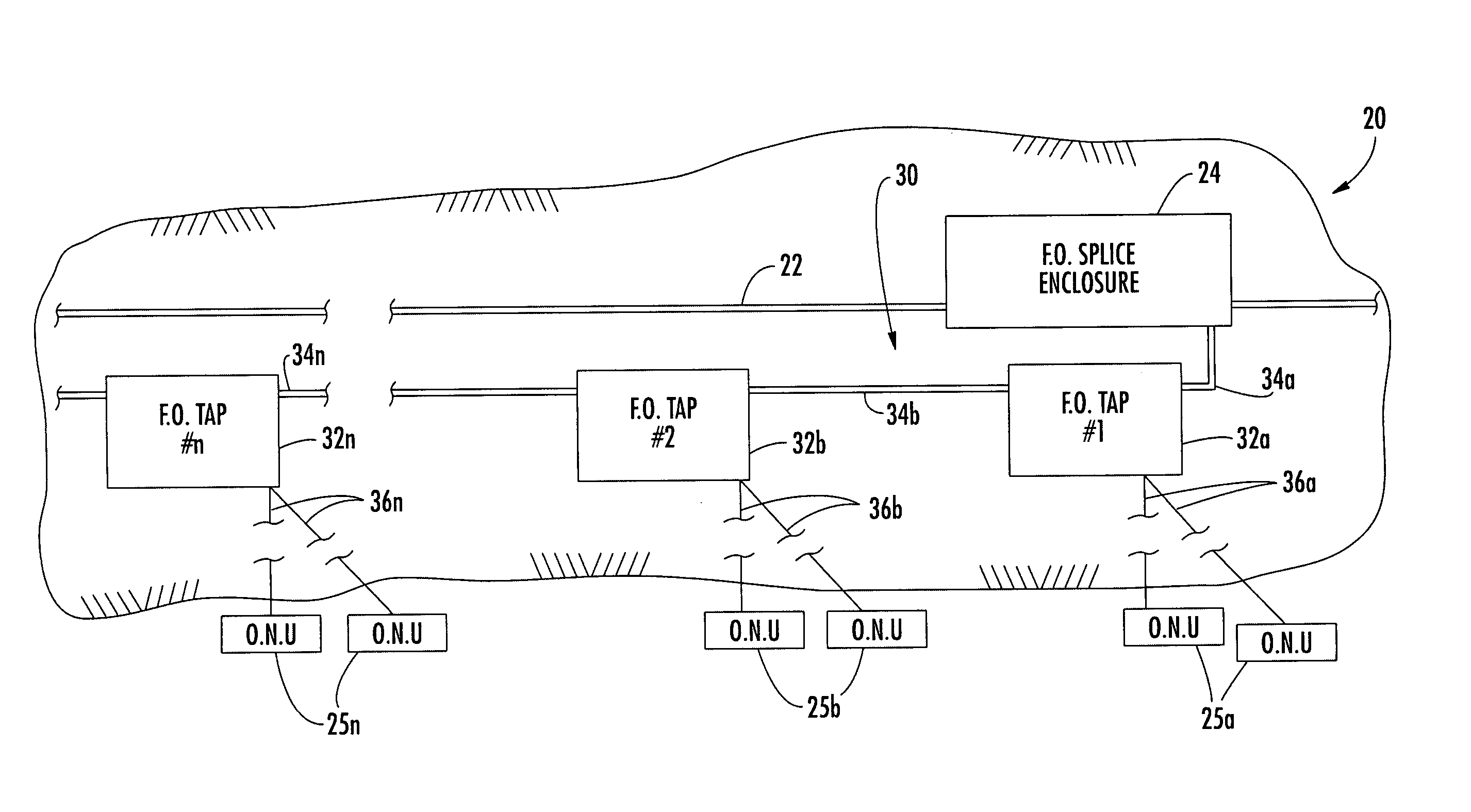
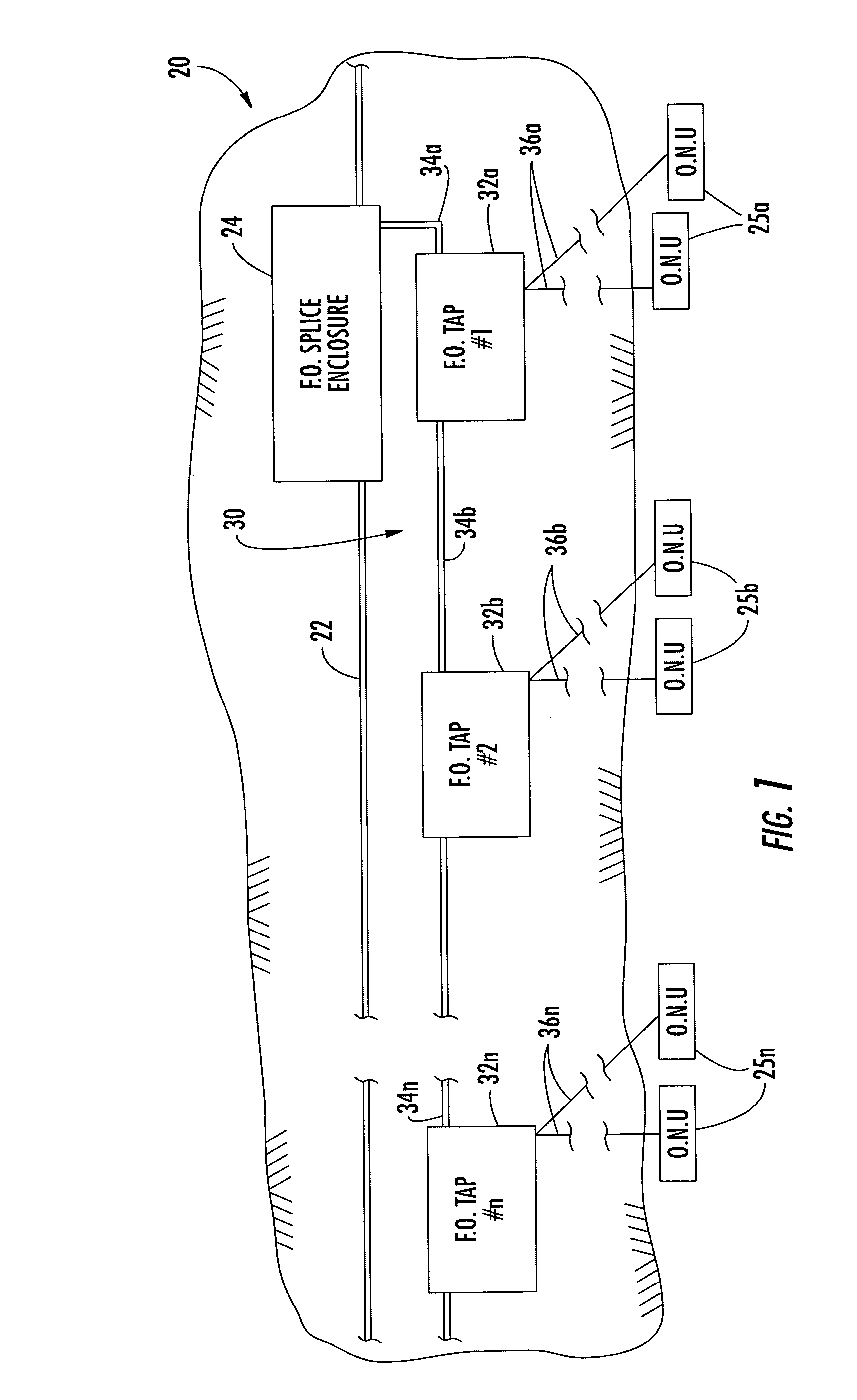
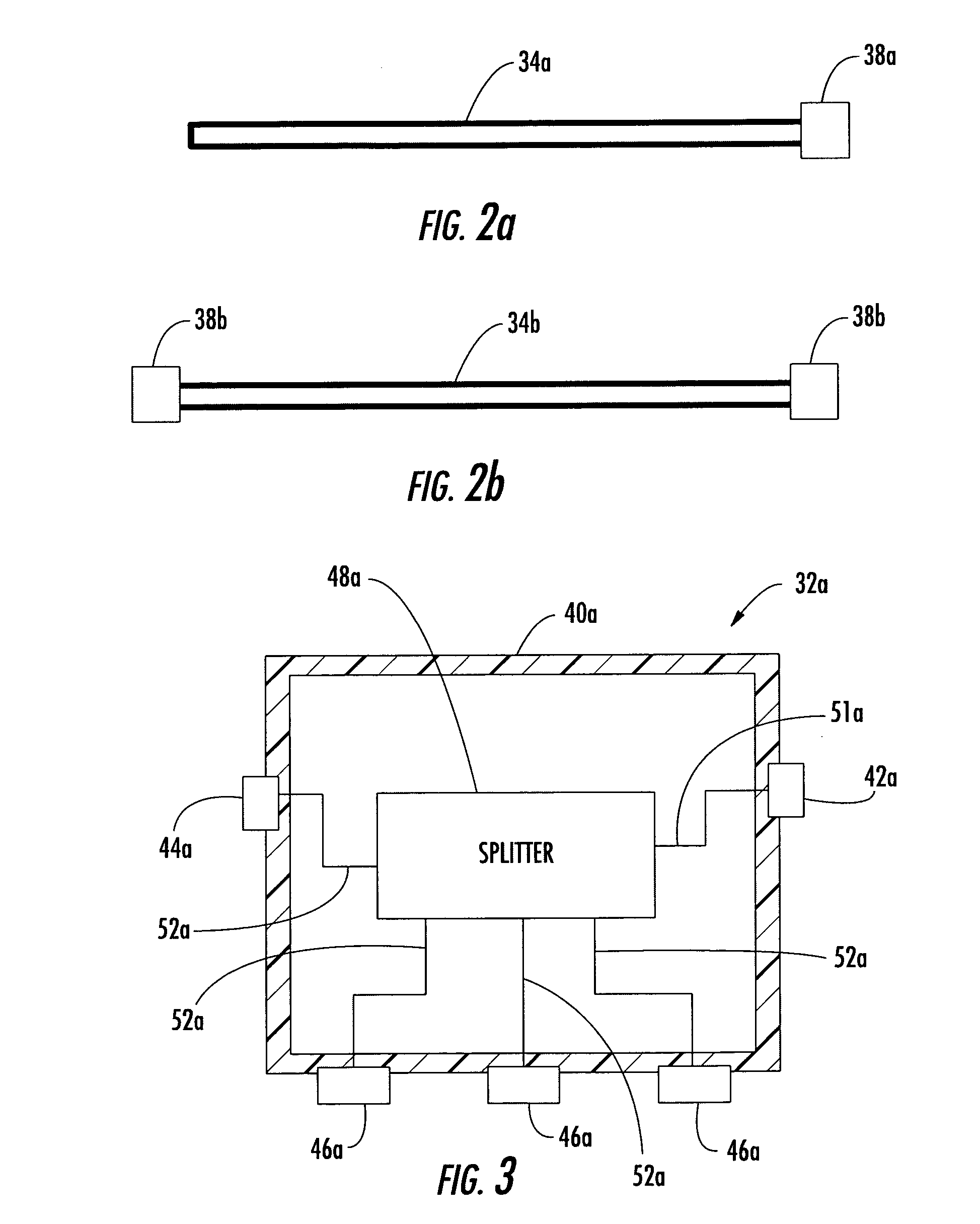
InactiveUS20050036749A1Reduce installation costsReduce exposureOptical fibre/cable installationFibre mechanical structuresFiberDistribution system
A buried fiber optic cable system includes a distribution cable extending along a buried route, a splice enclosure connected to the distribution cable along the buried route, and a first sub-distribution fiber optic system extending along the buried route in a first direction away from the fiber optic splice enclosure. The first sub-distribution system may include spaced apart fiber optic taps along the buried route, a first sub-distribution fiber optic cable between the fiber optic splice enclosure and a first fiber optic tap, and at least one second sub-distribution fiber optic cable between adjacent fiber optic taps so that the first sub-distribution fiber optic cable and the at least one second sub-distribution fiber optic cable are arranged in end-to-end relation. The system may also or alternately include a similar lateral sub-distribution system.
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
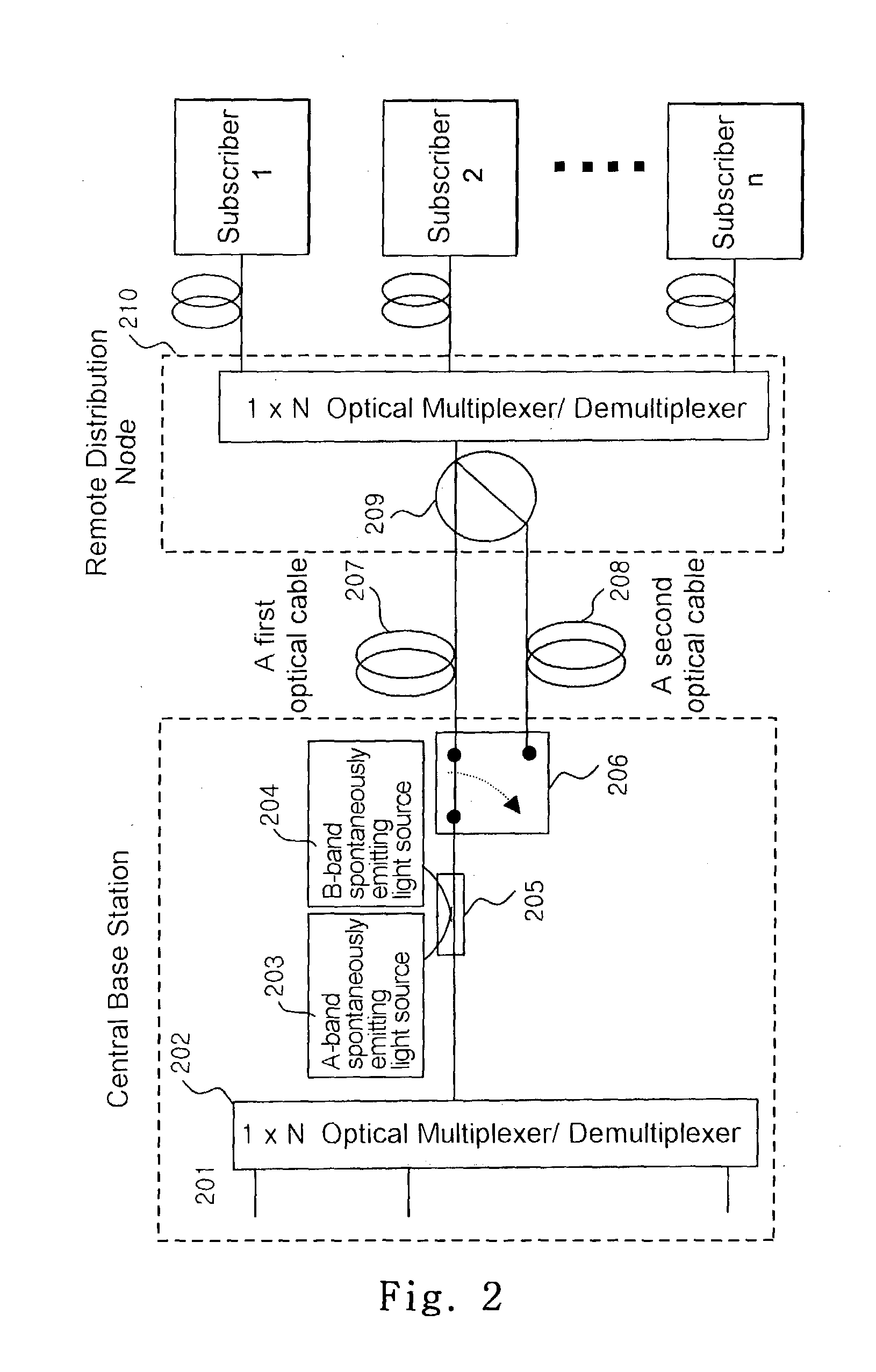
Optical access network of wavelength division method and passive optical network using the same
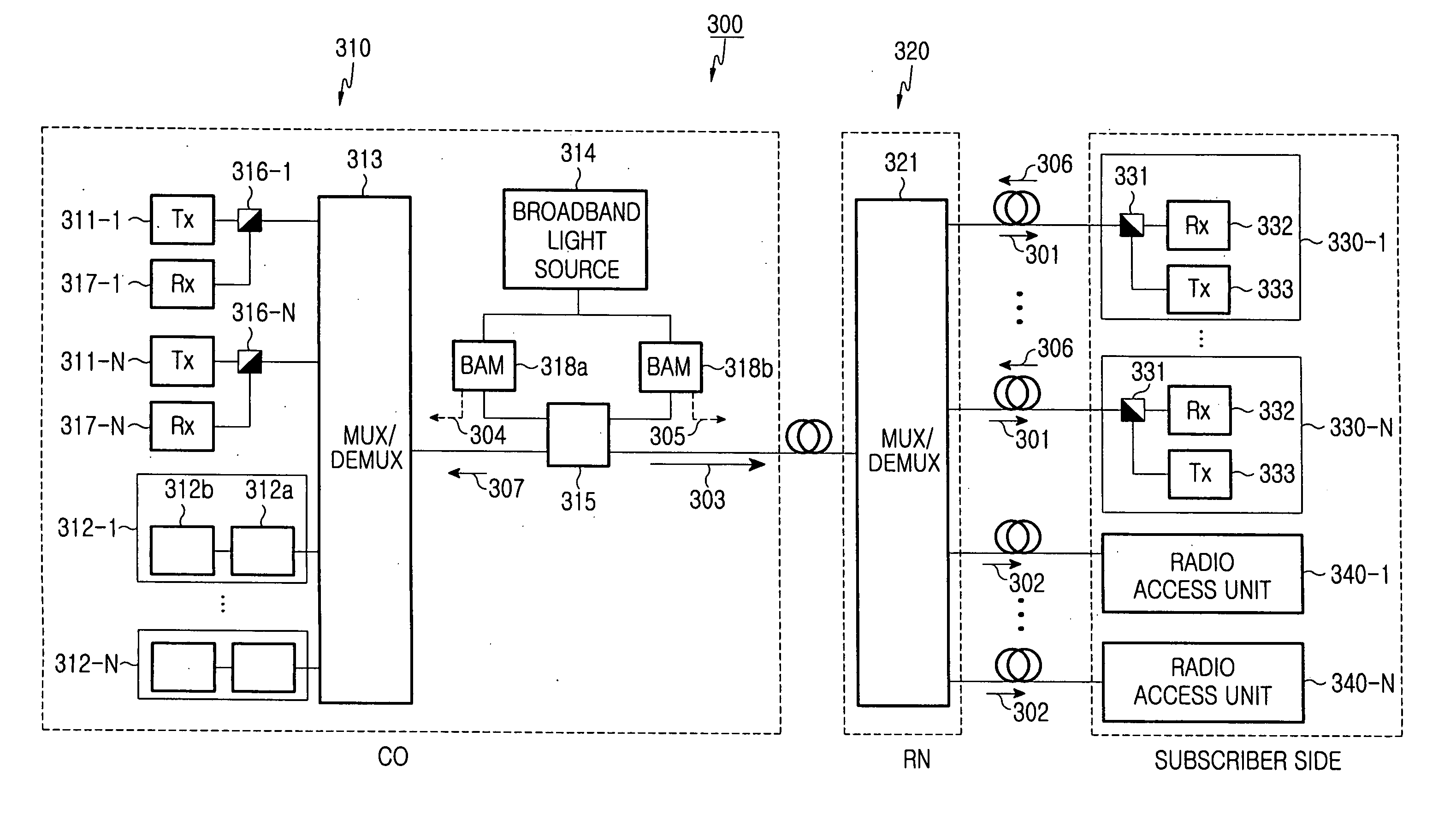
InactiveUS20060045525A1Low investment costWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar-type electromagnetic networksAccess networkWireless data services
A wavelength division multiplexed optical access network including a central office for multiplexing first optical signals used for transmitting a high-speed wire data service to a subscriber side and second optical signals used for transmitting a wireless data service to a remote subscriber terminal, a remote node connected to the central office through an optical fiber and for de-multiplexing a multiplexed optical signal received from the central office, a plurality of subscribers connected to the remote node, each subscriber receiving a first optical signal having a corresponding wavelength from among the de-multiplexed first optical signals, and a plurality of radio access units connected to the remote node, each radio access unit converting a second optical signal having a corresponding wavelength from among the de-multiplexed second optical signals into a wireless electric signal and wirelessly transmitting the wireless electric signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
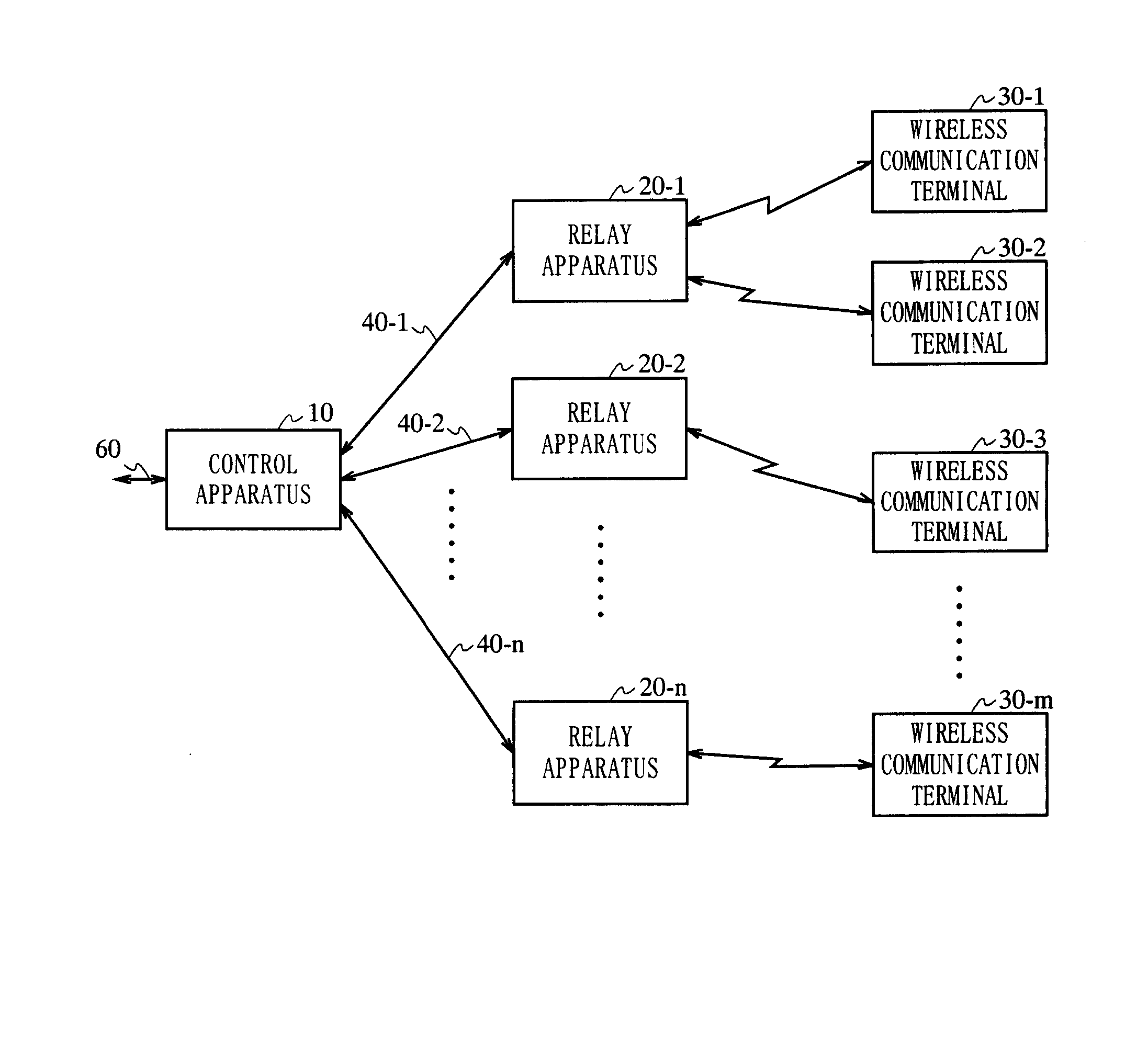
Radio communication system
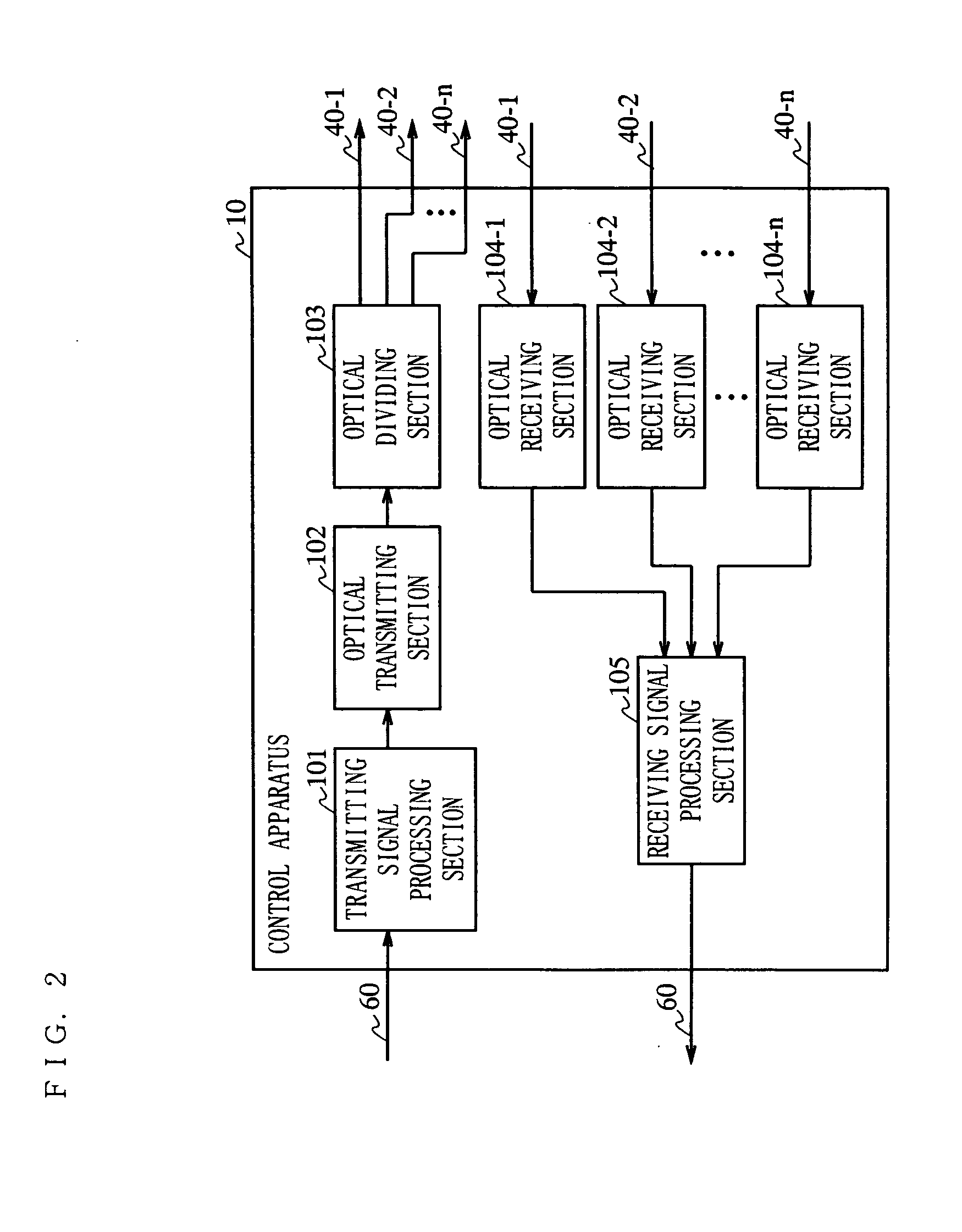
InactiveUS20050266797A1Quality improvementAvoid reflectionsPower managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemEngineering
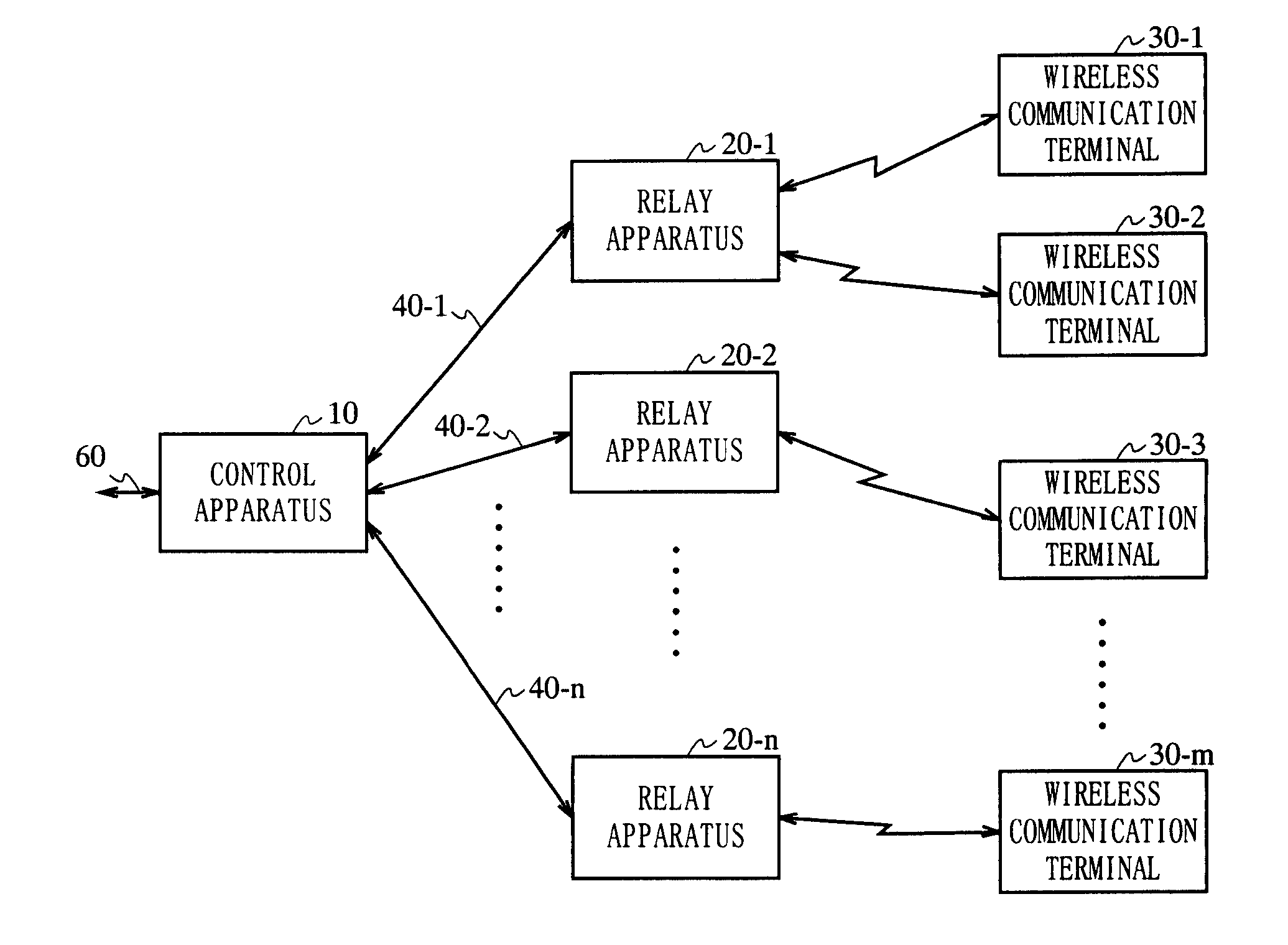
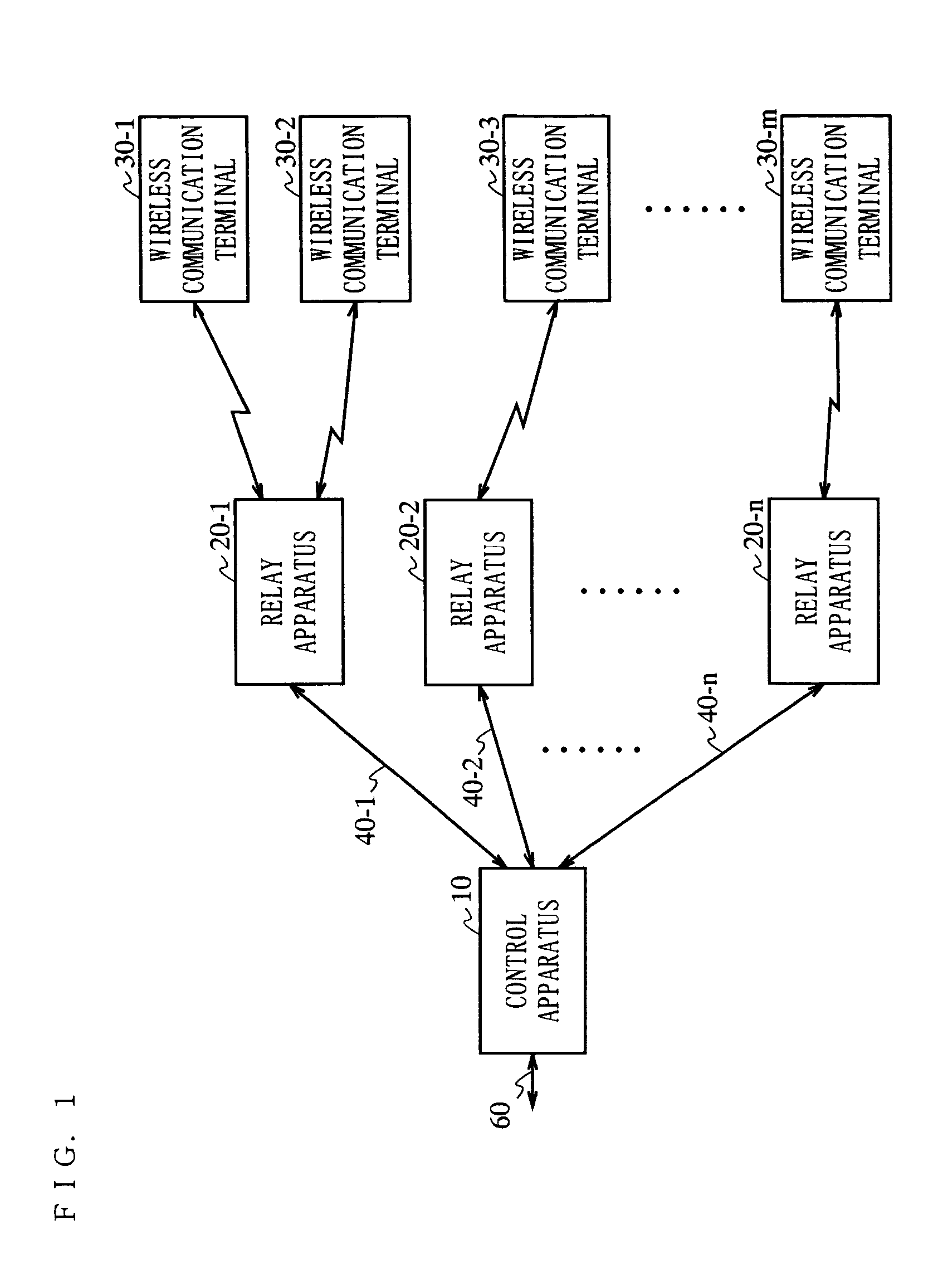
