Patents
Literature
8947 results about "Opto electronic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
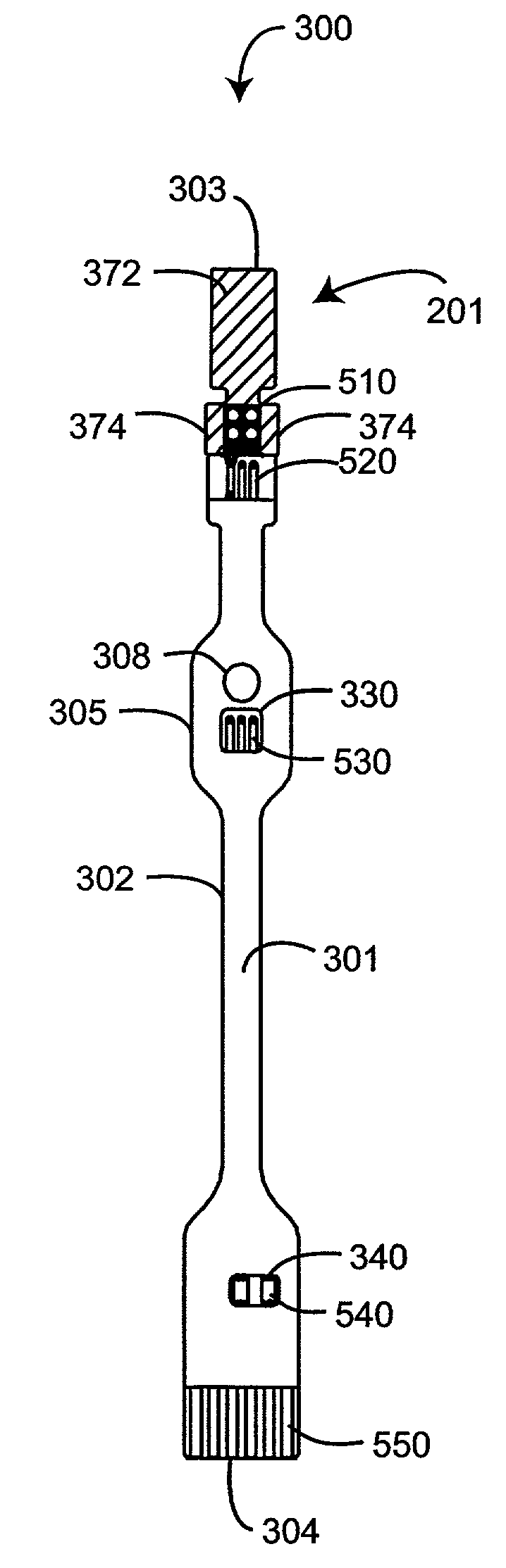
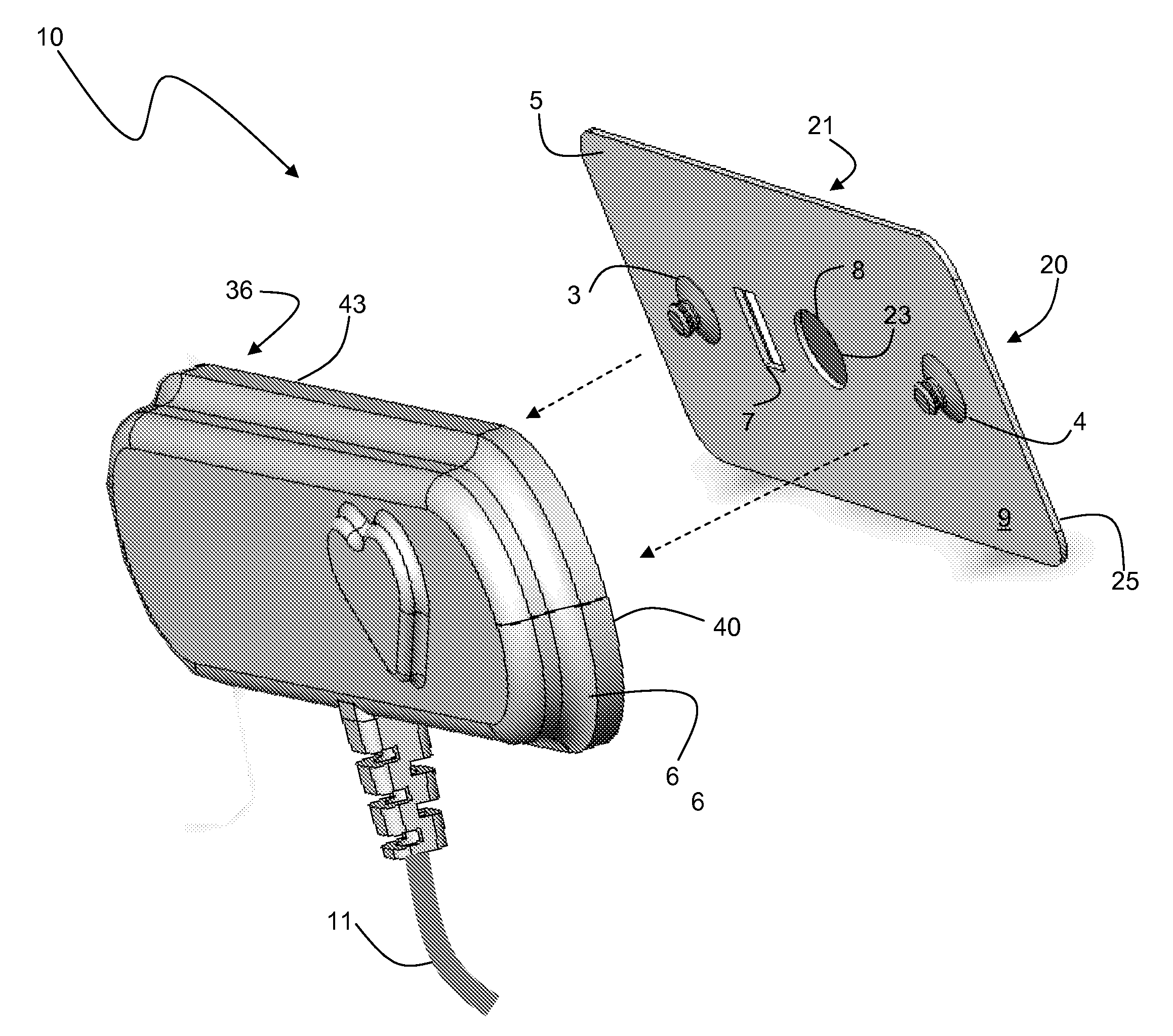
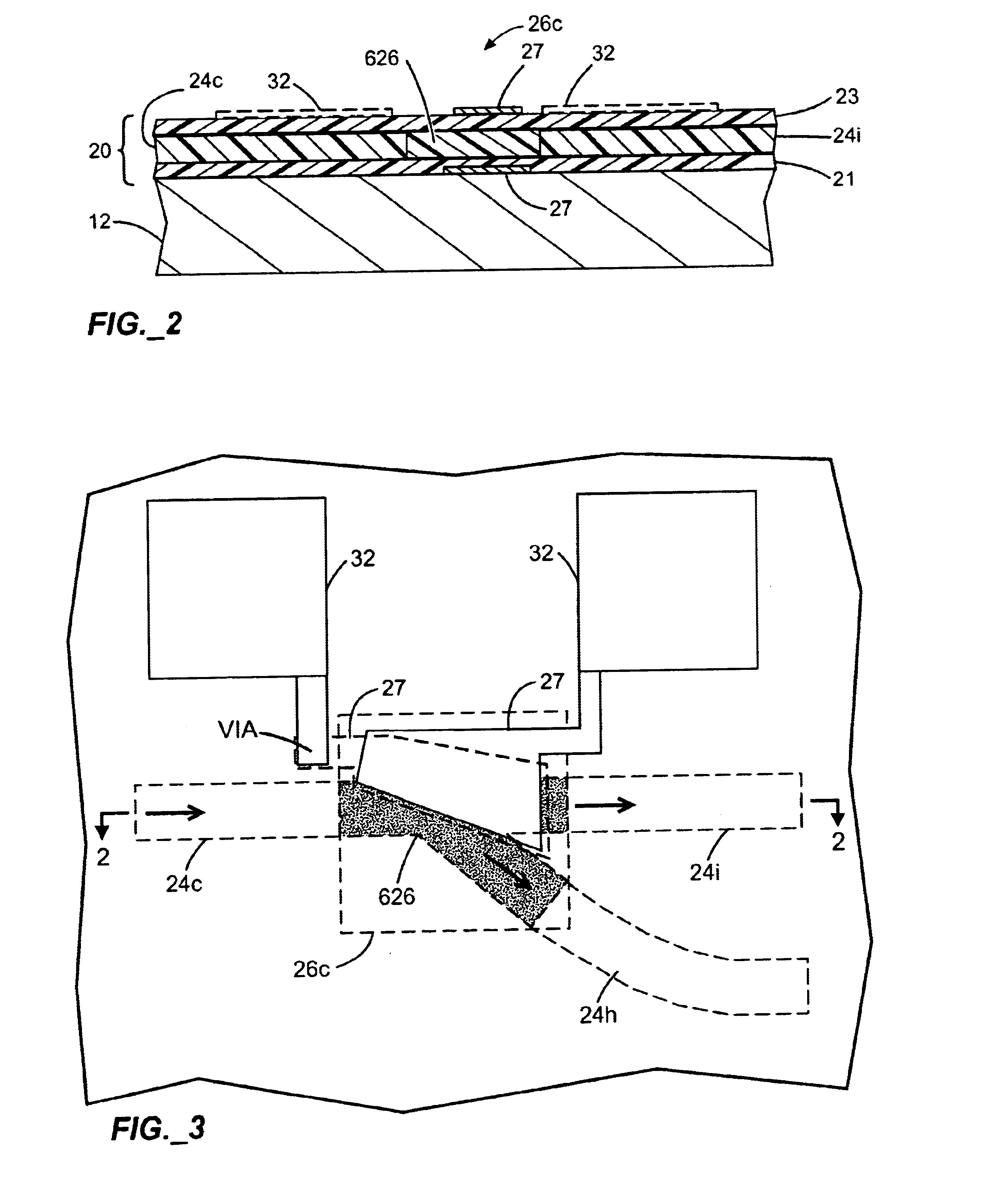
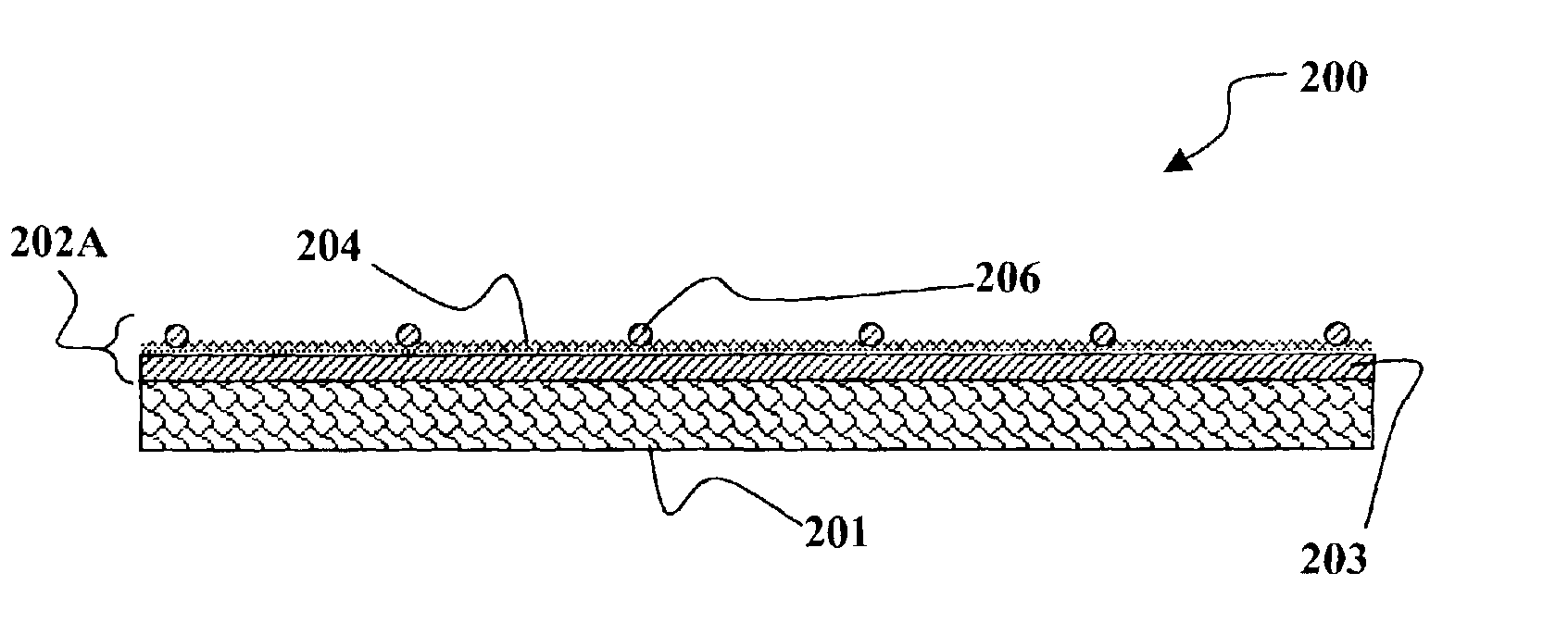
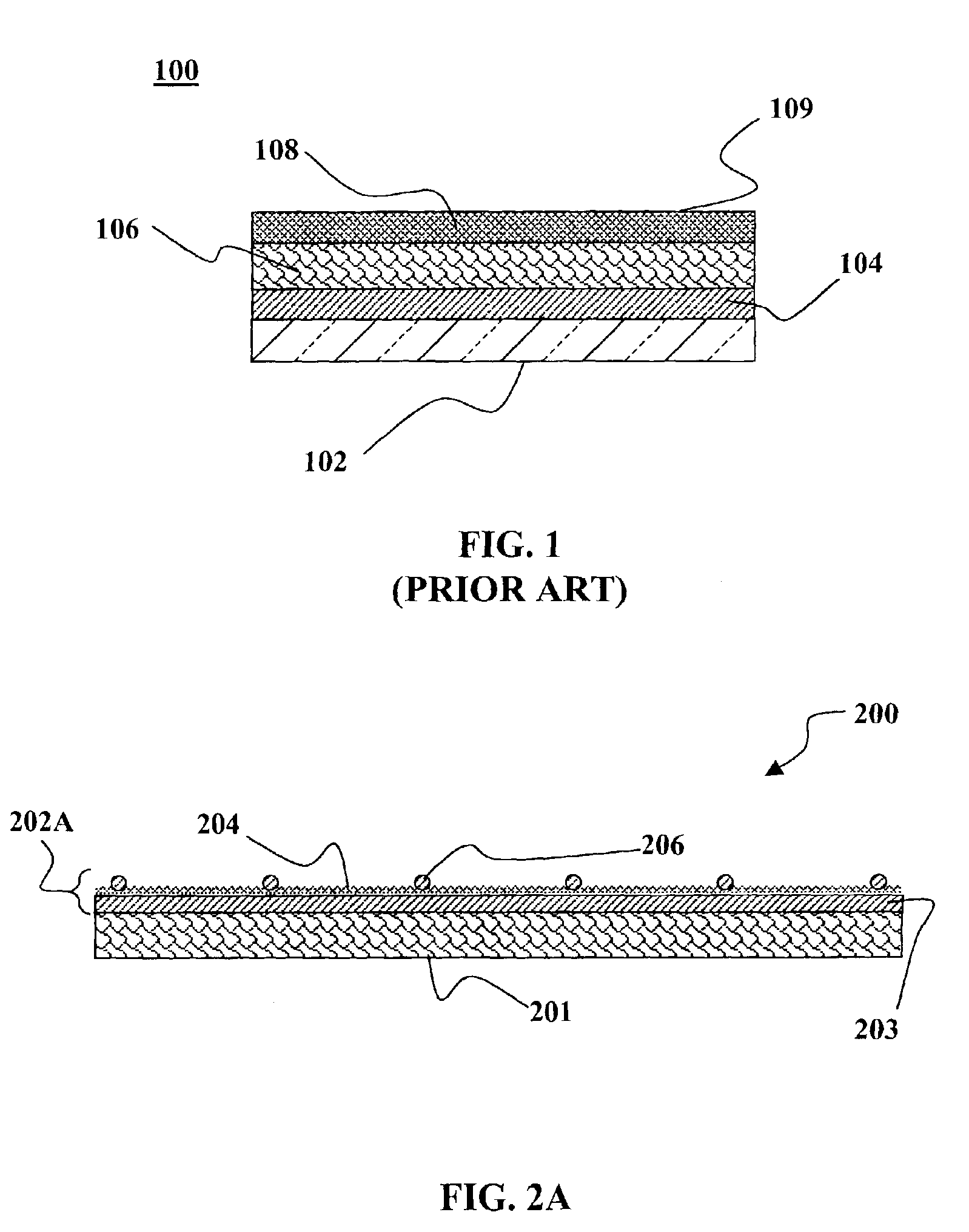
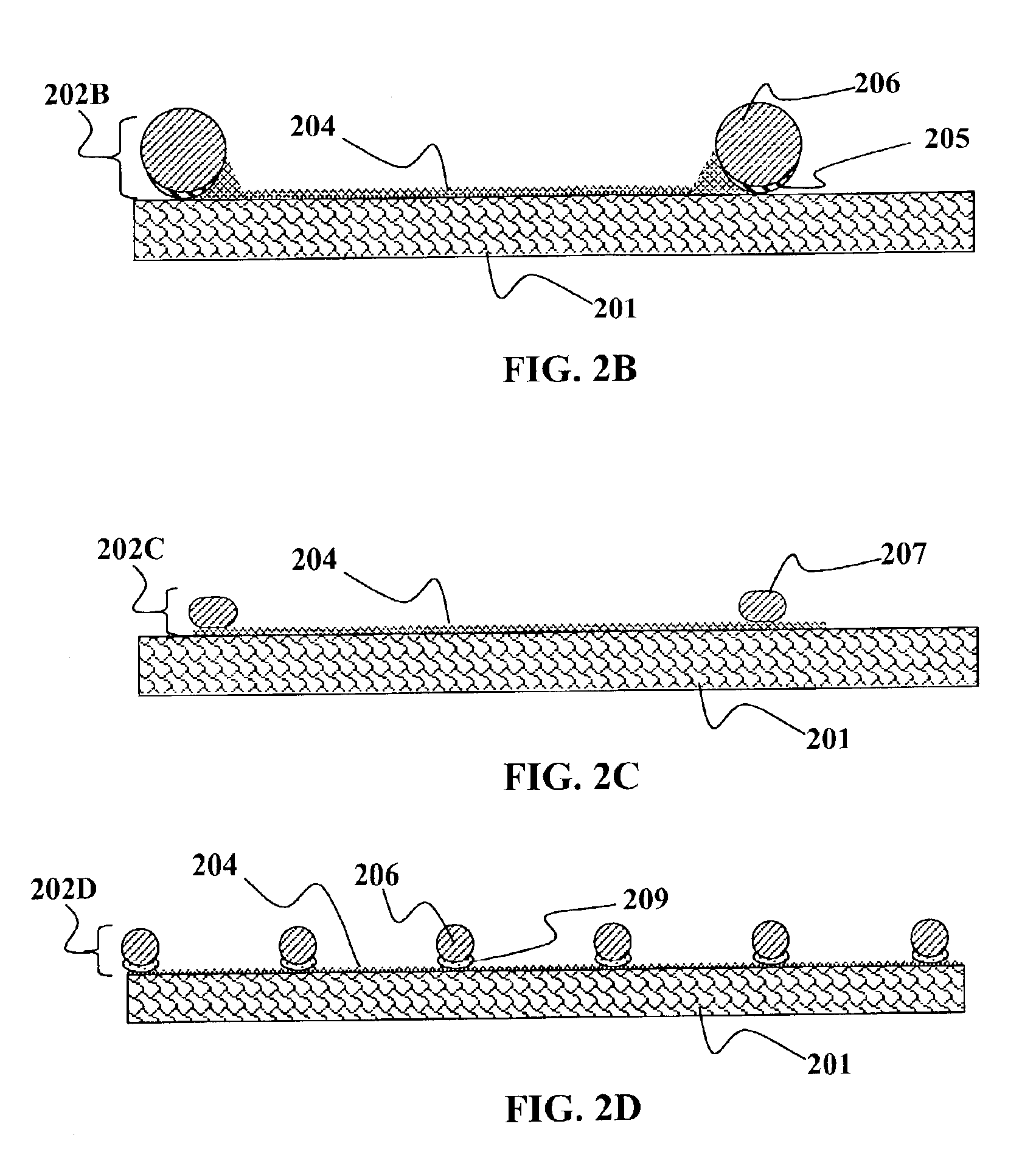
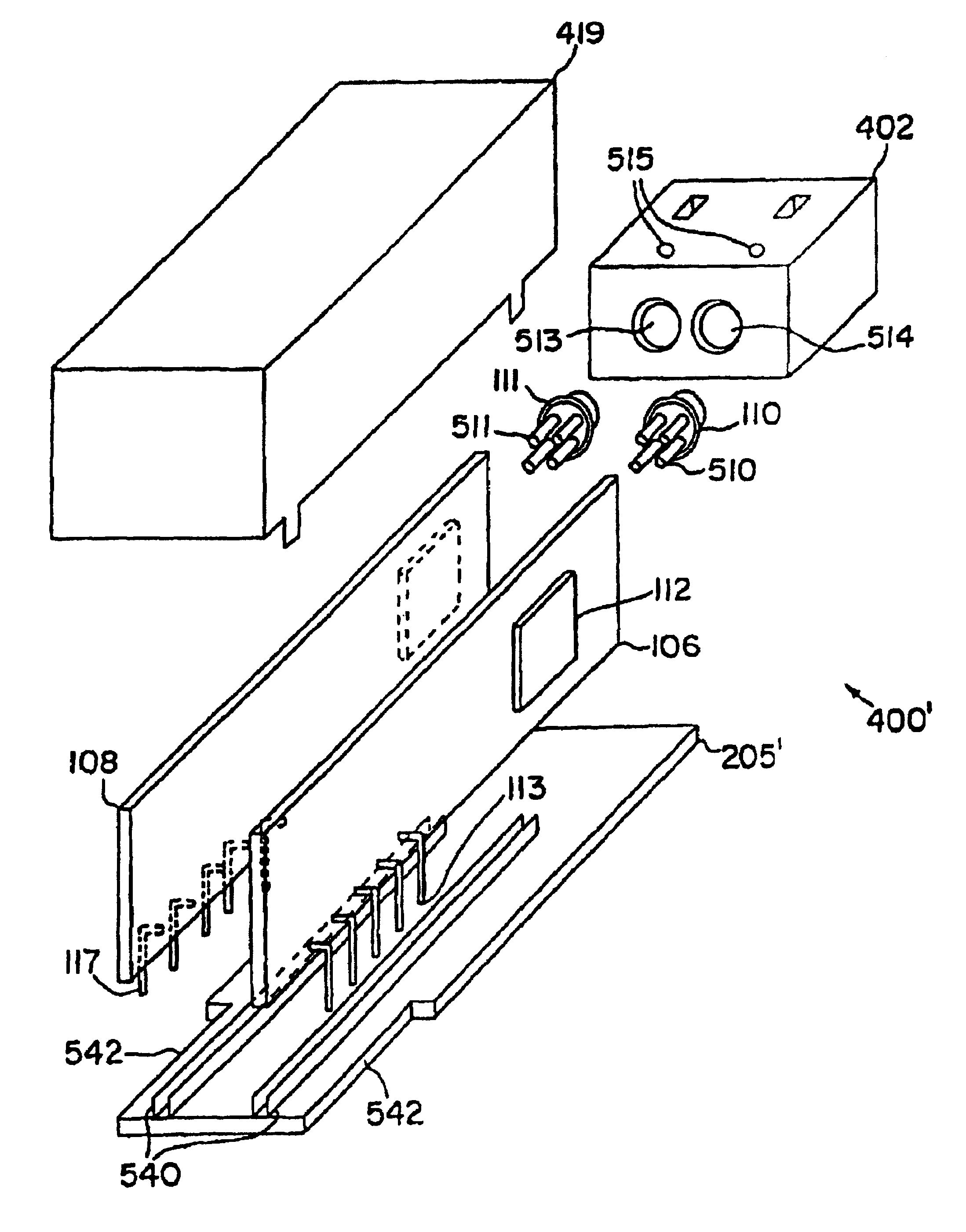
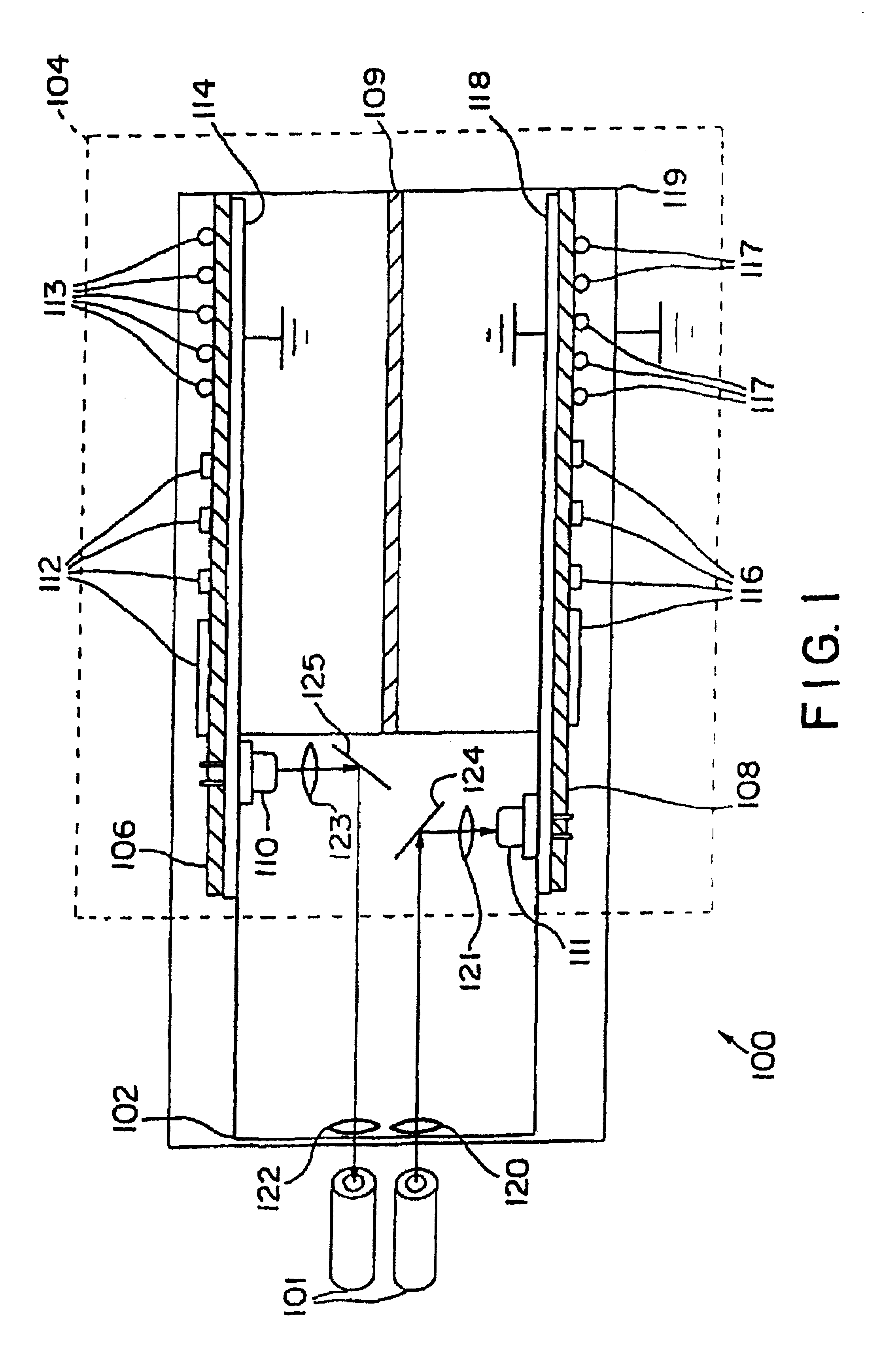
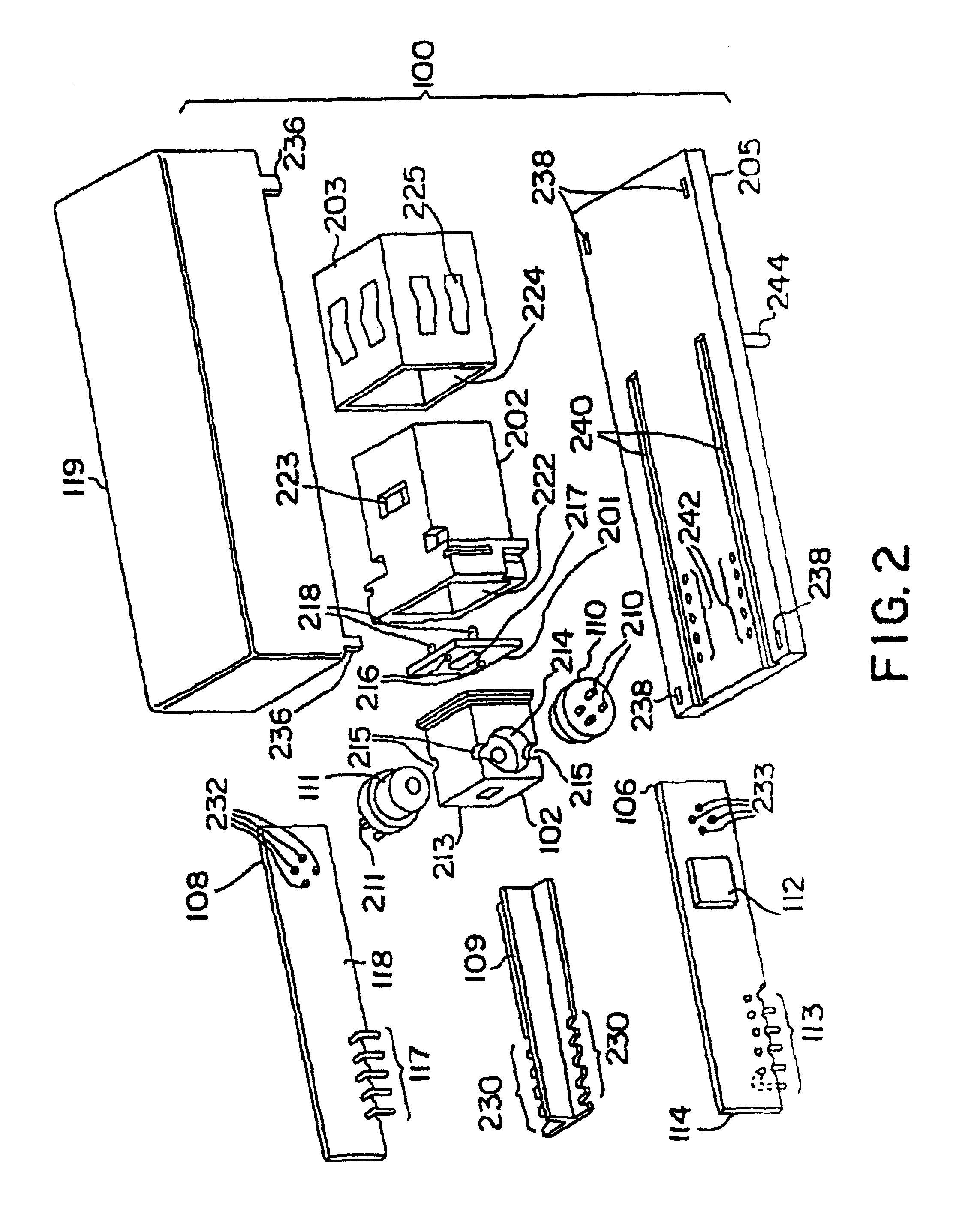
Flex circuit shielded optical sensor
InactiveUS6985764B2Cross-talk/noise/interference reductionColor/spectral properties measurementsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
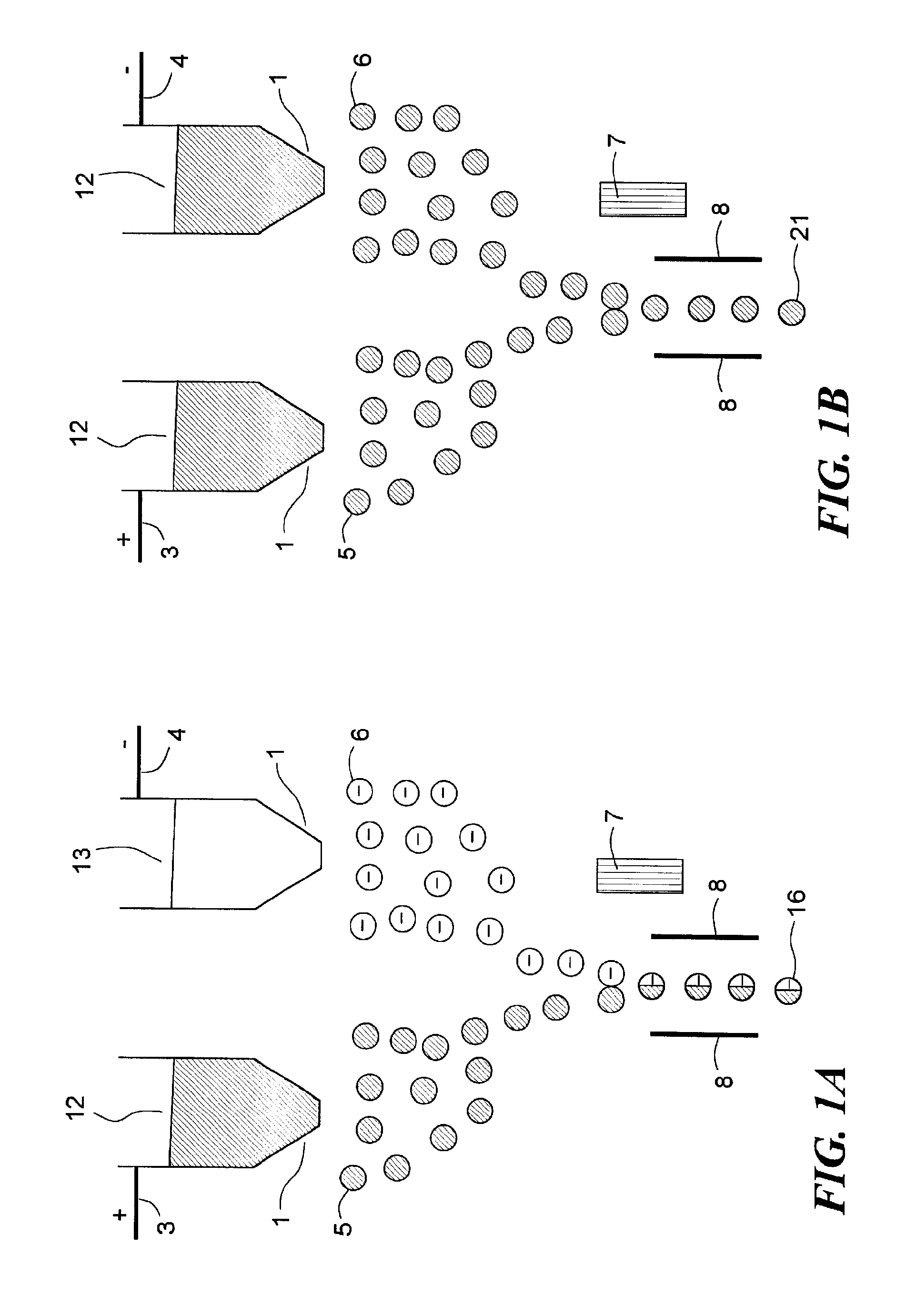
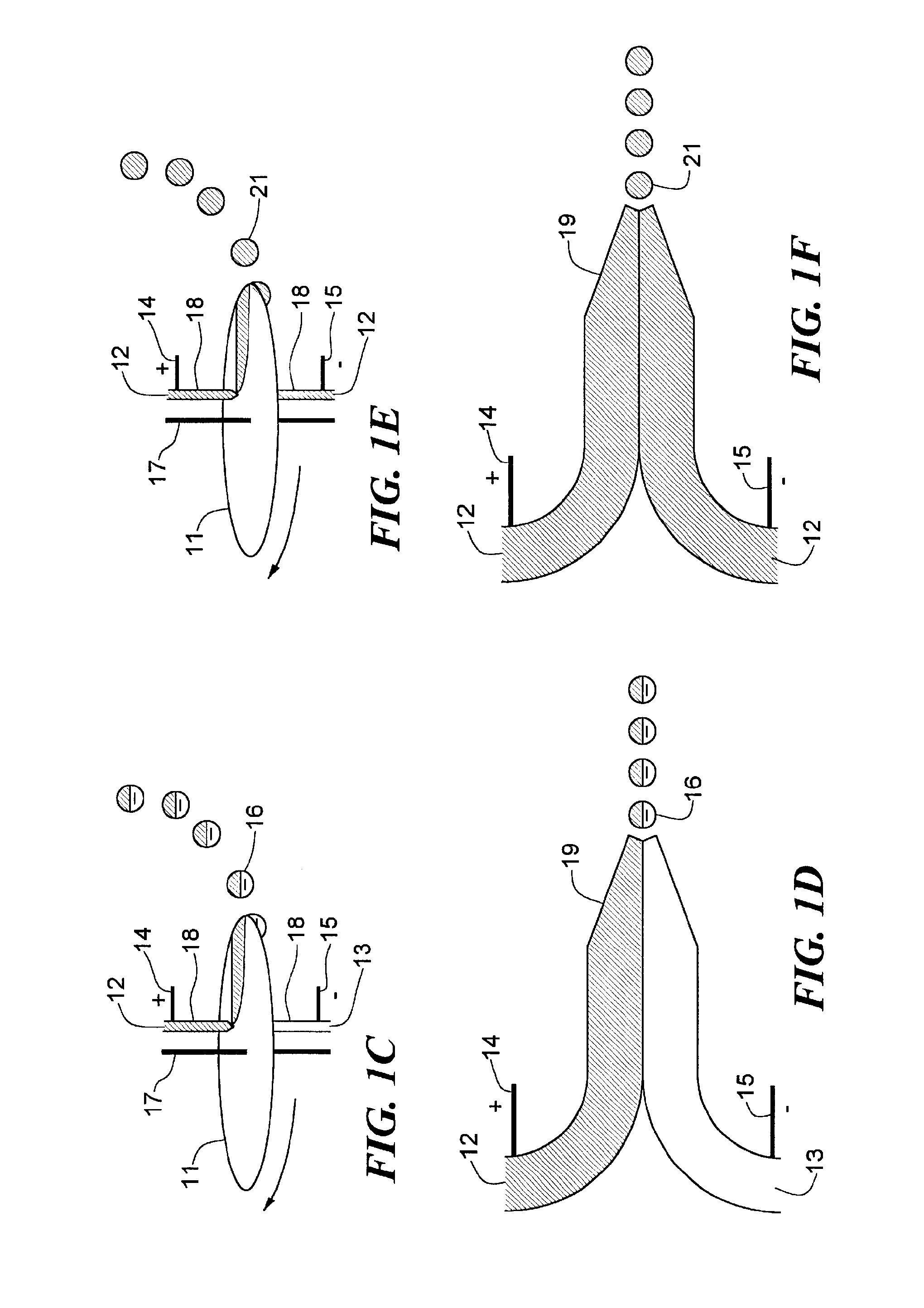
A flex circuit optical sensor has an integrated Faraday shield. A conductive trace layer disposed on a substrate is used to form a conductive grid which shields the face of a photodetector. A conductive ink layer is formed on a substrate side opposite the trace layer. The back and sides of the detector are shielded by flex circuit flaps that have the conductive ink layer but substantially exclude the trace layer so as to fold over and closely adhere to the detector body. The shielded substrate flaps advantageously eliminate a separate detector shield, which is typically fabricated with an etched copper part that must be attached to a flex circuit before mounting the detector.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Method and apparatus for non-invasive blood constituent monitoring
InactiveUS6181958B1Repeatable and reliableEasy to implementSensorsBlood characterising devicesNon invasiveHemoglobin G Szuhu
A system for determining a biologic constituent including hematocrit transcutaneously, noninvasively and continuously. A finger clip assembly includes including at least a pair of emitters and a photodiode in appropriate alignment to enable operation in either a transmissive mode or a reflectance mode. At least one predetermined wavelength of light is passed onto or through body tissues such as a finger, earlobe, or scalp, etc. and attenuation of light at that wavelength is detected. Likewise, the change in blood flow is determined by various techniques including optical, pressure, piezo and strain gage methods. Mathematical manipulation of the detected values compensates for the effects of body tissue and fluid and determines the hematocrit value. If an additional wavelength of light