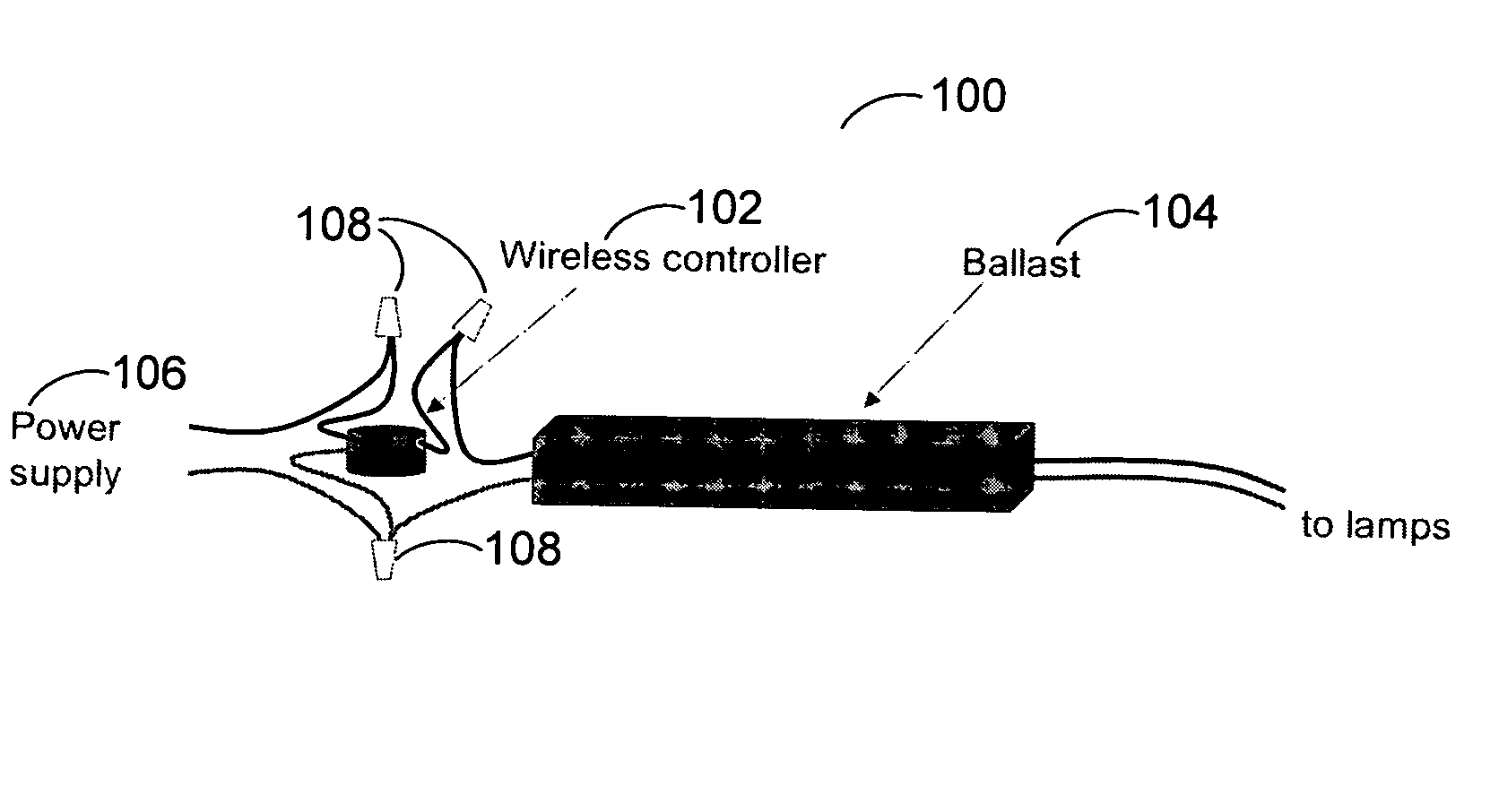
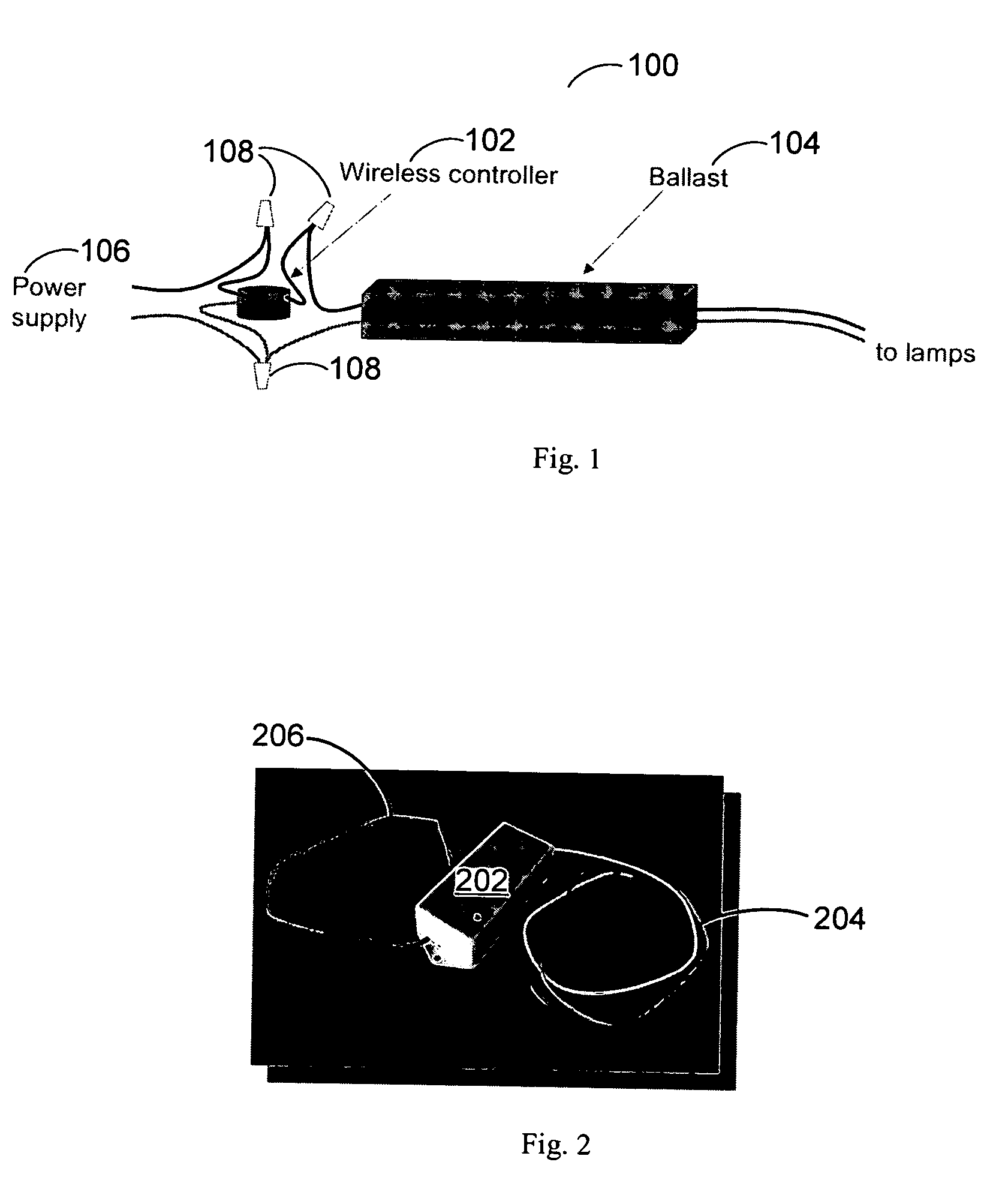
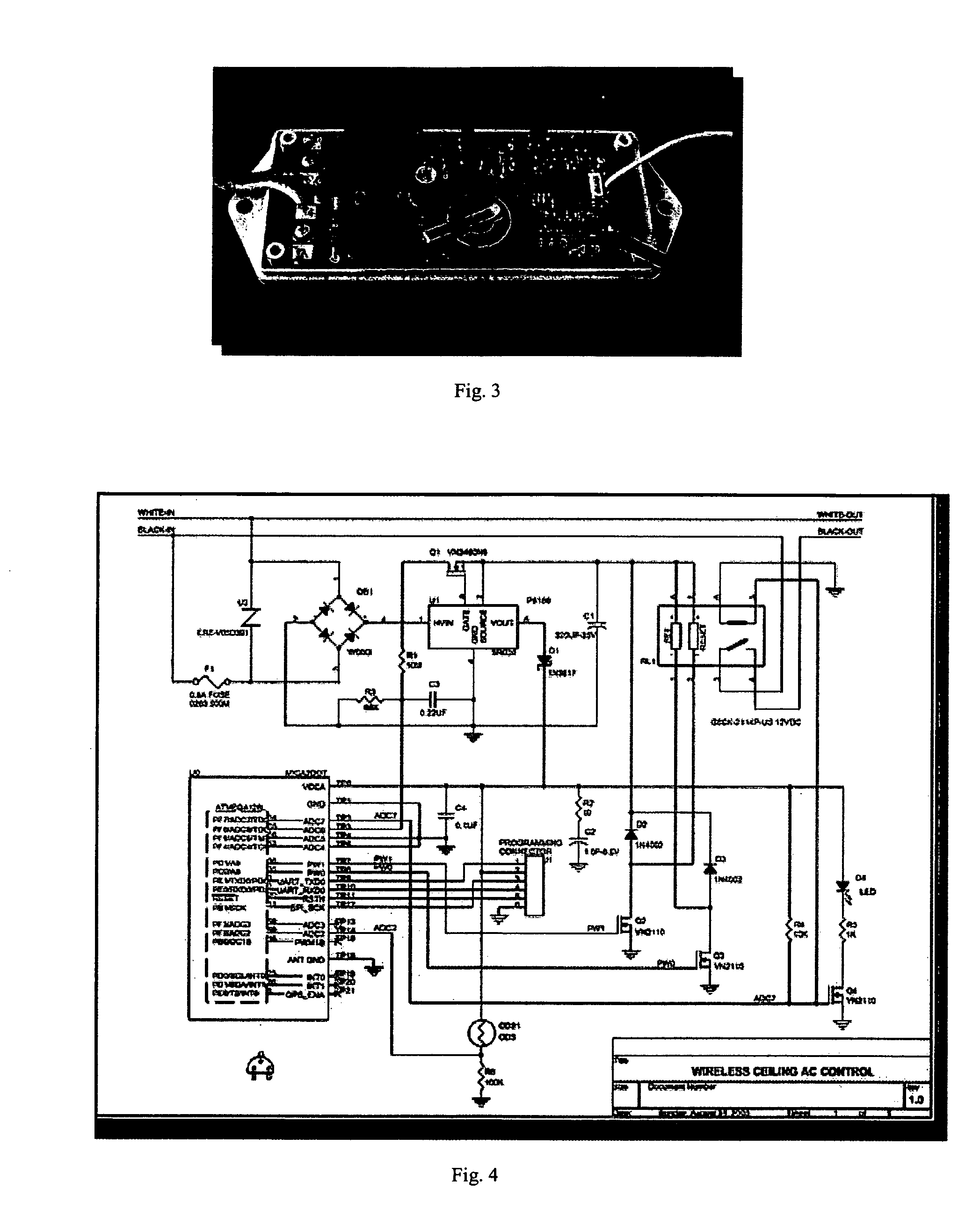
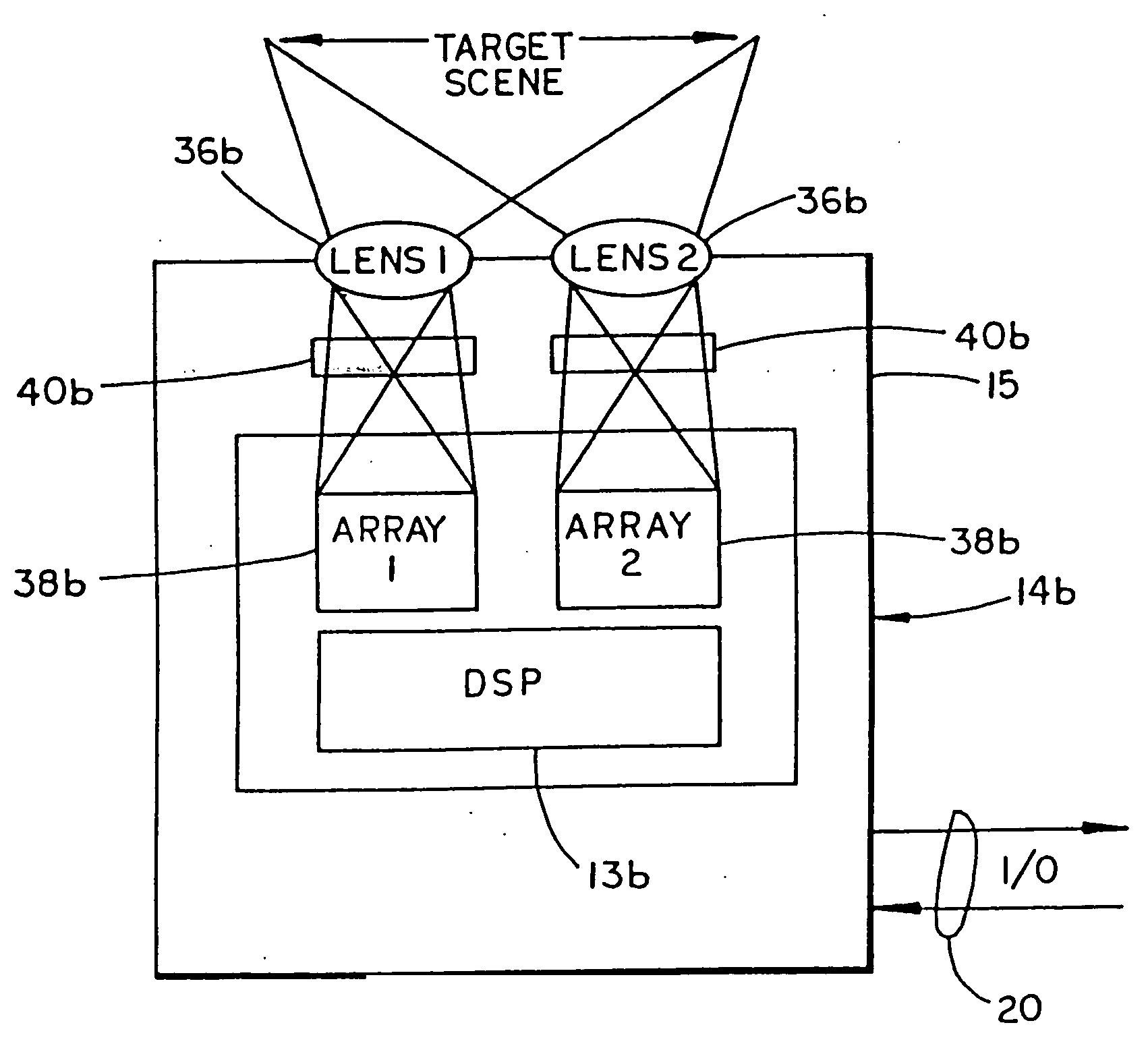
Patents
Literature
932 results about "Light level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
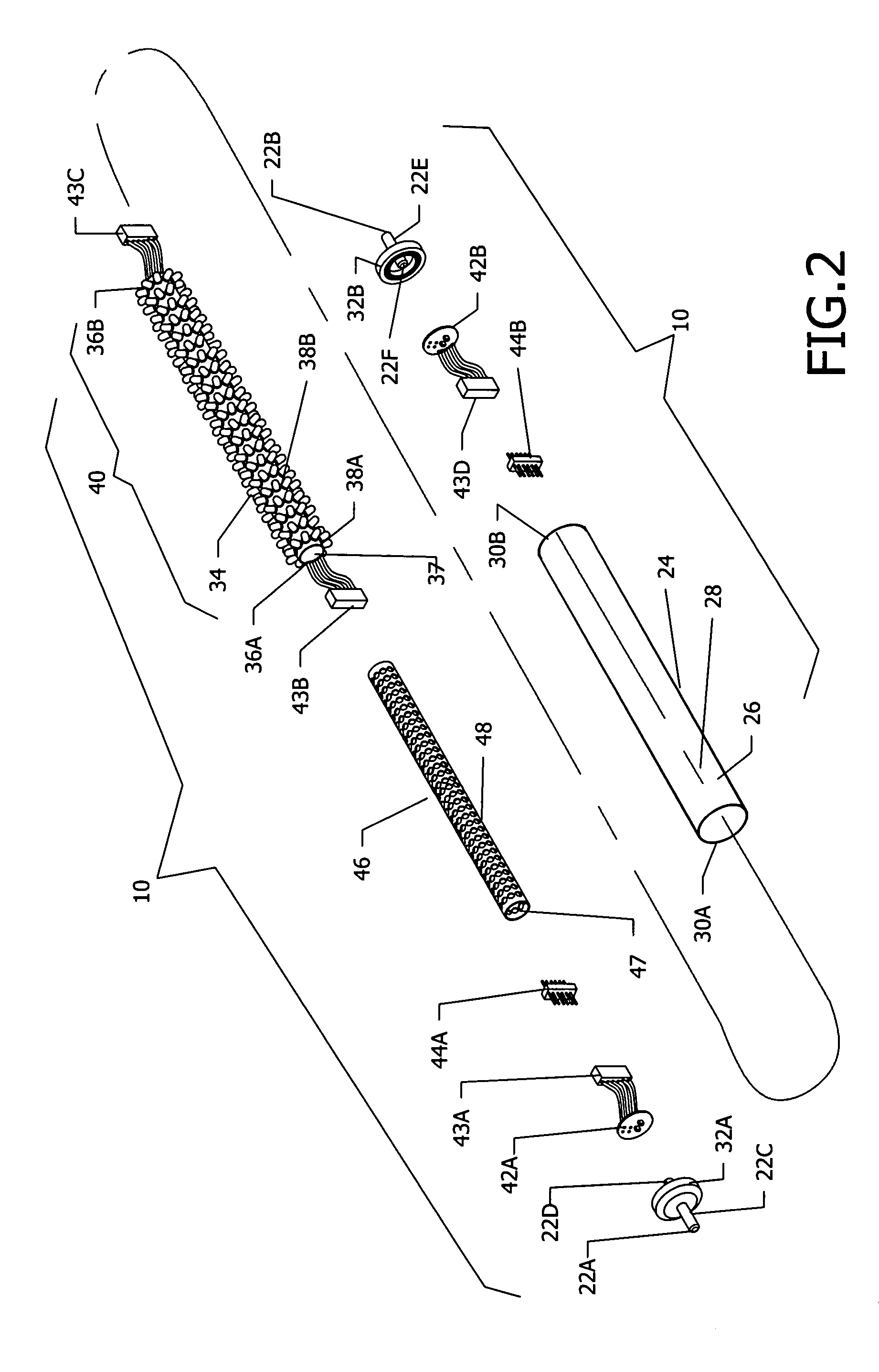
Edge-lit electronic-ink display device for use in indoor and outdoor environments
InactiveUS20100177076A1Easily identifiableCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingAmbient lightingControl signal
A wireless electronic-ink based display device for use in indoor and outdoor environments characterized by low and / or dynamic ambient lighting conditions. The wireless electronic-ink based display device has an ambient light level sensor for sensing ambient lighting conditions about the wireless electronic-ink based display device, and generating a drive control signal in response to sensed ambient lighting conditions. The wireless electronic-ink based display device also has an edge-lit LED-based illumination module, responsive to the drive control signal generated by the ambient light level sensor, for illuminating the display surface of its addressable electronic-ink display module during low-illumination ambient lighting conditions detected by the ambient light level sensor, under the control of a processor. In the illustrative embodiment, the processor runs a firmware routine which analyzes detected ambient light conditions made by the ambient light level sensor, and automatically generates the drive control signal provided to the edge-lit LED illumination module.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Retrofit LED lamp for fluorescent fixtures without ballast
ActiveUS20070228999A1Increase costLow costLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceFluorescenceNetwork communication
An energy saving device for an LED lamp mounted to an existing fixture for a fluorescent lamp where the ballast is removed or bypassed. The LEDs are positioned within a tube and electrical power is delivered from a power source to the LEDs. The LED lamp includes means for controlling the delivery of the electrical power from the power source to the LEDs, wherein the use of electrical power can be reduced or eliminated automatically during periods of non-use. Such means for controlling includes means for detecting the level of daylight in the illumination area of said least one LED, in particular a light level photosensor, and means for transmitting to the means for controlling relating to the detected level of daylight from the photosensor. The photosensor can be used in operative association with an on-off switch in power connection to the LEDs, a timer, or with a computer or logic gate array in operative association with a switch, timer, or dimmer that regulates the power to the LEDs. An occupancy sensor that detects motion or a person in the illumination area of the LEDs can be also be used in association with the photosensor and the computer, switch, timer, or dimmer, or in solo operation by itself. Two or more such LED lamps with a computer or logic gate array used with at least one of the lamps can be in network communication with at least one photosensor and / or at least one occupancy sensor to control the power to all the LEDs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Retrofit LED lamp for fluorescent fixtures without ballast