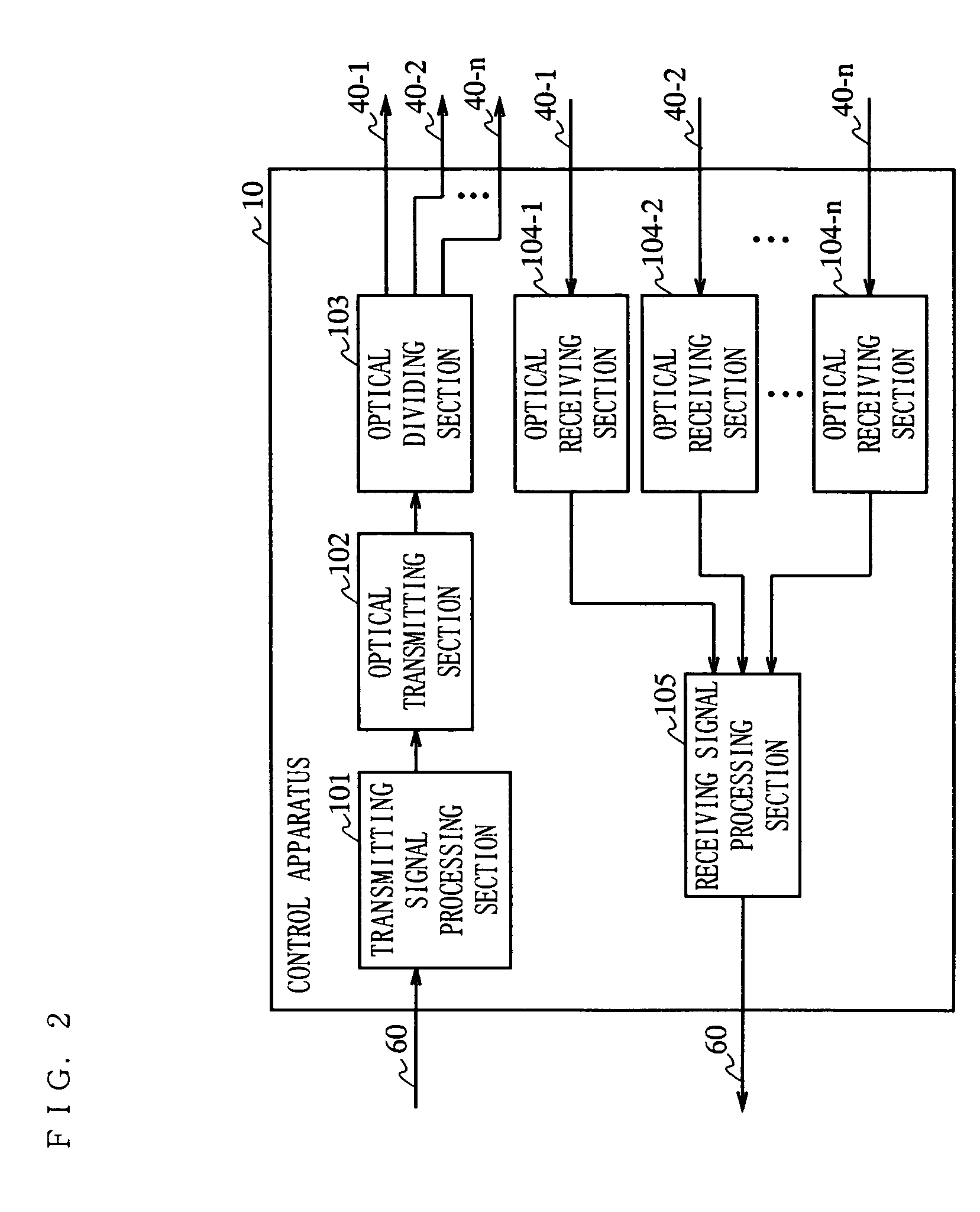
The present invention is directed to a wireless communication system capable of keeping a level of a wireless signal received by a relay apparatus (20) within a predetermined dynamic range. In a control apparatus (10), a transmitting section (102) converts a downstream electric signal into a downstream optical signal and transmits the downstream optical signal to the relay apparatus (20) via an optical transmission path (40). The relay apparatus (20) converts the received downstream optical signal into a downstream electric signal and transmits the downstream electric signal as a wireless signal to a wireless communication terminal (30) from a transmitting / receiving antenna section (204). In the relay apparatus (20), a level adjustment section (207) adjusts the level of the wireless signal transmitted by the relay apparatus (20) such that the receiving level of the wireless signal received by the relay apparatus is kept within a predetermined range.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Point-to-multipoint passive optical network that utilizes variable-length packets
InactiveUS7031343B1Reduce transmission overheadRemoves distance limitationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexVariable lengthTime-division multiplexing
A point-to-multipoint passive optical network transmits downstream data from an optical line terminal (OLT) to multiple optical network units (ONUs) in variable-length packets and upstream data from the ONUs to the OLT in variable-length packets utilizing time division multiplexing to avoid transmission collisions. In an embodiment, the variable-length downstream packets and the variable-length upstream packets are formatted according to IEEE 802.3. In an embodiment, the length of the variable-length downstream and upstream packets is related to the length of Internet protocol (IP) datagrams carried within the packets.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Passive optical network arrangement
InactiveUS6351582B1High loss pathPoint of failureMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringDual-homed
A passive optical network having a plurality of optical splitters / combiners each comprising first and second through ports and at least one drop port. The through ports of the plurality of splitters / combiners are concatenated to form a linear arrangement having two end through ports. Optical signals may be transmitted between the end through ports by means of the linear arrangement; and signals may be transmitted between at least one of the end through ports and one of the drop ports by means of the linear arrangement. The splitter / combiners can be inserted to form drop points in a ring or dual-homed passive optical network to provide flexibility in provision of protection and network reconfiguration.