is used which attenuates light substantially differently by oxyhemoglobin and reduced hemoglobin, then the blood oxygen saturation value, independent of hematocrit may be determined. Further, if an additional wavelength of light is used which greatly attenuates light due to bilirubin (440 nm) or glucose (1060 nm), then the bilirubin or glucose value may also be determined. Also how to determine the hematocrit with a two step DC analysis technique is provided. Then a pulse wave is not required, so this method may be utilized in states of low blood pressure or low blood flow.
Owner:HEMA METRICS
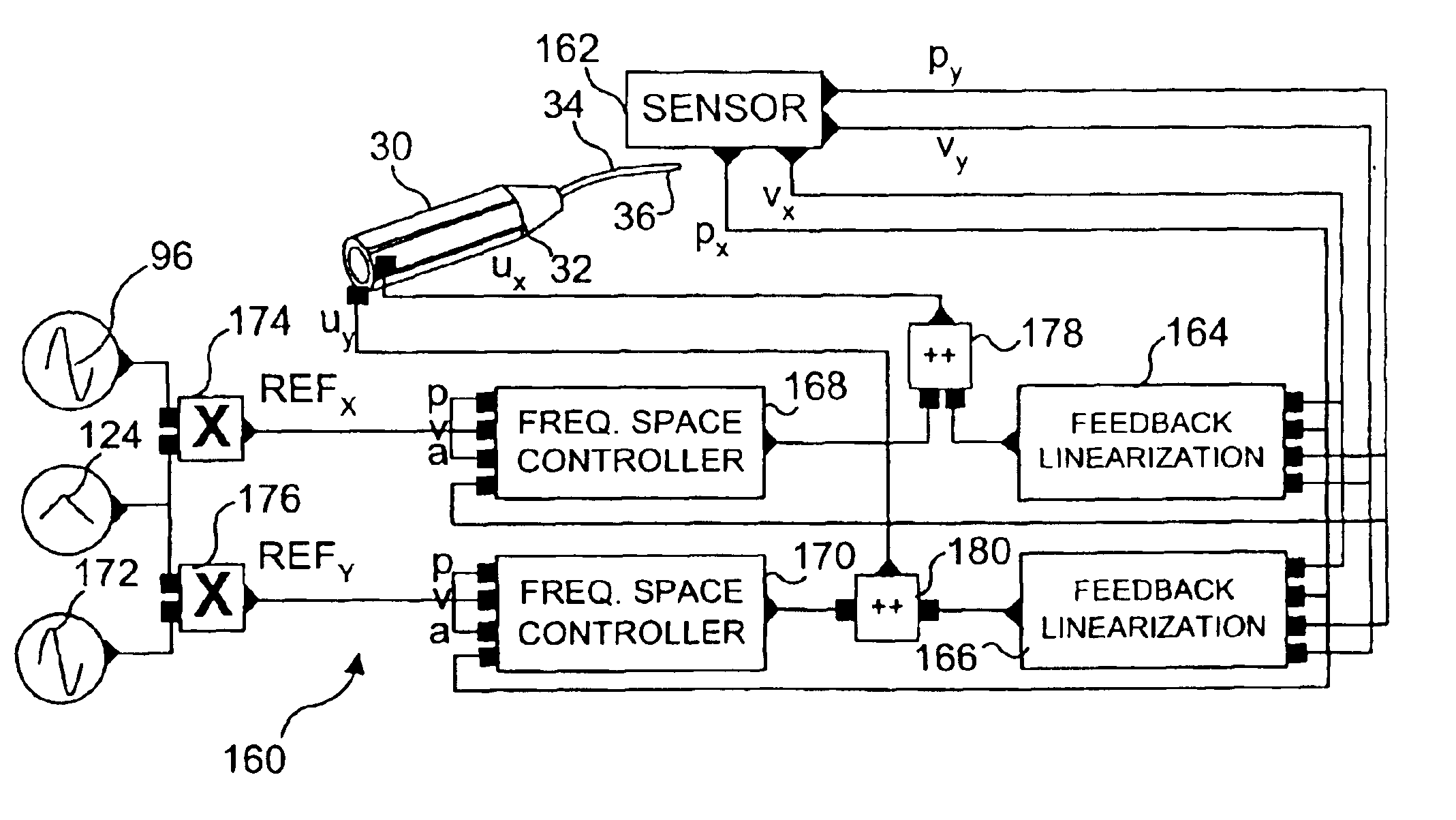
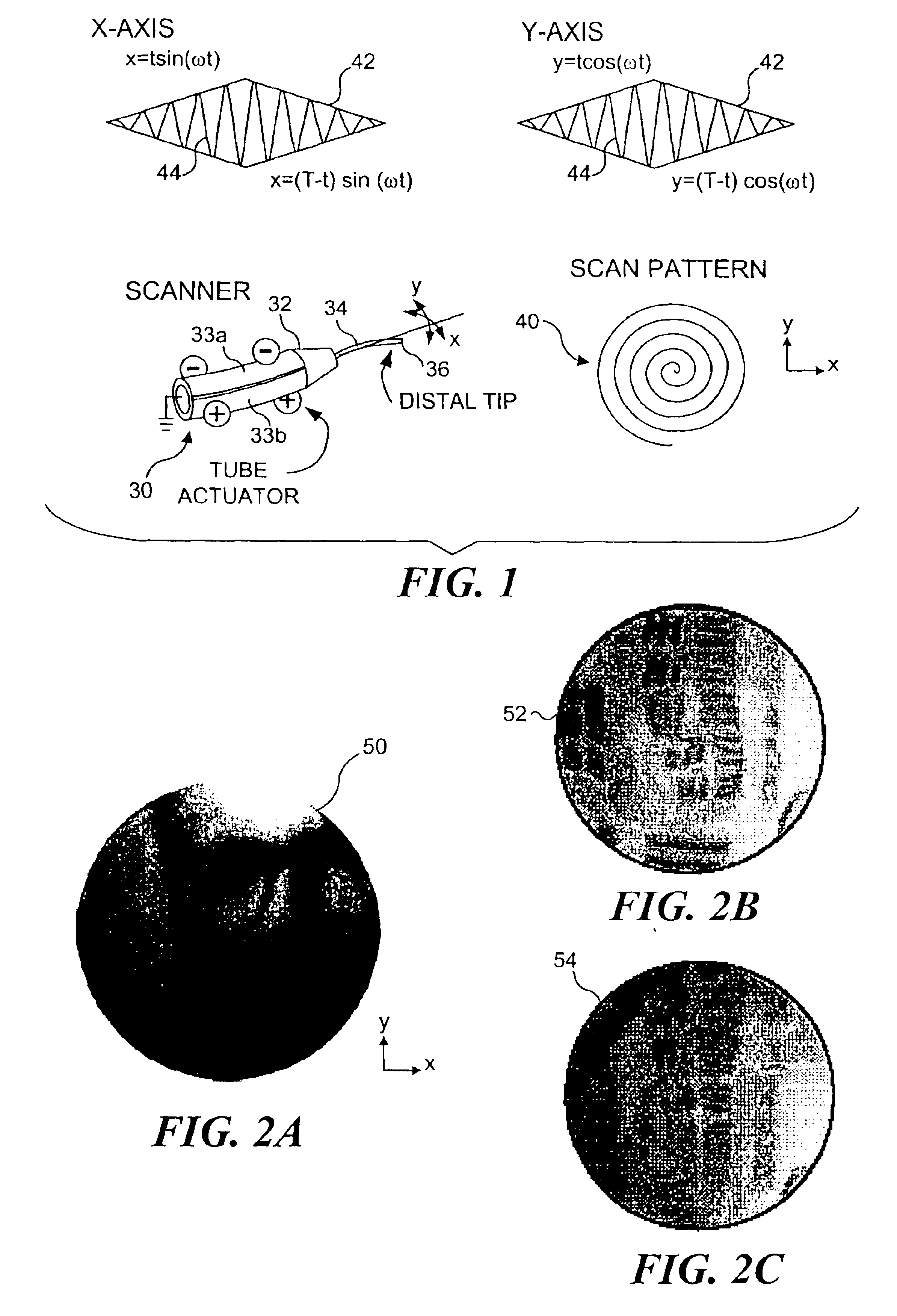
Control of an optical fiber scanner
InactiveUS6845190B1Remove nonlinear behaviorRobust cancellationSurgeryEndoscopesOptical scannersPhotodetector
Controls for an optical scanner, such as a single fiber scanning endoscope (SFSE) that includes a resonating optical fiber and a single photodetector to produce large field of view, high-resolution images. A nonlinear control scheme with feedback linearization is employed in one type of control to accurately produce a desired scan. Open loop and closed loops controllers are applied to the nonlinear optical scanner of the SFSE. A closed loop control (no model) uses either phase locked loop and PID controllers, or a dual-phase lock-in amplifier and two PIDs for each axis controlled. Other forms of the control that employ a model use a frequency space tracking control, an error space tracking control, feedback linearizing controls, an adaptive control, and a sliding mode control.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Solid-state imaging device, method of manufacturing the same, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20100201834A1Improve image qualityReduce colorTransistorTelevision system detailsInterconnectionPhotoelectric conversion
A solid-state imaging device includes: a pixel region in which a plurality of pixels composed of a photoelectric conversion section and a pixel transistor is arranged; an on-chip color filter; an on-chip microlens; and a multilayer interconnection layer in which a plurality of layers of interconnections is formed through an interlayer insulating film. The solid-state imaging device further includes a light-shielding film formed through an insulating layer in a pixel boundary of a light receiving surface in which the photoelectric conversion section is arranged.