ActiveUS7507001B2Reduce flickerReduce usageLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceFluorescenceNetwork communication
An energy saving device for an LED lamp mounted to an existing fixture for a fluorescent lamp where the ballast is removed or bypassed. The LEDs are positioned within a tube and electrical power is delivered from a power source to the LEDs. The LED lamp includes means for controlling the delivery of the electrical power from the power source to the LEDs, wherein the use of electrical power can be reduced or eliminated automatically during periods of non-use. Such means for controlling includes means for detecting the level of daylight in the illumination area of said least one LED, in particular a light level photosensor, and means for transmitting to the means for controlling relating to the detected level of daylight from the photosensor. The photosensor can be used in operative association with an on-off switch in power connection to the LEDs, a timer, or with a computer or logic gate array in operative association with a switch, timer, or dimmer that regulates the power to the LEDs. An occupancy sensor that detects motion or a person in the illumination area of the LEDs can be also be used in association with the photosensor and the computer, switch, timer, or dimmer, or in solo operation by itself. Two or more such LED lamps with a computer or logic gate array used with at least one of the lamps can be in network communication with at least one photosensor and / or at least one occupancy sensor to control the power to all the LEDs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
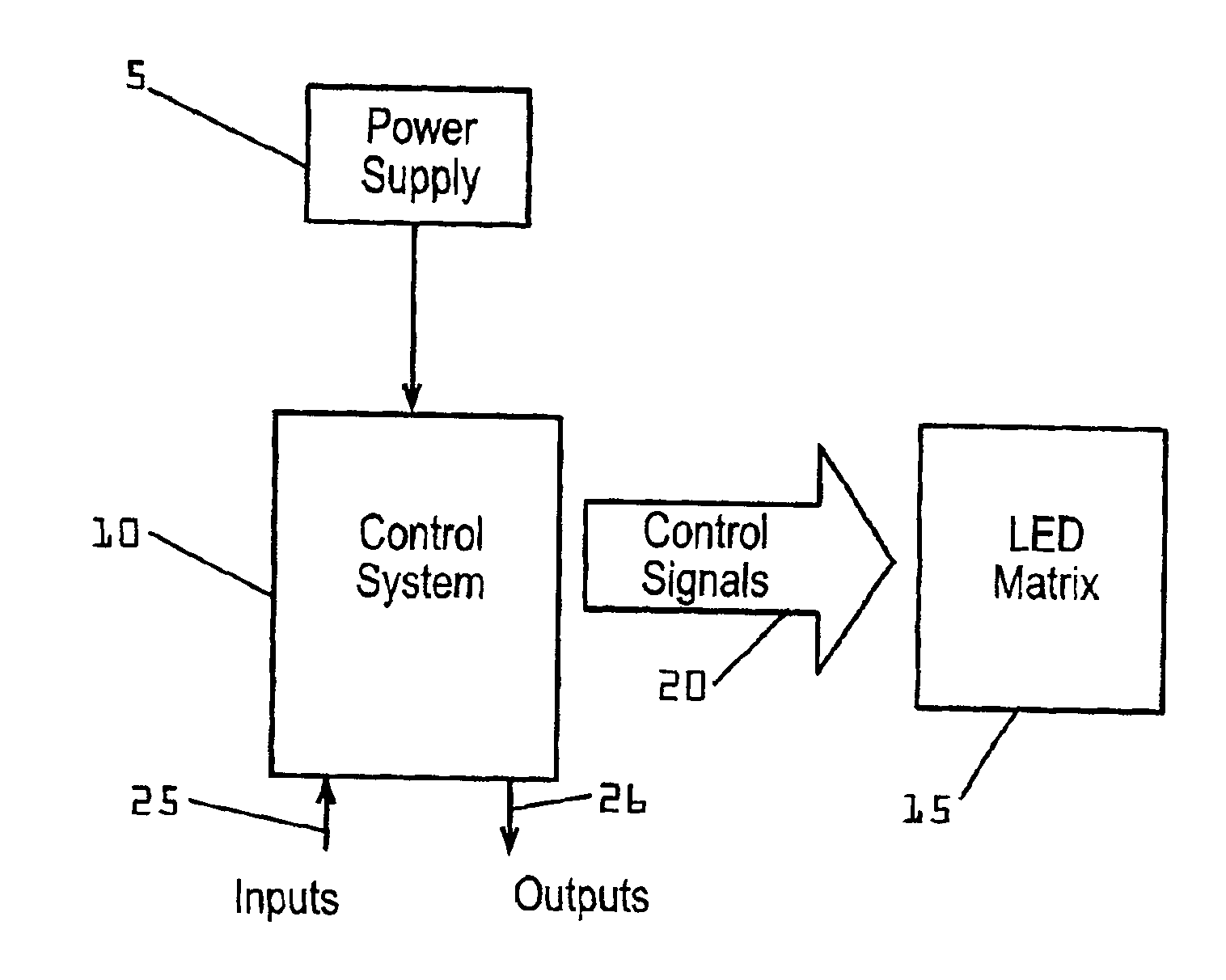
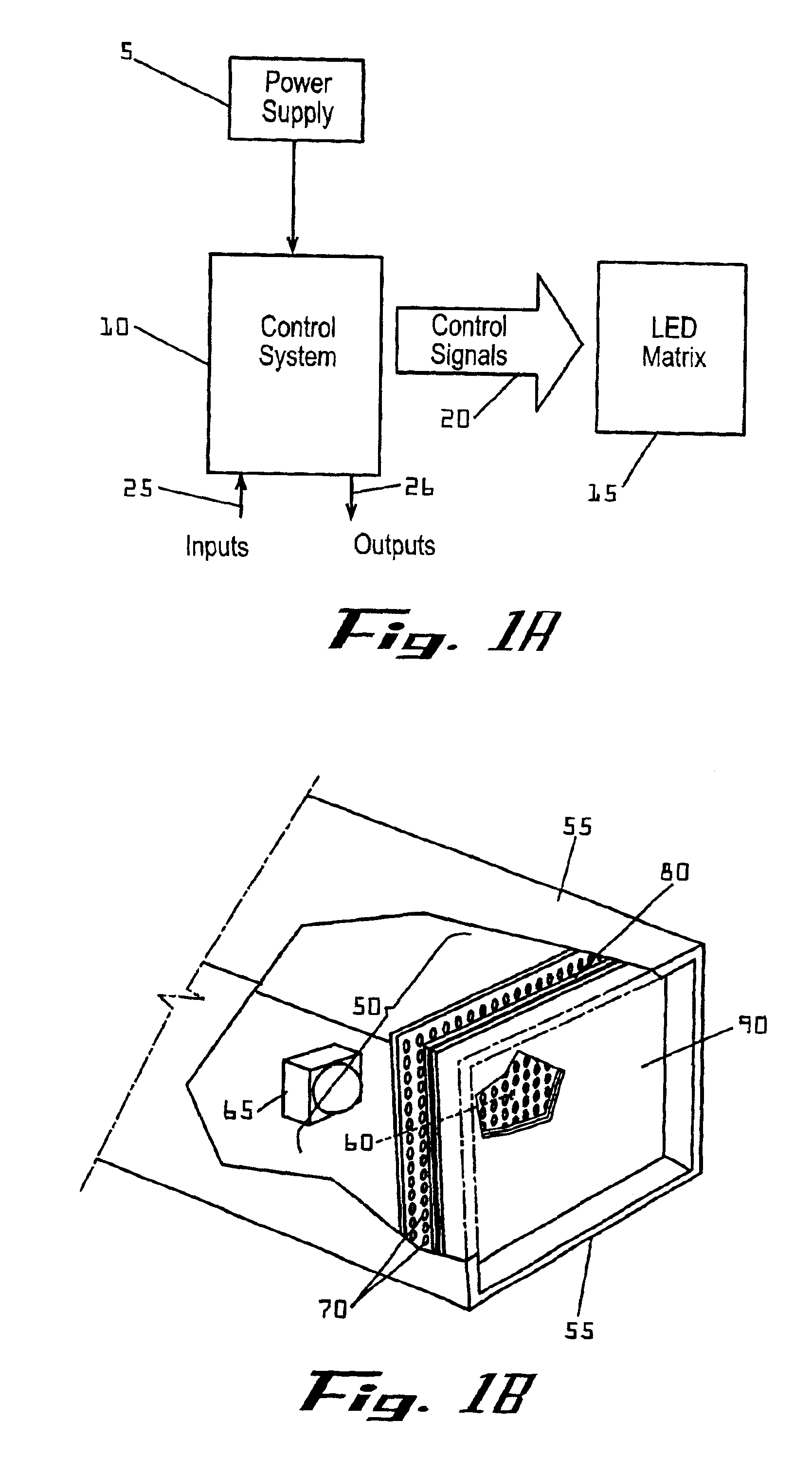
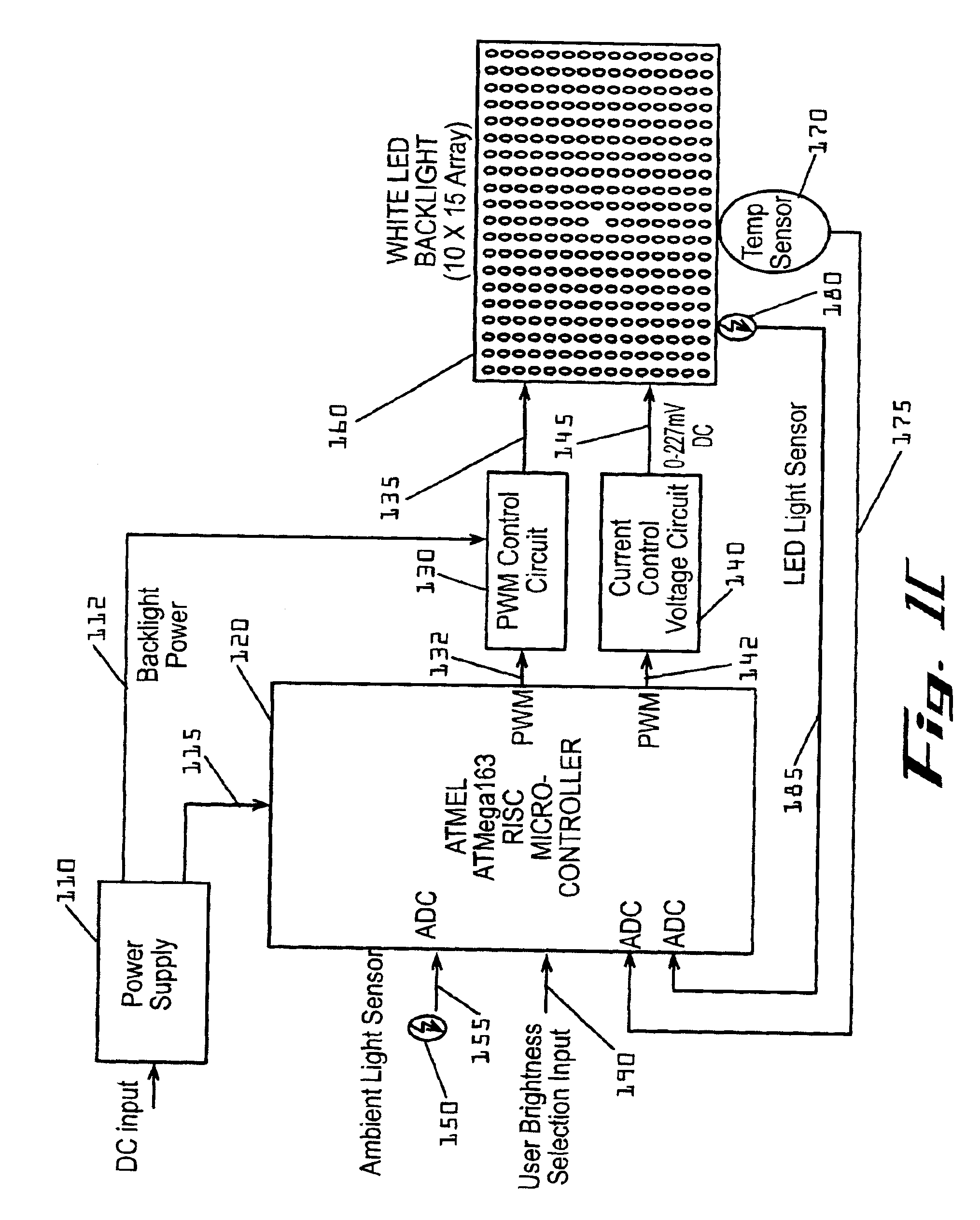
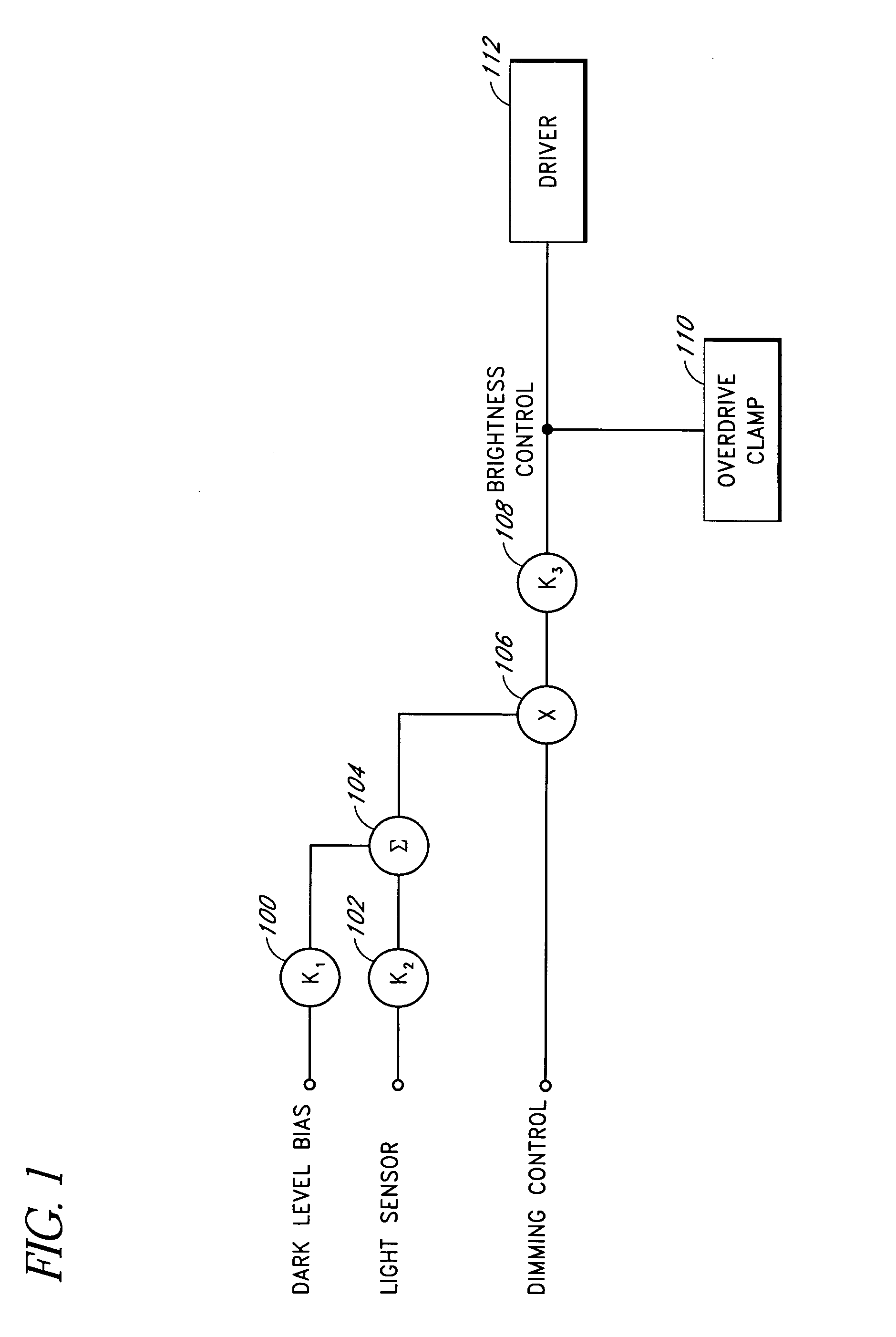
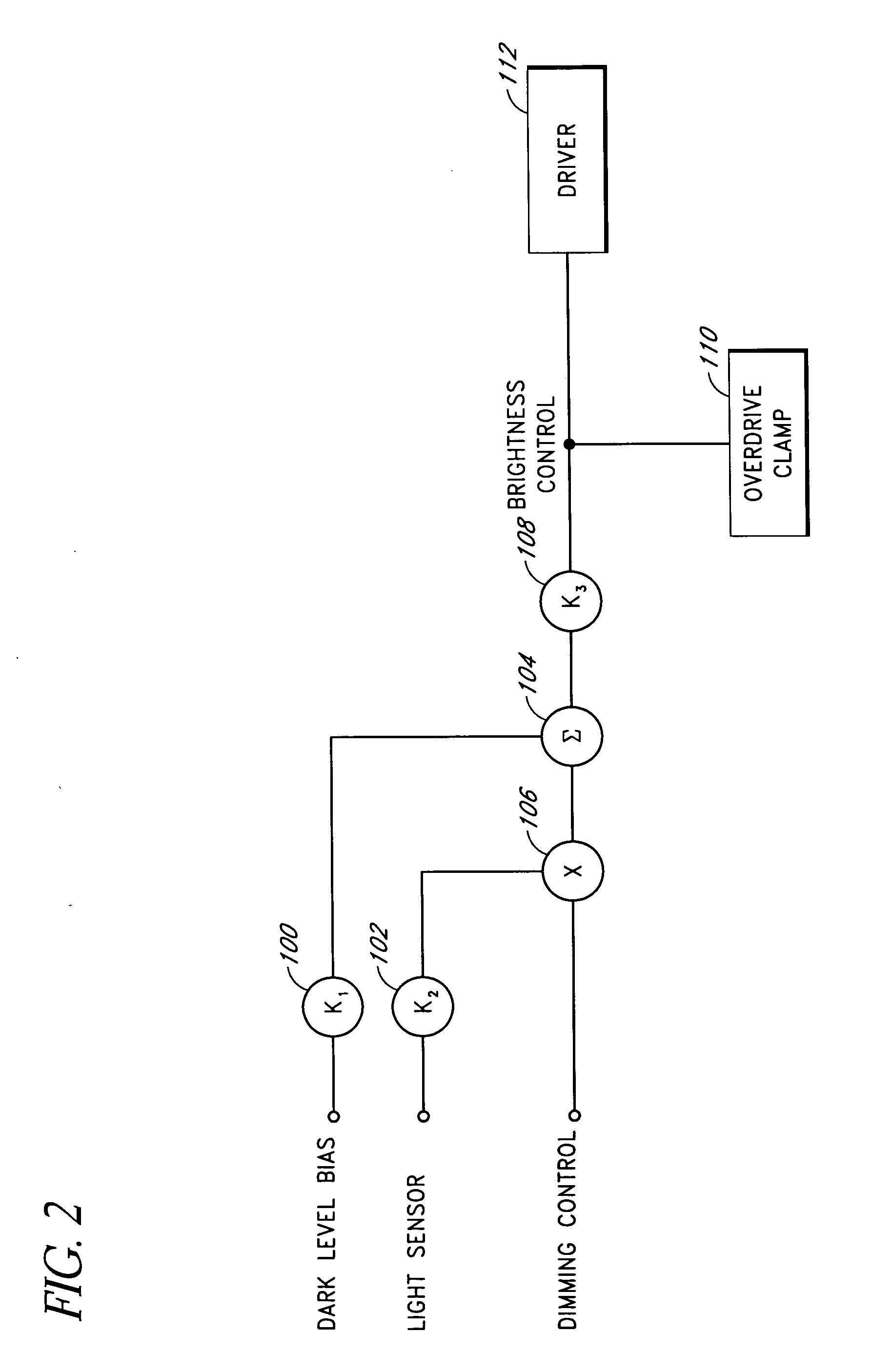
Systems and methods for controlling brightness of an avionics display
InactiveUS6841947B2Wide rangeAdversely effect readabilityElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesAmbient lightingDisplay device
The present invention provides for systems and methods for dimming a LED matrix functioning as a backlight to an avionics display. A system according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises a processor for receiving inputs of ambient lighting and temperature, as well as light generated by the LED matrix. The processor provides modulated pulse wave signals (square waves) to two control circuits for controlling the LED matrix in two modes. At low dimming levels, the processor modulates the duty cycle of a first square wave for affecting the light level and maintains a minimal duty cycle of a second square wave. Once the highest light level is obtained by increasing the duty cycle of the first square wave, the processor then modulates a second square wave by increasing its duty cycle. The duty cycle of the second square wave is modified by a circuit to produce a voltage level which is provided as an input to control light level of the LED matrix. As the duty cycle of the second signal is increased, so is the voltage level provided to the LED matrix and the light generated by the LED matrix.