Owner:CIENA
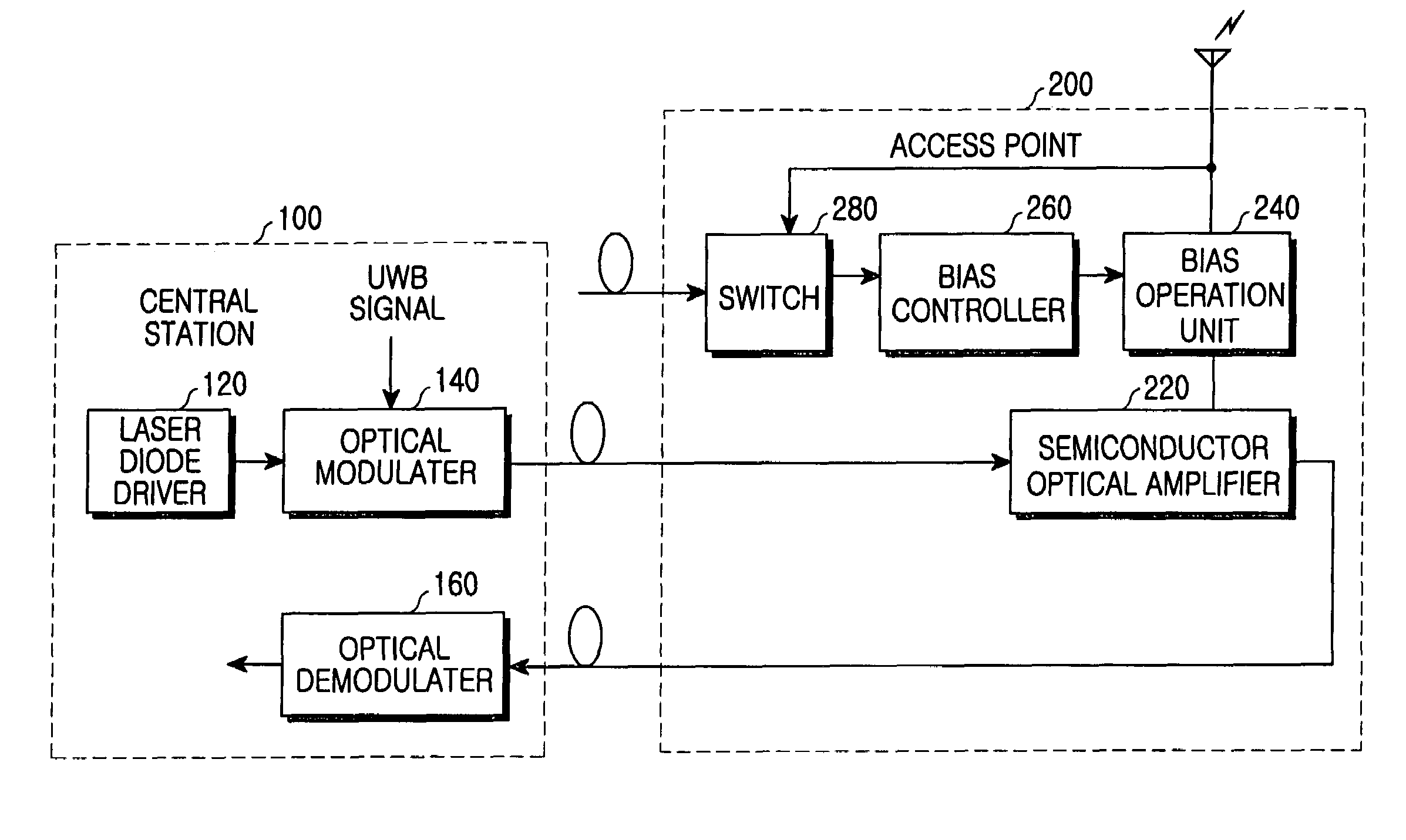
Access point for constructing optical fiber-based high-speed wireless network system
InactiveUS7349633B2Small sizeReduce manufacturing costTime-division optical multiplex systemsNetwork topologiesModulation functionNetworked system
An access point in an optical fiber-based high-speed optical wireless network is disclosed. The access point includes an antenna for receiving communication requirement signals, a switch for selectively outputting a corresponding signal according to the communication requirement signals, a bias control unit for selectively outputting bias current with variable intensity according to whether an output of the signal from the switch exists or not, on the basis of a threshold current; a bias operation unit for outputting input signals to the antenna when an input bias current is smaller than the threshold current and for outputting signals received by the antenna when an input bias current is larger than the predetermined threshold current, and a semiconductor optical amplifier for selectively performing an optical detection function of converting optical signals, which have been received through a first optical fiber from an central station, into electrical signals and sending the converted electrical signals to the bias operation unit, when a current smaller than the threshold current is input to the bias operation unit, and an optical modulation function of transmitting signals output from the bias operation unit through a second optical fiber to the central station, when a current larger than the threshold current is input to the bias operation unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for operating wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network
InactiveUS20060115271A1Avoid wastingEasy to useTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsControl channelLength wave
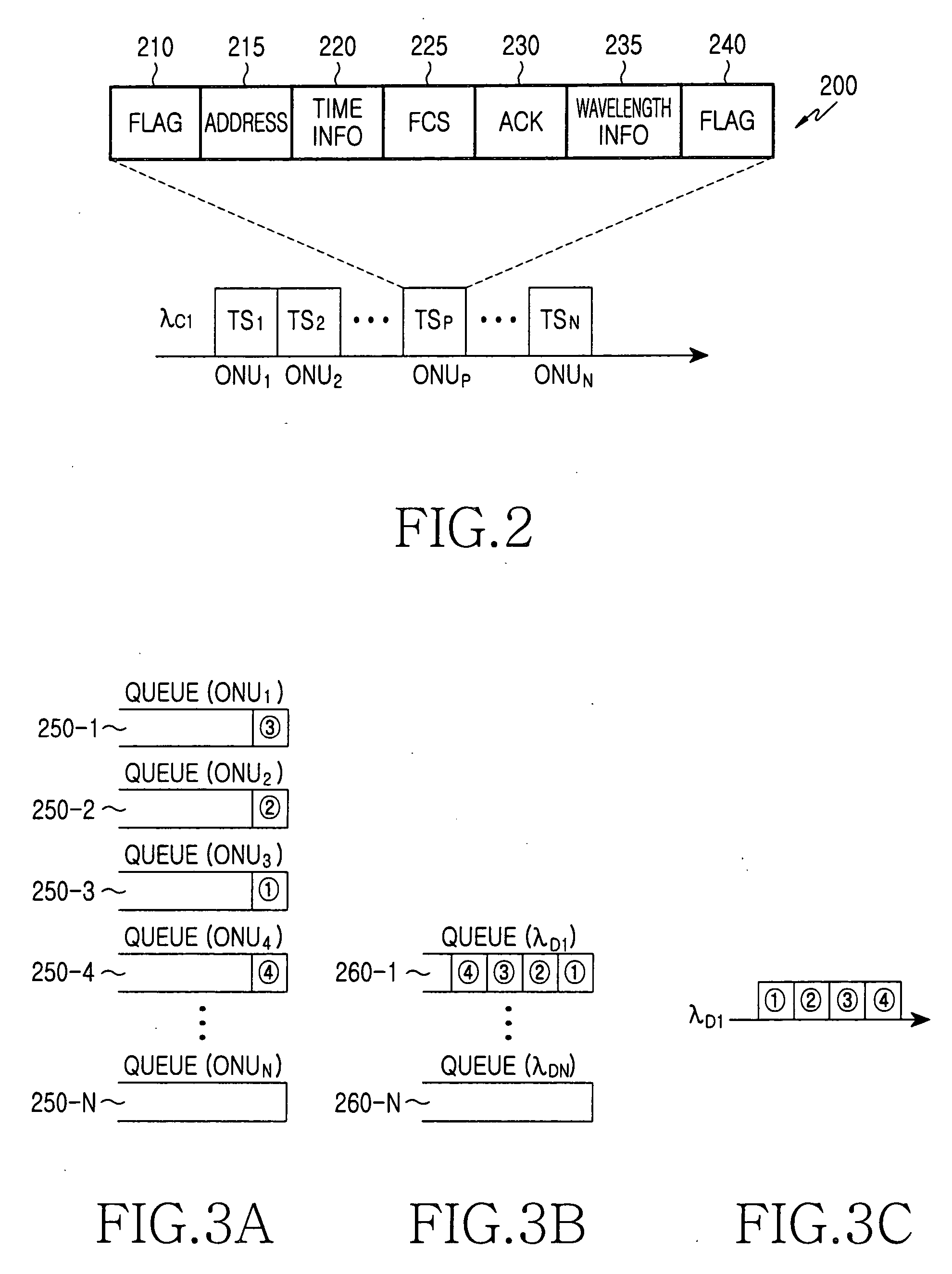
Disclosed is a method for operating a wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network (WDM-PON) including an optical line terminal (OLT) and a plurality of optical network units (ONUs), each of which is connected to the OLT and communicates with the OLT. The method comprises the steps of transmitting a first control channel including allocation information of downstream data channels and allocation information of time slots for the downstream data channels to each of the plurality of ONUs; and transmitting downstream data to the plurality of ONUs using their associated downstream data channels, each having at least one time slot, based on the information included in the first control channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
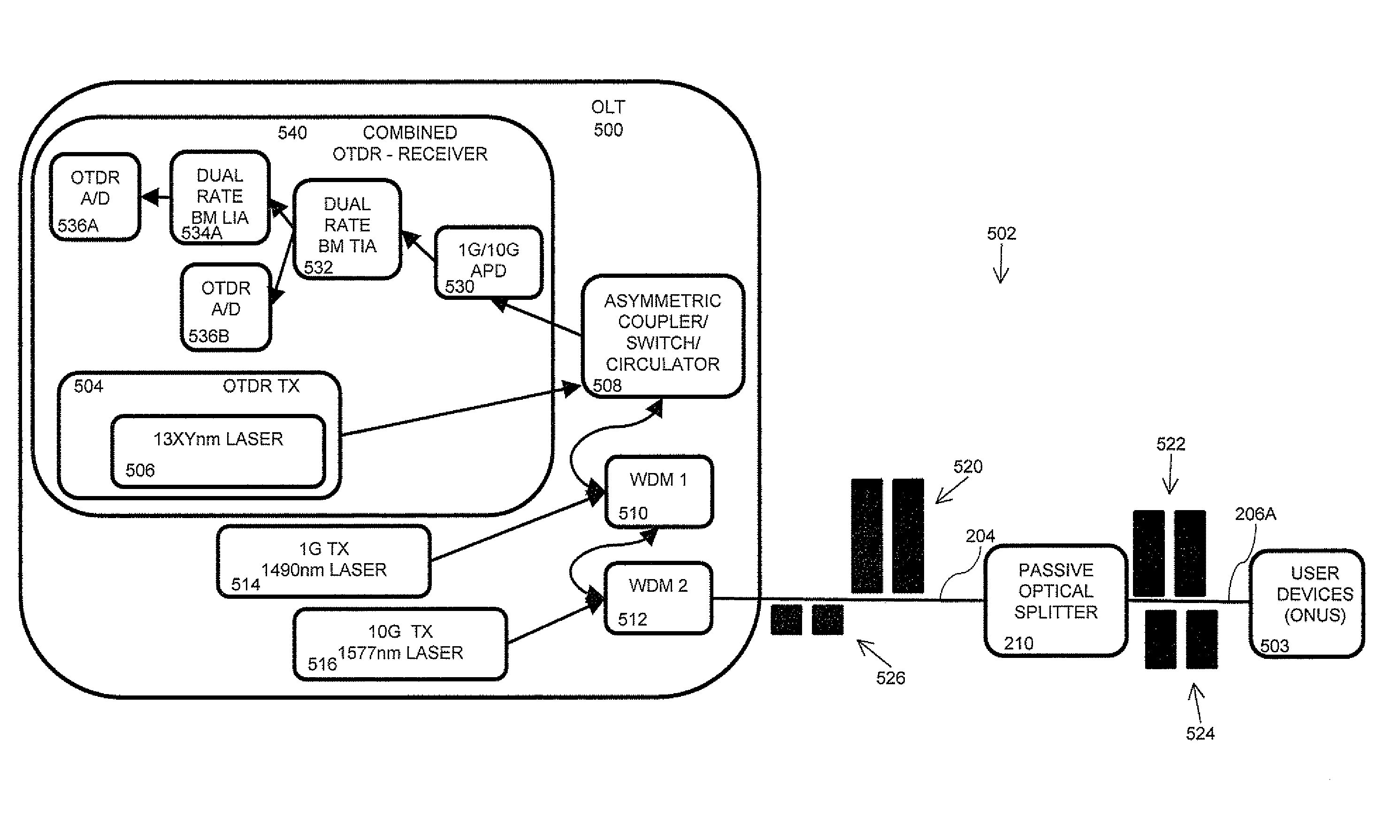
Passive optical network (PON) in-band optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR)
ActiveUS20110013904A1Material analysis by optical meansTransmission monitoringSignal onNetwork Communication Protocols
An in-band OTDR uses a network's communication protocols to perform OTDR testing on a link. Because the OTDR signal (probe pulse) is handled like a data signal, the time required for OTDR testing is typically about the same as the time required for other global network events, and is not considered an interruption of service to users. A network equipment includes an optical time domain reflectometry (OTDR) transmitter and receiver, each operationally connected to a link to transmit and receive, respectively, an OTDR signal. When an OTDR is to be performed, a network device operationally connected to the link actuates the OTDR transmitter to transmit the OTDR signal on the link during a determined test time based on a communications protocol of the link, during which data signals are not transmitted to the network equipment. A processing system processes the OTDR signal to provide OTDR test results.
Owner:MICROSEMI ISRAEL STORAGE SOLUTIONS LTD
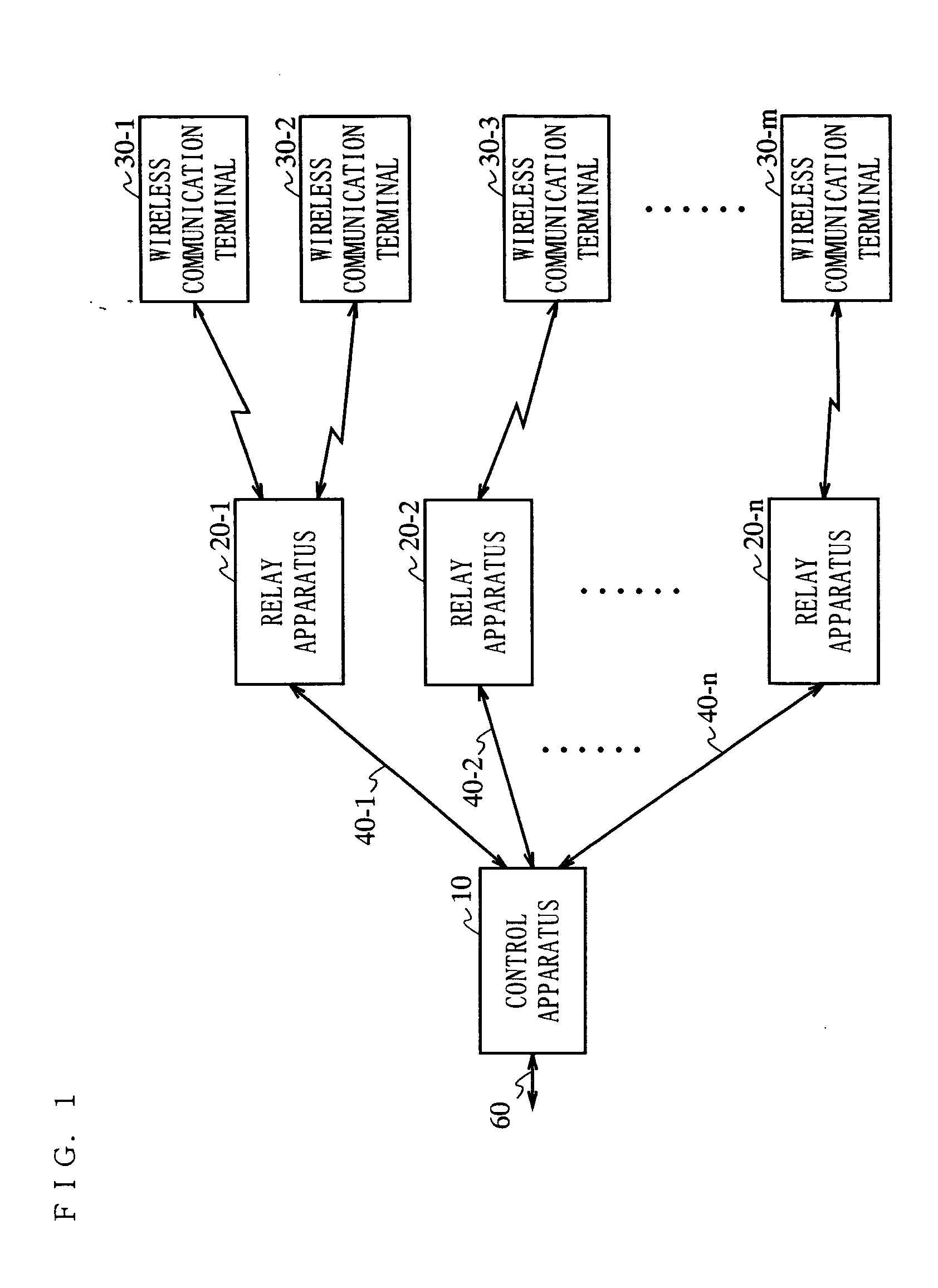
Wireless communication system
InactiveUS7460829B2Maintain standardReduce leakagePower managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemLight signal
A wireless communication system capable of keeping a level of a wireless signal received by a relay apparatus within a predetermined dynamic range. In a control apparatus, a transmitting section converts a downstream electric signal into a downstream optical signal and transmits the downstream optical signal to the relay apparatus via an optical transmission path. The relay apparatus converts the received downstream optical signal into a downstream electric signal and transmits the downstream electric signal as a wireless signal to a wireless communication terminal from a transmitting / receiving antenna section. In the relay apparatus, a level adjustment section adjusts the level of the wireless signal transmitted by the relay apparatus such that the receiving level of the wireless signal received by the relay apparatus is kept within a predetermined range.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Network for distributing signals to a plurality of users
InactiveUS6909821B2Easy accessImprove accuracyWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesEngineeringOpto electronic
A network for distributing signals to a plurality of user apparatuses having a distribution unit with a plurality of ports, and a plurality of optical-fiber cables connected to the ports and suitable to make the plurality of ports of the distribution unit communicate with the plurality of user apparatuses. At least one of the plurality of optical-fiber cables is an electrically terminated optical cable having an optical cable with a single-mode optical fiber and an opto-electronic end portion mechanically and permanently connected to an end of the optical cable, and the opto-electronic end portion has an opto-electronic conversion device having an optic port optically aligned with and mechanically connected to, an end of the single-mode optical fiber.