Owner:SONY CORP
Retrofit LED lamp for fluorescent fixtures without ballast
ActiveUS7507001B2Reduce flickerReduce usageLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceFluorescenceNetwork communication
An energy saving device for an LED lamp mounted to an existing fixture for a fluorescent lamp where the ballast is removed or bypassed. The LEDs are positioned within a tube and electrical power is delivered from a power source to the LEDs. The LED lamp includes means for controlling the delivery of the electrical power from the power source to the LEDs, wherein the use of electrical power can be reduced or eliminated automatically during periods of non-use. Such means for controlling includes means for detecting the level of daylight in the illumination area of said least one LED, in particular a light level photosensor, and means for transmitting to the means for controlling relating to the detected level of daylight from the photosensor. The photosensor can be used in operative association with an on-off switch in power connection to the LEDs, a timer, or with a computer or logic gate array in operative association with a switch, timer, or dimmer that regulates the power to the LEDs. An occupancy sensor that detects motion or a person in the illumination area of the LEDs can be also be used in association with the photosensor and the computer, switch, timer, or dimmer, or in solo operation by itself. Two or more such LED lamps with a computer or logic gate array used with at least one of the lamps can be in network communication with at least one photosensor and / or at least one occupancy sensor to control the power to all the LEDs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
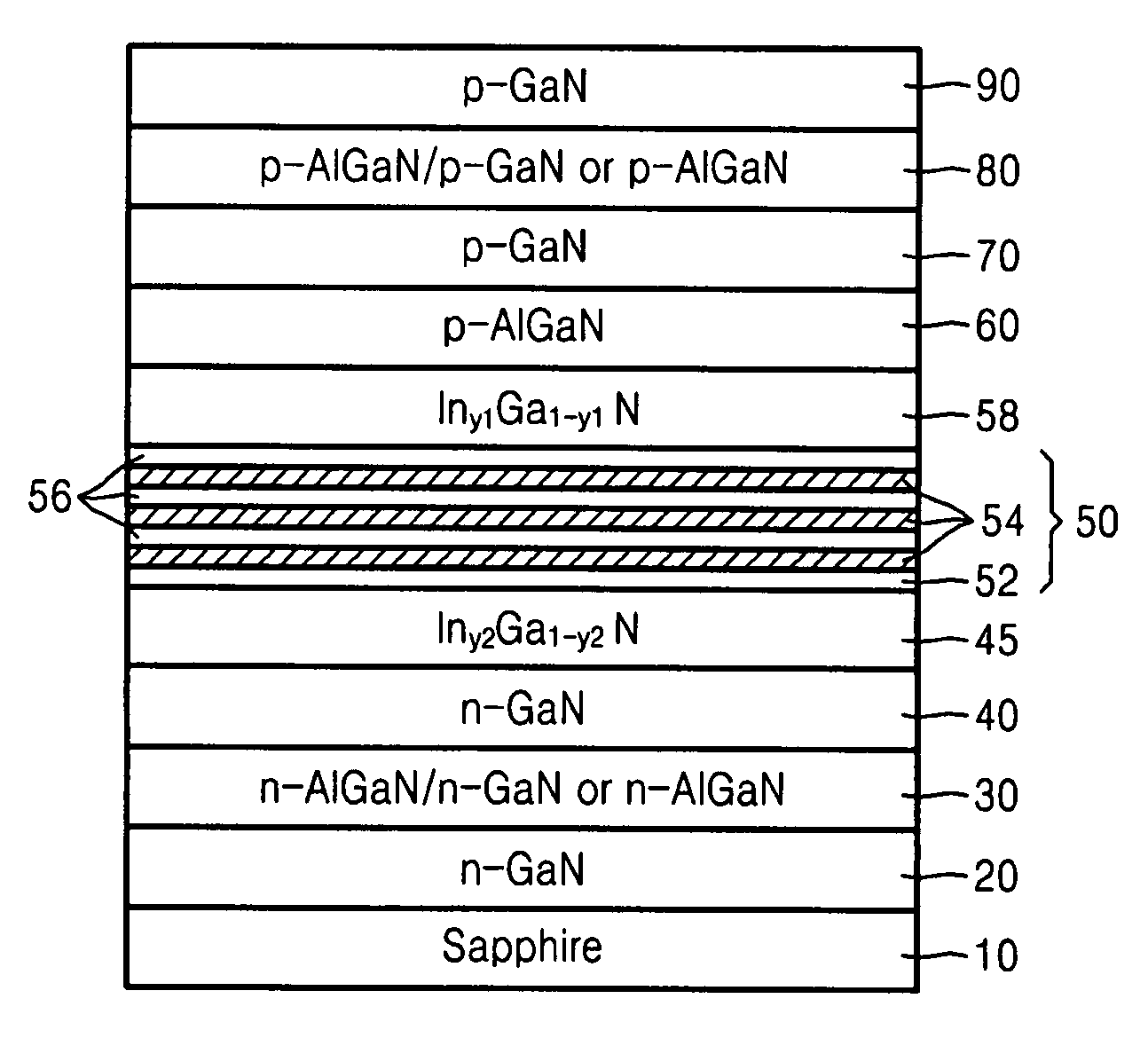
Method for achieving improved epitaxy quality (surface texture and defect density) on free-standing (aluminum, indium, gallium) nitride ((al,in,ga)n) substrates for opto-electronic and electronic devices
A III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structure comprising a III-V nitride homoepitaxial epi layer on a III-V nitride material substrate, e.g., of freestanding character. Various processing techniques are described, including a method of forming a III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer on a corresponding III-V nitride material substrate, by depositing the III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer by a VPE process using Group III source material and nitrogen source material under process conditions including V / III ratio in a range of from about 1 to about 105, nitrogen source material partial pressure in a range of from about 1 to about 103 torr, growth temperature in a range of from about 500 to about 1250 degrees Celsius, and growth rate in a range of from about 0.1 to about 500 microns per hour. The III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structures are usefully employed in device applications such as UV LEDs, high electron mobility transistors, and the like.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
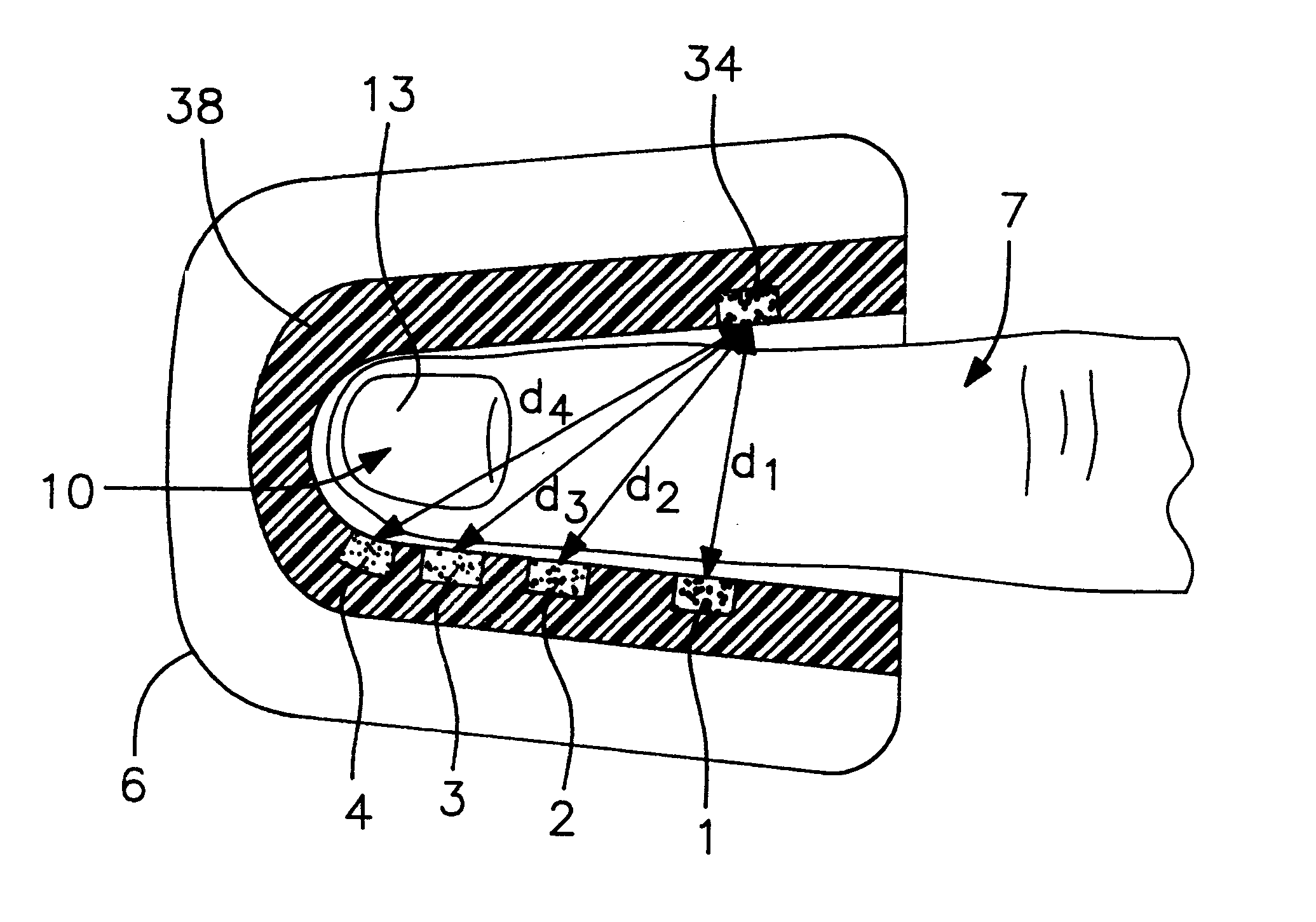
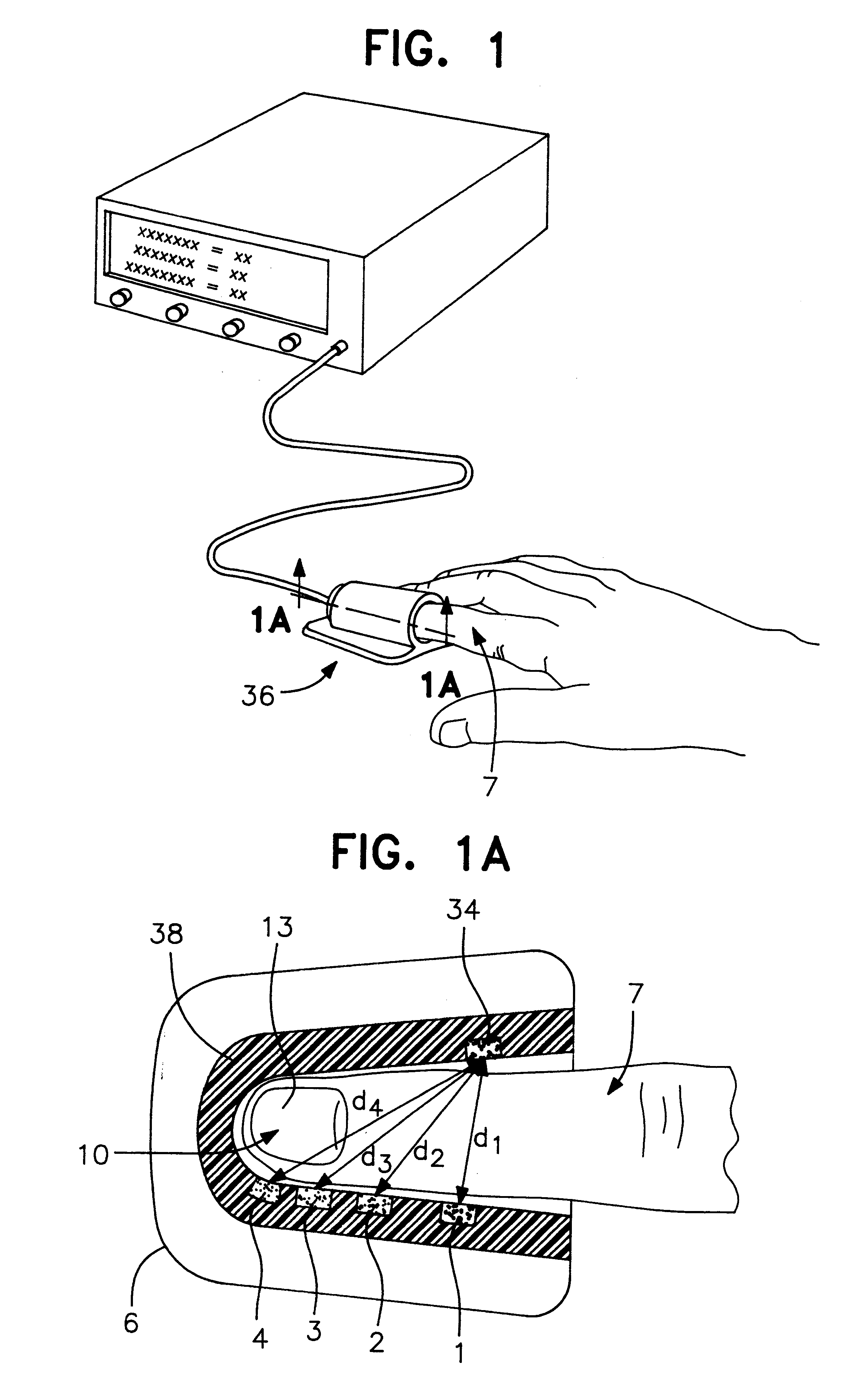
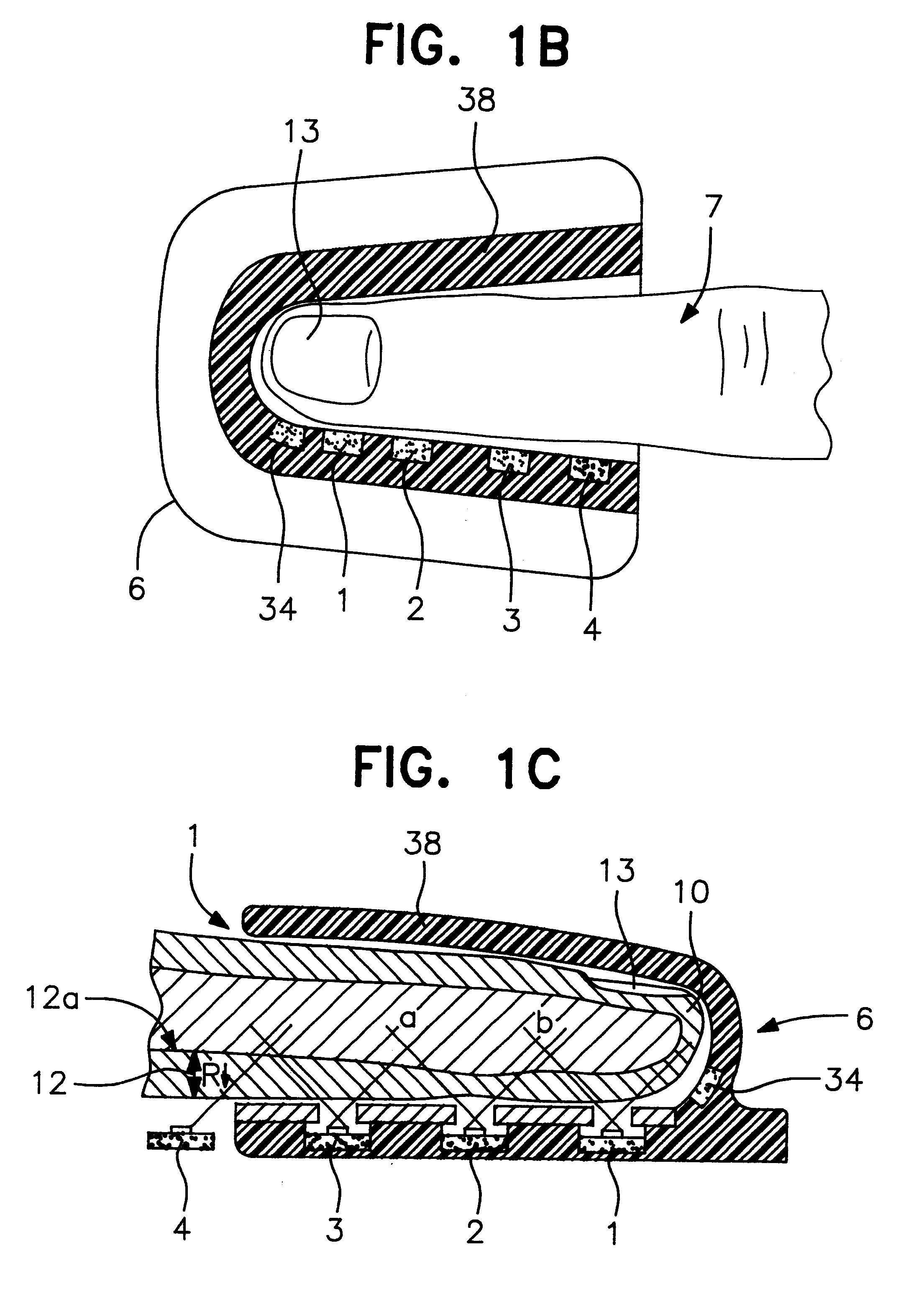
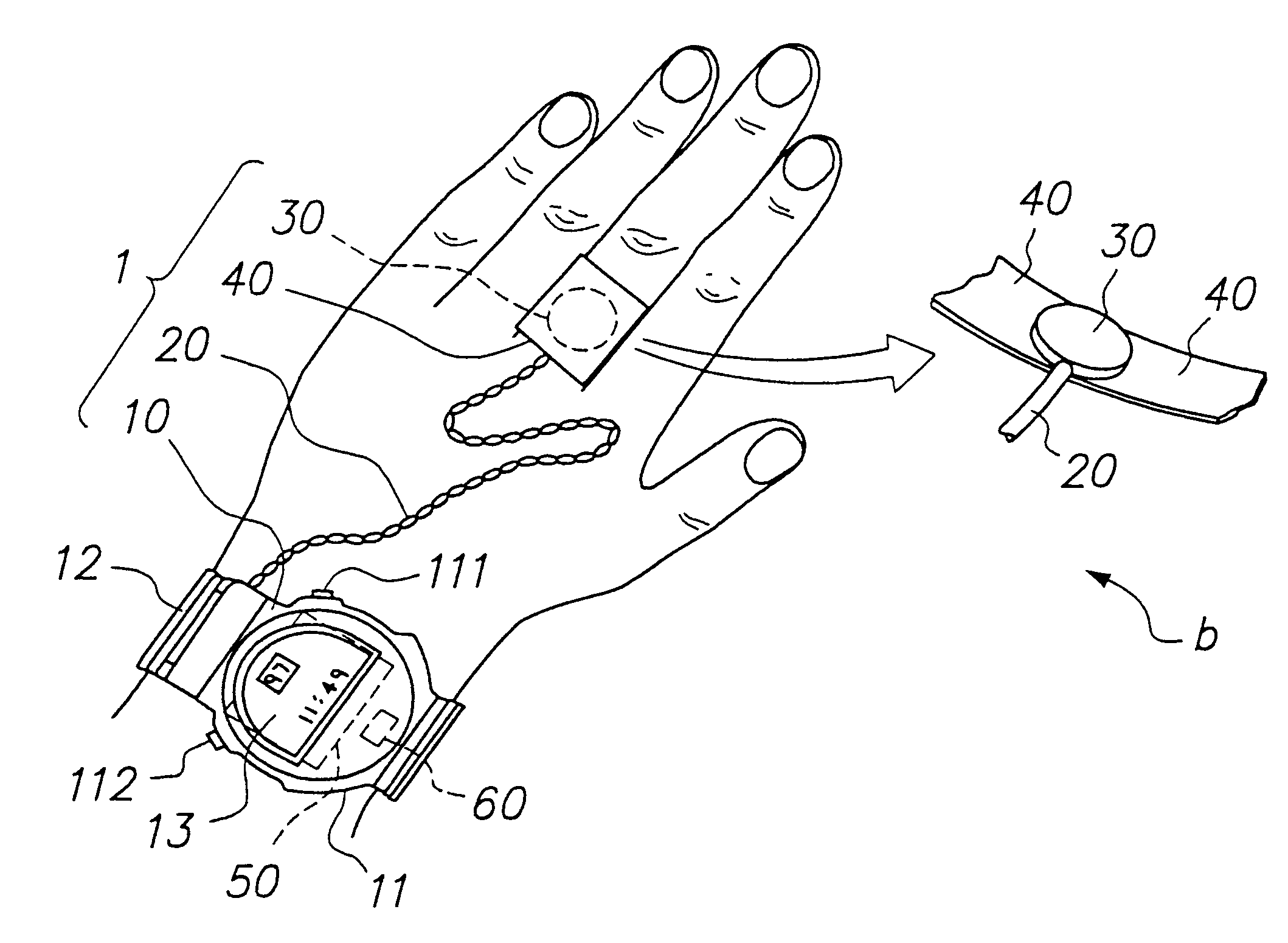
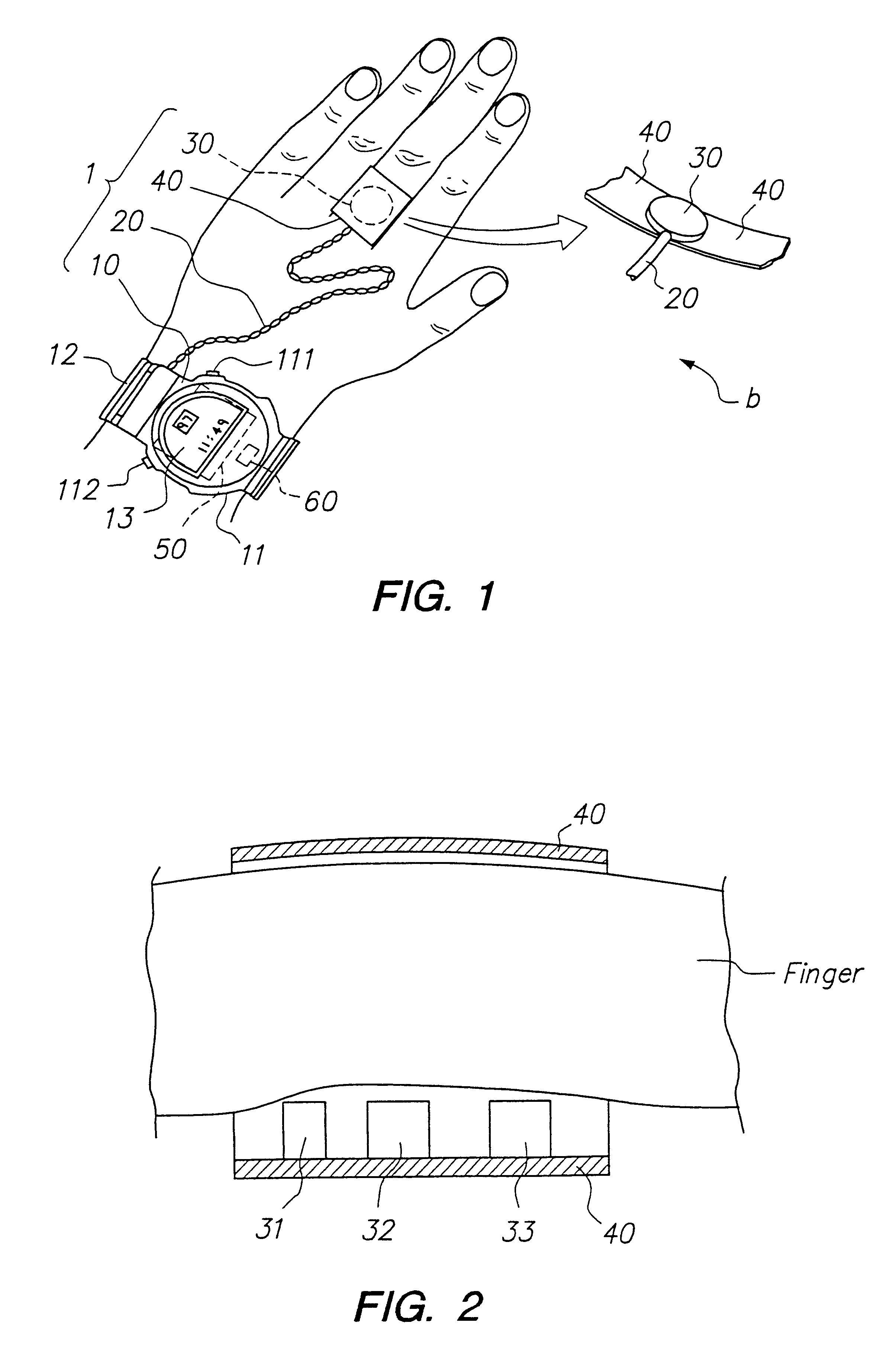
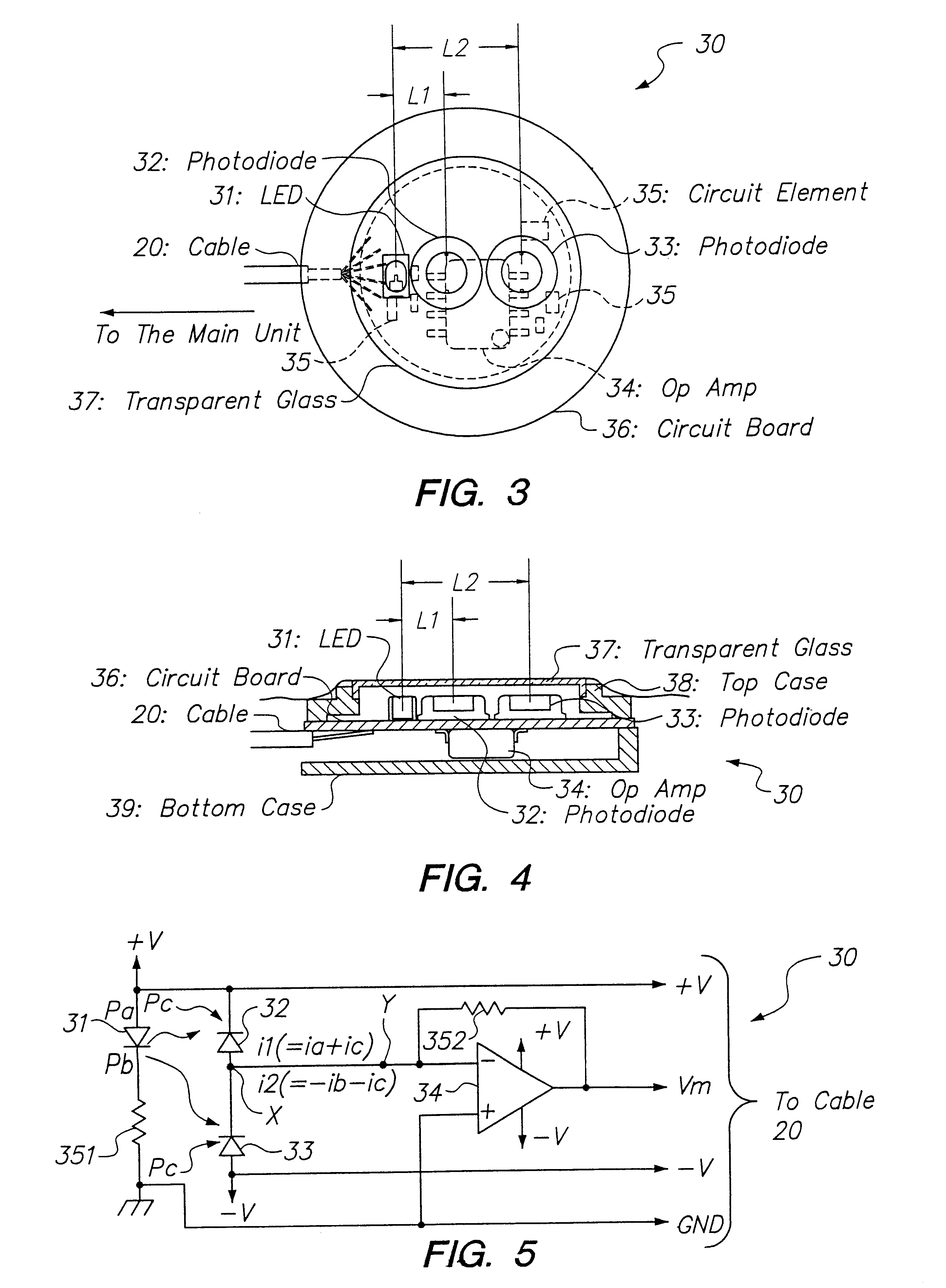
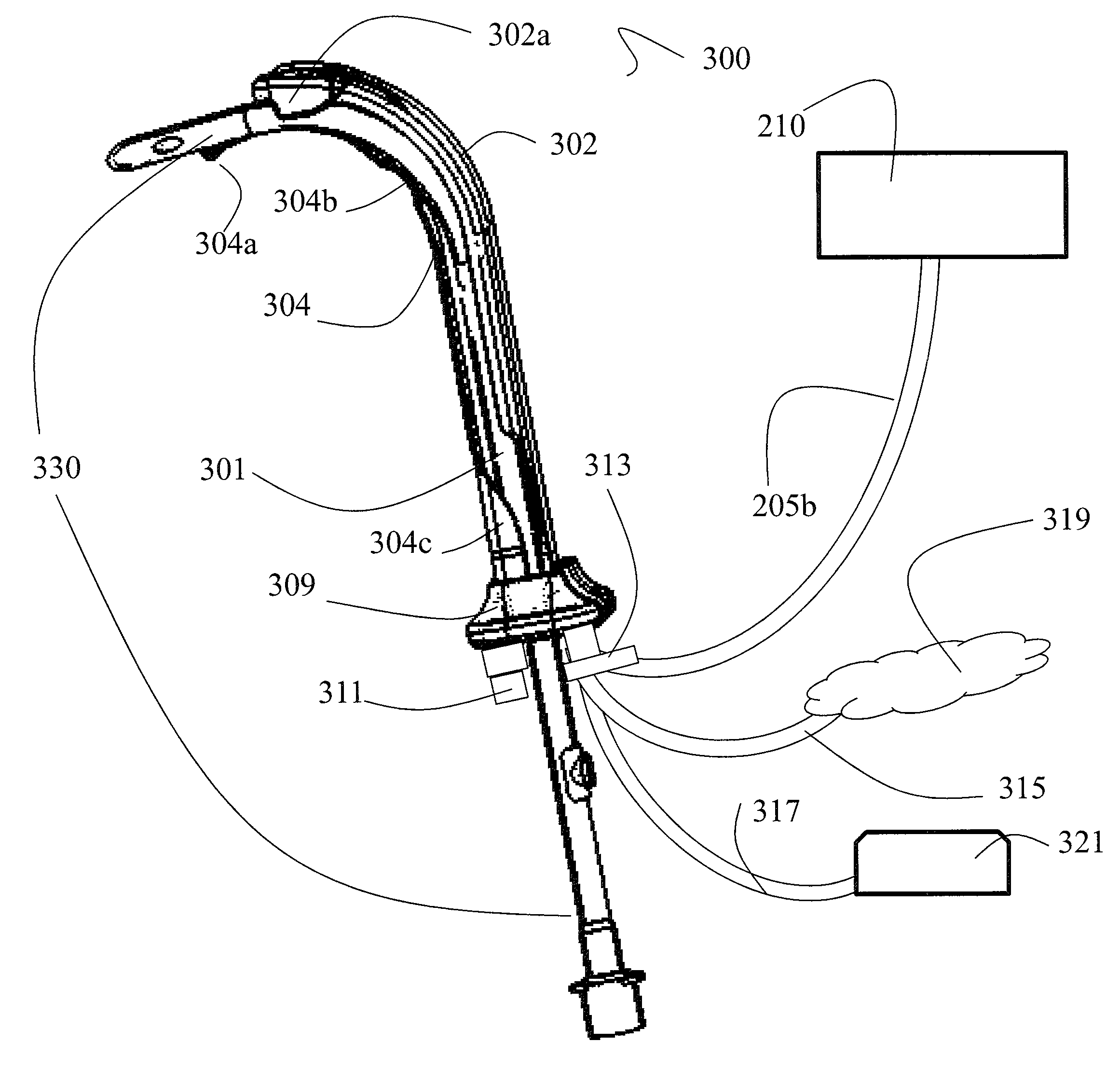
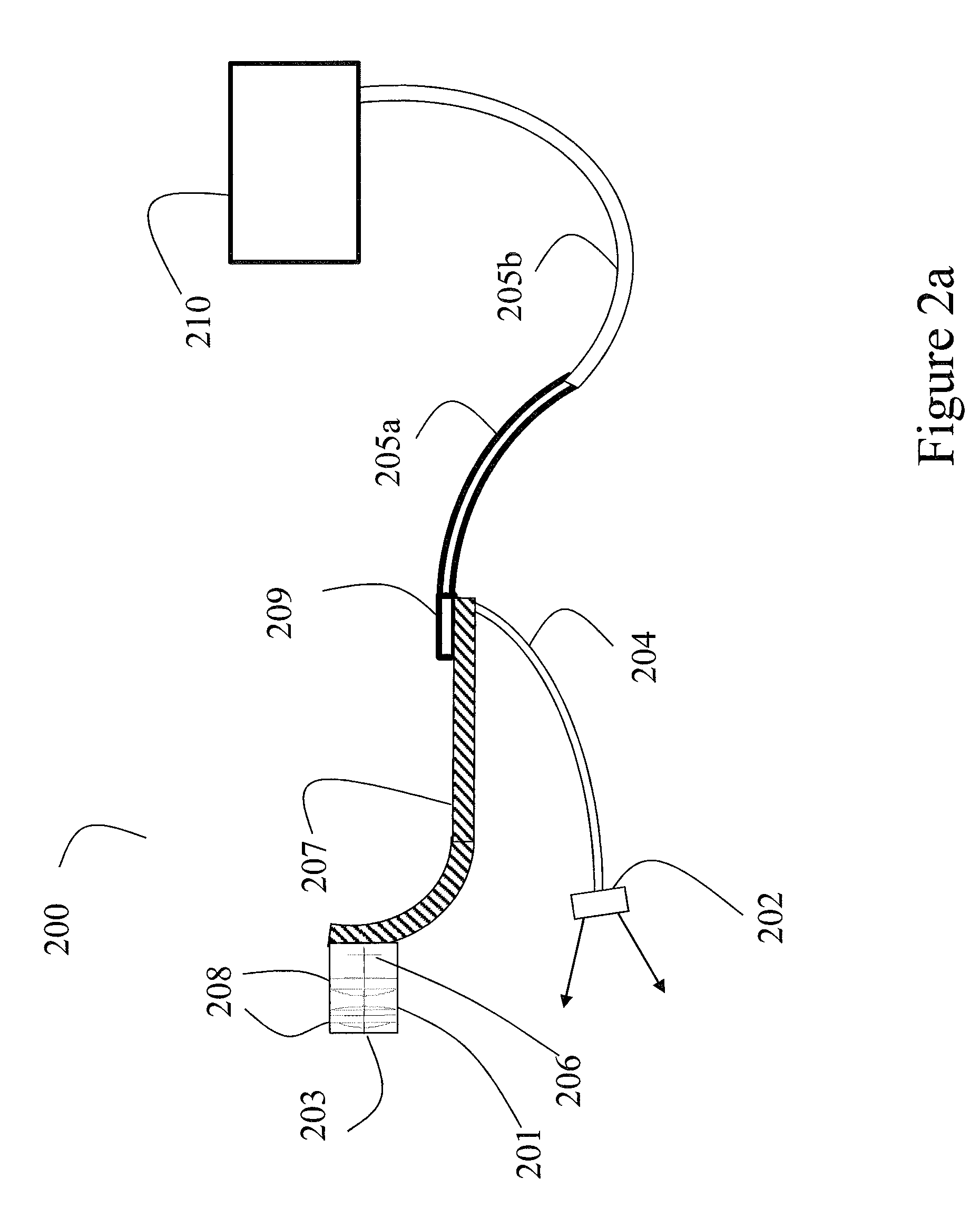
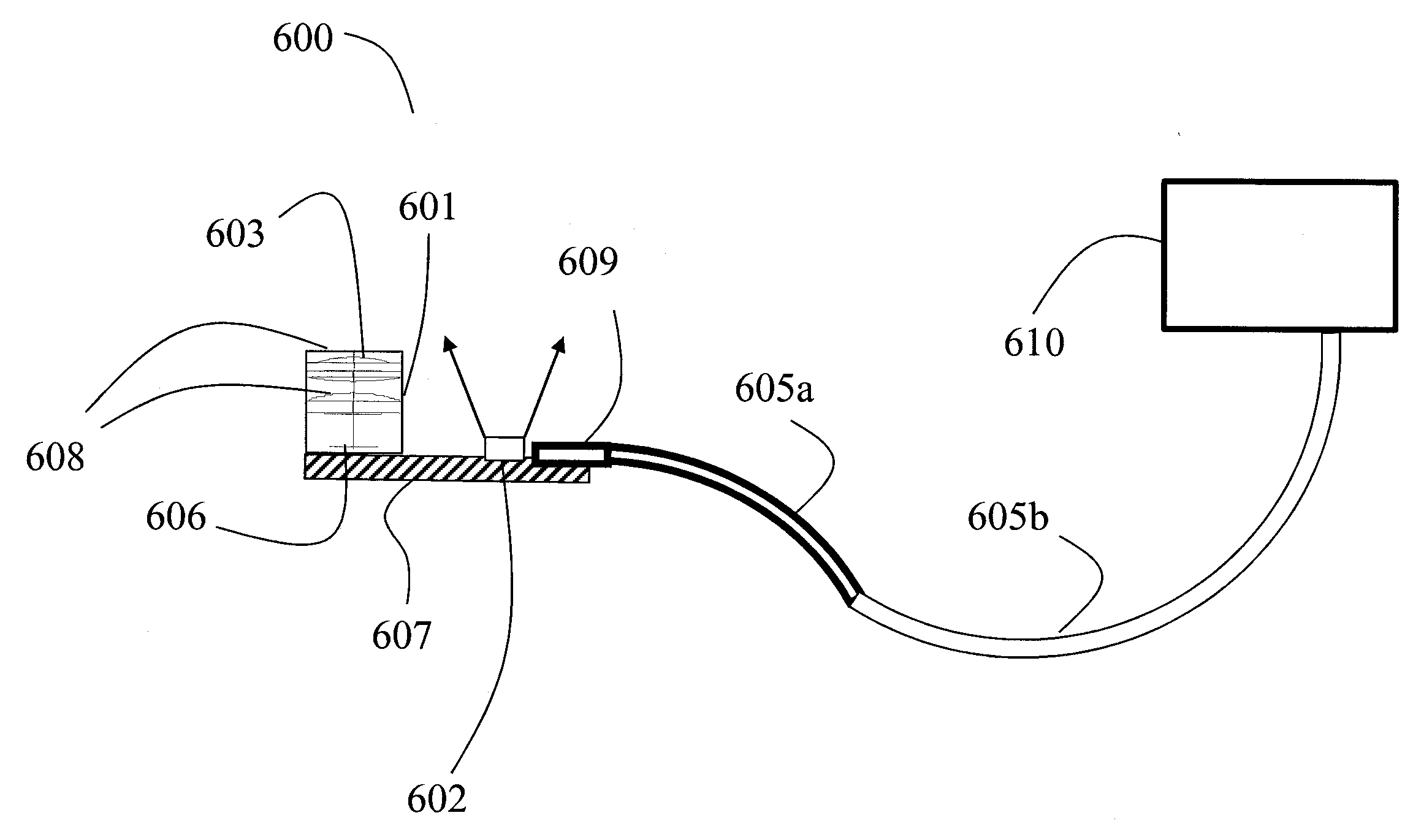
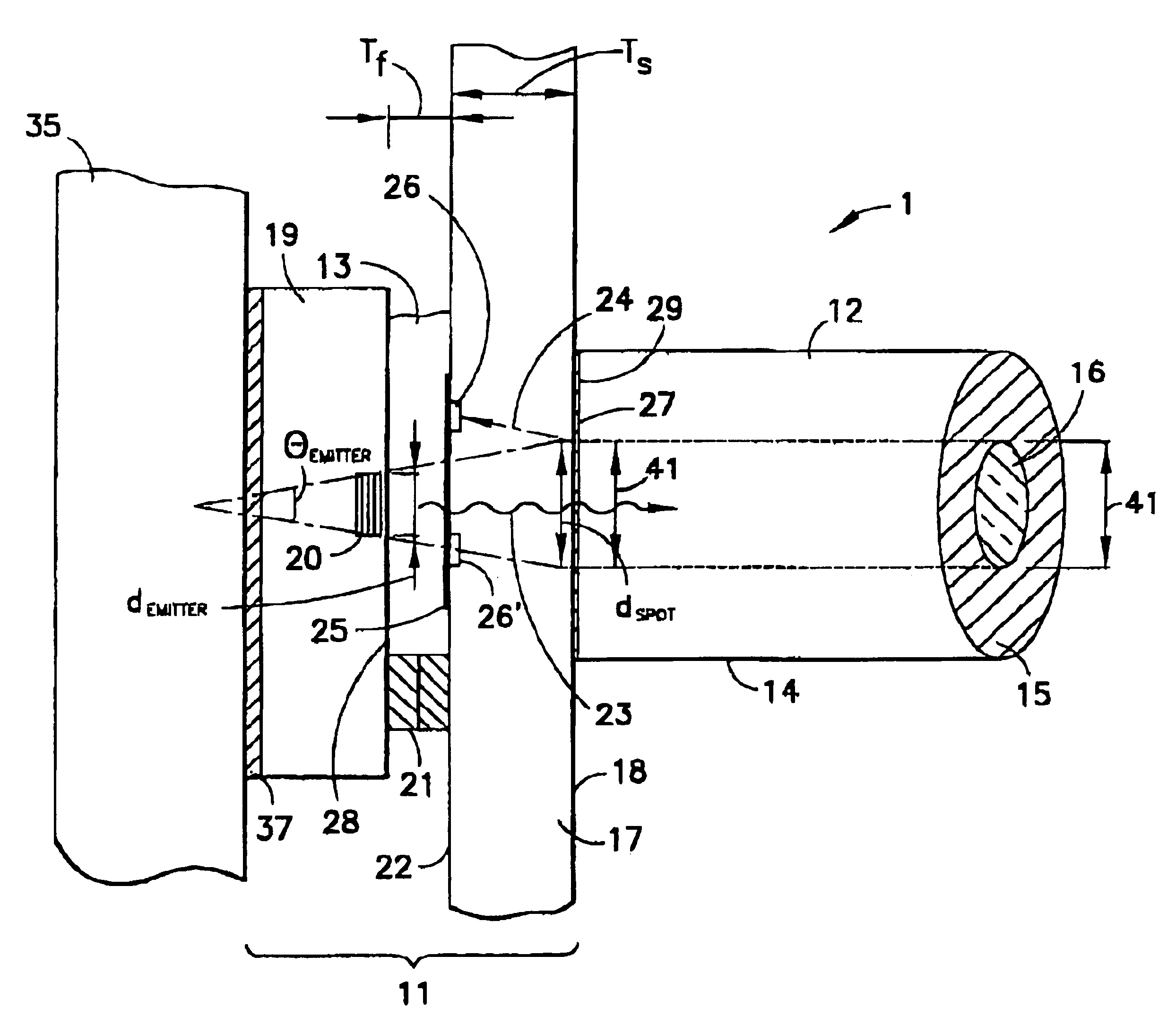
Reflection photodetector and biological information measuring instrument
InactiveUS6198951B1Inertial sensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse ratePower flowAudio power amplifier
When emitted light from LED 31 is incident on photodiodes 32 and 33 with luminance Pa and Pb, currents ia and ib are generated according to luminance Pa and Pb. When outside light is incident through the finger tissues on photodiodes 32 and 33 with luminance Pc, current ic is produced. The current i1 (=ia+ic) generated by photodiode 32, and the current i2 (=-ib-ic) generated by photodiode 33, are added at node X, and the current ic corresponding to outside light is thus cancelled. In addition, photodiodes 32 and 33 are disposed at different distances from LED 31. As a result, the current flowing to opamp 34 is current ia corresponding to luminance Pa because luminance Pb is extremely low. The opamp 34 then applies a current voltage conversion to generate pulse wave signal Vm.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
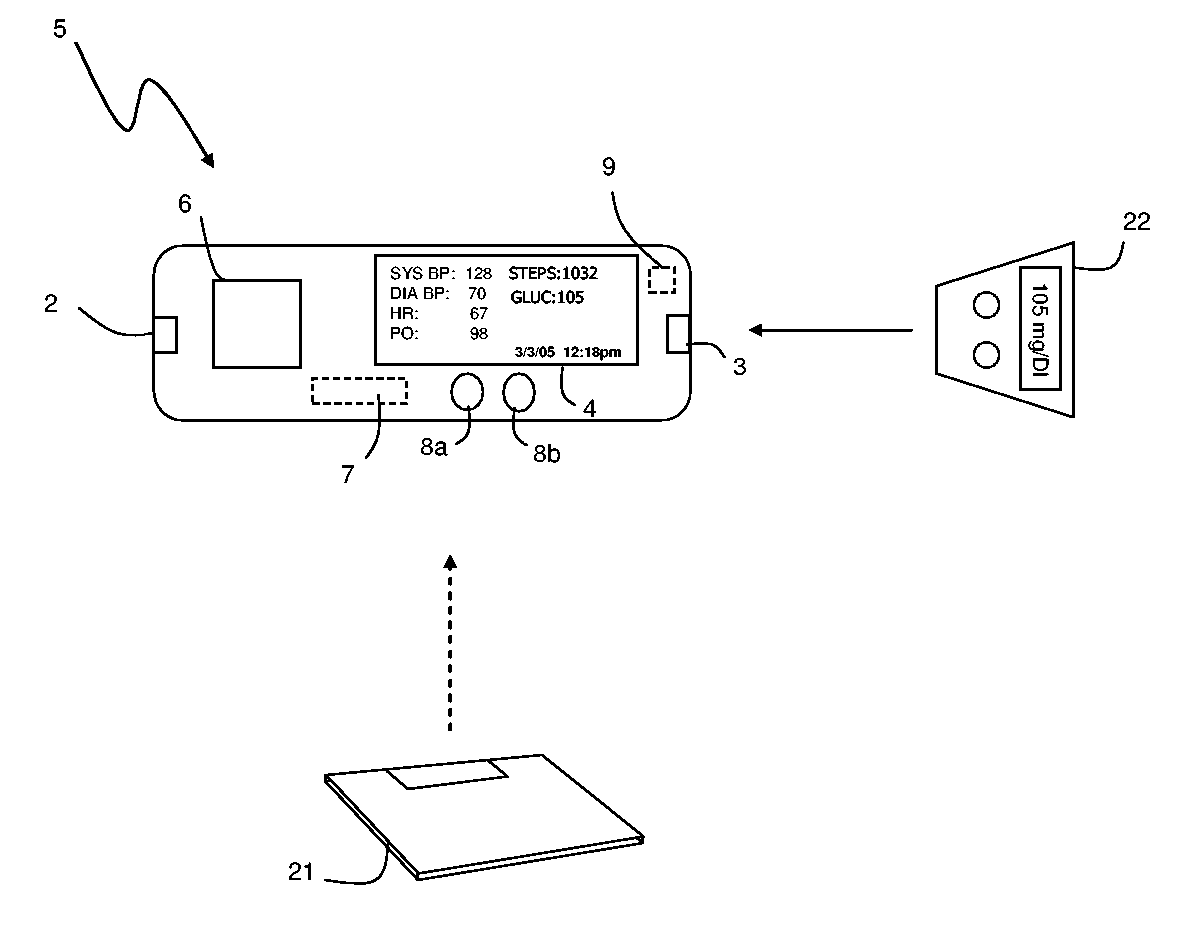
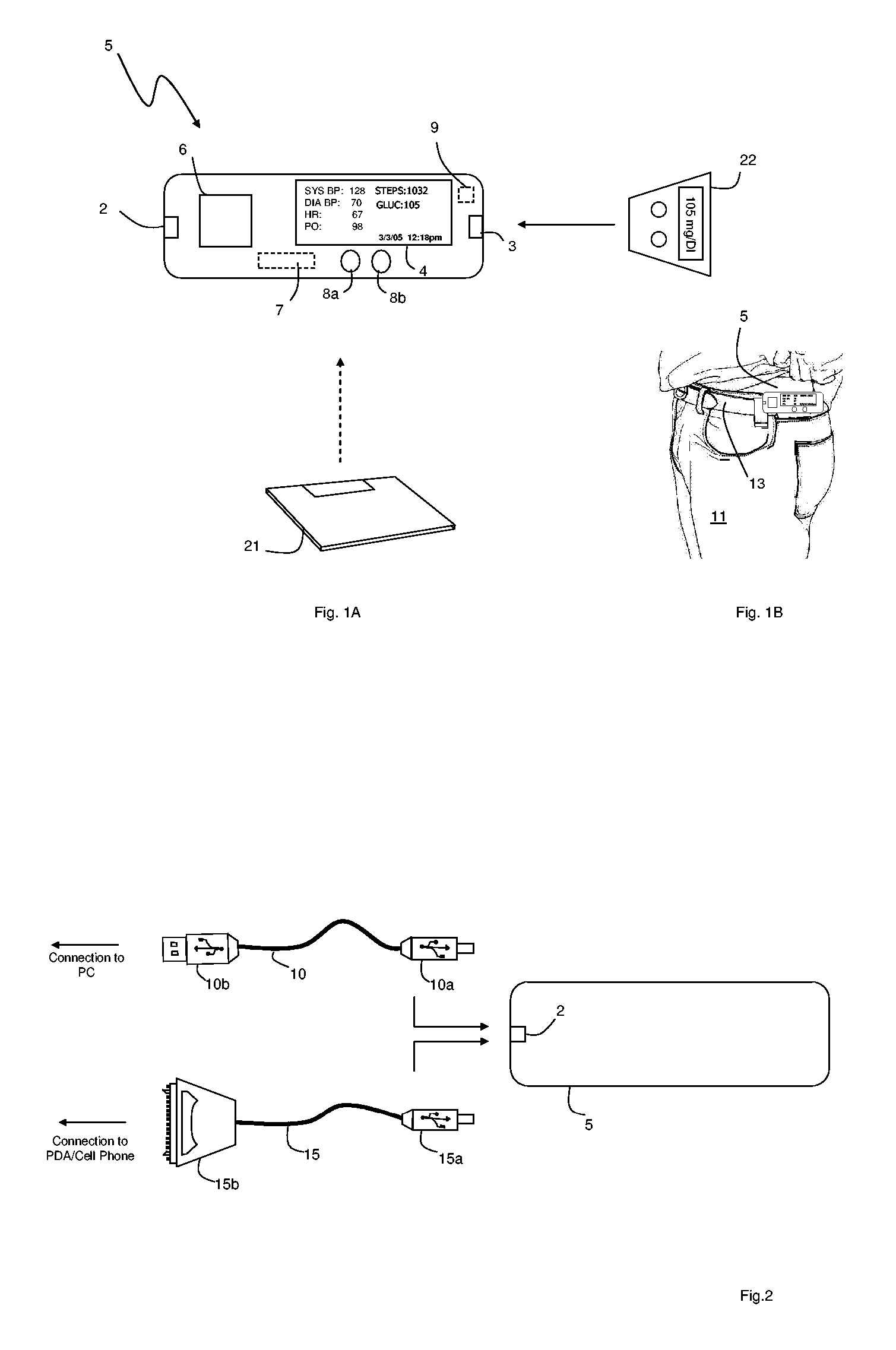
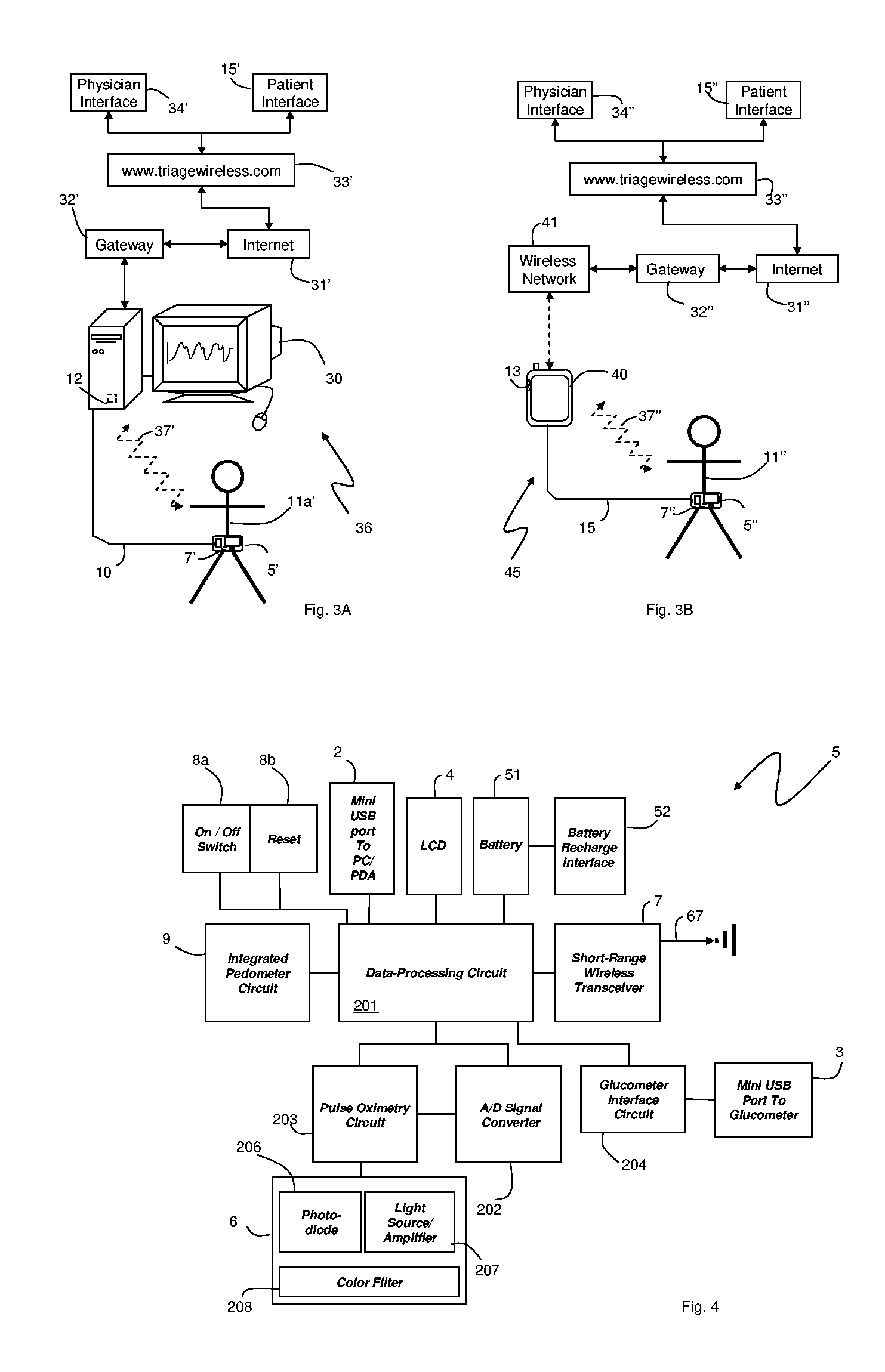
Small-scale, vital-signs monitoring device, system and method