Owner:GARMIN AT
System and method for adjusting display brightness levels according to user preferences
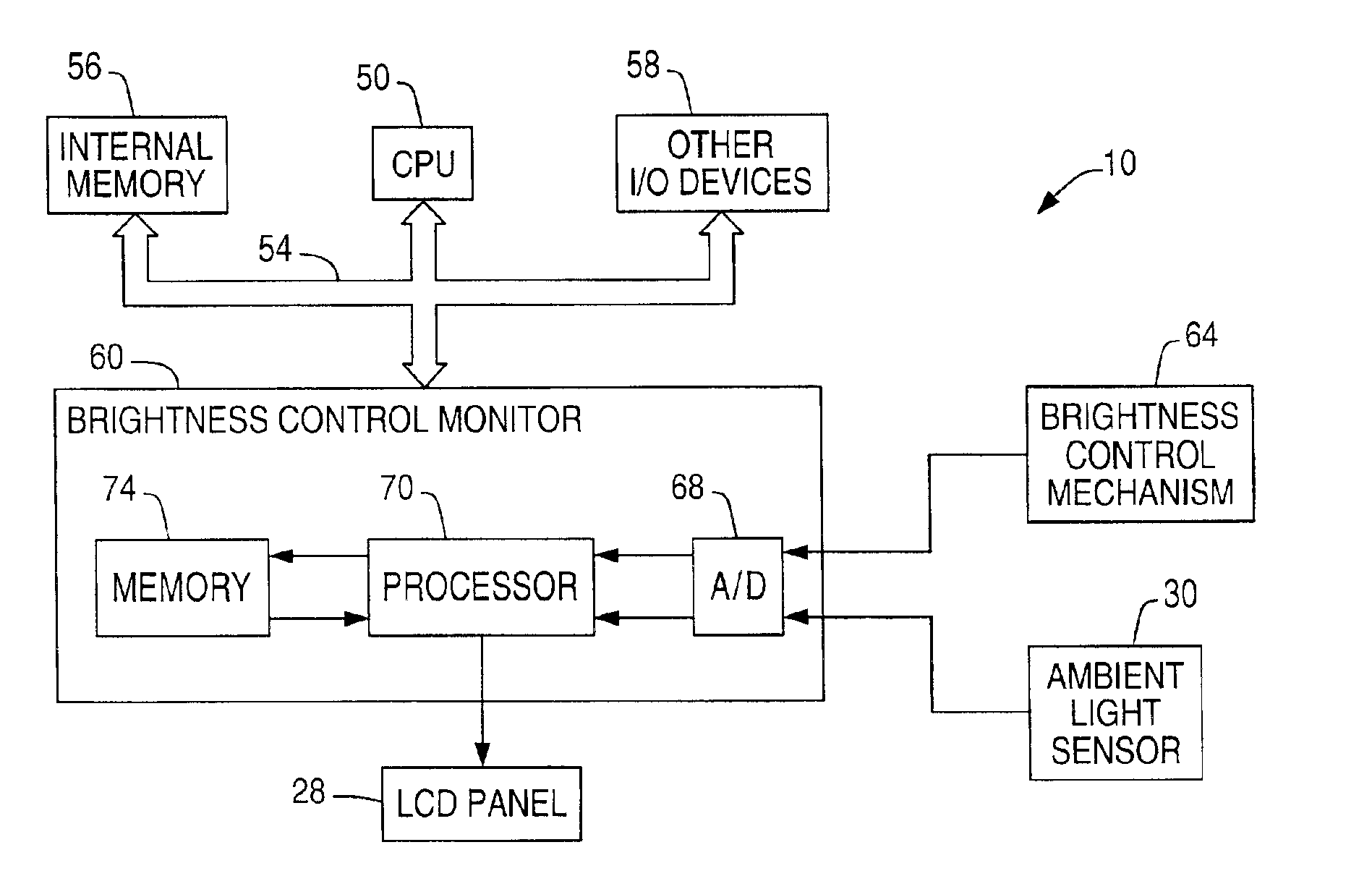
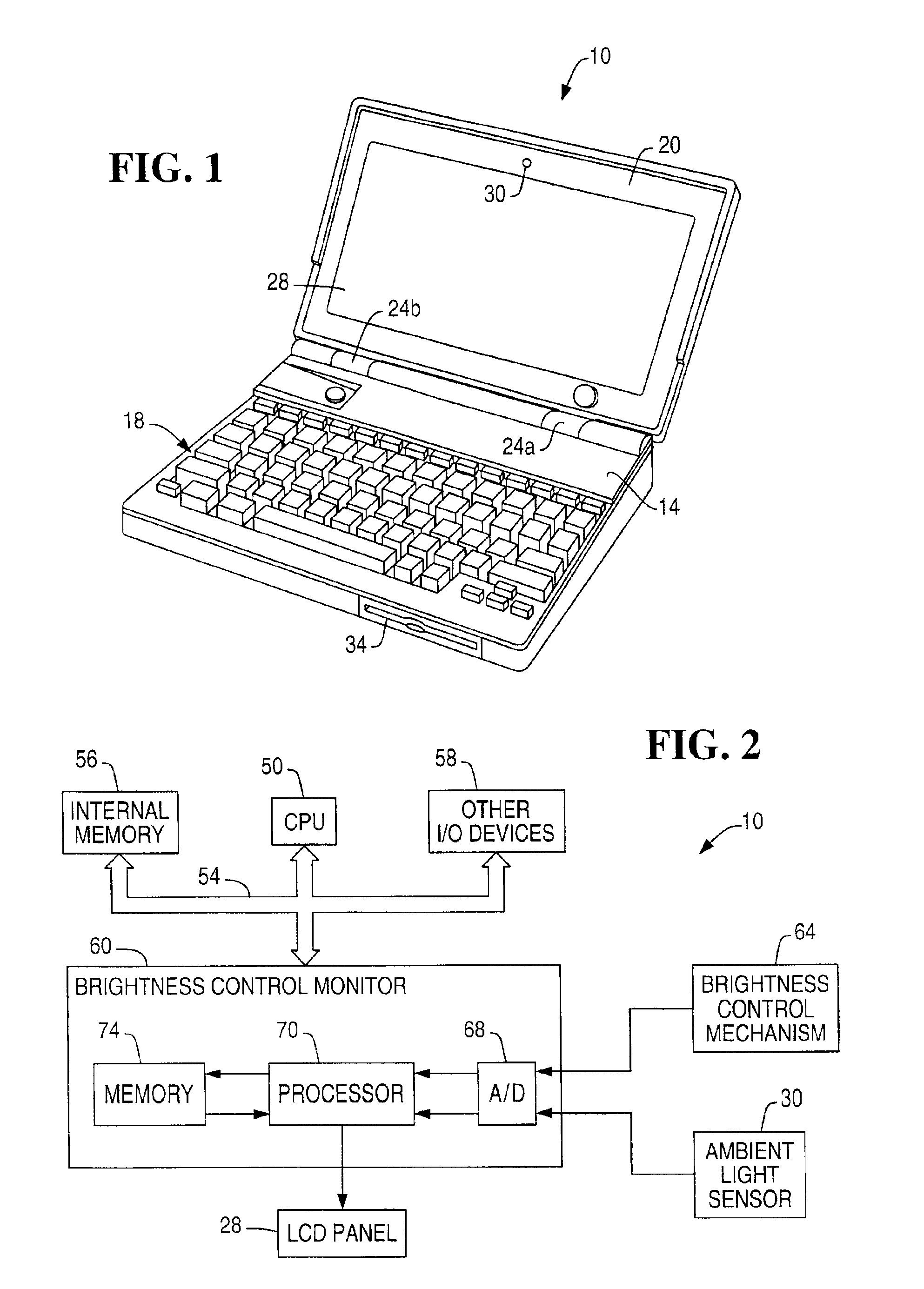
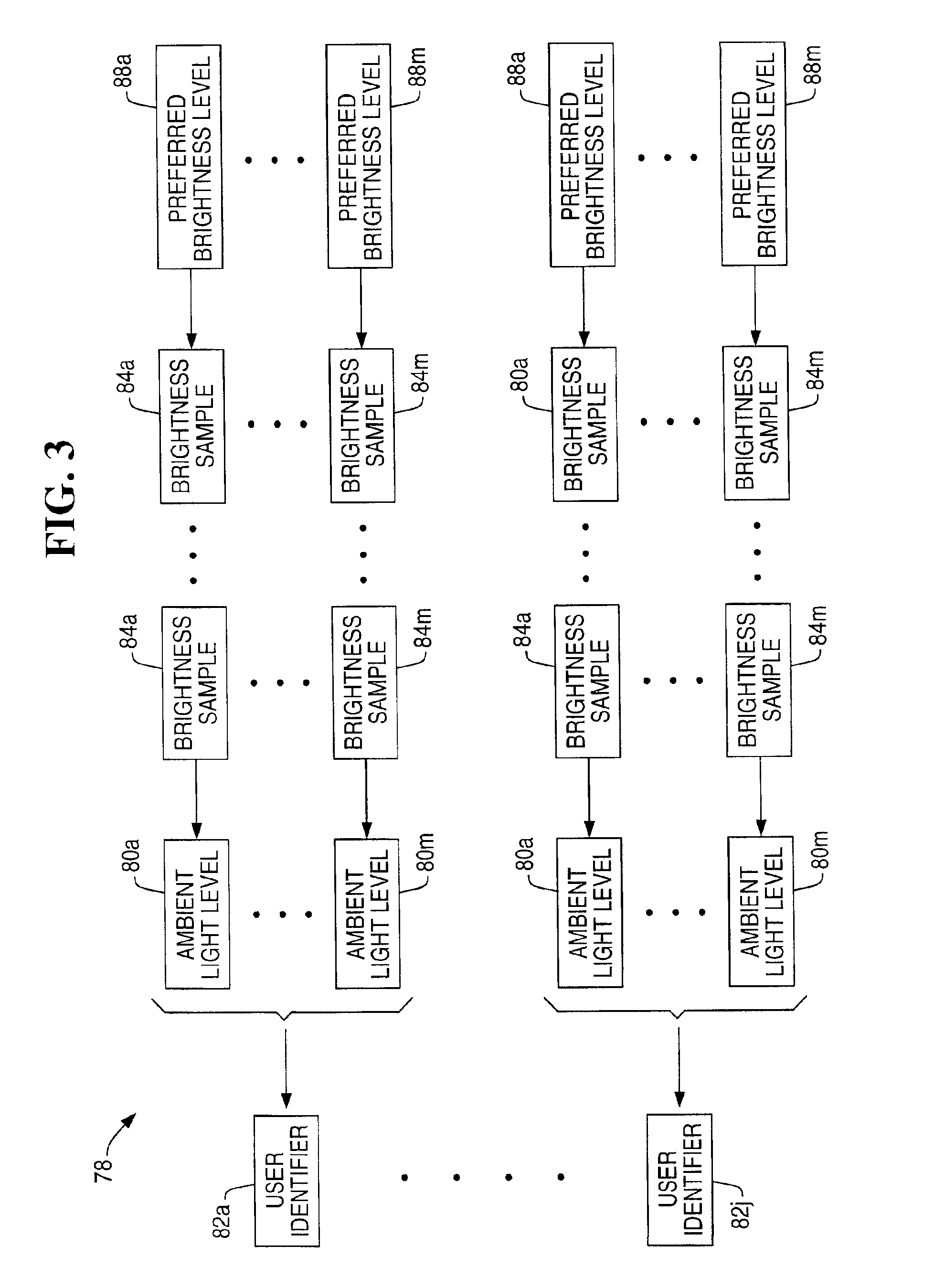
InactiveUS6870529B1Television system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Monitoring system
A display brightness monitoring system associates a brightness level and an ambient light level with a user identifier. Ambient light signals are received from an ambient light sensor mounted in proximity of an electronic display. Brightness levels are received from a brightness control mechanism for user selection of a display brightness. The monitoring system collects brightness levels and associates them with one of the ambient light levels associated with a user identifier. Preferably, a plurality of brightness levels are collected for each ambient light level and are used to compute a preferred brightness level indicative of a user's preferred display brightness for a given ambient light level. The brightness levels may be statistically averaged for computation of the brightness level. A data structure for associating brightness levels with ambient light levels and associating ambient light levels with a user identifier may be used to segregate one user's brightness levels from those of another. In this manner, the display may be driven using the preferred brightness levels for the user authorized to use a computer without altering the brightness levels stored for other users.
Owner:NCR CORP
Vehicle vision system
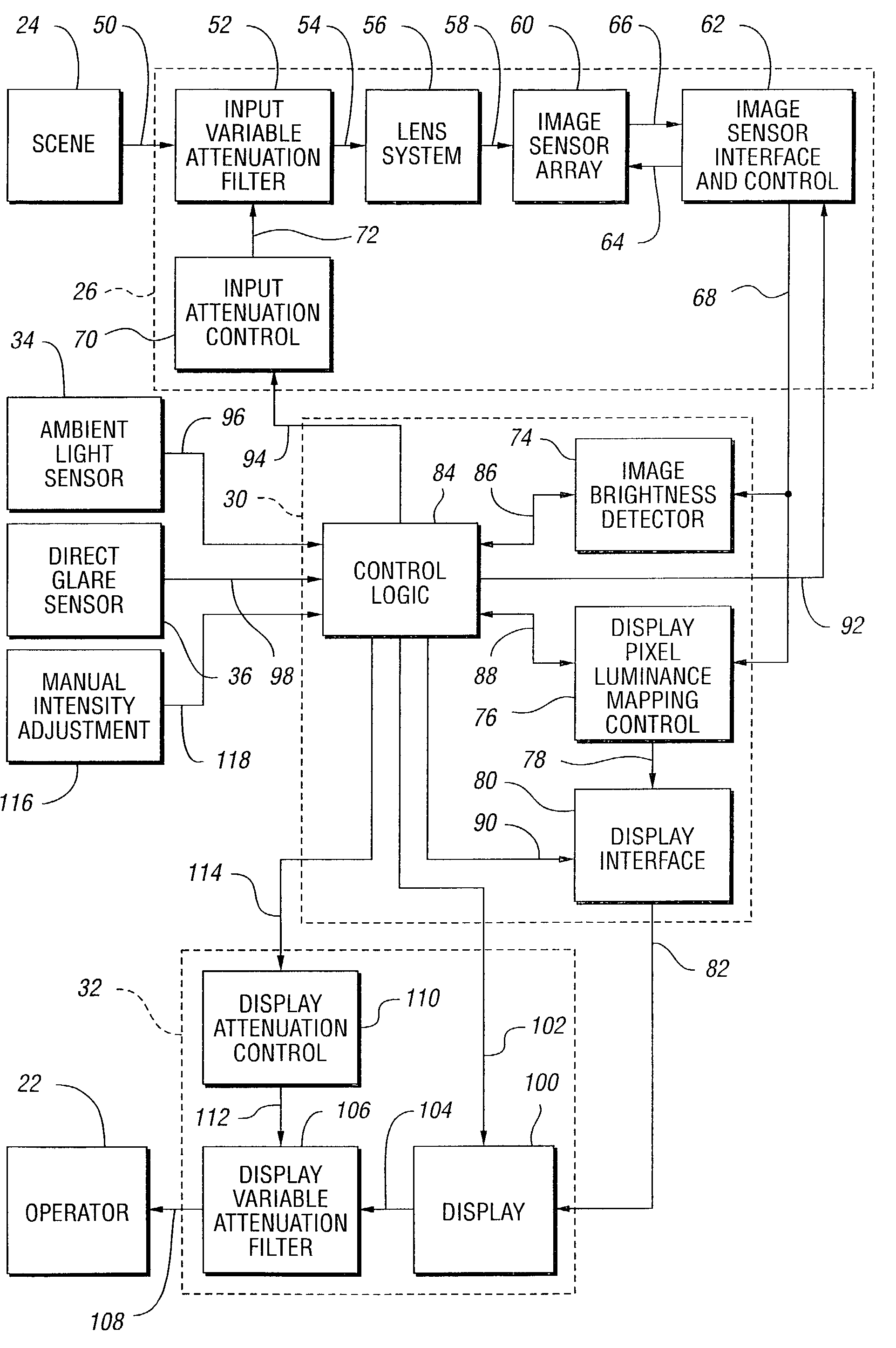
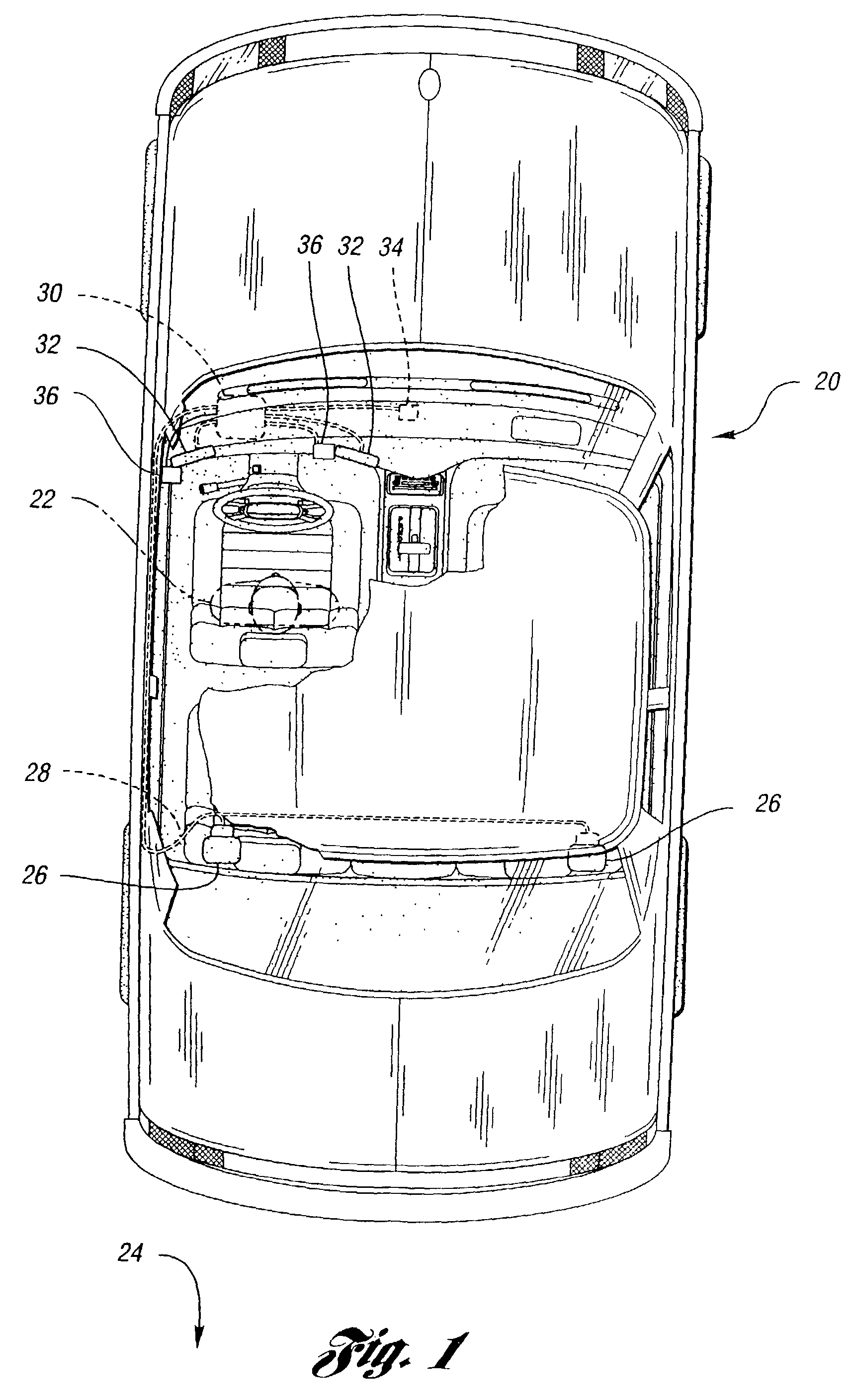
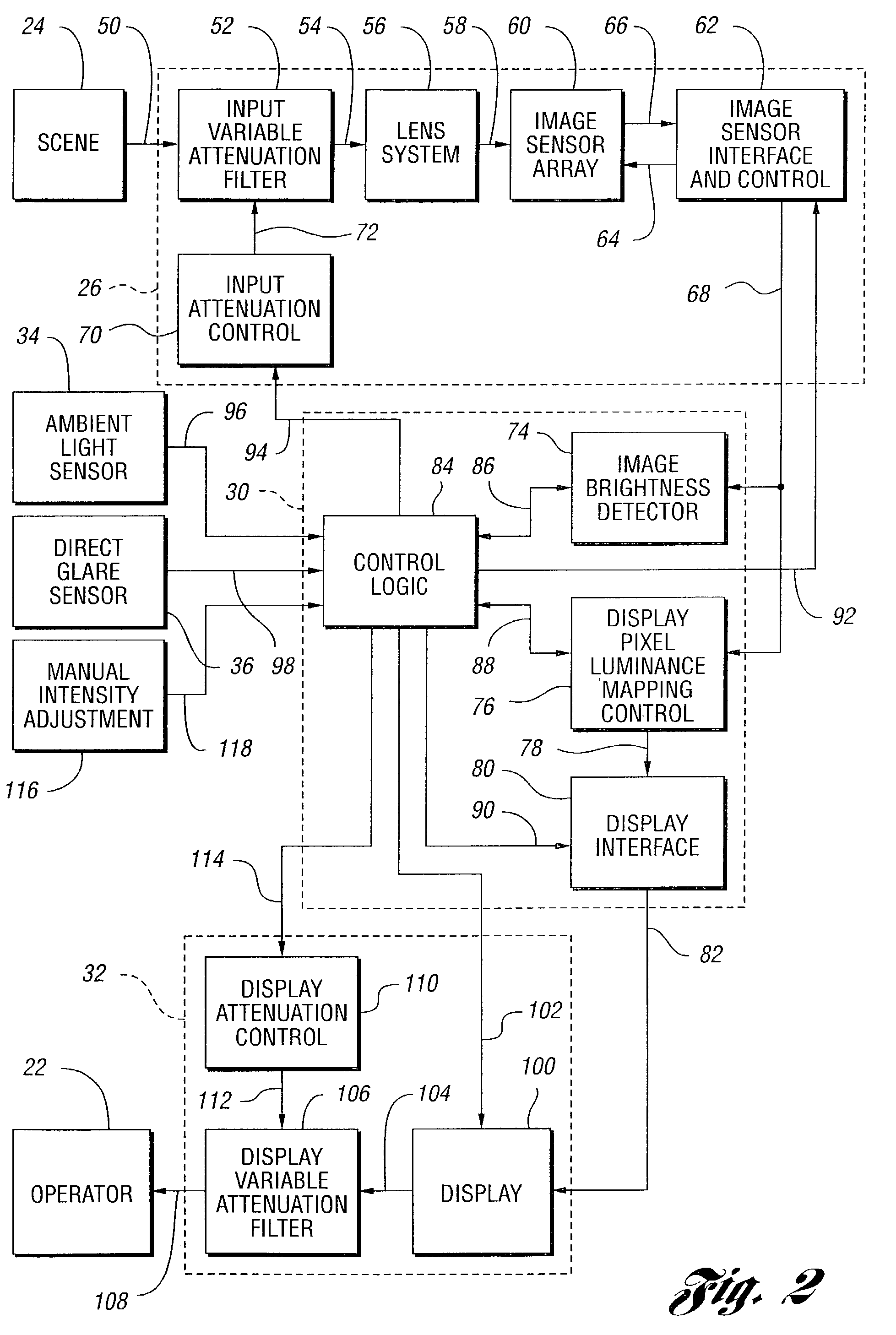
InactiveUS7567291B2Increase brightnessMinimal exposureTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDisplay deviceObservation system
A vehicle viewing system including a camera system for generating a signal corresponding to a scene by integrating light from the scene incident on pixel cells having a variable integration time, a display system for presenting a visual representation of the scene, and a processor system operable to determine the camera system integration time based on brightness levels in the scene. The camera system preferably includes and an input attenuating filter to limit light striking the optical array. The processor system includes an image brightness detector to determine overall image brightness and a display control to determine luminance settings for the display system. The processor system may determine the intensity of the display system based on the brightness of the scene, ambient light levels, and glare on the display. The display system includes a display and a display attenuation filter for limiting the intensity as viewed by the operator.
Owner:GENTEX CORP +1
Daylight control system device and method
ActiveUS7190126B1Simple and reliable processEasy to useElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementElectricityTransceiver
A system and device for and a method of programming and controlling light fixtures is disclosed. A system in accordance with the present invention includes a stationary controller unit that is electrically coupled to the light fixtures. The stationary controller unit is configured to be remotely programmed with a portable commissioning device to automatically control the lights fixtures. The stationary controller unit and the portable commissioning device include light sensors, micro-computers and transceivers for measuring light levels, running programs, storing data and transmitting data between the stationary controller unit and the portable commissioning device. In operation, target light levels selected with the portable commissioning device and the controller unit is remotely programmed to automatically maintain the target level.
Owner:THE WATT STOPPER
Lighting systems and methods of auto-commissioning
ActiveUS20110031897A1Electric signal transmission systemsElectrical apparatusMicrocontrollerEngineering
A lighting system for areal illumination is disclosed which includes a remote driver and a plurality of fixtures including luminaires, control devices, and / or standalone sensors. The luminaires include a light source whose output light level can be adjusted, a light sensor co-located therewith adapted to measure light received from adjacent fixtures, and a microcontroller capable of transmitting the output of the light sensor over wires to the remote driver. The remote driver is capable of bidirectional communication with the luminaires and provides independently controllable power for the light sources of the luminaires. A method of commissioning a lighting system is also disclosed which includes installing a plurality of luminaires above the area to be illuminated, causing a light source co-located with each luminaire to emit a signal, detecting the signal at light sensors co-located with each luminaire, converting the signals obtained by the light sensors into distance measurements between luminaires, creating a map recording the relative location of luminaires, and assigning luminaires to groups based on their relative locations in the map. A movable orb region large enough to containing a plurality of luminaires can also be defined and the light levels of individual luminaires can be set according to a defined mathematical function of their location within the orb region, where the defined mathematical function sets light levels which vary from the center to the periphery of said orb region.