Owner:PIRELLI CAVI E SISTEMI SPA
Passive optical network system and wavelength assignment method
InactiveUS20080166127A1Easy to useEasy to installWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar/tree networksLength waveLight source
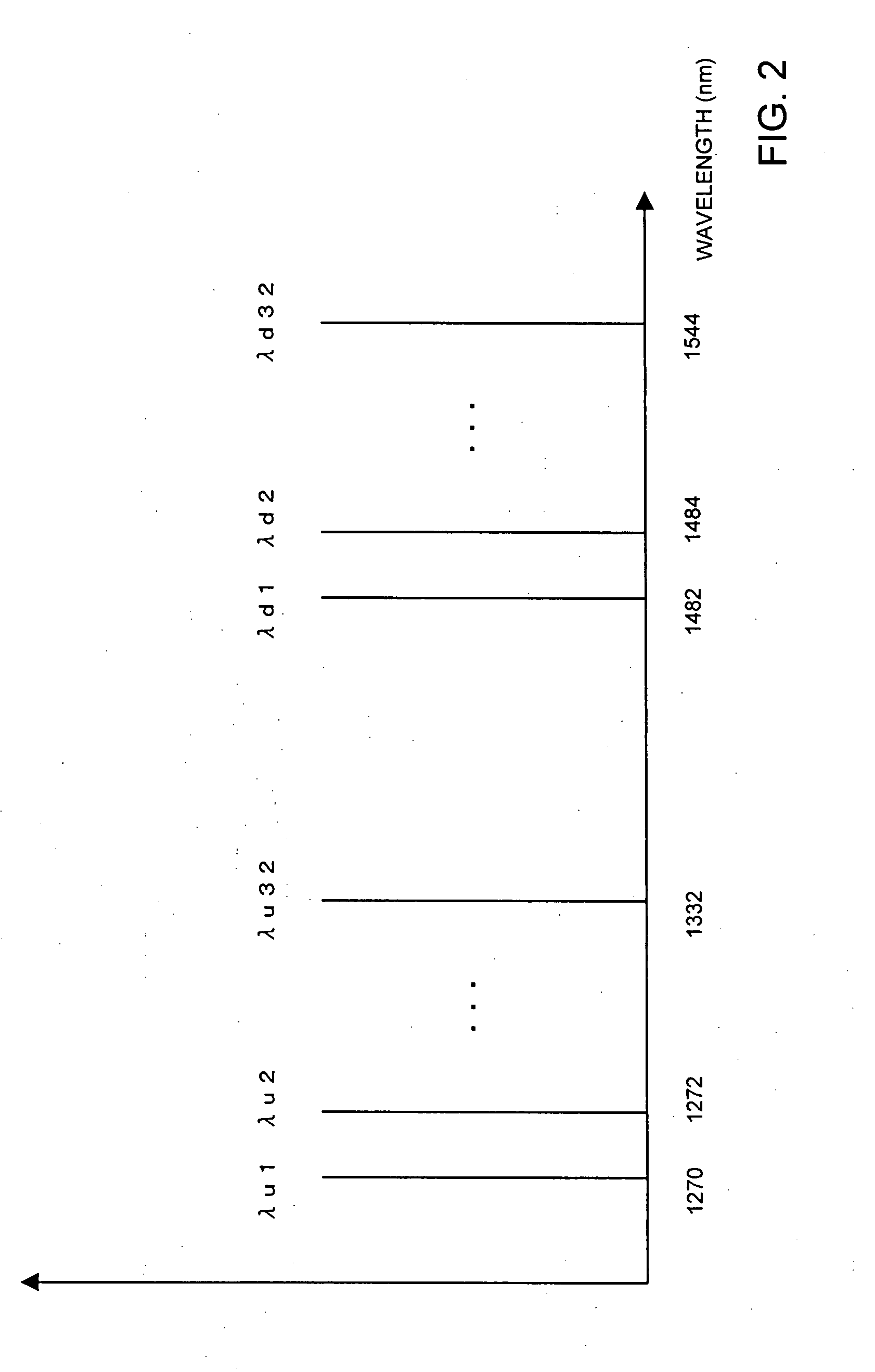
In a PON system with WDM, at the time of initial setting, each ONU negotiates with an OLT, and automatically acquires a wavelength which can be used by the ONU. One wavelength for negotiation of assigned wavelength is fixed as a default, and a newly connected ONU first uses the wavelength. The OLT 200 includes a plurality of light sources for downstream communication. The ONU 300 includes a wavelength variable filter selectively receiving one of wavelengths of downstream communication, and a wavelength variable light source selectively emitting light of one of plural wavelengths for upstream communication. The ONU 300 uses a transmission wavelength (for example, λu32) for negotiation and transmits a wavelength assignment request 1000 to the OLT 200. The OLT 200 selects a wavelength λu1 to be assigned from unused wavelengths, and transmits wavelength information to the ONU 300. The OLT 200 and the ONU 300 communicates using the notified wavelengths.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for level decision and optical receiver using same
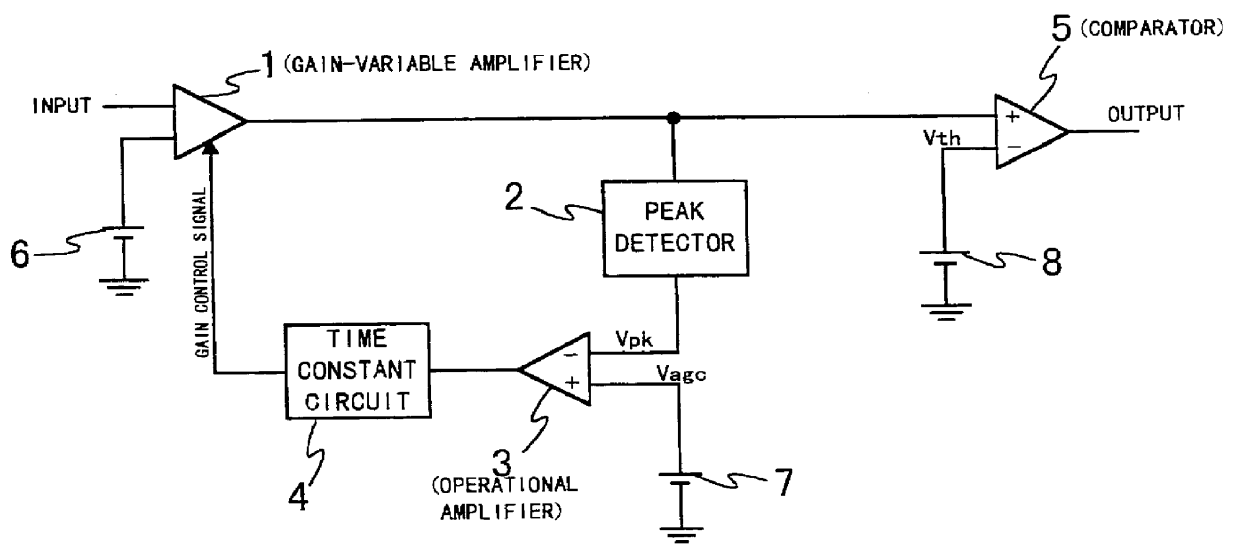
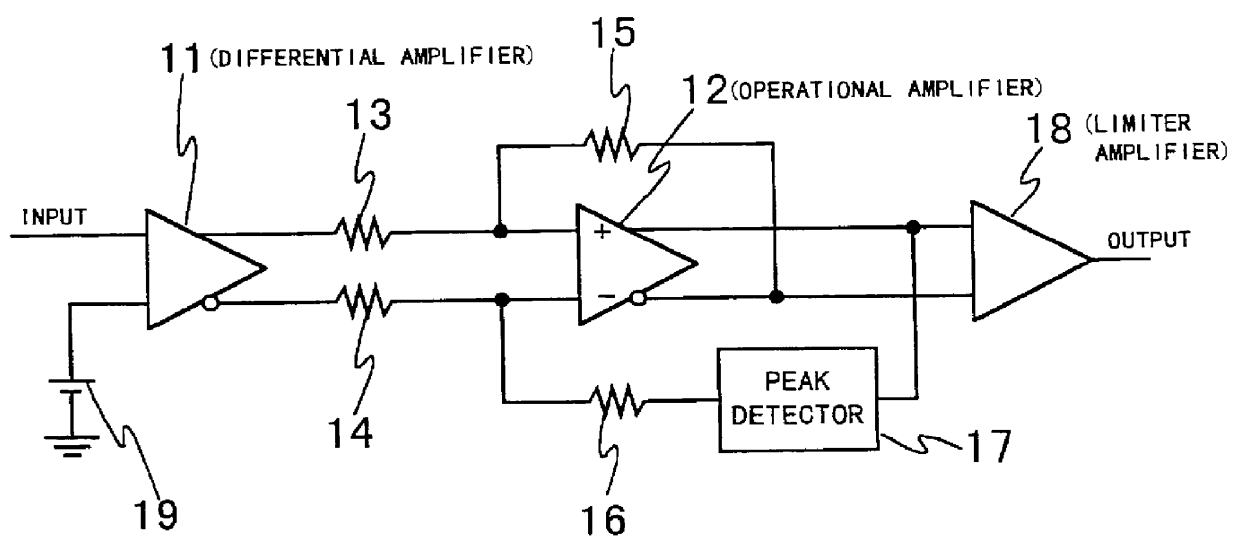
InactiveUS6151150ASimple designStart fastLaser detailsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionPeak valueEngineering
In a method for deciding the level of an input signal, positive and negative signals are provided in response to the input signal. A peak of the positive signal is detected to provide a positive-peak value. A peak of the negative signal is detected to provide a negative-peak value. The positive signal and the negative-peak value are combined to provide a first combination signal. The negative signal and the positive-peak value are combined to provide a second combination signal. The first and second combination signals are compared to provide an output signal of zero or one.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Method and system for processing downstream packets of an optical network
InactiveUS20030086140A1Efficient disseminationMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsQuality of serviceTransceiver
Unlike the conventional art which polices data at the entry points of a network, a transceiver node can police or monitor downstream bandwidths for quality of service at exit portions of an optical network. That is, the transceiver node can police downstream communication traffic near the outer edges of an optical network that are physically close to the subscribers of the optical network. In this way, a network provider can control the volume or content (or both) of downstream communications that are received by subscribers of the optical network. In addition to controlling the volume of communications that can be received by a subscriber, the transceiver node employs a plurality of priority assignment values for communication traffic. Some priority assignment values are part of a weighted random early discard algorithm that enables an output buffer to determine whether to drop data packets that are destined for a particular subscriber. In one exemplary embodiment, a weighted random early discard (WRED) priority value can be assigned according to the type of communication traffic supported by a packet.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS
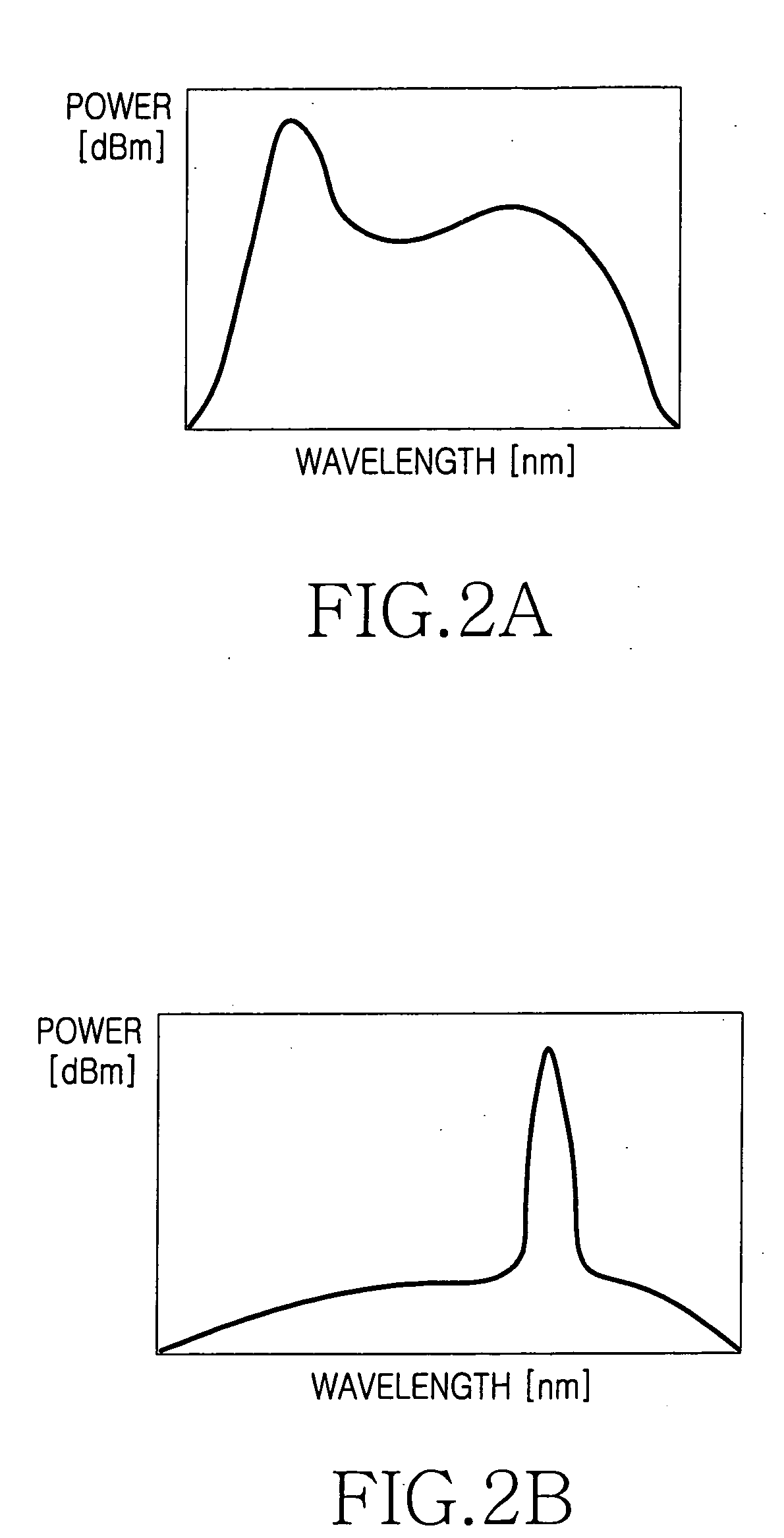
Method for decreasing and compensating the transmission loss at a wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network and an apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20030142978A1Decreasing and compensating optical lossLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveTransmission loss
The present invention relates to a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network. In particular, it relates to a technology for minimizing the optical loss at a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network based on wavelength-locked light source Thereby it improves the transmission quality and increases the transmission distance. A 4-port optical path setting device of the present invention increases the amount of light injected into an optical transmitter and thereby improves the wavelength-locking characteristic of a light source. In addition, it can decrease the optical transmission loss in an optical transmission path, and by an optical amplifier being inserted therein; it can also compensate the optical loss in an optical transmission path. In the present invention, a 4-port optical path setting device having the characteristics described above and a method for fault recovery without an additional optical loss are presented.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
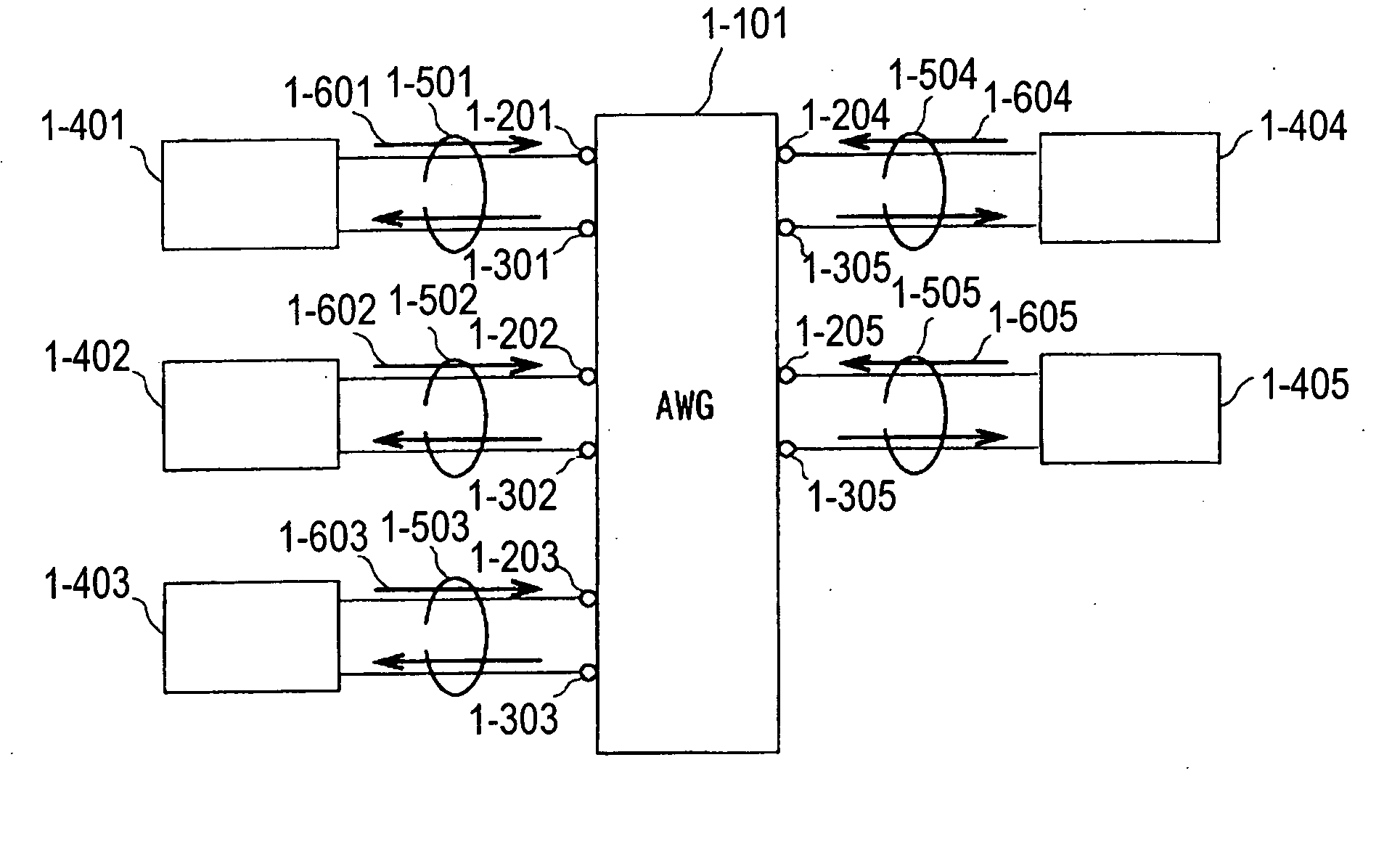
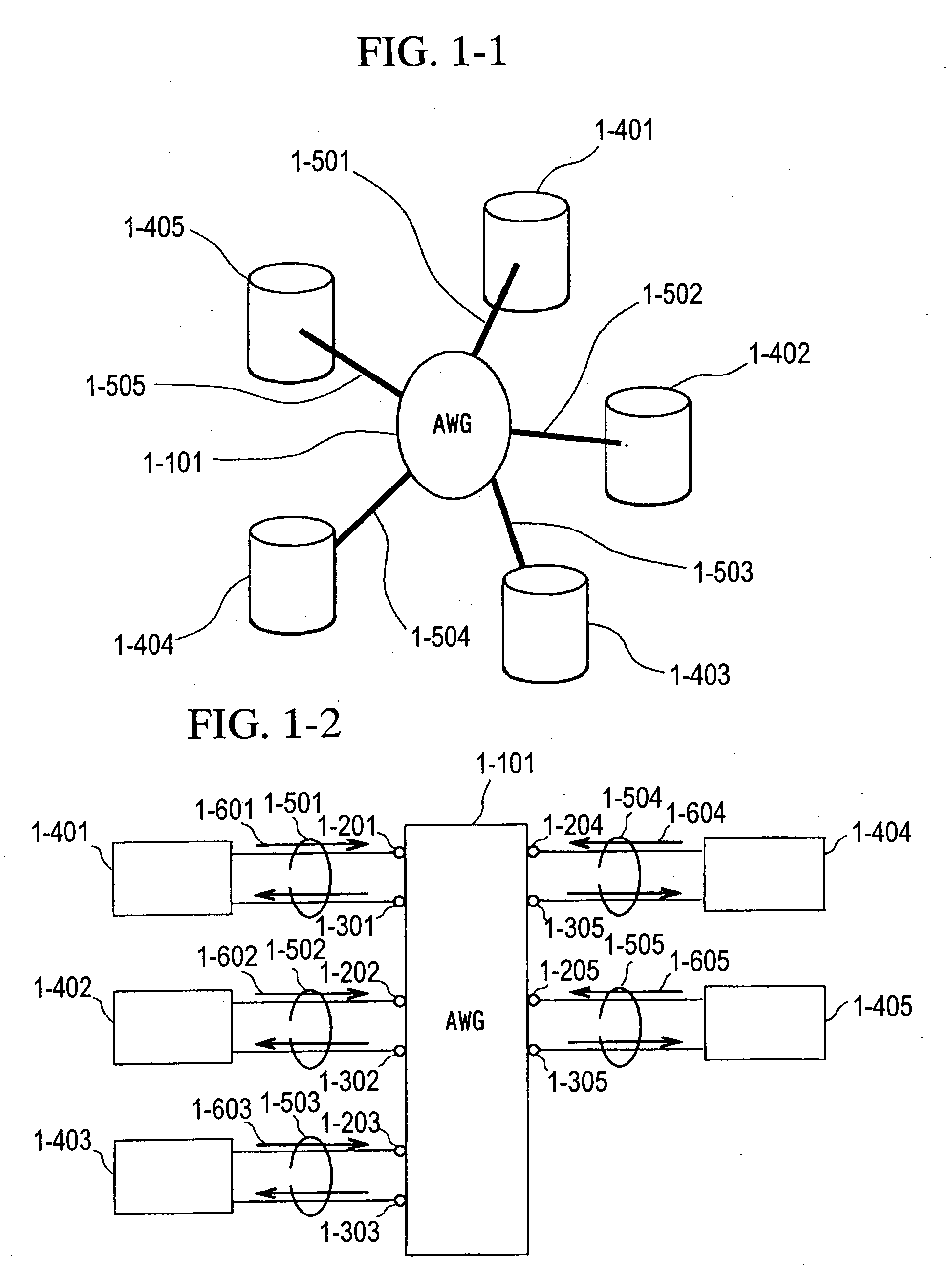
Optical communication network system
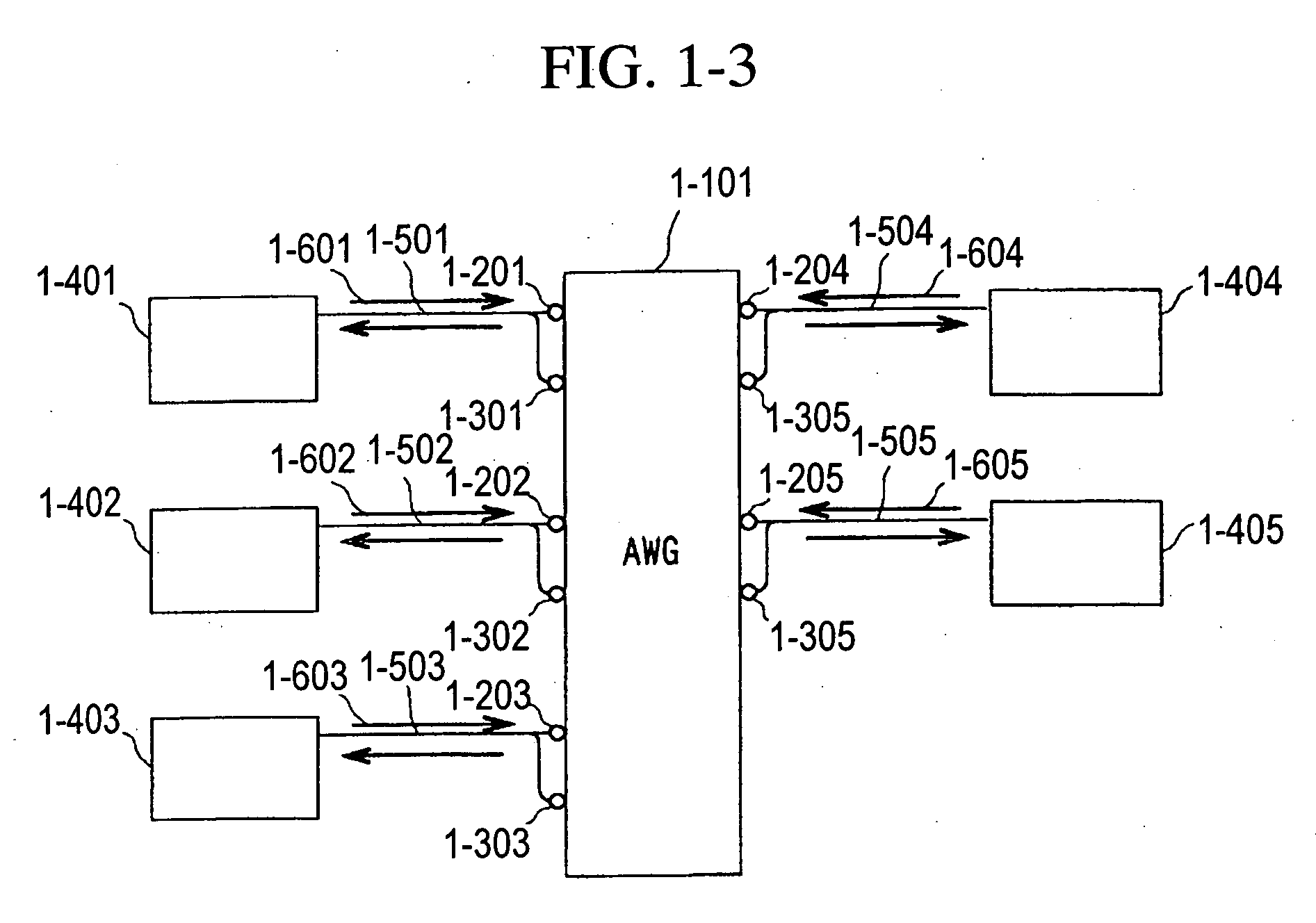
ActiveUS20060153496A1Quickly reconfiguredOptimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksGratingLength wave
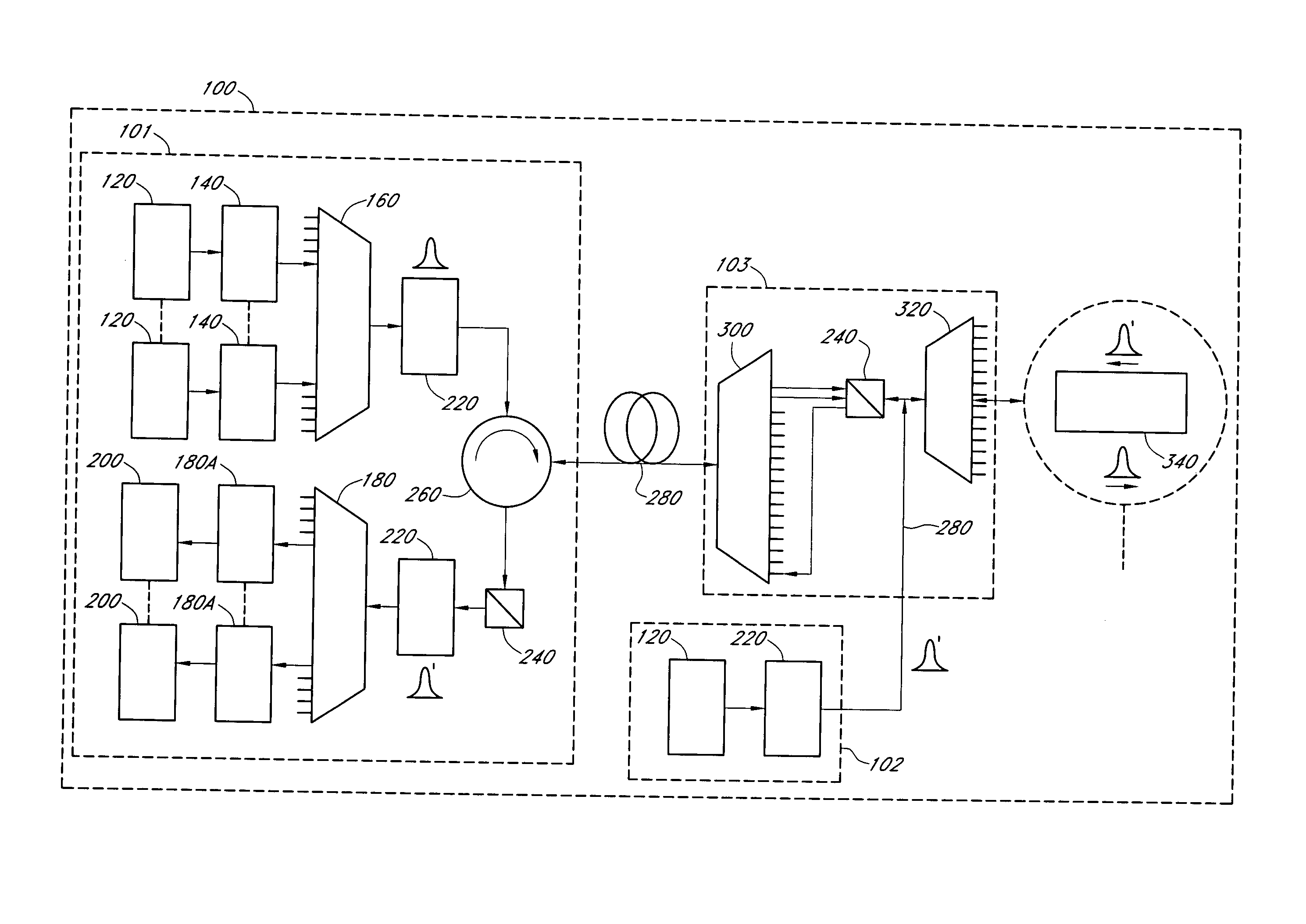