InactiveUS20050228244A1Quick measurementLow costEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The invention provides a monitoring device featuring: 1) a housing having a first surface; 2) a sensor pad, positioned on the first surface, that includes a first LED emitting red light, a second LED emitting infrared light, and a photodetector; 3) a data-processing circuit that analyzes a signal from the photodetector to generate a blood pressure value; and 4) means for transmitting the blood pressure value to an external device.
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
LED light communication system
InactiveUS20080310850A1Easy to transportFirmly connectedPower distribution line transmissionElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingTransceiverPhotovoltaic detectors
An LED light and communication system includes at least one optical transceiver, the optical transceiver including a light support and a processor. The light support has a plurality of light emitting diodes and at least one photodetector attached thereto, the light emitting diodes receiving power from a power source. The processor is in communication with the light emitting diodes and the at least one photodetector, the processor capable of illuminating the light emitting diodes to simultaneously create at least one first light signal, and at least one second light signal, the first light signal being observable to the unaided eyes of an individual and the second light signal not being observable to the unaided eyes of the individual. The second light signal includes at least one data packet. The at least one data packet comprises global positioning system (GPS) location information.
Owner:FEDERAL LAW ENFORCEMENT DEV SERVICES
Two-part patch sensor for monitoring vital signs
ActiveUS20080114220A1Quick measurementLittle and no discomfortUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyOptical radiationPhotodetector
A two-component monitoring device and system for monitoring blood pressure from a patient is disclosed herein. The two-component monitoring device includes a disposable component and a main component. The disposable component features: i) a backing structure having a first aperture; and ii) first and second electrodes, each electrode connected to the backing structure and including an electrical lead and a conductive electrode material, and configured to generate an electrical signal that passes through the electrical lead when the conductive electrode material contacts the patient. The main component includes: i) first and second connectors configured to connect to the first and second electrical leads to receive the first and second electrical signals; and ii) an optical component comprising a light source that generates optical radiation and a photodetector that detects the optical radiation. The optical component inserts into the first aperture of the disposable component. The main component optionally includes an acoustic sensor. The system utilizes a processing device, connected to the monitoring device by a cable which receives and processes a plurality of signals to determine real-time blood-pressure values for the patient.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Systems and methods for optical actuation of microfluidics based on opto-electrowetting
InactiveUS6958132B2Improve performanceSludge treatmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityMicrofluidics
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Opto-electronic package structure having silicon-substrate and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20090273005A1Simplify component complexityIncrease heatSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic structureOpto electronic
Owner:TOUCH MICRO SYST TECH
Disposable endoscopic access device and portable display
ActiveUS20110028790A1Minimal set-upLocation somewhat remoteBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesFlexible endoscopeDisplay device
Various embodiments for providing removable, pluggable and disposable opto-electronic modules for illumination and imaging for endoscopy or borescopy are provided for use with portable display devices. Generally, various rigid, flexible or expandable single use medical or industrial devices with an access channel, can include one or more solid state or other compact electro-optic illuminating elements located thereon. Additionally, such opto-electronic modules may include illuminating optics, imaging optics, and / or image capture devices, and airtight means for suction and delivery within the device. The illuminating elements may have different wavelengths and can be time-synchronized with an image sensor to illuminate an object for 2D and 3D imaging, or for certain diagnostic purposes.