Owner:WTEC GMBH
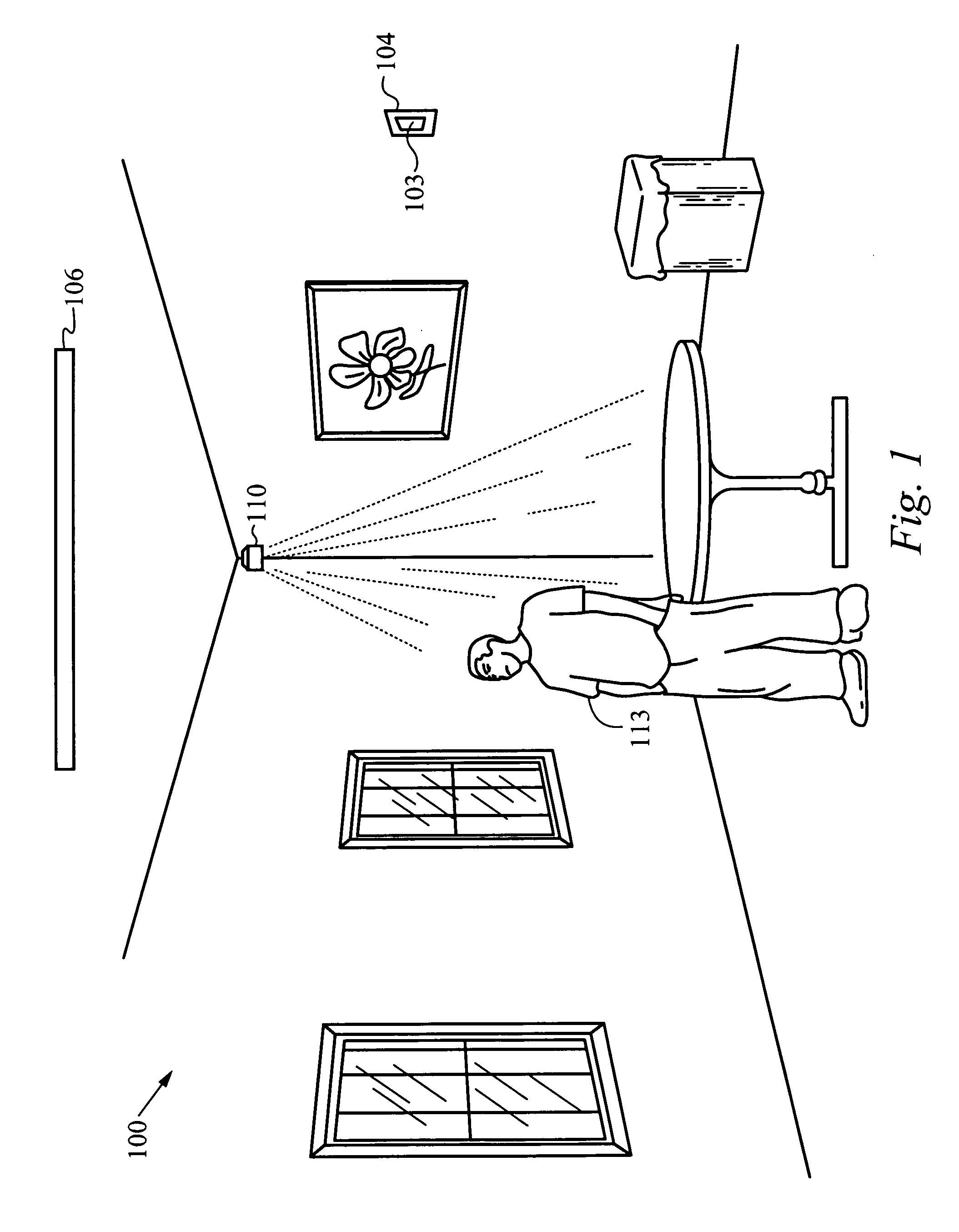
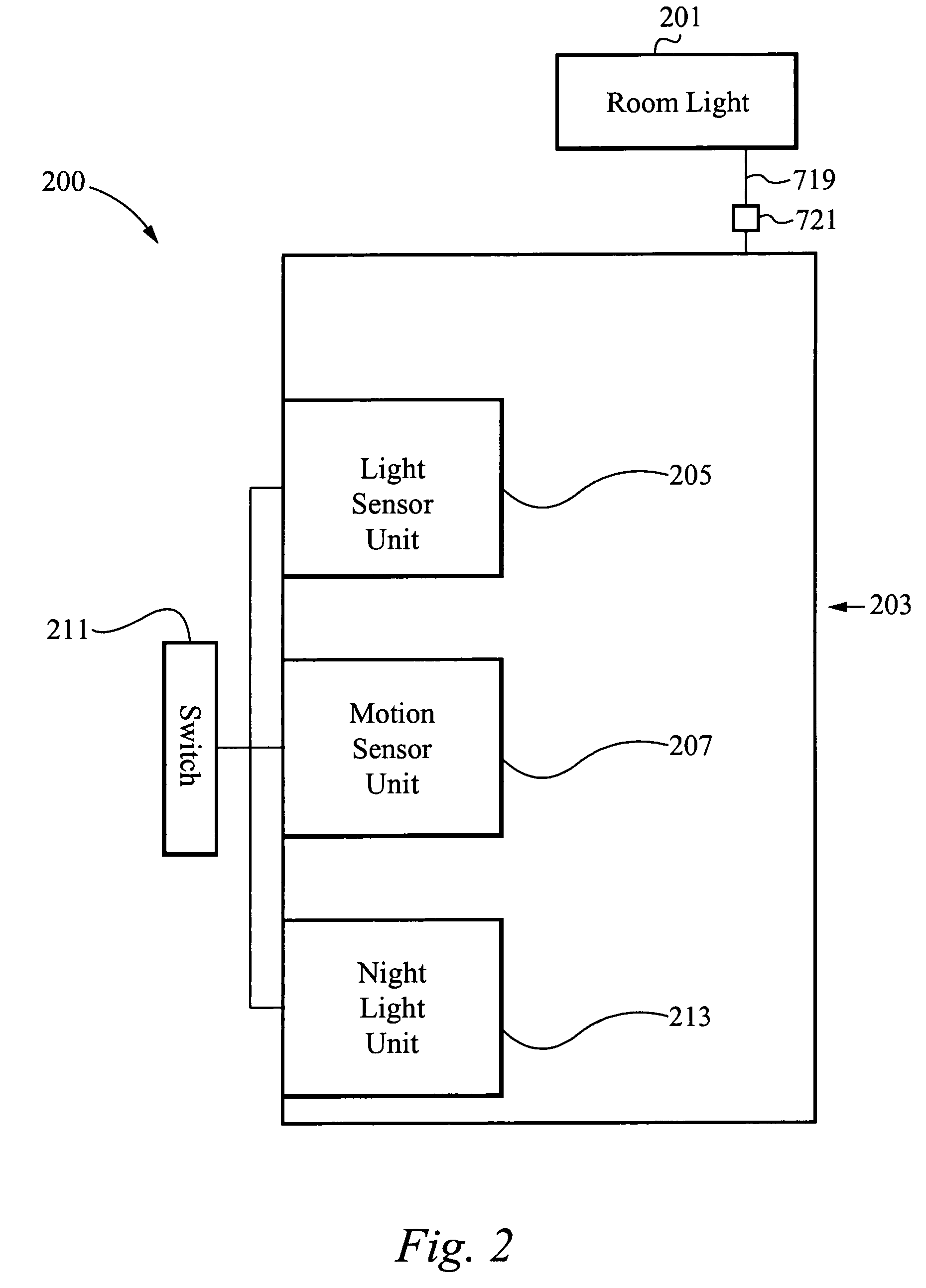
Light management system device and method
A lighting control system is disclosed. The lighting control system is electrically coupled to a load circuit for controlling indoor and / or outdoor lighting. The lighting control system includes a control module with a night light for providing low-level night light illumination and one or more sensors for operatively controlling the indoor and / or outdoor lighting and the night light in response to measured light levels and / or detected motion. The system is preferably configured to provide low-level night light from the night light when measured light levels and detected motion are below threshold values and to automatically turn on the indoor and / or outdoor lighting and simultaneously turn off the night light when measured light levels and detected motion are above the threshold values.
Owner:WATT STOPPER THE
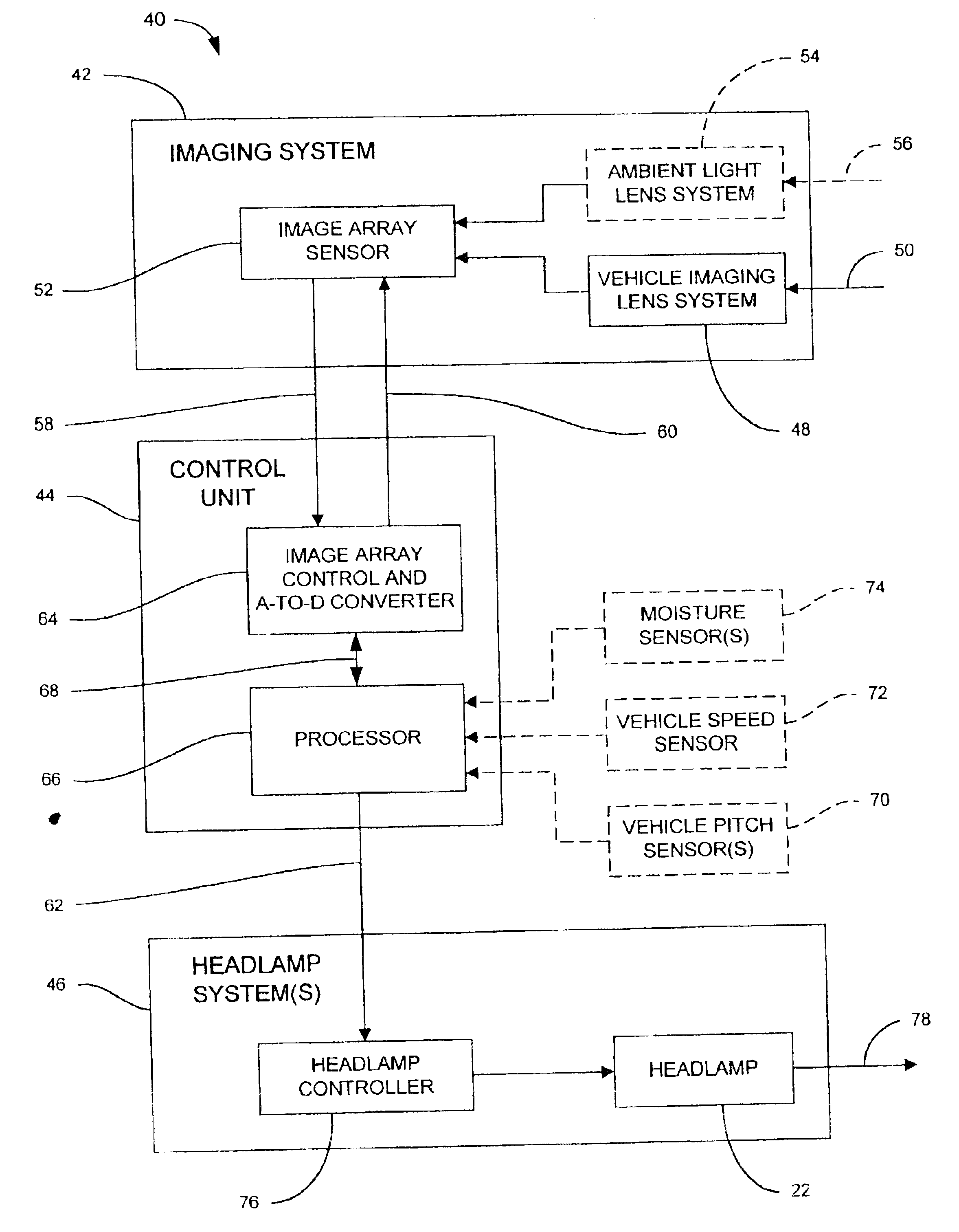
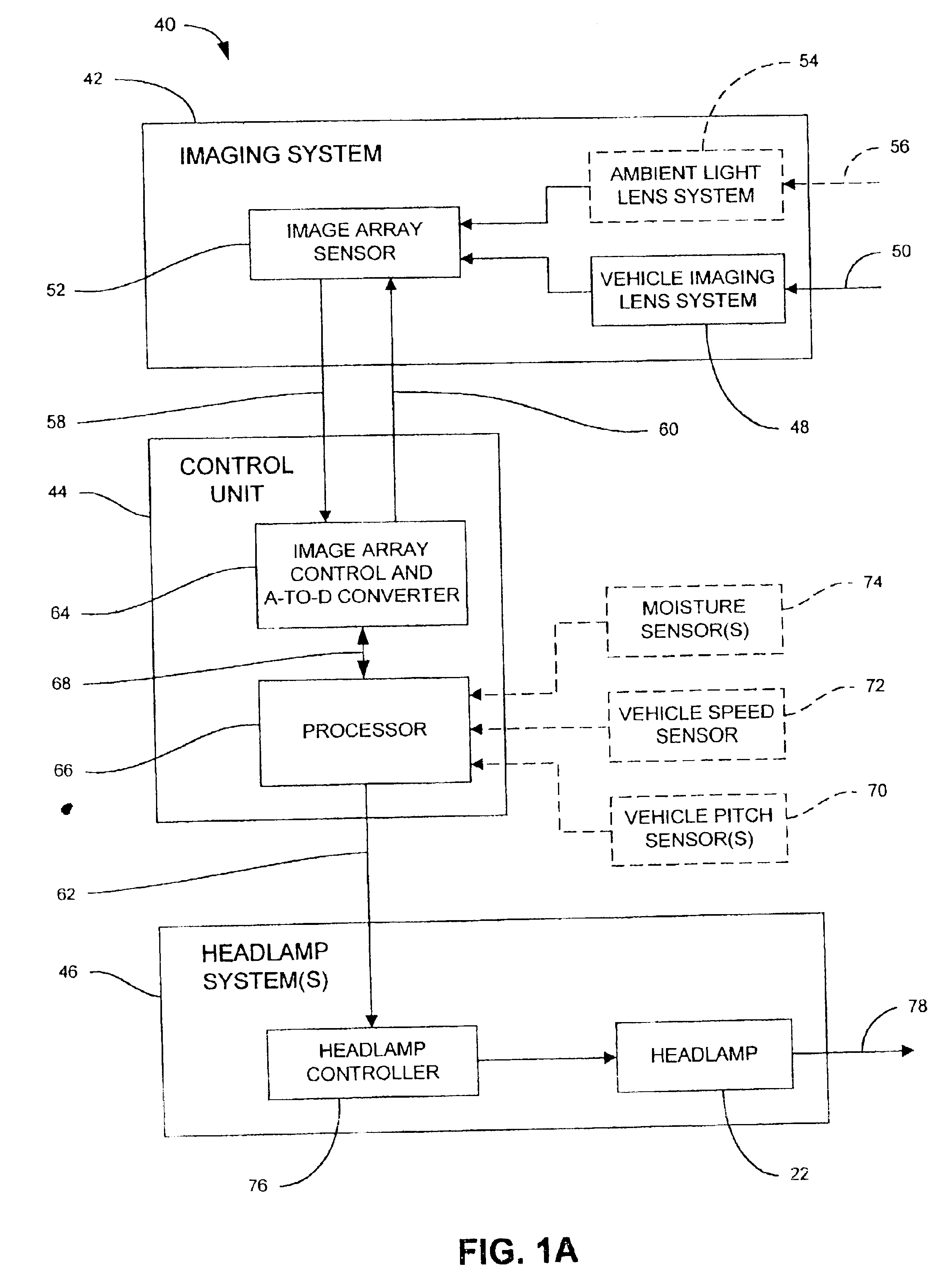
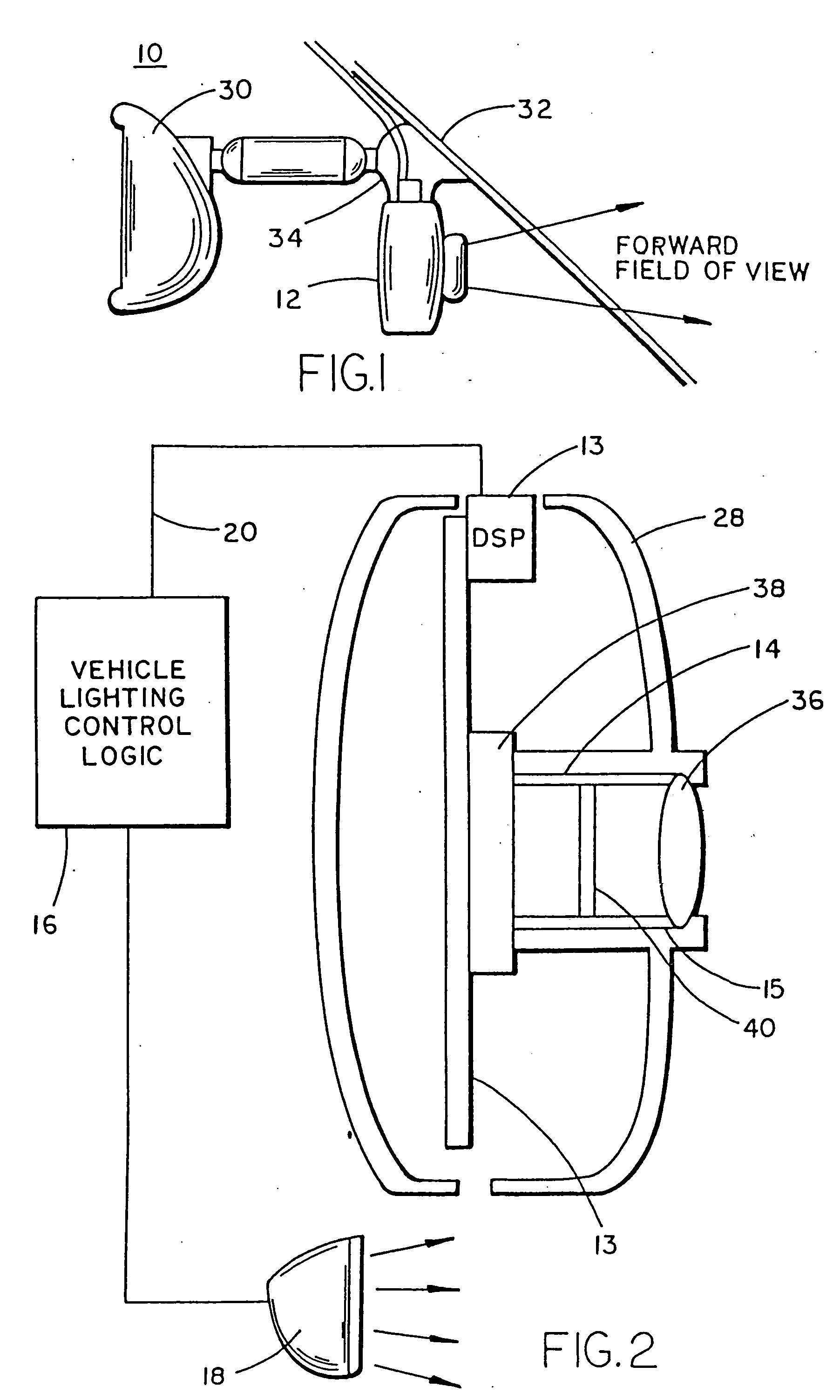
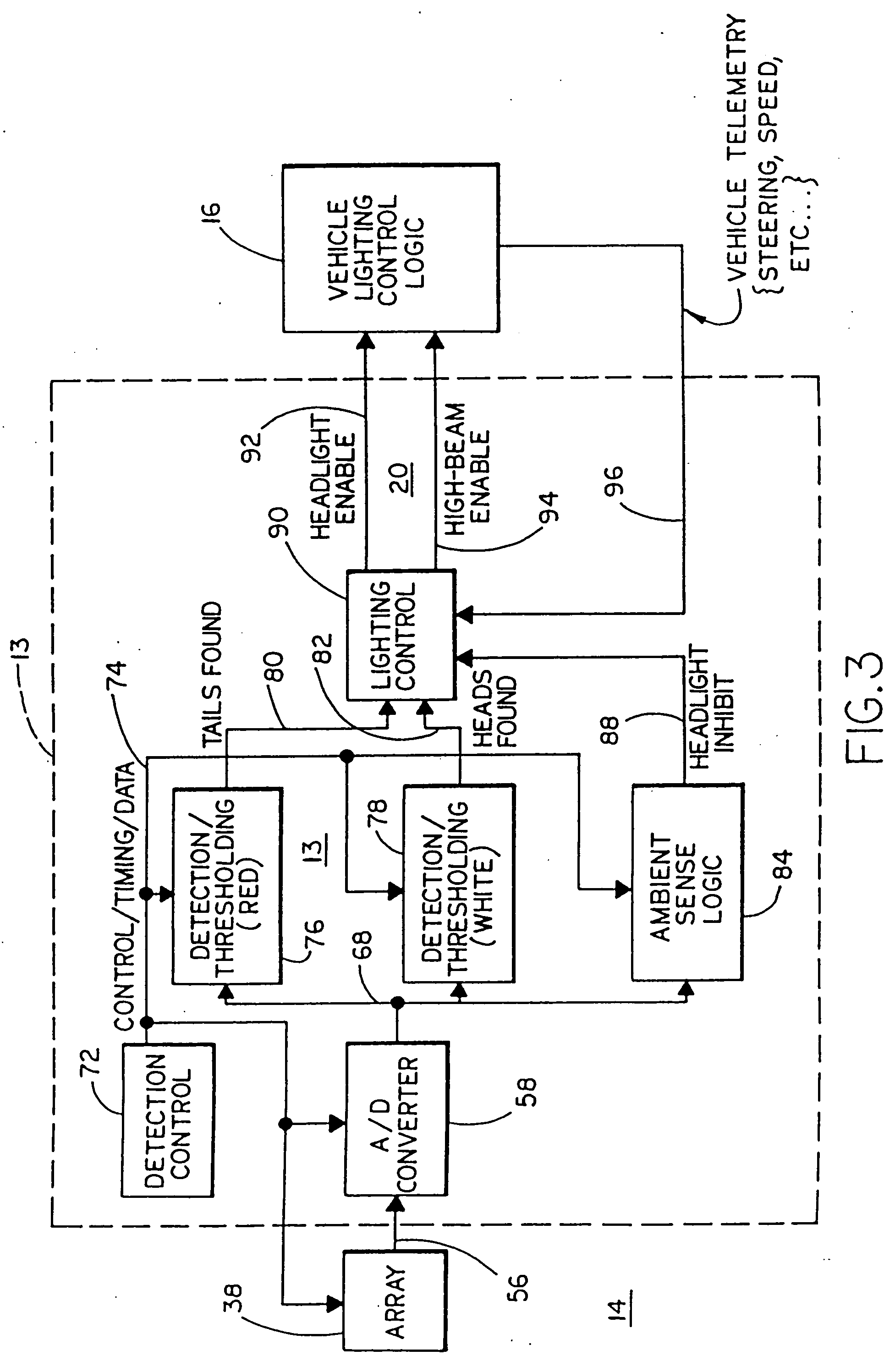
Headlamp control to prevent glare
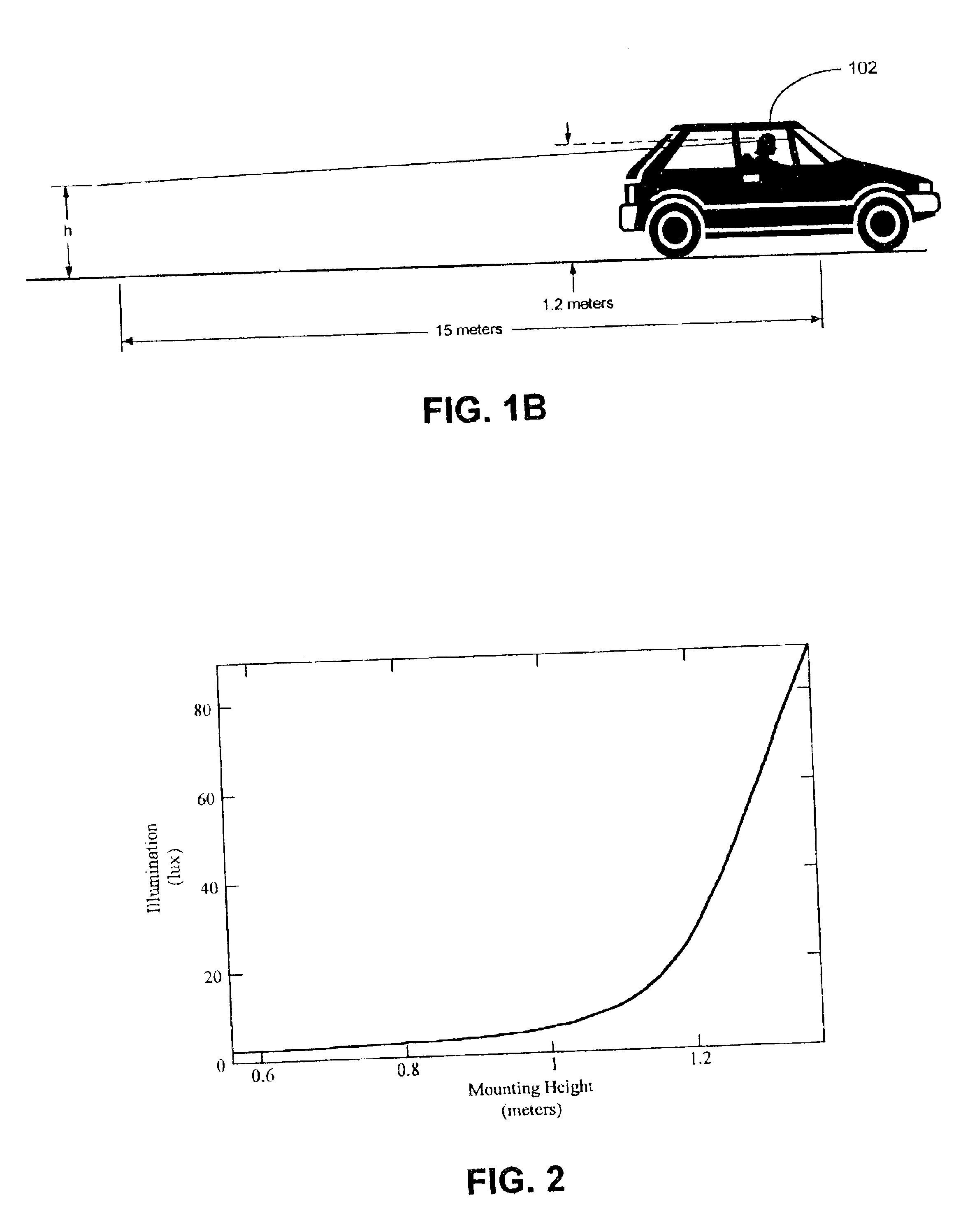
A system for controlling at least one exterior vehicle light of a controlled vehicle includes an array of sensors and a control unit. The array of sensors are capable of detecting light levels in front of the controlled vehicle. The control unit is in communication with the array of sensors and the at least one exterior vehicle light and determines a distance and an angle from the at least one exterior vehicle light of the controlled vehicle to a leading vehicle. The control unit is operable to control operation of the at least one exterior vehicle light as a function of the distance and angle, based on the output from the array of sensors, and prevent the at least one exterior vehicle light from providing a disruptive glare to a driver of the leading vehicle.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Electrochromic rearview mirror assembly incorporating a display/signal light
According to one embodiment of the present invention, an electrochromic rearview mirror assembly for a vehicle includes an electrochromic mirror having a variable reflectivity, a glare sensor for sensing levels of light directed towards the front element from the rear of the vehicle, an ambient sensor for sensing levels of ambient light, a display positioned behind the partially transmissive, partially reflective portion of the reflector for displaying information therethrough; and a control circuit coupled to the sensors and the display. The control circuit determines whether daytime or nighttime conditions are present as a function of the ambient light level sensed by the ambient sensor. During daytime conditions, the control circuit responds to light levels sensed by the glare sensor to control a contrast ratio of light originating from the display and light reflecting from the partially transmissive, partially reflective area of the reflector.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
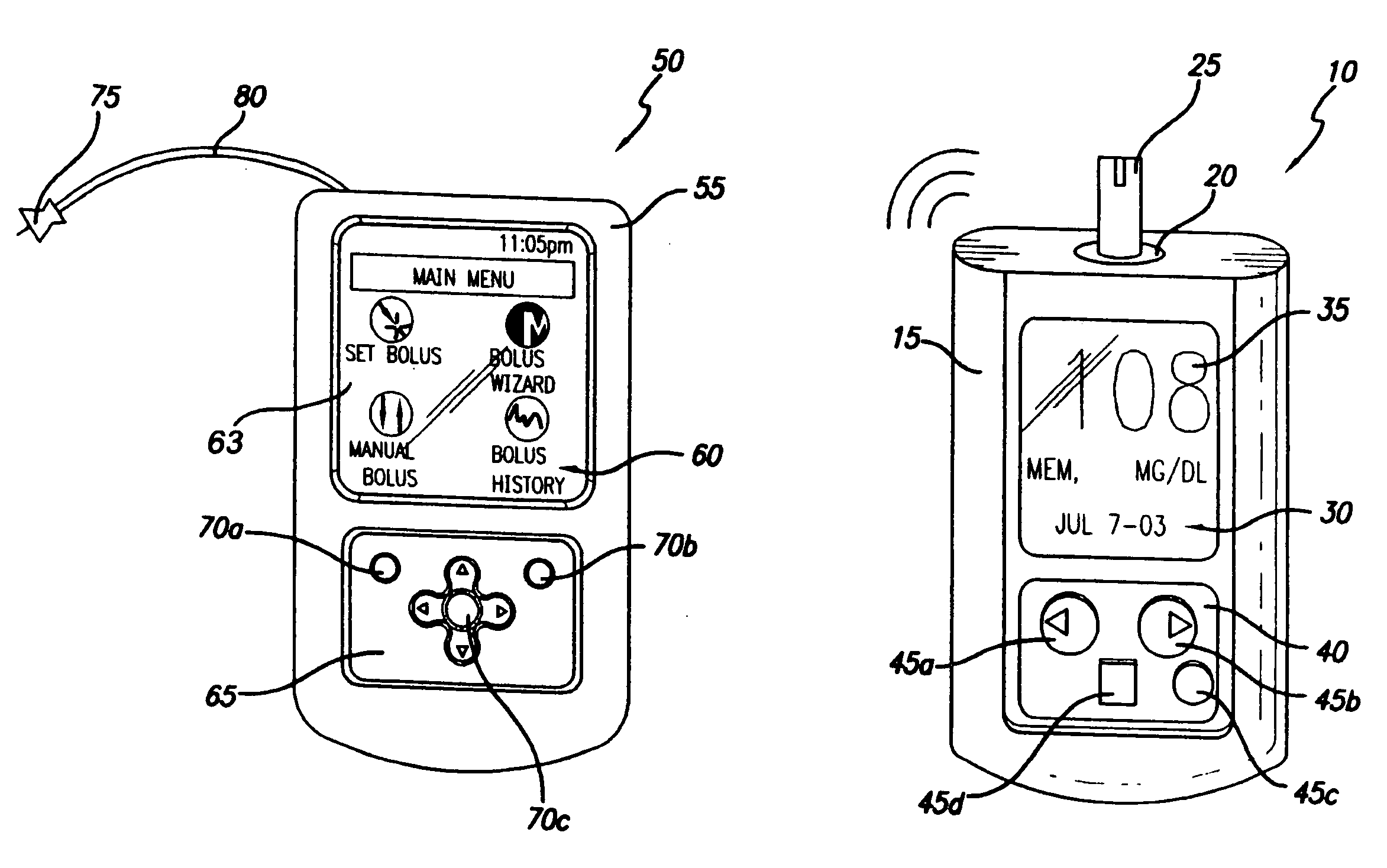
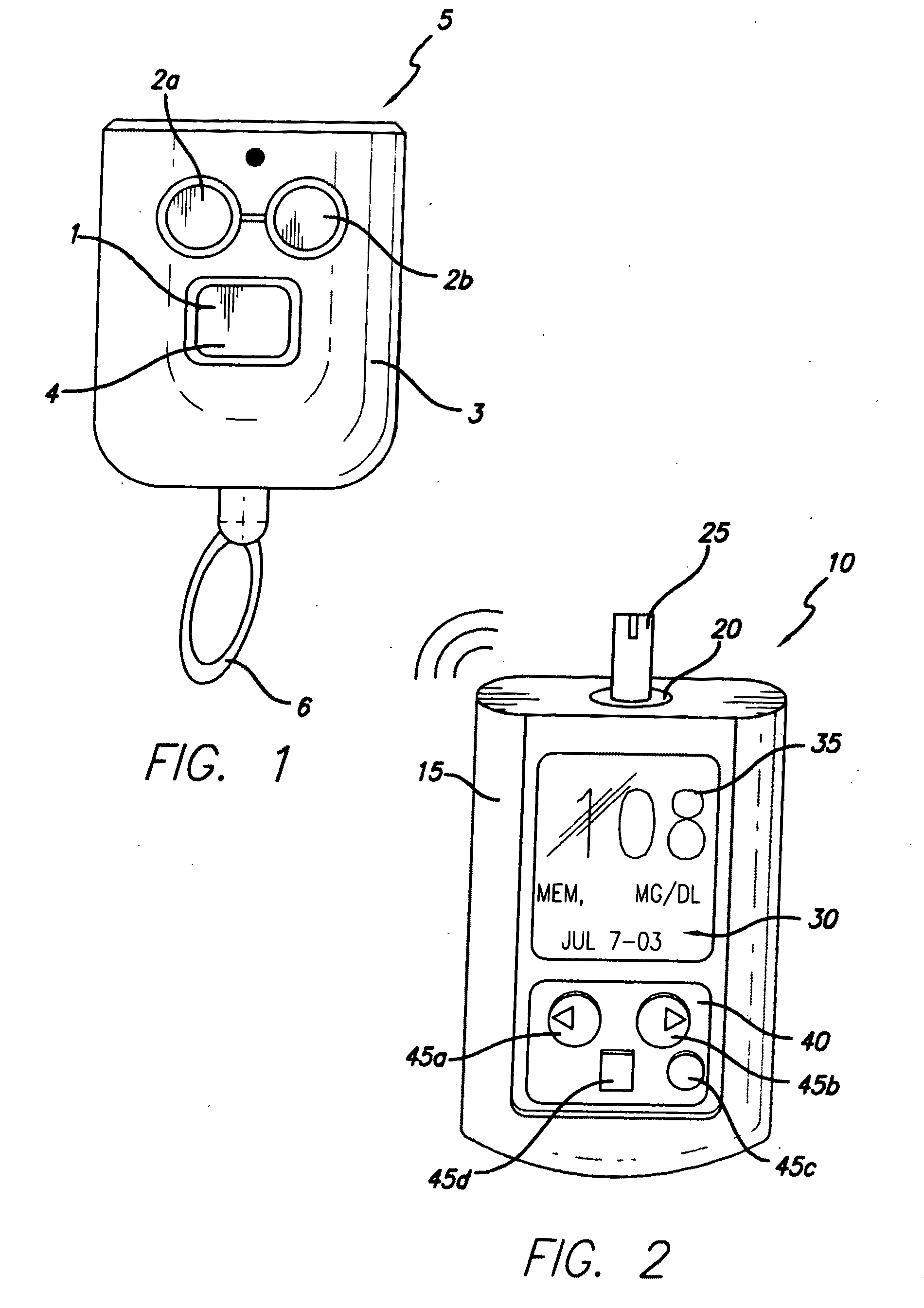
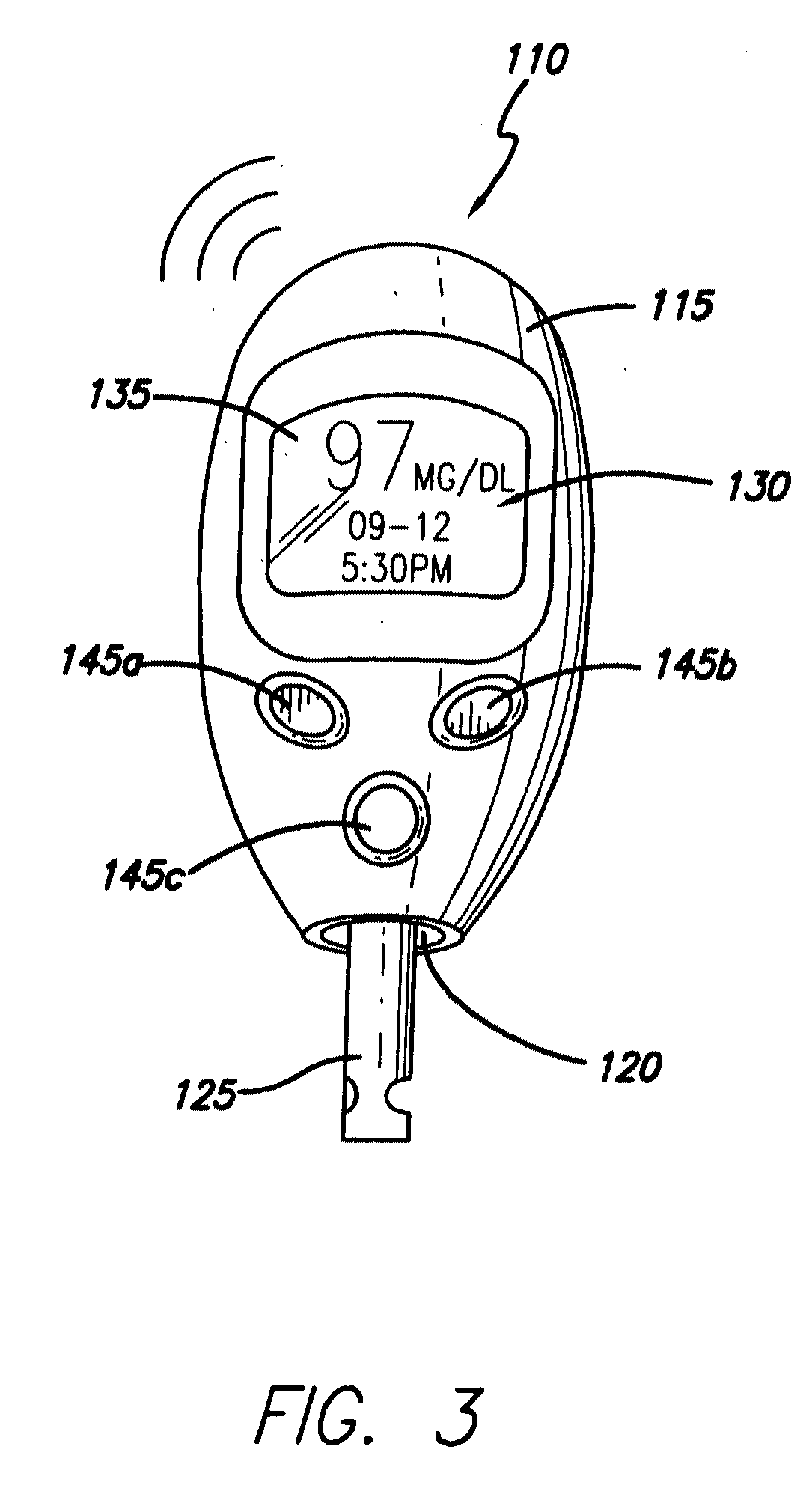
Controller device for an infusion pump
InactiveUS20090227855A1Minimizes potential for errorEasy to watchDrug and medicationsMedical devicesEngineeringInfusion pump
An infusion system that includes a controller device and a communication system to provide for two-way communication between the controller device and an infusion device that controls delivery of fluids to a user's body. Either the controller device or the infusion device may be integrated with a characteristic determining device in a single housing. The housing, in turn, may include a test-strip receptacle and an illuminator disposed so as to illuminate an area covering the receptacle and a test-strip inserted therein. The illuminator may be configured to be activated automatically when a test strip is inserted into the receptacle, selectively by the user via a button, key, or similar mechanism, and / or when the ambient light level, measured, e.g., with a light sensor, falls below a predetermined intensity. The illuminator may be a LED emitting white light, and may provide illumination at various levels of intensity.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Rearview assembly with display