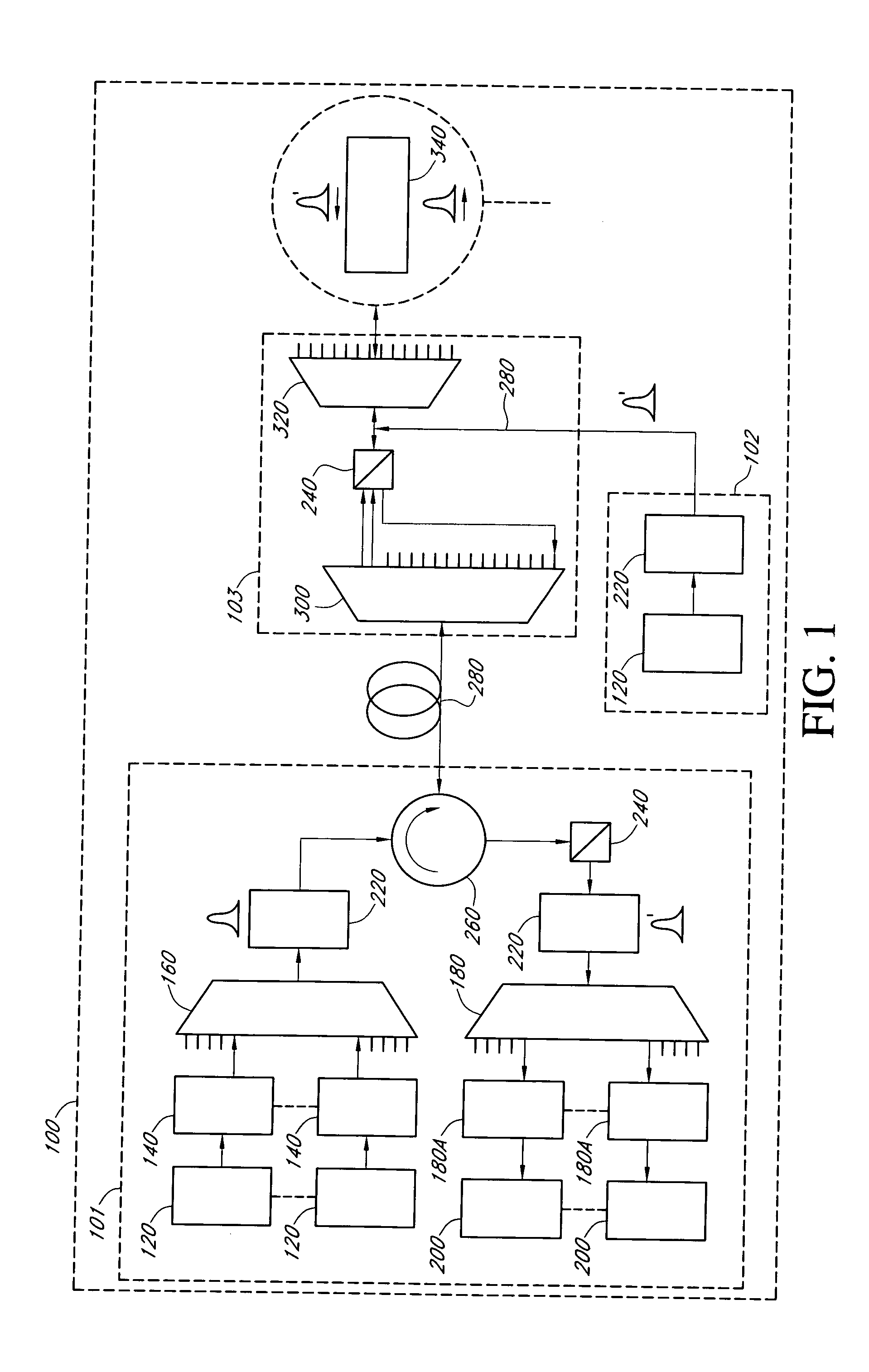
A fiber optic communication system includes a device of switching and setting wavelength of optical signals used in communication by network-node equipments, which sets the mapping of the wavelength of the optical signal used in communication by the network node equipments, and the input / output ports of an array waveguide grating (AWG), so as to construct a predetermined logical network topology by a plurality of network node equipments which are connected via optical fibers to the array waveguide grating that outputs optical signals inputted to optical input ports, to predetermined optical output ports in accordance with the wavelength thereof. As well as enabling a simple construction, it is easy to realize flexible network design, construction, and operation, and different network groups can also be easily connected to each other. Moreover, a fiber optic communication system having robust security and which can be stably operated even at the time of failure is realized at low cost.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
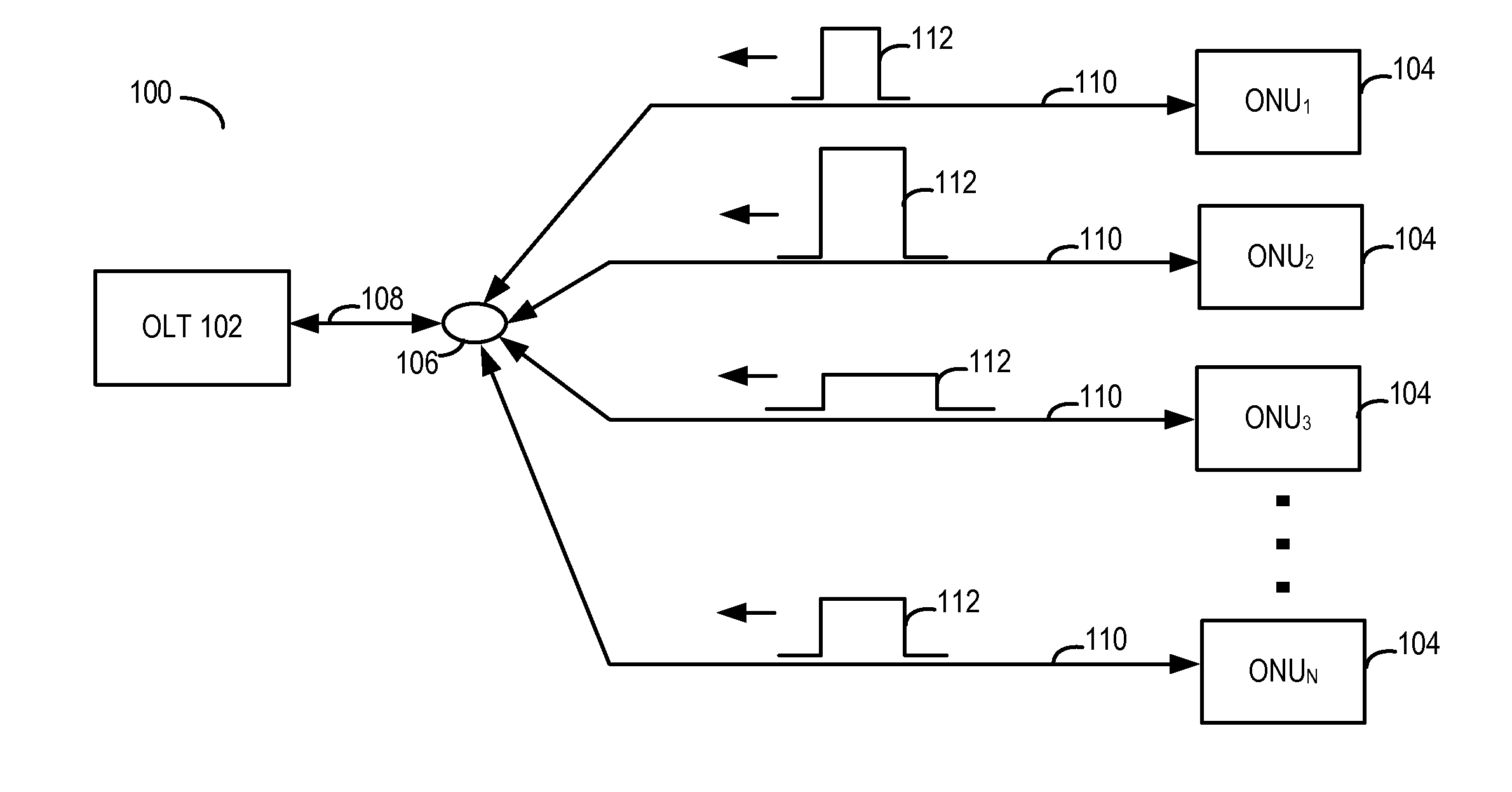
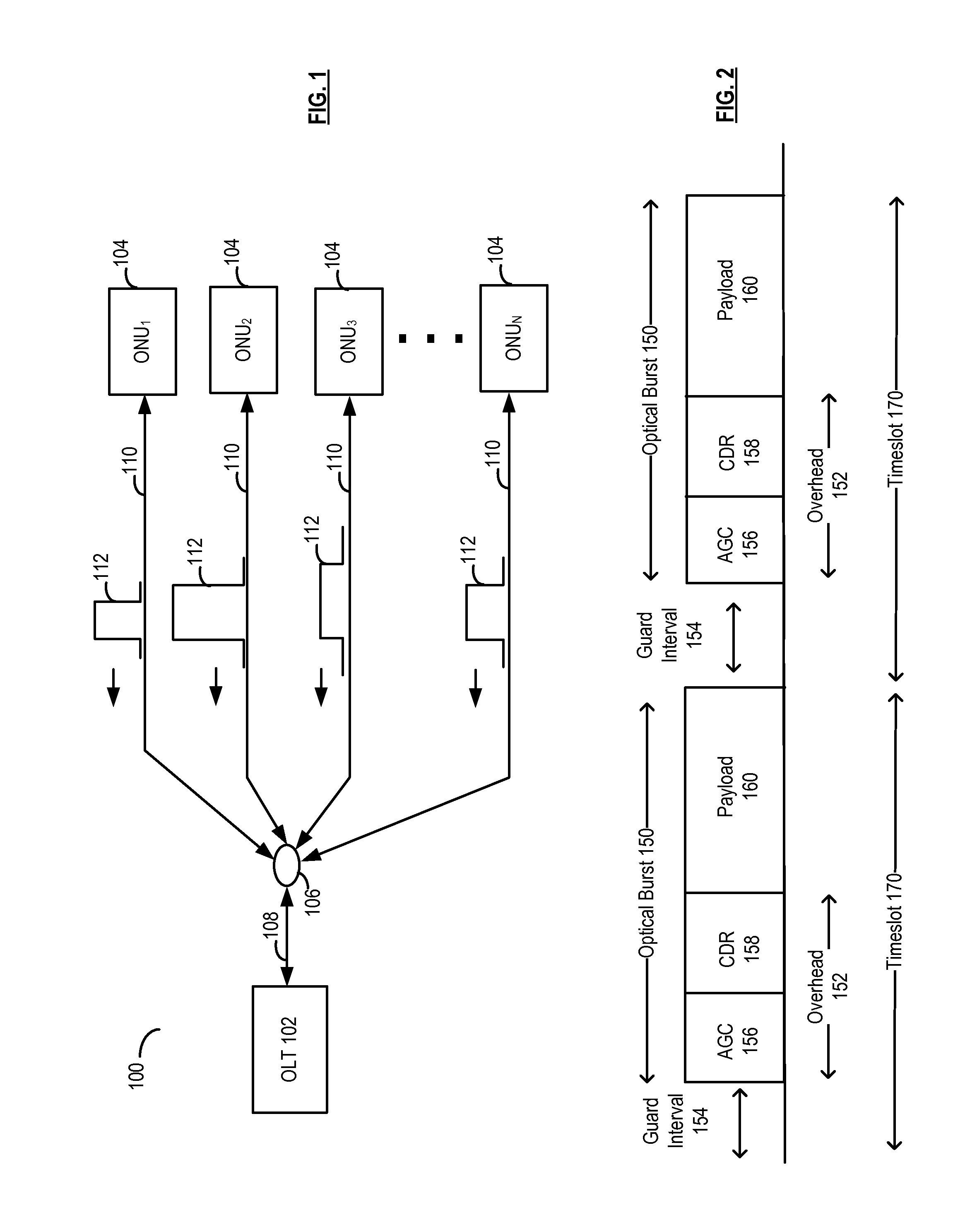
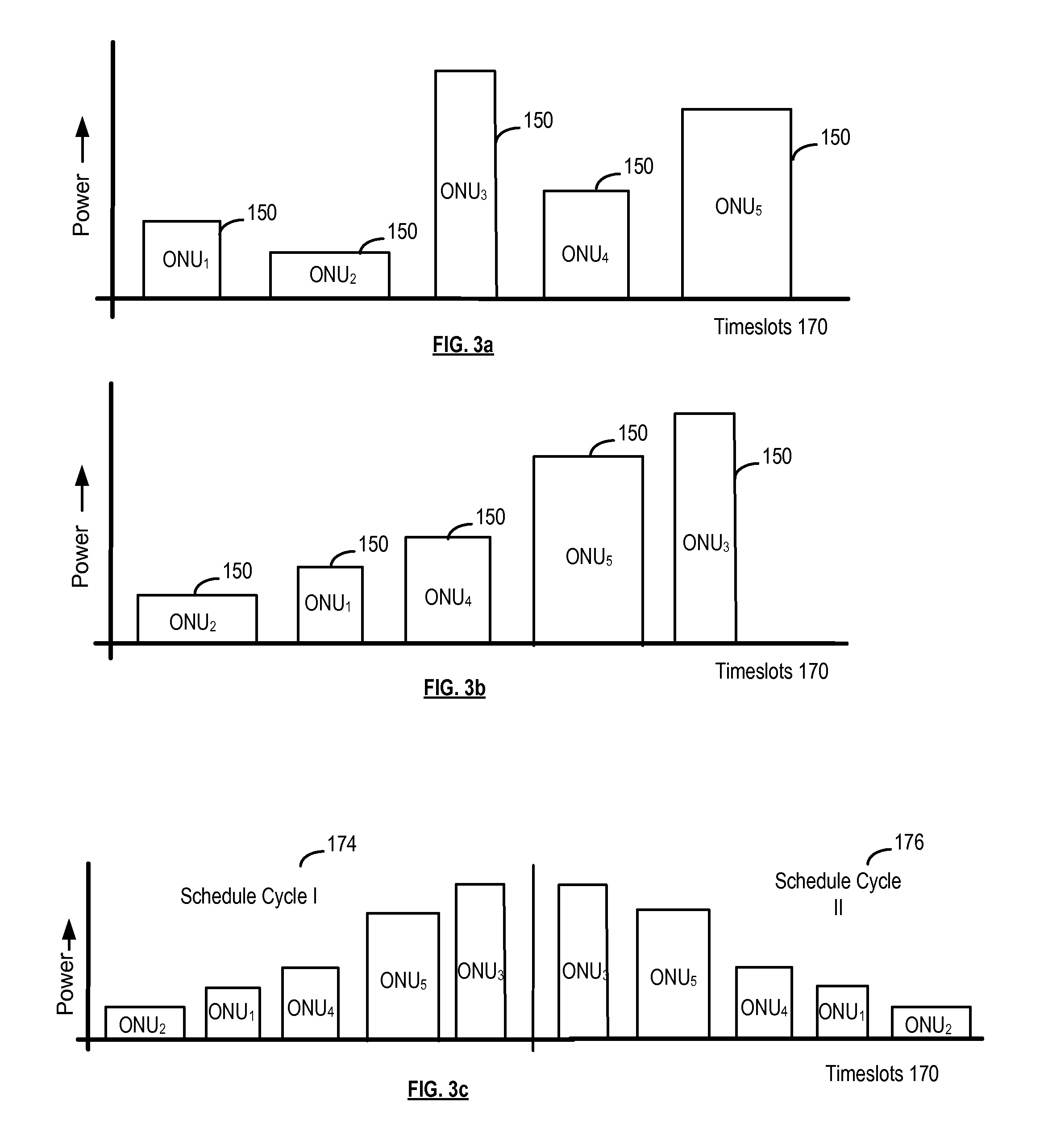
System and method for scheduling timeslots for transmission by optical nodes in an optical network
ActiveUS20110255866A1Time-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer networkOptical network unit
A signal strength corresponding to an incoming optical burst from each of a plurality of optical nodes is measured. The measurements can be performed at system start-up, configuration / installation of the optical nodes and / or at certain intervals of operation of the optical nodes. Signal strength information for the optical nodes based on the measurements is stored in memory. When scheduling the optical nodes for transmission, a preferred transmission order is determined in response to the stored signal strength information. In an embodiment, the preferred order is determined to reduce differences in signal strength levels between consecutive optical bursts.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and system for processing upstream packets of an optical network
InactiveUS7085281B2Avoid collisionReduce performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsGeneral purposeTransceiver
A protocol for an optical network can control the time at which subscriber optical interfaces of an optical network are permitted to transmit data to a transceiver node. The protocol can prevent collisions of upstream transmissions between the subscriber optical interfaces of a particular subscriber group. With the protocol, a transceiver node close to the subscriber can allocate additional or reduced upstream bandwidth based upon the demand of one or more subscribers. That is, a transceiver node close to a subscriber can monitor (or police) and adjust a subscriber's upstream bandwidth on a subscription basis or on an as-needed basis. The protocol can account for aggregates of packets rather than individual packets. By performing calculation on aggregates of packets, the algorithm can execute less frequently which, in turn, permits its implementation in lower performance and lower cost devices, such as software executing in a general purpose microprocessor.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
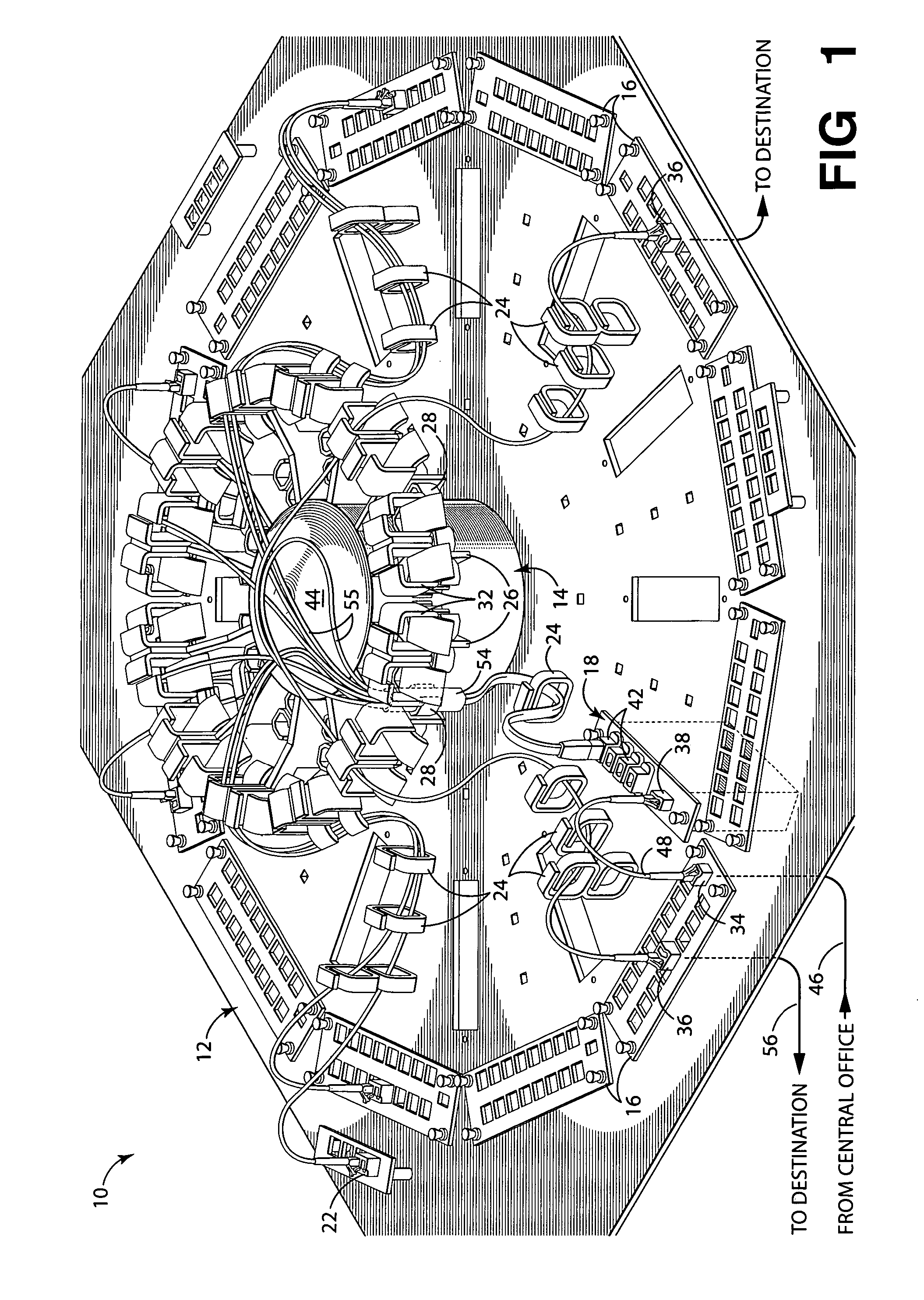
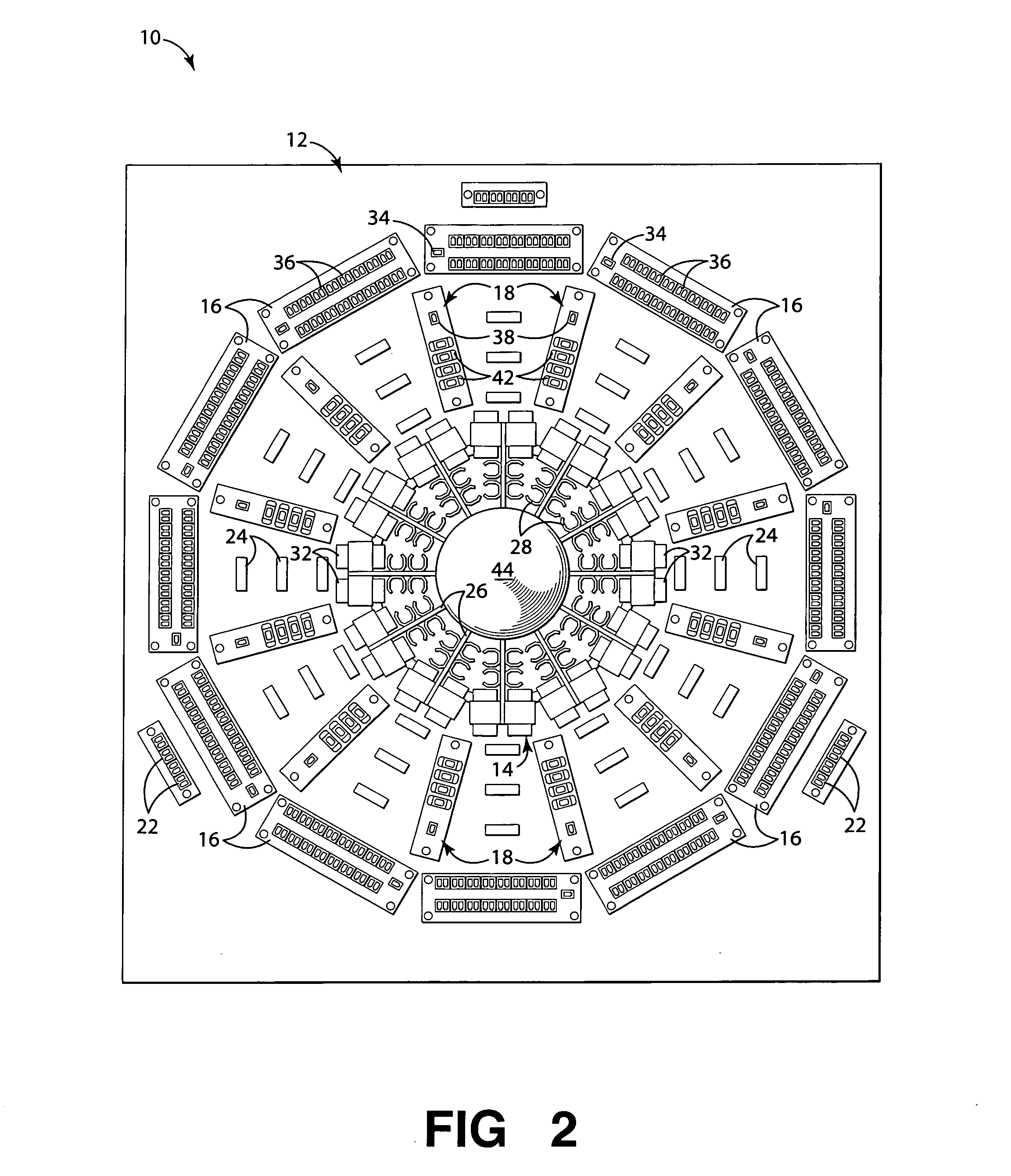
System and apparatus for radial optical distribution
ActiveUS20060165365A1Improving fiber organizationImproving routing managementRing-type electromagnetic networksOptical fibre/cable installationDistribution systemEngineering
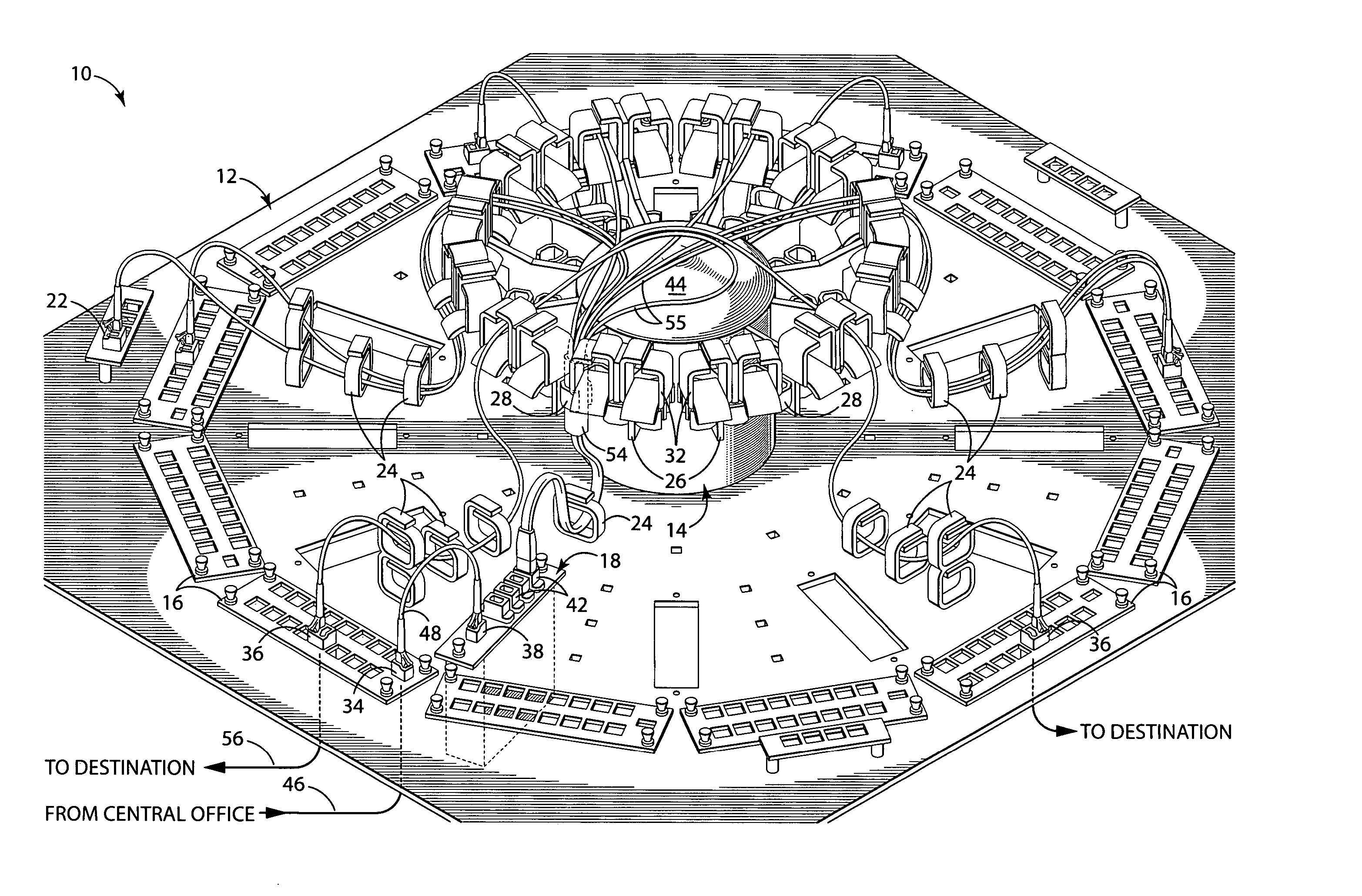
Embodiments of the invention include an apparatus and system for managing and radially distributing optical fibers from a first location, such as a central office, to a plurality of destination locations, such as homes within a neighborhood. The apparatus includes a distribution panel having a central hub or ring, and both a plurality of optical input elements and a plurality of optical output elements disposed radially around the central hub. The optical input elements split the fibers coupled from the first location into a plurality of individual fibers that are routed to the central hub. The central hub radially distributes the plurality of fibers to appropriate optical output elements, which are coupled to destination fibers routed to the plurality of destination locations. The radial configuration of the apparatus provides a central breakout point for fiber distribution, thus improving fiber organization and routing management compared to conventional routing and distribution systems.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
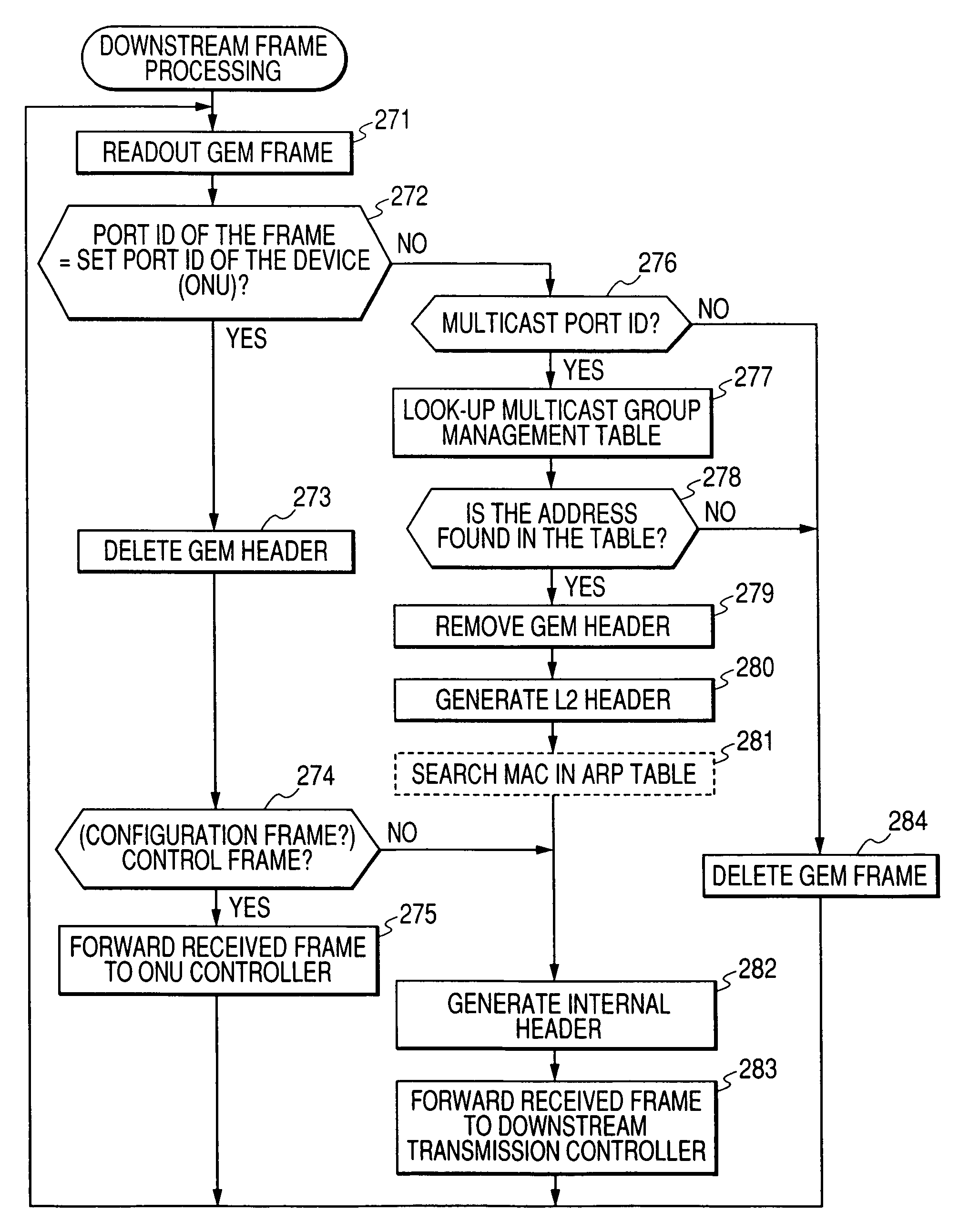
Passive optical network (PON) system
InactiveUS7675936B2Shorten the lengthEfficient use ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTransmission channelEmbedded system
A PON system capable of utilizing the bandwidth of an optical transmission channel in the PON section. In a PON system including an OLT and a plurality of ONUs, the OLT has: a downstream frame processing unit that removes at least part of the header information in a layer 2 header from a downstream frame received from a wide area network, and converts the remaining frame portion into a frame having a header specific to the PON section; and a downstream frame processing unit that extracts a downstream frame portion to be transferred to a user terminal, from a received frame from a PON, and adds the layer 2 header information deleted in the OLT.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access Based Virtual Passive Optical Network (VPON)