Owner:VIVID MEDICAL
Semiconductor optoelectronic device and method of fabricating the same
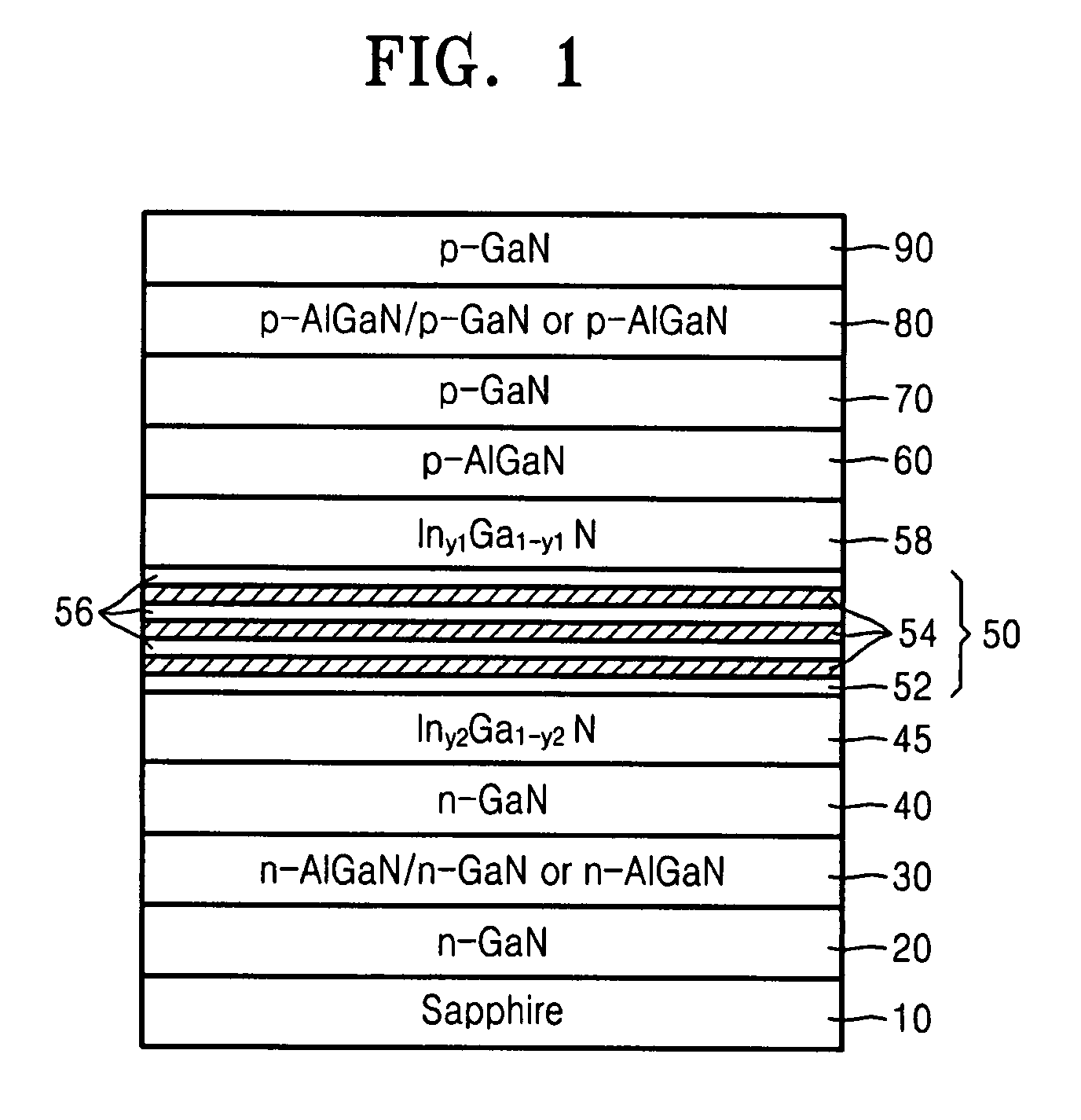
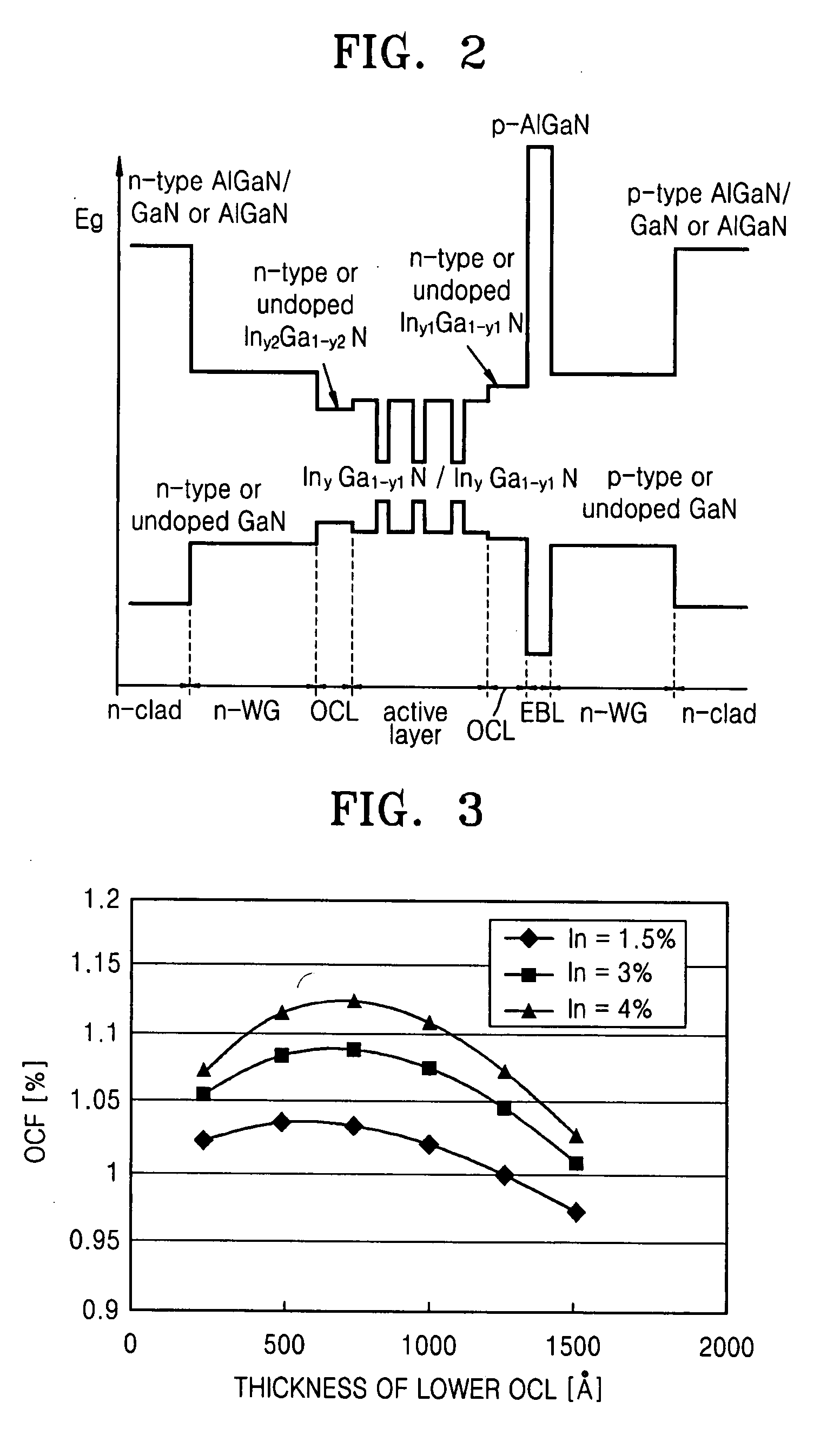
ActiveUS20080095492A1Reducing internal lossImprove internal quantum efficiencyNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersQuantum wellOpto electronic
Provided is a semiconductor opto-electronic device that may comprise an active layer including a quantum well and a barrier layer on a substrate, upper and lower waveguide layers on and underneath the active layer, respectively, and upper and lower clad layers on and underneath the upper and lower waveguide layers, respectively. The semiconductor opto-electronic device may further comprise an upper optical confinement layer (OCL) between the active layer and the upper waveguide layer and having an energy gap smaller than the energy gap of the upper waveguide layer and equal to or larger than the energy gap of the barrier layer, and a lower OCL between the active layer and the lower waveguide layer and having an energy gap smaller than the energy gap of the lower waveguide layer and equal to or smaller than the energy gap of the barrier layer. Also provided is a method of fabricating the semiconductor opto-electronic device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-layer opto-electronic substrates with electrical and optical interconnections and methods for making
InactiveUS6845184B1Reduce area requirementsOptical coupling efficiency improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityThin layer
Opto-electrical systems having electrical and optical interconnections formed in thin layers are disclosed. In one set of preferred embodiments, optical signals are conveyed between layers by respective vertical optical couplers disposed on the layers. In other preferred embodiments, optical signals are conveyed by stack optical waveguide coupling means. Yet other preferred embodiments have electrical via means formed in one or more layers to covey electrical signals between two or more layers.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Disposable endoscope and portable display
ActiveUS20100198009A1Location somewhat remoteFull connectivityCannulasEndoscopesFlexible endoscopeDisplay device
Various embodiments for providing removable, pluggable and disposable opto-electronic modules for illumination and imaging for endoscopy or borescopy are provided for use with portable display devices. Generally, various medical or industrial devices can include one or more solid state or other compact electro-optic illuminating elements located thereon. Additionally, such opto-electronic modules may include illuminating optics, imaging optics, and / or image capture devices. The illuminating elements may have different wavelengths and can be time-synchronized with an image sensor to illuminate an object for imaging or detecting purpose or other conditioning purpose. The removable opto-electronic modules may be plugged onto the exterior surface of another medical device, deployably coupled to the distal end of the device, or otherwise disposed on the device.
Owner:VIVID MEDICAL
Transparent electrode, optoelectronic apparatus and devices
InactiveUS6936761B2Large scaleSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive polymerOpto electronic
Transparent conductive electrodes, optoelectronic apparatus, optoelectronic devices and methods for making such electrodes, apparatus and devices are disclosed. The transparent conducting electrode (TCE) includes a layer of transparent electrically conducting polymer material and an array of electrically conductive wires distributed across the layer of transparent electrically conducting polymer material. The TCE may be made by distributing an array of conductive wires across a conductive polymer layer and attaching polymer layer to the wire array. An optoelectronic apparatus may comprise an active layer in electrical contact with the TCE. An optoelectronic device may incorporate an active layer disposed between two electrodes, at least one of which is the TCE. An optoelectronic device may be made by disposing an active layer between a base electrode and a TCE and attaching all three together.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