InactiveUS20090201137A1Spread the wordDegradation of display imageMirrorsOptical signallingDisplay deviceControl circuit
A rearview assembly for a vehicle includes a mirror element having a partially reflective, partially transmissive coating and a video display positioned behind the mirror element such that a display image is viewable through the partially reflective, partially transmissive coating. The video display may generate a viewable display image that has an intensity of at least 250 cd / m2. The video display may generate a display image that extends along and abuts at least a portion of curved edges of a housing. The assembly may include a forward facing light sensor for sensing a first light level forward of the vehicle, a rearward facing light sensor sensing a second light level to the rear of the vehicle, and a control circuit for comparing the first and second light levels and generating a warning signal when the second light level exceeds the first light level by at least threshold amount.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS INC
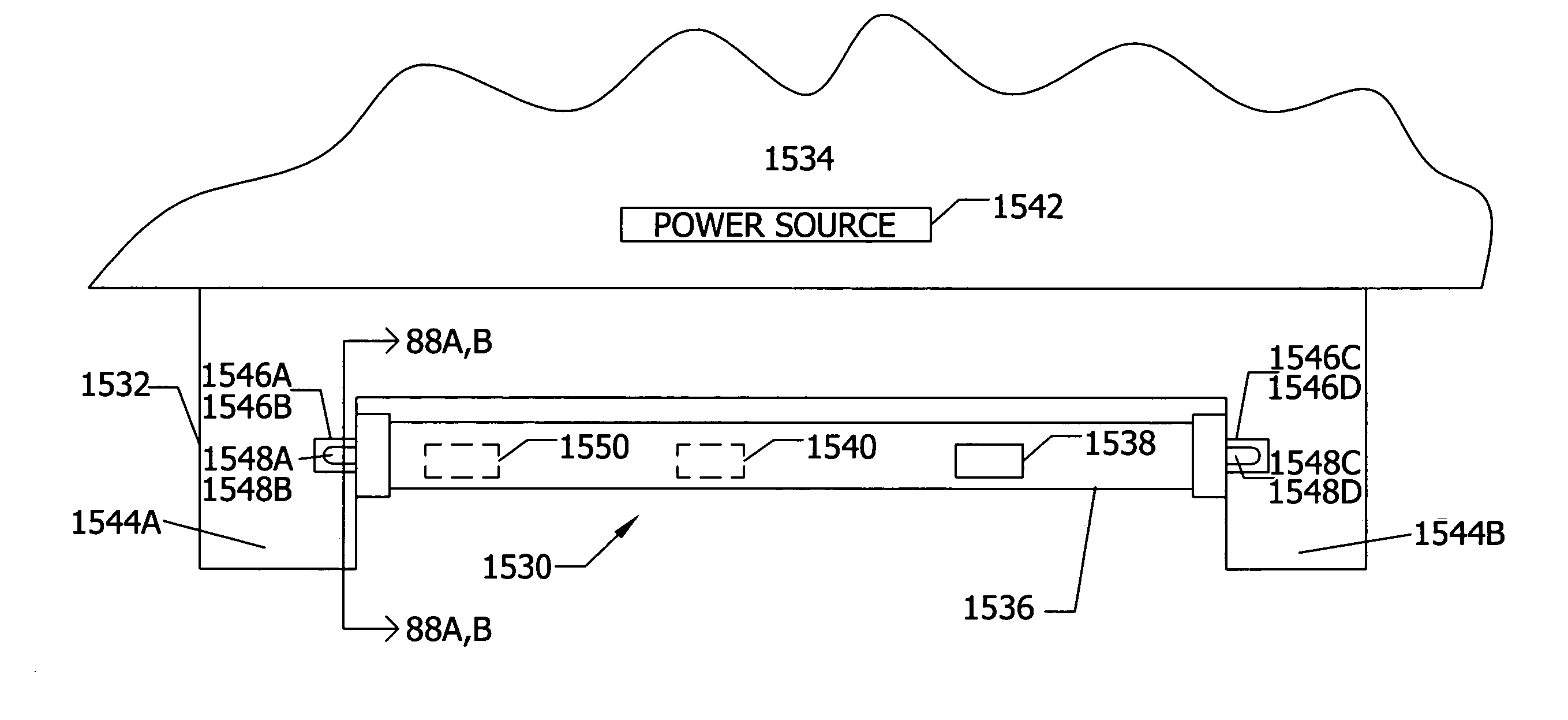
Power controls with photosensor for tube mounted LEDs with ballast
InactiveUS20050281030A1Easy to controlReduce flickerPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesControl signalNetwork communication
A power saving device for a light emitting diode (LED) lamp mounted to an existing fixture for a fluorescent lamp having a ballast assembly and LEDs positioned within a tube and electrical power delivered from the ballast assembly to the LEDs. The LED lamp includes means for controlling the delivery of the electrical power from the ballast assembly to the LEDs wherein the use of electrical power can be reduced or eliminated automatically during periods of non-use. Such means for controlling include means for detecting the level of daylight in the illumination area of said least one LED in particular a light level photosensor and means for transmitting to the means for controlling a control signal relating to the detected level of daylight from the photosensor. The photosensor can be used in operative association with an on-off switch in power connection to the LEDs, or with a computer or logic gate array in operative association with a dimmer that controls the power to the LEDs. An occupancy sensor that detects motion or a person in the illumination area of the LEDs can be optionally used in association with the photosensor and the computer and dimmer. Two or more such LED lamps with one or more computers or logic gate arrays can be in network communication with the photosensors and the occupancy sensors to control the power to the LEDs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
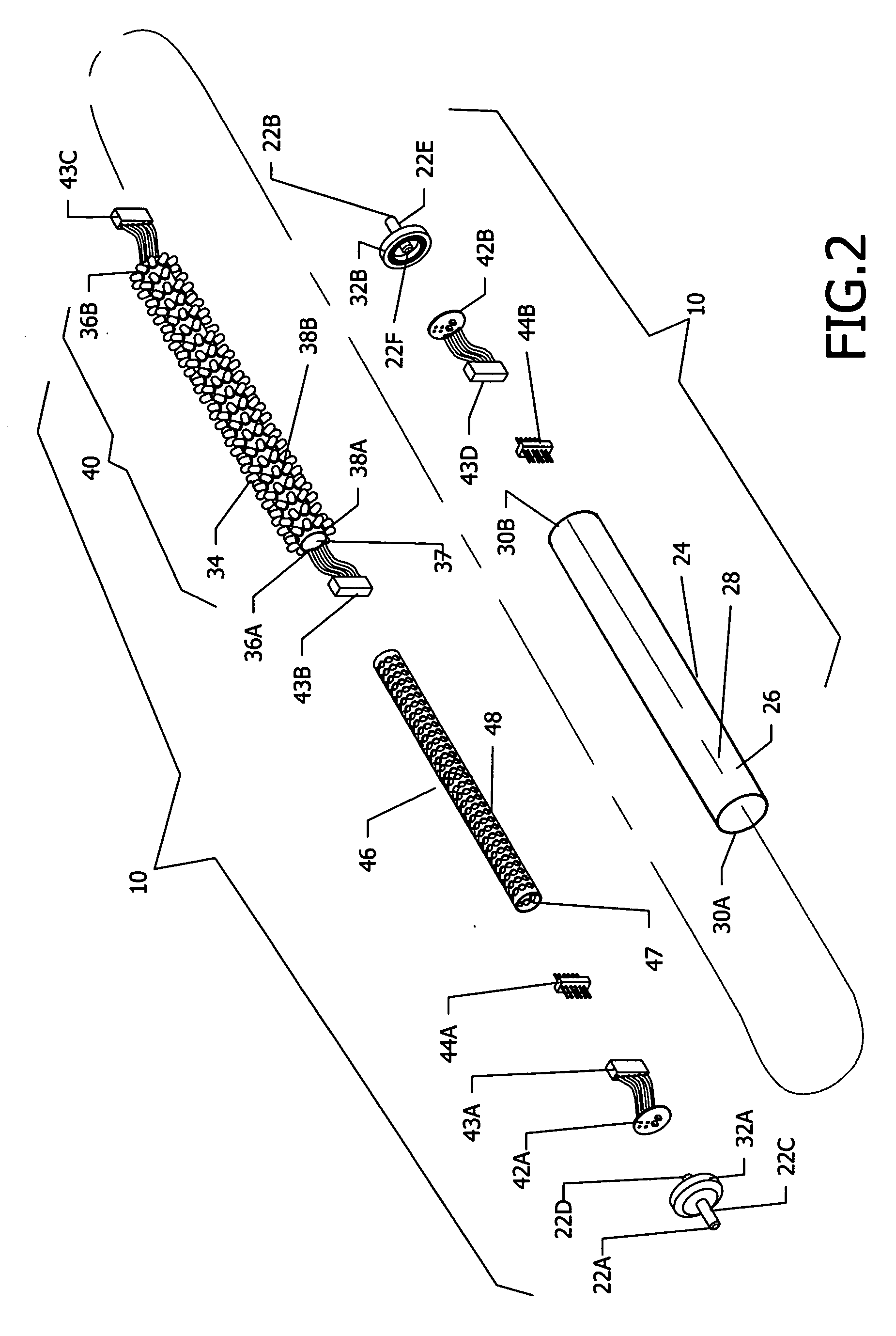
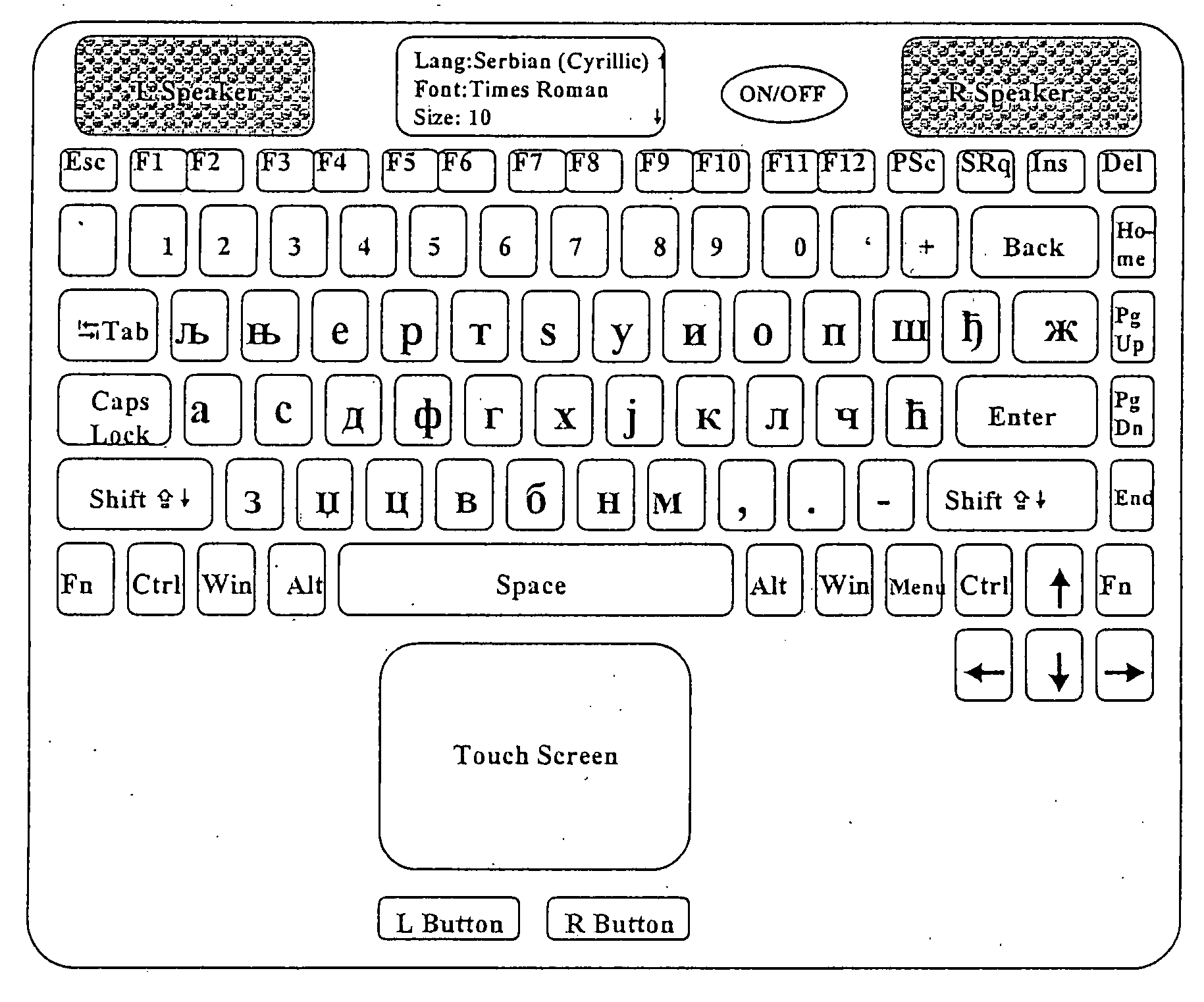
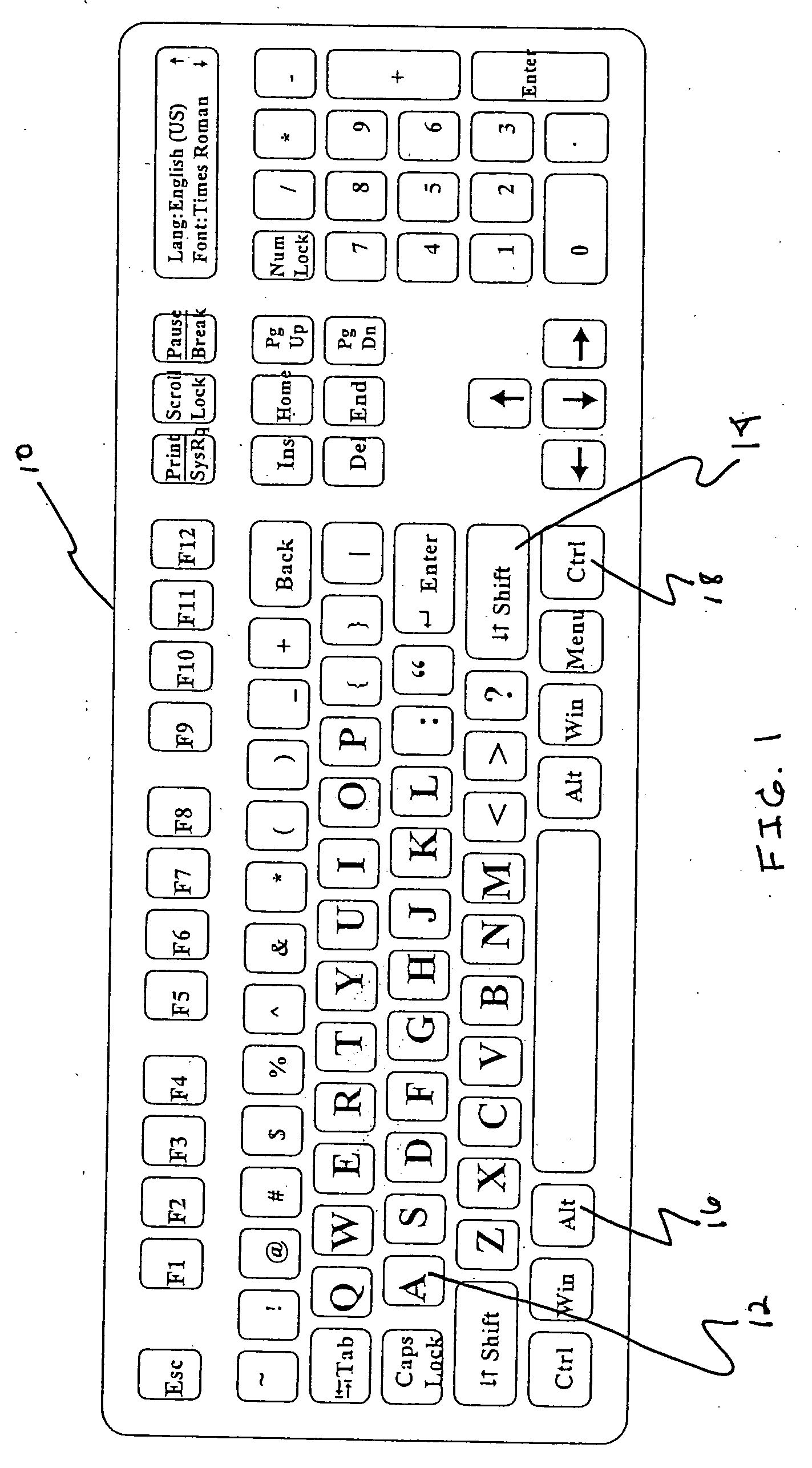
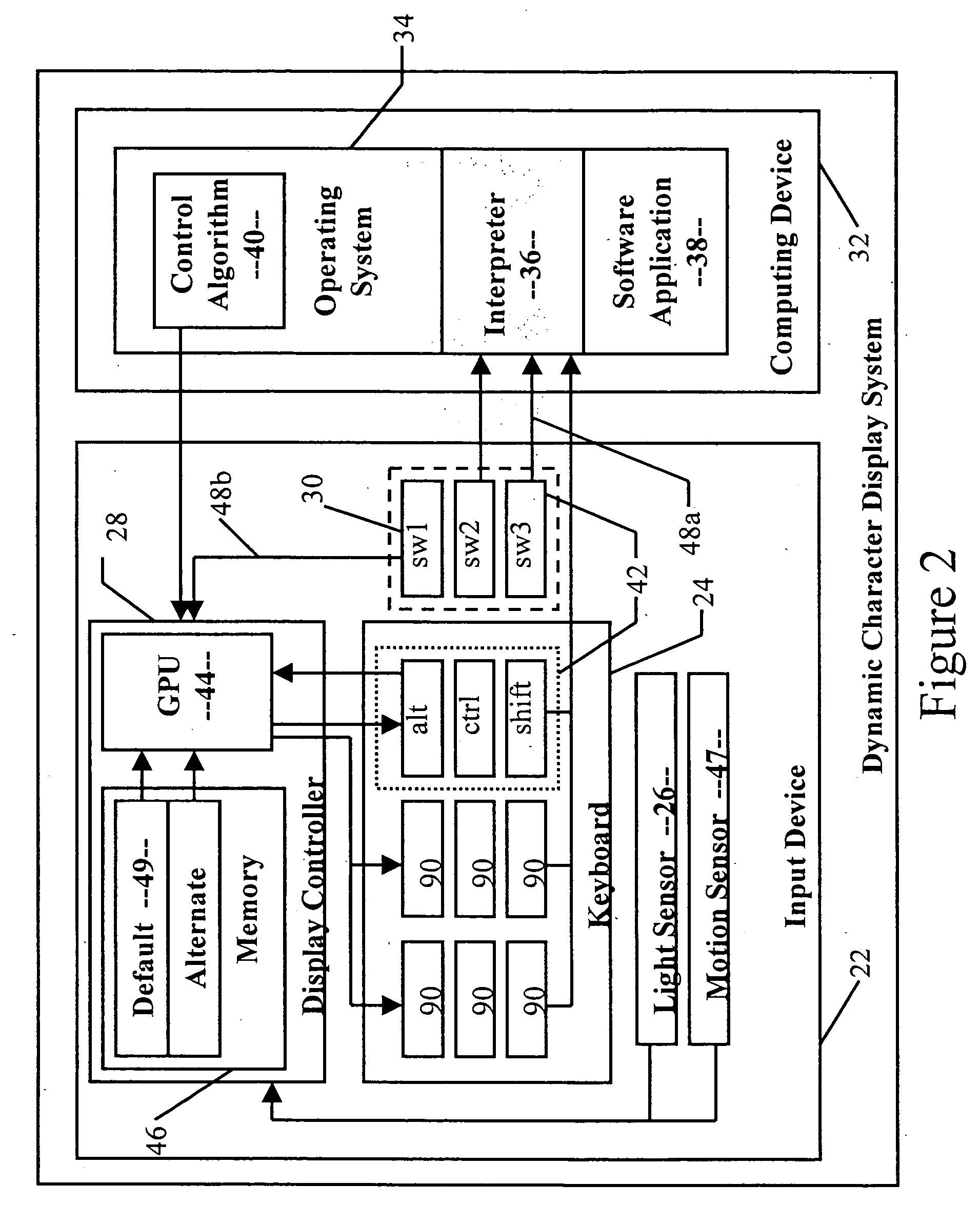
Dynamic character display input device
InactiveUS20060061542A1Eliminate needCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingOperational systemOutput device
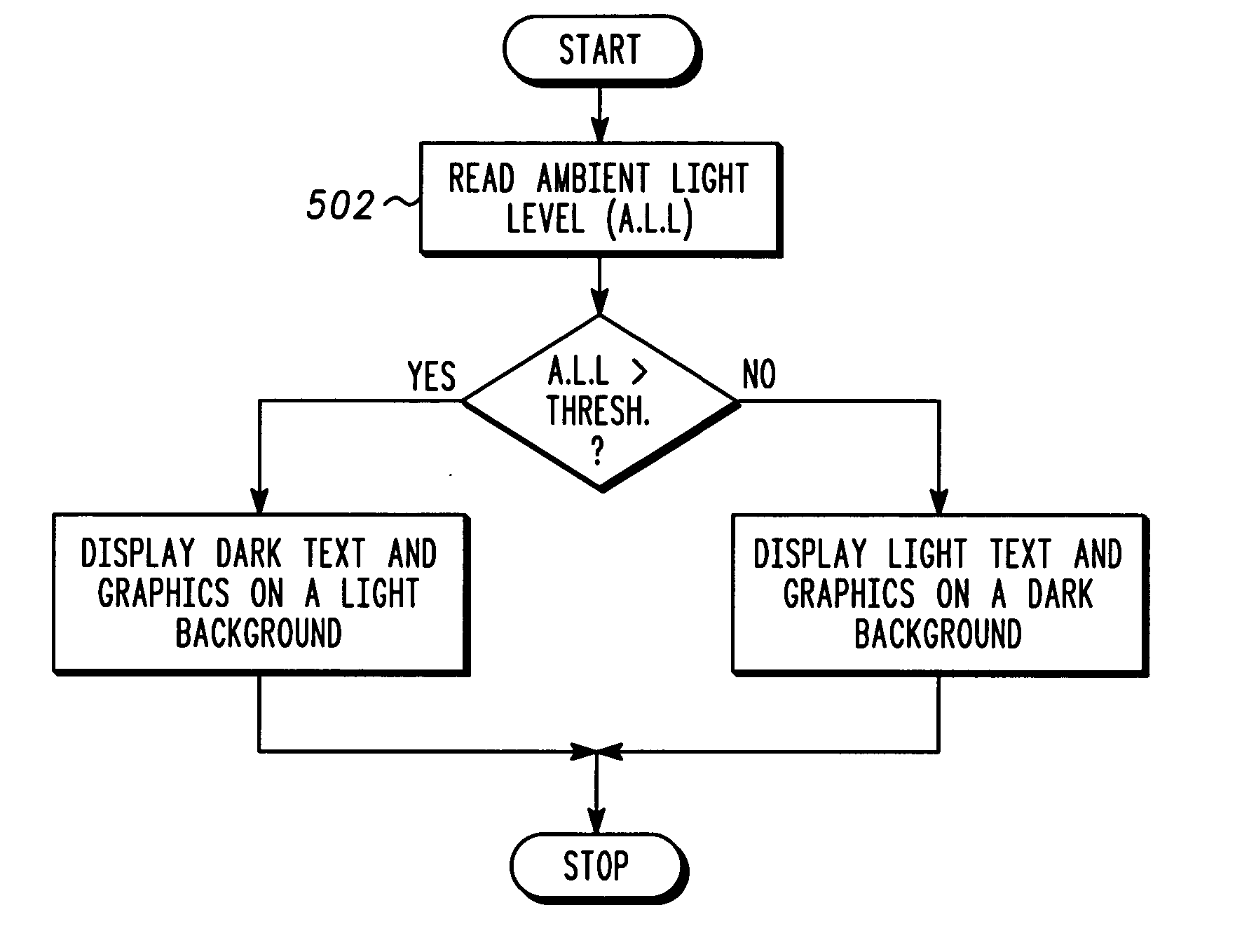
An input device including an illuminated keyboard and a display controller for displaying characters on depressible keyboard locations or buttons. The display controller changes the displayed characters according to a selection of a character set and application of modifiers, such as shift, alternate, or control. The input / output device also includes a light sensor for sampling the ambient light level in the vicinity of the input / output device. Based on the ambient light level, the display controller adjusts the intensity of the displayed character, its background, and the contrast between the displayed character and its background. The depressible keyboard locations may be buttons connected to mechanical switches to allow a user to rapidly type information into the input device. The display controller can be controlled by either user-selectable switches or by the operating system or software applications of an attached computing device.