InactiveUS20090092394A1Effective bandwidthWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar-type electromagnetic networksEngineeringLength wave
Various types of passive optical networks operate simultaneously in one passive optical network system comprising an optical line terminal, a passive remote node, and multiple optical network units. Downstream data is orthogonal frequency division multiplexed onto a single wavelength optical carrier transmitted on a primary downstream optical beam from the optical line terminal to a splitter in the passive remote node. The primary downstream optical beam is split into multiple secondary downstream optical beams; each is transmitted to a specific optical network unit. Upstream data is orthogonal frequency division multiplexed onto a single wavelength optical carrier transmitted on a secondary upstream optical beam from each optical network unit to a coupler in the passive remote node. The upstream wavelength for each optical network unit is different. The wavelength division multiplexed optical beam is transmitted from the passive remote node to a parallel signal detector in the optical line terminal.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
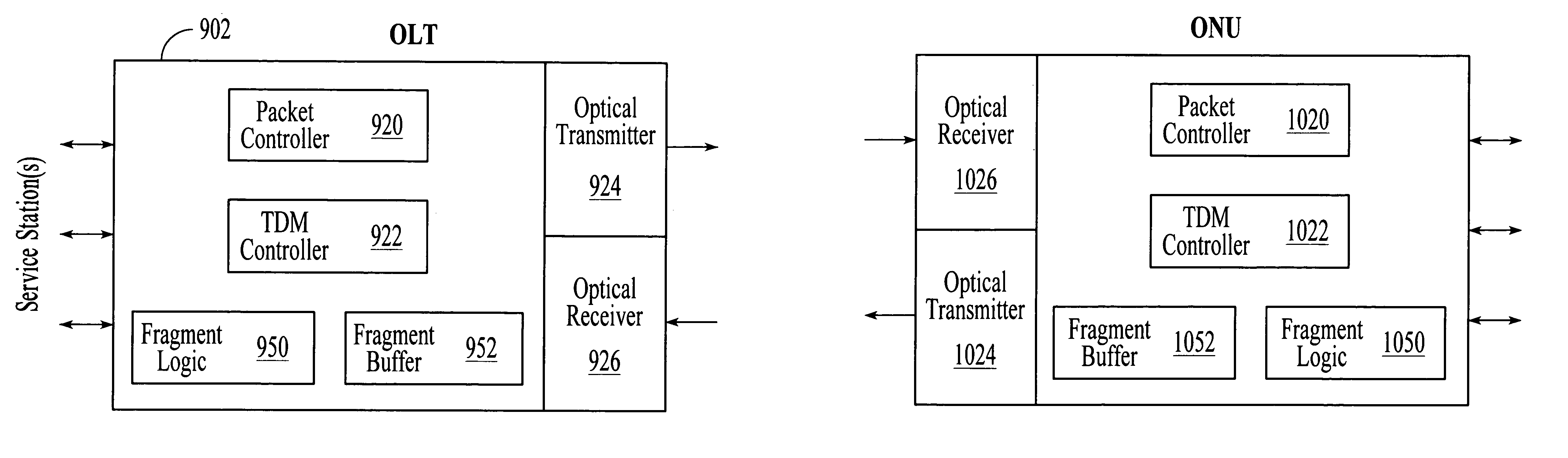
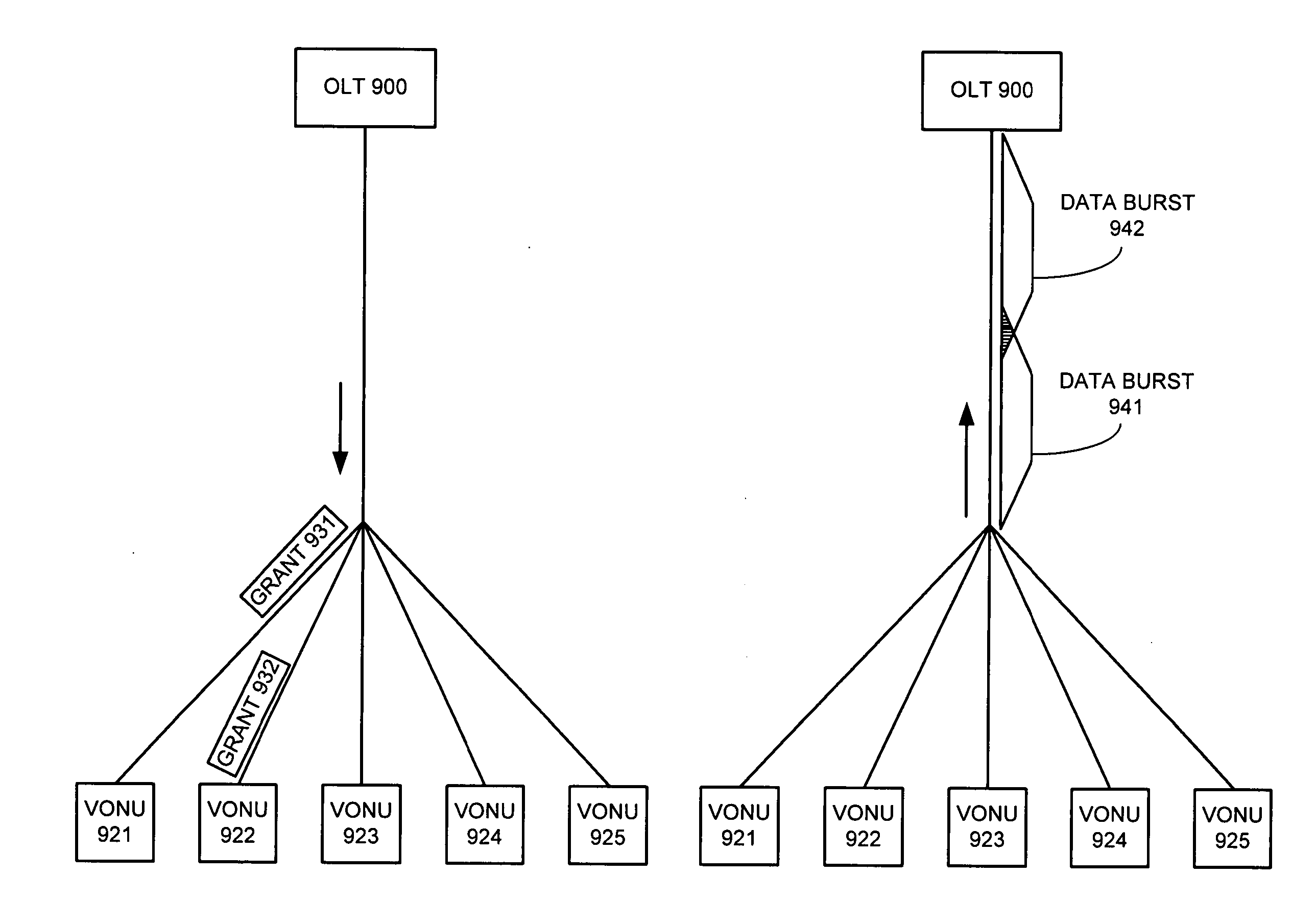
Method and apparatus for reducing data burst overhead in an ethernet passive optical network
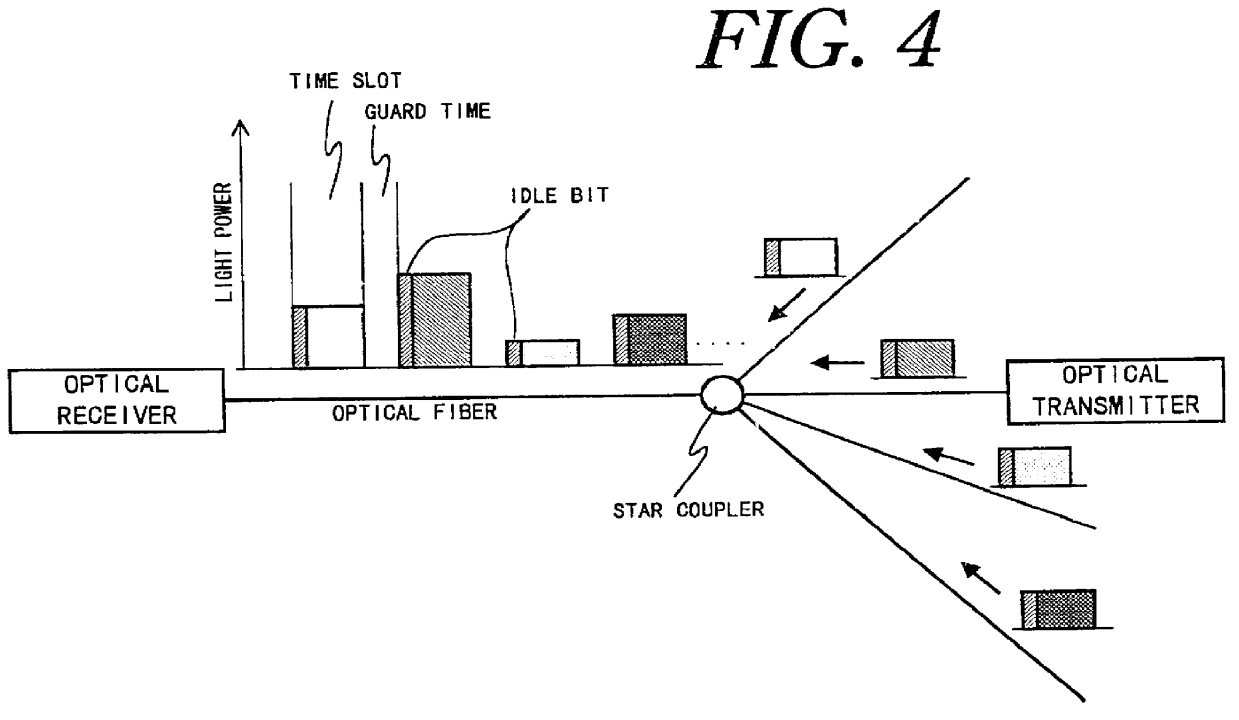
InactiveUS20050041682A1Reduces data burst overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexStart timeEthernet
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that reduces data burst overhead in an Ethernet passive optical network which includes a central node and at least one remote node, wherein downstream data from the central node is broadcast to the remote nodes, and wherein upstream data from a remote node is transmitted to the central node in a unicast manner. During operation, the central node transmits grant messages to a number of remote nodes, wherein a grant message for a specified remote node assigns a start time and a duration of a transmission timeslot in which the specified remote node may transmit an upstream data burst. In response to the grant messages, the central node then receives a number of upstream data bursts, wherein the time gap between two consecutive upstream data bursts is less than the summation of a default laser turn-on time, a default laser turn-off time, an AGC period, and a CDR period.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Wavelength-division multiplexing-passive optical network
InactiveUS20060153567A1Enhanced advantageWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar/tree networksEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
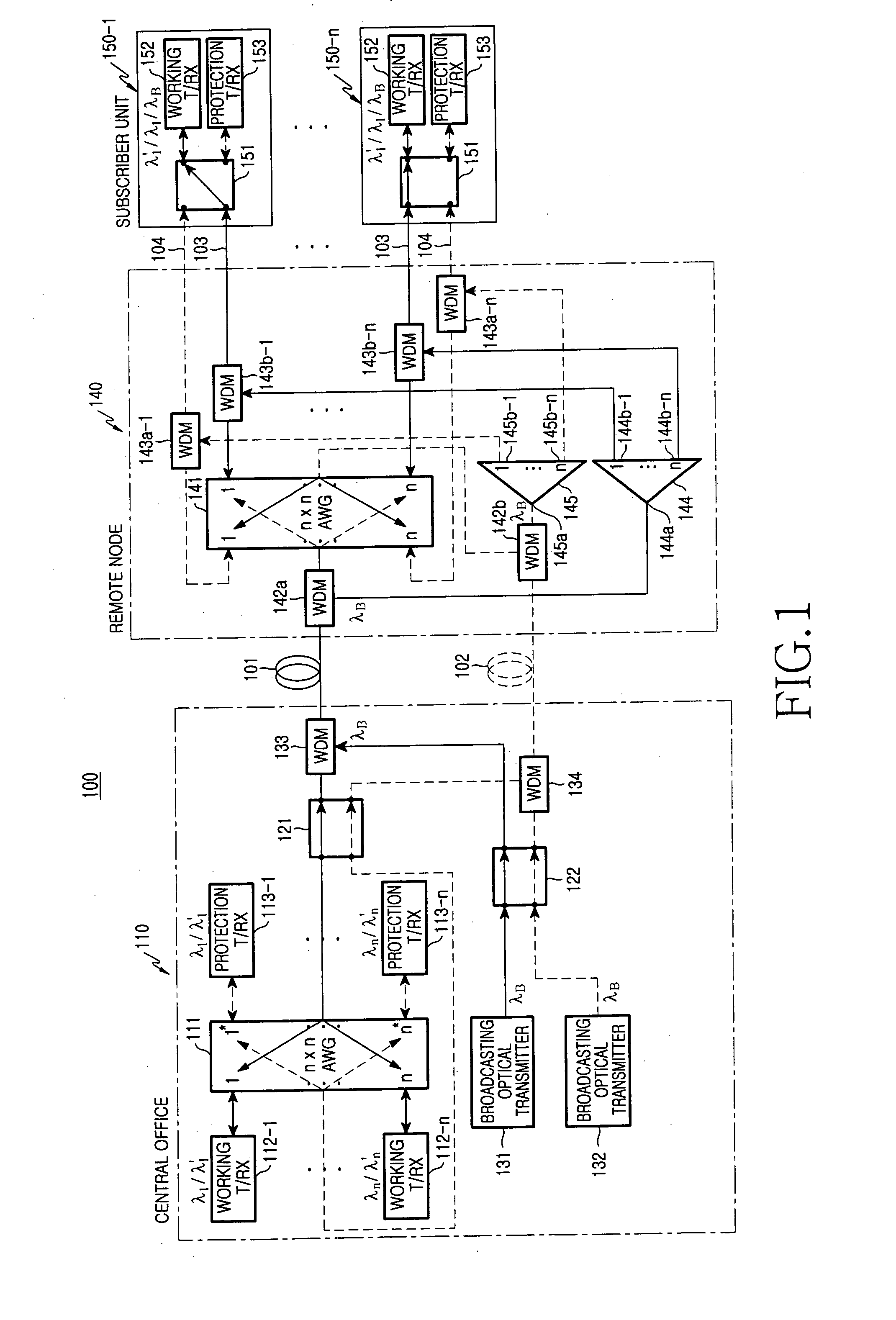
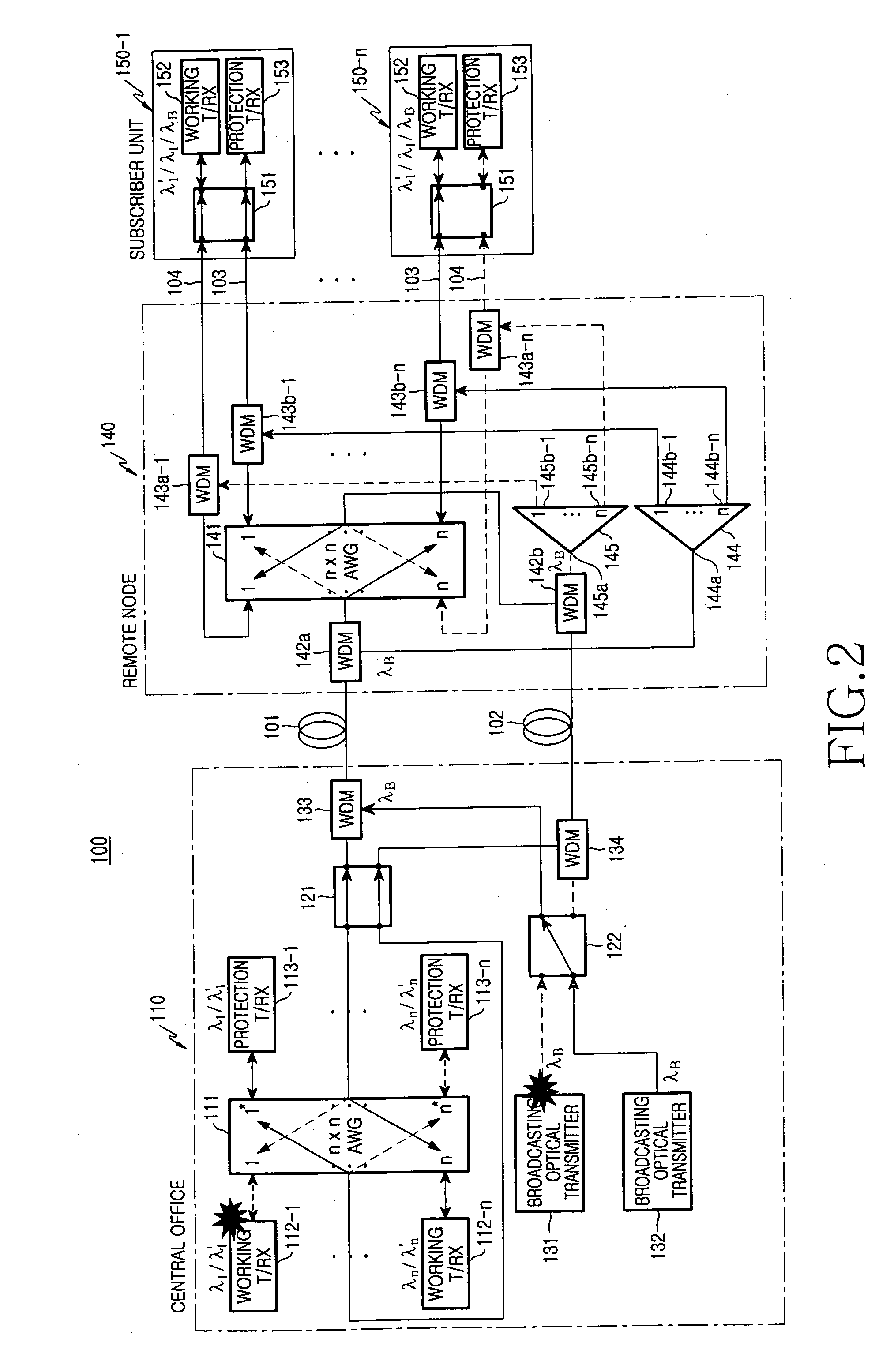
Disclosed is a wavelength-division multiplexing-passive optical network having a central office including a plurality of first working and protection transmit / receive modules, working and protection optical transmitters, and a plurality of first optical switches, the first working and protection transmit / receive modules generating downstream optical signals and detecting upstream optical signals having corresponding wavelengths, the working and protection optical transmitters generating broadcasting optical signals, the first optical switches performing a switching operation when faults occur, a plurality of subscriber units for receiving broadcasting optical signals and downstream optical signals having corresponding wavelengths and generating upstream optical signals, the subscriber units including second optical switches, a remote node including working and protection optical splitters for dividing intensity of the broadcasting optical signals, the remote node being positioned between the subscriber units and the central office, working and protection main optical fibers for linking the central office with the remote node; and a plurality of working and protection branch optical fibers for linking the remote node with the subscriber units, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dynamic intelligent bidirectional optical access communication system with object/intelligent appliance-to-object/intelligent appliance interaction
ActiveUS20110158653A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsPersonalizationSoftware modules
Reduced Rayleigh backscattering effect enables a longer-reach optical access communication network-thus it eliminates significant costs. Furthermore, a wavelength to an intelligent subscriber subsystem can be dynamically varied for bandwidth on-Demand and service on-Demand. A software module renders intelligence (and context awareness) to a subscriber subsystem and an appliance. An object can sense / measure / collect / aggregate / compare / map and connect / couple / interact (via one or more or all electrical / optical / radio / electro-magnetic / sensor / bio-sensor communication network(s) within and / or to and / or from an object) with another object, an intelligent subscriber subsystem and an intelligent appliance utilizing an Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) and its subsequent versions.A construction of a near-field communication (NFC) enabled intelligent micro-subsystem and / or intelligent appliance with key applications (e.g., an intelligent, location based and personalized social network and an intelligent, location based and personalized direct and peer-to-peer marketing) are also described.