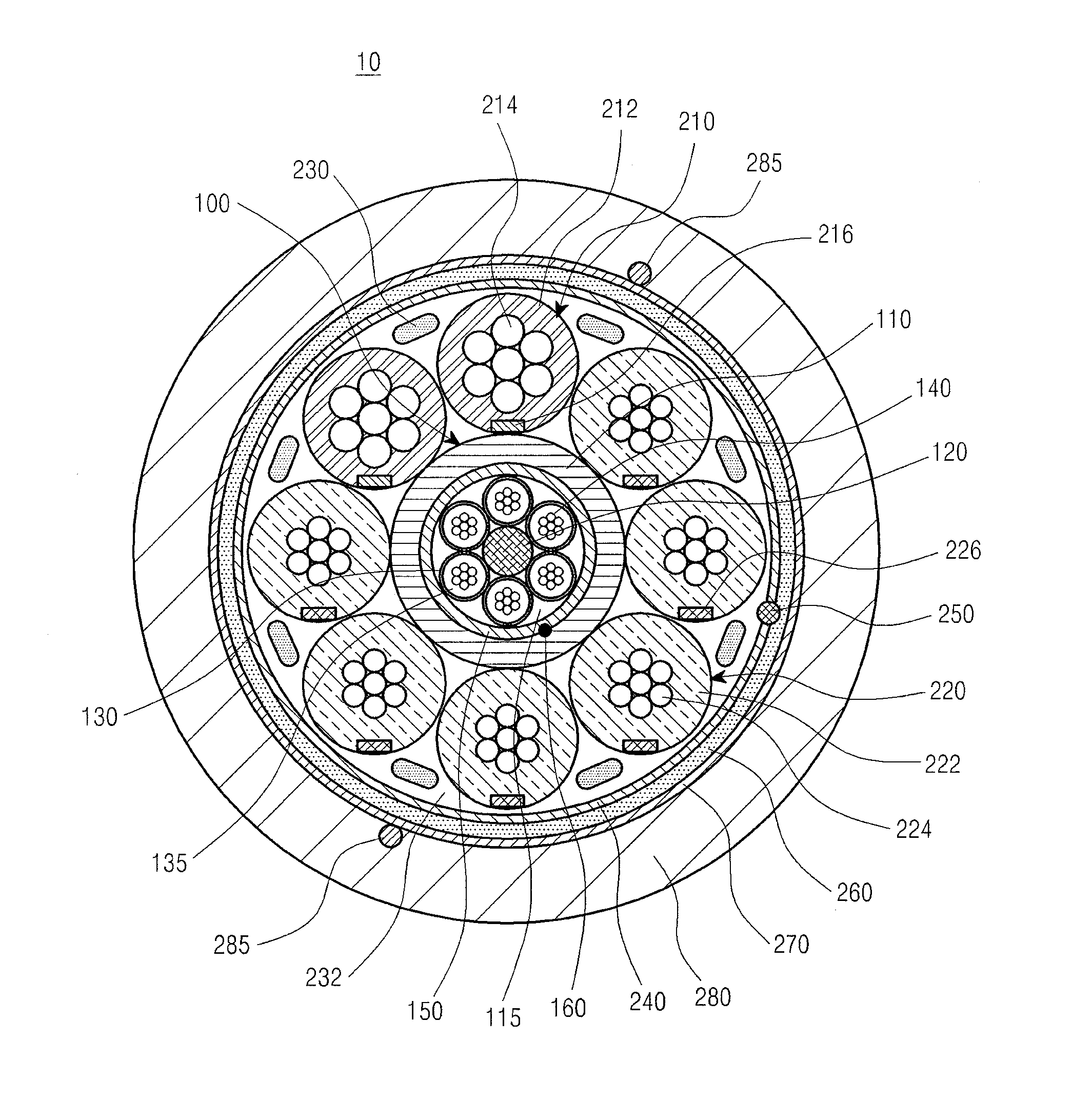
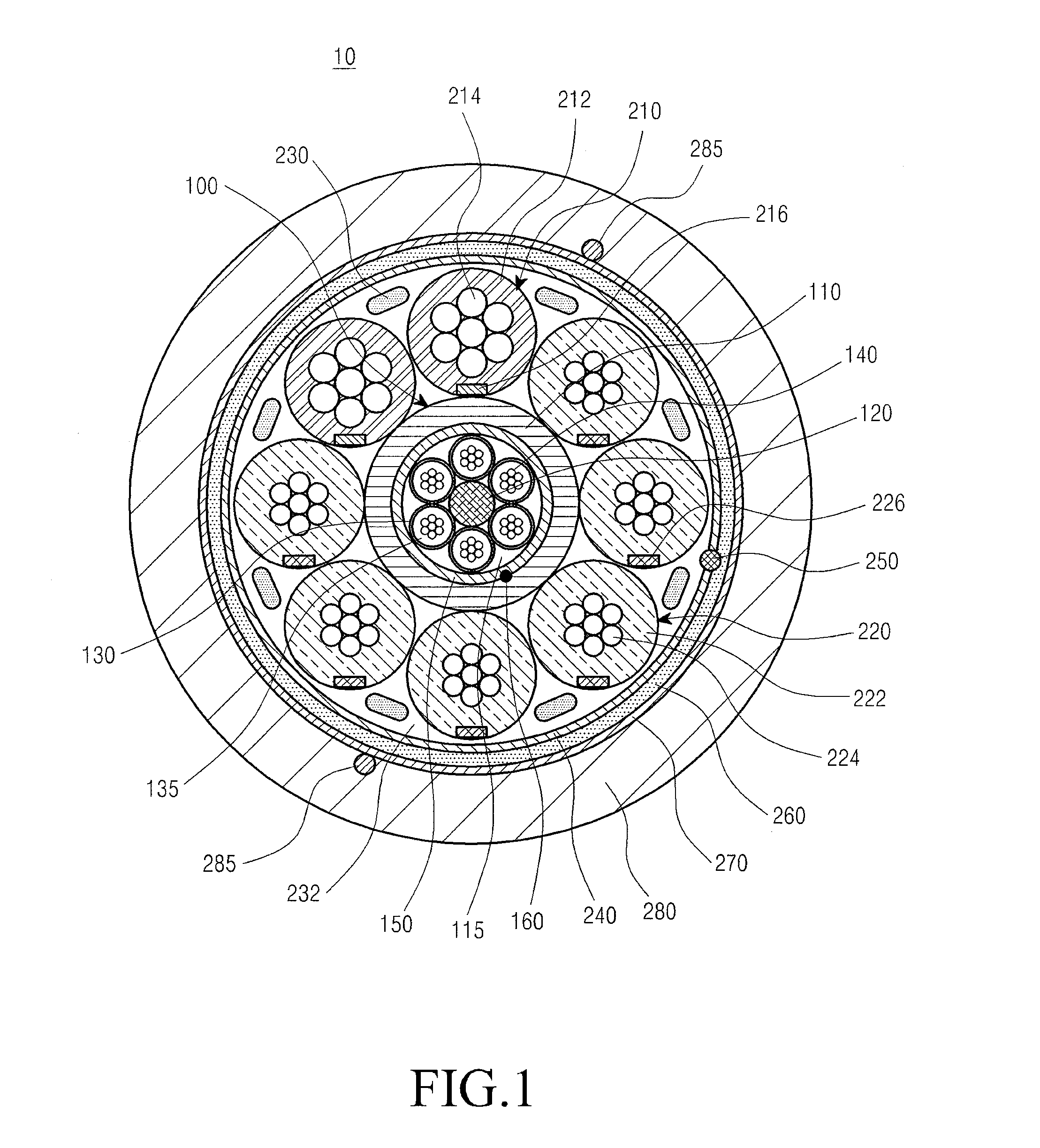
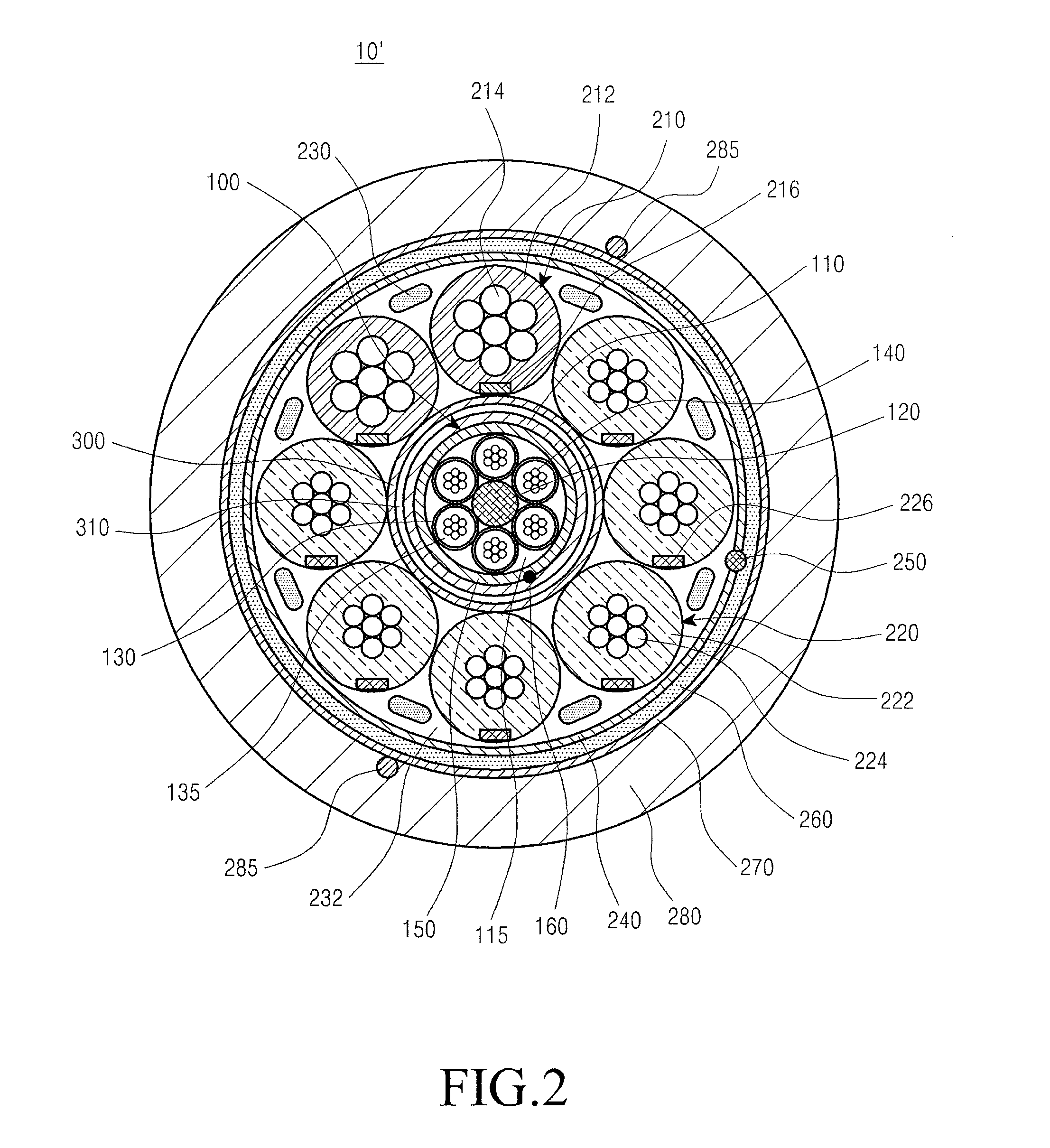
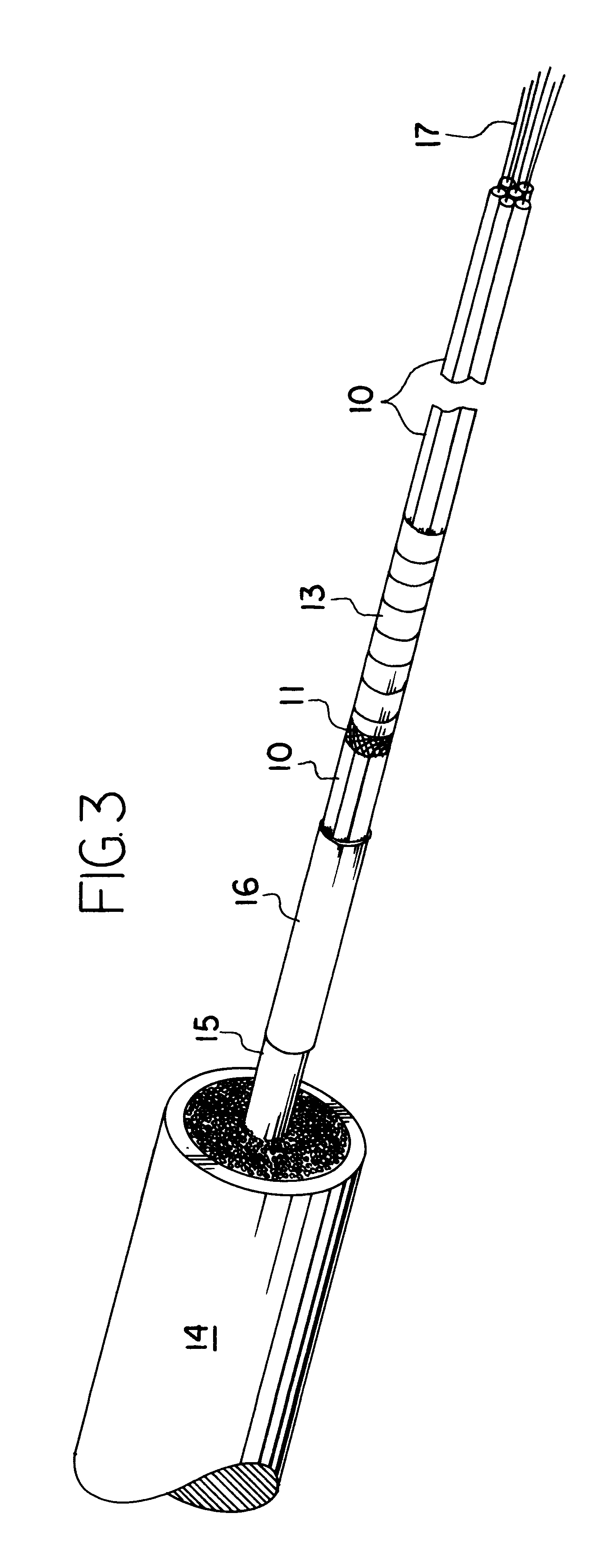
Optical electrical hybrid cable
InactiveUS8792760B2Reduce the overall diameterThe process is stable and efficientCommunication cablesCoupling light guidesFiberElectric force
An optical electrical hybrid cable for transmitting an optical signal and an electrical signal simultaneously is provided. The optical electrical hybrid cable includes a fiber-optic cable disposed in the center of the optical electrical hybrid cable, and including a plurality of tubes each of which comprises a plurality of optical fibers operatively mounted in an inner space thereof, and a first binder disposed around the plurality of tubes, a plurality of power cables disposed around the fiber-optic cable, each of the power cables comprising a plurality of conducting wires, and a second binder disposed around the plurality of power cables.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for pluggable fiber optic modules
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
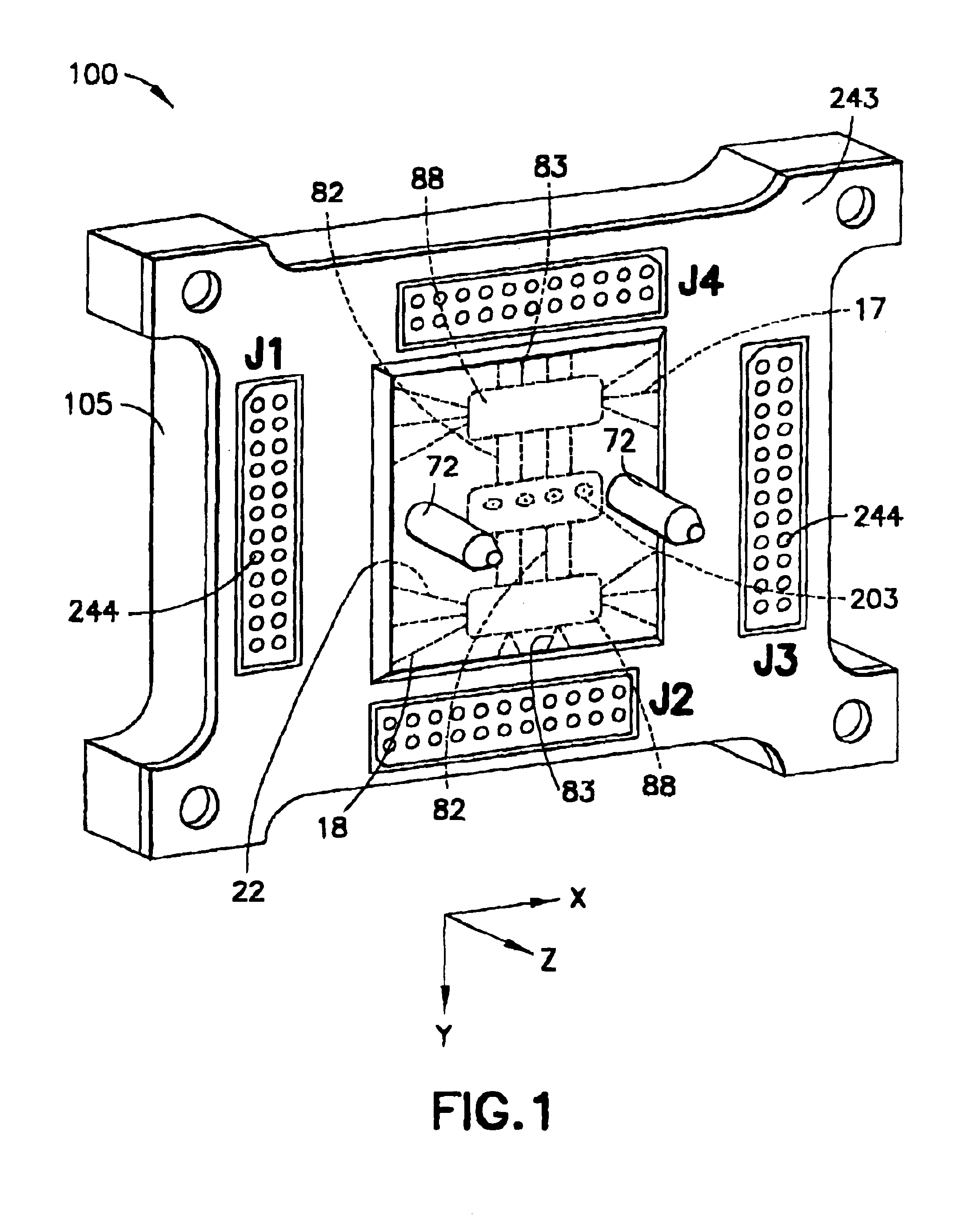
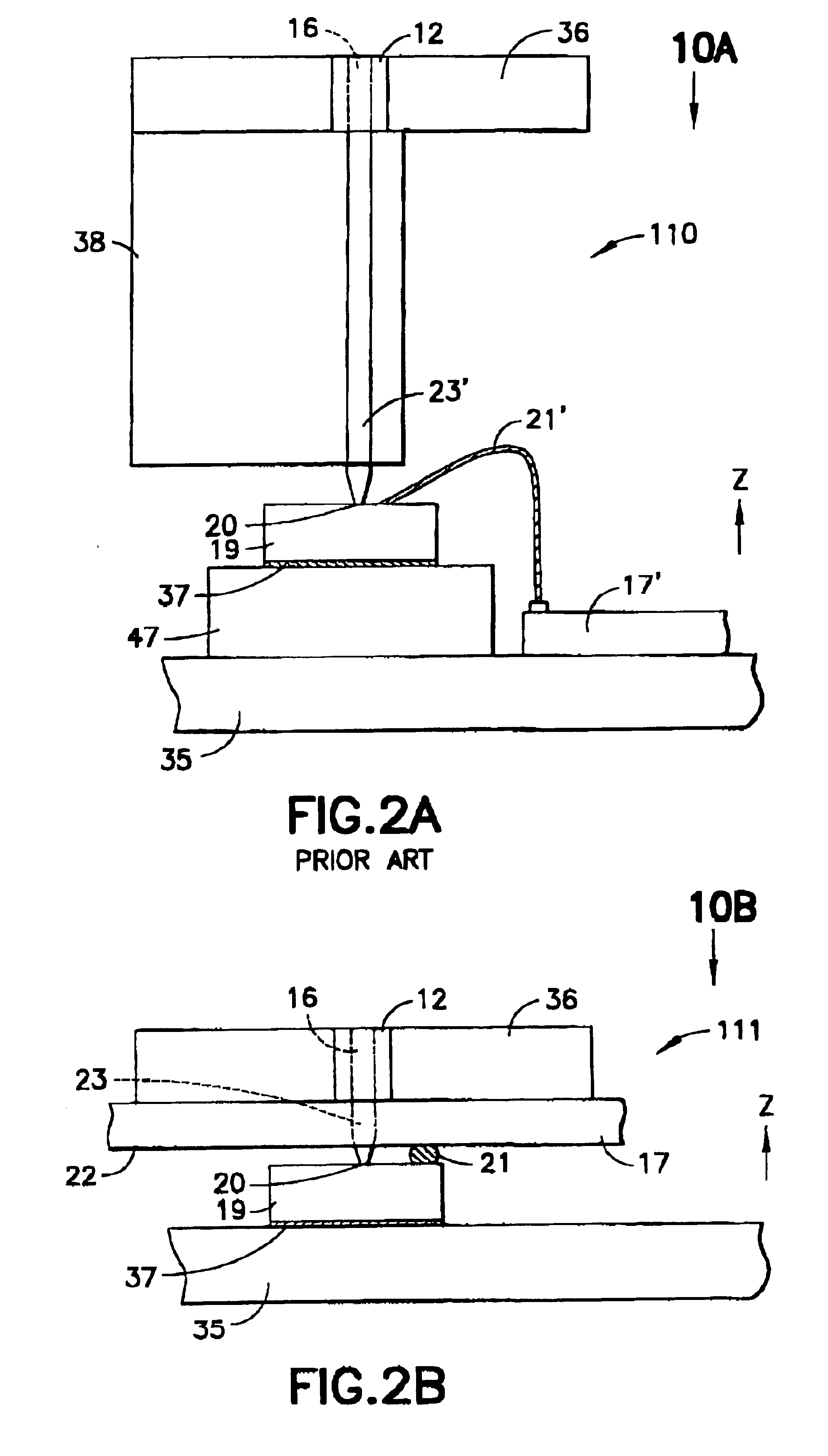
Small-scale optoelectronic package
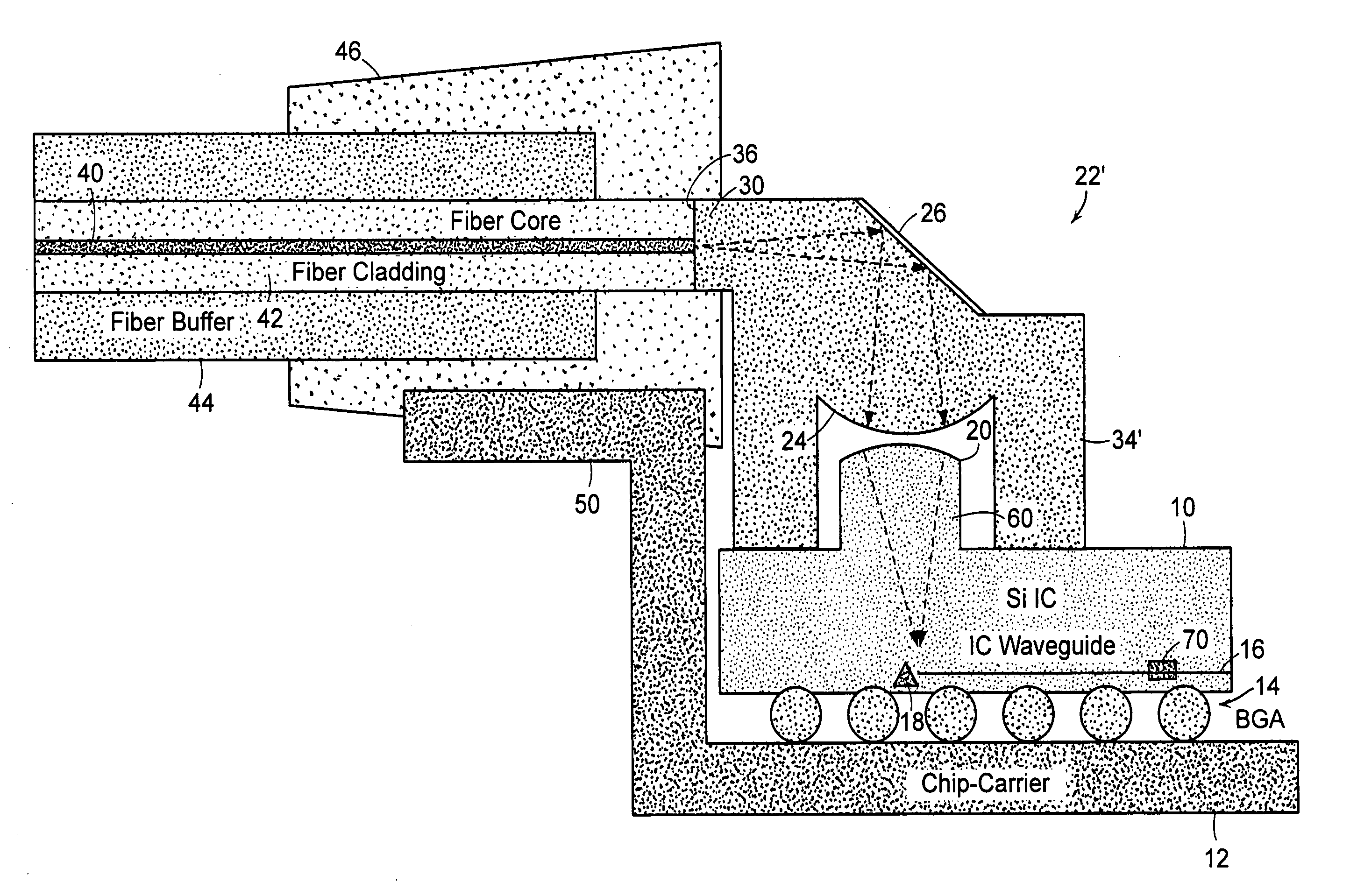
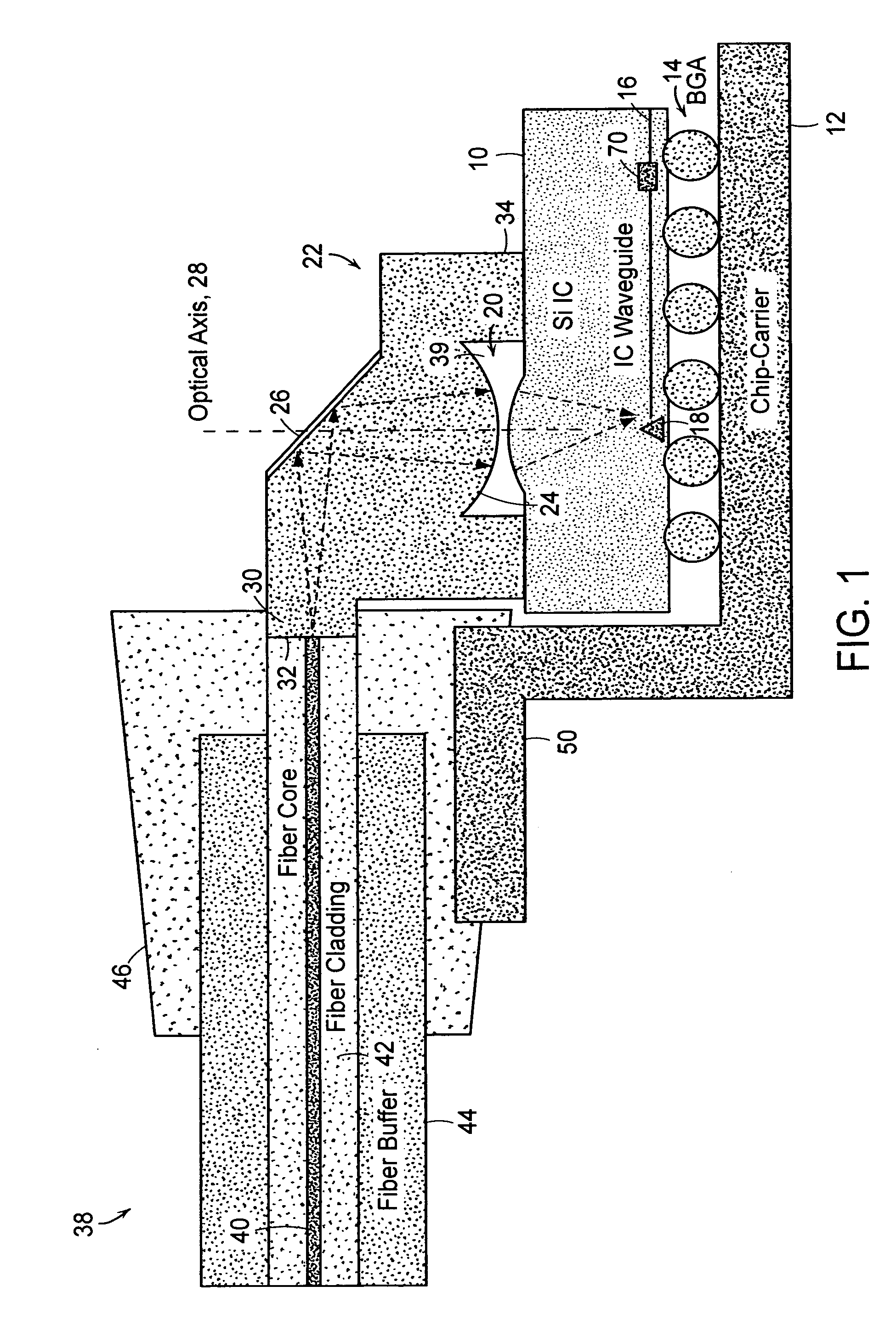
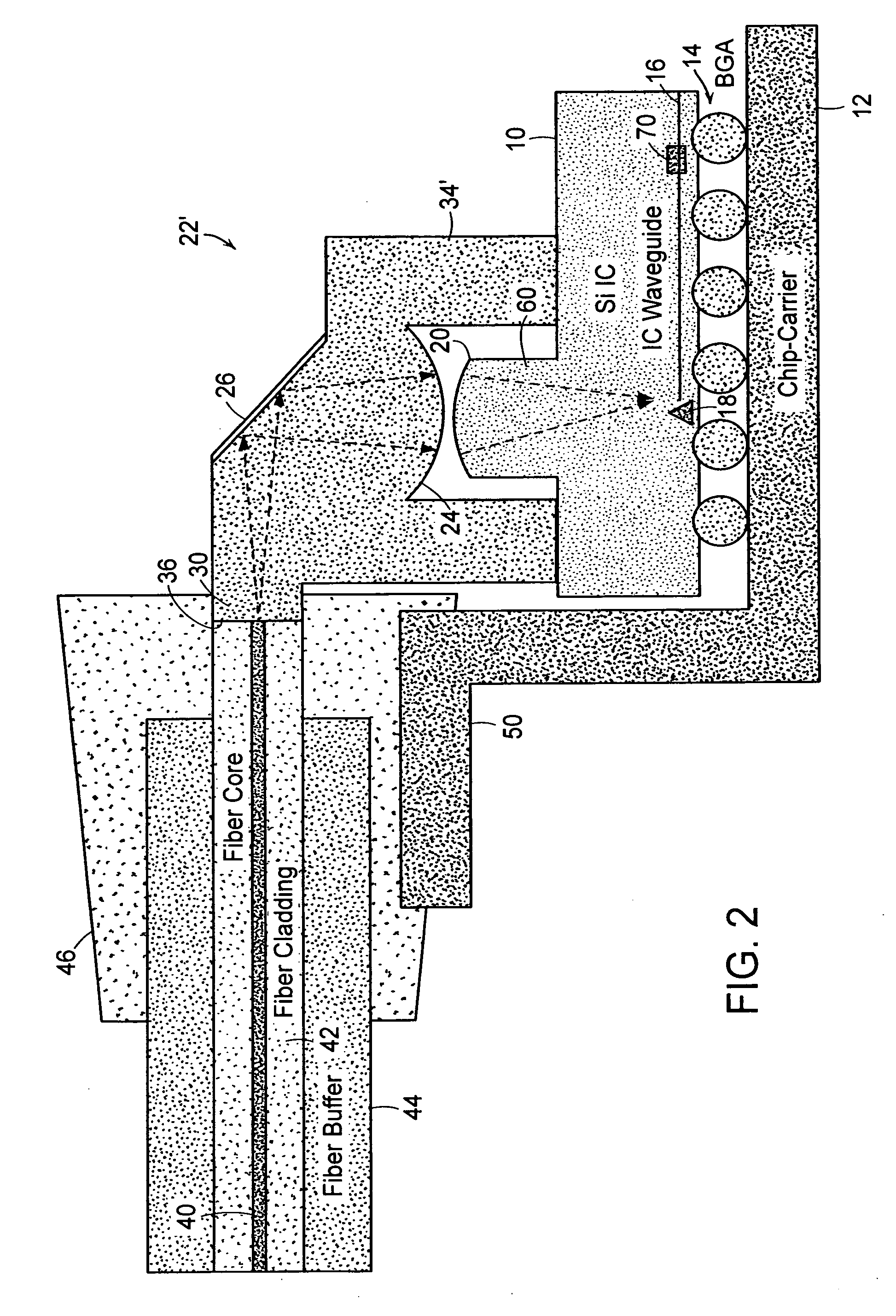
InactiveUS6910812B2Easy to manufactureSacrifice speedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFiberElectricity
An integrated circuit / optoelectronic packaging system (100) which comprises OE and IC components packaged to provide electrical input / output, thermal management, an optical window, and precise passive or mechanical alignment to external optical receivers or transmitters. A transparent insulating substrate having electrical circuitry in a thin silicon layer formed on its top side is positioned between the optical fiber and the optoelectronic device such that an optical path is described between the optoelectronic device and the optical fiber core through the transparent insulating substrate. The optoelectronic devices are mounted on the transparent insulating substrate in a precise positional relationship to guide holes in the substrate. The optical fibers are fixed in an optical fiber connector and are held in a precise positional relationship to guide holes in the connector. Alignment is accomplished with complementary guide pins that pass through guide holes in the fiber optic connector and in the transparent substrate.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
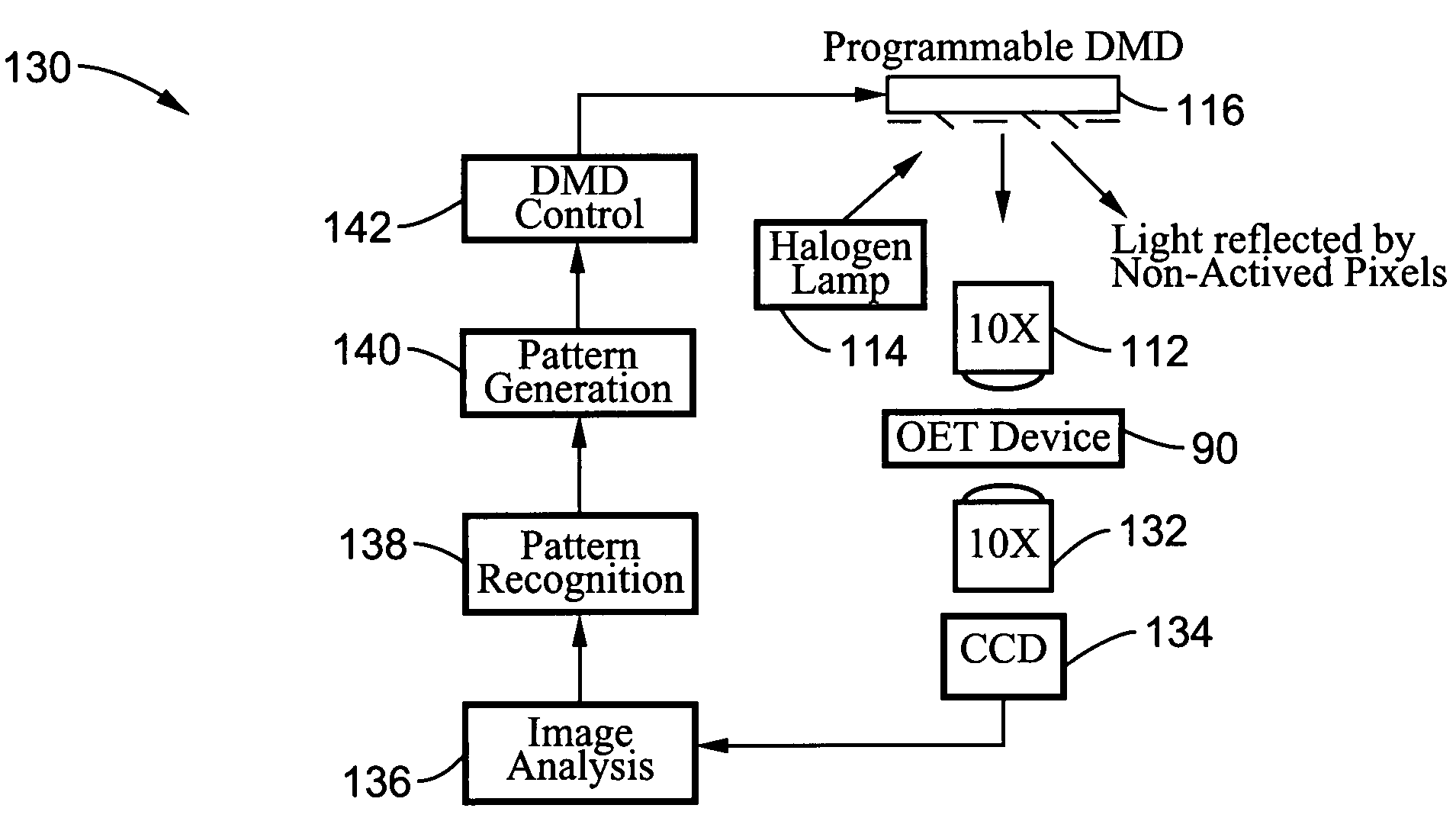
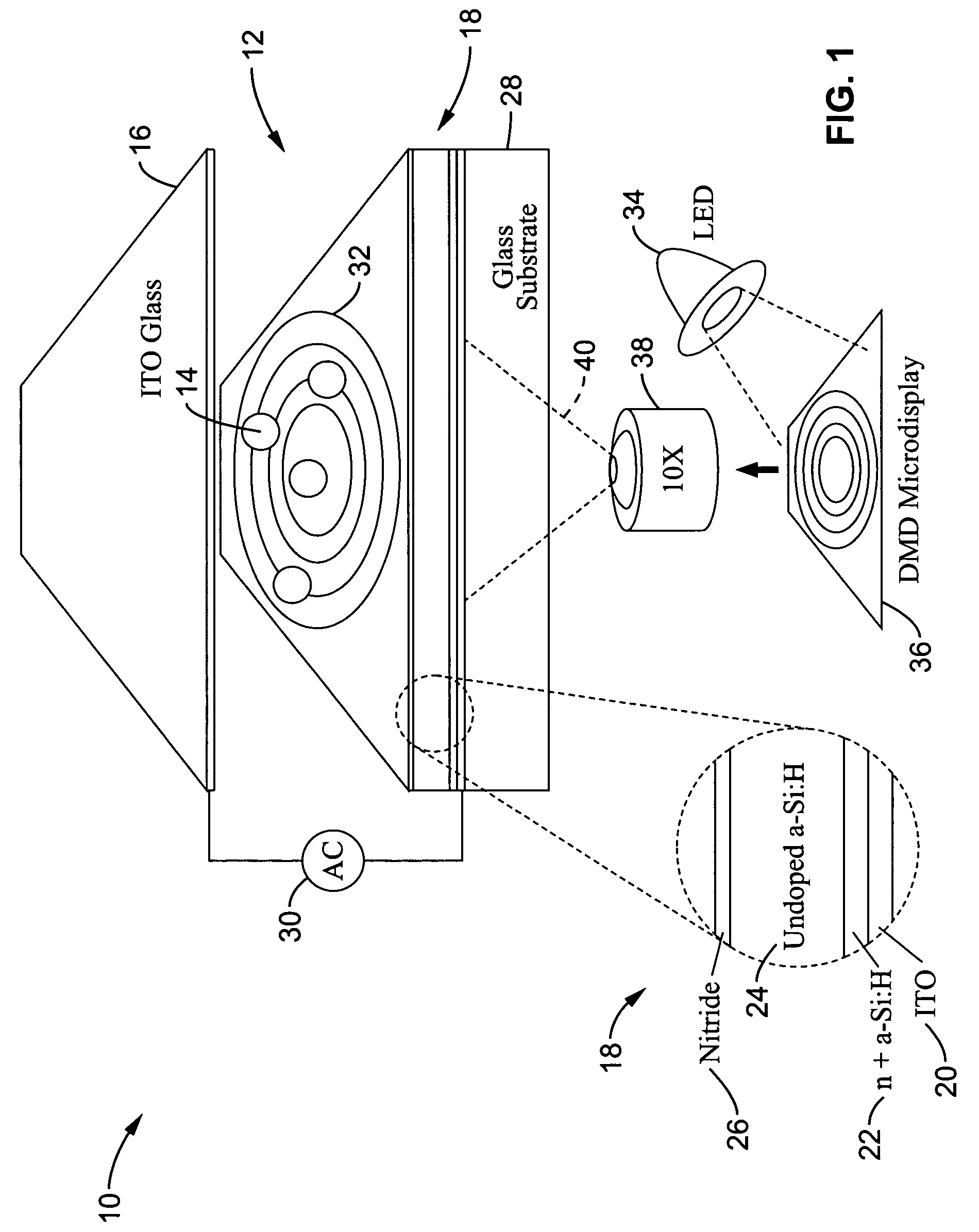
Optoelectronic tweezers for microparticle and cell manipulation
ActiveUS7612355B2Easy to operateEasy to createElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicroparticleOpto electronic
An optical image-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and method are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells with a diameter on the order of 100 μm or less. The apparatus is referred to as optoelectric tweezers (OET) and provides a number of advantages over conventional optical tweezers, in particular the ability to perform operations in parallel and over a large area without damage to living cells. The OET device generally comprises a planar liquid-filled structure having one or more portions which are photoconductive to convert incoming light to a change in the electric field pattern. The light patterns are dynamically generated to provide a number of manipulation structures that can manipulate single particles and cells or groups of particles / cells. The OET preferably includes a microscopic imaging means to provide feedback for the optical manipulation, such as detecting position and characteristics wherein the light patterns are modulated accordingly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electronically addressable microencapsulated ink and display thereof