Owner:STOKIC DRAGAN Z
Power controls with photosensor for tube mounted LEDs with ballast
InactiveUS7490957B2Reduce flickerReduce usageLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceControl signalNetwork communication
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Method and apparatus to control display brightness with ambient light correction
ActiveUS20050190142A1Improve comfortPrevents premature aging of light sourceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingInformation display systemsControl signal
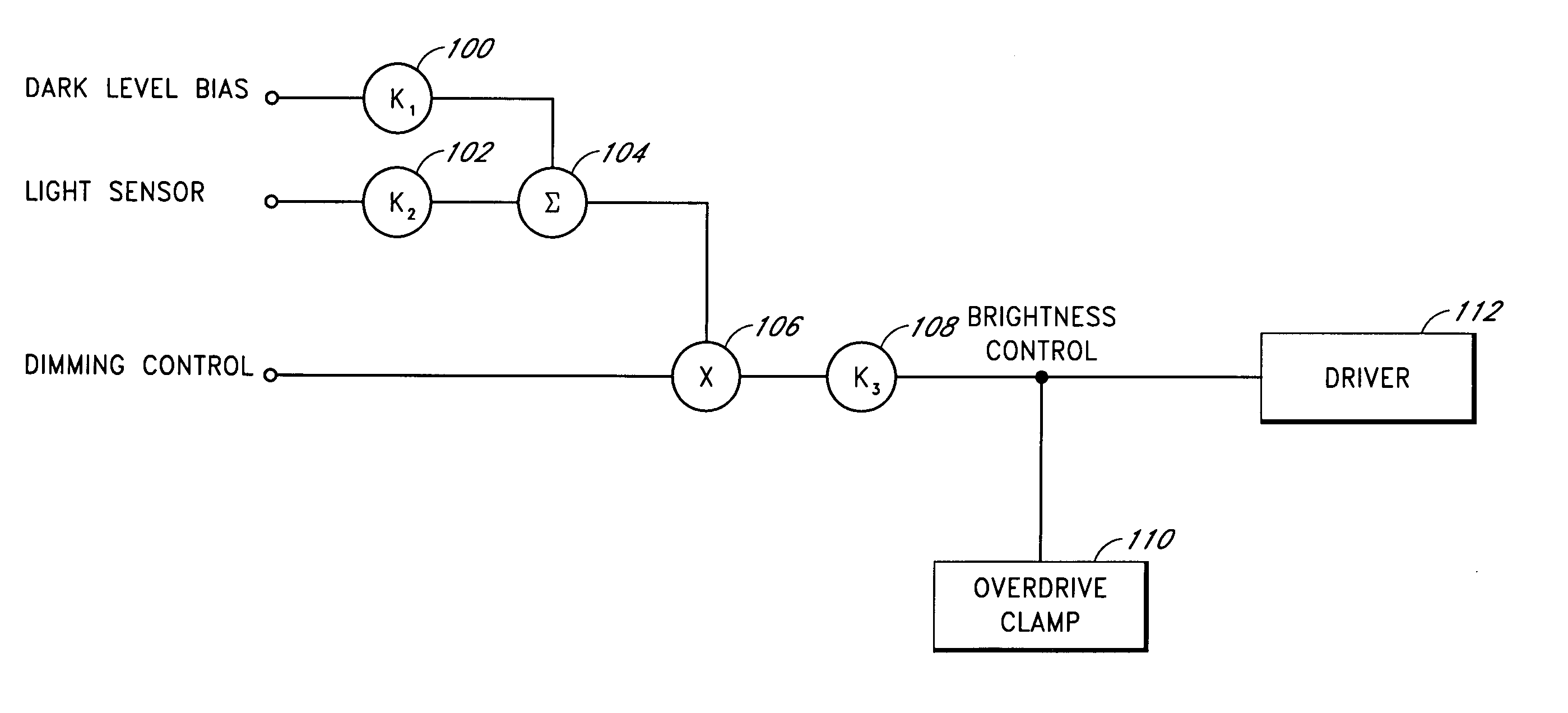
An ambient light sensor produces a current signal that varies linearly with the level of ambient light. The current signal is multiplied by a user dimming preference to generate a brightness control signal that automatically compensates for ambient light variations in visual information display systems. The multiplying function provides noticeable user dimming control at relatively high ambient light levels.
Owner:POLARIS POWERLED TECH LLC
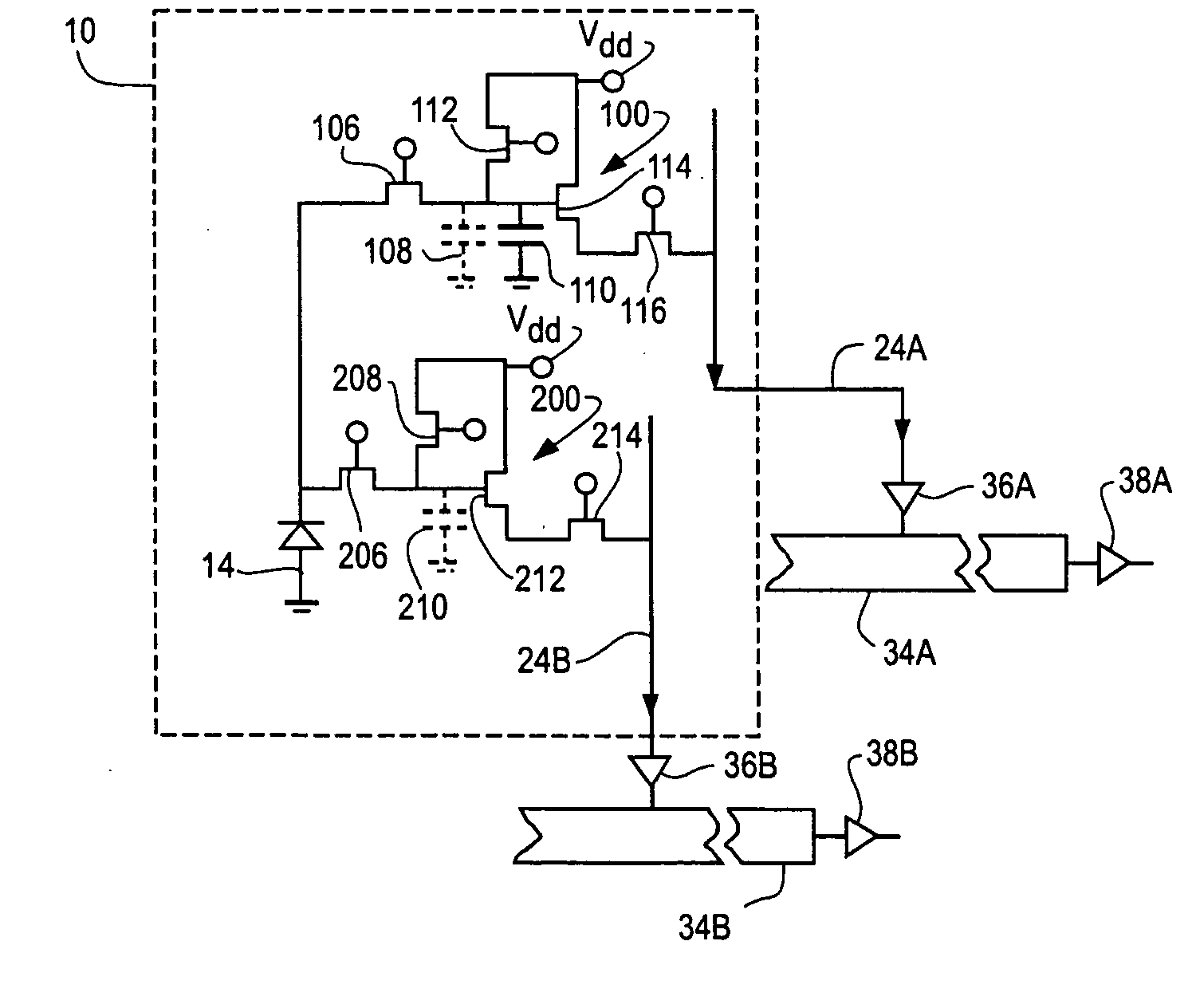
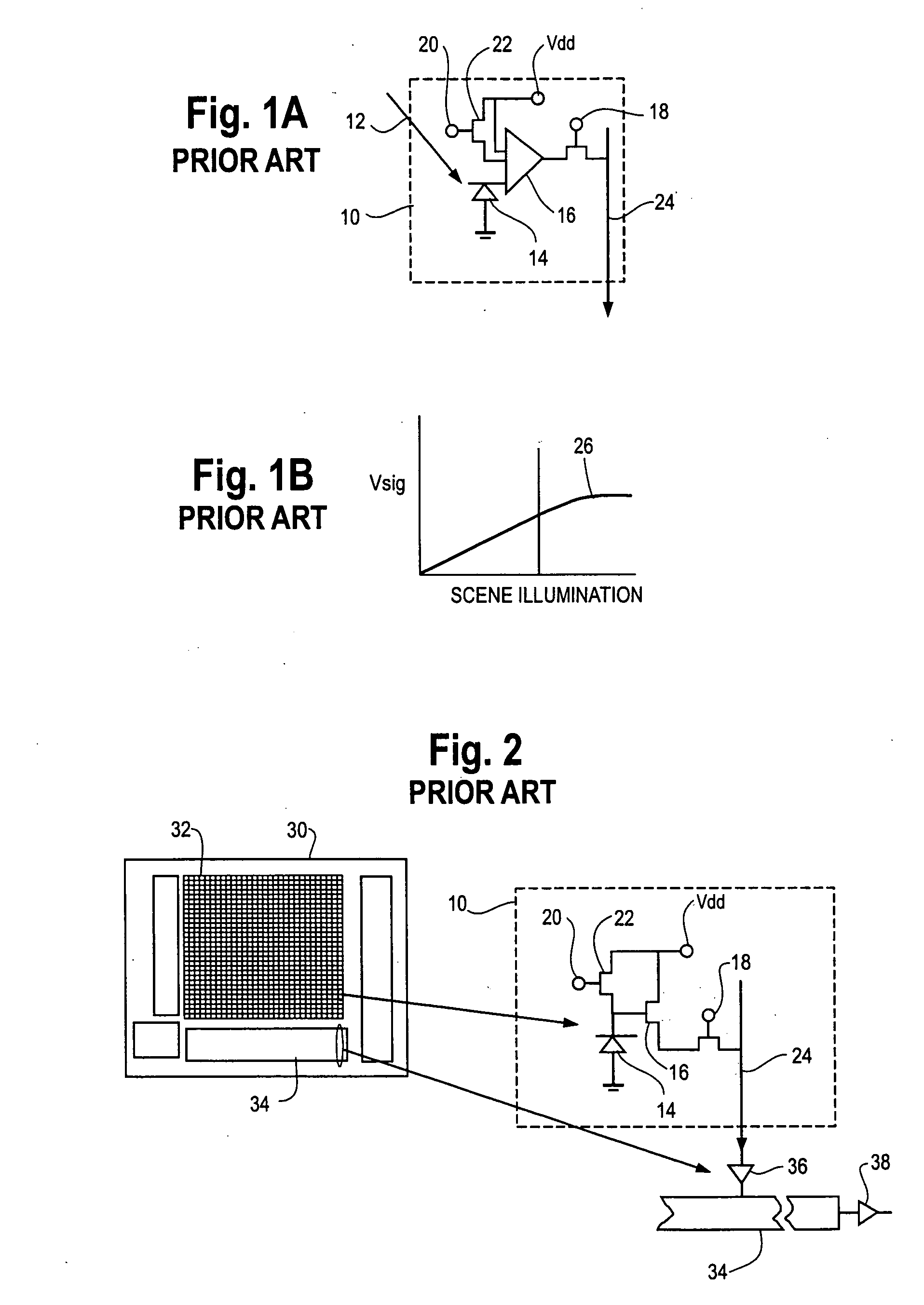
Hybrid infrared detector array and CMOS readout integrated circuit with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS20060181627A1High gainReduced dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsIndium bumpDetector array
A hybrid image sensor includes an infrared detector array and a CMOS readout integrated circuit (ROIC). The CMOS ROIC is coupled to at least one detector of the IR detector array, e.g., via indium bump bonding. Each pixel of the CMOS ROIC includes a first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals from the IR detector. Each pixel also includes a second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals from the IR detector (or from a second IR detector). A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Color translating UV microscope
A color translating UV microscope for research and clinical applications involving imaging of living or dynamic samples in real time and providing several novel techniques for image creation, optical sectioning, dynamic motion tracking and contrast enhancement comprises a light source emitting UV light, and visible and IR light if desired. This light is directed to the condenser via a means of selecting monochromatic, bandpass, shortpass, longpass or notch limited light. The condenser can be a brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast or DIC. The slide is mounted in a stage capable of high speed movements in the X, Y and Z dimensions. The microscope uses broadband, narrowband or monochromat optimized objectives to direct the image of the sample to an image intensifier or UV sensitive video system. When an image intensifier is used it is either followed by a video camera, or in the simple version, by a synchronized set of filters which translate the image to a color image and deliver it to an eyepiece for viewing by the microscopist. Between the objective and the image intensifier there can be a selection of static or dynamic switchable filters. The video camera, if used, produces an image which is digitized by an image capture board in a computer. The image is then reassembled by an overlay process called color translation and the computer uses a combination of feedback from the information in the image and operator control to perform various tasks such as optical sectioning and three dimensional reconstruction, coordination of the monochromater while collecting multiple images sets called image planes, tracking dynamic sample elements in three space, control of the environment of the slide including electric, magnetic, acoustic, temperature, pressure and light levels, color filters and optics, control for microscope mode switching between transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, Raman, scanning, confocal, area limited, autofluorescent, acousto-optical and other modes.