Owner:MAZED MOHAMMAD
Method and system for providing a return path for signals generated by legacy terminals in an optical network
InactiveUS7190901B2Small sizeIncrease transfer speedMultiplex system selection arrangementsBroadband local area networksNetwork architectureThe Internet
A return path system includes inserting RF packets between regular upstream data packets, where the data packets are generated by communication devices such as a computer or internet telephone. The RF packets can be derived from analog RF signals that are produced by legacy video service terminals. In this way, the present invention can provide an RF return path for legacy terminals that shares a return path for regular data packets in an optical network architecture.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS
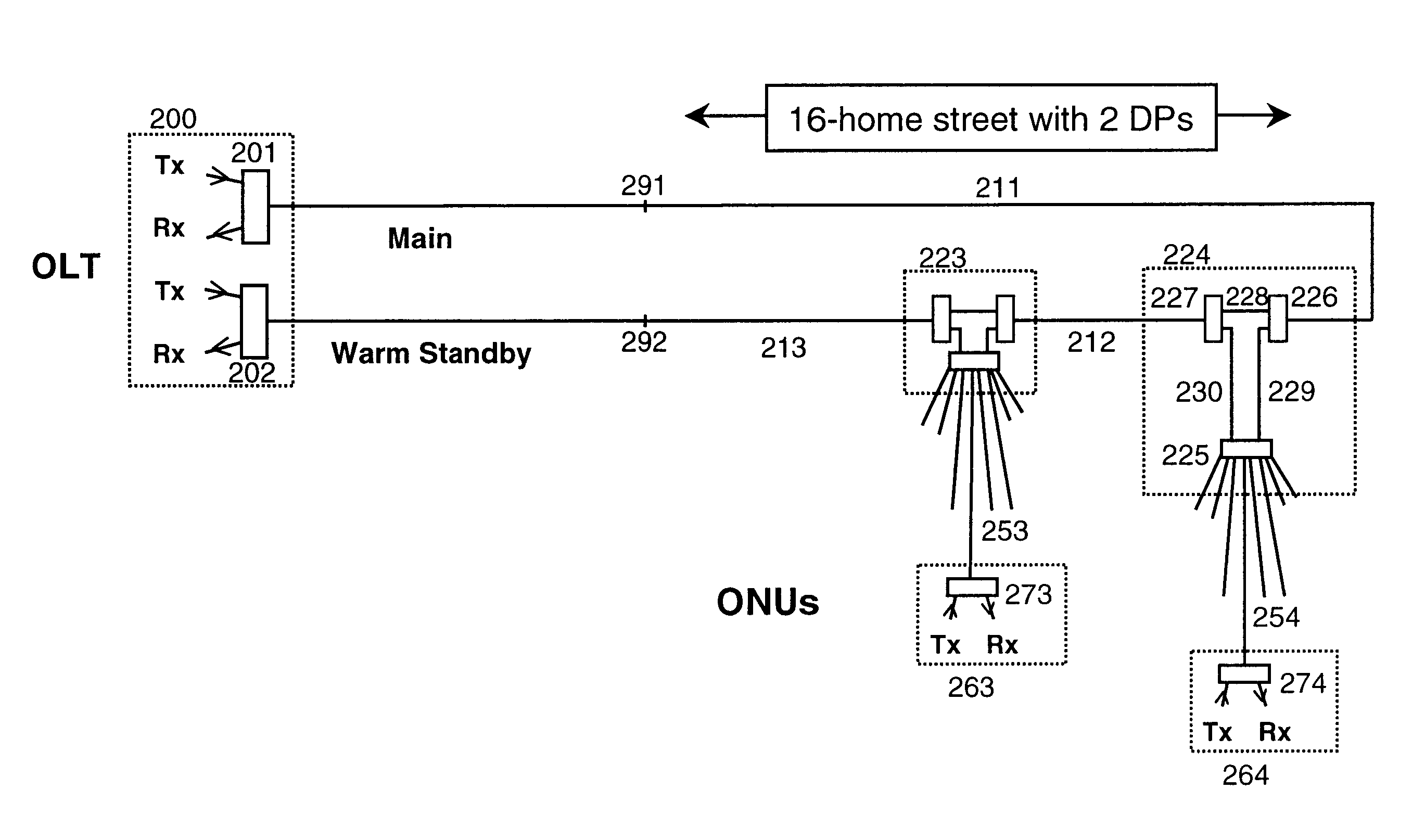
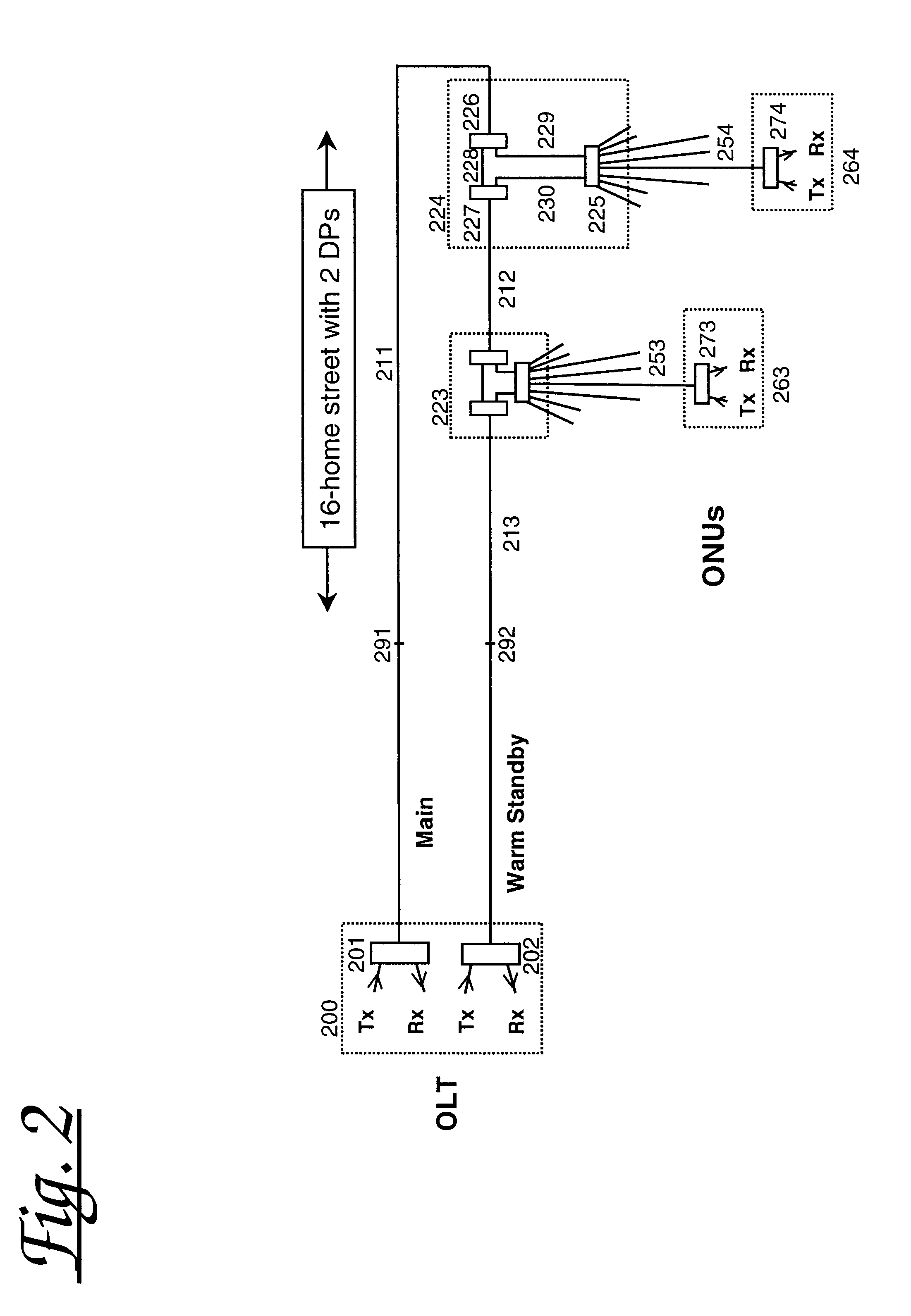
Optical termination system
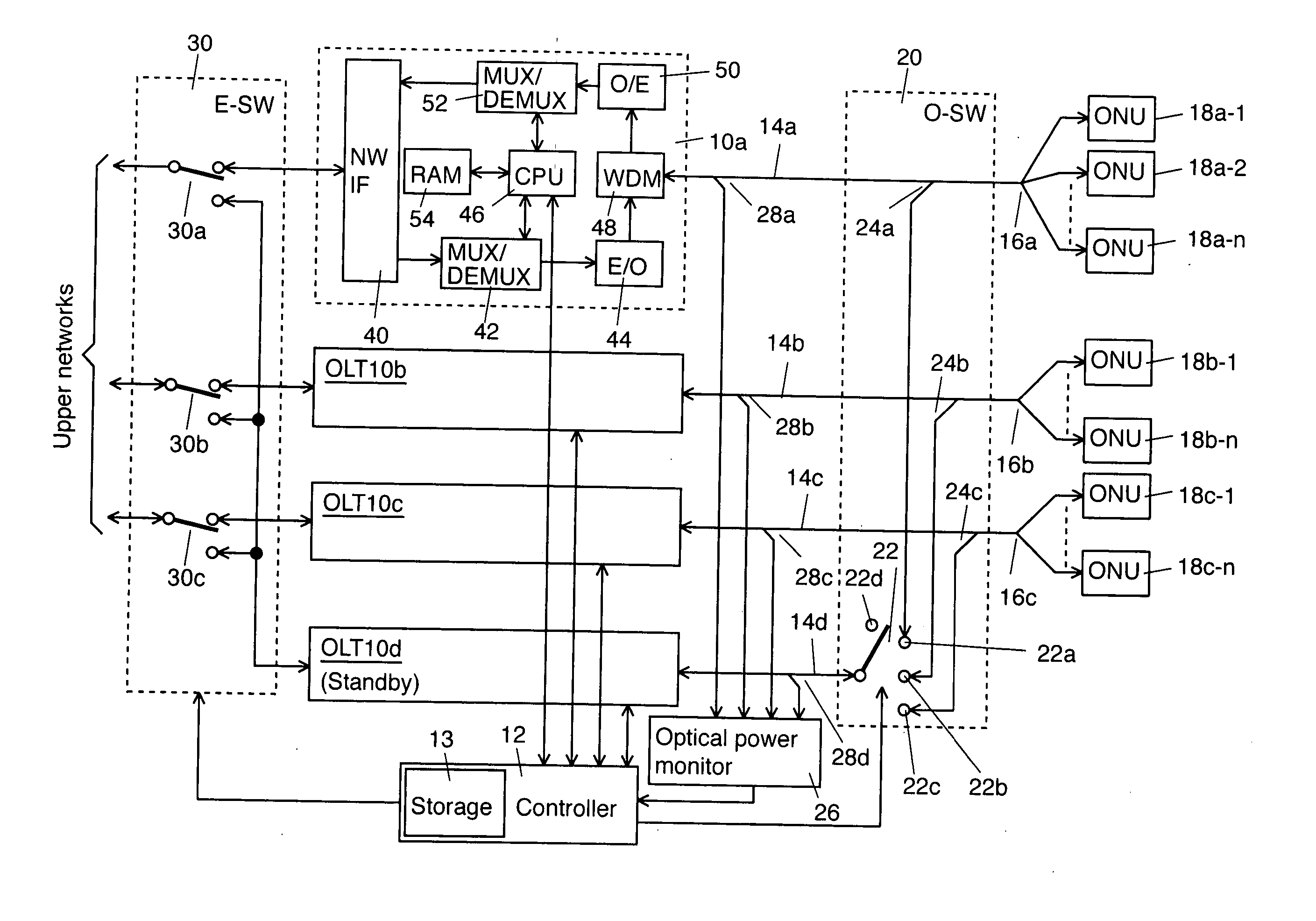
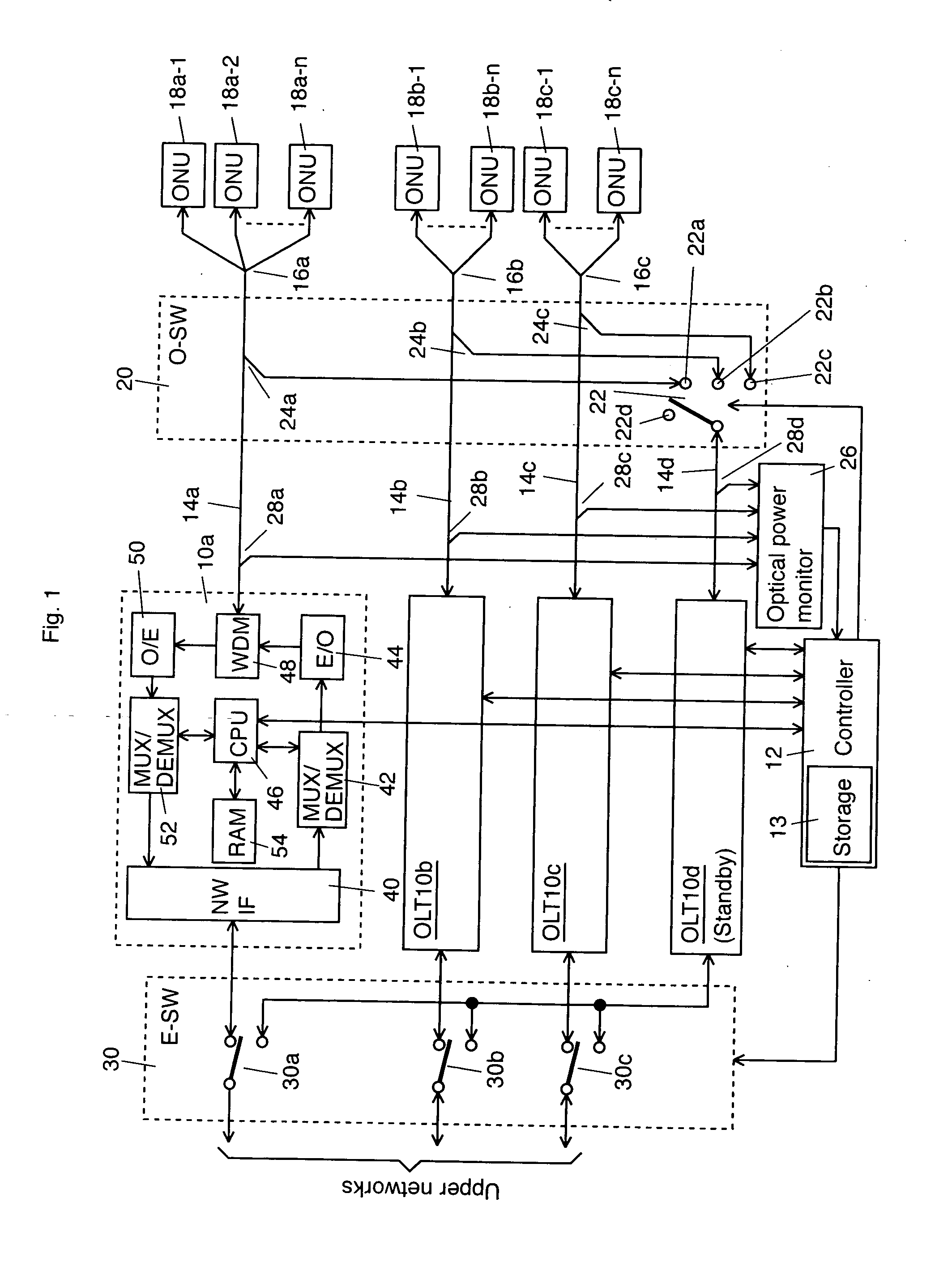
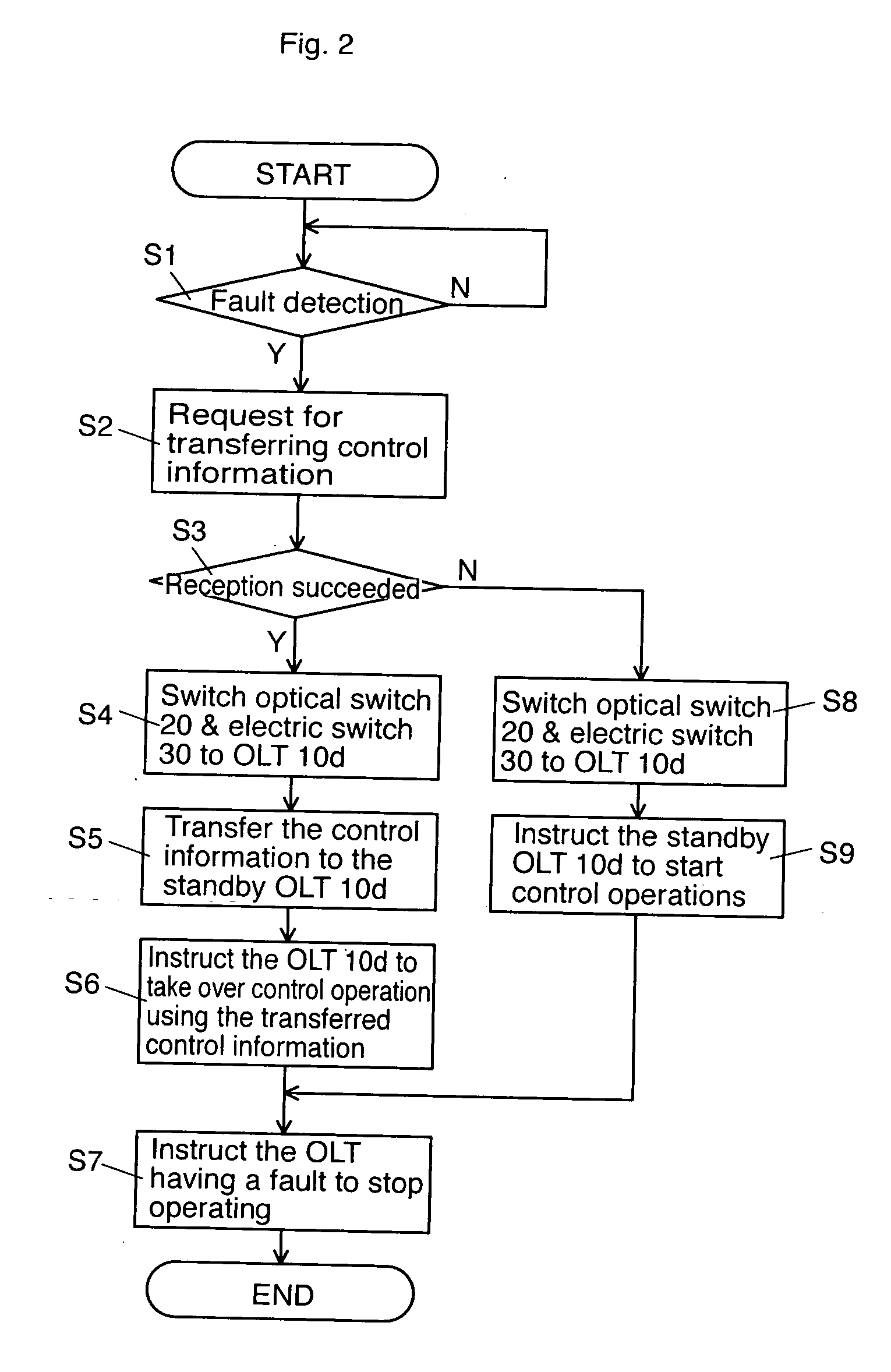
InactiveUS20070058973A1Reduce switchingLaser detailsError preventionEngineeringOptical line termination
An optical termination system is provided. The optical termination system includes a working Optical Line Terminal (OLT) that communicates with a plurality of Optical Network Units (ONUs) near end users through an optical transmission line. The OLT includes a control information storage to store control information of the plurality of ONUs. In addition, the optical termination system includes a standby OLT, which includes a storage to store the control information to be transmitted from the working OLT. Furthermore, the optical termination system includes a controller that controls switching from the working OLT to the standby OLT.