InactiveUS20070052757A1Inexpensive displayMechanical clocksVisual indicationsElectrical conductorSemiconductor materials
A system of electronically active inks is described which may include electronically addressable contrast media, conductors, insulators, resistors, semiconductive materials, magnetic materials, spin materials, piezoelectric materials, optoelectronic, thermoelectric or radio frequency materials. We further describe a printing system capable of laying down said materials in a definite pattern. Such a system may be used for instance to: print a flat panel display complete with onboard drive logic; print a working logic circuit onto any of a large class of substrates; print an electrostatic or piezoelectric motor with onboard logic and feedback or print a working radio transmitter or receiver.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Optical receptacle, transceiver and cage
InactiveUS6854894B1Prevent exitAvoid radiationCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresFiberTransceiver
The present invention provides multi-optoelectronic assemblies in which a plurality of multi-receiver cages in which are mounted multi-optical receptacle assemblies associated with a plurality of transceivers are mounted on a printed wire assembly. The multi-optical receptacle assemblies includes a plurality of receptacles having shared walls, unitary walls or no walls. The multi-optoelectronic assemblies are compatible with multi-fiber assemblies.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
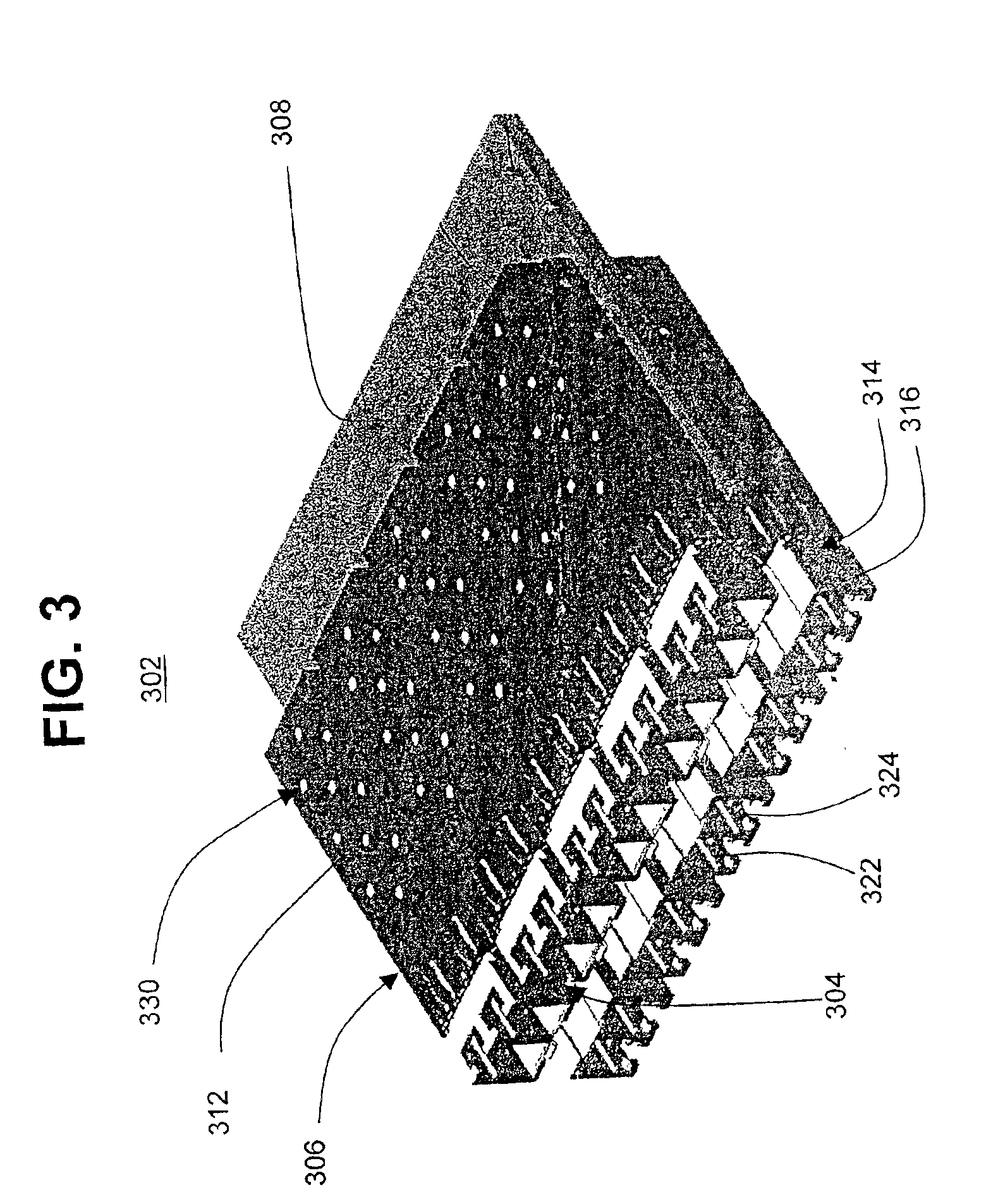
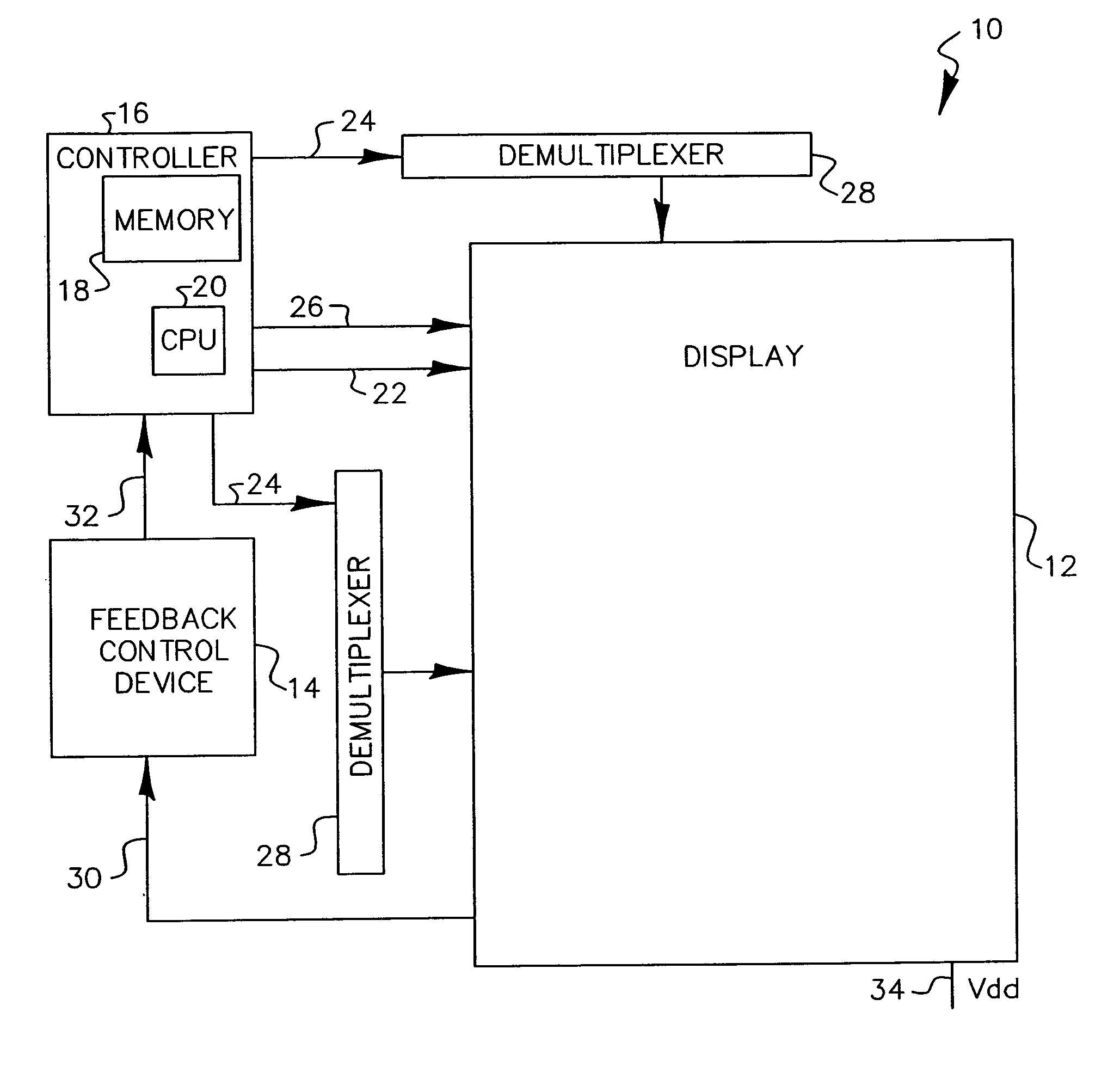
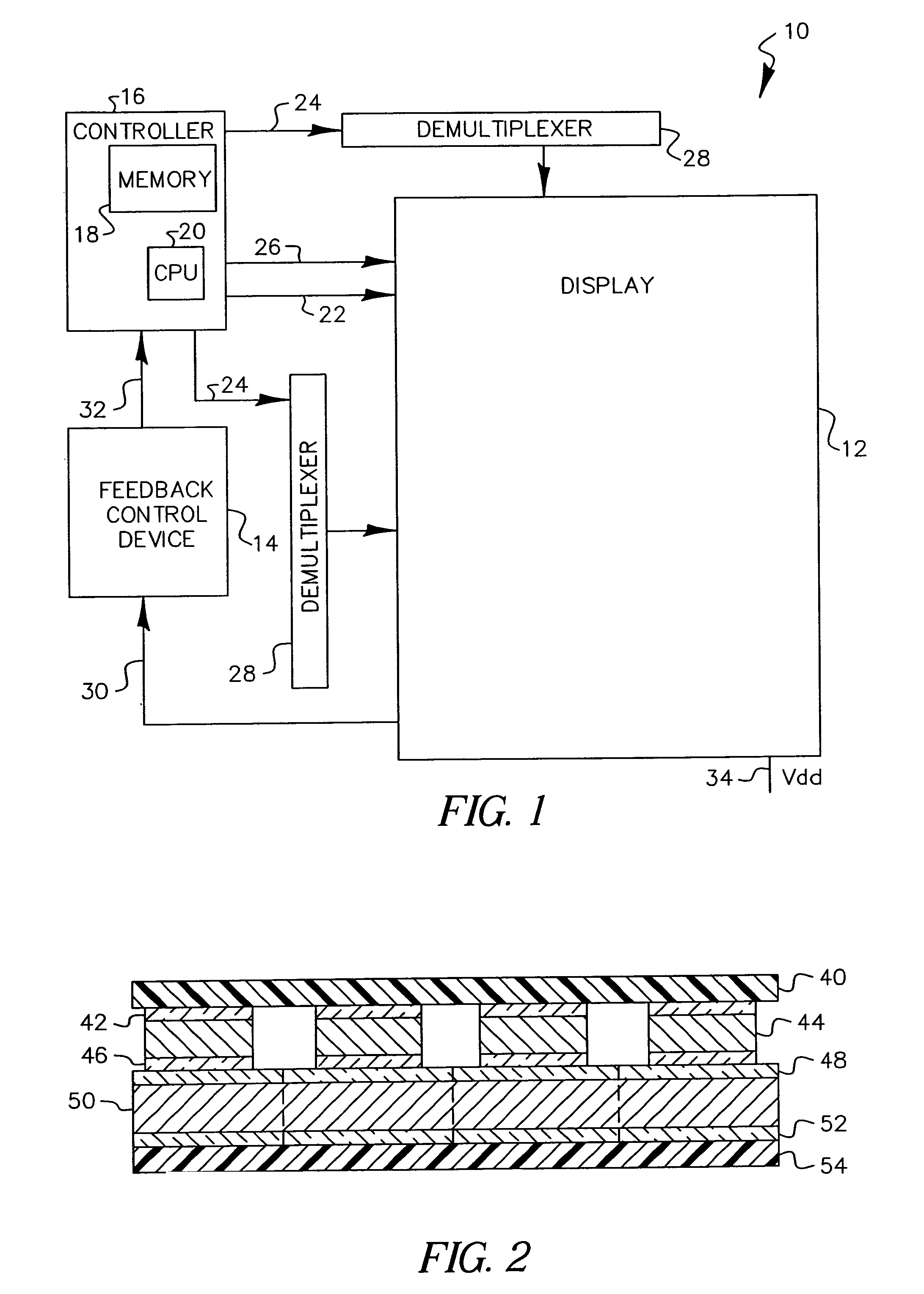
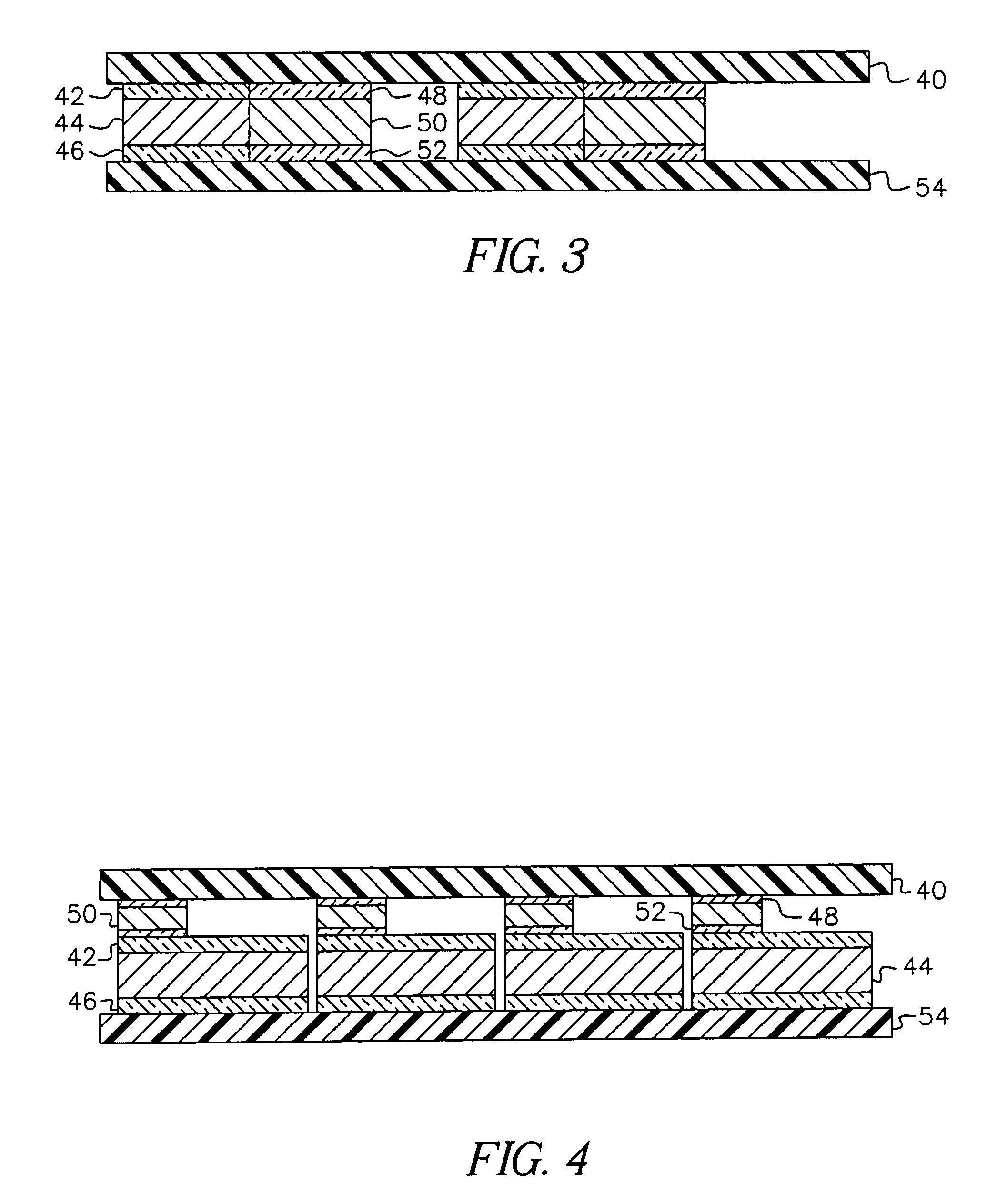
Flat-panel display with luminance feedback
InactiveUS7064733B2Improve performanceIncrease brightnessTelevision system detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceOpto electronic
An image display, includes a substrate; a light emitter formed on the substrate; and a photo-sensor formed on the substrate and optically coupled directly to the light emitter.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Optical coupling to IC chip
InactiveUS20060239605A1Low costEnhanced couplingOptical articlesCoupling light guidesOpto electronicWaveguide
An optoelectronic circuit including: an IC chip made up of a substrate in which an optical waveguide and a mirror have been fabricated, the substrate having a first lens formed thereon, wherein the mirror is aligned with the optical waveguide and the first lens is aligned with the mirror to form an optical path connecting the first lens, the mirror, and the optical waveguide; and an optical coupler including a second lens, the optical coupler affixed to the substrate and positioned to align the second lens with the first lens so as to couple an optical signal into or out of the optical waveguide within the IC chip.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
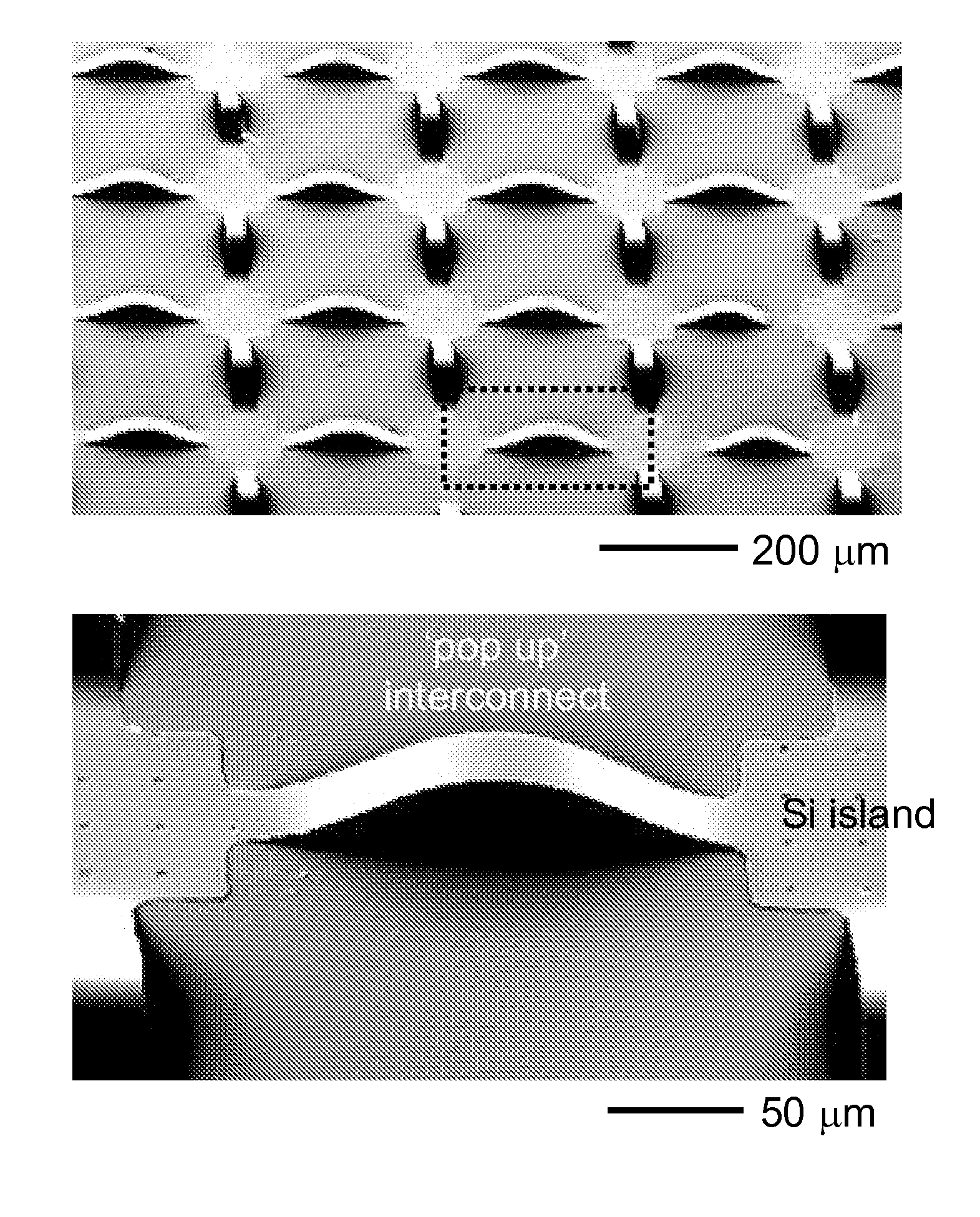
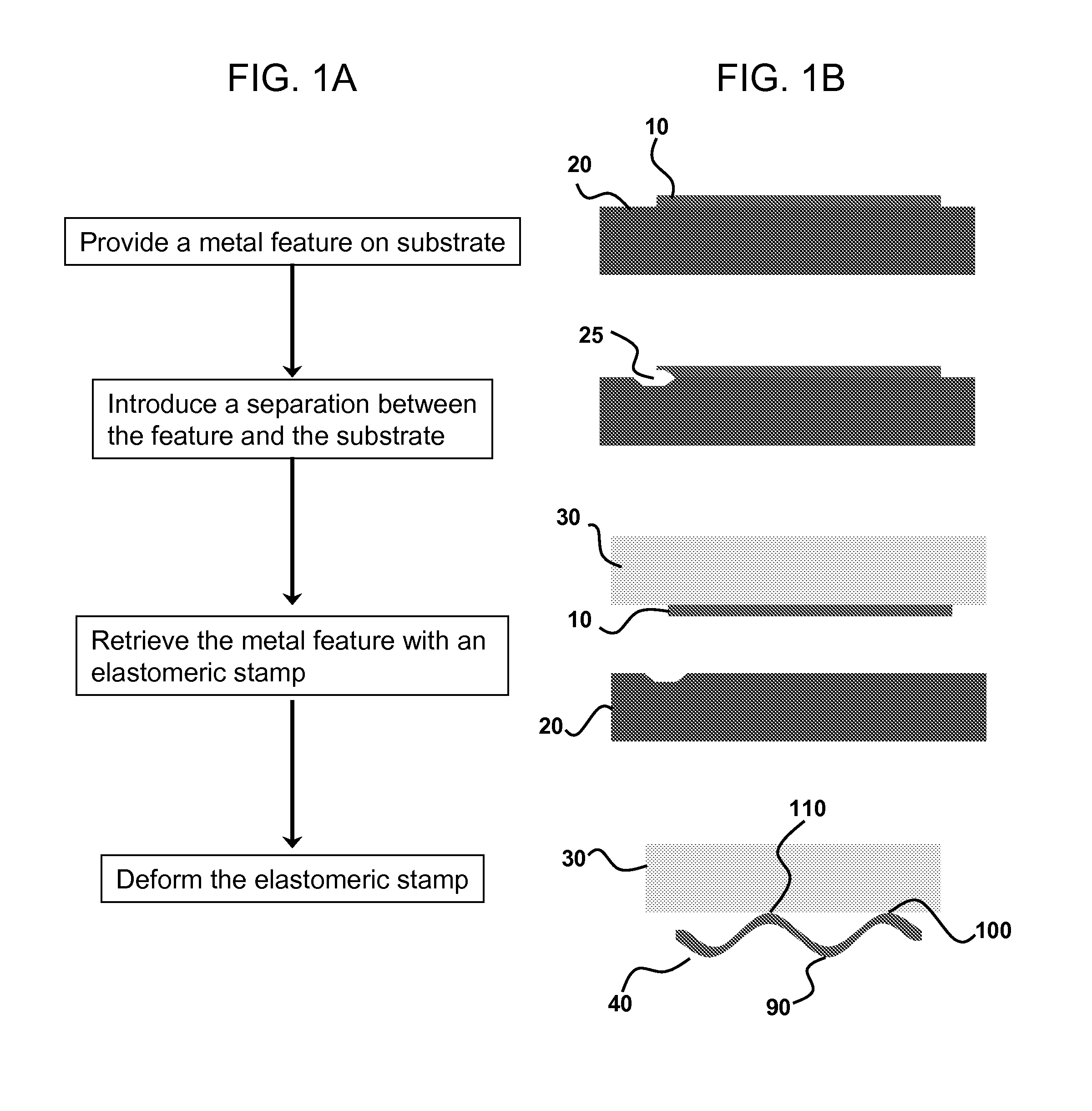
Controlled buckling structures in semiconductor interconnects and nanomembranes for stretchable electronics
ActiveUS8217381B2Without adversely impacting performanceFlexibilityTransistorCircuit bendability/stretchabilityStretchable electronicsEngineering
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
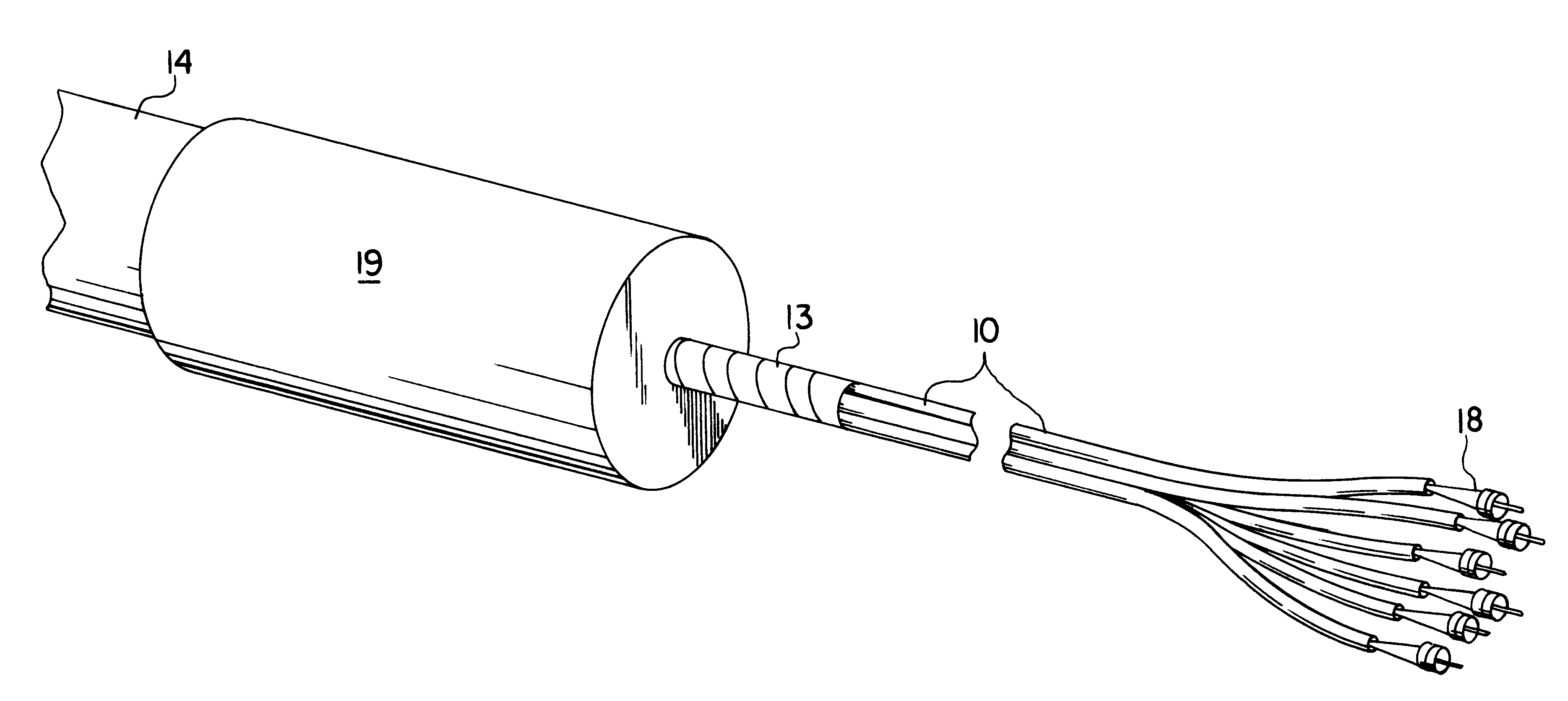
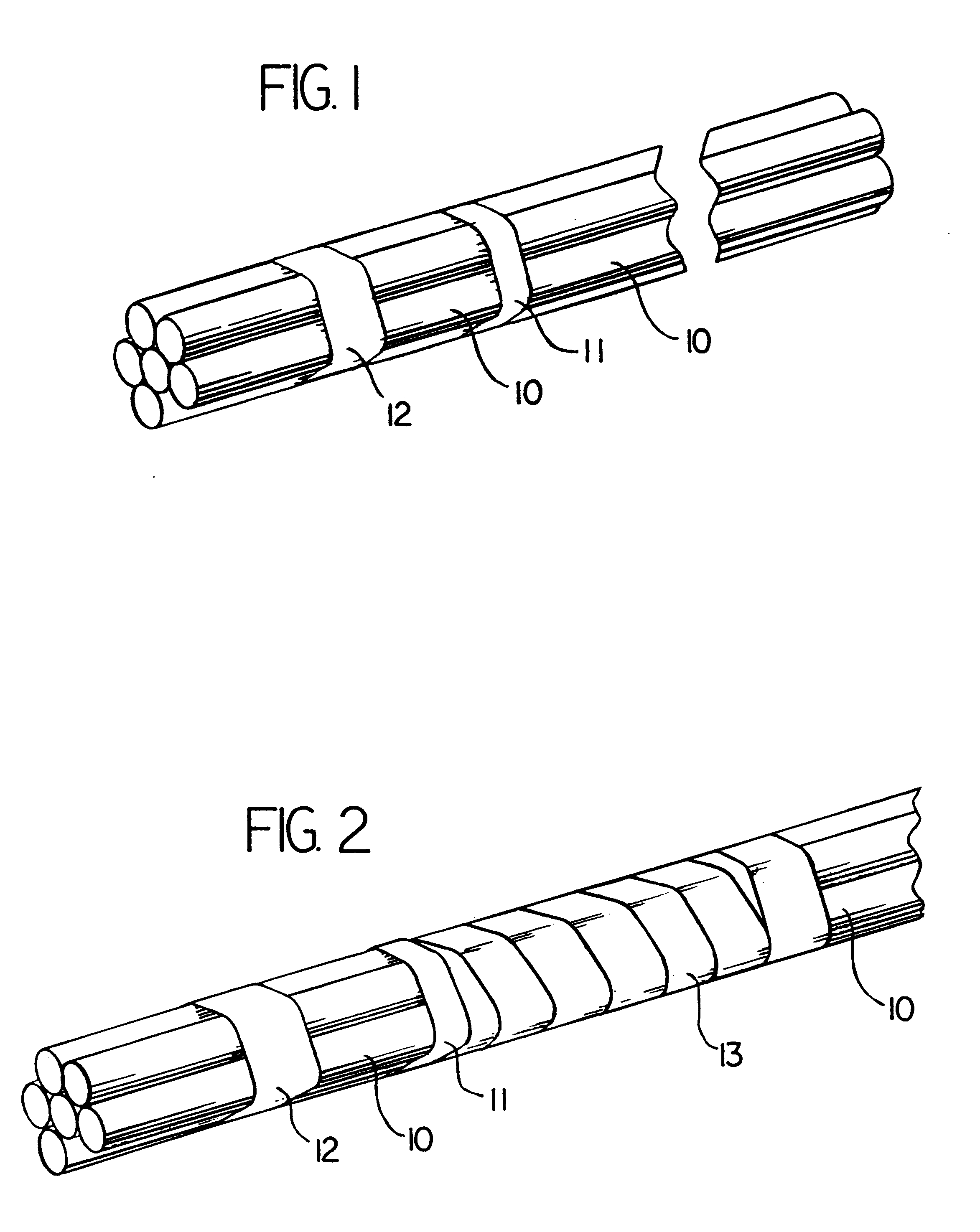
Cable assembly for use with opto-electronic equipment enclosures
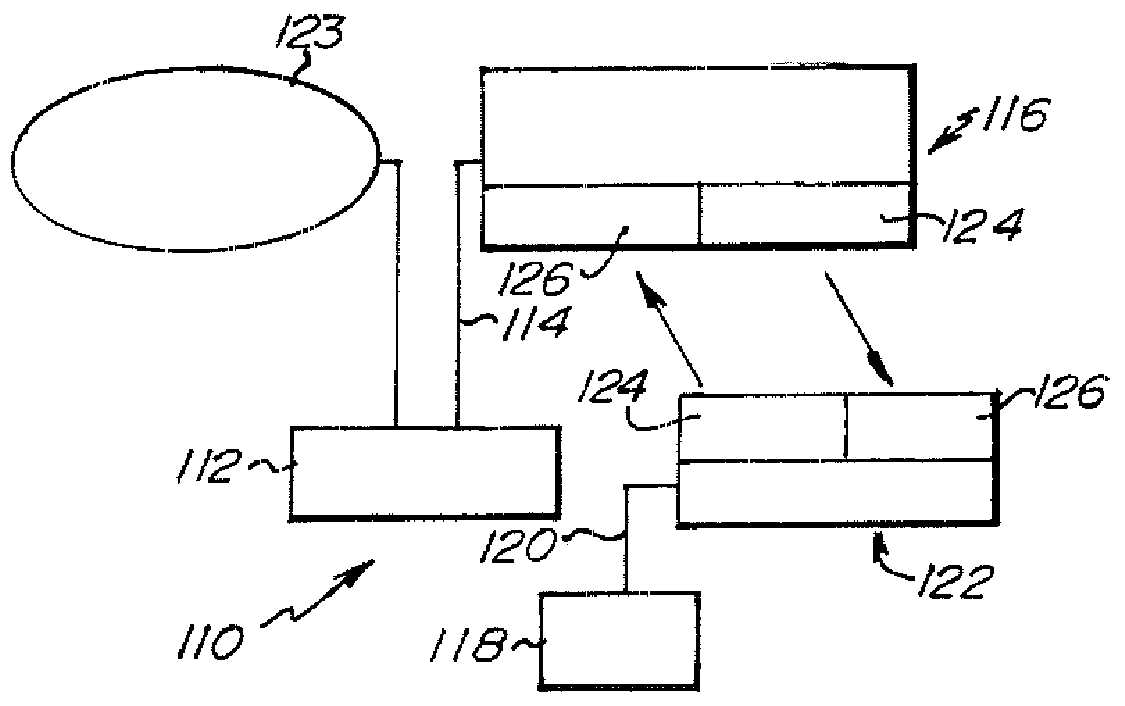
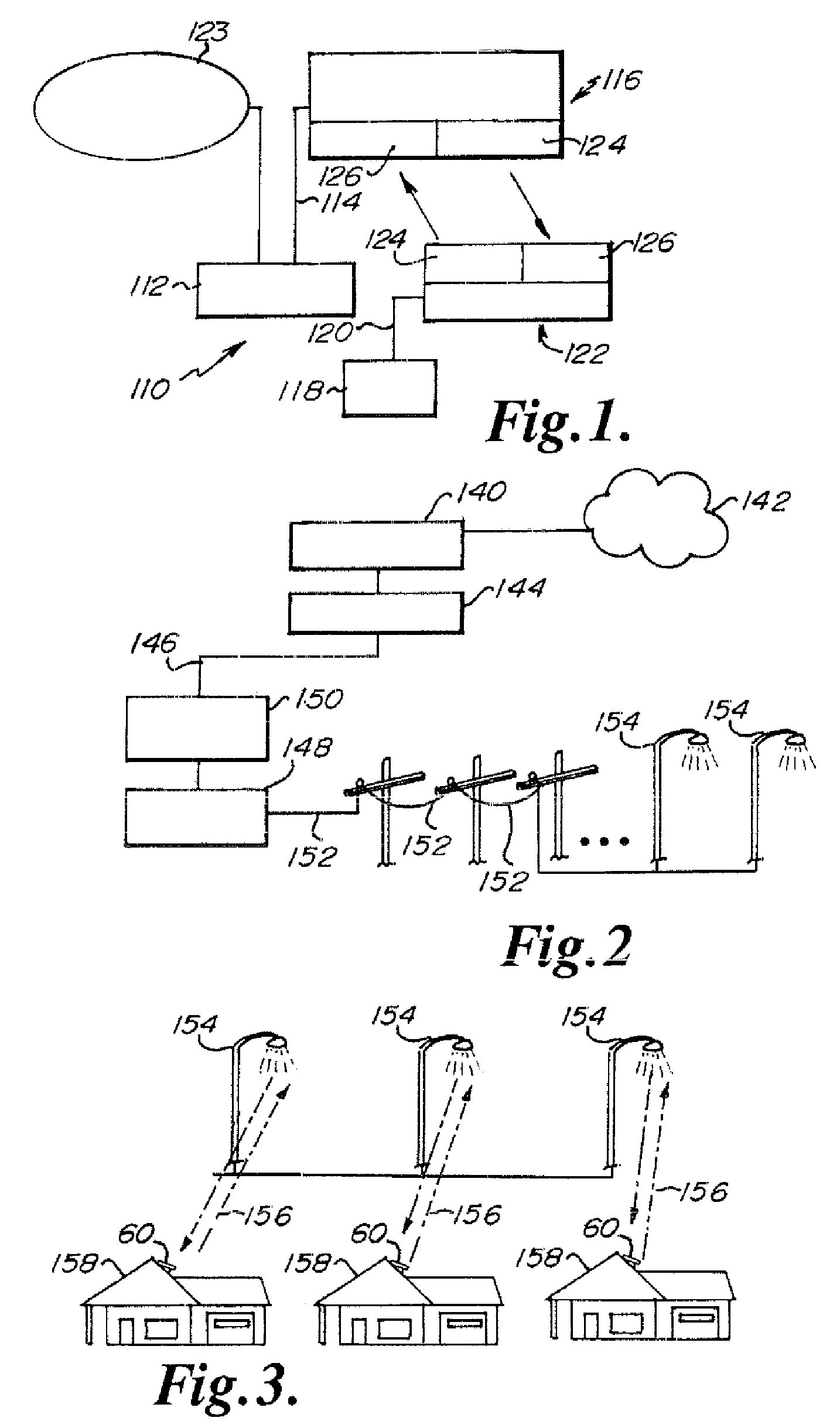
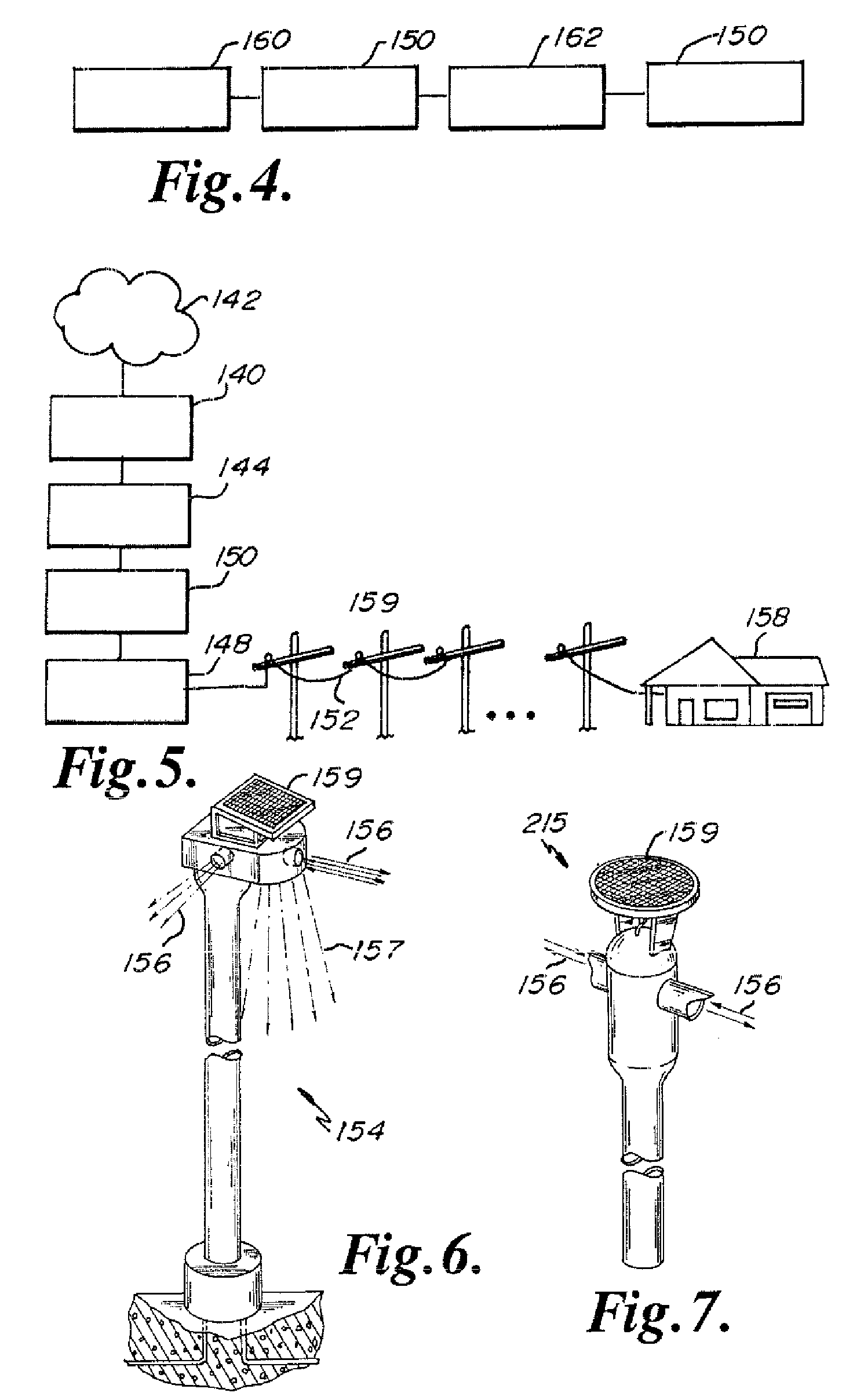
Light, flexible tubes are placed around optical fibers extending from the end of a cable jacket. A water impervious plug encases the end of the cable jacket and a portion of the flexible tubes. Couplers are attached to the light waveguide terminal ends and the optical couplers and the plug are placed in an opto-electronic equipment closure. The assembly is designed for use with cable television system aerial closures.