Owner:RICHARDSON TECH
Wireless network control for building lighting system
Wireless control of lighting fixtures via a wireless radio network using a radio-controlled relay device located between a lighting fixture or a ballast of a fluorescent fixture and its power supply. The radio-controlled device receives signals from remote controllers or via a computer interface. The wireless device is also configured to monitor the power consumption of a lighting fixture (or ballast) and send that information to the network. In the wireless control network, light level sensors and motion sensors also send information to the network to allow lights to respond to daylight levels or occupancy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Vehicle headlight control using imaging sensor
InactiveUS20070023613A1Photometry using reference valueVehicle headlampsField of viewSpectral signature
A vehicle headlamp control method and apparatus includes providing an imaging sensor that senses light in spatially separated regions of a field of view forward of the vehicle. Light levels sensed in individual regions of the field of view are evaluated in order to identify light sources of interest, such as oncoming headlights and leading taillights. The vehicle's headlights are controlled in response to identifying such particular light sources or absence of such light sources. Spectral signatures of light sources may be examined in order to determine if the spectral signature matches that of particular light sources such as the spectral signatures of headlights or taillights. Sensed light levels may also be evaluated for their spatial distribution in order to identify light sources of interest.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS
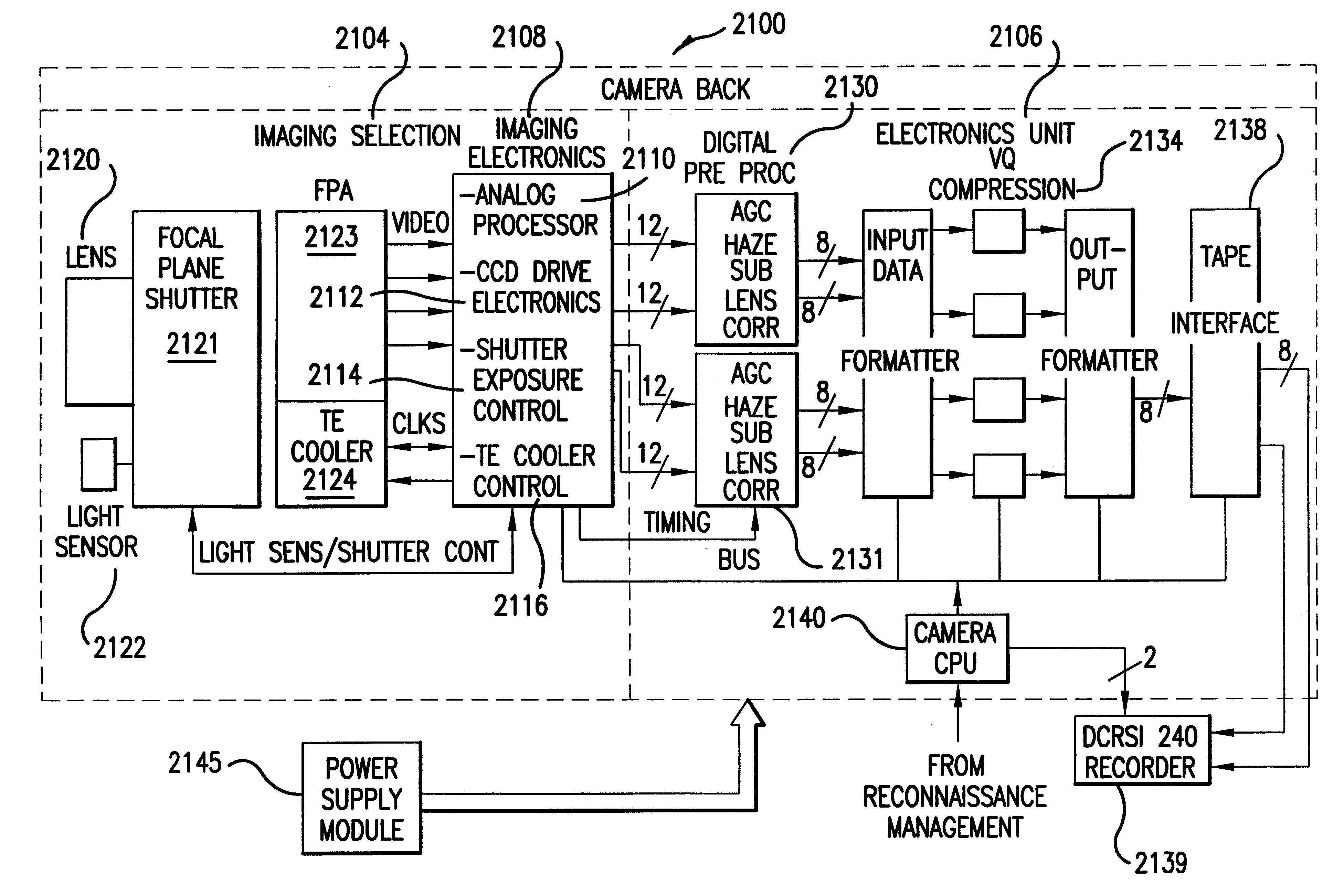
Electro-optical reconnaissance system with forward motion compensation
InactiveUS6256057B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage transferImage motion
An electro-optical framing camera forward motion compensation (FMC) reconnaissance system comprising a moving shutter and a full frame focal plane array detector is designed to minimize the variation of image motion from a target scene across the focal plane array. The full frame focal plane array, such as a Charge Coupled Device (CCD), is designed to transfer and add the image from pixel to pixel at a predetermined rate of image motion corresponding to the region exposed by the focal plane shutter. The focal plane shutter aperture and velocity are set to predetermined values coordinated with the available illumination. The CCD image transfer rate is set to minimize the smear effects due to image motion in the region of the scene exposed by the focal plane shutter. This rate is variable with line of sight depression angle, aircraft altitude, and aircraft velocity / altitude ratio. Further, a method of FMC utilizes a comparison of a measured light level to a standard value in order to determine the appropriate exposure time and shutter motion rate. An optimal FMC clocking signal is calculated based on image motion equations incorporated in the processing unit of the reconnaissance system.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Oximeter sensor with digital memory recording sensor data
InactiveUS20020038081A1Improve abilitiesEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsMemory chipDriving current
The present invention provides a memory chip for use in an oximeter sensor, or an associated adapter or connector circuit. The memory chip allows the storing of different data to provide enhanced capabilities for the oximeter sensor. In addition to providing unique data to store in such a memory, the invention describes unique uses of data stored in such a memory. The data stored in the memory chip may include information relating to use of the oximeter sensor. For example, the memory chip may encode a sensor model identification that can be displayed on a display screen when the sensor is connected to an oximeter monitor. The memory may also encode a range of operating parameters such as light levels over which the sensor can function or a maximum drive current. The operating parameters are read and interpreted by a controller circuit to control the pulse oximetry system.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
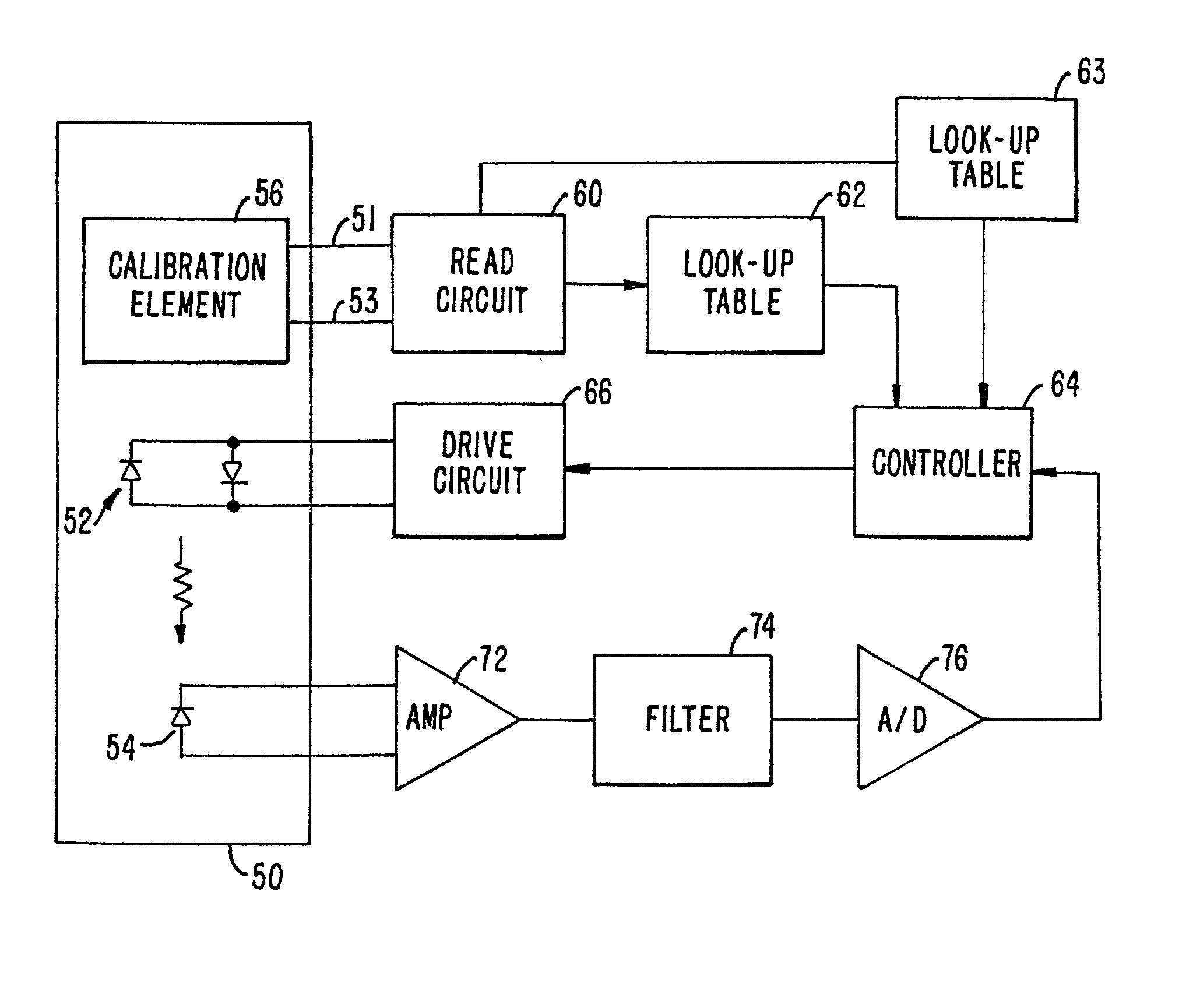
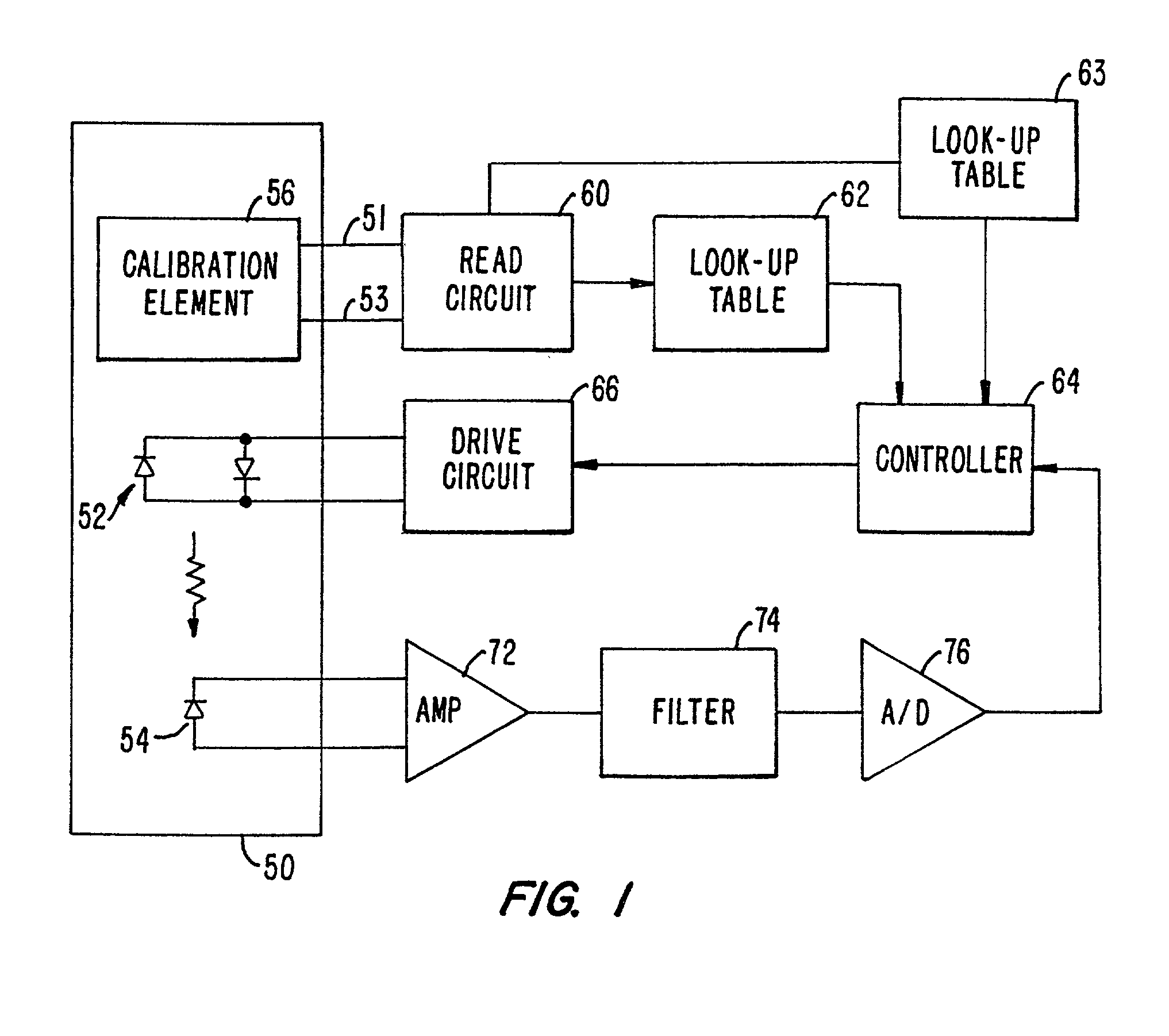
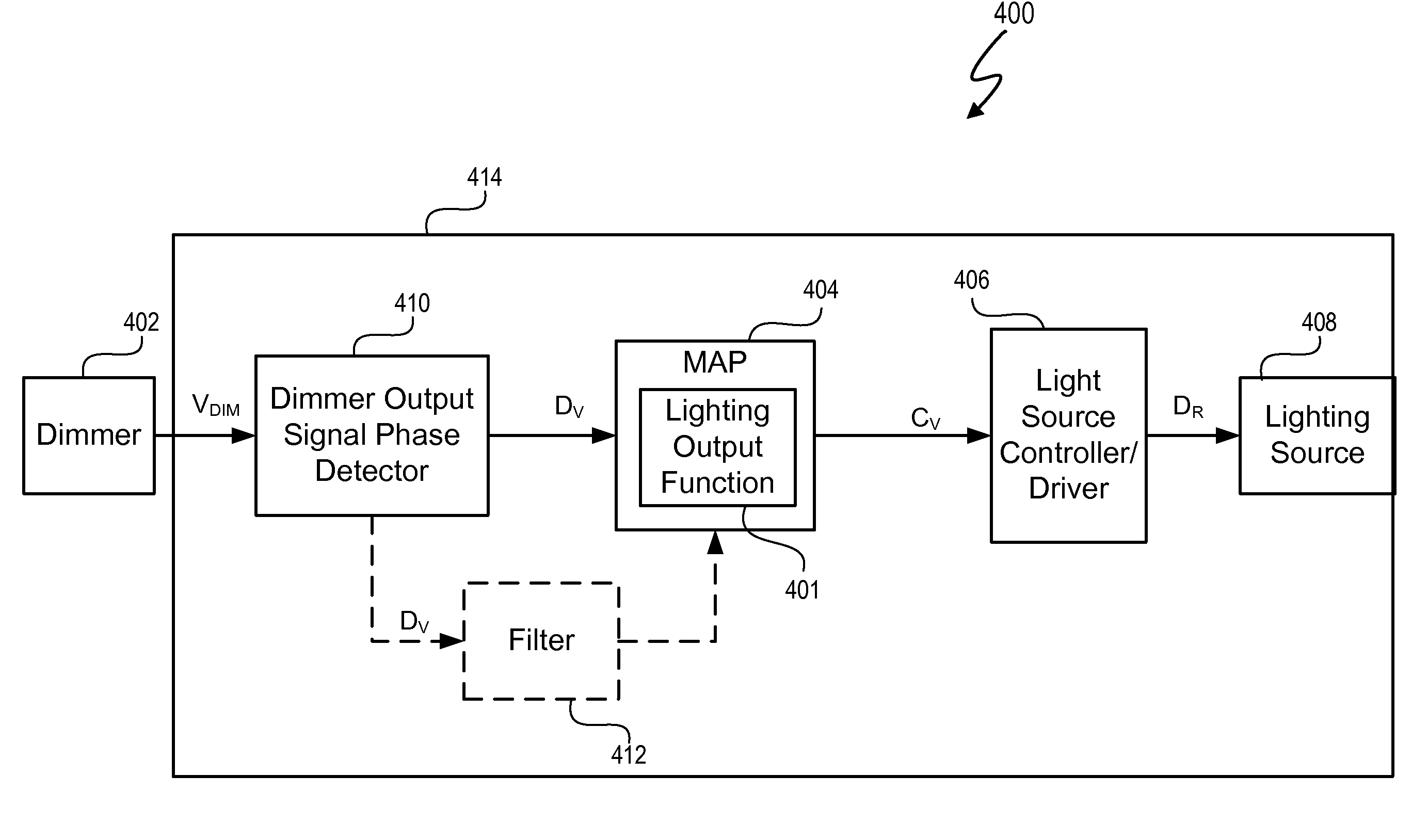
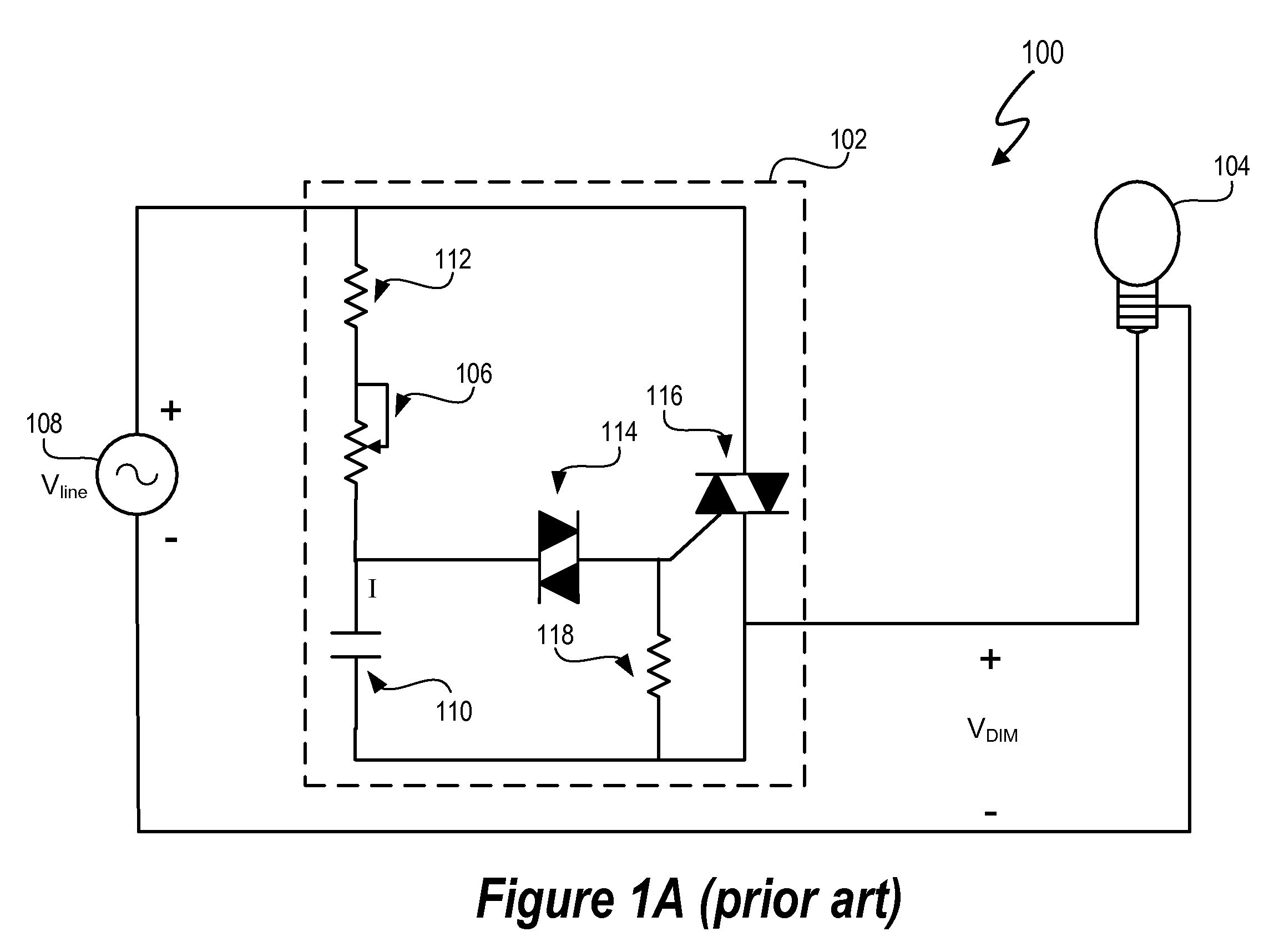
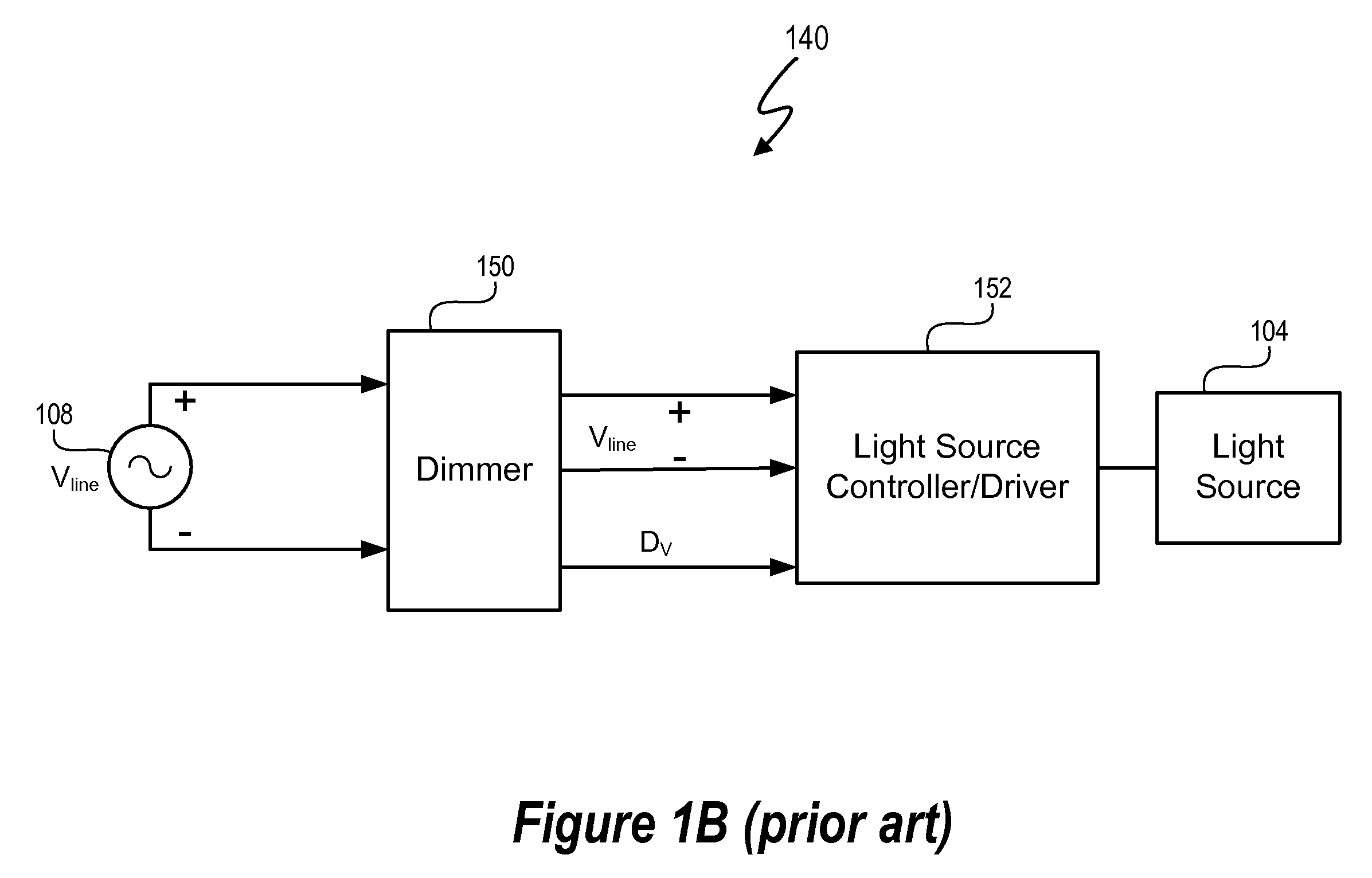
Lighting System with Lighting Dimmer Output Mapping
A system and method map dimming levels of a lighting dimmer to light source control signals using a predetermined lighting output function. The dimmer generates a dimmer output signal value. At any particular period of time, the dimmer output signal value represents one of multiple dimming levels. In at least one embodiment, the lighting output function maps the dimmer output signal value to a dimming value different than the dimming level represented by the dimmer output signal value. The lighting output function converts a dimmer output signal values corresponding to measured light levels to perception based light levels. A light source driver operates a light source in accordance with the predetermined lighting output function. The system and method can include a filter to modify at least a set of the dimmer output signal values prior to mapping the dimmer output signal values to a new dimming level.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Method for calibrating a lighting control system that facilitates daylight harvesting
ActiveUS20070185675A1Minimize visual impactMinimize impactNon-electric lightingPhotometry using reference valueLighting control consoleHigh energy
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for calibrating a lighting control system. The lighting control system is a daylight-harvesting system that controls the output of the lighting system based on available daylight and / or other light sources to reduce energy usage while providing lighting for an area. The lighting system includes multi-level lighting capabilities for one or more light sources. First, the system measures the light levels for the area when the lighting system: is turned on at a high energy-level; is turned on at an intermediate energy-level; and is turned off. The system determines from these measured light levels the light output of the lighting system in the different states. Then, during operation, the system measures a present light level for the area. The system then adjusts the light output of the lighting system for the area based on a lighting control parameter (e.g an on set-point and an off set-point pair), the present light output of the lighting system, and the present light level for the area.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electronic image sensor
InactiveUS20060164533A1Avoid complicationsAccurate exposureTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringFrame rate
An electronic imaging sensor. The sensor includes an array of photo-sensing pixel elements for producing image frames. Each pixel element defines a photo-sensing region and includes a charge collecting element for collecting electrical charges produced in the photo-sensing region, and a charge storage element for the storage of the collected charges. The sensor also includes charge sensing elements for sensing the collected charges, and charge-to-signal conversion elements. The sensor also includes timing elements for controlling the pixel circuits to produce image frames at a predetermined normal frame rate based on a master clock signal (such as 12 MHz or 10 MHz). This predetermined normal frame rate which may be a video rate (such as about 30 frames per second or 25 frames per second) establishes a normal maximum per frame exposure time. The sensor includes circuits (based on prior art techniques) for adjusting the per frame exposure time (normally based on ambient light levels) and novel frame rate adjusting features for reducing the frame rate below the predetermined normal frame rate, without changing the master clock signal, to permit per frame exposure times above the normal maximum exposure time. This permits good exposures even in very low light levels. (There is an obvious compromise of lowering of the frame rate in conditions of very low light levels, but in most cases this is preferable to inadequate exposure.) These adjustments can be automatic or manual.