Owner:KDDI CORP
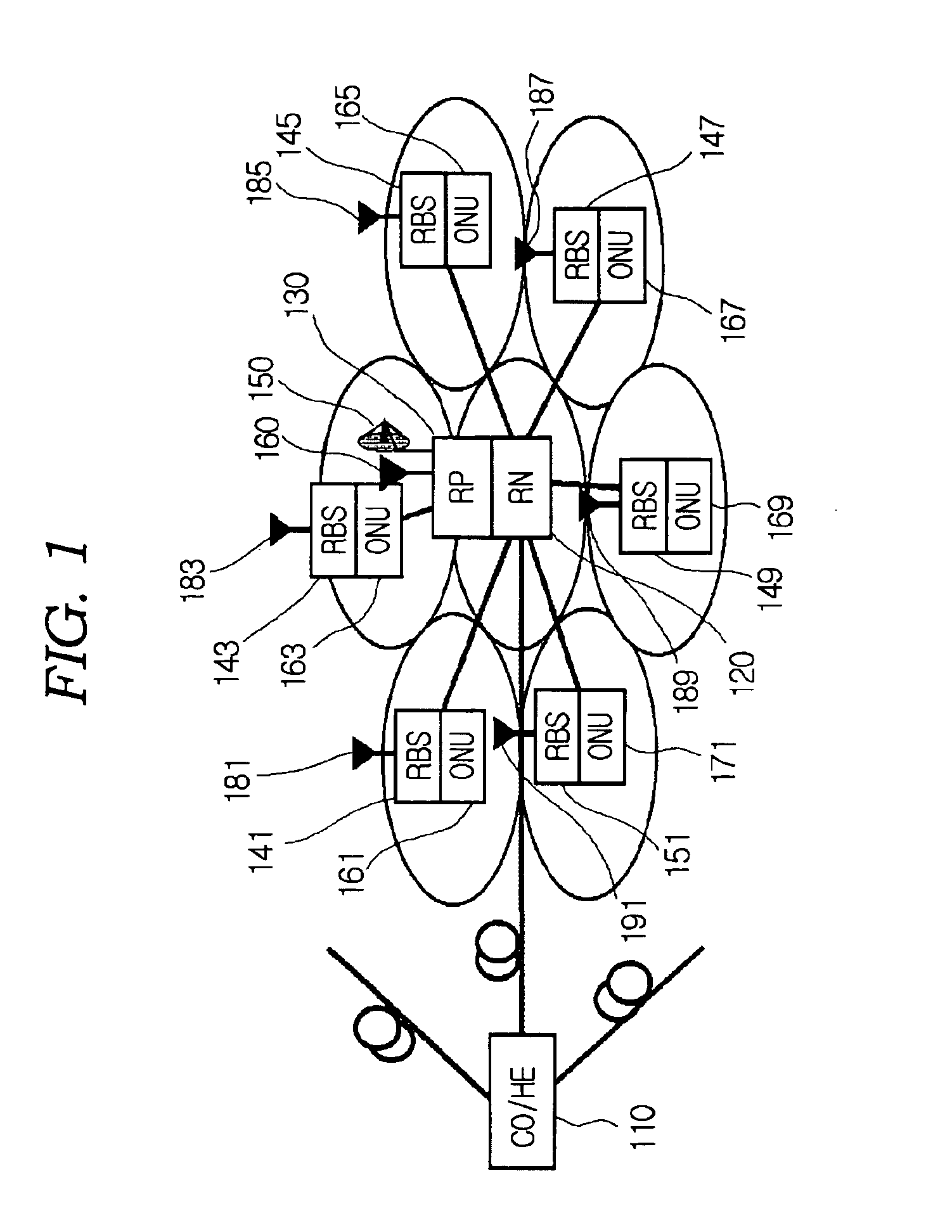
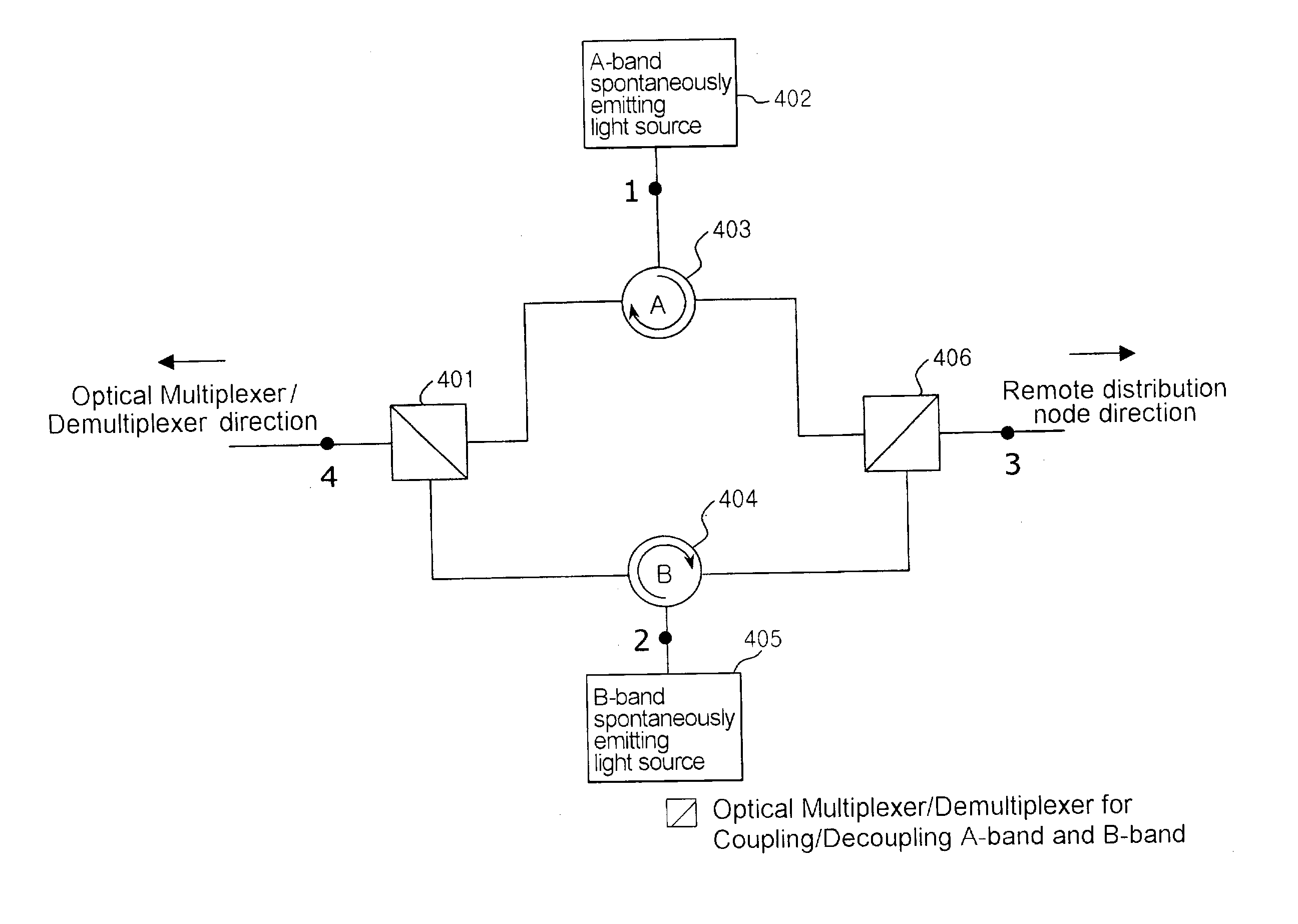
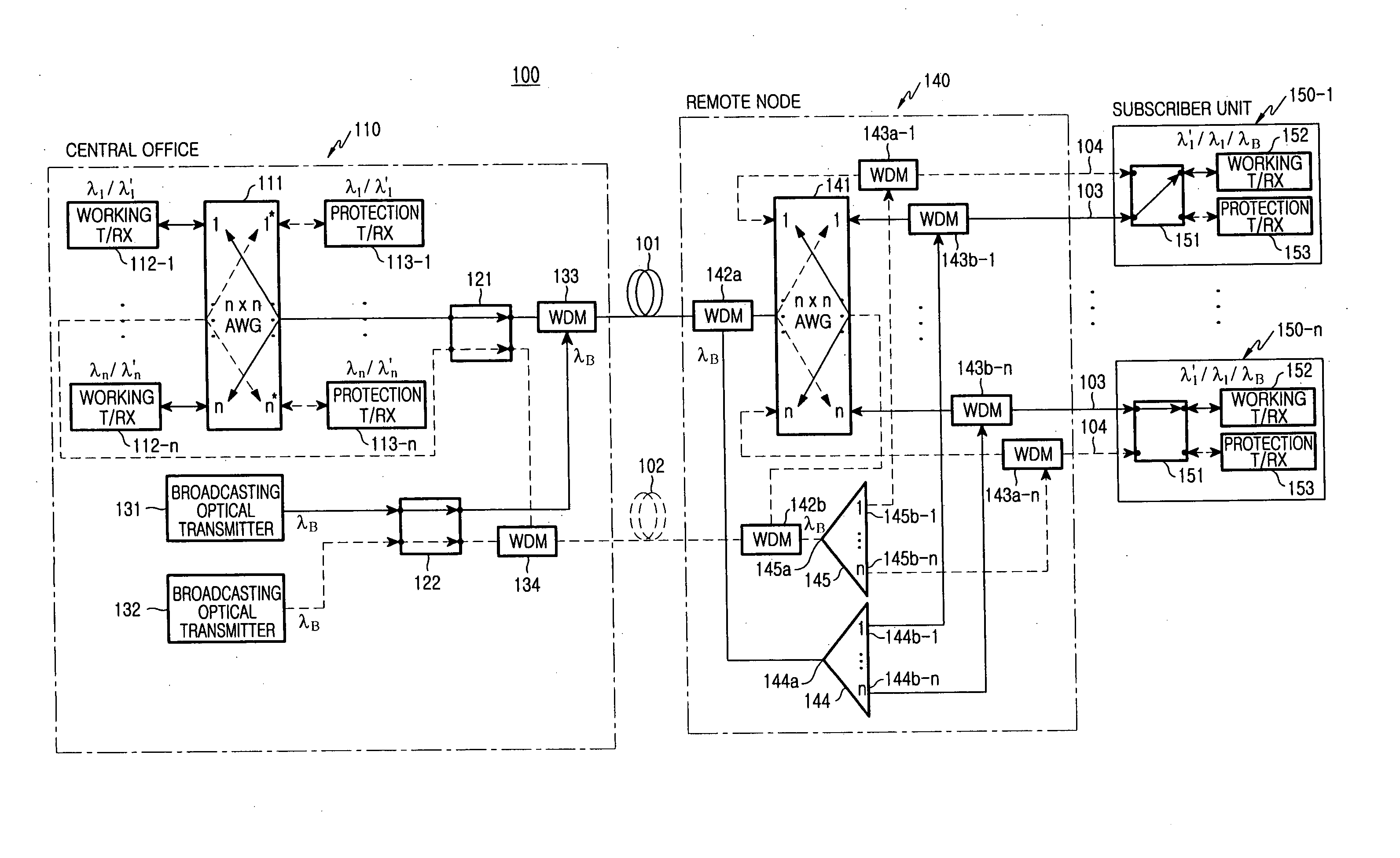
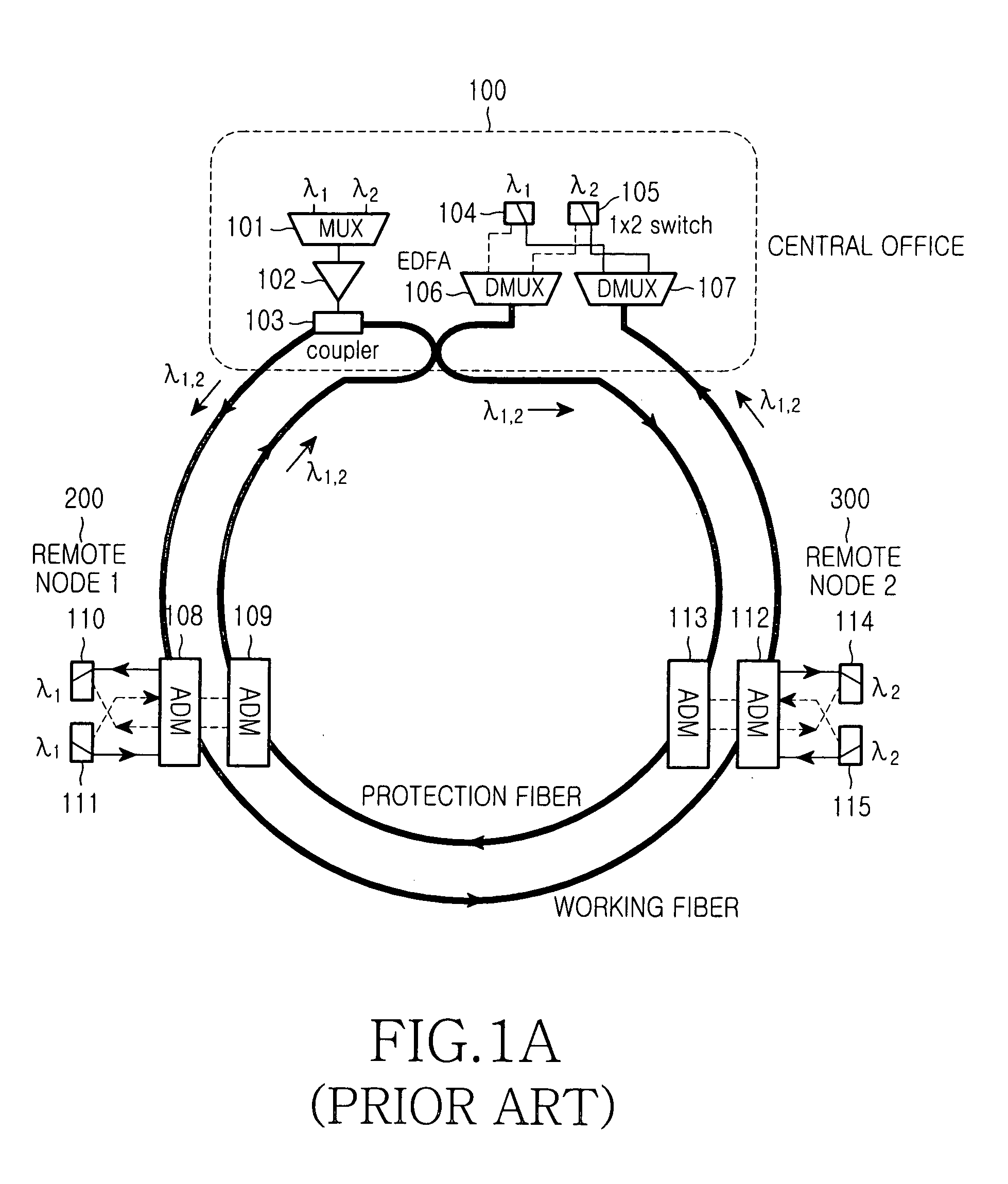
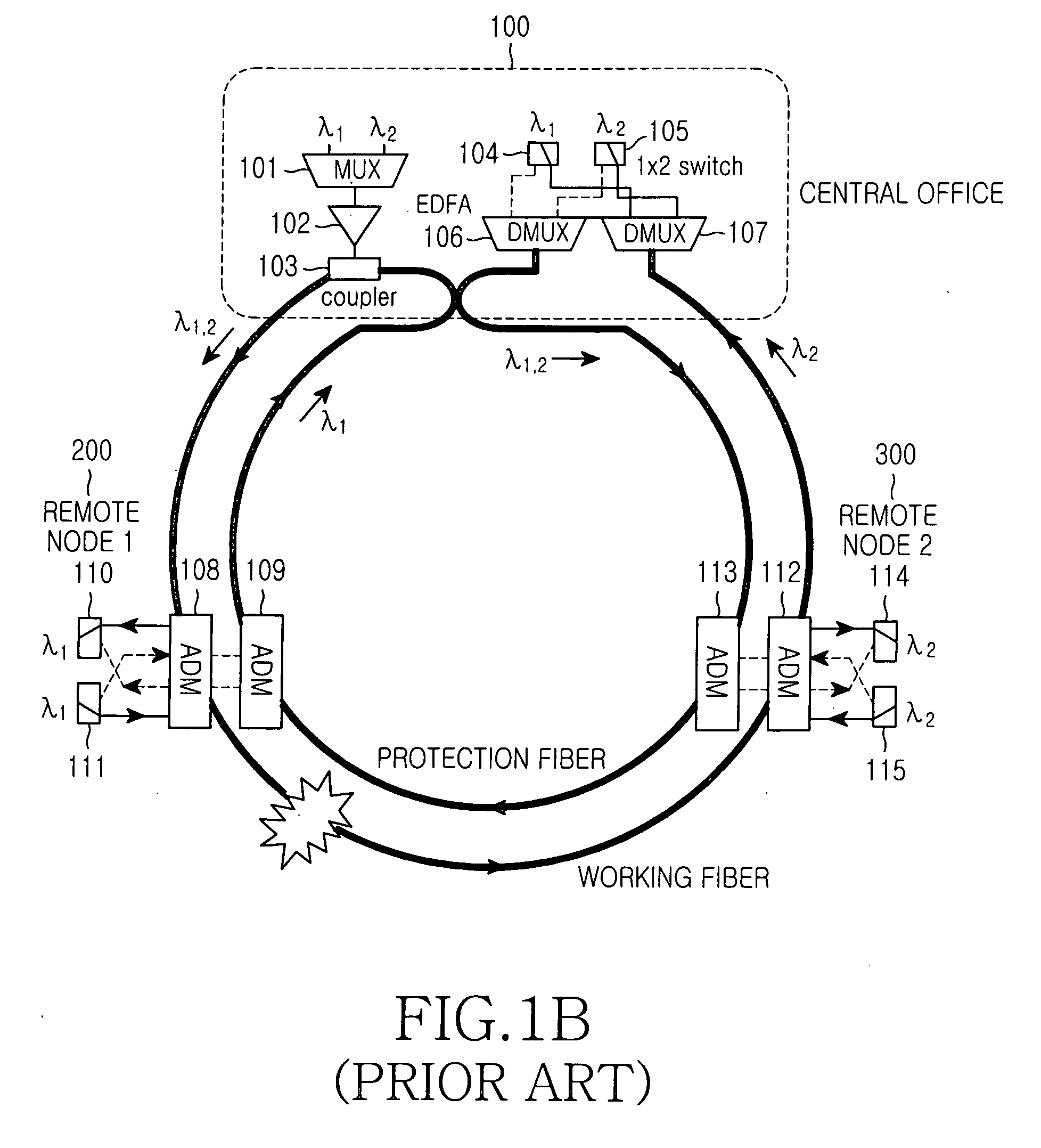
Wavelength-division multiplexed self-healing passive optical network
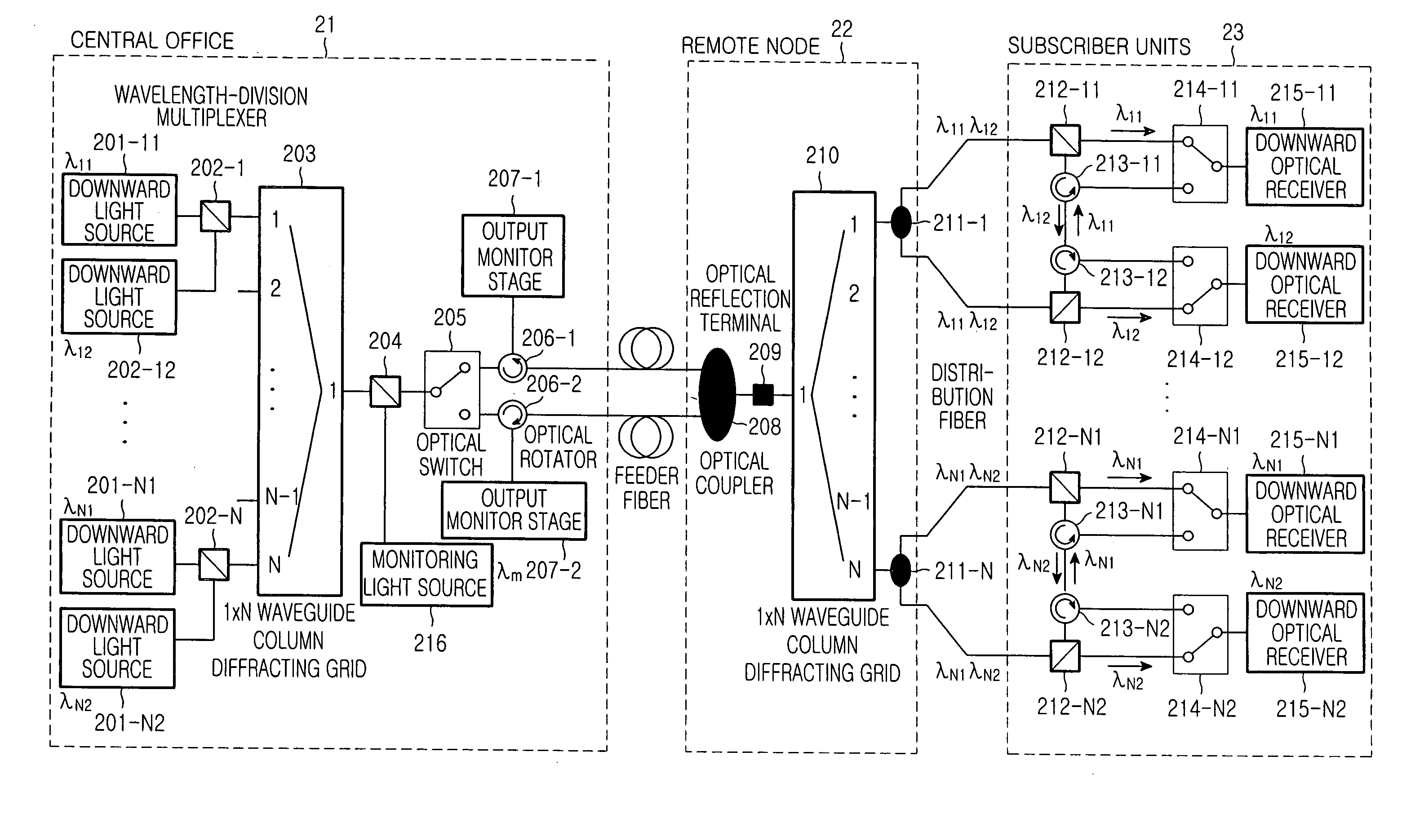
InactiveUS20050141892A1Detected accidentallyRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsTelecommunicationsControl signal
A wavelength-division multiplexed self-healing passive optical network is capable of detecting cut-off and deterioration of feeder fiber and distribution fiber and restoring a network with a star structure. The network includes a central office, a remote node, and a plurality of subscriber units. Working and protection feeder fibers connect the central office to the remote node. A reflection unit at an end of the remote node connects to the central office for reflecting a monitoring optical signal transmitted from the central office. An output monitor stage at an end of the central office connects to the remote node for detecting the reflected monitoring optical signal and generating a control signal based on the presence of abnormality of the working and protection feeder fibers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com