Owner:SIECOR A DELAWARE
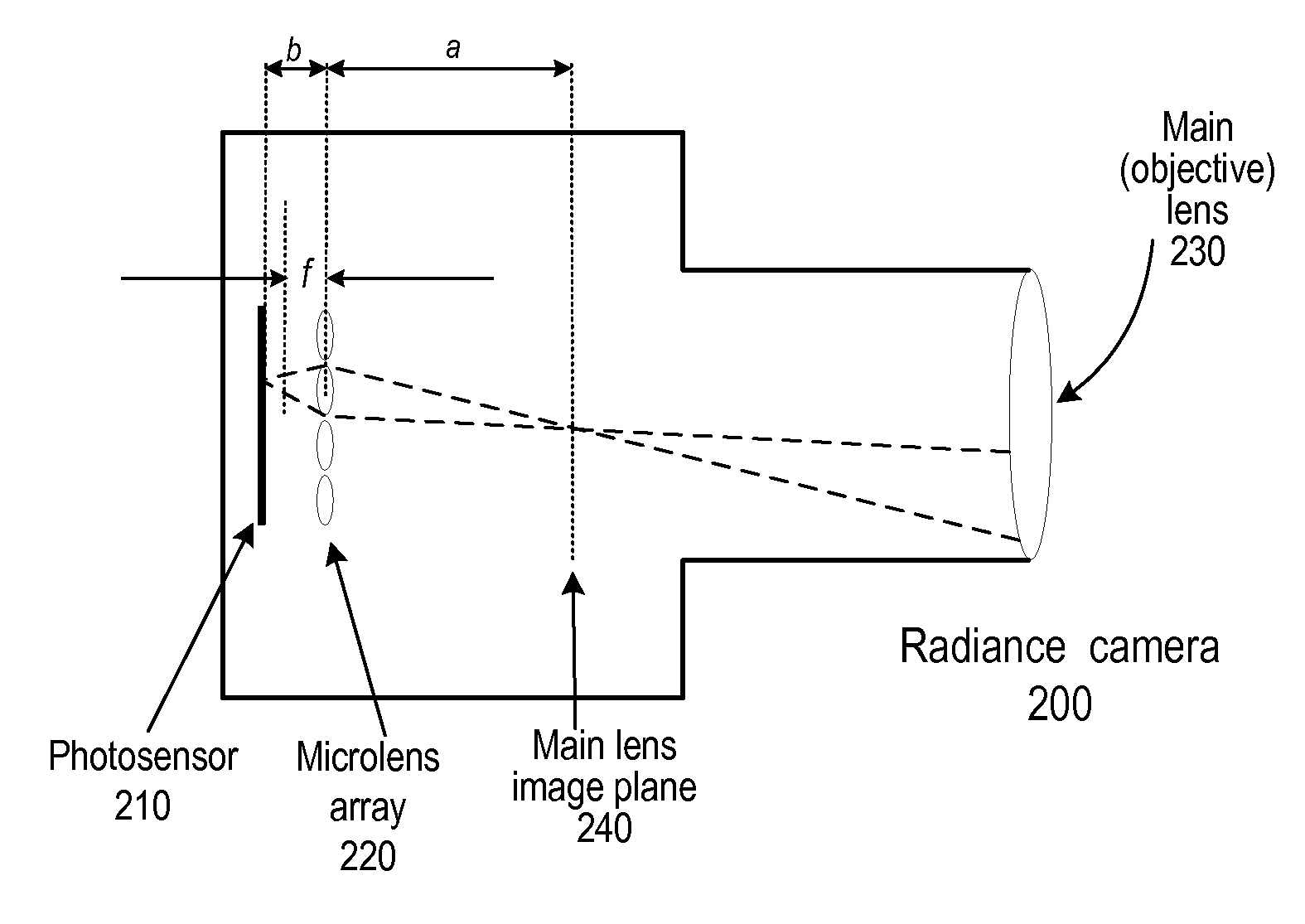
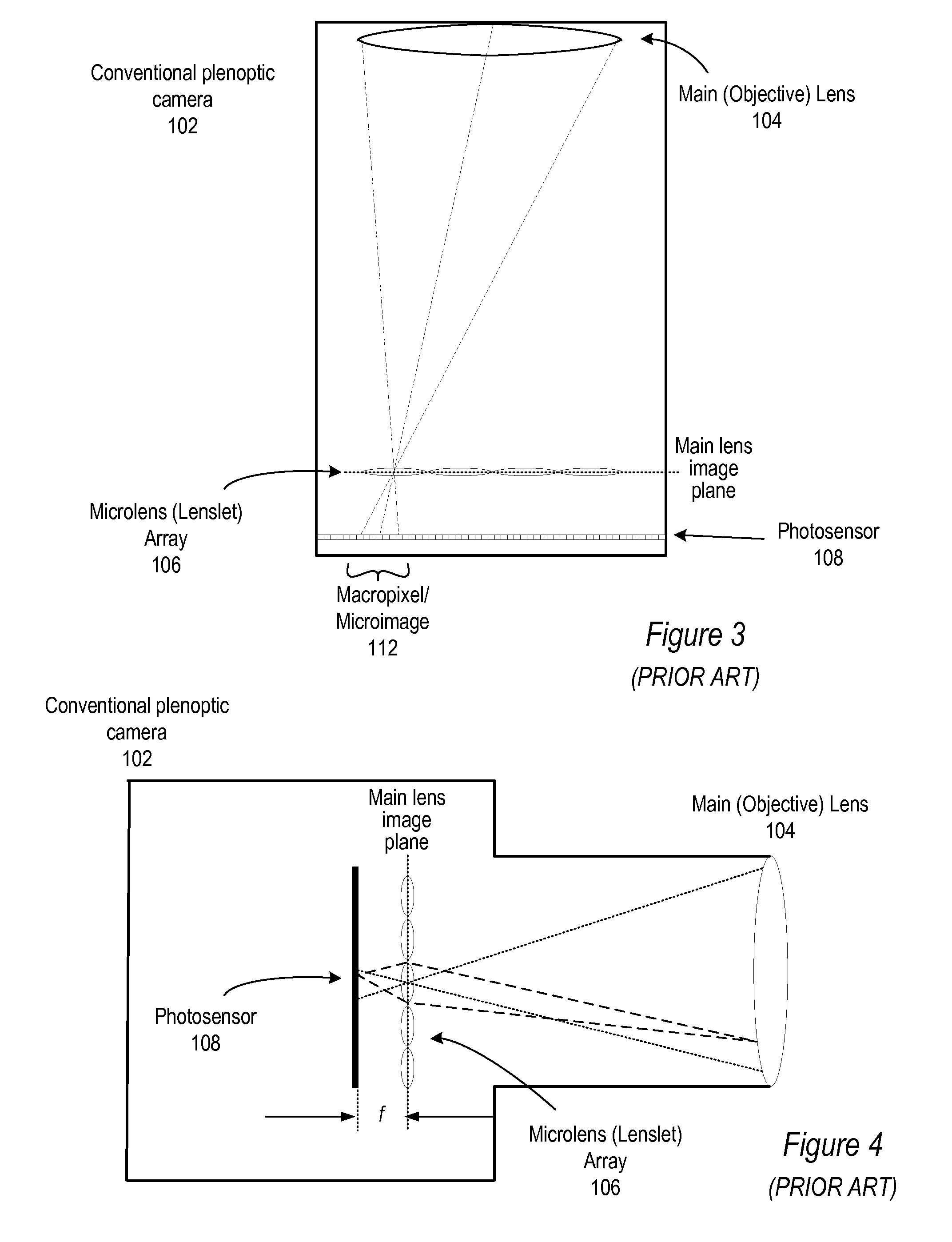
Methods and Apparatus for Full-Resolution Light-Field Capture and Rendering
ActiveUS20090185801A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionRadiance
Method and apparatus for full-resolution light-field capture and rendering. A radiance camera is described in which the microlenses in a microlens array are focused on the image plane of the main lens instead of on the main lens, as in conventional plenoptic cameras. The microlens array may be located at distances greater than f from the photosensor, where f is the focal length of the microlenses. Radiance cameras in which the distance of the microlens array from the photosensor is adjustable, and in which other characteristics of the camera are adjustable, are described. Digital and film embodiments of the radiance camera are described. A full-resolution light-field rendering method may be applied to light-fields captured by a radiance camera to render higher-resolution output images than are possible with conventional plenoptic cameras and rendering methods.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Optical device utilizing optical waveguides and mechanical light-switches
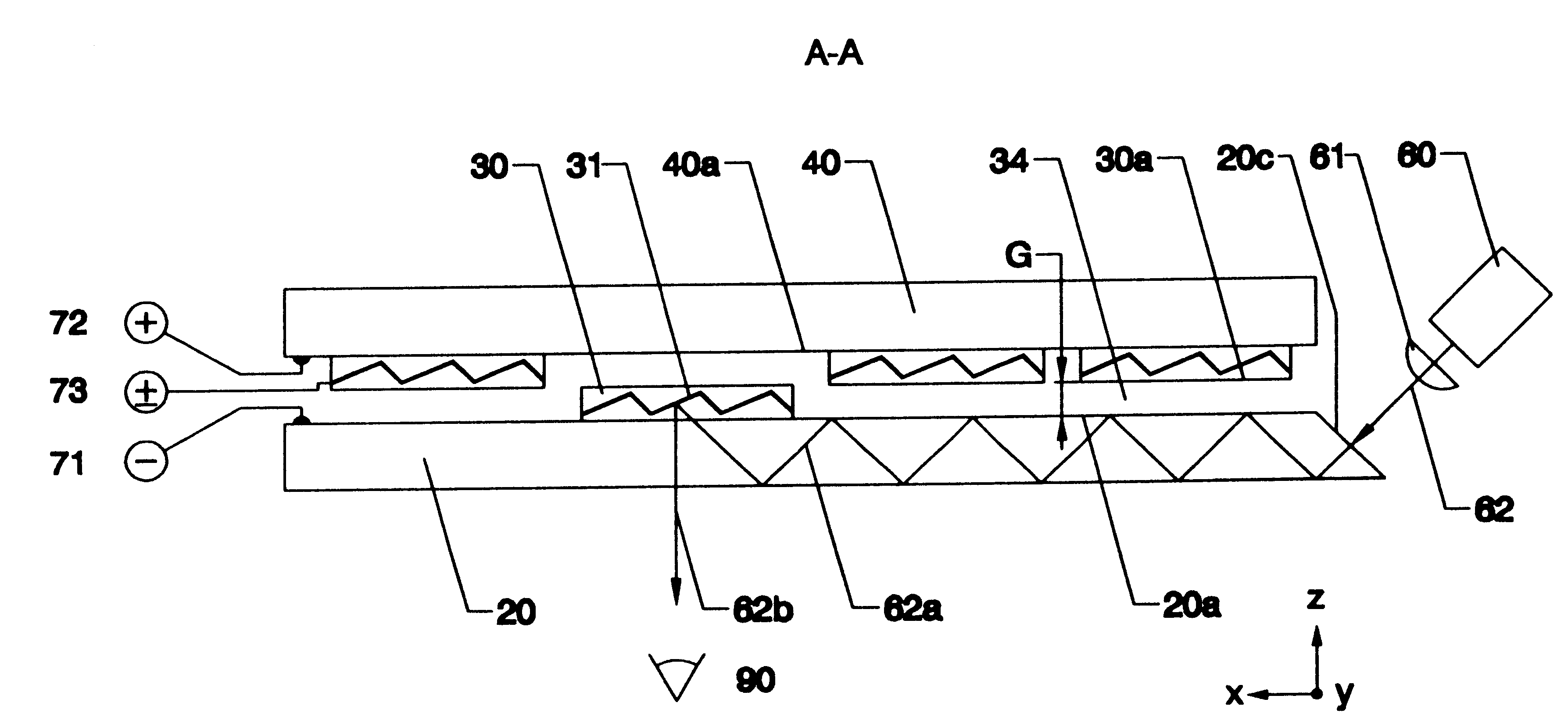
InactiveUS6650822B1High refractive indexReduction factorCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An optical device consists of one or more optical waveguides and mechanical light switches 30. When a light switch 30 is turned on, it extracts light beam 62a from a waveguide core 20 and redirect the light beam 62b into free space, it redirects an incoming light beam 80 from free space and injects the light beam 80a into the waveguide core 20, or it performs both functions at the same time, depending on specific applications. On and off states of a light switch 30 are achieved by pulling the light switch 30 into a close vicinity of the waveguide core 20 and by pushing the light switch 30 away from the waveguide core 20, respectively. An interactive fiat-panel display can be built based on this invention. A plurality of parallel channel waveguides forms a display panel. An array of light beams 62a, injected from an array light source 60, propagates along waveguide cores 20 until reaches a location where a light switch 30 is turned on. At this location, the light switch 30 redirects the light beams towards a viewer. An image is produced when the light switches 30 are turned on sequentially while the light-intensity distribution on the array light source 60 is synchronically updated. The panel display is capable of responding to an input optical signal by detecting an incoming light beam 80 from a light pen 100. An array of photodetectors 81 is used to identify the location of the incoming light beam 80 on the display panel and a computer is used to execute a corresponding action accordingly.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
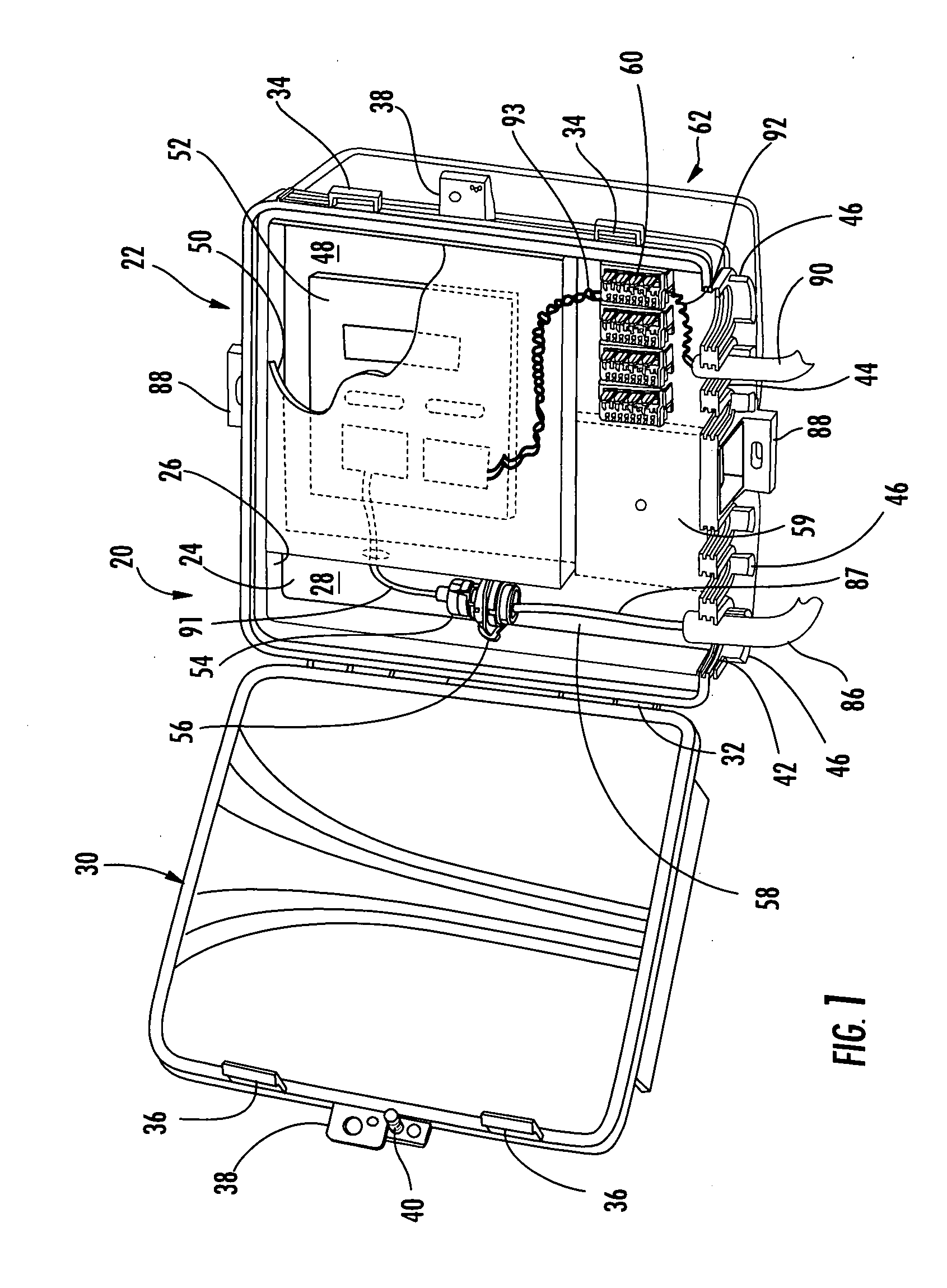
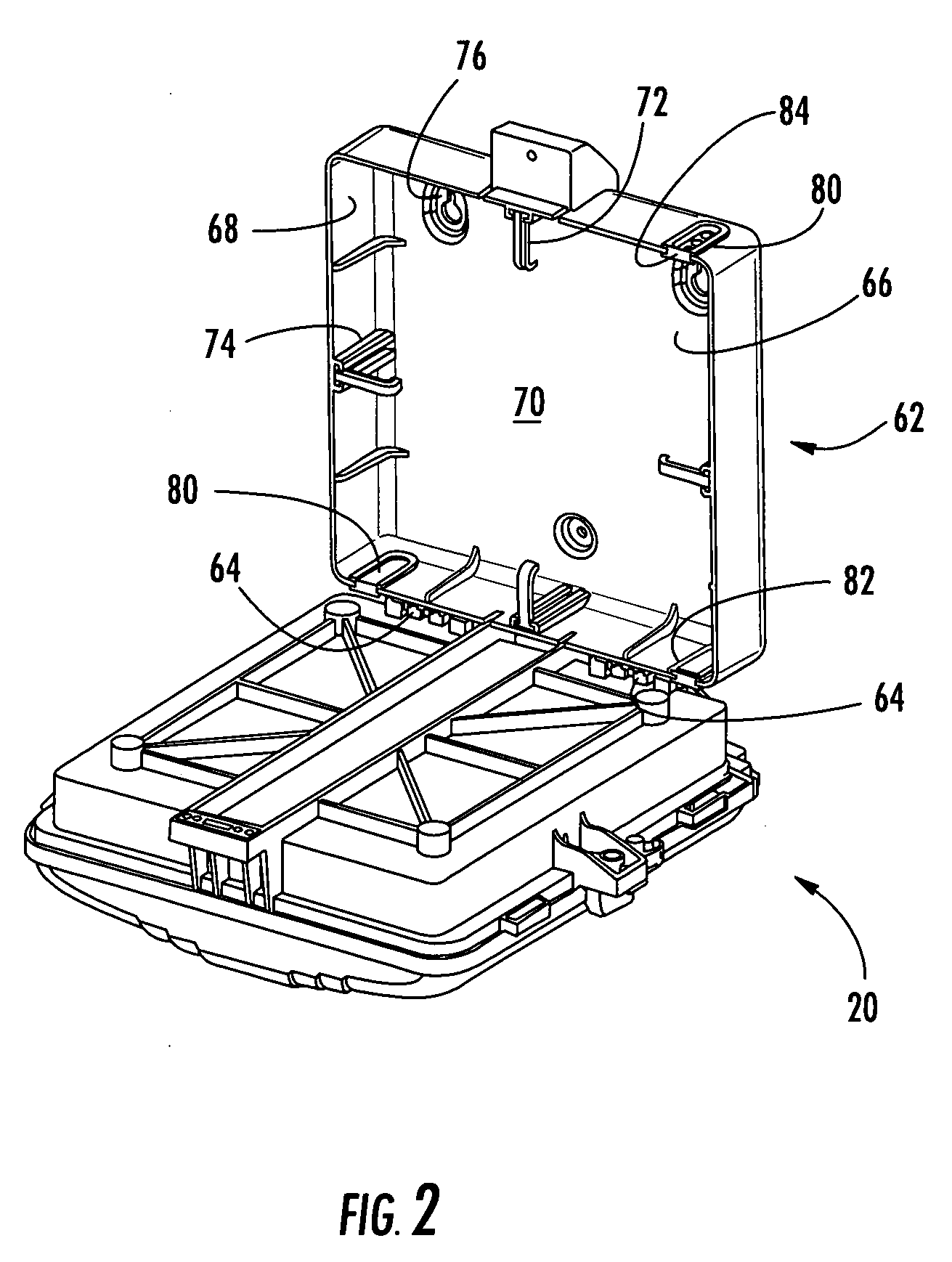
Network interface device having integral slack storage compartment
A network interface device (NID) for a fiber optic communications network is provided for housing optical, electrical and / or coaxial connections and active and / or passive components. The NID includes a base and a movable panel defining a connections area and a components area. In one embodiment, a first base defines a first compartment for housing the panel and a second base defining a second compartment for storing drop cable slack, the first base being movably attached to the second base to provide access to the drop cable slack without disturbing the connections. In another embodiment, the panel defines a first compartment for optical and electrical connections and a second compartment for active and passive components, the second compartment being accessible to only the service provider. In another embodiment, the panel is removable and interchangeable to permit the service provider to upgrade the services or to expand services provided to a subscriber.
Owner:CORNING CABLE SYST LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com