Owner:E PHOCOS
Information display system for a vehicle
InactiveUS7488080B2Easy to install and arrangeReduce light leakageMirrorsElectrical apparatusInformation display systemsLuminous intensity
An interior rearview mirror assembly suitable for use in a vehicle includes a variable reflectance reflective element, which includes an electrochromic medium, a first information display positioned to the rear of the variable reflectance reflective element, and a second information display. The mirror assembly further includes a single control for adjusting the luminous intensity of the first information display and the second information display and at least one light sensor, with the output of the control being generated responsive to a light level sensed by the at least one light sensor. In addition, the luminous intensity of the first information display and of the second information display increases responsive to the output of the control to compensate for any decrease in transmission of the electrochromic medium.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Solid-state lighting fixtures
ActiveUS20090046457A1Easy to changeTurn easilyLight source combinationsPoint-like light sourceFluorescenceEffect light
Owner:EVERHART ROBERT L
Ambient light controlled display and method of operation
InactiveUS20050037815A1Devices with sensorCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Display device
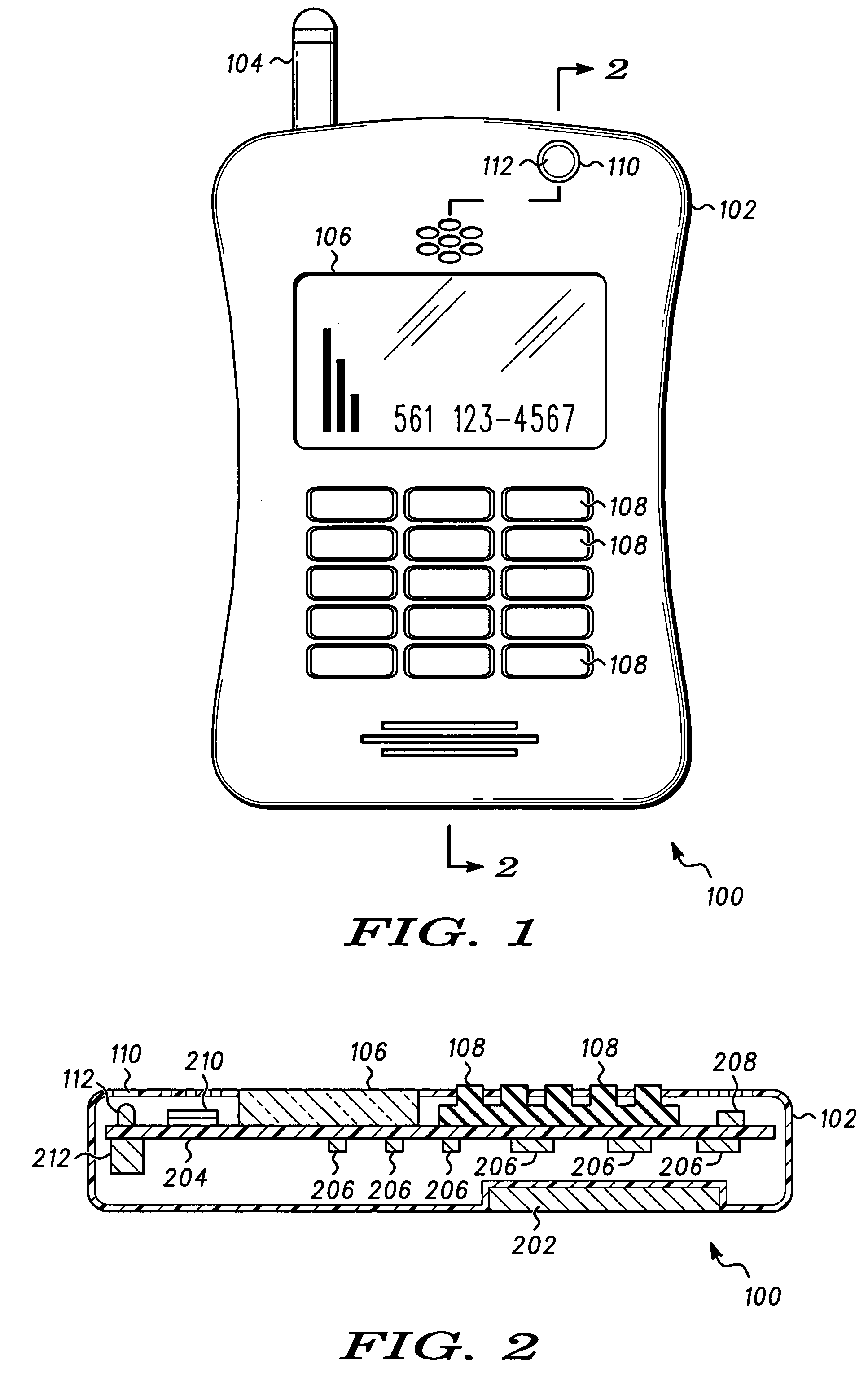
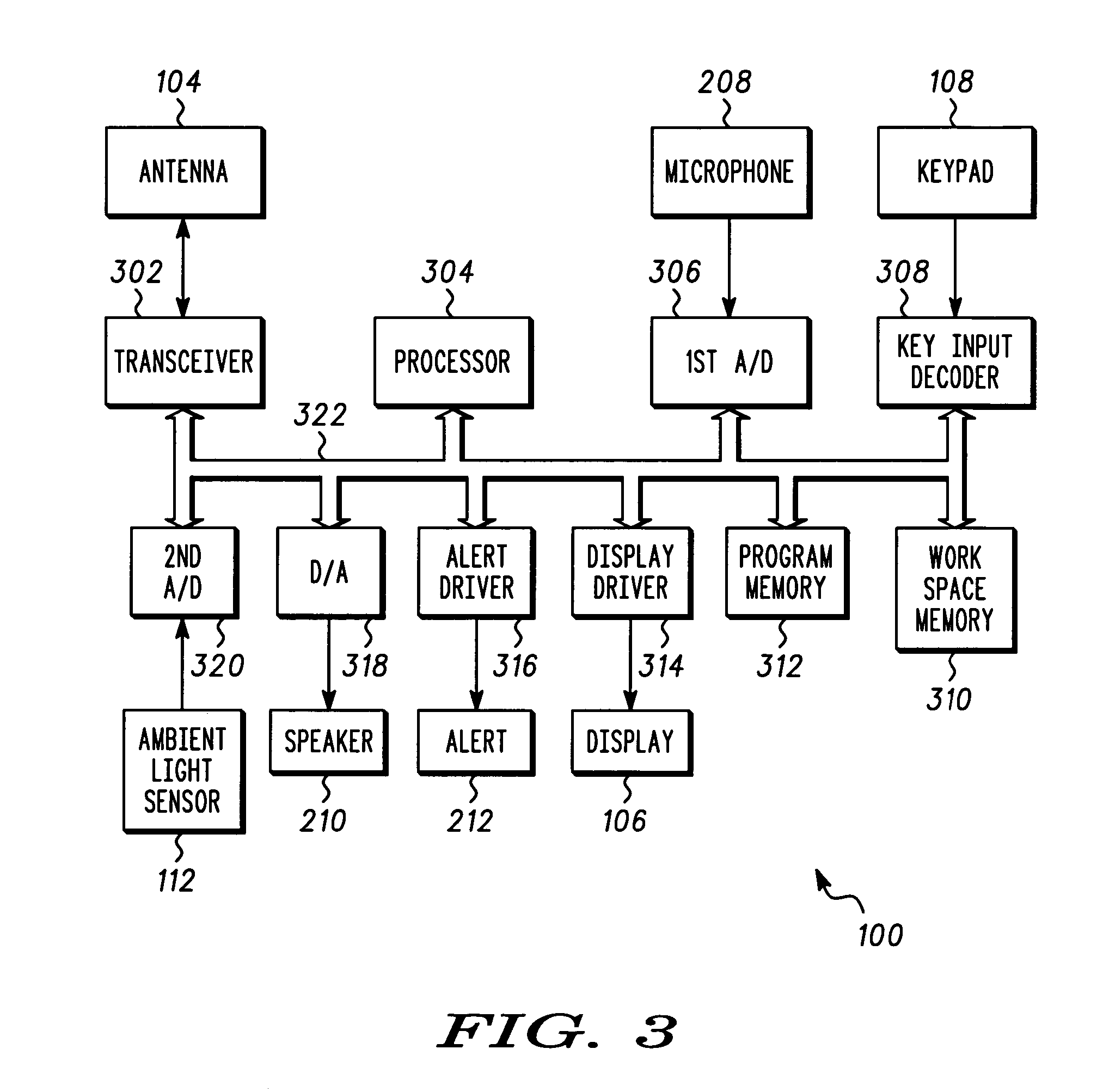
A portable electronic apparatus (100) includes a ambient light sensor (112) for measuring ambient light levels, a display (106) for displaying text and icons, on a background, and a processor (304) coupled to the display (106), and the light sensor for causing indicia to be displayed on the display (106), and adjusting the color and / or size characteristics of the indicia and / or background according to the ambient light level measured through the ambient light sensor (112)
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Method for dynamically adjusting the operating parameters of a tof camera according to vehicle speed
ActiveUS20140152975A1More time for speed adjustmentIncrease rangePhotogrammetry/videogrammetryActive open surveying meansEngineeringVisual perception
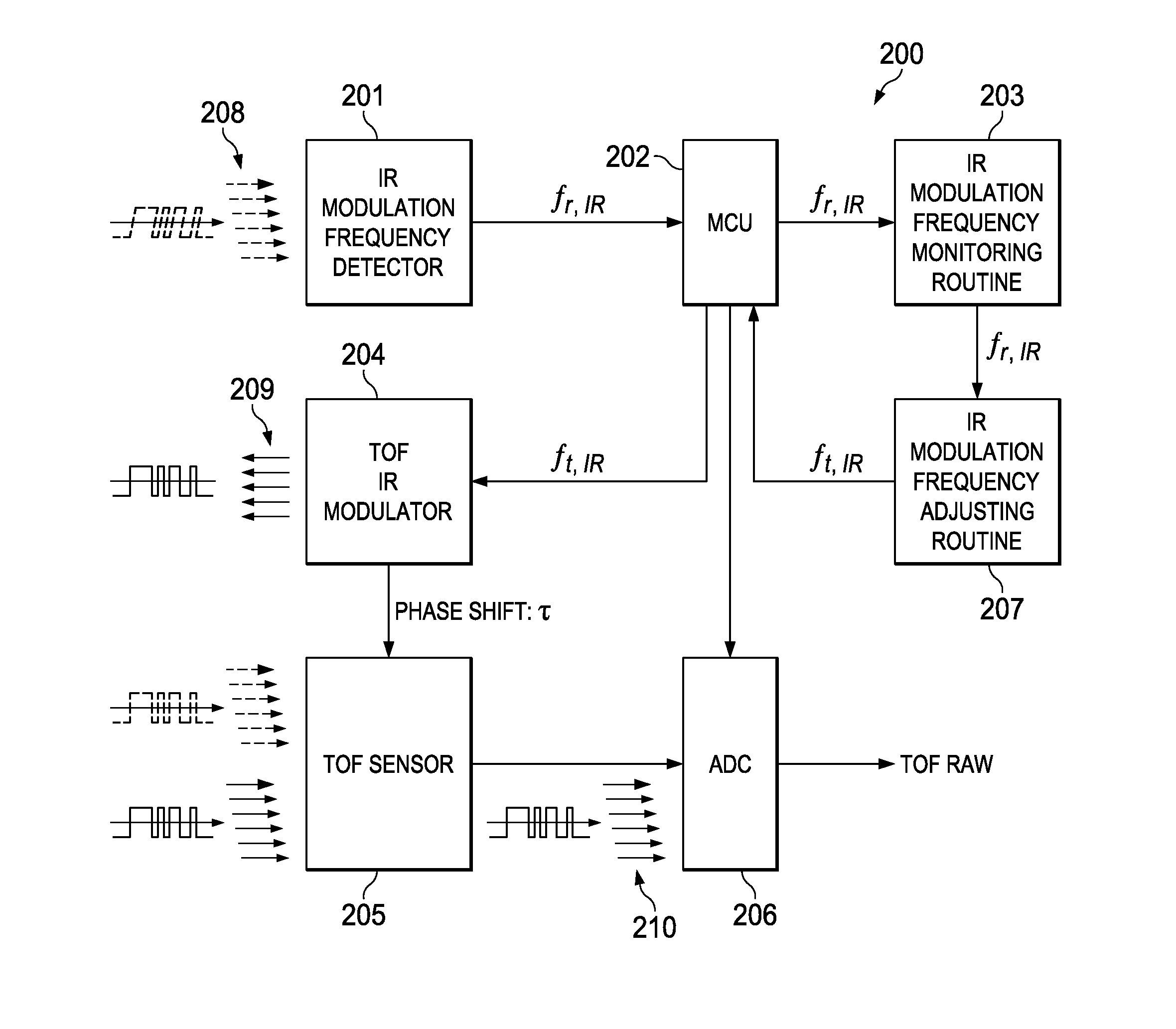
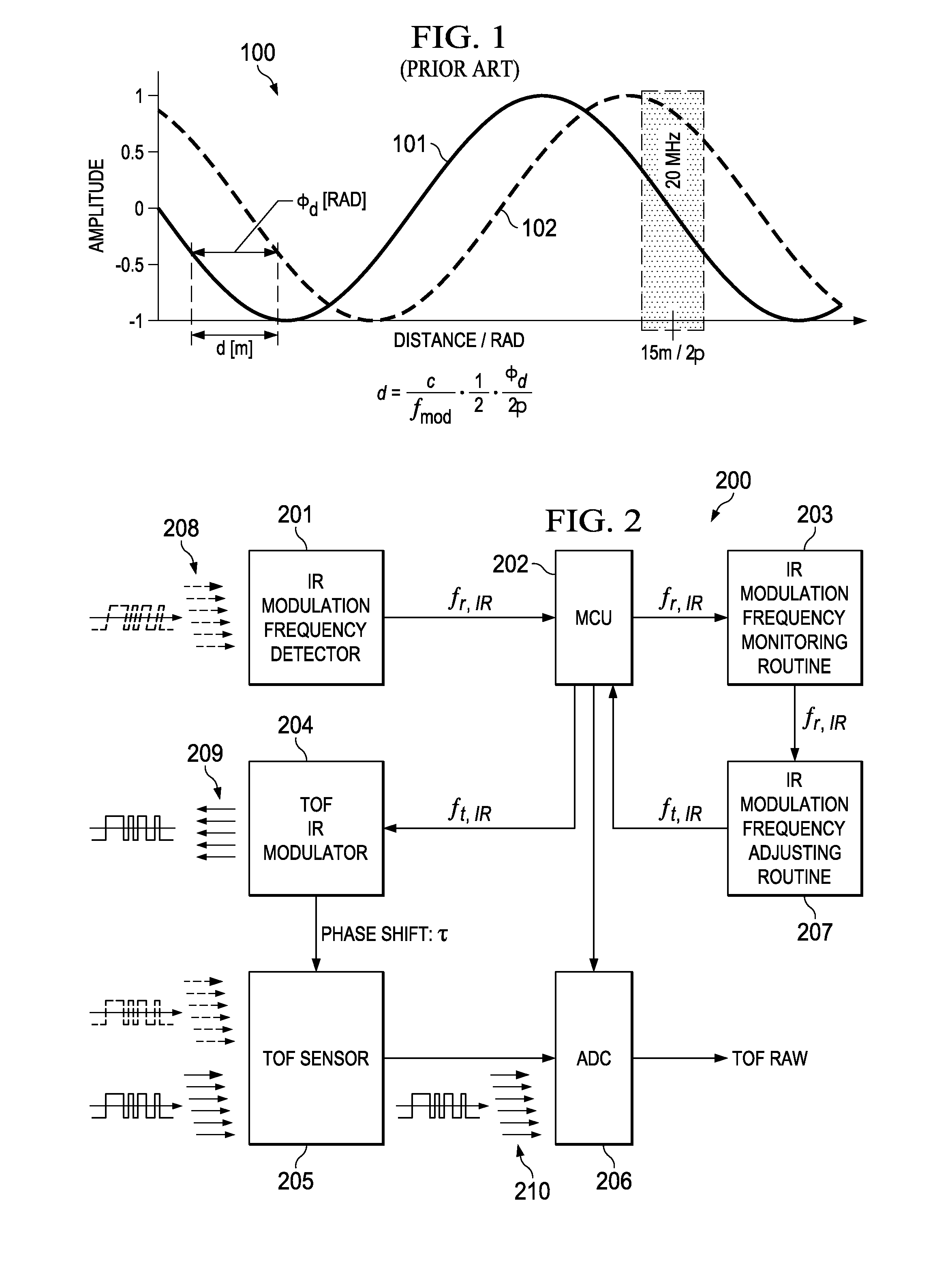
A method for adjusting the modulating frequency and the intensity of the IR illumination of a Time of Flight measurement system proportionally to the speed of movement and the ambient light level of the TOF system, thus adjusting the range of vision of the system dependent on speed. In an alternate embodiment the modulating frequency of a TOF measurement system is periodically adjusted to cover a larger range of vision of the TOF.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com